Patents
Literature
2203 results about "Cutoff frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced (attenuated or reflected) rather than passing through.
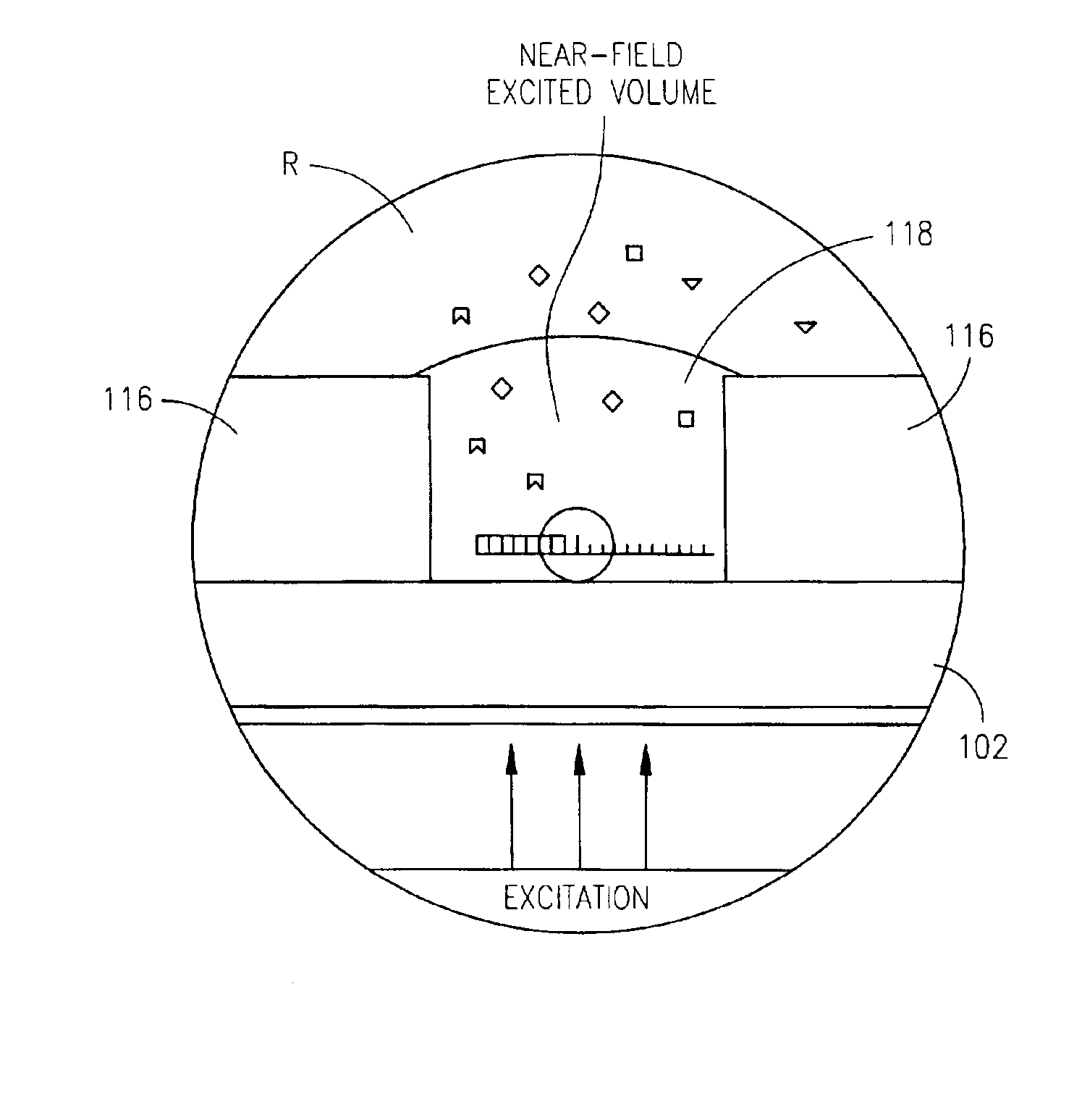
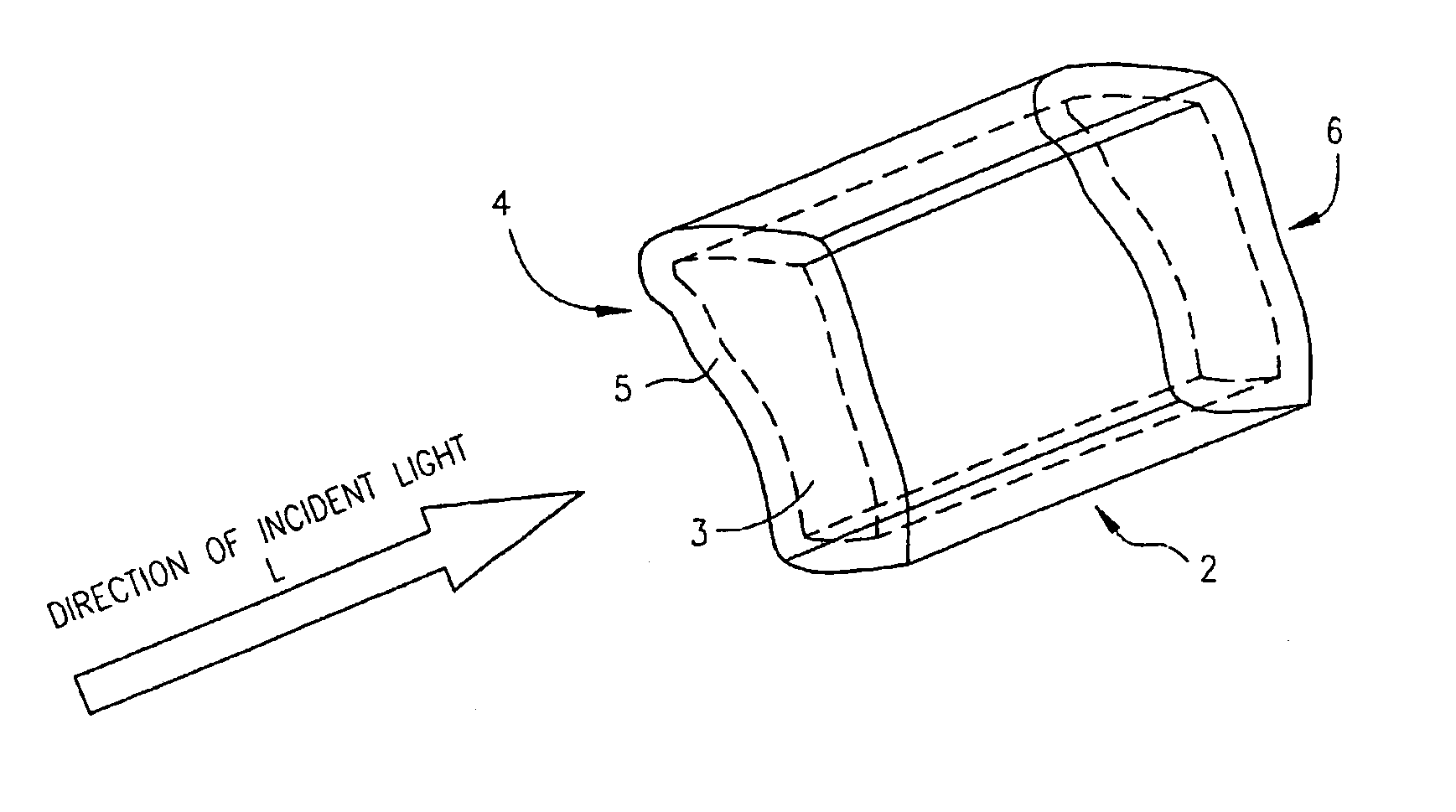
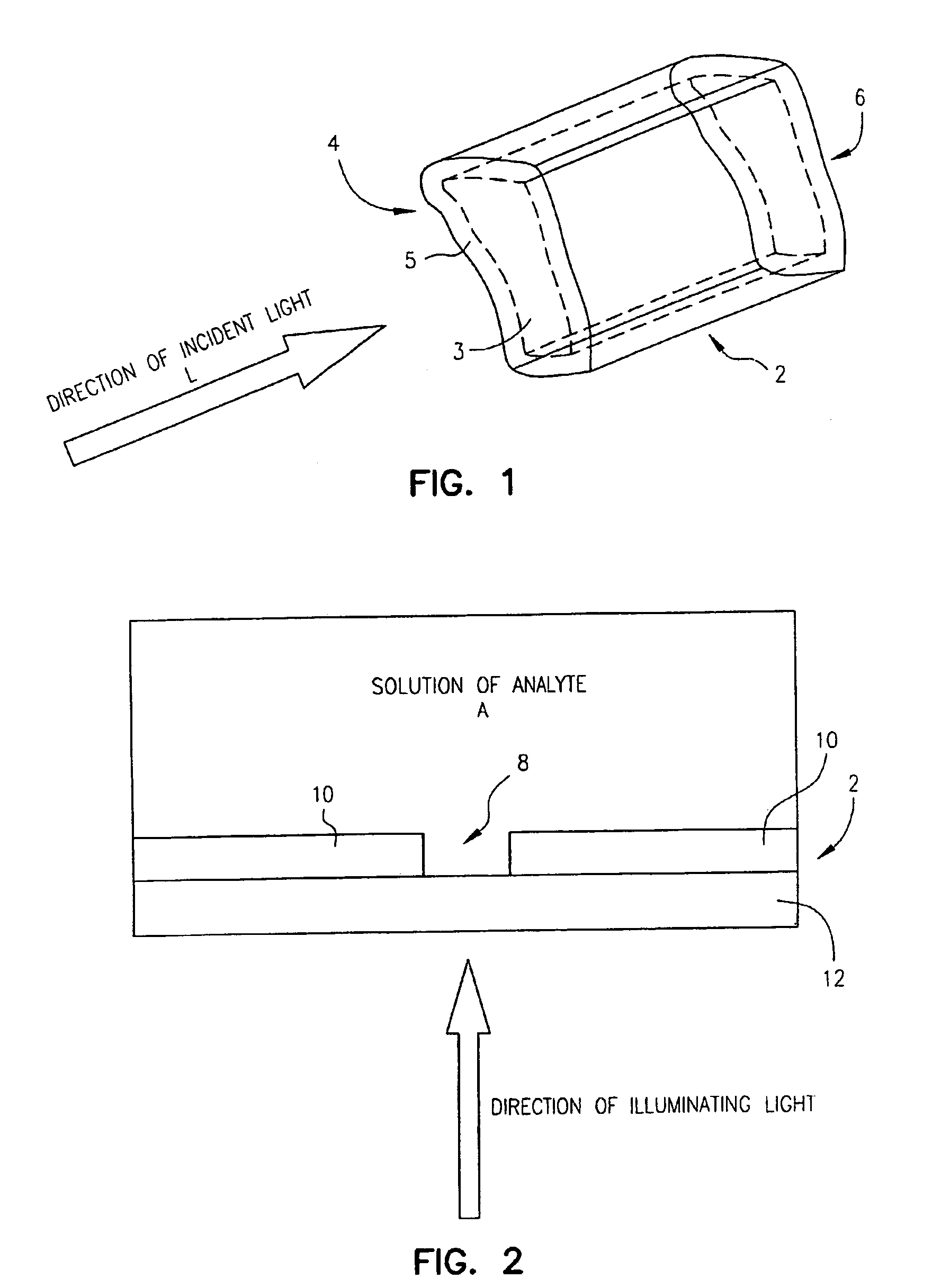
Zero-mode clad waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS6917726B2Effective volumeEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
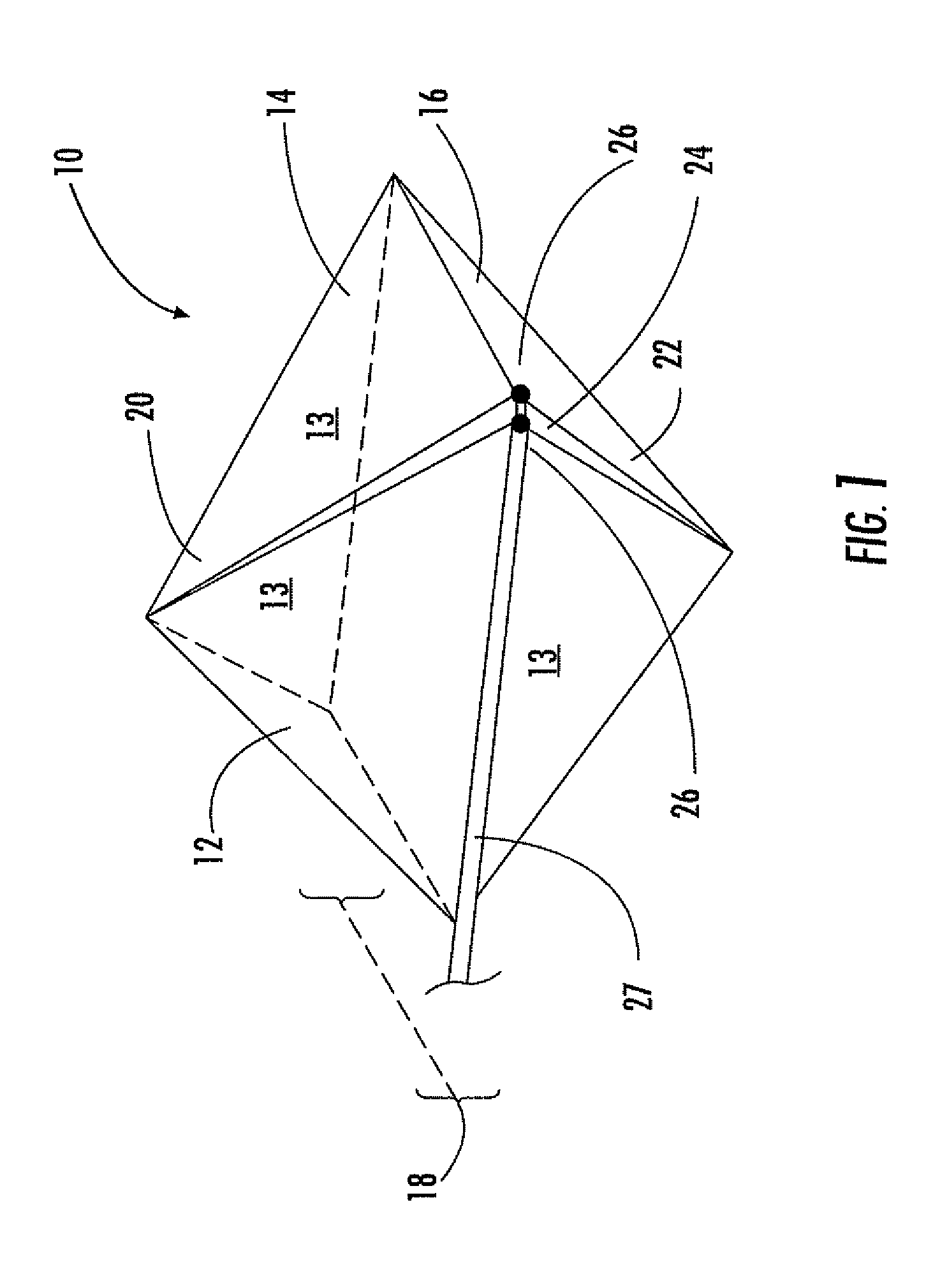
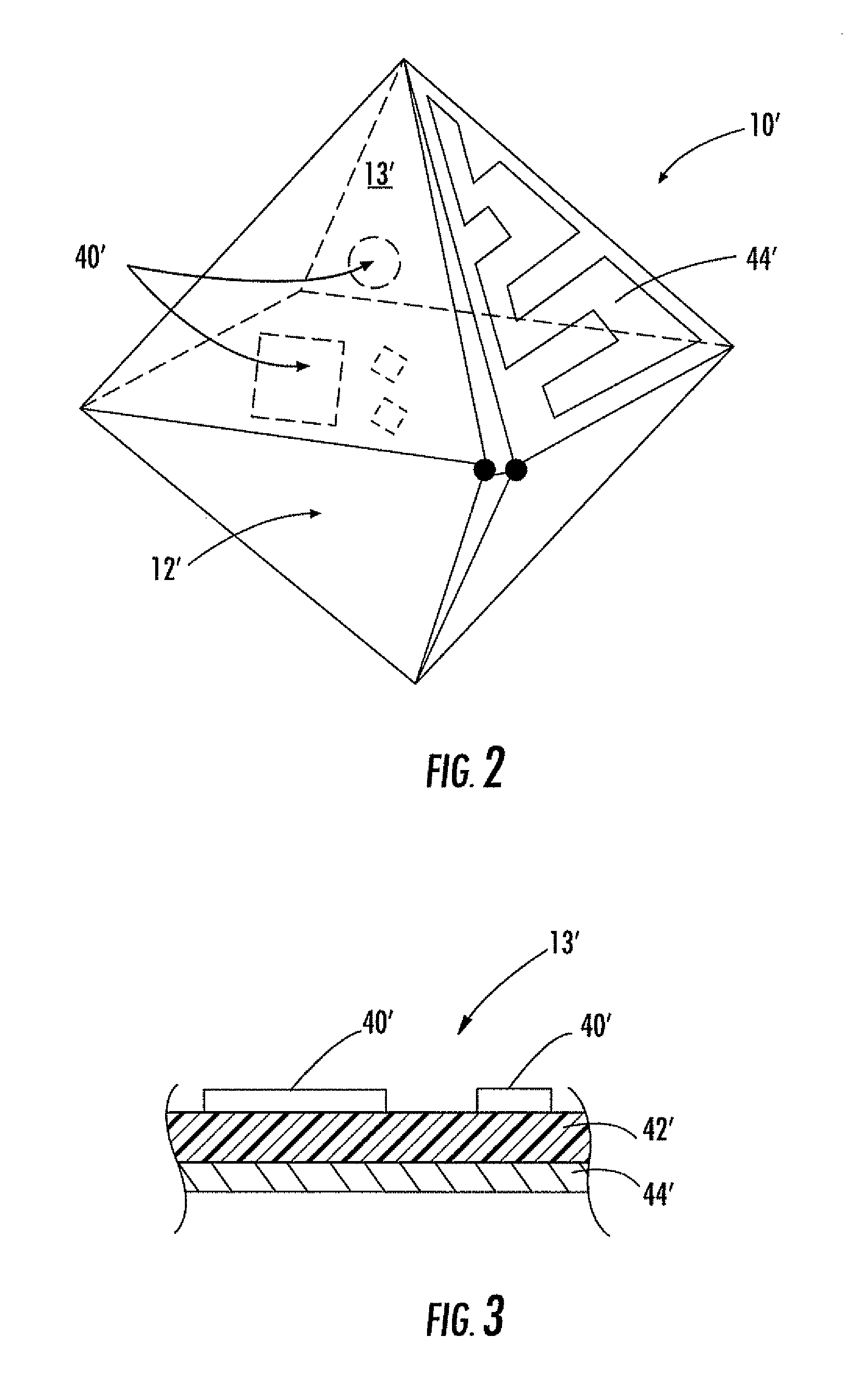
Polyhedral antenna and associated methods
The antenna includes an electrically conductive antenna body having a polyhedral shape with opposing first and second ends and a medial portion therebetween. The medial portion of the electrically conductive antenna body is wider than the opposing first and second ends thereof, and the electrically conductive antenna body has a slot therein extending from at least adjacent the first end to at least adjacent the second end. The polyhedral antenna has an omnidirectional pattern, is horizontally polarized and broad in bandwidth above a lower cutoff frequency.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
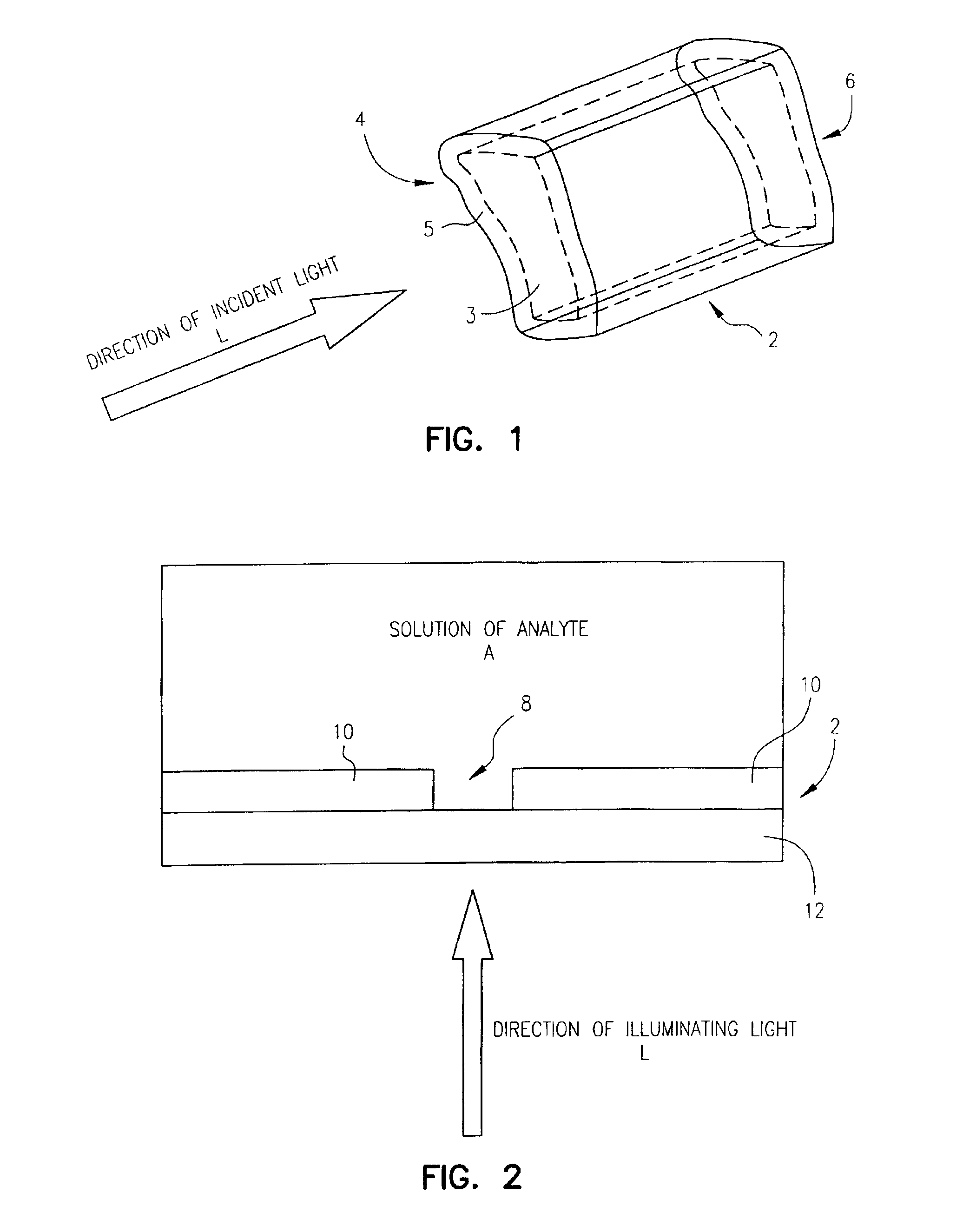
Waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS7013054B2Effective volumeEasy to useCladded optical fibreMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
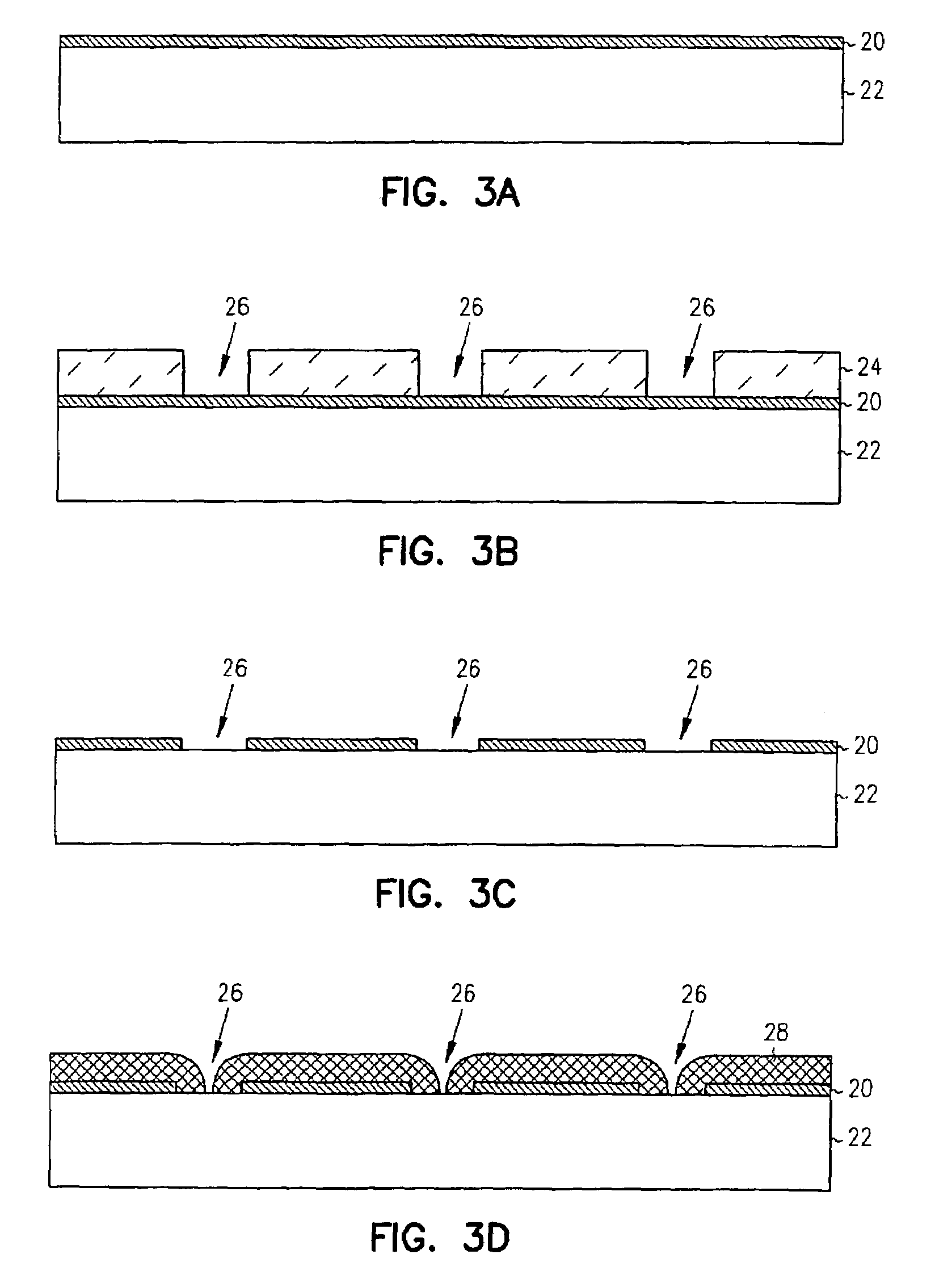
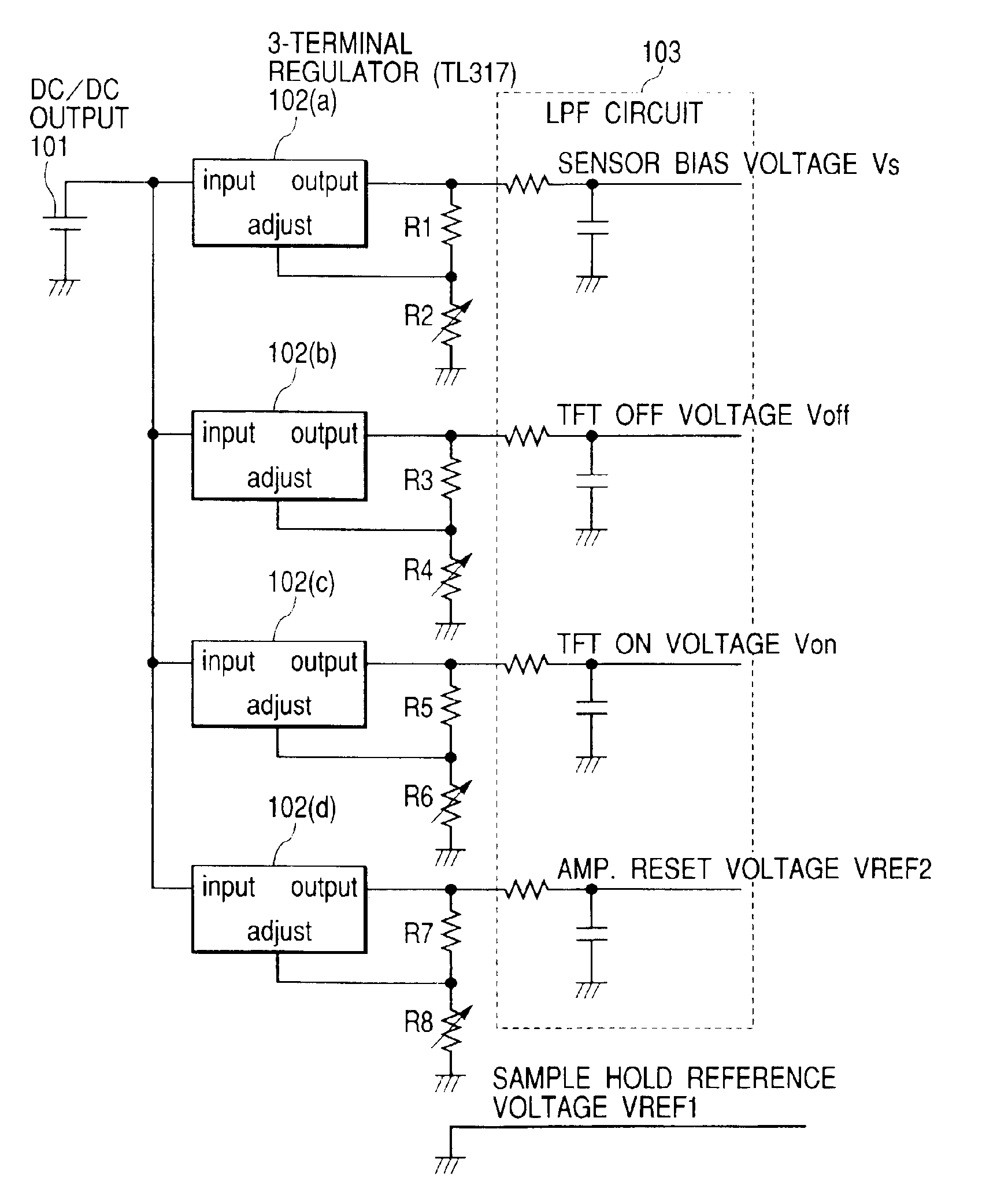
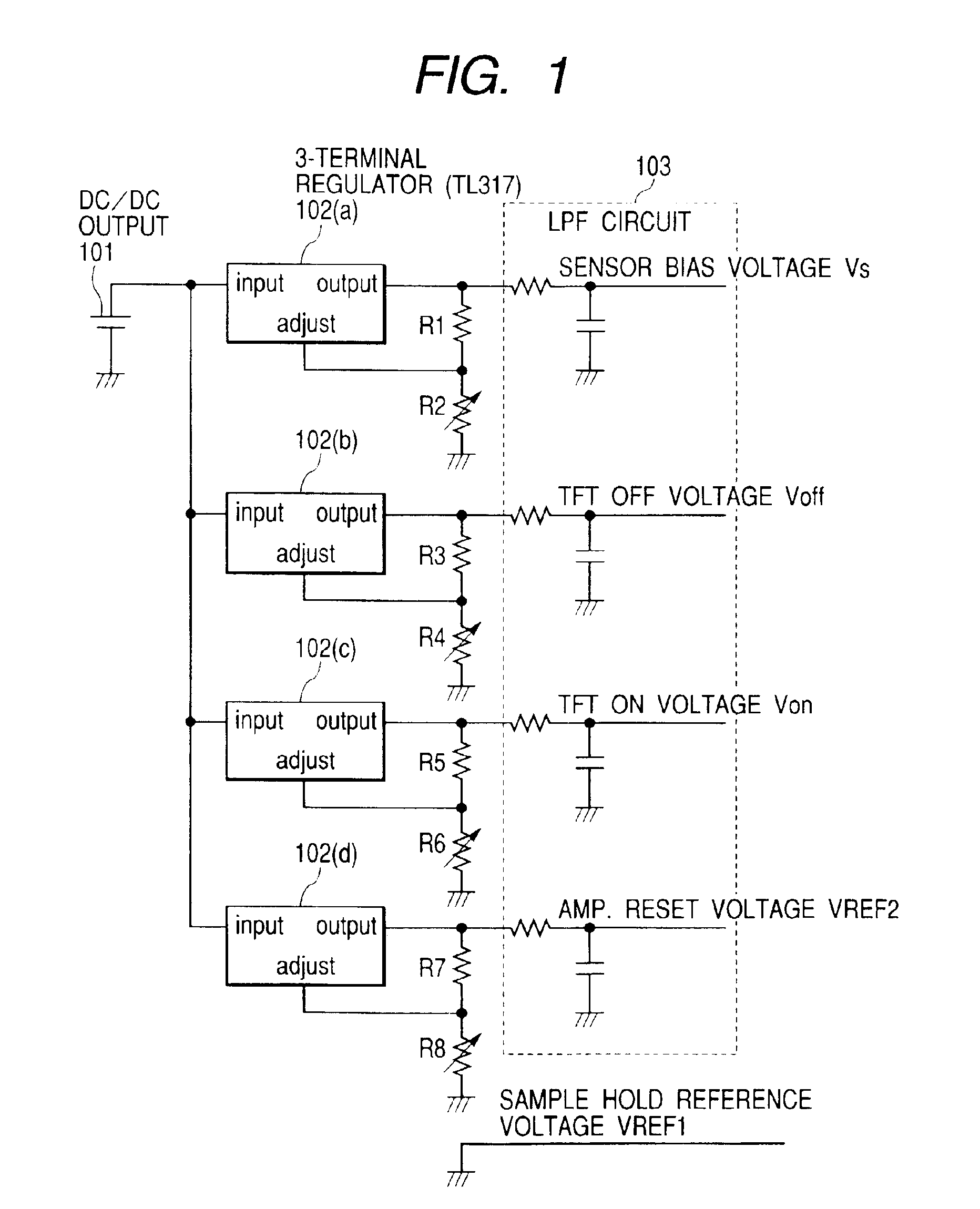
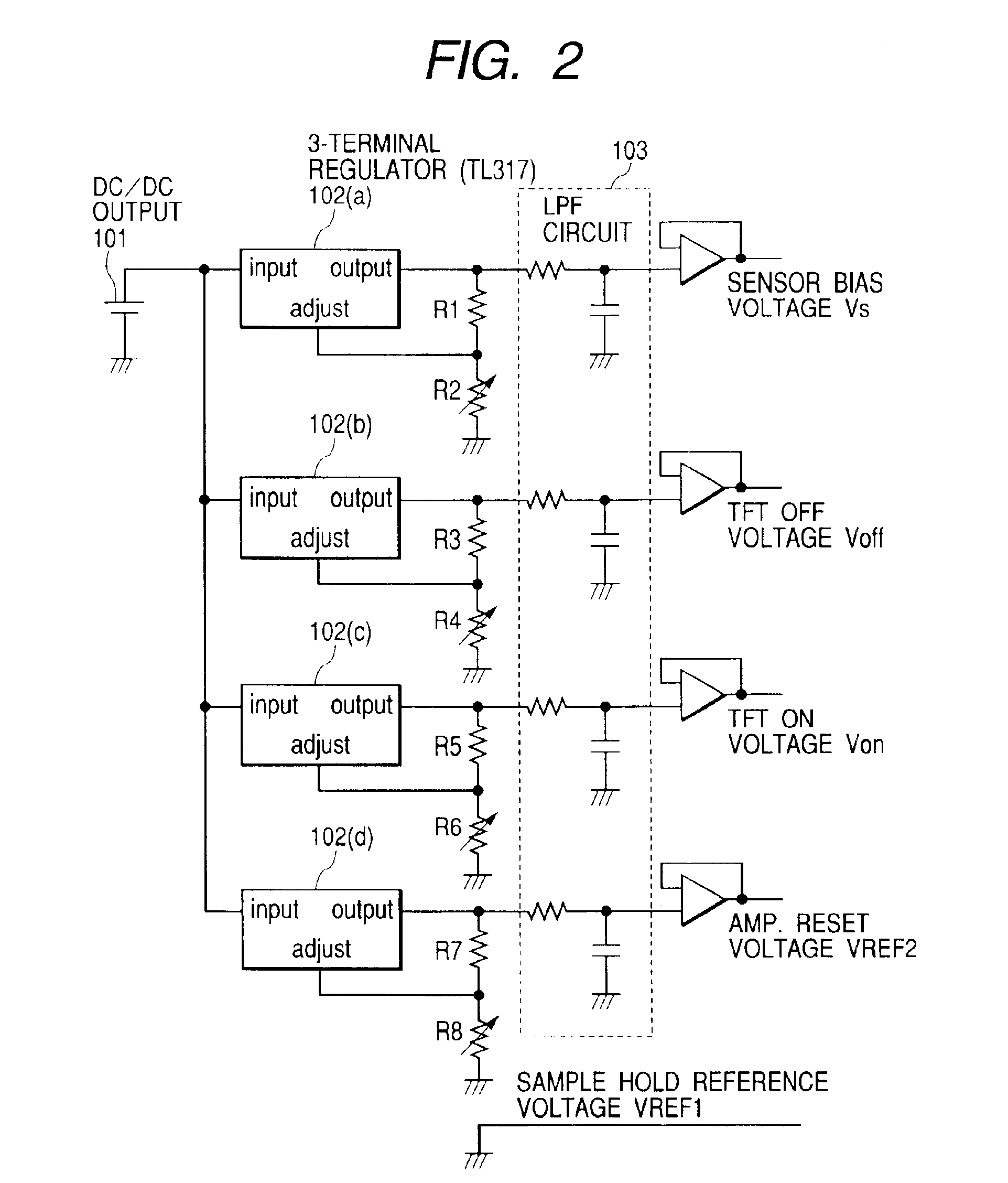
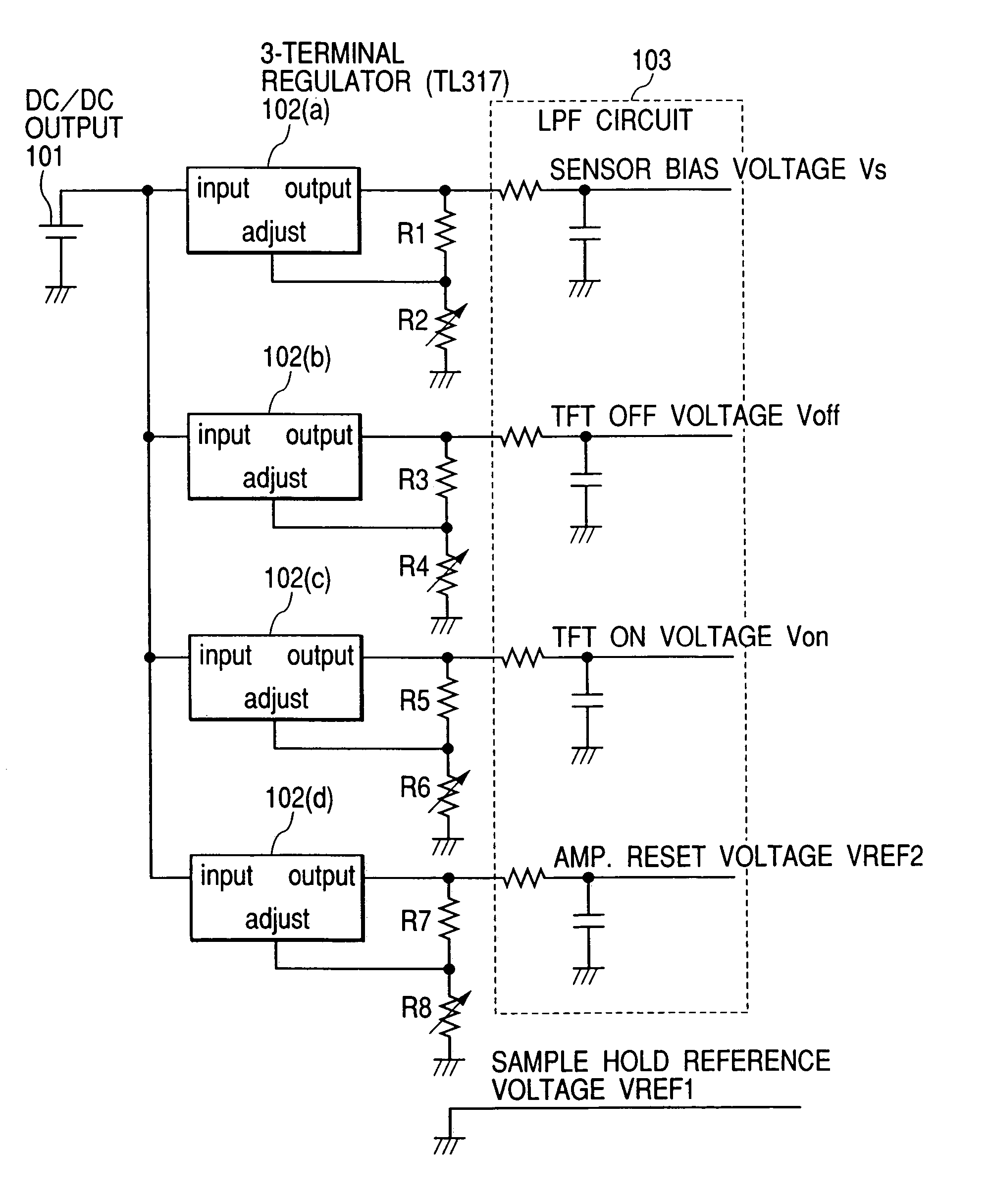
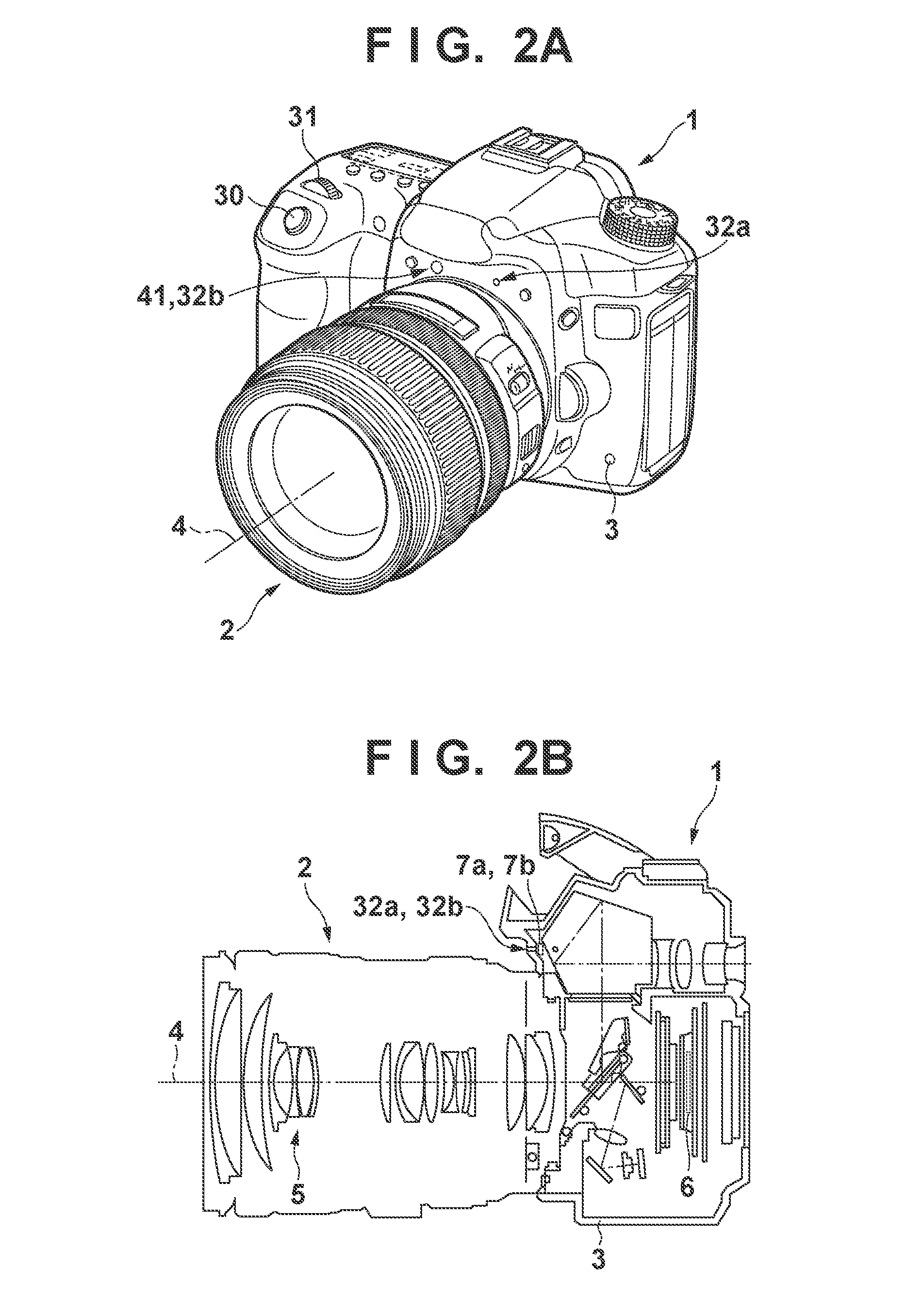
Image pick-up apparatus and image pick-up system
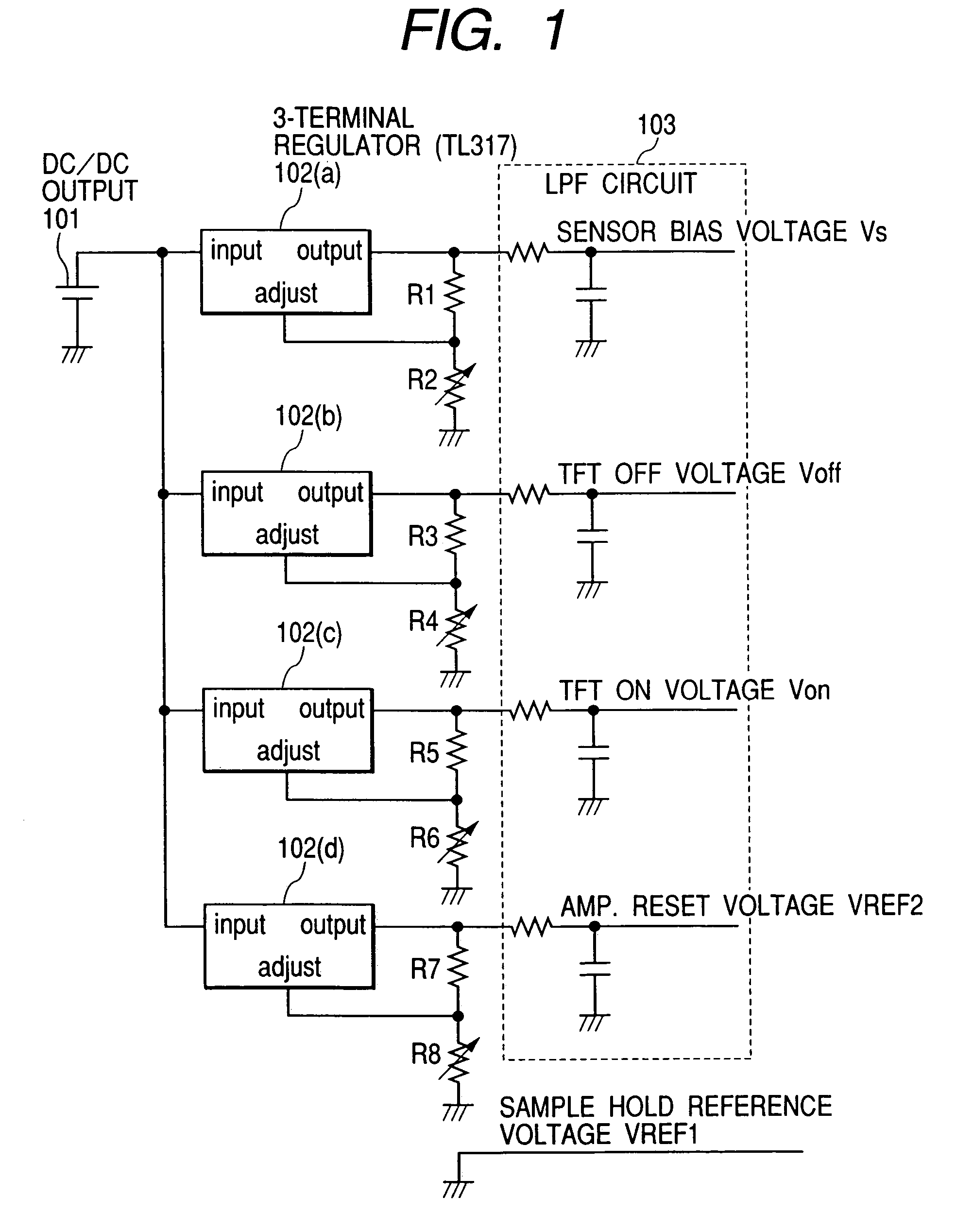
An image pick-up apparatus and an image pick-up system constructed to prevent occurrence of random noise in a photographed image due to a random noise component produced in a reference supply circuit. An image pick-up apparatus has an area sensor driven by matrix driving, and a reference supply circuit for supplying a reference voltage for driving of the area sensor, and the reference voltage is supplied through a low-pass filter (LPF) coupled to the reference supply circuit. Further, a cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter preferably is determined so that an effective value of noise of the reference voltage having passed through the low-pass filter becomes not more than one-tenth of an effective value of random noise produced in pixels of the area sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
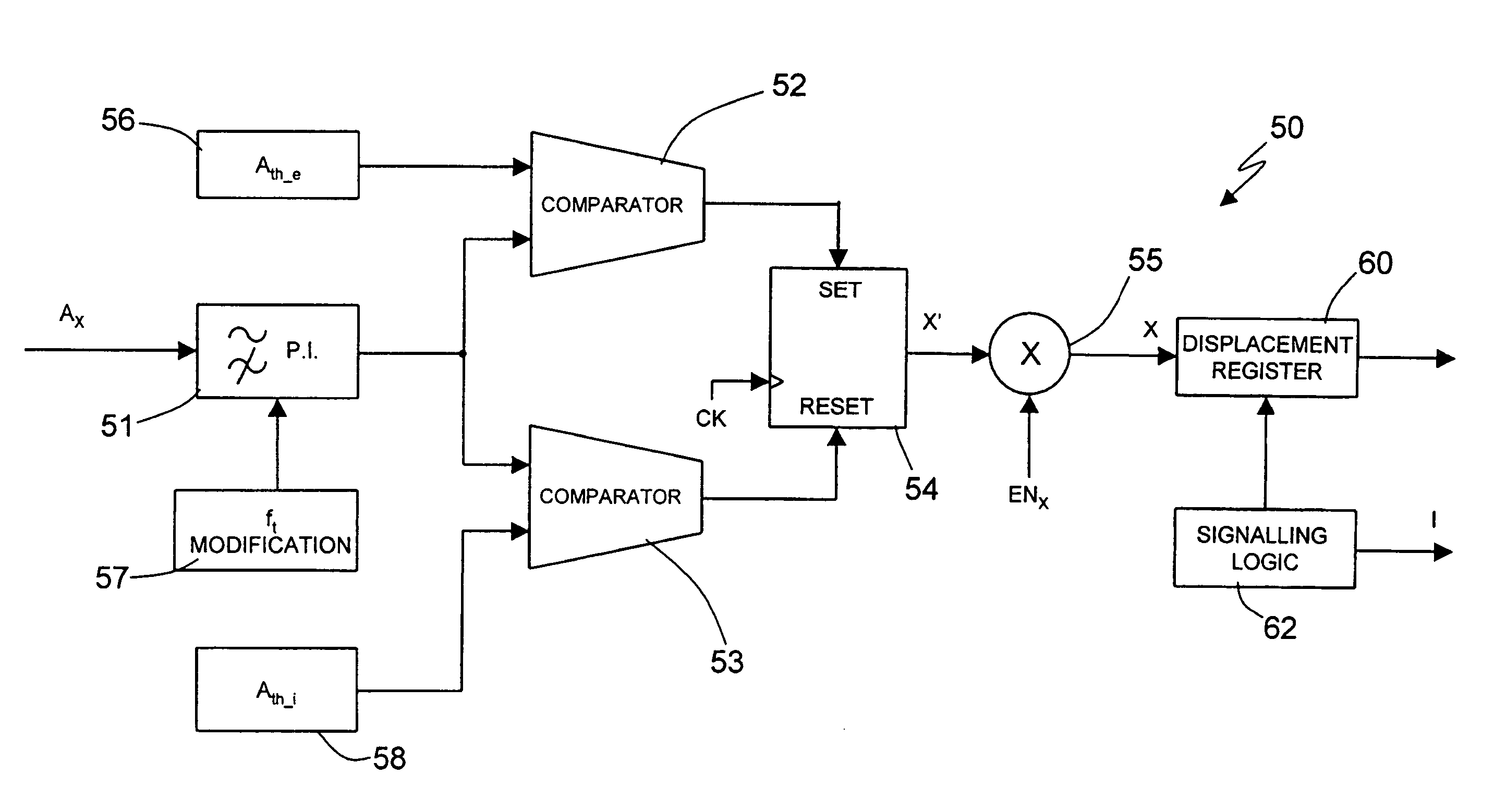
Displacement detection device for a portable apparatus
ActiveUS7672806B2Overcomes drawbackAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDigital computer detailsClassical mechanicsBand-pass filter
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
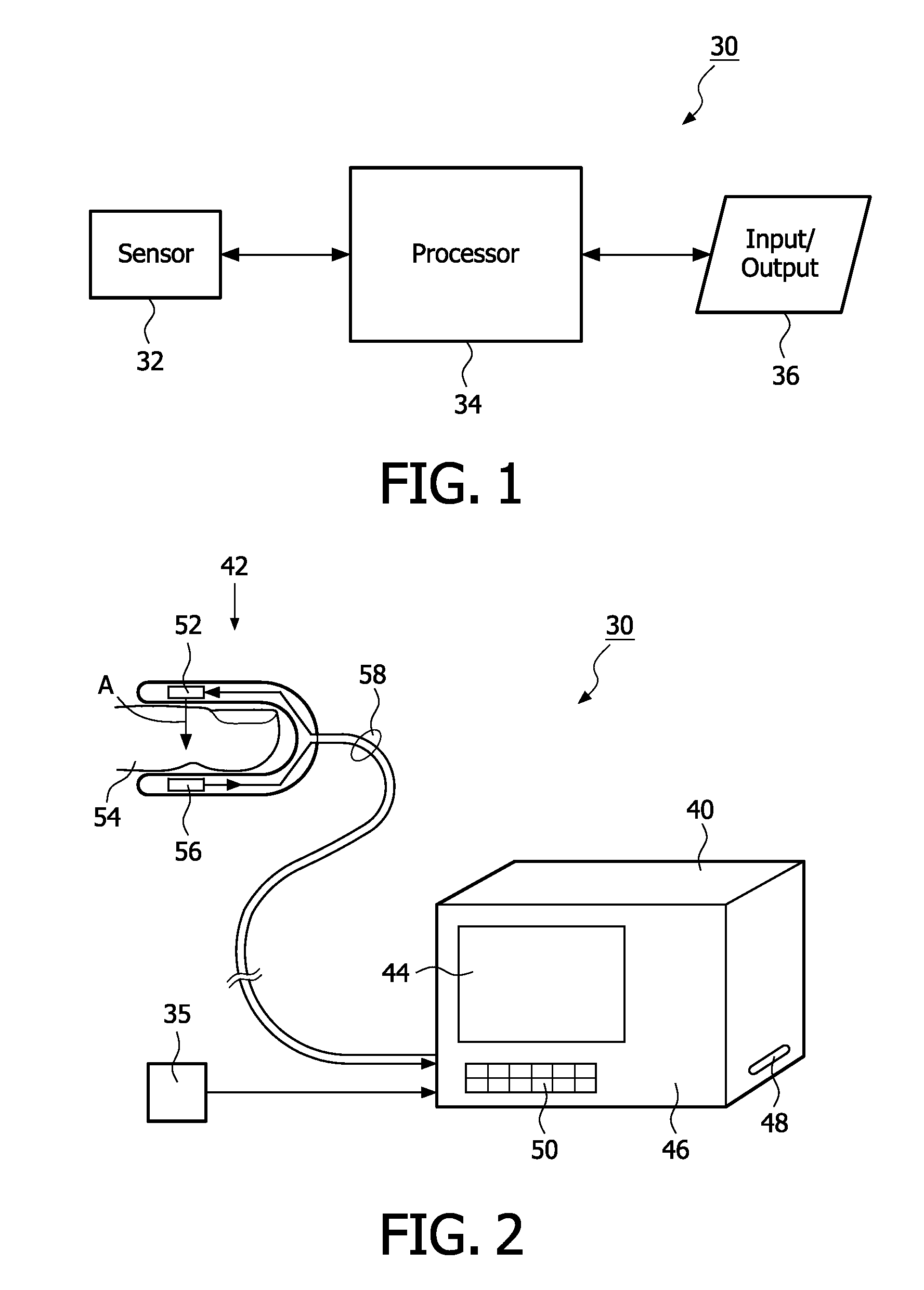
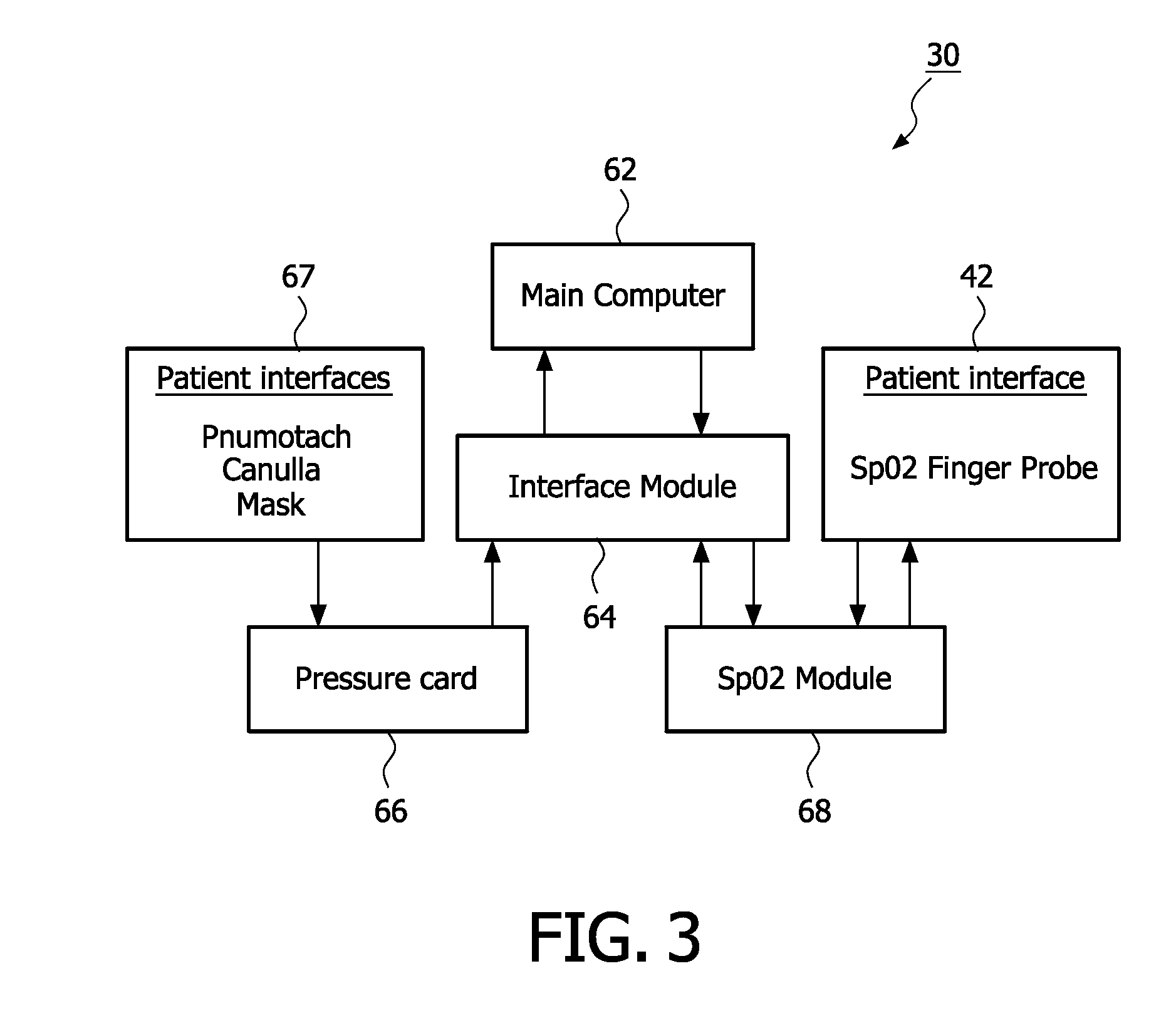
Apparatus and method for monitoring pressure related changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system
ActiveUS20100222655A1Overcome disadvantagesEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFrequency spectrumCardiac functioning
A method and apparatus for monitoring changes in the intra-thoracic pressure of a patient due to the patient's respiratory activity or volumetric changes in the extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system due to cardiac function based on the changes in pressure in the patient's extra-thoracic arterial circulatory system as measured by a plethysmography sensor, such as an photoplethysmograph. A frequency spectrum is generated for the plethysmograph signal and the frequencies of interest is isolated from the frequency spectrum by setting appropriate cutoff frequencies for the frequency spectrum. This isolated frequency is used to filter the plethysmograph signal to provide a signal indicative of the patient's respiratory activity or cardiac function.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
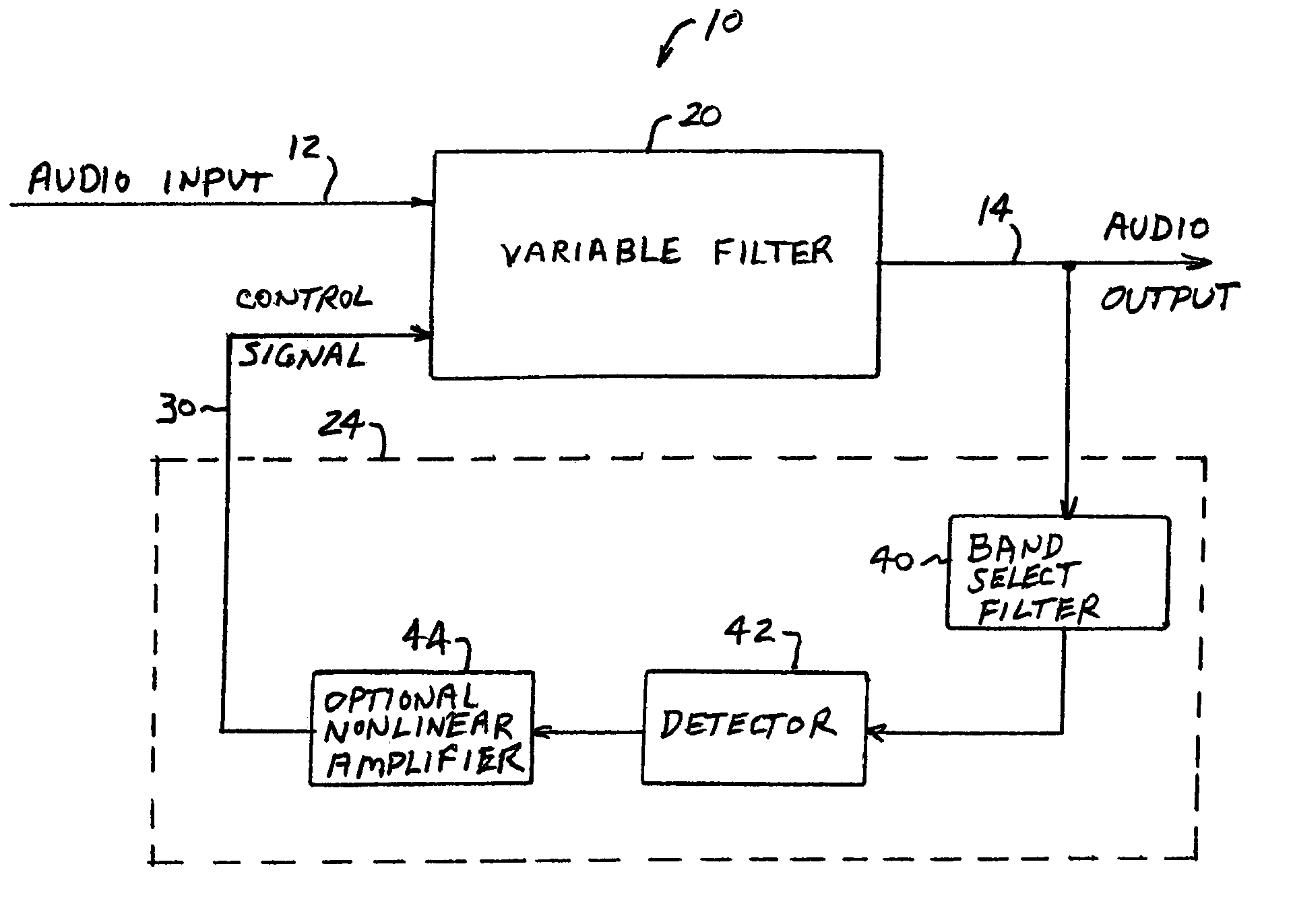
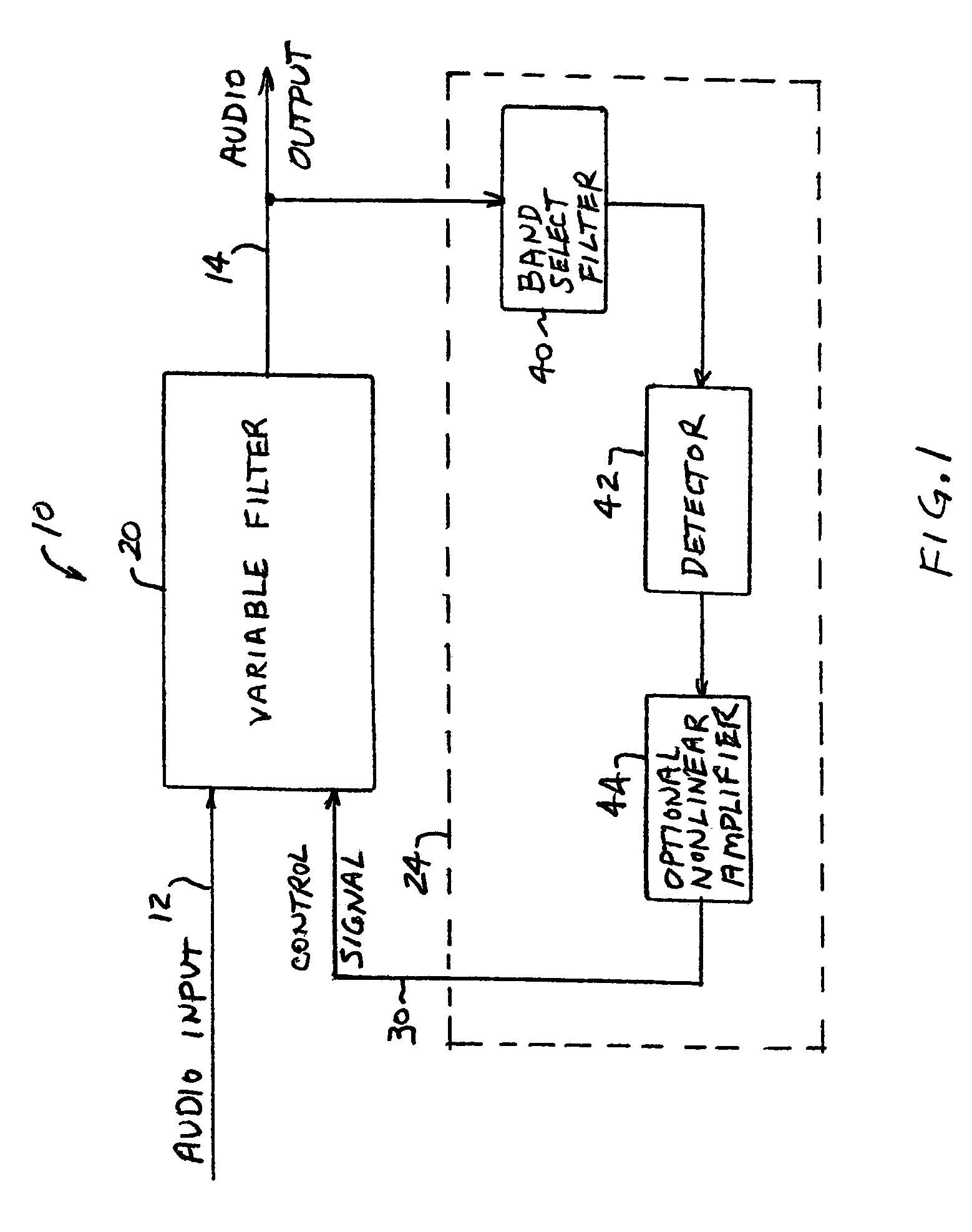
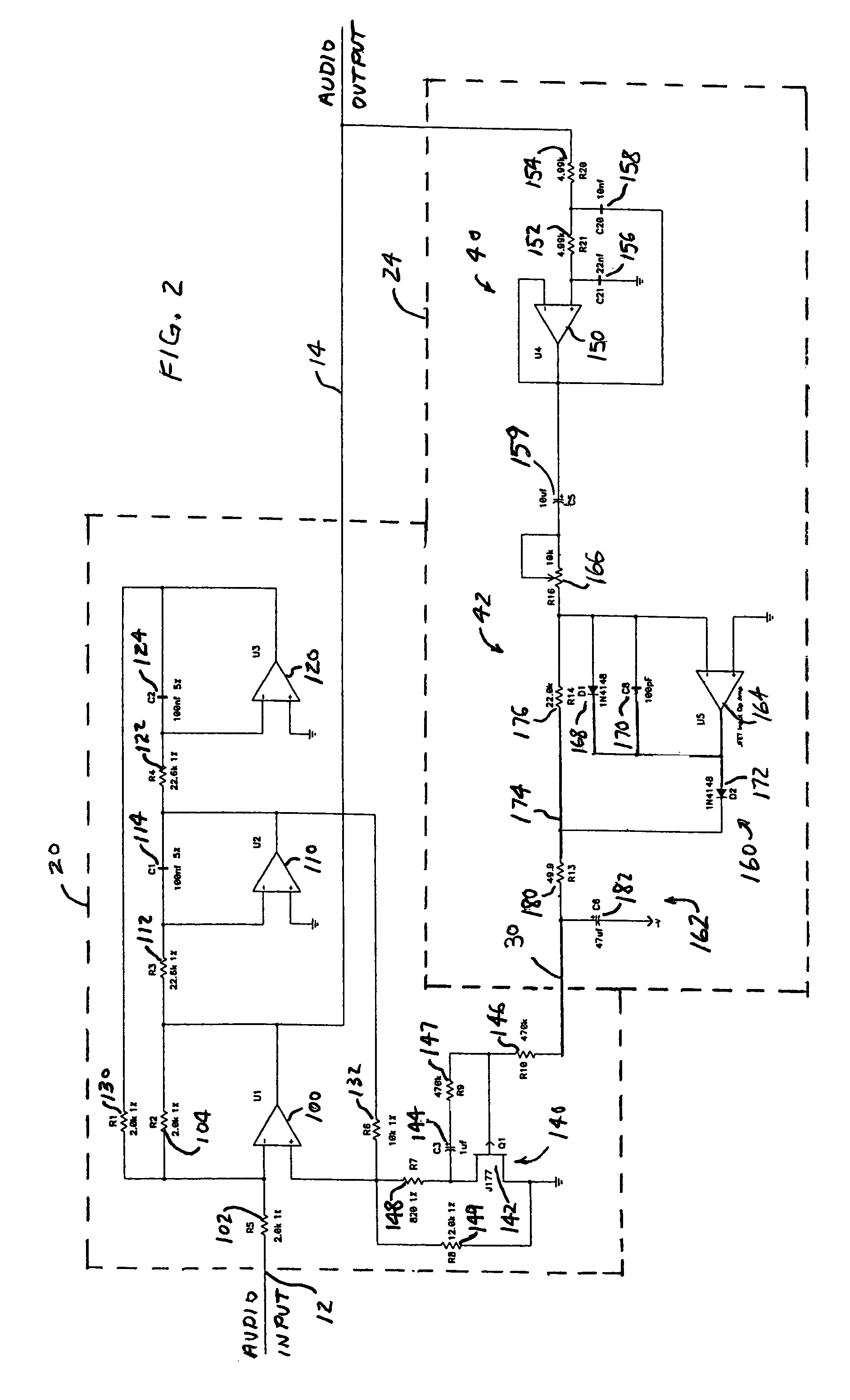
Dynamic bass boost apparatus and method
ActiveUS7171010B2Digital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsLow-pass filterControl signal
Audio processing methods and apparatus are provided for at least partially compensating for the Fletcher-Munson effect. An audio processor includes a variable filter receiving an input signal and providing a filtered output signal, the variable filter having a fixed cutoff frequency and a quality factor that is controllable in response to a control signal, and a control circuit configured to detect a signal level representative of input signal level in a selected band and to generate the control signal in response to the detected signal level. The control circuit may include a low-pass band select filter and a detector for detecting a signal level in the band selected by the low-pass filter and for generating the control signal.
Owner:BOSTON ACOUSTICS INC
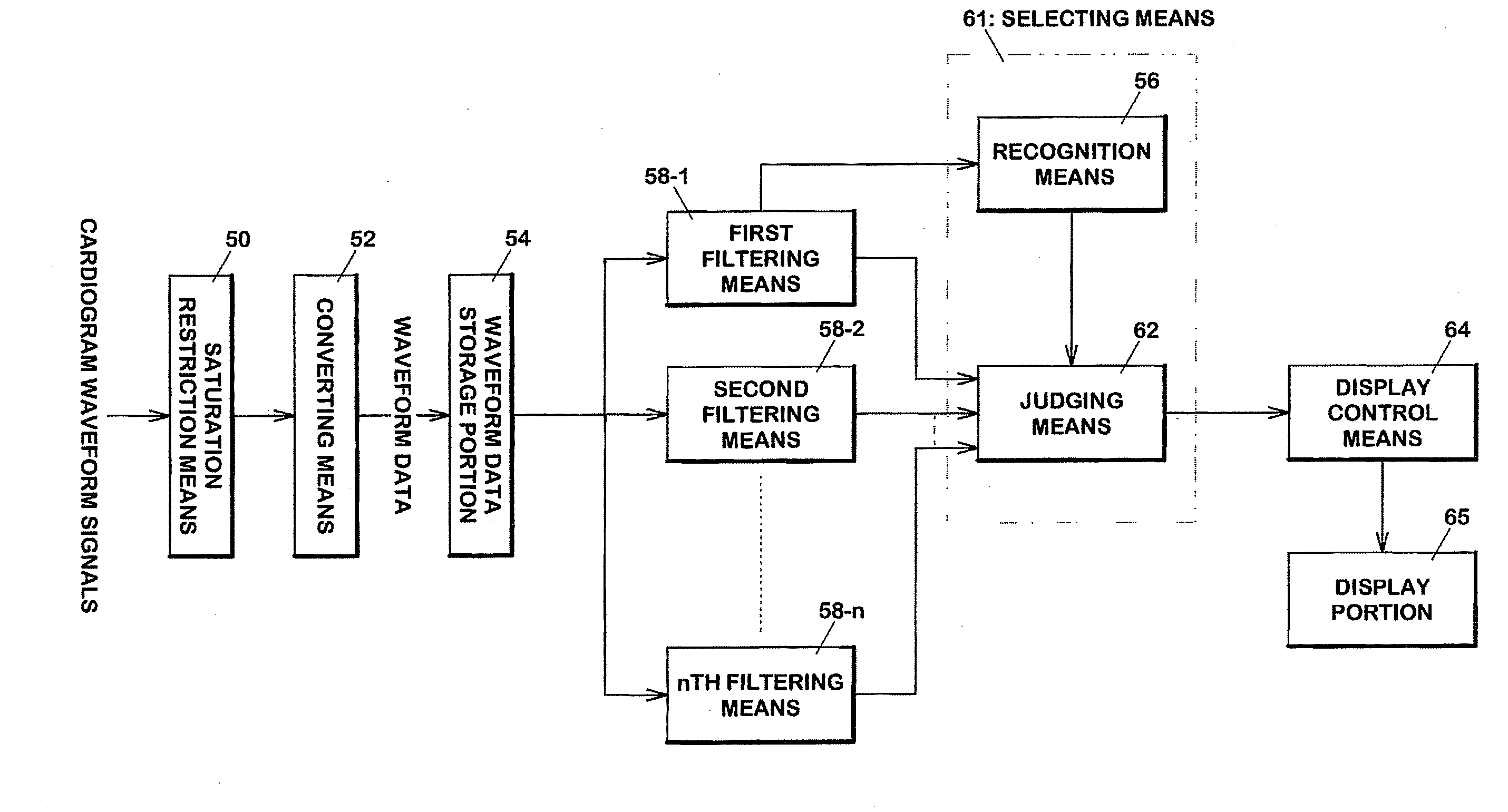
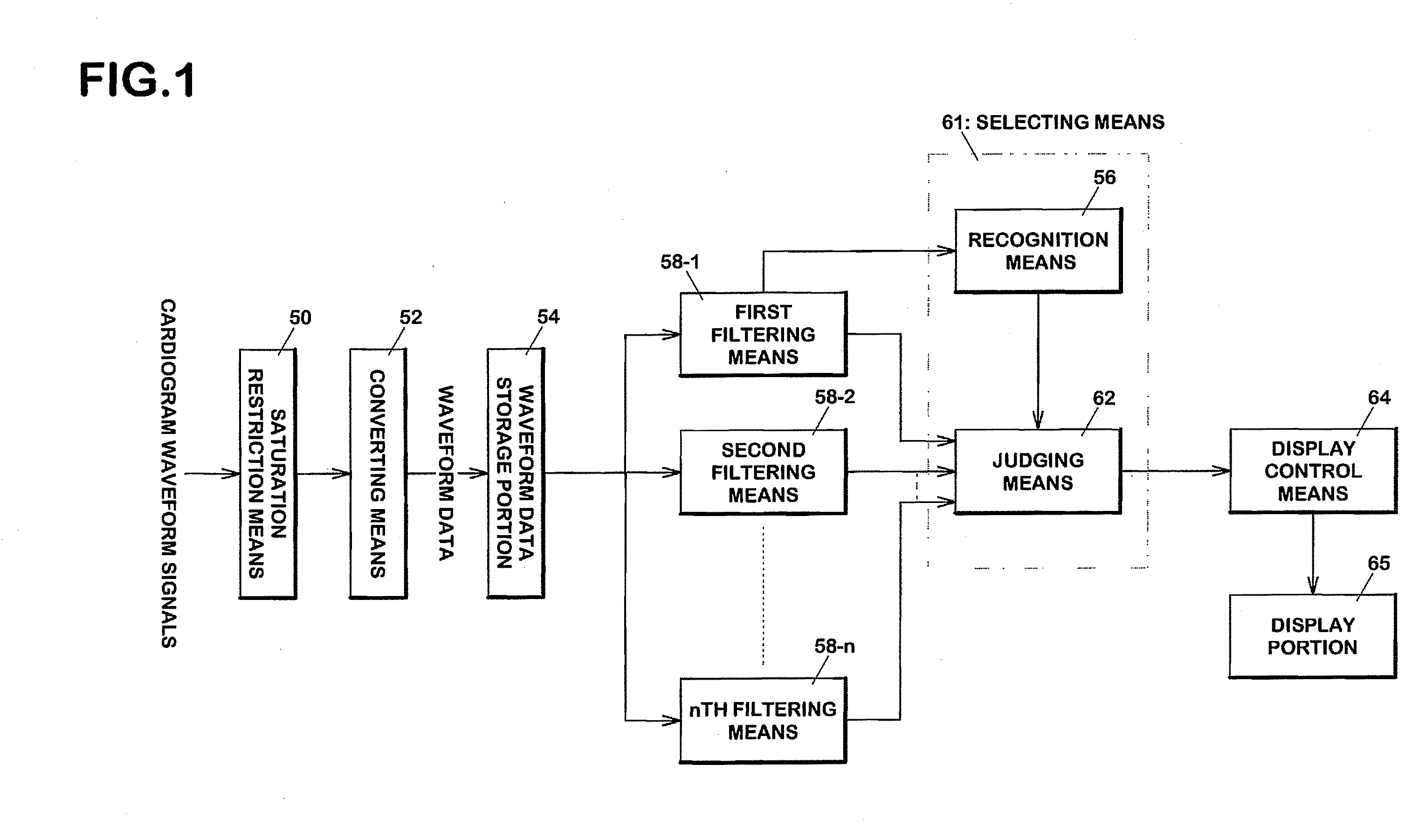
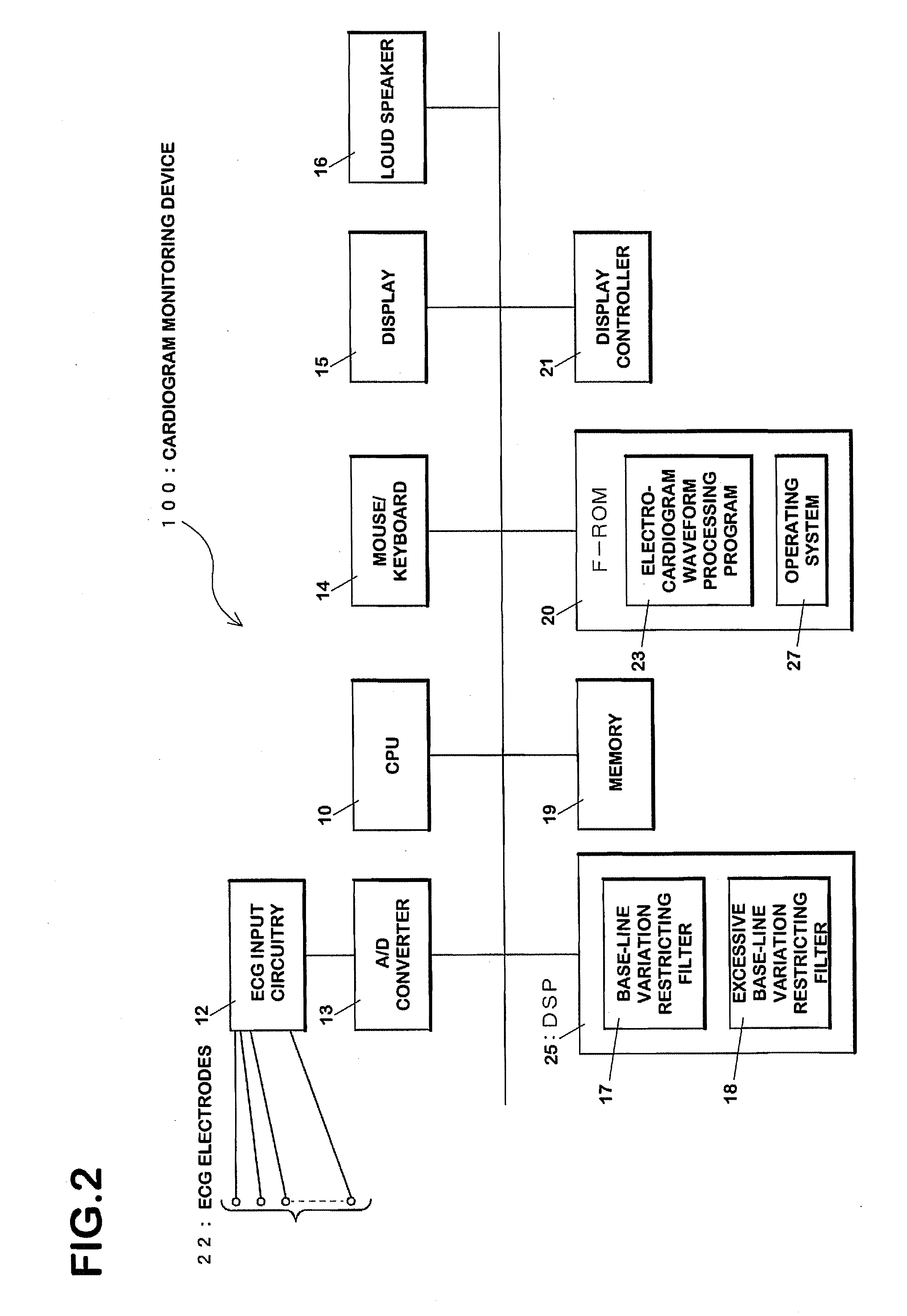
Electrocardiogram Waveform Correction Display and Electrocardiogram Waveform Correction Display Method
The present invention provides a cardiogram waveform correcting and displaying device capable of facilitating visibility of cardiogram waveforms. A first filtering means 58-1 through n th filtering means 58-n are low-cut filters, each having a first cutoff frequency fc1 through an n th cutoff frequency fcn respectively. Recognition means 56 recognizes feature values of waveforms related to variation of the waveforms in accordance with any outputs of the first filtering means 58-1 through the n th filtering means 58-n. Judging means 62 selects which of the first through the n th filter is used based on the recognized feature values with the recognition means 56. A filter which restricts base-line variation is used when the base-line variation is large, and a filter having less influence to waveforms is used when the base-line variation is small. Display control means 64 displays on a display portion 65 output of the selected filter.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
System for transferring energy wirelessly
ActiveUS8536738B2Near-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectromagnetic field
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
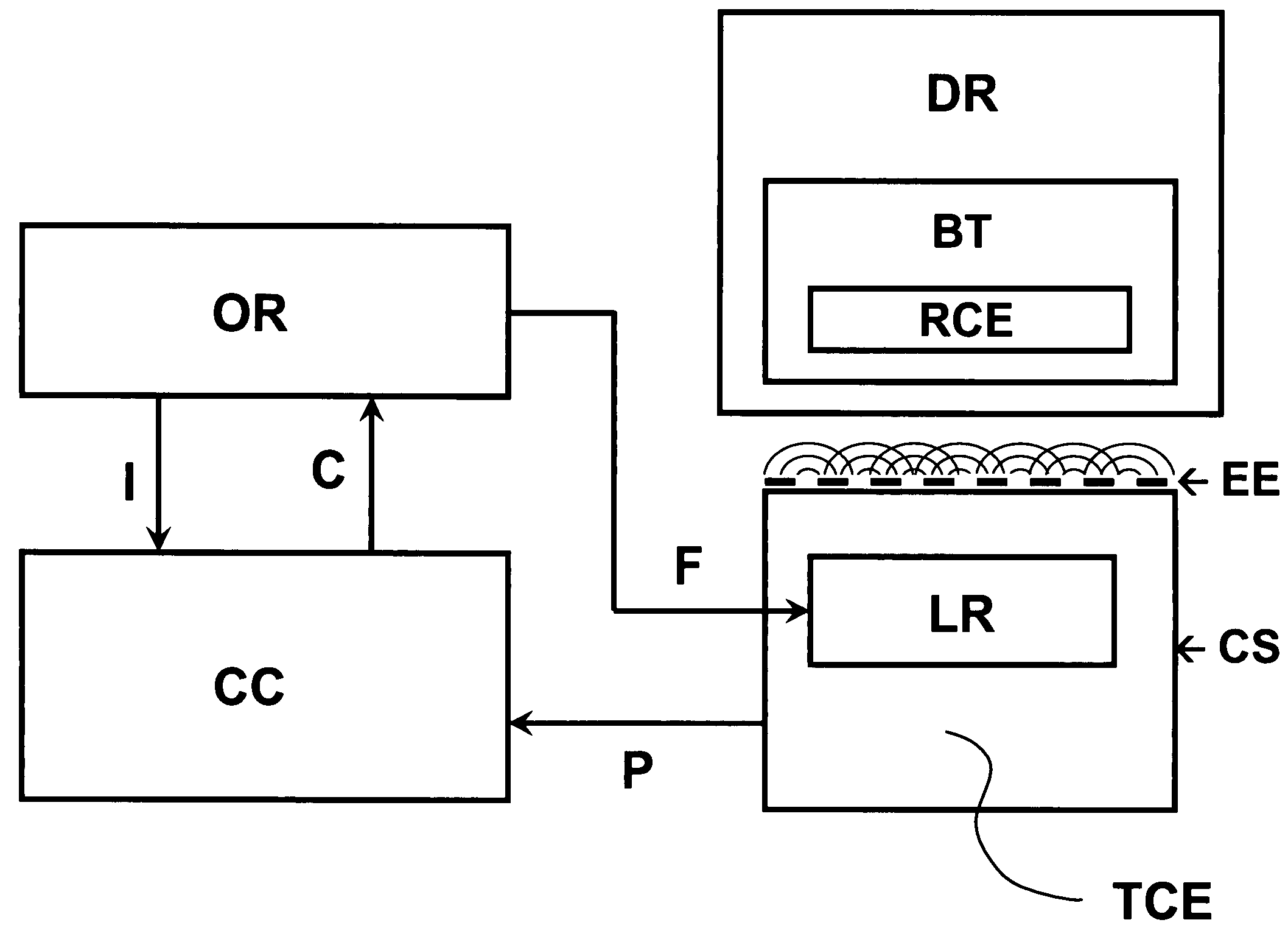
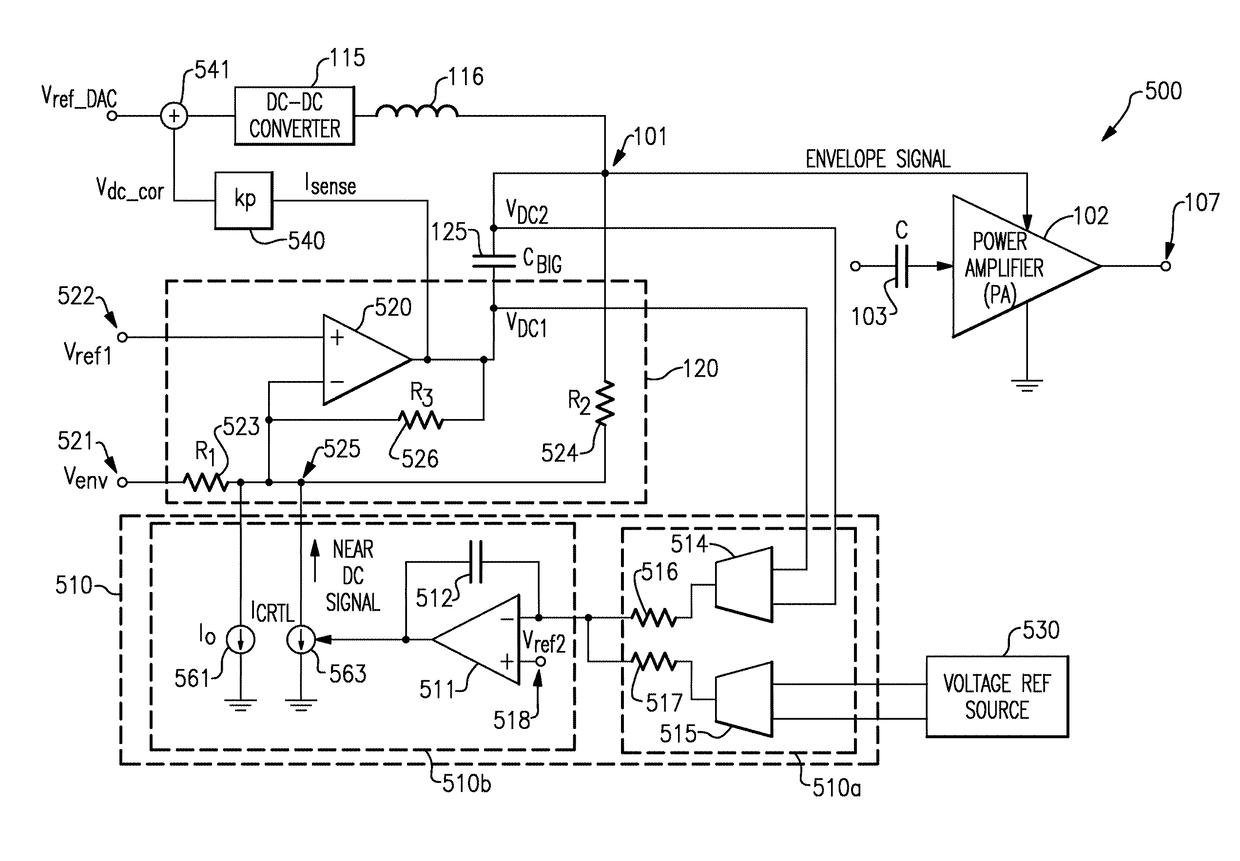
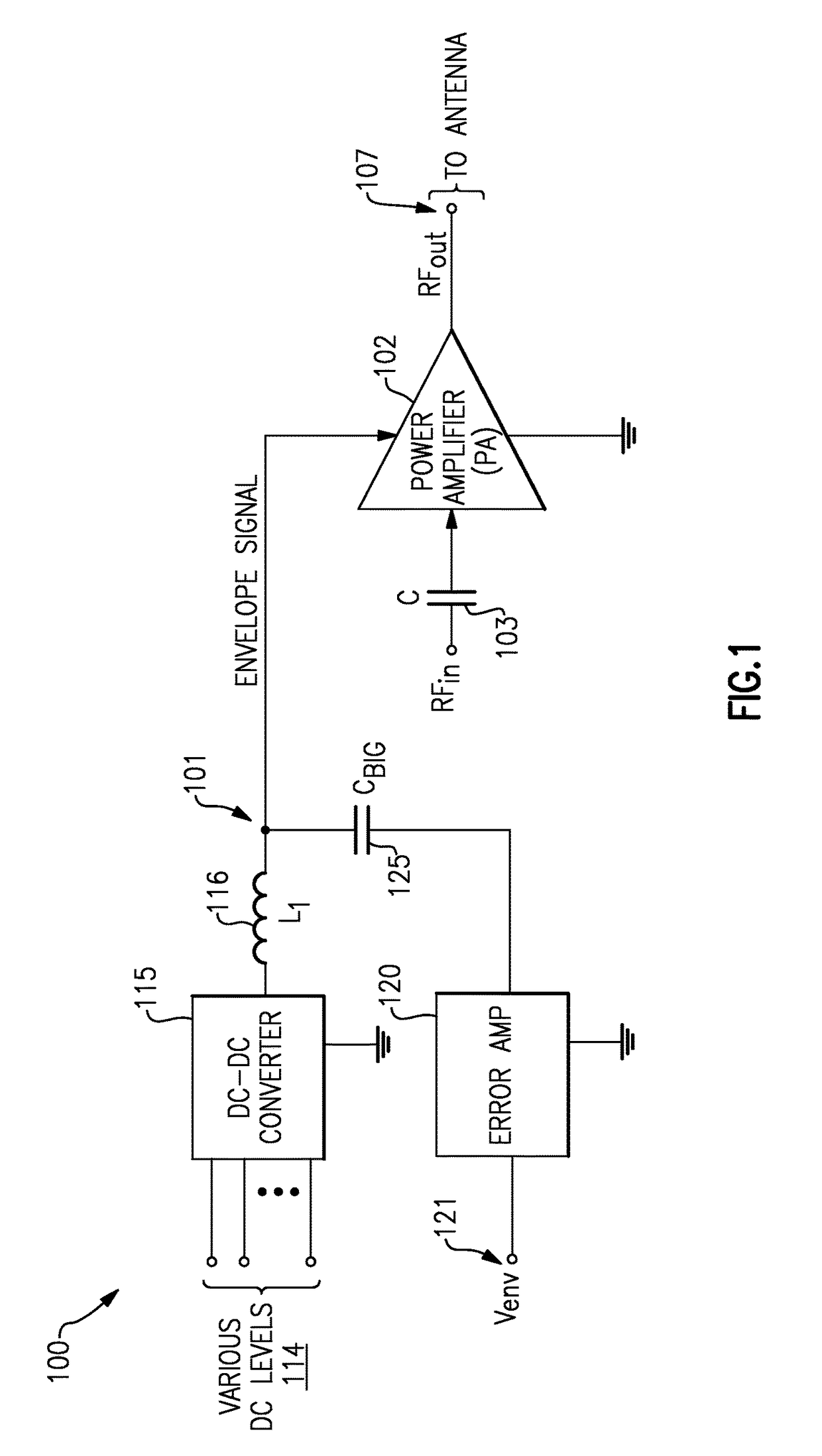
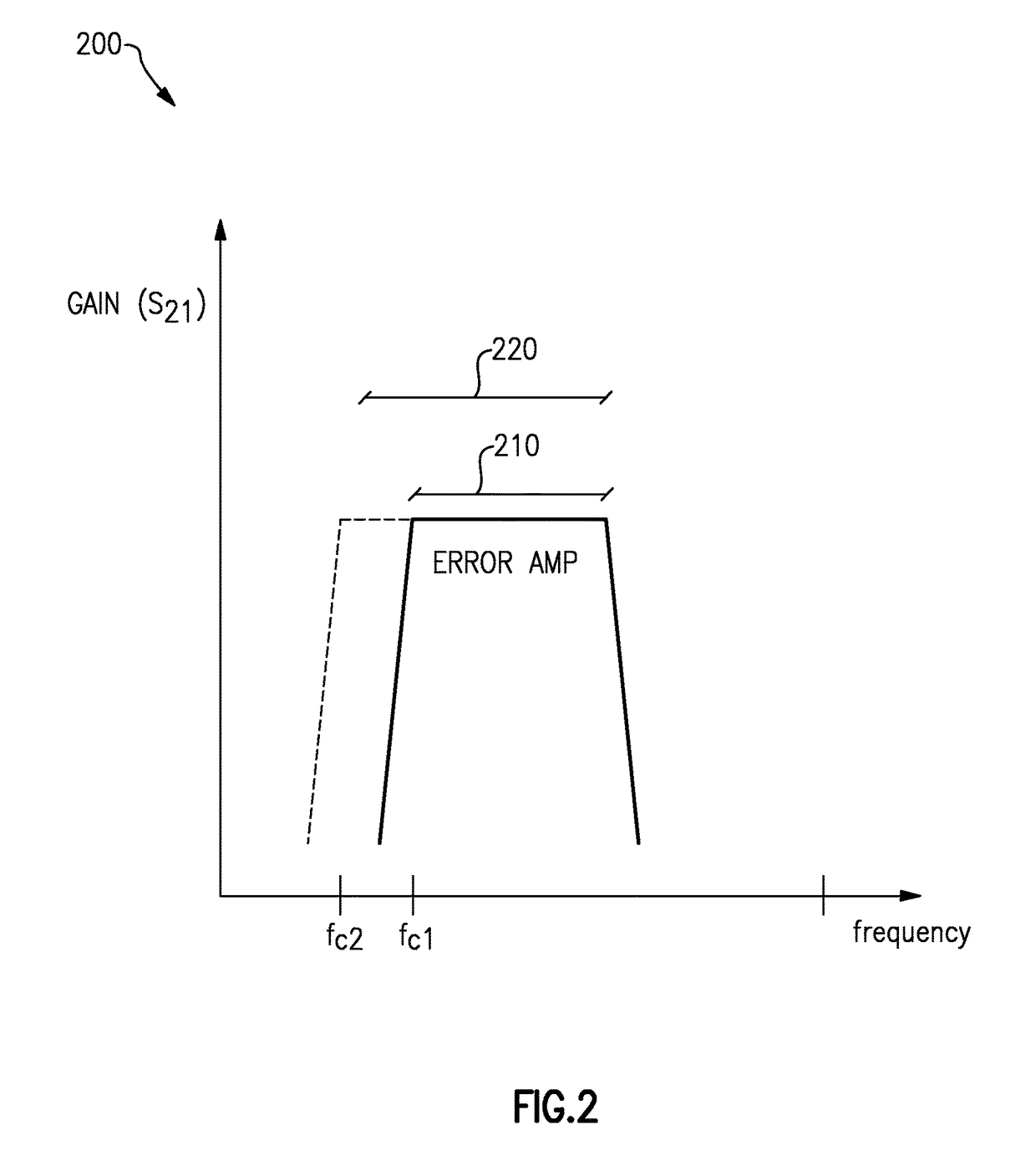
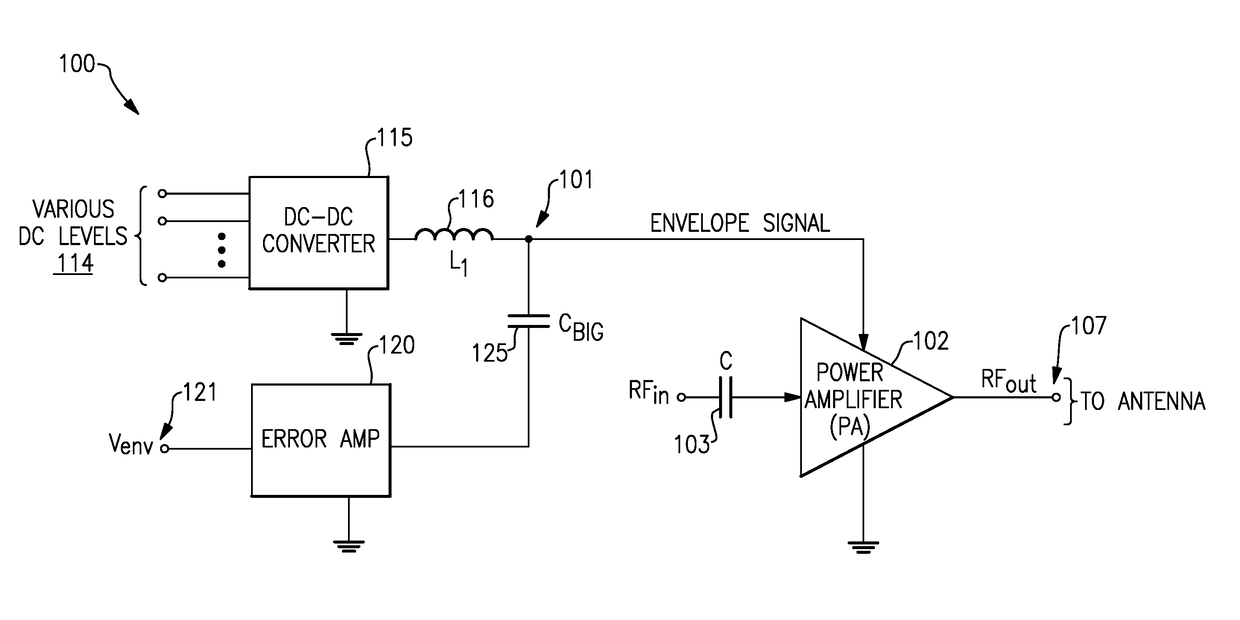
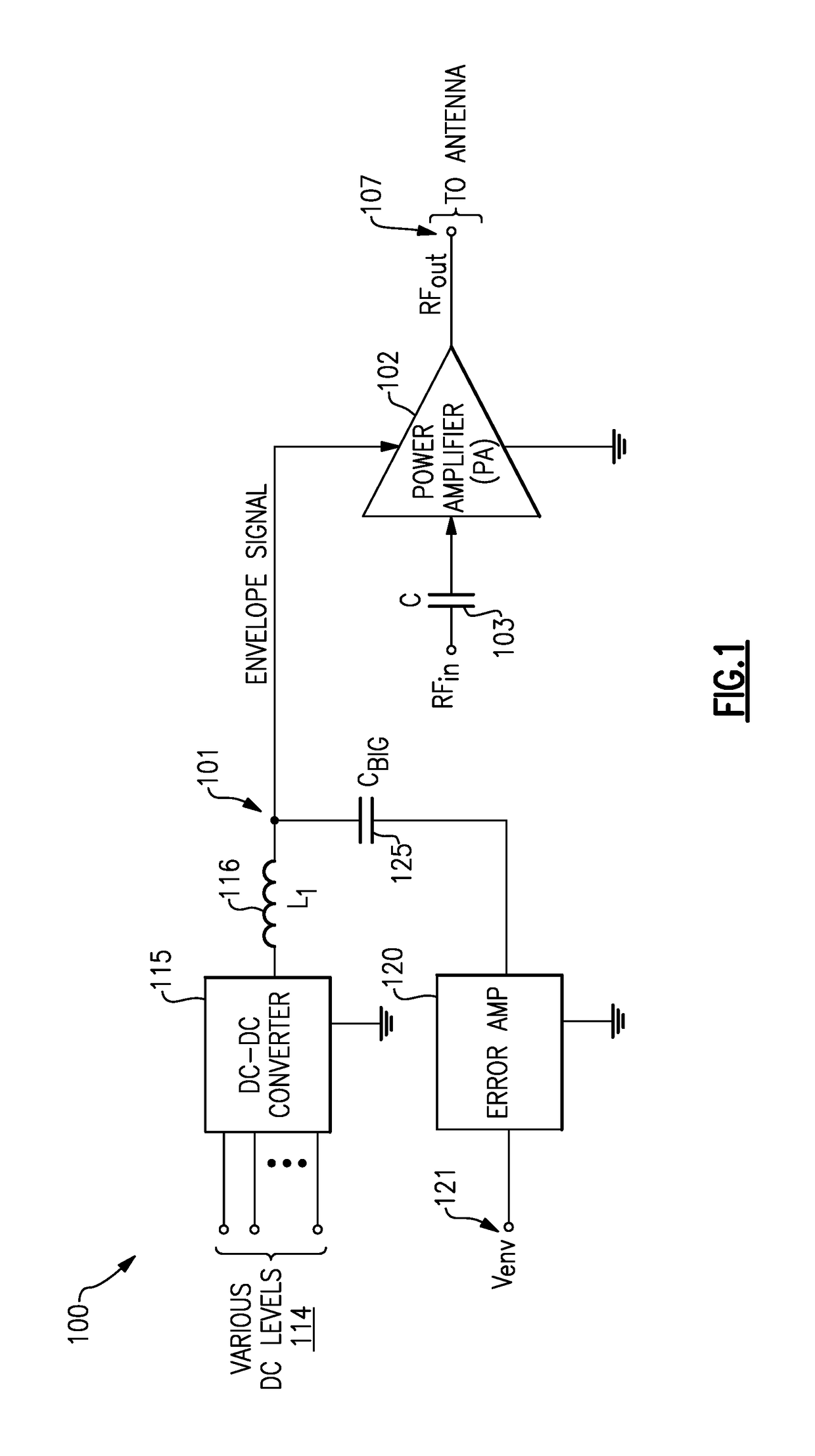
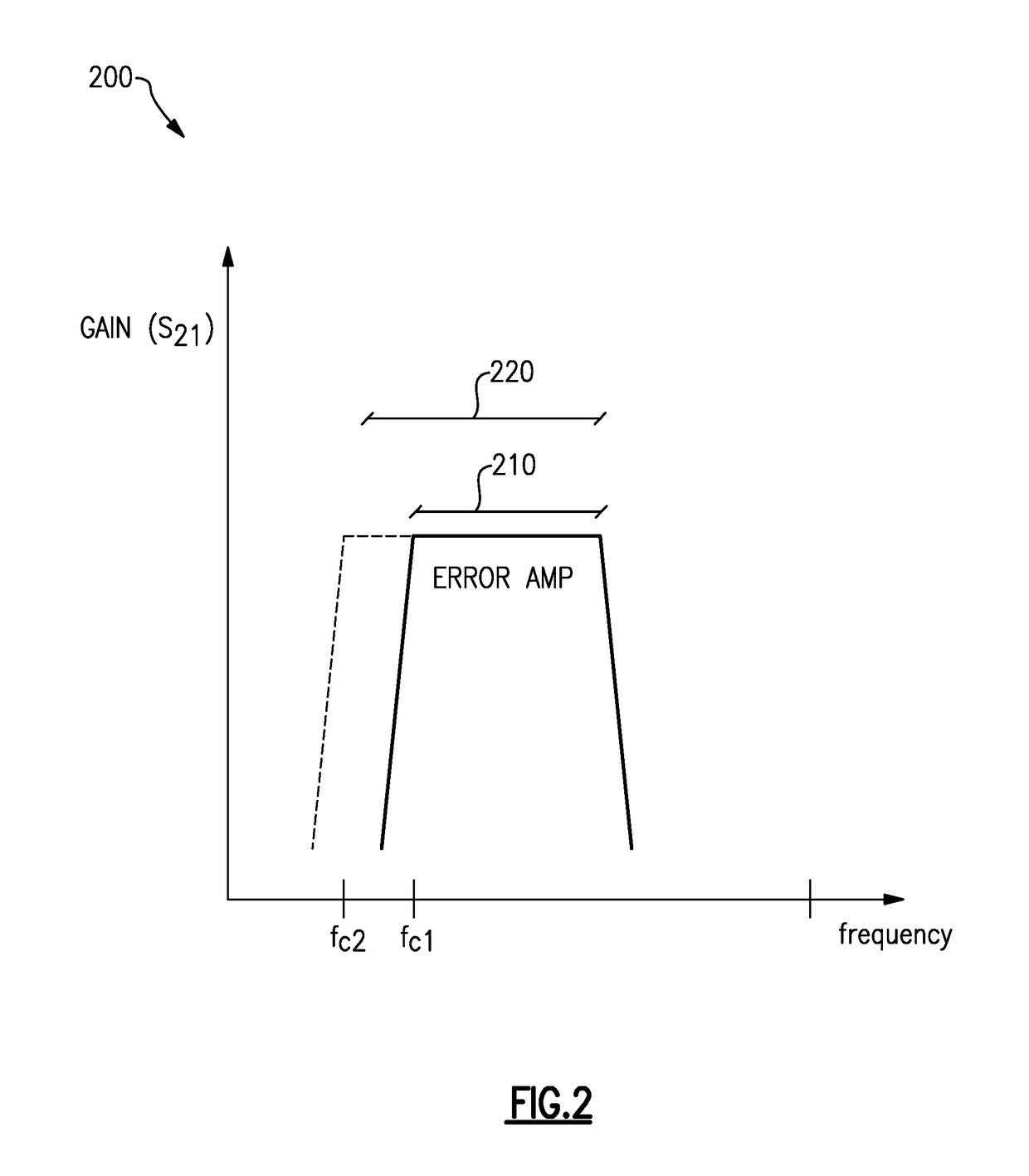
Envelope tracking with low frequency loss correction
ActiveUS9831834B2Improve power efficiencyGated amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
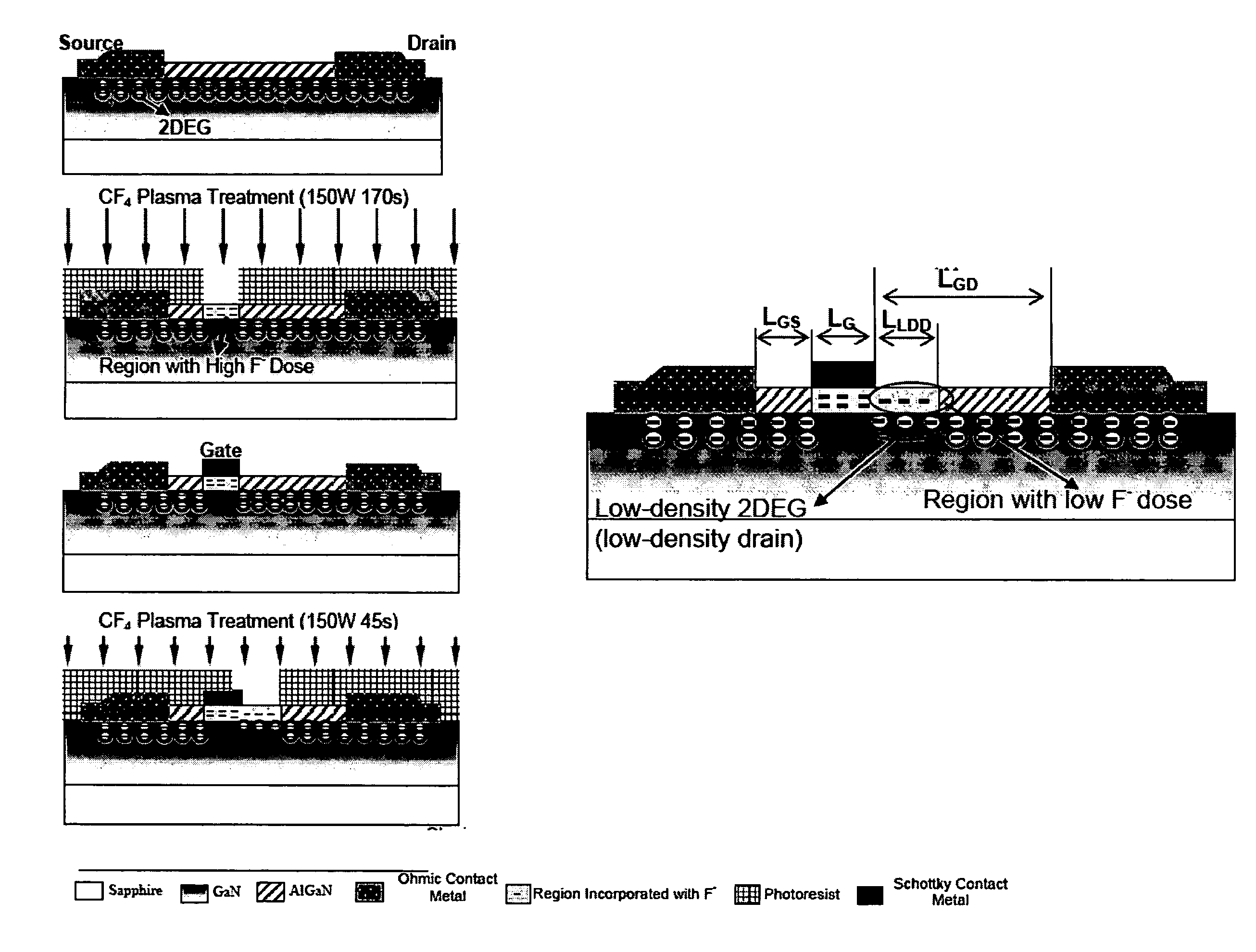
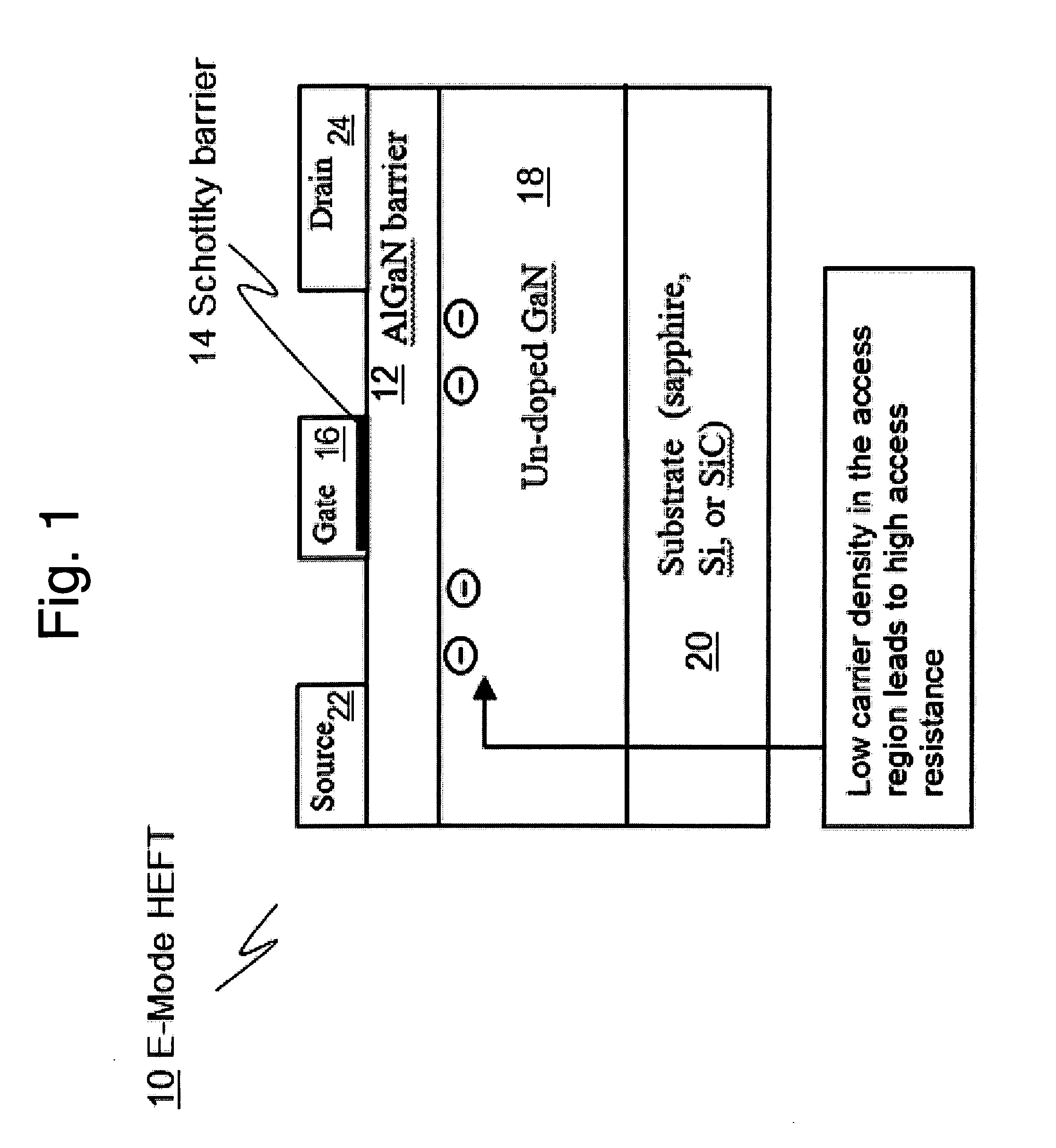
Low Density Drain HEMTs
ActiveUS20070295993A1Simple circuit configurationFavorable operating condition for device safetySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIon implantationBreakdown voltage
Methods and devices for fabricating AlGaN / GaN normally-off high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs). A fluorine-based (electronegative ions-based) plasma treatment or low-energy ion implantation is used to modify the drain-side surface field distribution without the use of a field plate electrode. The off-state breakdown voltage can be improved and current collapse can be completely suppressed in LDD-HEMTs with no significant degradation in gains and cutoff frequencies.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
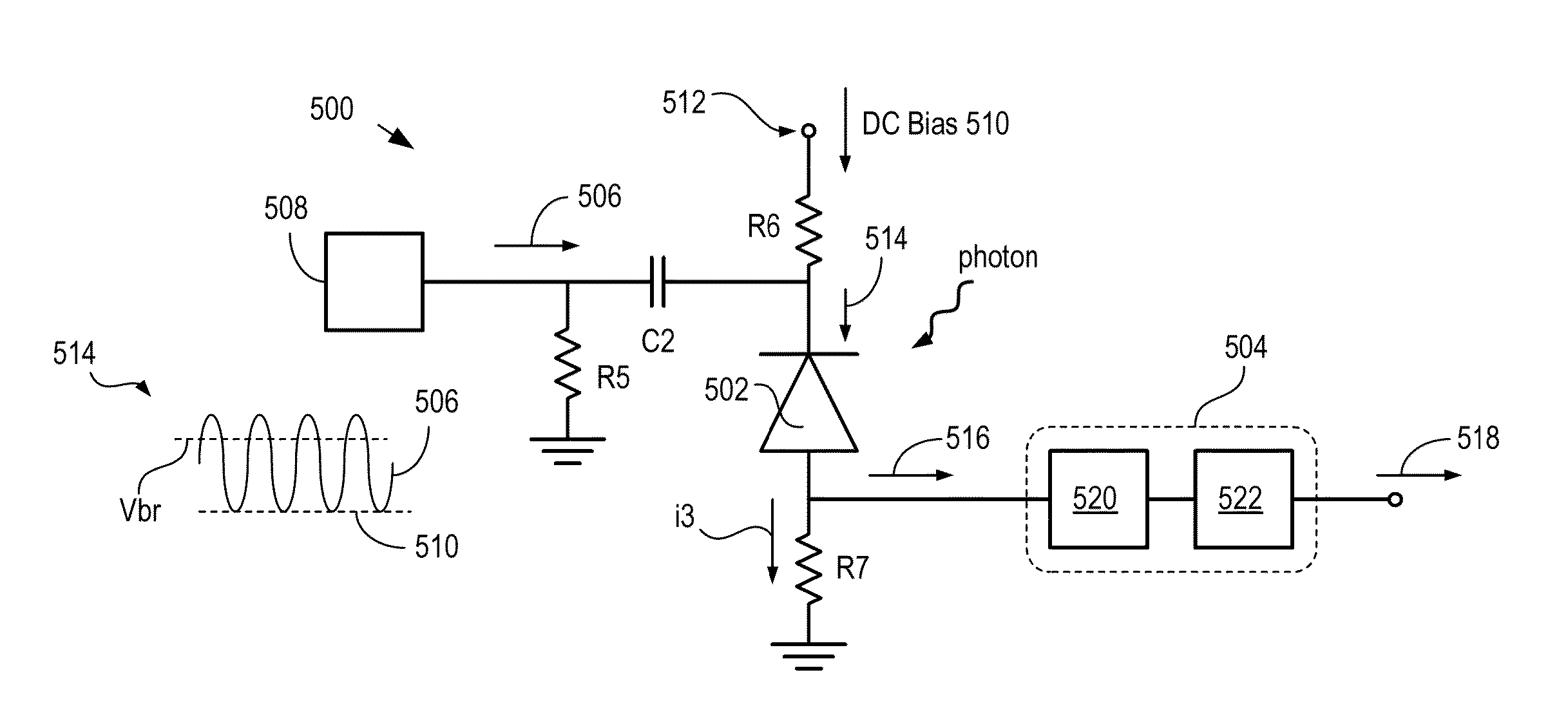
High-repetition-rate single-photon receiver and method therefor
ActiveUS8796605B2Material analysis by optical meansElectronic switchingSignal qualityLow-pass filter
A single-photon receiver and method for detecting a single-photon are presented. The receiver comprises a SPAD that receives a gating signal having a fundamental frequency in the 100 MHz to multiple GHz range. The receiver further comprises a two-stage frequency filter for filtering the output of the SPAD, wherein the filter has: (1) a notch filter response at the fundamental frequency; and (2) a low-pass filter response whose cutoff frequency is less than the first harmonic of the fundamental frequency. As a result, the frequency filter removes substantially all the frequency components in the SPAD output without significant degradation of the signal quality but with reduced complexity, cost, and footprint requirement relative to receivers in the prior art.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
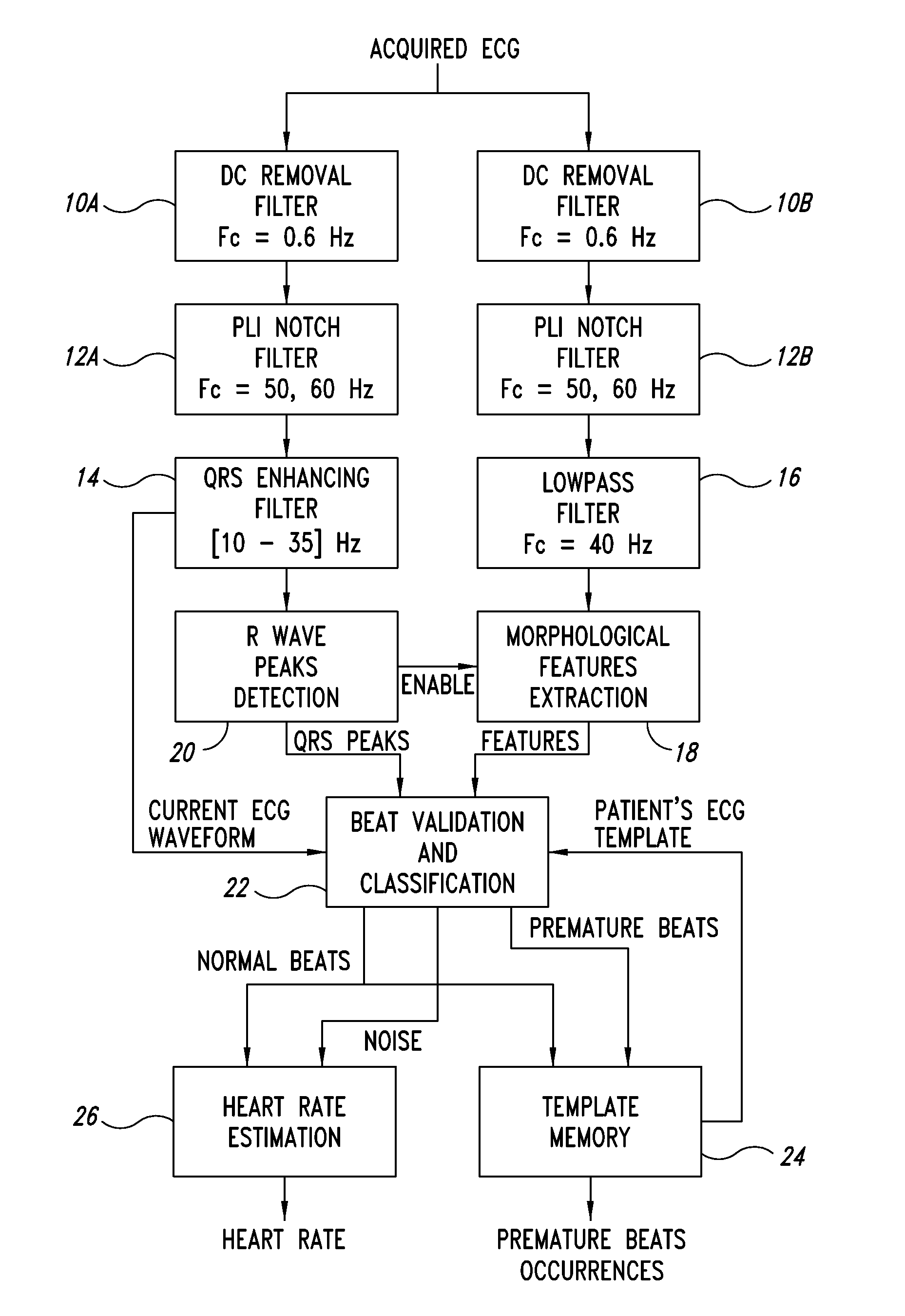
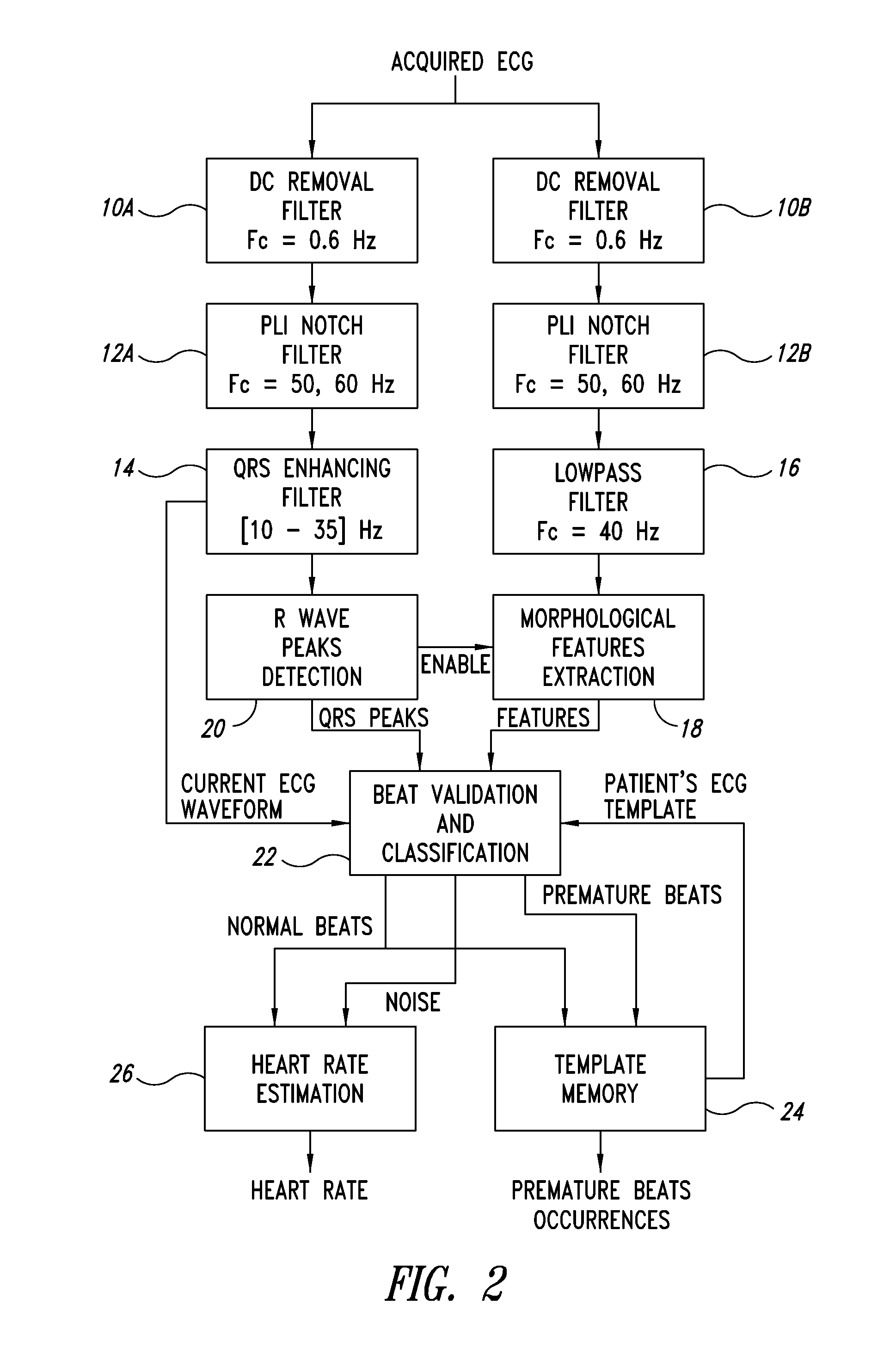
Method and device for estimating morphological features of heart beats
ActiveUS20110184297A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioDetect arrhythmiaElectrocardiographySensorsBandpass filteringEcg signal
A method estimates morphological features of heart beats from an ECG signal. Peaks of the R wave of the ECG are detected and classified using a parallel filtering structure. The first branch implements a bandpass filtering with cut off frequencies of about 10 Hz and 35 Hz, enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the QRS complex. The second branch estimates morphological features of the heart beat from an alternating current (AC) replica of the ECG signal, that may be used to classify the beat and potentially detect arrhythmias.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
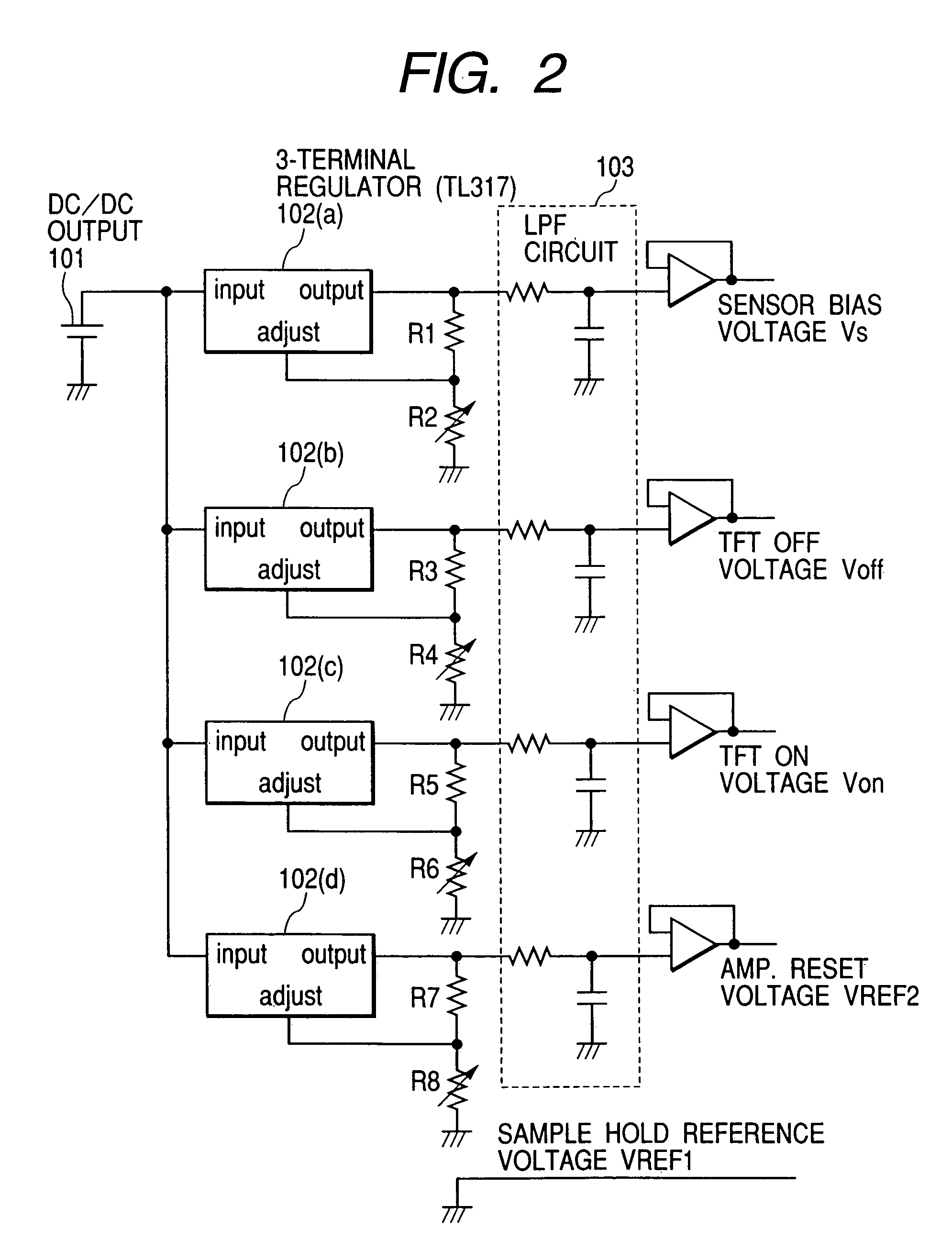
Image pick-up apparatus and image pick-up system
An image pick-up apparatus and an image pick-up system constructed to prevent occurrence of random noise in a photographed image due to a random noise component produced in a reference supply circuit. An image pick-up apparatus has an area sensor driven by matrix driving, and a reference supply circuit for supplying a reference voltage for driving of the area sensor, and the reference voltage is supplied through a low-pass filter (LPF) coupled to the reference supply circuit. Further, a cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter is preferably determined so that an effective value of noise of the reference voltage having passed through the low-pass filter becomes not more than one-tenth of an effective value of random noise produced in pixels of the area sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
Low conversion rate digital dispersion compensation
ActiveUS20090201796A1Eliminate the effects ofIncrease speedModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexPhase distortionLow-pass filter
A method of suppressing effects of aliasing in a system for digitally processing a high speed signal having a symbol rate of 1 / T. The high speed signal is sampled at a fractional multiple (N) of the symbol rate, wherein 1<N<2, to generate a corresponding sample stream, and filtered using a low-pass filter characteristic having a cut-off frequency corresponding to 1 / 2T. Phase distortions due to the filtering are compensated by digitally processing the sample stream.
Owner:CIENA
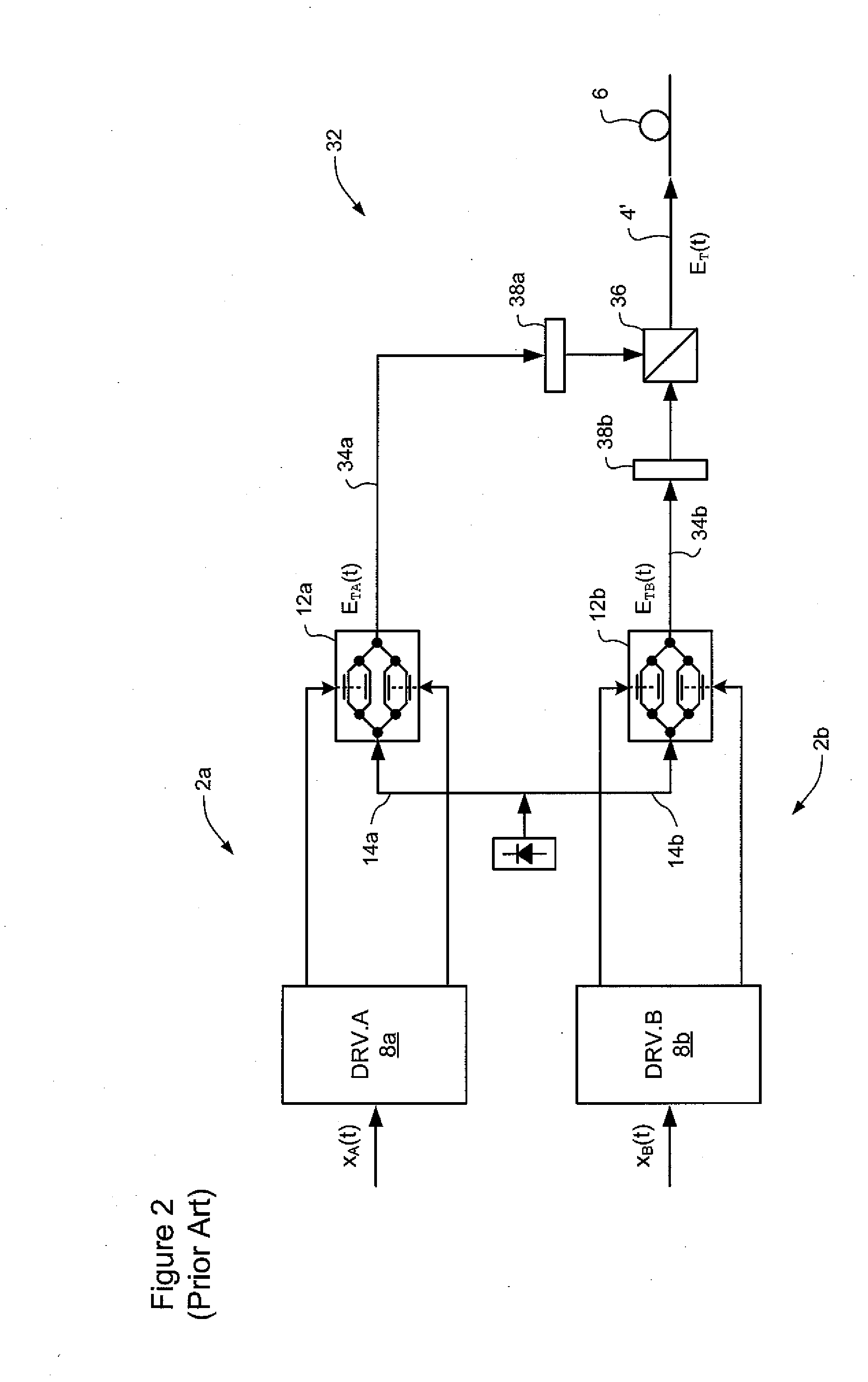
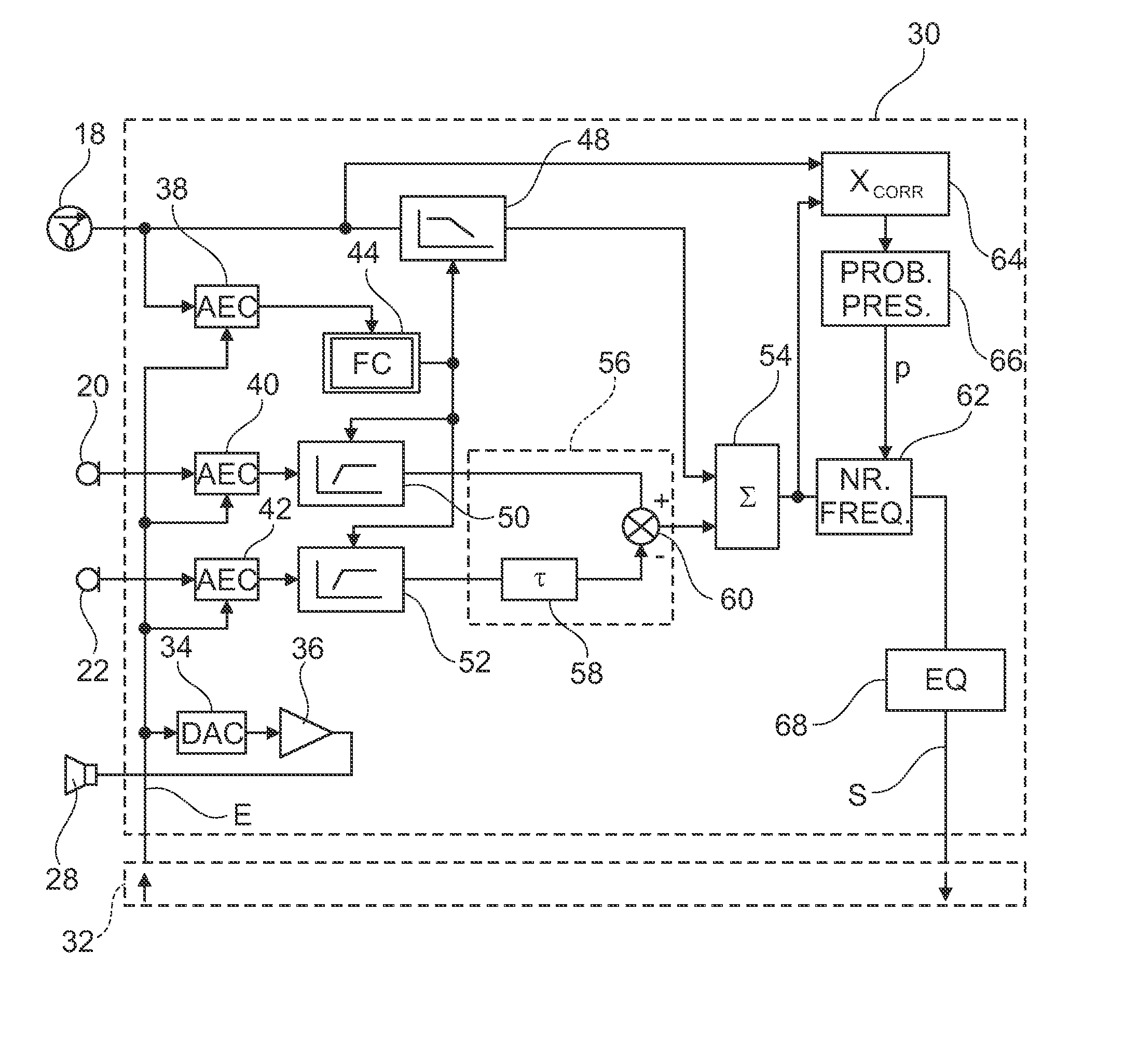
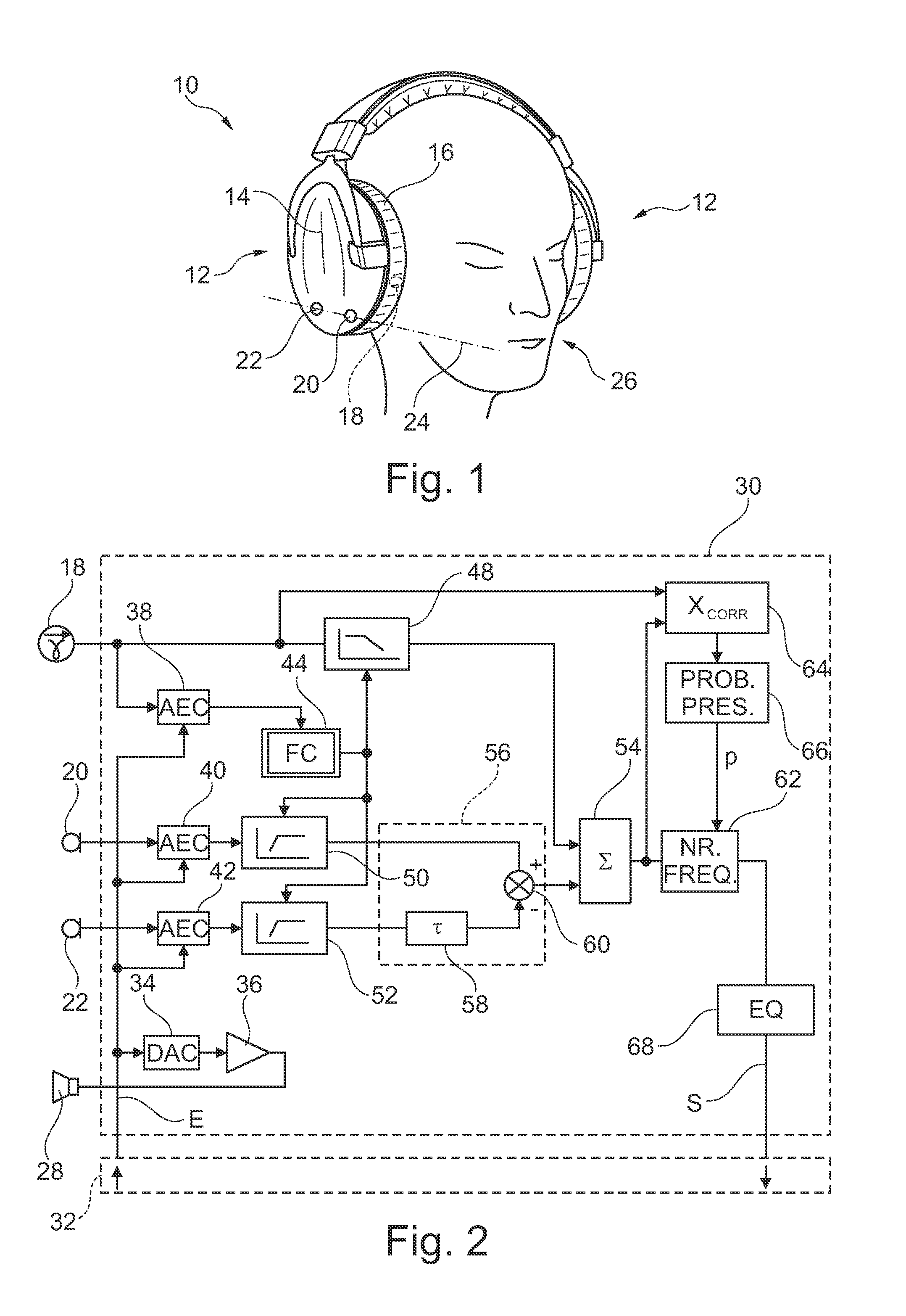
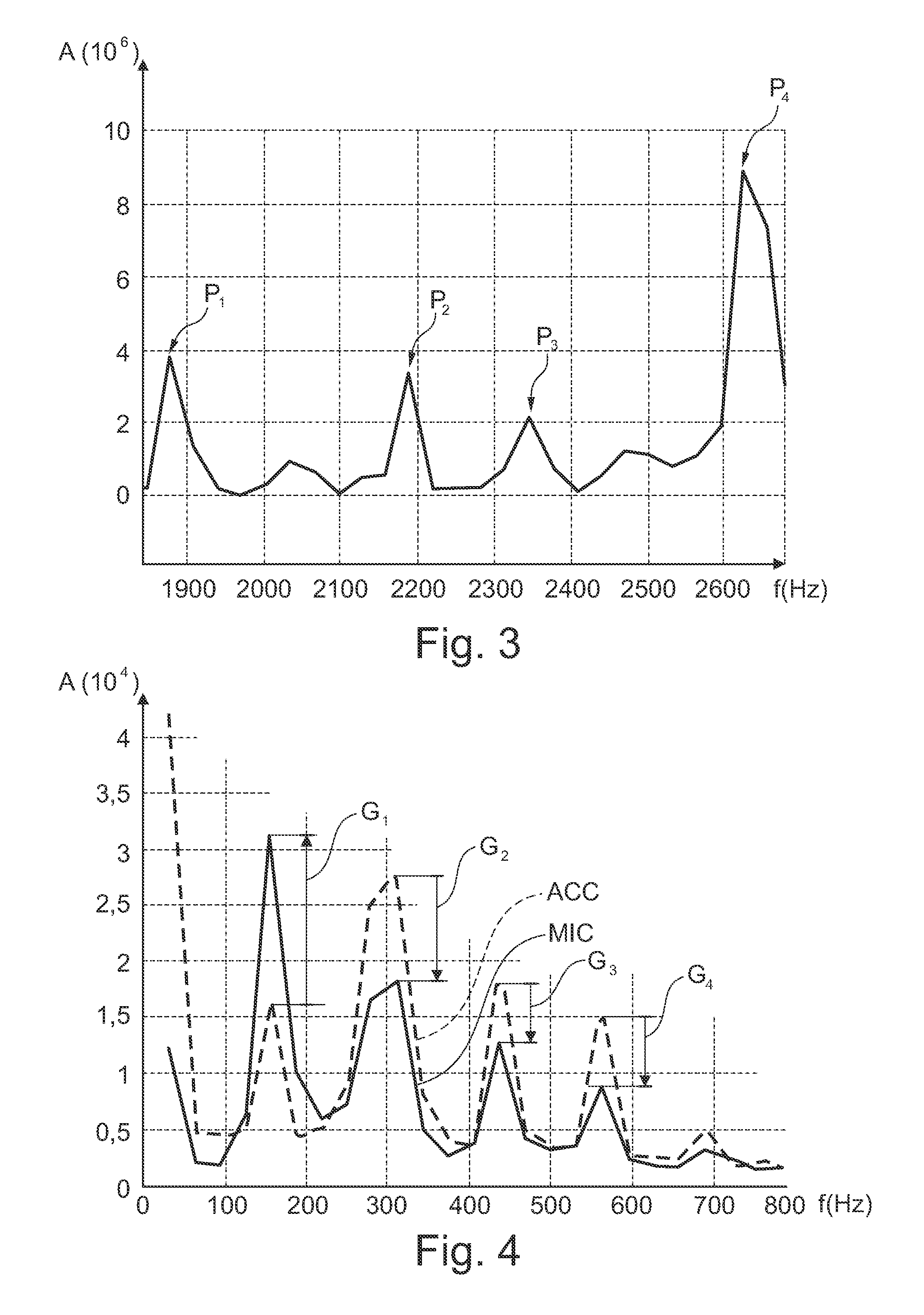
Combined microphone and earphone audio headset having means for denoising a near speech signal, in particular for a " hands-free" telephony system
InactiveUS20120278070A1Reduce noiseEasy to useBone conduction transducer hearing devicesSpeech analysisEngineeringHands free
The headset comprises: a physiological sensor suitable for being coupled to the cheek or the temple of the wearer of the headset and for picking up non-acoustic voice vibration transmitted by internal bone conduction; lowpass filter means for filtering the signal as picked up; a set of microphones picking up acoustic voice vibration transmitted by air from the mouth of the wearer of the headset; highpass filter means and noise-reduction means for acting on the signals picked up by the microphones; and mixer means for combining the filtered signals to output a signal representative of the speech uttered by the wearer of the headset. The signal of the physiological sensor is also used by means for calculating the cutoff frequency of the lowpass and highpass filters and by means for calculating the probability that speech is absent.
Owner:PARROT
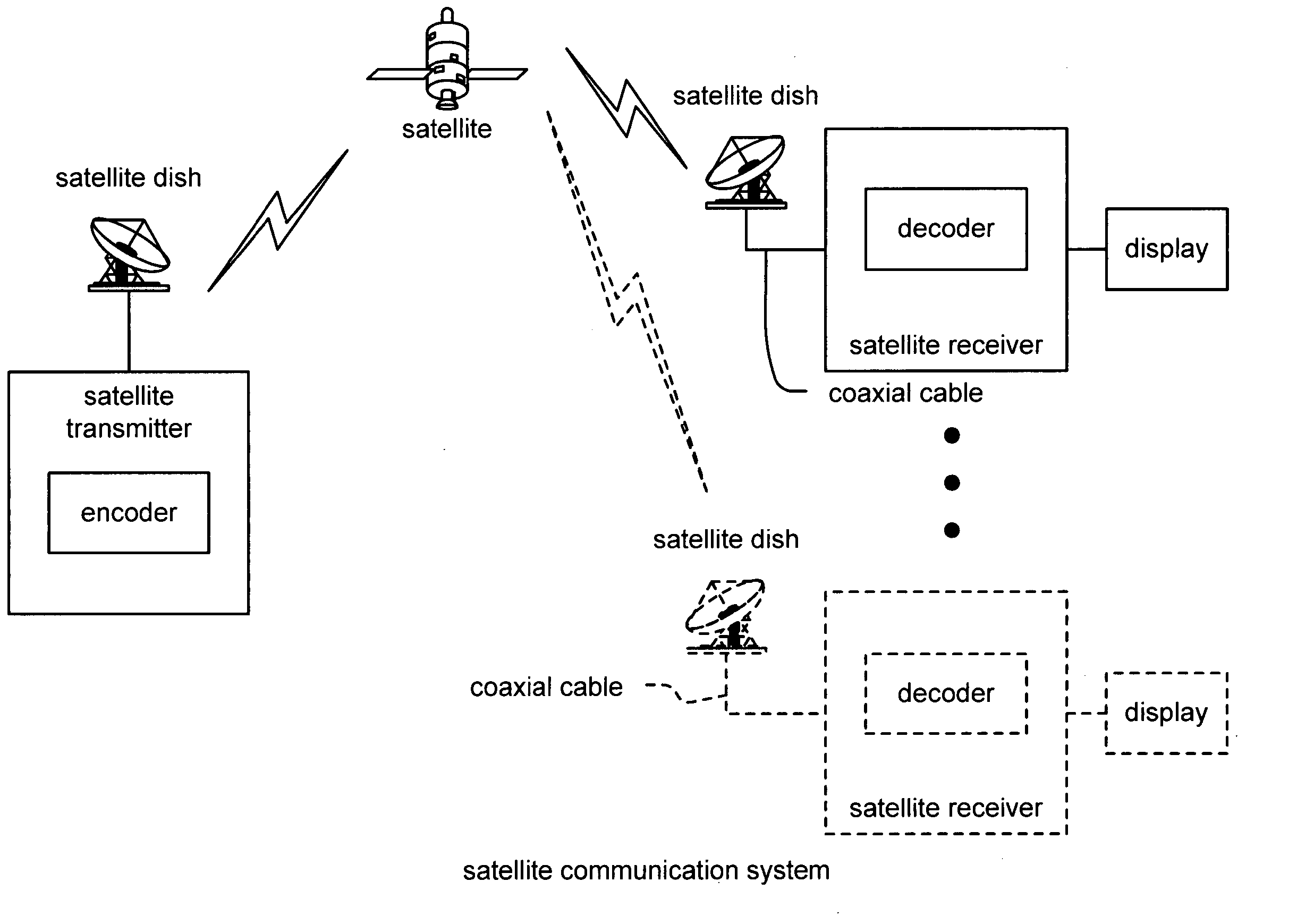
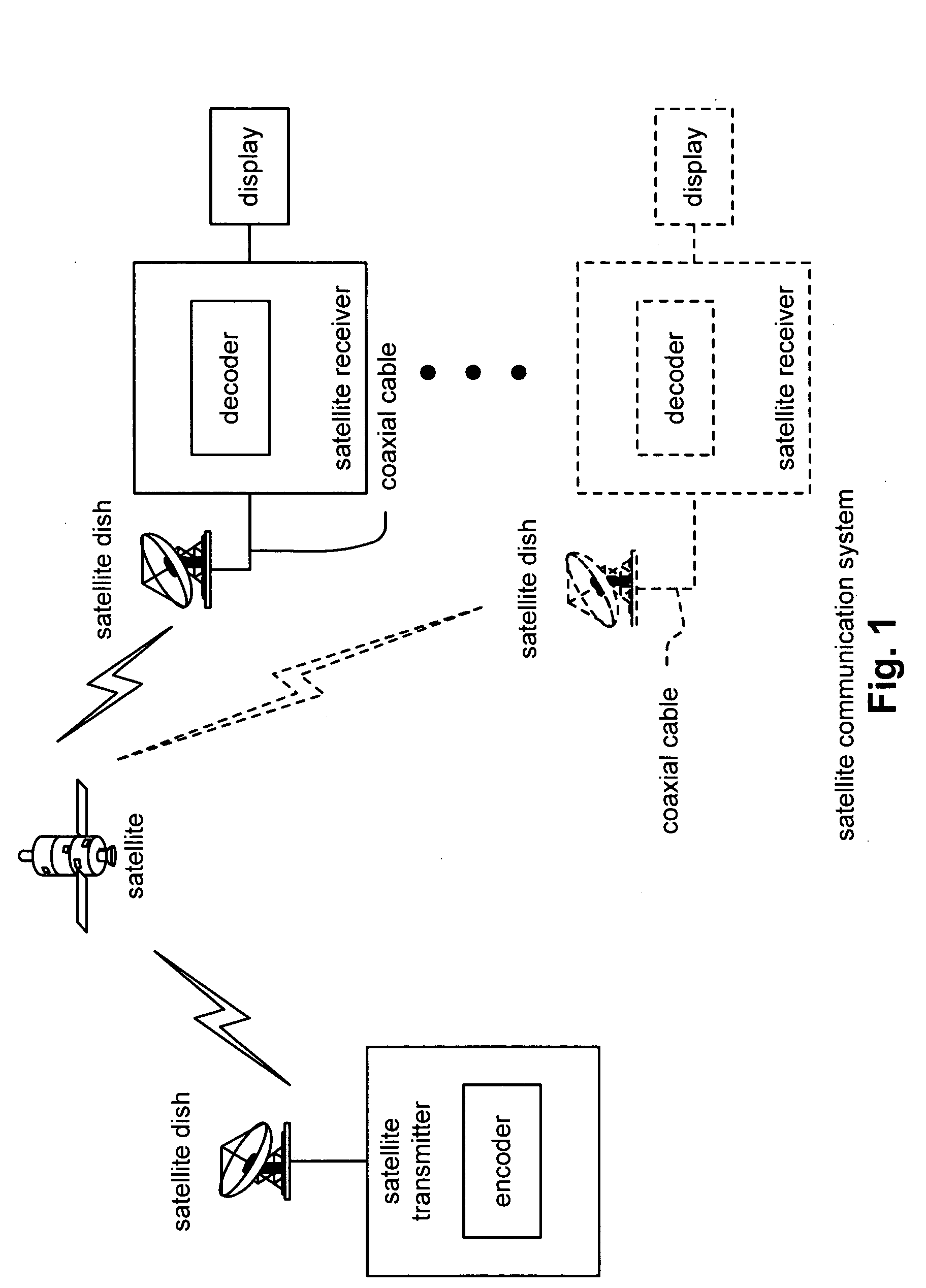
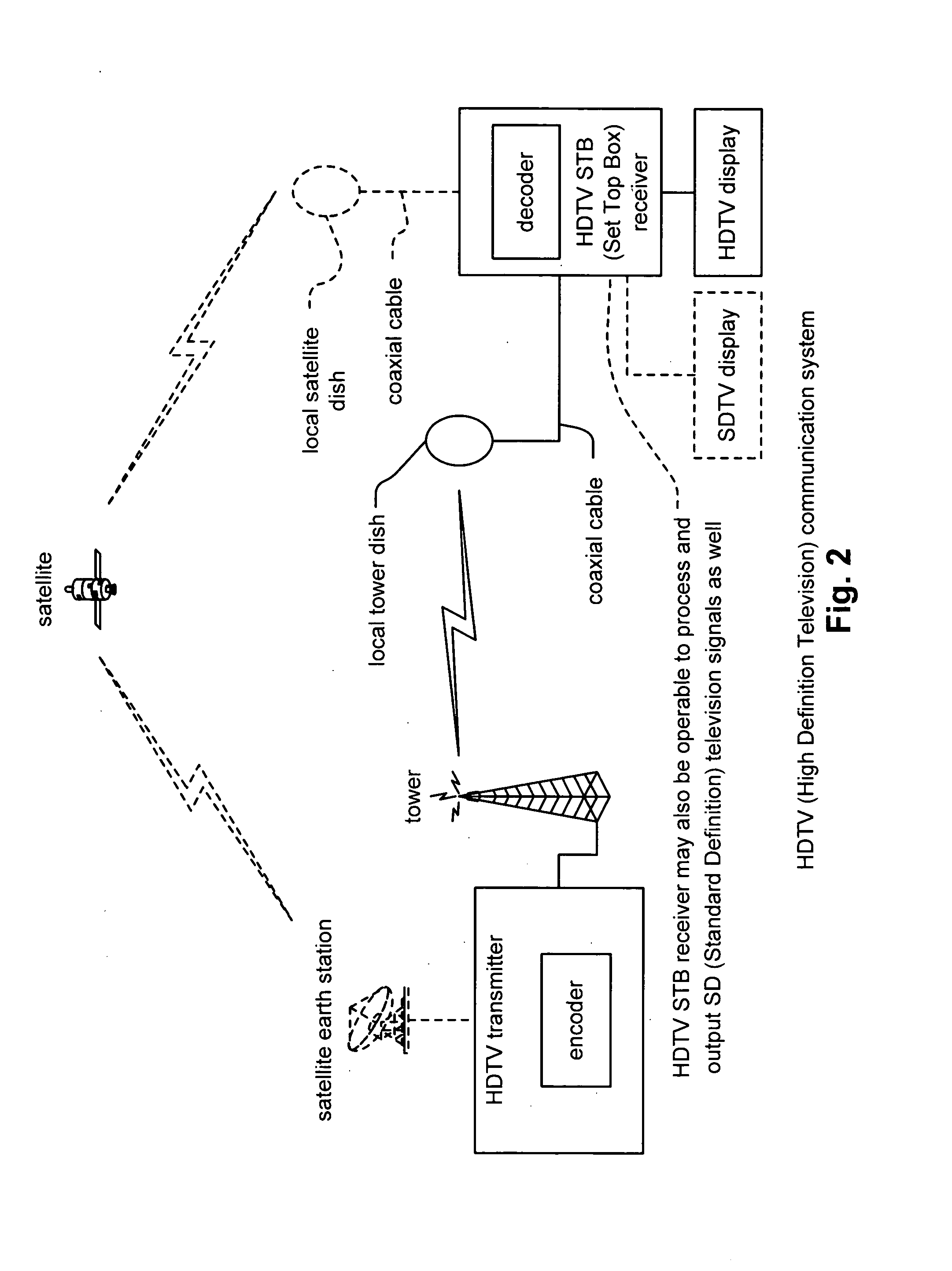
Satellite downstream porting interface API
InactiveUS20050071877A1Satellite broadcast receivingGHz frequency transmissionLow noiseEmbedded software
Satellite downstream porting interface API. A novel solution is presented to support various integrated and non-integrated functional blocks within the front-end of a satellite receiver STB (Set Top Box) system. Embedded software, running on an integrated microprocessor within a single chip STB device, is implemented to govern various devices within the satellite STB system. The embedded software may control operational parameters of an external LNB (Low Noise Block) on a satellite dish employed by a user; this may include controlling the polarization of the LNB as well as the associated voltages levels employed by the LNB. The embedded software may also direct the tuning frequency and cut-off frequency of 1 or more SDSs (integrated downstream satellite receivers) receiving output from the satellite dish. The embedded software may also direct many of the various operational parameters of 1 or more SDSs including modulation, code rate, and / or symbol rate of received signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
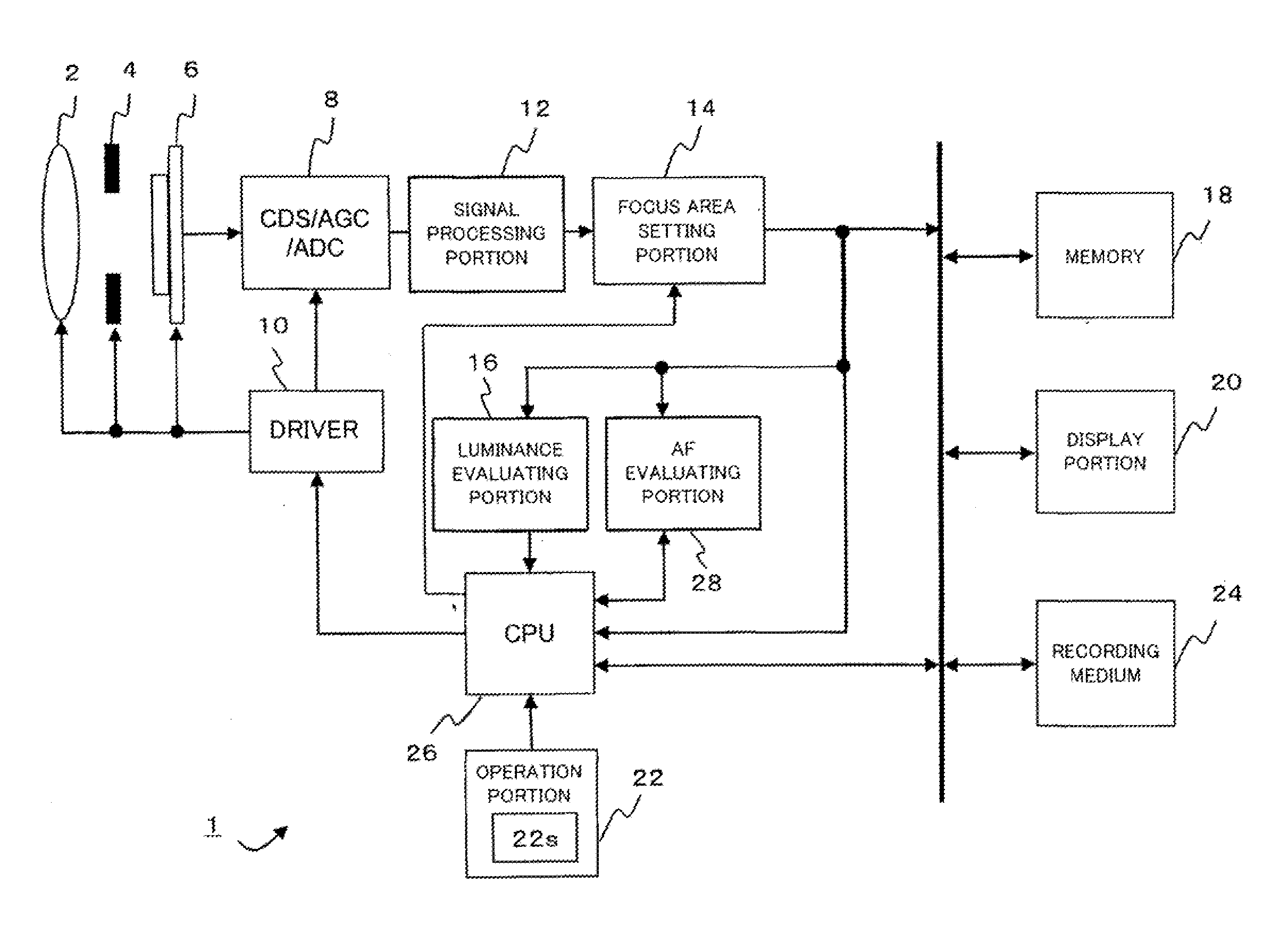
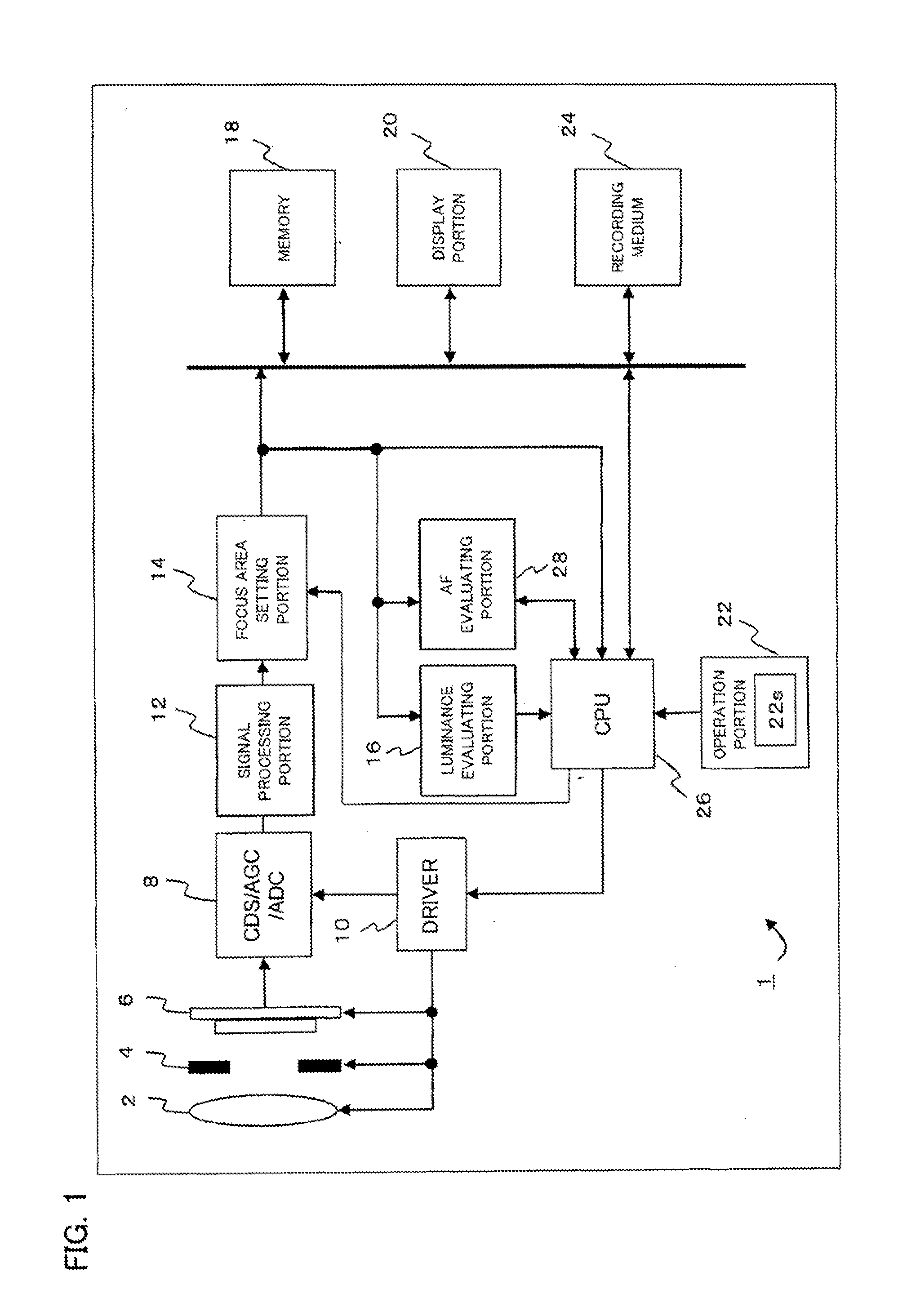
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20130016245A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging equipmentImage signal
An imaging apparatus includes an imager which acquires an image signal of a subject. A first filter processer performs a filer process on a luminance signal included in the image signal in a focus area. A second filter processor performs a filter process on the luminance signal included in the image signal in the focus area and to which a cutoff frequency different from the cutoff frequency of the first filter processor is set. A first determiner determines whether or not a point light source is included in the subject. A calculator calculates an evaluation value from the luminance signal included in the image signal in the focus area. A focuser performs focus control based on the evaluation value. When it is determined that the point light source is included in the subject, the calculator calculates the evaluation value based on outputs of the first and second filter processor.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Circuit for capacitive touch applications
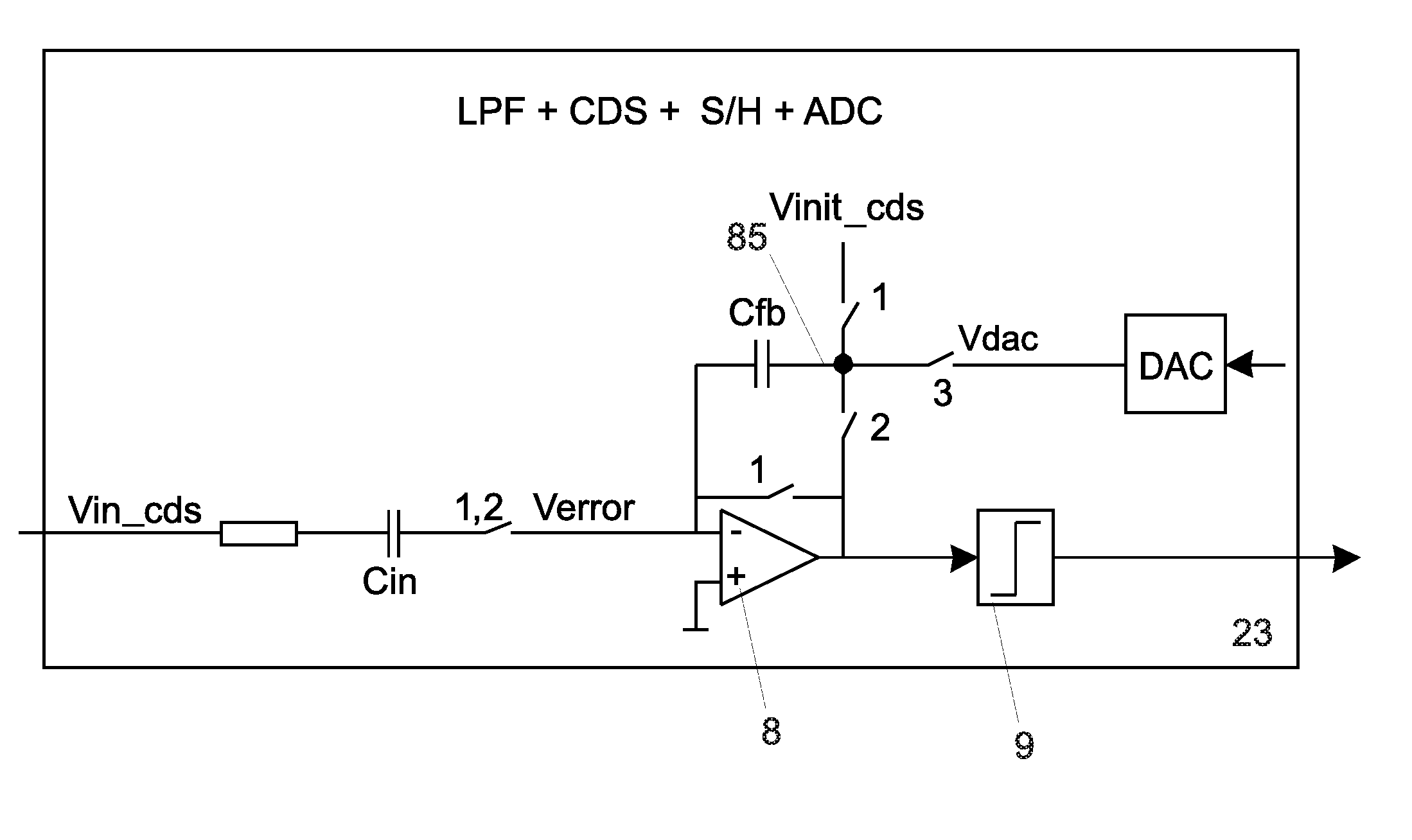
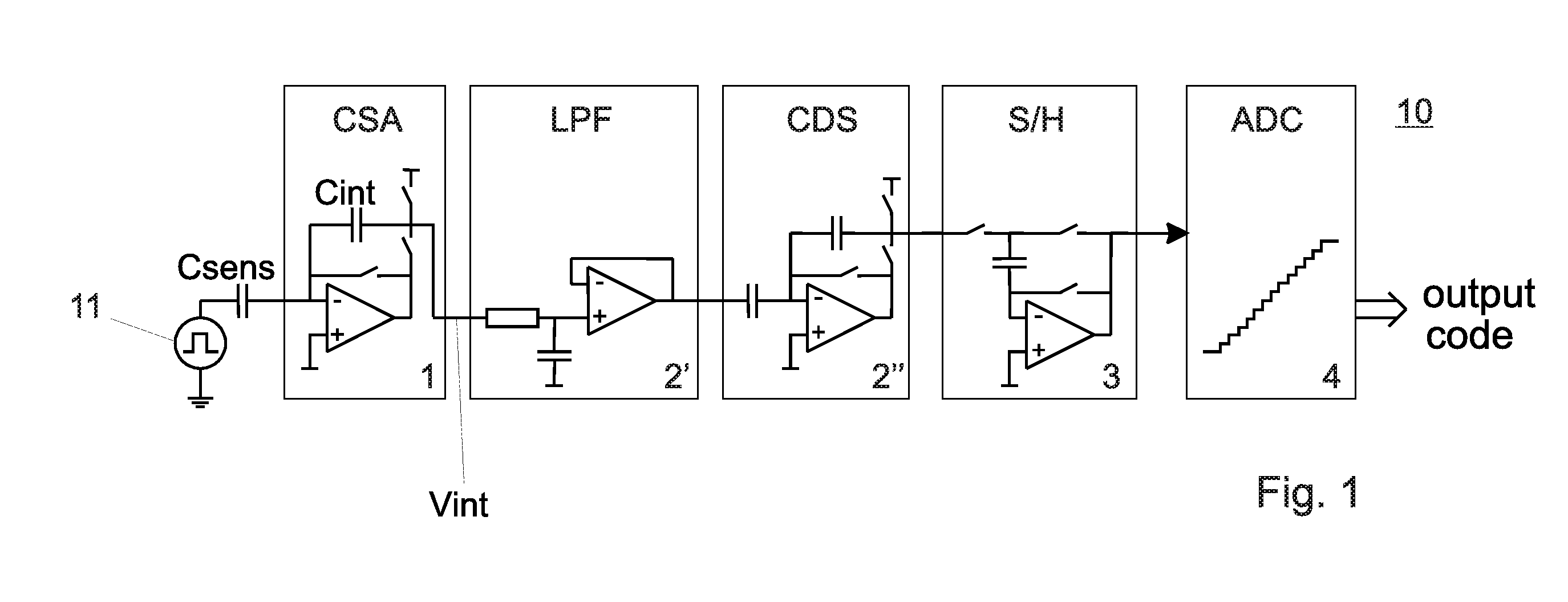
ActiveUS20110001492A1Reduce in quantityReduce consumptionAnalogue/digital conversionResistance/reactance/impedenceIntegratorLow-pass filter
A circuit for capacitive touch applications comprisinga charge integratora low pass-filtera correlated double sampler comprising an input capacitora sampler and holderan analog to digital convertersaid low pass-filter having a cut-off frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency of the sampler and holdersaid low pass filter comprising said input capacitor and a serial resistor.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON
Digital crossover and parametric equalizer
InactiveUS6405227B1Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsBand-pass filterEqualization
A DSP-based and multi-channel digital filter chip providing crossover filtering and parametric equalization. Crossovers can be low-pass, high-pass, or band-pass filters with programmable cutoff frequencies. Each equalizer band has independently adjustable center frequency band, and levels over a -60 dB to +16 dB range. The chip can work either with a microprocessor controlling the chip or in a stand-alone mode having the filter settings downloaded automatically from an external EEPROM. The chip is ideal for applications that require precise digital filtering or software programmable filters, and is also an alternative to analog filters, eliminating passive components and reducing circuit size.
Owner:NJR CORP
Optical element and solid-state imaging device
ActiveUS20100176280A1Lower-profile structureRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesElectrical conductorPhotoelectric conversion
An optical element includes a first filter having the function to transmit a component at a lower frequency than a first cutoff frequency in incident light, a second filter having the function to transmit a component at a higher frequency than a second cutoff frequency in the incident light, and a light-receiving element for photoelectrically converting the components transmitted through the first filter and the second filter in the incident light. A metal optical filter composed of a conductor thin film is used as at least one of the first filter and the second filter.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
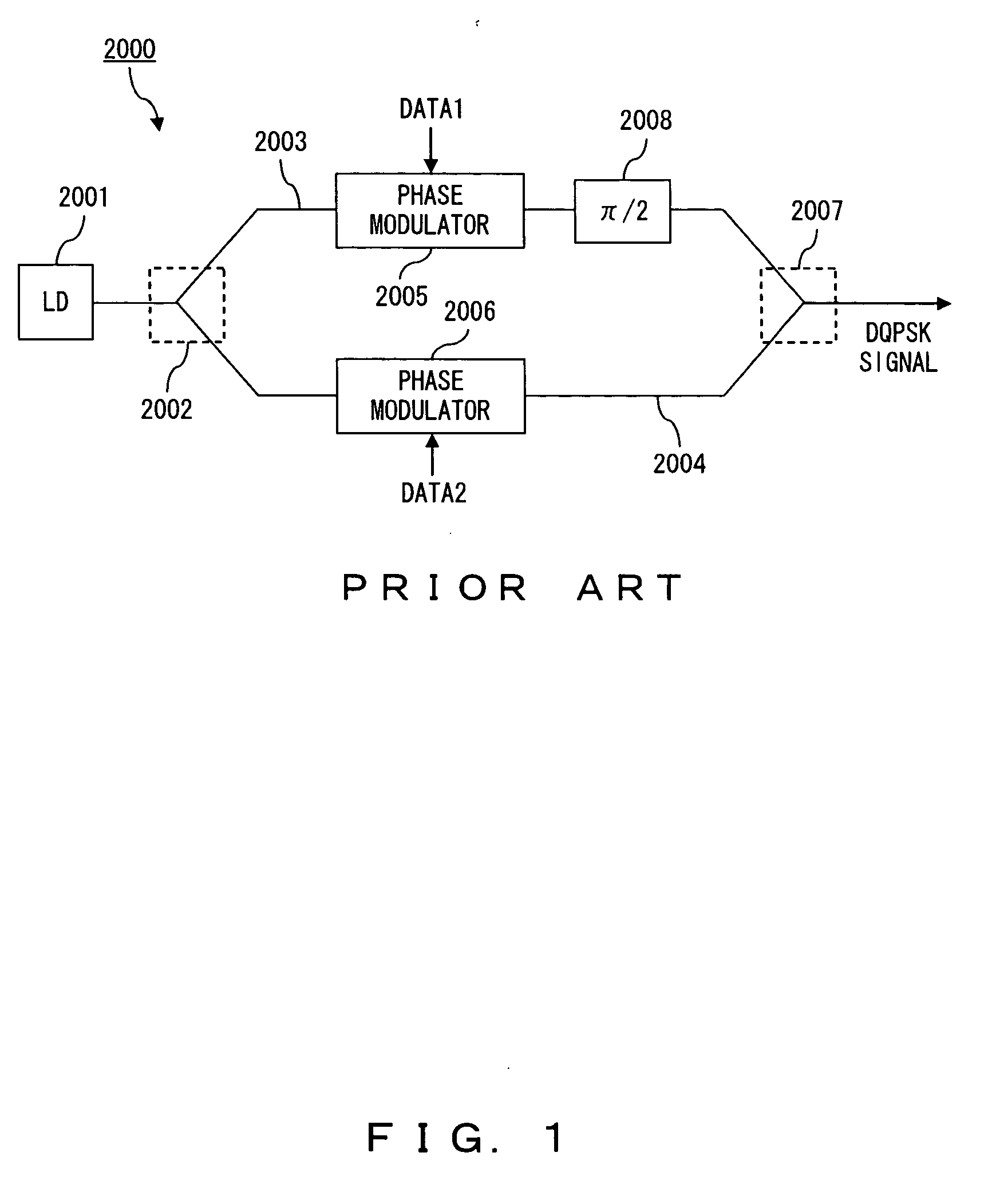
Optical transmitting apparatus and optical communication system
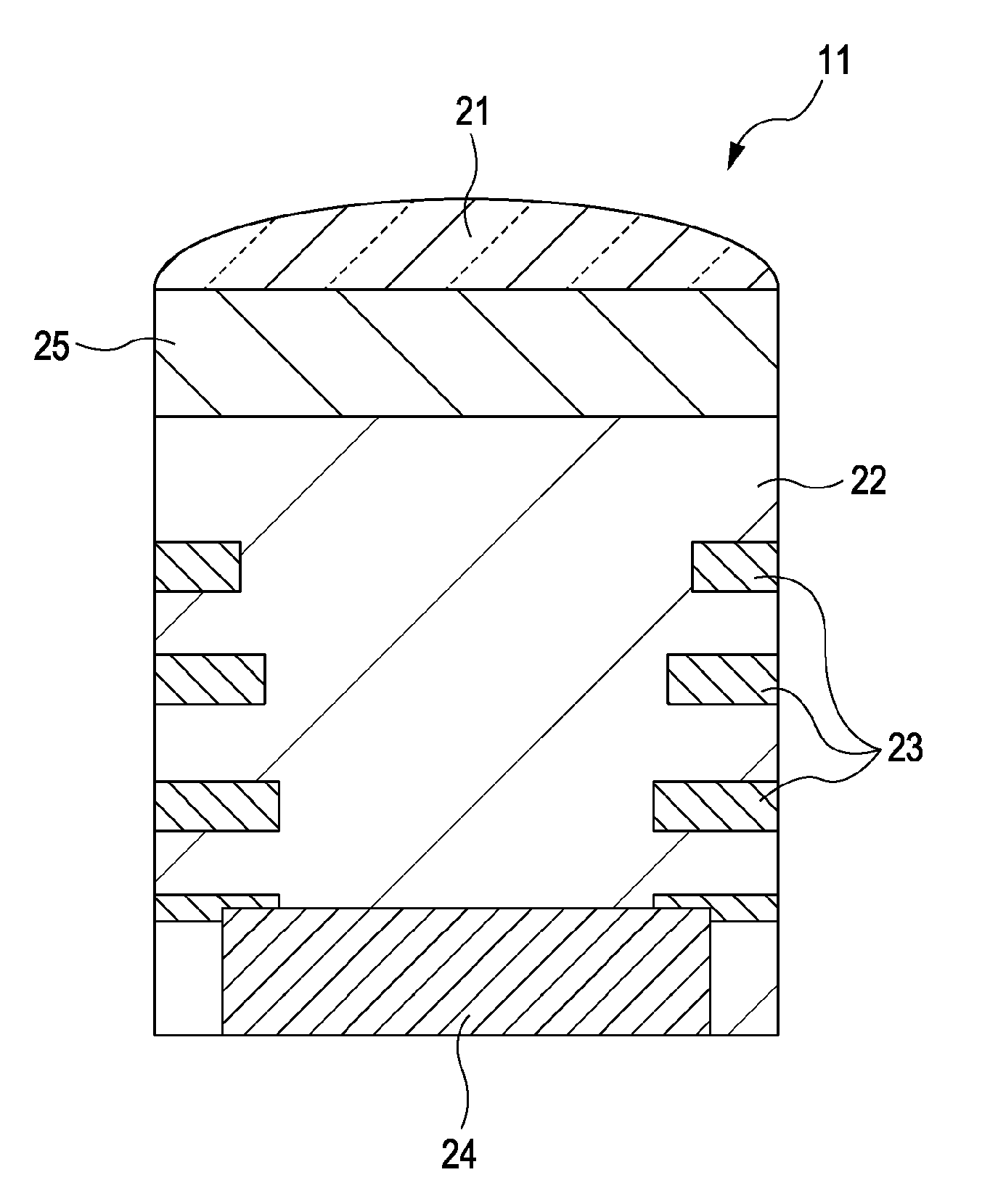
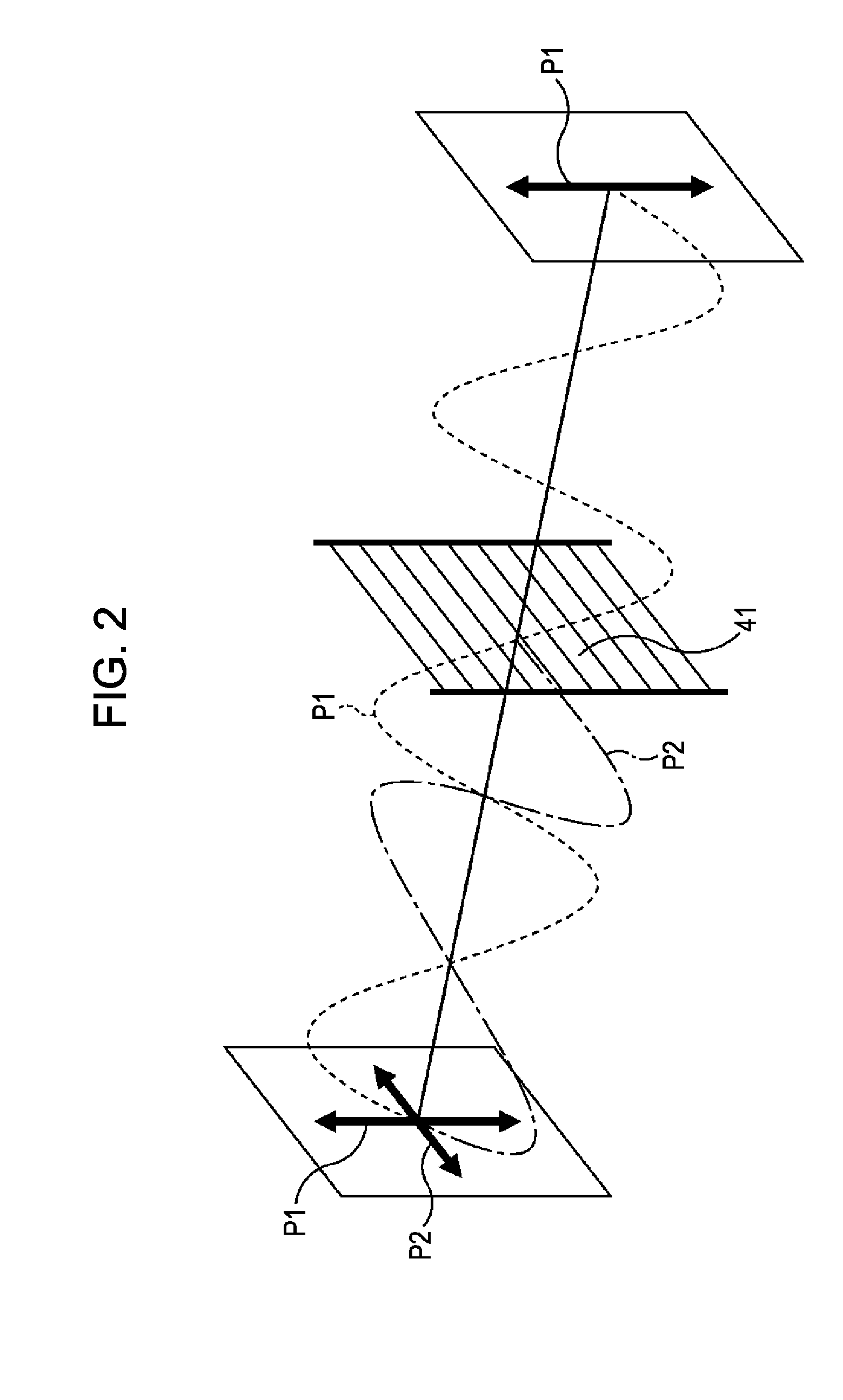
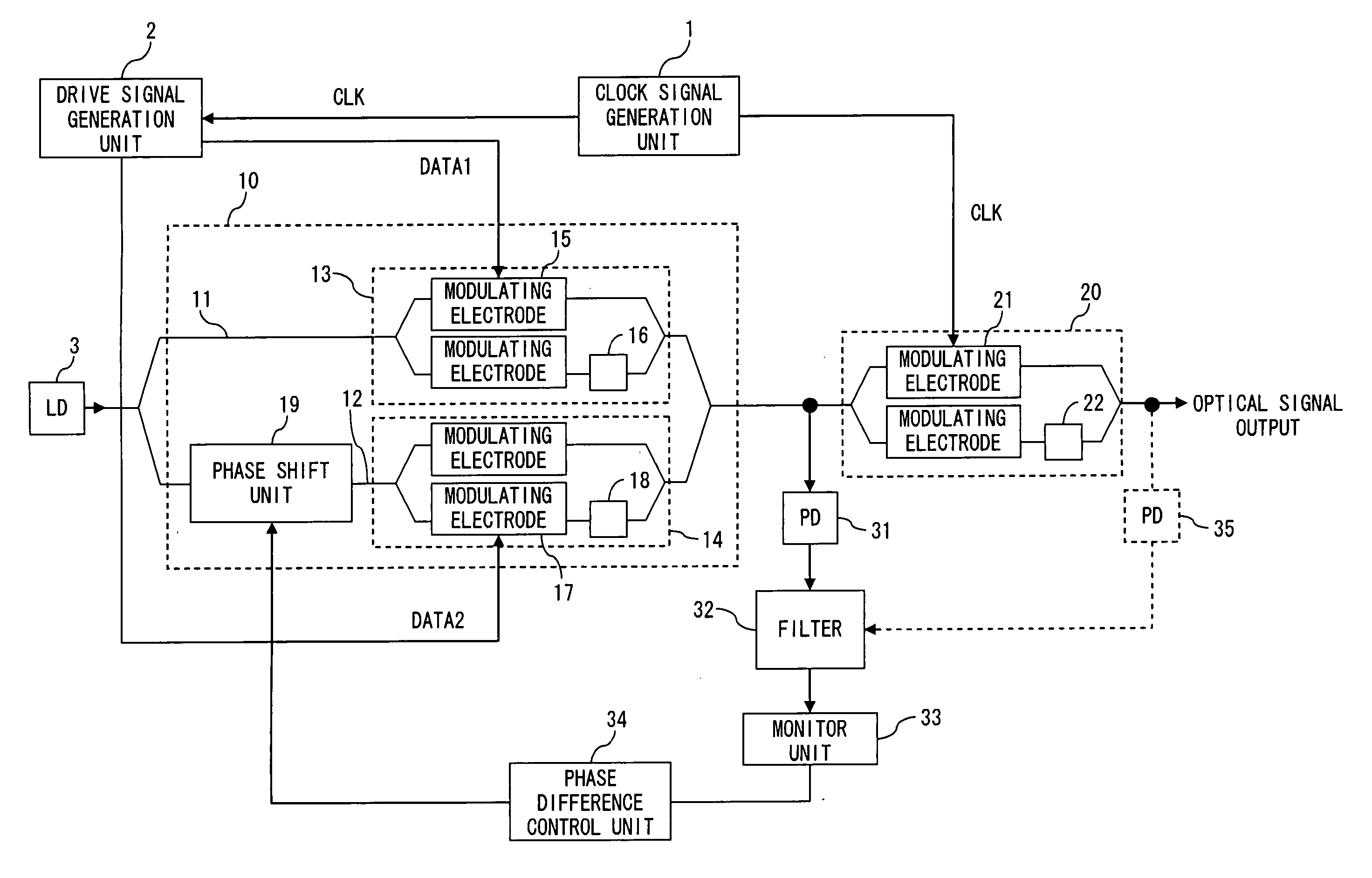
ActiveUS20070065161A1Inhibit deteriorationDrop in communication qualityElectromagnetic transmittersTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsPhase shiftedPhotodetector
A data modulator unit generates a DQPSK optical signal in accordance with a data signal. A phase shift unit provides a phase difference of π / 2 between a pair of arms. A photodetector converts an output signal of the data modulator unit into an electrical signal. A filter is a low-pass filter with a cut-off frequency lower than a symbol frequency, and filters an output signal of the photodetector. A monitor unit detects power of an output signal of the filter. A phase difference control unit adjusts the amount of phase shift in the phase shift unit so as to minimize power of an output signal of the filter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
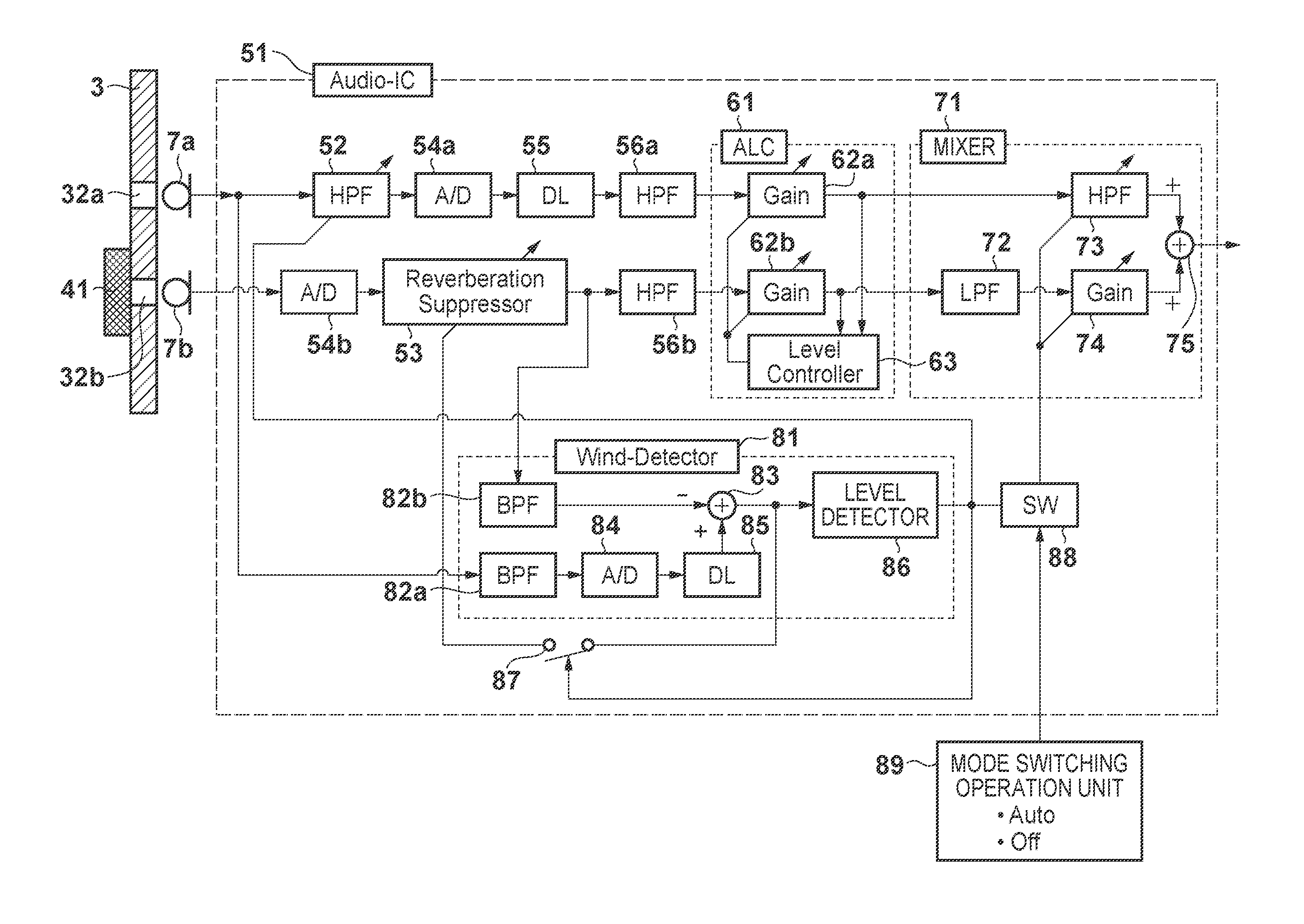
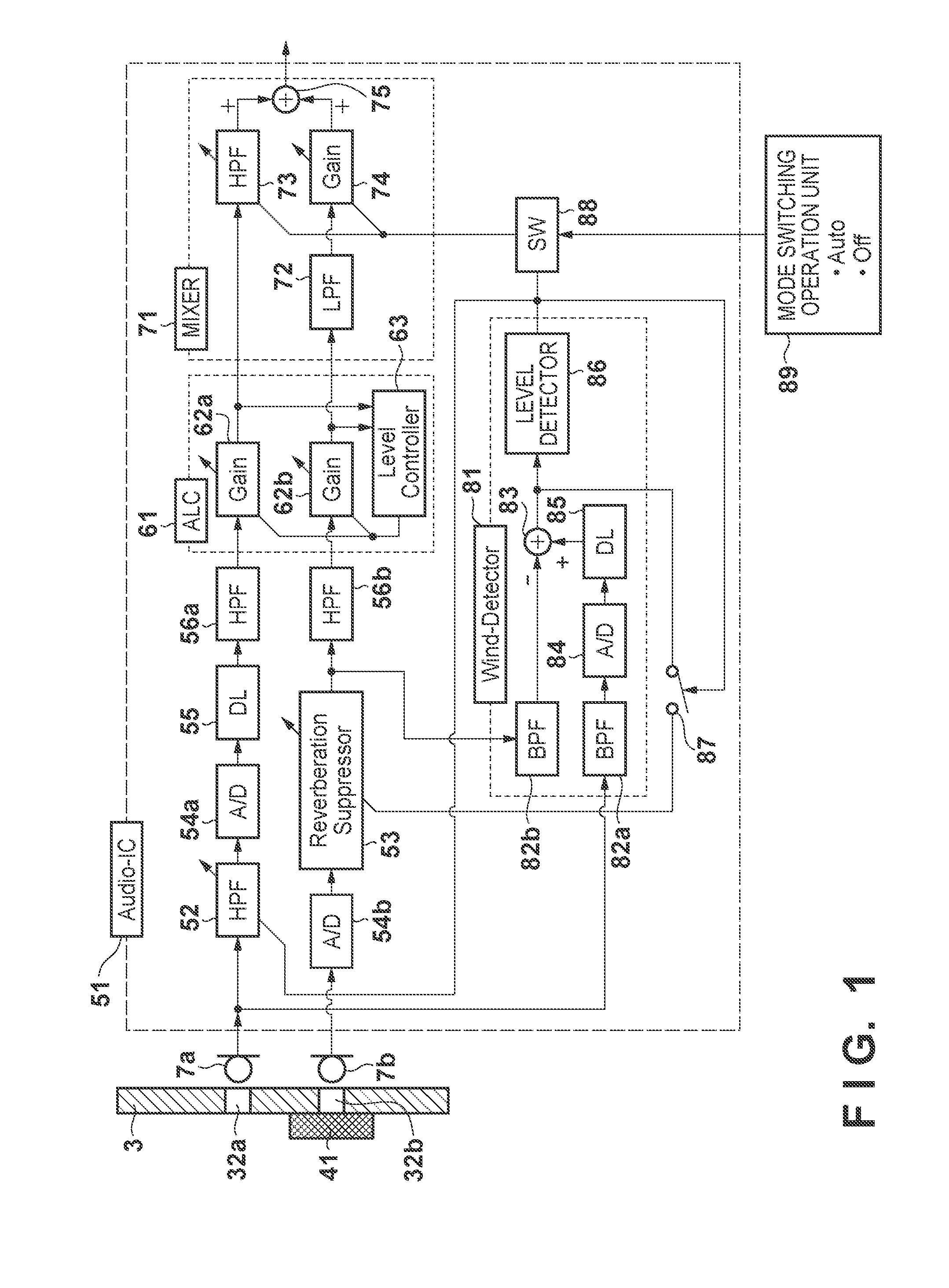
Audio processing apparatus and method of controlling the audio processing apparatus
InactiveUS20120207315A1Easy to quantifyHigh-quality audioMicrophonesSignal processingComputer scienceAudio frequency
An audio processing apparatus includes first and second audio pickup units. The second audio pickup unit includes an audio resistor provided to cover a sound receiving portion to suppress external wind introduction while passing an external audio. A first filter attenuates a signal having a frequency lower than a first cutoff frequency of the output signal of a first A / D converter. A second filter attenuates a signal having a frequency higher than a second cutoff frequency of the output signal of a second A / D converter. A third filter is provided between the first audio pickup unit and the first A / D converter to attenuate a signal having a frequency lower than a third cutoff frequency for suppressing the wind noise.
Owner:CANON KK
Envelope tracking for radio-frequency applications
InactiveUS20180159476A1Improve power efficiencyGated amplifiersPower amplifiersEnvelope TrackingLow frequency
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
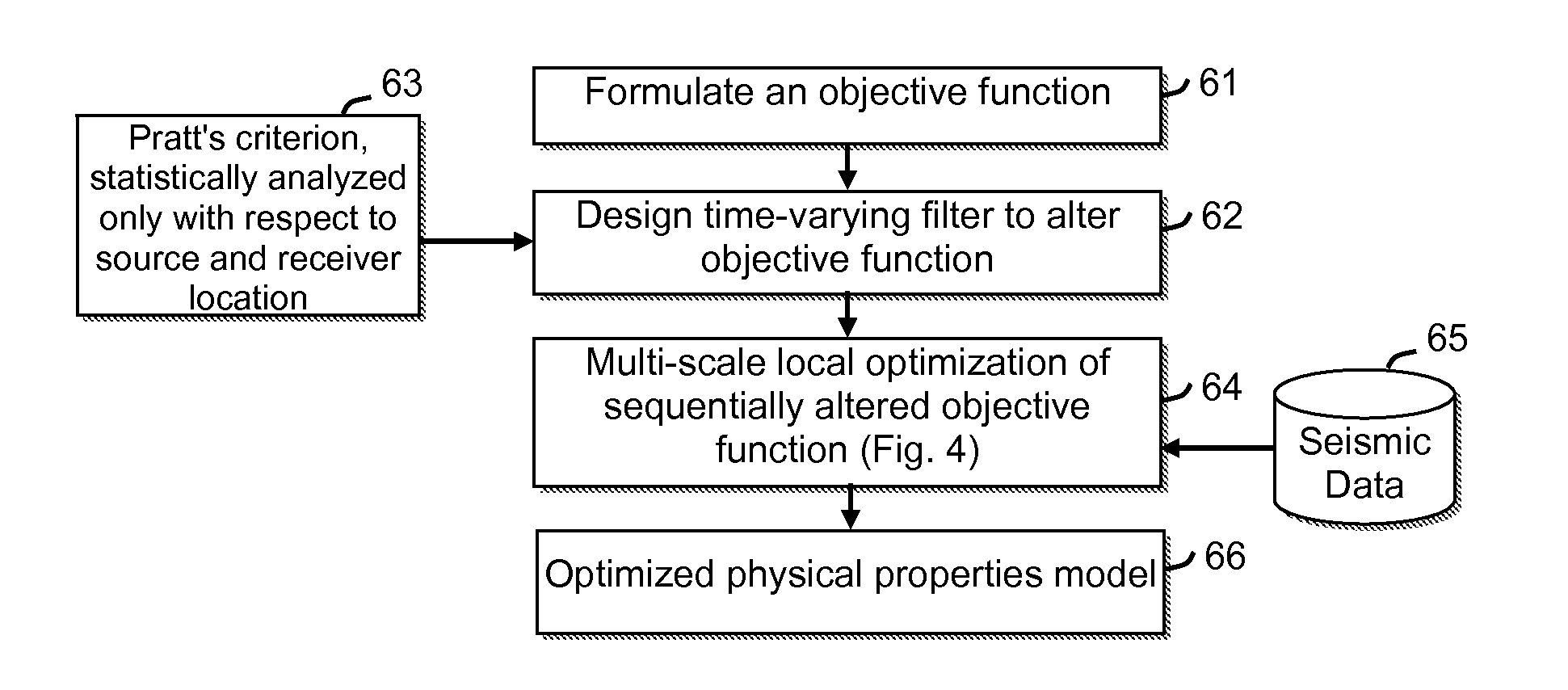
Full Wavefield Inversion Using Time Varying Filters
ActiveUS20110238390A1Reduce in quantityReduce computing timeError detection/correctionSeismologyLow-pass filterTime changes
An improved method for reducing the accuracy requirements on the starting model when performing multi-scale inversion of seismic data (65) by local objective function optimization (64). The different scales of inversion are brought about by incorporating a low-pass filter into the objective function (61), and then decreasing the amount of high-frequency data that is filtered out from one scale to the next. Moreover, the filter is designed to be time varying, wherein the filter's low-pass cutoff frequency decreases with increasing traveltime of the seismic data being filtered (62). The filter may be designed using Pratt's criterion for eliminating local minima, and performing averages (or other statistical measure) of the period and the traveltime error only with respect to source and receiver location but not traveltime (63).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Optical waveguide structures
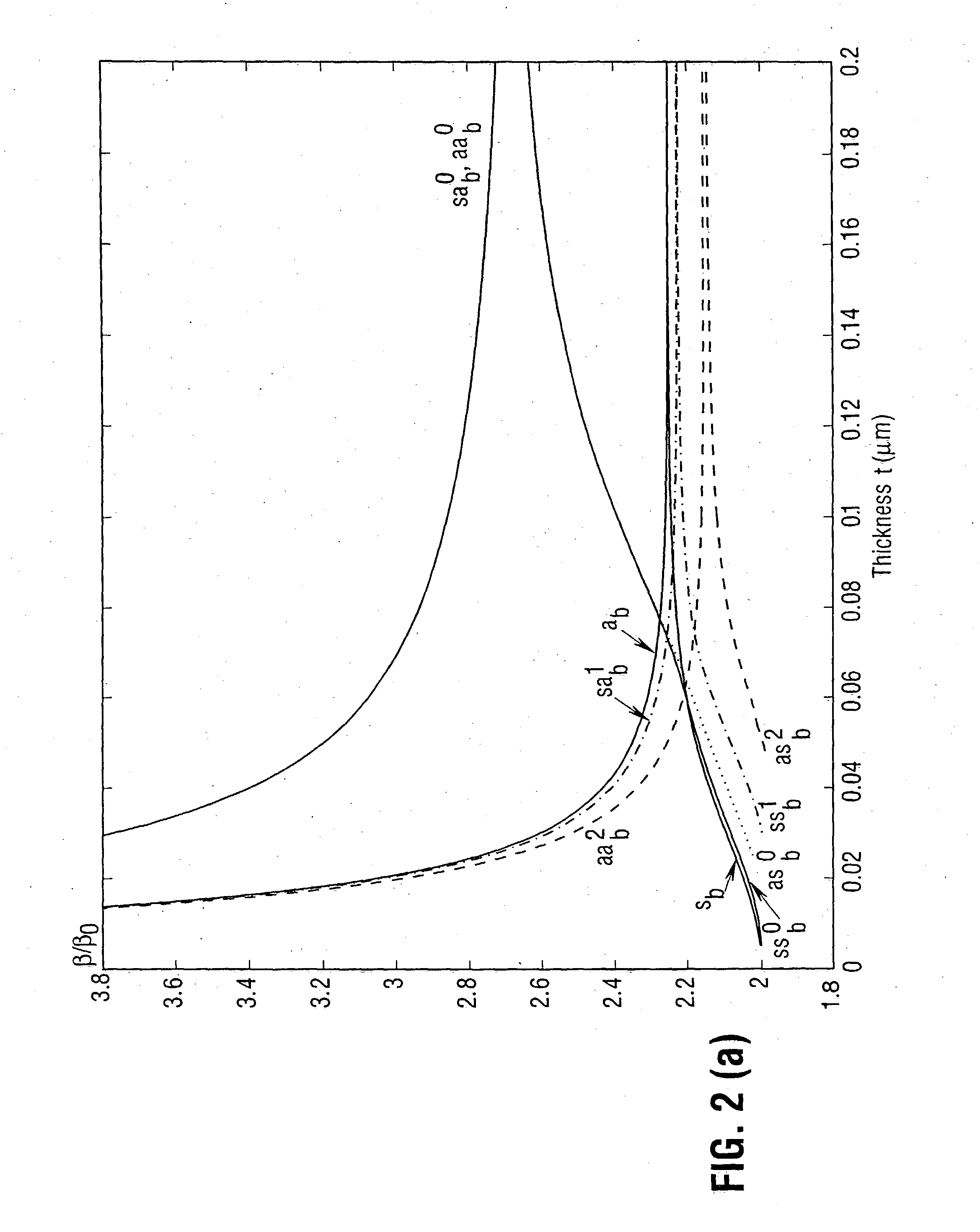
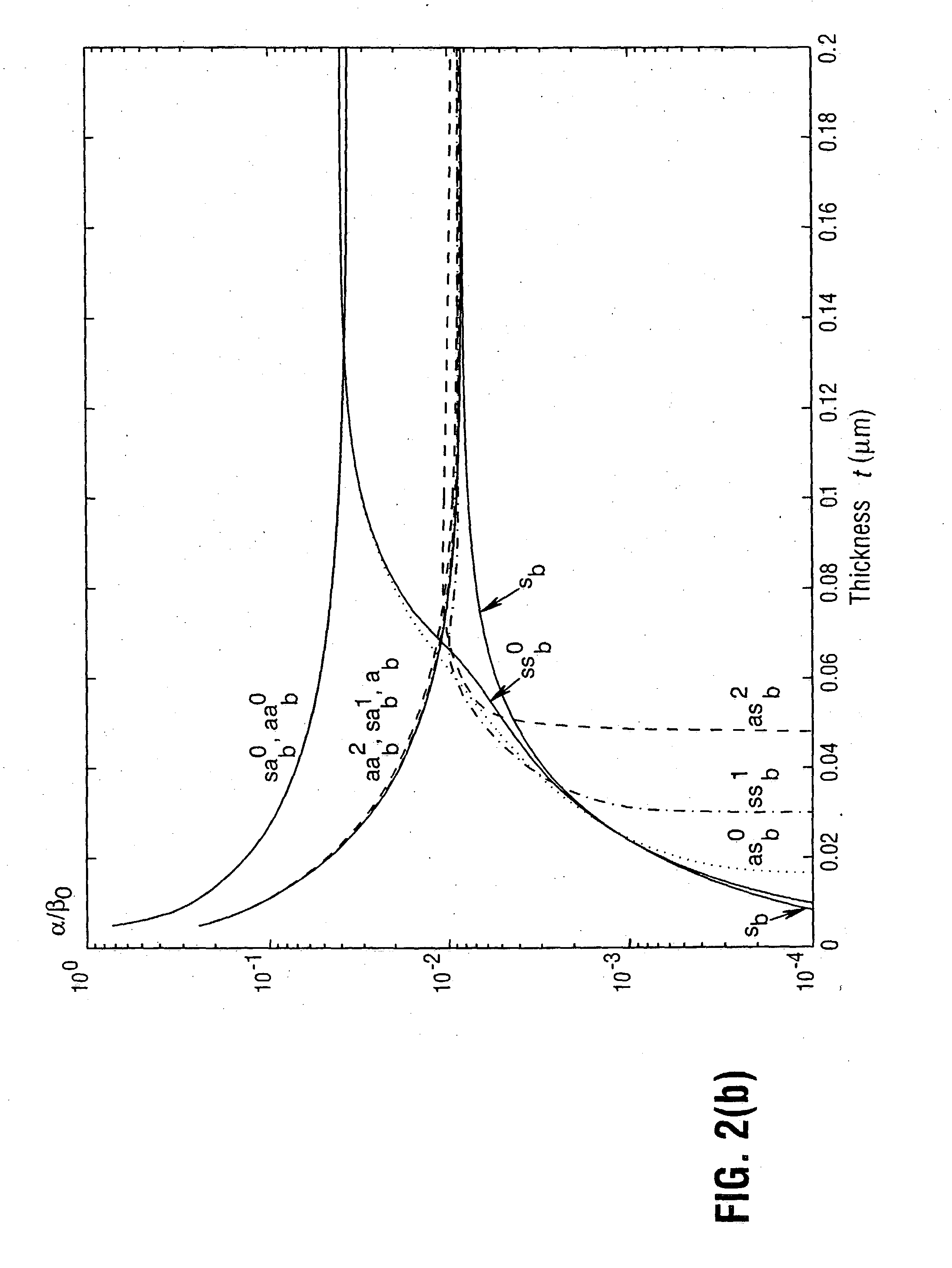
The purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation supported by waveguide structures comprised of a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric have been characterized at optical wavelengths. One of the fundamental modes supported by the structure exhibits very interesting characteristics and is potentially quite useful. It evolves with decreasing film thickness and width towards the TEM wave supported by the background (an evolution similar to that exhibited by the sb mode in symmetric metal film slab waveguides), its losses and phase constant tending asymptotically towards those of the TEM wave. Attenuation values can be well below those of the sb mode supported by the corresponding metal film slab waveguide. Low mode power attenuation in the neighbourhood of 10 to 0.1 dB / cm is achievable at optical communications wavelengths, with even lower values being possible. Carefully selecting the film's thickness and width can make this mode the only long-ranging one supported. In addition, the mode can have a field distribution that renders it excitable using an end-fire approach. The existence of this mode renders the finite-width metal film waveguide attractive for applications requiring short propagation distances and 2-D field confinement in the transverse plane, enabling various devices to be constructed, such as couplers, splitters, modulators, interferometers, switches and periodic structures. Under certain conditions, an asymmetric structure can support a long-ranging mode having a field distribution that is suitable to excitation using an end-fire technique. Like asymmetric slab waveguides. The attenuation of the long-ranging mode near cutoff decreases very rapidly, much more so than the attenuation related to the long-ranging mode in a similar symmetric structure. The cutoff thickness of a long-ranging mode in an asymmetric finite-width structure is larger than the cutoff thickness of the sb mode in a similar asymmetric slab waveguide. This implies that the long-ranging mode supported by an asymmetric finite-width structure is more sensitive to the asymmetry in the structure compared to the sb mode supported by a similar slab waveguide. This result is interesting and potentially useful in that the propagation of such a mode can be affected by a smaller change in the dielectric constant of the substrate or superstrate compared with similar slab structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
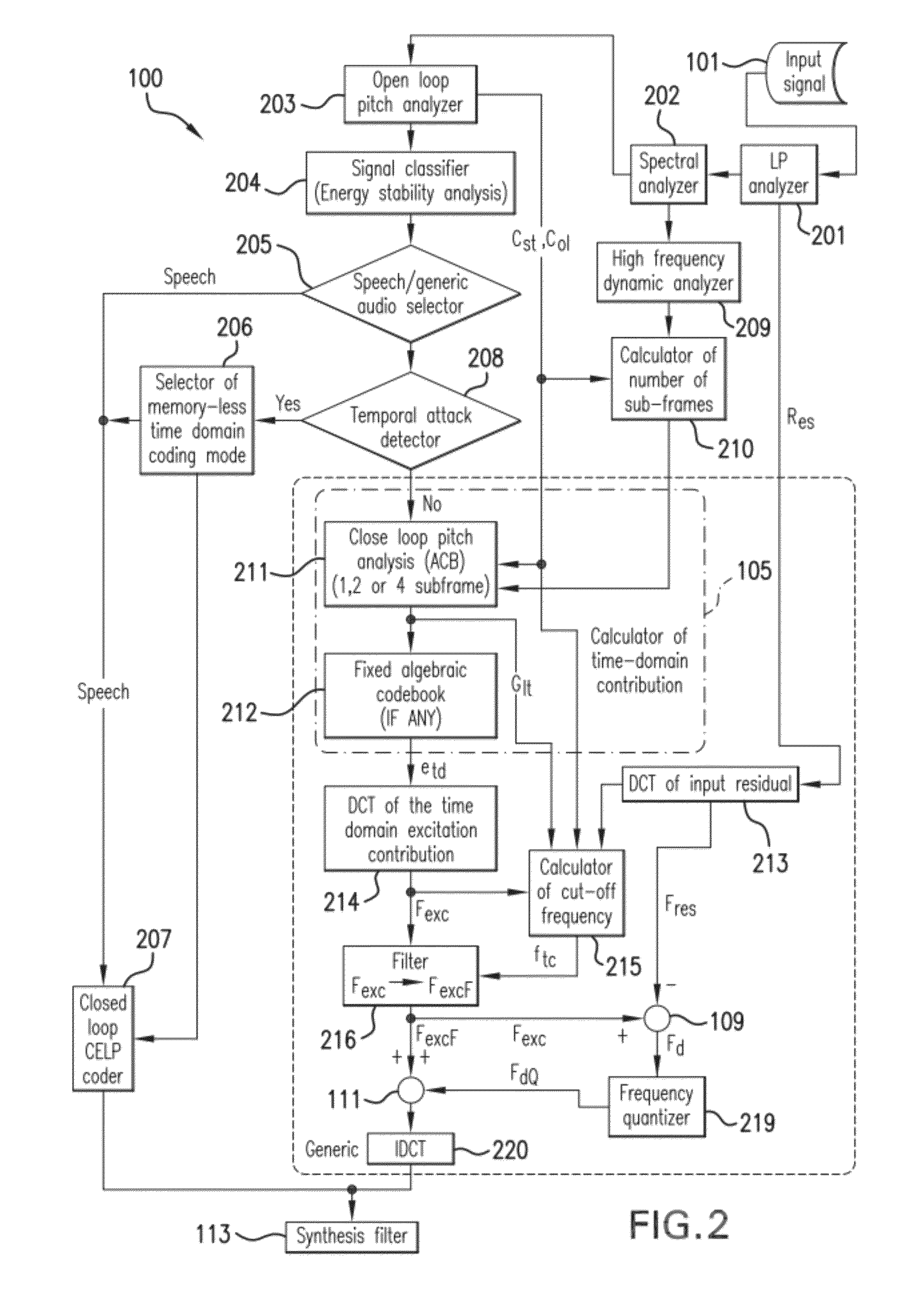
Coding Generic Audio Signals at Low Bitrates and Low Delay
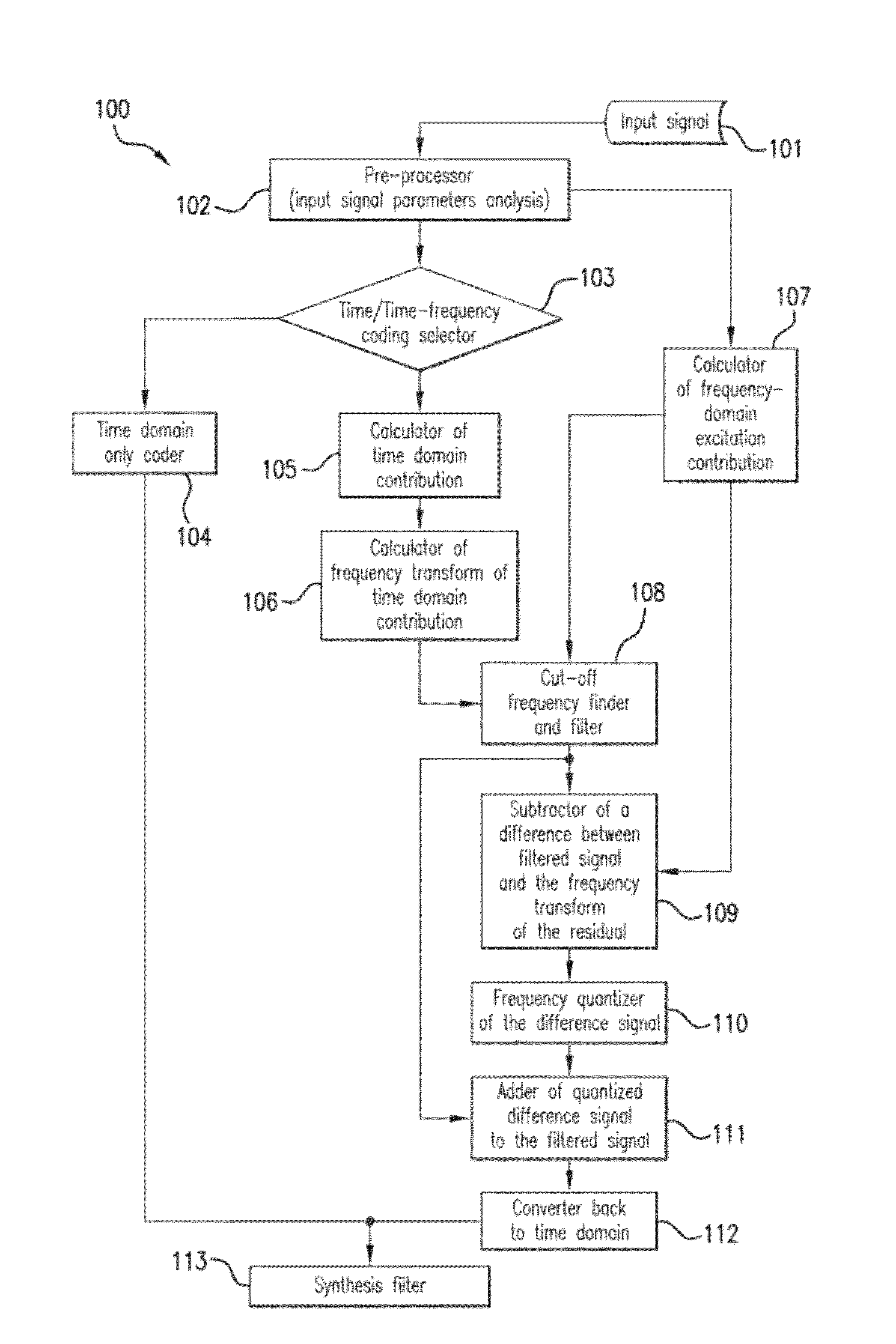
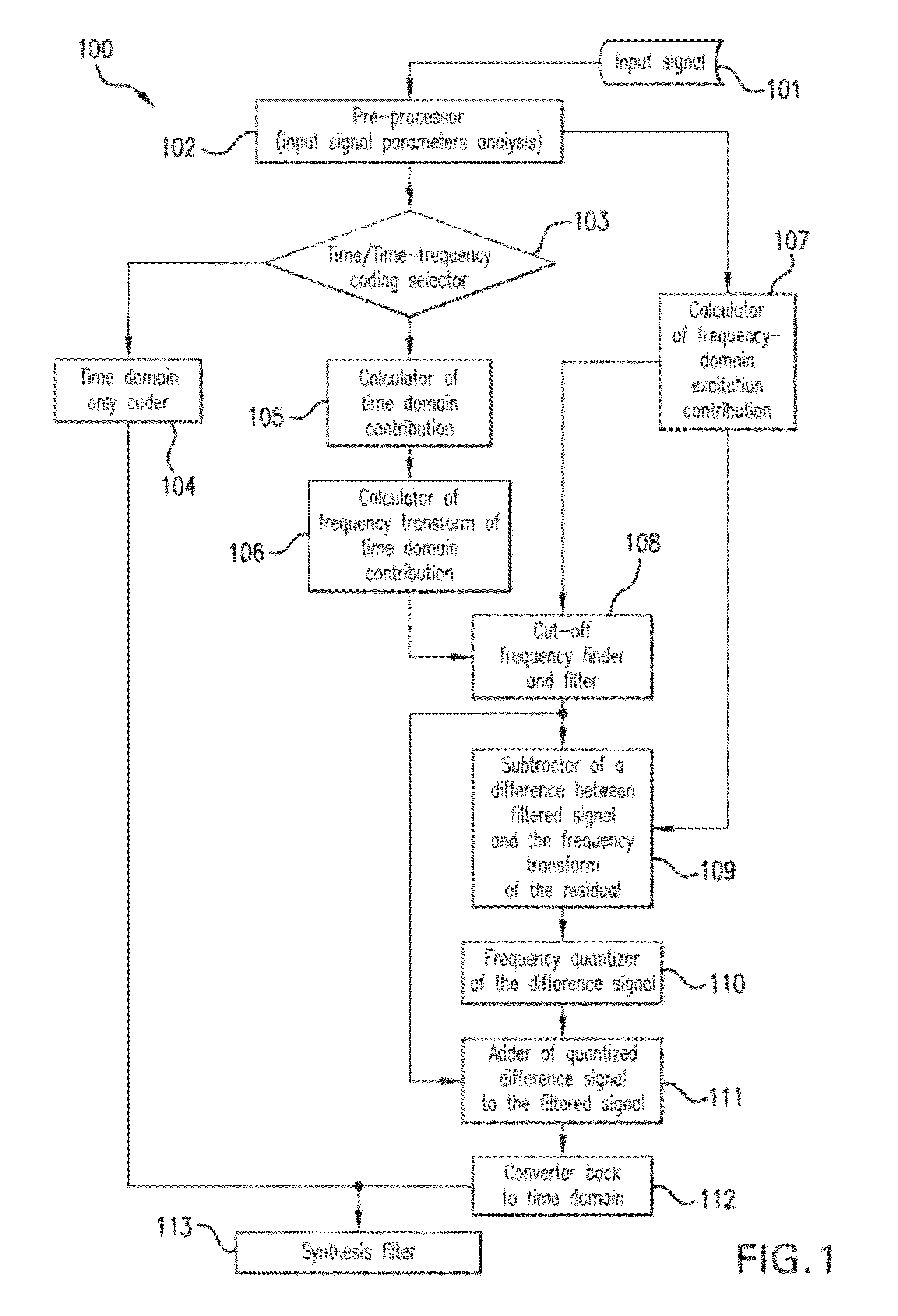
A mixed time-domain / frequency-domain coding device and method for coding an input sound signal, wherein a time-domain excitation contribution is calculated in response to the input sound signal. A cut-off frequency for the time-domain excitation contribution is also calculated in response to the input sound signal, and a frequency extent of the time-domain excitation contribution is adjusted in relation to this cut-off frequency. Following calculation of a frequency-domain excitation contribution in response to the input sound signal, the adjusted time-domain excitation contribution and the frequency-domain excitation contribution are added to form a mixed time-domain / frequency-domain excitation constituting a coded version of the input sound signal. In the calculation of the time-domain excitation contribution, the input sound signal may be processed in successive frames of the input sound signal and a number of sub-frames to be used in a current frame may be calculated.
Owner:VOICEAGE EVS LLC
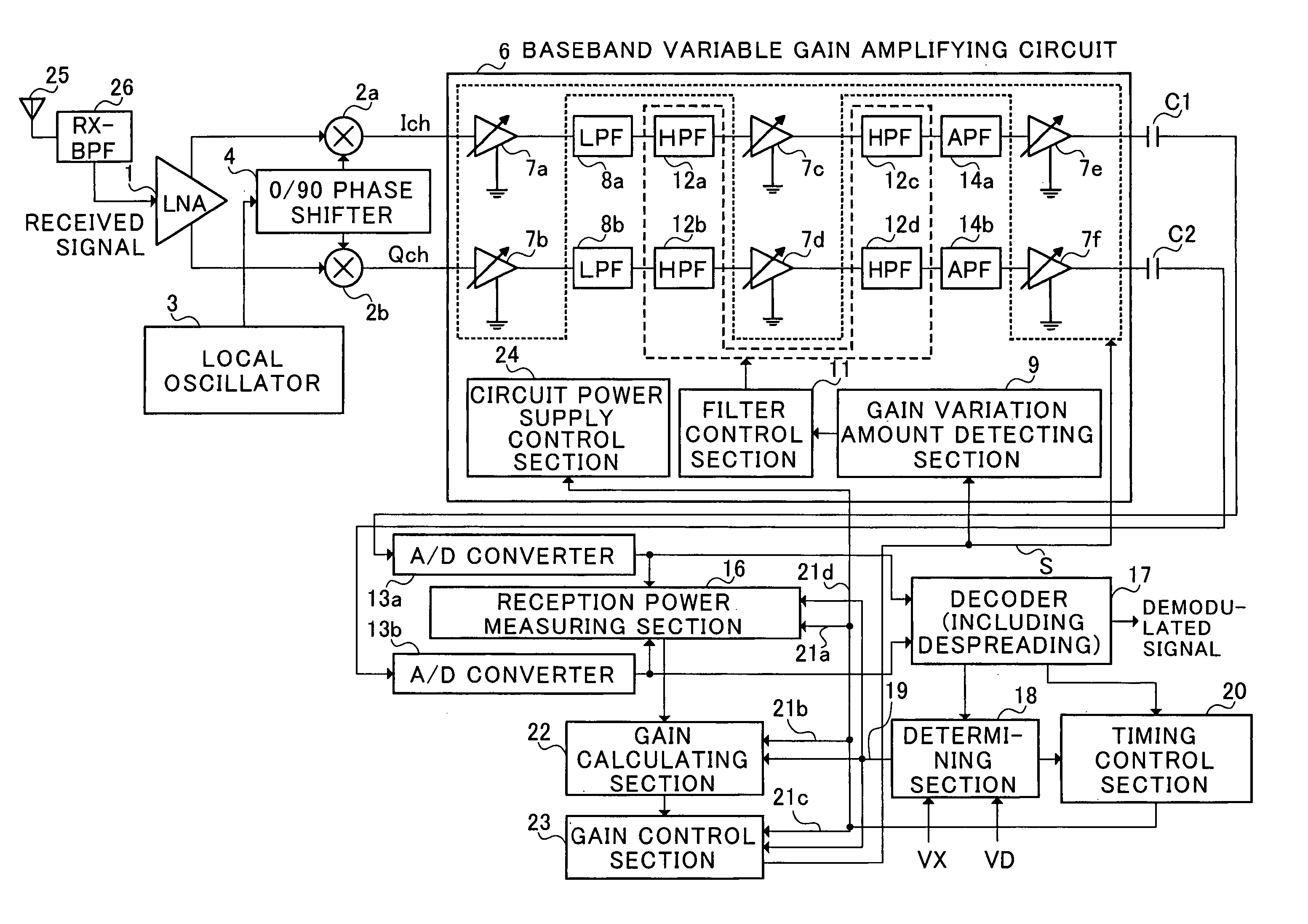
Direct conversion receiver and DC offset reducing method
InactiveUS7171185B2Reduced DC offsetAccurate and fast AGCGain controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDirect-conversion receiverEngineering
A determining section (18) and gain variation amount detecting section (9) detect a period having a possibility of a DC-component offset in an internal circuit of a direct conversion receiver increasing beyond an allowable value due to AGC operation, and during the period, a cut-off frequency of each of high-pass filters (12a to 12d) is set at a frequency higher than that in general operation, thereby rapidly converging transient responses of signals passed through the high-pass filters, while controlling precisely operation timings of reception power measuring section (16), gain calculating section (22), gain control section (23) and circuit power supply control section (24) composing an AGC loop, whereby the DC offset is prevented from increasing and stable circuit operation is assured. It is thereby possible to achieve further reductions in size and power consumption of a CDMA receiver using the direct conversion receiver.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
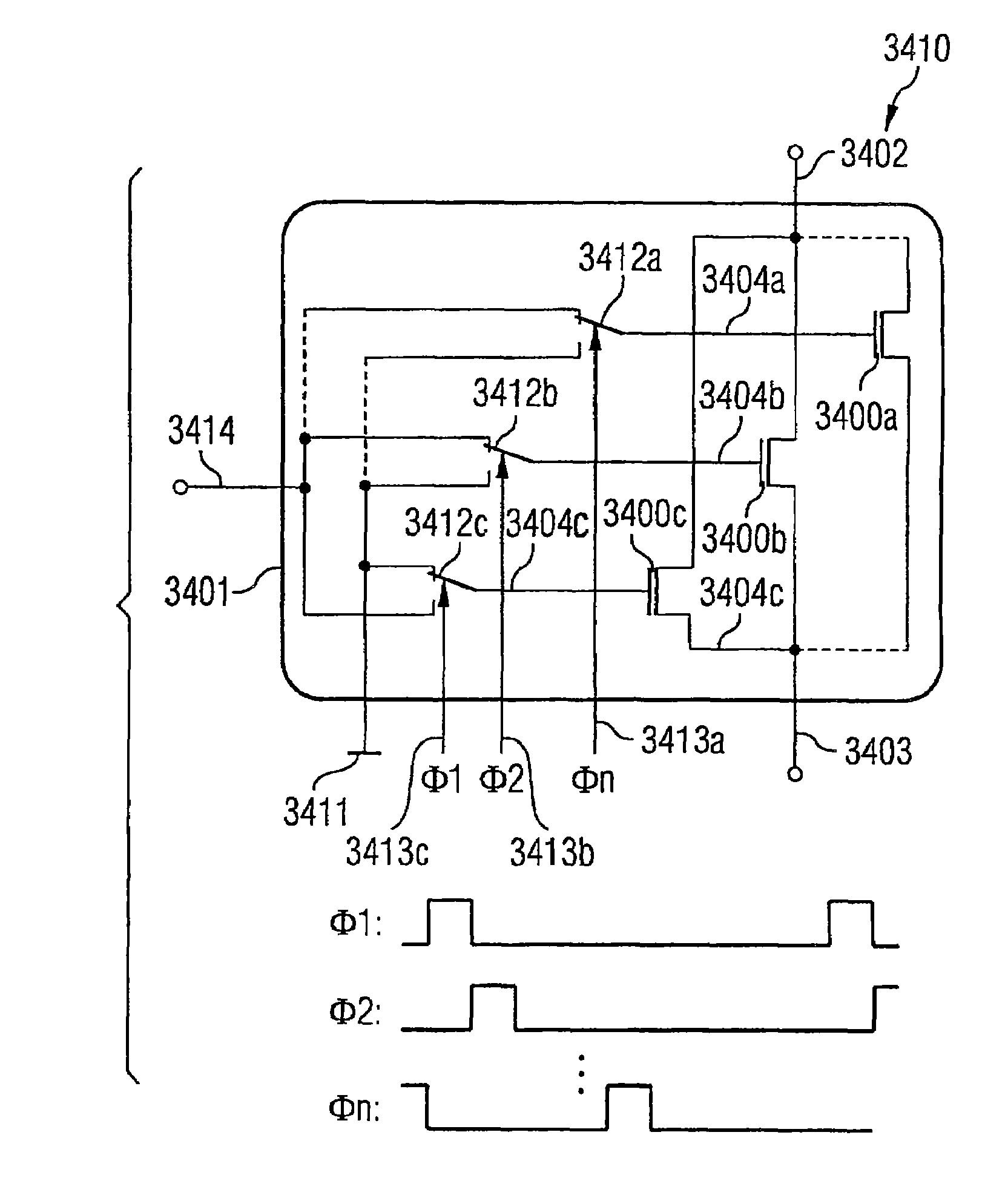
Noise-reducing transistor arrangement
Noise-reducing transistor arrangement having first and second field effect transistors (FETs) having source terminals coupled together, drain terminals coupled together, and control terminals for application of a first or second signal. A clock generator unit is configured to provide the first and second signals alternately to the FETs with an alternating frequency which is at least as great as the cut-off frequency of the noise characteristic of the FETs, or with a reciprocal alternating frequency which is less than a mean lifetime of an occupation state of a defect in the boundary region between channel region and gate insulating layer of the FETs. The first signal is applied to the control terminal of the first FET and, simultaneously, the second signal to the control terminal of the second FET. The second signal is applied to the control terminal of the first FET and, simultaneously, the first signal to the control terminal of the second FET.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
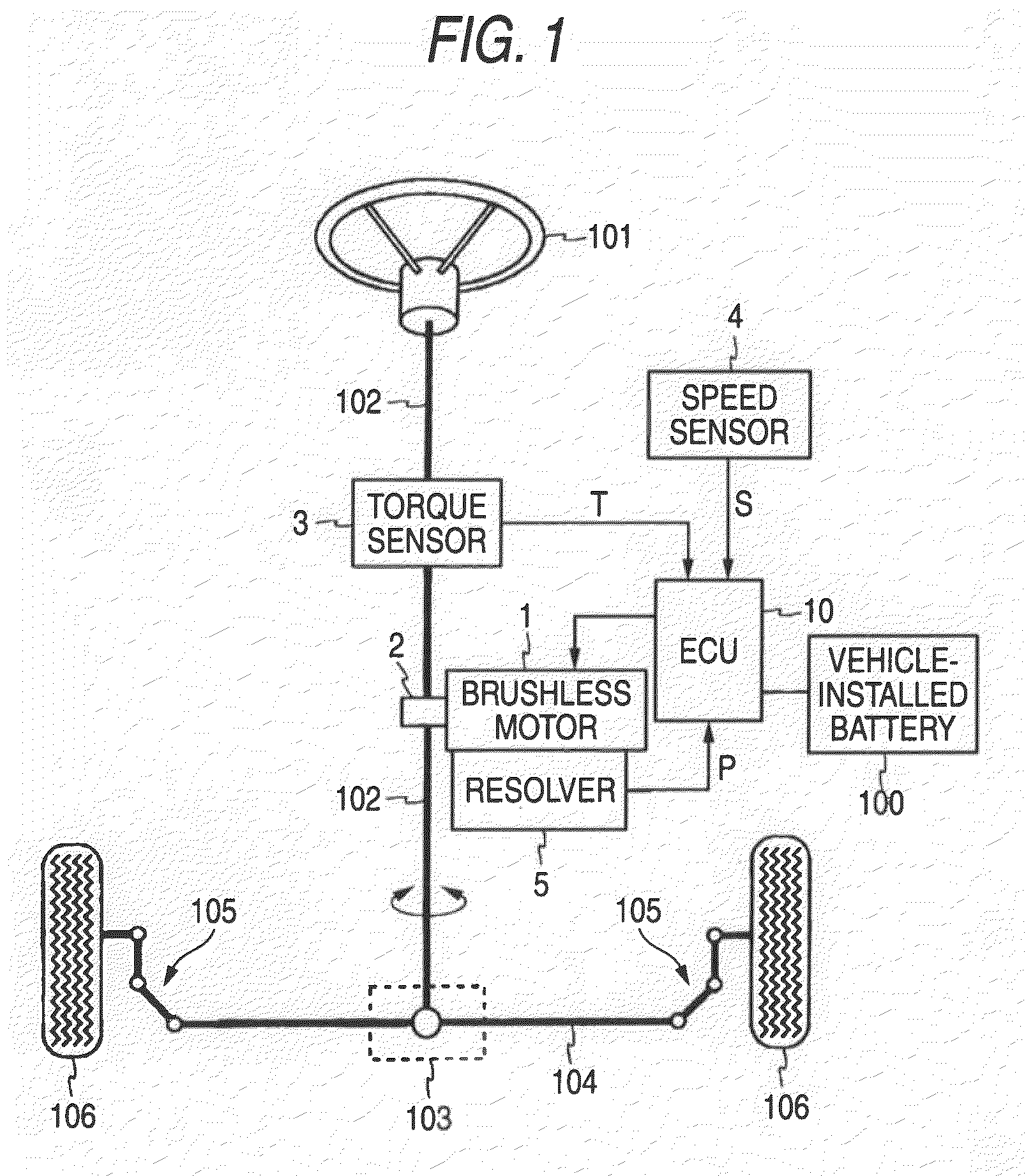
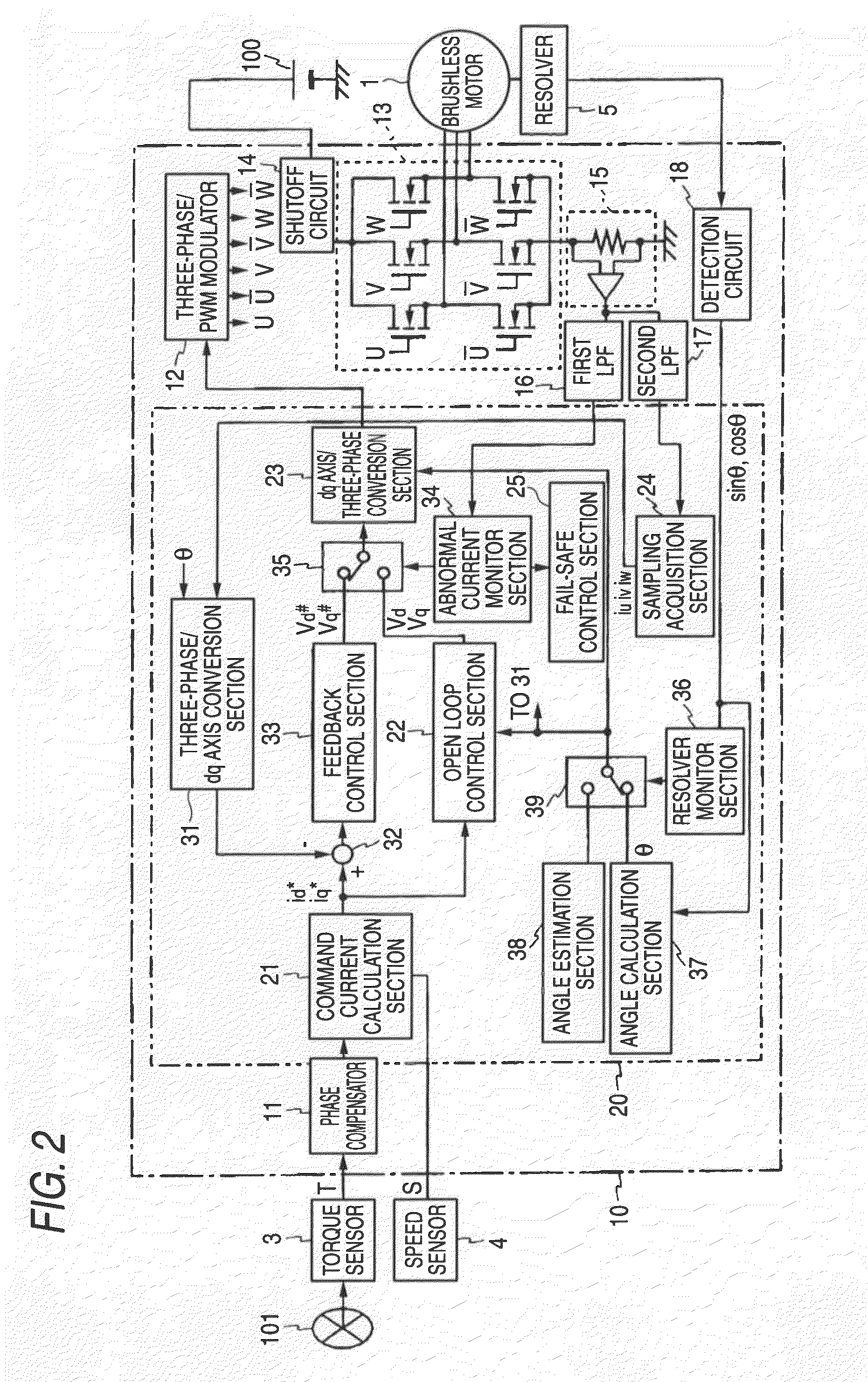
Motor controller and electric power steering system
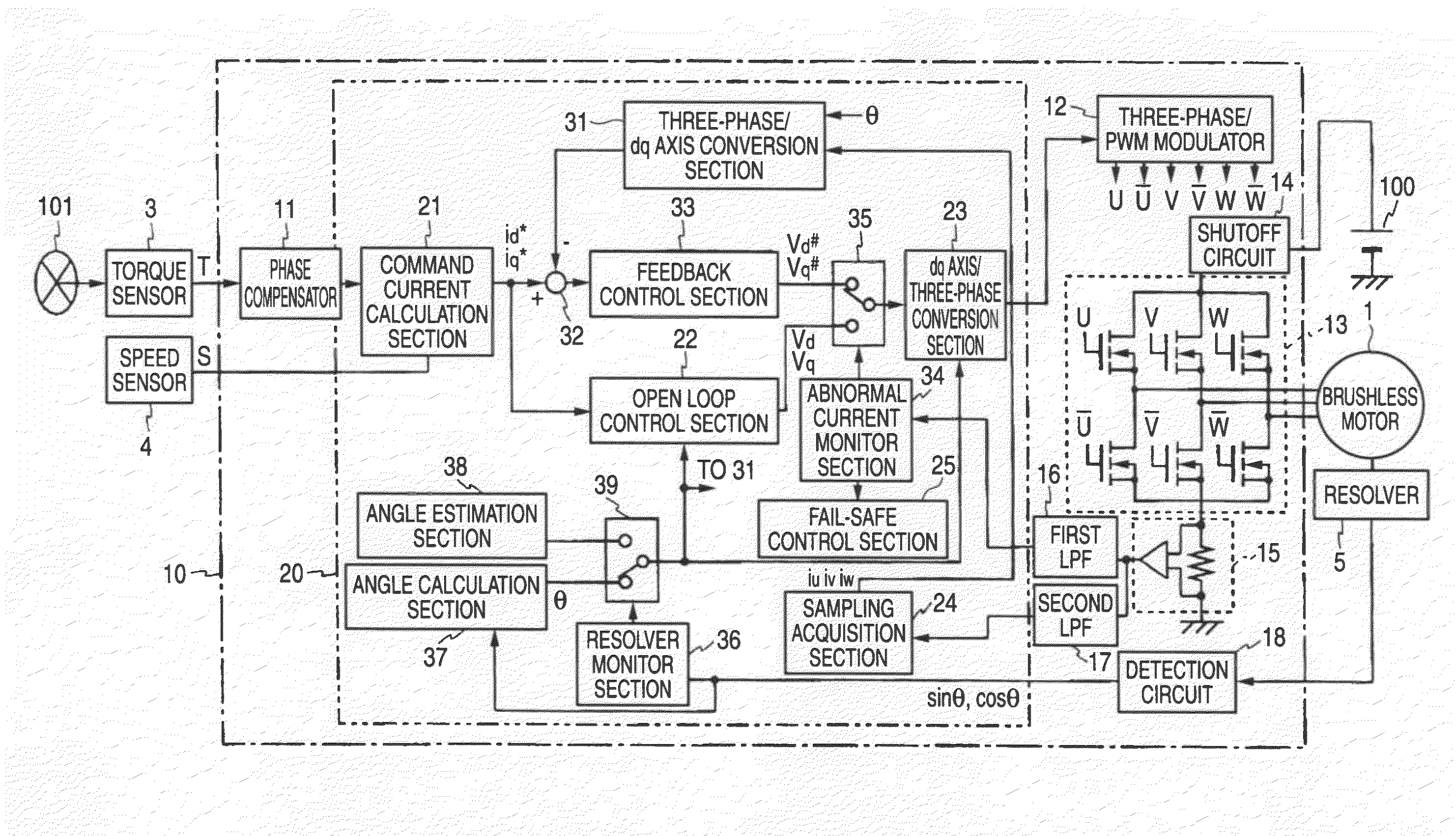
InactiveUS20090079373A1Lower cutoff frequencySafe steering assistingCommutation monitoringAC motor controlElectric power steeringMicrocomputer
A current sensor of a motor controller detects the current applied to a motor drive circuit and thus a phase where a failure cannot be detected would occur without taking any measures. However, an abnormal current monitor section contained in a microcomputer receives a voltage signal of an average value of the currents detected in the current sensor by allowing a signal to pass through a first LPF having a cutoff frequency sufficiently lower than the frequency of a PWM signal. Therefore, whether or not the value is within a predetermined normal range is checked, whereby whether or not some failure containing a failure of the current sensor occurs can be easily determined about every phase.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com