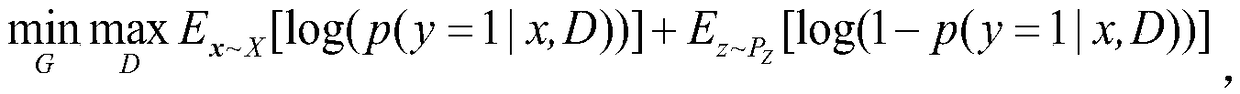Patents
Literature
1560 results about "Random noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
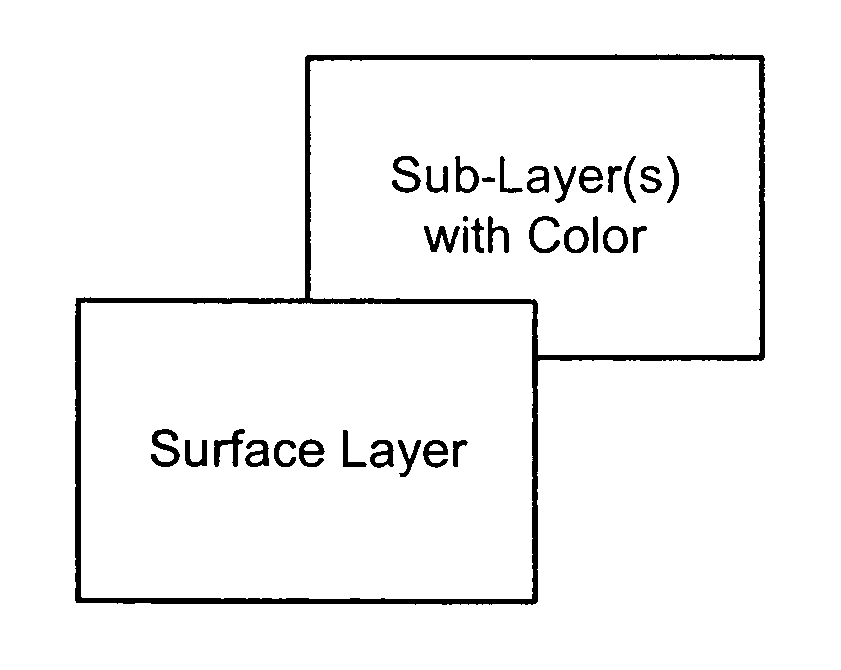
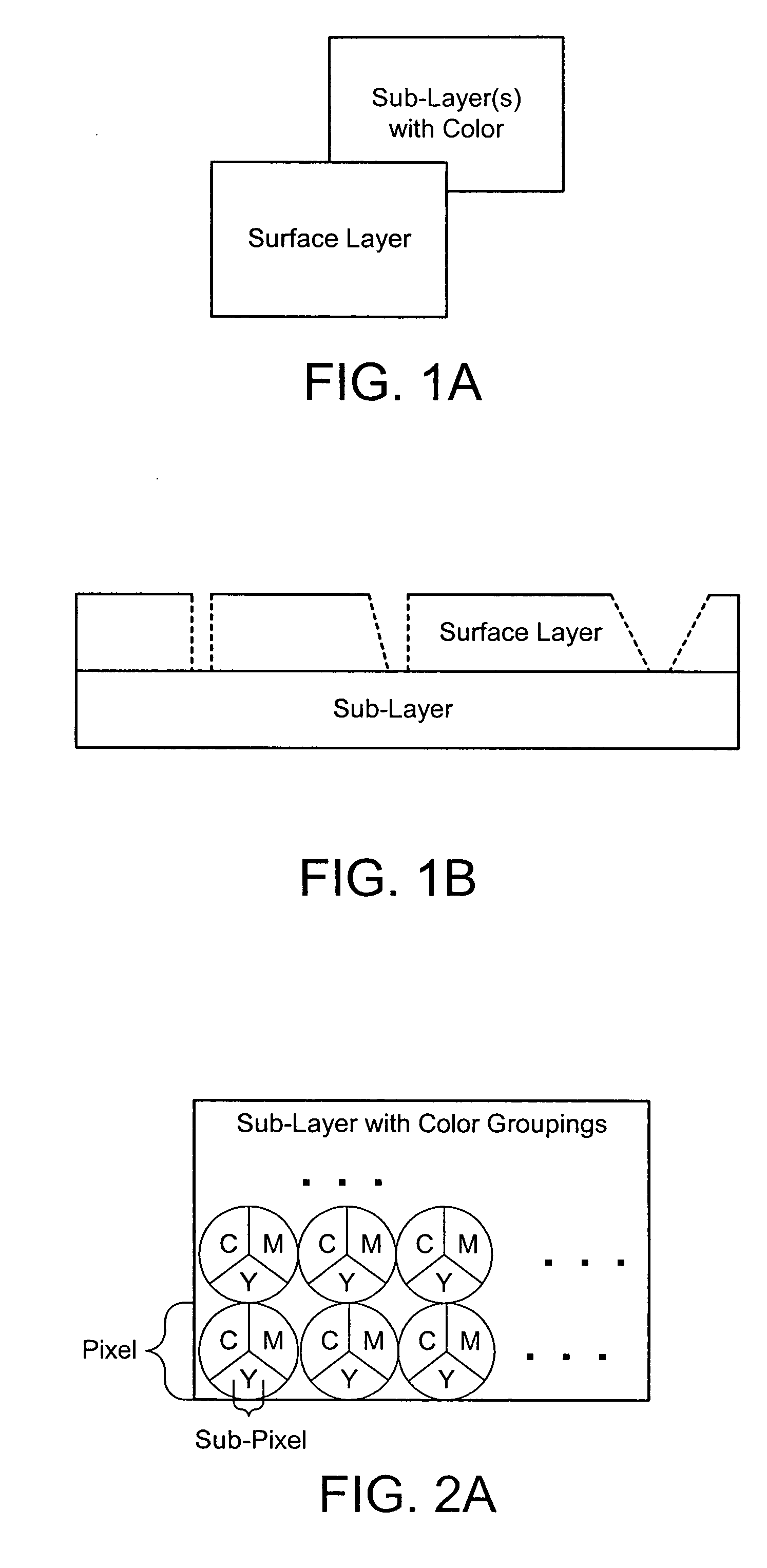
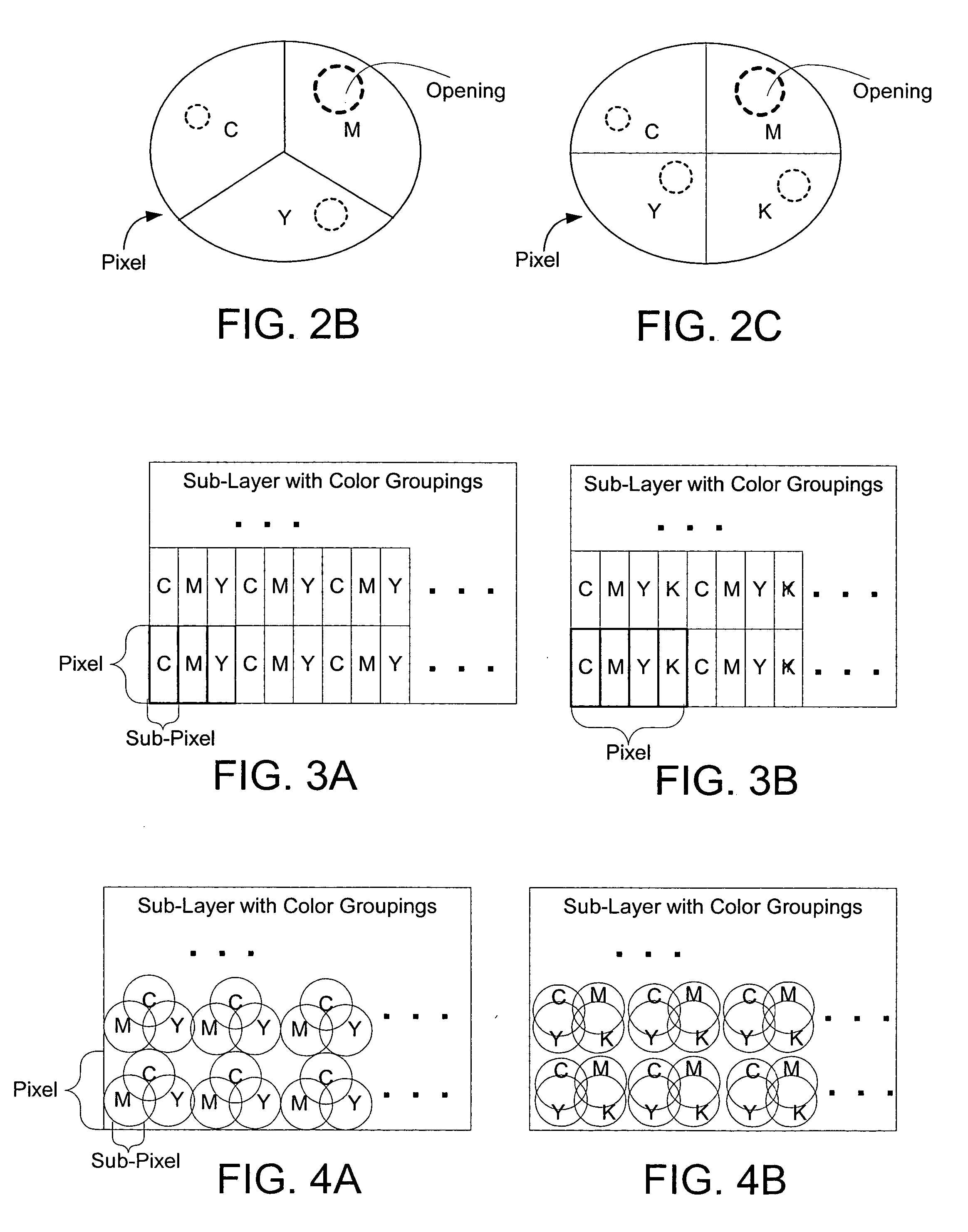
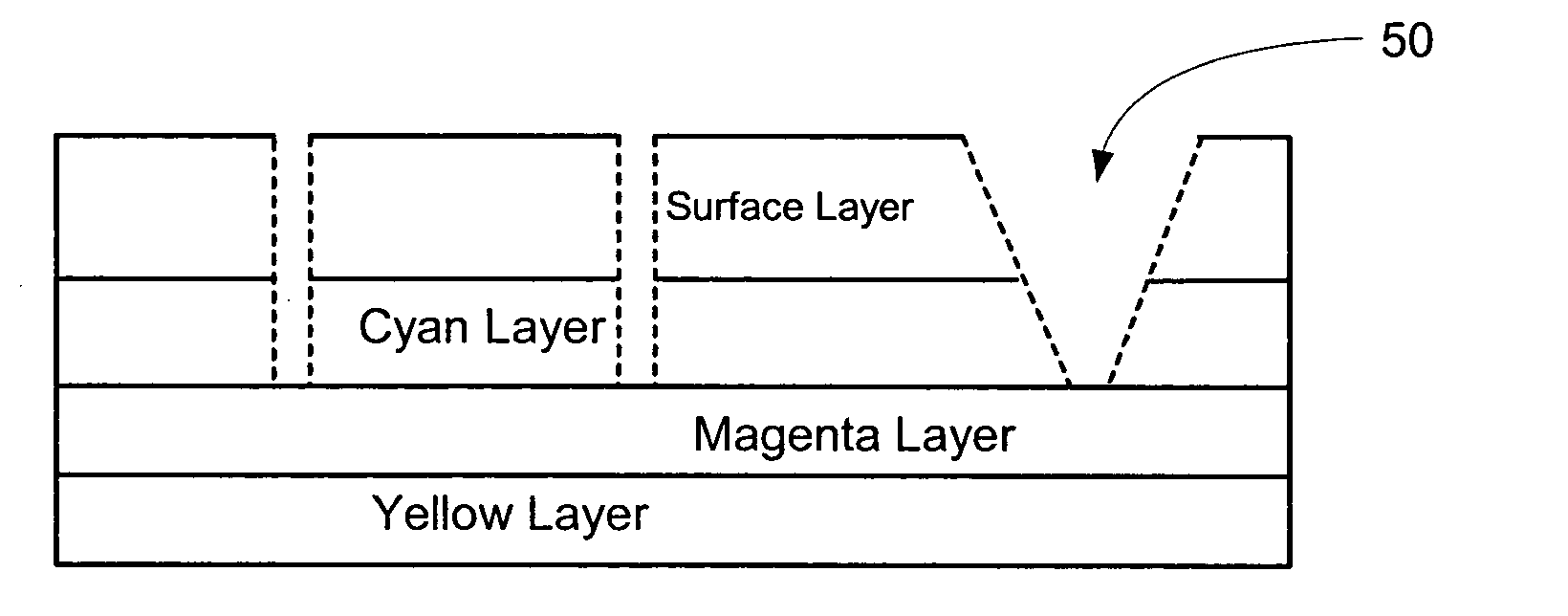
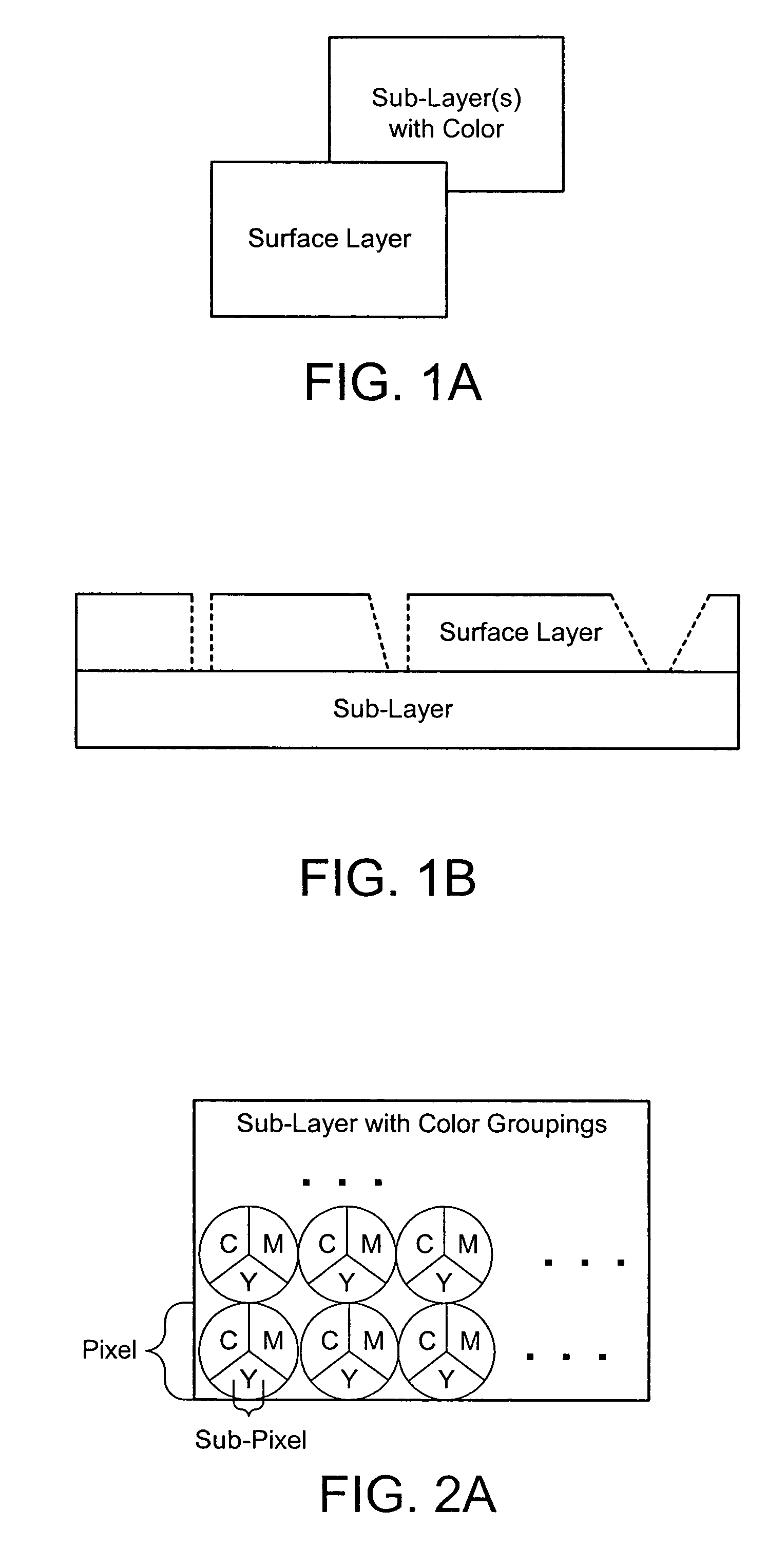
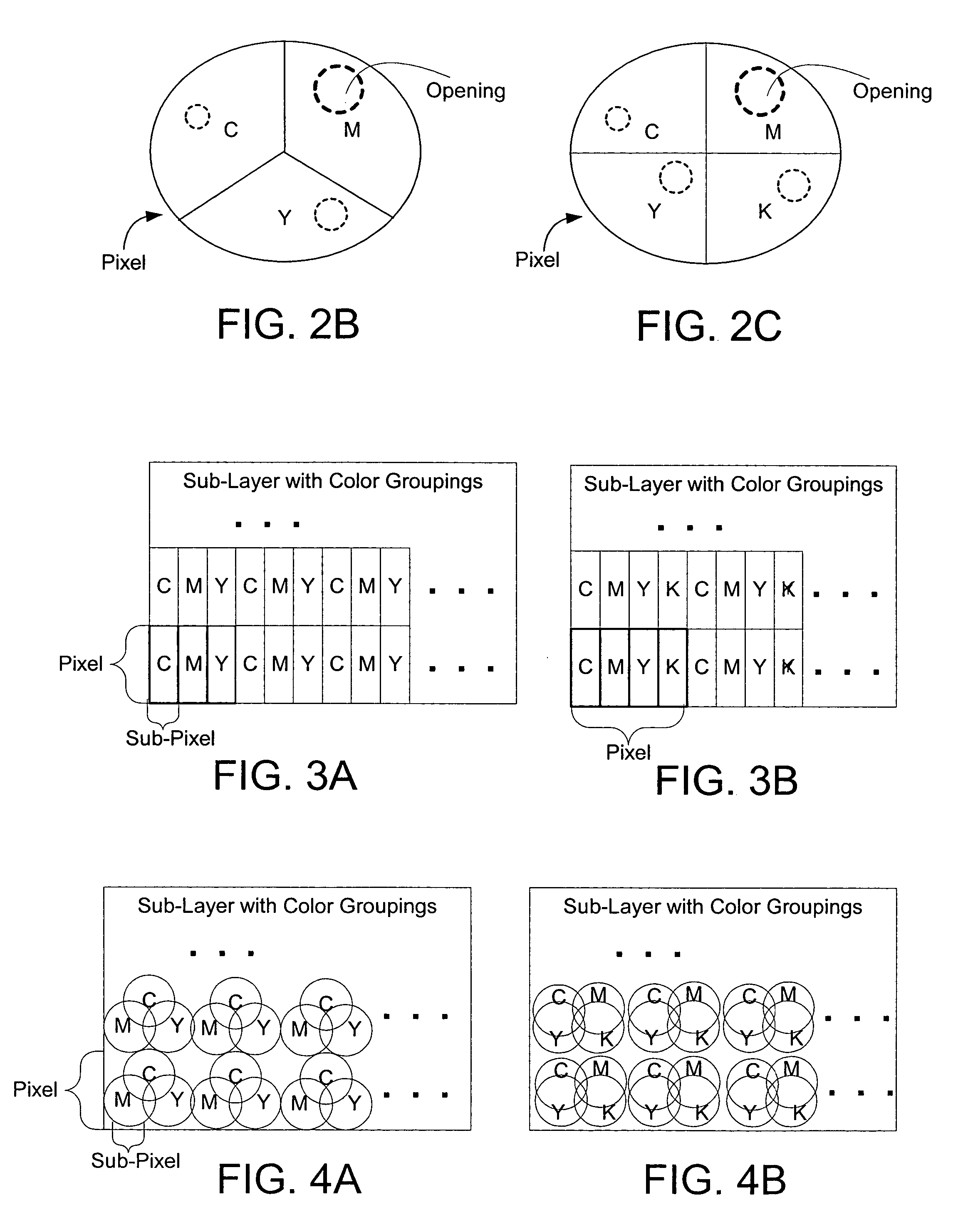
Color laser engraving and digital watermarking
A color laser engraving method engraves a document including a surface layer and one or more sub-layers. The sub-layer includes different colors and orientations of ink. A laser provides openings in the surface layer—to expose color ink in the sub-layer—to create color images and / or text. The different orientations of the colored inks include, e.g., circular, linear and overlapped groupings of ink. A sub-layer preferably includes many repeated instances of the grouping. A digital watermark is embedded in a document via transfer of the digital watermark in an embedded image or text, or by pre-embedding the document via altering intensity of colored inks on the original document card stock. A digital watermark can be carried via modulation with a pseudo-random noise sequence.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
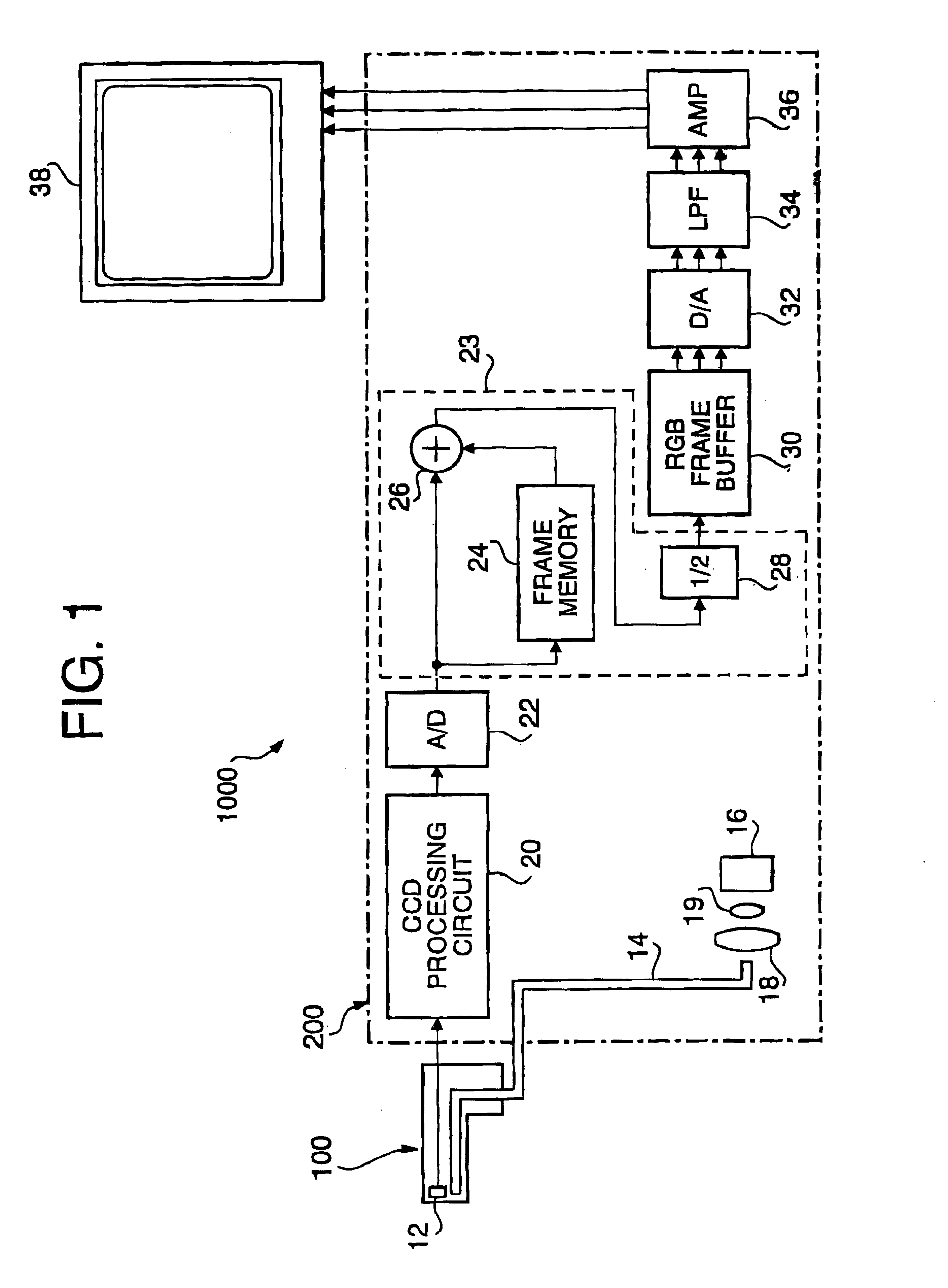
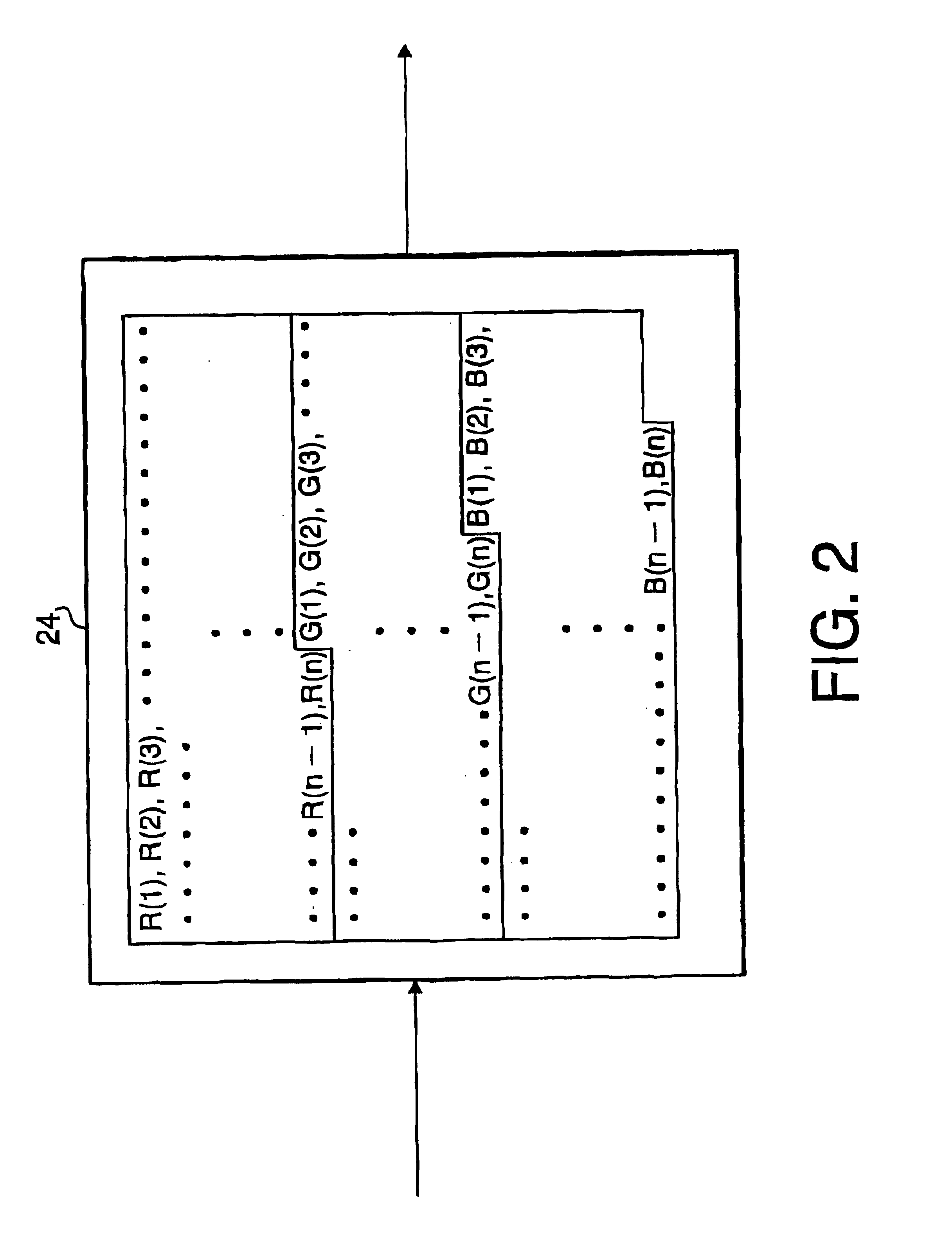
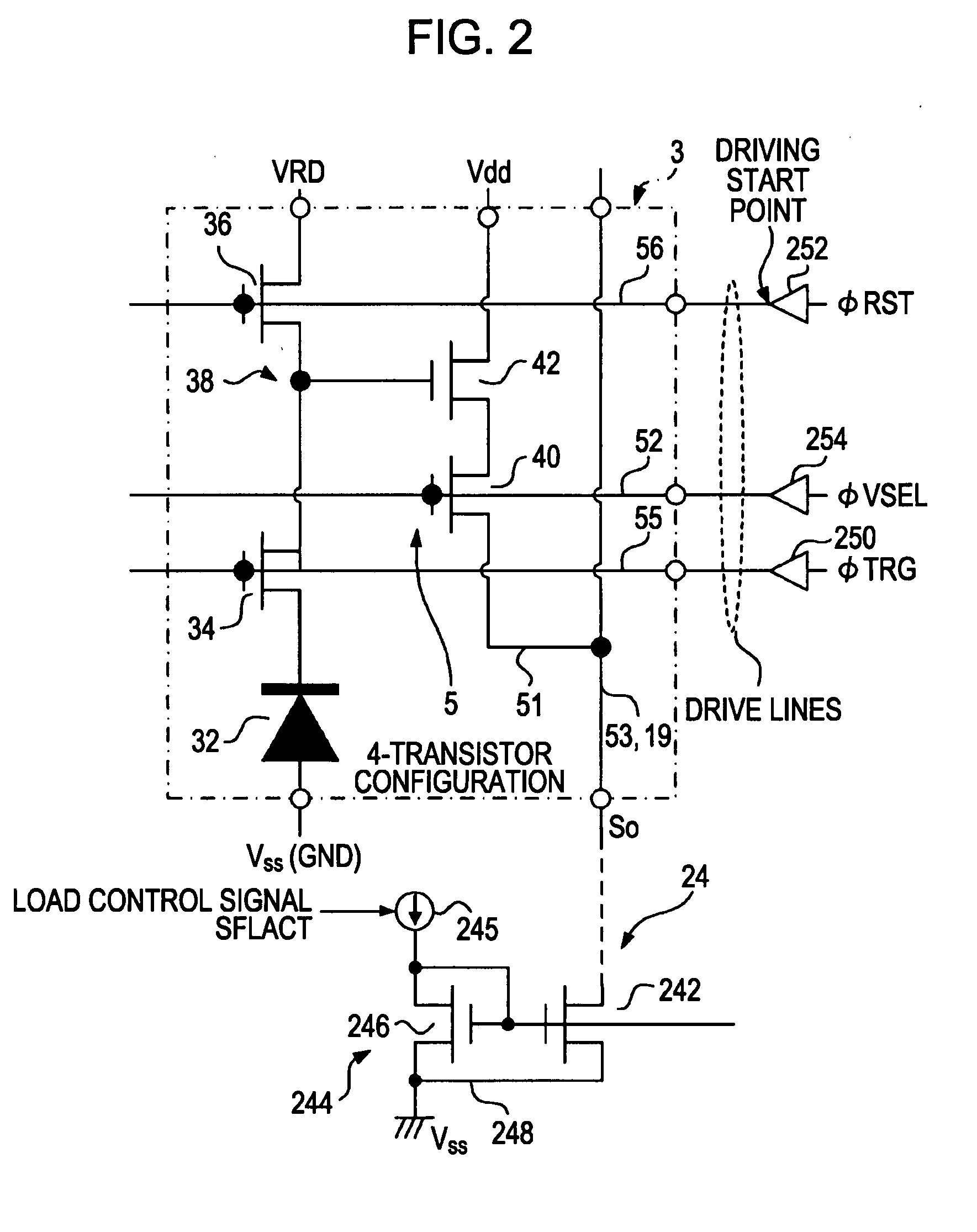
Electronic endoscope system for reducing random noise of a video signal
InactiveUS6900829B1Reduce random noiseClear imagingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image
An electronic endoscope system which captures an image of an object and displays the same on a display device is provided with a noise reduction system. The noise reduction system reduces noise included in a frame of an image signal for each color component. The noise-reduced color components are stored in a buffer, and then output as a video signal to be transmitted to a display where a color image of the object is displayed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
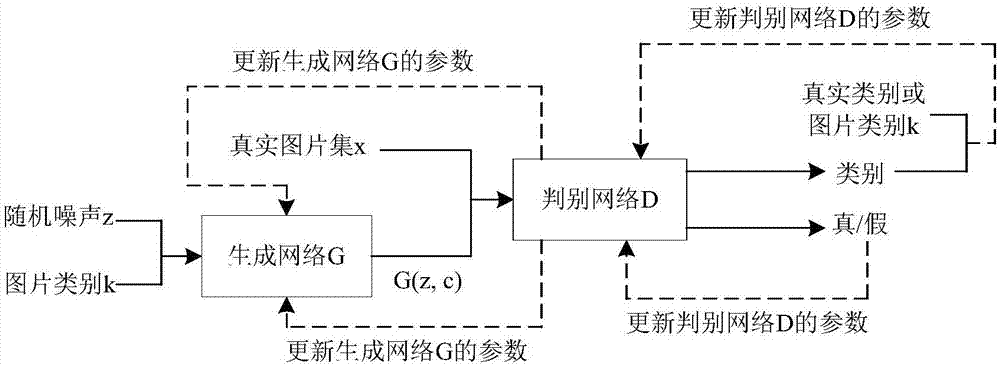
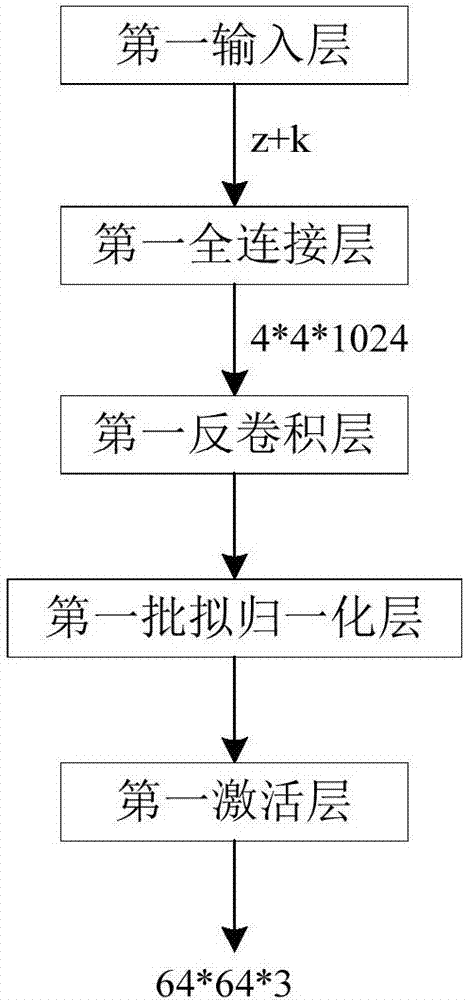
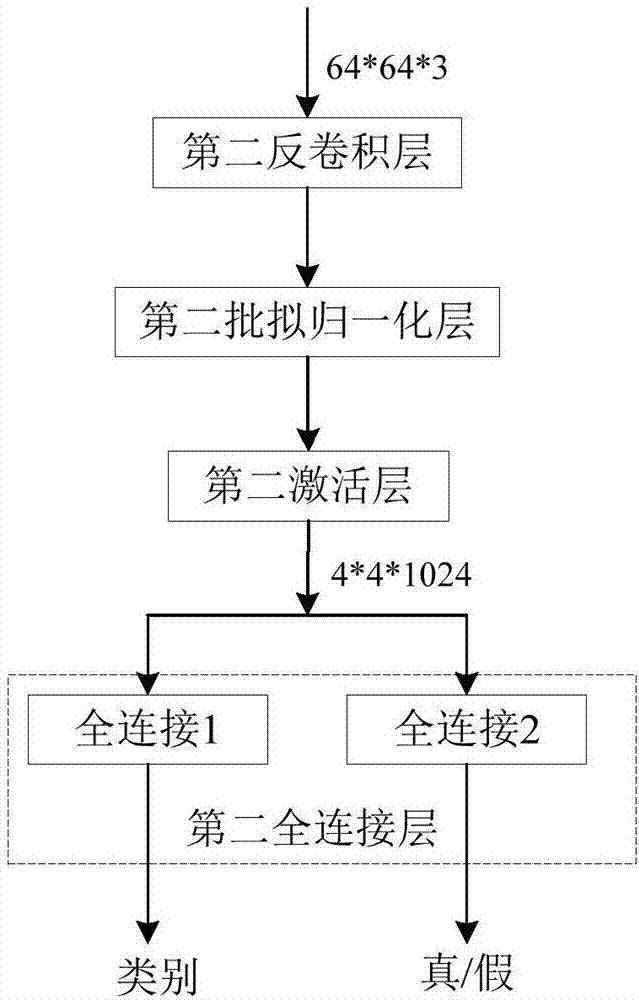
Picture generation method based on depth learning and generative adversarial network
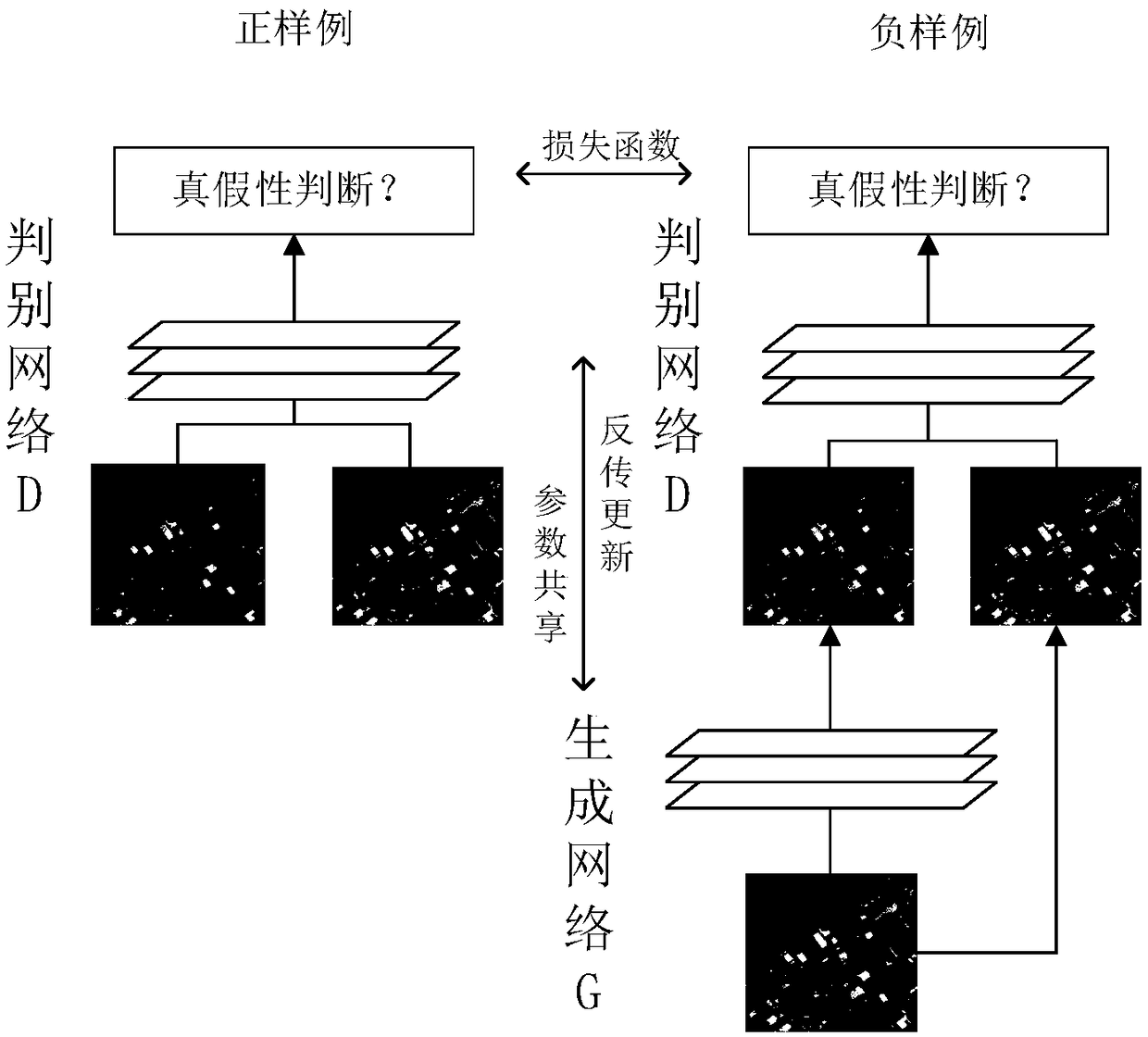
The invention discloses a picture generation method based on depth learning and a generative adversarial network. The method comprises steps that (1), a picture database is established, multiple real pictures are collected and are further classified and marked, and each picture has a unique class label k corresponding to the each picture; (2), the generation network G is constructed, a vector combined by a random noise signal z and the class label k is inputted to the generation network G, and generated data is taken as input of a discrimination network D; (3), the discrimination network D is constructed, and a loss function of the discrimination network D comprises a first loss function used for determining true and false pictures and a second loss function used for determining picture classes; (4), the generation network is trained; (5), needed pictures are generated, the random noise signal z and the class label k are inputted to the generation network G trained in the step (4) to acquire pictures in a designated class. The method is advantaged in that not only can the pictures can be generated, but also the designated generation picture classes can be further realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
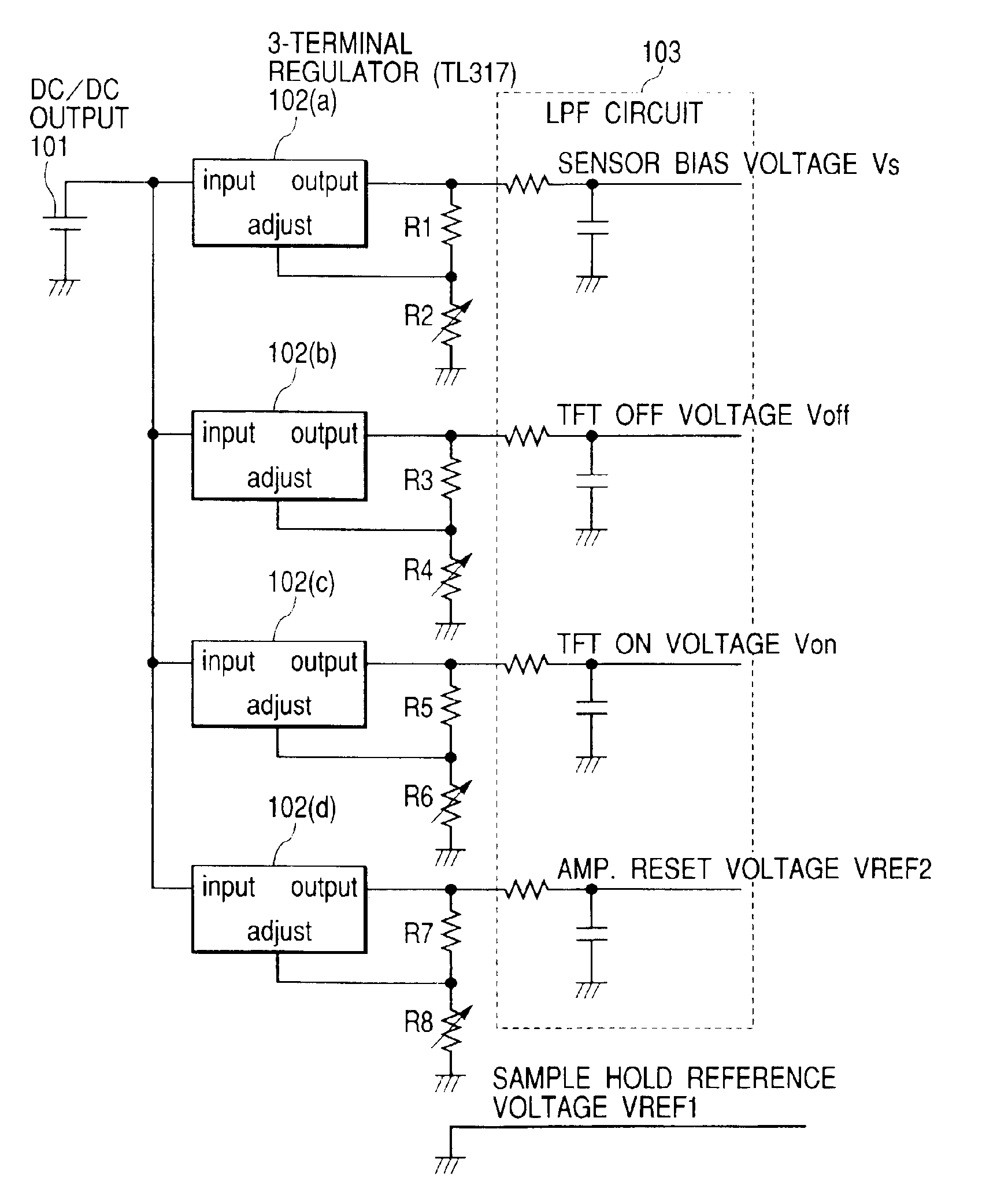
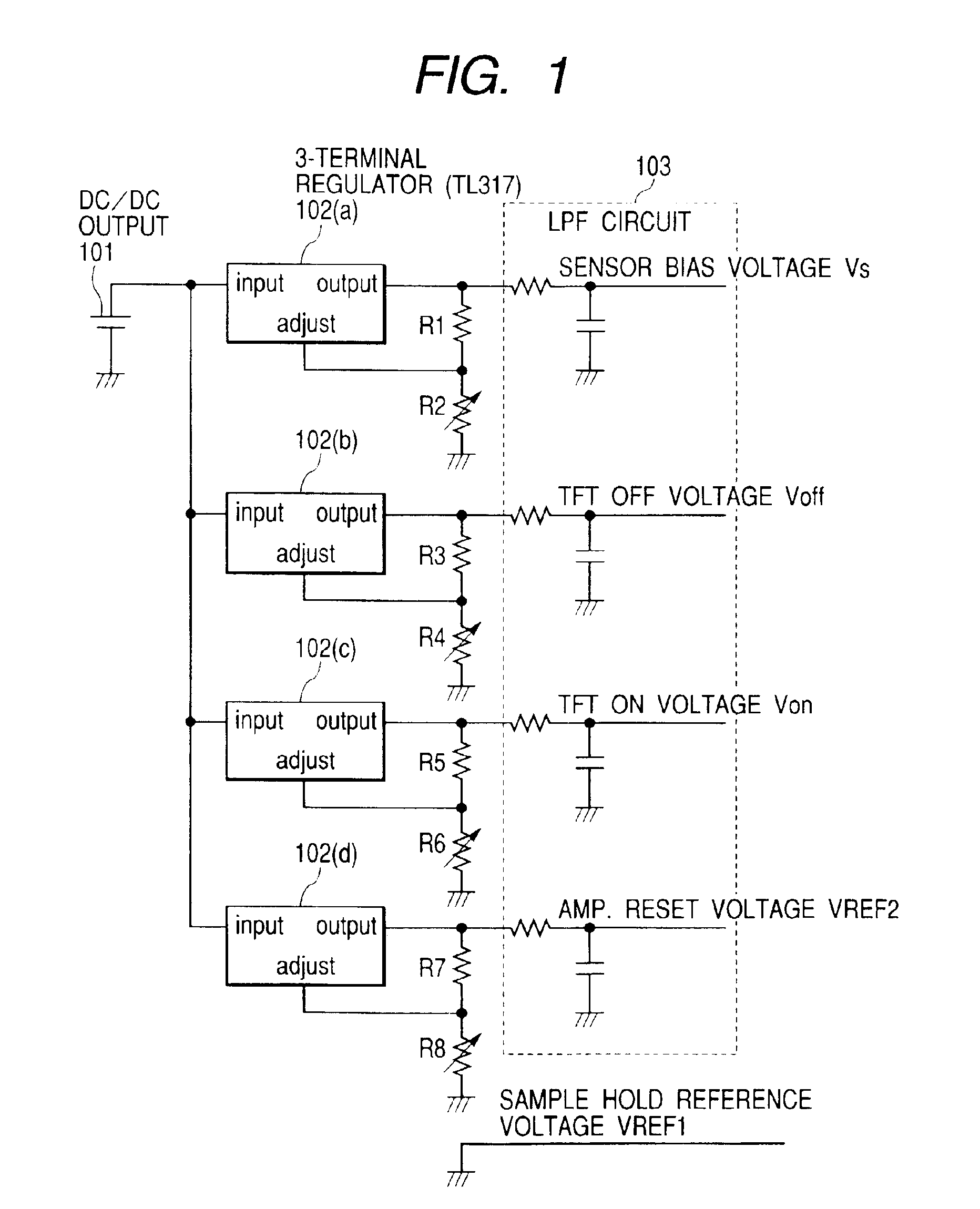
Image pick-up apparatus and image pick-up system
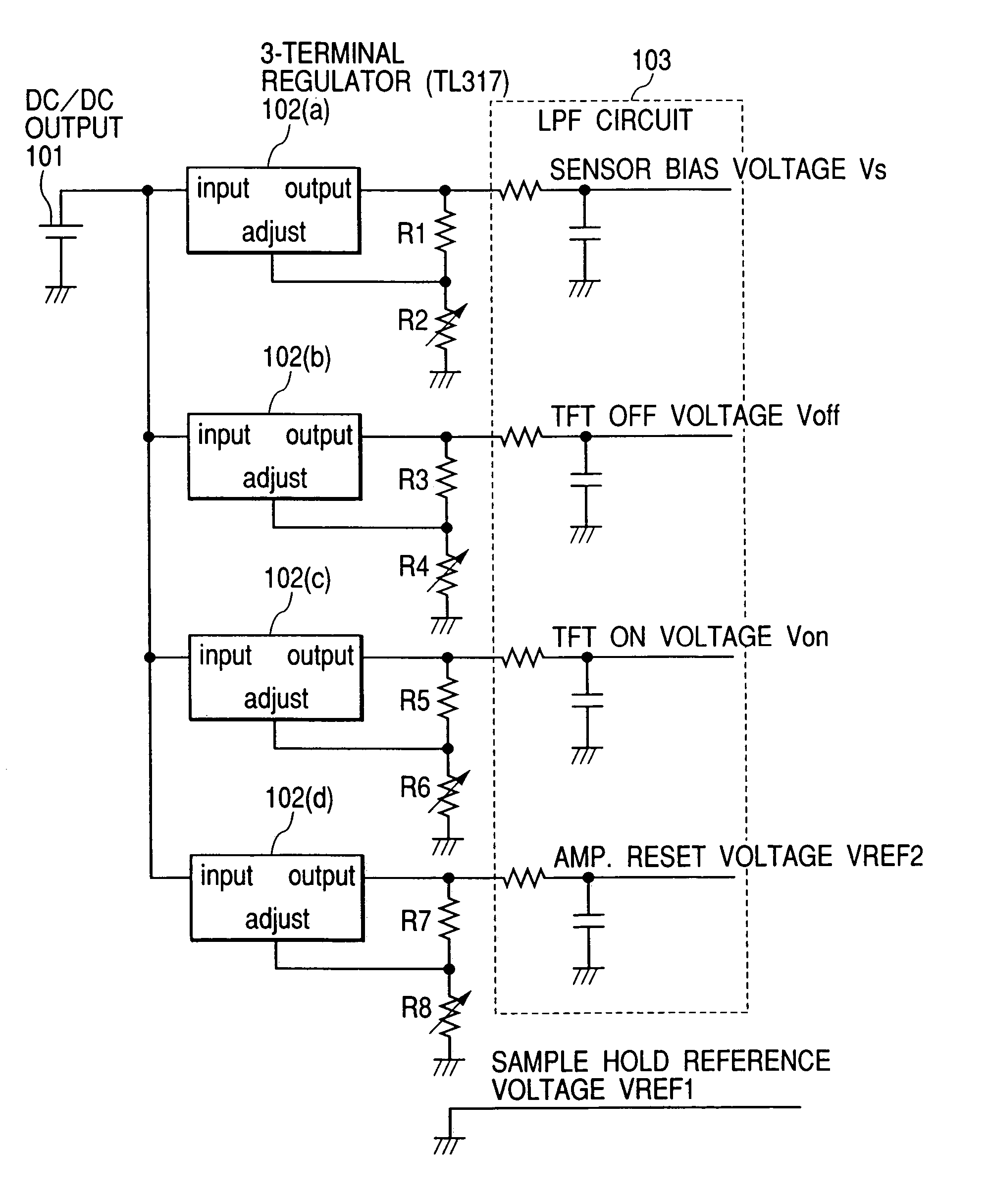
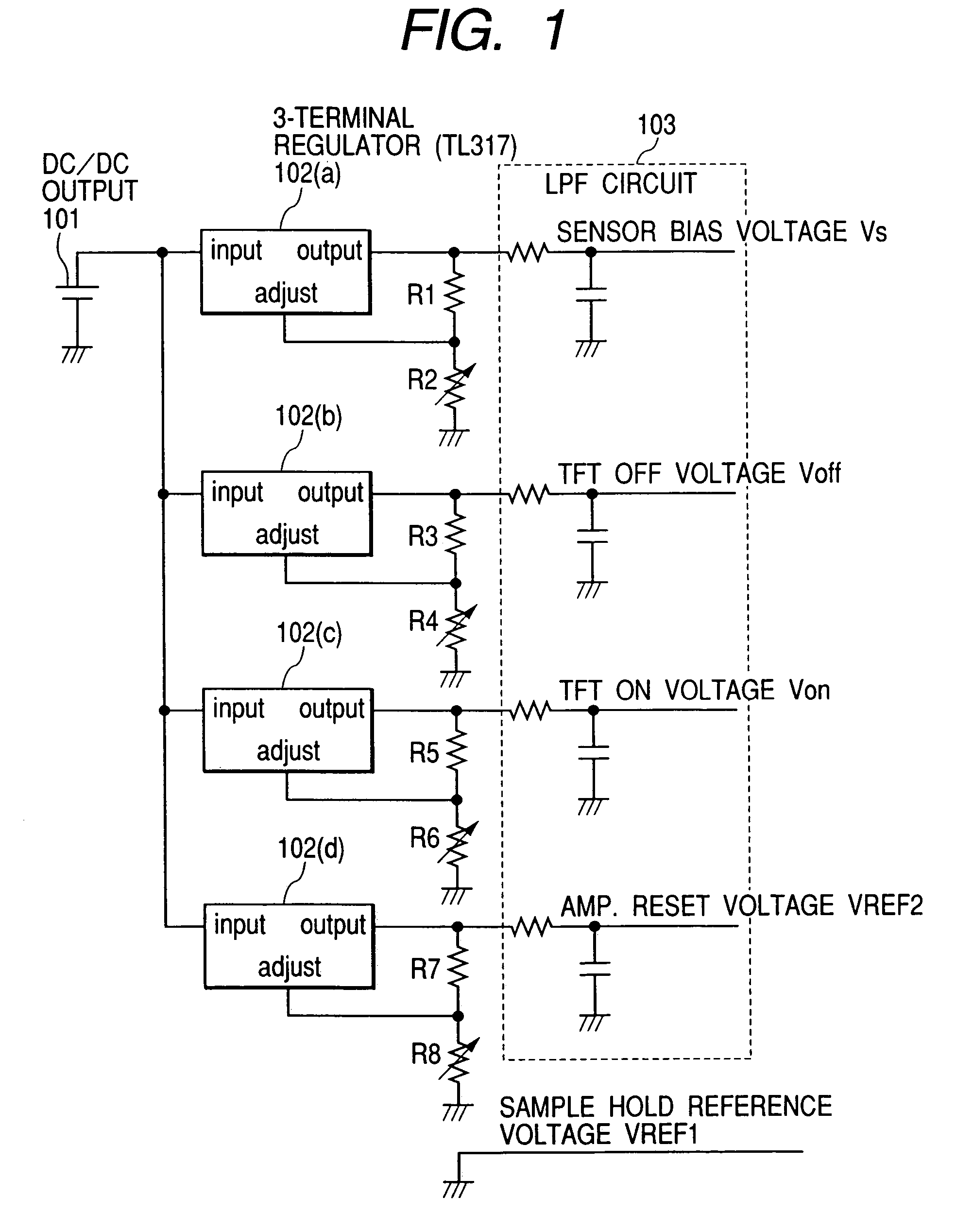
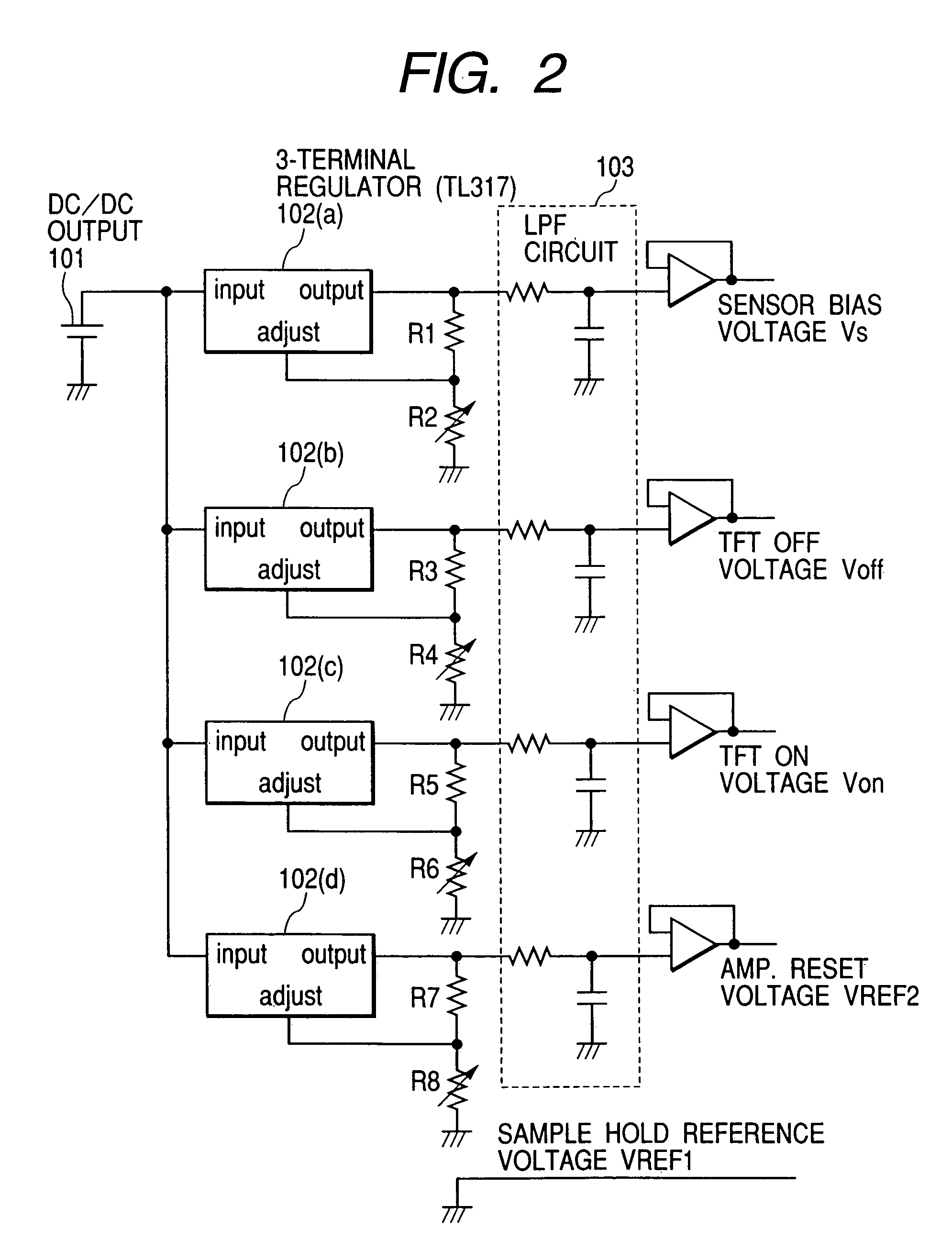
An image pick-up apparatus and an image pick-up system constructed to prevent occurrence of random noise in a photographed image due to a random noise component produced in a reference supply circuit. An image pick-up apparatus has an area sensor driven by matrix driving, and a reference supply circuit for supplying a reference voltage for driving of the area sensor, and the reference voltage is supplied through a low-pass filter (LPF) coupled to the reference supply circuit. Further, a cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter preferably is determined so that an effective value of noise of the reference voltage having passed through the low-pass filter becomes not more than one-tenth of an effective value of random noise produced in pixels of the area sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
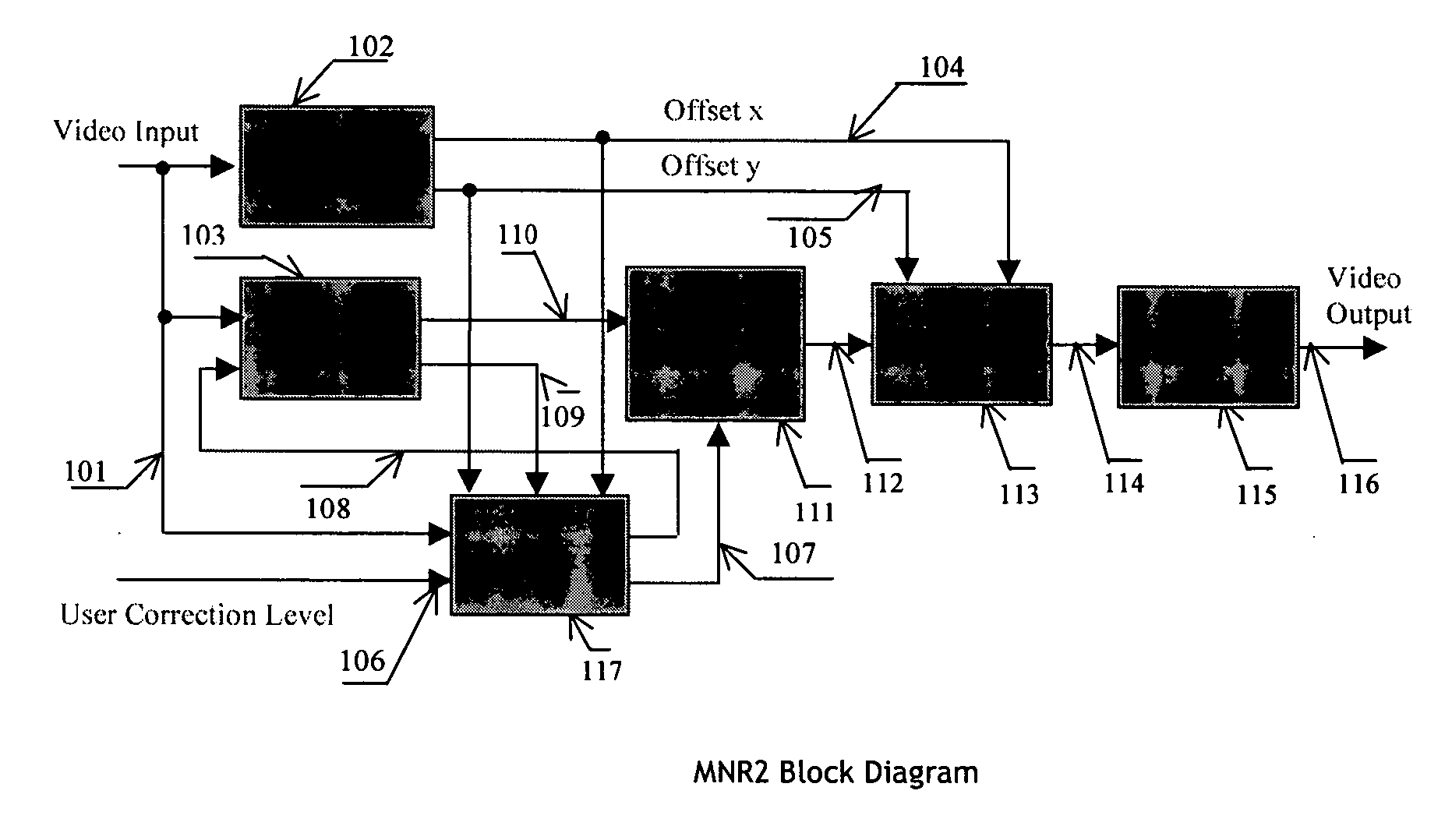
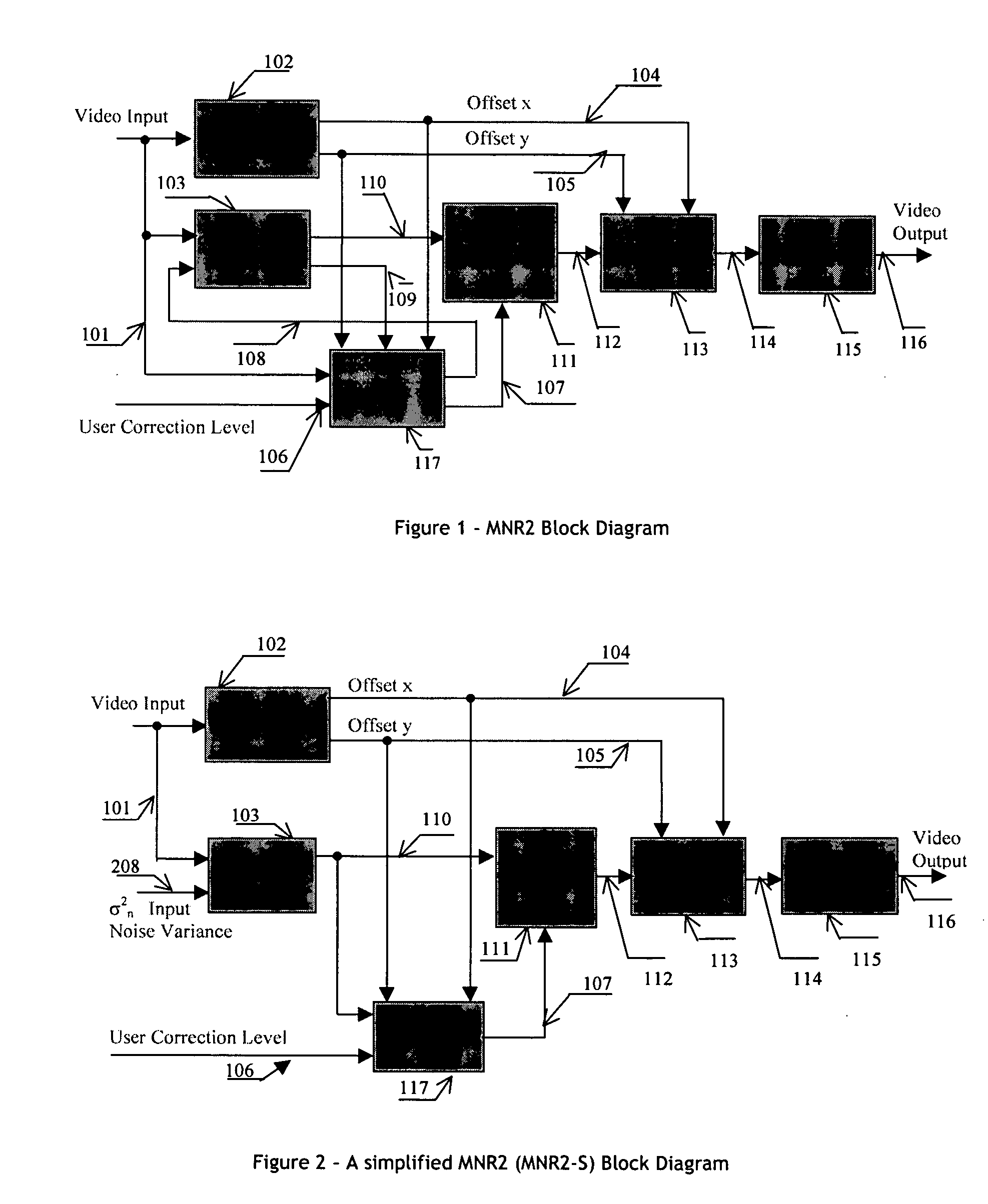
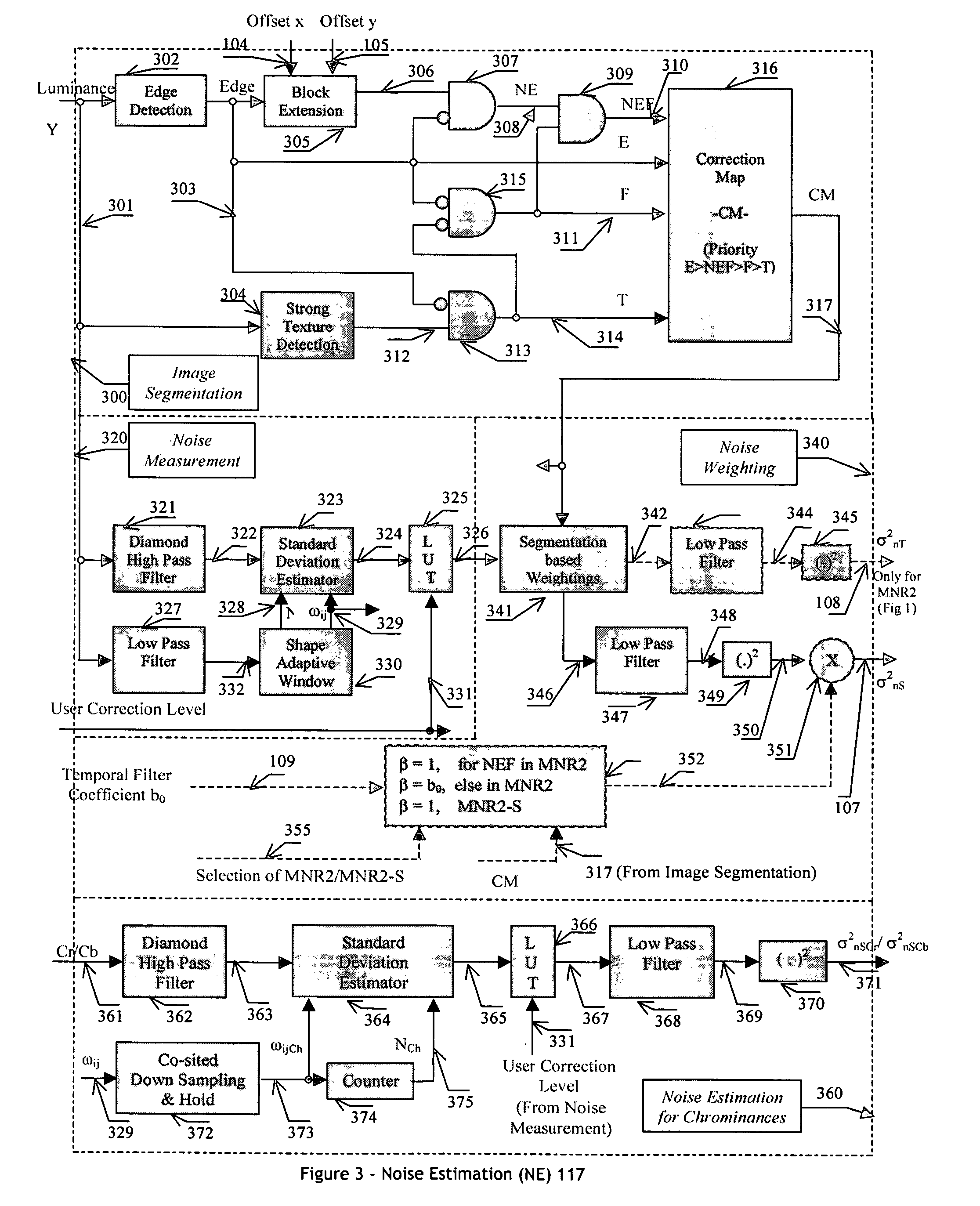
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
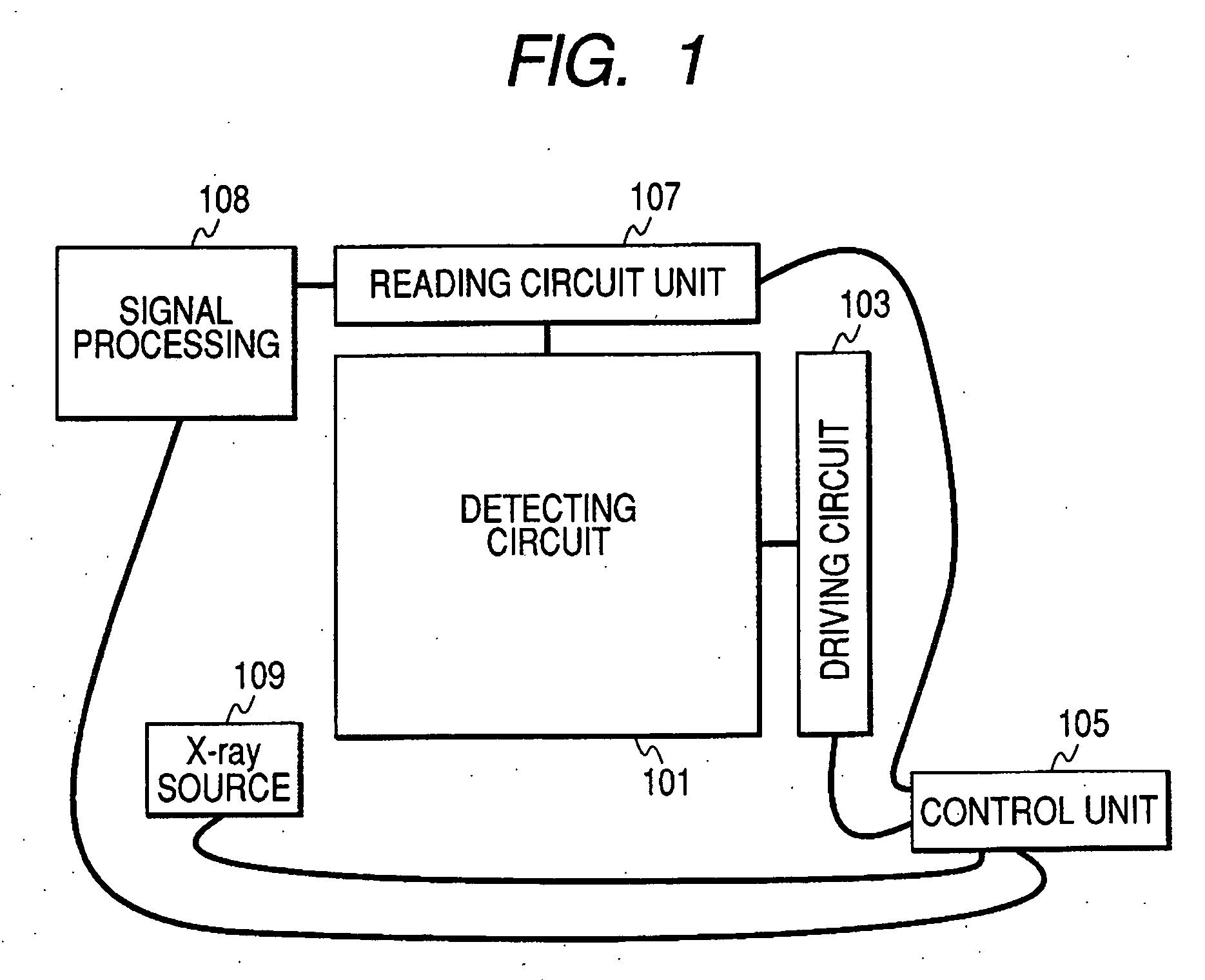
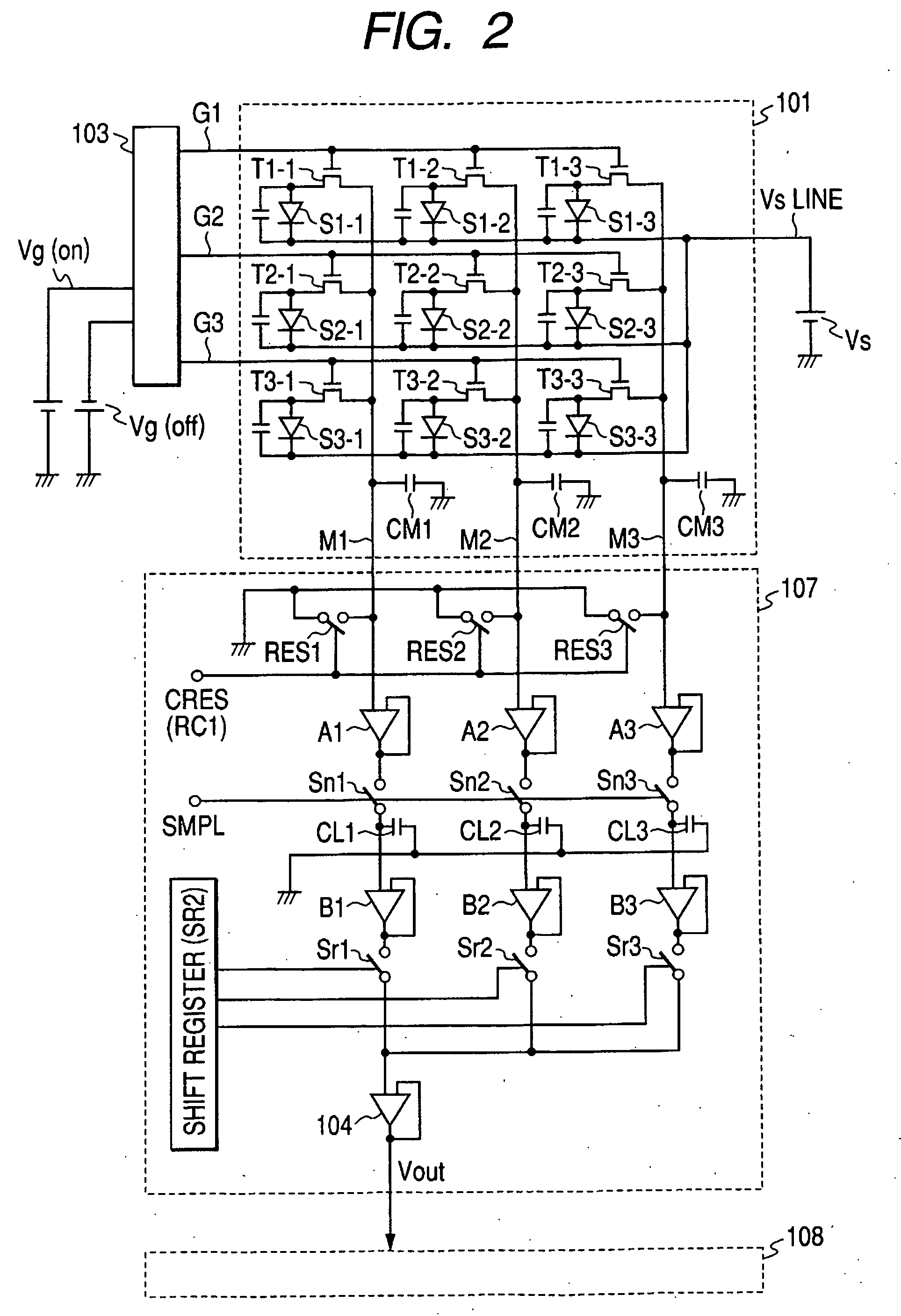
Radiation image pickup apparatus, radiation image pickup system, their control method and their control program
InactiveUS20070040099A1Improve image qualityImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesRandom noiseRadiation exposure
A radiation image pickup apparatus which selectively executes a first reading operation driving a detection unit irradiated with the radiation to read a first signal value, a second reading operation driving the detection unit without being irradiated with any radiations before the first reading operation to read a second signal value, and a third reading operation driving the detection unit without being irradiated with any radiations after the first reading operation to read a third signal value, and subtracts a signal value produced by the processing of the second signal value and the third signal value from the first signal value, thereby reducing an offset component and random noises without lowering a frame rate and its control method are provided.
Owner:CANON KK
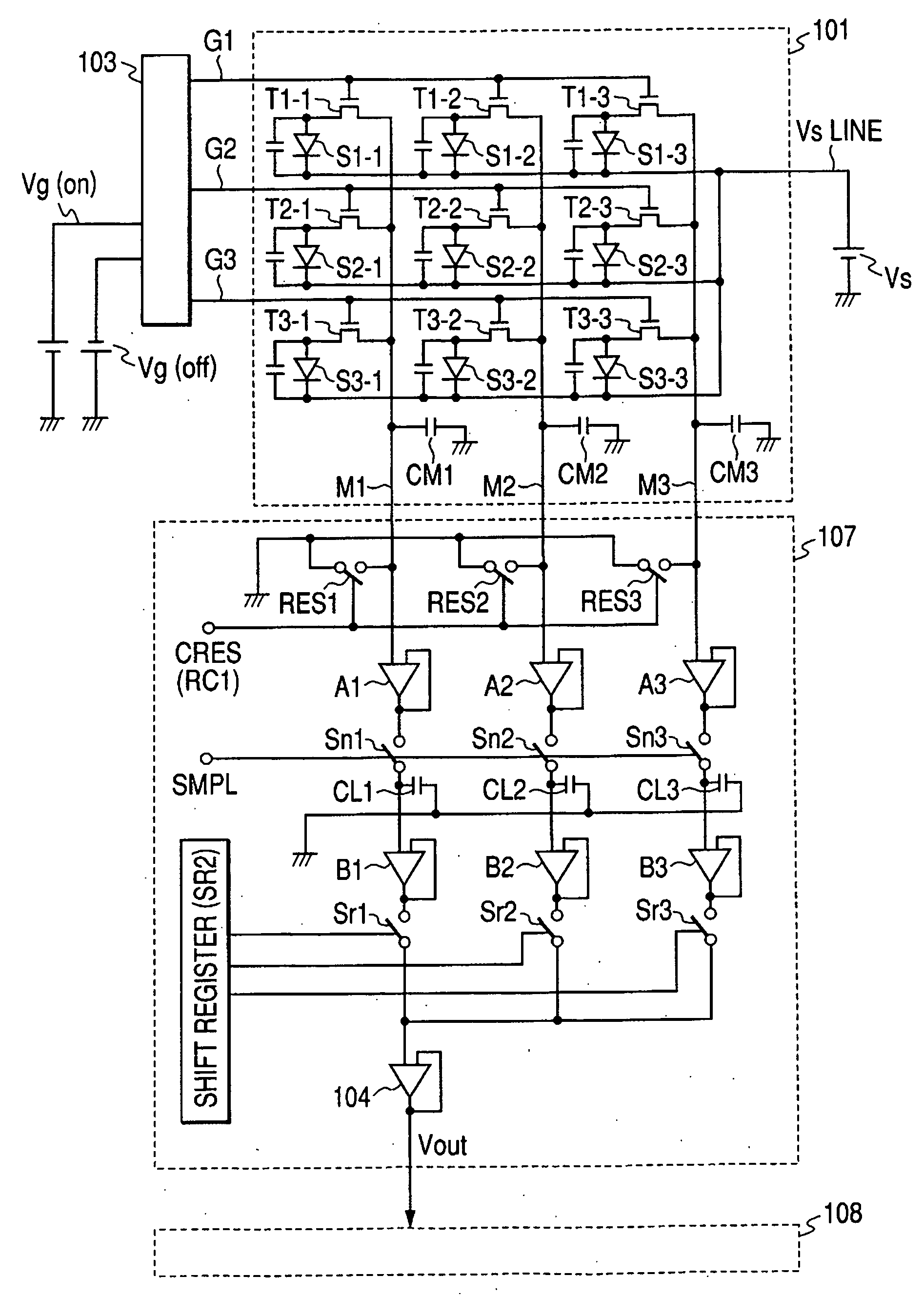
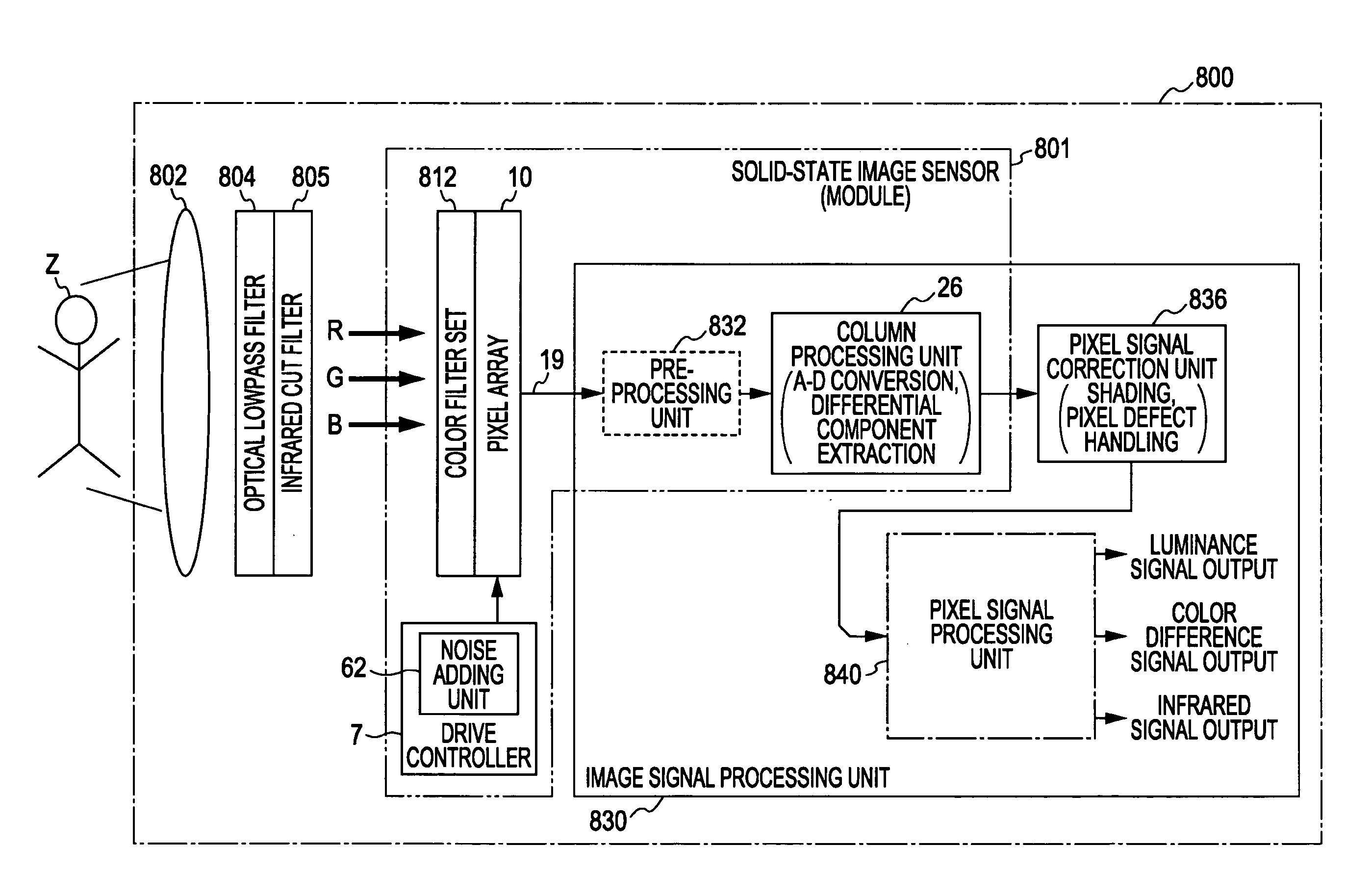
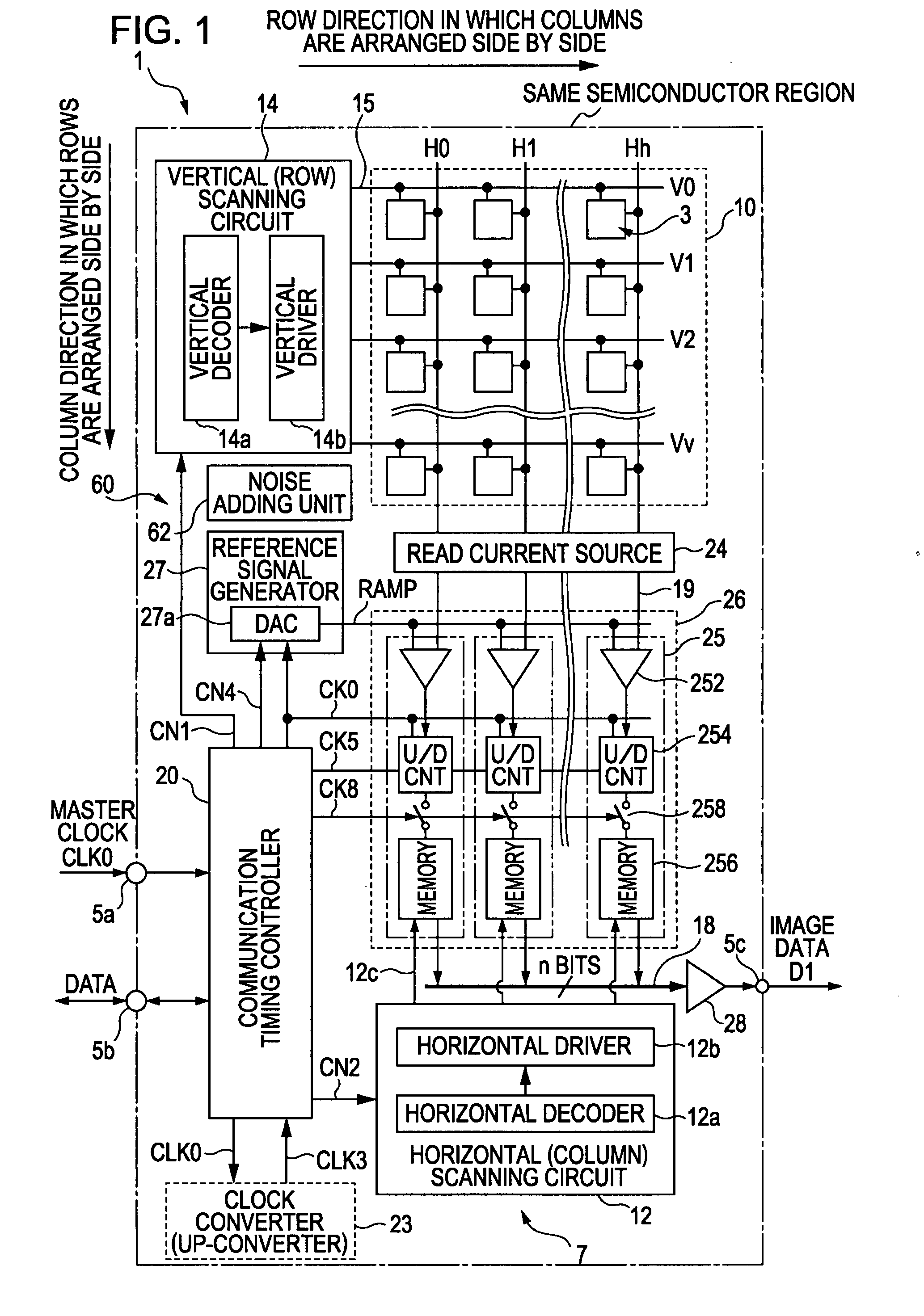
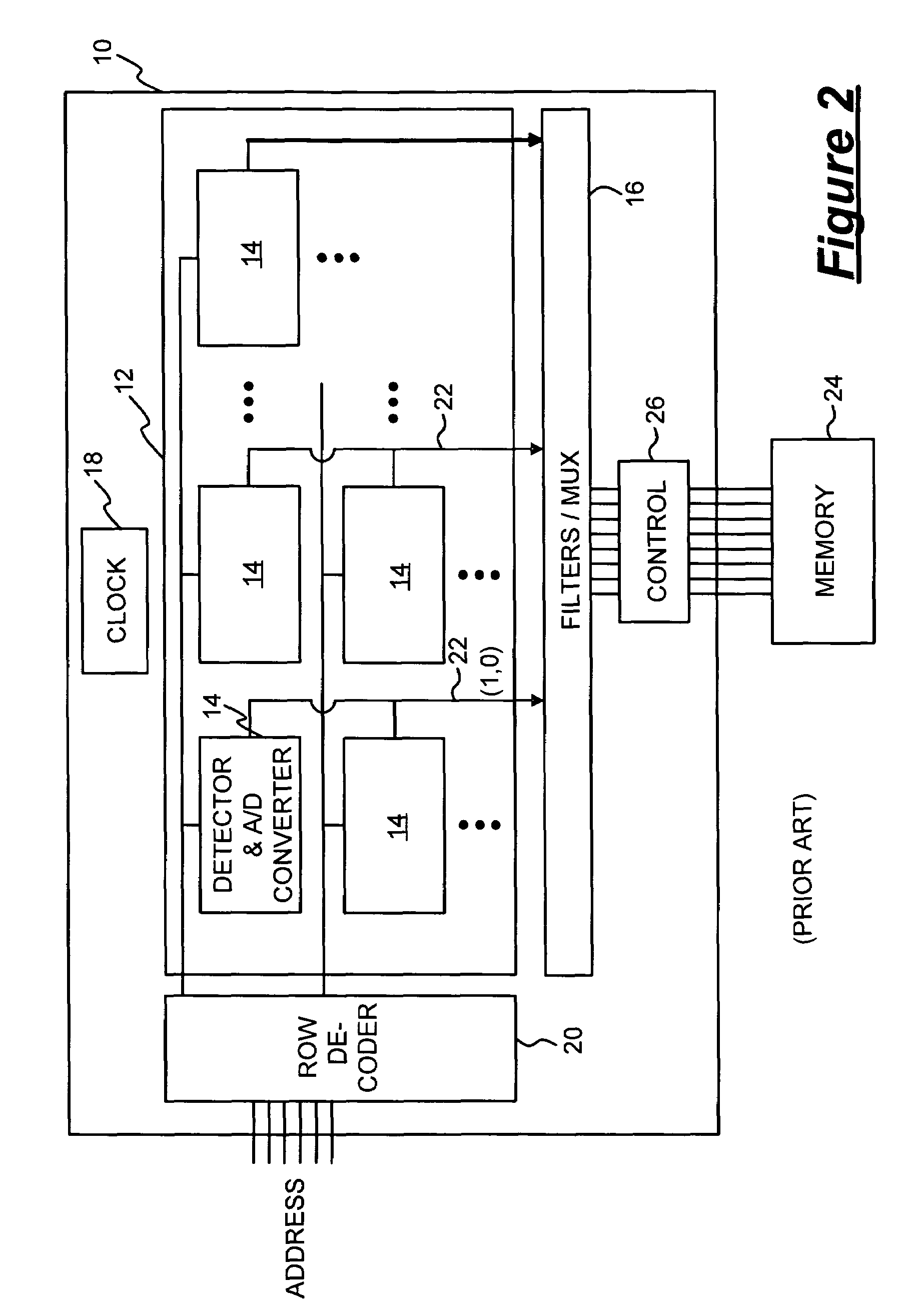
Solid-state image sensor and image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS20080055432A1Suppress vertical streak noiseSuppress noiseTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsRandom noiseAnalog-to-digital converter
A solid-state image sensor includes a pixel array unit including a plurality of pixels arranged in the form of an array, column signal lines adapted to transmit pixel signals output from pixels in respective columns, a noise adding unit adapted to add temporally constant and two-dimensional spatially random noise to the pixel signals transmitted via the column signal lines, and an analog-to-digital converter adapted to convert a signal level and a reference level of each pixel signal including the noise added thereto by the noise adding unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Color laser engraving and digital watermarking
A color laser engraving method engraves a document including a surface layer and one or more sub-layers. The sub-layer includes different colors and orientations of ink. A laser provides openings in the surface layer—to expose color ink in the sub-layer—to create color images and / or text. The different orientations of the colored inks include, e.g., circular, linear and overlapped groupings of ink. A sub-layer preferably includes many repeated instances of the grouping. A digital watermark is embedded in a document via transfer of the digital watermark in an embedded image or text, or by pre-embedding the document via altering intensity of colored inks on the original document card stock. A digital watermark can be carried via modulation with a pseudo-random noise sequence.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
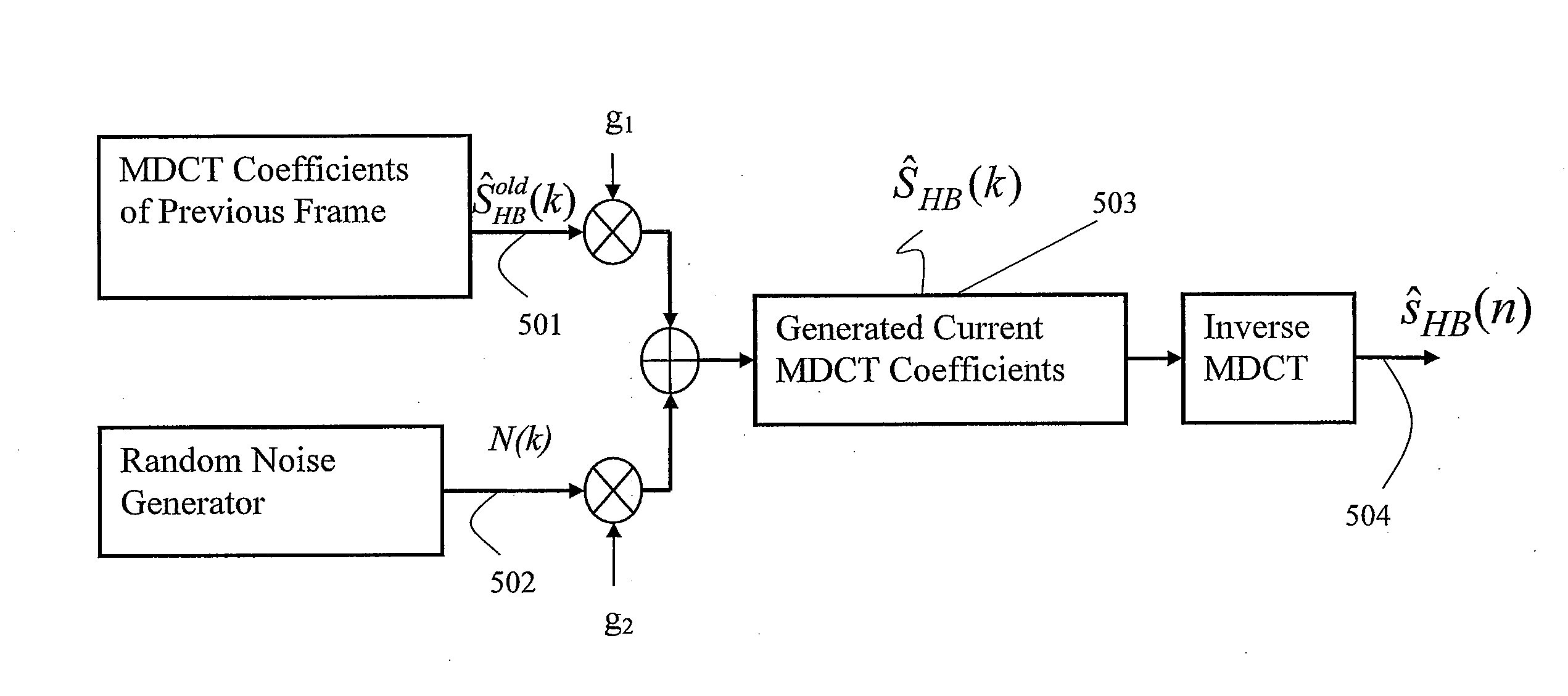
System and Method for Correcting for Lost Data in a Digital Audio Signal
ActiveUS20100286805A1Speech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsRandom noiseDigital audio signals
In an embodiment, a method of receiving a digital audio signal, using a processor, includes correcting the digital audio signal from lost data. Correcting includes copying frequency domain coefficients of the digital audio signal from a previous frame, adaptively adding random noise coefficients to the copied frequency domain coefficients, and scaling the random noise coefficients and the copied frequency domain coefficients to form recovered frequency domain coefficients. Scaling is controlled with a parameter representing a periodicity or harmonicity of the digital audio signal. A corrected audio signal is produced from the recovered frequency domain coefficients.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
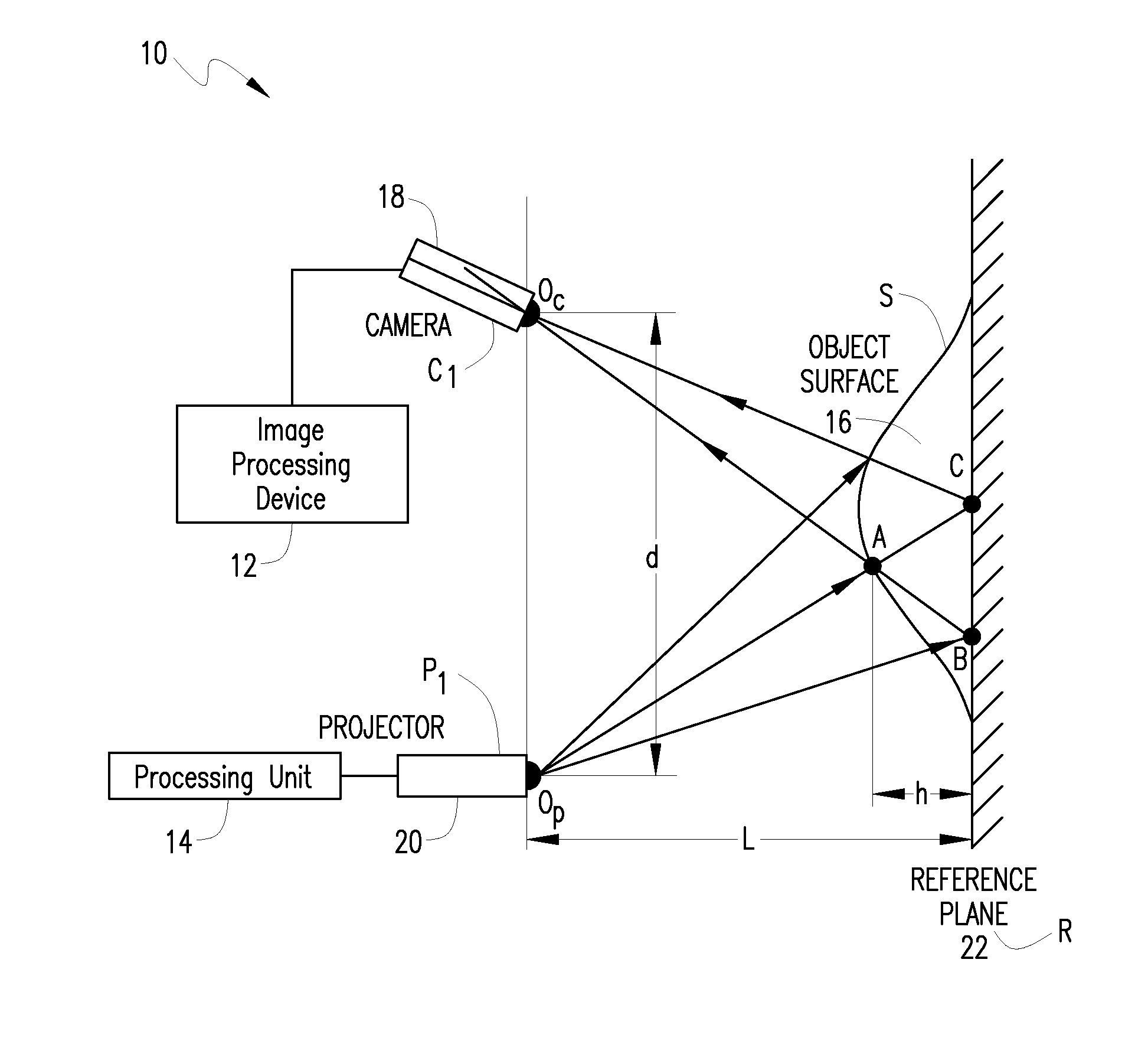
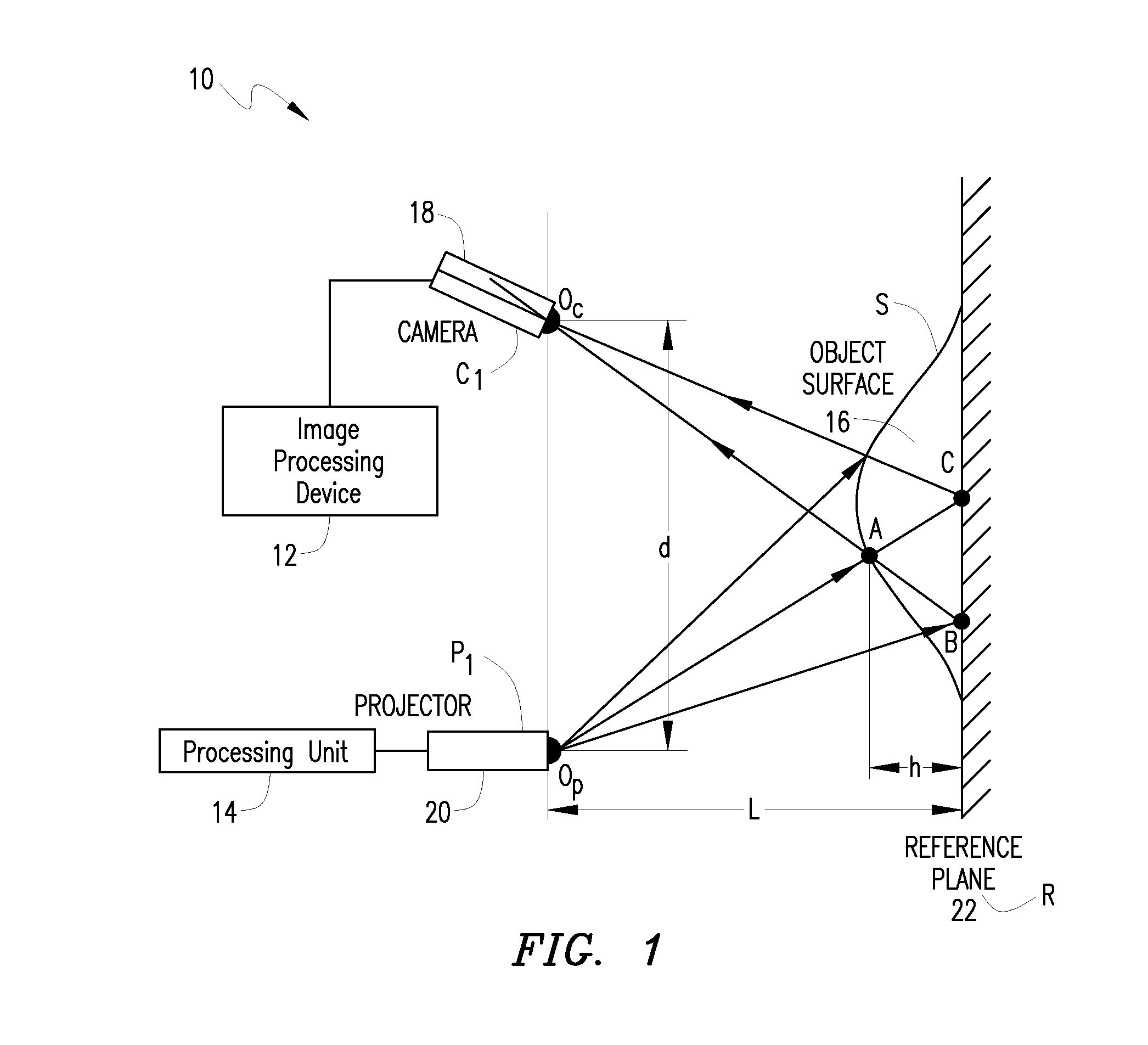
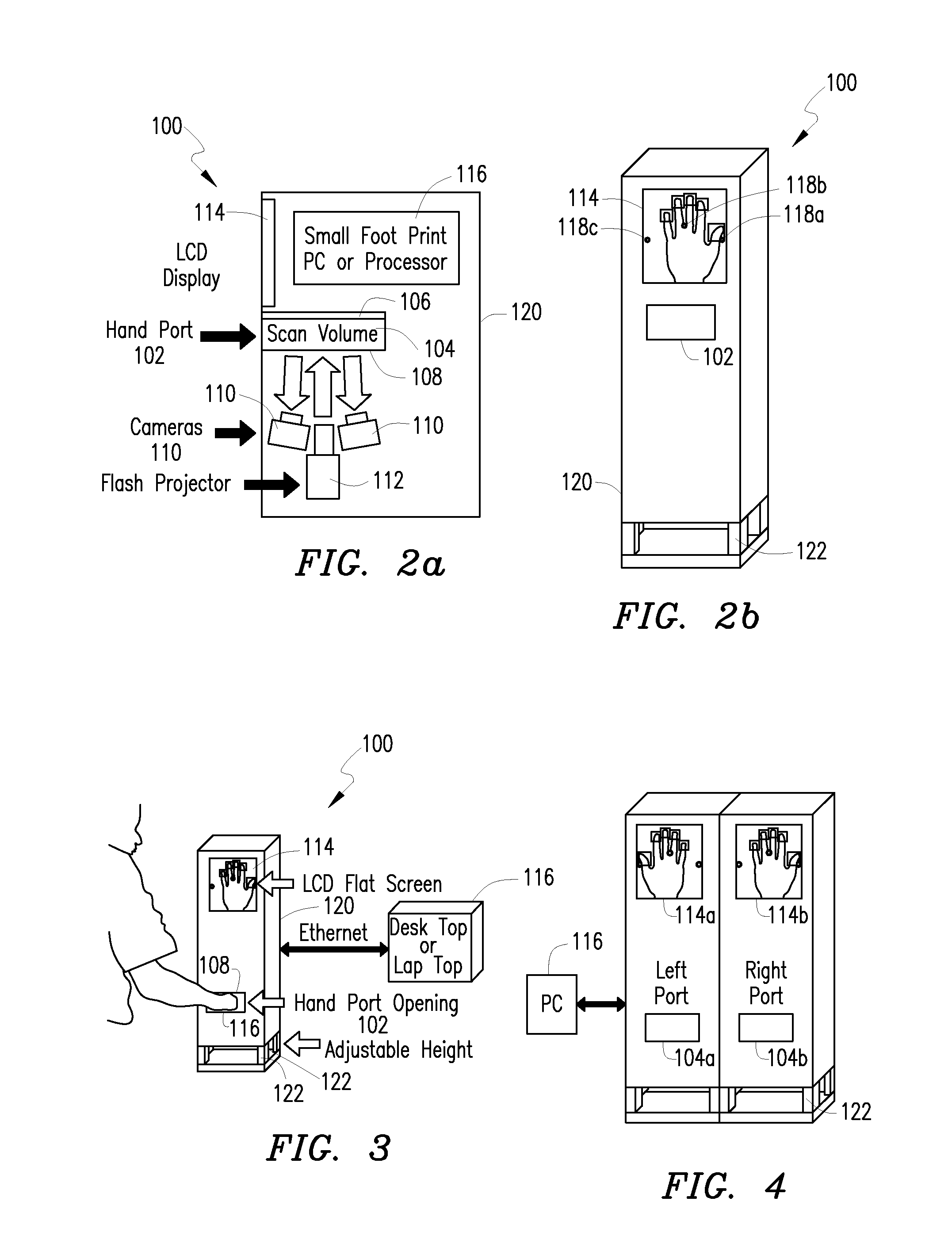
System and method for 3D imaging using structured light illumination
InactiveUS8224064B1Acquisition speed is fastMore robust to extremely worn ridges of the fingersImage enhancementImage analysisRandom noiseComputer science
A biometrics system captures and processes a handprint image using a structured light illumination to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The biometrics system includes an enclosure with a scan volume for placement of the hand. A reference plane with a backdrop pattern forms one side of the scan volume. The backdrop pattern is preferably a random noise pattern and the coordinates of the backdrop pattern are predetermined at system provisioning. The biometrics system further includes at least one projection unit for projecting a structured light pattern onto a hand positioned in the scan volume on or in front of the backdrop pattern and at least two cameras for capturing a plurality of images of the hand, wherein each of the plurality of images includes at least a portion of the hand and the backdrop pattern. A processing unit calculates 3D coordinates of the hand from the plurality of images using the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern to align the plurality of images and mapping the 3D coordinates to a 2D flat surface to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The processing unit can also adjust calibration parameters for each hand scan from calculating coordinates of the portion of backdrop pattern in the at least one image and comparing with the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
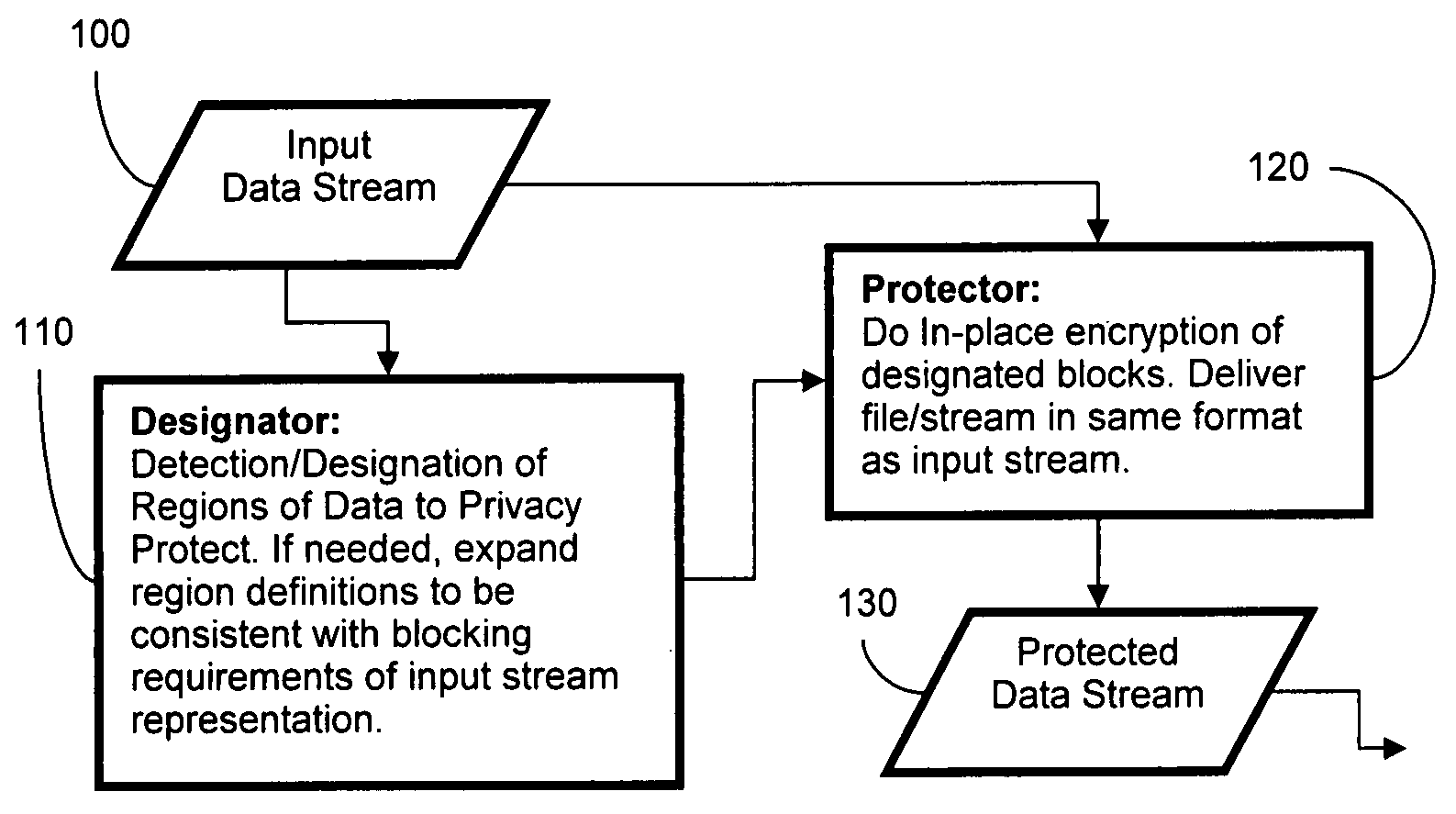
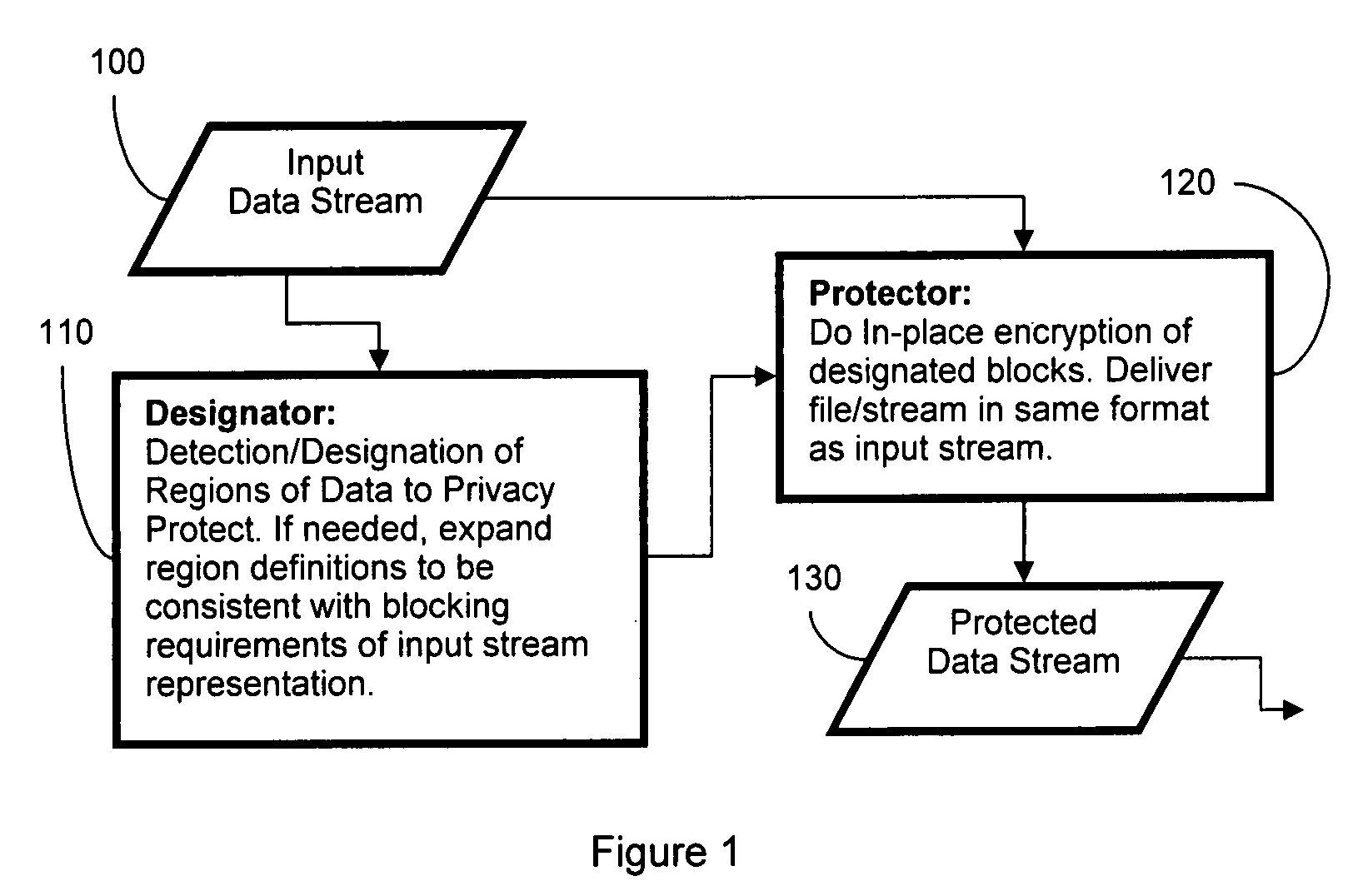
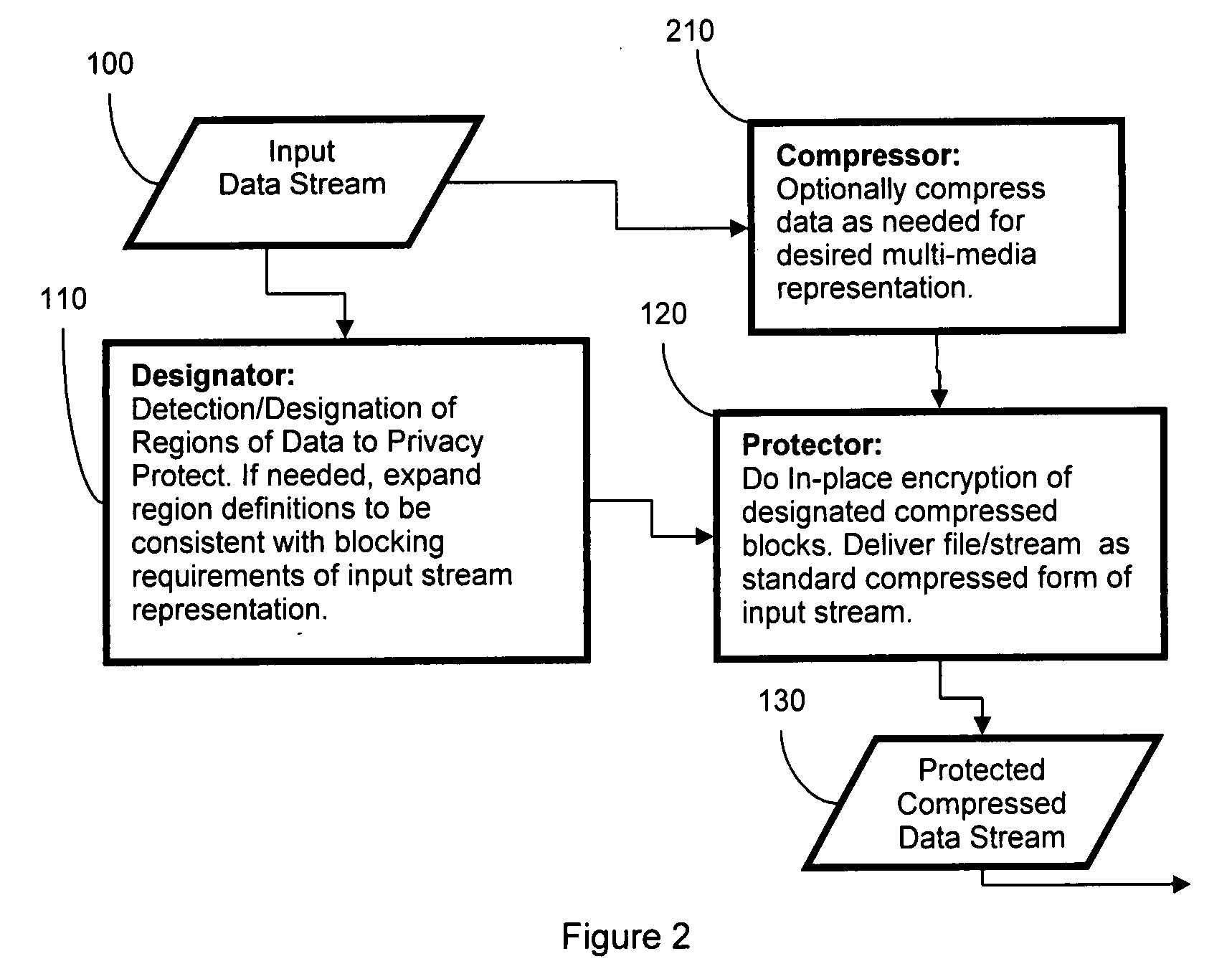
System and method for privacy enhancement via adaptive cryptographic embedding
InactiveUS20080267403A1Improve securityPrivacy protectionSecret communicationSecuring communicationData streamInternet privacy
The system and method enhances privacy and security by determining parts of a data stream that should not be publicly available and doing in-place encryption of that data while leaving the remaining data unencrypted for direct usage in security. The system is composed of a designator, that determines what parts of the data stream require protection, and a protector, that performs the in-place encryption. The resulting protected data stream can be played / displayed using the same standard technology as for the original data stream, with the encrypted portions appearing as random noise. The system also supports an extractor, which can, given access to the appropriate keys, invert the encryption and provide back the original data stream.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Dynamic offset and feedback threshold
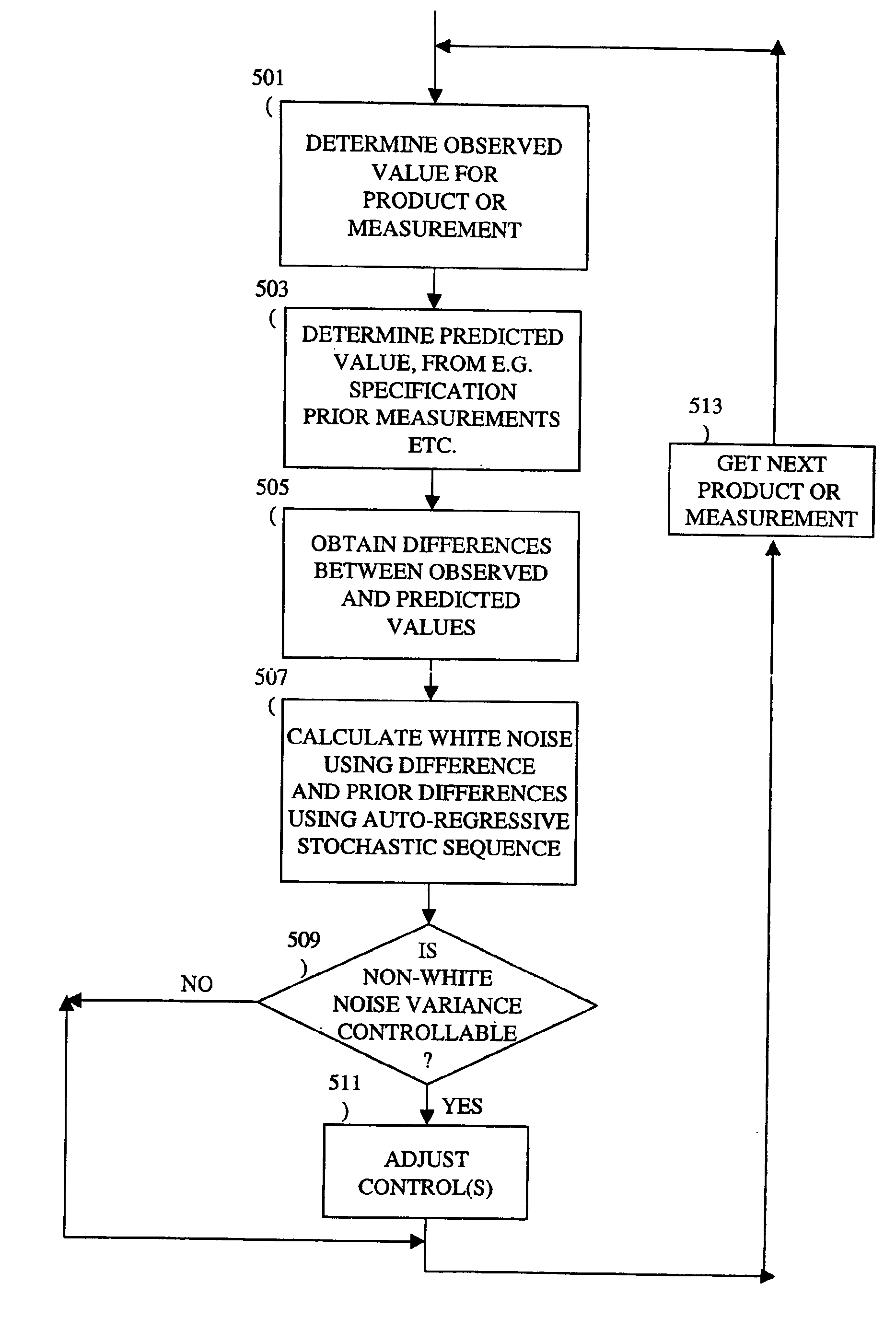
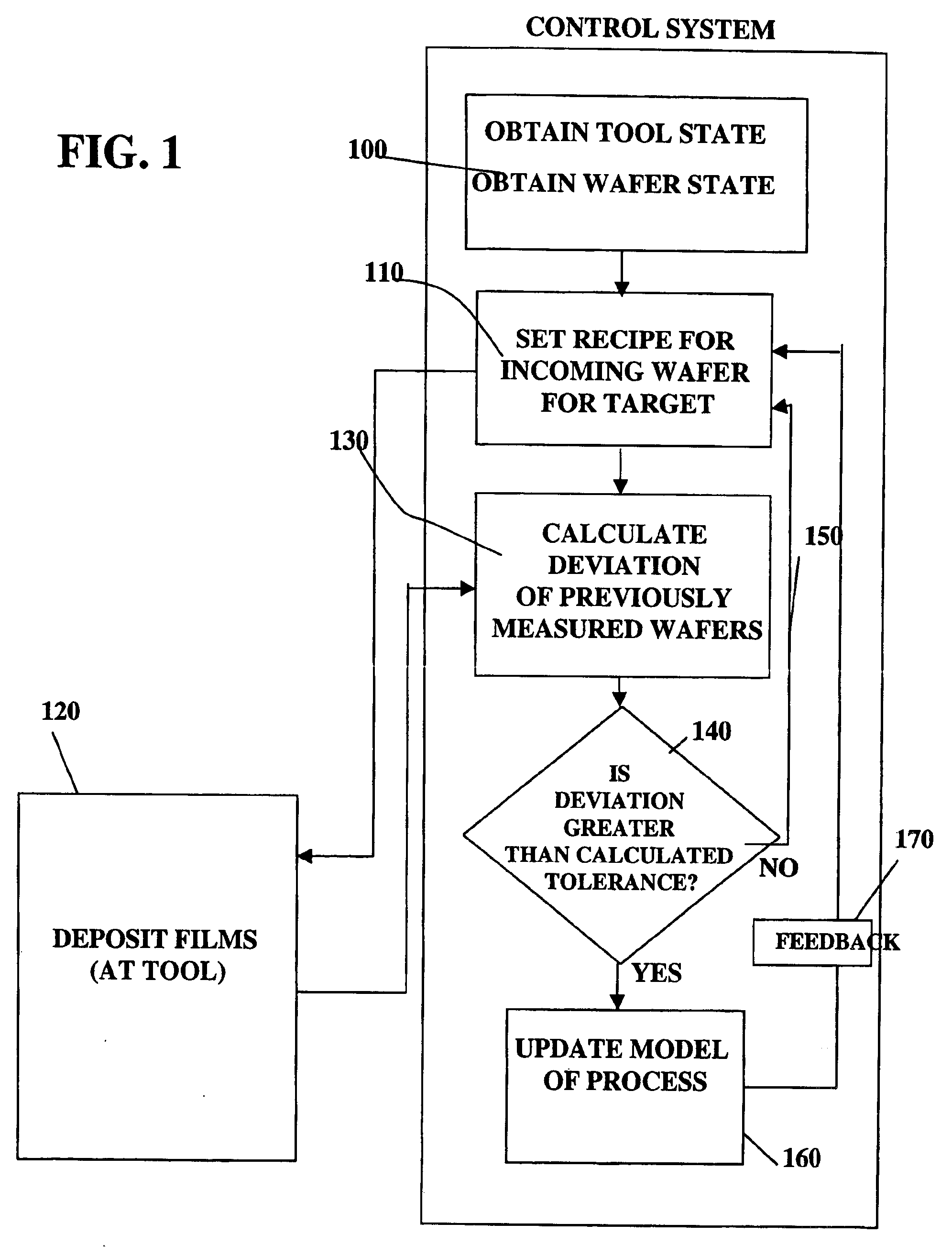
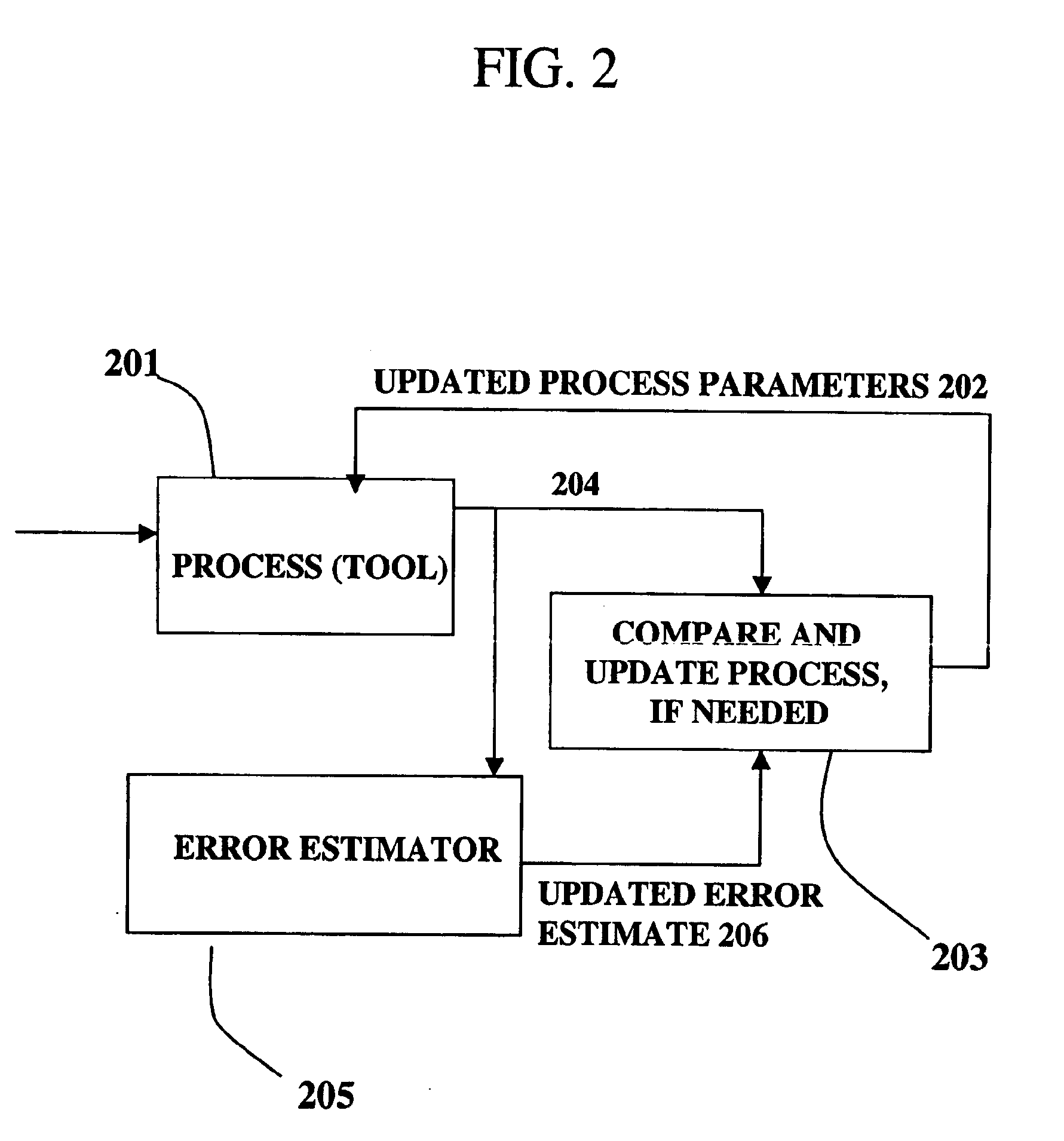
InactiveUS6961626B1Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsProcess varianceSemiconductor chip
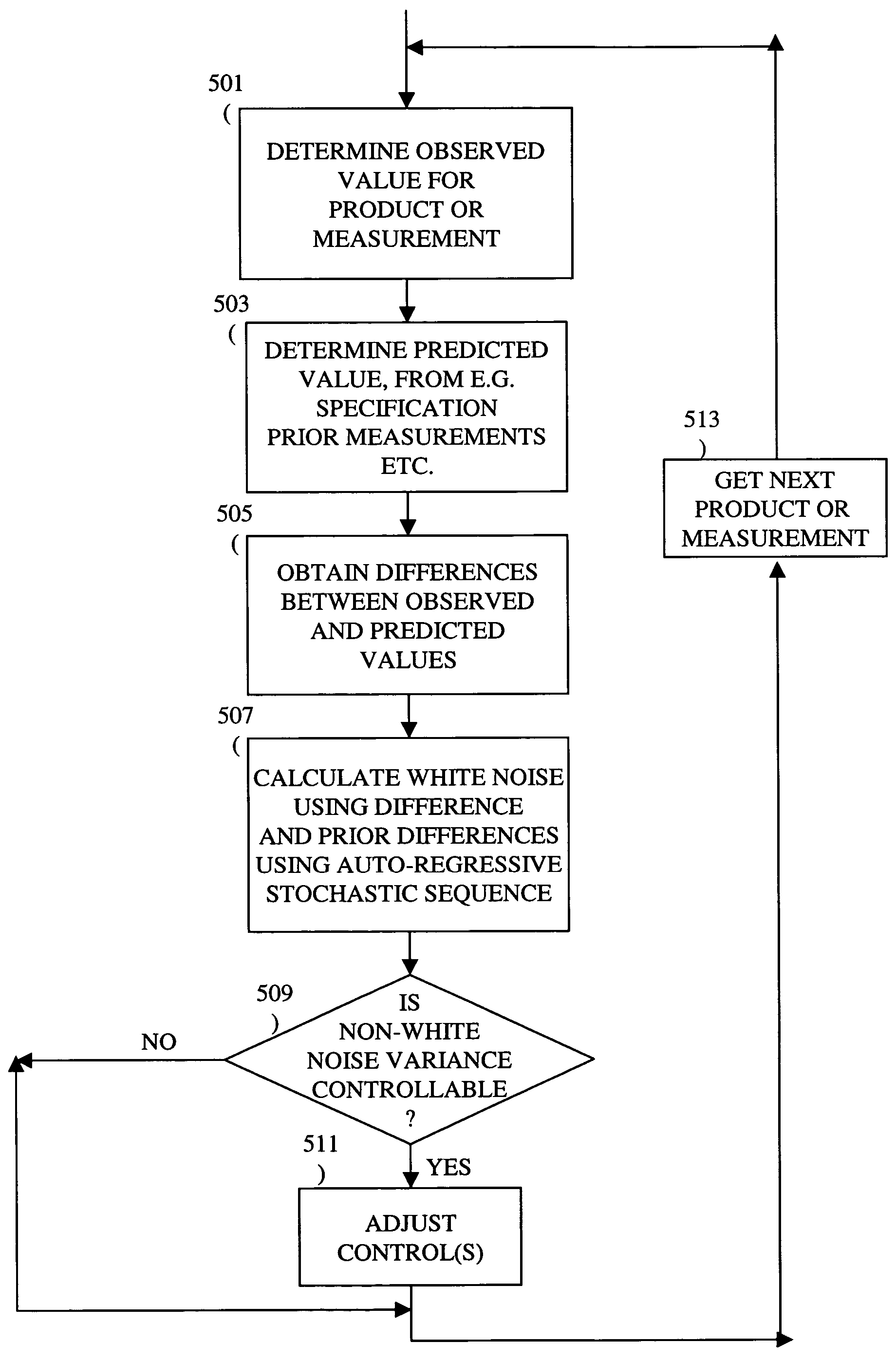
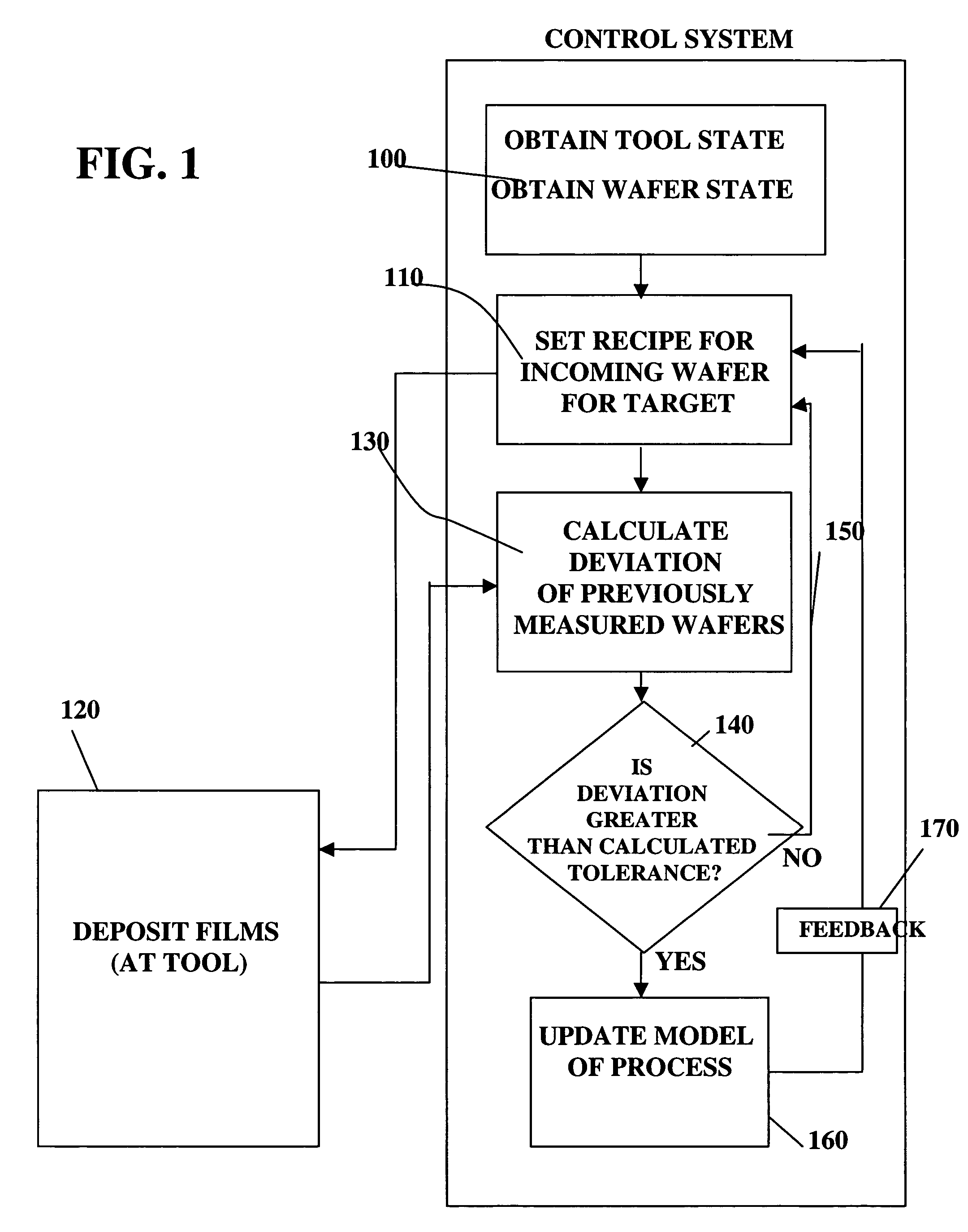
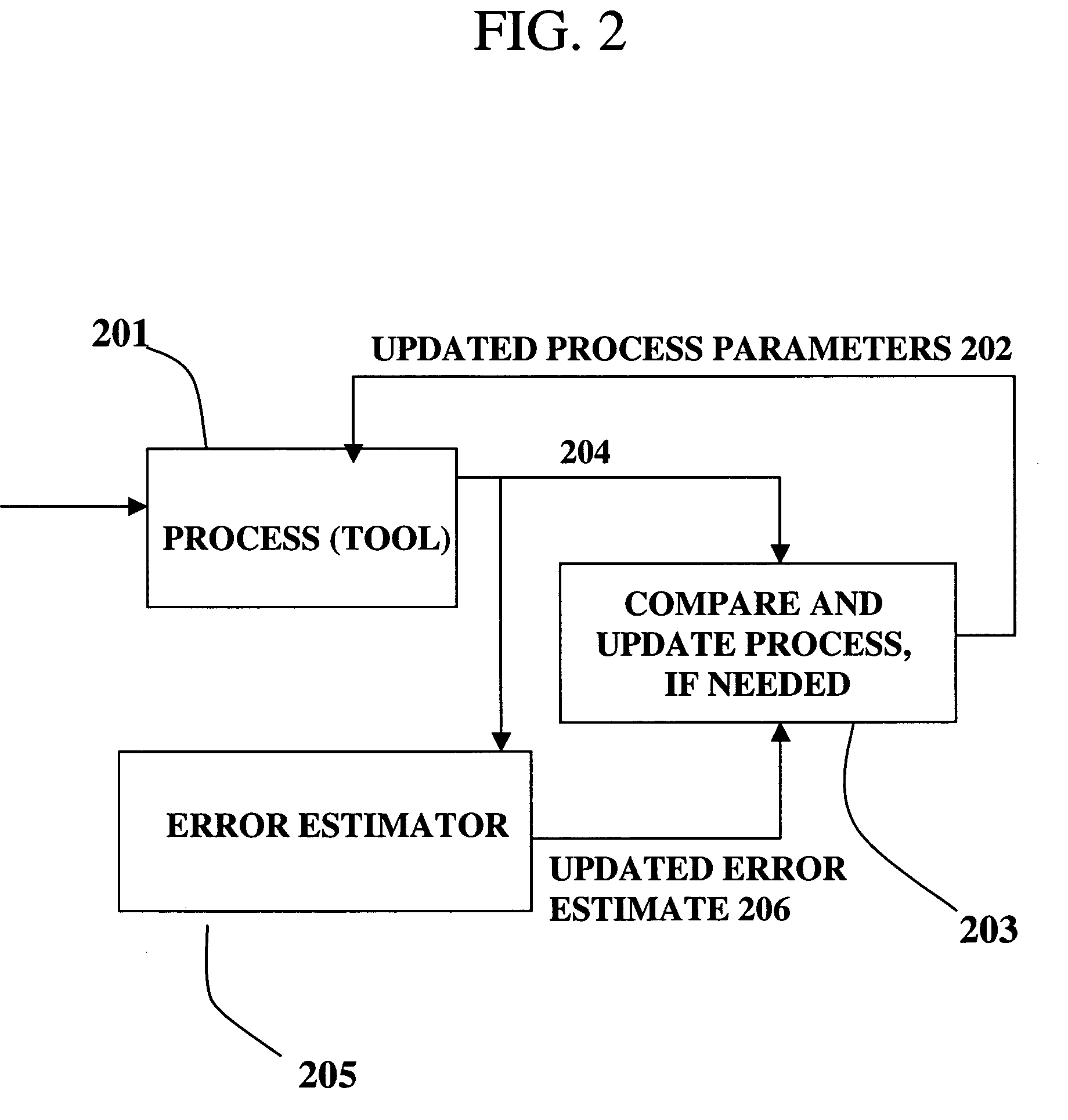
A method, system and medium are provided for enabling improved feedback and feedforward control. An error, or deviation from target result, is observed during manufacture of semi conductor chips. The error within standard deviation is caused by two components: a white noise component and a signal component (such as systematic errors). The white noise component is random noise and therefore is relatively non-controllable. The systematic error, in contrast, may be controlled by changing the control parameters. A ratio between the two components is calculated autoregressively. Based on the ratio and using the observed or measured error, the actual value of the error caused by the signal component is calculated utilizing an autoregressive stochastic sequence. The actual value of the error is then used in determining when and how to change the control parameters. The autoregressive stochastic sequence addresses the issue of real-time control of the effects of run-to-run deviations, and provides a mechanism that can extract white noise from the statistical process variance in real time. This results in an ability to provide tighter control of feedback and feedforward variations.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
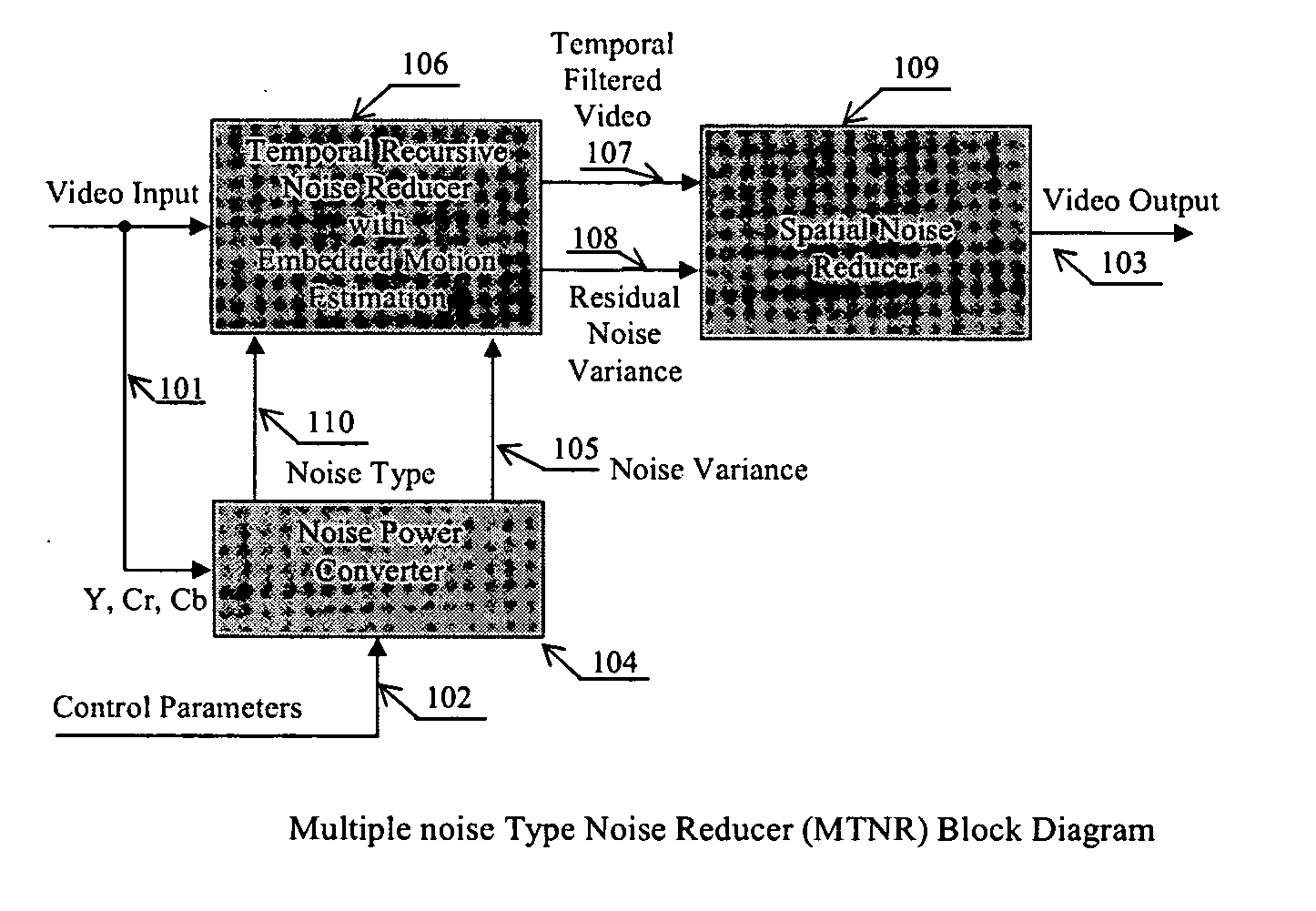
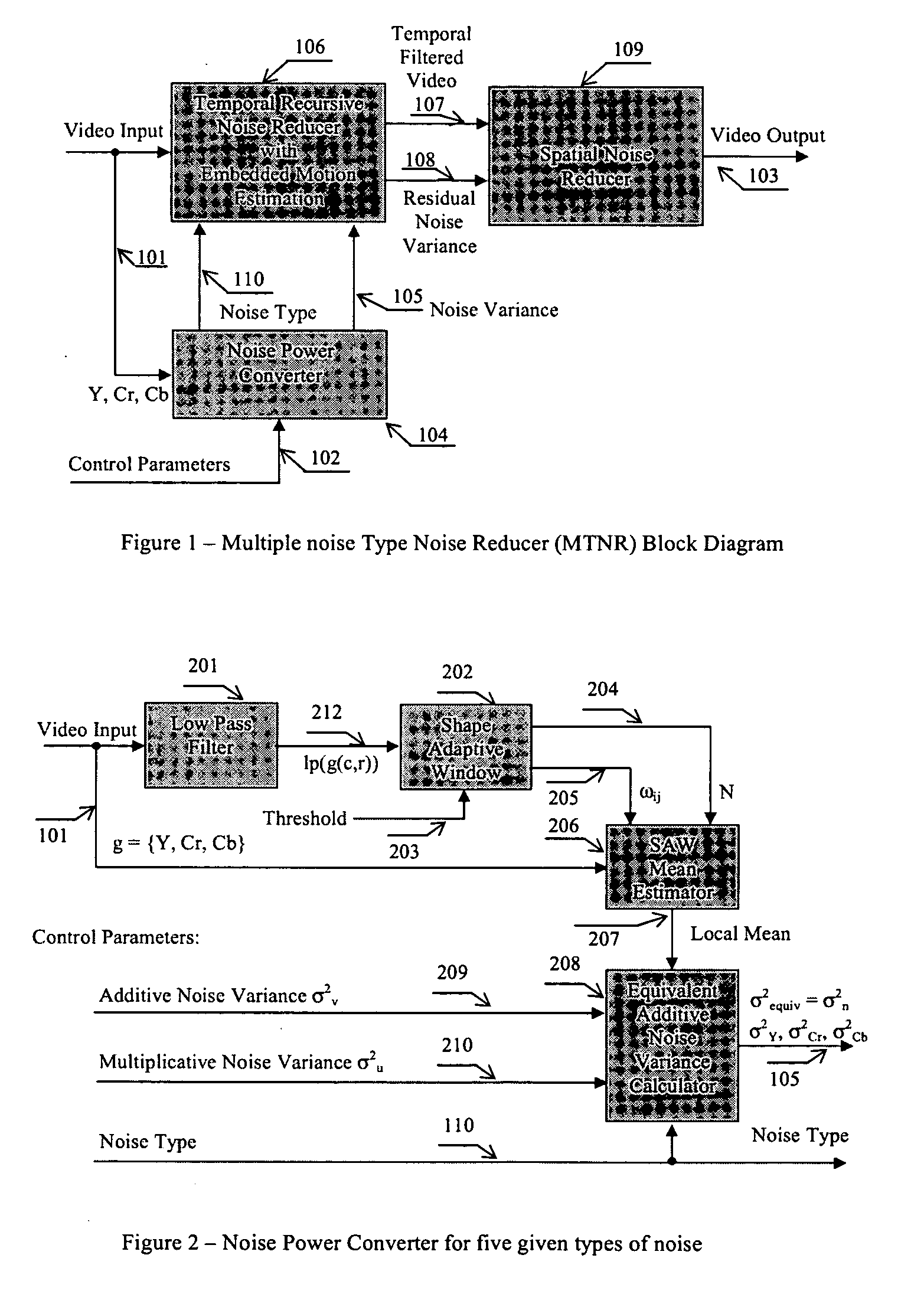
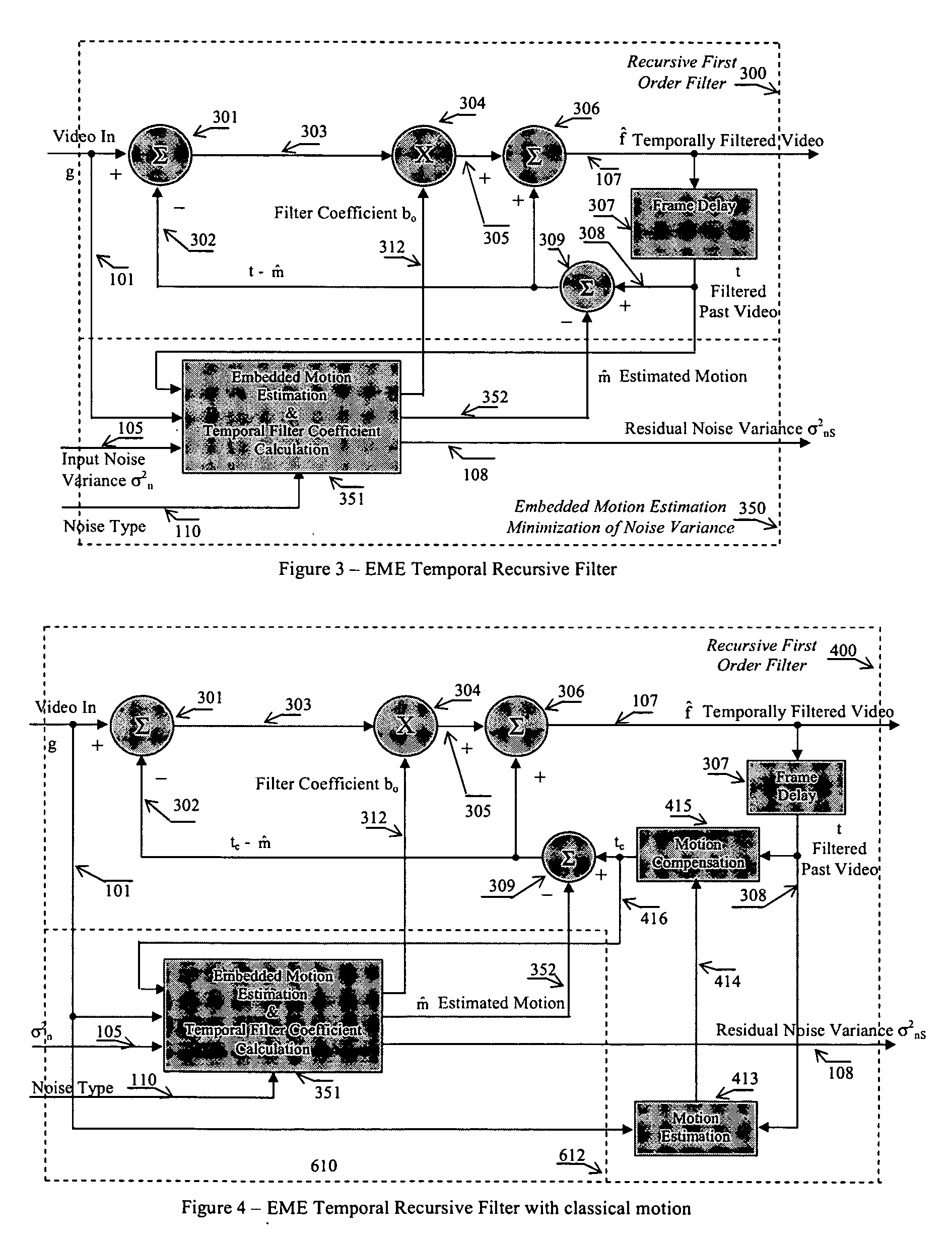
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D noise reduction
InactiveUS20060056724A1Reduce noiseType of reductionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
A non-iterative 3D processing method and system is disclosed for generic noise reduction. The 3D noise reducer is based on a simple conversion of the five types of noise to equivalent additive noise of varying statistics. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient temporal filtering technique which combines Minimization of Output Noise Variance (MNV) and Embedded Motion Estimation (EME). The proposed temporal filtering technique may be furthermore combined with classical motion estimation and motion compensation for more efficient noise reducer. The proposed technique comprises also a spatial noise reducer which combines Minimum Mean Squared Error (MMSE) with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing (SAW) is utilized for smoothing random noise in the whole image, particularly for edge regions. Another modification to MMSE is also introduced for handling banding effect for eventual excessive filtering in slowly varying regions.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
Image processor with noise reduction circuit
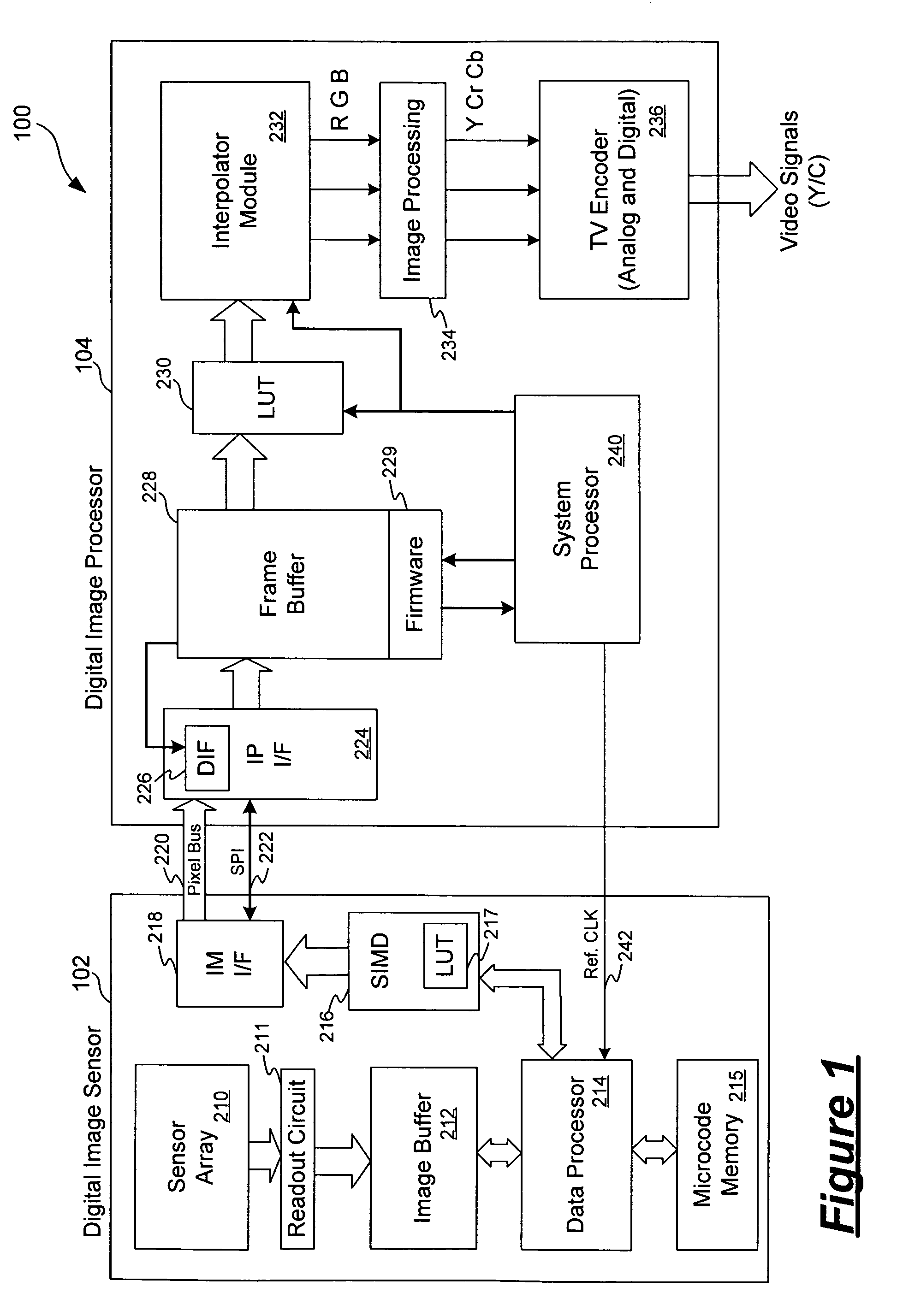
ActiveUS7265784B1Reduce noiseRemove random noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital imagingRandom noise
A digital imaging system includes an image sensor, an interface circuit, a frame buffer and an image processor. The image sensor includes a two-dimensional array of pixel elements and outputs digital signals on a pixel bus as pixel data representing an image of a scene. The interface circuit is coupled to receive the pixel data from the pixel bus. The frame buffer is coupled to store pixel data provided by the interface circuit. The image processor operates to process the pixel data stored in the frame buffer to generate image data for displaying the image of the scene. The interface circuit includes a noise reduction circuit operated to perform signal processing on the pixel data received on the pixel bus for noise reduction. Thus, random noise such as readout noise can be eliminated as pixel data are being transferred from the image sensor and stored in the frame buffer.
Owner:PIXIM
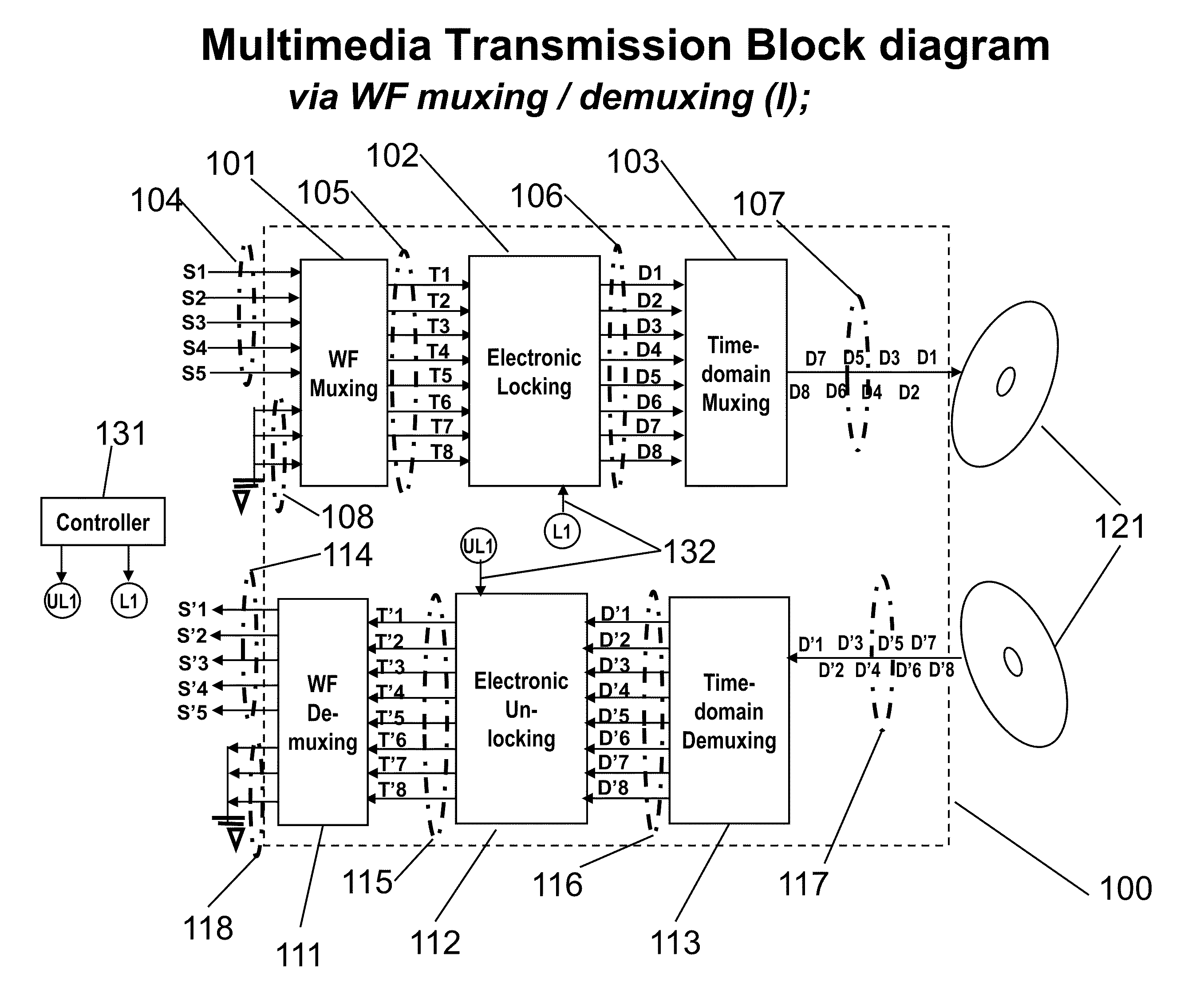
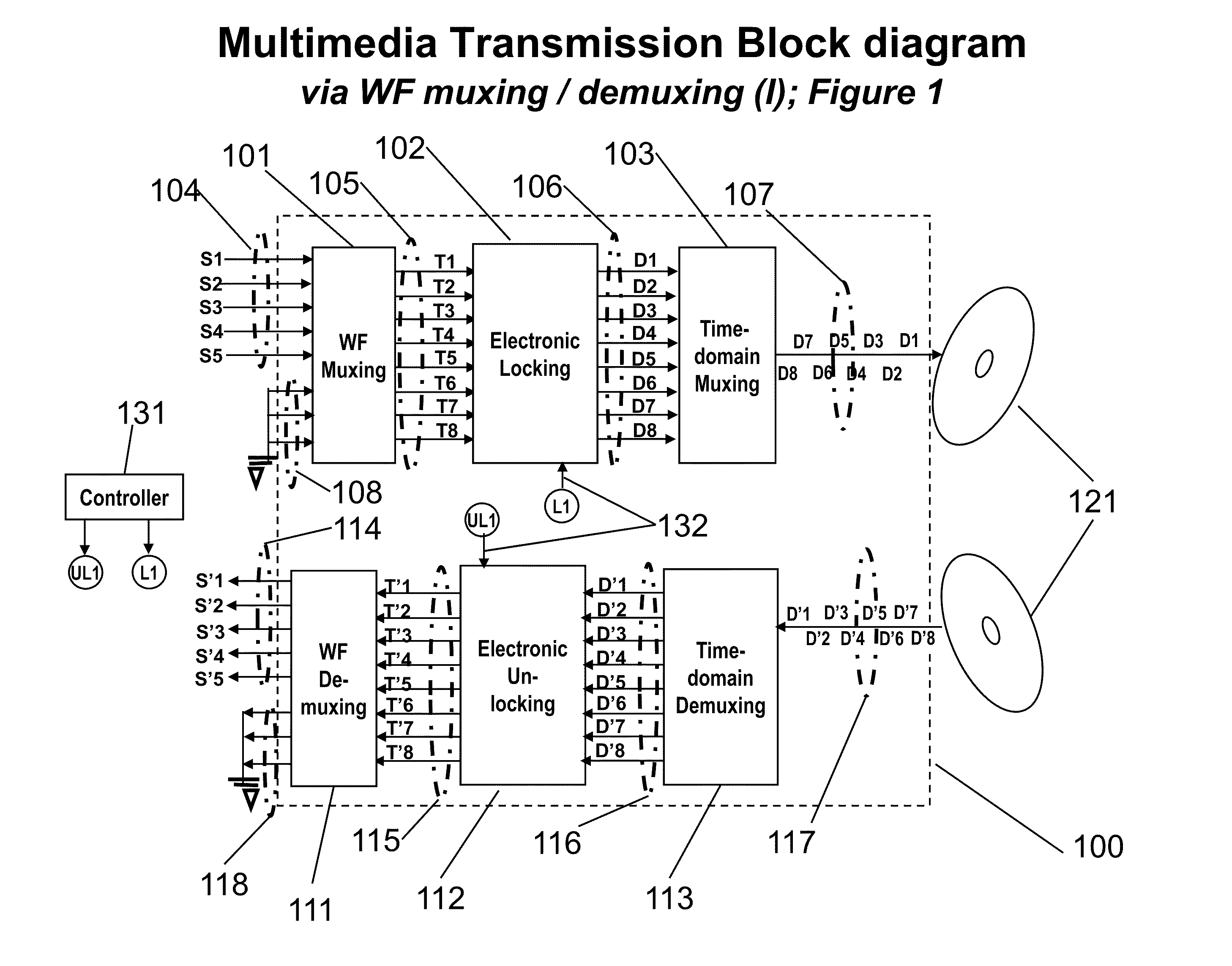
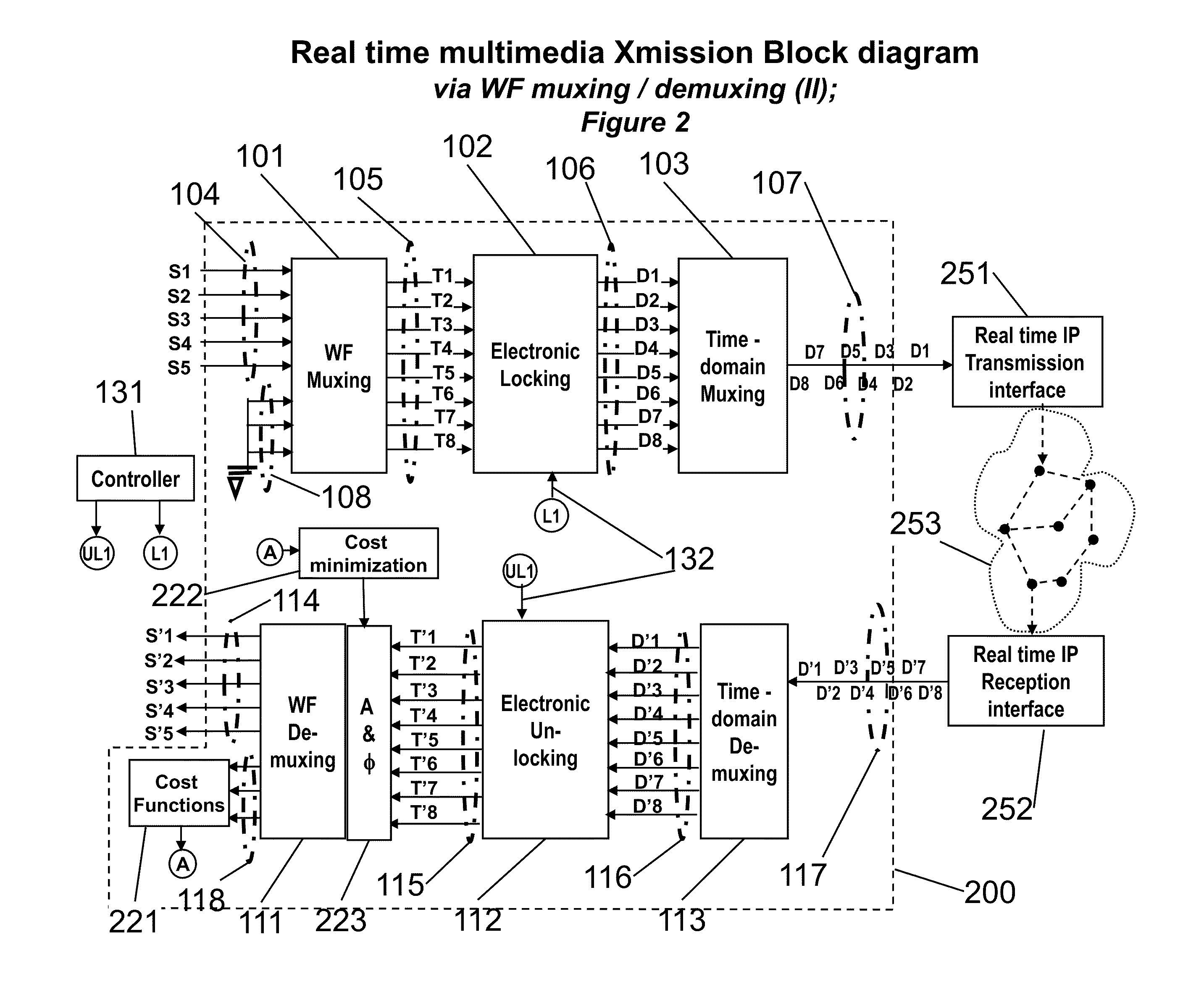
Novel Karaoke and Multi-Channel Data Recording / Transmission Techniques via Wavefront Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
InactiveUS20110197740A1Quality improvementEnhance security and integrityElectrophonic musical instrumentsTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
An advanced channel storage and retrieving system is achieved that is capable of simultaneously transporting multiple-stream data concurrently, with encryptions and error detection and limited correction capability using wavefront (WF) multiplexing (muxing) at the pre-processing and WF demultiplexing (de-muxing) in the post-processing. The WF muxing and demuxing processing can be applied for multiple signal streams with similar contents and format such as cable TV delivery systems or multiple signal streams with very distinct contents and format such as Karaoke multimedia systems. The stored or transported data are preprocessed by a WF muxing processor and are in the formats of multiple sub-channels. Signals in each sub-channel are results of unique linear combination of all the input signals streams. Conversely, an input signal stream is replicated and appears on all the sub-channels. Furthermore the replicated streams in various sub-channels are “linked” together by a unique phase weighting vector, which is called “wavefront” or WF. Various input signal streams will feature different WFs among their replicated signal streams in the sub-channels. The WF muxing processing is capable to generating a set of orthogonal WFs, and the WF demuxing processing is capable of reconstituting the input signal streams based on the retrieved sub-channel data only if the orthogonal characteristics of a set of WFs are preserved. Without the orthogonality among the WF, the signals in sub-channels are mixed and become effectively pseudo random noise. Therefore, an electronic locking mechanism in the preprocessing is implemented to make the WFs un-orthogonal among one another. Similarly, an electronic un-locking mechanism in the post-processing is implemented to restore the orthogonal characteristics among various WFs embedded in the sub-channel signals. Some of the phenomena due to the selected locking mechanisms are reproducible in nature, such as wave propagating effects, and other are distinctively man-made; such as switching sub-channel sequences. There are other conventional encryption techniques using public and private keys which can be applied in conjunction with the WF muxing and de-muxing processor, converting plain data streams into ciphered data streams which can be decoded back into the original plain data streams. An encryption algorithm along with a key is used in the encryption and decryption of data. As to the optional parallel to serial and serial to parallel conversions in the pre and post processing, respectively, we assume that transmissions with single carrier are more efficient than those with multiple carriers. We also assume single channel recording is more cost effective than multiple channel recording. However, there are occasions that continuous spectrum is hard to come-by. We may use fragmented spectrum for transmissions. There are techniques to convert wideband waveforms using continuous spectra into multiple fragmented sub-channels distributed on non-continuous frequency slots. Under these conditions we may replace the parallel to serial conversion processing by a frequency mapping processor.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
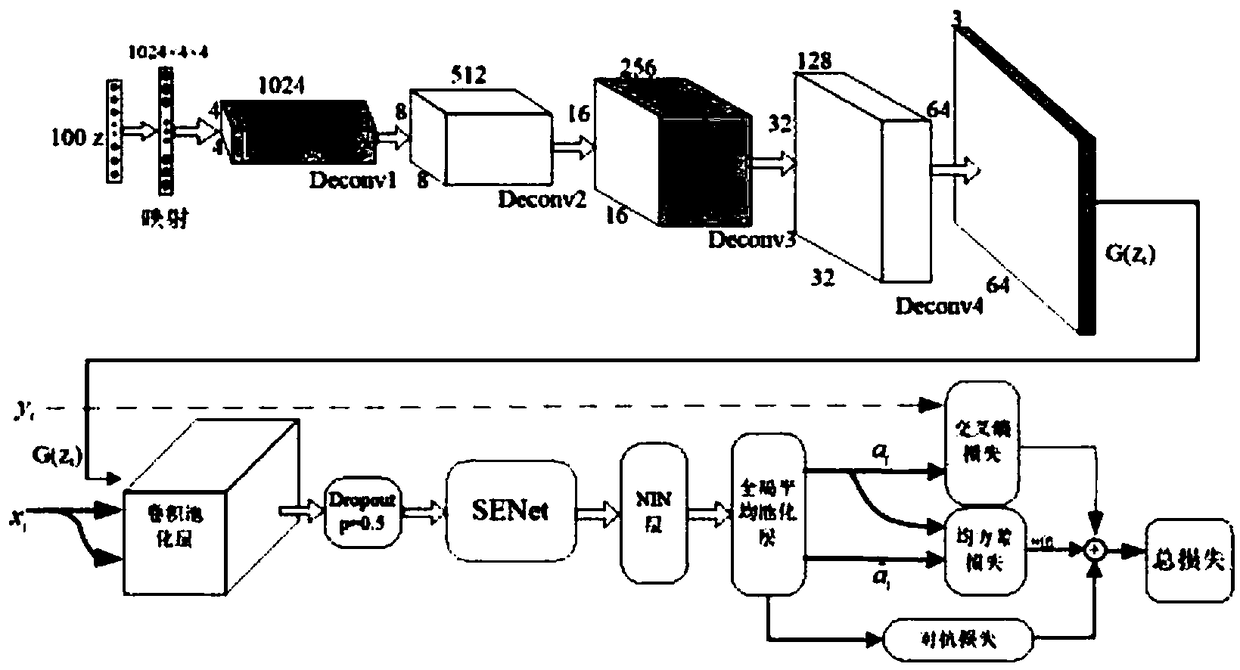
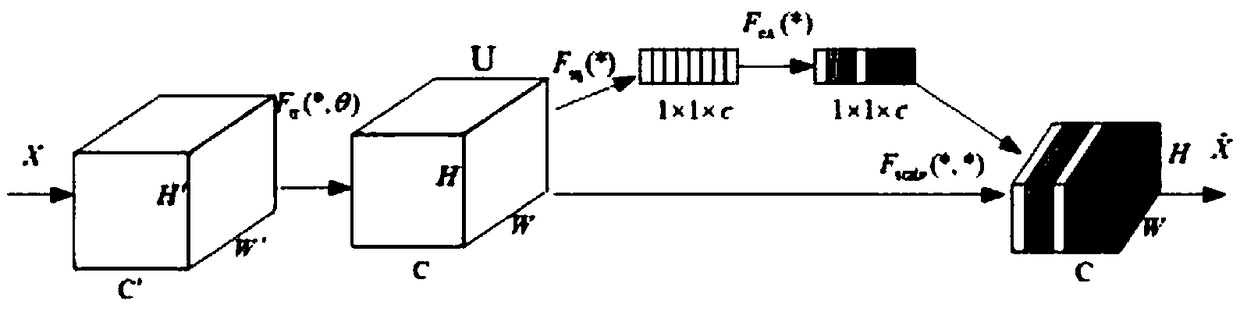
Image classification method based on confrontation network generated through feature recalibration
ActiveCN108805188AImprove generalization abilityClassification task performance improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesGenerative adversarial networkClassification methods
The invention discloses an image classification method based on a confrontation network generated through feature recalibration. The image classification method based on the confrontation network generated through feature recalibration is suitable for the field of machine learning and comprises the steps that to-be-classified image data are input into a confrontation network model for network training; a generator and a discriminator which are constituted by a convolutional network are constructed; random noise is initialized and input into the generator; the random noise is subjected to multilevel deconvolution operation in the generator through the convolutional network, and finally, generated samples are obtained; the generated samples and authentic samples are input into the discriminator; and the input samples are subjected to convolution and pooling operation in the discriminator through the convolutional network, thus a feature graph is obtained, a compressed and activated SENetmodule is imported into an intermediate layer of the convolutional network to calibrate the feature graph, thus the calibrated feature graph is obtained, global average pooling is used, and finally,image data classification is output. The SENet module is imported into the intermediate layer of the discriminator, the importance degree of each feature channel is automatically learned, useful features relevant to a task are extracted, features irrelevant to the task are restrained, and thus semi-supervised learning performance is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU YUNYI ELECTRIC
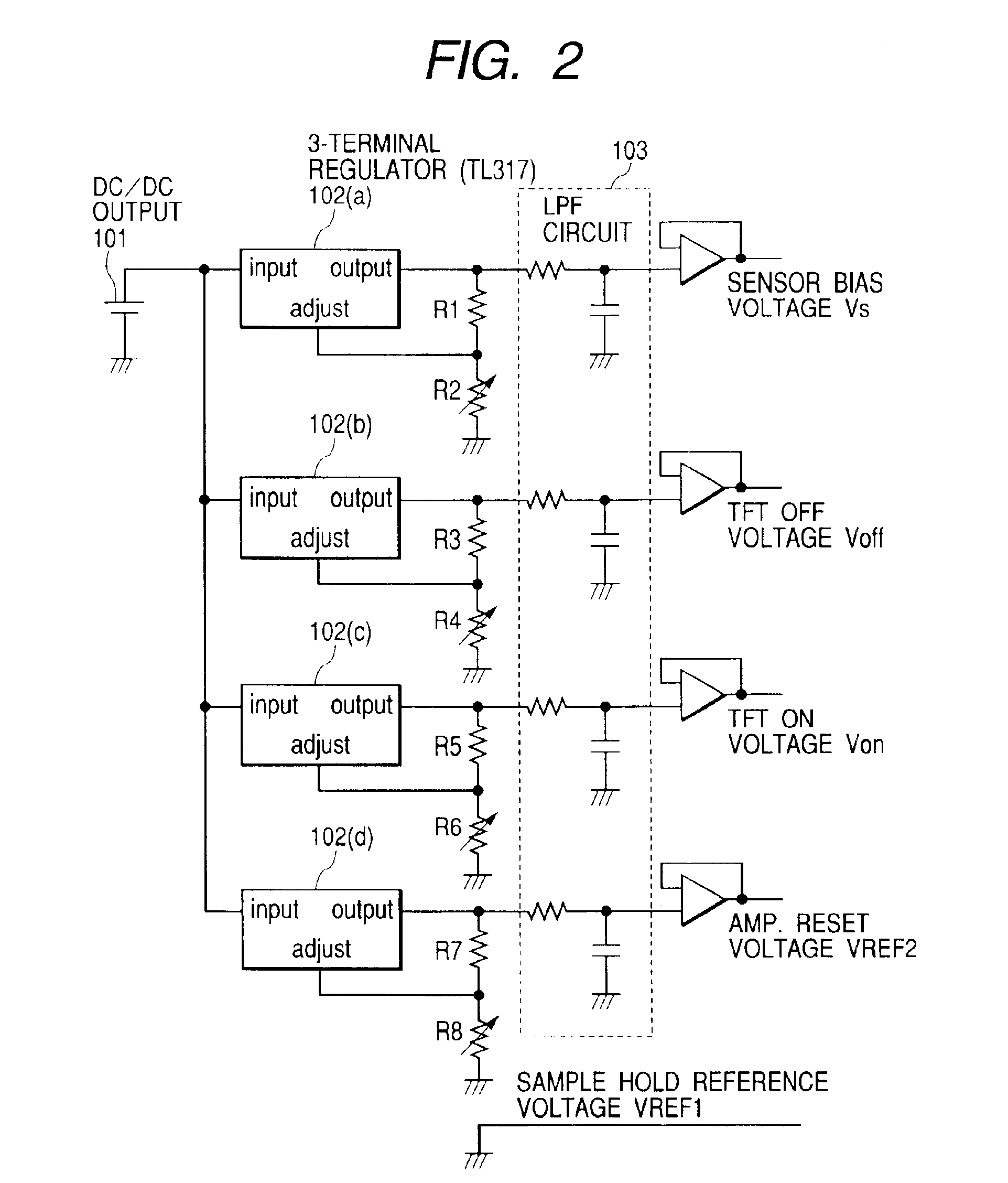
Image pick-up apparatus and image pick-up system
An image pick-up apparatus and an image pick-up system constructed to prevent occurrence of random noise in a photographed image due to a random noise component produced in a reference supply circuit. An image pick-up apparatus has an area sensor driven by matrix driving, and a reference supply circuit for supplying a reference voltage for driving of the area sensor, and the reference voltage is supplied through a low-pass filter (LPF) coupled to the reference supply circuit. Further, a cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter is preferably determined so that an effective value of noise of the reference voltage having passed through the low-pass filter becomes not more than one-tenth of an effective value of random noise produced in pixels of the area sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
Adjusting manufacturing process control parameter using updated process threshold derived from uncontrollable error
InactiveUS7349753B2Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductor chipRandom noise
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
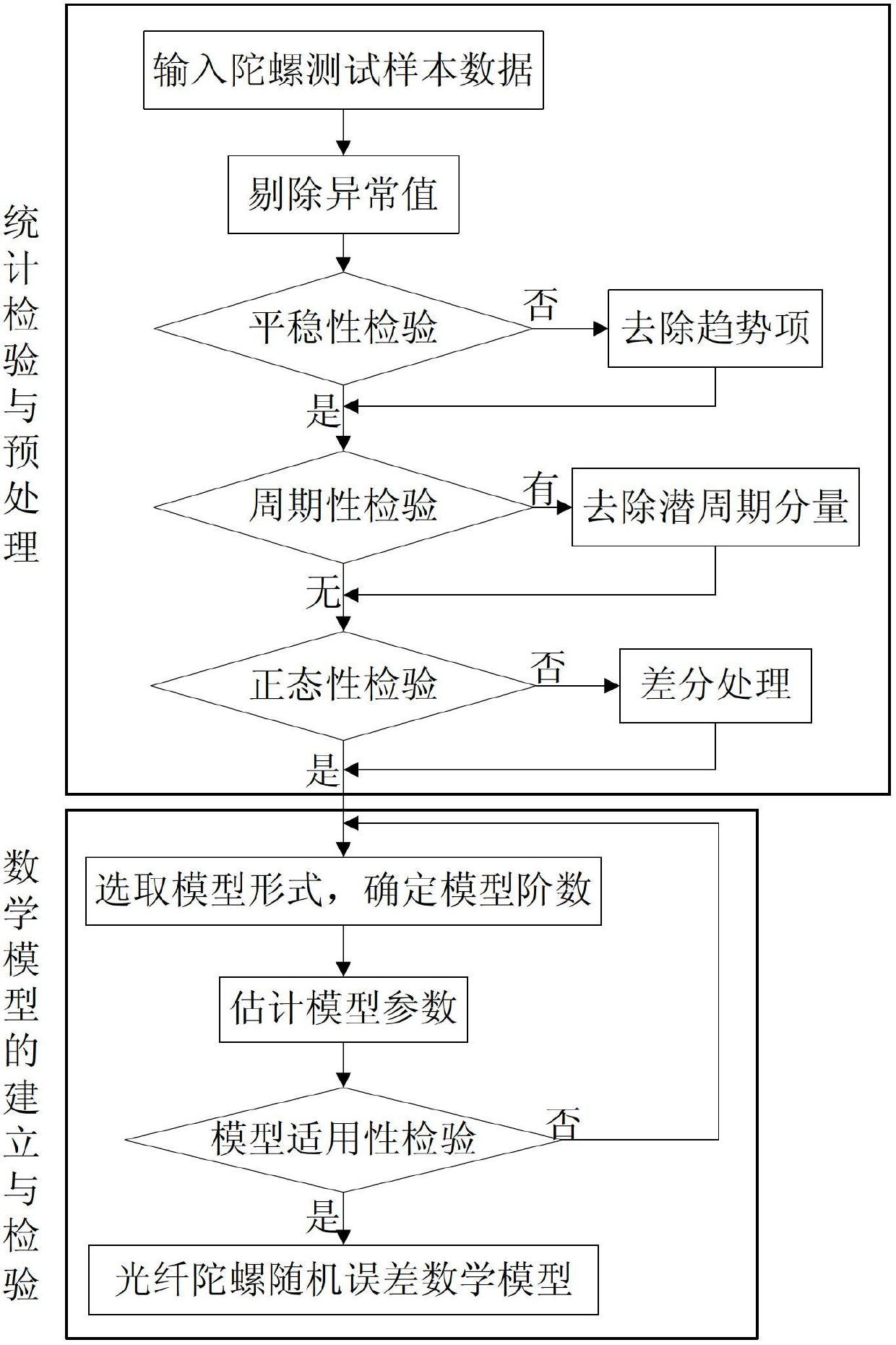
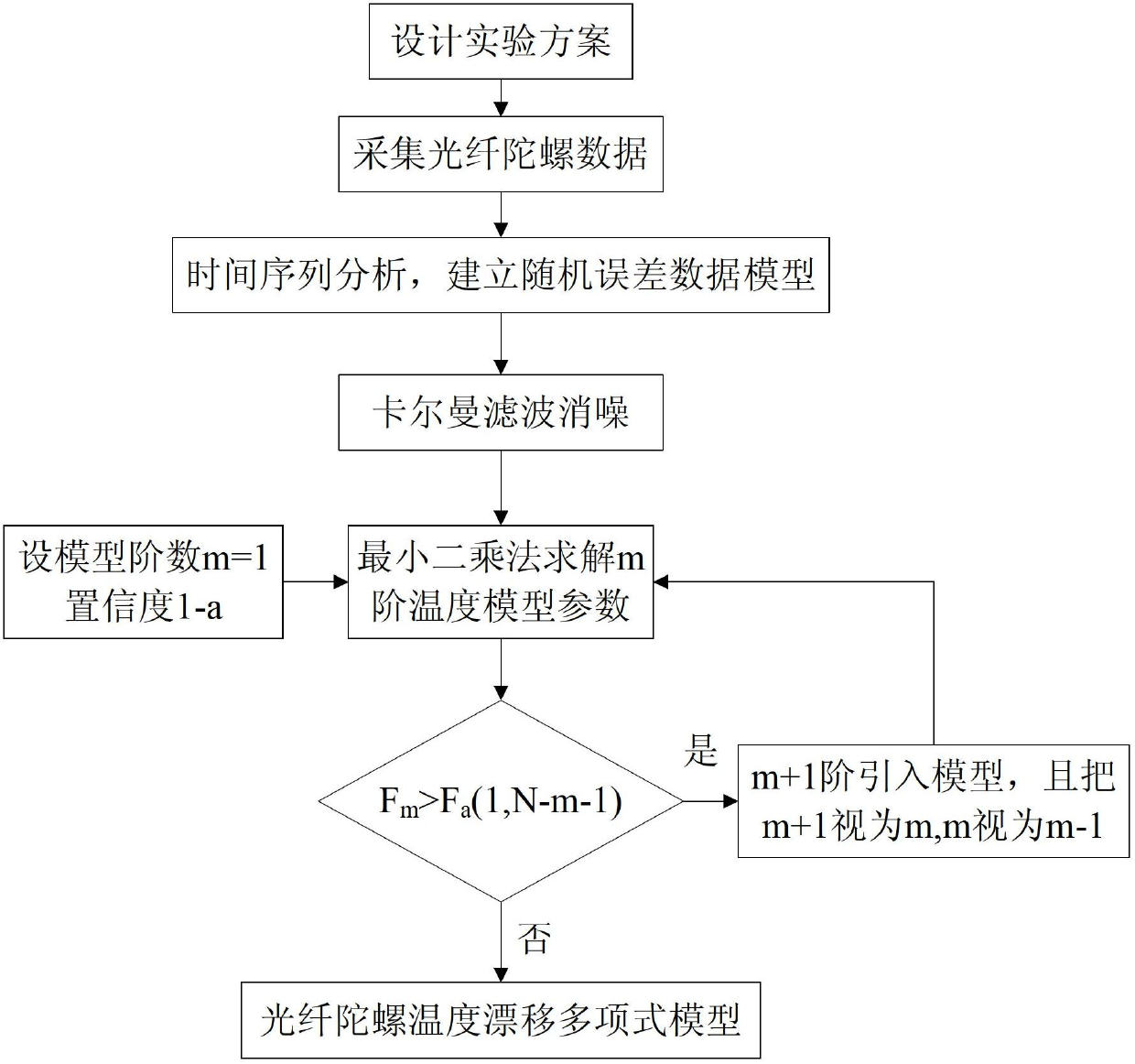
Temperature compensation method for denoising fiber-optic gyroscope on basis of time series analysis
A temperature compensation method for denoising a fiber-optic gyroscope on the basis of time series analysis comprises four steps of: step 1, designing an experimental scheme, performing fixed point low and high temperature testing experiment on the fiber-optic gyroscope, and utilizing acquisition software for data acquisition; step 2, performing time series analysis on the zero offset data of the gyroscope, and establishing the mathematical model of the random error of the fiber-optic gyroscope; step 3, adopting a kalman filtering algorithm to filter random noise in the zero offset data of the fiber-optic gyroscope; and step 4, utilizing the data which is de-noised by the kalman filtering to identify the model structure of the temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope, and calculating the parameters of the identified model. The method establishes the multinomial model of the static temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope through time series analysis, kalman filtering denoising treatment and identification of the temperature shift error model structure and parameters. The method completely meets the real-time compensation requirement on the project, and has a better practicable value and a wide application prospect in the technical field of aerospace navigation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Bit-depth extension of digital displays via the use of models of the impulse response of the visual system
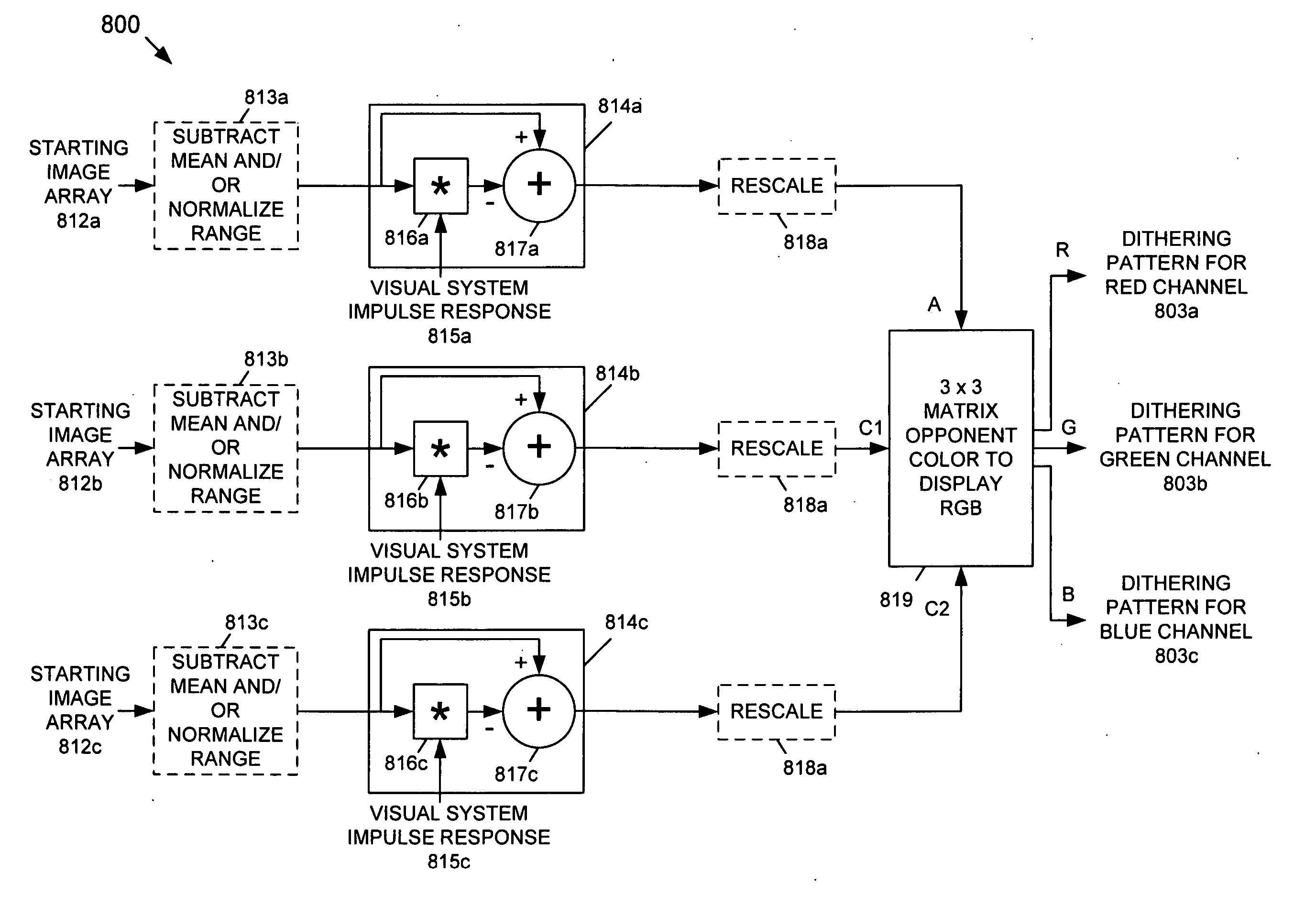
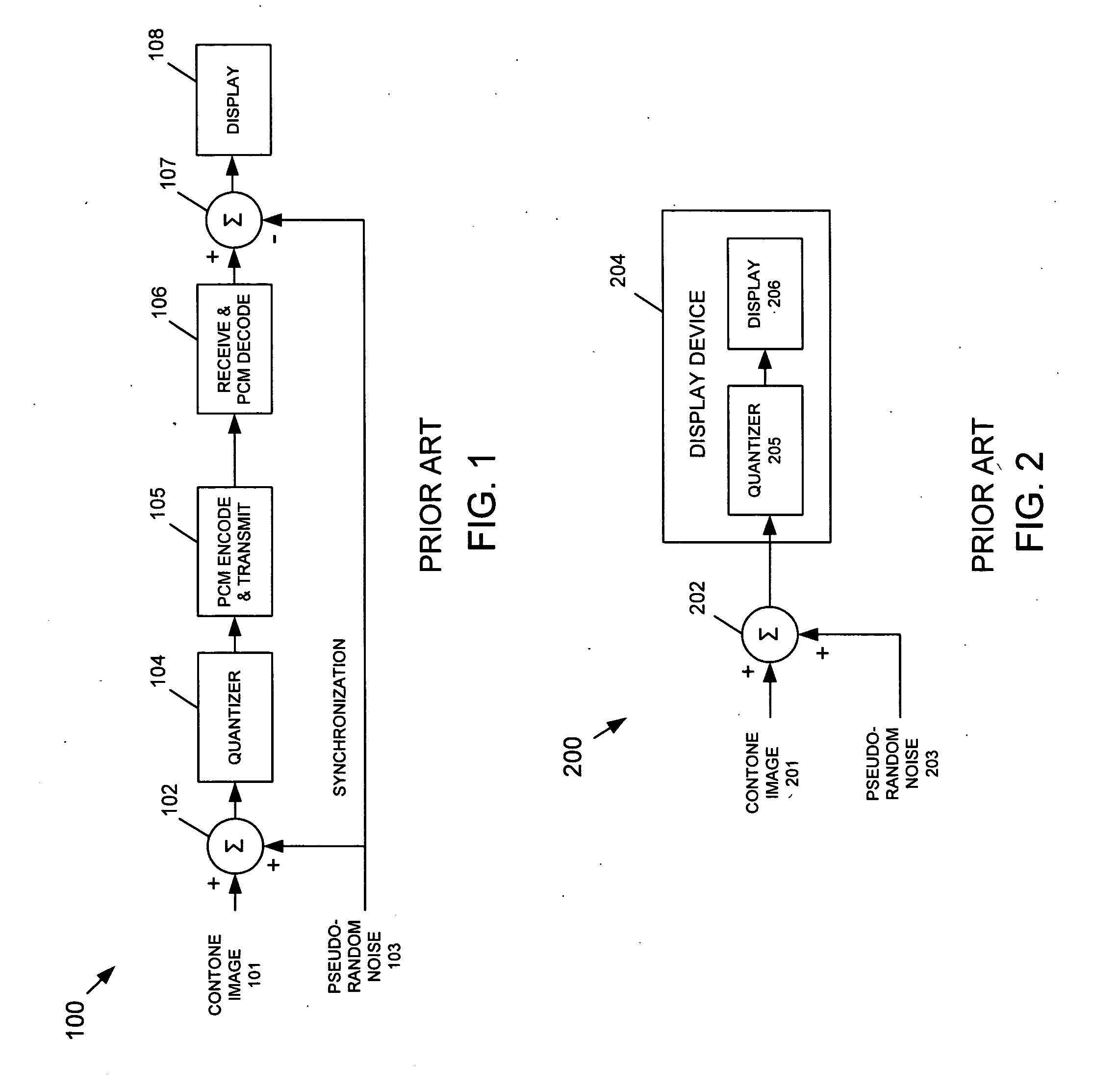
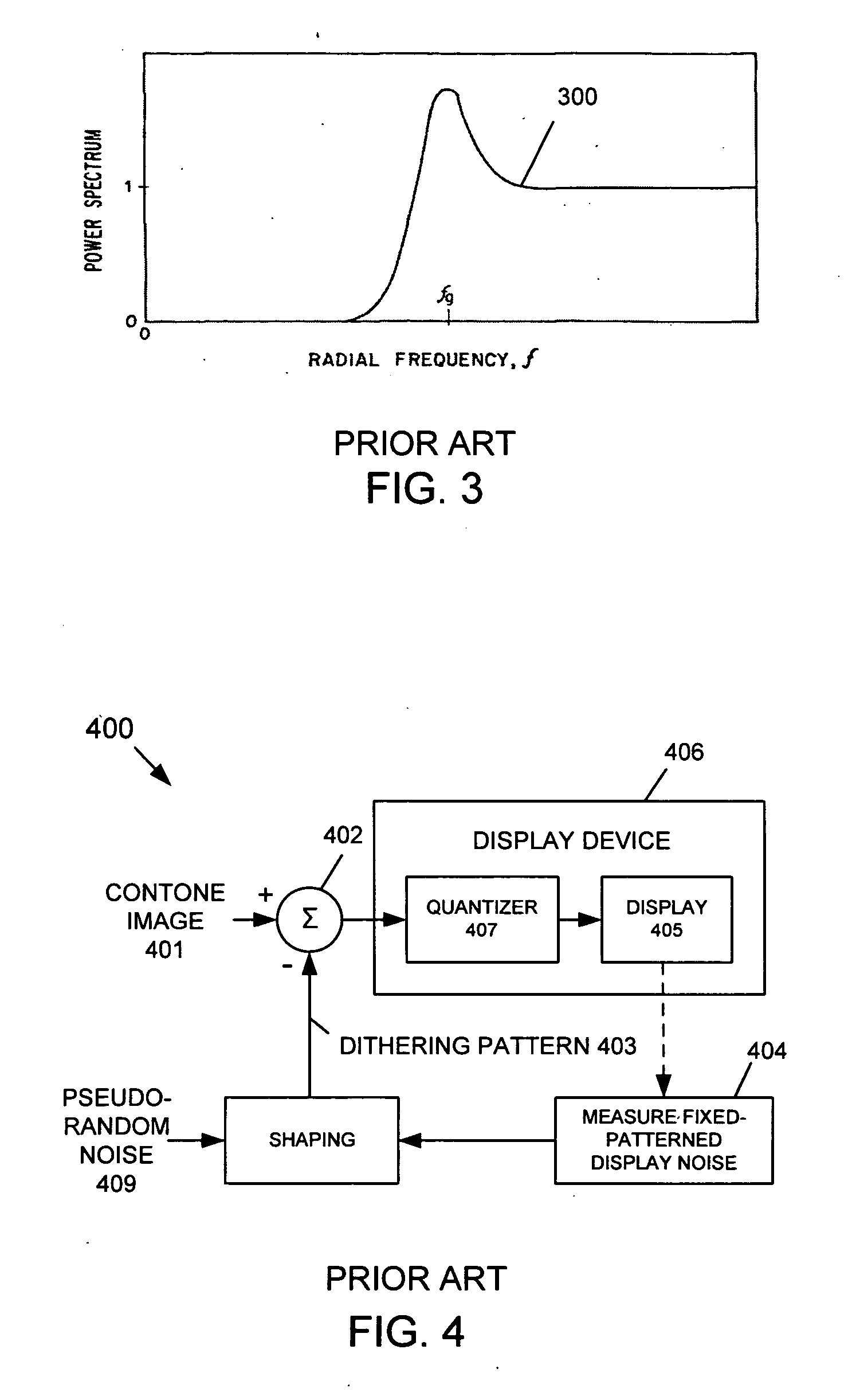
InactiveUS20060038826A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionDisplay device
A dithering pattern that is generated based on a spatial operation is used for a Bit-Depth Extension (BDE) technique for preventing contouring artifacts in an image displayed by a display having a bit-depth that-is less than the bit-depth of the image. The dithering pattern can be based on achromatic visual model or a spatio-chromatic visual model. The dither pattern is formed by shaping a pseudo-random noise signal by an equivalent noise visual model that is based on an array of pixels. Alternatively, the array of pixels is based on an image, or a determinate array of pixels.
Owner:SHARP KK
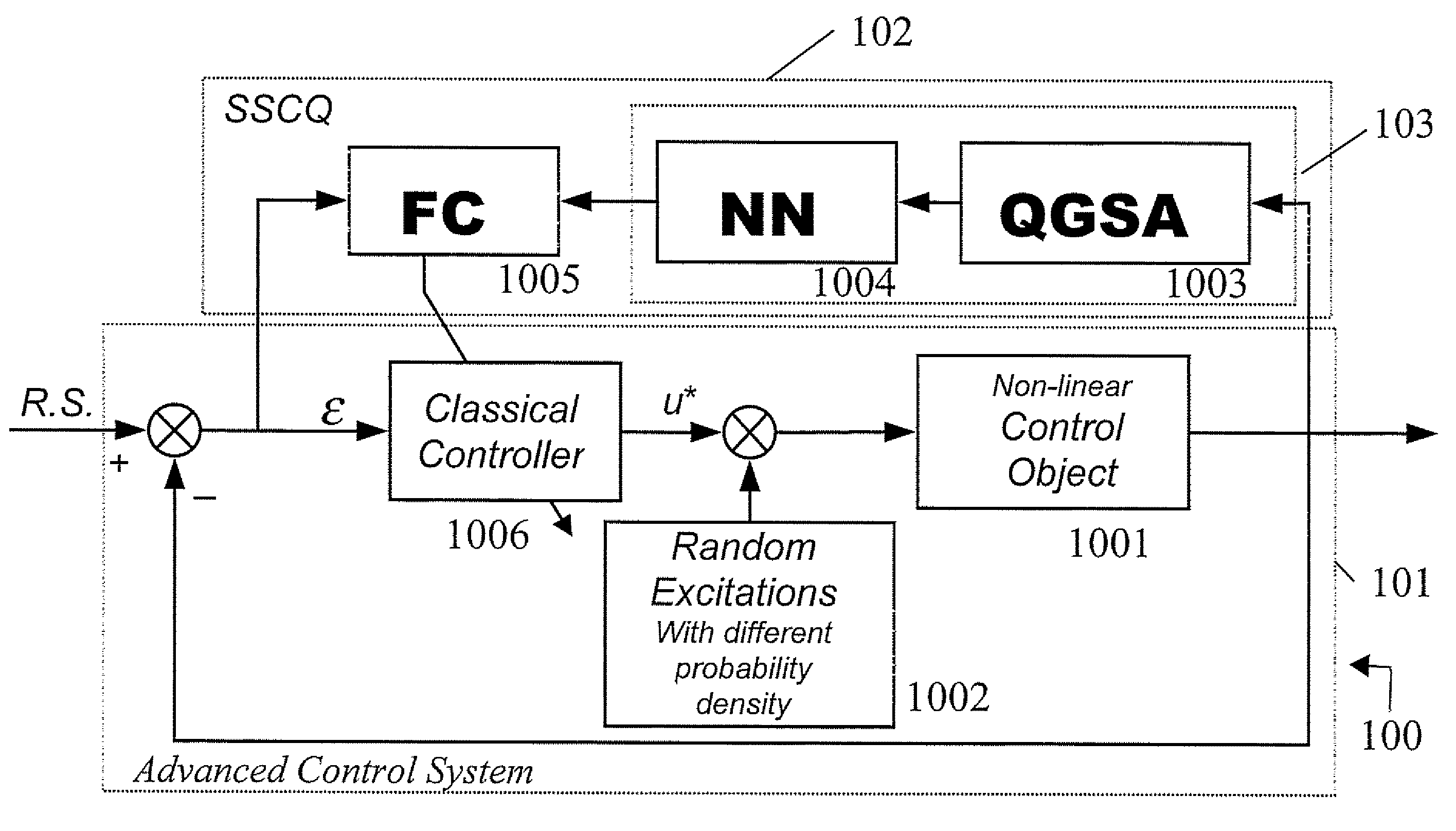
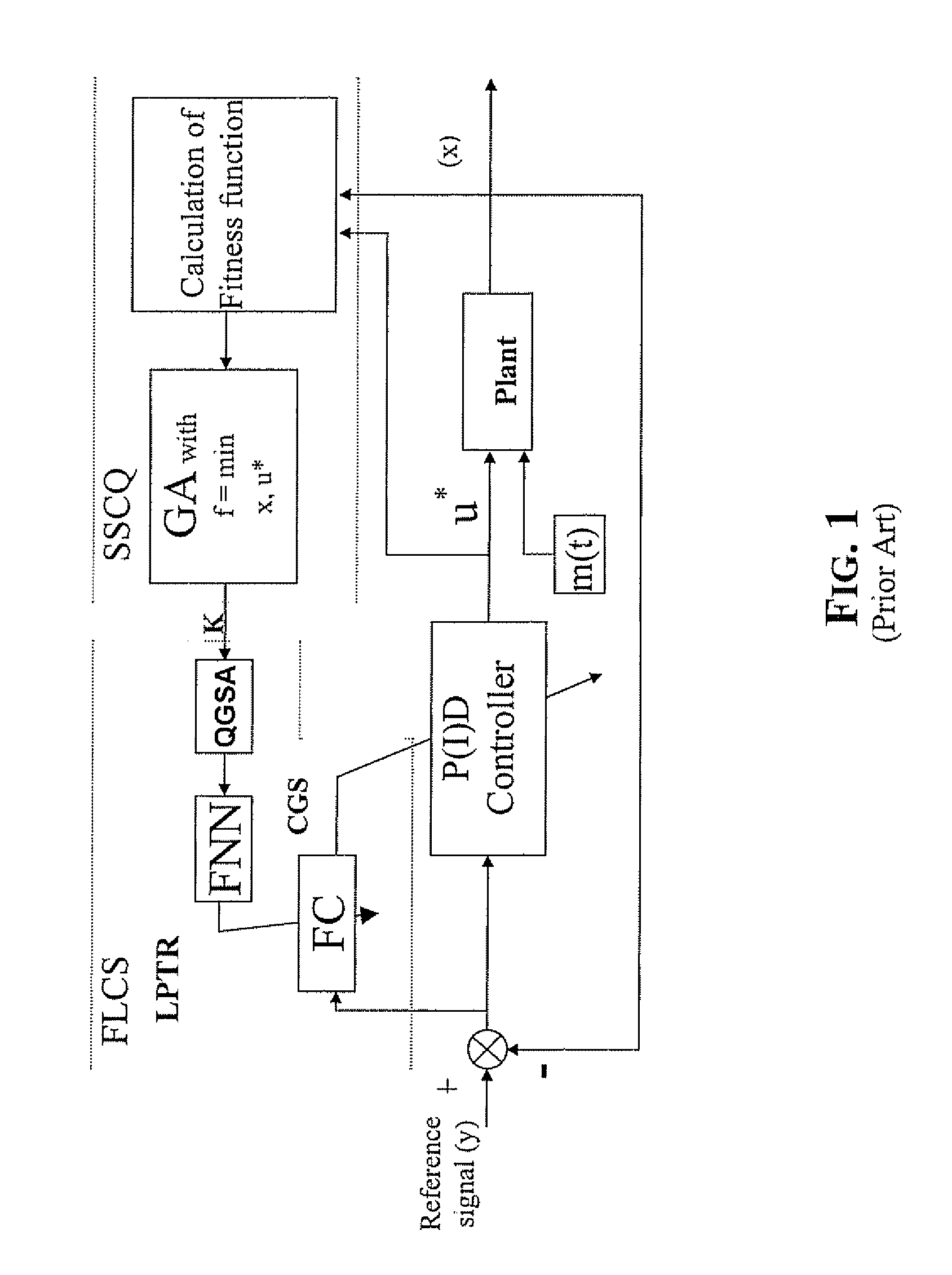
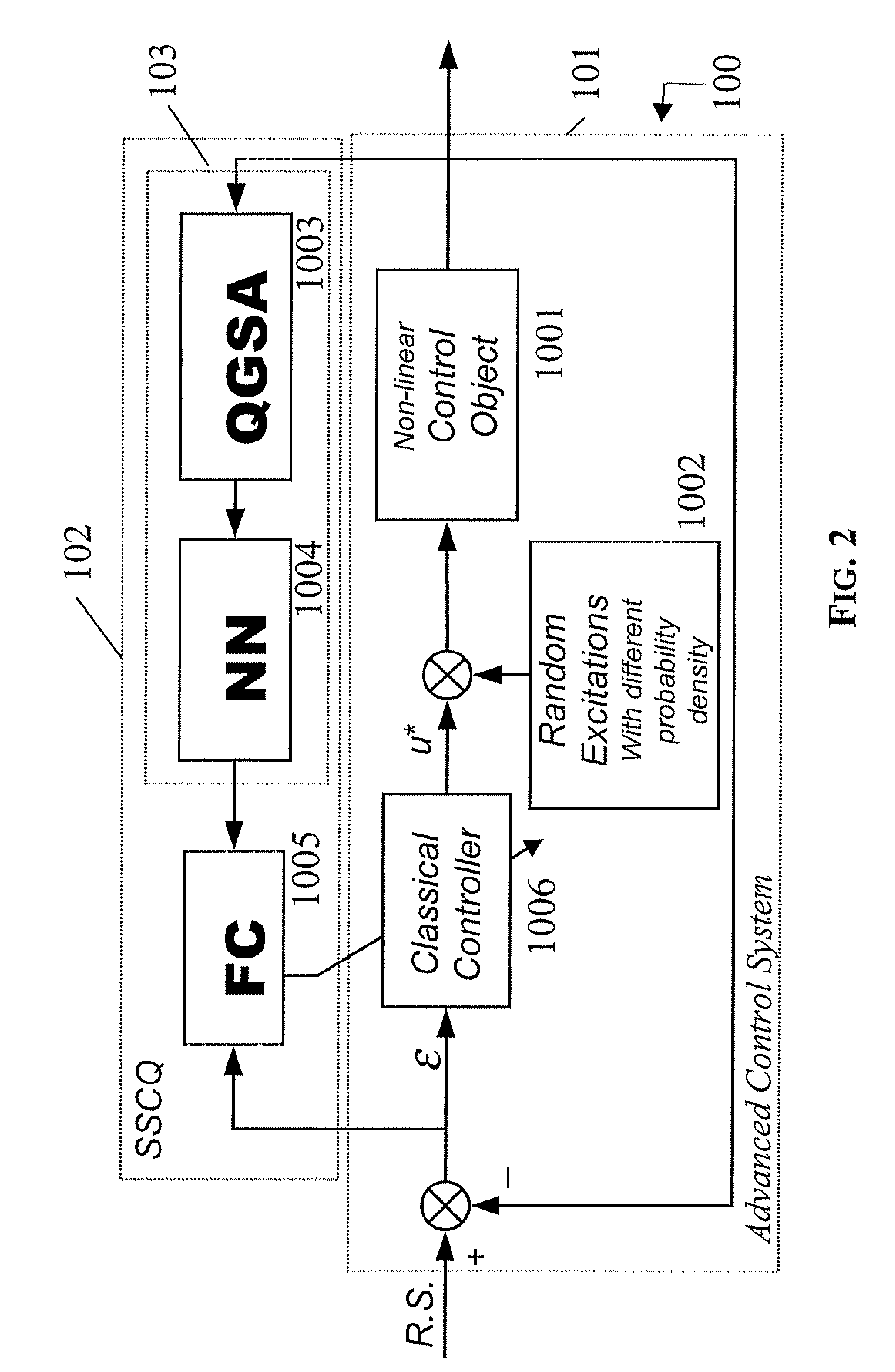
Method and device for performing a quantum algorithm to simulate a genetic algorithm
InactiveUS20080140749A1Increase diversityEasy searchQuantum computersNanoinformaticsAlgorithmQuantum algorithm
A method and device for performing a quantum algorithm where the superposition, entanglement with interference operators determined for performing selection, crossover, and mutation operations based upon a genetic algorithm. Moreover, entanglement vectors generated by the entanglement operator of the quantum algorithm may be processed by a wise controller implementing a genetic algorithm before being input to the interference operator. This algorithm may be implemented with a hardware quantum gate or with a software computer program running on a computer. Further, the algorithm can be used in a method for controlling a process and a relative control device of a process which is more robust, requires very little initial information about dynamic behavior of control objects in the design process of an intelligent control system, or random noise insensitive (invariant) in a measurement system and in a control feedback loop.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
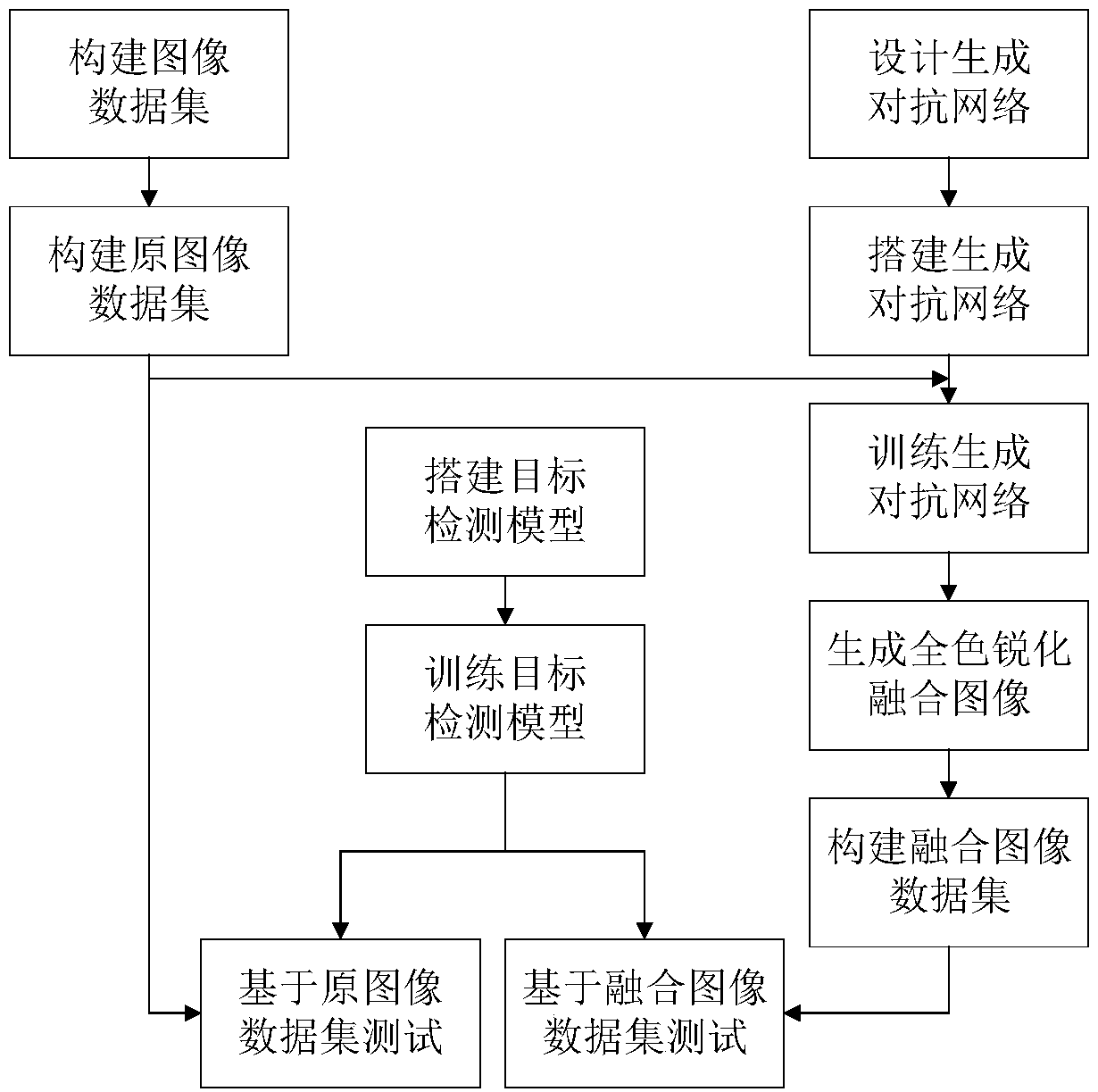
Remote sensing image panchromatic sharpening method based on generative adversarial networks
ActiveCN108537742AAdd jump linkReduce lossesImage enhancementImage analysisData setGenerative adversarial network
The invention relates to a remote sensing image panchromatic sharpening method based on generative adversarial networks (GAN). The remote sensing image panchromatic sharpening method based on generative adversarial networks includes the steps: 1) constructing a data set: performing target classification and marking on remote sensing image data, and constructing an original image data set includingpanchromatic images and spectral images; 2) designing to a GAN model and a discrimination network model, wherein the GAN model G of GAN learns the random noise vector and the images in the data set and trains a mapping to the generated sample image y, and the sample image generated from the trained G cannot be discriminated as false by the discrimination network model while the discrimination network model D uses the convolutional neural network, and after training, the discrimination network model D can discriminate true and false of the generated data, thus being able to preferably completediscrimination of the classification problem of true or false of generated sample images; and 3) training the GAN model.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Device for and method of signal synchronization in a communication system
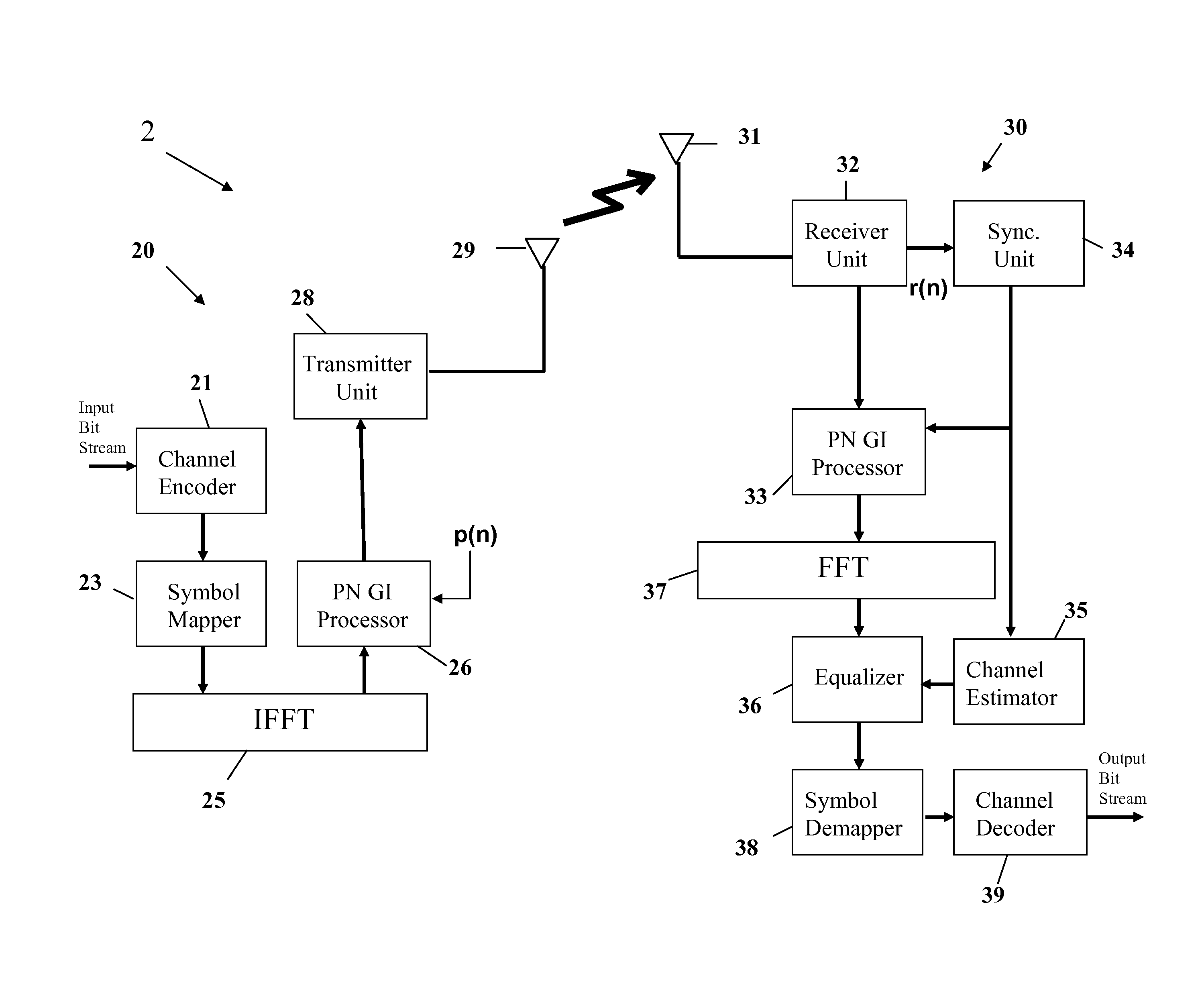
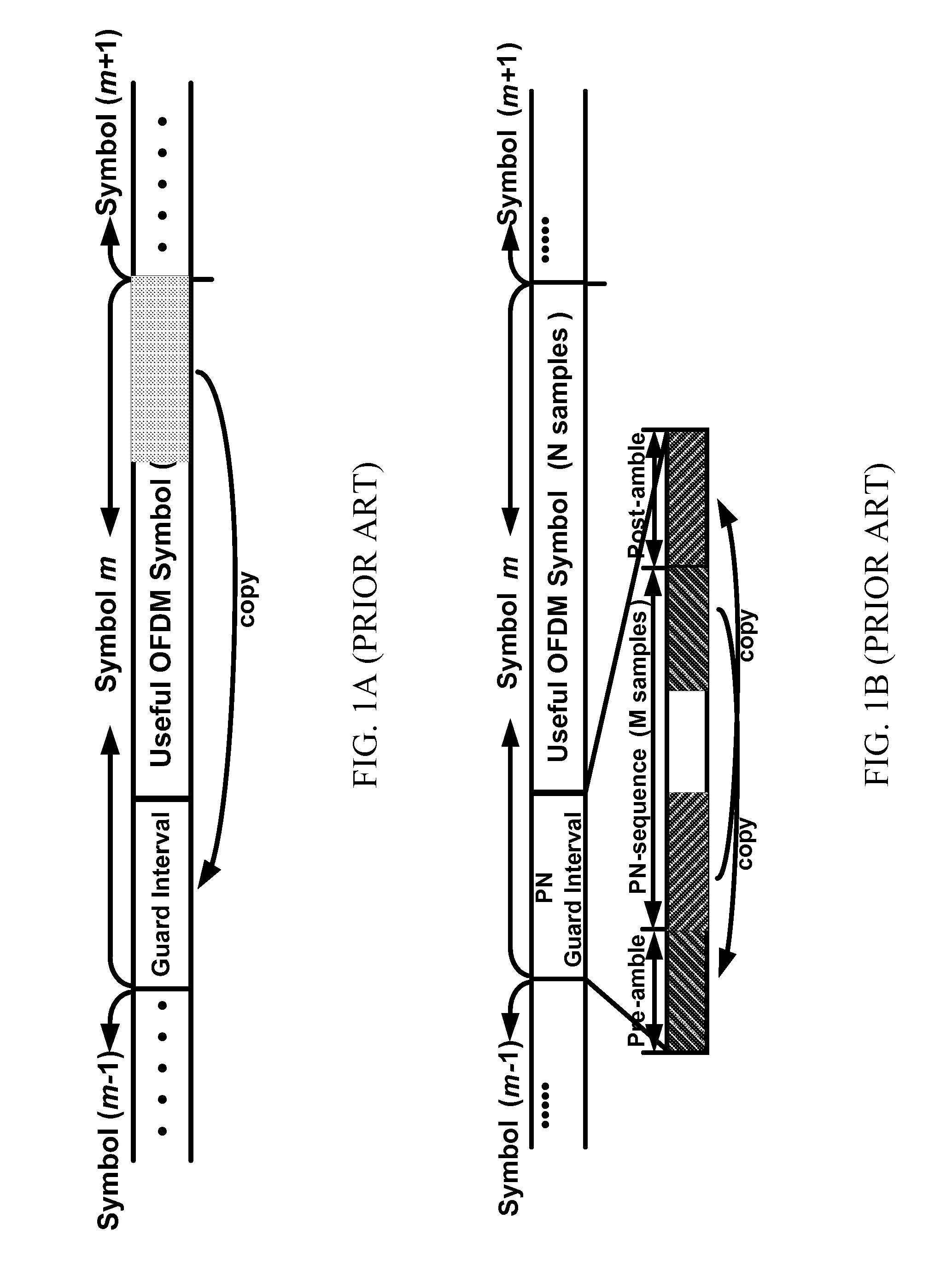
ActiveUS20090135977A1Compensation effectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCommunications systemGuard interval
A device for signal synchronization in a communication system, the device comprising a first detector configured to perform a first sliding correlation for a received signal and a pseudo-random noise (PN) sequence to obtain information on symbol timing, a second detector configured to identify a fractional carrier frequency offset (FCFO) using the information on symbol timing and the cyclic extension property of the PN guard interval (GI), a first multiplier configured to provide a first product by multiplying the received signal with the FCFO, and a third detector comprising a set of second multipliers configured to provide a set of second products by multiplying the first product with each of a set of phases related to integral carrier frequency offsets (ICFOs), a set of sliding correlators each being configured to perform a second sliding correlation for the PN sequence and one of the set of the second products, the set of sliding correlators providing a set of peak values, and a peak detector configured to identify an ICFO by detecting an index number of a maximal value among the set of peak values.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS20070244575A1Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
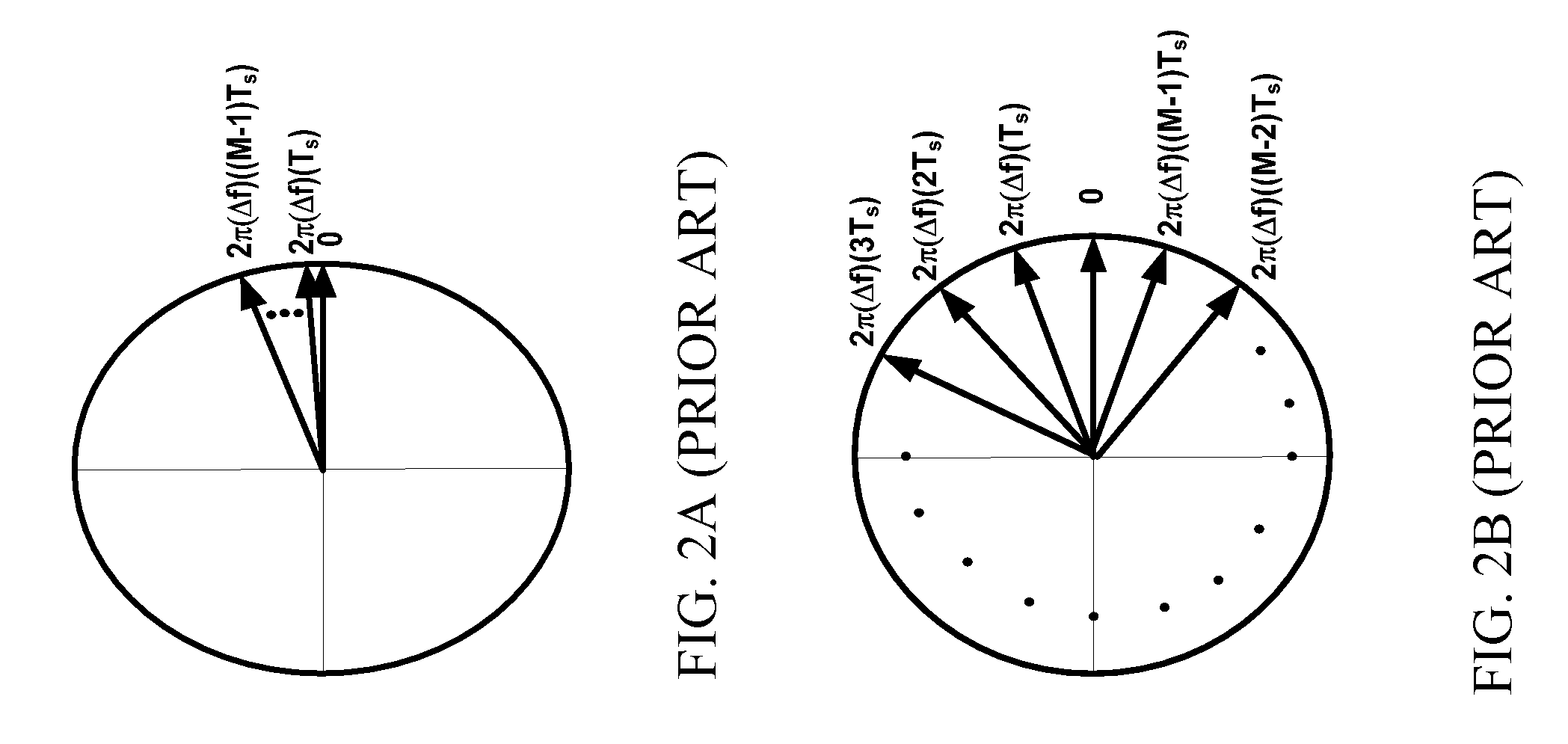
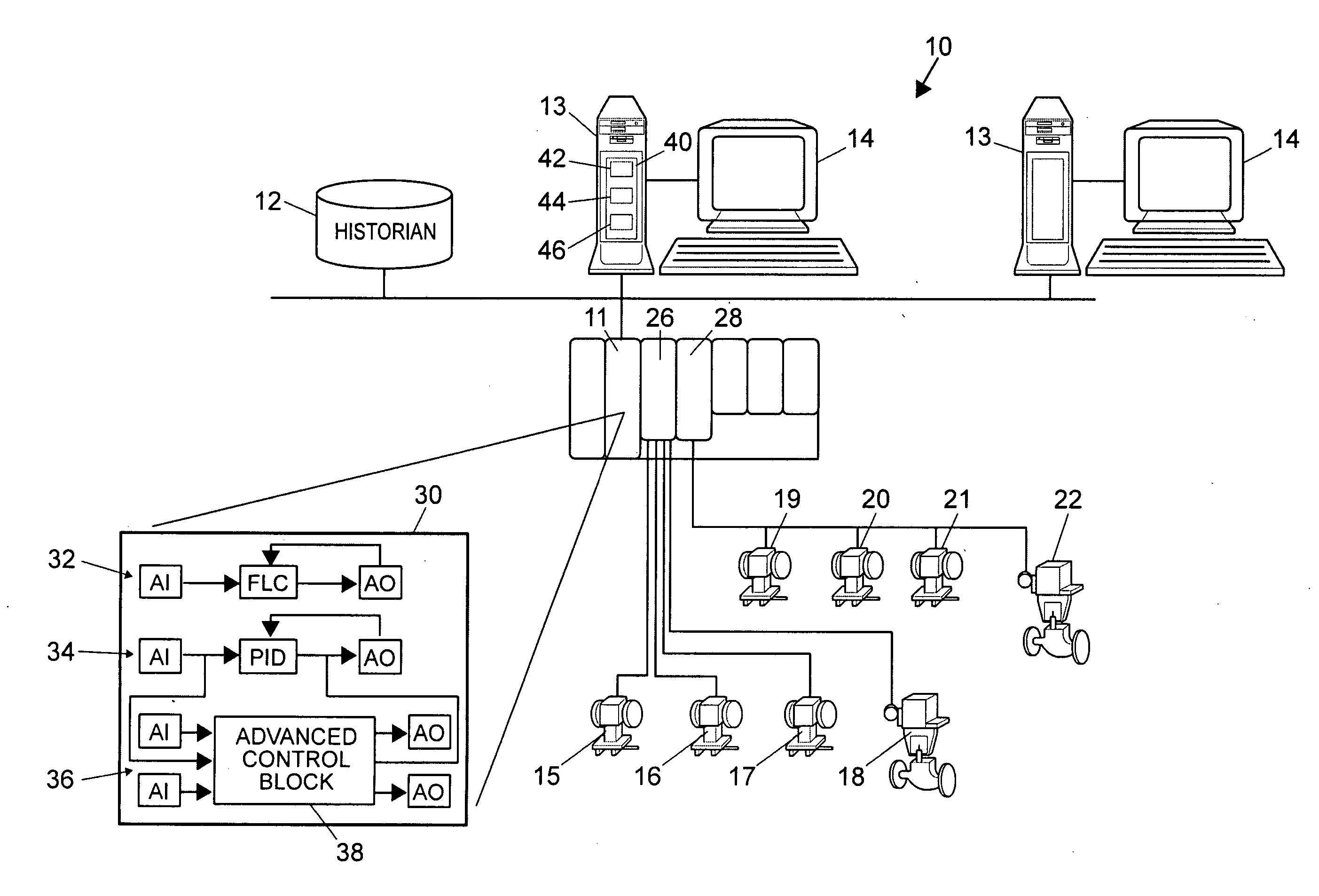
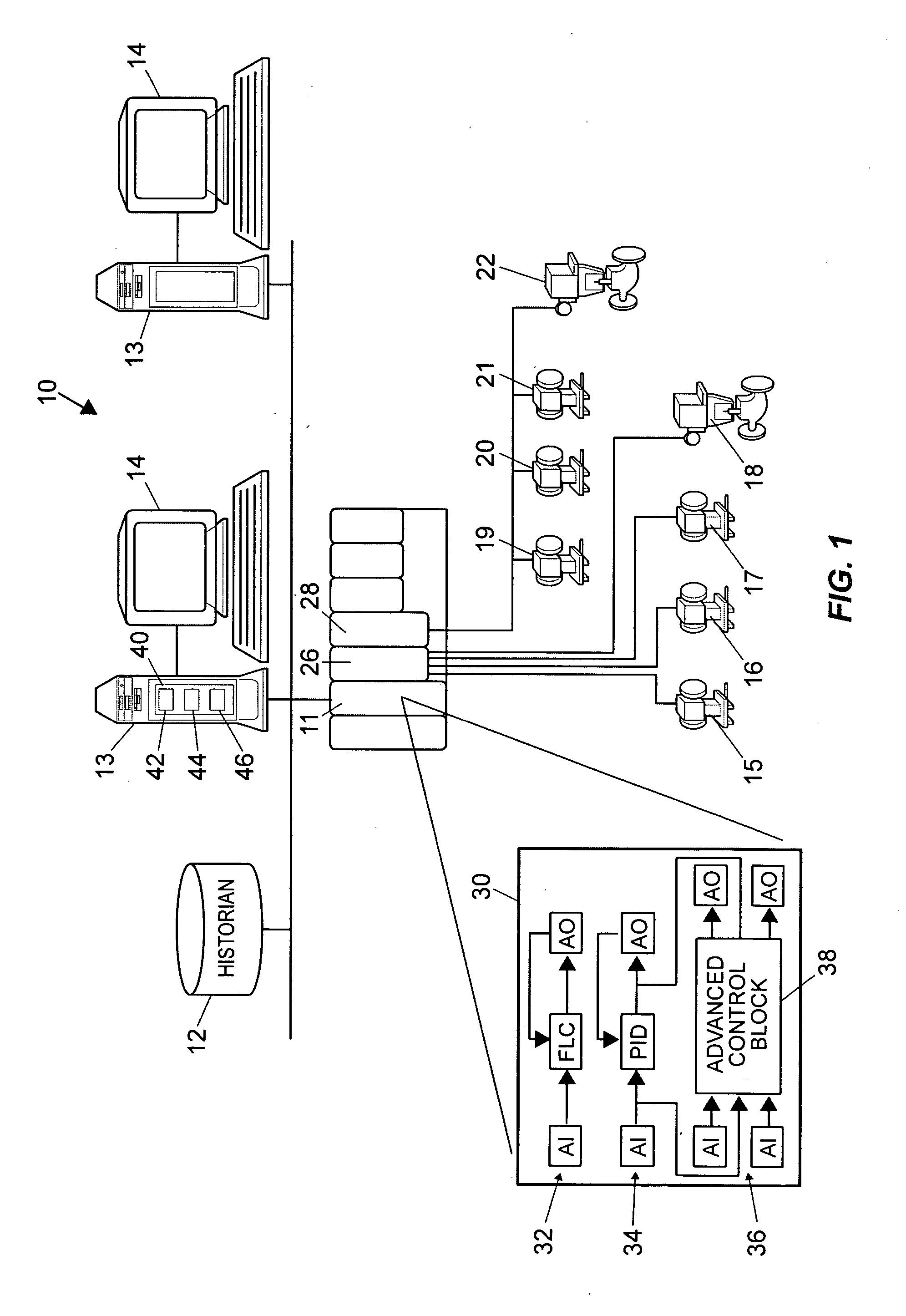
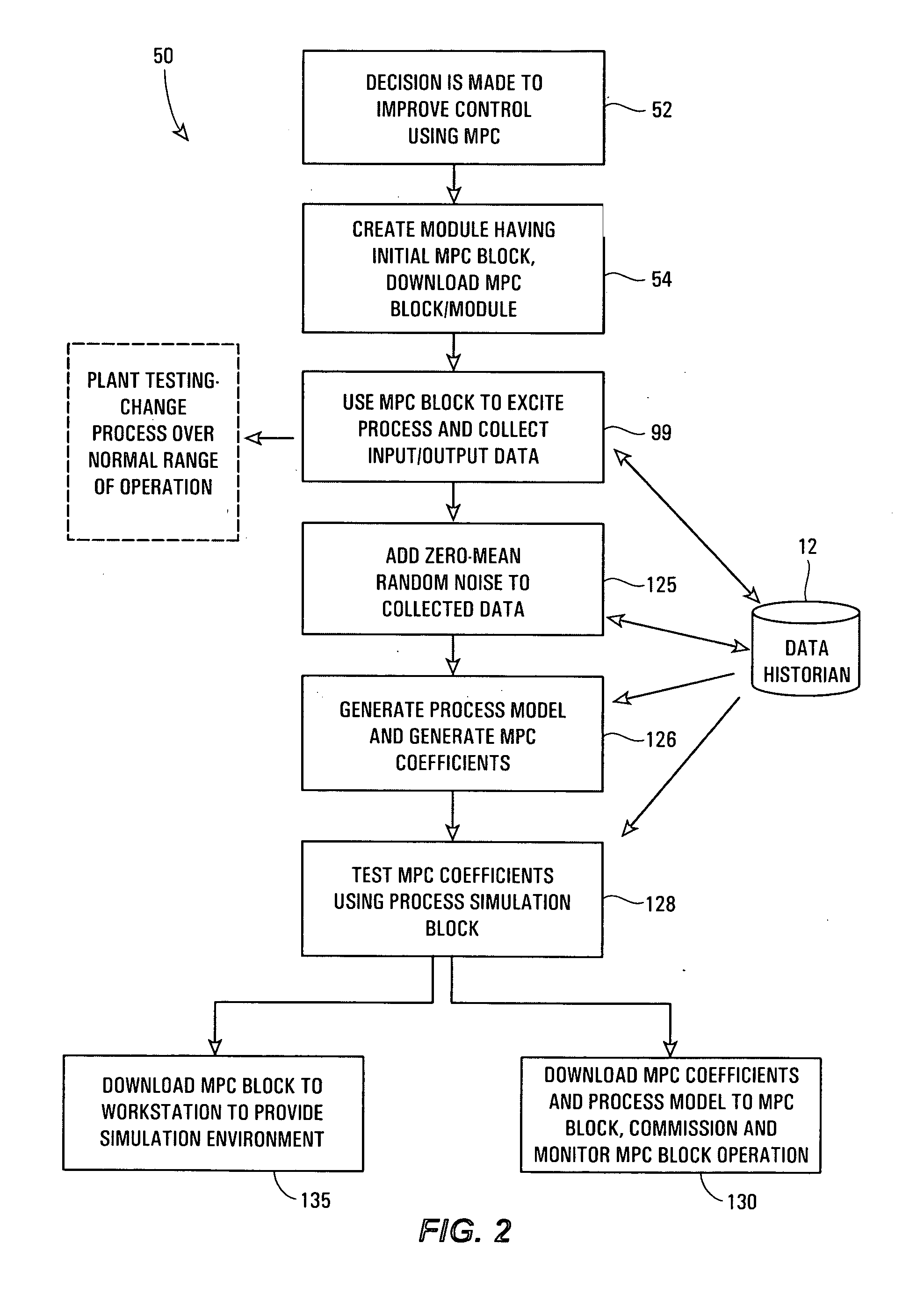
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
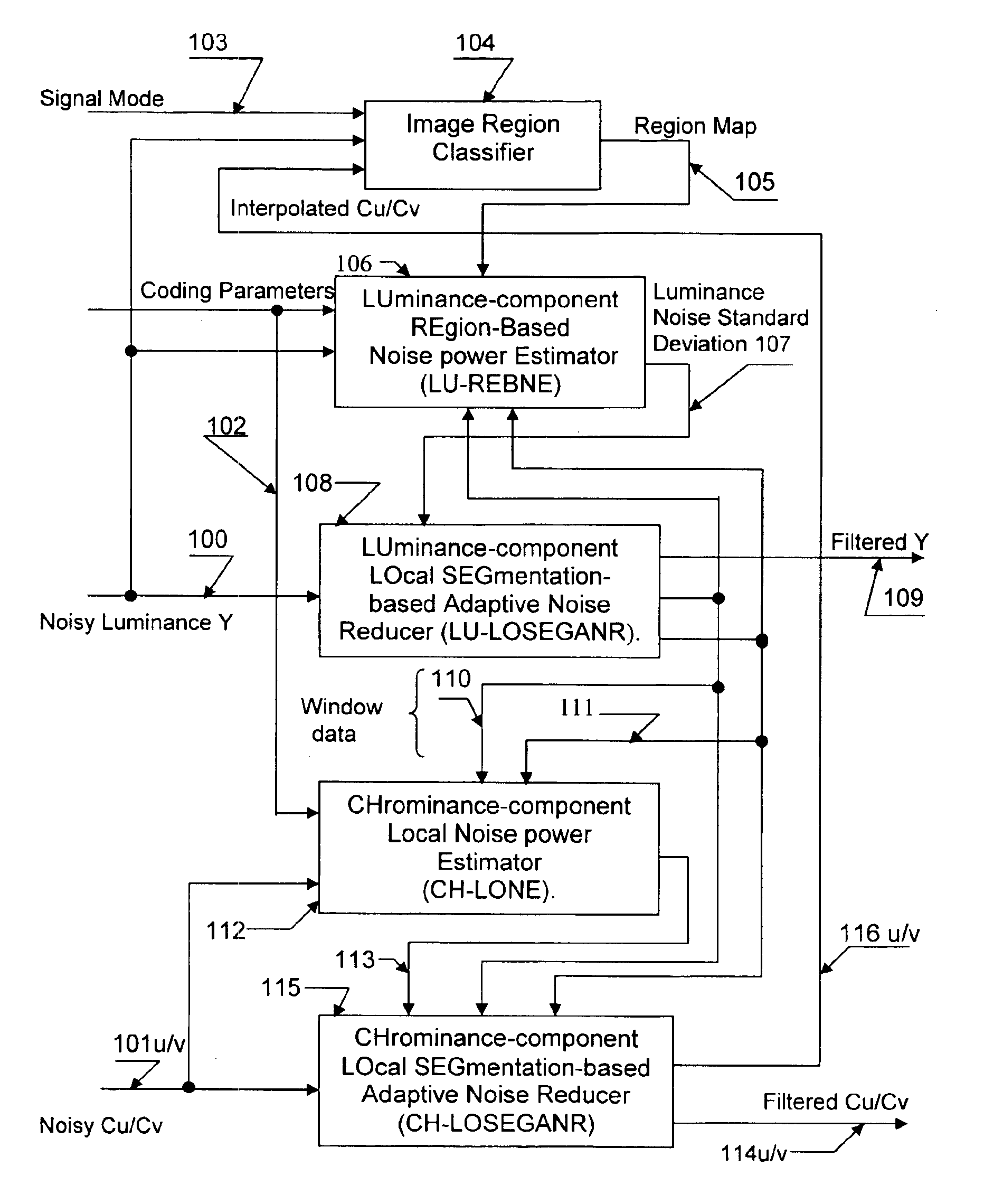
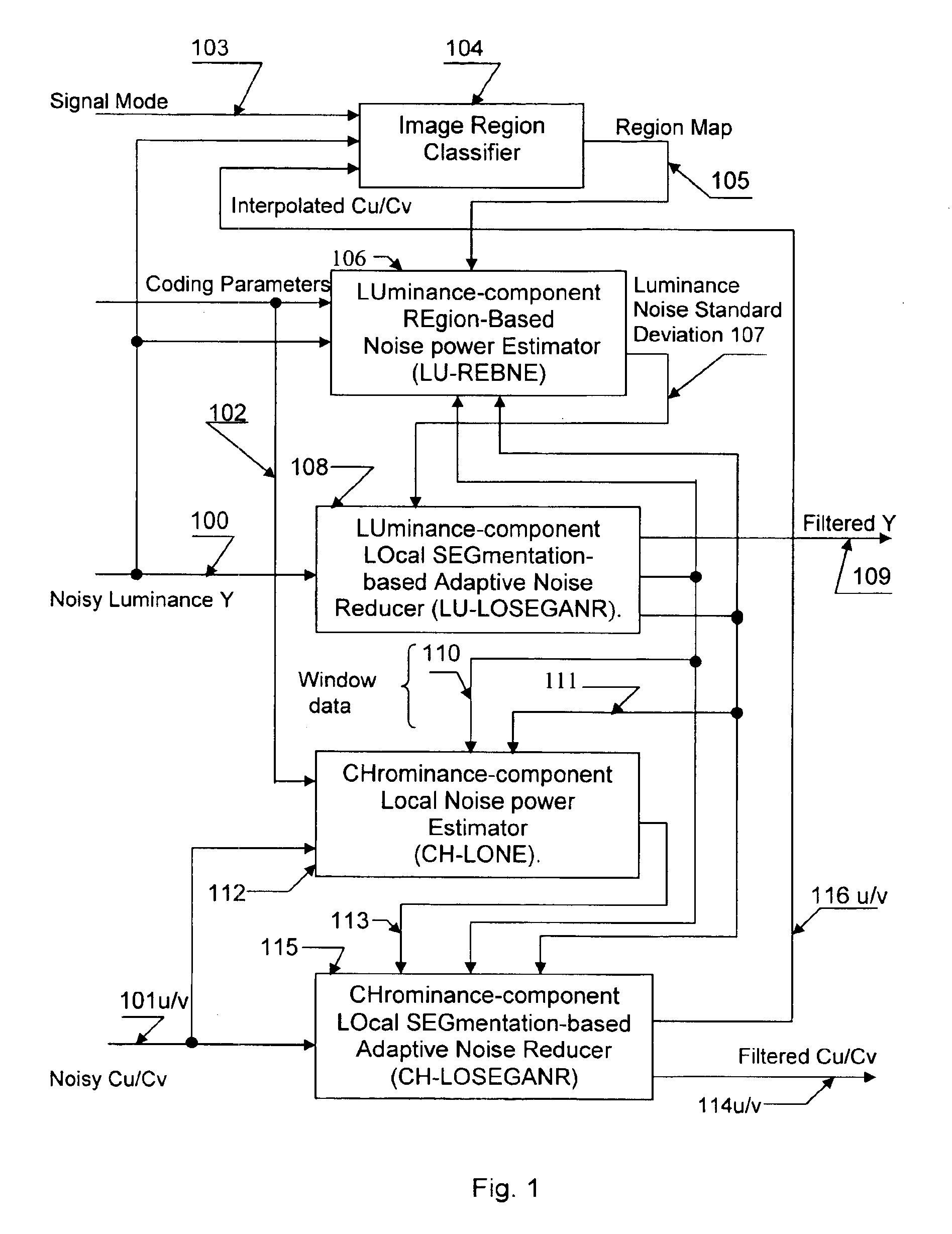
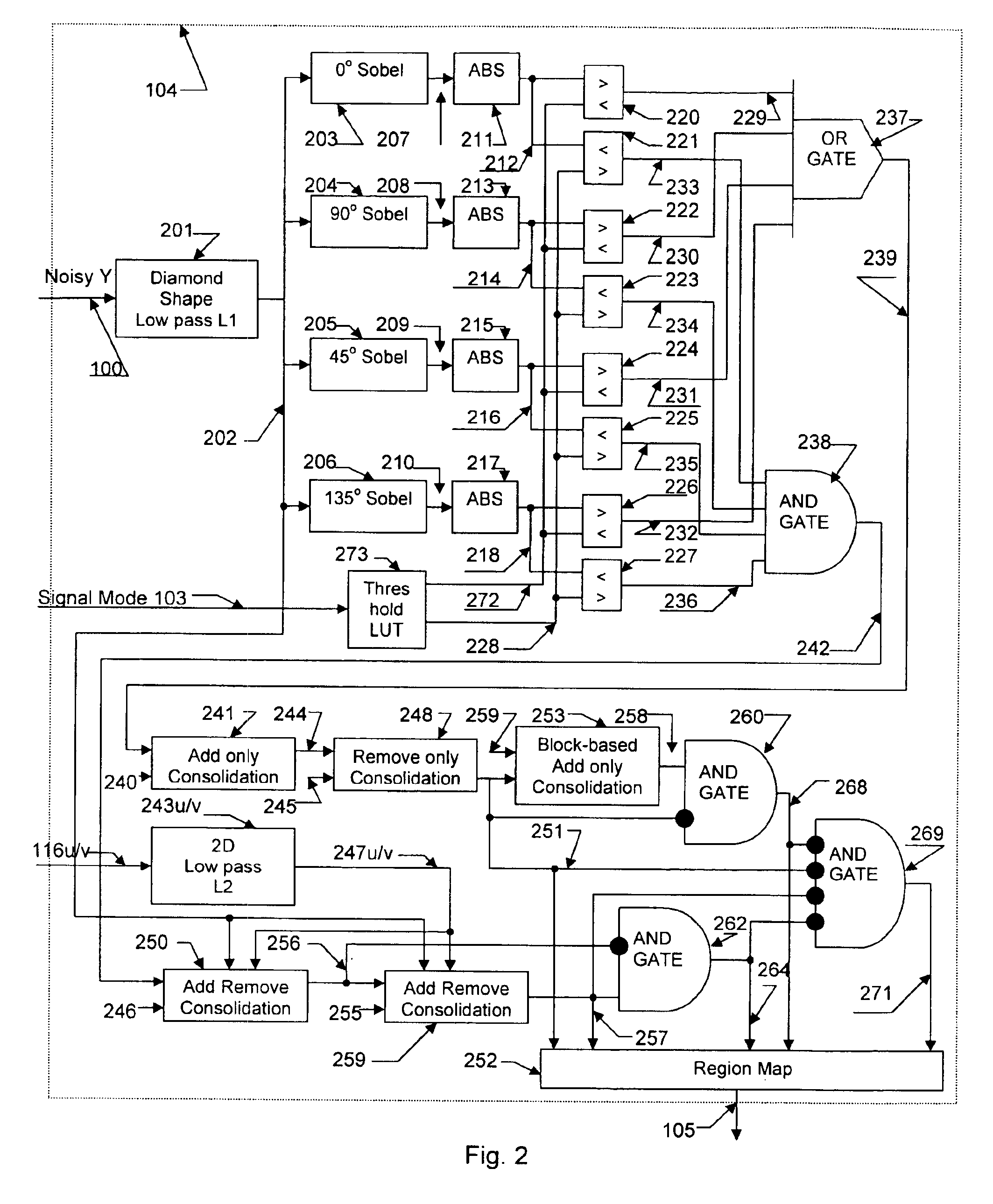
Apparatus and method for adaptive spatial segmentation-based noise reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS7076113B2Reduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionRandom noise
An efficient and non-iterative post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction in DCT block-based decoded images. The post-processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. An MMSE or MMSE-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. Finally, the proposed technique comprises also, for chrominance components, efficient shape adaptive local noise power estimation and correction.
Owner:BANK OF MONTREAL +1
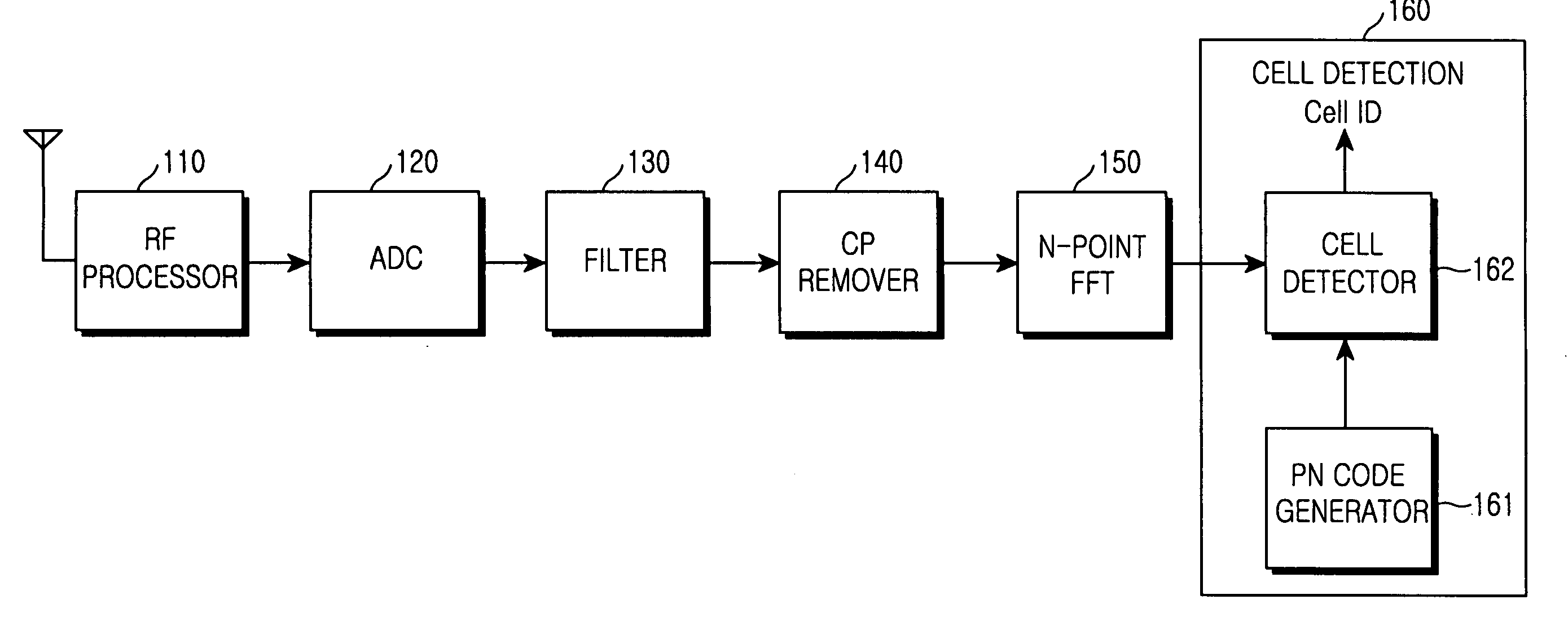
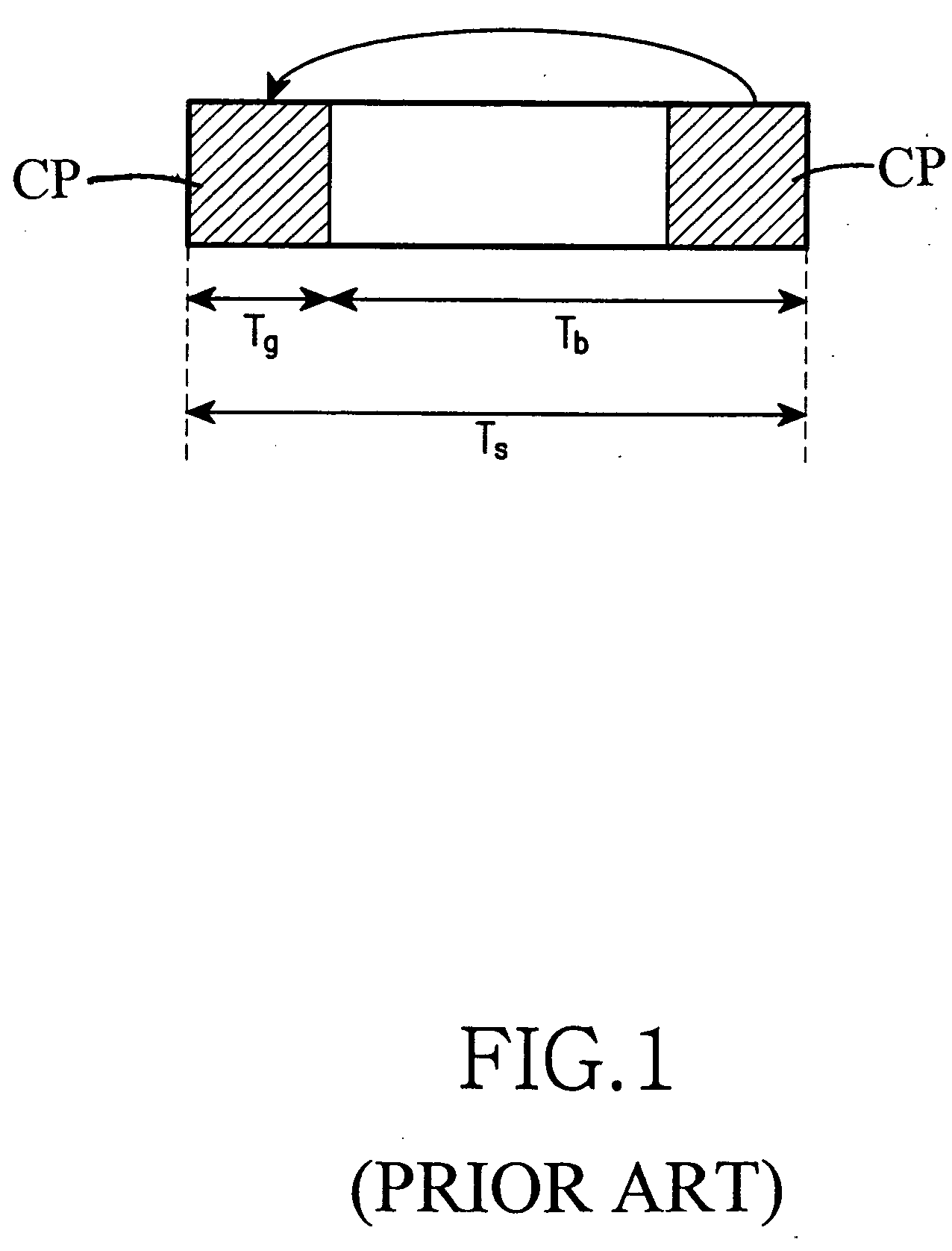
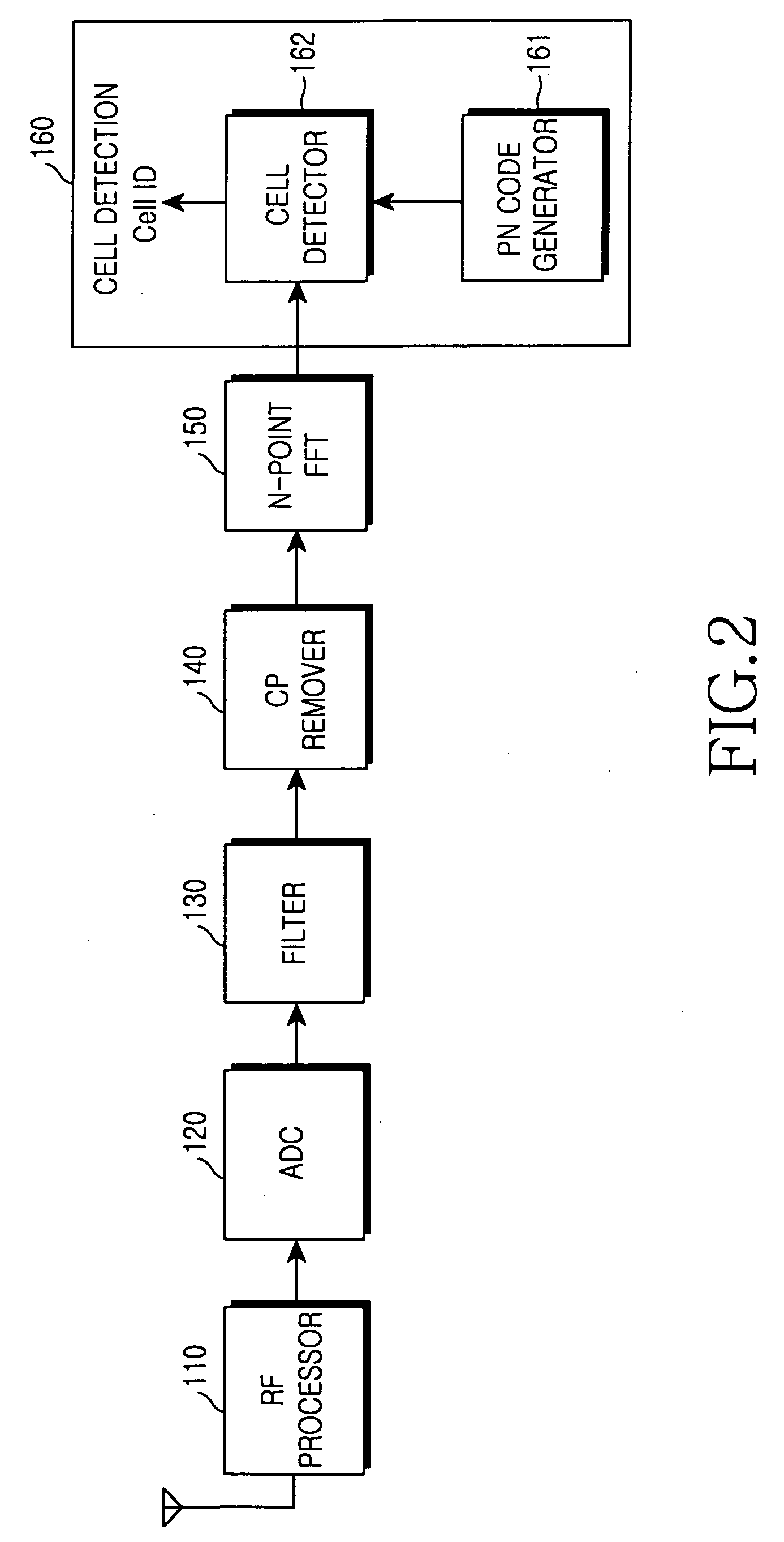
Method and apparatus for detecting a cell in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access system
InactiveUS20050271026A1Radio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformRandom noise
An apparatus and method are provided for detecting via a mobile station a cell in which the mobile station is located in order to initiate communication in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) system including a plurality of base stations transmitting signal with a pseudo-random noise (PN) code to the mobile station. The apparatus and method include receiving the signal from the base station and performing fast Fourier transform (FFT) on the received signal; generating a PN code for comparison with a base station's PN code included in the signal; and detecting a cell where the mobile station is located by searching for a PN code synchronized in the FFT-processed signal using the generated PN code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
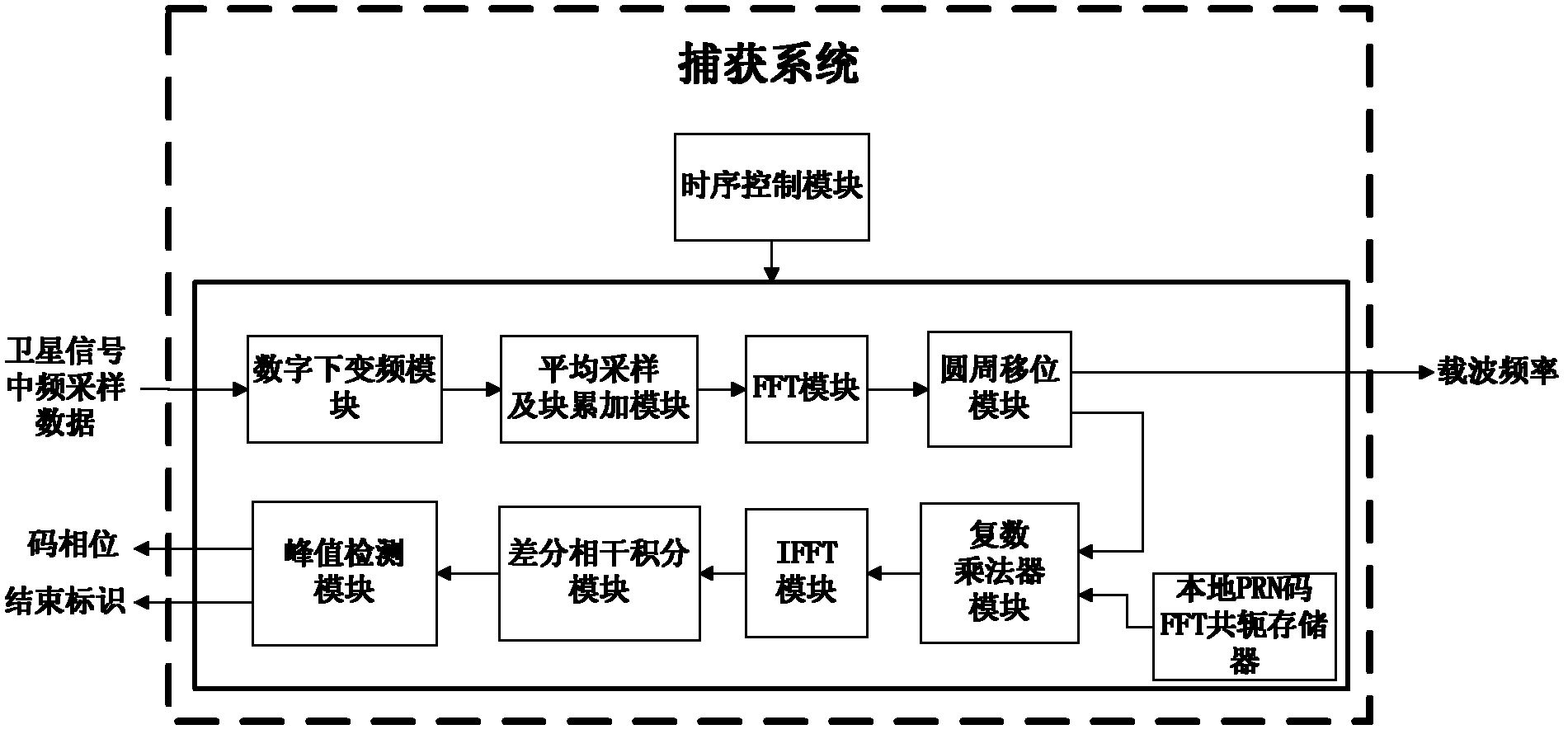
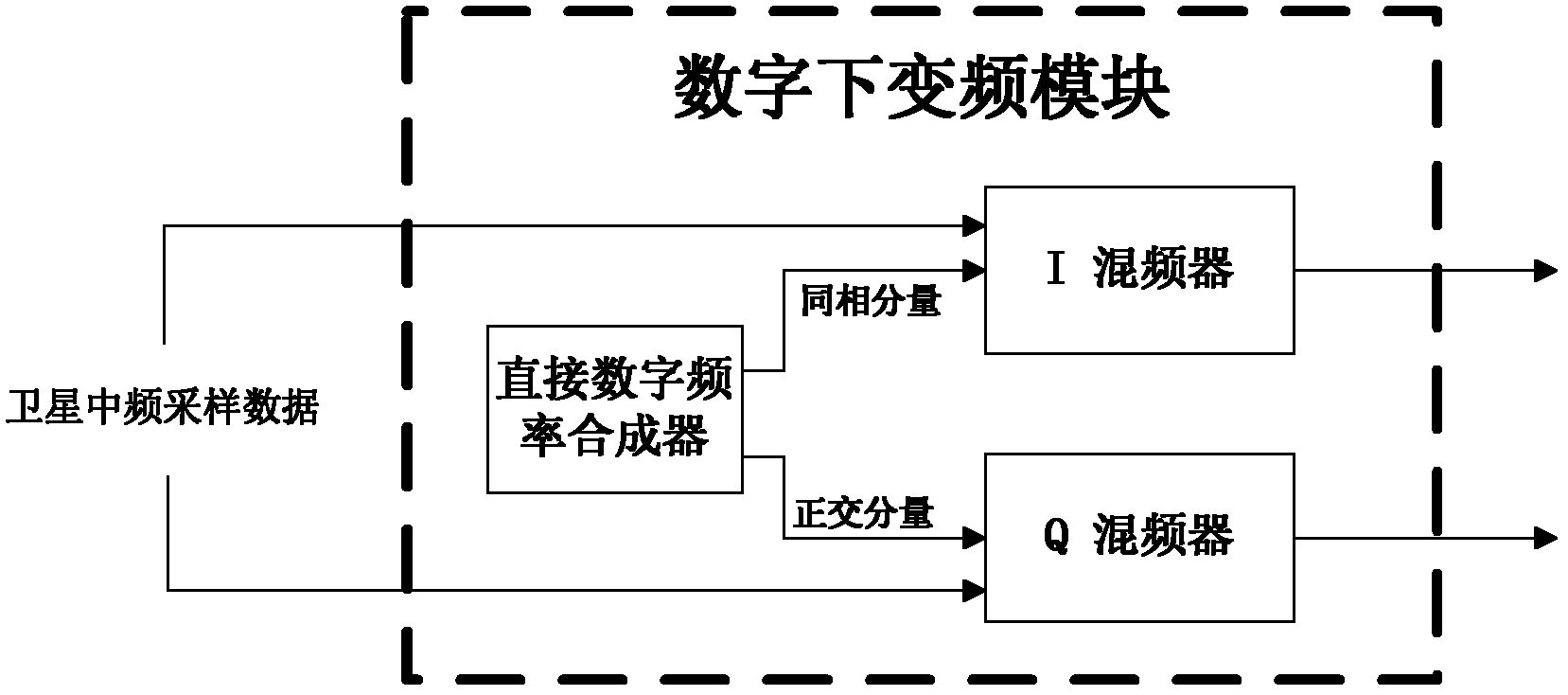
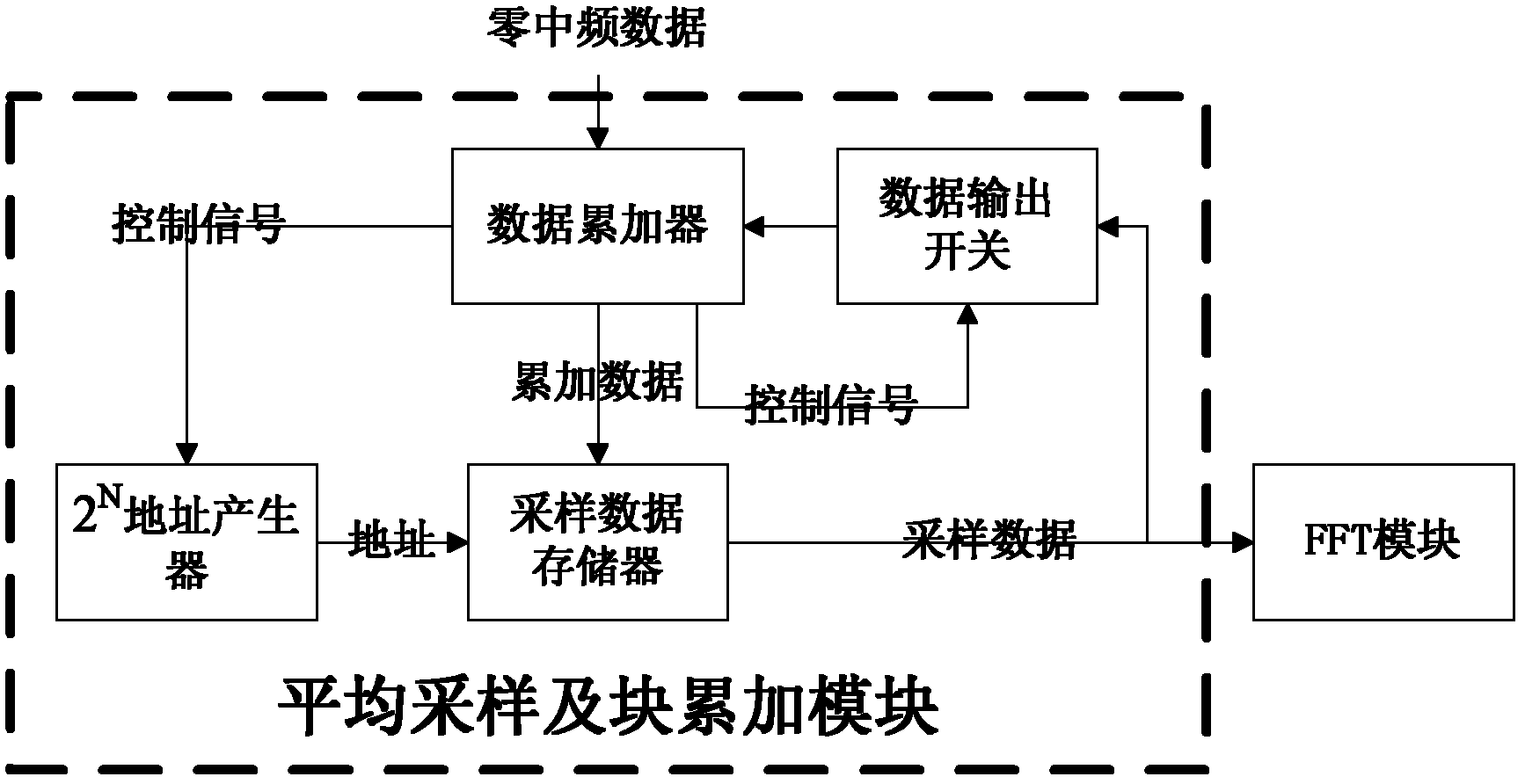
High-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and system
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and a system. The system comprises a digital down-conversion module, an average sampling and block accumulation module, an FFT (fast Fourier transform) module, a circumference shifting module, a local PRN (pseudo random noise) code FFT conjugate memory, a complex multiplier module, an IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) module, a differential coherence integration module, a peak detection module and a sequential control module. The digital down-conversion module realizes digital down-conversion operation for satellite digital intermediate frequency signals; the average sampling and block accumulation module averagely samples satellite data and completes a block accumulation function; the FFT module searches code phase frequency domains; the circumference shifting module utilizes Doppler circumference shifting search to replace frequency compensation; the local PRN code FFT conjugate memory stores a local PRN code FFT conjugate result; the complex multiplier module realizes signal de-spreading; the IFFT module calculates different code phase coherence results; the differential coherence integration module accumulates differential coherence energy of de-spread satellite signals; the peak detection module realizes signal capturing output; and the sequential control module controls timing sequence of the various modules of the system. Weak signal capturing speed and sensitivity of a satellite navigation receiver are improved, and parameters can be configured flexibly.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
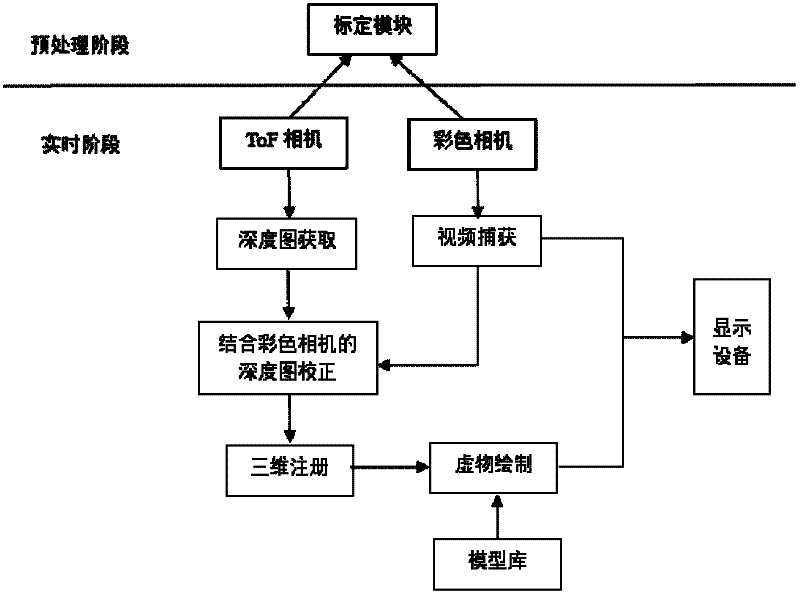
Three-dimensional registering method based on ToF (Time-of-Flight) depth camera
InactiveCN102609941AImprove real-time performanceImprove applicabilityImage enhancementImage analysisVisual field lossRandom noise
The invention provides a three-dimensional registering method based on a ToF (Time-of-Flight) depth camera, comprising the following steps of: (1) establishing a double-eye camera system composed of the ToF depth camera and a color camera and calibrating the system; (2) finishing the elimination of abnormal points and random noises of a depth image by the ToF camera to improve the precision of depth data; and (3) projecting the depth image obtained by the ToF camera to a visual field of the color camera to establish a corresponding relation between the depth image and a colorful image. The tracking of marks in a real-time video streaming can be realized by using a Camshift algorithm, so that a three-dimensional position and a direction of the marks in a space can be obtained according to the projected depth image.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Matched filtration with experimental noise determination for denoising, peak picking and quantitation in lc-ms
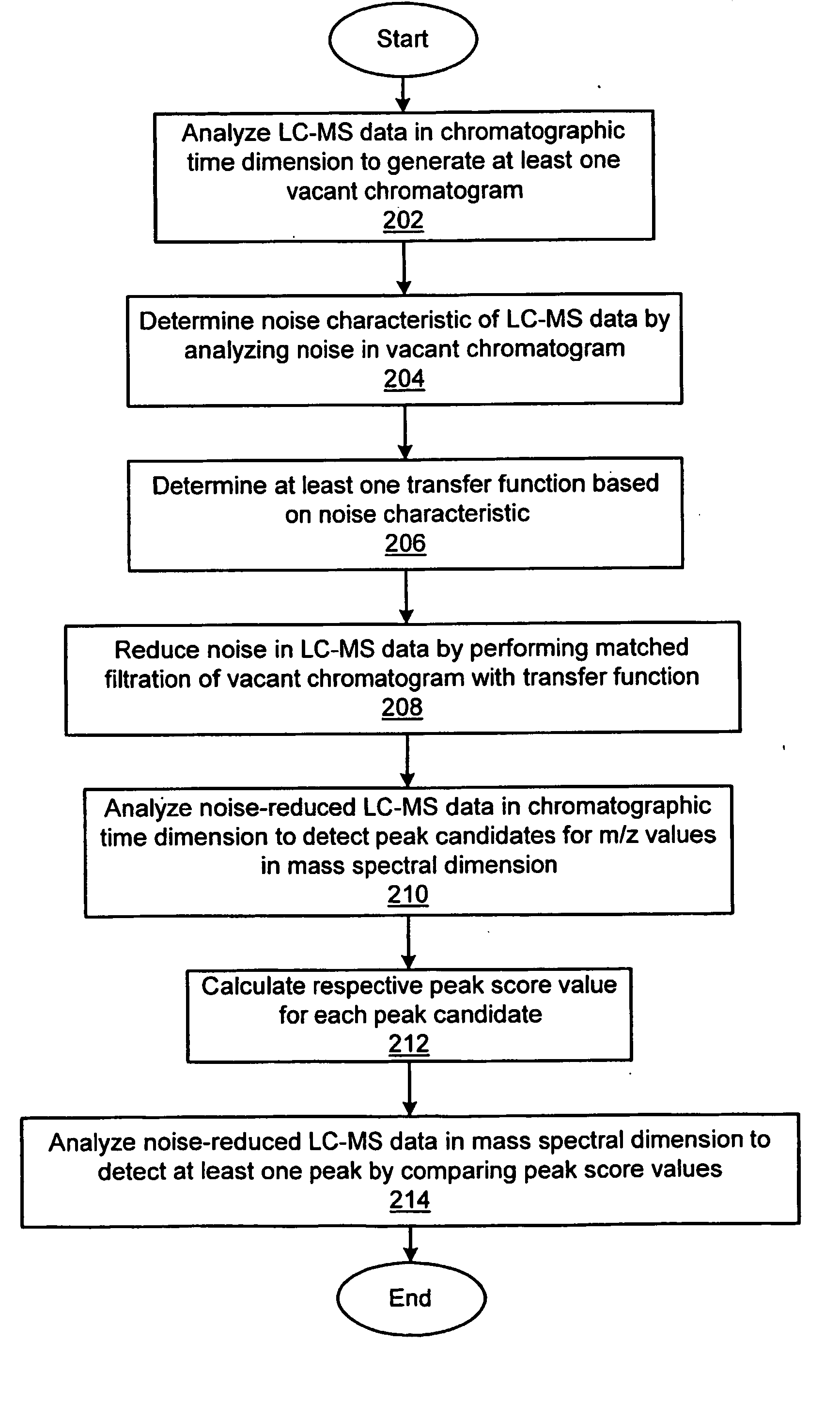
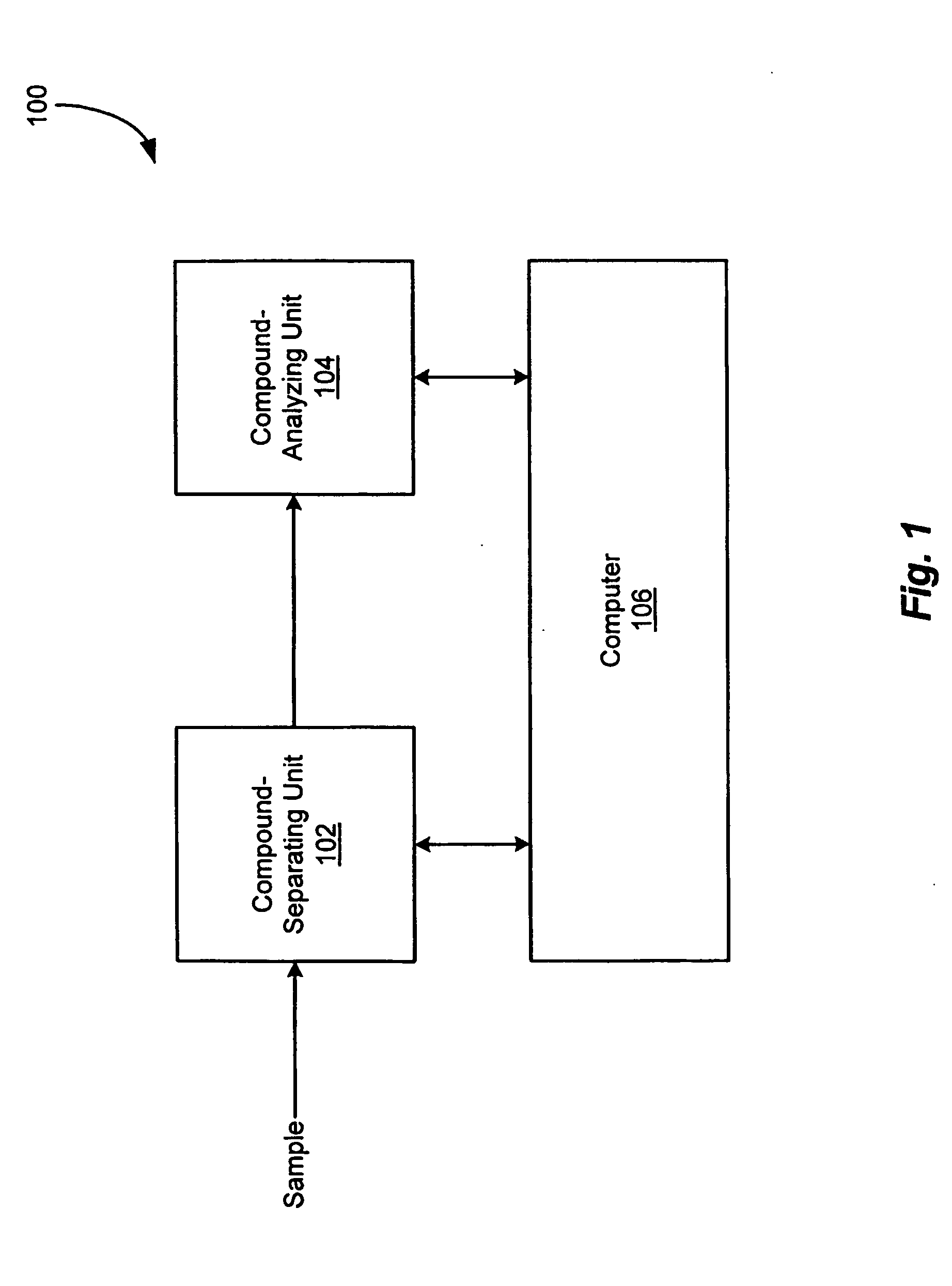
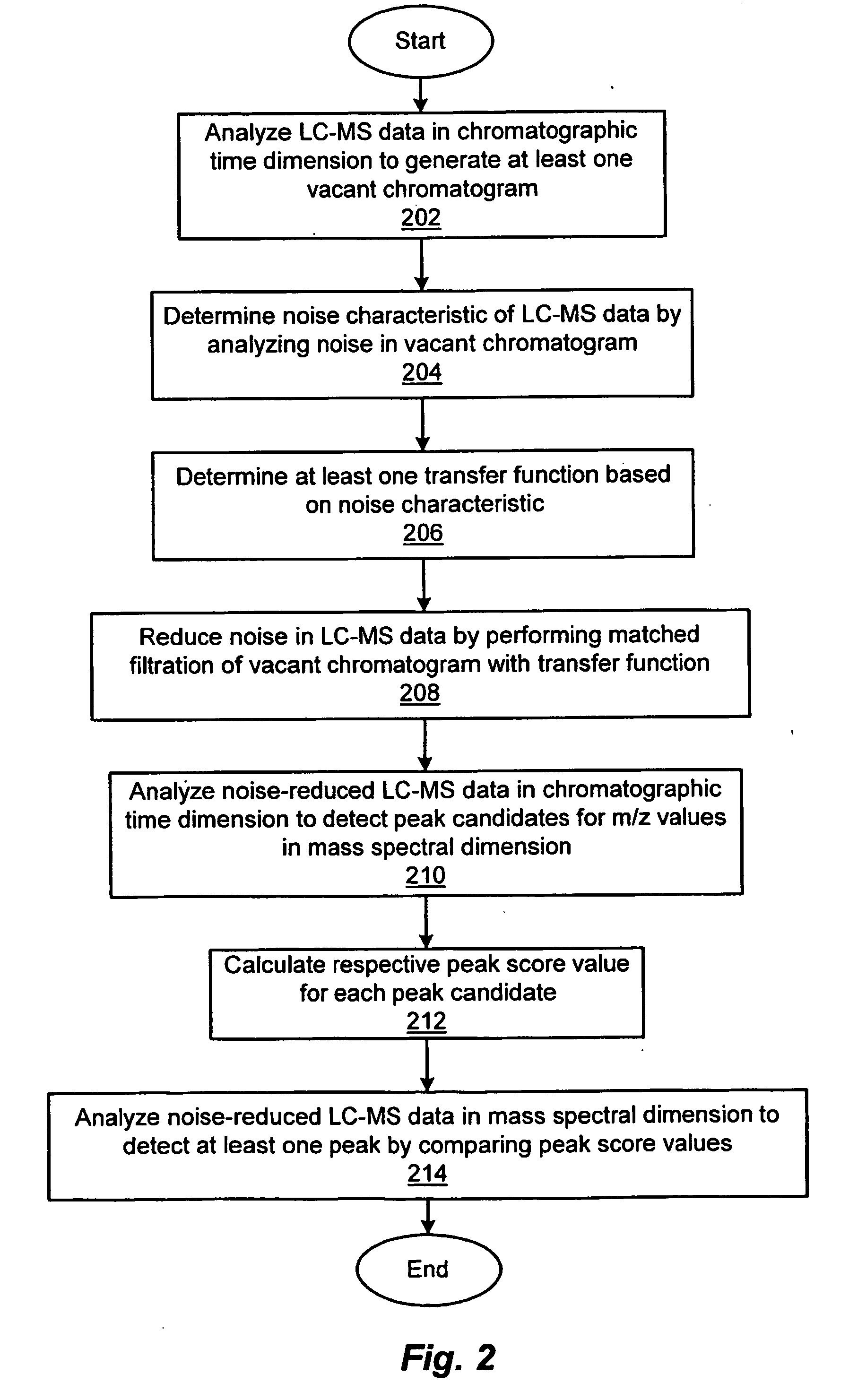
InactiveUS20050261838A1Improve reliabilityReduce noiseMolecular entity identificationComponent separationData setFiltration
An improved system and method of analyzing sample data that increases the reliability of peak (compound) detection and identification in the presence of chemical and / or random noise. The sample analysis system includes a compound-separating unit for separating constituent compounds in a sample mixture, a compound-analyzing unit for identifying and quantitating at least one of the separated compounds, and a computer for acquiring data from the compound-separating and compound-analyzing units, for generating a multi-dimensional data set incorporating the acquired data, for executing an algorithm for reducing noise in the data set and for detecting peaks (compounds) in the noise-reduced data set, and for identifying / quantitating the detected compounds.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
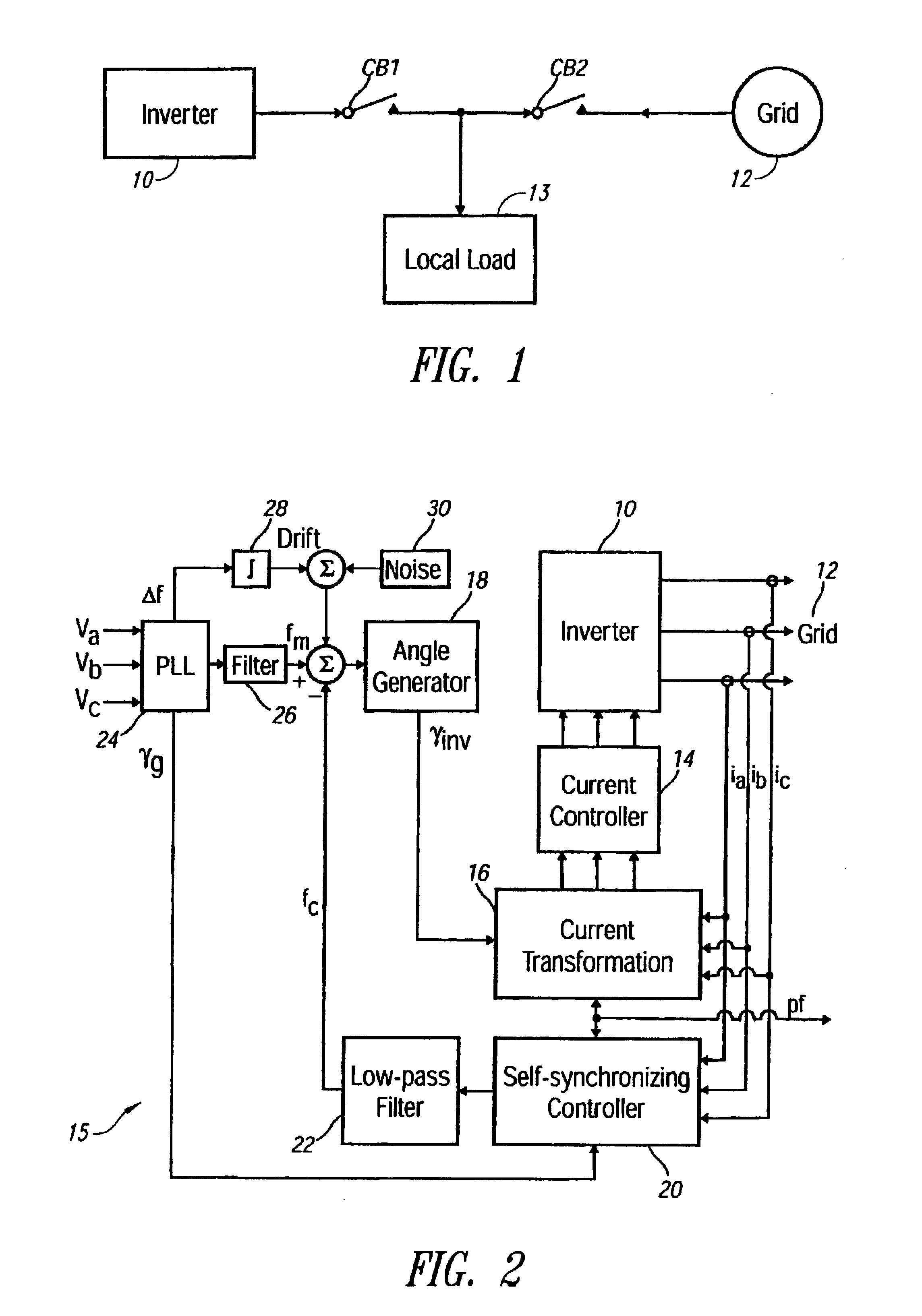
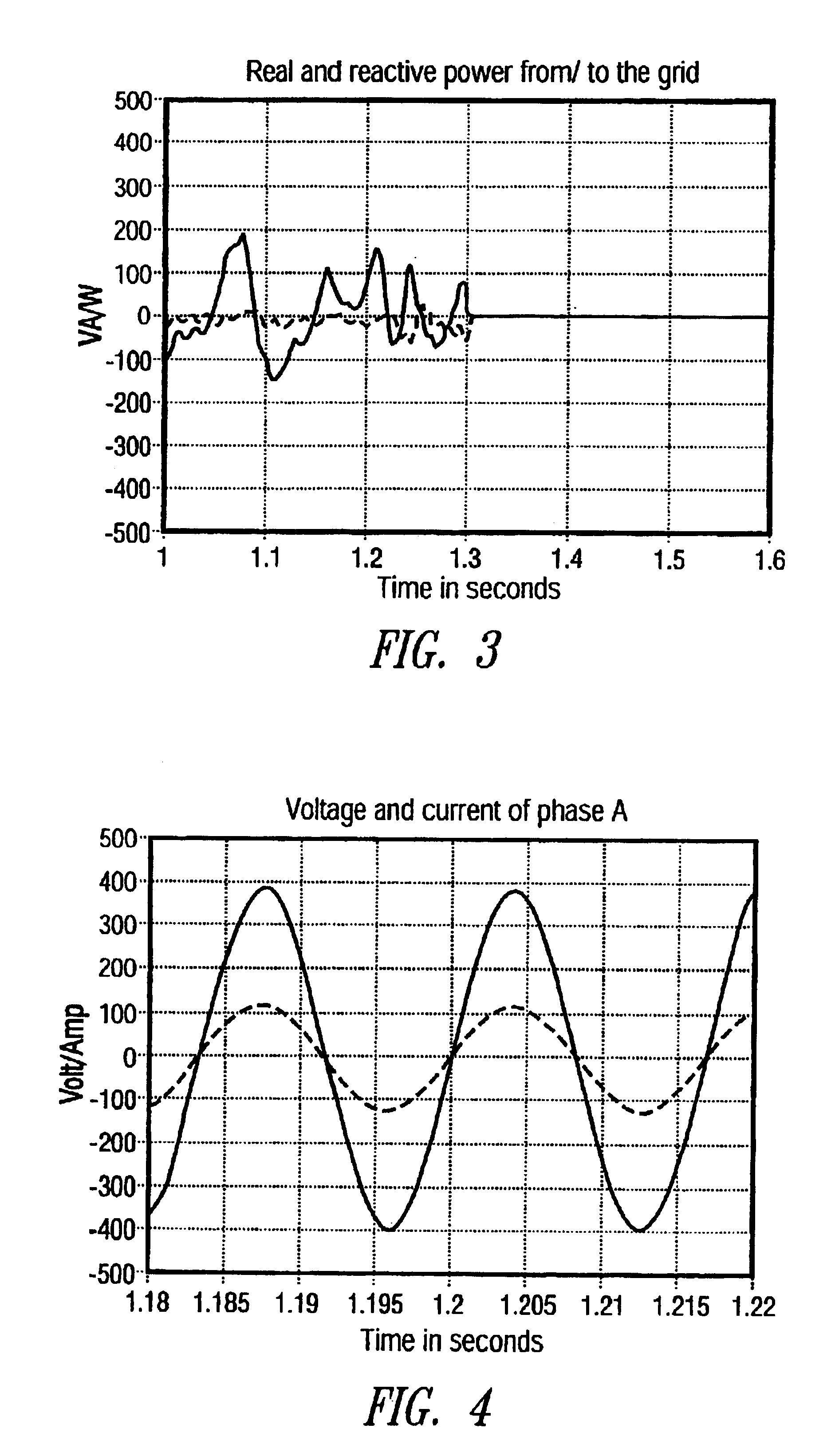
Anti-islanding device and method for grid connected inverters using random noise injection
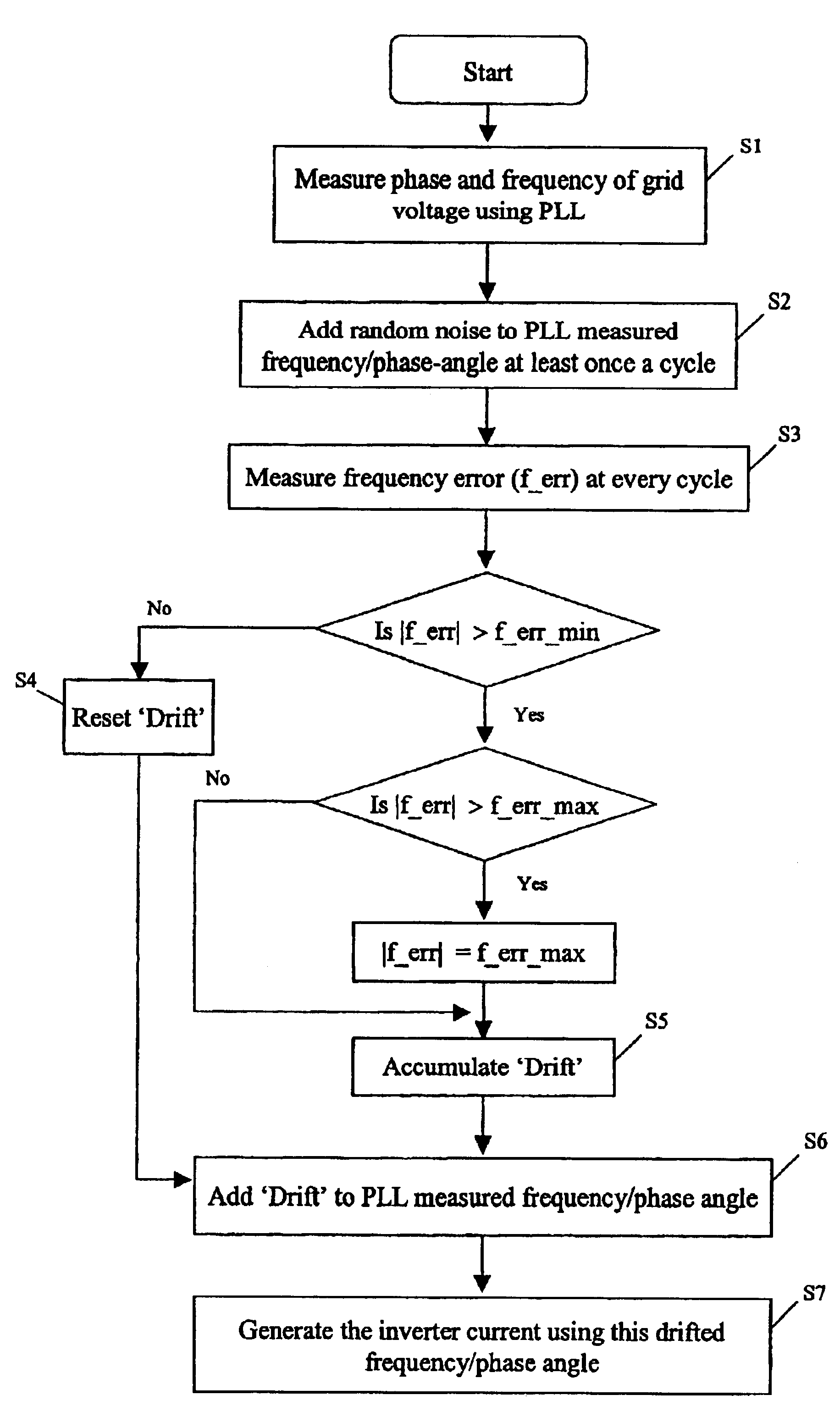
InactiveUS6853940B2Improves harmonic contentImproves direct current (dc) offset of currentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical measurementsIslandingGrid-tie inverter
A device and method for detecting islanding of a grid connected inverter makes use of an injected white noise as a perturbing force on the output voltage of the inverter. The white noise is injected at least once in every cycle and can be generated at different rates in implementation. On loss of the grid, a frequency drift of the output voltage is detected and a positive feedback is activated that accelerates the drift.
Owner:RHOMBUS ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com