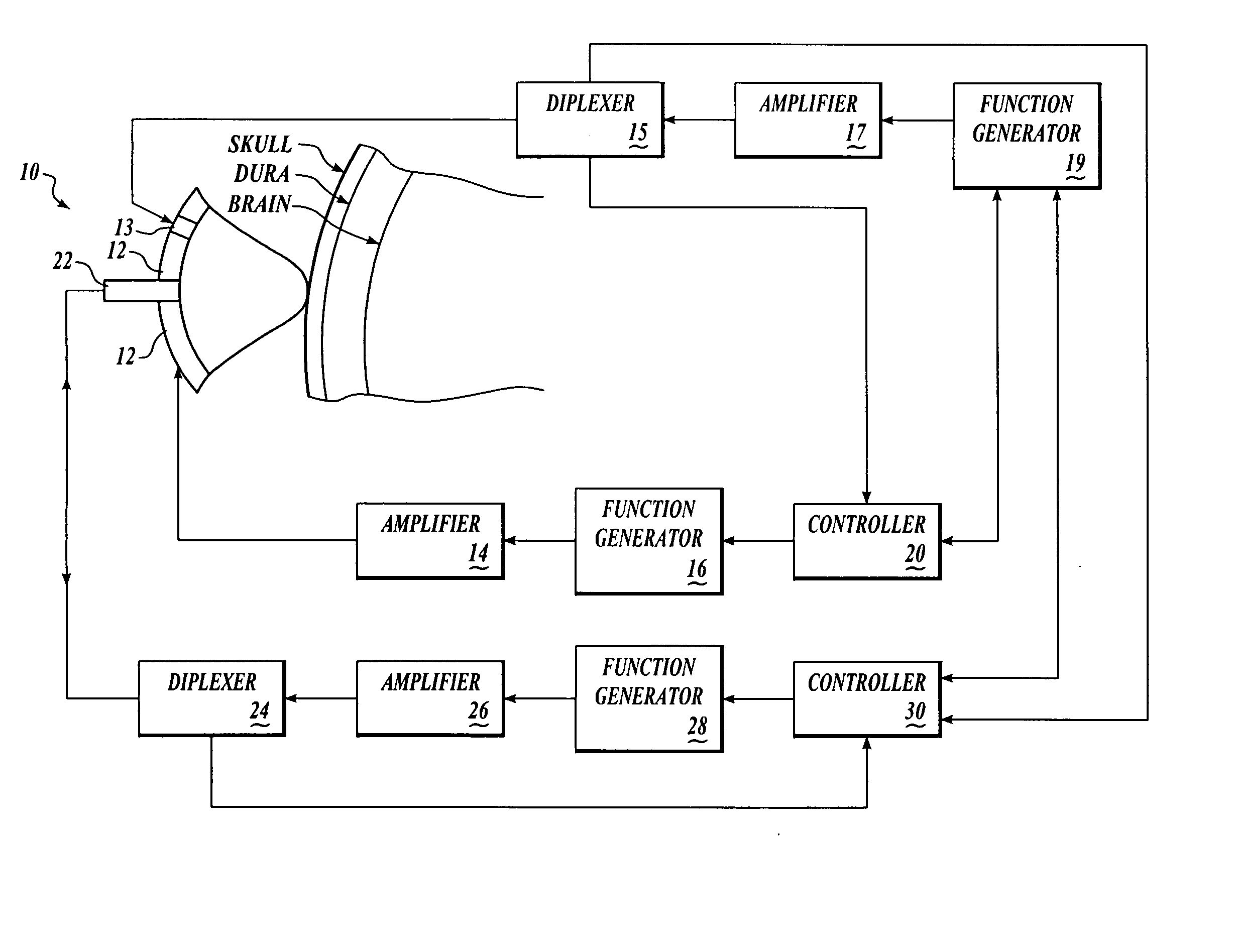
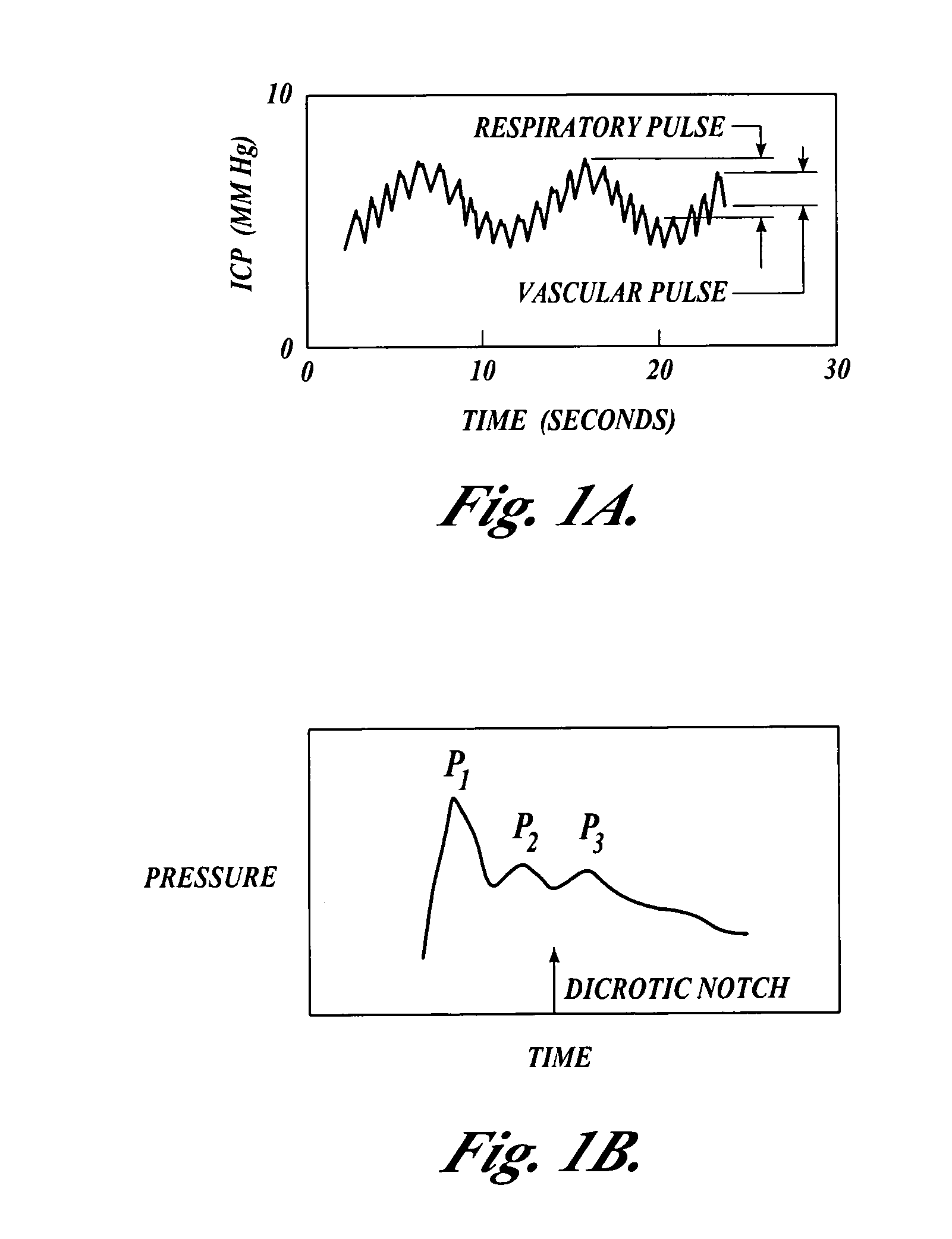
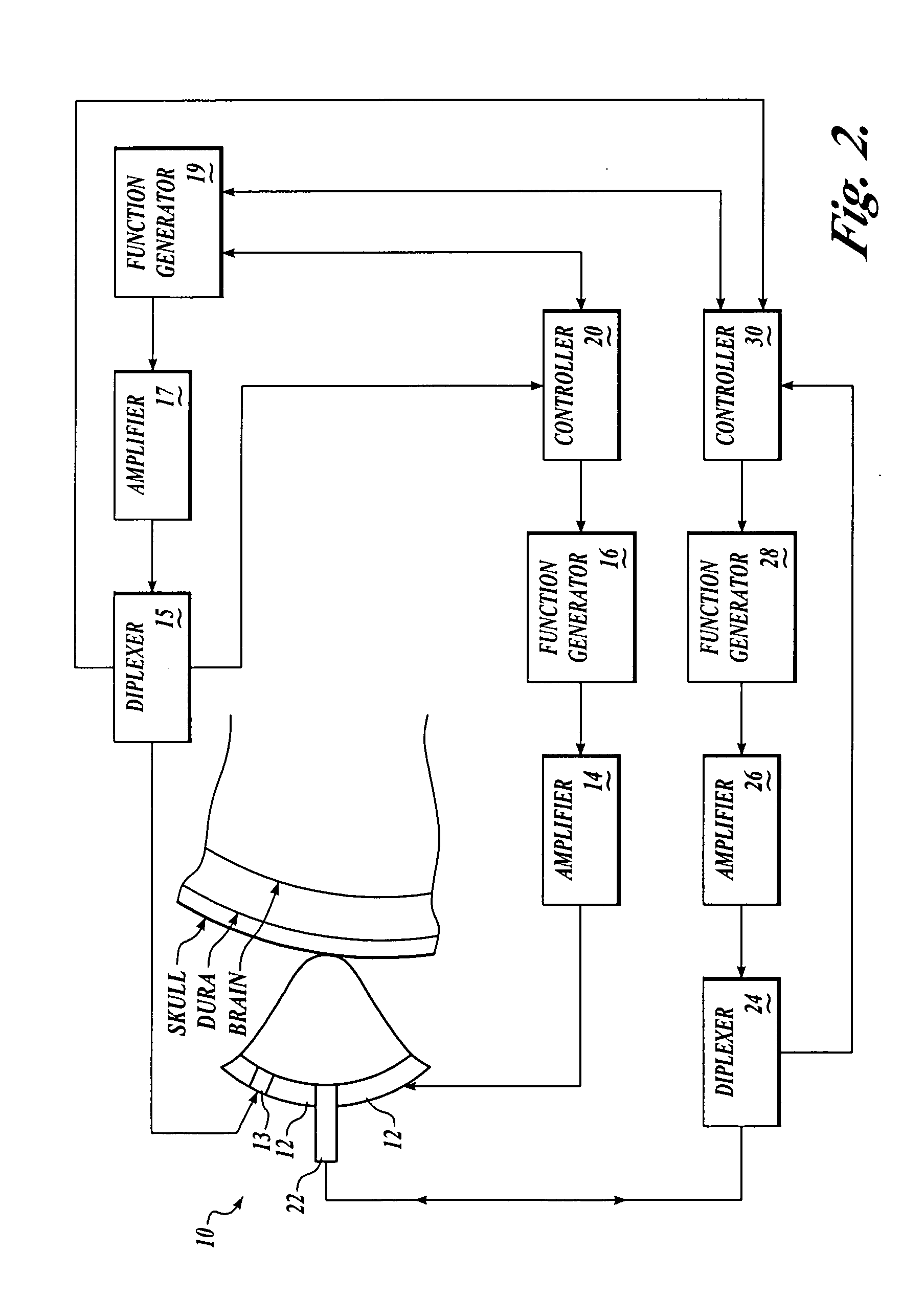
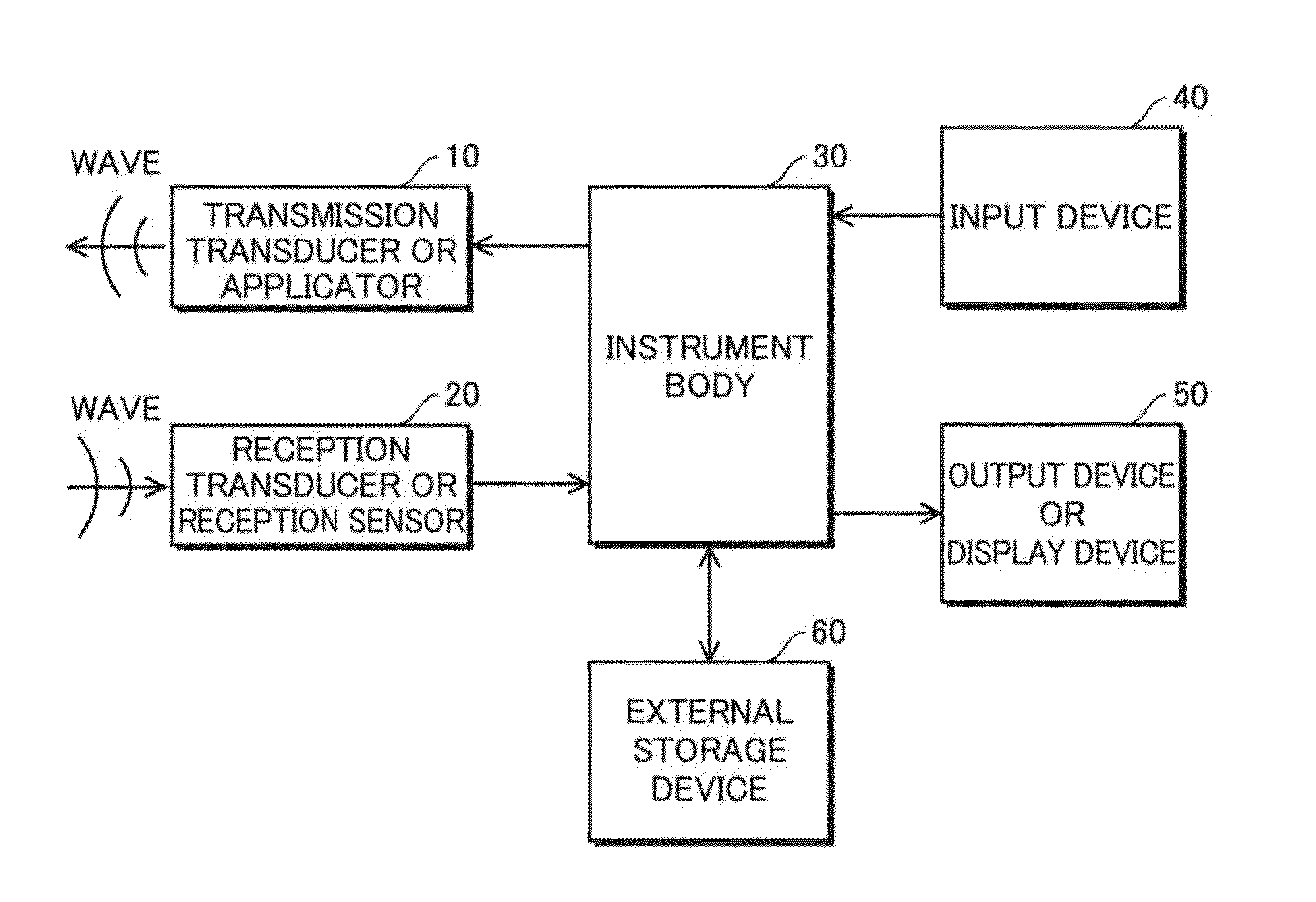
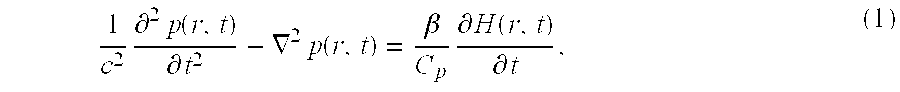Patents
Literature
4010results about How to "Improve spatial resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
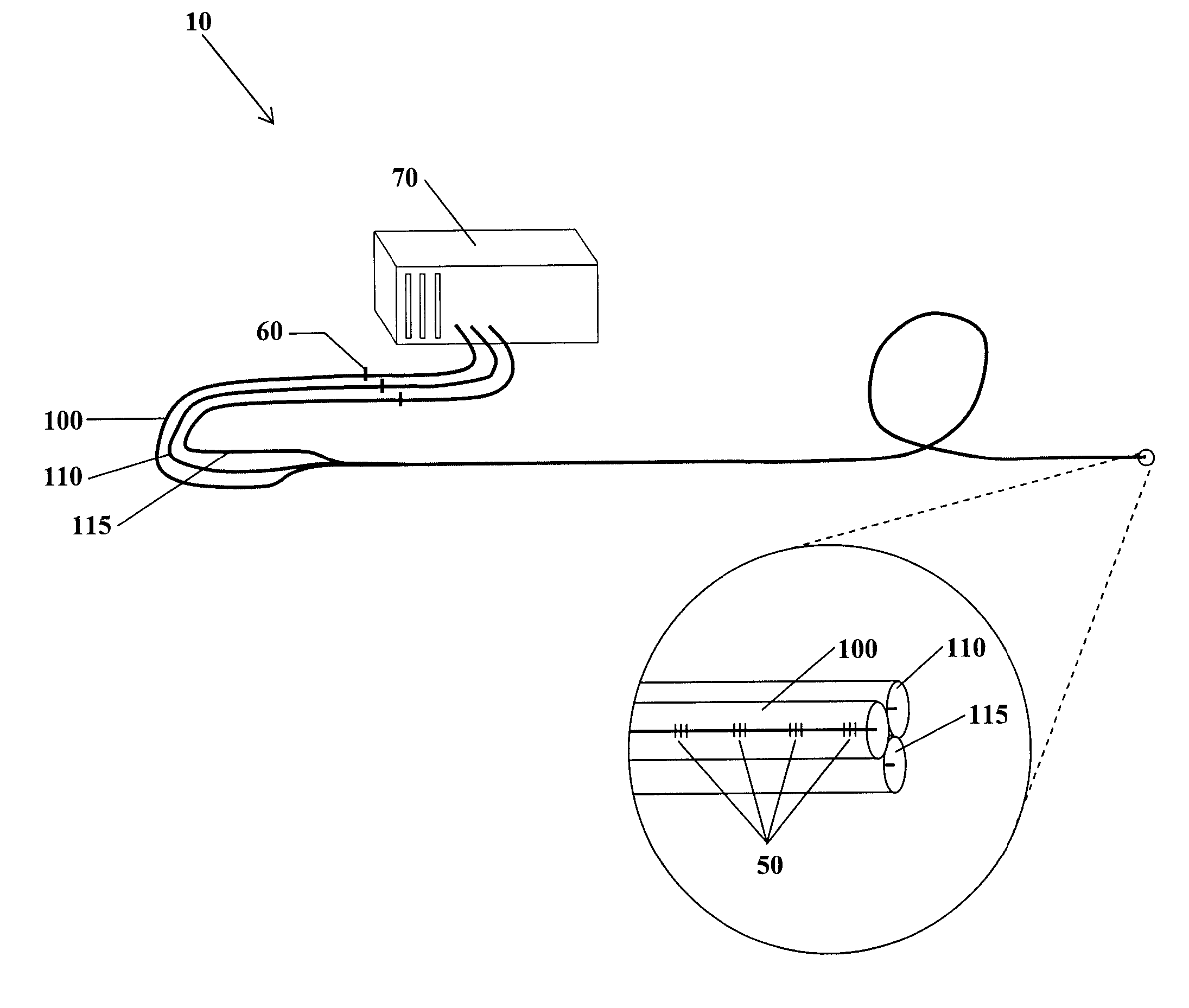
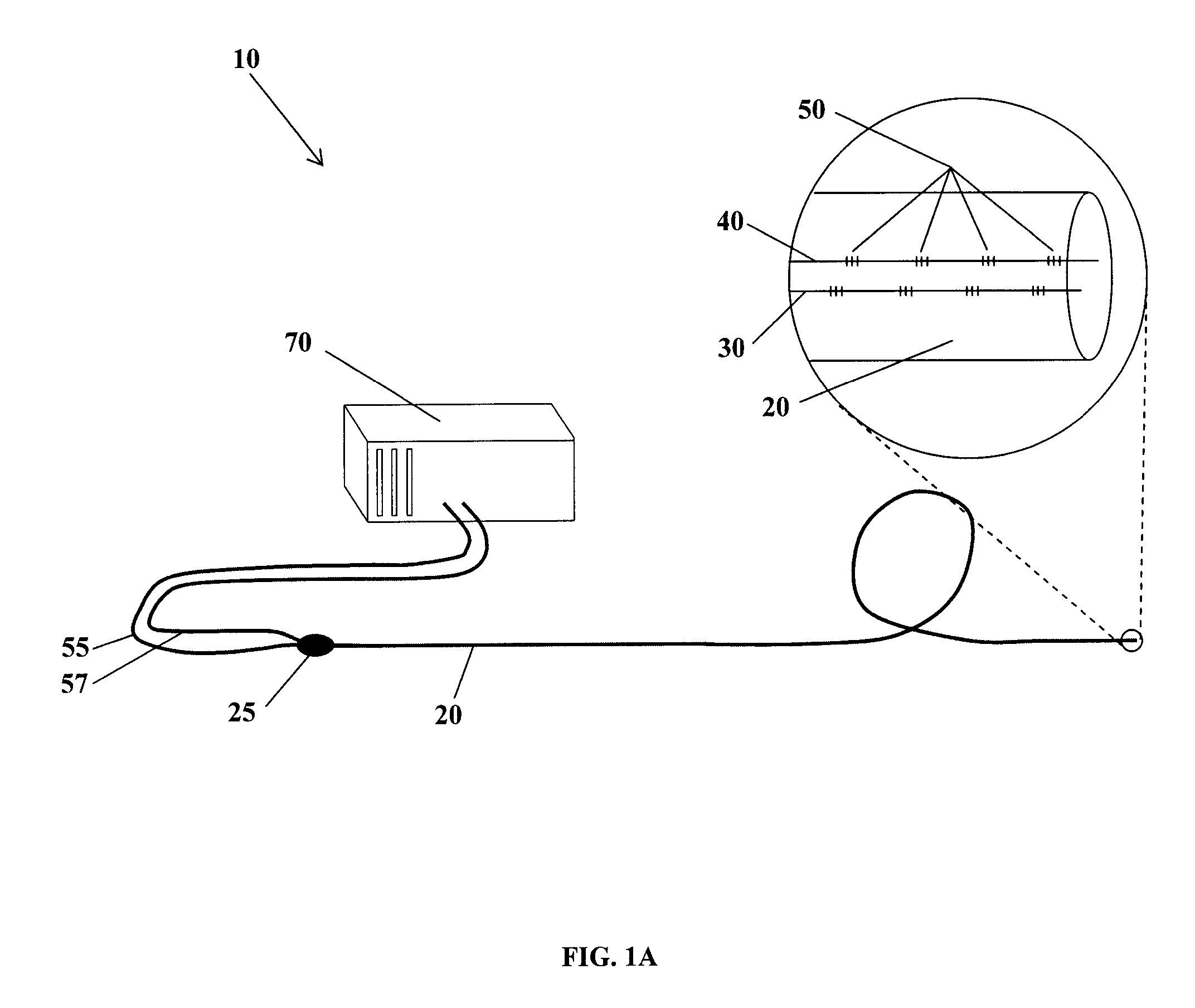
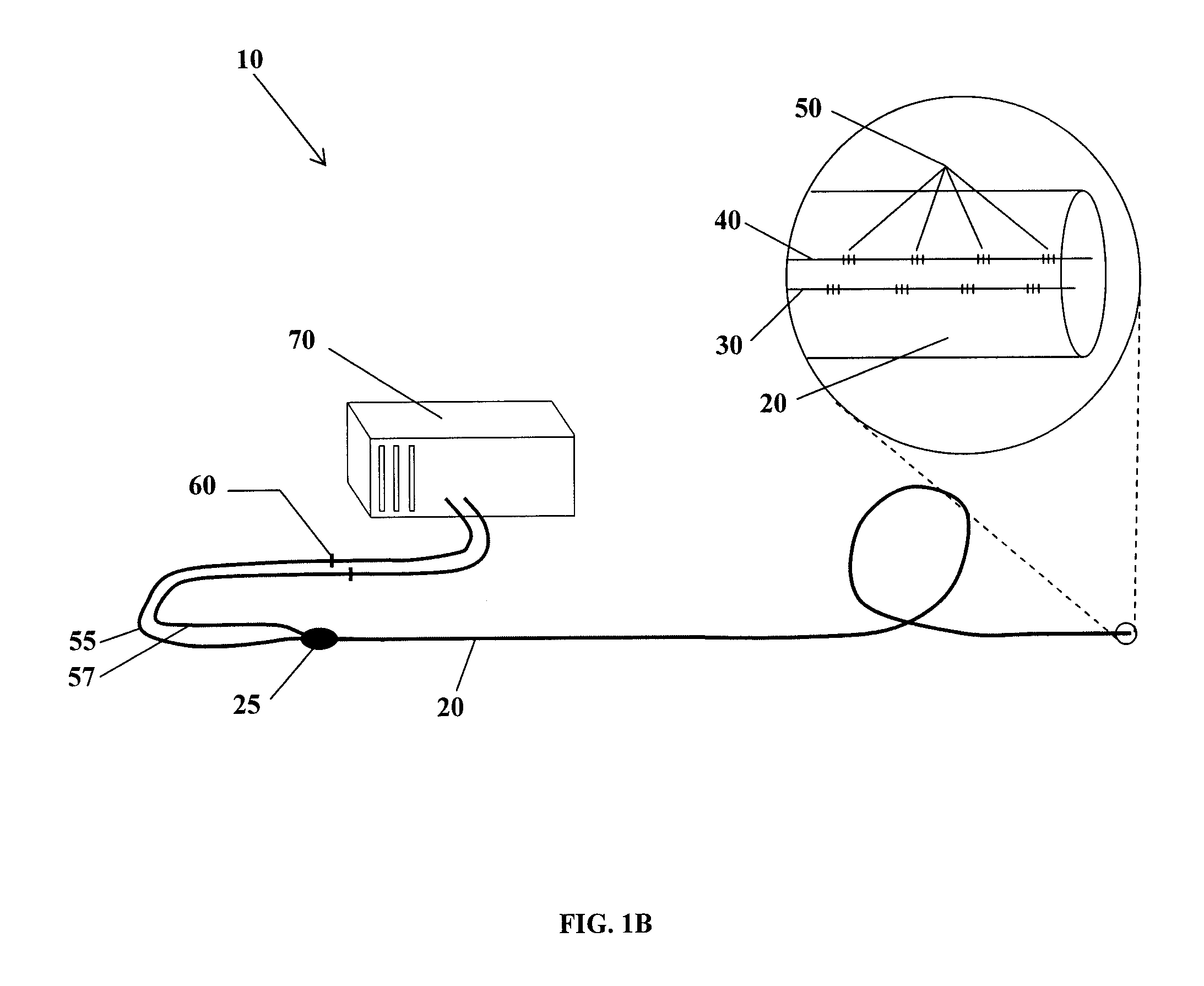
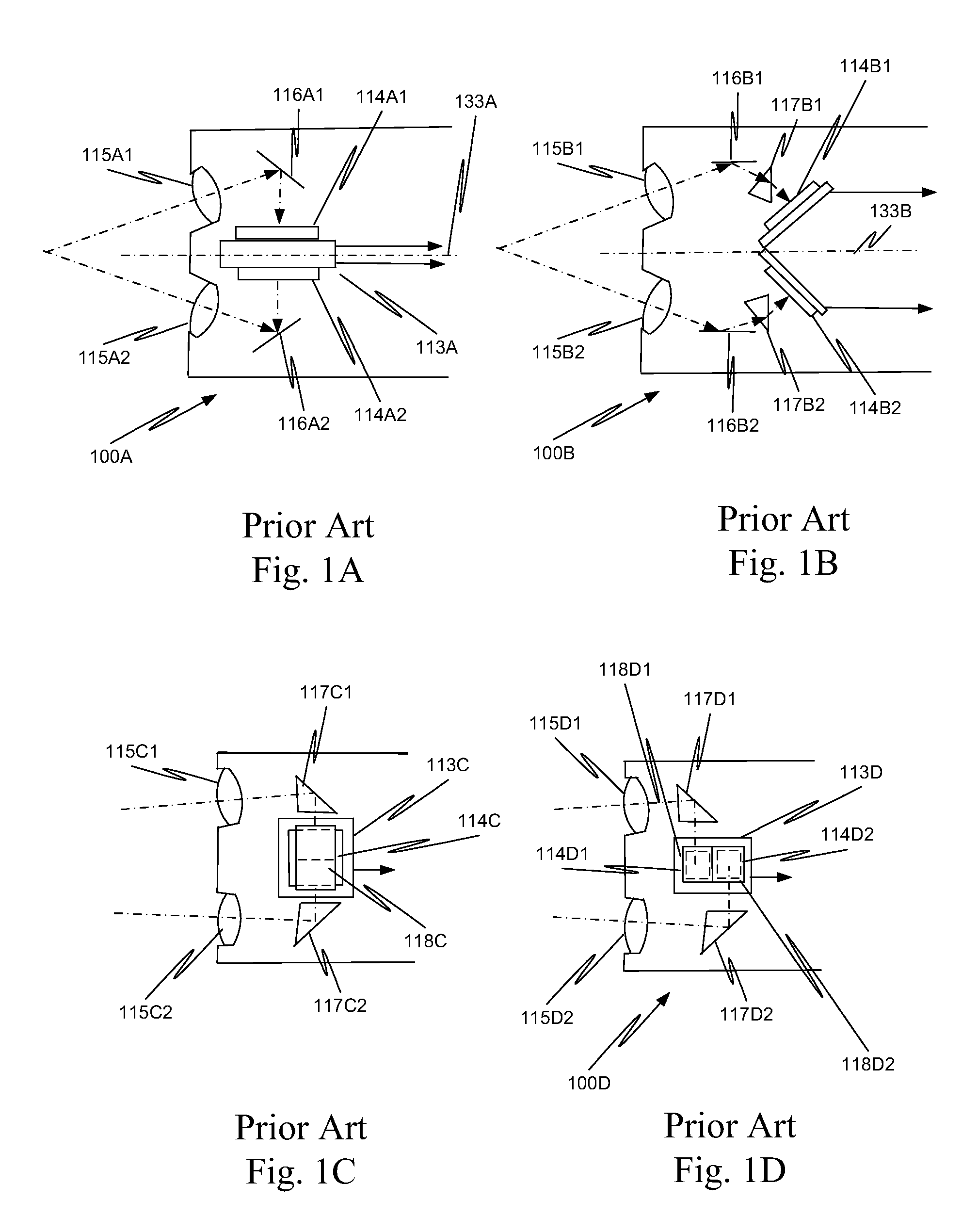
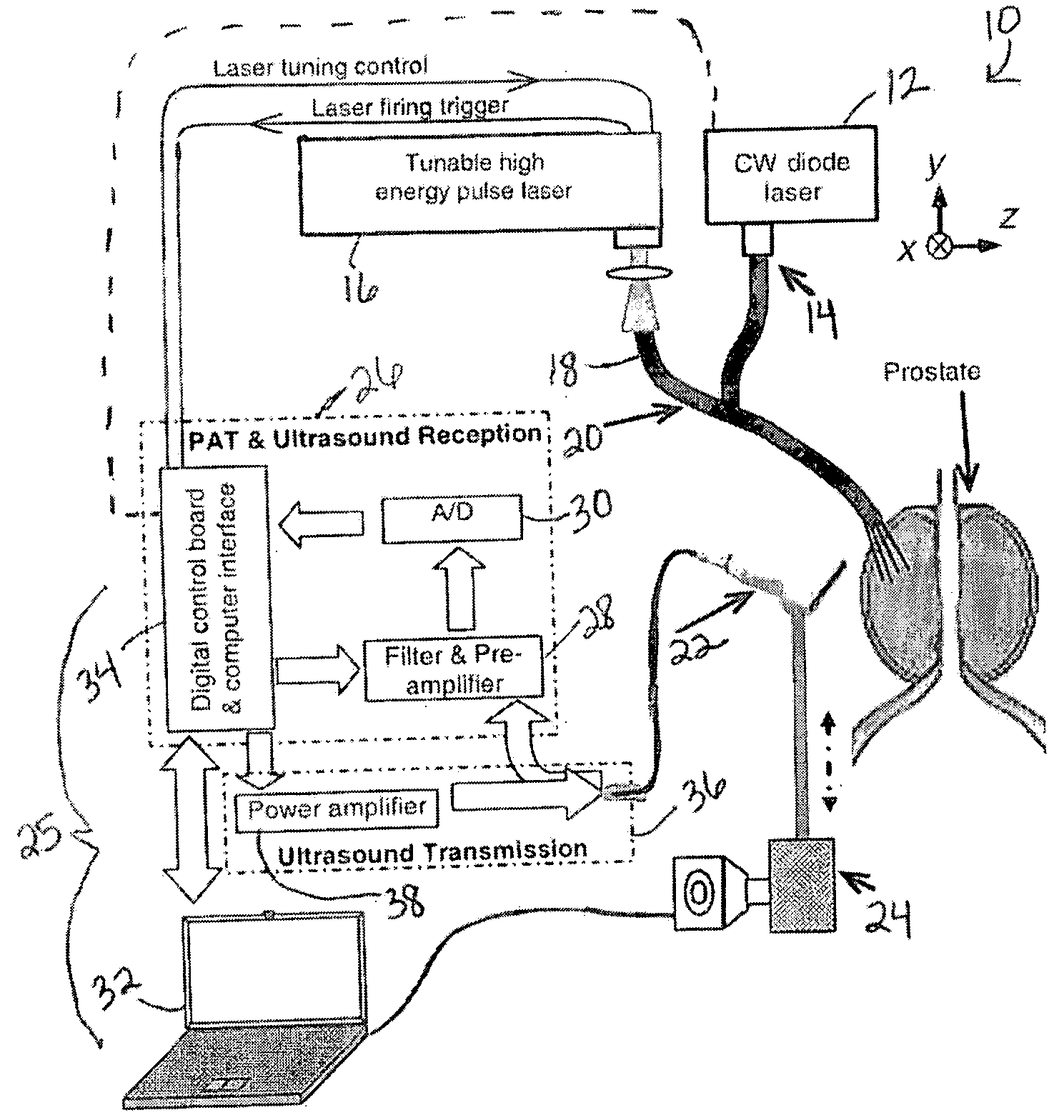
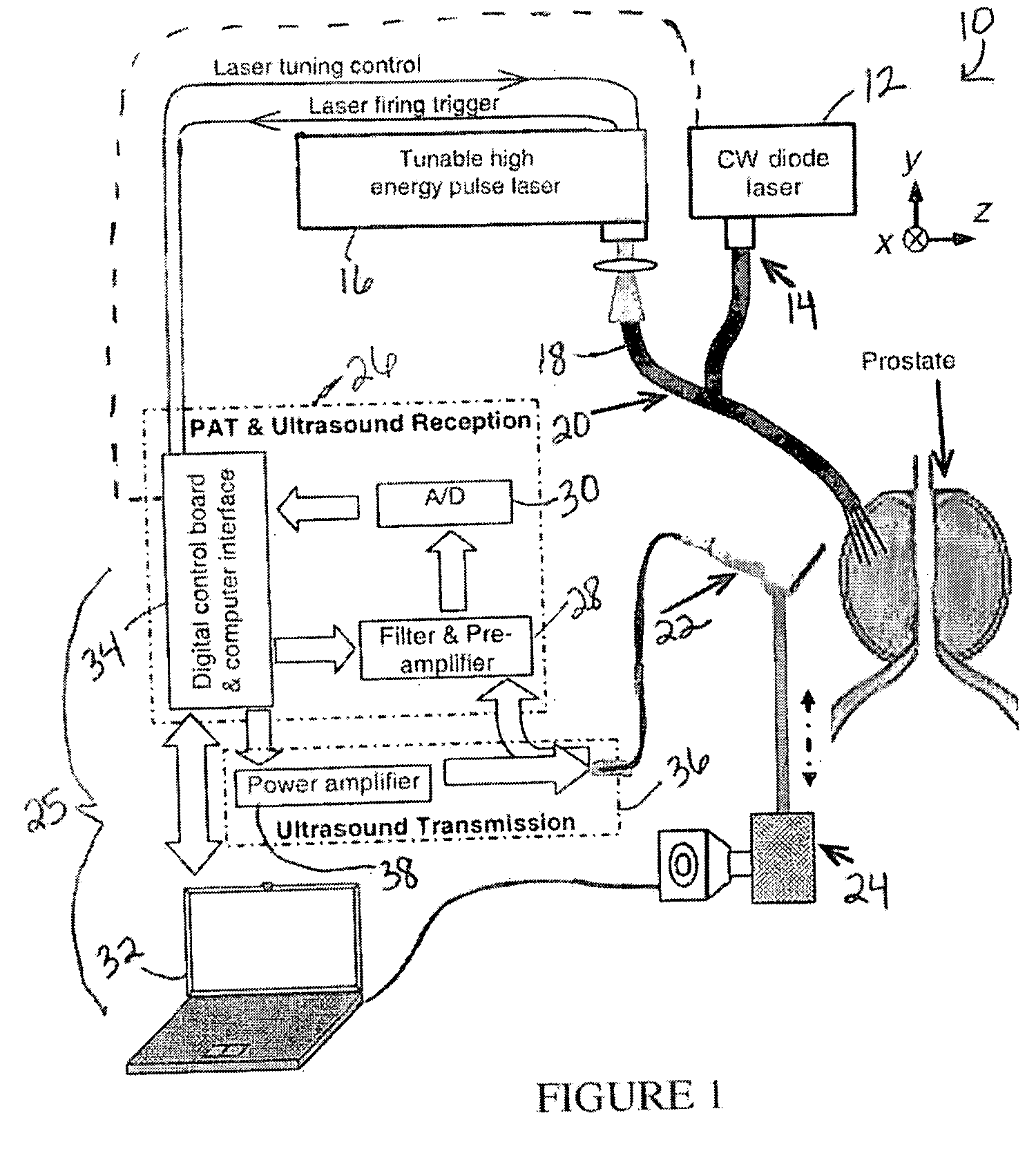
Fiber optic position and shape sensing device and method relating thereto
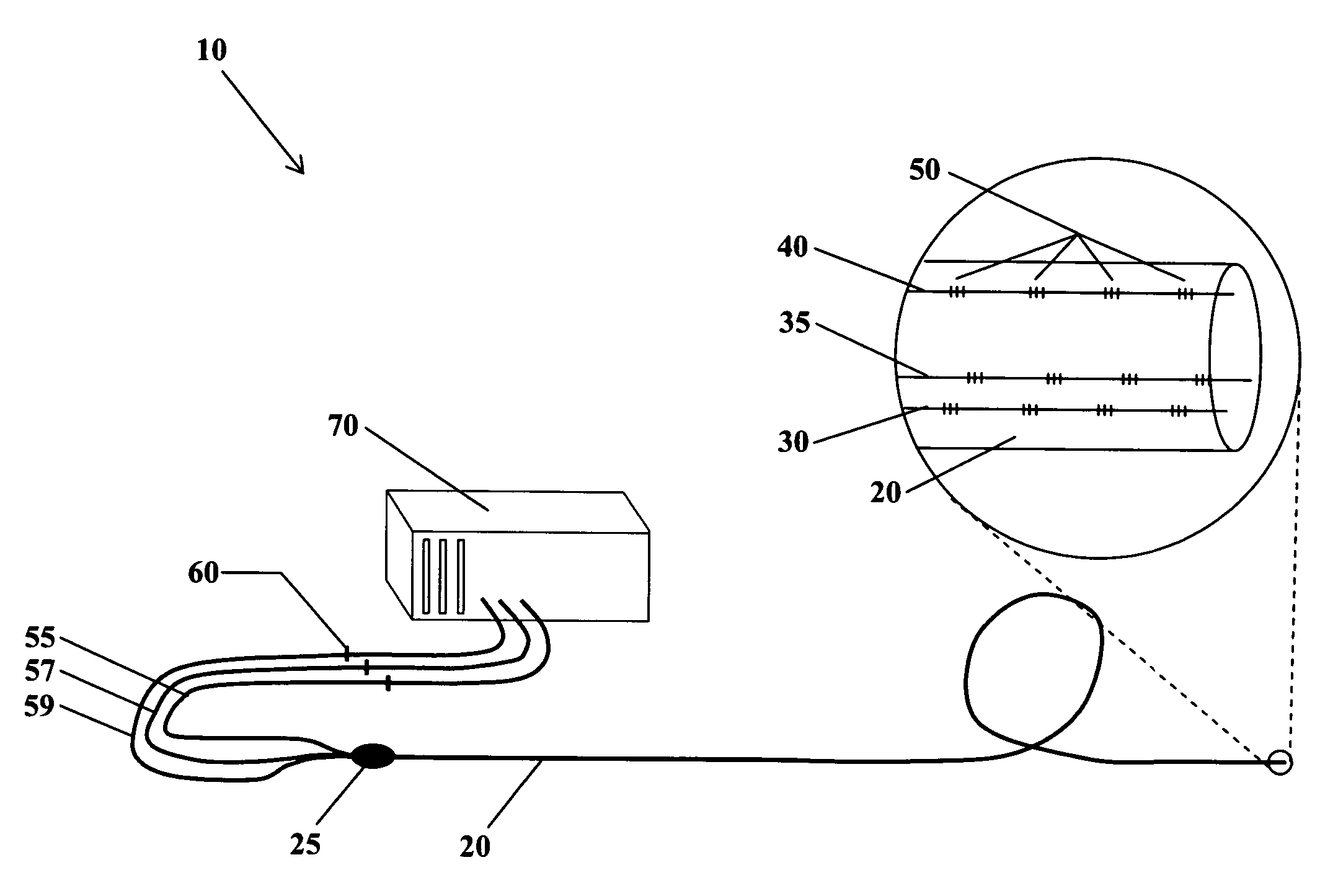
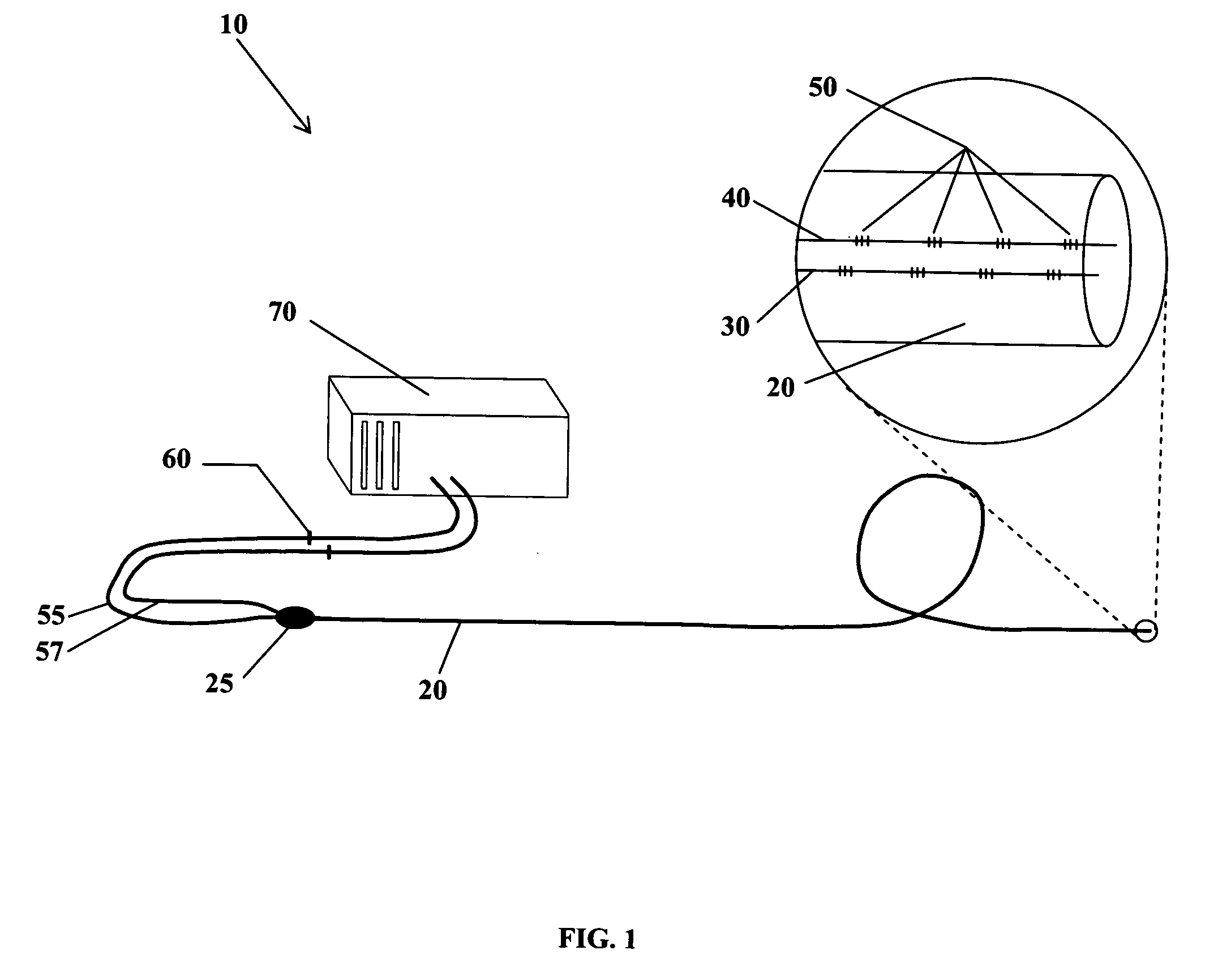
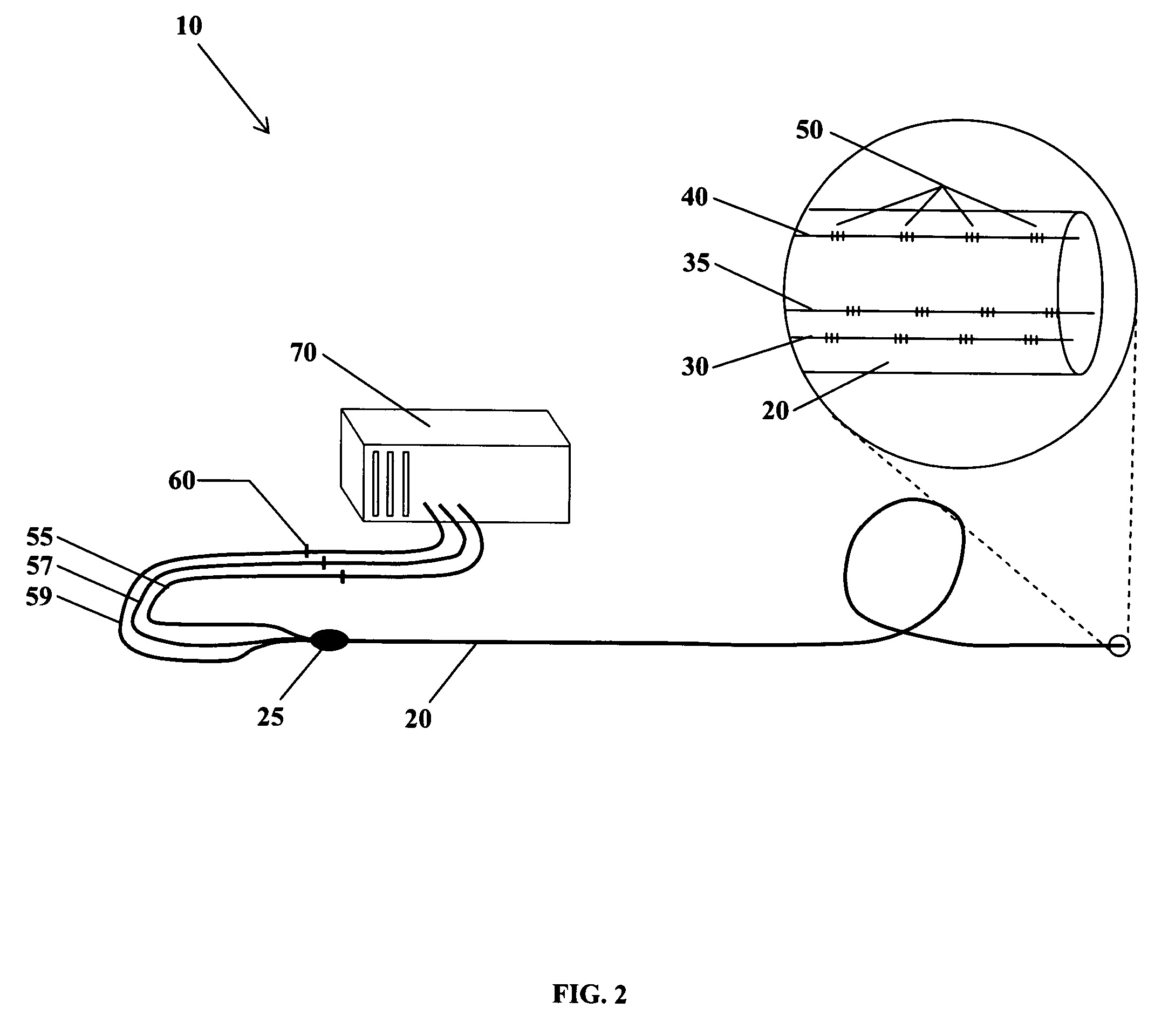
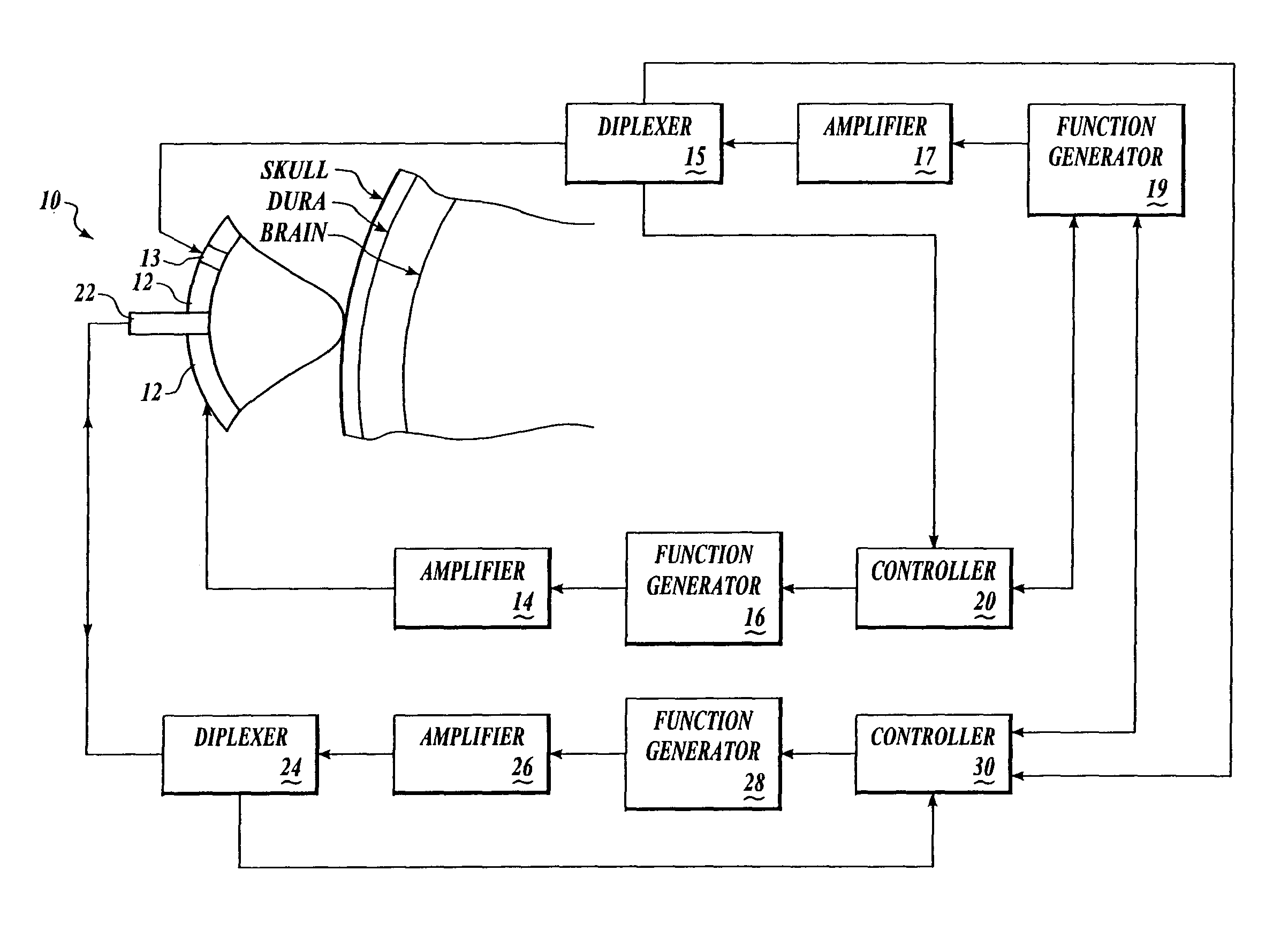
The present invention is directed toward a fiber optic position and shape sensing device and the method of use. The device comprises an optical fiber means. The optical fiber means comprises either at least two single core optical fibers or a multicore optical fiber having at least two fiber cores. In either case, the fiber cores are spaced apart such that mode coupling between the fiber cores is minimized. An array of fiber Bragg gratings are disposed within each fiber core. A broadband reference reflector is positioned in an operable relationship to each fiber Bragg grating wherein an optical path length is established for each reflector / grating relationship. A frequency domain reflectometer is positioned in an operable relationship to the optical fiber means. In use, the device is affixed to an object. Strain on the optical fiber is measured and the strain measurements correlated to local bend measurements. Local bend measurements are integrated to determine position or shape of the object.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Digital imaging system and method using multiple digital image sensors to produce large high-resolution gapless mosaic images
InactiveUS20090268983A1Avoid smallNot easy to produceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayCamera lens
A digital imaging system and method using multiple cameras arranged and aligned to create a much larger virtual image sensor array. Each camera has a lens with an optical axis aligned parallel to the optical axes of the other camera lenses, and a digital image sensor array with one or more non-contiguous pixelated sensors. The non-contiguous sensor arrays are spatially arranged relative to their respective optical axes so that each sensor images a portion of a target region that is substantially different from other portions of the target region imaged by other sensors, and preferably overlaps adjacent portions imaged by the other sensors. In this manner, the portions imaged by one set of sensors completely fill the image gaps found between other portions imaged by other sets of sensors, so that a seamless mosaic image of the target region may be produced.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
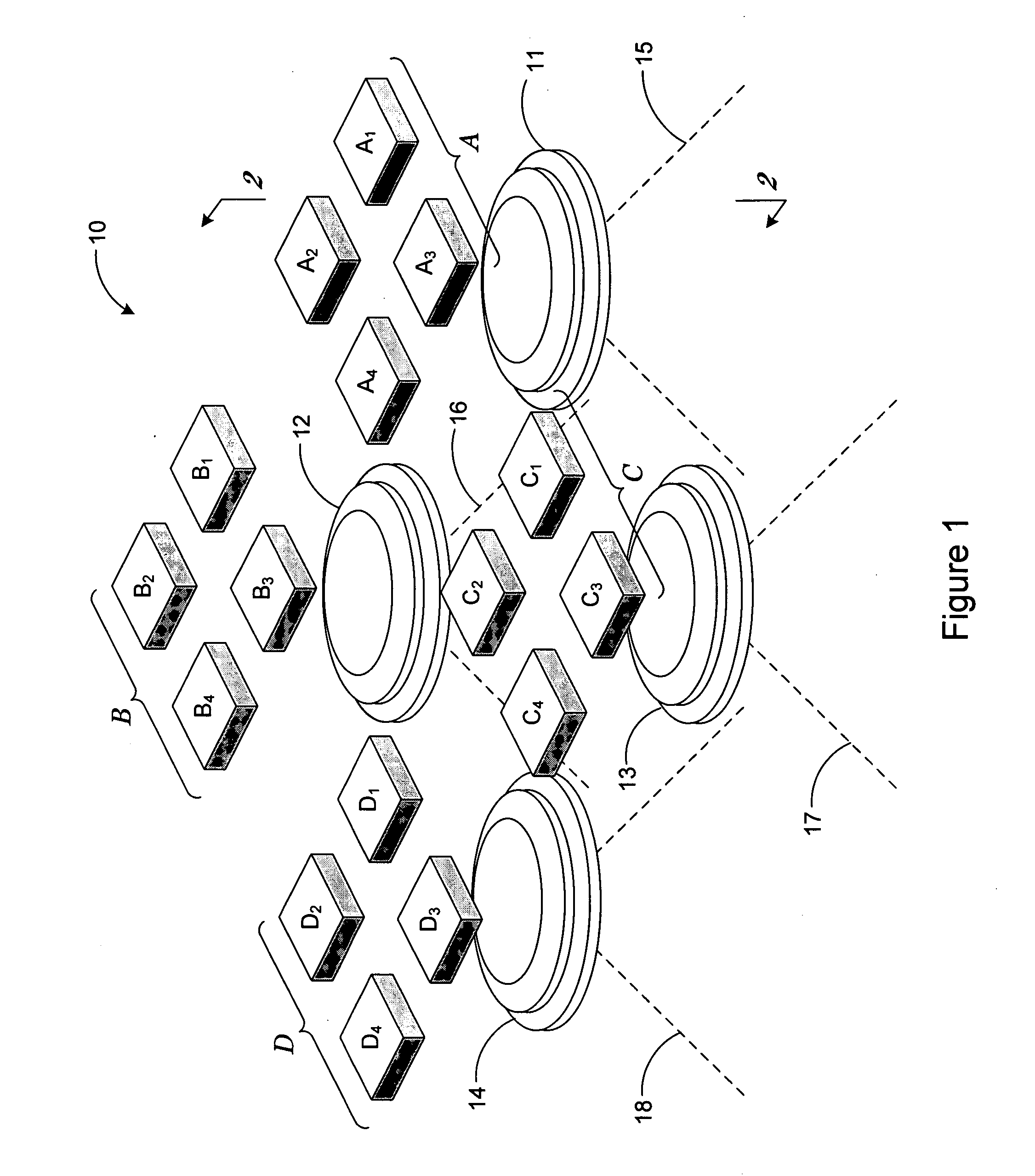
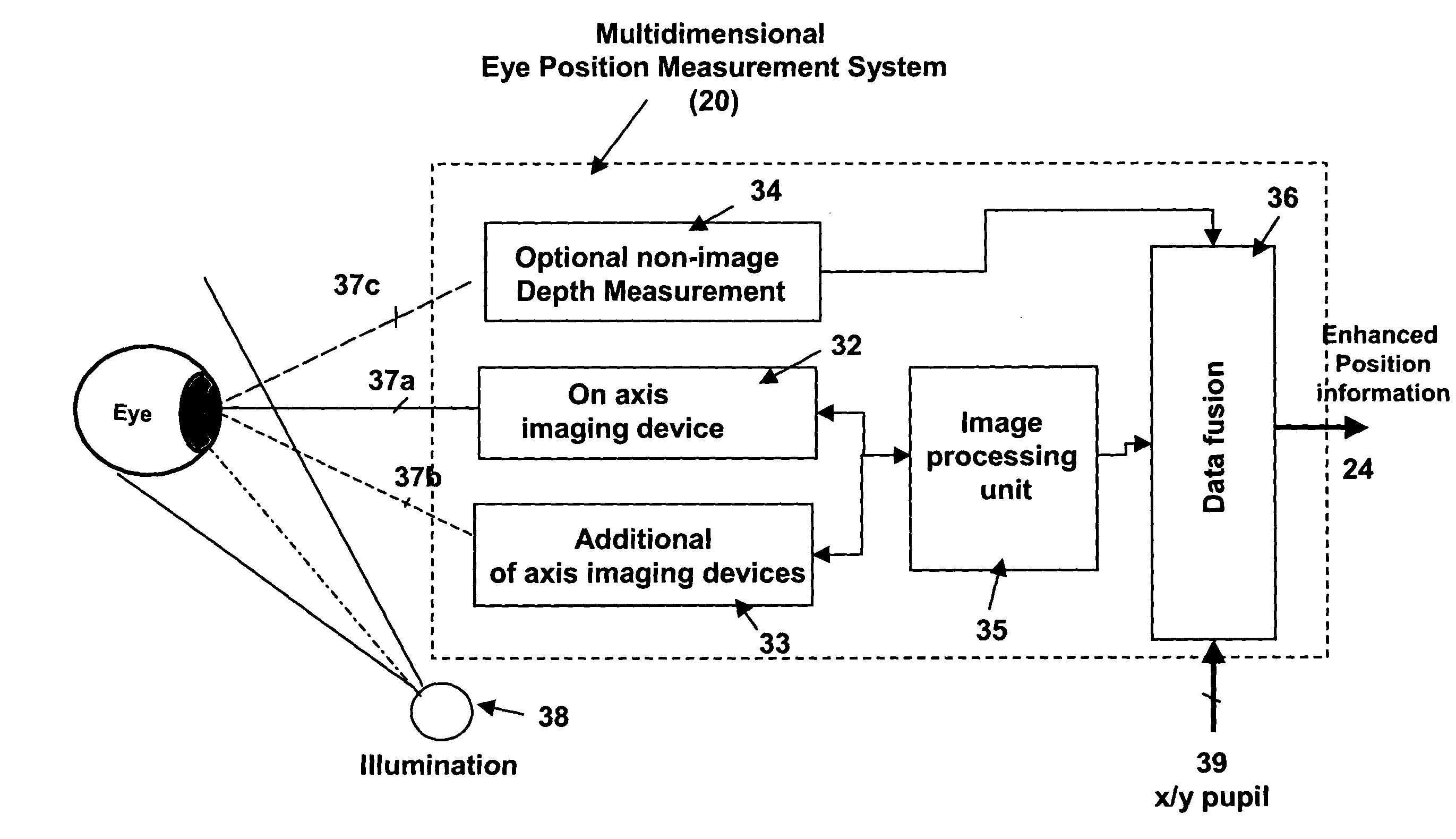
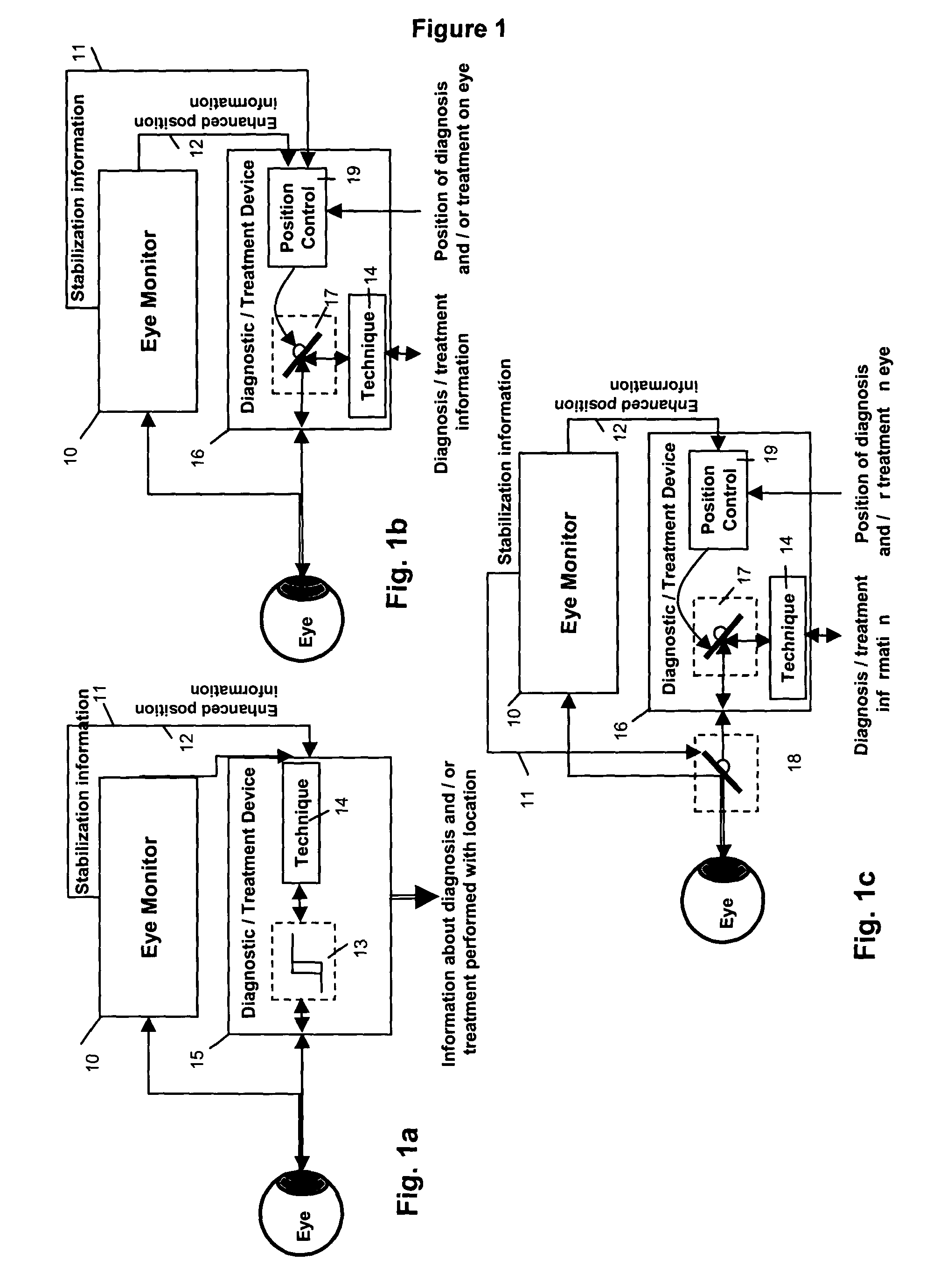
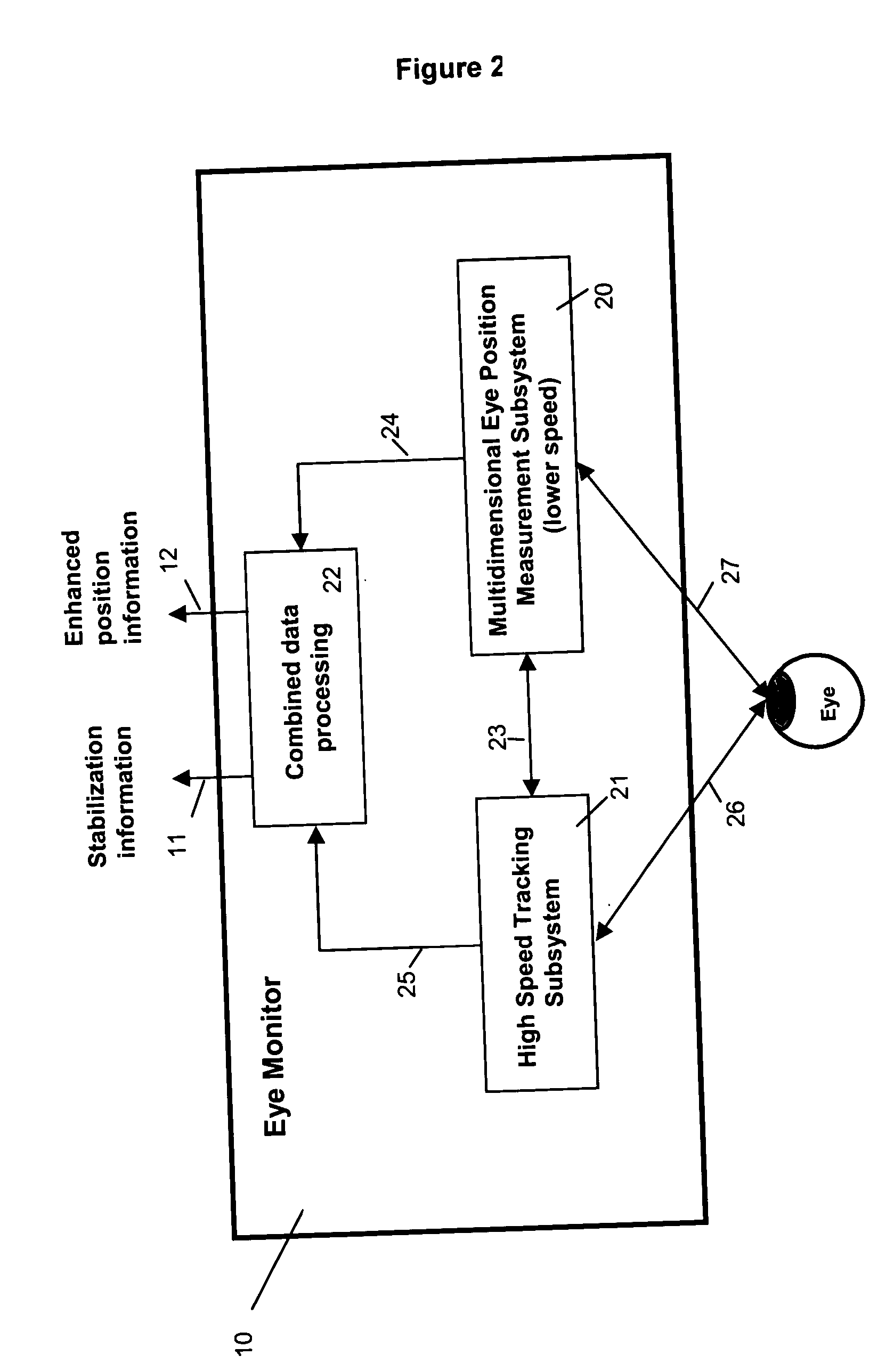
Multidimensional eye tracking and position measurement system for diagnosis and treatment of the eye
ActiveUS20050024586A1Improve spatial resolutionLess field of viewLaser surgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceSaccadic movements
The present invention relates to improved ophthalmic diagnostic measurement or treatment methods or devices, that make use of a combination of a high speed eye tracking device, measuring fast translation or saccadic motion of the eye, and an eye position measurement device, determining multiple dimensions of eye position or other components of eye, relative to an ophthalmic diagnostic or treatment instrument.
Owner:SENSOMOTORIC INSTR FUR INNOVATIVE SENSORIK MBH D B A SENSOMOTORIC INSTR
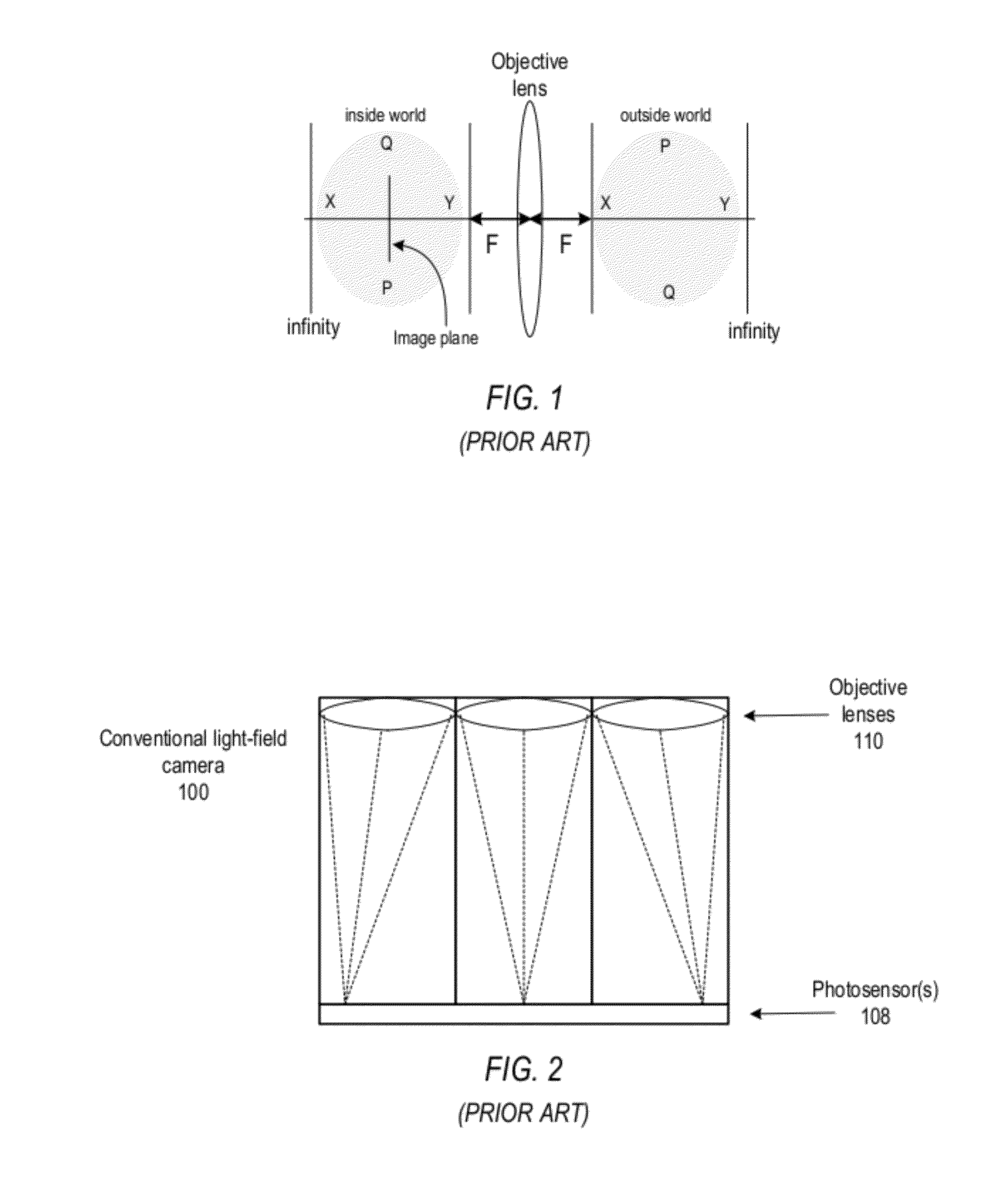
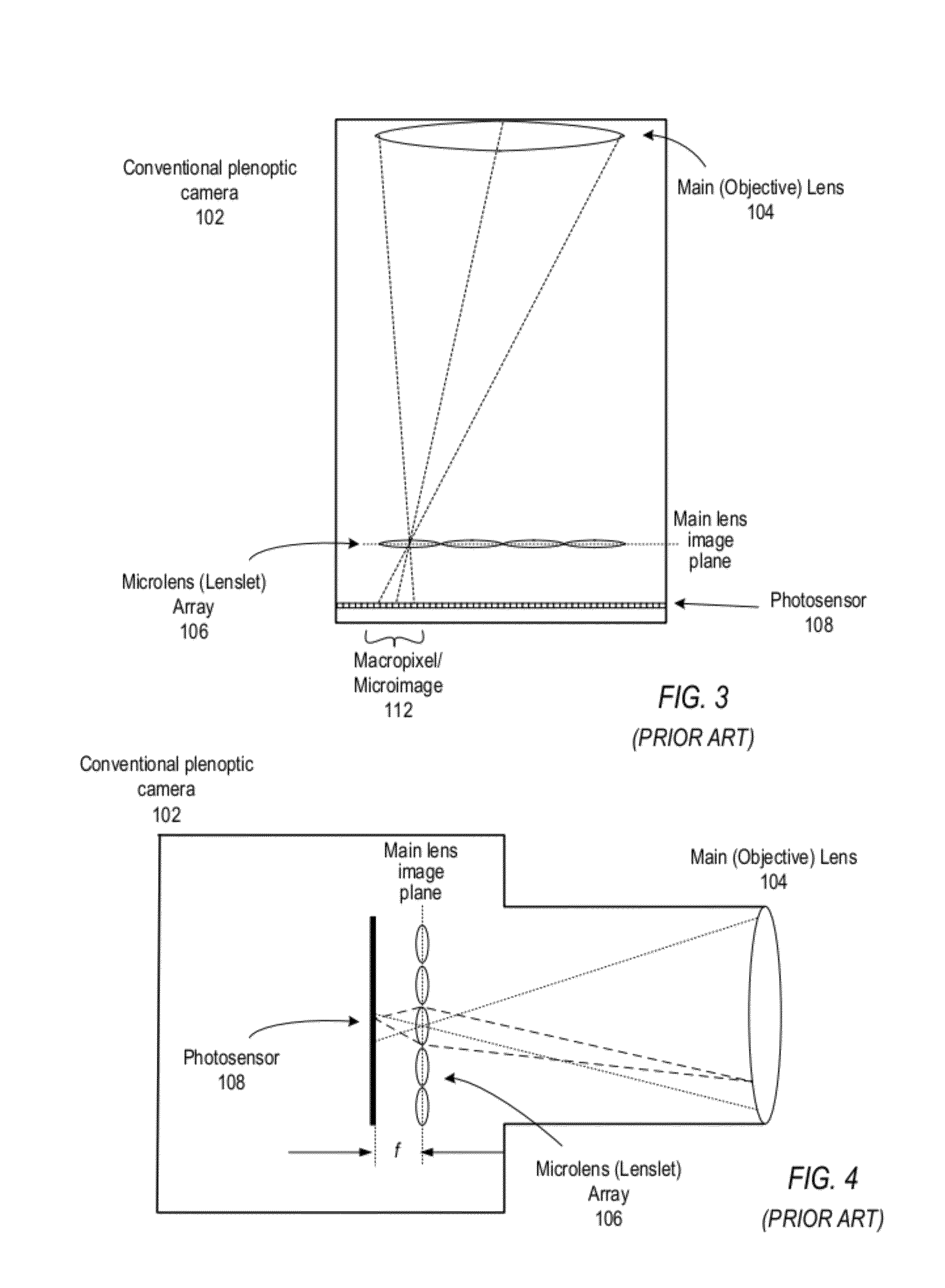
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging
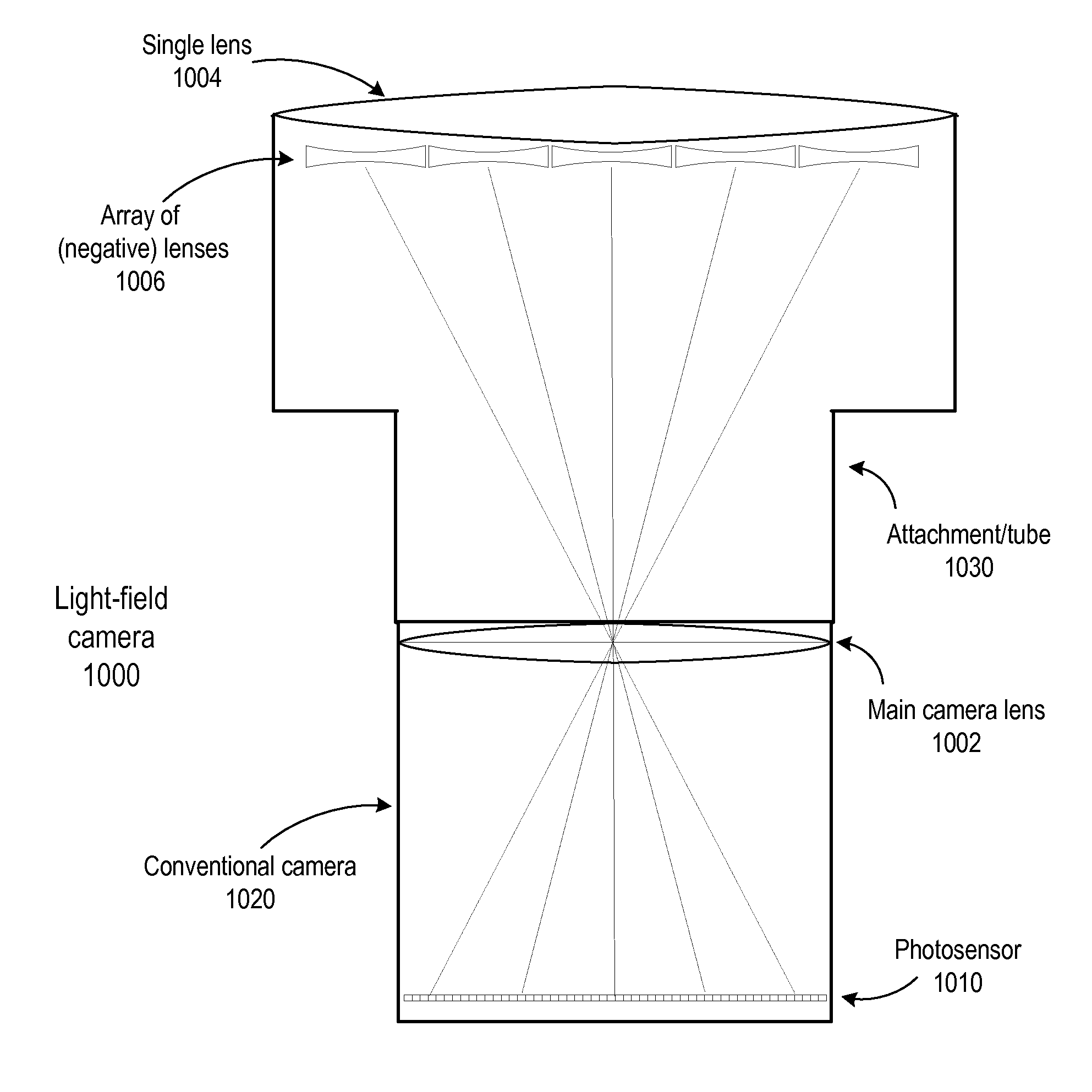
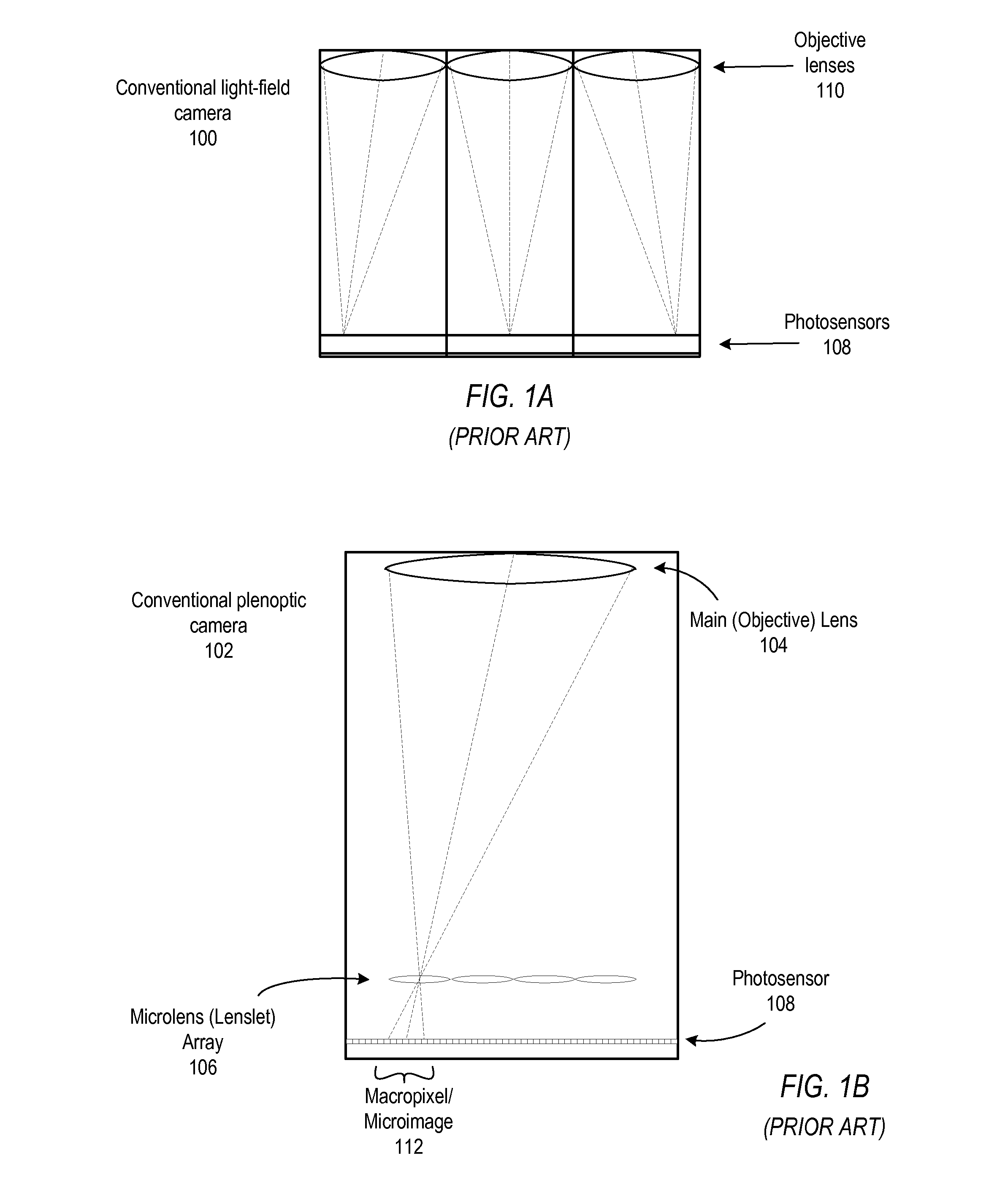
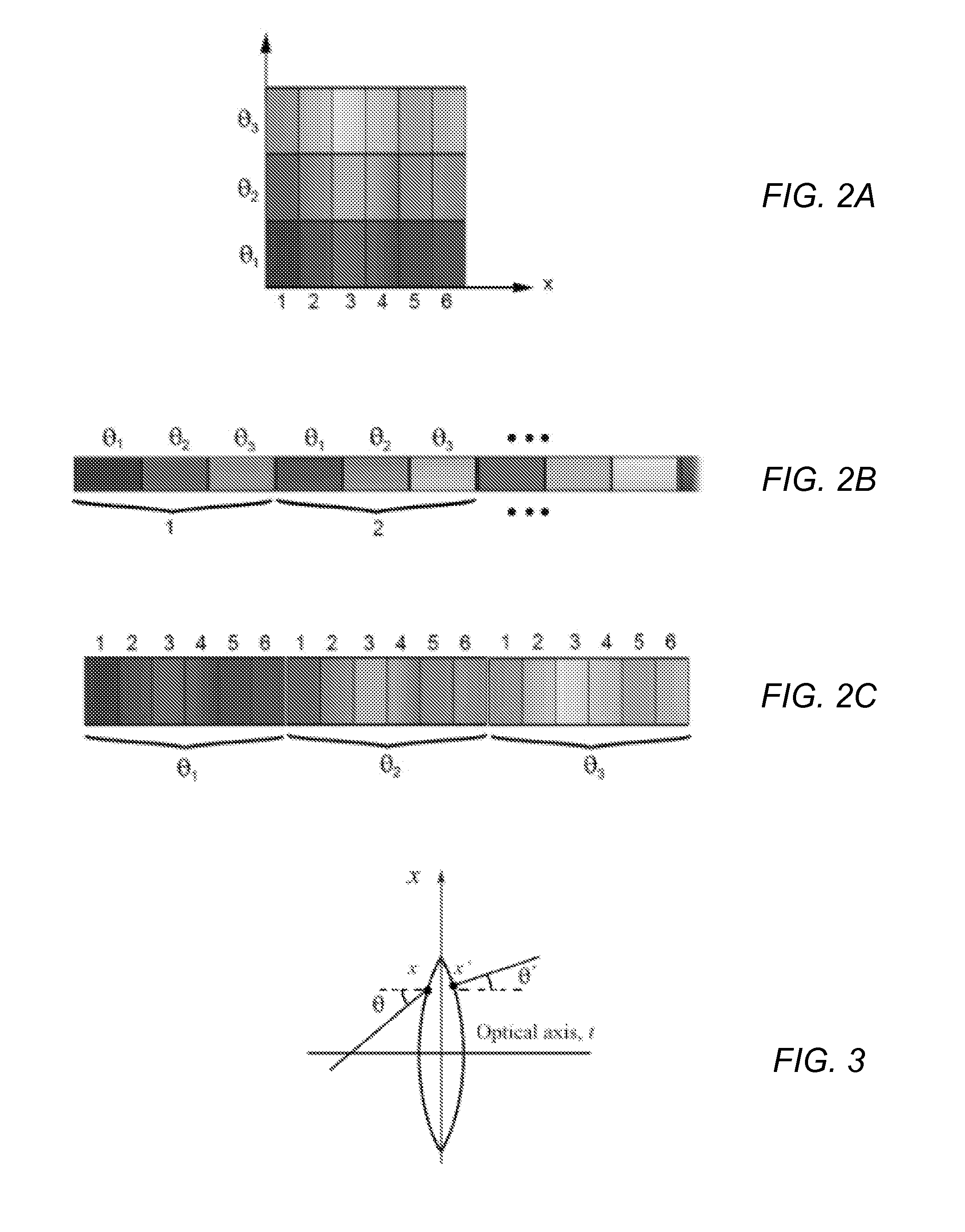
ActiveUS8290358B1Minimal loss in qualityImprove spatial resolutionStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsCamera lensHand held
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging. Light-field camera designs are described that produce higher spatial resolution than conventional plenoptic camera designs, while trading-off the light-field's angular sampling density. This lower angular resolution may be compensated for by a light-field image processing method that inserts data synthesized by view interpolation of the measured light-field. In one embodiment, a light-field image processing method that performs three-view morphing may be used to interpolate the missing angular samples of radiance. The light-field camera designs may be implemented in hand-held light-field cameras that may capture a light-field with a single exposure. Some of the light-field camera designs are internal to the camera, while others are external to the camera. One light-field camera design includes a single, relatively large lens and an array of negative lenses that are placed in front of (external to) the main lens of a conventional camera.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Fiber optic position and shape sensing device and method relating thereto
The present invention is directed toward a fiber optic position and shape sensing device and the method of use. The device comprises an optical fiber means. The optical fiber means comprises either at least two single core optical fibers or a multicore optical fiber having at least two fiber cores. In either case, the fiber cores are spaced apart such that mode coupling between the fiber cores is minimized. An array of fiber Bragg gratings are disposed within each fiber core and a frequency domain reflectometer is positioned in an operable relationship to the optical fiber means. In use, the device is affixed to an object. Strain on the optical fiber is measured and the strain measurements correlated to local bend measurements. Local bend measurements are integrated to determine position and / or shape of the object.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
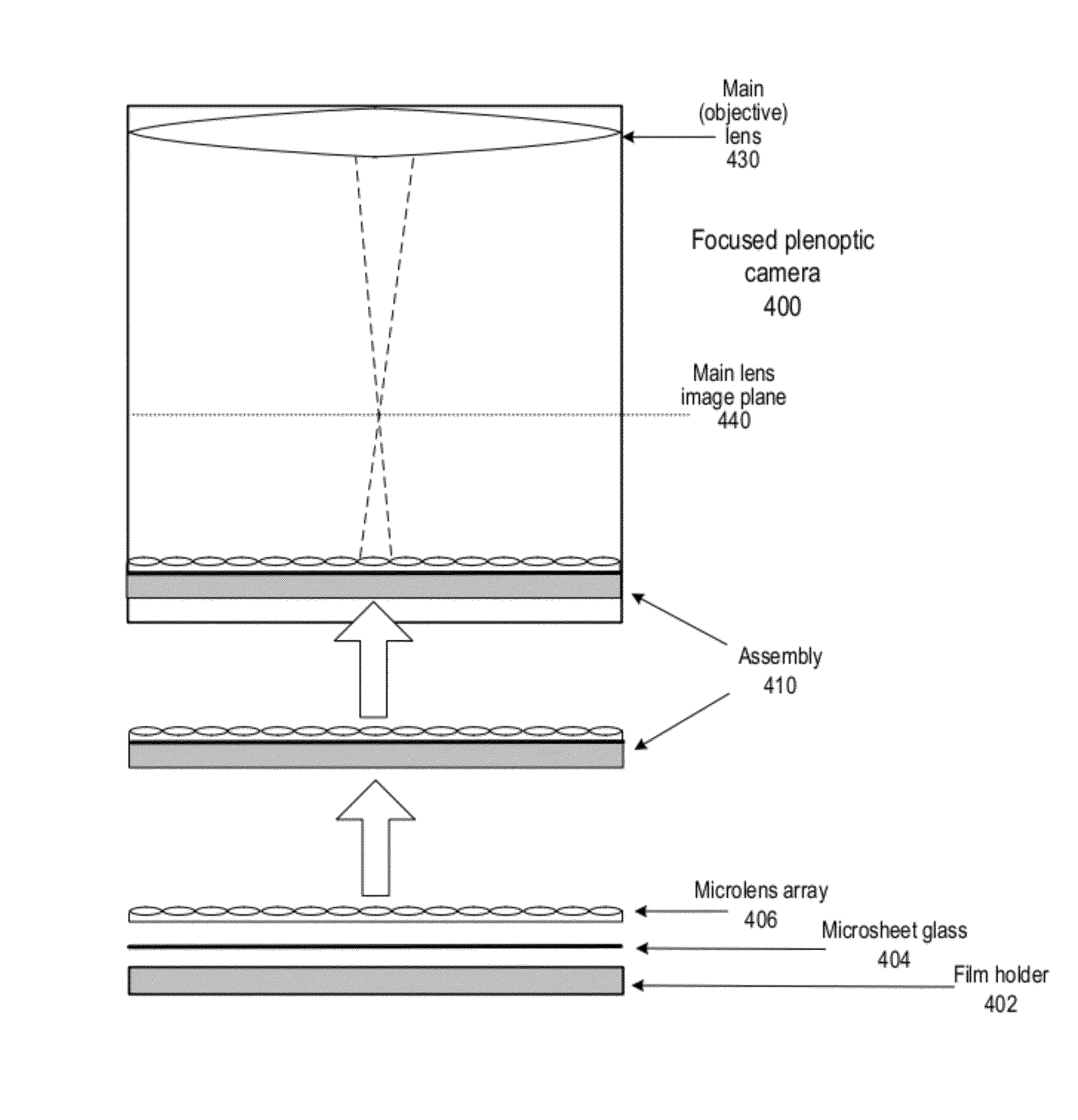
Super-resolution with the focused plenoptic camera
ActiveUS8315476B1Improve spatial resolutionAvoid estimationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicrolensImage resolution
Methods and apparatus for super-resolution in focused plenoptic cameras. By examining the geometry of data capture for super-resolution with the focused plenoptic camera, configurations for which super-resolution is realizable at different modes in the focused plenoptic camera are generated. A focused plenoptic camera is described in which infinity is super resolved directly, with registration provided by the camera geometry and the microlens pitch. In an algorithm that may be used to render super-resolved images from flats captured with a focused plenoptic camera, a high-resolution observed image is generated from a flat by interleaving pixels from adjacent microlens images. A deconvolution method may then be applied to the high-resolution observed image to deblur the image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Digital camera using multiple image sensors to provide improved temporal sampling
InactiveUS20080211941A1Keep for a long timeImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceImage resolutionExposure period
A method and apparatus for capturing image data from multiple image sensors and generating an output image sequence are disclosed. The multiple image sensors capture data with one or more different characteristics, such as: staggered exposure periods, different length exposure periods, different frame rates, different spatial resolution, different lens systems, and different focal lengths. The data from multiple image sensors is processed and interleaved to generate an improved output motion sequence relative to an output motion sequence generated from an a single equivalent image sensor.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Tomography-Based and MRI-Based Imaging Systems
InactiveUS20110142316A1Comparable image qualityImproved temporalReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisElastography
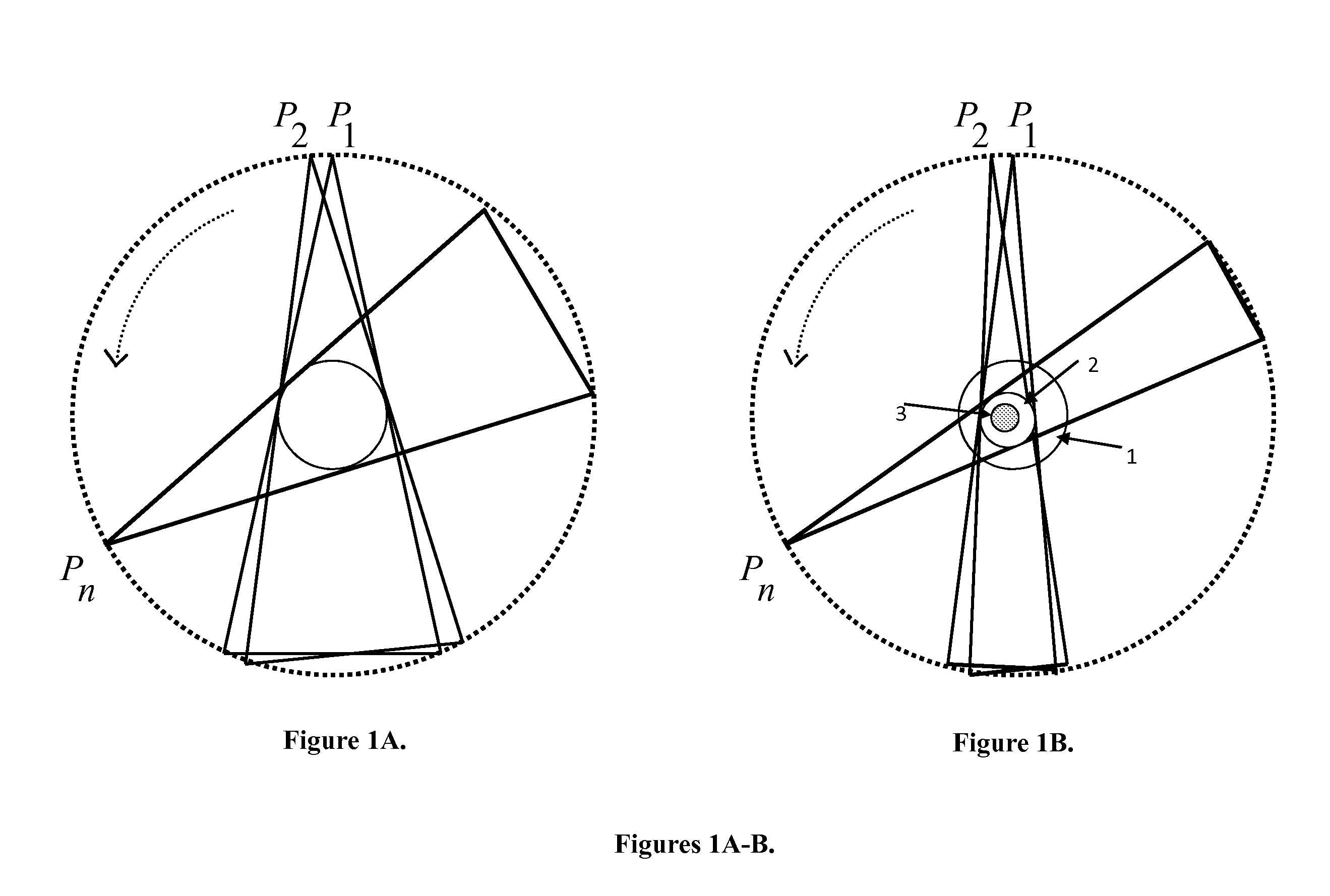
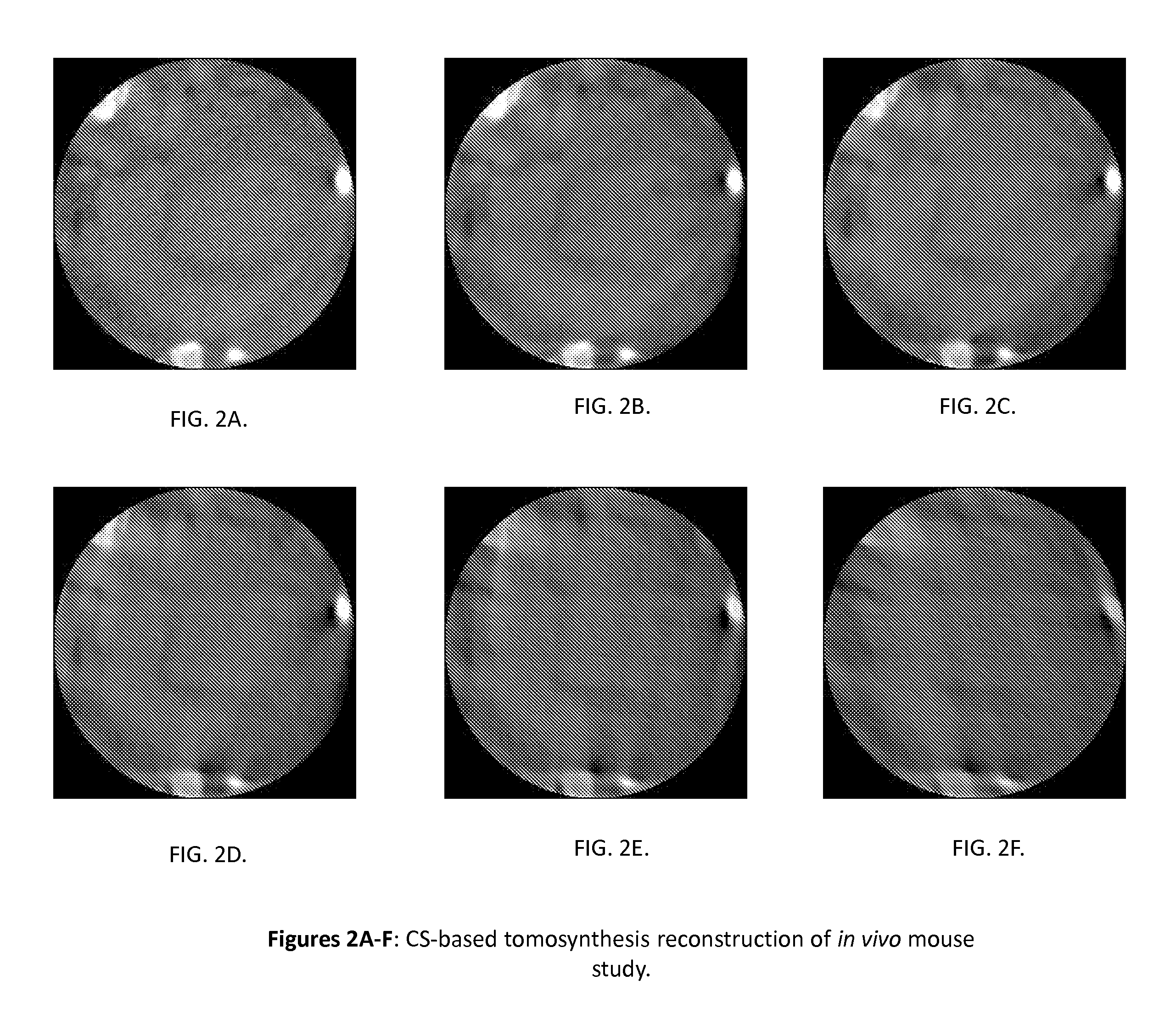
Tomography limitations in vivo due to incomplete, inconsistent and intricate measurements require solution of inverse problems. The new strategies disclosed in this application are capable of providing faster data acquisition, higher image quality, lower radiation dose, greater flexibility, and lower system cost. Such benefits can be used to advance research in cardiovascular diseases, regenerative medicine, inflammation, and nanotechnology. The present invention relates to the field of medical imaging. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to methods, systems, and devices for imaging, including tomography-based and MRI-based applications. For example, included in embodiments of the invention are compressive sampling based tomosynthesis methods, which have great potential to reduce the overall x-ray radiation dose for a patient. To name a few, compressive sensing based carbon nano-tube based interior tomosynthesis systems, tomography-based dynamic cardiac elastography systems, cardiac elastodynamic biomarkers from interior MR imaging, exact and stable interior ROI reconstructions for radial MRI, and interior reconstruction based ultrafast tomography systems are provided.
Owner:WANG GE +5
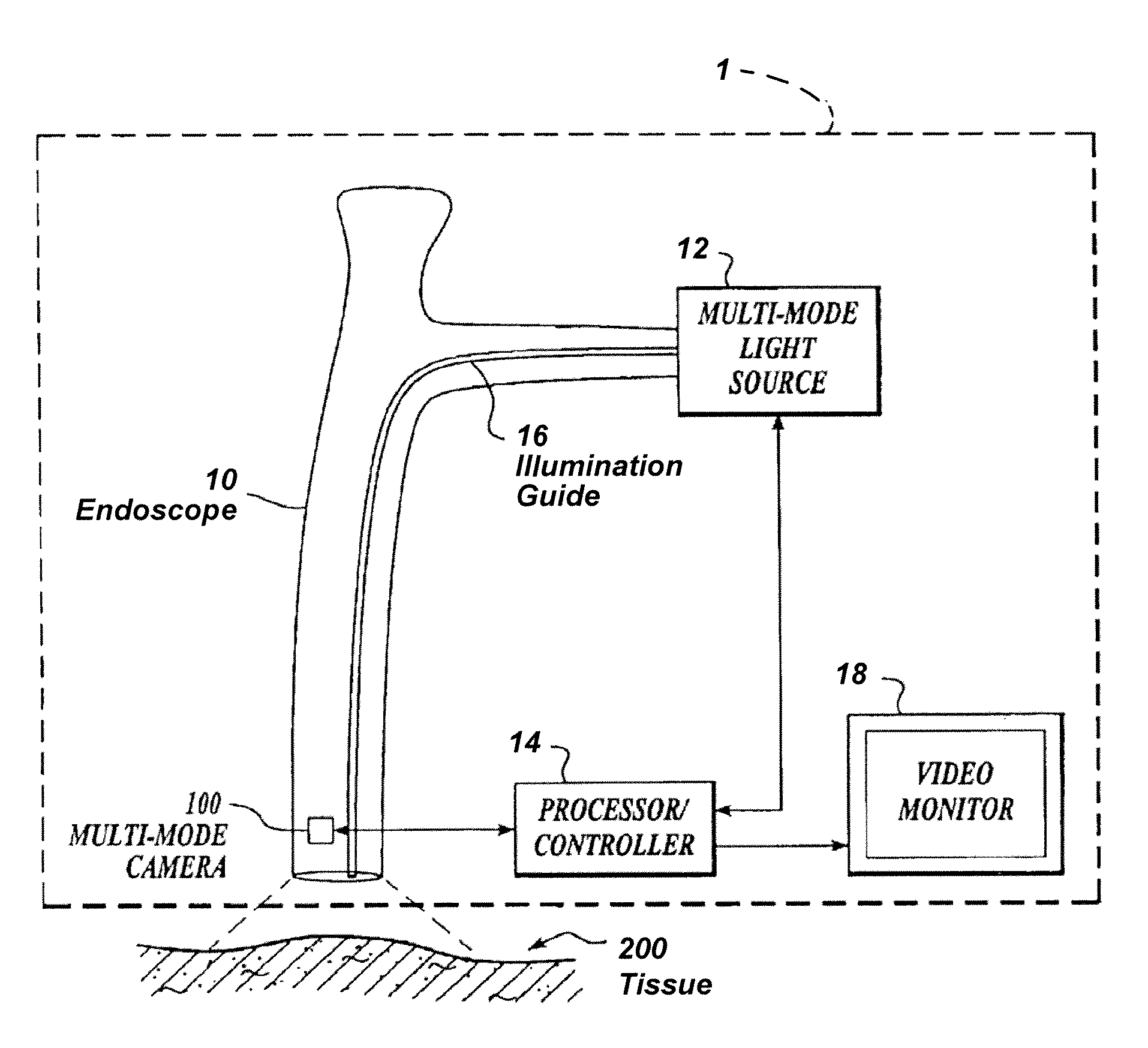
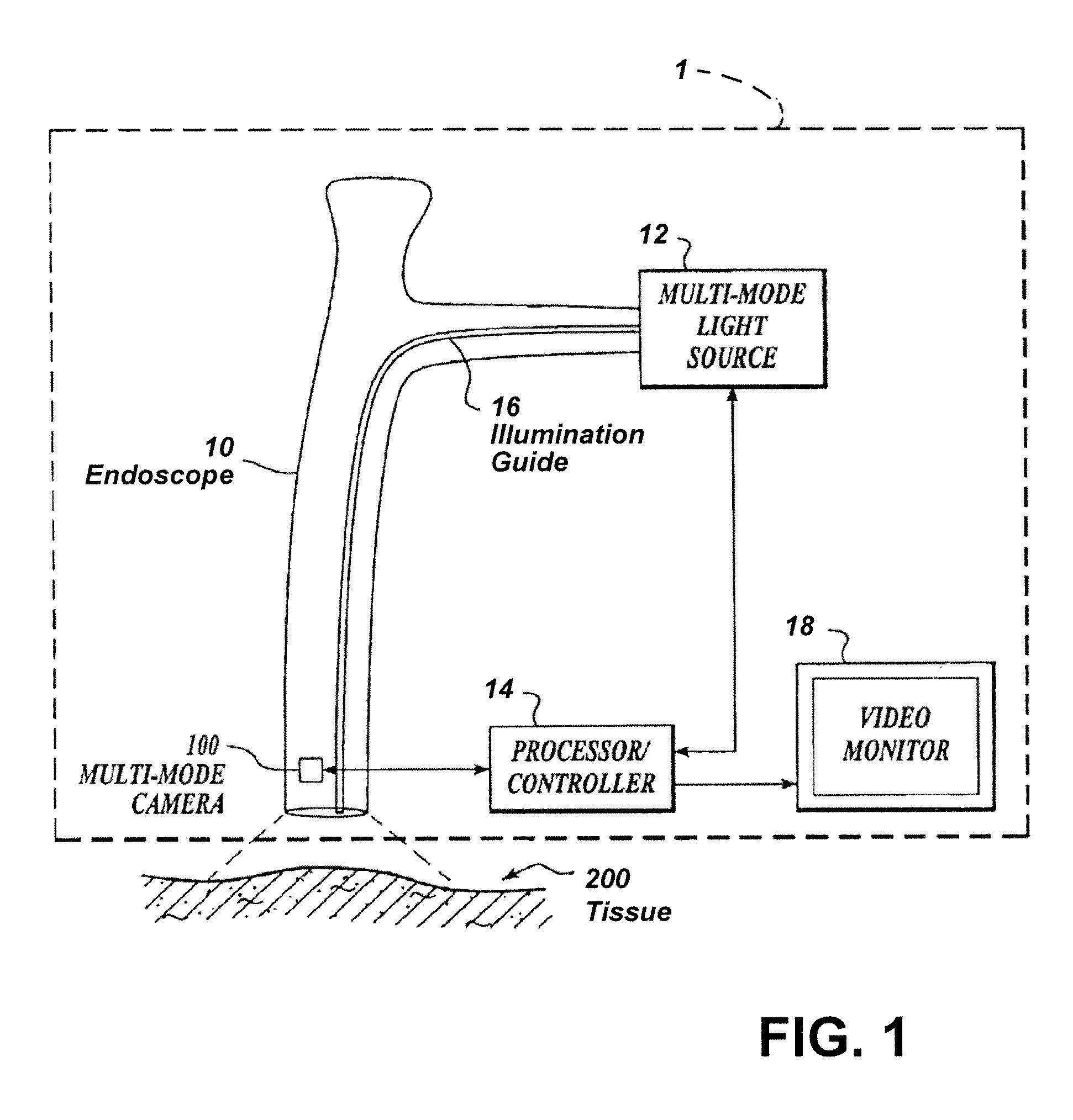
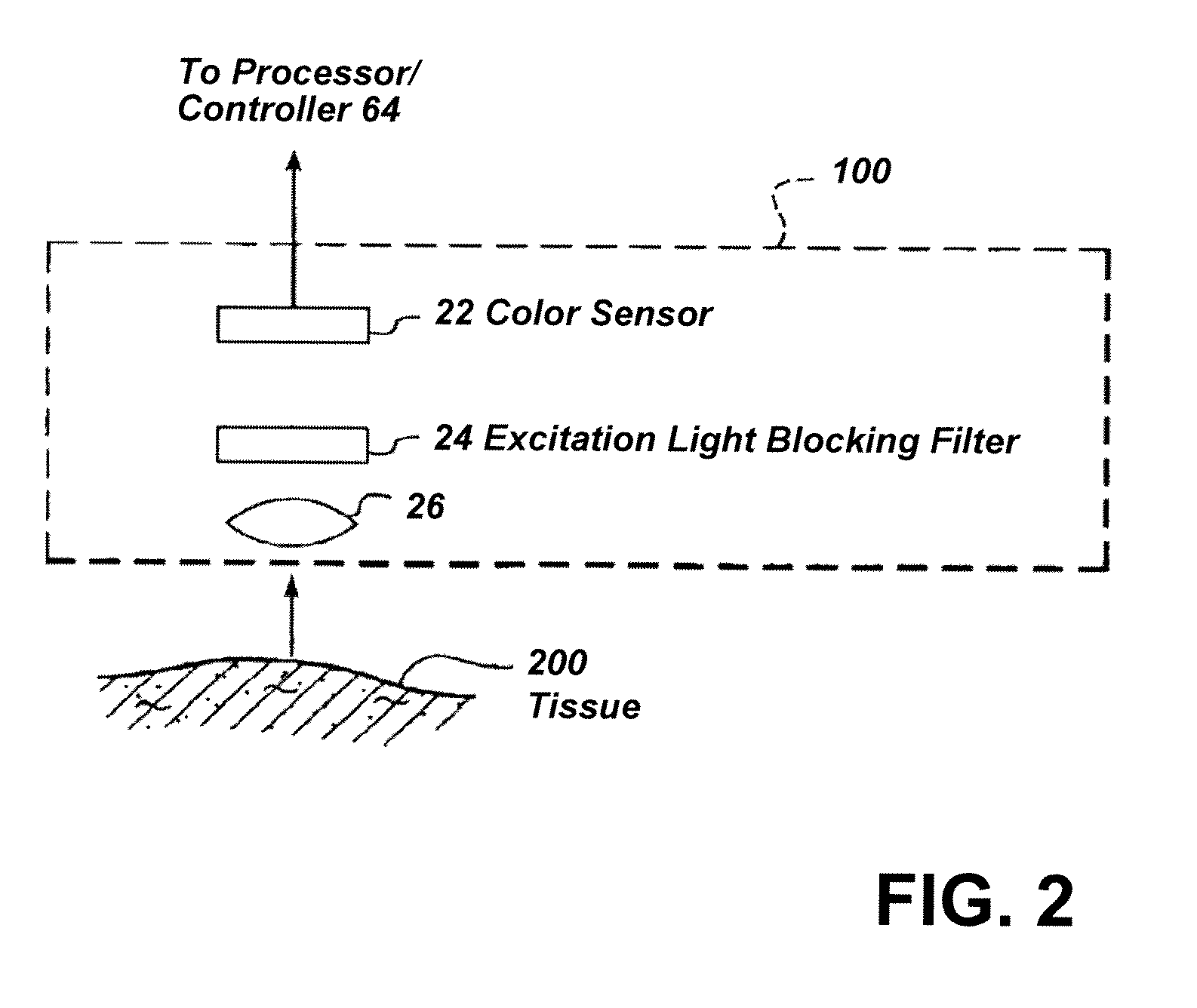
Imaging system with a single color image sensor for simultaneous fluorescence and color video endoscopy
ActiveUS20080239070A1Enhanced attainable spatial resolutionHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsSurgeryVideo rateMonochrome Image
An endoscopic video system and method using a camera with a single color image sensor, for example a CCD color image sensor, for fluorescence and color imaging and for simultaneously displaying the images acquired in these imaging modes at video rates in real time is disclosed. The tissue under investigation is illuminated continuously with fluorescence excitation light and is further illuminated periodically using visible light outside of the fluorescence excitation wavelength range. The illumination sources may be conventional lamps using filters and shutters, or may include light-emitting diodes mounted at the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
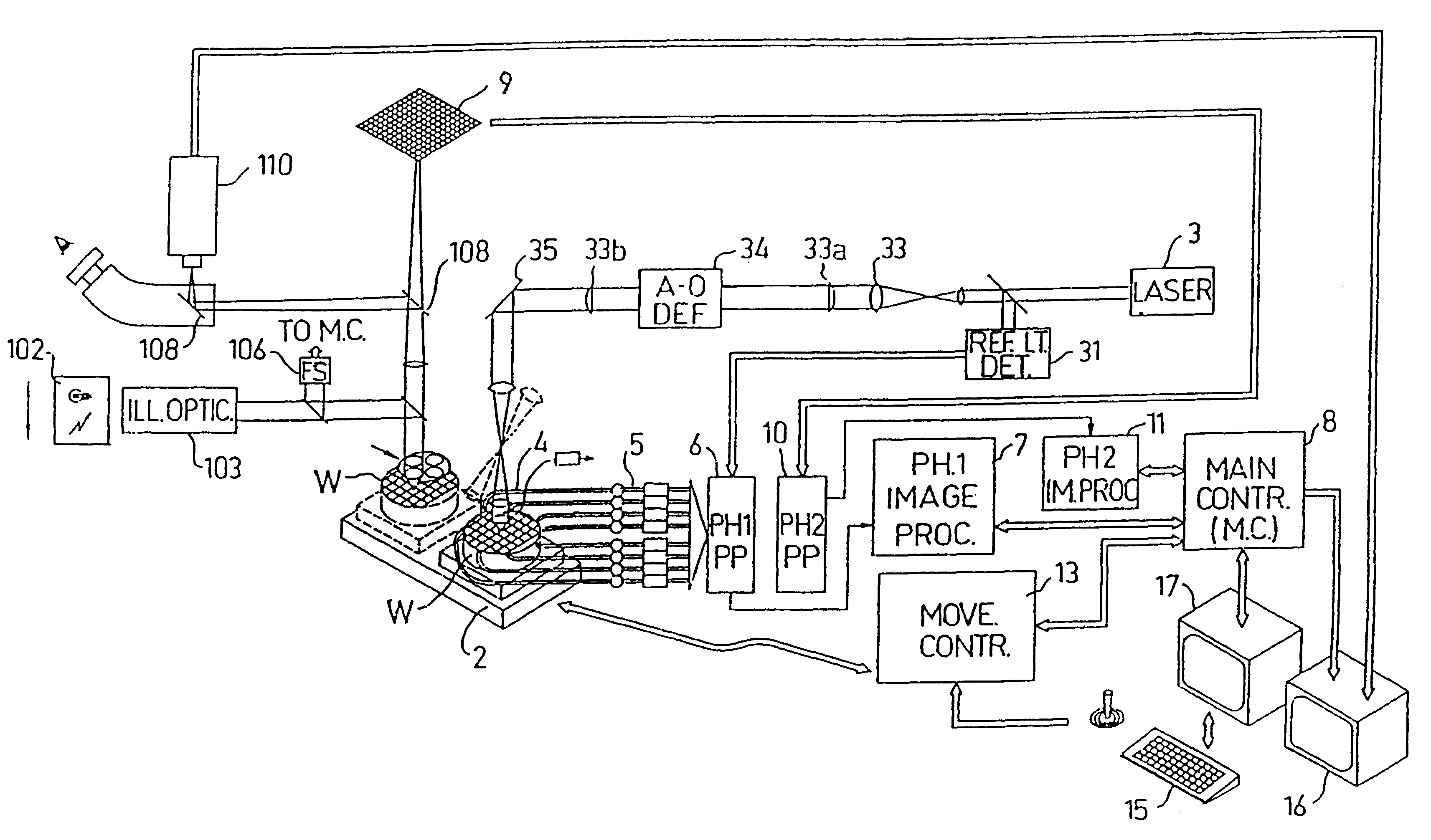
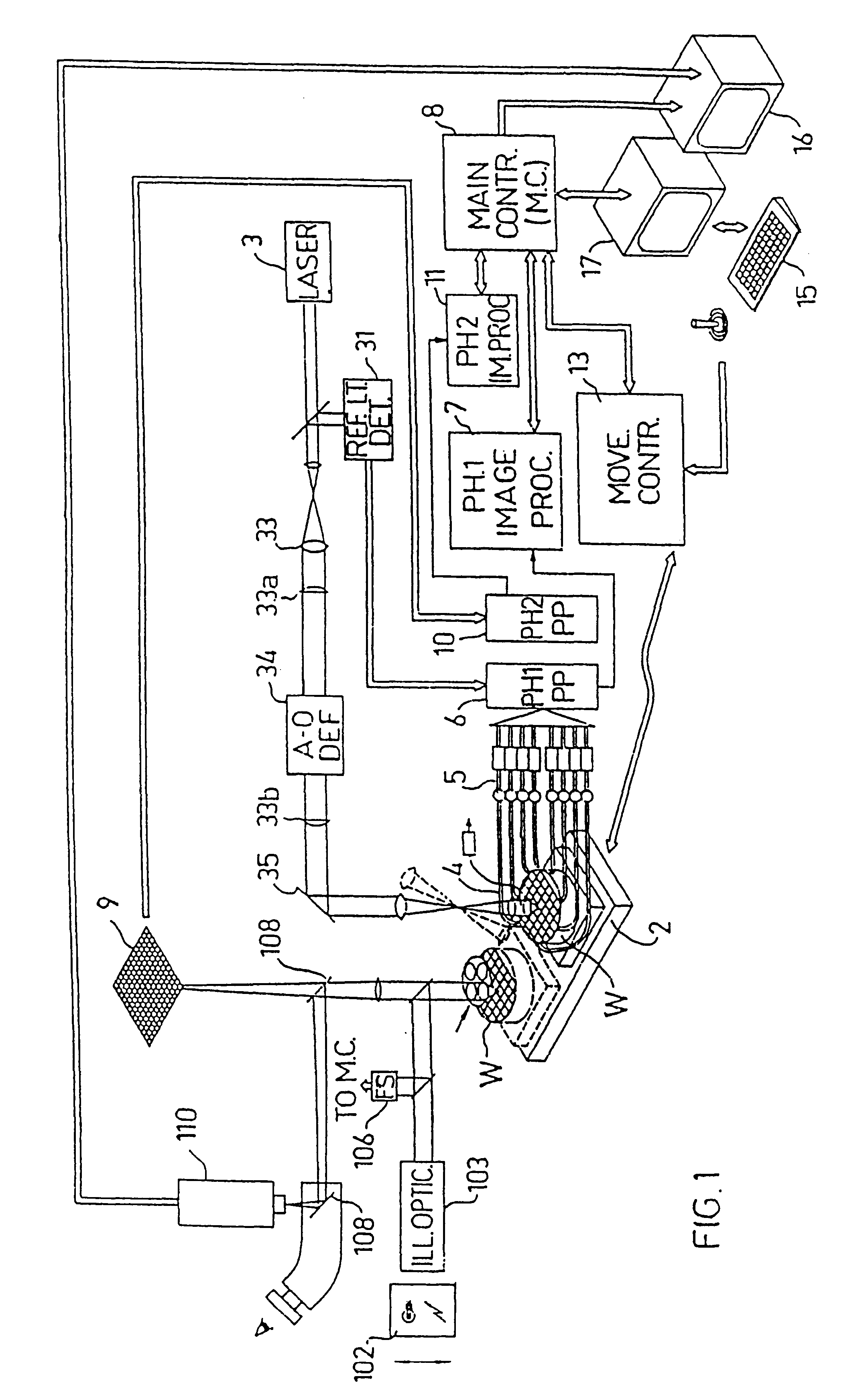
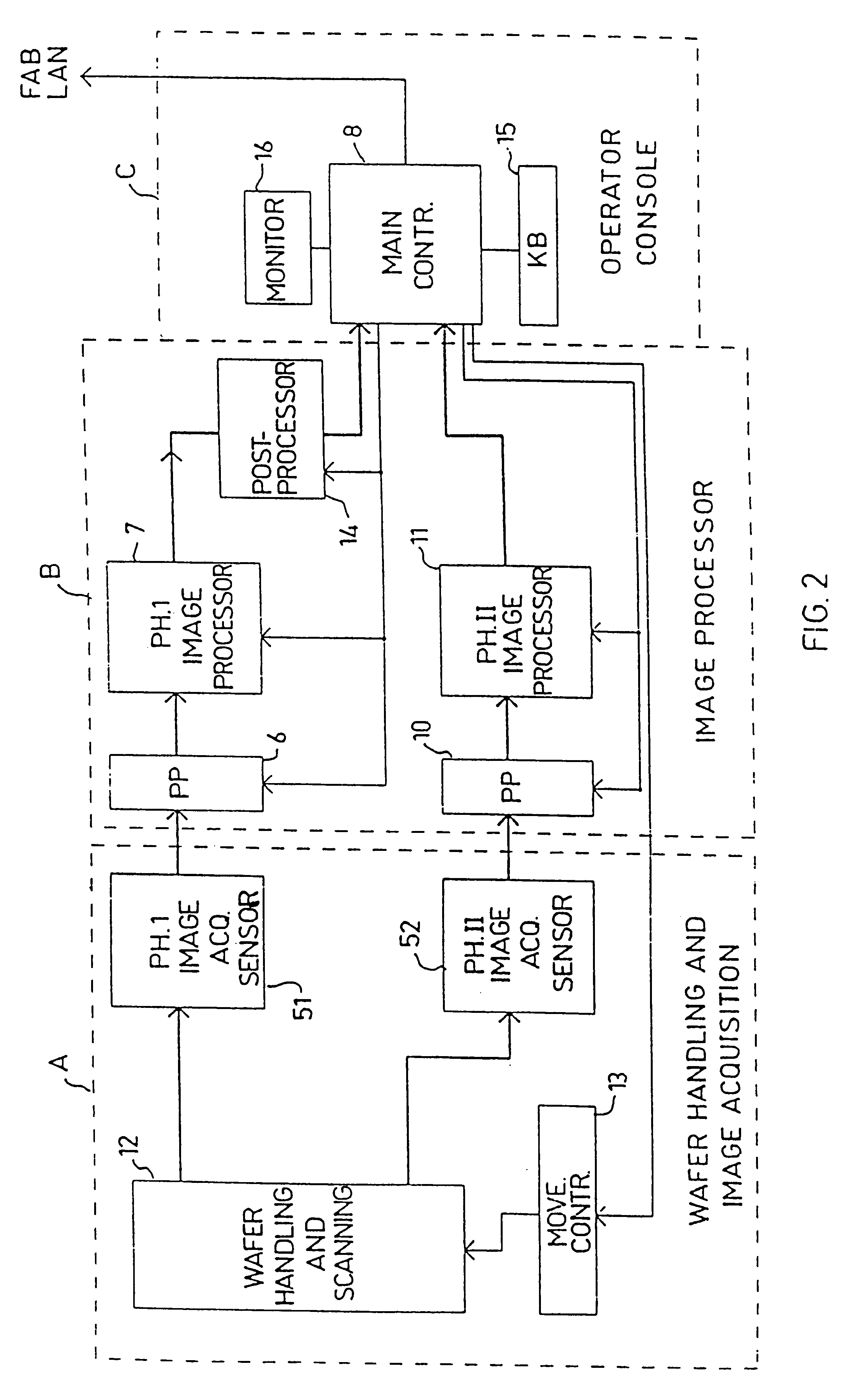
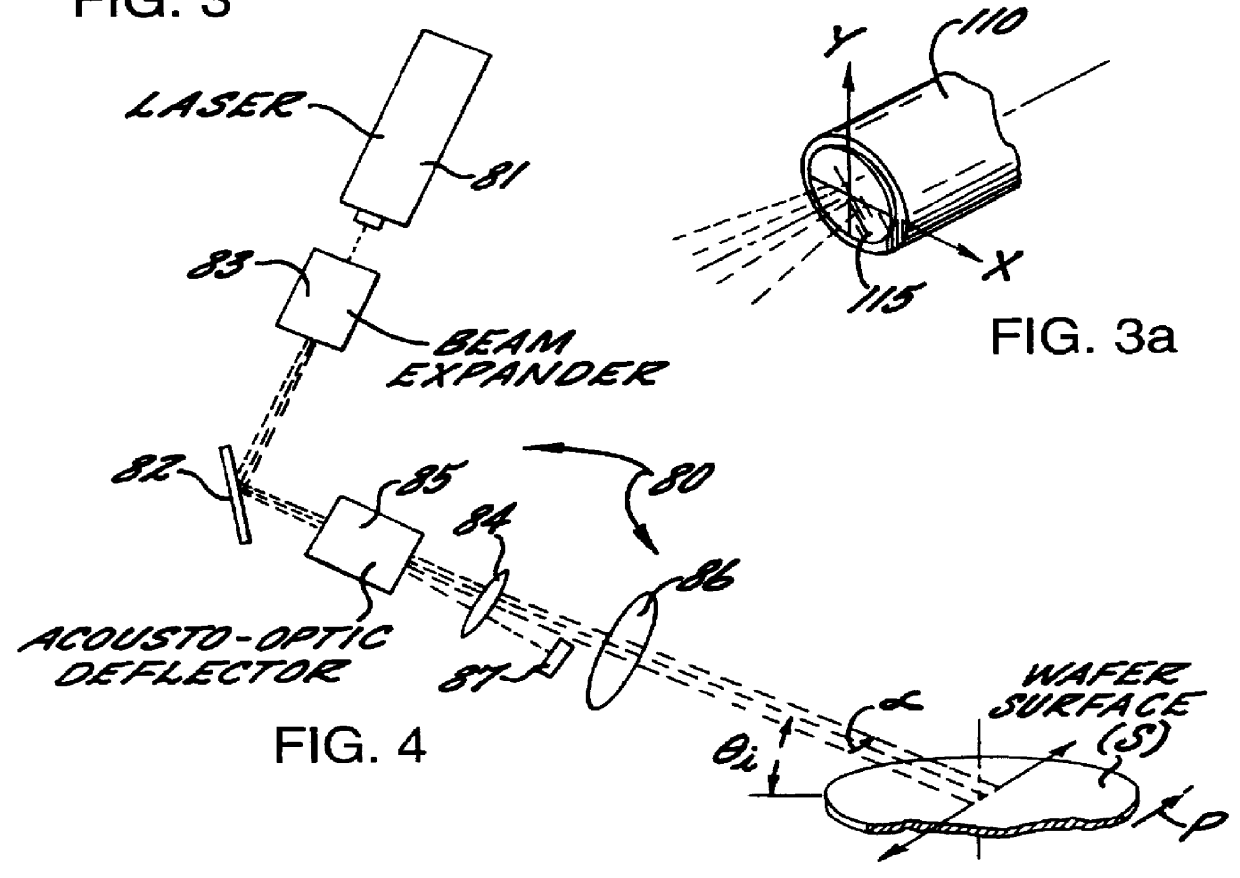
Substrate inspection method and apparatus
InactiveUS6178257B1High throughputIncrease sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method and apparatus for inspecting the surface of articles, such as chips and wafers, for defects, includes a first phase of optically examining the complete surface of the article inspected at a relatively high speed and with a relatively low spatial resolution, and a second phase of optically examining with a relatively high spatial resolution only the suspected locations for the presence or absence of a defect therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
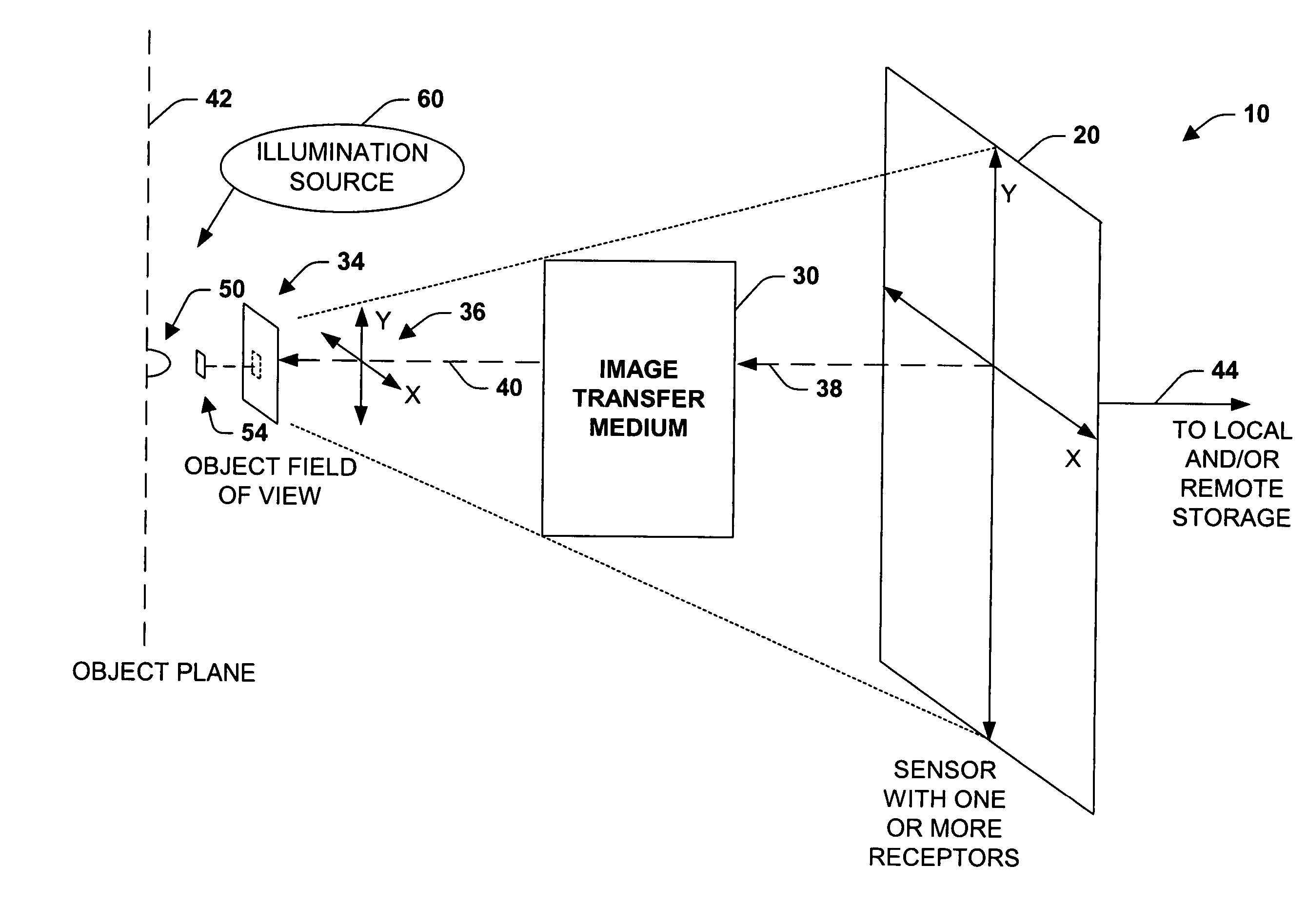
Imaging system and methodology
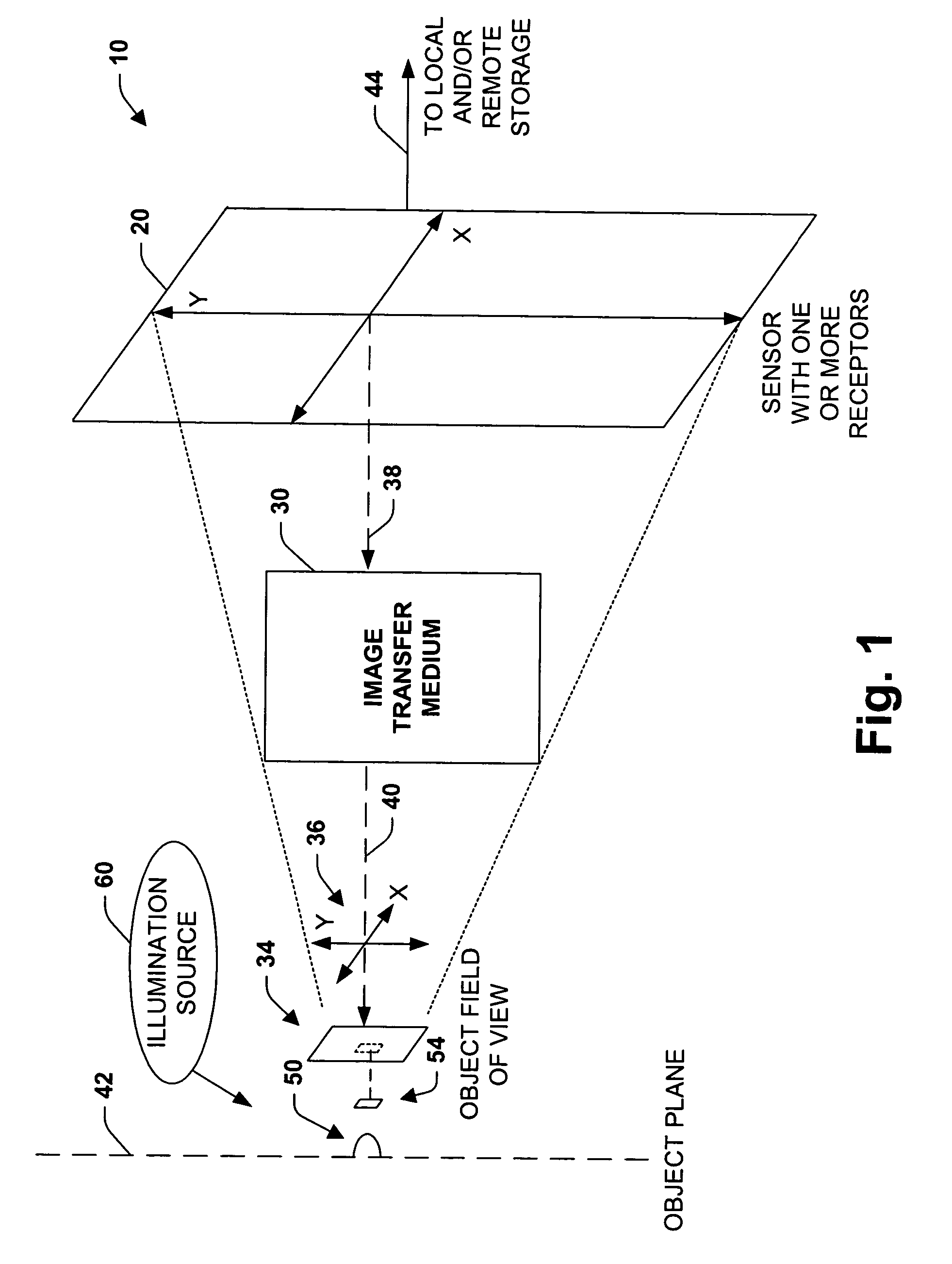
InactiveUS7151246B2Improve performanceEffectively scaledTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage transferDisplay device
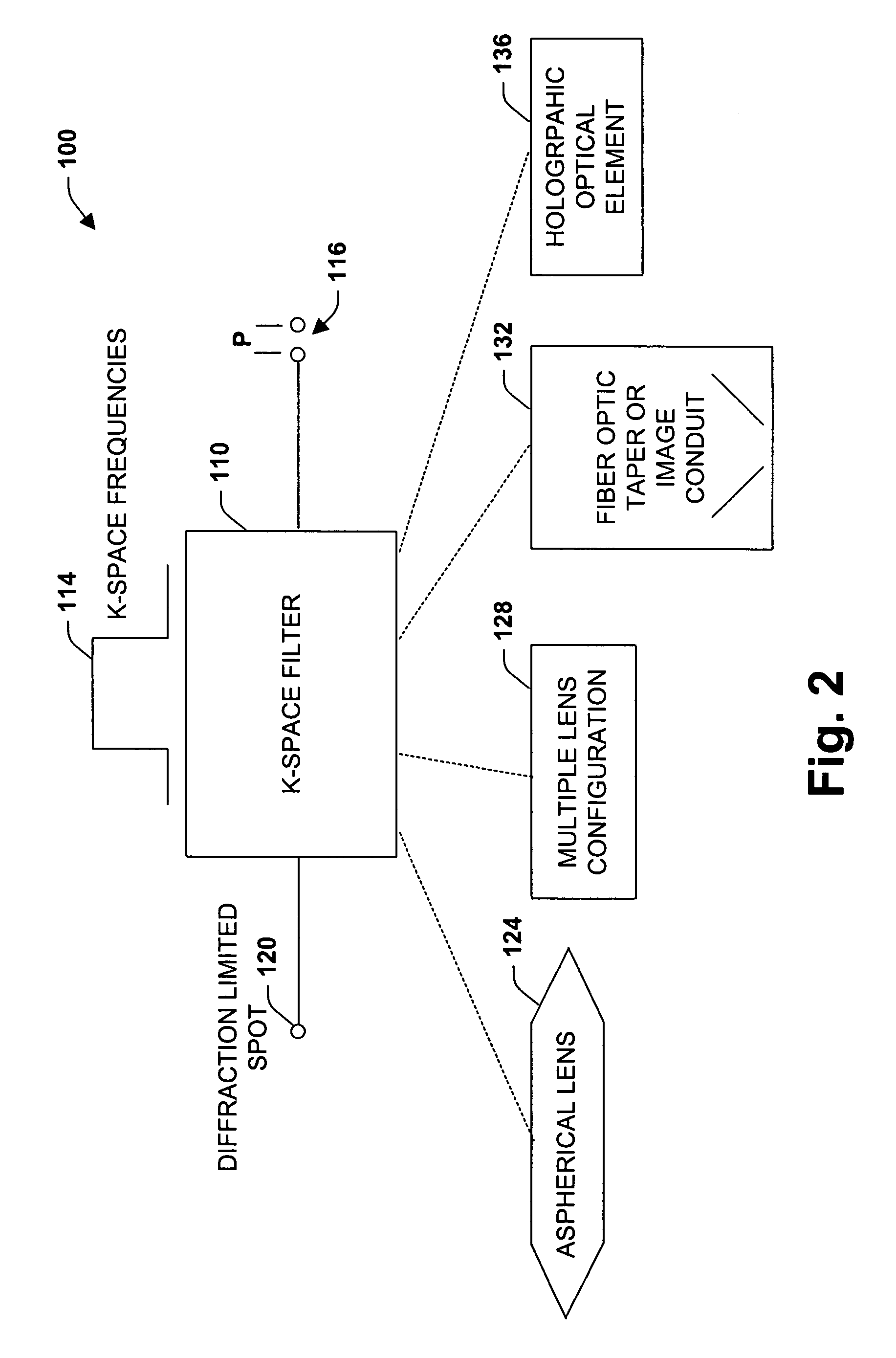
An imaging system, methodology, and various applications are provided to facilitate optical imaging performance. The system contains a sensor having one or more receptors and an image transfer medium to scale the sensor and receptors in accordance with resolvable characteristics of the medium, and as defined with certain ratios. A computer, memory, and / or display associated with the sensor provides storage and / or display of information relating to output from the receptors to produce and / or process an image, wherein a plurality of illumination sources can also be utilized in conjunction with the image transfer medium. The image transfer medium can be configured as a k-space filter that correlates projected receptor size to a diffraction-limited spot associated with the image transfer medium, wherein the projected receptor size can be unit-mapped within a certain ratio to the size of the diffraction-limited spot, both in the object plane.
Owner:HIMANSHU S AMIN +3
Optical imaging of blood circulation velocities
InactiveUS7113817B1Reduce the impactImprove accuracyTesting eggsDiagnostics using lightDigital imagingDetector array
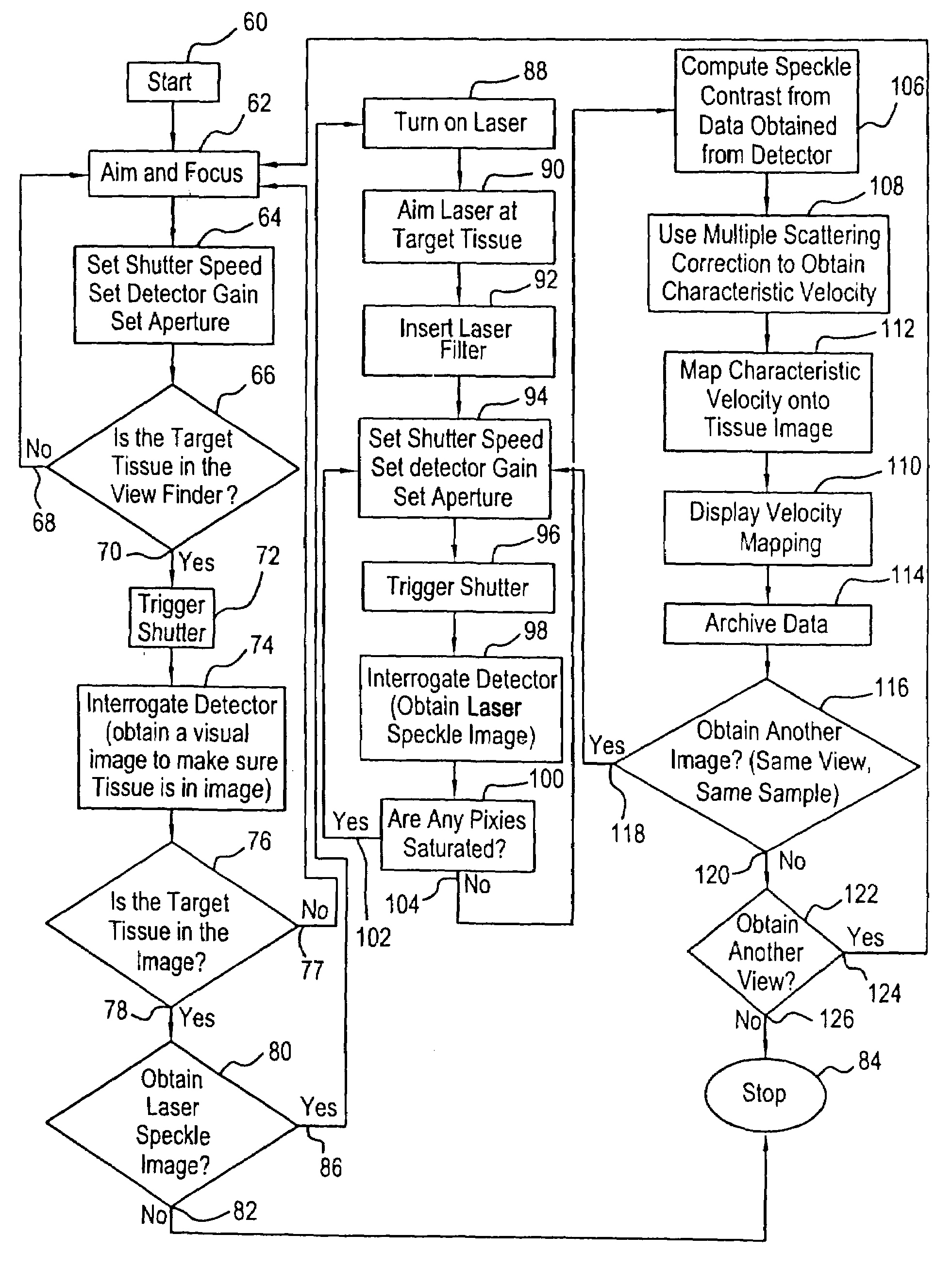
New devices and methods are provided for noninvasive and noncontact real-time measurements of tissue blood velocity. The invention uses a digital imaging device such as a detector array that allows independent intensity measurements at each pixel to capture images of laser speckle patterns on any surfaces, such as tissue surfaces. The laser speckle is generated by illuminating the surface of interest with an expanded beam from a laser source such as a laser diode or a HeNe laser as long as the detector can detect that particular laser radiation. Digitized speckle images are analyzed using new algorithms for tissue optics and blood optics employing multiple scattering analysis and laser Doppler velocimetry analysis. The resultant two-dimensional images can be displayed on a color monitor and superimposed on images of the tissues.
Owner:WINTEC LLC
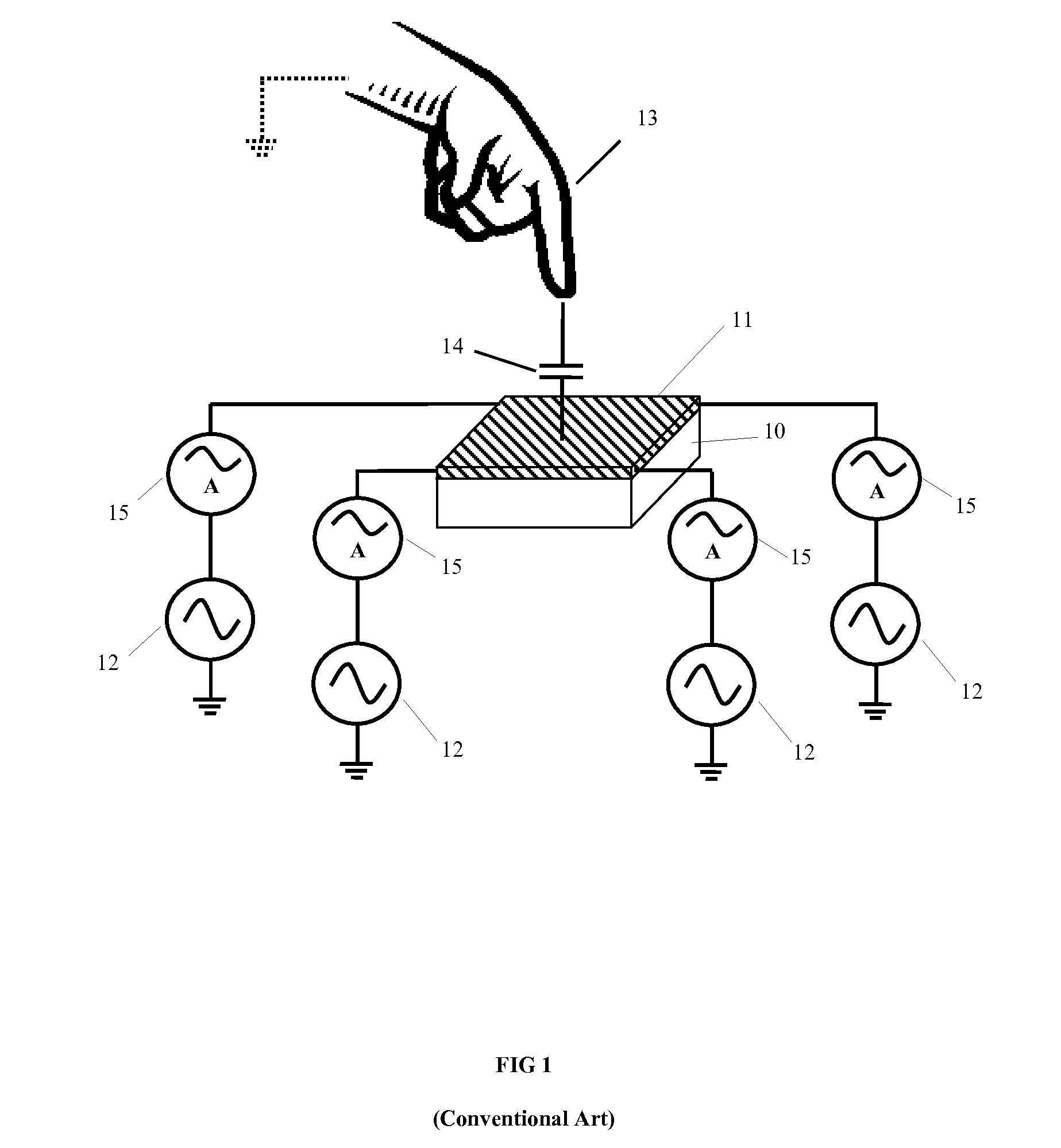
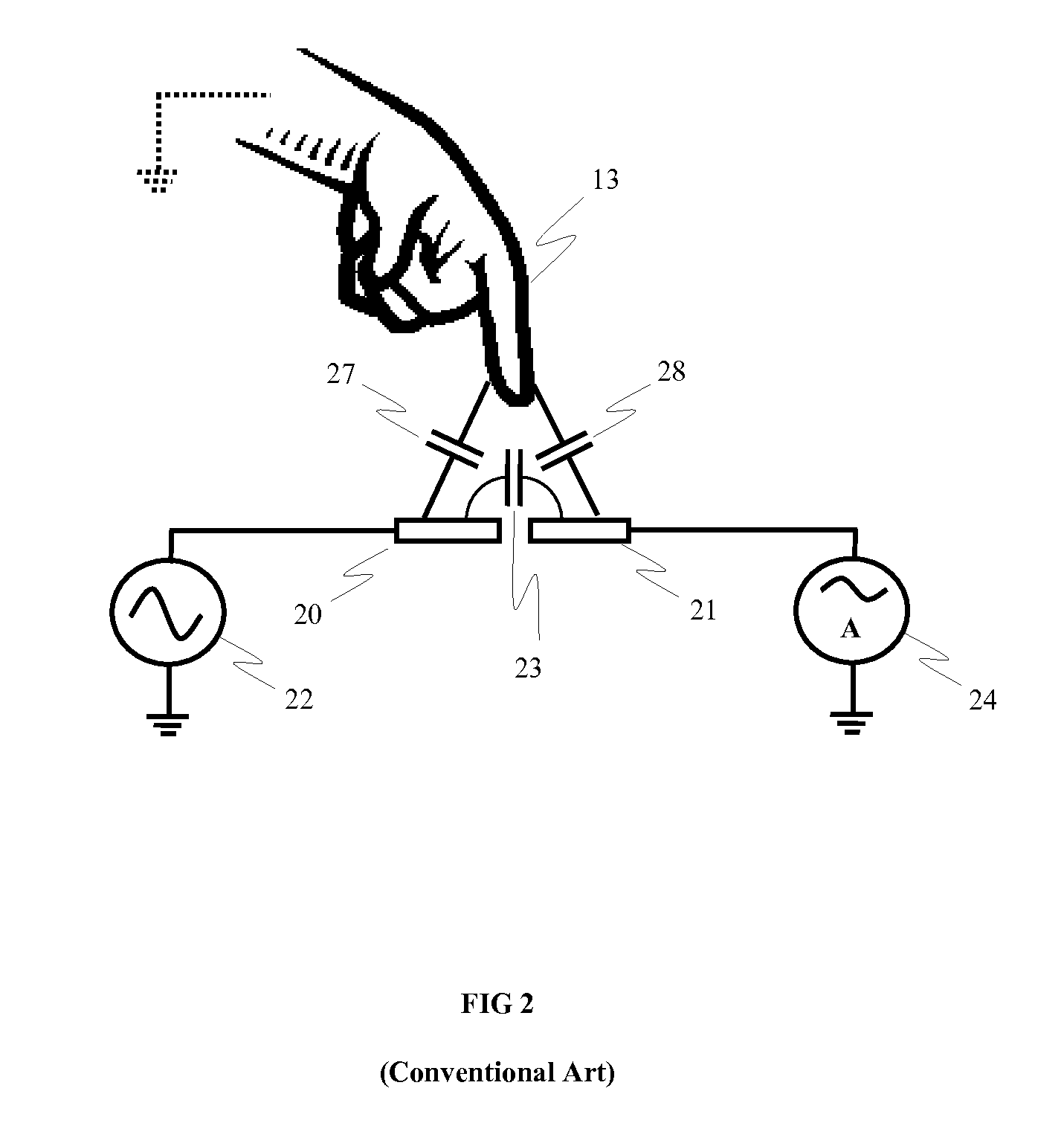
Capacitive touch panel with force sensing
ActiveUS20140062934A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh sensitivityTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouch Senses
A capacitive type touch sensing device includes a first electrode array including a plurality of drive electrodes and a plurality of sense electrodes, and a second electrode array spaced apart from the first electrode array and including a plurality of discrete, electrically floating conductive regions. At least part of the second electrode array positionally overlaps with at least part of the first electrode array to define a separation distance therebetween, the separation distance varying with a force applied to a surface of the touch sensing device. Further, each conductive region is positioned relative to a respective drive electrode and sense electrode of the first electrode array so that a capacitance between certain pairs of drive and sense electrodes is more sensitive to a variation in the separation distance than a capacitance between other pairs of drive and sense electrodes.
Owner:SHARP KK
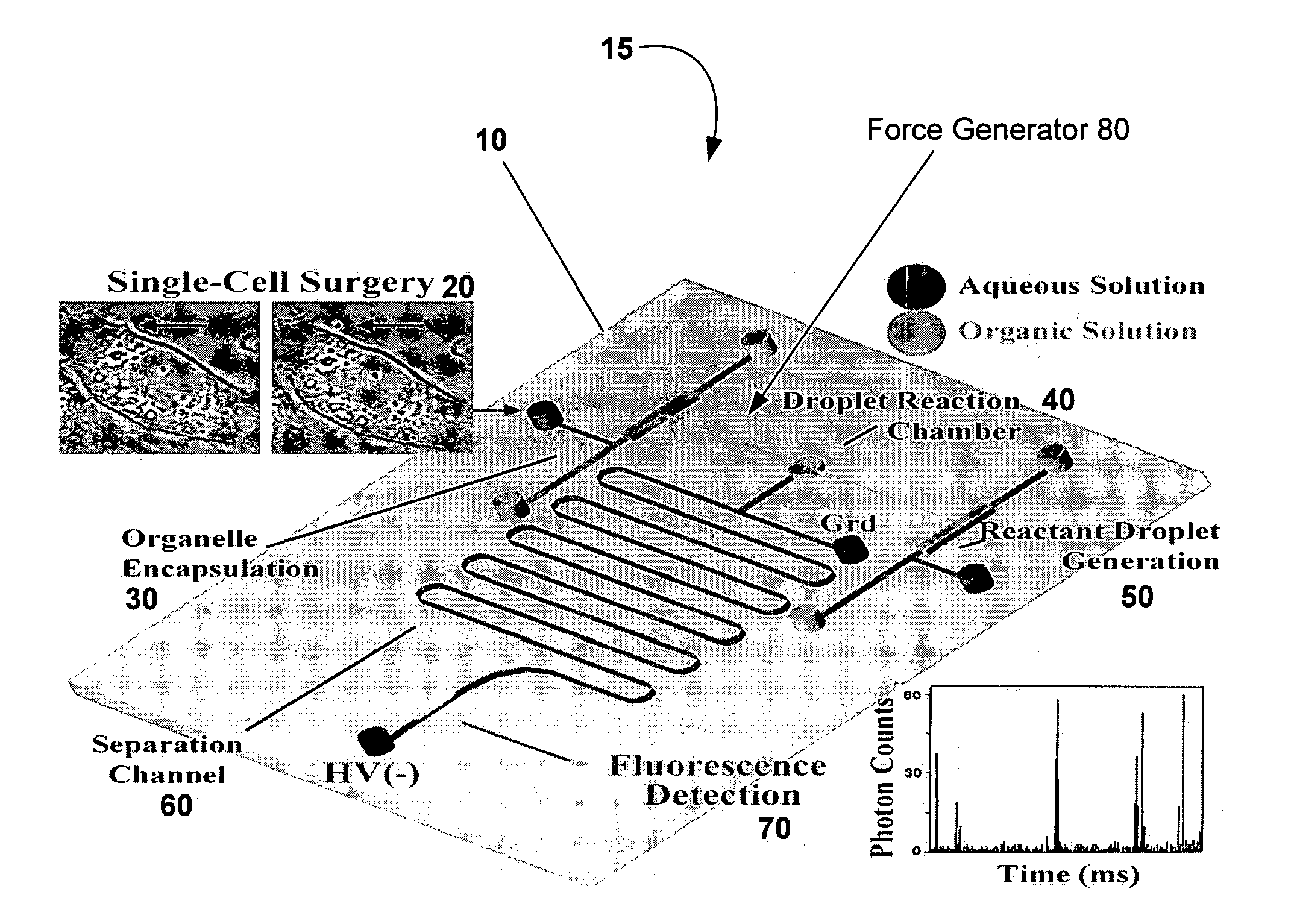
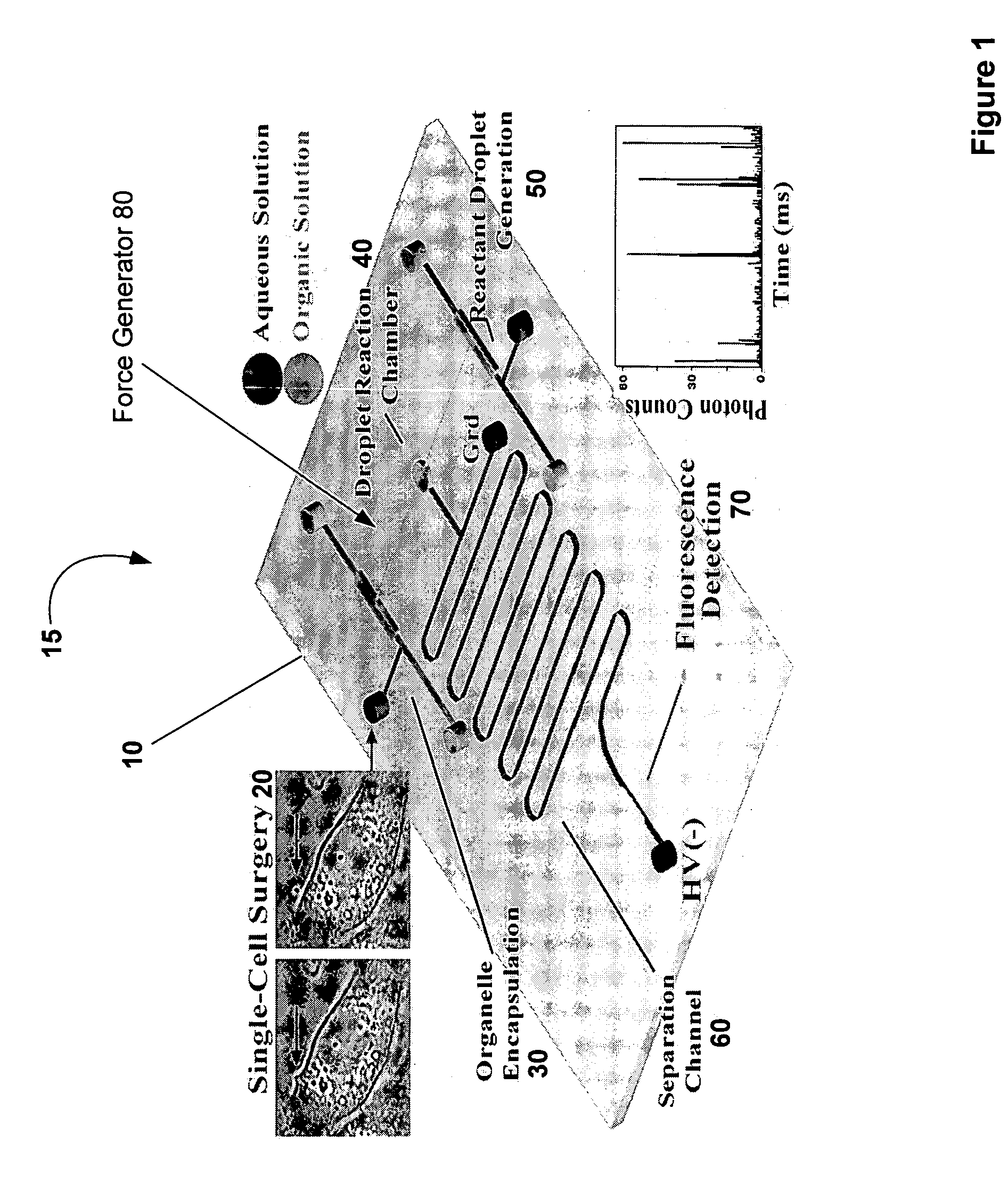
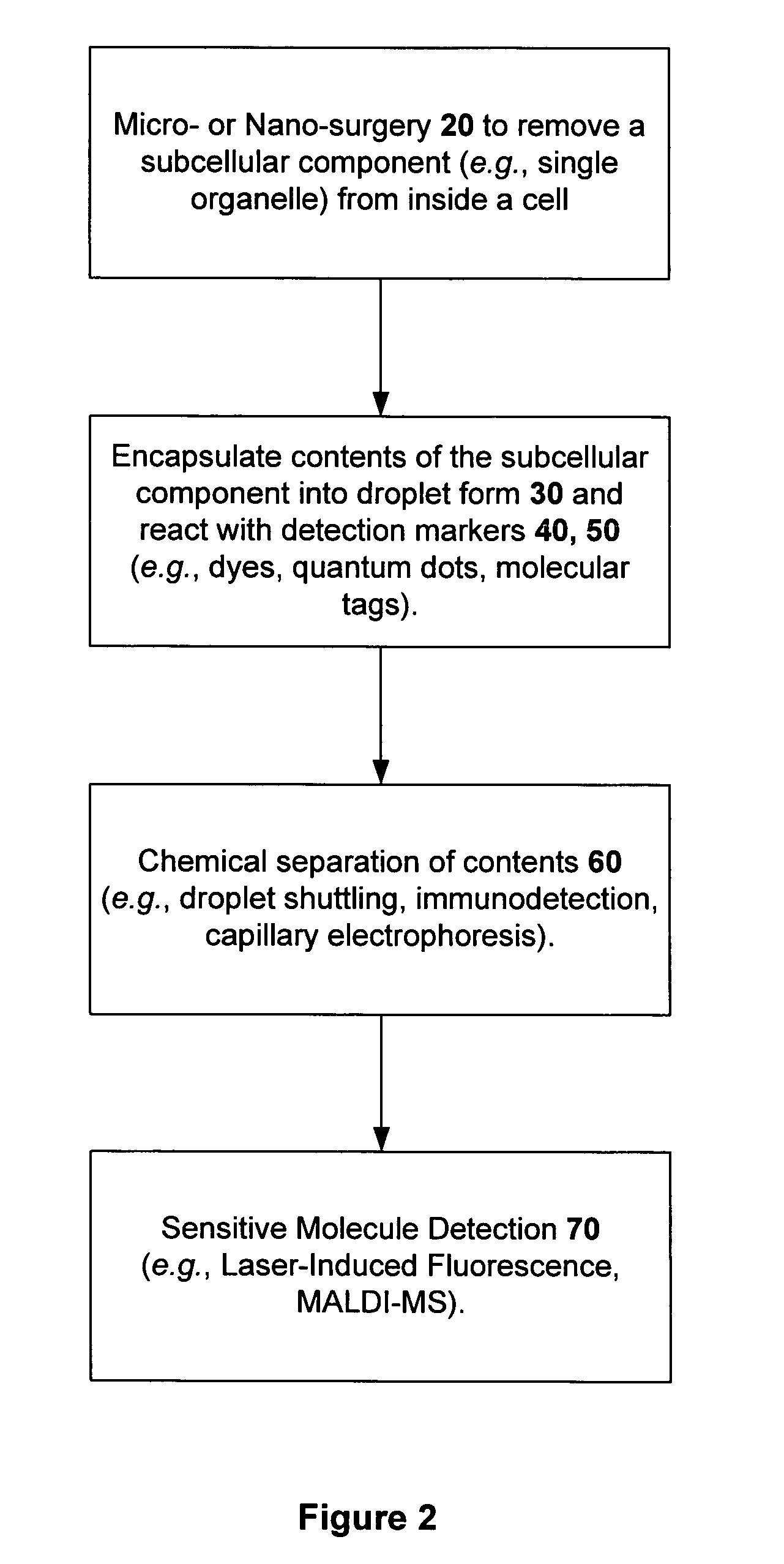
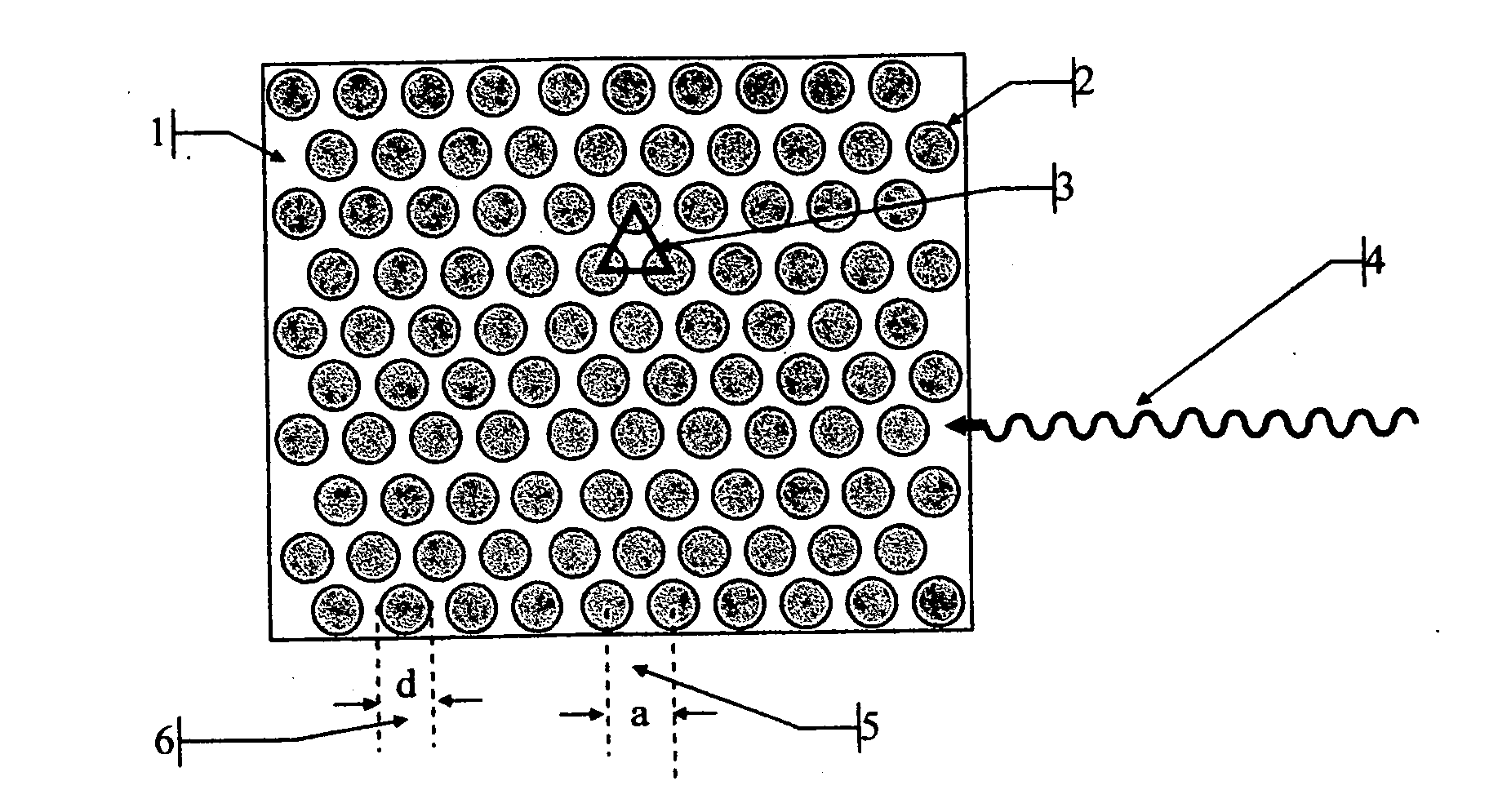
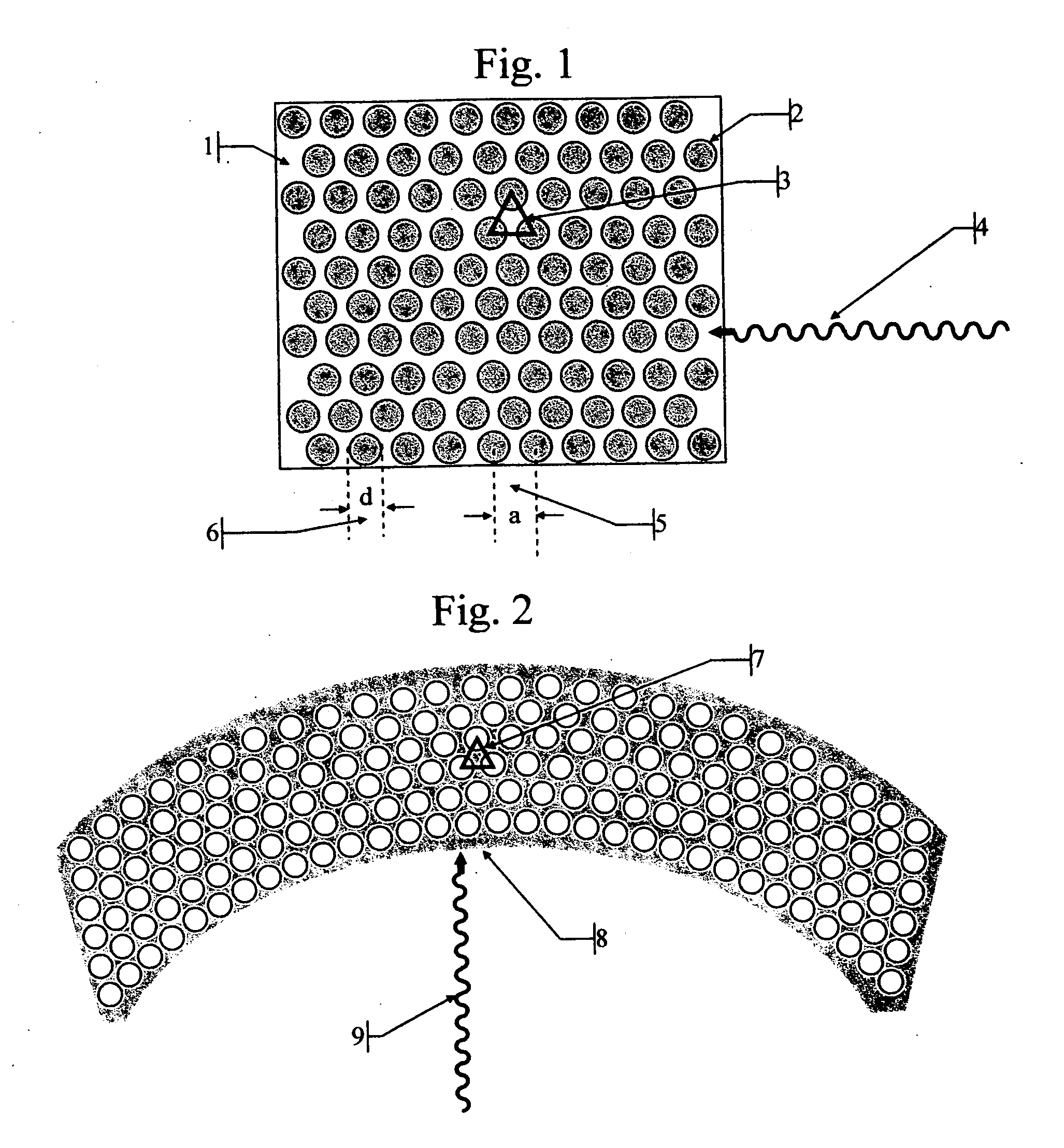
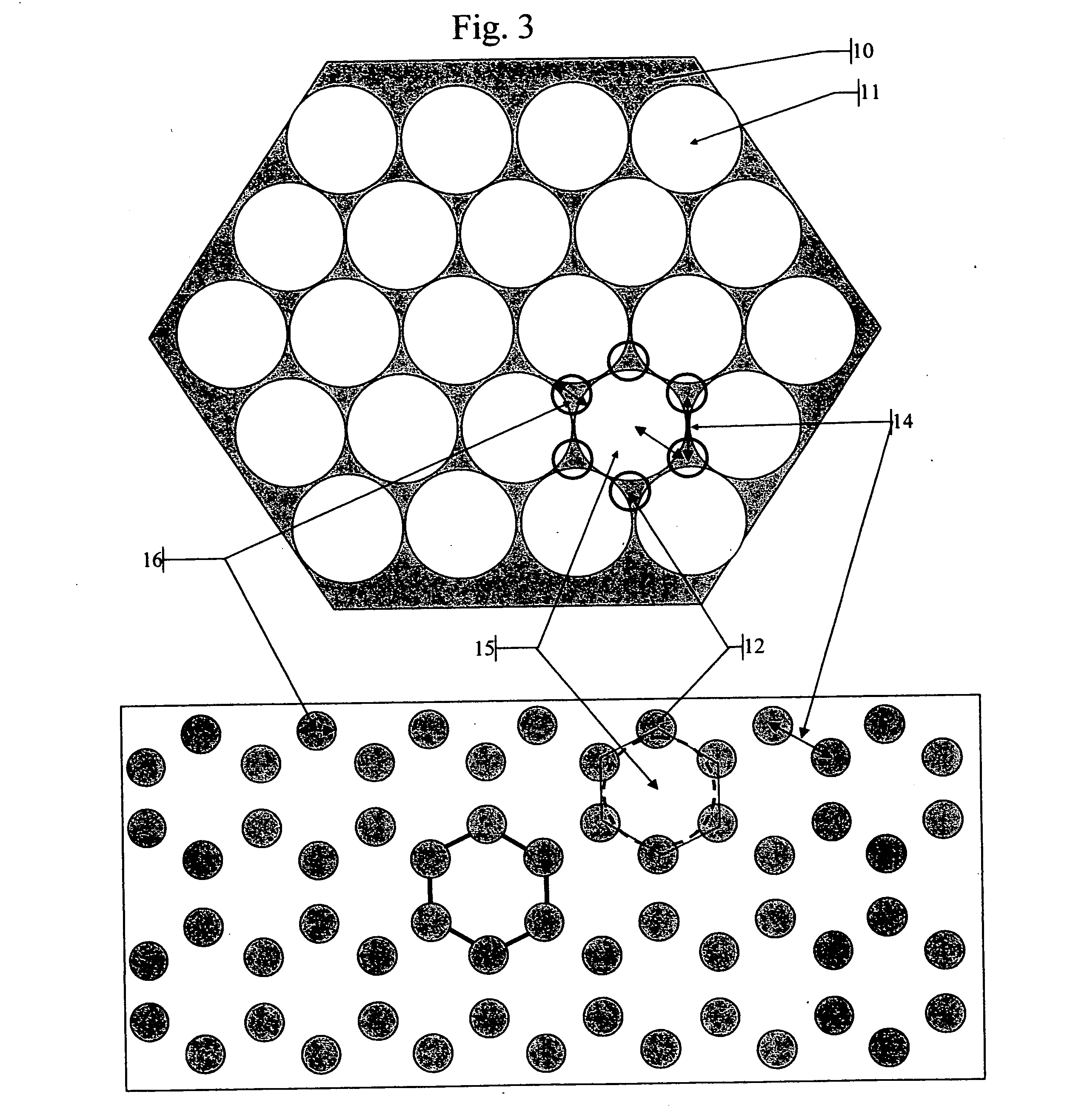
Method and device for biochemical detection and analysis of subcellular compartments from a single cell
InactiveUS20050048581A1Improve spatial resolutionMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiophysicsBiochemical detection
A method and system for performing biochemical detection or analysis on micro- and nano-scale subcellular component within a single biological cell is provided. An integrated platform device and method to perform the biochemical analysis is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS20060202125A1Thinner sliceImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are decribed.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
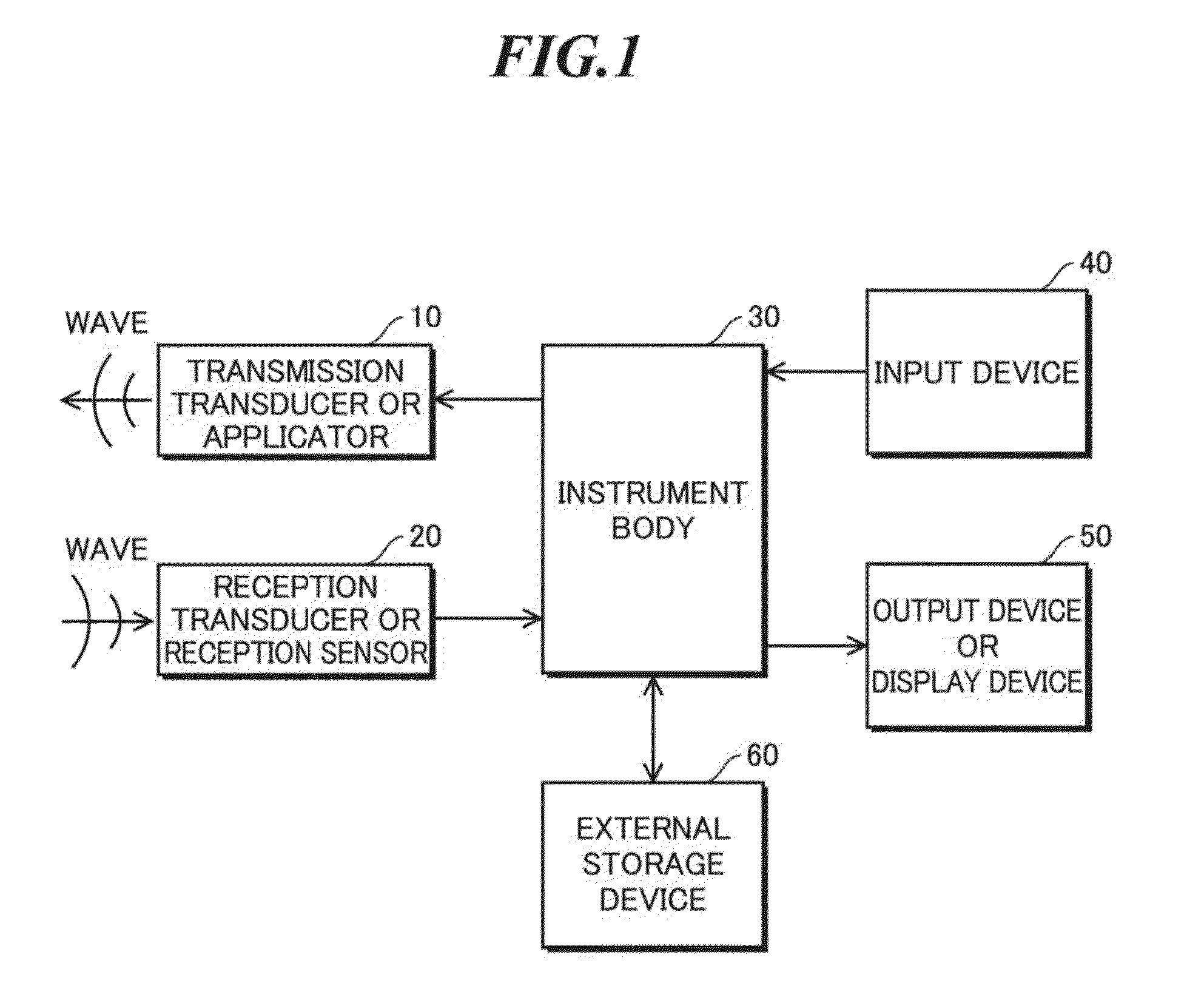
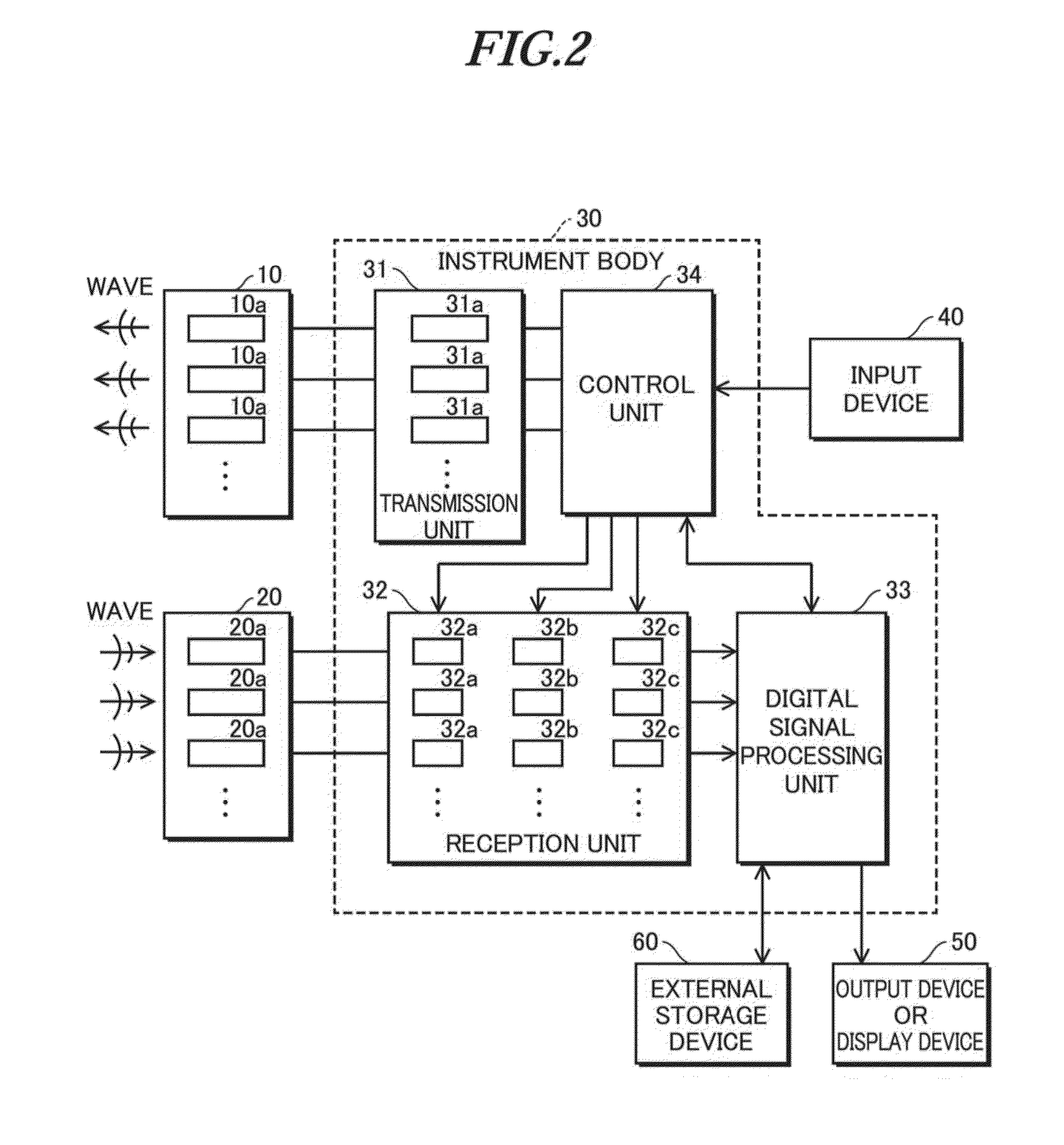
Beamforming method, measurement and imaging instruments, and communication instruments
ActiveUS20160157828A1Increase speedImprove accuracyProcessing detected response signalCatheterEngineeringWavenumber
Beamforming method that allows a high speed and high accuracy beamforming with no approximate interpolations. This beamforming method includes step (a) that generates reception signals by receiving waves arrival from a measurement object; and step (b) that performs a beamforming with respect to the reception signals generated by step (a); and step (b) including without performing wavenumber matching including approximate interpolation processings with respect to the reception signals, and the reception signals are Fourier's transformed in the axial direction and the calculated Fourier's transform is multiplied to a complex exponential function expressed using a wavenumber of the wave and a carrier frequency to perform wavenumber matching in the lateral direction and further, the product is Fourier's transformed in the lateral direction and the calculated result is multiplied to a complex exponential function, from which an effect of the lateral wavenumber matching is removed, to perform wavenumber matching in the axial direction, by which an image signal is generated.
Owner:CHIKAYOSHI SUMI
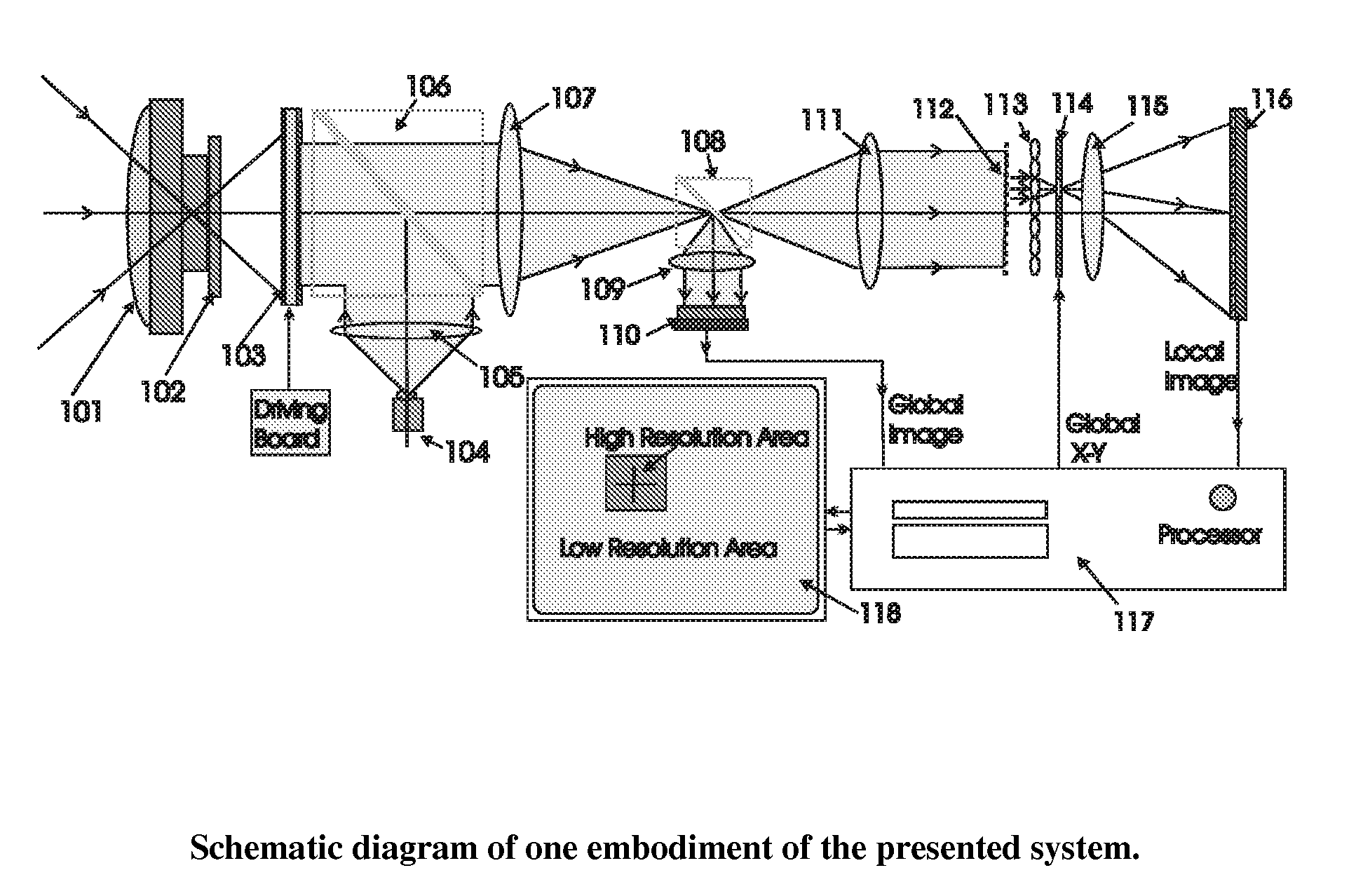
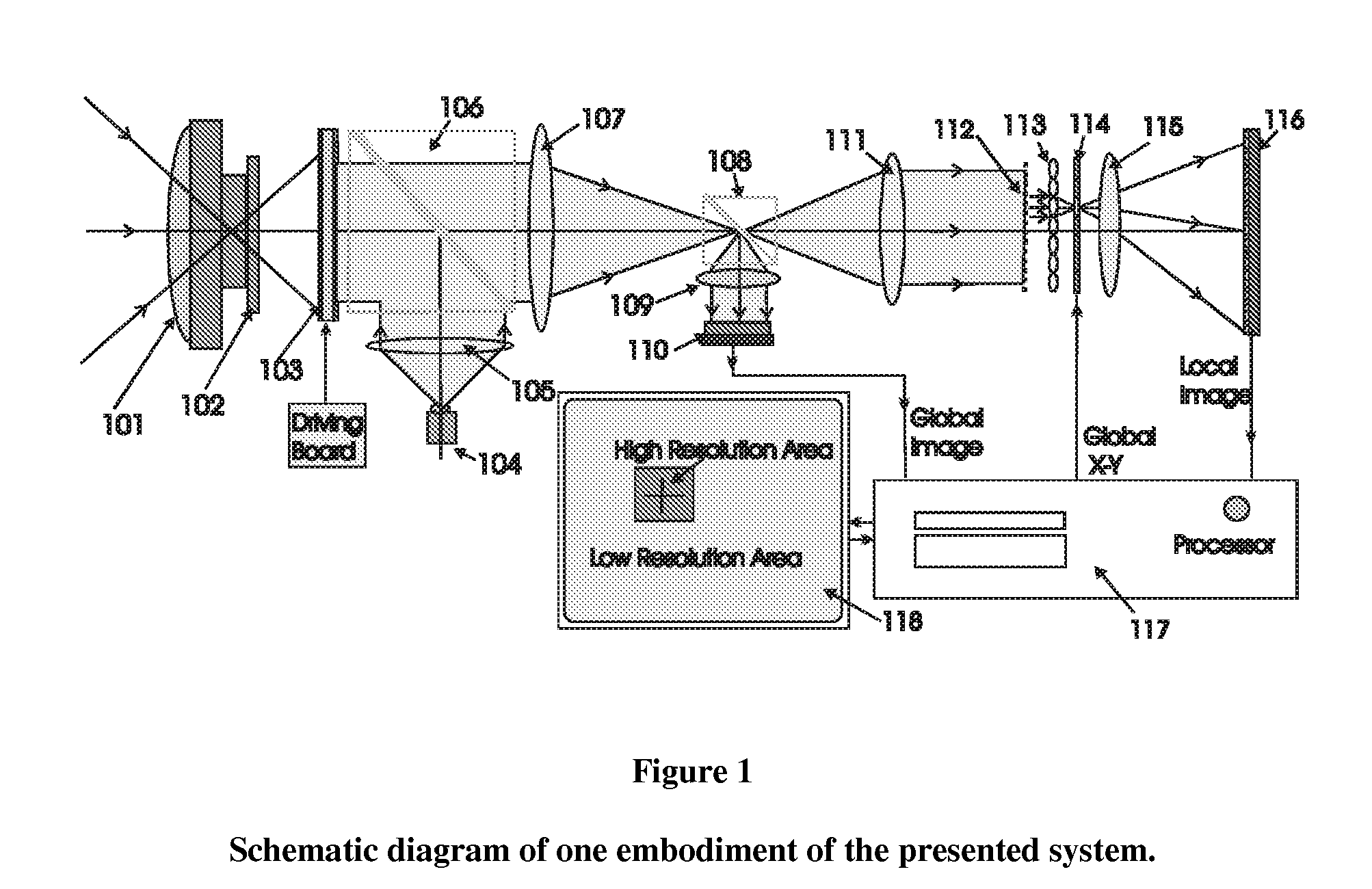
Electro-optical foveated imaging and tracking system
InactiveUS7973834B2Improve spatial resolutionWide field-of-viewTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayHigh resolution image
Conventional electro-optical imaging systems can not achieve wide field of view (FOV) and high spatial resolution imaging simultaneously due to format size limitations of image sensor arrays. To implement wide field of regard imaging with high resolution, mechanical scanning mechanisms are typically used. Still, sensor data processing and communication speed is constrained due to large amount of data if large format image sensor arrays are used. This invention describes an electro-optical imaging system that achieves wide FOV global imaging for suspect object detection and local high resolution for object recognition and tracking. It mimics foveated imaging property of human eyes. There is no mechanical scanning for changing the region of interest (ROI). Two relatively small format image sensor arrays are used to respectively acquire global low resolution image and local high resolution image. The ROI is detected and located by analysis of the global image. A lens array along with an electronically addressed switch array and a magnification lens is used to pick out and magnify the local image. The global image and local image are processed by the processor, and can be fused for display. Three embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
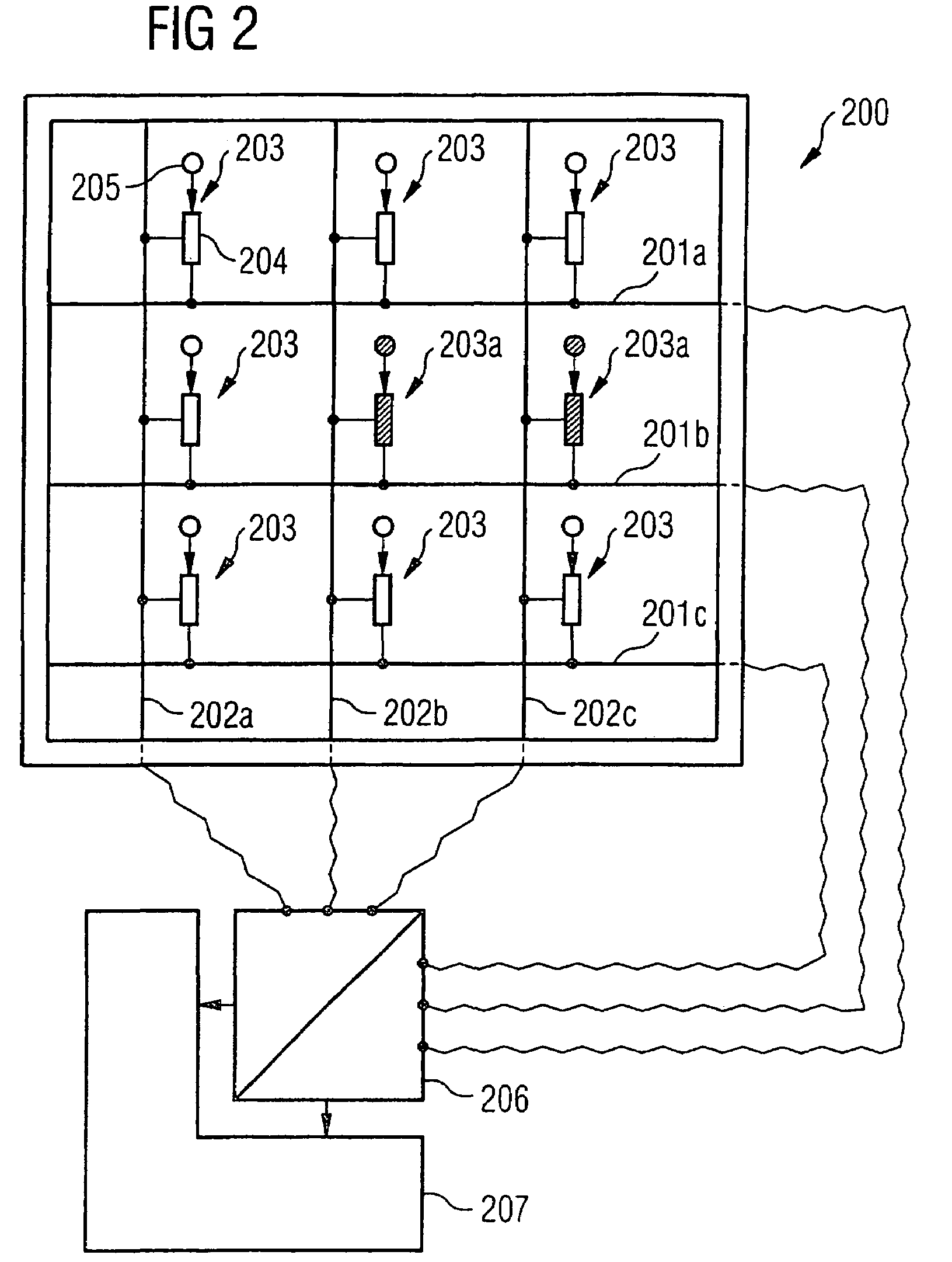
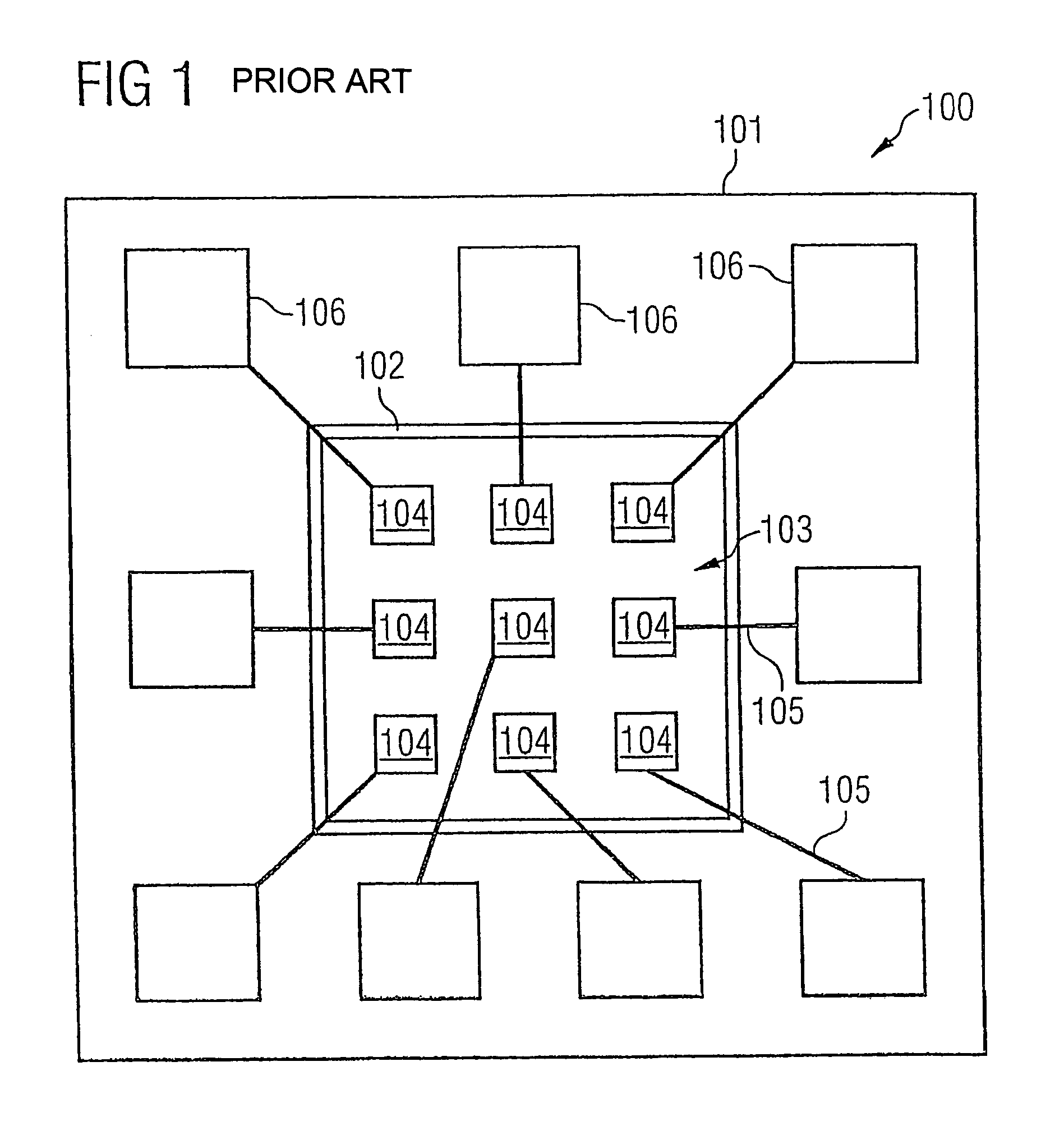
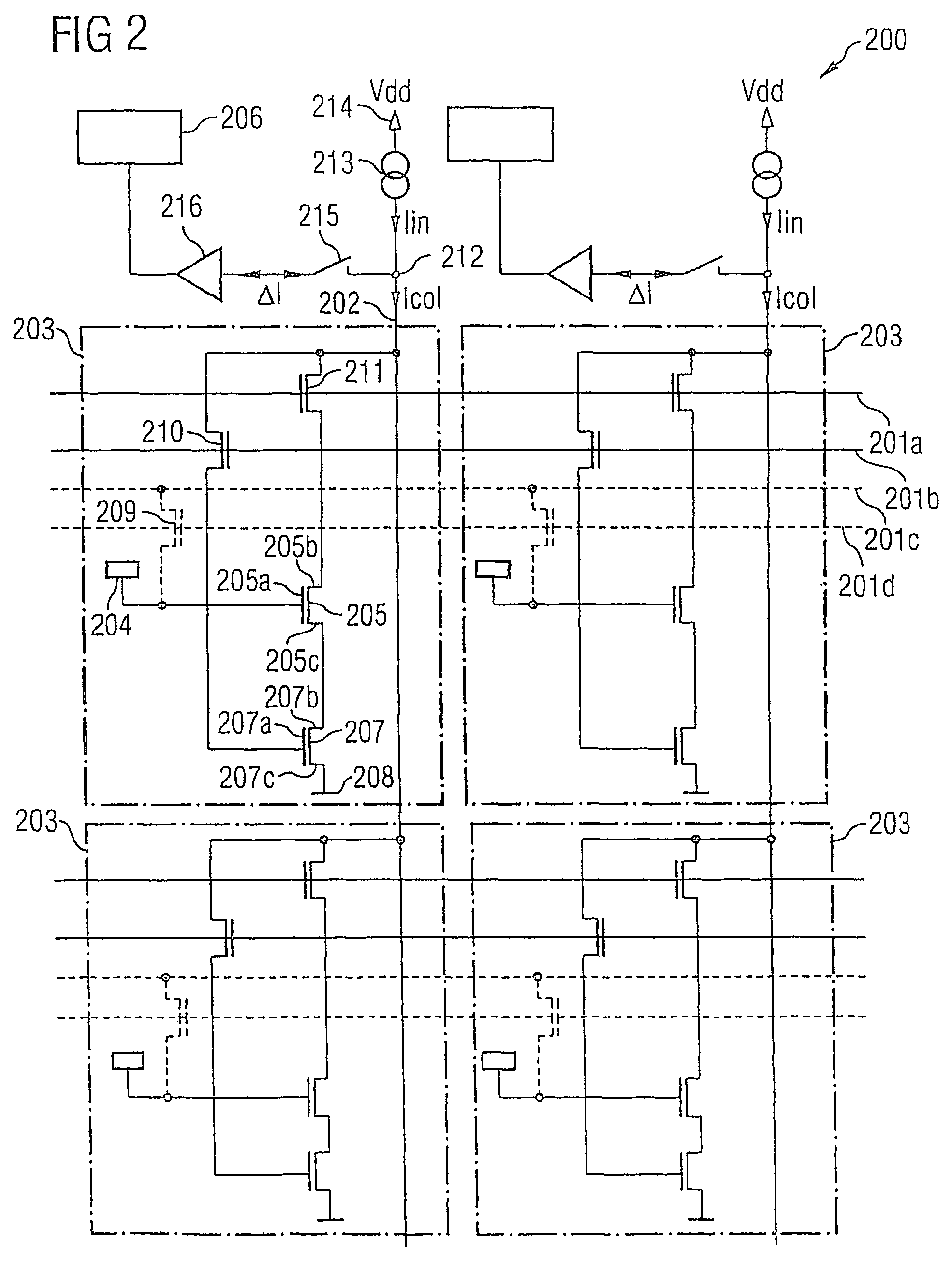
Sensor arrangement
ActiveUS7470352B2Reduced dimensionImprove read rateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSensor arrayElectricity
Sensor arrangement having row and column lines arranged in first and second directions, respectively, sensor arrays arranged in crossover regions of the row and column lines, a detector, and a decoding device. The sensor arrays have a coupling device for electrically coupling respective row and column lines, and a sensor element to influence electric current flow through the coupling device. The detector is electrically coupled to a respective end section of at least a portion of the row and column lines, and detects a respective accumulative current flow from the individual electrical current flows provided by the sensor arrays of the respective lines. The decoding device is coupled to the row and column lines, and evaluates at least a portion of the accumulative electric current flows fed to the decoding device via the row and column lines to determine at which of the sensor elements a sensor signal is present.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Biological specimen imaging method and biological specimen imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090086314A1Improve spatial resolutionShort exposure timeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFocal positionField of view
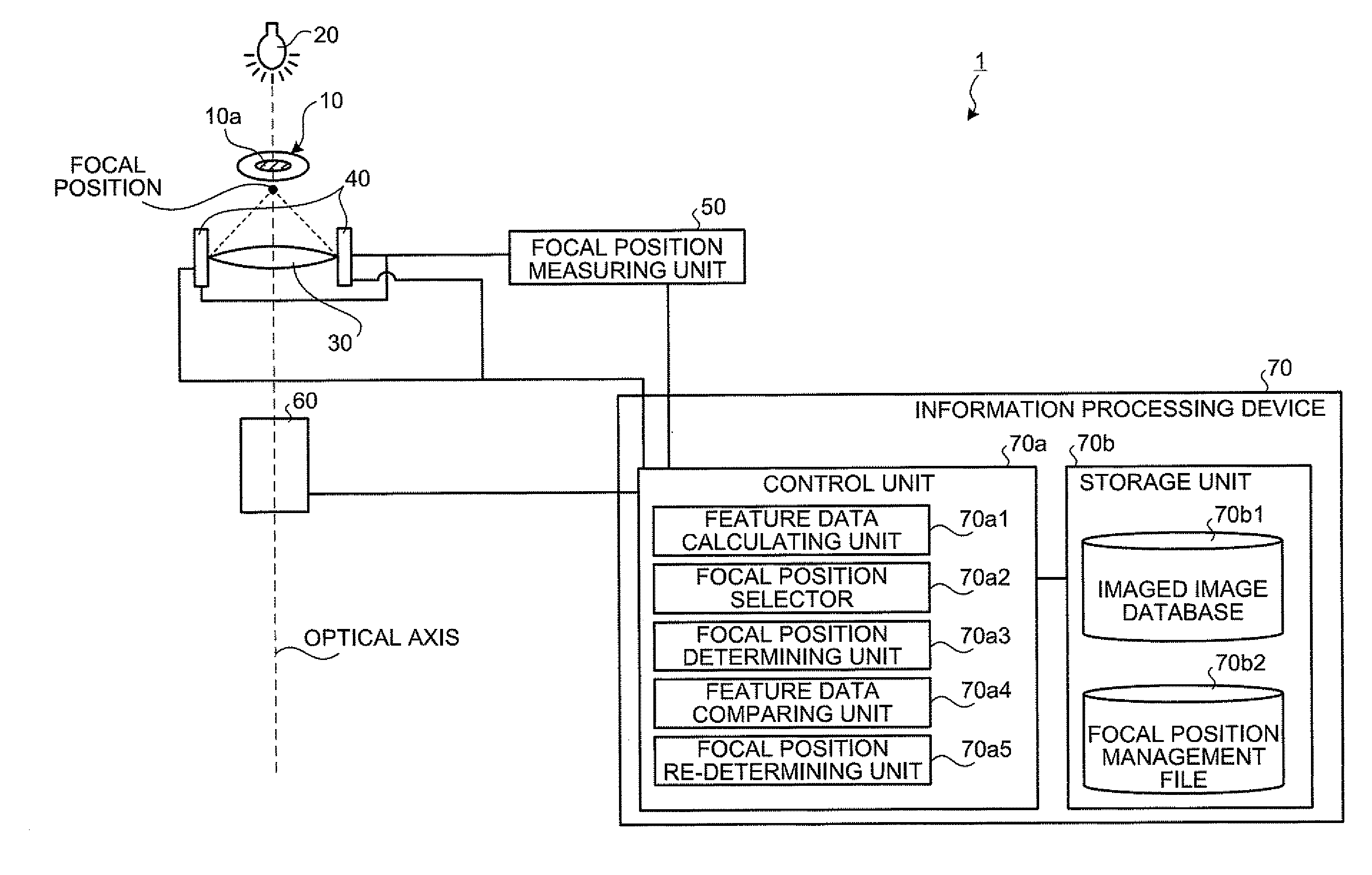
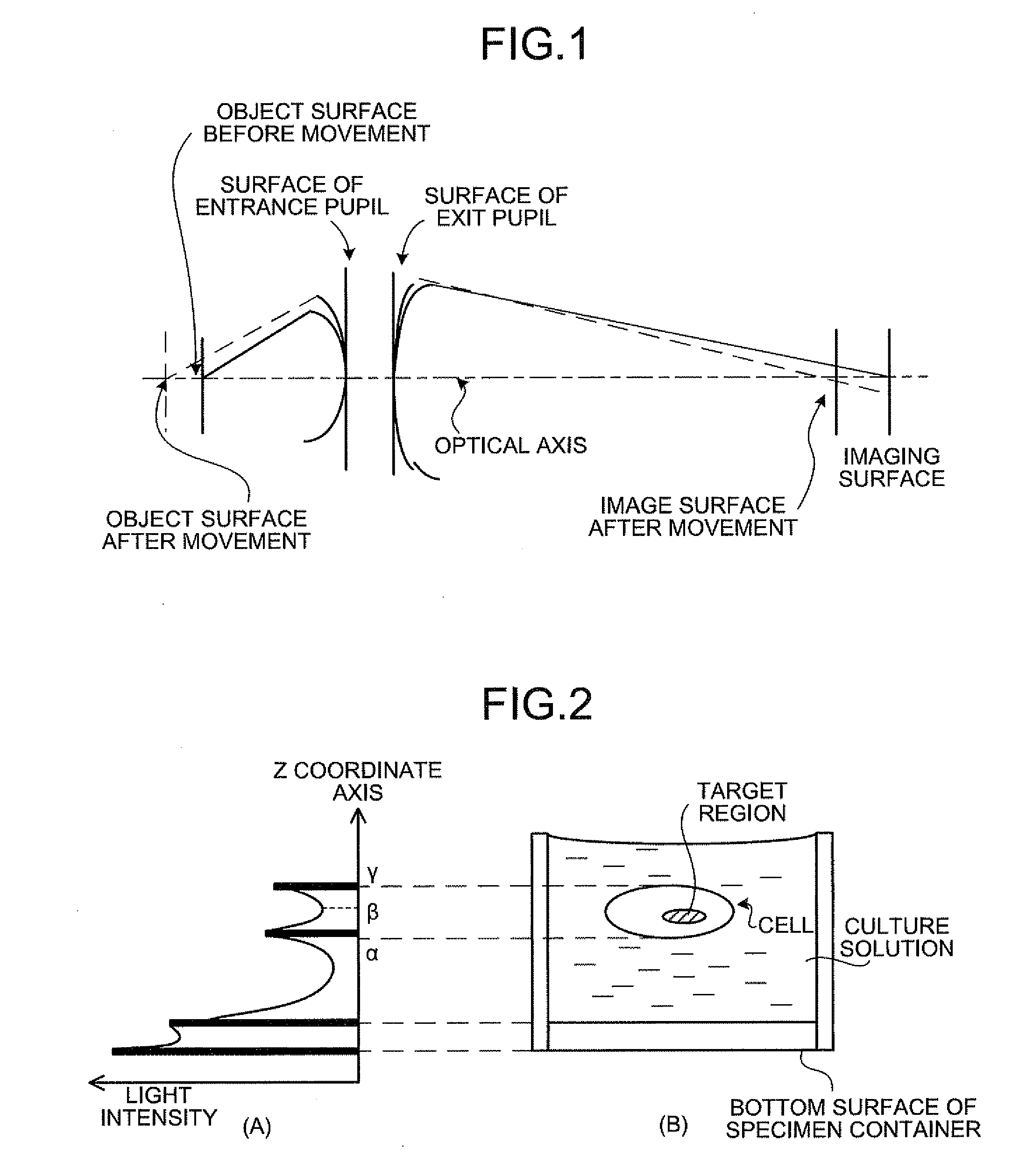
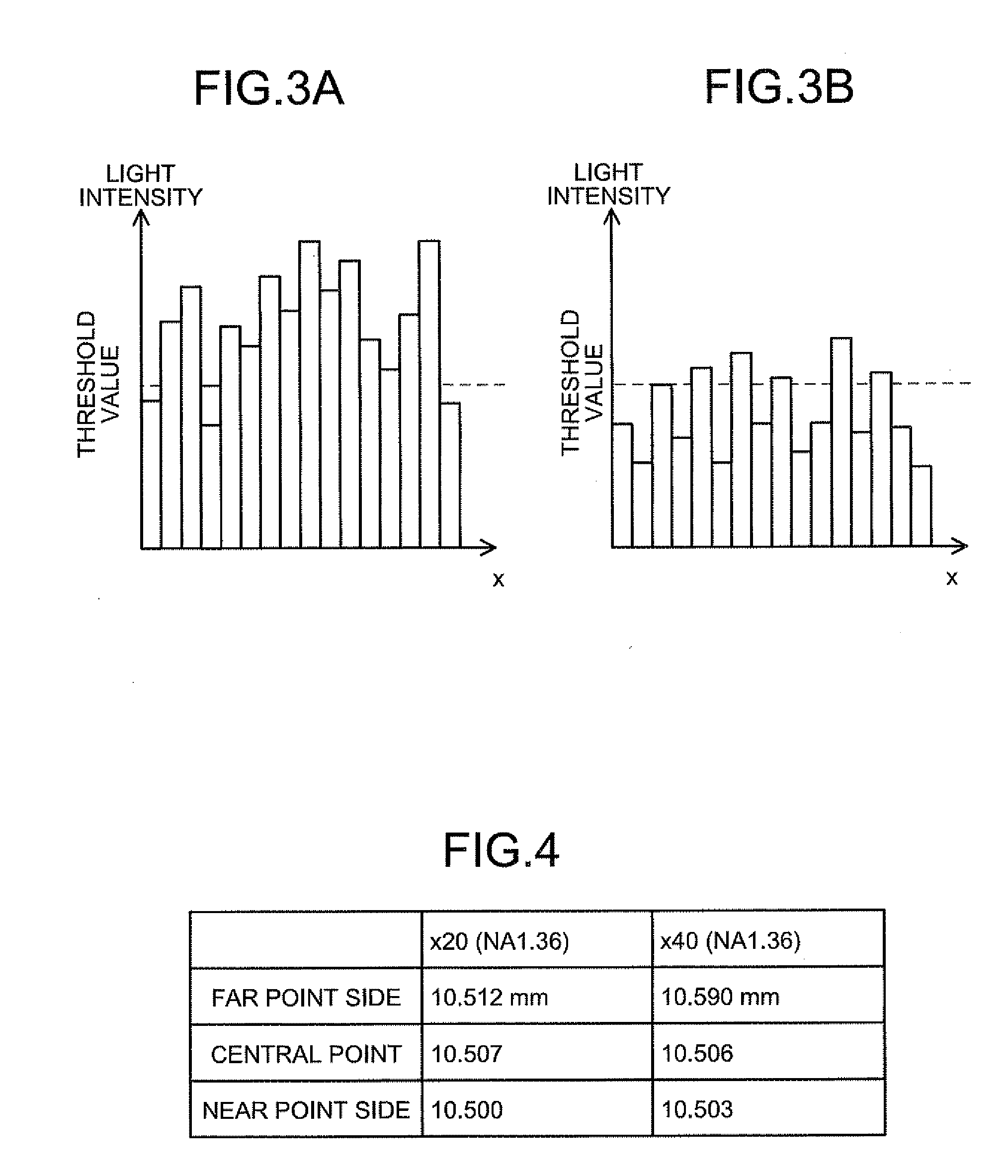
In a biological specimen imaging method, a biological specimen which is stored in a storing section of a substrate having plural storing sections and emitting a feeble light is imaged through an objective lens. The biological specimen imaging method includes moving any one of the substrate and the objective lens or both until the desired storing section falls within the field of view of the objective lens, measuring any one of a focal position at a near point and the focal position at a far point of the objective lens or both, determining the focal position of the objective lens focused on an observed target region in the biological specimen stored in the desired storing section based on the measured focal position, and adjusting the focal position of the objective lens to the determined focal position so as to image the biological specimen through the objective lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
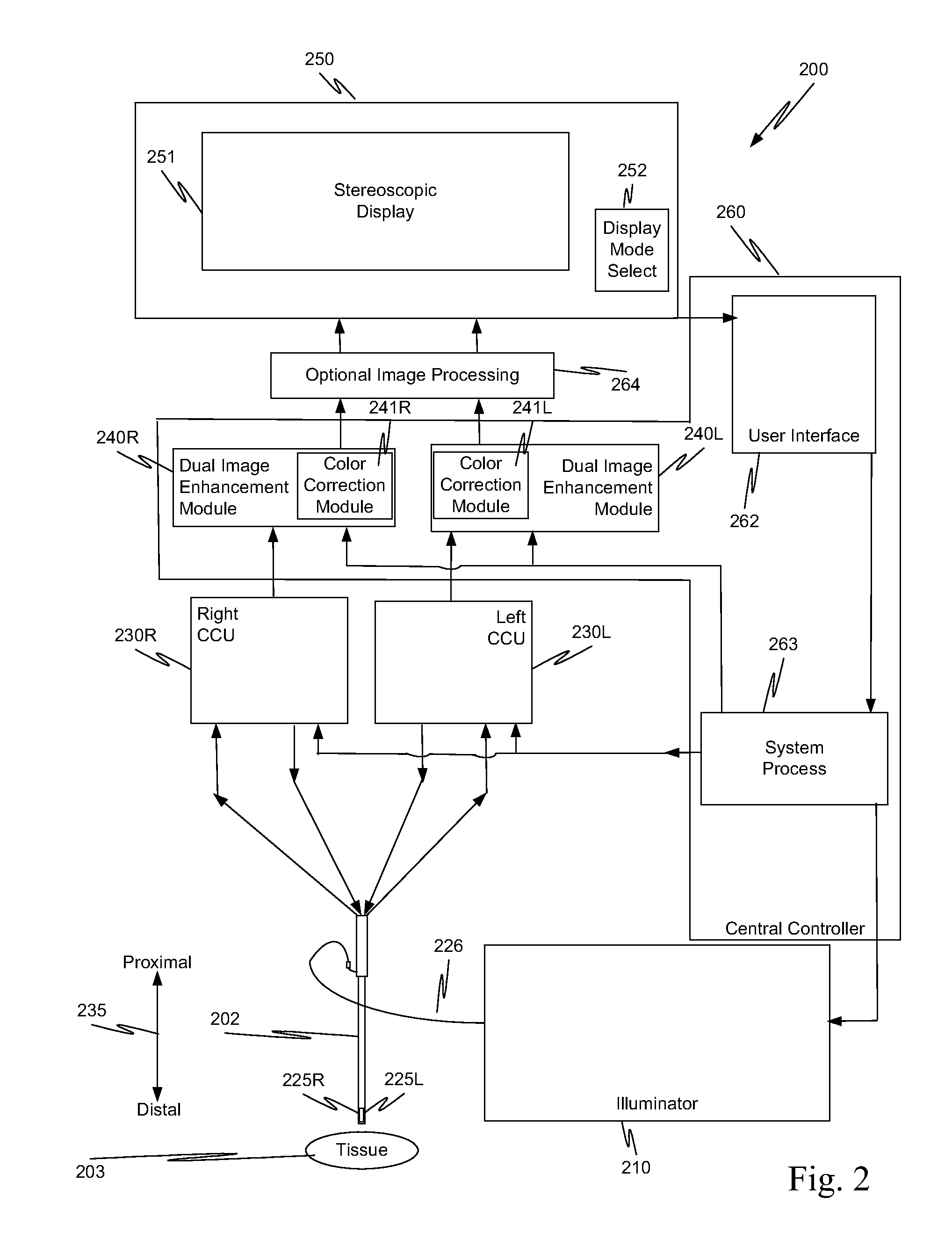
Image capture unit and method with an extended depth of field
ActiveUS20130038689A1Overcomes shortcomingMore capabilityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsBeam splitterImage resolution
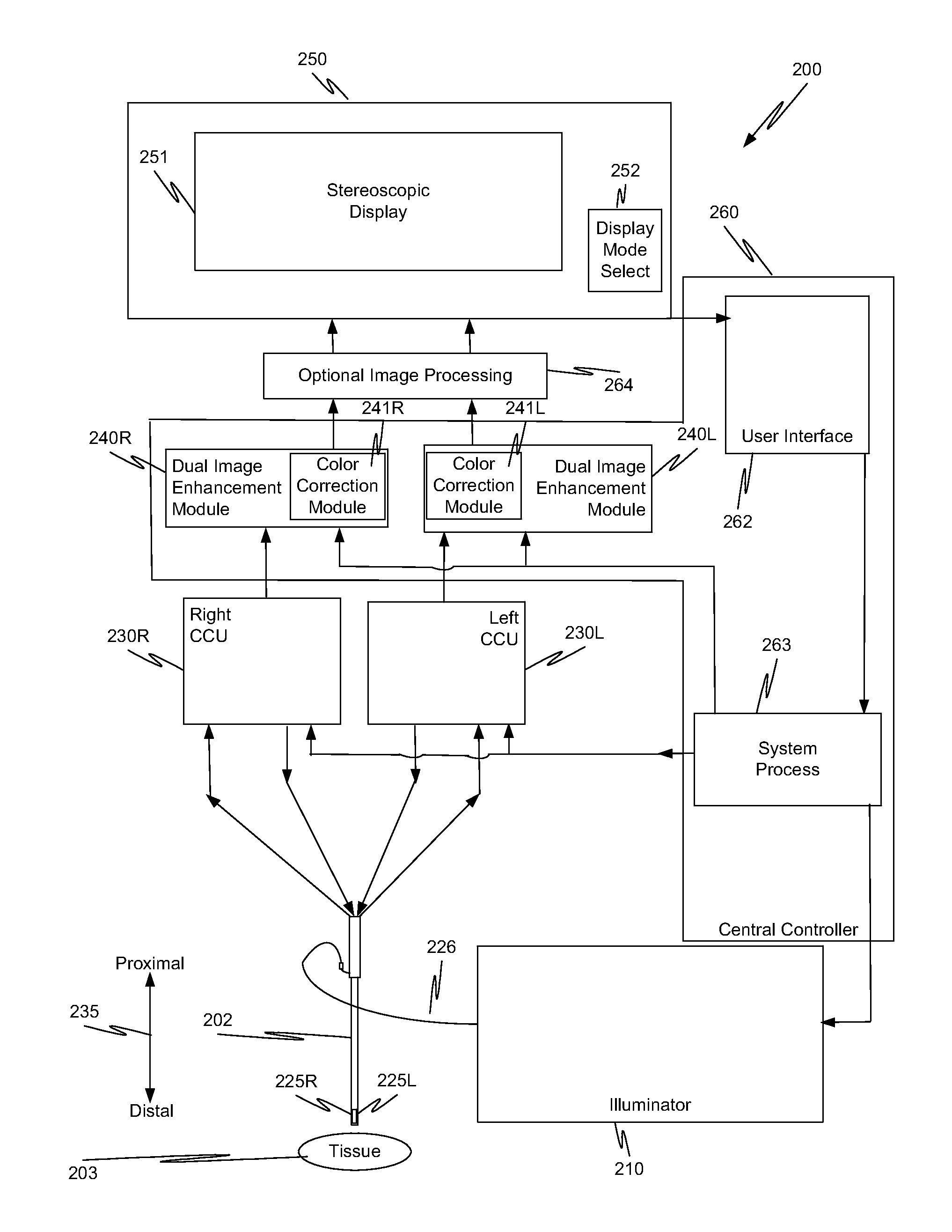
In a minimally invasive surgical system, an image capture unit includes a prism assembly and sensor assembly. The prism assembly includes a beam splitter, while the sensor assembly includes coplanar image capture sensors. Each of the coplanar image capture sensors has a common front end optical structure, e.g., the optical structure distal to the image capture unit is the same for each of the sensors. A controller enhances images acquired by the coplanar image capture sensors. The enhanced images may include (a) visible images with enhanced feature definition, in which a particular feature in the scene is emphasized to the operator of minimally invasive surgical system; (b) images having increased image apparent resolution; (c) images having increased dynamic range; (d) images displayed in a way based on a pixel color component vector having three or more color components; and (e) images having extended depth of field.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Wafer inspection system for distinguishing pits and particles
InactiveUS6118525AEasy to classifyEasy to identifySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInvestigating moving sheetsLight beamSilicon
A surface inspection system and method is provided which detects defects such as particles or pits on the surface of a workpiece, such as a silicon wafer, and also distinguishes between pit defects and particle defects. The surface inspection system comprises an inspection station for receiving a workpiece and a scanner positioned and arranged to scan a surface of the workpiece at the inspection station. The scanner includes a light source arranged to project a beam of P-polarized light and a scanner positioned to scan the P-polarized light beam across the surface of the workpiece. The system further provides for detecting differences in the angular distribution of the light scattered from the workpiece and for distinguishing particle defects from pit defects based upon these differences.
Owner:ADE OPTICAL SYST
Dual-Purpose Lasso Catheter with Irrigation
ActiveUS20100168548A1Electrical resistance is minimizedDrag minimizationElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical connectionDual purpose
Cardiac catheters, including a lasso catheter, are provided for use in a system for electrical mapping of the heart has an array of raised, perforated electrodes, which are in fluid communication with an irrigating lumen. There are position sensors on a distal loop section and on a proximal base section of the catheter. The electrodes are sensing electrodes that may be adapted for pacing or ablation. The raised electrodes securely contact cardiac tissue, forming electrical connections having little resistance.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
System and method for monitoring photodynamic therapy
InactiveUS20080221647A1High electromagnetic contrastHighly sensitive detection and monitoringSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotodynamic therapyUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for monitoring photodynamic therapy of a target tissue, where the target tissue contains a photosensitizing substance, include a first light source configured to deliver light to the target tissue, the first light source having a wavelength capable of exciting the photosensitizing substance. An ultrasonic transducer receives photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of light energy by the target tissue, and a control unit in communication with the ultrasonic transducer reconstructs photoacoustic tomographic images from the received photoacoustic signals to provide an indication of optical energy deposition due to the photosensitizing substance in the target tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Miniaturized terahertz radiation source
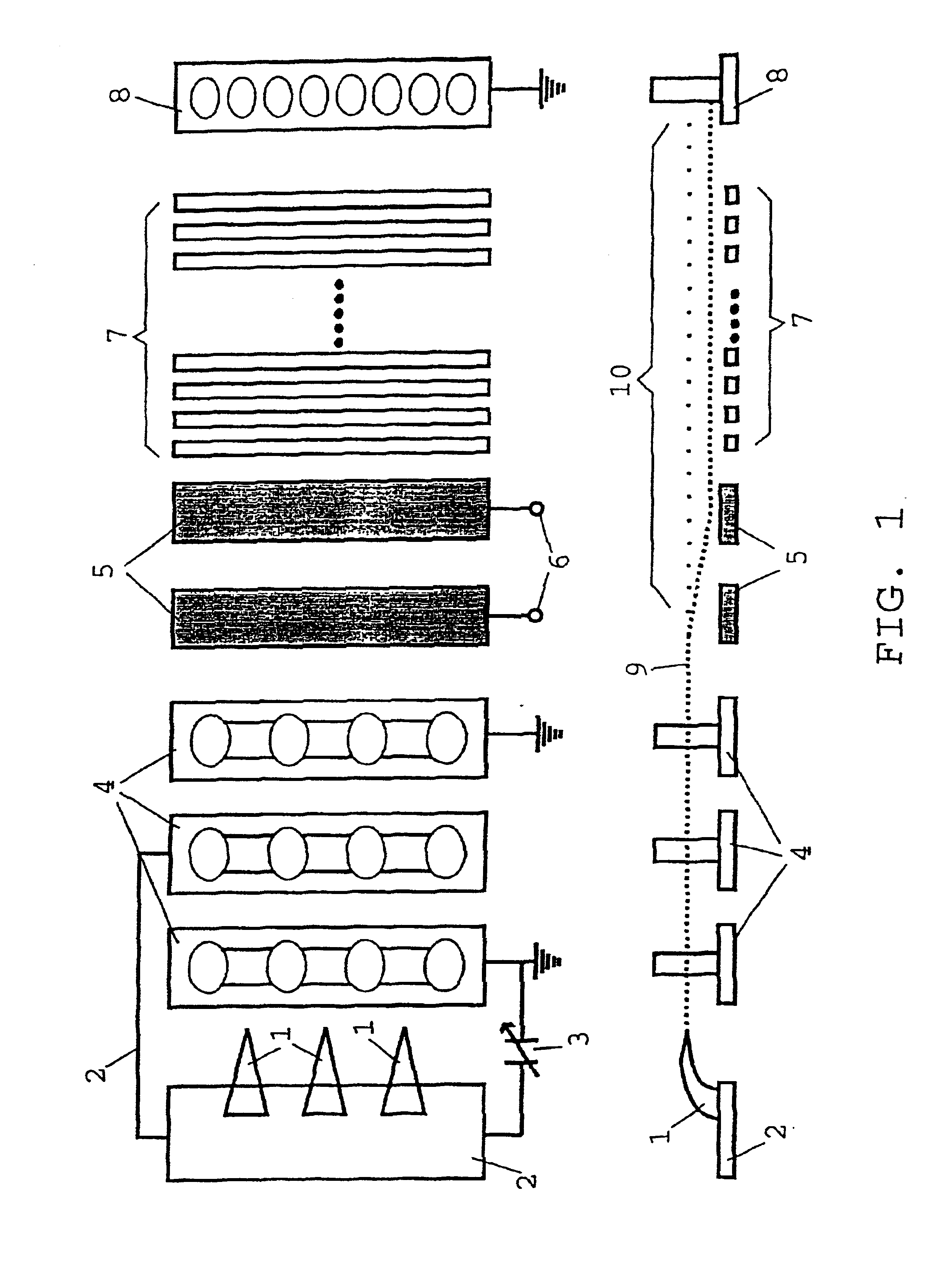
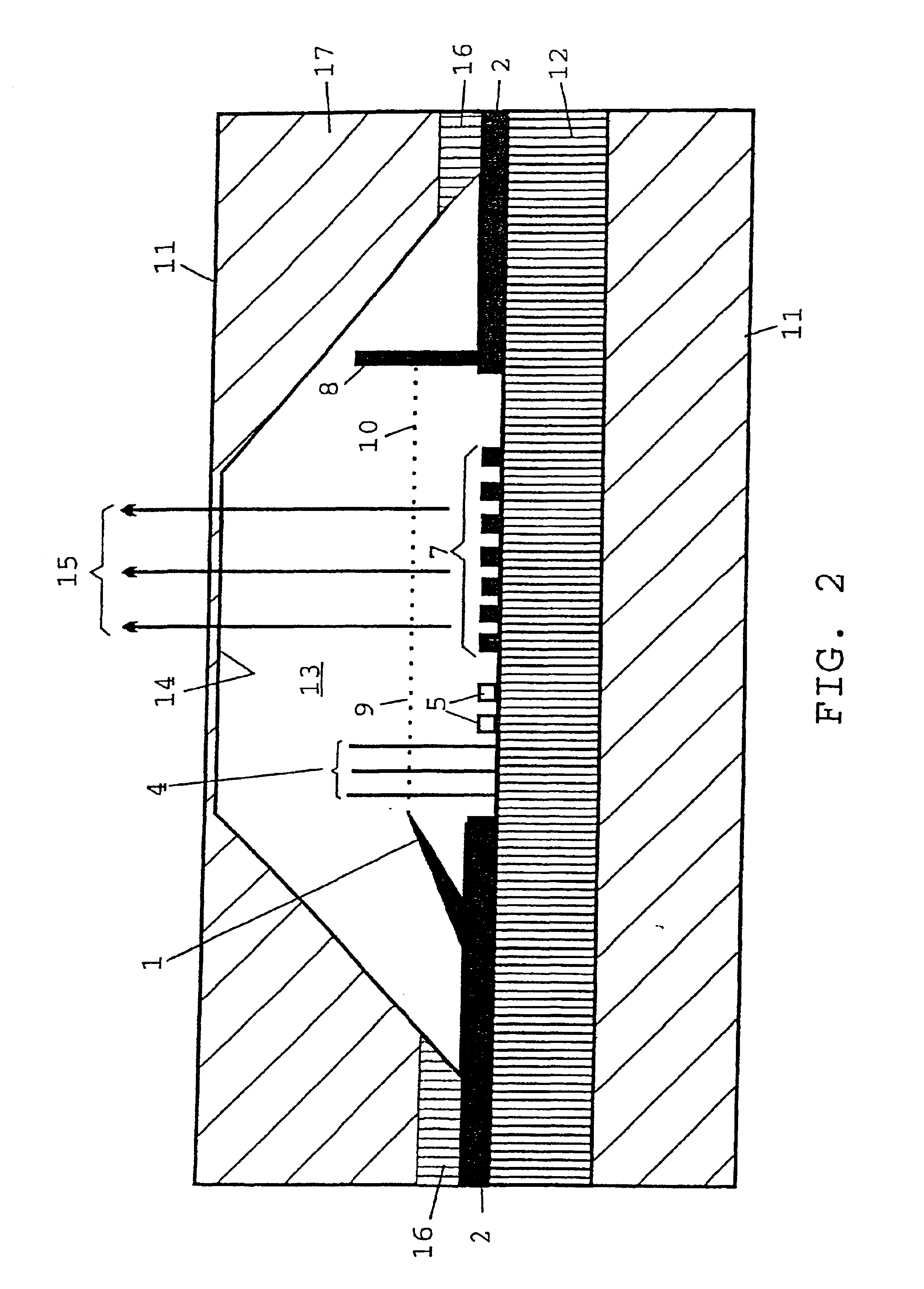
InactiveUS6909104B1High spatial resolutionHighly coherentLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusPhysicsElectrostatic lens
A miniaturized terahertz radiation source based on the Smith-Purcell effect is provided, in which, from a focused electron source, a high-energy bundle of electrons is transmitted at a defined distance over a reflection diffraction grating composed of transversely disposed grating rods, so that, in response to oscillating image charges, electromagnetic waves of one wavelength are emitted, the wavelength being adjustable as a function of the periodicity of the lines and of the electron velocity. The elements of the radiation source, such as field emitter (1), electrostatic lens (4), beam deflector (5), grating (7) of metal, and a second anode (8), are integrated on a semiconductor chip using additive nanolithographic methods. The field electron source is constructed to project, as a wire, out of the surface, using additive nanolithography, and is made of readily conductive material having stabilizing series resistance. The wire is constructed, using computer-controlled deposition lithography, in a straight or curved, free-standing design. In its surface area, the base material bears a conductor structure for the electrical terminals and connections (2), including controllable voltage sources (3) for supplying the field emitter tips (1), lens (4), and control electrodes (5, 8). The terahertz radiation source is designed to be a powerful component that is available in modular form and is usable in any spatial situation.
Owner:NAWOTEC
Apparatus and method for efficiently increasing the spatial resolution of images
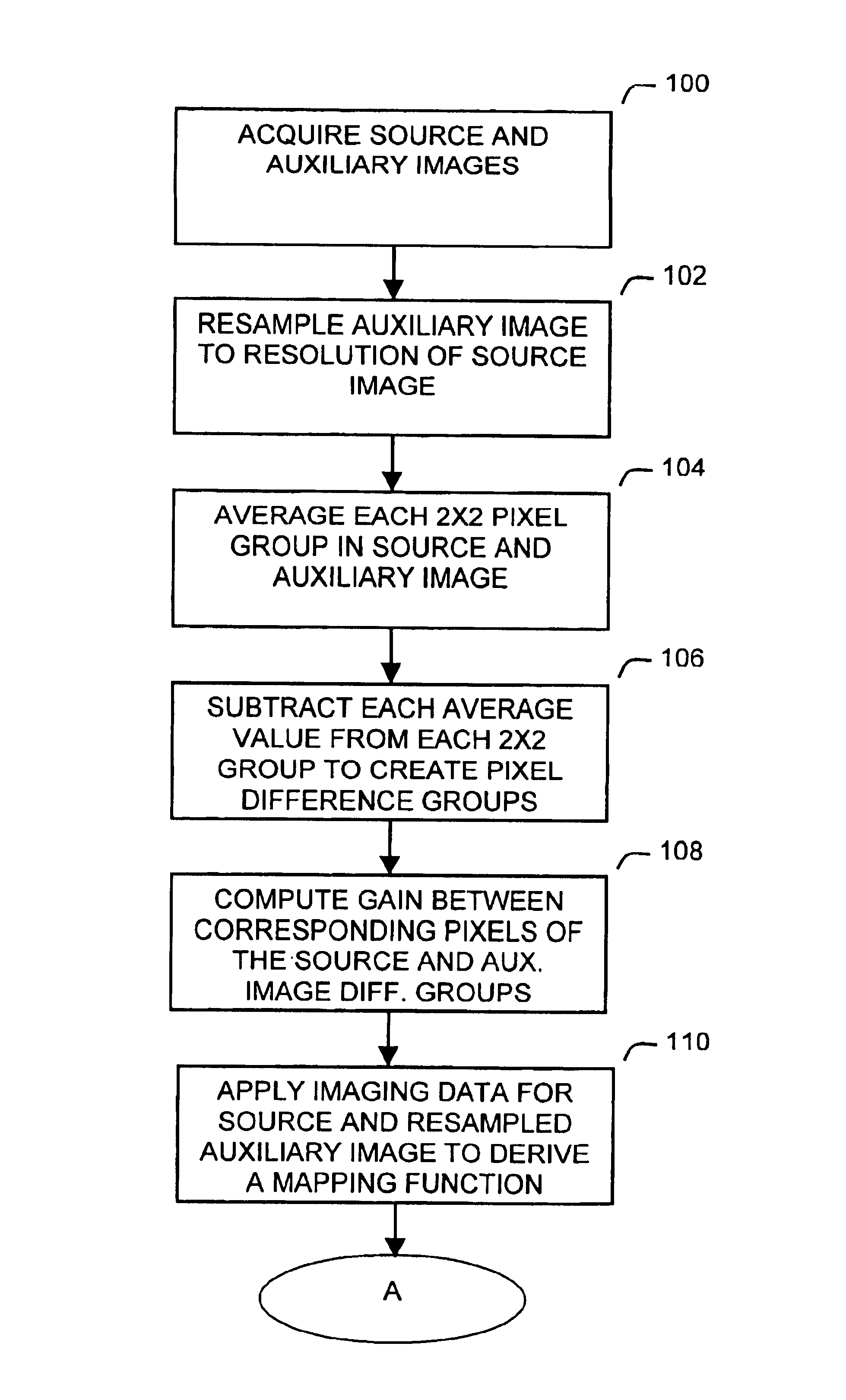
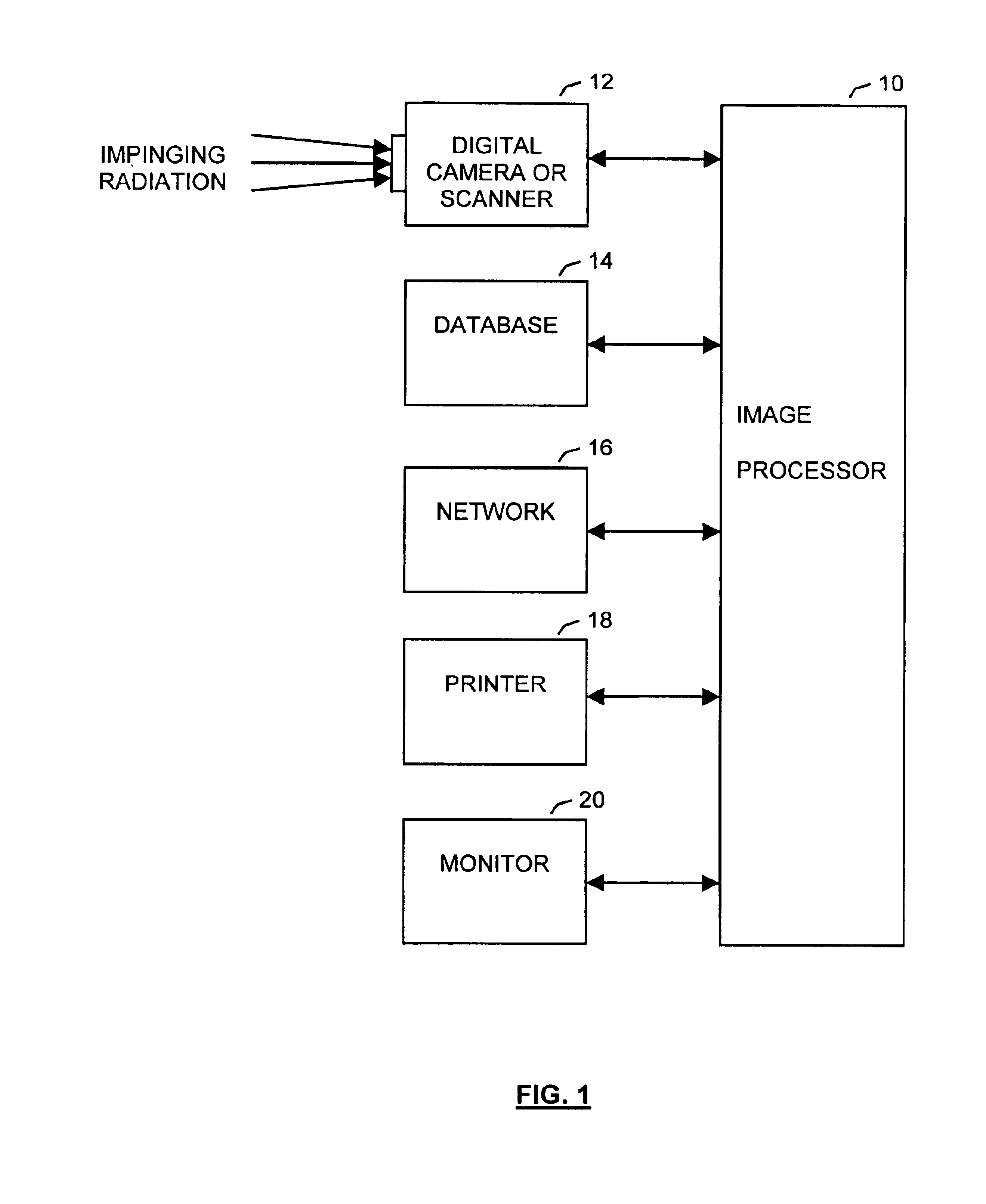
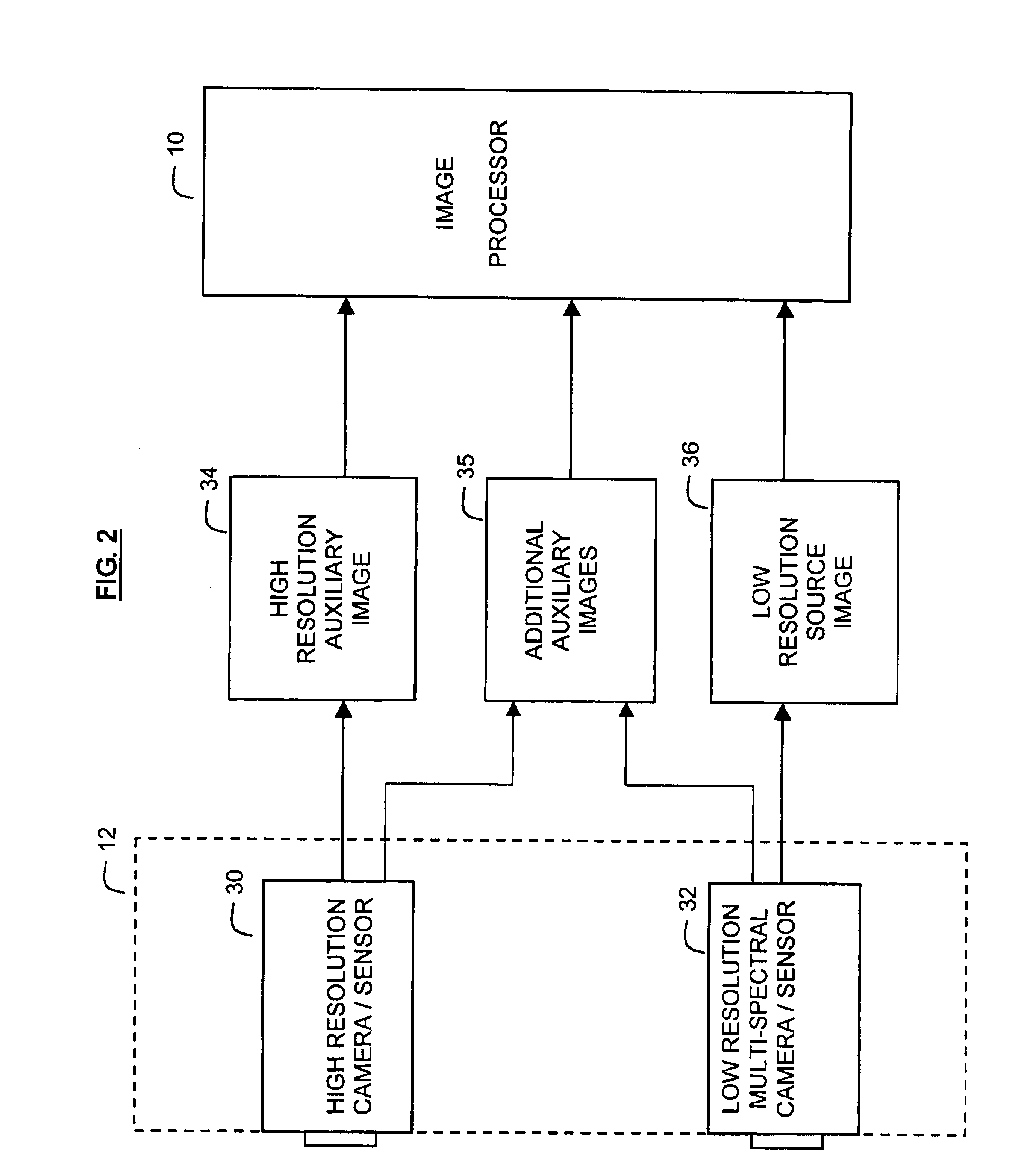
InactiveUS6937774B1Improve spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method increases the spatial resolution of a source image based on an auxiliary, co-registered image of a higher spatial resolution. Each of the source and auxiliary images includes a plurality of pixels with corresponding spectral intensities and the method includes reducing, identifying, deriving, subdividing and modifying steps. Multiple auxiliary images can be used with the method.In the reducing step, a spatial resolution of the auxiliary image is reduced to a common resolution with the source image. Then in the identifying step, corresponding groups of pixels at the common resolution in the source and auxiliary images are identified. Then in the deriving step, a mapping function is derived which relates the rate of change of intensity of each group in the auxiliary image and the corresponding rate of change of intensity in the corresponding group in the source image to the intensity vector. This map can be conditioned on any number of auxiliary image planes.In the subdividing step, each source pixel is subdivided. Then in the modifying step, the spectral intensity of each subdivided source pixel is modifying based on the map and the local intensity variations of the auxiliary image. This results in increasing the resolution of the source image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
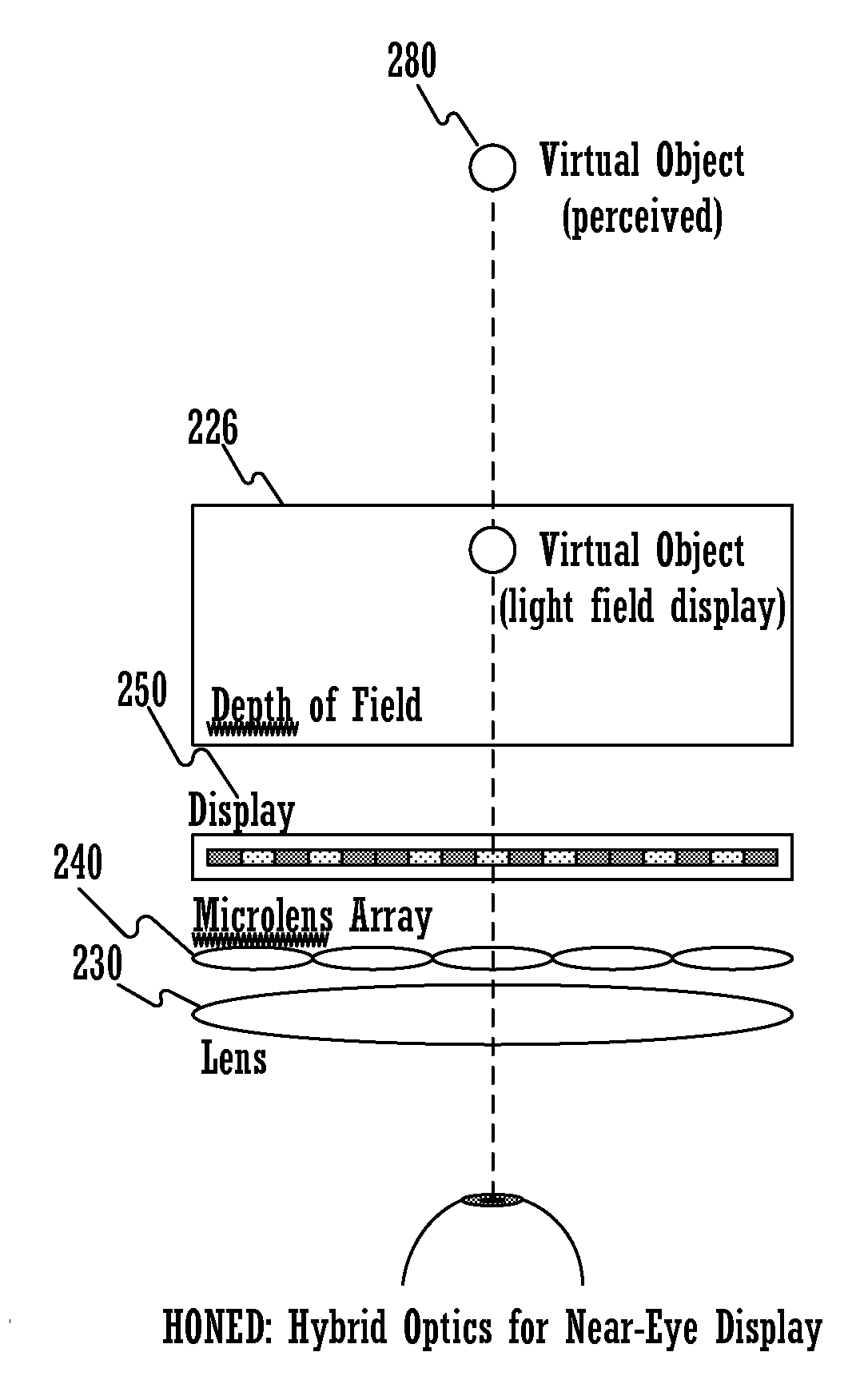
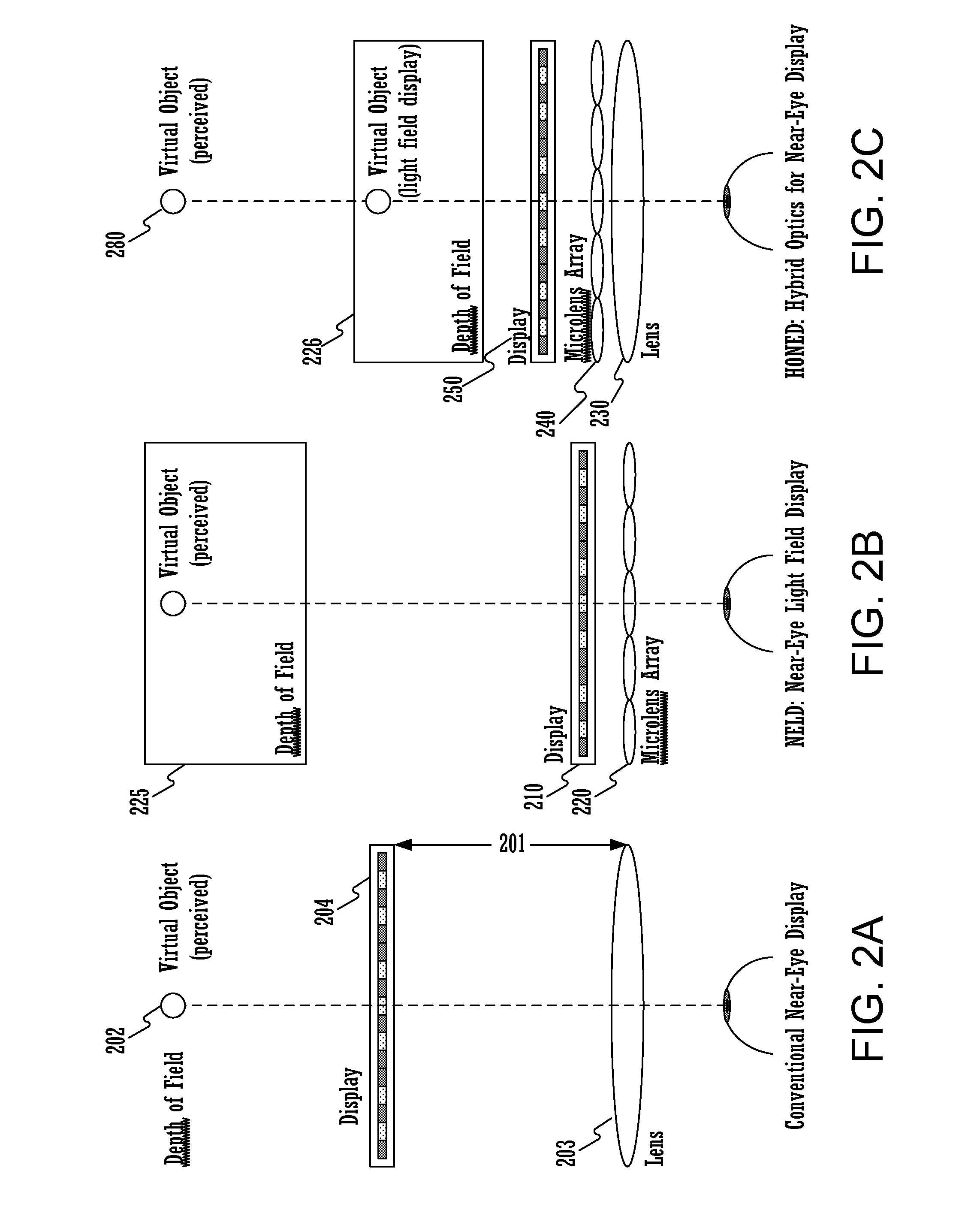
Hybrid optics for near-eye displays
ActiveUS20150049390A1Reduce depthGreat percentageStatic indicating devicesDetails for portable computersImage resolutionDisplay device
A method for displaying a near-eye light field display (NELD) image is disclosed. The method comprises determining a pre-filtered image to be displayed, wherein the pre-filtered image corresponds to a target image. It further comprises displaying the pre-filtered image on a display. Subsequently, it comprises producing a near-eye light field after the pre-filtered image travels through a microlens array adjacent to the display, wherein the near-eye light field is operable to simulate a light field corresponding to the target image. Finally, it comprises altering the near-eye light field using at least one converging lens, wherein the altering allows a user to focus on the target image at an increased depth of field at an increased distance from an eye of the user and wherein the altering increases spatial resolution of said target image.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus for forming an image that shows information about a subject
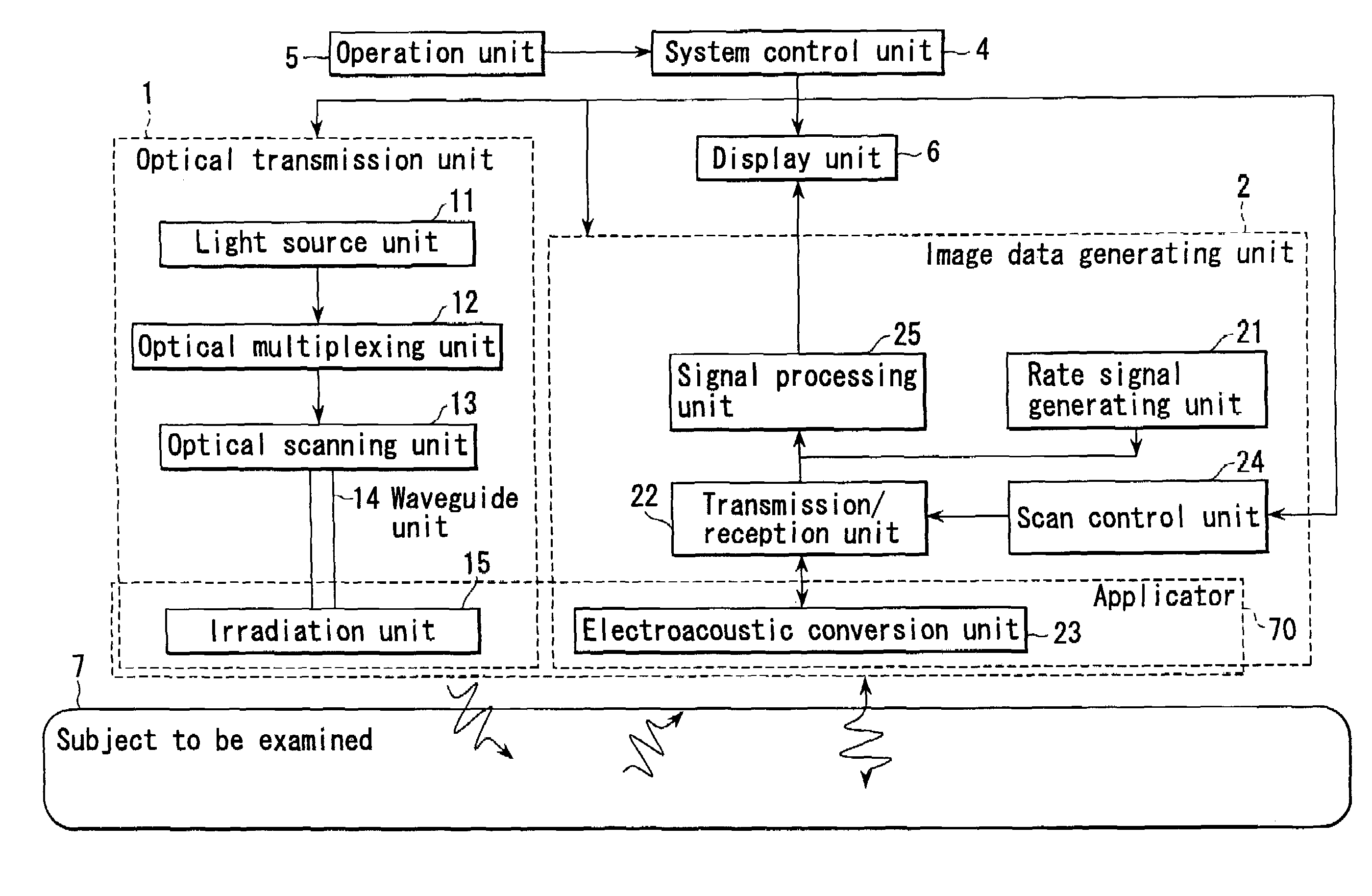
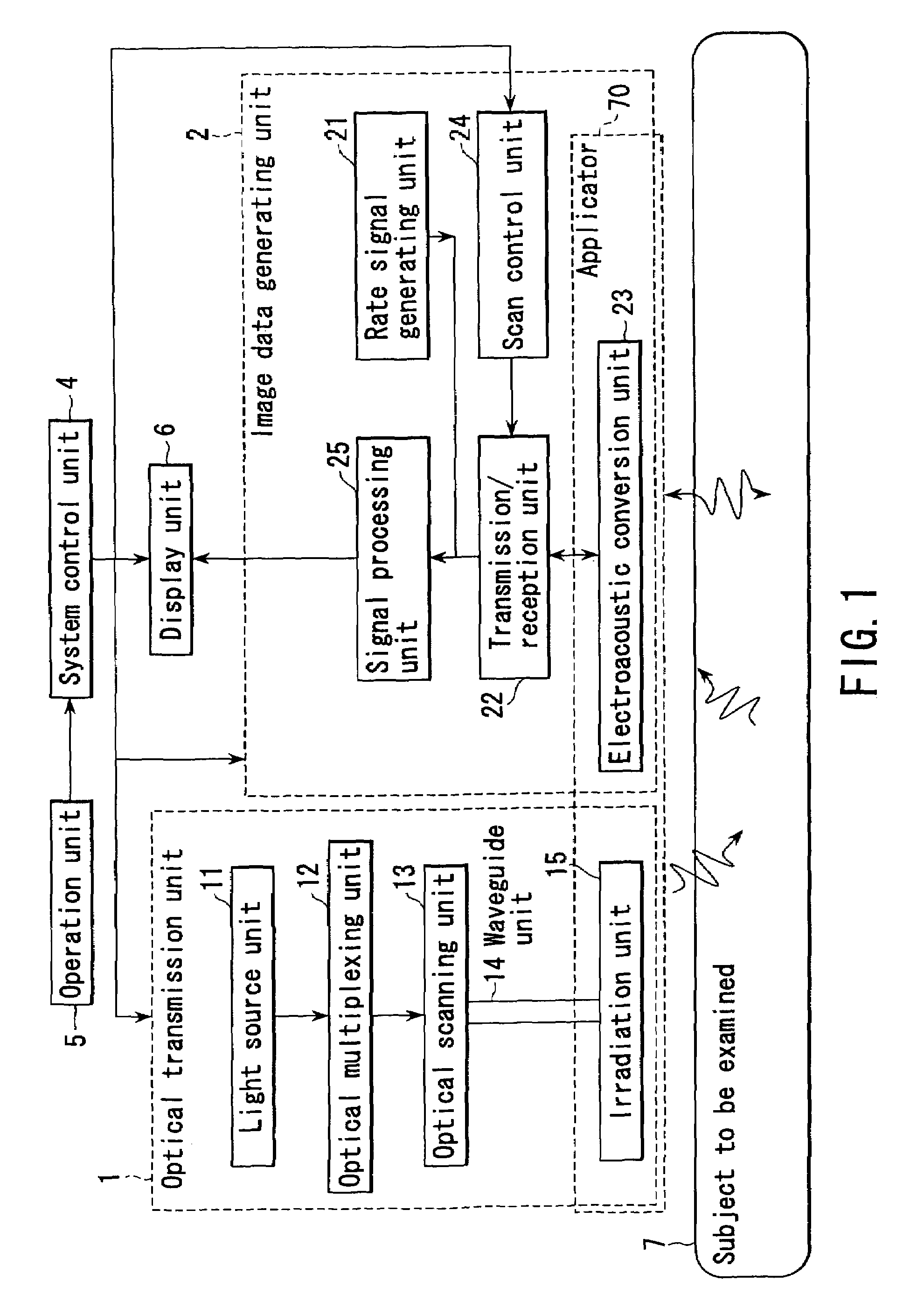
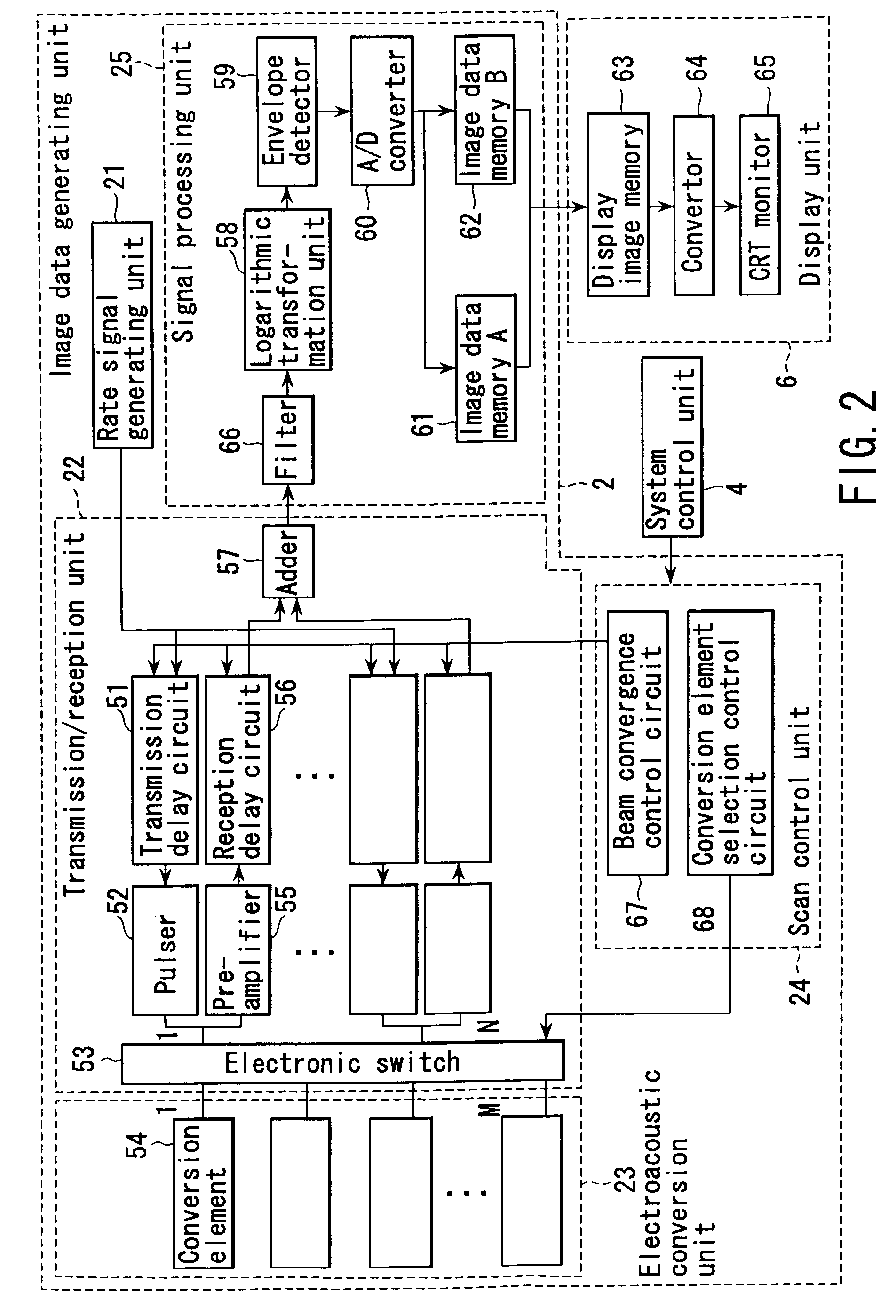
InactiveUS6979292B2Easy to operateImprove spatial resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionElectricitySonification
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
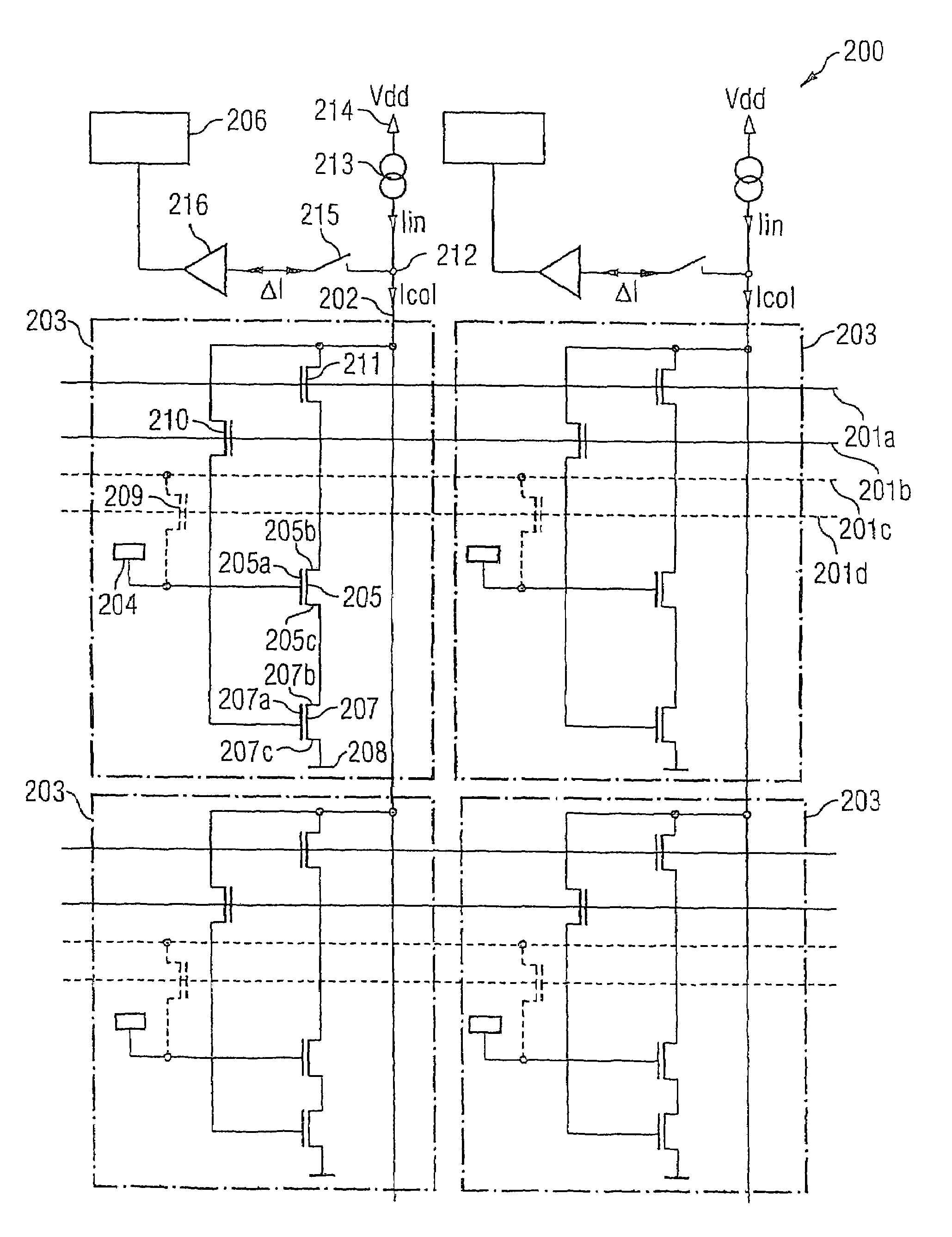
Biosensor circuit and sensor array consisting of a plurality of said biosensor circuits and biosensor array
InactiveUS7019305B2Highly integratedHigh degree of miniaturizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayDevice form
Biosensor circuit arrangement including a substrate, a sensor element formed in or on a surface region of the substrate with a physical parameter, which is coupled to a substance to be examined, the type of coupling having a resistive component, the sensor element having an electrically conductive sensor electrode that is coupled to the substance to be examined, the sensor element having a measuring transistor the gate terminal of which is coupled to the electrically conductive sensor electrode, and the physical parameter being the threshold voltage of the measuring transistor, and a calibration device formed in or on the substrate, the calibration device being set up such that it is used to at least partly compensate for an alteration of the value of the physical parameter of the sensor element.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com