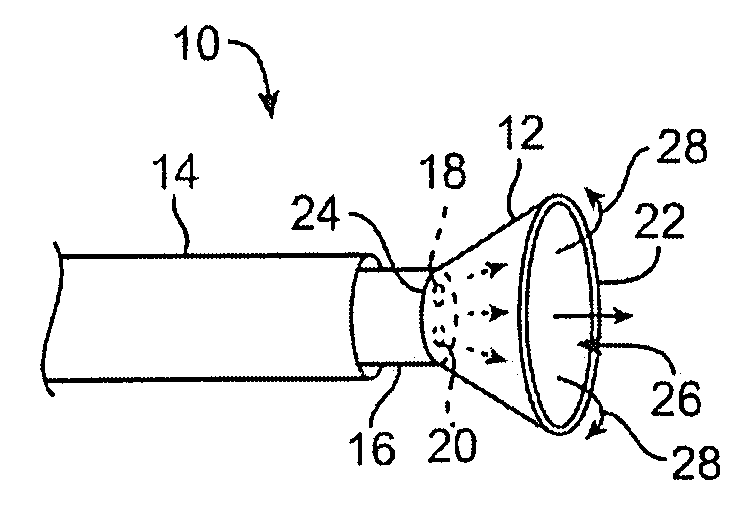
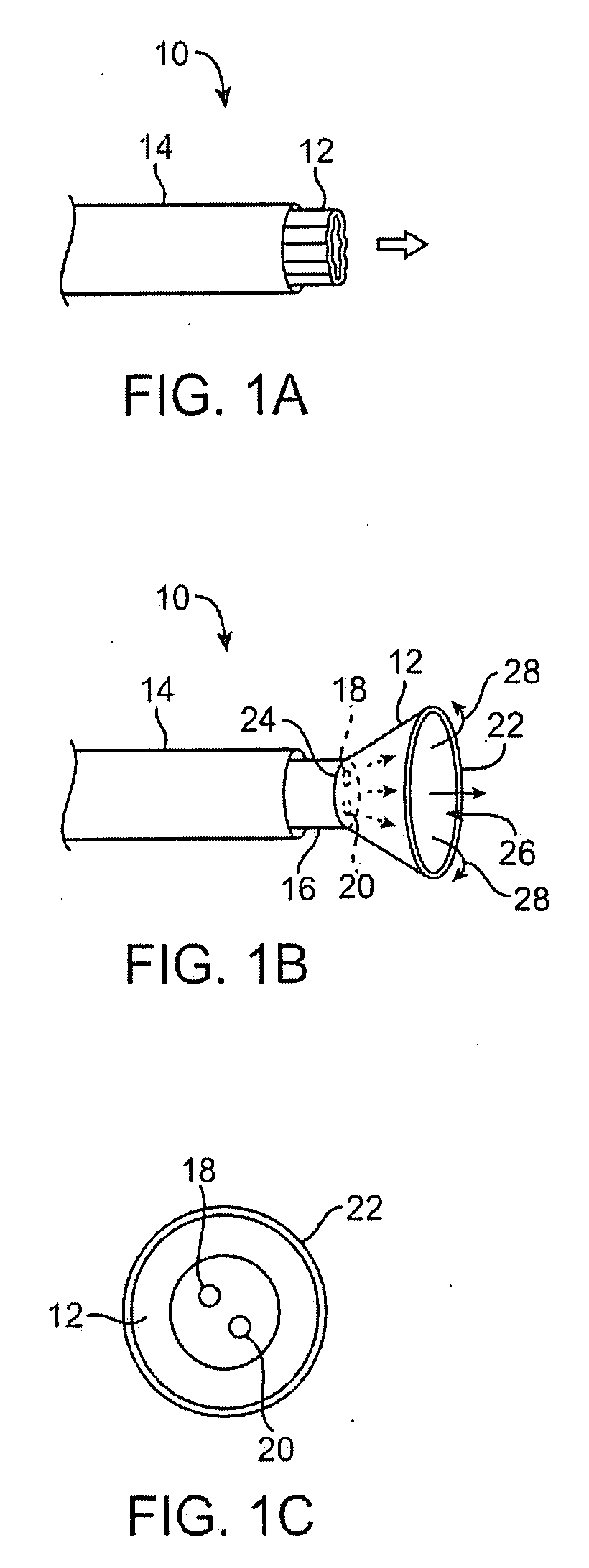
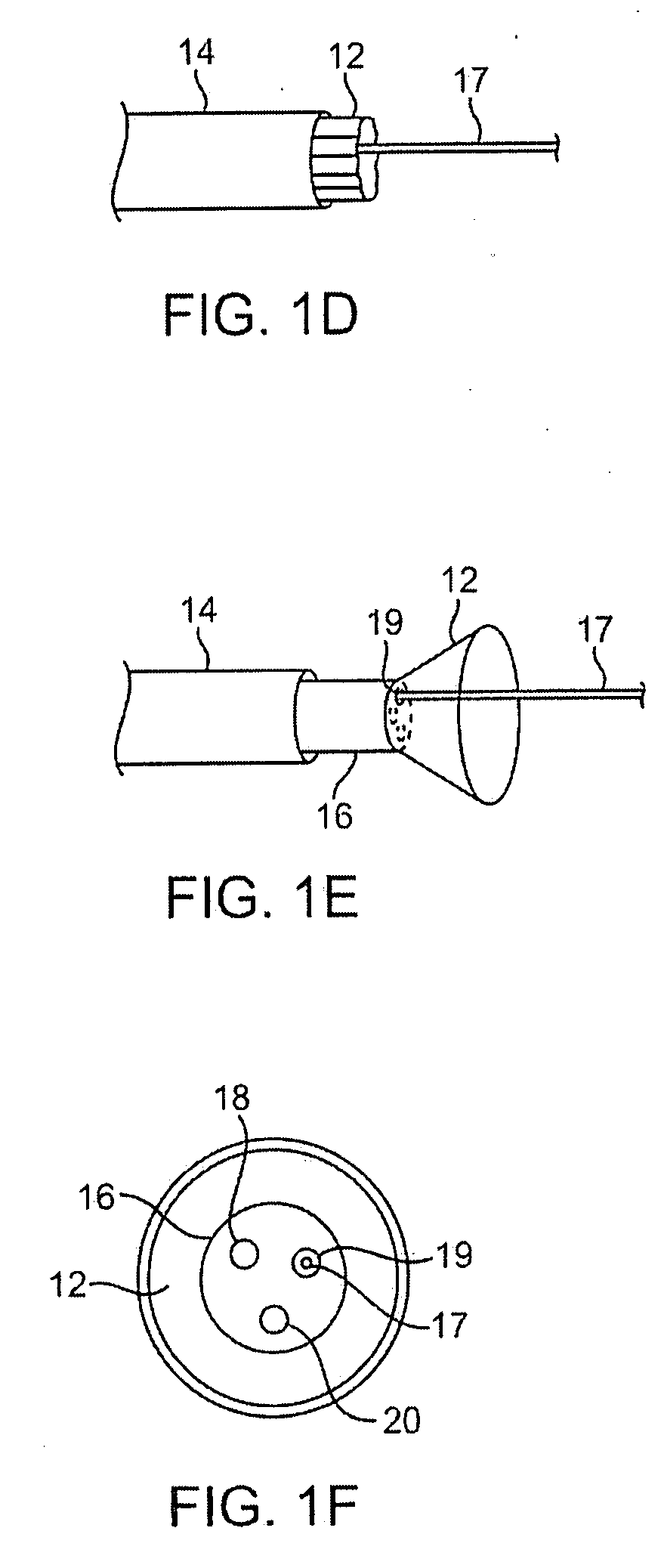
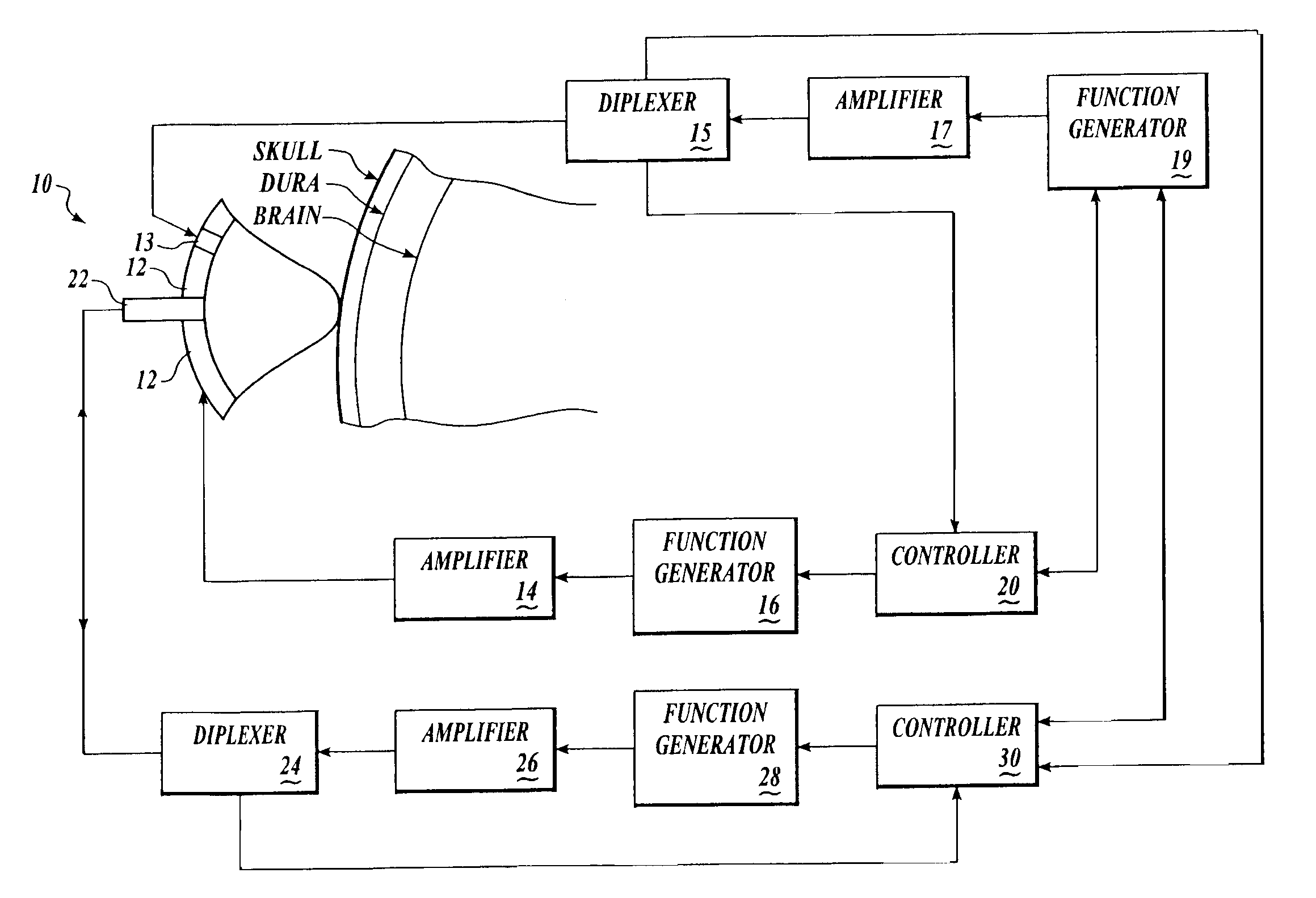
Patents
Literature
419 results about "Infarction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as an infarct (from the Latin infarctus, "stuffed into").
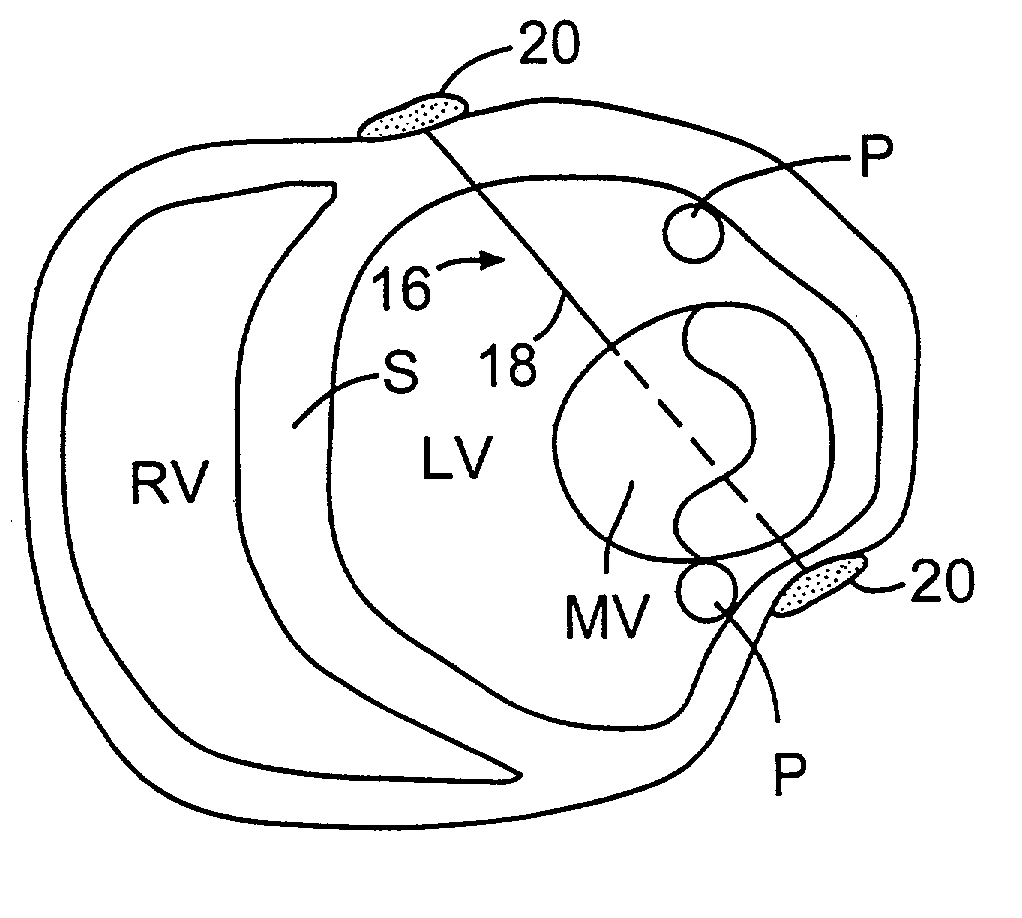
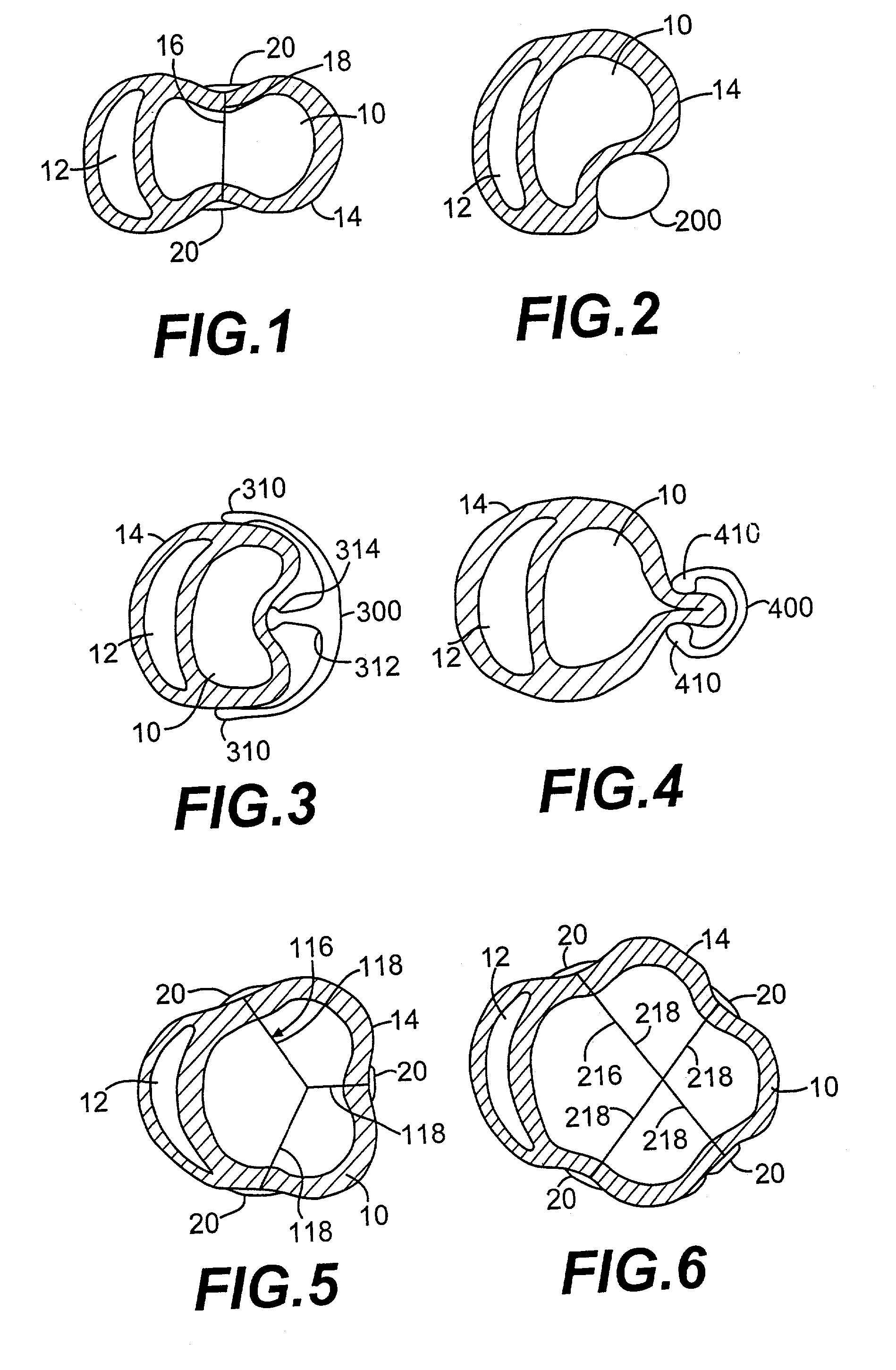
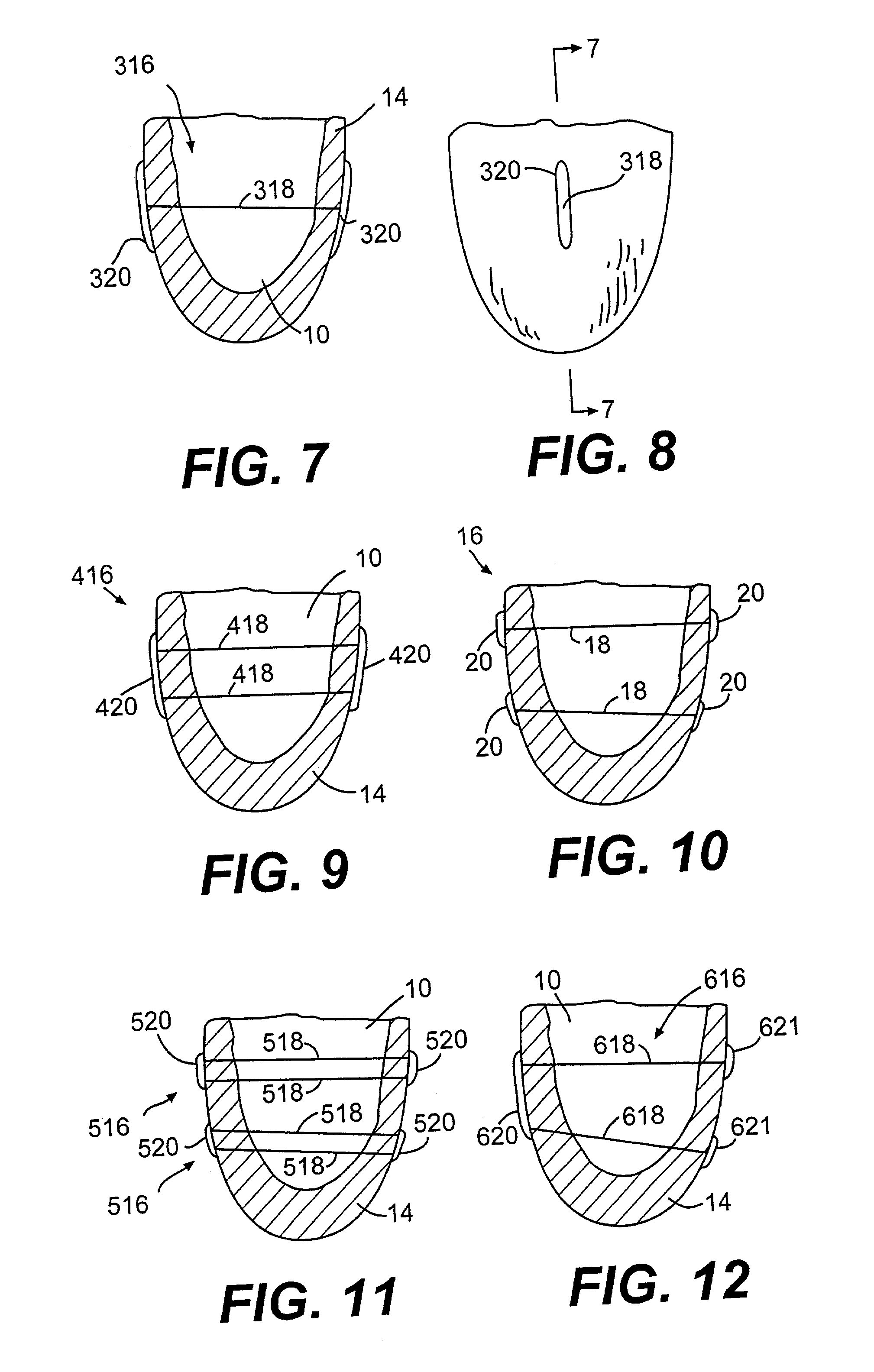
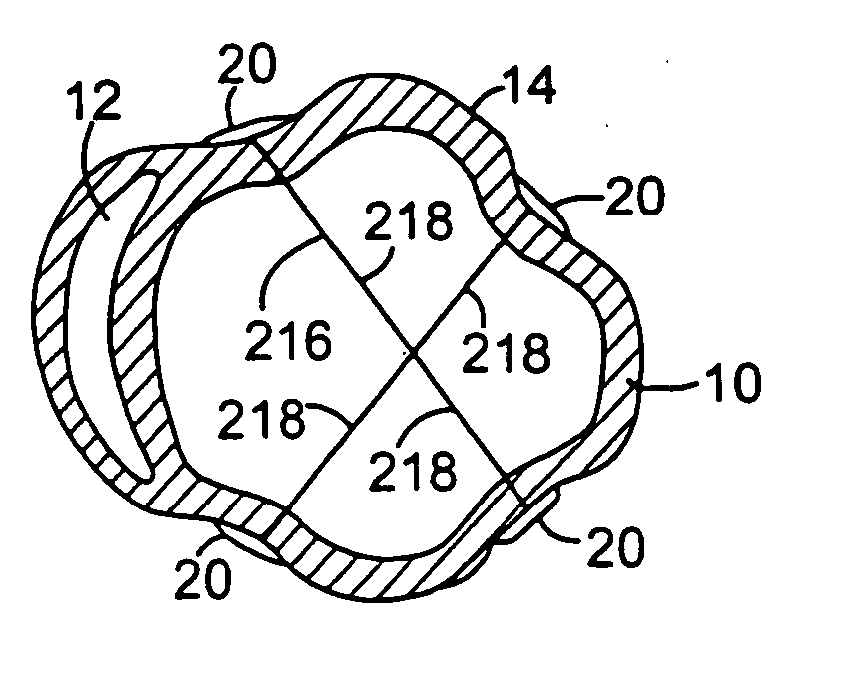
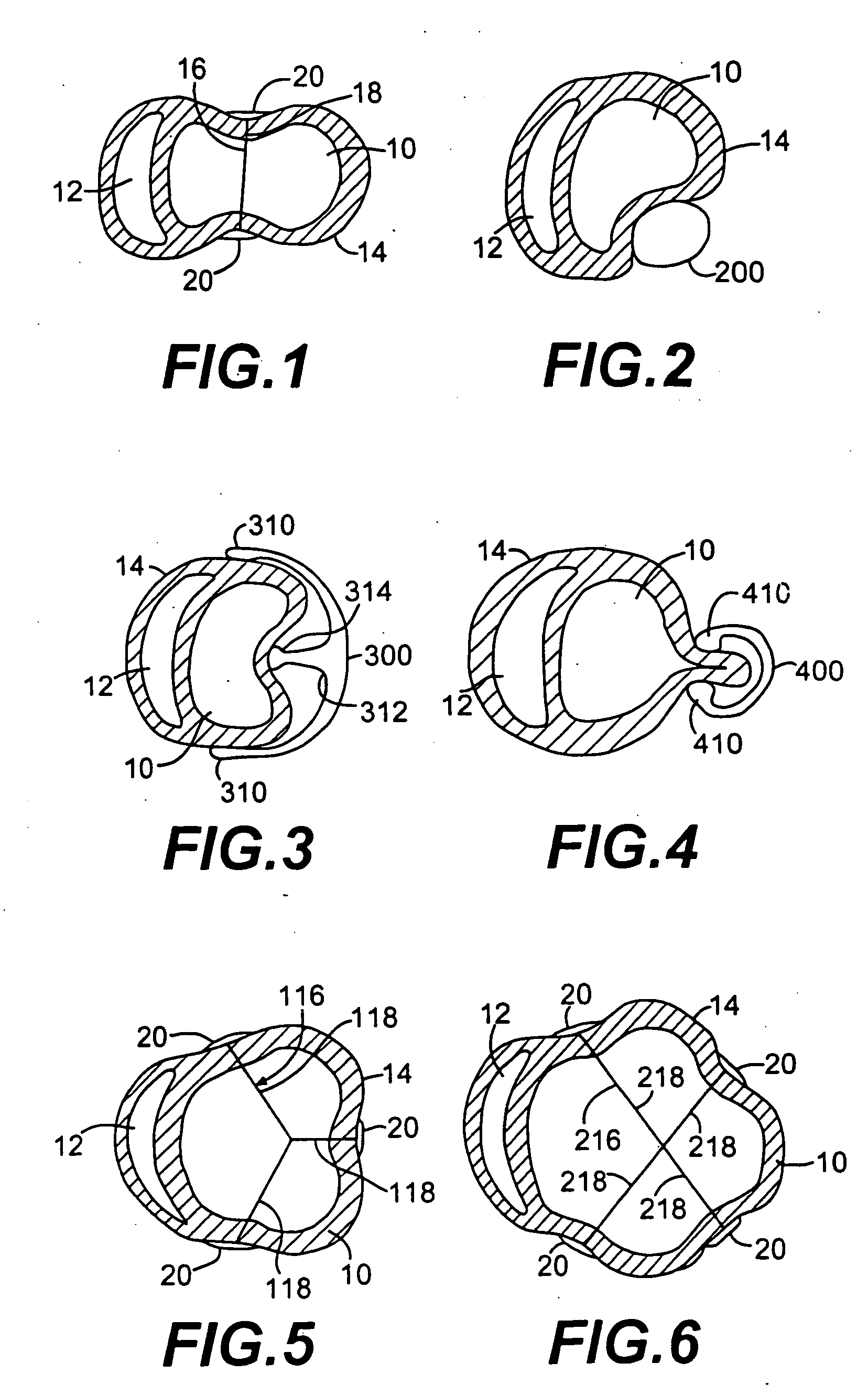
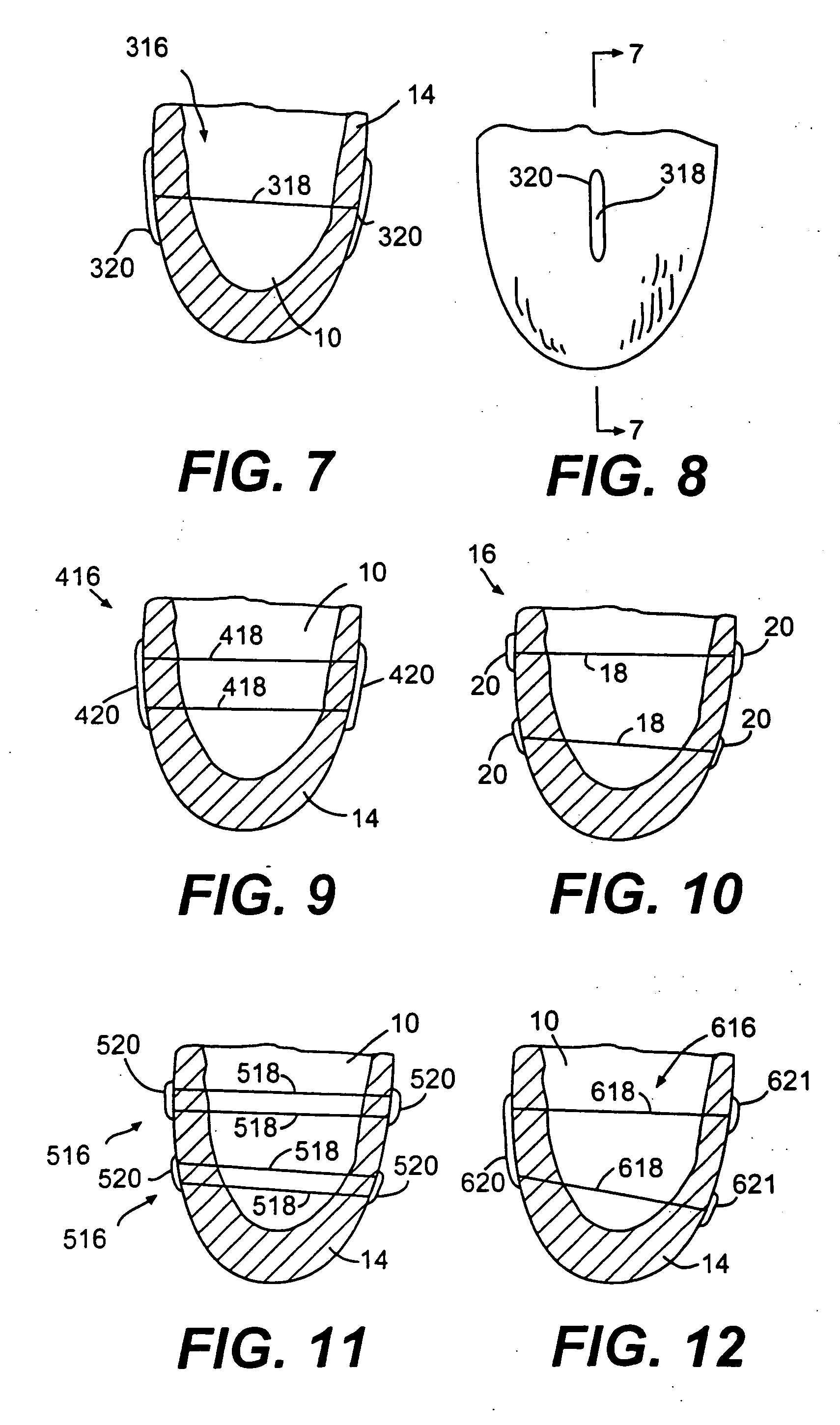
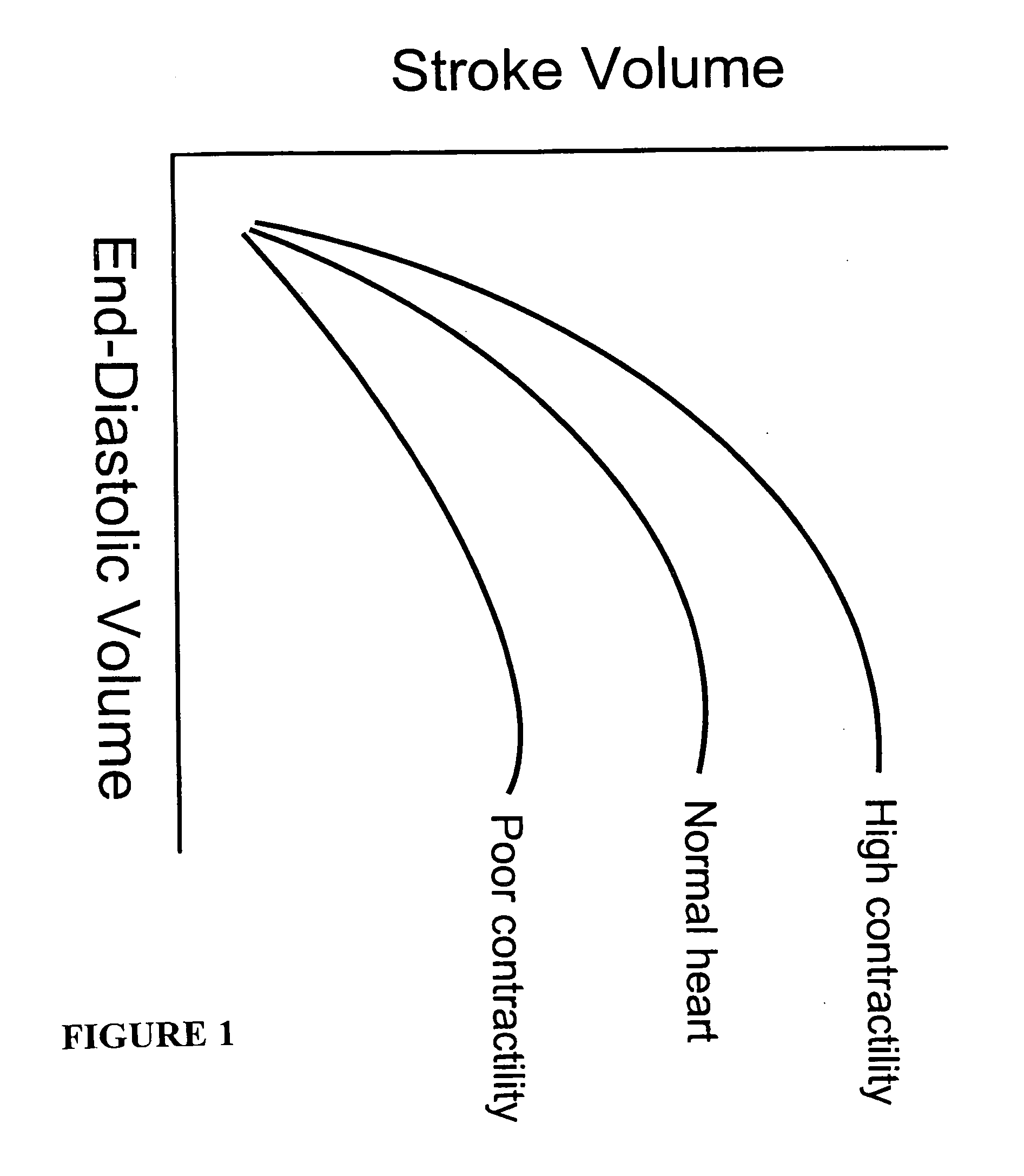
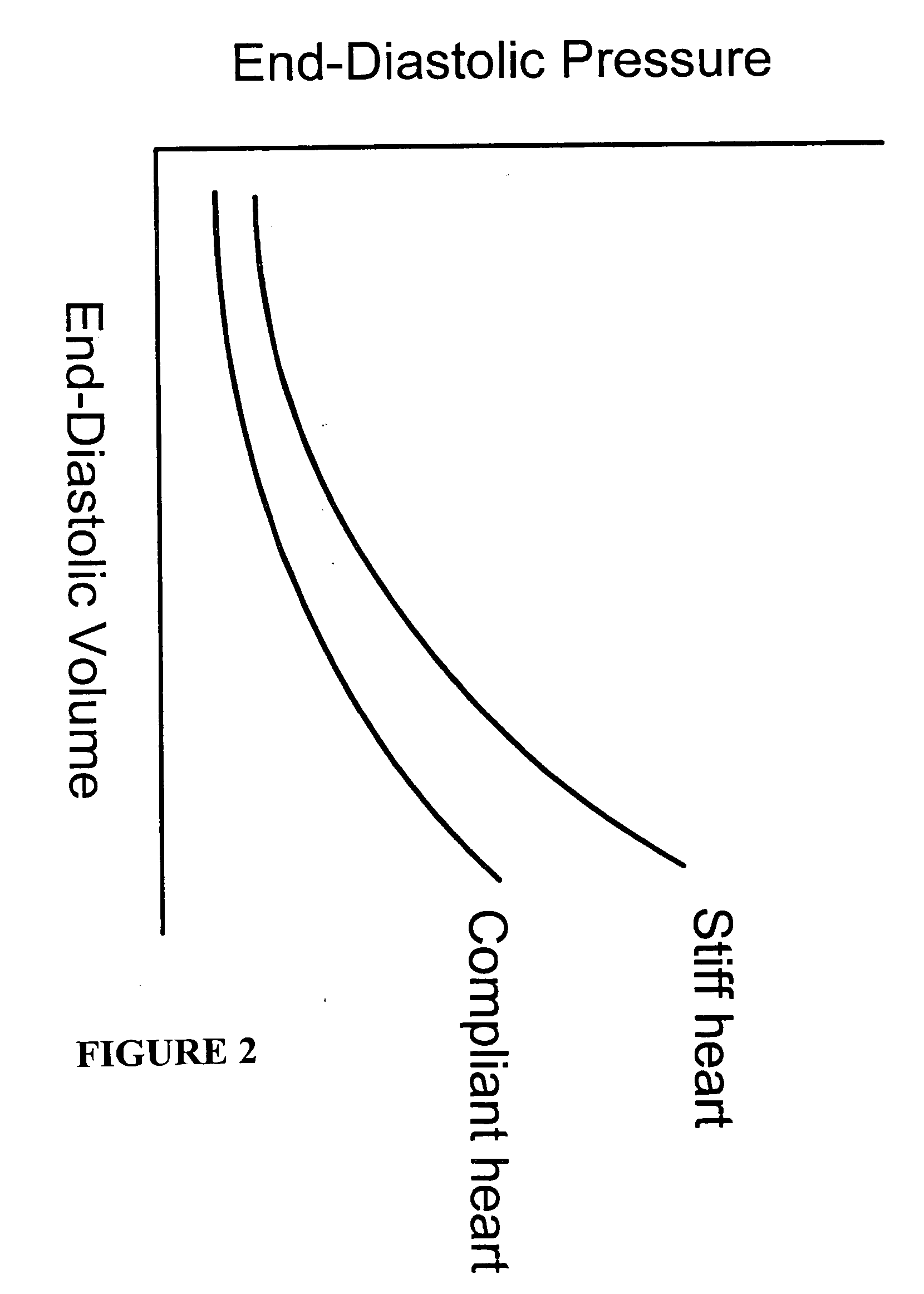
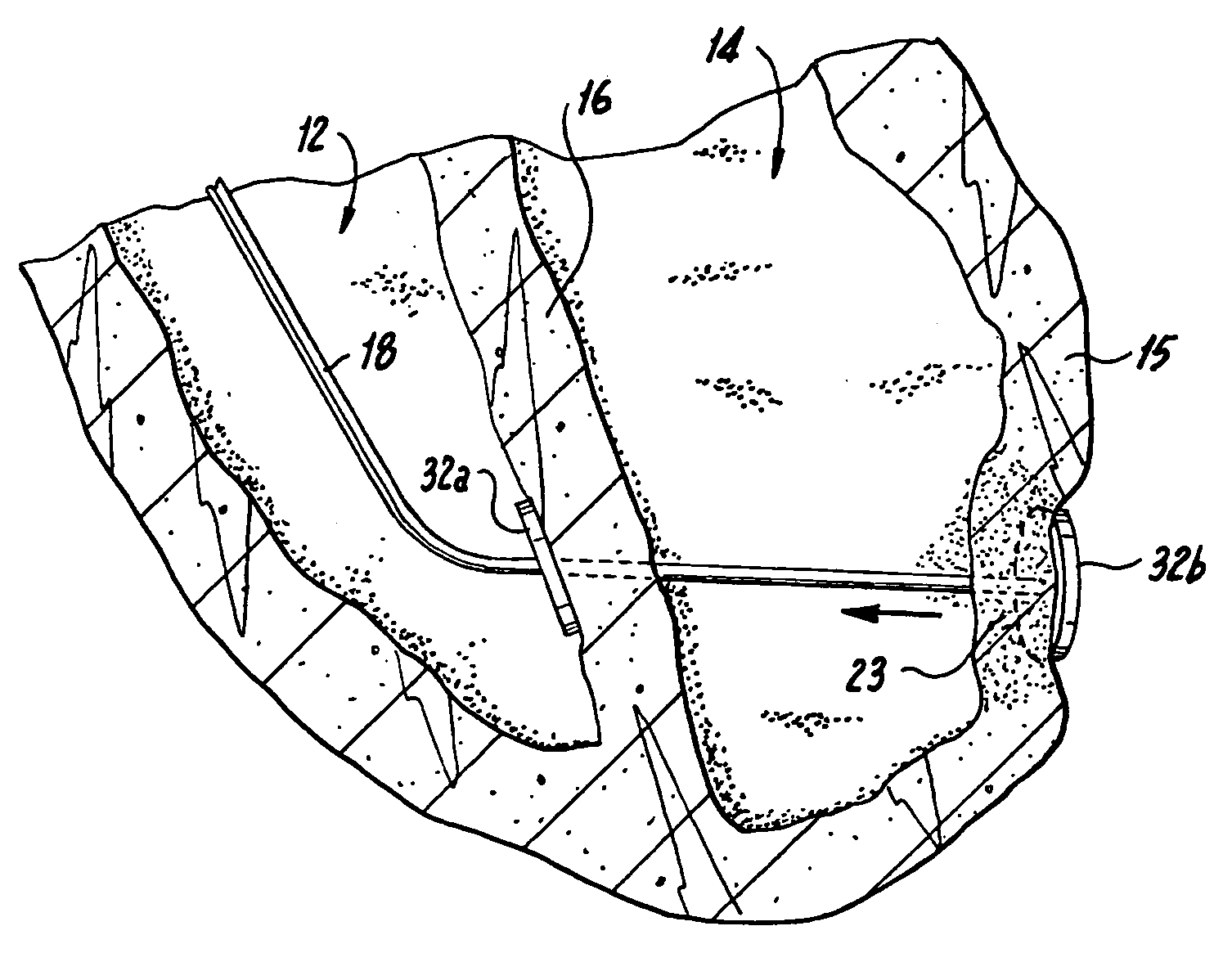
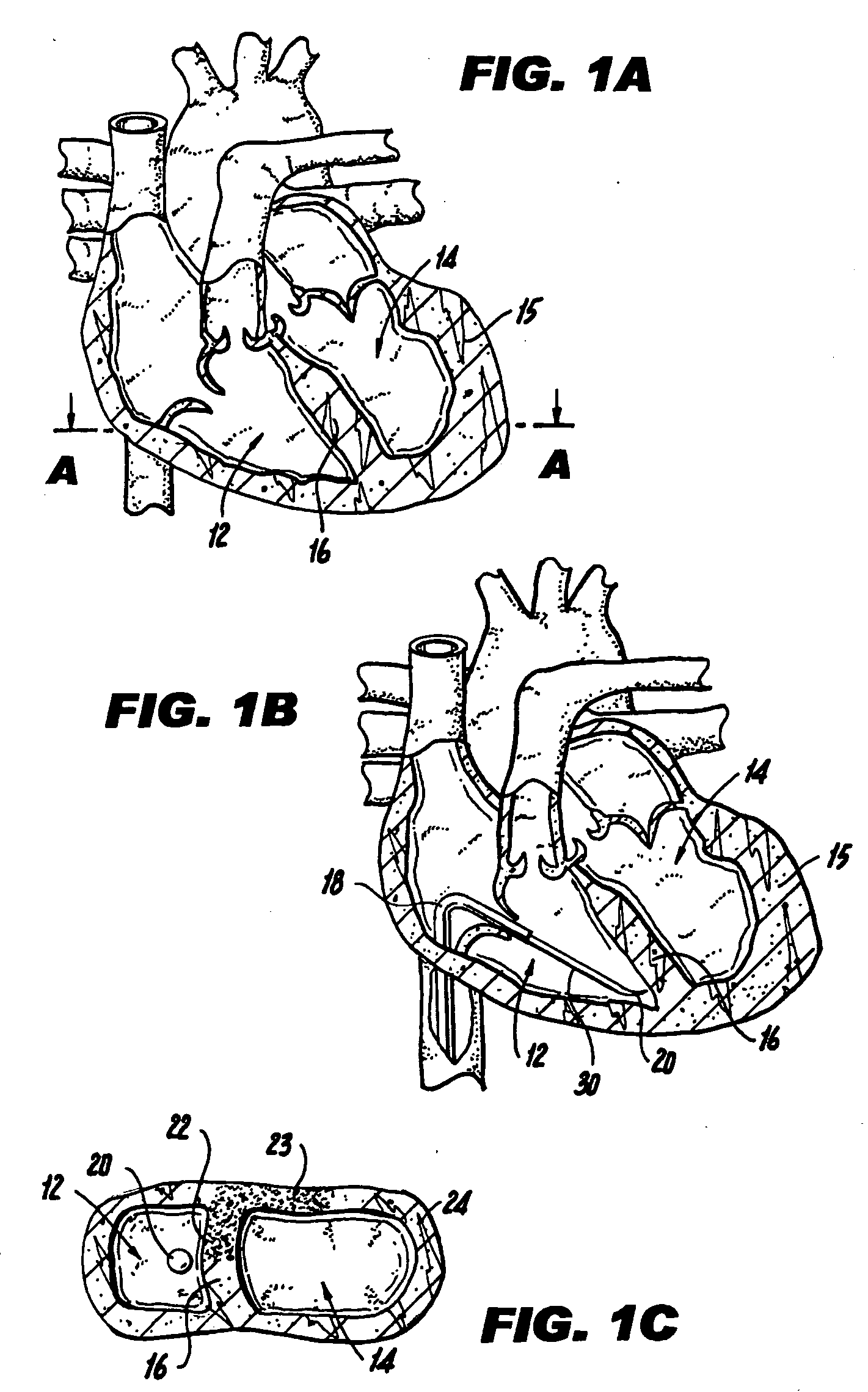
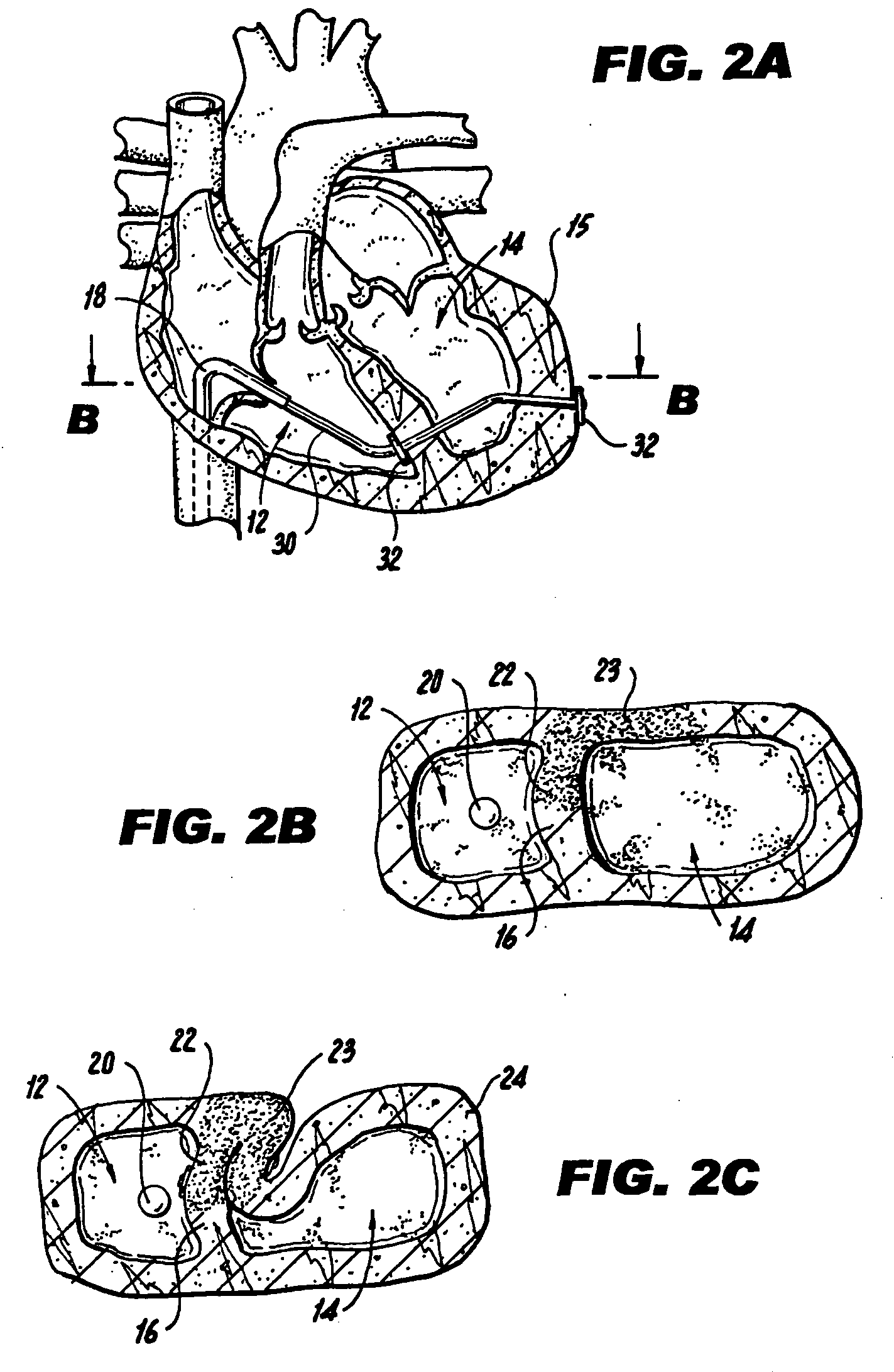
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS7189199B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesIliac AneurysmWall stress
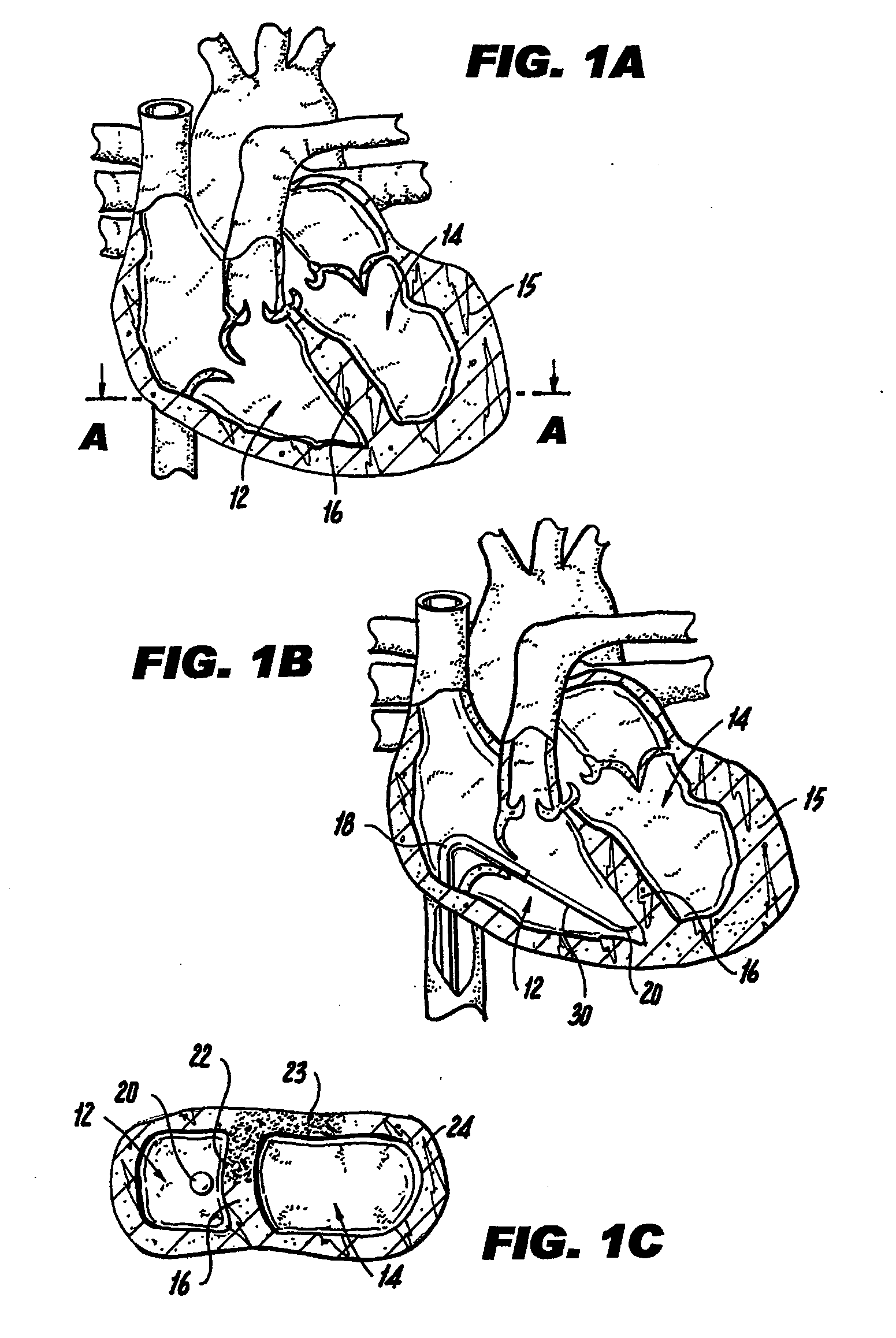
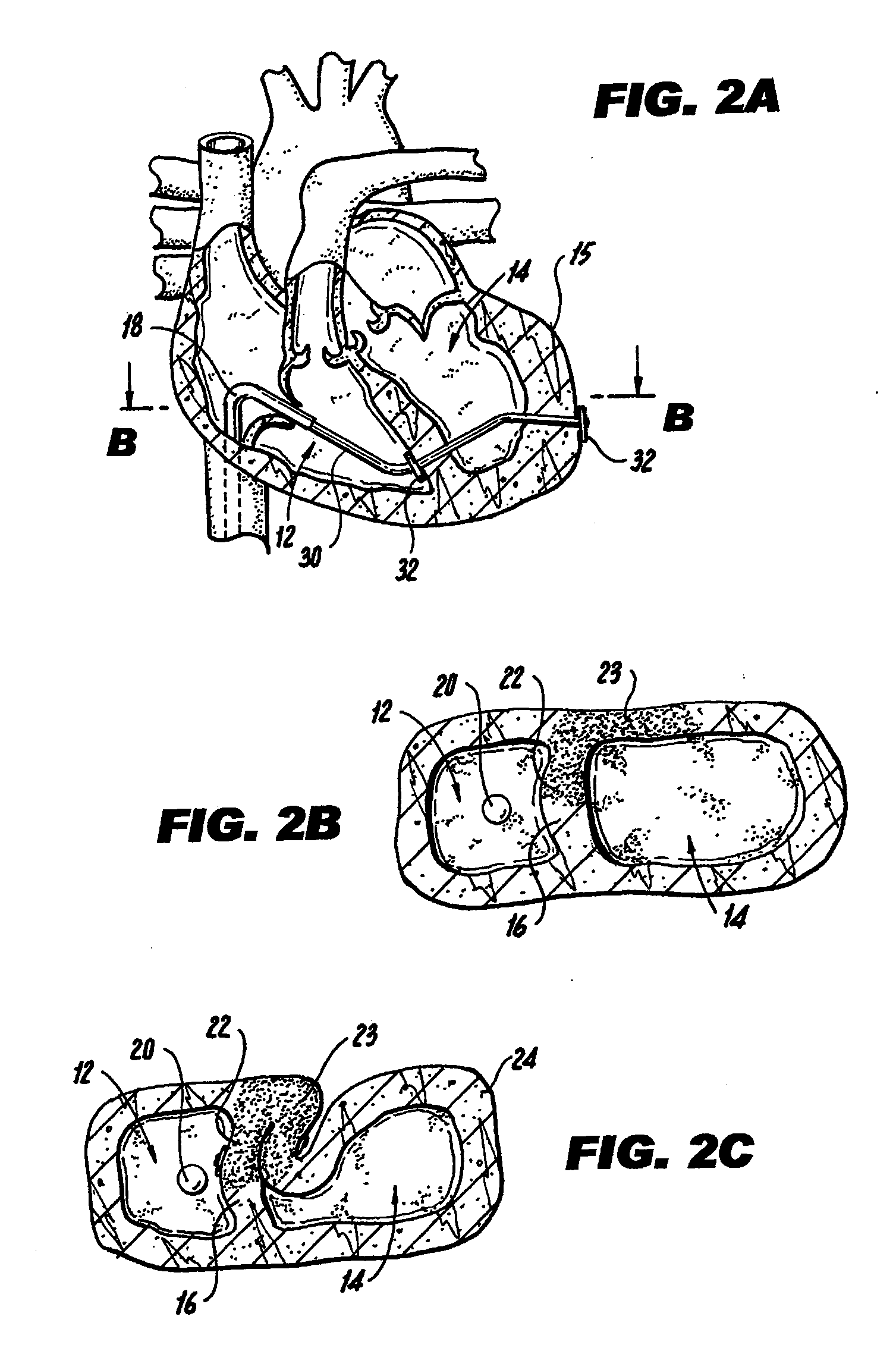
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS20060161040A1Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMedicineCardiac wall
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
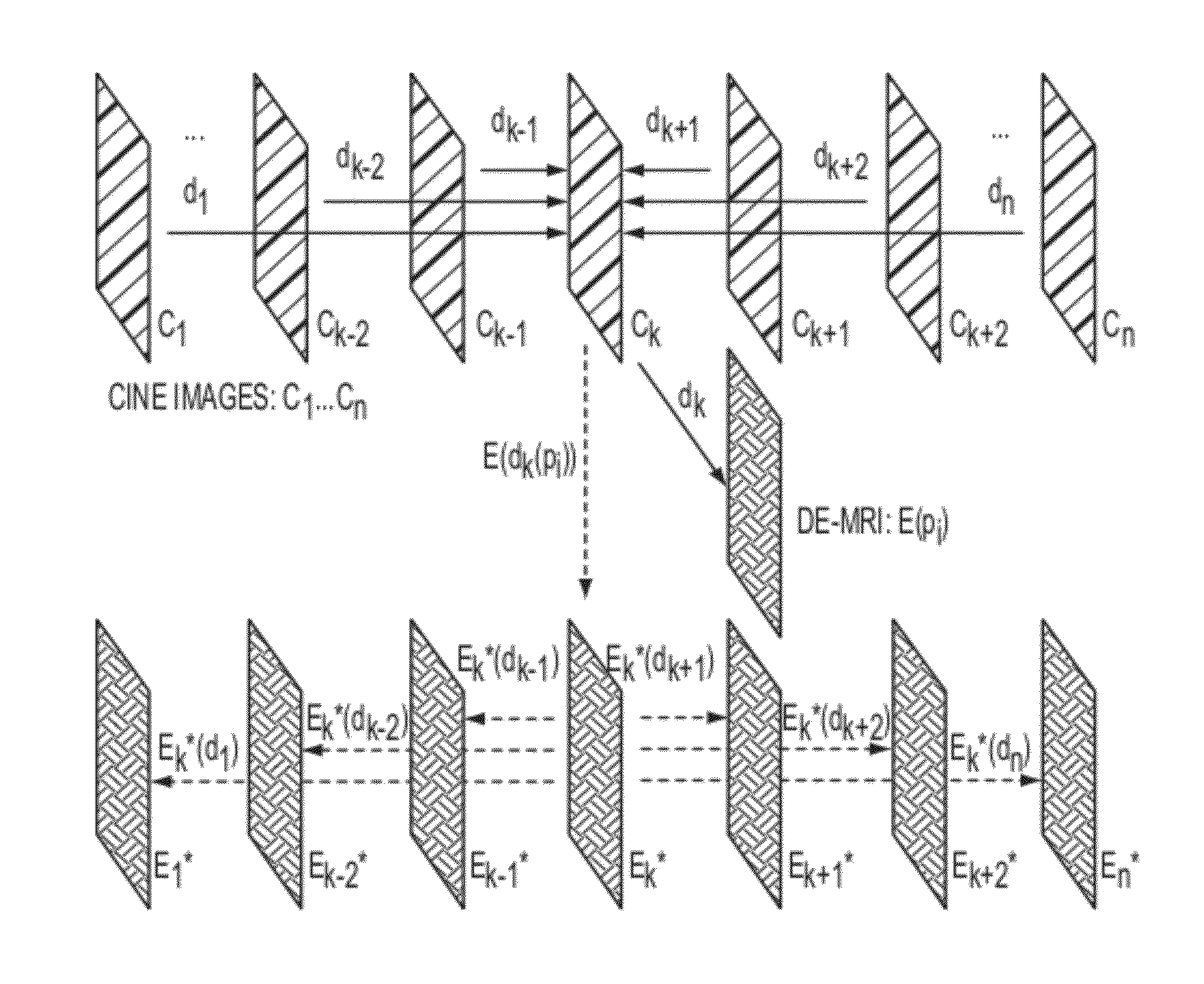
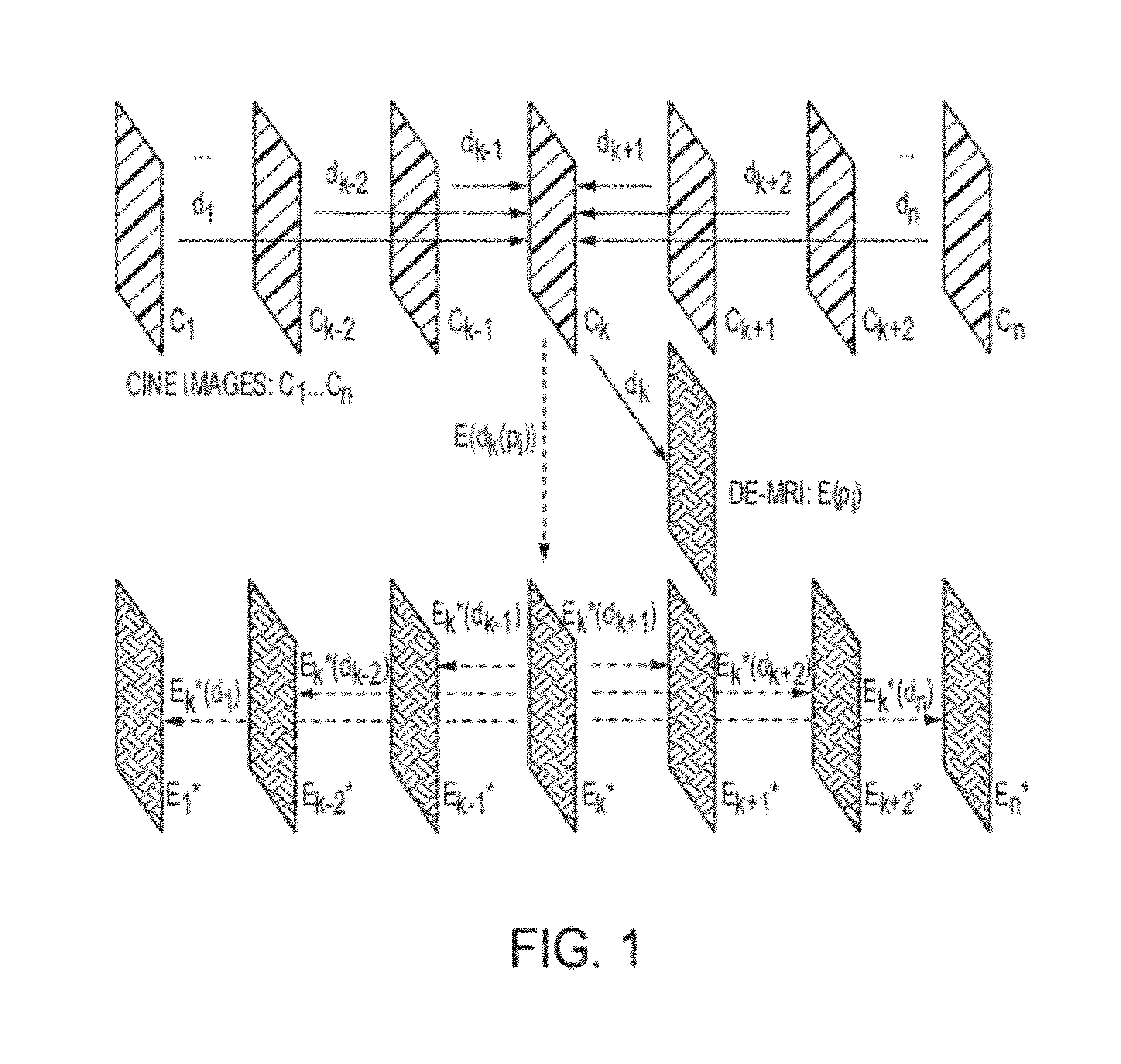
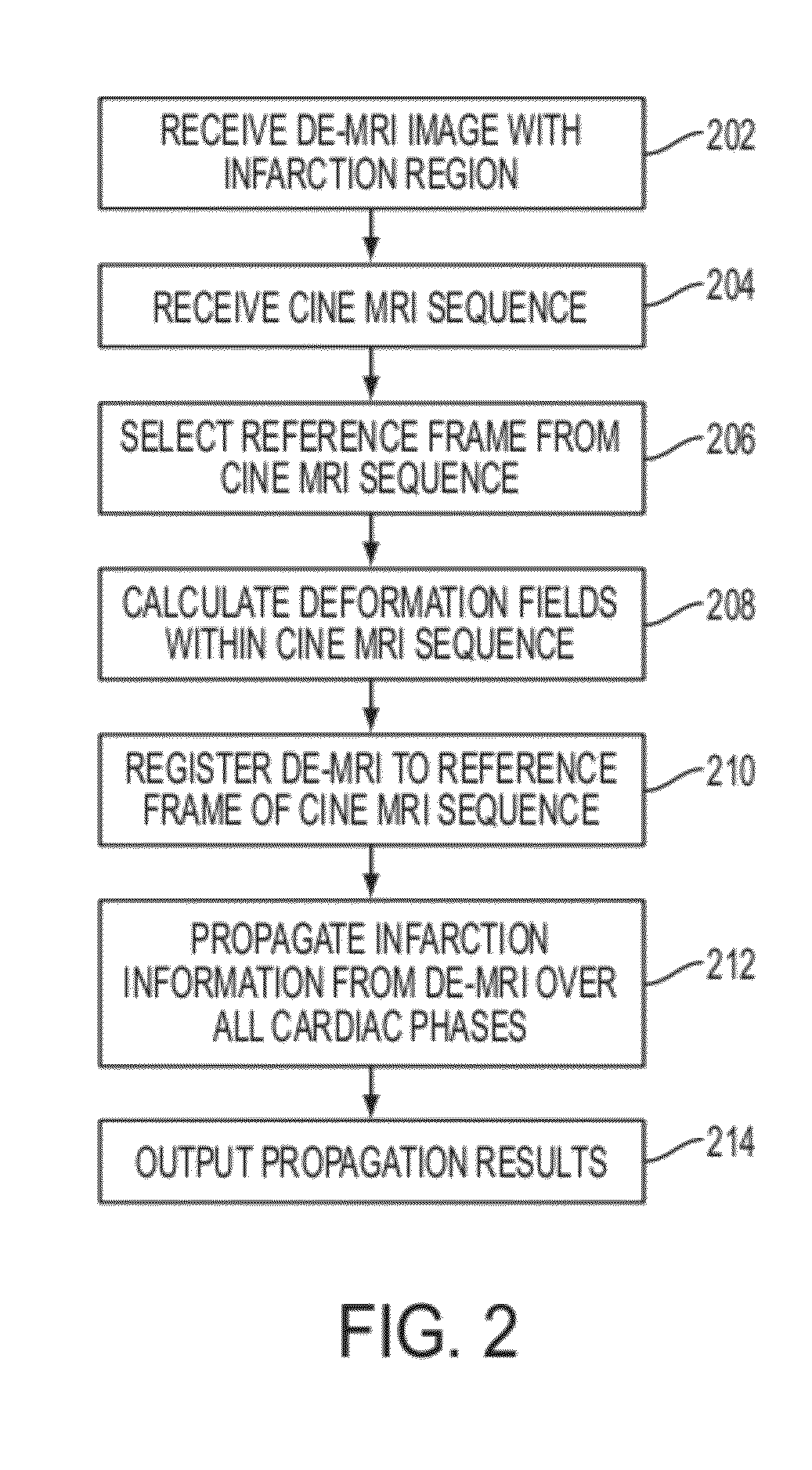
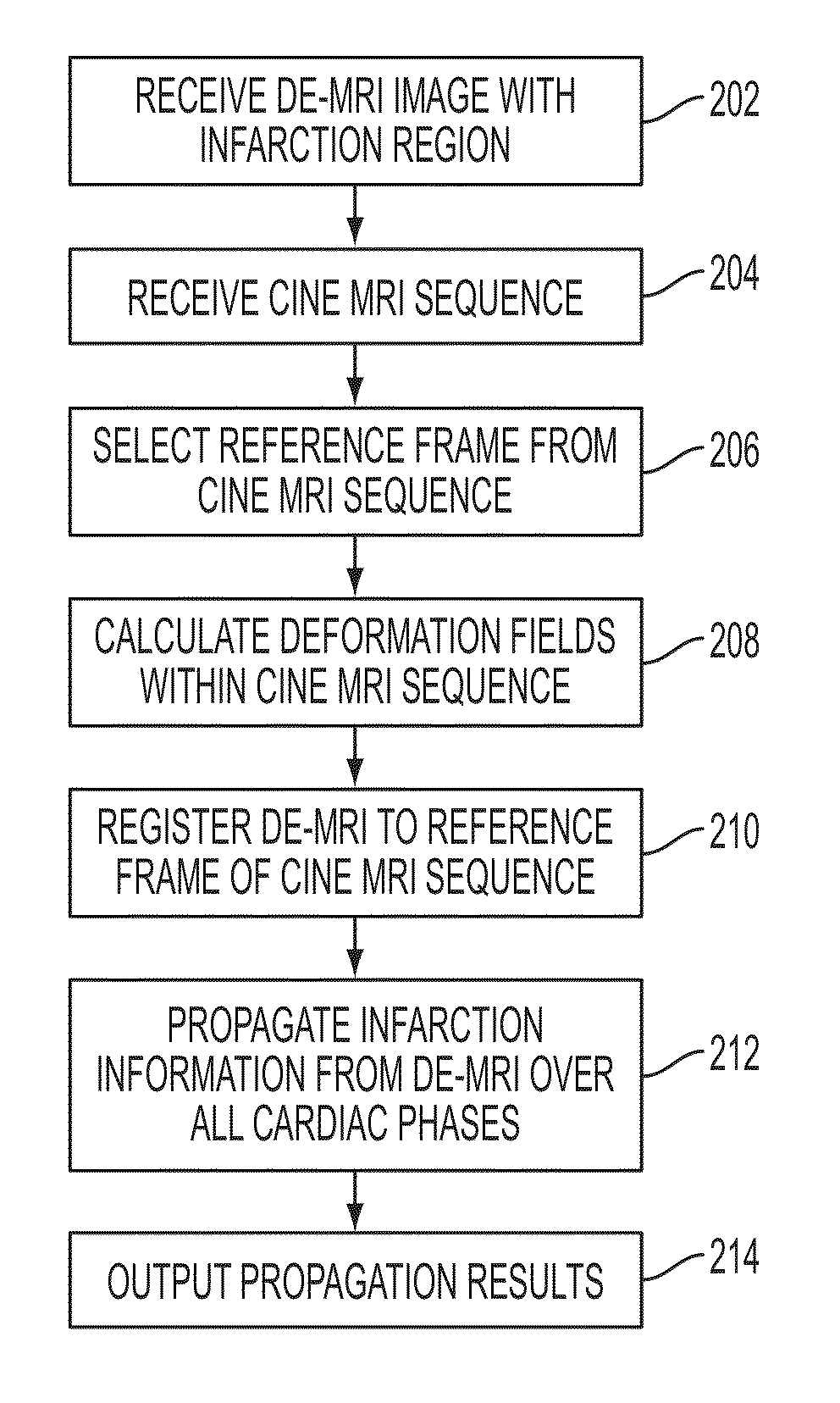
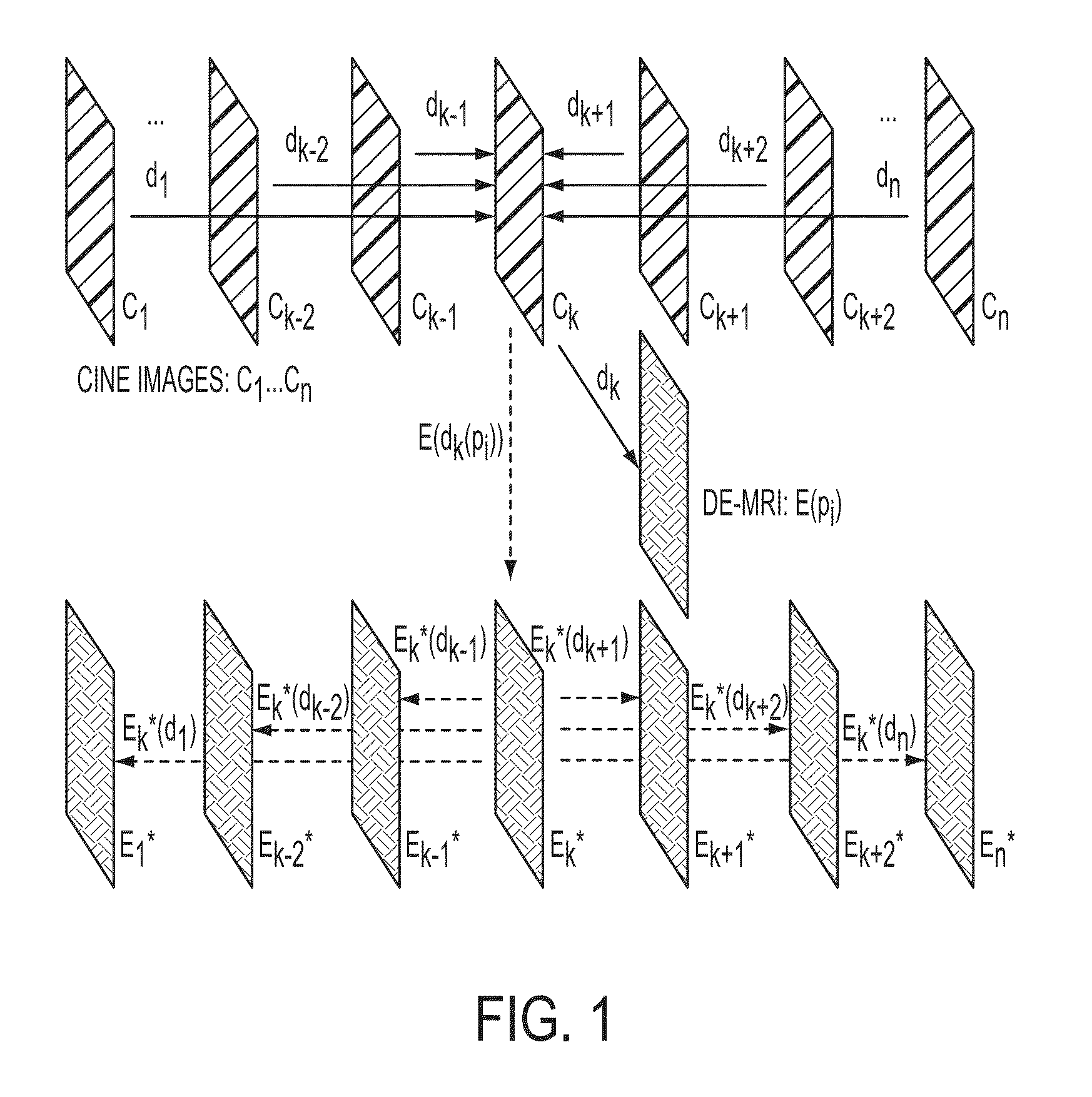
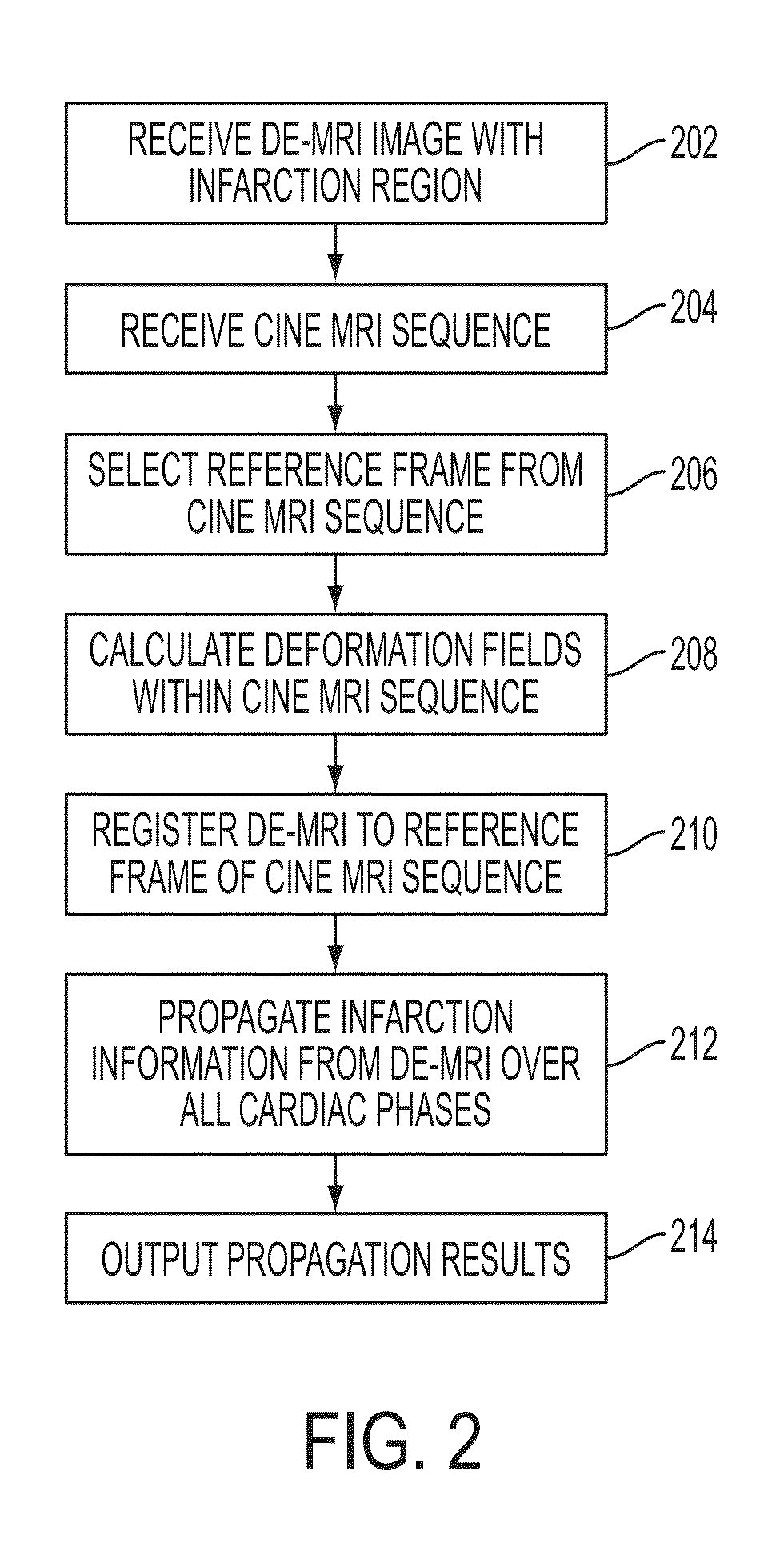
Method and System for Propagation of Myocardial Infarction from Delayed Enhanced Cardiac Imaging to Cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Hybrid Image Registration
ActiveUS20120121154A1Correction of deformationAccurate alignment and deformation correctionImage enhancementImage analysisCine mriCardiac phase
A method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) to cine MRI is disclosed. A reference frame is selected in a cine MRI sequence. Deformation fields are calculated within the cine MRI sequence to register the frames of the cine MRI sequence to the reference frame. A DE-MRI image having an infarction region is registered to the reference frame of the cine MRI sequence. The DE-MRI image may be registered to the infarction region using a hybrid registration algorithm that unifies both intensity and feature points into a single cost function. Infarction information in the DE-MRI image is then propagated cardiac phases of the frames in the cine MRI sequence based on the registration of the DE-MRI image to the reference frame and the plurality of deformation fields calculated within the cine MRI sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced cardiac imaging to cine magnetic resonance imaging using hybrid image registration
ActiveUS8682054B2Accurate alignment and deformation correctionImage enhancementImage analysisCine mriCardiac phase
A method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) to cine MRI is disclosed. A reference frame is selected in a cine MRI sequence. Deformation fields are calculated within the cine MRI sequence to register the frames of the cine MRI sequence to the reference frame. A DE-MRI image having an infarction region is registered to the reference frame of the cine MRI sequence. The DE-MRI image may be registered to the infarction region using a hybrid registration algorithm that unifies both intensity and feature points into a single cost function. Infarction information in the DE-MRI image is then propagated cardiac phases of the frames in the cine MRI sequence based on the registration of the DE-MRI image to the reference frame and the plurality of deformation fields calculated within the cine MRI sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS20070112244A1Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesWall stressAneurysm
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Heart disease detection patch
InactiveUS20060030782A1Inexpensive and simple to useSuitable for self-administrationElectrocardiographySensorsFibrillationNon invasive
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for the non-invasive detection of heart disease. The patch is placed on a person's chest area for automatic analysis of ECG. The heart condition is indicated via an indicator integrated within the patch. The patch is inexpensive and simple for self-administration. In one embodiment, the status of the heart is indicated via multiple LEDs. The detection and indication typically occurs, within 24 hours or sooner if a condition is readily identifiable. The patch is thin, flexible, and incorporates a battery, ECG amplifier, and a processor for analyzing ECG waveform and indicating the heart condition. A software algorithm searches for a cardiac abnormality such as arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation, mycocardial infarction, ischemia, long-QT syndrome, blocks, late potentials, and premature contractions. In another embodiment, results and relevant ECG data are stored in memory for later retrieval.
Owner:CARDIOVU
Treatment of infarct expansion by partially occluding vena cava
InactiveUS20060064059A1Reduces severity and complicationReduce expansionBalloon catheterSurgeryVeinVenous blood flow
A method and apparatus for prevention and reduction of myocardial infarct size and / or expansion and heart remodeling by partial, controllable and reversible obstruction of the venous blood flow to the heart. As a result, the ventricular wall stress and dilation are reduced. Blood flow is maintained at a safe level for the duration of treatment. The apparatus consists of a catheter with an occlusion balloon and a control and monitoring system.
Owner:GELFAND MARK +1
Delivery of biological compounds to ischemic and/or infarcted tissue
The delivery of biological compounds to ischemic and / or infarcted tissue are described herein where such a system may include a deployment catheter and an attached imaging hood deployable into an expanded configuration. In use, the imaging hood is placed against or adjacent to a region of tissue to be imaged in a body lumen that is normally filled with an opaque bodily fluid such as blood. A translucent or transparent fluid, such as saline, can be pumped into the imaging hood until the fluid displaces any blood, thereby leaving a clear region of tissue to be imaged via an imaging element in the deployment catheter. Additionally, any number of therapeutic tools can also be passed through the deployment catheter and into the imaging hood for performing any number of procedures on the tissue for identifying, locating, and / or accessing ischemic and / or infarcted tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Method and device for percutaneous left ventricular reconstruction
InactiveUS20060079736A1Reduce volumeMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsElectrocardiographyVentricular volumeChest surgery
A method for reducing left ventricular volume, which comprises identifying infarcted tissue during open chest surgery; reducing left ventricle volume while preserving the ventricular apex; and realigning the ventricular apex, such that the realigning step comprises closing the lower or apical portion of said ventricle to achieve appropriate functional contractile geometry of said ventricle in a dyskinetic ventricle of a heart.
Owner:CHF TECH A CALIFORNIA CORP
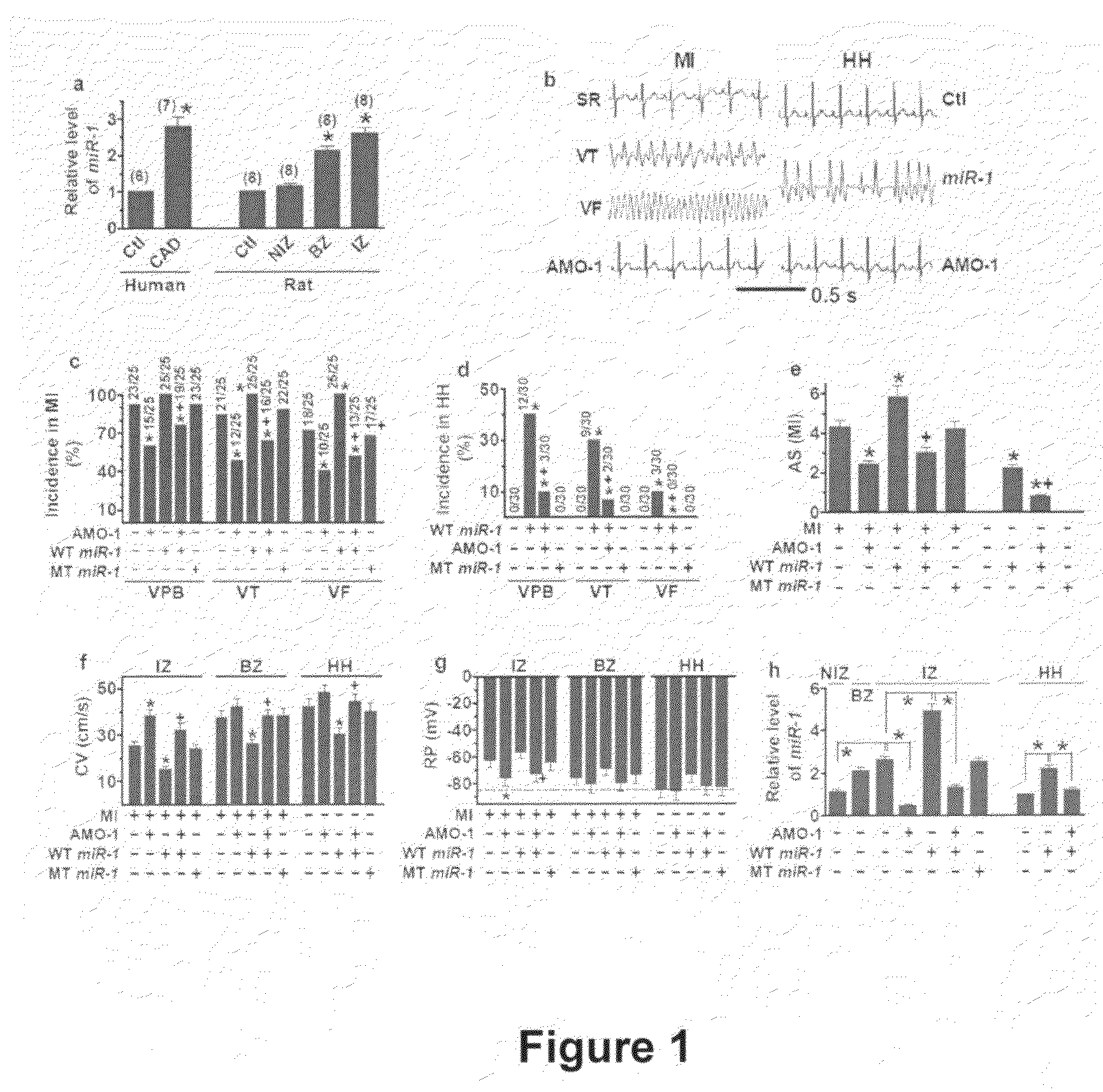
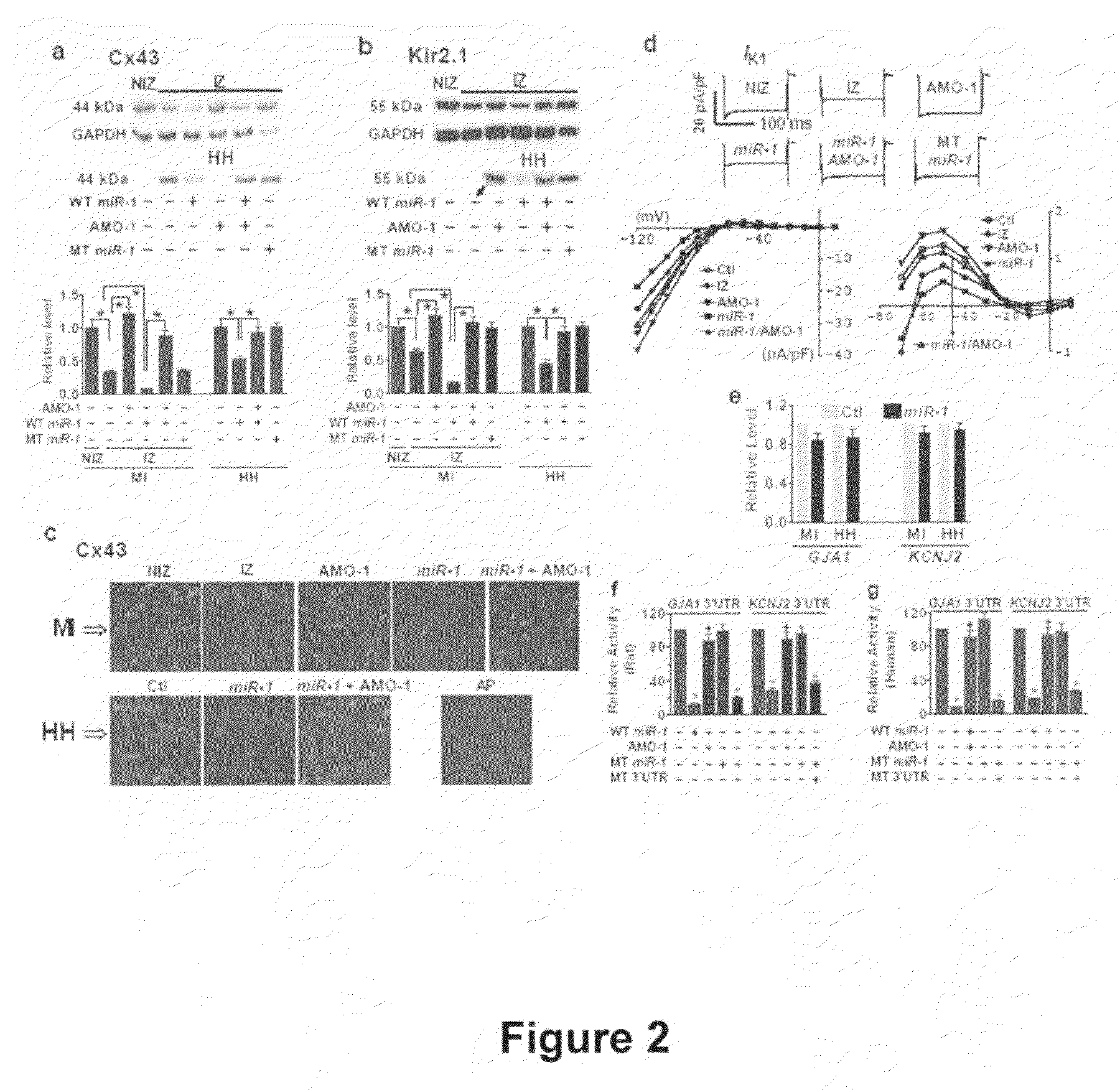
Use of the microRNA miR-1 for the treatment, prevention, and diagnosis of cardiac conditions
InactiveUS20090005336A1High expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseCoronary artery disease
Among >300 miRNAs known to date, miR-1 is considered muscle-specific. Here we show that that miR-1 overexpressed in individuals with coronary artery disease, and when overexpressed, it exacerbated arrhythmogenesis in both infarcted and normal hearts of rats whereas elimination of miR-1 by its antisense inhibitor relieved it. MiR-1 rendered slowed conduction and depolarized membrane by post-transcriptionally repressing KCNJ2 and GJA1 genes, likely accounting for its arrhythmogenic potential. Thus, miR-1 may have important pathophysiological functions in heart, being a novel antiarrhythmic target useful in the treatment and prevention of various cardiac pathologies.
Owner:WANG ZHIGUO
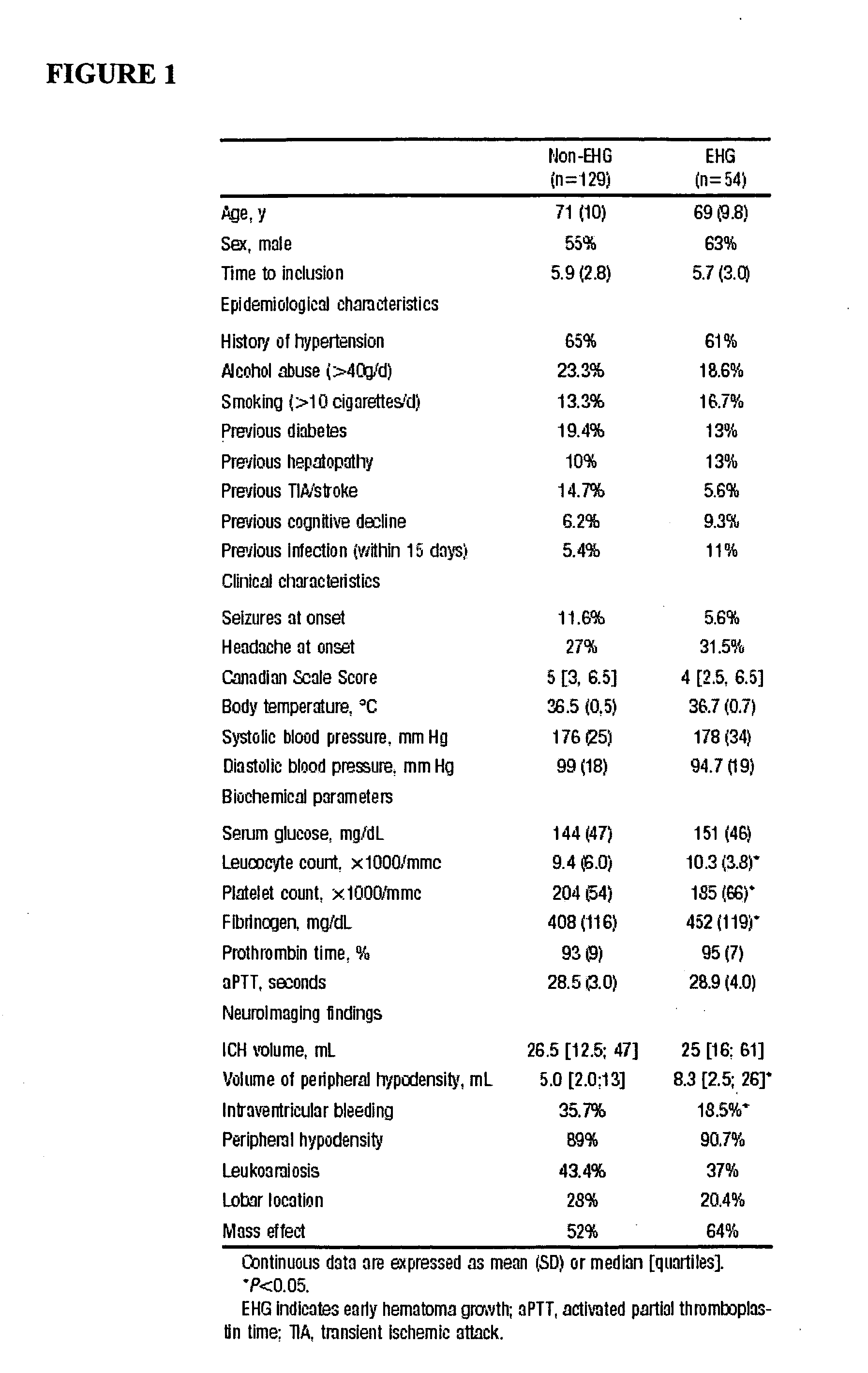
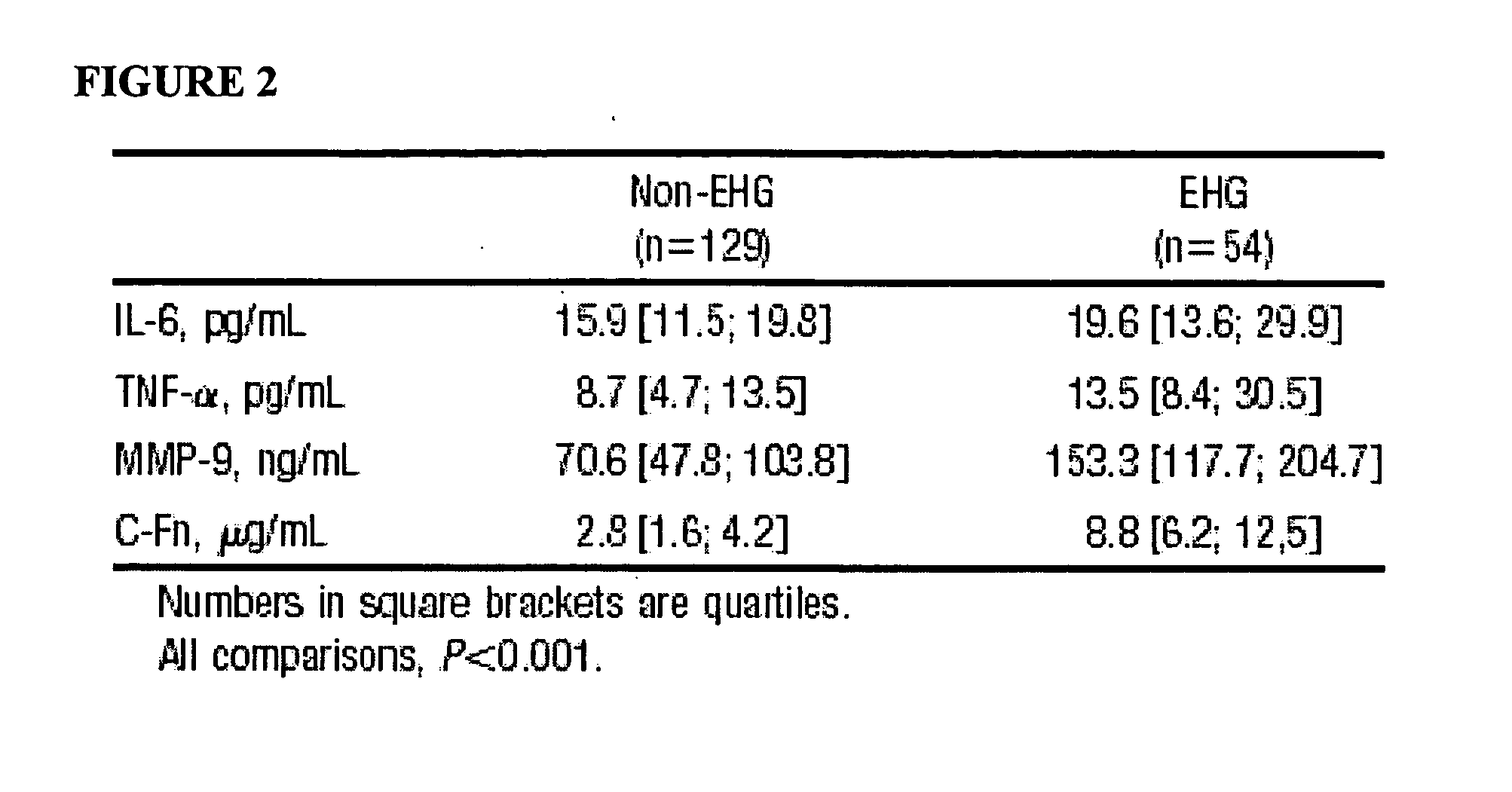
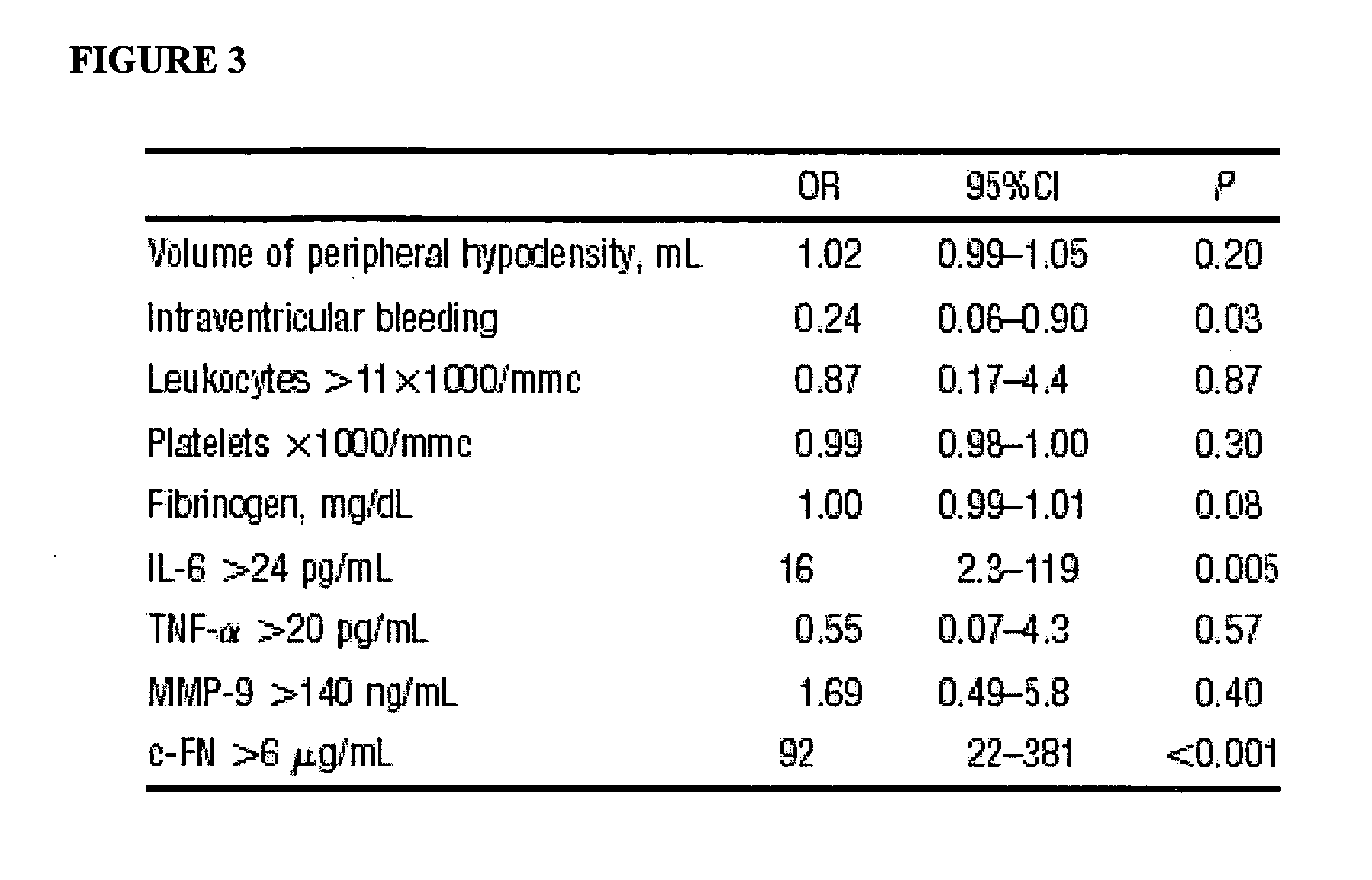
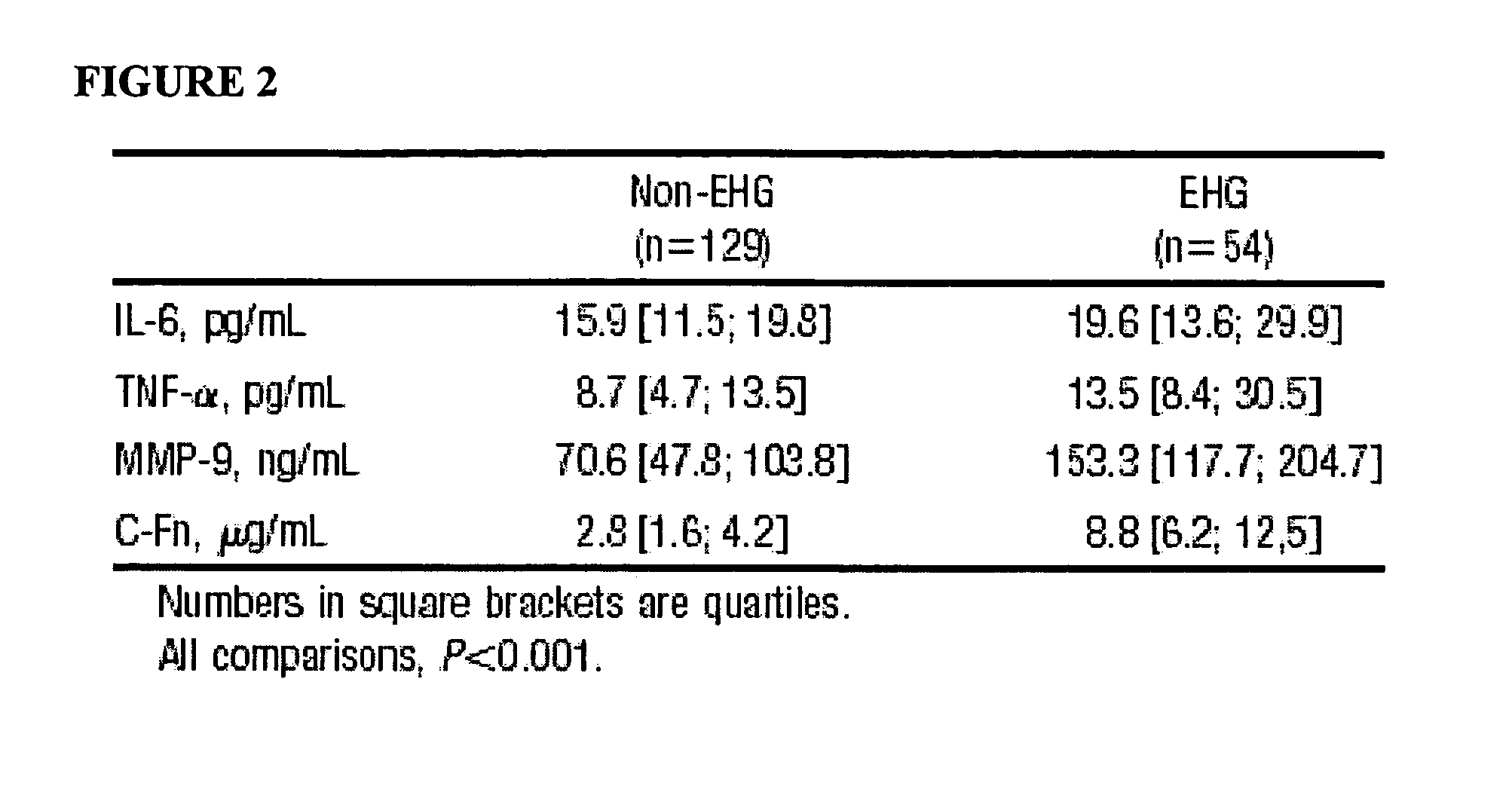
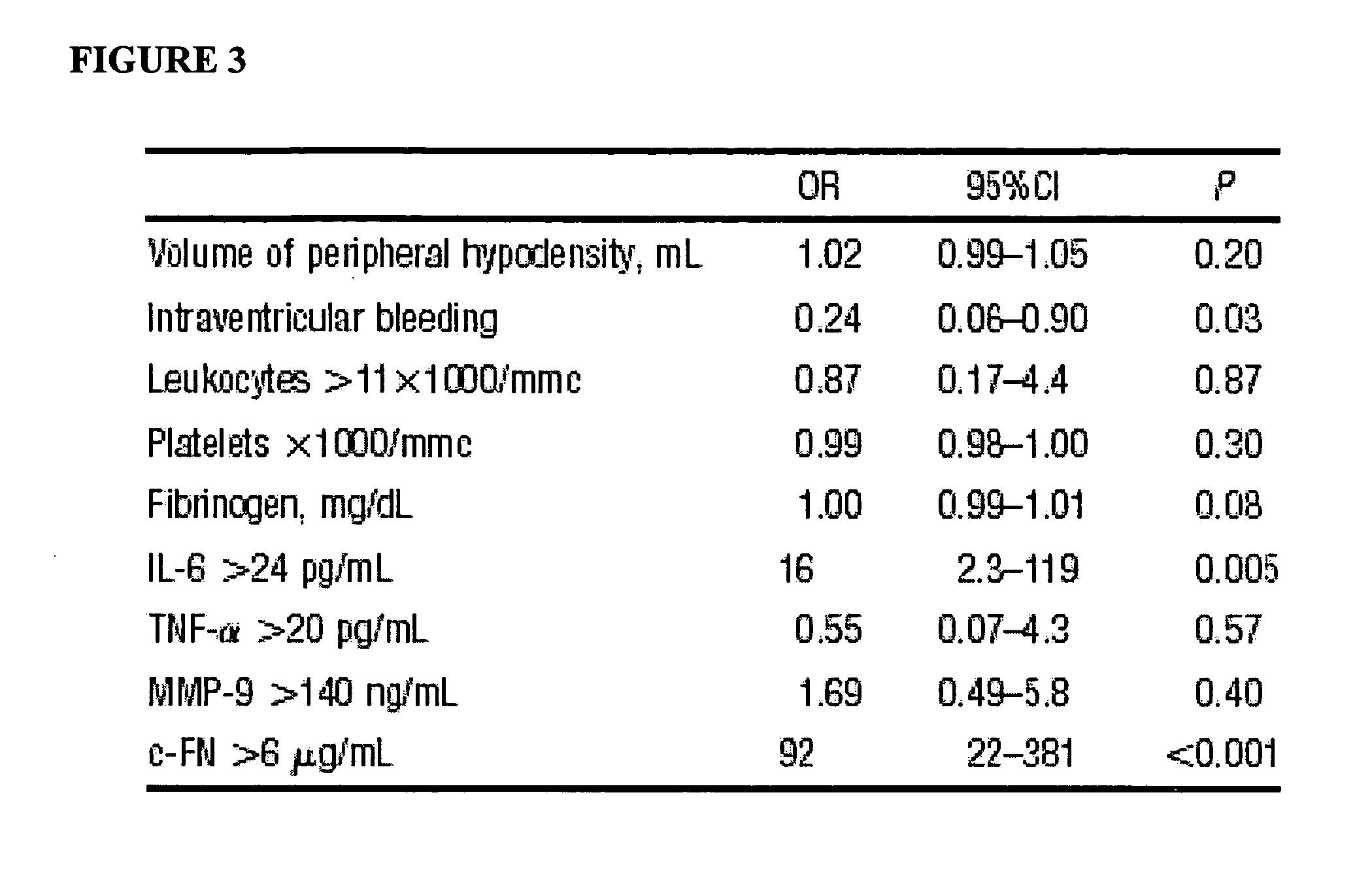
Cellular fibronectin as a diagnostic marker in stroke and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070005261A1Rapidly and accurately determinedMaximal sensitivityMedical data miningDisease diagnosisStroke subtypeBiomarker (petroleum)
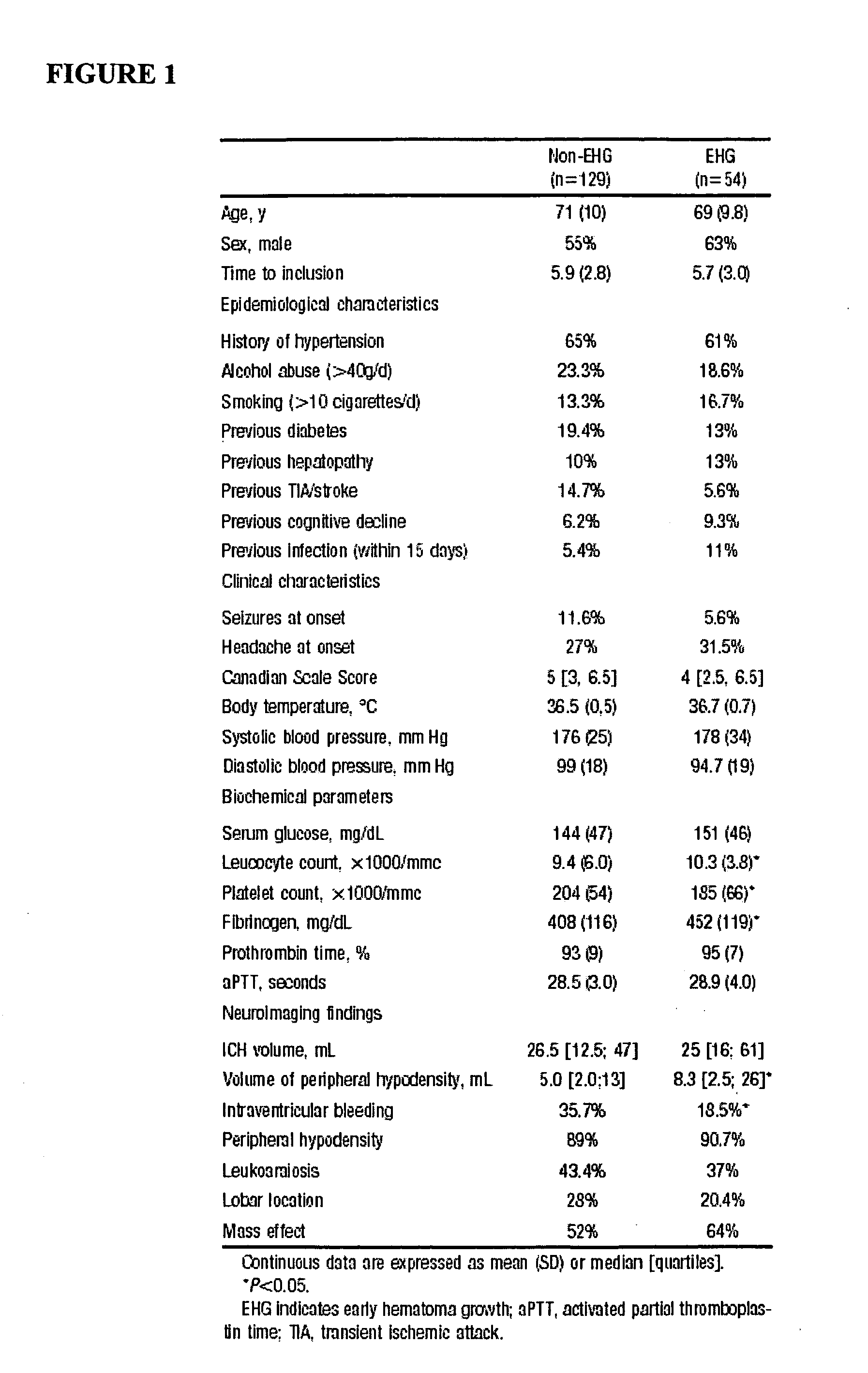
Methods for the diagnosis and evaluation of stroke and stroke sub-type employ a variety of bio-markers including cellular fibronectin (c-Fn) assembled as a panel for stoke diagnosis and evaluation. Methods are disclosed for selecting markers and correlating their combined levels with a clinical outcome of interest. In various aspects the methods permit early detection and differentiation of stroke subtypes, determination of the prognosis of a patient presenting stroke symptoms, and identification of a patient at risk for early hematoma growth and / or malignant massive cerebral artery infarction. The disclosed methods provide rapid, sensitive and specific assays to greatly increase the number of patients that can receive beneficial stroke treatment and therapy, and to reduce the human and economic costs associated with incorrect stroke diagnosis.
Owner:PREDICTION SCI
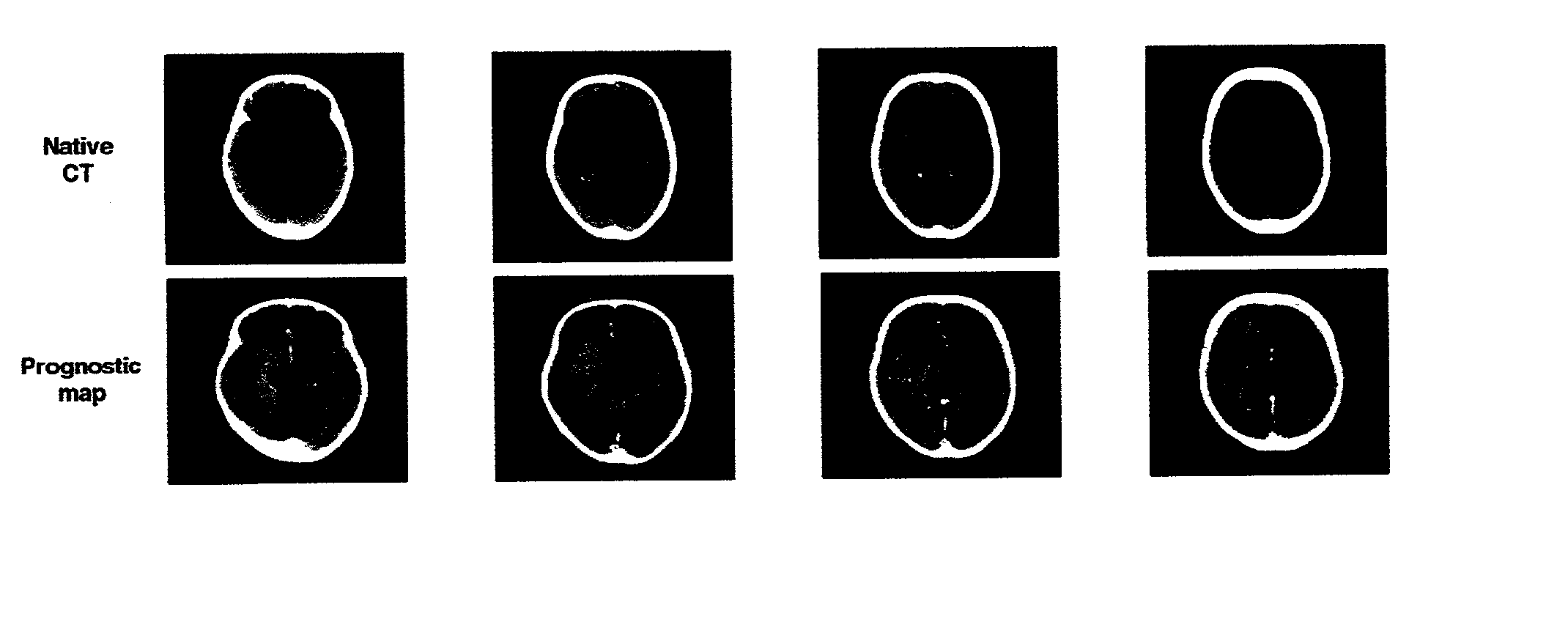
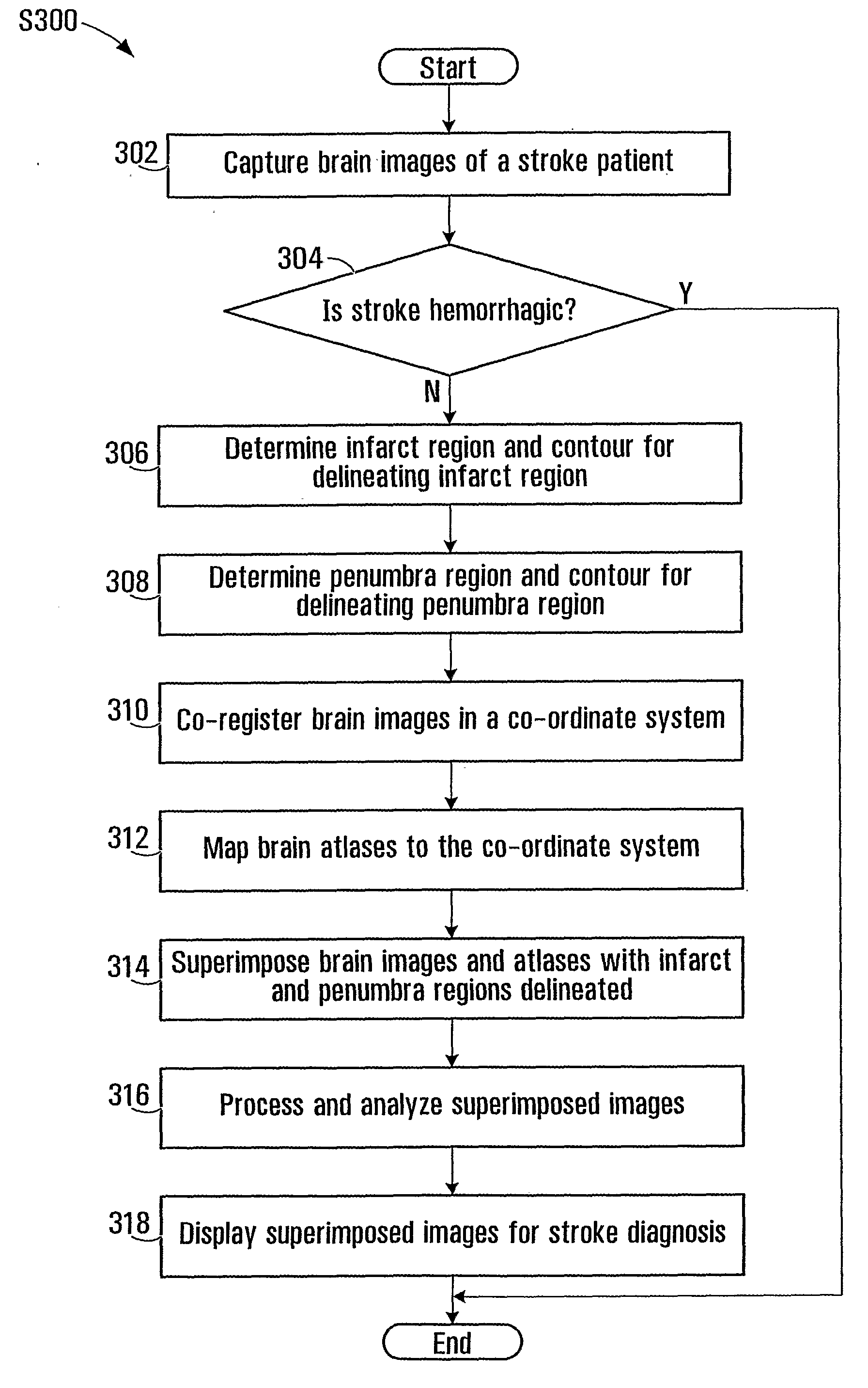
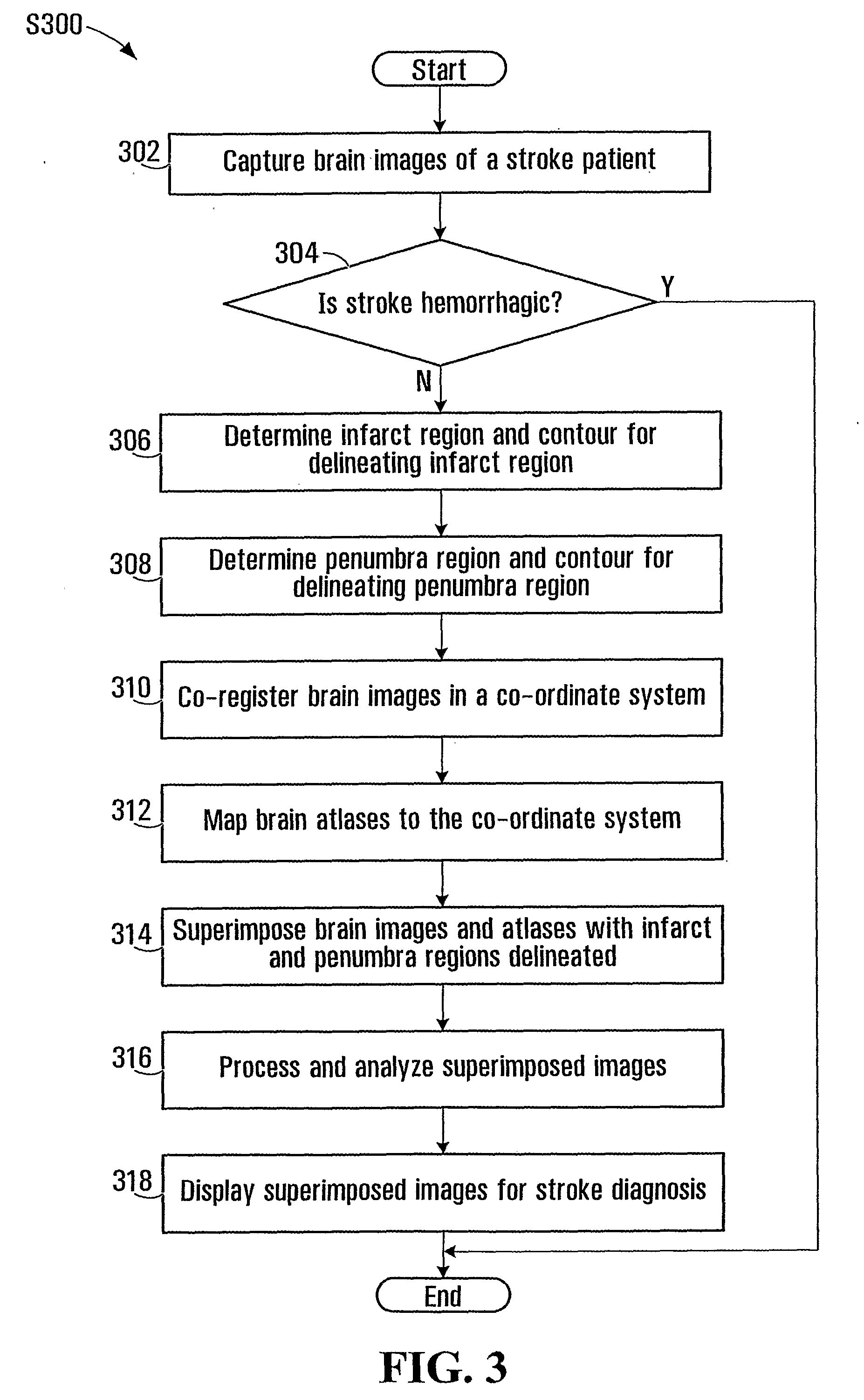
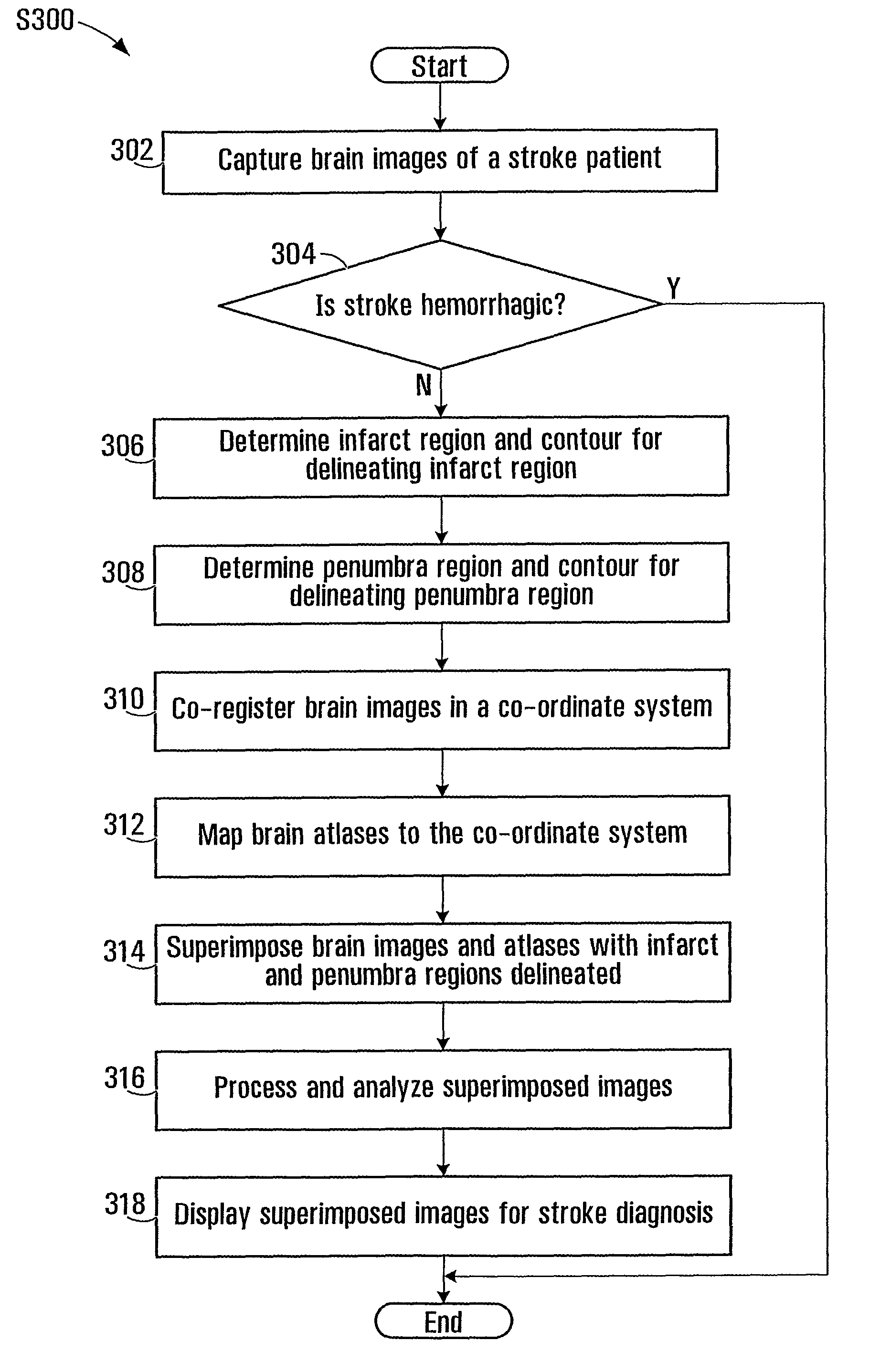
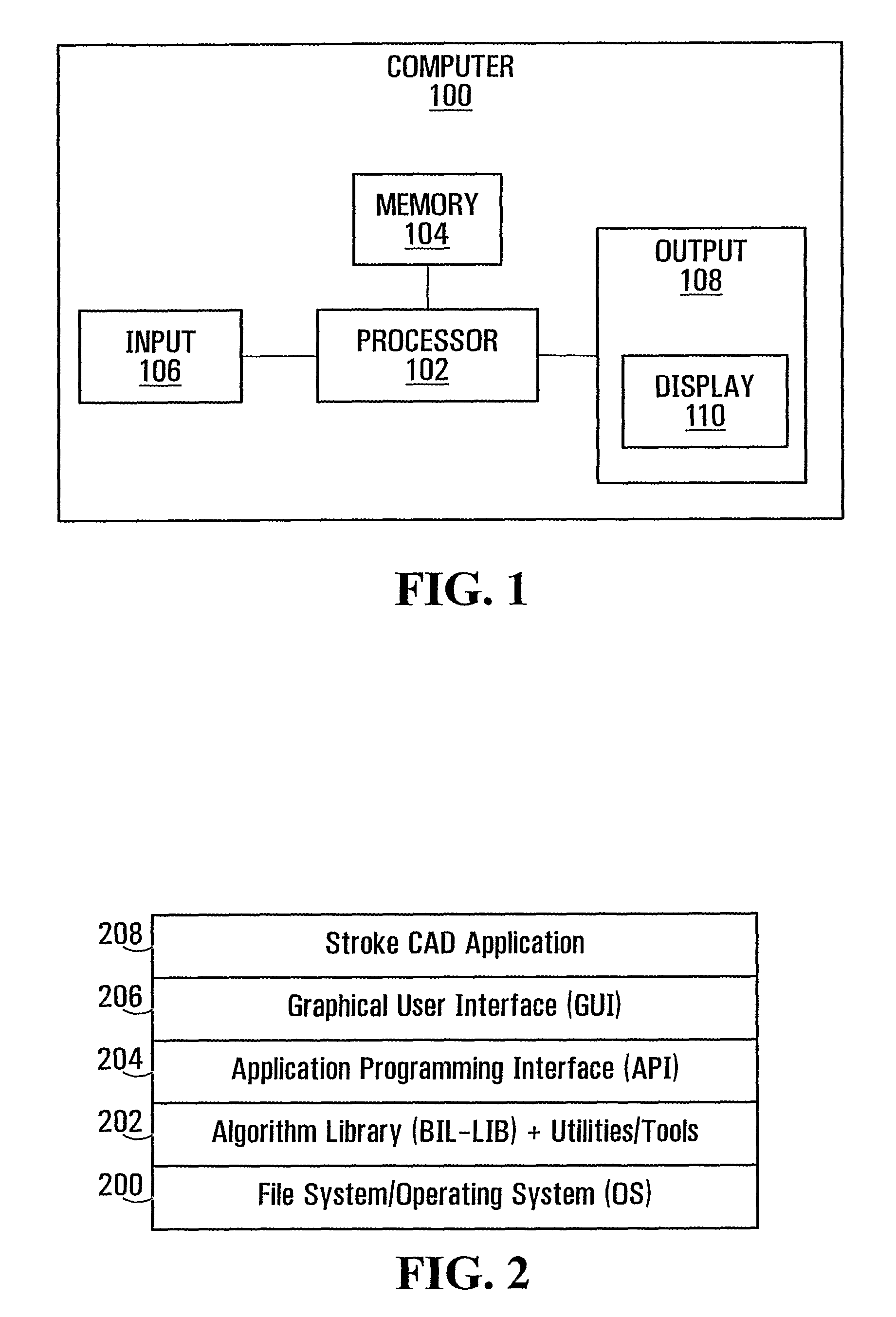
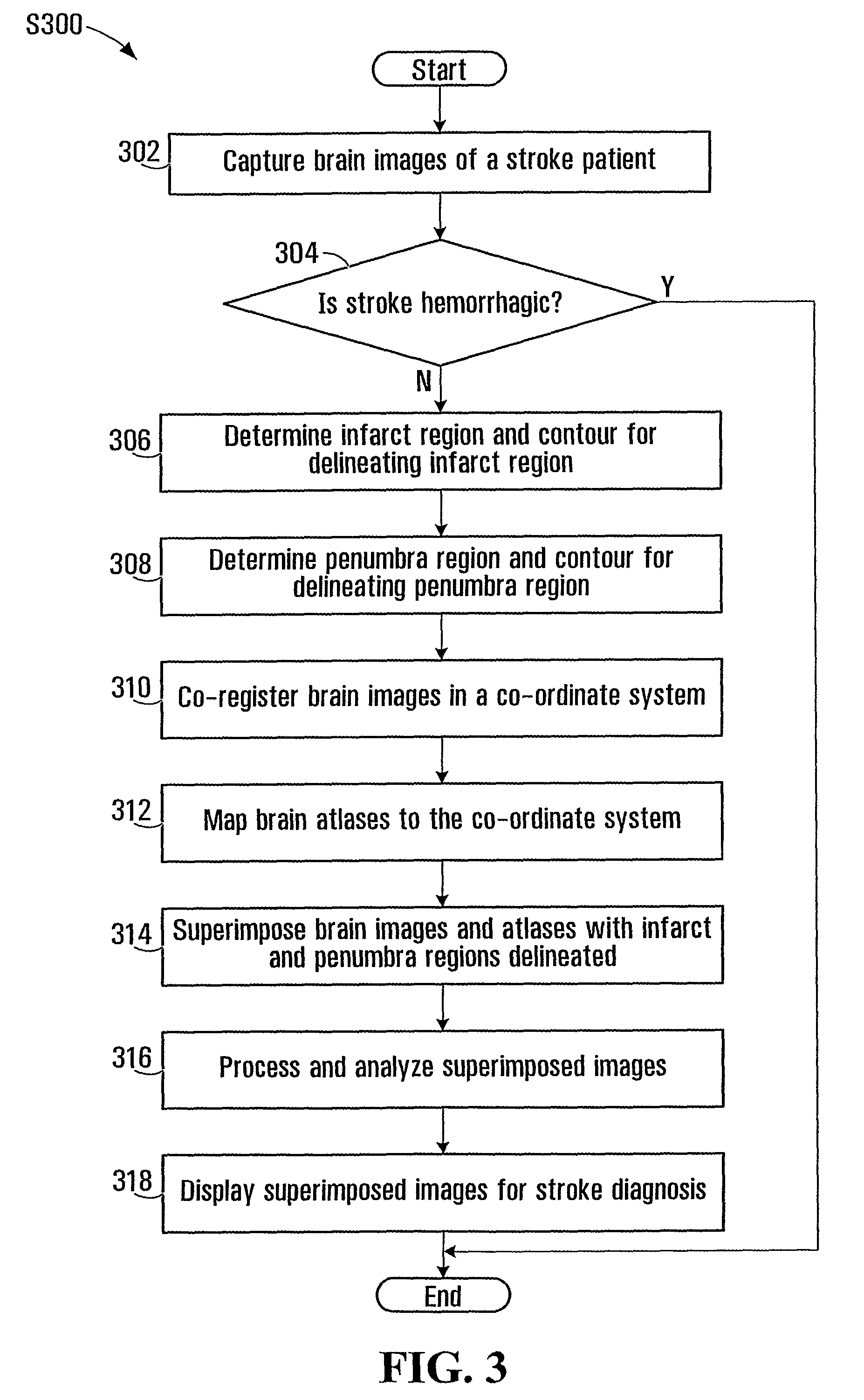
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS20090034812A1Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRisk stroke
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Implantable myocardial ischemia detection, indication and action technology
InactiveUS7277745B2Reduce capacityReduce mechanical performance requirementsElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsThoracic structureCardiac muscle
One embodiment enables detection of MI / I and emerging infarction in an implantable system. A plurality of devices may be used to gather and interpret data from within the heart, from the heart surface, and / or from the thoracic cavity. The apparatus may further alert the patient and / or communicate the condition to an external device or medical caregiver. Additionally, the implanted apparatus may initiate therapy of MI / I and emerging infarction.
Owner:INFINITE BIOMEDICAL TECH
Agents for treating cardiopathy
ActiveUS20090220500A1Improve the situationSuppressing left ventricular remodelingAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCardiac echoLeft ventricular size
The present inventors investigated the effects of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies on improving the condition of infarcted areas in myocardial infarction, and on suppressing left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. As a result, the administration of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies significantly suppressed the increase of MPO activity in the infarcted area and suppressed myocardial MCP-1 expression in both the infarcted area and the non-infarcted area. Furthermore, echocardiography and histological examinations revealed that cardiac hypertrophy is also suppressed.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for treating infarcted regions of tissue following acute myocardial infarction
ActiveUS20060074399A1Extended stayIncreasing stem cell residence timeBalloon catheterSurgeryProgenitorCoronary arteries
Apparatus and methods are provided for treating an infarcted region of myocardium following acute myocardial infarction by reducing the rate of blood flow through infarcted region, and then injecting a solution containing stem cells, endothelial progenitor cells or mediators of stem cell mobilization, migration and attachment into the effected region so that the stem cells become embedded therein and promote tissue regeneration. In a first embodiment, delivery of the stem cells, endothelial progenitor cells or mediators of stem cell mobilization, migration and attachment is accomplished using a catheter that relies upon antegrade flow through the coronary artery and a flow control catheter placed in the coronary sinus. In an alternative embodiment, the delivery catheter delivers the stem cells in a retrograde manner through the coronary sinus, and the delivery catheter further comprises an occlusion balloon for controlling outflow through the coronary sinus ostium.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method and device for percutaneous left ventricular reconstruction
ActiveUS20080097148A1Reduce volumeReducing ventricular volumeSuture equipmentsElectrocardiographyVentricular volumeLeft ventricular size
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
Systems and methods to obtain a myocardial mass index indicative of an at-risk myocardial region
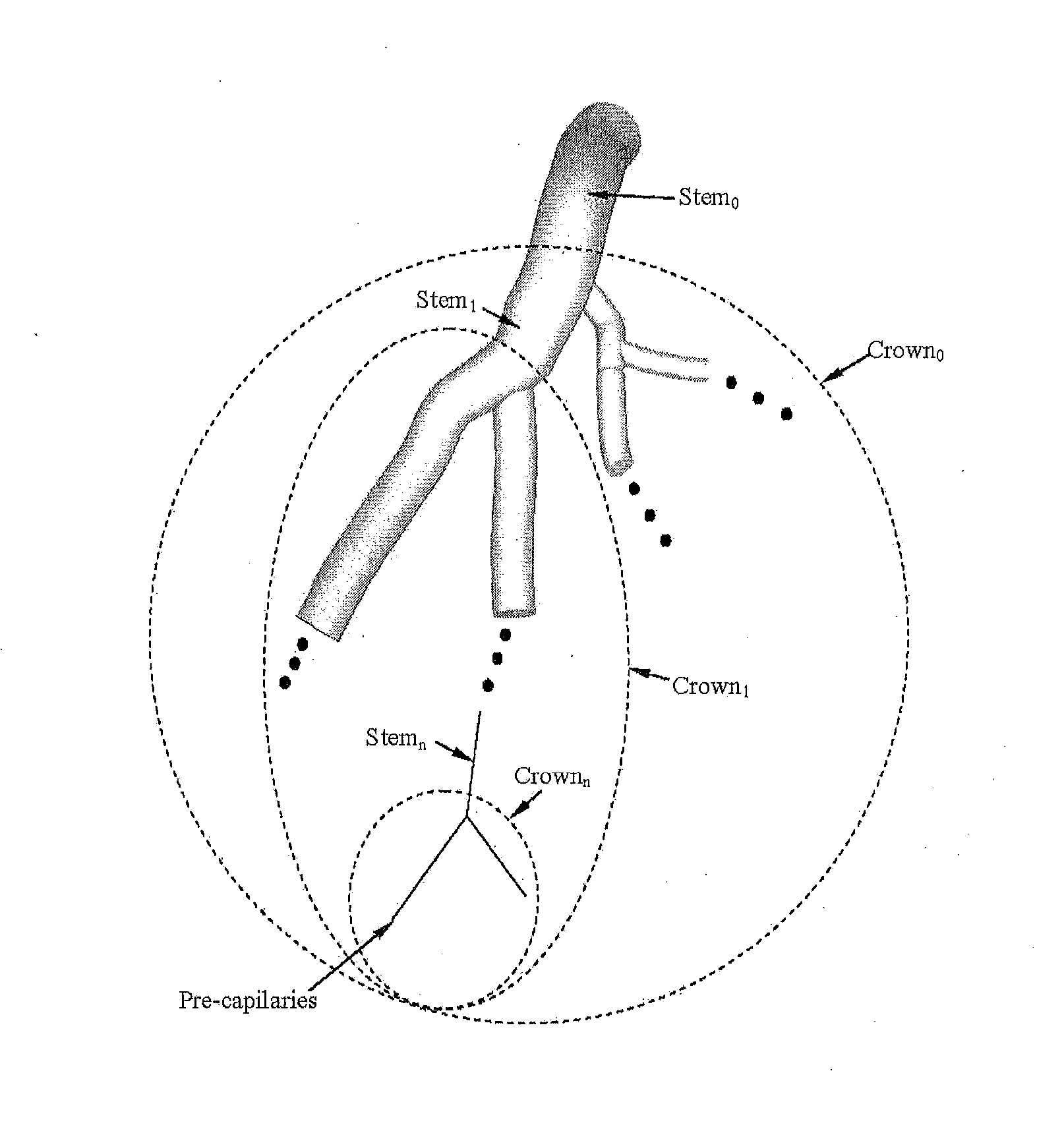
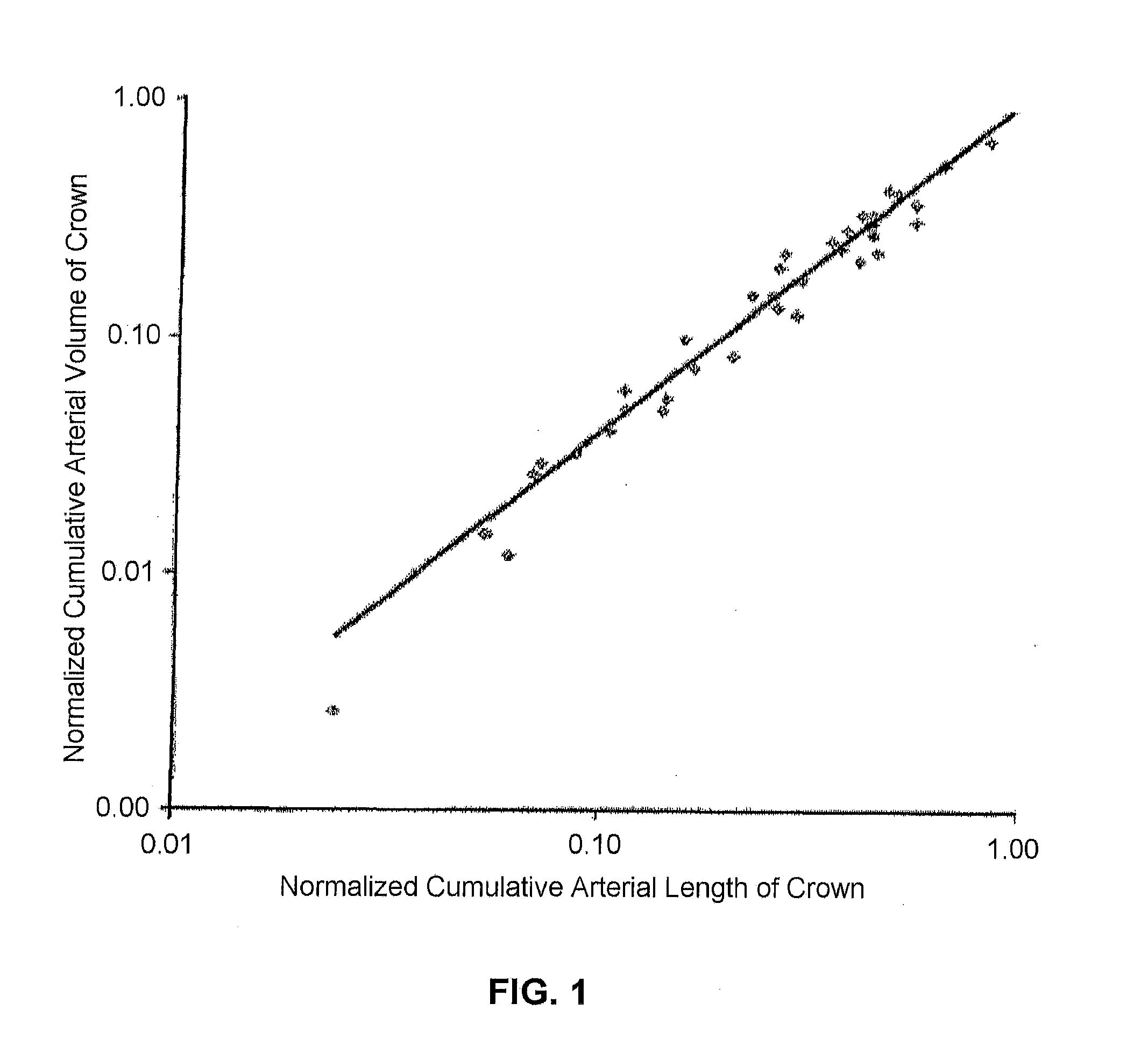
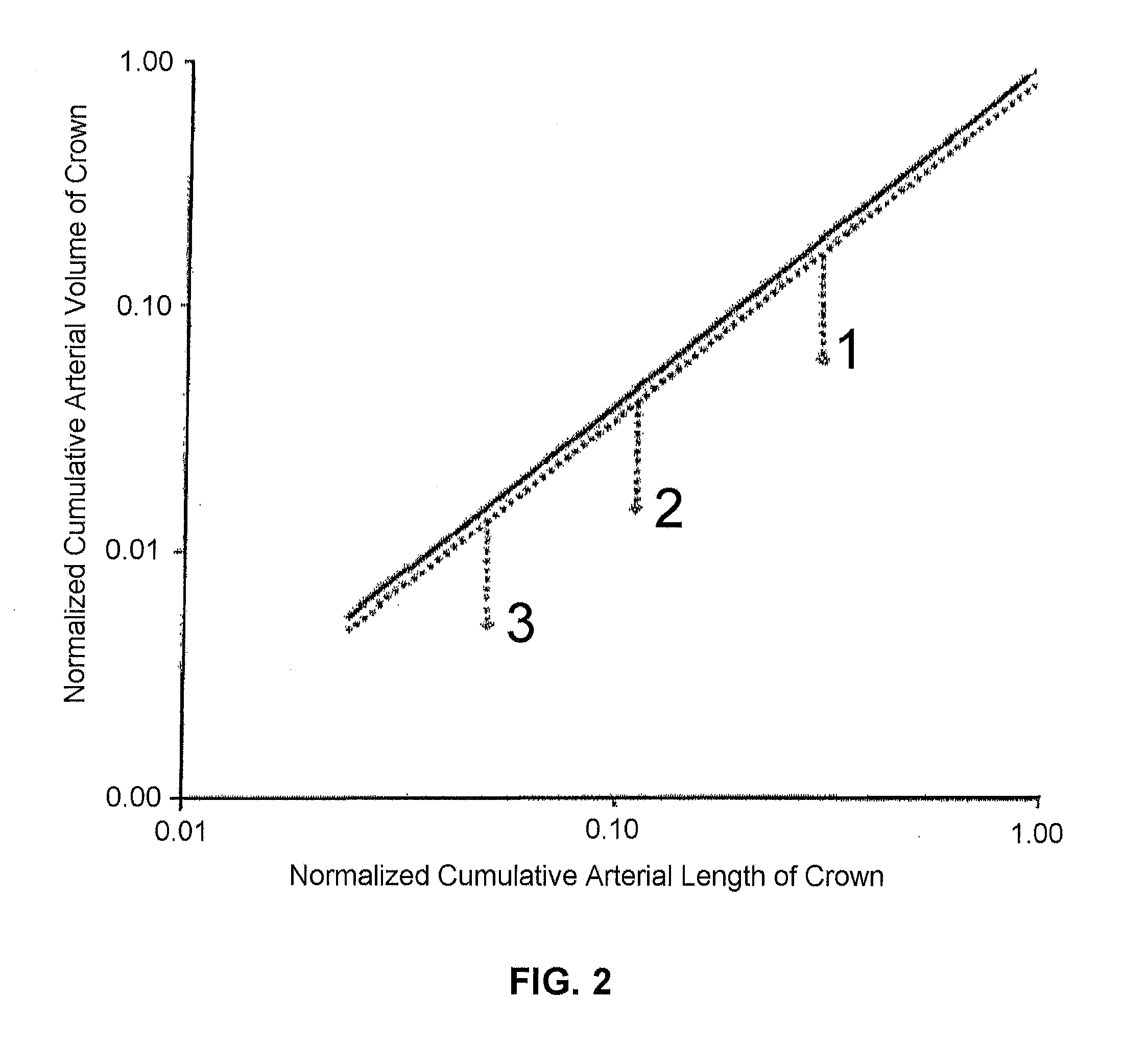
Systems and methods to obtain a myocardial mass index indicative of an at-risk myocardial region. In at least one embodiment, a method for diagnosing a risk of cardiac disease is provided, the method comprising the steps of identifying a luminal cross-sectional area of a side branch vessel, identifying a luminal cross-sectional area of a main artery most proximal to the side branch vessel, determining a myocardial region at risk for infarct from side branch occlusion relative to a mass perfused by the most proximal artery, wherein such region is based on a relationship between the cross-sectional areas of the side branch and the most proximal main artery, and diagnosing a risk of cardiac disease based on a diameter of the side branch and the size of the myocardial region at risk for infarct perfused by the side branch.
Owner:DTHERAPEUTICS
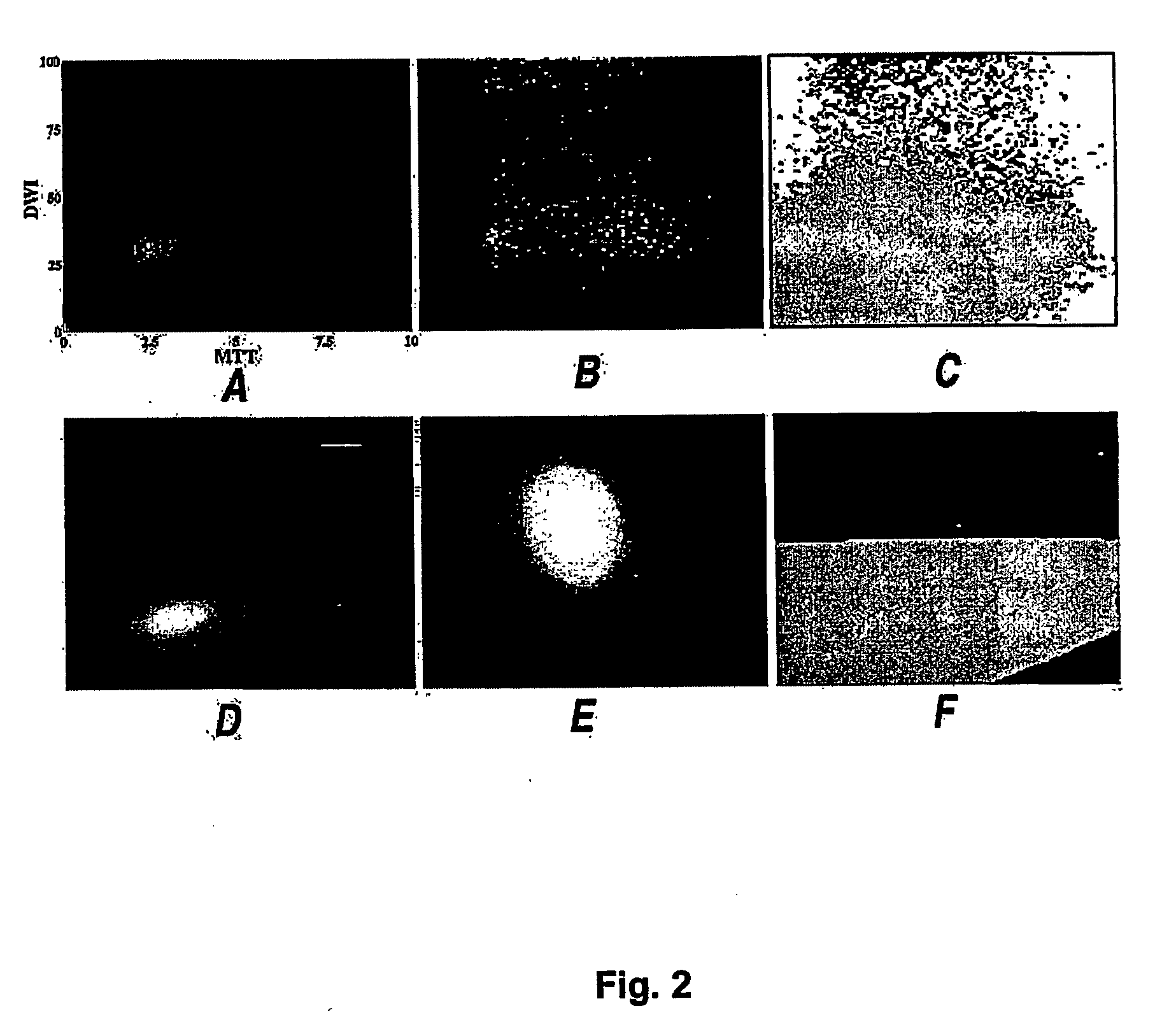
Method of predicting stroke evolution utilising mri
InactiveUS20040106864A1Minimize impactLess-intensive therapyImage enhancementOrganic active ingredientsResonanceRisk stroke
A method predicting stroke evolution uses magnetic resonance diffusion and perfusion images obtained shortly after the onset of stroke symptoms to automatically estimate the eventual volume of dead cerebral tissue resulting from the stroke. The diffusion and perfusion images are processed to extract region(s) of interest presenting tissue at risk of infarction. A midplane algorithm is also used to calculate ratio and diffusion and perfusion measures for modelling infarct evolution. A parametric normal classifier algorithm is used to predict infarct growth using the calculated measures.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Devices, systems, and methods for promotion of infarct healing and reinforcement of border zone
ActiveUS20100185140A1Convenient introductionPromote blood flowEpicardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsInfusion catheterSurgery
Devices, systems, and methods for accessing tissue, including the internal and external tissues of the heart, are disclosed. At feast some of the embodiments disclosed herein provide access to the tissues surrounding the heart to facilitate myocardial infarct healing and border zone reinforcement. In at least one embodiment, a suction / infusion catheter is used to provide localized suction to an area of myocardial infarct. In another embodiment, a suction infusion catheter is used to deliver a glue-like substance and magnetic cells to a myocardial infarct border zone.
Owner:CVDEVICES
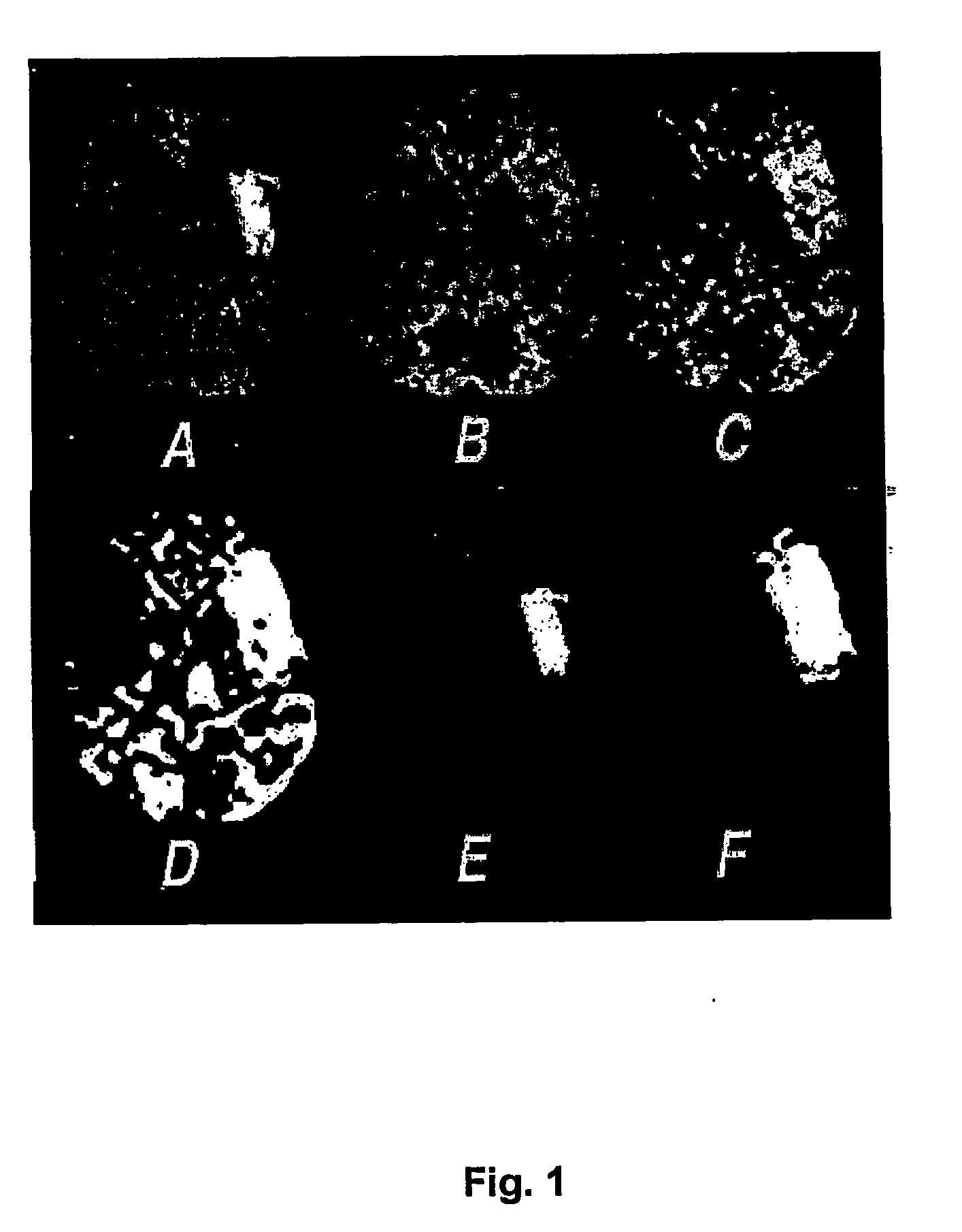
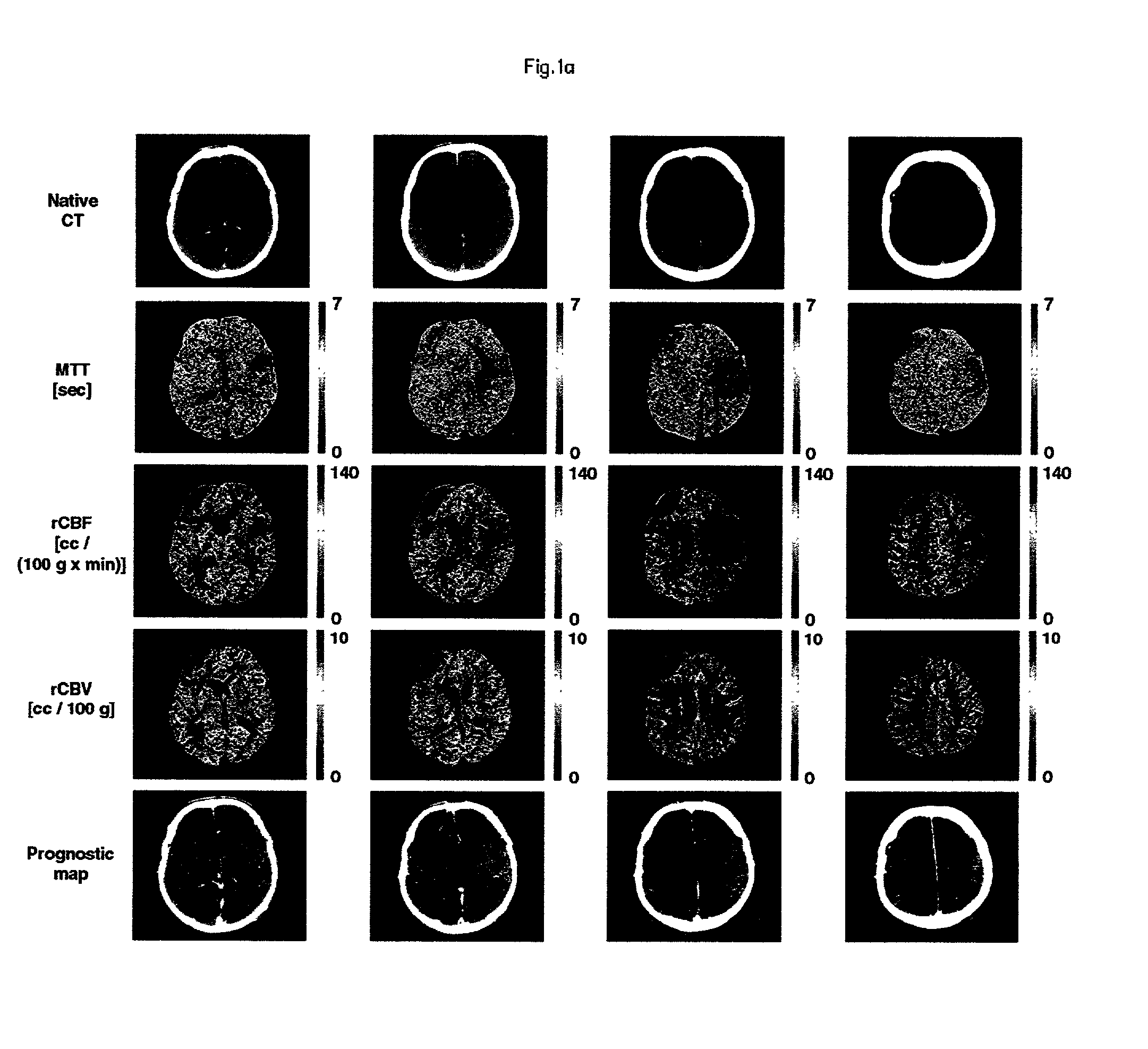
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
InactiveUS20020161292A1Computerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyCerebral blood volume
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second value. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
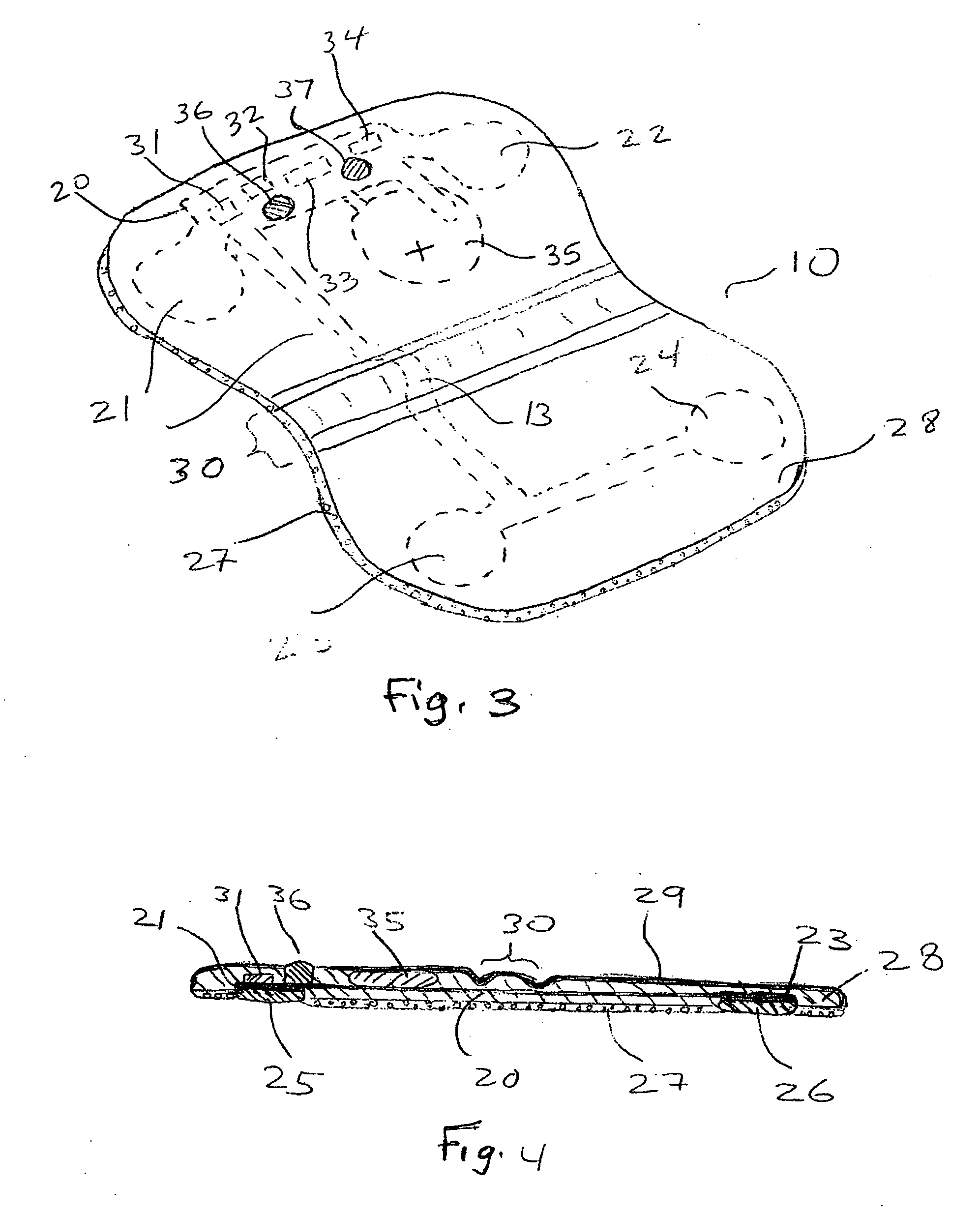
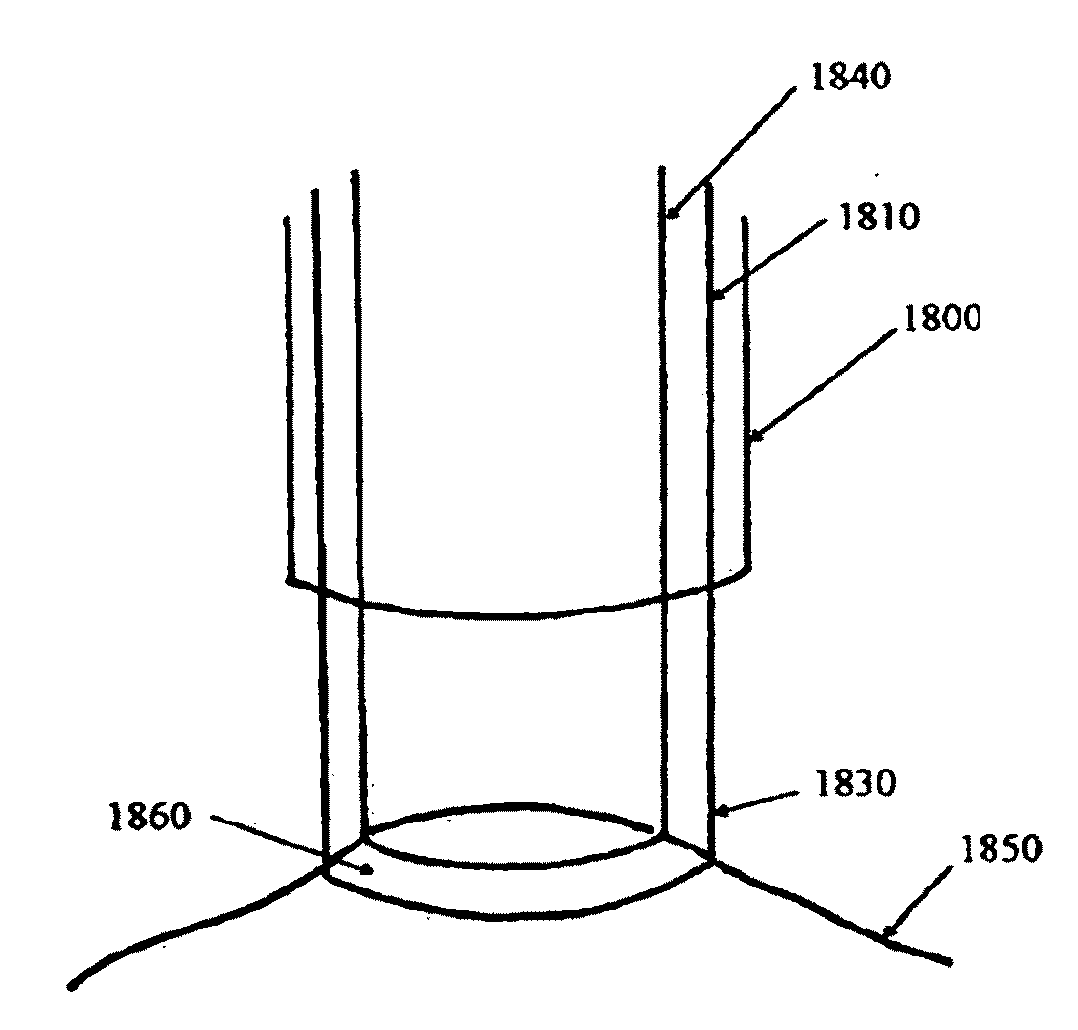
Method for producing a device applicable to biological tissues, particularly a patch for treating damaged tissues, and a device obtained by said method
ActiveUS20120070485A1Slow kineticsEasy to controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHaemostatic functionCross-link
The present invention relates to a device consisting of cross-linked nanofibrillary fibrin supported on and rooted to a microporous nonwoven fabric consisting of a biocompatible synthetic polymer material. An active ingredient is advantageously dispersed in the fibrin layer. The fibrin layer does not have a haemostatic function, but is suitable for retaining the active ingredient and releasing it with controlled kinetics. The device forming the object of the invention, preferably in the form of patches, is useful for in vitro cell cultures or for treating tissues damaged by wounds or necrosis, such as cardiac walls bearing the sequelae of infarction, or a tissue damaged by a diabetic ulcer. The patch according to the invention can be manufactured by inducing the polymerisation of the fibrin, under suitable conditions, directly on the support layer, which is suitably impregnated with thrombin (at least in a superficial portion of its thickness), and which has been conveniently prepared by means of a spray phase-inversion technique.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE +1
Cellular fibronectin as a diagnostic marker in stroke and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7392140B2Convenient treatmentAdditional diagnostic and/or prognostic indicatorsMedical data miningDisease diagnosisStroke subtypeGastroenterology
Methods for the diagnosis and evaluation of stroke and stroke sub-type employ a variety of bio-markers including cellular fibronectin (c-Fn) assembled as a panel for stoke diagnosis and evaluation. Methods are disclosed for selecting markers and correlating their combined levels with a clinical outcome of interest. In various aspects the methods permit early detection and differentiation of stroke subtypes, determination of the prognosis of a patient presenting stroke symptoms, and identification of a patient at risk for early hematoma growth and / or malignant massive cerebral artery infarction. The disclosed methods provide rapid, sensitive and specific assays to greatly increase the number of patients that can receive beneficial stroke treatment and therapy, and to reduce the human and economic costs associated with incorrect stroke diagnosis.
Owner:PREDICTION SCI
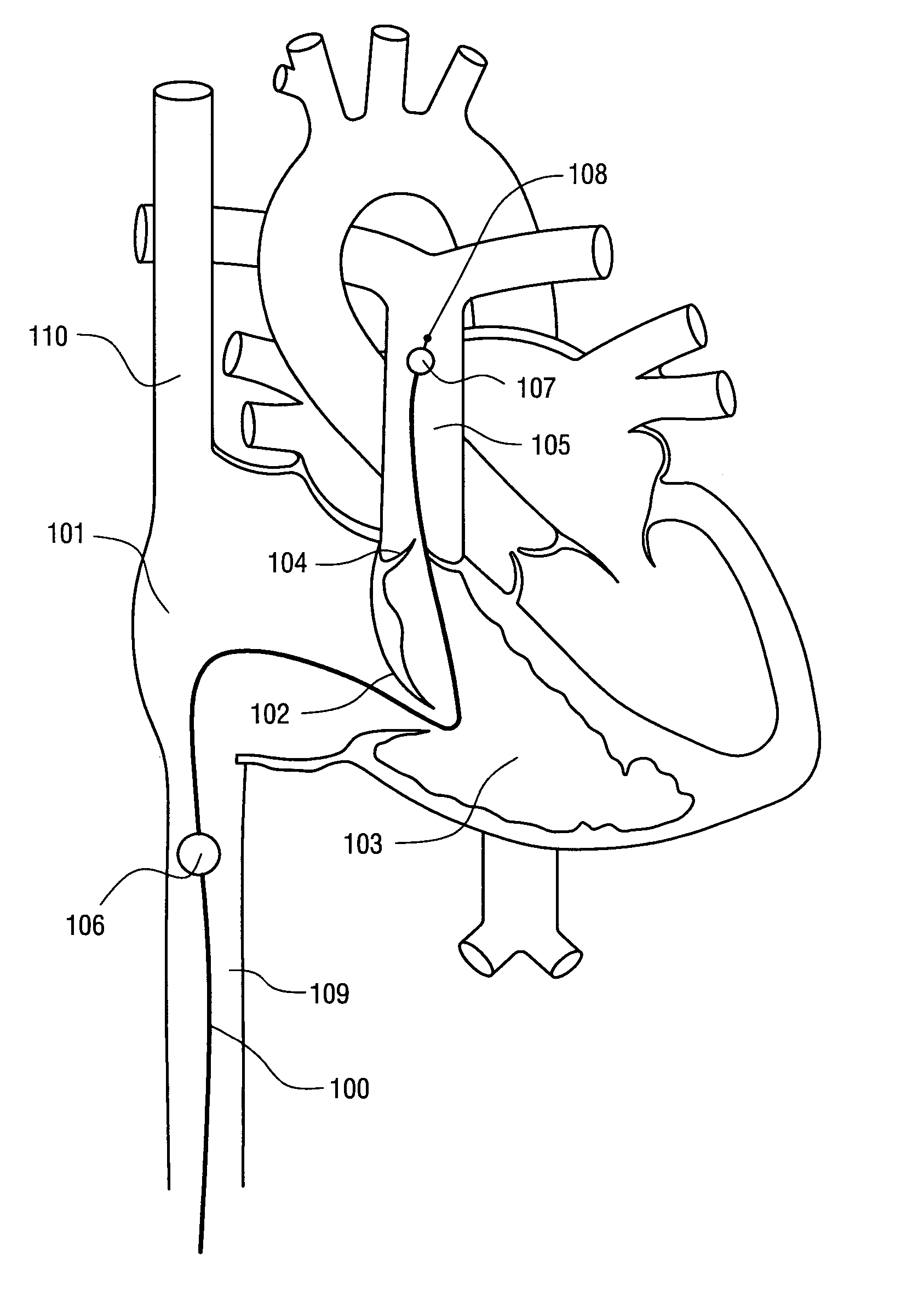
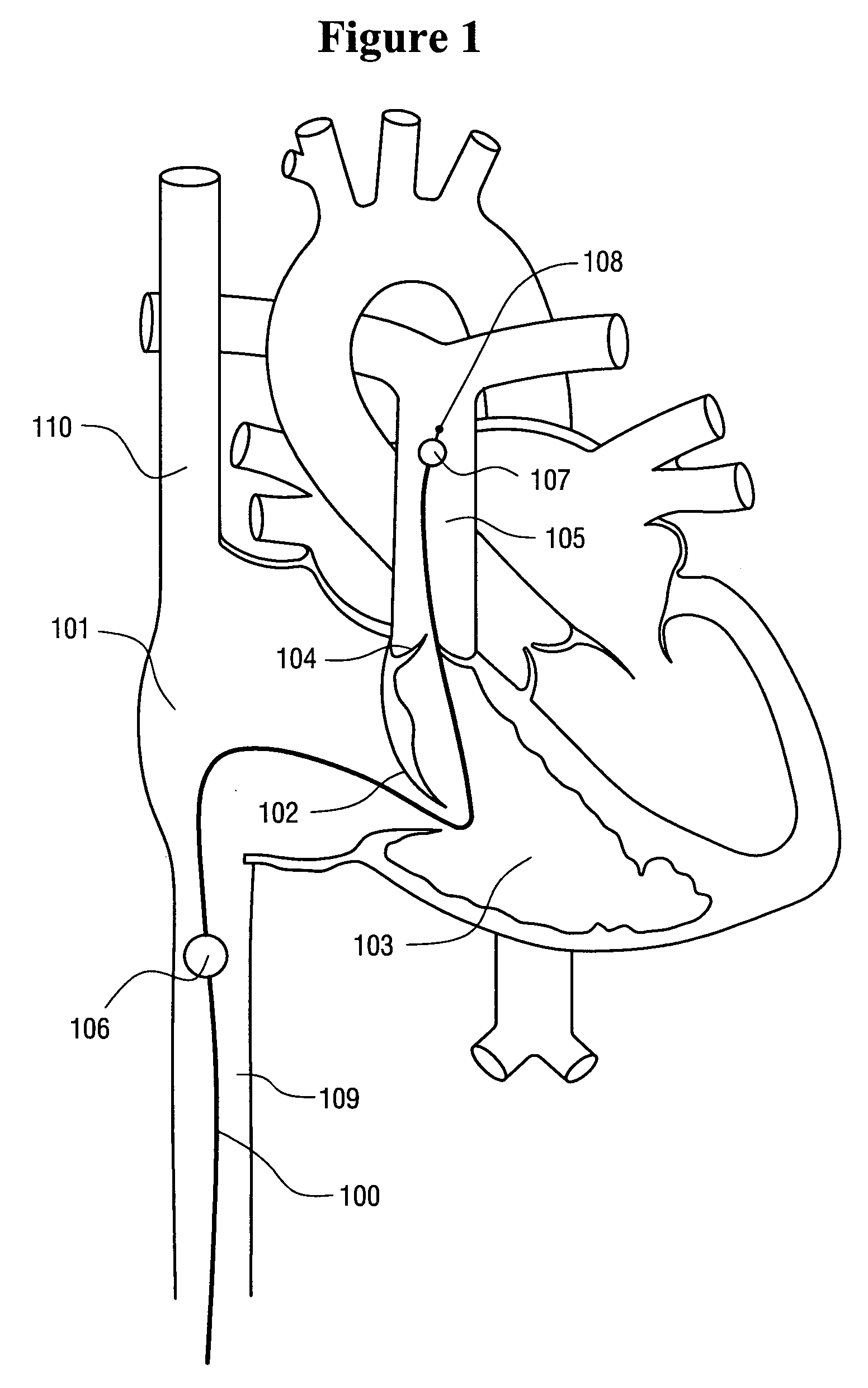
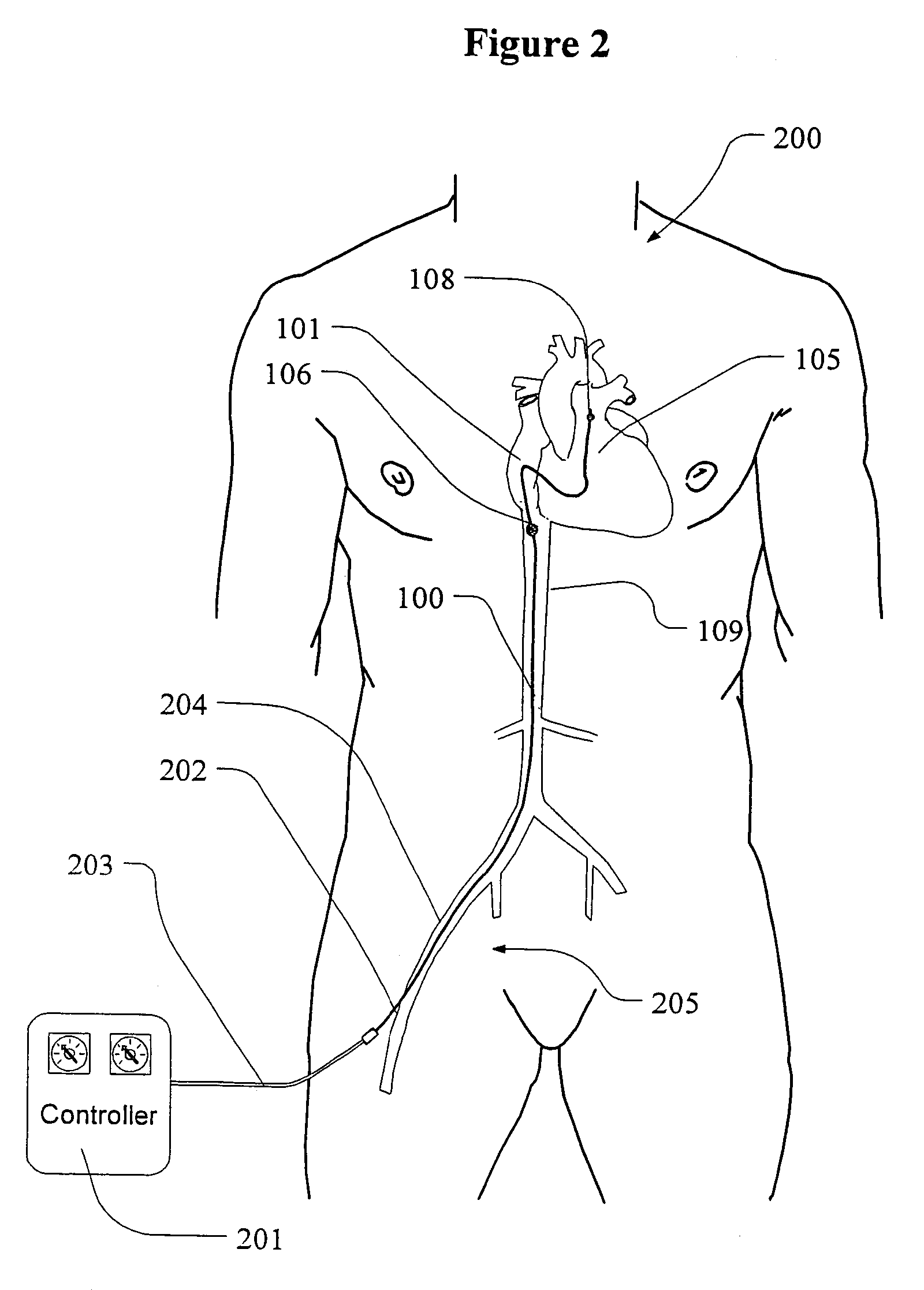
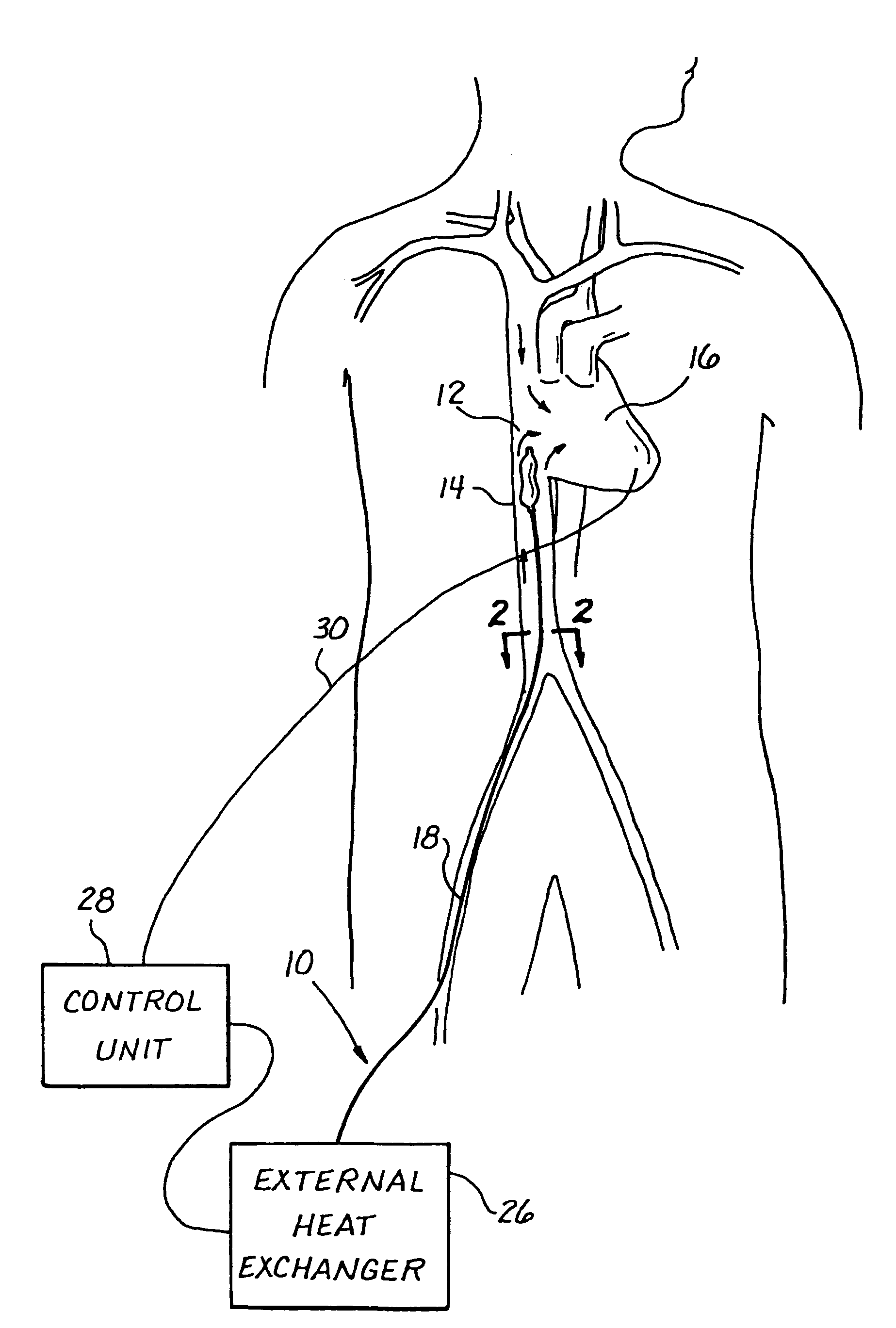
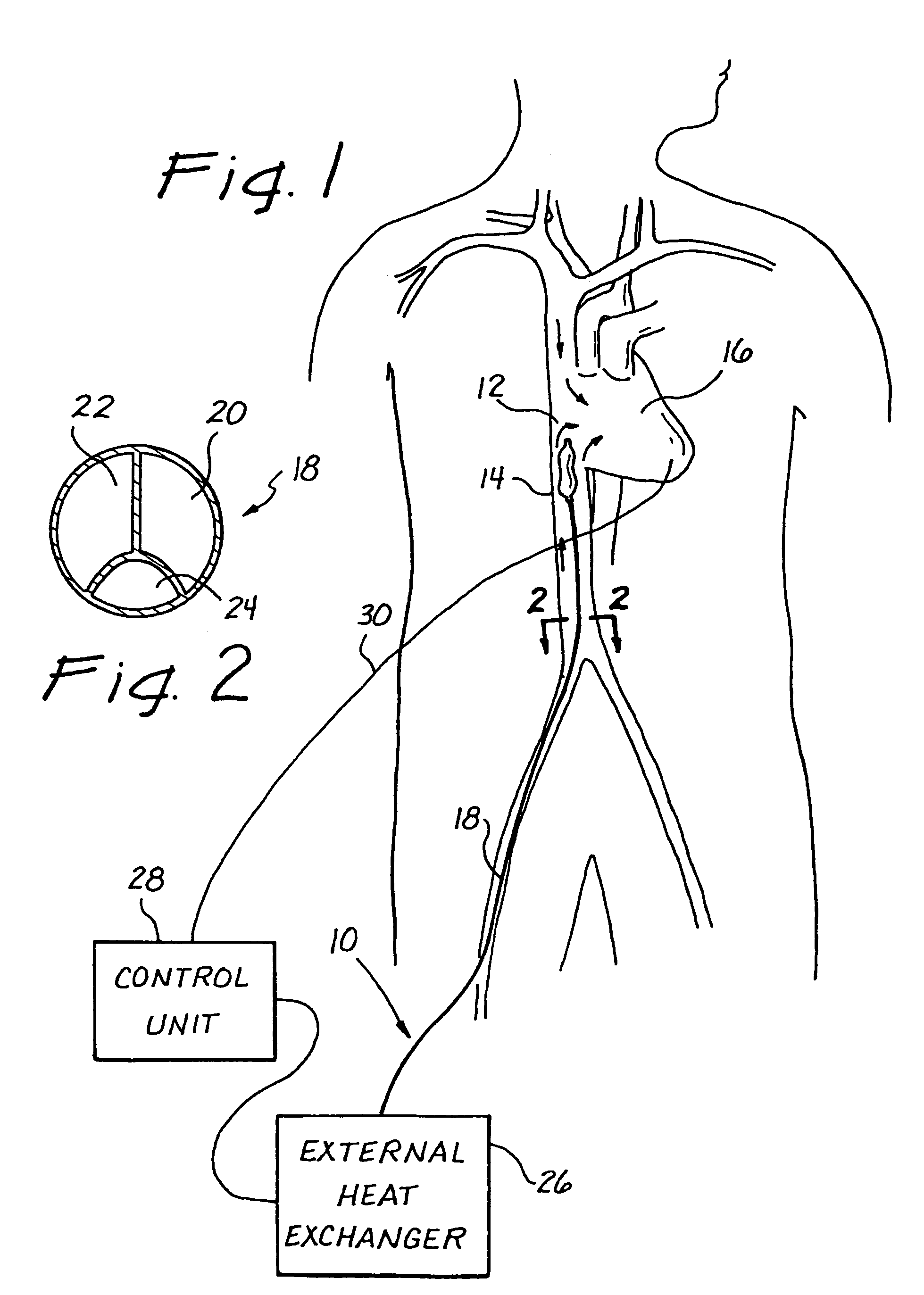
Use of intravascular hypothermia during angioplasty procedures
InactiveUS7510569B2Prevent and deter and minimize and treat other type of damagePrevent and lessen myocardial infarctionStentsCatheterPercutaneous angioplastyIschemic myocardium
Methods and apparatus for preventing myocardial infarction, or lessening the size / severity of an evolving myocardial infarction, by cooling at least the affected area of the myocardium using an intravascular heat exchange catheter. The heat exchange catheter may be inserted into the vasculature (e.g., a vein) and advanced to a position wherein a heat exchanger on the catheter is located in or near the heart (e.g., within the vena cava near the patient's heart). Thereafter, the heat exchange catheter is used to cool the myocardium (or the entire body of the patient) to a temperature that effectively lessens the metabolic rate and / or oxygen consumption of the ischemic myocardial cells or otherwise protects the ischemic myocardium from undergoing irreversible damage or infarction.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
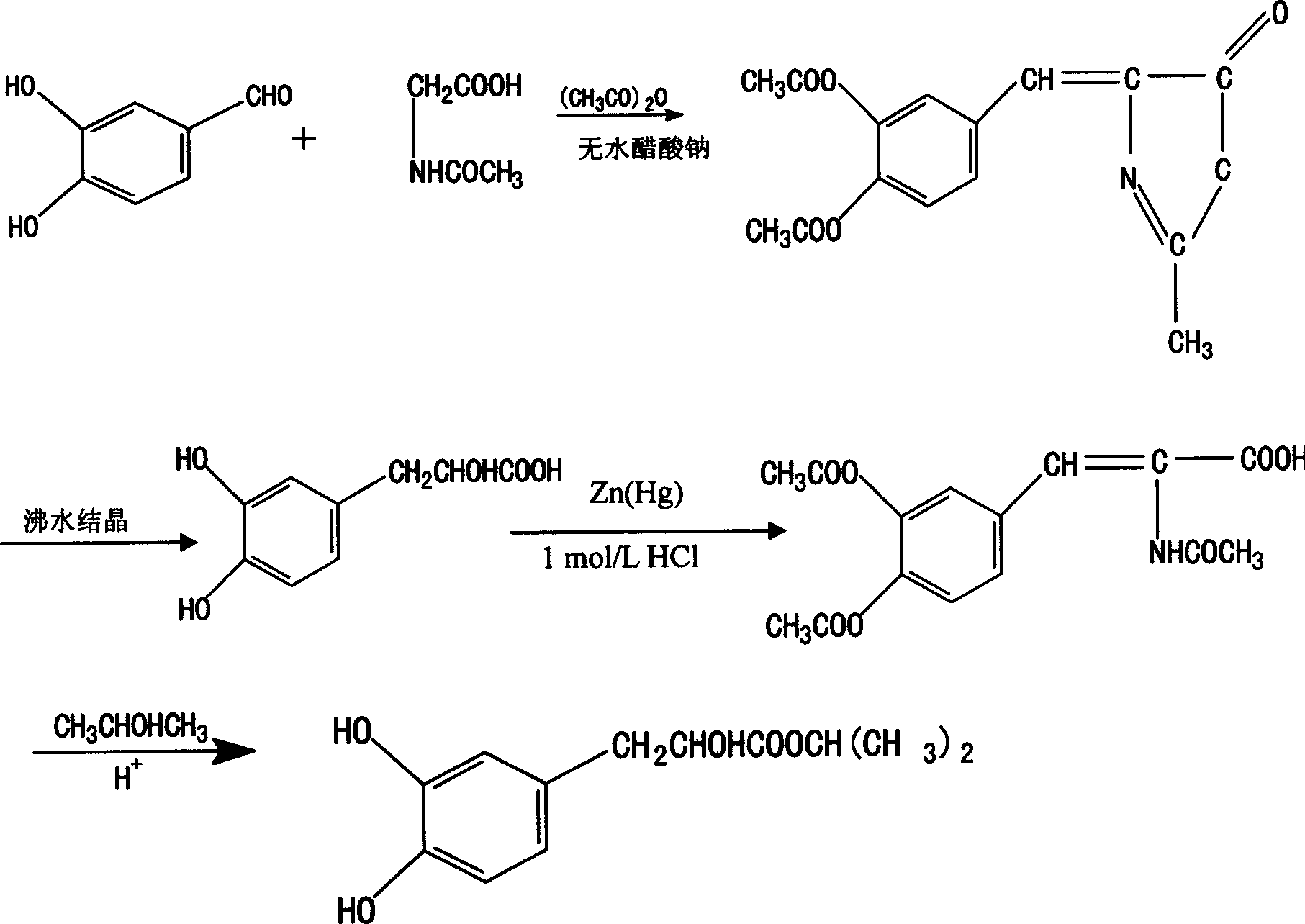
Beta (3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-hydroxyisopropyl propionate and its synthesis
InactiveCN1583710AReduce frequencyReduce morbidityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical structureDisease
The invention relates to effective components of root of red-rooted salvia to treat disease and its chemical structure and synthesize technique. It is used to treat heart and blood vessel of brain diseases. Filter the main metabolite-beta(-3,4- dihydric phenyl)-alpha hydric propionic acid isopropyl ester in human blood serum after taking medicine. The purity is 98.0%. The results demonstrate the medicine to have varies function in blood vessel dilatation, anti cerebral ischemia, oxidation resisting in vitro, and protect heart and brain and remission the diabetes caused miocardial infarction.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Use of timosaponin for preparing medicine for preventing and treating brain apoplexy
InactiveCN1451384AReduce edemaReduce volumeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderReperfusion injuryCerebral edema
An use of common timosaponin in preparing medicine or food for preventing and treating cerebral apoplexy is disclosed.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating cardiac, cerebral and vascular diseases and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101690764ARestore elasticityPrevent agglutinationHeavy metal active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsOysterCoronary heart disease
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine for treating cardiac, cerebral and vascular diseases; the drug is composed of forty kinds of crude drugs by weight parts: milk veteh, salvia miltiorrhiza, root of common peony, ligusticum wallichii, lumbricus, sanguisuga, rhizoma acori graminei, polygala root, red ocher, oyster, angelica, the root of kudzu vine, arisaema cum bile and the like; the preparation method is that: (1) the crude drugs are prepared into water extract liquid; (2) the water extract liquid is prepared into oral liquid; (3)the water extract liquid obtained by the step (1) is dried, crushed, sieved, undersize material is extracted powder; (4) the extracted powder prepared by the step (3) is prepared into various dosage forms. The preparation method of crude powder is that: lime earth of the crude drugs is sieved, and then the crude drugs are crushed and sieved, the undersize material is taken out and is sterilized to be crude powder, and the crude powder is prepared into various dosage forms. The traditional Chinese medicine has the major functions of treating miocardial infarction and angina caused by coronary heart disease, high blood pressure and cerebral thrombosis, hemiplegia, cerebral infarction, cerebrovascular accident, sequel of apoplexy and other symptoms, and the medicine has obvious effect on headache, dizziness and heart cerebrovascular diseases caused by high blood pressure and cerebral circulation insufficiency.
Owner:卢速江
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS8019142B2Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMedicine
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
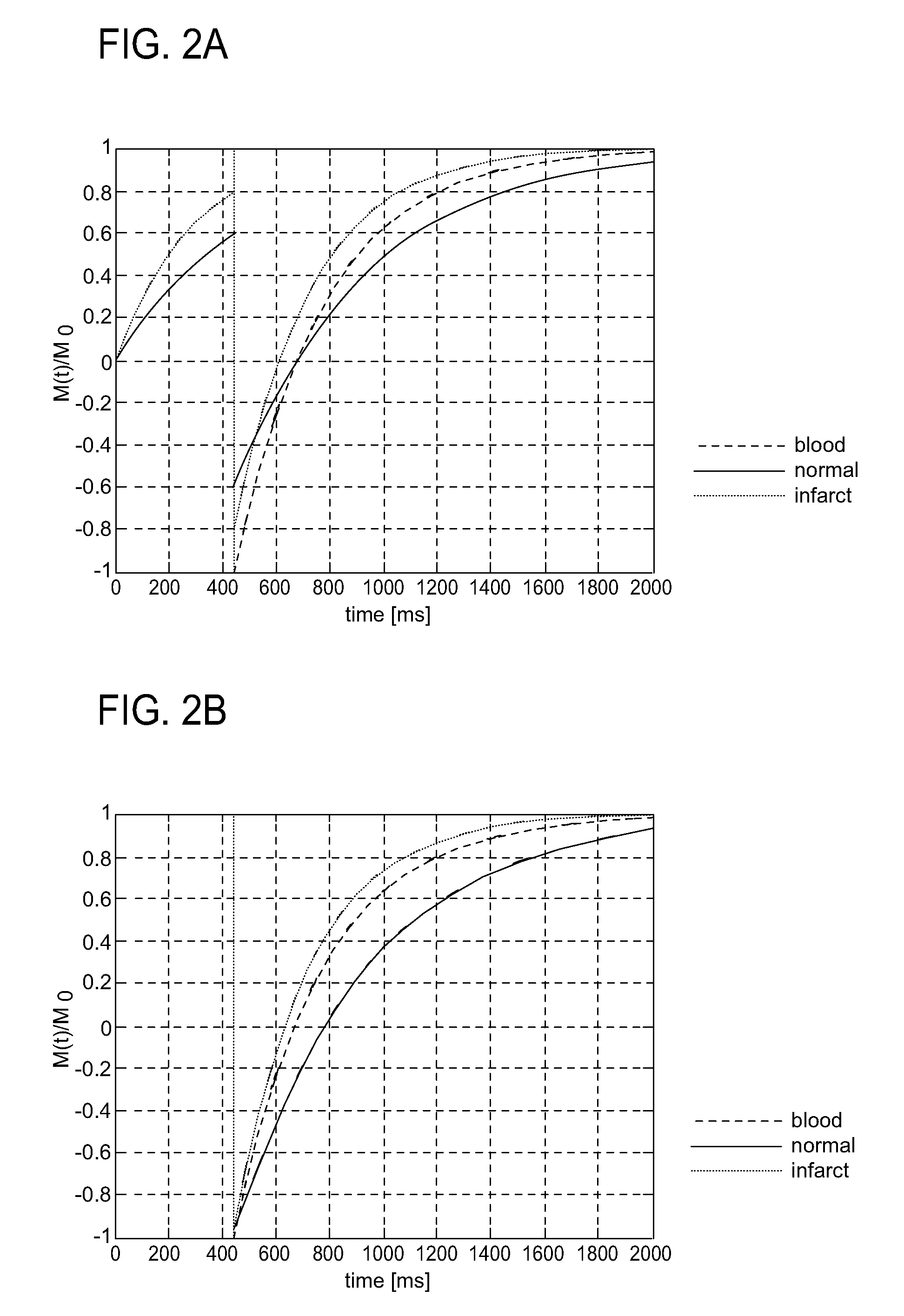
Dark blood delayed enhancement magnetic resonance viability imaging techniques for assessing subendocardial infarcts
ActiveUS20090005673A1Improve image contrastRaise modalDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRelaxation curveCardiac cycle
The technology herein provides a dark blood delayed enhancement technique that improves the visualization of subendocardial infarcts that may otherwise be disguised by the bright blood pool. The timed combination of a slice-selective and a non-selective preparation improves the infarct / blood contrast by decoupling their relaxation curves thereby nulling both the blood and the non-infarcted myocardium. This causes the infarct to be imaged bright and the blood and non-infarct to both be imaged dark. The slice-selective preparation occurs early enough in the cardiac cycle so that fresh blood can enter the imaged slice.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com