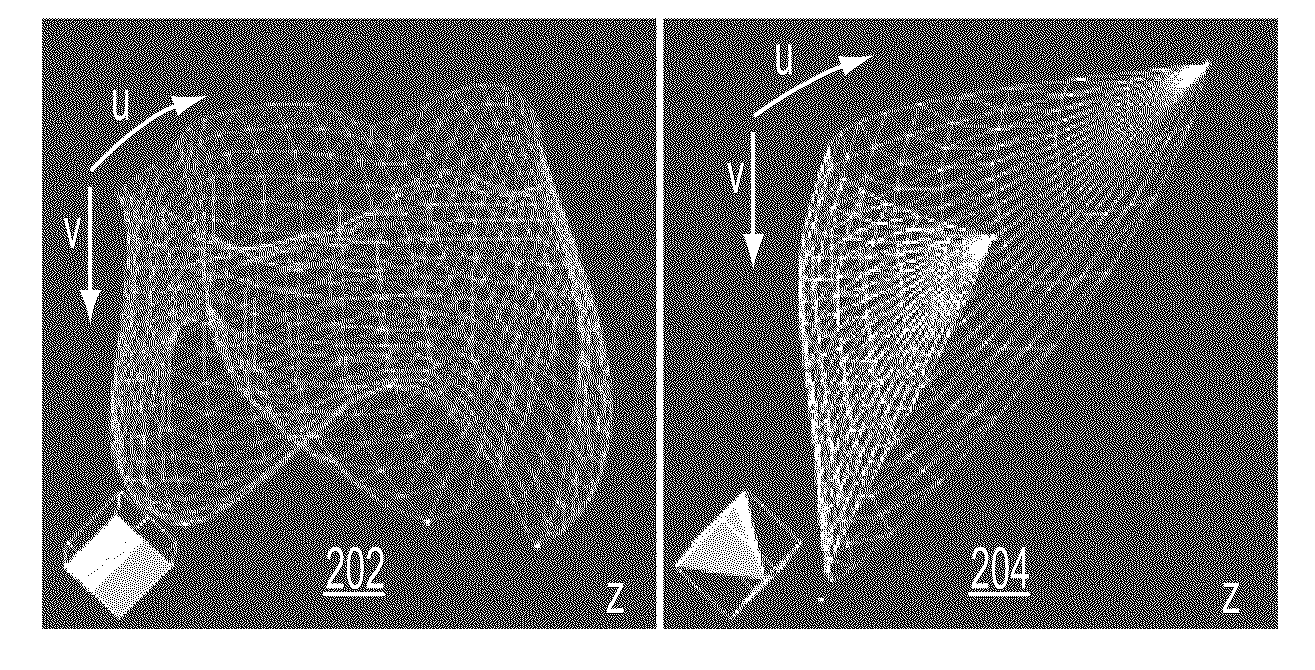Patents
Literature
123 results about "Cardiac echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>Normal results are inferred when the images produced do not show any complications.</li><li>Abnormal results are signified when images show defects in heart size, shape, muscles or valves.</li></ul>
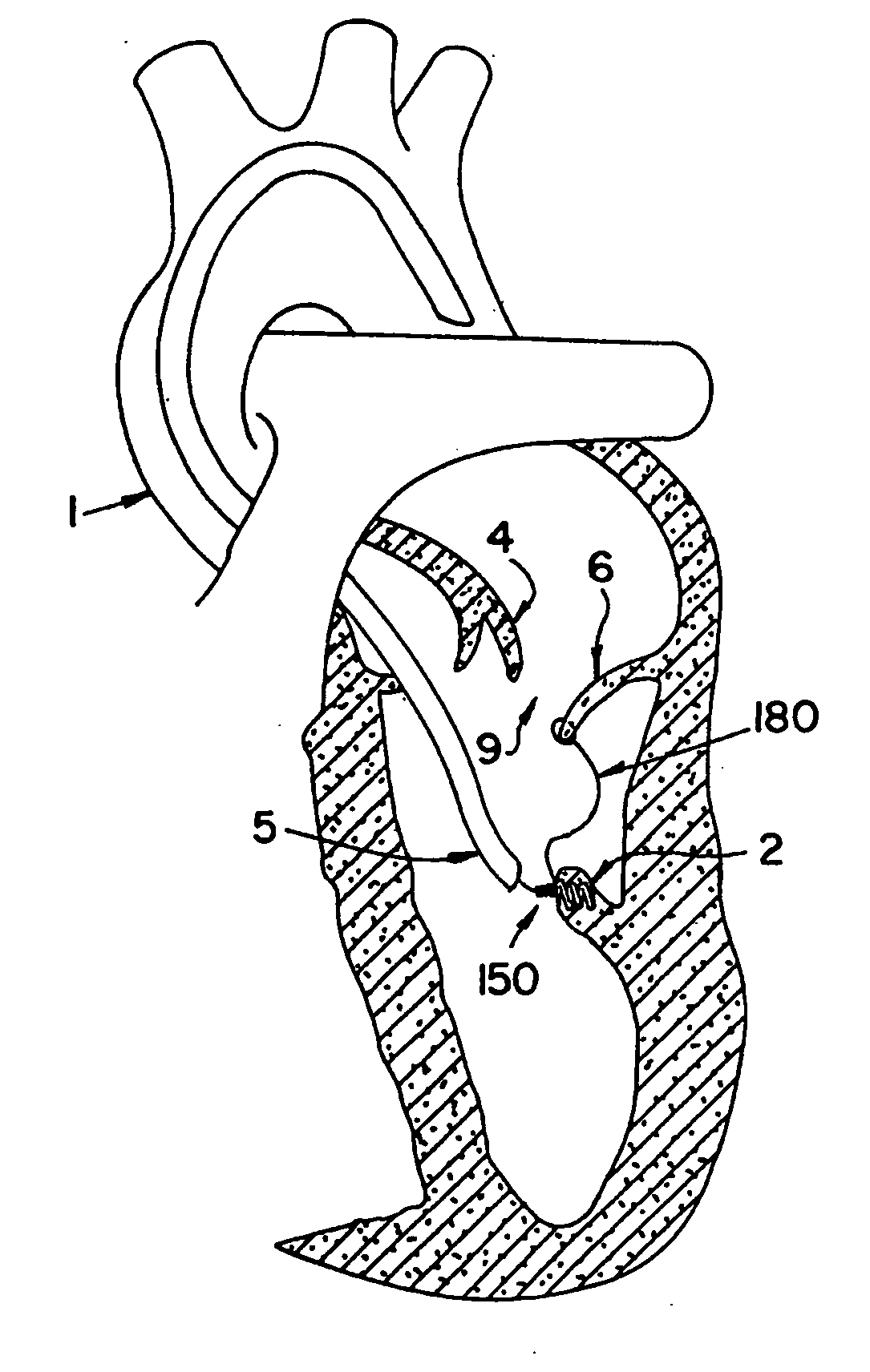
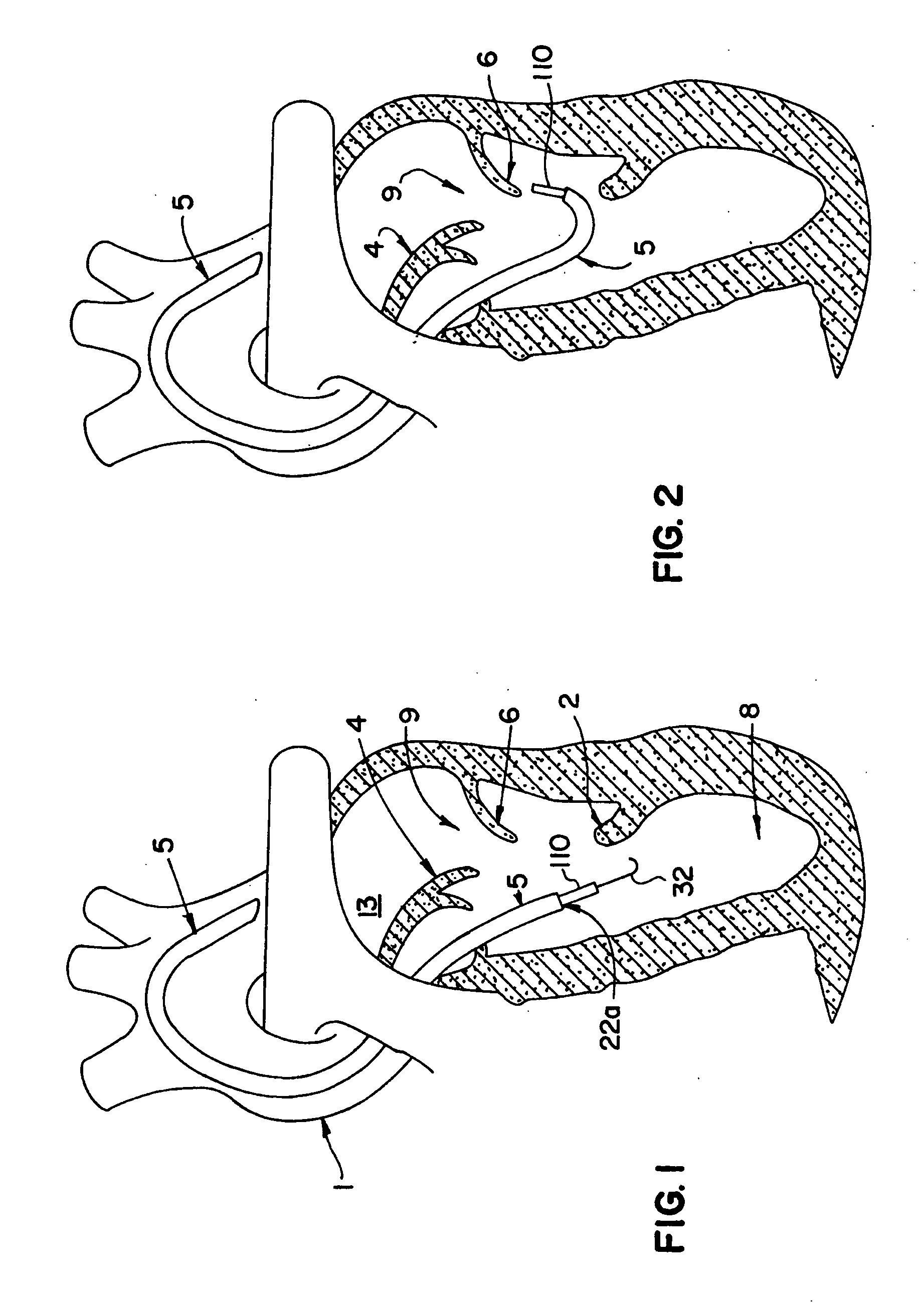
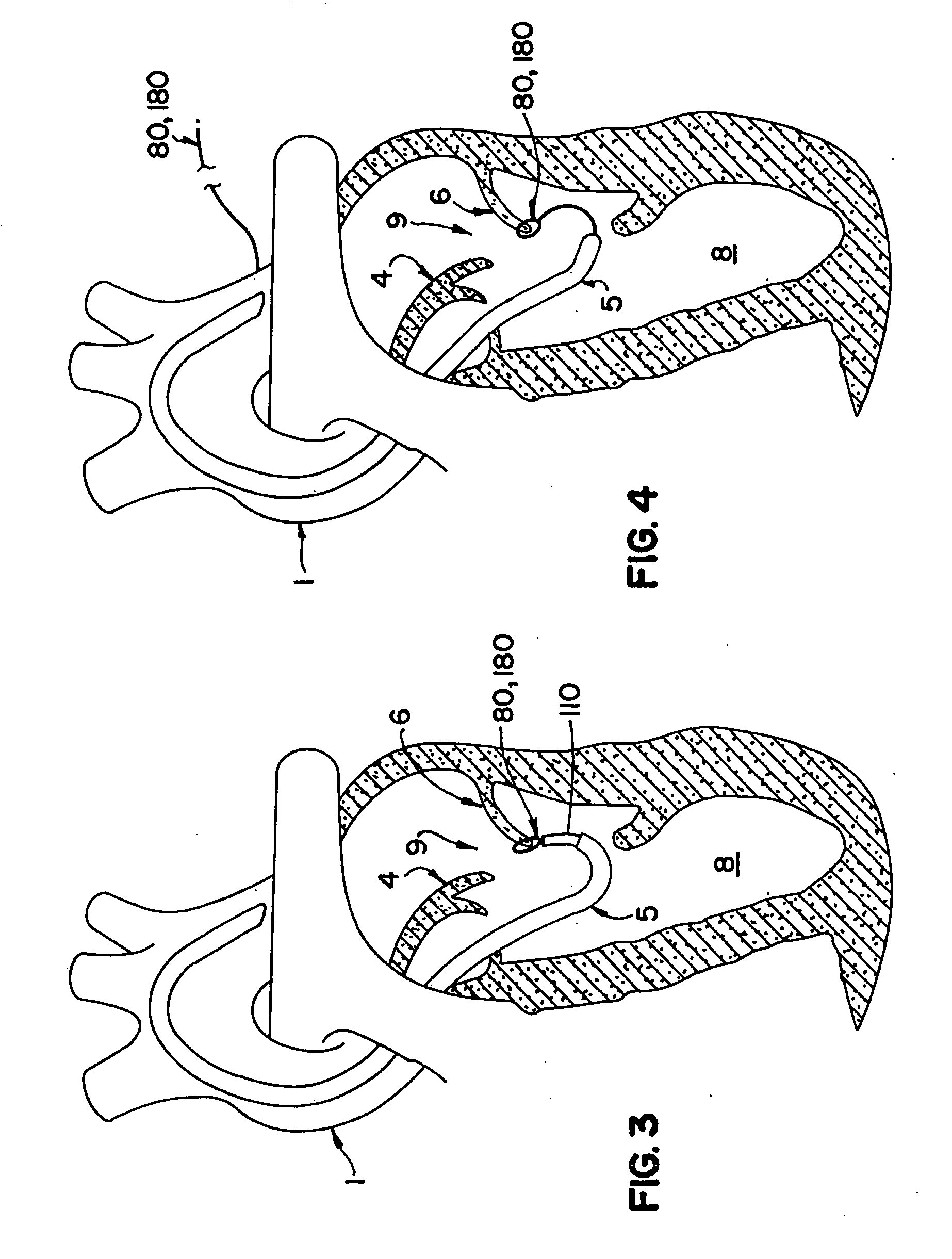
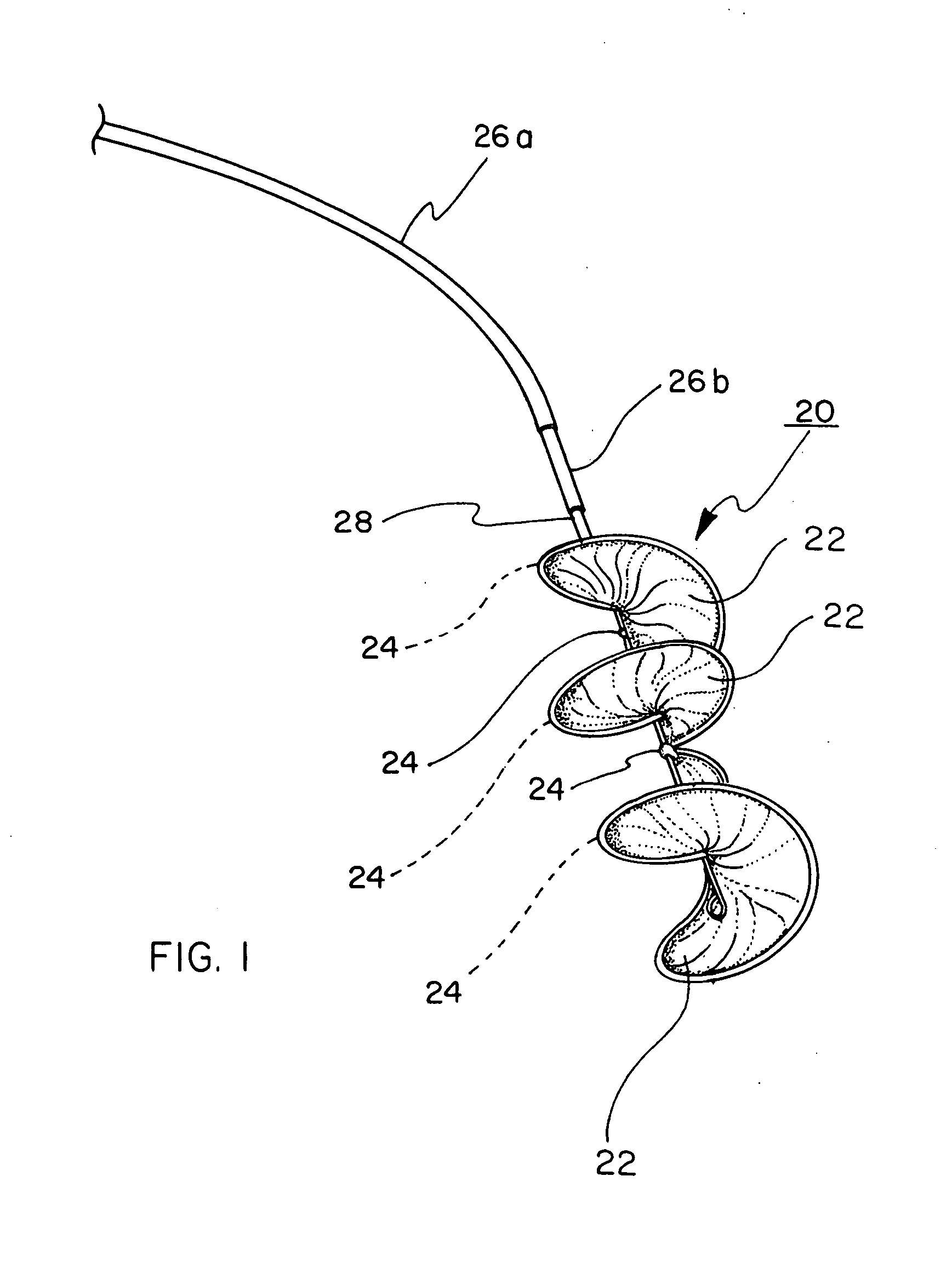
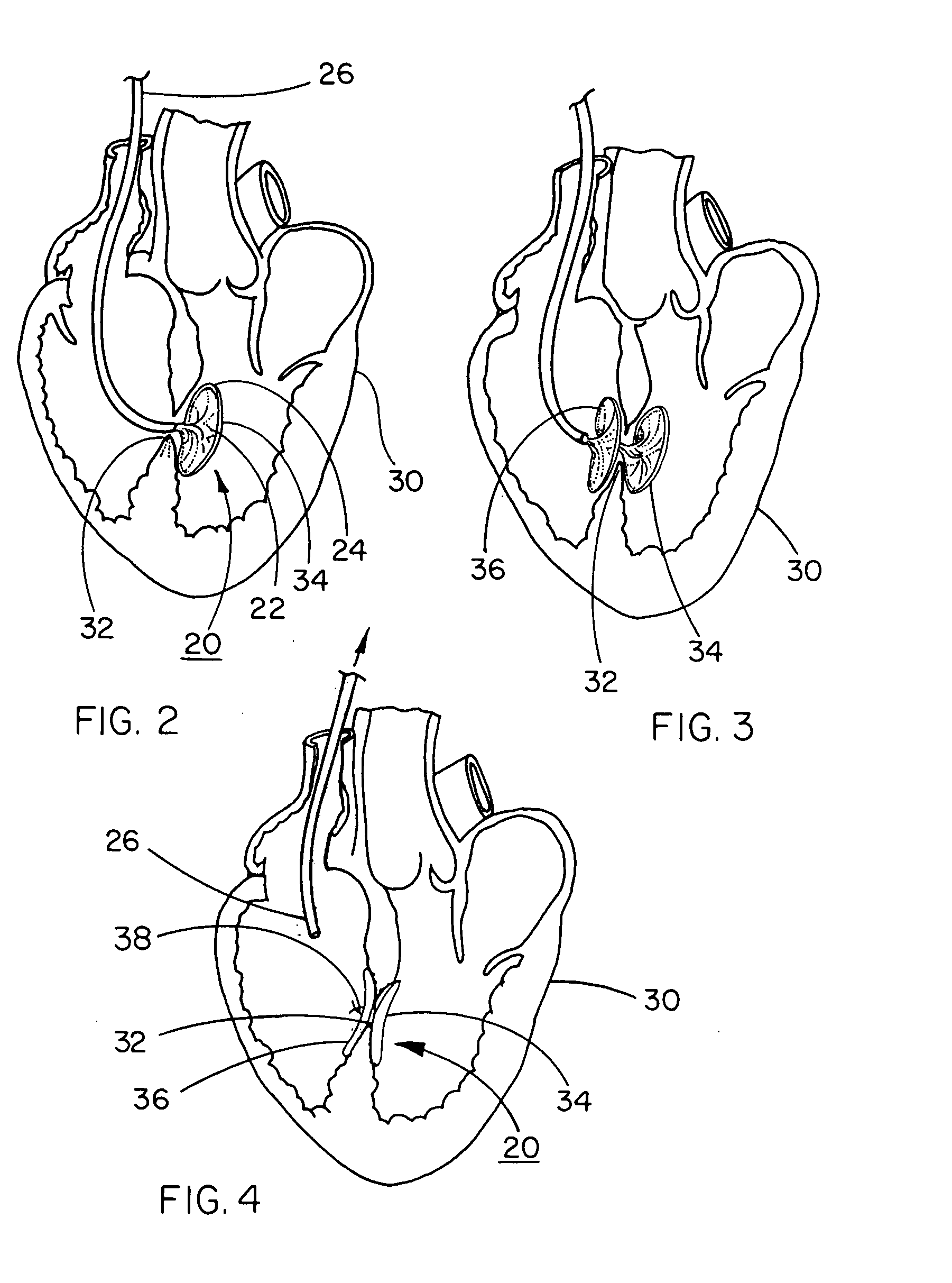
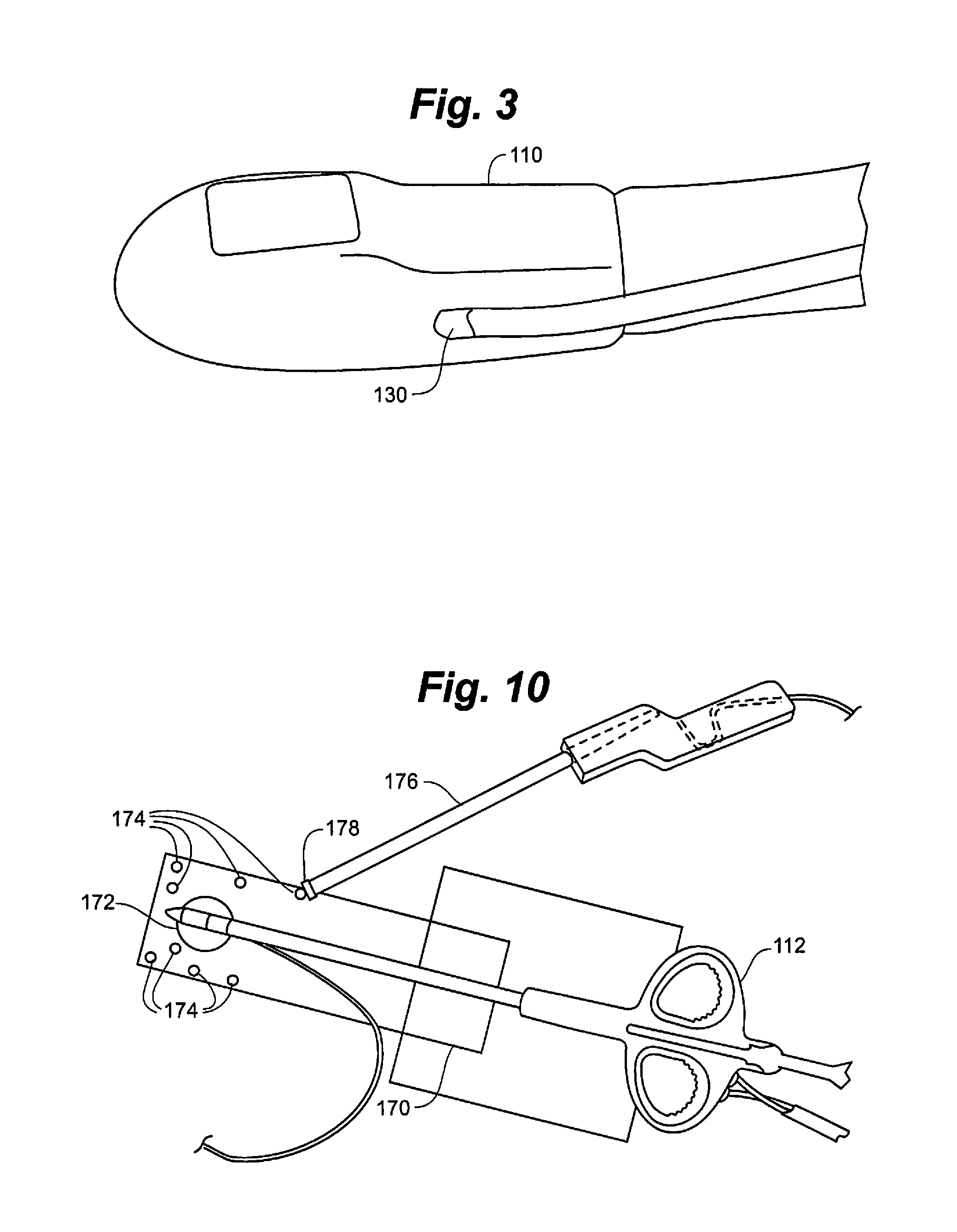
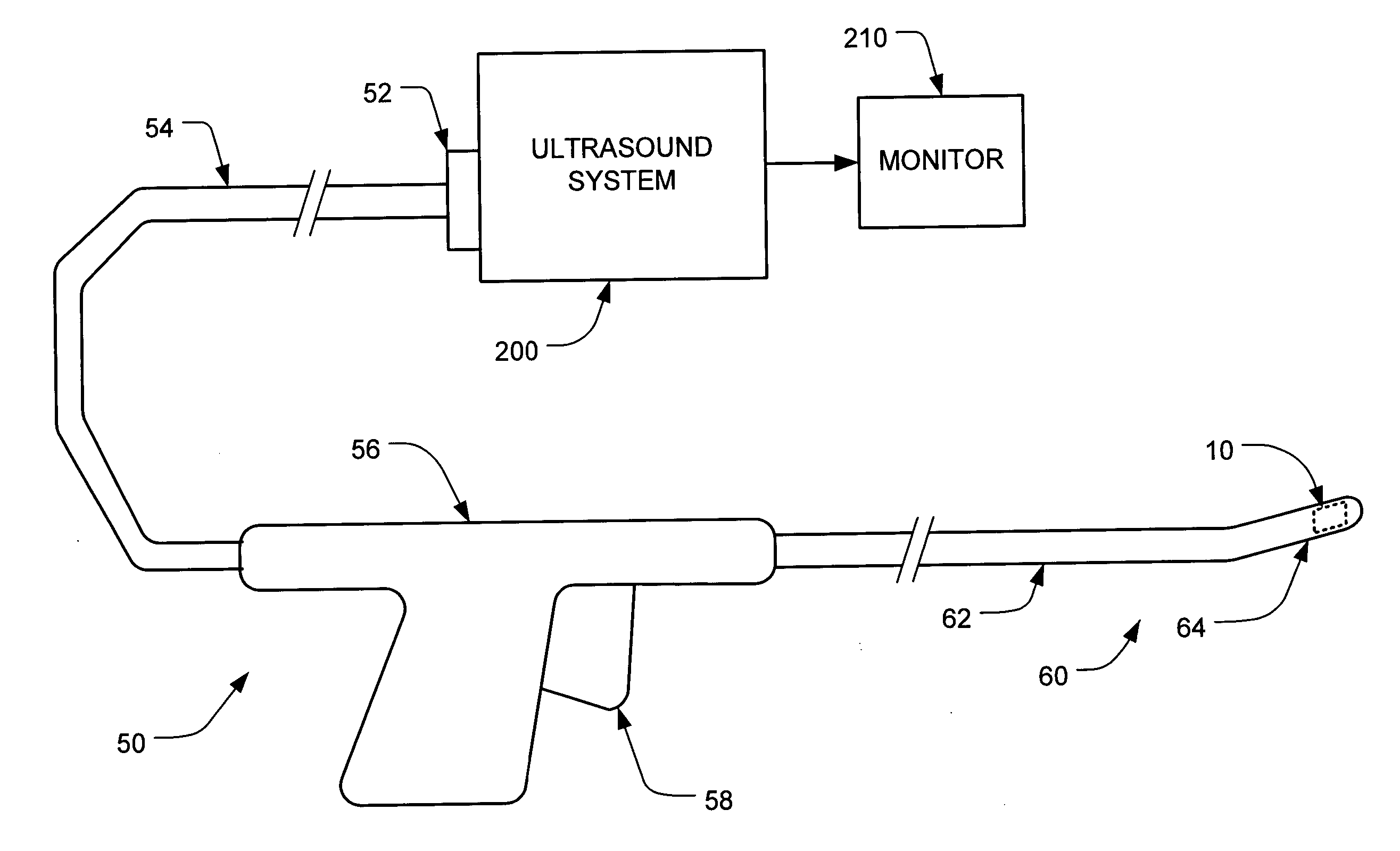
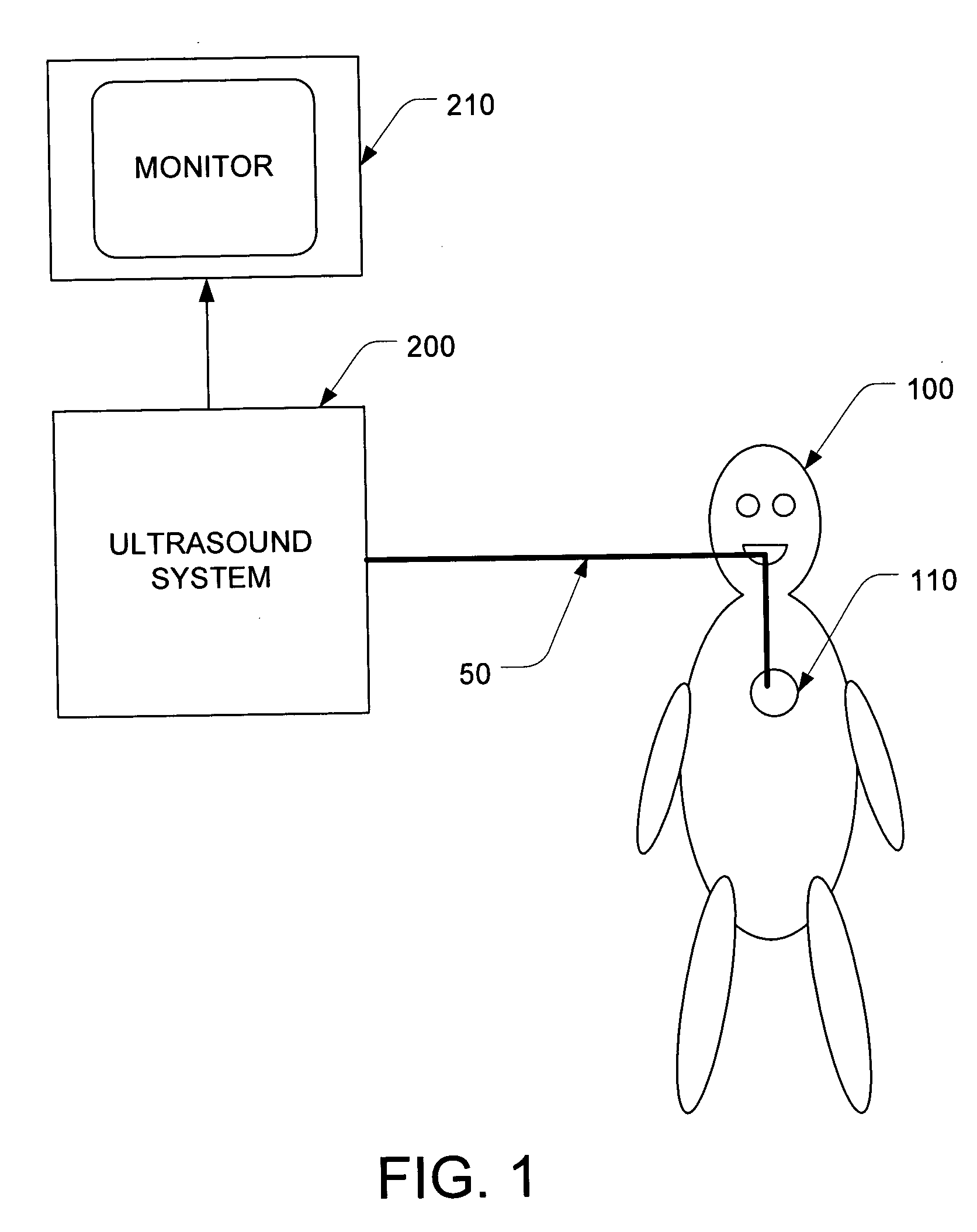
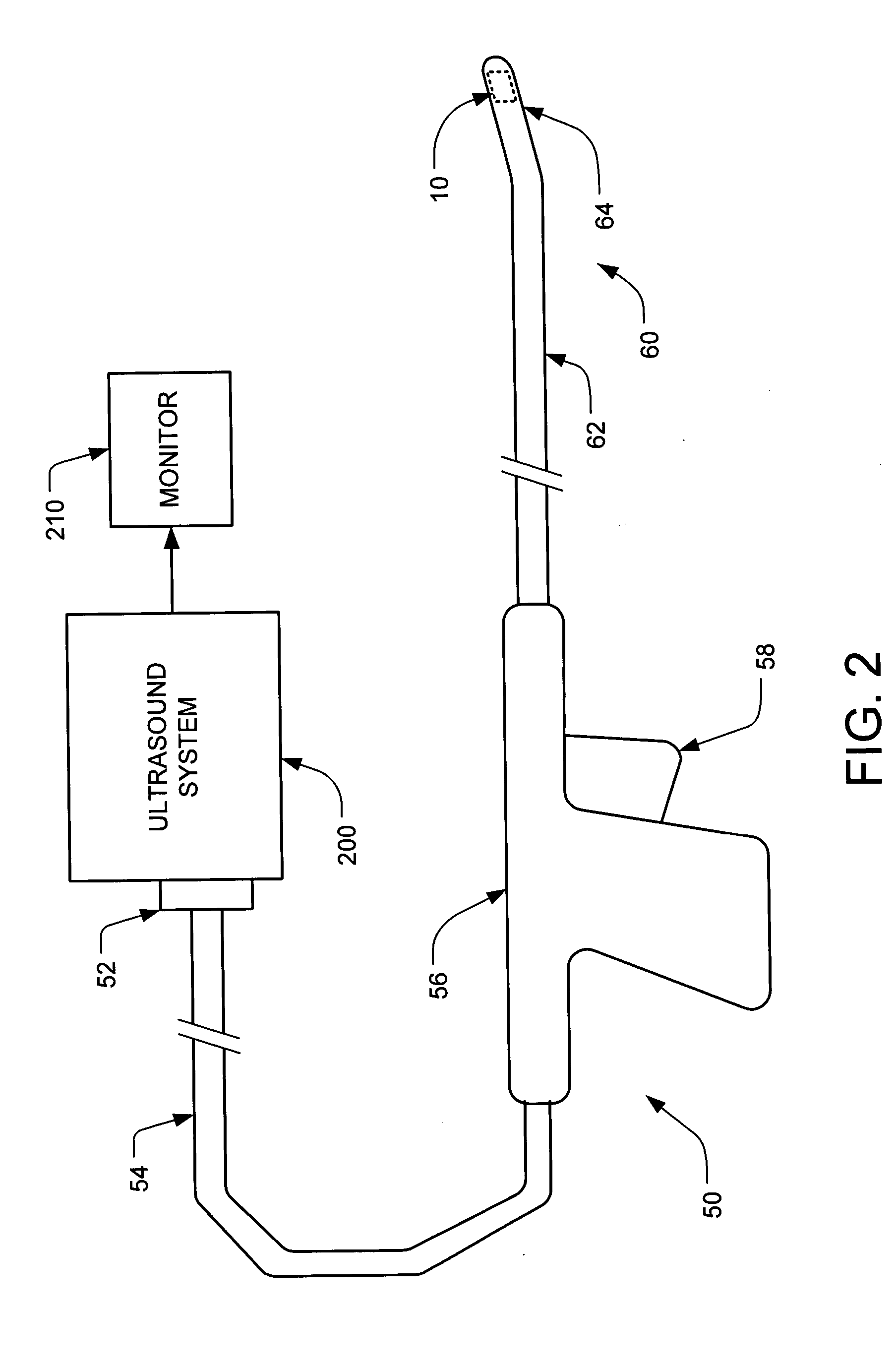
Percutaneous cardiac valve repair with adjustable artificial chordae
InactiveUS20070118151A1Reduction of mitral valve regurgitationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
The invention includes a novel method and system to achieve leaflet coaptation in a cardiac valve percutaneously by creation of neochordae to prolapsing valve segments. This technique is especially useful in cases of ruptured chordae, but may be utilized in any segment of prolapsing leaflet. The technique described herein has the additional advantage of being adjustable in the beating heart. This allows tailoring of leaflet coaptation height under various loading conditions using image-guidance, such as echocardiography. This offers an additional distinct advantage over conventional open-surgery placement of artificial chordae. In traditional open surgical valve repair, chord length must be estimated in the arrested heart and may or may not be correct once the patient is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. The technique described below also allows for placement of multiple artificial chordae, as dictated by the patient's pathophysiology.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Implantable product with improved aqueous interface characteristics and method for making and using same
InactiveUS20050129735A1Rapidly and accurately visualizedEliminates air-interference issueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsLaparoscopyCardiac echo
An implantable medical device including a porous membrane that is treated with a hydrophilic substance to obtain rapid optimum visualization using technology for viewing inside of a mammalian body. These technologies include ultrasound echocardiography and video imaging such as that used during laparoscopic procedures.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Methods and systems for ultrasound imaging of the heart from the pericardium
InactiveUS20050203410A1Low costOptimize locationSurgeryHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasound imagingThoracic structure
A peritoneal ultrasound imager includes an elongated body less than about 20 inches in length that is adapted to be inserted through a cannula into or near the pericardium space, and an ultrasound transducer array at one end of the body that is suitable for ultrasound echocardiography. The cannula and ultrasound imager may be of a single piece construction. A method for imaging the heart includes introducing a cannula into the wall of a patient's chest, inserting the elongated body into the cannula, moving the inserted elongated body to a position near the heart, and imaging the heart with ultrasound echo.
Owner:EP MEDSYST
Method and System for Computational Modeling of the Aorta and Heart
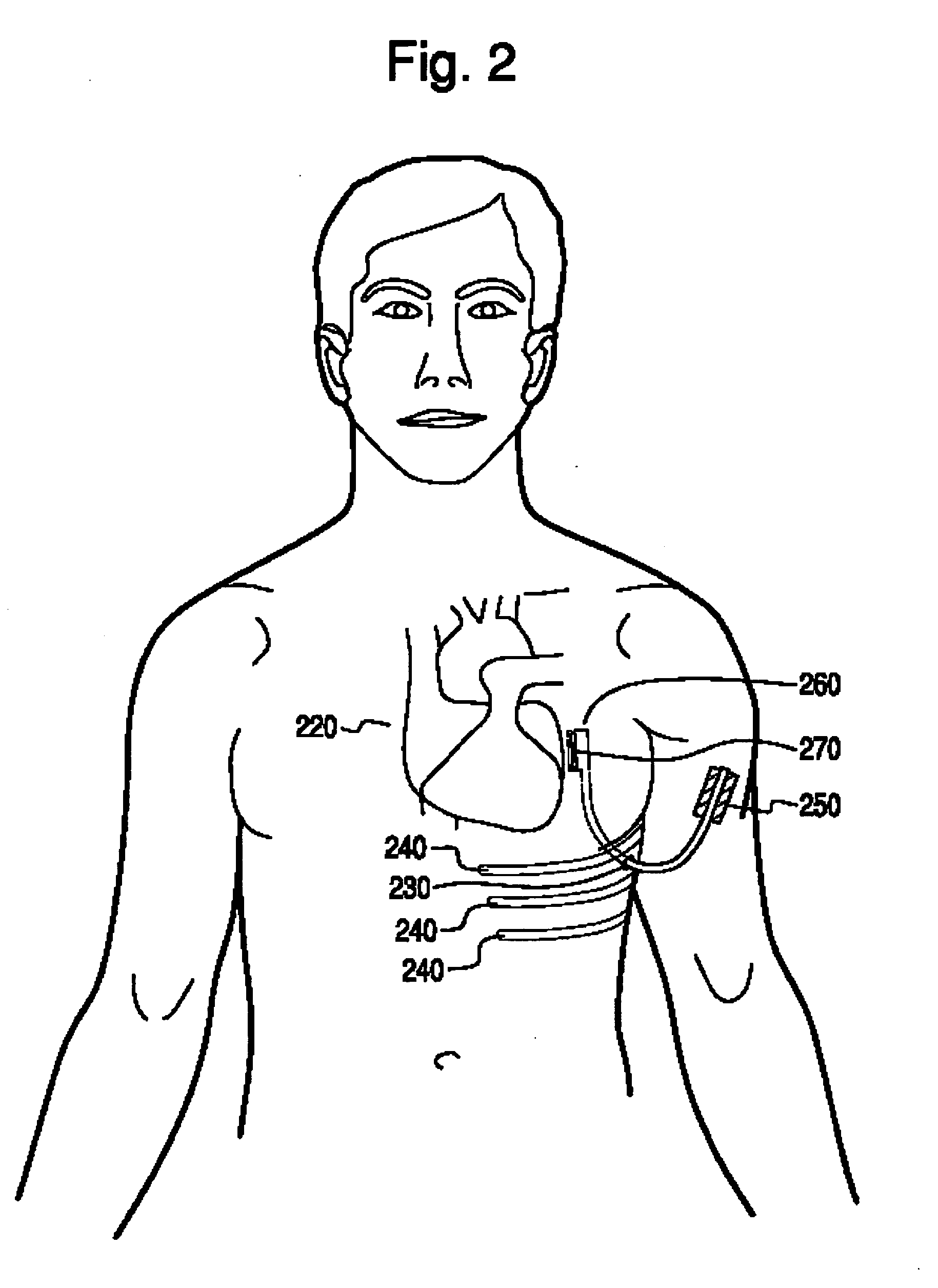
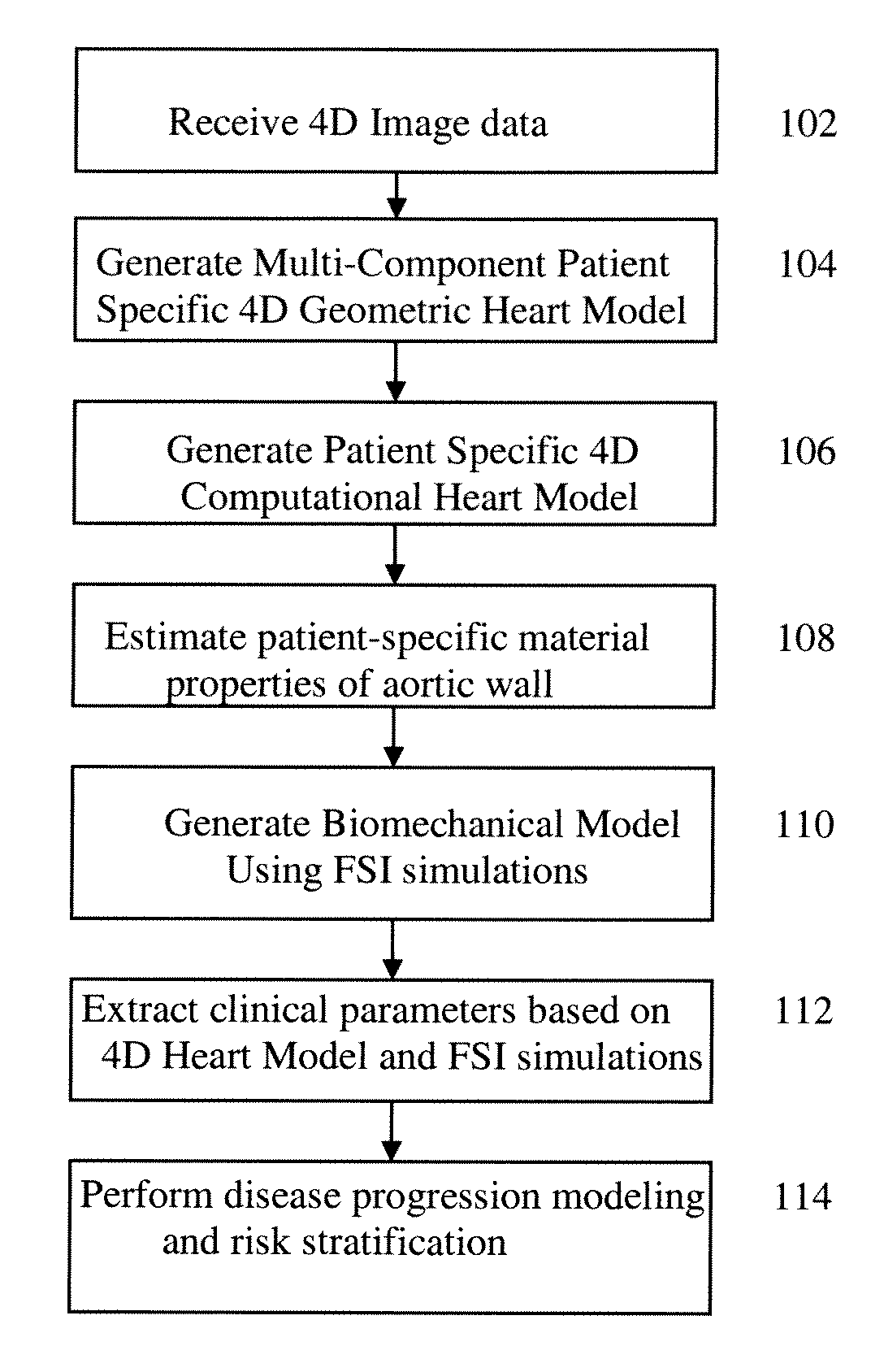
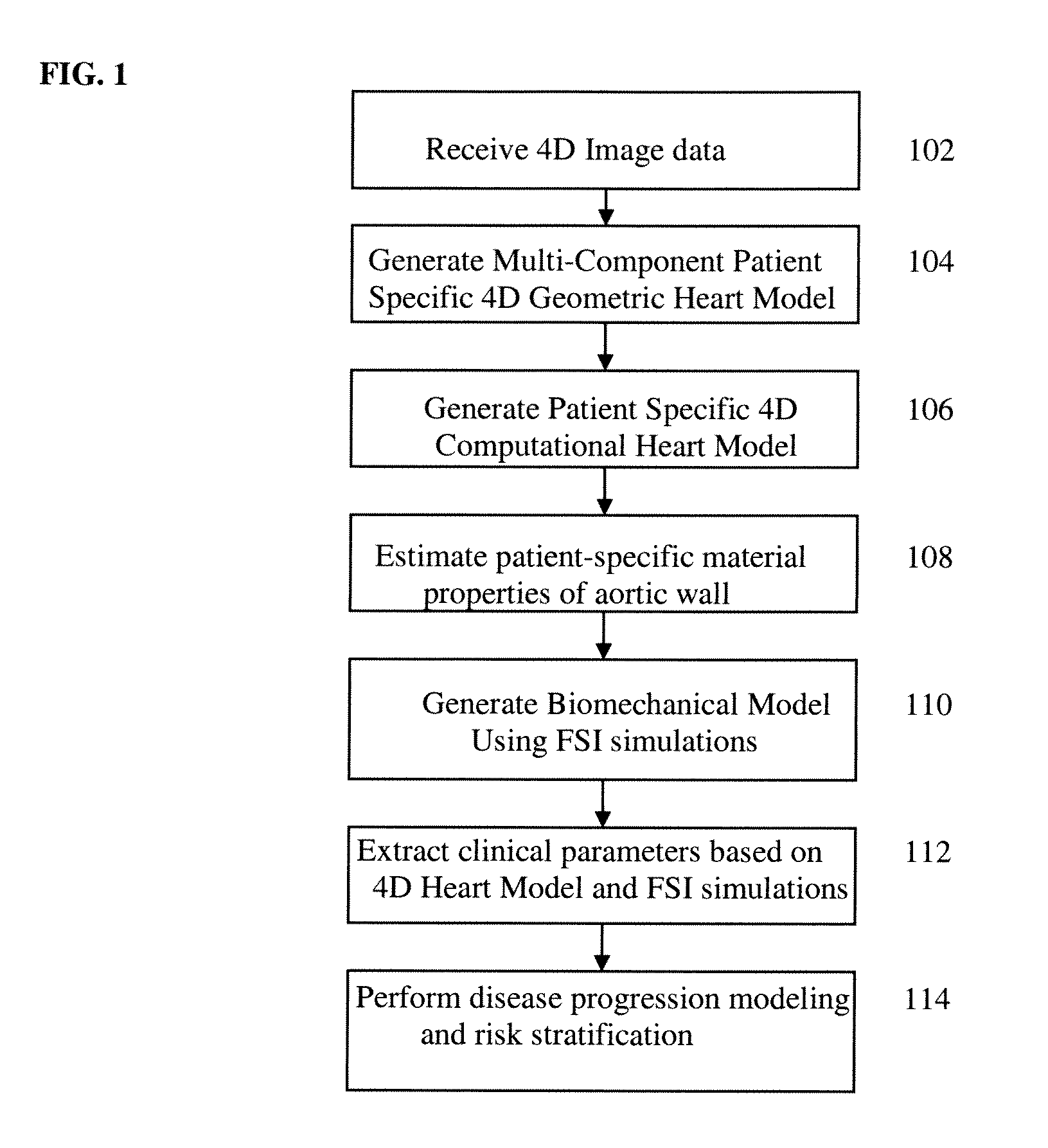
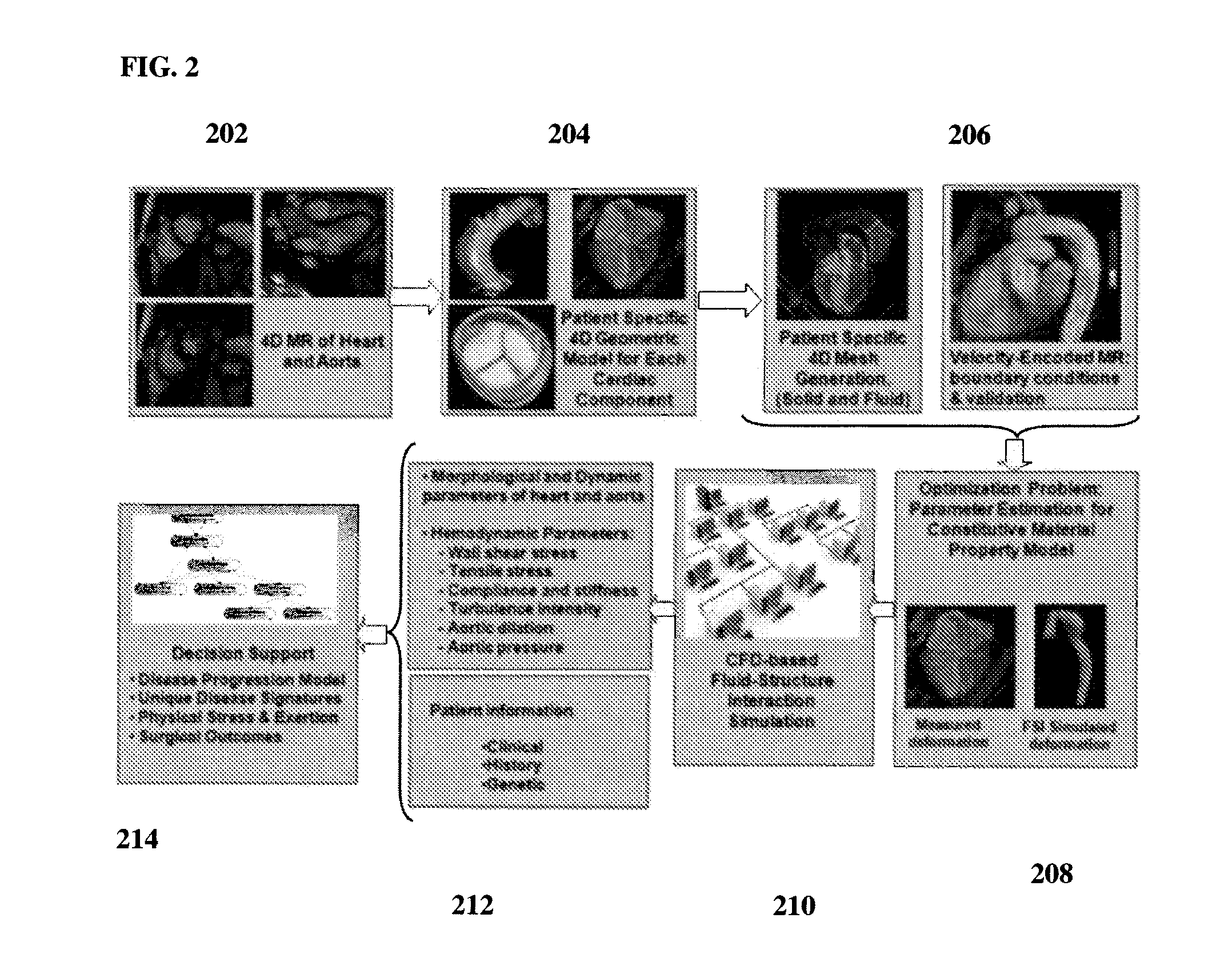
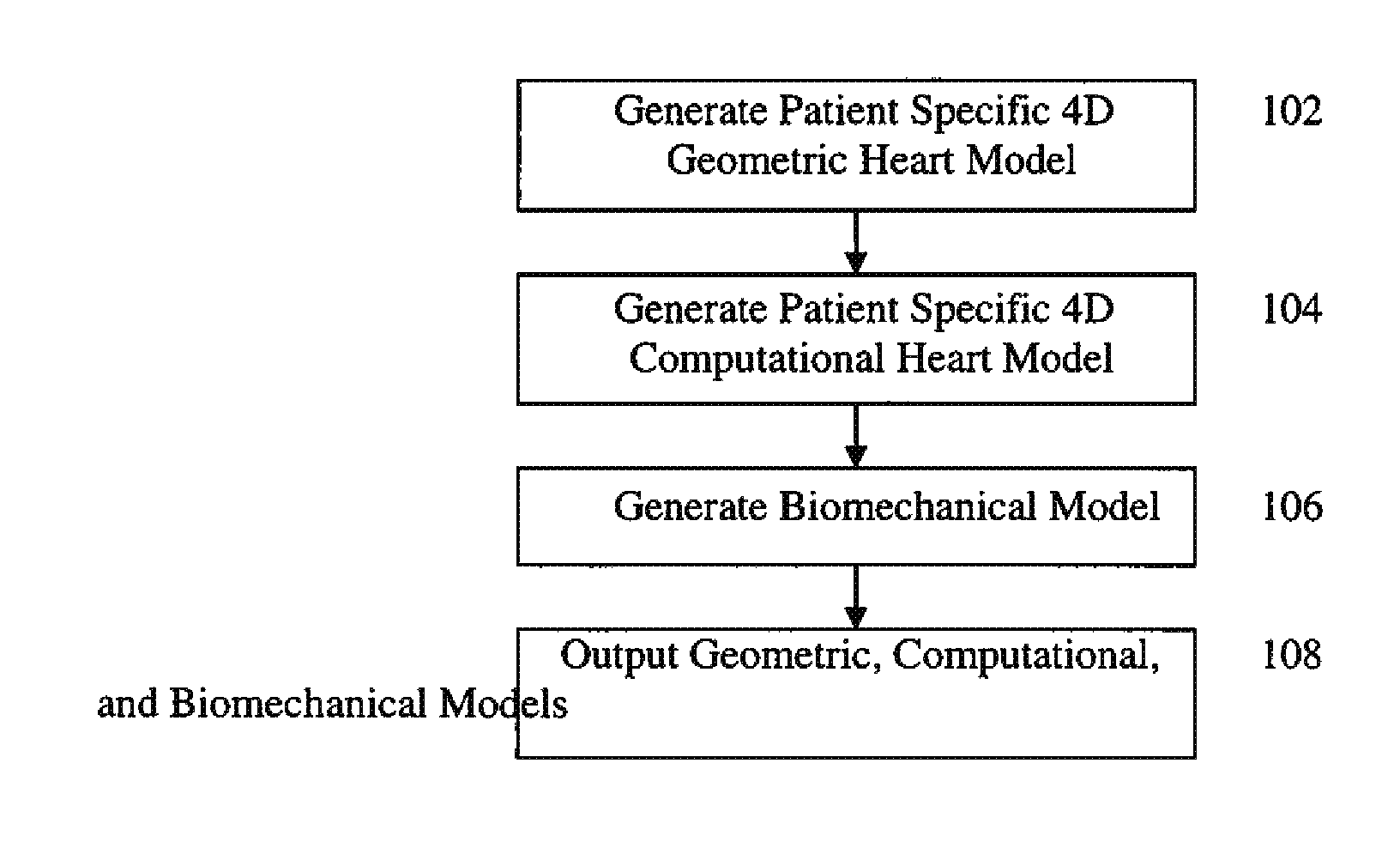
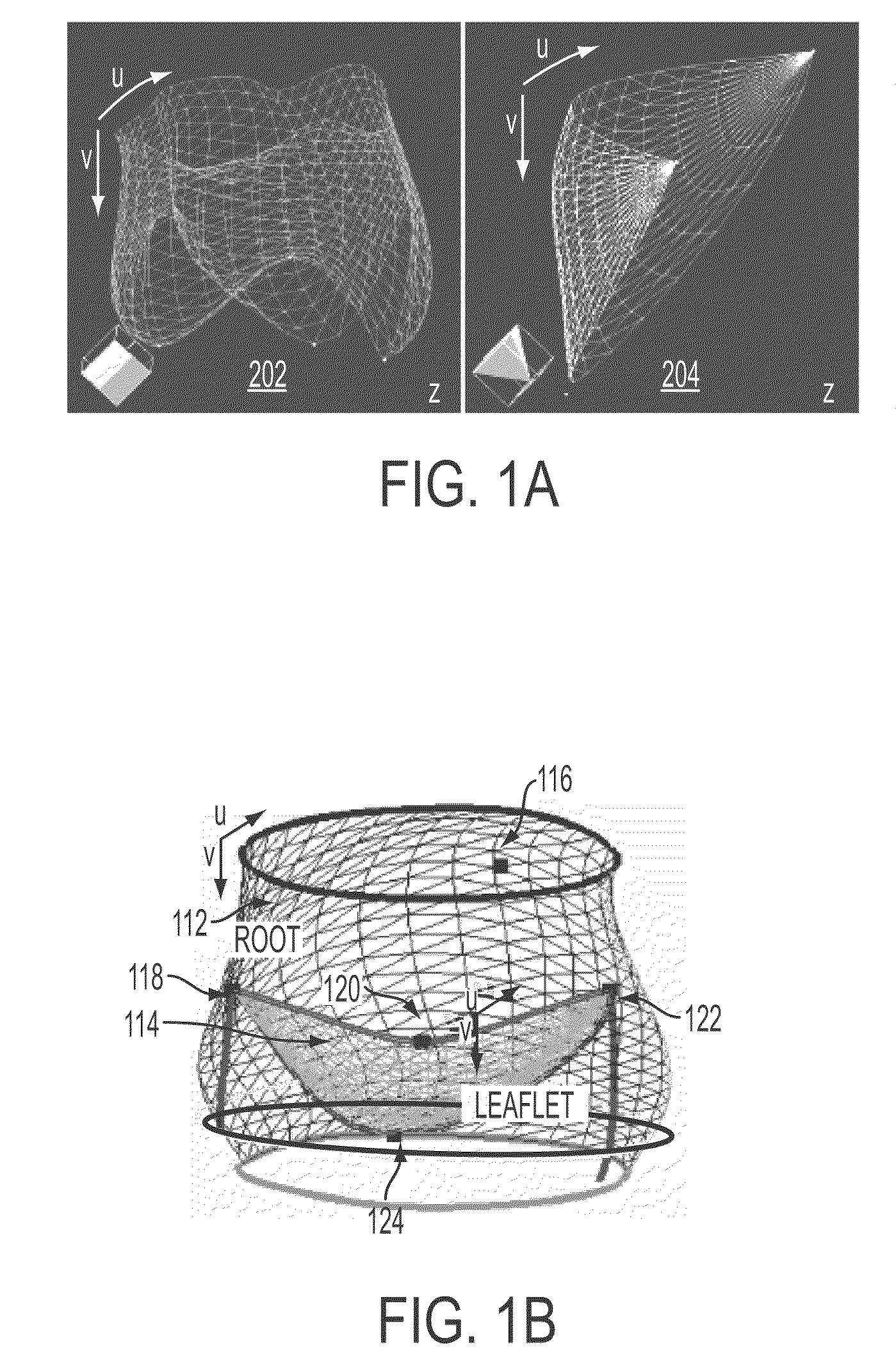
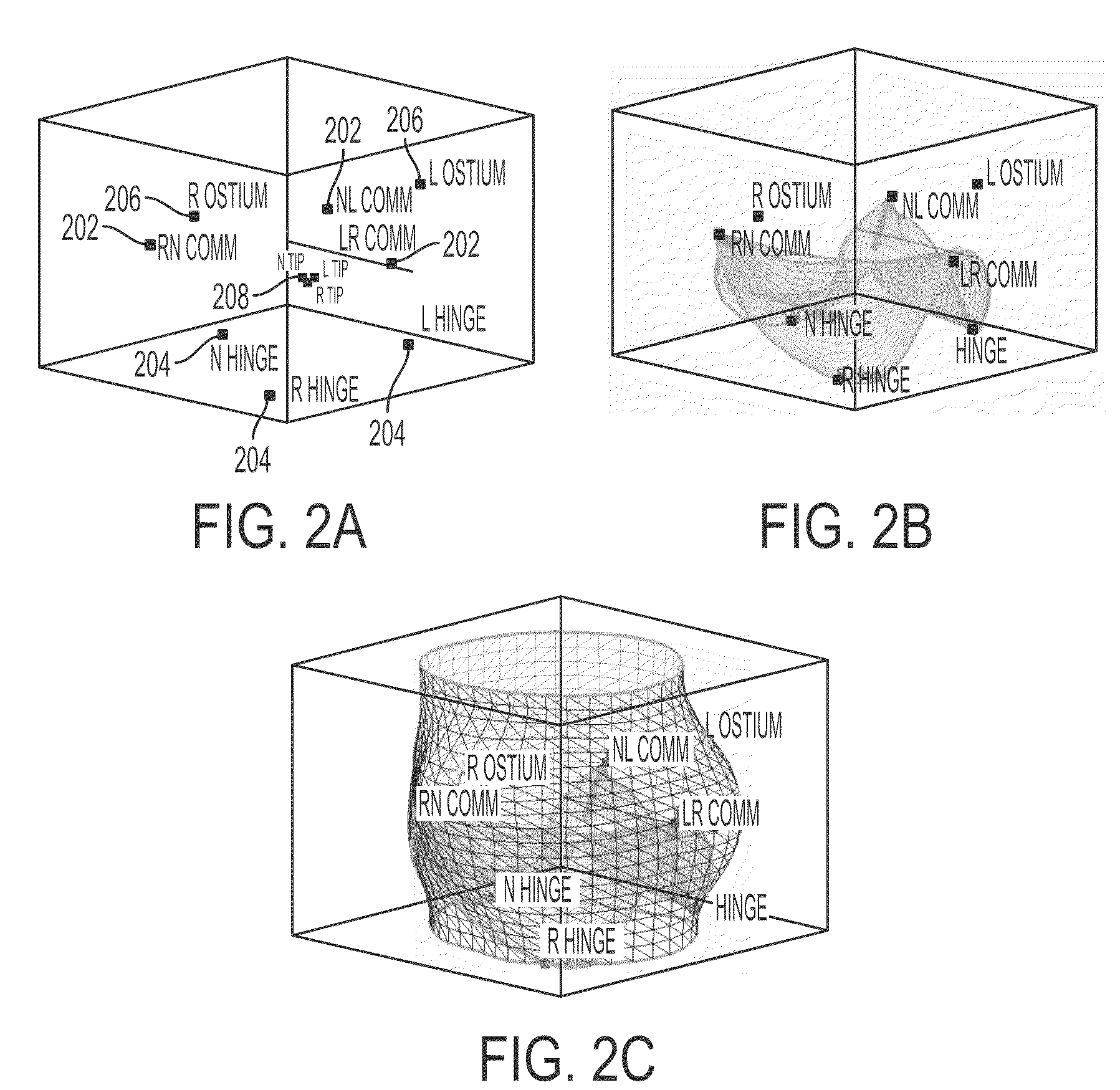
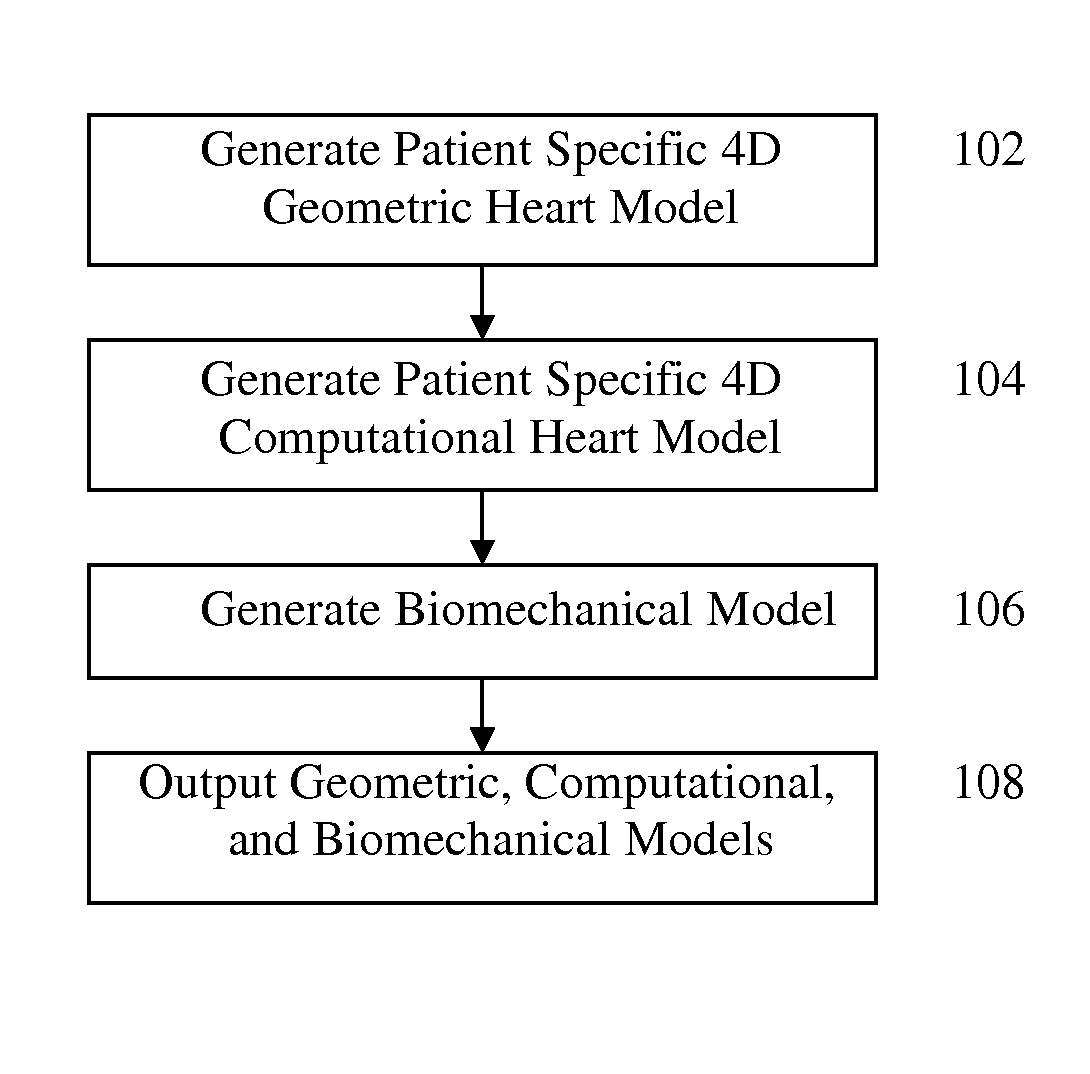
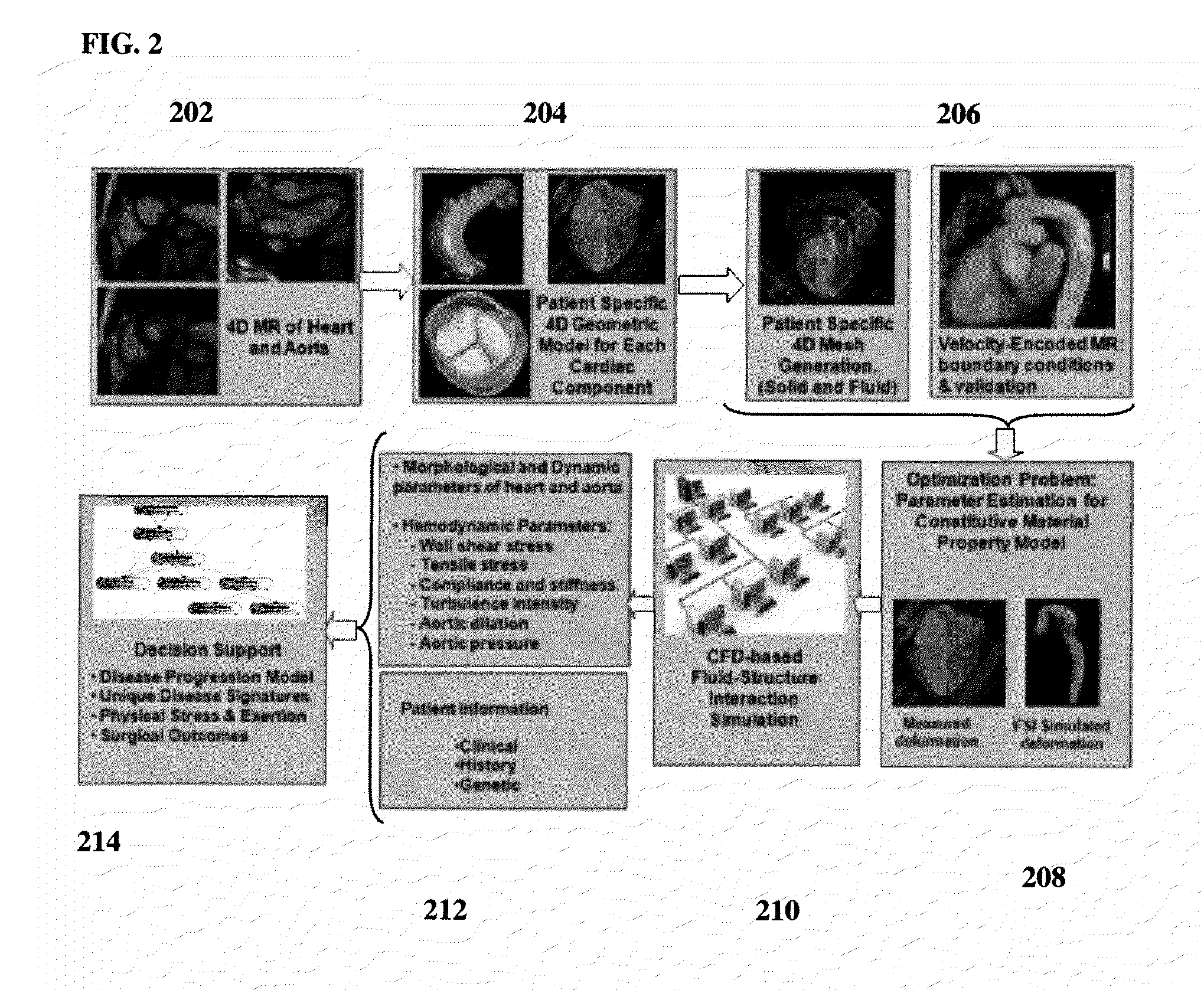
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Generating a Personalized Anatomical Heart Model
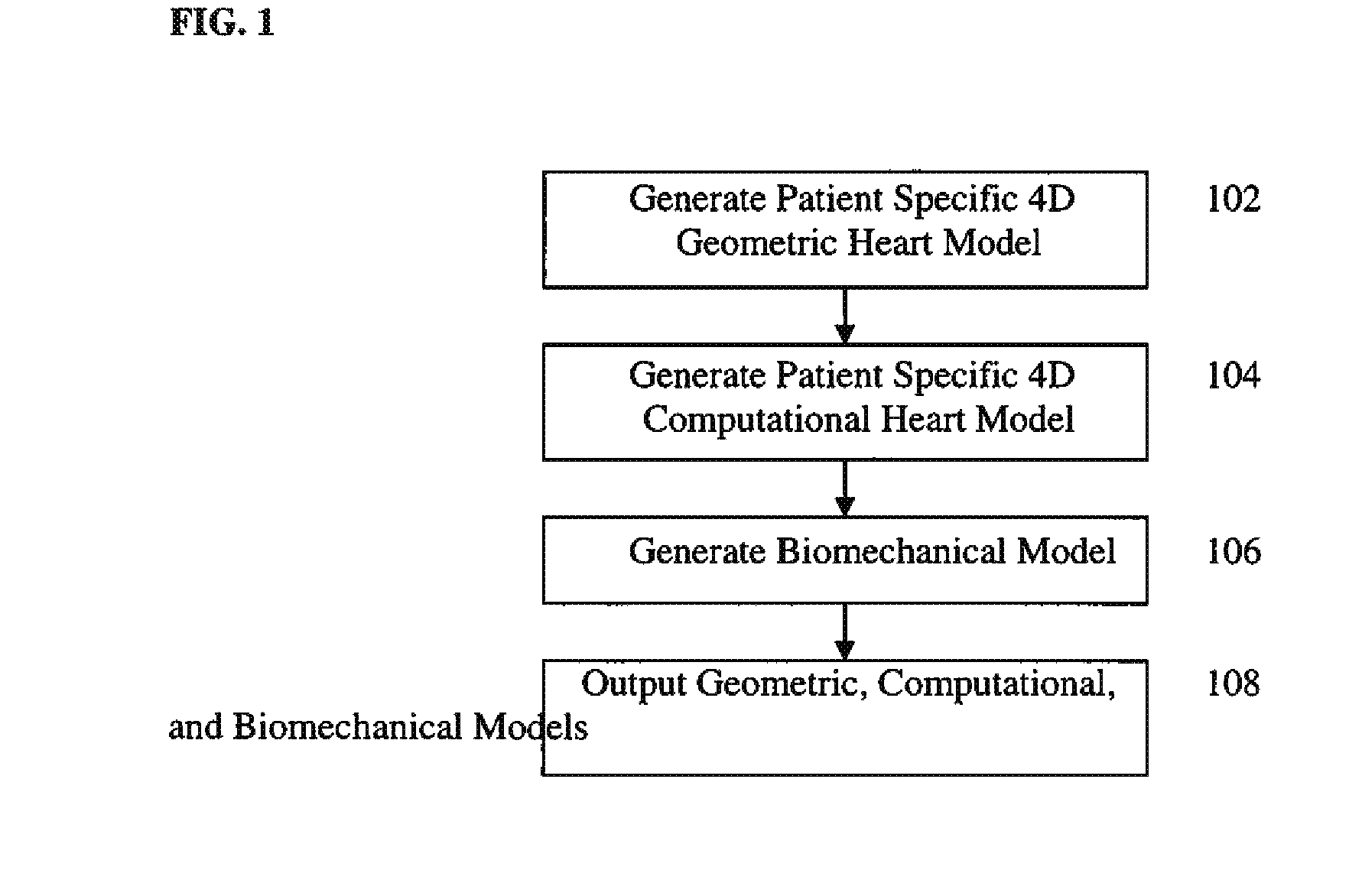
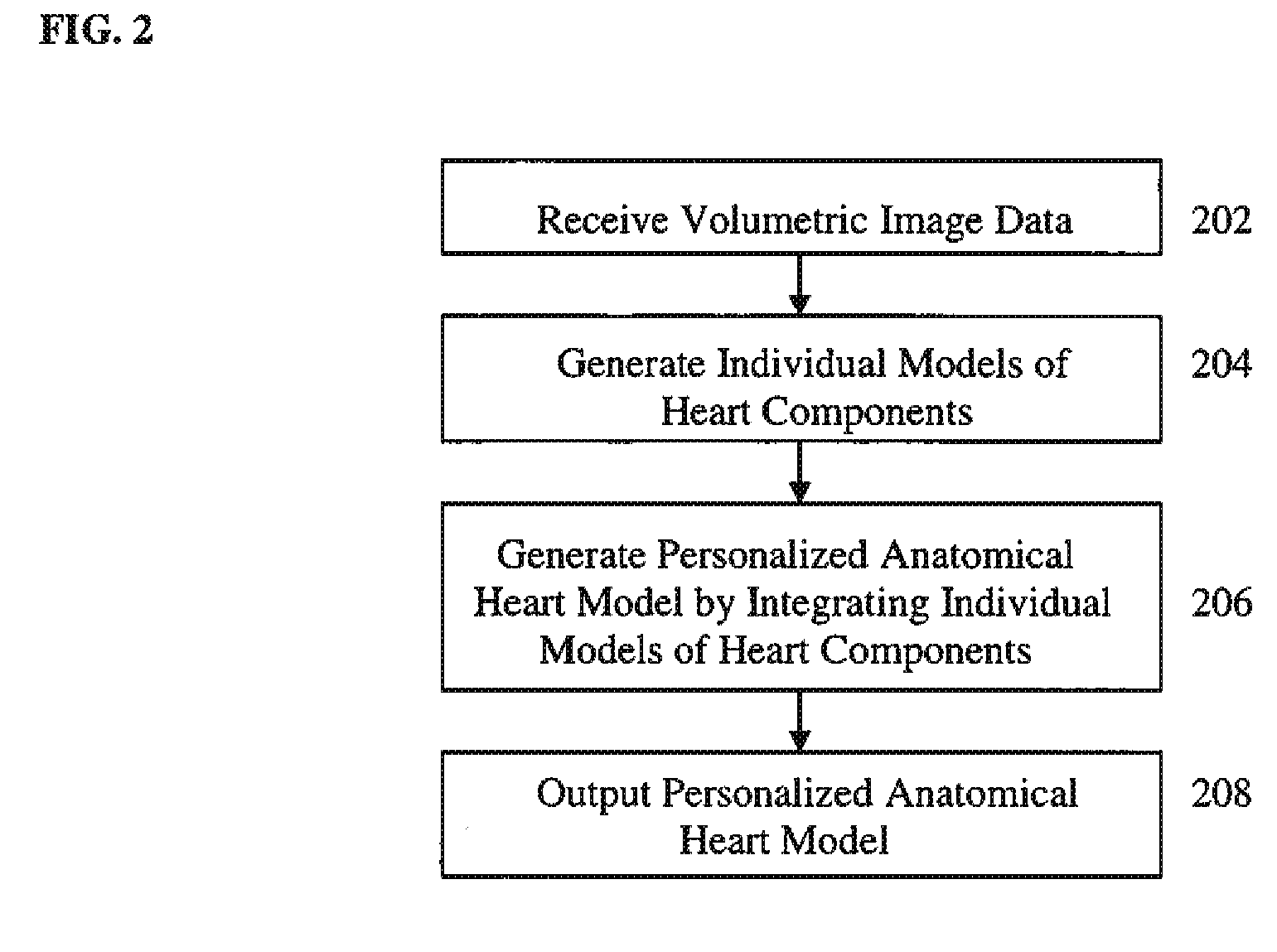
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. Volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT) or echocardiography image data, of a patient's cardiac region is received. Individual models for multiple heart components, such as the left ventricle (LV) endocardium, LV epicardium, right ventricle (RV), left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), mitral valve, aortic valve, aorta, and pulmonary trunk, are estimated in said volumetric cardiac image data. A patient specific anatomical heart model is generated by integrating the individual models for each of the heart components.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
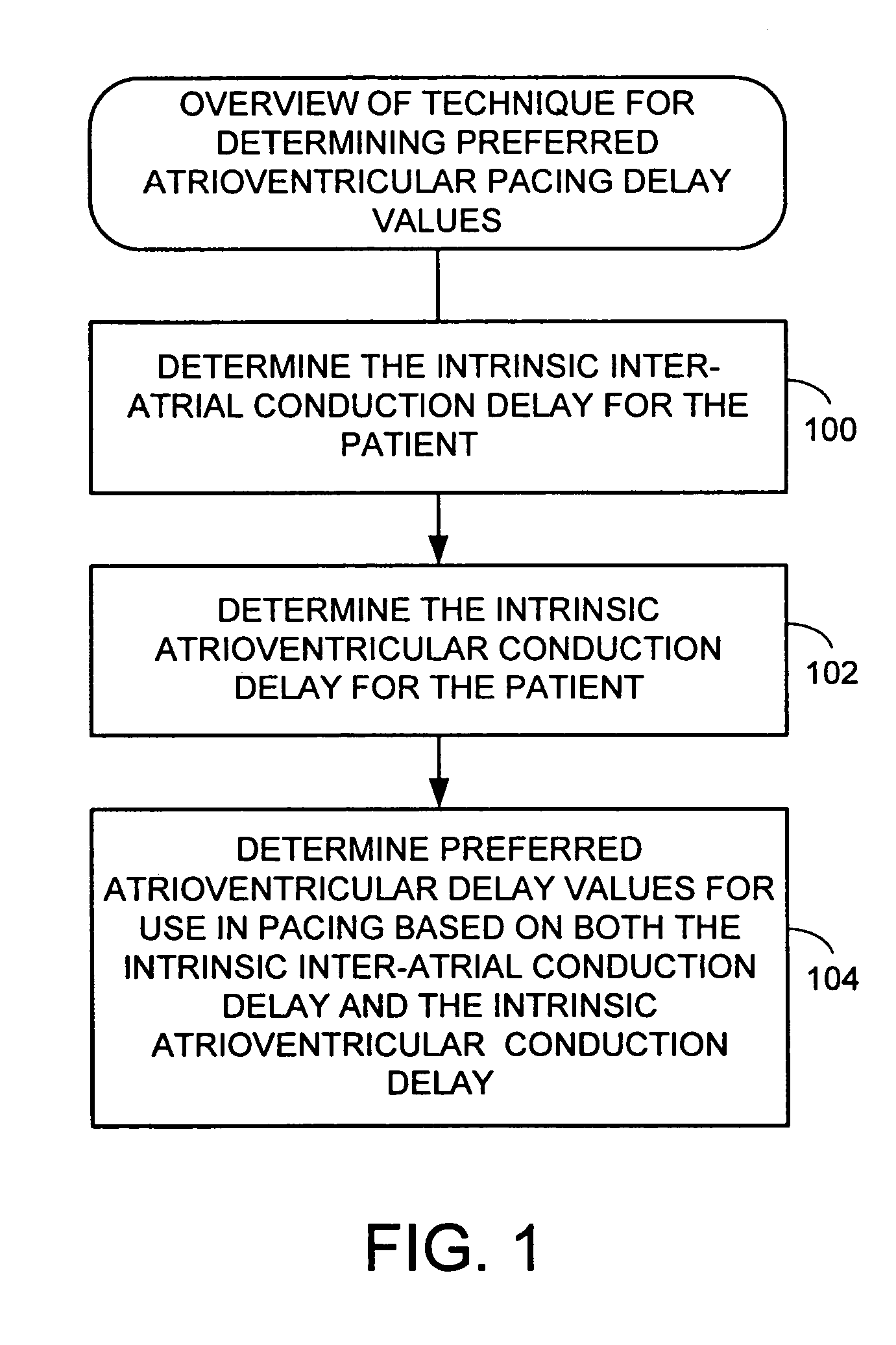
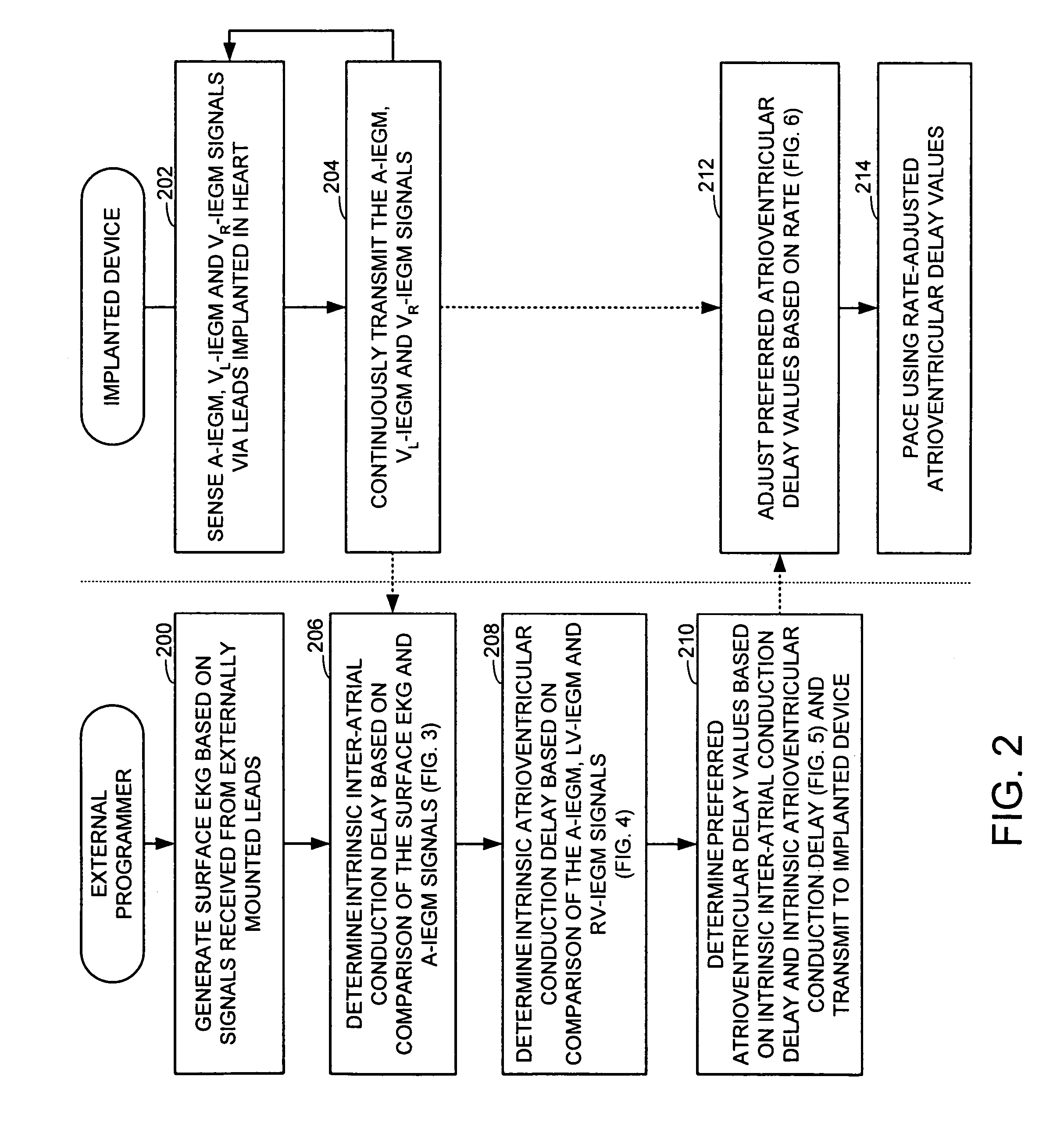
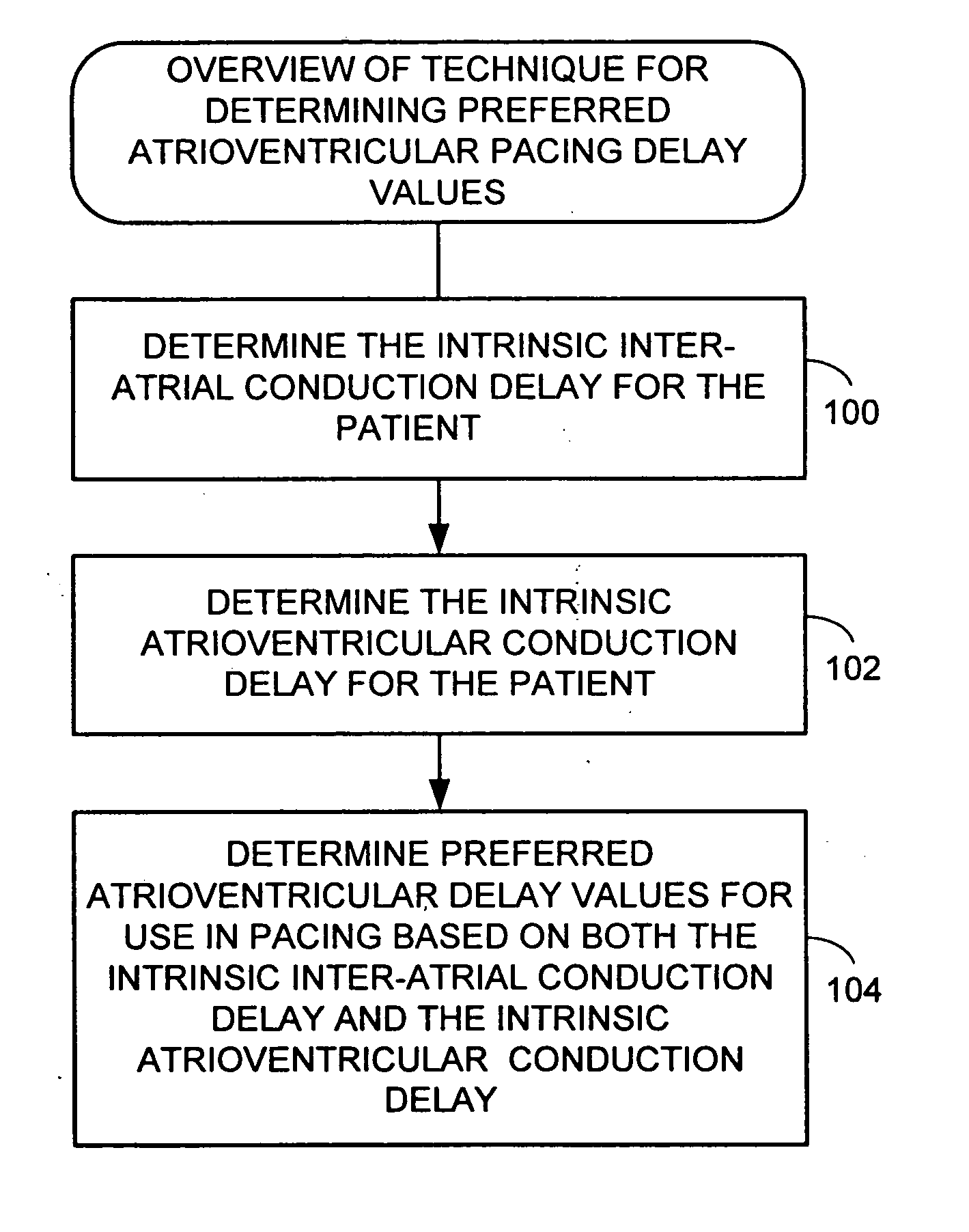
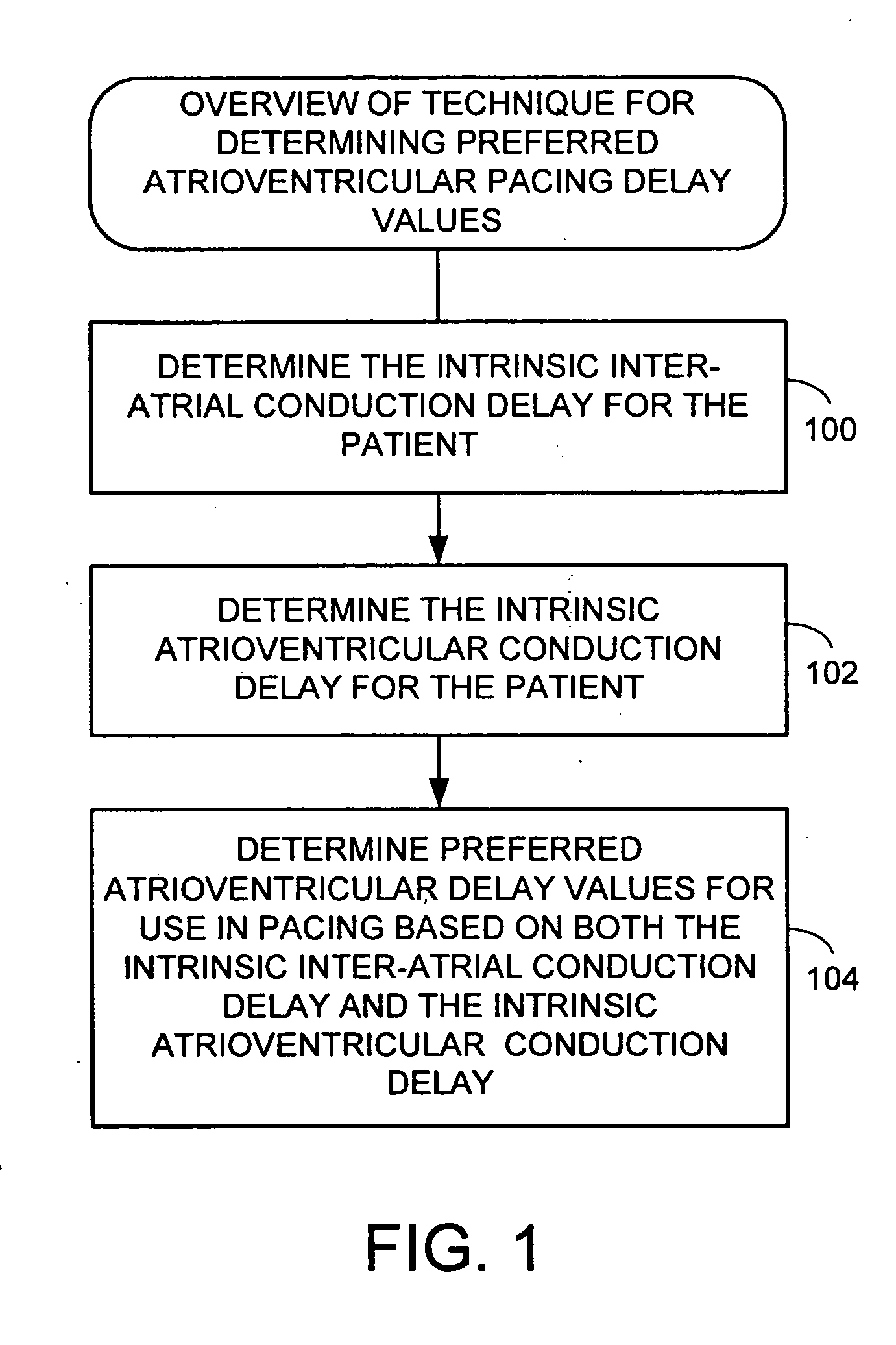
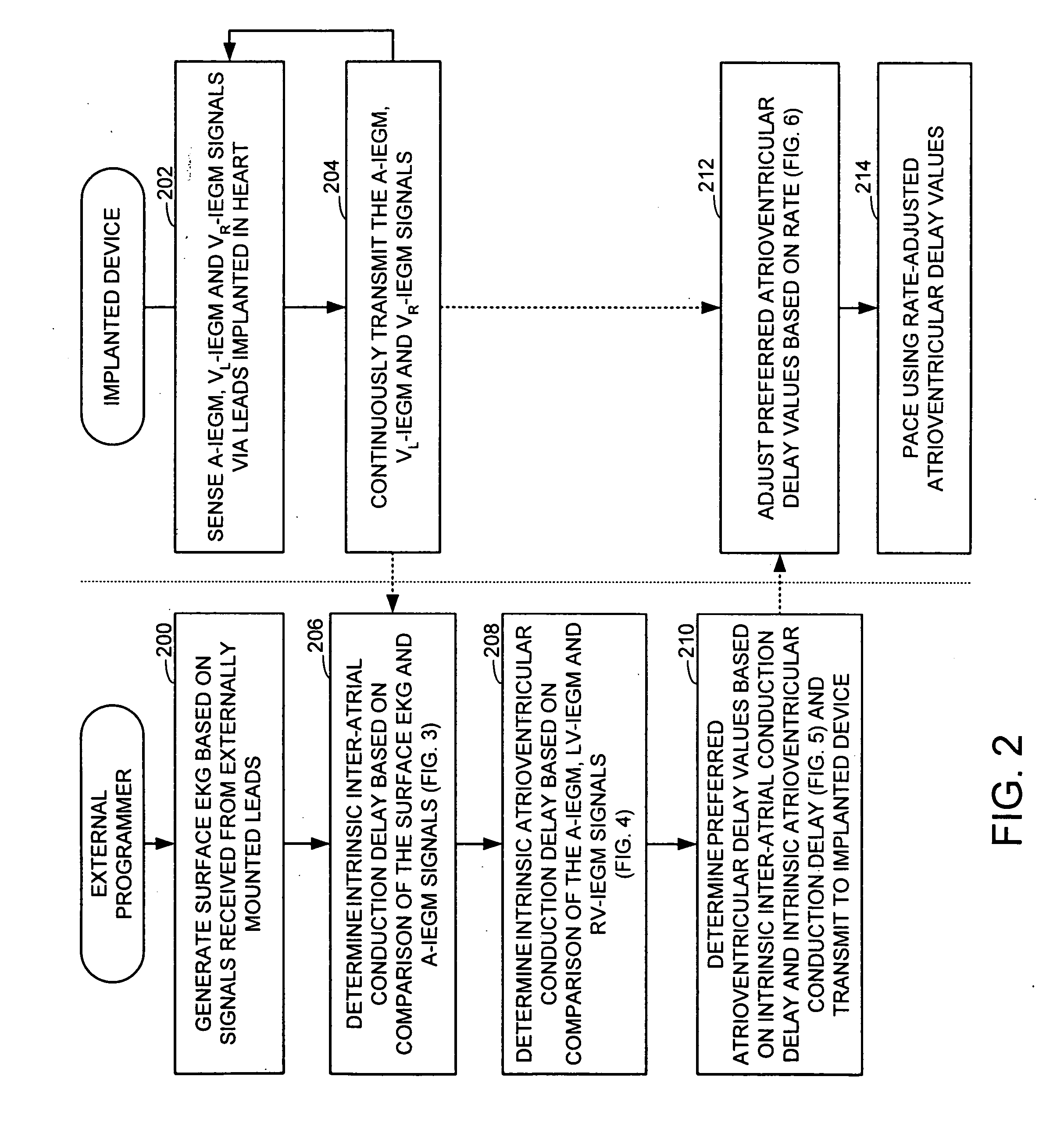
System and method for determining optimal atrioventricular delay based on intrinsic conduction delays
ActiveUS7248925B2ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationIntracardiac ElectrogramSurface electrocardiogram
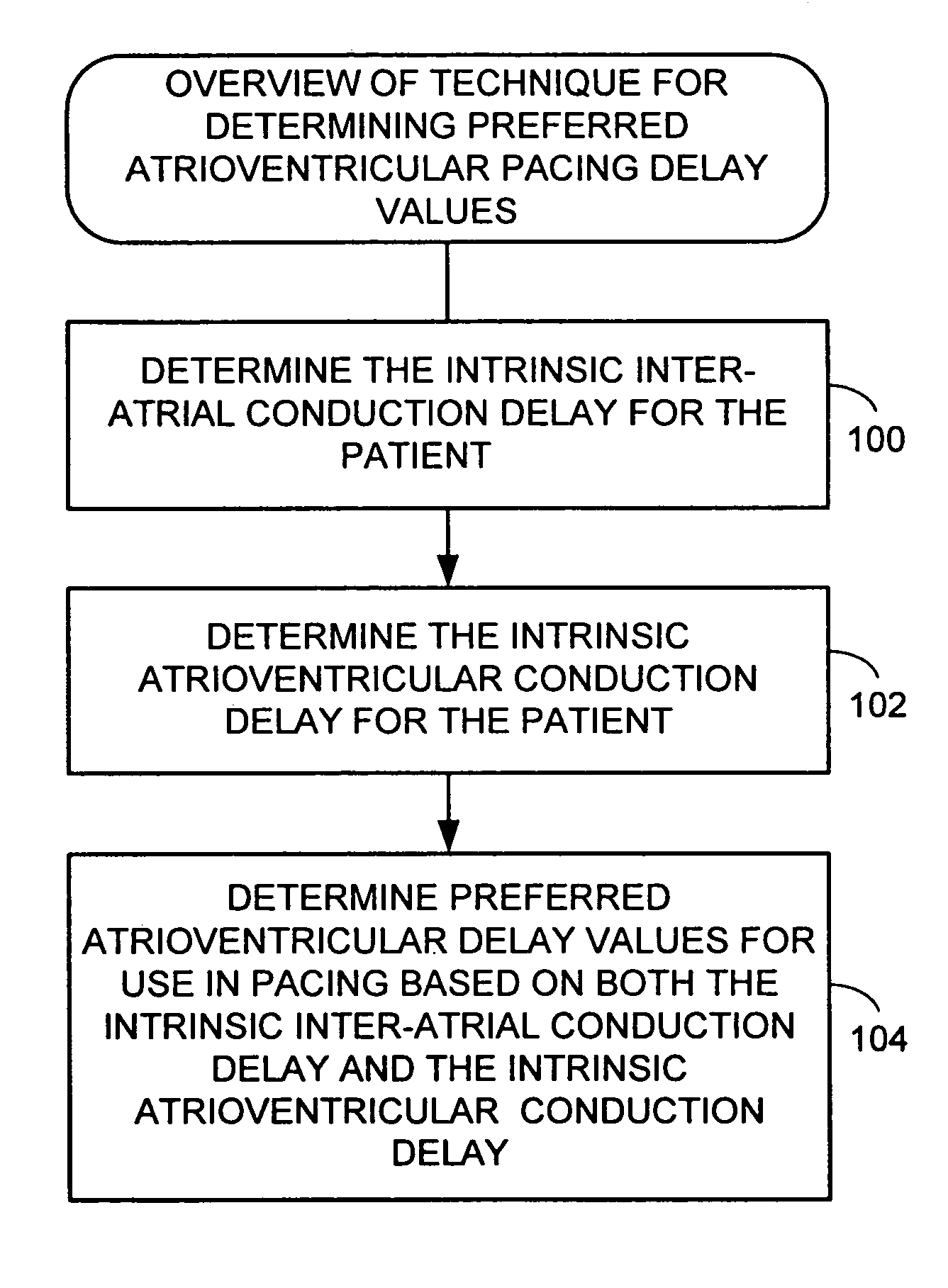
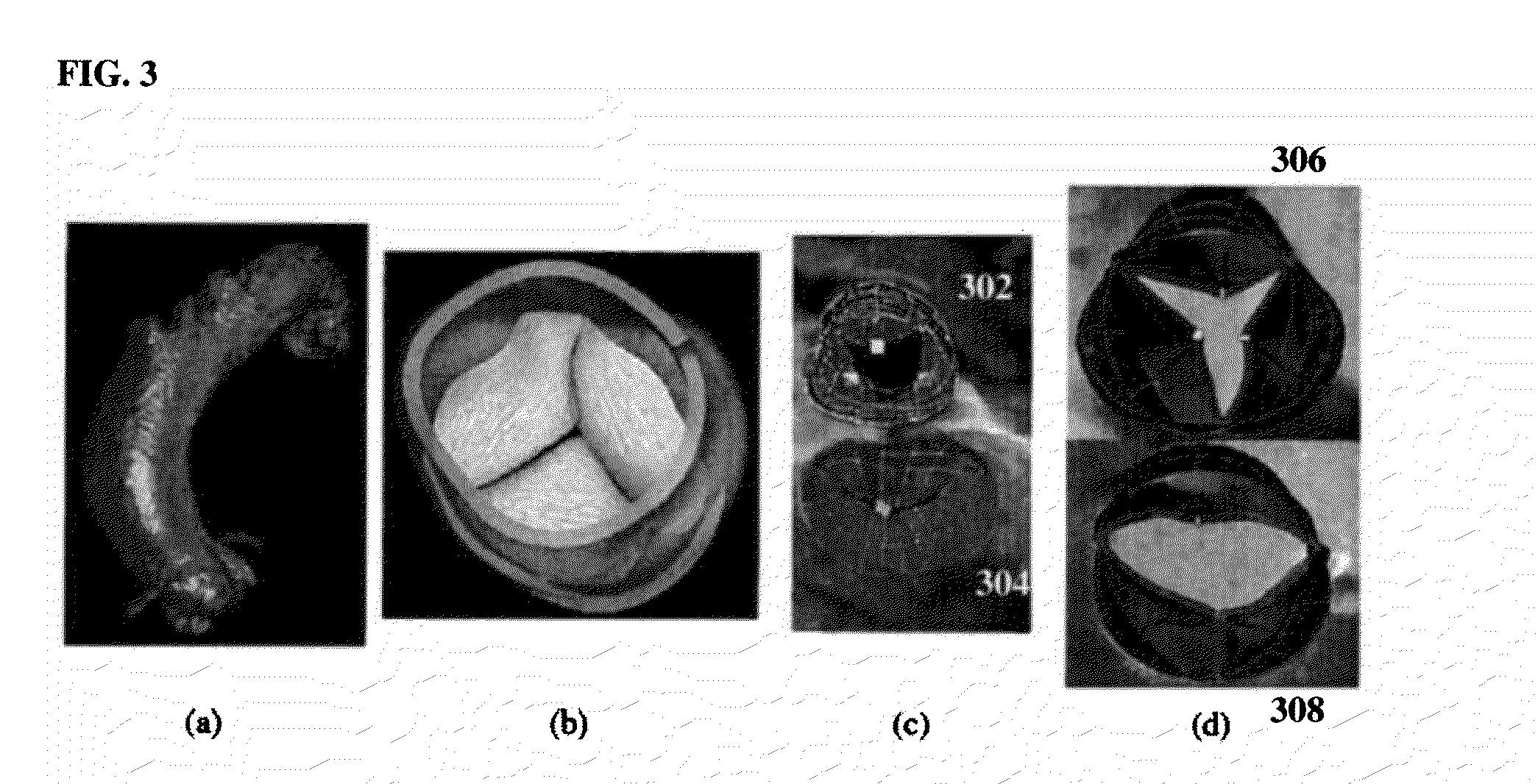
A system and method for estimating optimal atrioventricular delay values for use in pacing the ventricles. Both the intrinsic inter-atrial conduction delay and the intrinsic atrioventricular conduction delay are determined for the patient and then the preferred atrioventricular pacing delay is derived therefrom. By taking into account intrinsic inter-atrial delay along with intrinsic atrioventricular delay, a more reliable estimate of the true optimal atrioventricular delay values for the patient can be achieved than with techniques that only take into account intrinsic atrioventricular delay values. In one example, the technique uses intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals and surface electrocardiogram (EKG) signals and hence can be performed by an external programmer without requiring Doppler echocardiography or other cardiac performance monitoring techniques. In another example, wherein the implanted device is equipped with a coronary sinus lead, the technique uses only IEGM signals and hence can be performed by the device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system
A cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system and method is disclosed, wherein a dedicated fast, sensitive, compact and economical imaging gamma camera system that is especially suited for heart imaging and functional analysis is employed. The cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system of the present invention can be used as a dedicated nuclear cardiology small field of view imaging camera. The disclosed cardiovascular imaging system and method has the advantages of being able to image physiology, while offering an inexpensive and portable hardware, unlike MRI, CT, and echocardiography systems.The cardiovascular imaging system of the invention employs a basic modular design suitable for cardiac imaging with one of several radionucleide tracers. The detector can be positioned in close proximity to the chest and heart from several different projections, making it possible rapidly to accumulate data for first-pass analysis, positron imaging, quantitative stress perfusion, and multi-gated equilibrium pooled blood (MUGA) tests..In a preferred embodiment, the Cardiovascular Non-Invasive Screening Probe system can perform a novel diagnostic screening test for potential victims of coronary artery disease. The system provides a rapid, inexpensive preliminary indication of coronary occlusive disease by measuring the activity of emitted particles from an injected bolus of radioactive tracer. Ratios of this activity with the time progression of the injected bolus of radioactive tracer are used to perform diagnosis of the coronary patency (artery disease).
Owner:NORTH COAST IND INC
Optical transesophageal echocardiography probe
InactiveUS6884220B2Reduce traumaUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGastroscopesOesophageal tubeCardiac echo
The present invention concerns an optical transesophageal echocardiography probe (OPTEE) having an optical fiber bundle, a suction channel and light channels for illumination, wherein the OPTEE has a circumference along its distal tip that allows both safe insertion and insures the stability of the probe. The probe tip is generally circular in circumference, but levels off to a flat surface for a portion of the circumference, and is provided with beveled edges and corner throughout so that there are no sharp edges to traumatize the patient. The invention also concerns an optically-recessed OPTEE comprising an optical transesophageal probe comprising a longitudinally extending main body having an outer surface and a substantially circular cross-section and a distal portion having an outer surface and a distal tip, wherein an optical bundle having a distal tip is positioned on the outer surface of the main body and the outer surface of the distal portion and the distal tip of the optical bundle does not extend as far as the distal tip of the distal portion.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Agents for treating cardiopathy
ActiveUS20090220500A1Improve the situationSuppressing left ventricular remodelingAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCardiac echoLeft ventricular size
The present inventors investigated the effects of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies on improving the condition of infarcted areas in myocardial infarction, and on suppressing left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. As a result, the administration of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies significantly suppressed the increase of MPO activity in the infarcted area and suppressed myocardial MCP-1 expression in both the infarcted area and the non-infarcted area. Furthermore, echocardiography and histological examinations revealed that cardiac hypertrophy is also suppressed.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
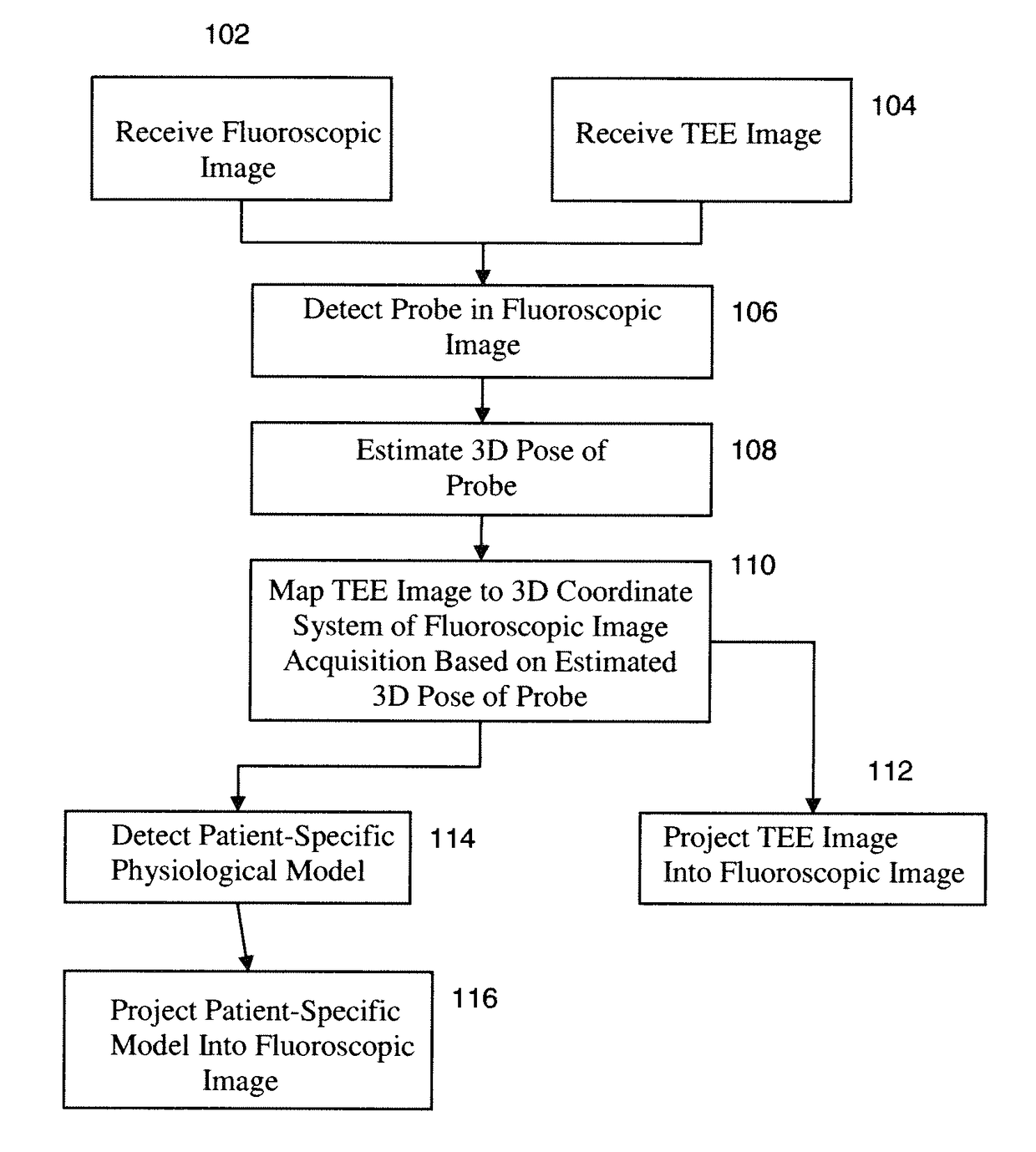
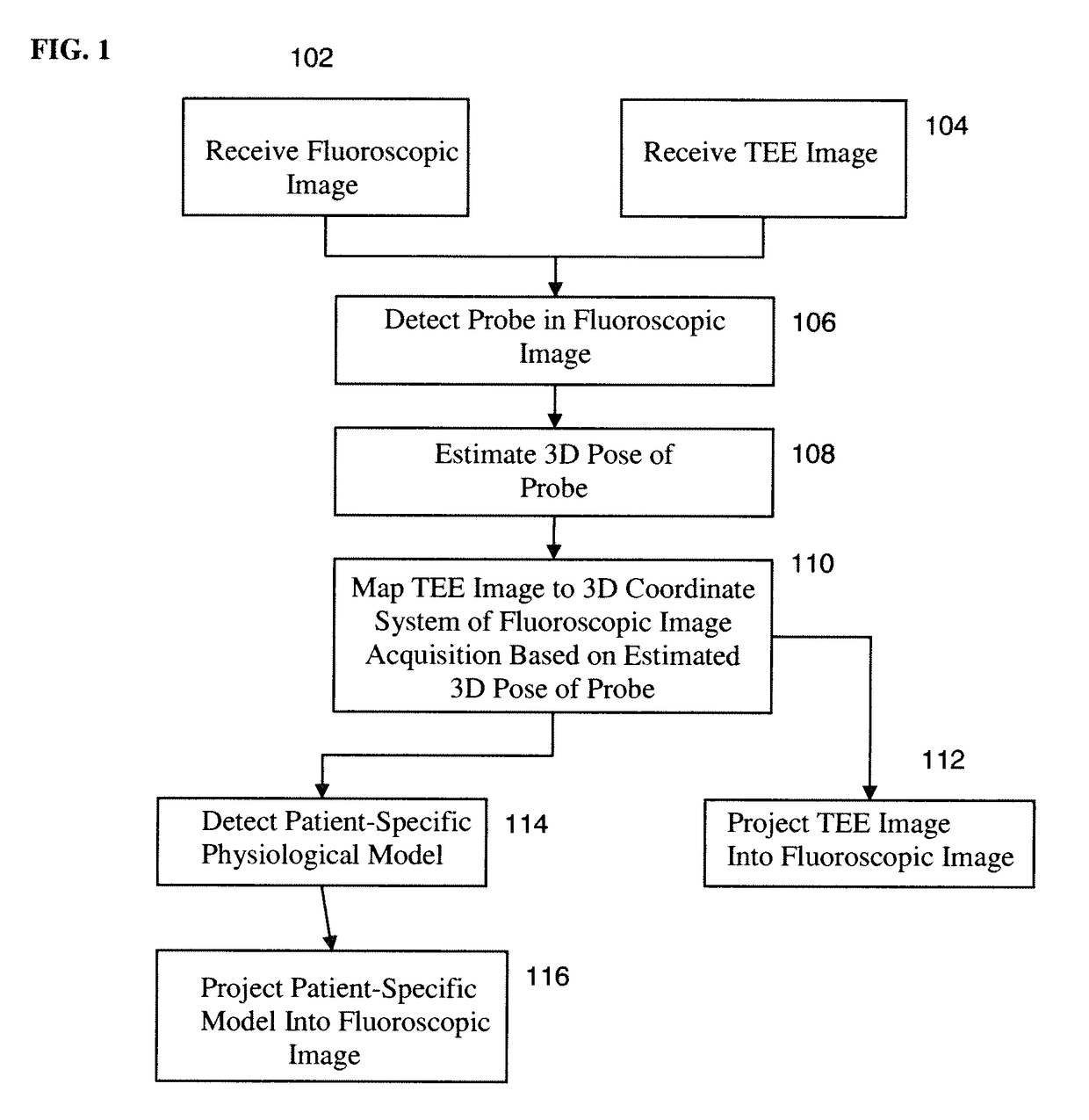
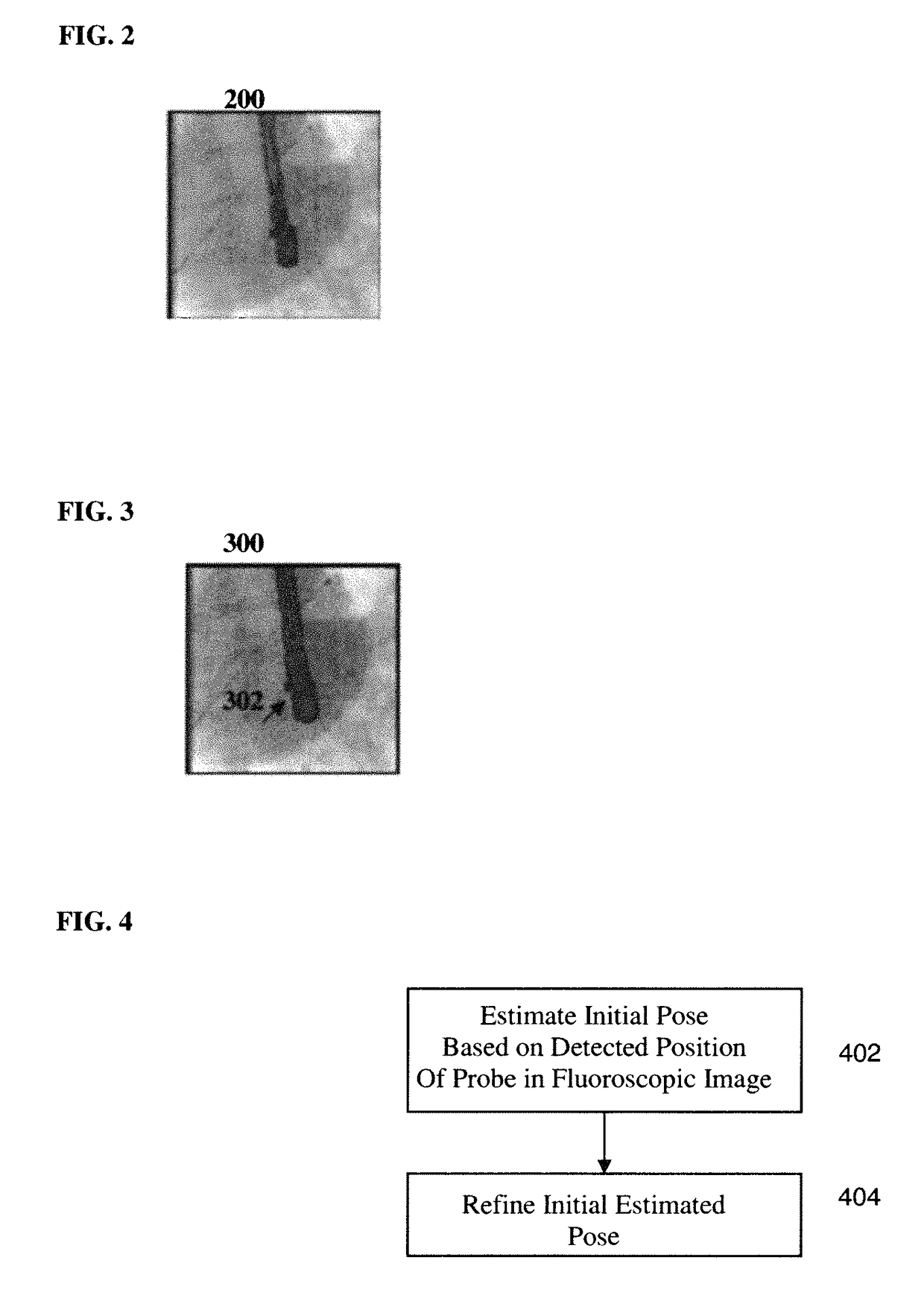
Method and System for Registration of Ultrasound and Physiological Models to X-ray Fluoroscopic Images
A method and system for registering ultrasound images and physiological models to x-ray fluoroscopy images is disclosed. A fluoroscopic image and an ultrasound image, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) image, are received. A 2D location of an ultrasound probe is detected in the fluoroscopic image. A 3D pose of the ultrasound probe is estimated based on the detected 2D location of the ultrasound probe in the fluoroscopic image. The ultrasound image is mapped to a 3D coordinate system of a fluoroscopic image acquisition device used to acquire the fluoroscopic image based on the estimated 3D pose of the ultrasound probe. The ultrasound image can then be projected into the fluoroscopic image using a projection matrix associated with the fluoroscopic image. A patient specific physiological model can be detected in the ultrasound image and projected into the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
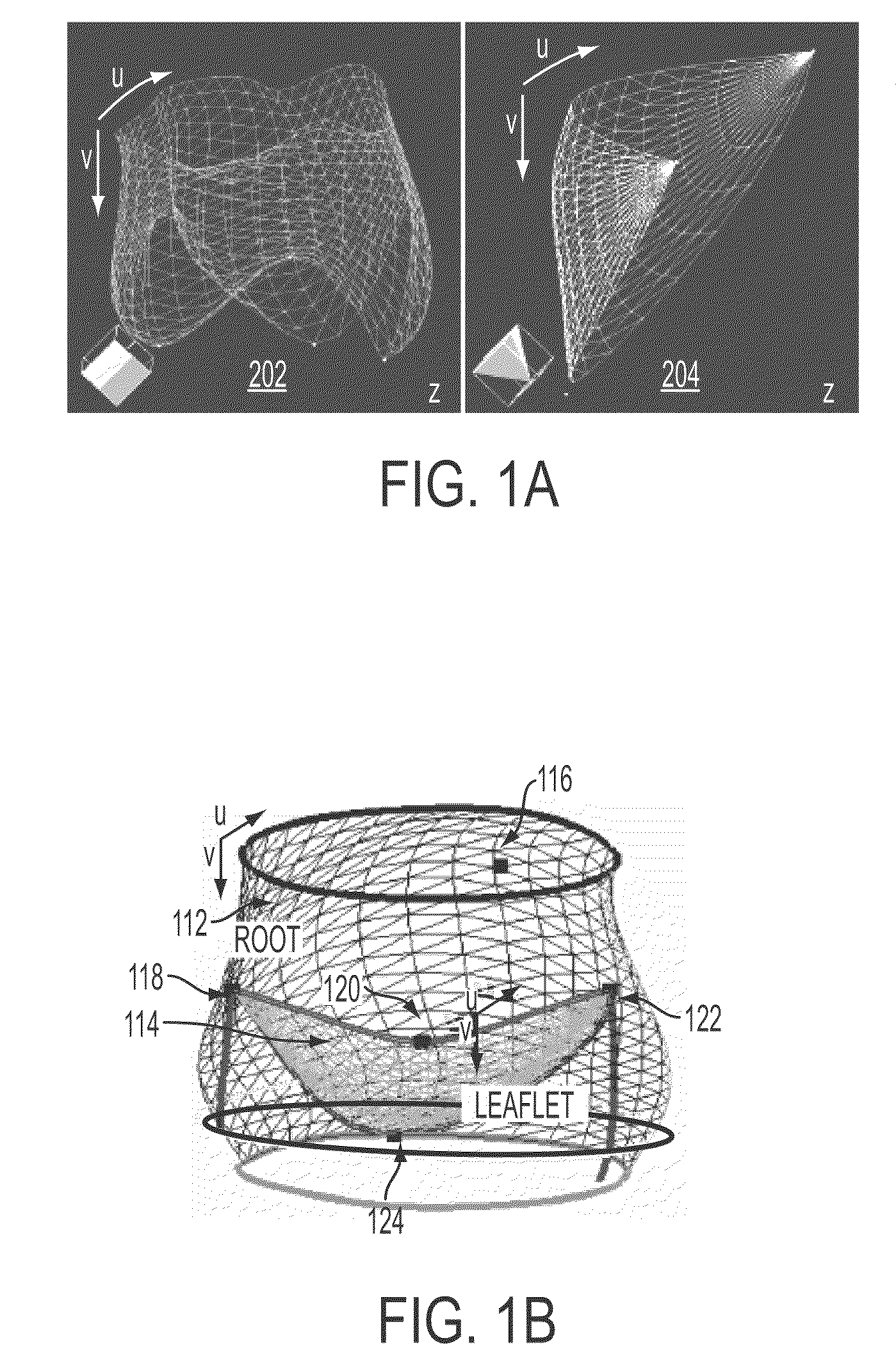
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
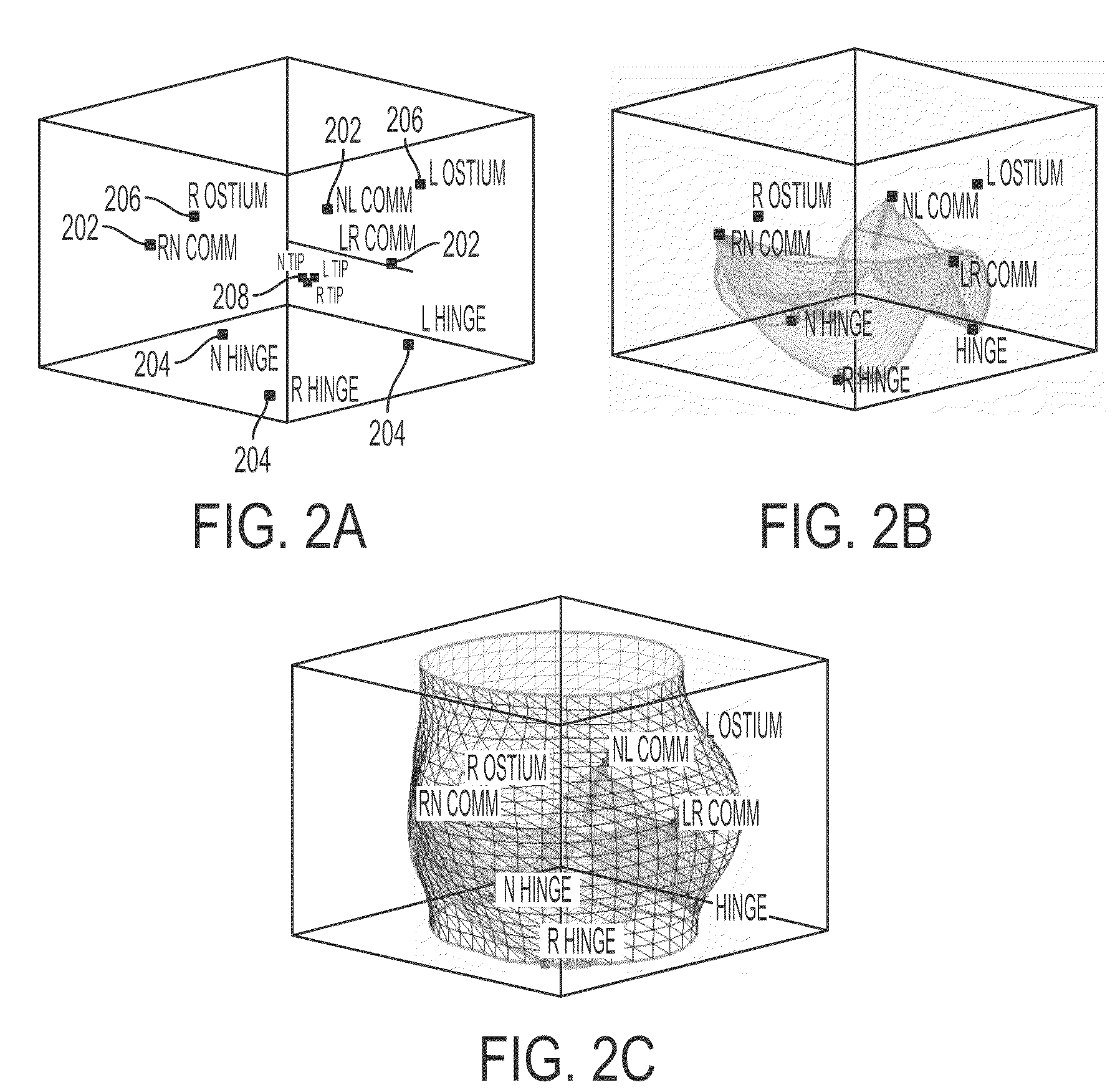
Surgical navigation for repair of heart valve leaflets
ActiveUS20130150710A1Improve overall navigation processHigh areaSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac echoMedicine
To improve the overall navigation process for minimally invasive repair of heart valve leaflets, an augmented reality technique capable of providing a robust three-dimensional context for transesophogeal echocardiography data has been developed. In the context of various embodiment of the invention, augmented reality essentially refers to a system in which the primary environment is virtual but the environment is augmented by real elements. In this real-time environment, the surgeon can easily and intuitively identify the tool, surgical targets, and high risk areas, and view tool trajectories and orientations.
Owner:NEOCHORD
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
Method and system for generating a personalized anatomical heart model
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. Volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT) or echocardiography image data, of a patient's cardiac region is received. Individual models for multiple heart components, such as the left ventricle (LV) endocardium, LV epicardium, right ventricle (RV), left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), mitral valve, aortic valve, aorta, and pulmonary trunk, are estimated in said volumetric cardiac image data. A patient specific anatomical heart model is generated by integrating the individual models for each of the heart components.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for computational modeling of the aorta and heart
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for determining optimal atrioventricular delay based on intrinsic conduction delays
Techniques are provided for estimating optimal atrioventricular delay values for use in pacing the ventricles. Both the intrinsic inter-atrial conduction delay and the intrinsic atrioventricular conduction delay are determined for the patient and then the preferred atrioventricular pacing delay is derived therefrom. By taking into account intrinsic inter-atrial delay along with intrinsic atrioventricular delay, it is believed that a more reliable estimate of the true optimal atrioventricular delay values for the patient can be achieved than with techniques that only take into account intrinsic atrioventricular delay values. In one example, the technique uses intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals and surface electrocardiogram (EKG) signals and hence can be performed by an external programmer without requiring Doppler echocardiography or other cardiac performance monitoring techniques. In another example, wherein the implanted device is equipped with a coronary sinus lead, the technique uses only IEGM signals and hence can be performed by the device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
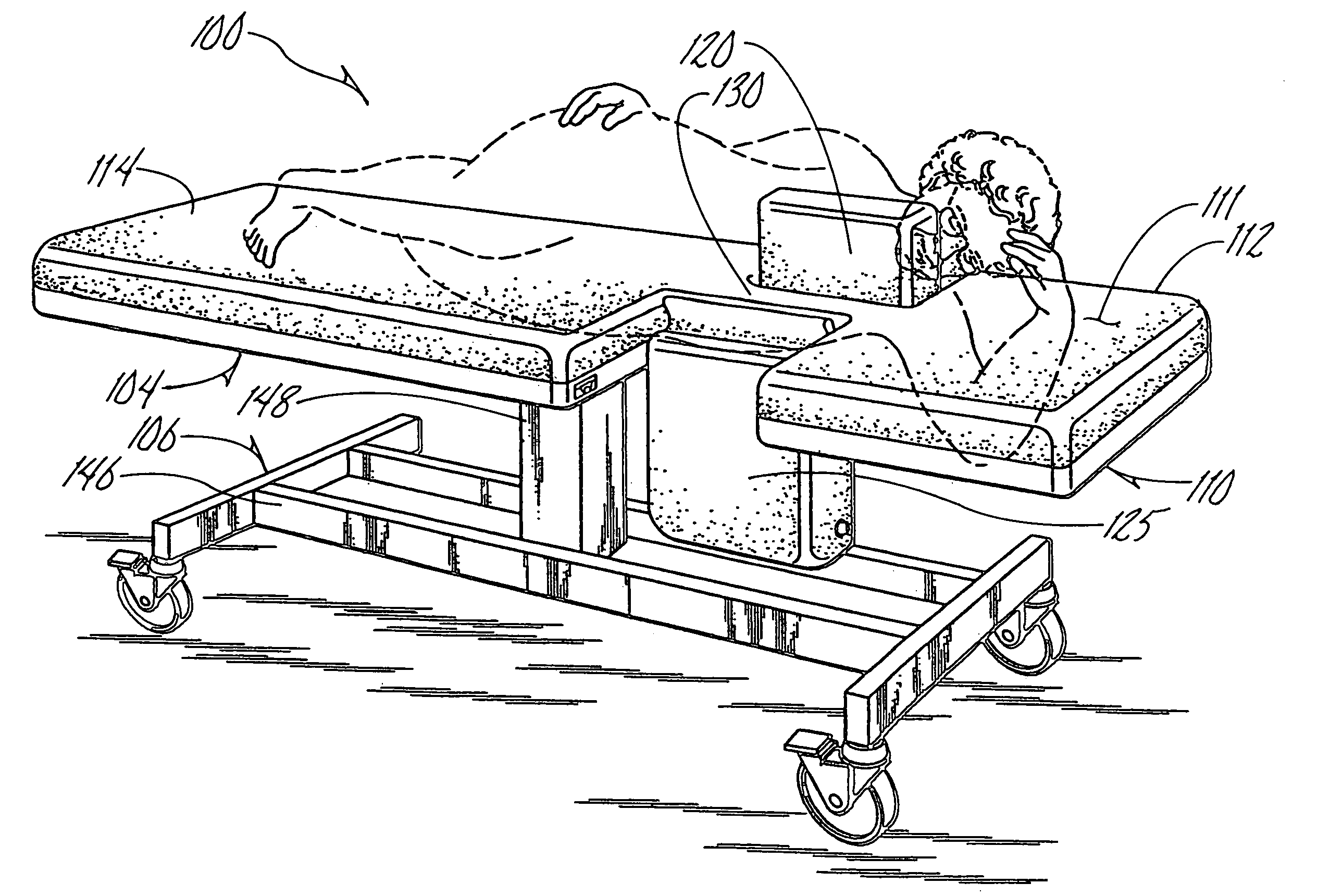
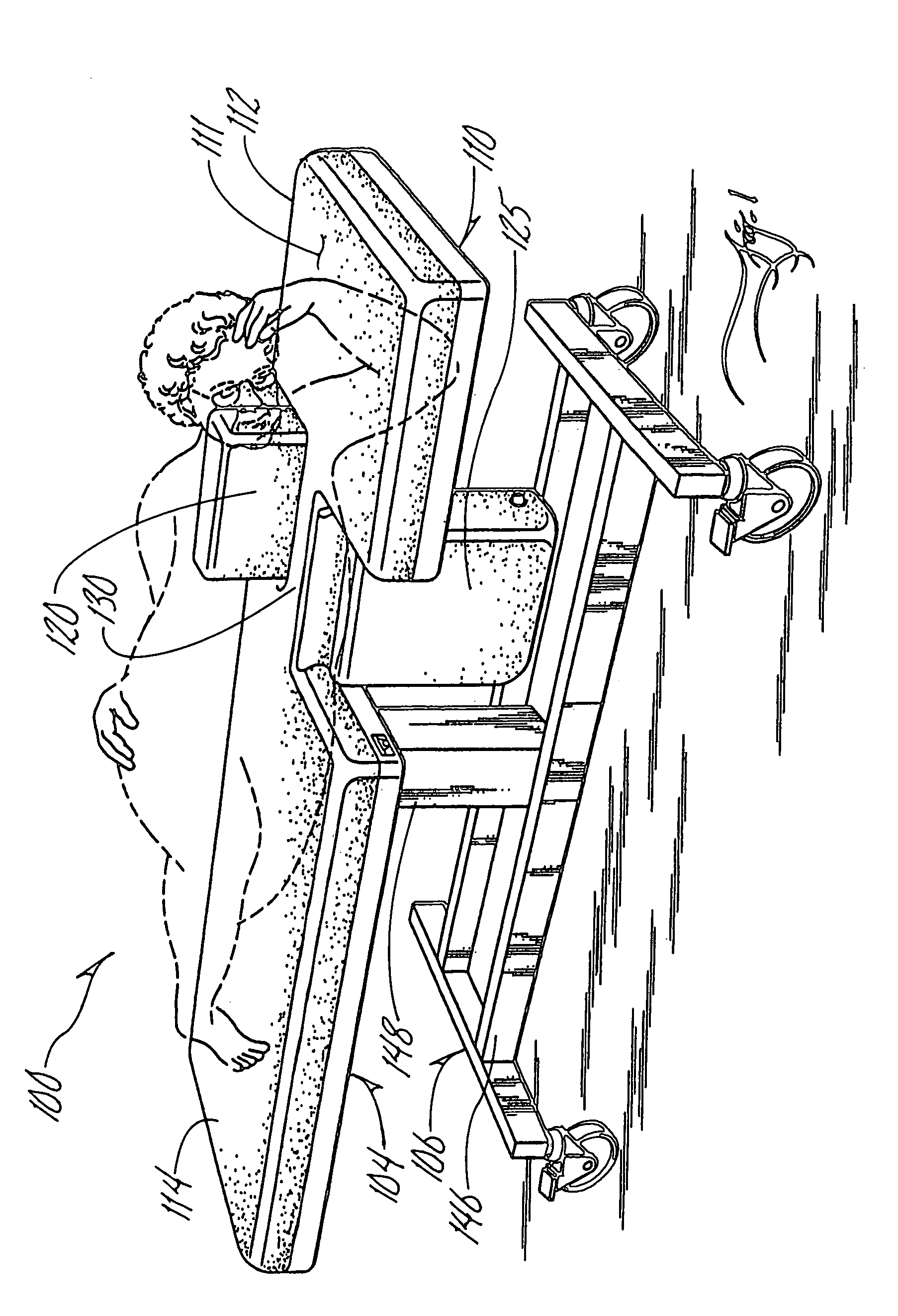
Sonography bed having patient support and sonographer access provisions
A patient exam bed useful for sonograms including echocardiography exams has a mattress provided with one or more pop-up wedges as well as one or more access bays formed through a side edge of the mattress. The access bays provide reach up access to a patient from below a plane of the mattress top, and can be filled-in when not needed by movable or removable in-fill sections. The pop-up wedges act to chock or support a patient to hold steady in a specific angle-of-roll or attitude chosen from various angles of lying down on one's side. The mattress optionally might have one or more folding sections to convert the bed into more like a chair or reclining chair. Additionally, any of the various foregoing options may be enhanced with power equipment to drive the movable components through their movements.
Owner:STASNEY T GLEN +1
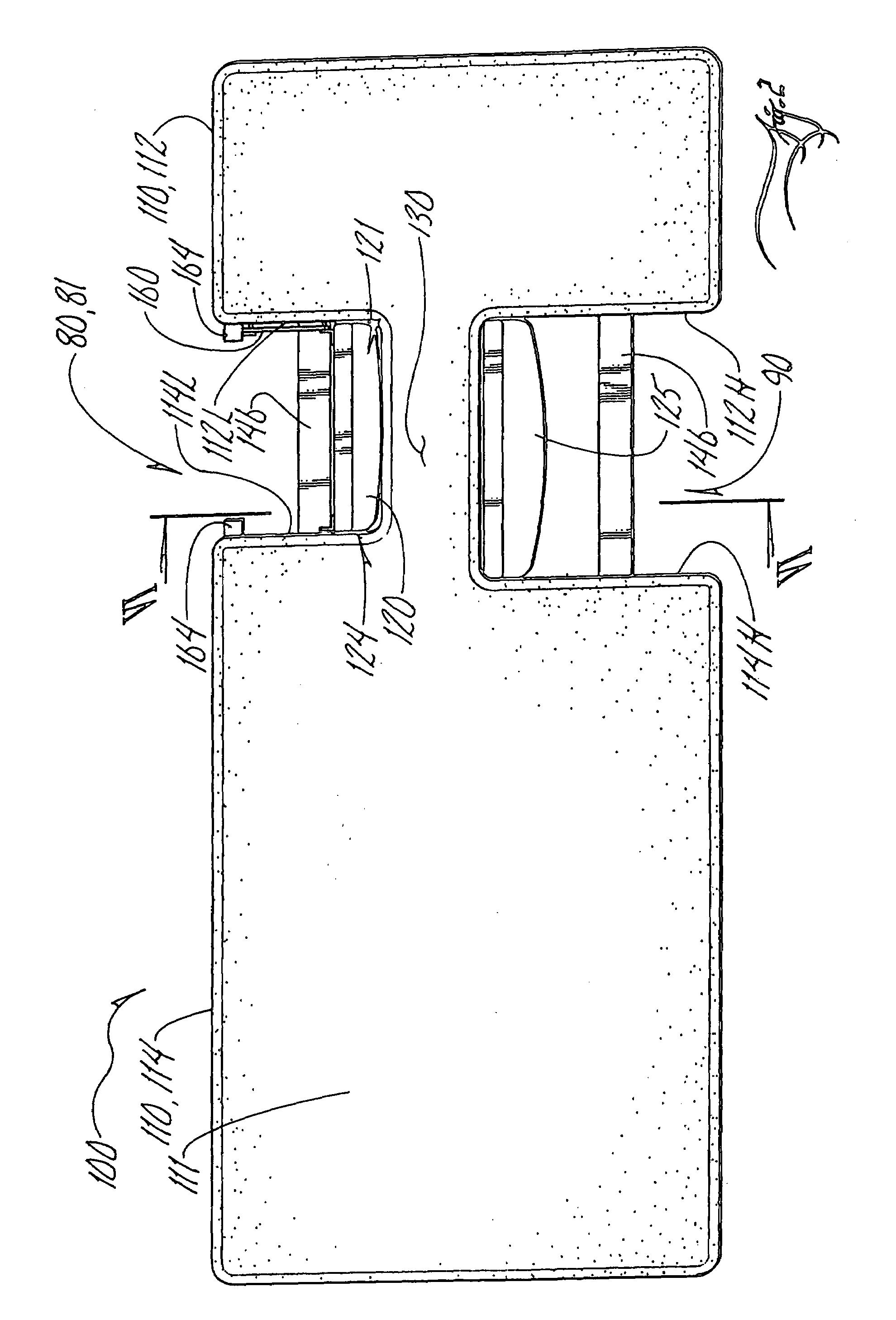
Echocardiography table swing out patient support cushion
InactiveUS7103932B1Support moreStably support more weightPatient positioningOperating tablesCardiac echoEngineering
Echocardiography table with an access cushion hinged within an access recess and a patient support cushion that swings out about a pivot from a swung in position within a patient support recess and a swung out position clear of the patient support recess. Retainers such as locking elements keep the patient support cushion in either the swung in or swung out position, as applicable. The patient support recess may have opposite walls that diverge and complement the tapering sides of the patient support cushion. The access cushion may be hinged to either rotate upright or swing to a hanging position.
Owner:MIRION TECH (CAPINTEC) INC
Surgical navigation for repair of heart valve leaflets
To improve the overall navigation process for minimally invasive repair of heart valve leaflets, an augmented reality technique capable of providing a robust three-dimensional context for transesophogeal echocardiography data has been developed. In the context of various embodiment of the invention, augmented reality essentially refers to a system in which the primary environment is virtual but the environment is augmented by real elements. In this real-time environment, the surgeon can easily and intuitively identify the tool, surgical targets, and high risk areas, and view tool trajectories and orientations.
Owner:NEOCHORD
Respiratory referenced imaging
InactiveUS20050187464A1Accurate measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsRespiratory gatingSonification
Methods, systems and devices are presented that provide improved medical diagnostic and intervention procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging, cardiac imaging, cardiac nuclear scintigraphy, computed tomography, echocardiography, imaging to direct laser ablation, imaging to direct radio frequency radiation ablation, imaging to direct gamma knife radiation therapy, and imaging to direct radiation therapy by respiratory gating. In a preferred embodiment, one or more balloon pressure probes within a catheter are placed into the esophagus and detect pressure within the esophagus to infer respiratory air-flow. Other probes such as those based on fiber optics and other useful materials are described. Many of these devices interact poorly or not at all with magnetic and electromagnetic fields, and are particularly useful for use in respiratory gating of MRI.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Combined display method of multimode image of coronary artery
The invention discloses a combined display method of a multimode image of a coronary artery. In the method of the invention, a Chinese visible human (CVH) data set and a dual source CT (DSCT) data set are respectively used to establish a three-dimensional visual model of surface rendering and a three-dimensional model of volume rendering. According to a nonrigid change mode, registration is performed to a transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) section image and a corresponding volume rendering section image. Then, a surface rendering section of a corresponding space coordinate is superposed with the TTE section image so as to overcome a difficult existing in a TTE teaching training. Abstract understanding to the TTE image is greatly influenced by subjective consciousness. Therefore, it is not convenient for understanding and mastering. By using the method provided in the invention, a medical student can visually understand and grasp the TTE and two and three level branches of the coronary artery corresponding to a corresponding myocardial segment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
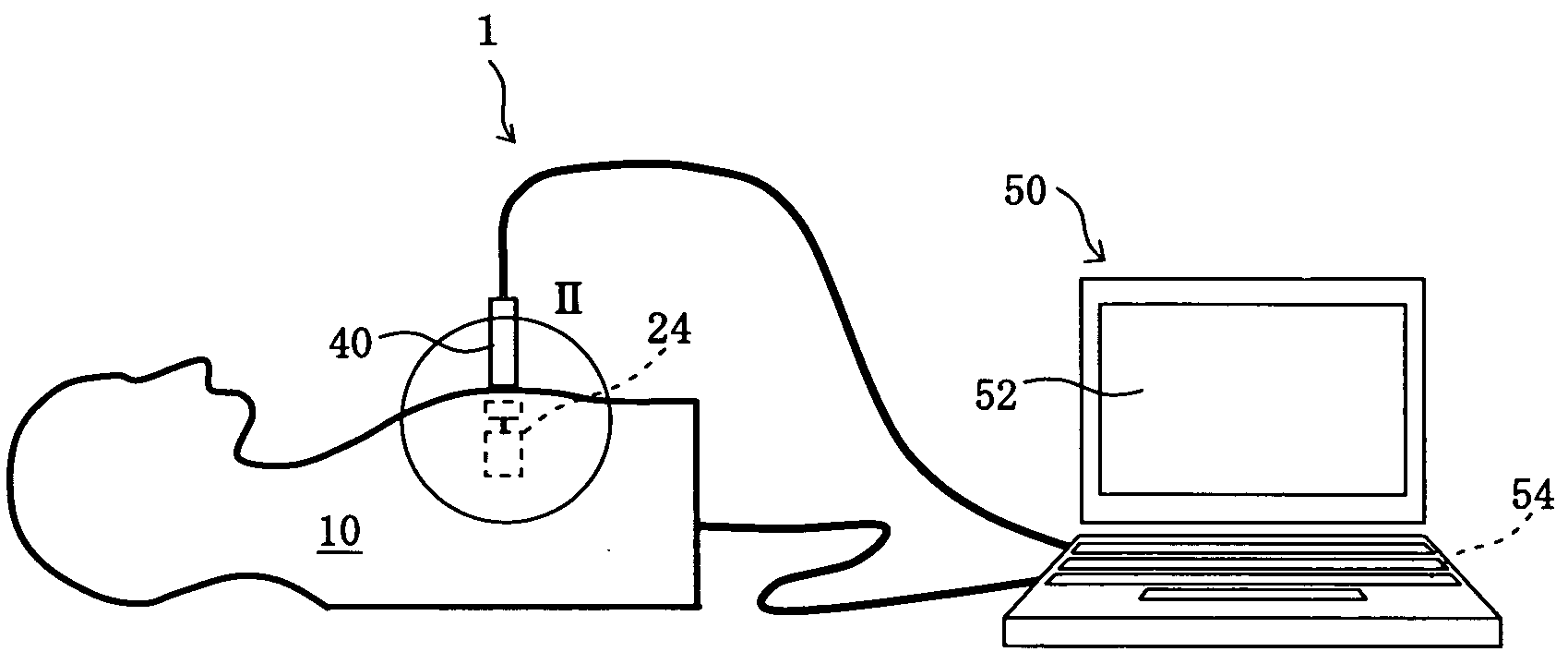
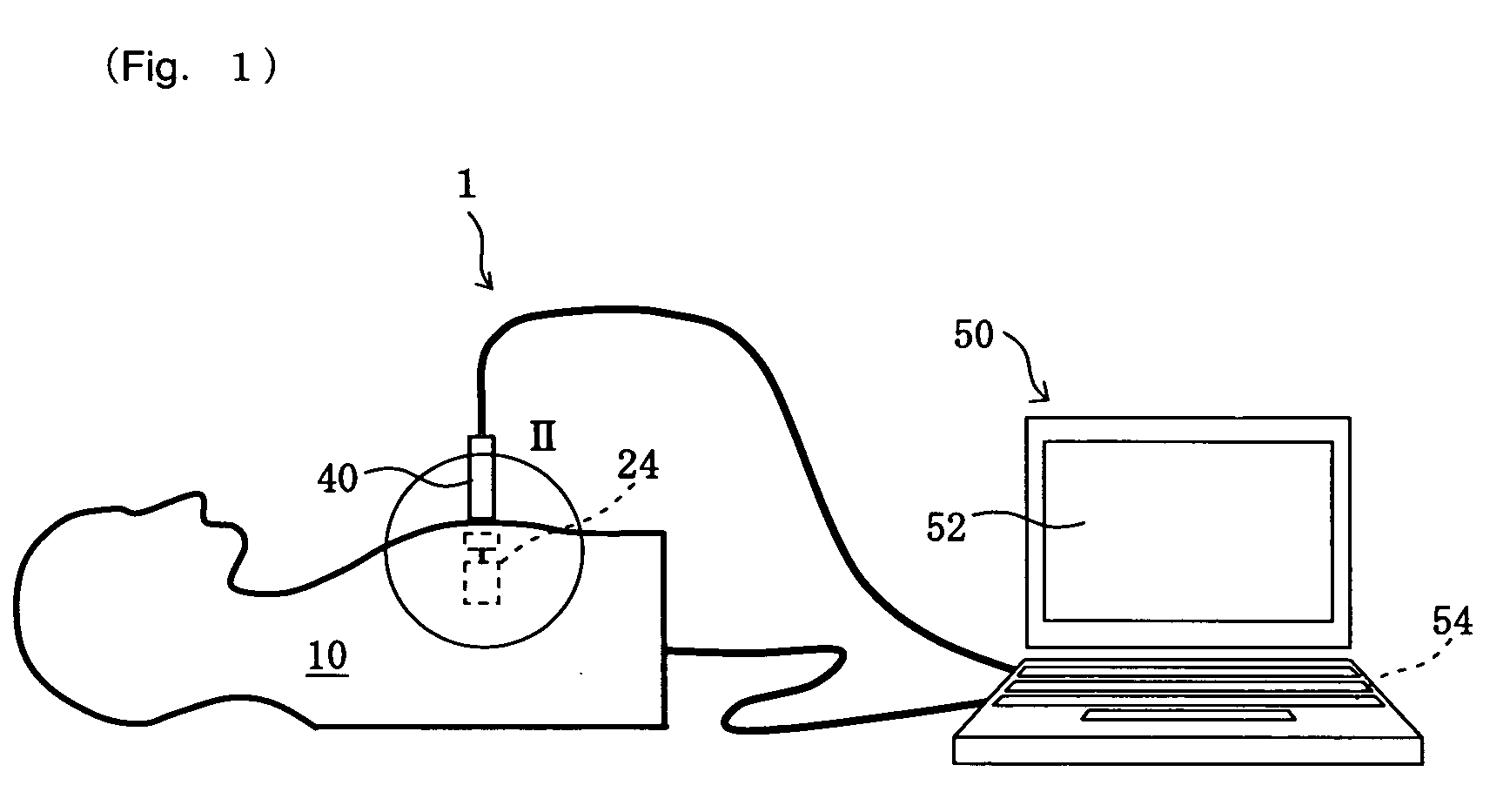
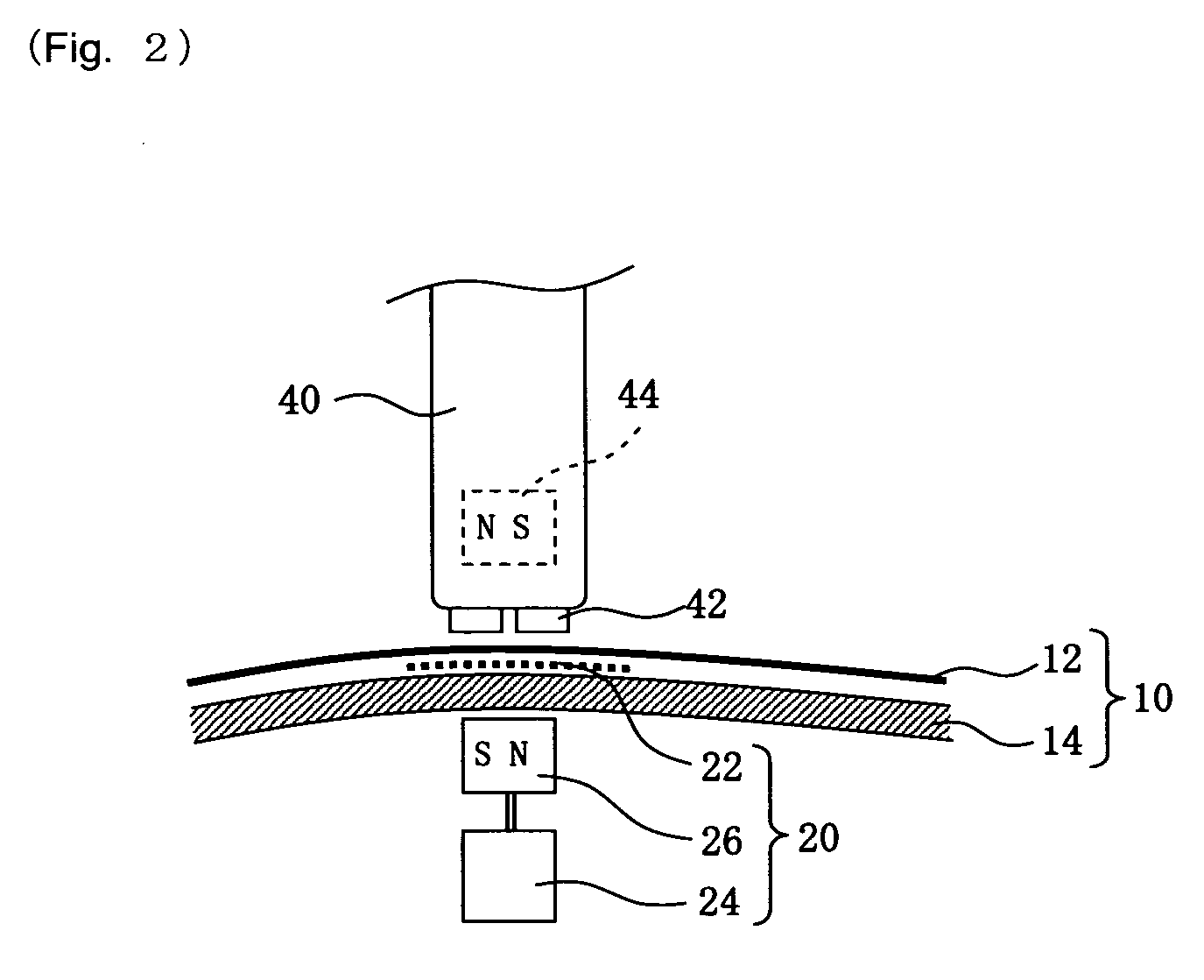
Educational Simulator for Transthoracic Echocardiography
InactiveUS20090130642A1Improve portabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsContrast echocardiographySonification
The present invention relates to a simulation device for ultrasonic diagnosis targeting a heart and its object is to provide an educational simulator for transthoracic echocardiography which can run simulations in a feeling like actual ultrasonic diagnosis. The educational simulator for transthoracic echocardiography is composed of a chest phantom with position sensors embedded at prescribed positions beneath the chest surface, a dummy probe in which a magnet is embedded and which is provided with an inclination sensor placed in the acral part, a memory section which stores three-dimensional image data of echocardiography, a CPU which calculates the position, inclination and pressing force of the dummy probe on the basis of information from each said sensor and clips two-dimensional image data from the three-dimensional image data on the basis of the calculation, and a display section which shows the clipped two-dimensional data.
Owner:HRS CONSULTANT SERVICE
Methods for treating myocardial infarction comprising administering an IL-6 inhibitor
ActiveUS8945558B2Improve the situationSuppressing left ventricular remodelingPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsCardiac echoLeft ventricular size
The present inventors investigated the effects of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies on improving the condition of infarcted areas in myocardial infarction, and on suppressing left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. As a result, the administration of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies significantly suppressed the increase of MPO activity in the infarcted area and suppressed myocardial MCP-1 expression in both the infarcted area and the non-infarcted area. Furthermore, echocardiography and histological examinations revealed that cardiac hypertrophy is also suppressed.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method and system for registration of ultrasound and physiological models to X-ray fluoroscopic images
A method and system for registering ultrasound images and physiological models to x-ray fluoroscopy images is disclosed. A fluoroscopic image and an ultrasound image, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) image, are received. A 2D location of an ultrasound probe is detected in the fluoroscopic image. A 3D pose of the ultrasound probe is estimated based on the detected 2D location of the ultrasound probe in the fluoroscopic image. The ultrasound image is mapped to a 3D coordinate system of a fluoroscopic image acquisition device used to acquire the fluoroscopic image based on the estimated 3D pose of the ultrasound probe. The ultrasound image can then be projected into the fluoroscopic image using a projection matrix associated with the fluoroscopic image. A patient specific physiological model can be detected in the ultrasound image and projected into the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
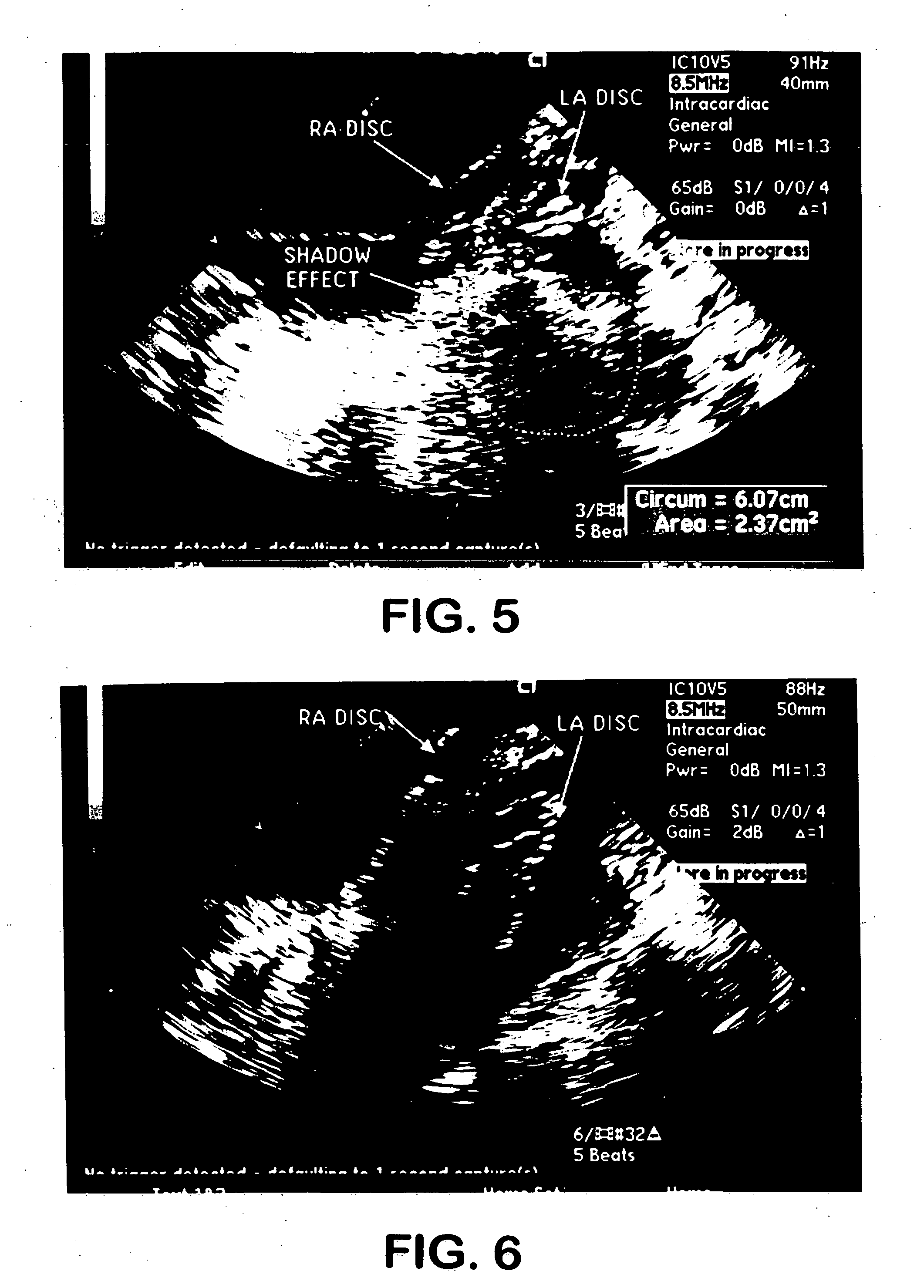
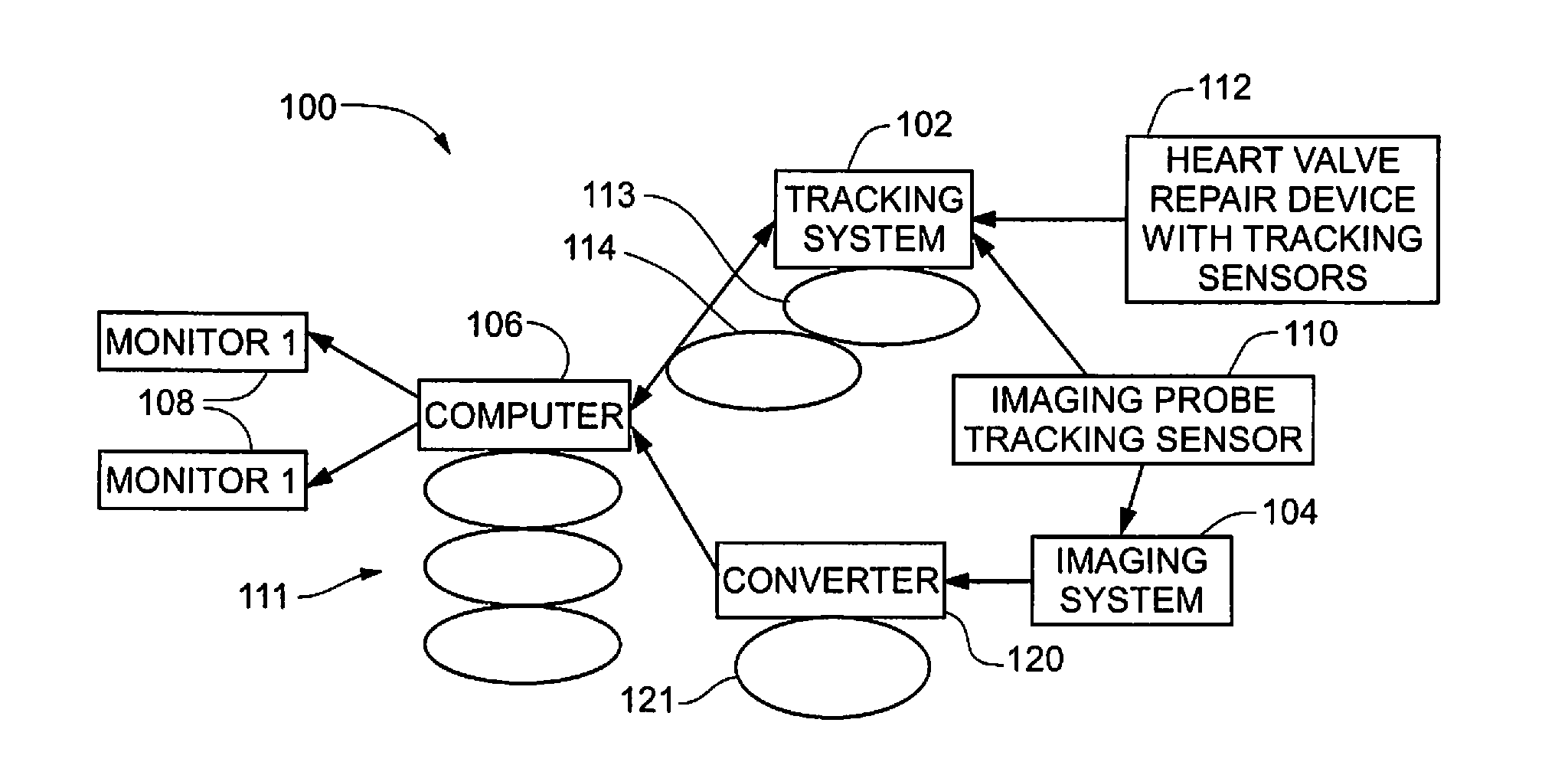
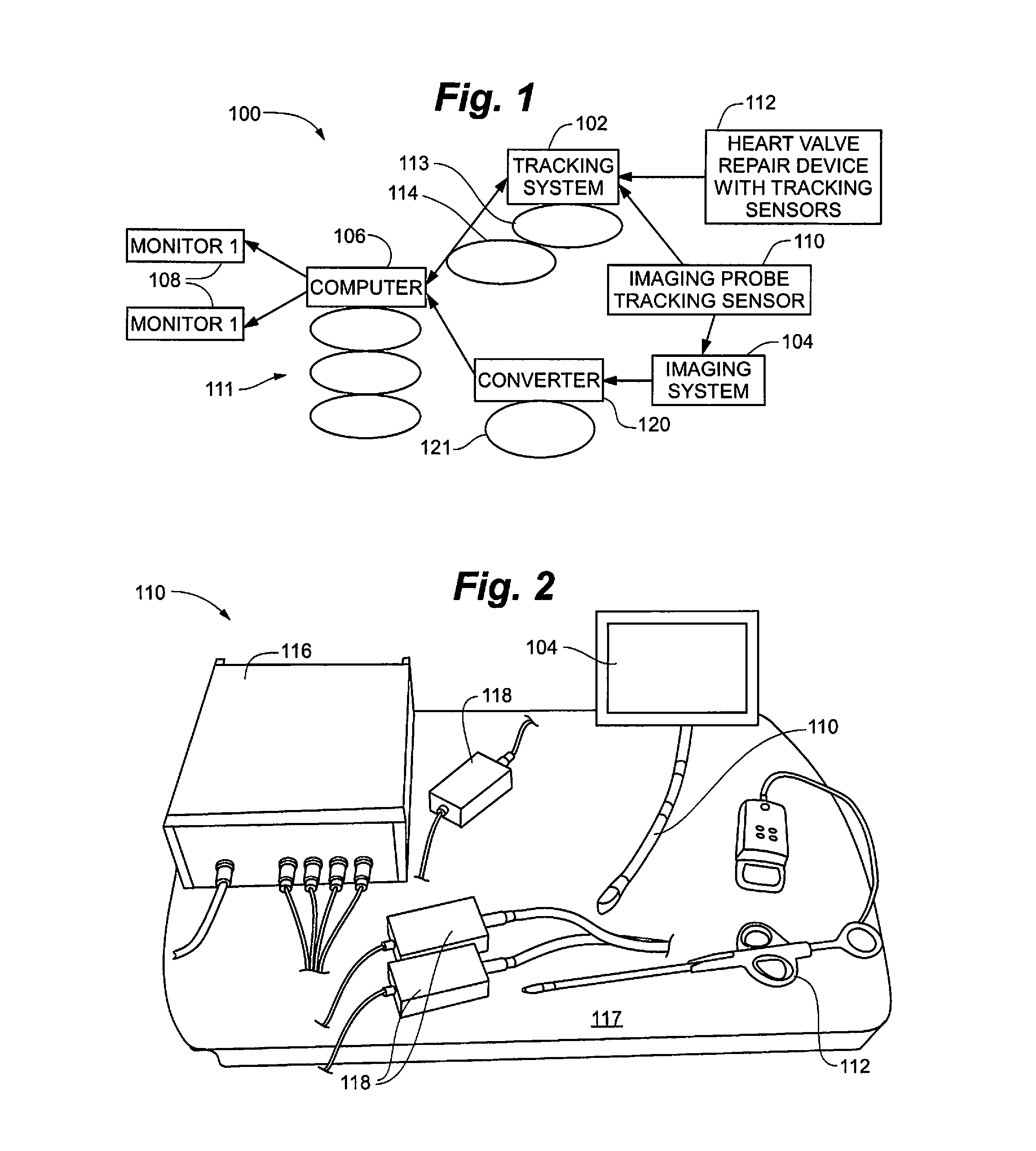
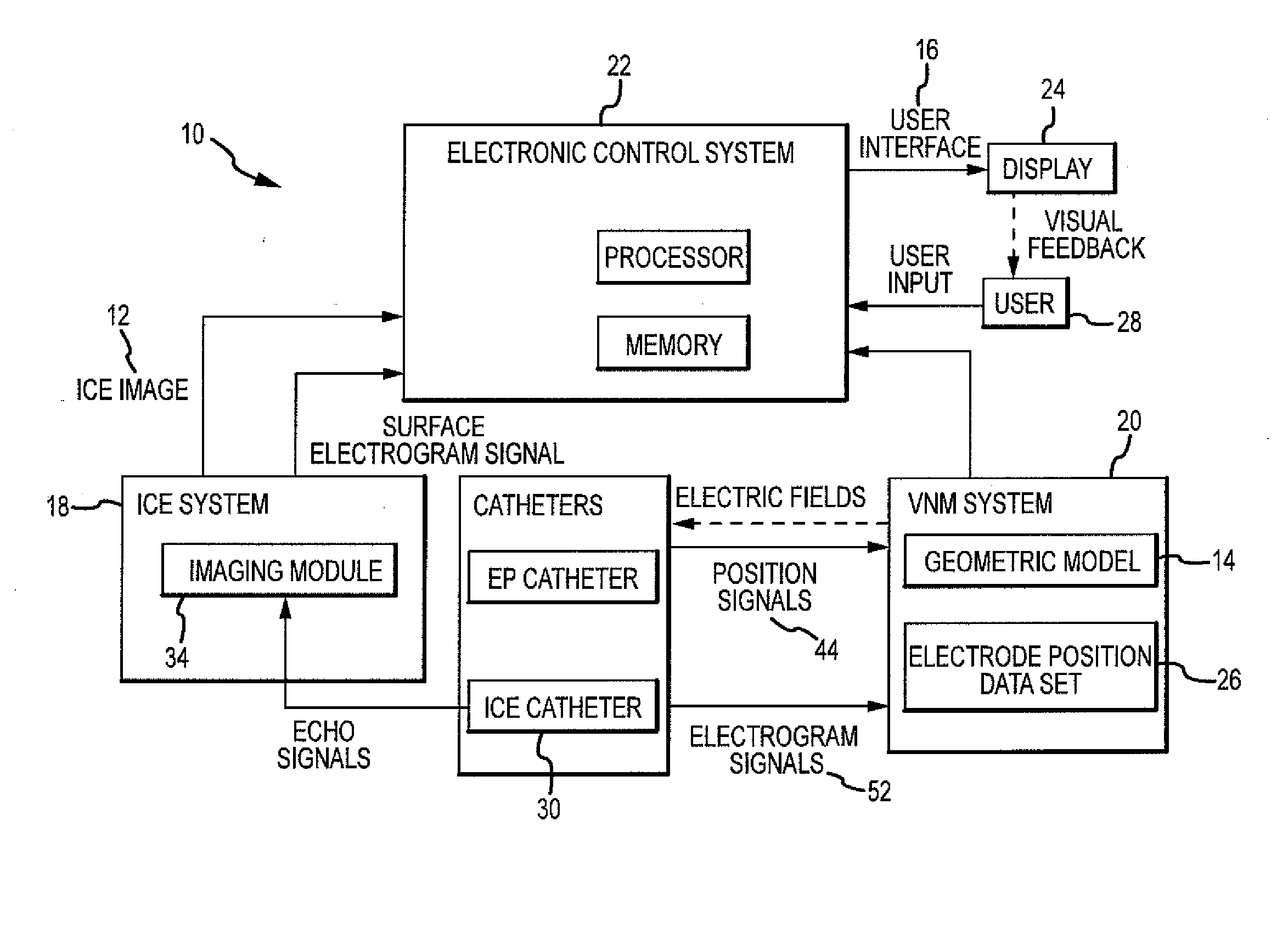
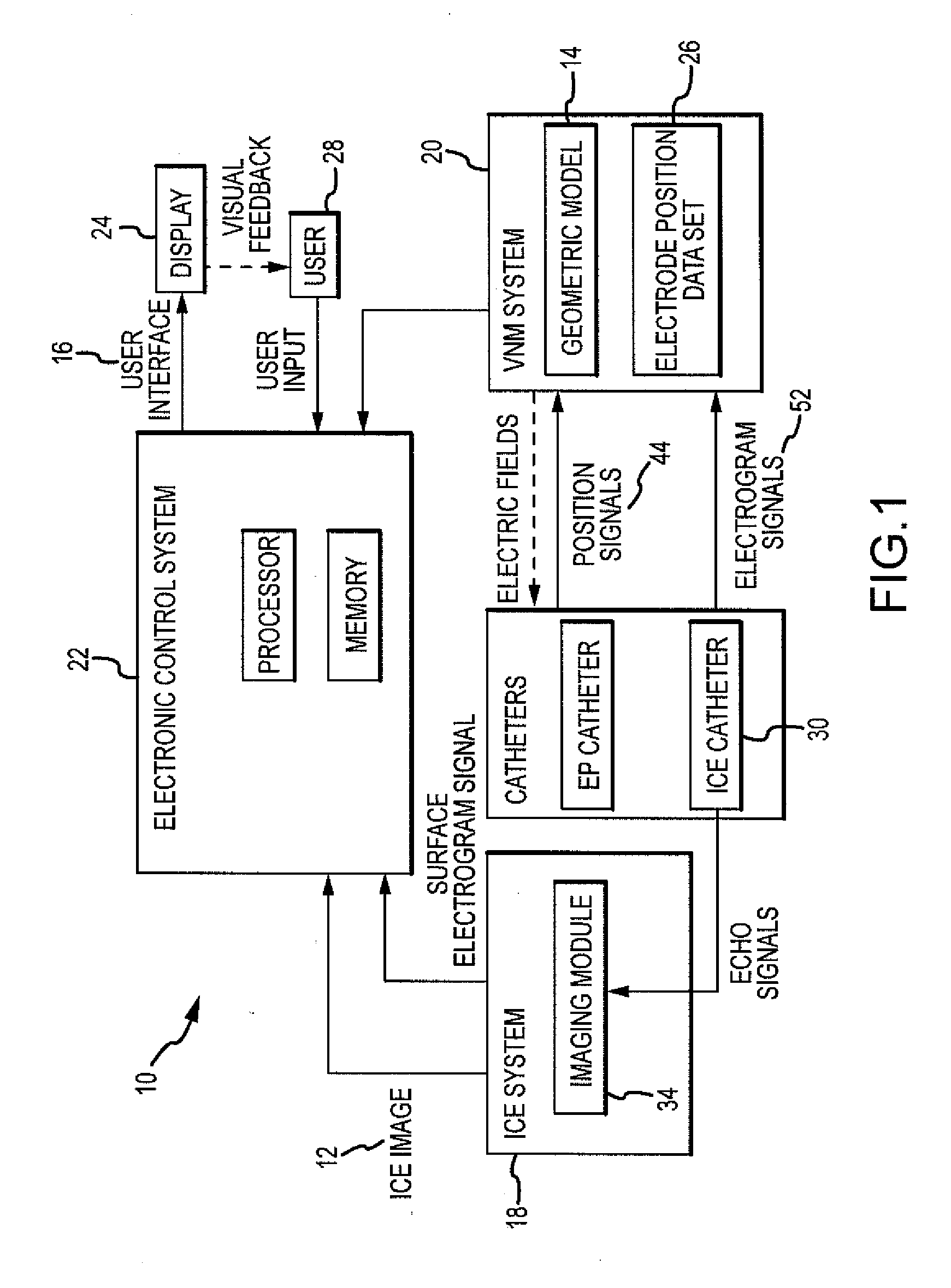
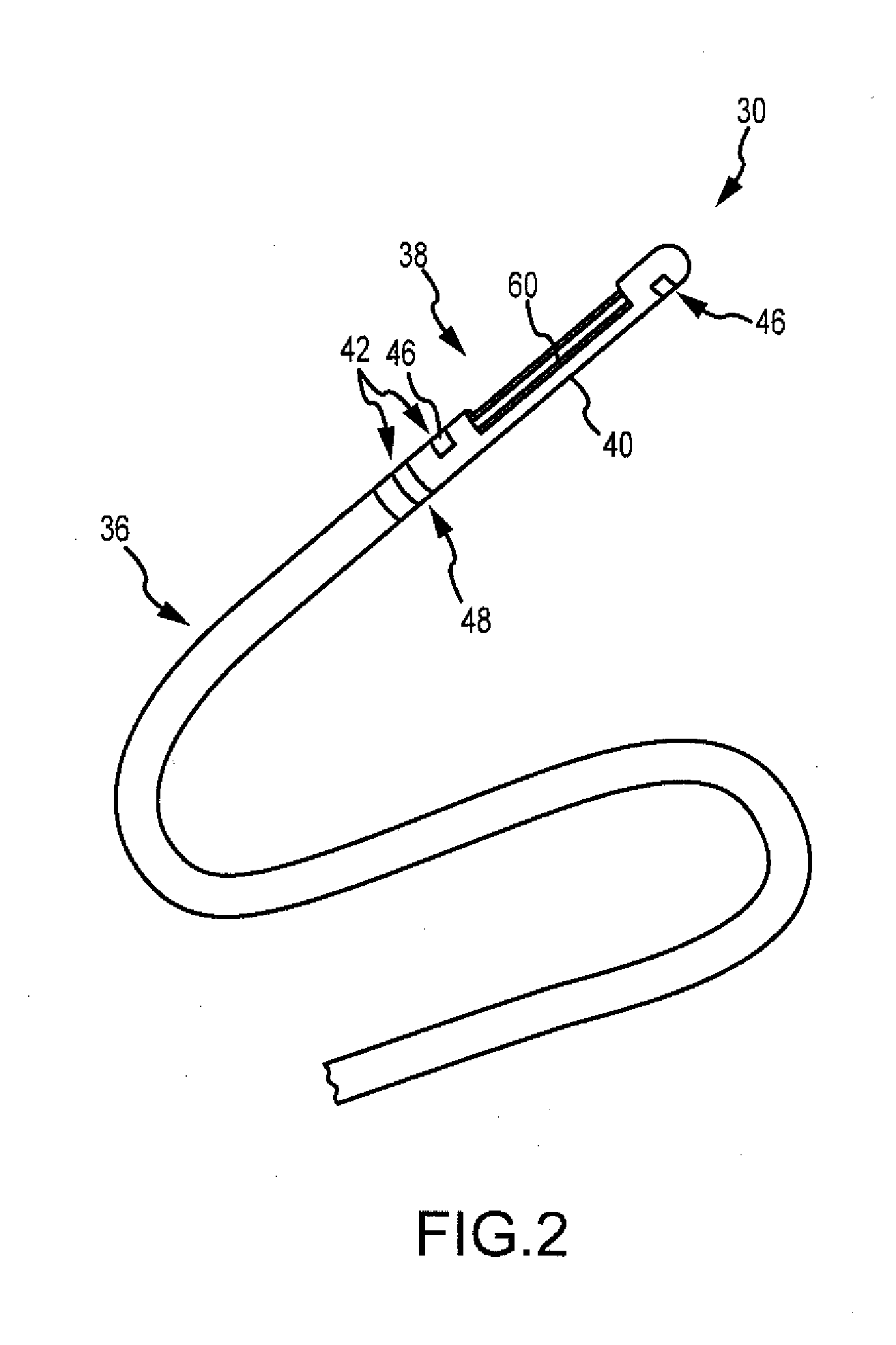
Intracardiac imaging system utilizing a multipurpose catheter
ActiveUS20110160593A1Accurate projectionAccurate displayUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSonificationCardiac echo
A three dimensional physiological mapping system utilizing an intracardiac echo catheter capable of being located in six degrees of freedom by a visualization, navigation, or mapping system. An echocardiography image of the intracardiac echo catheter may be projected within a geometric model of the visualization, navigation, or mapping system where the location of the projected image is adjusted in response to user input identifying a structure present in the echocardiography image and the geometric model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
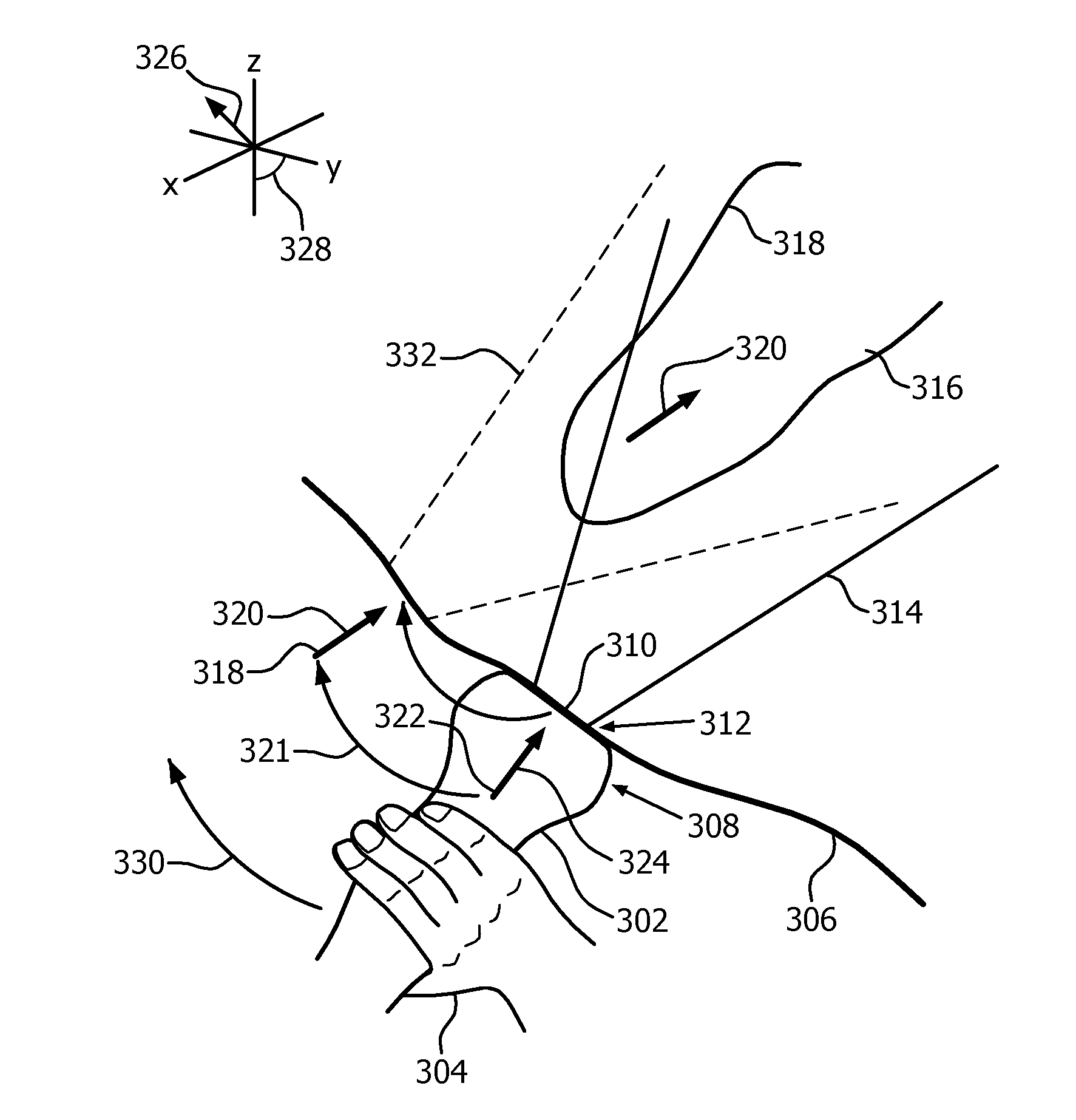
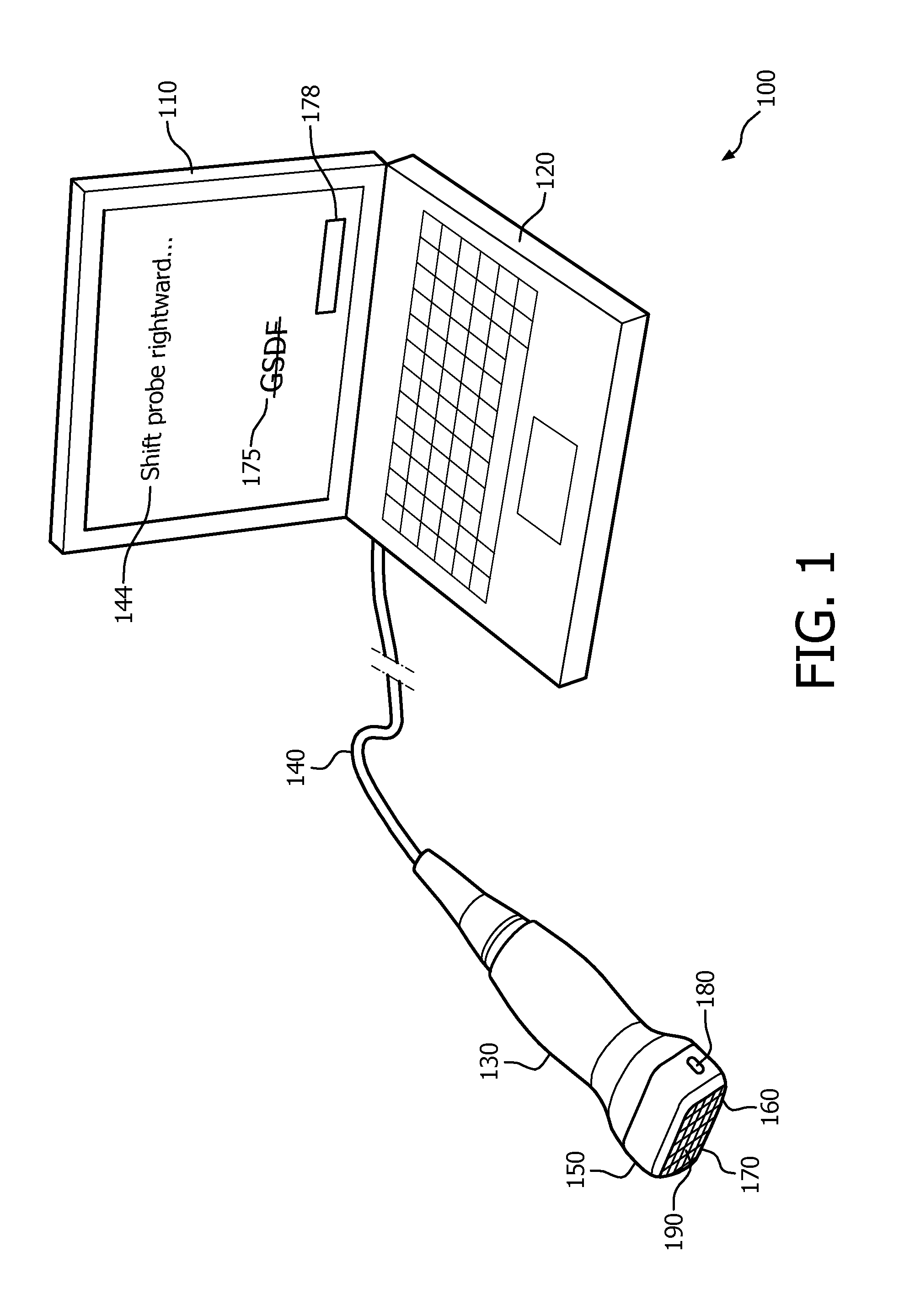
Anatomically intelligent echocardiography for point-of-care
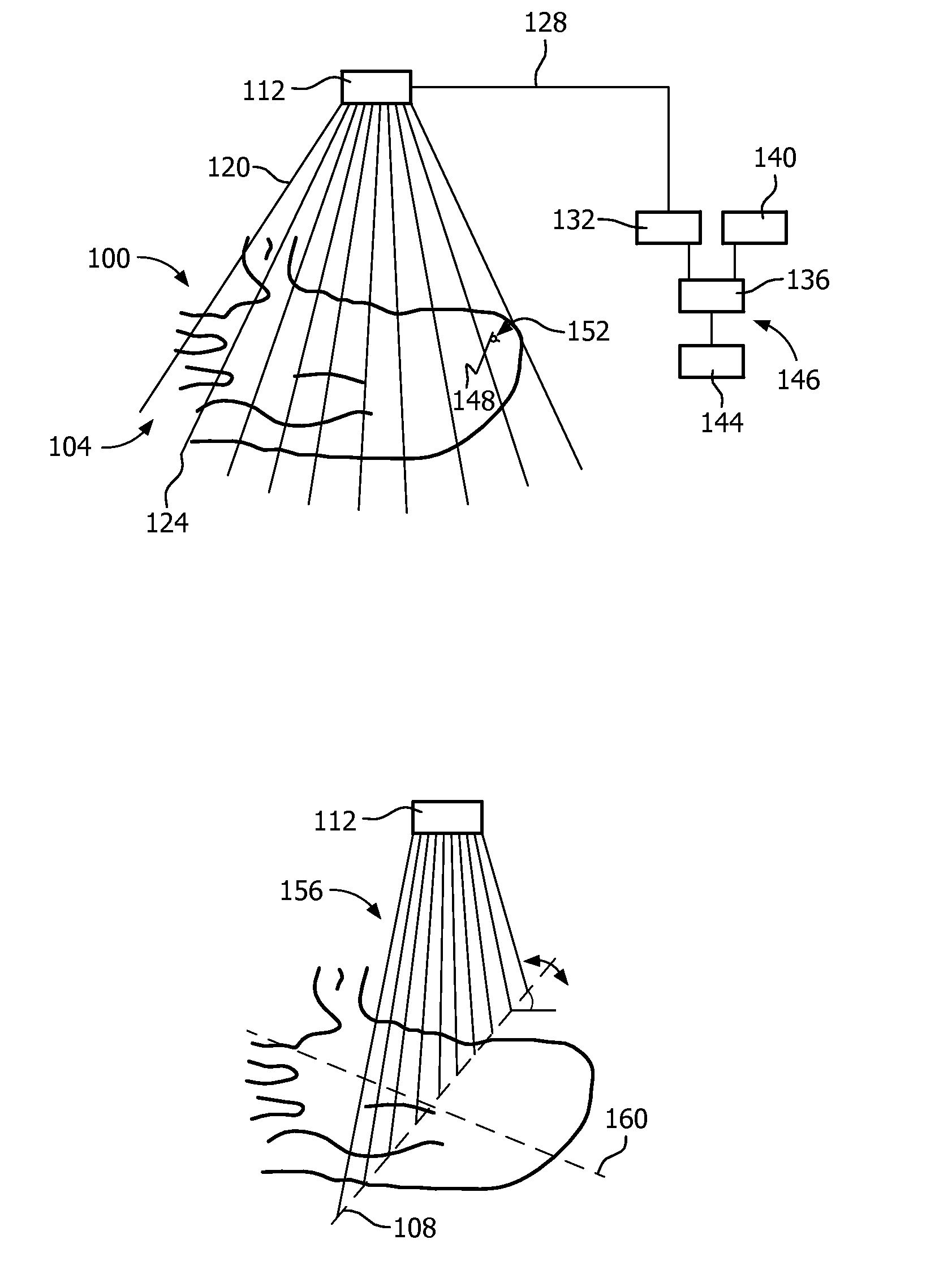
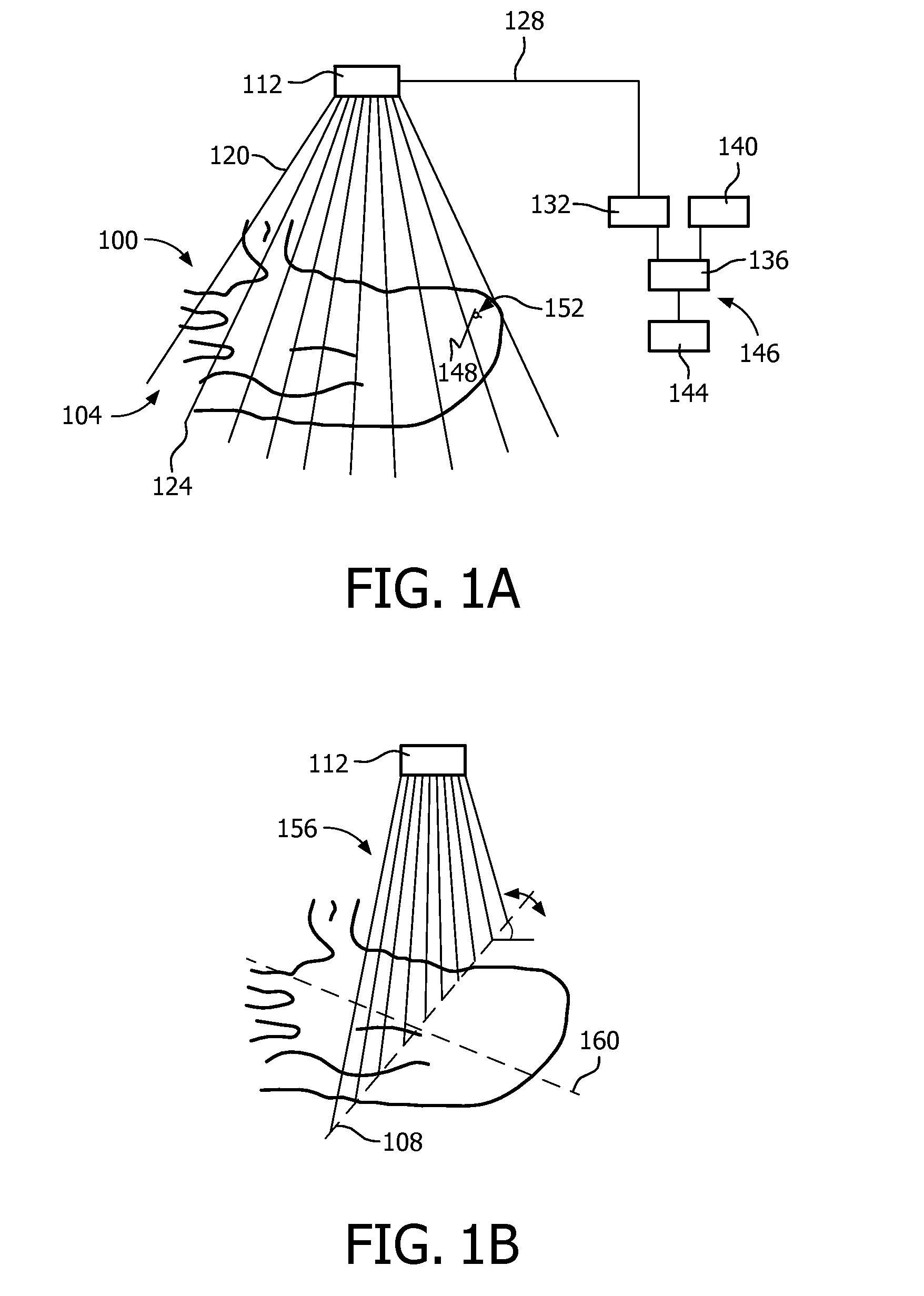
ActiveUS20150310581A1Lower the barrierImprove treatmentImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint of careSonification
An apparatus includes an imaging probe and is configured for dynamically arranging presentation of visual feedback (144) for guiding manual adjustment, via the probe, of a location, and orientation, associated with the probe. The arranging is selectively based on comparisons (321) between fields of view of the probe and respective results of segmenting image data acquired via the probe. In an embodiment, the feedback does not include (175) a grayscale depiction of the image data. Coordinate system trans formations corresponding to respective comparisons may be computed. The selecting may be based upon and dynamically responsive to content of imaging being dynamically acquired via the probe.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Automatic imaging plane selection for echocardiography
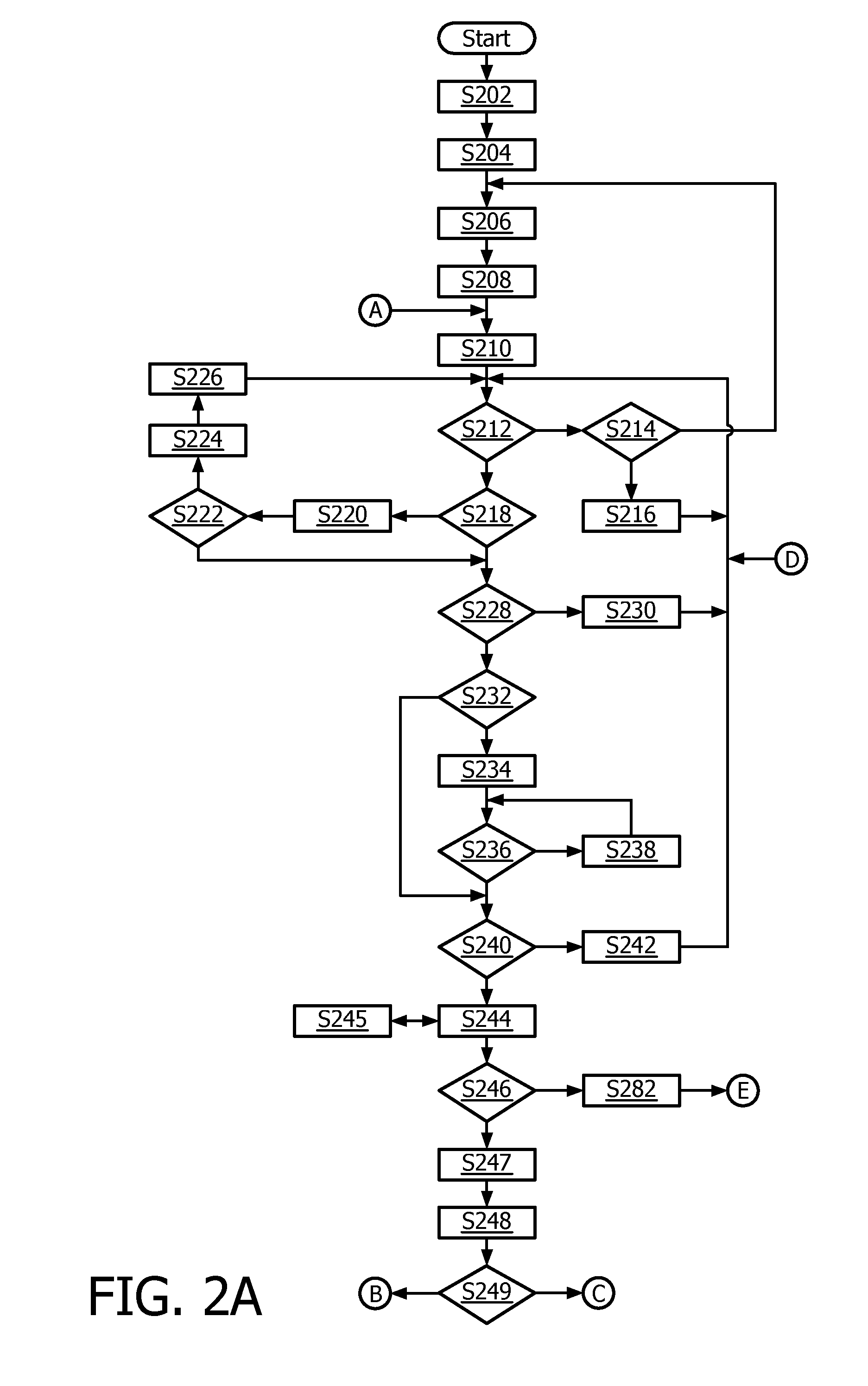
InactiveUS20150011886A1High resolutionRapid diagnosisWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical structuresTime response
Based on anatomy recognition from three-dimensional live imaging of a volume, one or more portions (204, 208) of the volume are selected in real time. In further real time response, live imaging or the portion(s) is performed with a beam density (156) higher than that used in the volume imaging. The one or more portion may be one or more imaging plane selected for optimal orientation in making an anatomical measurement (424) or display. The recognition can be based on an anatomical model, such as a cardiac mesh model. The model may be pre-encoded with information that can be associated with image locations to provide the basis for portion selection, and for placement of indicia (416, 420, 432, 436) displayable for initiating measurement within an image provided by the live portion imaging. A single TEE or TTE imaging probe (112) may be used throughout. On request, periodically or based on detected motion of the probe with respect to the anatomy, the whole process can be re-executed, starting back from volume acquisition (S508).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Echocardiography
InactiveUS20150327838A1Improved test-retest reproducibility of measurementImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac echoVelocity vector
Various methods for automatically processing an ultrasound image for echocardiography are disclosed in which the regions of interest in the ultrasound image are identified by determining velocity vectors for tissue movement in the image. A novel construction of ultrasound probe is also disclosed.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
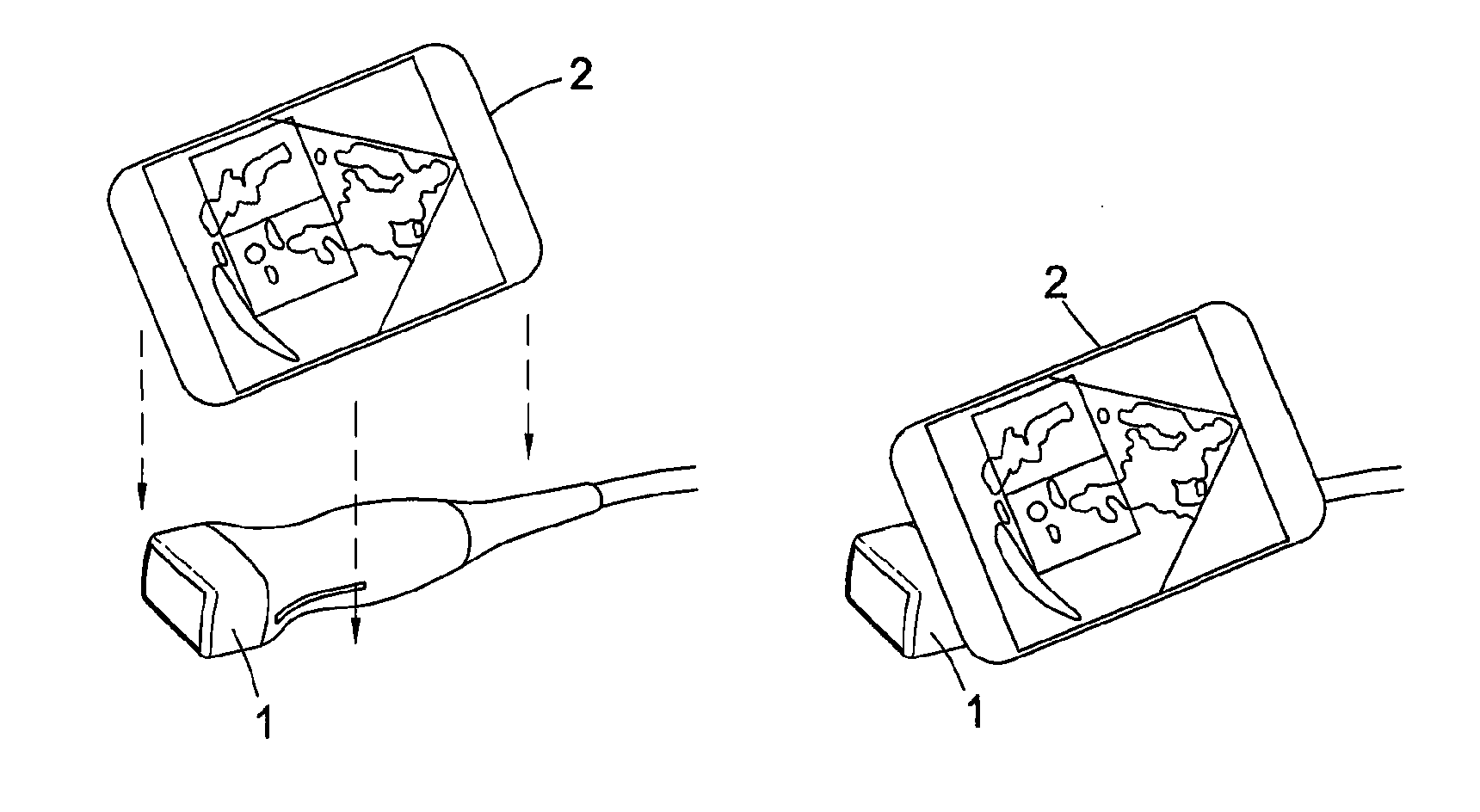
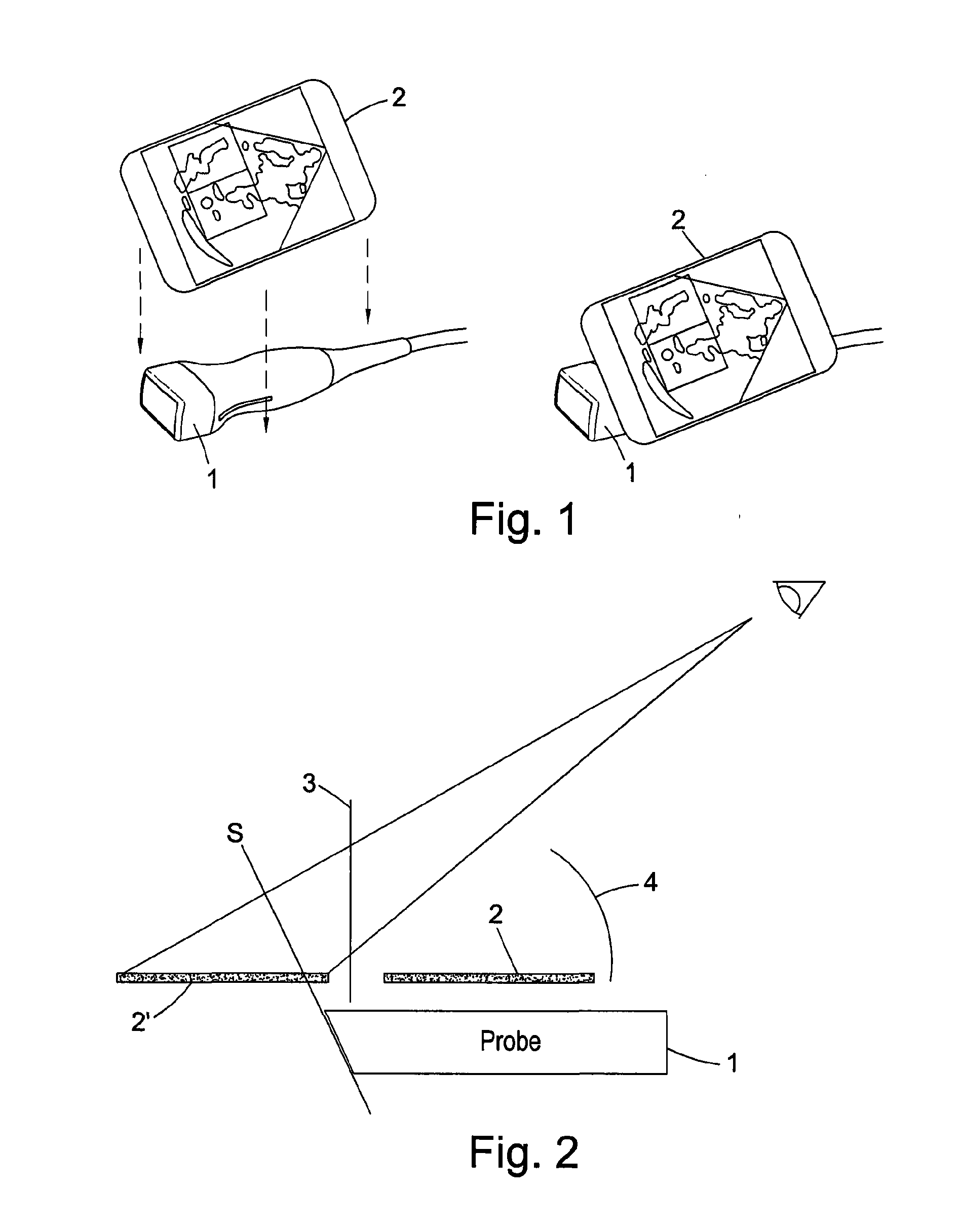
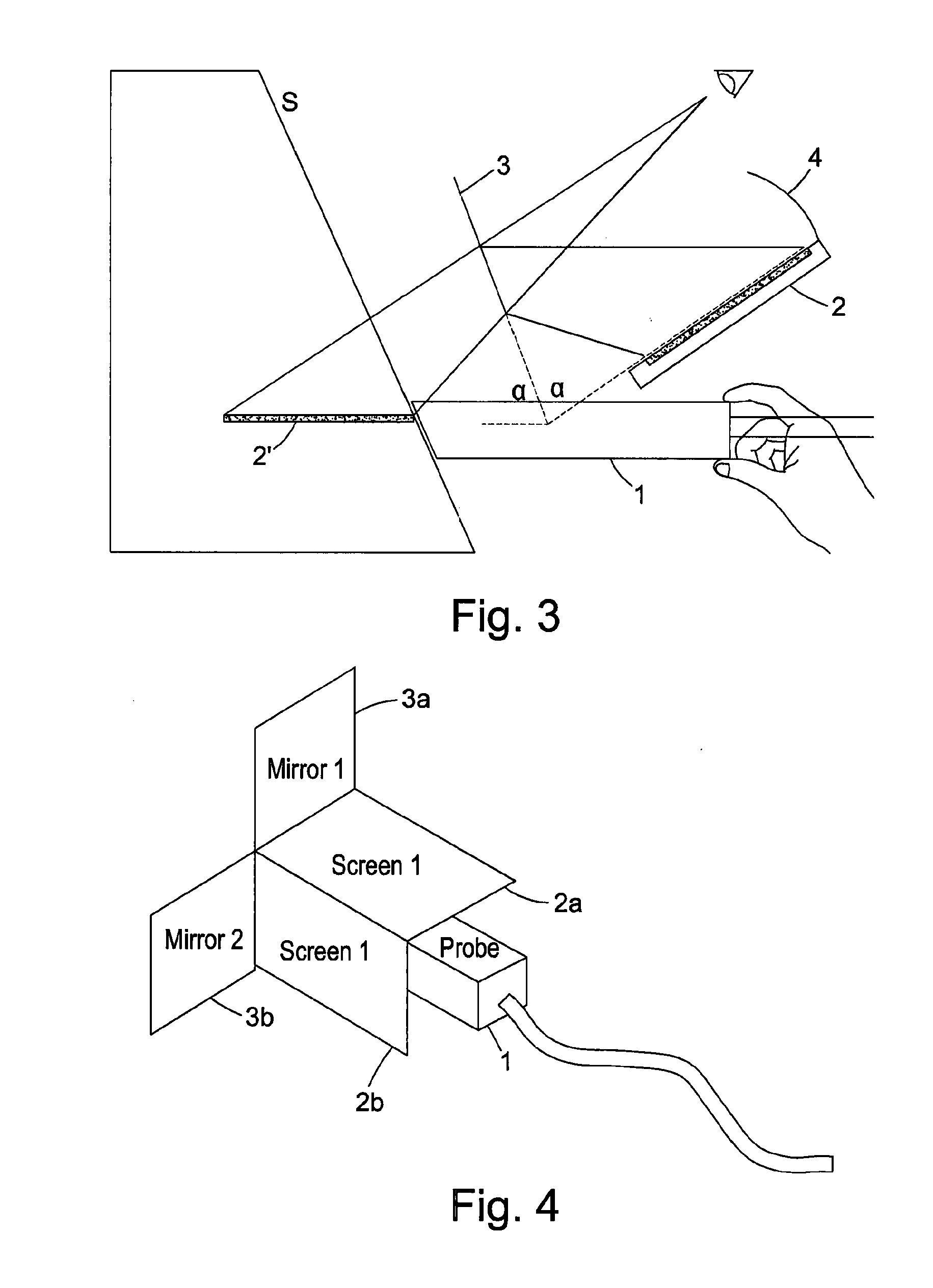
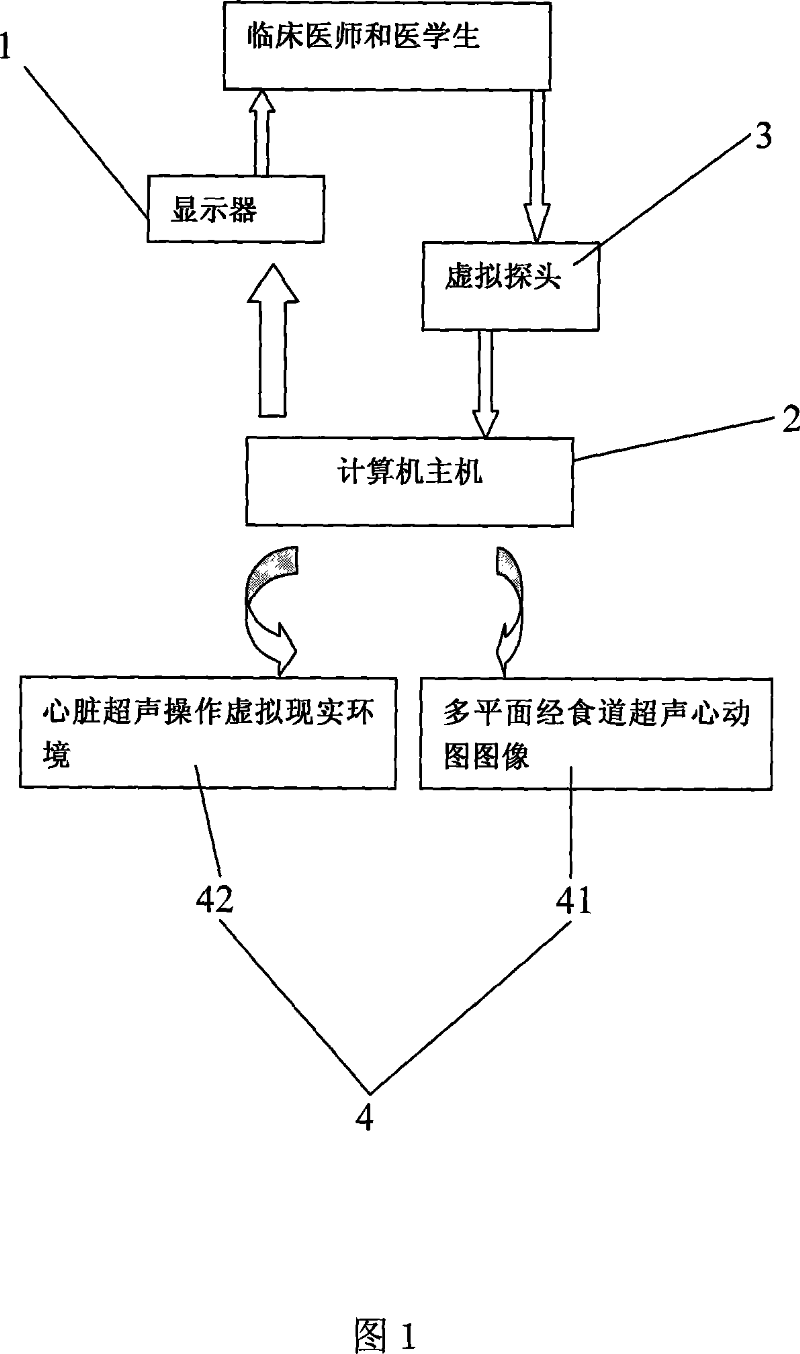
System of obtaining the echocardiography by the dummy gullet passing and the method for realizing the same
InactiveCN101036585ADifficult to solveProblem Solved and MasteredUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCosmonautic condition simulationsAnatomical structuresSonification
The invention discloses an ultrasonic cadiogram system and the realizing method through the esophagus virtually, wherein the system includes a display, a main frame connected to the display and a virtual probe connected to the main frame; a virtual multiple plane ultrasonic cadiogram system module via the esophagus is arranged in the main frame, wherein the system module includes a multiple plane ultrasonic cadiogram data base via the esophagus and a virtual reality environment for the heart ultrasonic operation; the system is applied in the clinic and the practical work, for solving the a plurality of problems which are not identified by the esophagus ultrasonic cadiogram image and are hard to popularize and master by the esophagus ultrasonic cadiogram, in addition, the clinicians and the medicos can grasp the anatomical structure of different esophagus depth and the angle via the ultrasonic cadiogram image on said system, which is favorable for the popularization of the ultrasonic cadiogram via the esophagus and advances the accuracy for diagnosing the heart disease via the esophagus ultrasonic cadiogram, thereby avoiding from adding the pain to the sufferer and reducing the incidence rate of the complication.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Transesophageal ultrasound using a narrow probe
ActiveUS20050143657A1Easy to optimizeIncrease penetration depthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonificationCardiac echo
Transesophageal echocardiography is implemented using a miniature transversely oriented transducer that is preferably small enough to fit in a 7.5 mm diameter probe, and most preferably small enough to fit in a 5 mm diameter probe. Signal processing techniques improve the depth of penetration to the point where the complete trans-gastric short axis view of the left ventricle can be obtained, despite the fact that the transducer is so small. The reduced diameter of the probe (as compared to prior art probes) reduces risks to patients, reduces or eliminates the need for anesthesia, and permits long term direct-visualization monitoring of patients' cardiac function.
Owner:IMACOR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com