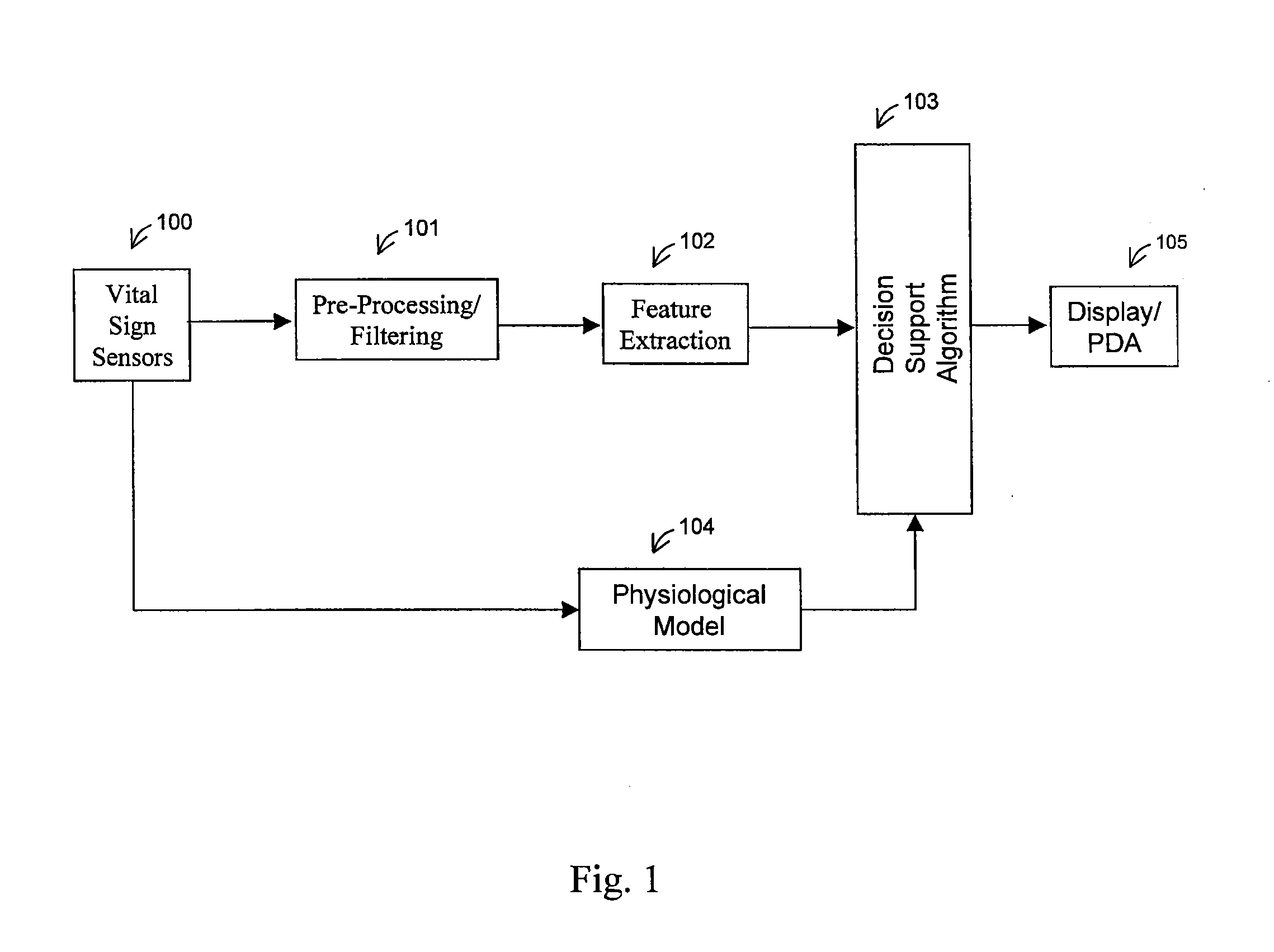
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Physiological model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
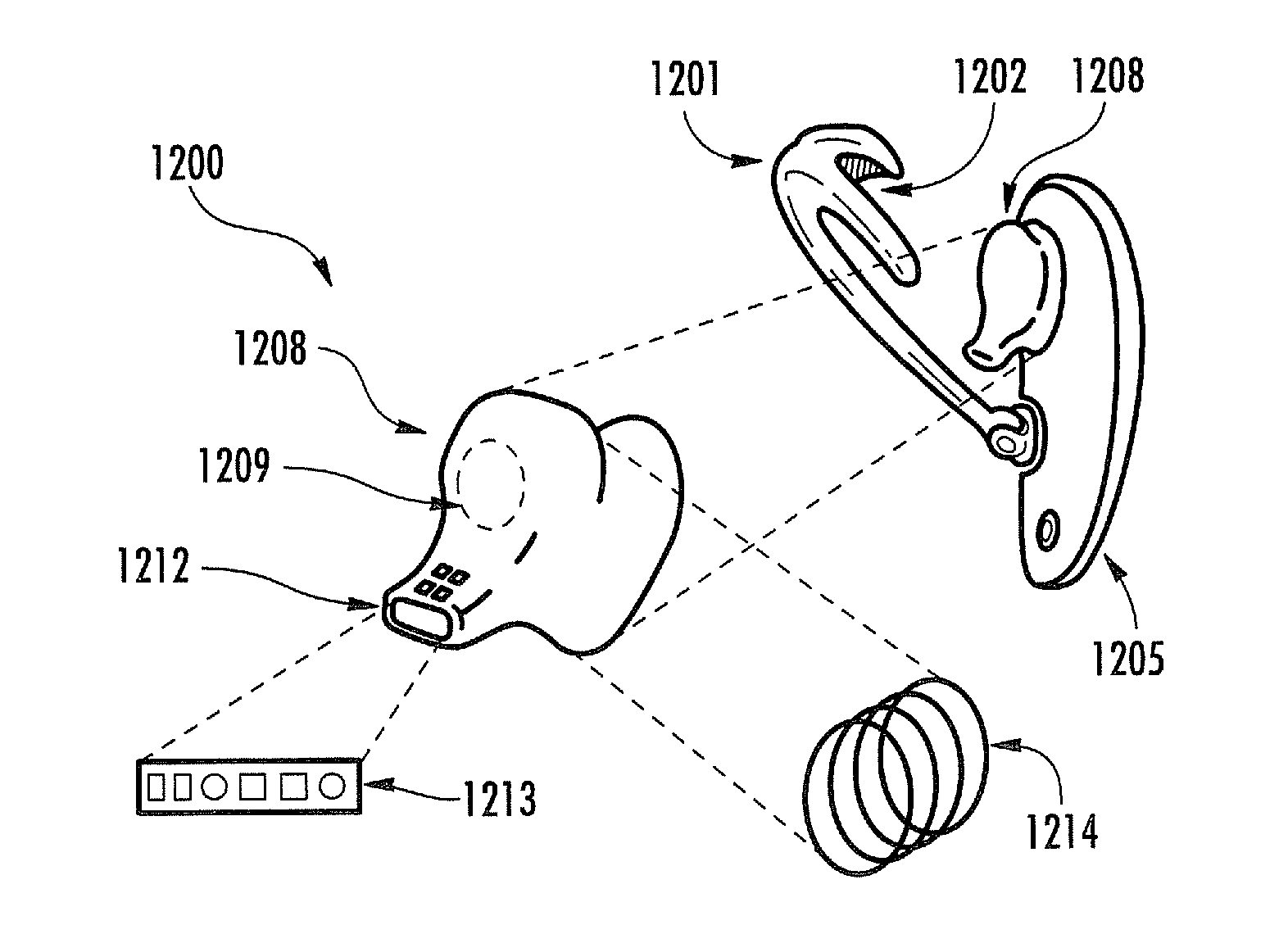
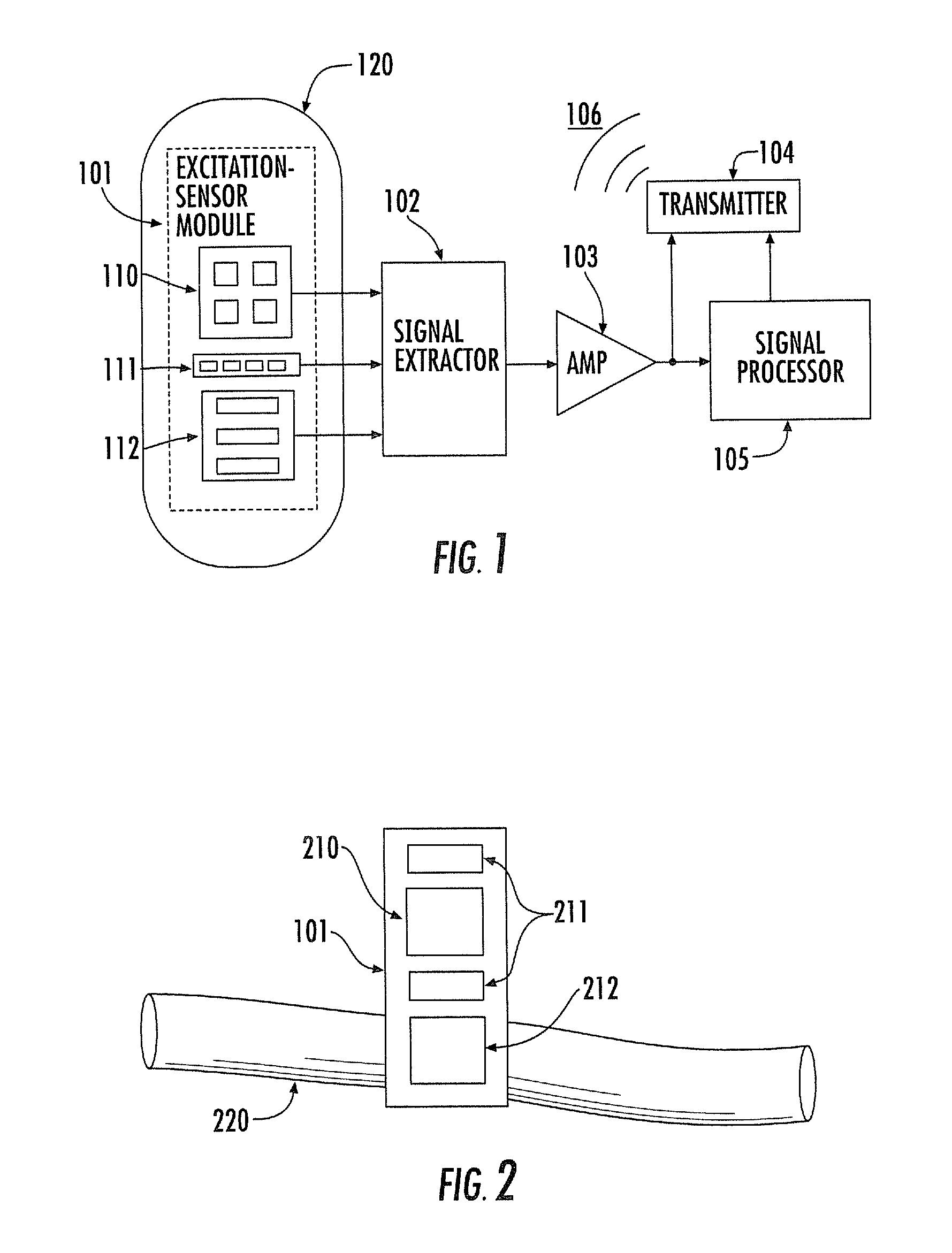
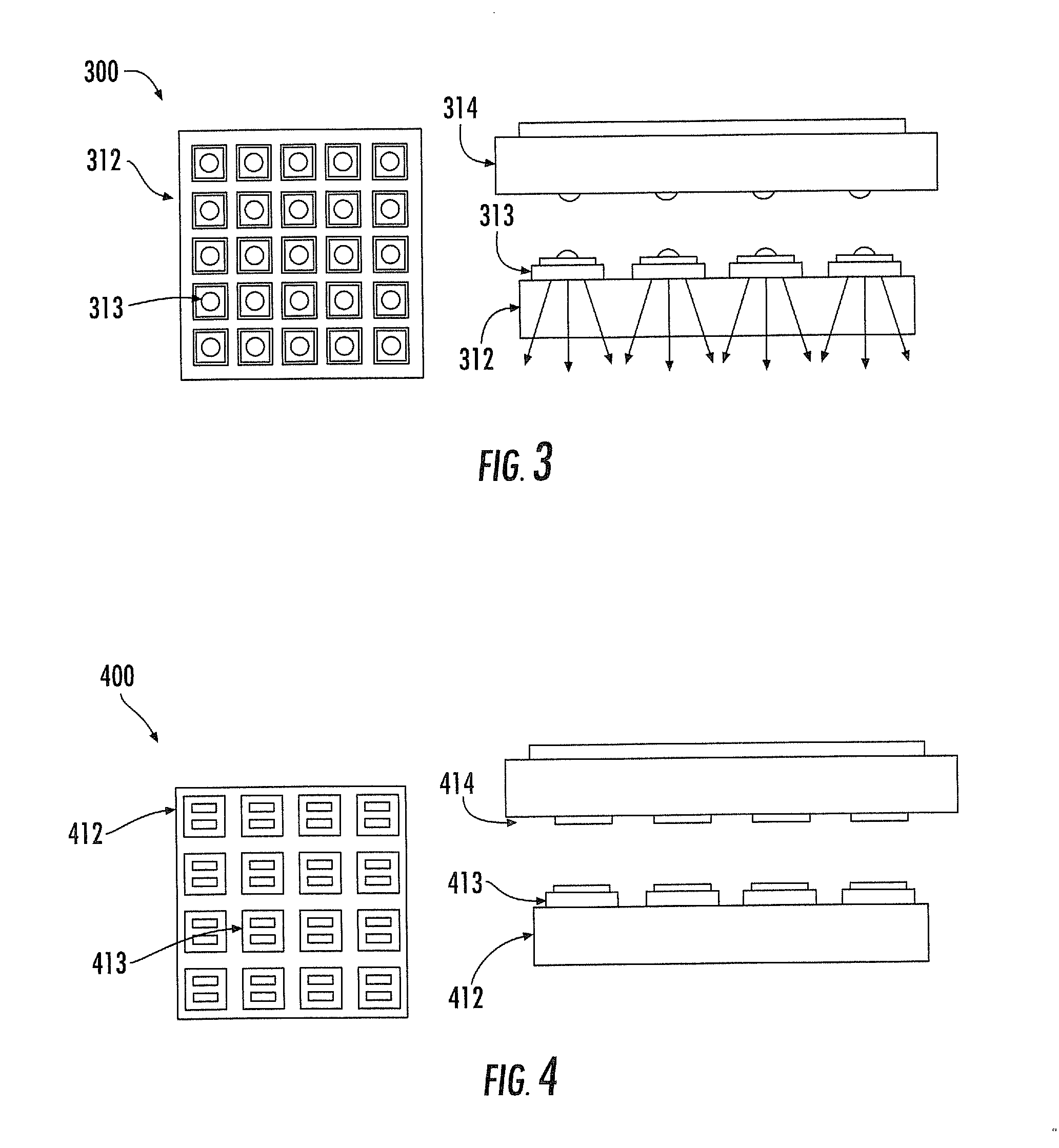
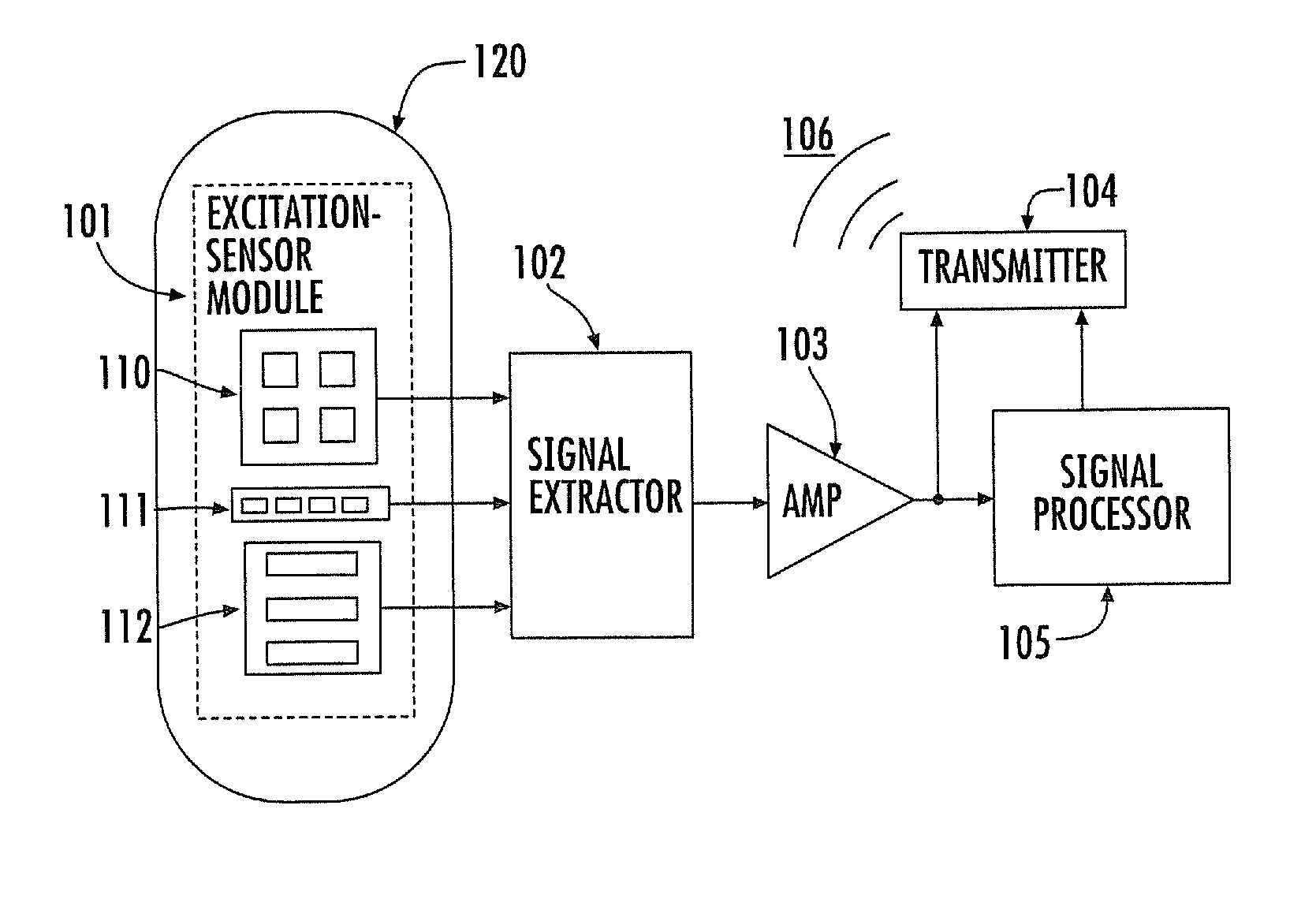
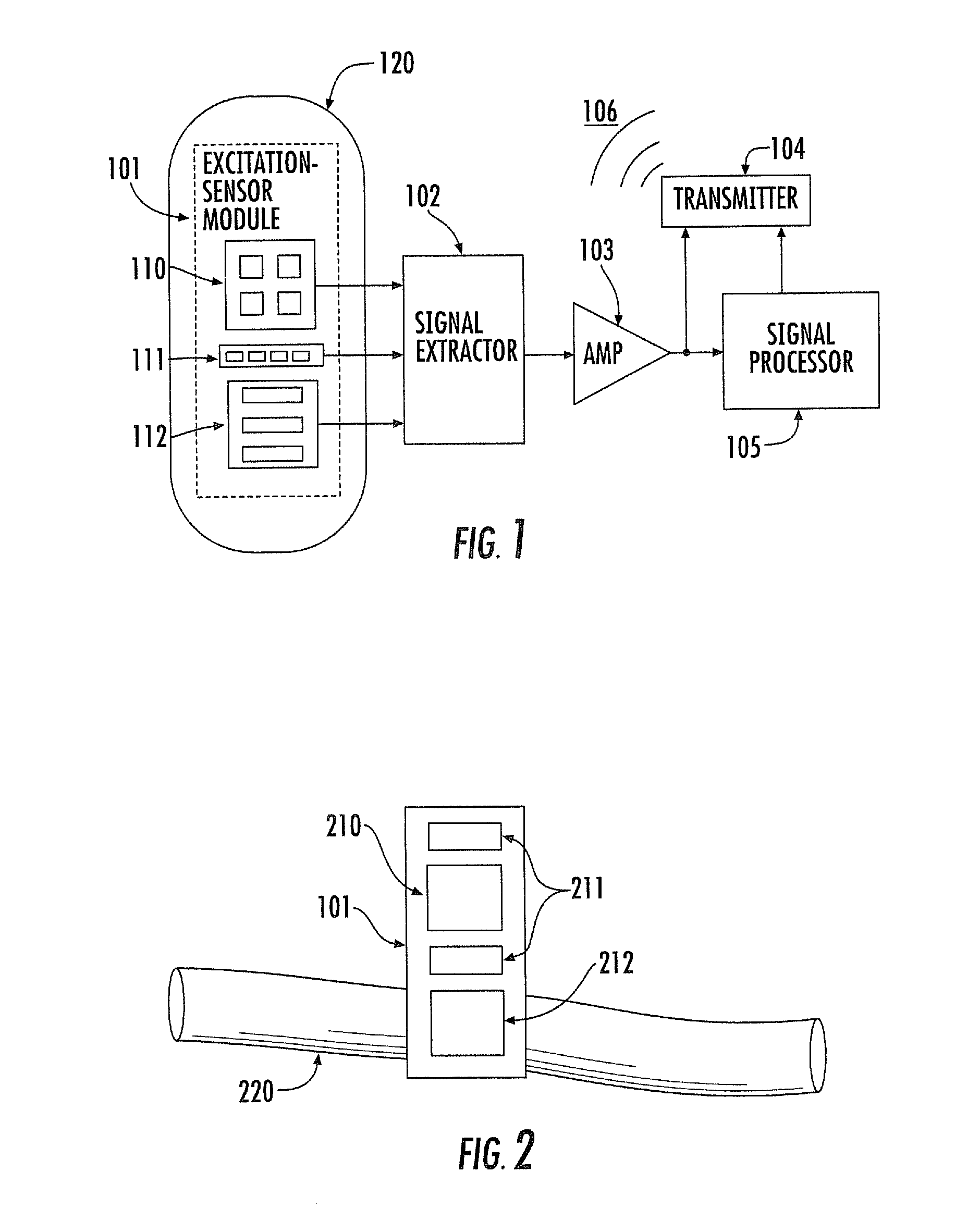
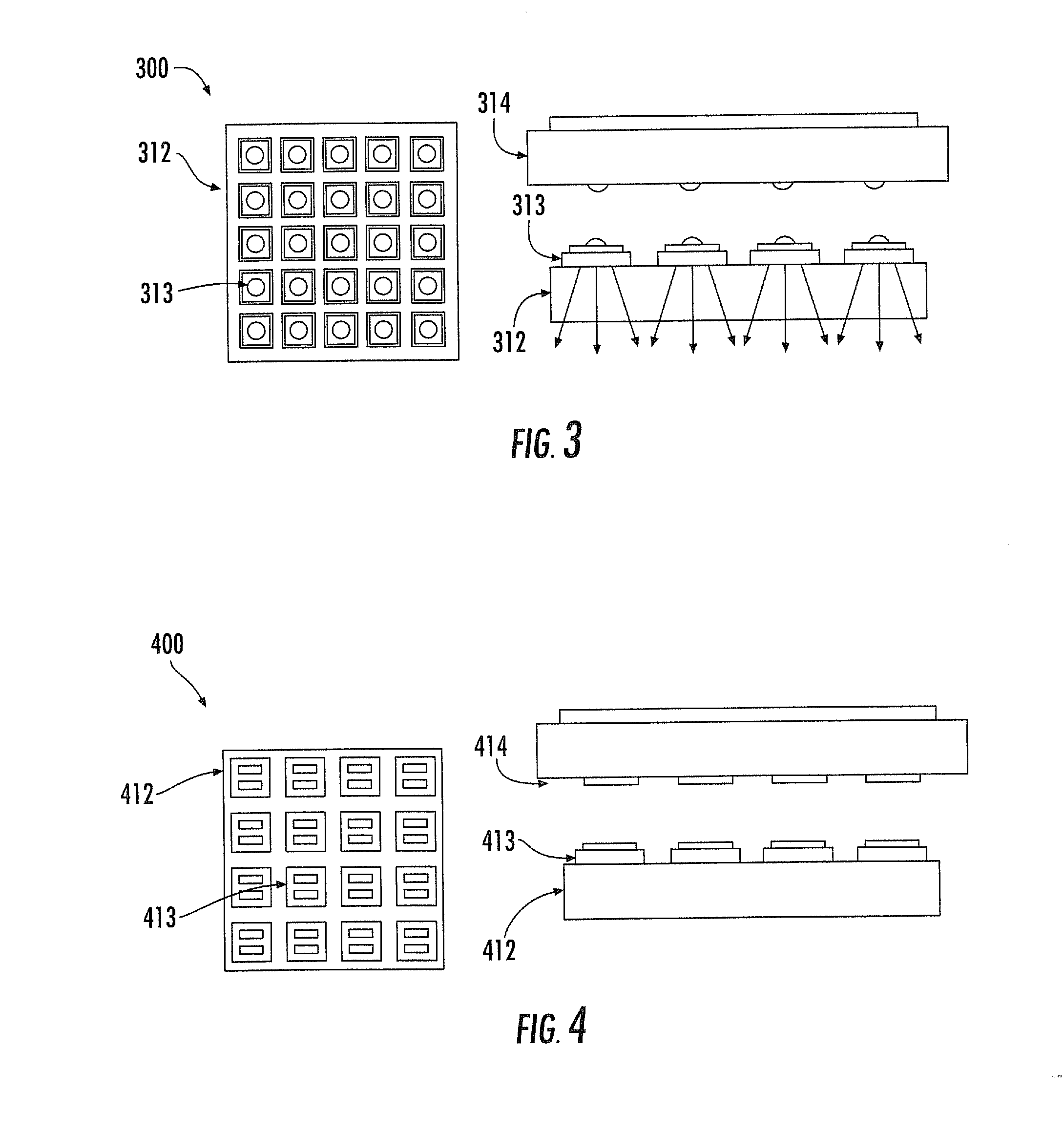
Noninvasive physiological analysis using excitation-sensor modules and related devices and methods
Methods and apparatus for qualifying and quantifying excitation-dependent physiological information extracted from wearable sensors in the midst of interference from unwanted sources are provided. An organism is interrogated with at least one excitation energy, energy response signals from two or more distinct physiological regions are sensed, and these signals are processed to generate an extracted signal. The extracted signal is compared with a physiological model to qualify and / or quantify a physiological property. Additionally, important physiological information can be qualified and quantified by comparing the excitation wavelength-dependent response, measured via wearable sensors, with a physiological model.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
Noninvasive physiological analysis using excitation-sensor modules and related devices and methods
Methods and apparatus for qualifying and quantifying excitation-dependent physiological information extracted from wearable sensors in the midst of interference from unwanted sources are provided. An organism is interrogated with at least one excitation energy, energy response signals from two or more distinct physiological regions are sensed, and these signals are processed to generate an extracted signal. The extracted signal is compared with a physiological model to qualify and / or quantify a physiological property. Additionally, important physiological information can be qualified and quantified by comparing the excitation wavelength-dependent response, measured via wearable sensors, with a physiological model.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
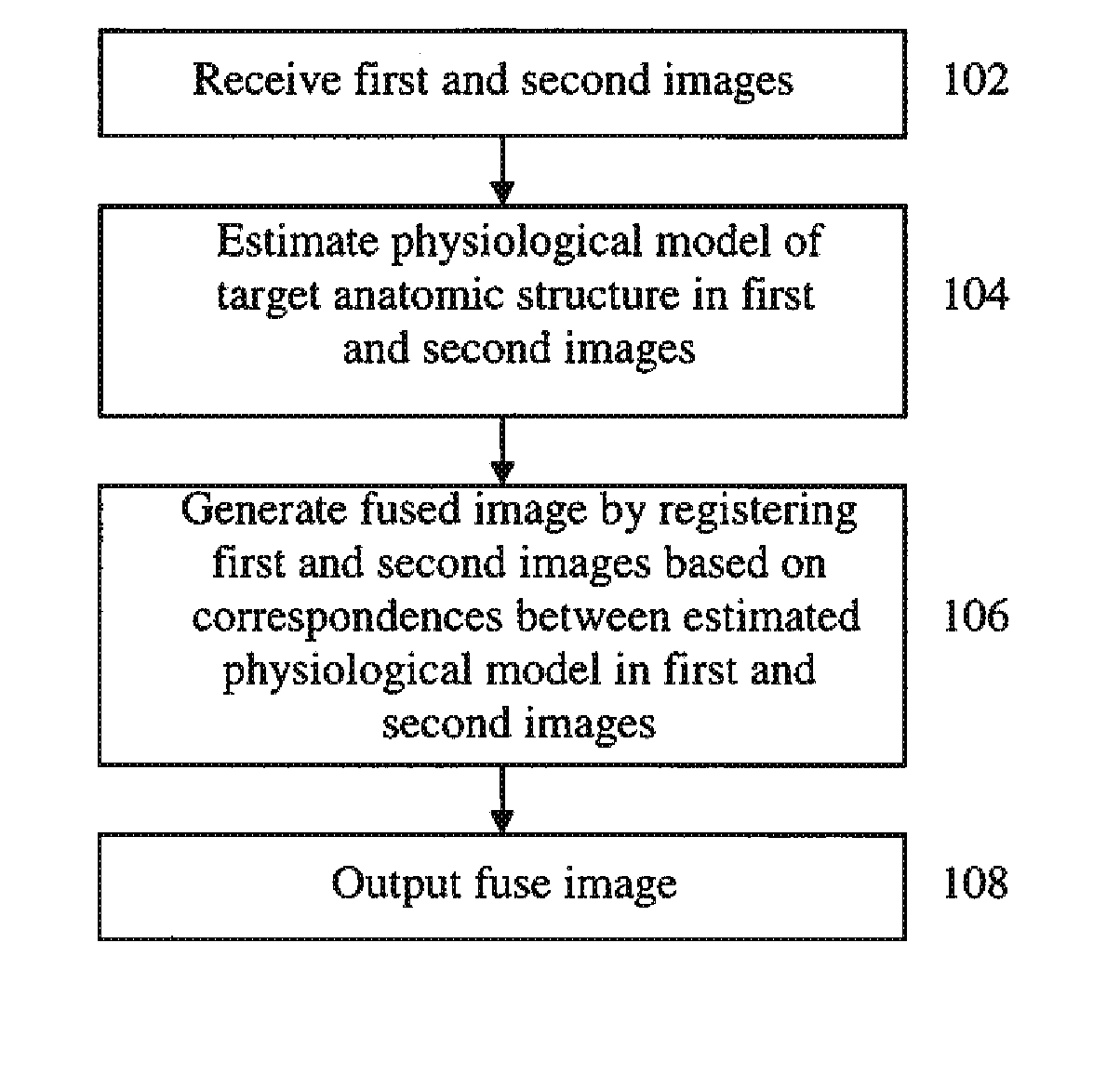
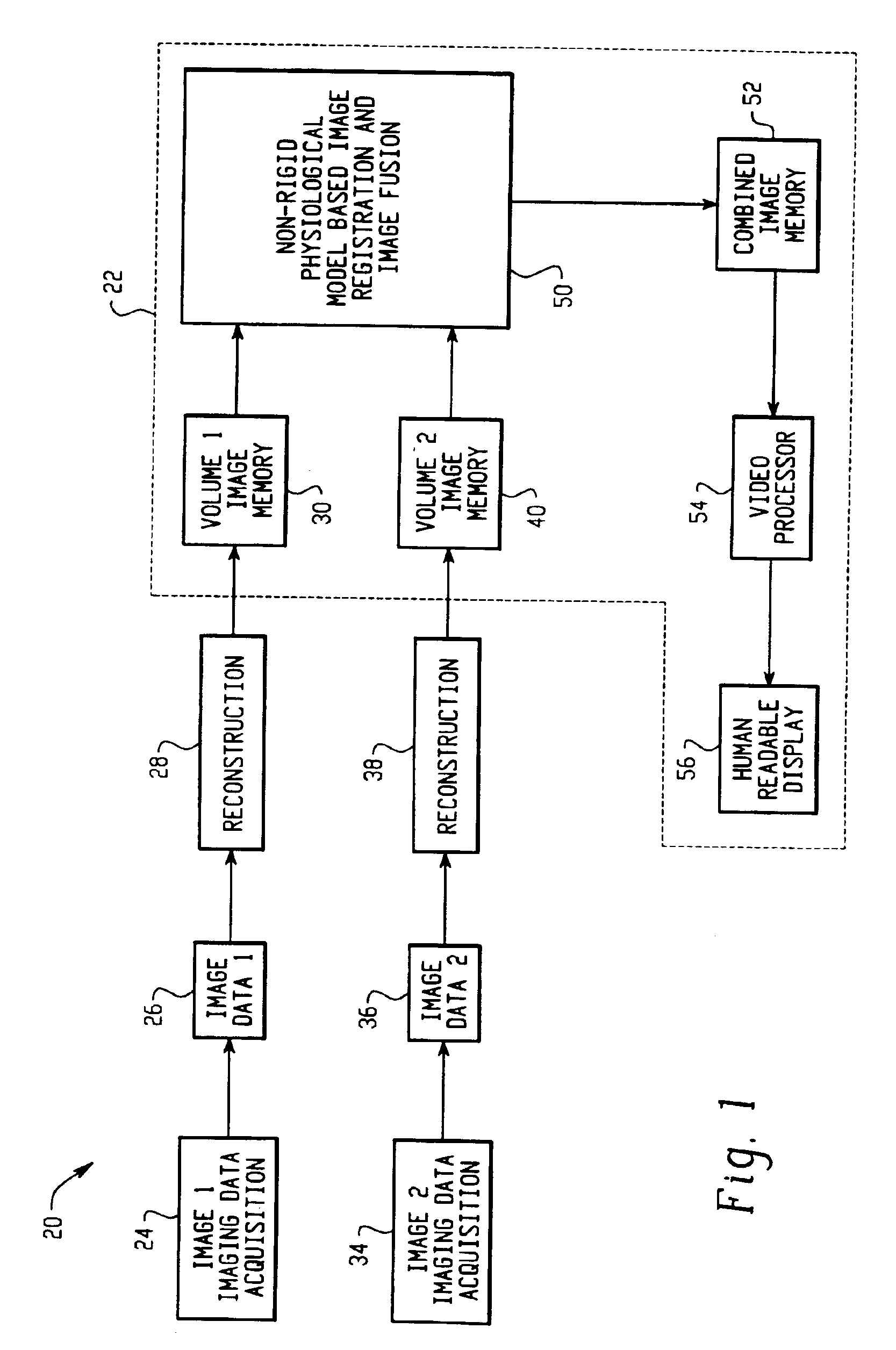
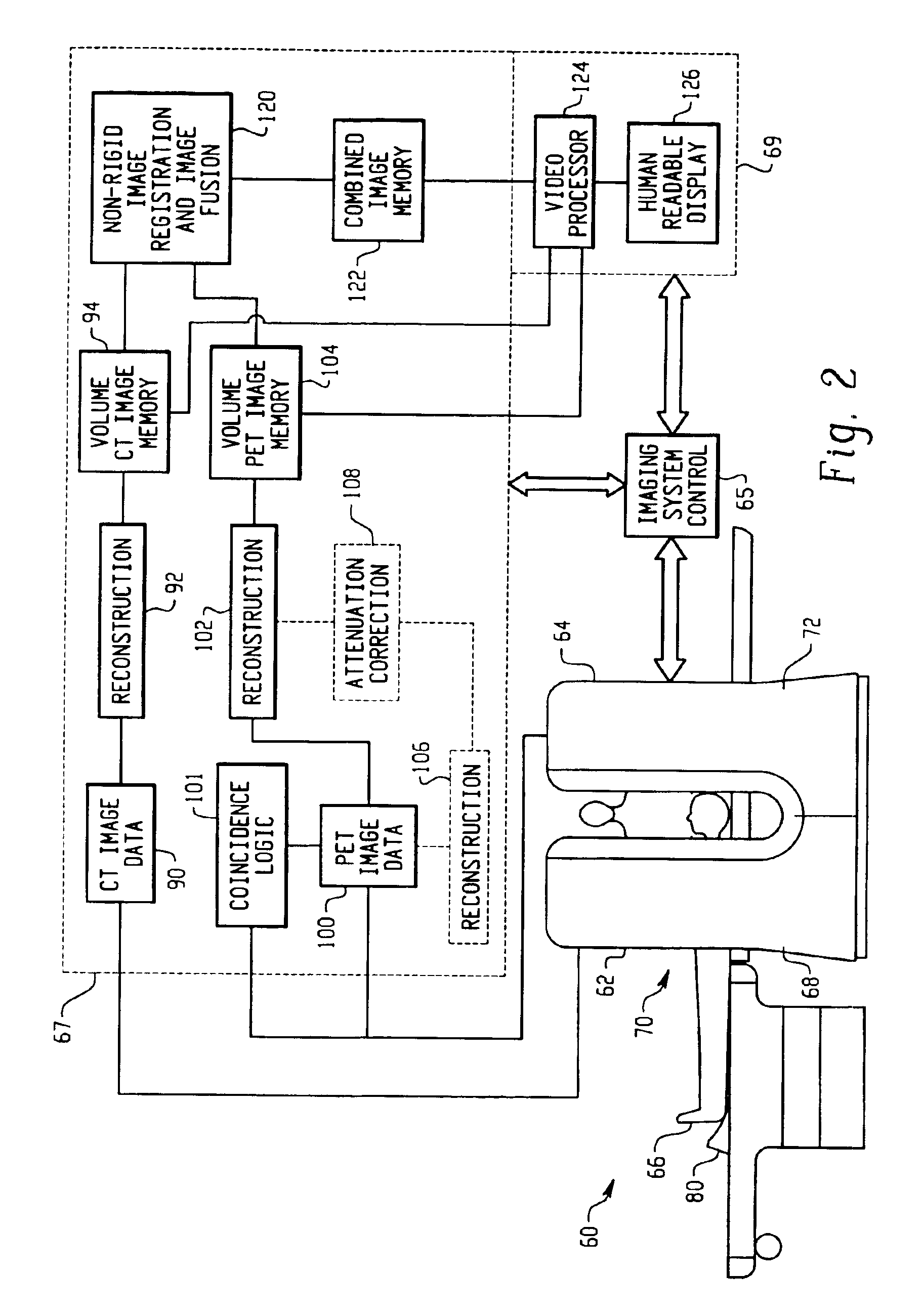
Method and System for Physiological Image Registration and Fusion
ActiveUS20100067768A1Accurate and robust alignmentImage analysisRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsAnatomical structuresLearning based
A method and system for physiological image registration and fusion is disclosed. A physiological model of a target anatomical structure in estimated each of a first image and a second image. The physiological model is estimated using database-guided discriminative machine learning-based estimation. A fused image is then generated by registering the first and second images based on correspondences between the physiological model estimated in each of the first and second images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
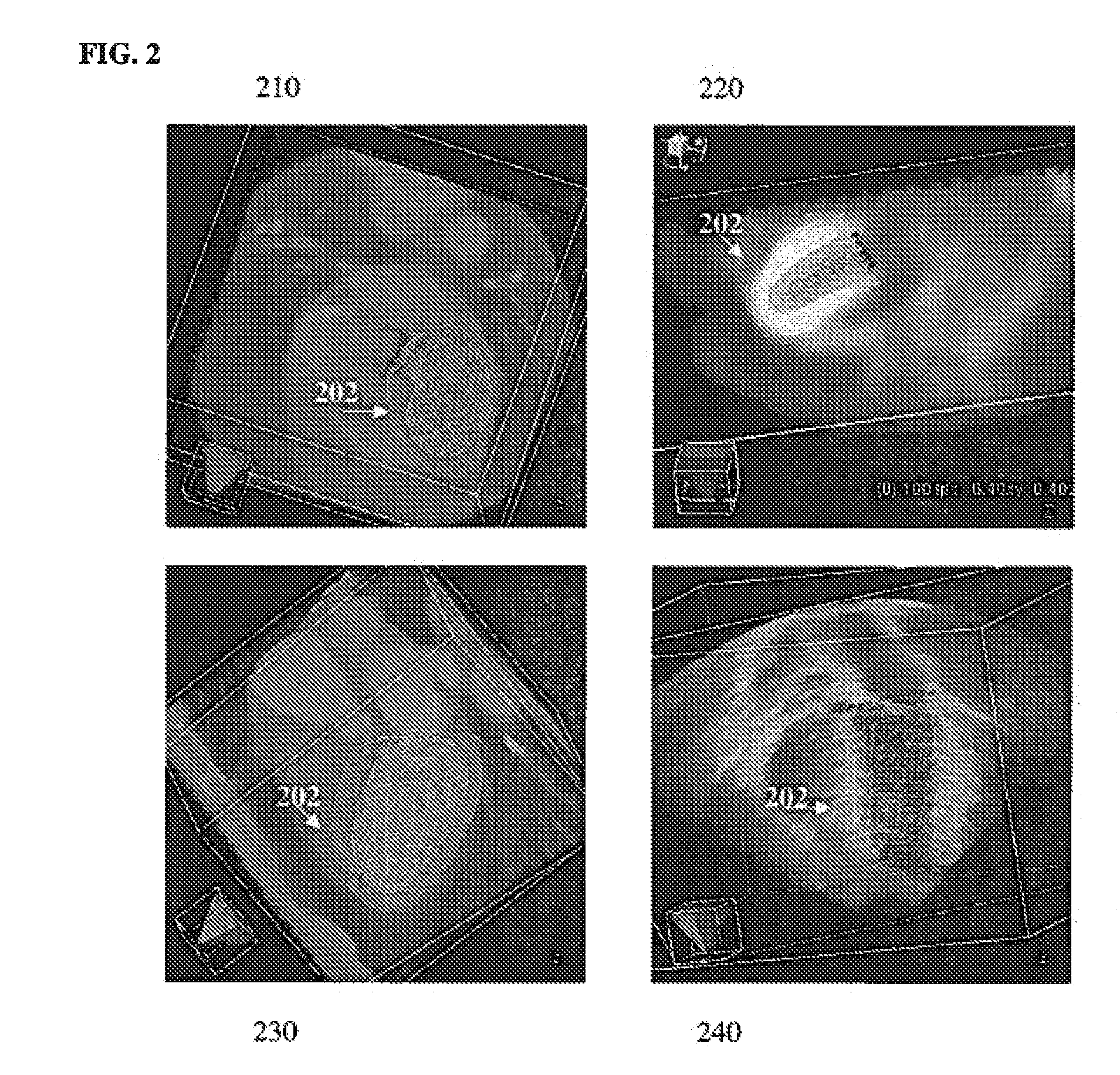
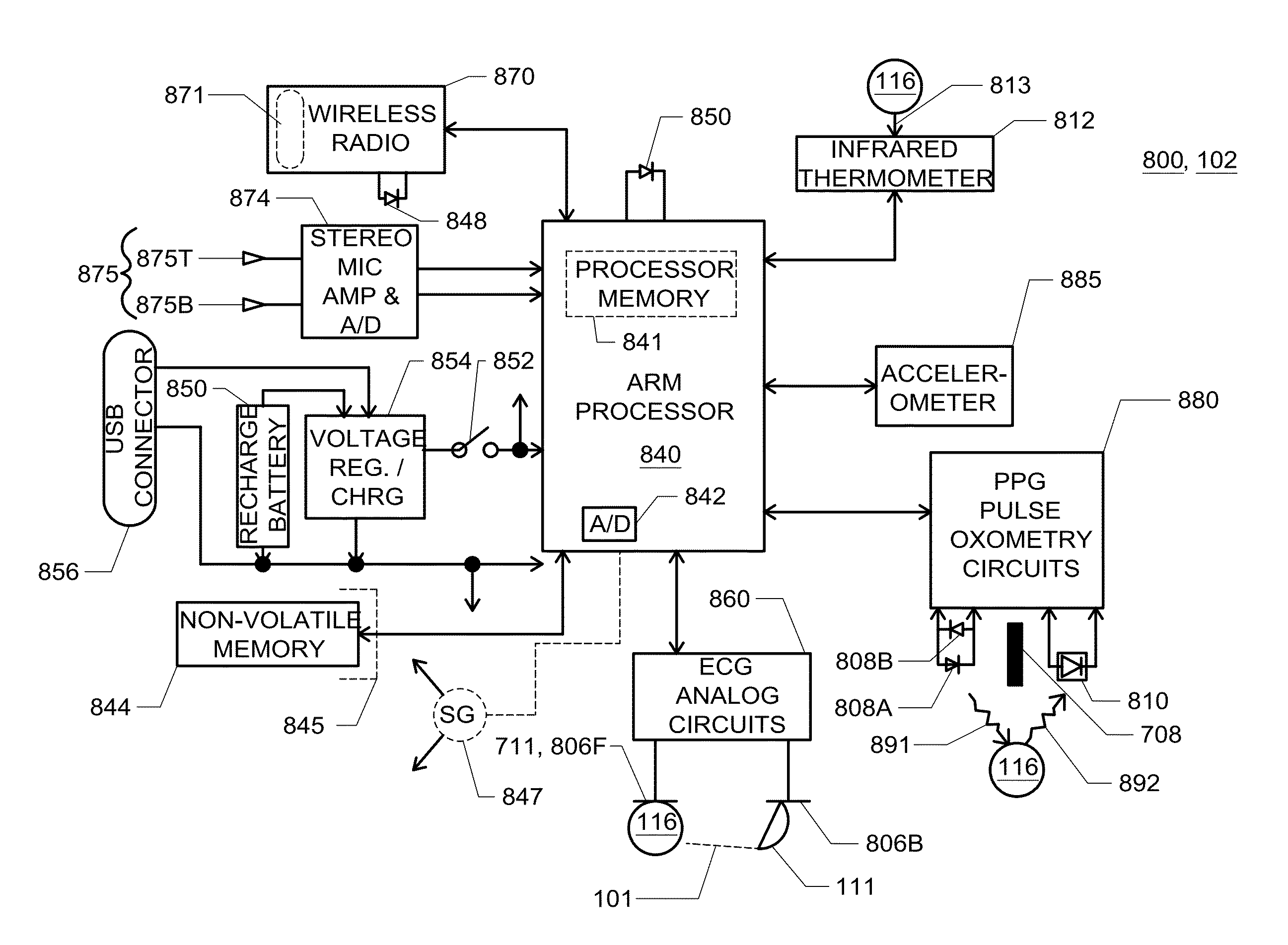
Portable device with multiple integrated sensors for vital signs scanning
InactiveUS20150313484A1Easy to installShorten the timeElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAccelerometerMultiple sensor
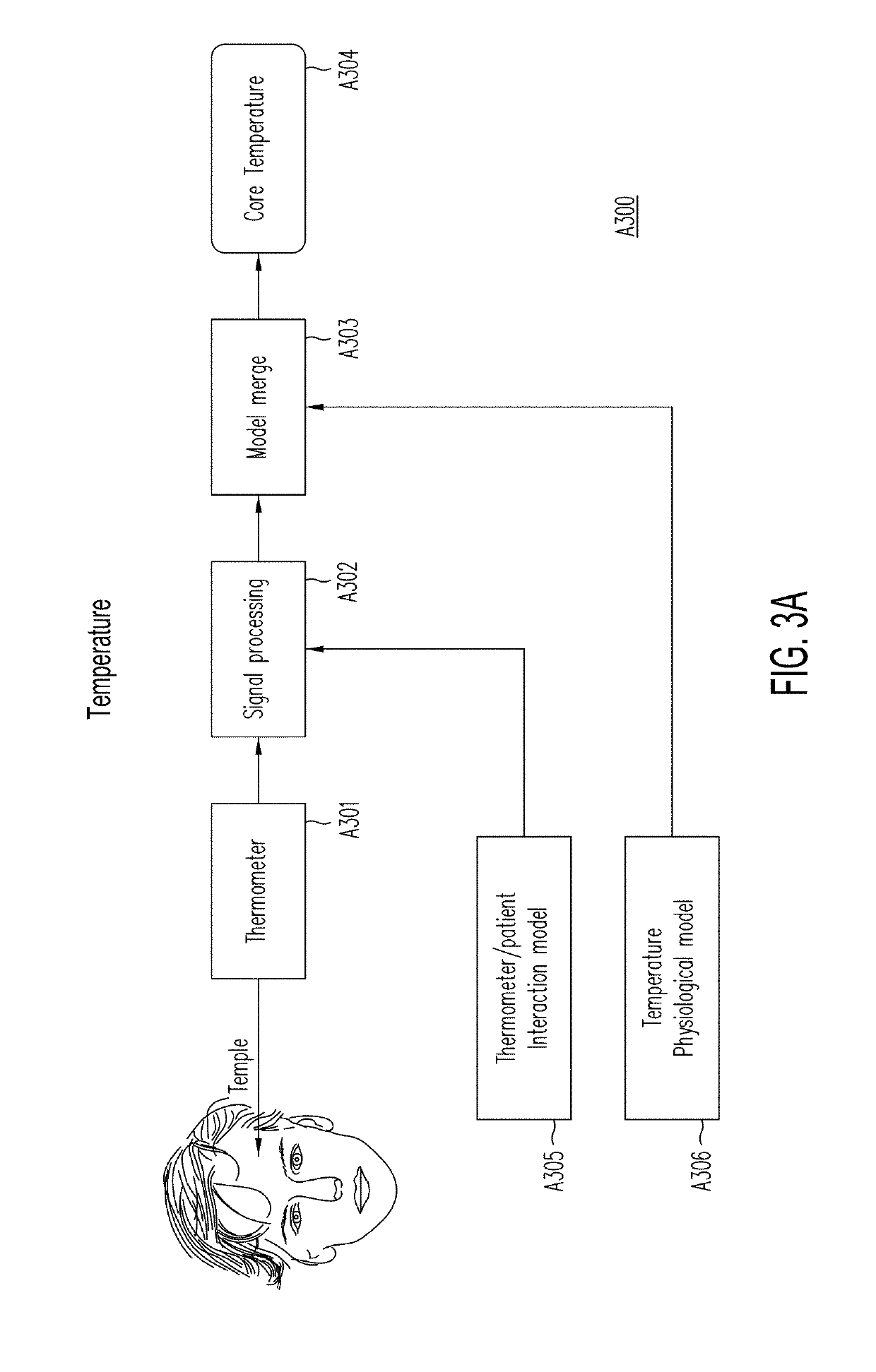
In one embodiment of the invention, a portable device with multiple integrated sensors for vital signs scanning and method of using said device is disclosed. The portable personal scanning device includes multiple sensors such as a plurality of ECG, thermometer, PPG, accelerometer, and microphone for determining a user's vital signs. The method includes concurrently scanning with one or more sensors, validating and enhancing the results of each sensor scan with other concurrent sensor scan and patient interaction models, processing the sensor scans separately or in combination to extract user's vital signs, validating the vital signs extracted by comparison to physiological models, and fusing the similar vital signs extracted from more than one process according to a determination of the measure of quality of the process that produced the vital sign.
Owner:SCANADU
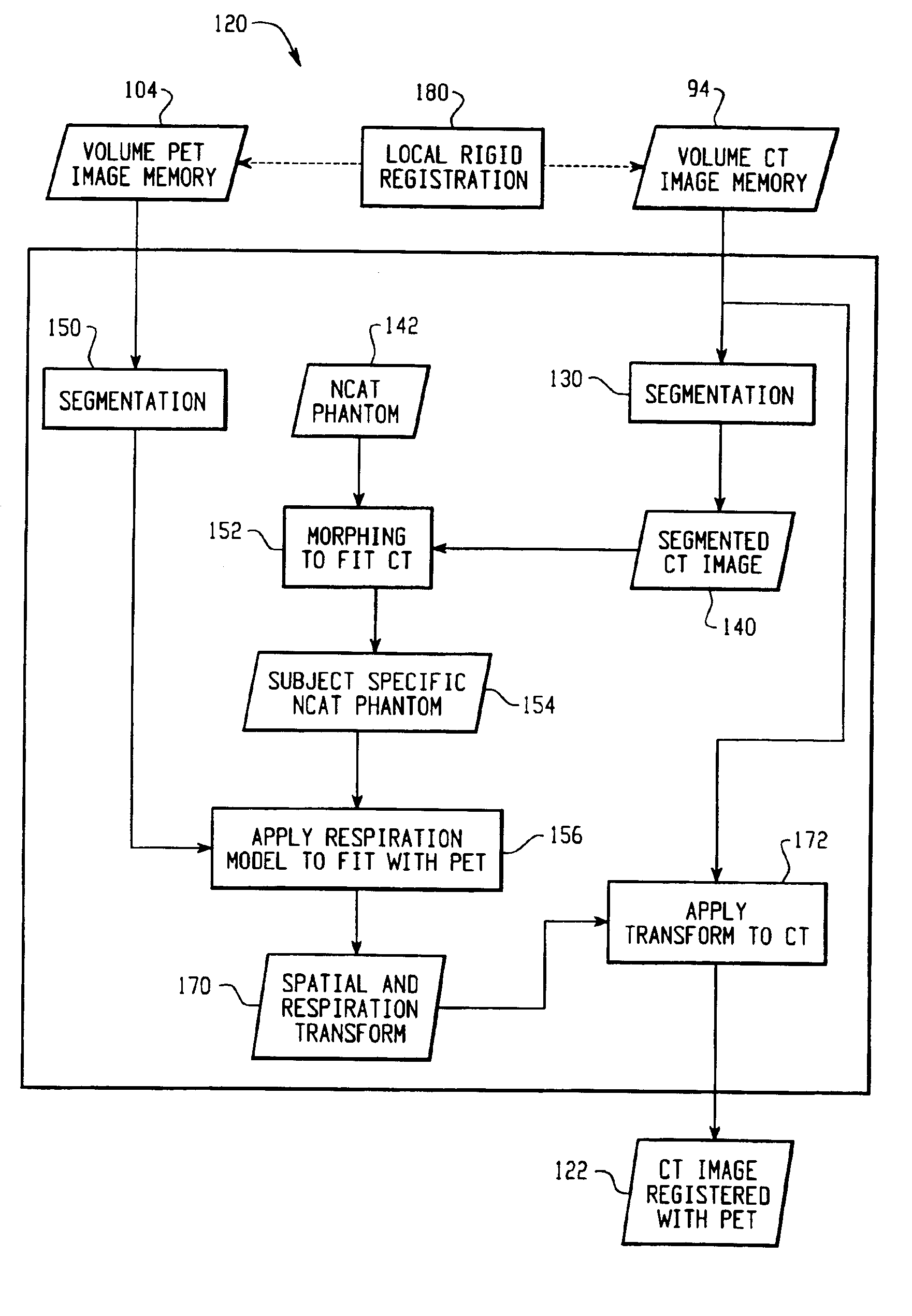
Physiological model based non-rigid image registration
InactiveUS7117026B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionData set
A method for non-rigid registration and fusion of images with physiological modeled organ motions resulting from respiratory motion and cardiac motion that are mathematically modeled with physiological constraints. A method of combining images comprises the steps of obtaining a first image dataset (24) of a region of interest of a subject and obtaining a second image dataset (34) of the region of interest of the subject. Next, a general model of physiological motion for the region of interest is provided (142). The general model of physiological motion is adapted with data derived from the first image data set (140) to provide a subject specific physiological model (154). The subject specific physiological model is applied (172) to the second image dataset (150) to provide a combined image (122).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
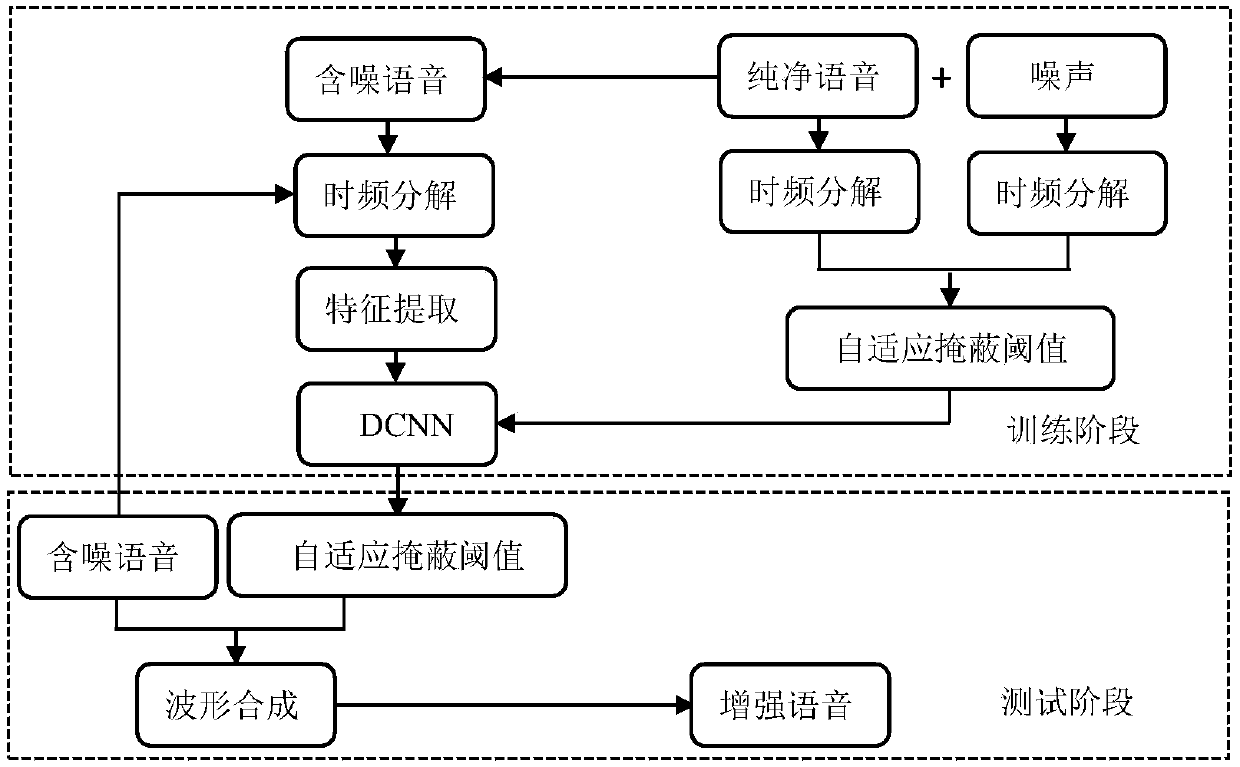
Voice enhancing method based on multiresolution auditory cepstrum coefficient and deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN107845389AReduce complexityCompatible with auditory perception characteristicsSpeech recognitionMasking thresholdHuman ear
The invention discloses a voice enhancing method based on a multiresolution auditory cepstrum system and a deep convolutional neural network. The voice enhancing method comprises the following steps:firstly, establishing new characteristic parameters, namely multiresolution auditory cepstrum coefficient (MR-GFCC), capable of distinguishing voice from noise; secondly, establishing a self-adaptivemasking threshold on based on ideal soft masking (IRM) and ideal binary masking (IBM) according to noise variations; further training an established seven-layer neural network by using new extracted characteristic parameters and first / second derivatives thereof and the self-adaptive masking threshold as input and output of the deep convolutional neural network (DCNN); and finally enhancing noise-containing voice by using the self-adaptive masking threshold estimated by the DCNN. By adopting the method, the working mechanism of human ears is sufficiently utilized, voice characteristic parameters simulating a human ear auditory physiological model are disposed, and not only is a relatively great deal of voice information maintained, but also the extraction process is simple and feasible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
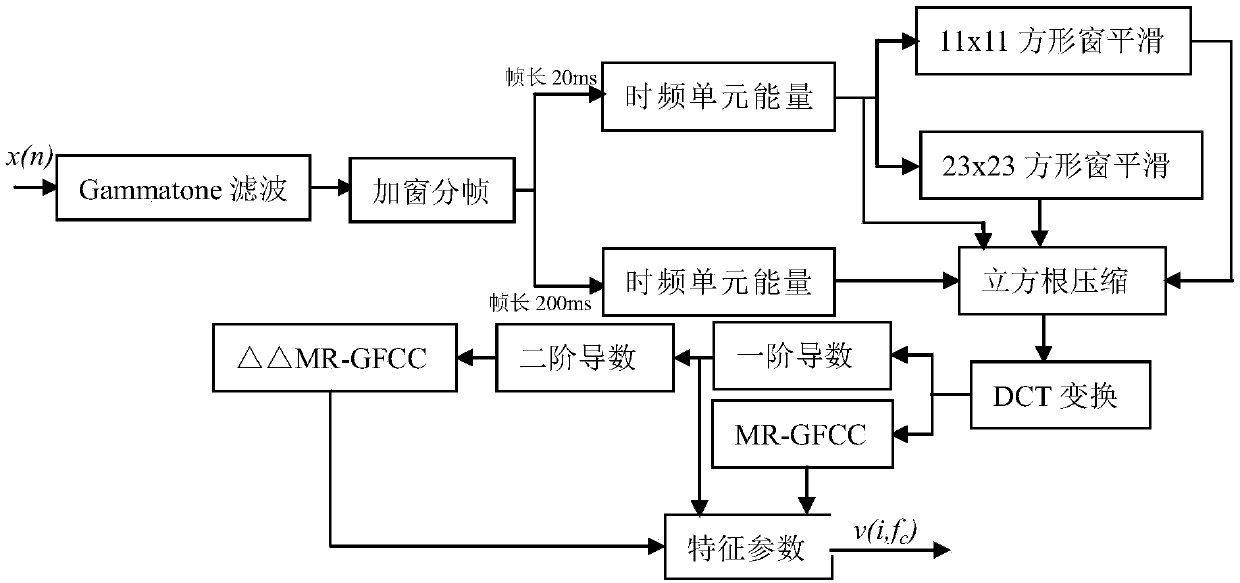
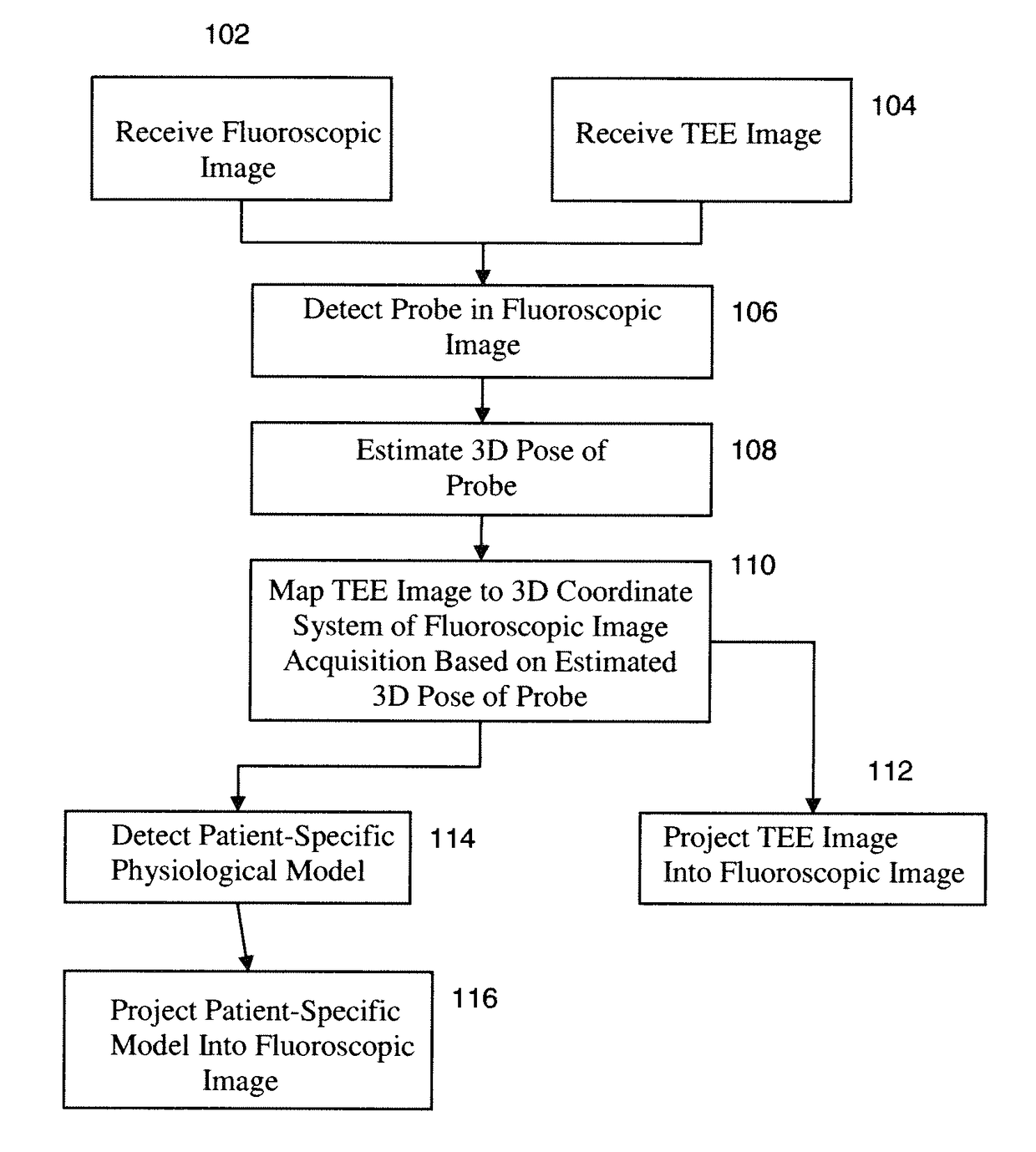
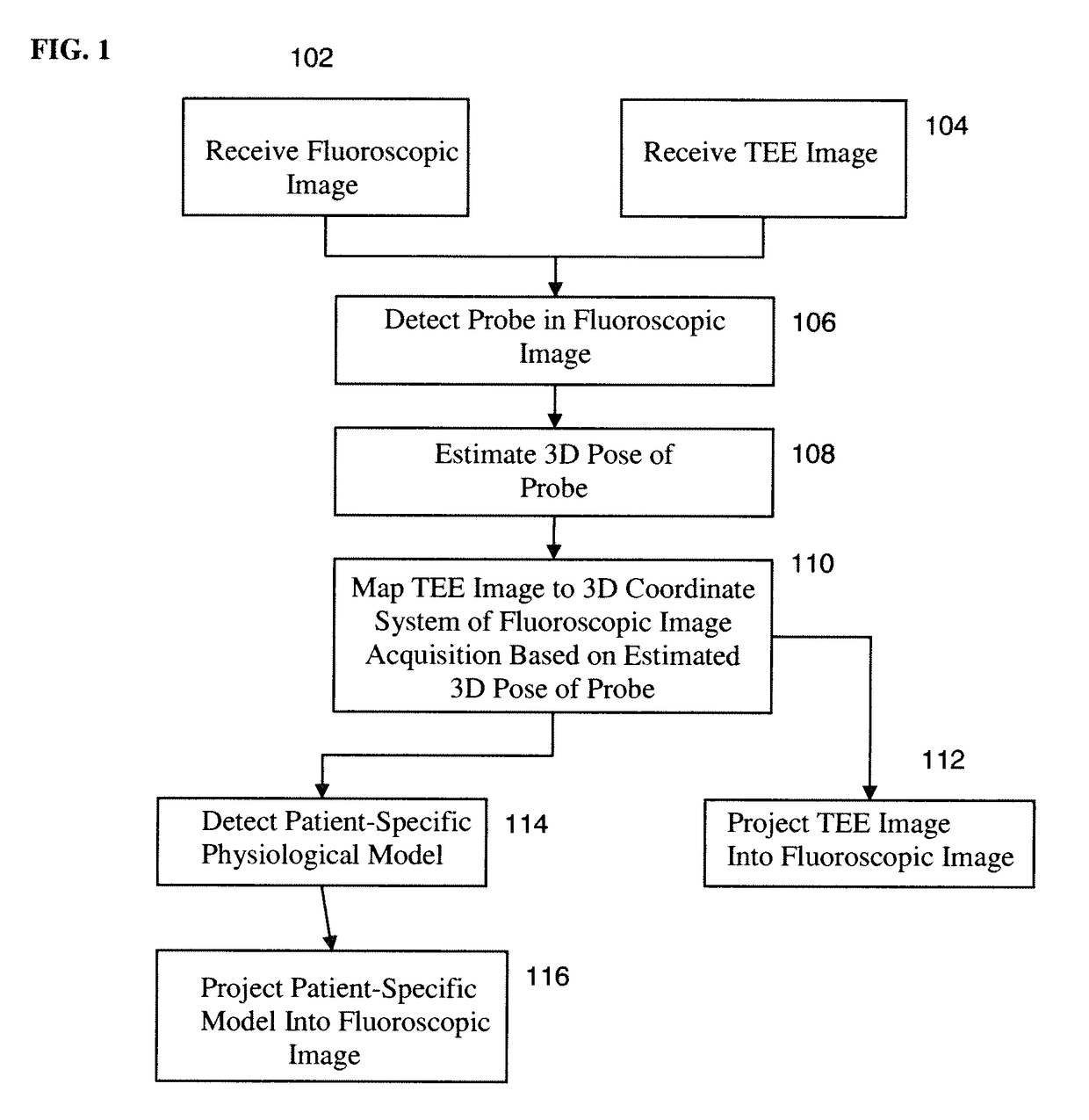
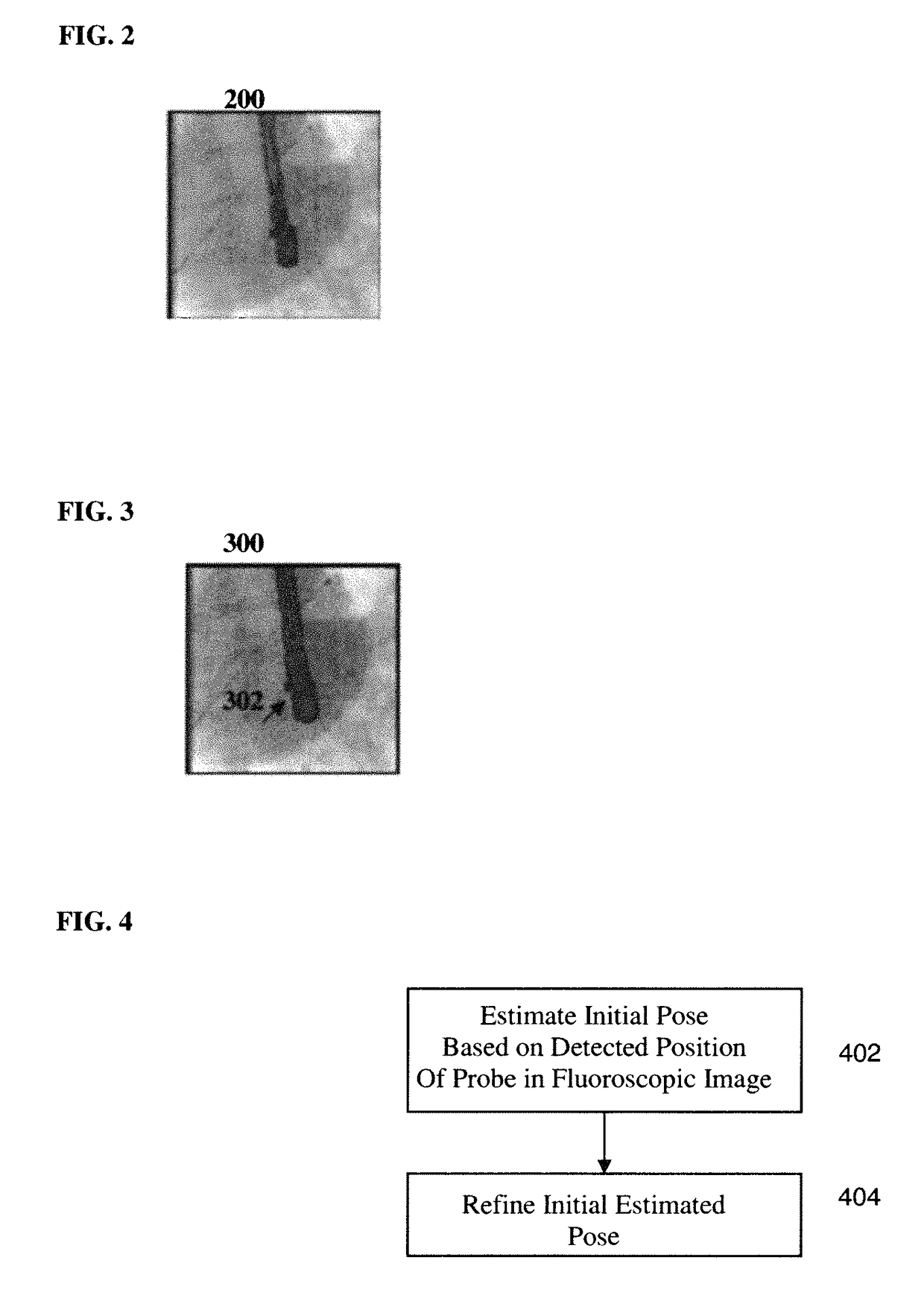
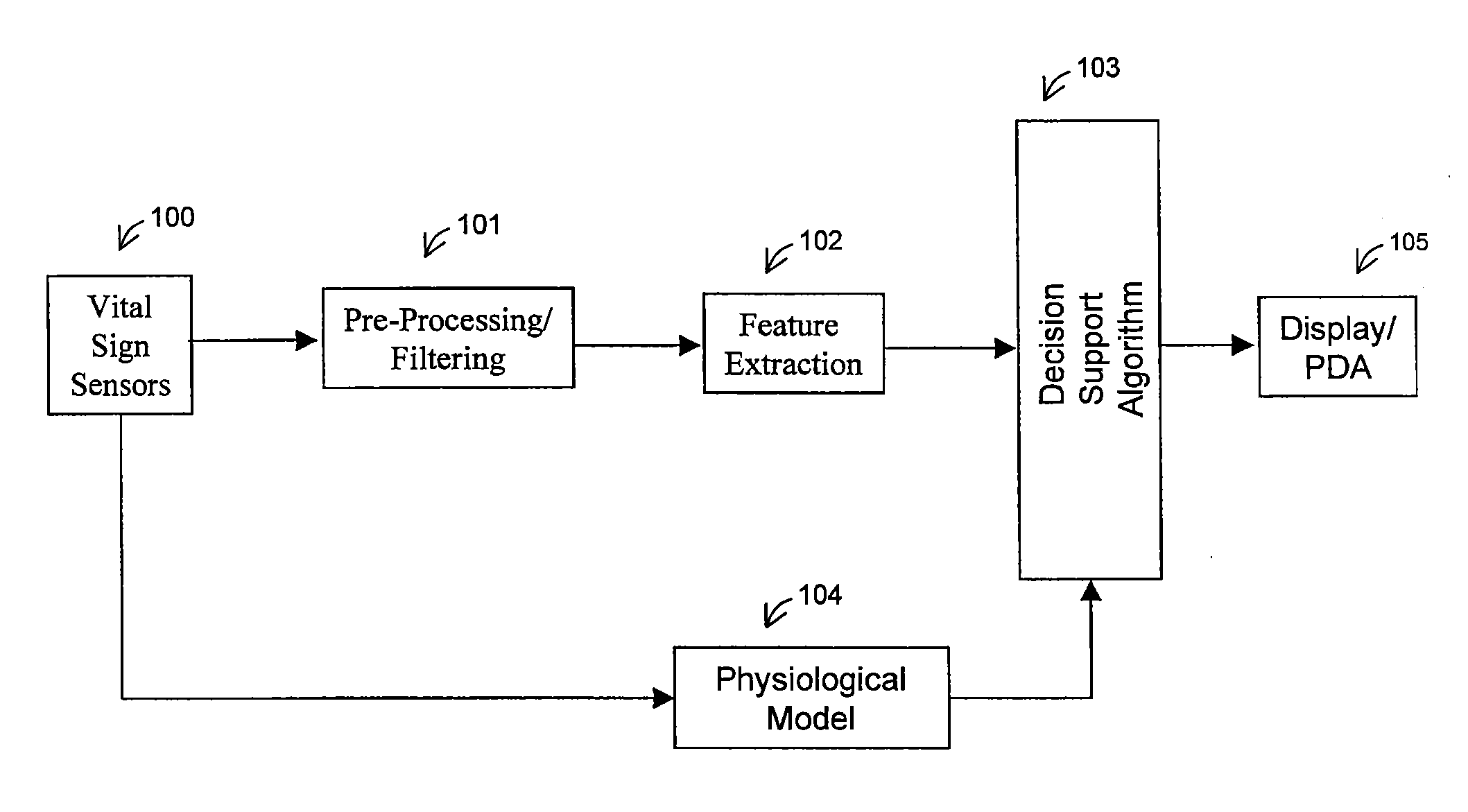
Method and System for Registration of Ultrasound and Physiological Models to X-ray Fluoroscopic Images
A method and system for registering ultrasound images and physiological models to x-ray fluoroscopy images is disclosed. A fluoroscopic image and an ultrasound image, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) image, are received. A 2D location of an ultrasound probe is detected in the fluoroscopic image. A 3D pose of the ultrasound probe is estimated based on the detected 2D location of the ultrasound probe in the fluoroscopic image. The ultrasound image is mapped to a 3D coordinate system of a fluoroscopic image acquisition device used to acquire the fluoroscopic image based on the estimated 3D pose of the ultrasound probe. The ultrasound image can then be projected into the fluoroscopic image using a projection matrix associated with the fluoroscopic image. A patient specific physiological model can be detected in the ultrasound image and projected into the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
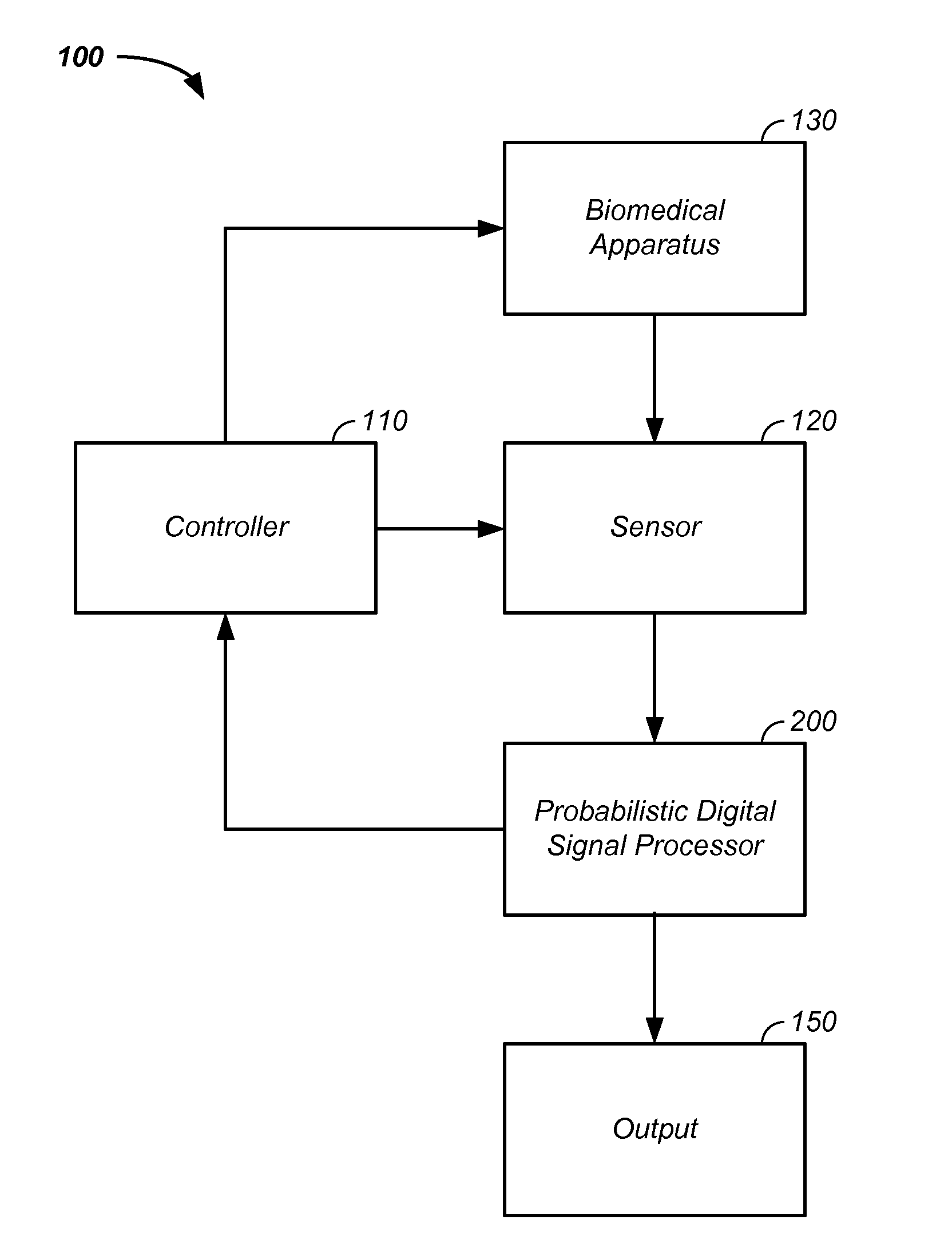
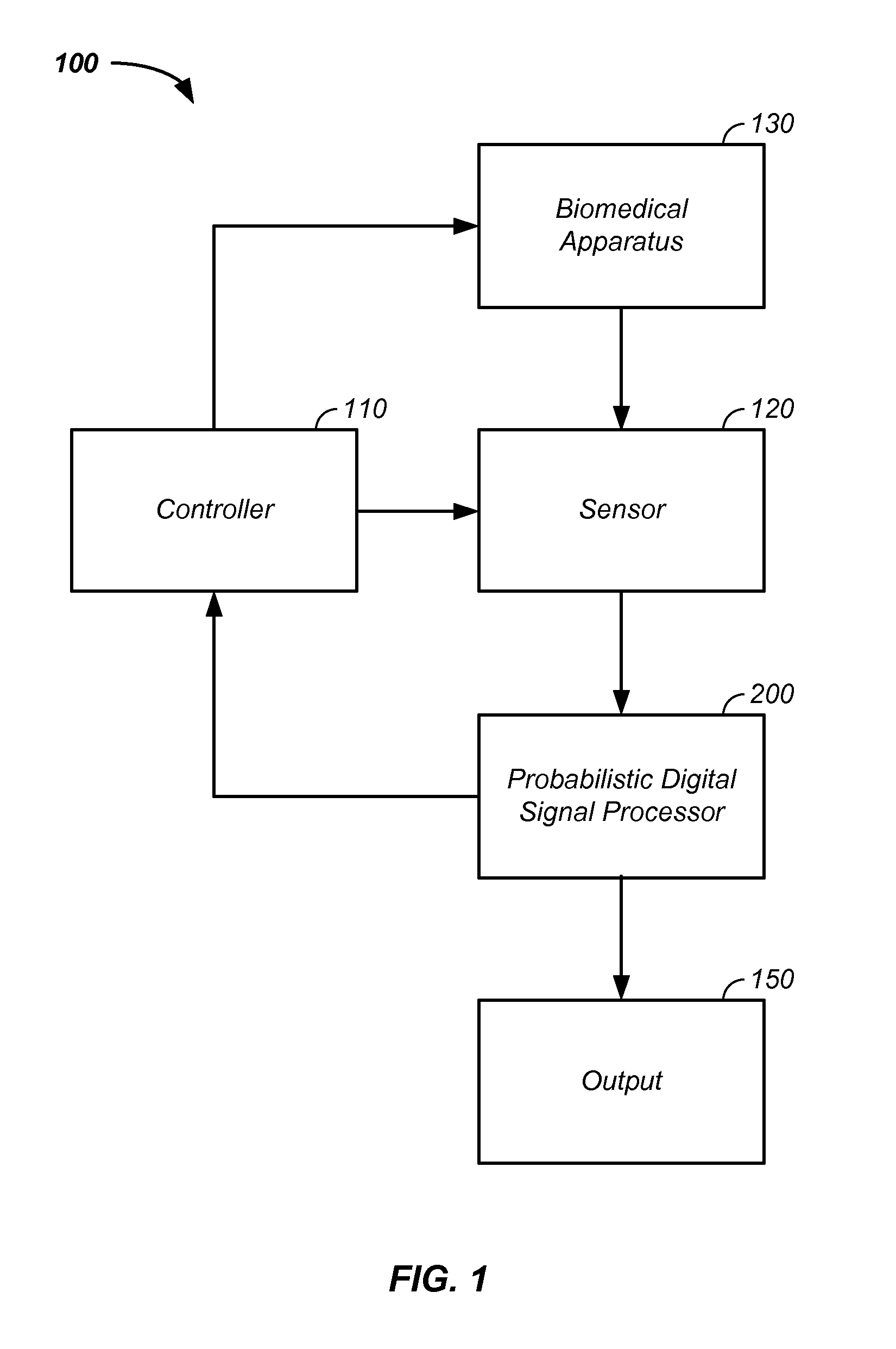
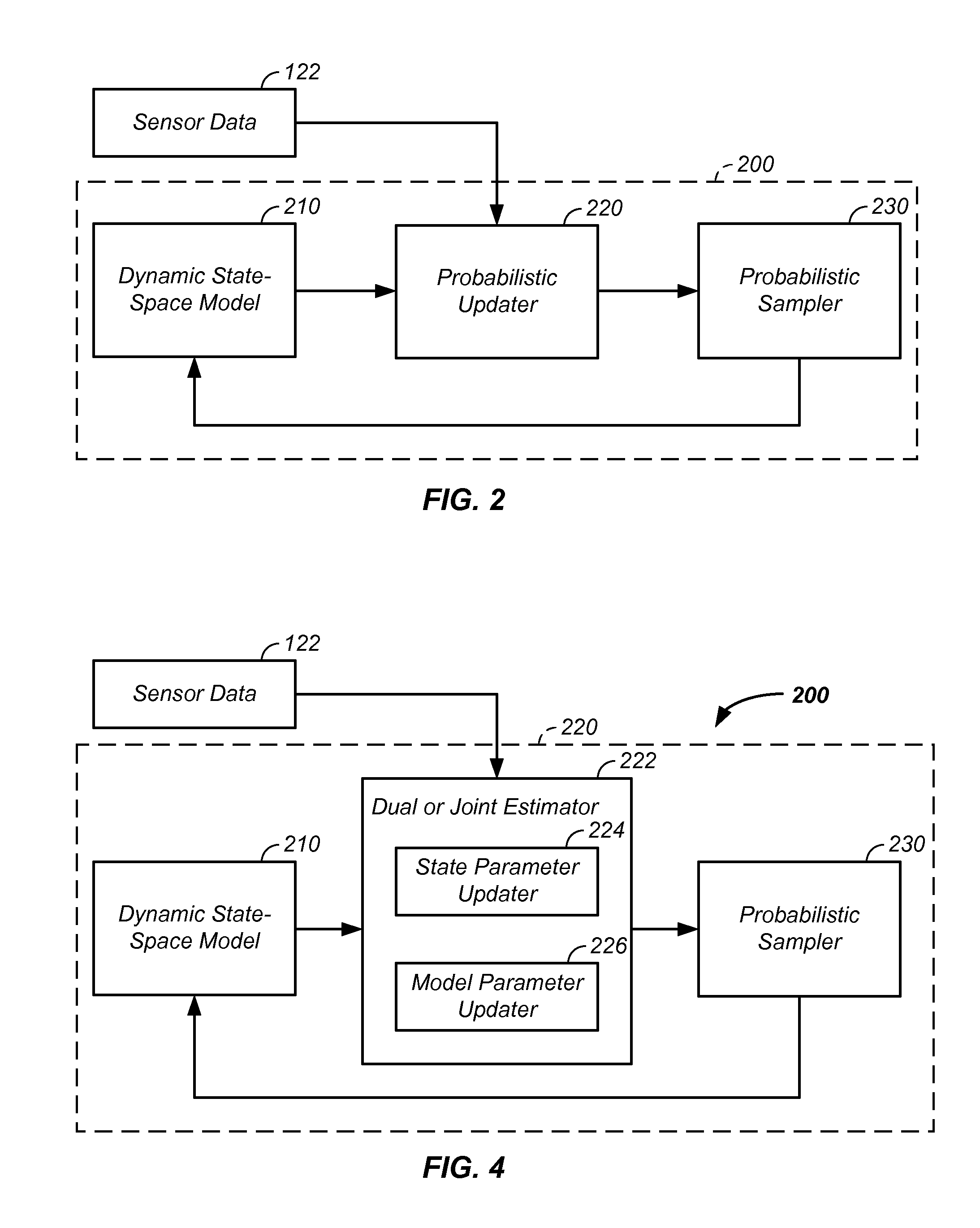
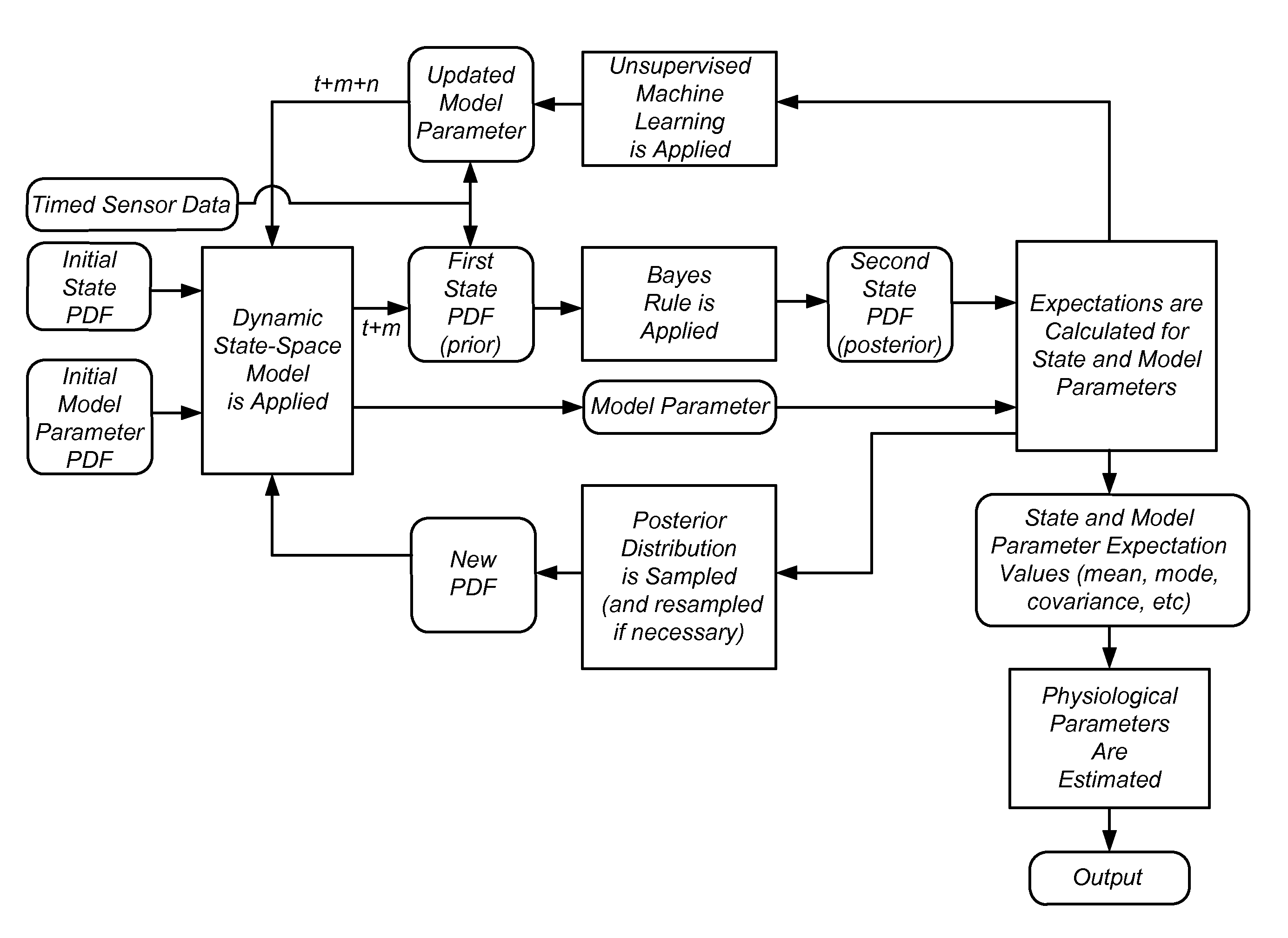
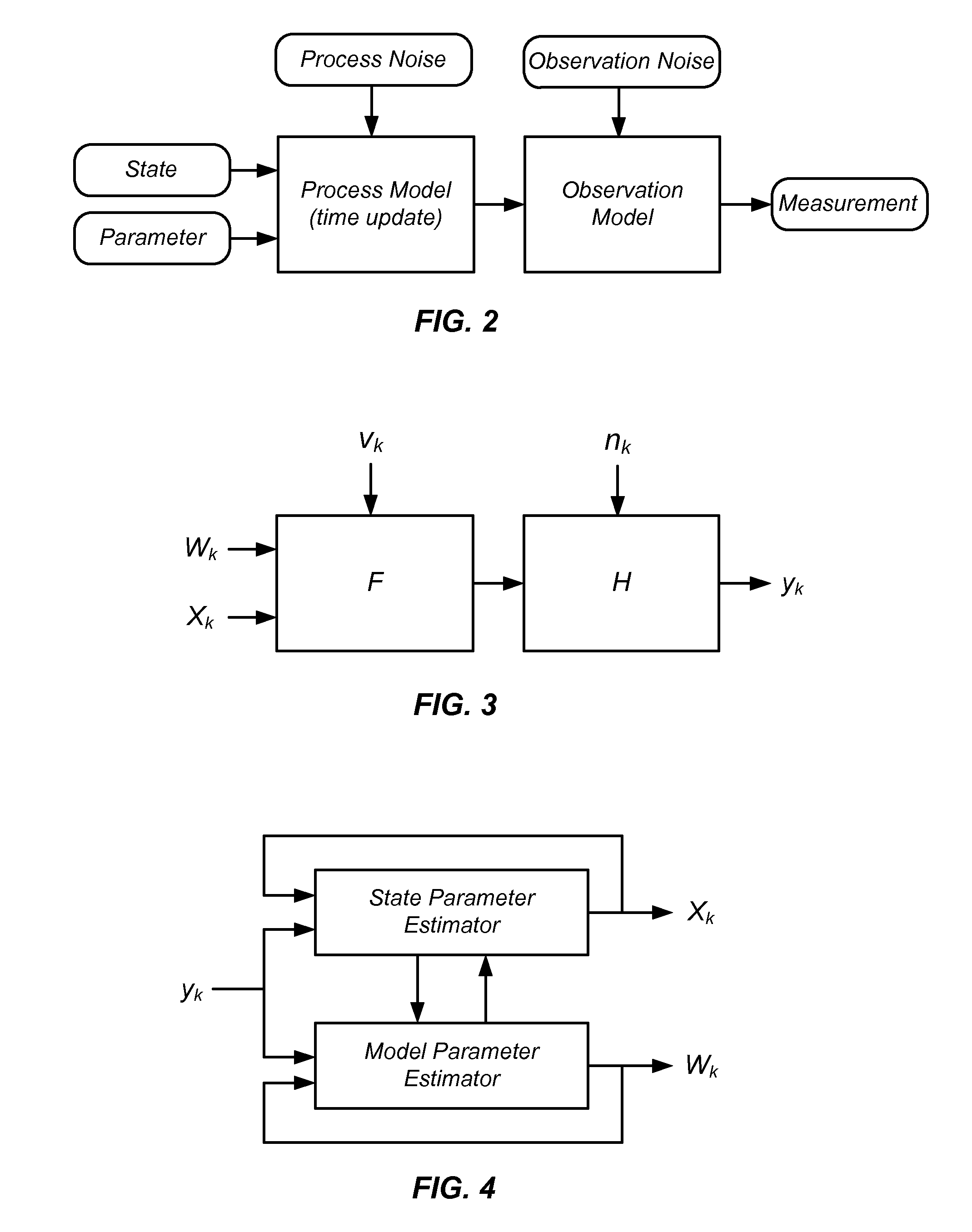
Iterative probabilistic parameter estimation apparatus and method of use therefor
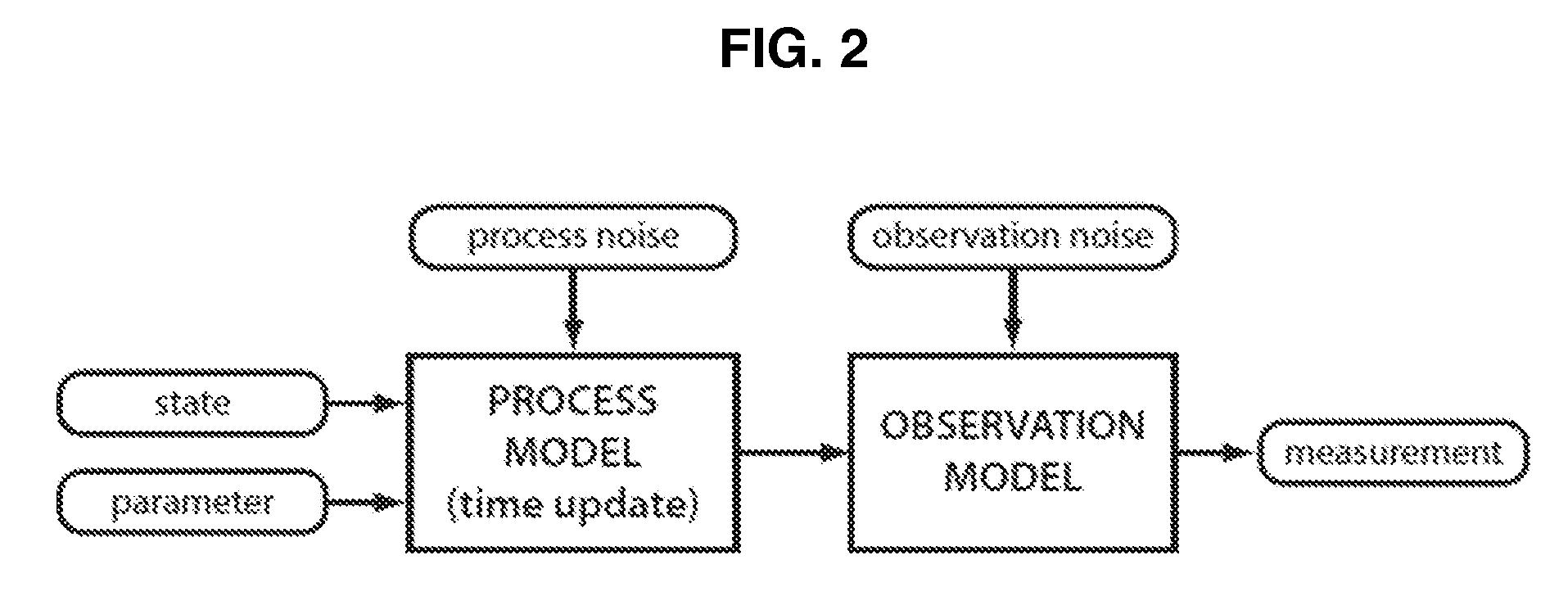
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. In one example, a digital signal processor is integrated into a biomedical device. The processor is configured to: use a dynamic state-space model configured with a physiological model of a body system to provide a prior probability distribution function; receive sensor data input from at least two data sources; and iteratively use a probabilistic updater to integrate the sensor data as a fused data set and generate a posterior probability distribution function using all of: (1) the fused data set; (2) an application of Bayesian probability; and (3) the prior probability distribution function. The processor further generates an output of a biomedical state using the posterior probability function.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
Processing Physiological Sensor Data Using a Physiological Model Combined with a Probabilistic Processor
InactiveUS20100274102A1Reliable and accurate measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse oximetersSigma point
A pulse oximeter system comprises a data processor configured to perform a method that combines a sigma point Kalman filter (SPKF) or sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) algorithm with Bayesian statistics and a mathematical model comprising a cardiovascular model and a plethysmography model to remove contaminating noise and artifacts from the pulse oximeter sensor output and measure blood oxygen saturation, heart rate, left-ventricular stroke volume, aortic pressure and systemic pressures.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveUS8682626B2Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesAnatomical structuresEntire heart
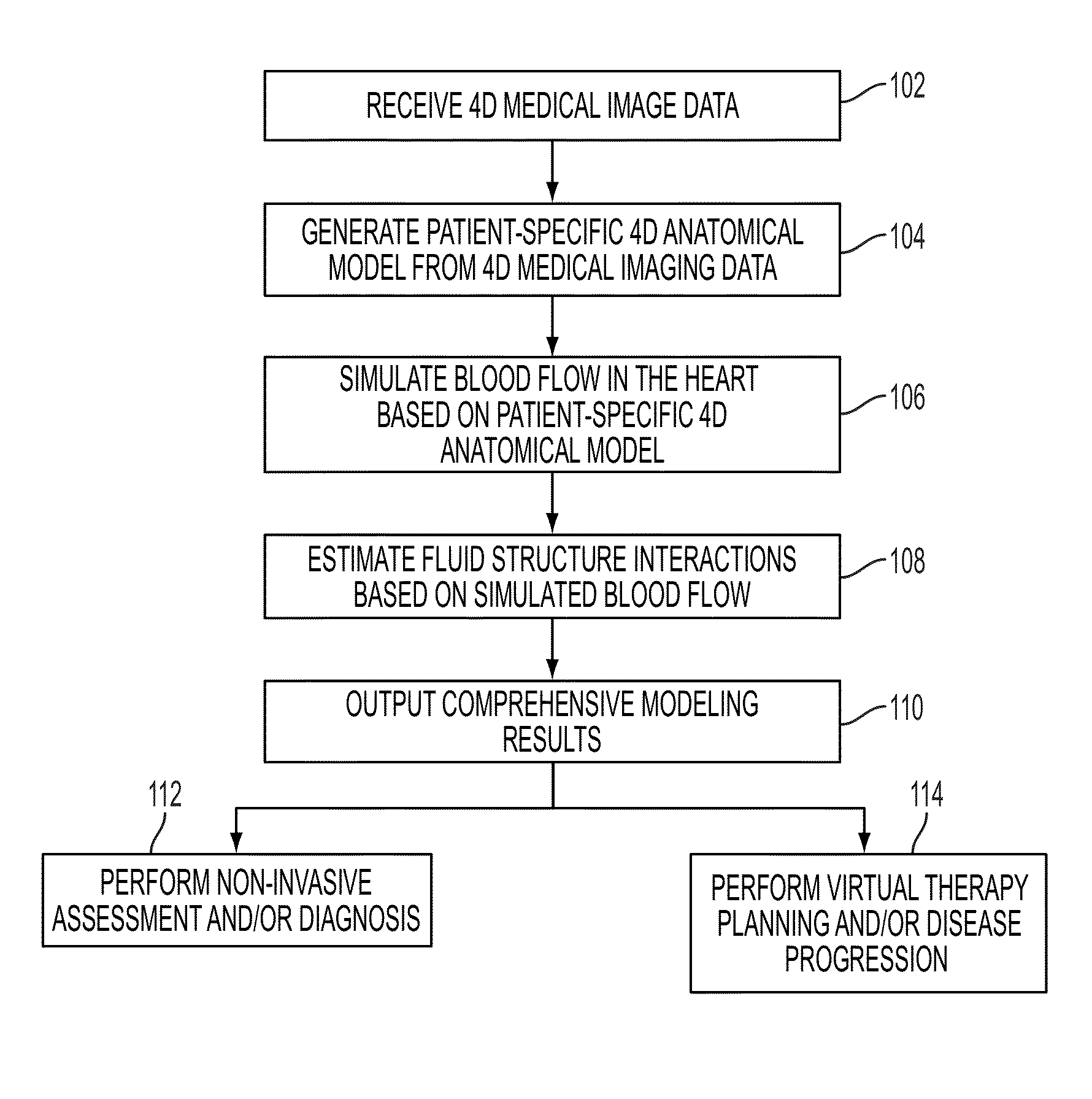
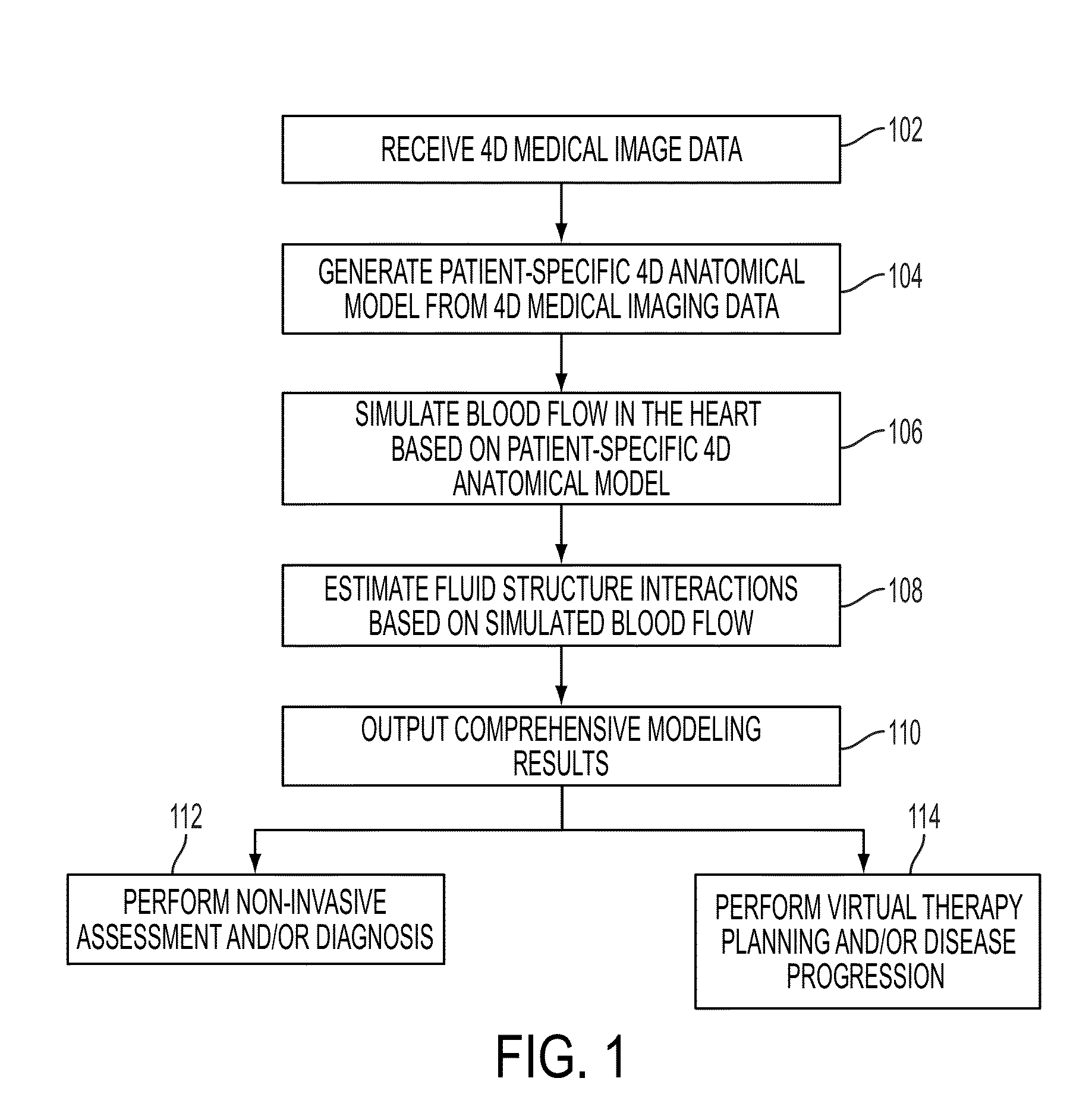
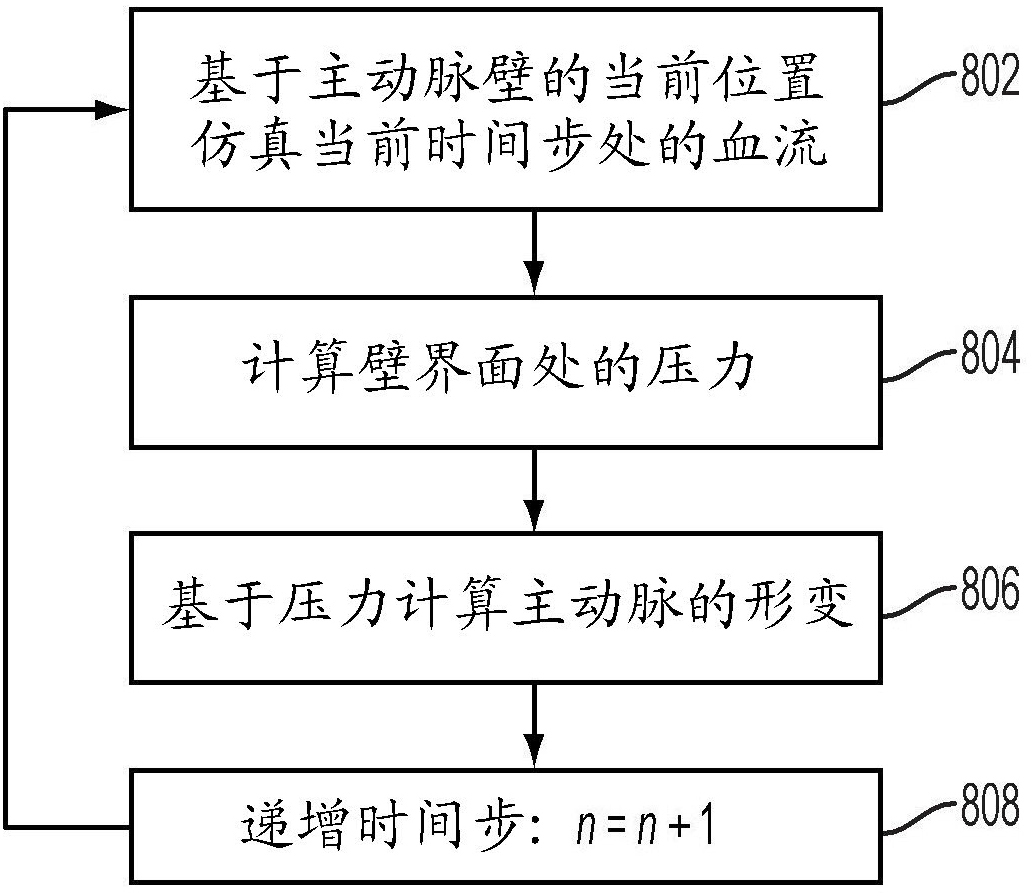
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System for determining the position of a sound source
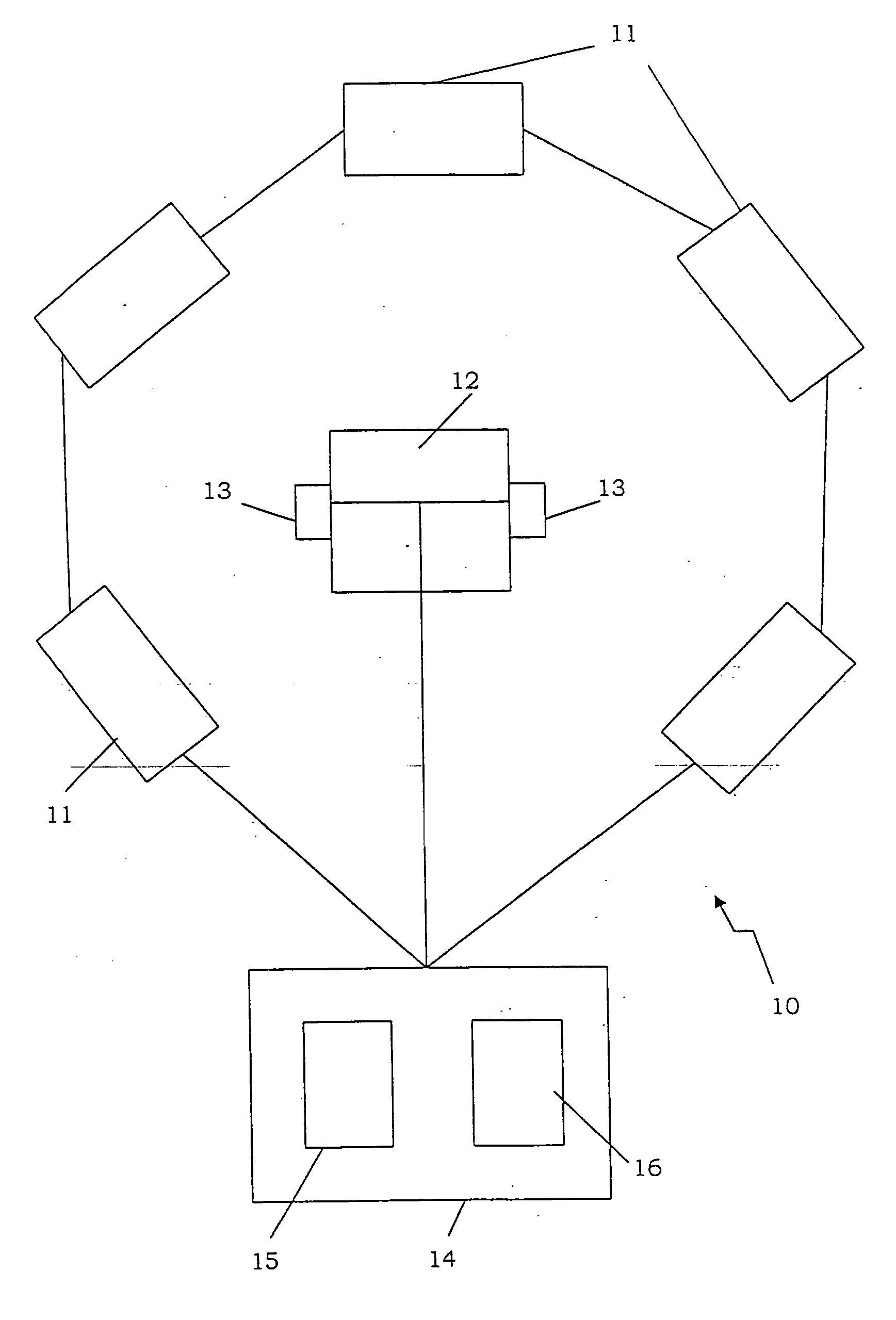
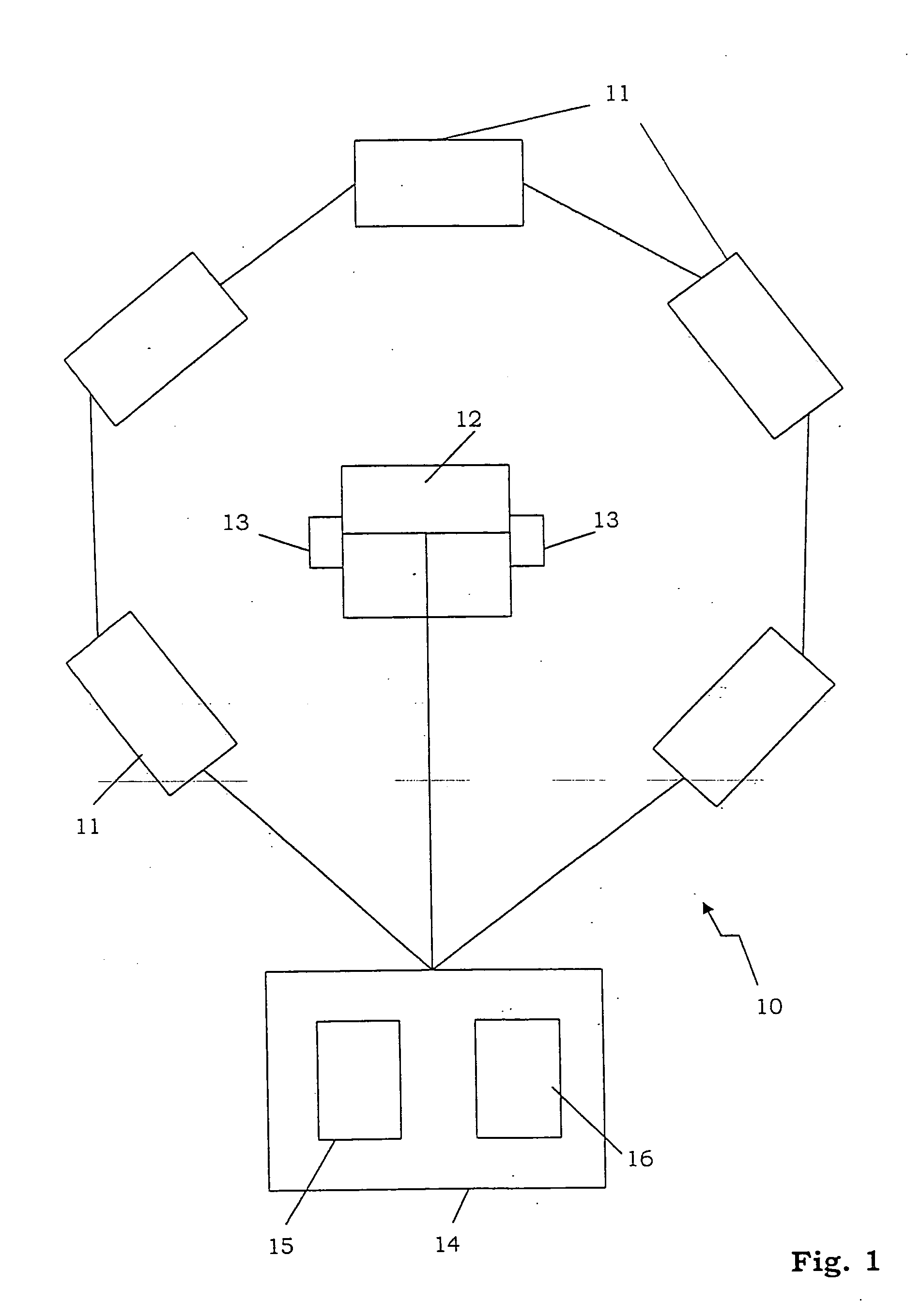
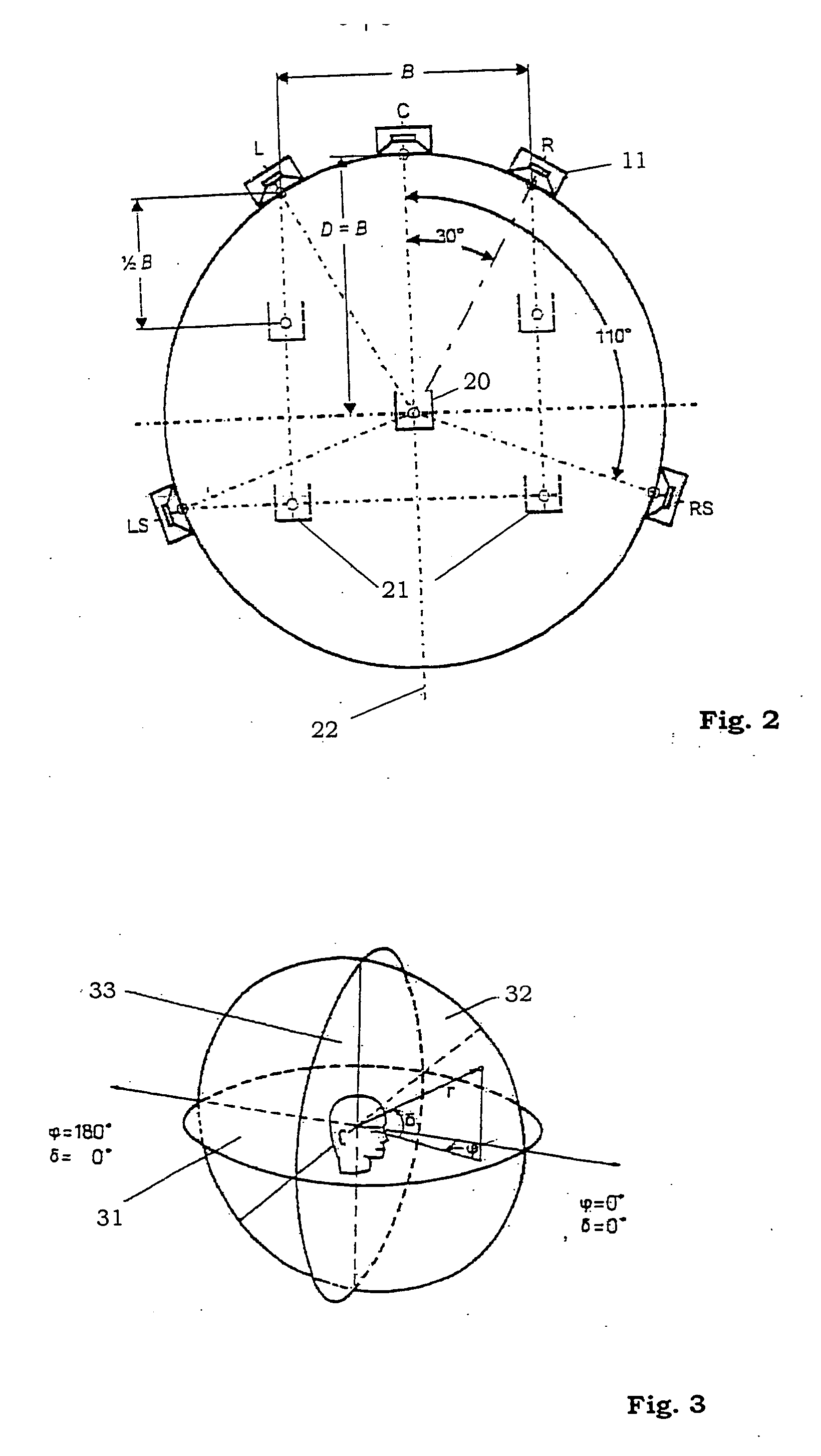
ActiveUS20050078833A1Cutting can not be obtainedPosition fixationDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesTime delays
A method and system for determining the position of a sound source in relation to a reference position, comprising the steps of generating a sound signal emitted from the sound source, detecting the emitted sound signal, processing the sound signal by the use of a physiological model of the ear, deducing at least one of lateral deviation in relation to the reference position, time delay of the sound signal from the sound source to the reference position, and the sound level of the detected sound signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
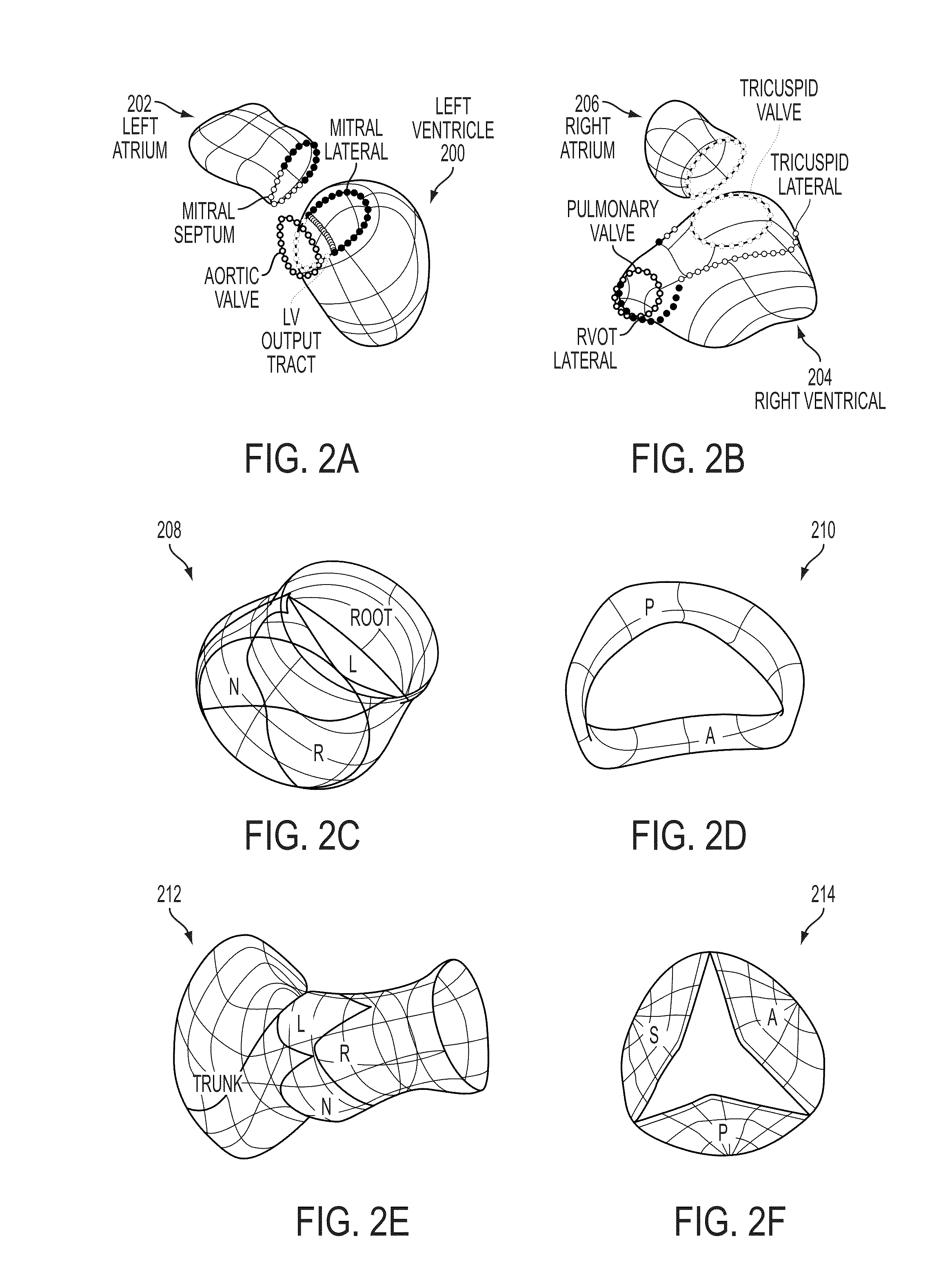
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
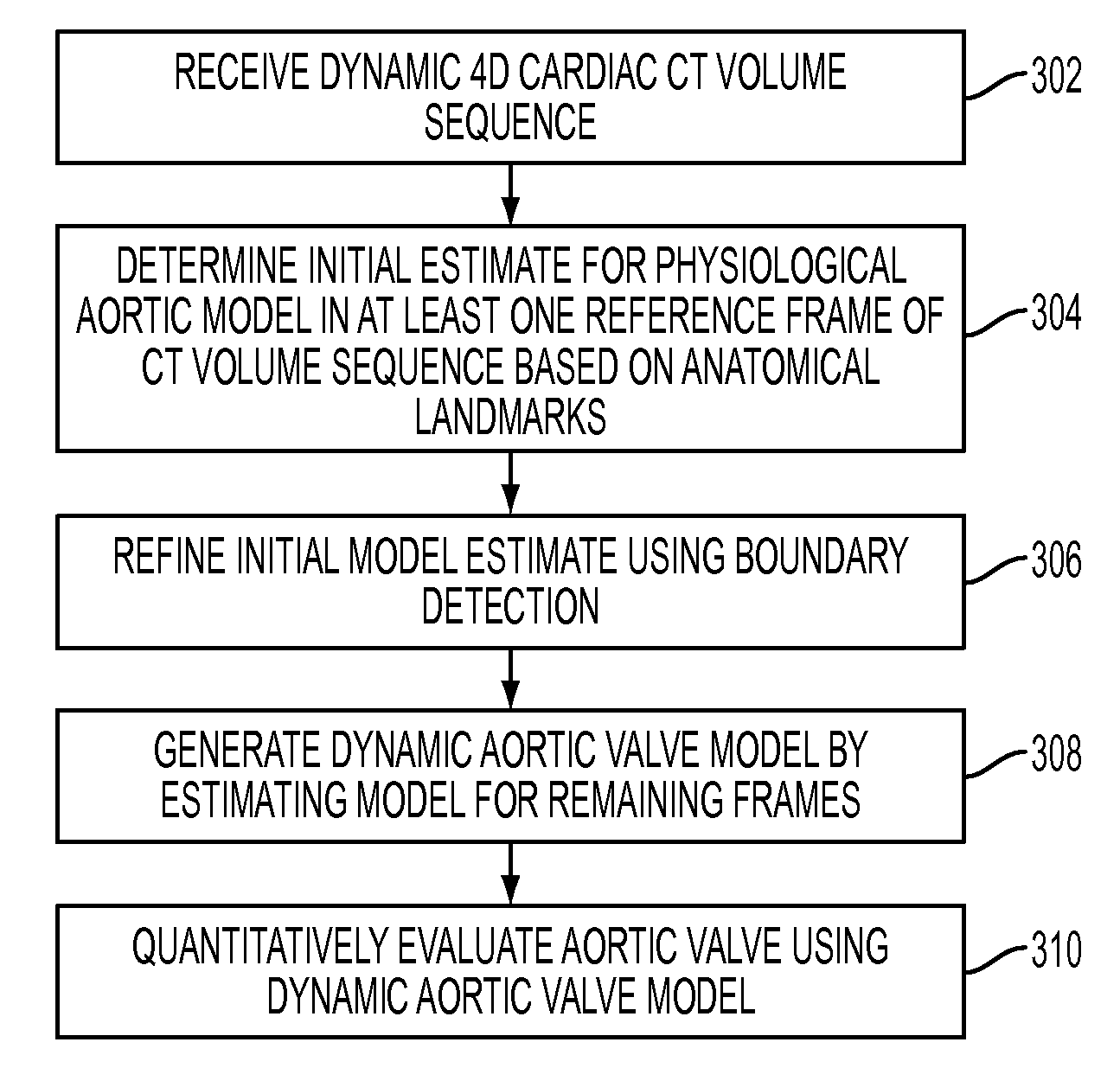
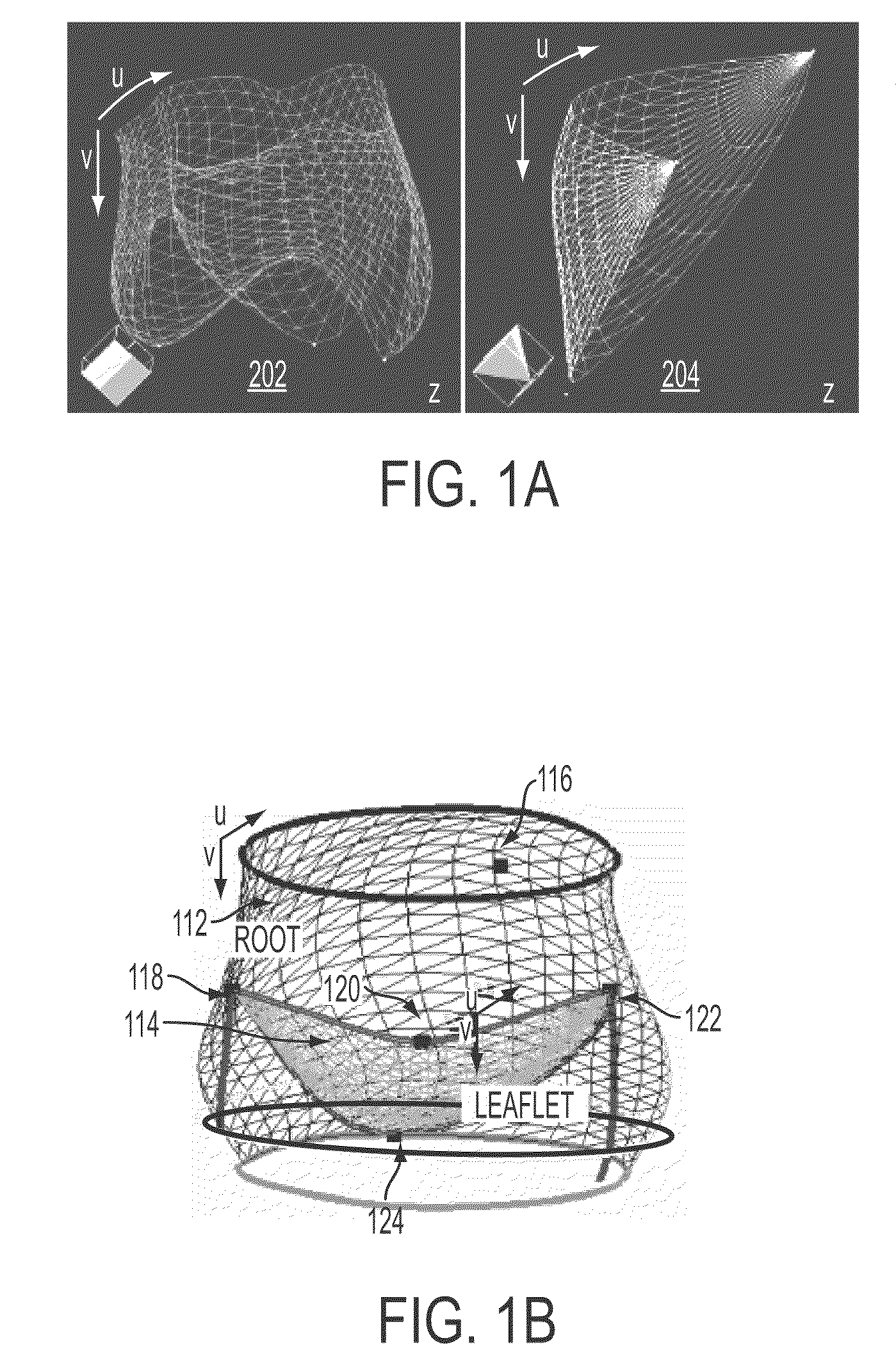
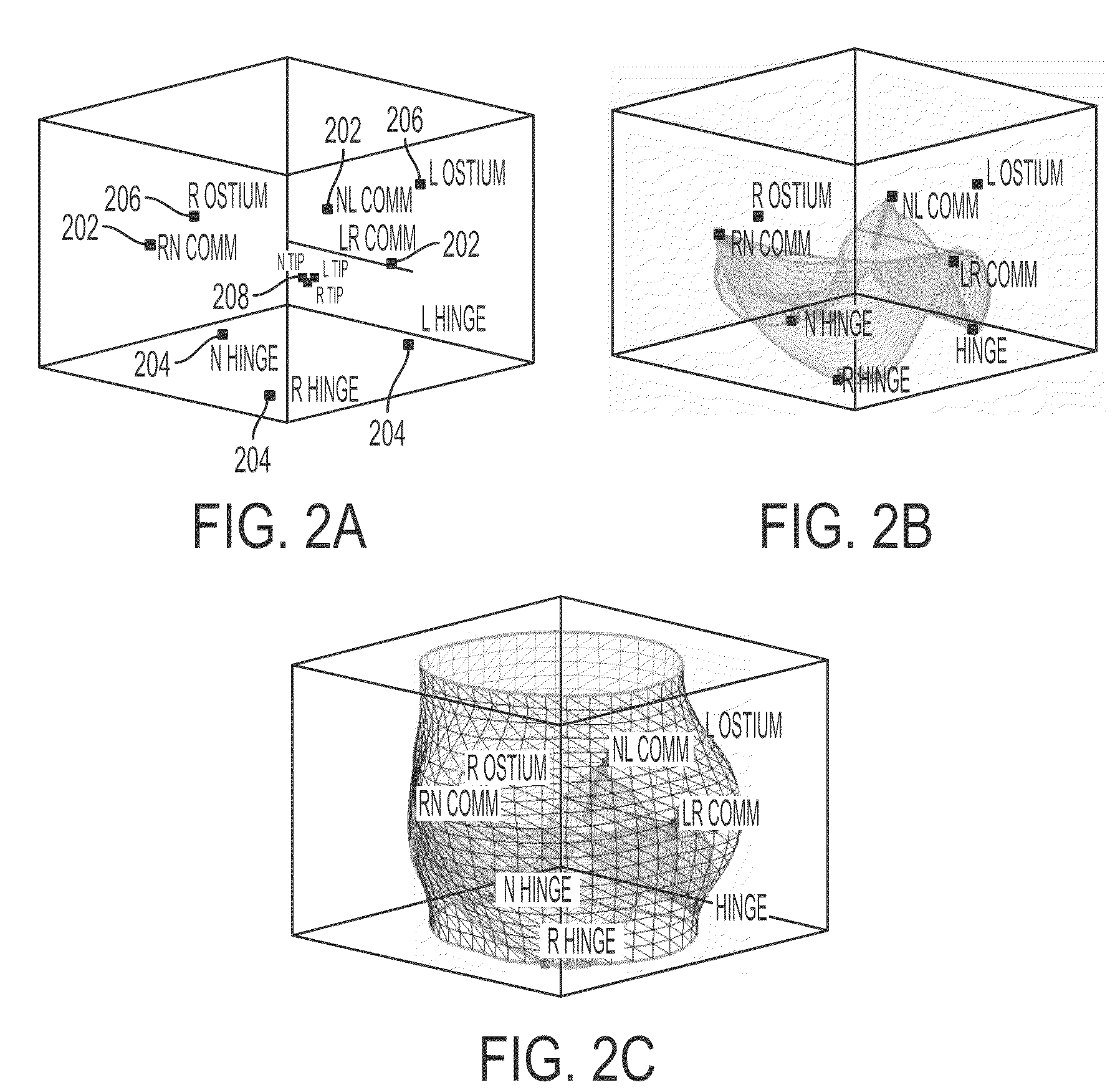
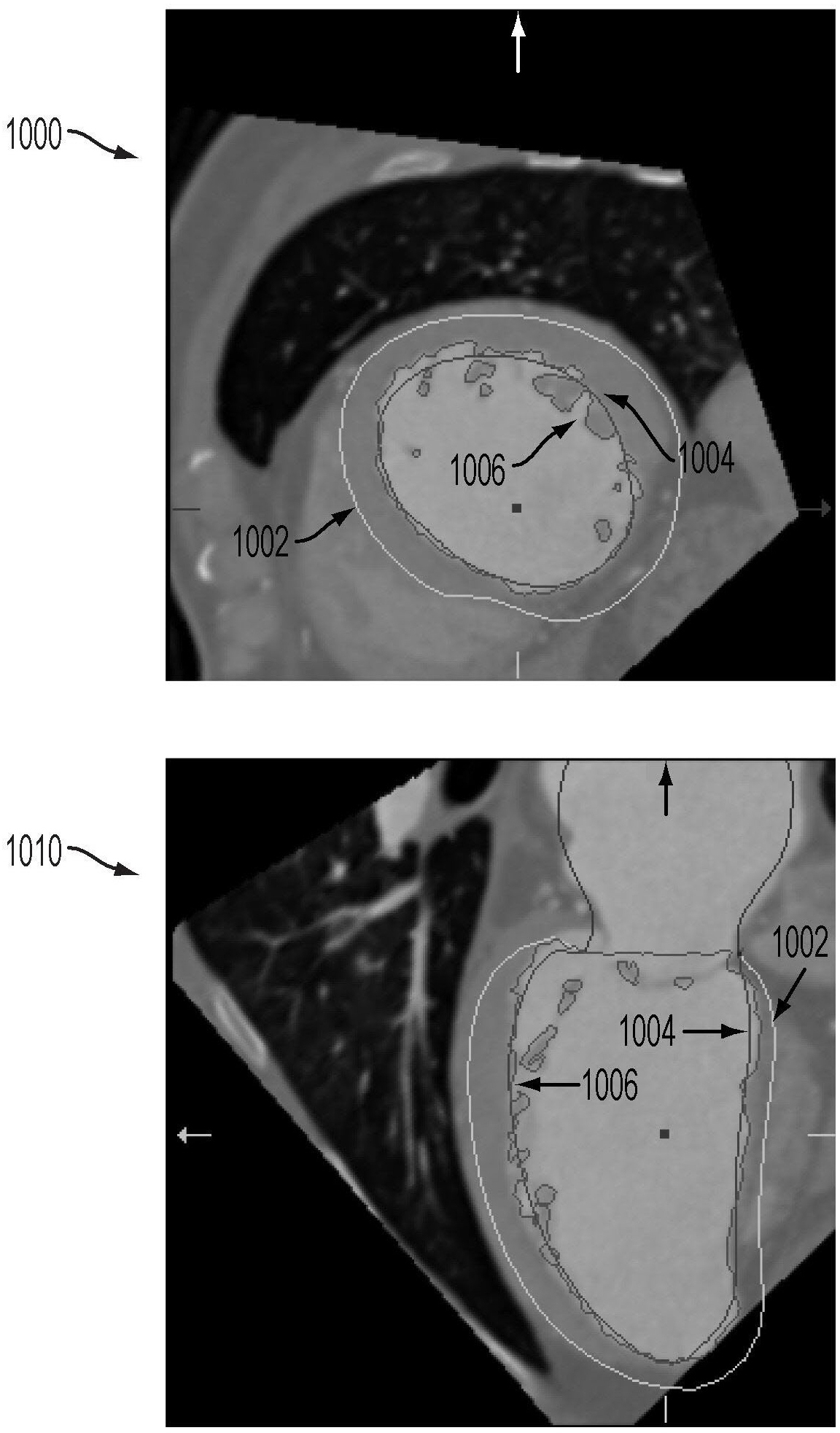
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveCN102346811ADescription of measurement accuracySpecial data processing applicationsTreatment optionsEntire heart
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
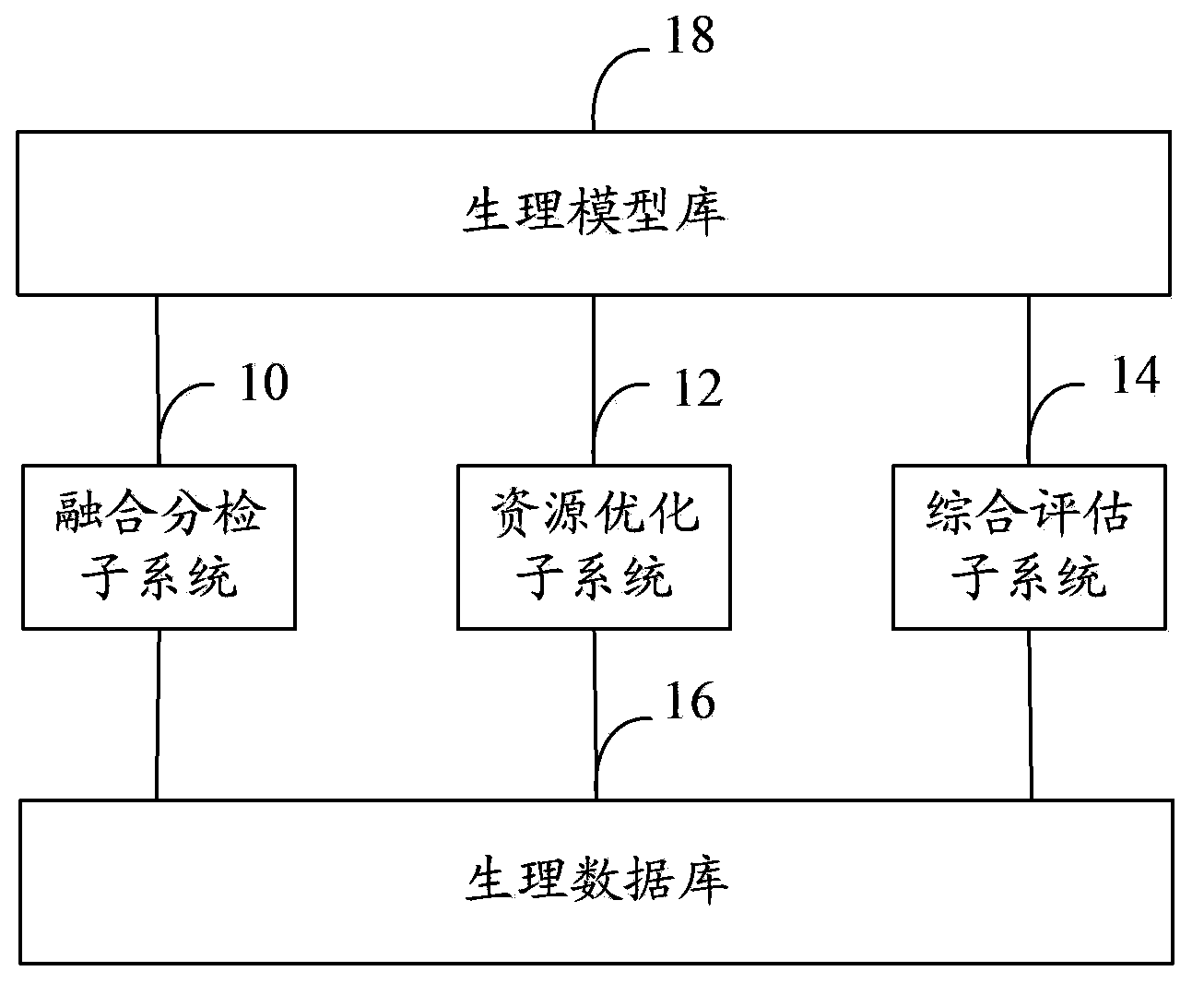
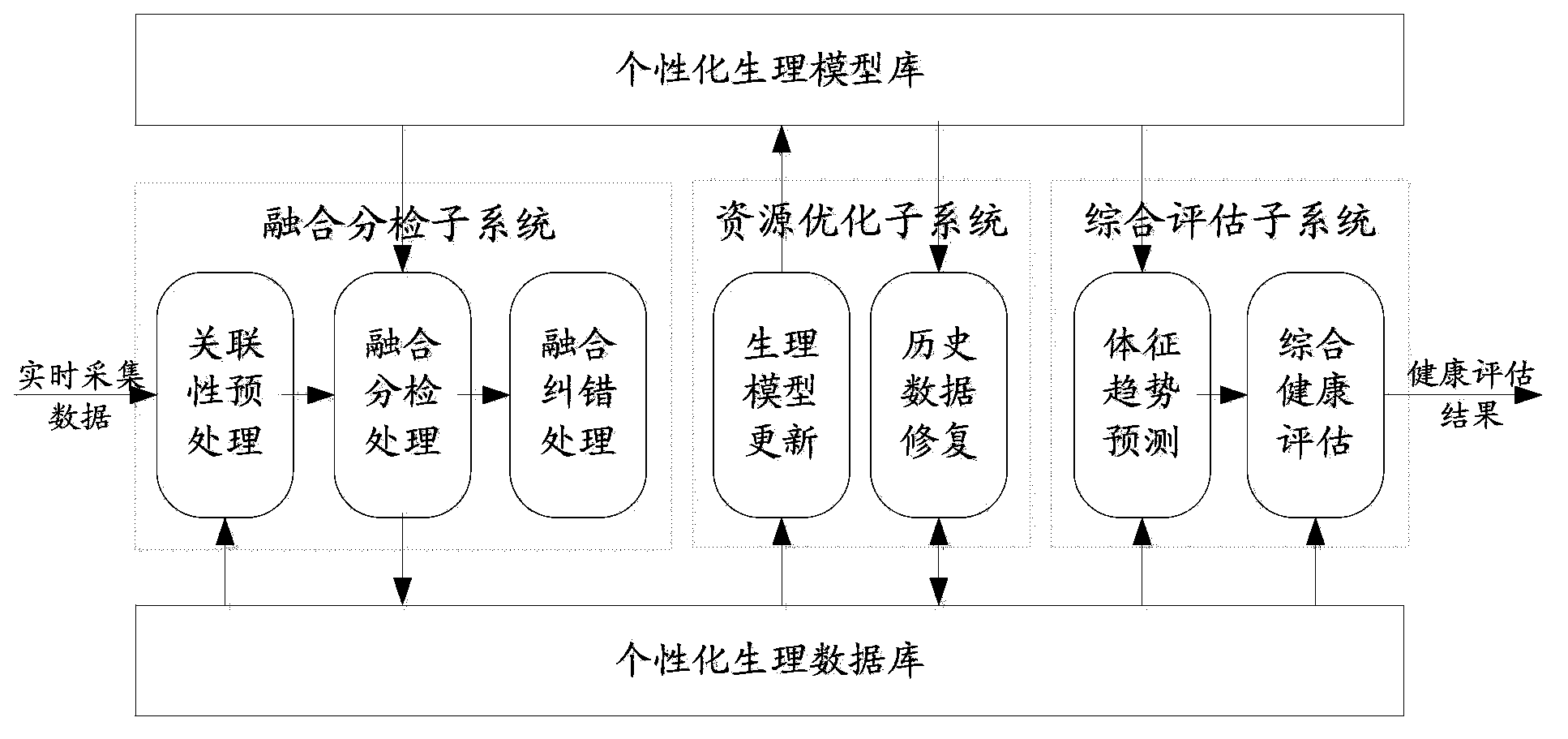
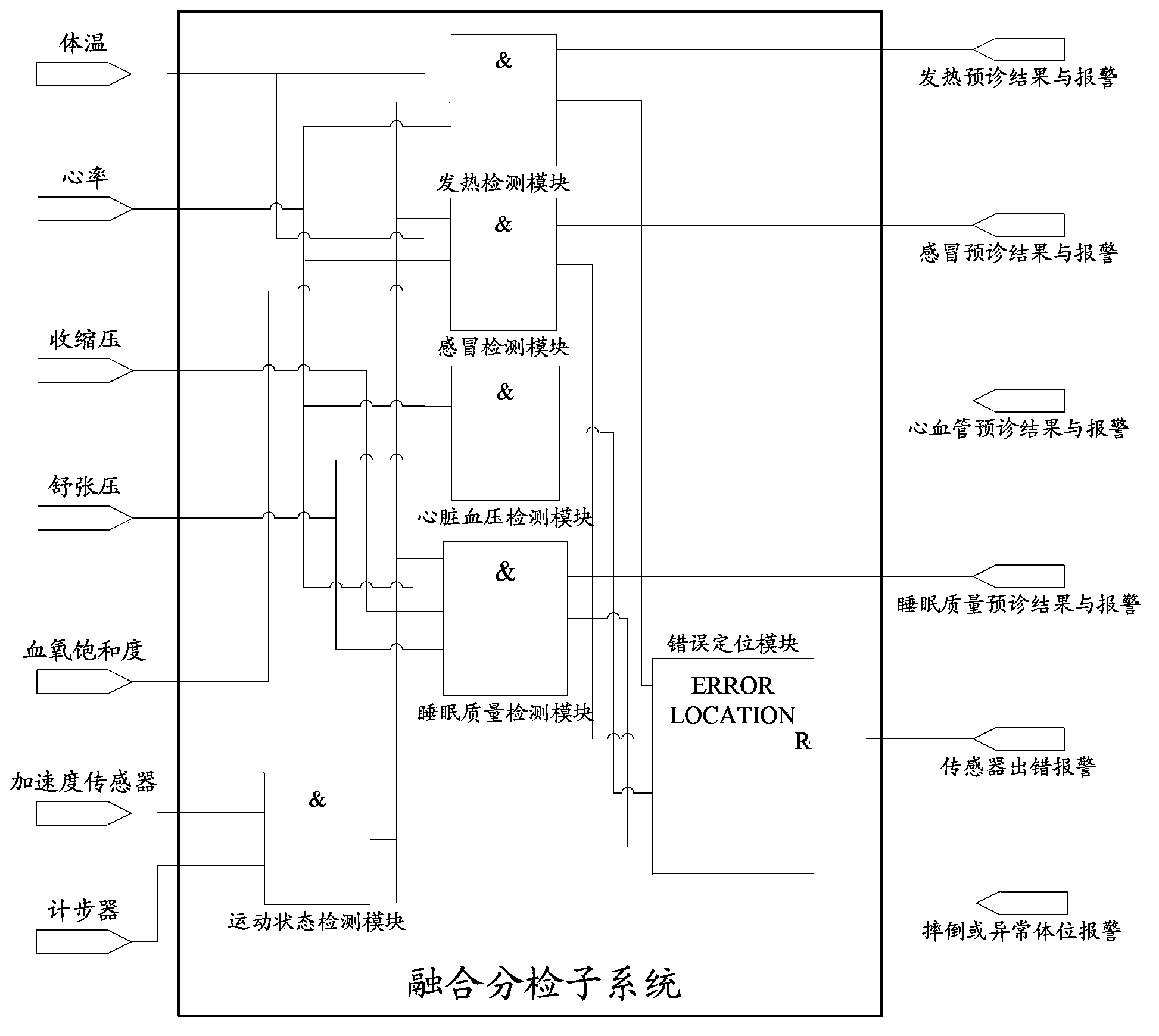
Remote home health care system
ActiveCN103778312ASolve the high false alarm rateSolve historical data errors and omissionsEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPersonalizationSign changing
The invention discloses a remote home health care system. The home health care system comprises a fusion sorting subsystem used for receiving physical sign data parameters collected by a sensor in real time, conducting fusion sorting processing on the physical sign data parameters and diagnosing and feeding back the body condition of a user in real time according to physiological data and physiological models in a physiological model library, a resource optimization subsystem used for regularly optimizing the physiological data in a physiological database, generating an individualized physiological model for the user according to the historical physiological data in the physiological database, storing the physiological model in the physiological model library, and updating the physiological models in the physiological model library according to the latest physiological data in the physiological database and a comprehensive assessment subsystem used for predicting the physical sign change tread and the physical sign dynamic change range of the user according to the physiological data in the physiological database and the physiological models in the physiological model library and assessing the health of the user according to the physiological data and a predicating result.
Owner:ZTE CORP
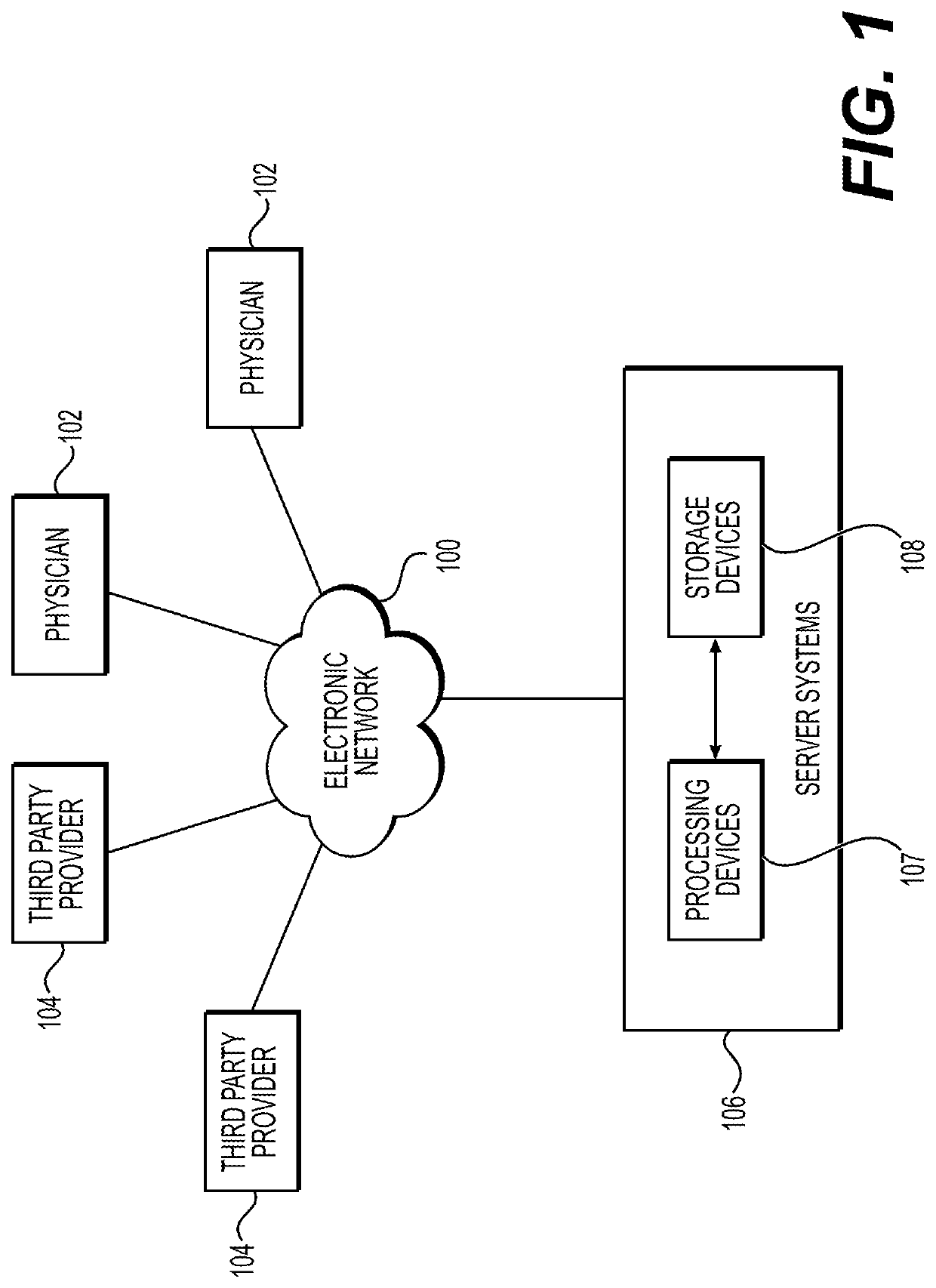
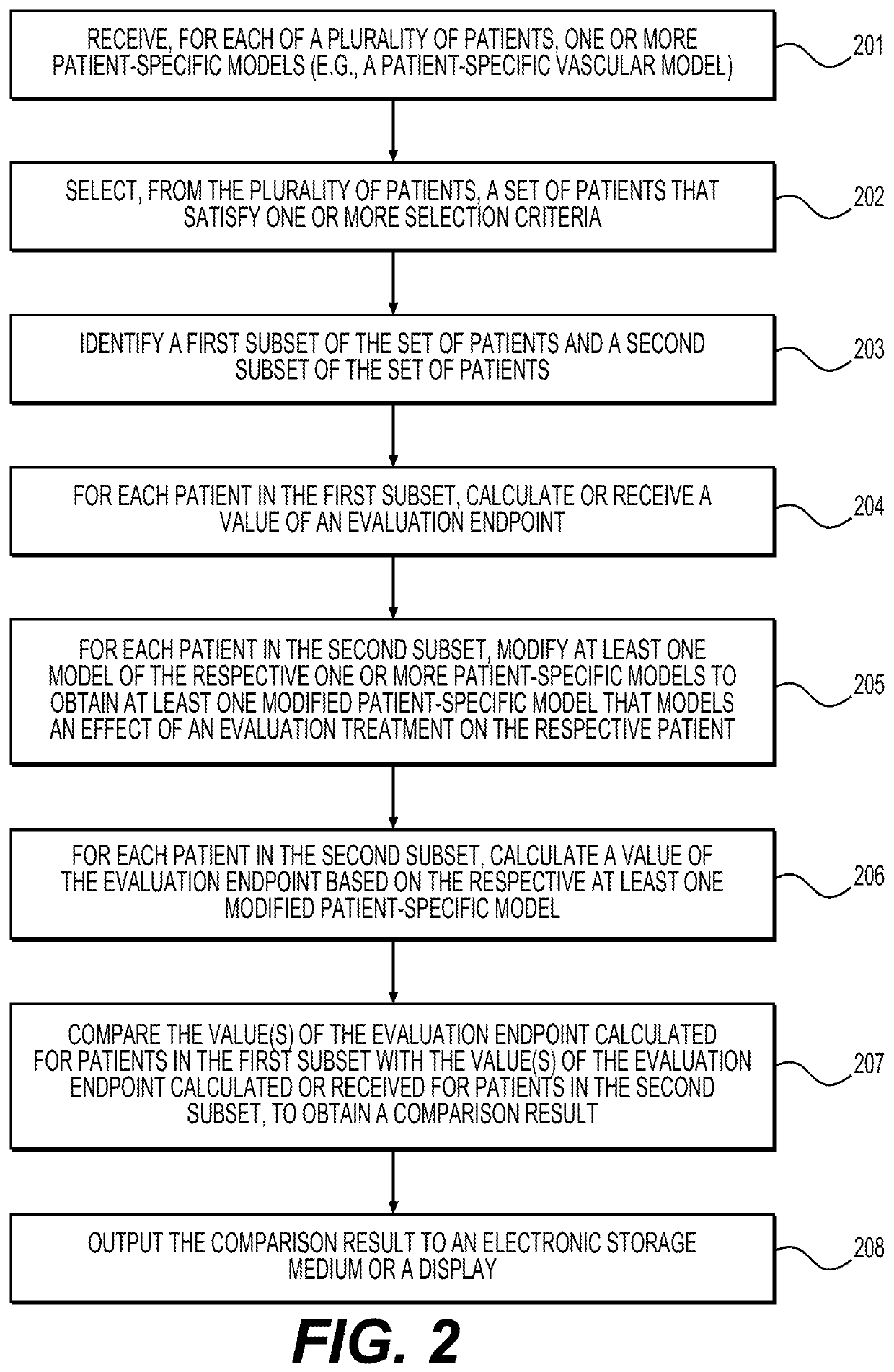
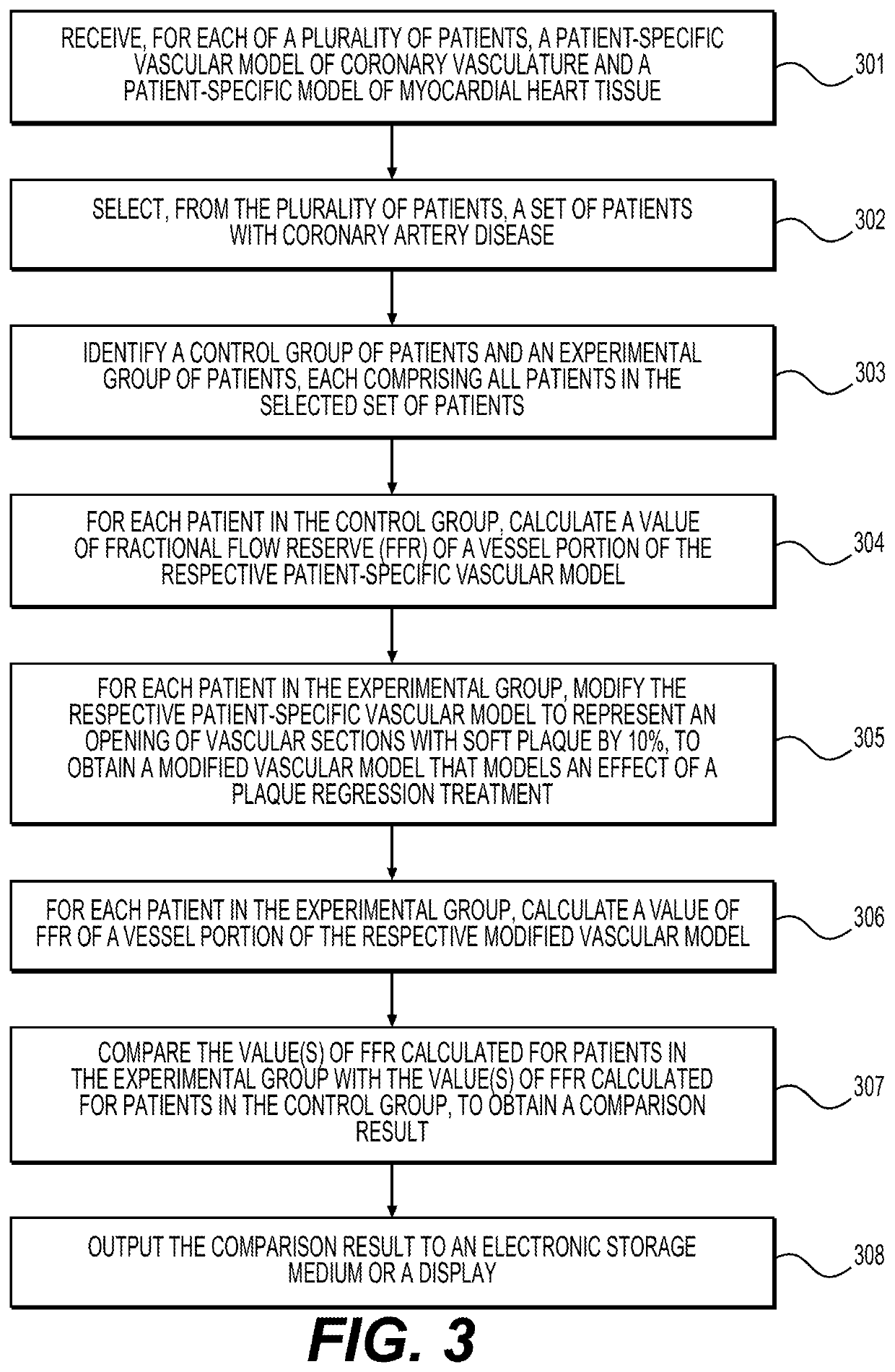
Systems and methods for performing computer-simulated evaluation of treatments on a target population
ActiveUS10991465B2Medical simulationPathological referencesSpecific modelTreatment and control groups
Owner:HEARTFLOW
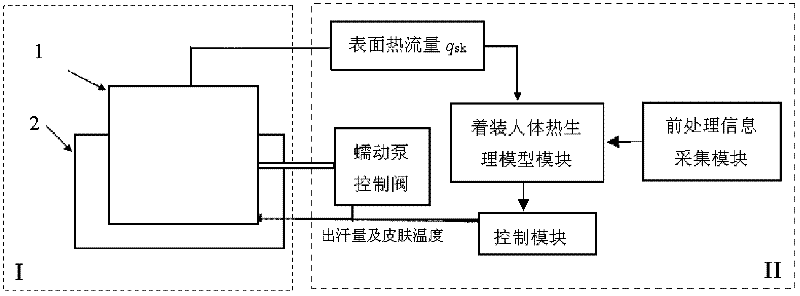
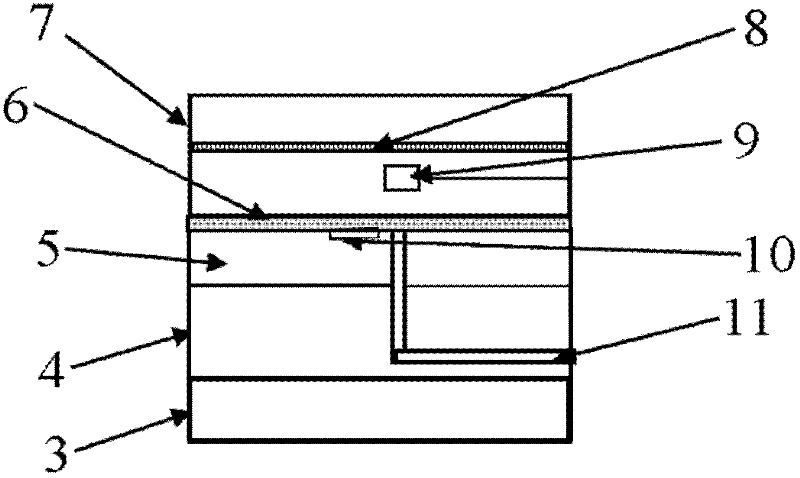
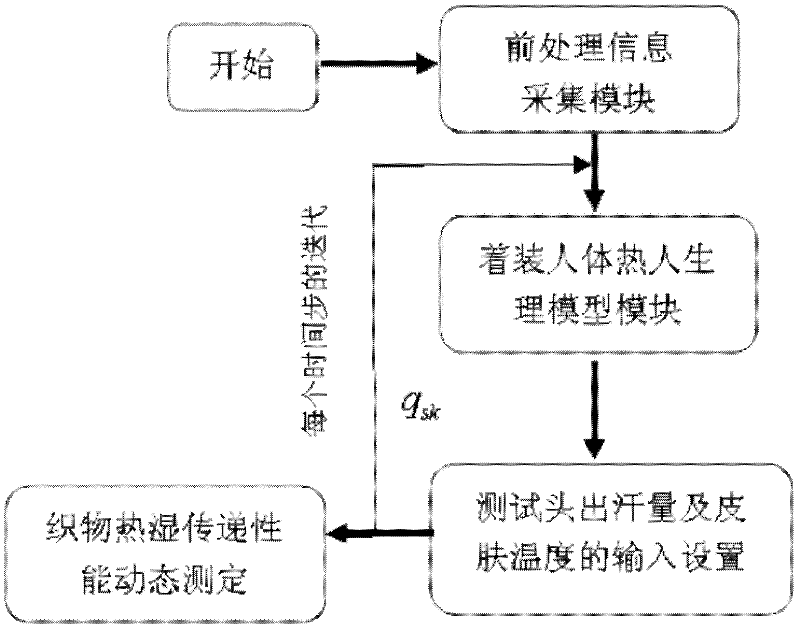
Self-adapting testing instrument for heat-moisture comfort performance of fabric and coupled testing method using same
InactiveCN102507641AActual measurement of dynamic heat and moisture transfer characteristicsThe experimental results are accurate and reliableMaterial heat developmentTextile testingHuman bodyPeristaltic pump
The invention relates to a self-adapting testing instrument and a testing method for heat-moisture comfort performance of fabric. The testing instrument comprises a testing main body and a testing accessory body, wherein the testing main body comprises a testing head; the testing head sequentially comprises a heating plate, a copper plate, a simulated skin, a simulated skin and a sample clamp clamped with a sample bottom to top; a temperature and humidity sensor is arranged between the sample and the simulated skin; a membrane couple is attached to the surface of the simulated skin device; multiple sweating micropores connected with a control valve of a peristaltic pump are disposed on the simulated skin device; the testing accessory body comprises a clothed human body heat physiological model module, a control module and a surface heat flow calculation module; the surface heat flow calculation module is used for calculating the surface heat flow according to the sweating amount of the sweating micropores and the temperature of the membrane couple; and the clothed human body heat physiological model module is used for real-time sending signals for controlling the peristaltic pump and the heating plate to the control module by taking the calculated surface heat flow as a boundary condition. The self-adapting testing instrument can simulate human body heat physiological characteristics changing along with the ambient change.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method and system for registration of ultrasound and physiological models to X-ray fluoroscopic images
A method and system for registering ultrasound images and physiological models to x-ray fluoroscopy images is disclosed. A fluoroscopic image and an ultrasound image, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) image, are received. A 2D location of an ultrasound probe is detected in the fluoroscopic image. A 3D pose of the ultrasound probe is estimated based on the detected 2D location of the ultrasound probe in the fluoroscopic image. The ultrasound image is mapped to a 3D coordinate system of a fluoroscopic image acquisition device used to acquire the fluoroscopic image based on the estimated 3D pose of the ultrasound probe. The ultrasound image can then be projected into the fluoroscopic image using a projection matrix associated with the fluoroscopic image. A patient specific physiological model can be detected in the ultrasound image and projected into the fluoroscopic image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and systems for non-invasive, internal hemorrhage detection
InactiveUS20110319724A1Increase chances of survivalElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisInternal hemorrhagePhotoplethysmogram
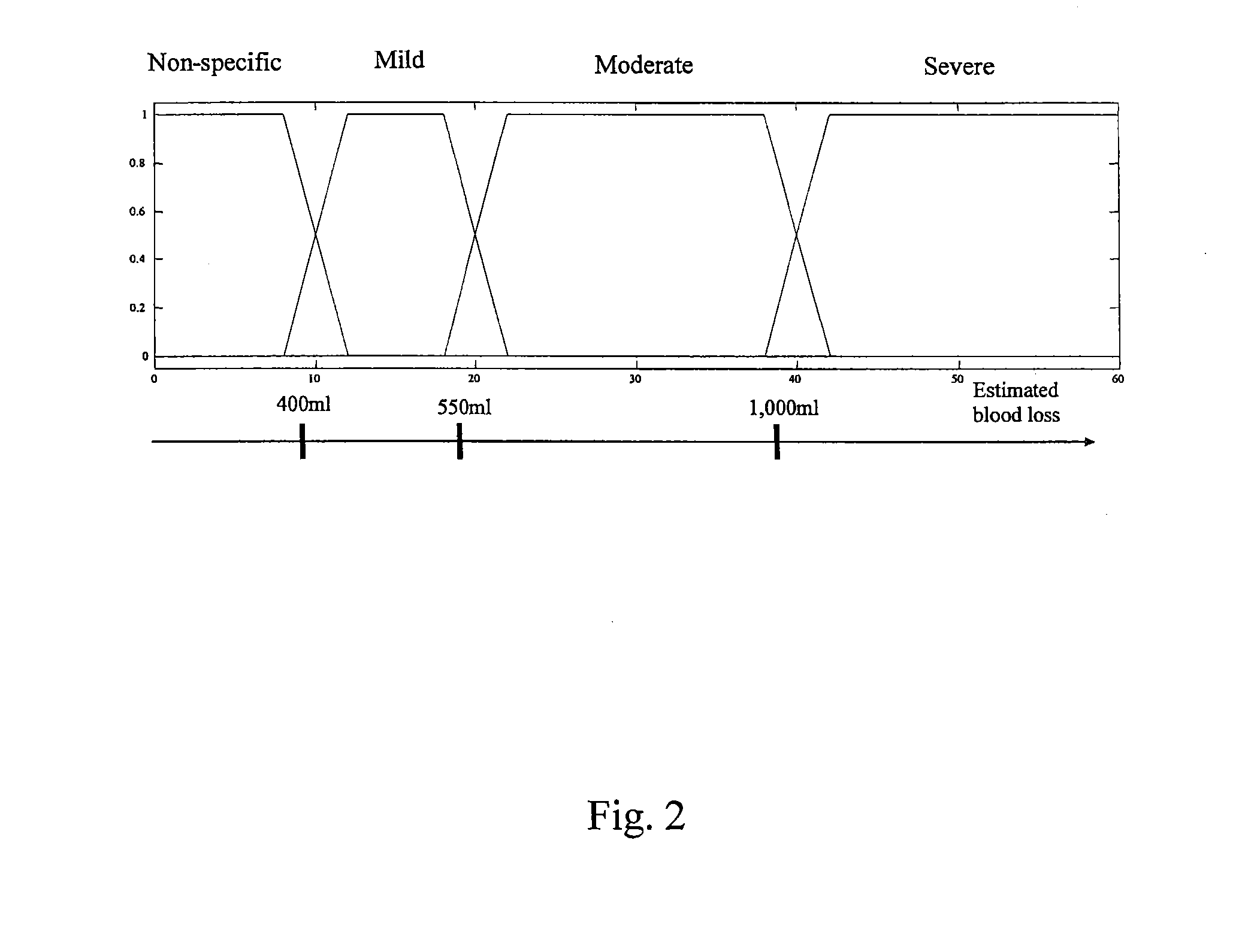
Methods and systems for detecting internal hemorrhaging in a person are provided. In an exemplary embodiment, one method includes the steps of measuring physiological conditions associated with the person and processing the measured physiological conditions using a probabilistic network to determine if the person has internal hemorrhaging. The method also includes the steps of determining the severity of any internal hemorrhaging by determining the amount of blood lost by the person and classifying this loss as non-specific, mild, moderate, and severe. The physiological measurements include an electrocardiogram, a photoplethysmogram, and oxygen saturation, respiratory, skin temperature, and blood pressure measurements. The probabilistic network included with one system determines whether there is internal hemorrhaging based on a number of factors including a physiological model, medical personnel inputs, transfer function, statistical, and spectral information, short and long term trends, and previous hemorrhage decisions.
Owner:COX PAUL G
System and apparatus for the non-invasive measurement of glucose levels in blood
A system for estimating the glucose levels in blood is developed in the present invention. Said system establishes a physiological model of the pulse wave and its energy, which are also correlated with the glucose metabolic function, for generating a fixed length vector containing the values of the previous model combined with other variables related to the user such as, for example, age, sex, height, weight, etc. . . . This fixed length vector is used as an excitation of a function estimation system based on “random forests” for the calculation of the interest variable. The main advantage of this parameter estimation system lays in the fact that it does not apply any restriction a priori on the function to be estimated, and that it is robust in front of heterogeneous data, such as in the case of the present invention.
Owner:SABIRMEDICAL
Systems and method for homeostatic blood states
InactiveUS20070178167A1The process is simple and fastReliable and accurate evaluationMammal material medical ingredientsBiological testingBlood test resultMedical record
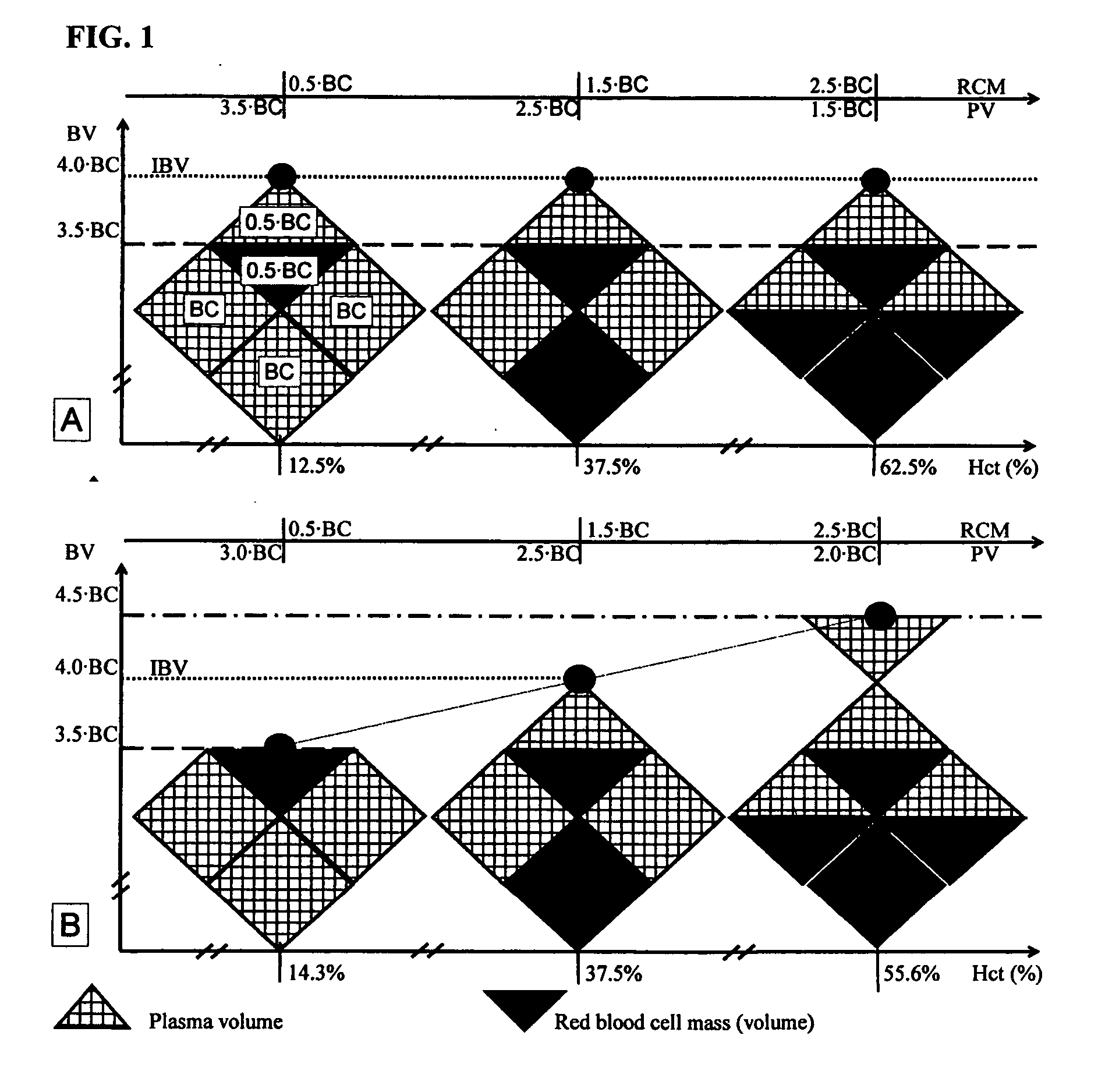
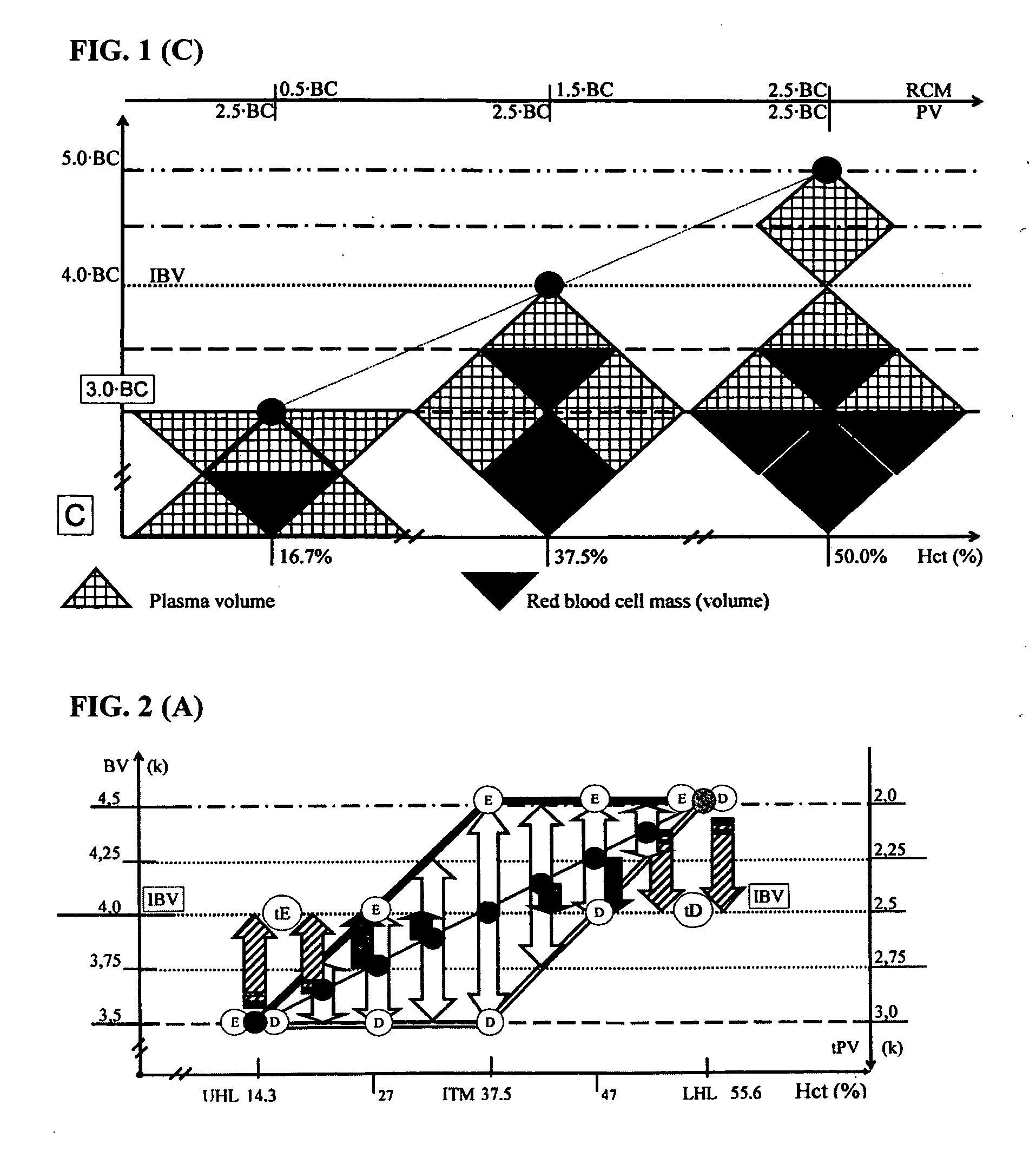
Decades of investigations were focused on finding “gold standard” for evaluation of plasma dilution and osmolality, blood loss evaluation and prediction of bleeding or transfusion induced changes in hematocrit and hemoglobin concentration. Addressing deficiencies of existing methods, the current invention created new combined mathematical-physiological model applicable to manually operated nomograms and software in medical monitors. The mathematical model HBS Trends is used in blood transfusion and infusion therapy nomogram—HBS Nomogram—which is based on blood hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit. It is also an easy and practical tool for recording and dynamical interpretation of plasma osmolality, blood hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration. The HBS Nomogram is a practical system for organizing blood test results in a patient's medical records. It can be used alone or, in line with existing guidelines for infusion and transfusion therapy making them more practical, cost effective and time saving in decision making.
Owner:MEDITASKS
Portable device with multiple integrated sensors for vital signs scanning
ActiveUS20190298183A1Easy to installShorten the timeElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAccelerometerMultiple sensor
In one embodiment of the invention, a portable device with multiple integrated sensors for vital signs scanning and method of using said device is disclosed. The portable personal scanning device includes multiple sensors such as a plurality of ECG, thermometer, PPG, accelerometer, and microphone for determining a user's vital signs. The method includes concurrently scanning with one or more sensors, validating and enhancing the results of each sensor scan with other concurrent sensor scan and patient interaction models, processing the sensor scans separately or in combination to extract user's vital signs, validating the vital signs extracted by comparison to physiological models, and fusing the similar vital signs extracted from more than one process according to a determination of the measure of quality of the process that produced the vital sign.
Owner:HEALTHY IO LTD
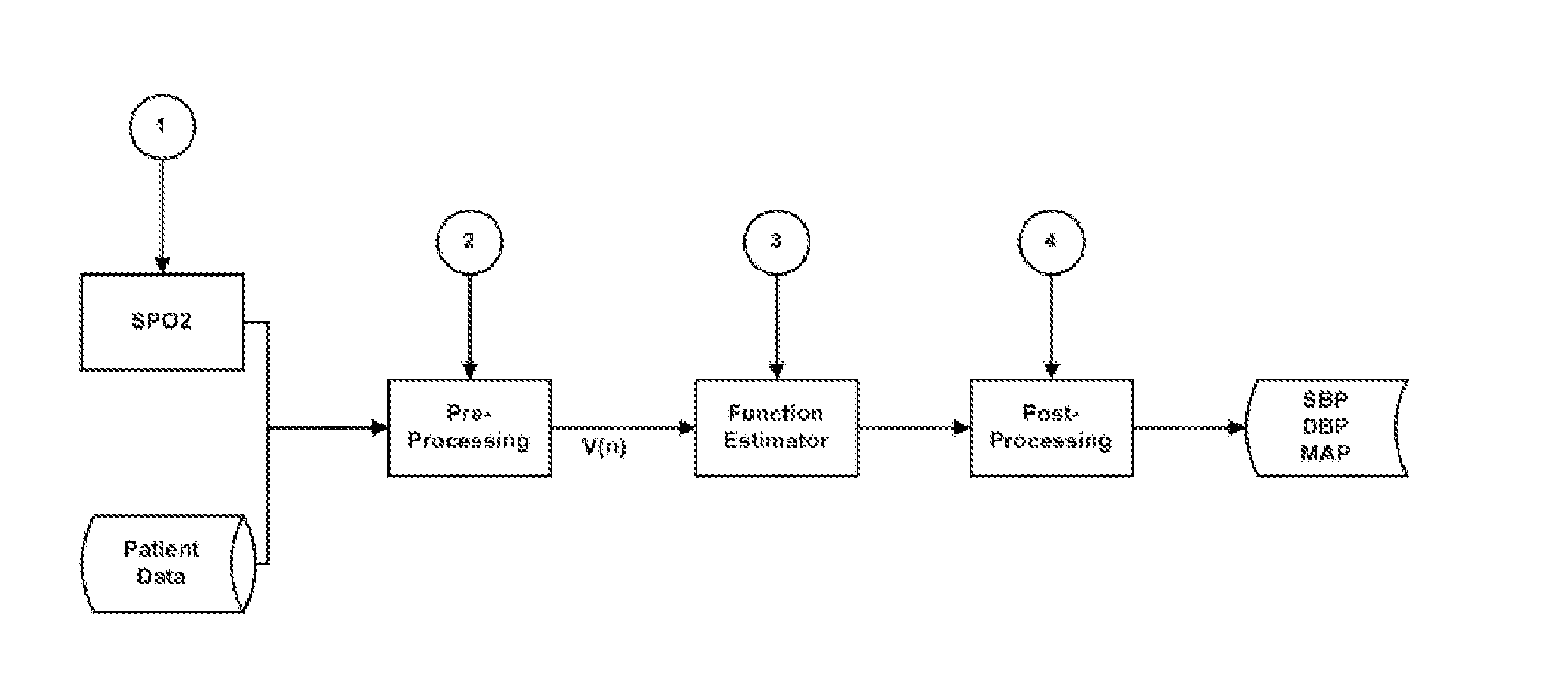
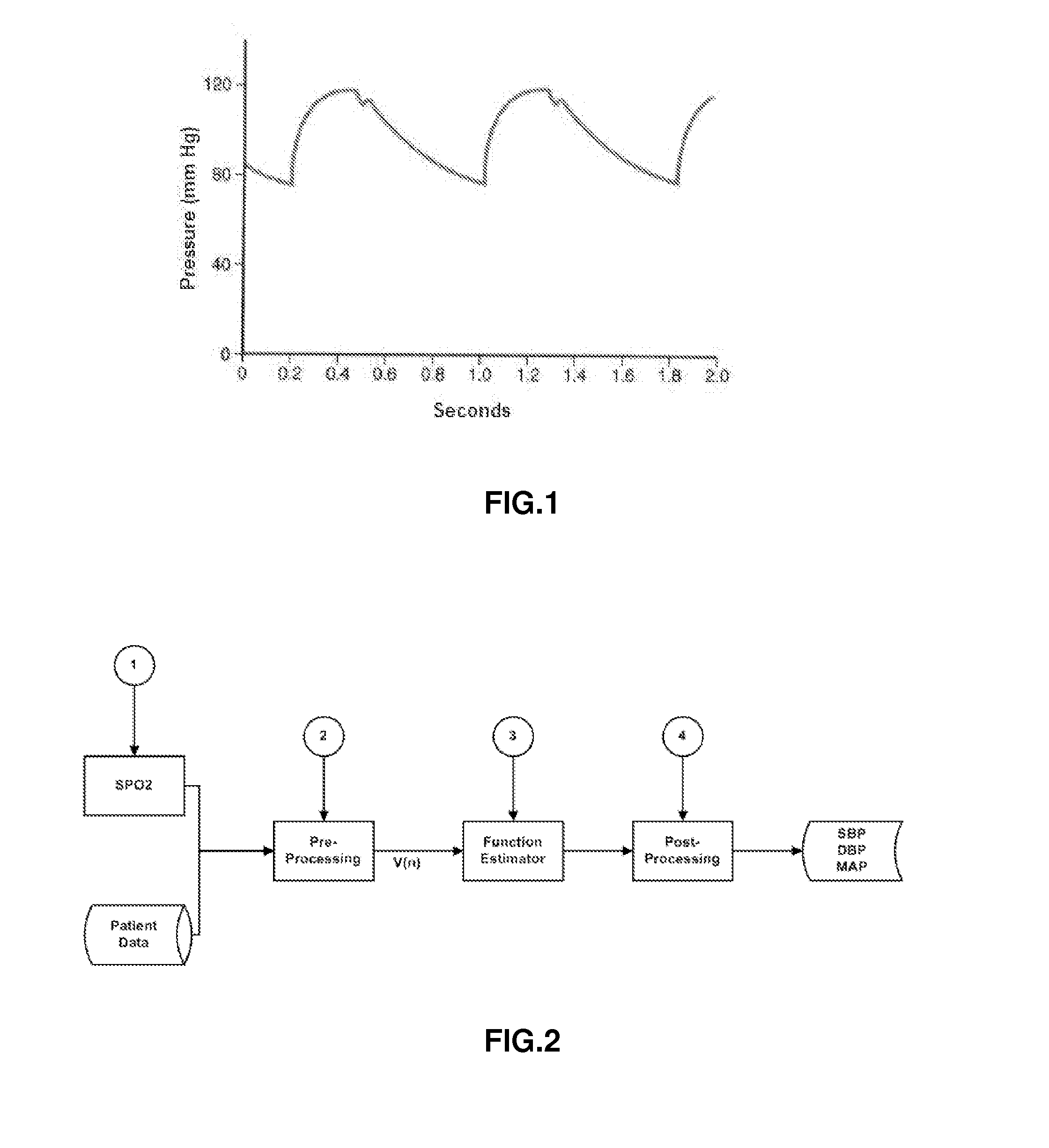
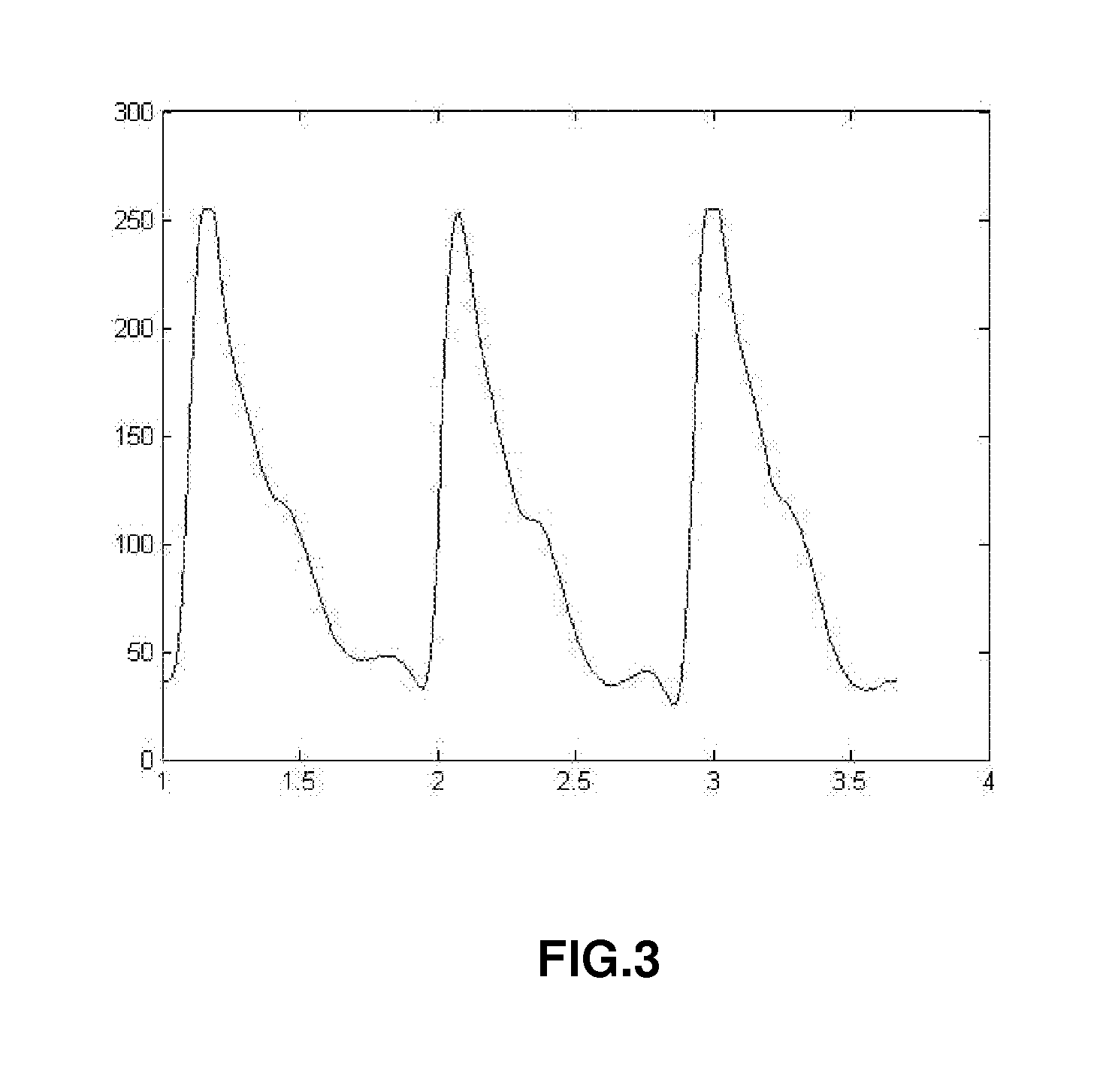
System and apparatus for the non-invasive measurement of blood pressure
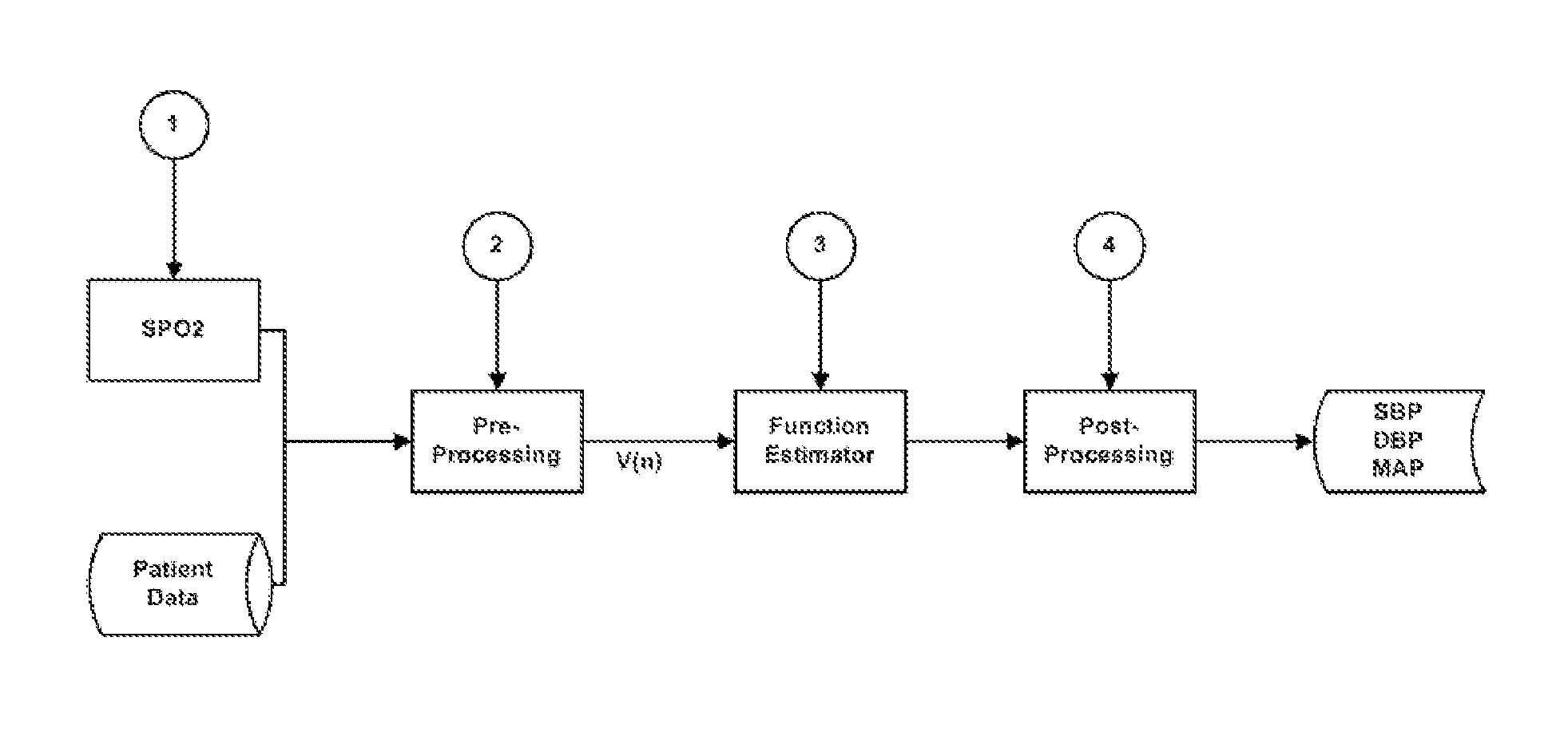
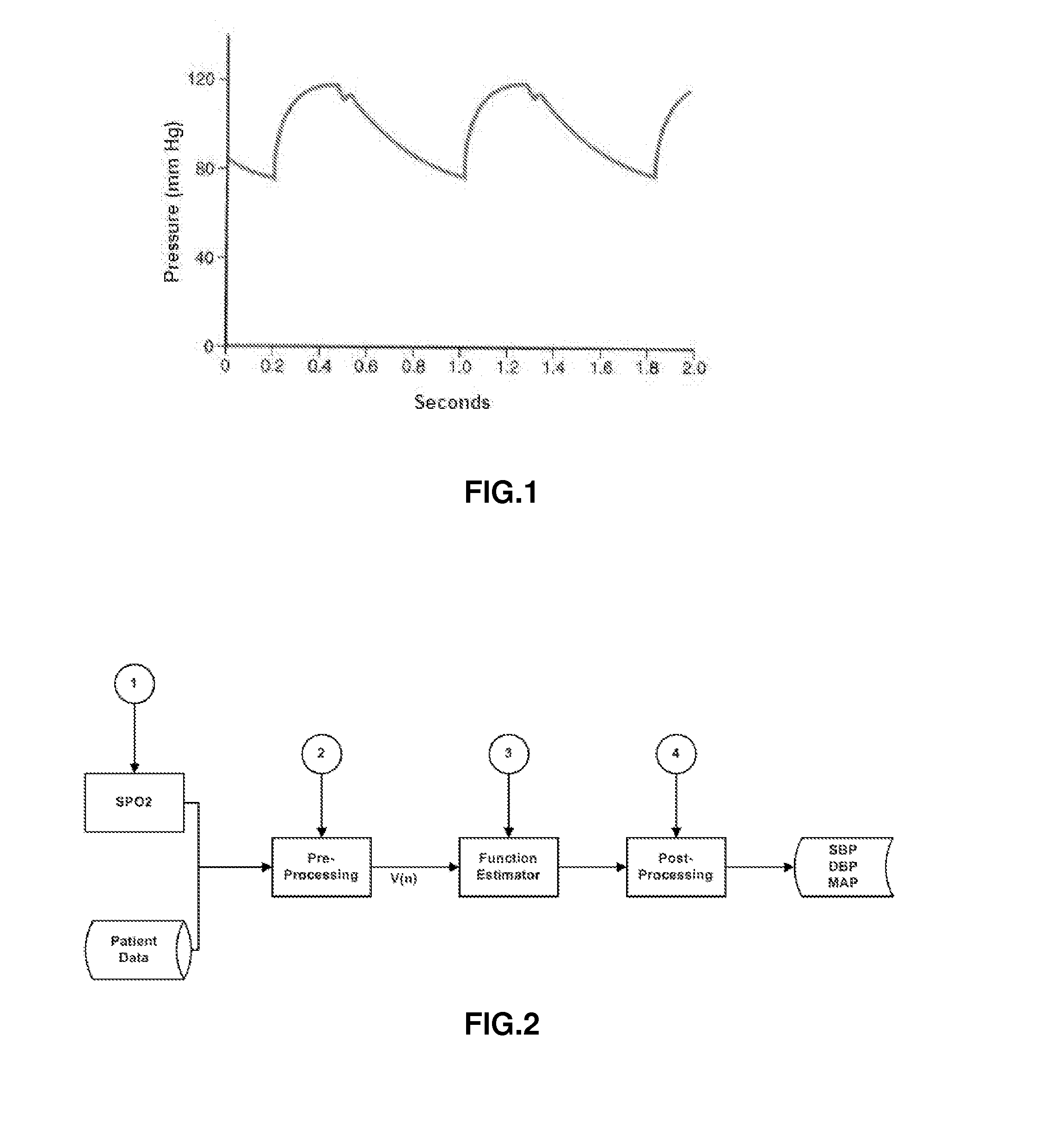
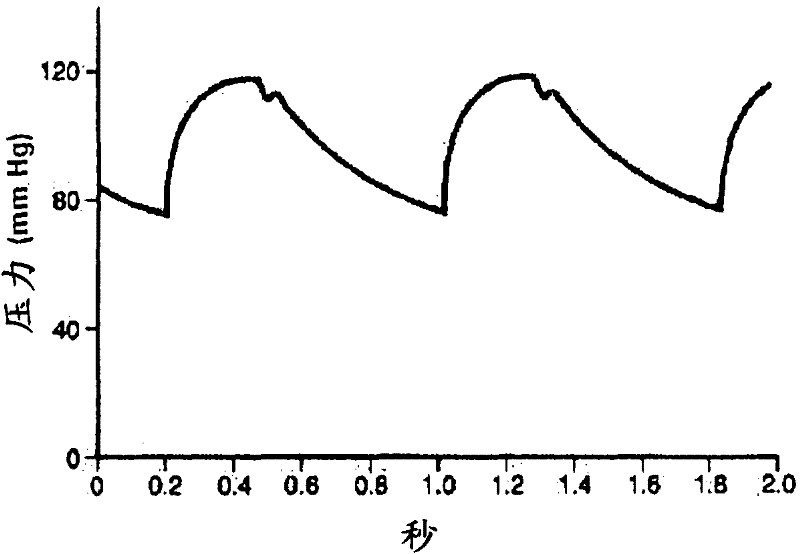
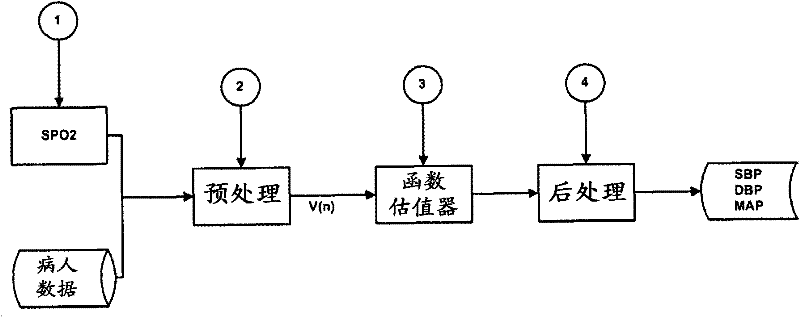
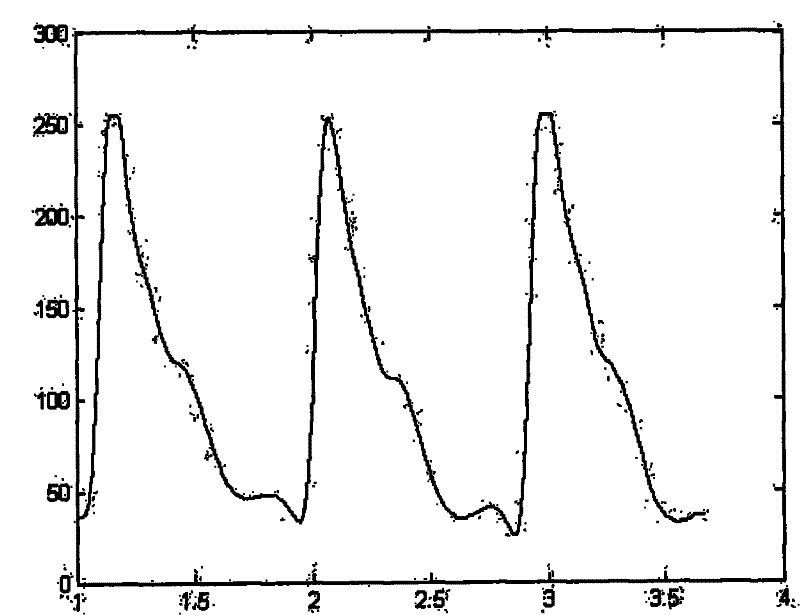
The present invention relates to a system for the estimation of the systolic (SBP), diastolic (DBP) and average (MAP) blood pressure. Said system establishes a physiological model of the pulse wave combined with its energy for, afterwards, generating a fixed length vector containing the previous model's values with other variables related to the user like, for example, age, sex, height, weight, etc. . . . This fixed length vector is used as an input of a function estimator system based on “random forests” for the calculation of the three variables of interest. The main advantage of this function estimator lies in that it does not impose any restriction beforehand over the function to be estimated, and it is also very reliable with heterogeneous data, as in the present invention's case.
Owner:SABIRMEDICAL
System and apparatus for the non-invasive measurement of blood pressure
Owner:SABIRMEDICAL
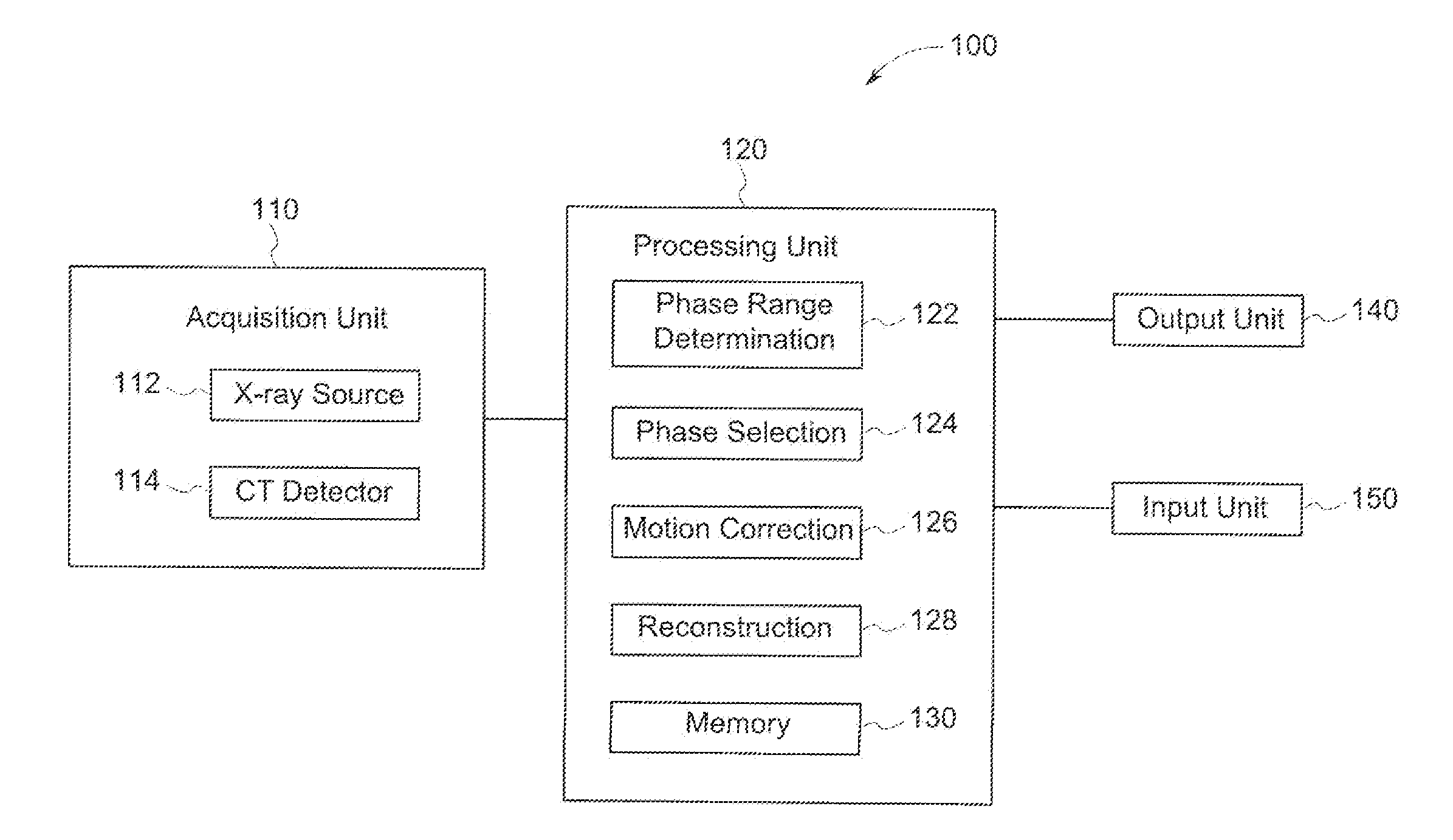
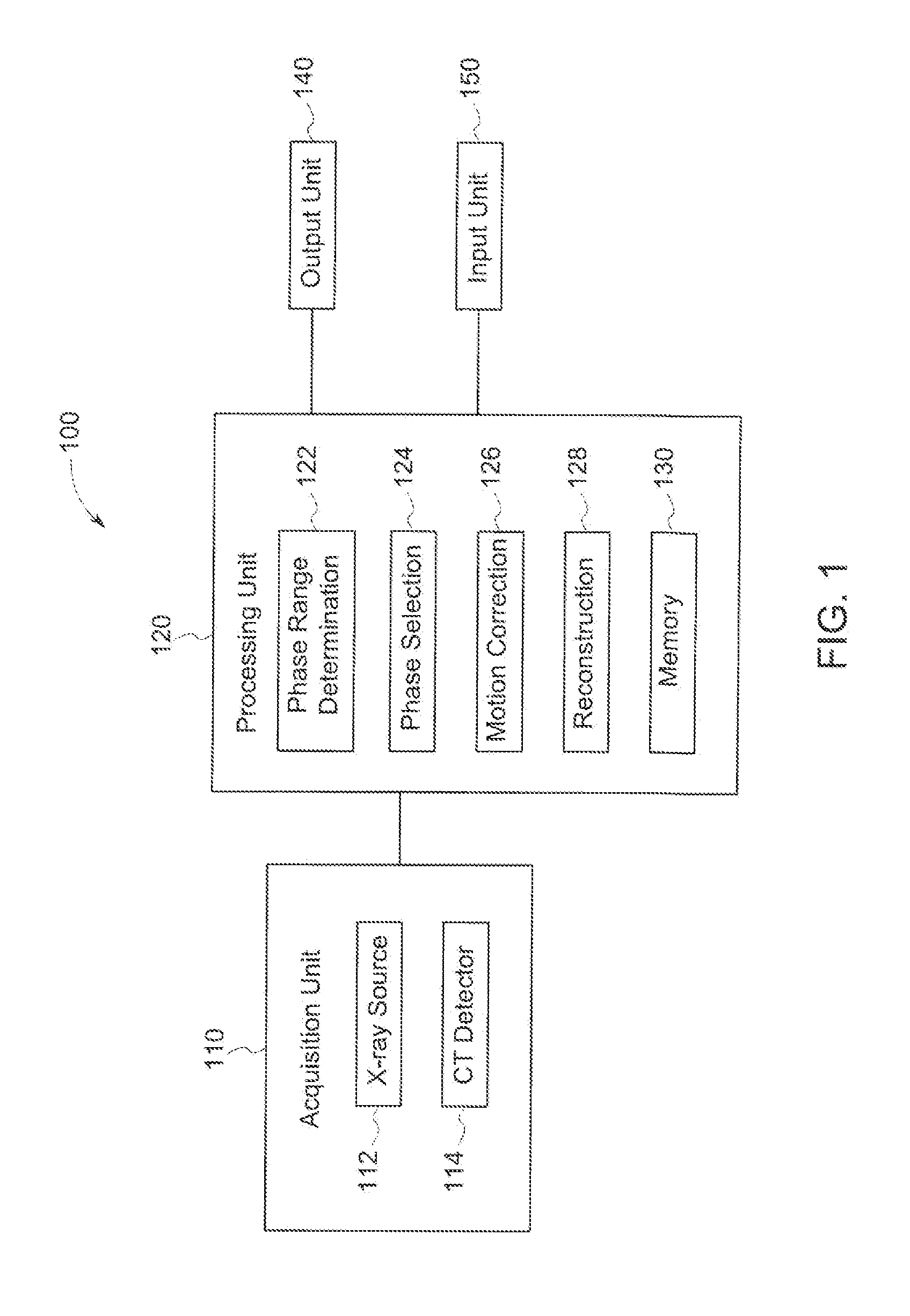
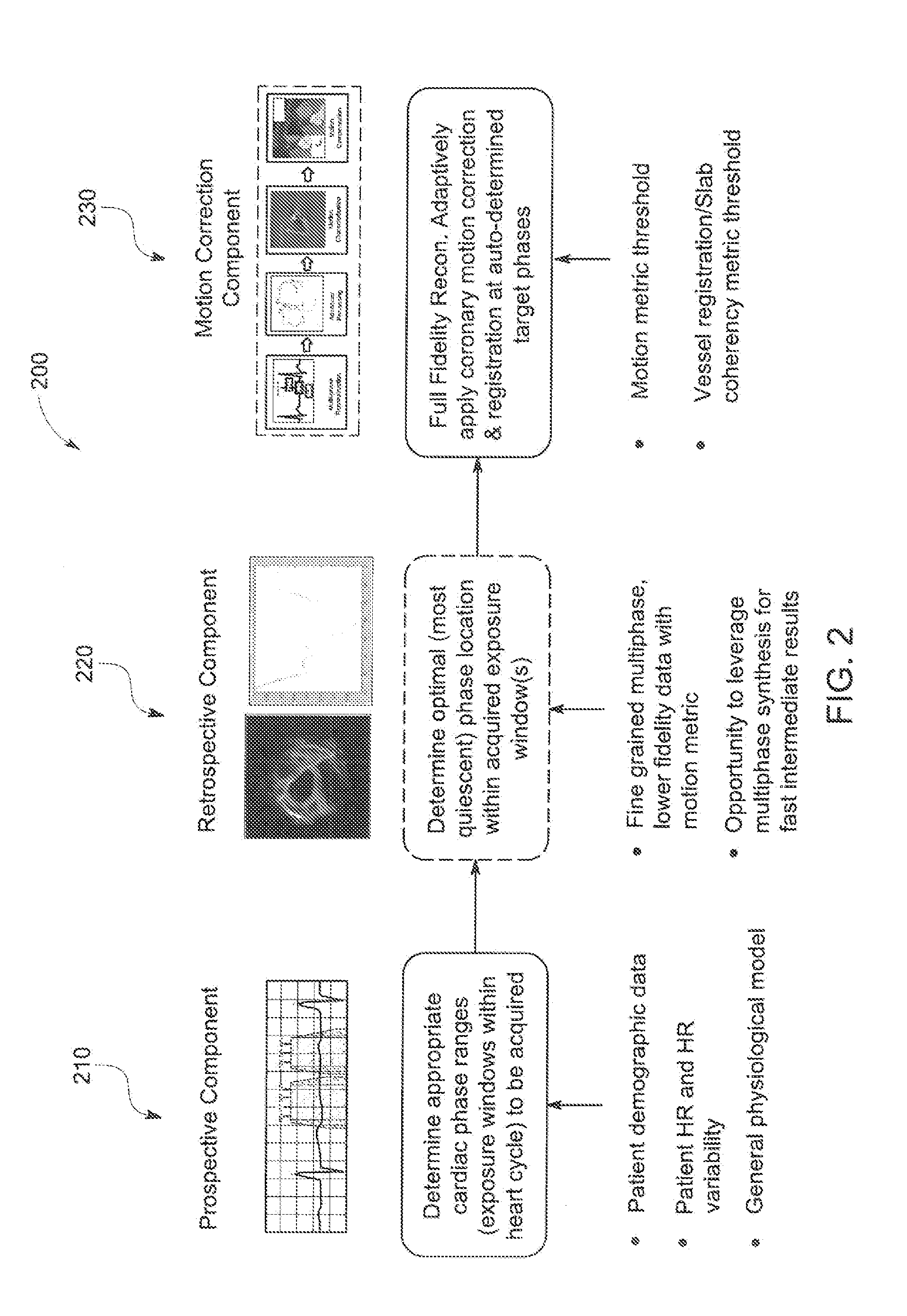
Systems and methods for coronary imaging
A method is provided including determining at least one range of phases of a cardiac cycle from which to select a selected phase based on at least one of patient demographic information, patient physiological information, or a general physiological model. The method also includes generating corresponding intermediate images for each of the phases of the at least one range of phases. Further, the method includes selecting the selected phase based on at least one image quality (IQ) metric of the intermediate images. Also, the method includes generating an image for diagnostic use using imaging information from the selected phase.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods, systems, and devices for optimal positioning of sensors
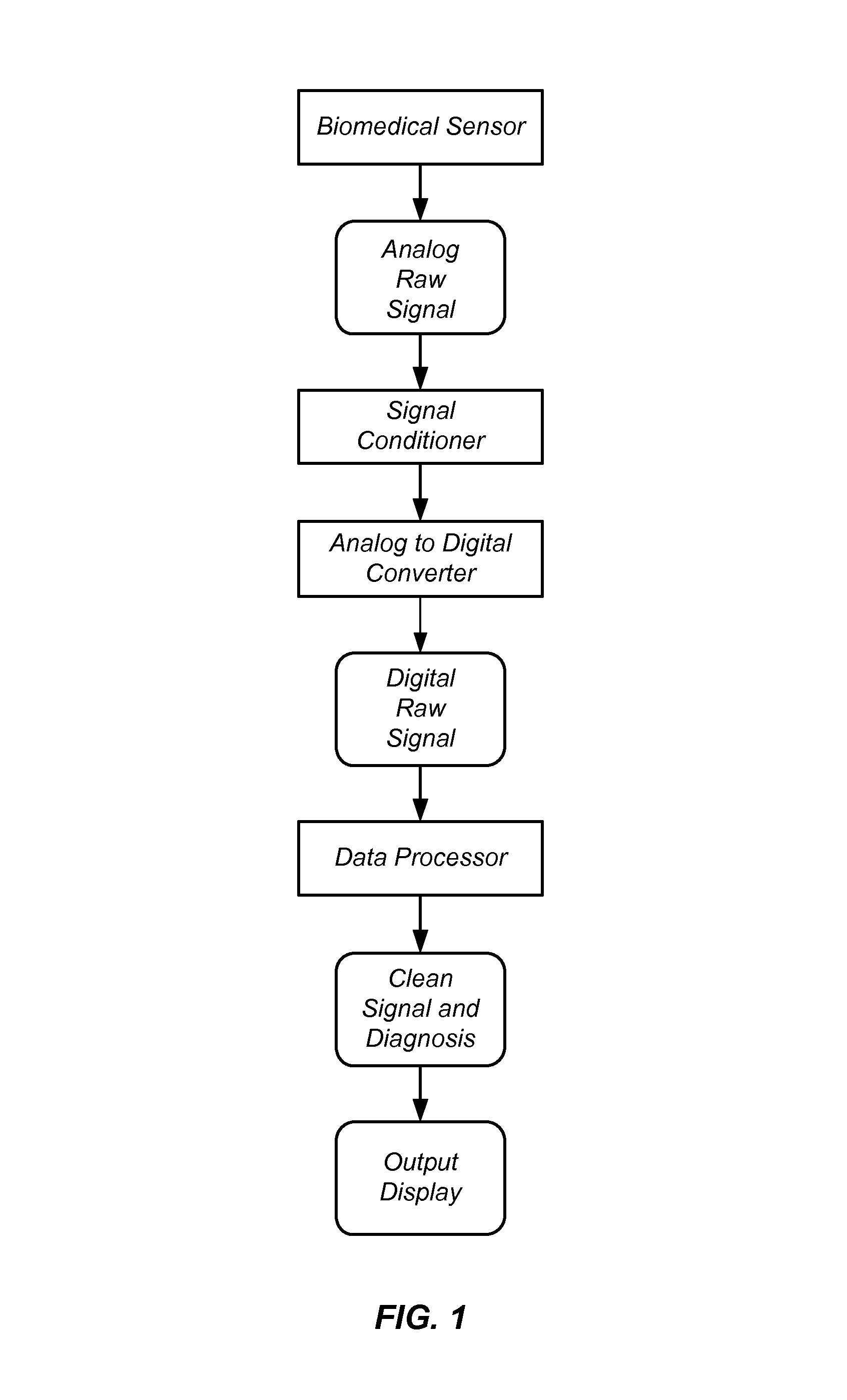
ActiveUS20160317088A1Easy to FeedbackWay accurateElectroencephalographyElectromyographyBiomedical sensorsTest measurement
A biomedical sensor has conducting elements disposed at least partly over a skin-facing surface. A sensing element detects a signal representative of a physiological parameter of a body using the conducting elements. A storage device stores a physiological model. A processor determines sensor placement quality by comparing the signal to the model and operates an indicator to indicate the determined quality. A method of measuring using the sensor includes computing a measurement acceptance criterion using numerous measurements, determining whether a subsequent test measurement corresponds to the measurement acceptance criterion obtained from the computing step, and indicating the results via the indicator. A system for measuring a physiological property of the body includes the sensor, a user interface device to receive measurements from the sensor, and a processor associated with the user interface device and configured to provide feedback if the measurement does not meet a selected acceptance criterion.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
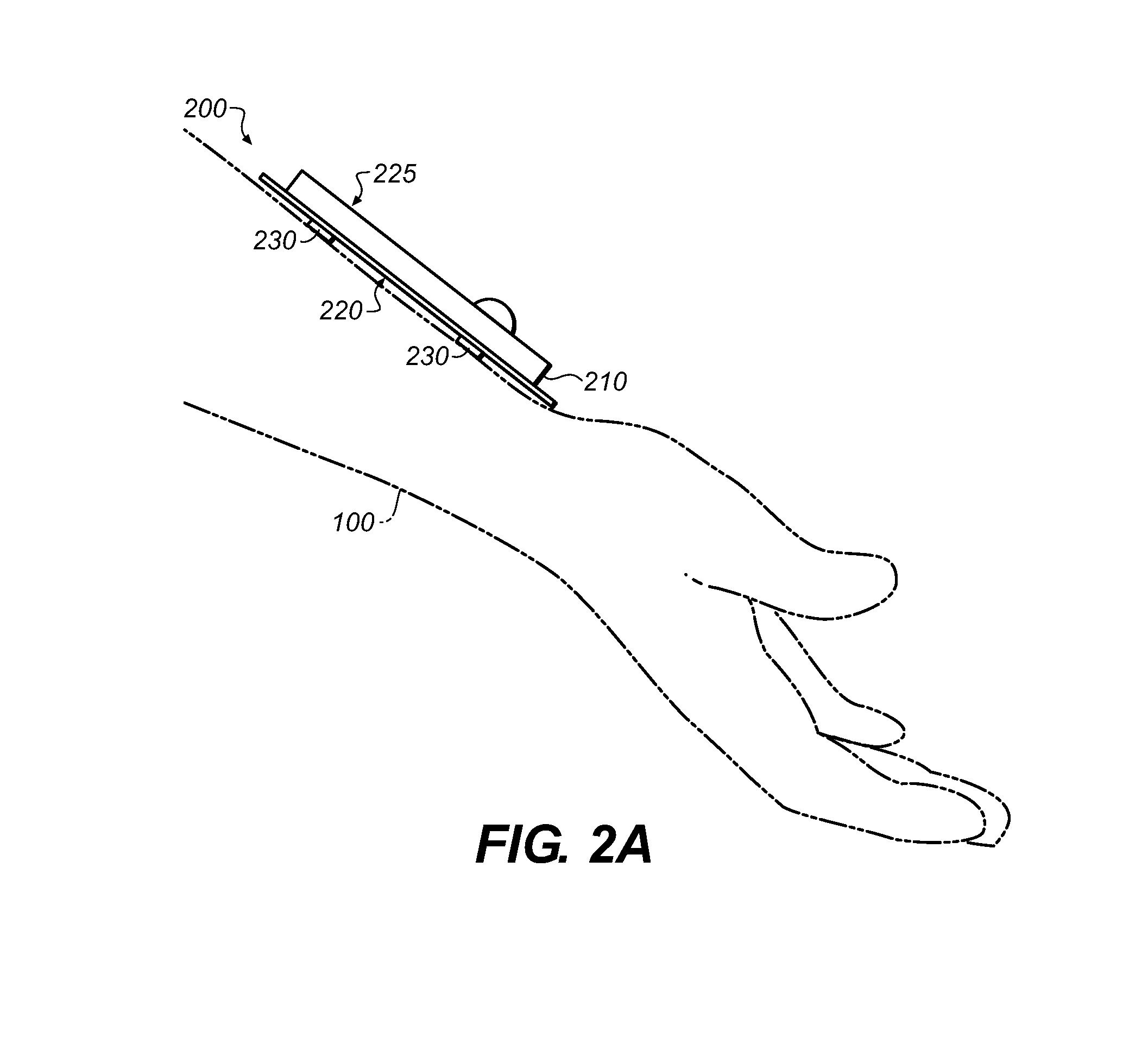
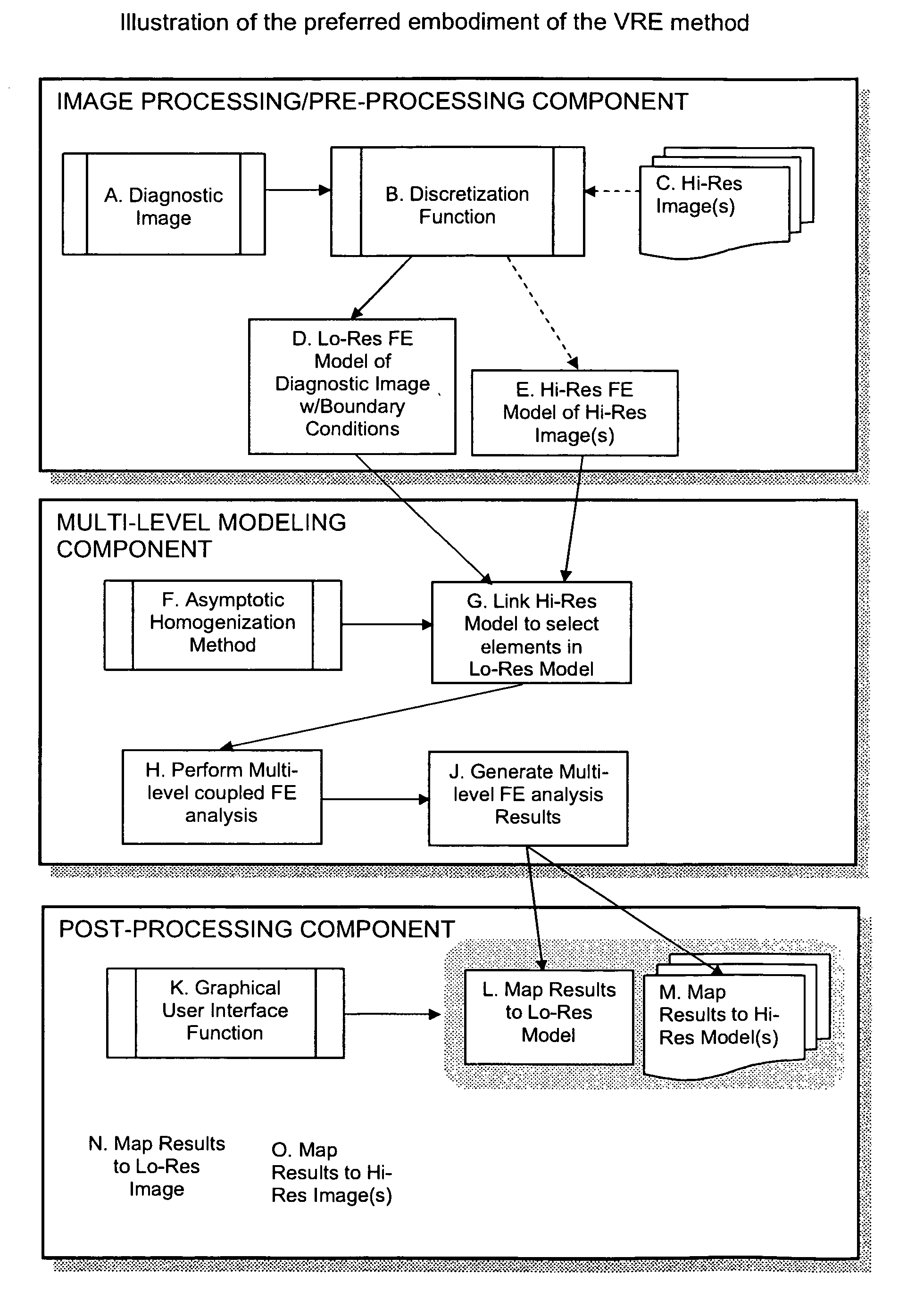
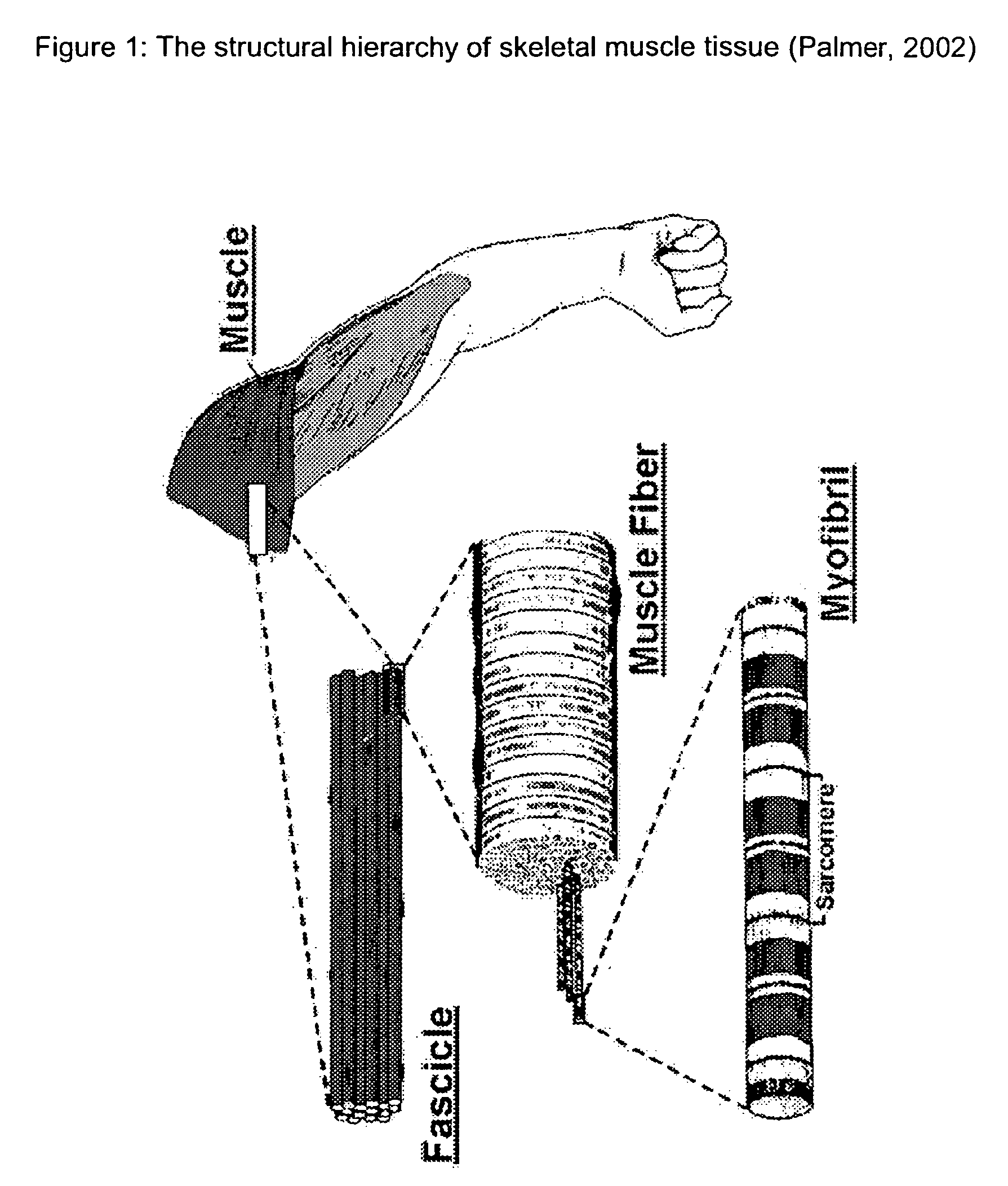
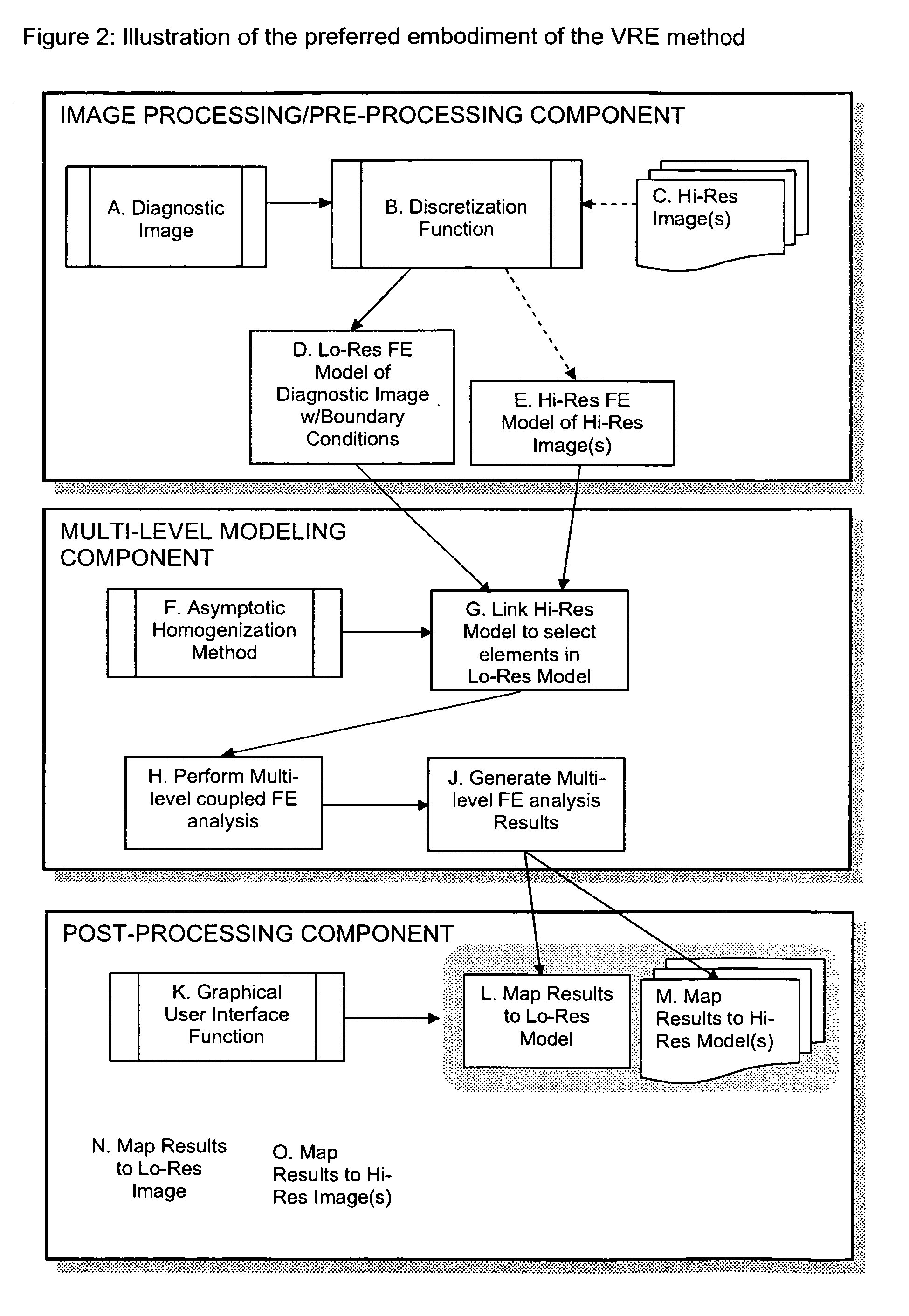
Virtual resolution enhancement in diagnostic imaging using FEA
InactiveUS20070014459A1Low costCheap imaging modalityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionDiscretization
A method is described for achieving resolutions beyond the resolution of a diagnostic imaging using multilevel computational analysis. This is accomplished by coupling the diagnostic image with images obtained at higher resolutions or with physiological models constructed at size scales beyond the resolution of the original diagnostic image. Using a discretization function, the image data or models are converted or generated so that they can be processed by a multilevel computational analysis function. The multilevel analysis then mathematically couples the models across two or more length scales generating parameters of interest at each level of analysis. A post-processing function provides the interface for the user to view the parameters of interest in the model derived from the original diagnostic image and / or the image itself and then “zoom-in” to a region by accessing the higher resolution image and / or model associated with it and viewing the parameters of interest.
Owner:PALMER MARK L
Rice plant type quantitative control method integrating crop virtual growth model
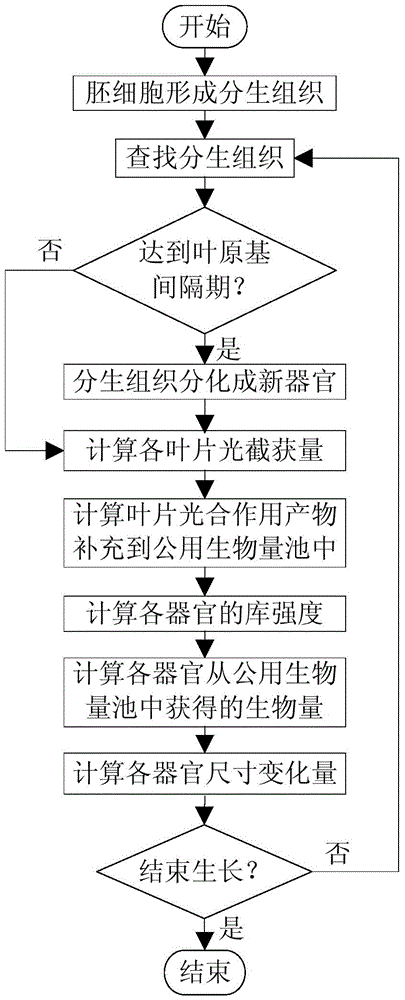
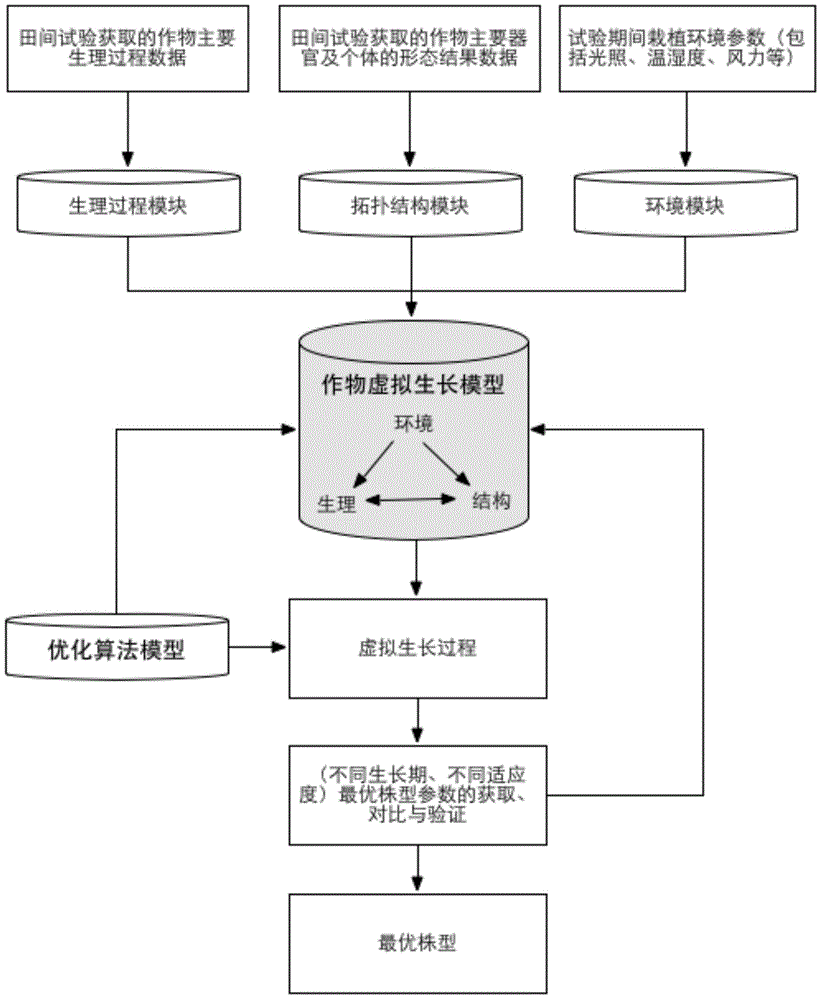
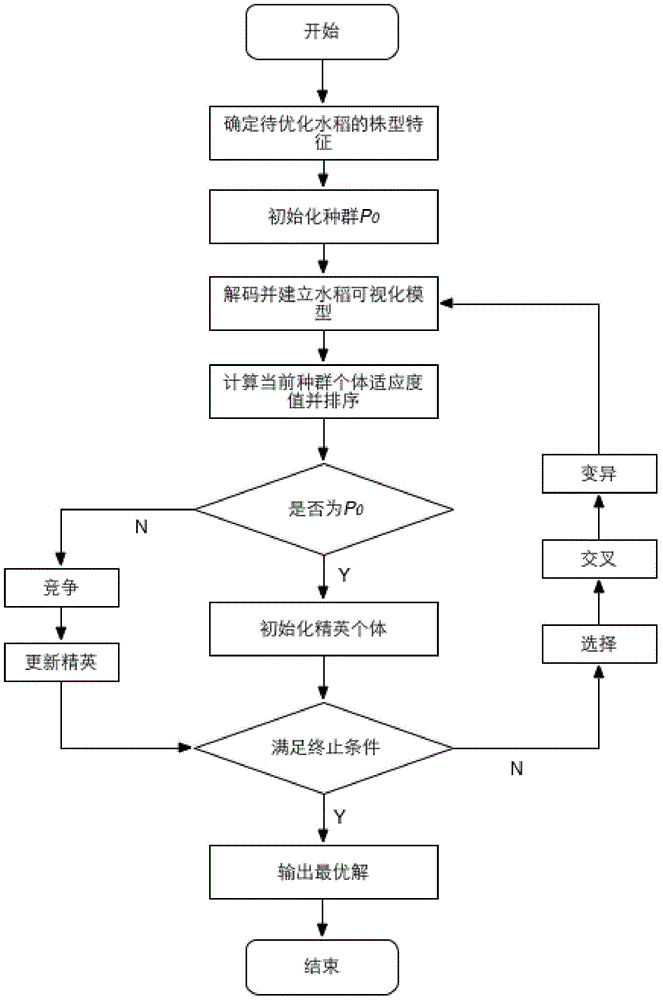
ActiveCN104376142AEasy to breedImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applications3D modellingEnvironmental modelPhysiological model
Provided is a rice plant type quantitative design method integrating a crop virtual growth model. The crop virtual growth model is constructed, effective correlation and combination of the main plant physiological process, morphological structures and a light environmental model are achieved, and visual virtual growth of crop plants can be achieved; in the crop virtual growth model, morphologies of crops at different growth periods are set up through a structure model, a physiological model is used for realizing dynamic prediction of production, distribution and final yield of crop assimilates, and the light environmental model is used for computing crop canopy light radiation quantity and crop individual fractional interception of photosynthetic active radiation; the crop plant type structure is continuously changed through an optimization algorithm, so that simulation results of different adaption degrees are obtained, and the optimal crop plant type based on different targets can be obtained; the different adaption degrees are used as optimization results of the targets and set as morphological parameters of the virtual growth model, analog operation is carried out, horizontal and longitudinal comparison is carried out, and the optimal plant type data of crops are verified and determined.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus for processing physiological sensor data using a physiological model and method of operation therefor
A pulse oximeter system comprises a data processor configured to perform a method that combines a sigma point Kalman filter (SPKF) or sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) algorithm with Bayesian statistics and a mathematical model comprising a cardiovascular model and a plethysmography model to remove contaminating noise and artifacts from the pulse oximeter sensor output and measure blood oxygen saturation, heart rate, left-ventricular stroke volume, aortic pressure and systemic pressures.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
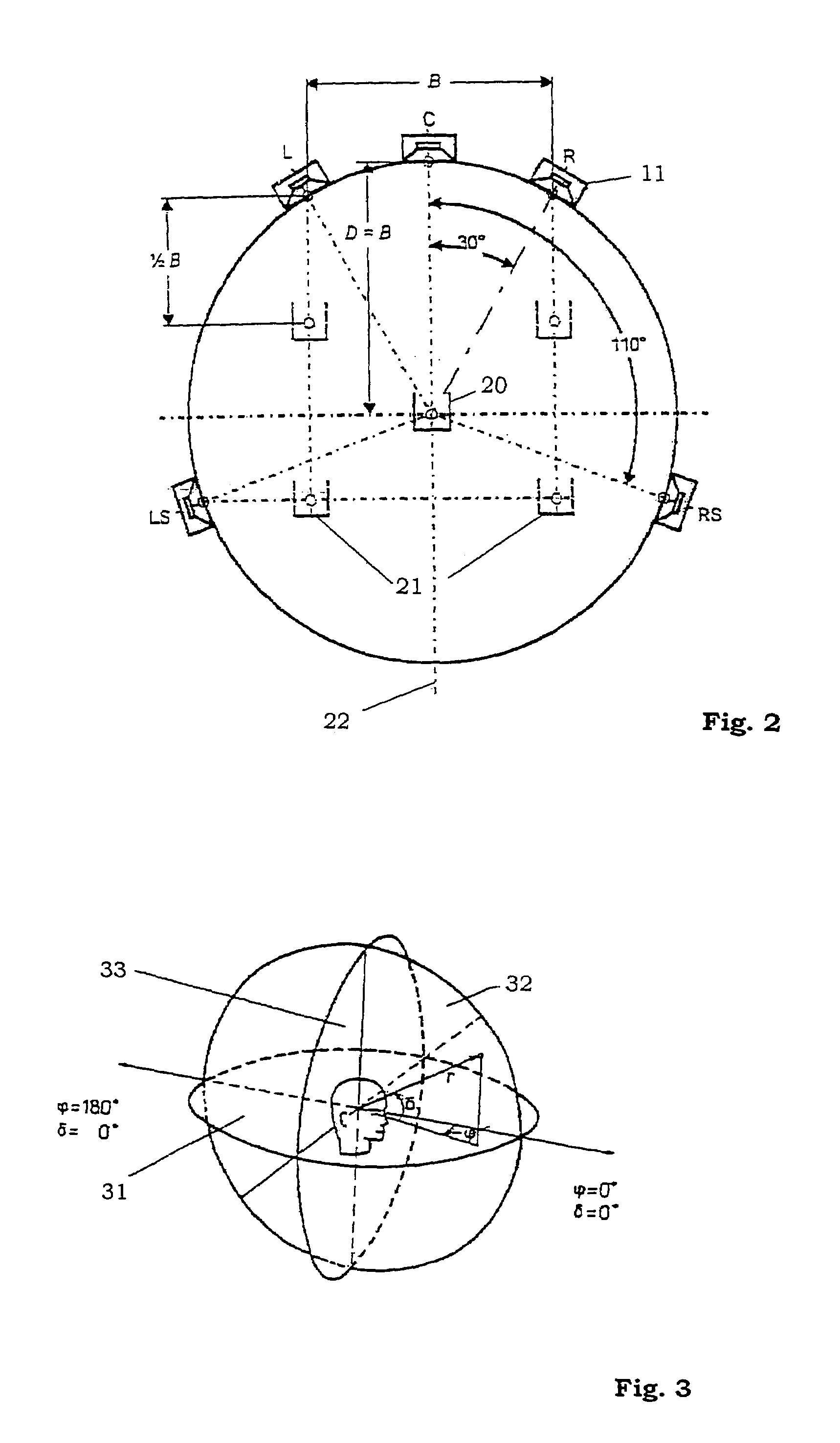
System for determining the position of a sound source
ActiveUS7386133B2Cutting can not be obtainedPosition fixationDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesPhysiological model
A method and system for determining the position of a sound source in relation to a reference position, comprising the steps of generating a sound signal emitted from the sound source, detecting the emitted sound signal, processing the sound signal by the use of a physiological model of the ear, deducing at least one of lateral deviation in relation to the reference position, time delay of the sound signal from the sound source to the reference position, and the sound level of the detected sound signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com