Patents
Literature
365 results about "Respiratory motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
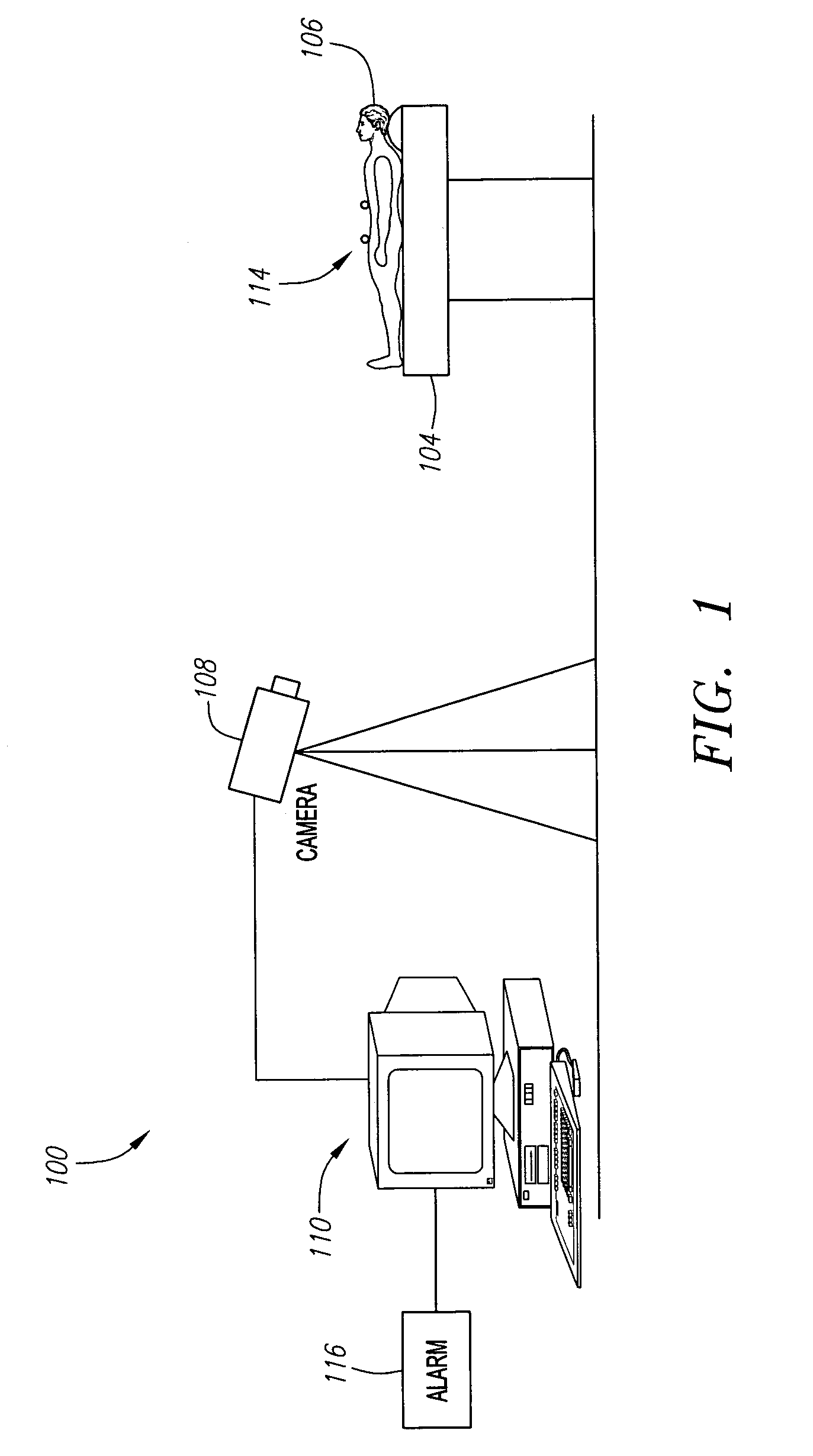
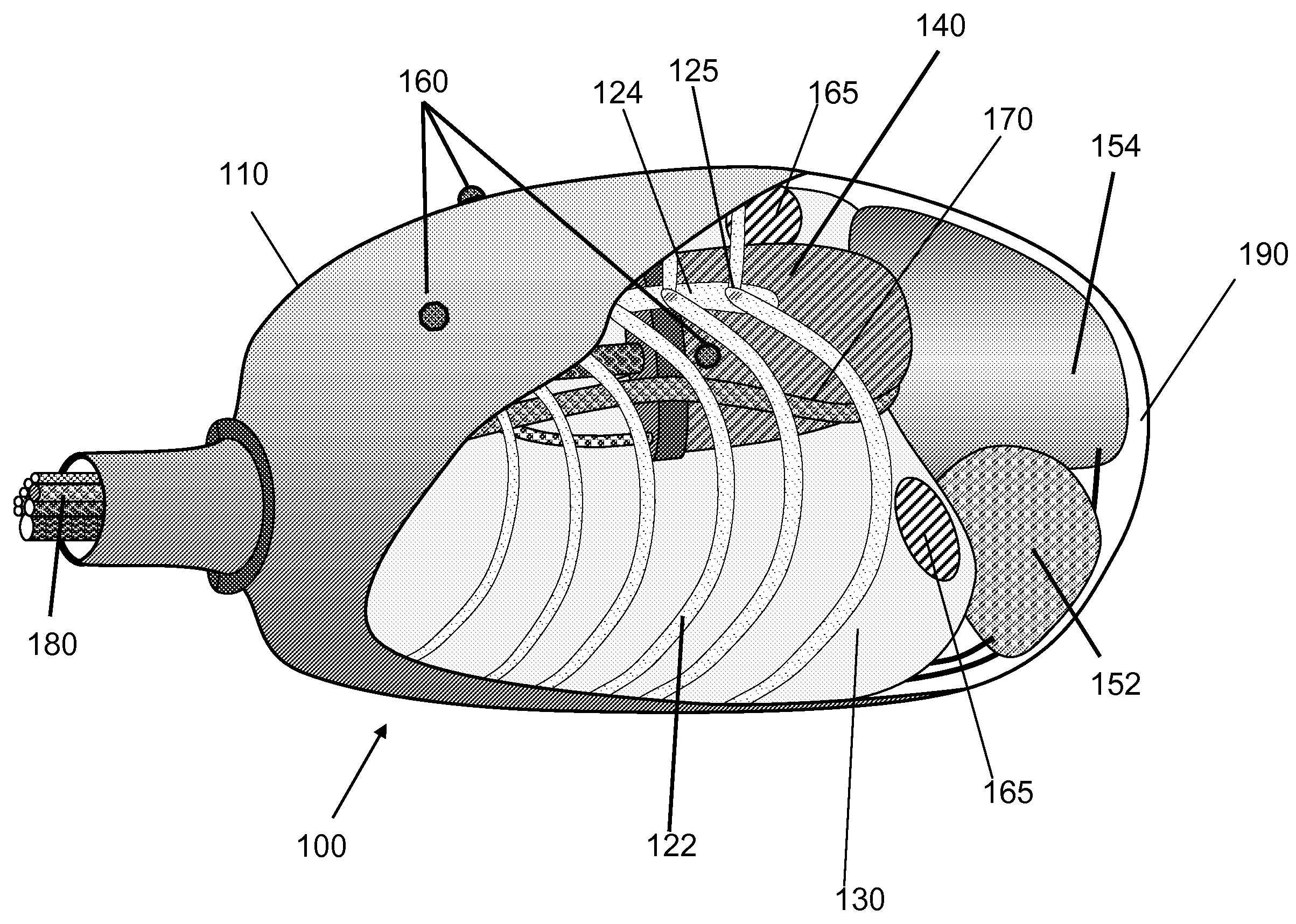
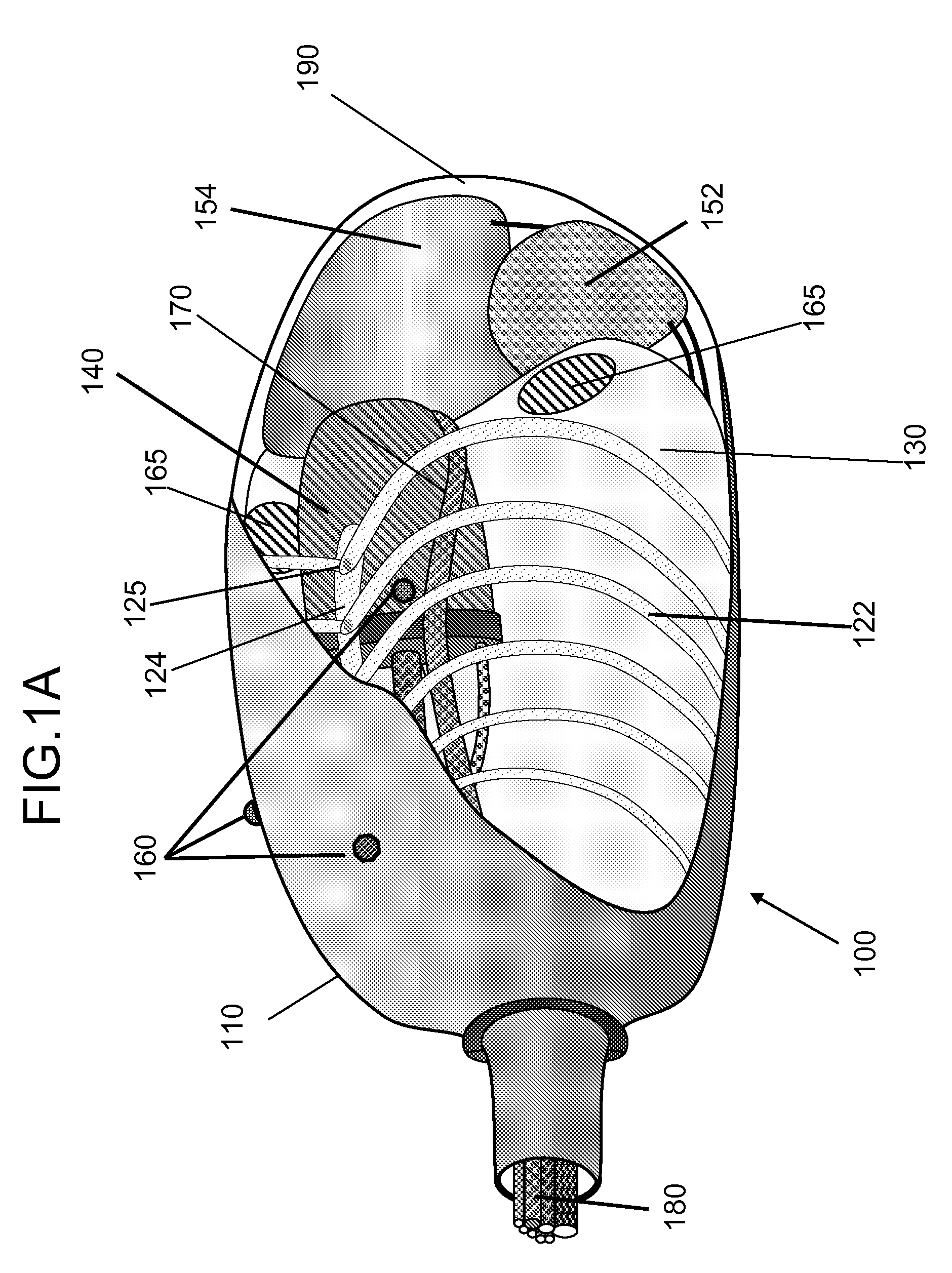
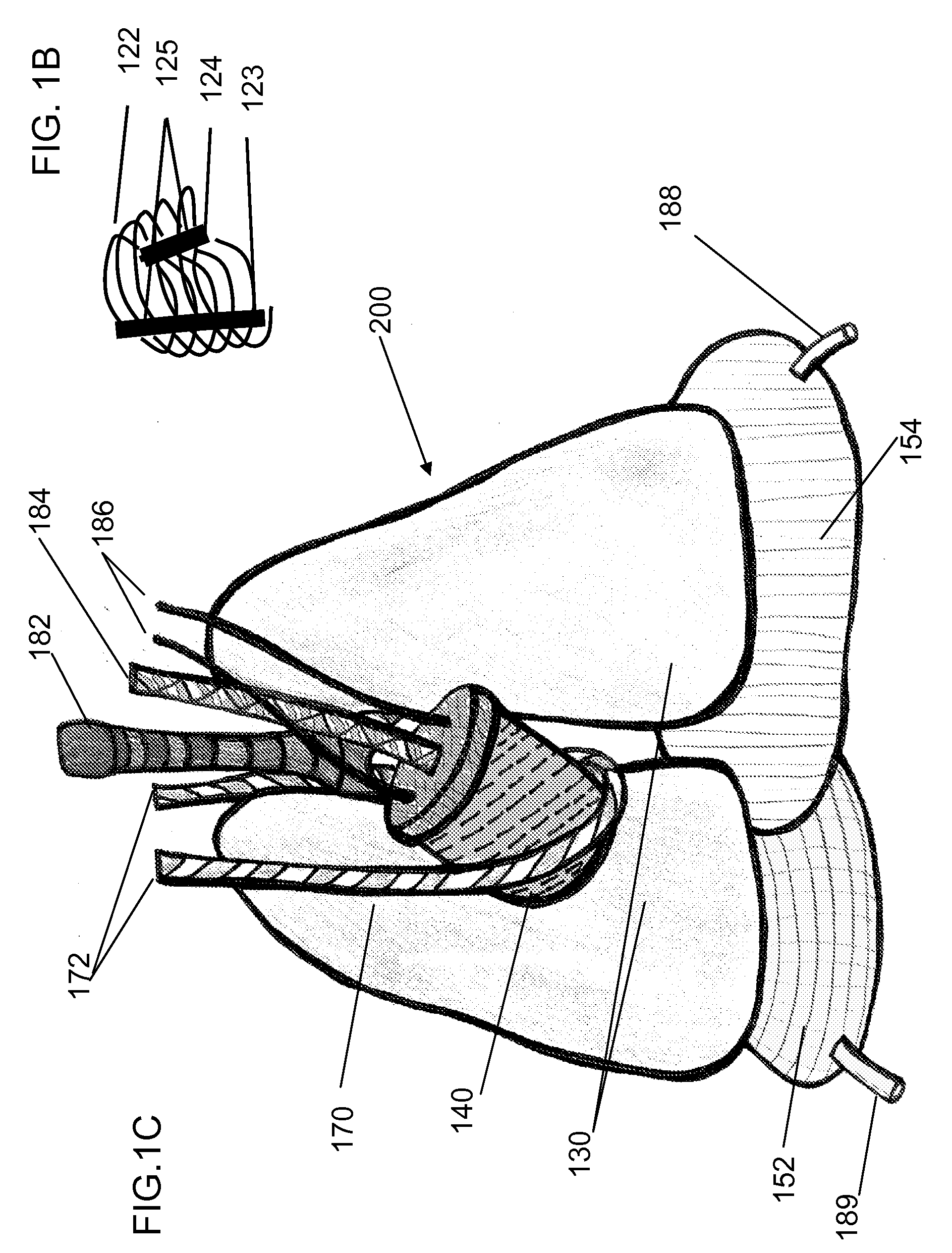
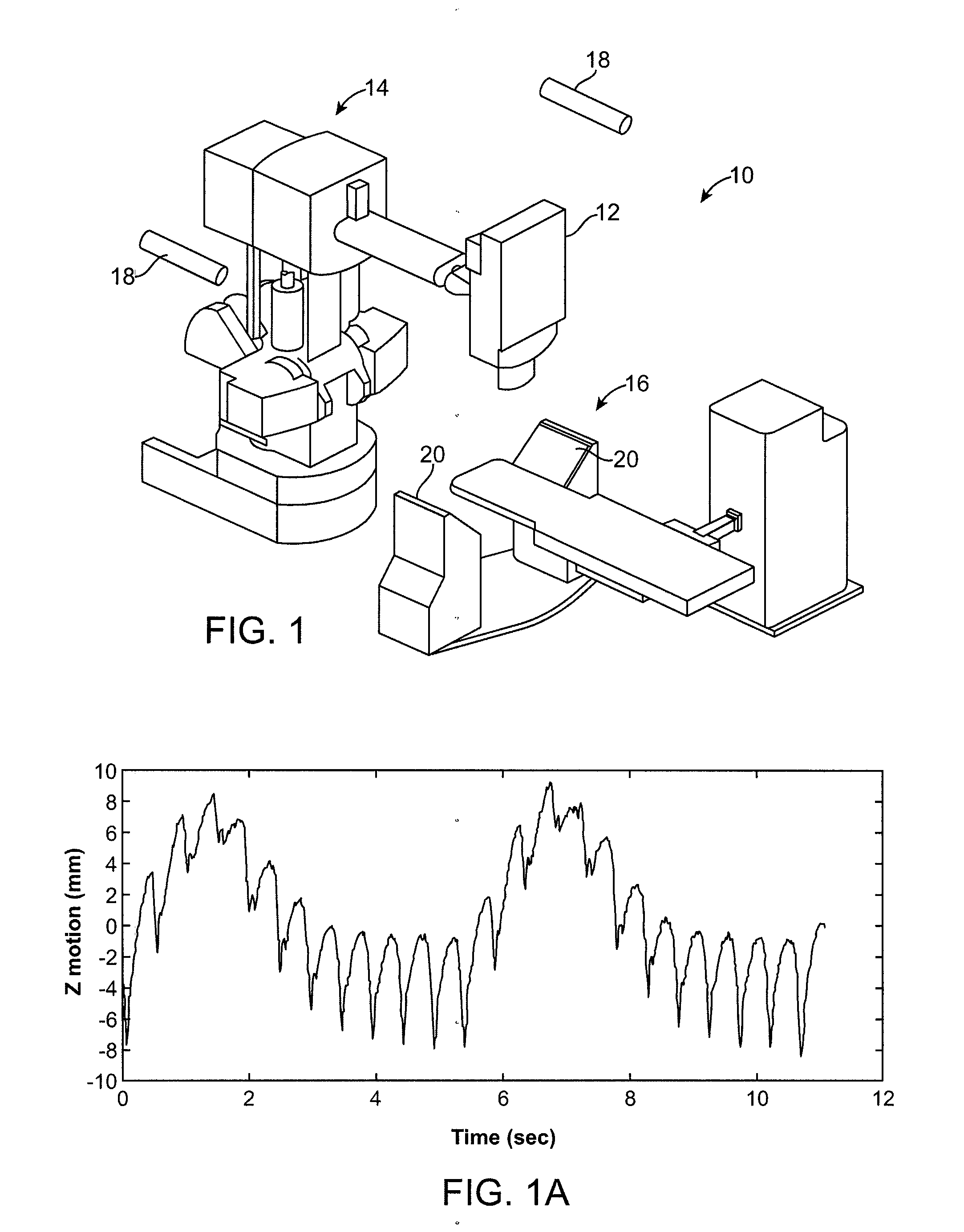
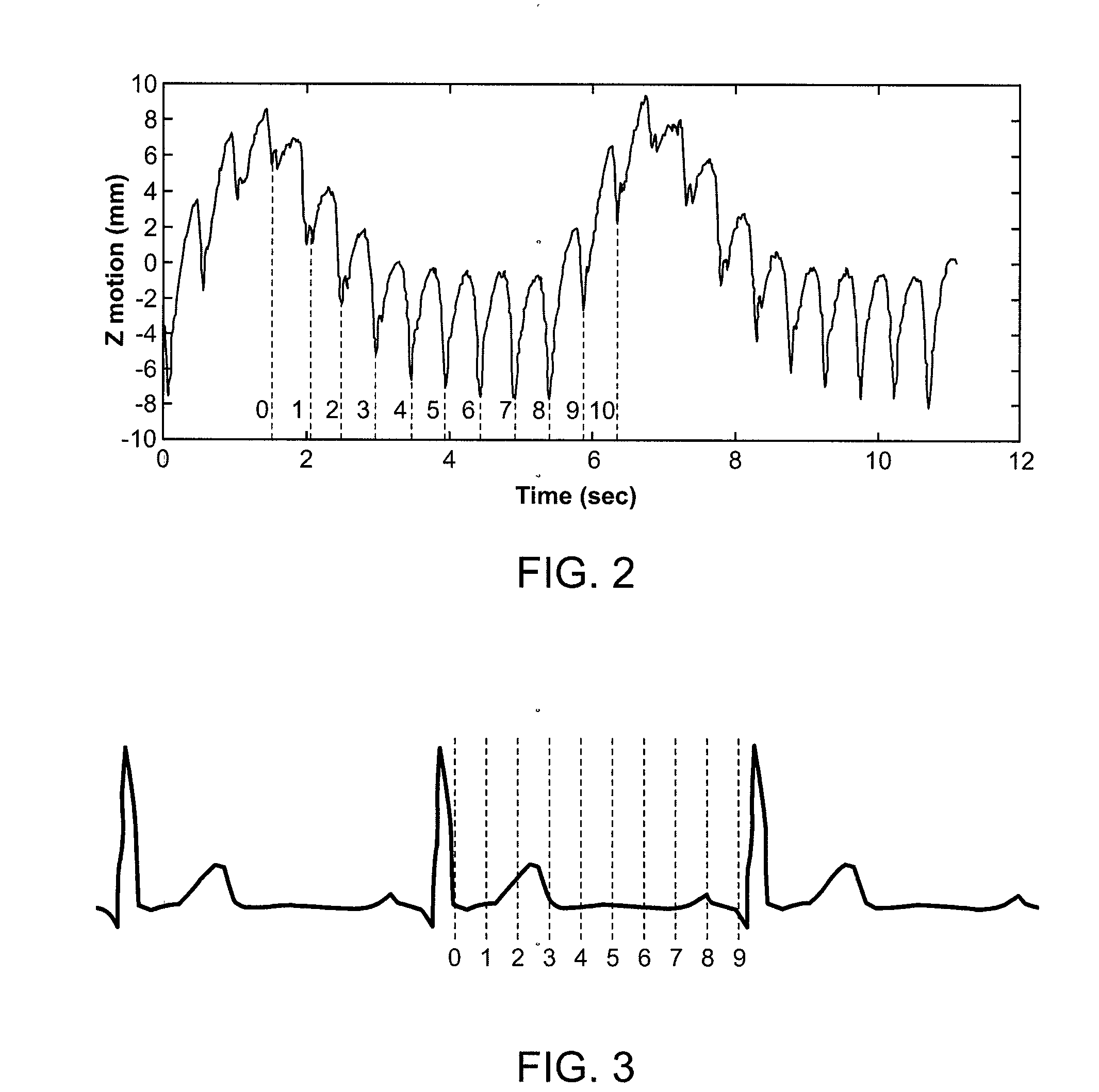
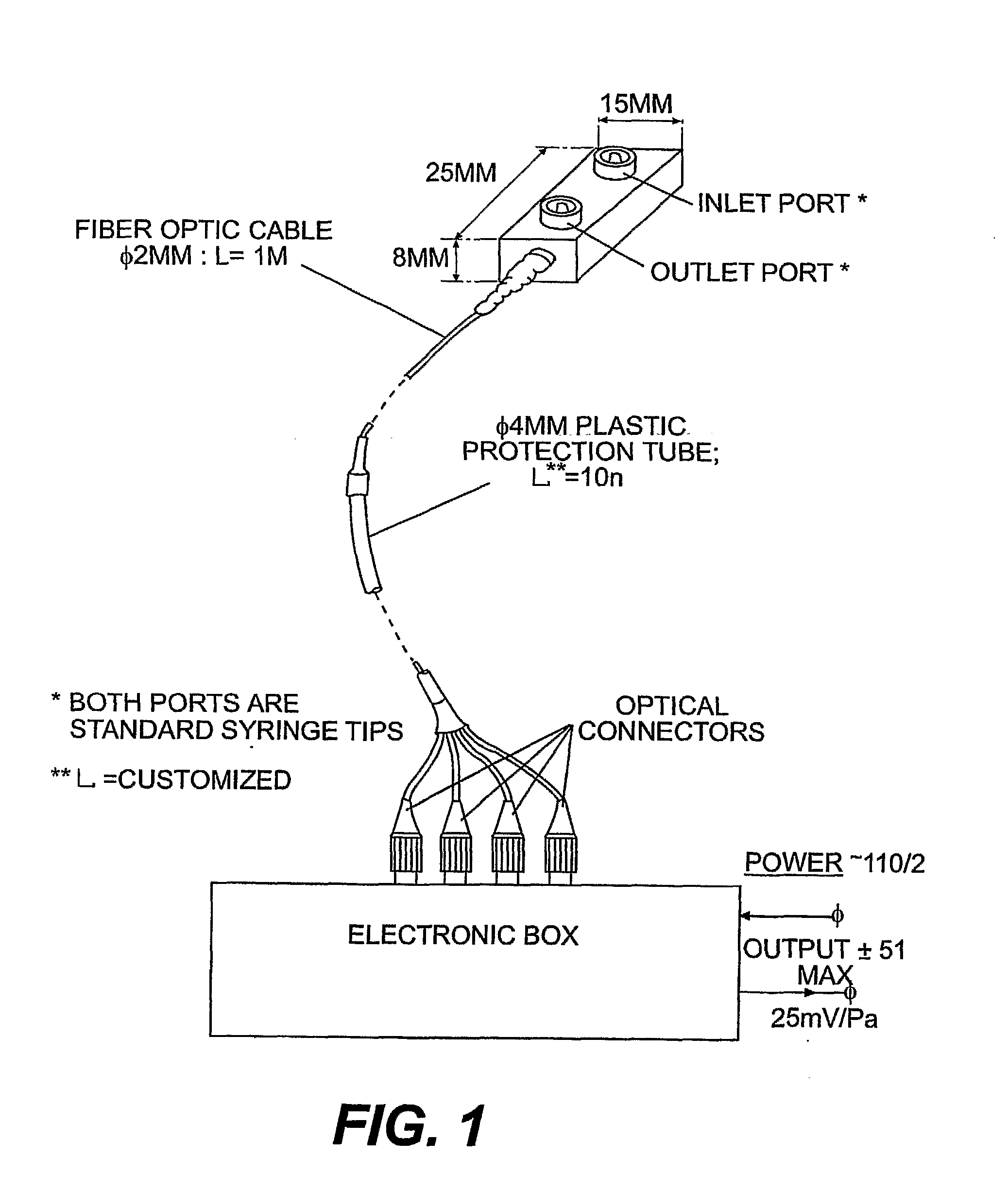
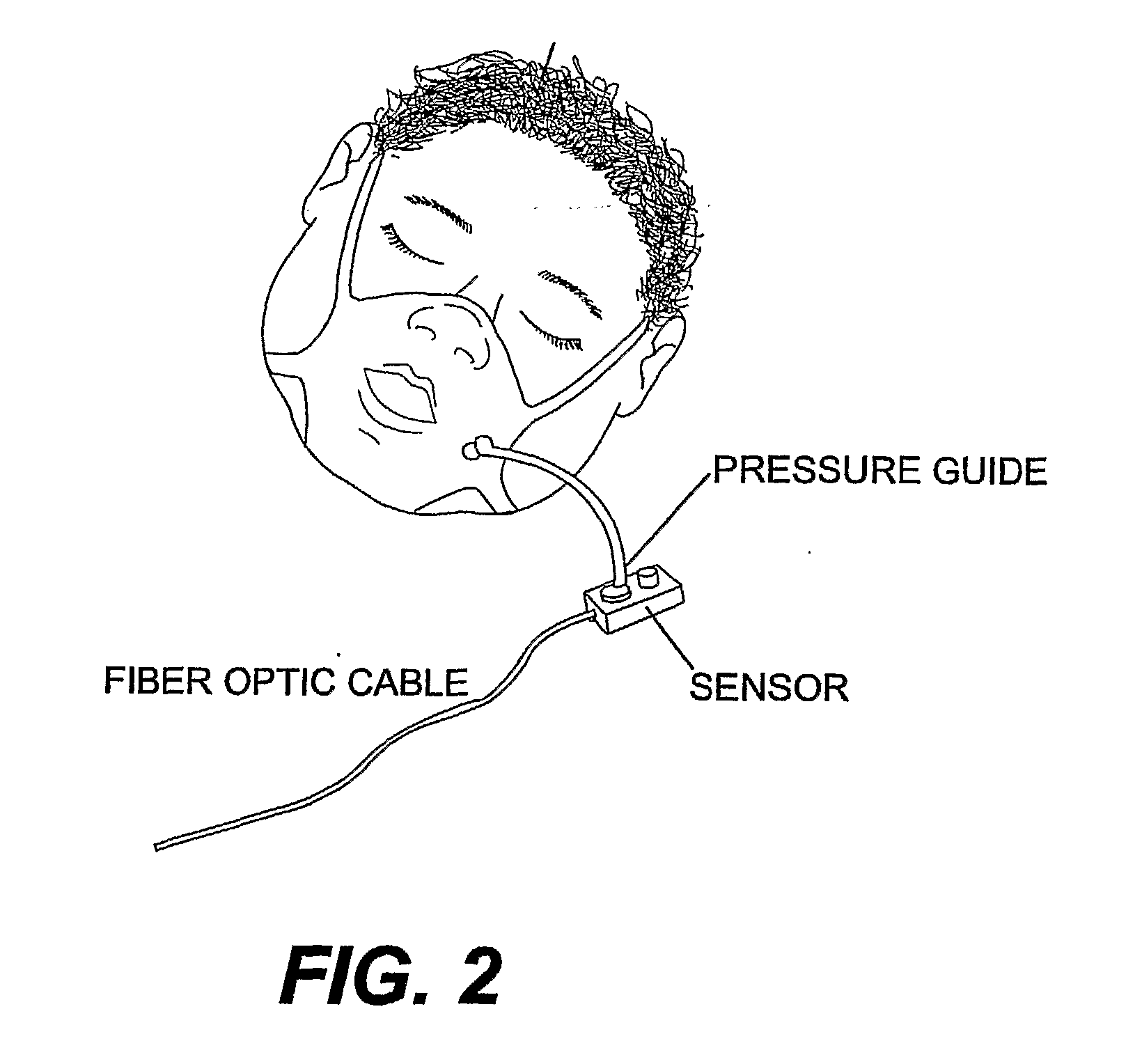
Respiration Motion Detection and Health State Assesment System
InactiveUS20070293781A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce bandwidth requirementsDiagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationBody shapeAccelerometer
A wearable platform embodied in a belt or flattened patch-like central body shaped to conform to the abdomen provides physiological monitoring of soldiers during field operations or trauma victims at accident sites and makes health state assessments. The platform includes sensors for heart rate, body motion, respiration rate and intensity, and temperature and further contains a microprocessor and short range transmitter. The respiration sensor uses conductive ink in a novel manner. A small square of the ink is coated on an arched structure so that flexing of the arch either to increase or decrease its radius of curvature modifies the resistance of the structure. This is utilized to set the unstressed resistance of the arch structure and to allow a greater range of resistance values capable of measuring distortions in different deformations of the arch. The respiration sensor supplements the motion information provided by an accelerometer sensor.
Owner:SIMS NATHANIEL +4
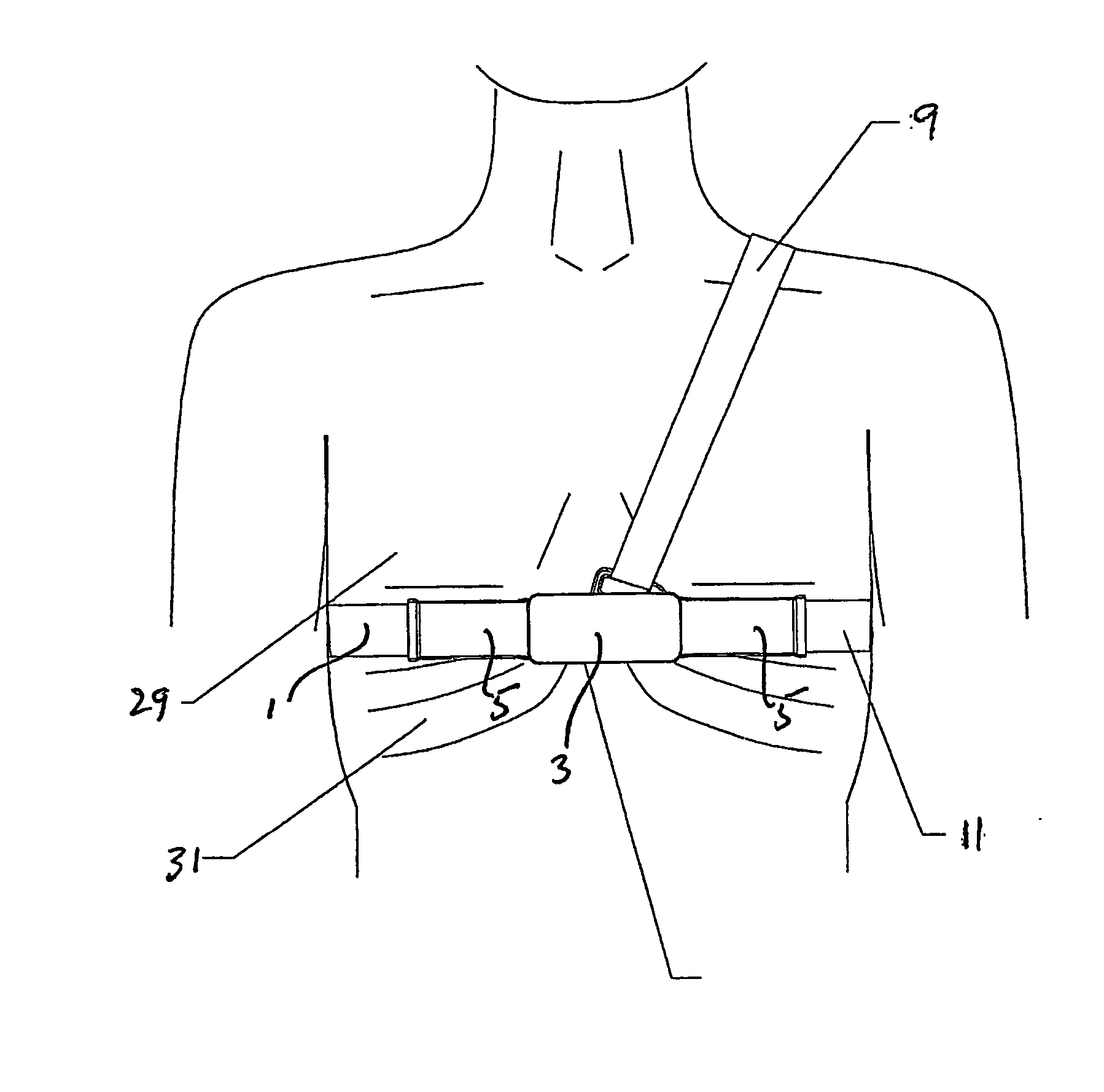
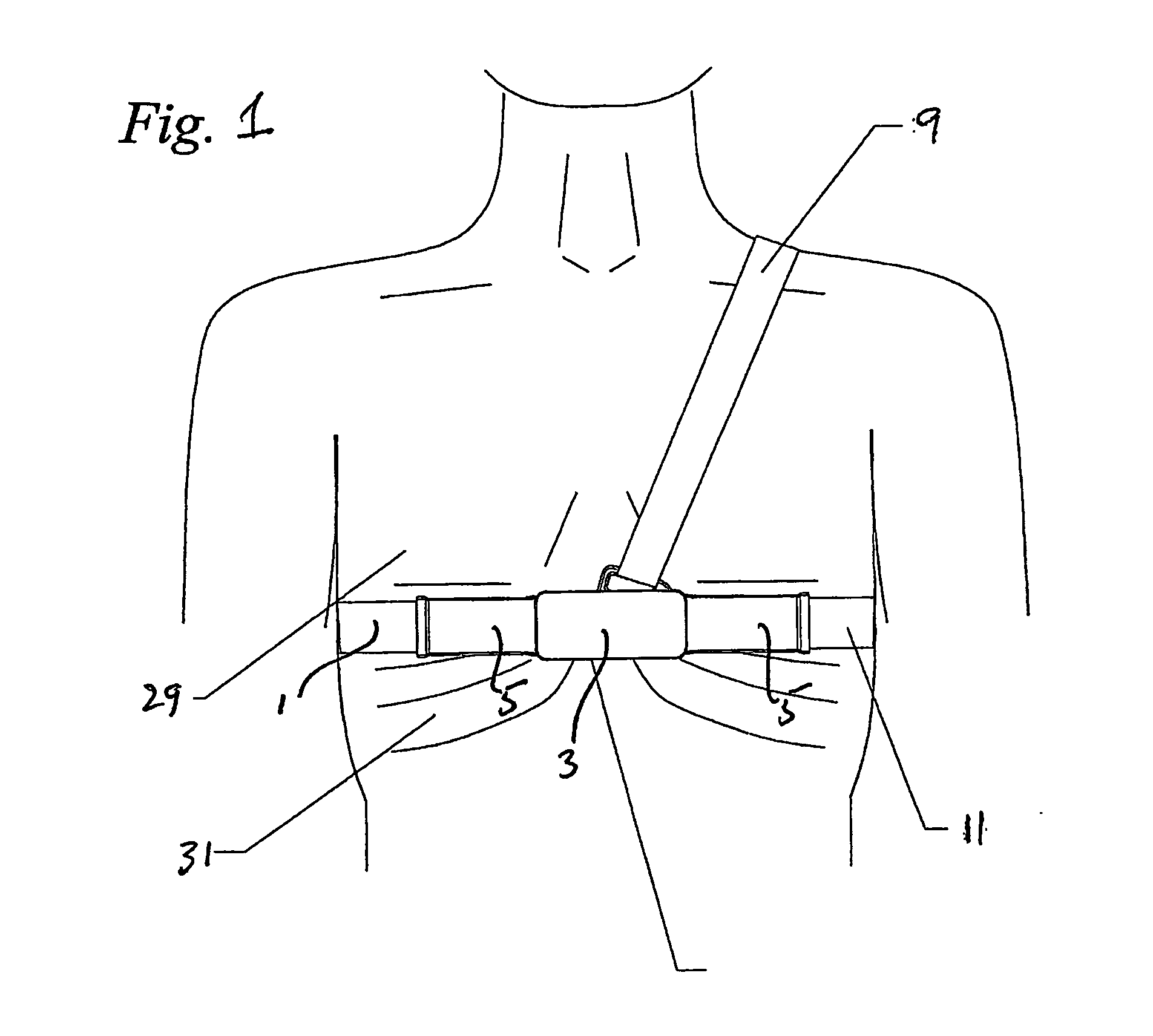
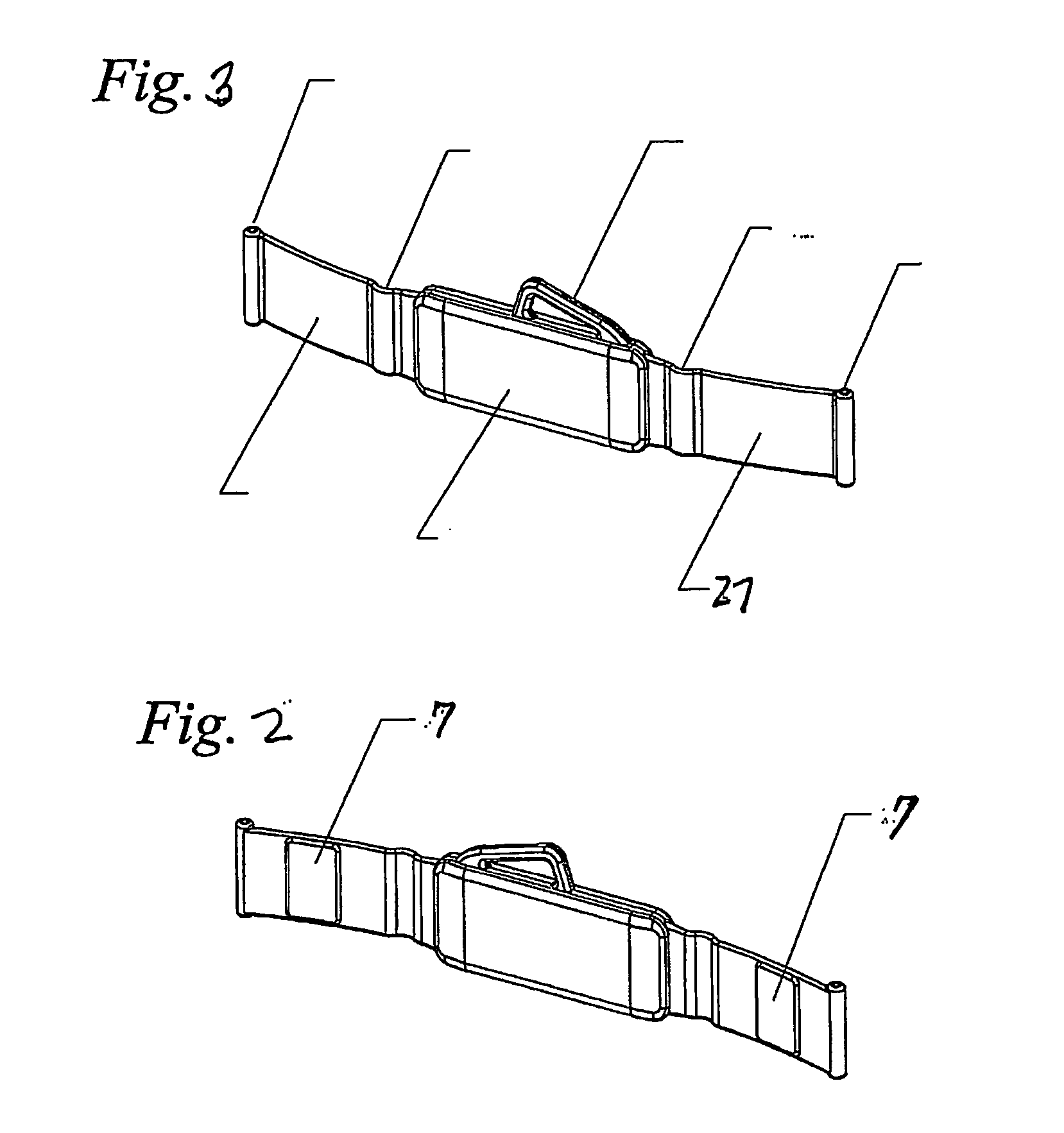
Apparatus and method for radiosurgery
A method and system is presented for treating moving target regions in a patient's anatomy by creating radiosurgical lesions. The method includes determining a pulsating motion of a patient separately from a determining of a respiratory motion, and directing a radiosurgical beam, from a radiosurgical beam source, to a target in the patient based on the determining of the pulsating motion. Directing the radiosurgical beam to the target may include creating a lesion in the heart to inhibit atrial fibrillation. The method may further include determining the respiratory motion of the patient, and compensating for movement of the target, due to the respiratory motion and the pulsating motion of the patient, in the directing of the radiosurgical beam based on the determining of the respiratory motion and the determining of the pulsating motion.
Owner:ACCURAY
System and method for patient positioning for radiotherapy in the presence of respiratory motion
A system and method for positioning a patient for radiotherapy is provided. The method comprises: acquiring a first x-ray image sequence of a target inside the patient at a first angle; acquiring first respiratory signals of the patient while acquiring the first x-ray image sequence; acquiring a second x-ray image sequence of the target at a second angle; acquiring second respiratory signals of the patient while acquiring the second x-ray image sequence; synchronizing the first and second x-ray image sequences with the first and second respiratory signals to form synchronized first and second x-ray image sequences; identifying the target in the synchronized first and second x-ray image sequences; and determining three-dimensional (3D) positions of the target through time in the synchronized first and second x-ray image sequences.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
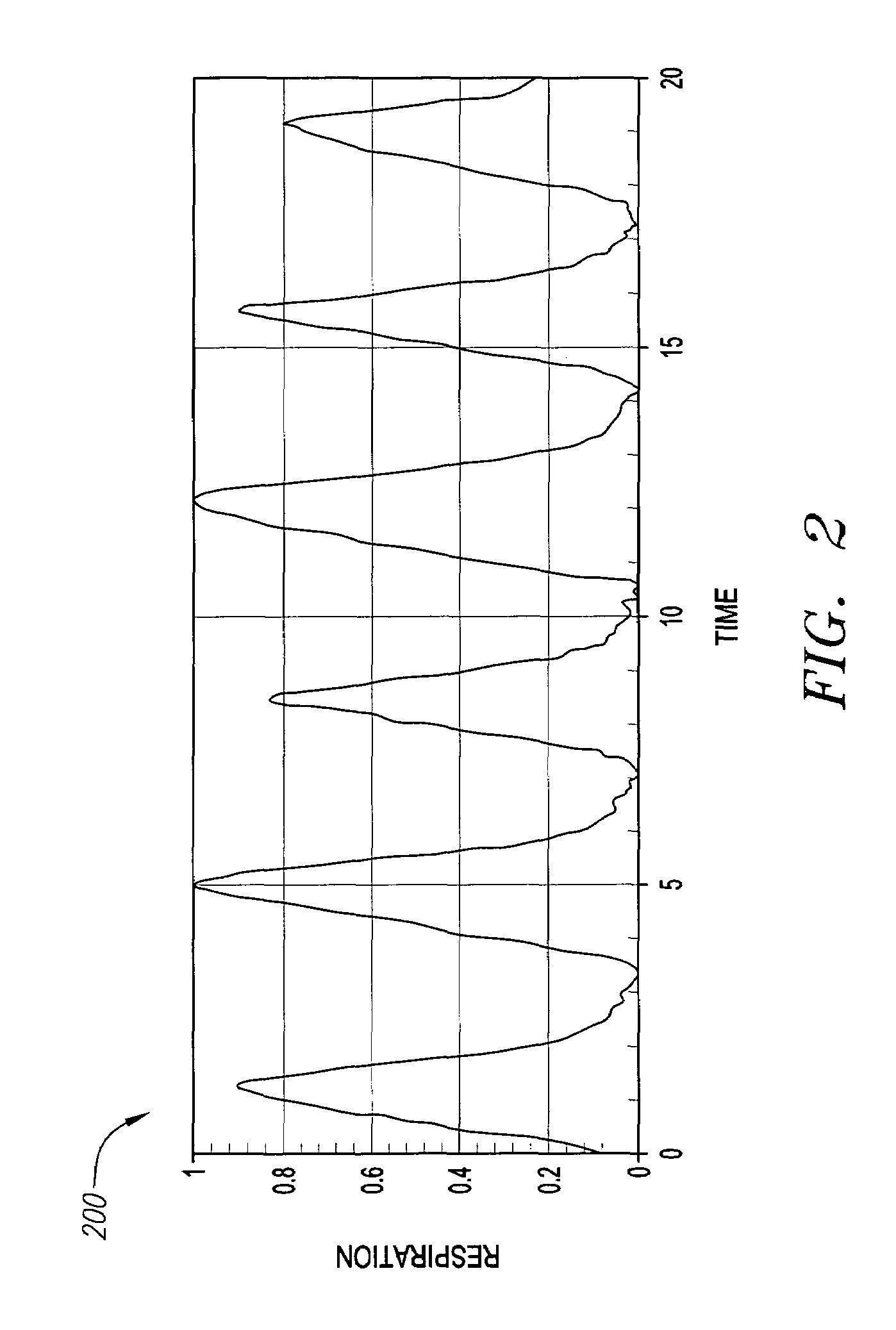
Method and system for monitoring breathing activity of a subject
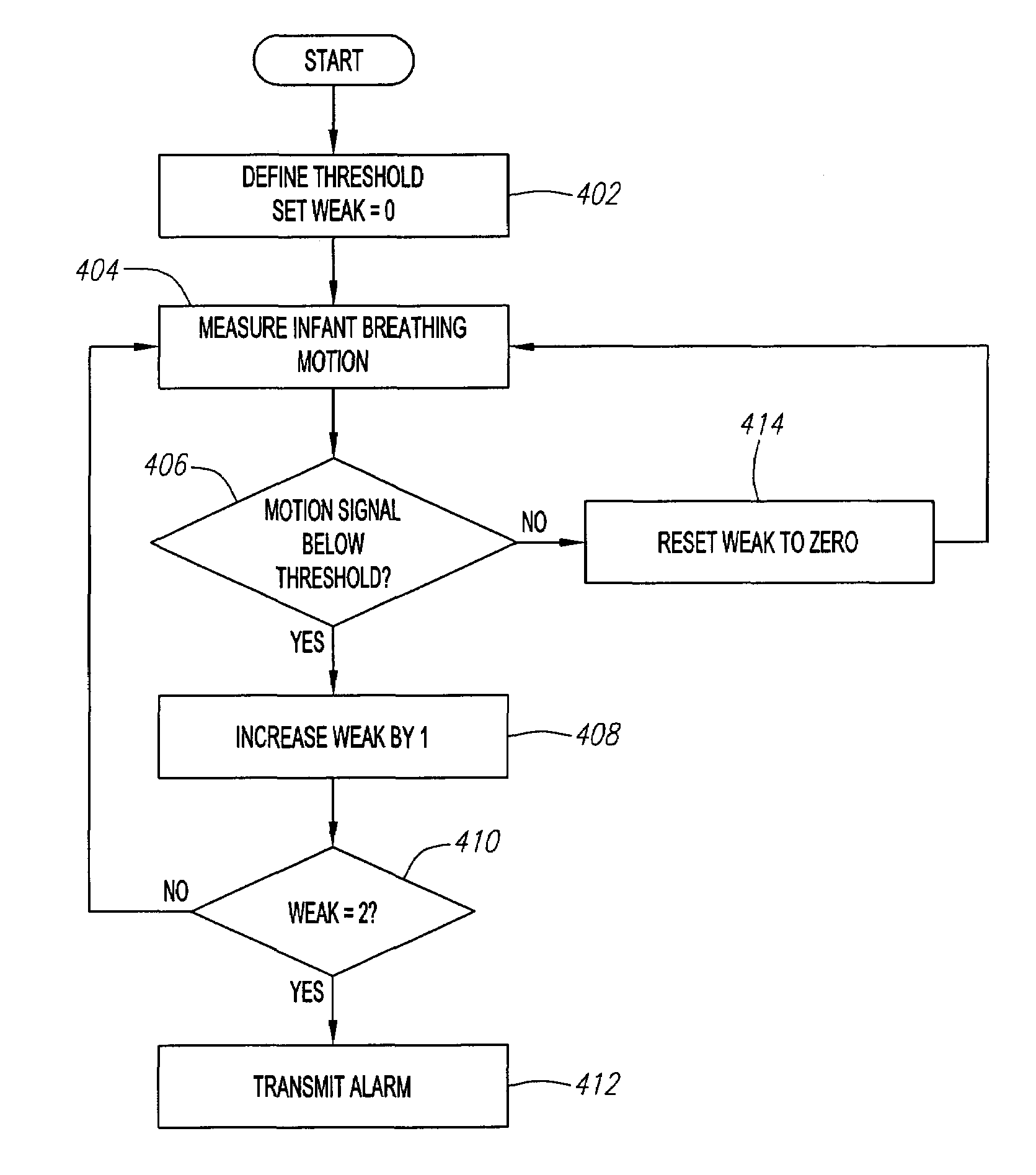
A method and system for monitoring breathing movement of an infant is disclosed. A method and system for detecting and predictably estimating regular cycles of breathing movements is disclosed. Another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to detect and report irregularity of breathing activity of an infant, such as cessation and non-periodicity, which suggests a likelihood of SIDS.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
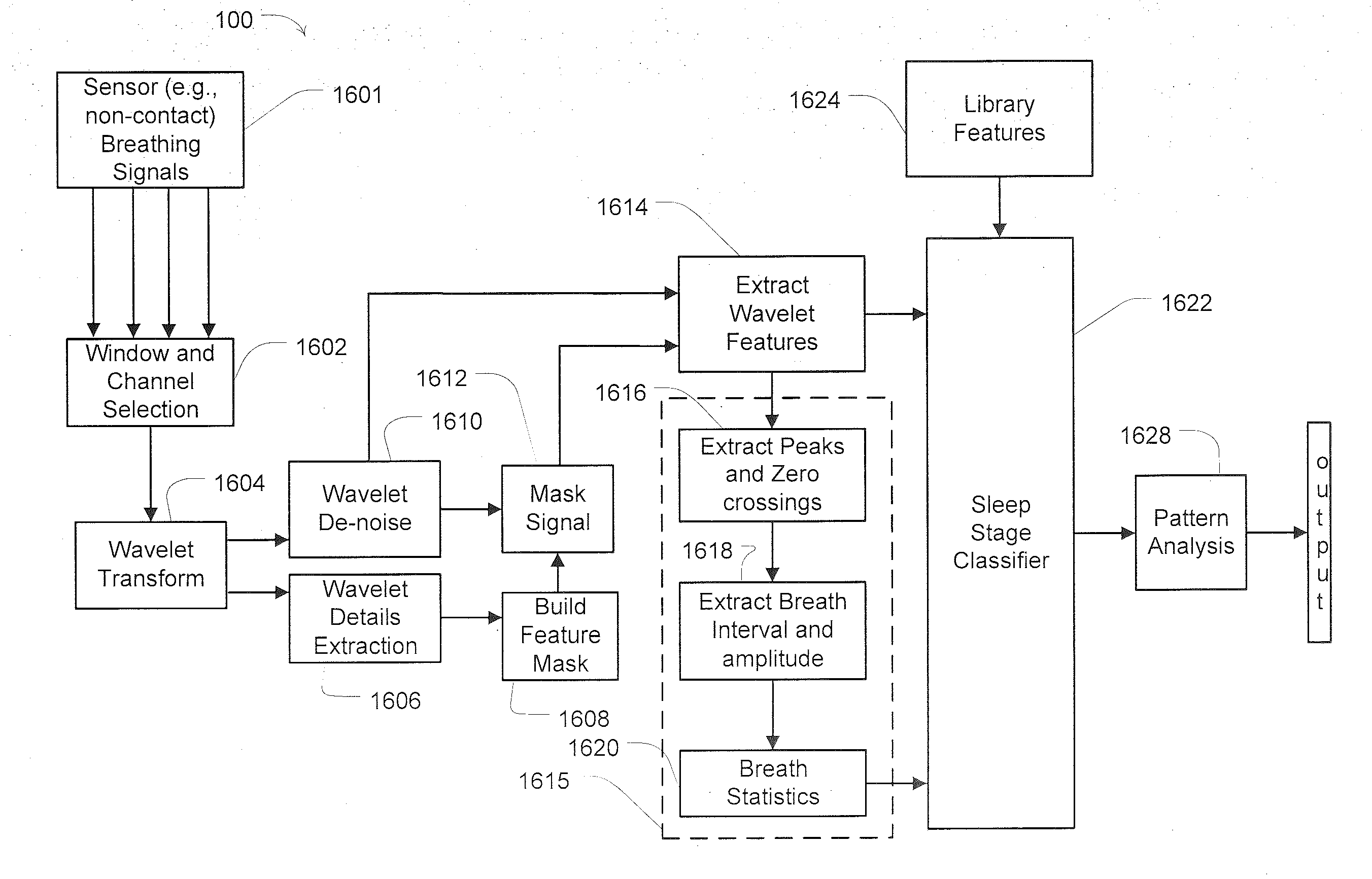
System and method for determining sleep stage
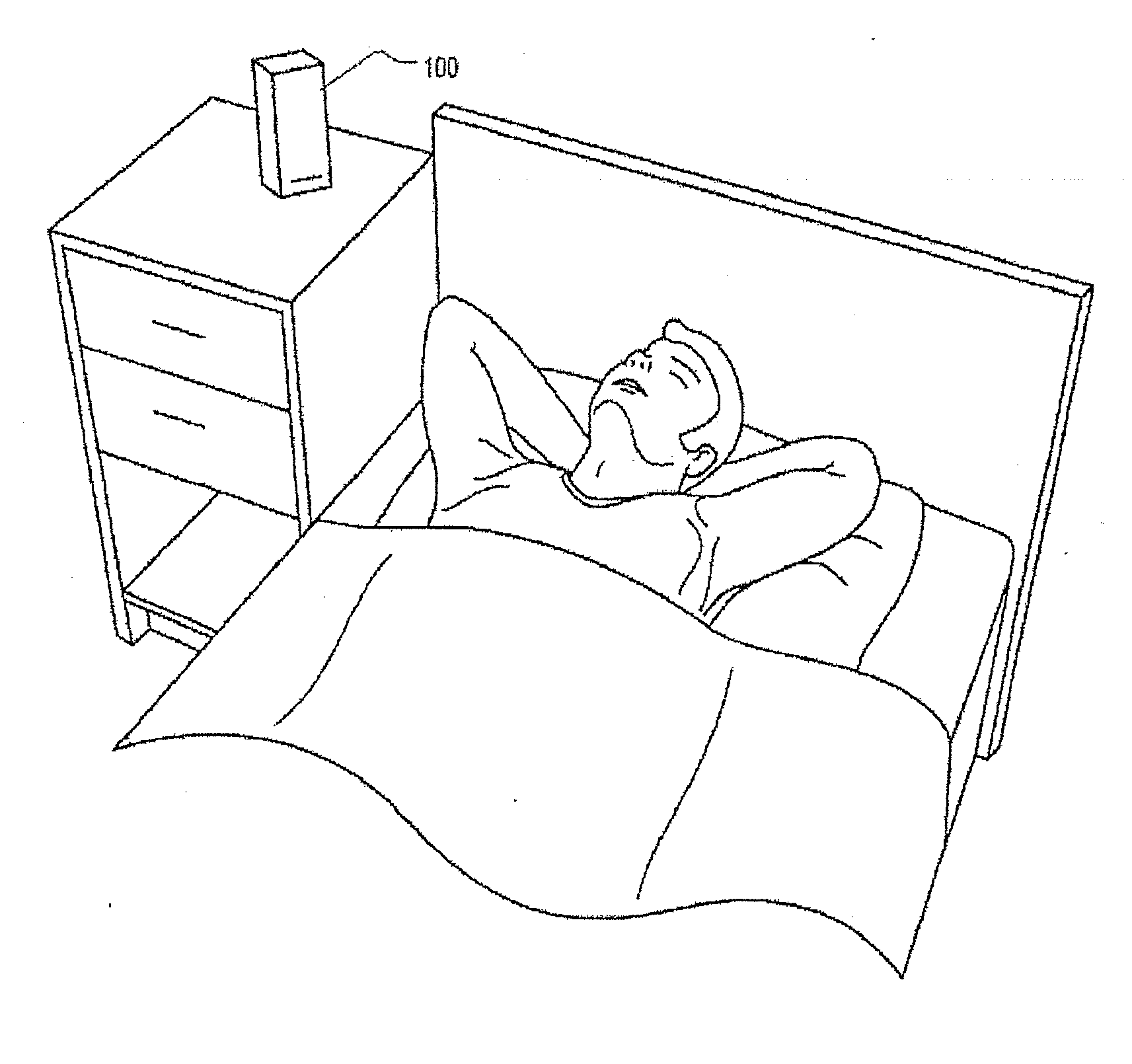
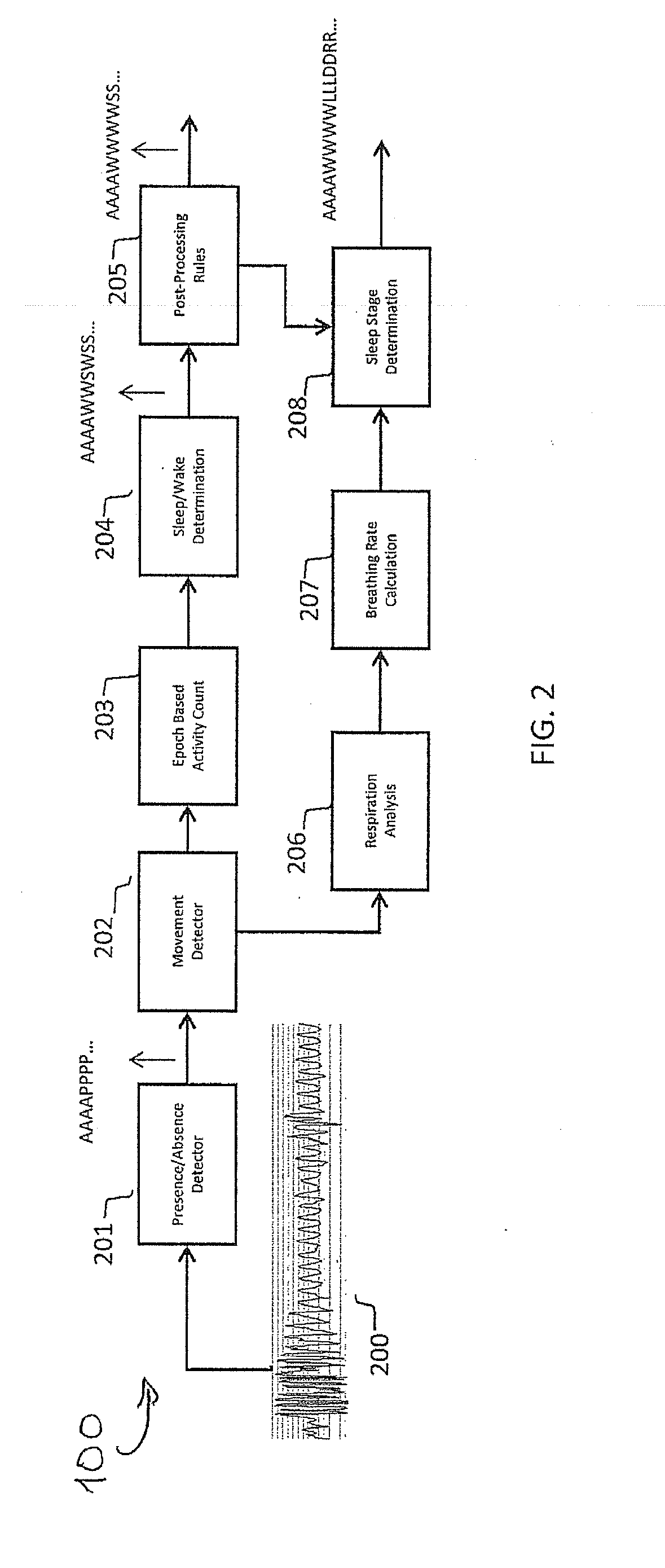
Methods and apparatus monitor health by detection of sleep stage. For example, a sleep stage monitor may access sensor data signals related to bodily movement and respiration movements. At least a portion of the detected signals may be analyzed to calculate respiration variability. The respiration variability may include variability of respiration rate or variability of respiration amplitude. A processor may then determine a sleep stage based on a combination bodily movement and respiration variability. The determination of sleep stages may distinguish between deep sleep and other stages of sleep, or may differentiate between deep sleep, light sleep and REM sleep. The bodily movement and respiration movement signals may be derived from one or more sensors, such as non-invasive sensor (e.g., a non-contact radio-frequency motion sensor or a pressure sensitive mattress).
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
Method and system for monitoring breathing activity of a subject
A method and system for monitoring breathing movement of a subject is disclosed. A method and system for detecting and predictably estimating regular cycles of breathing movements is disclosed. Another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to detect and report irregularity of breathing activity of an infant, such as cessation and non-periodicity, which suggests a likelihood of SIDS.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Monitoring physiological condition of a subject
InactiveUS20130165809A1Cheap, non invasive, accurate, small and disposableImprove securityRespiratory organ evaluationTelemetric patient monitoringResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
A system for monitoring breathing of a subject, the system comprising: (a) a wearable subject unit comprising: an elastic resistive sensor positionable such that breathing motion of the subject applies mechanical pressure to said elastic resistive sensor, wherein said elastic resistive sensor is configured to change its resistance responsive to the mechanical pressure, and a transmitter configured to wirelessly transmit a signal based on the change in resistance of the elastic resistive sensor; and (b) a platform unit comprising a receiver and being positionable in wireless transmission range with said subject unit, said platform unit configured to receive said signal from said subject unit and to issue an advisory signal indicative of the breathing of the subject.
Owner:DIGISENSE
Apparatus and method using synchronized breathing to treat tissue subject to respiratory motion
ActiveUS7778691B2Simple methodAnalogue computers for chemical processesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicinePhases of clinical research
Radiation treatment of the lung or surrounding tissue during continuous breathing is made possible by preparing a treatment plan linked to motion phase and then synchronizing the plan to motion phase as the patient follows a regular breathing schedule.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
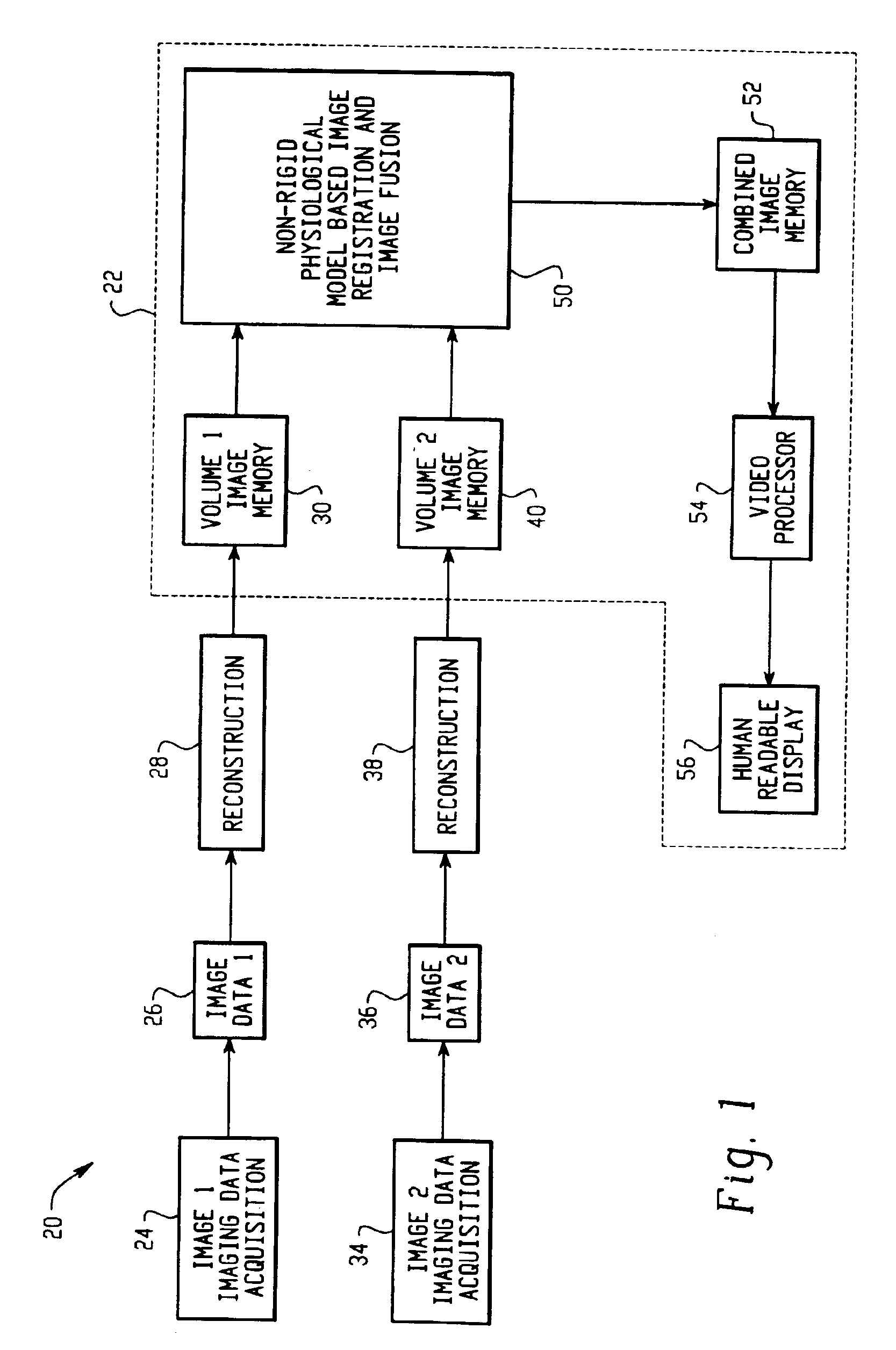
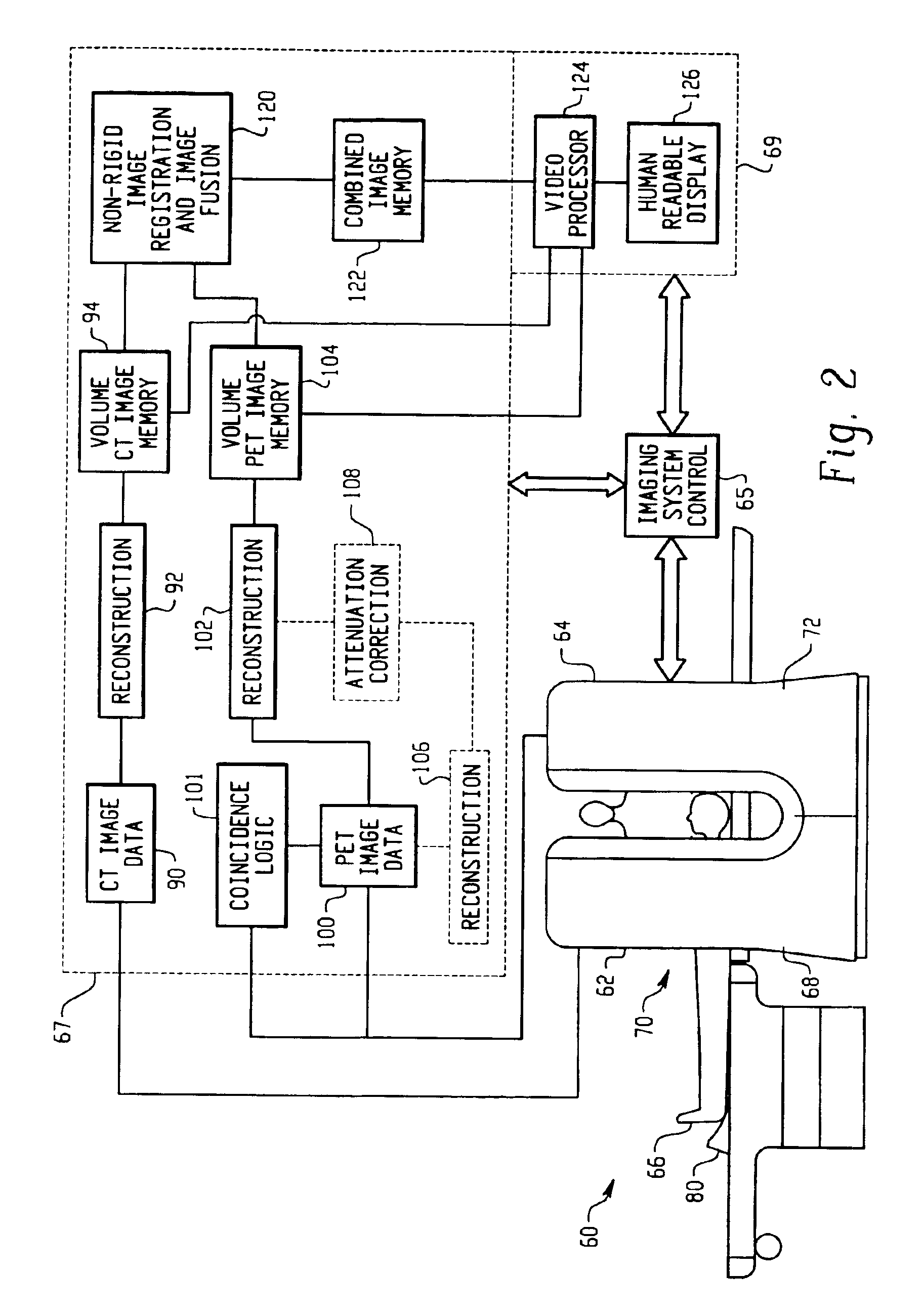
Physiological model based non-rigid image registration
InactiveUS7117026B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionData set
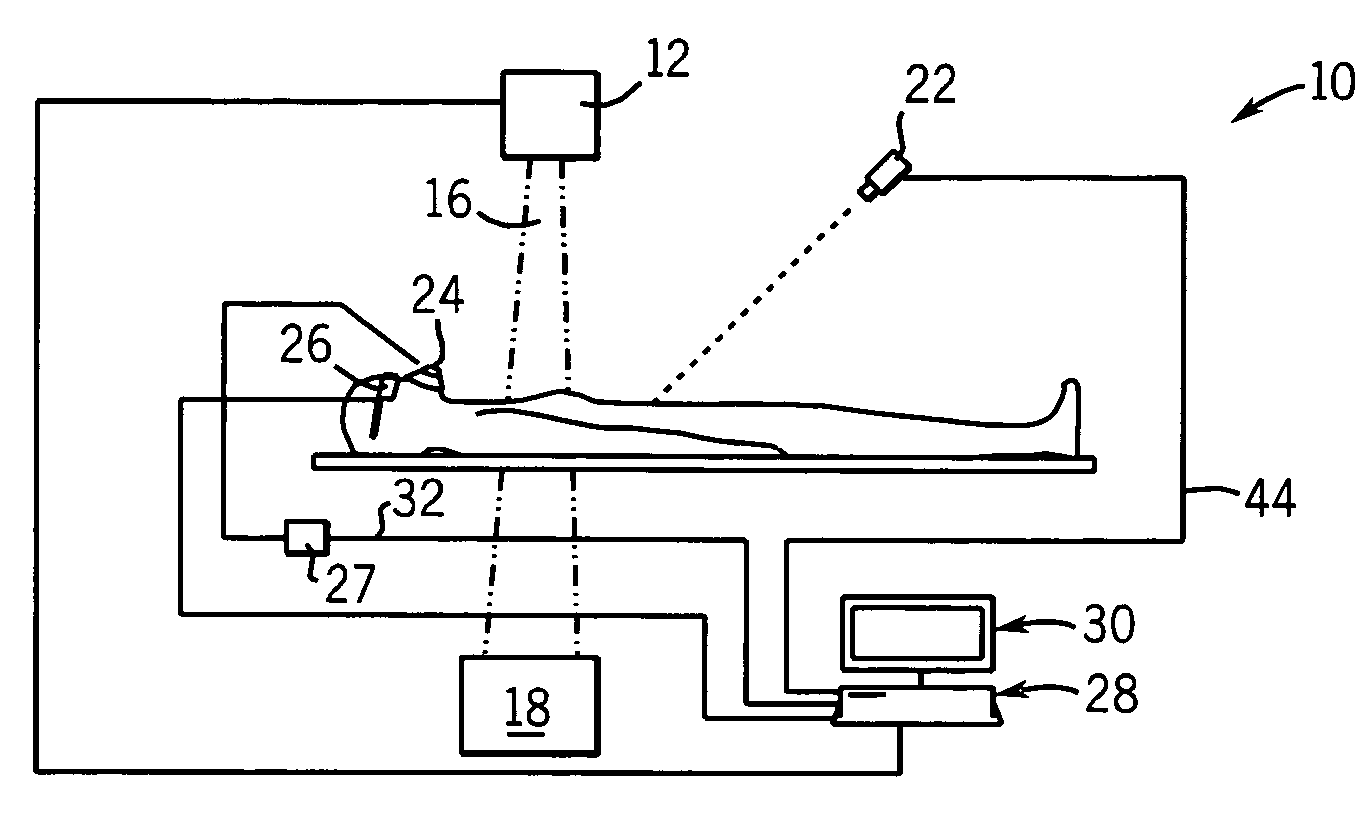
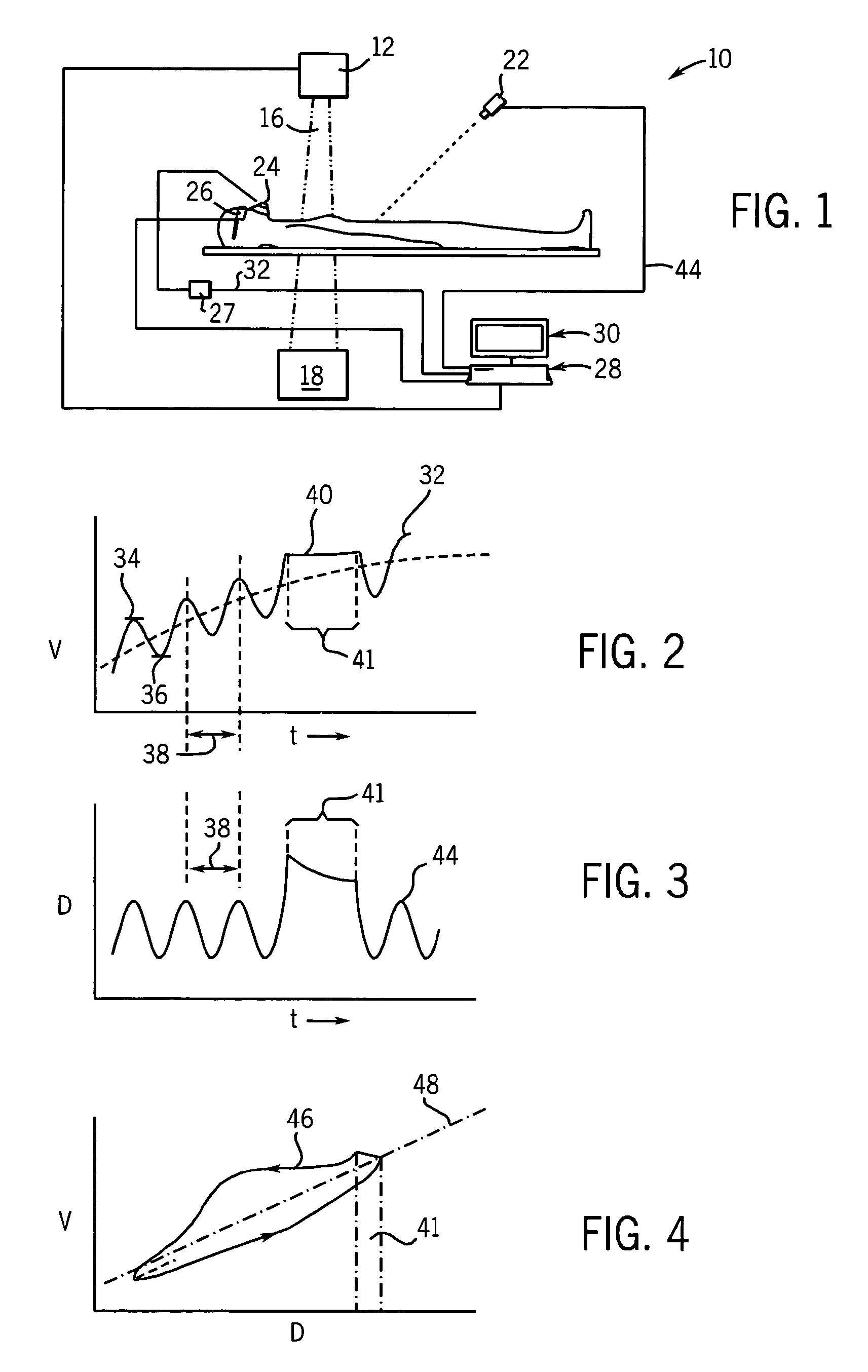
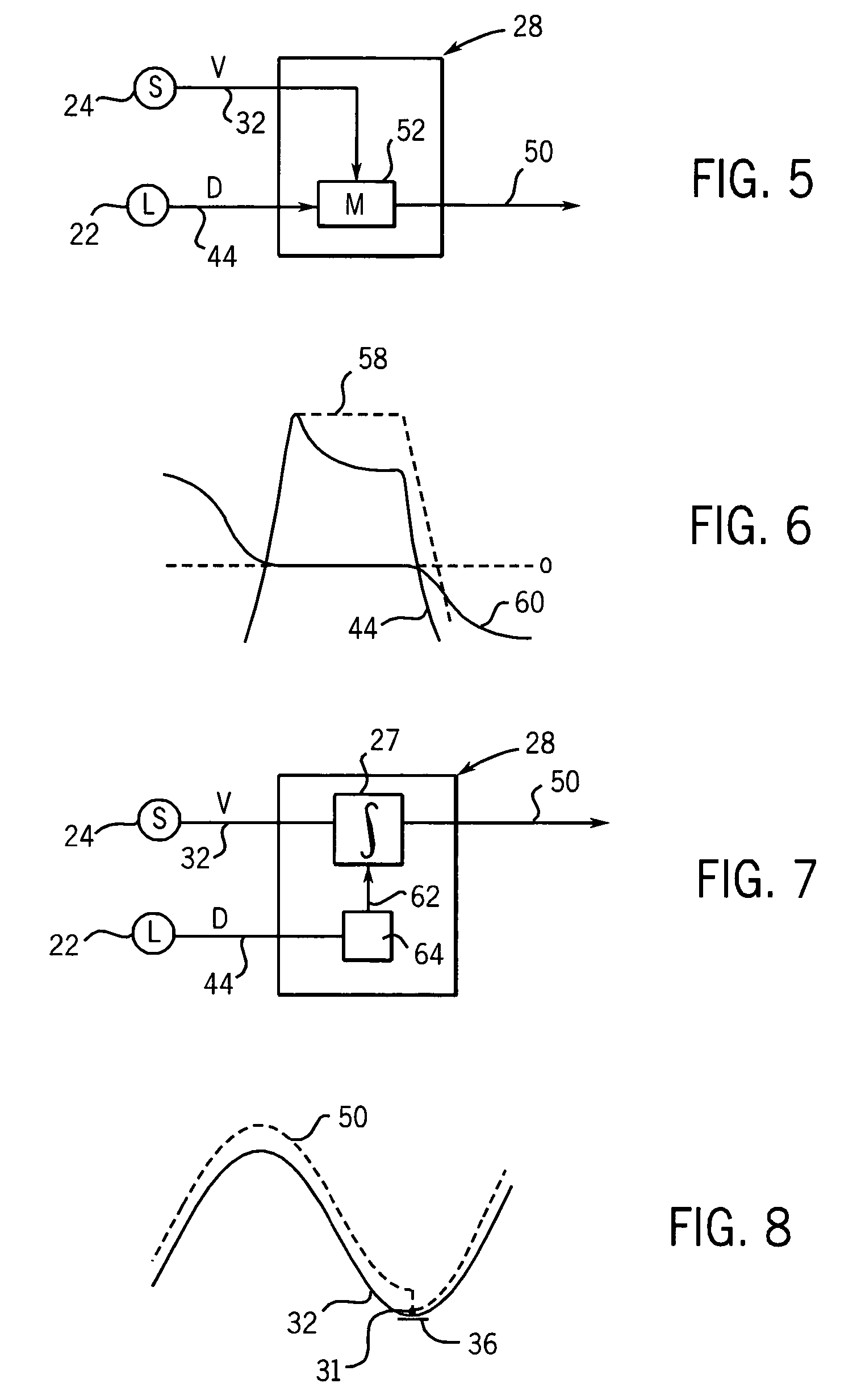
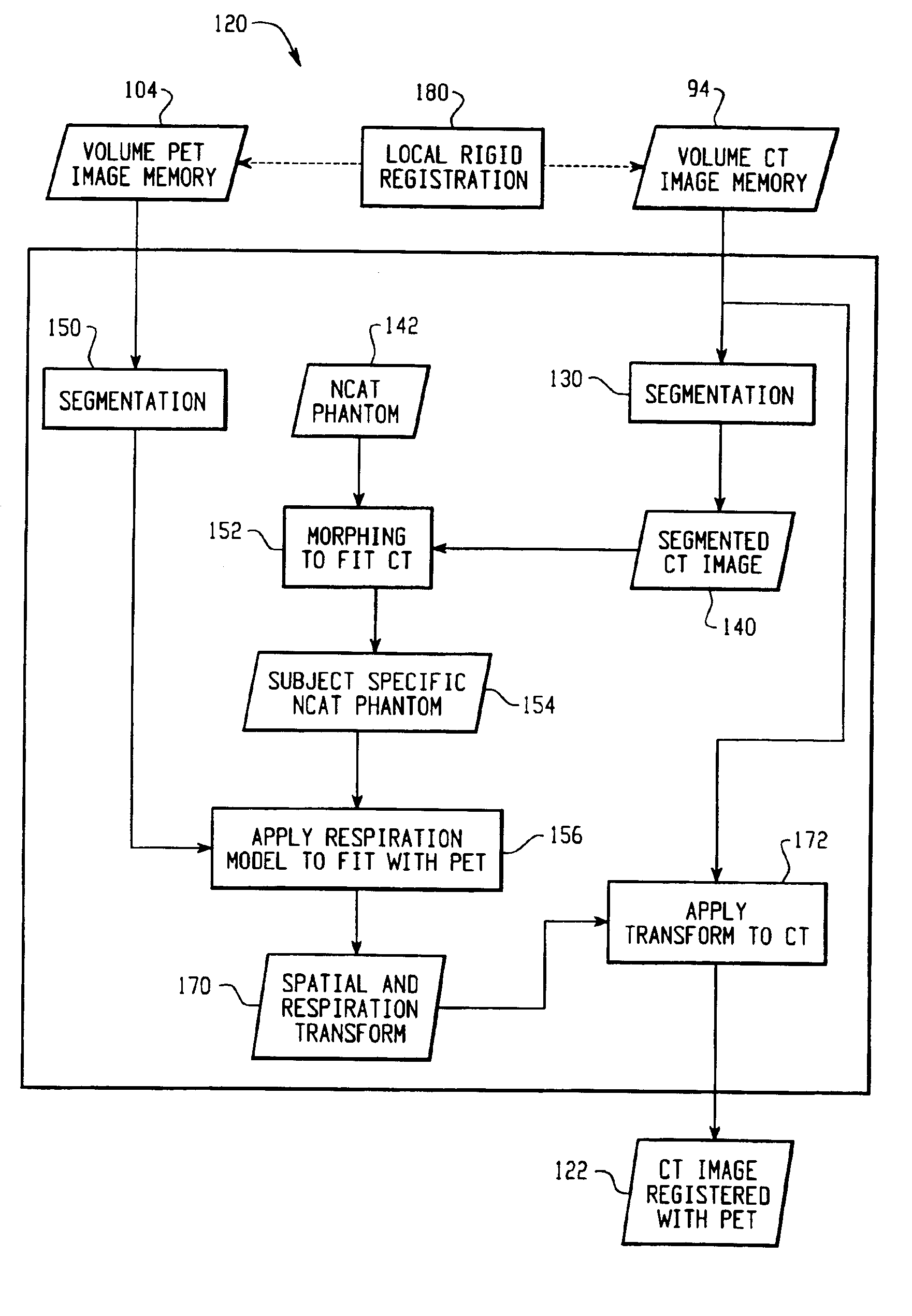
A method for non-rigid registration and fusion of images with physiological modeled organ motions resulting from respiratory motion and cardiac motion that are mathematically modeled with physiological constraints. A method of combining images comprises the steps of obtaining a first image dataset (24) of a region of interest of a subject and obtaining a second image dataset (34) of the region of interest of the subject. Next, a general model of physiological motion for the region of interest is provided (142). The general model of physiological motion is adapted with data derived from the first image data set (140) to provide a subject specific physiological model (154). The subject specific physiological model is applied (172) to the second image dataset (150) to provide a combined image (122).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Implantable generating system
An implantable generating system includes a generator assembly for converting mechanical motion into electrical energy. A linkage assembly, which is mechanically coupled to the generator assembly, converts respiratory motion into mechanical motion.
Owner:BAKER III REX M +1
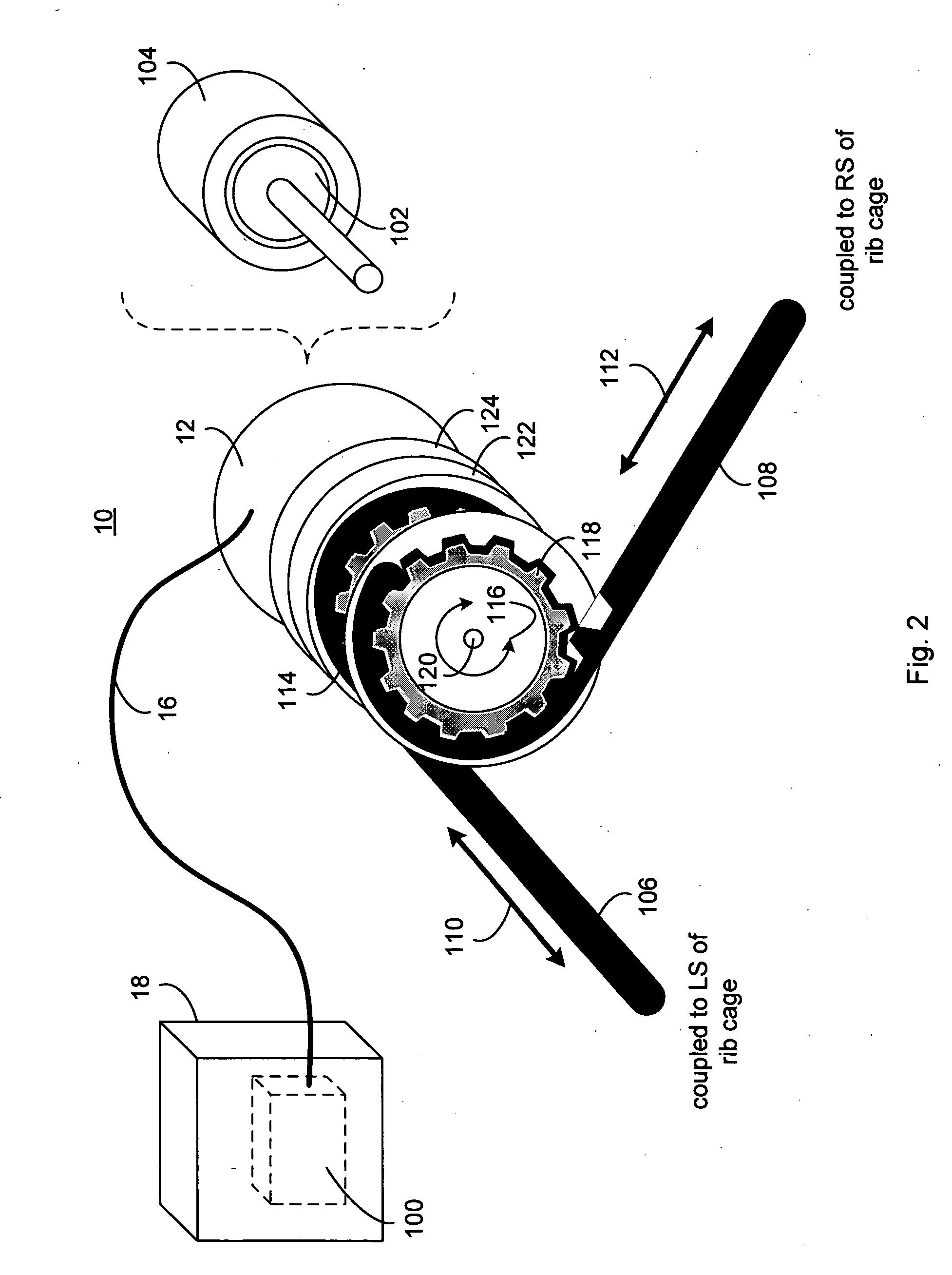
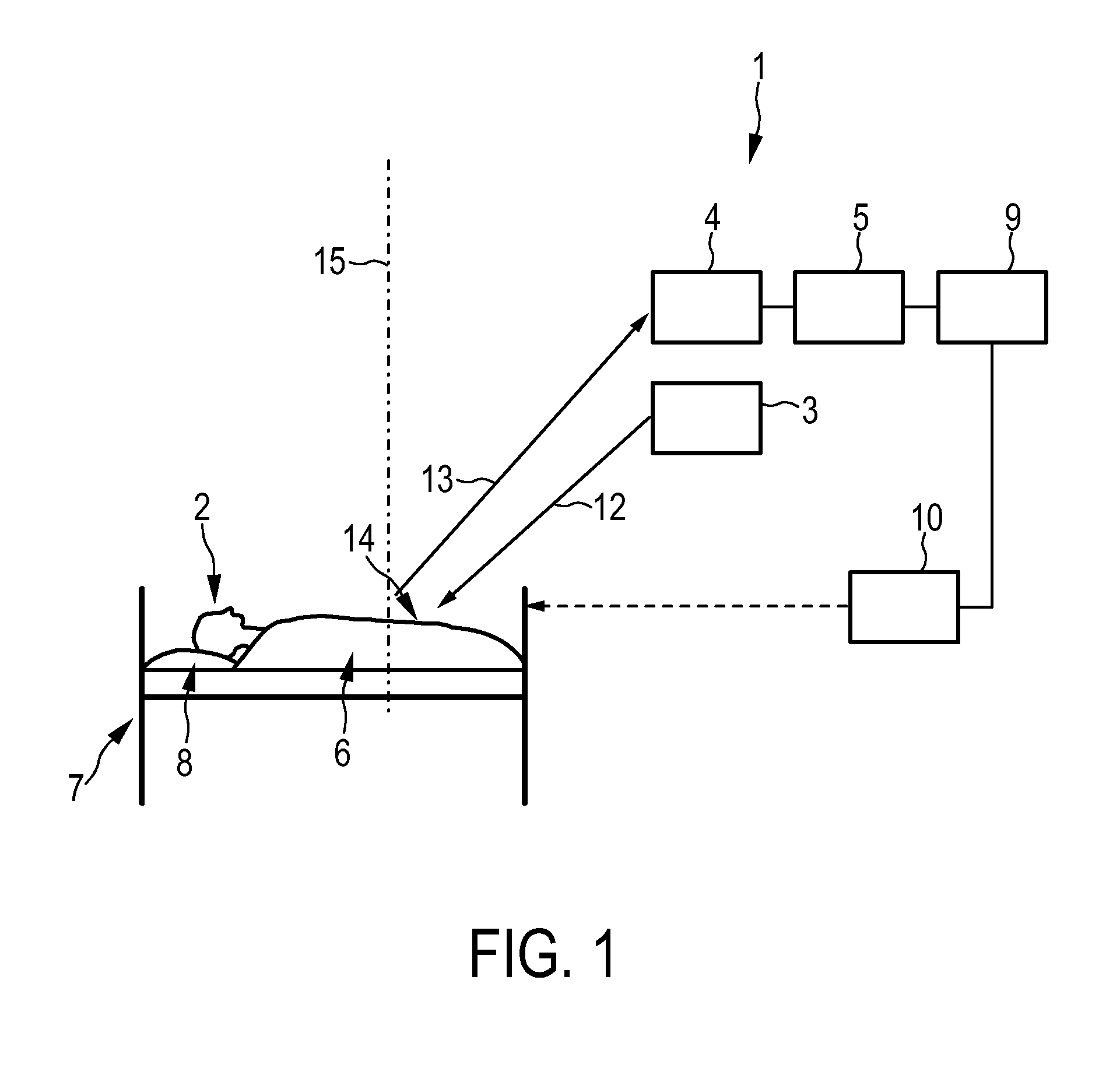
Respiratory motion detection apparatus
ActiveUS20130035599A1High detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisAnesthesiaRespiratory motion
The invention relates to a respiratory motion detection apparatus (1) for detecting respiratory motion of a person. An illuminator (3) illuminates the person (2) with an illumination pattern (11), and a detector (4) detects the illumination pattern (11) on the person (2) over time. A temporal respiratory motion signal being indicative of the respiratory motion of the person (2) is determined from the detected illumination pattern by a respiratory motion signal determination unit (5). The illumination pattern deforms significantly with slight movements of the person. Thus, since the respiratory motion signal determination unit (5) is adapted to determine the temporal respiratory motion signal from the detected illumination pattern, even slight respiratory movements of the person can be determined. The sensitivity of detecting respiratory movements of a person can therefore be improved.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Human torso phantom for imaging of heart with realistic modes of cardiac and respiratory motion
A human torso phantom and its construction, wherein the phantom mimics respiratory and cardiac cycles in a human allowing acquisition of medical imaging data under conditions simulating patient cardiac and respiratory motion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
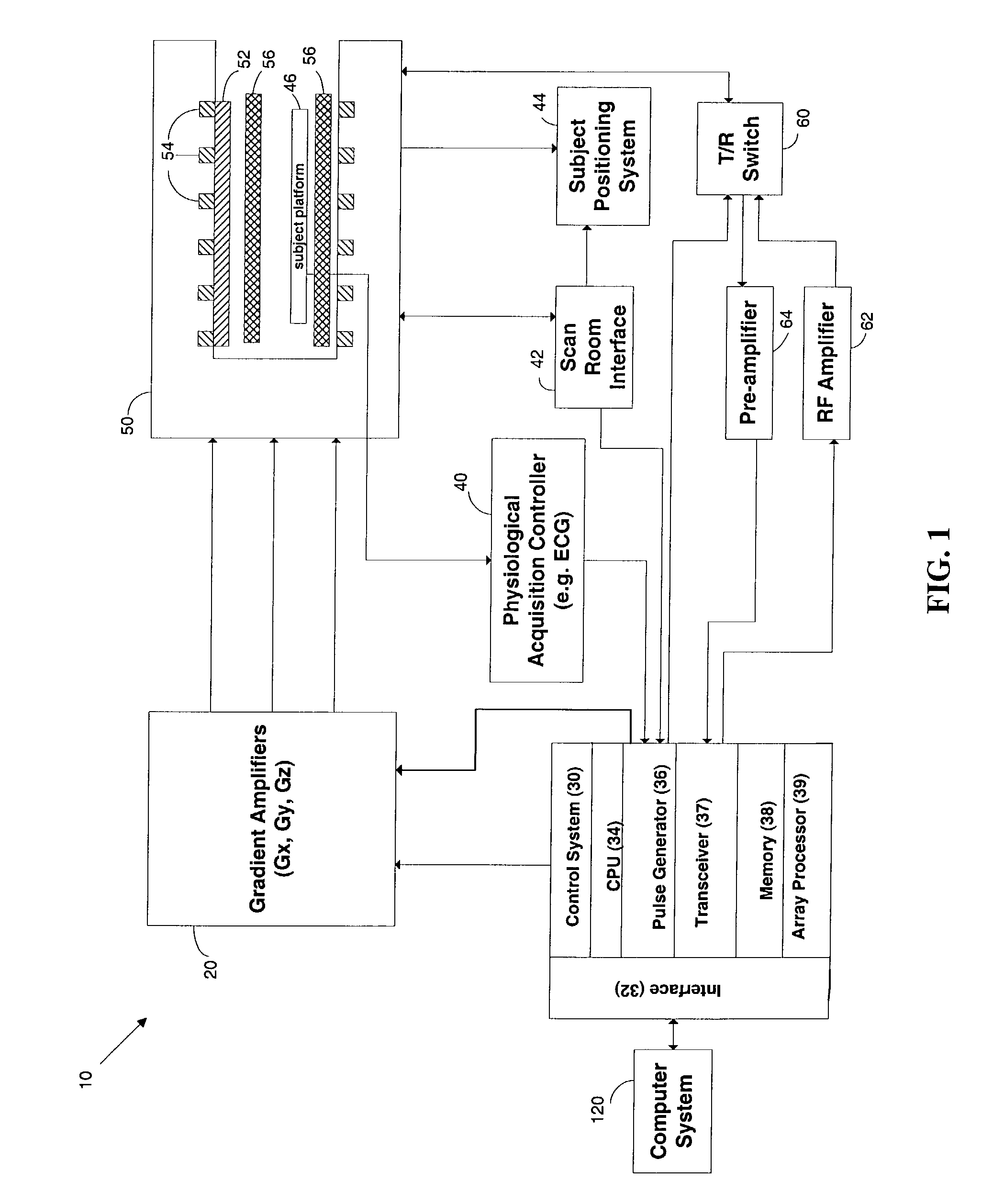
MRI navigator methods and systems
ActiveUS7561909B1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage resolutionNormal blood volume
Navigator methods are disclosed that are based on detecting a flow-sensitive signal within a subject, and using the position of the signal to track subject motion between imaging sequences. In a disclosed embodiment, the fast-moving blood volume in the left ventricle of the heart is detected and used as a reference point to correct for cardiac motion that results from respiratory motion in a subject. The navigator based on the position of the fast-moving blood volume in the left ventricle may be applied prospectively to shift a subsequent imaging slice to compensate for subject motion, and thereby provide MRI images with increased clarity and resolution.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
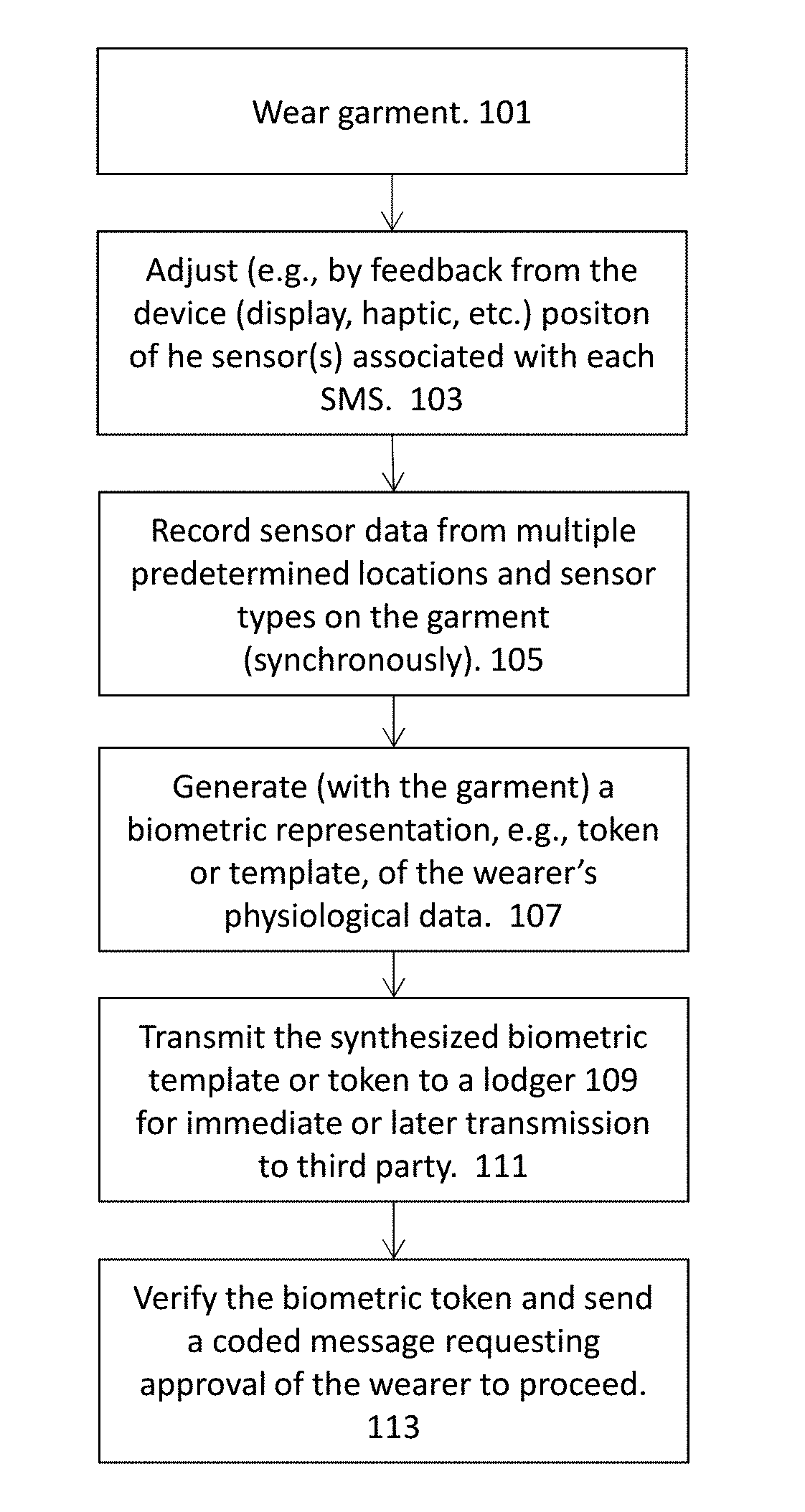
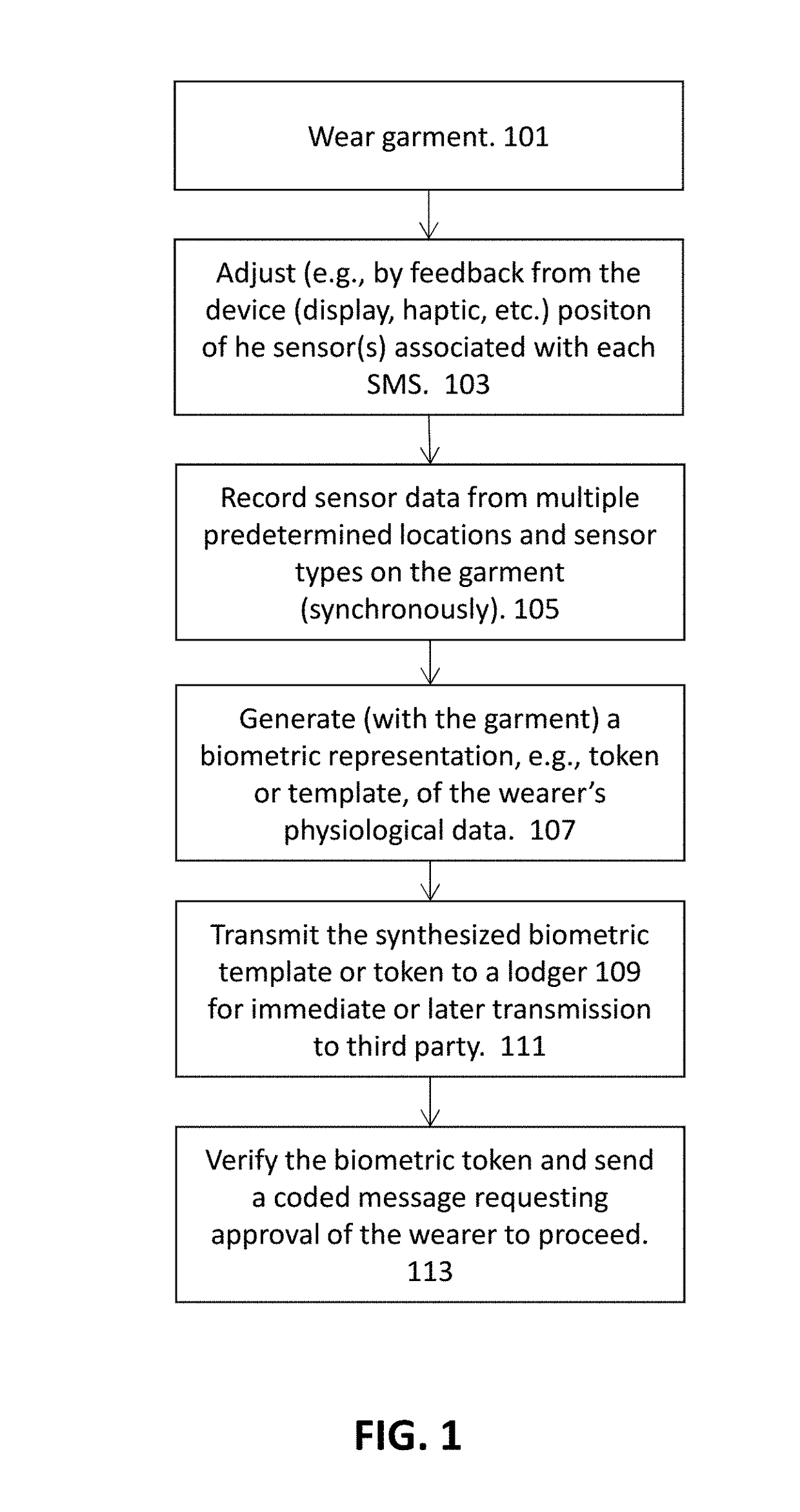
Biometric identification by garments having a plurlity of sensors
ActiveUS20180000367A1Reduce gapEasy to measureElectrocardiographyPerson identificationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityEngineering
Biometric identification methods and apparatuses (including devices and systems) for uniquely identifying one an individual based on wearable garments including a plurality of sensors, including but not limited to sensors having multiple sensing modalities (e.g., movement, respiratory movements, heart rate, ECG, EEG, etc.).
Owner:L I F E
System and method for determining sleep stage
ActiveUS20150230750A1Improve comfortIncrease costRespiratory masksMedical devicesSommeil paradoxalNon invasive
Methods and apparatus monitor health by detection of sleep stage. For example, a sleep stage monitor (100) may access sensor data signals related to bodily movement and / or respiration movements. At least a portion of the detected signals may be analyzed to calculate respiration variability. The respiration variability may include one or more of variability of respiration rate and variability of respiration amplitude. A processor may then determine a sleep stage based on one or more of respiration variability and bodily movement, such as with a combination of both. The determination of sleep stages may distinguish between deep sleep and other stages of sleep, or may differentiate between deep sleep, light sleep and REM sleep. The bodily movement and respiration movement signals may be derived from one or more sensors, such as non-invasive sensor (e.g., a non-contact radio-frequency motion sensor or a pressure sensitive mattress).
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
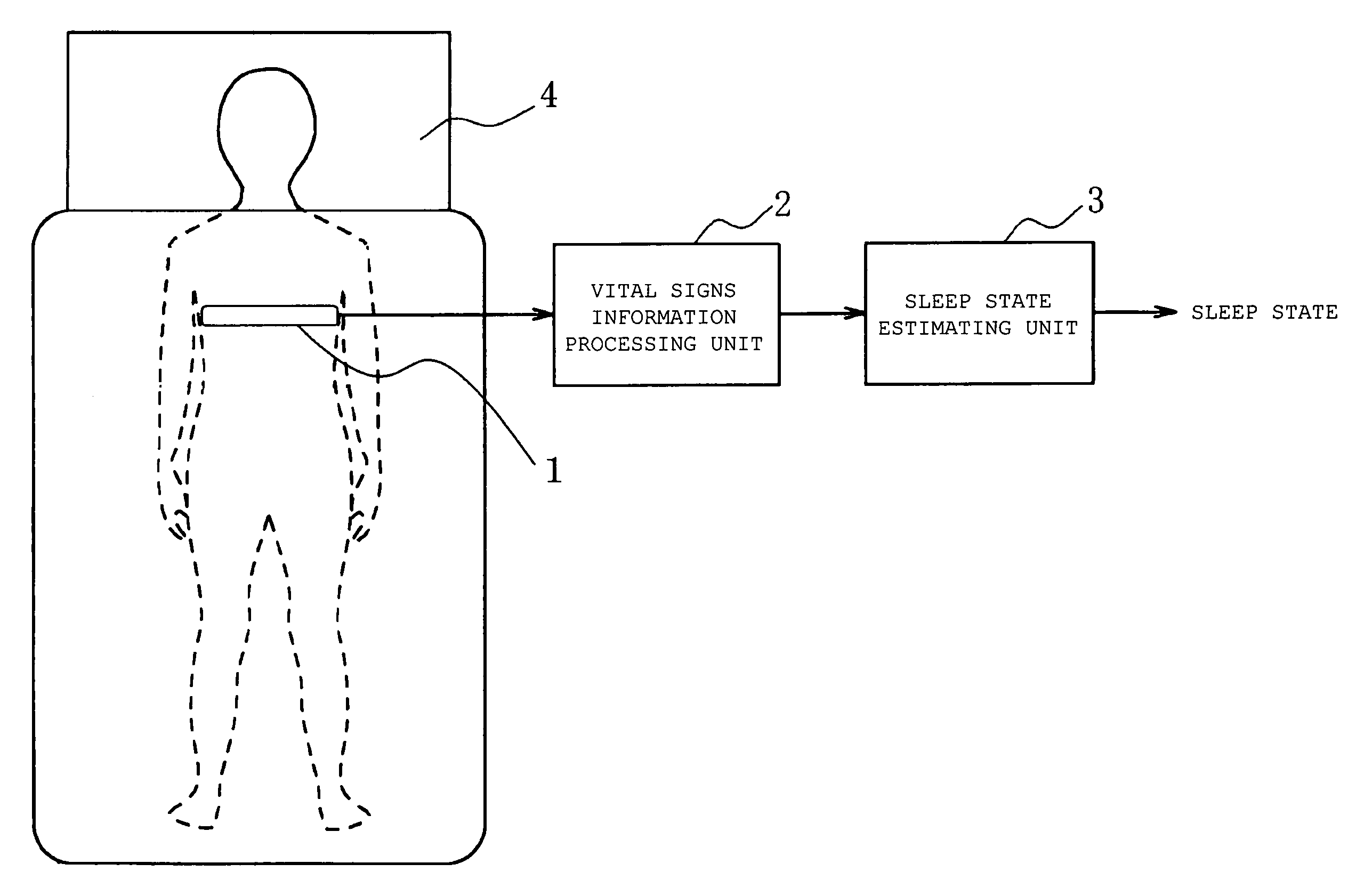
Sleep state estimation device and program product for providing a computer with a sleep state estimation function
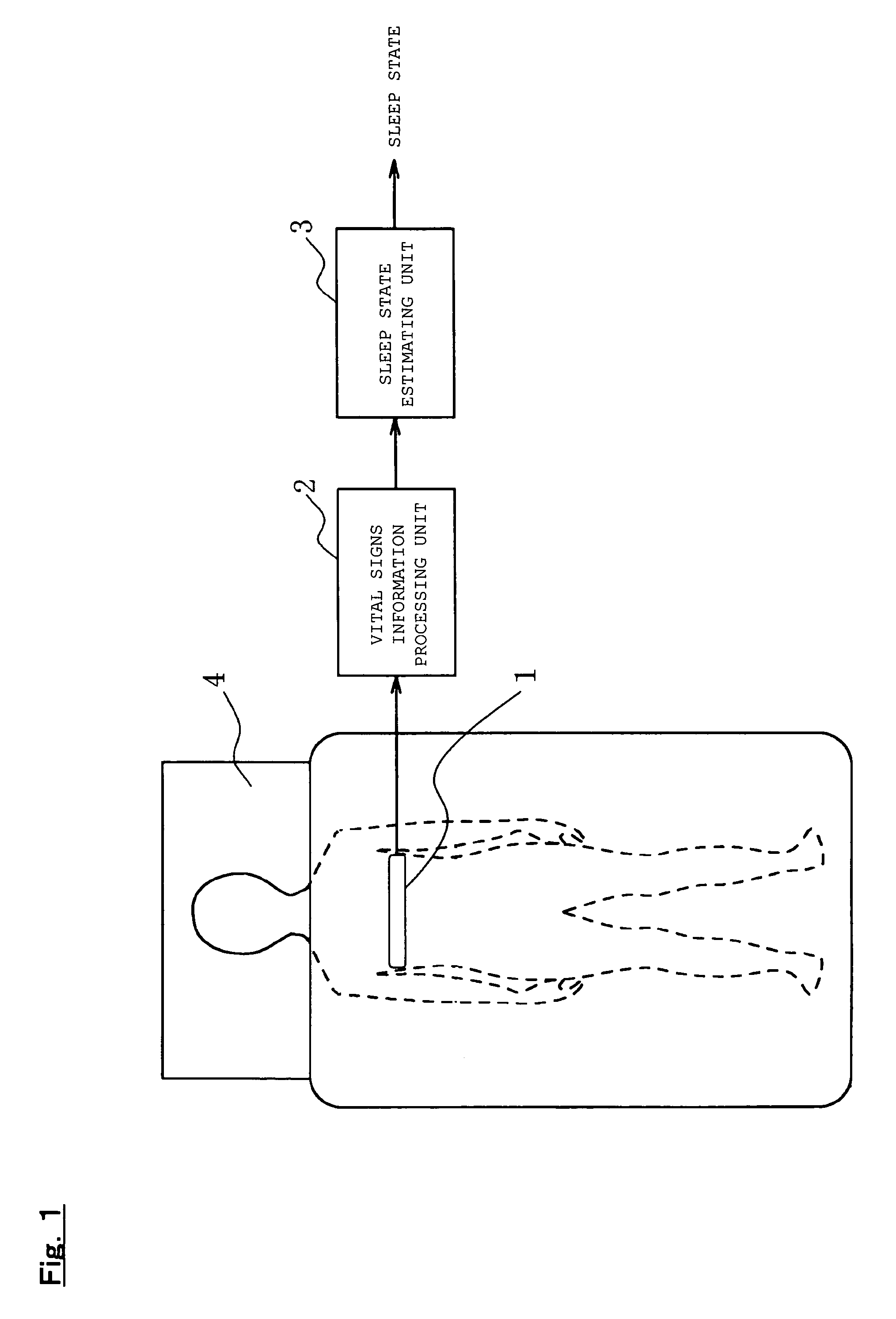
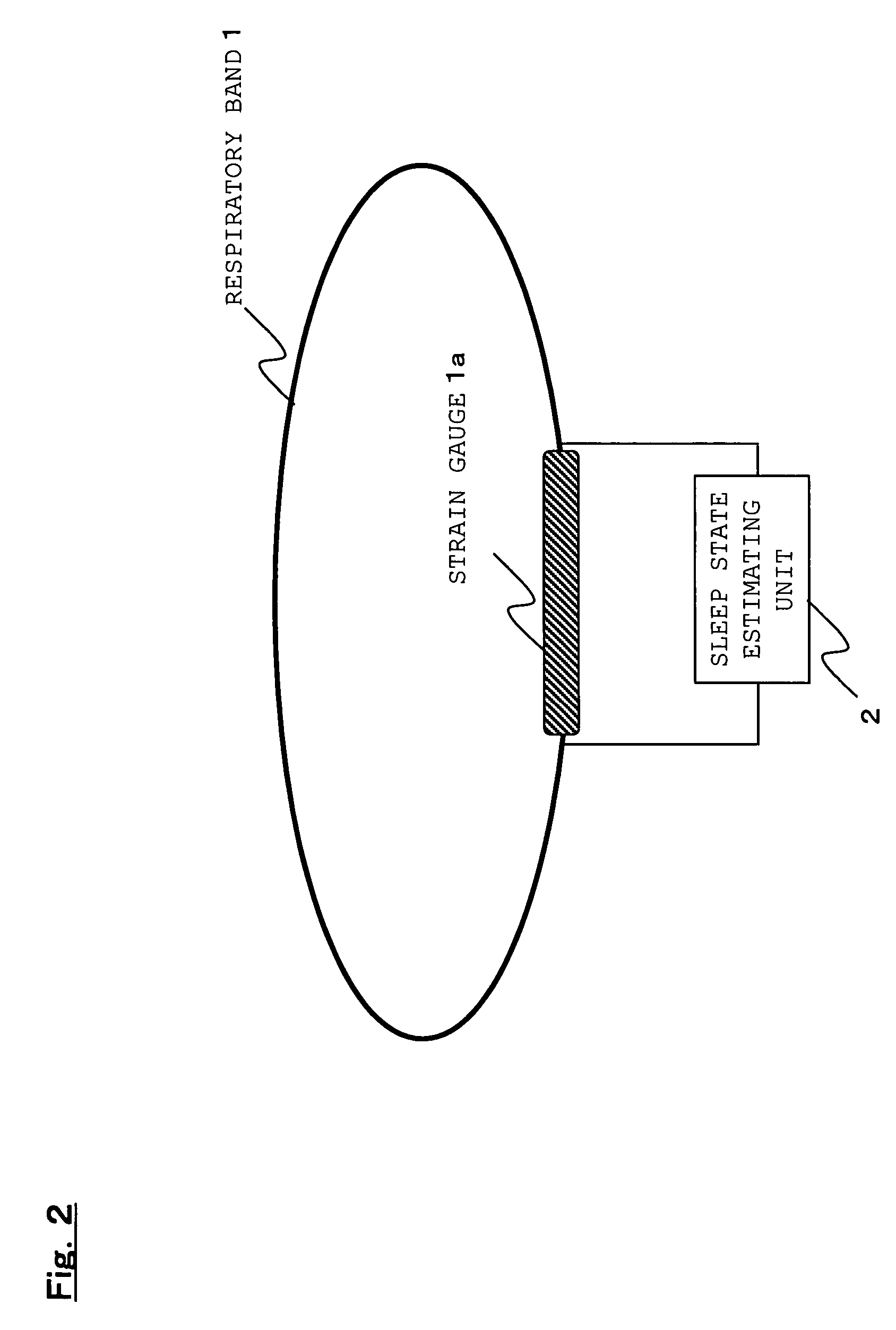
InactiveUS7150718B2Simple processGood estimateStrain gaugeRespiratory organ evaluationSleep stateLight sleep
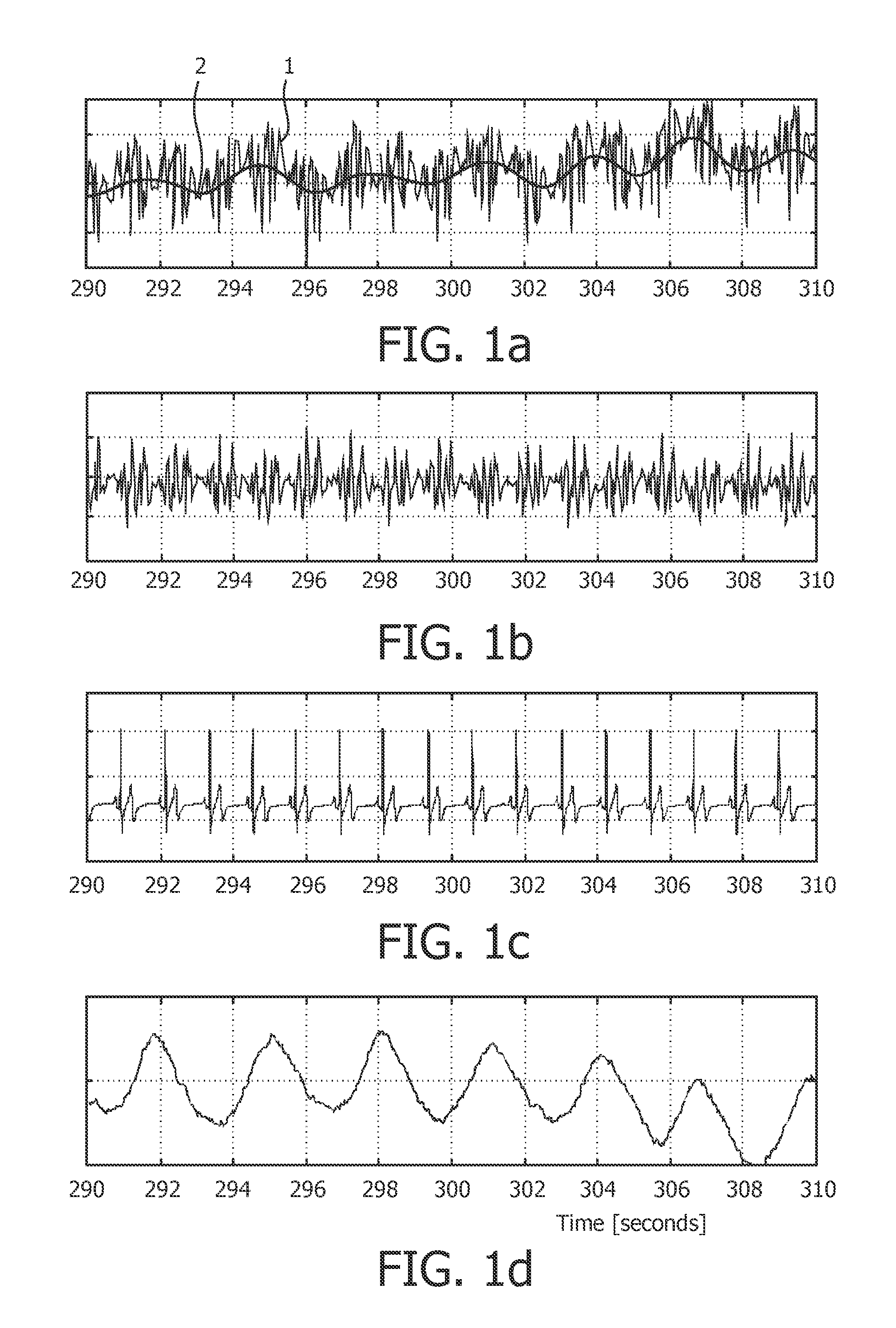
An object of the present invention is to provide a sleep state estimation device capable of estimating a sleep state (deep sleep, light sleep) in real time with relative simplicity. Voltage variations resulting from human respiratory movement are measured for each given period to calculate from the measurement results positive voltage peak values and time intervals between adjacent peaks. The obtained peak values and peak intervals are used to calculate a mean peak interval value A, a coefficient of variation B based on dispersion of the peak intervals, and a coefficient of variation C based on the peak values. The sleep state in this period is estimated from the calculation results. More specifically, referring to FIG. 5, the sleep state is estimated as a “wakeful state” or a “hypnagogic state” by checking whether the mean value A is larger or smaller than a threshold a and whether the coefficient of variation C is larger or smaller than a threshold c (S105) whereas the sleep state is estimated as the “hypnagogic state”, “light sleep” or “deep sleep” by checking whether the coefficient of variation B is larger or smaller than a threshold b and whether the coefficient of variation C is larger or smaller than the threshold c (S109, S113, S116, S117).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for dynamic road mapping
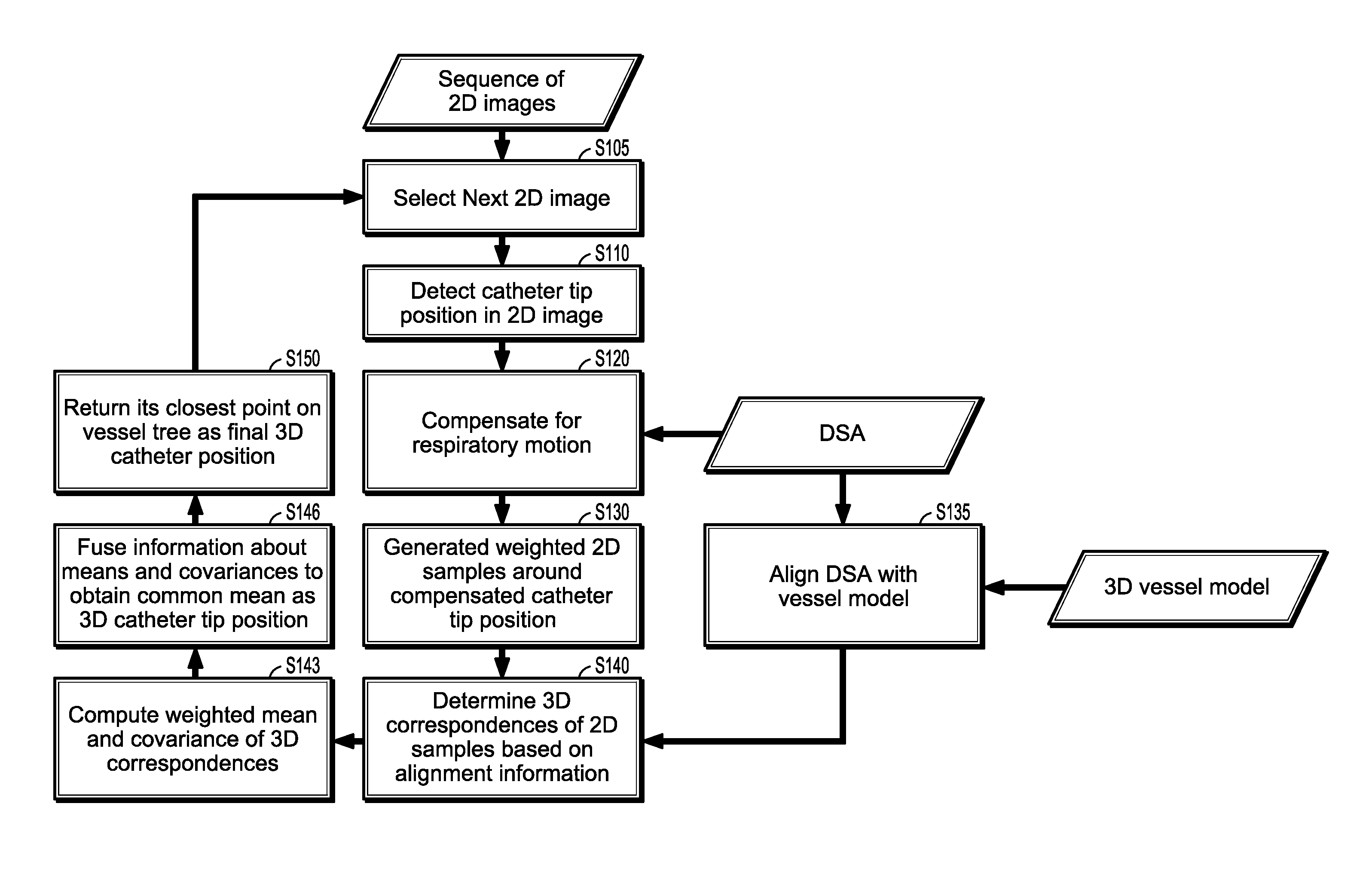
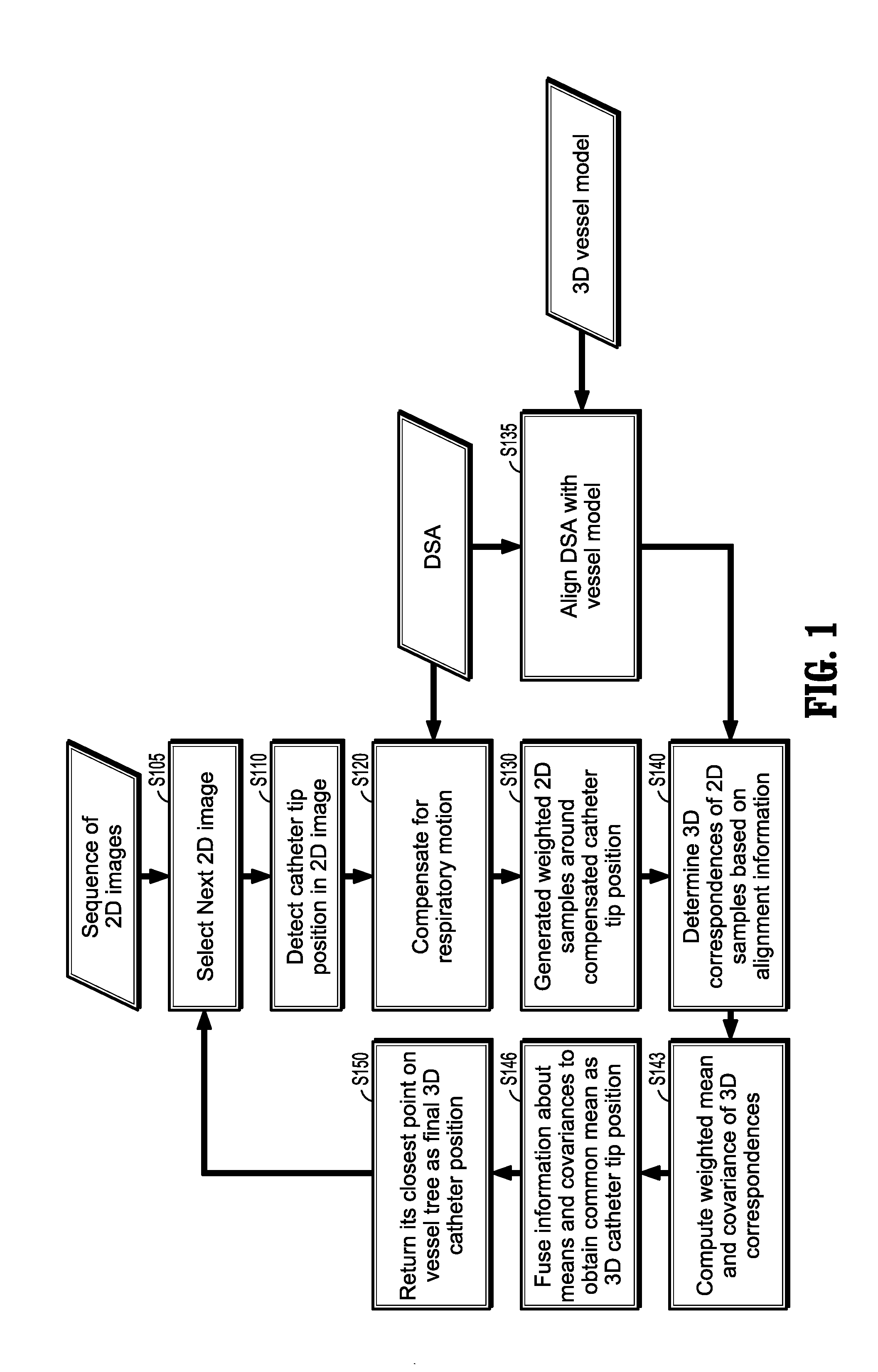
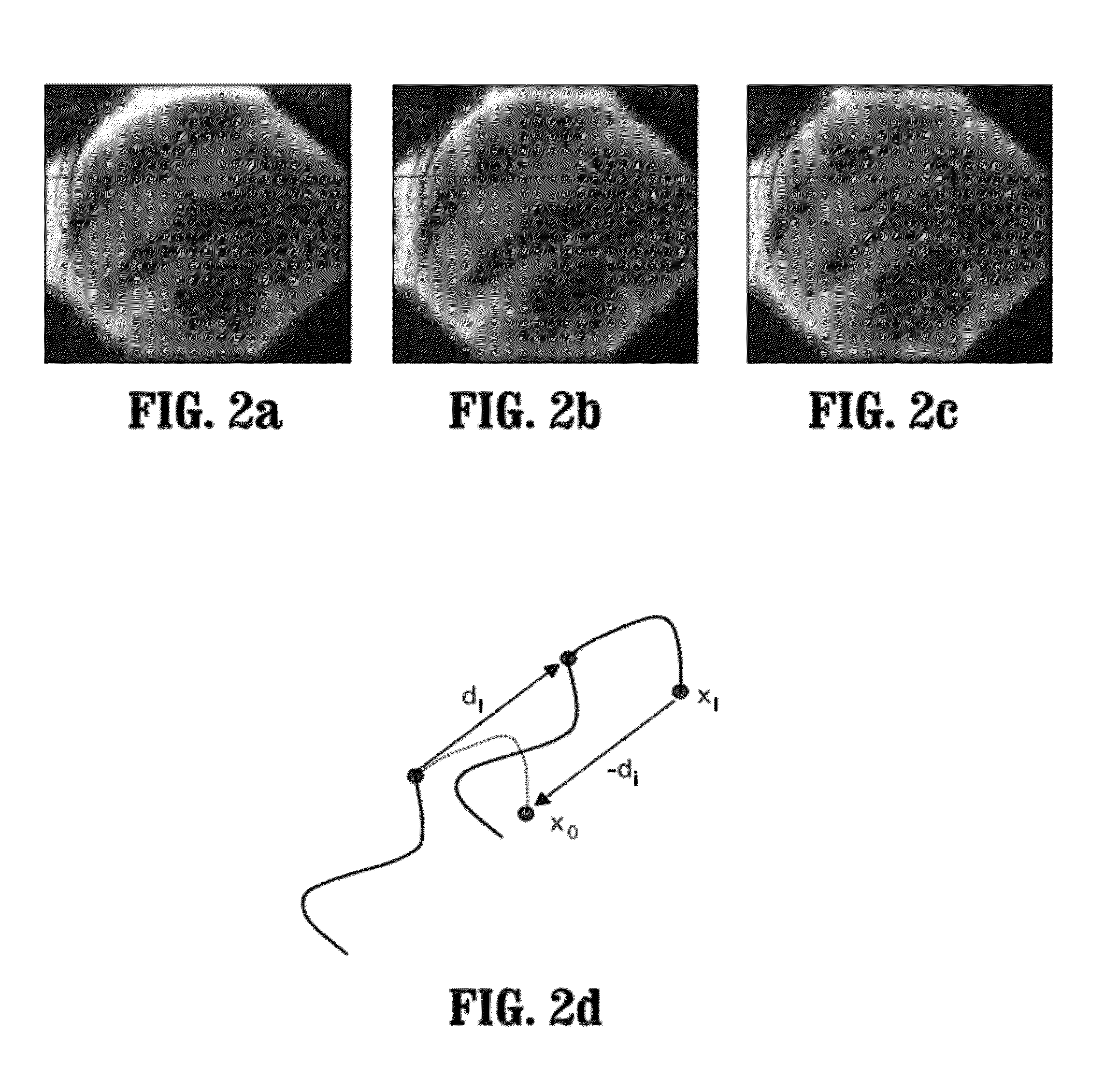
A method of determining a three-dimensional (3D) position of a catheter tip includes: compensating a 2D position of the tip of the catheter for respiratory motion to generate a compensated 2D catheter position, generating weighted sample points around the compensated 2D catheter position, determining correspondent points of the weighted sample points in a 3D image, computing a weighted mean and a weighted covariance of each correspondent point, and determining the 3D position of the catheter tip in the 3D image from a fusion of the weighted means and weighted covariances.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
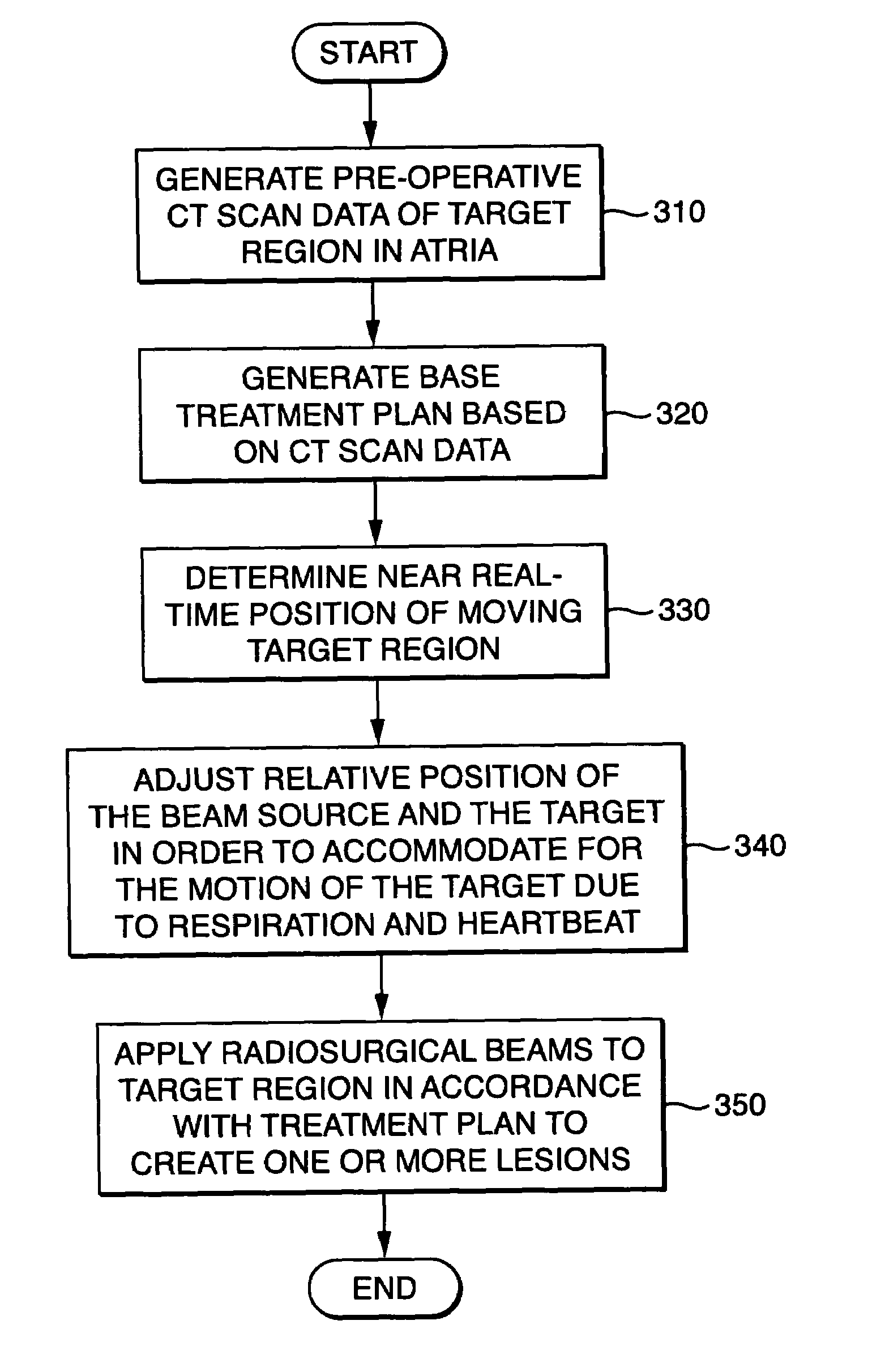
Method for Depositing Radiation in Heart Muscle
InactiveUS20080177280A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic recording/measuringX-raySurgical department
Radiosurgical treatment of tissues of the heart to mitigate arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or the like. Radiosurgical targeting of the relatively rapid movement of heart tissues may be enhanced by generating a moving model volume using a time-sequence of three dimensional acquired tissue volumes. A digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) may be generated from the model at a desired cardiac and / or respiration motion phase and compared to an X-ray or the like taken immediately before or during treatment. When a series of radiation beams will be directed to a heart tissue to alleviate an arrhythmia, the treatment system may alter the radiation beam series in response to the type of the arrhythmia.
Owner:CYBERHEART
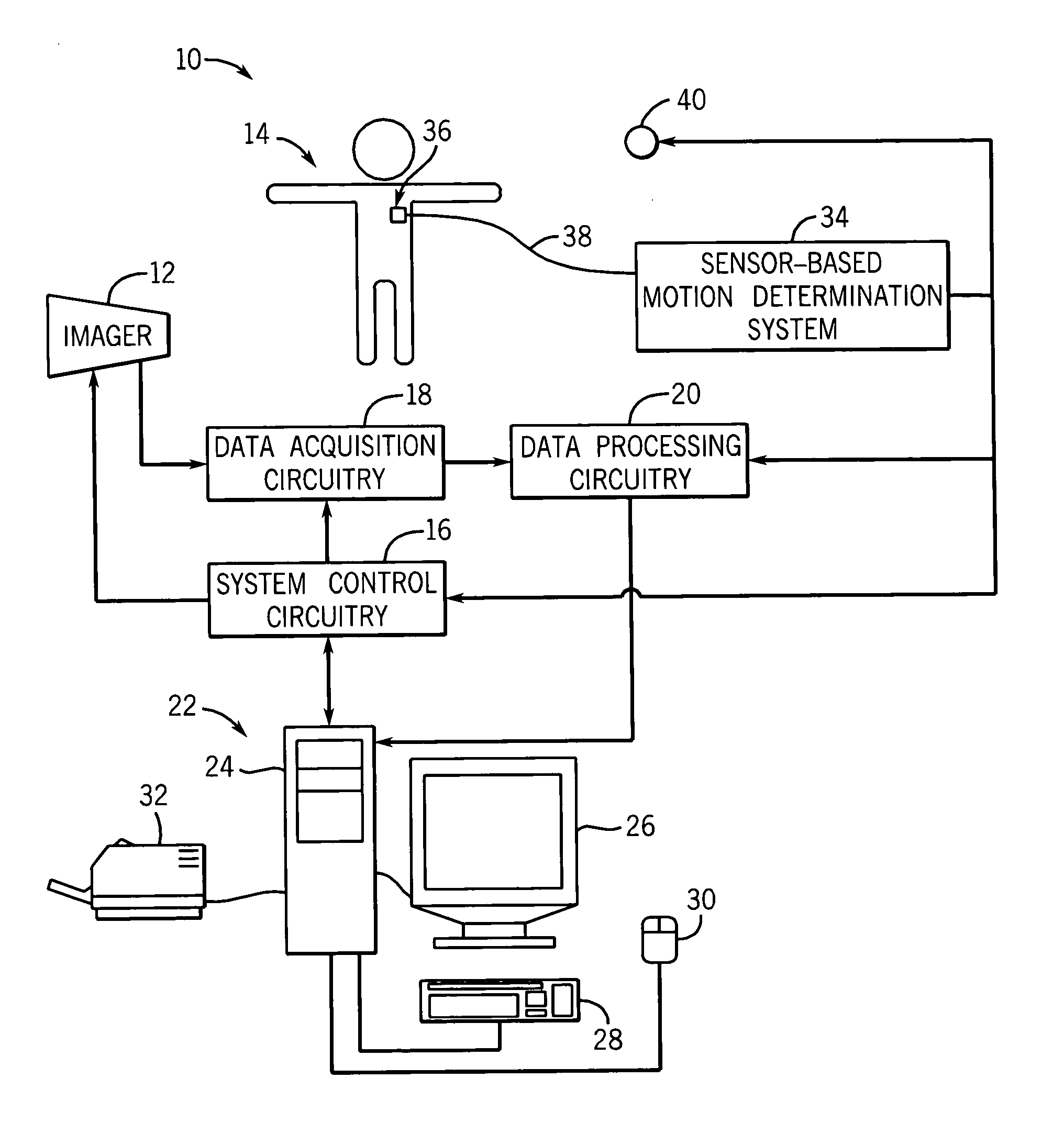
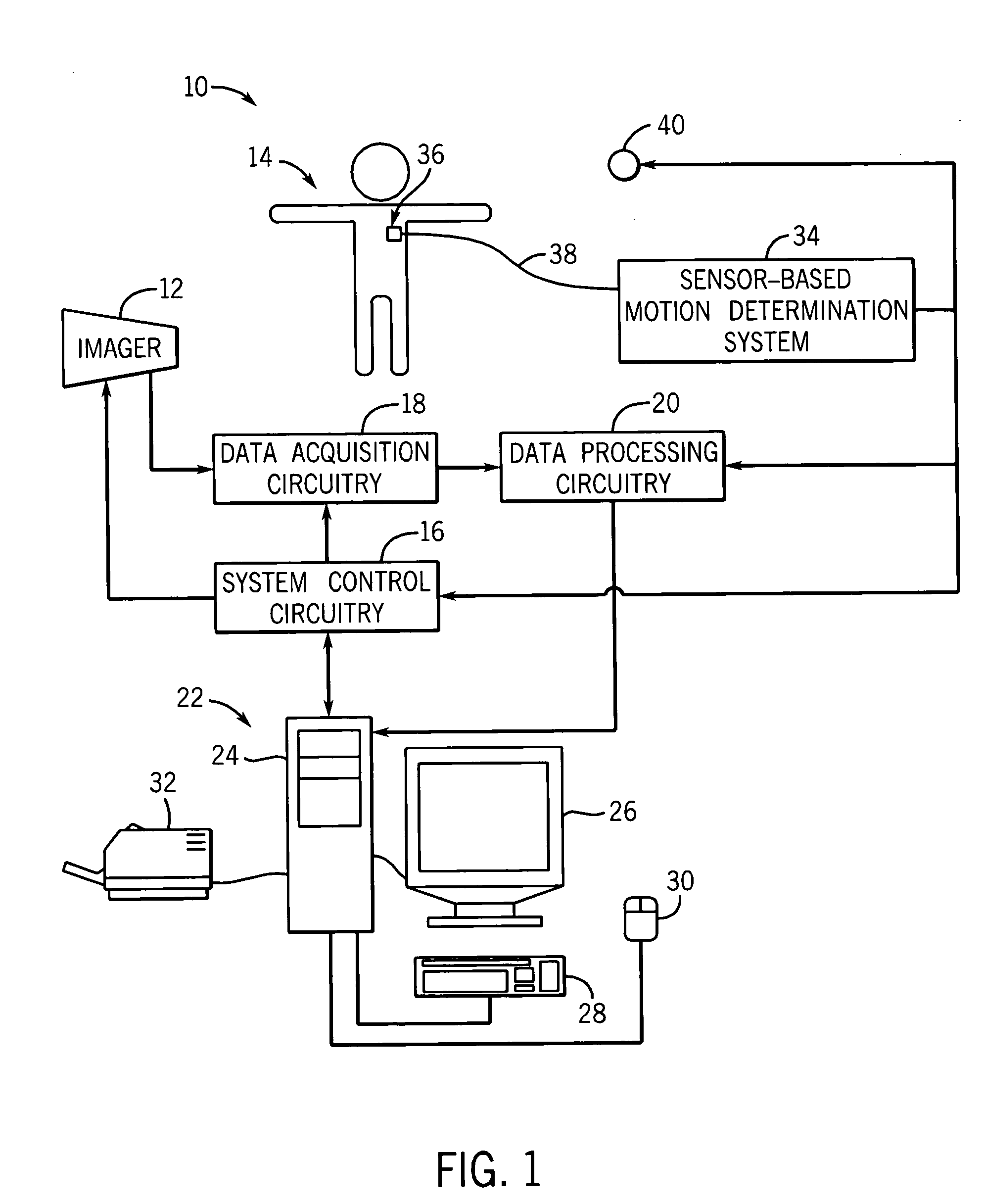
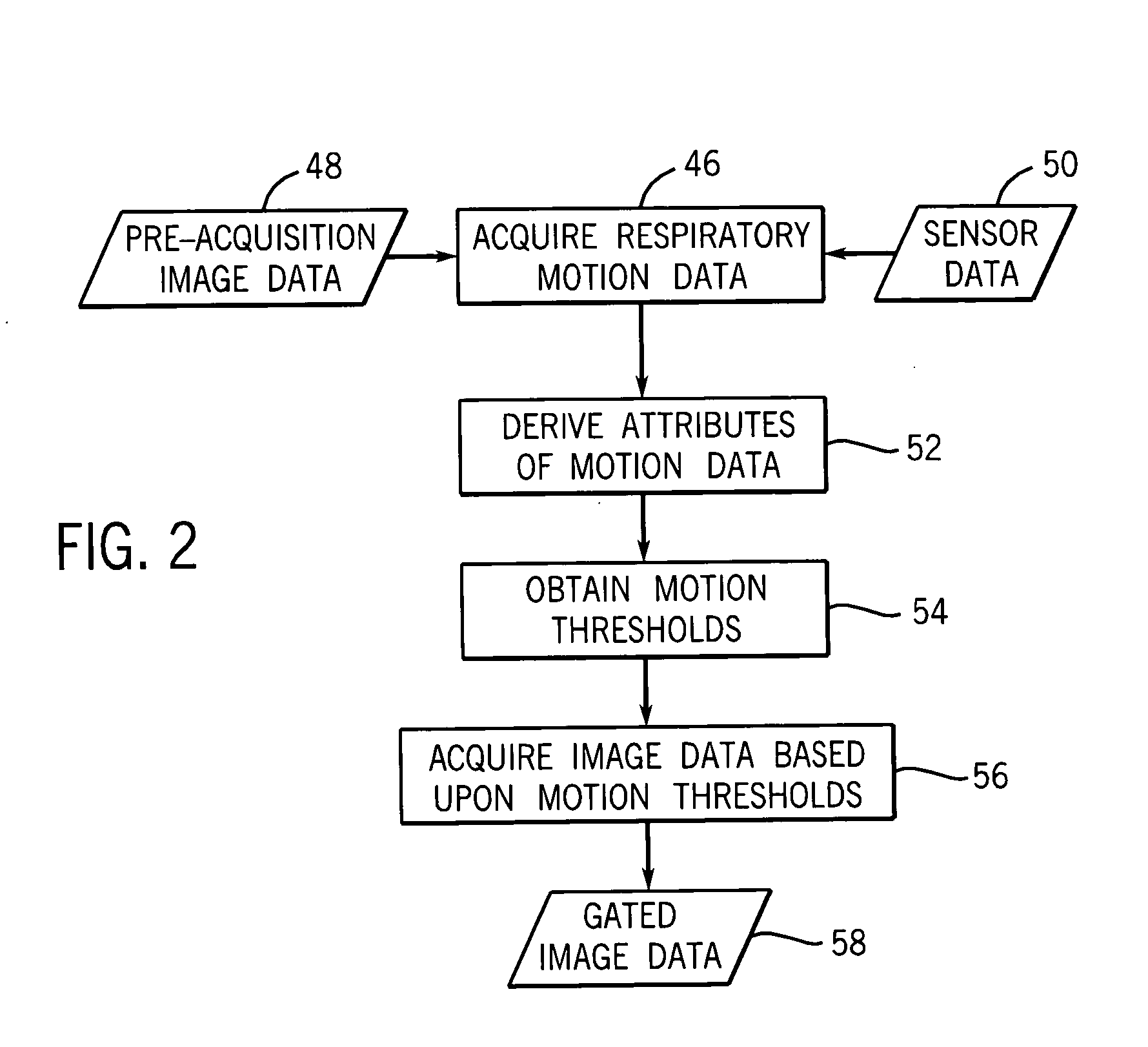
Method and system to reduce motion-related image artifacts during breath holding
One or more techniques are provided for gating the acquisition or selection of image data based upon the respiration of a patient. The technique provides for the acquisition of respiratory motion data from the image system or from one or more sensor-based motion determination systems. Various attributes of respiratory motion may be derived from the respiratory motion data and motion thresholds determined from the attributes. Based upon the respiratory motion of the patient and the determined thresholds, image data may be acquired or selected which corresponds to one or more breath-holds by the patient or low respiratory motion quiet periods within the breath-holds. The technique may be implemented in a fully automated or operator assisted or supervised manner.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
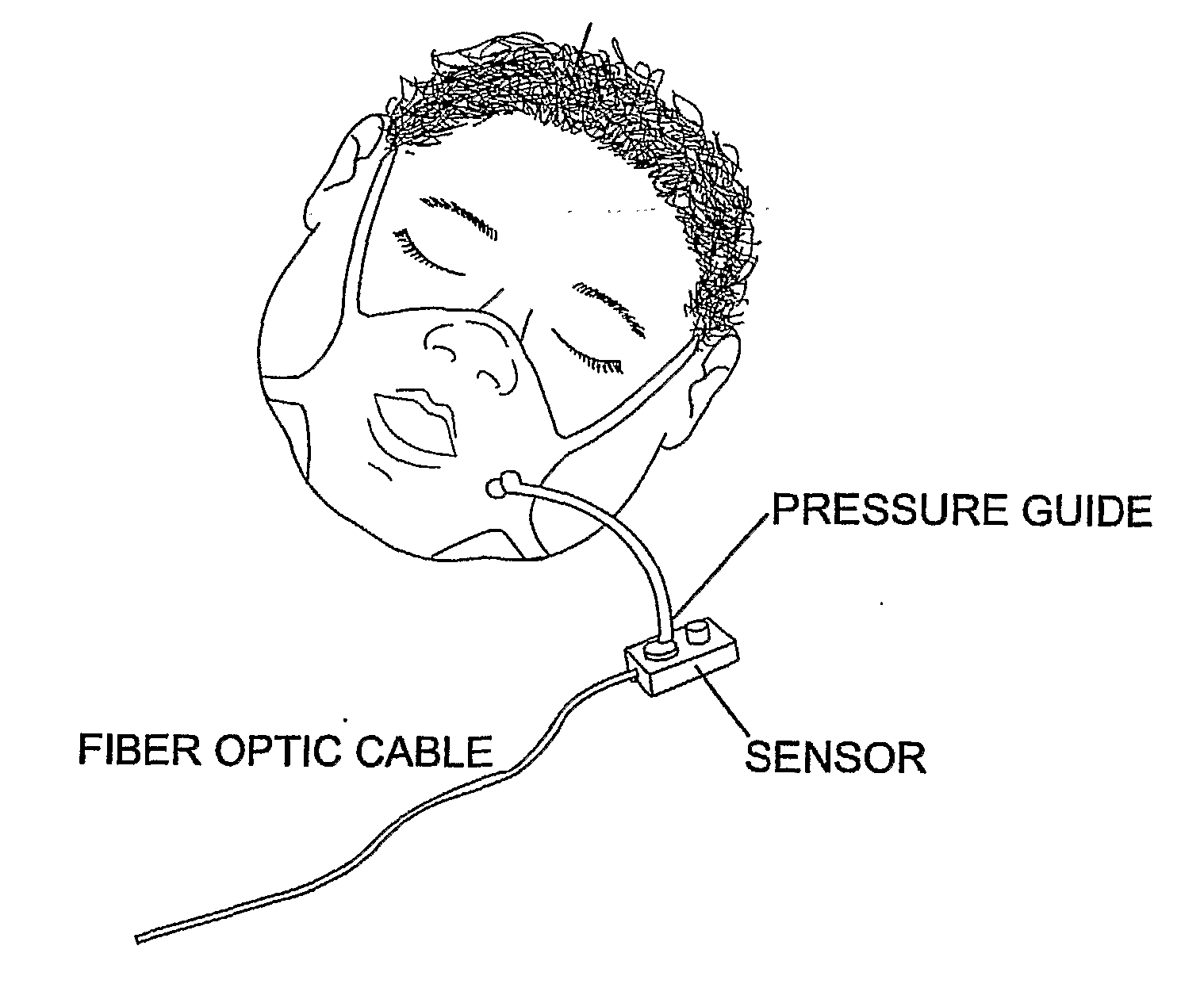
Respiratory Volume/Flow Gating, Monitoring, and Spirometry System for Mri
InactiveUS20080077038A1Improve accuracyHigh precisionMagnetic measurementsRespiratory organ evaluationForced expiratory vital capacityLung volumes
A respiratory volume / flow monitoring system, including a pneumotach that measures micromovements of a membrane in a MRI environment, gates (triggers) a MRI machine to start image acquisition at specific lung volumes or airflow rates during the breathing cycle or other breathing maneuvers of a patient. The system provides breathing motion artifact suppression for any imaging test susceptible to breathing motion artifact, allows respiratory monitoring of the subject during an MRI procedure, and provides the capability to perform spirometric testing while the subject is in the MRI environment. Embodiments of the invention are also applicable for patients undergoing CT imaging or any other imaging modality that allows external triggering.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
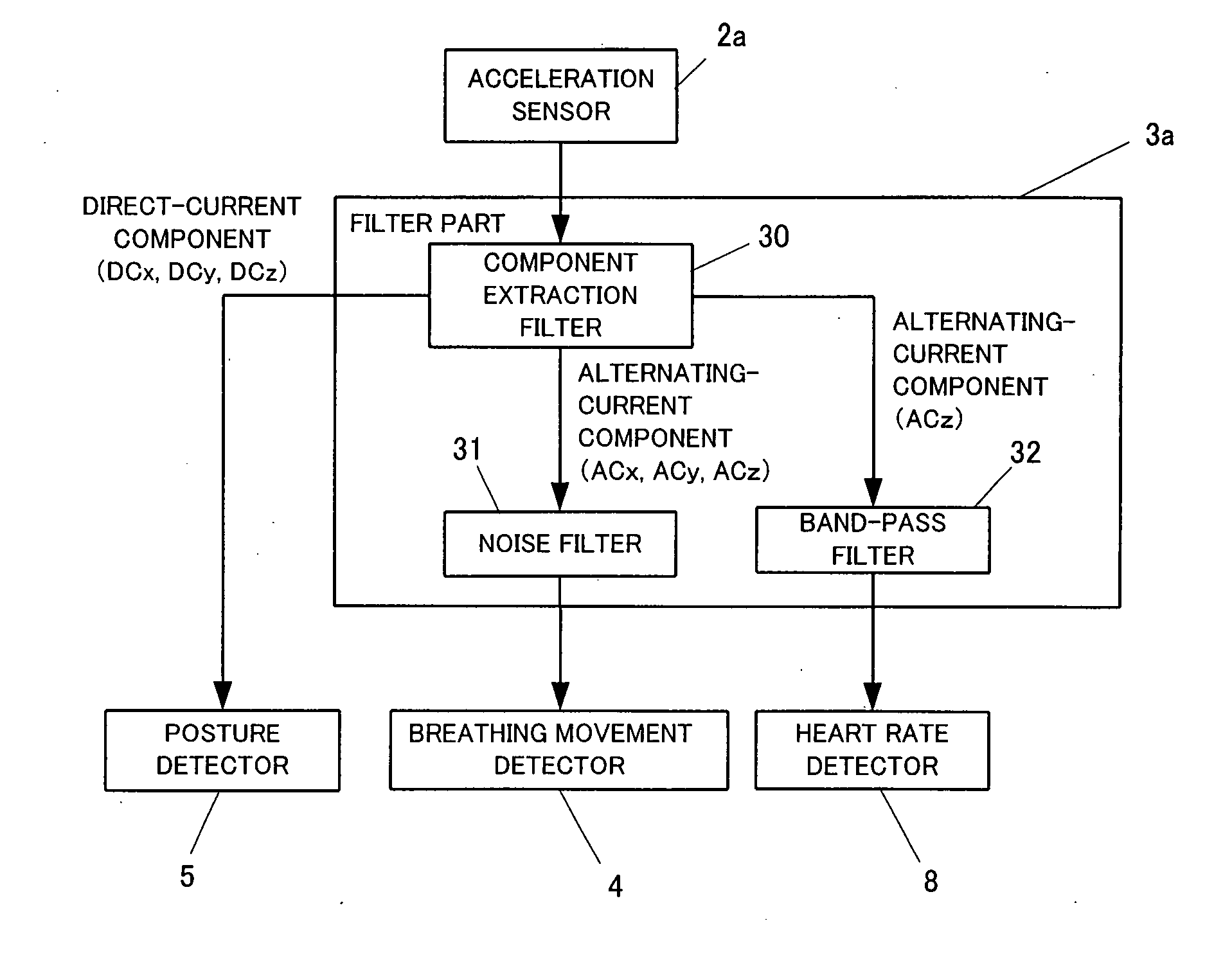
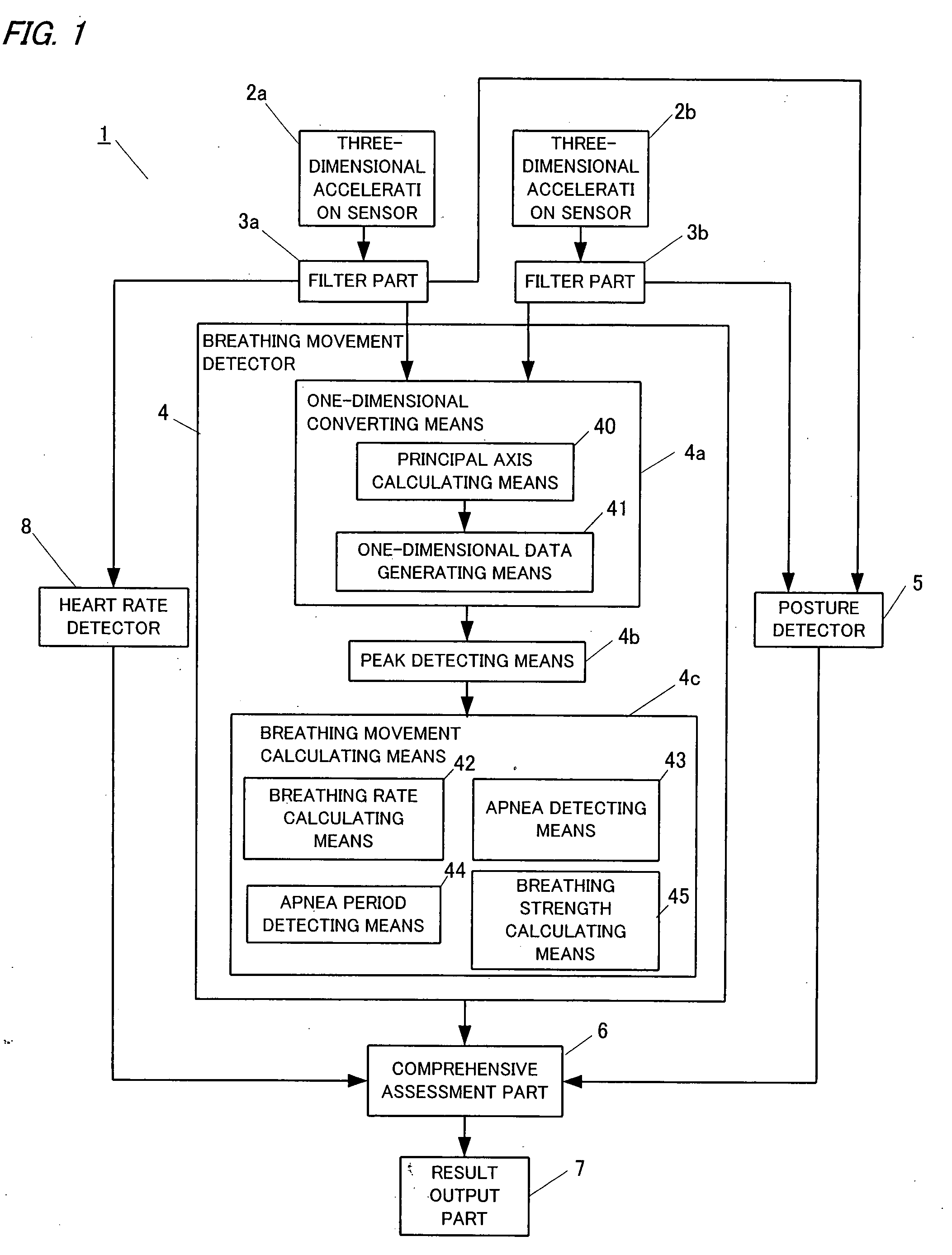
Sleep diagnosis device
InactiveUS20090062628A1Reduce the burden onReduce in quantityInertial sensorsCatheterRespiratory motionPostural orientation
The sleep diagnosis device 1 of the present invention comprises three-dimensional acceleration sensors 2a and 2b, a posture detector 5 which detects a posture of the patient from a DC component of the three-dimensional acceleration sensors, and a breathing movement detector 4 which detects a breathing movement of the patient from the AC component of the three-dimensional acceleration sensors. The sleep diagnosis device of the present invention can detect the posture (sleeping posture) and the breathing movement of the patient by using one three-dimensional acceleration sensor, so it is possible to reduce the number of sensors. Furthermore, the sleep diagnosis device can detect the breathing movement accurately by the three-dimensional acceleration sensors.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
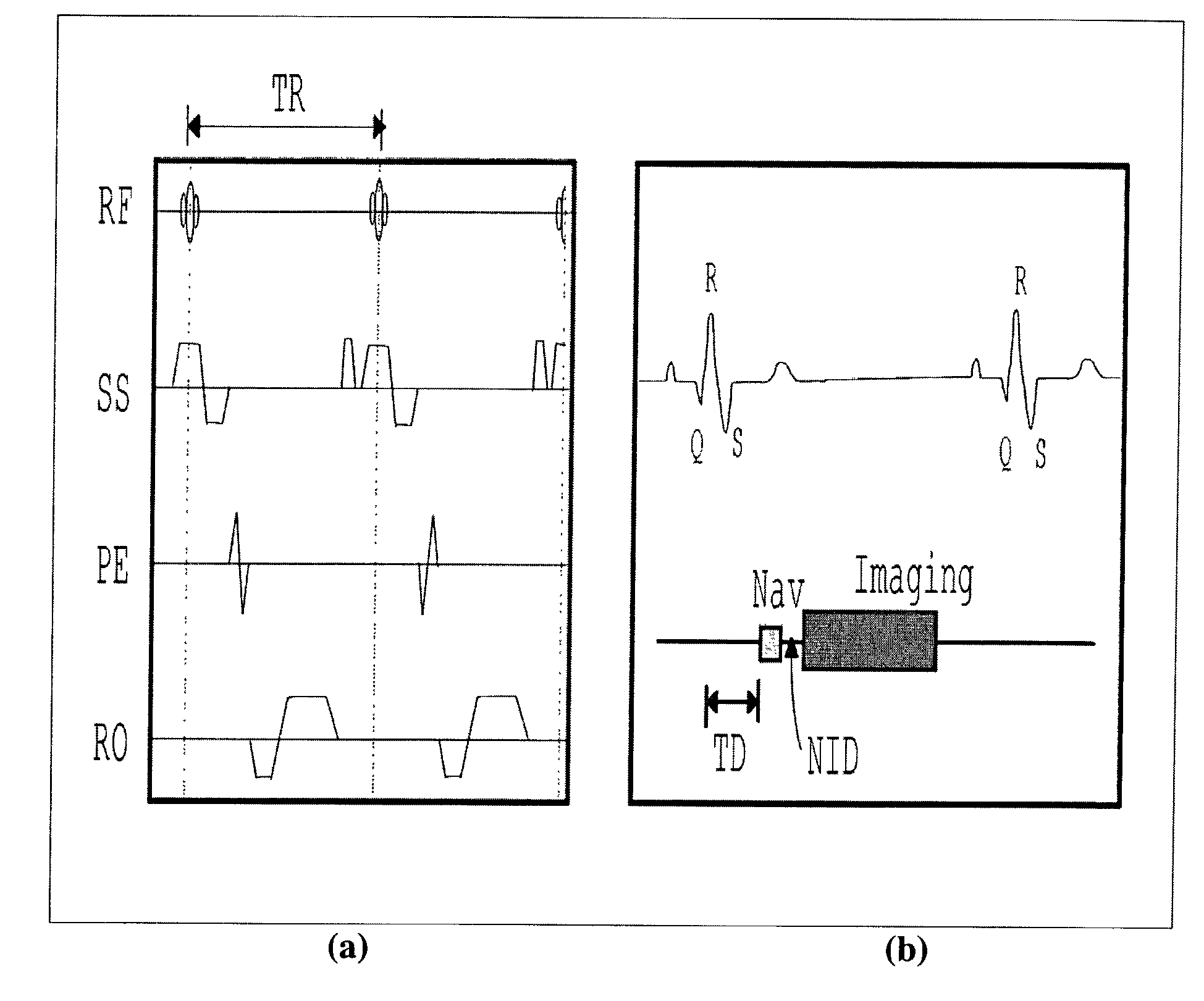
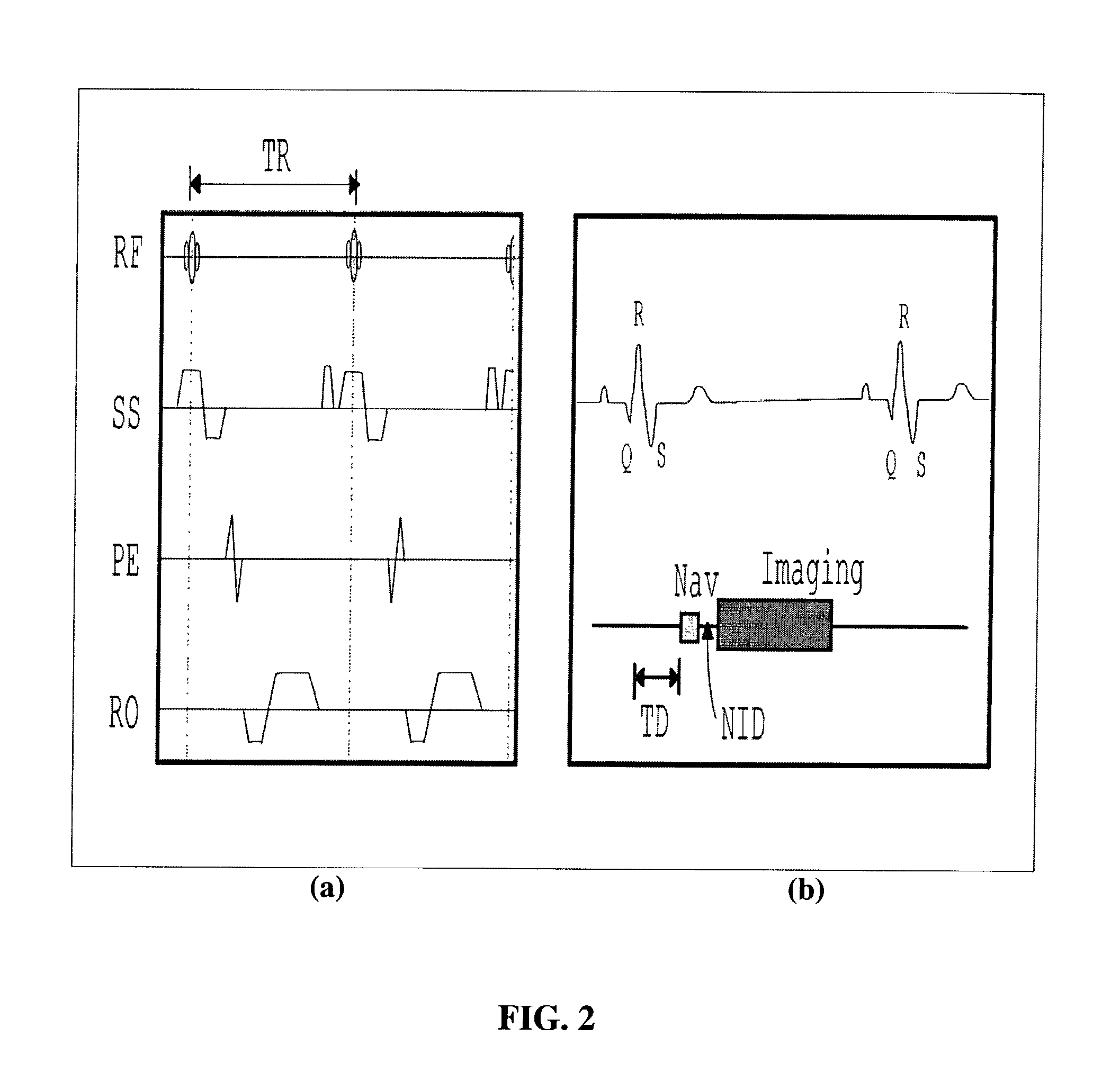
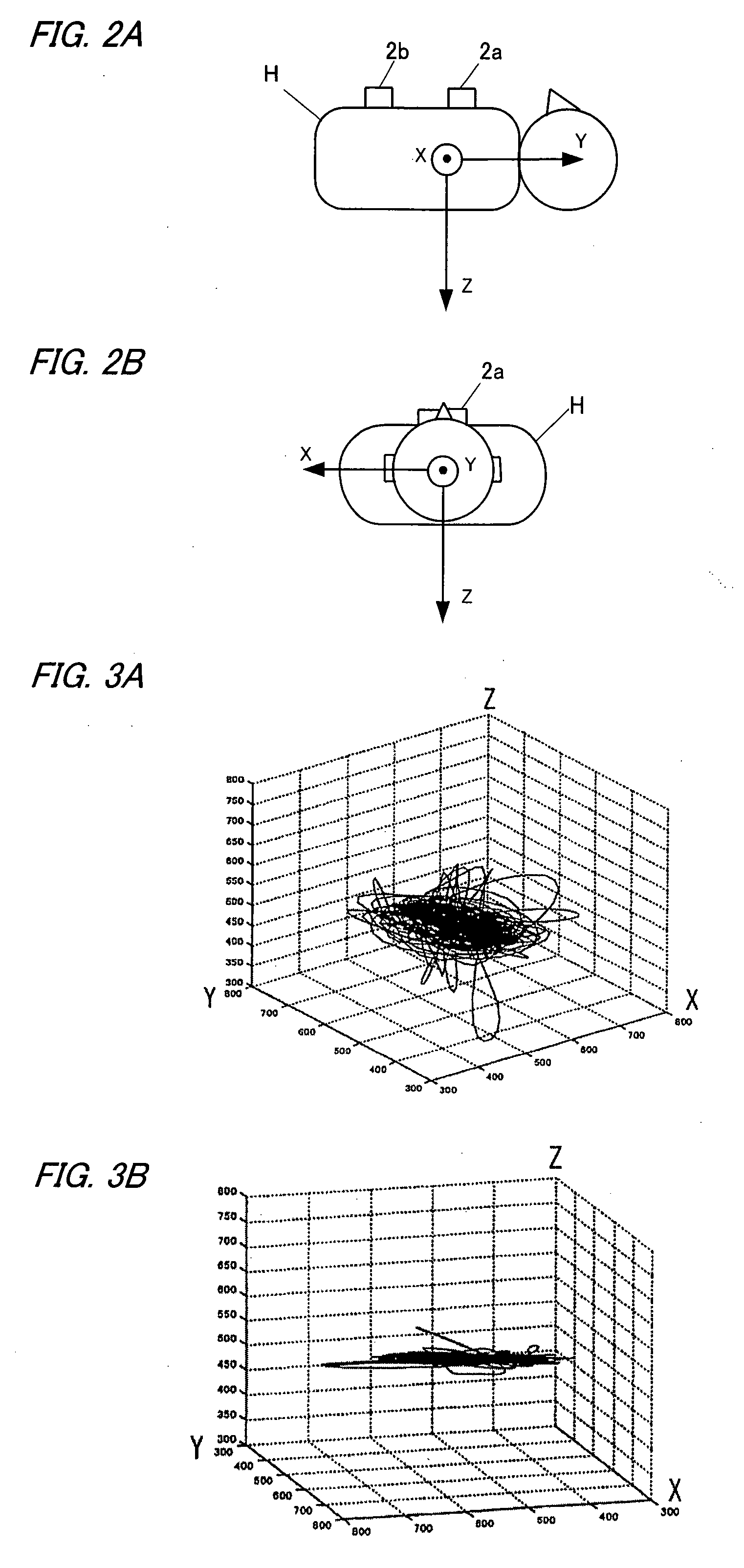
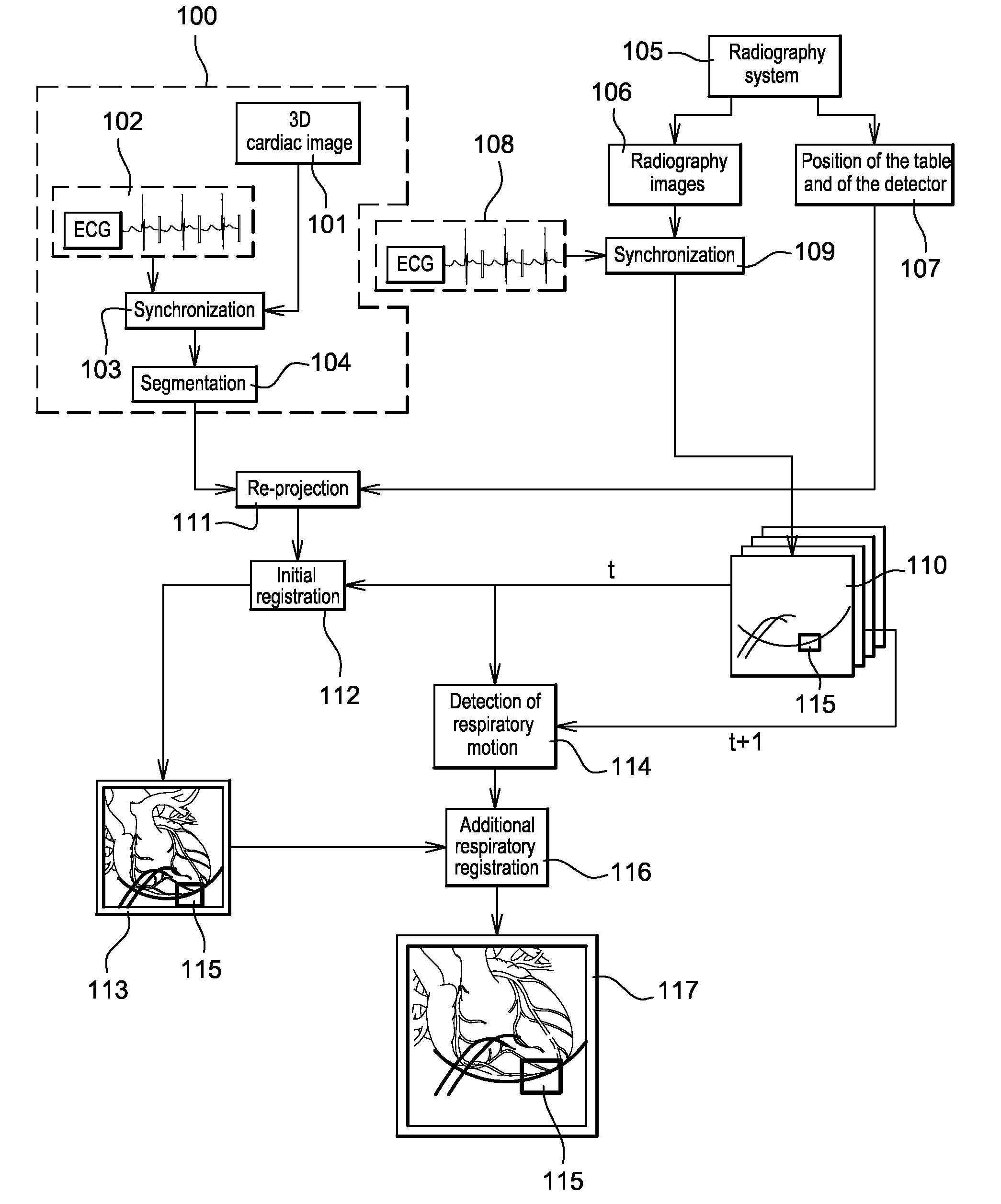
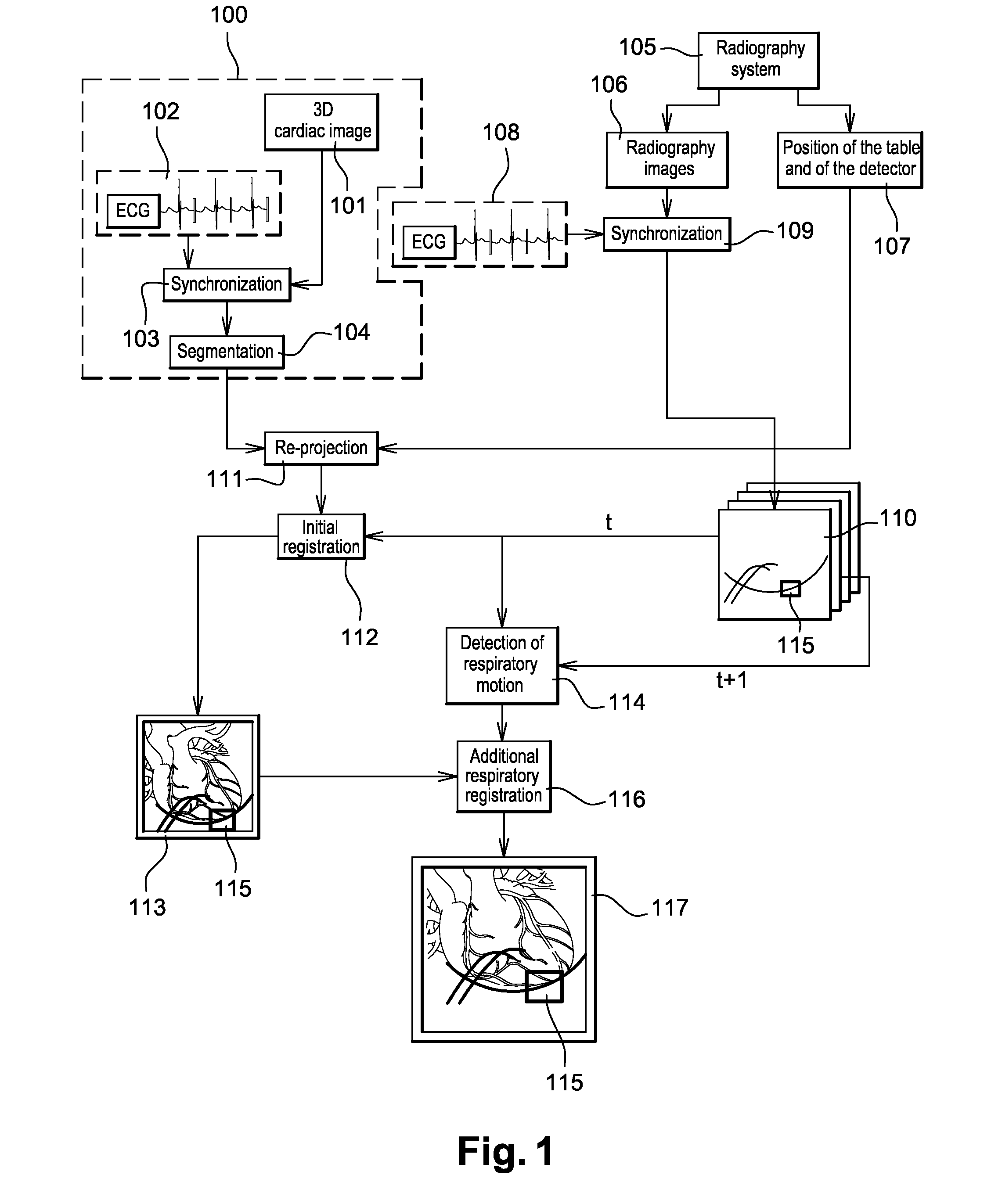
Method of detection and compensation for respiratory motion in radiography cardiac images synchronized with an electrocardiogram signal
ActiveUS20080240536A1Effective registrationGreat precision and simplicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHealth-index calculationX-rayX ray image
A method of detection and compensation for respiratory motion improves the registration between a 3D pre-operation image and X-ray images acquired during a cardiac intervention. By synchronizing the X-ray images with the electrocardiogram, the disclosed method thus eliminates the motion related to the heart cycle from these images, thus isolating the contribution of the respiratory motion. From this point, an algorithm is proposed capable of attributing the motion remaining in the radiography images to respiration. The algorithm also enables this motion to be detected and compensated for in order to obtain a registration between 3D cardiac images and radiography images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
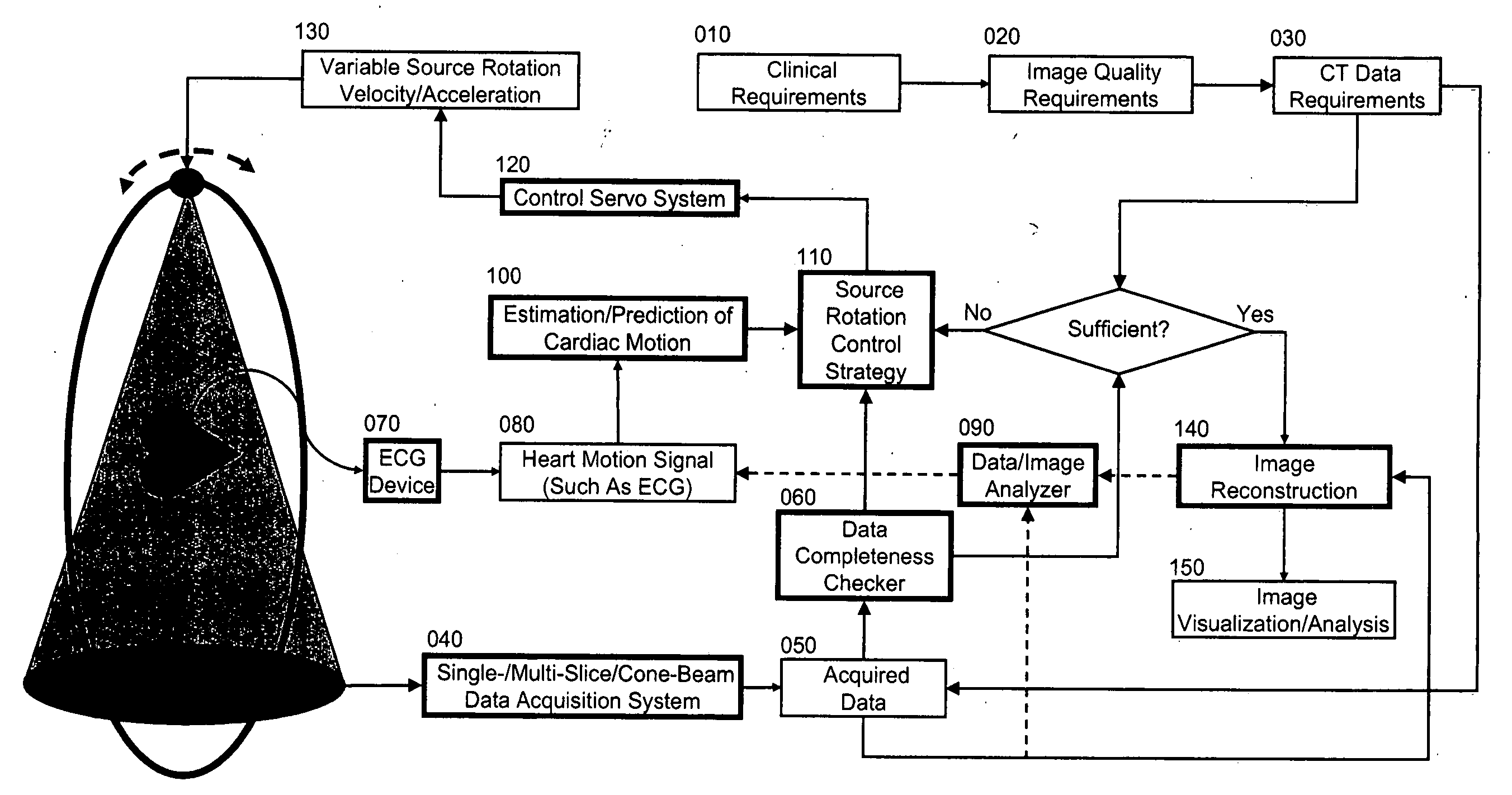
Controlled cardiac computed tomography
InactiveUS20070153971A1Minimize impactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCardiac computed tomographyData acquisition
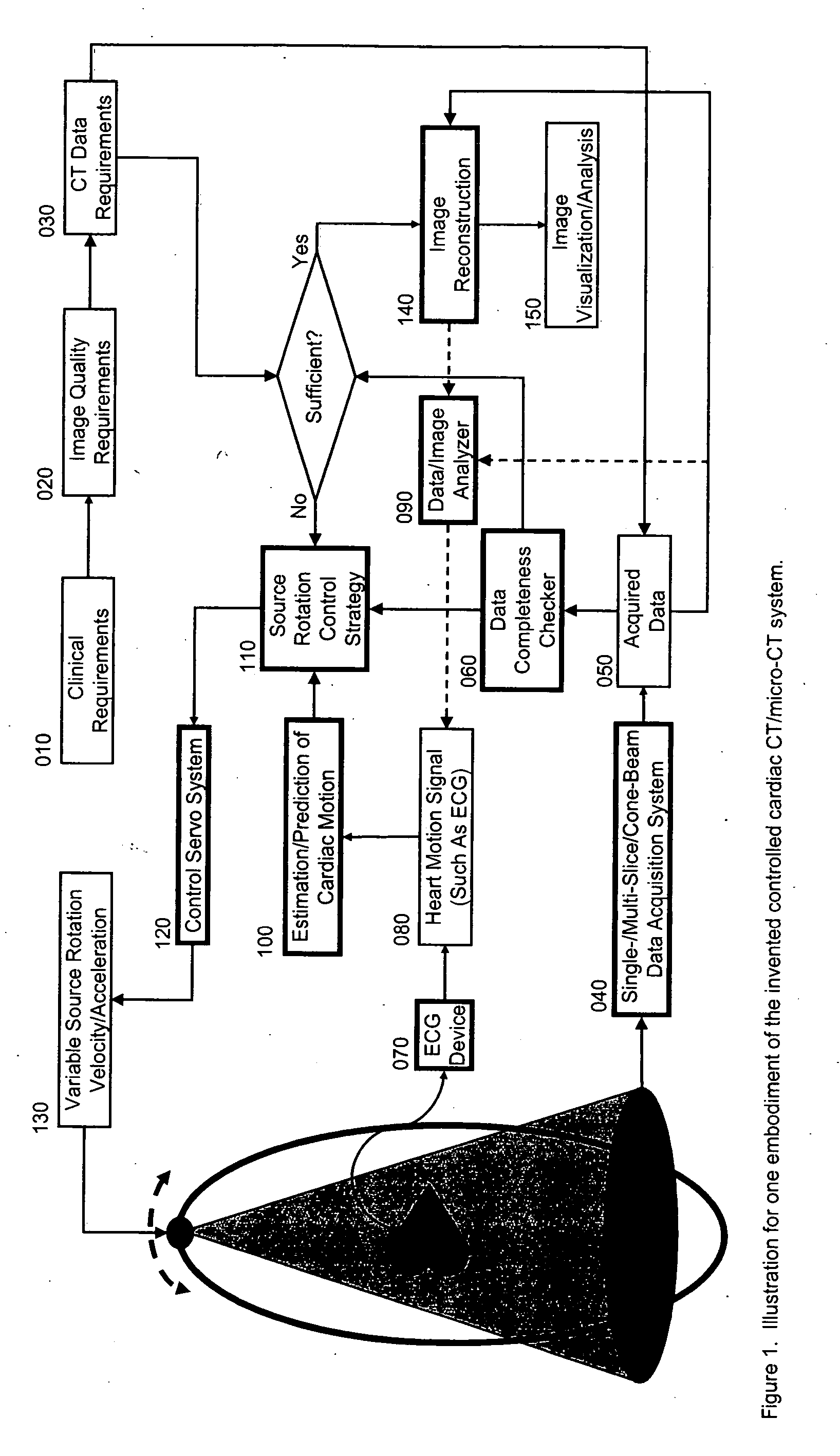
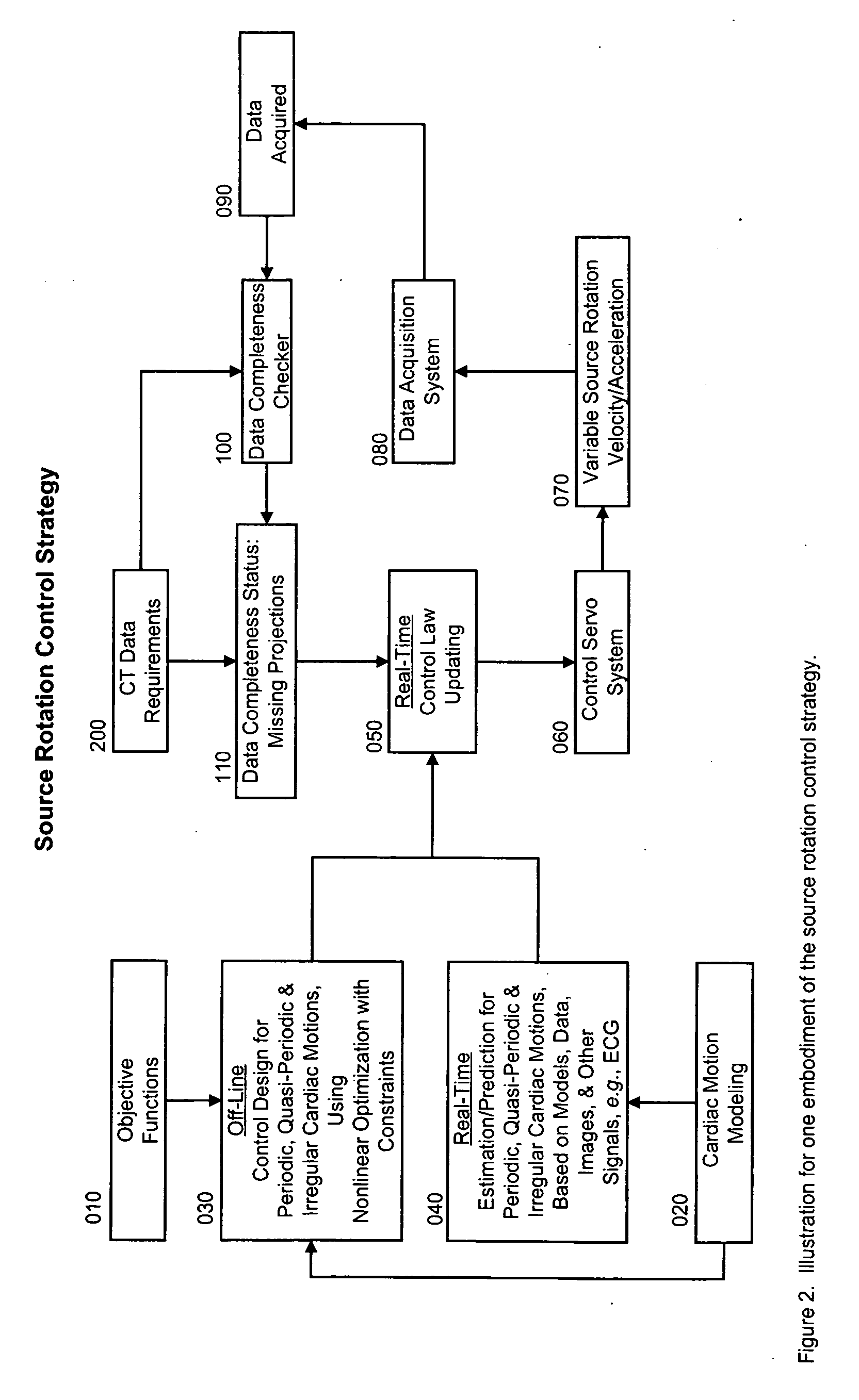
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) has been a hot topic for years because of the clinical importance of cardiac diseases and the rapid evolution of CT systems. In this application, we disclose a novel strategy for controlled cardiac CT (CCCT) that may effectively reduce image artifacts due to cardiac and respiratory motions and reduce the scan time. Our approach is radically different from existing ones and is based on controlling the x-ray source rotation velocity and powering status in reference to the cardiac motion. By such a control-based intervention the data acquisition process can be optimized for cardiac CT in the cases of periodic and quasi-periodic cardiac motions. Specifically, we present the corresponding coordination / control schemes for either exact or approximate matches between the ideal and actual source positions.
Owner:WANG CHENGLIN +1
Method and apparatus for determining a respiration signal
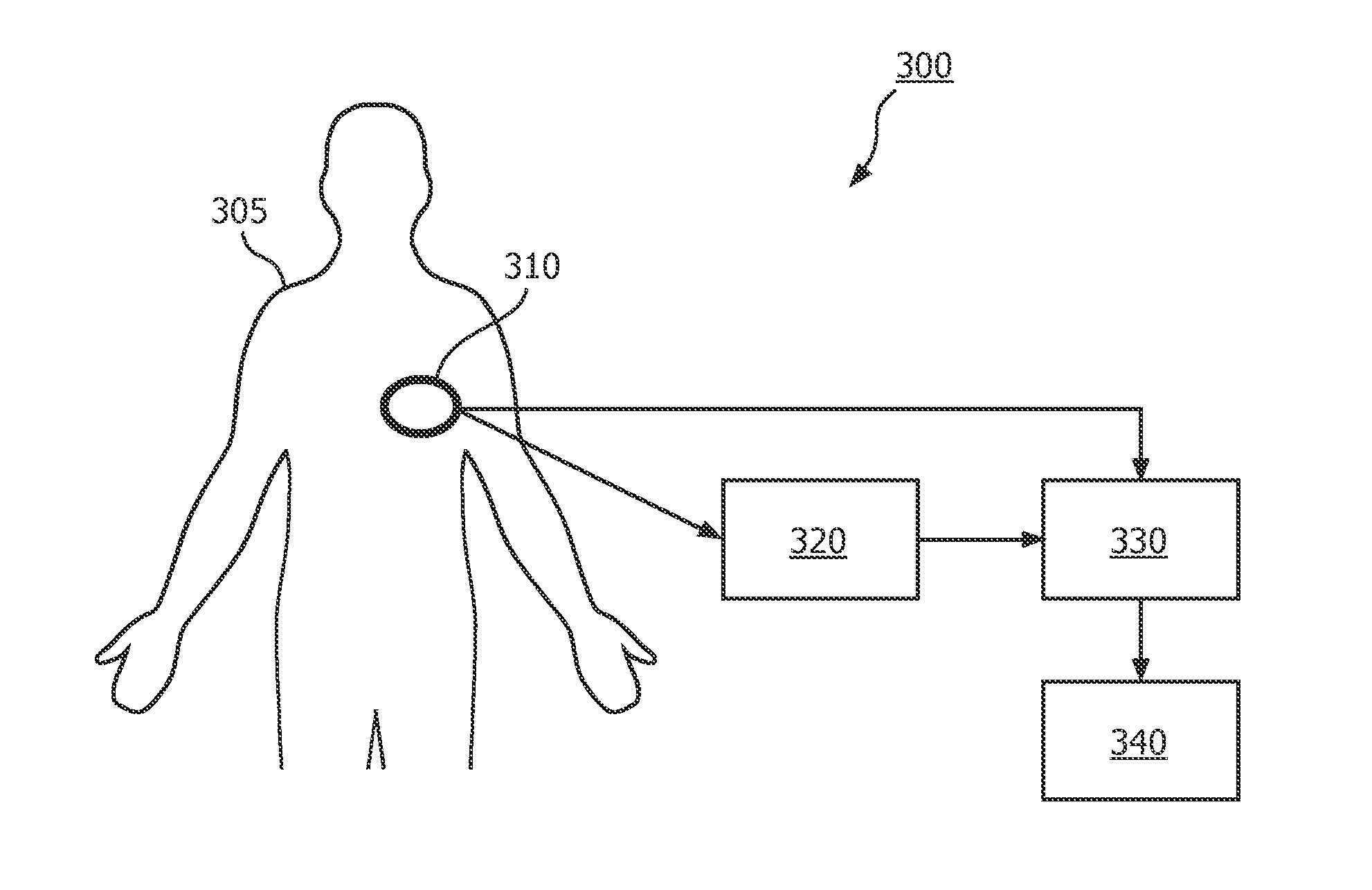
ActiveUS20120296221A1Efficiently determineAccurate representationInertial sensorsCatheterAccelerometerClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for determining a respiration of a subject (305) in which, with a single multi-axial accelerometer (310) positioned on a body of the subject (305), accelerometer signals are generated (101) indicative of the acceleration of the subject (305) along different spatial axes, a vector magnitude signal of the acceleration of the subject (305) along the different spatial axes is calculated (102) from the accelerometer signals, a non-respiratory motion contribution to the acceleration along the different spatial axes is identified (103, 203) from the vector magnitude signal, which non-respiratory motion contribution is not caused by the respiration, and a respiration signal indicative of the respiration of the subject is determined (104, 204) by filtering the non-respiratory motion contribution from at least one of the accelerometer signals. In this way a method is provided which determines the respiration of a subject (305) with a single accelerometer (310) in an efficient and, for a patient, comfortable way.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
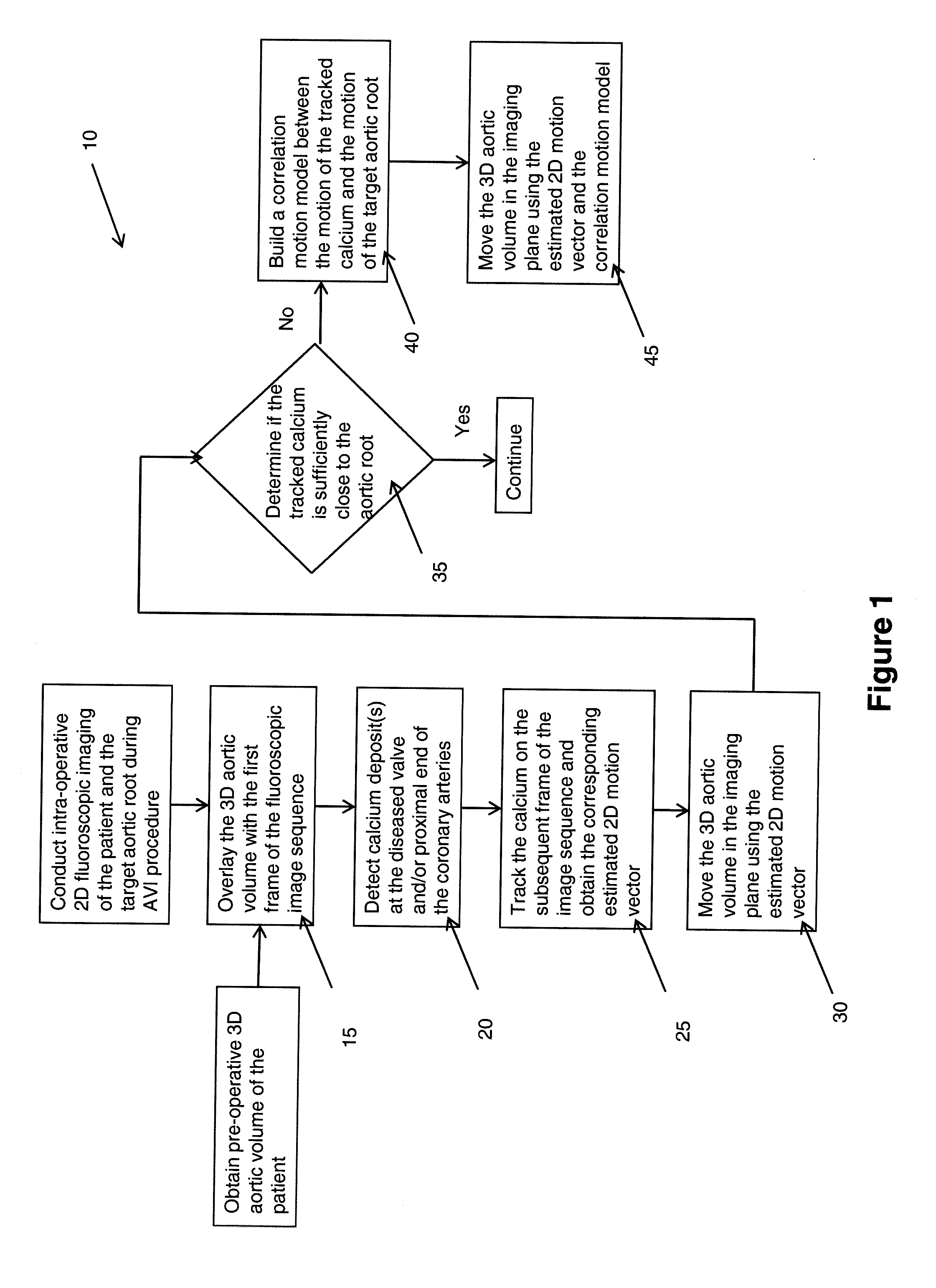
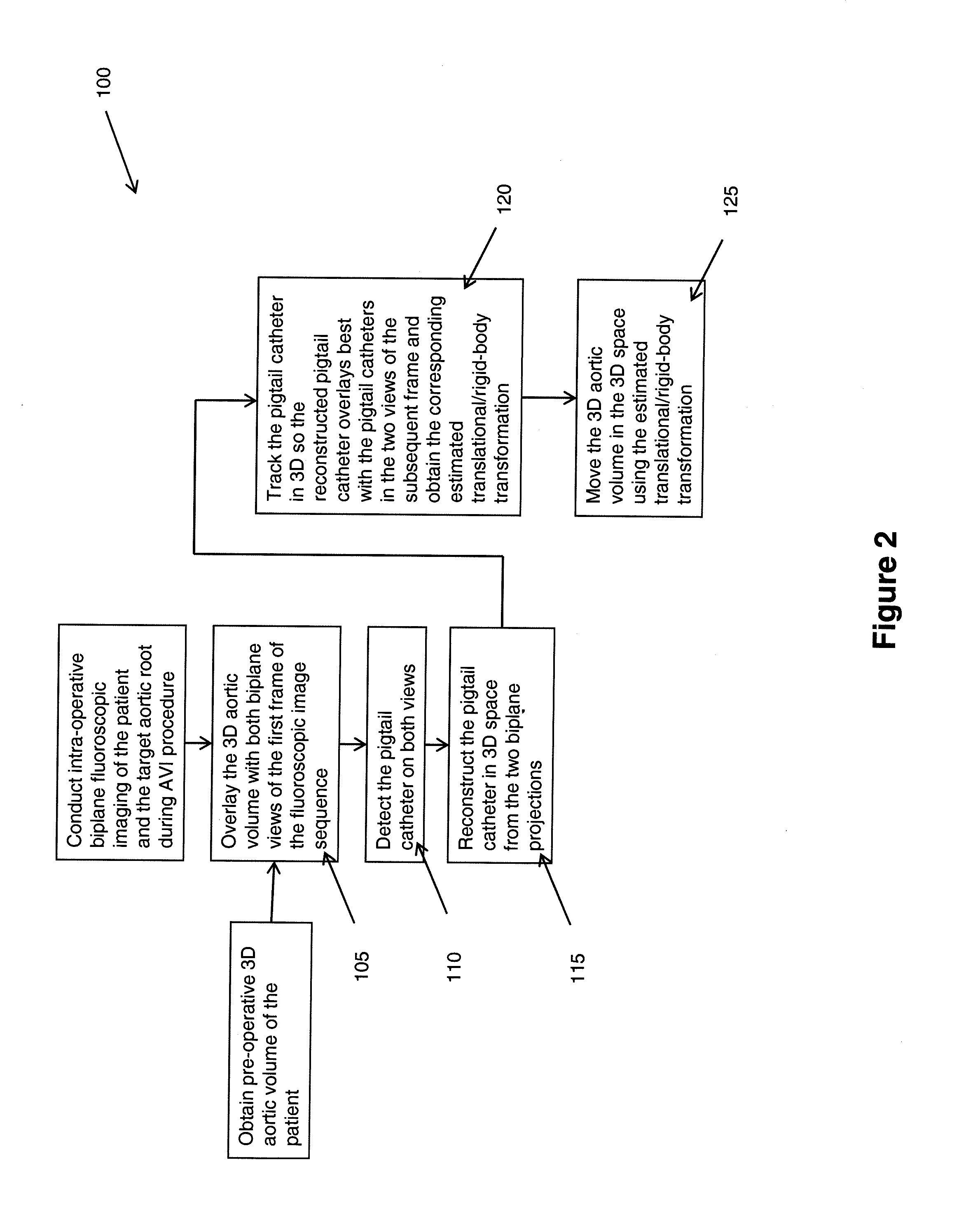
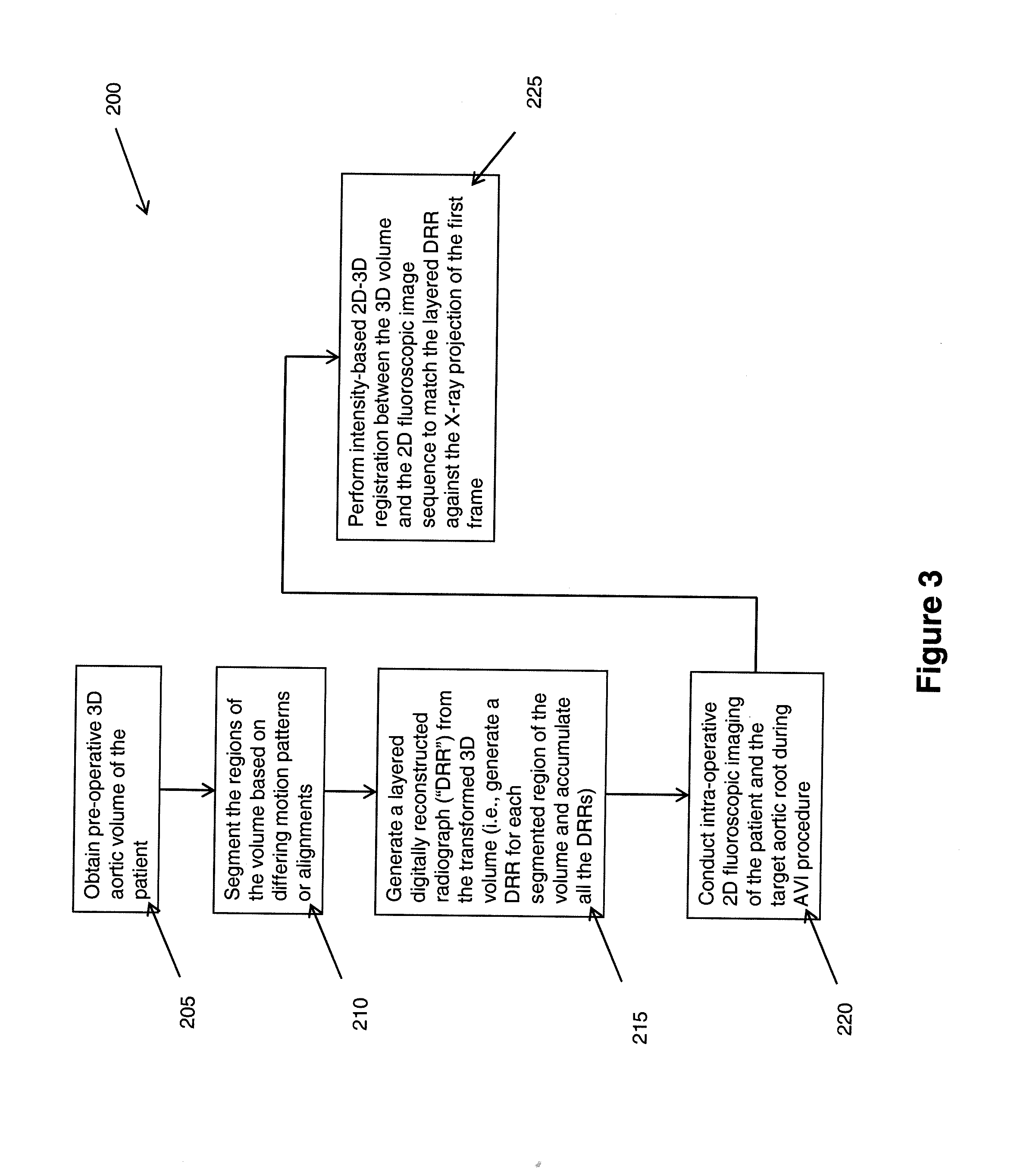
Method of motion compensation for trans-catheter aortic valve implantation
ActiveUS20110164035A1Not utilizeMotion compensationImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCardiac imaging
A method (10) to compensate for cardiac and respiratory motion in cardiac imaging during minimal invasive (e.g., trans-catheter) AVI procedures by image-based tracking (20, 25) on fluoroscopic images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Breathing movement measurements and apparatus
InactiveUS6893404B2Medical automated diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationMedicineMovement measurement
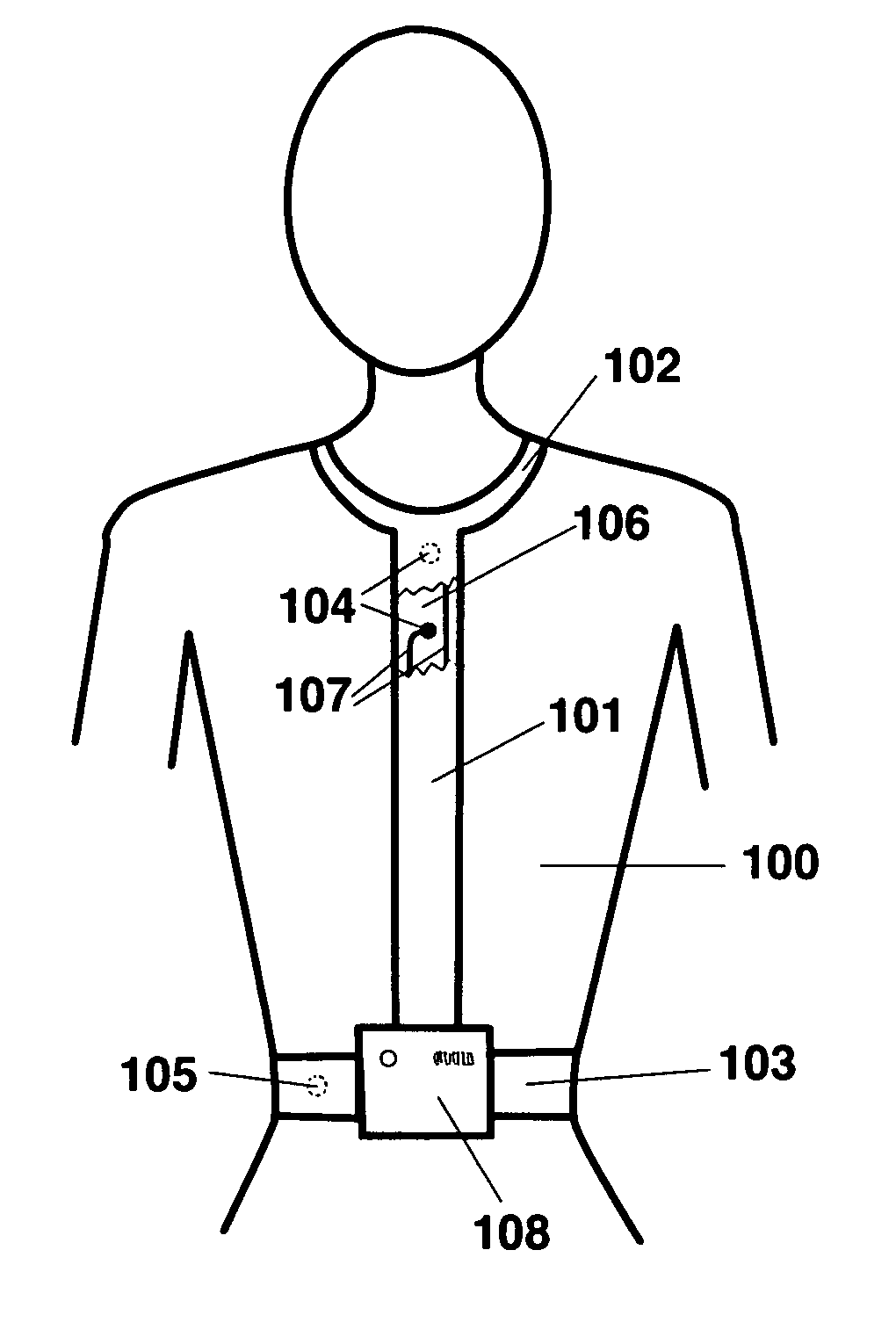
A method and apparatus for measuring breathing movements and determining breathing patterns, by measuring the simultaneous movement of a plurality of points of a human subject, such that a breathing pattern may be determined based on data obtained in a single acquisition. The method provides a symmetry breathing pattern parameter.
Owner:REMO EHF
Breathing detection apparatus and method
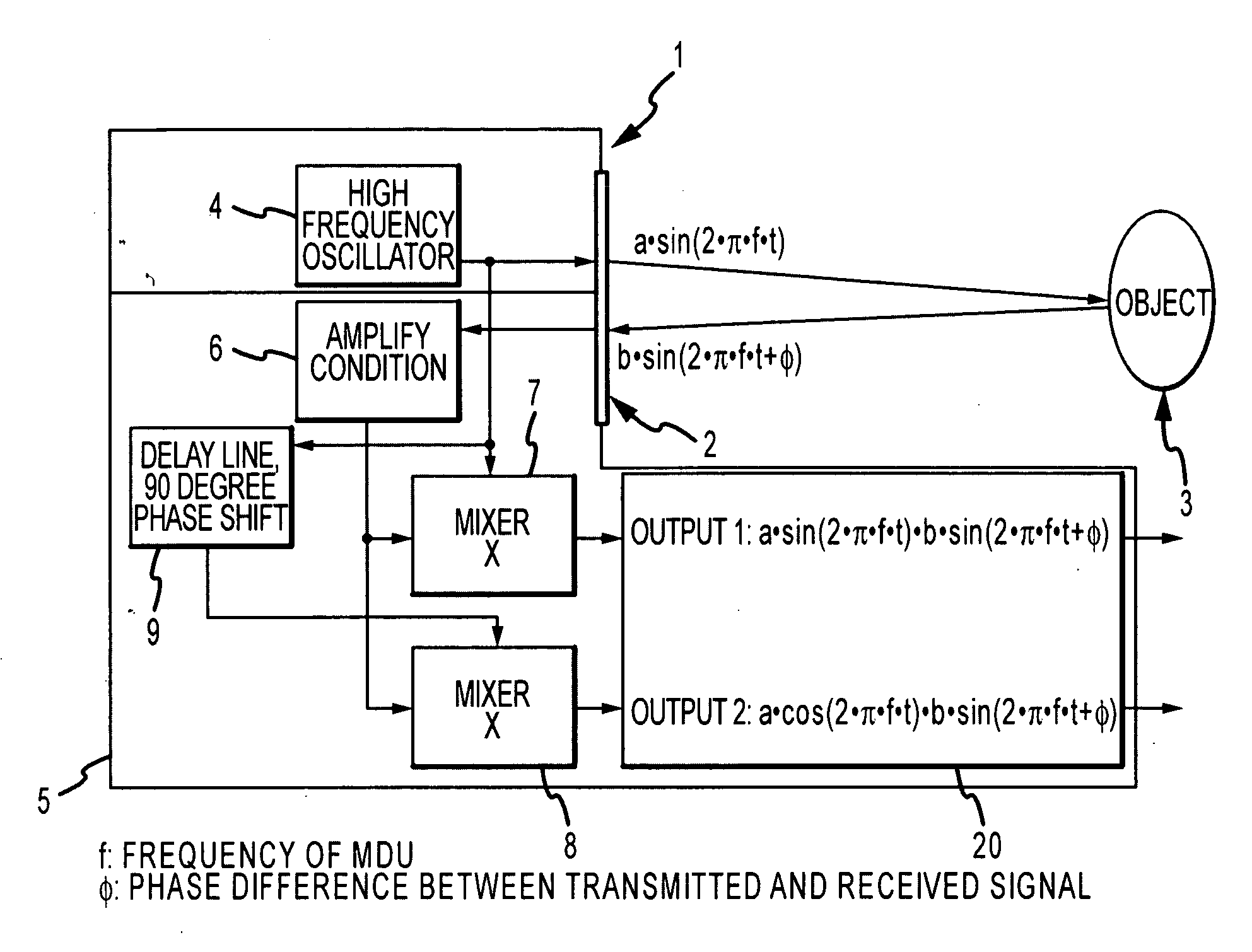
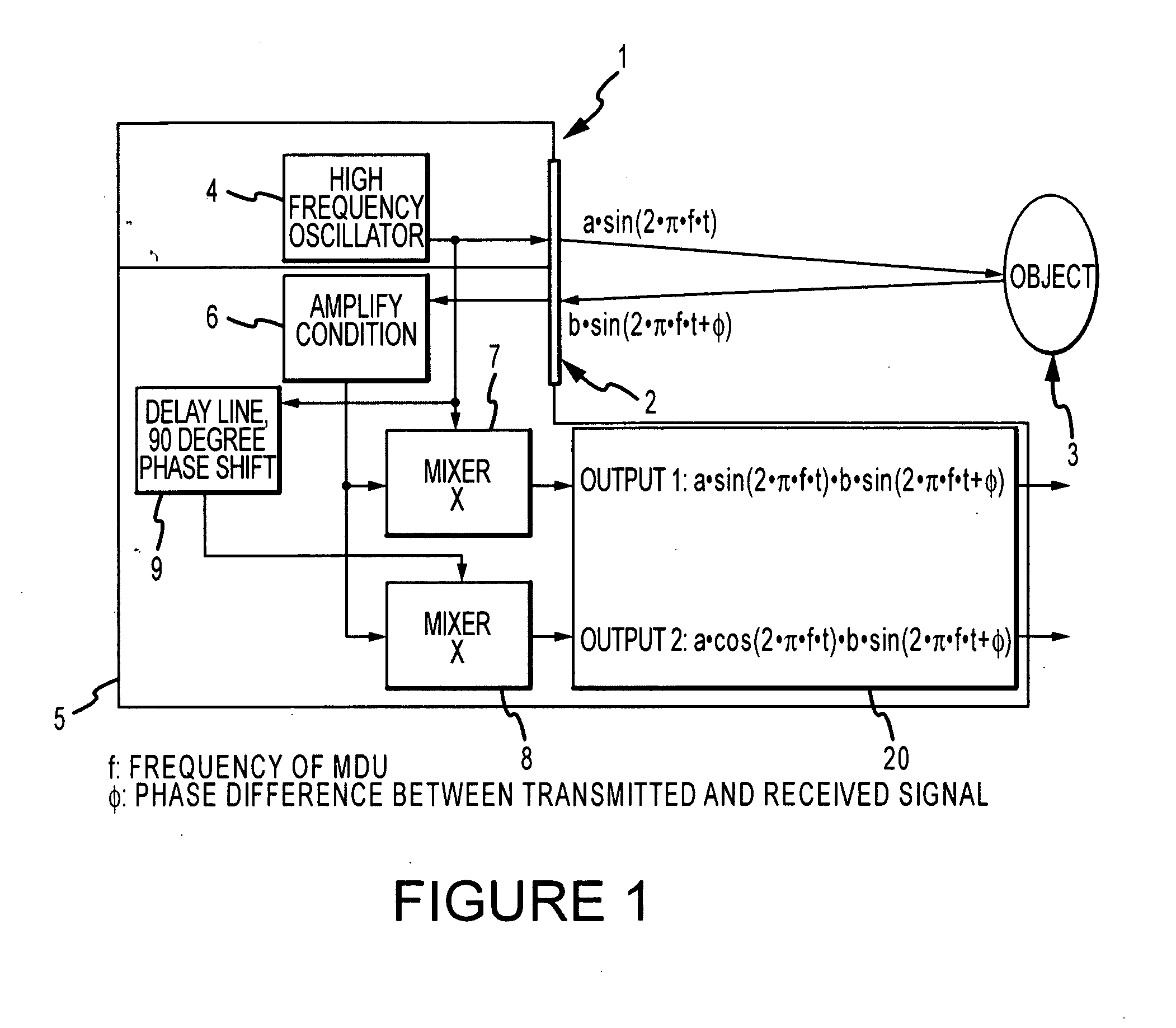
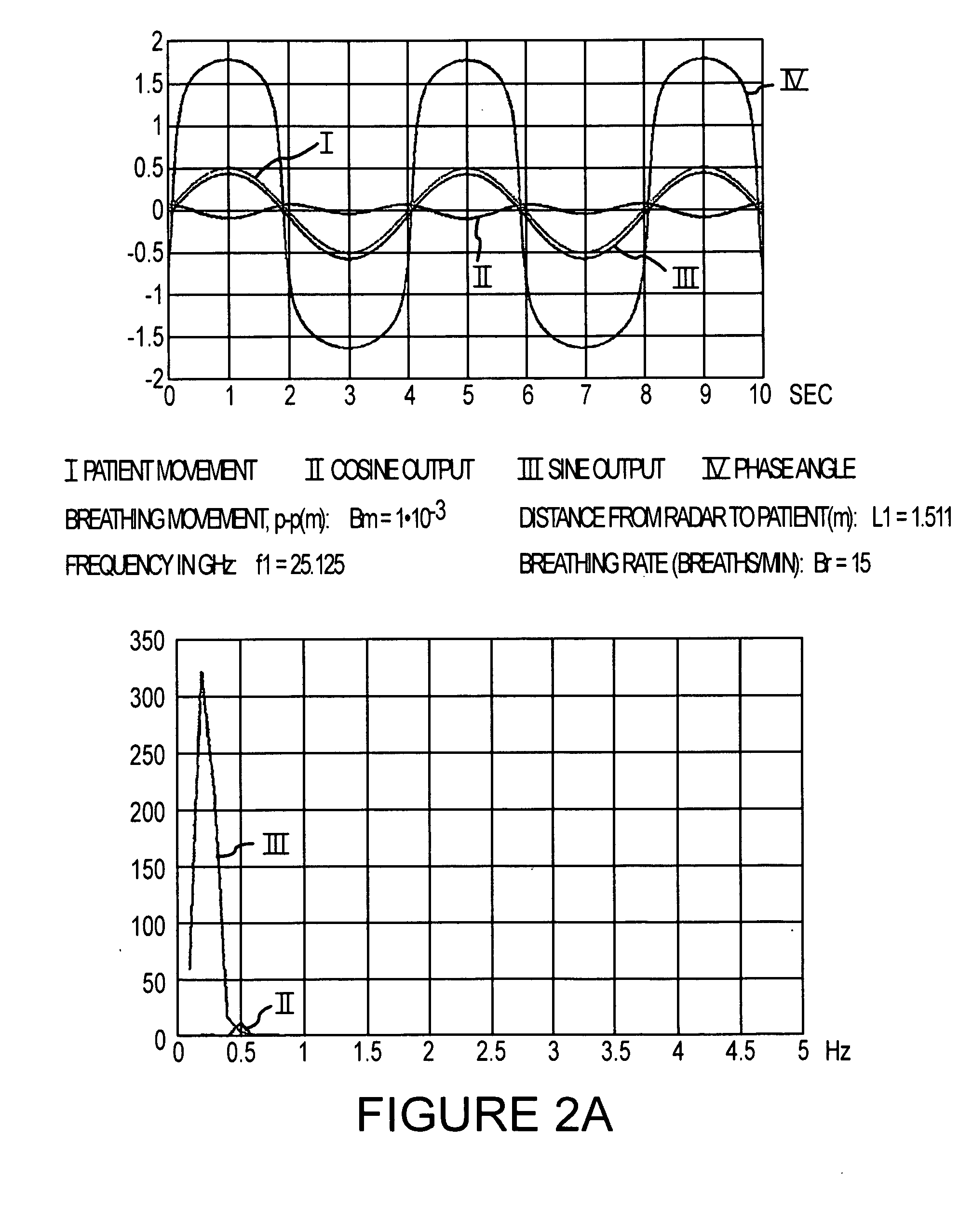
A device is disclosed for remote monitoring of breathing movements of a patient, comprising a sender transmitting a microwave signal toward the patient, a receiver arranged to receive a signal reflected by the patient, and a processor. The processor mixes the received signal with the transmitted signal and with a signal in quadrature with the transmitted signal to determine a breathing frequency of the patient. In some embodiments, two signals at different frequencies are emitted toward the patient and processed in order to compensate for breathing patterns that are not uniquely resolvable at a single frequency.
Owner:LAERDAL MEDICAL AS
Relaxation inducing apparatus
A wearable relaxation inducing apparatus comprises either a harness or a garment made of elastically flexible fabric tightly worn on the torso; electromechanical sensors attached to the fabric translating the breathing movements of a wearer into electric signals representing breathing rate and depth; electrically operated transducers attached to the fabric providing tactile feedback to the body about breathing; and electronic circuitry for processing the electrical signals produced by the electromechanical sensors and for operating the transducers at selected adjustable sequences and rates.
Owner:MURPHY MARTIN PAUL
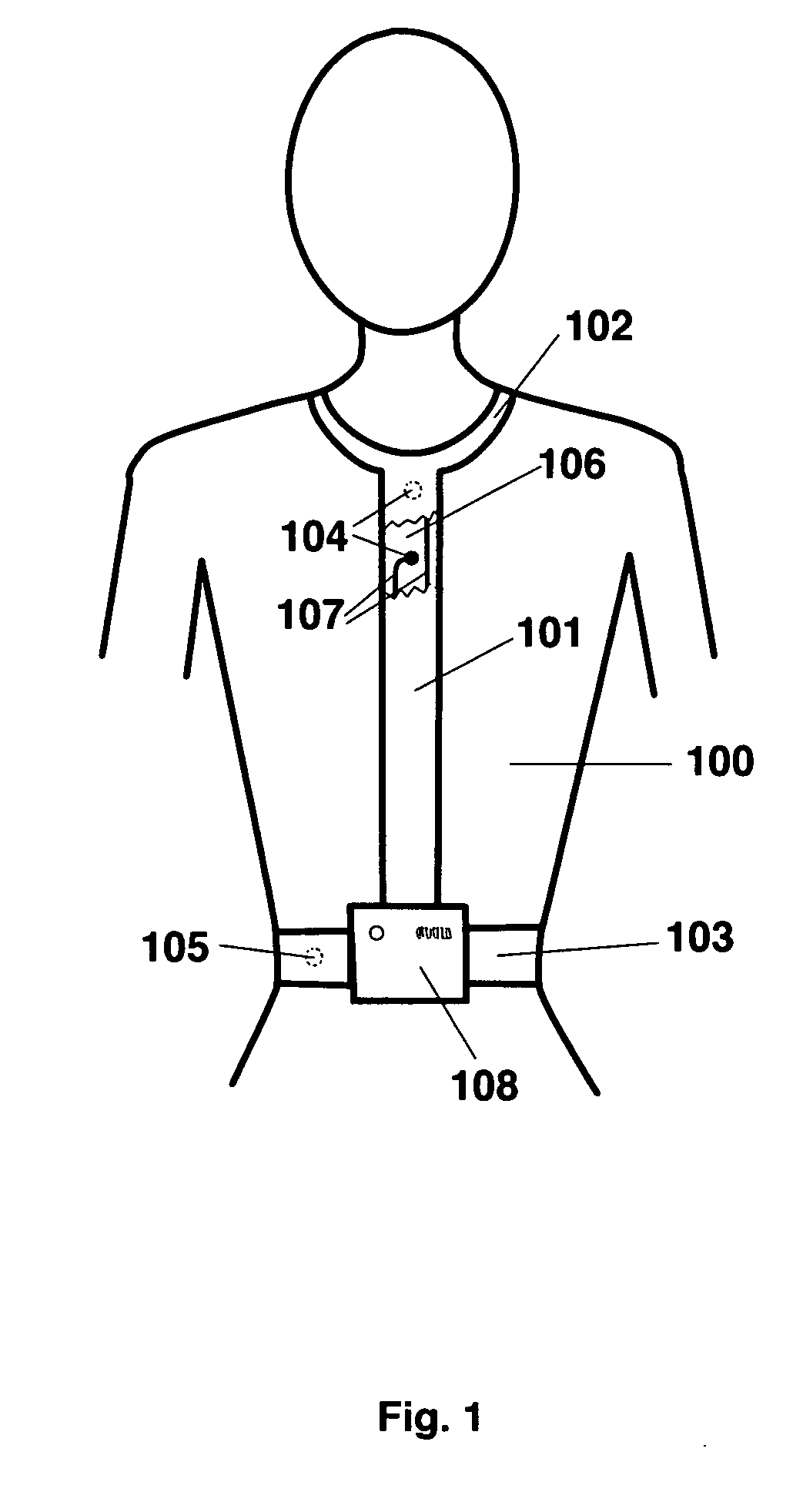
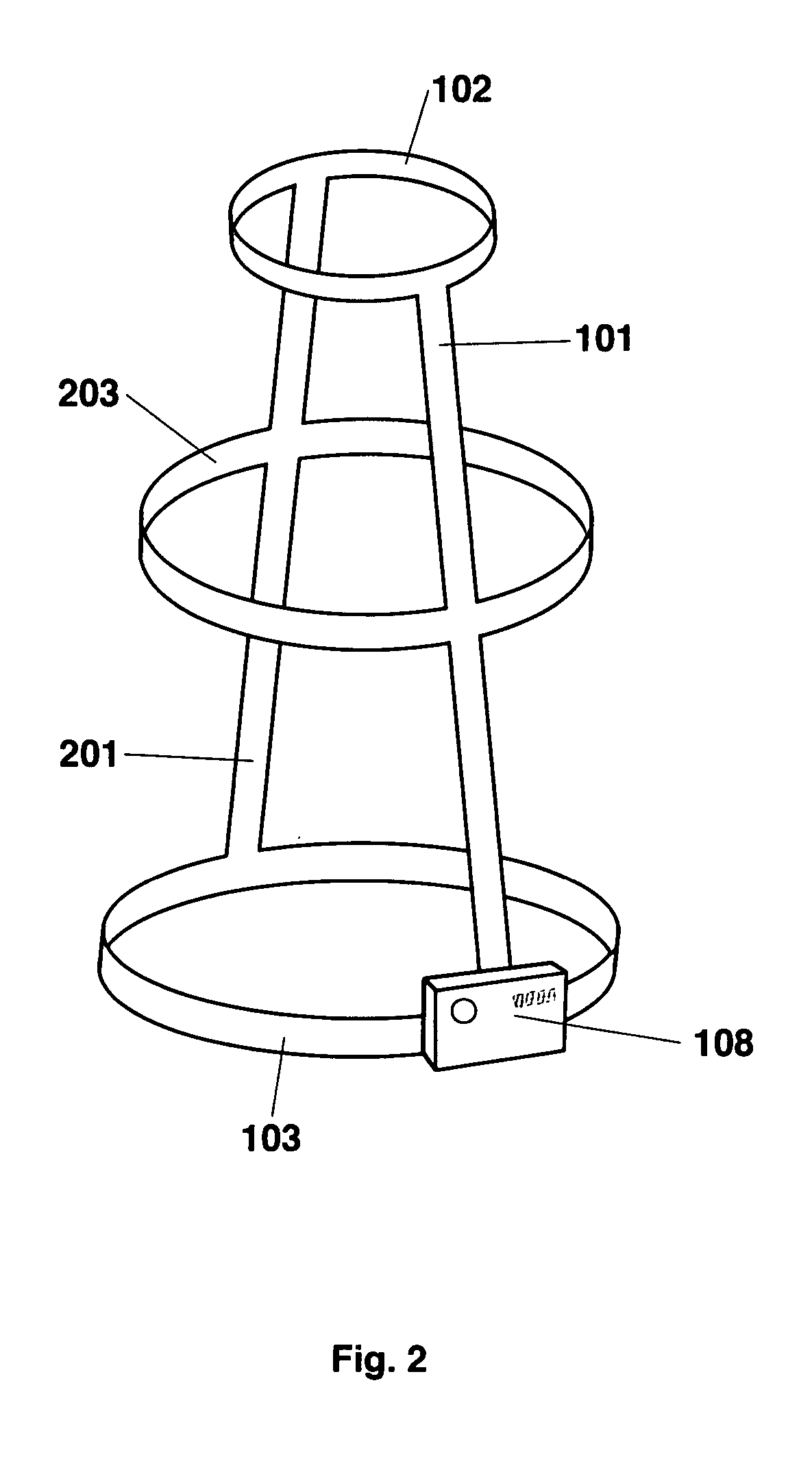
Comprehensive feedback type pulmonary rehabilitation assessment treatment instrument
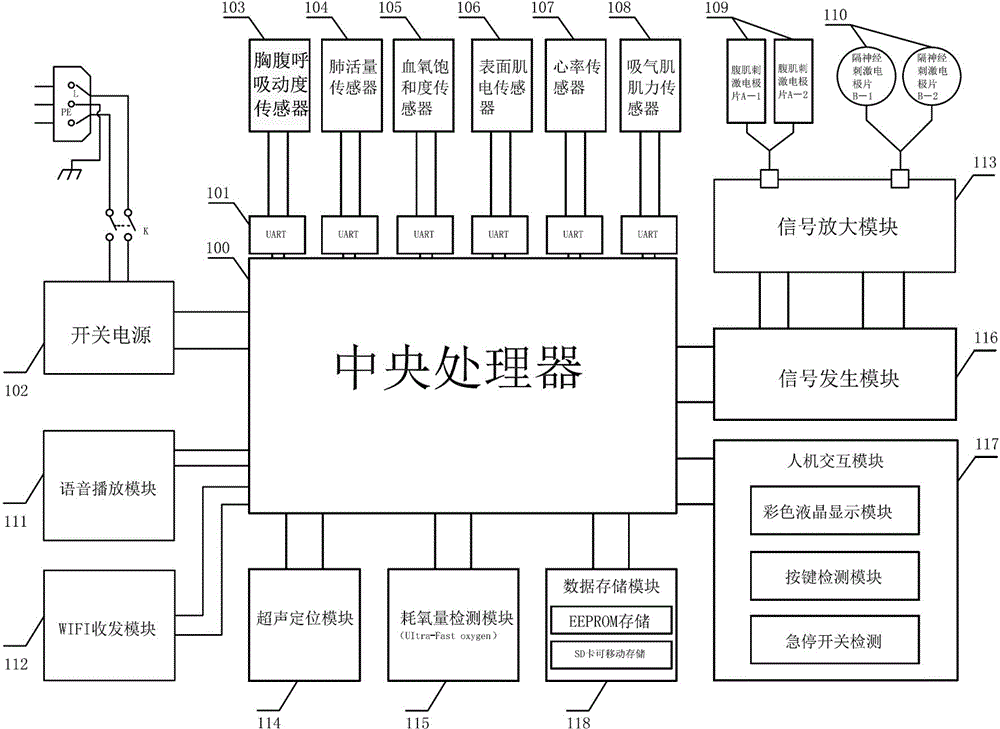
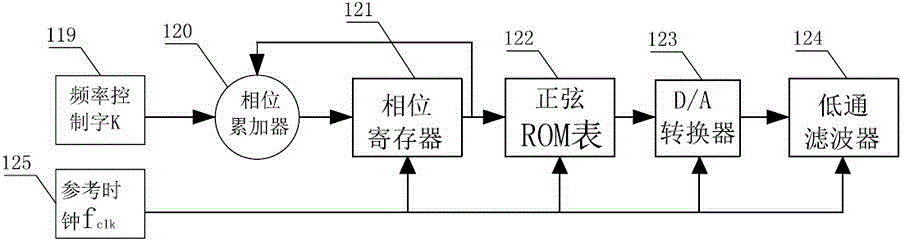
ActiveCN104939815AReal-time human-computer interactionReal-time data display for synchronous real-time human-computer interactionDiagnostic signal processingGymnastic exercisingUniversal asynchronous receiver/transmitterVital capacity
The invention relates to a comprehensive feedback type pulmonary rehabilitation assessment treatment instrument. The instrument comprises a central processor (100), a UART (universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter), a switching power supply (102), a thoracoabdominal breathing movement sensor (103), a vital capacity sensor (104), a blood oxygen saturation degree sensor (105), a surface myoelectricity sensor (106), a heart rate sensor (107), an inspiratory muscle force sensor (108), a signal generation module (116), a signal amplification module (113), an abdominal muscle stimulation electrode (109), a phrenic nerve stimulation electrode (110), a voice playing module (111), a WIFI (wireless fidelity) transceiving module (112), an ultrasonic positioning module (114), an oxygen consumption detection module (115), a man-machine interaction module (117) and a data storage module (118). The sensors of the instrument are used for monitoring various indexes including breathing, circulation, myoelectricity and the like respectively; the sensors are independently or unitedly used for various feedback treatment and also sequential low-frequency current stimulation on phrenic nerves on the neck and abdominal muscles, and a patient is trained to master correct and effective breathing movement. Various data are displayed and processed synchronously in real time, so that man-machine interaction is more convenient and more efficient.
Owner:张鸣生
Motion Compensated MR Imaging System
ActiveUS20130251225A1Reduces respiratory related motion artifactMinimal impactMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiologyThresholding
A method provides motion corrected MR image data in an MR imaging system. The method employs an imaging method for acquiring k-space data of a k-space data array during an imaging scan and the k-space data represents image data of a patient anatomical region. The method acquires k-space data associated with a central region of the k-space data array and subsequently acquires k-space data external to the central region of the k-space data array. The method acquires a motion signal indicating respiratory motion at least during the acquisition of the k-space data external to the central region and compares the motion signal with a predetermined threshold. The method identifies acquired k-space data corresponding to acquisition periods when the motion signal exceeds the threshold and excludes use of the identified acquired k-space data in image reconstruction using the remaining acquired k-space data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com