Patents
Literature
788 results about "Scan time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scan Time (SCT) The total scan time is the time required to collect all data needed to generate the programmed images. The scan time is related to the used pulse sequence and dependent on the assemble of parameters like e.g., repetition time (TR), Matrix, number of signal averages (NSA), TSE- or EPI factor and flip angle.
System and method for managing network vulnerability analysis systems
ActiveUS7926113B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionSystems managementDistributed security
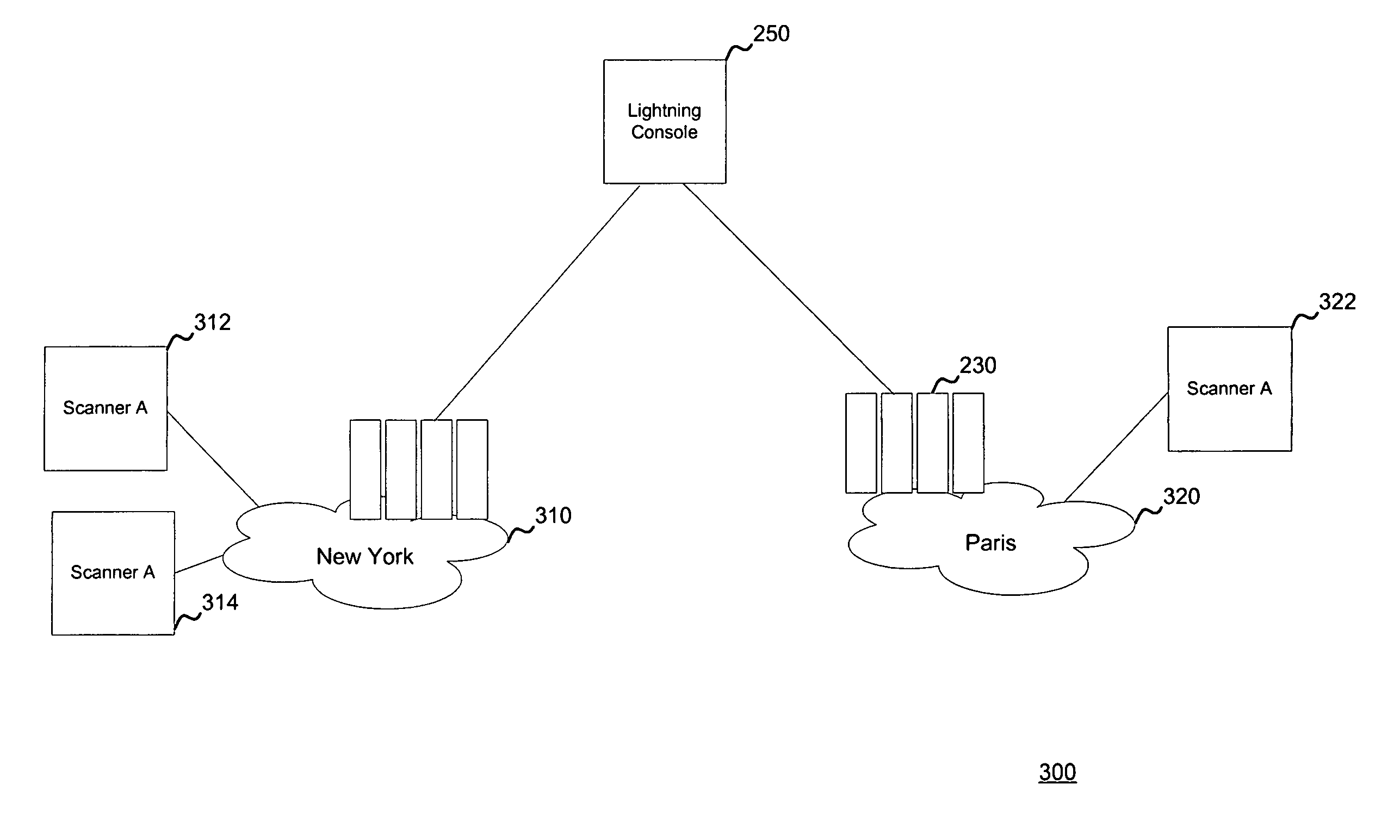
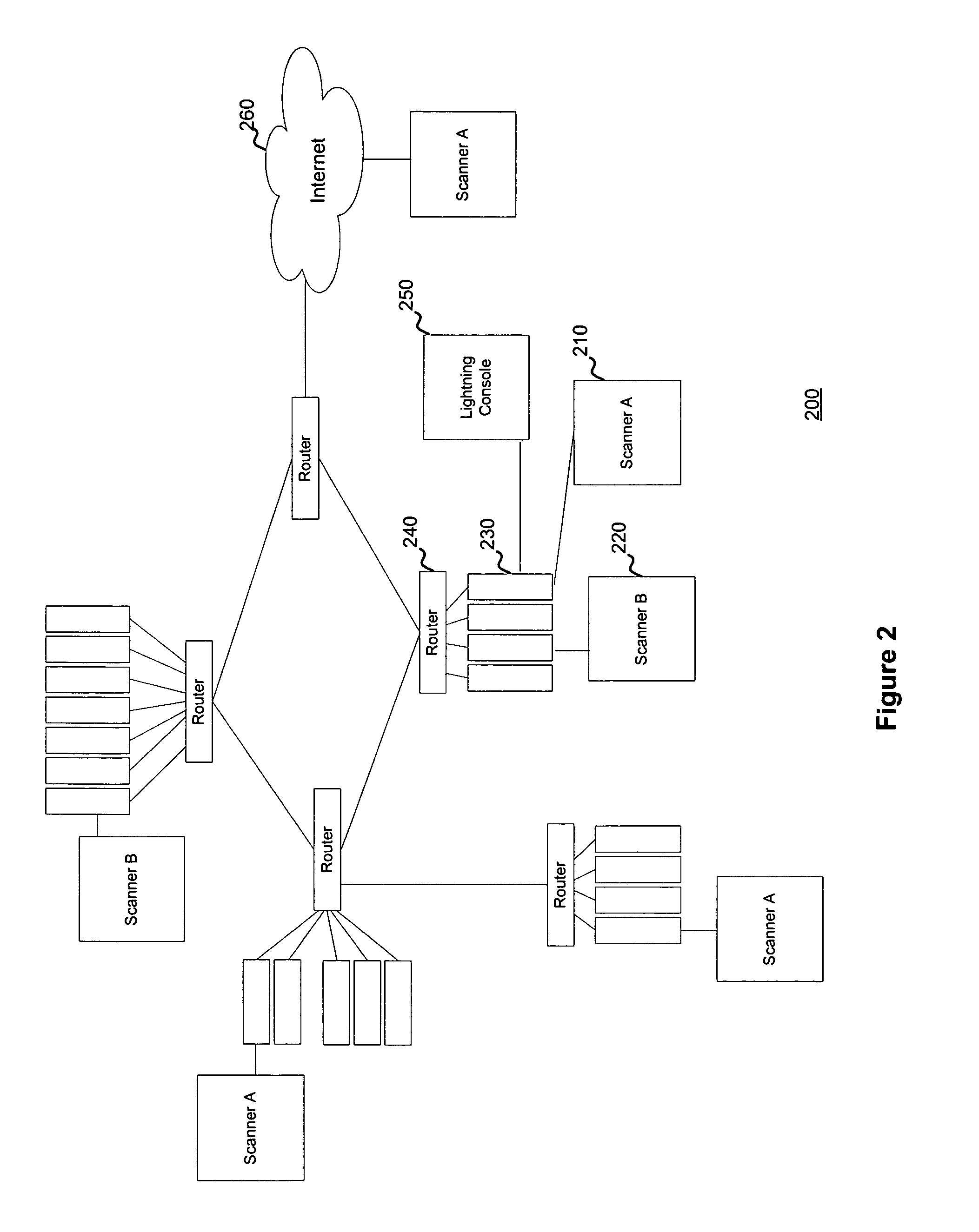
Systems and methods to manage multiple vulnerability scanners distributed across one or more networks using a distributed security management system, herein called a Lightning Console. By distributing multiple scanners across a network, the work load of each scanner may be reduced to significantly reduce the impact on the network routing and switching infrastructure. In addition, scanners may be placed directly behind firewalls for more thorough scanning. Further, scanners may be placed closer to their scanned networks. By placing vulnerability scanners closer, the actual scanning traffic does not cross the core network switch and routing fabric, thereby avoiding potential network outages due to scanning activity. In addition, the closer distance of the scanners to the scanned targets speeds scan times by reducing the distance that the packets must traverse.
Owner:TENABLE INC
Compressed sensing theory-based reconstruction method of magnetic resonance image
InactiveCN102389309AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove visual effectsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReconstruction methodObservation matrix
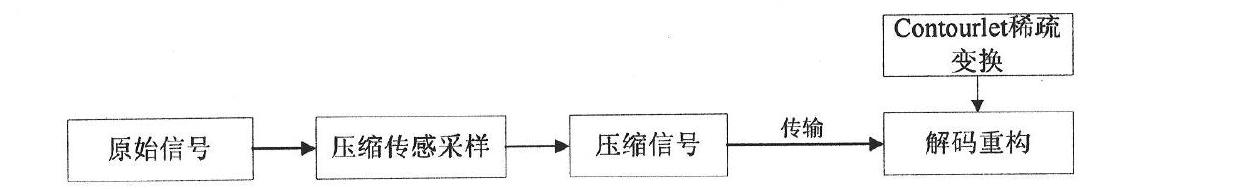
The invention provides a compressed sensing theory-based reconstruction method of a magnetic resonance random sampled K space data image. The reconstruction method applies a contourlet conversion and iterative soft thresholding method to realize reconstruction of a magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the following steps: collecting K space data in a magnetic resonance image scanner according to a preset observation matrix phi to generate a measurement value, and keeping y; acquiring y from a coil of the magnetic resonance image scanner, and transmitting y to a computer; and finallyconstructing a same phi, constructing any orthogonal transformation psi, and recovering from y by adopting a compressed sensing theory-based magnetic resonance random sampled K space data image reconstruction method according to reconstruction. According to the method, scanning time is saved, quick imaging is realized, high-quality reliable image information is provided to medical nuclear magnetic resonance imaging detection, and solid theoretical and practical foundation is established for further development and large-scale popularization and application of the medical imaging detection technology.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
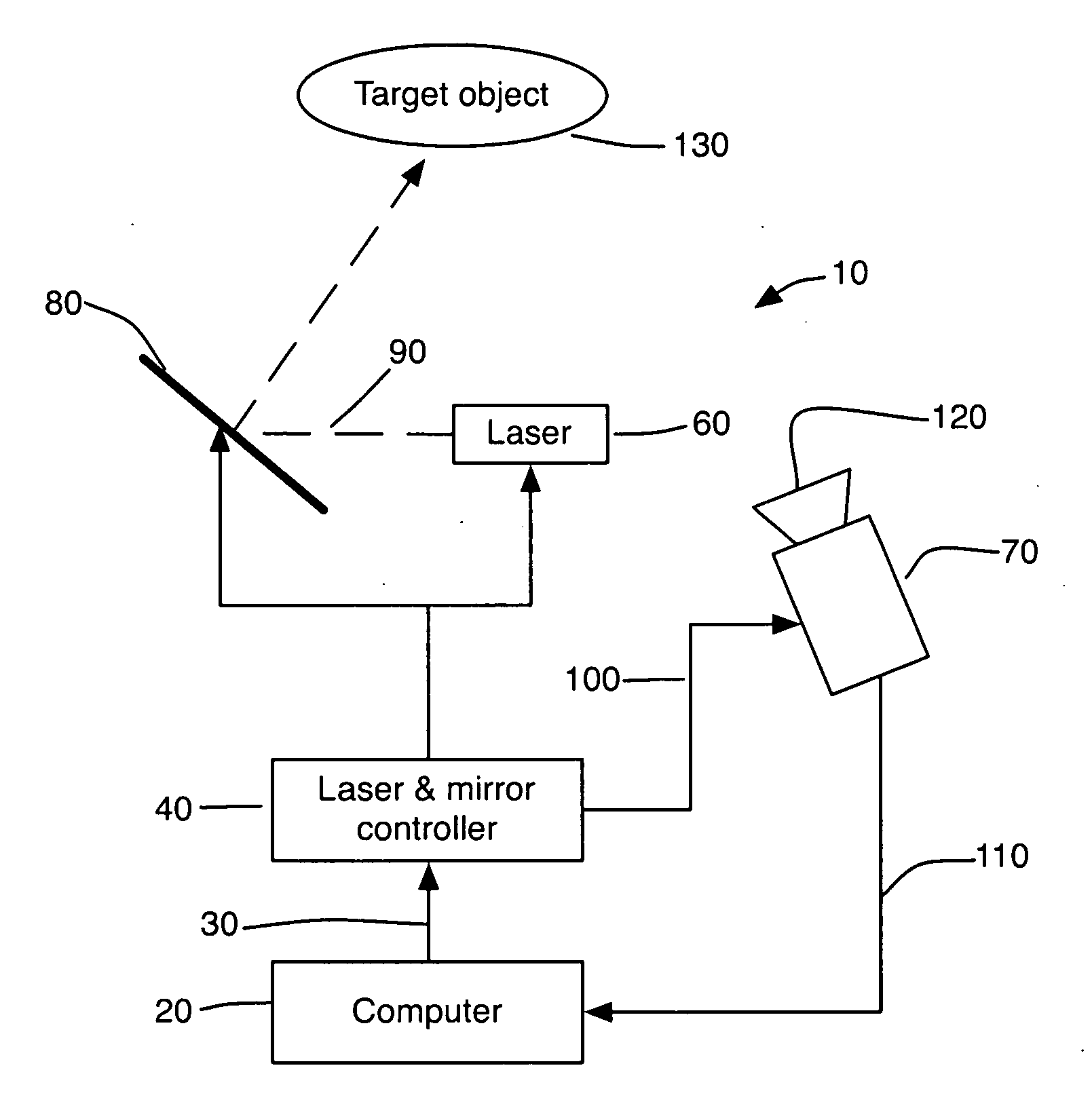
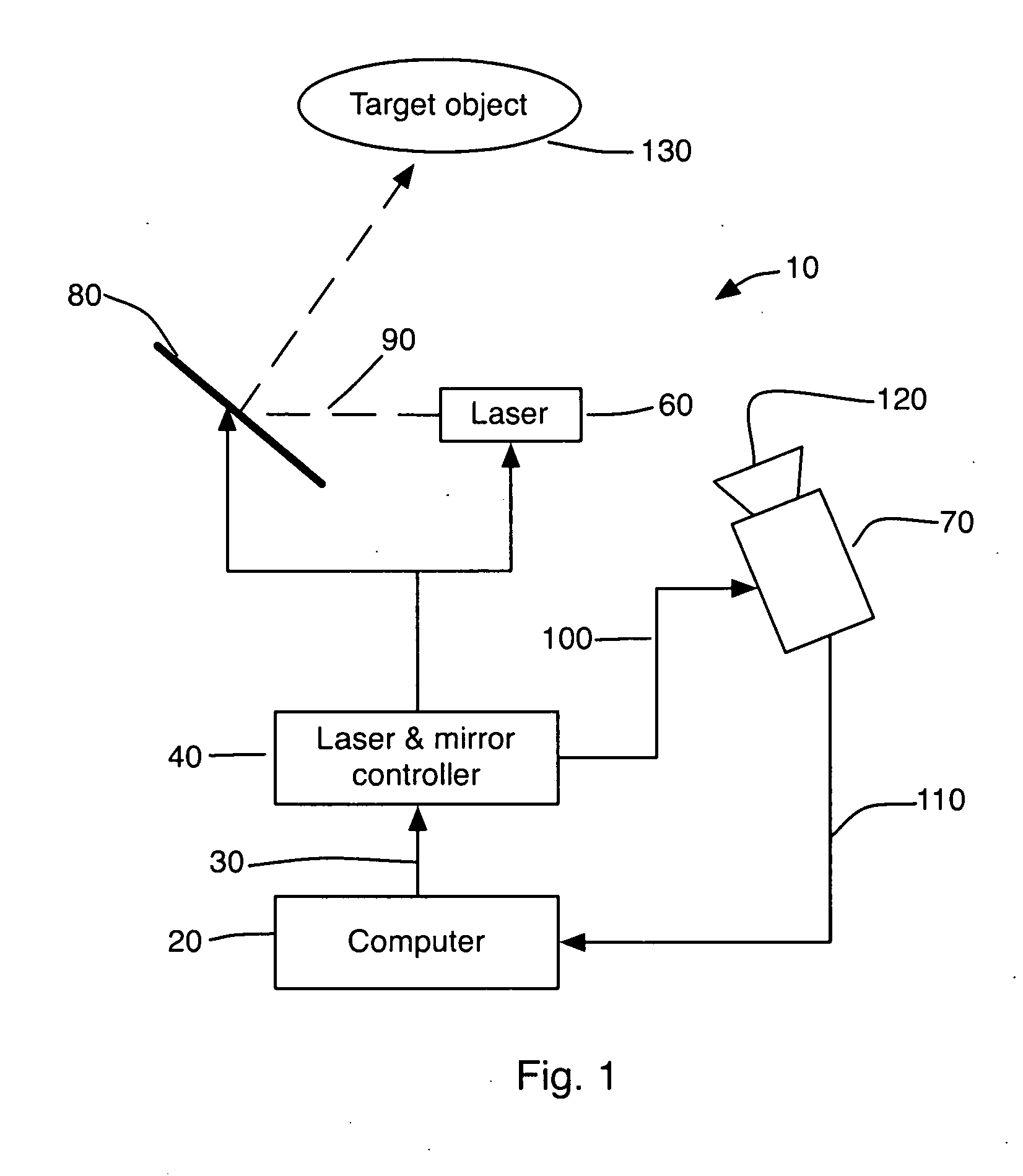
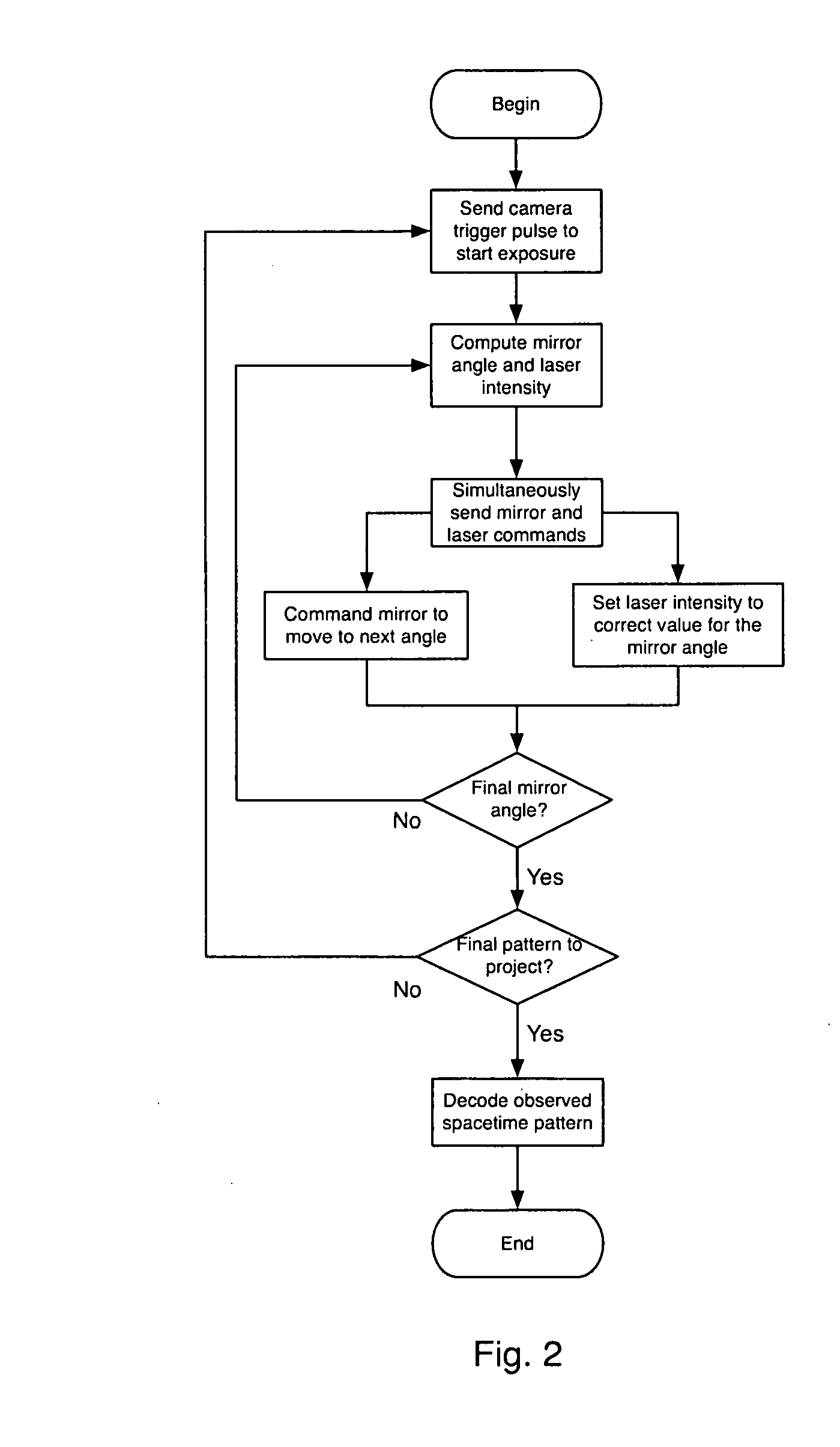
Method and System for 3D Imaging Using a Spacetime Coded Laser Projection System
A desktop three-dimensional imaging system and method projects a modulated plane of light that sweeps across a target object while a camera is set to collect an entire pass of the modulated plane of light over the object in one image to create a line stripe pattern. A spacetime coding scheme is applied to the modulation controller whereby a plurality of images of line stripe patterns can be analyzed and decoded to yield a three-dimensional image of the target object in a reduced scan time and with better accuracy than existing close range scanners.
Owner:THREERIVERS 3D
System and Method for Low Dose Tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20090213987A1Reduces patient doseHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisBreast cancer screening
A breast imaging system leverages the combined strengths of two-dimensional and three-dimensional imaging to provide a breast cancer screening with improved sensitivity, specificity and patient dosing. A tomosynthesis system supports the acquisition of three-dimensional images at a dosage lower than that used to acquire a two-dimensional image. The low-dose three-dimensional image may be used for mass detection, while the two-dimensional image may be used for calcification detection. Obtaining tomosynthesis data at low dose provides a number of advantages in addition to mass detection including the reduction in scan time and wear and tear on the x-ray tube. Such an arrangement provides a breast cancer screening system with high sensitivity and specificity and reduced patient dosing.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Image forming method, image forming apparatus, optical scan device, and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7256815B2Correct position shiftSave energyPrintingOptical elementsOptical beam deflectionLight beam
An optical scan device having an optical deflector reflecting a light beam from a light beam source so as to deflect the light beam and having a surface to be scanned on which information is written such that the light beam deflected by the deflector scans the surface is disclosed. Optical detectors are arranged at least in two locations, a start side of writing and an end side of writing, which locations are outside an effective writing area. A measuring part measures a scan time required by the light beam deflected by the optical deflector to scan a range between the optical detectors. A correcting part corrects each dot position of image data in the effective writing area to an arbitrary position based on a variation amount of the measured scan time.
Owner:RICOH KK
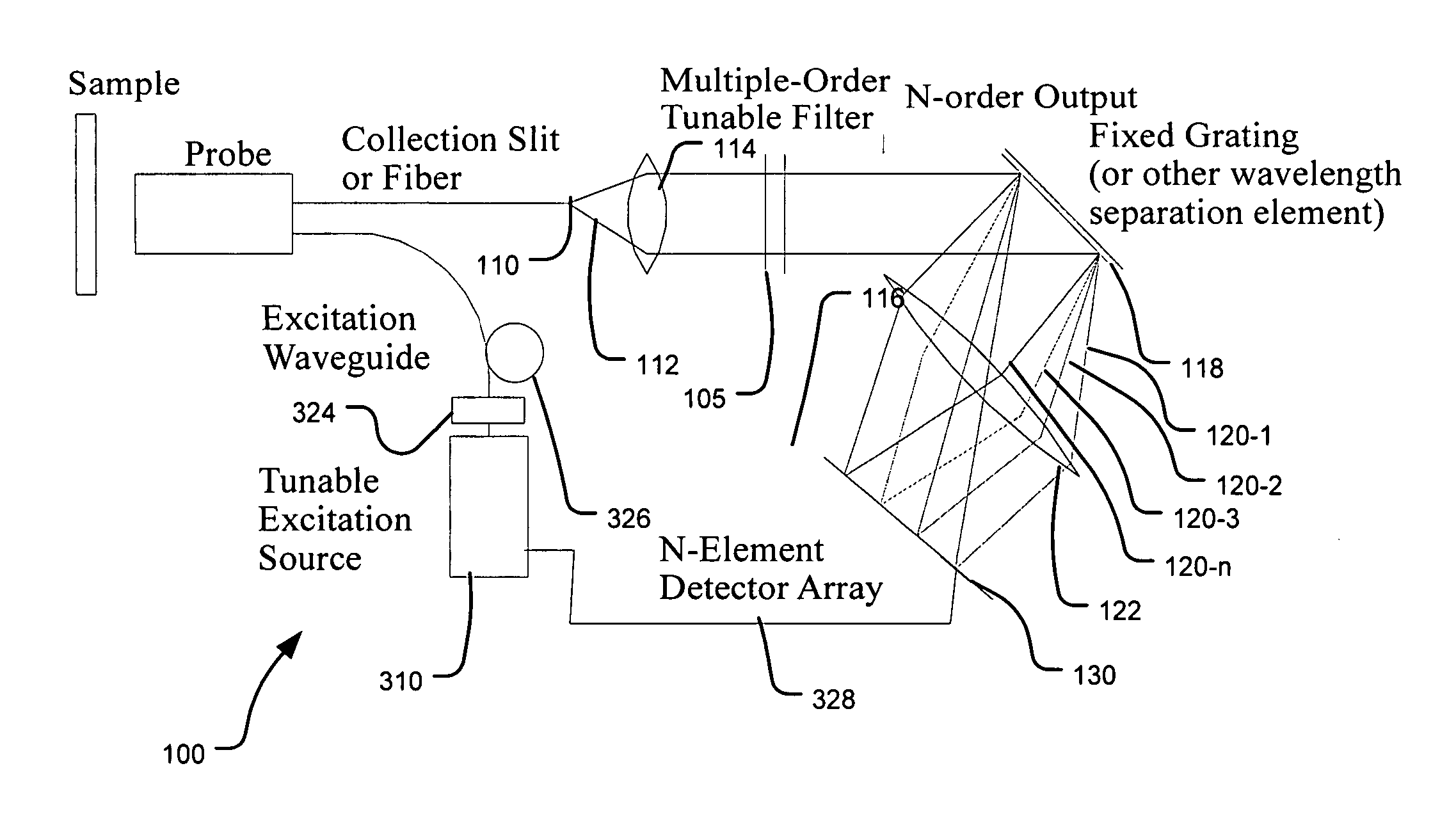
Multi channel Raman spectroscopy system and method
InactiveUS20050264808A1High resolutionReduce power consumptionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingDetector array
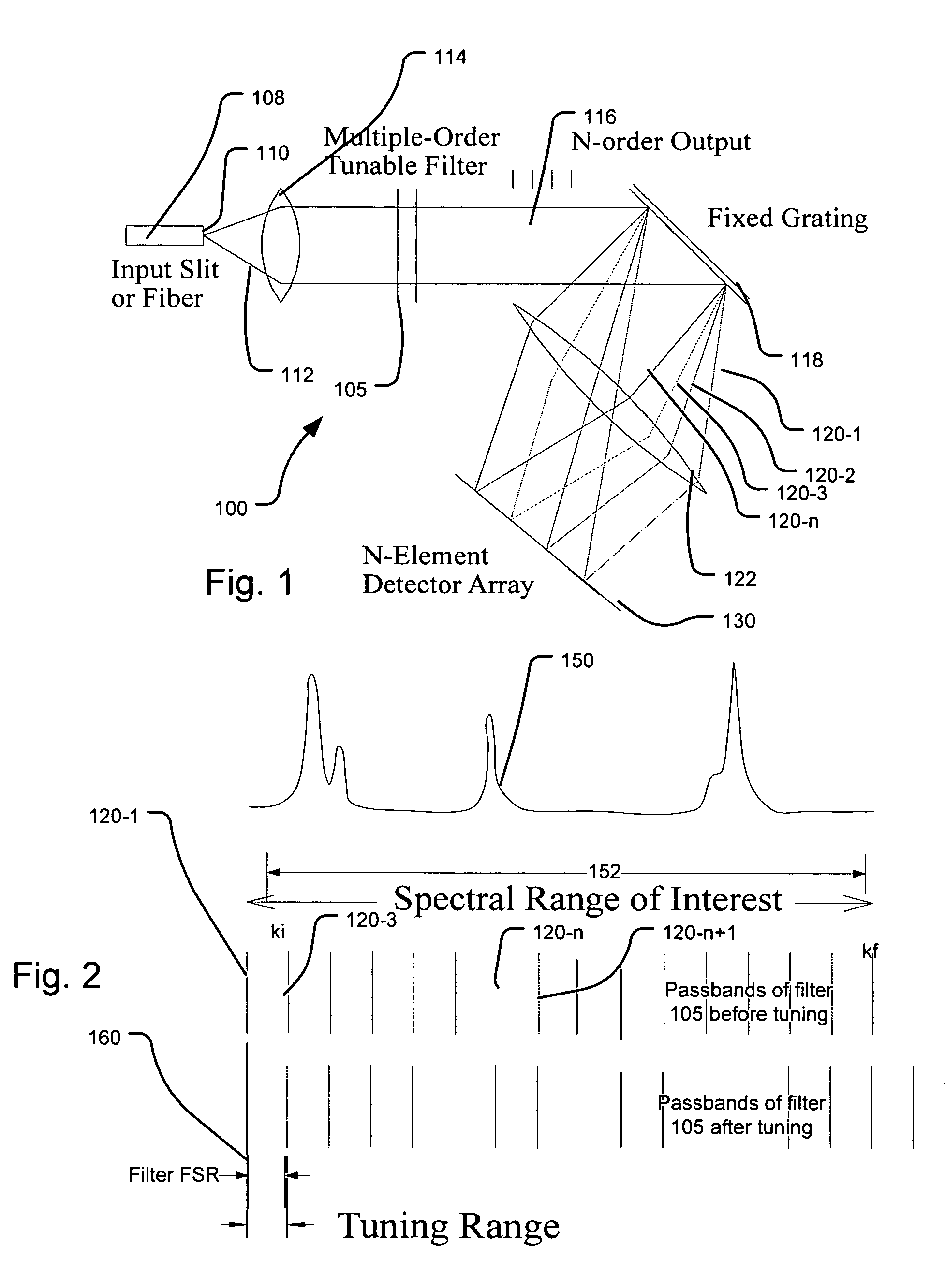
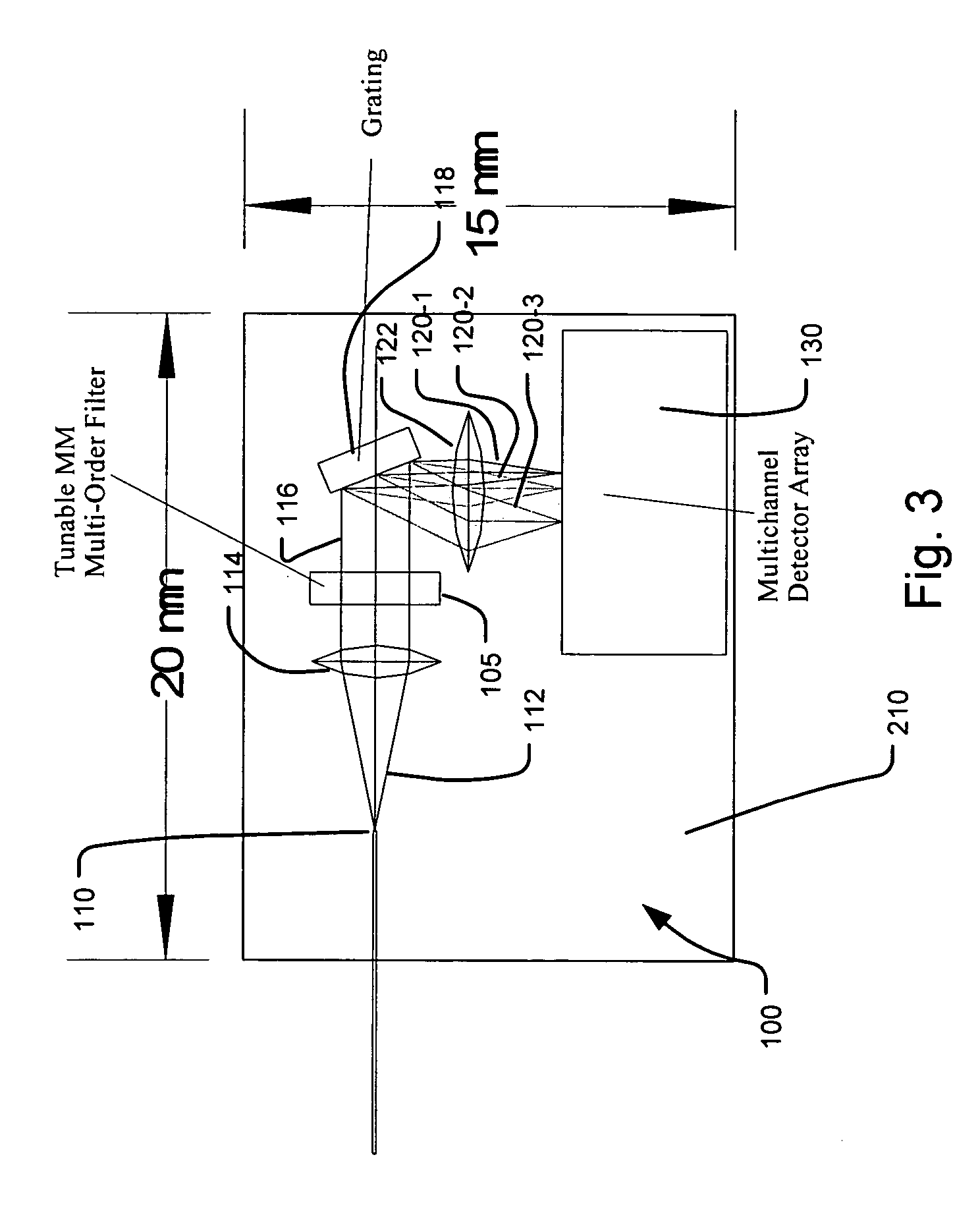
A spectrometer that provides the ability to combine the advantages of high resolution, compactness, ruggedness, and low-power consumption of Fabry-Perot (FP) tunable filter spectrometer, with the multi-channel multiplexing advantage of FT and / or grating / detector array. The key concept is to design and operate a tunable FP filter in a multiple-order condition. This filter is then followed by a “low-resolution” fixed grating, which disperses the filtered n-order signal into a preferably matched N-element detector array for parallel detection. The spectral resolution in this system is determined by the FP filter, which can be designed to have very high resolution. The N-order parallel detection scheme reduces the total integration or scan time by a factor of N to achieve the same signal to noise ratio (SNR) at the same resolution as the single channel tunable filter method. This design is also very flexible, allowing spectrometer systems with appropriate order N to thereby optimize the system performance for spectral resolution and scan integration time. In addition to the significant reduction in scan integration time, there are two other advantages to this approach. The first, because the FP tunable filter is designed and operated under n-orders, the fabrication tolerances of the FP filter cavity and operating conditions are significantly loosened.
Owner:AXSUN TECH
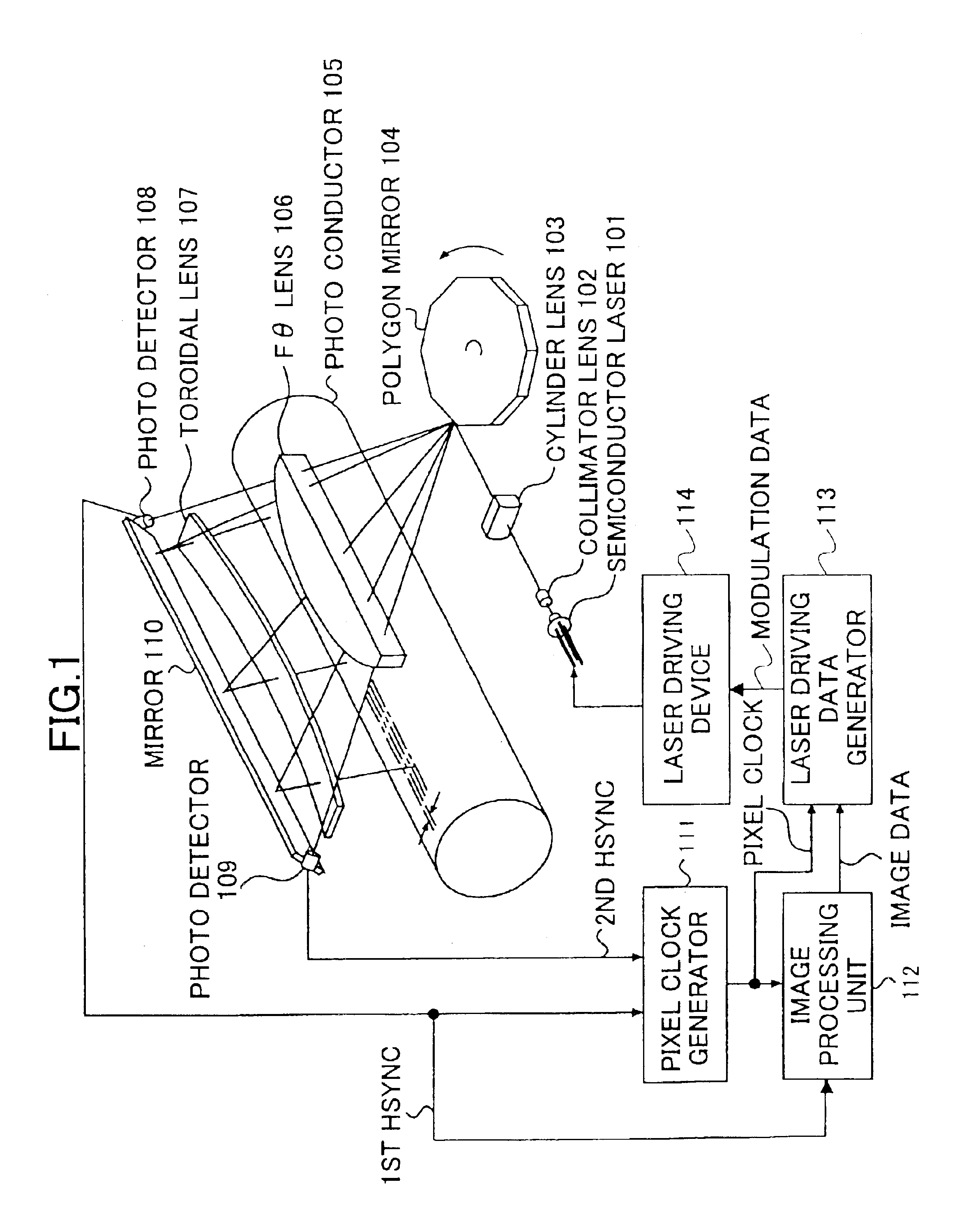
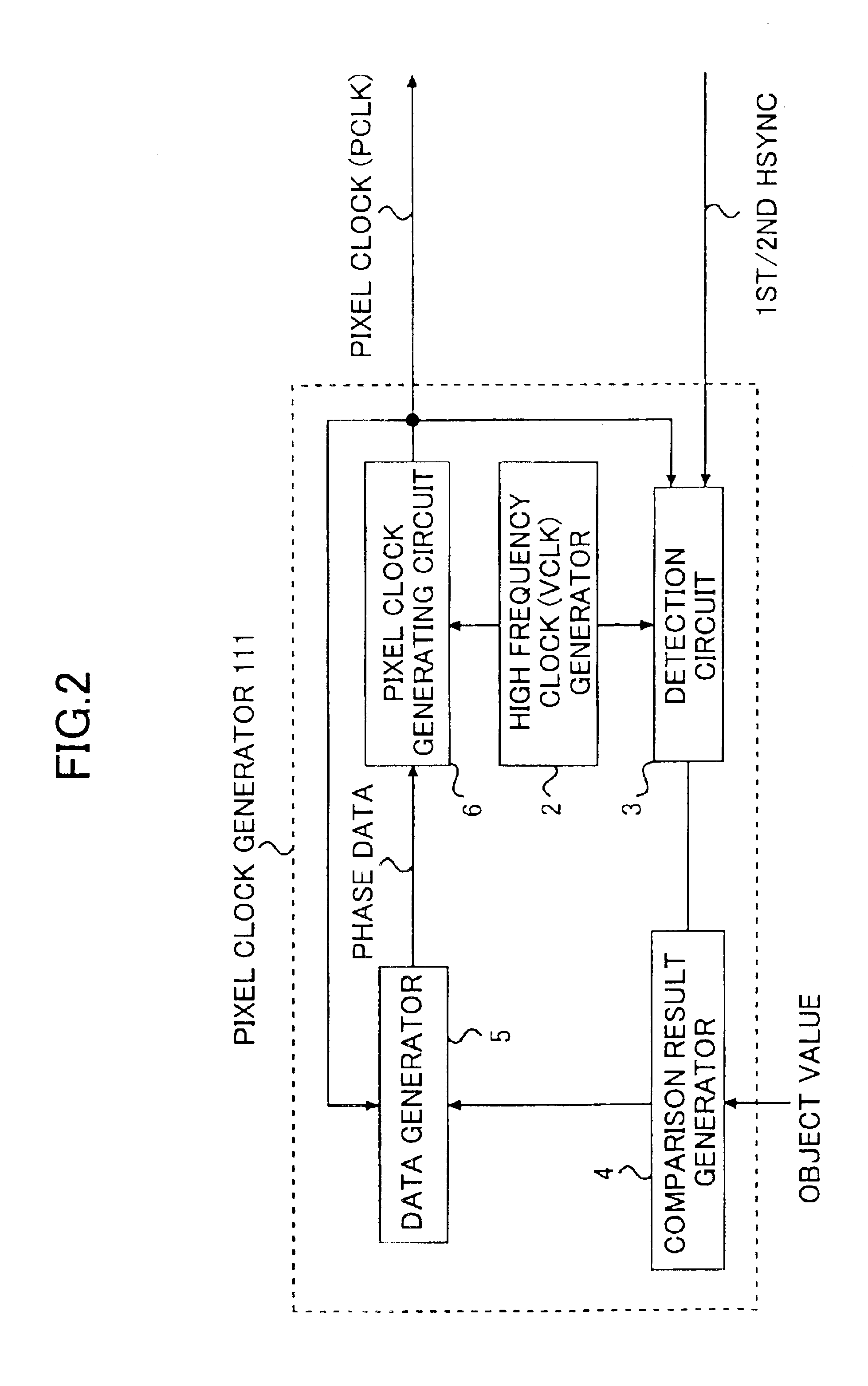
Pixel clock generating device, laser scanning device, and image forming device
InactiveUS6927789B2Simple configurationCorrect fluctuationElectrographic process apparatusPrintingComputer hardwareImage formation
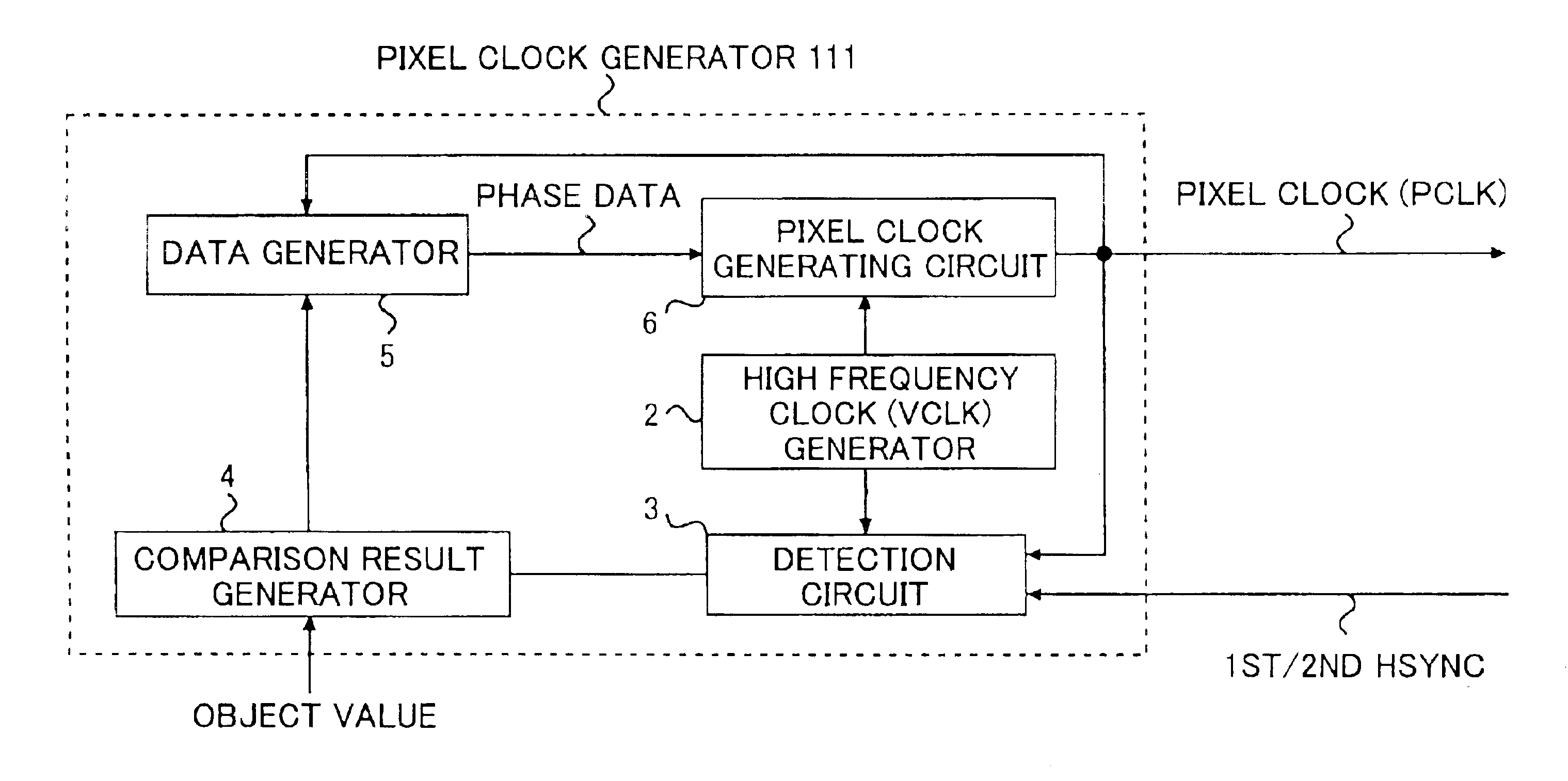
A pixel clock generating device includes a measurement unit that measures a scanning time required for scanning a length and outputs a measured value, a pixel clock generating unit that generates a pixel clock, and a reference clock generating unit that generates a reference clock having a frequency higher than the pixel clock. A phase of the pixel clock is controlled based on (i) the reference clock and (ii) a comparison result between the measured scanning time and a preset scanning time.
Owner:RICOH KK
Reduction of scan time in imaging mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20070141719A1Raise the possibilityReduced target region spacingCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging particle spectrometryImage resolutionTissue sample
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Active matrix liquid crystal display
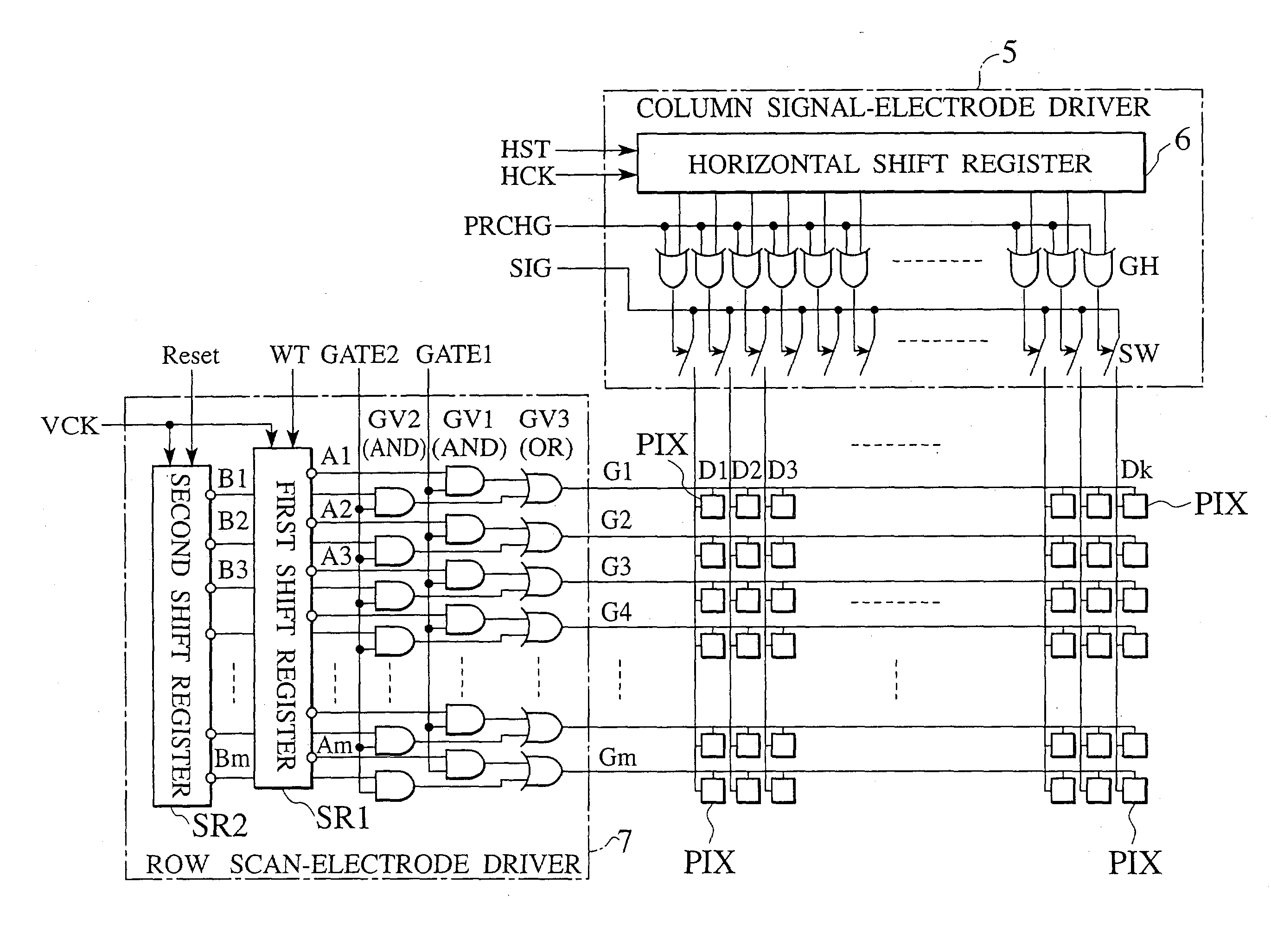
An active matrix LCD defines a display signal period and a reset period in each vertical scan period. The display signal period is a period to write and hold display signals in pixels in response to a row select pulse generated from an output pulse of a first shift register (SR1). The reset period is a period to write and hold a reset voltage in the pixels in response to a row select pulse generated from an output pulse of a second shift register (SR2). The ratio of the display signal period to the reset period is adjustable in units of horizontal scan time by changing the number "n" of horizontal scan periods to be passed between the time when the first shift register receives a scan start signal (WT) and the time when the second shift register receives a scan start signal (Reset).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Reduction of scan time in imaging mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070141718A1Raise the possibilityBig spaceImaging particle spectrometryBiological testingImage resolutionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Techniques are disclosed for reducing scan times in mass spectral tissue imaging studies. According to a first technique, a tissue imaging boundary is defined that closely approximates the edges of a tissue sample. According to a second technique, a low-resolution scan is performed to identify one or more areas of interest within the tissue sample, and the identified areas of interest are subsequently scanned at higher resolution.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
PET-CT scanning imaging method and related imaging method
ActiveCN105078495AIncrease scan timeIncreased CT radiation doseComputerised tomographsTomographyPET-CTComputed tomography
The invention discloses a PET-CT scanning imaging method and a related imaging method. The PET-CT scanning imaging method comprises that an area to be imaged is positioned and scanned, the positioning image of the area to be imaged is obtained and displayed, and the displayed positioning image is used for a user to determine the scanning area; the scanning area information which is input by the user is received, the PET total scanning area is determined according to the scanning area information; the PET total scanning area generates a plurality of PET sub scanning areas, each PET sub scanning area corresponds to a PET scanning bed, and the PET sub scanning areas are superposed to cover the PET total scanning area completely,; multi-bed PET scanning is carried out; CT scanning is carried out; and scanning data are reconstructed to obtain PET-CT images. According to the invention, unrelated scanning areas in the PET-CT scanning imaging process are eliminated, the PET-CT scanning time is shortened, and the CT radiation dose received by a patient in the PET-CT scanning imaging process is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
User input utilizing dual line scanner apparatus and method
ActiveUS20120189166A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational scienceLine sensor
A user input method and apparatus may comprise a two line object imaging sensor having a primary line scan-sensor providing a primary line scan-sensor output and a secondary line scan-sensor providing a secondary line scan-sensor output, representing pixels in a current primary scan row and a current secondary scan row, and adapted to scan an object; storing for each scan time each current primary line scan-sensor output and each current secondary line scan-sensor output and a correlation unit correlating at least one of the current representations of pixels in a primary line sensor output with stored representations and the current representations of pixels in a secondary line sensor output with stored representations and, the correlation unit providing as an output a motion indicator.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Improved techniques for magnetic particle imaging
ActiveUS20110089942A1Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
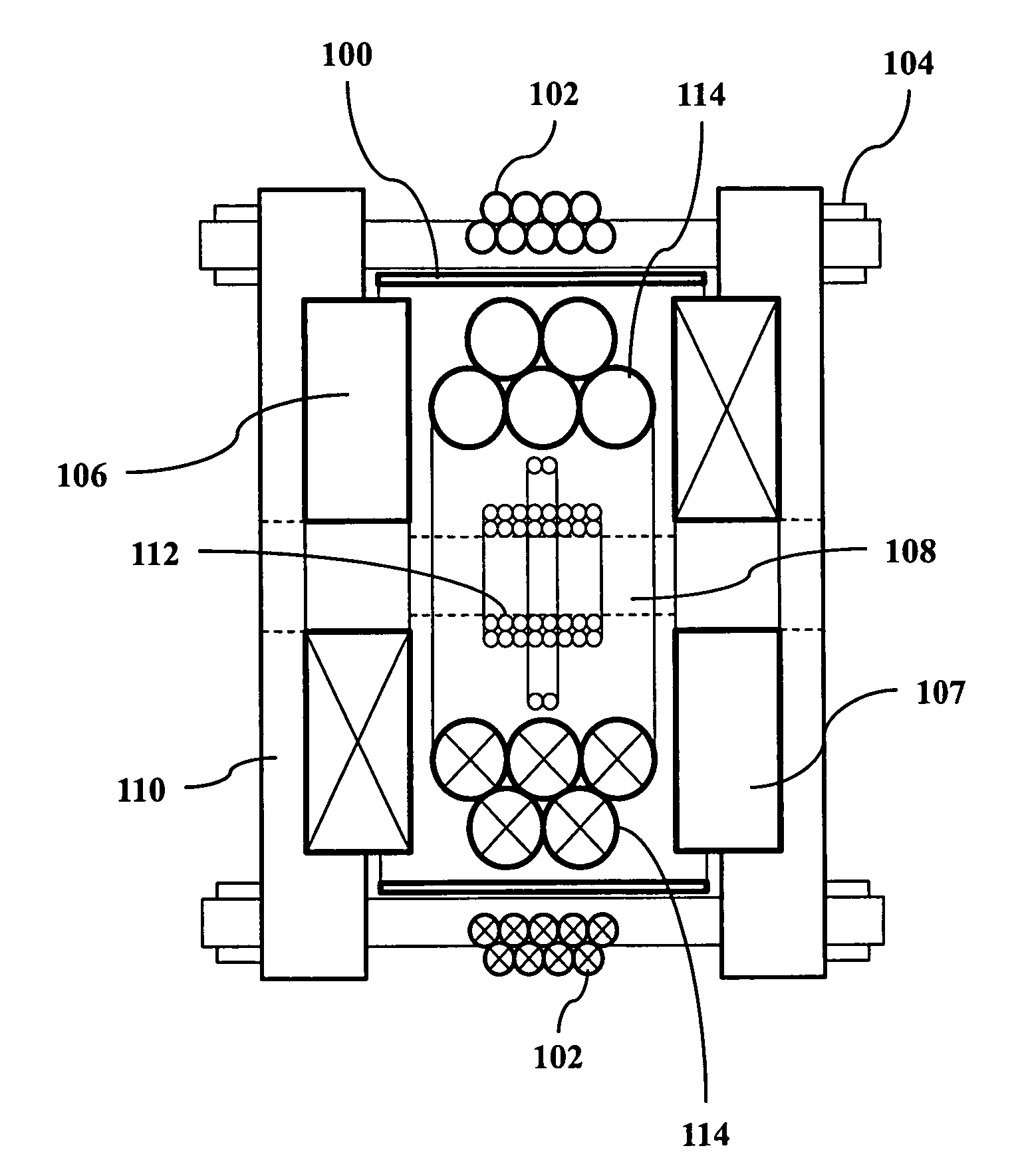
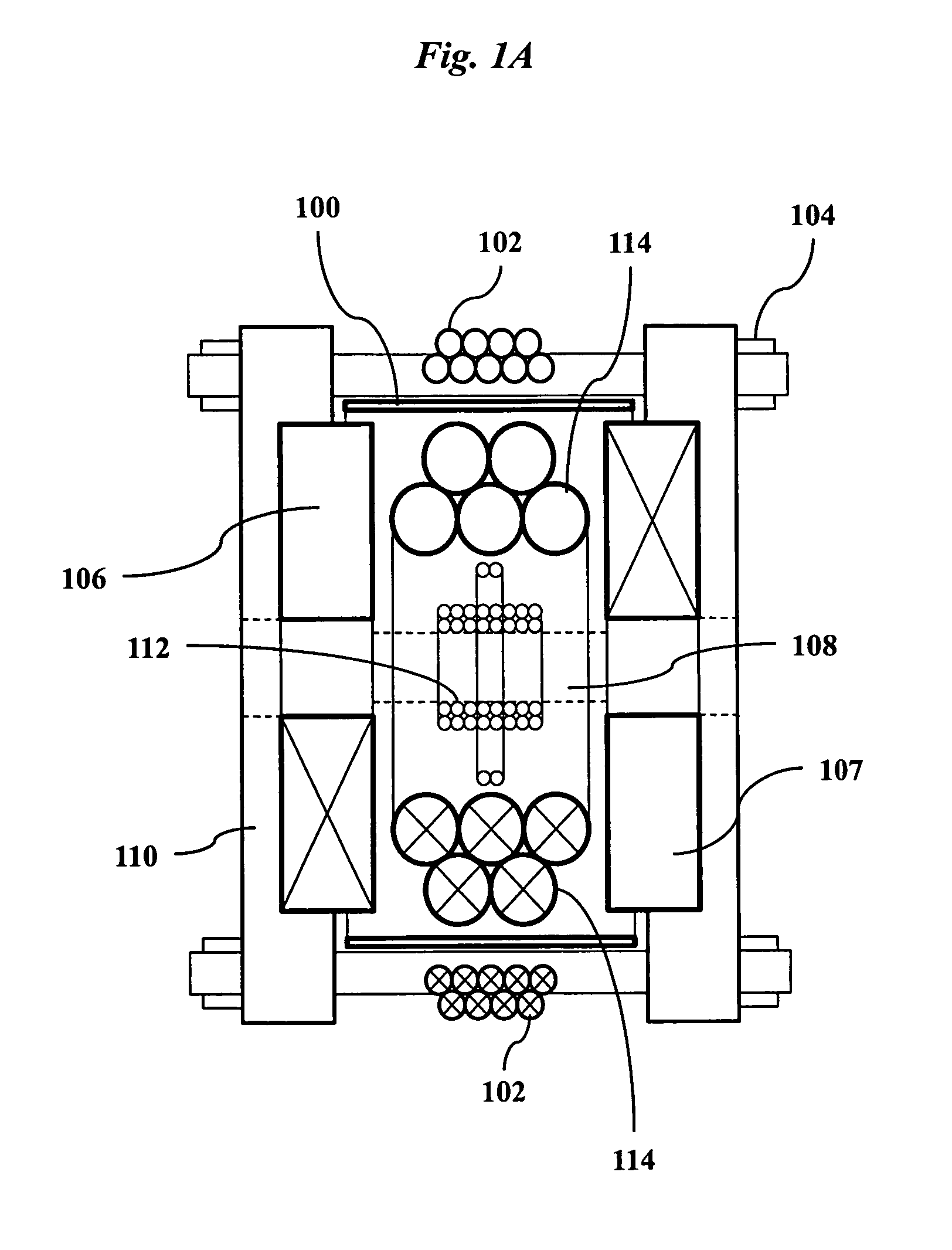
A magnetic particle imaging apparatus includes magnets [106,107] that produce a gradient magnetic field having a field free region (FFR), excitation field electromagnets [102,114] that produce a radiofrequency magnetic field within the field free region, high-Q receiving coils [112] that detect a response of magnetic particles in the field free region to the excitation field. Field translation electromagnets create a homogeneous magnetic field displacing the field-free region through the field of view (FOV) allowing the imaging region to be scanned to optimize scan time, scanning power, amplifier heating, SAR, dB / dt, and / or slew rate. Efficient multi-resolution scanning techniques are also provided. Intermodulated low and radio-frequency excitation signals are processed to produce an image of a distribution of the magnetic nanoparticles within the imaging region. A single composite image is computed using deconvolution of multiple signals at different harmonics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and apparatus for reducing artifacts in computed tomography images
InactiveUS20080273651A1Reduce artifactsHigh error rateReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHigh resolution imageReconstruction algorithm
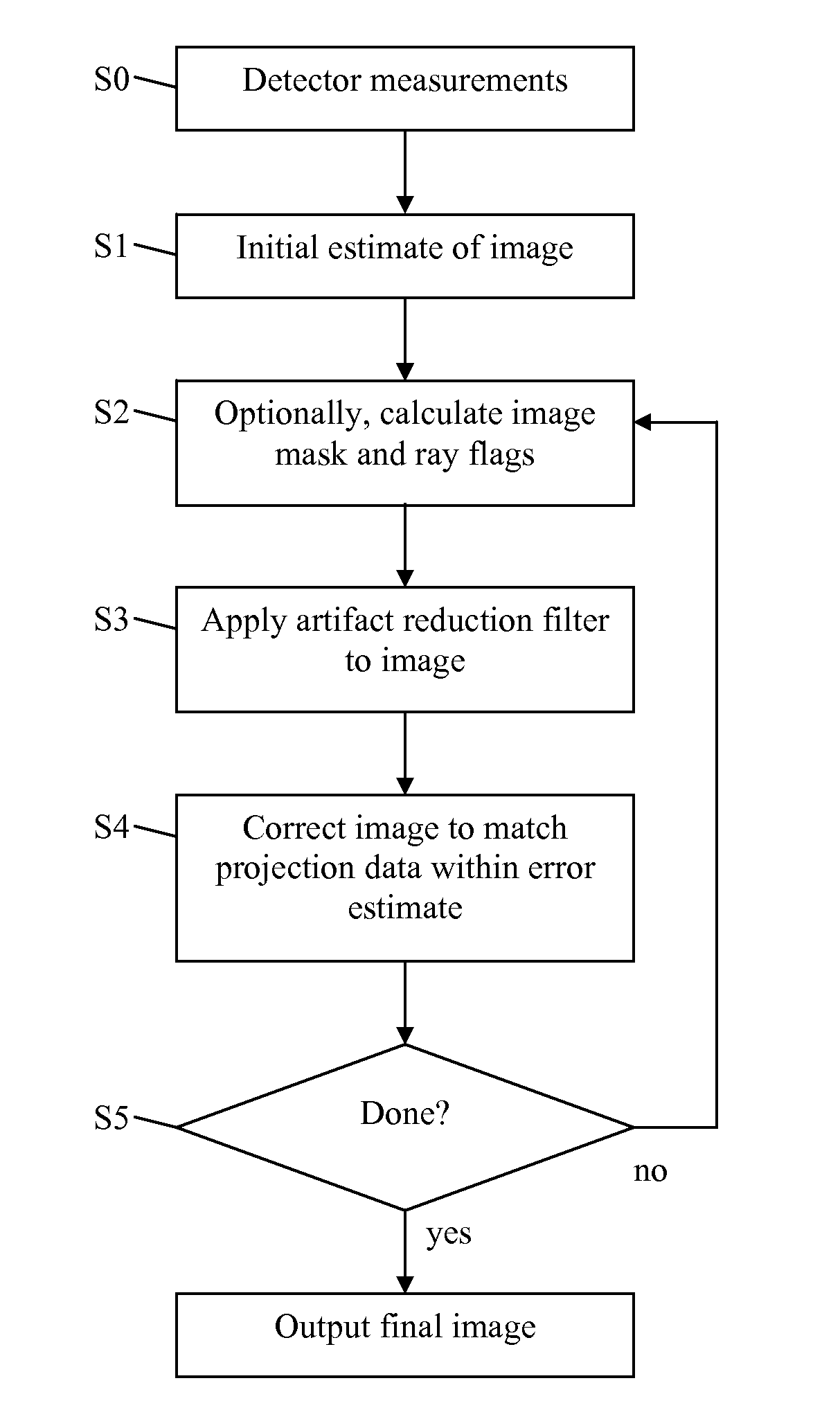
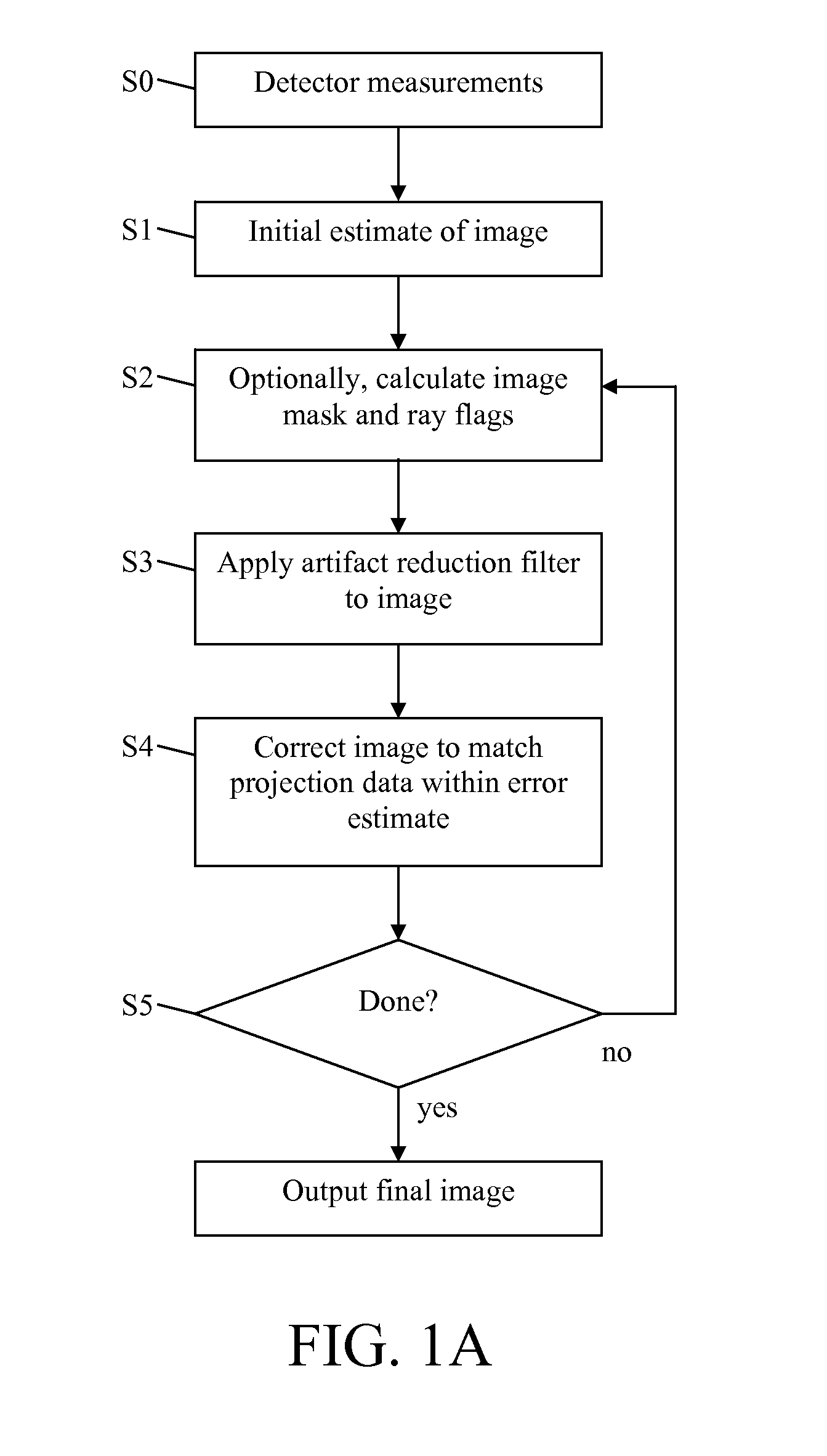
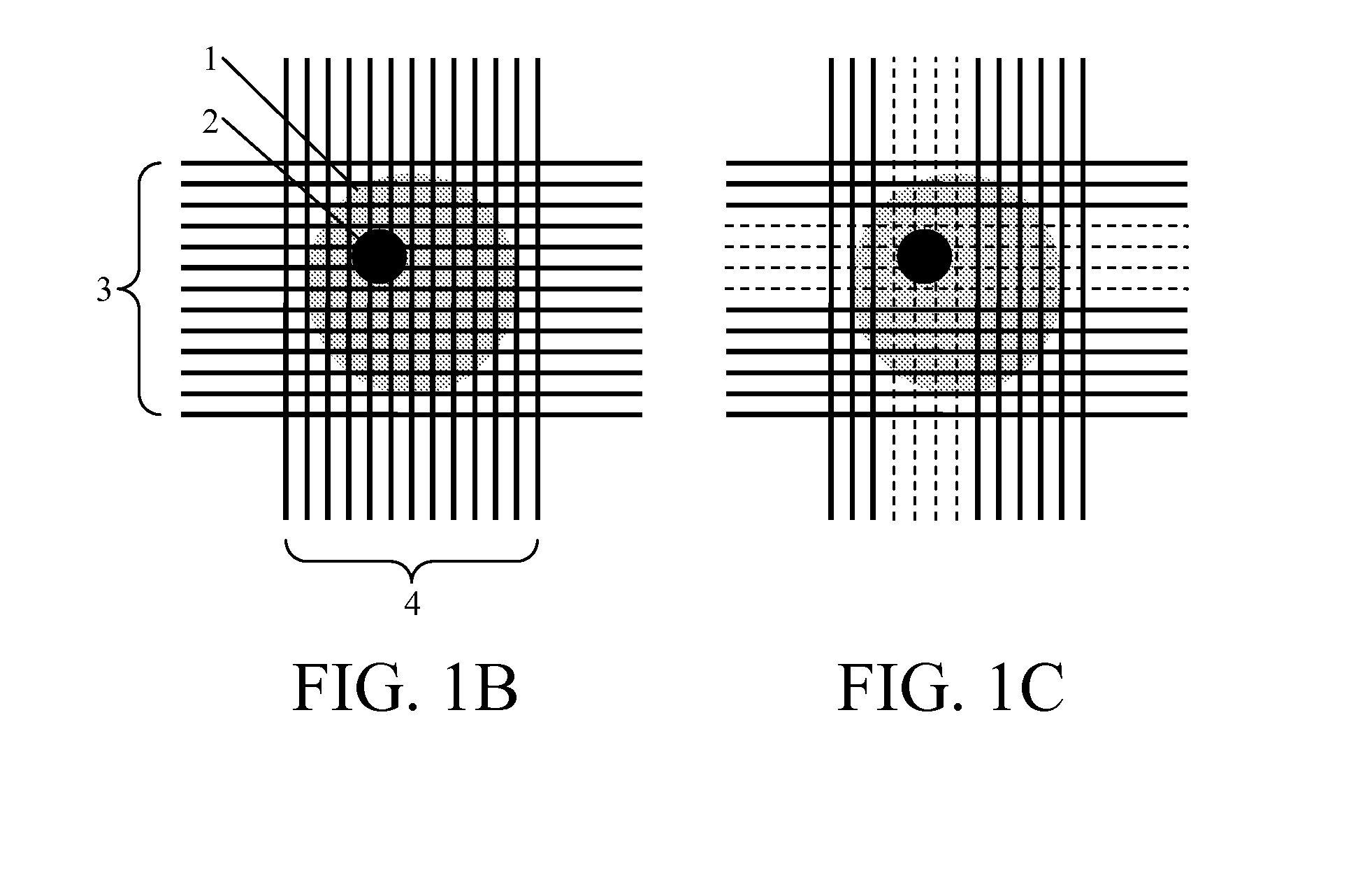
We present an iterative method for reducing artifacts in computed tomography (CT) images. In each iteration, constraints such as non-negativity are applied, then the image is blurred to guide convergence to a smoother image. Next, the image is modified using an algebraic reconstruction algorithm to try to match the projection data to within the experimental error. A mask is calculated which specifies which parts of the image to update during each iteration. The mask allows us to first solve regions of the image that are determined by rays with low photon counts (and thus high error). Then, regions of the image determined by rays with higher photon counts (and thus lower error), are solved using those ray sums. Reducing CT scan artifacts results in clearer and higher resolution images, faster scan times, and less radiation use.
Owner:BOAS FRANZ EDWARD
Scan locating method for independent keyboard
InactiveCN103226391AAvoid jitter effectsEliminate disturbing effectsInput/output for user-computer interactionKey pressingComputer hardware
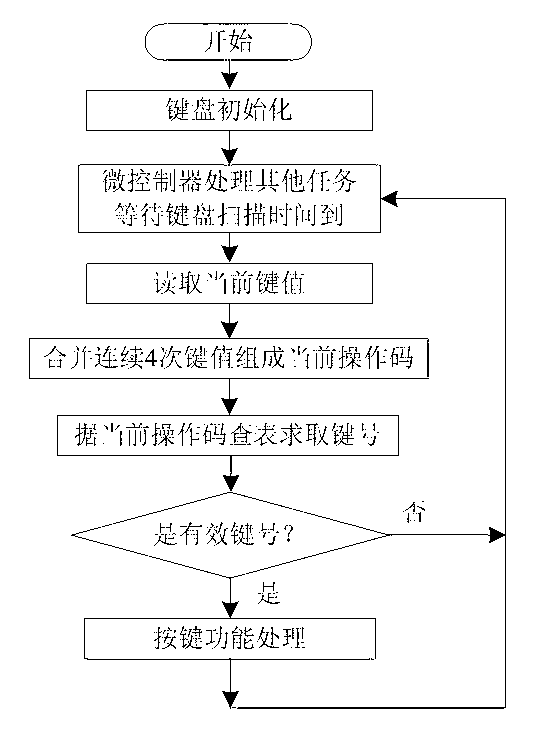
The invention discloses a scan locating method for an independent keyboard, which is suitable for the design on an independent keyboard of an electronic product. The method comprises the following steps of: initializing a keyboard, reading the current key value when the keyboard scanning time is reached, merging the latest four key values to form an identification code, looking up a table according to the identification code to obtain a key number, and carrying out corresponding processing according to the key number. The key number is obtained in a way of looking up the table, single-key operation and combination-key operation can be simultaneously processed, only the size of an effective identification code table needs to be increased or reduced or the order of identification codes in the effective identification code table needs to be adjusted when the operation functions of keys are increased or reduced or adjusted, and the independent keyboard is simple in algorithm and convenient to maintain.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method and system
ActiveCN102018514AAcquisition speed is fastFast imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComplete dataRapid imaging
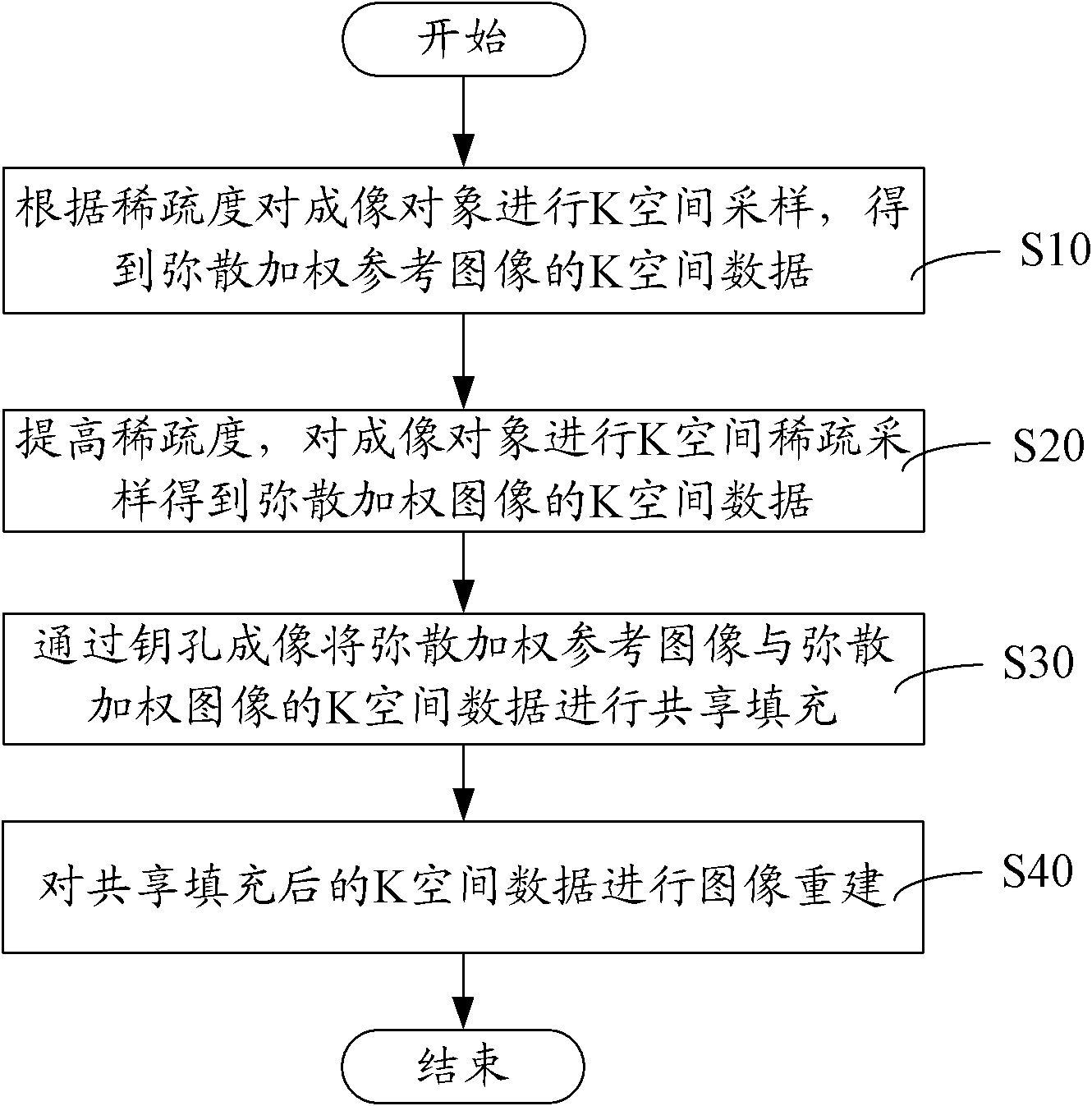
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method which comprises the following steps: performing K space sparse sampling on an imaging object to obtain K space data of a diffusion weighted reference image; performing K space sparse sampling on the imaging object to obtain the K space data of a diffusion weighted image; performing share filling on the K space data of the diffusion weighted reference image and the diffusion weighted image by keyhole imaging; and performing image reconstruction on the K space data after share filling. The magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method and system provided by the invention have the advantages of reconstructing complete data, shortening the scanning time, improving the data acquiring speed and achieving rapid imaging by adopting sparse sampling rapidly and continuously to acquire K space data and performing share filling under the action of the keyhole imaging technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
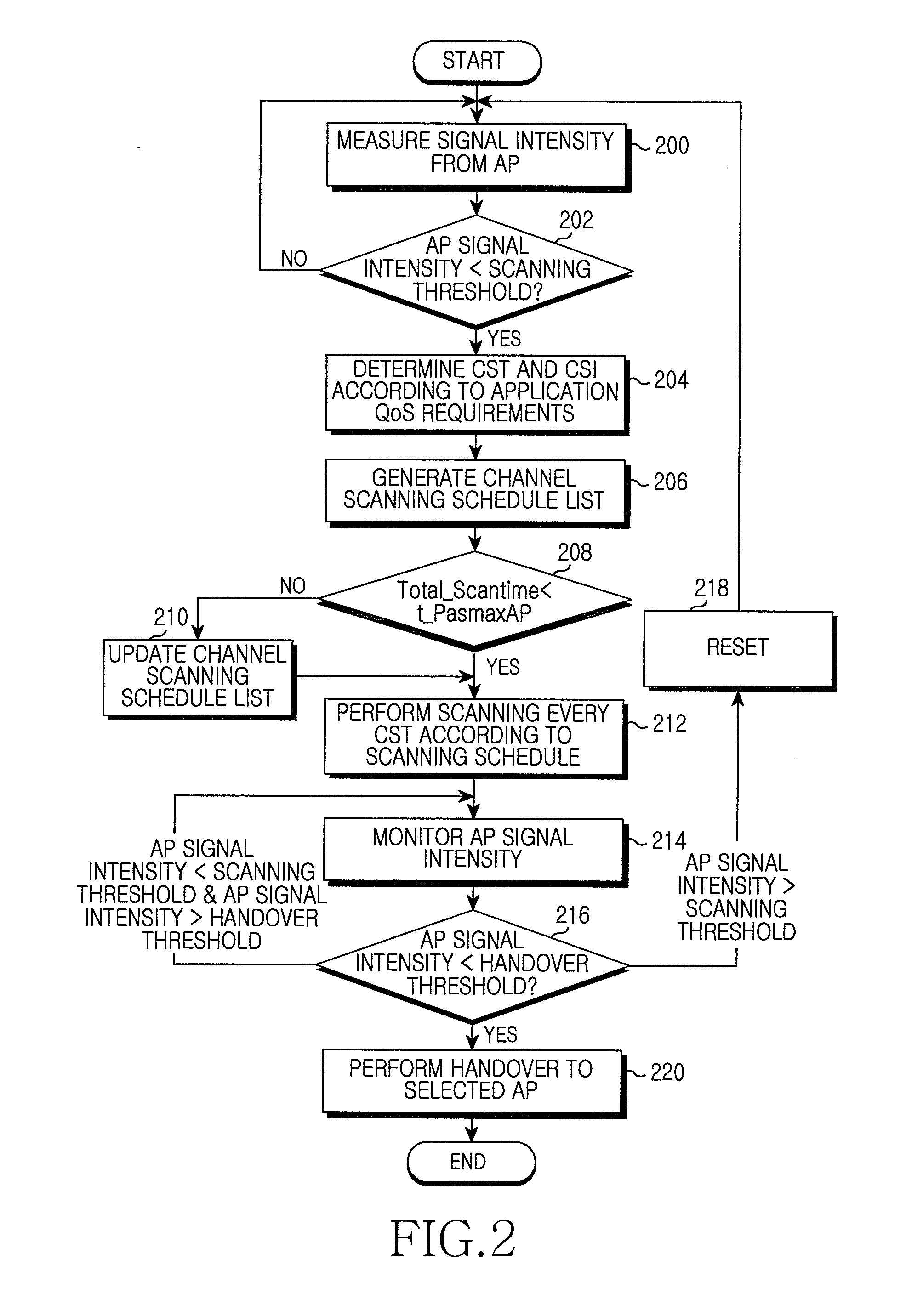
Method and apparatus for channel scanning in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110243013A1Reduce latencyIncrease overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemComputer science
A method and apparatus perform channel scanning in a wireless communication system. A signal intensity of an Access Point (AP) is compared with a scanning threshold, when the AP signal intensity not less than the scanning threshold, a channel scanning schedule list is generated in consideration of a scan time based on a passive channel scan scheme and a scan time based on an active channel scan scheme. The channel scanning is performed every channel scanning time, according to the channel scanning schedule list.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
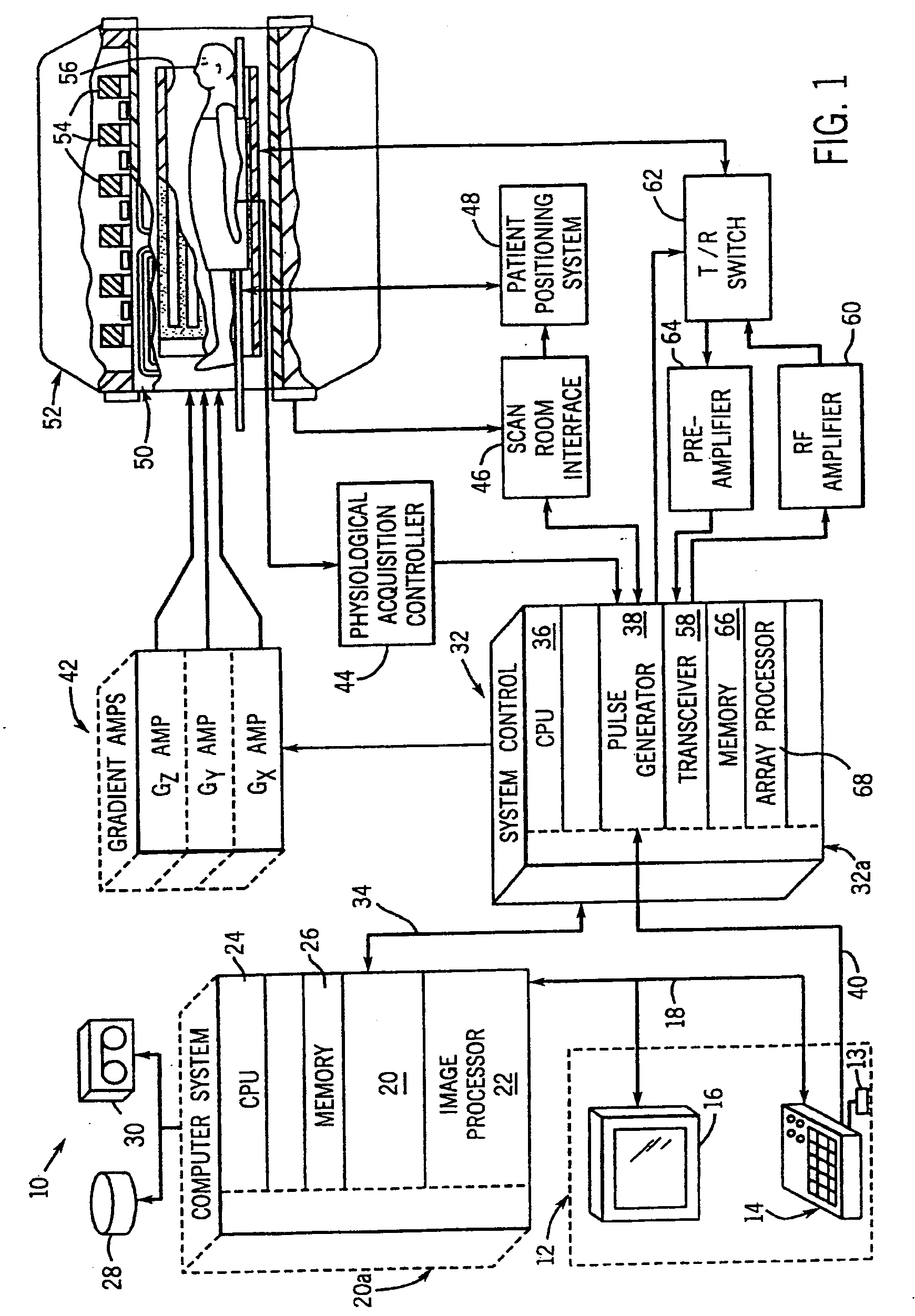
Method and apparatus to reduce RF power deposition during MR data acquisition
ActiveUS20050110487A1Efficient managementFaithful productionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAudio power amplifierCoil array
A system composed of multiple transmit coils with corresponding RF pulse synthesizers and amplifiers is disclosed. A method of designing RF pulses specific to each transmit coil to dynamically control RF power deposition across an imaging volume is also disclosed, where parallel excitation with the transmit coils allows for management of RF power deposition on a subject while facilitating faithful production of a desired excitation profile. The present invention also supports reduction in scan time and is applicable to any coil array geometry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
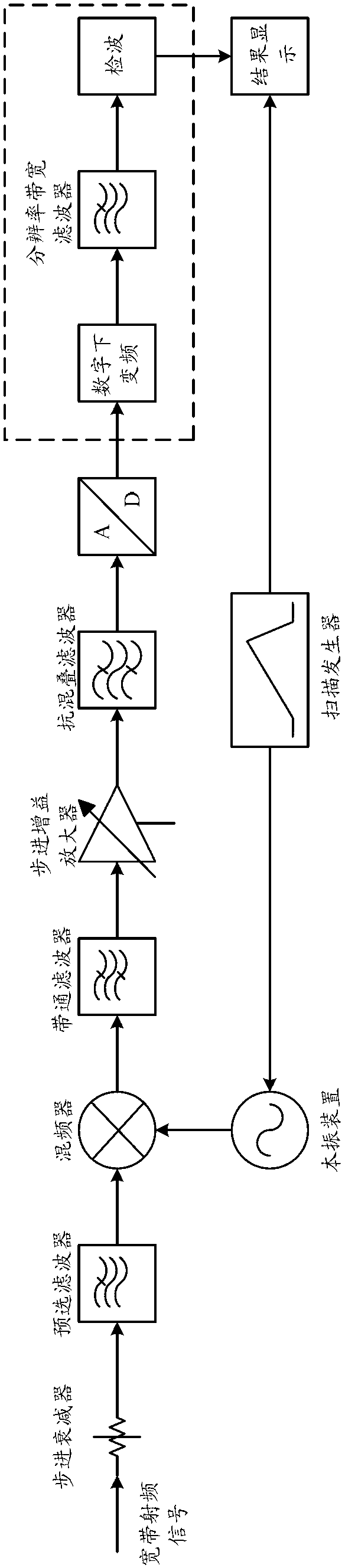
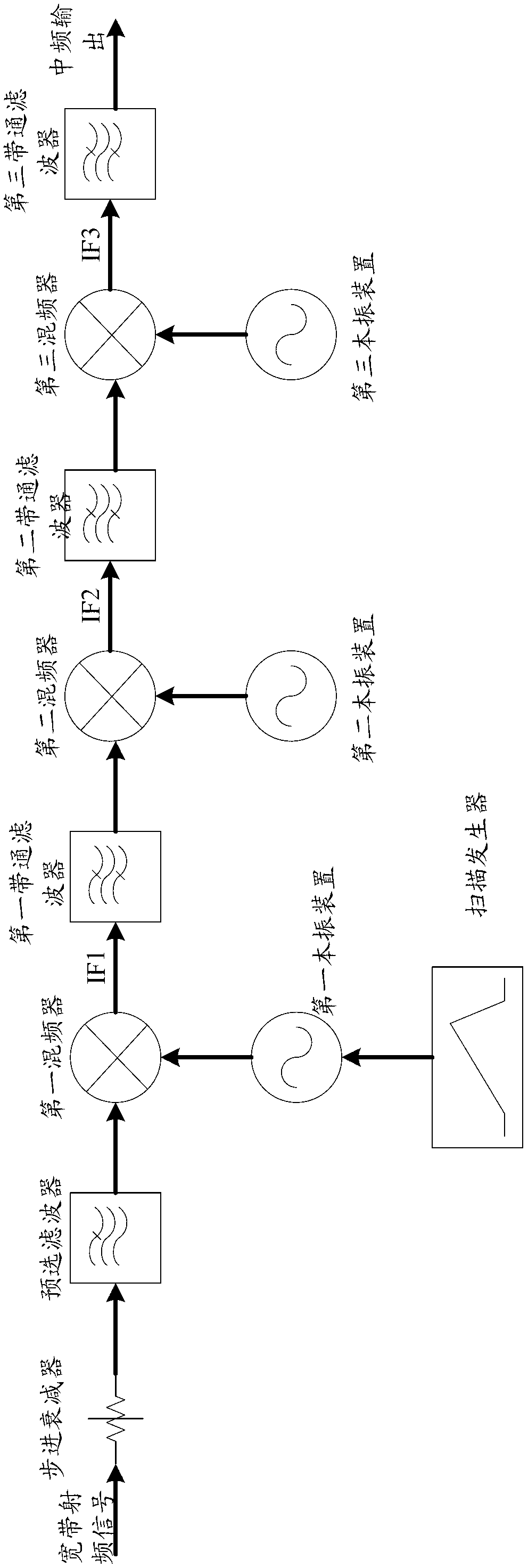
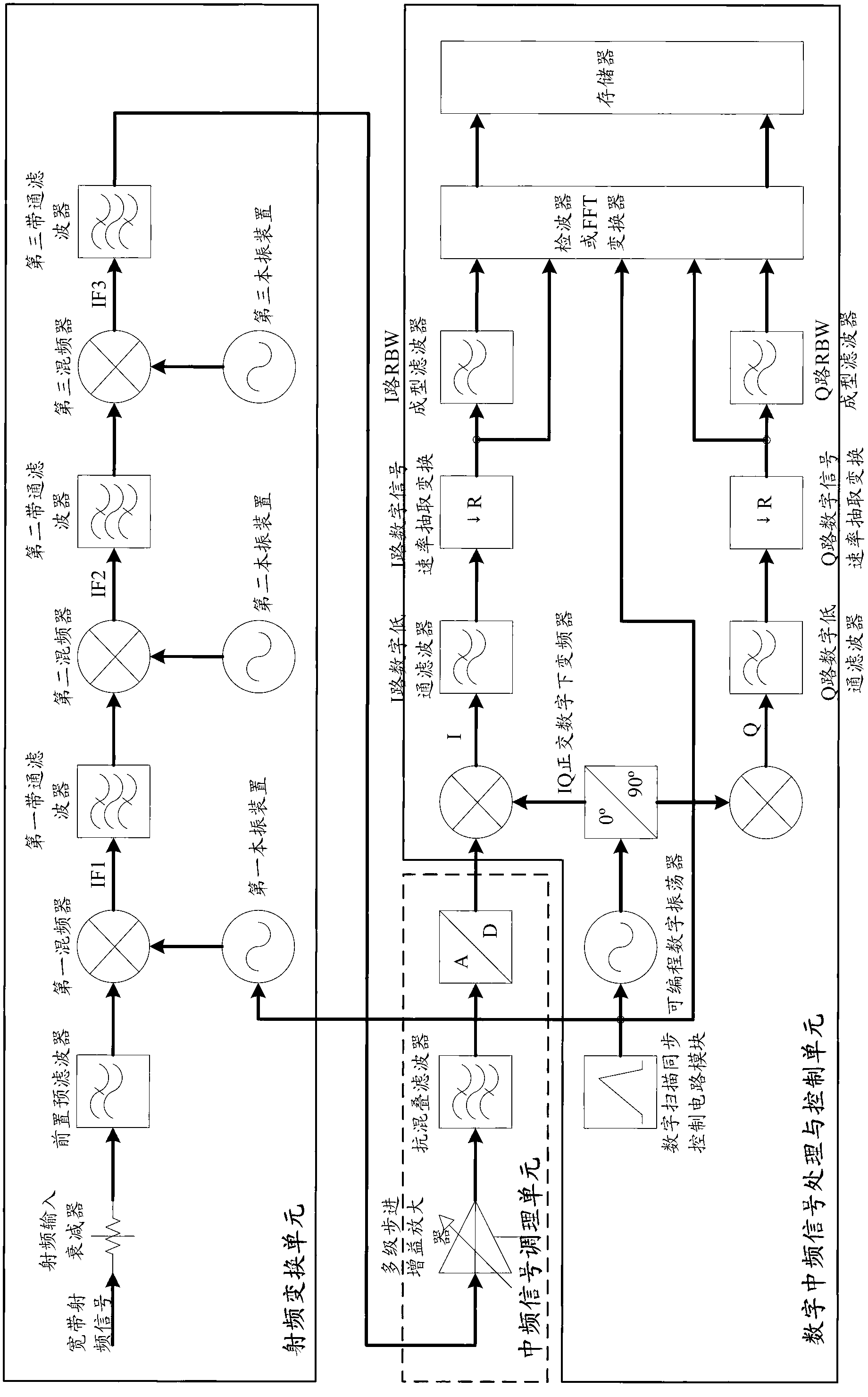
System and method for measuring radio-frequency signal high-speed sweeping frequency spectrum based on digital local oscillator
ActiveCN103067104ASimplify design difficultySimplify Design ComplexitySpectral/fourier analysisTransmission monitoringFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a system for measuring a radio-frequency signal high-speed sweeping frequency spectrum based on a digital local oscillator. The system comprises a radio frequency conversion unit, an intermediate frequency signal conditioning unit and a digital intermediate frequency signal processing and controlling unit which are sequentially connected in series. The digital intermediate frequency signal processing and controlling unit is provided with a digital scan synchronous control circuit module and a programmable digital oscillator, wherein the digital scan synchronous control circuit module is connected with an in-phase quadrature (IQ) signal shunt processing circuit module through the programmable digital oscillator, the digital scan synchronous control circuit module is connected with a first local oscillator device, a detector, or a fast fourier transform (FFT) convertor. The invention further relates to a method which is based on the system and achieves synchronous control for the scanning in high-speed sweeping frequency spectrum measurement. Due to the fact that the system and method for measuring radio-frequency signal high-speed sweeping frequency spectrum based on the digital local oscillator are adopted, scanning time is greatly shortened, local frequency accuracy in a scanning process is improved, circuit hardware is simplified, cost is reduced, working performance is stable and reliable, and range of application is wide.
Owner:TRANSCOM INSTR
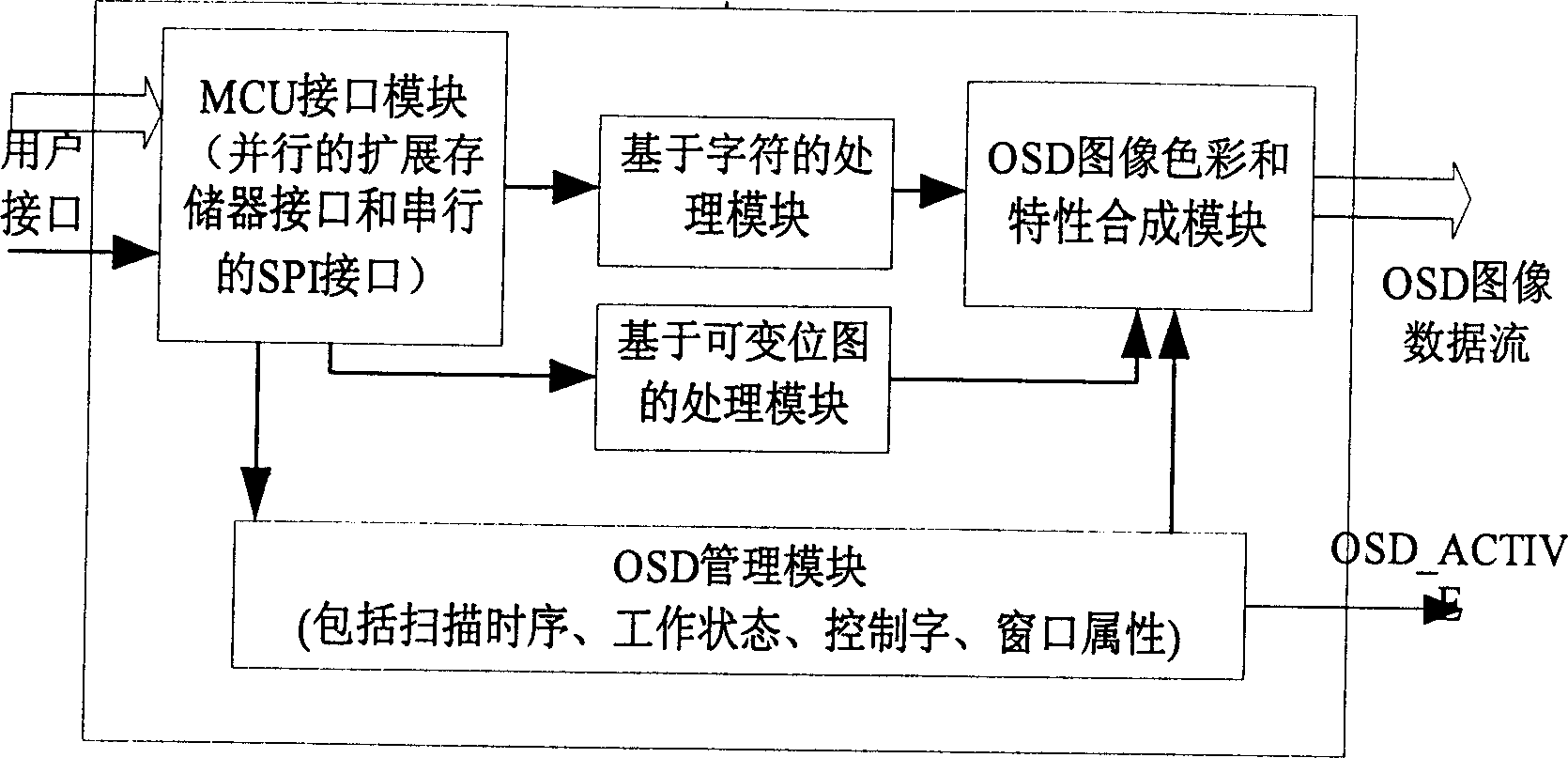
Digital OSD controller based on FRGA
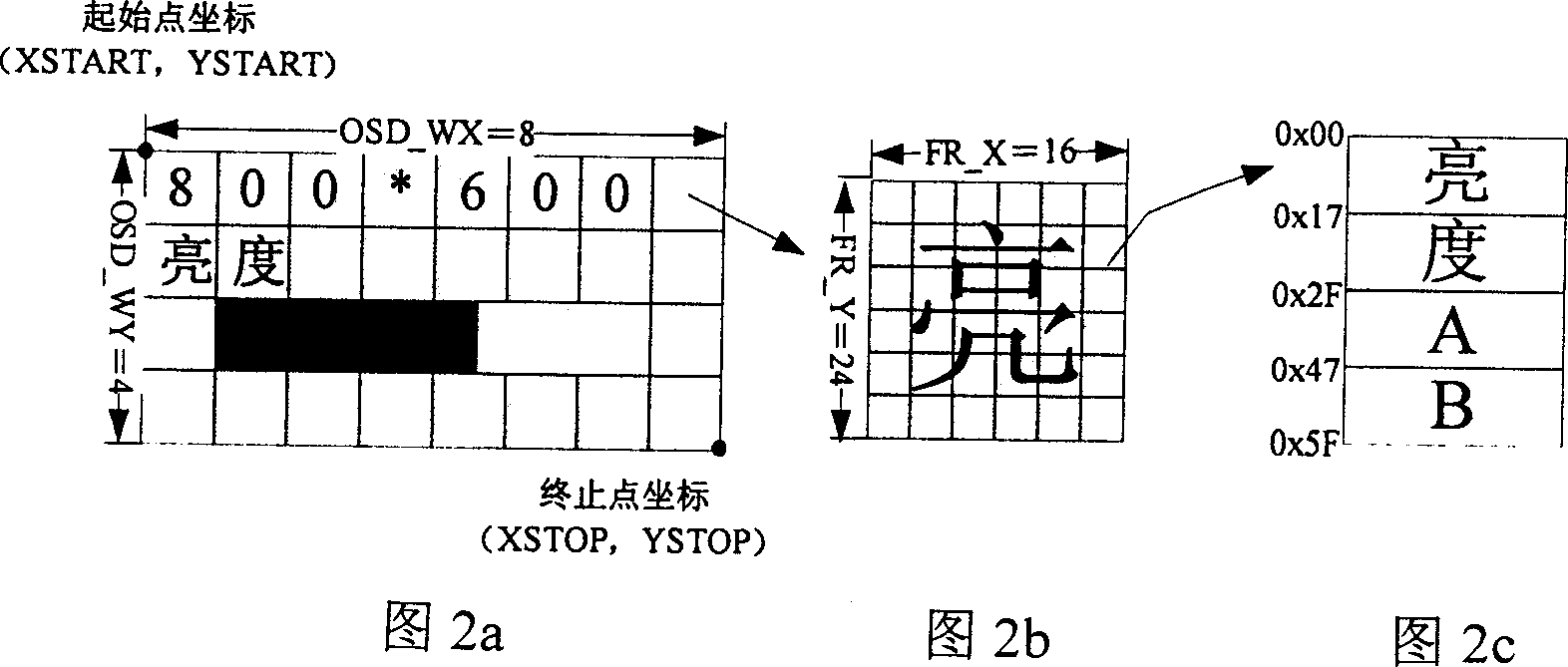
InactiveCN1713264ARealize generationSimple structureStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A digital OSD controller based on FPGA consists of character processing module, variable bit map processing module, MCU interface module of micro-controller, synthetic module of OSD image color and feature as well as OSD management module. It is featured as using three different storages to synthesize scan time sequence and signal stream for overlapping them with original image at output end then displaying OSD menu image with variable size, variable character, etc on LCD.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
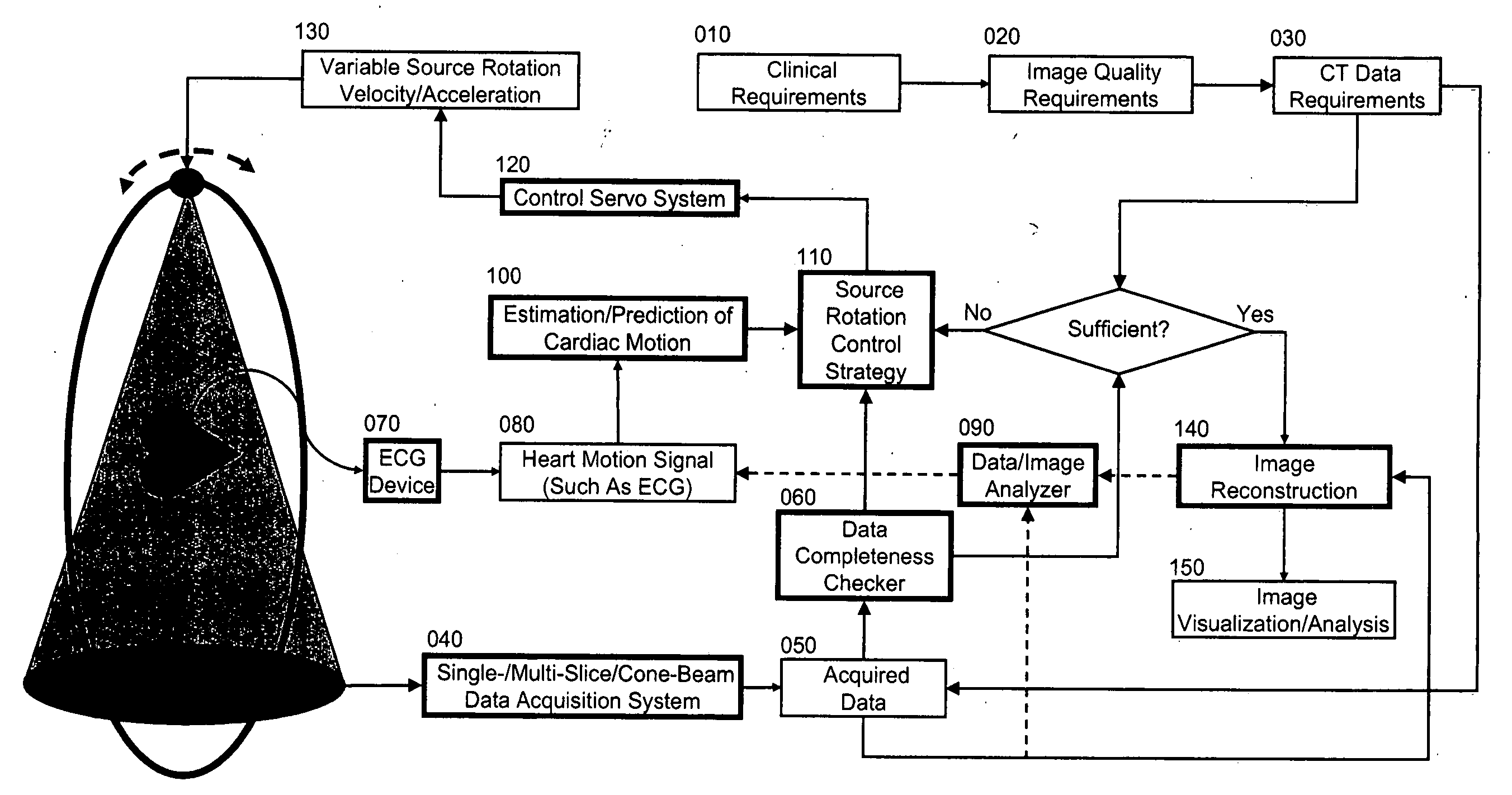
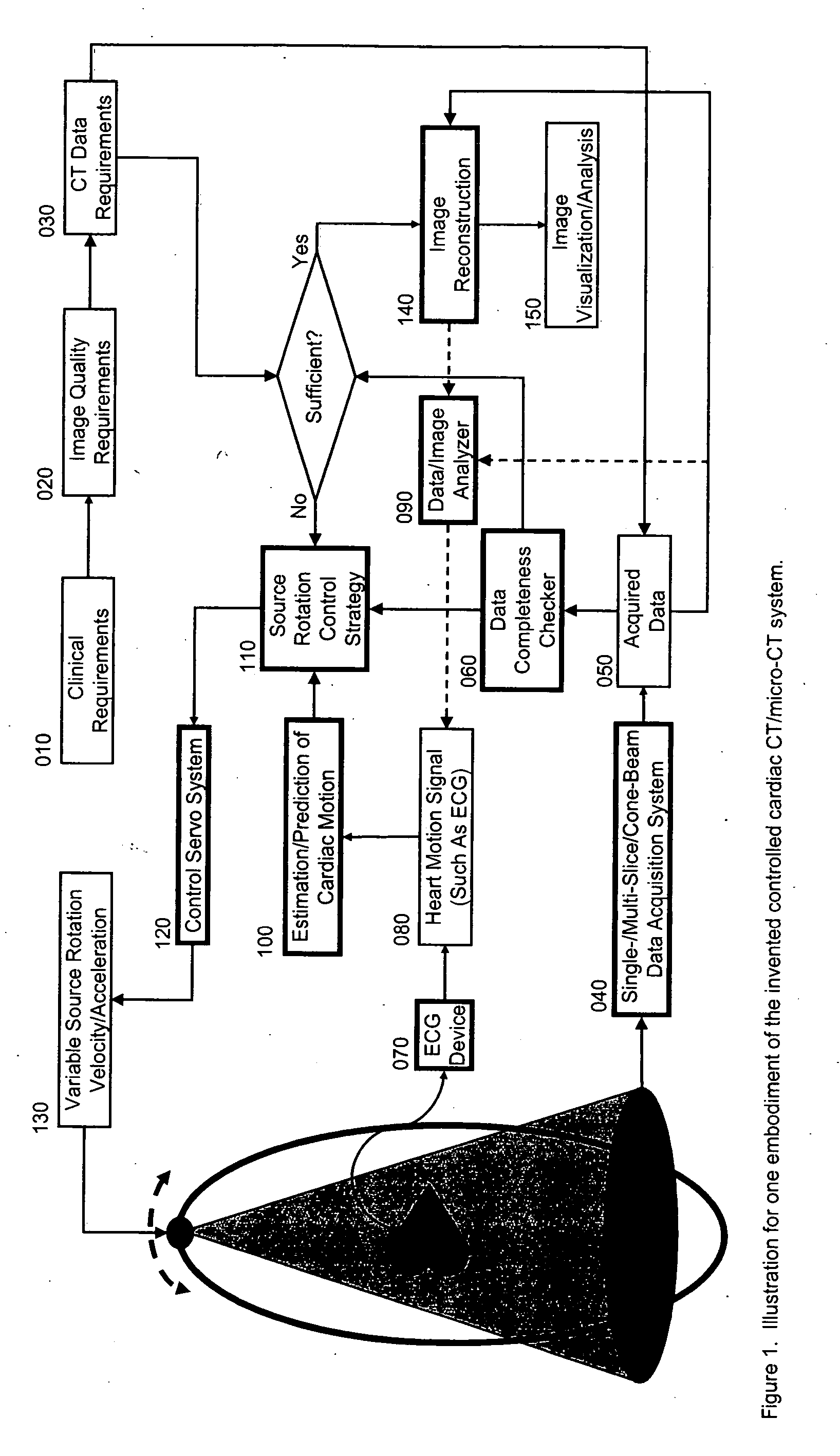
Controlled cardiac computed tomography
InactiveUS20070153971A1Minimize impactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCardiac computed tomographyData acquisition
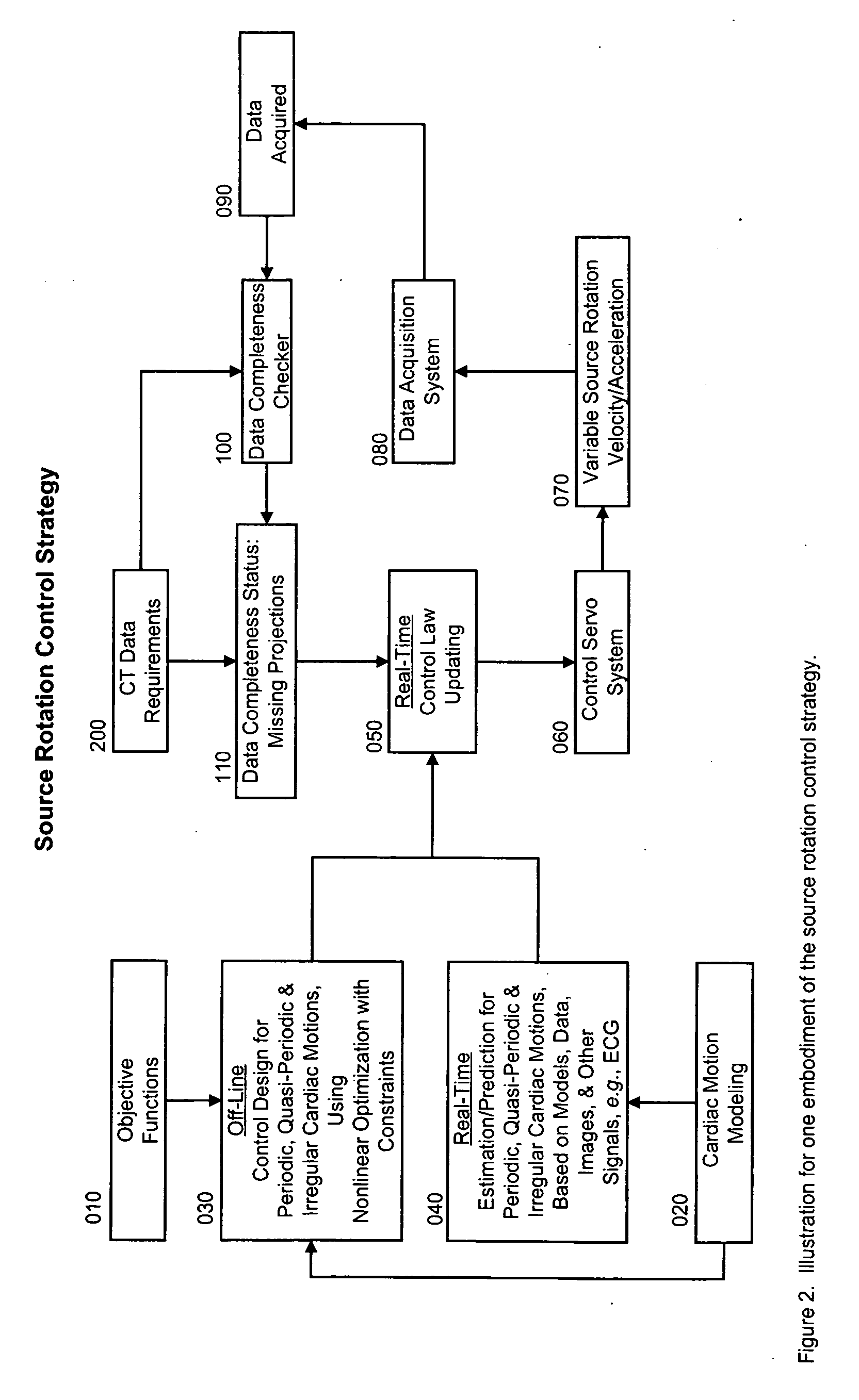
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) has been a hot topic for years because of the clinical importance of cardiac diseases and the rapid evolution of CT systems. In this application, we disclose a novel strategy for controlled cardiac CT (CCCT) that may effectively reduce image artifacts due to cardiac and respiratory motions and reduce the scan time. Our approach is radically different from existing ones and is based on controlling the x-ray source rotation velocity and powering status in reference to the cardiac motion. By such a control-based intervention the data acquisition process can be optimized for cardiac CT in the cases of periodic and quasi-periodic cardiac motions. Specifically, we present the corresponding coordination / control schemes for either exact or approximate matches between the ideal and actual source positions.
Owner:WANG CHENGLIN +1
Method and system to regulate cooling of a medical imaging device
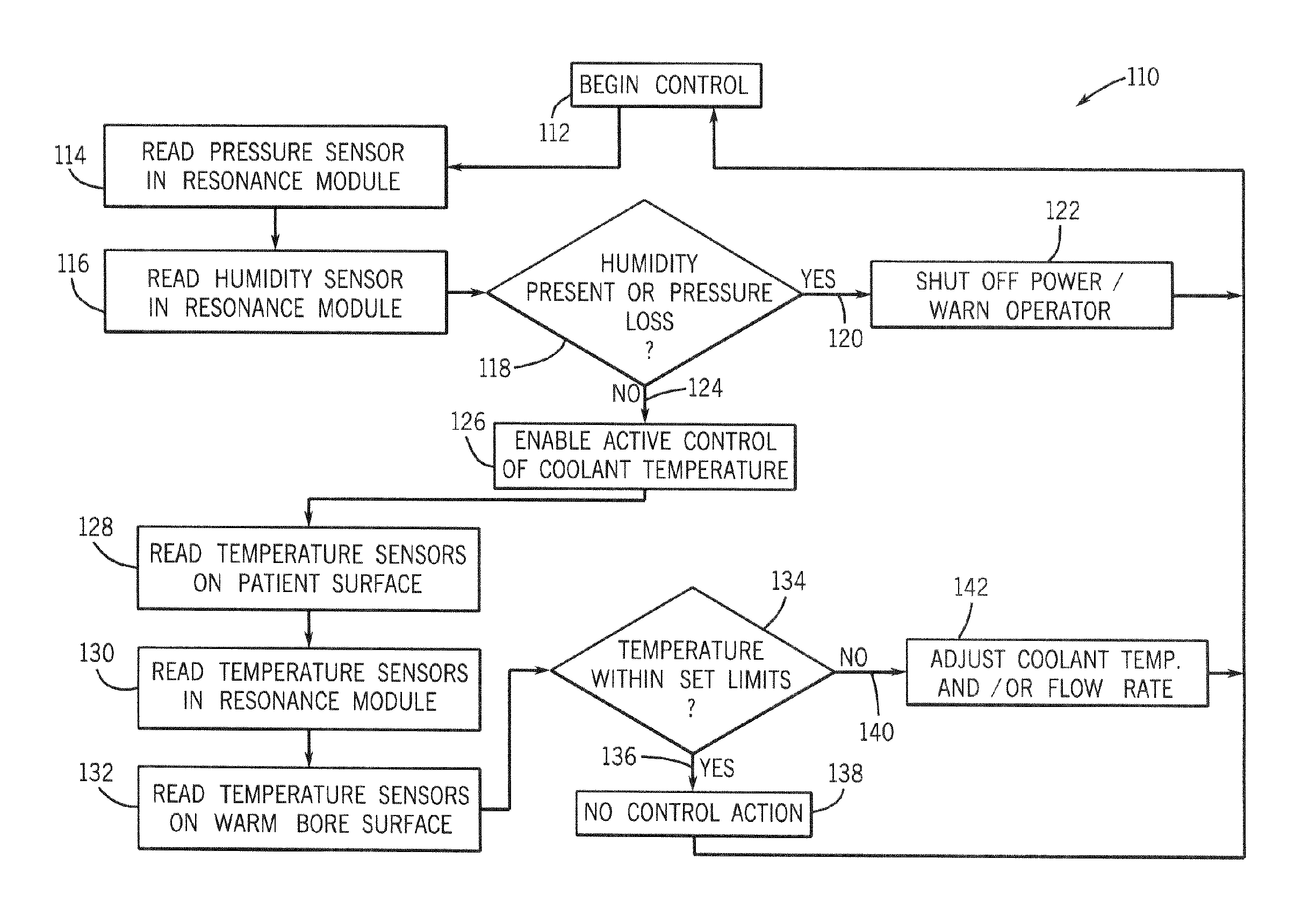
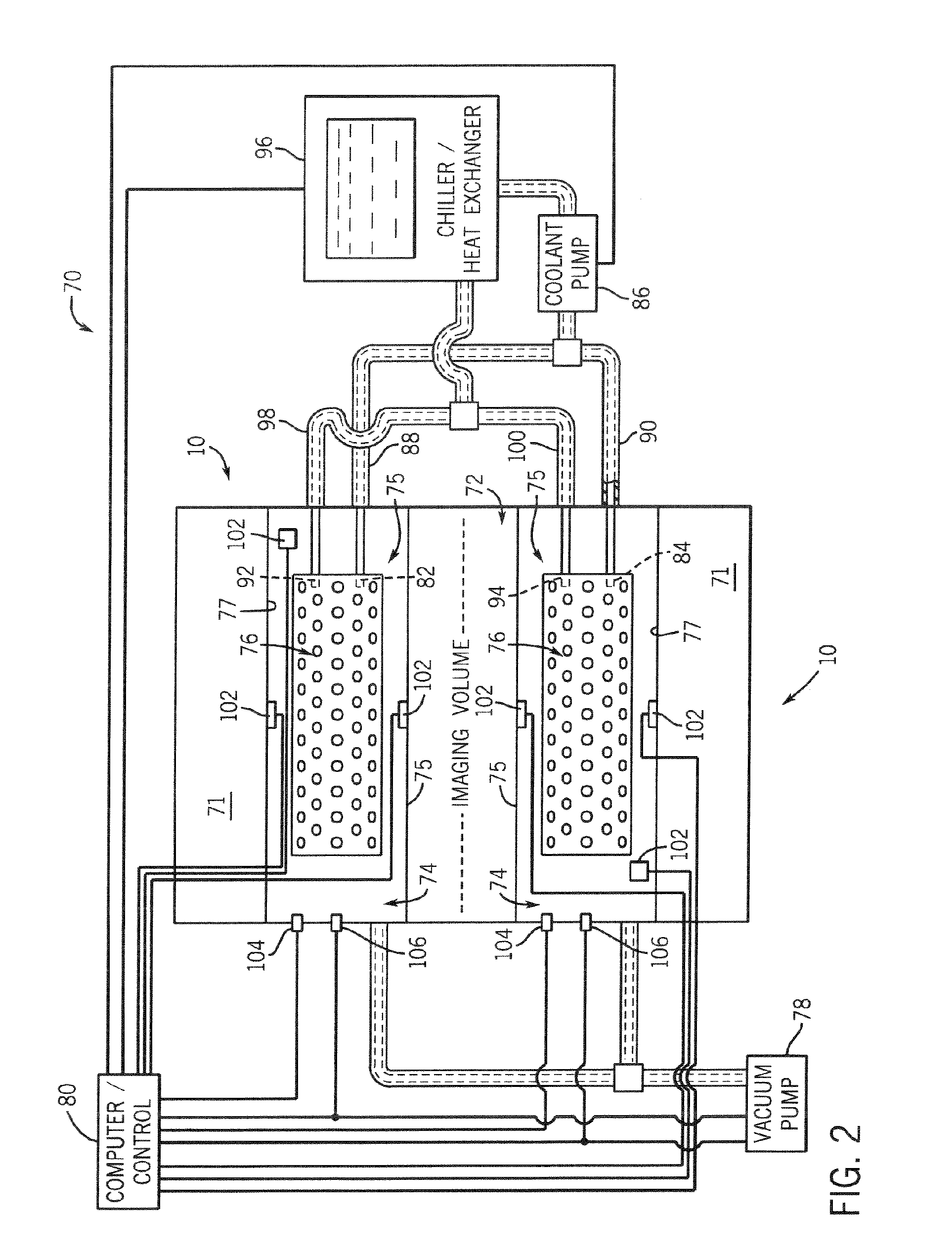
InactiveUS6992483B1Increase powerFast imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method of removing heat from an MR imaging device while maintaining internal and external temperatures below maximum operating limits, thereby enabling higher power applications for faster imaging with improved image quality as well as, allowing longer scan times for interventional procedures. The system includes a vacuum chamber housing the gradient coils and a vacuum pump connected thereto to regulate the pressure and humidity within the chamber. A heat exchanger, coolant pump, and controller are provided to regulate the temperature of coolant designed to dissipate heat from the gradient coils in response to at least one temperature sensor.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
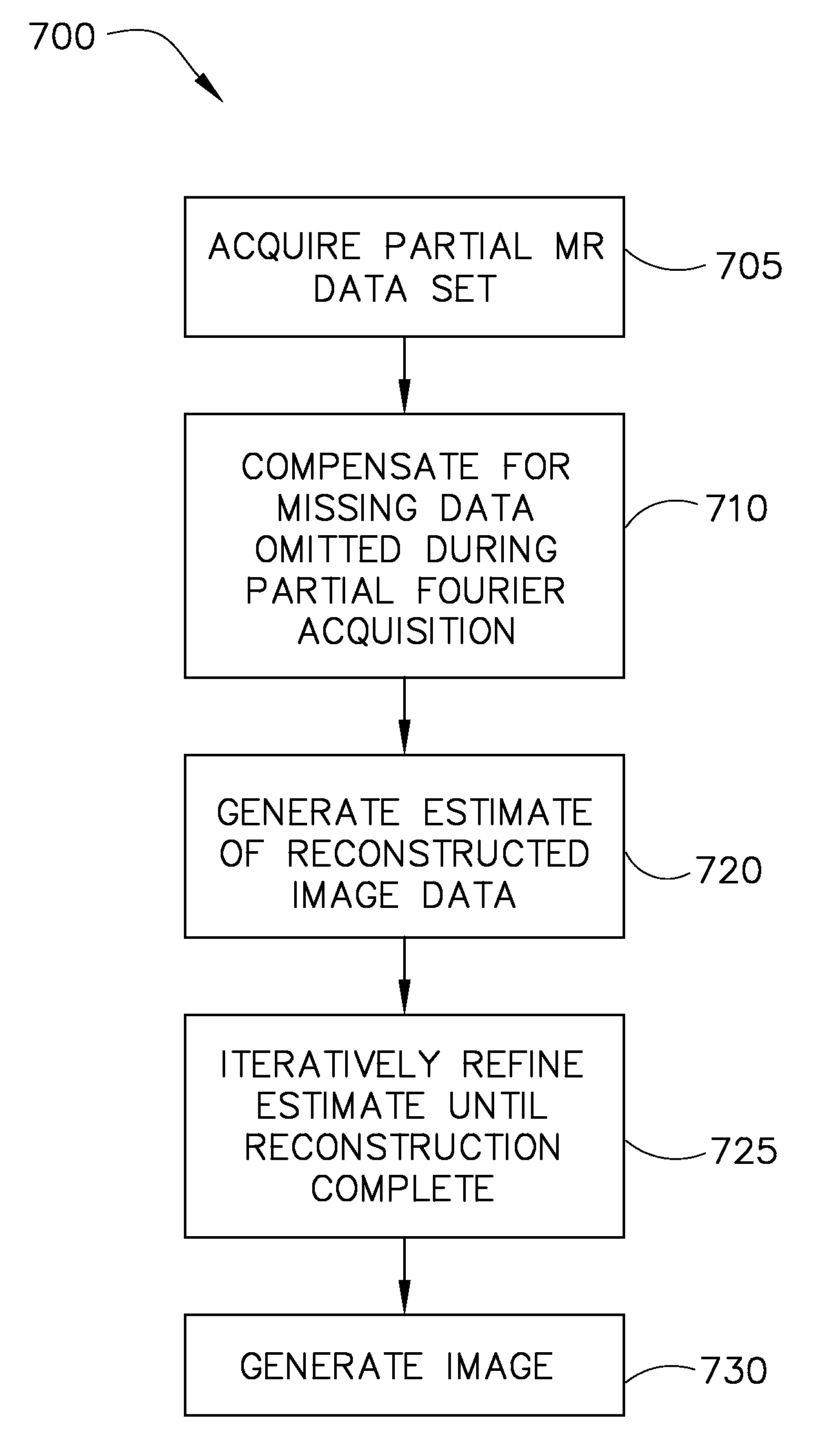
System and method for reducing MR scan time using partial fourier acquisition and compressed sensing
A system and method for reducing the scan time of an MR imaging system using a data acquisition technique that combines partial Fourier acquisition and compressed sensing includes a computer programmed to acquire a partial MR data set in k-space along a phase encoding direction, the data set having missing data in the phase encoding direction due to the omission of phase encoding steps. The computer is further programmed to generate an estimate of a reconstructed image, compensate the partial MR data set for the missing data, and reconstruct an MR image by iteratively minimizing the total squared difference between the k-space data of the estimate of the reconstructed image and the measured k-space data of the compensated partial MR data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
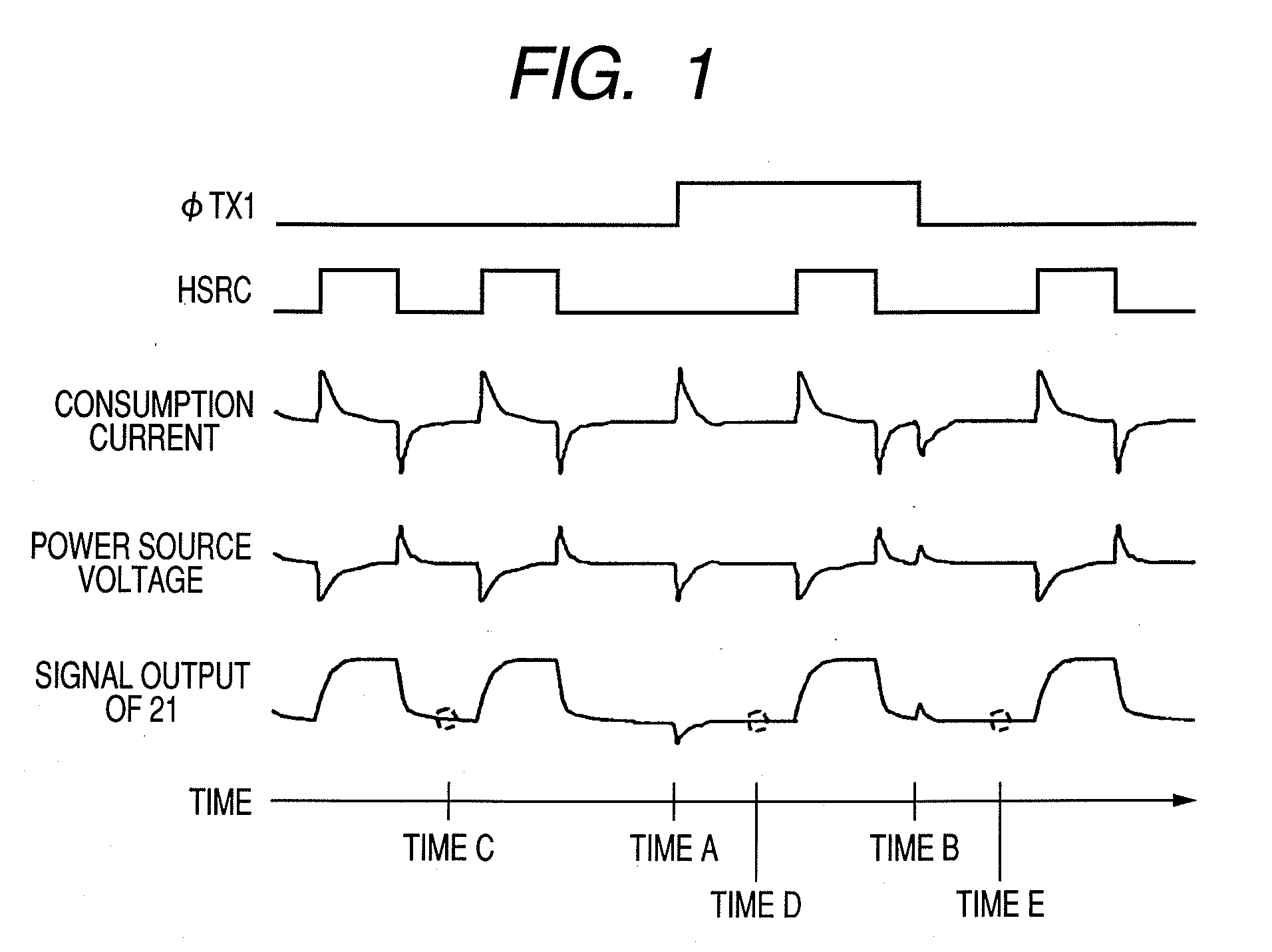
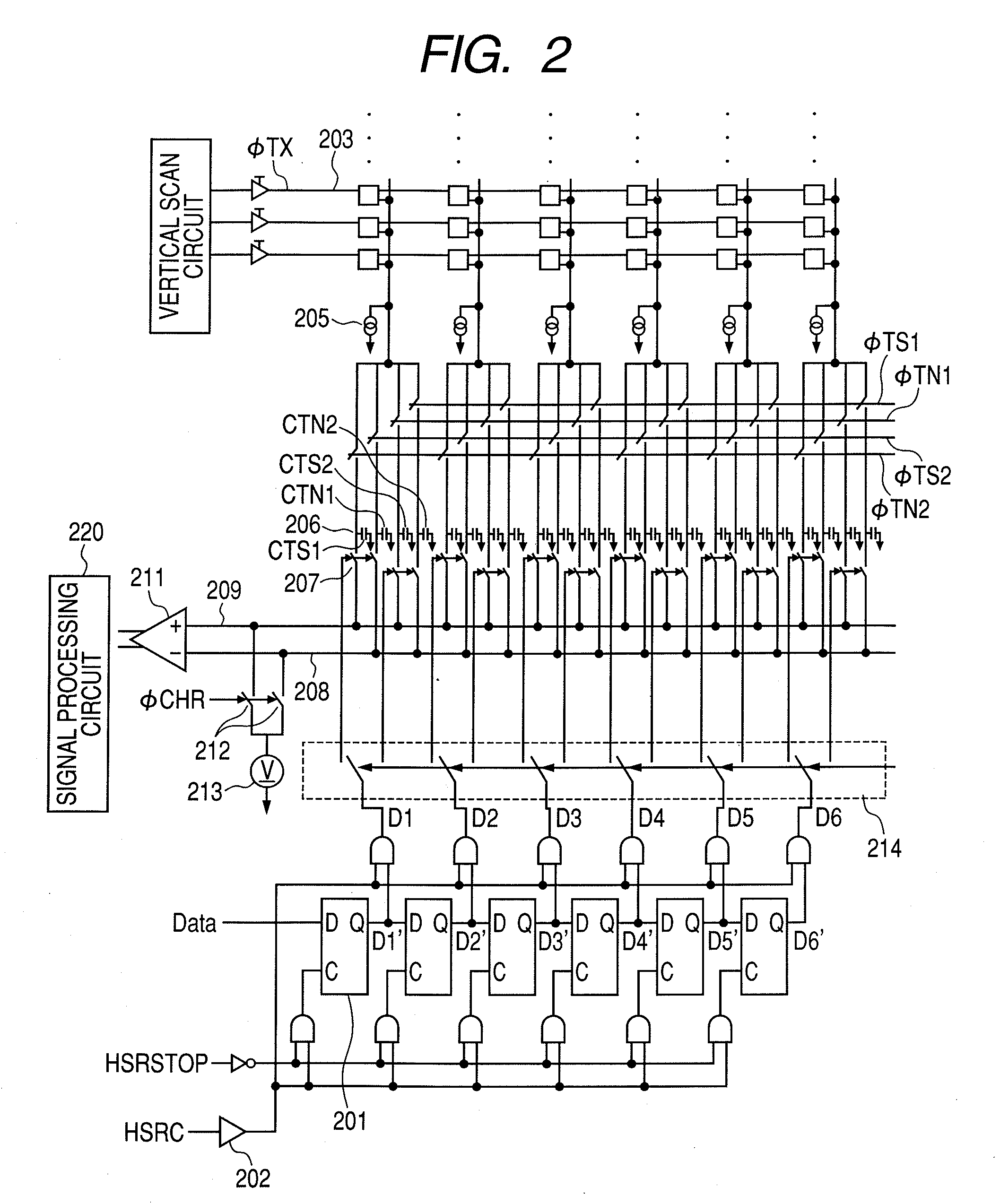
Solid-state imaging apparatus, method of driving solid-state imaging apparatus, and imaging system
InactiveUS20090219429A1Avoid mixingAvoid noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionCapacitor
There is provided a solid-state imaging apparatus which, while shortening the reading time period, can prevent noise from being mixed. There are included: multiple pixels (203), wherein the pixel includes a photoelectric conversion element converting light into electric charge, and outputs, responsive to a reading out signal, a signal based on the electric charge obtained by the conversion by the photoelectric conversion element; multiple capacitors (206) to hold the signal output from the plurality of pixels; and a horizontal scanning circuit (201) for sequentially transferring data pulse responsive to a clock pulse and thereby reading the signals held by the plurality of capacitors, wherein the horizontal scanning circuit includes a mask signal input portion for receiving a mask signal, and when the plurality of pixels output the signal to the plurality of capacitors during a horizontal scanning time period in which the horizontal scanning circuit reads out the signal of one row of the pixels, the mask signal is input to the mask signal input portion at the time of changing of the reading out signal, so that the horizontal scanning circuit is disabled from transferring the data pulse responsive to the clock pulse.
Owner:CANON KK
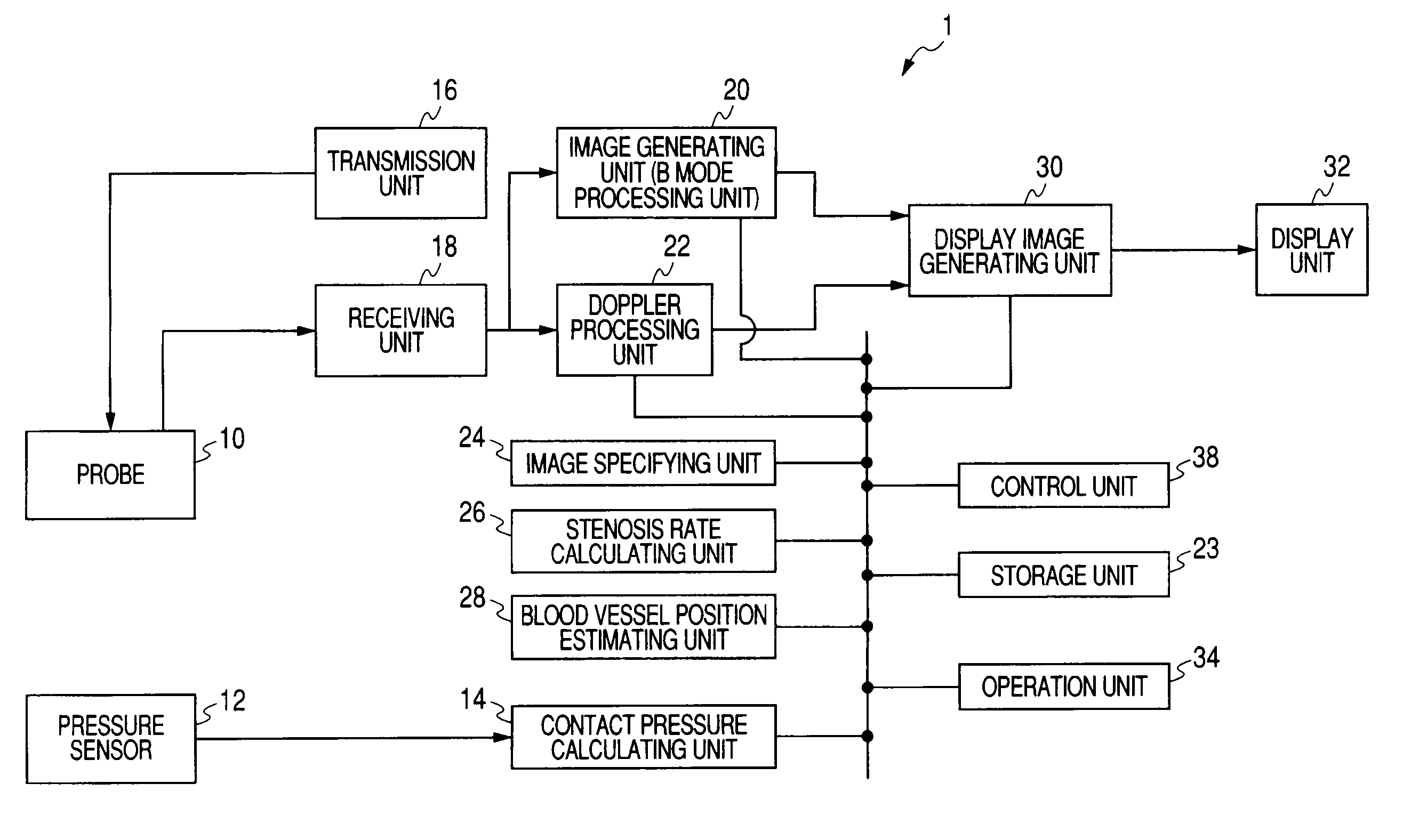
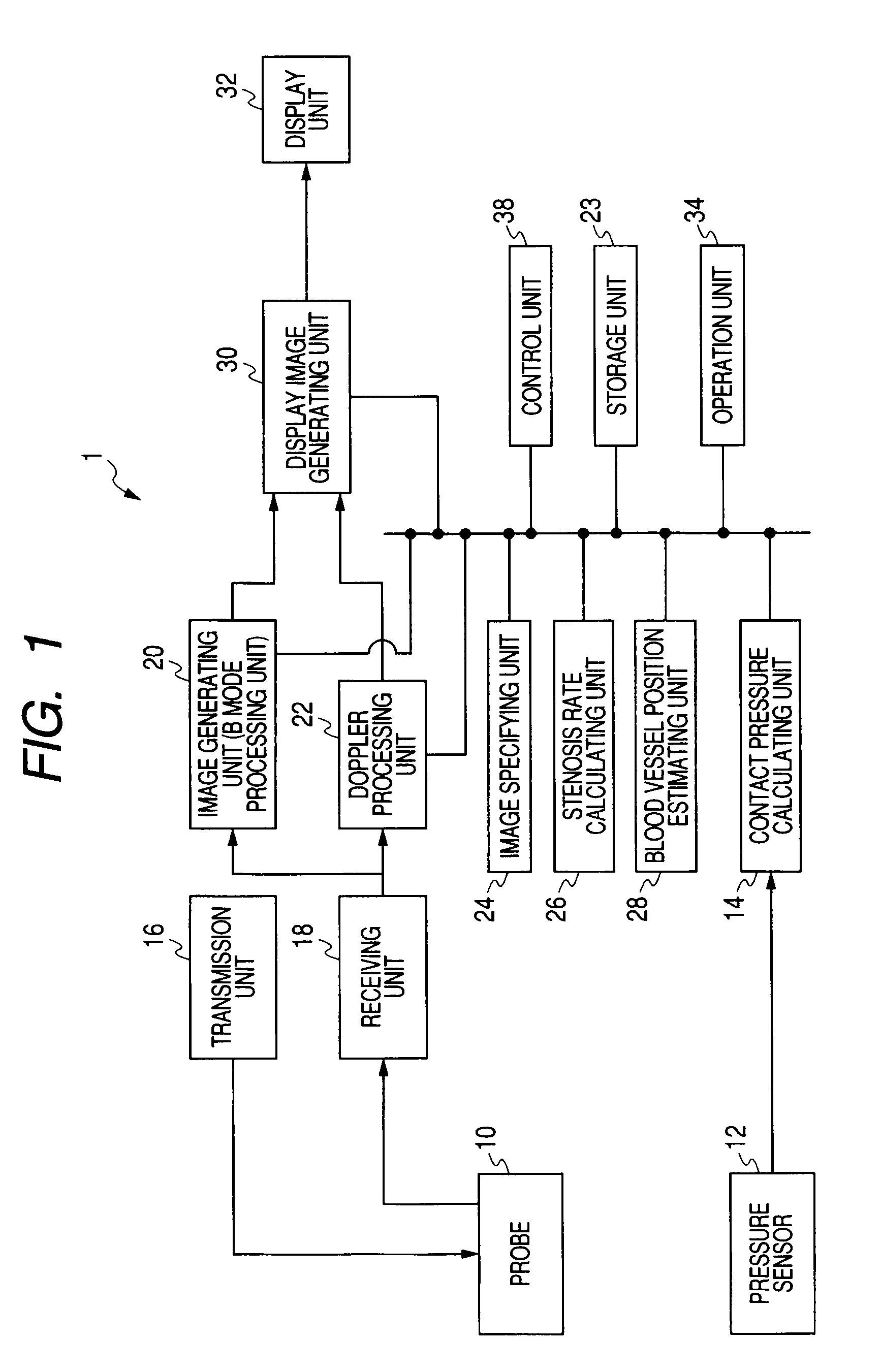
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and image display method thereof
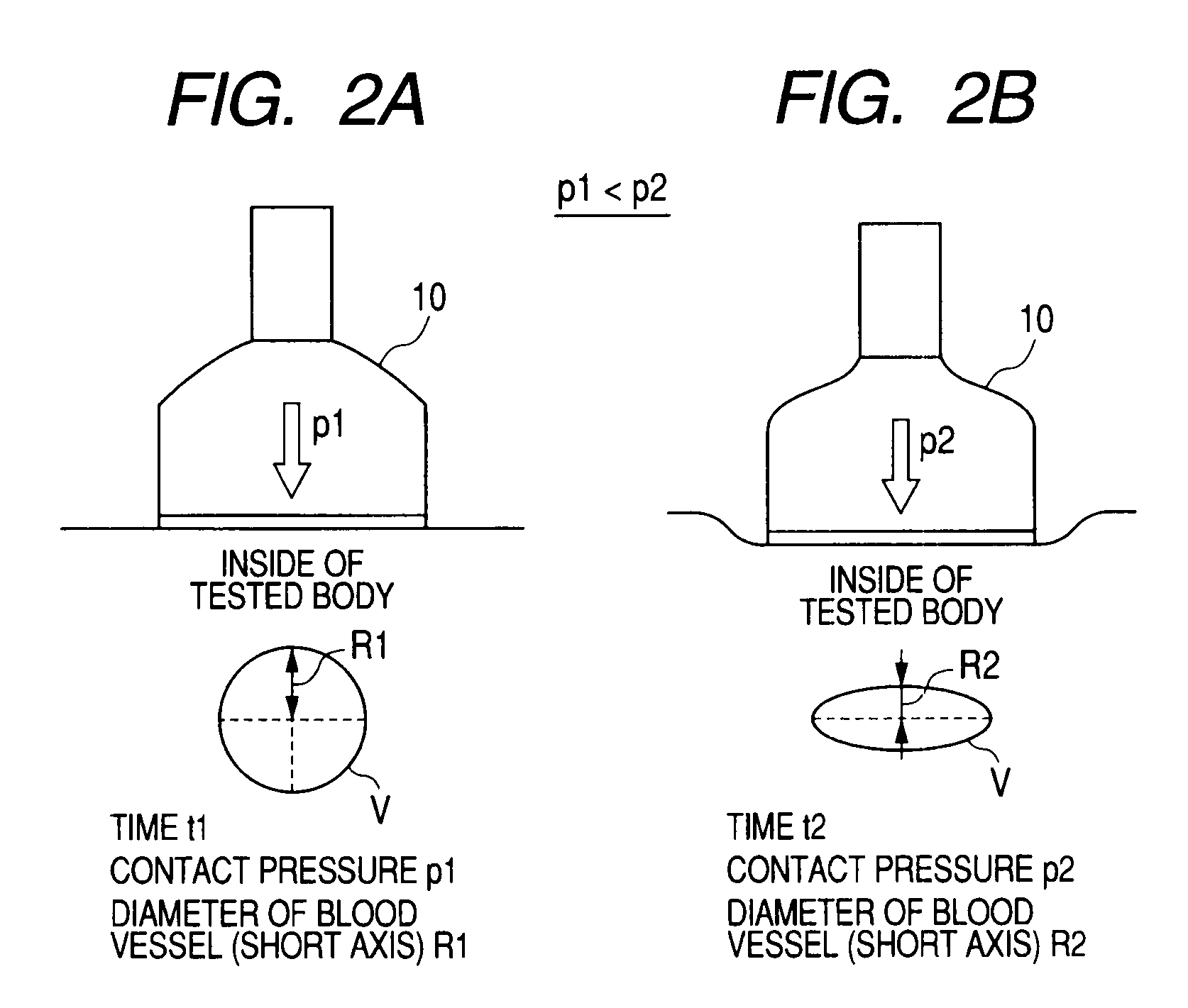
ActiveUS20080269605A1Easily determining deformationDiagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesPhysical quantityUltrasound diagnostics
A generation unit generates data of a plurality of images whose scan time is different on the basis of an output of the probe. A calculation unit calculates a plurality of index values related to pressure of the probe against the tested body on the basis of a physical quantity changing with the strength of the pressure. A specifying unit specifies a first image, which corresponds to a first index value of the plurality of calculated index values, and a second image, which corresponds to a second index value, among the plurality of generated images. A display unit displays the specified first and second images side by side.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
X-ray computed tomography apparatus and image processing apparatus
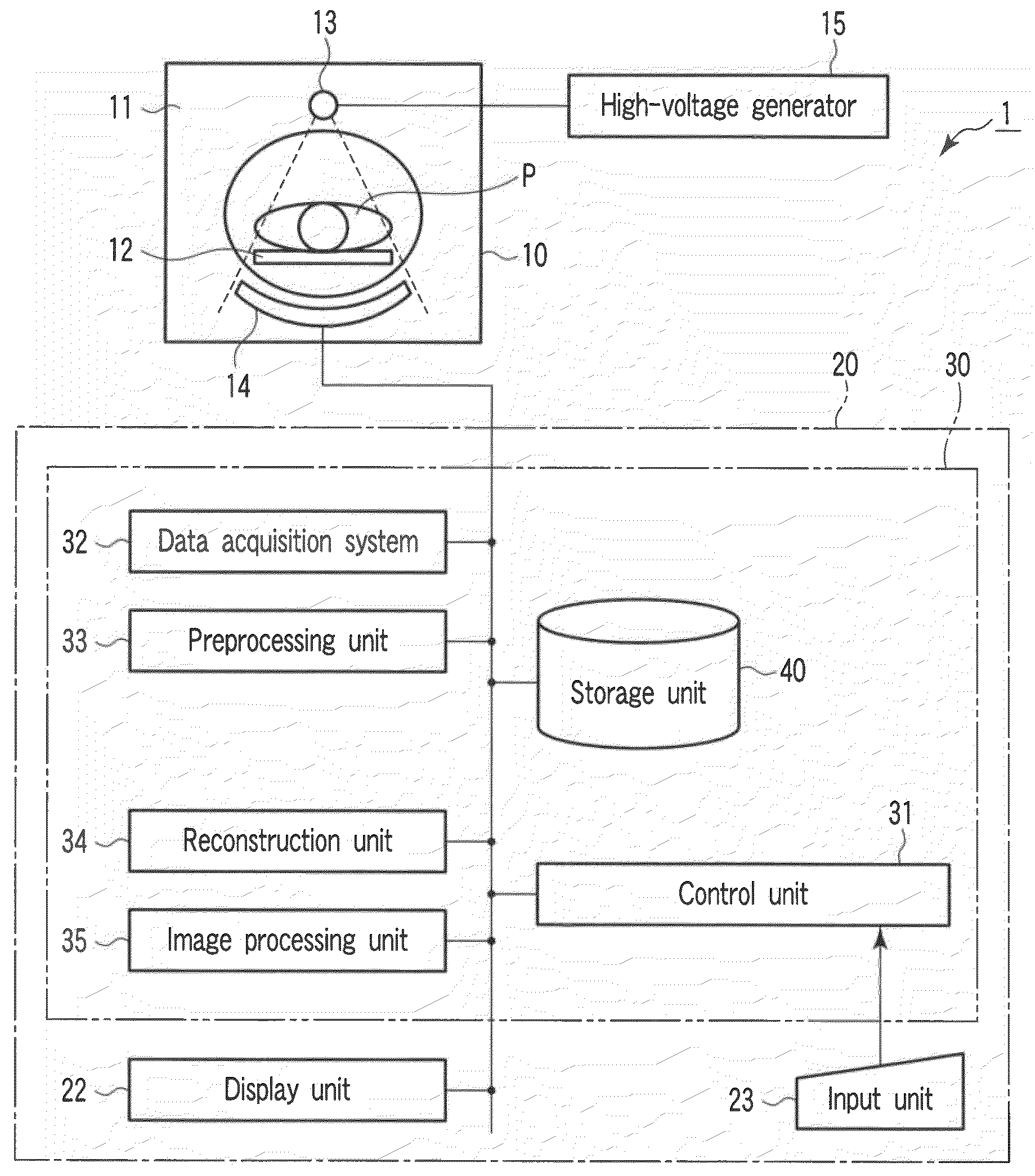
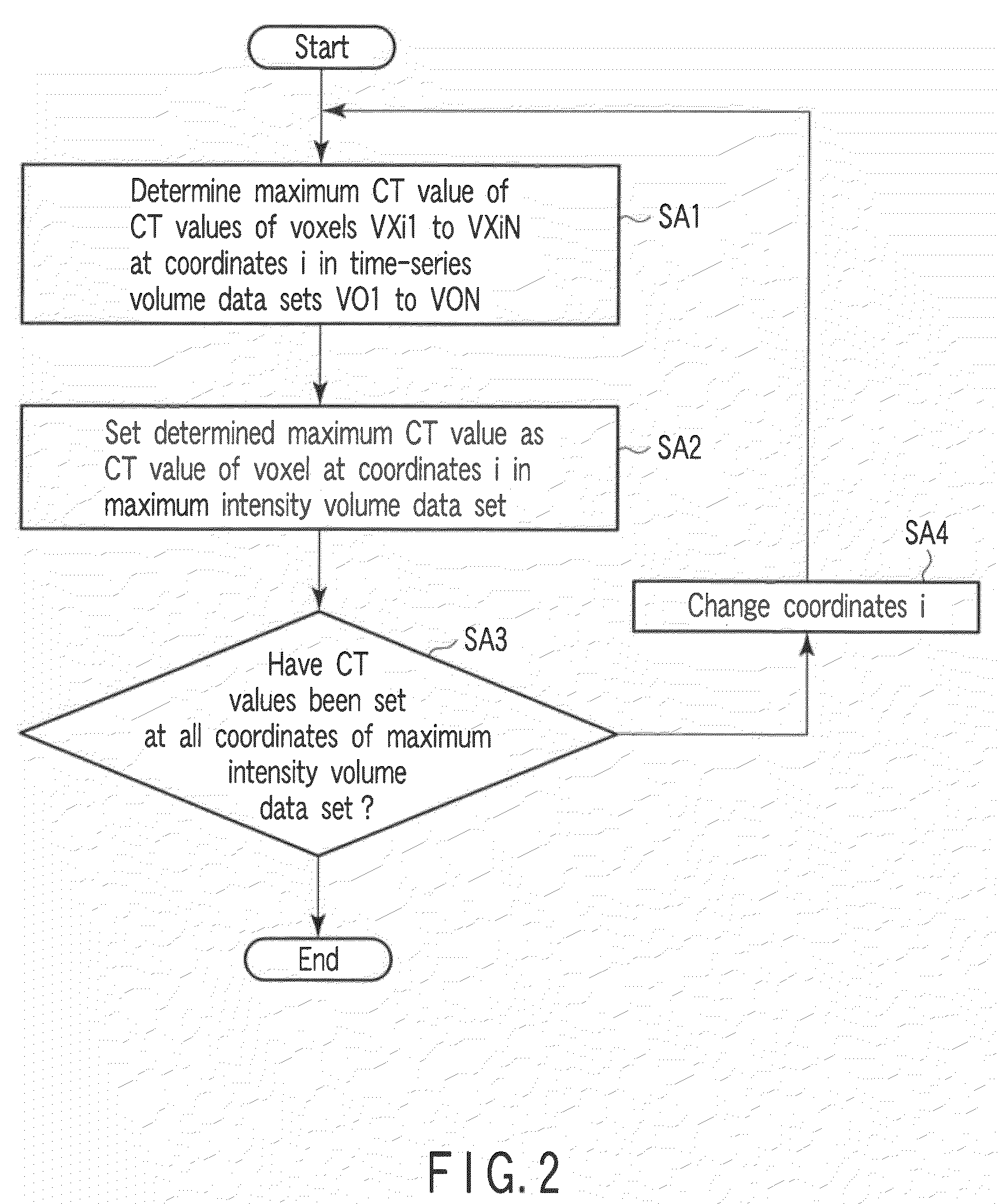
InactiveUS20090028409A1Improve diagnostic efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayData set
An X-ray tube generates X-rays. An X-ray detector detects X-rays generated from the X-ray tube and transmitted through an object to be examined. A rotating frame continuously rotates the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector around the object. A reconstruction unit reconstructs a plurality of first volume data sets with different scan times for the same scan area of the object on the basis of an output from the X-ray detector. An image processing unit generates single second volume data set corresponding to a maximum value, an average value, a median value, or minimum value of the plurality of reconstructed first volume data sets in the temporal direction.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and method for interactive image contrast control in a magnetic resonance imaging system
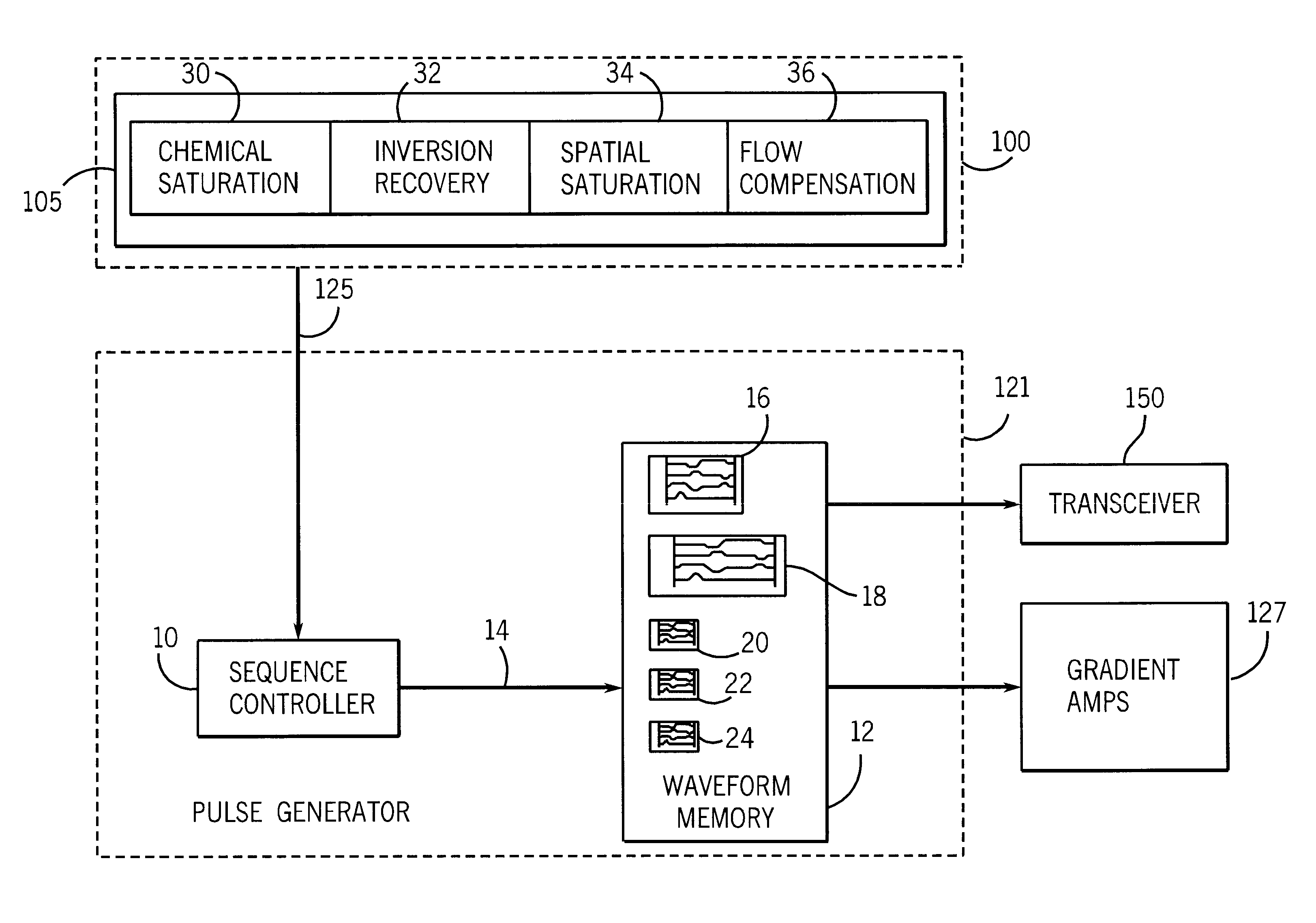
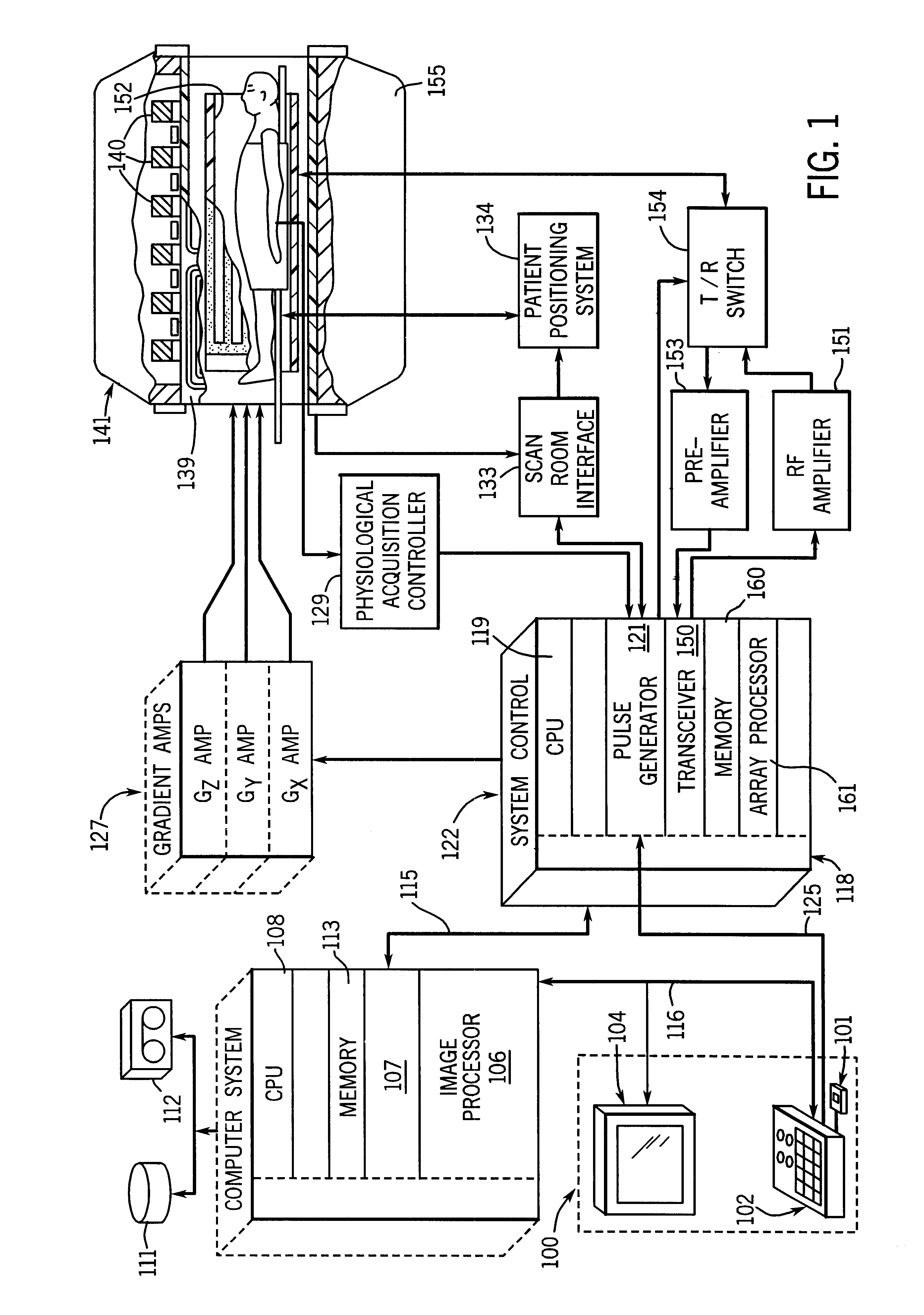
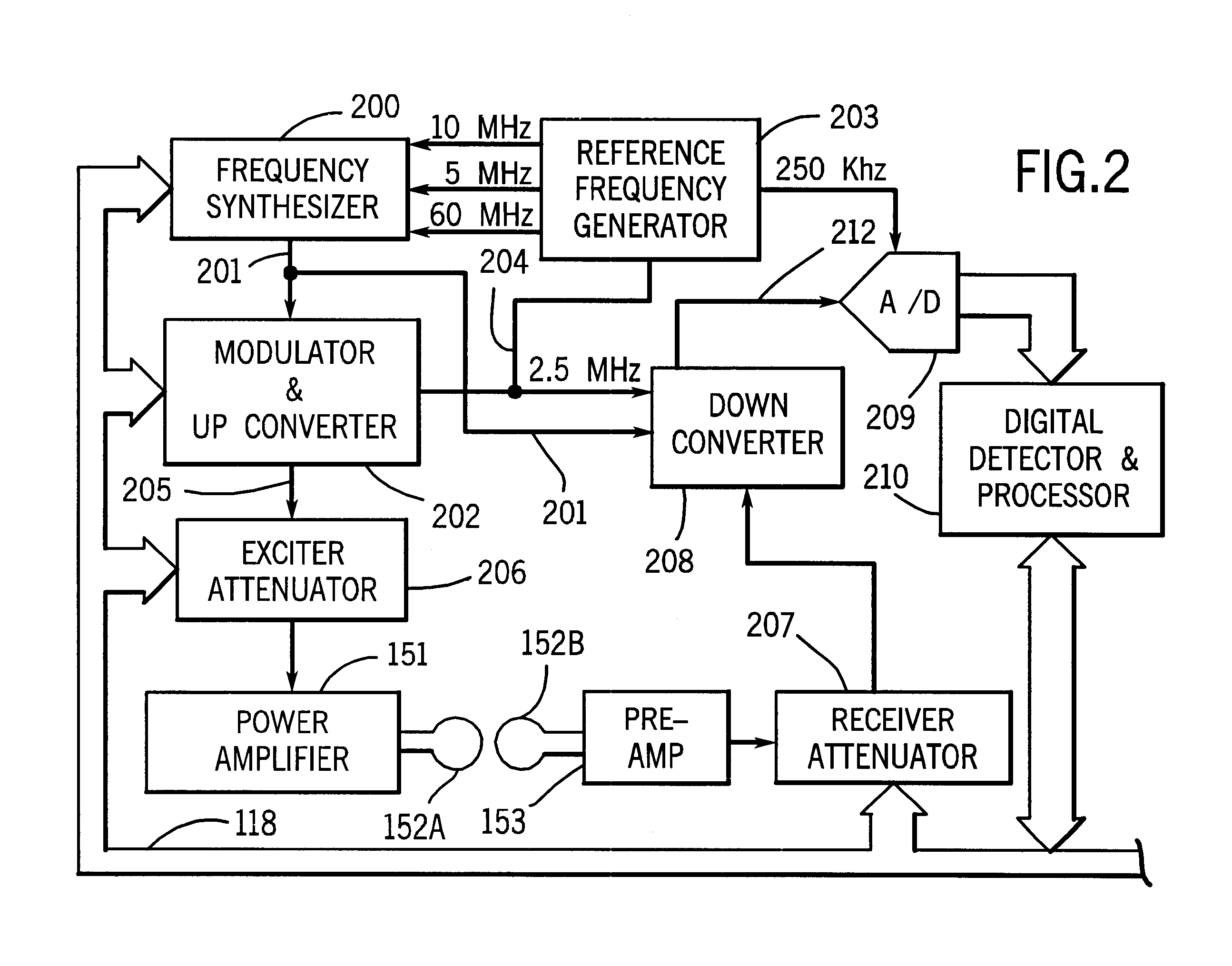
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging system equipped with real-time imaging capability and method of interactively prescribing image contrast are disclosed herein. The MR imaging system includes a sequence controller for constructing MR imaging pulse sequences and a waveform memory for storing waveform segments. The MR imaging system allows an operator to interactively prescribe image contrast mechanism prior to and / or during real-time imaging. The use of image contrast waveform segments, only as needed, minimizes unnecessary MR scan time.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
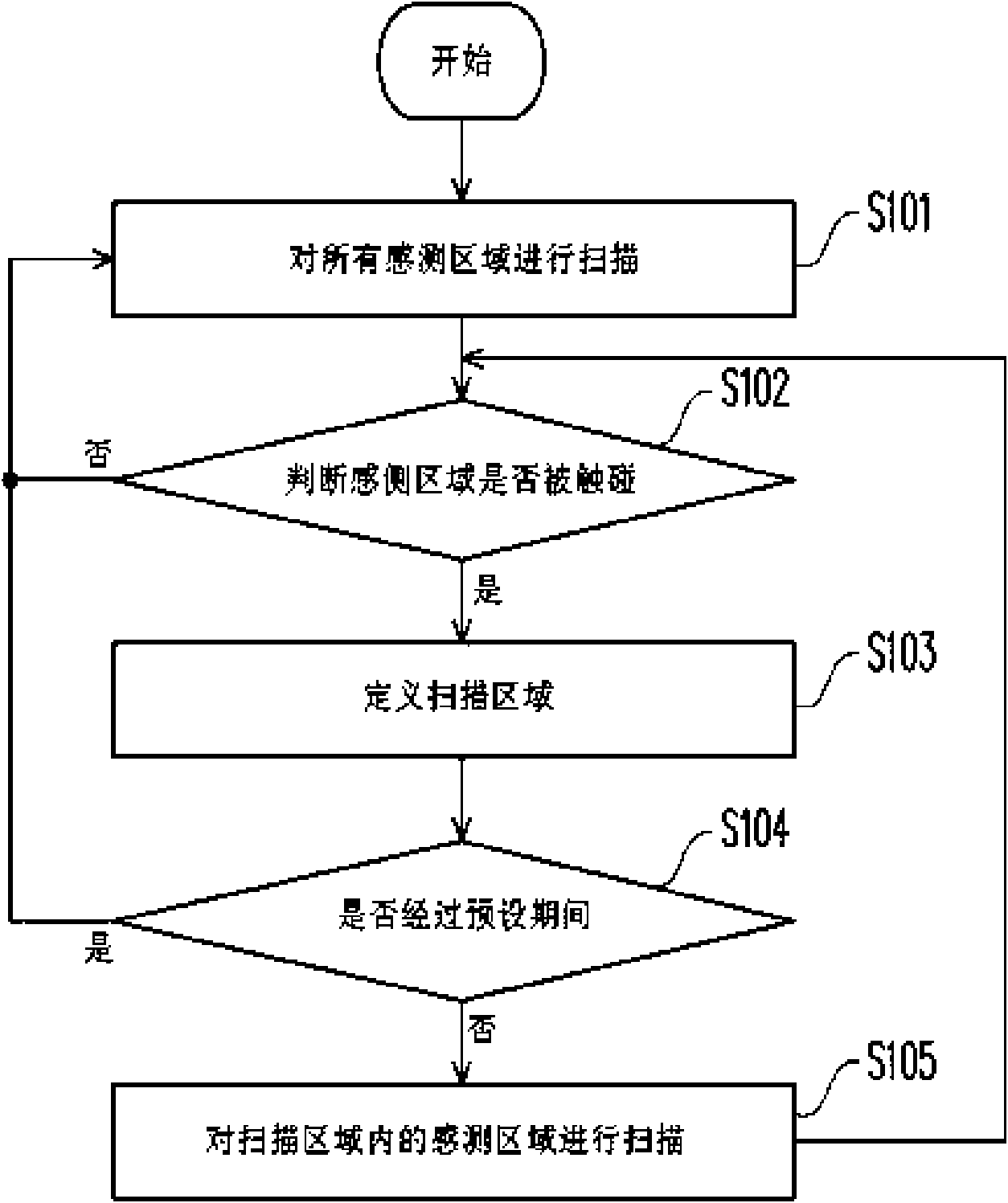
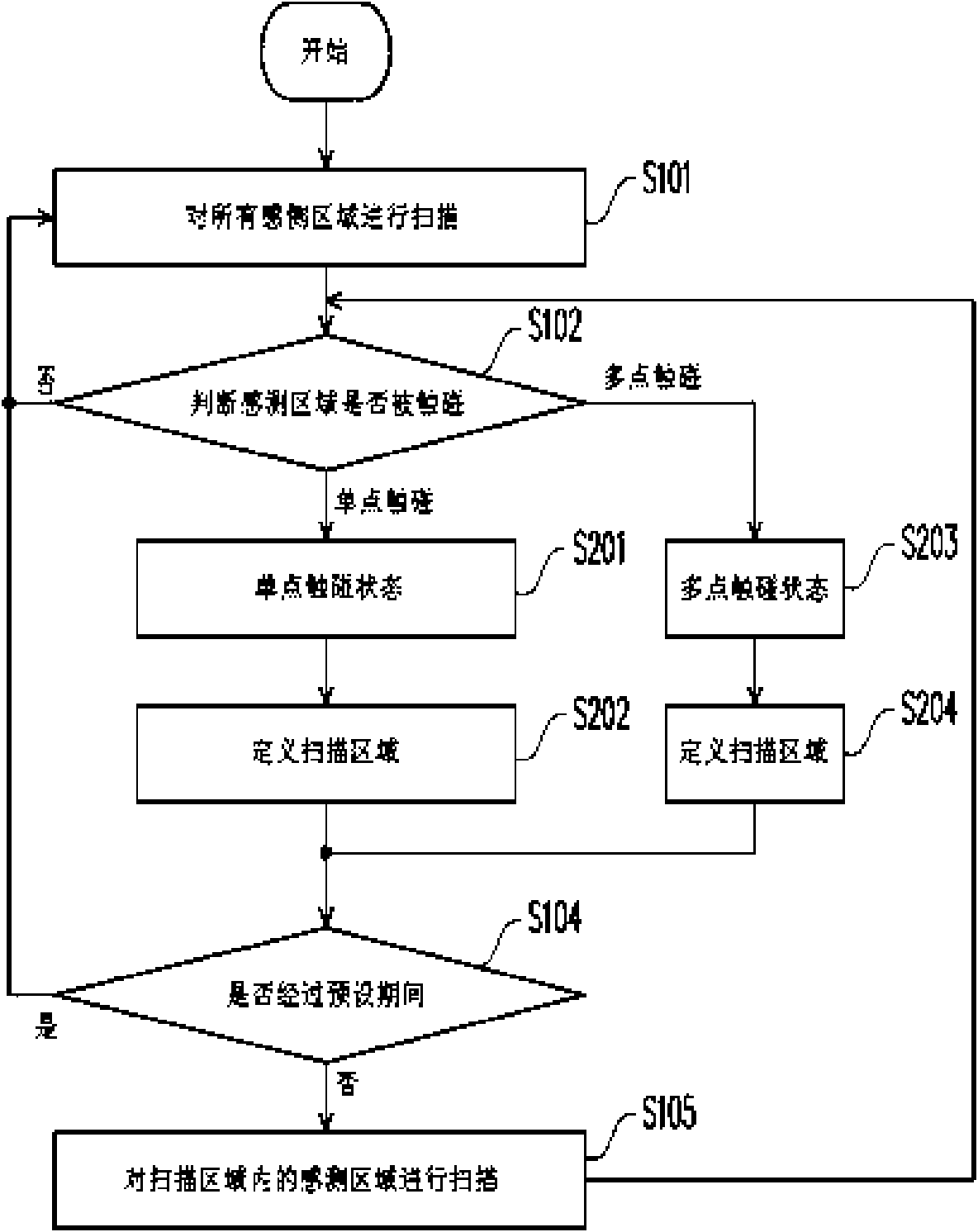
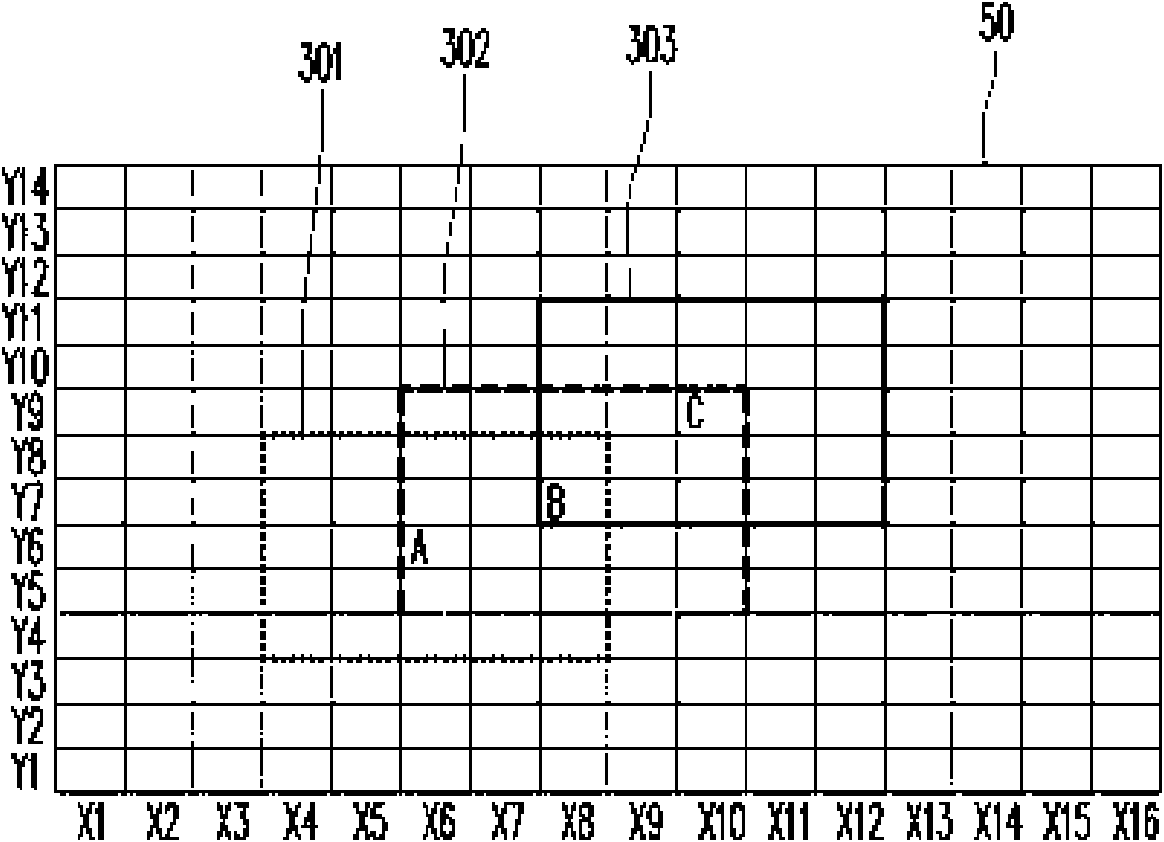
Scanning method for touch panel
InactiveCN101615097AReduce scan timeReduce power consumptionInput/output processes for data processingComputer scienceTouch panel
The invention relates to a scanning method for a touch panel, in particular to a scanning method capable of adjusting a dynamic area of a scanning area according to a touch signal. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, defining the scanning area according to coordinates corresponding to the detected touch signal; then, scanning the scanning area in a preset period to detect a next touch signal; and after the preset period, scanning a sensing range of the touch panel to redefine the scanning area. Because the scanning area is smaller than the sensing range of the whole touch panel, the scanning method can reduce the scanning time and power consumption by using the scanning area to detect the next touch signal.
Owner:CPTF VISUAL DISPLAY (FUZHOU) LTD +1
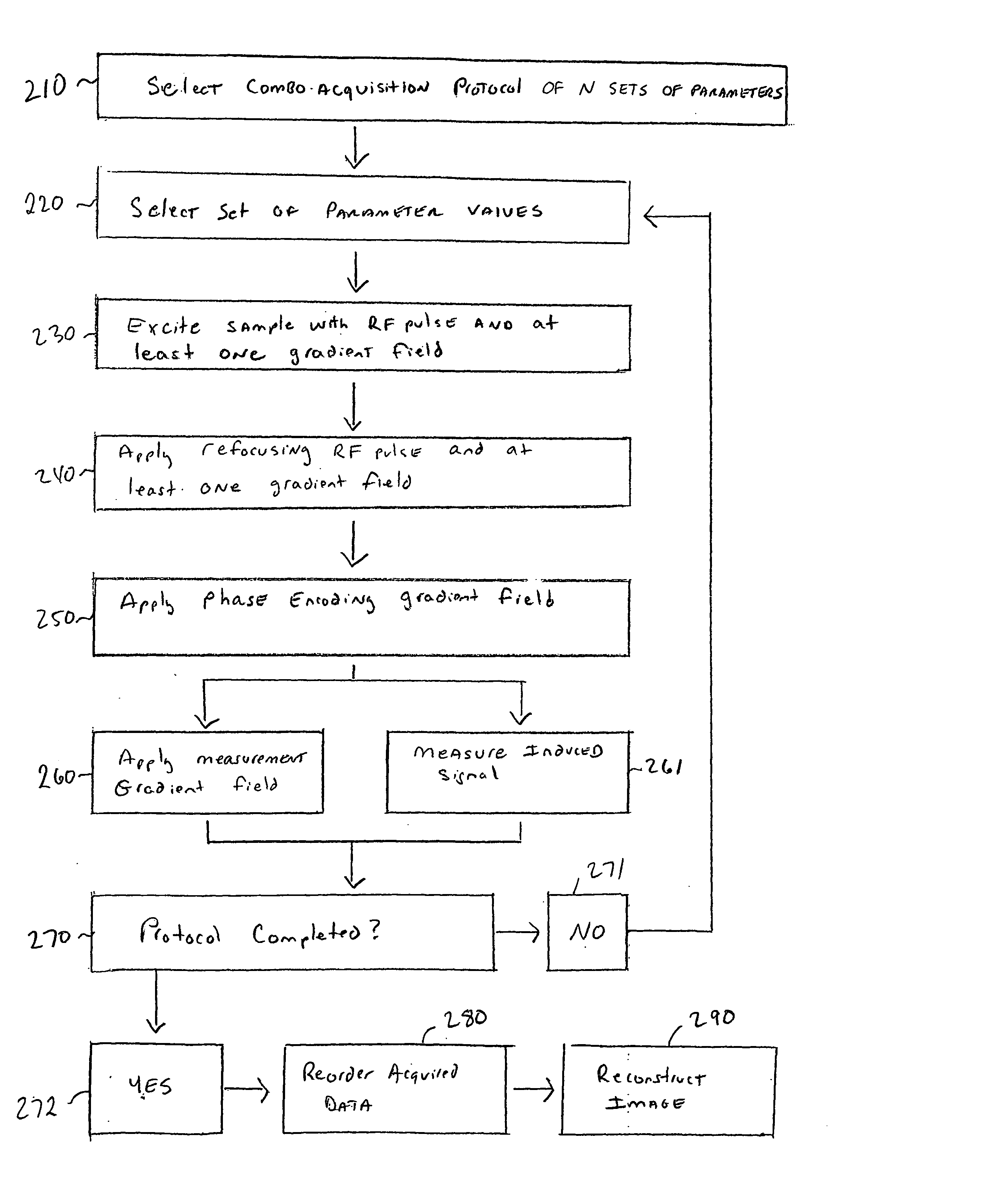
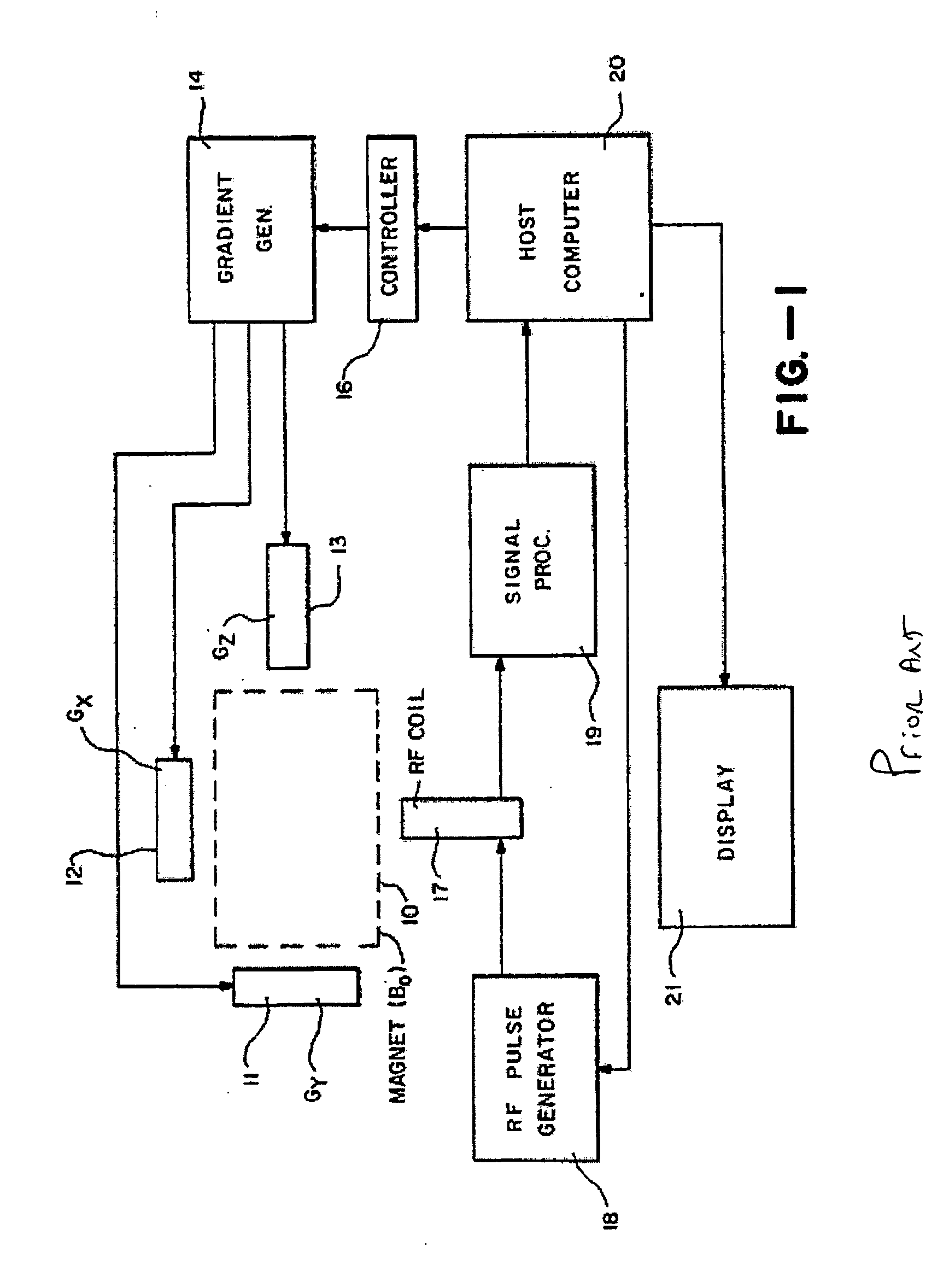
Combined magnetic resonance data acquisition of multi-contrast images using variable acquisition parameters and k-space data sharing
InactiveUS20050033151A1Reduce scan timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceData acquisition
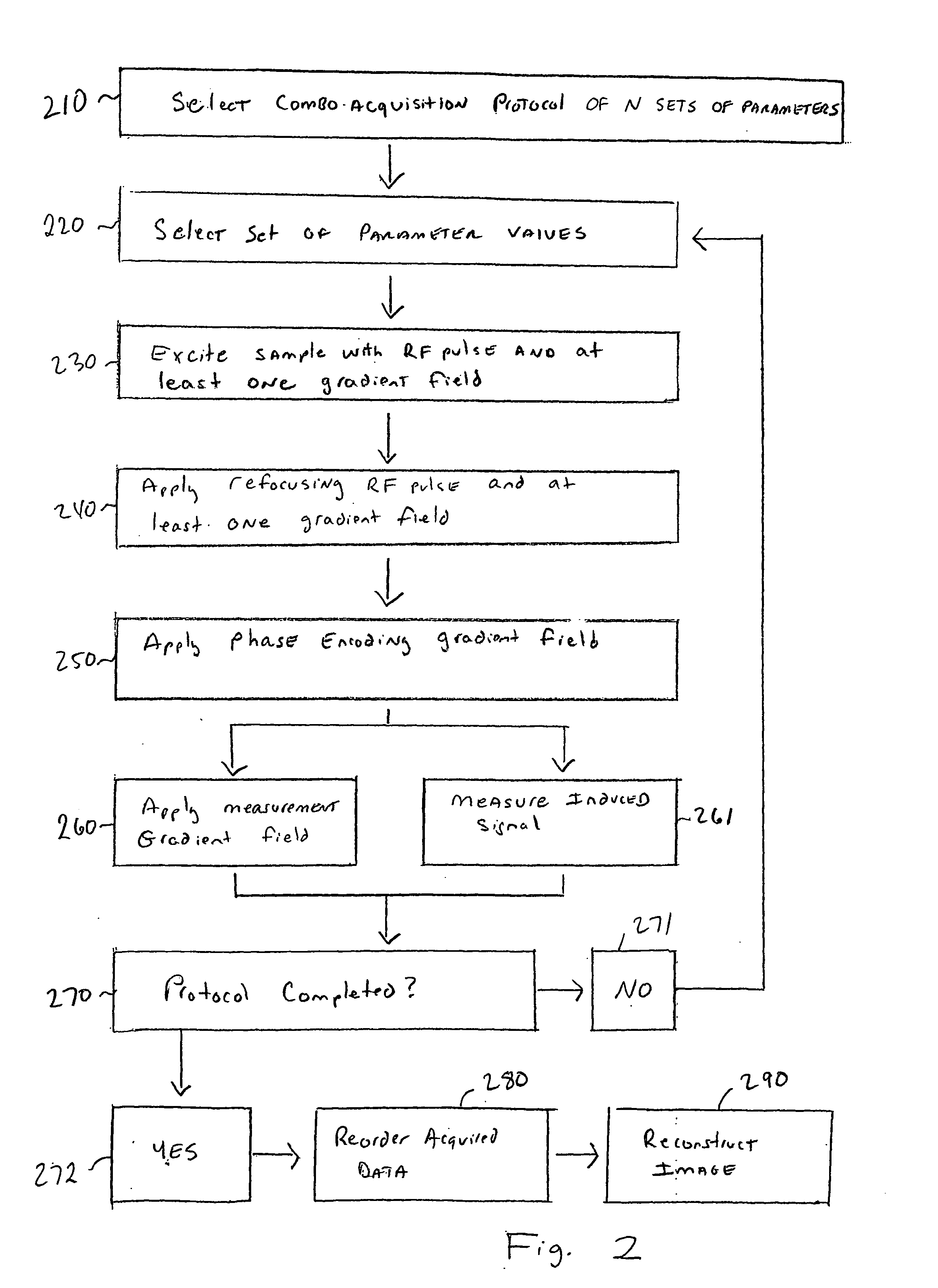
Techniques for reducing the scan time required for the acquisition of two or more magnetic resonance imaging images of a subject having differing contrasts. In one arrangement, a combo acquisition protocol of N sets of parameters is selected prior to imaging. In order to image a subject, a first set of parameter values is selected from the protocol, a first RF pulse and at least one gradient field are used to excite the subject, a refocusing RF pulse and at least one gradient field is applied to the subject, a phase encoding gradient field is applied to the subject, and then a measurement gradient field is applied to the subject simultaneously while an induced signal is measured. The process is repeated to obtain N measurements, which are then processed into two or more reconstructed images of differing contrast, and where some of the measurements are used during the reconstruction of two or more of the images.
Owner:WU ED X +2
Method for recognizing multiple touch point at infrared touch screen
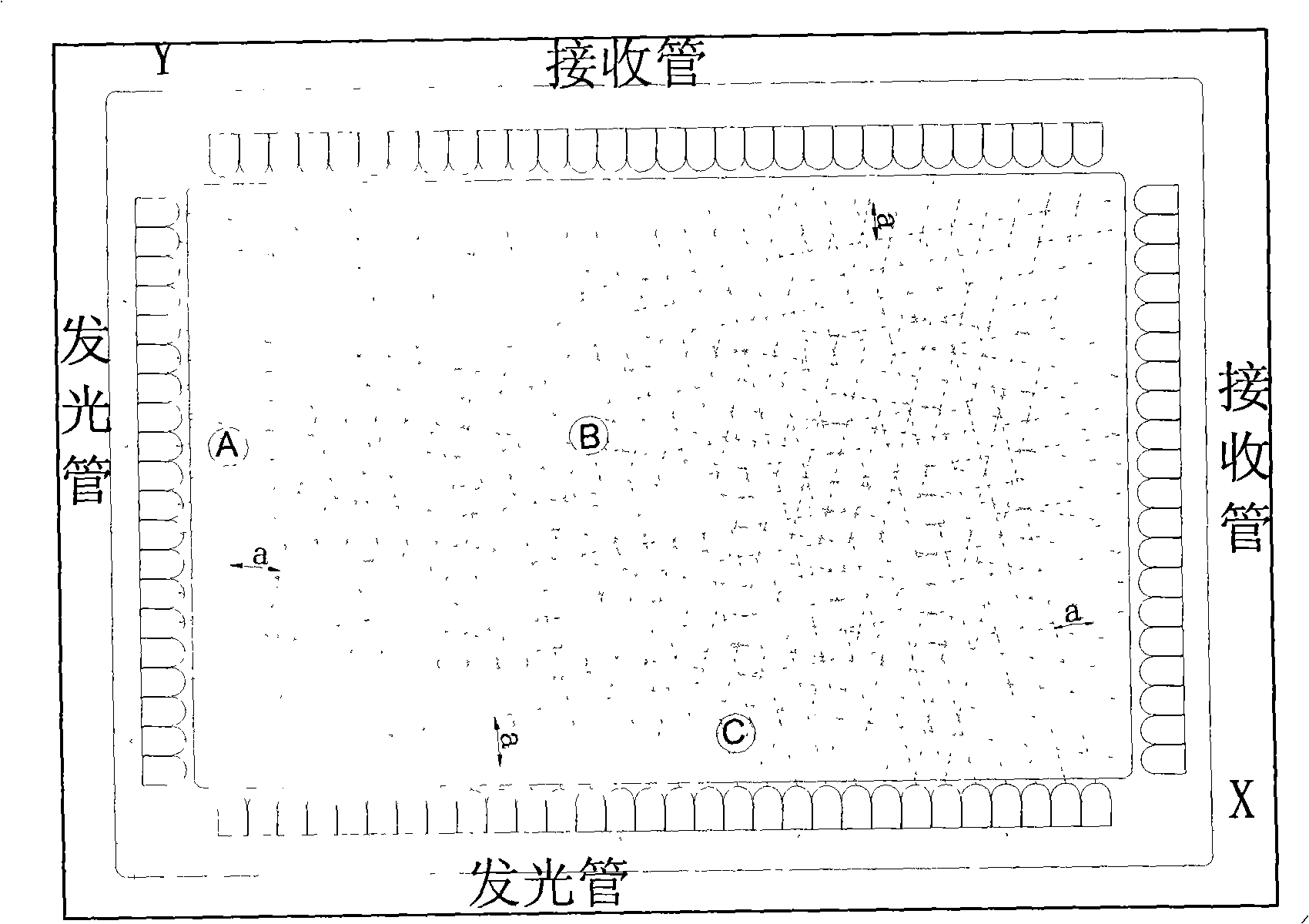
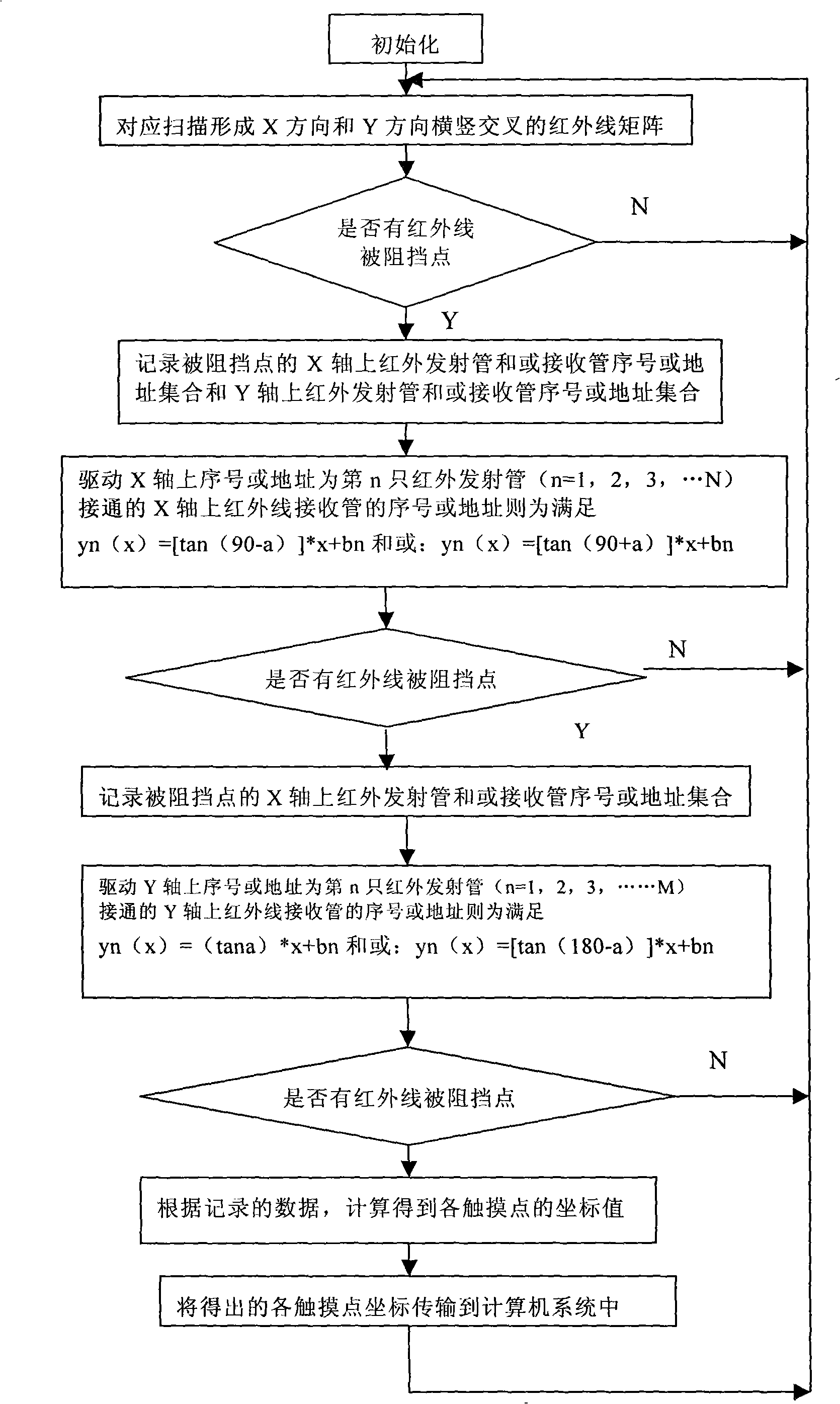
ActiveCN101286104ARealize detectionLow application costInput/output processes for data processingHardware structureImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a plurality of touch points on an infrared touch screen, comprising the steps of: starting the infrared touch screen, driving an infrared emitter and an infrared receiver and forming transverse and longitudinal infrared arrays by corresponding scan; determining the transverse coordinates sets and longitudinal coordinates sets of all touch points, driving the infrared emitter and the infrared receiver, forming an infrared array with the functional relation of that y(x) is equal to f(x) in the touch area by corresponding scan, gaining a set of function value that y(x) is equal to f(x) of the touch points in the touch area, through calculating the sets of two scans by a controller, gaining the coordinates of all touch points and disposing and removing false touch points. The invention can complete the detection of a plurality of touch points without changing the hardware structure of existing touch screen, has no incorrect area of multi-point detection at four corners of the screen body, has higher sensitiveness to adjacent multi-point detection, higher resolution, short scan time and quick response.
Owner:GENERALTOUCH TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com