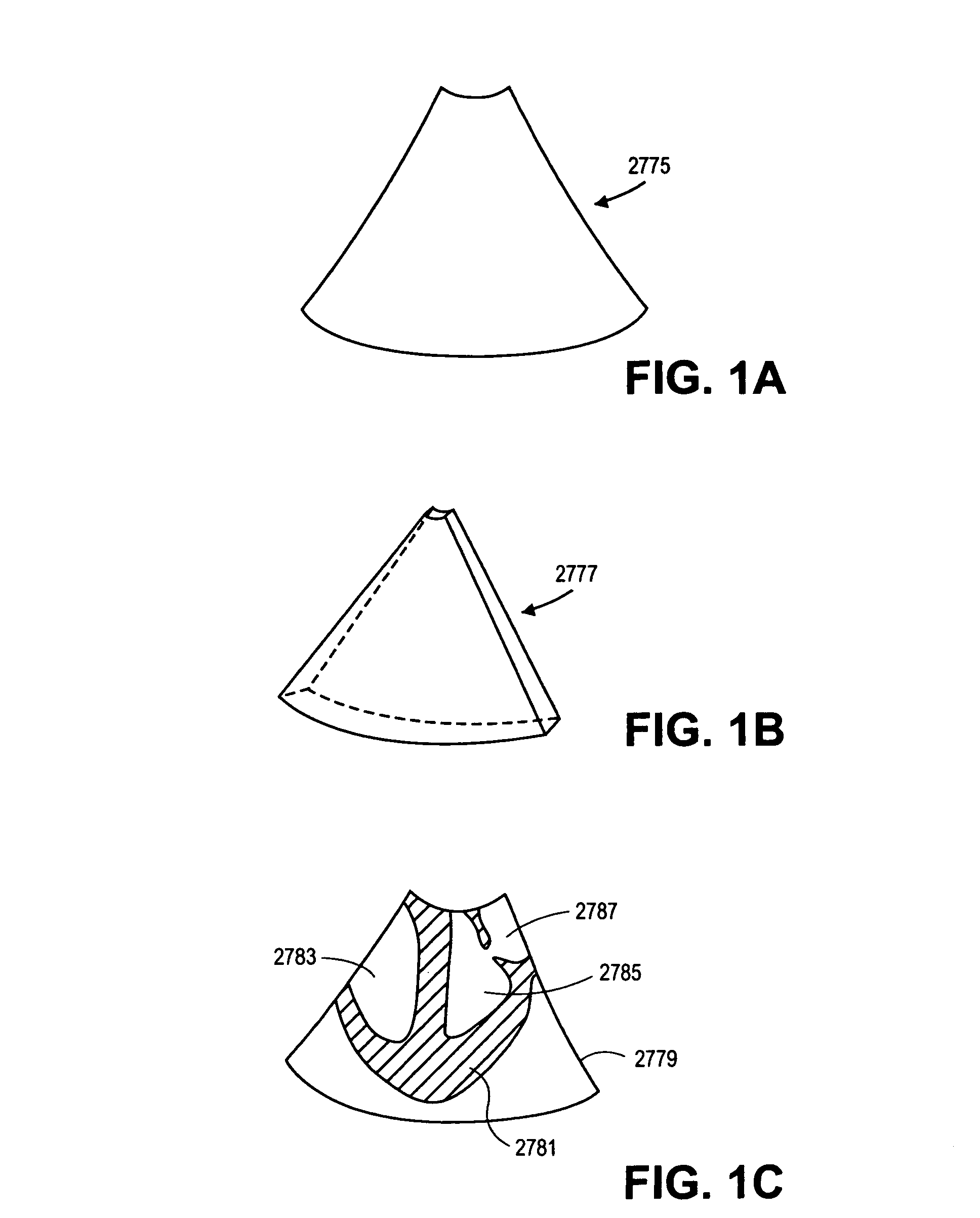
Patents
Literature
12411 results about "Image processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
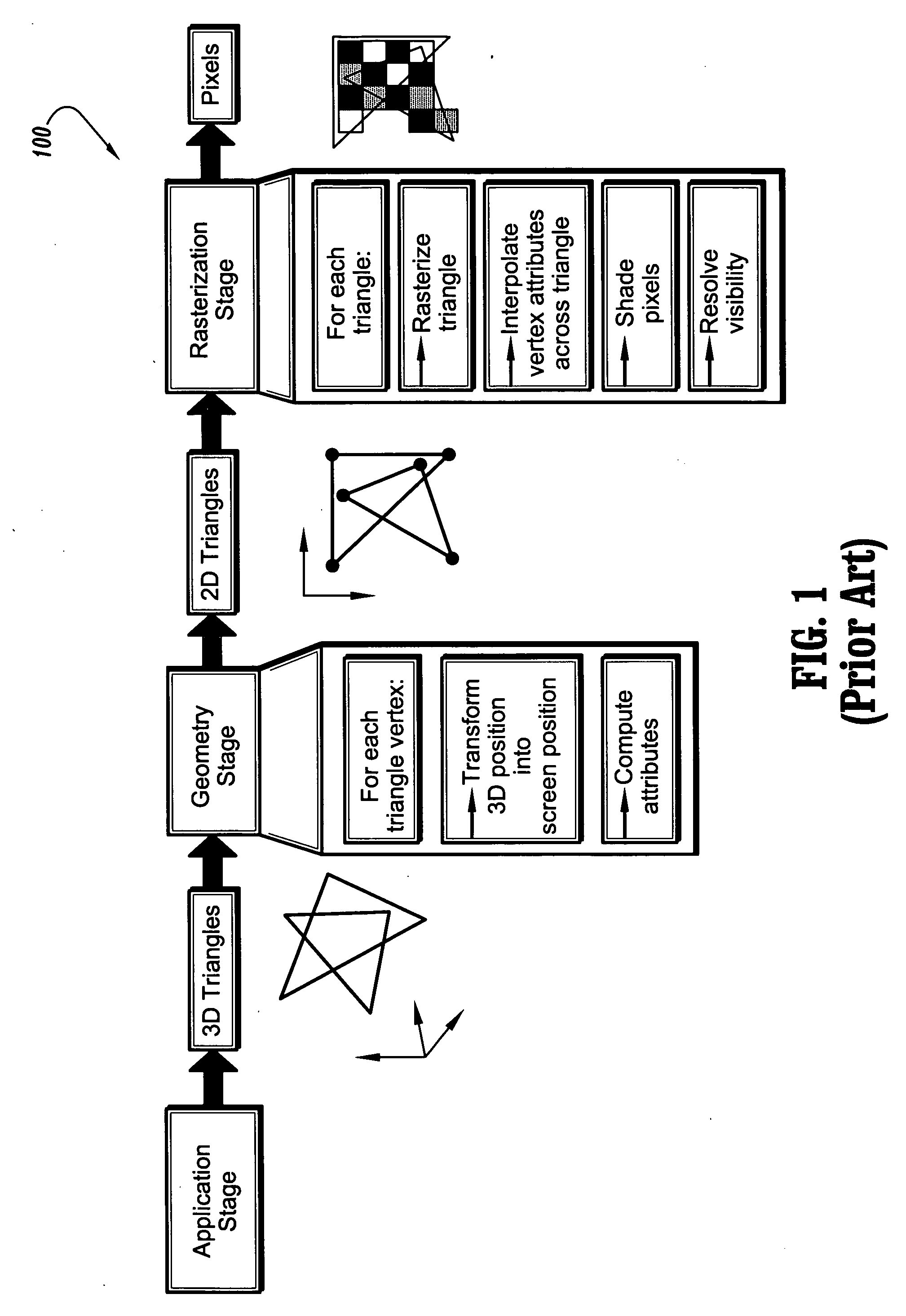
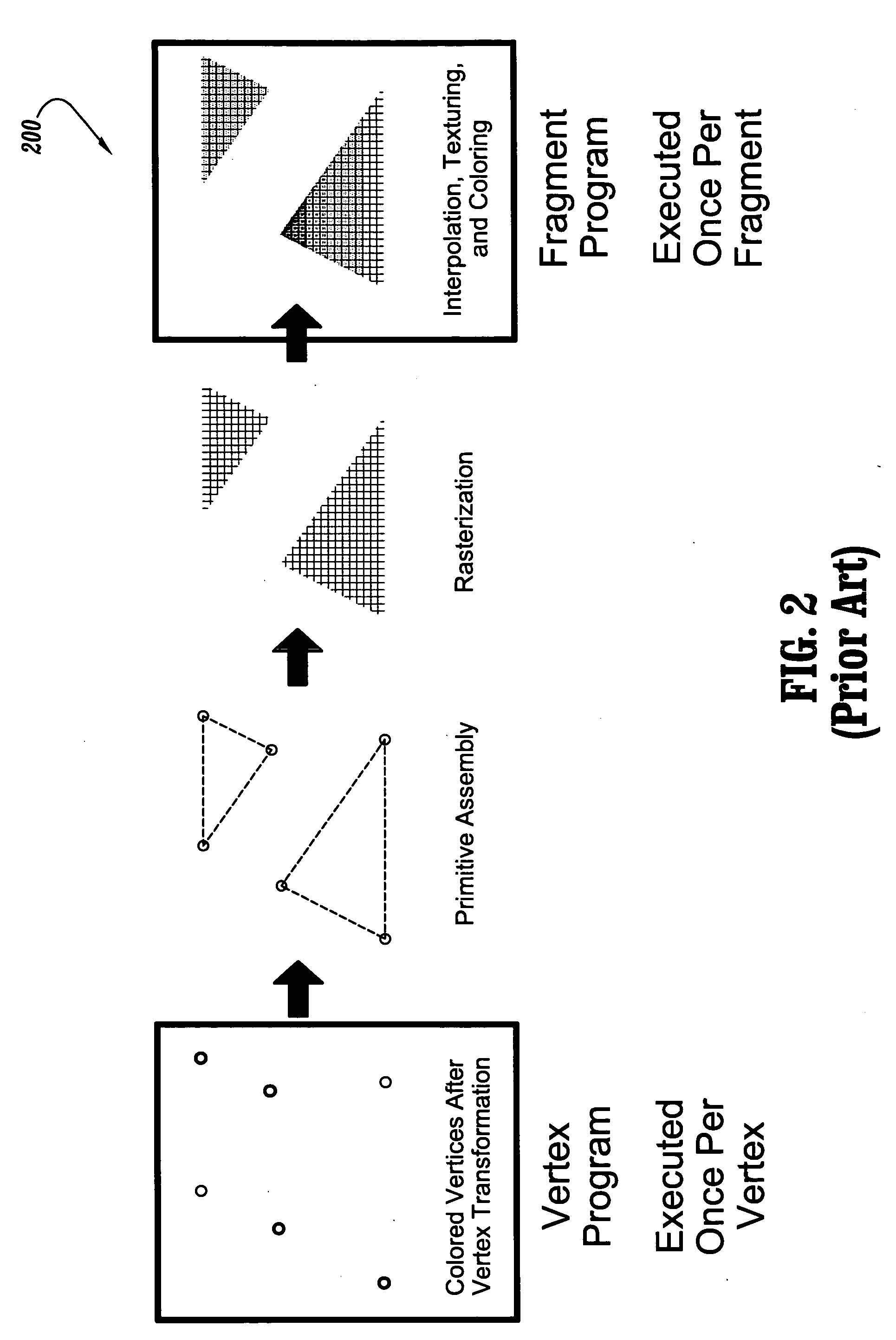
In imaging science, image processing is any form of signal processing for which the input is an image, such as a photograph or video frame; the output of image processing may be either an image or a set of characteristics or parameters related to the image. Most image-processing techniques involve treating the image as a two-dimensional signal and applying standard signal-processing techniques to it. Image processing usually refers to digital image processing, but optical and analog image processing also are possible. This article is about general techniques that apply to all of them. The acquisition of images is referred to as imaging. Closely related to image processing are computer graphics and computer vision. In computer graphics, images are manually made from physical models of objects, environments, and lighting, instead of being acquired from natural scenes, as in most animated movies. Computer vision, on the other hand, is often considered high-level image processing out of which a machine/computer/software intends to decipher the physical contents of an image or a sequence of images.
Dimensioning system with multipath interference mitigation
ActiveUS20160109224A1Reducing multipath distortionReduce distortionUsing optical meansMultipath interferenceLight beam
A system and method for measuring an item's dimensions using a time-of-flight dimensioning system is disclosed. The system and method mitigate multipath distortion and improve the accuracy of the measurements, especially in a mobile environment. To mitigate the multipath distortion, an imager captures an image of an item of interest. This image is processed to determine an illumination region corresponding item-of-interest's size, shape, and position. Using this information, an adjustable aperture's size, shape, and position are controlled so the light beam used in the time-of-flight analysis substantially illuminates the illumination region without first being reflected.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
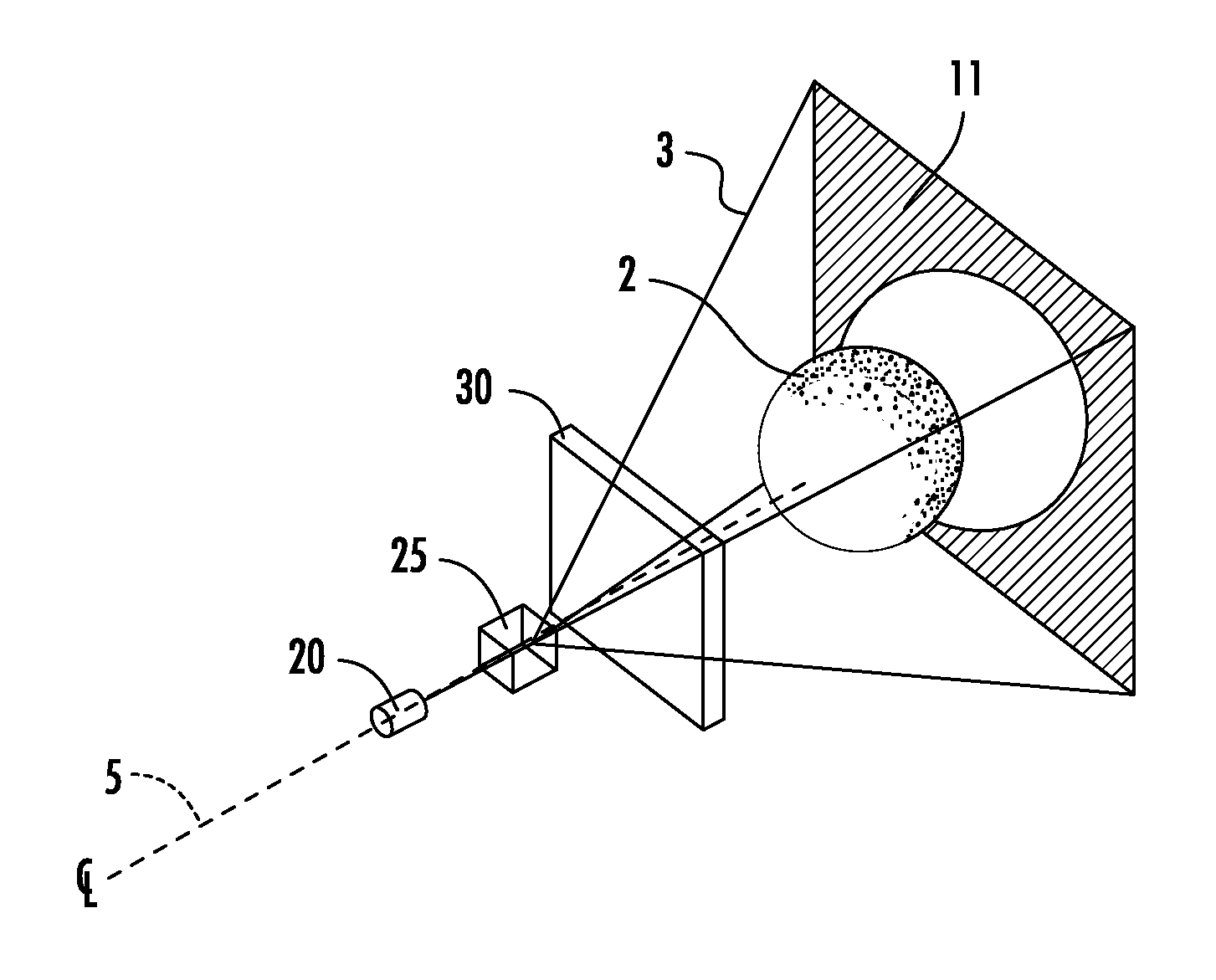
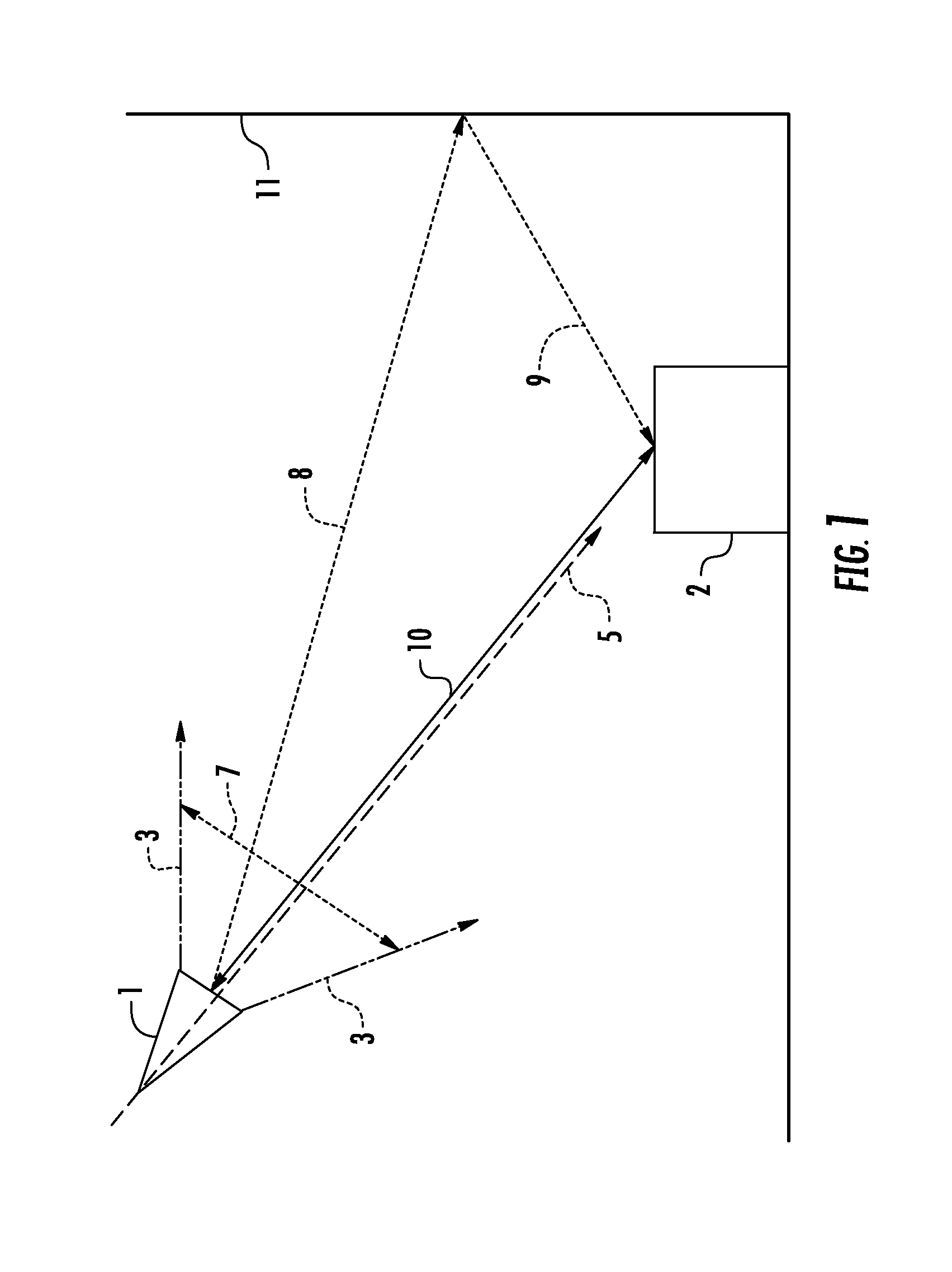
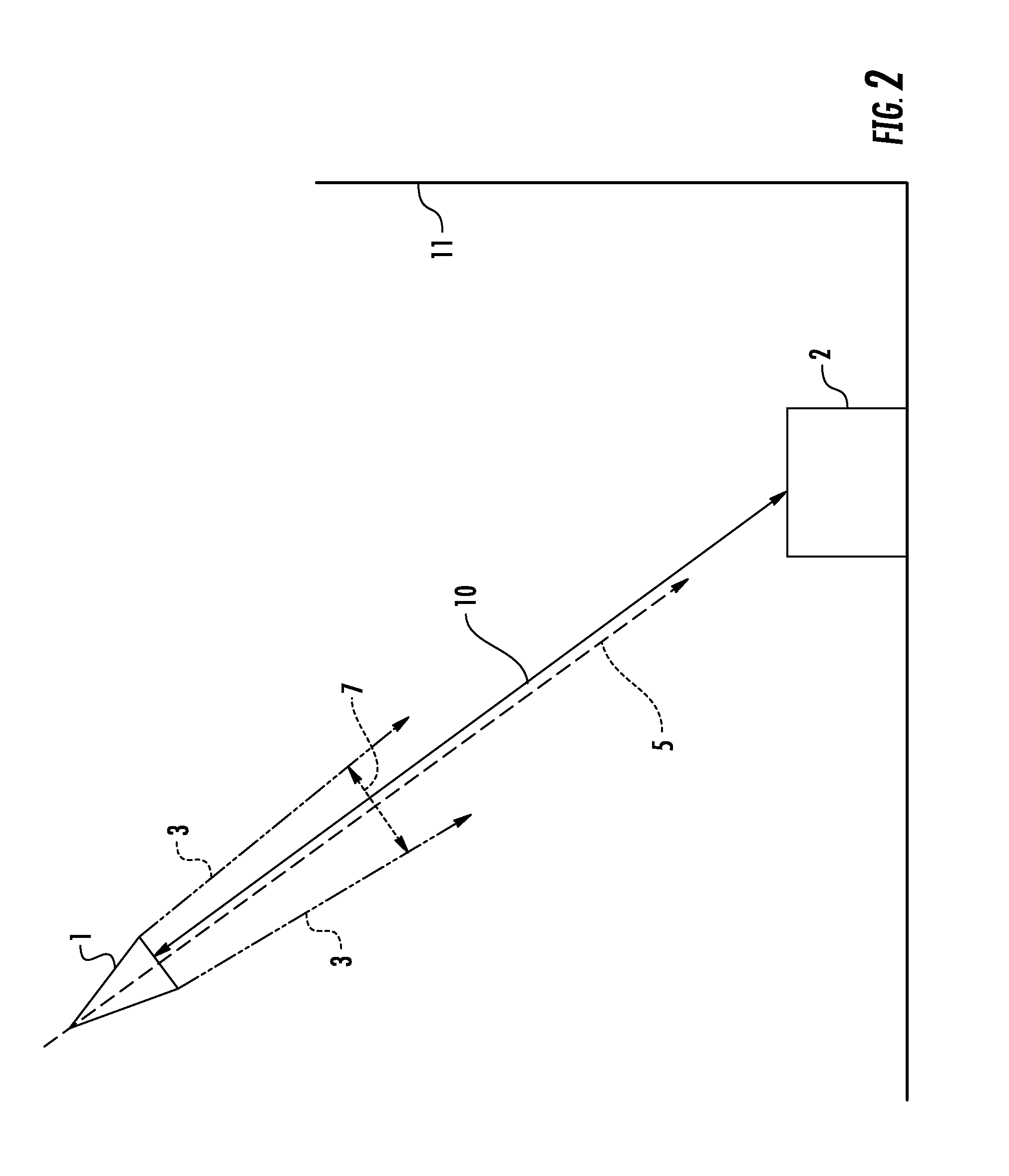
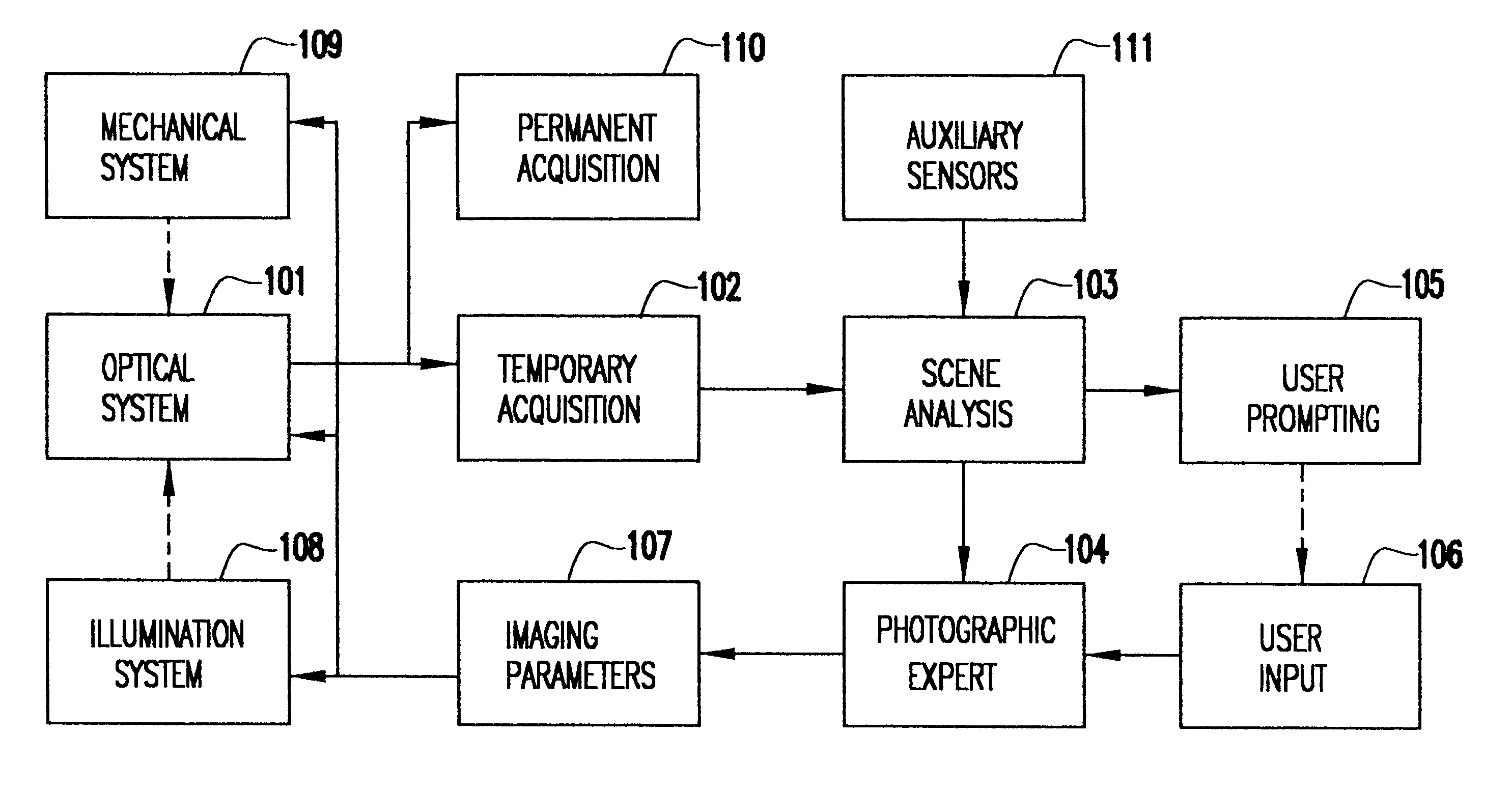
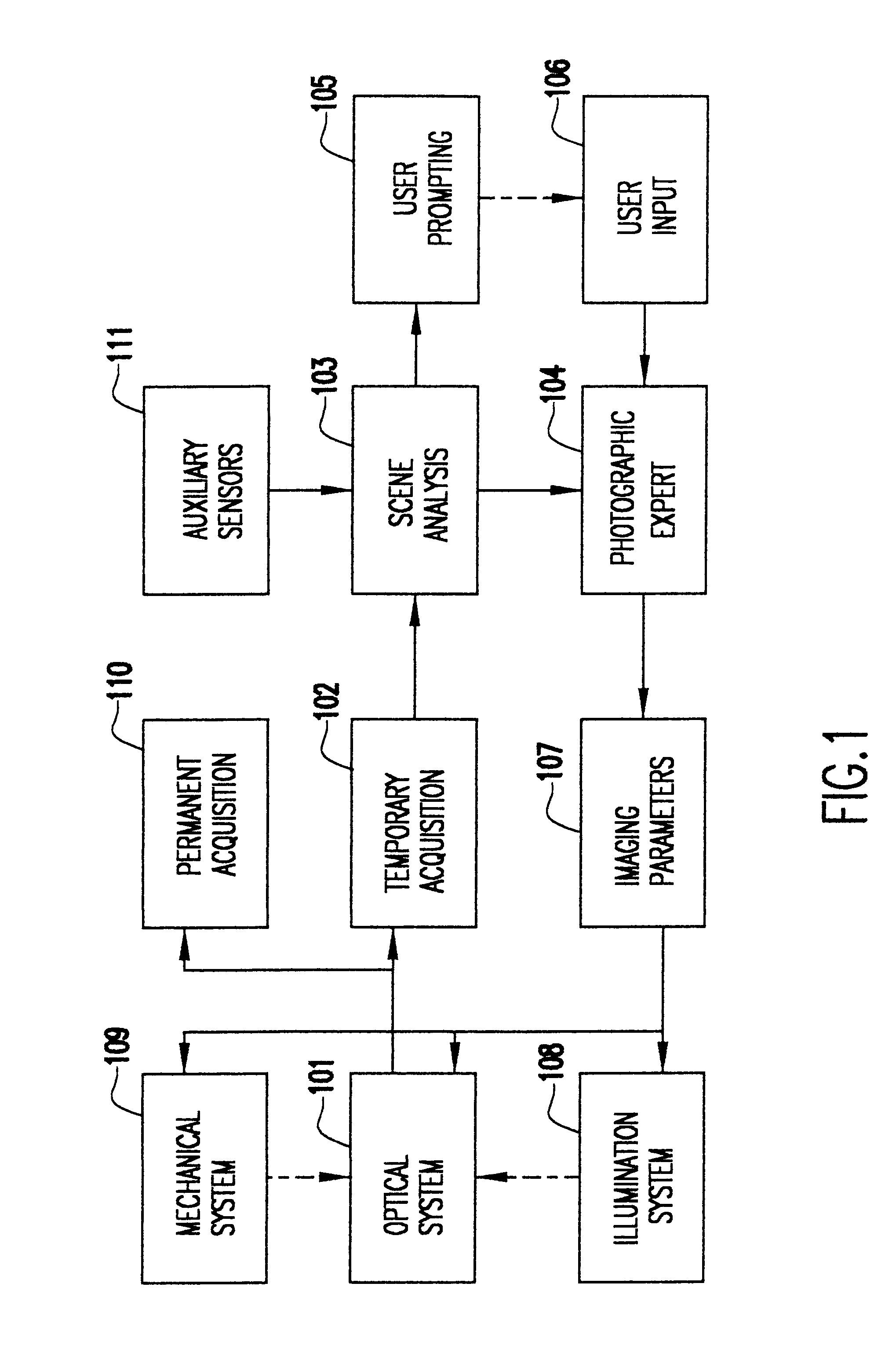
System and method for automatically setting image acquisition controls
InactiveUS6301440B1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementSubject matterComputer image
A system and method use computer image processing for setting the parameters for an image acquisition device of a camera. The image parameters are set automatically by analyzing the image to be taken, and setting the controls according to the subject matter, in the same manner as an expert photographer would be able to. The system can run in a fully automatic mode choosing the best image parameters, or a "guided mode" where the user is prompted with choices where a number of alternate settings would be reasonable.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
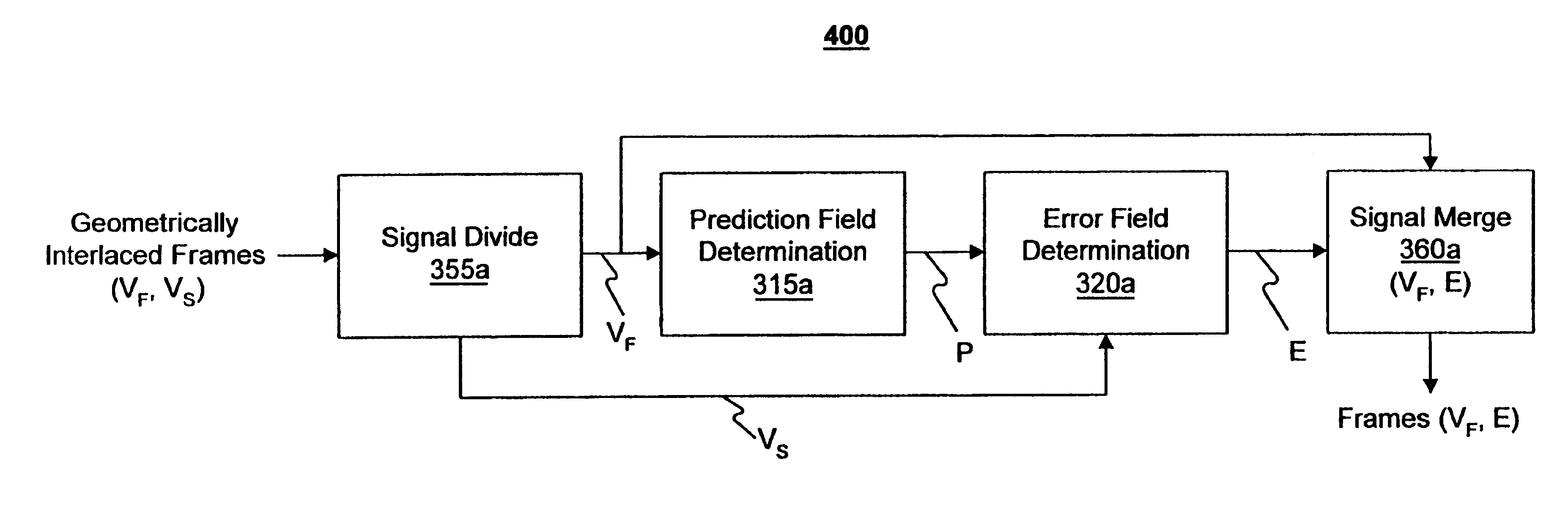
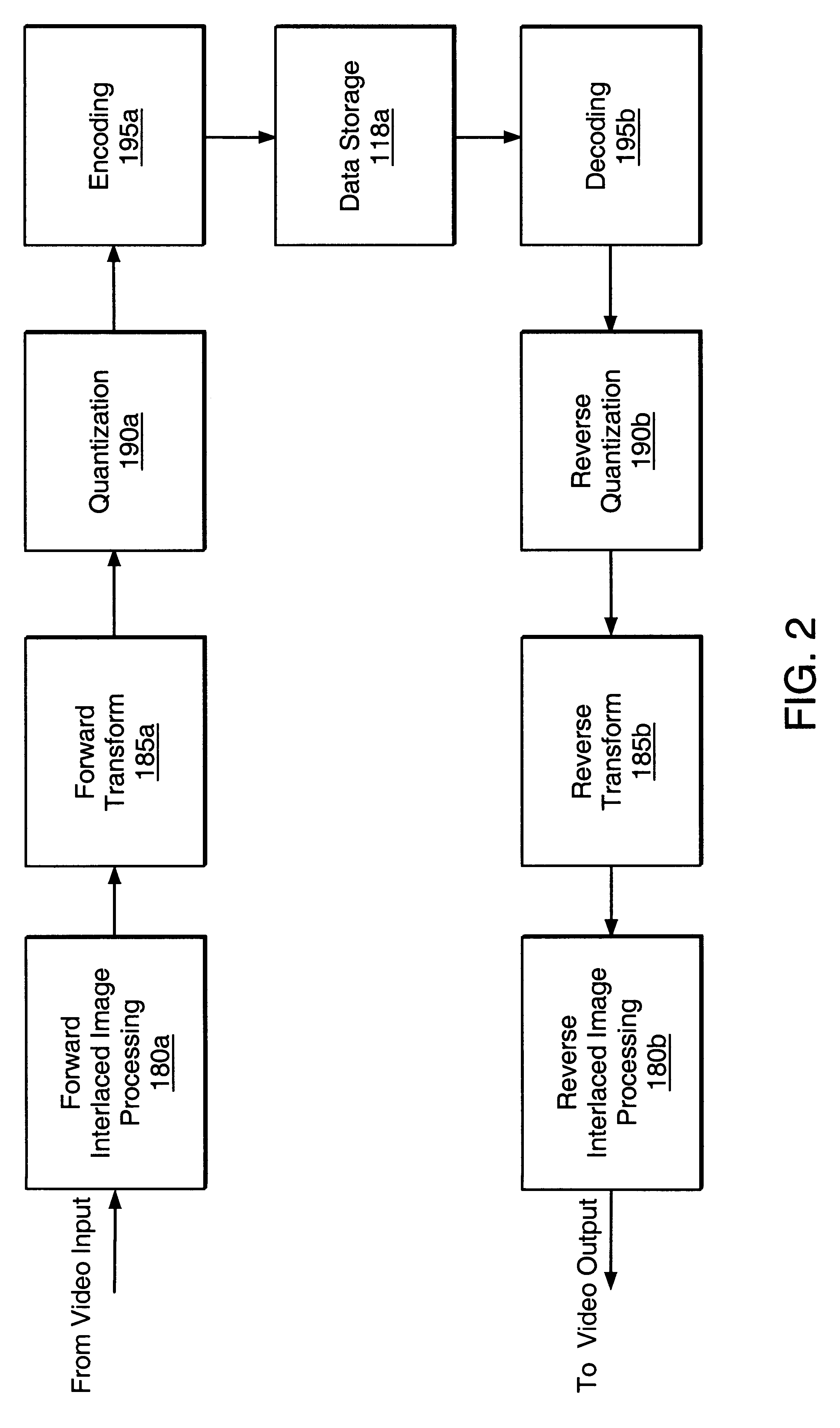
Apparatus and method for optimized compression of interlaced motion images
InactiveUS6289132B1Easy to compressAvoid inefficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImaging processingInterlaced video
Owner:QUVIS +1
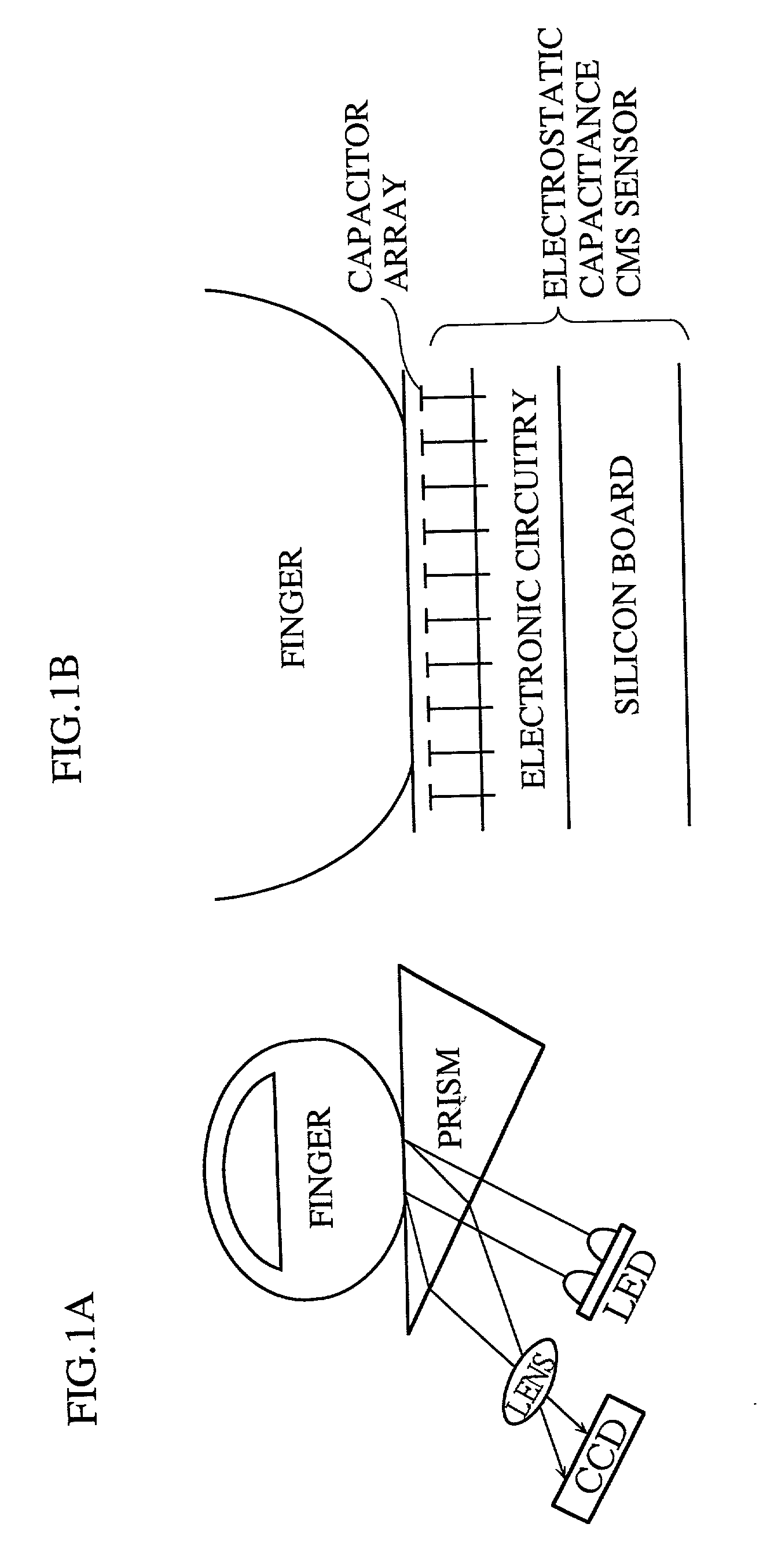
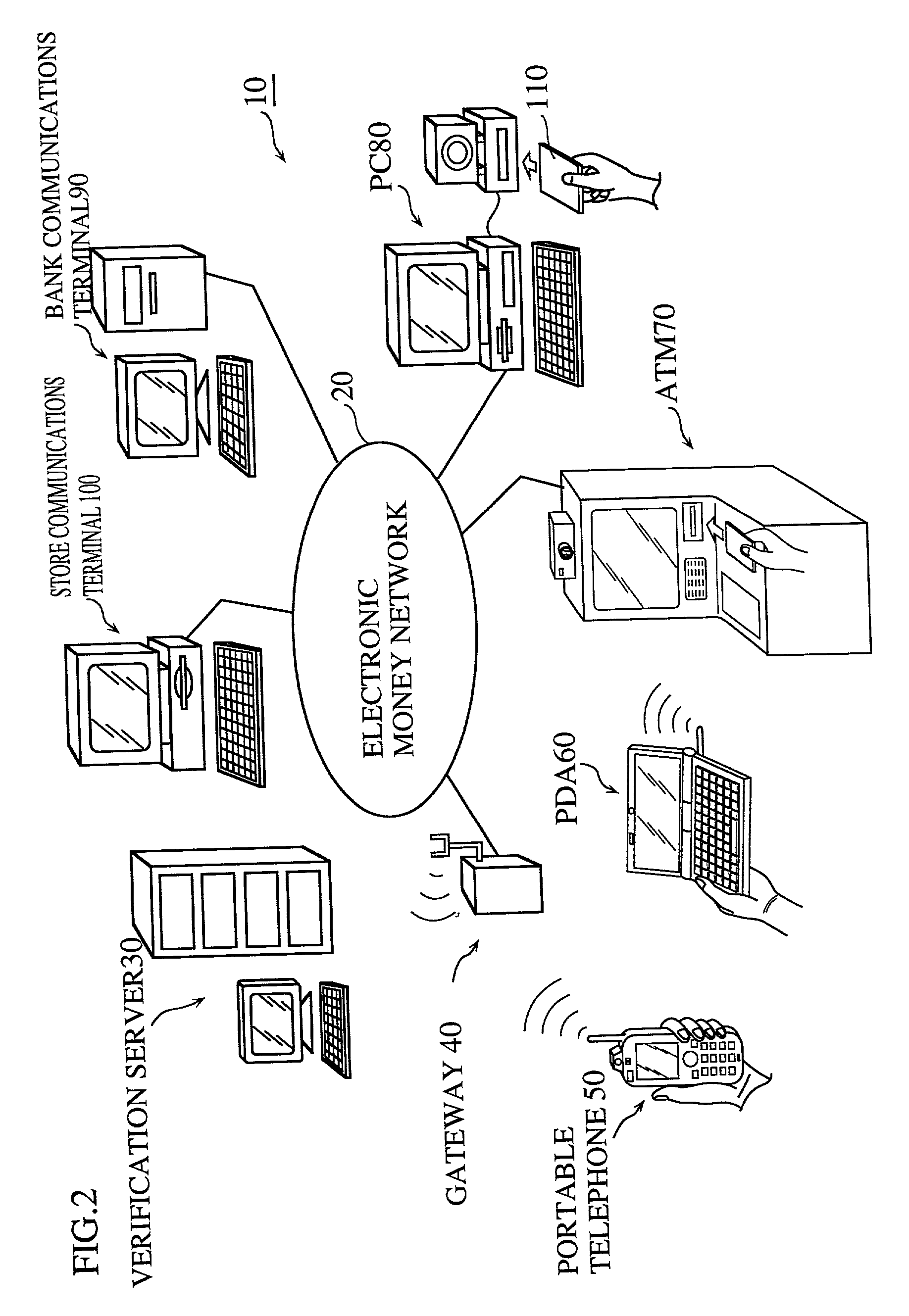
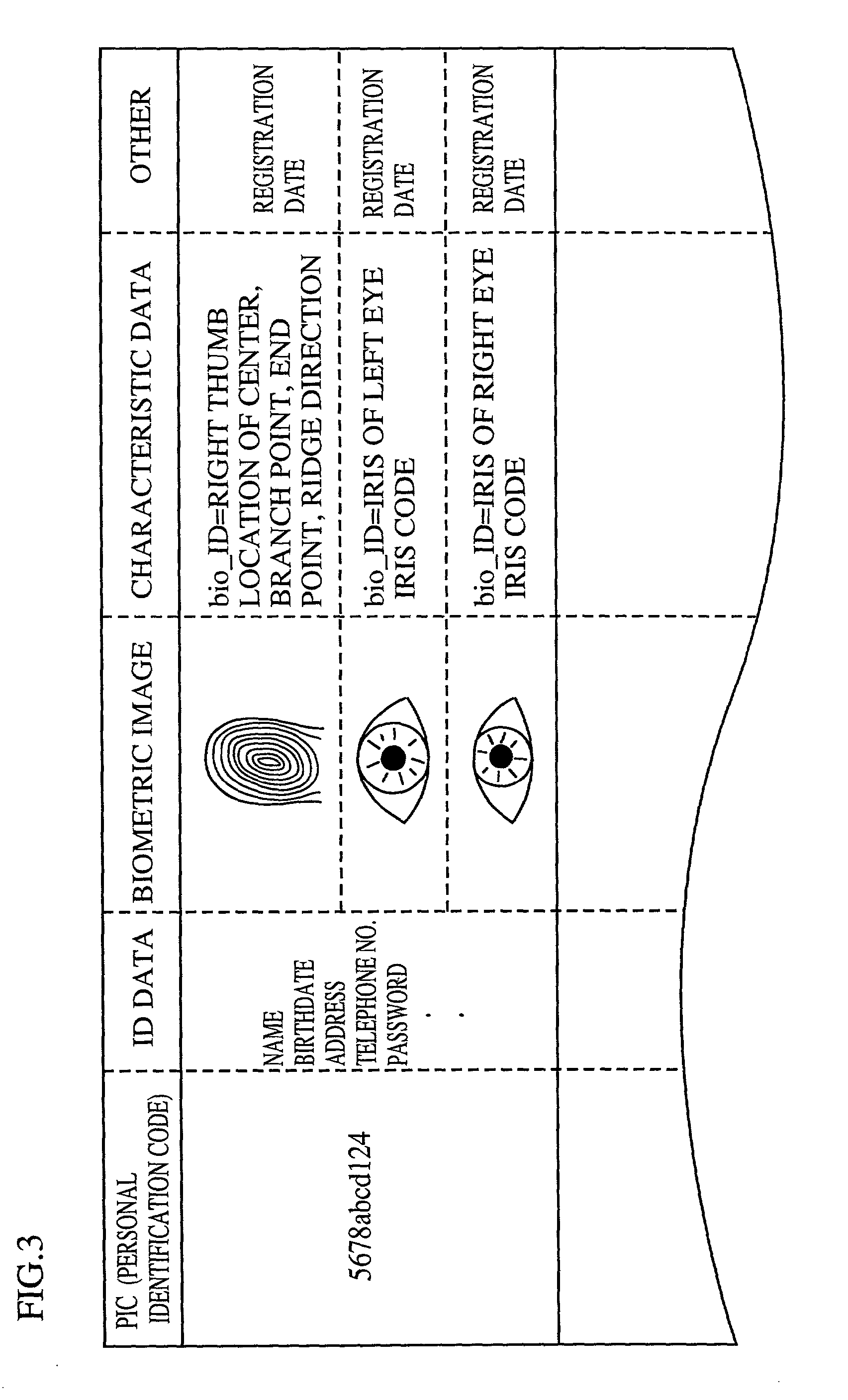
Apparatus for identity verification, a system for identity verification, a card for identity verification and a method for identity verification, based on identification by biometrics
InactiveUS20010026632A1Improve reliabilityLow costImage analysisUser identity/authority verificationCommunication interfaceImaging processing
An identity verification system is used to identify persons with high accuracy, while avoiding direct contact with the device to prevent any negative psychological reaction from a user. The system includes: a camera unit and an image processing unit for obtaining object images of body parts (such as fingerprints and irides) by scanning, without physical contact; an image display unit for displaying layered images of the body part as scanned and a guide showing the body part in an optimal position; a control unit for extracting biometric characteristic data from object images and sending the data to a verification server after encrypting by an encryption unit; and a communications interface unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
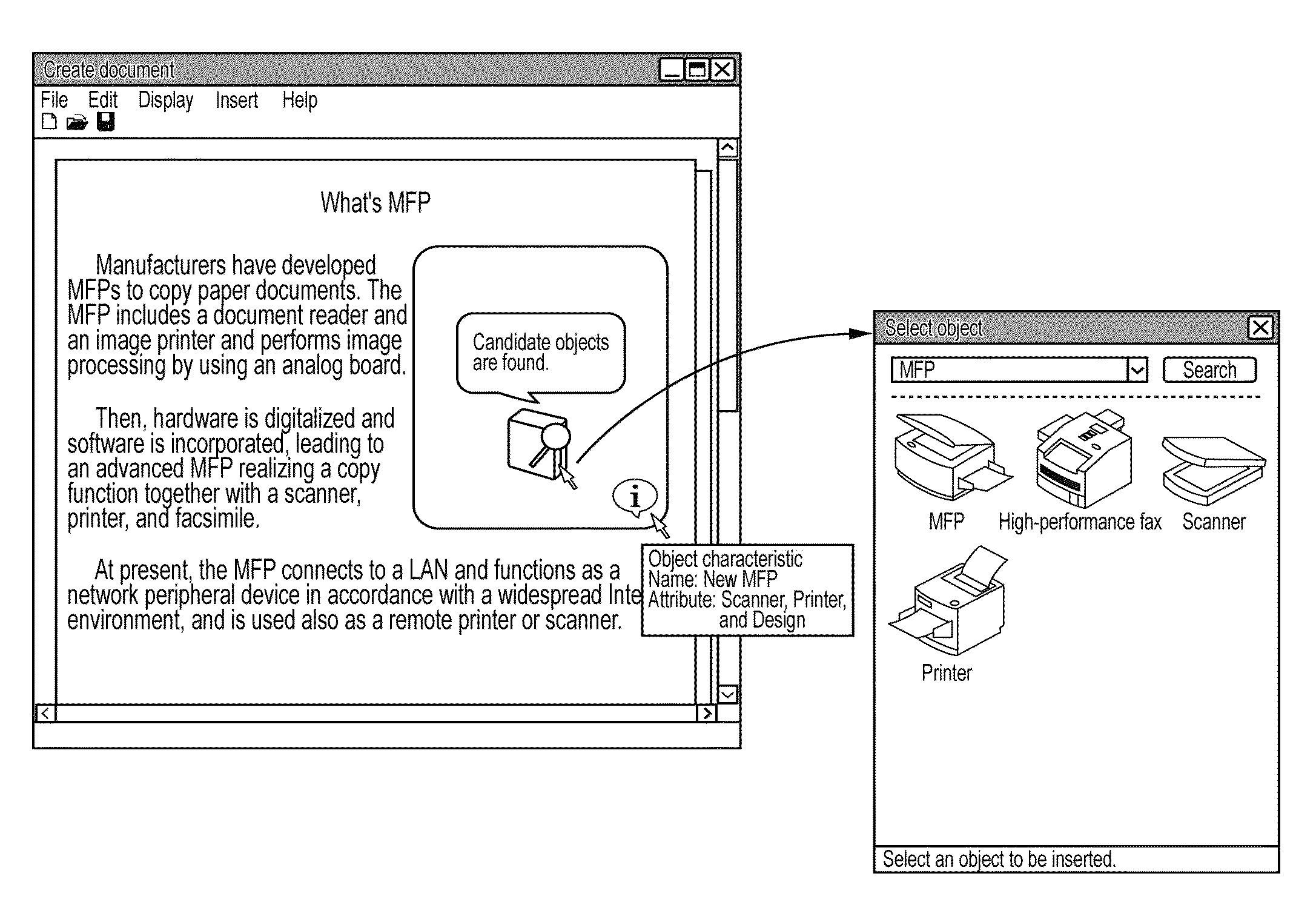
Managing apparatus, image processing apparatus, and processing method for the same, wherein a first user stores a temporary object having attribute information specified but not partial-area data, at a later time an object is received from a second user that includes both partial-area data and attribute information, the storage unit is searched for the temporary object that matches attribute information of the received object, and the first user is notified in response to a match
InactiveUS8339645B2Easy to useDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsDocumentationDatabase
A temporary object is registered in a document managing system in advance on the basis information about an object that a user wants to use. Then, when an object is registered by another user, it is determined whether the registered object is a similar object corresponding to the temporary object. If the registered object is a similar object, the user is notified of that fact, and the temporary object in target document data is updated with the similar object.
Owner:CANON KK
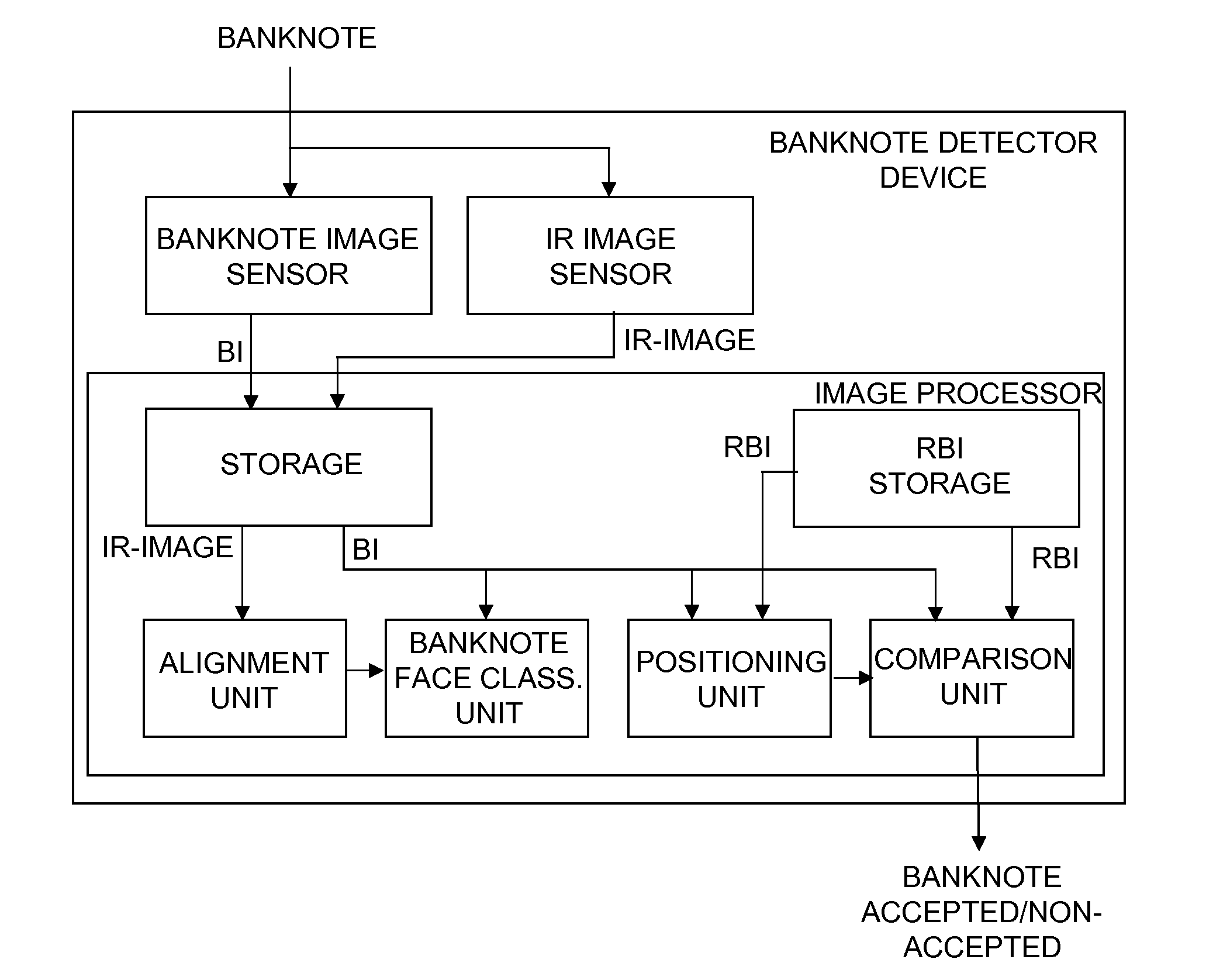
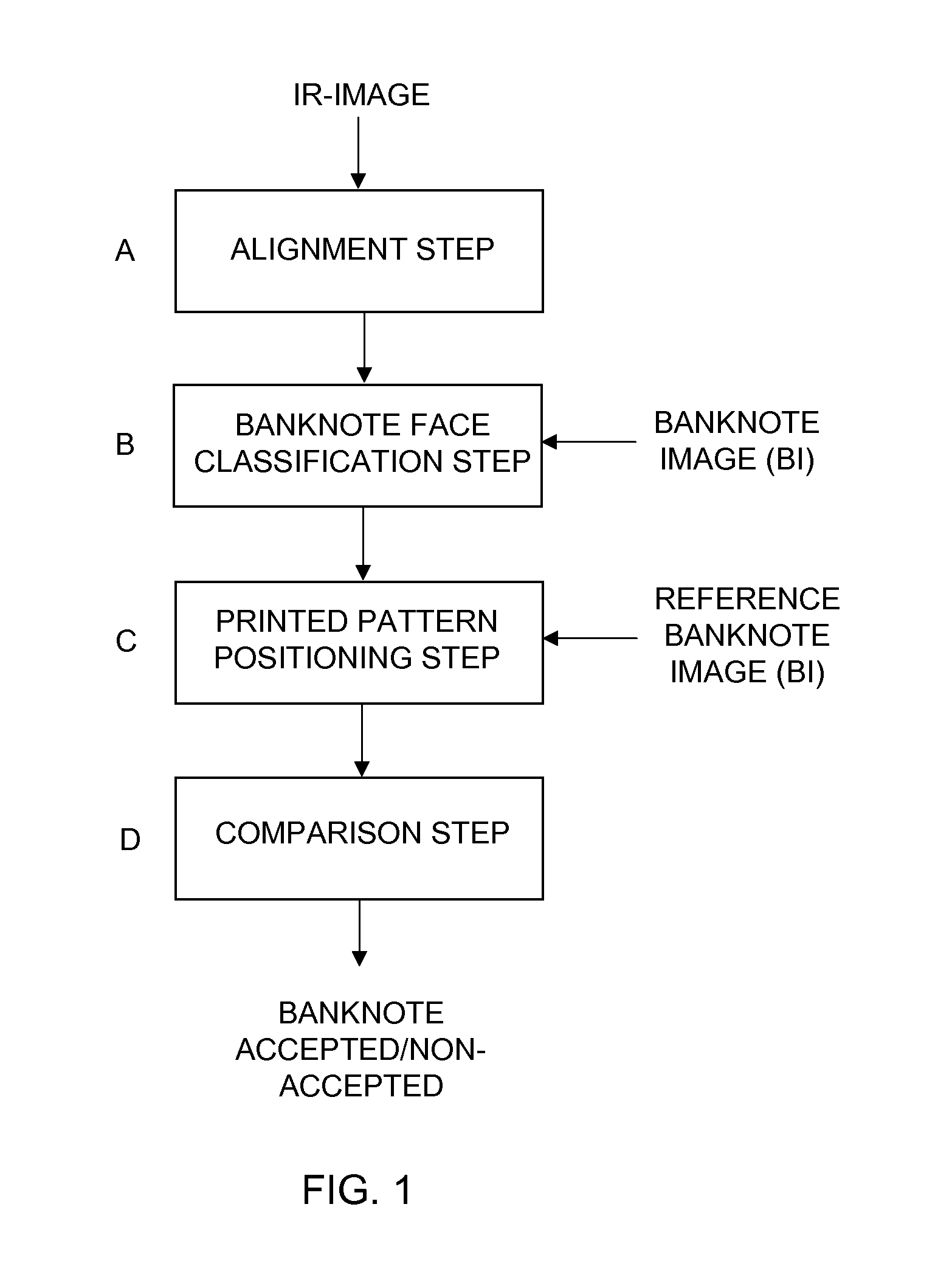
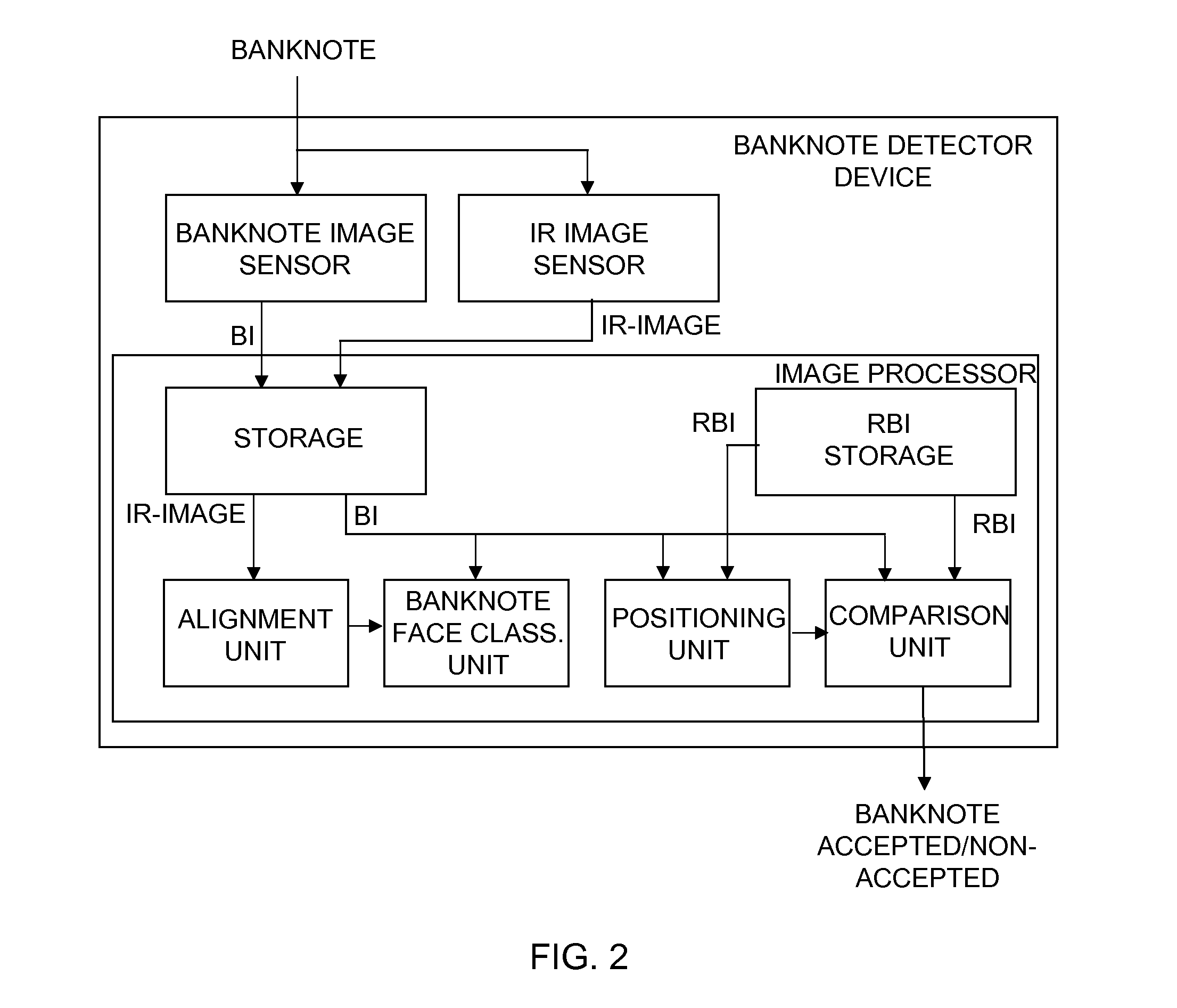
Method for a banknote detector device, and a banknote detector device
ActiveUS20120045112A1Increase capacityPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging dataImage processing
A banknote detector device for an automatic teller machine, for differentiating between non-accepted and accepted banknotes, includes a banknote image sensor to receive and scan at least one face of an input banknote and to store a banknote image (BI) of each scanned. The image includes image data in the form of a number of pixels; and a reference banknote image (RBI) storage where one reference banknote image, being processed from a predetermined number of banknote images from accepted banknotes, is stored for each face of each banknote. The device includes an alignment, a banknote face classification unit, a printed pattern positioning unit and a comparison unit where, for at least one face of the banknote, the BI and RBI, being in exact pattern position in relation to each other, are compared pixel per pixel according to a predefined comparison procedure to classify the banknote as accepted or non-accepted.
Owner:NCR CORP
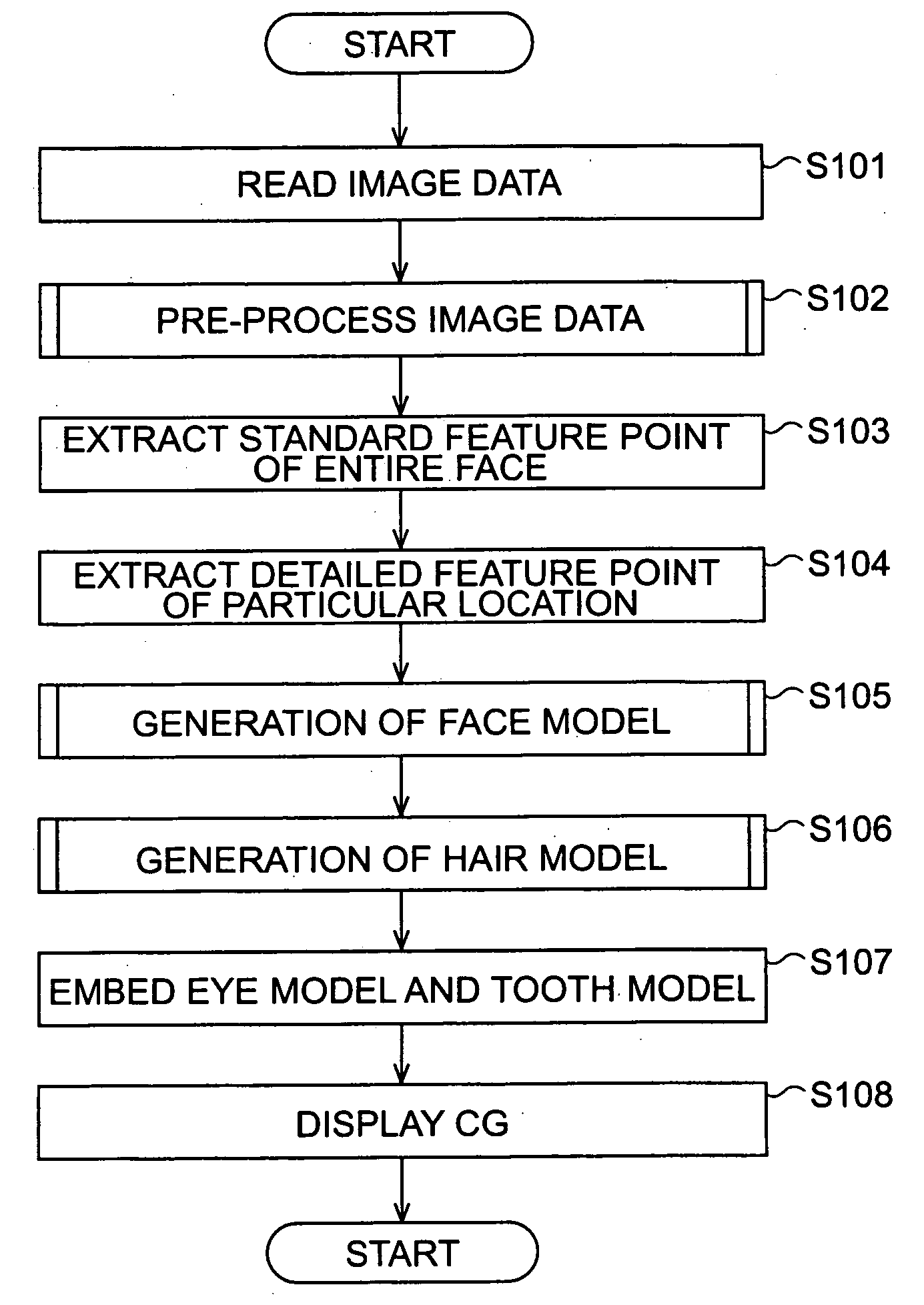
Method, apparatus, and computer program for processing image
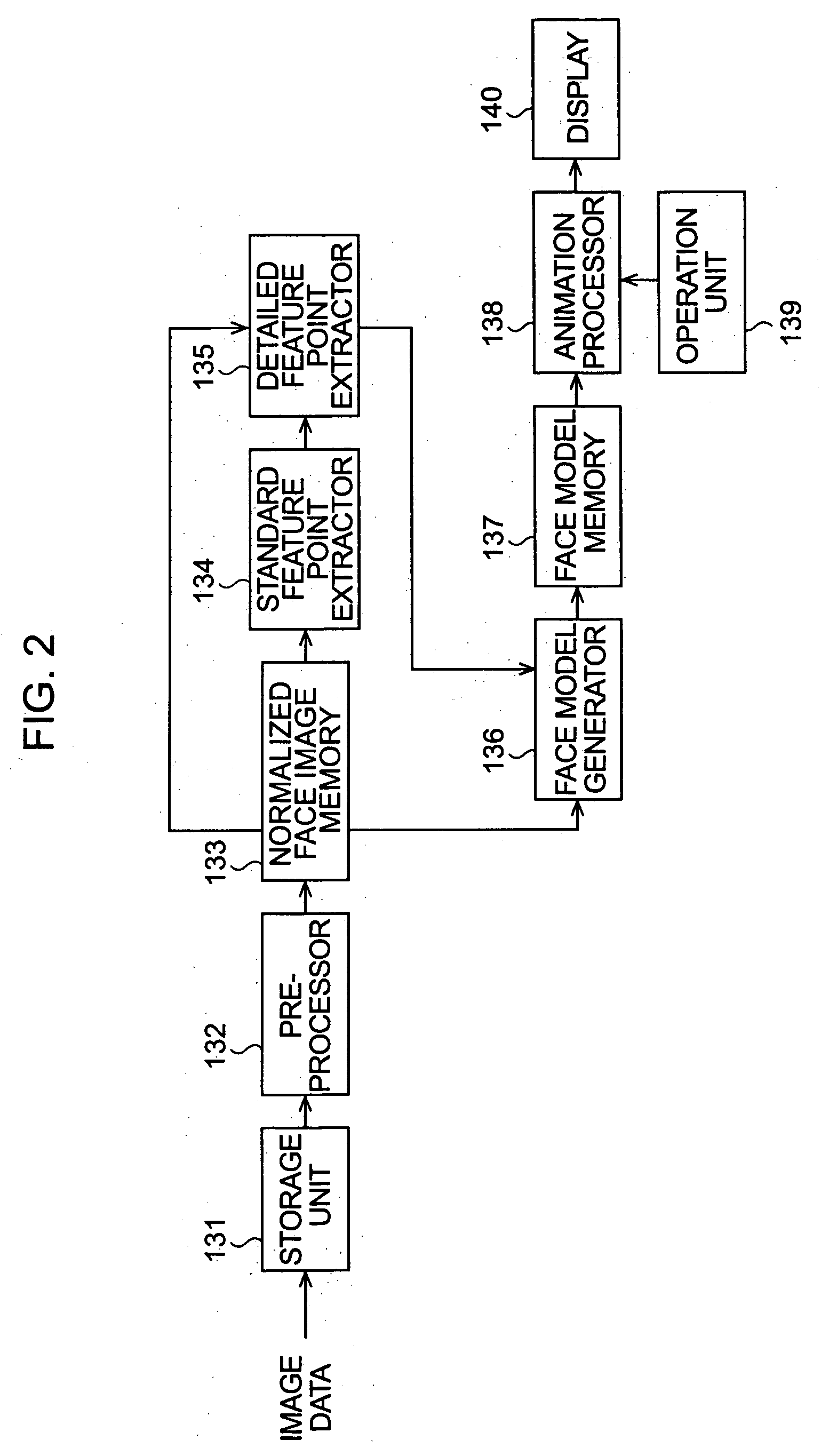
ActiveUS20060188144A1Easy to getRealistic animationCharacter and pattern recognitionAnimationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus for generating a three-dimensional model of a three-dimensional object from an image displaying the object in two dimensions includes a three-dimensional model generator operable to generate the three-dimensional model of the object from the image, and an extender operable to extend a lateral region of the three-dimensional model in a depth direction orthogonal to the two dimensions.
Owner:AX INC +1
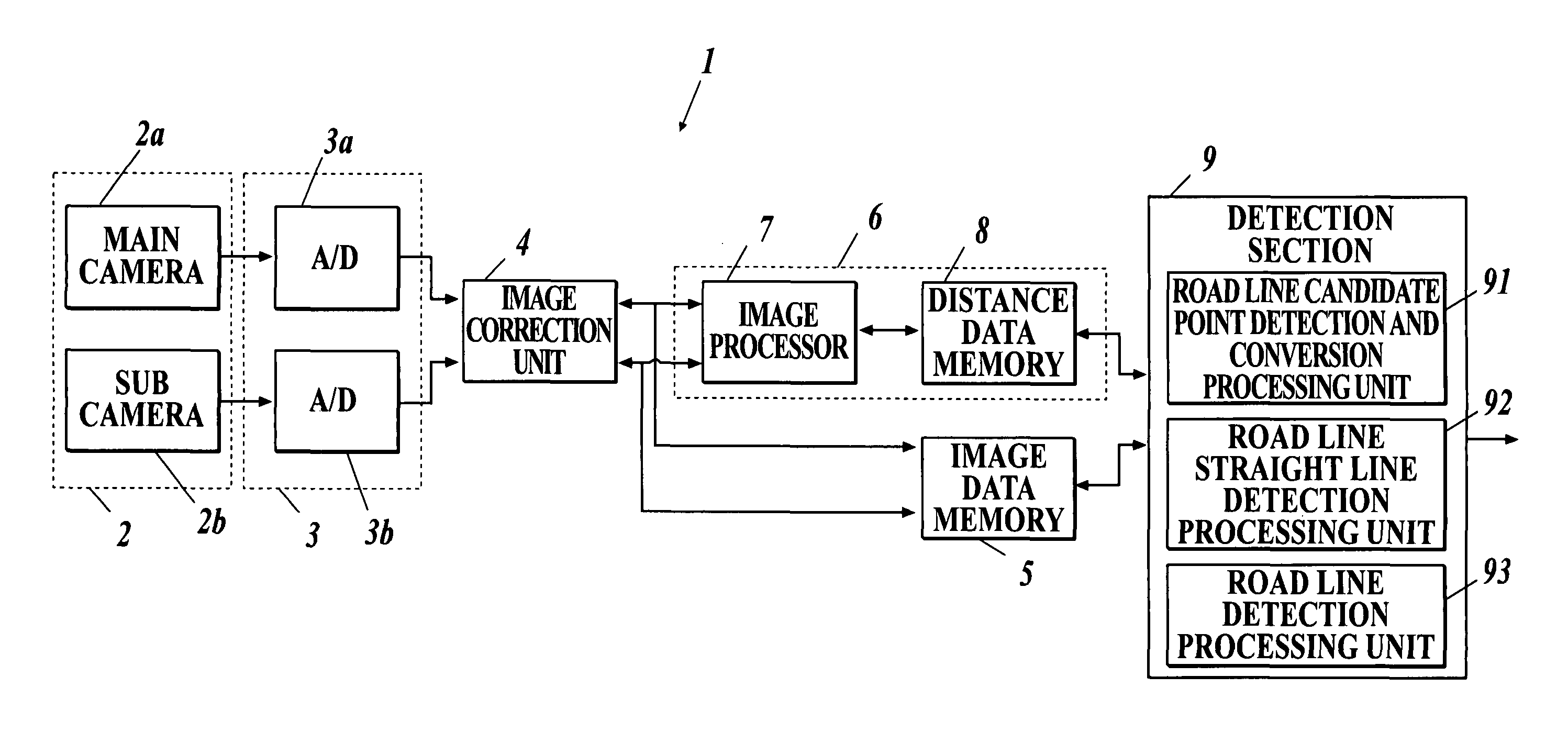
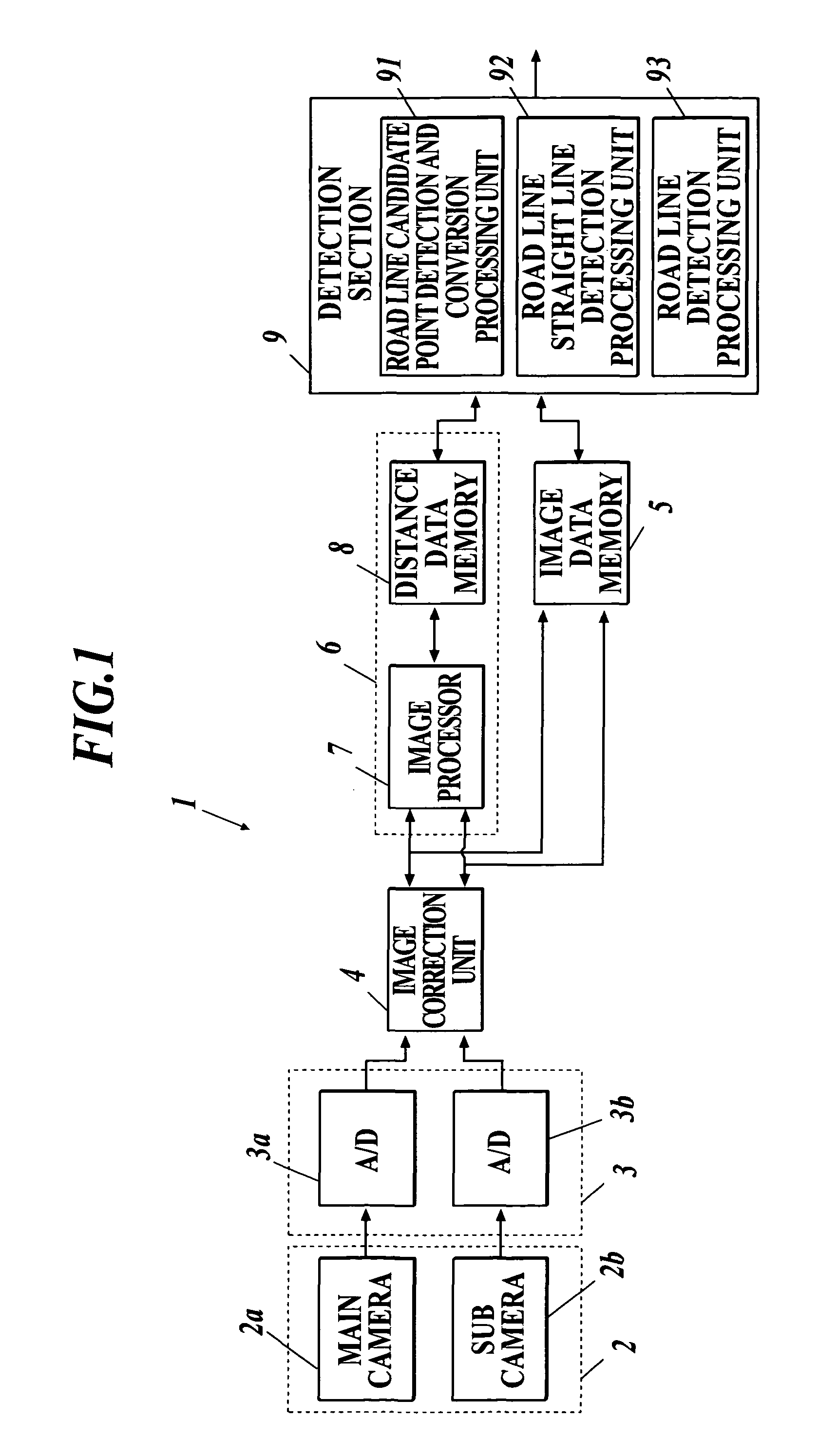
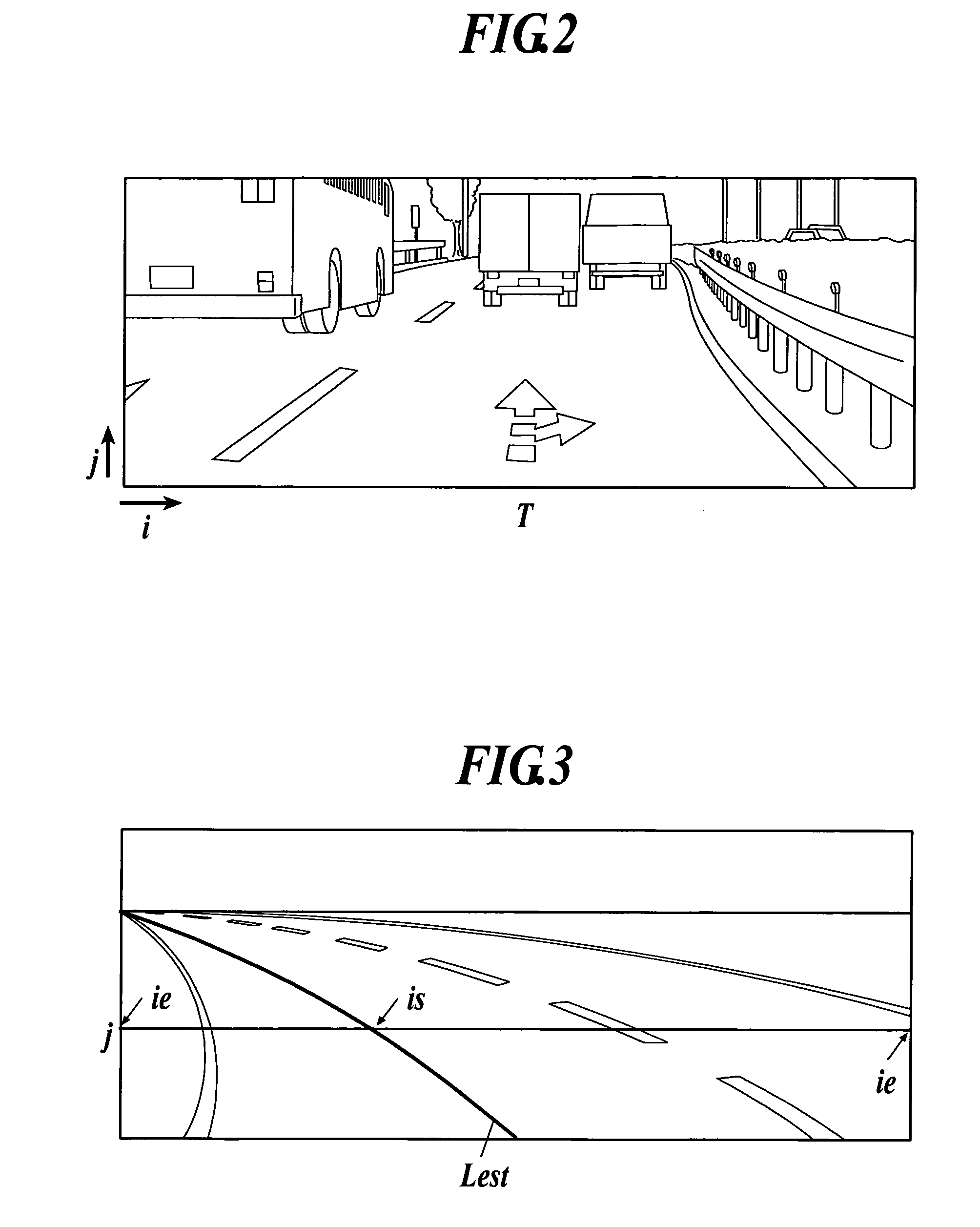
Road line recognition apparatus
ActiveUS8224031B2Stable detectionAccurate detectionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficImaging processingRoad surface
A road line recognition apparatus, including: an imaging section imaging a progress path of a own vehicle including a road to output a couple of images; an image processing section calculating a distance in a real space in a set region of at least an image on one side based on the imaged couple of images; and a detection section detecting a road line; wherein the detection section includes: a road line candidate point detection and conversion processing unit detecting a pixel on a road surface as a road line candidate point based on luminance and the distance with regard to the image on one side, and performing Hough conversion of the road line candidate point; a road line straight line detection processing unit detecting one straight line proper to the road line on each of a right side and a left side of the own vehicle based on at least a position or a behavior of the own vehicle between straight lines obtained by the Hough conversion; and a road line detection processing unit detecting the road line of a shape of a straight line or a curved line by recording a road line position which is a road line candidate point indicating a road line among the road line candidate points based on the detected straight line.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
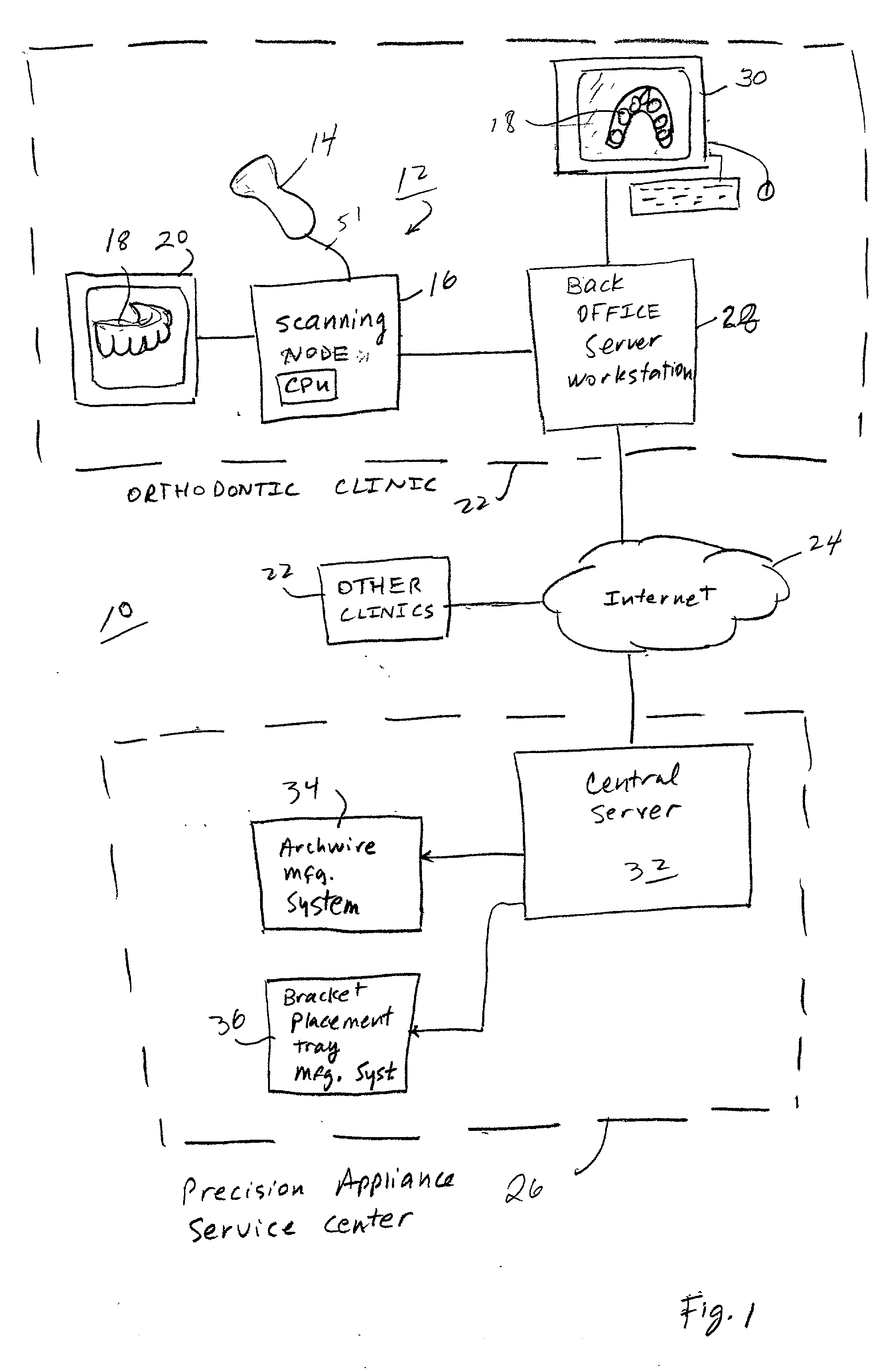
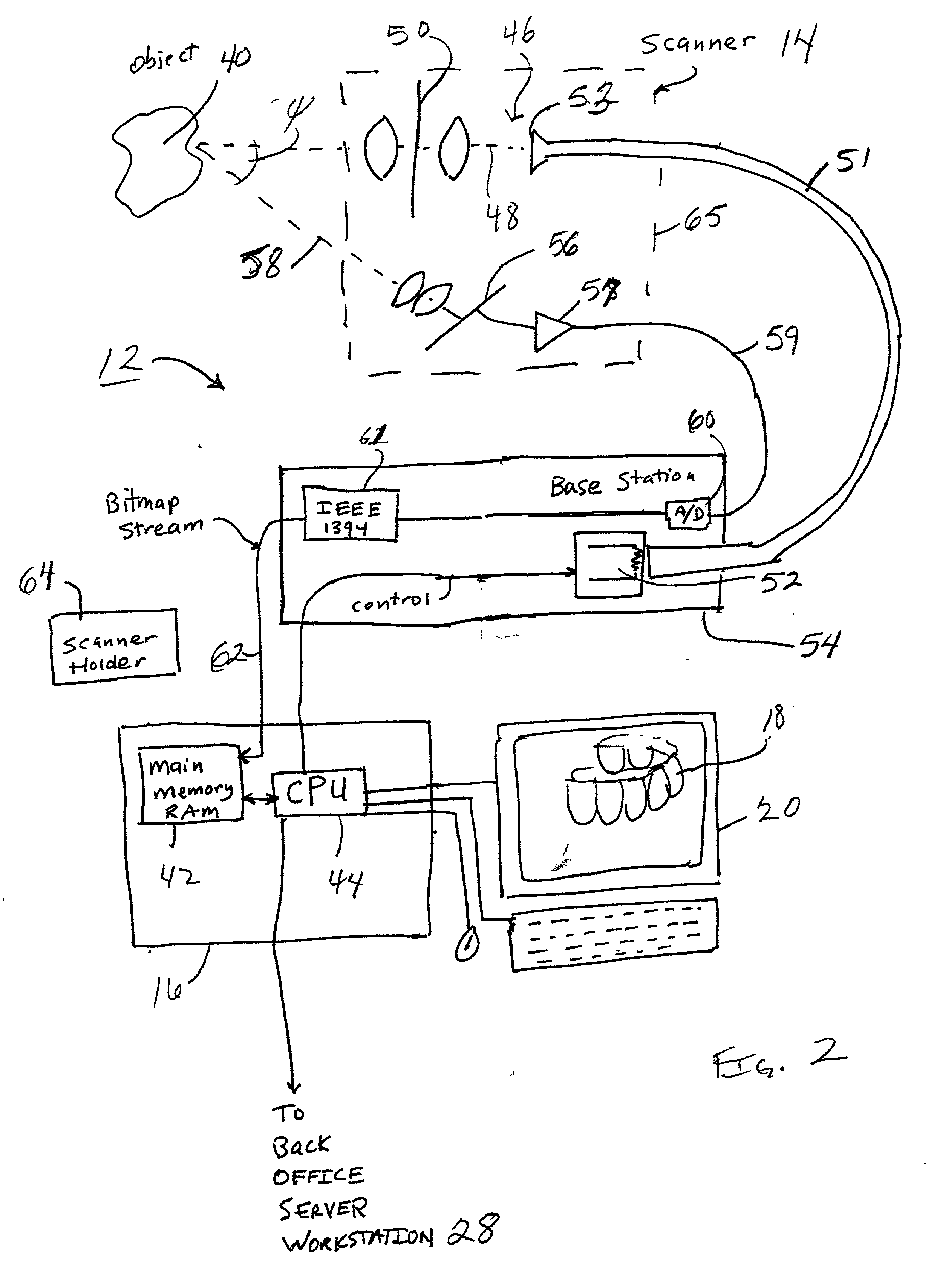
Scanning system and calibration method for capturing precise three-dimensional information of objects
A scanning system includes a hand-held scanning device that generates two-dimensional images of a pattern reflected off an object. The system also includes a memory and processing unit. The memory stores a calibration table for the scanner and received scanned bitmap images. The processing unit generates three-dimensional information as to a scanned object. The scanning can be performed without knowledge or even precise control of the position of the object relative to the scanner. Random movement of the object during scanning is also possible. For example, the scanner is simply swept over the surface of the object by hand. Three-dimensional information of the object is obtained from the captured images using a calibration table for the scanner. A method of calibration of the scanner in X, Y and Z directions is also described. The scanner can be used for a variety of purposes, including medical and industrial purposes. The illustrated embodiment is in-vivo scanning of human teeth for purposes of orthodontic treatment planning and diagnosis.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
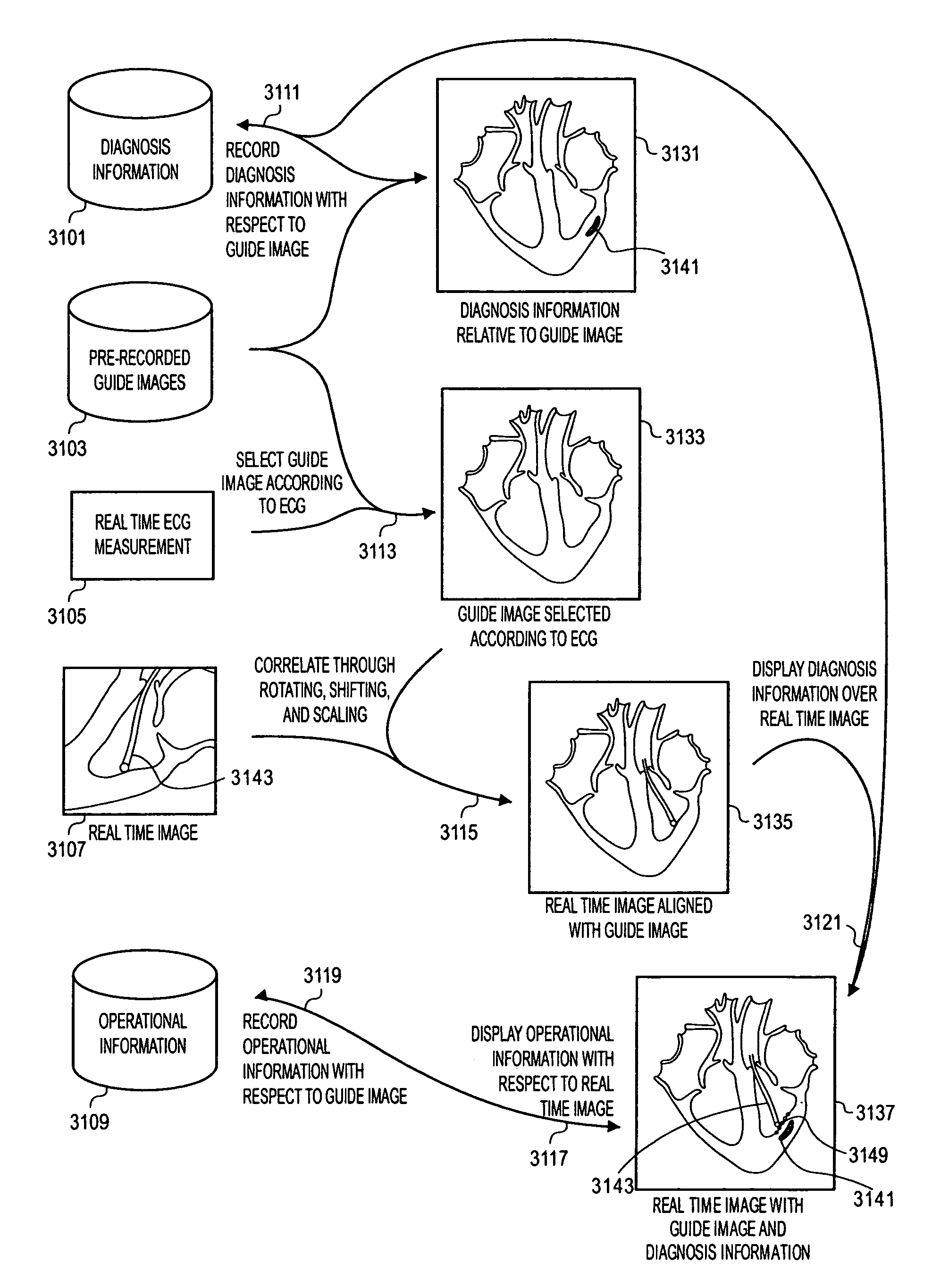
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
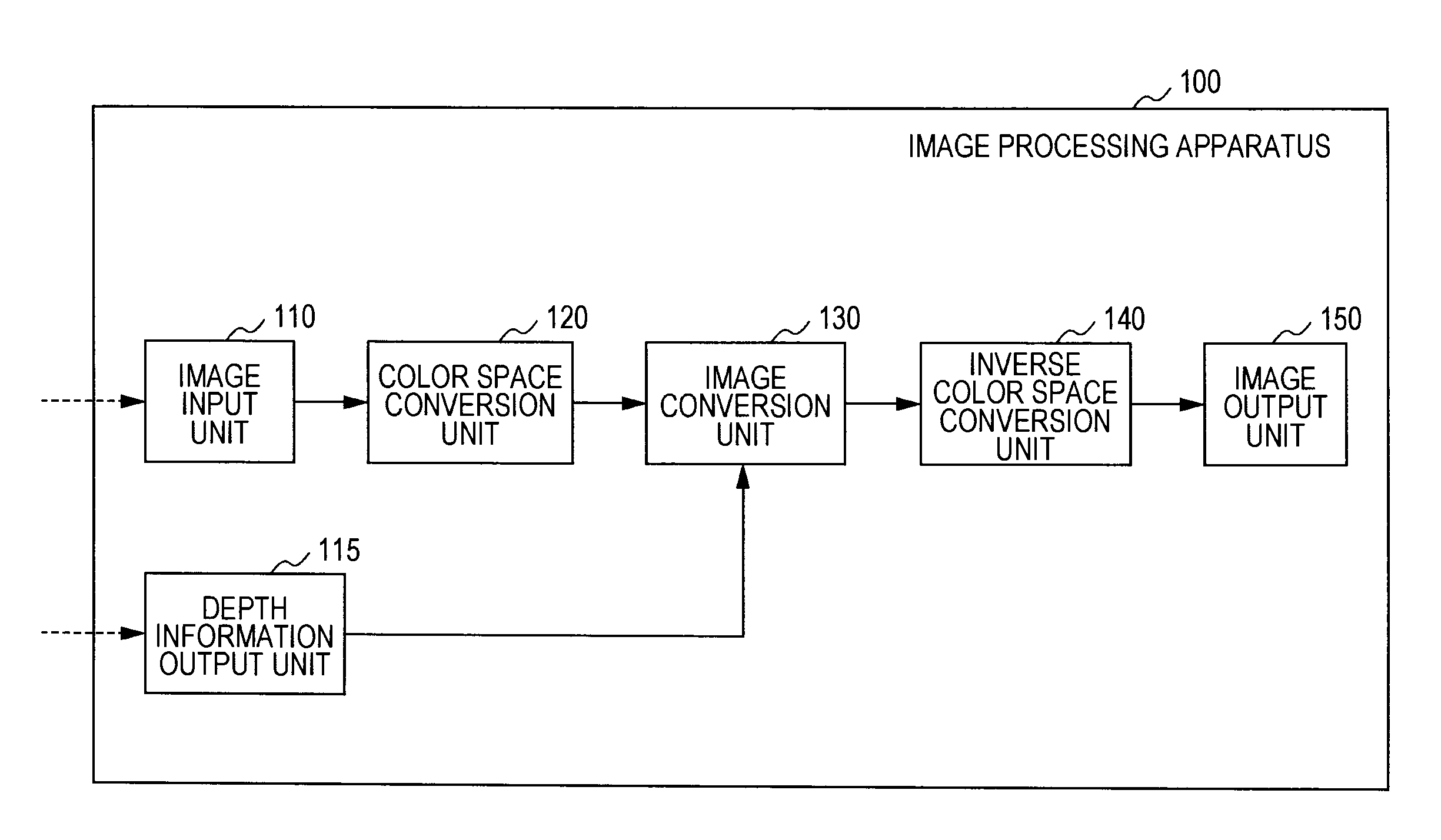
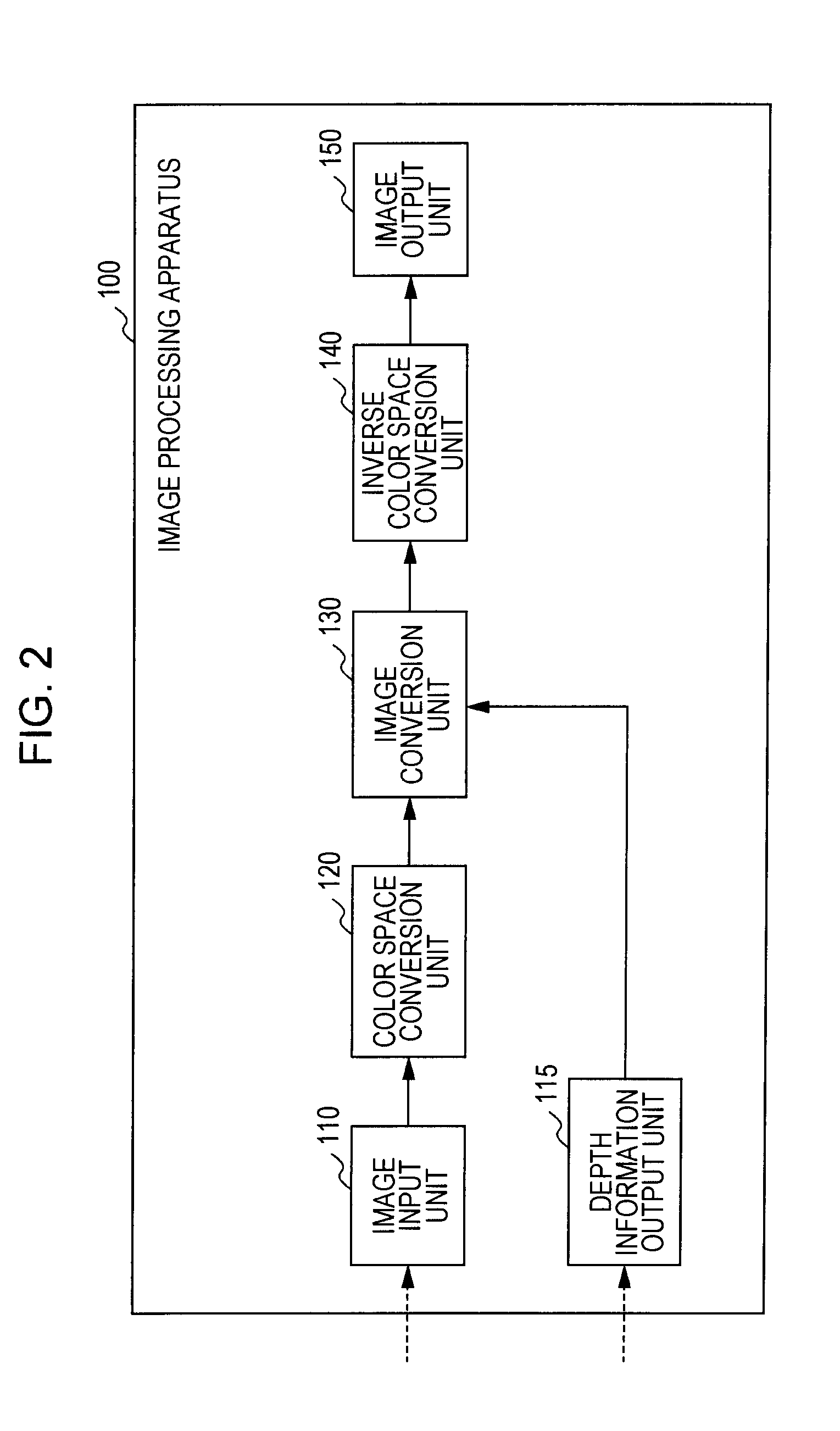
Image processing apparatus, image processing method and program
An image processing apparatus includes an image input unit that inputs a two-dimensional image signal, a depth information output unit that inputs or generates depth information of image areas constituting the two-dimensional image signal, an image conversion unit that receives the image signal and the depth information from the image input unit and the depth information output unit, and generates and outputs a left eye image and a right eye image for realizing binocular stereoscopic vision, and an image output unit that outputs the left and right eye images. The image conversion unit extracts a spatial feature value of the input image signal, and performs an image conversion process including an emphasis process applying the feature value and the depth information with respect to the input image signal, thereby generating at least one of the left eye image and the right eye image.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
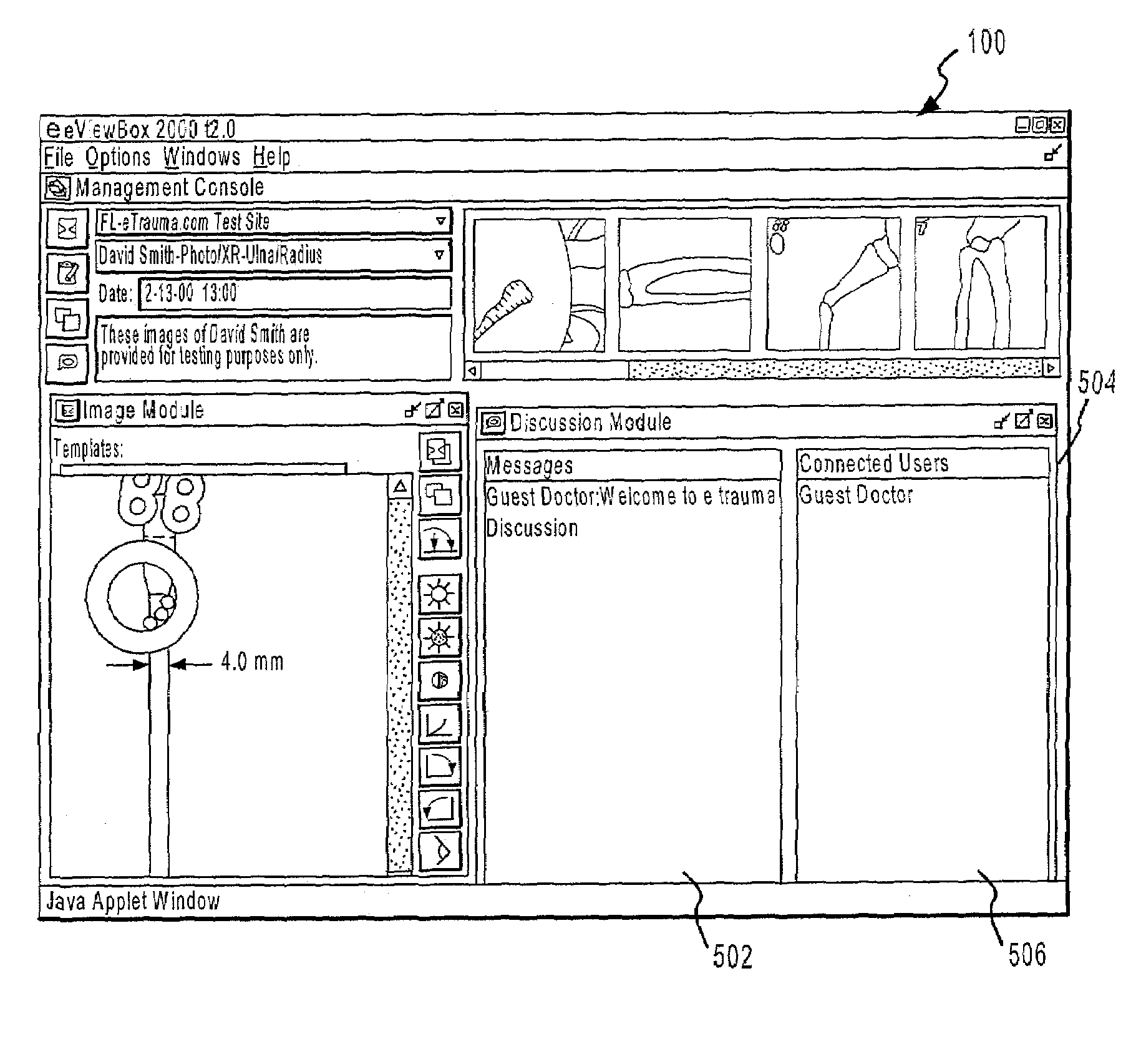
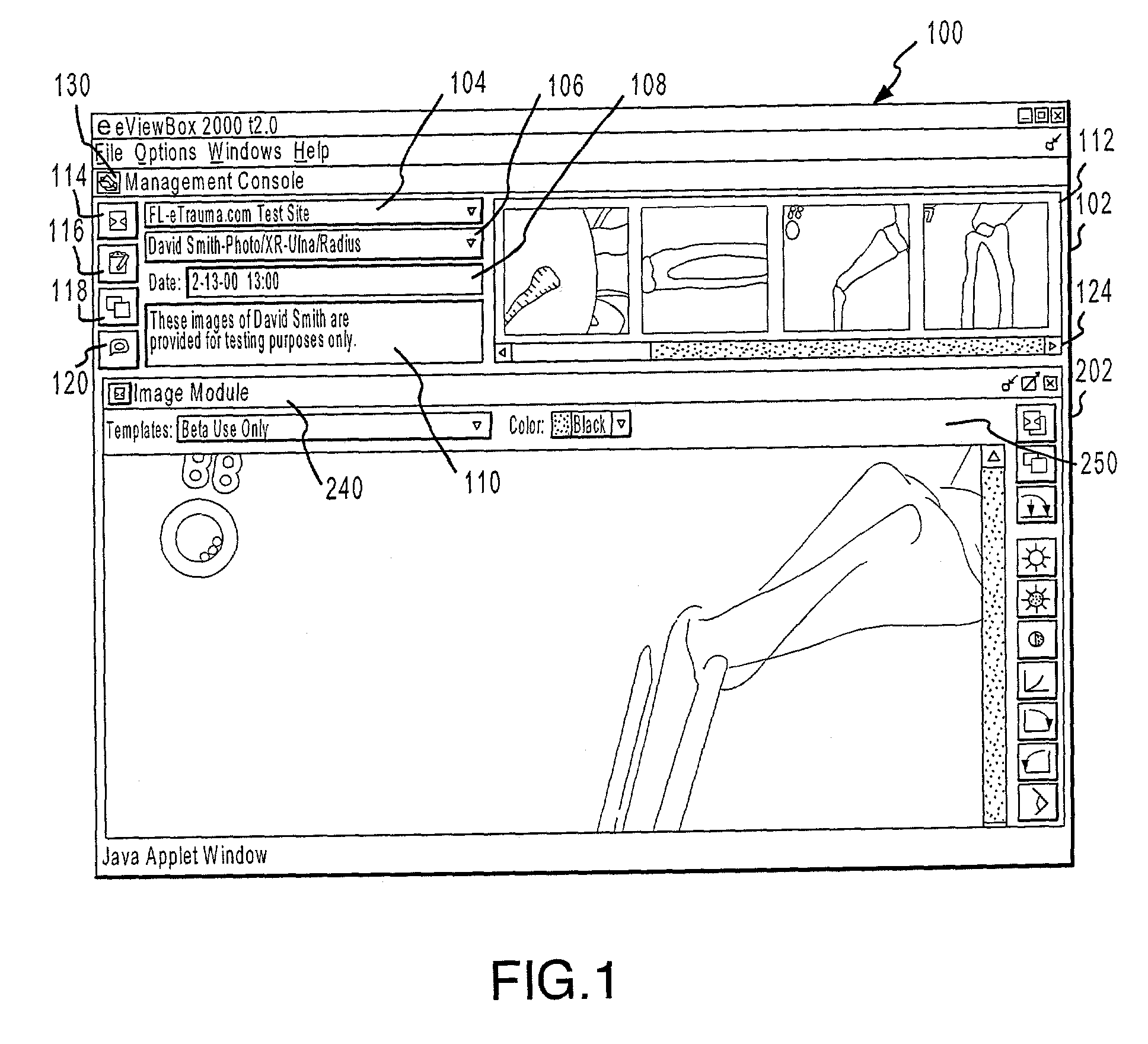
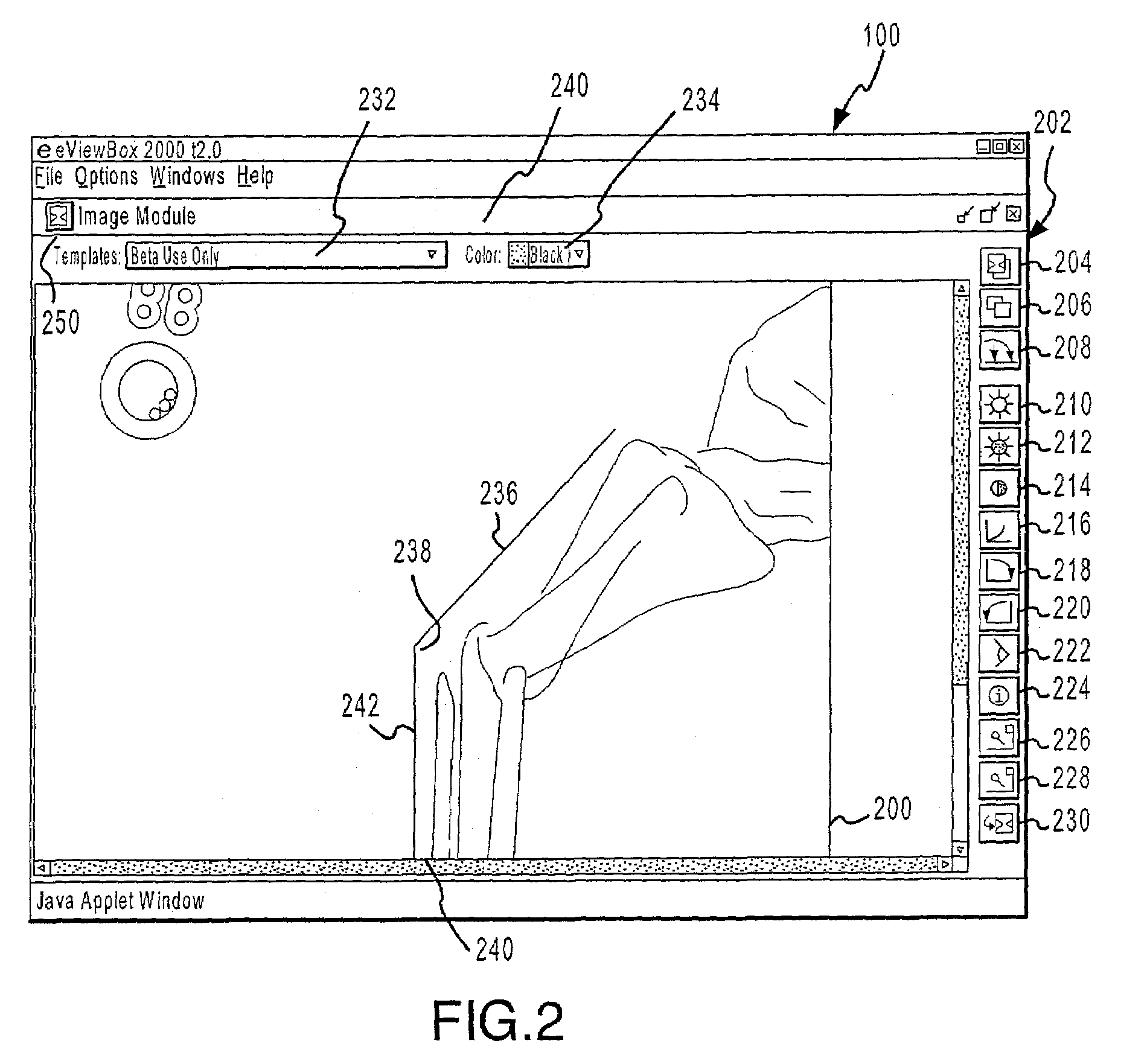
Systems and methods for enhancing the viewing of medical images
ActiveUS7106479B2Improve viewing effectImage enhancementLocal control/monitoringGoniometerMedical device
The present invention provides systems and methods for enhancing the delivery and display of medical images over a network. Authorized users may access and view images by accessing a secure server and selecting images for viewing. Various characteristics of the image or images being viewed may be manipulated. Additionally, measuring devices, such as a goniometer, may be placed on an image to measure distances, angles and the like. In one embodiment, one or more templates, for example of medical devices, may be placed on an image and manipulated. In another embodiment, two or more users may view the same image simultaneously, while also viewing a template, measuring device, image manipulations and the like simultaneously. In yet another embodiment, two or more users may discuss one or more images via a discussion board.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
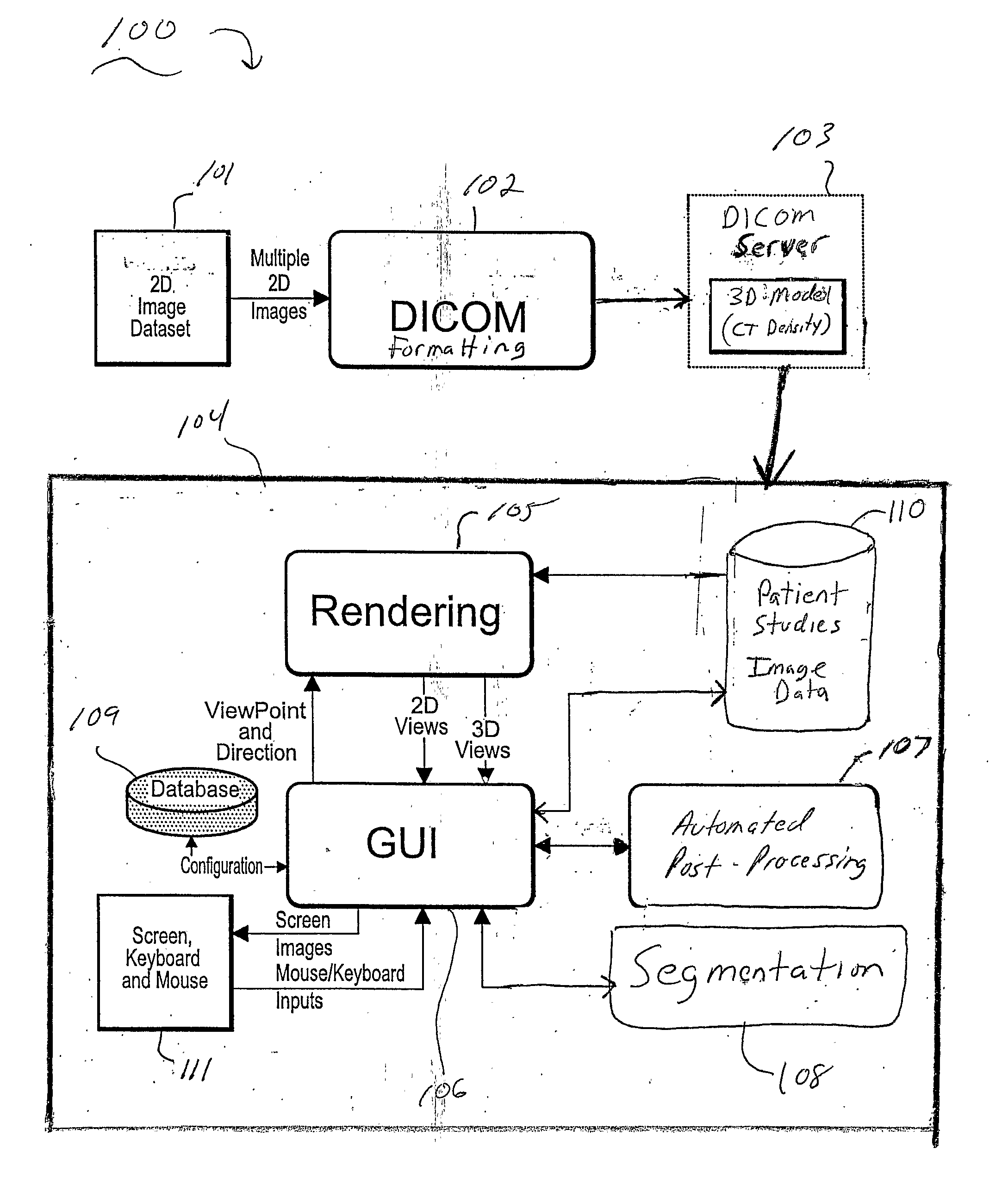
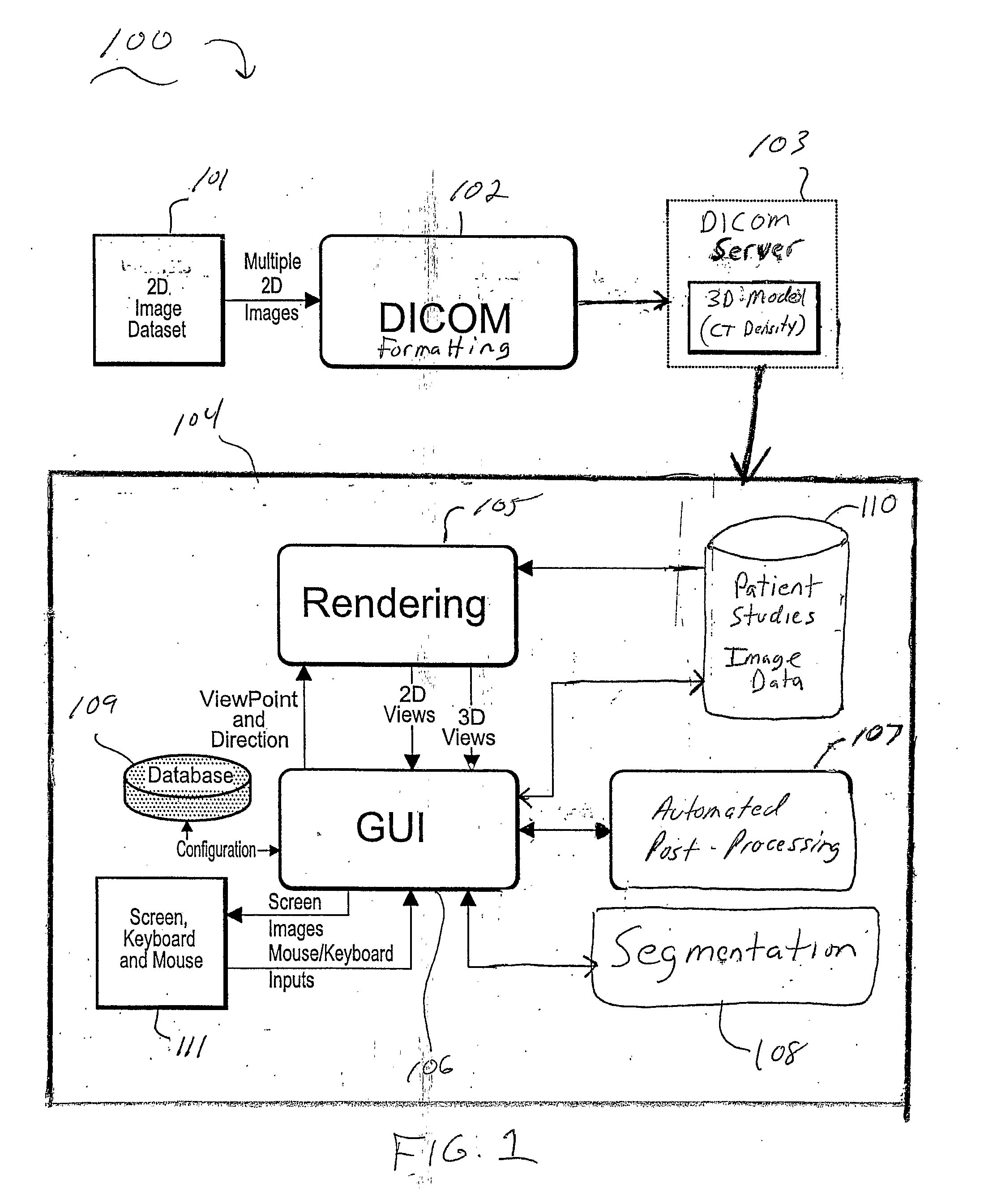
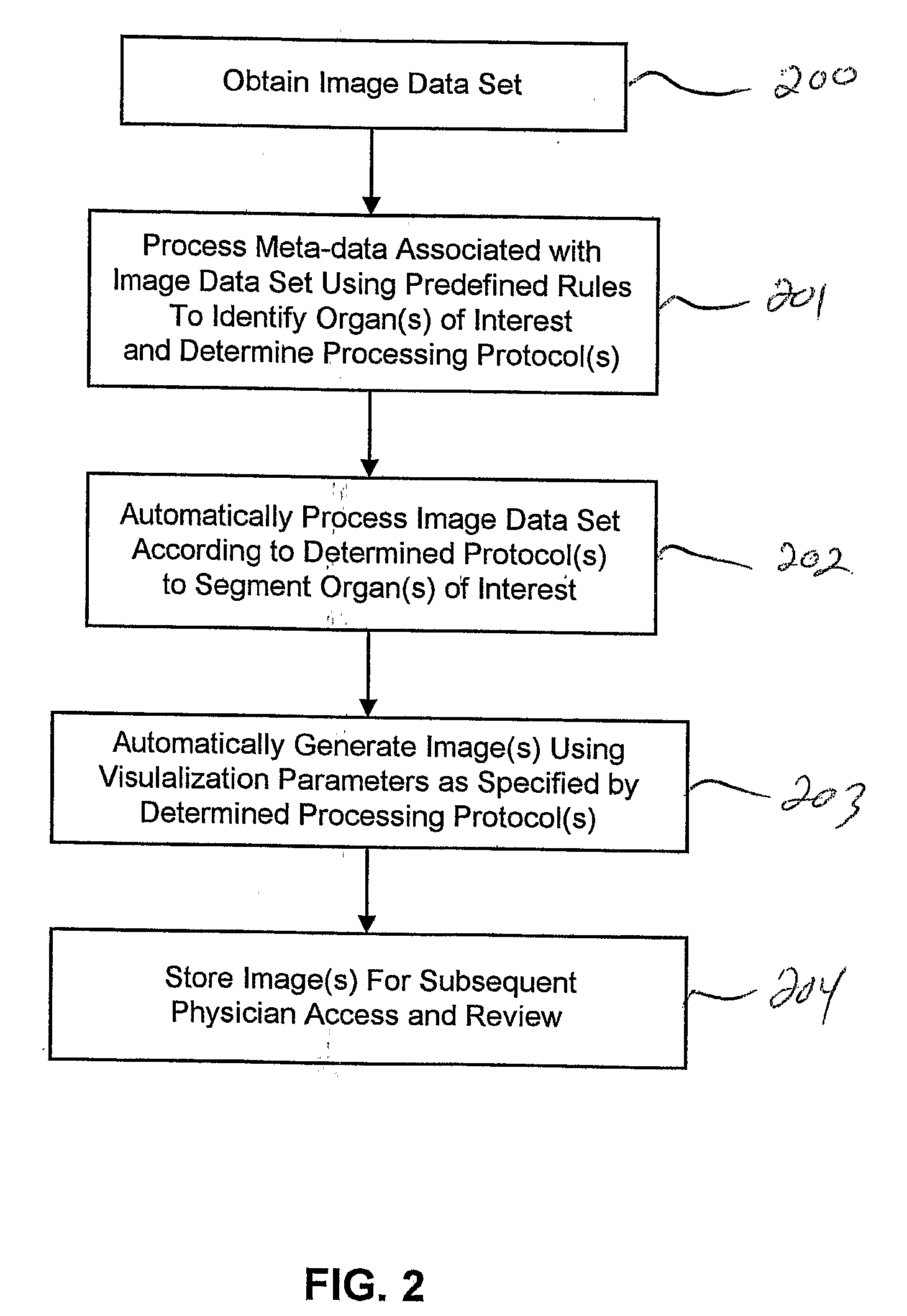
Systems and Methods for Automated Segmentation, Visualization and Analysis of Medical Images
An imaging system for automated segmentation and visualization of medical images (100) includes an image processing module (107) for automatically processing image data using a set of directives (109) to identify a target object in the image data and process the image data according to a specified protocol, a rendering module (105) for automatically generating one or more images of the target object based on one or more of the directives (109) and a digital archive (110) for storing the one or more generated images. The image data may be DICOM-formatted image data (103), wherein the imaging processing module (107) extracts and processes meta-data in DICOM fields of the image data to identify the target object. The image processing module (107) directs a segmentation module (108) to segment the target object using processing parameters specified by one or more of the directives (109).
Owner:VIATRONIX
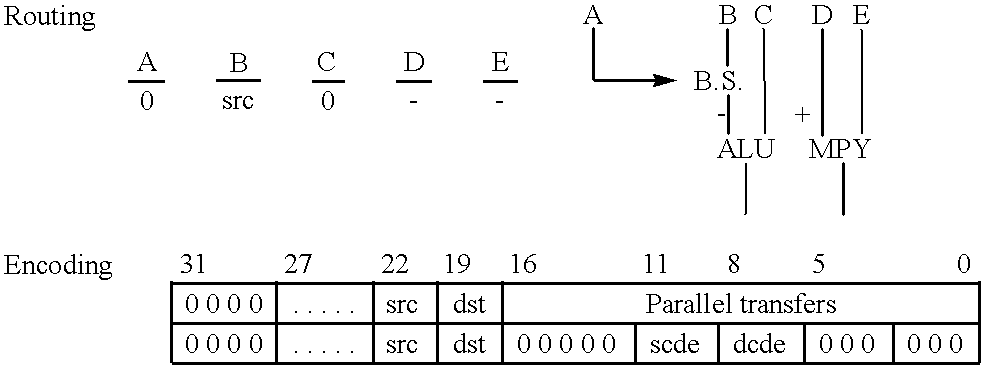
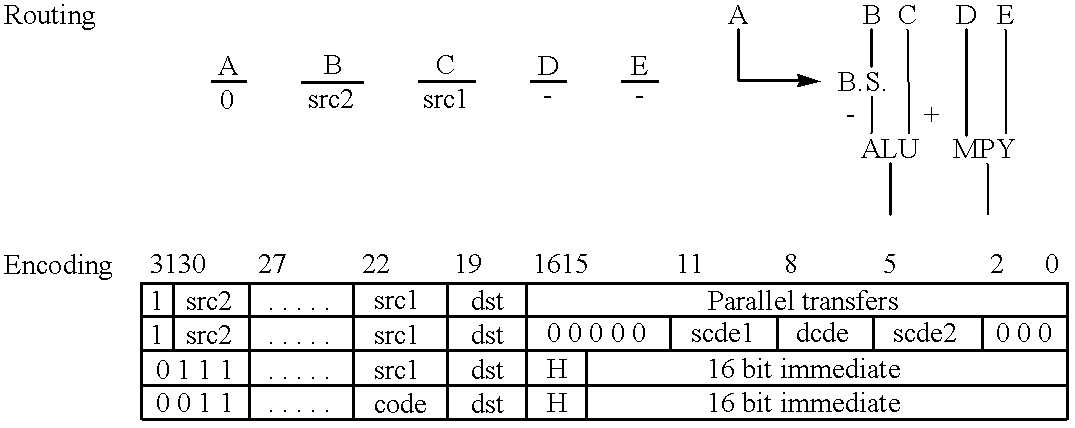
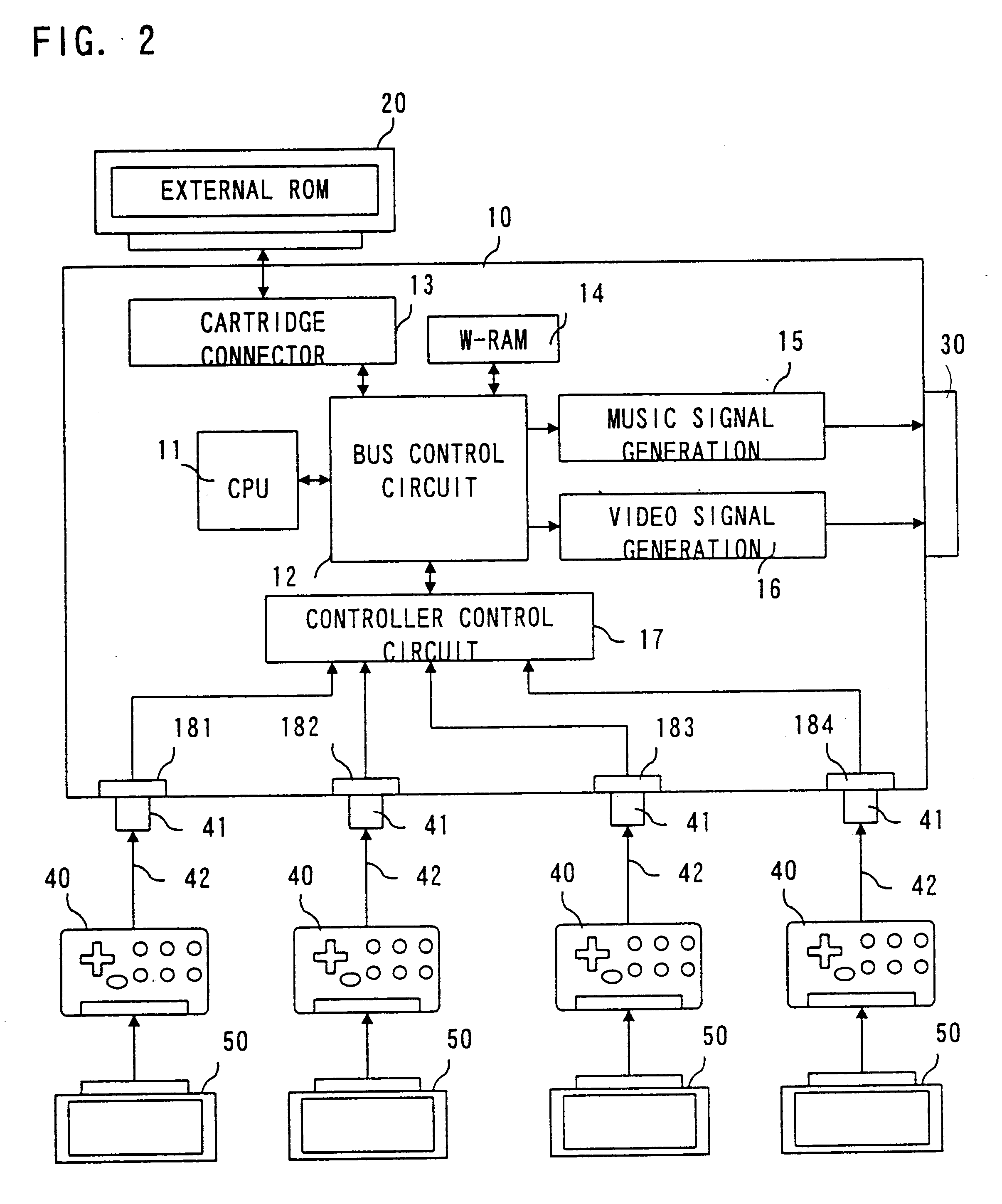
Single integrated circuit embodying a risc processor and a digital signal processor
InactiveUS6260088B1Save spaceImprove versatilityGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital signal processingComputer image
A single integrated circuit includes first and second data processors operating on different instruction sets independently operating on disjoint programs and data. The single integrated circuit preferably includes an external interface, a shared data transfer controller and shared memory divided into plural independently accessible memory banks. The two data processors are preferably a digital signal processor (DSP) and a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) processor. The DSP and RISC processors are suitably programmed to perform differing aspects of computer image processing.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
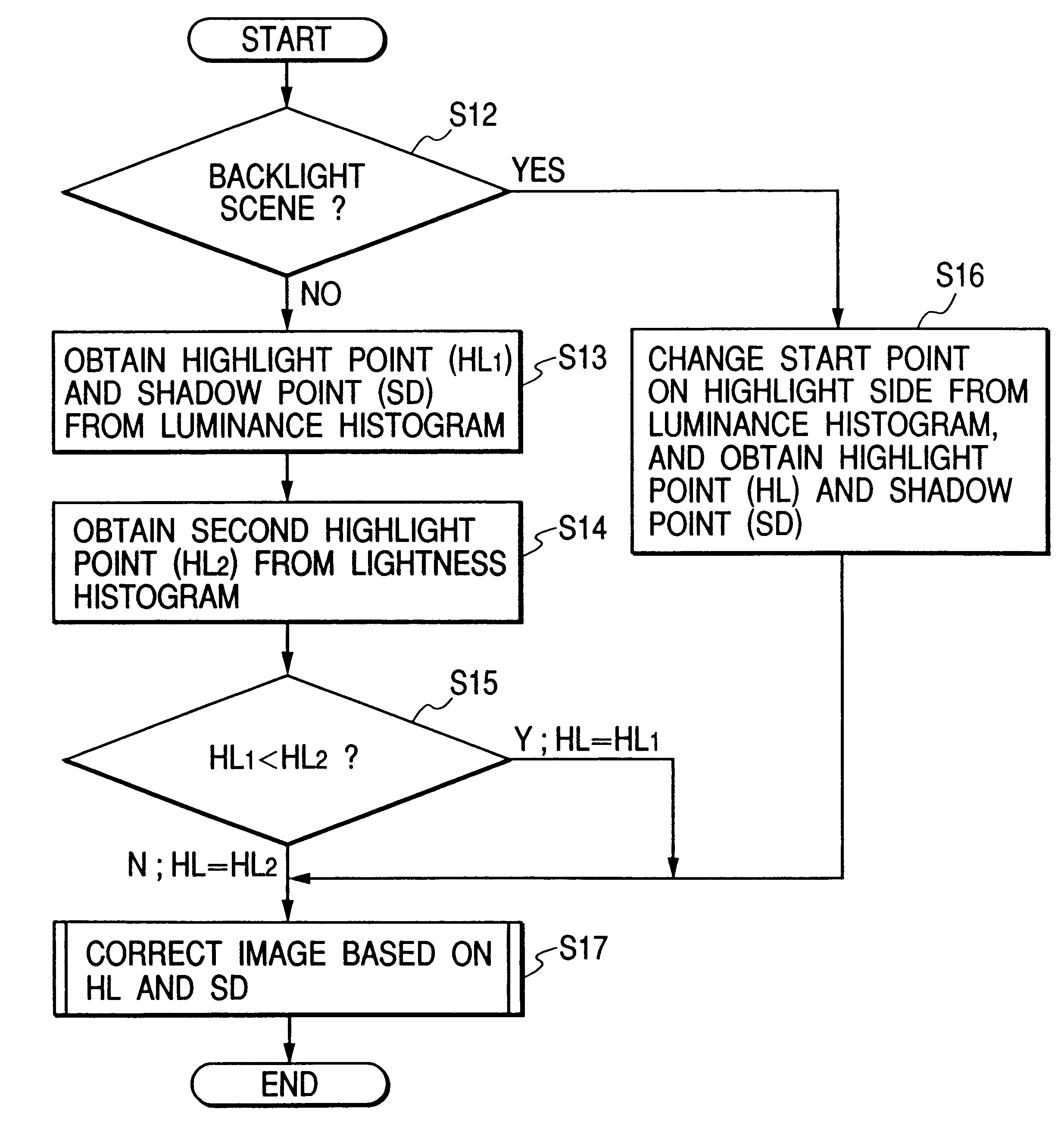
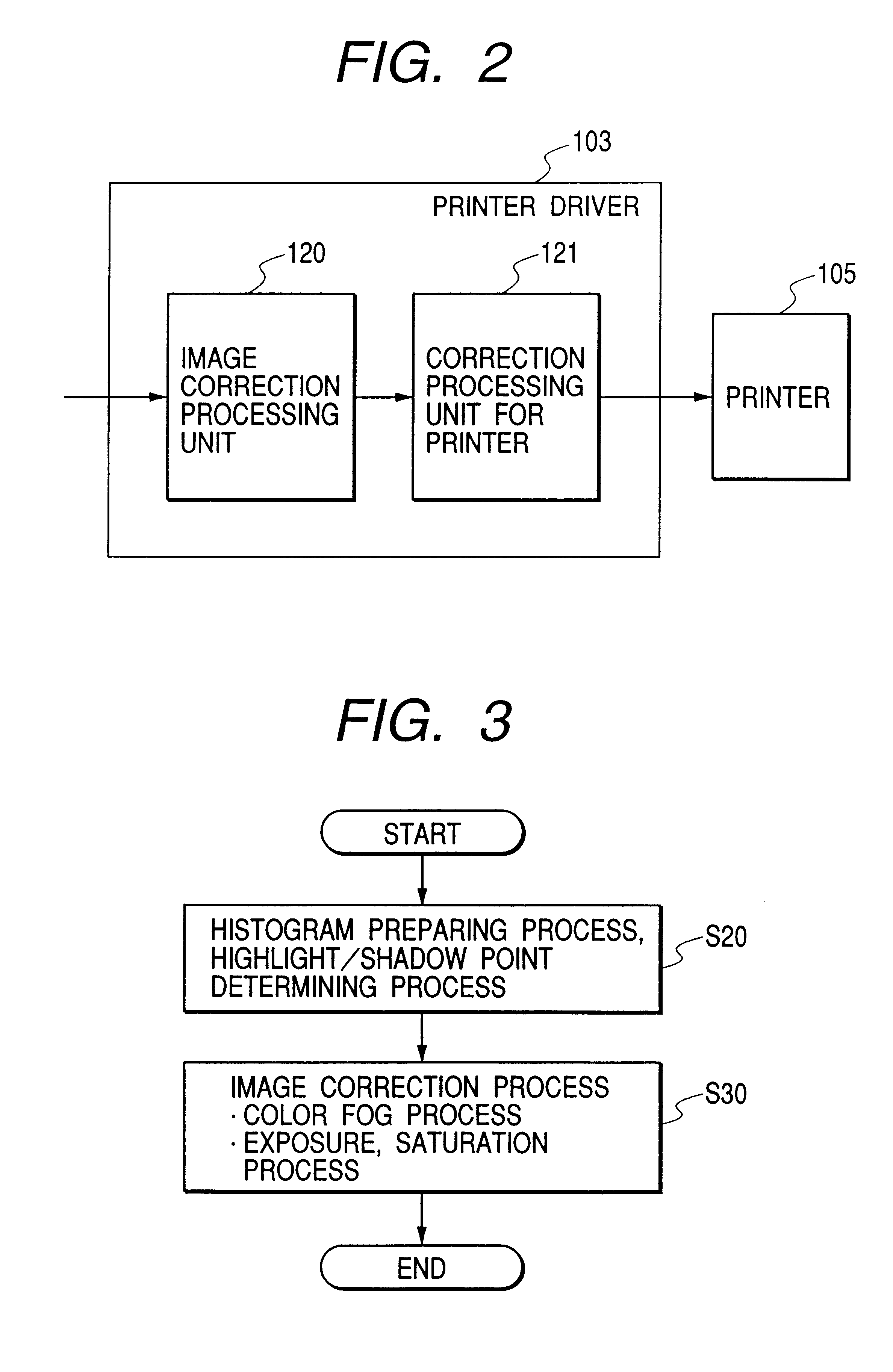
Image processing method, image processing apparatus and recording medium
An image processing method, an image processing system and a recording medium capable of reproducing images in colors which are close to those memorized by man including a process to create a histogram of an original image, a process to adequately locate a highlight point on the histogram by comparing peaks of the histogram and setting image processing conditions dependently on a shape of a selected peak.
Owner:CANON KK
Synthesizing training data for broad area geospatial object detection
A system for broad area geospatial object recognition, identification, classification, location and quantification, comprising an image manipulation module to create synthetically-generated images to imitate and augment an existing quantity of orthorectified geospatial images; together with a deep learning module and a convolutional neural network serving as an image analysis module, to analyze a large corpus of orthorectified geospatial images, identify and demarcate a searched object of interest from within the corpus, locate and quantify the identified or classified objects from the corpus of geospatial imagery available to the system. The system reports results in a requestor's preferred format.
Owner:MAXAR INTELLIGENCE INC
Medical Image Processing
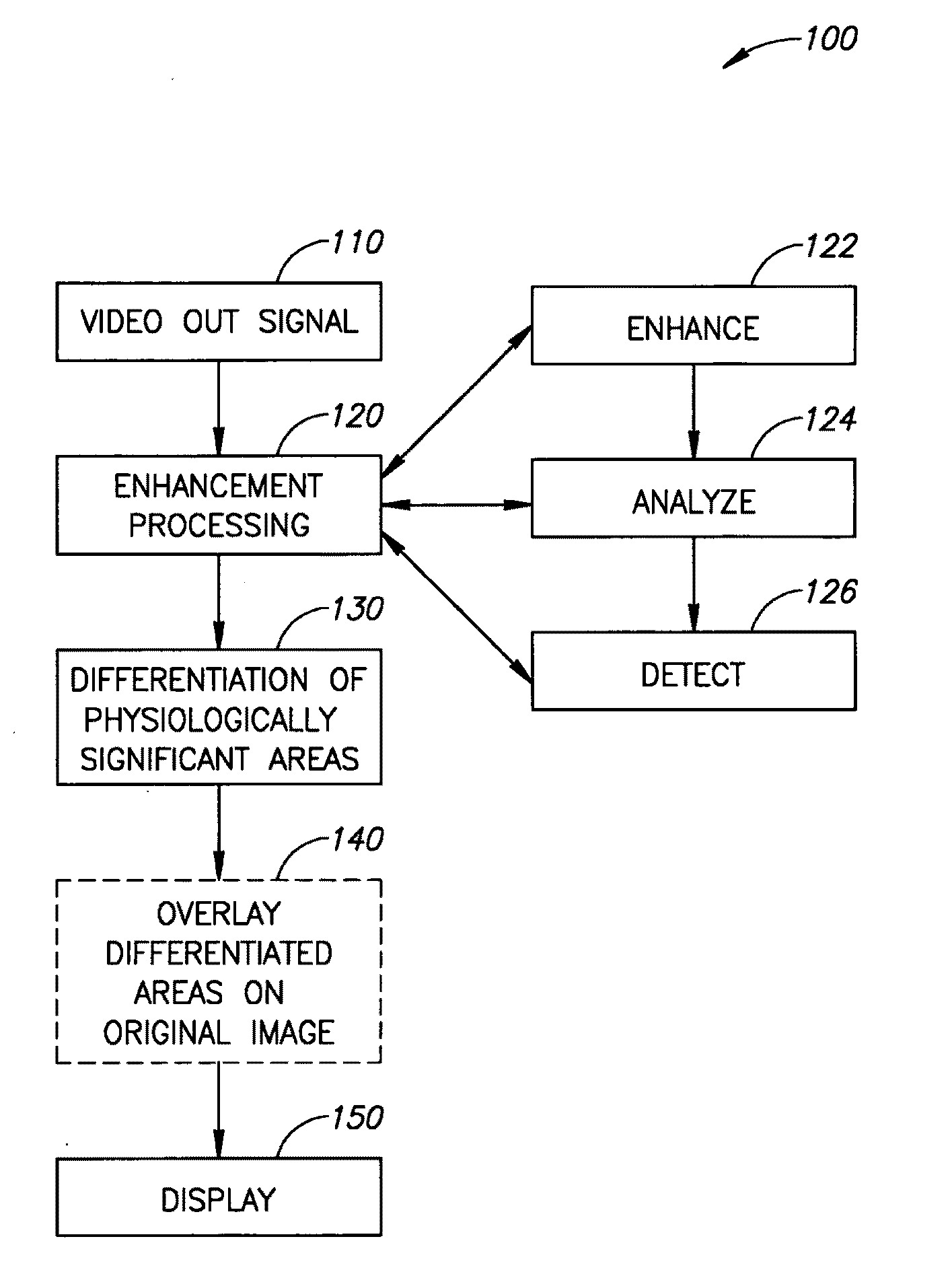
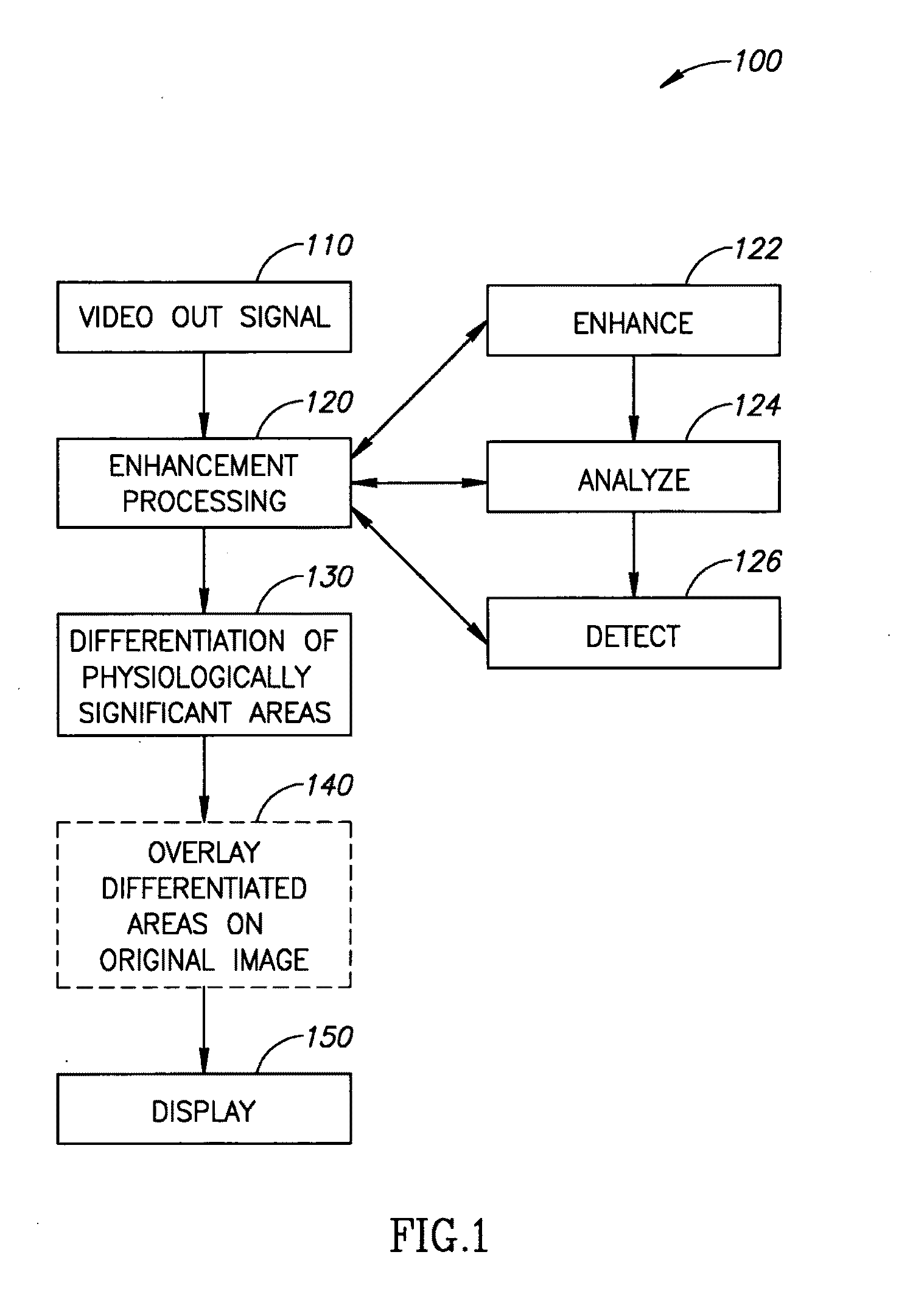
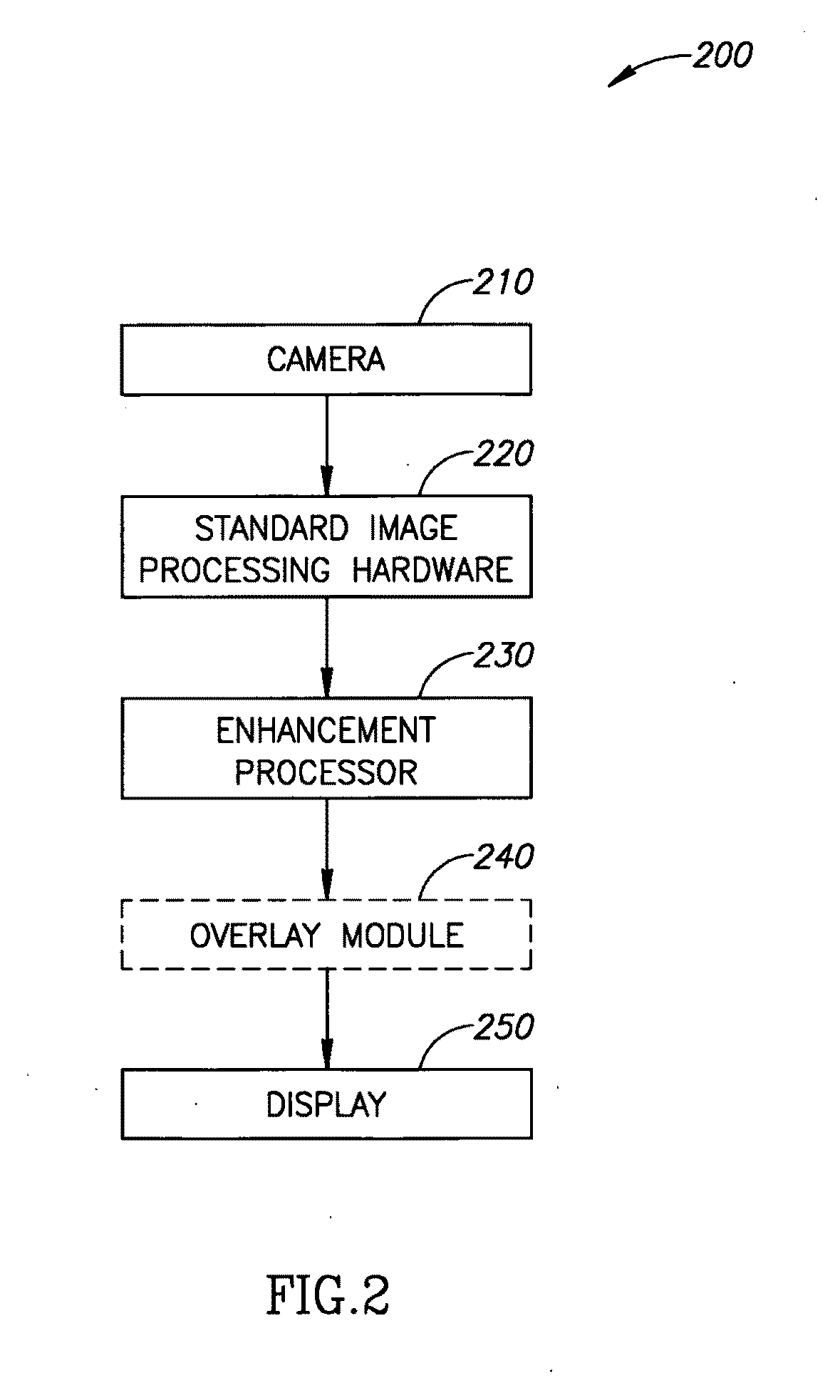
A method of image processing, including:(a) calculating at least one pixel color feature (PCF) value for each pixel in a color medical image to generate a set of PCF data; and(b) filtering the PCF data with at least one spatial adaptive bandpass filter (ABPF) to sort the pixels into physiologically significant regions;wherein the at least one PCF value for at least one pixel depends on at least 2 color components of the medical image.
Owner:D V P TECH
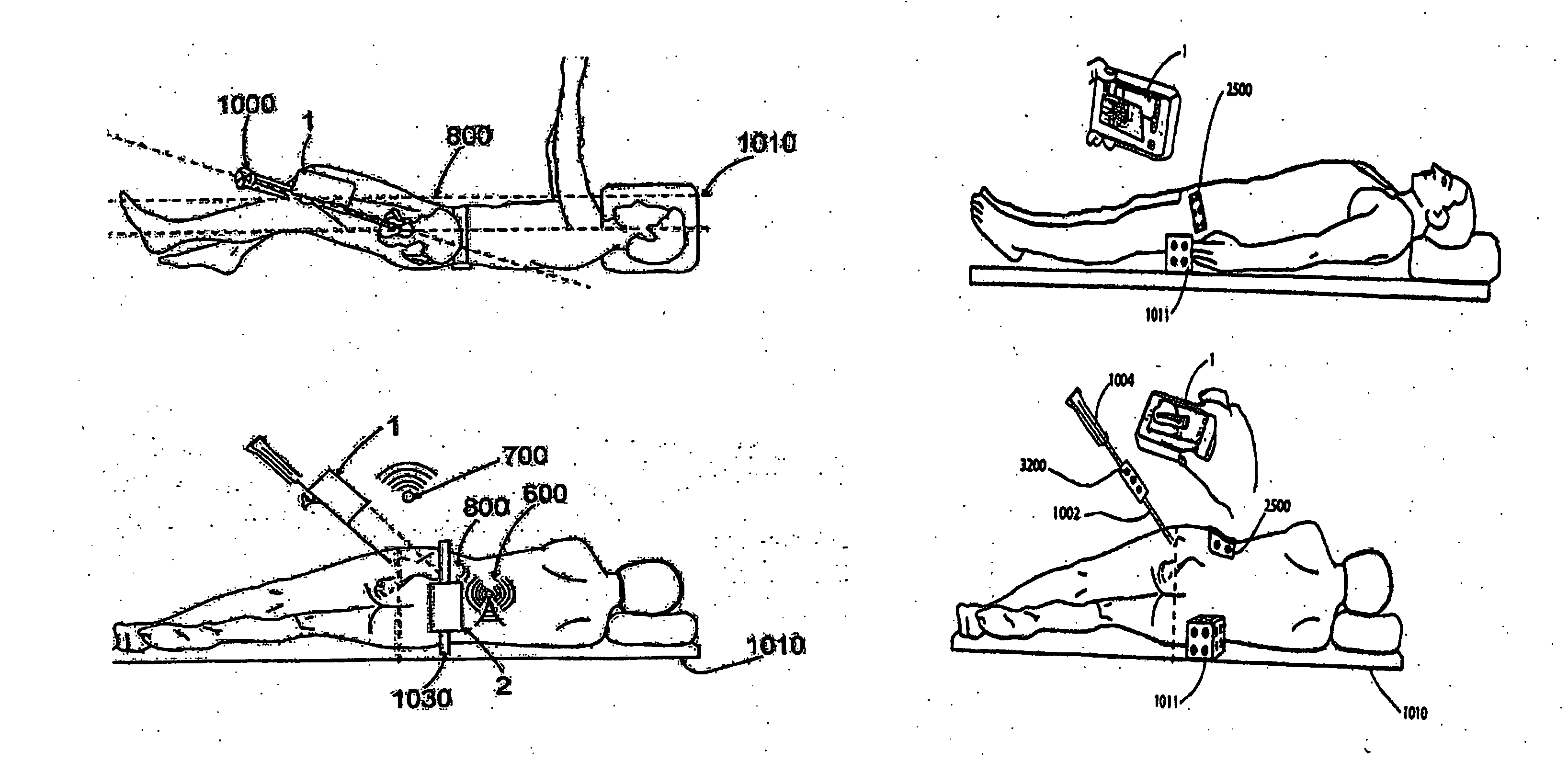
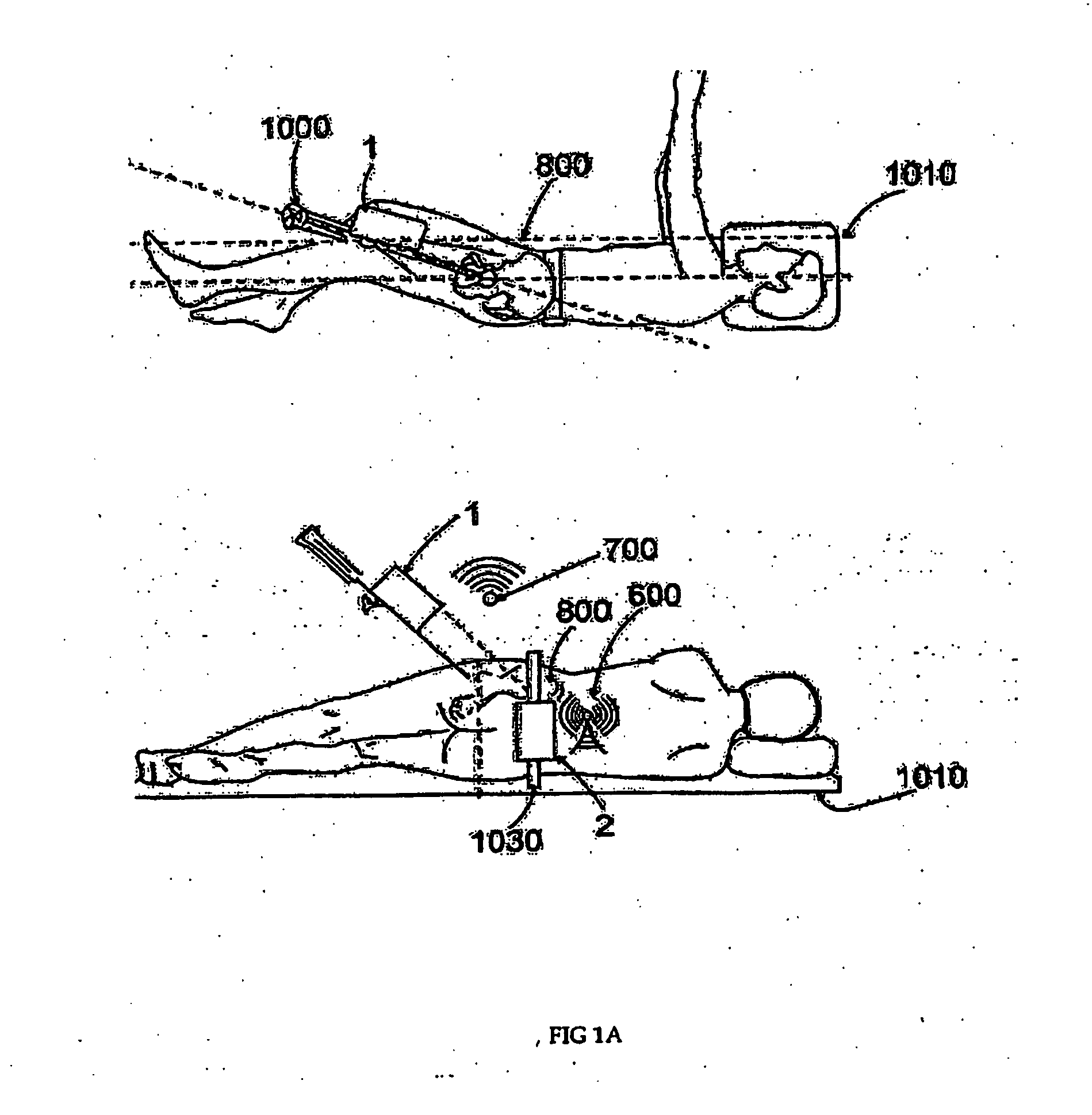
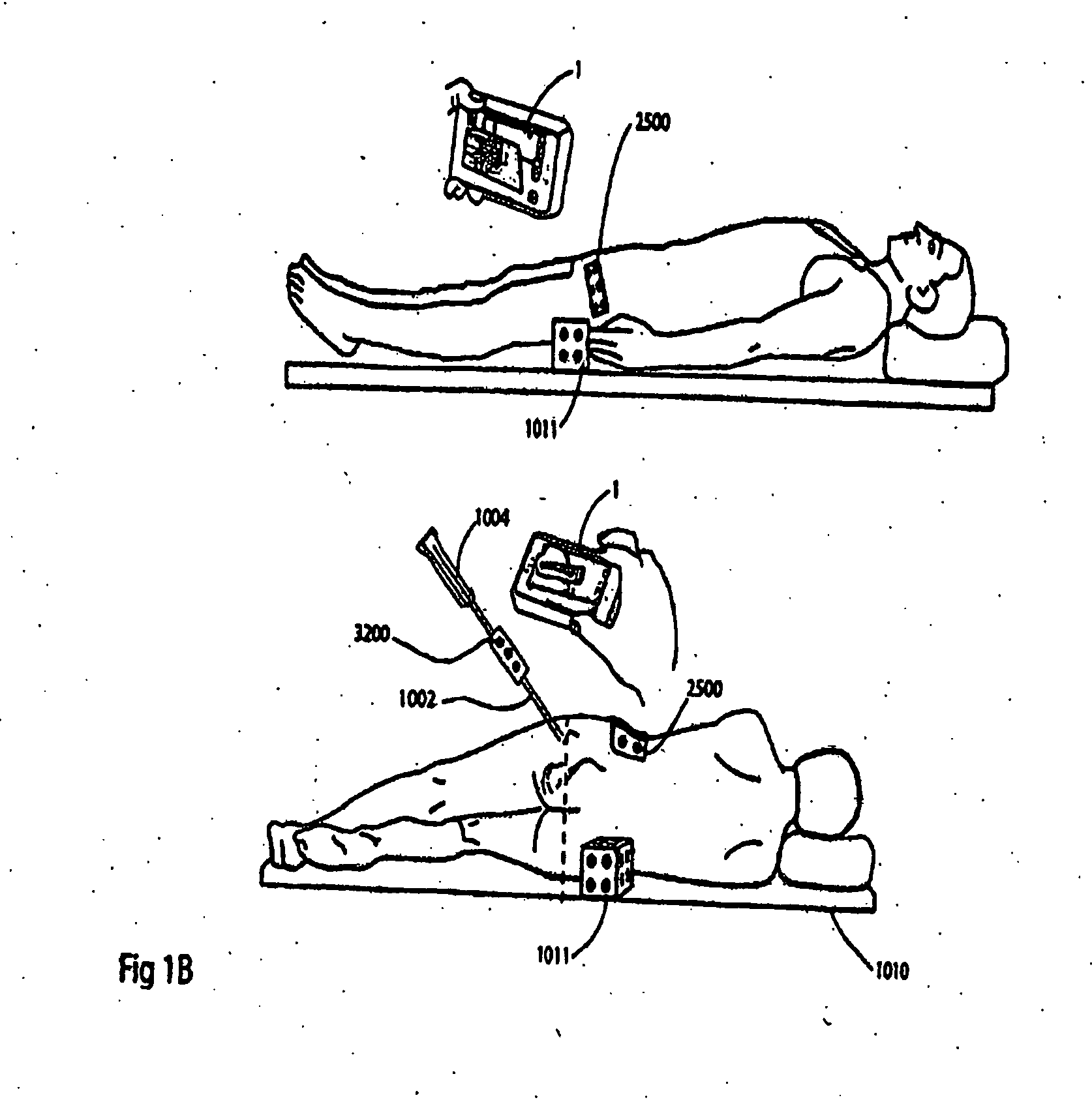
Handheld tracking system and devices for aligning implant systems during surgery
InactiveUS20150133945A1Accurate placementPrevent any length discrepancy in leg lengthSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsSterile environmentScheie operation
The present invention discloses handheld tracking systems and devices comprising of at least one handheld tracking device for intra-operative aligning or positioning of surgical implant systems and instruments with reference to the anatomy of a patient. The handheld tracking system further comprises of at least one trackable element. The handheld device is mounted at the proposed implantation site using the holding means while trackable element(s) is / are mounted at predetermined location(s) such that data from said deployed trackable element(s) relating to the position of the patient and the surgical instruments are input continuously into the handheld devices. The handheld device then processes the data on the basis of pre-loaded preoperative scanned images in the processing means to monitor the accurate placement of said implant system onsite in sterile environment.
Owner:STRYKER GLOBAL TECH CENT
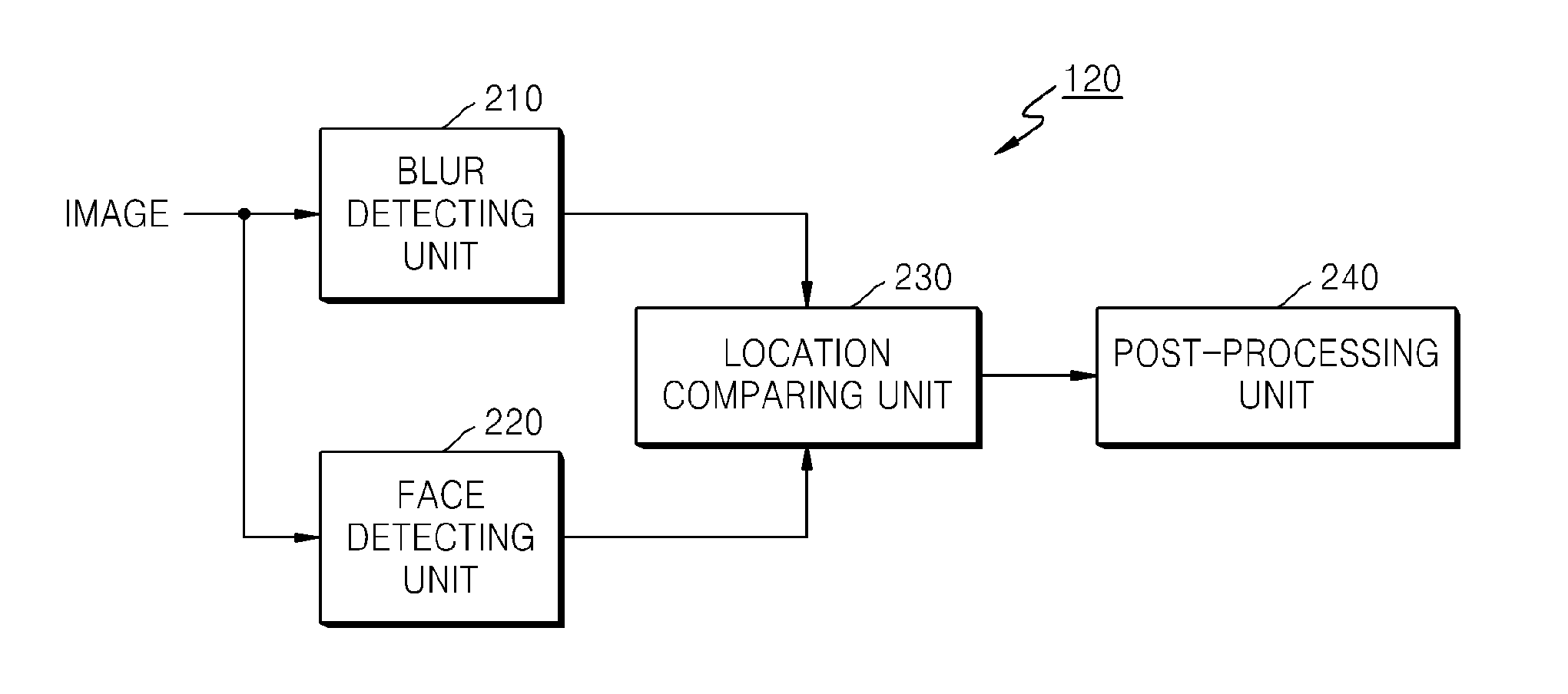
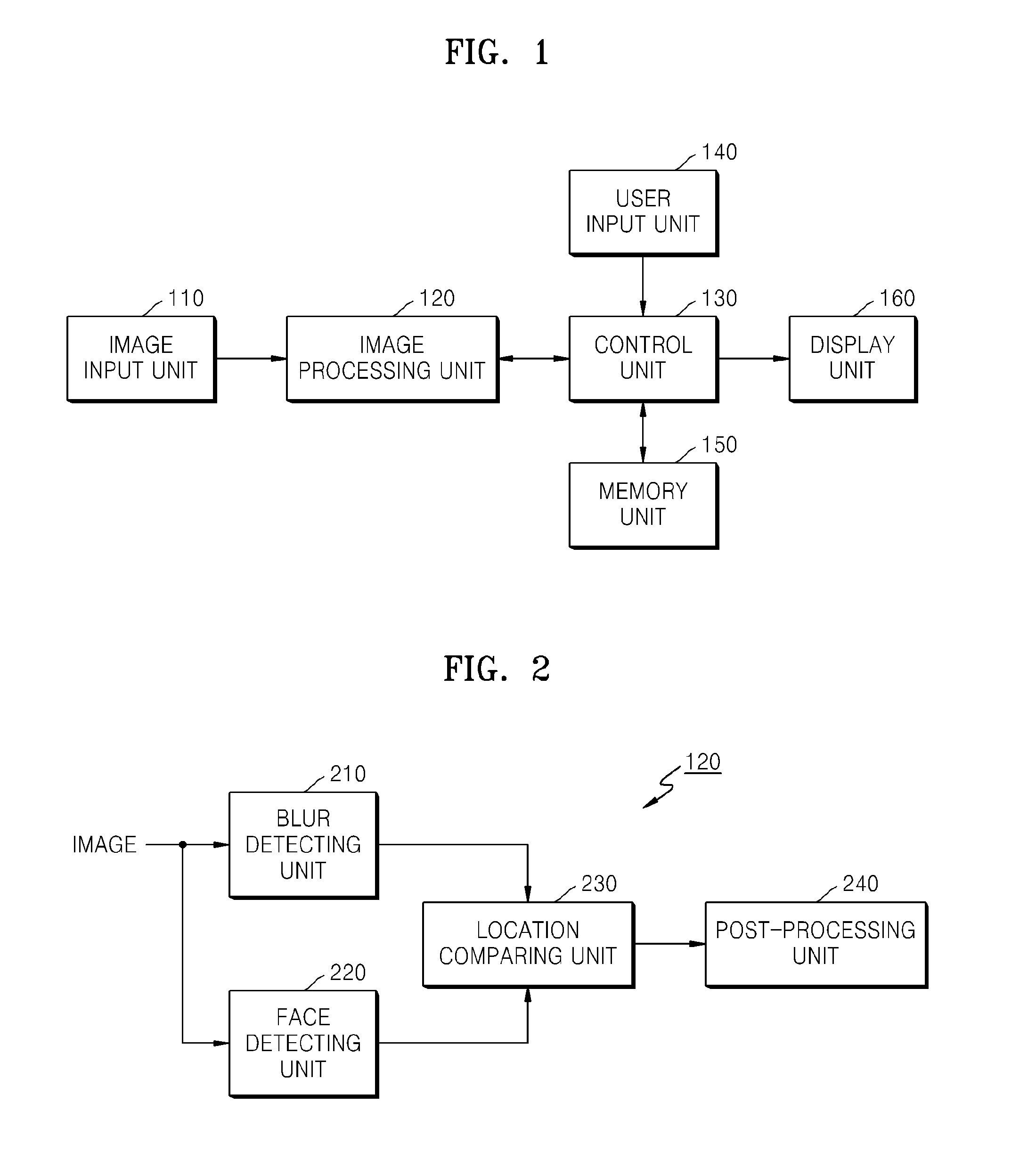
Method and apparatus for processing image
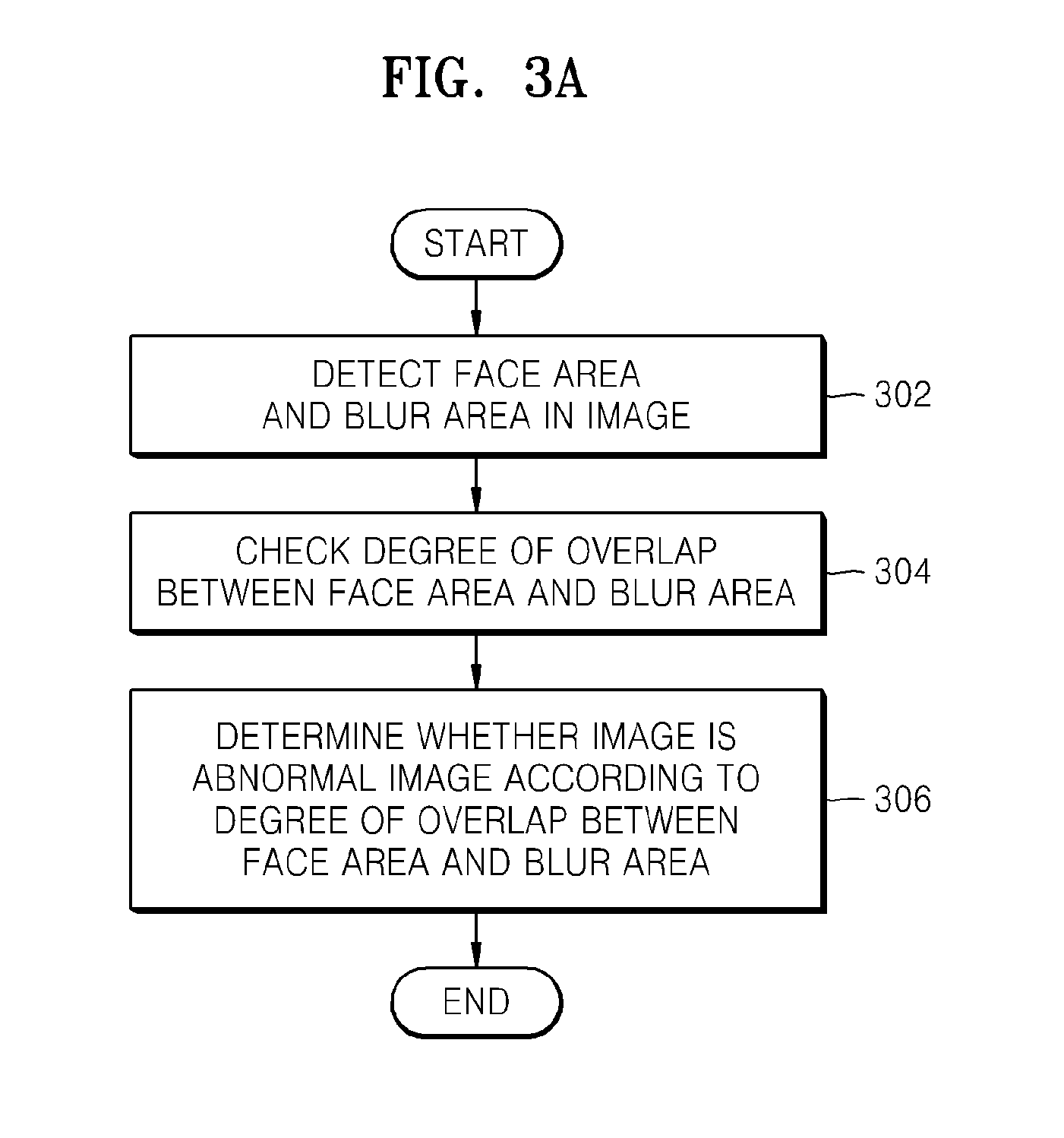
ActiveUS20110116716A1Efficient managementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage processingRecording media
A method, apparatus, and computer readable recording medium for processing an image. The method includes detecting a face area and a blur area from an image; checking a degree of overlap between the face area and the blur area by comparing a location of the face area with a location of the blur area; and determining whether the image is an abnormal image according to the degree of overlap between the face area and the blur area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dual-mode stereo imaging system for tracking and control in surgical and interventional procedures
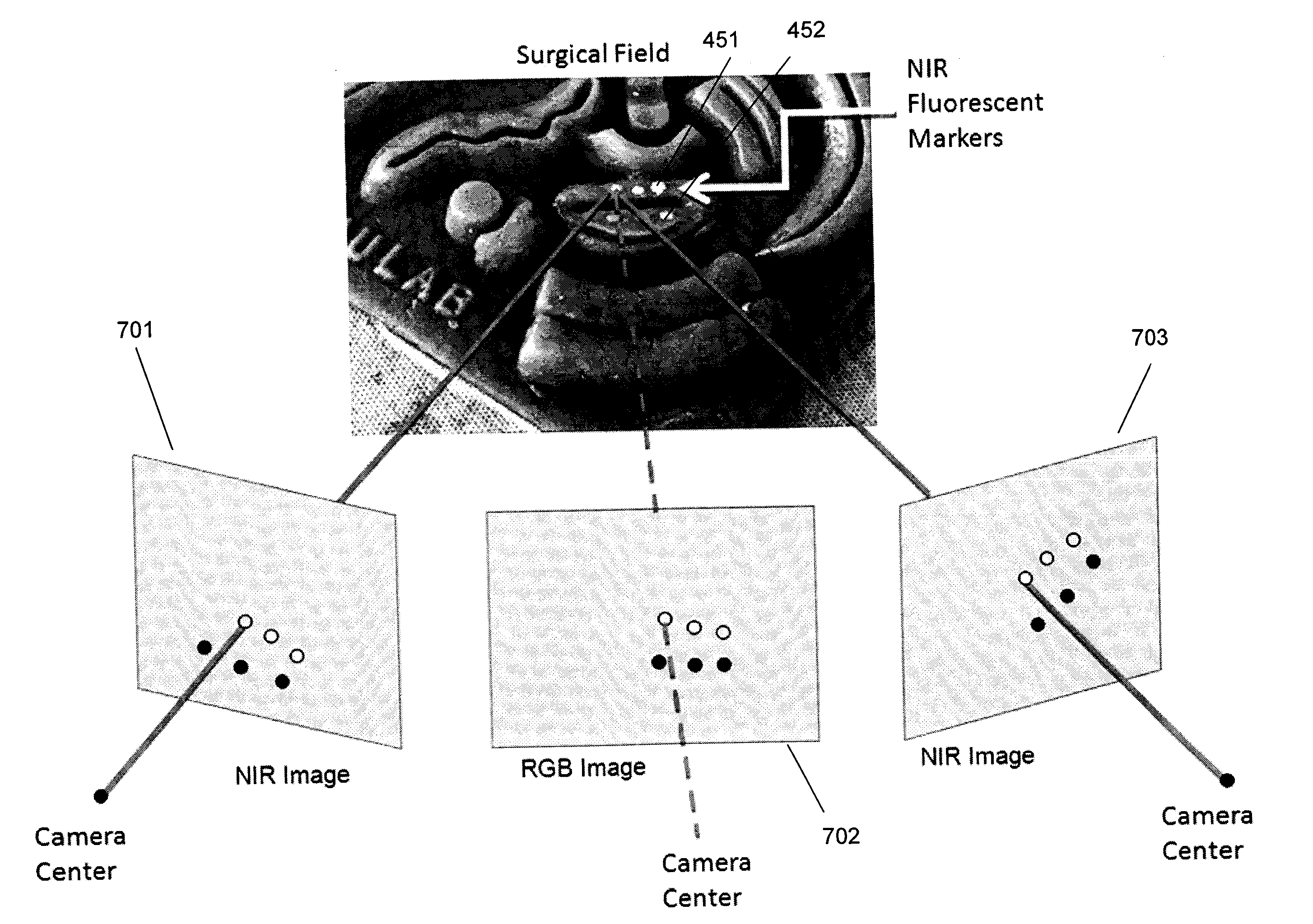
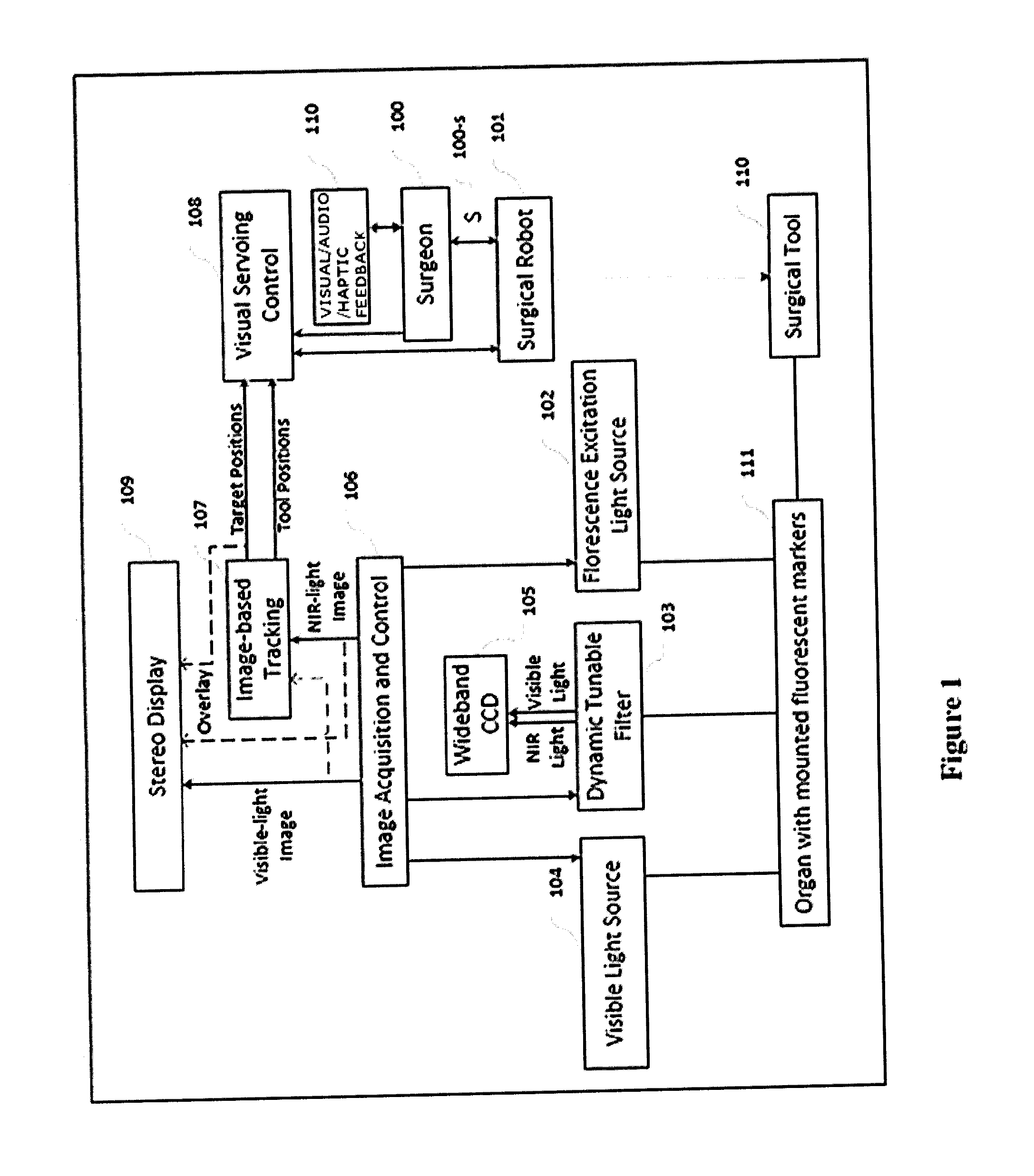
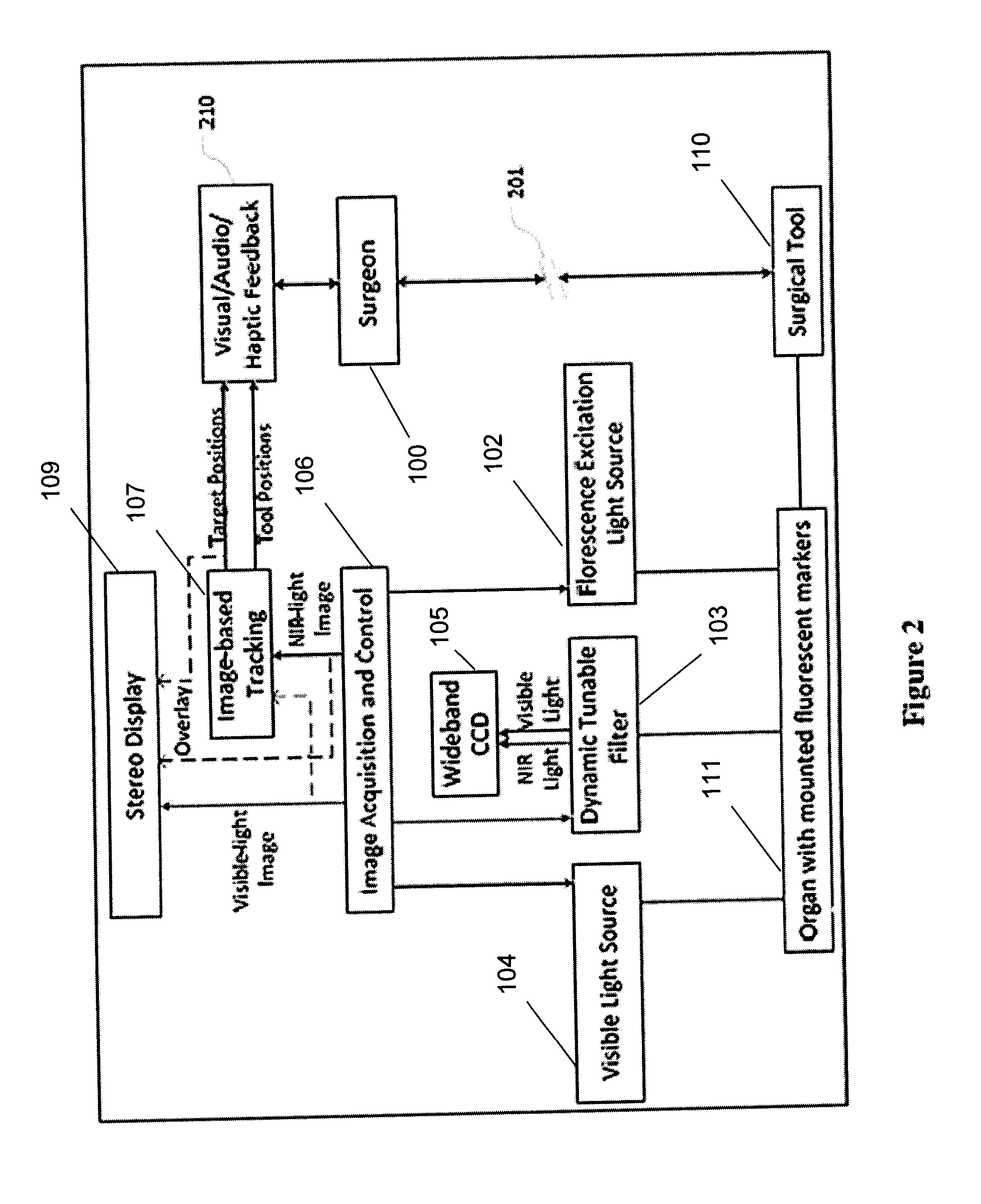
InactiveUS20130274596A1Change is minimalSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostics using spectroscopyDual modeFluorescent light
System and method for tracking and control in medical procedures. The system including a device that deploys fluorescent material on at least one of an organ under surgery and a surgical tool, a visual light source, a fluorescent light source corresponding to an excitation wavelength of the fluorescent material, an image acquisition and control element that controls the visual light source and the fluorescent light source, and captures and digitizes at least one of resulting visual images and fluorescent images, and an image-based tracking module that applies image processing to the visual and fluorescent images, the image processing detecting fluorescent markers on at least one of the organ and the surgical tool.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
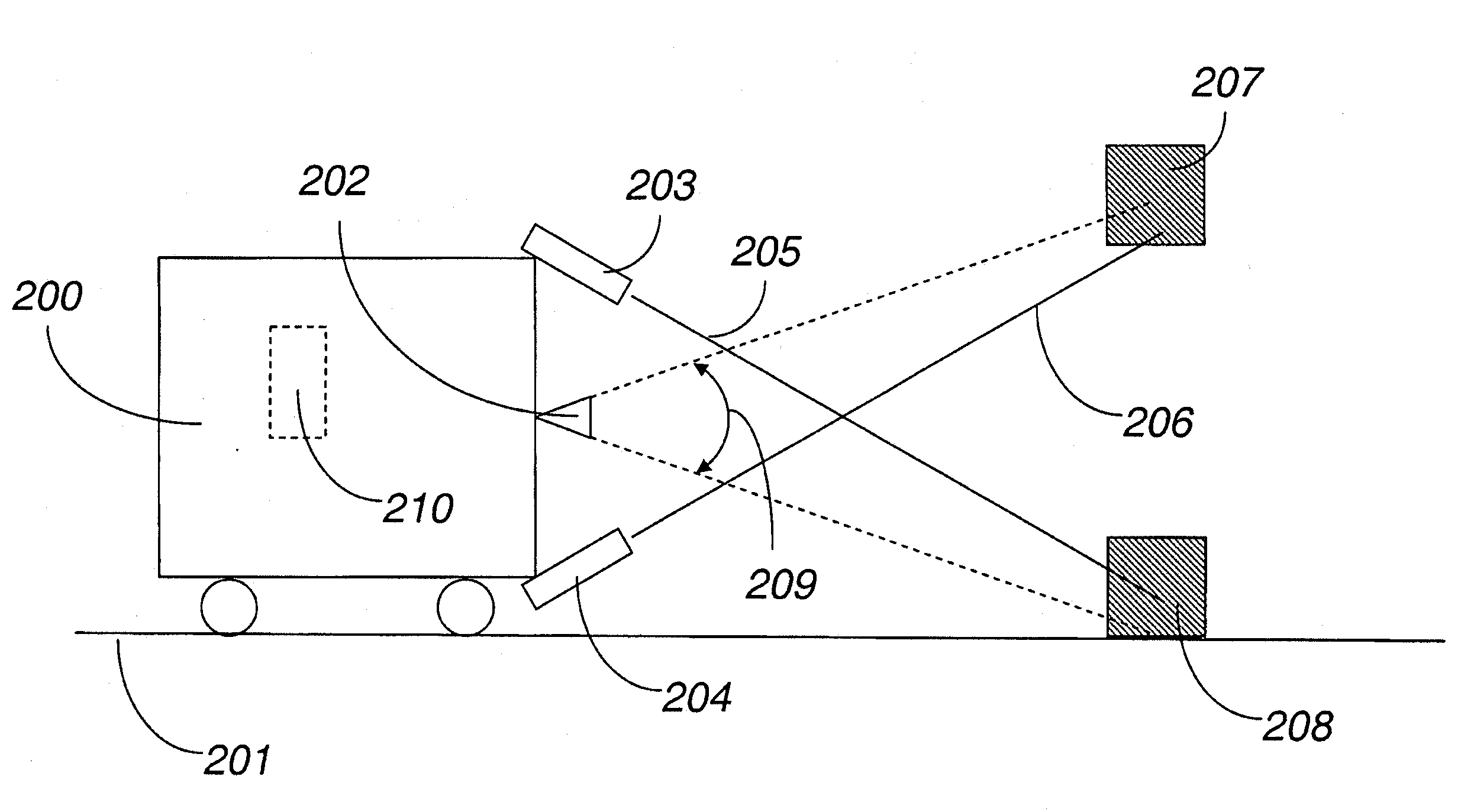
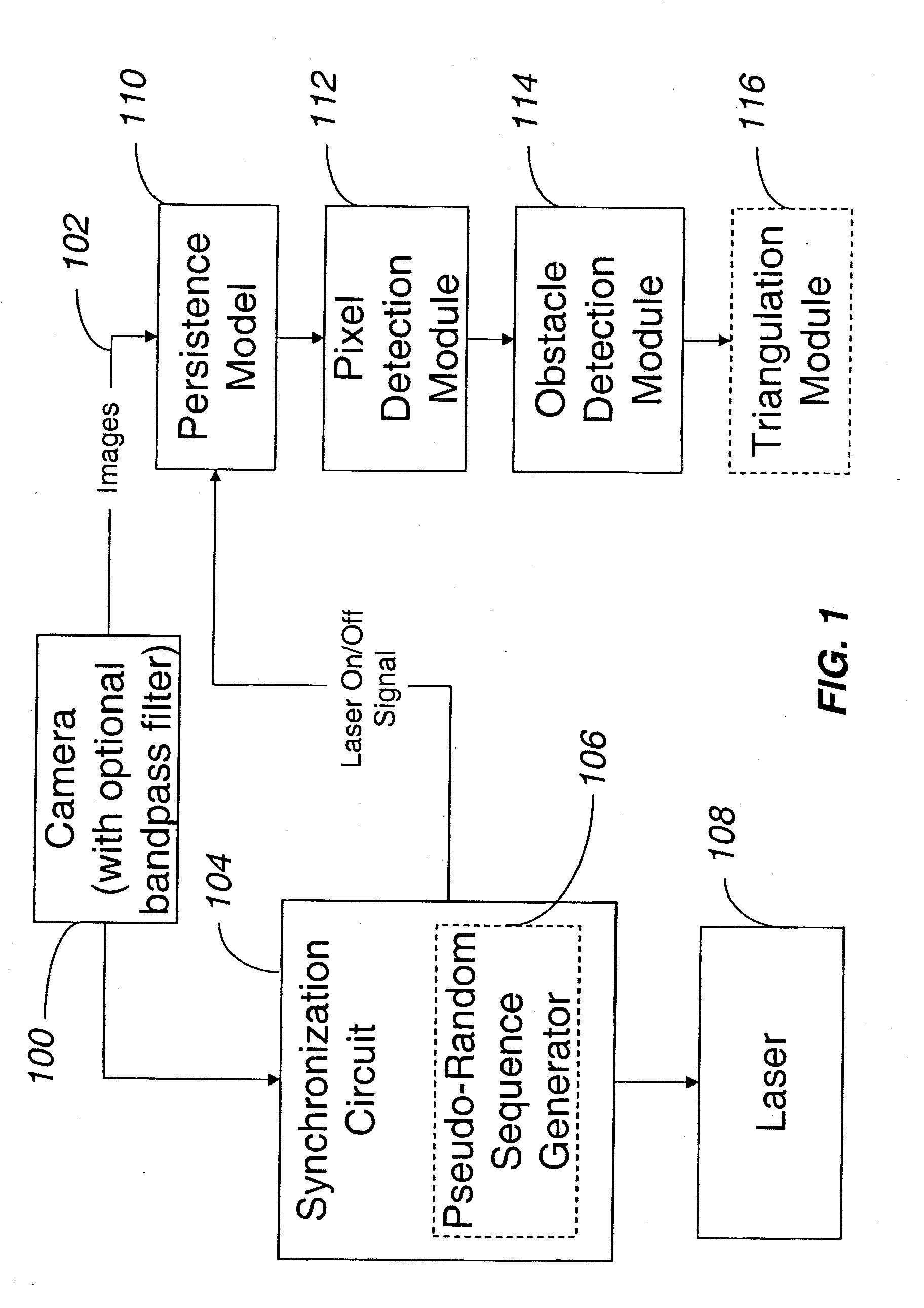
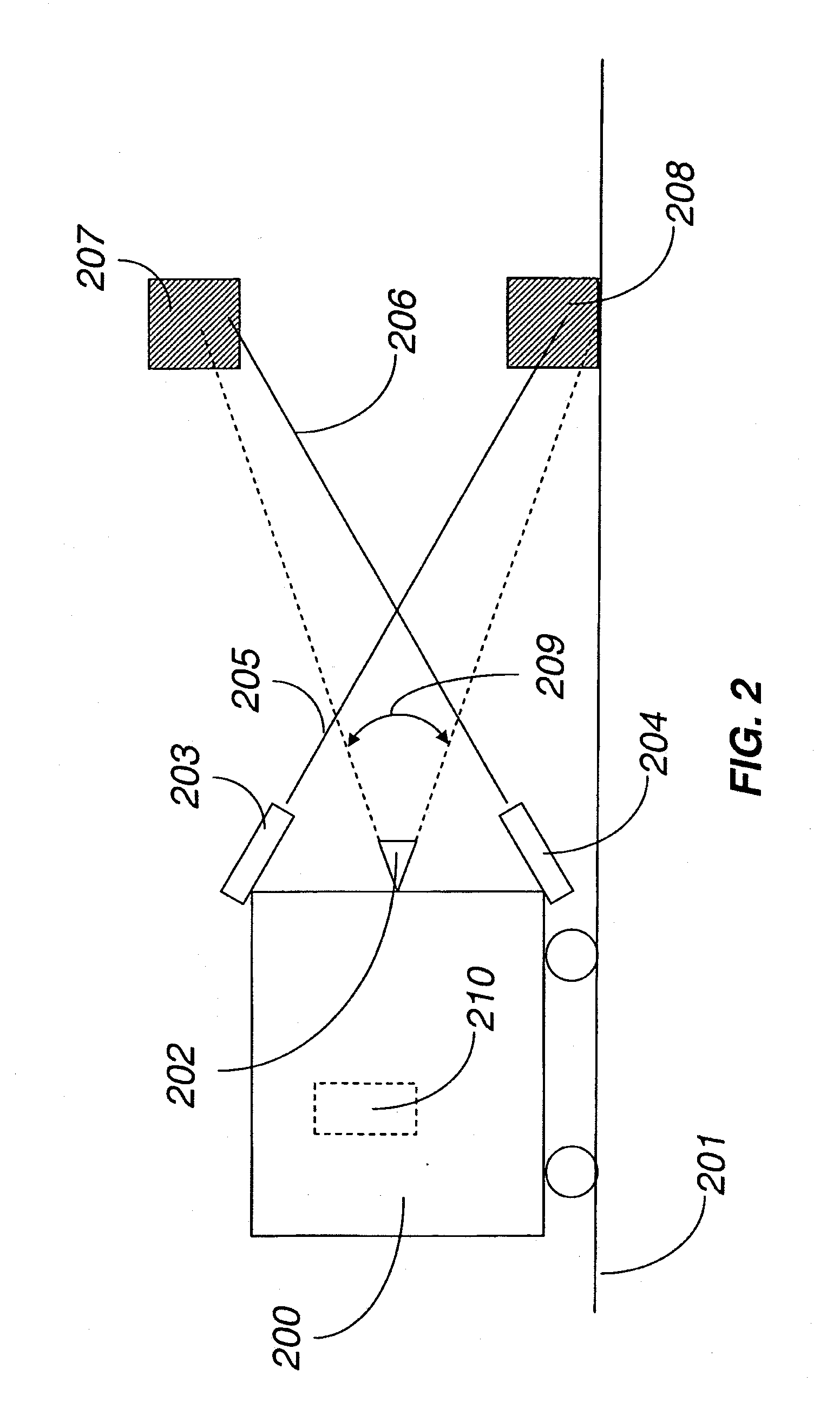
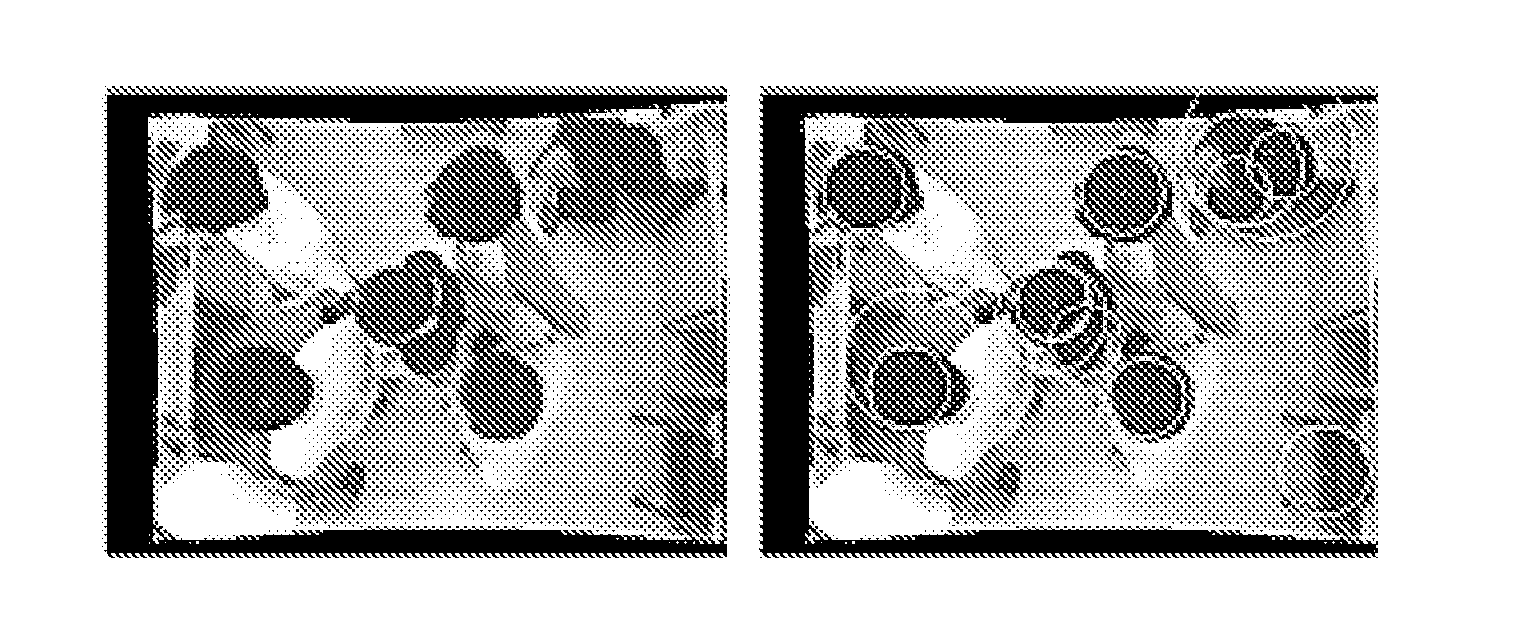
Methods and systems for obstacle detection using structured light
ActiveUS20150168954A1Robust detectionImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlProcessing elementVision sensor
An obstacle detector for a mobile robot while the robot is in motion is disclosed. The detector preferably includes at least one light source configured to project pulsed light in the path of the robot; a visual sensor for capturing a plurality of images of light reflected from the path of the robot; a processing unit configured to extract the reflections from the images; and an obstacle detection unit configured to detect an obstacle in the path of the robot based on the extracted reflections. In the preferred embodiment, the reflections of the projected light are extracted by subtracting pairs of images in which each pair includes a first image captured with the at least one light source on and a second image captured with the at least one light source off, and then combining images of two or more extracted reflections to suppress the background.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
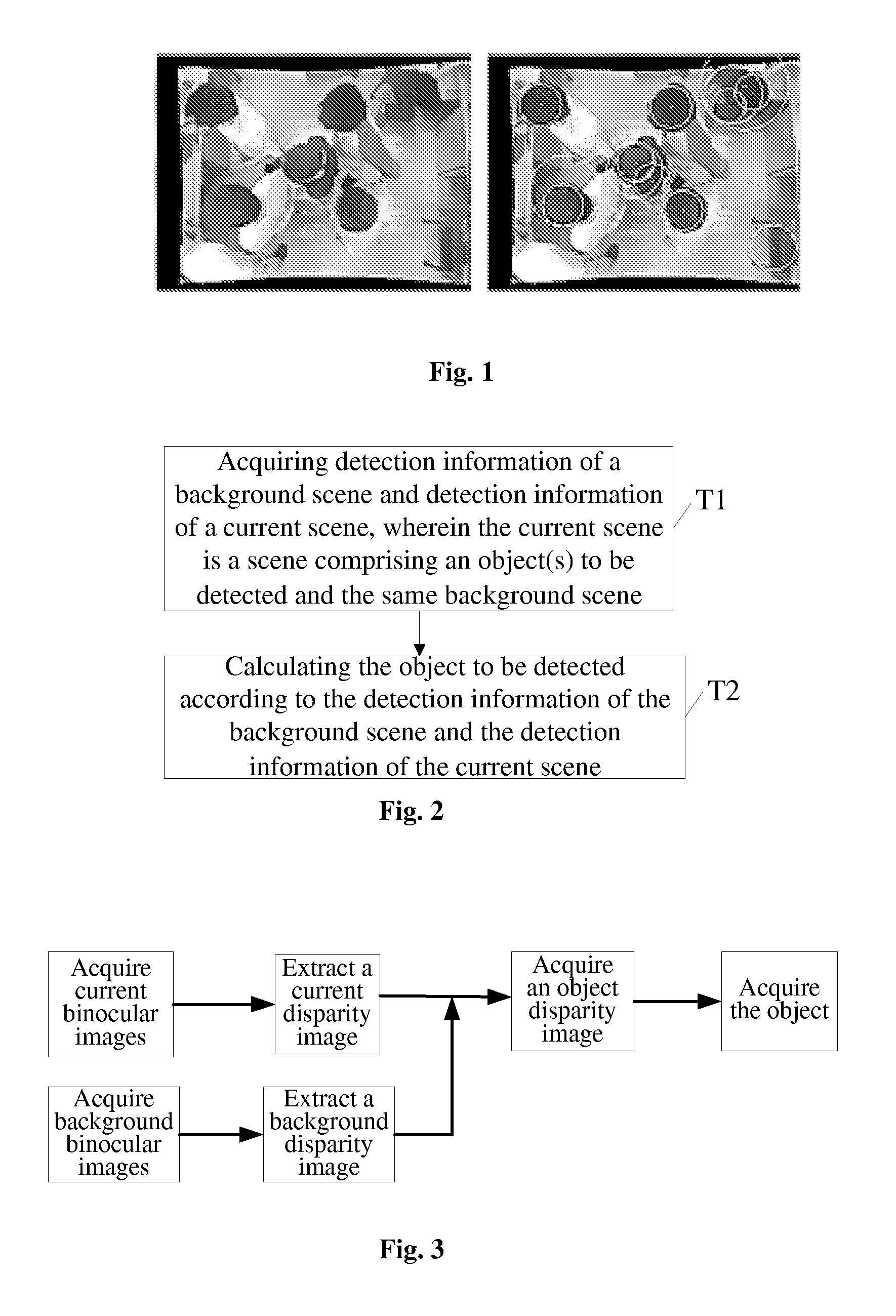
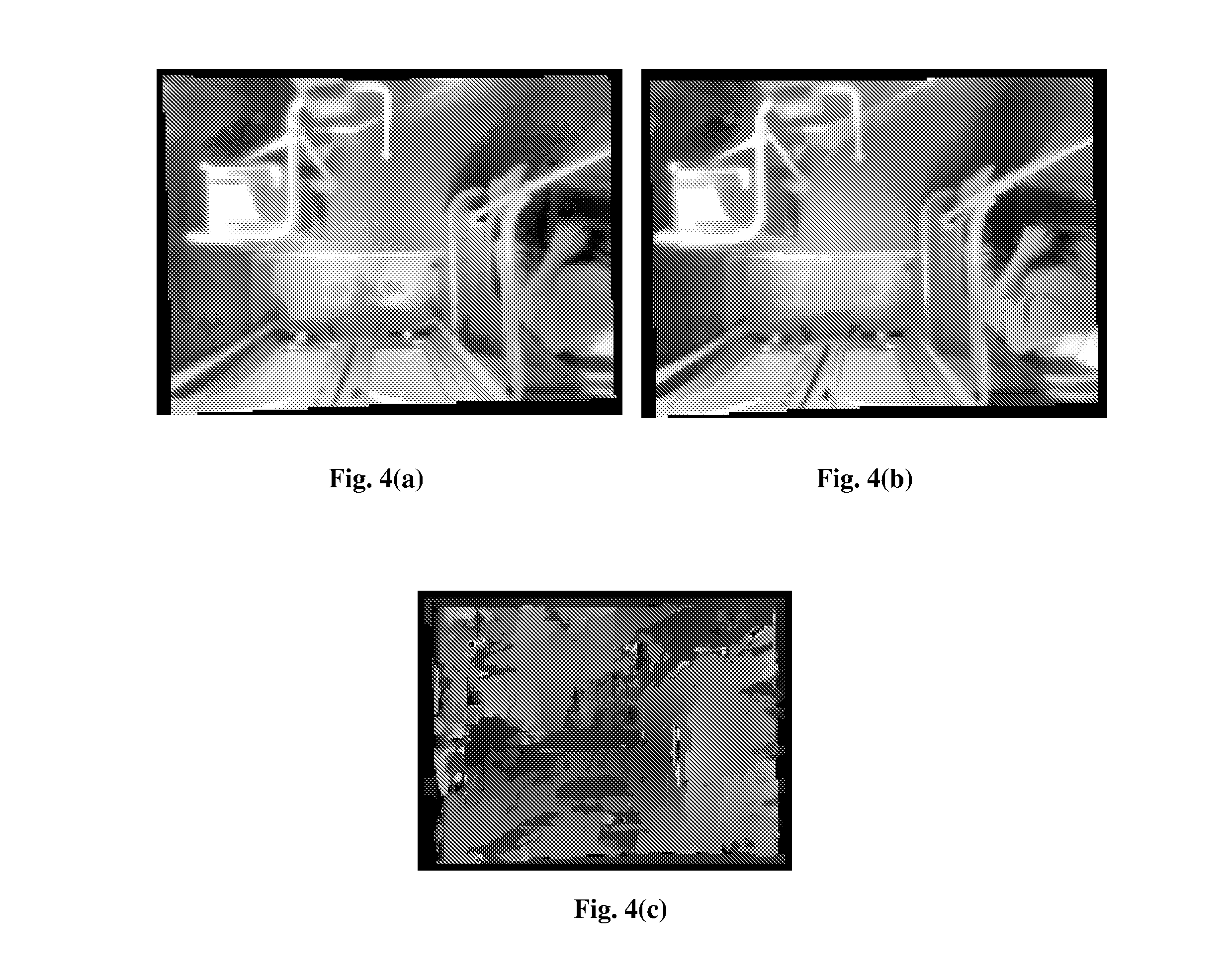
Motion detection method, apparatus and system
ActiveUS20110044502A1Reduce computational complexityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVideo imageLightness
A motion detection method, apparatus and system are disclosed in the present invention, which relates to the video image processing field. The present invention can effectively overcome the influence of the background on motion detection and the problem of object “conglutination” to avoid false detection, thereby accomplishing object detection in complex scenes with a high precision. The motion detection method disclosed in embodiments of the present invention comprises: acquiring detection information of the background scene and detection information of the current scene, wherein the current scene is a scene comprising an object(s) to be detected and the same background scene; and calculating the object(s) to be detected according to the detection information of the background scene and the detection information of the current scene. The present invention is applicable to any scenes where moving objects need to be detected, e.g., automatic passenger flow statistical systems in railway, metro and bus sectors, and is particularly applicable to detection and calibration of objects in places where brightness varies greatly.
Owner:HISENSE
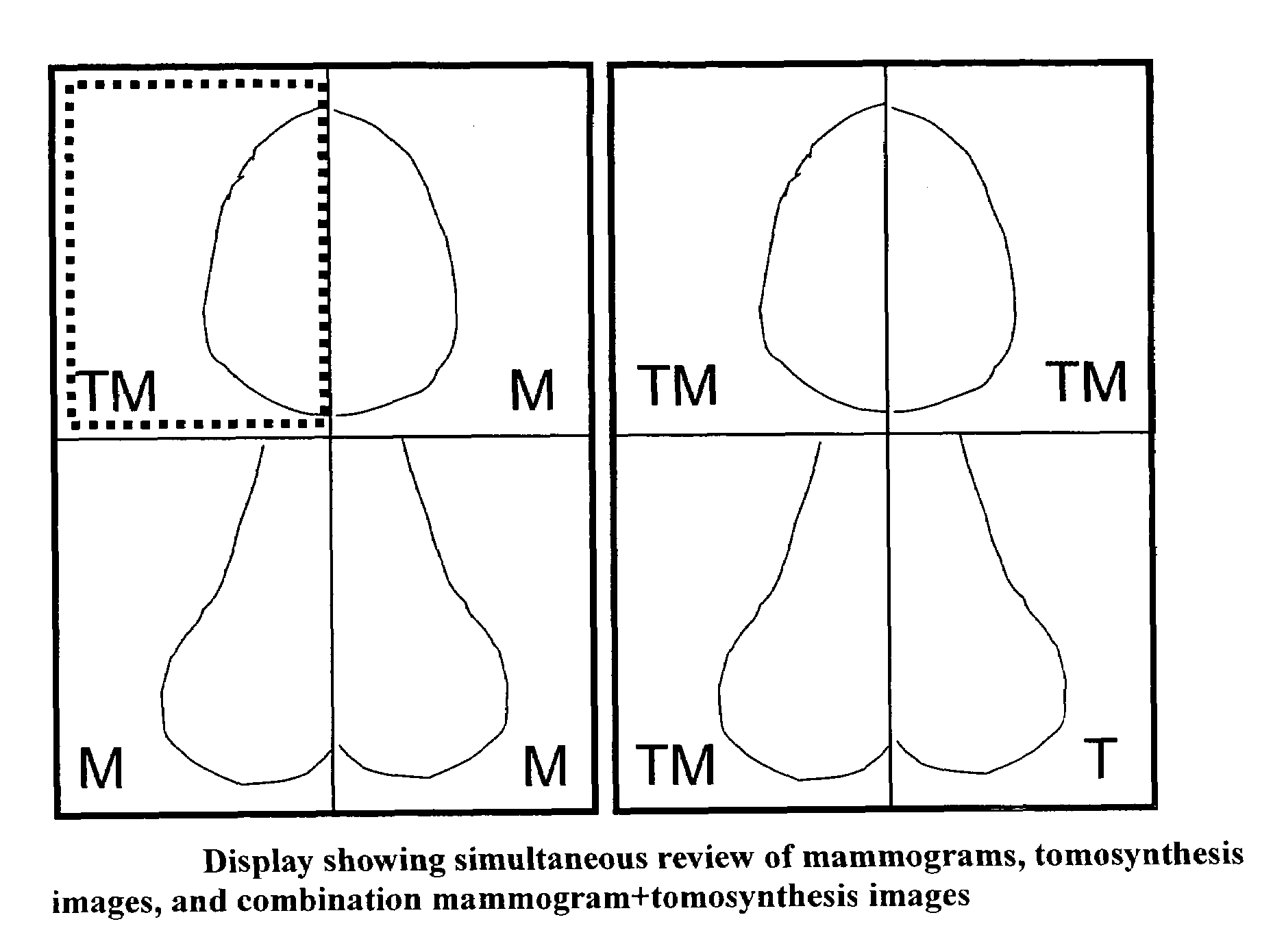
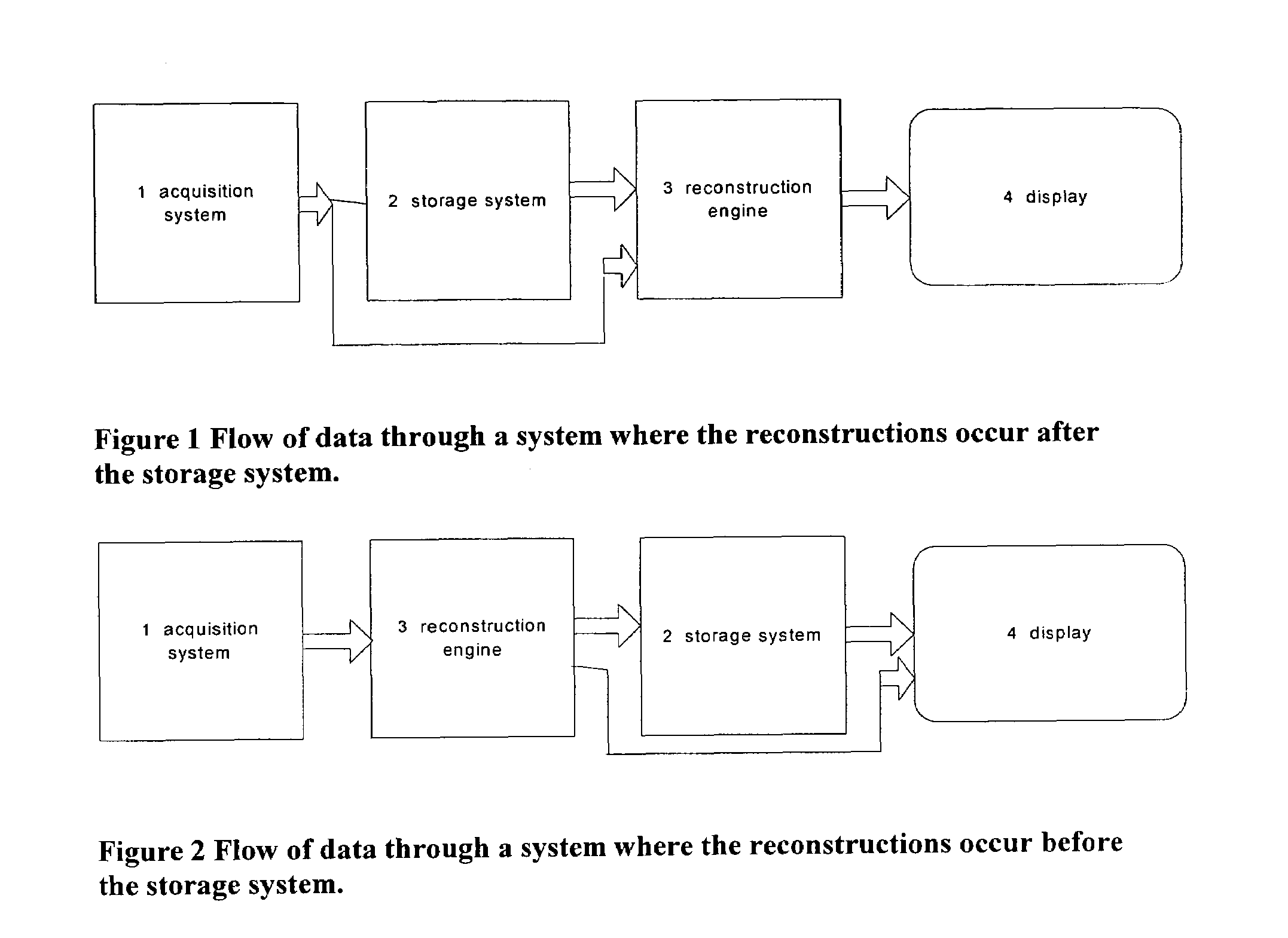
Image handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Apparatus for communicating over a network images captured by a digital camera
InactiveUS20050036034A1Data augmentationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCable transmissionWireless data
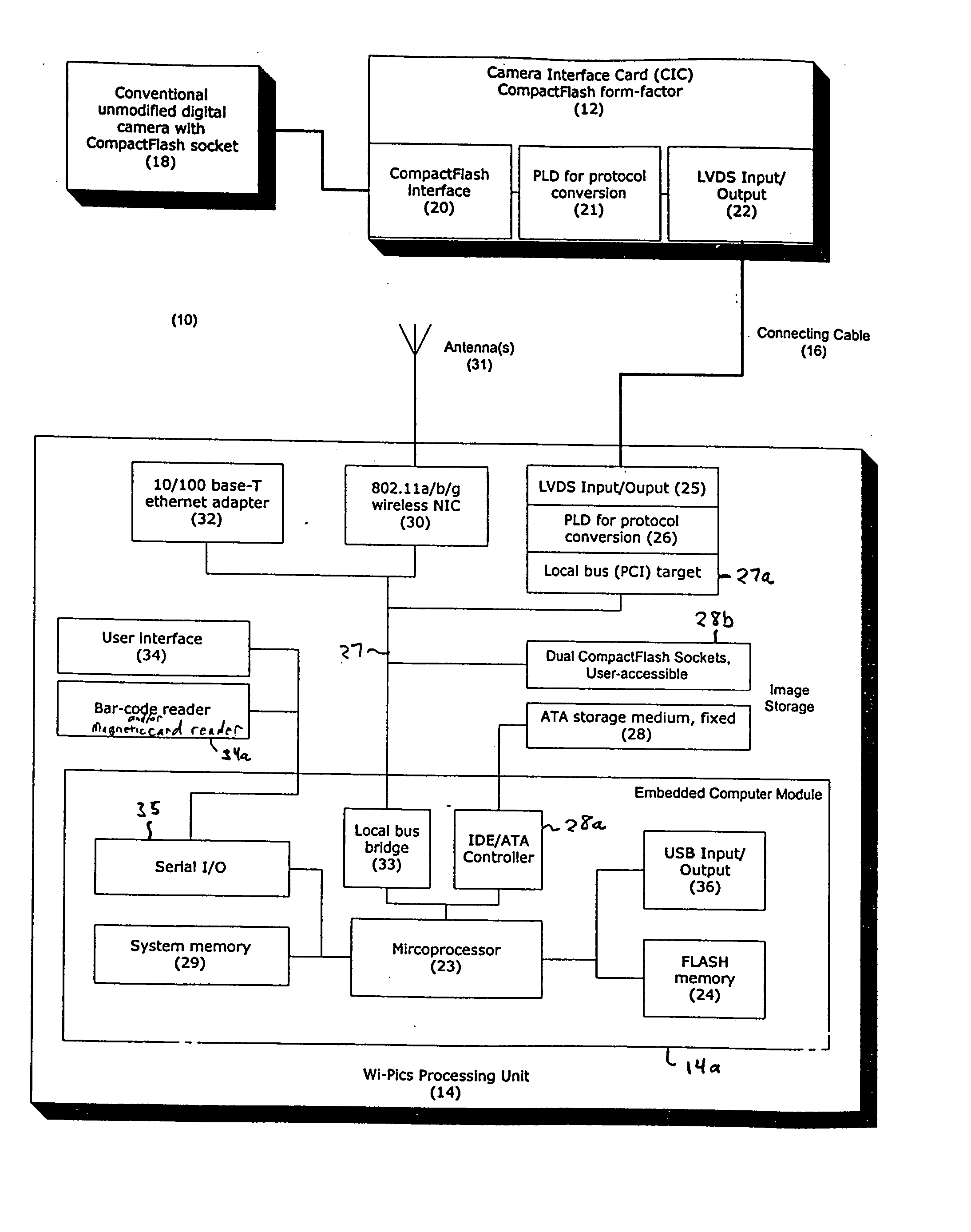
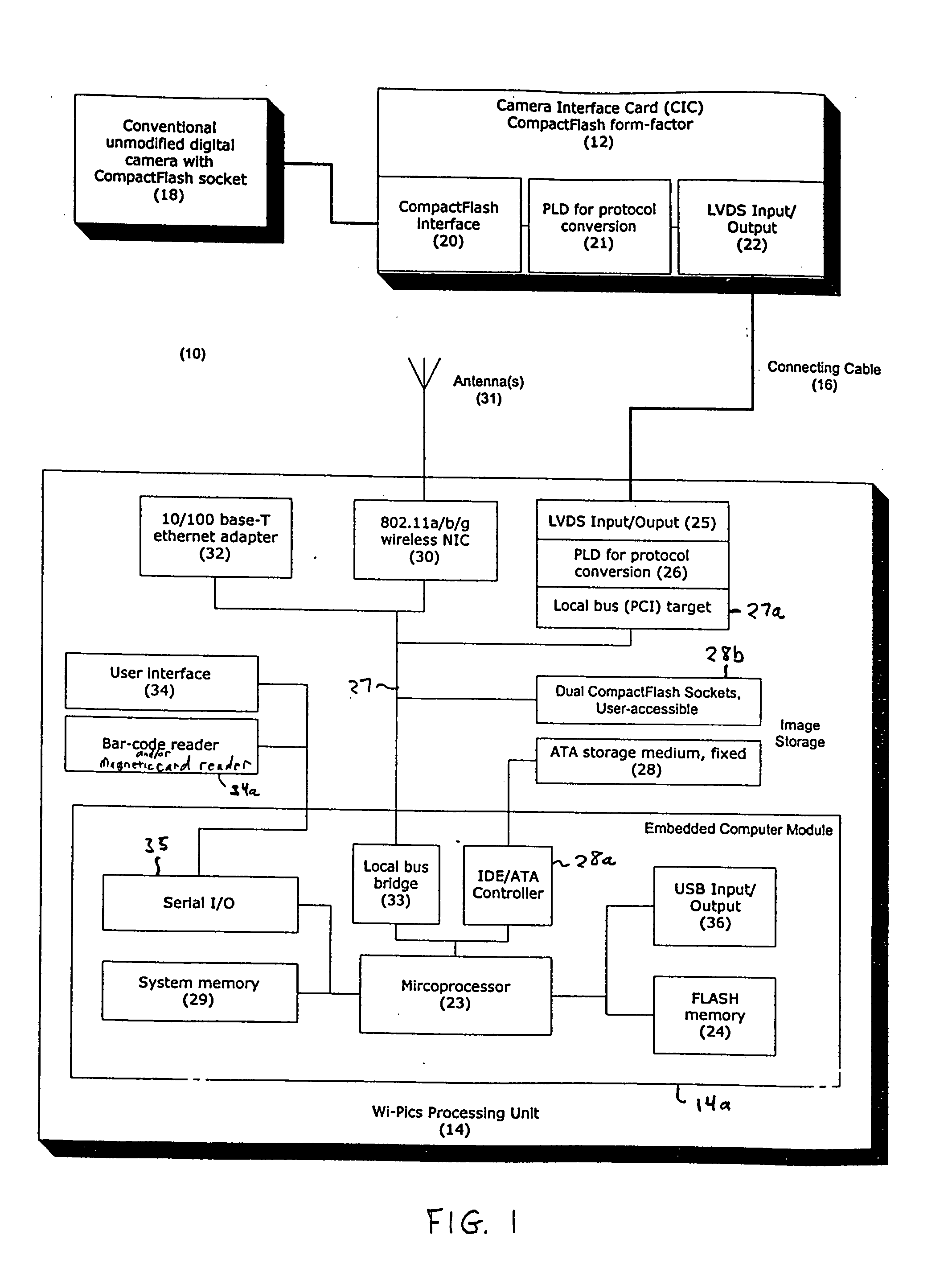
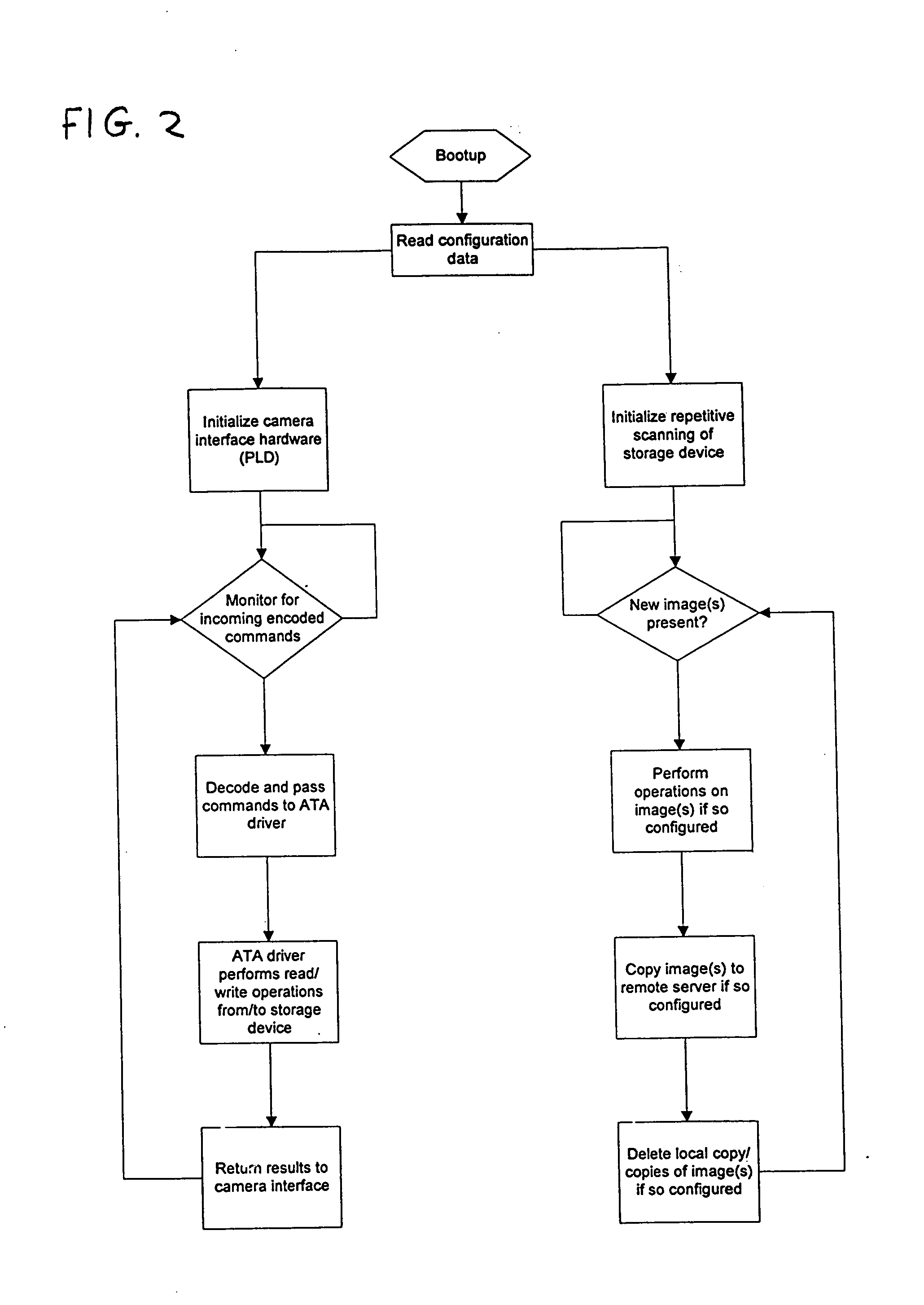
An apparatus is provided for communicating over a network images captured by a digital camera, such as a digital camera without an on-board network interface. The apparatus includes a housing separate from the digital camera having a processing unit with memory for storage of images, a camera interface card received in a memory card slot of the digital camera, and a cable or wireless connection coupling the camera interface card to the processing unit for data communication. The apparatus emulates a memory card to the digital camera, such that the digital camera's electronics operate with the memory of the processing unit through the camera interface card, as if such memory was on a memory card located in slot of the digital camera. Images captured by the digital camera are transferred, via the camera interface card and cable, to memory of the processing unit, and the digital camera can access images stored in memory of the processing unit. The processing unit has a wireless data network interface and Ethernet communication interface, whereby captured images stored in memory of the processing unit are queued in real-time for network transfer, and subsequently transferred via one of the network communication interfaces, to a computer system, such as an web site or file server, at a network destination address configurable in the processing unit. Data may be inputted by the user before and / or after image capture for association with images prior to their network transfer. The housing for the processing unit may be shaped like a motor drive unit and attached to the bottom of the camera, or worn by the user of the camera in the form of a belt pack or backpack.
Owner:UNITED IMAGING SOLUTIONS
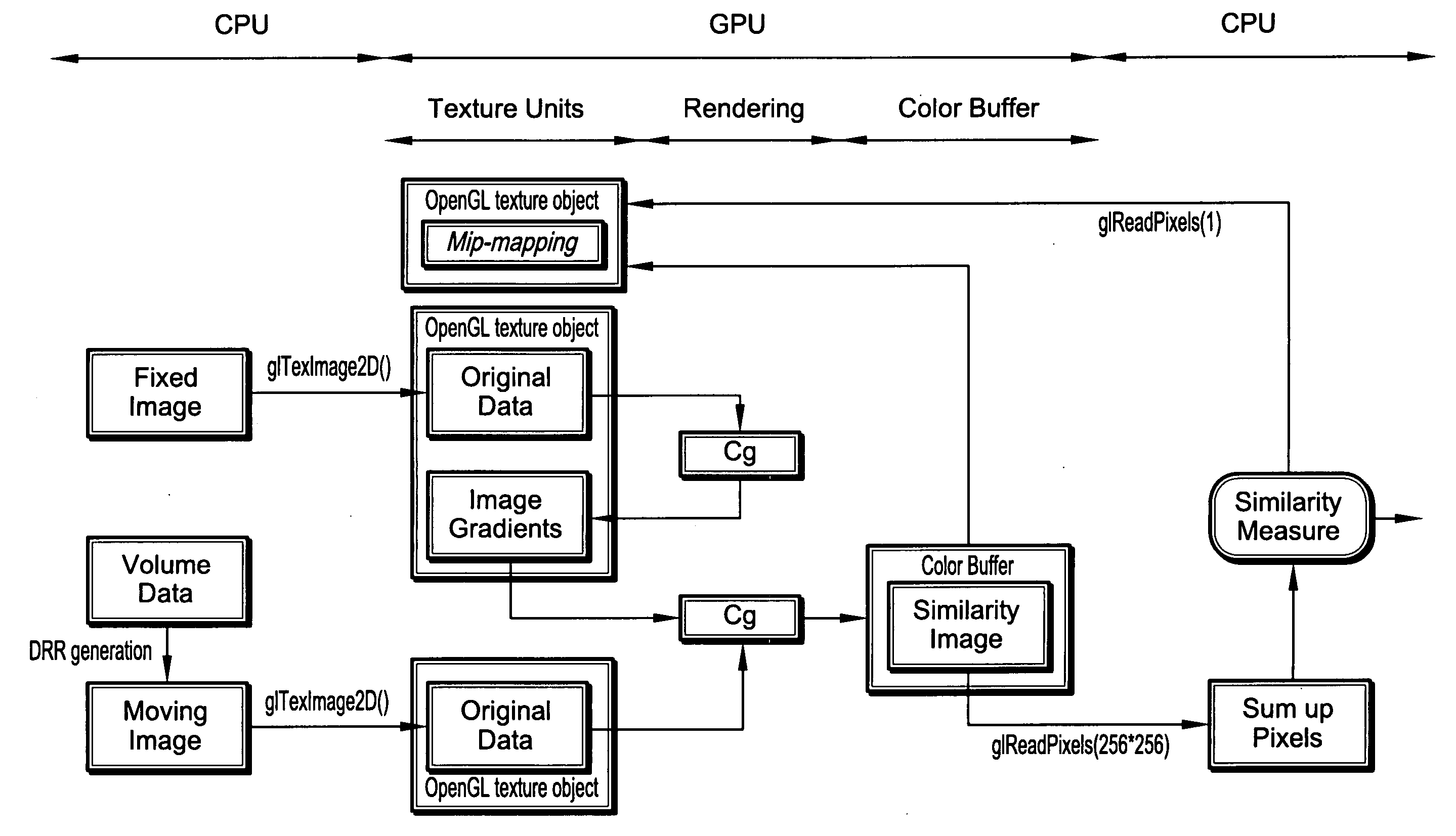
GPU-based image manipulation method for registration applications
Exemplary systems and methods for performing registration applications are provided. An exemplary system includes a central processing unit (CPU) for transferring a plurality of images to a graphics processing unit (GPU); wherein the GPU performs a registration application on the plurality of images to produce a registration result, and wherein the GPU returns the registration result to the CPU. An exemplary method includes the steps of transferring a plurality of images from a central processing unit (CPU) to a graphics processing unit (GPU); performing a registration application on the plurality of images using the GPU; transferring the result of the step of performing from the GPU to CPU.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Computer vision systems
ActiveUS20180018508A1High degreePromote exchangeCharacter and pattern recognitionReal-time dataHome environment
Owner:UNIFAI HLDG LTD
Image processing apparatus, image display method, and image display program
ActiveUS8875044B2Fast imagingEasy to findInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingLocation detectionComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus includes an image display element, an instruction position detection unit for accepting an instruction operation from a user through an operation face provided to a display screen of the image display element and detecting and outputting an instruction position of the instruction operation with respect to the operation face, a storage unit for storing and holding image data of images, and a display control unit for performing a control for displaying an image in accordance with the stored and held image data on the image display element, in which when the user performs a continuous movement on the operation face, the display control unit performs a control for scrolling the display image while being reduced together with images before and after the display image in accordance with a direction of the operation determined on the basis of a detection output from the instruction position detection unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Three-dimensional image processing apparatus
InactiveUS6421056B1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementImaging processingThree-dimensional space
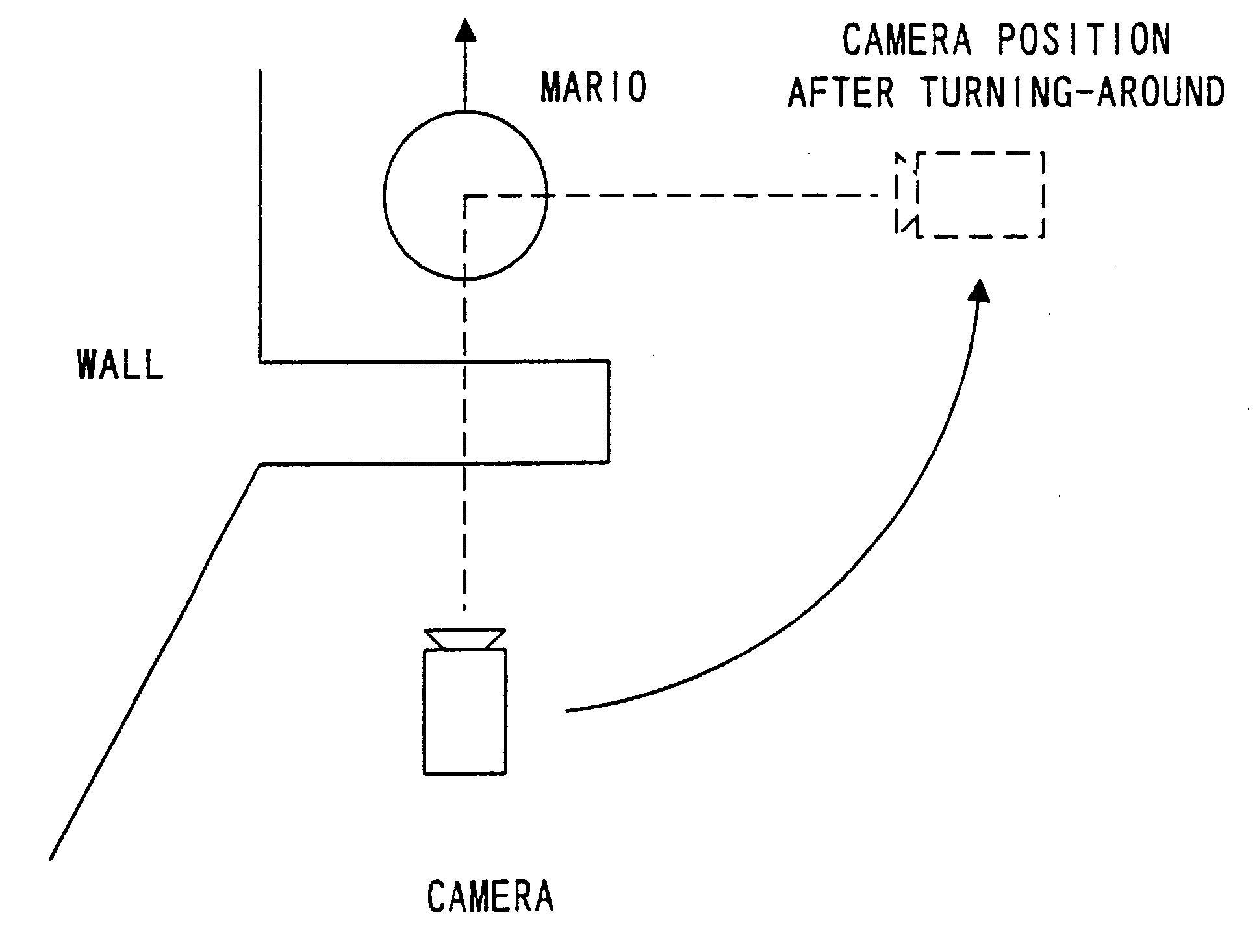
A three-dimension image processing apparatus includes a CPU. When the CPU detects by collision determination that another object, e.g., a wall, is existent between an operable object and a camera, it calculates such a moving angle of the camera that an eye of the camera to the operable object is not obstructed by the other object. The camera is moved in accordance with the moving angle to a position where the operable object and the other object existing in a photographed three-dimensional space are displayed on a display.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Image data processing system and image data processing server
InactiveUS20030163833A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsSubstation equipmentData processing systemImaging data
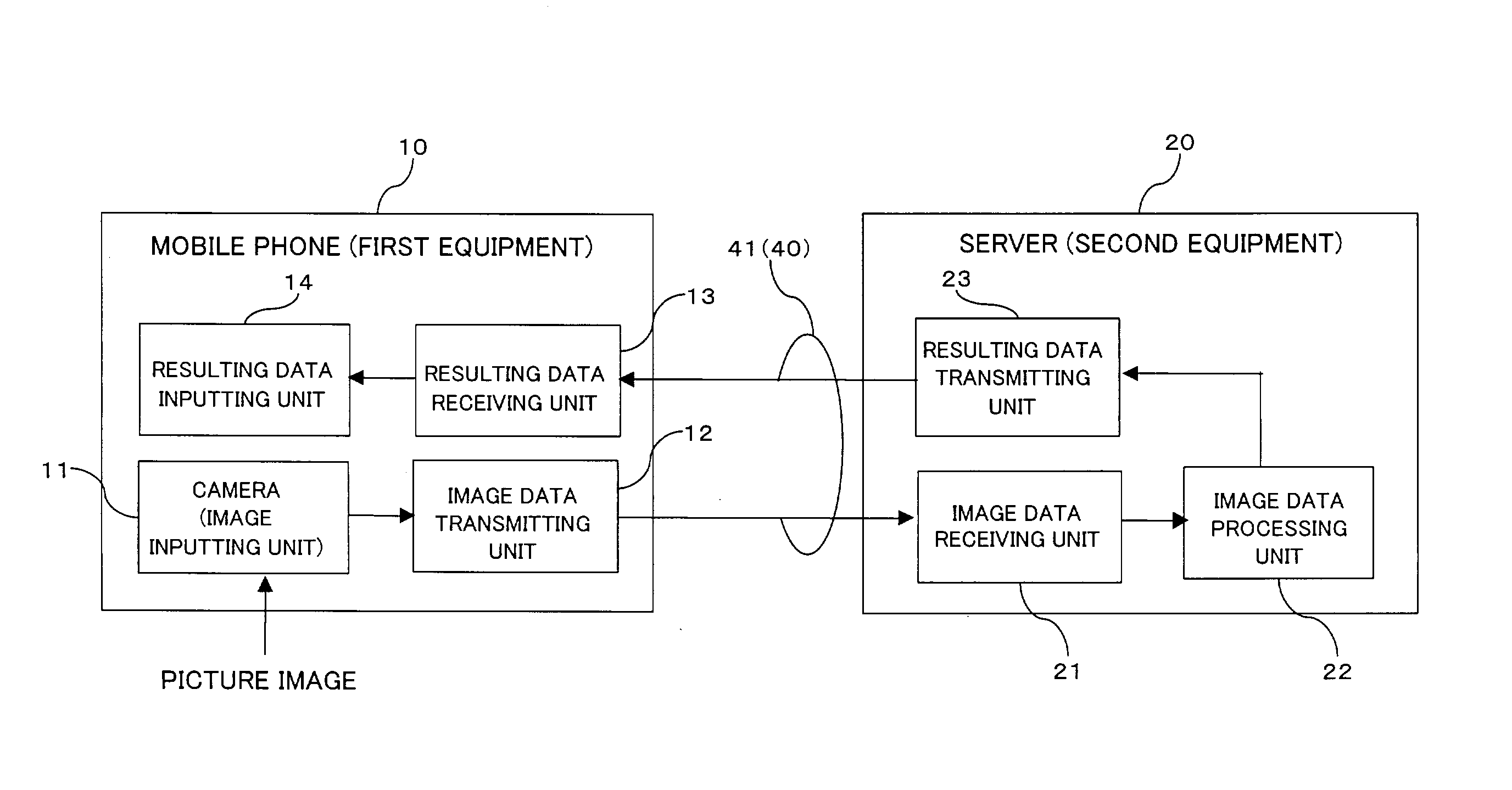
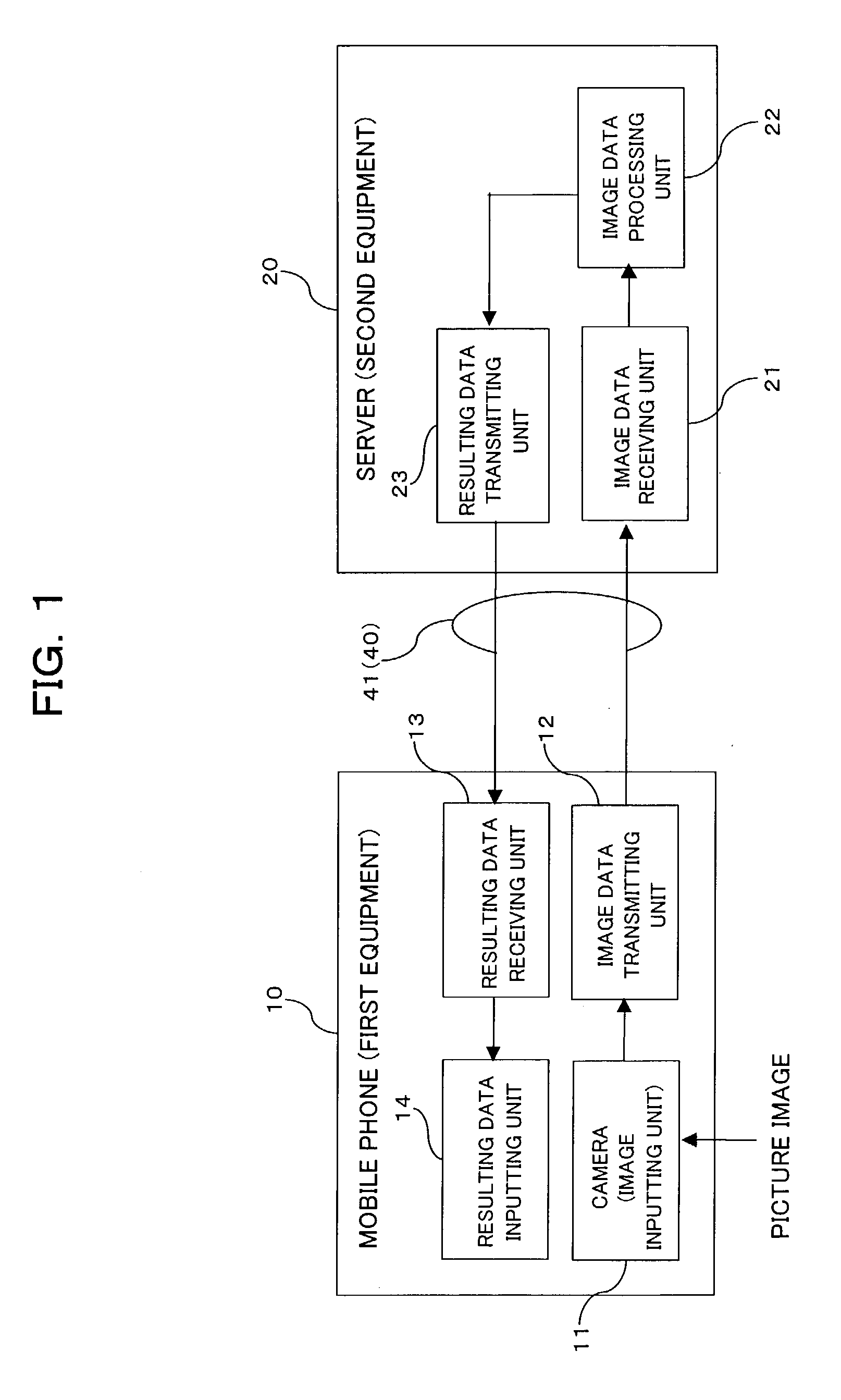
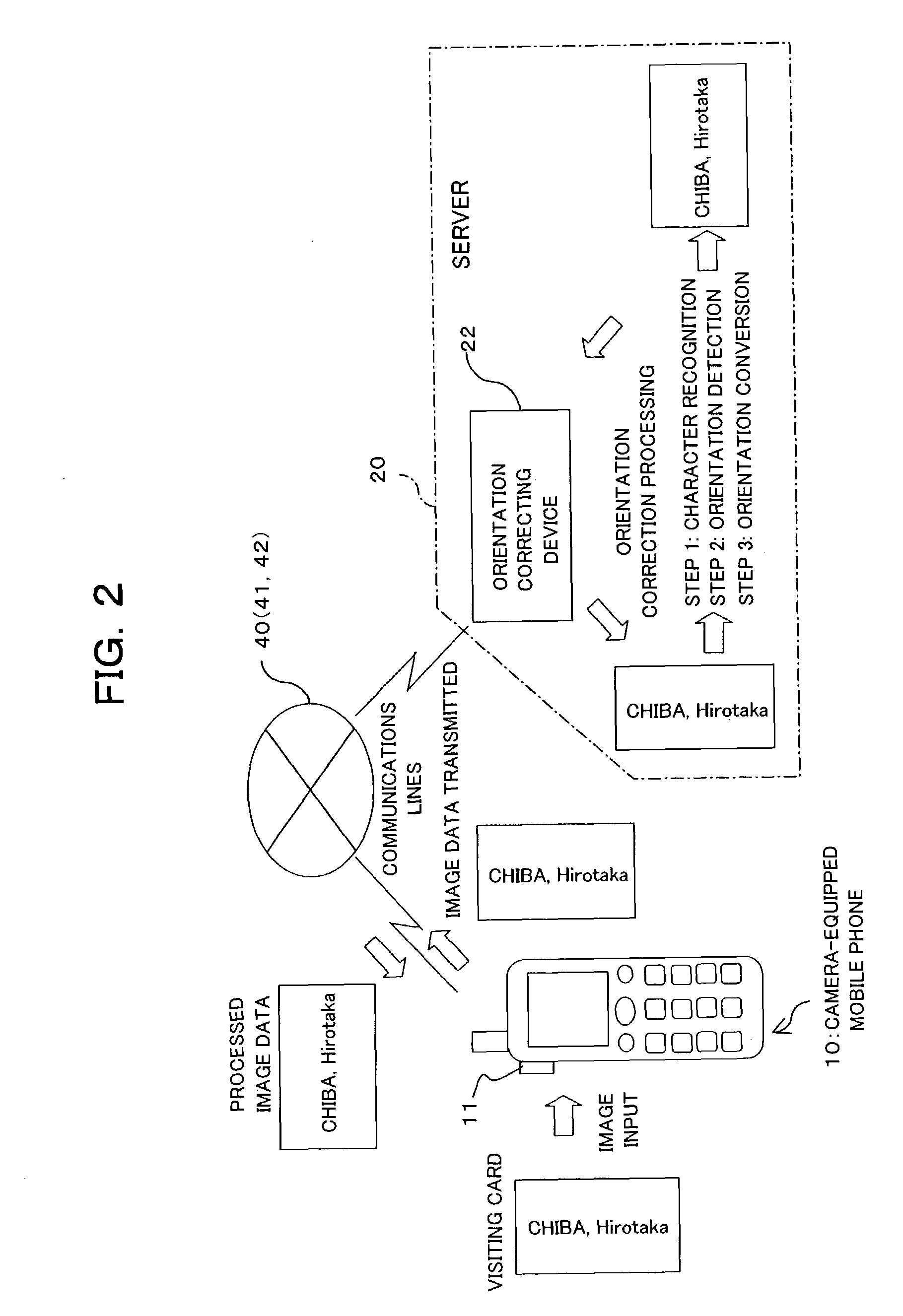
The system performs complicated processing at high speed on image data which is obtained by a camera-equipped mobile phone, thereby reducing the time required for image data processing. The system includes first equipment and second equipment, communicably interconnected each other with a first communication path. The first equipment includes: an image inputting unit for obtaining image information in the form of image data; and an image data transmitting unit for transmitting the image data, which has been obtained by the image inputting unit, to the second equipment over the first communication path. The second equipment includes: an image data receiving unit for receiving the image data, which has been transmitted over the first communication path, from the first equipment; and an image data processing unit for processing the image data, which has been obtained by the image data receiving unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
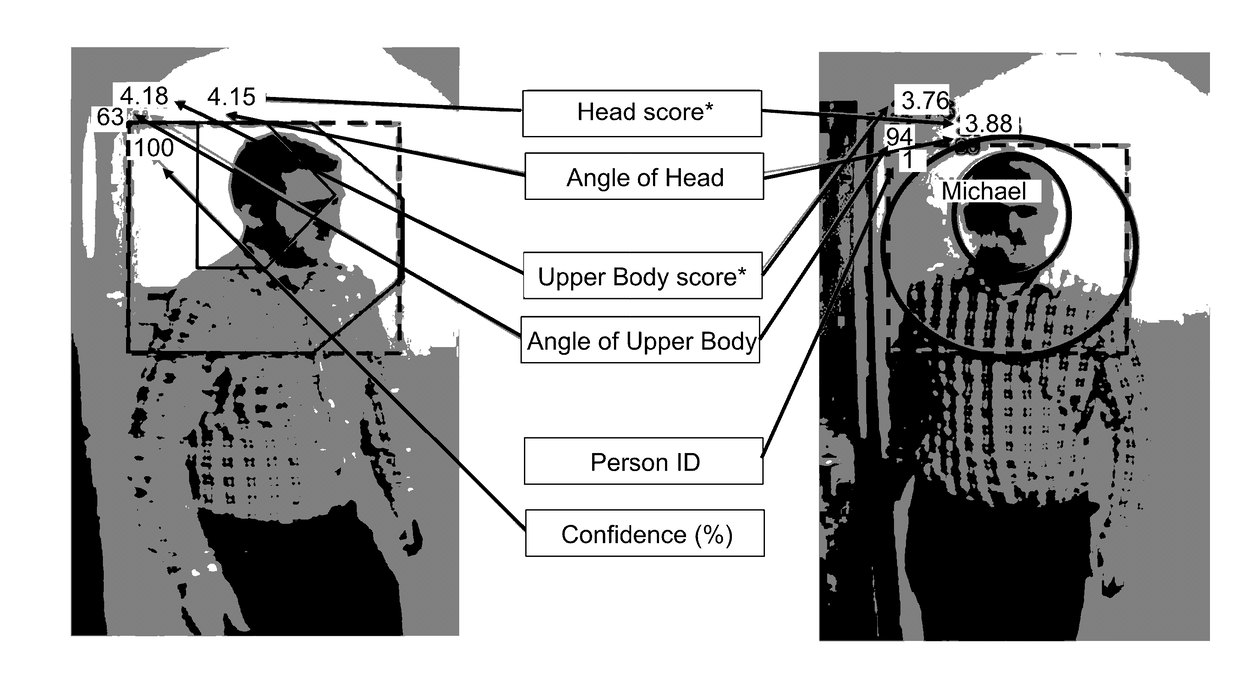
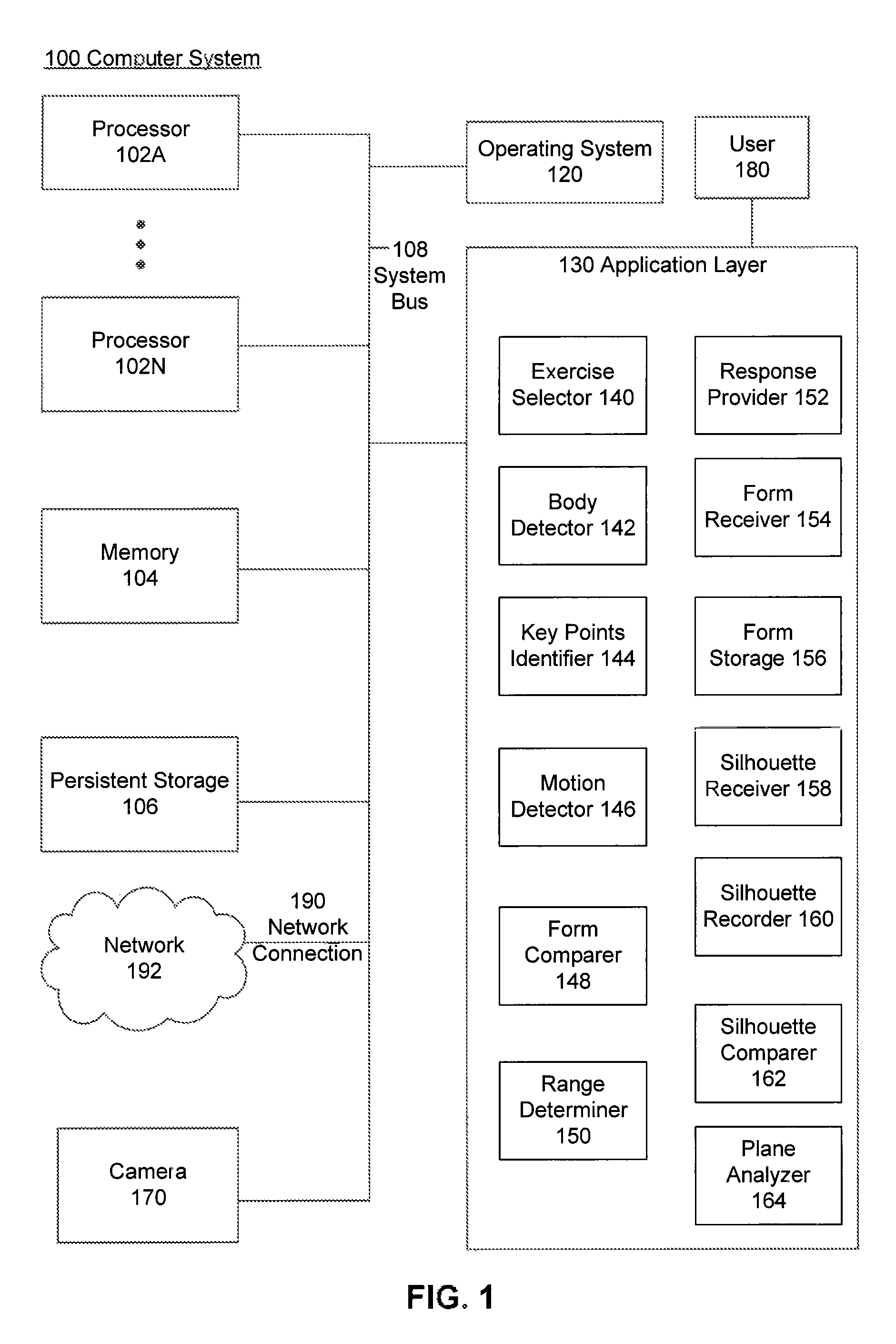
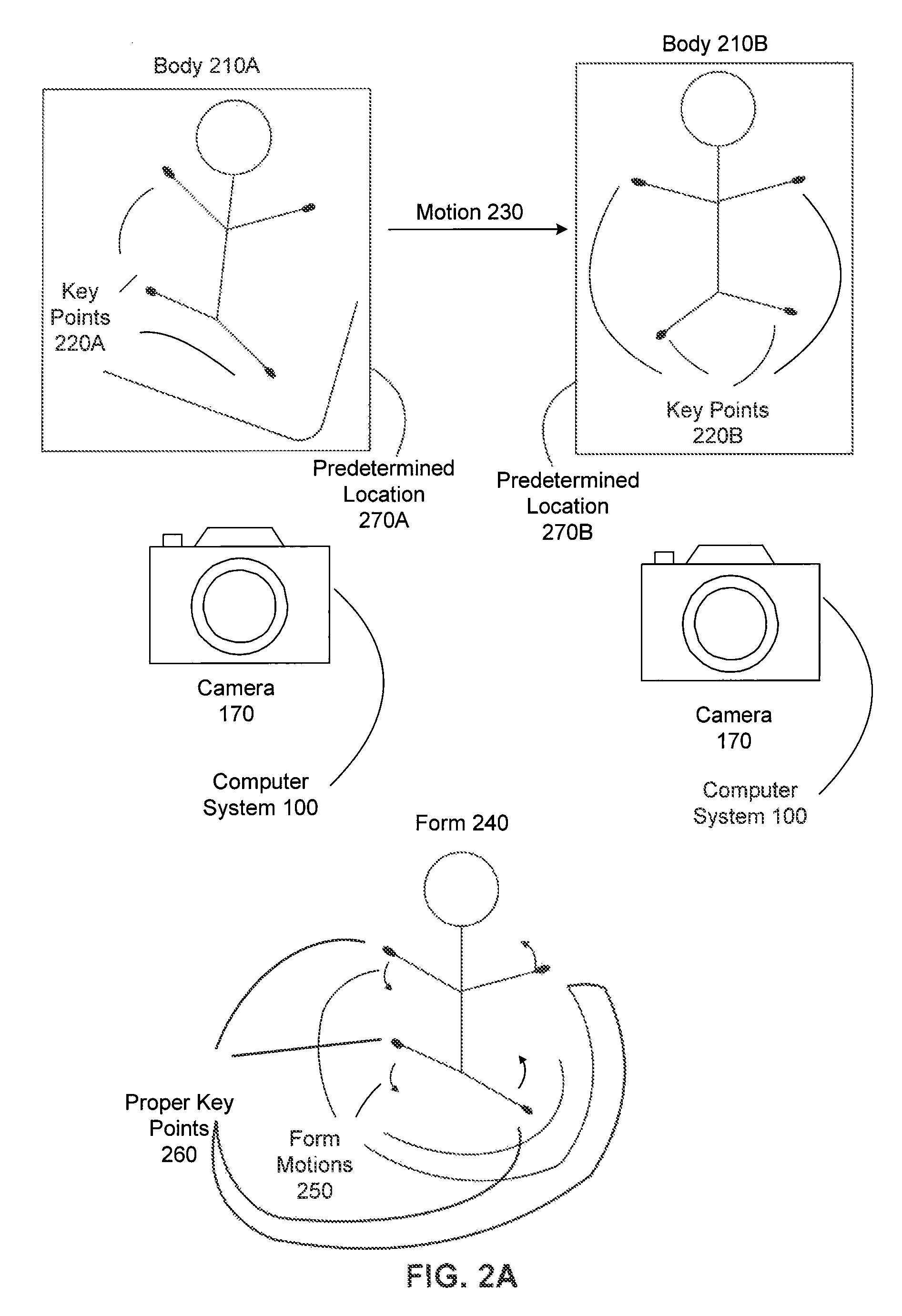
Physical training assistant system
InactiveUS9154739B1Physical therapies and activitiesImage enhancementCrucial pointHuman–computer interaction
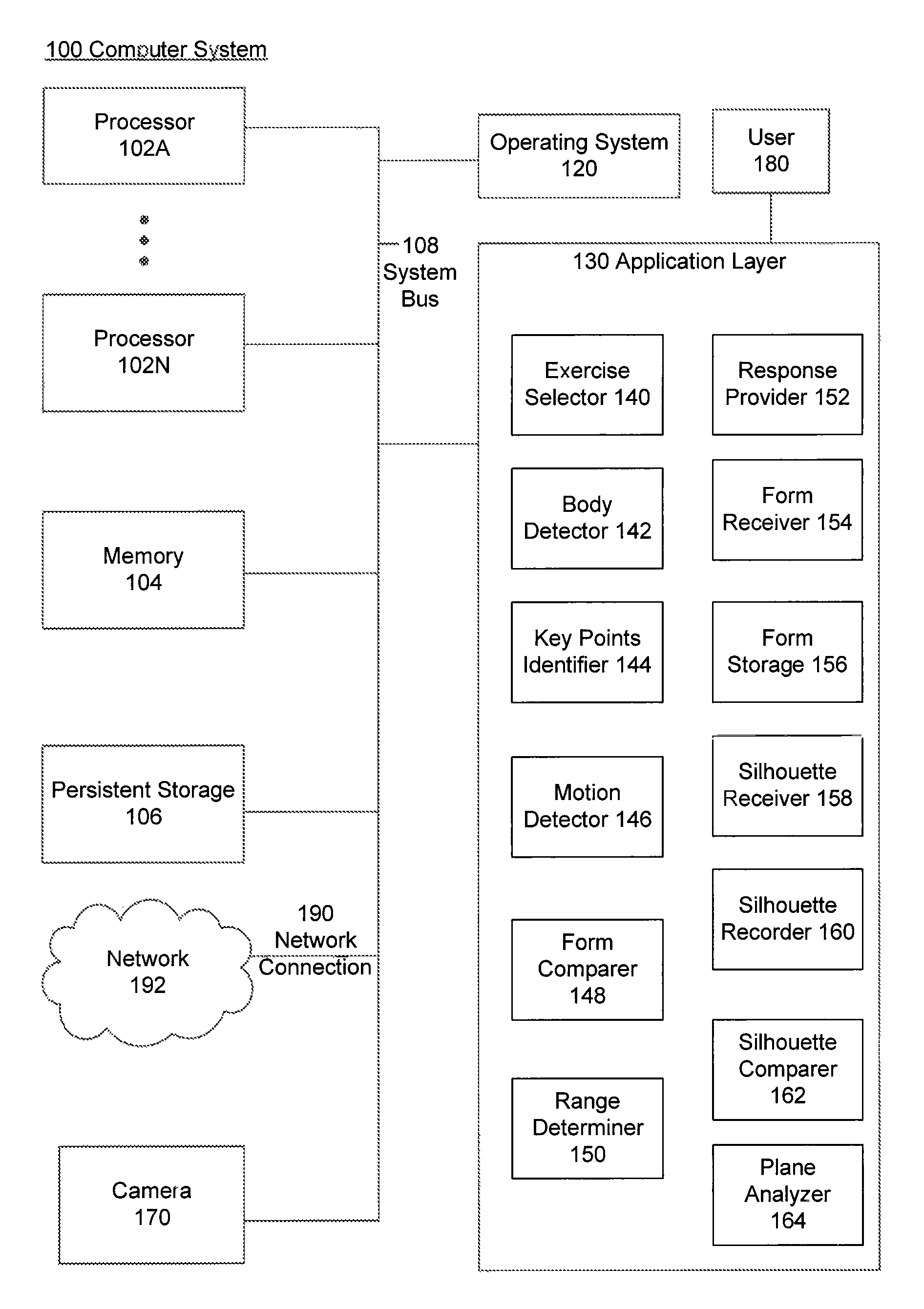
A computer-implemented method, a system and a computer-readable medium provide useful feedback for a user involved in exercise. A camera is used to track user motion by using image processing techniques to identify key points on a user's body and track their motion. The tracked points are compared to proper form for an exercise, and an embodiment gives feedback based on the relationship between the actual movement of the user and the proper form. Alternatively, silhouette information may be used in a similar manner in another embodiment.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com