Patents
Literature
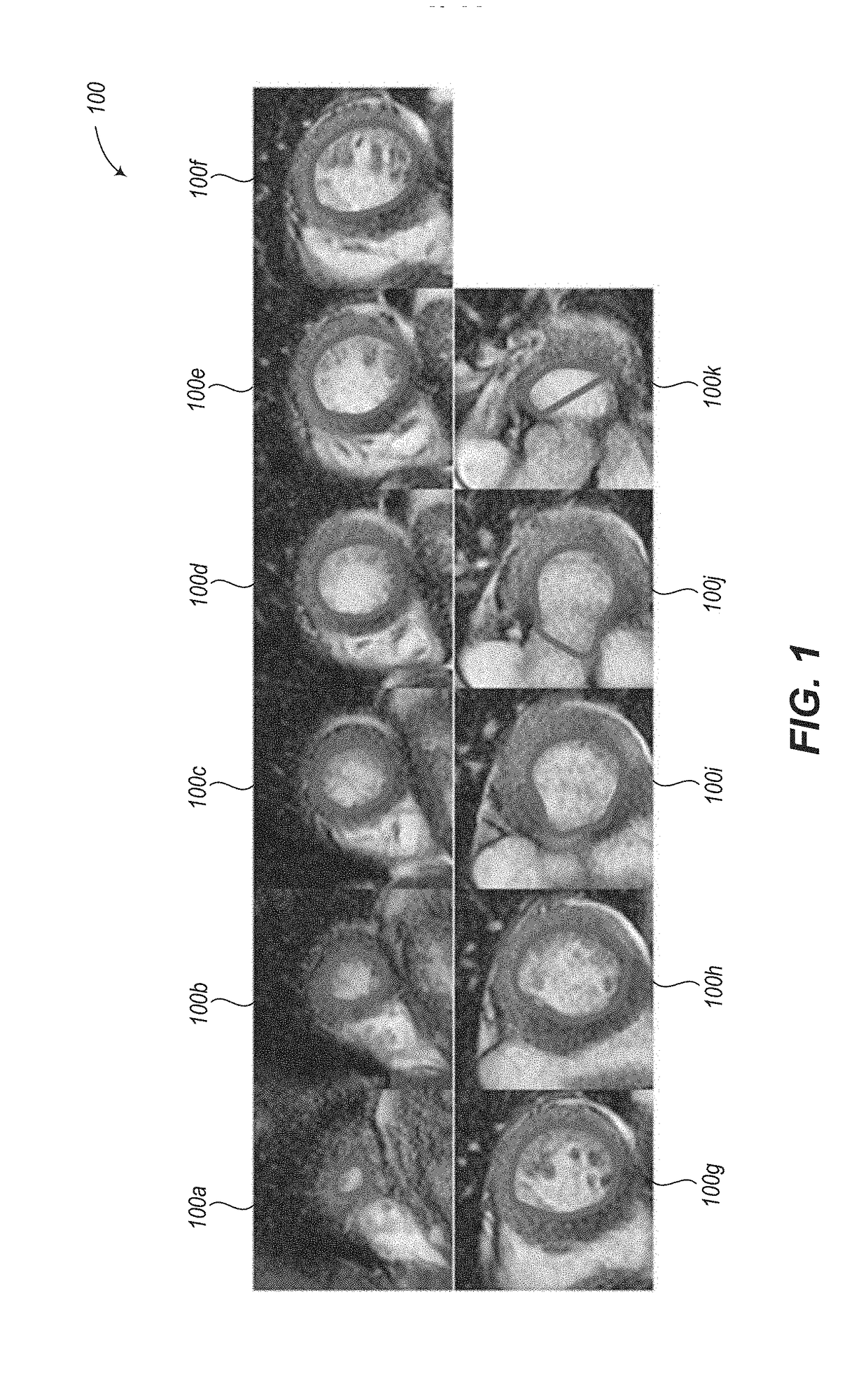
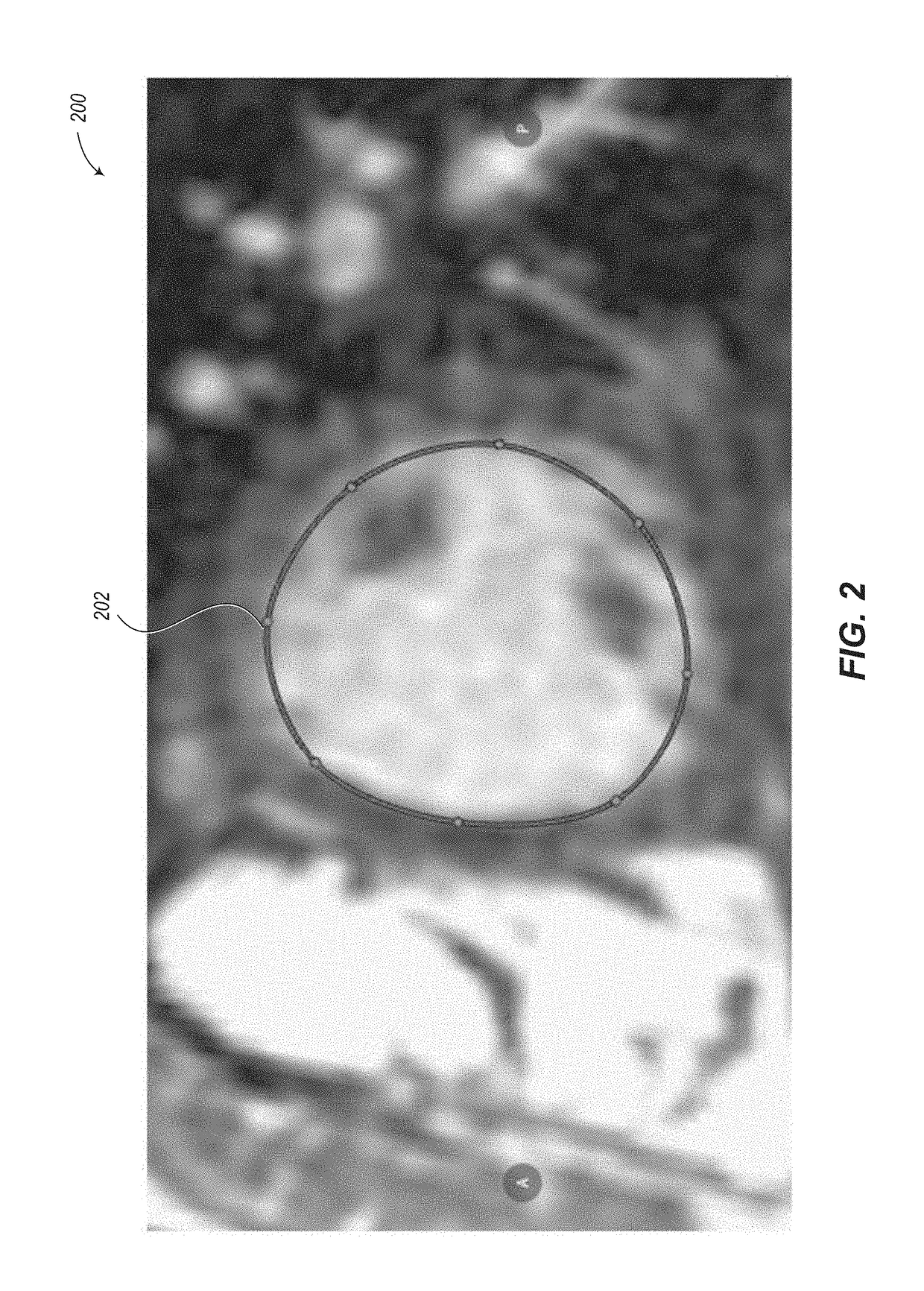
561 results about "Automated segmentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
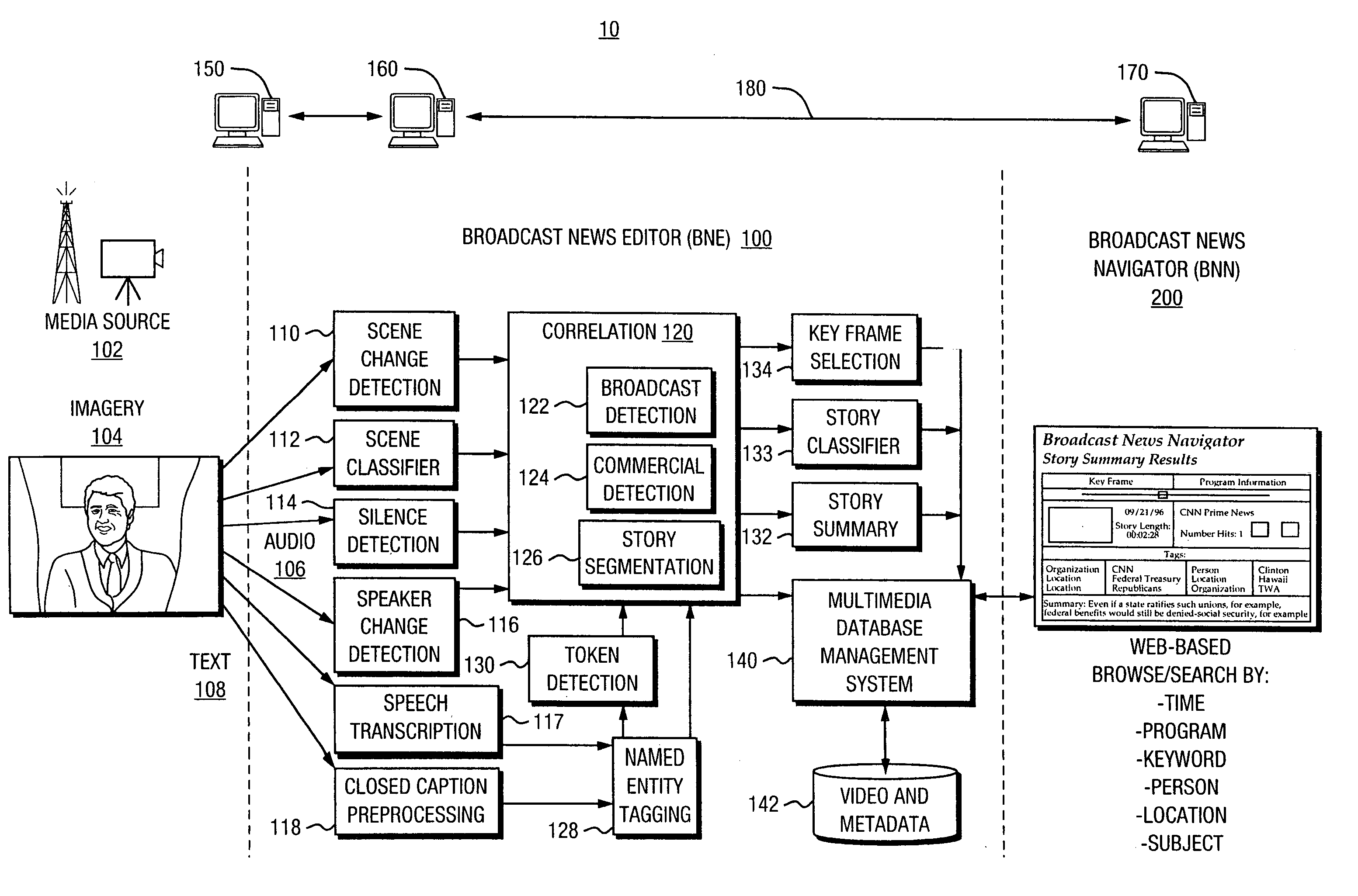
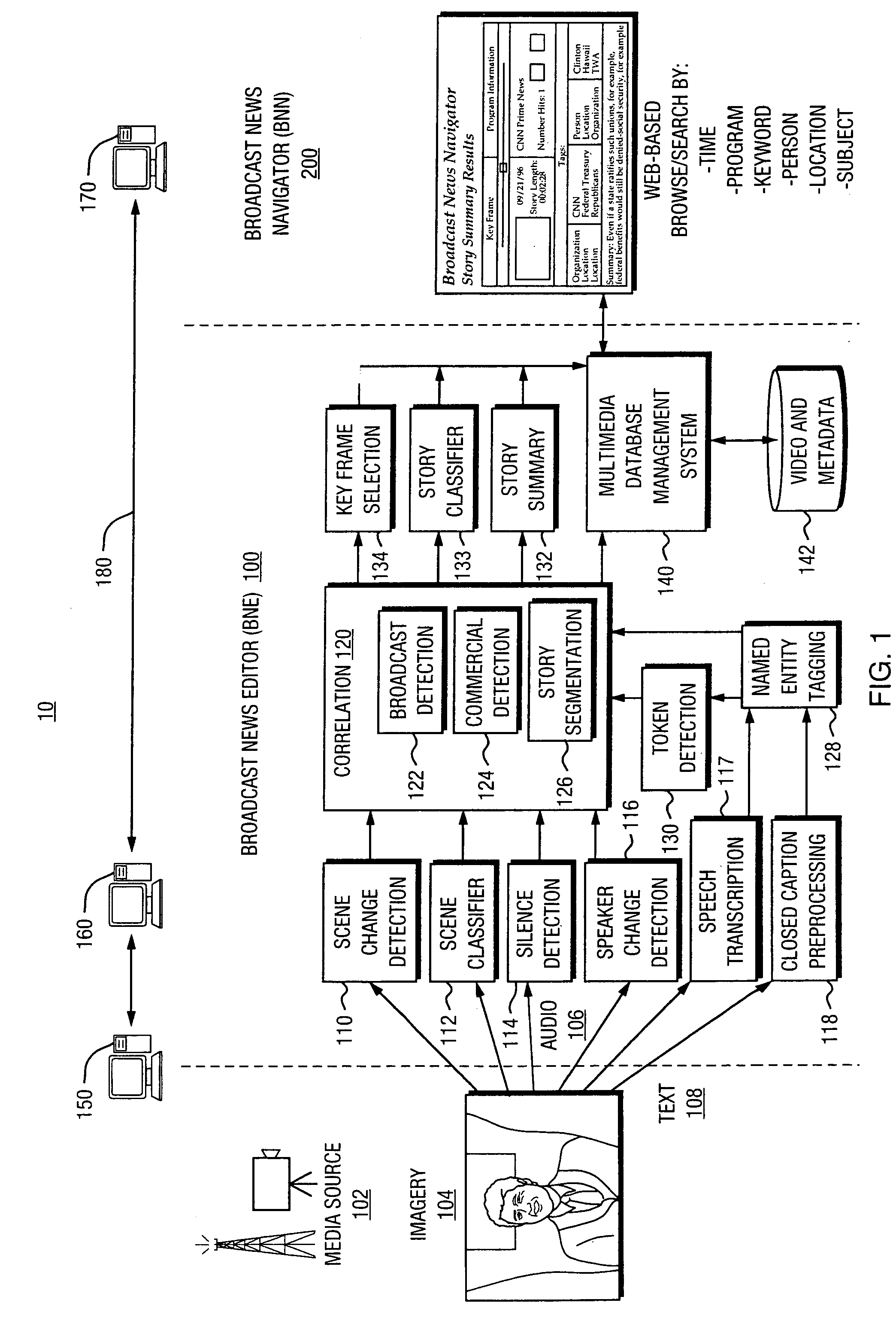
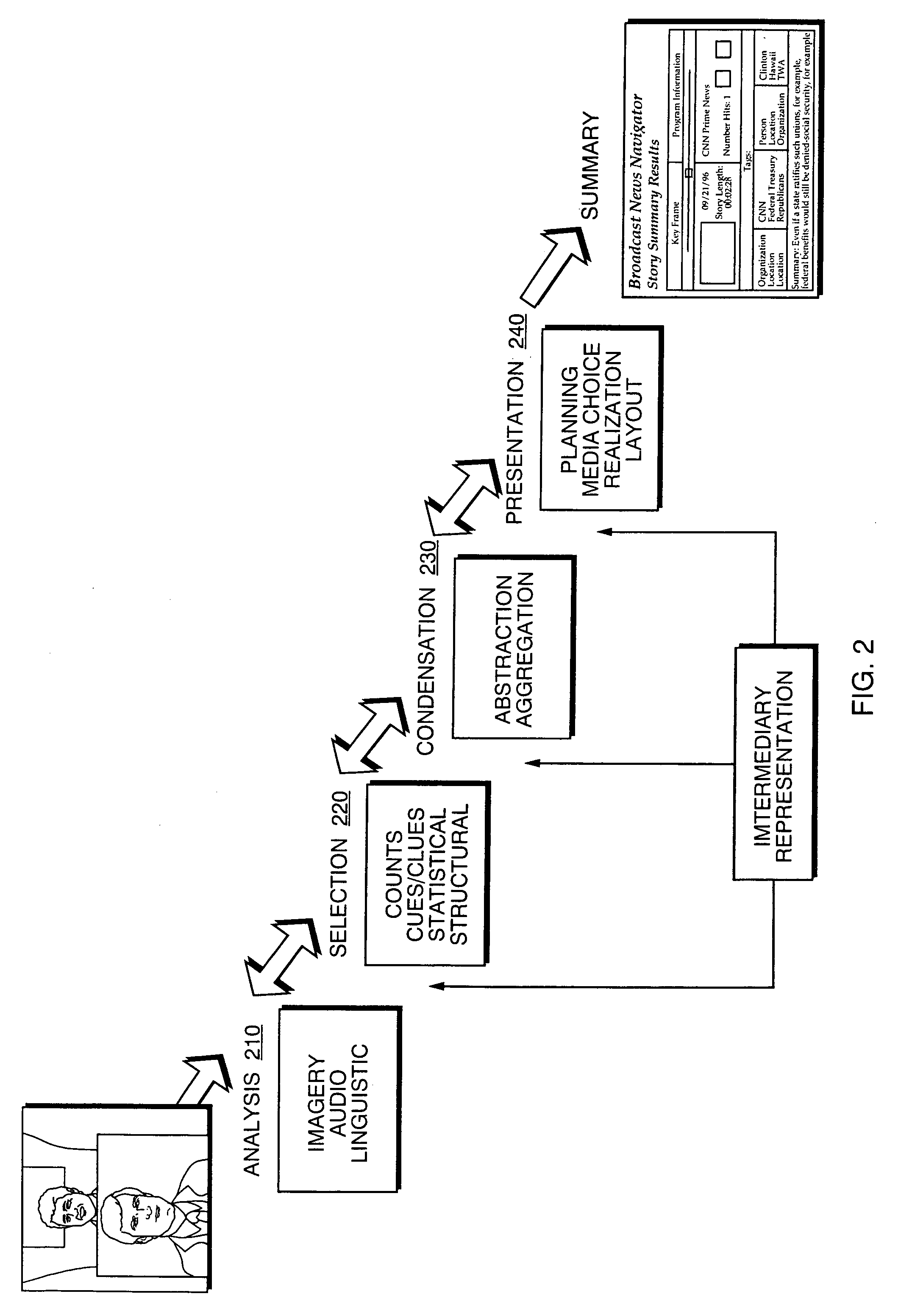
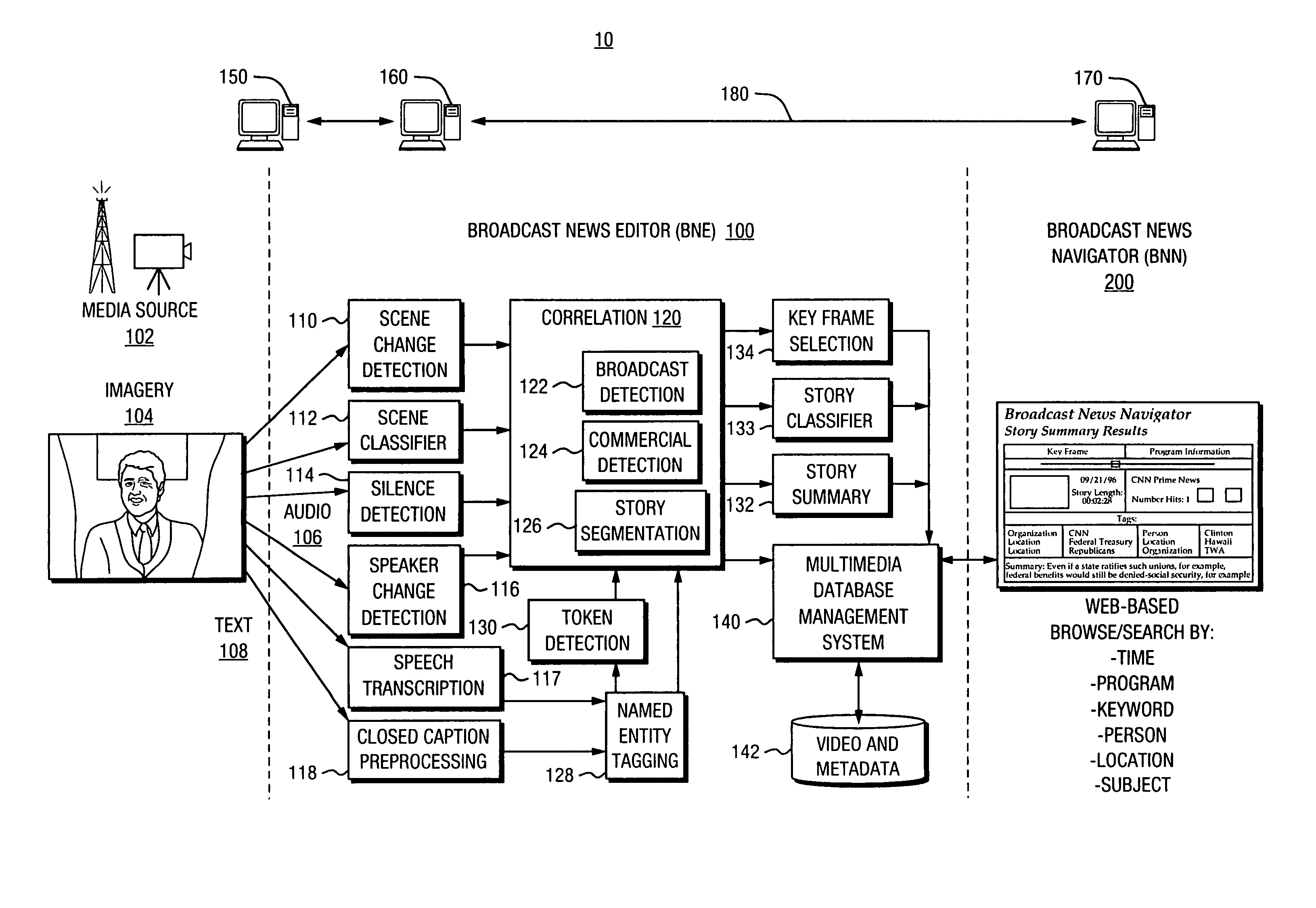
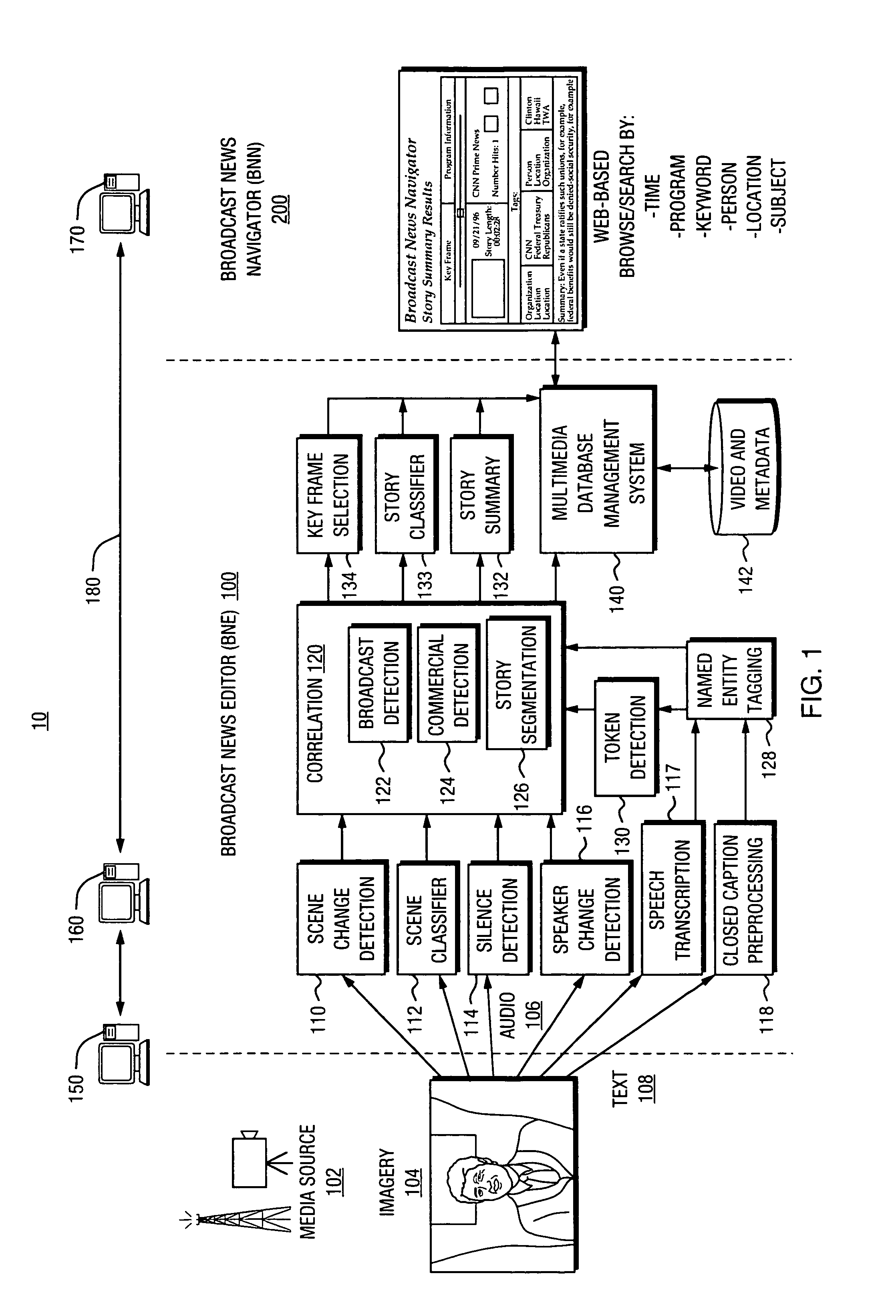
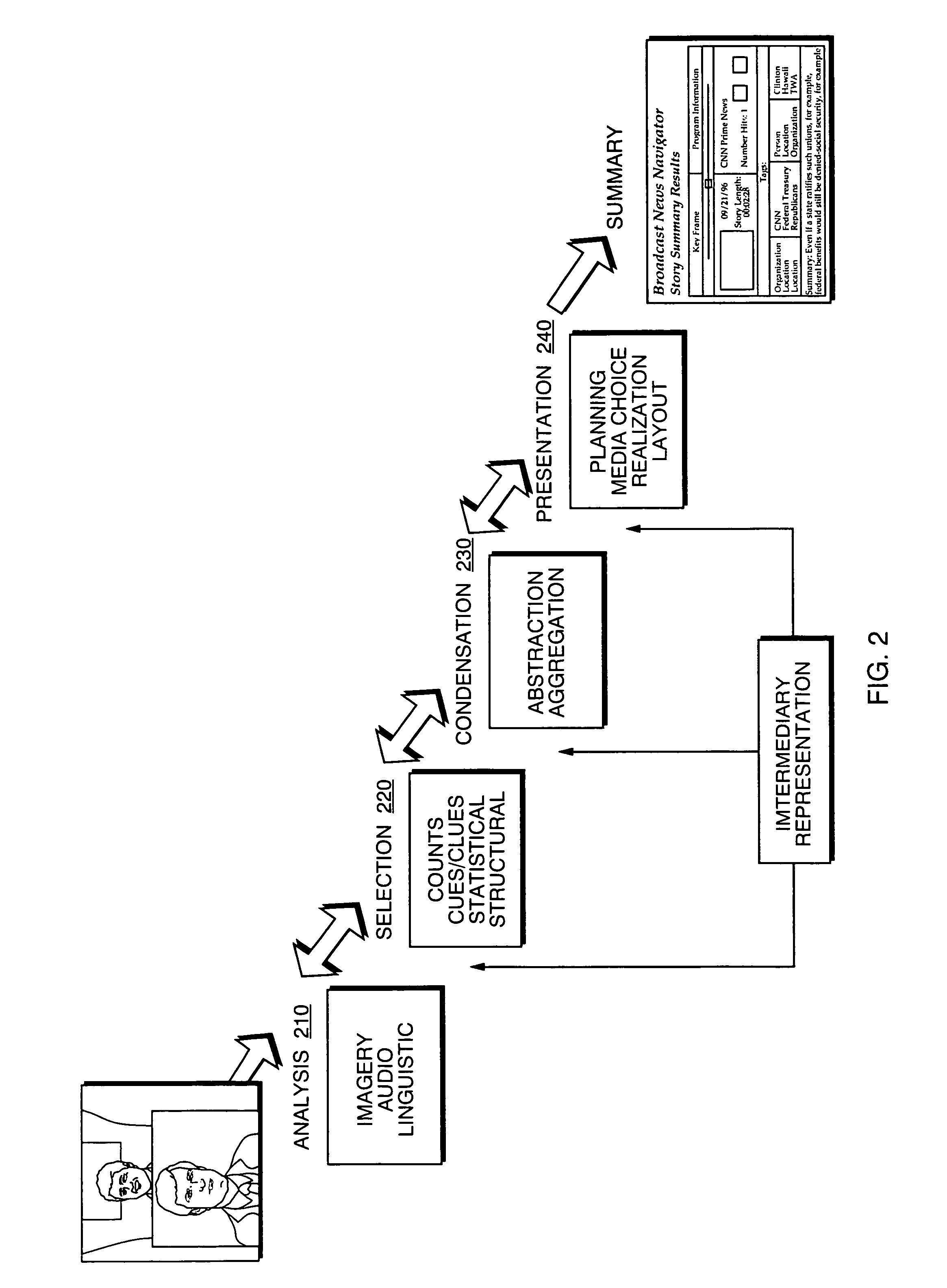
Automated segmentation, information extraction, summarization, and presentation of broadcast news
InactiveUS6961954B1More efficientMore timelyTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsSystems analysisWeb browser
A technique for automated analysis of multimedia, such as, for example, a news broadcast. A Broadcast News Editor and Broadcast News Navigator system analyze, select, condense, and then present news summaries. The system enables not only viewing a hierarchical table of contents of the news, but also summaries tailored to individual needs. This is accomplished through story segmentation and proper name extraction which enables the use of common information retrieval methodologies, such as Web browsers. Robust segmentation processing is provided using multistream analysis on imagery, audio, and closed captioned stream cue events.
Owner:OAKHAM TECH
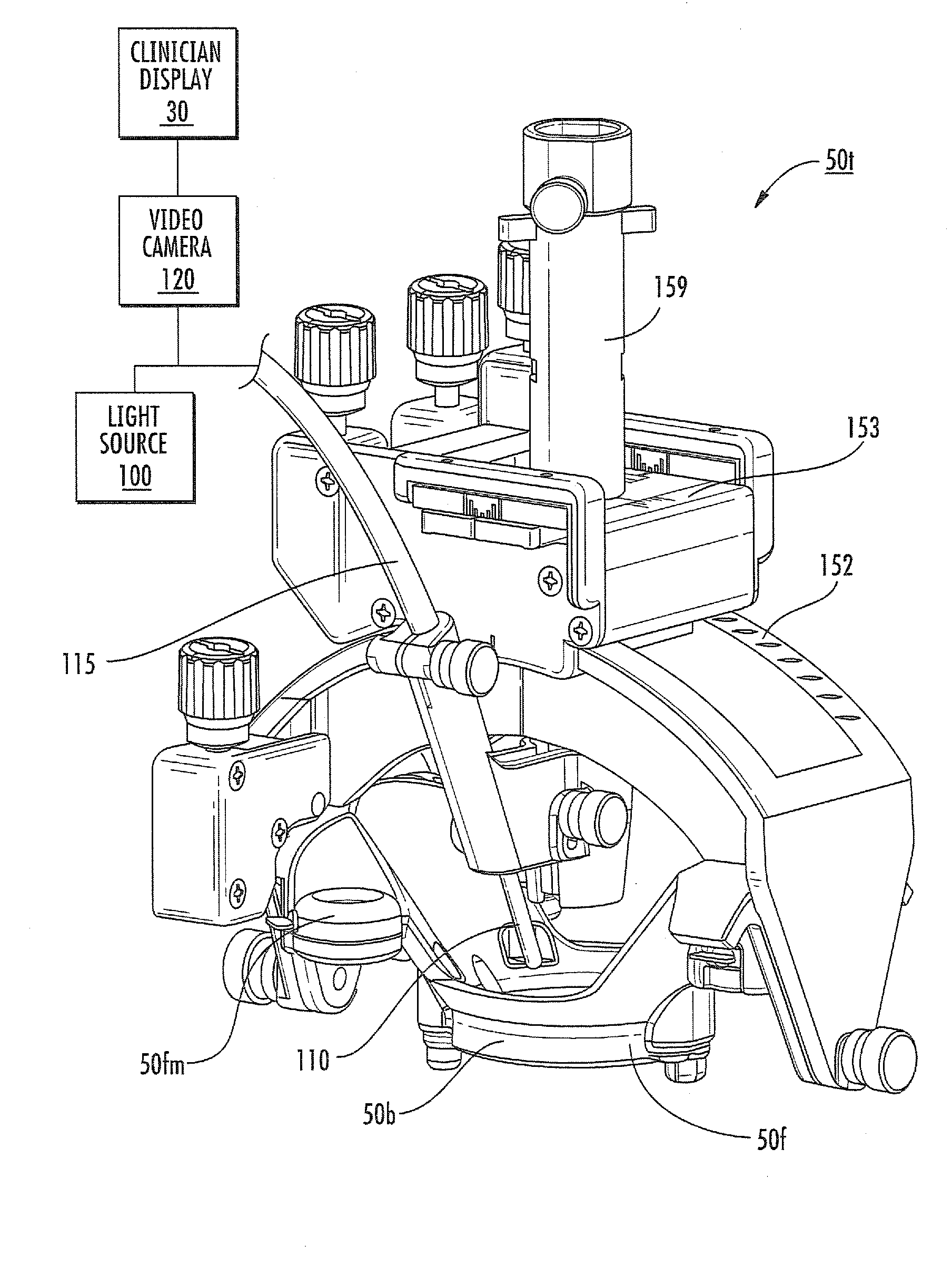
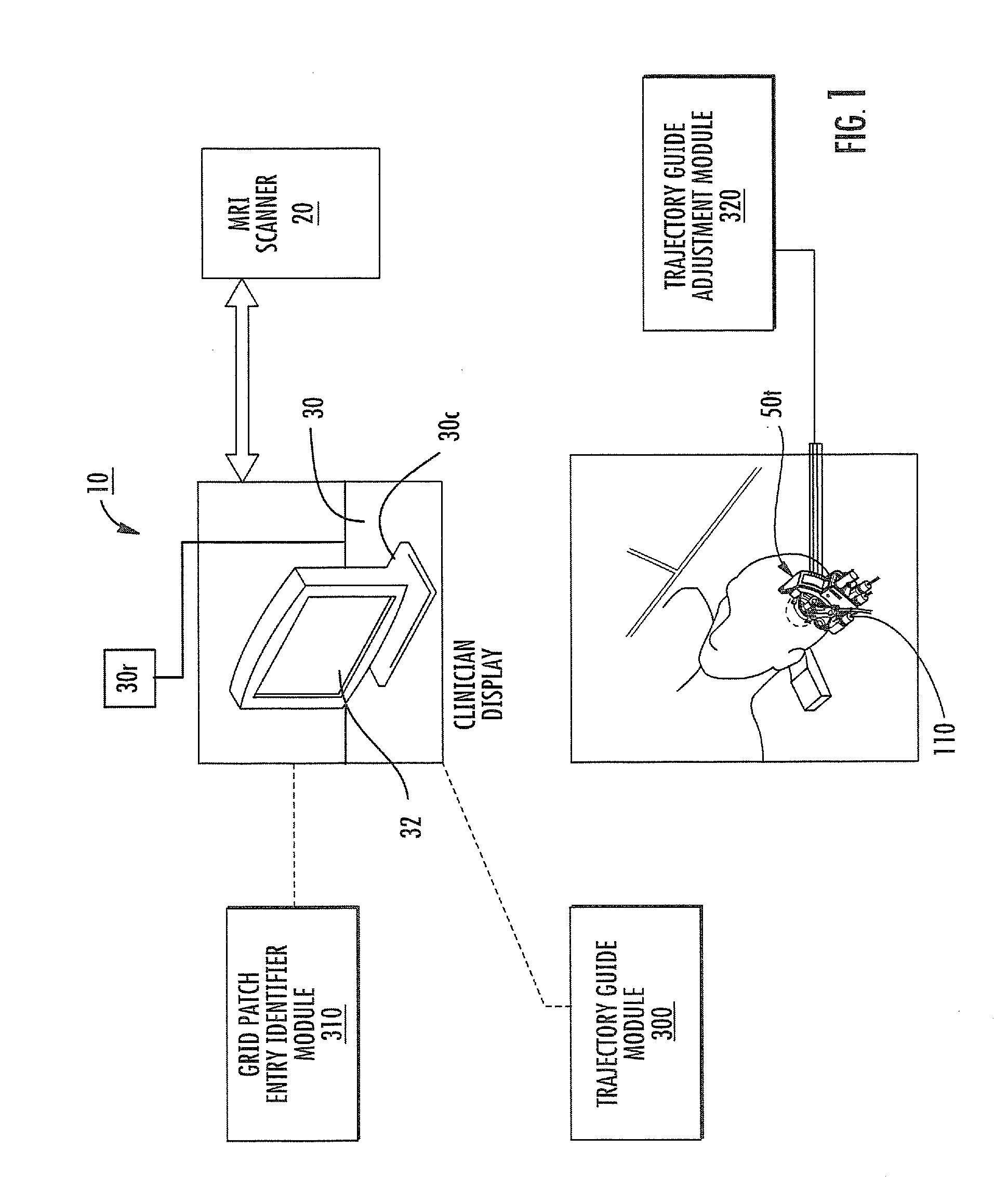
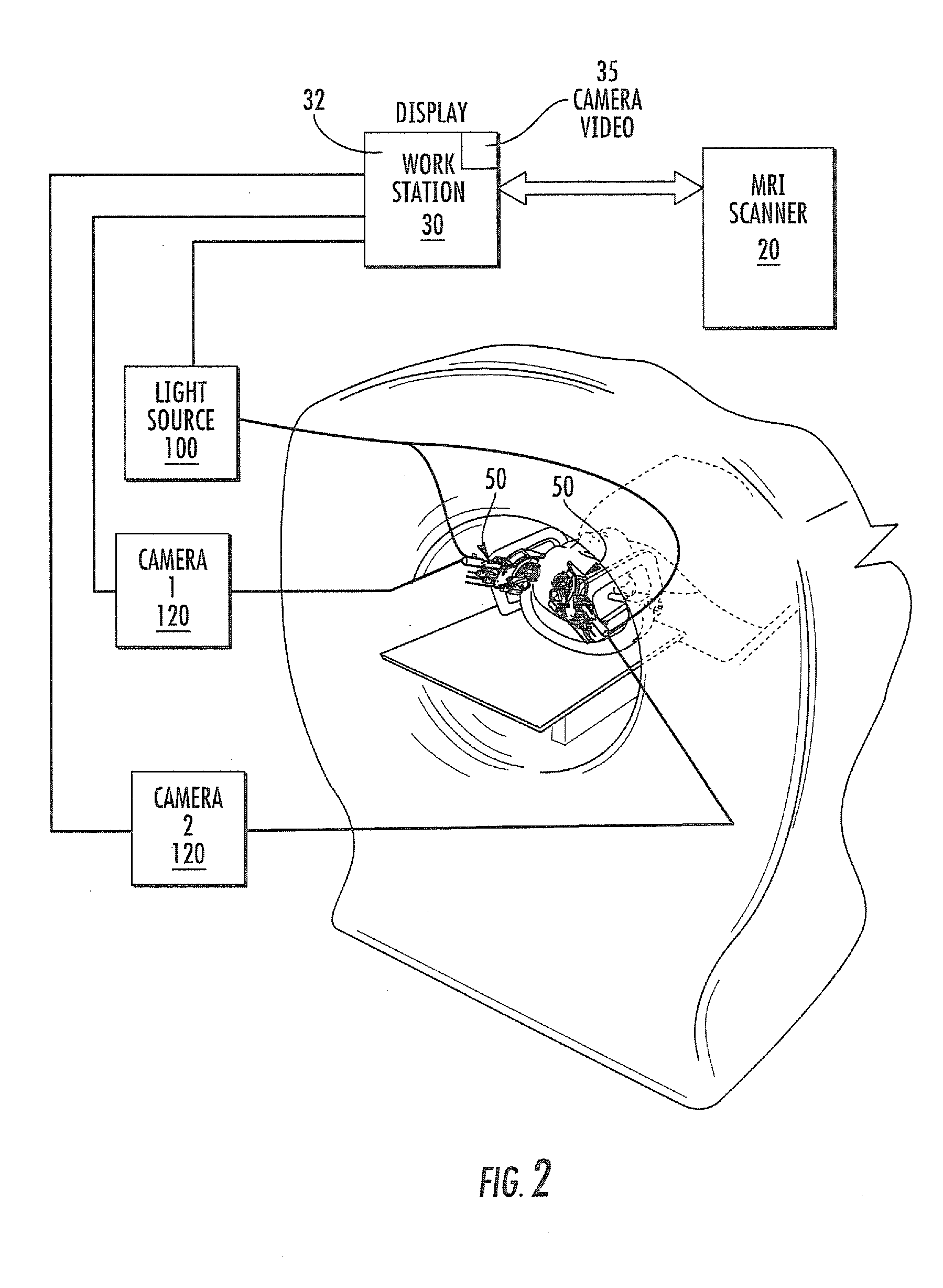
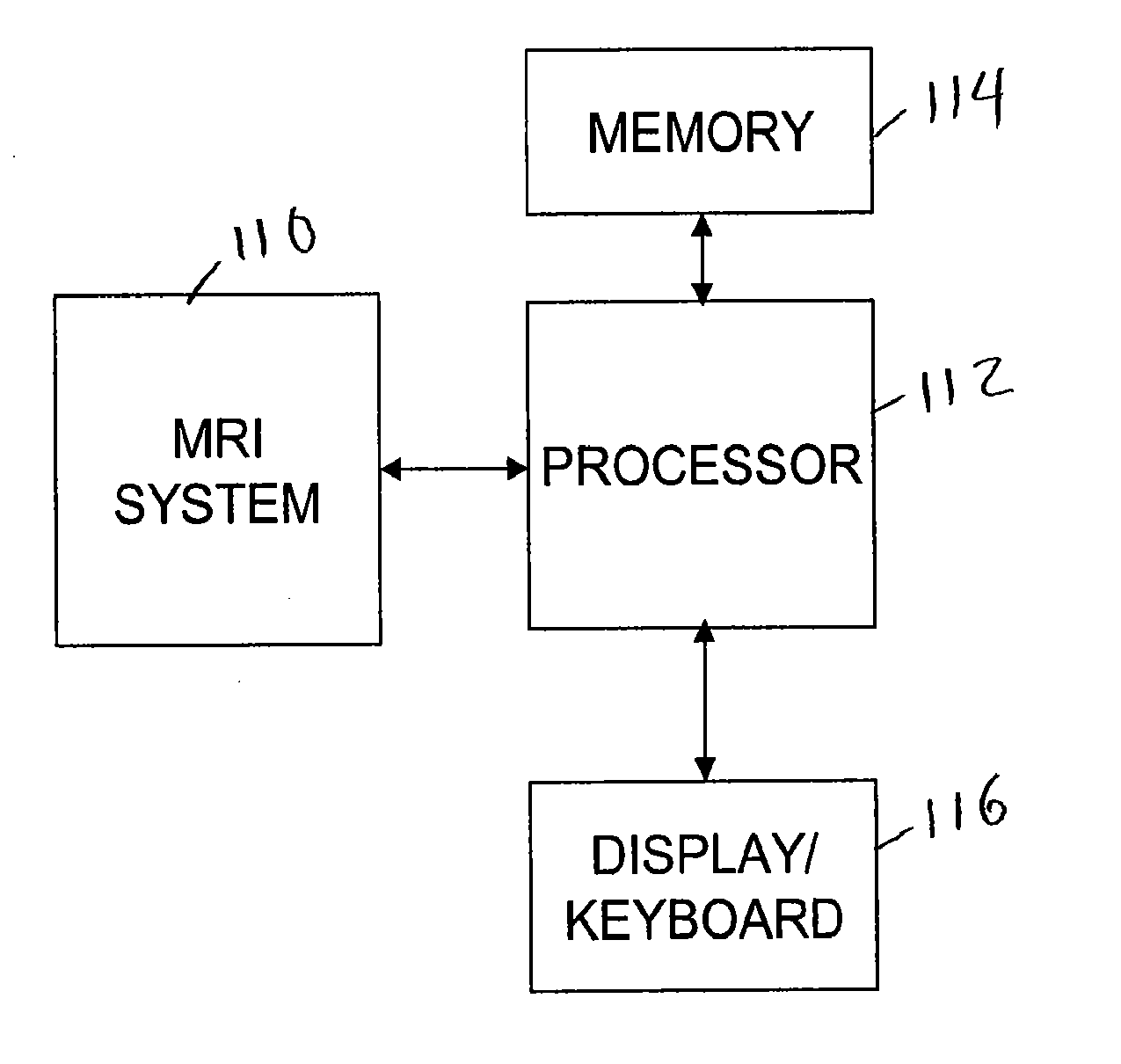
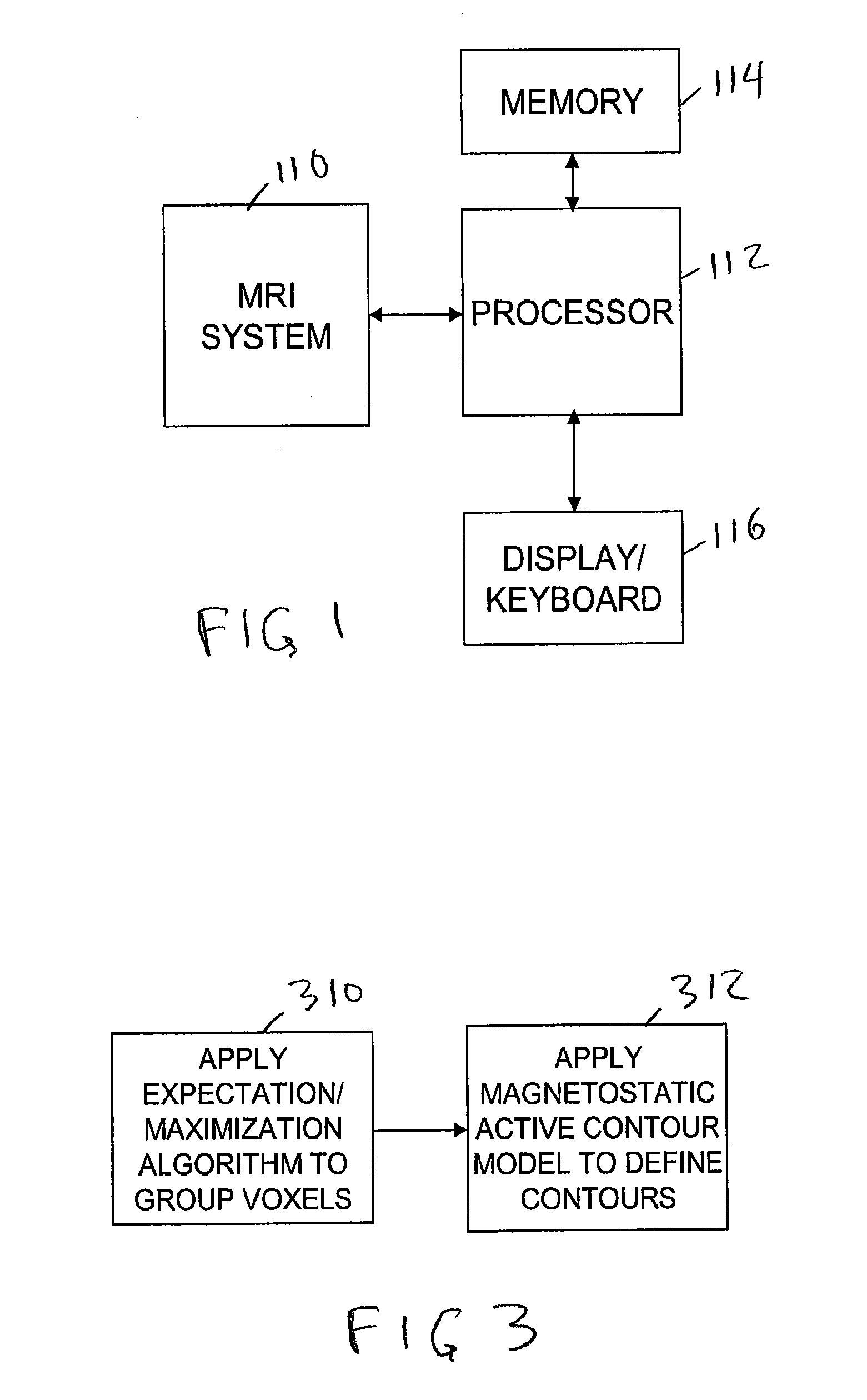
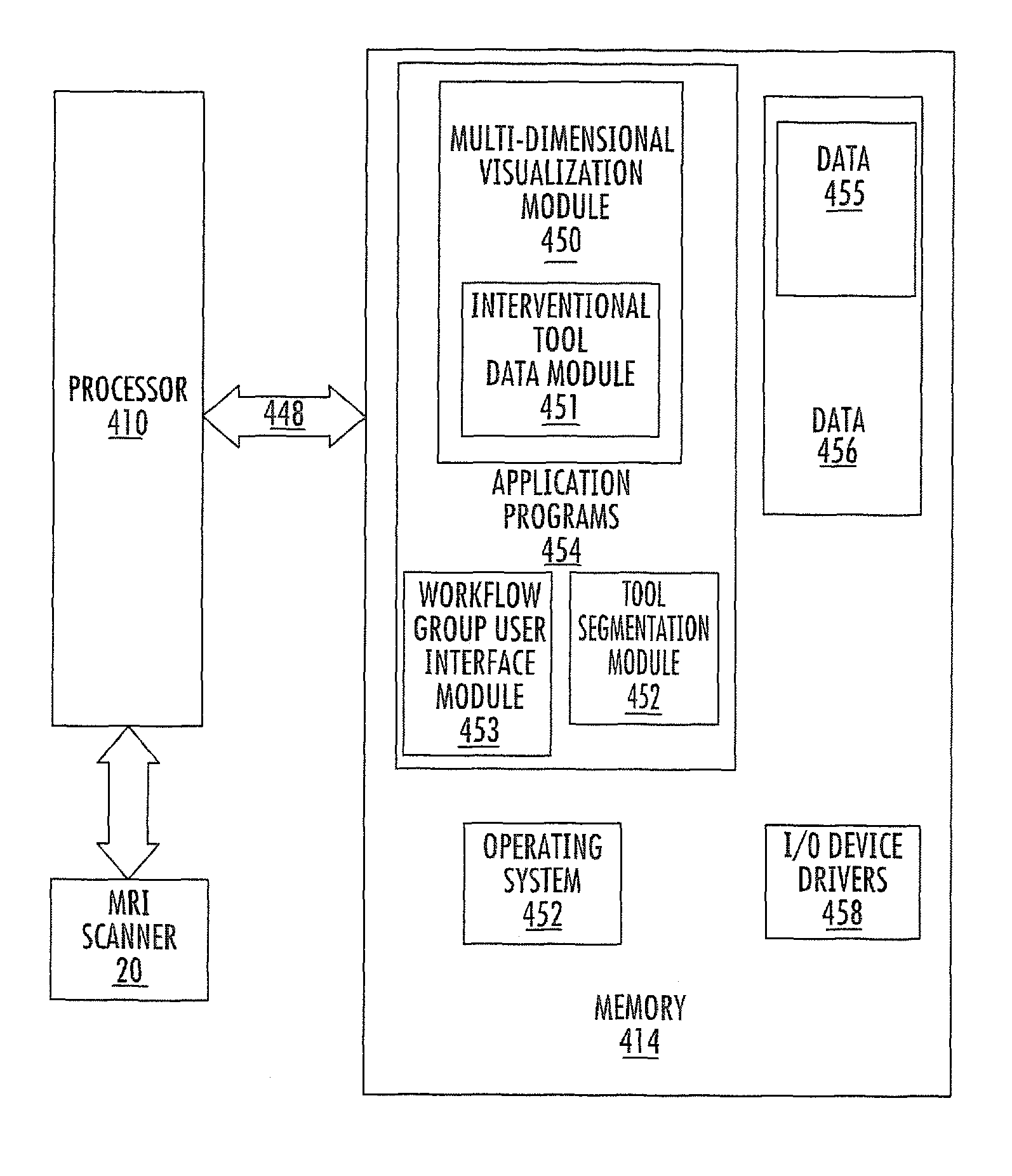
MRI surgical systems for real-time visualizations using MRI image data and predefined data of surgical tools
ActiveUS20090171184A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityMagnetic measurementsSurgical needlesMri guidedDisplay device
MRI-Surgical systems include: (a) at least one MRI-compatible surgical tool; (b) a circuit adapted to communicate with an MRI scanner; and (c) at least one display in communication with the circuit. The circuit electronically recognizes predefined physical characteristics of the at least one tool to automatically segment MR image data provided by the MRI scanner whereby the at least one tool constitutes a point of interface with the system. The circuit is configured to provide a User Interface that defines workflow progression for an MRI-guided surgical procedure and allows a user to select steps in the workflow, and wherein the circuit is configured to generate multi-dimensional visualizations using the predefined data of the at least one tool and data from MRI images of the patient in substantially real time during the surgical procedure.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
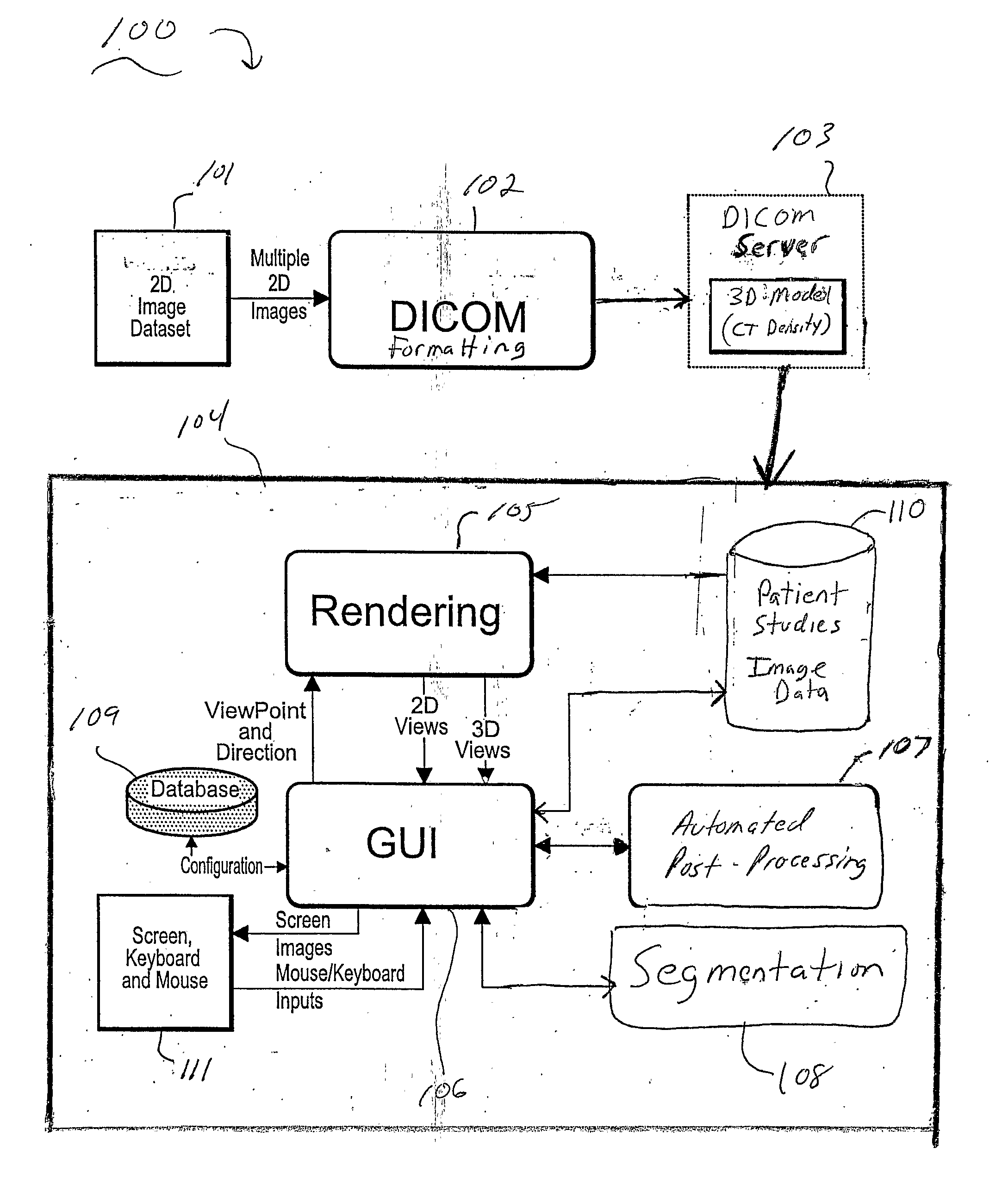
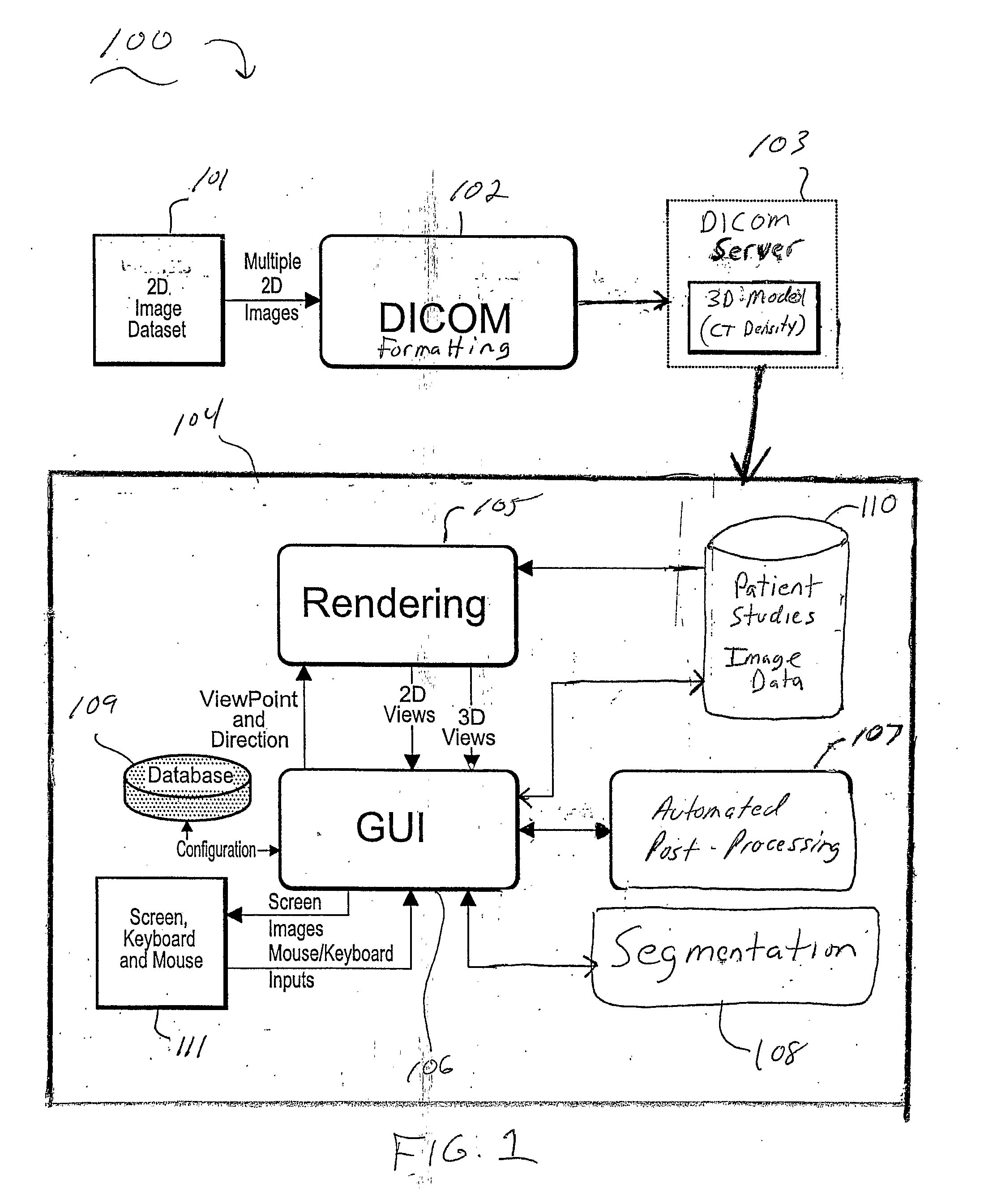
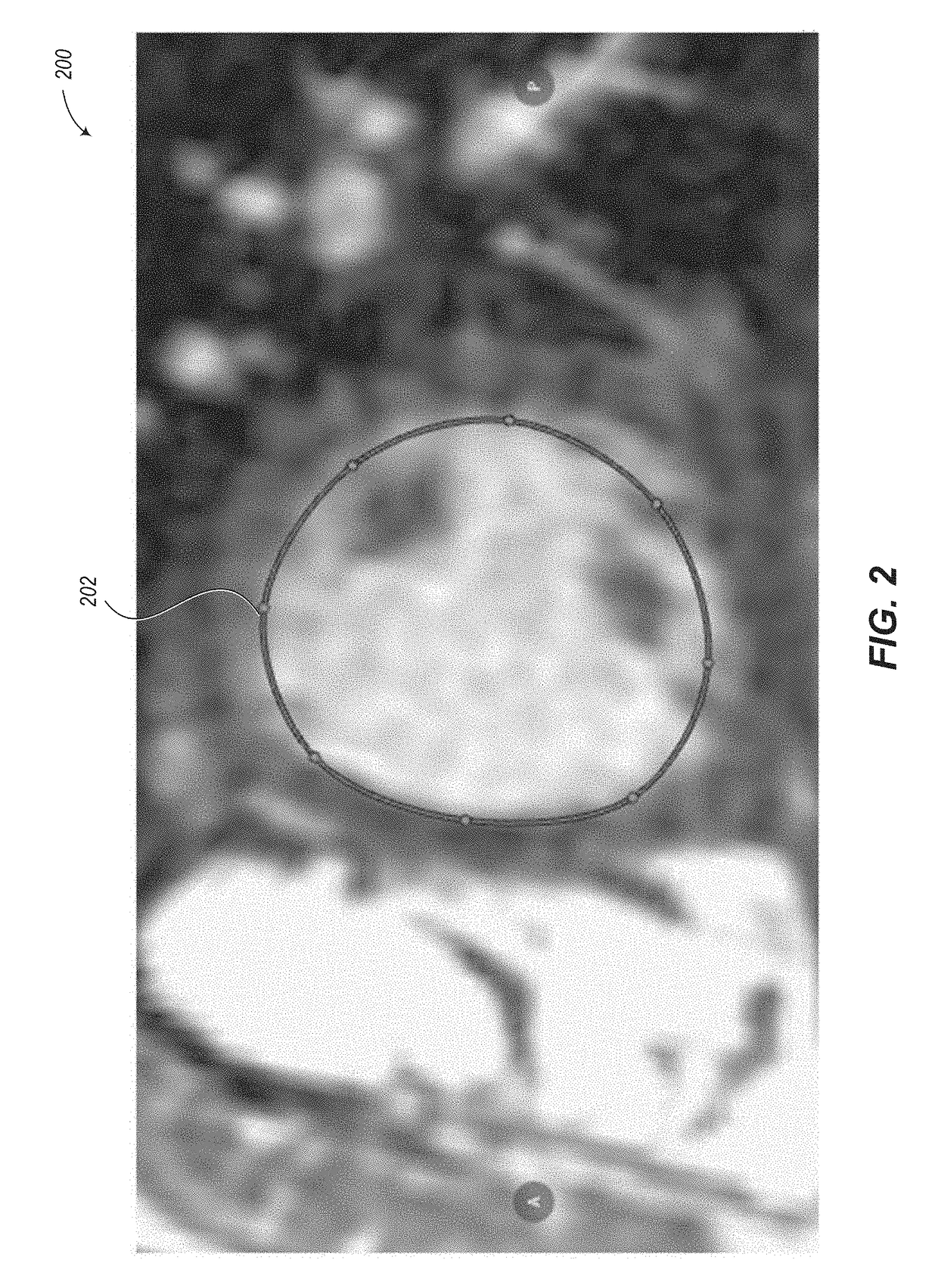
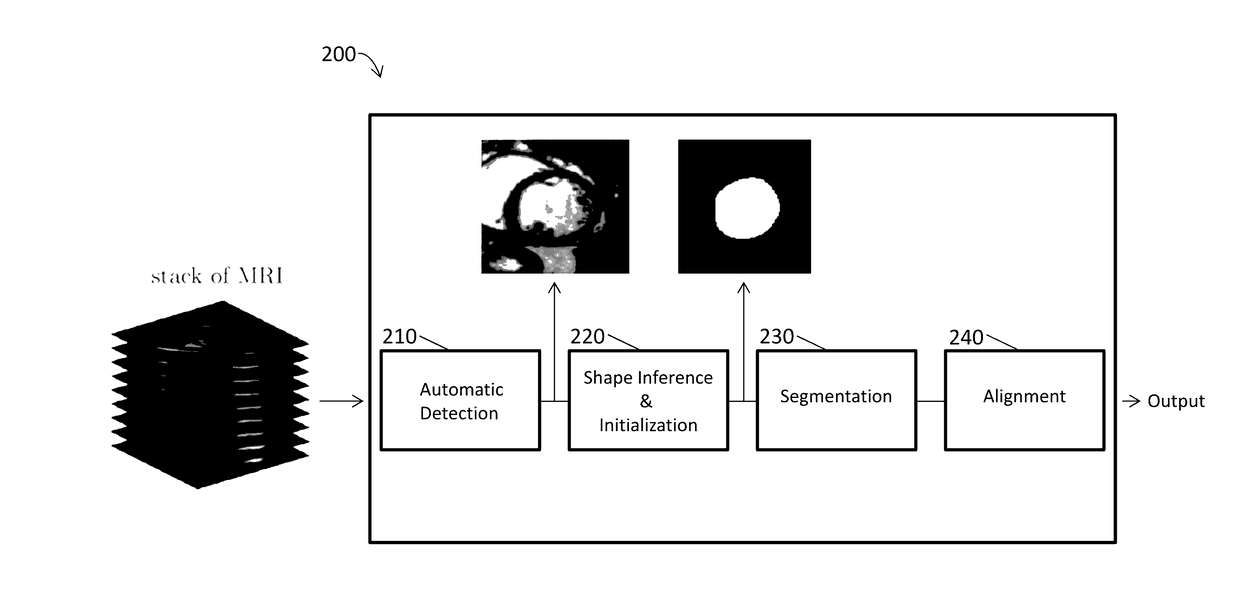
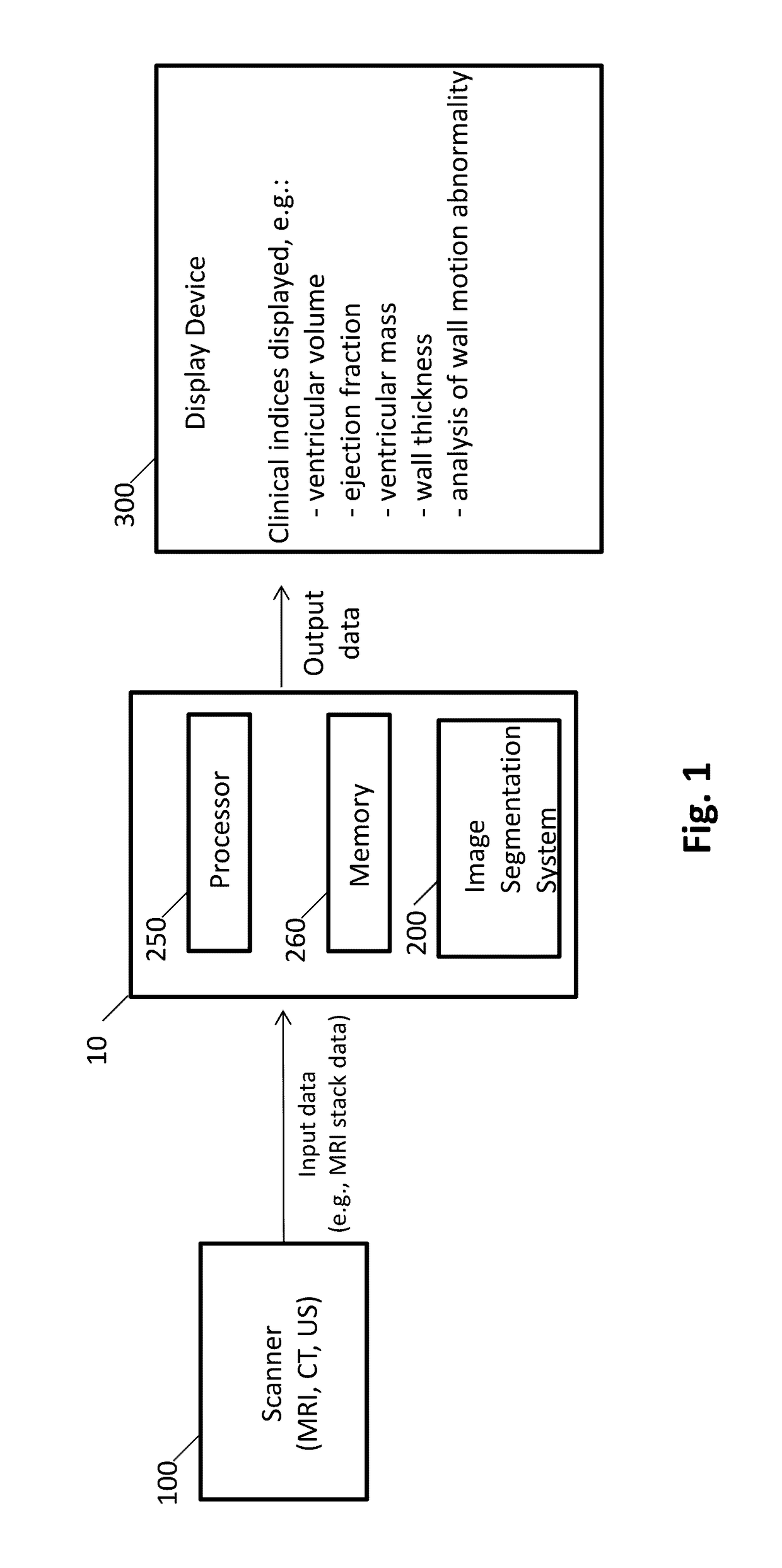
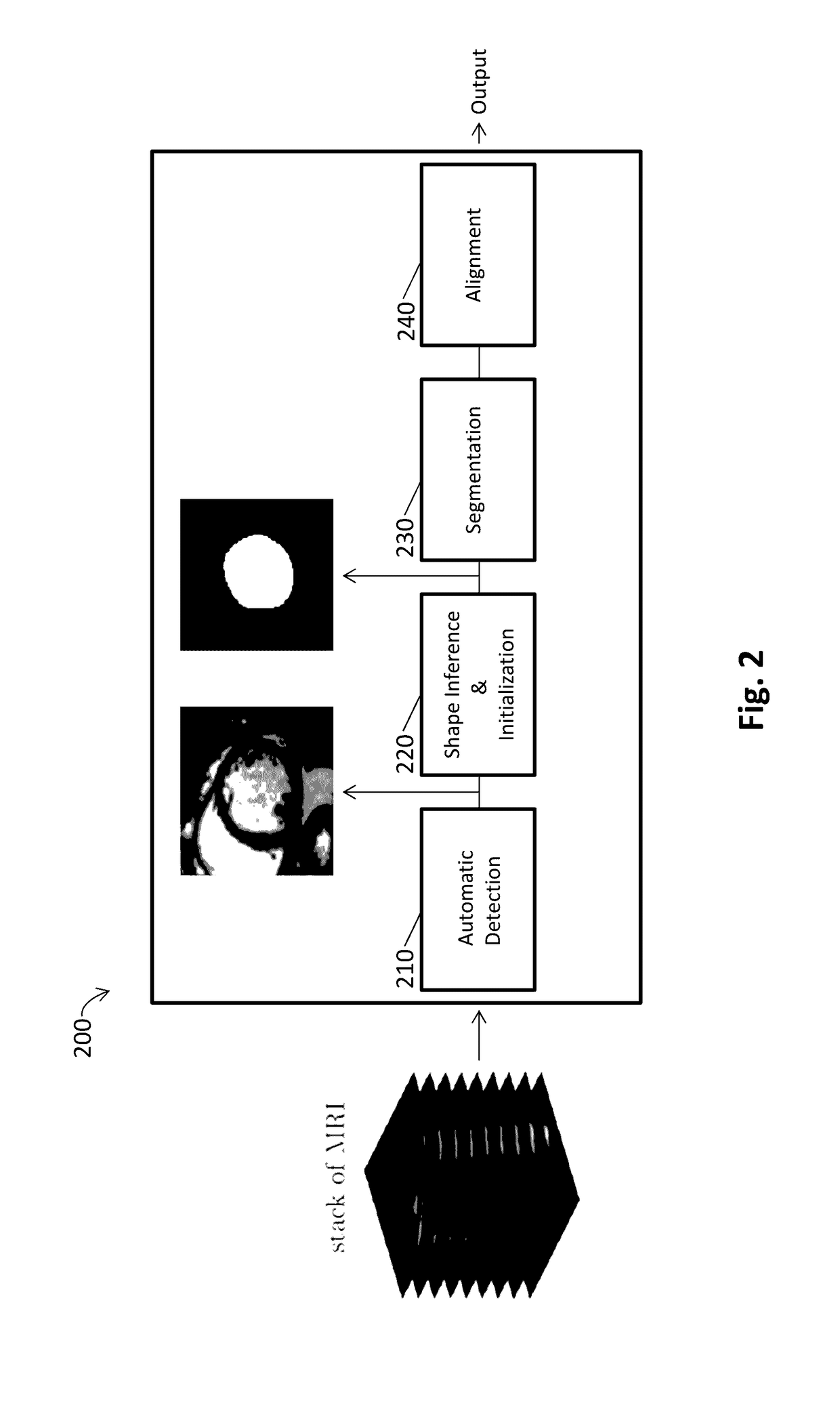
Systems and Methods for Automated Segmentation, Visualization and Analysis of Medical Images
An imaging system for automated segmentation and visualization of medical images (100) includes an image processing module (107) for automatically processing image data using a set of directives (109) to identify a target object in the image data and process the image data according to a specified protocol, a rendering module (105) for automatically generating one or more images of the target object based on one or more of the directives (109) and a digital archive (110) for storing the one or more generated images. The image data may be DICOM-formatted image data (103), wherein the imaging processing module (107) extracts and processes meta-data in DICOM fields of the image data to identify the target object. The image processing module (107) directs a segmentation module (108) to segment the target object using processing parameters specified by one or more of the directives (109).
Owner:VIATRONIX
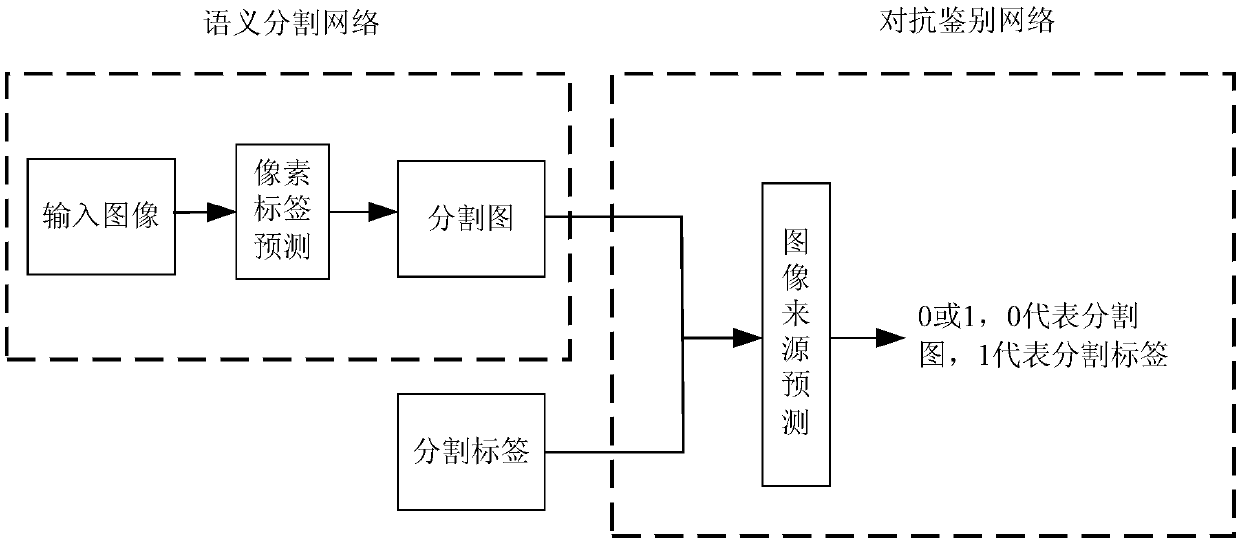
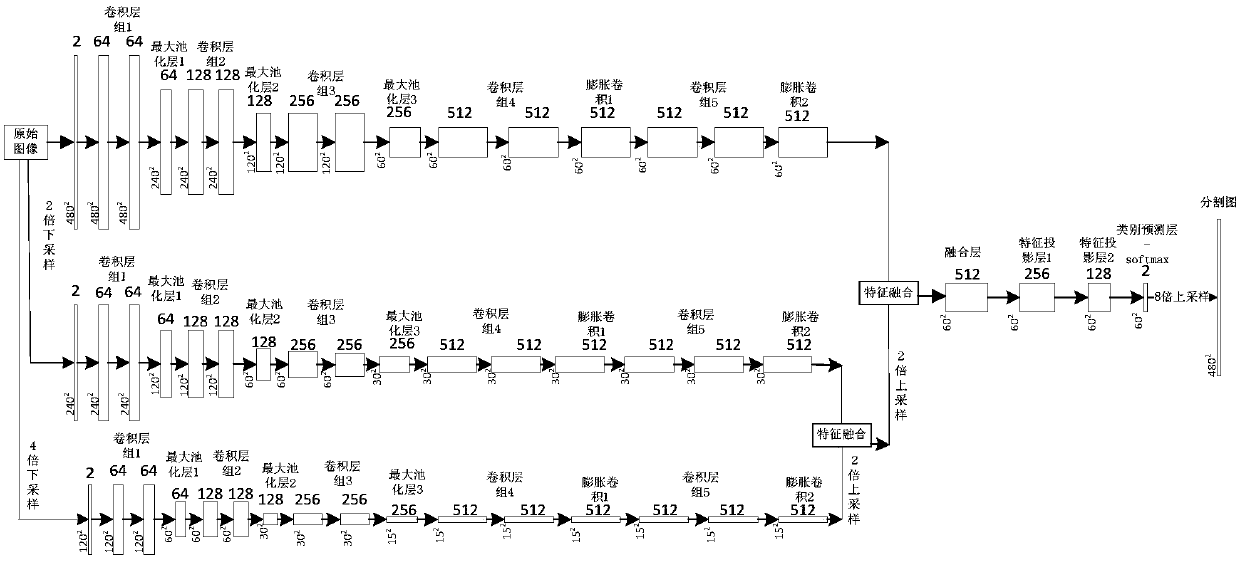
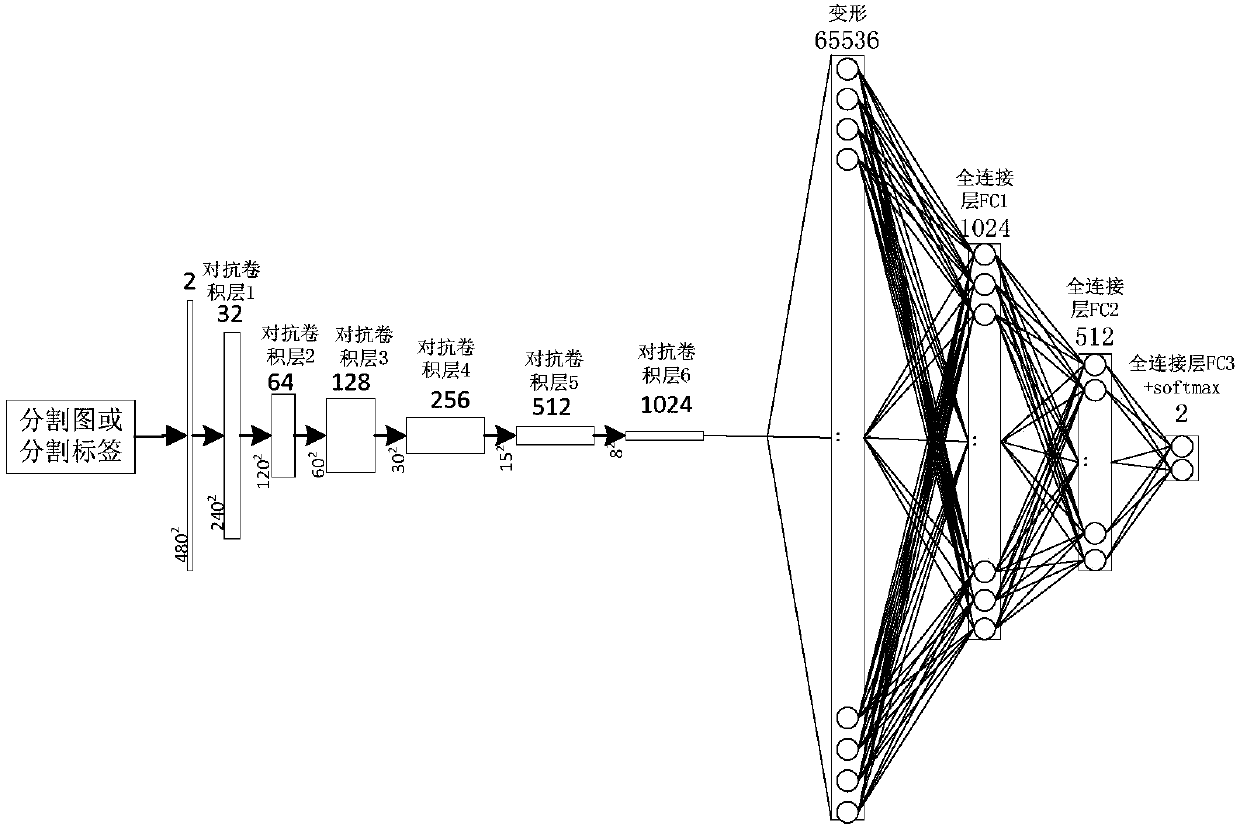
Multi-scale feature fusion ultrasonic image semantic segmentation method based on adversarial learning
ActiveCN108268870AImprove forecast accuracyFew parametersNeural architecturesRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsPattern recognitionAutomatic segmentation
The invention provides a multi-scale feature fusion ultrasonic image semantic segmentation method based on adversarial learning, and the method comprises the following steps: building a multi-scale feature fusion semantic segmentation network model, building an adversarial discrimination network model, carrying out the adversarial training and model parameter learning, and carrying out the automatic segmentation of a breast lesion. The method provided by the invention achieves the prediction of a pixel class through the multi-scale features of input images with different resolutions, improvesthe pixel class label prediction accuracy, employs expanding convolution for replacing partial pooling so as to improve the resolution of a segmented image, enables the segmented image generated by asegmentation network guided by an adversarial discrimination network not to be distinguished from a segmentation label, guarantees the good appearance and spatial continuity of the segmented image, and obtains a more precise high-resolution ultrasonic breast lesion segmented image.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Automated segmentation and information extraction of broadcast news via finite state presentation model
InactiveUS7765574B1More efficientMore timelyTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalWeb browserPublic information
Owner:OAKHAM TECH
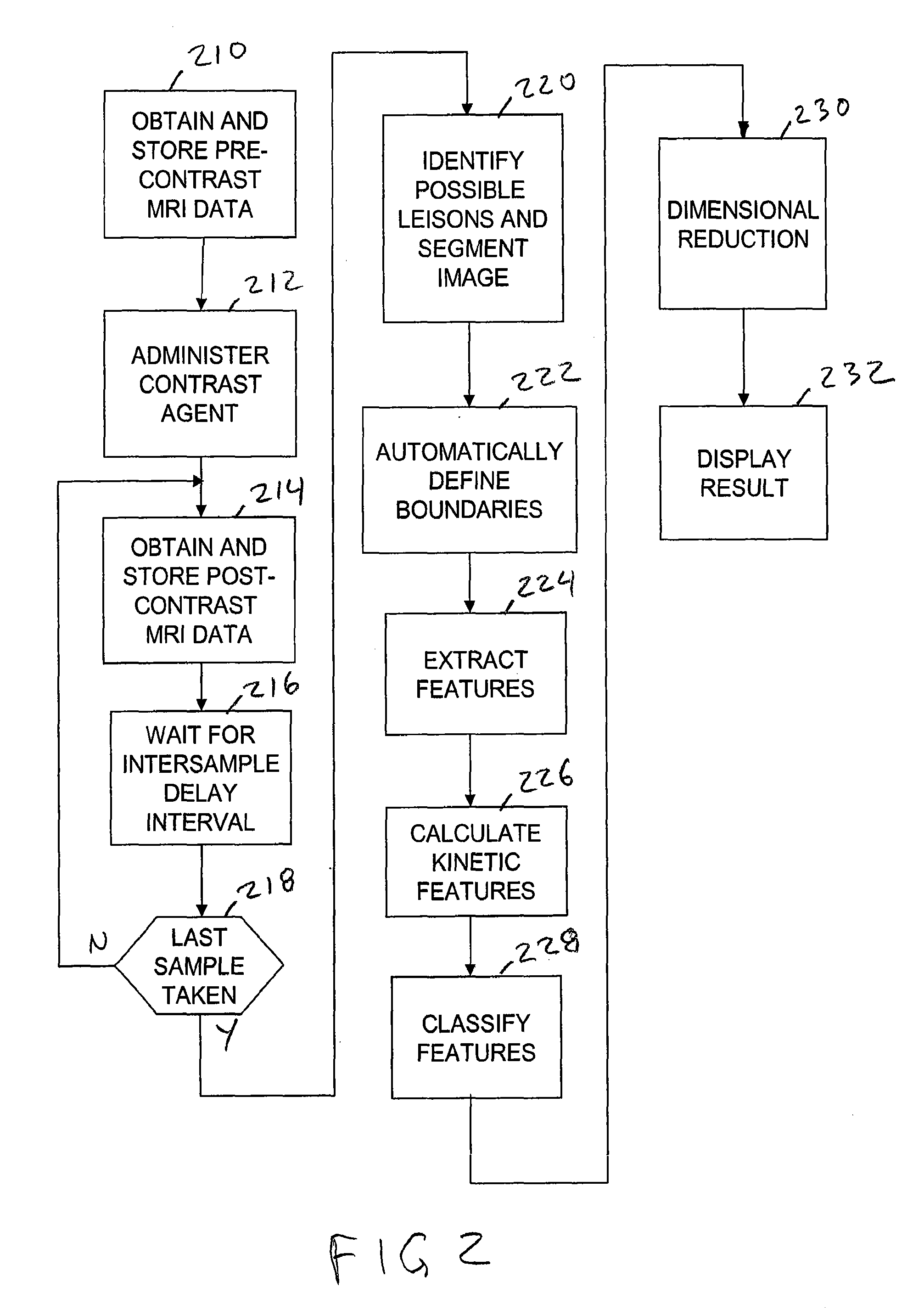
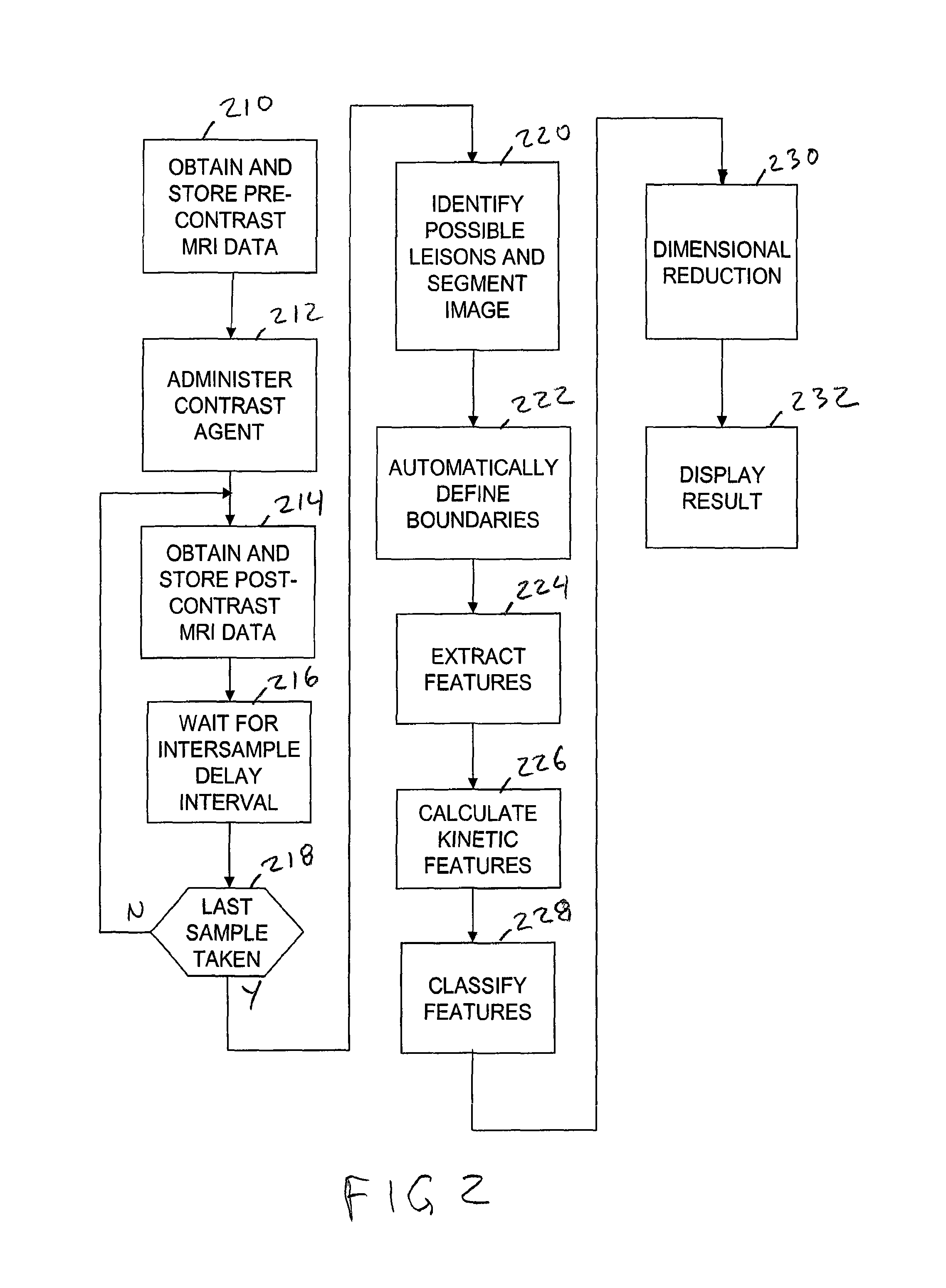
System and method for automated segmentation, characterization, and classification of possibly malignant lesions and stratification of malignant tumors
A method and apparatus for classifying possibly malignant lesions from sets of DCE-MRI images includes receiving a set of MRI slice images obtained at respectively different times, where each slice image includes voxels representative of at least one region of interest (ROI). The images are processed to determine the boundaries of the ROIs and the voxels within the identified boundaries in corresponding regions of the images from each time period are processed to extract kinetic texture features. The kinetic texture features are then used in a classification process which classifies the ROIs as malignant or benign. The malignant lesions are further classified to separate TN lesions from non-TN lesions.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Medical image reporting system and method
ActiveUS20100310146A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomated algorithmGraph theoretic
This invention relates generally to medical imaging and, in particular, to a method and system for reconstructing a model path through a branched tubular organ. Novel methodologies and systems segment and define accurate endoluminal surfaces in airway trees, including small peripheral bronchi. An automatic algorithm is described that searches the entire lung volume for airway branches and poses airway-tree segmentation as a global graph-theoretic optimization problem. A suite of interactive segmentation tools for cleaning and extending critical areas of the automatically segmented result is disclosed. A model path is reconstructed through the airway tree.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Automated segmentation utilizing fully convolutional networks
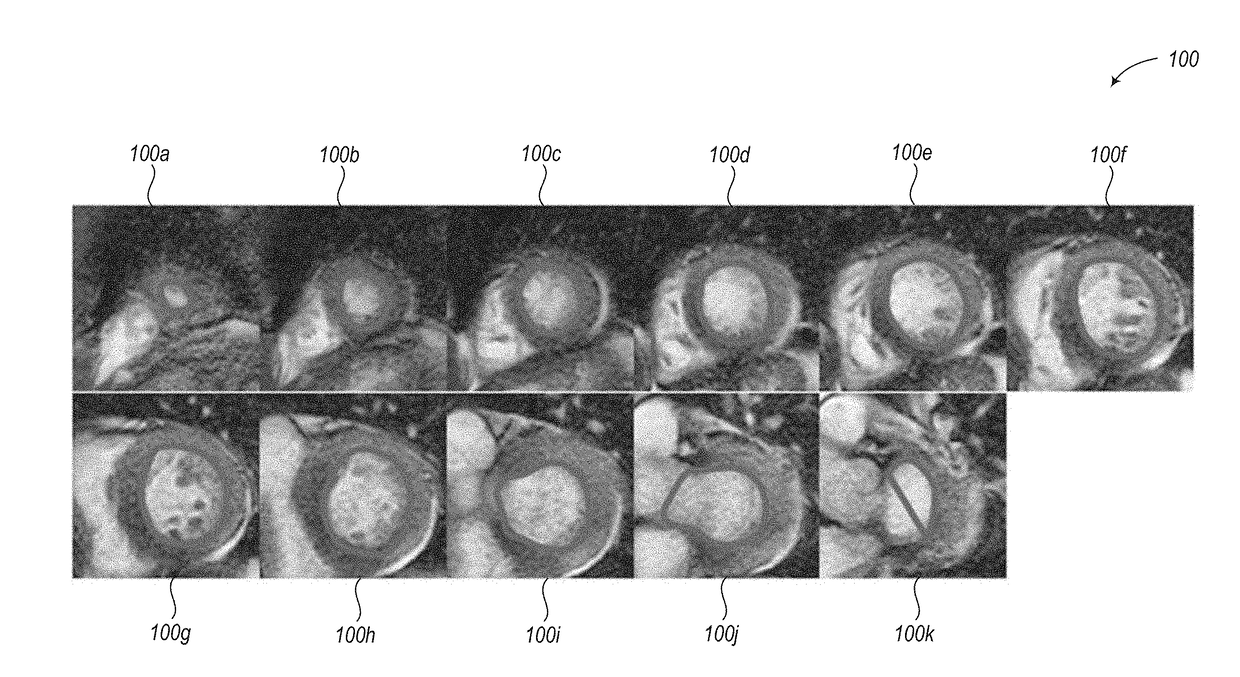
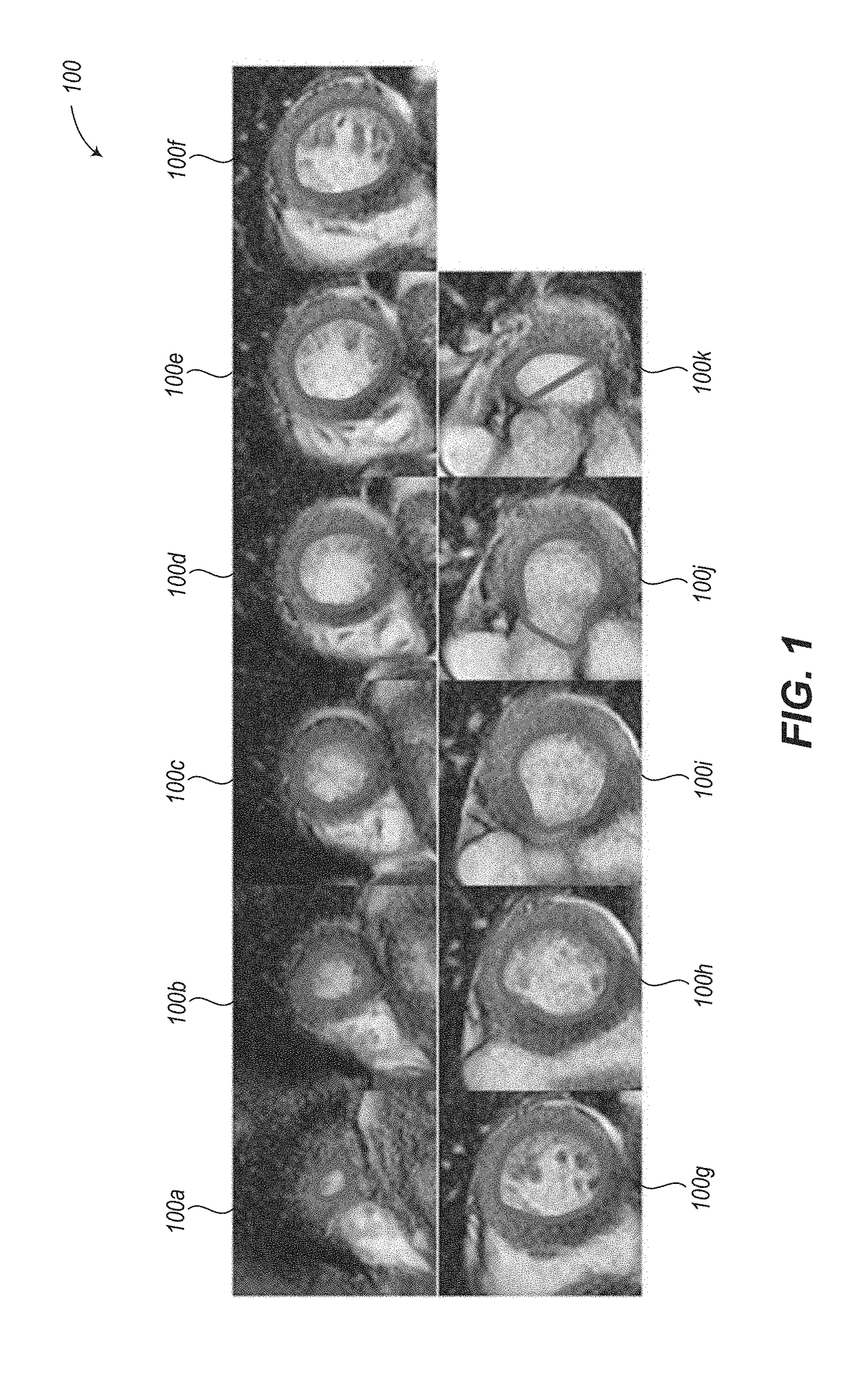
ActiveUS20180218502A1Quantity minimizationReduce identified areaImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresCardiac muscle
Systems and methods for automated segmentation of anatomical structures (e.g., heart). Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) may be employed to autonomously segment parts of an anatomical structure represented by image data, such as 3D MRI data. The CNN utilizes two paths, a contracting path and an expanding path. In at least some implementations, the expanding path includes fewer convolution operations than the contracting path. Systems and methods also autonomously calculate an image intensity threshold that differentiates blood from papillary and trabeculae muscles in the interior of an endocardium contour, and autonomously apply the image intensity threshold to define a contour or mask that describes the boundary of the papillary and trabeculae muscles. Systems and methods also calculate contours or masks delineating the endocardium and epicardium using the trained CNN model, and anatomically localize pathologies or functional characteristics of the myocardial muscle using the calculated contours or masks.
Owner:ARTERYS INC
Automated segmentation of organ chambers using deep learning methods from medical imaging
Systems and methods are disclosed for automatically segmenting a heart chamber from medical images of a patient. The system may include one or more hardware processors configured to: obtain image data including at least a representation of the patient's heart; obtain a region of interest from the image data; organize the region of interest into an input vector; apply the input vector through a trained graph; obtain an output vector representing a refined region of interest corresponding to the heart based on the application of the input vector through the trained graph; apply a deformable model on the obtained output vector representing the refined region of interest; and identify a segment of a heart chamber from the application of the deformable model on the obtained output vector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
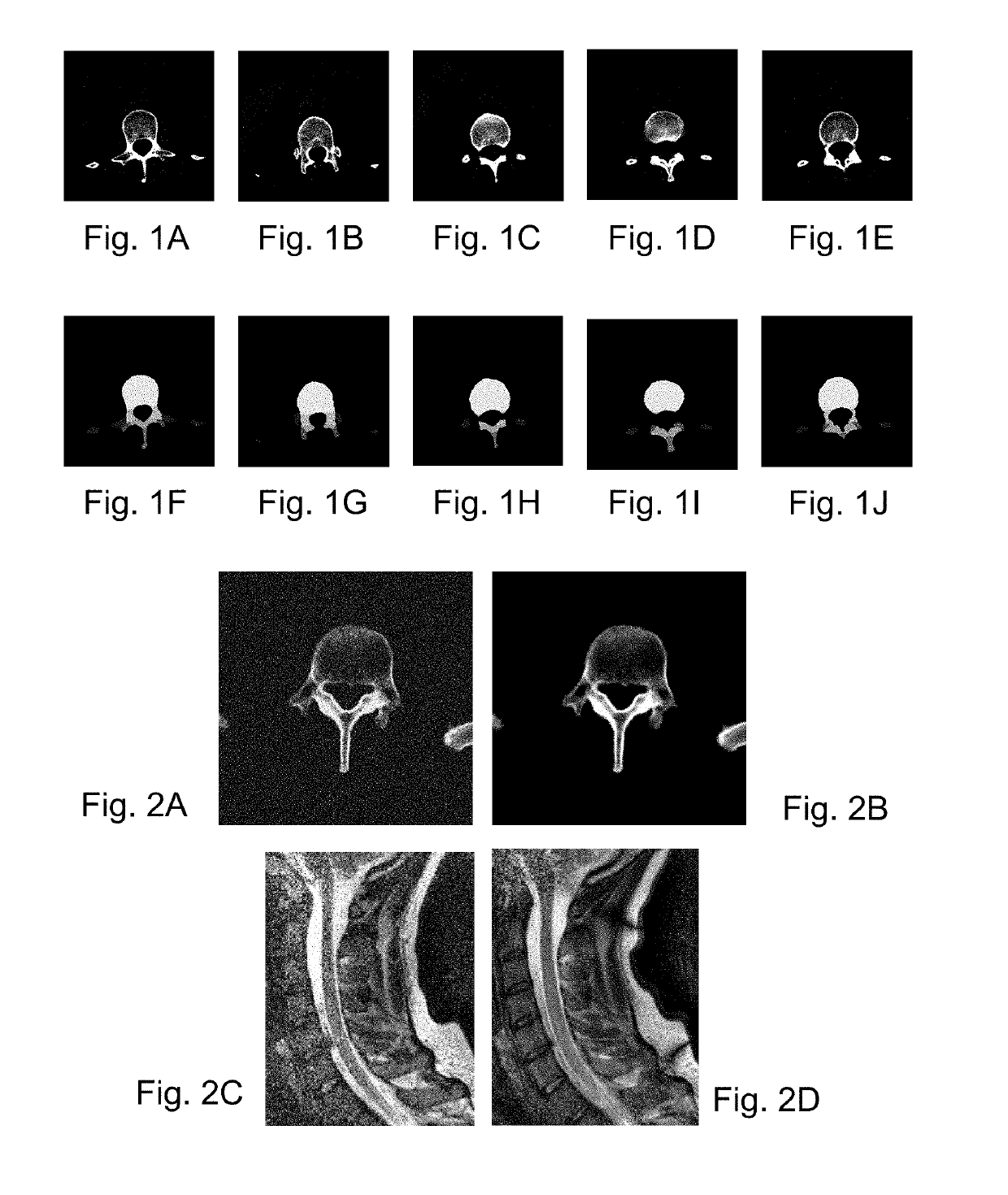
Method for Automatic Segmentation of Images
InactiveUS20100215238A1Simplify the segmentation processSimple processImage enhancementImage analysisContour segmentationPattern recognition
A method for automatic left ventricle segmentation of cine short-axis magnetic resonance (MR) images that does not require manually drawn initial contours, trained statistical shape models, or gray-level appearance models is provided. More specifically, the method employs a roundness metric to automatically locate the left ventricle. Epicardial contour segmentation is simplified by mapping the pixels from Cartesian to approximately polar coordinates. Furthermore, region growing is utilized by distributing seed points around the endocardial contour to find the LV myocardium and, thus, the epicardial contour. This is a robust technique for images where the epicardial edge has poor contrast. A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is utilized to smooth both the determined endocardial and epicardial contours. In addition to determining endocardial and epicardial contours, the method also determines the contours of papillary muscles and trabeculations.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
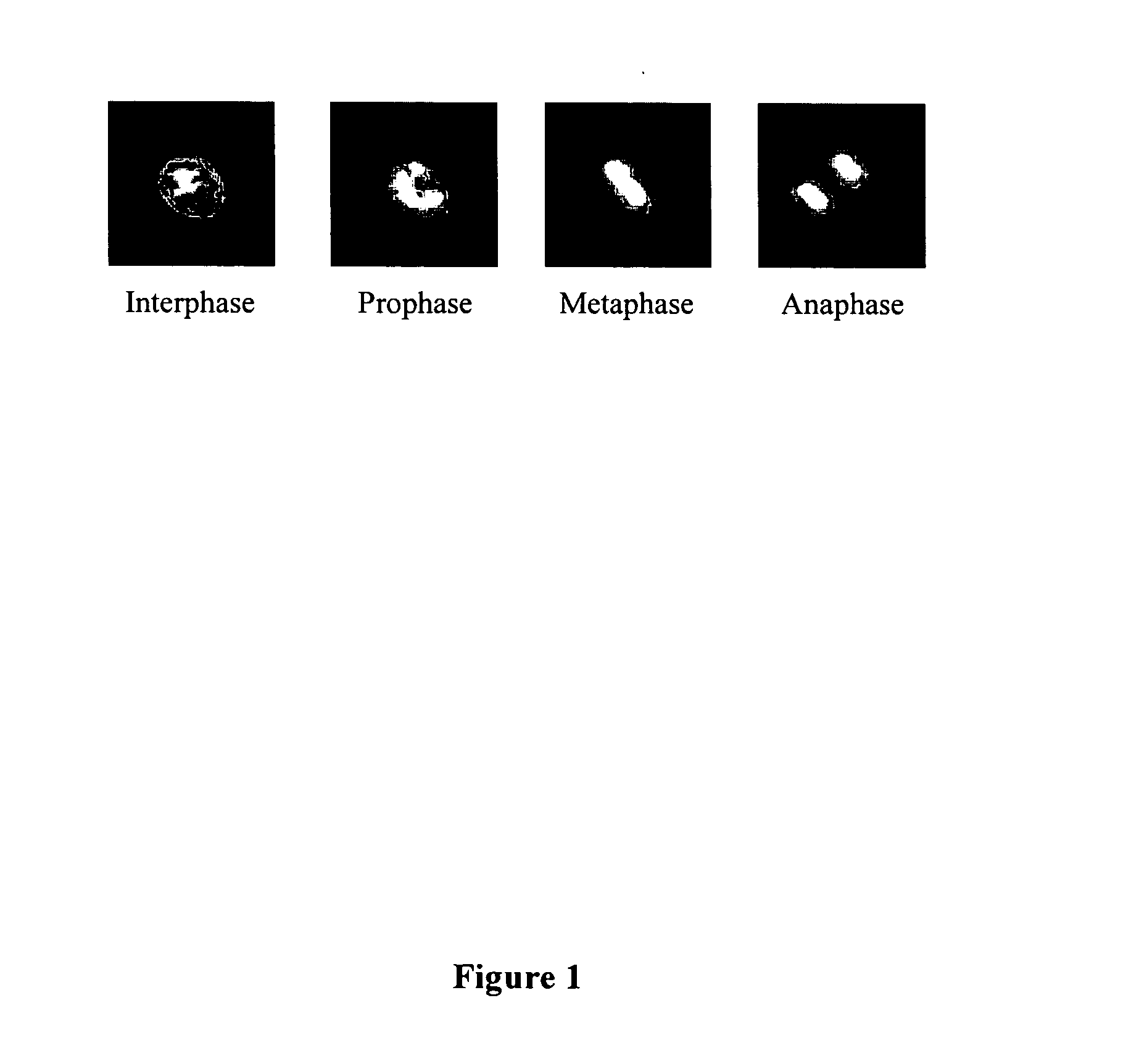
Automated segmentation, classification, and tracking of cell nuclei in time-lapse microscopy
InactiveUS20060127881A1Efficient dynamic cell imaging studyIncrease capacityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomated segmentationInterphase Cell
Methods and apparatus are provided for the automated analysis of images of living cells acquired by time-lapse microscopy. The new methods and apparatus can be used for the segmentation, classification and tracking of individual cells in a cell population, and for the extraction of biologically significant features from the cell images. Based upon certain extracted features, the inventive image analysis methods can characterize a cell as mitotic or interphase and / or can classify a cell into one of the following mitotic phases: prophase, metaphase, arrested metaphase, and anaphase with high accuracy.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC
Automated cardiac volume segmentation
ActiveUS20180259608A1Verify accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMissing data
Systems and methods for automated segmentation of anatomical structures, such as the human heart. The systems and methods employ convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to autonomously segment various parts of an anatomical structure represented by image data, such as 3D MRI data. The convolutional neural network utilizes two paths, a contracting path which includes convolution / pooling layers, and an expanding path which includes upsampling / convolution layers. The loss function used to validate the CNN model may specifically account for missing data, which allows for use of a larger training set. The CNN model may utilize multi-dimensional kernels (e.g., 2D, 3D, 4D, 6D), and may include various channels which encode spatial data, time data, flow data, etc. The systems and methods of the present disclosure also utilize CNNs to provide automated detection and display of landmarks in images of anatomical structures.
Owner:ARTERYS INC
Semi-automated segmentation method for 3-dimensional ultrasound
InactiveUS6251072B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationTherapy planning
The present invention provides a semi-automated method for three-dimensional ultrasound for constructing and displaying 3-D ultrasound images of luminal surfaces of blood vessels. The method comprises acquiring a 3-D ultrasound image of a target vessel and segmenting the luminal surfaces acquired from the 3-D ultrasound image of the target vessel to generate a 3-D ultrasound image of the lumen of the target vessel, wherein an inflating balloon model is used for segmenting the luminal surfaces of the target vessel. The method is useful for diagnostic assessment of bodily vessels as well as provides for therapy planning and as a prognostic indicator.
Owner:THE JOHN P ROBARTS RES INST
Image segmentation
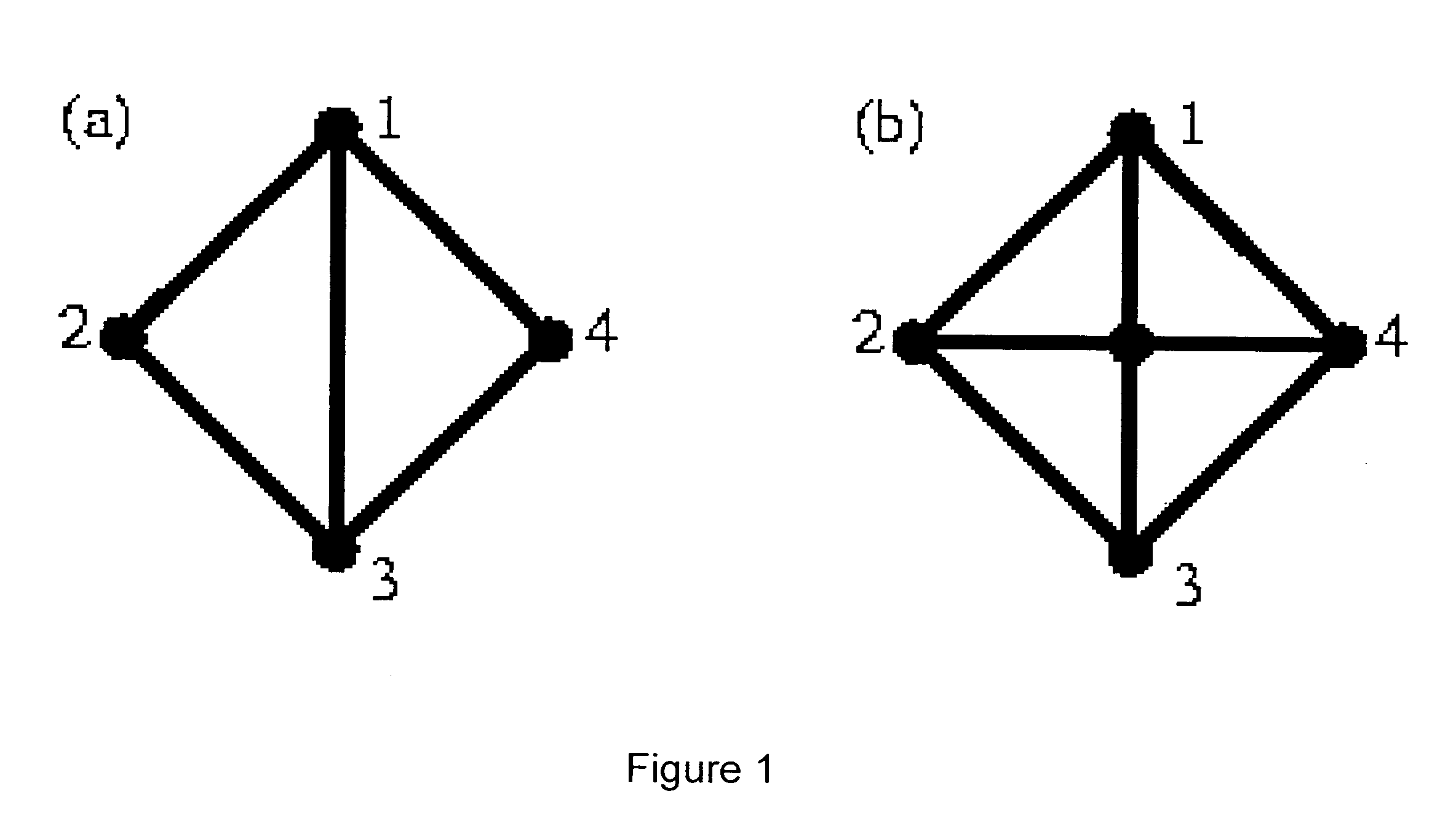
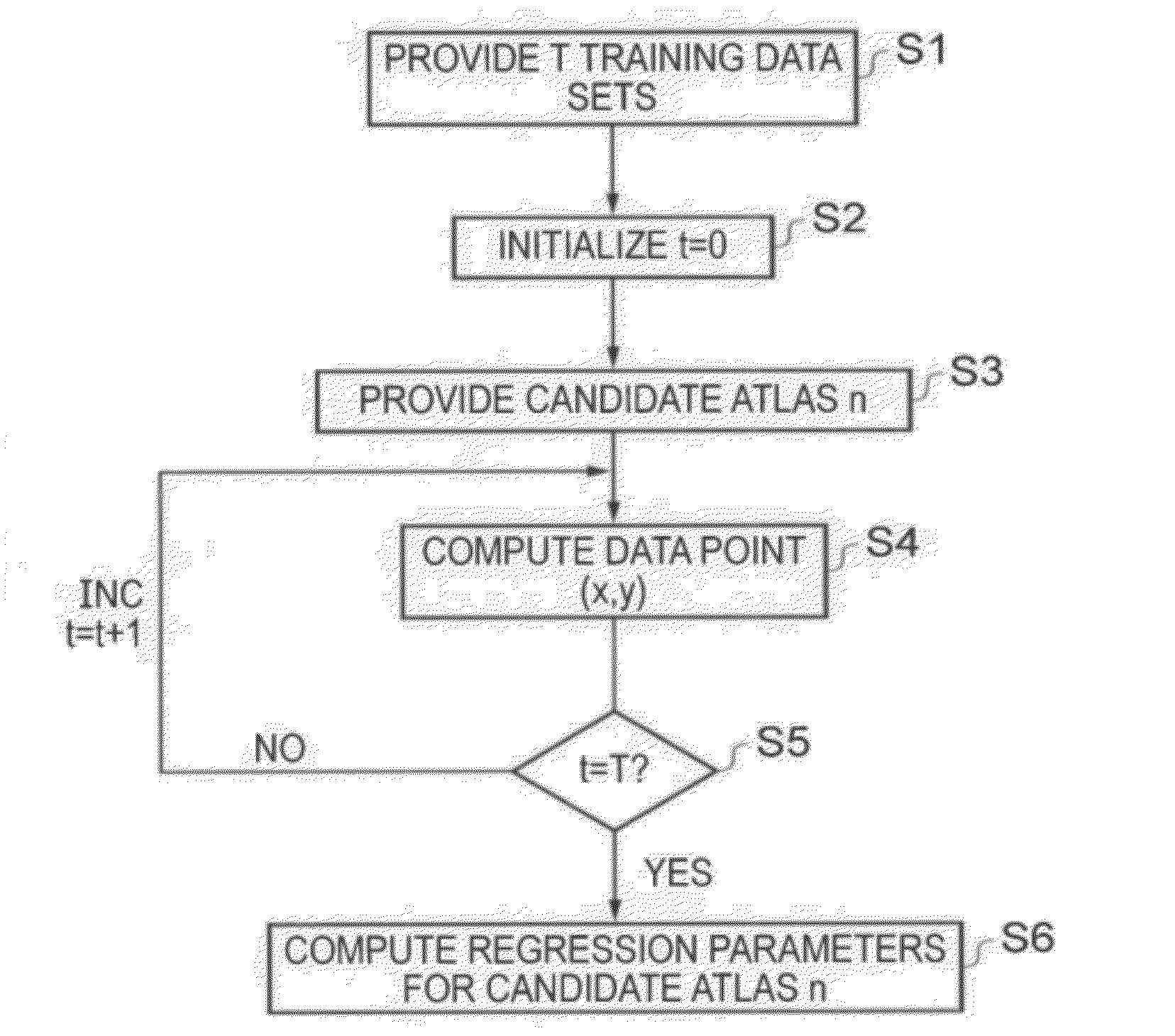
According to one embodiment there is provided a method of selecting a plurality of M atlases from among a larger group of N candidate atlases to form a multi-atlas data set to be used for computer automated segmentation of novel image data sets to mark objects of interest therein. A set of candidate atlases is used containing a reference image data set and segmentation data. Each of the candidate atlases is segmented against the others in a leave-one-out strategy, in which the candidate atlases are used as training data for each other. For each candidate atlas in turn, the following is carried out: registering; segmenting; computing an overlap; computing a value of the similarity measure for each of the registrations; and obtaining a set of regression parameters by performing a regression with the similarity measure being the independent variable and the overlap being the dependent variable. The M atlases are then selected from among all the N candidate atlases to form the multi-atlas data set, the M atlases being those atlases determined to collectively provide the highest aggregate overlap over all the training data image sets.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
MRI surgical systems for real-time visualizations using MRI image data and predefined data of surgical tools
ActiveUS8315689B2Increase speedImprove reliabilityMagnetic measurementsSurgical needlesMri guidedDisplay device
MRI-Surgical systems include: (a) at least one MRI-compatible surgical tool; (b) a circuit adapted to communicate with an MRI scanner; and (c) at least one display in communication with the circuit. The circuit electronically recognizes predefined physical characteristics of the at least one tool to automatically segment MR image data provided by the MRI scanner whereby the at least one tool constitutes a point of interface with the system. The circuit is configured to provide a User Interface that defines workflow progression for an MRI-guided surgical procedure and allows a user to select steps in the workflow, and wherein the circuit is configured to generate multi-dimensional visualizations using the predefined data of the at least one tool and data from MRI images of the patient in substantially real time during the surgical procedure.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
Automated segmentation utilizing fully convolutional networks
ActiveUS20180218497A1Quantity minimizationReduce identified areaImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresTunica intima
Systems and methods for automated segmentation of anatomical structures (e.g., heart). Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) may be employed to autonomously segment parts of an anatomical structure represented by image data, such as 3D MRI data. The CNN utilizes two paths, a contracting path and an expanding path. In at least some implementations, the expanding path includes fewer convolution operations than the contracting path. Systems and methods also autonomously calculate an image intensity threshold that differentiates blood from papillary and trabeculae muscles in the interior of an endocardium contour, and autonomously apply the image intensity threshold to define a contour or mask that describes the boundary of the papillary and trabeculae muscles. Systems and methods also calculate contours or masks delineating the endocardium and epicardium using the trained CNN model, and anatomically localize pathologies or functional characteristics of the myocardial muscle using the calculated contours or masks.
Owner:ARTERYS INC
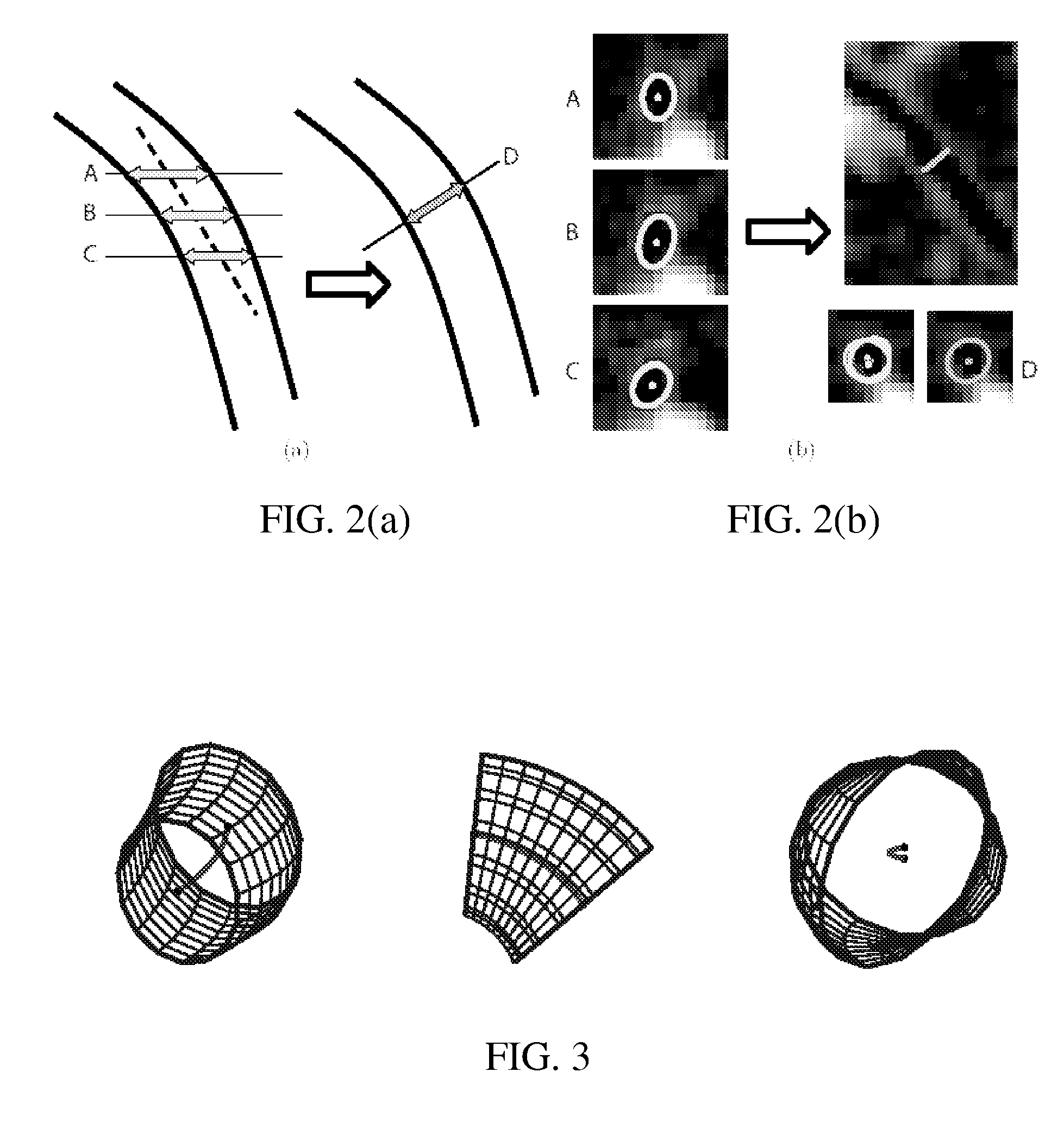
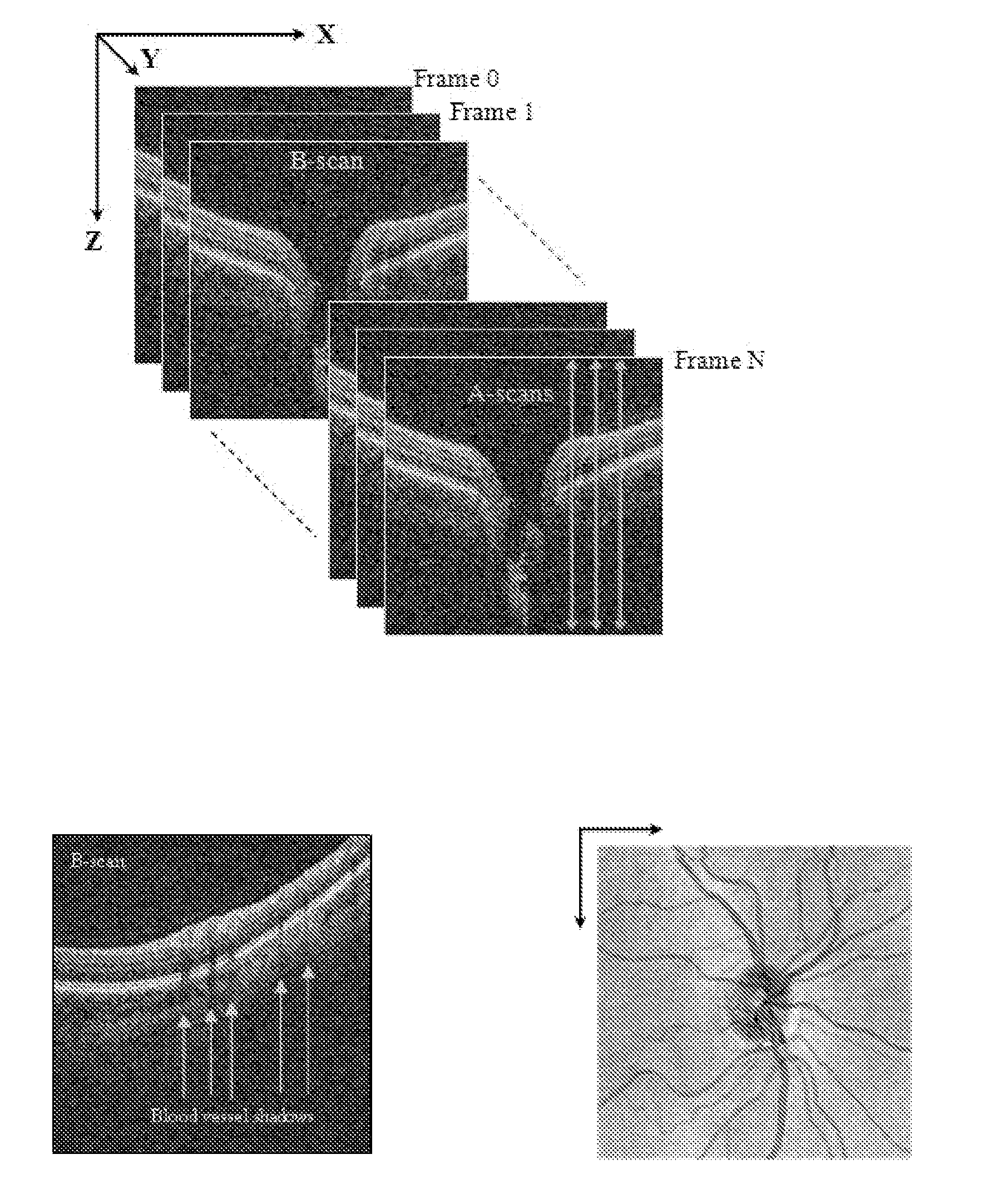
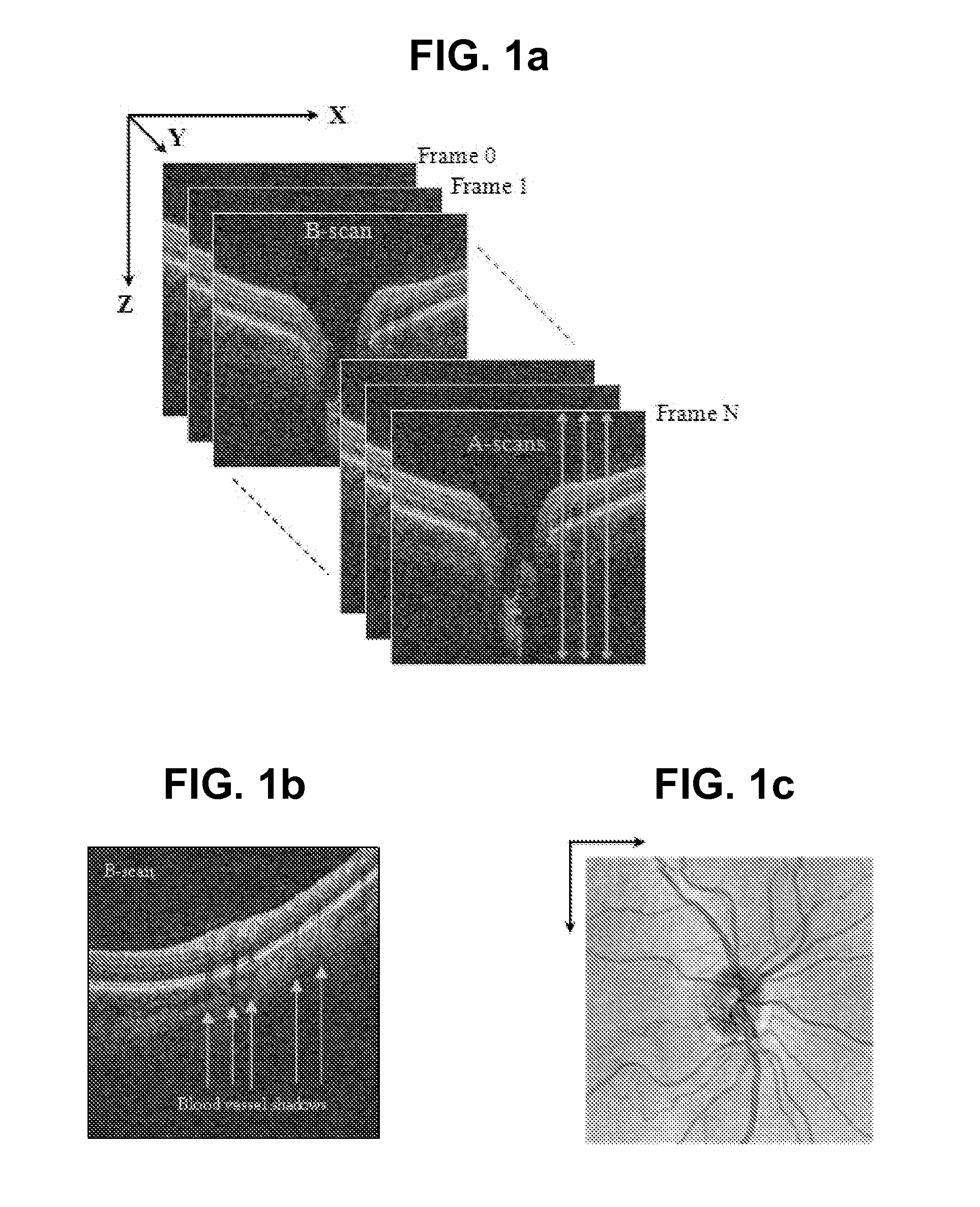
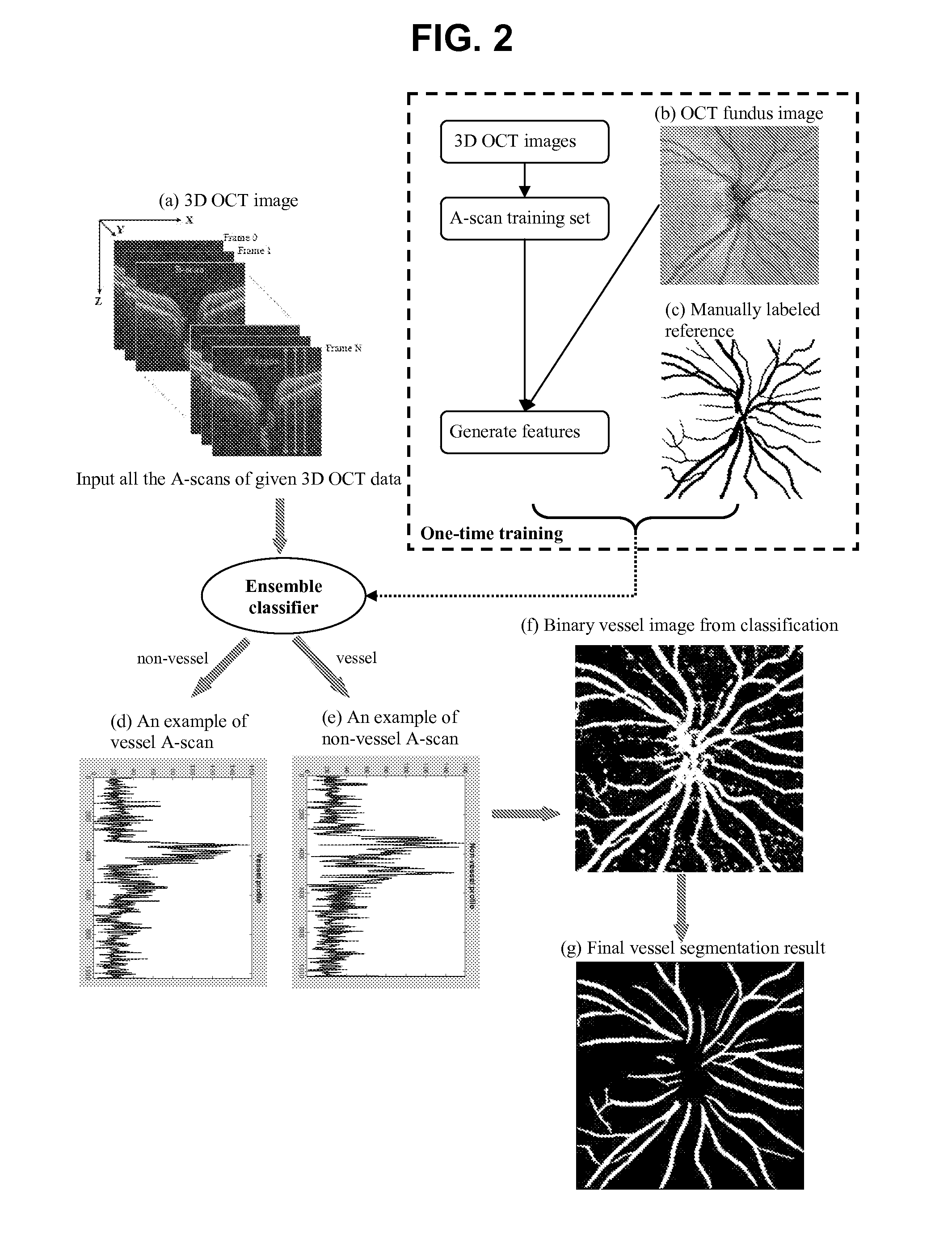
Blood vessel segmentation with three dimensional spectral domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20120213423A1Precise patternImage enhancementImage analysisStudy methodsRetinal image registration
In the context of the early detection and monitoring of eye diseases, such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, the use of optical coherence tomography presents the difficulty, with respect to blood vessel segmentation, of weak visibility of vessel pattern in the OCT fundus image. To address this problem, a boosting learning approach uses three-dimensional (3D) information to effect automated segmentation of retinal blood vessels. The automated blood vessel segmentation technique described herein is based on 3D spectral domain OCT and provides accurate vessel pattern for clinical analysis, for retinal image registration, and for early diagnosis and monitoring of the progression of glaucoma and other retinal diseases. The technique employs a machine learning algorithm to identify blood vessel automatically in 3D OCT image, in a manner that does not rely on retinal layer segmentation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
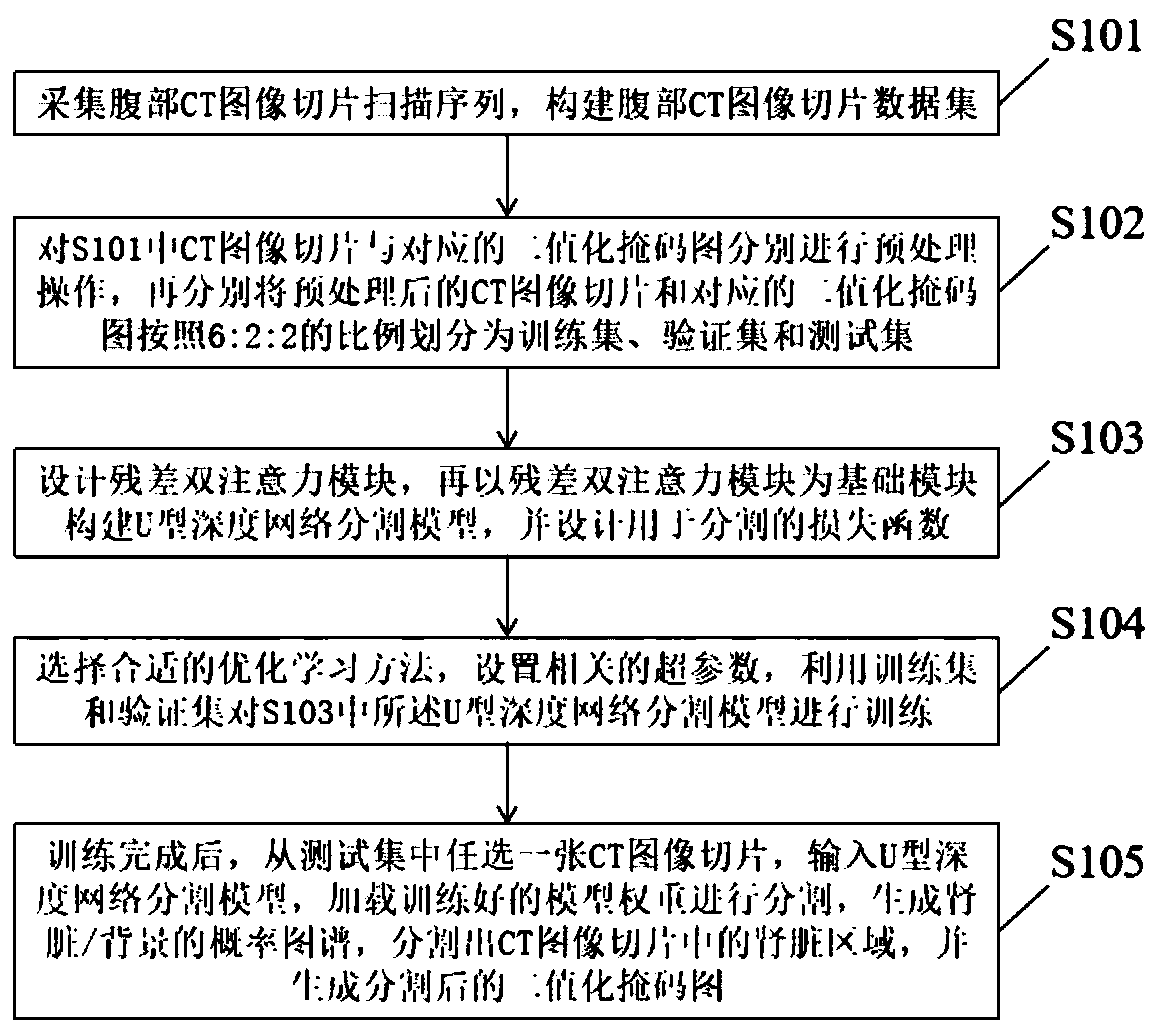
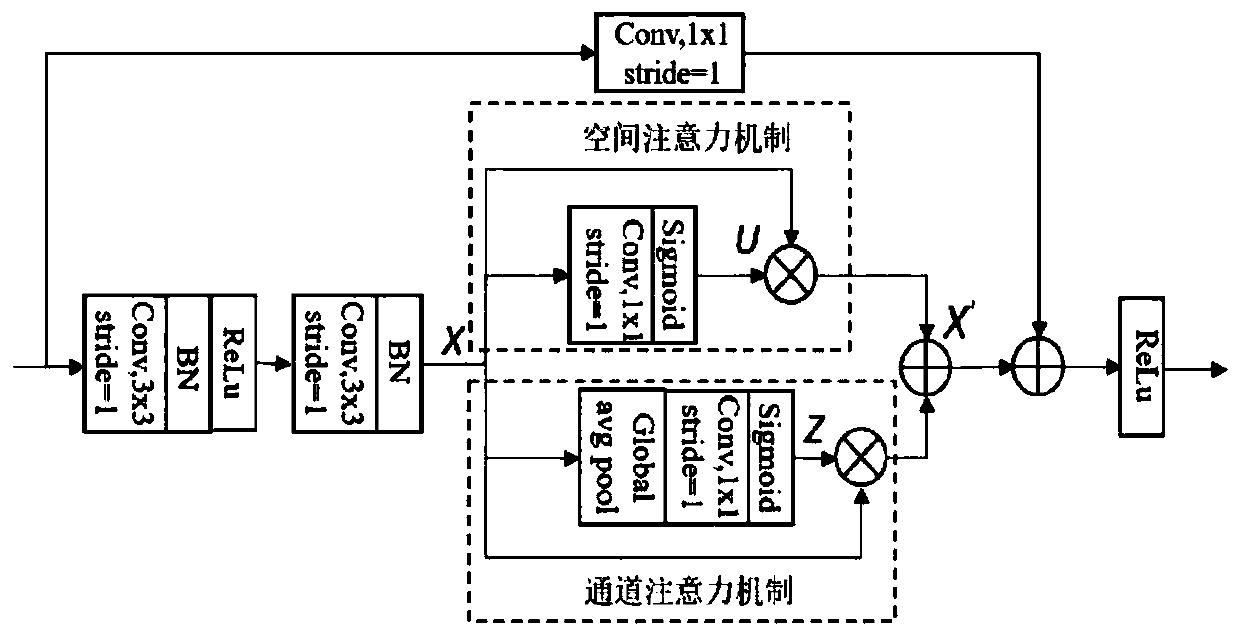
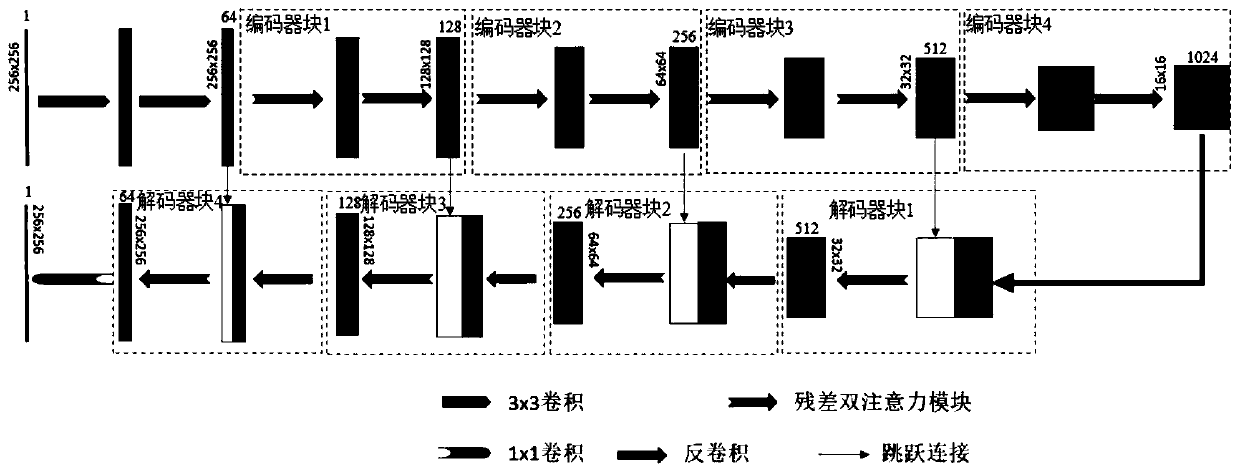
CT image kidney segmentation algorithm based on residual double-attention deep network
PendingCN110675406AResponds effectively to shape changesRobust to shape changesImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationFeature learning
The invention discloses a CT image kidney segmentation algorithm based on a residual double-attention deep network. According to the method, the advantage that the residual error unit can repeatedly utilize the features and the excellent feature learning capability of the double attention mechanism are combined; a residual double attention module is designed; and a residual double attention moduleis used as a basic module to construct a U-shaped deep network segmentation model, and a loss function for segmentation is designed at the same time, so that the U-shaped deep network segmentation model can pay more attention to kidney region features, can effectively cope with shape changes of the kidney with cystic lesions, and can maintain robustness for the shape changes of the kidney with cystic lesions. Therefore, the boundary of the kidney area is accurately positioned, and automatic segmentation of the kidney area in the CT image is achieved, and a good segmentation effect is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
System and methods for rapid and automated screening of cells
A system for performing automated cell screening in drug discovery, including an automated microscope, a fast autofocus device and a digital imaging system. Processes are implemented in software through which relevant cellular material is segmented and quantified with minimal user interaction. Improvements in the following areas: known methods for image processing are implemented in such a way that automated segmentation is achieved; sets of known measurements (pixel counting, etc.) are implemented as methods which demonstrate aspects of biology in a reliable fashion; components for automated positioning, focusing, imaging and processing of a multiplicity of samples are integrated as systems within which the segmentation and measurement methods may be mounted; and components and methods are adapted into systems which yield more highly automated and more rapid cell screening.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
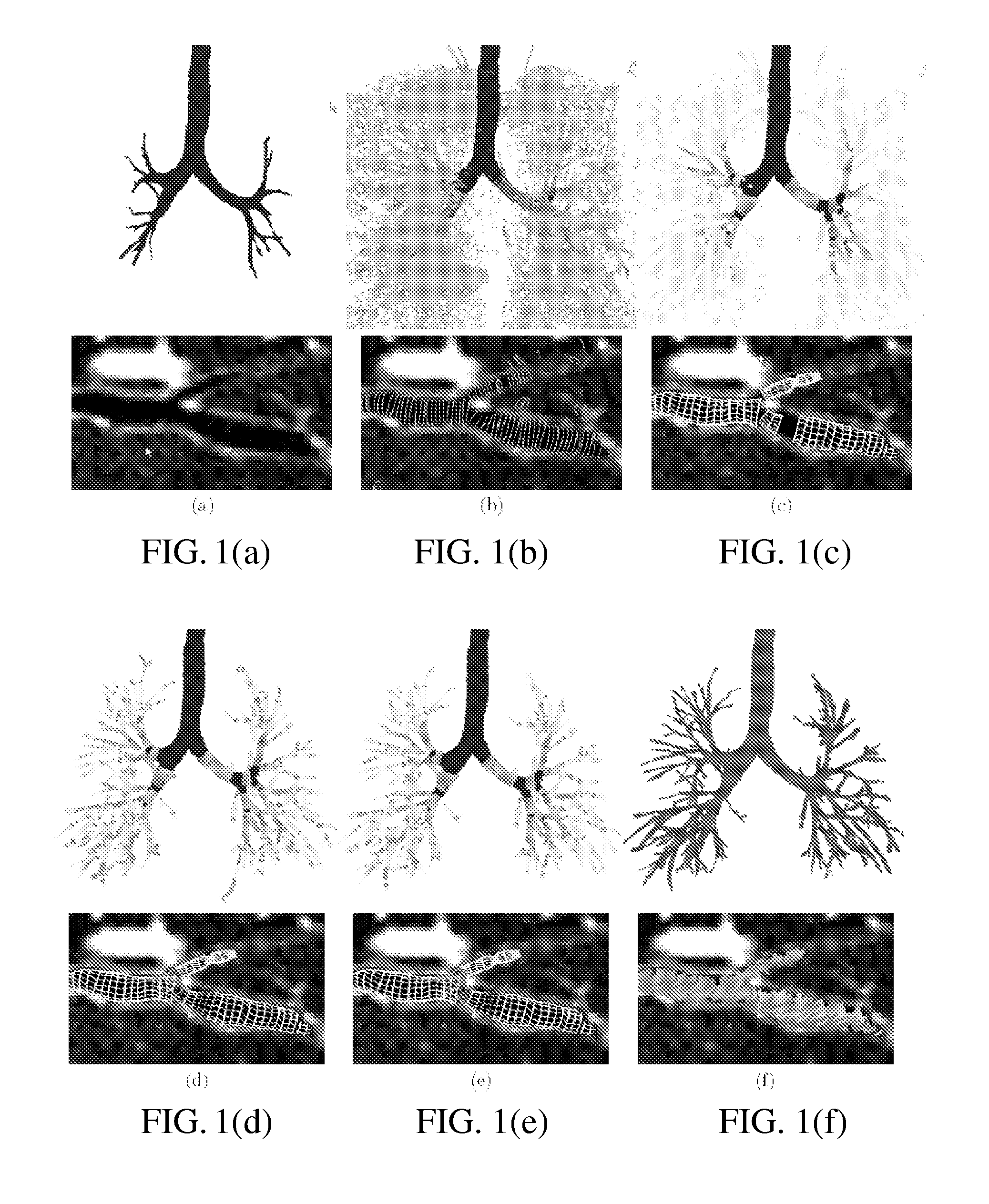
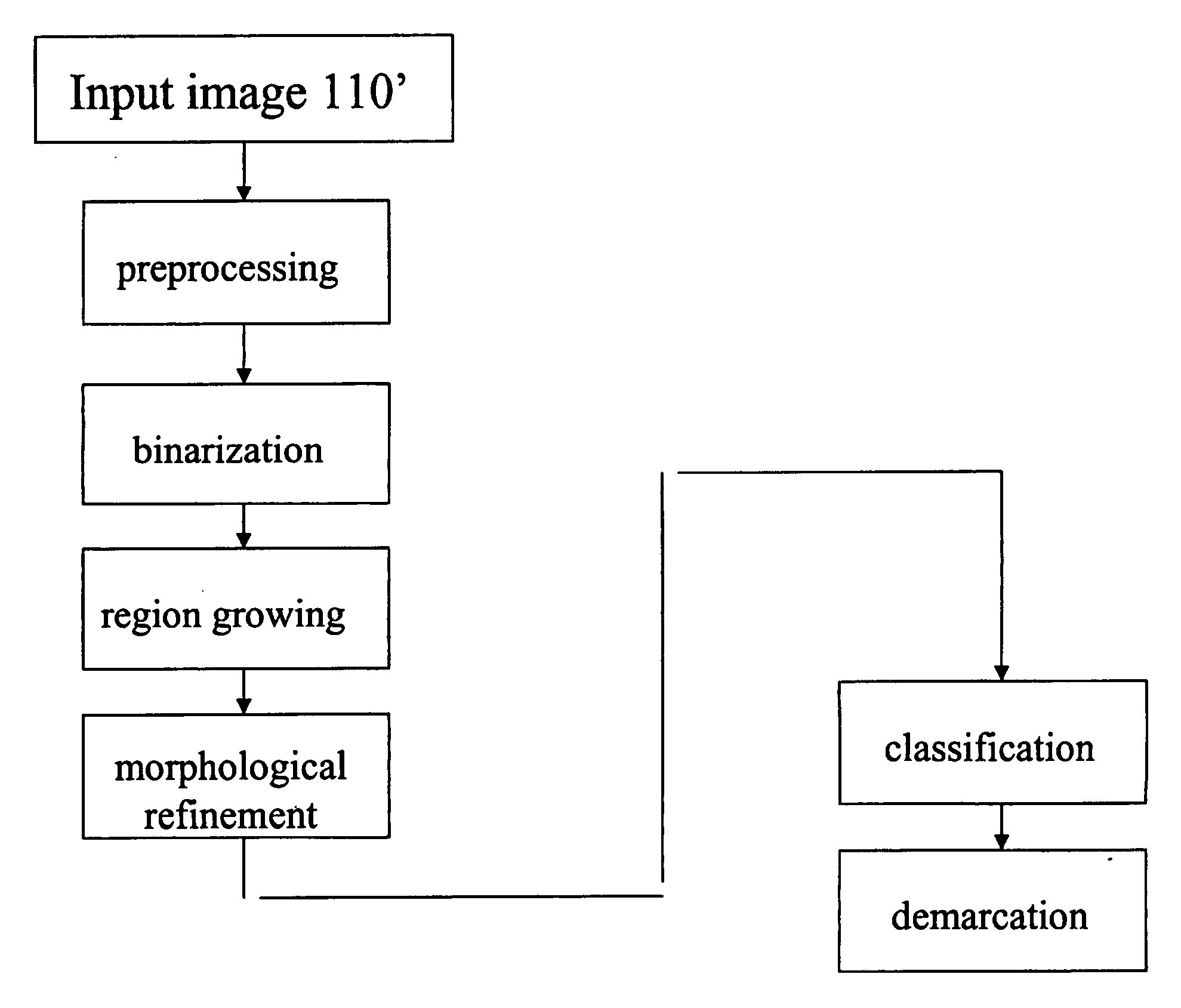
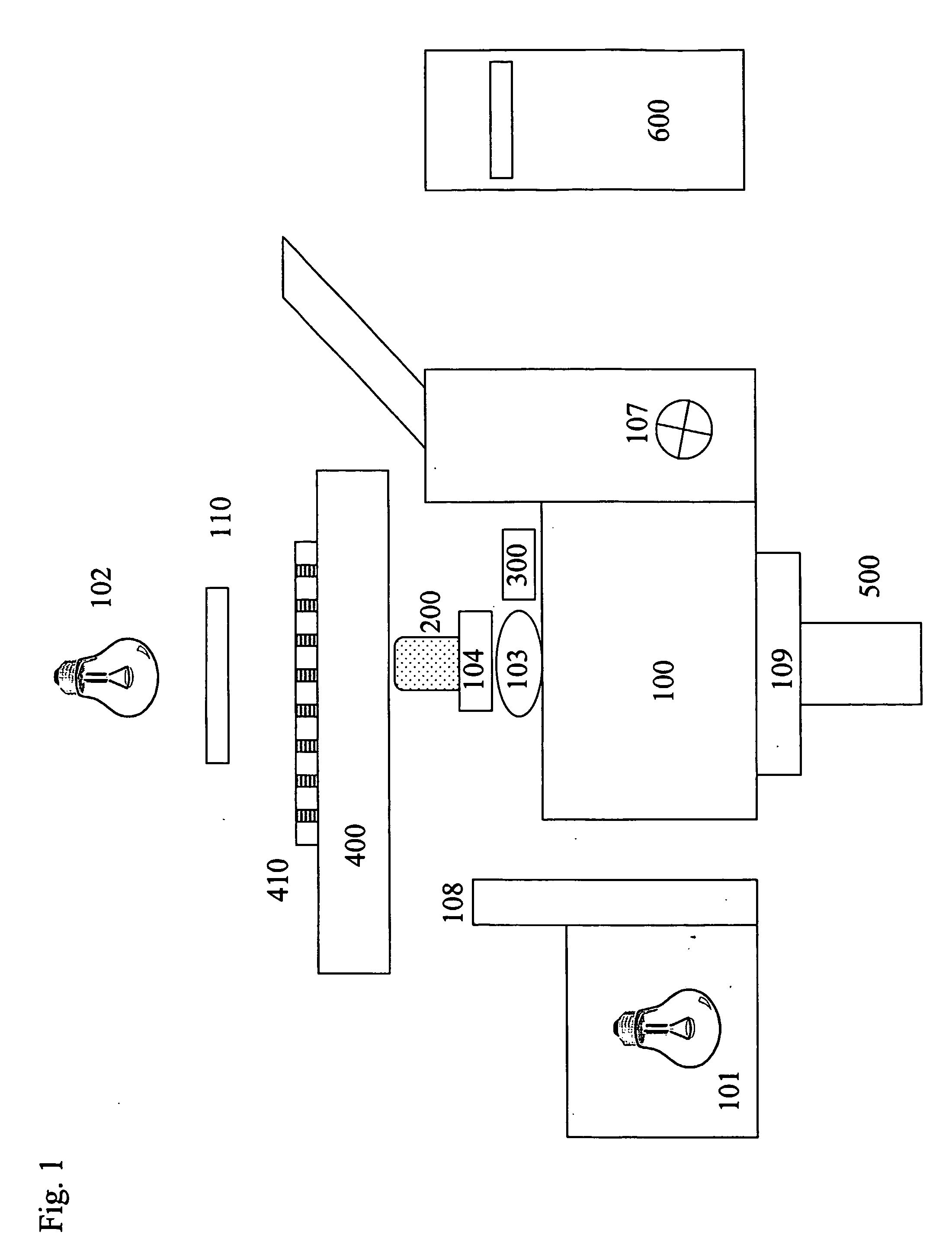
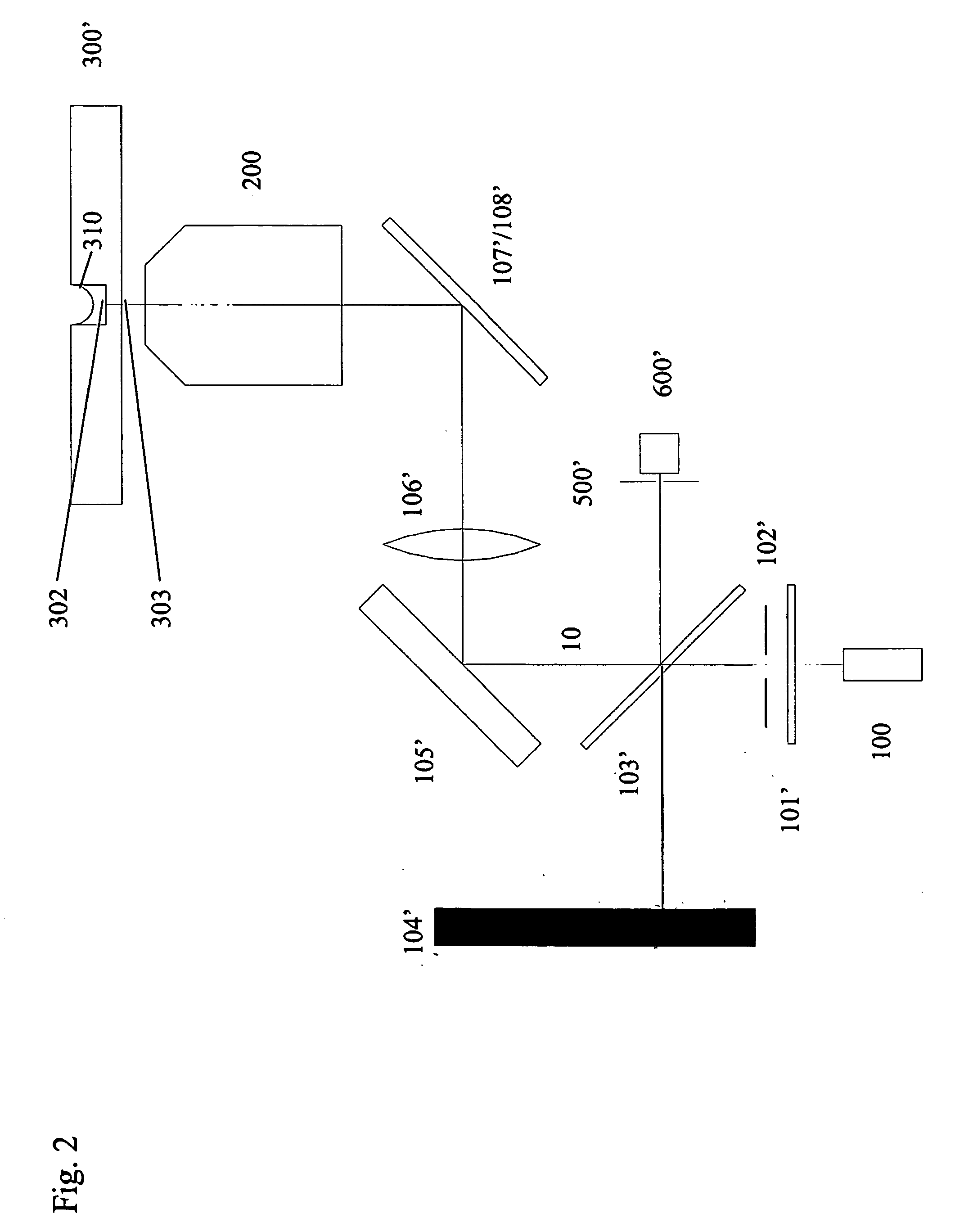
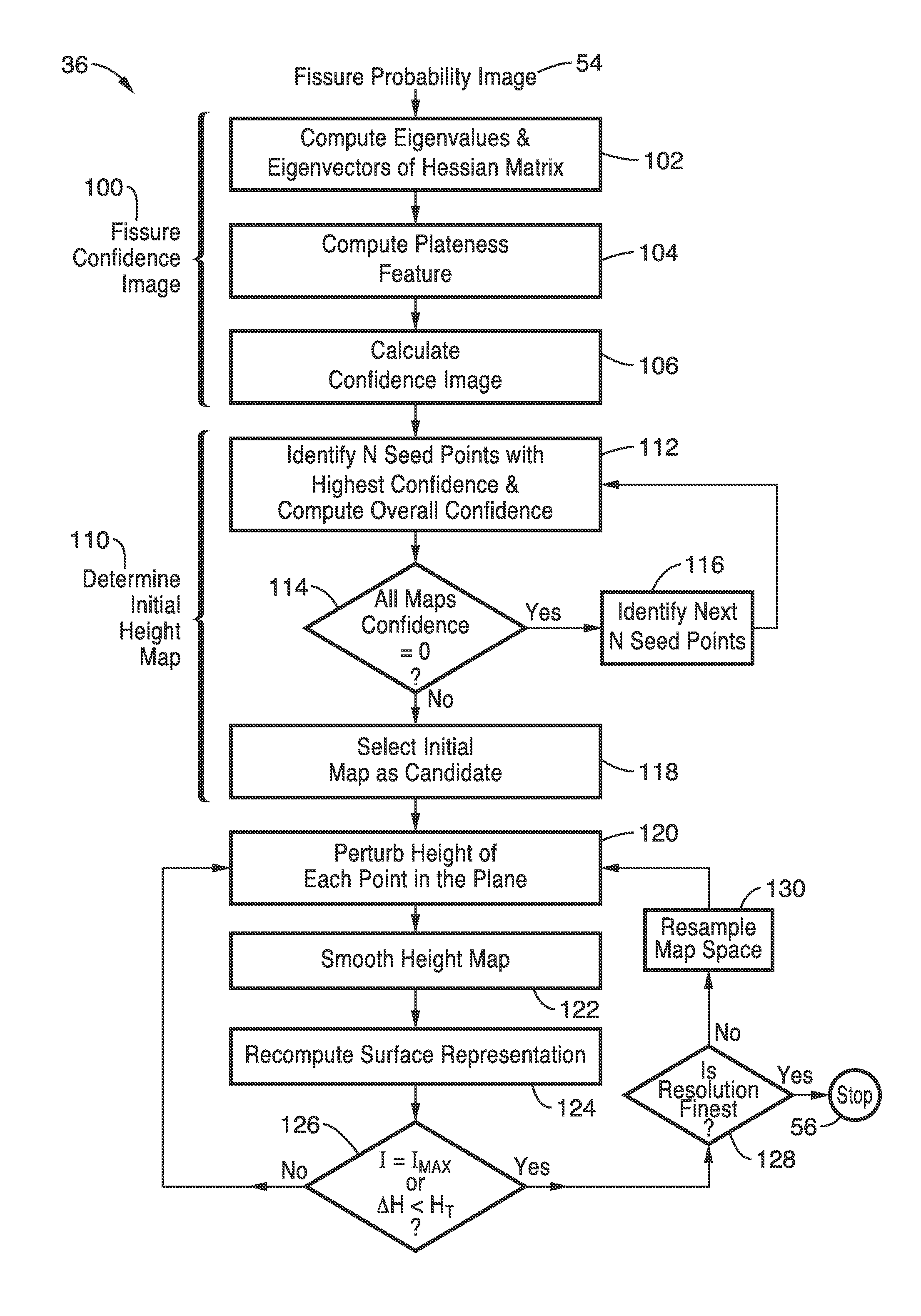
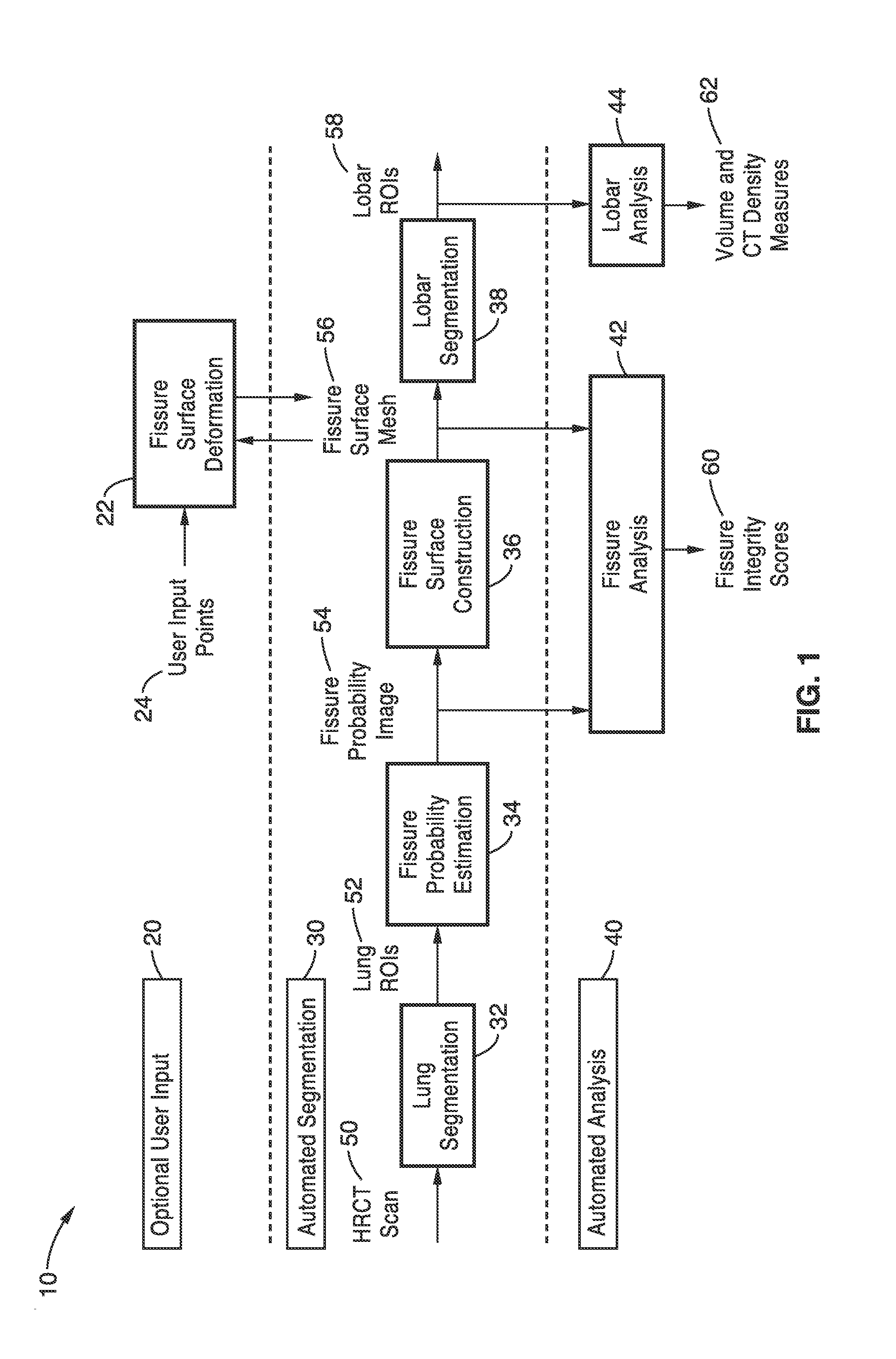
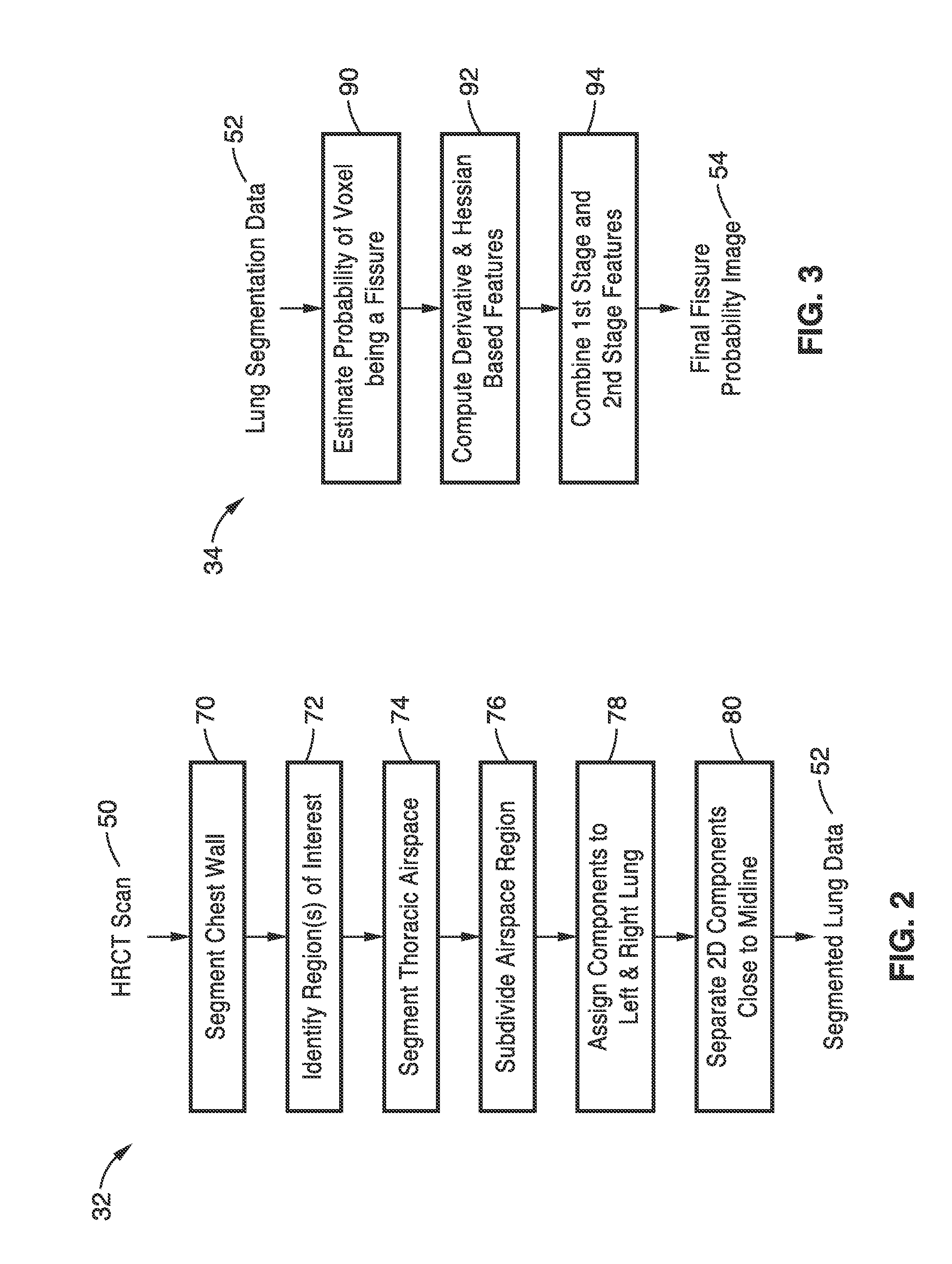
Lung, lobe, and fissure imaging systems and methods
An automated or semi-automated system and methods are disclosed that provide a rapid and repeatable method for identifying lung, lobe, and fissure voxels in CT images, and allowing for quantitative lung assessment and fissure integrity analysis. An automated or semi-automated segmentation and editing system and methods are also disclosed for lung segmentation and identification of lung fissures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
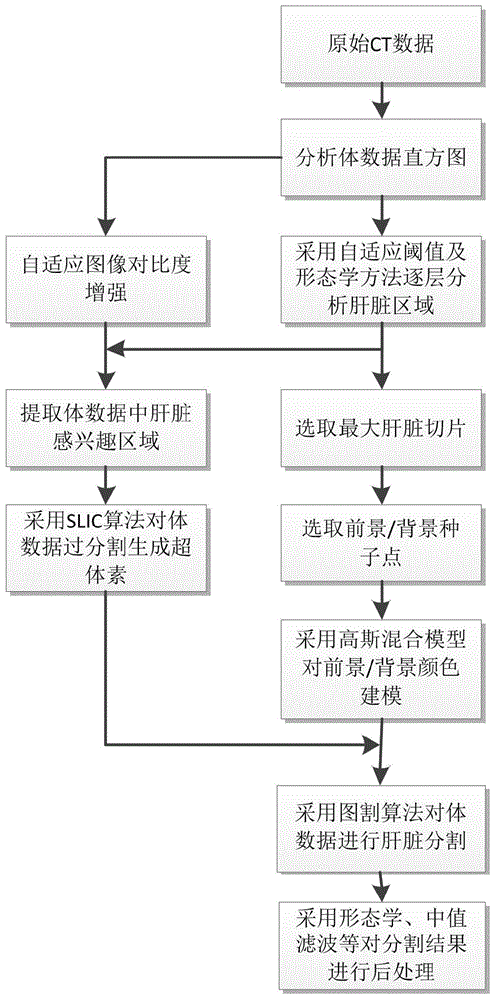
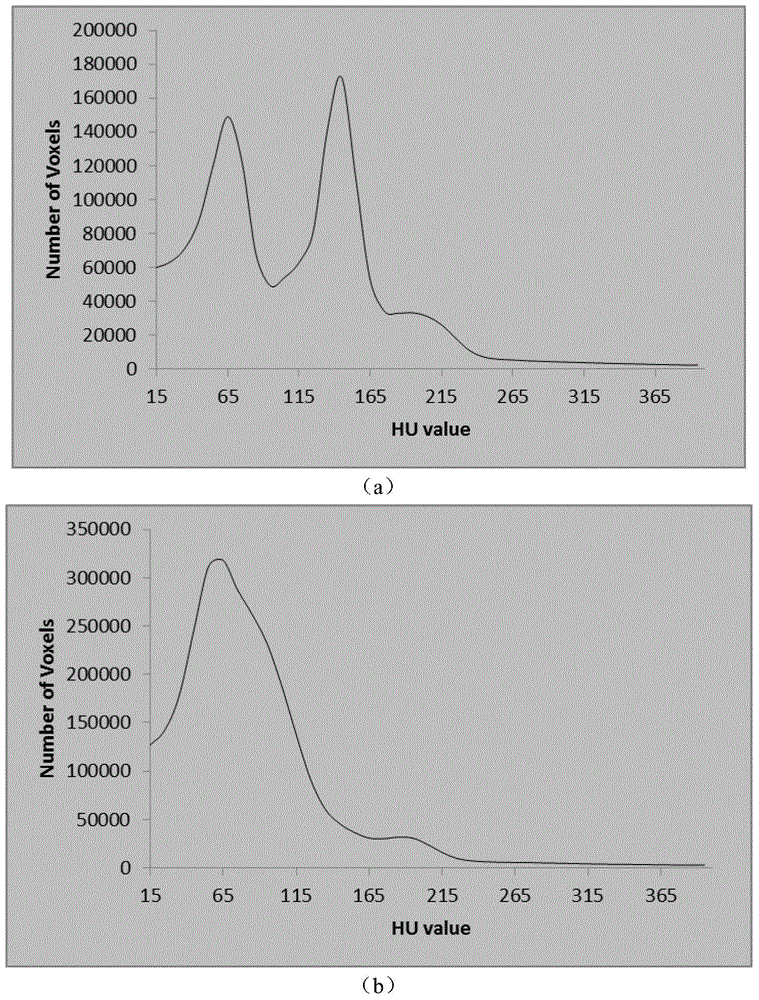
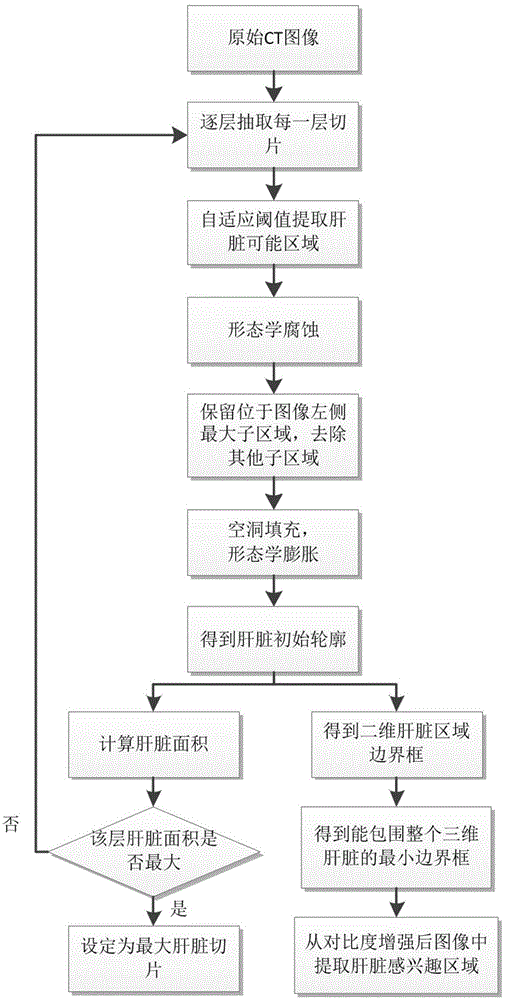
Three-dimensional liver CT (computed tomography) image automatically segmenting method based on hyper voxels and graph cut algorithm
InactiveCN104809723AAvoid robustness effectsIncrease the level of automationImage analysisImage contrastComputed tomography
Disclosed is a three-dimensional liver CT image automatically segmenting method based on hyper voxels and the graph cut algorithm. The method comprises analyzing a volume data histogram to adaptively enhance the image contrast; performing primary liver contour segmentation layer by layer through an adaptive threshold and an morphological method, selecting the largest liver segment to compute and extract a liver interest area; selecting seed points on the largest liver segment according to a primary liver contour, modelling foreground and background colors through a Gaussian mixed model; generating hyper voxels on the contrast-enhanced liver interest area through an SLIC (simple linear iterative clustering) algorithm, structuring an undirected weighted graph by taking the hyper voxels as the vertex, and segmenting the undirected weighted graph through the graph cut algorithm; performing postprocessing on segmentation results through a morphological algorithm. The three-dimensional liver CT image automatically segmenting method based on the hyper voxels and the graph cut algorithm can achieve rapid and accurate automatic segmentation of the liver in a three-dimensional abdominal CT image.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
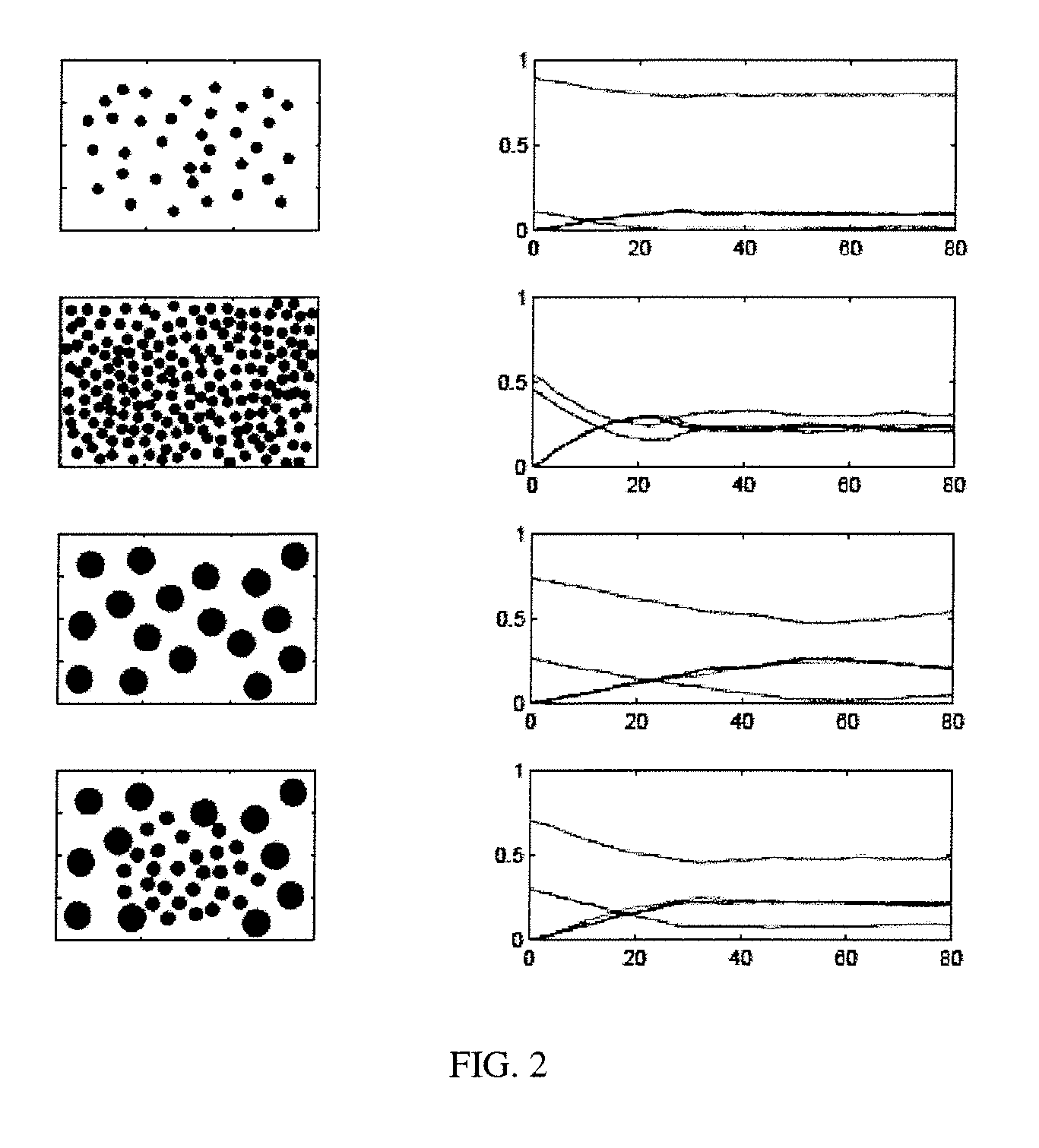
Methods and systems for automated segmentation of dense cell populations
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
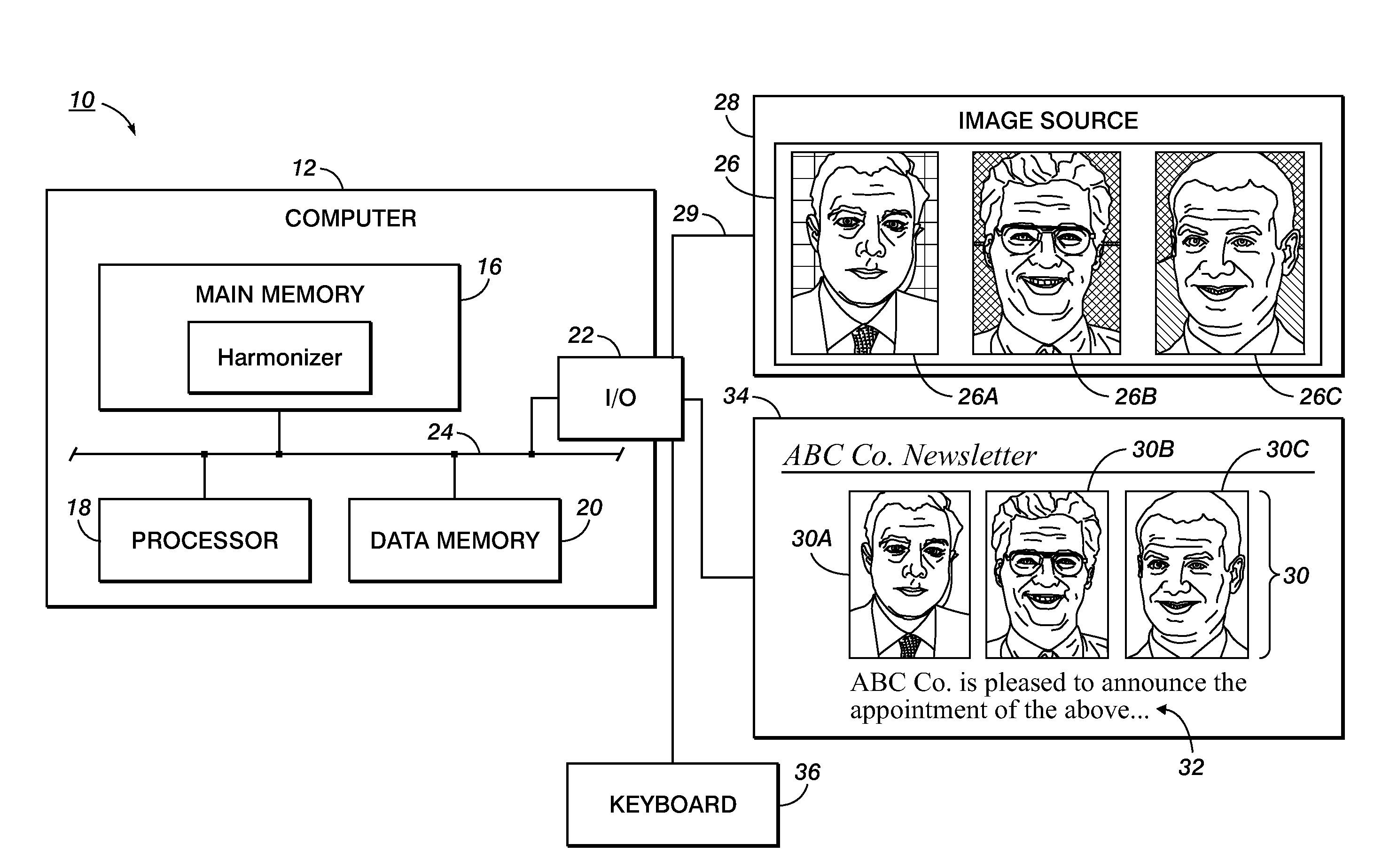
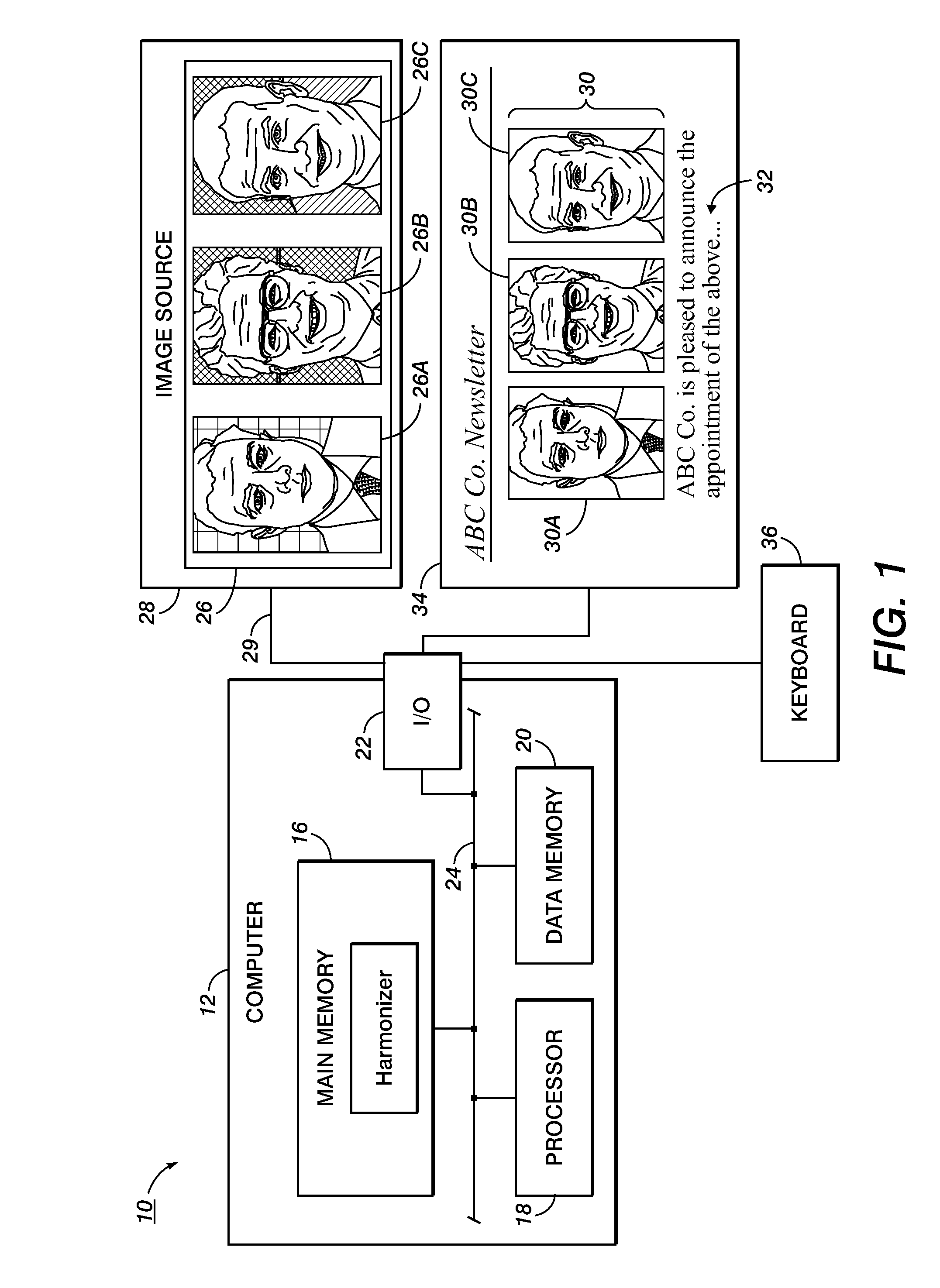
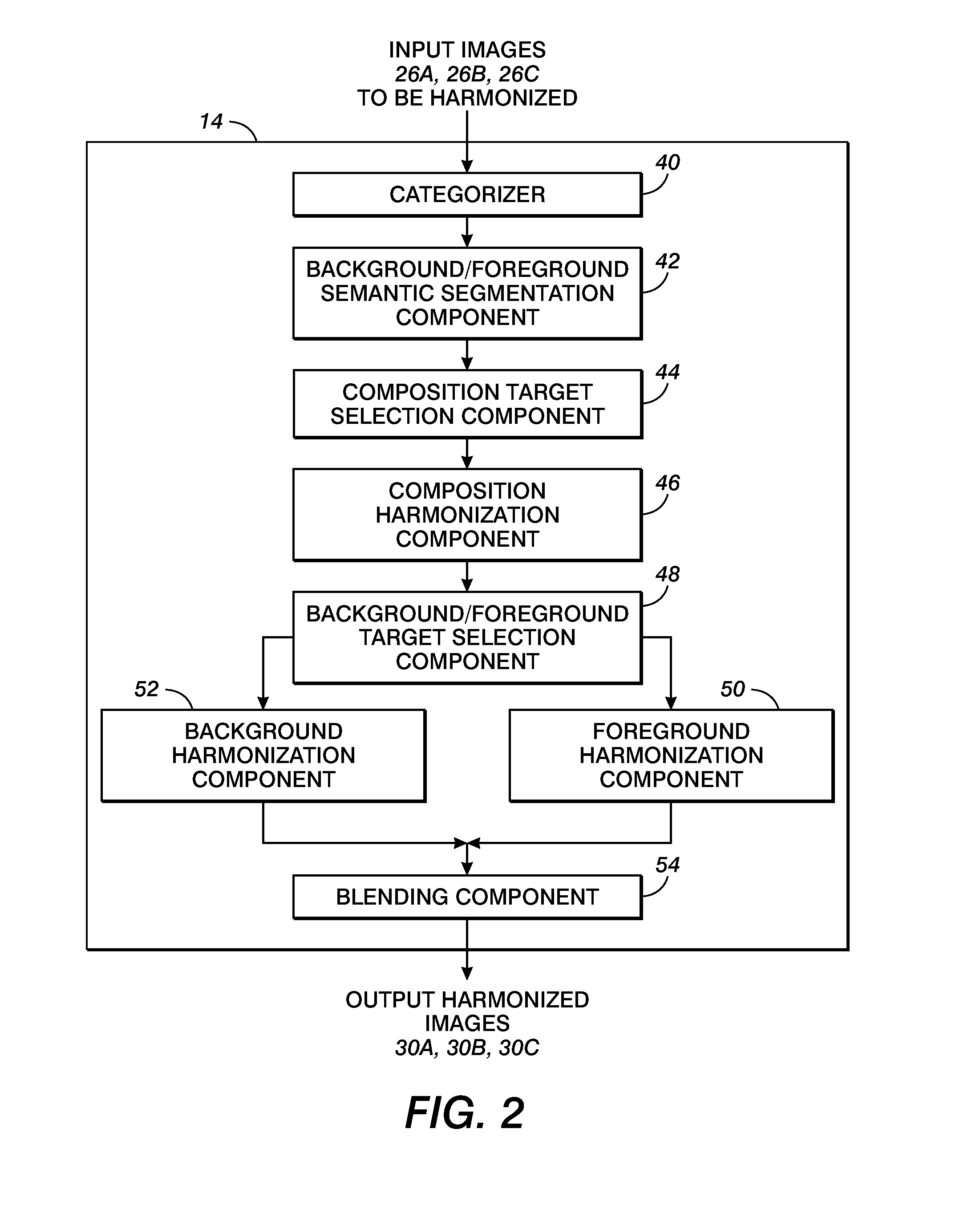
Content-based image harmonization
A harmonization system and method are disclosed which allow harmonization of a set of digital images. The images are automatically segmented into foreground and background regions and the foreground and background regions are separately harmonized. This allows region-appropriate harmonization techniques to be applied. The segmenting and harmonizing may be category dependent, allowing object-specific techniques to be applied.
Owner:XEROX CORP
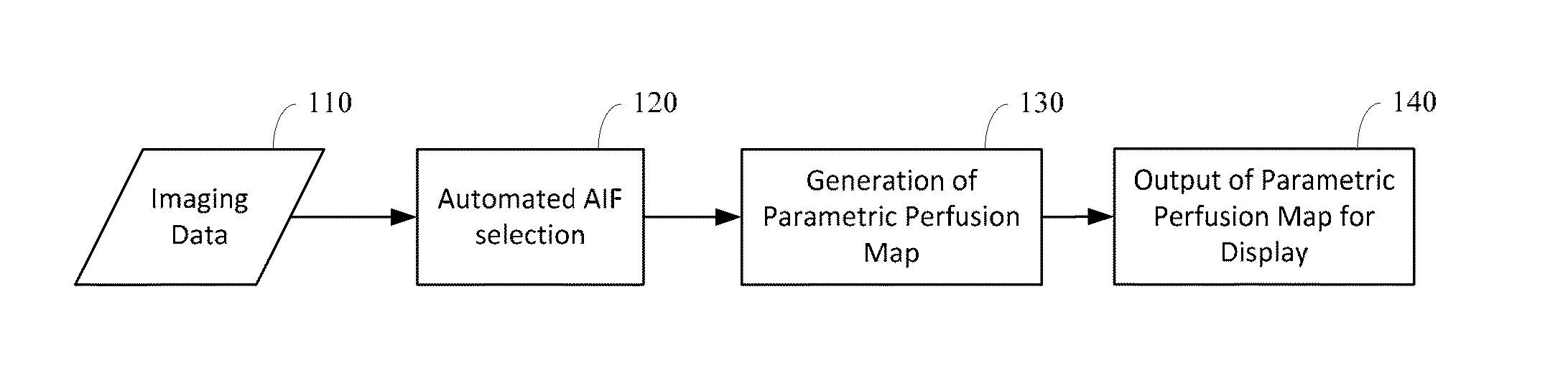
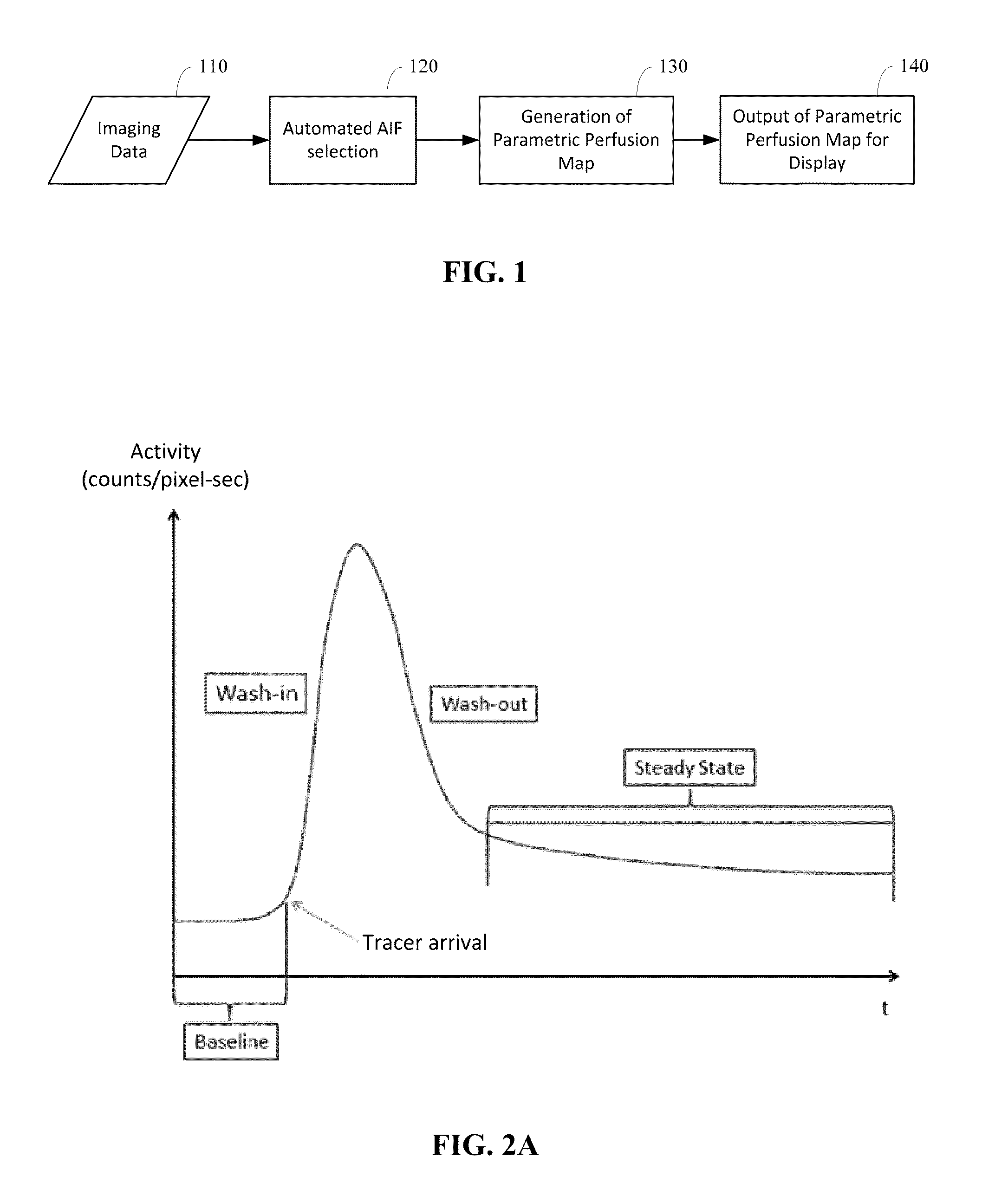
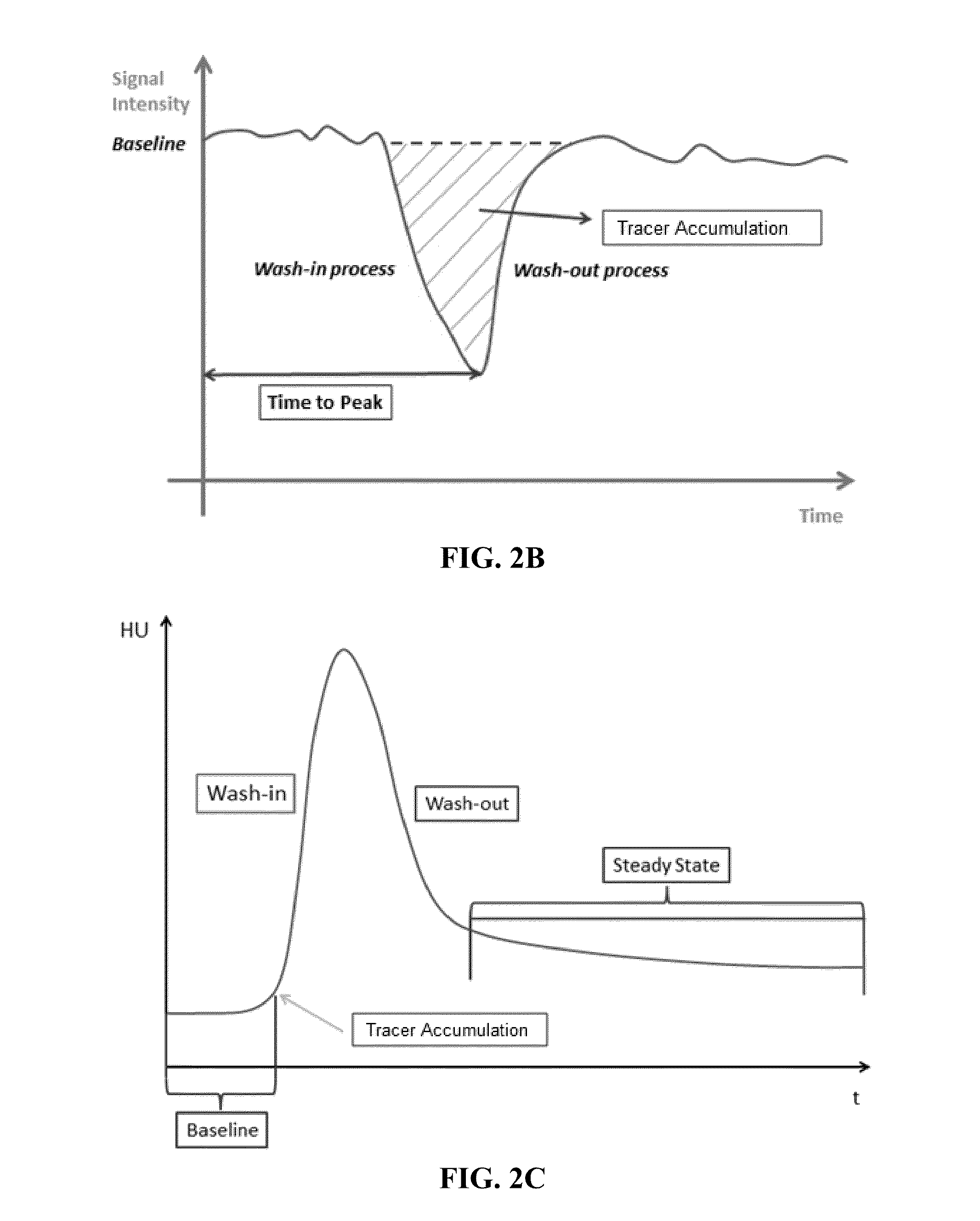
Automated determination of arterial input function areas in perfusion analysis
InactiveUS20140163403A1Well formedMagnetic measurementsCatheterImaging modalitiesArterial input function
Automatic arterial input function (AIF) area determination is provided that can be used to facilitate the generation of parametric maps for perfusion studies based on various imaging modalities and covering a variety of tissues. Automatic AIF determination can be accomplished by extracting characteristic parameters such as maximum slope, maximum enhancement, time to peak, time to wash-out, and wash-out slope. Characteristic parameter maps are generated to show relationships among the extracted characteristic parameters, and the characteristic parameter maps are converted to a plurality of two-dimensional plots. Automated segmentation of non-AIF tissues and determination of AIF areas can be accomplished by automatically finding peaks and valleys of each phase of AIF areas on the plurality of two-dimensional plots.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
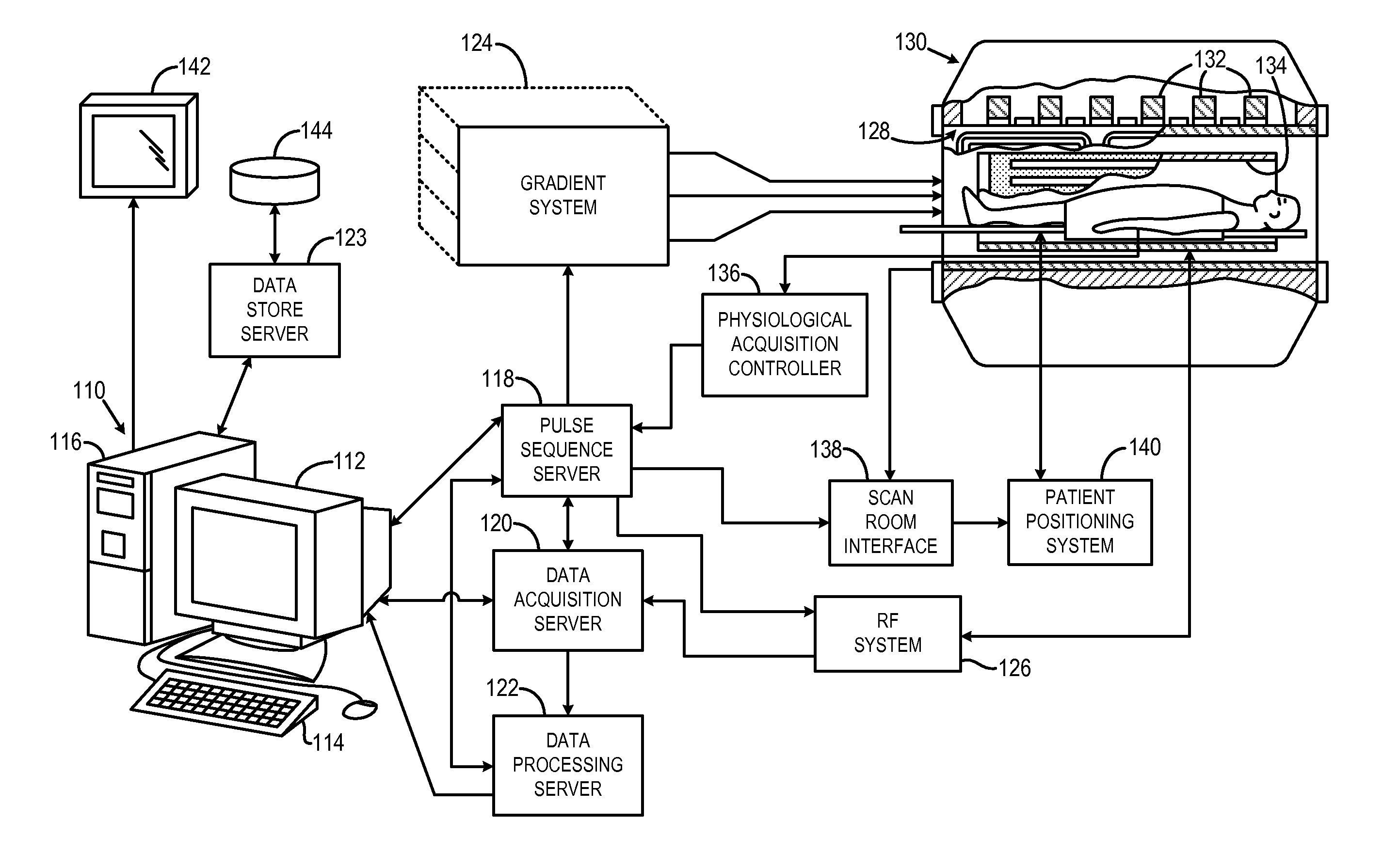
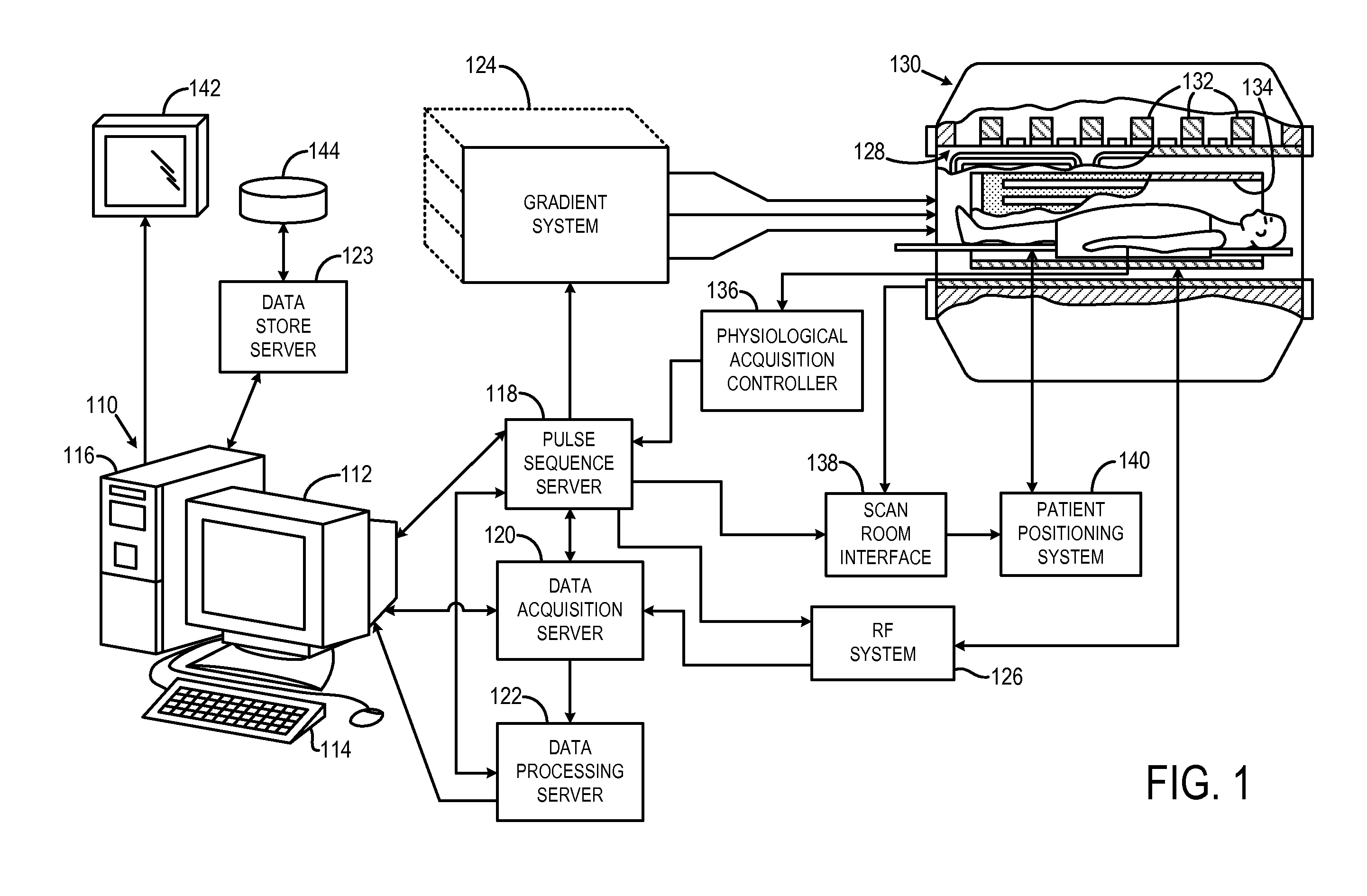
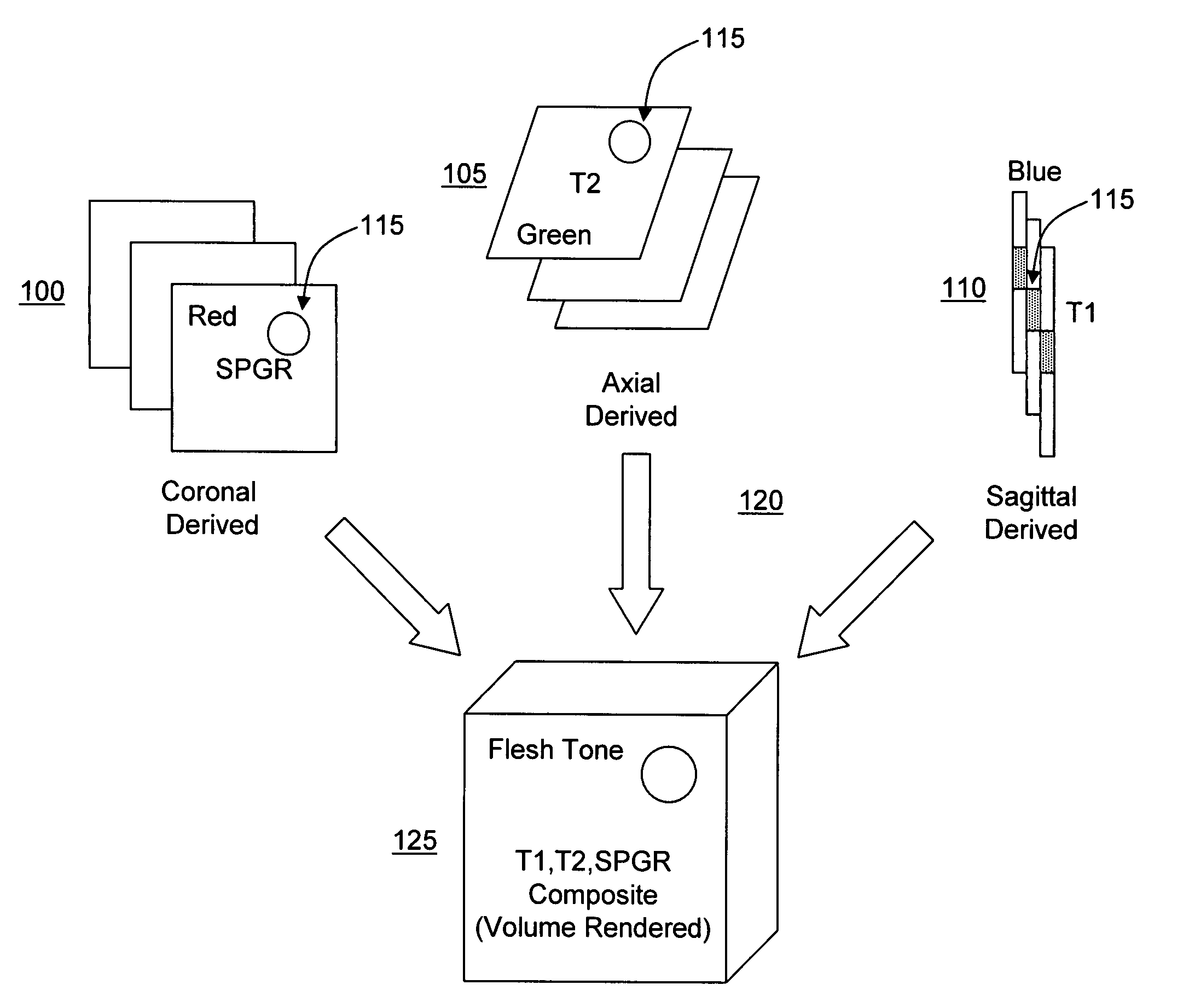
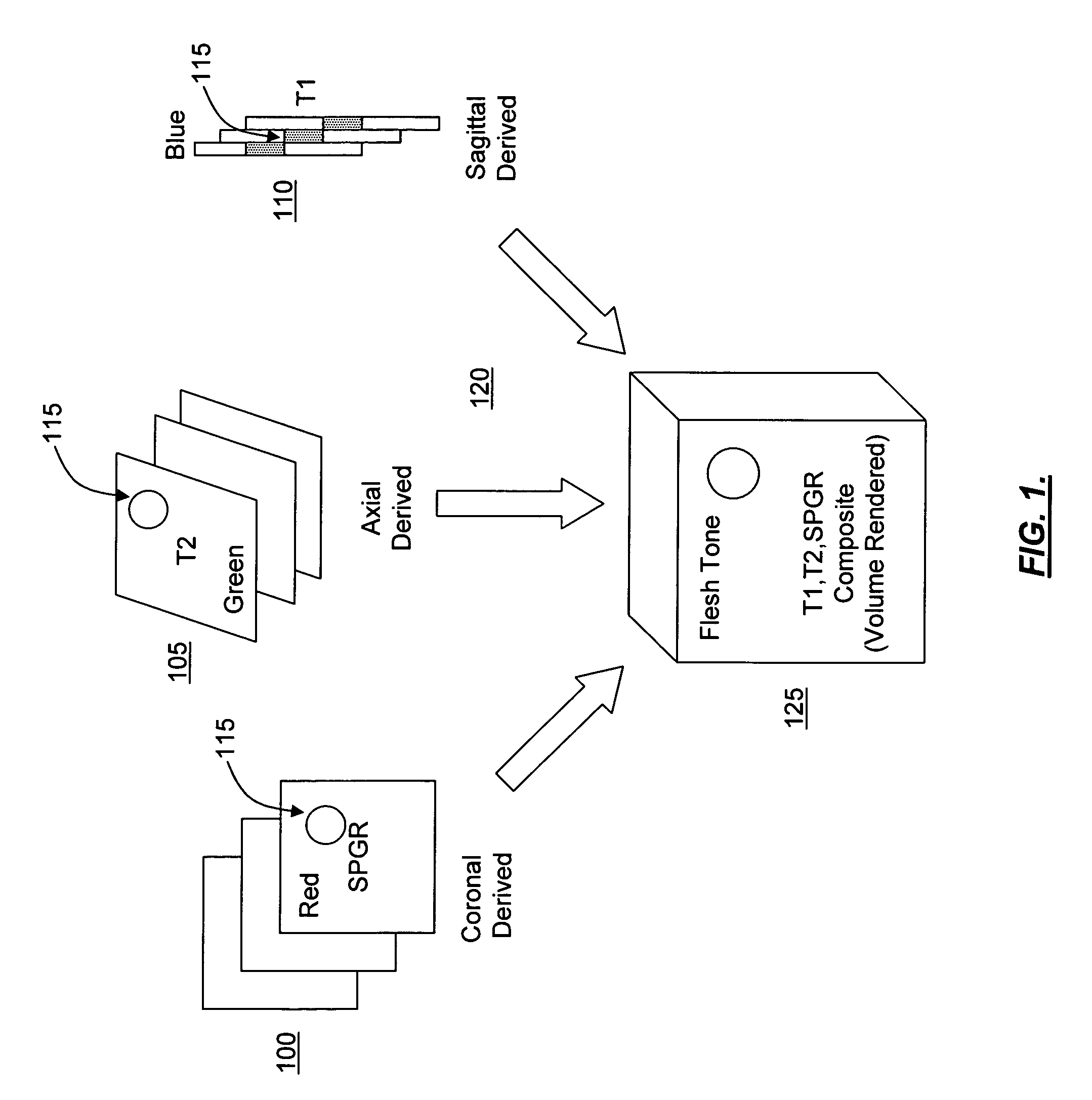
Opposed orthogonal fusion system and method for generating color segmented MRI voxel matrices
InactiveUS6956373B1Easy to understandCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelTissue characterization
Systems and methods for producing multi-dimensional tissue characterization images are described. By combining colorized MRI images composited from multiple gray tone MRI images, riffle stacks can be formed and combined to render multidimensional reconstruction of anatomical, physiological and pathological features. Biophysical parameters are therefore automatically segmented, characterized, tagged, mapped and otherwise labeled. In another embodiment, gray tone images are collected by acquiring orthogonally opposed pulse sequences, the images of which are color masked and uniquely rendered in three dimensions to obtain voxels in which the color is determined by the summative color masks applied to original gray tone pixels. This method can be embodied as specific applications designed for the brain, abdomen, breast, pelvis, musculoskeletal and other organs and biophysical systems to facilitate diagnosis, surgical planning and virtual exploration.
Owner:BROWN HUGH KEITH +1
System and method for automated segmentation, characterization, and classification of possibly malignant lesions and stratification of malignant tumors
A method and apparatus for classifying possibly malignant lesions from sets of DCE-MRI images includes receiving a set of MRI slice images obtained at respectively different times, where each slice image includes voxels representative of at least one region of interest (ROI). The images are processed to determine the boundaries of the ROIs and the voxels within the identified boundaries in corresponding regions of the images from each time period are processed to extract kinetic texture features. The kinetic texture features are then used in a classification process which classifies the ROIs as malignant or benign. The malignant lesions are further classified to separate TN lesions from non-TN lesions.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
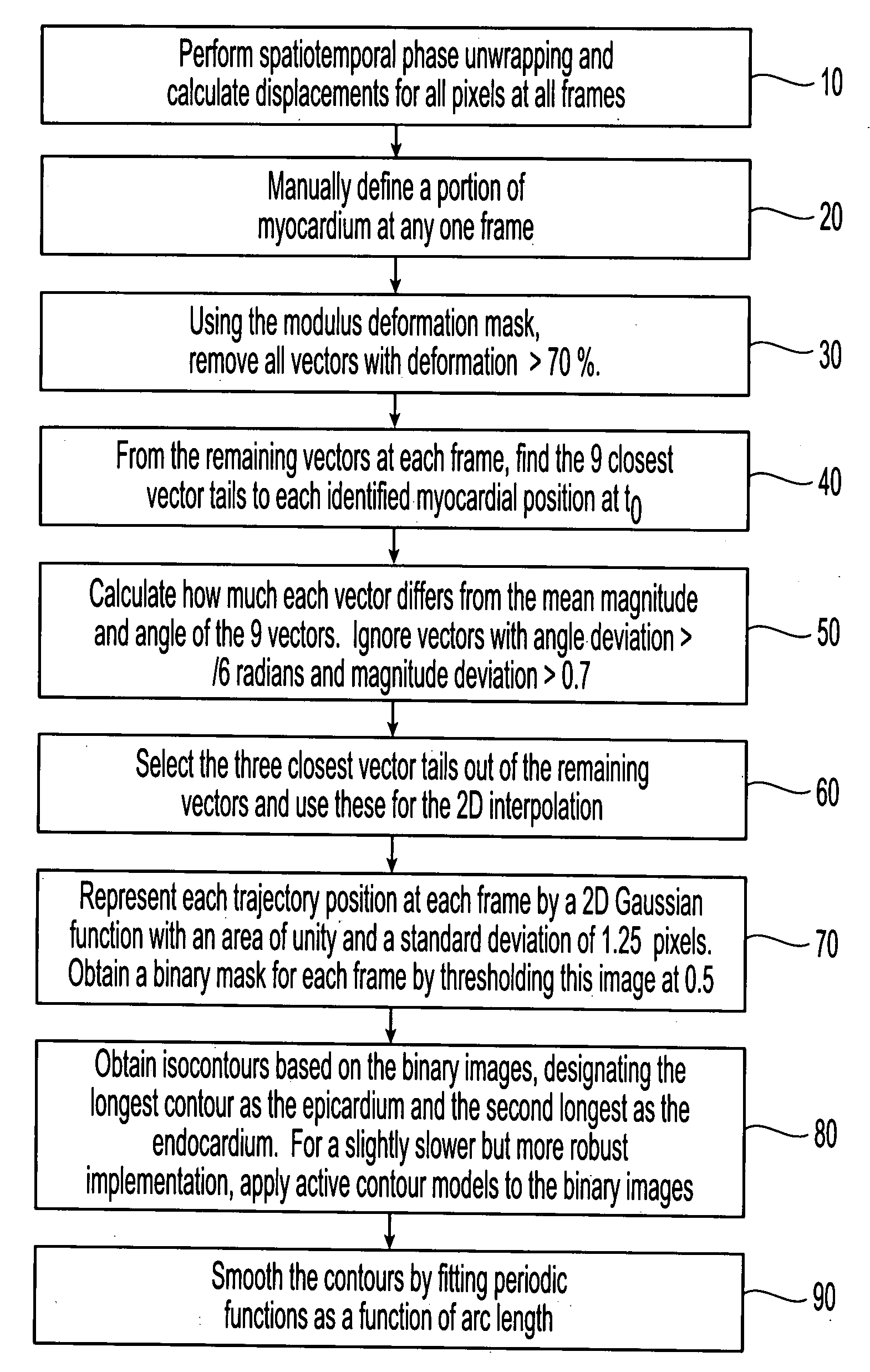
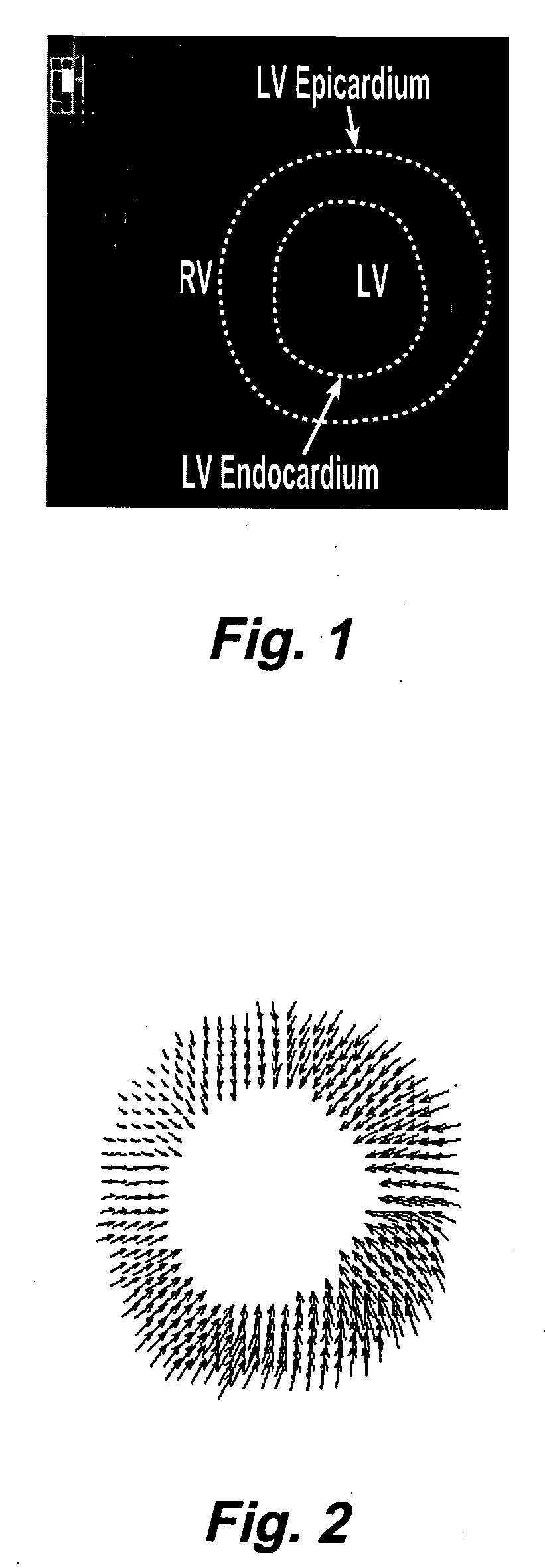
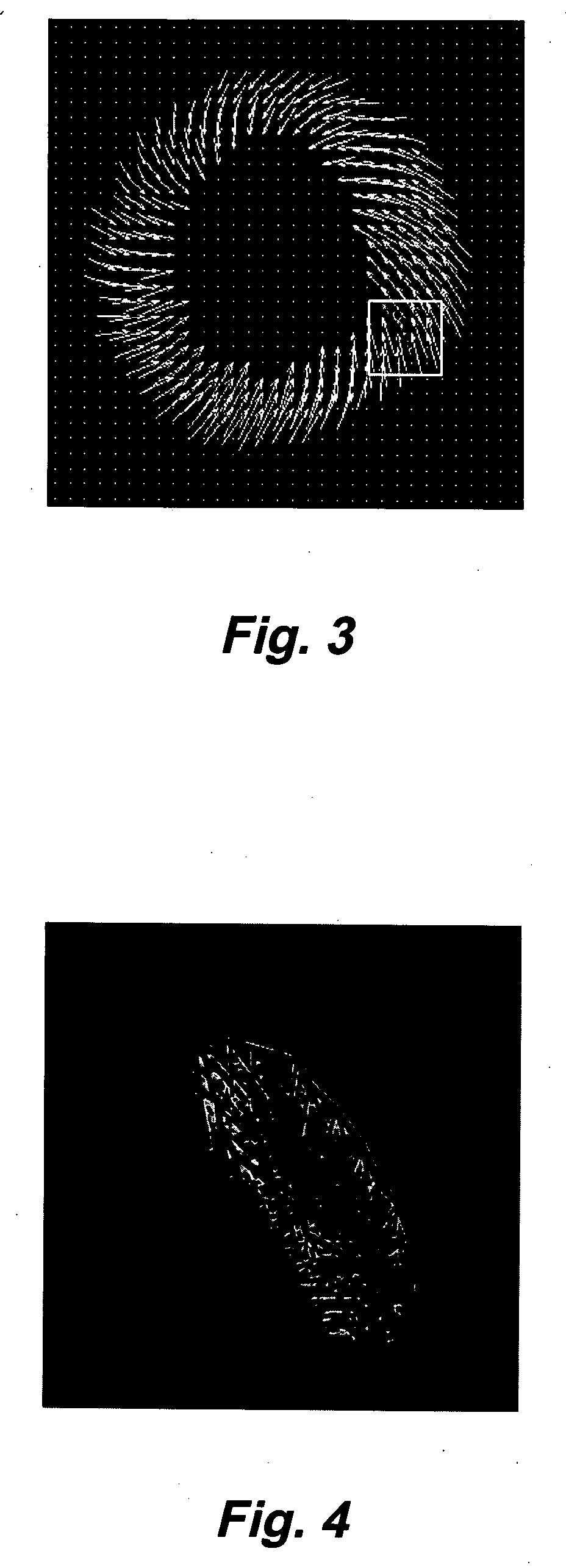
Motion-guided segmentation for cine dense images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
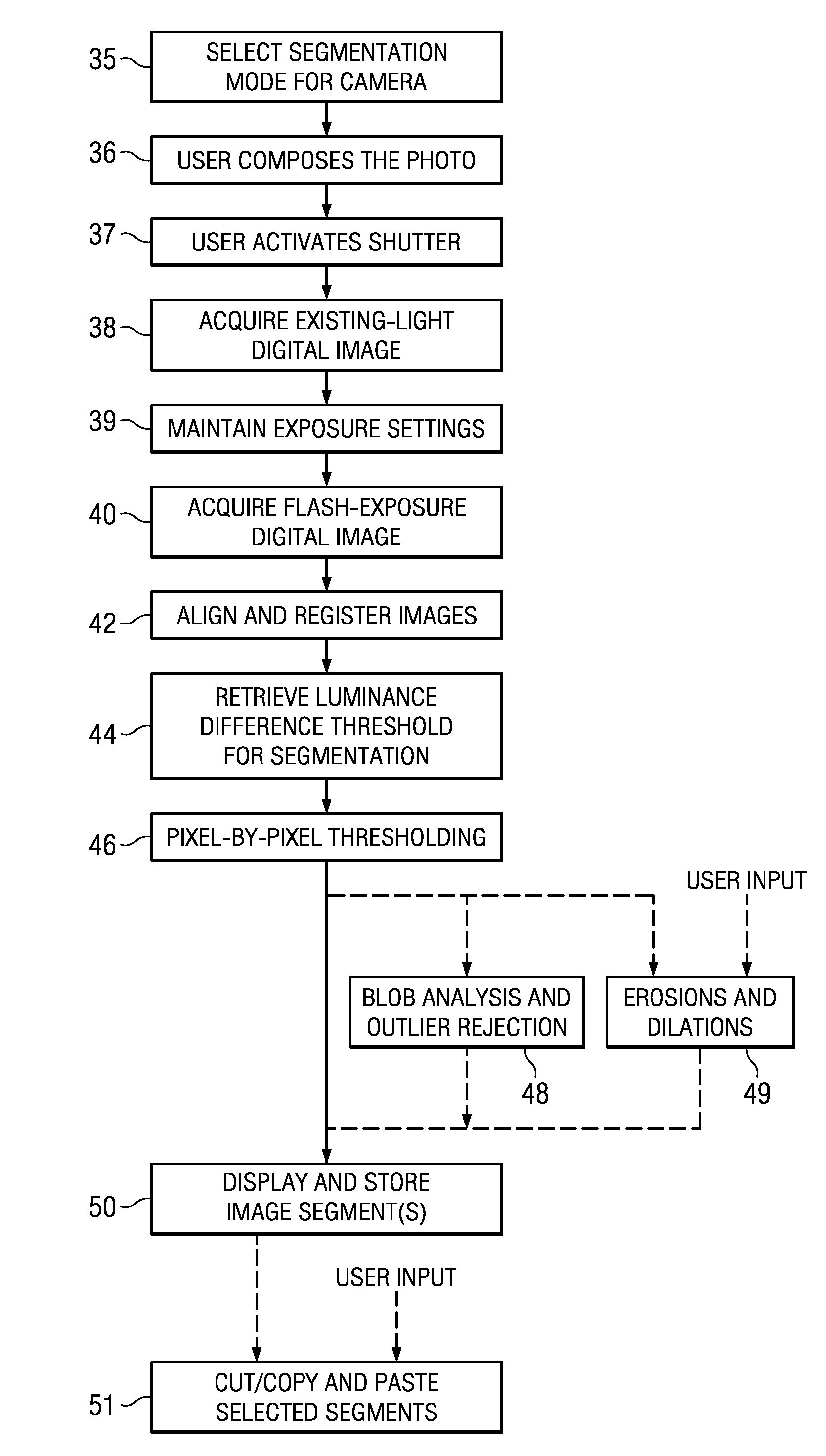
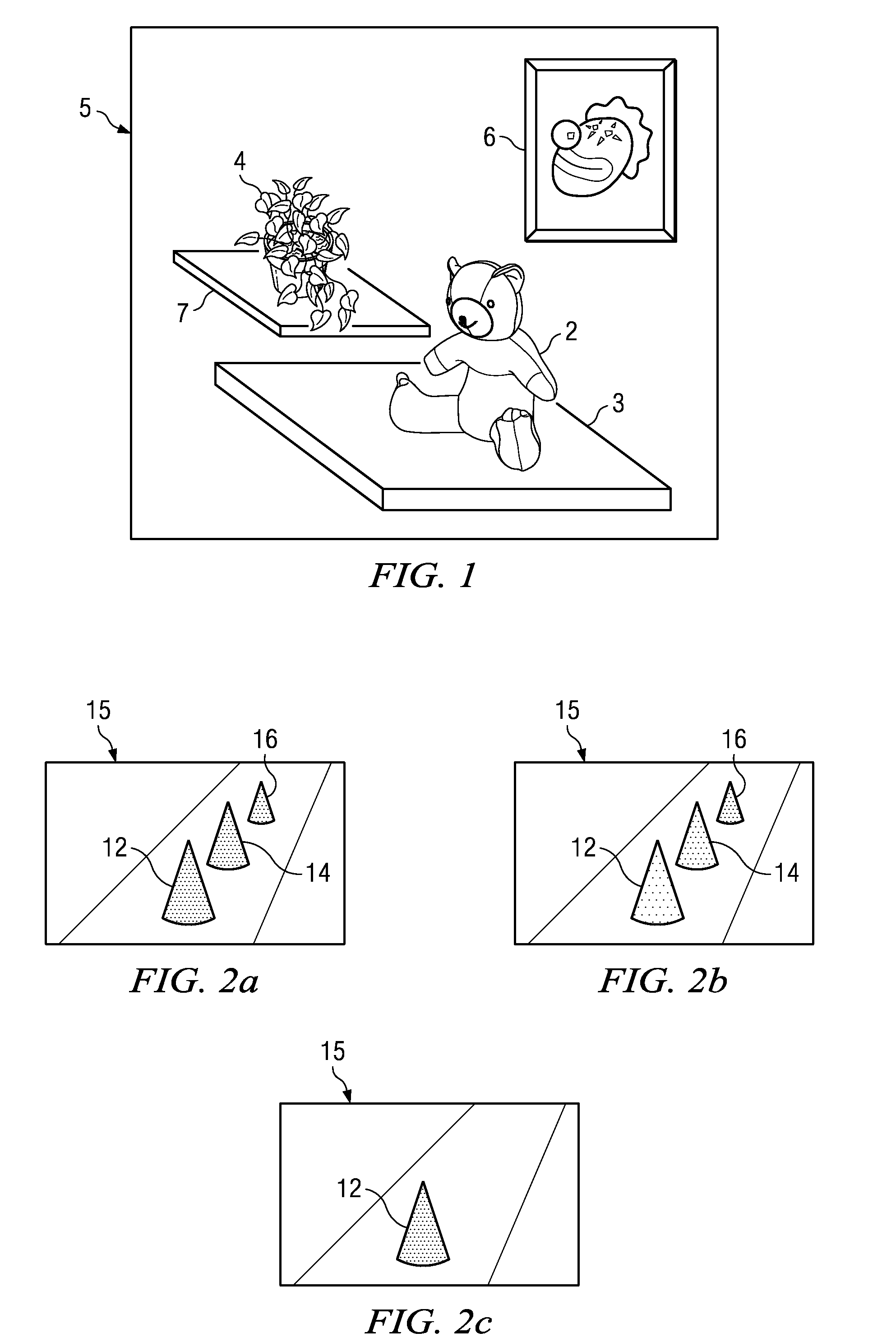
Digital Image Segmentation Using Flash
ActiveUS20100245609A1Easy to adjustAutomatically performTelevision system detailsImage enhancementDigital imageComputer science
A digital camera function, such as can be implemented in a cellular telephone handset, and that includes automated segmentation of foreground subjects in acquired digital photos and images. Successive images are captured by the digital camera function at different flash exposure levels, for example using existing light only and using flash exposure. After alignment and registration of the images, luminance difference values in the two images are determined for each pixel, and the luminance difference values compared against a threshold value on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Those pixels with luminance difference values exceeding the threshold are segmented from the image as foreground subjects.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Automated segmentation of three dimensional bony structure images
ActiveUS20190105009A1Meet constraintsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLearning dataImaging data
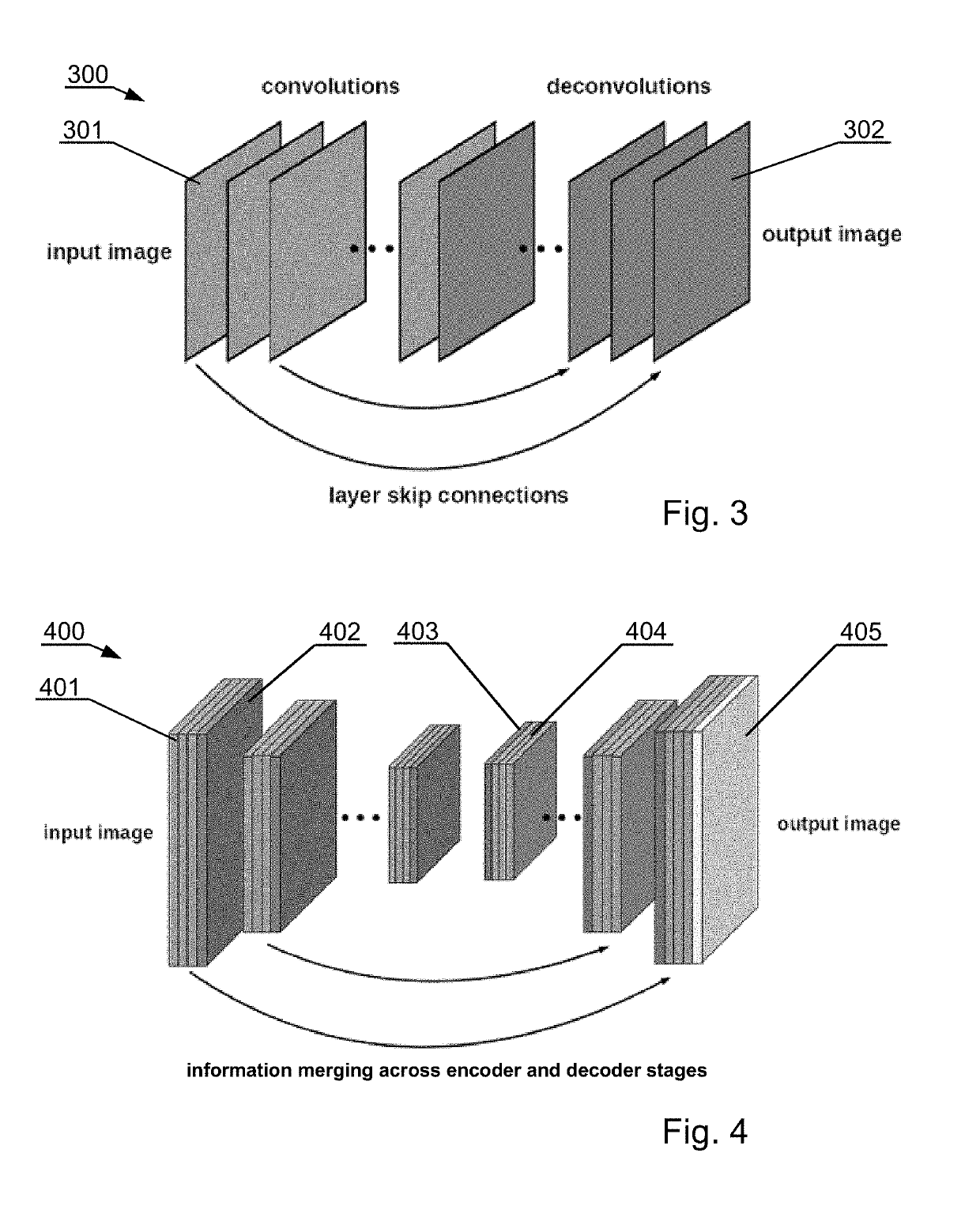
A computer-implemented system: at least one processor communicably coupled to at least one nontransitory processor-readable storage medium storing processor-executable instructions or data receives segmentation learning data comprising a plurality of batches of labeled anatomical image sets, each image set comprising image data representative of a series of slices of a three-dimensional bony structure, and each image set including at least one label which identifies the region of a particular part of the bony structure depicted in each image of the image set, wherein the label indicates one of a plurality of classes indicating parts of the bone anatomy; trains a segmentation CNN, that is a fully convolutional neural network model with layer skip connections, to segment semantically at least one part of the bony structure utilizing the received segmentation learning data; and stores the trained segmentation CNN in at least one nontransitory processor-readable storage medium of the machine learning system.
Owner:HOLO SURGICAL INC
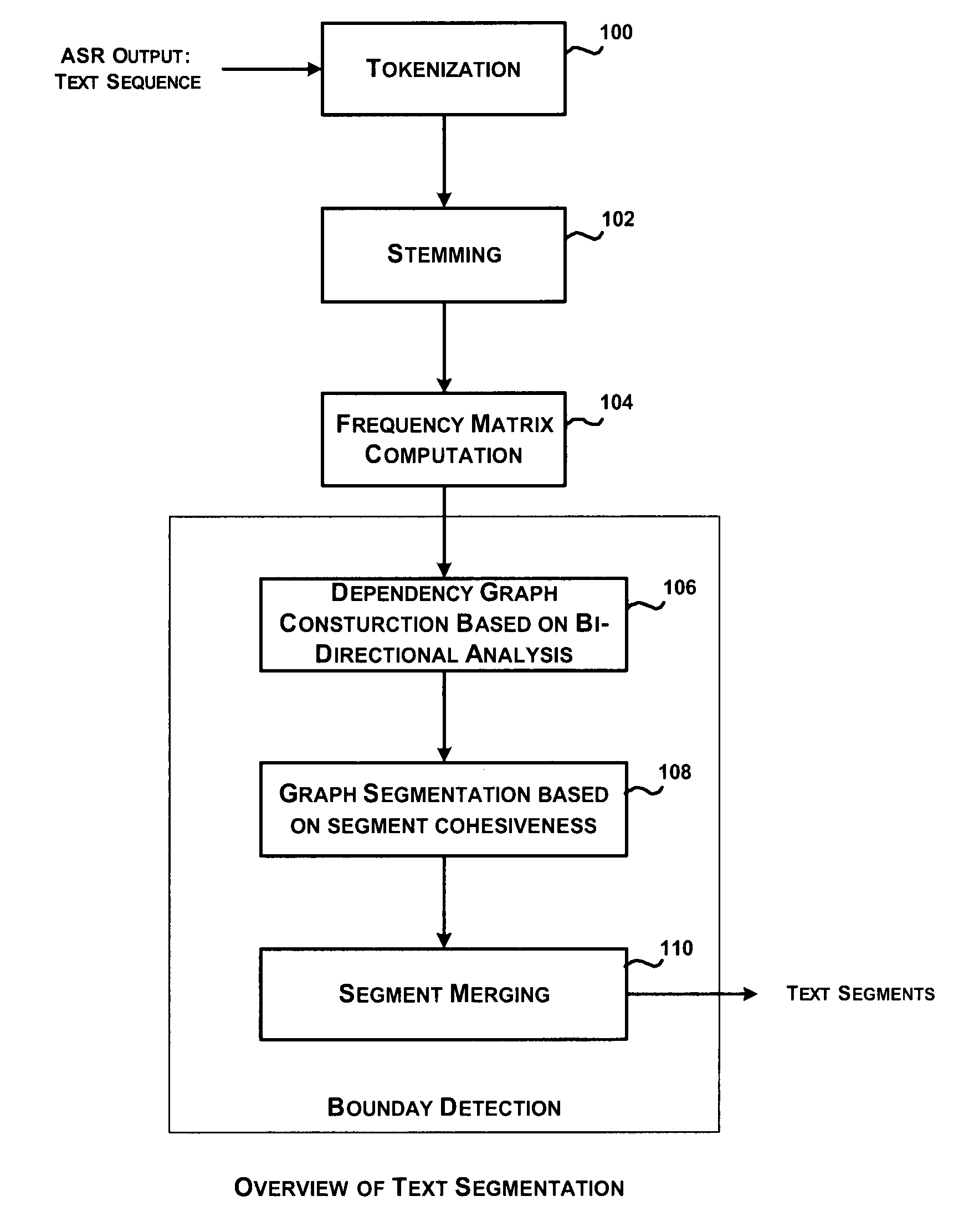
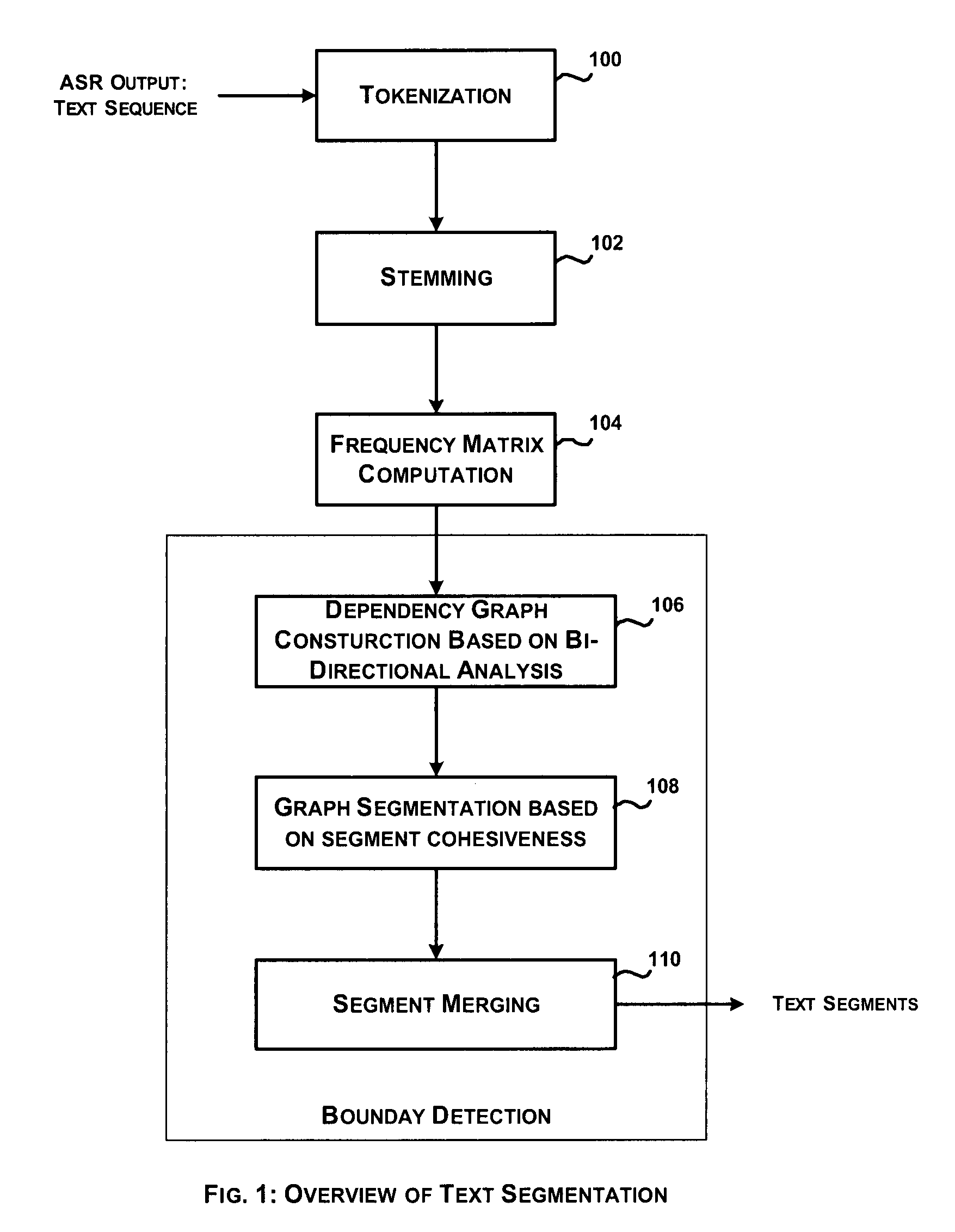
System and method for automatic segmentation of ASR transcripts
InactiveUS8036464B2Character and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingPattern recognitionAutomatic segmentation
Text segmentation based on topic boundary detection has been an industry problem in automating information dissemination to targeted users. A system for automatic segmentation of ASR output text involves boundary identification based on “topic” changes. The proposed approach is based on building a weighted graph to determine dependency in input sentences based on bi-directional analysis of the input sentences. Furthermore, the input sentences are segmented based on the notion of segment cohesiveness and the segmented sentences are merged based on preamble and postamble analyses.
Owner:TECH MAHINDRA INDIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com