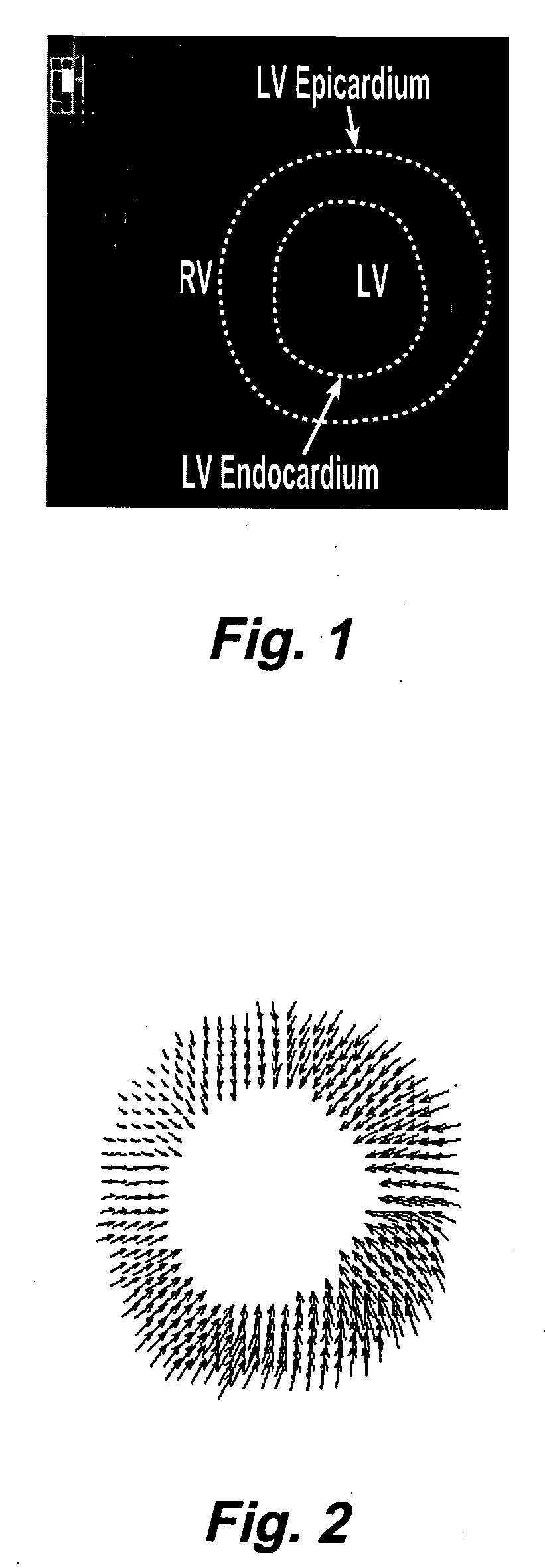
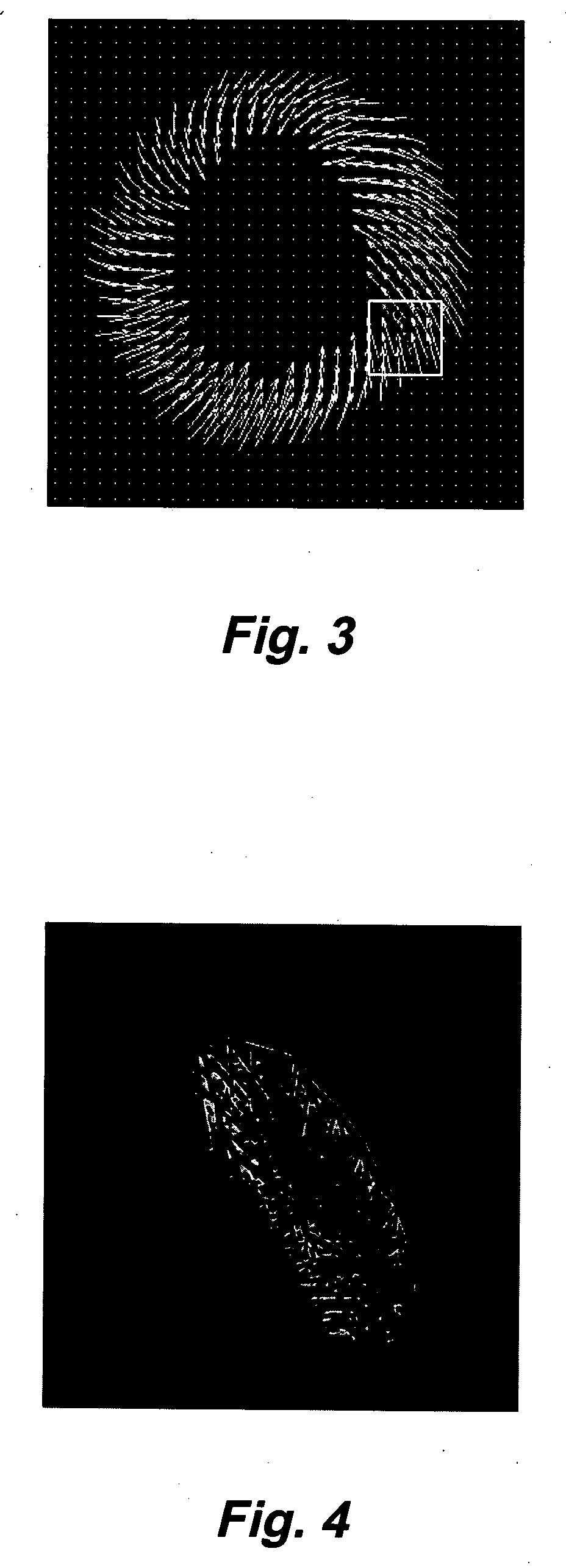
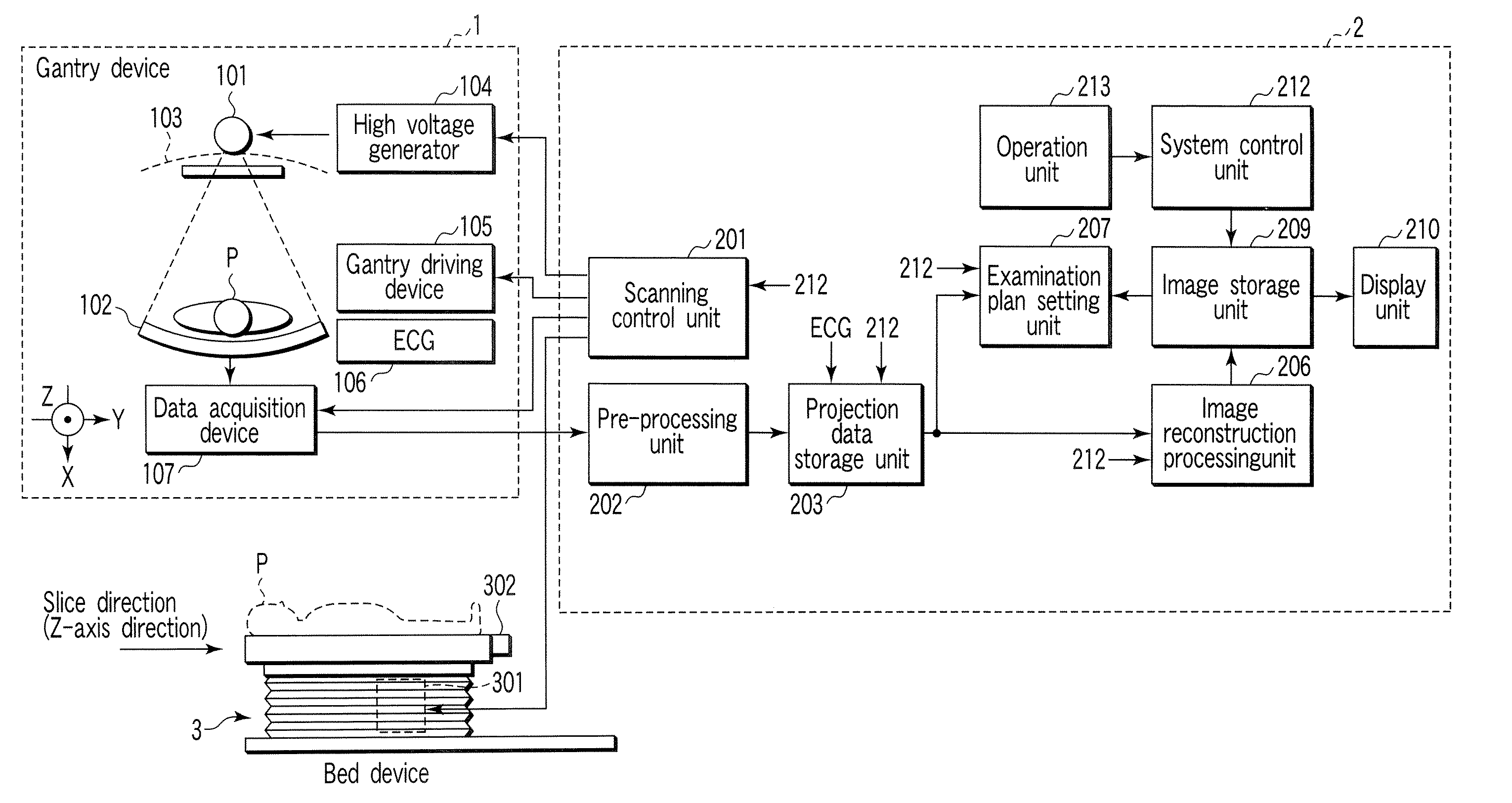
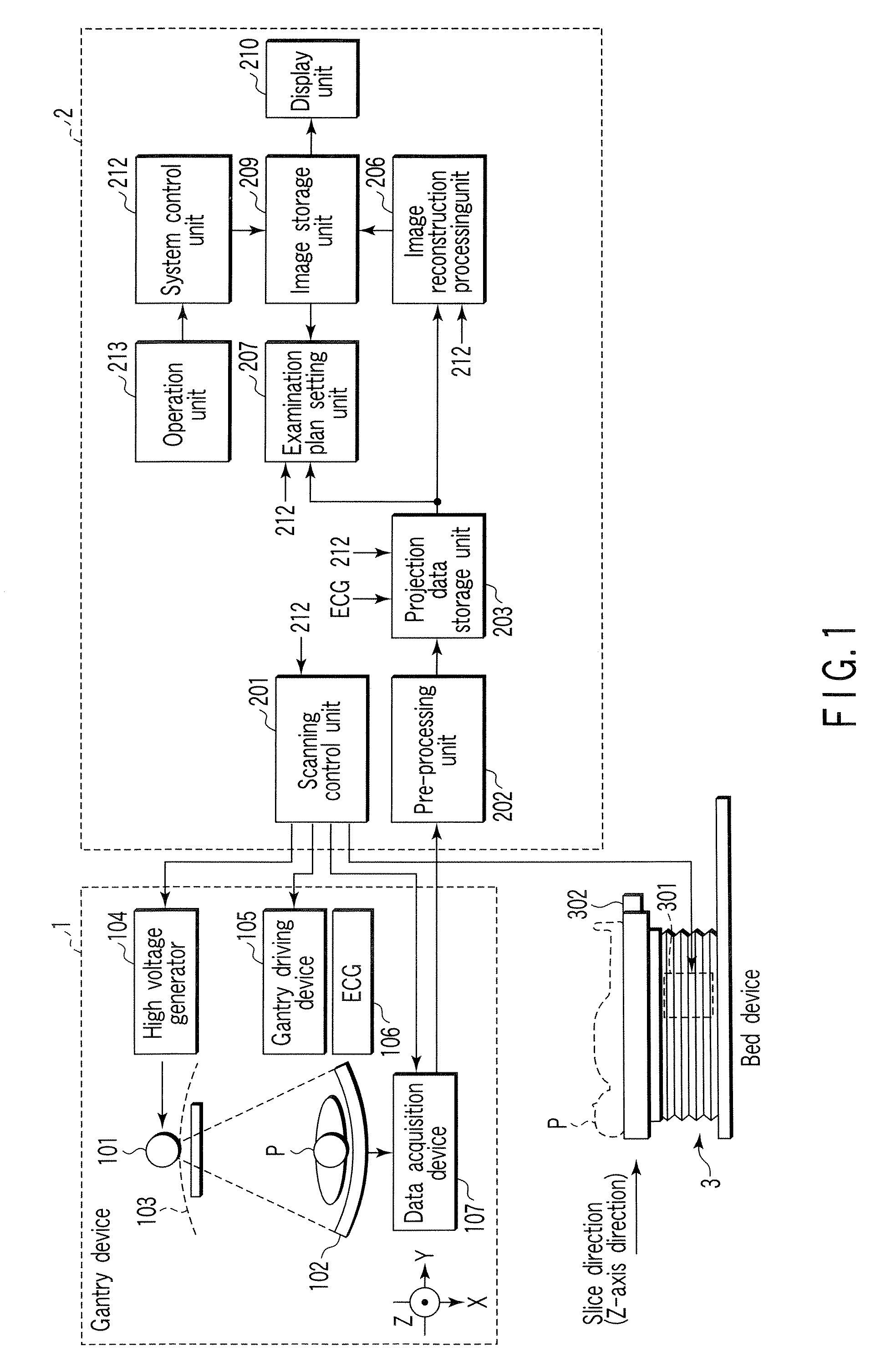
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Cardiac phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
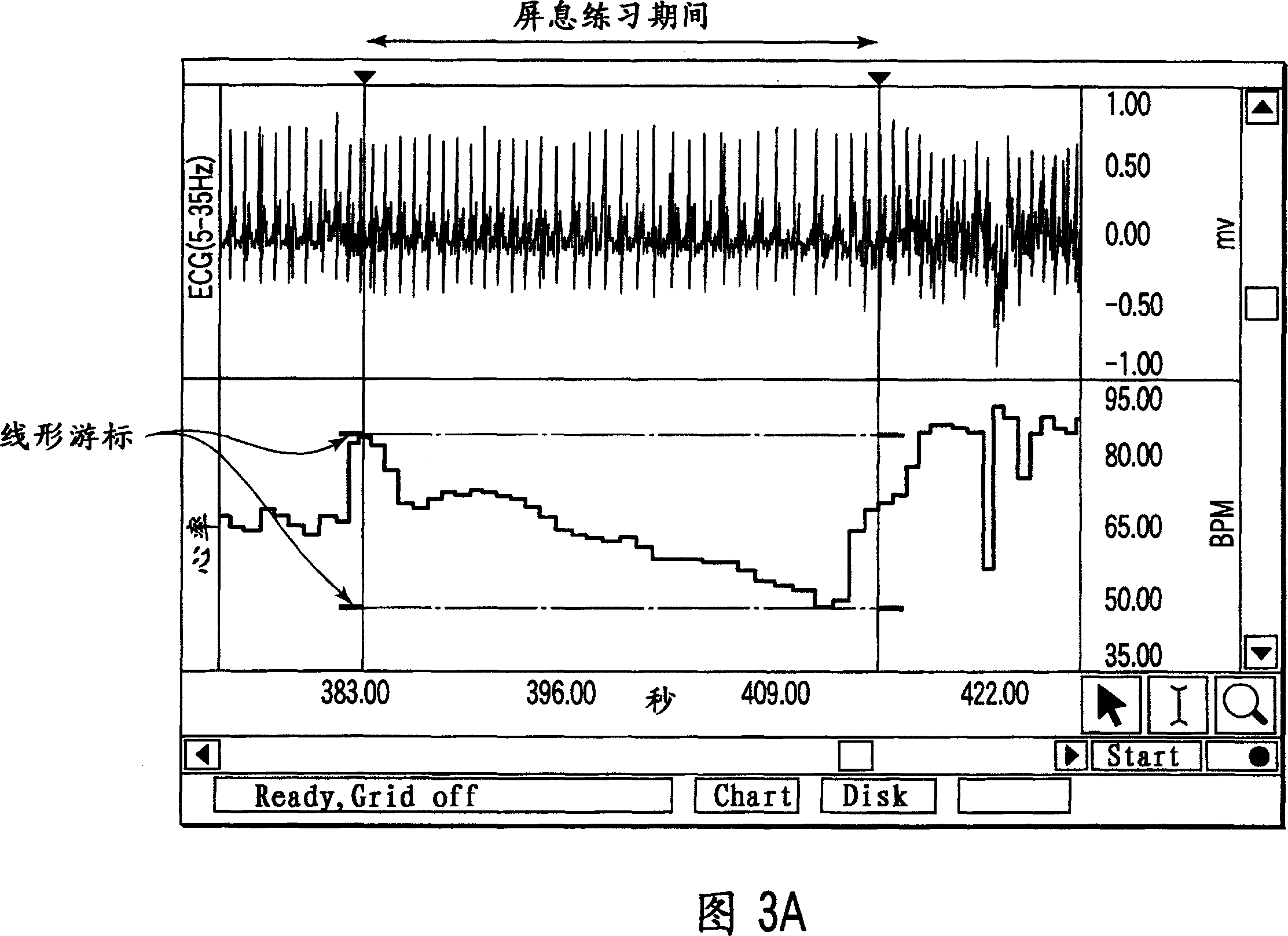
Phases of Cardiac Cycle. As stated earlier, the length of a cardiac cycle is divided into the diastole and systole phases. The phase in which the heart muscles contract is called the systole, and the phase in which the muscles relax after the systole is known as the diastole. The diastole and systole too are sub-divided into first and second phases.
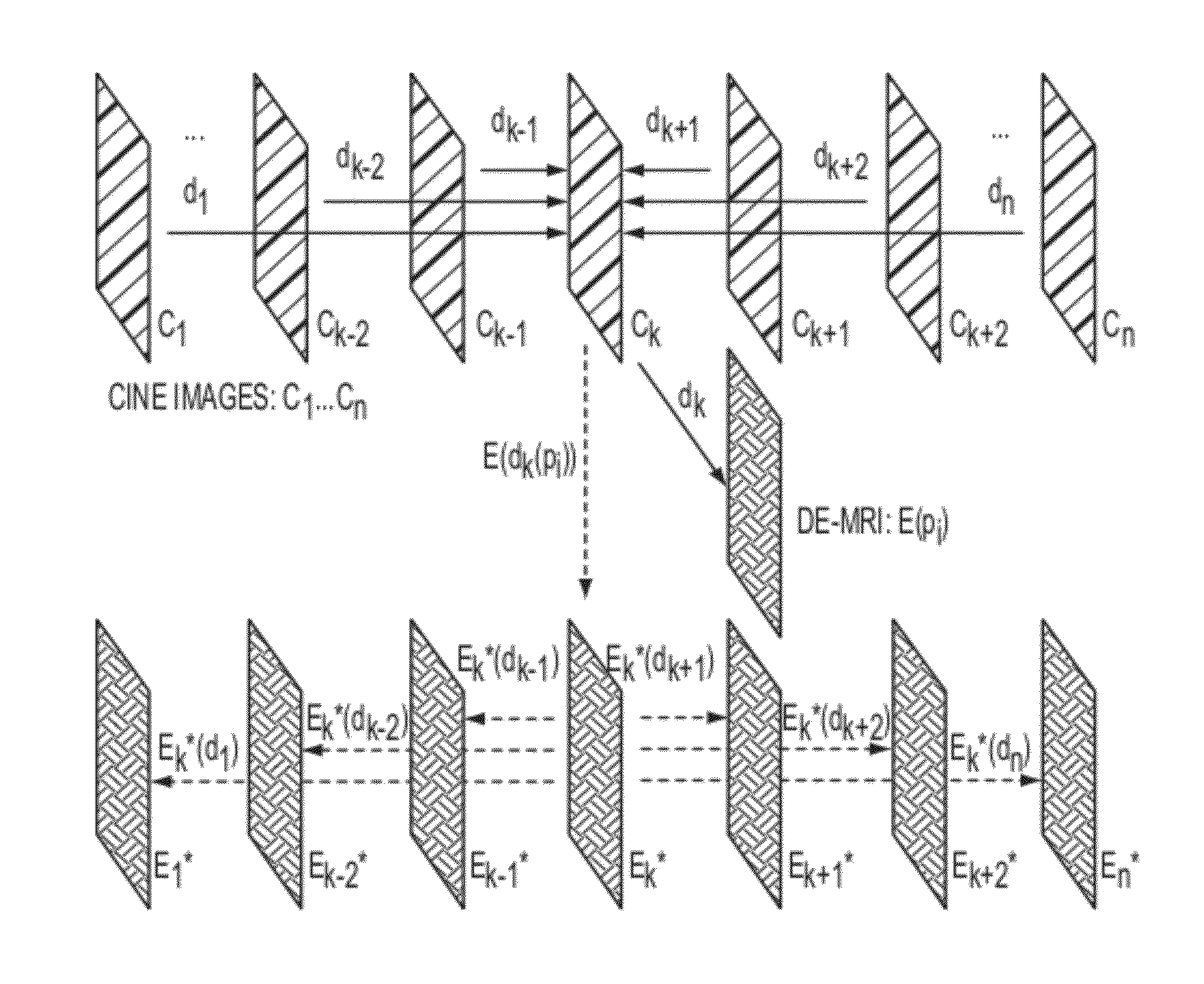
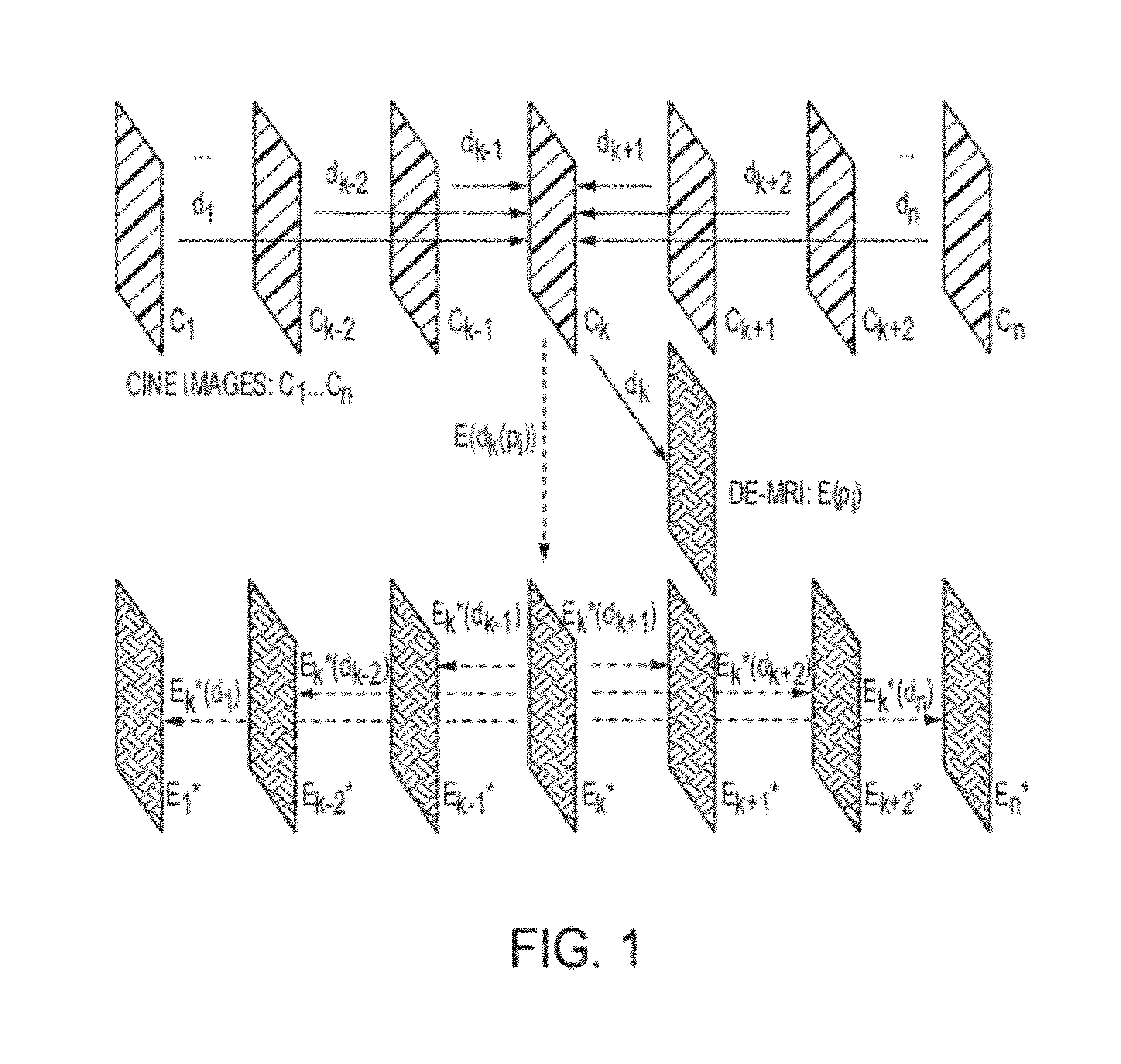
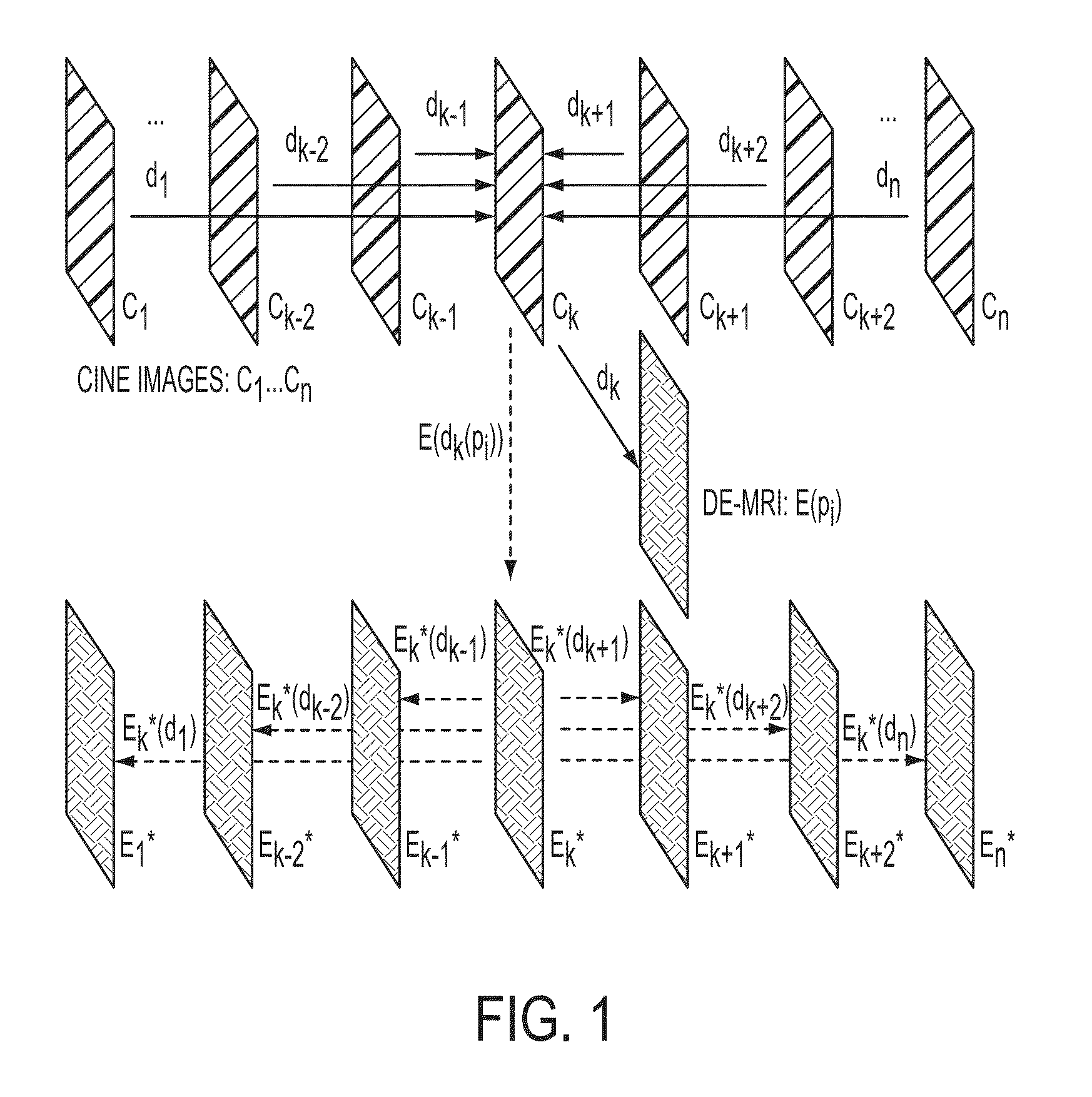
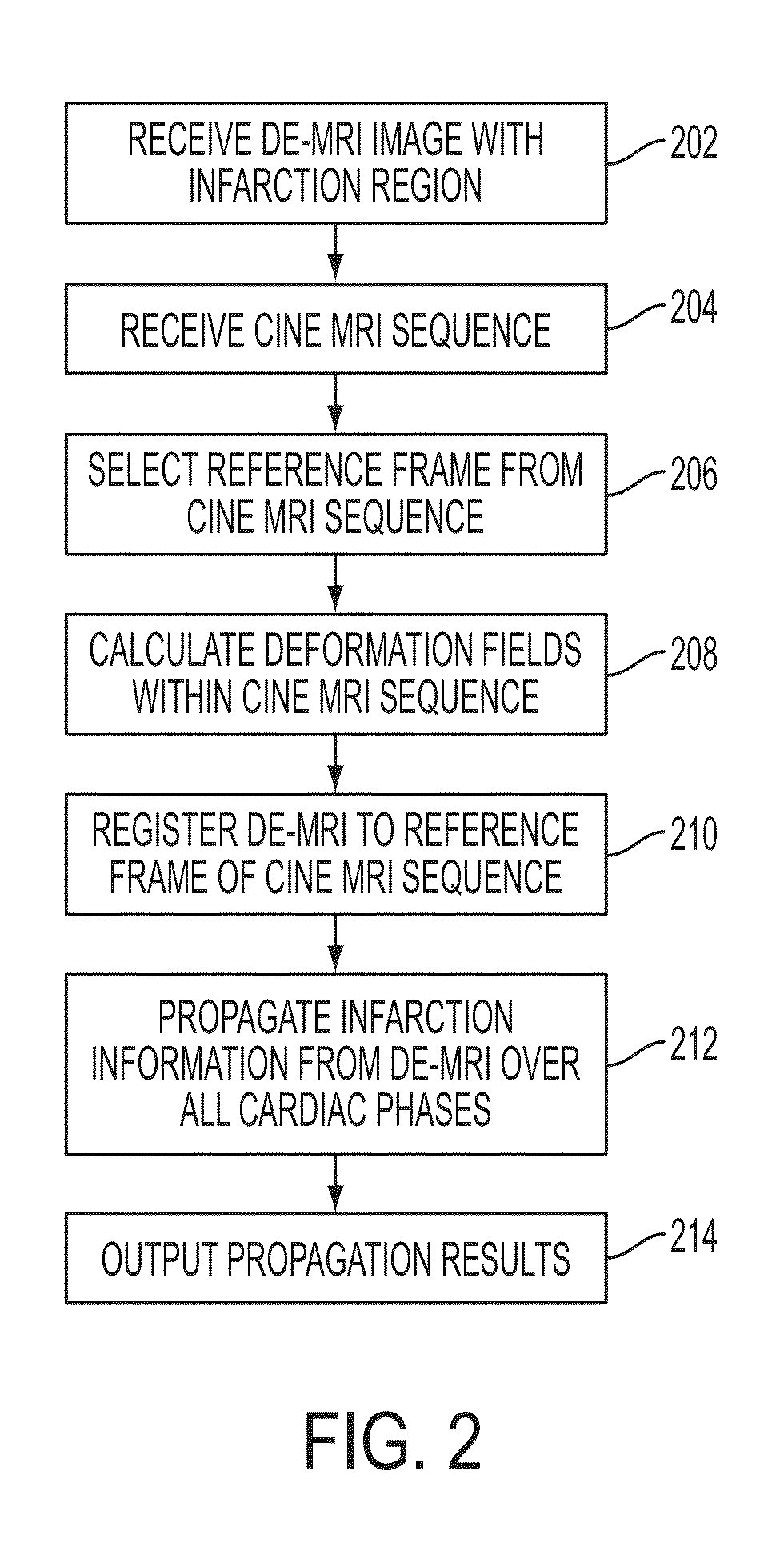
Method and System for Propagation of Myocardial Infarction from Delayed Enhanced Cardiac Imaging to Cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Hybrid Image Registration
ActiveUS20120121154A1Correction of deformationAccurate alignment and deformation correctionImage enhancementImage analysisCine mriCardiac phase
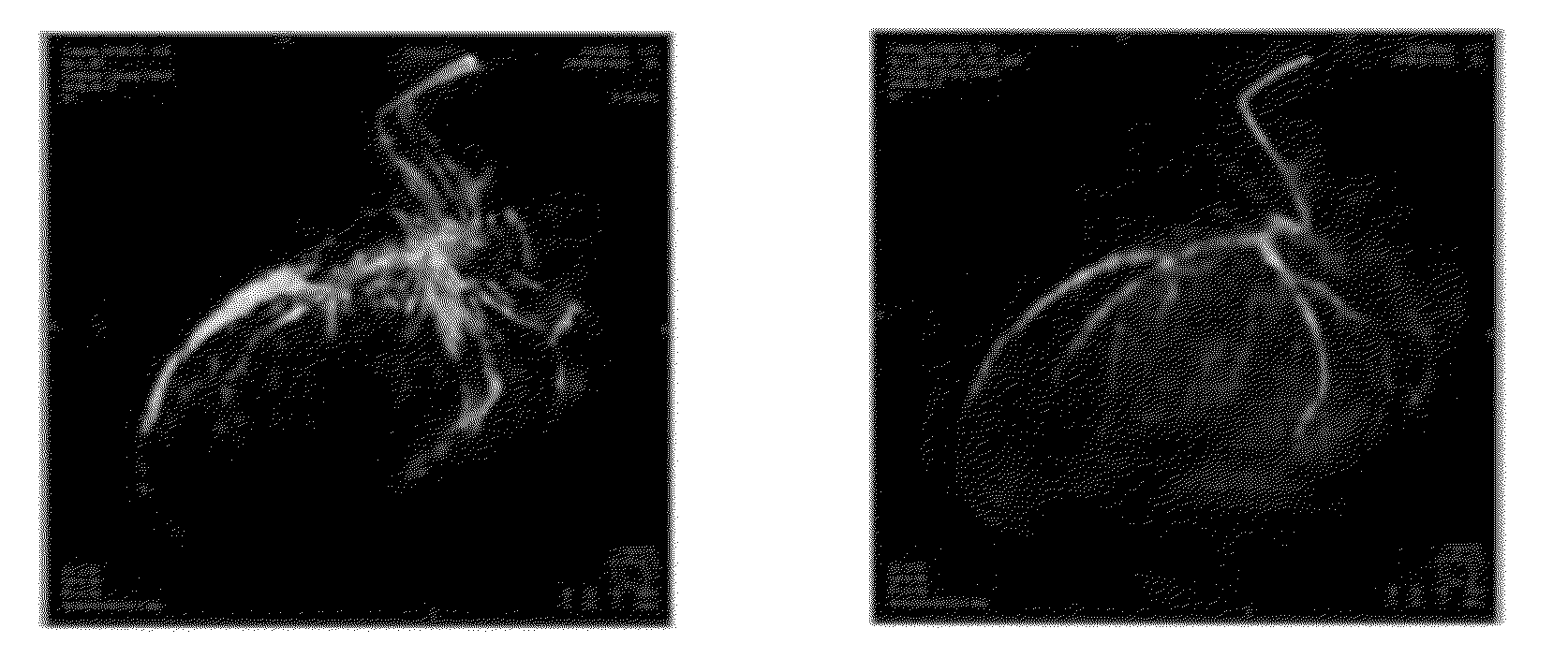
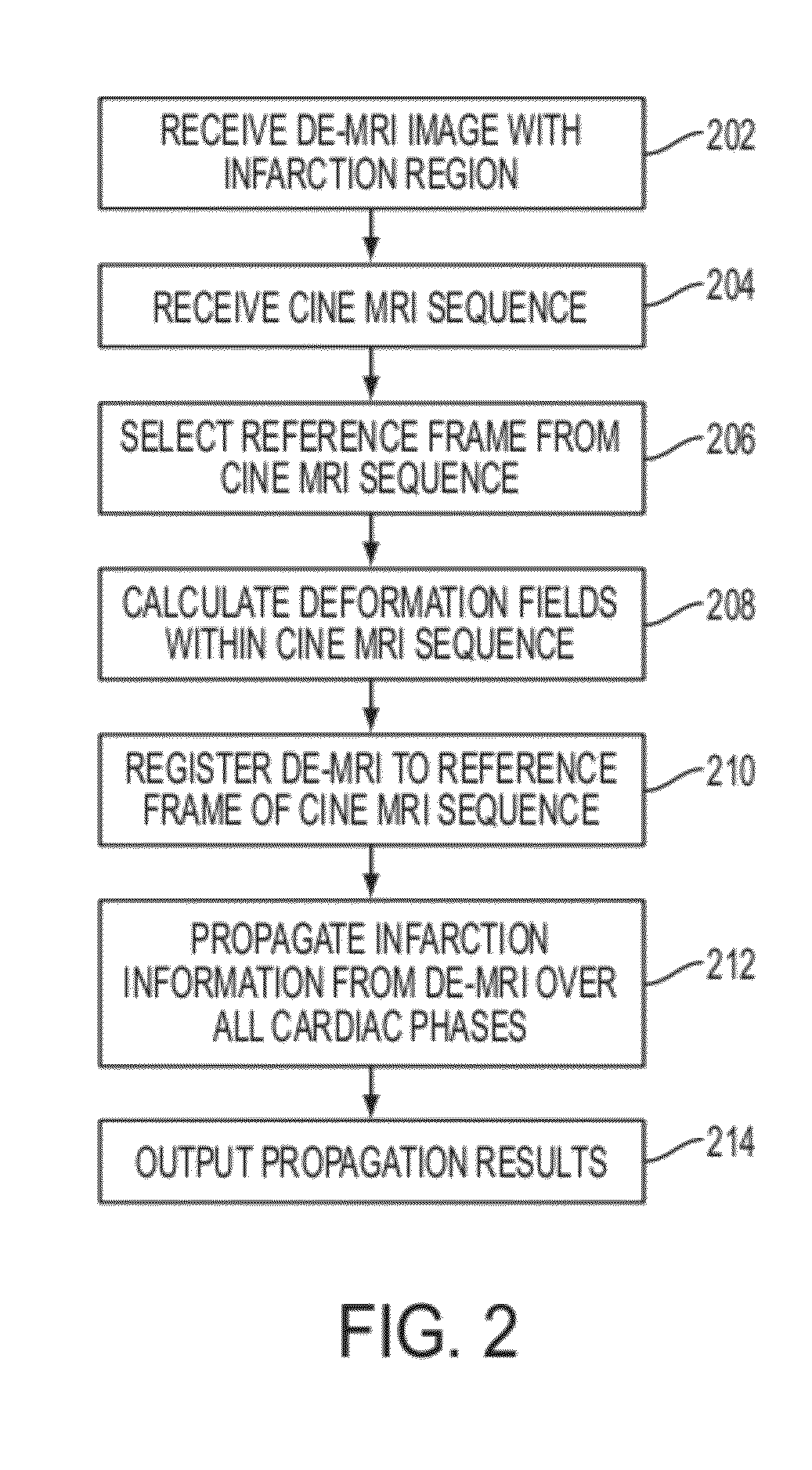
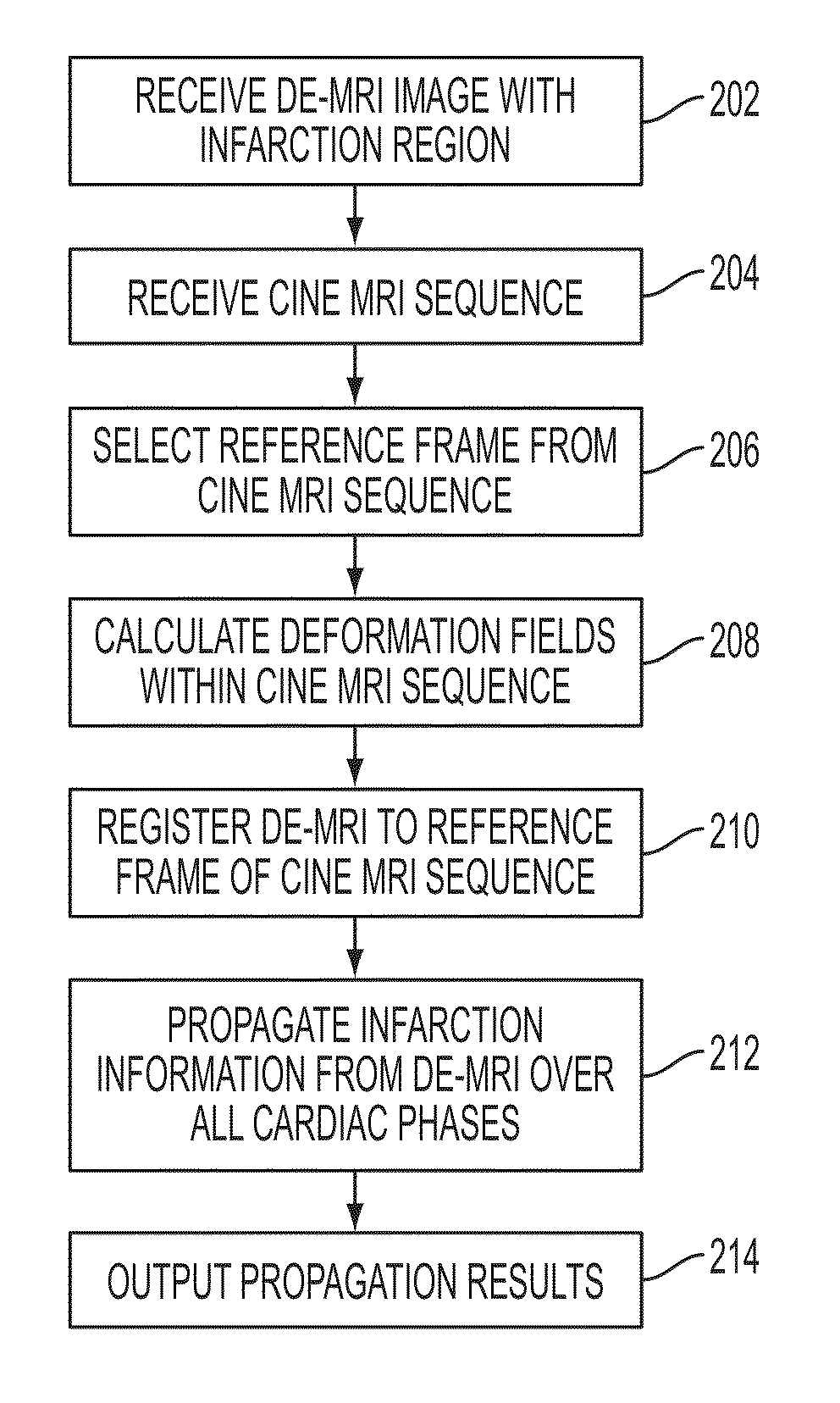
A method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) to cine MRI is disclosed. A reference frame is selected in a cine MRI sequence. Deformation fields are calculated within the cine MRI sequence to register the frames of the cine MRI sequence to the reference frame. A DE-MRI image having an infarction region is registered to the reference frame of the cine MRI sequence. The DE-MRI image may be registered to the infarction region using a hybrid registration algorithm that unifies both intensity and feature points into a single cost function. Infarction information in the DE-MRI image is then propagated cardiac phases of the frames in the cine MRI sequence based on the registration of the DE-MRI image to the reference frame and the plurality of deformation fields calculated within the cine MRI sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced cardiac imaging to cine magnetic resonance imaging using hybrid image registration
ActiveUS8682054B2Accurate alignment and deformation correctionImage enhancementImage analysisCine mriCardiac phase
A method and system for propagation of myocardial infarction from delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) to cine MRI is disclosed. A reference frame is selected in a cine MRI sequence. Deformation fields are calculated within the cine MRI sequence to register the frames of the cine MRI sequence to the reference frame. A DE-MRI image having an infarction region is registered to the reference frame of the cine MRI sequence. The DE-MRI image may be registered to the infarction region using a hybrid registration algorithm that unifies both intensity and feature points into a single cost function. Infarction information in the DE-MRI image is then propagated cardiac phases of the frames in the cine MRI sequence based on the registration of the DE-MRI image to the reference frame and the plurality of deformation fields calculated within the cine MRI sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
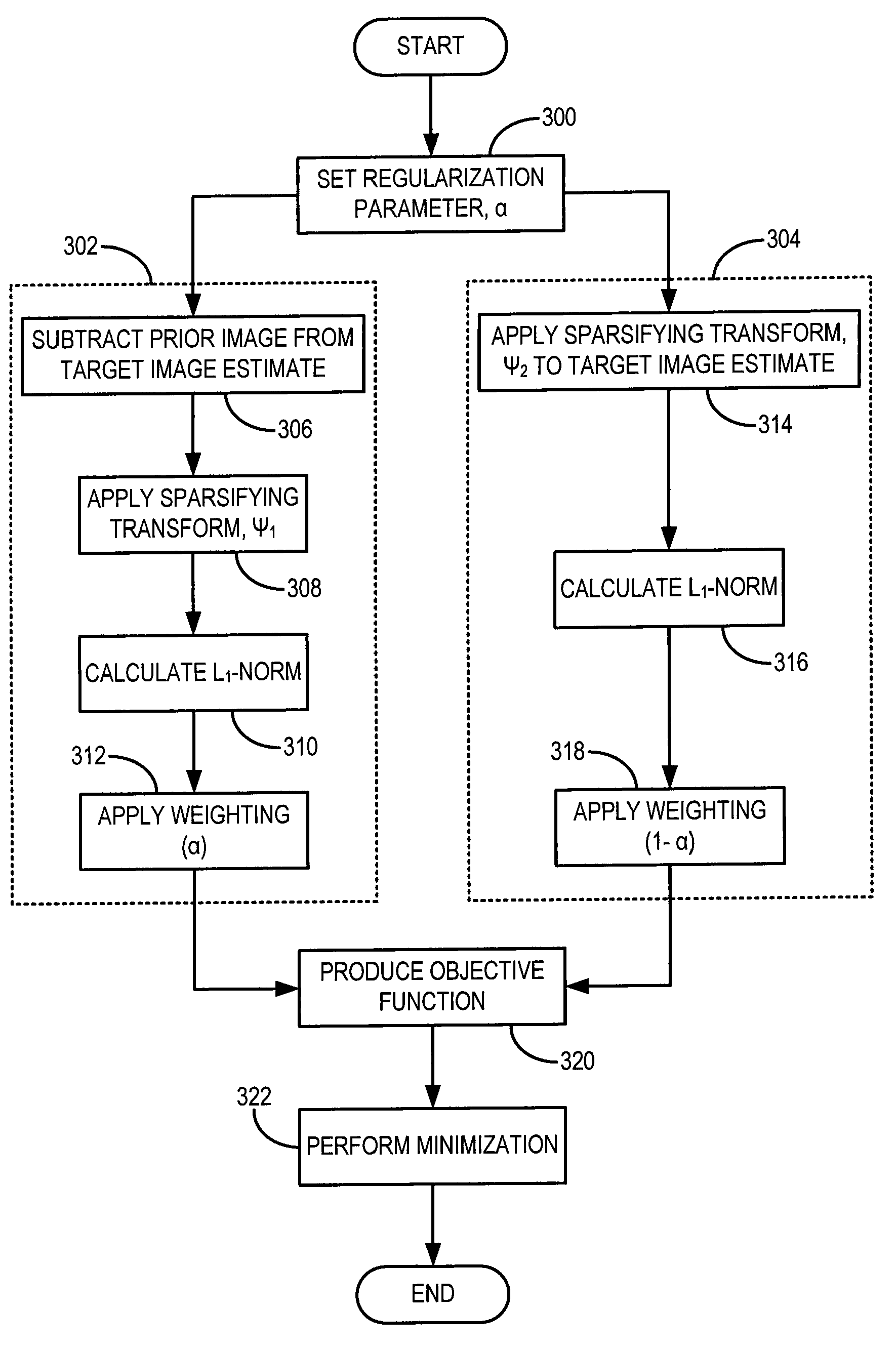
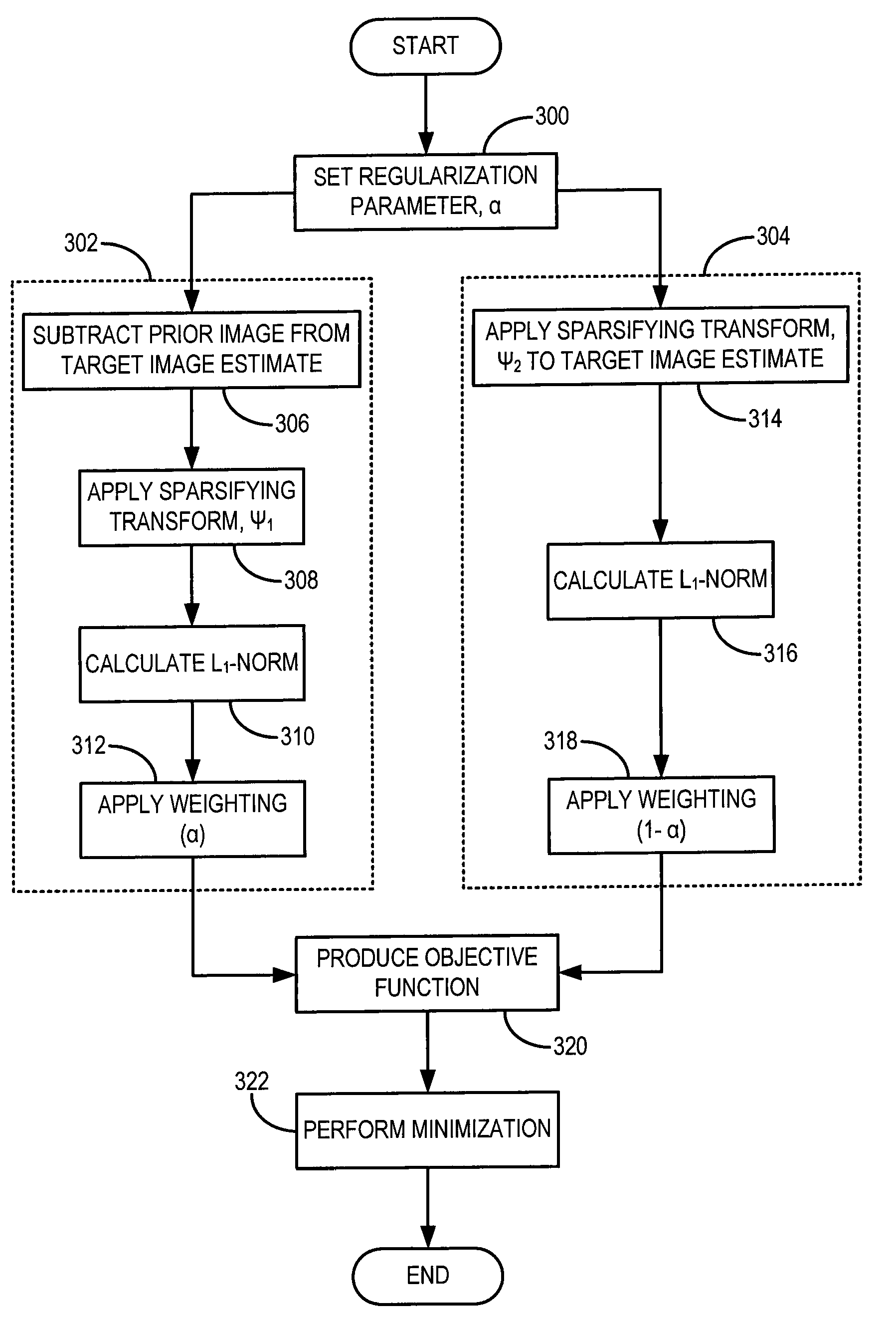
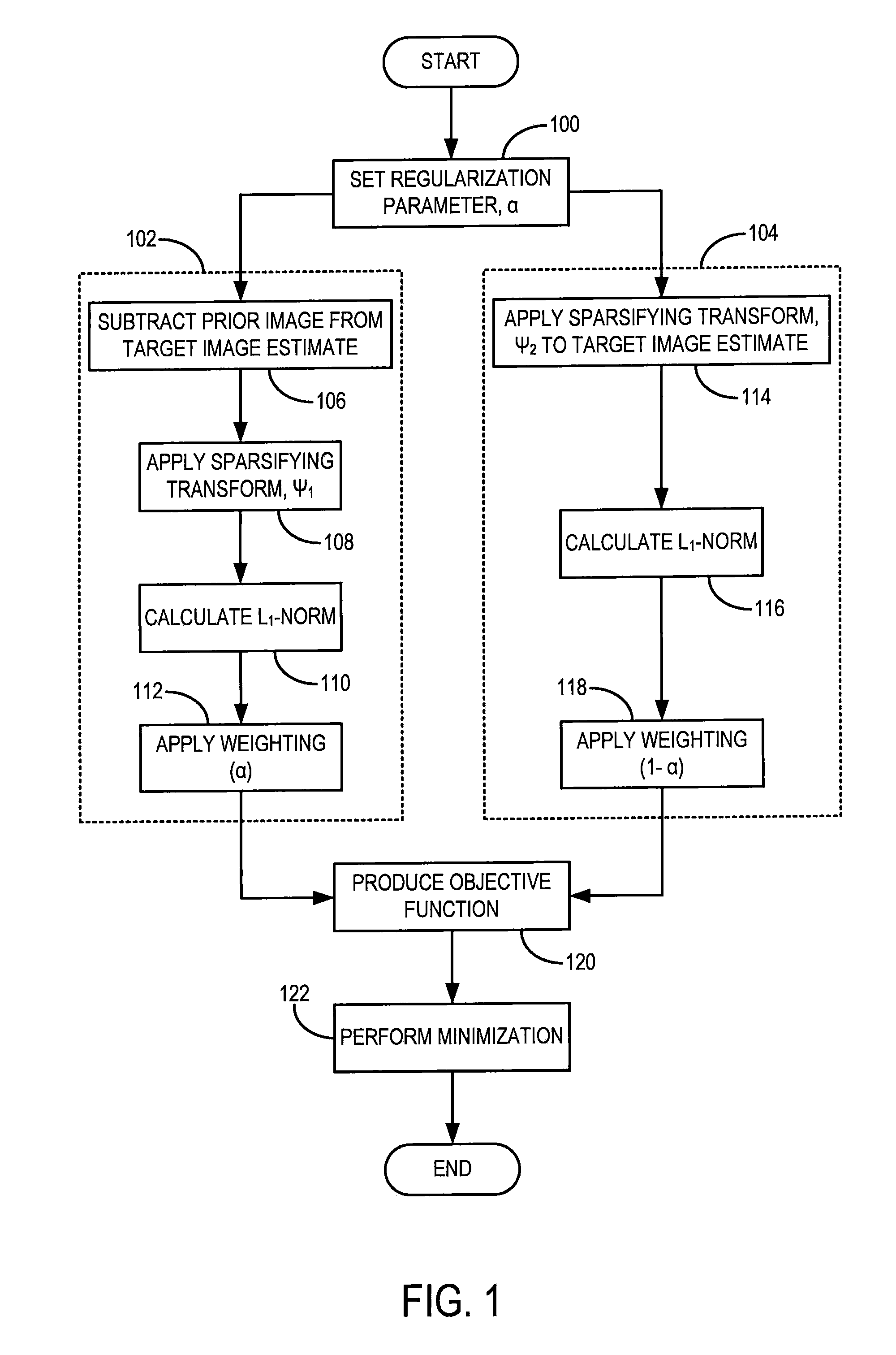
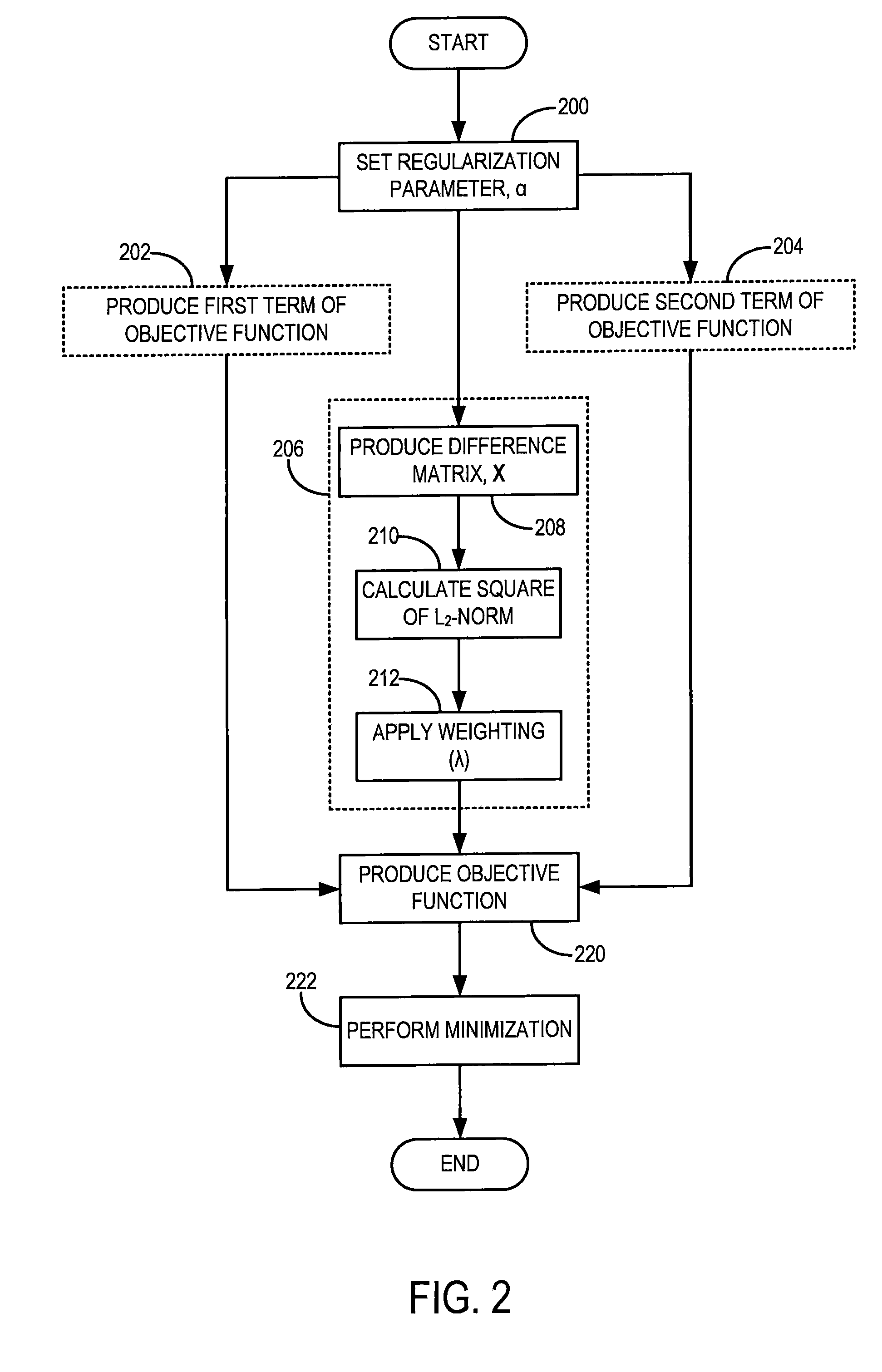
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS20090161933A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
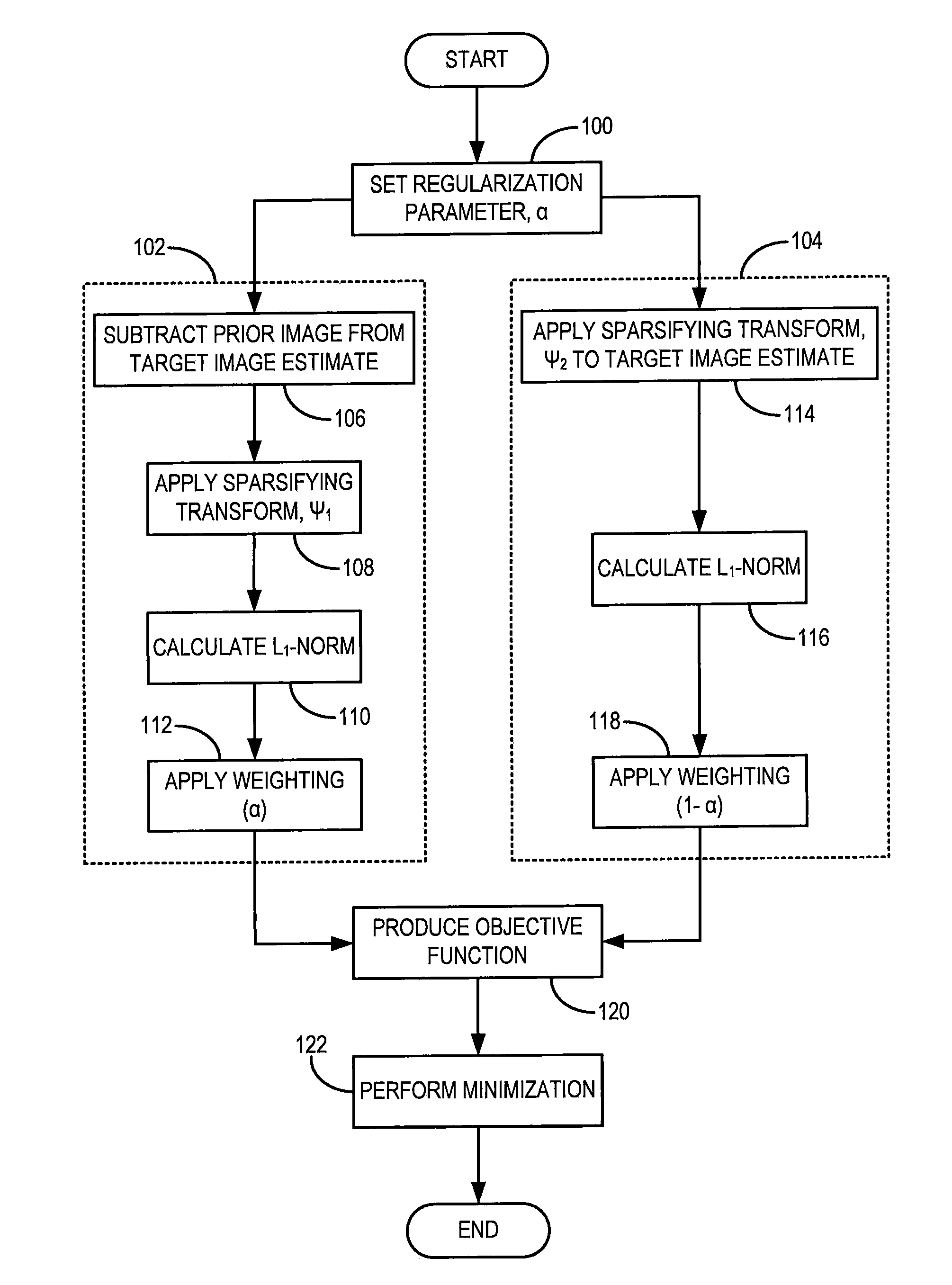
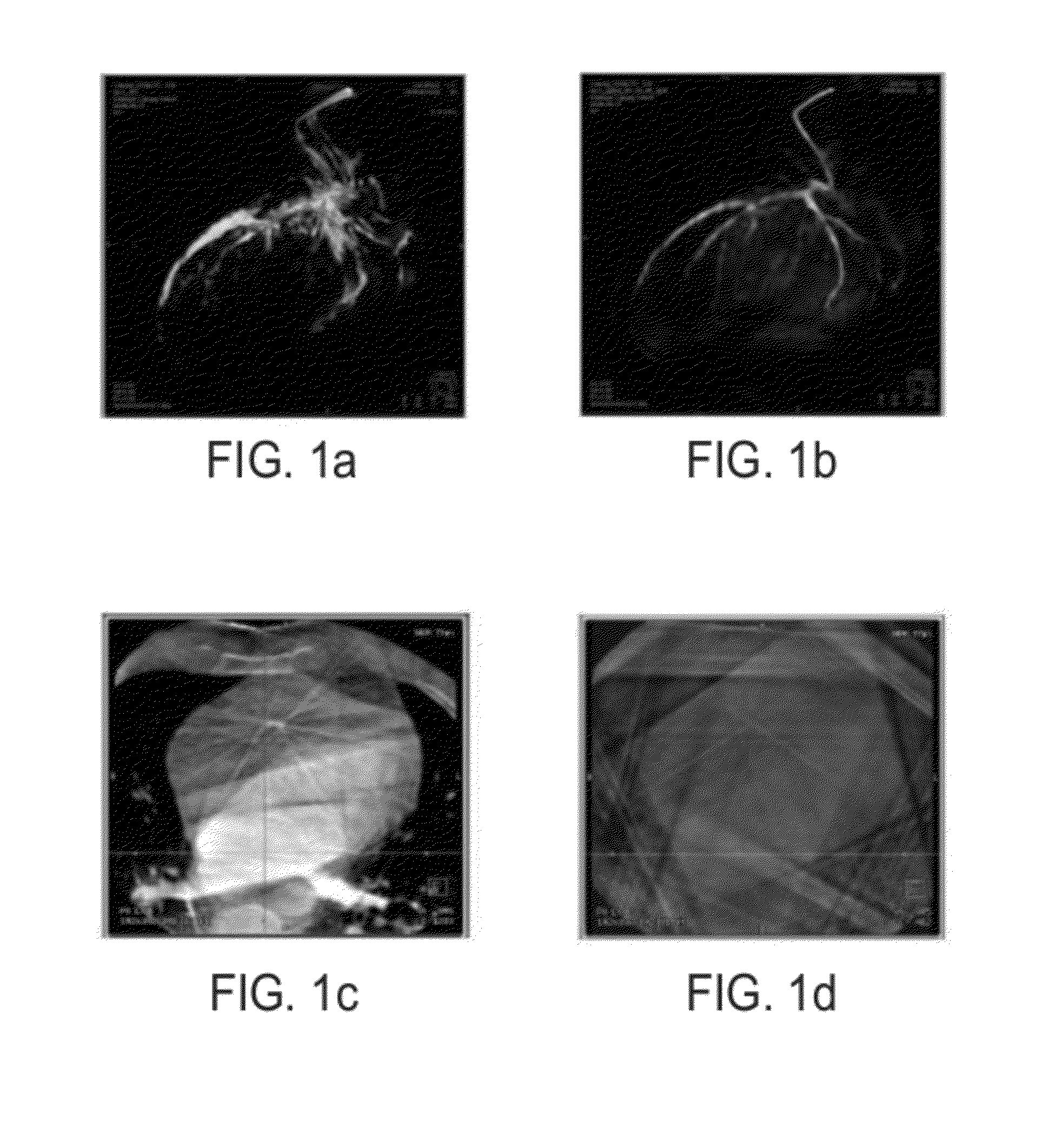
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. Thus, one aspect of the present invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that requires less number of data samples to reconstruct an accurate reconstruction of a desired image than previous methods, such as, compressed sensing. Another aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution (e.g., 20 milliseconds) using a CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System for multi-dimensional anatomical functional imaging
InactiveUS20100081917A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresData set
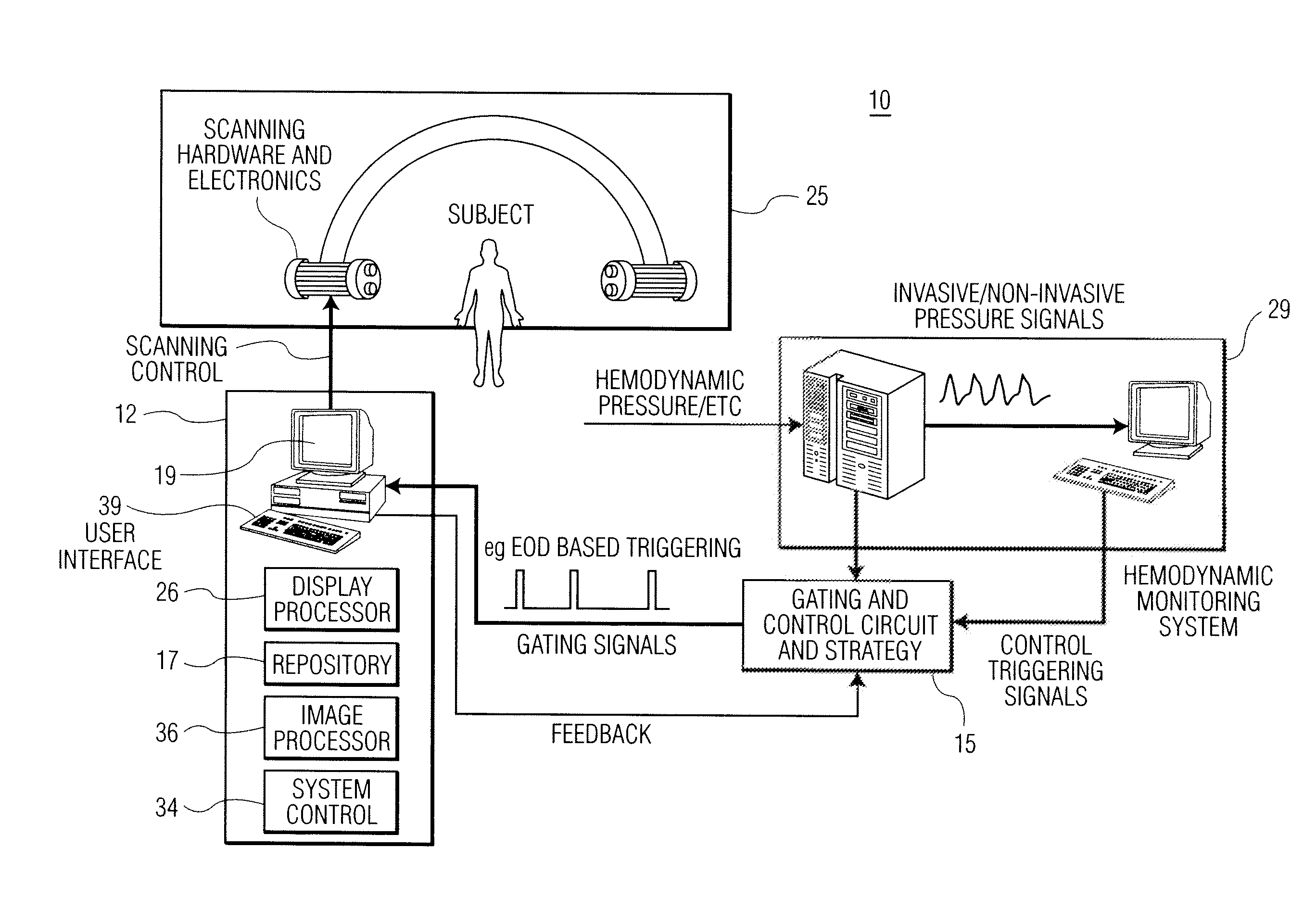
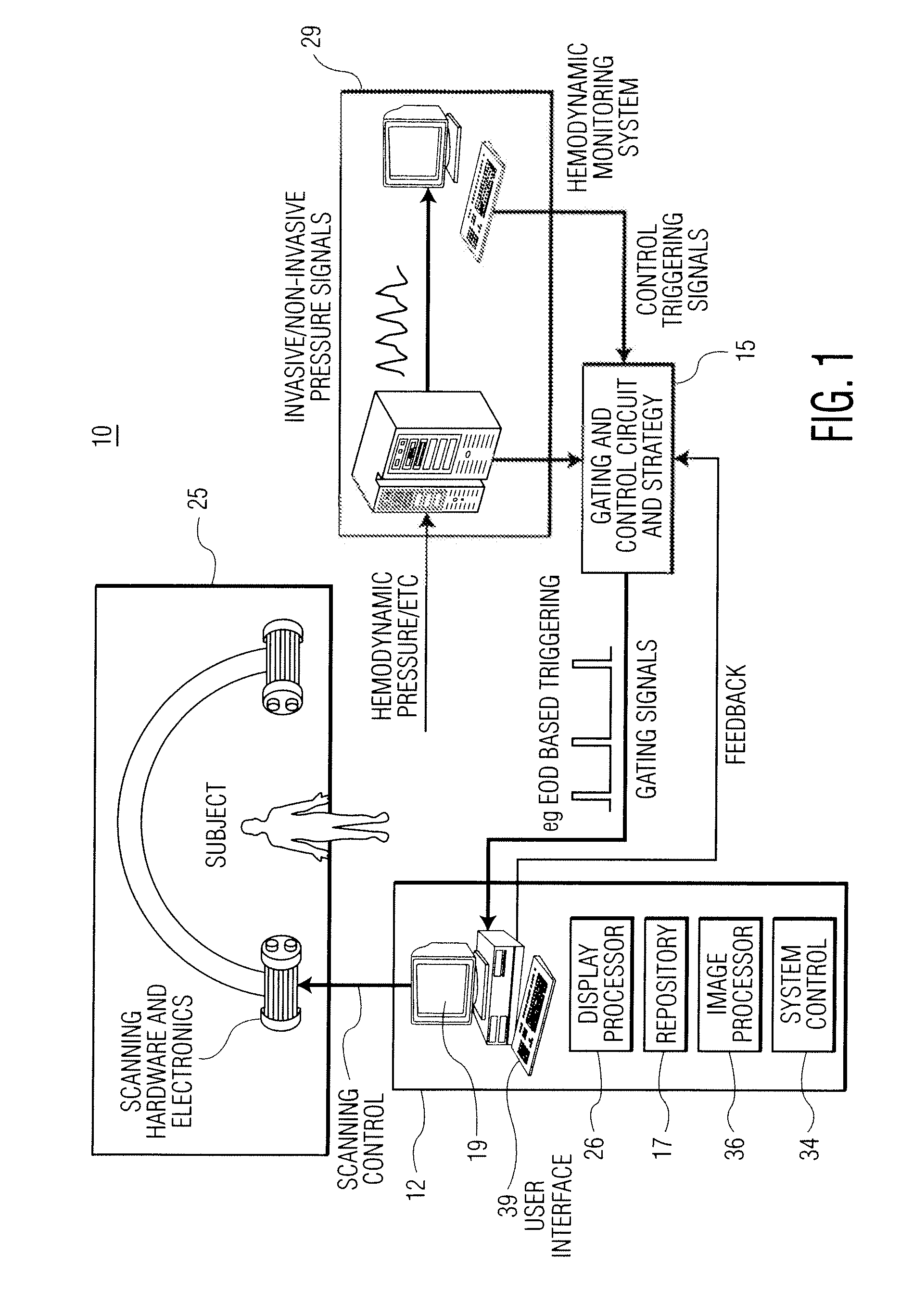
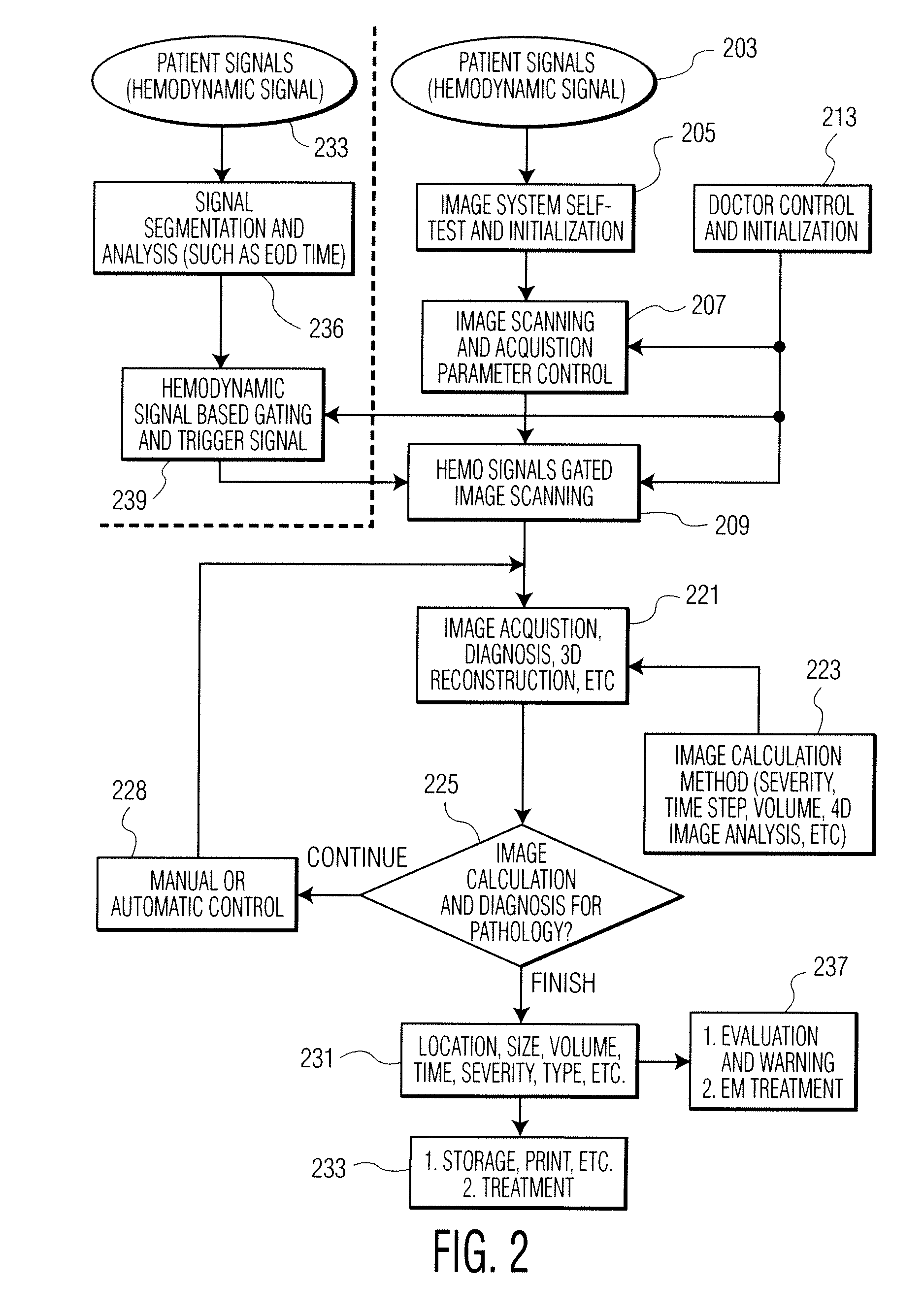
A cardiac functional analysis system reconstructs a 3D anatomical image volume using image frames acquired at predetermined cardiac phases over multiple cardiac cycles in response to a trigger derived from hemodynamic signals. A medical imaging system generates 3D anatomical imaging volume datasets from acquired 2D anatomical images. The system includes an image acquisition device for acquiring 2D anatomical images of a portion of patient anatomy in selectable angularly variable imaging planes in response to a synchronization signal derived from a patient blood flow related parameter. A synchronization processor provides the synchronization signal derived from the patient blood flow related parameter. An image processor processes 2D images acquired by the image acquisition device of the portion of patient anatomy in multiple different imaging planes having relative angular separation, to provide a 3D image reconstruction of the portion of patient anatomy.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
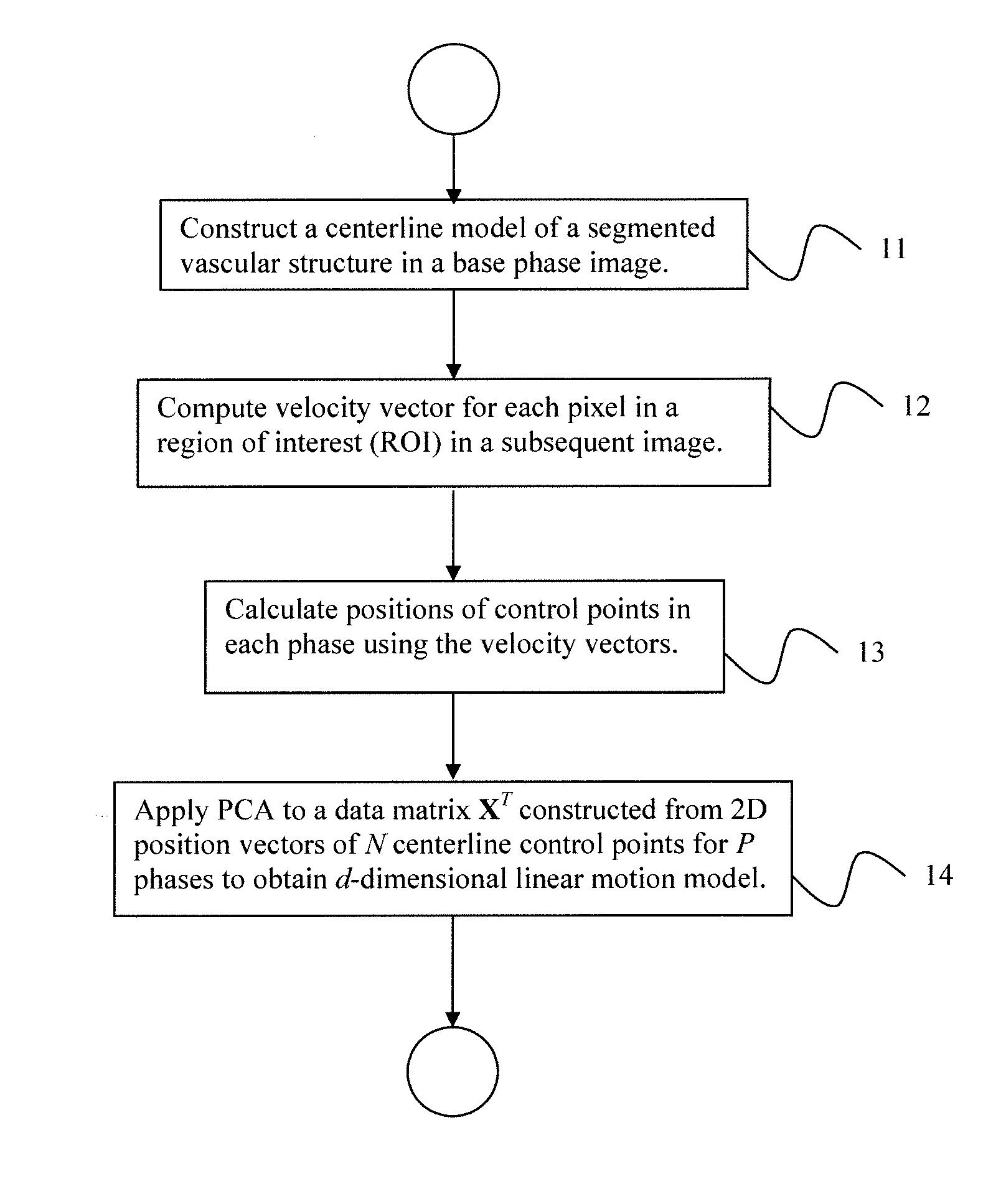
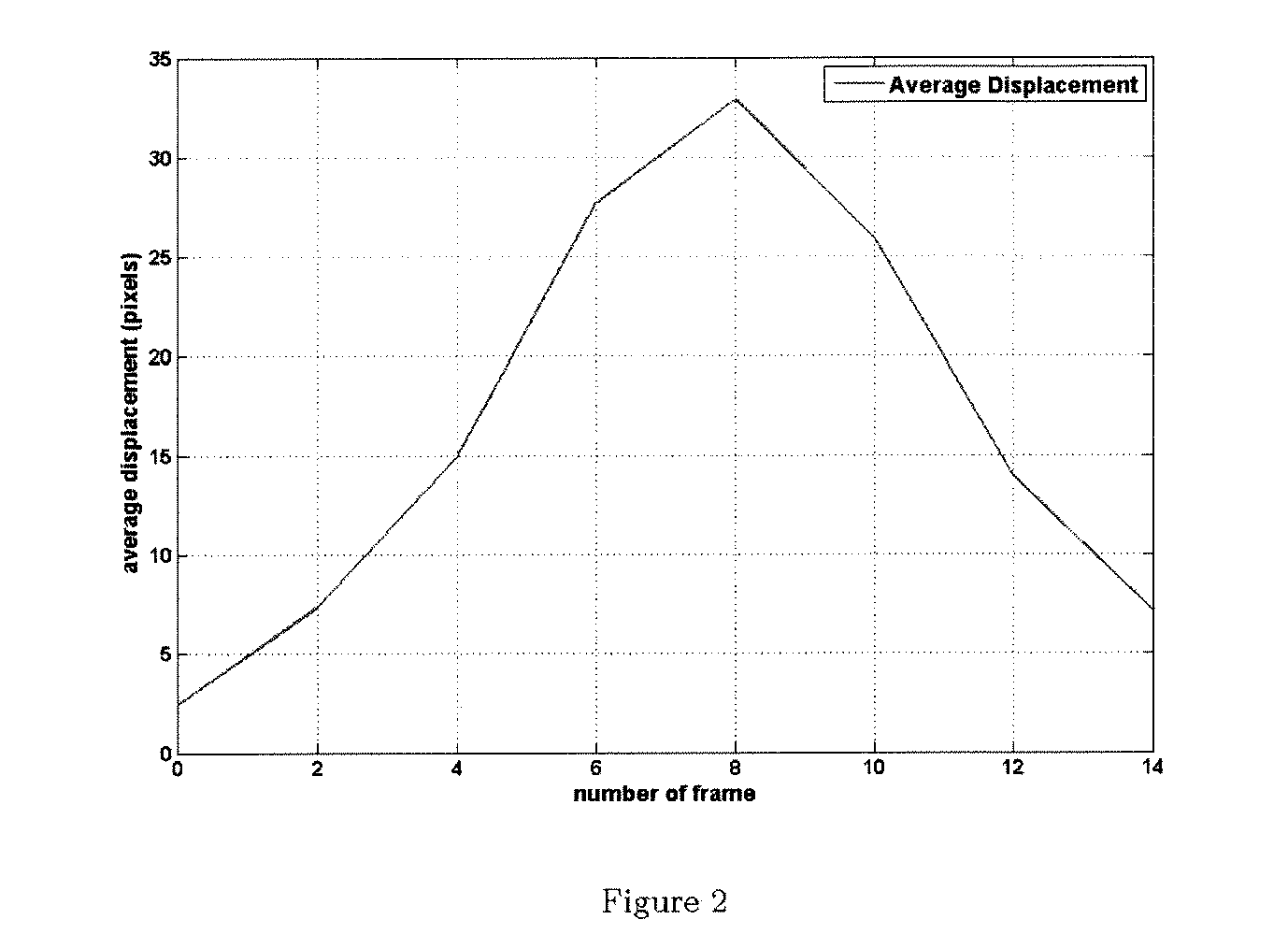
Coronary artery motion modeling
ActiveUS20130101187A1Real-time performanceImage enhancementImage analysisLinear motionCoronary arteries
A method for tracking coronary artery motion includes constructing (11) a centerline model of a vascular structure in a base phase image in a sequence of 2D images of coronary arteries acquired over a cardiac phase, computing (12), for each pixel in a region-of-interest in each subsequent image, a velocity vector that represent a change in position between the subsequent image and base phase image, calculating (13) positions of control points in each phase using the velocity vectors, and applying (14) PCA to a P×2N data matrix XT constructed from position vectors (x, y) of N centerline control points for P phases to identify d eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues of XXT to obtain a d-dimensional linear motion model {circumflex over (α)}p, in which a centerline model for a new image at phase p+1 is estimated by adding {circumflex over (α)}p to each centerline control point of a previous frame at phase p.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
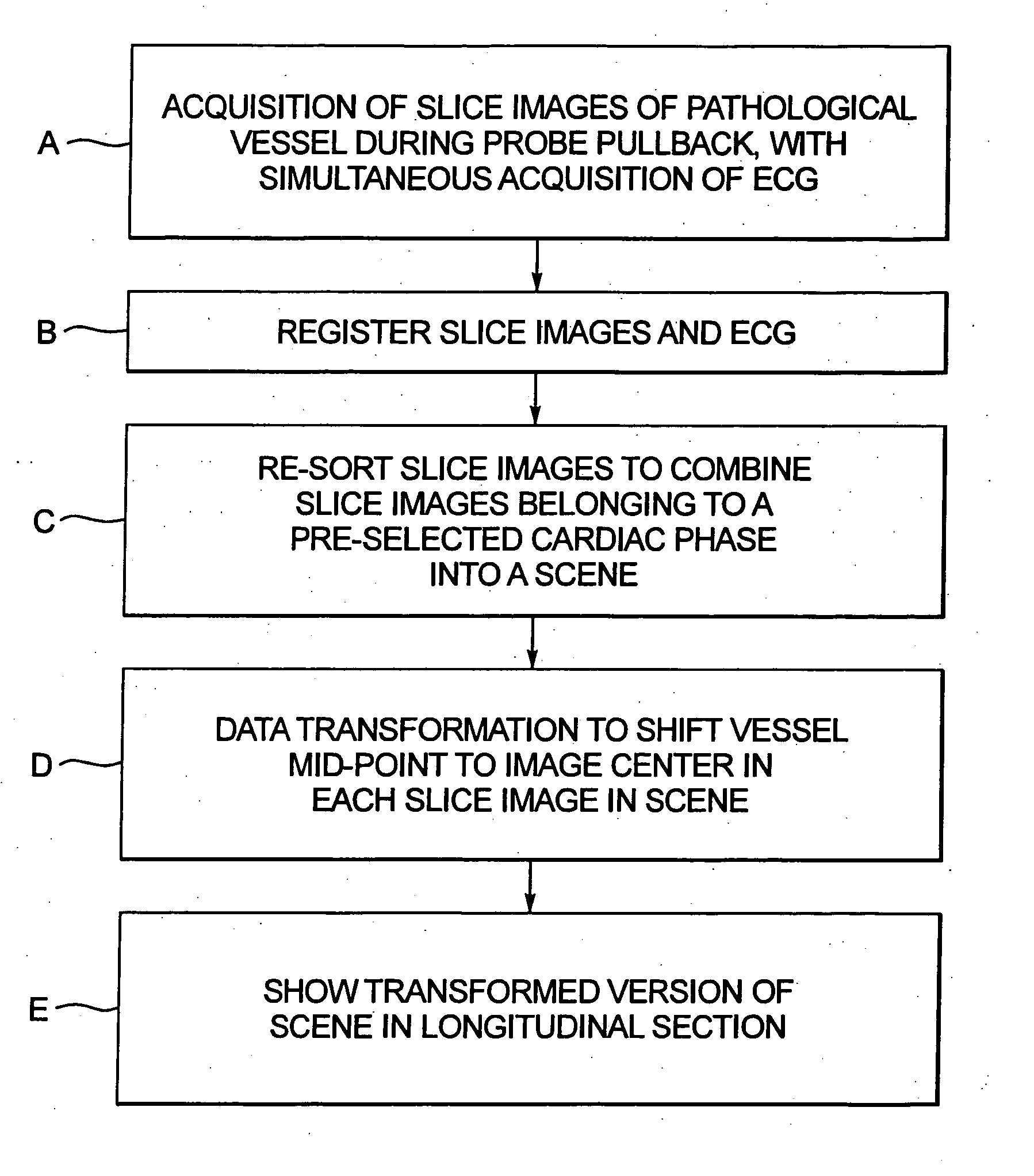
Method and apparatus for ECG-synchronized optically-based image acquisition and transformation
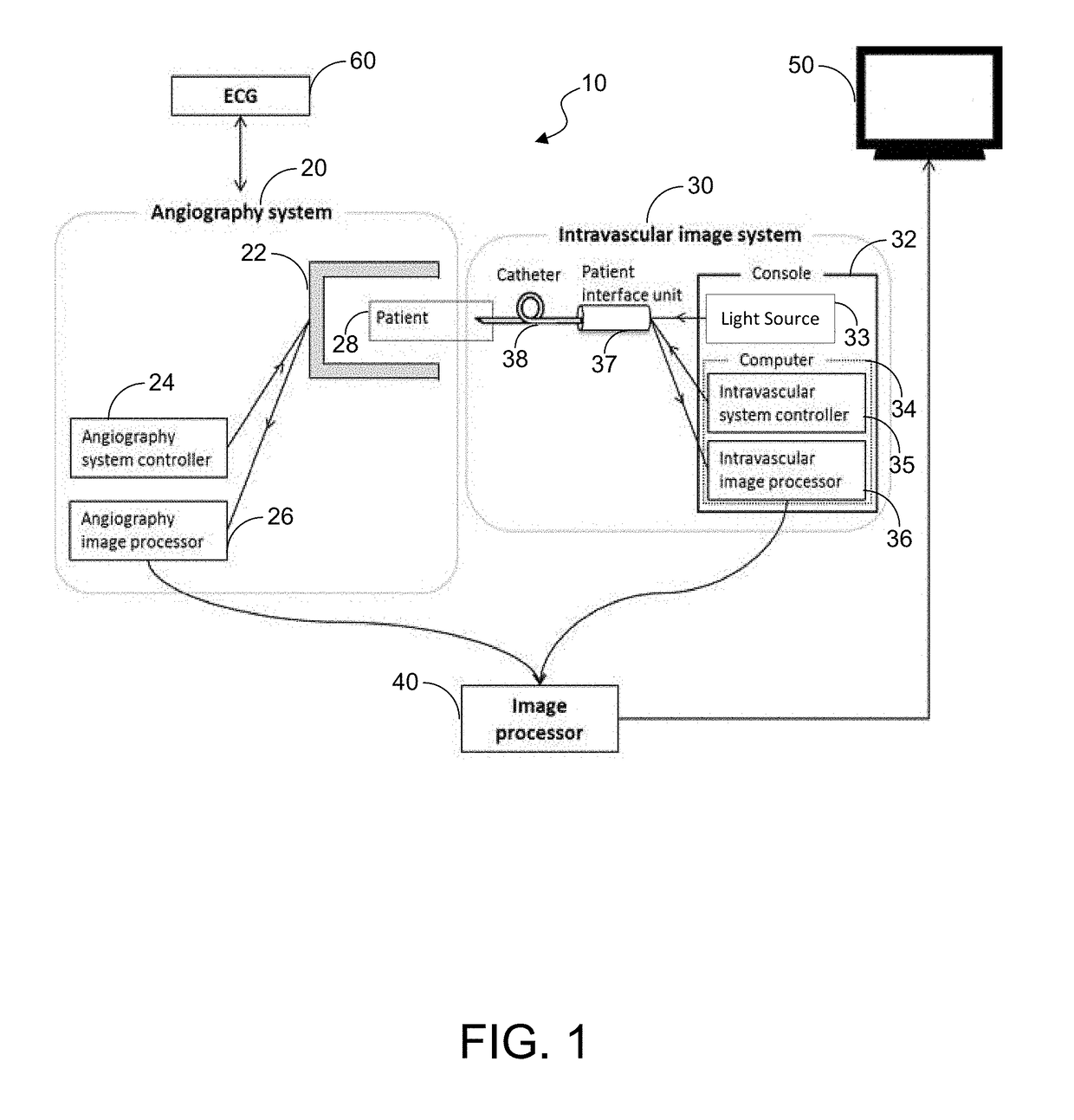
InactiveUS20070167833A1Increased radiation exposureSolve the lack of resolutionElectrocardiographyCatheterEcg signalData transformation
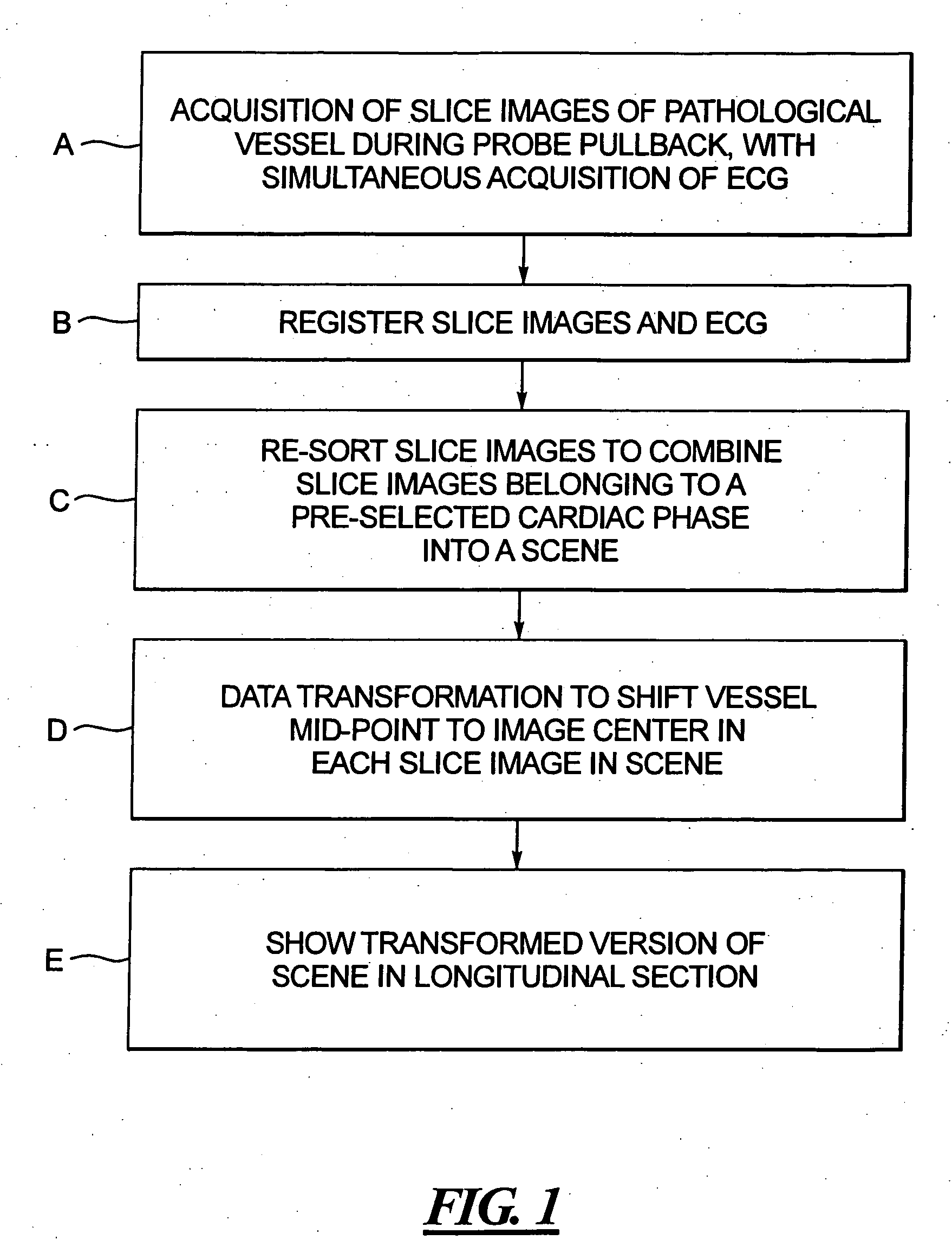
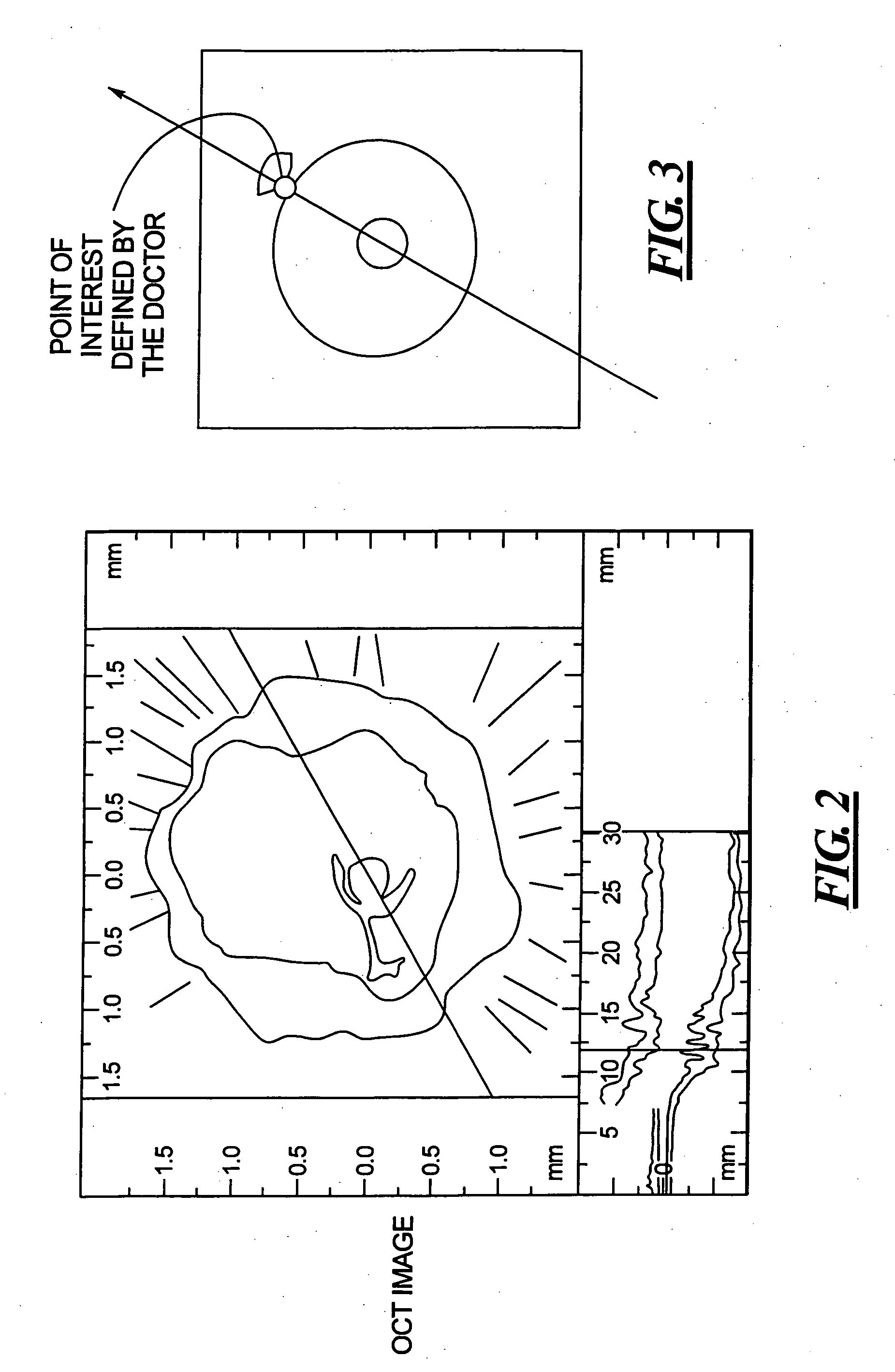
In a method and apparatus for optically-based acquisition of slice images from a vessel of a subject, and for combining the slice images to provide an intuitively recognizable visualization of a pathology in the vessel, slice images of the vessel are acquired during pullback of an optical probe of the optically-based slice imaging system, while simultaneously acquiring an ECG signal from the subject. The slice images and the ECG signal are registered, and slice images acquired at a selected cardiac phase are combined into a scene. The slice images in the scene are subjected to a first data transformation to shift the vessel midpoint in each slice image to the image center of each slice image. After the first data transformation, the slice images in the scene are subjected to a second data transformation to produce the visualization. The second transformation, for example, can be a curved planar reformation to allow the vessel to be shown in longitudinal section.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
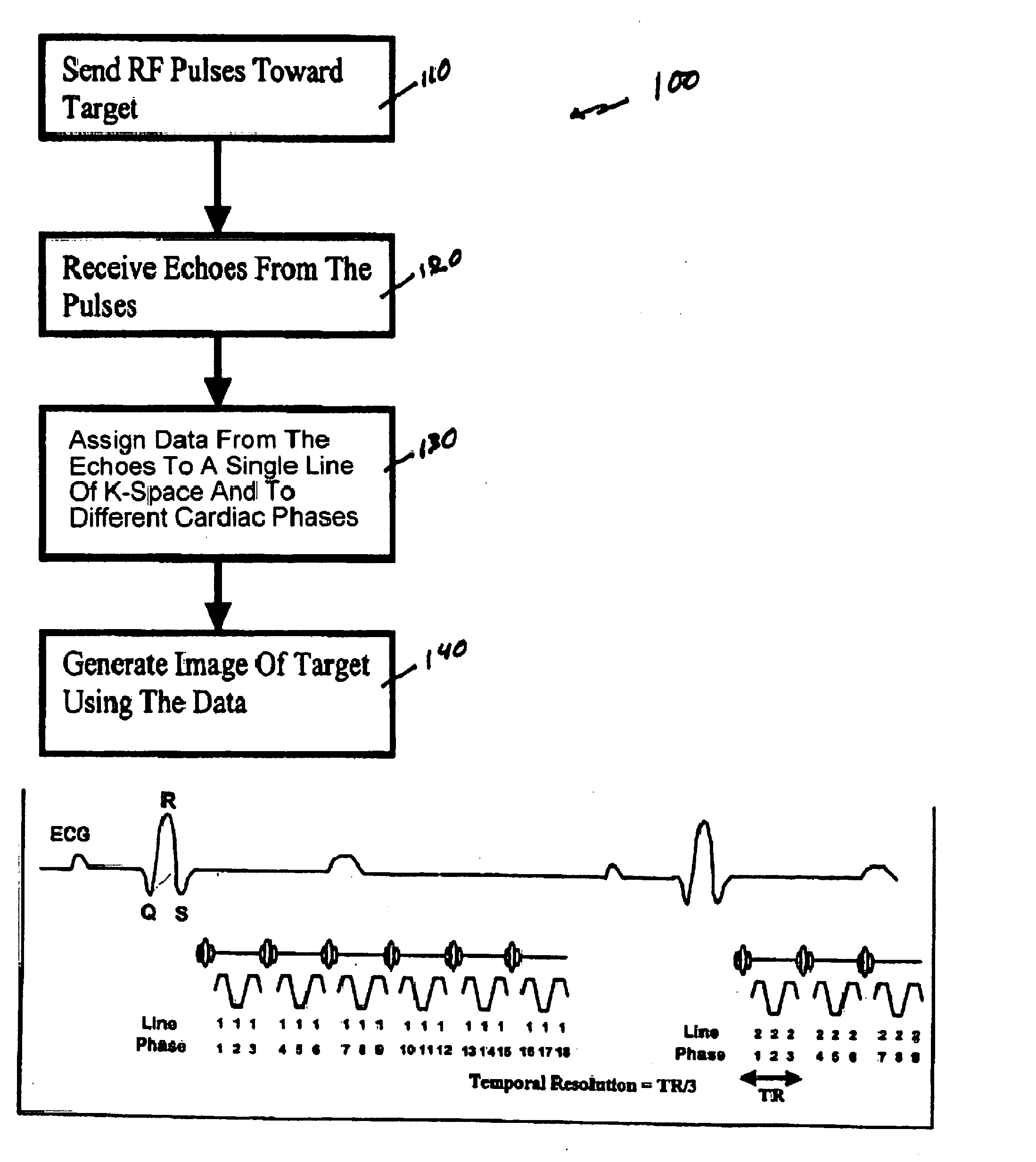
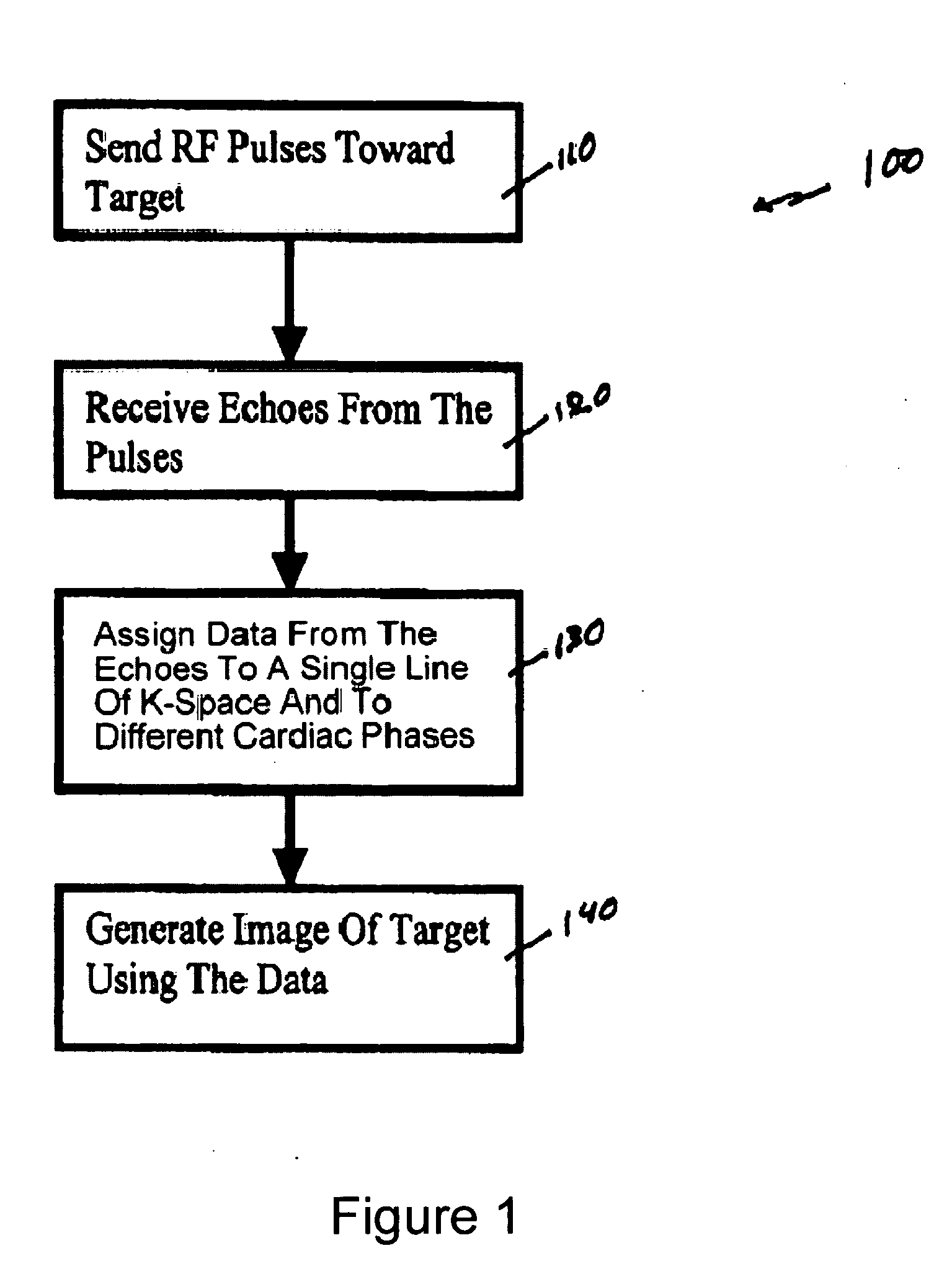
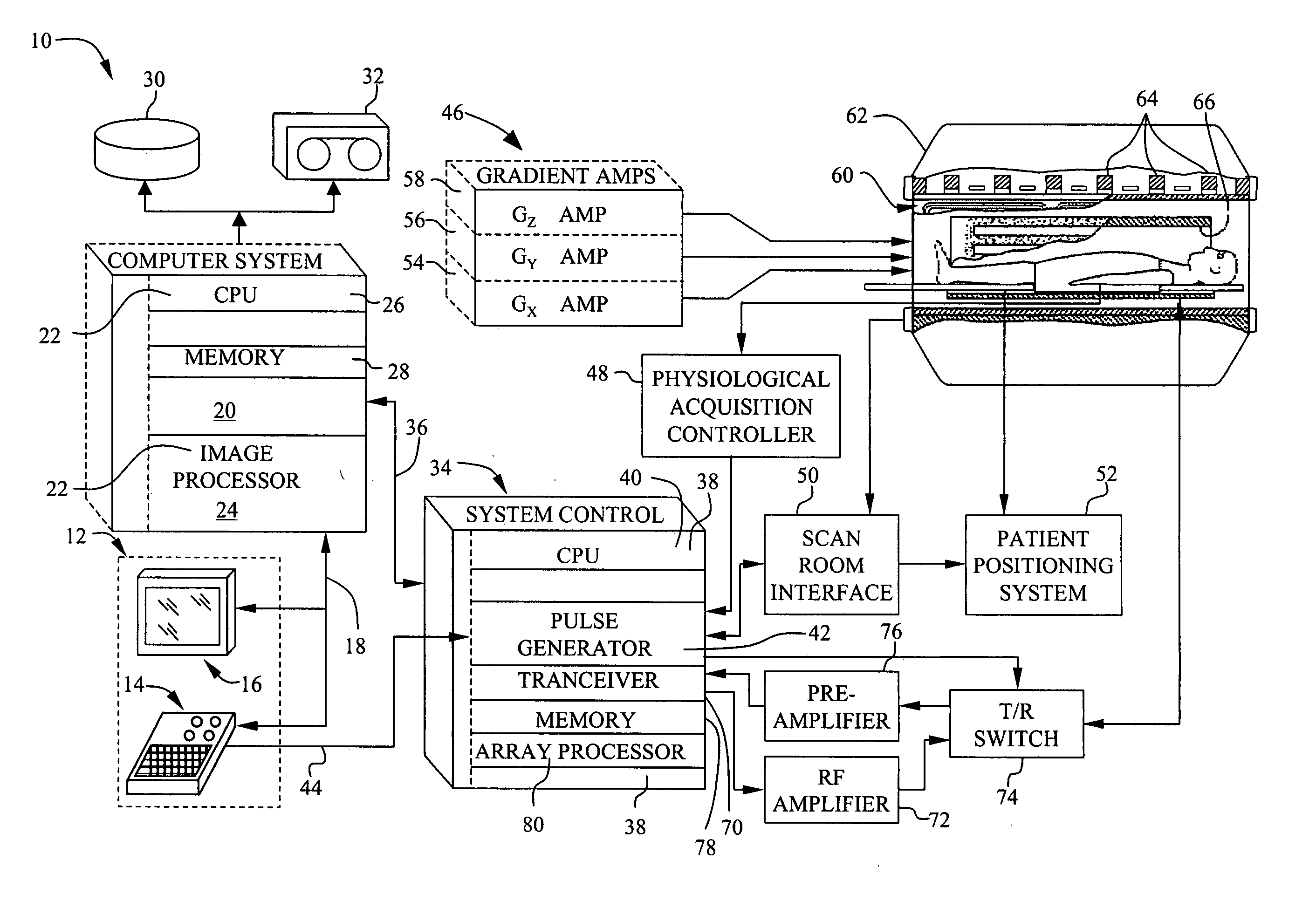
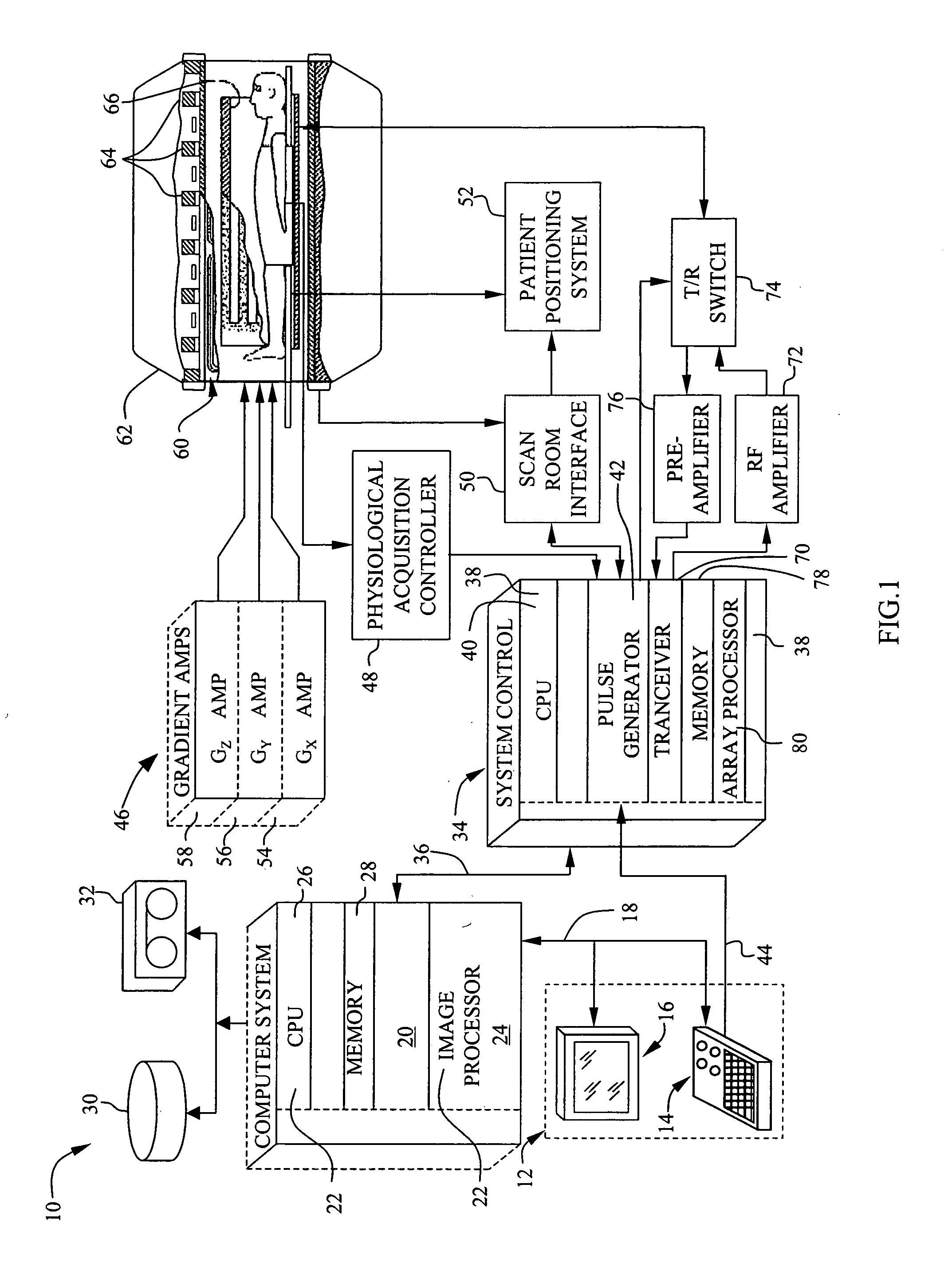
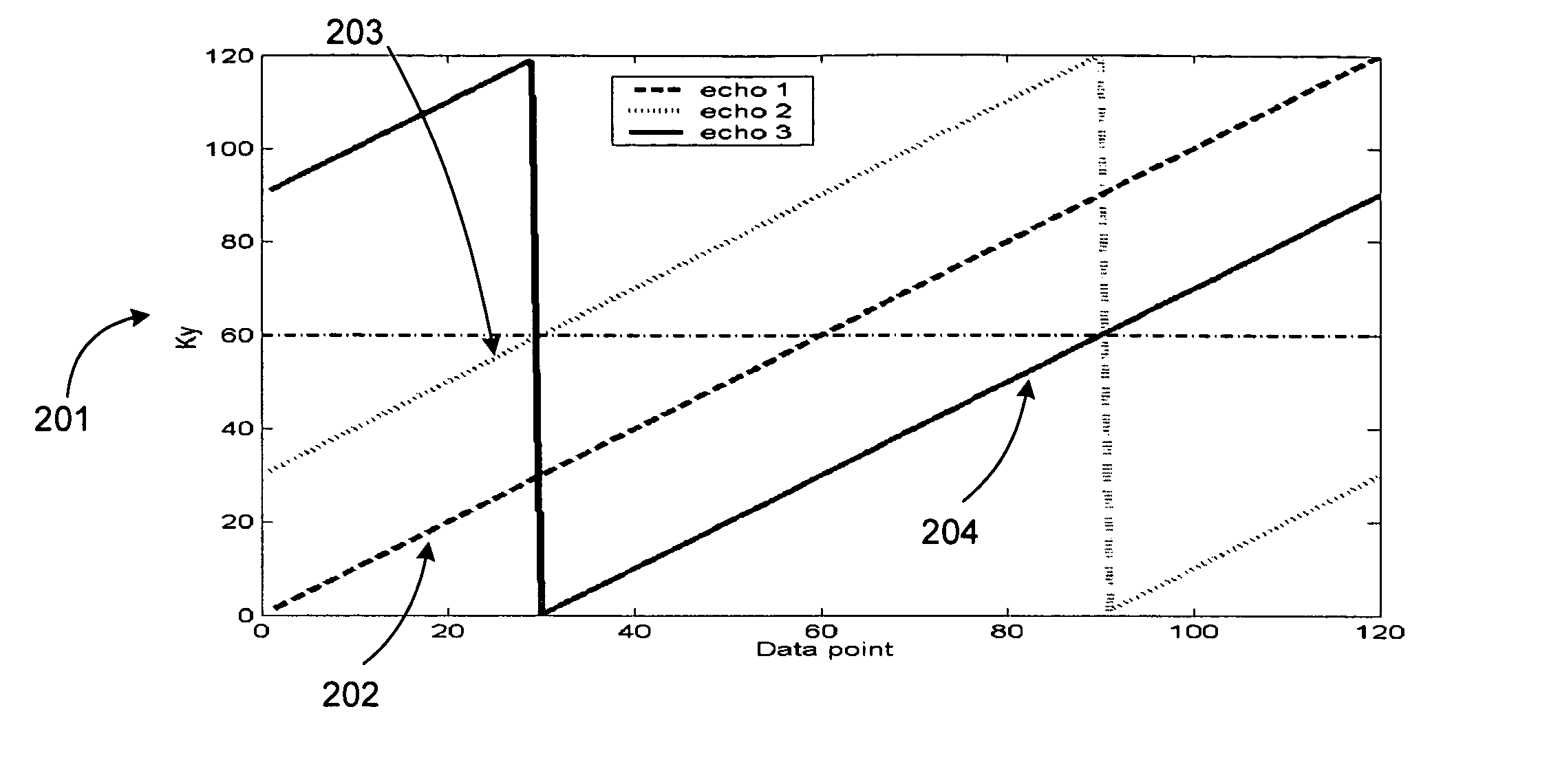
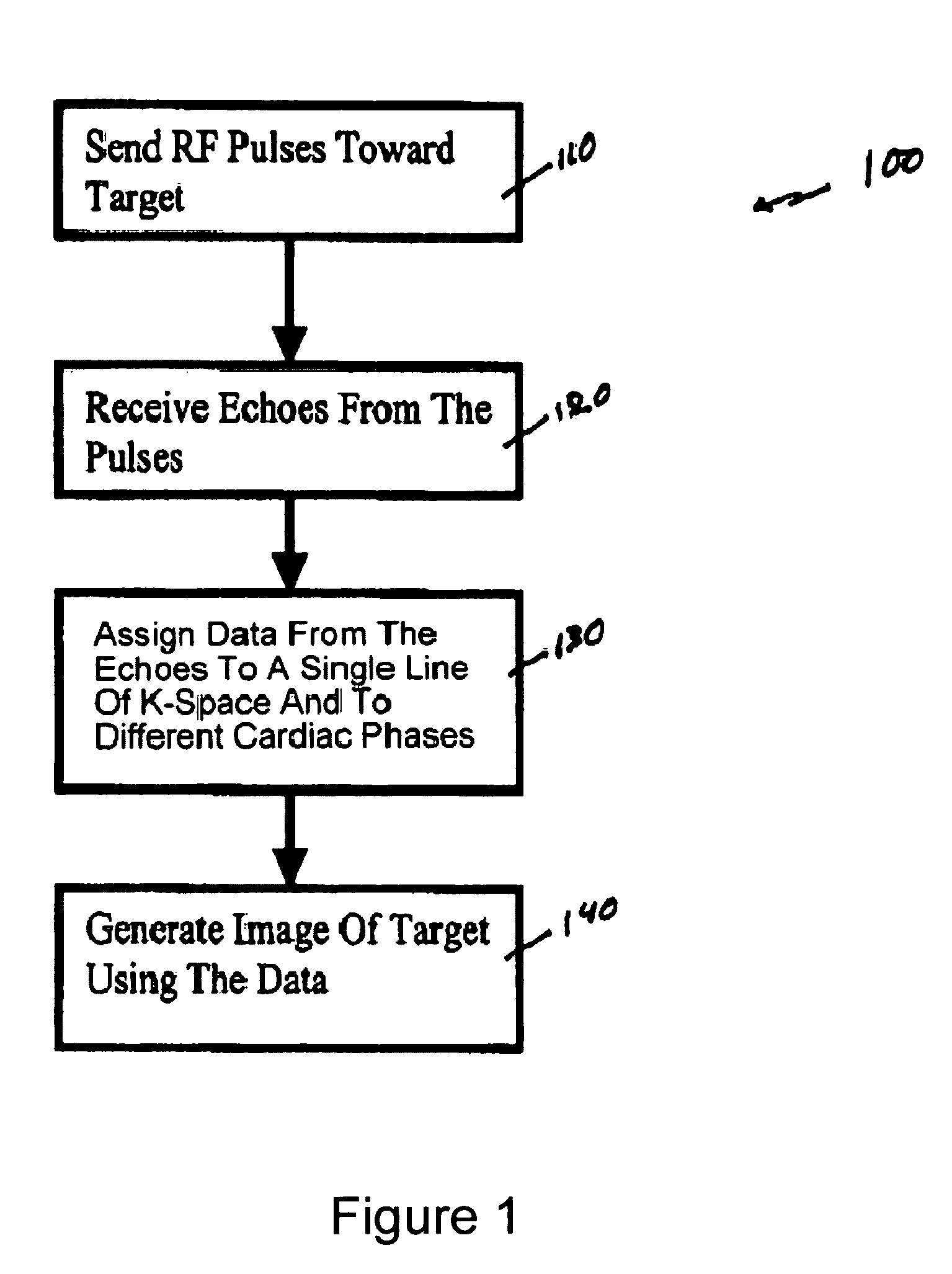
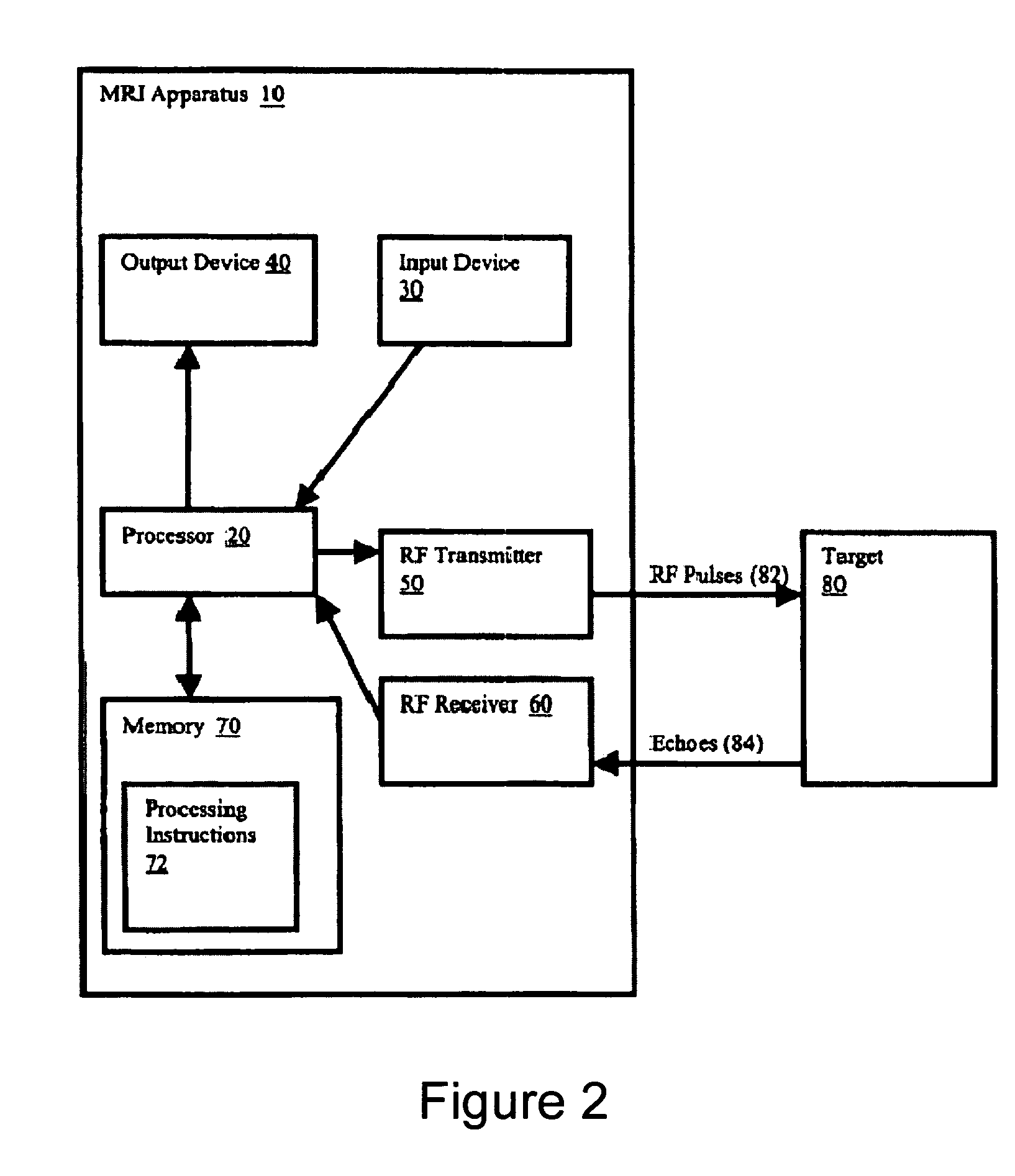
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
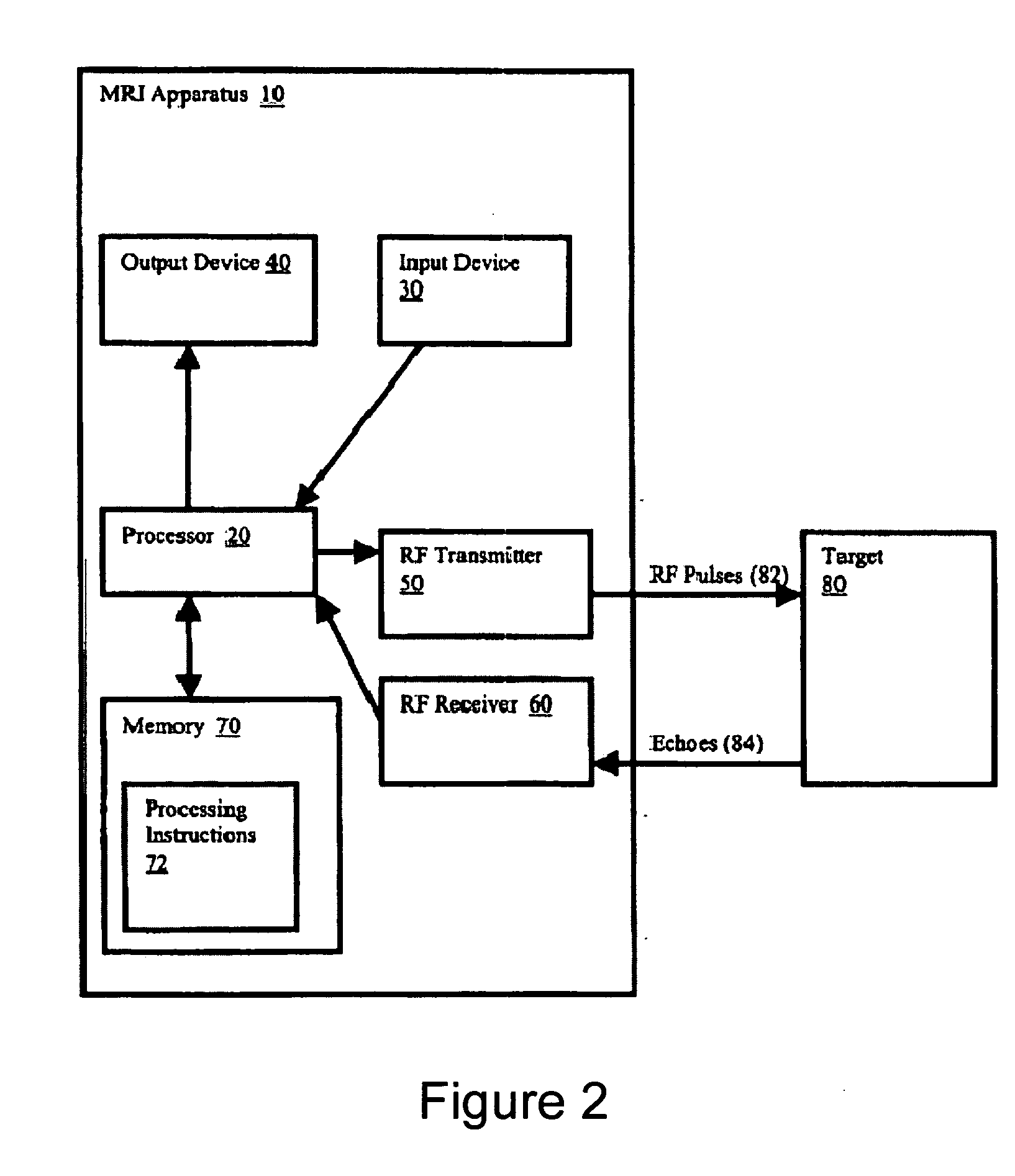
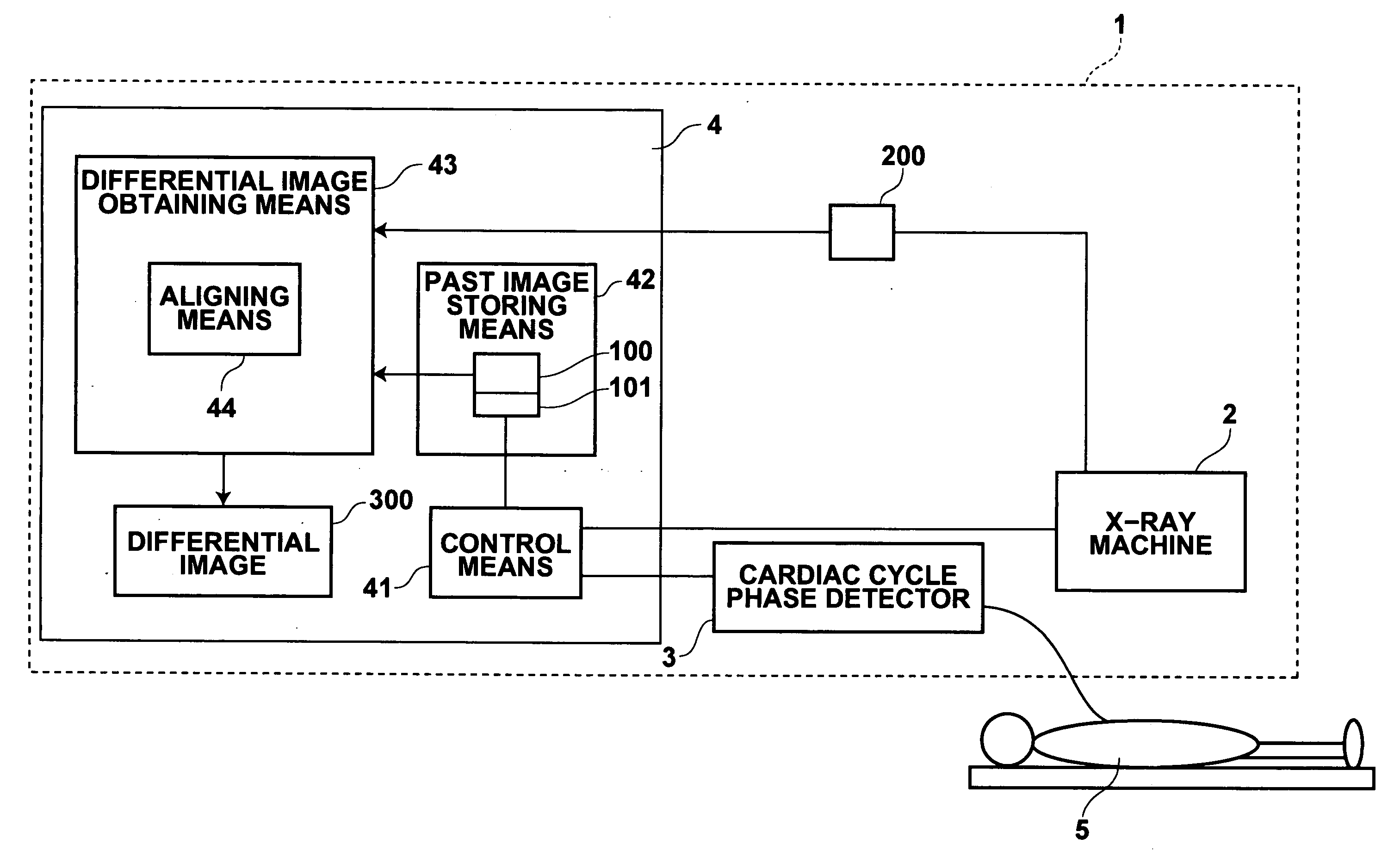
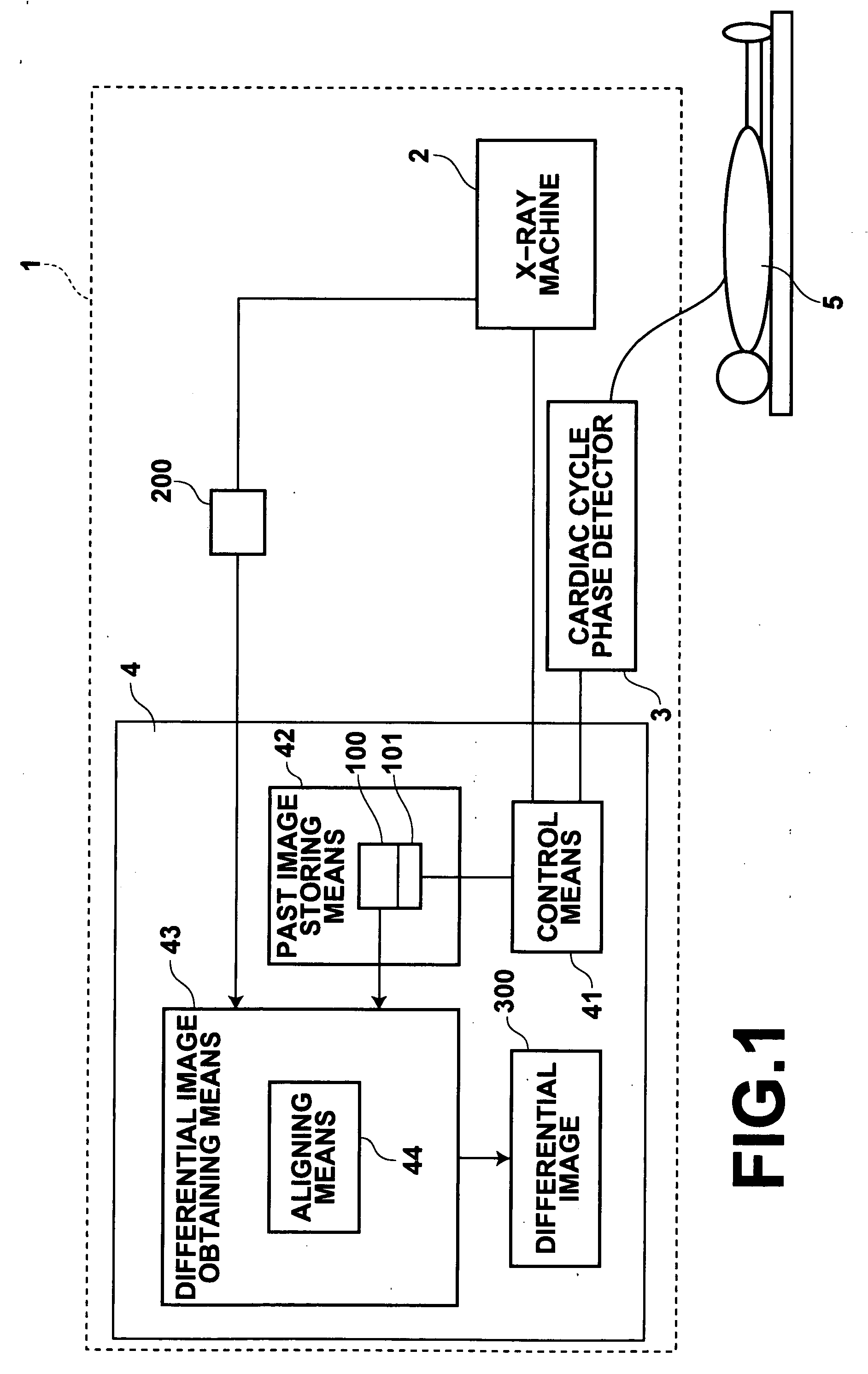
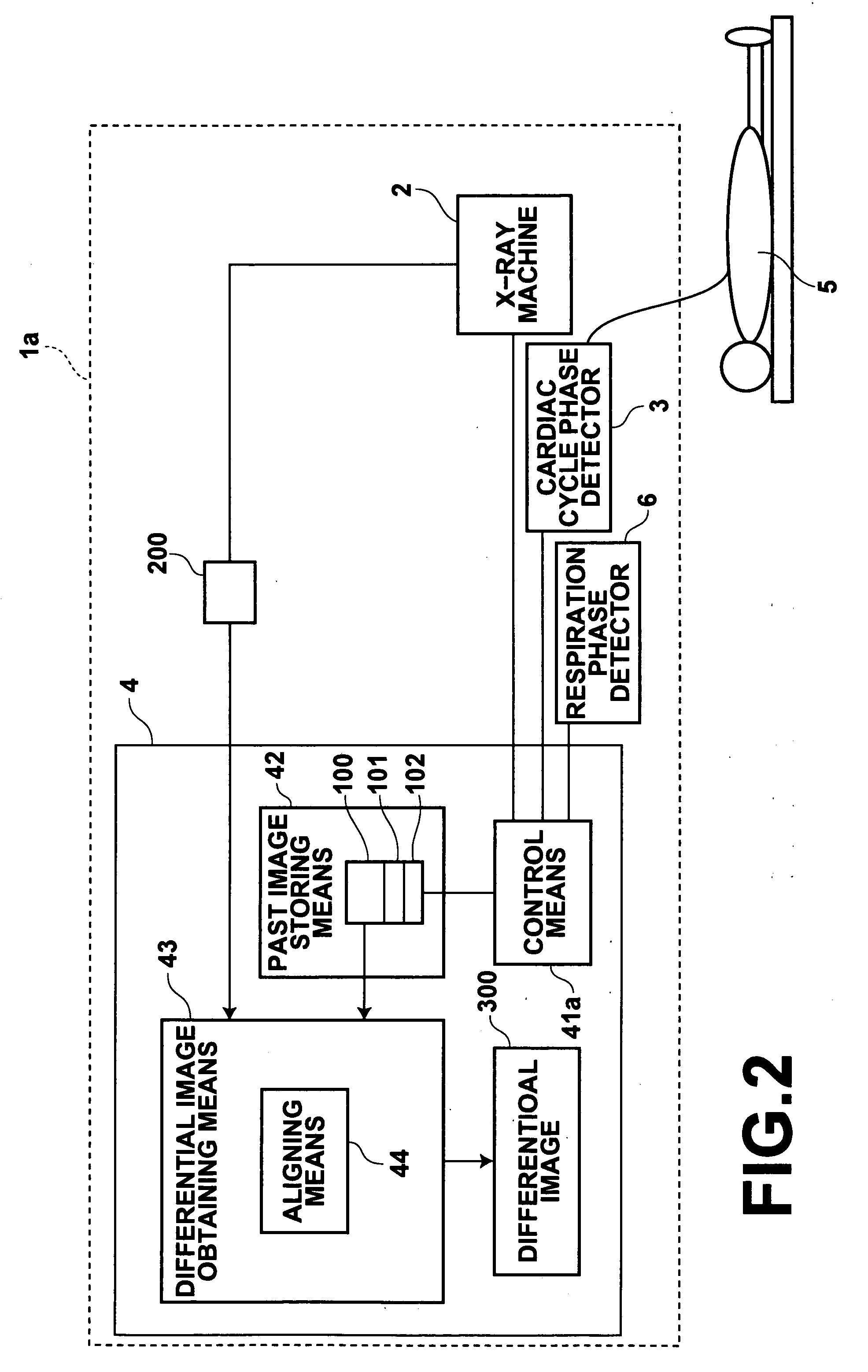
Method, apparatus and program for obtaining differential image
InactiveUS20050234331A1Efficient identificationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCardiac phaseImage detection
Detection of the difference between images of the same subject obtained at different times is performed effectively. The cardiac phases of the subject are detected, and a current image is obtained through X-raying the subject at the time when the detected cardiac phase corresponds to that of the past image. Thereafter, a differential image is obtained from the current and past images by obtaining the difference between them.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS8194937B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. Thus, one aspect of the present invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that requires less number of data samples to reconstruct an accurate reconstruction of a desired image than previous methods, such as, compressed sensing. Another aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution (e.g., 20 milliseconds) using a CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
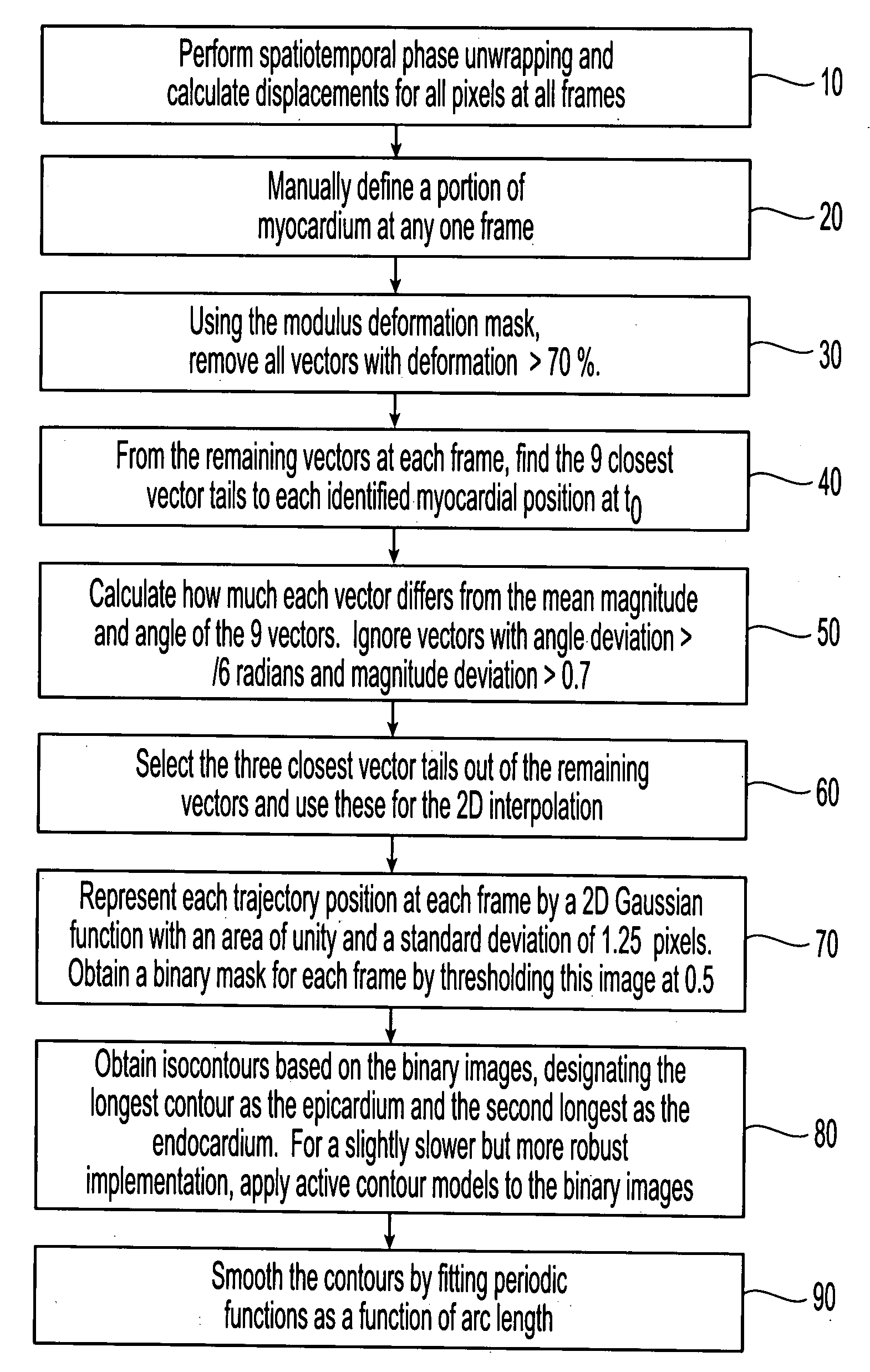
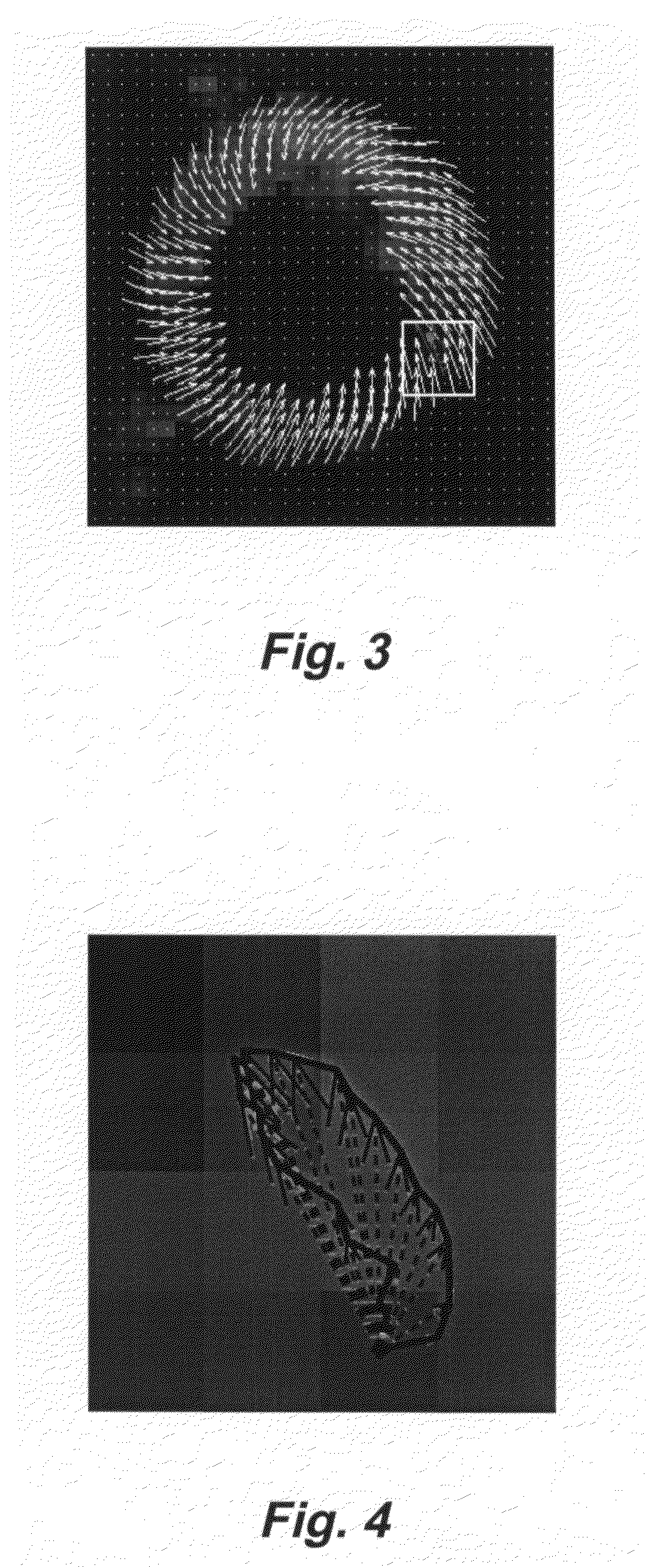
Motion-guided segmentation for cine dense images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
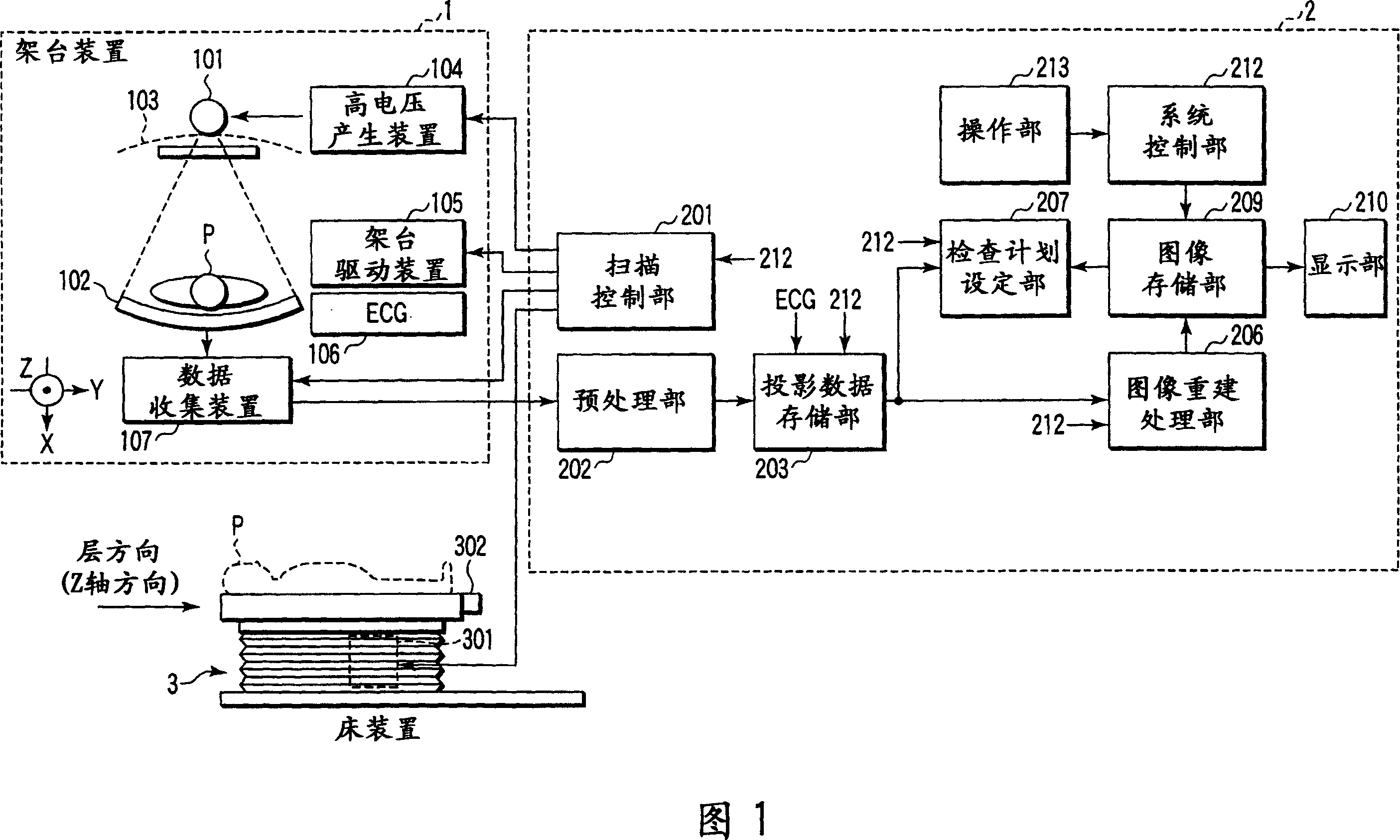
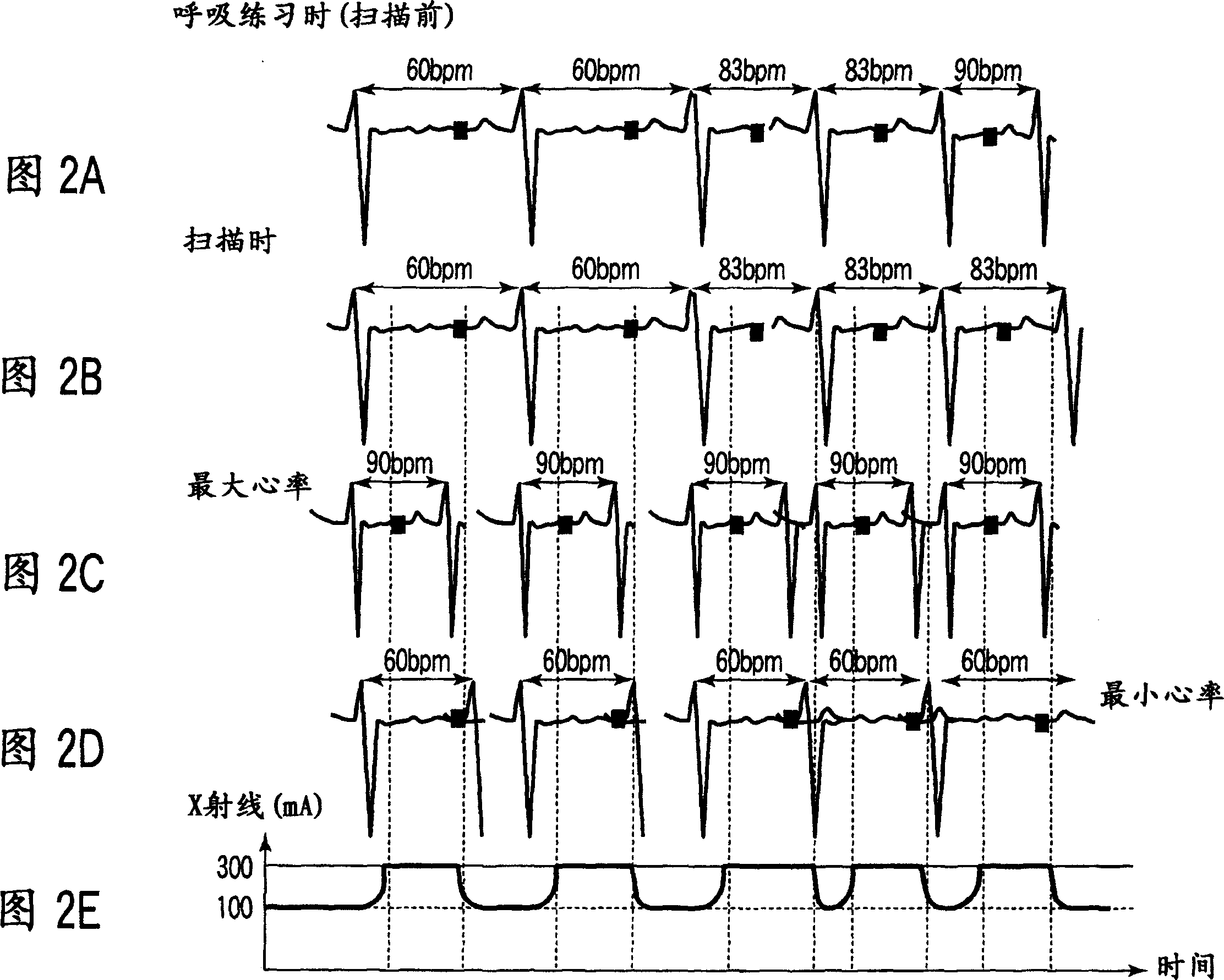
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
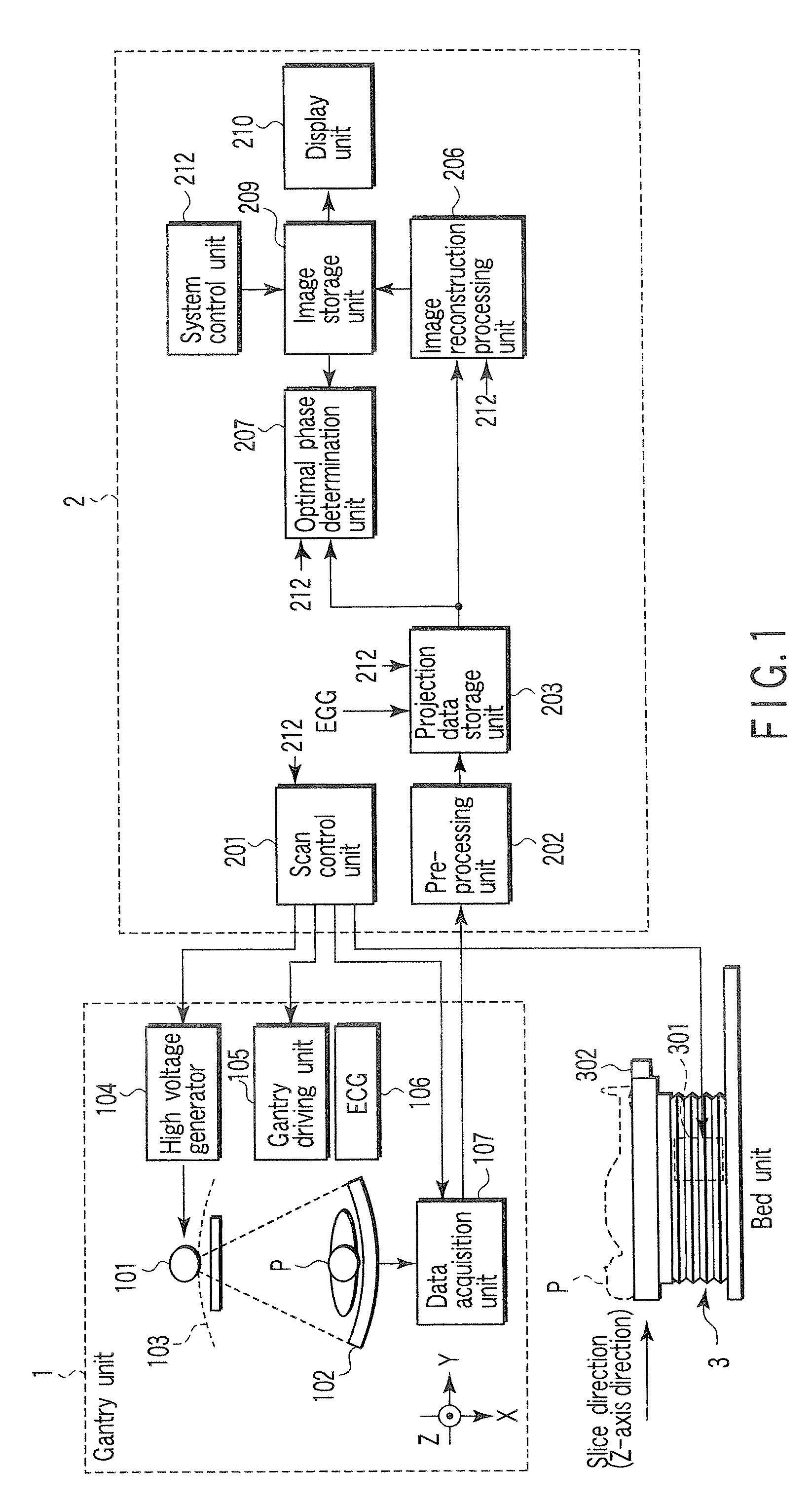
ActiveUS20070053483A1Avoid partialMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData setCycle control
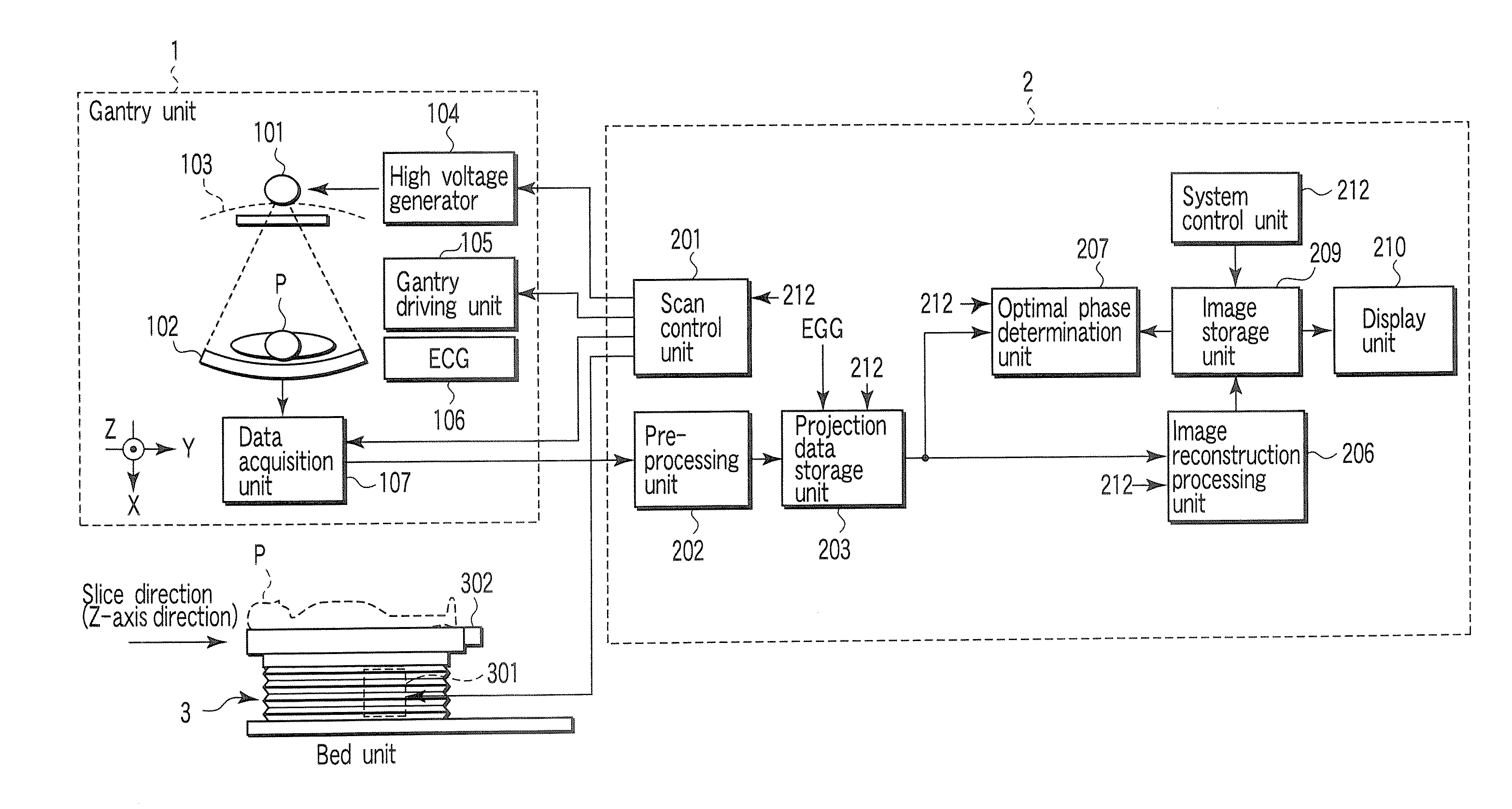
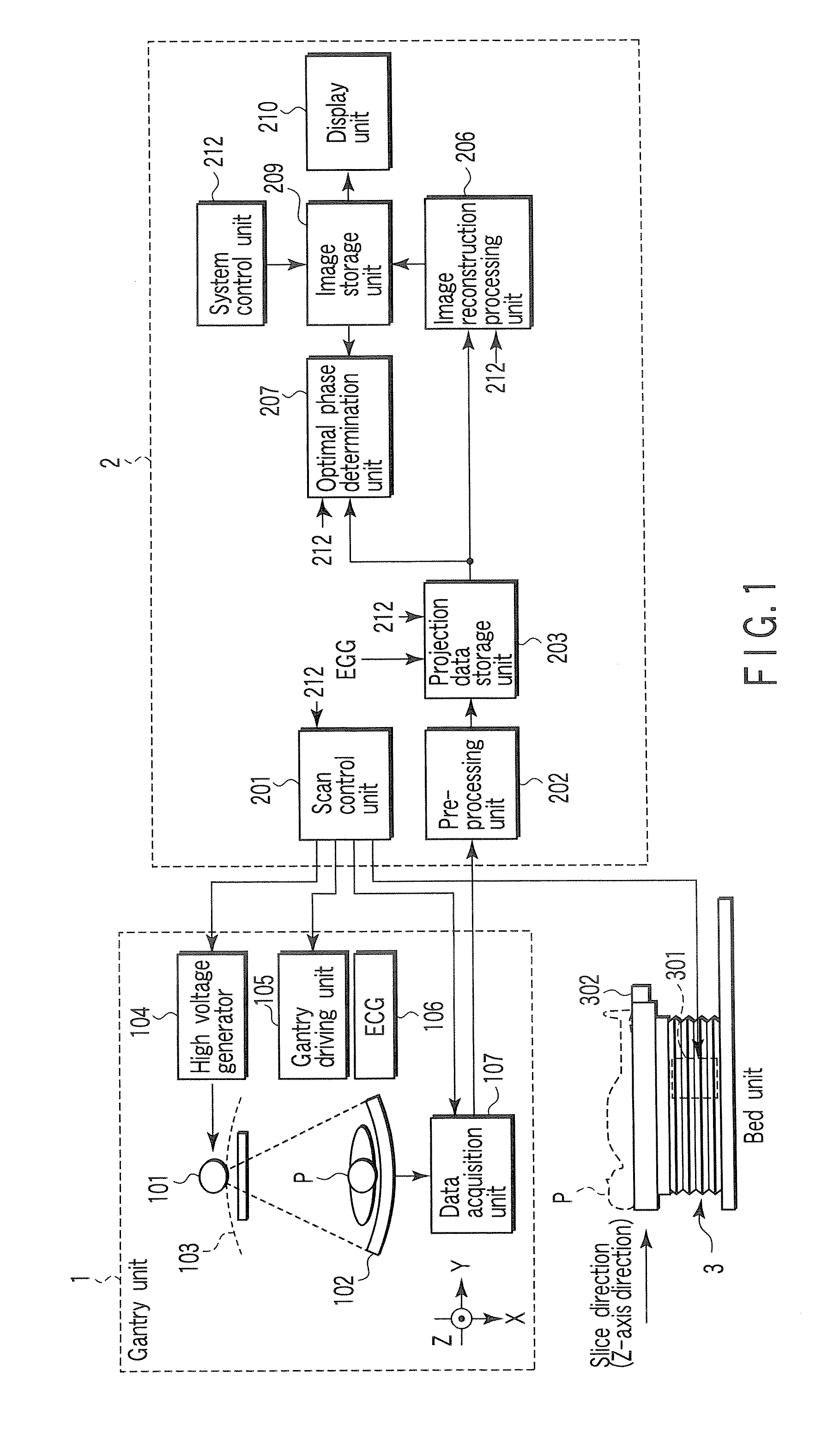
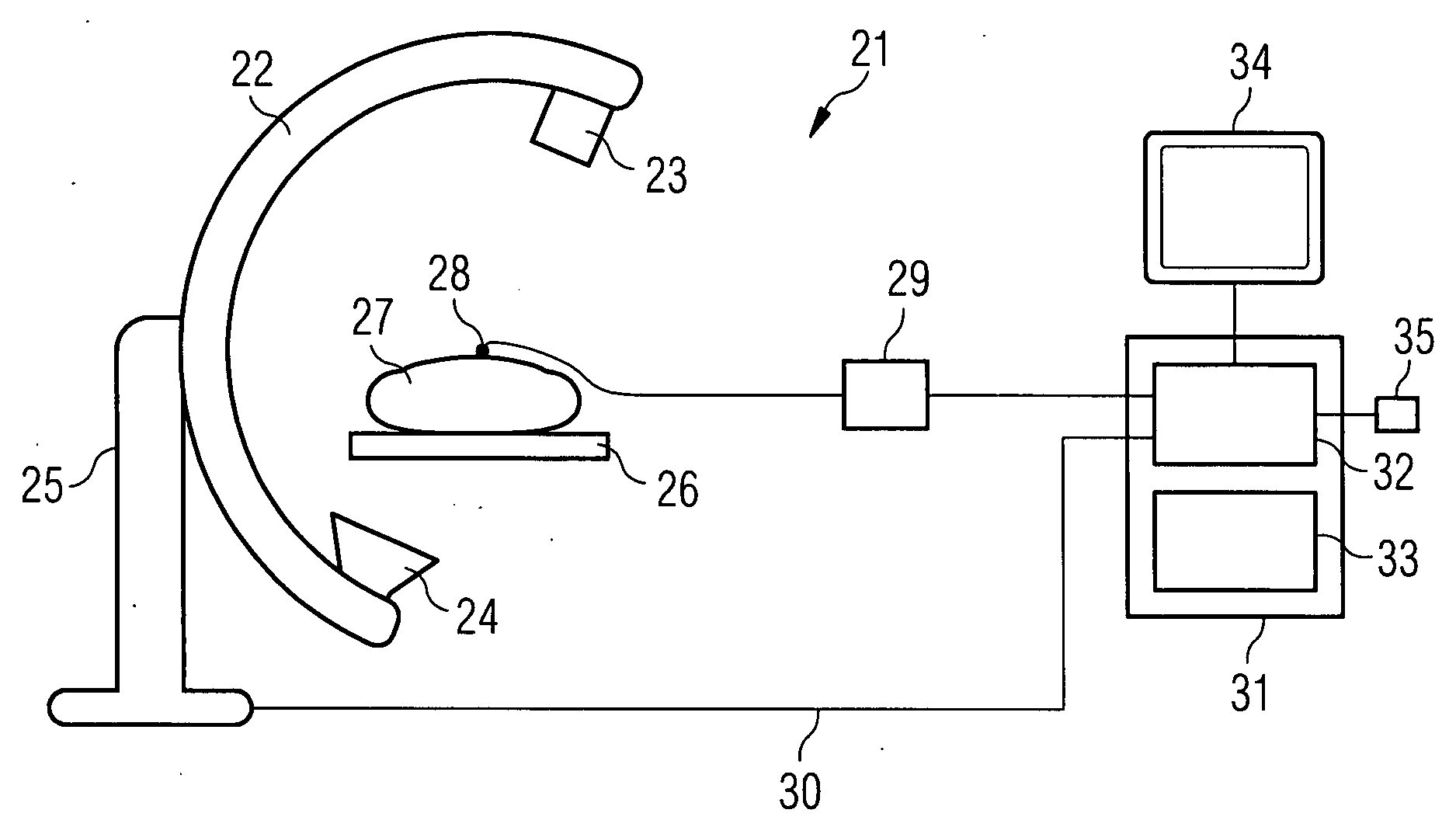
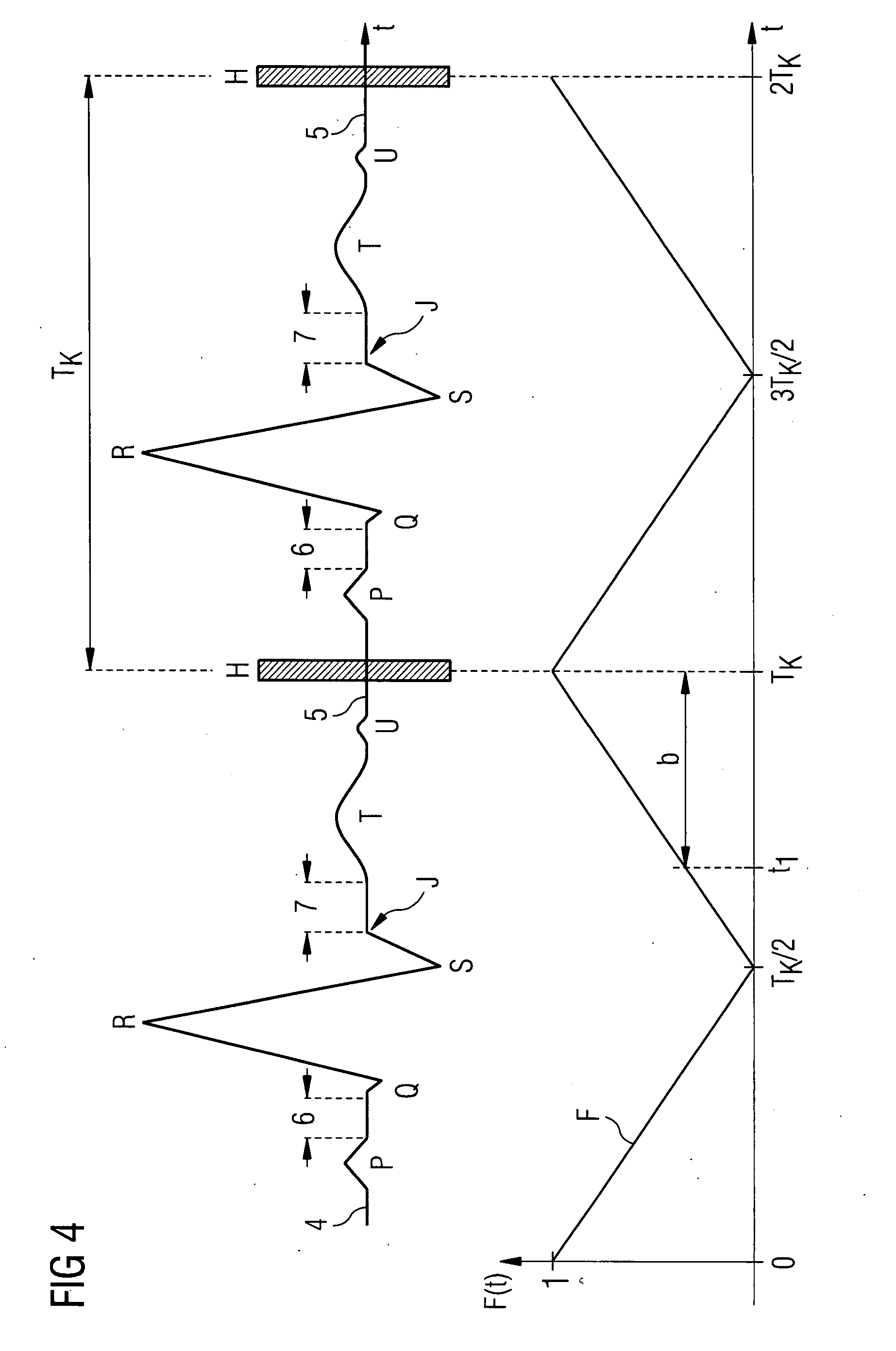
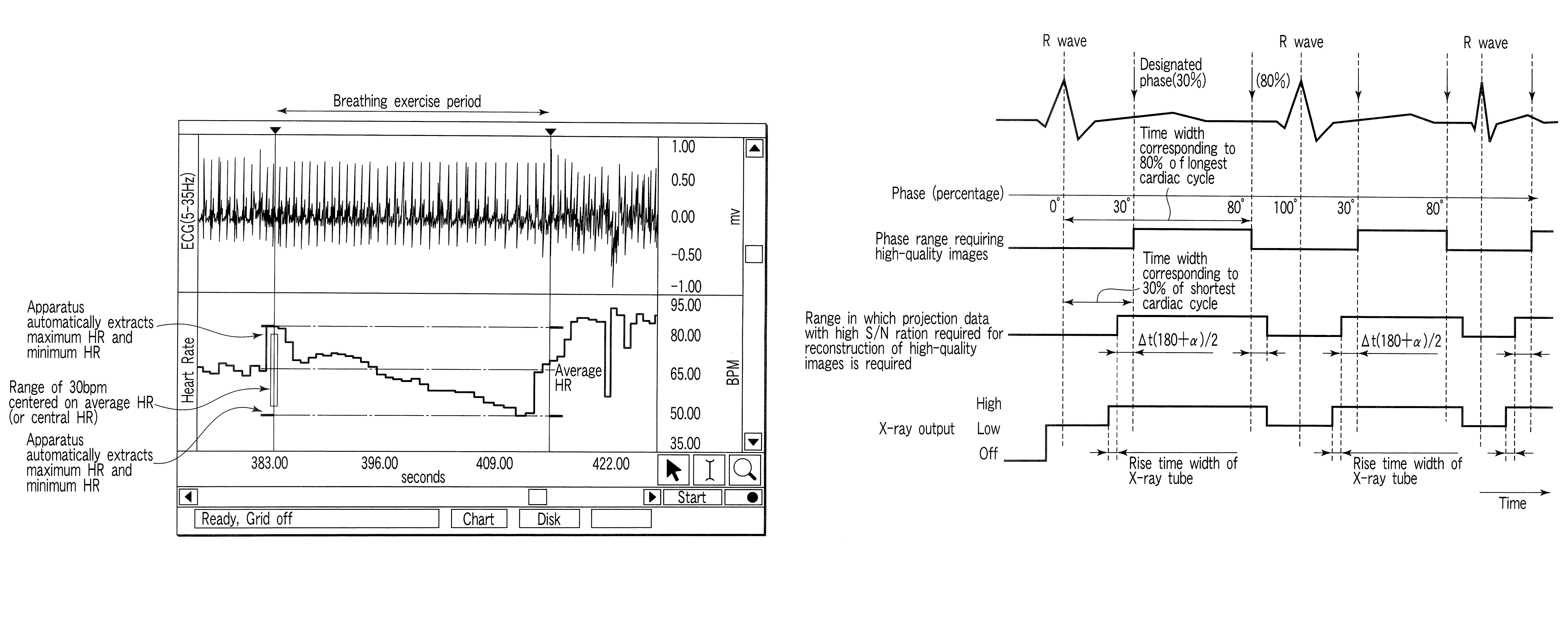
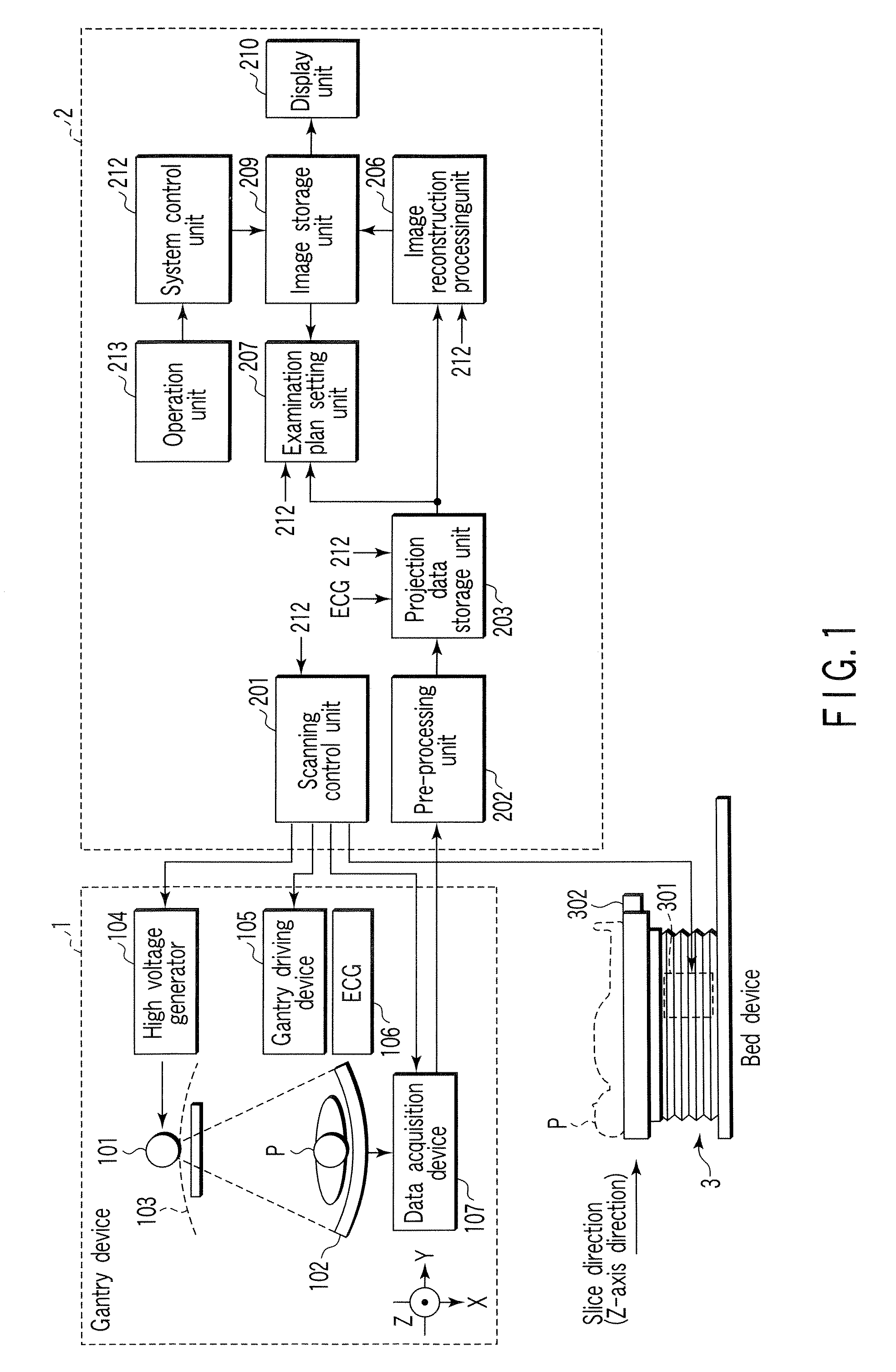
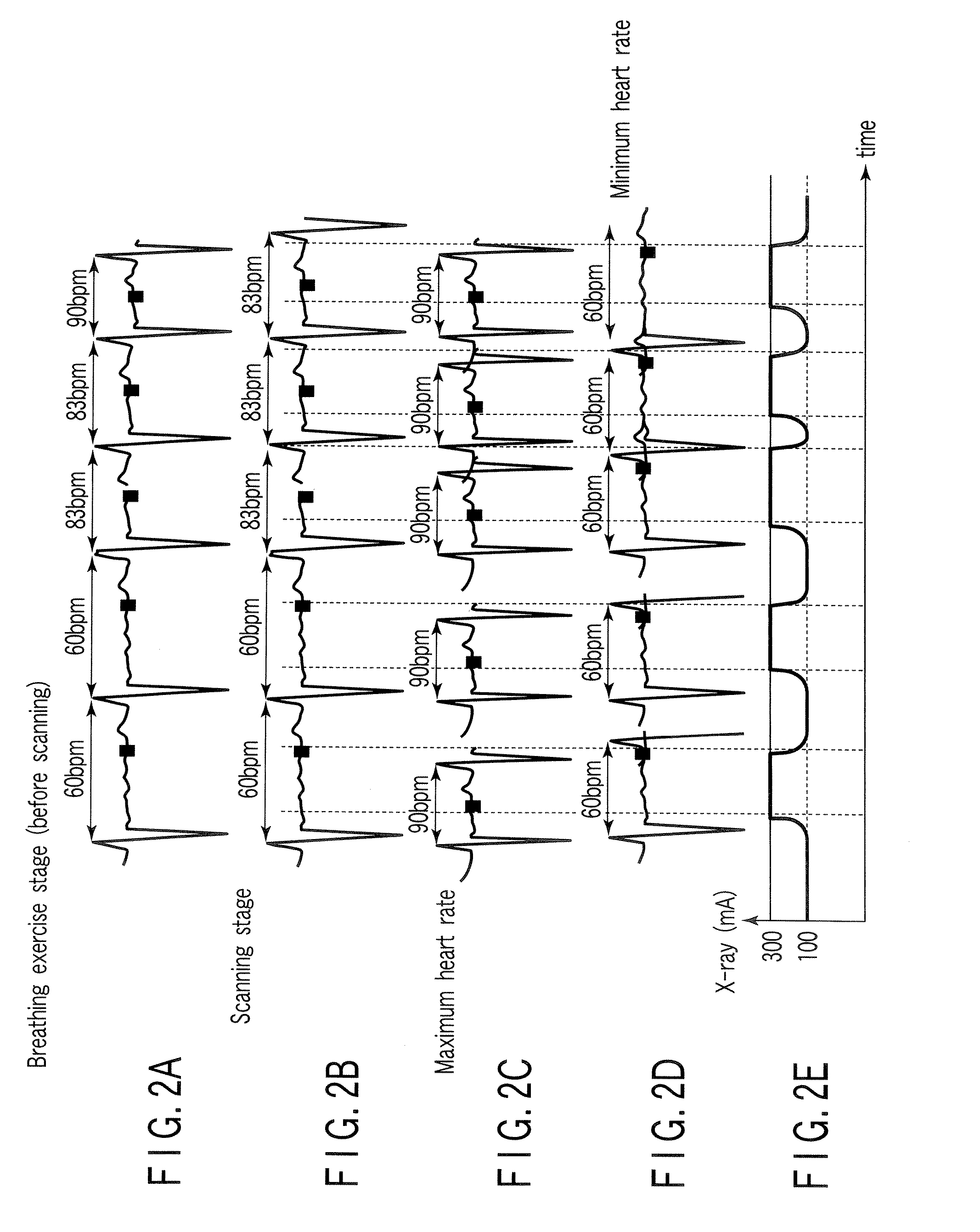
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes an X-ray source, a high voltage generating unit, an X-ray detector detecting X-rays transmitted through a subject to generate projection data, a storage unit storing the projection data in association with electrocardiographic data of the subject, a setting unit setting a specific cardiac phase in accordance with an operator's instruction, a reconstruction unit reconstructing a tomogram based on projection data sets acquired in specific periods centered on the specific cardiac phase throughout cardiac cycles, a period extending unit extending the specific period on the basis of a heart rate fluctuation range of the subject, and a control unit controlling the high voltage generating unit to generate a relatively high dose of X-rays in the extended specific period and generate a relatively low dose of X-rays in a period other than the extended specific period.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
ECG driven image reconstruction for cardiac imaging
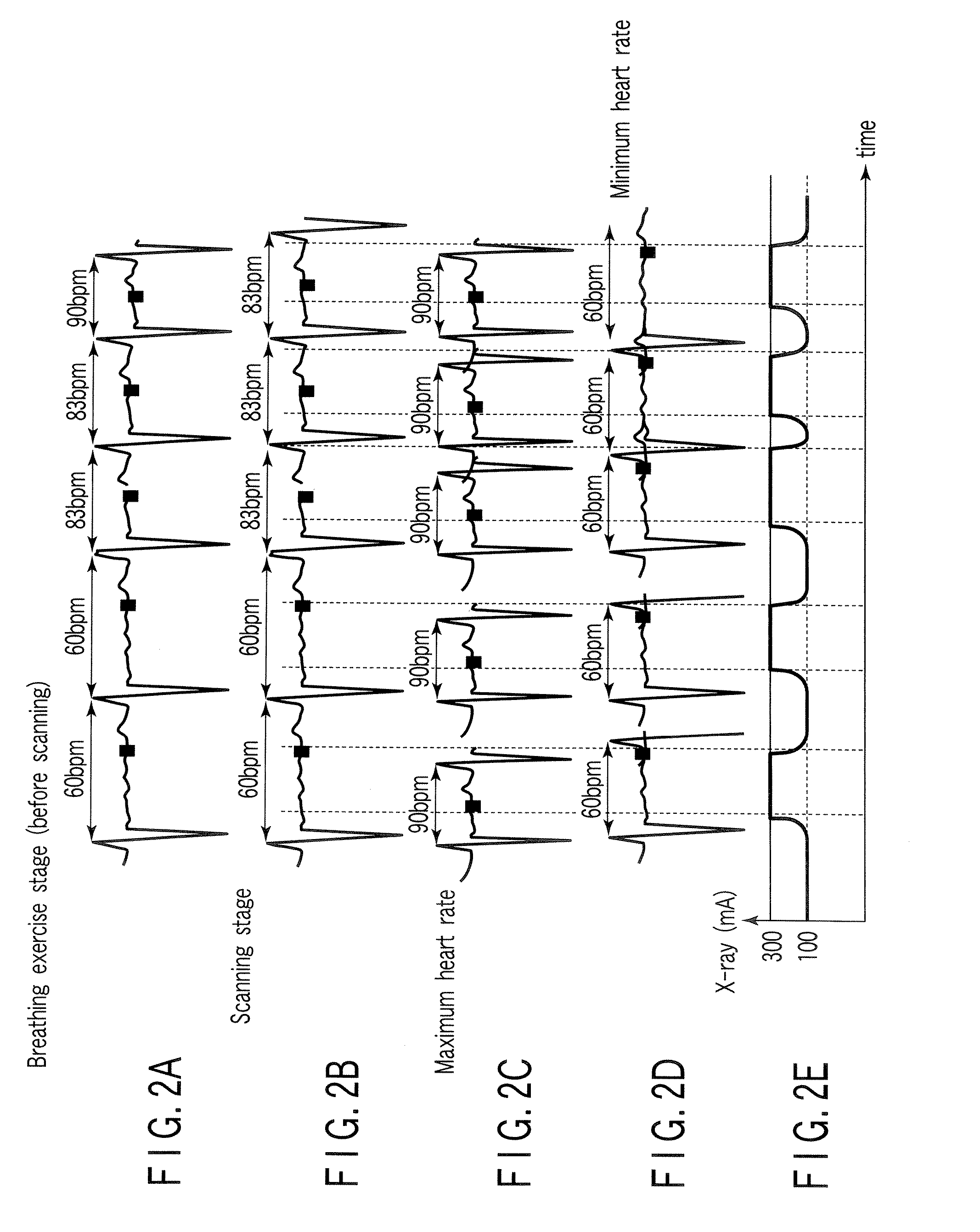
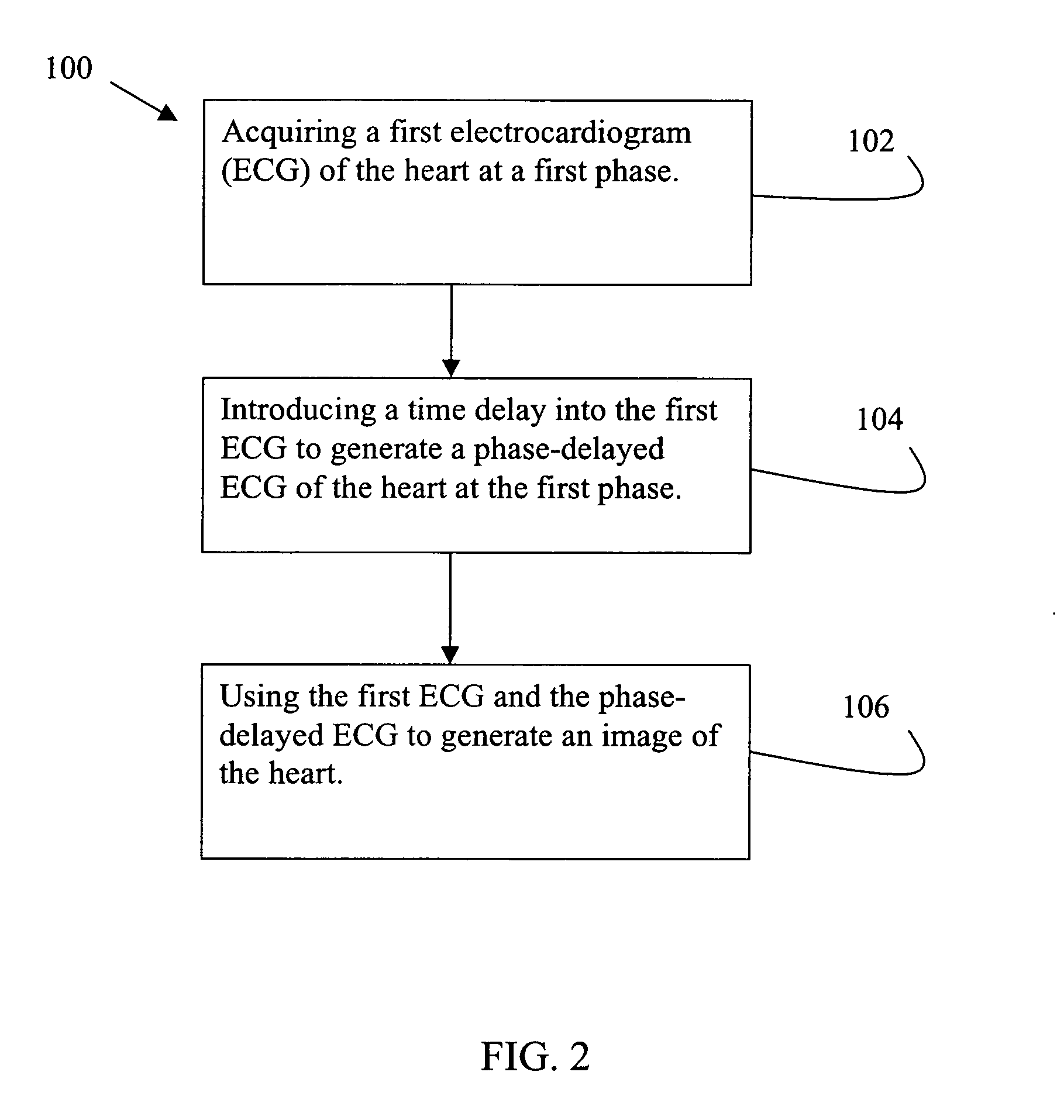
A method for generating an image of a heart at a selected cardiac phase is described. The method includes acquiring a first electrocardiogram (ECG) of the heart at a first phase, introducing a time delay into the first ECG to generate a phase-delayed ECG of the heart at the first phase, and using the first ECG and the phase-delayed ECG to generate an image of the heart.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
InactiveUS20070030946A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData setCardiac phase
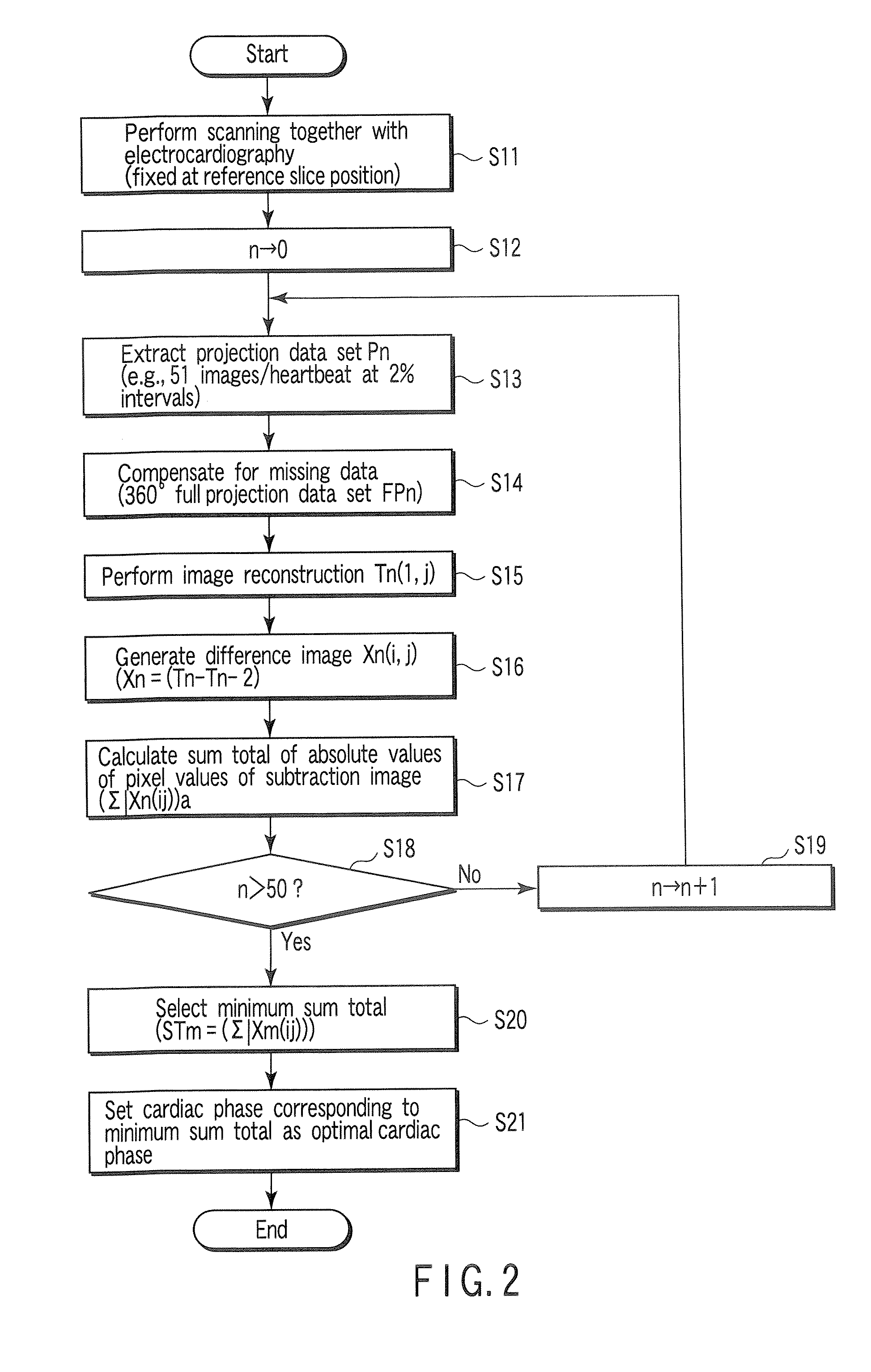
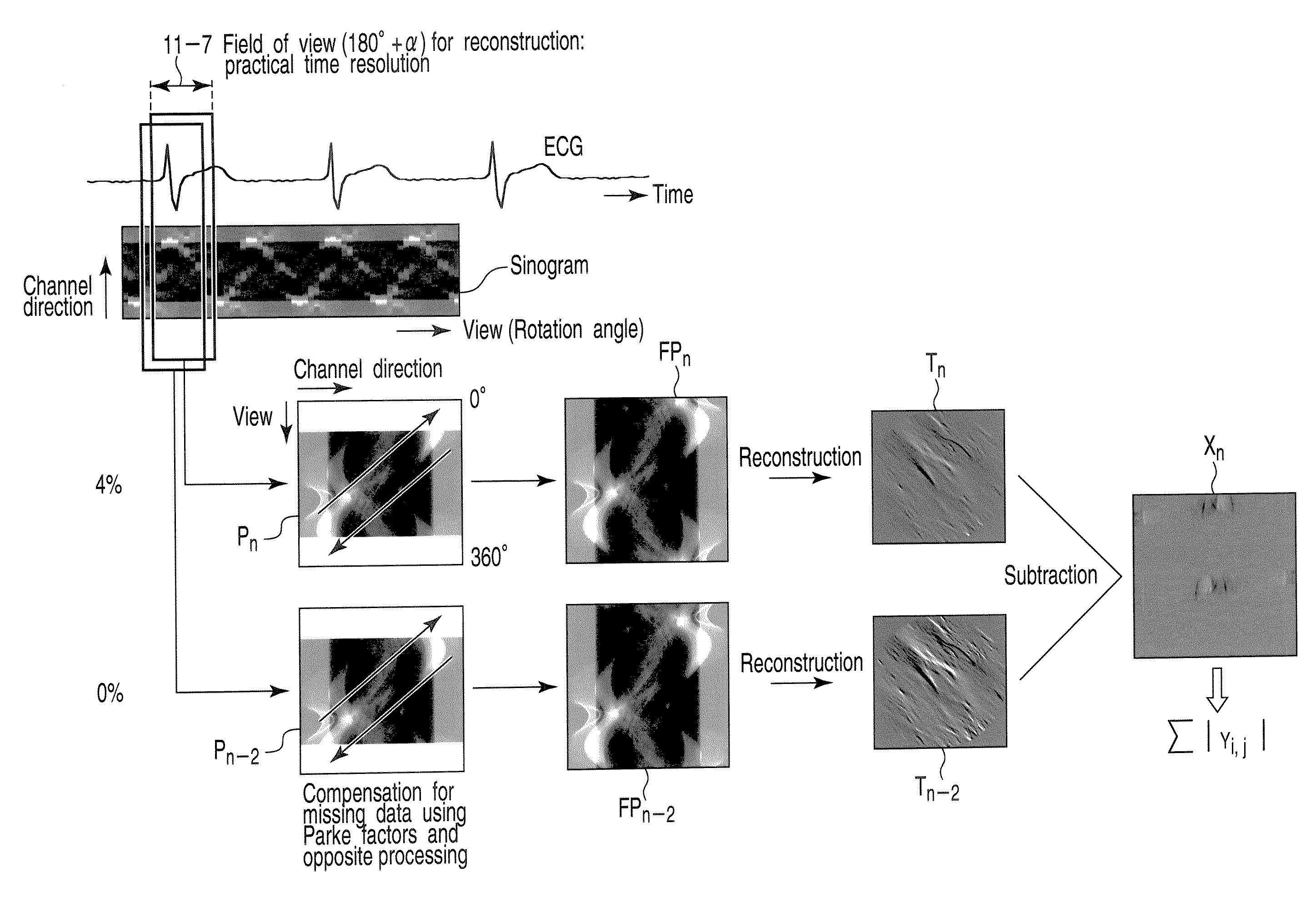
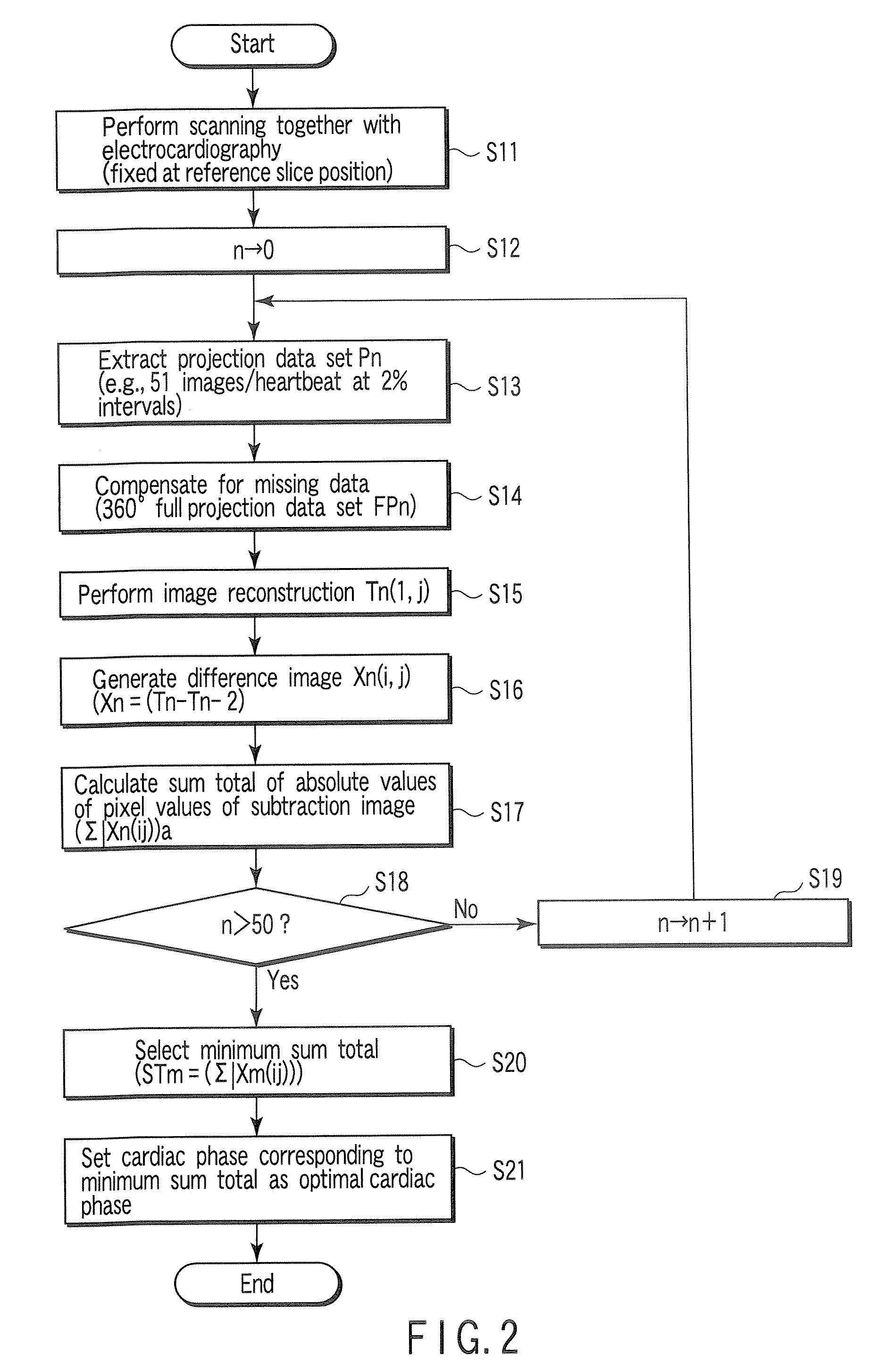
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes an X-ray tube which generates X-rays, an X-ray detector which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined, a mechanism which continuously rotates the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector, a storage unit which stores projection data detected by the X-ray detector, a read unit which reads out projection data sets of parts of a pair spaced apart from each other by 360° from the storage unit, an index generating unit which generates a plurality of indices indicating movement of a heart on the basis of a difference between the projection data sets of the parts of the pair, a cardiac phase determination unit which determines a cardiac phase on the basis of the indices, and a reconstruction unit which reconstructs an image on the basis of a full projection data set corresponding to the determined cardiac phase.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS8111893B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. One aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system, while mitigating undesired image artifacts. This is generally achieved by incorporating a limited amount of additional image data into the data consistency condition imposed during a prior image constrained image reconstruction. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution using a state-of-the-art multi-detector CT system with either fast gantry rotation speed or CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
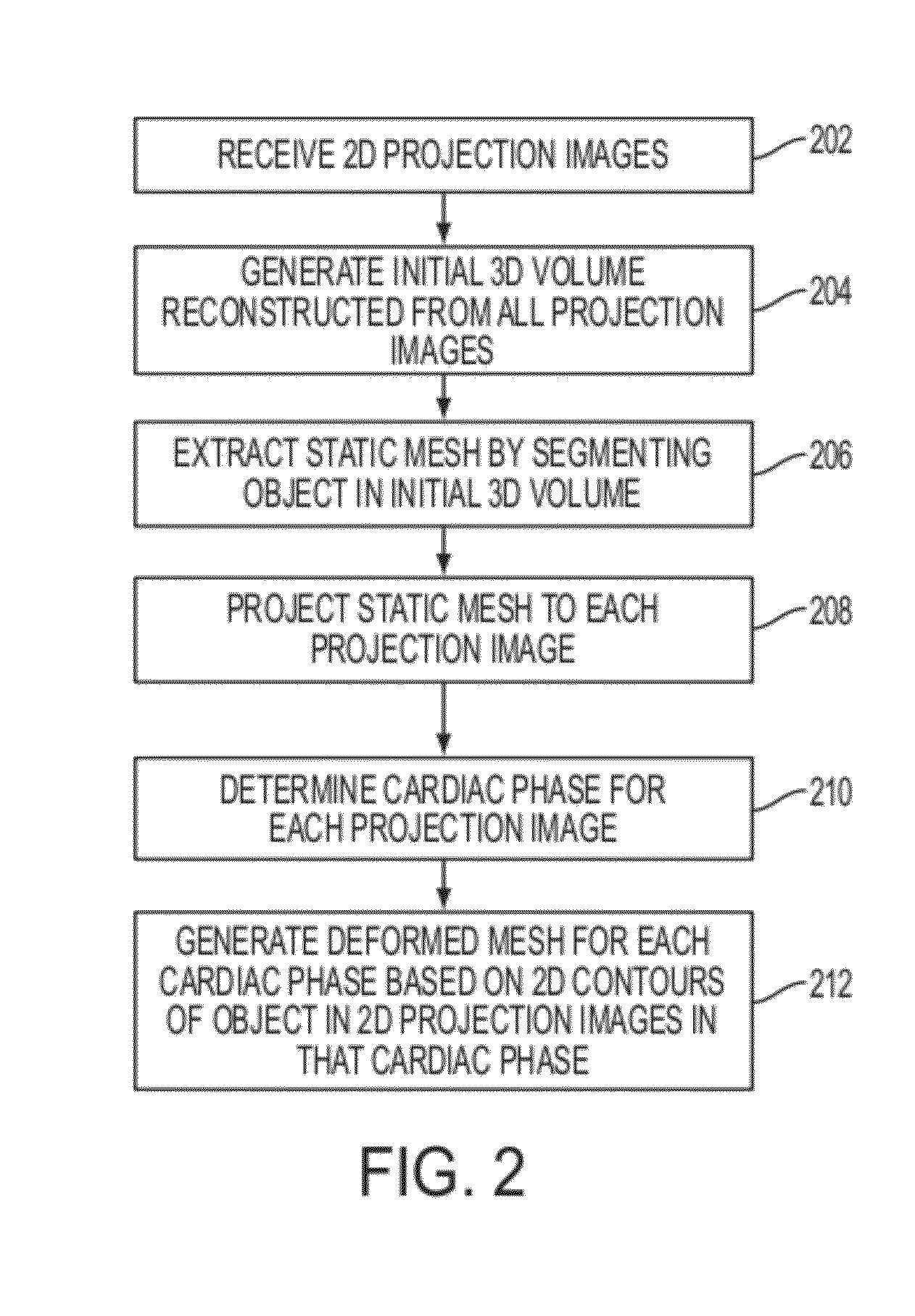
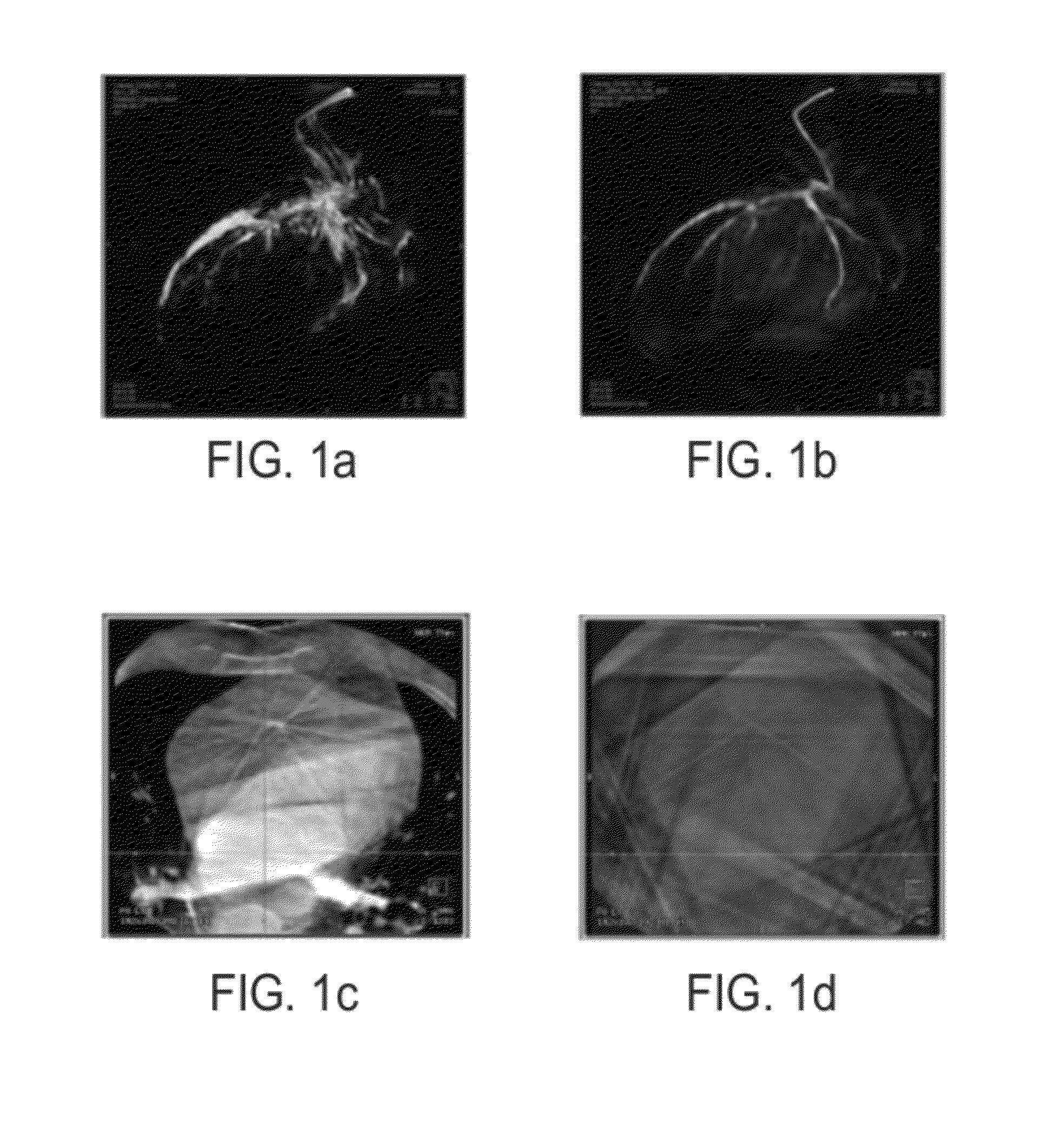
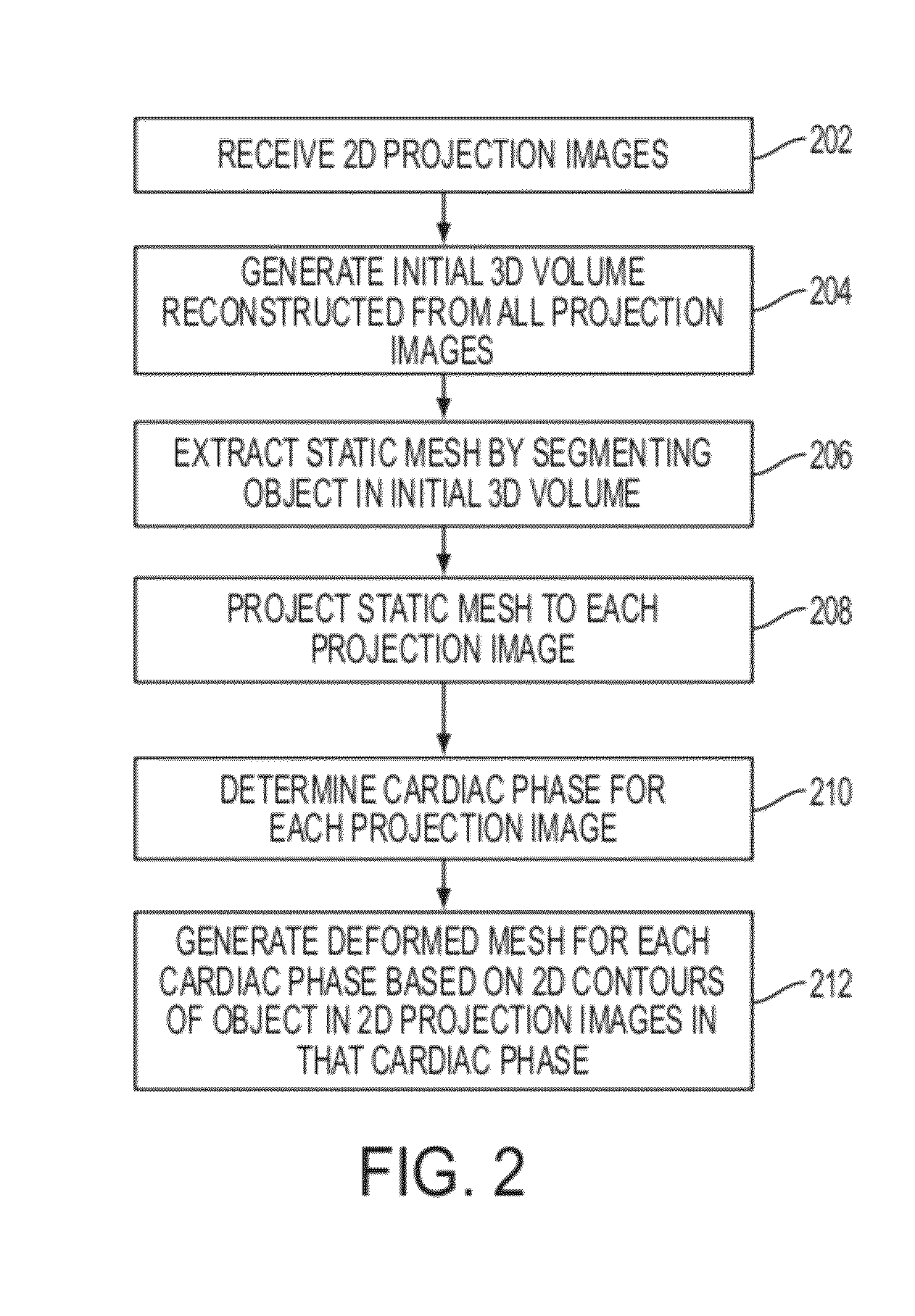
Method and System for 3D Cardiac Motion Estimation from Single Scan of C-Arm Angiography
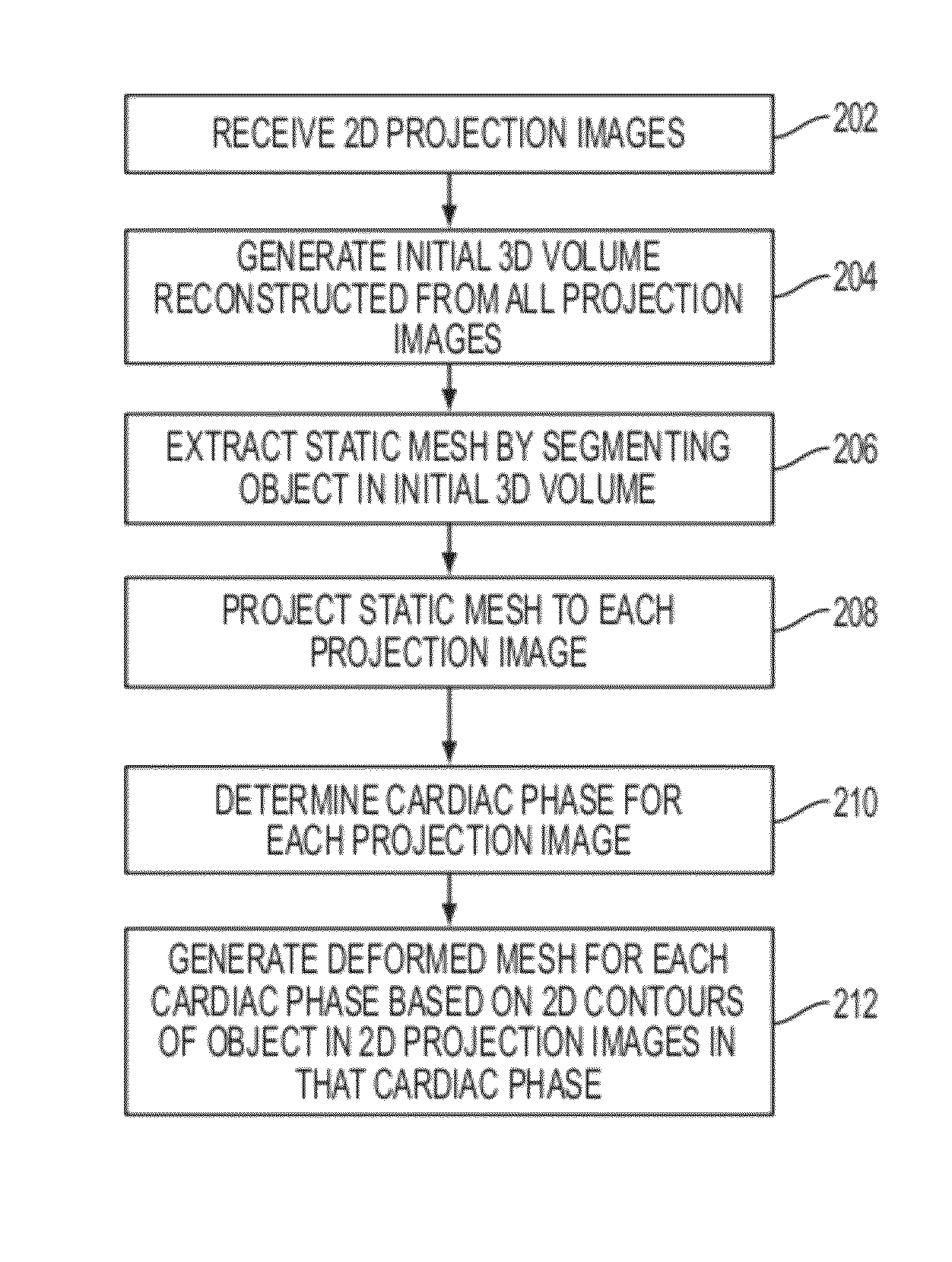
A method and system for estimating 3D cardiac motion from a single C-arm angiography scan is disclosed. An initial 3D volume is reconstructed from a plurality of 2D projection images acquired in a single C-arm scan. A static mesh is extracted by segmenting an object in the initial 3D volume. The static mesh is projected to each of the 2D projection images. A cardiac phase is determined for each of the 2D projection images. A deformed mesh is generated for each of a plurality of cardiac phases based on a 2D contour of the object and the projected mesh in each of the 2D projection images of that cardiac phase.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
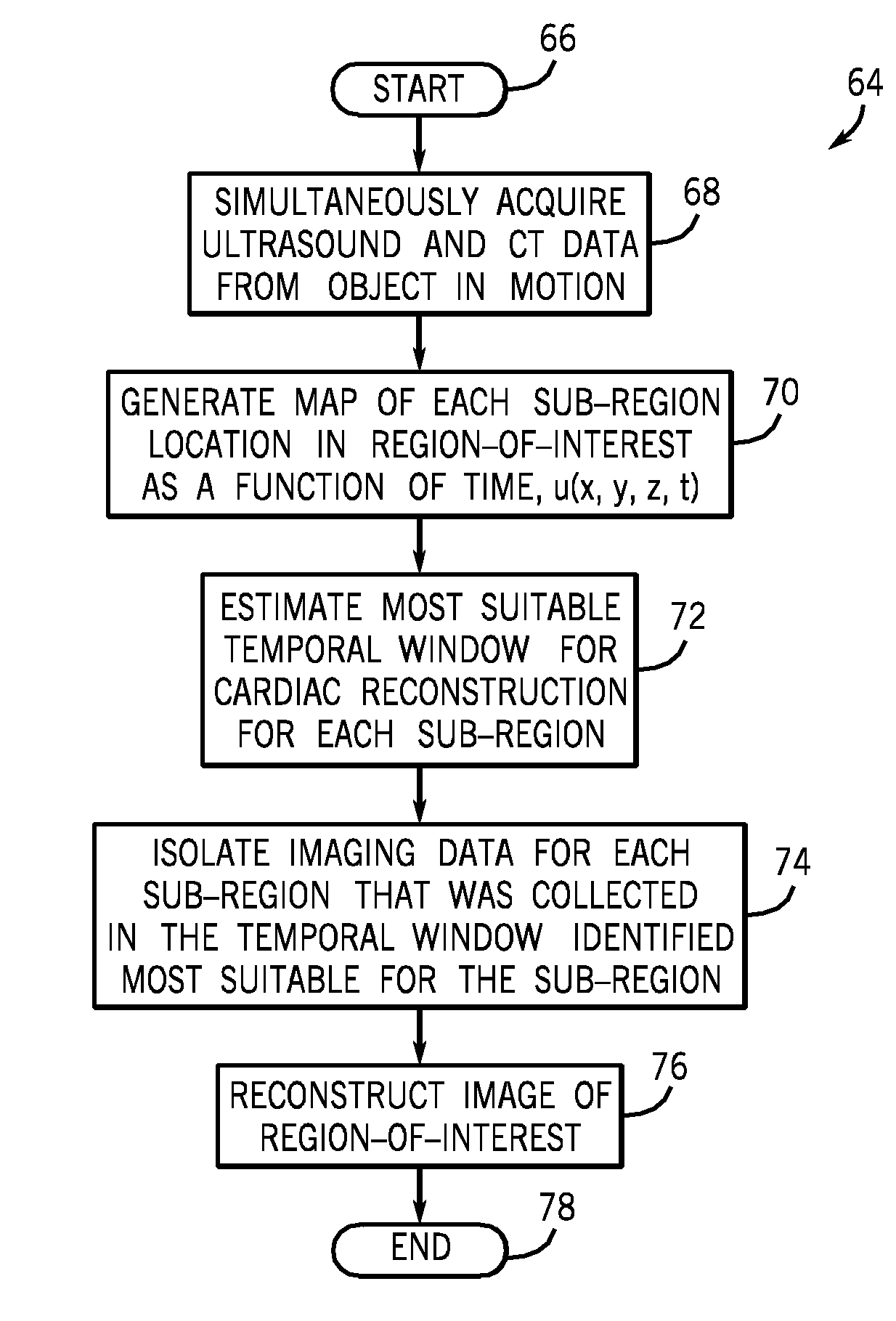
Method and apparatus to compensate imaging data with simultaneously acquired motion data
ActiveUS8155729B1Correction errorReduce noiseDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionSystoleCardiac phase
Motion data is acquired simultaneously and in real-time with image data. The motion data provides accurate and near-instant information as to the state and position of an object prone to motion. The present invention is particularly applicable for cardiac CT or MR imaging and other physiologically gated acquisitions. In the context of cardiac imaging, the motion data includes information regarding size and location of the heart during the cardiac phases (diastole, systole, etc.) during each cardiac cycle.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance imaging system for non-contrast MRA and magnetic resonance signal acquisition method employed by the same
ActiveUS20060100503A1Imposes burdenPreventing Image Quality DeteriorationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCardiac phaseMri image
A magnetic resonance imaging system comprises a first RF coil for acquiring a magnetic resonance signal from a subject, and a device for estimating a cardiac phase of the subject based on the magnetic resonance signal acquired by the first RF coil. The first RF coil, for example, is an RF coil exclusive to cardiac phase estimation. The magnetic resonance imaging system further comprises a second RF coil for acquiring a magnetic resonance signal based on the estimated cardiac phase, and a device for reconstructing a magnetic resonance image of the subject based on the magnetic resonance signal acquired by the second RF coil. Thus, MRA can be performed by estimating a cardiac phase.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes an X-ray source (101) which generates X-rays, a high voltage generating unit (104) which generates a high voltage to be applied to the X-ray source, an X-ray detector (102) which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined to generate projection data, a storage unit (203) which stores the projection data in association with electrocardiographic data of the subject, a setting unit (207) which sets a specific cardiac phase in accordance with an operator's instruction, a reconstruction unit (206) which reconstructs a tomogram on the basis of a plurality of projection data sets acquired in a plurality of specific periods centered on the specific cardiac phase throughout a plurality of cardiac cycles, a period extending unit (207) which extends the specific period on the basis of a heart rate fluctuation range of the subject, and a control unit (212) which controls the high voltage generating unit to generate a relatively high dose of X-rays in the extended specific period and generate a relatively low dose of X-rays in a period other than the extended specific period.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
InactiveUS7630472B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayData set
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes an X-ray tube which generates X-rays, an X-ray detector which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined, a mechanism which continuously rotates the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector, a storage unit which stores projection data detected by the X-ray detector, a read unit which reads out projection data sets of parts of a pair spaced apart from each other by 360° from the storage unit, an index generating unit which generates a plurality of indices indicating movement of a heart on the basis of a difference between the projection data sets of the parts of the pair, a cardiac phase determination unit which determines a cardiac phase on the basis of the indices, and a reconstruction unit which reconstructs an image on the basis of a full projection data set corresponding to the determined cardiac phase.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and device for the combined representation of 2D fluoroscopic images and a static 3D image data set
InactiveUS20080175455A1Increase impressionSimple methodImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageData set
The invention relates to a method and a device for the combined representation of a series of 2D fluoroscopic images of the beating heart with a static 3D image data set of the same heart. The fluoroscopic images are registered with the 3D image data set and from this a 2D pseudo-projection on to the image plane of each fluoroscopic image generated in each case. This is then represented with the associated fluoroscopic image overlaid. The method is characterized in that the pseudo-projection is represented differently in each case or is not represented depending on the interval of the cardiac phase of the currently represented fluoroscopic image relative to the cardiac phase of the 3D image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
ActiveUS7715520B2Avoid partialMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData setCardiac phase
An X-ray computed tomography apparatus includes an X-ray source, a high voltage generating unit, an X-ray detector detecting X-rays transmitted through a subject to generate projection data, a storage unit storing the projection data in association with electrocardiographic data of the subject, a setting unit setting a specific cardiac phase in accordance with an operator's instruction, a reconstruction unit reconstructing a tomogram based on projection data sets acquired in specific periods centered on the specific cardiac phase throughout cardiac cycles, a period extending unit extending the specific period on the basis of a heart rate fluctuation range of the subject, and a control unit controlling the high voltage generating unit to generate a relatively high dose of X-rays in the extended specific period and generate a relatively low dose of X-rays in a period other than the extended specific period.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
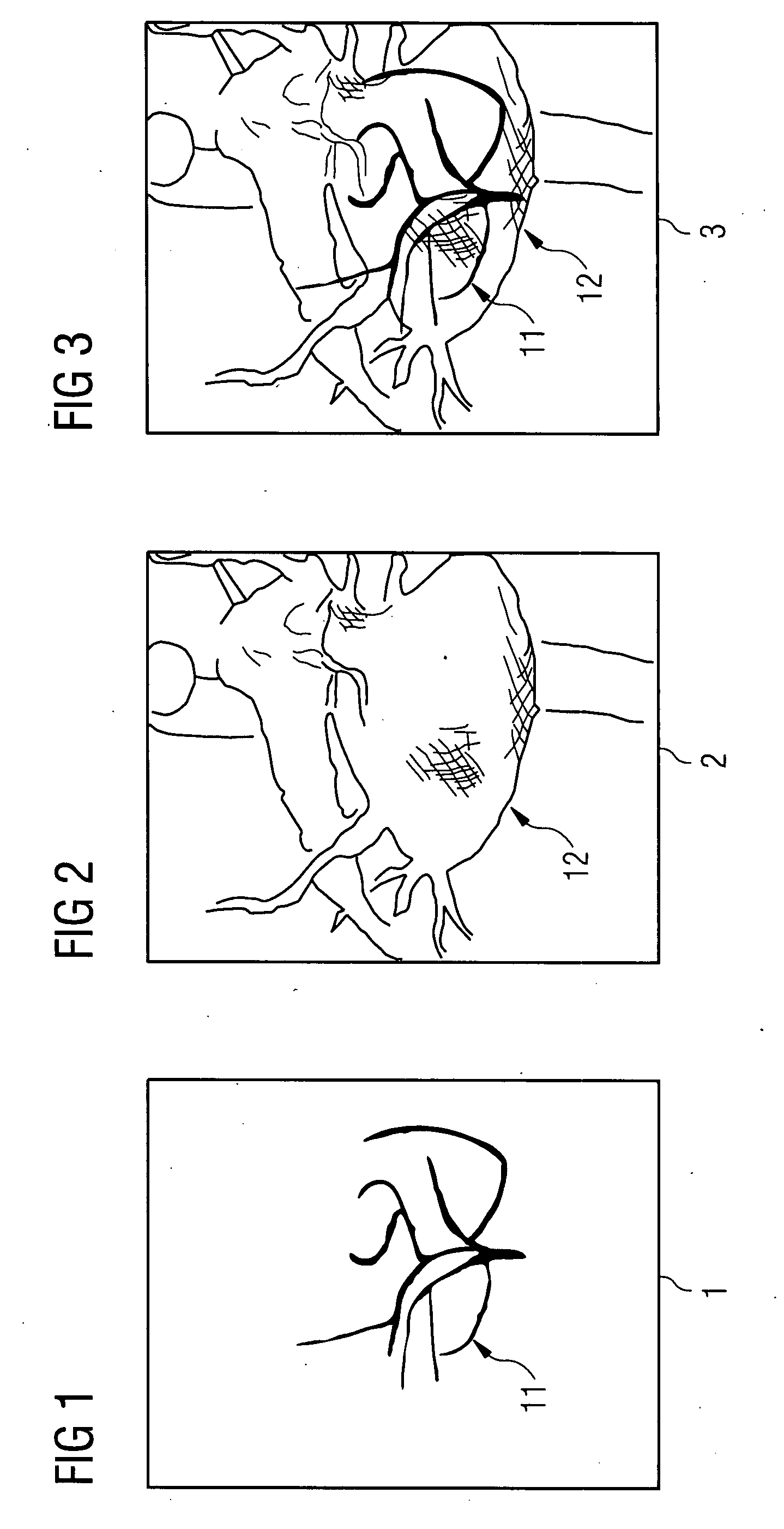
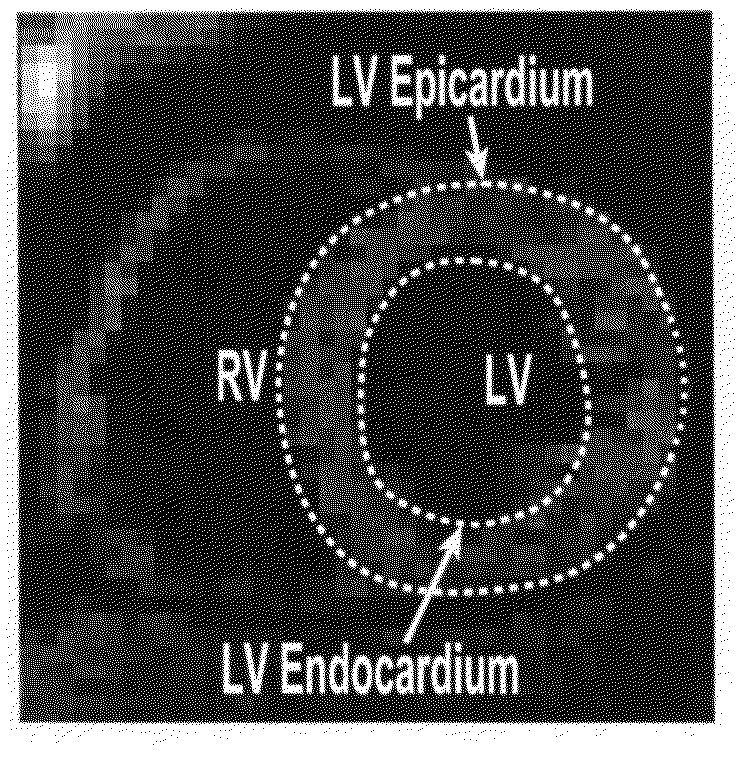
Method for segmenting a myocardial wall and device for detecting a coronary artery with pathological changes
InactiveUS20090003680A1Improve visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesCardiac phase
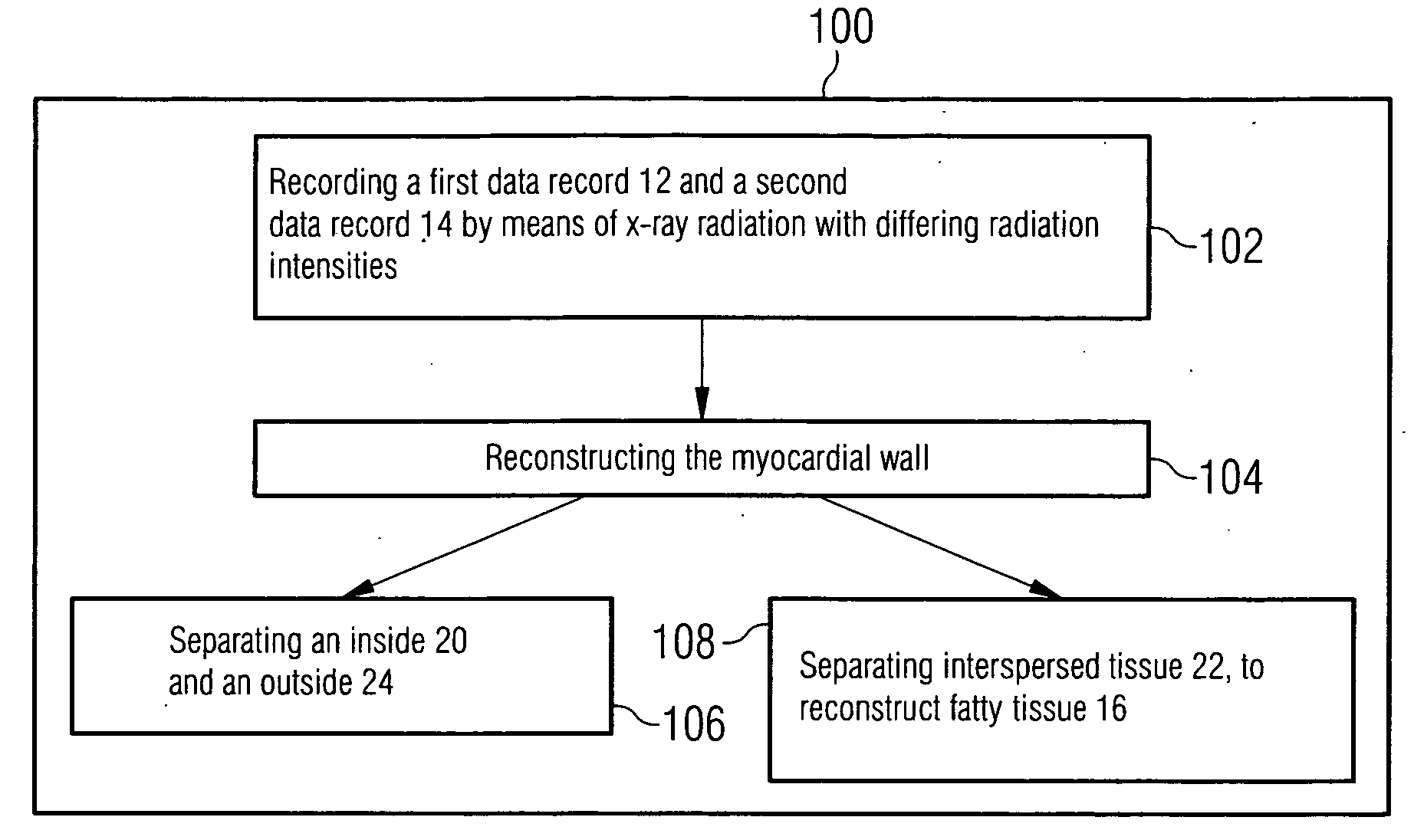
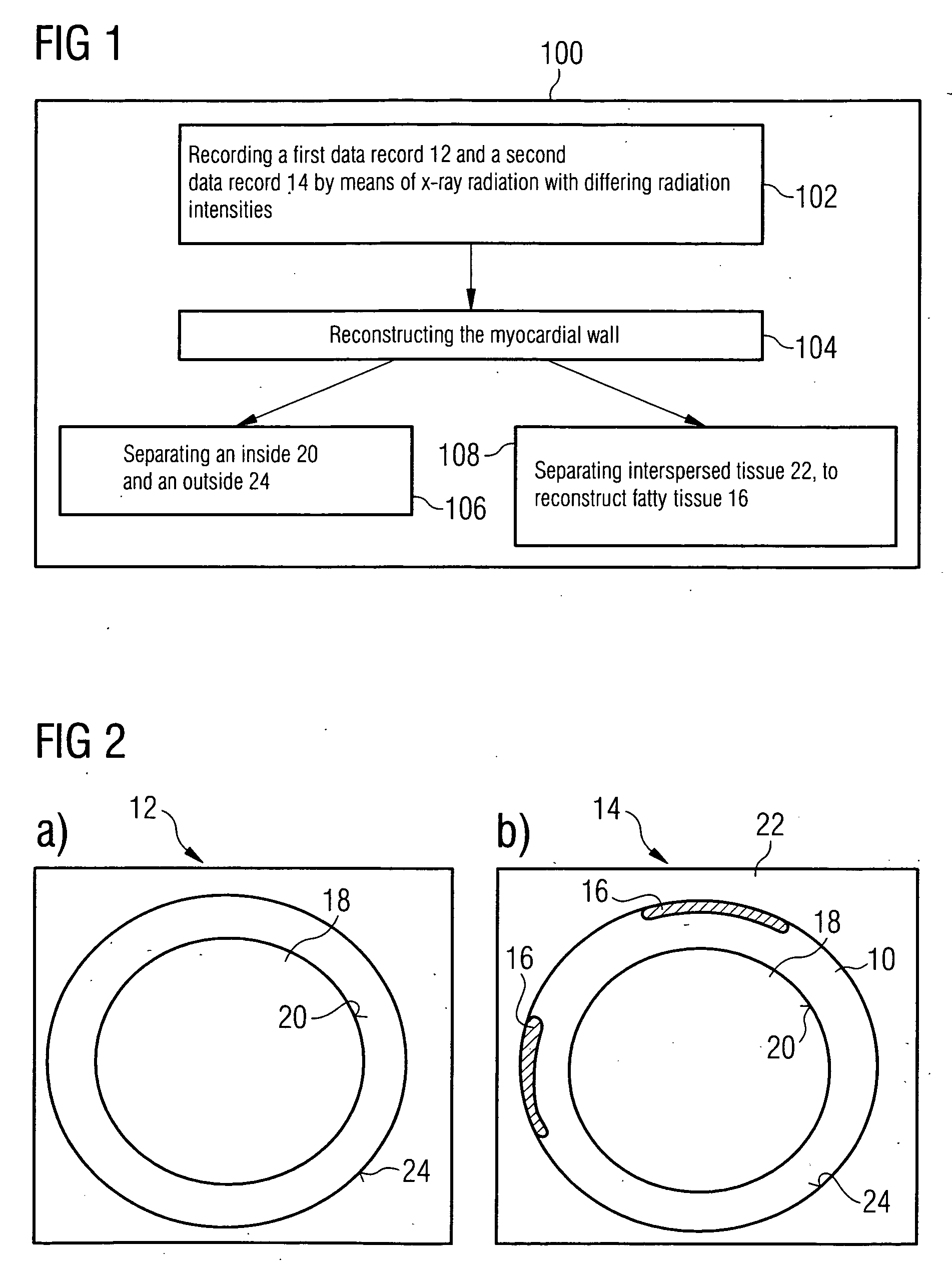
The present invention relates to a method for segmenting a myocardial wall with the following steps: recording a first data record and a second data record in the same cardiac phase by means of x-ray radiation with differing radiation intensities, reconstructing the myocardial wall from the first and second data record. To generate a detailed and complete reconstruction of the myocardial wall, it is proposed that the method be supplemented by the following steps: separating an inside and an outside of the myocardial wall from the data record recorded with higher radiation intensity, and separating tissue interspersing the myocardial wall between the inside and the outside, in particular fatty tissue, from the data record recorded with lower radiation intensity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
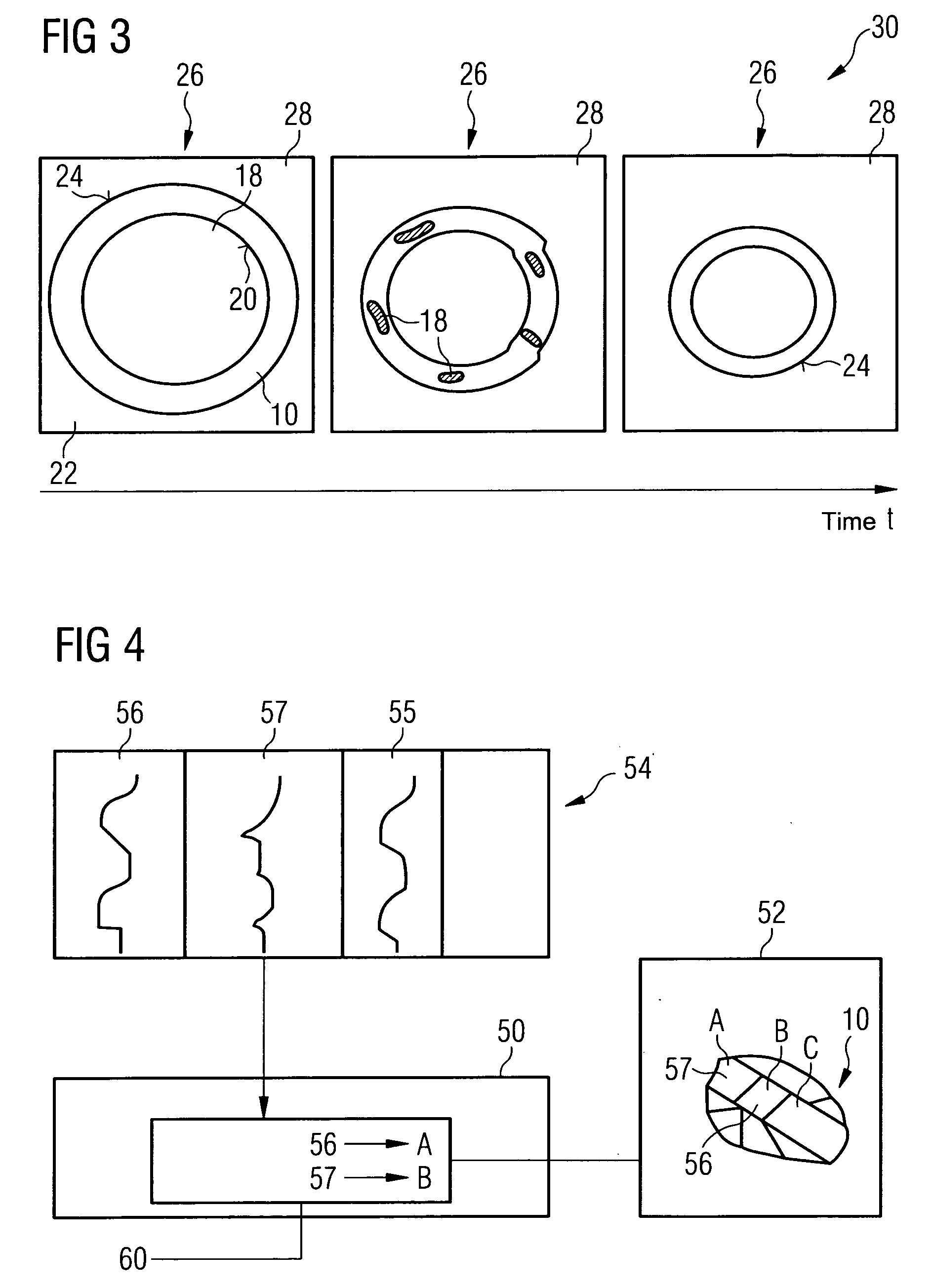
Three dimensional image processing apparatus and x-ray diagnosis apparatus
ActiveUS20090052613A1Stabilize image quality of imageSuppress mutationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging processingCardiac phase
A three dimensional image processing apparatus includes a storage unit storing data of images in different radiographing directions together with information concerning cardiac phases, a key image selection unit selecting key images from the images, a feature point designation unit designatting feature points on the selected key images in accordance with operation by an operator, and an image reconstruction unit reconstructing a three dimensional image from the images on the basis of positions of the designated feature points, wherein the key image selection unit selects, as the key images, a pair of images which are located at the same cardiac phase and whose radiographing directions are different by a substantially predetermined angle and images spaced apart from each other by an angle obtained by substantially equally dividing an interval between the pair of images by a predetermined number.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
InactiveUS8060180B2Improve time resolutionHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceCardiac phase
Exemplary method, systems and arrangements can be provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target. For example, radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by a RF transmitter of a MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to each pulse may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space of a distinct image, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, velocity data and / or acceleration data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes can be assigned to the same k-space line and to different cardiac phases. The exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method and system for 3D cardiac motion estimation from single scan of C-arm angiography
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Motion-guided segmentation for cine DENSE images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
X-ray ct apparatus
ActiveUS20080253505A1Relieve pressureImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectrocardiographyHelical scanCardiac phase
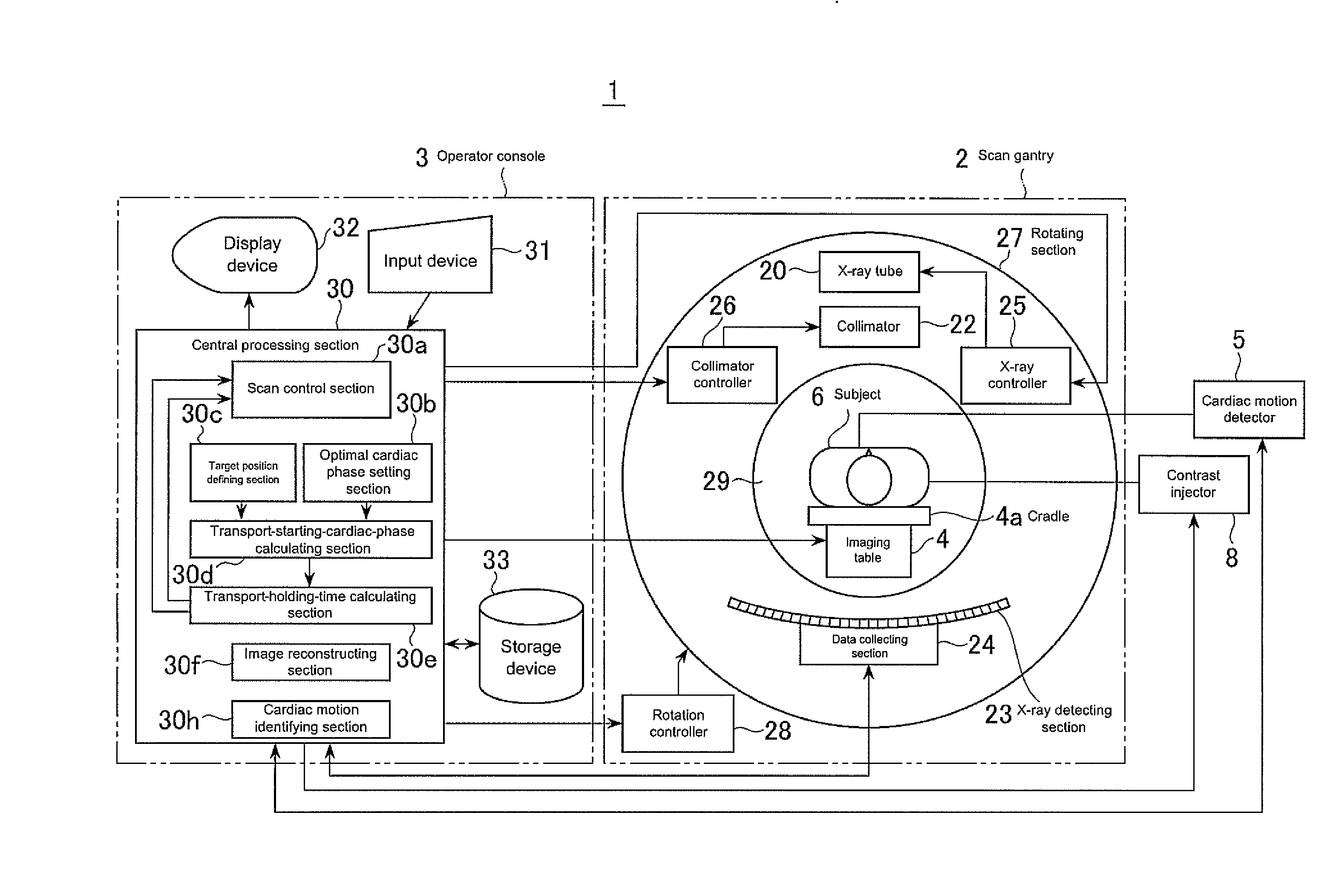
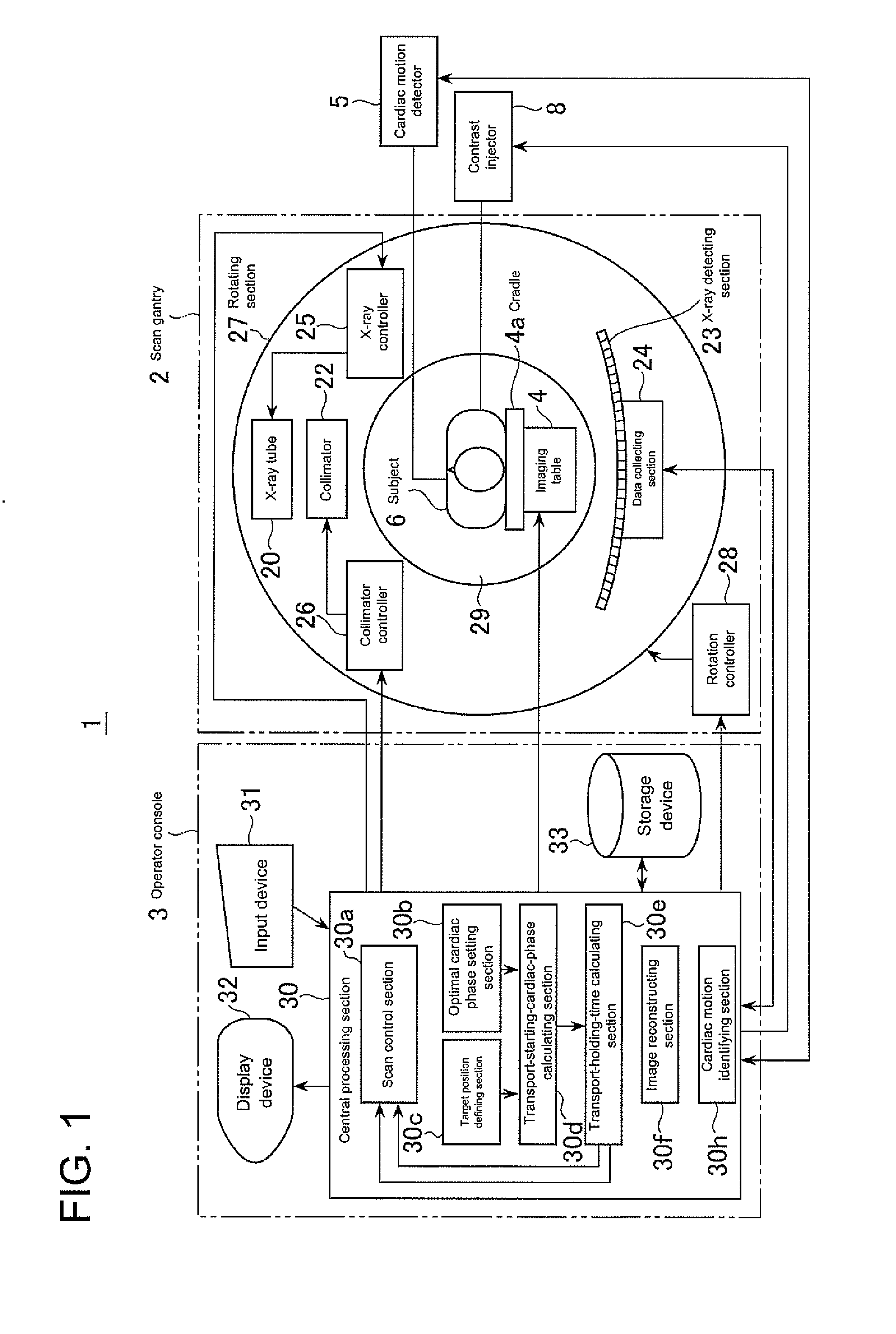
For the purpose of X-ray CT imaging a heart of a subject with high image quality while reducing stress on the subject, once an optimal cardiac phase has been set by an optimal cardiac phase setting section 30b and a target position in a subject to be scanned when the cardiac phase of the subject is at an optimal cardiac phase is defined at a target position defining section 30c, a transport-starting-cardiac-phase calculating section 30b calculates a transport-starting cardiac phase such that the target position is scanned at the optimal cardiac phase, using the optimal cardiac cycle, target position, scan start position, transport speed of an imaging table, and approach-run time for the imaging table. A scan control section starts transport at the imaging table 4 when the cardiac phase of the subject coincides with the transport-starting cardiac phase, and performs a helical scan with a helical pitch of one or more, for example.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
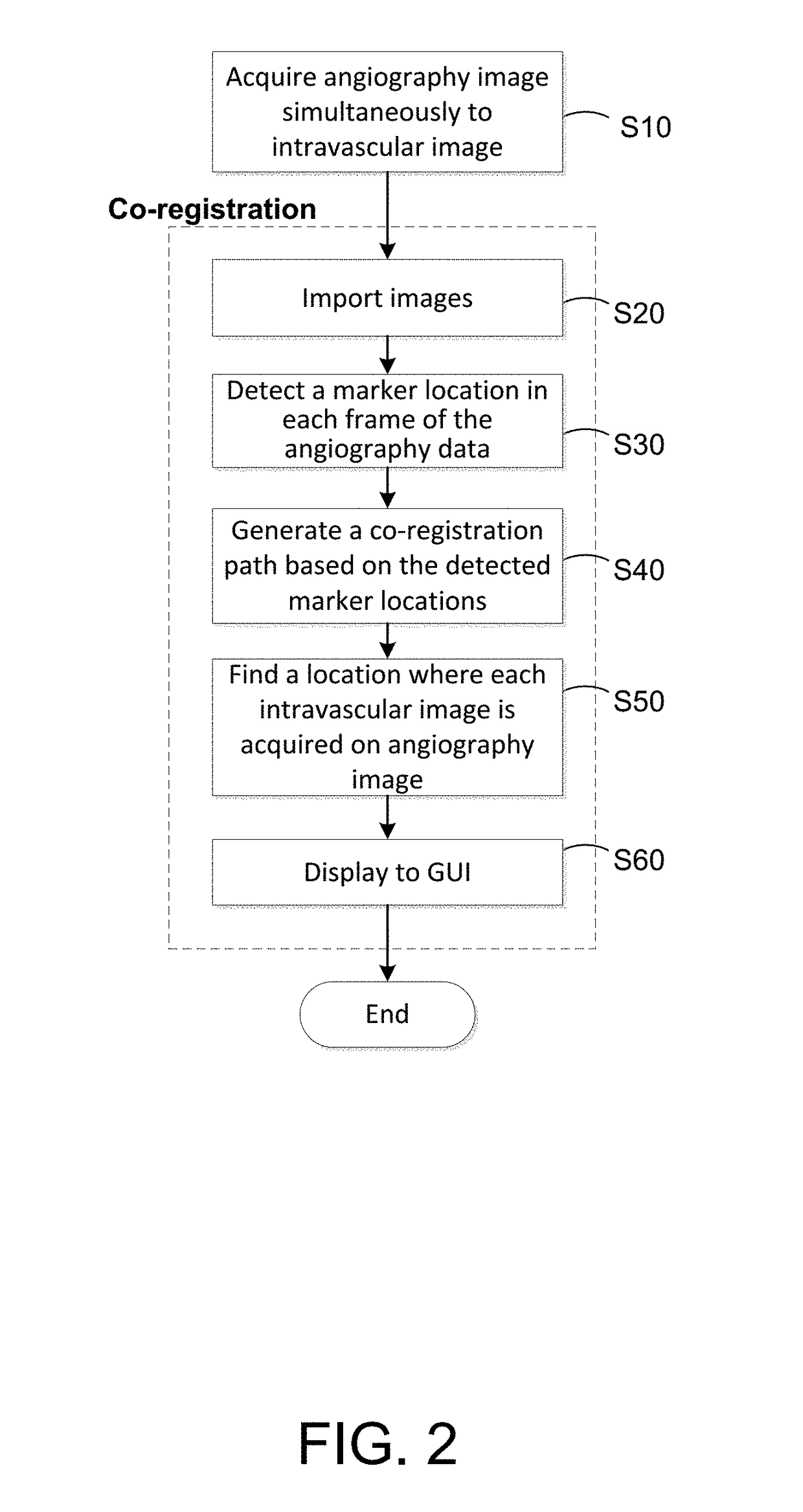
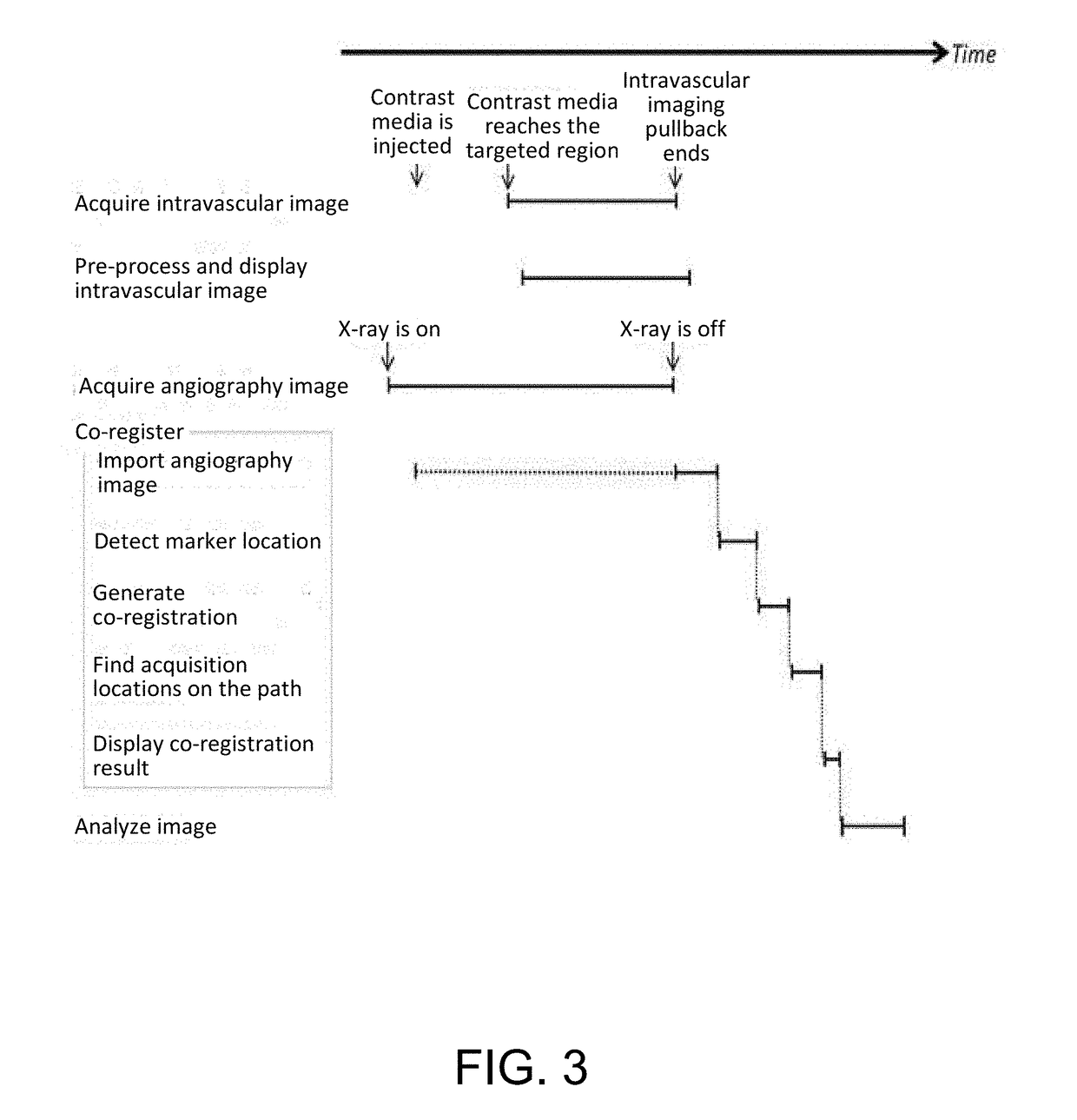
Method for co-registering and displaying multiple imaging modalities
ActiveUS20190029624A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCardiac phase
A method for processing angiography image data by using an imaging catheter path that is directly detected from the angiography data as a co-registration path or using detected marker locations from the angiography data to generate a co-registration path. If the acquired angiography data includes synchronized cardiac phase signals and a predetermined quantity of angiography image frames not including contrast media, then a directly detected imaging catheter path is used as the co-registration path. Otherwise the co-registration path is determined based upon detected marker locations from the angiography image data.
Owner:CANON USA
Method and apparatus of multi-phase cardiac imaging
ActiveUS7774040B1Improve system throughputImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityCardiac phase
A method and apparatus for multi-phase cardiac CT imaging includes an adaptive, selective reconstruction process that, when possible, implements an image or non-phase location driven reconstruction process to reconstruct cardiac CT images. If the hardware parameters support an image location driven reconstruction for the particular imaging session then the image location driven reconstruction is implemented. However, if image location driven reconstruction is not supported, a default phase location driven reconstruction is employed. Image location driven reconstruction improves system throughput and improves image quality as more cardiac phase locations can routinely be generated to better “freeze” the motion of the heart of a patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for determining a personalized cardiac model using a magnetic resonance imaging sequence
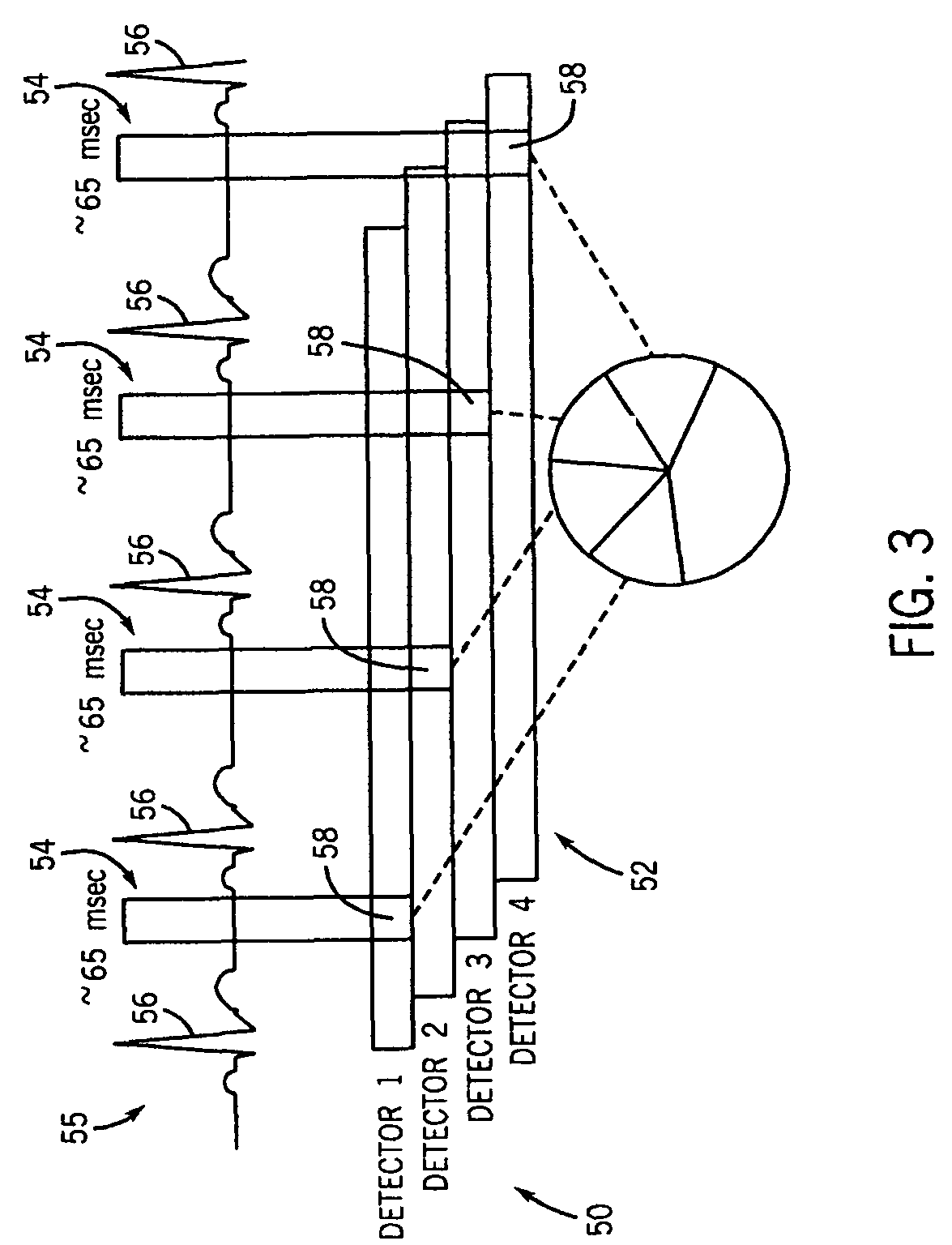
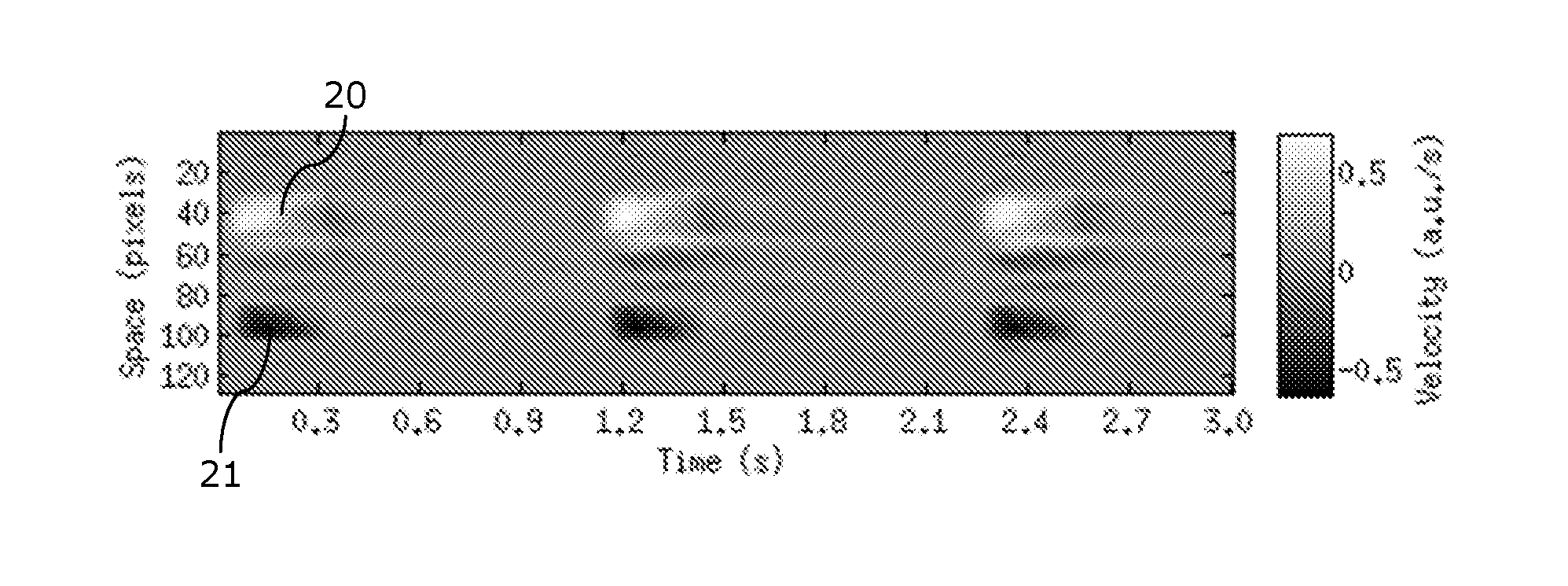
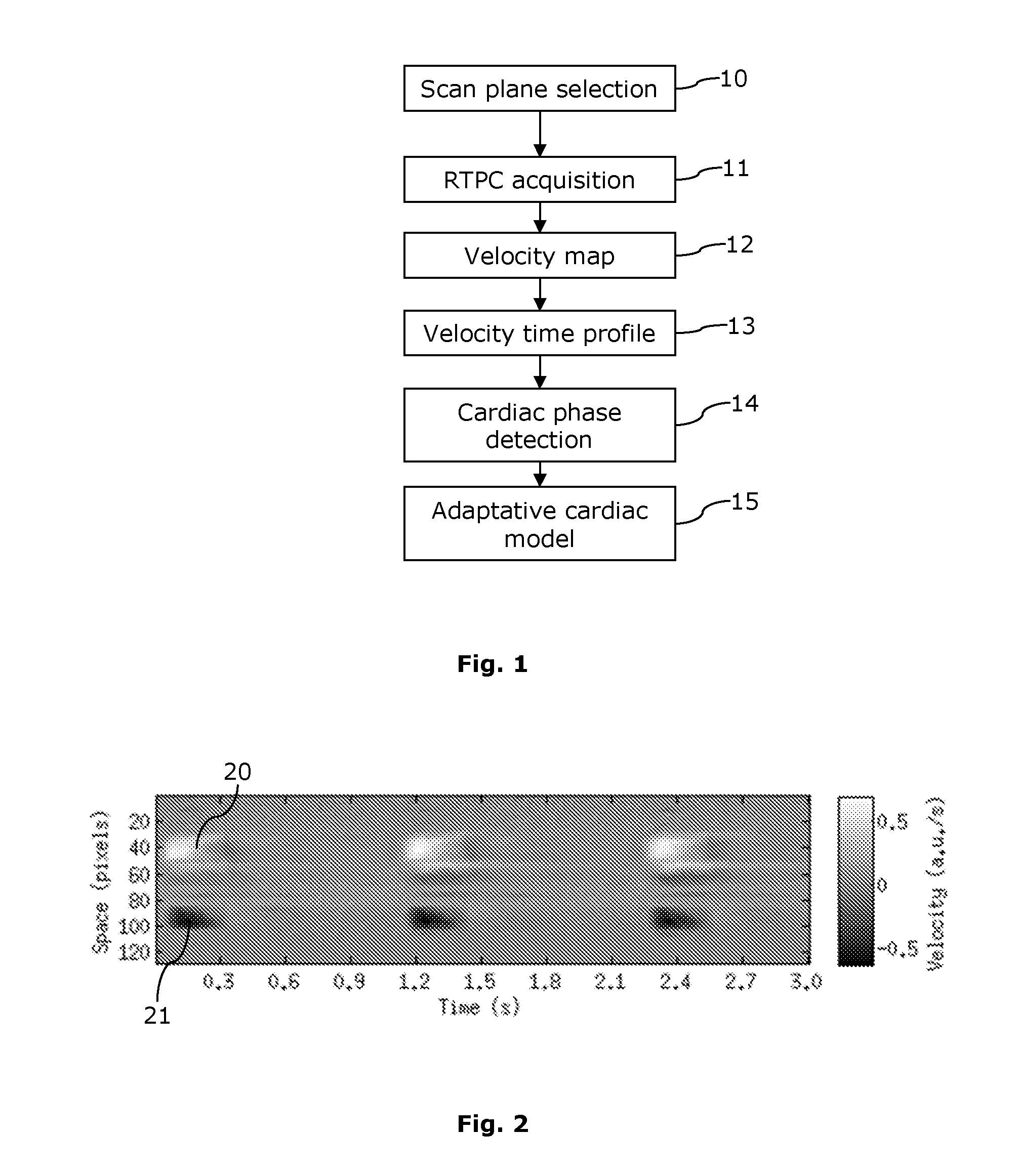
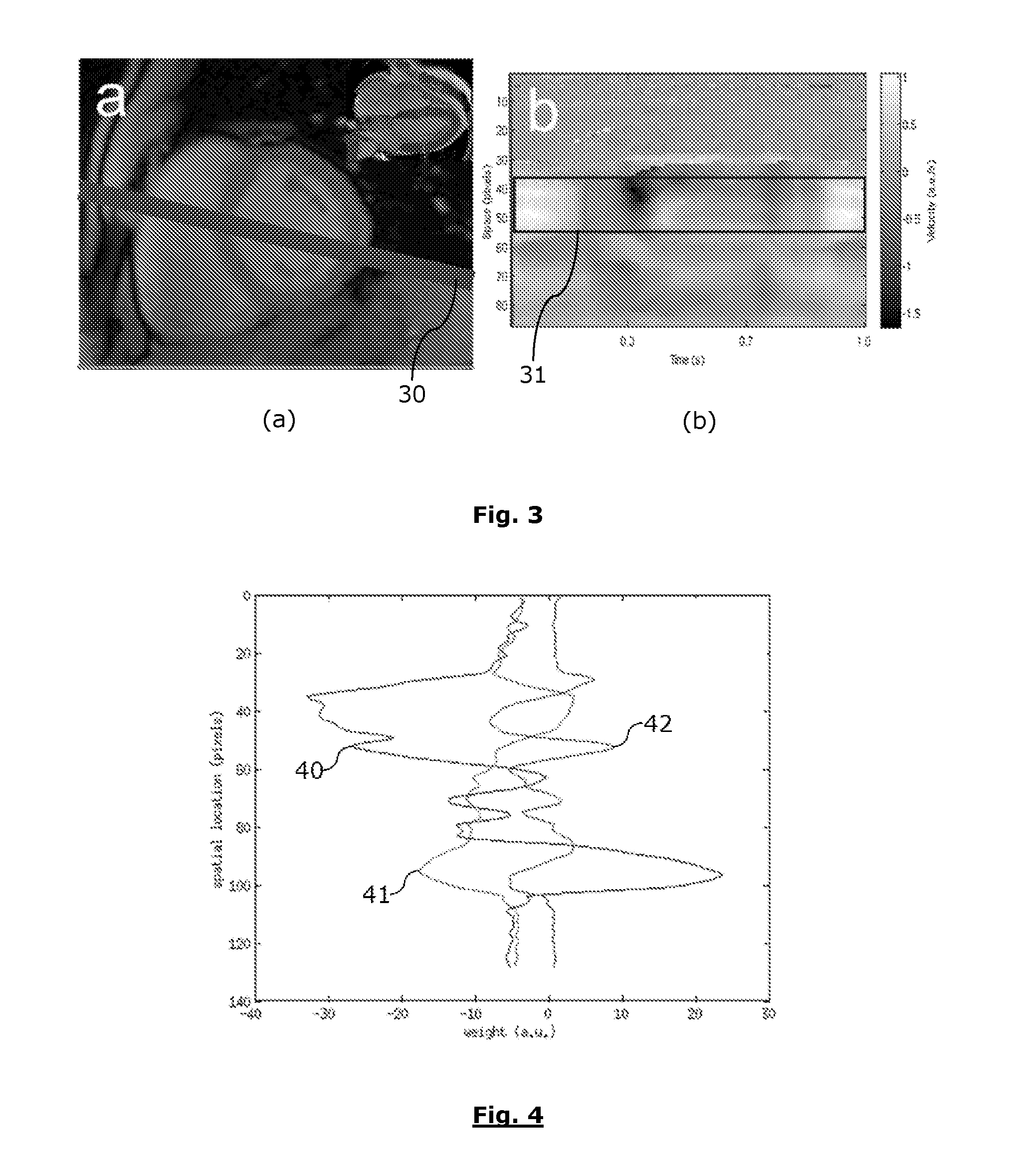
ActiveUS20160324427A1Easy to predictImproving time resolution precisionMagnetic measurementsSensorsCardiac phaseTime profile
A method is provided for determining a personalized cardiac model, including steps of (i) computing a velocity time profile of a blood flow across a selected area of the heart or the aorta during at least one cardiac cycle, using data acquired with a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) device; (ii) performing a segmentation of the velocity time profile so as to identify cardiac phases according to a predefined generic cardiac model; and (iii) computing normalized time location and / or duration of the cardiac phases within cardiac cycles so as to define a personalized cardiac model.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LORRAINE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com