Patents
Literature
148 results about "Circumflex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The circumflex is a diacritic in the Latin and Greek scripts that is used in the written forms of many languages and in various romanization and transcription schemes. It received its English name from Latin circumflexus "bent around"—a translation of the Greek περισπωμένη (perispōménē). The circumflex in the Latin script is chevron-shaped ( ˆ ), while the Greek circumflex may be displayed either like a tilde ( ˜ ) or like an inverted breve ( ̑ ).
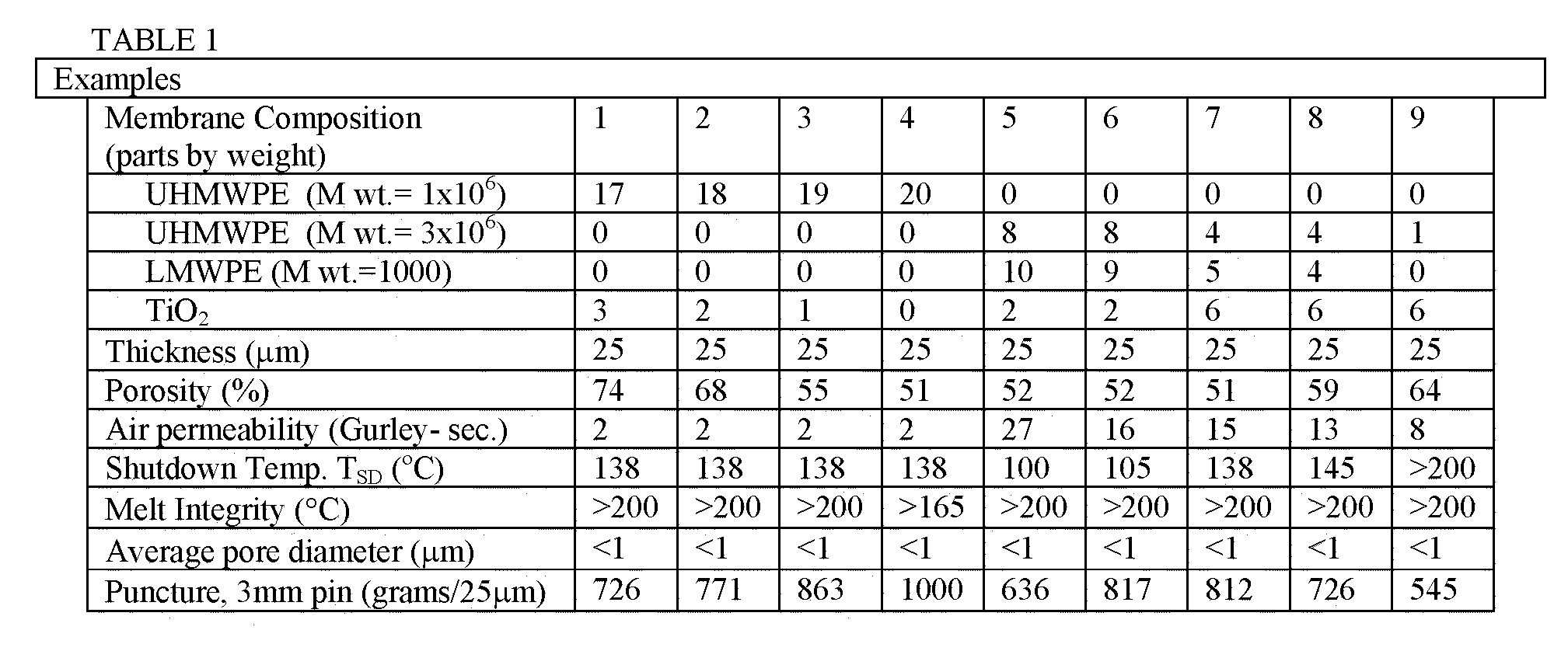
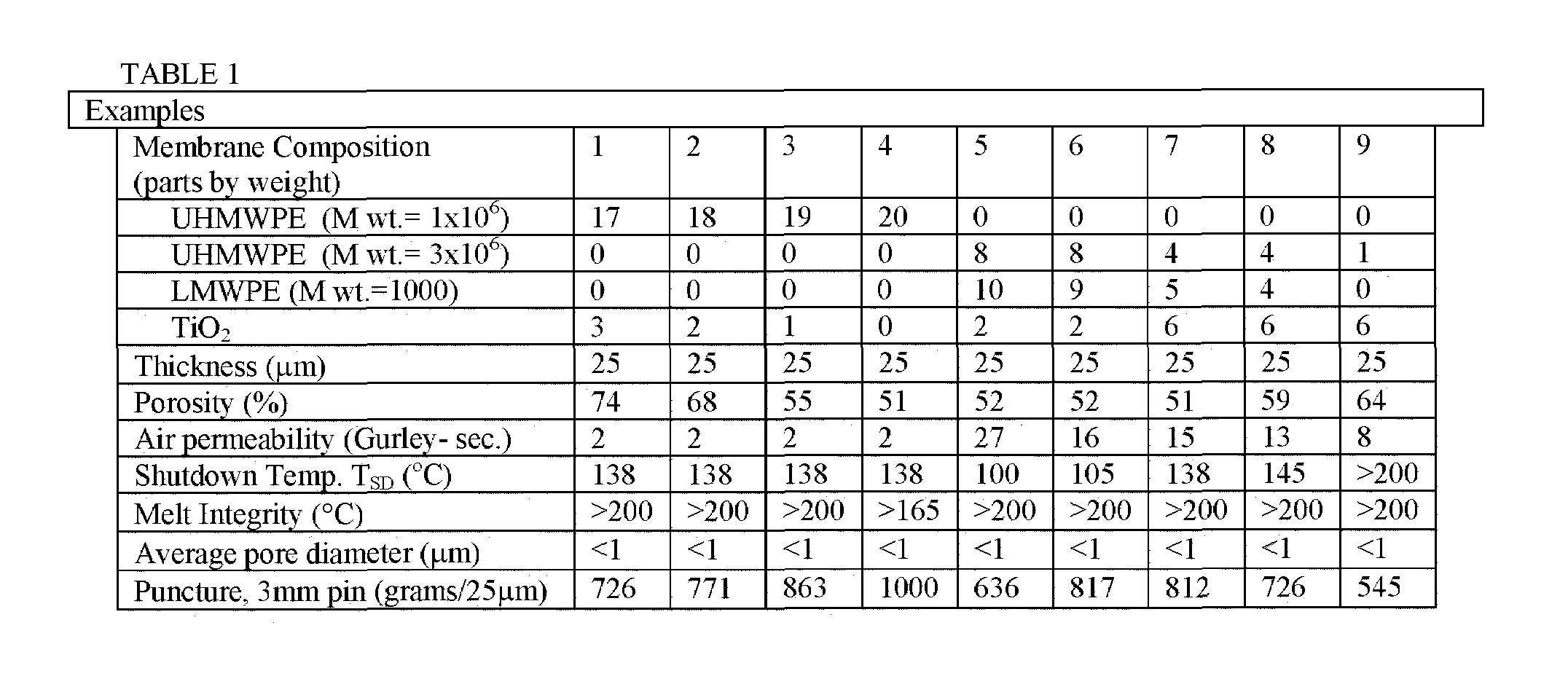
Shutdown separators with improved properties
InactiveUS6949315B1Improve propertiesReduced flexibilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Owner:ADVANCED MEMBRANE SYST INC
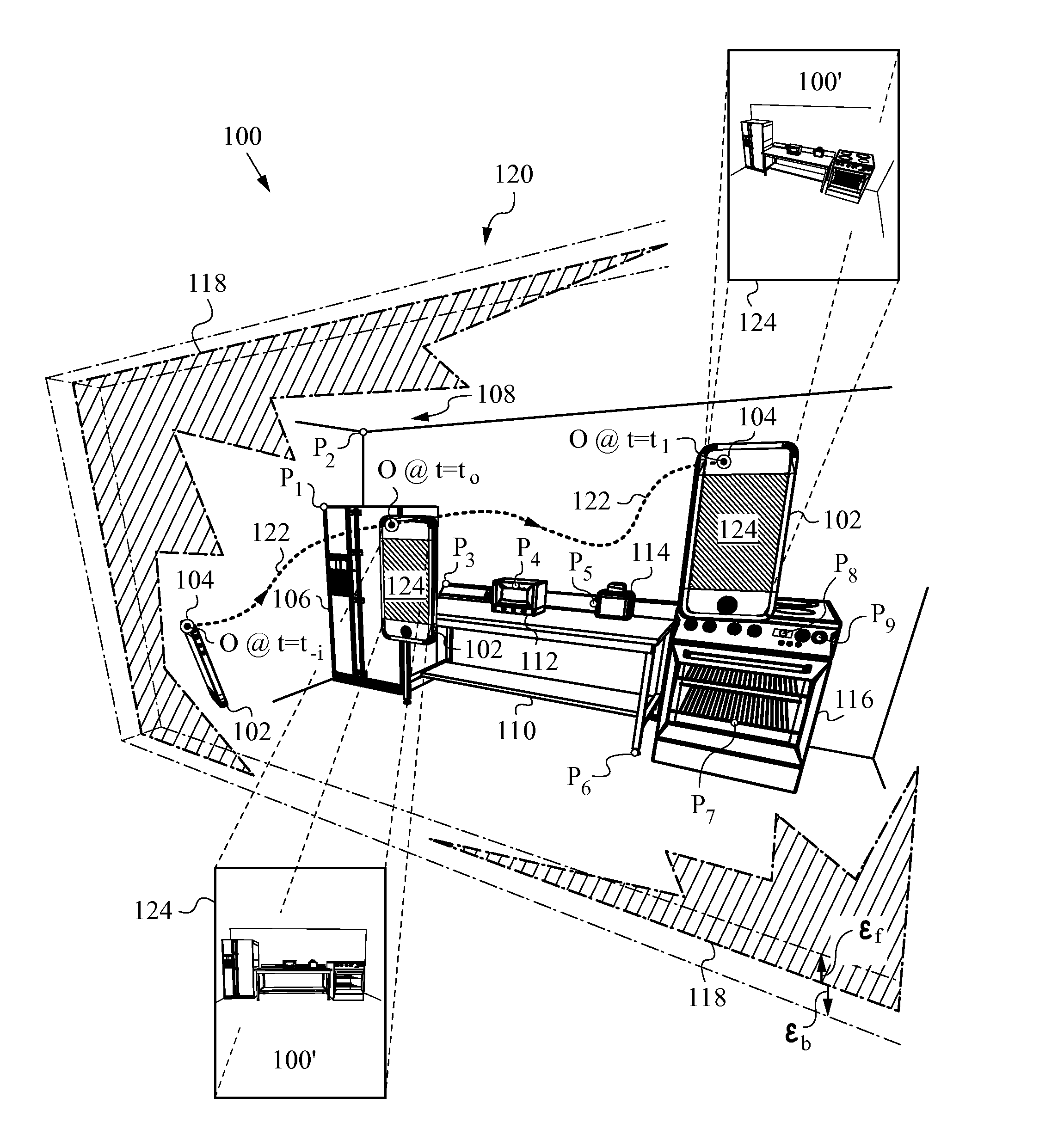
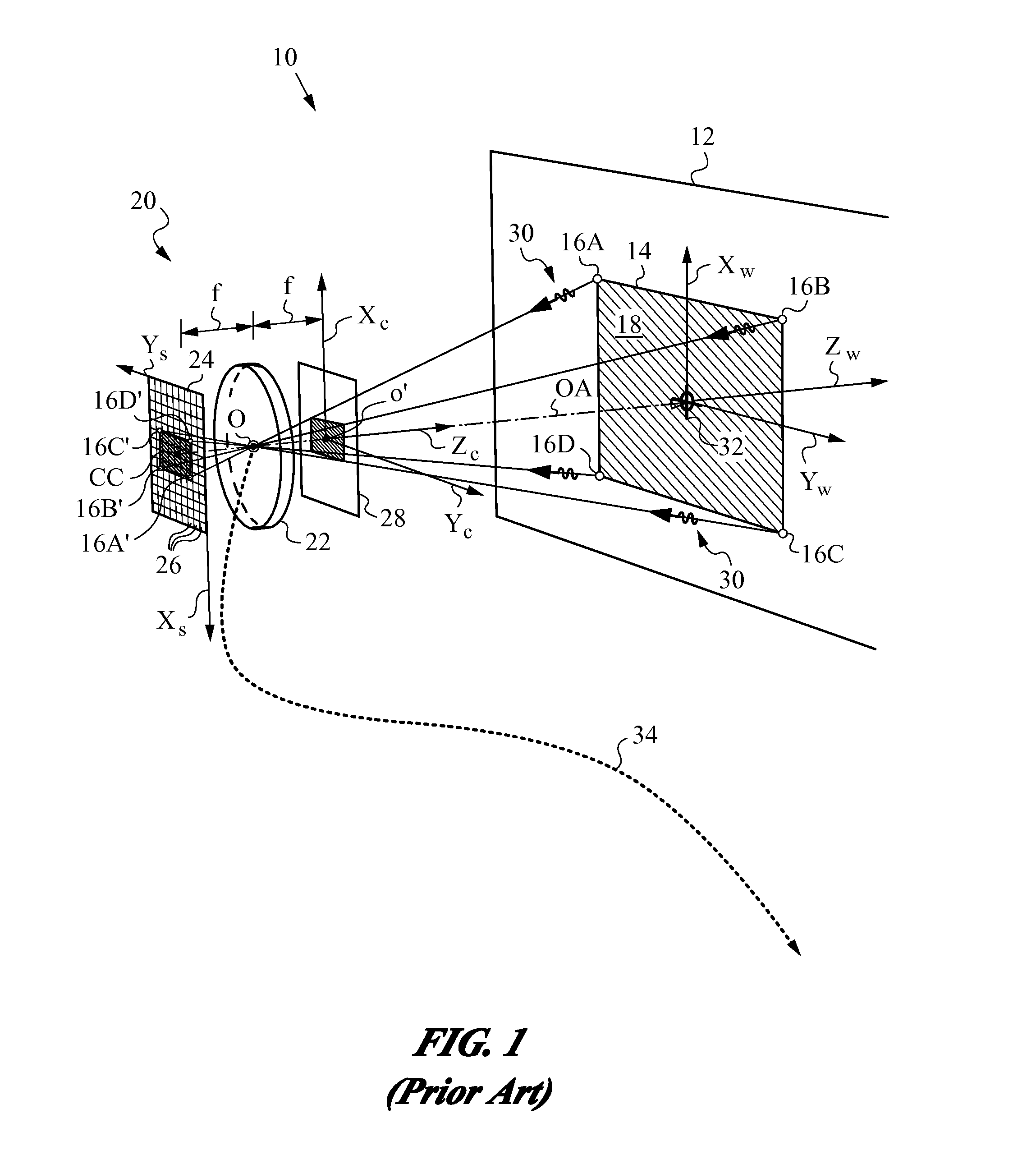
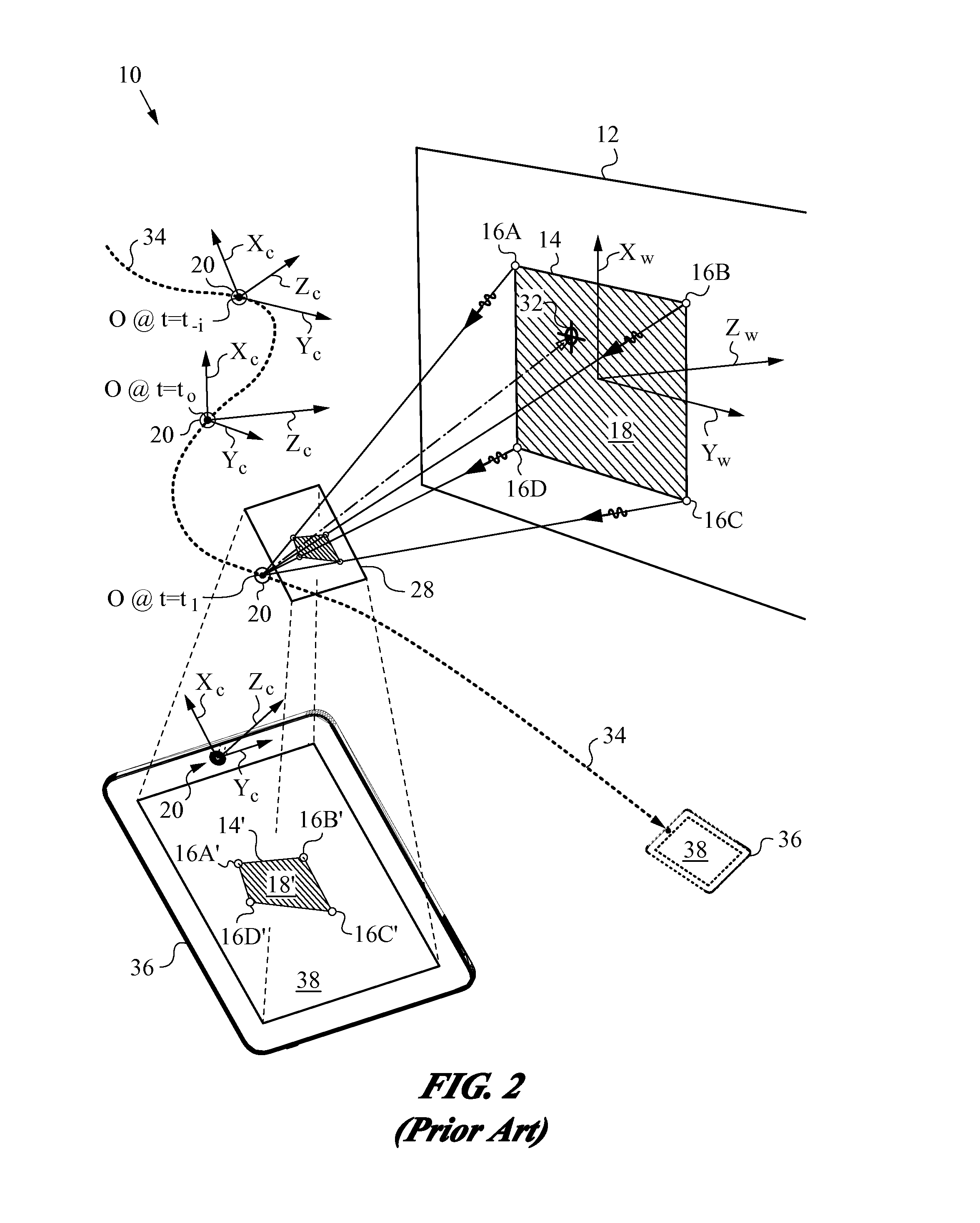
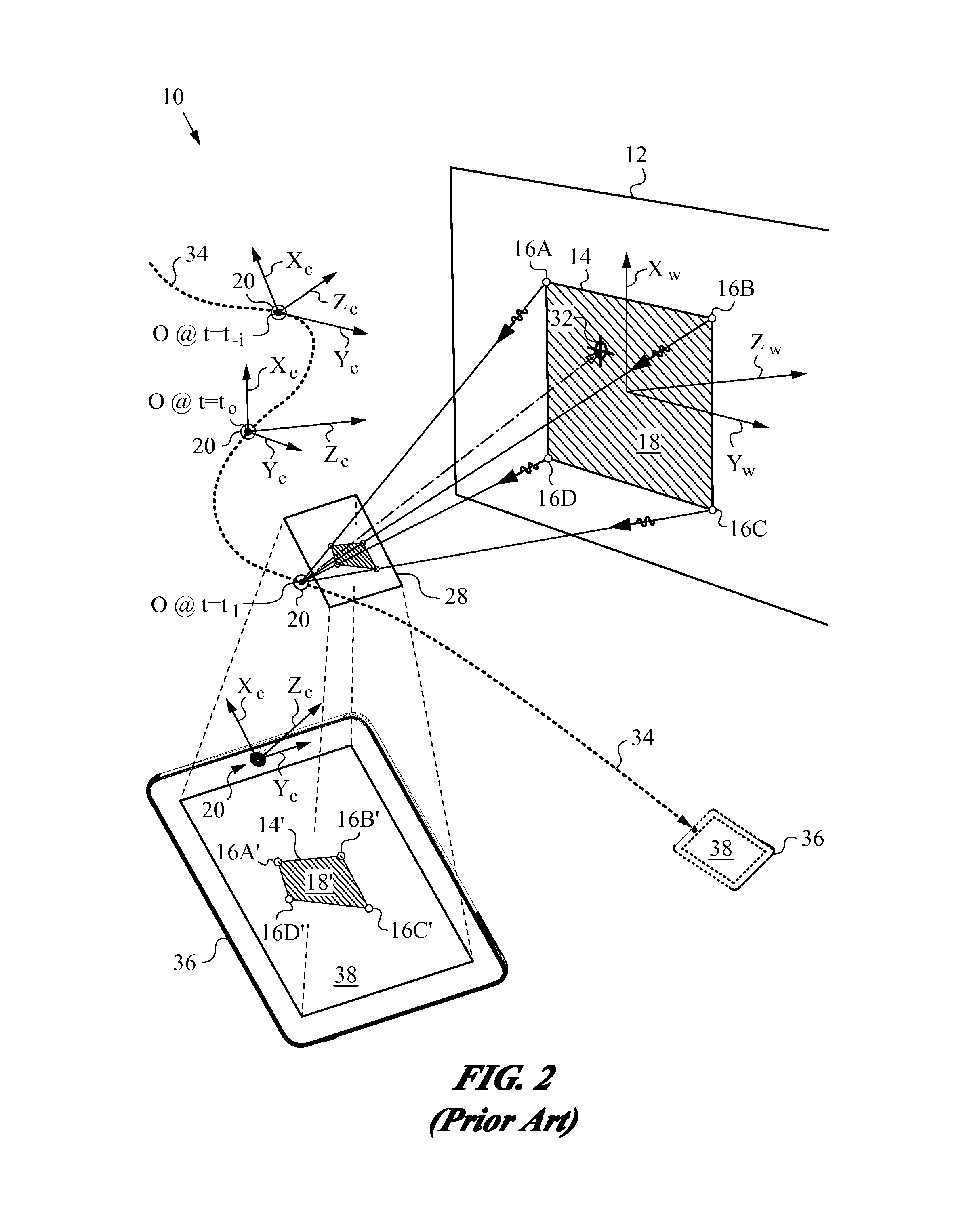
Reduced Homography for Recovery of Pose Parameters of an Optical Apparatus producing Image Data with Structural Uncertainty
A reduced homography H for an optical apparatus to recover pose parameters from imaged space points Pi using an optical sensor. The electromagnetic radiation from the space points Pi is recorded on the optical sensor at measured image coordinates. A structural uncertainty introduced in the measured image points is determined and a reduced representation of the measured image points is selected based on the type of structural uncertainty. The reduced representation includes rays {circumflex over (r)}i defined in homogeneous coordinates and contained in a projective plane of the optical apparatus. At least one pose parameter of the optical apparatus is then estimated by applying the reduced homography H and by applying a condition on the motion of the optical apparatus, the condition being consonant with the reduced representation employed in the reduced homography H.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
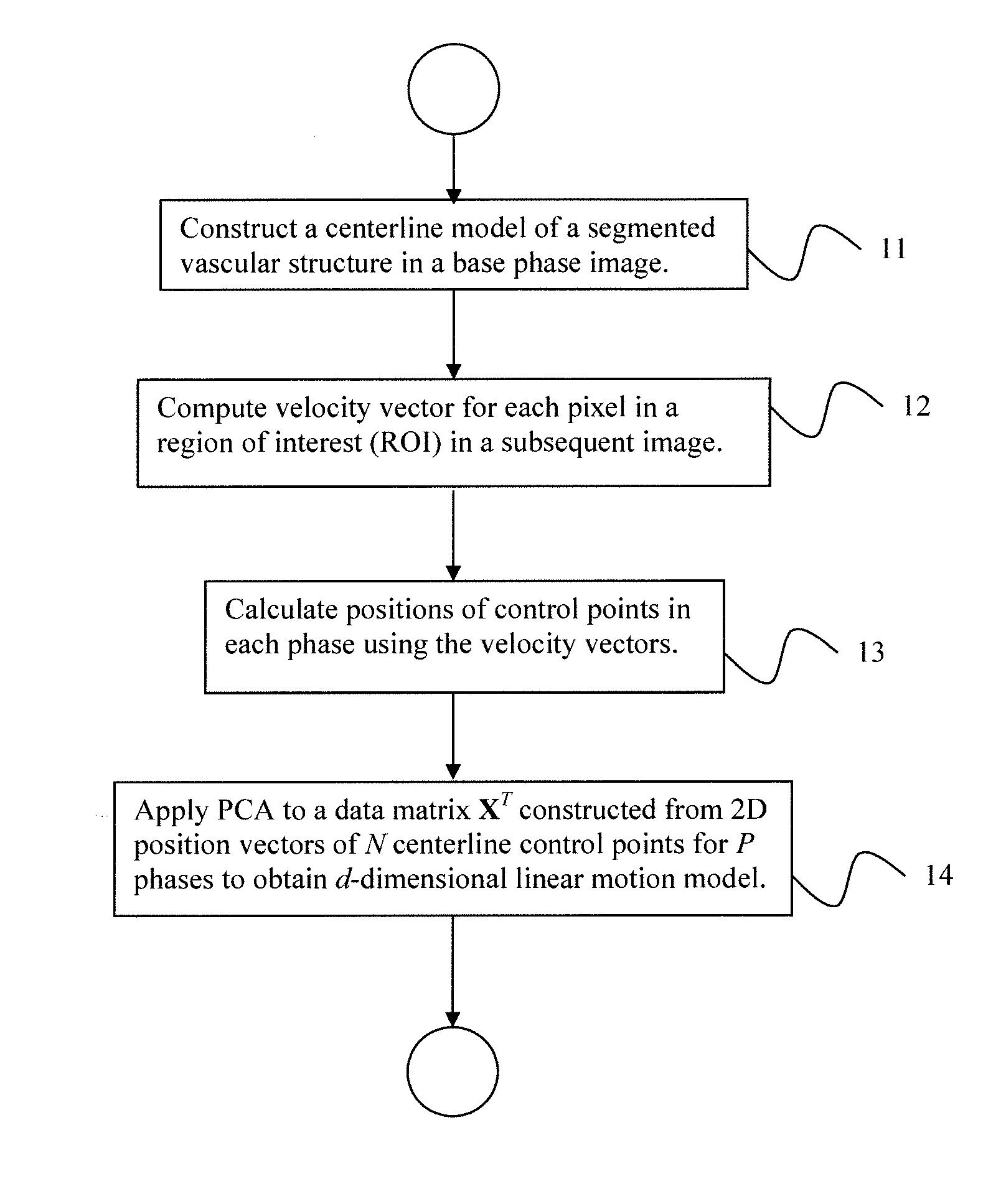
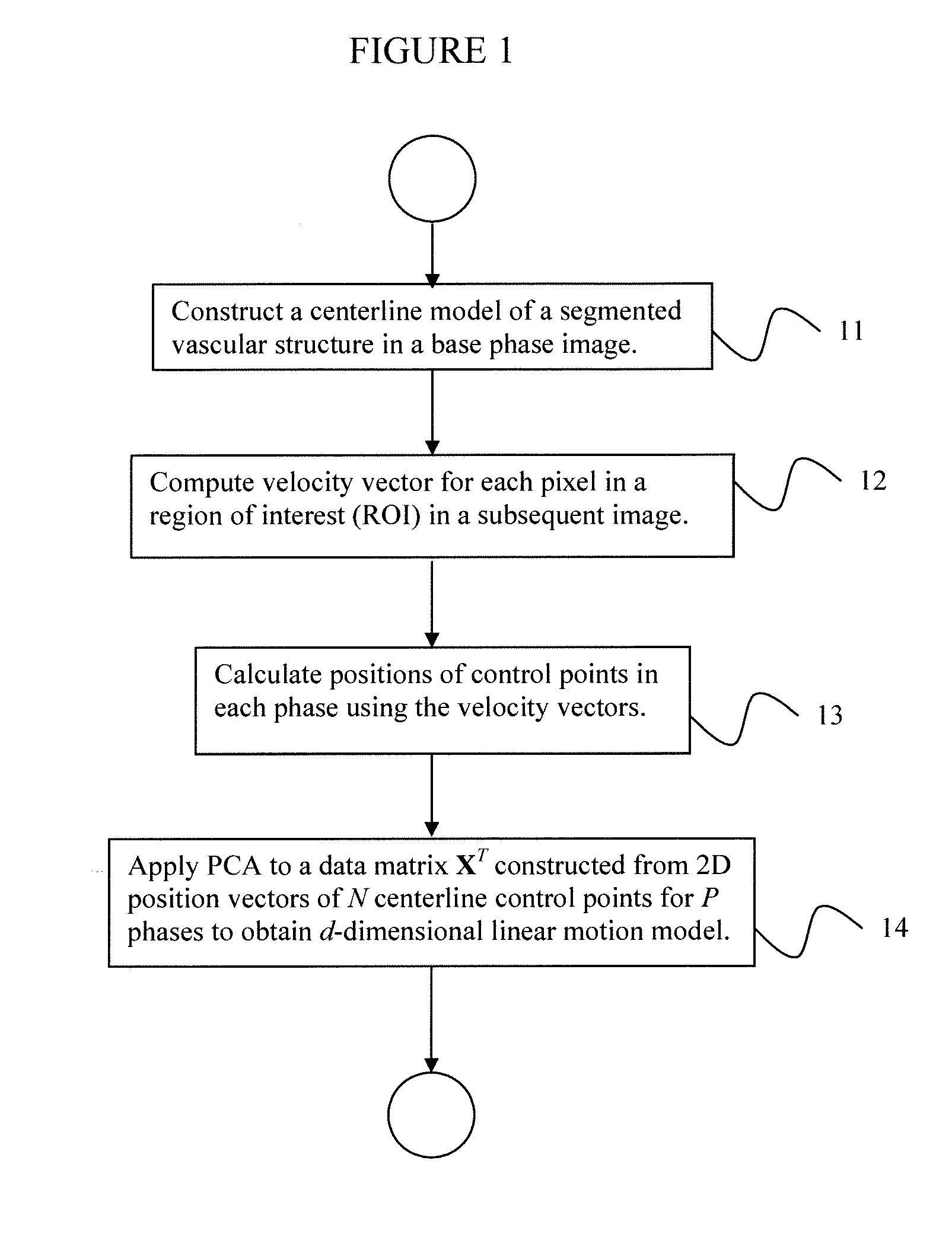
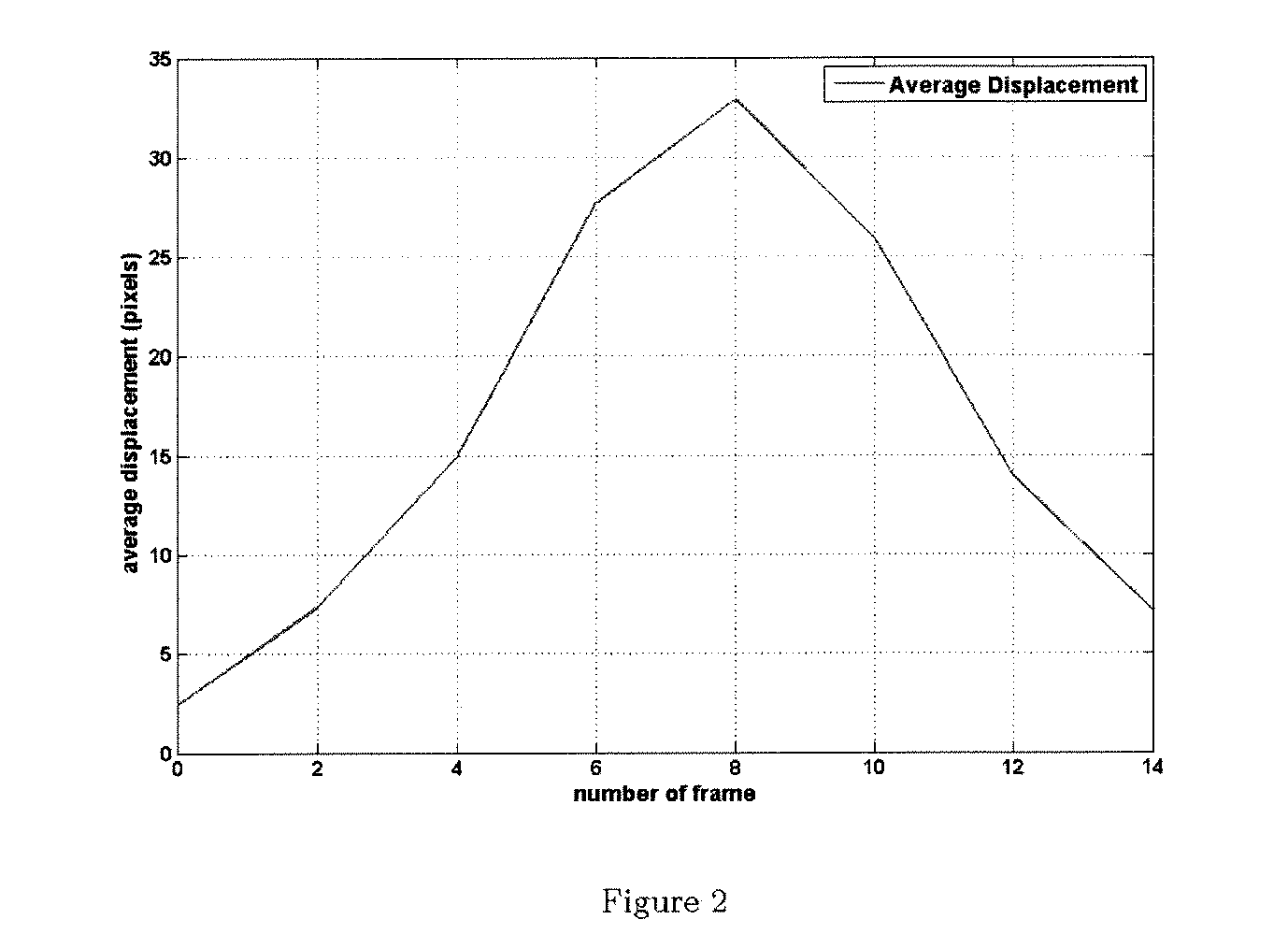
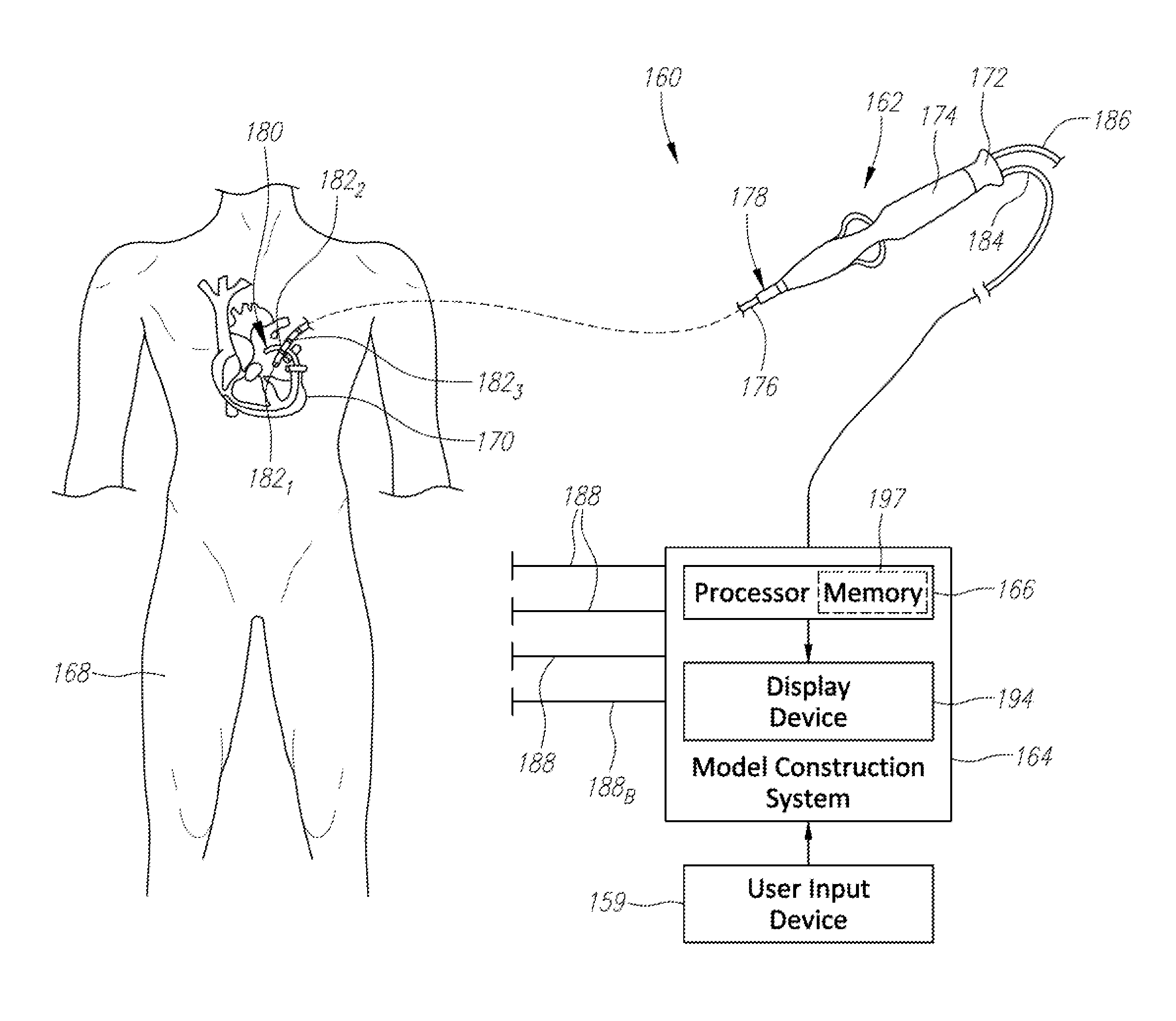
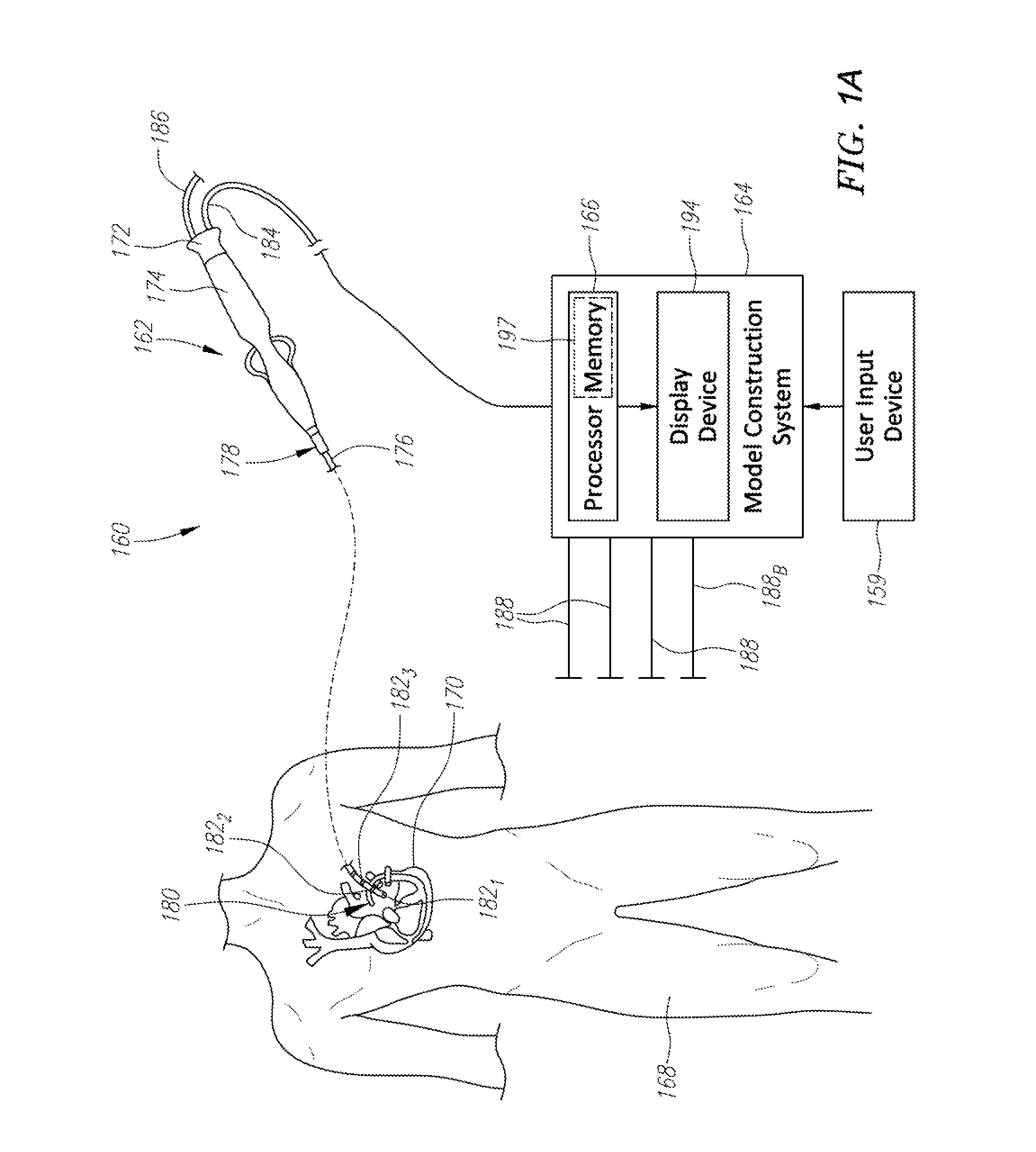
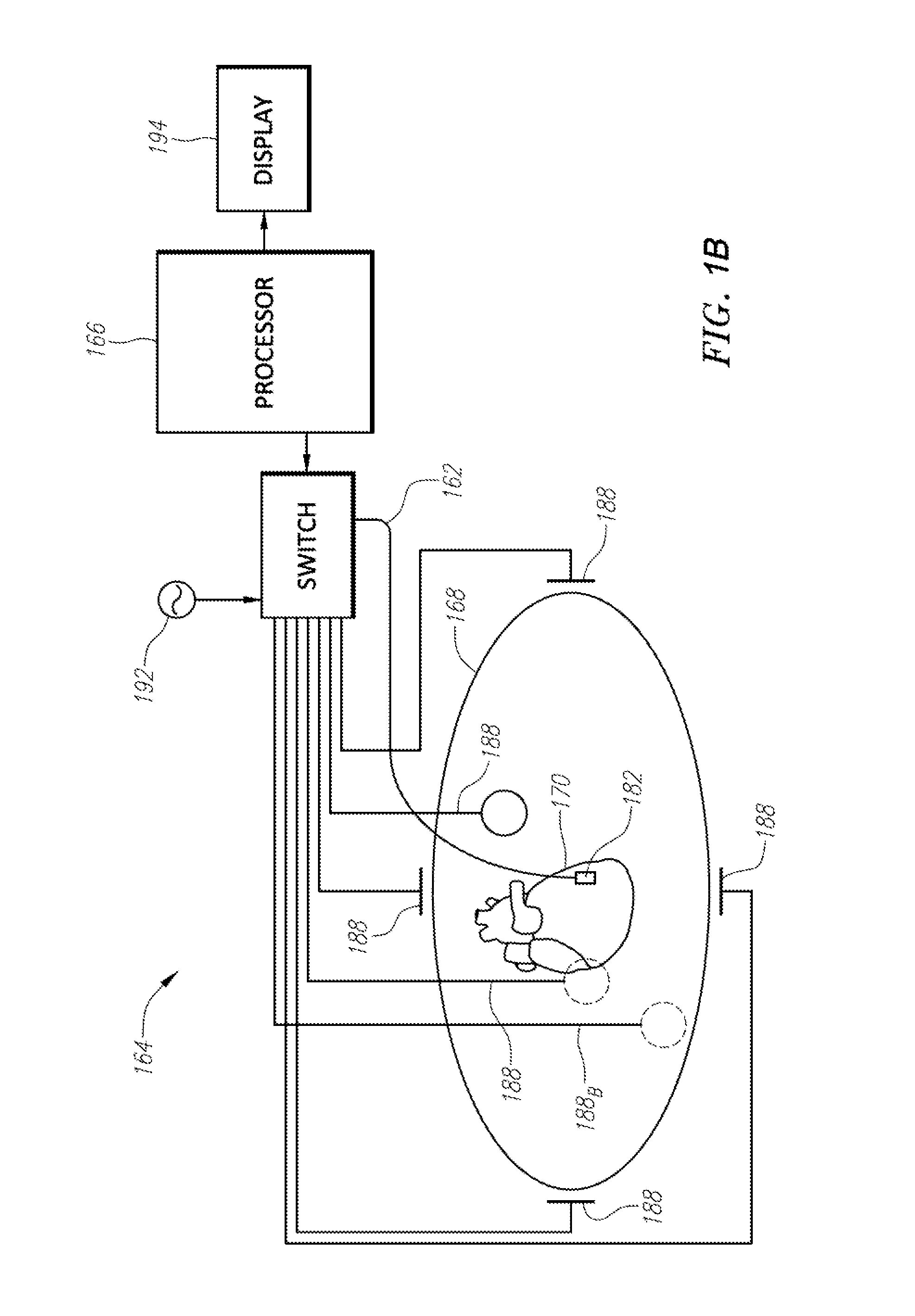
Coronary artery motion modeling
ActiveUS20130101187A1Real-time performanceImage enhancementImage analysisLinear motionCoronary arteries
A method for tracking coronary artery motion includes constructing (11) a centerline model of a vascular structure in a base phase image in a sequence of 2D images of coronary arteries acquired over a cardiac phase, computing (12), for each pixel in a region-of-interest in each subsequent image, a velocity vector that represent a change in position between the subsequent image and base phase image, calculating (13) positions of control points in each phase using the velocity vectors, and applying (14) PCA to a P×2N data matrix XT constructed from position vectors (x, y) of N centerline control points for P phases to identify d eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues of XXT to obtain a d-dimensional linear motion model {circumflex over (α)}p, in which a centerline model for a new image at phase p+1 is estimated by adding {circumflex over (α)}p to each centerline control point of a previous frame at phase p.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for orientation independent sensing
A system and method for obtaining an OIS coordinate frame comprising an electronic control unit configured to determine a local 3D electric field loop, create a zero mean version of E(t) over a depolarization interval, compute an Ė value at each of a plurality of time intervals, compute an initial estimate of ŵ from a cross product of E and the Ė value for each of the plurality of time intervals, average the initial estimate of ŵ from each of the plurality of time for a best estimate of ŵ, determine a plurality of â(θ) values and using the corresponding {circumflex over (n)}(θ) values, compute a composite match score, and choose at least one best value for â and a best value for {circumflex over (n)}.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
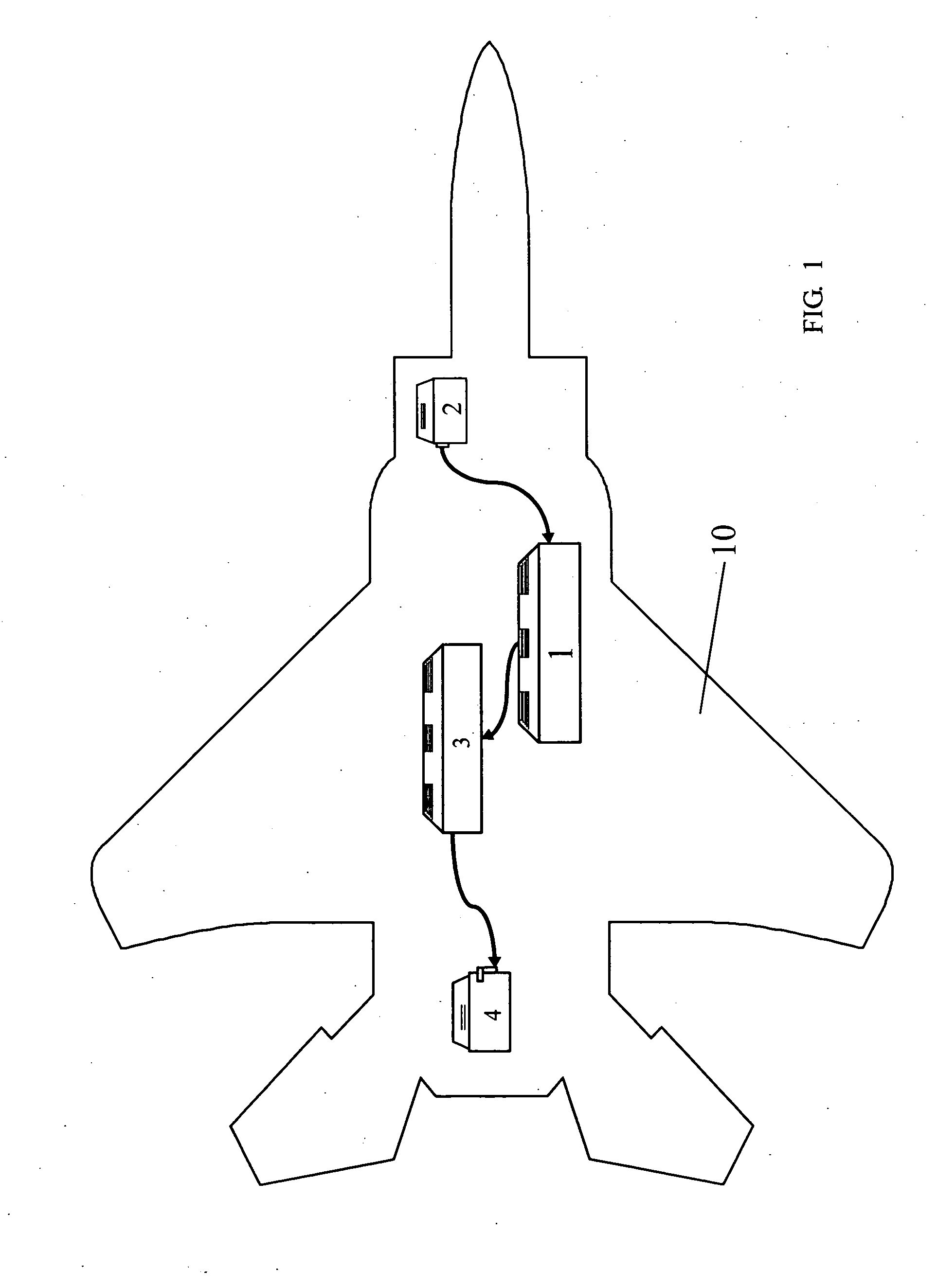
Sensor Fusion System and Method for Estimating Position, Speed and Orientation of a Vehicle, in Particular an Aircraft
InactiveUS20070213889A1Increase computational costOptical rangefindersDigital data processing detailsBody axisKinematics equations
This invention relates to a system for estimating the position, speed and orientation of a vehicle (10), comprising means for determining the components of two noncollinear constant unit vectors b, b according to vehicle body axes; means for determining the components of said noncollinear constant unit vectors {right arrow over (g)}t, {right arrow over (e)}t according to Earth's axes; means for determining the three components of angular velocity b of the vehicle in body axes; means for correcting said angular velocity b with a correction uω and obtaining a corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω; a control module (14) implementing a control law to calculate said correction uω, where said control law is: uω=σ(b×ĝb+<?img id="custom-character-00007" he="3.13mm" wi="1.78mm" file="US20070213889A1-20070913-P00901.TIF" alt="custom character" img-content="character" img-format="tif" ?>b×êb) [1]where σ is a positive scalar, such that upon using said corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω as input to a module for integrating the kinematic equations, the latter are stable in the ISS sense and the error in the estimation of the direction cosine matrix {circumflex over (B)} and of the Euler angles {circumflex over (Φ)} is bounded.
Owner:INST NACIONAL DE TECNICA AEROESPACIAL
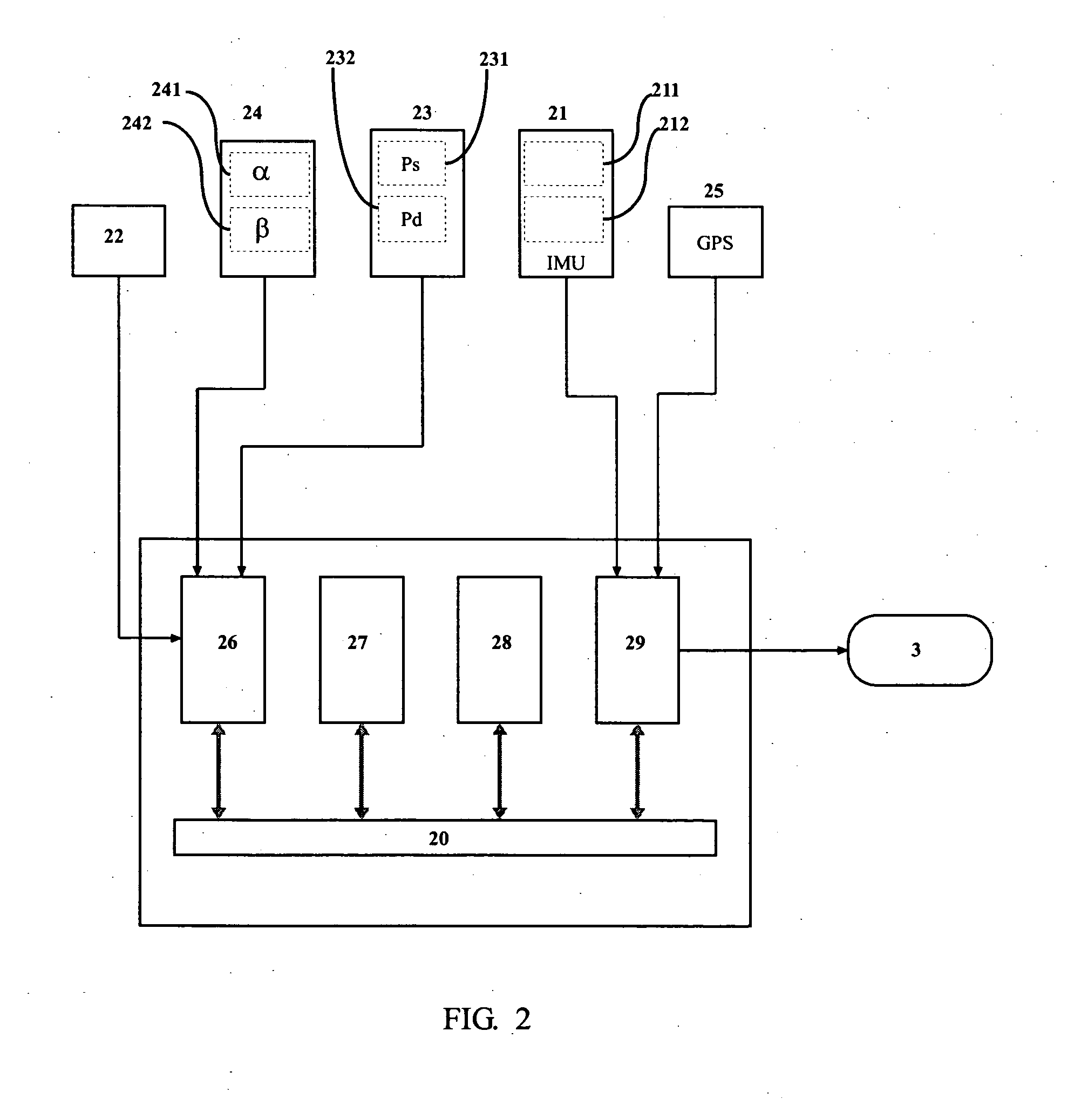
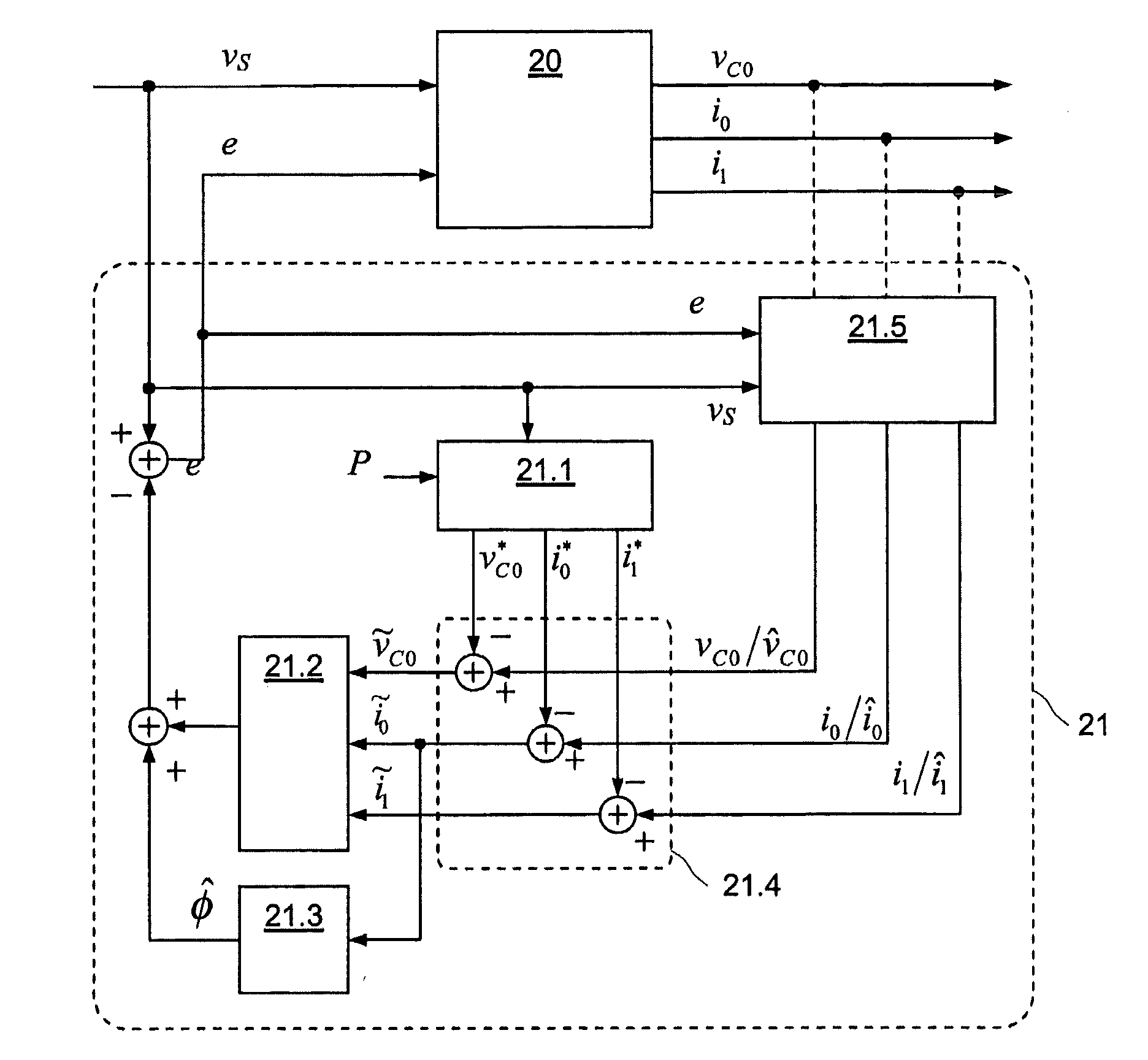
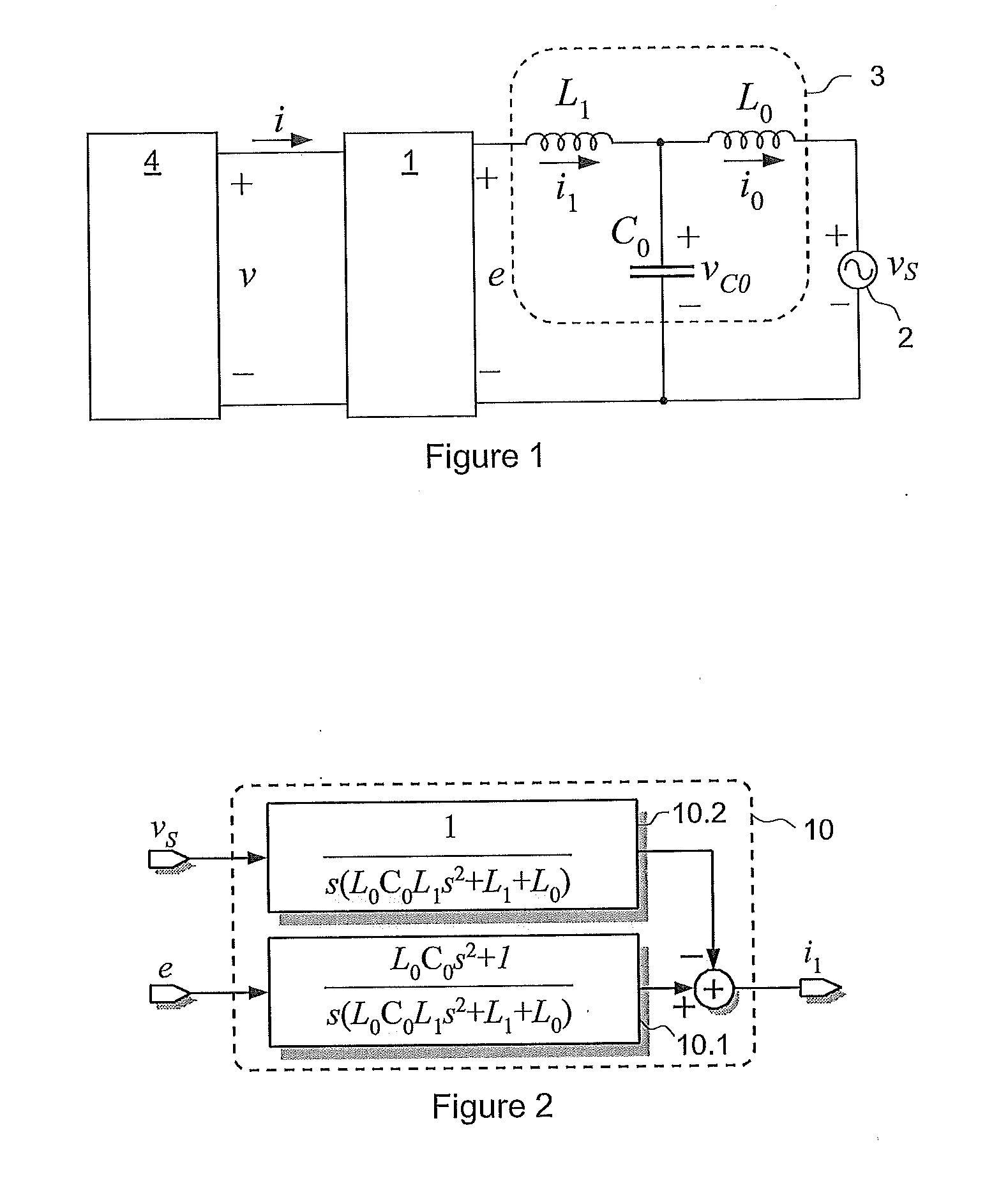
Control method for single-phase grid-connected lcl inverter
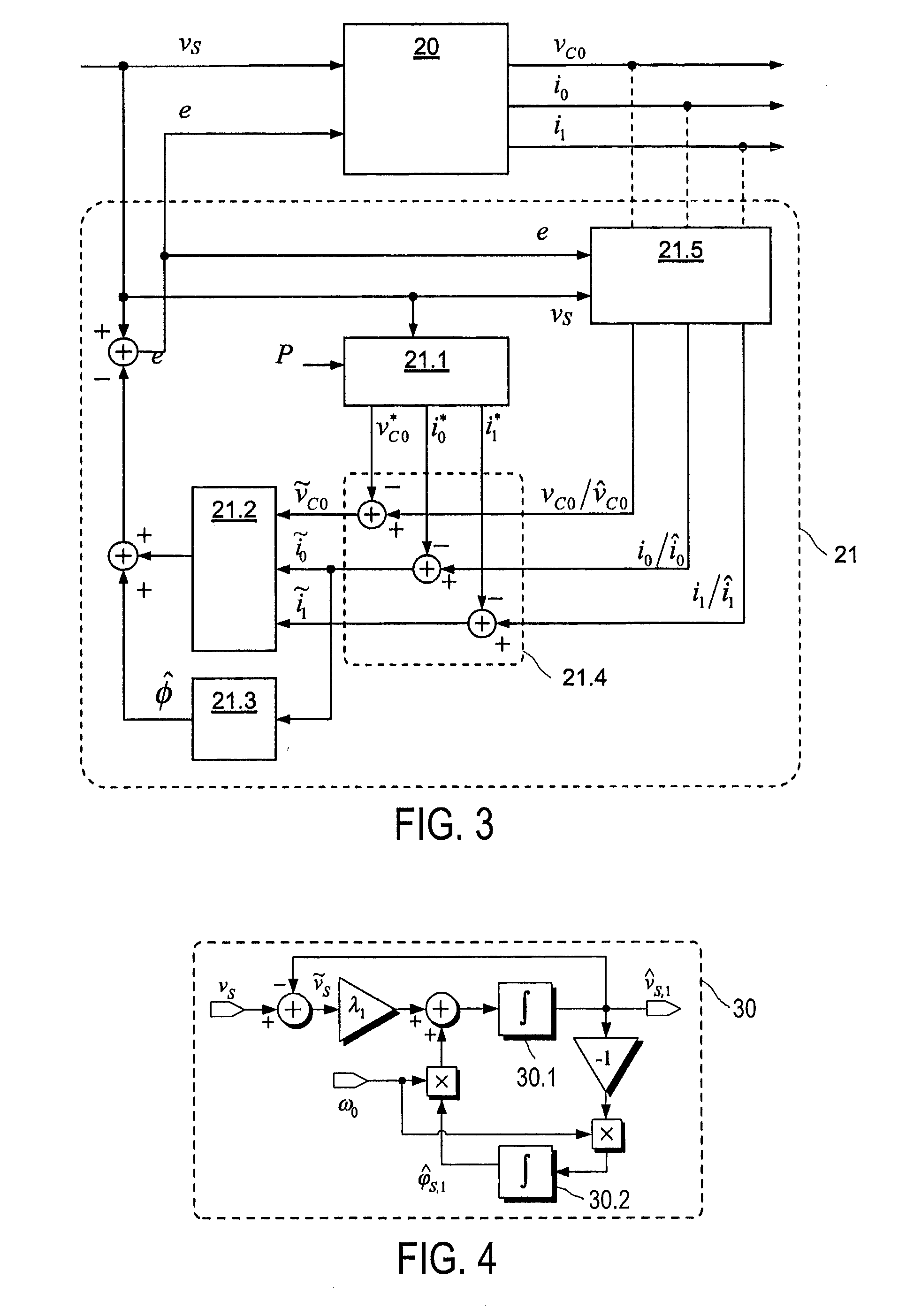
ActiveUS20110221420A1Improve performanceReduce resonanceVariable inductancesFixed transformers or mutual inductancesResonanceCapacitor voltage
A method of controlling the grid-side current of a single-phase grid-connected converter having an LCL filter connected between the output of the converter and the grid. The method includes measuring a grid voltage (vS) and at least one signal in a group of signals consisting of a grid-side current (i0), a converter-side current (i1) and a capacitor voltage (vC0). The method includes estimating the fundamental component (vS,1) of the grid voltage (vS), forming a grid-side current reference (i0*), a converter-side current reference (i1*) and a capacitor voltage reference (vC0*) for the grid-side current of the LCL filter using the fundamental component of the grid voltage (vS,1), forming estimates for the non-measured signals in said group of signals, forming a grid-side current difference term (ĩ0), a converter-side current difference term (ĩ1) and a capacitor voltage difference term ({tilde over (v)}C0) from the differences between the references and measured / estimated values of said signals, forming an injection term for damping the resonance of the LCL filter by using an active damping injection mechanism (ADI), in which the grid-side current difference term (ĩ0), the converter-side current difference term (ĩ1) and the capacitor voltage difference term ({tilde over (v)}C0) are used, forming an estimate of harmonic distortion term ({circumflex over (φ)}) using the grid-side current difference term (ĩ0), and controlling the output voltage (e) of the converter on the basis of the grid voltage, formed injection term and formed estimate of the harmonic distortion term ({circumflex over (φ)}) to produce a grid side (i0) current corresponding to the current reference.
Owner:MARICI HLDG THE NETHERLANDS BV
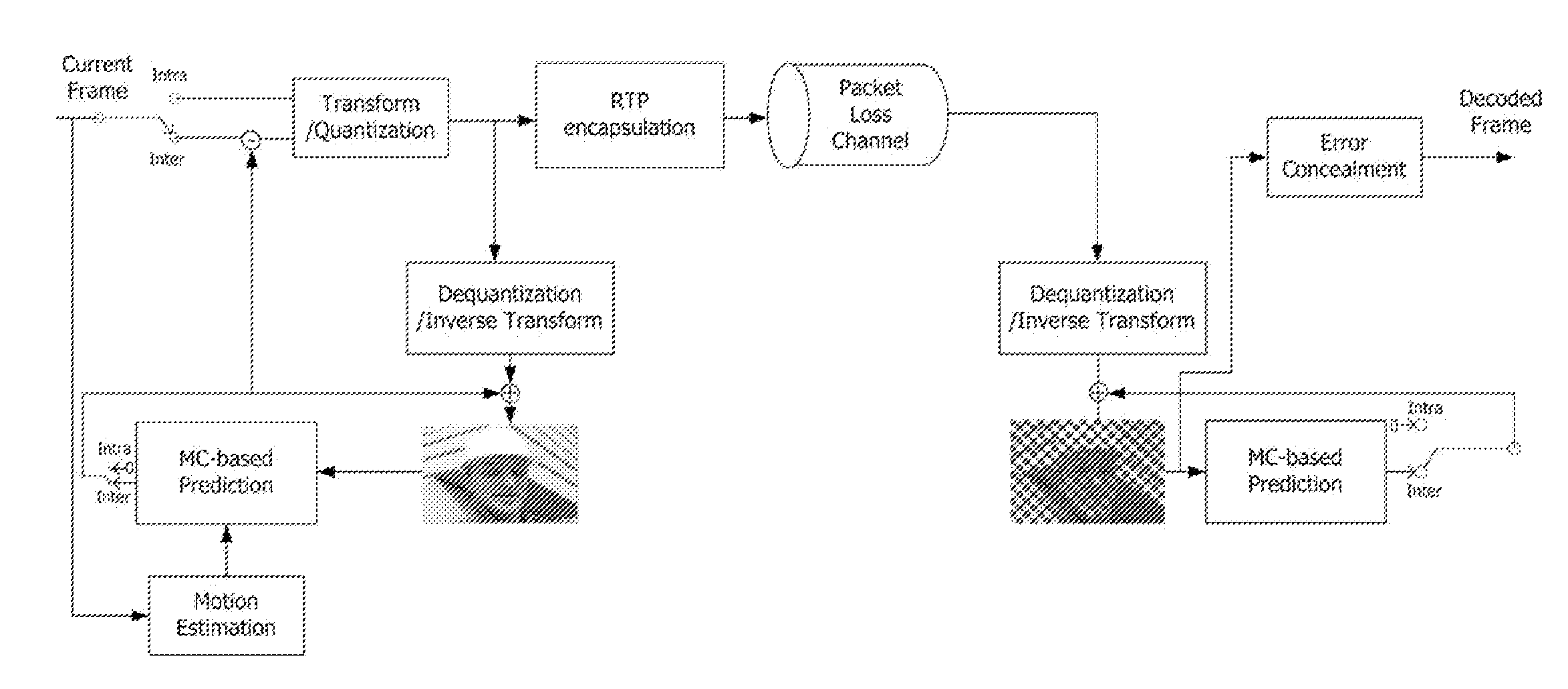
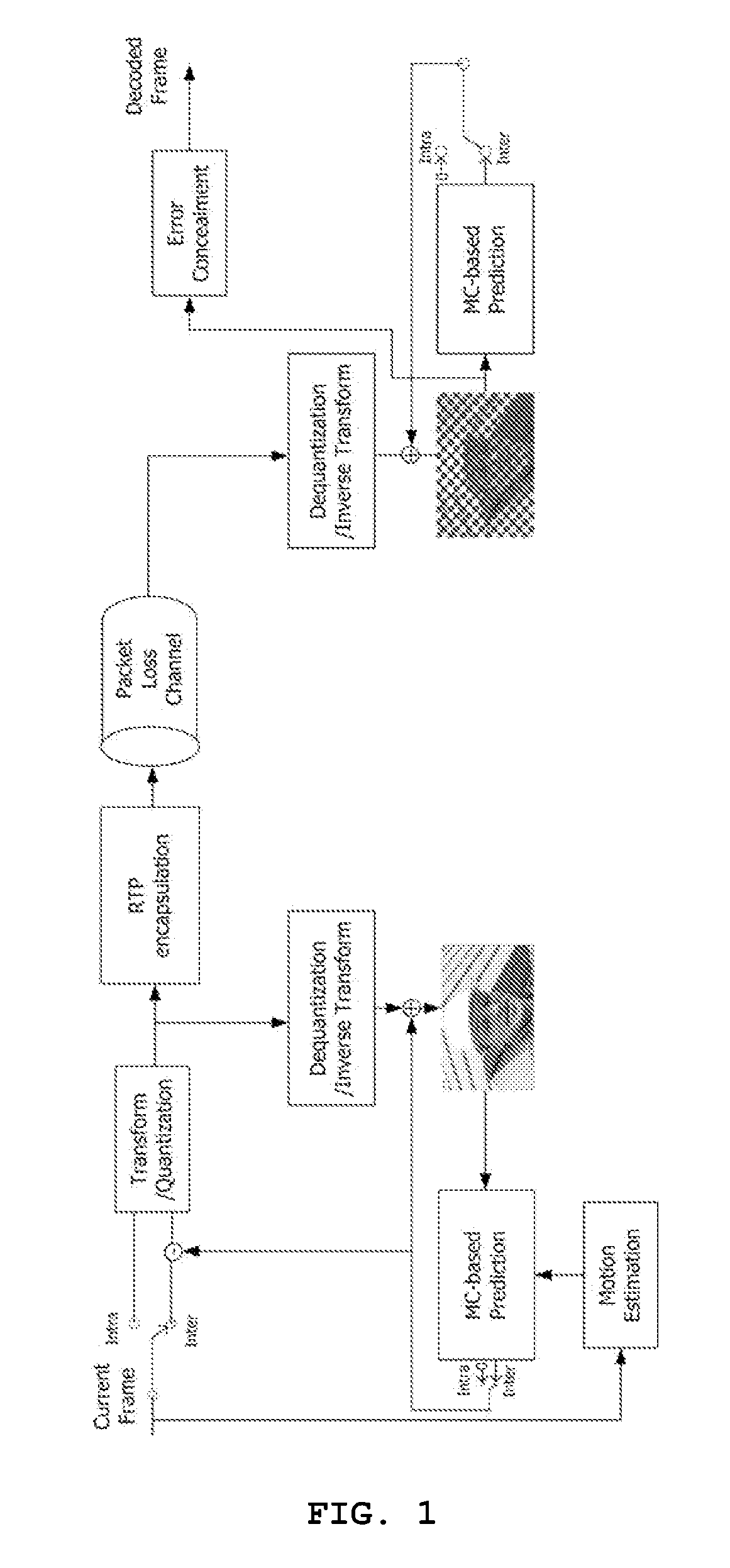
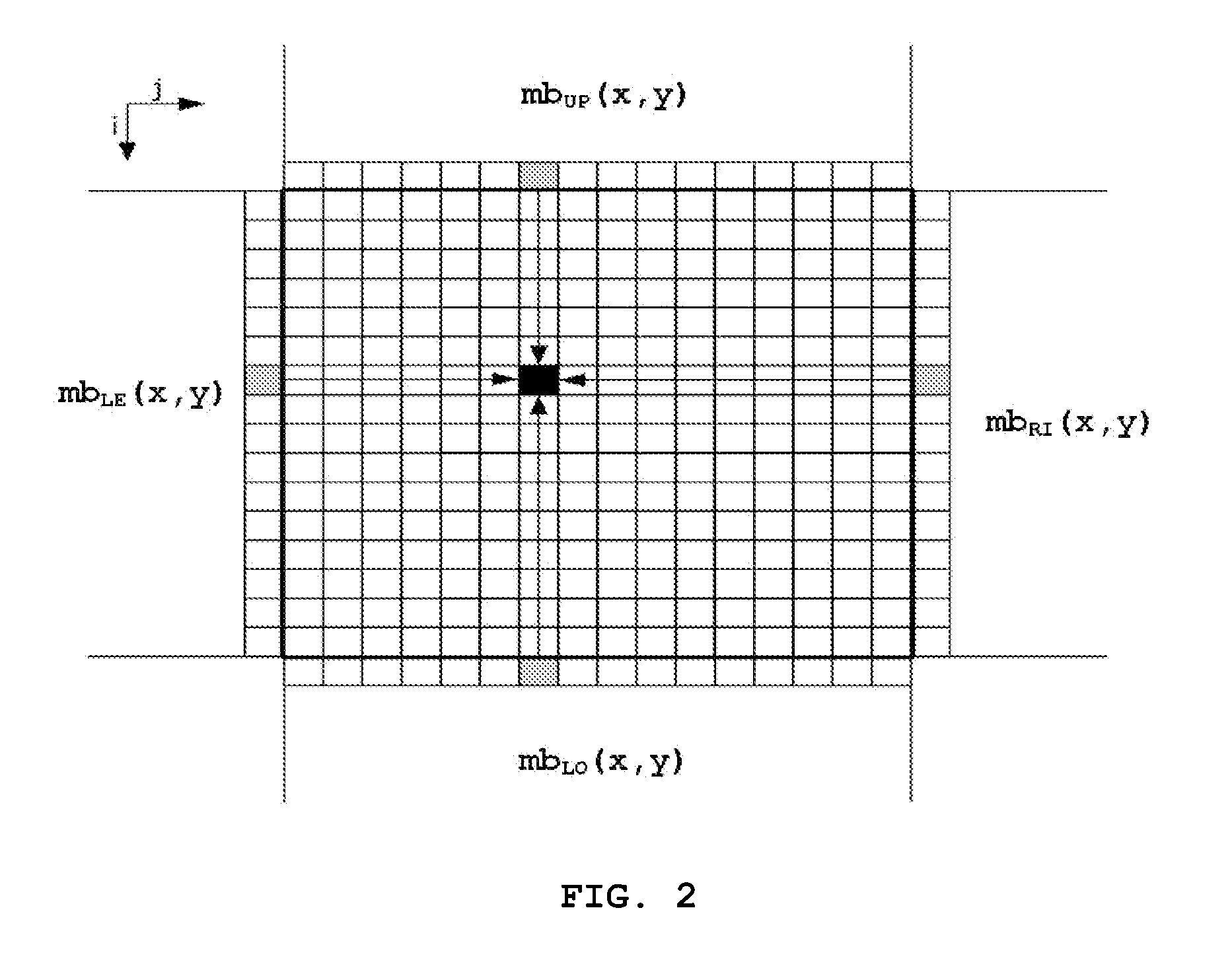
Hybrid error concealment method
InactiveUS20070153898A1Reduce bitrateHigh loss rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorCircumflex
Disclosed herein is a hybrid error concealment method. The hybrid error concealment method of the present invention includes a first step of calculating a side match distortion, measured when a motion vector for an arbitrary intra-frame is assumed to be zero, and the intra-frame is temporally reconstructed, a second step of applying temporal error concealment when the side match distortion, calculated at the first step, is less than a predetermined low threshold value, a third step of applying spatial error concealment when the side match distortion, calculated at the first step, is greater than a predetermined high threshold value, and a fourth step of performing error concealment based on {circumflex over (m)}{circumflex over (b)}(x,y)=α·{circumflex over (m)}{circumflex over (b)}t(x,y)+β·{circumflex over (m)}{circumflex over (b)}s(x,y) when the side match distortion, calculated at the first step, exists between the low threshold value and the high threshold value. According to the present invention, the hybrid error concealment method improves PSNR performance compared to a conventional spatial error concealment algorithm used in H.264, and obtains greatly improved performance characteristics, particularly when motion is small and the value of a quantization parameter is relatively low.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP +1
Device for estimating a sequence of N bits corresponding to a received sequence of M digital data and associated method
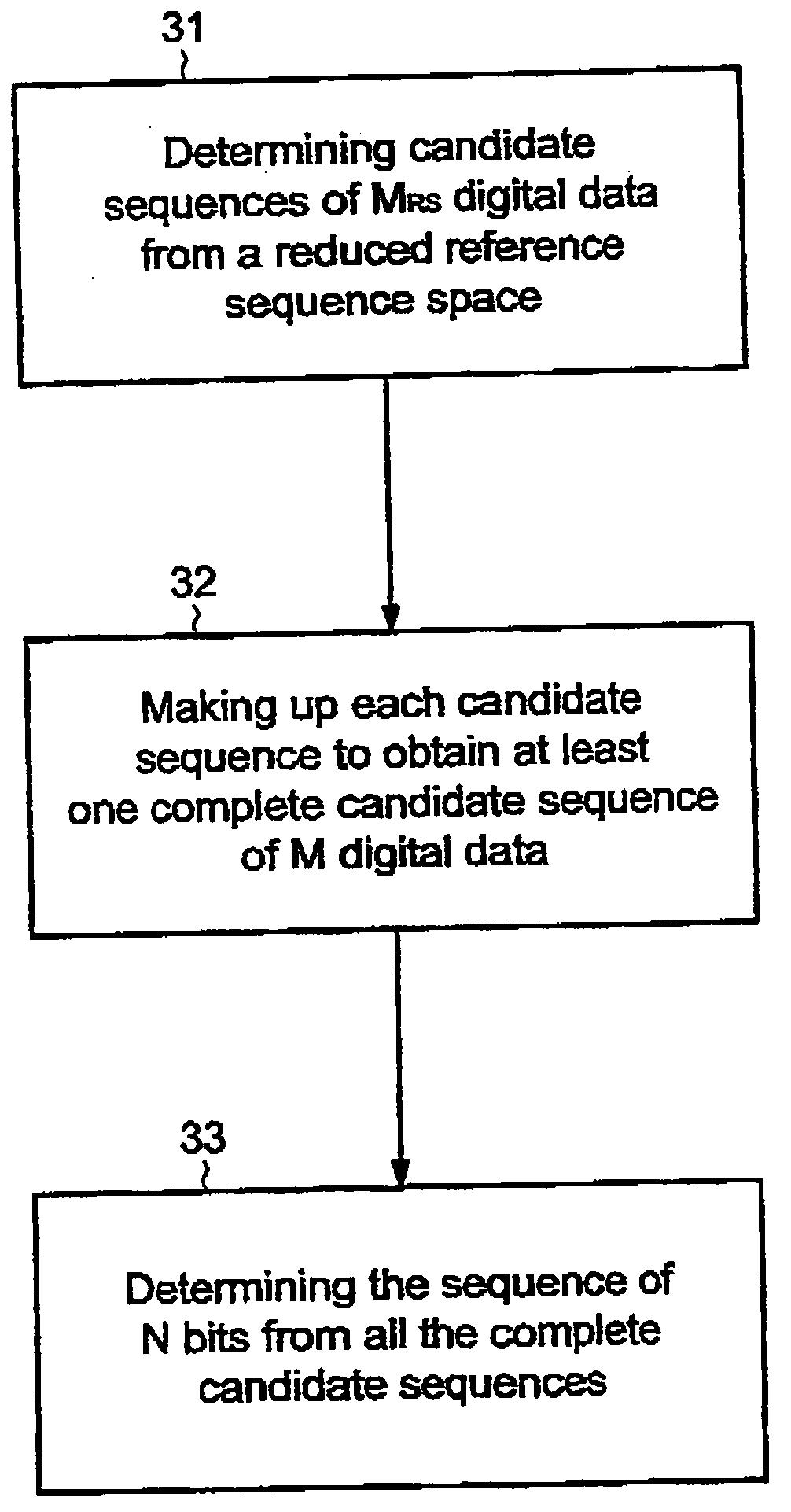
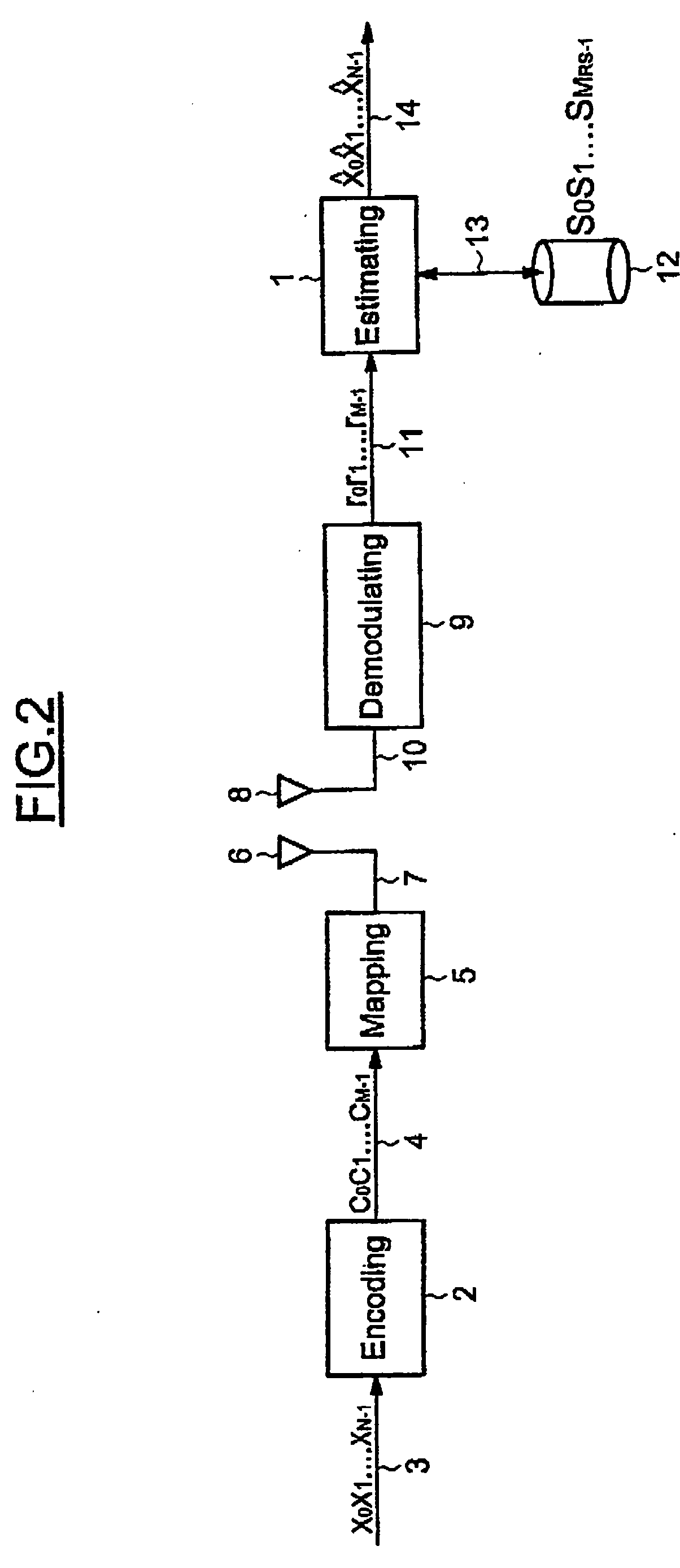
ActiveUS20050180531A1Reducing sequence spaceReduce spacingError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesDigital dataCircumflex
A system and method is provided for estimating a sequence of N bits ({circumflex over (x)}0{circumflex over (x)}1 . . . {circumflex over (x)}N−1) corresponding to a received sequence of M digital data (r0r1 . . . rM−1). The method includes determining candidate sequences of MRS digital data from a reduced reference sequence space comprising 2N<sub2>RS < / sub2>reduced reference sequences of MRS reference digital data (s0s1 . . . sM<sub2>RS< / sub2>−1), MRS being less than M, and 2N<sub2>RS < / sub2>being less than or equal to 2N. The method further includes making up each candidate sequence with remaining reference symbols to obtain at least one complete candidate sequence of M digital data, and determining the sequence of N bits ({circumflex over (x)}0{circumflex over (x)}1 . . . {circumflex over (x)}N−1) from the complete candidate sequences.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Method and arrangement for demodulating data symbols
InactiveUS6269116B1Improve the level ofMinimize impactMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCircumflexResult set
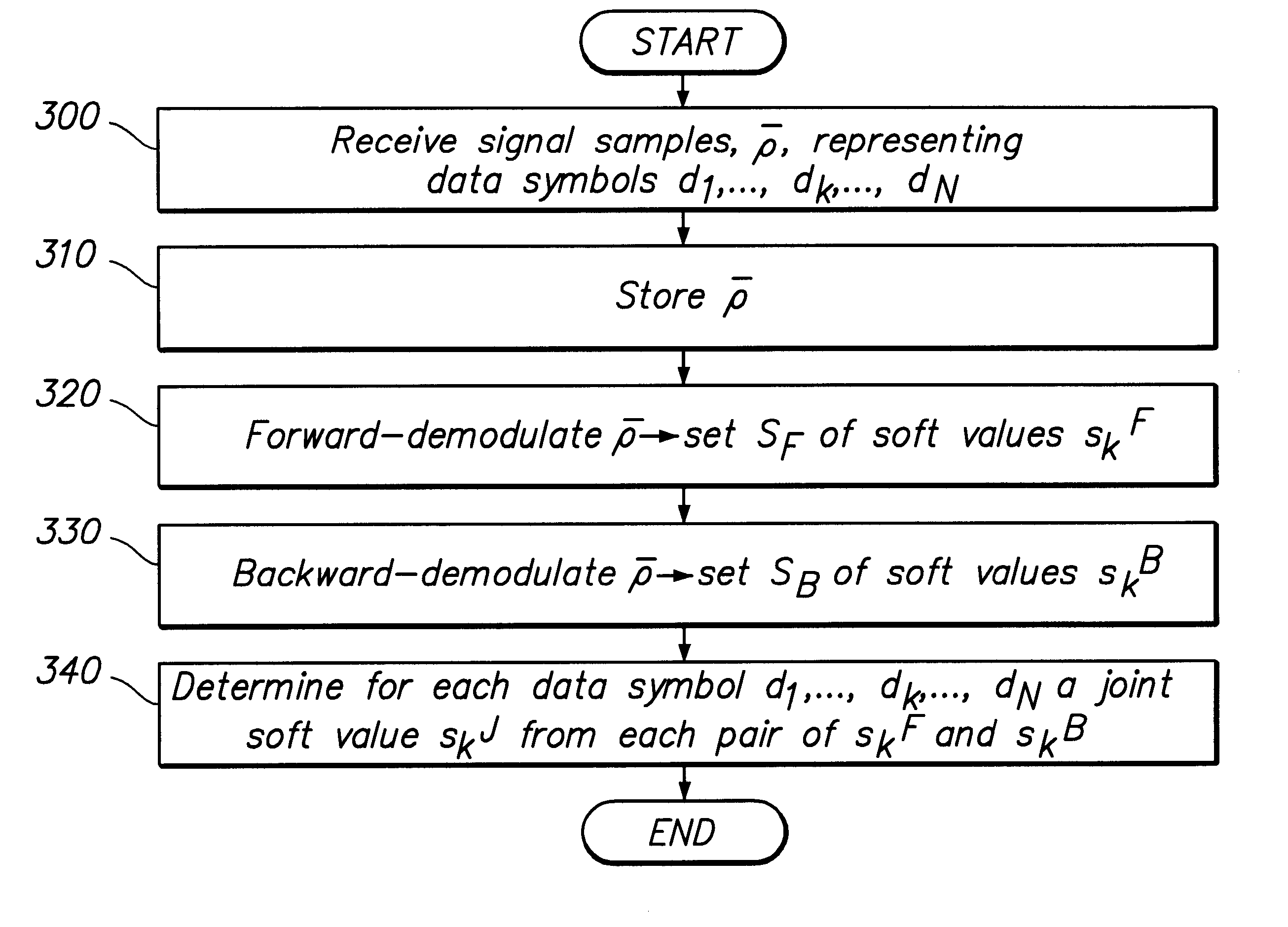
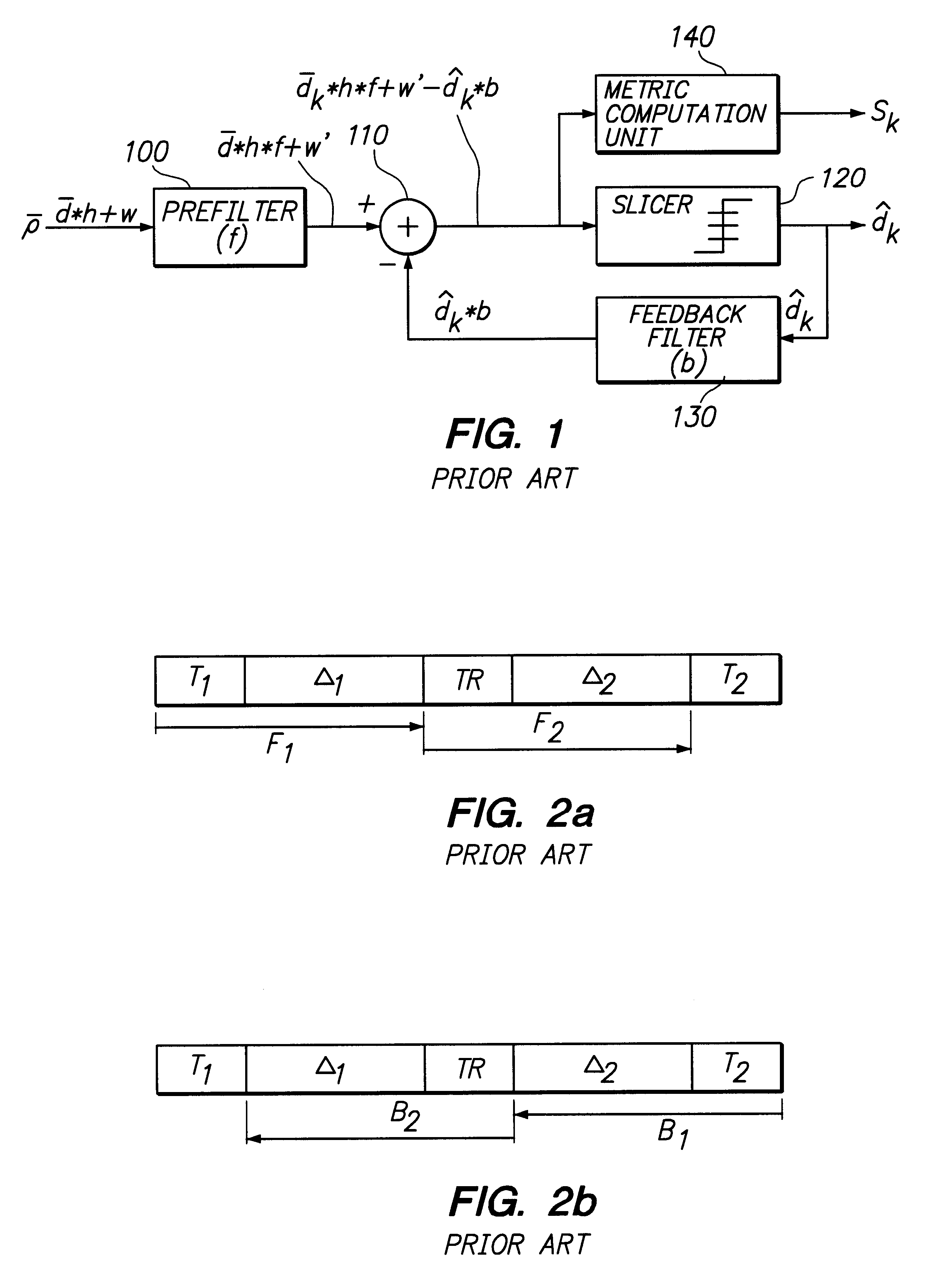
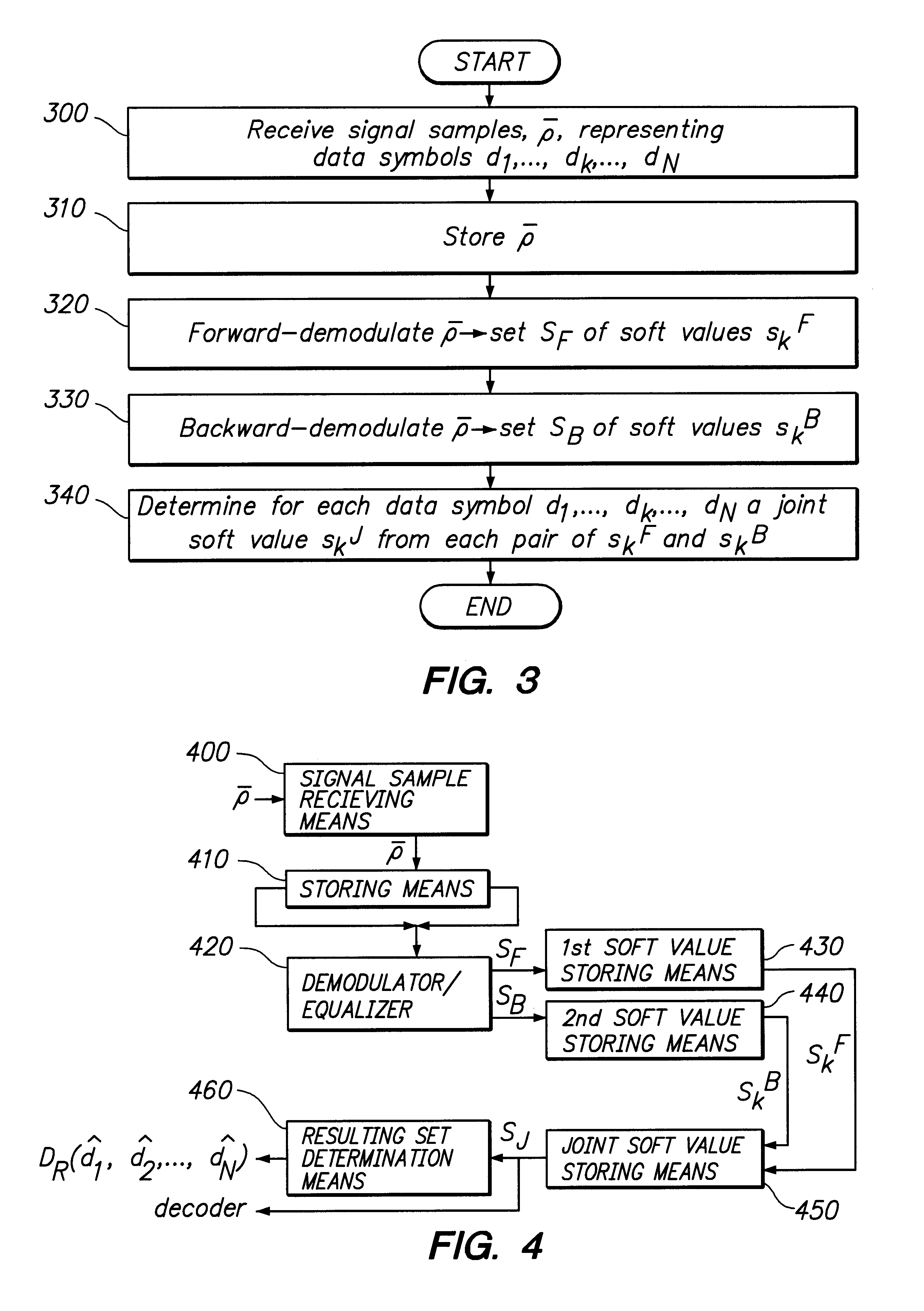
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for demodulating data symbols (d1-dN) having been transmitted through a communication channel, particularly a channel suffering from one or more impairments. Received signal samples ({overscore (rho)}), representing the sent data symbols (d1-dN), are stored (310) and demodulated in both the forward (320) and the backward direction (330), via a demodulator / equaliser. In course of the demodulations are produced a first (SF) and a second (SB) respective set of soft values (skF; skB), which each is associated with a certain data symbol (dk). (340) From every pair of soft values (skF; skB) is then determined a joint soft value (SkJ), which e.g. may be utilised for deriving a resulting set of data symbols ({circumflex over (d)}1-{circumflex over (d)}N) or for directly decoding the payload information contained in the data symbols (d1-dN).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Reduced homography for recovery of pose parameters of an optical apparatus producing image data with structural uncertainty
A reduced homography H for an optical apparatus to recover pose parameters from imaged space points Pi using an optical sensor. The electromagnetic radiation from the space points Pi is recorded on the optical sensor at measured image coordinates. A structural uncertainty introduced in the measured image points is determined and a reduced representation of the measured image points is selected based on the type of structural uncertainty. The reduced representation includes rays {circumflex over (r)}i defined in homogeneous coordinates and contained in a projective plane of the optical apparatus. At least one pose parameter of the optical apparatus is then estimated by applying the reduced homography H and by applying a condition on the motion of the optical apparatus, the condition being consonant with the reduced representation employed in the reduced homography H.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
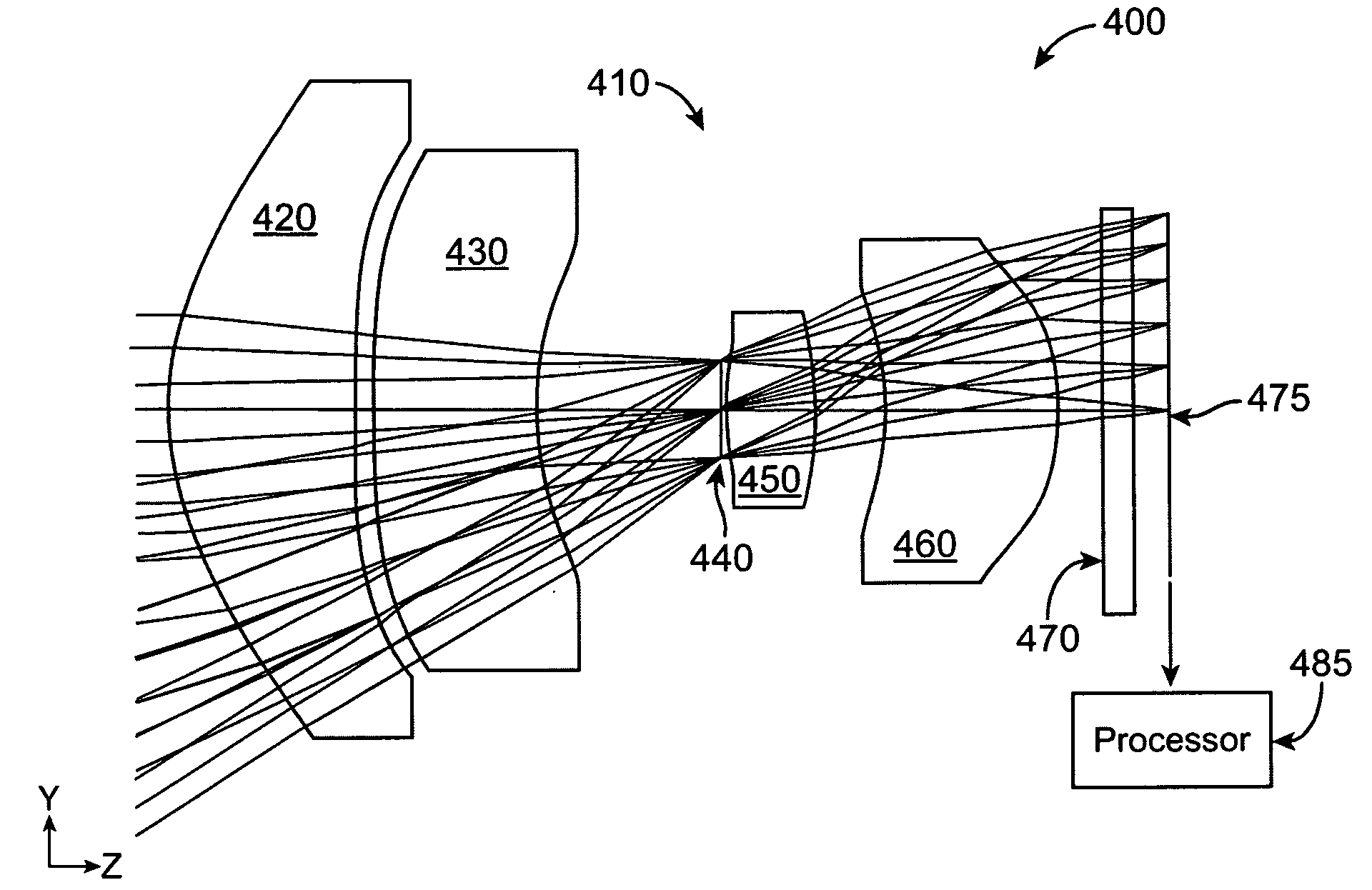
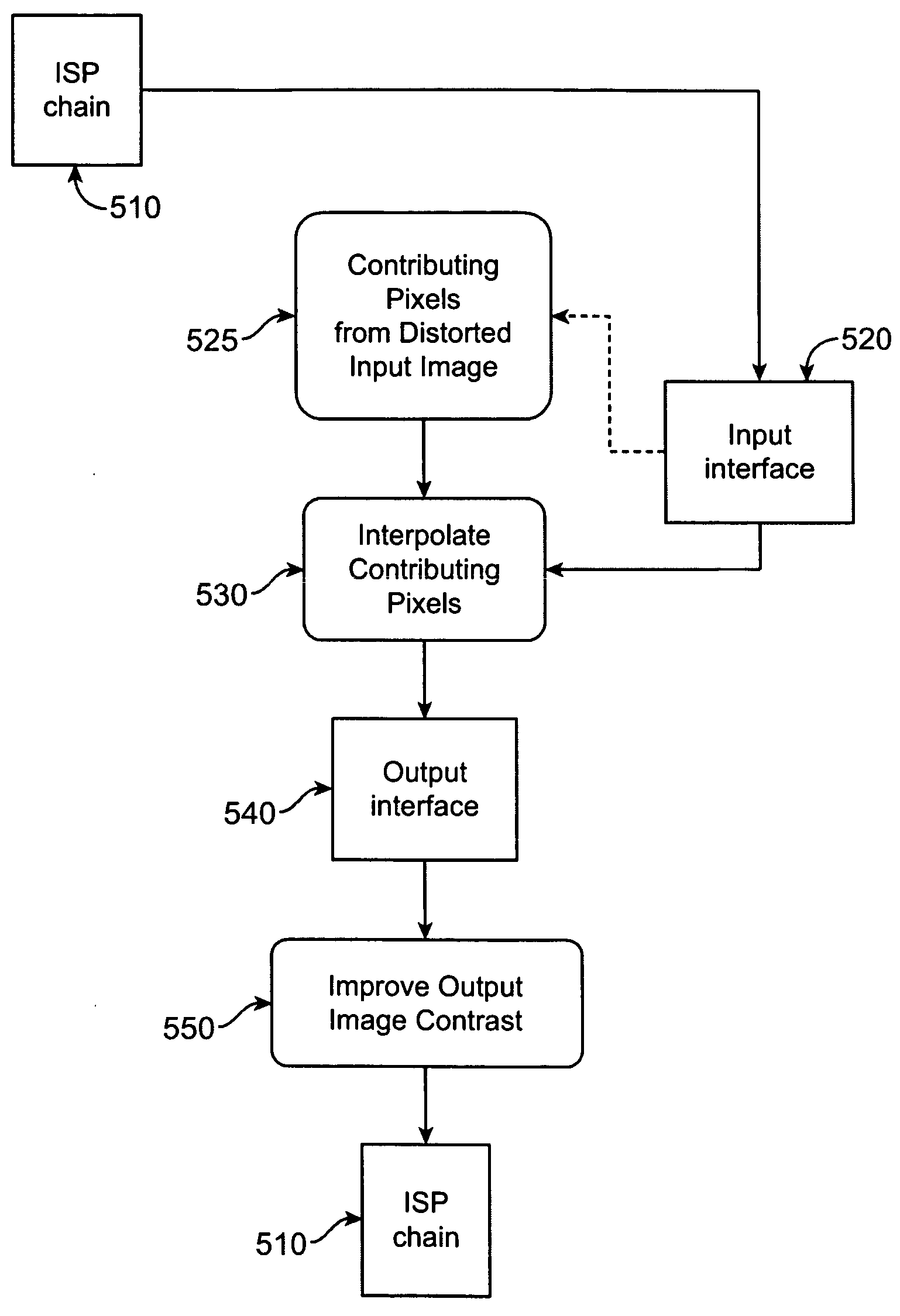
Imaging system with improved image quality and associated methods
InactiveUS20090115885A1Reduce resolutionIncrease the areaTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionImaging quality
An image capturing device may include a detector including a plurality of sensing pixels, and an optical system adapted to project a distorted image of an object within a field of view onto the sensing pixels, wherein the optical system expands the image in a center of the field of view and compresses the image in a periphery of the field of view, wherein a first number of sensing pixels required to realize a maximal zoom magnification {circumflex over (Z)} at a minimum resolution of the image capturing device is less than a square of the maximal zoom magnification times a second number of sensing pixels required for the minimum resolution.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS EURO
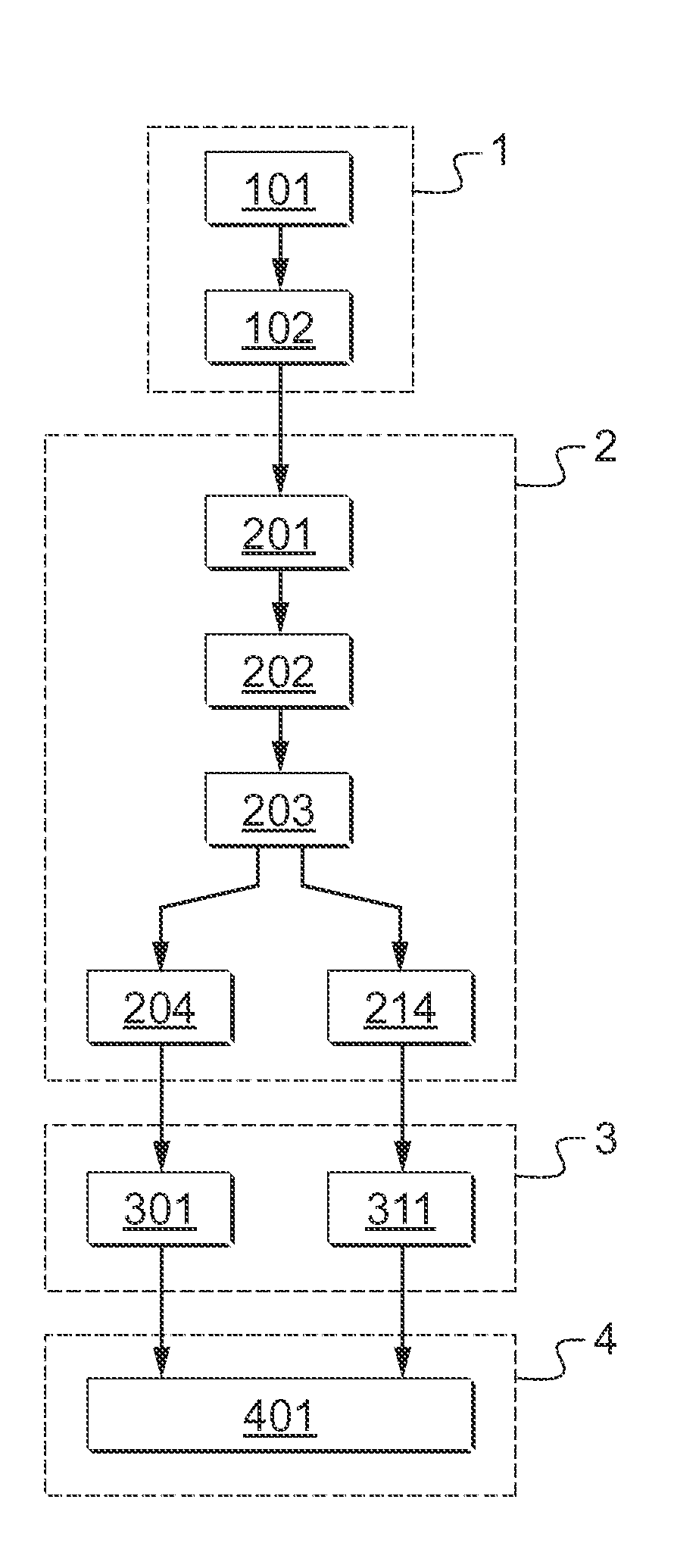
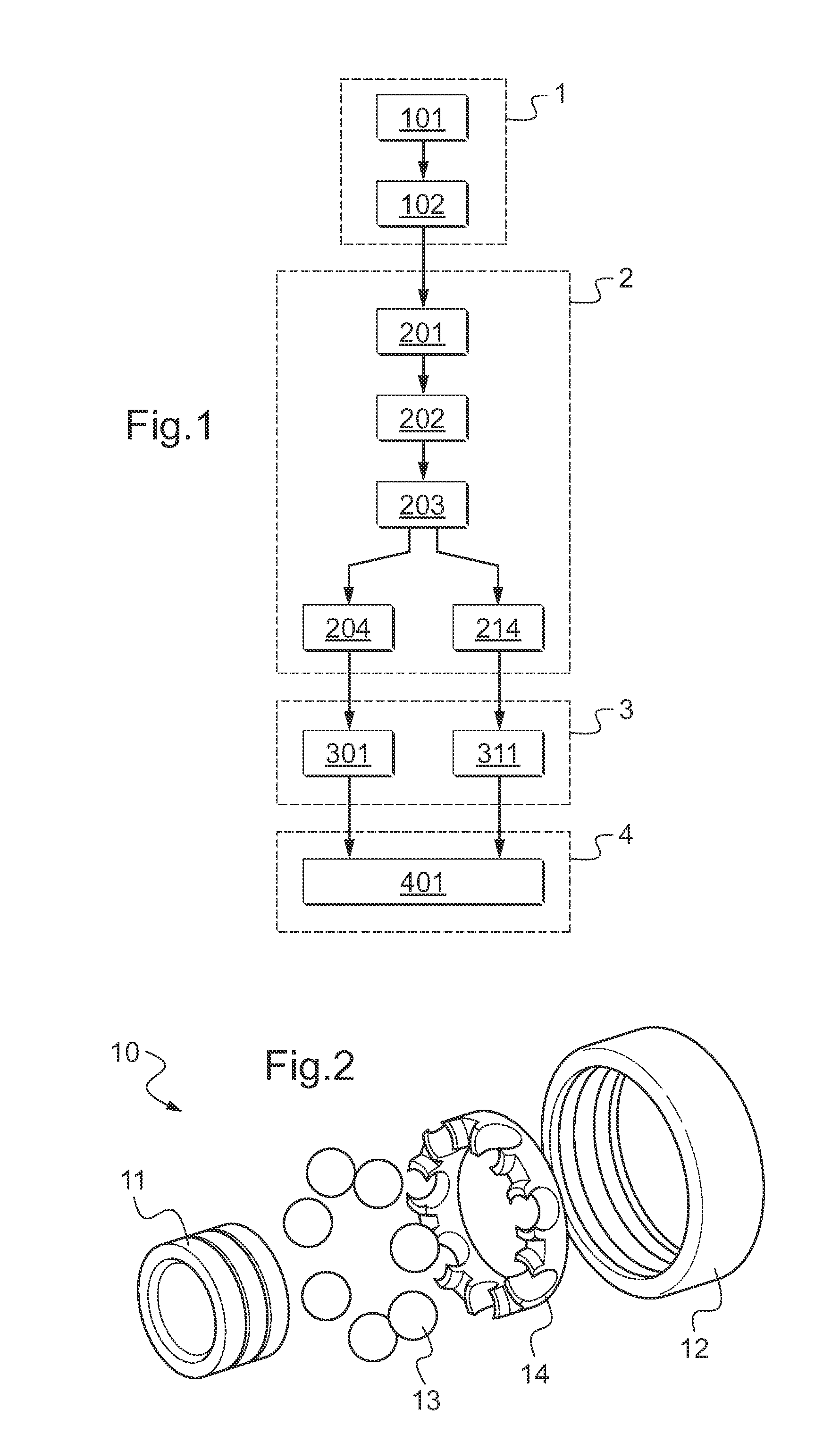
Method of detecting defects of a rolling bearing by vibration analysis
A method of detecting defects in a rolling bearing (10). The method includes acquiring a time-domain vibration signal An; filtering said time-domain vibration signal An; and then resolving it to obtain a deterministic time-domain vibration signal Fn and a random time-domain vibration signal Gn. Thereafter, the time-domain vibration signals Fn and Gn are transformed respectively into a deterministic frequency-domain vibration signal Jn and into a random frequency-domain vibration signal Kn, and then, for each element (11, 12, 13) and for each frequency-domain vibration signal Jn, Kn, a defect-presence frequency {circumflex over (α)} is determined corresponding to a maximum probability of the presence of a defect in said element (11, 12, 13) and to an associated reliability level p({circumflex over (α)}). An alert message indicating at least one defect in at least one element (11, 12, 13) is potentially delivered depending on the values of each defect-presence frequency {circumflex over (α)} and on each associated reliability level p({circumflex over (α)}).
Owner:EUROCOPTER
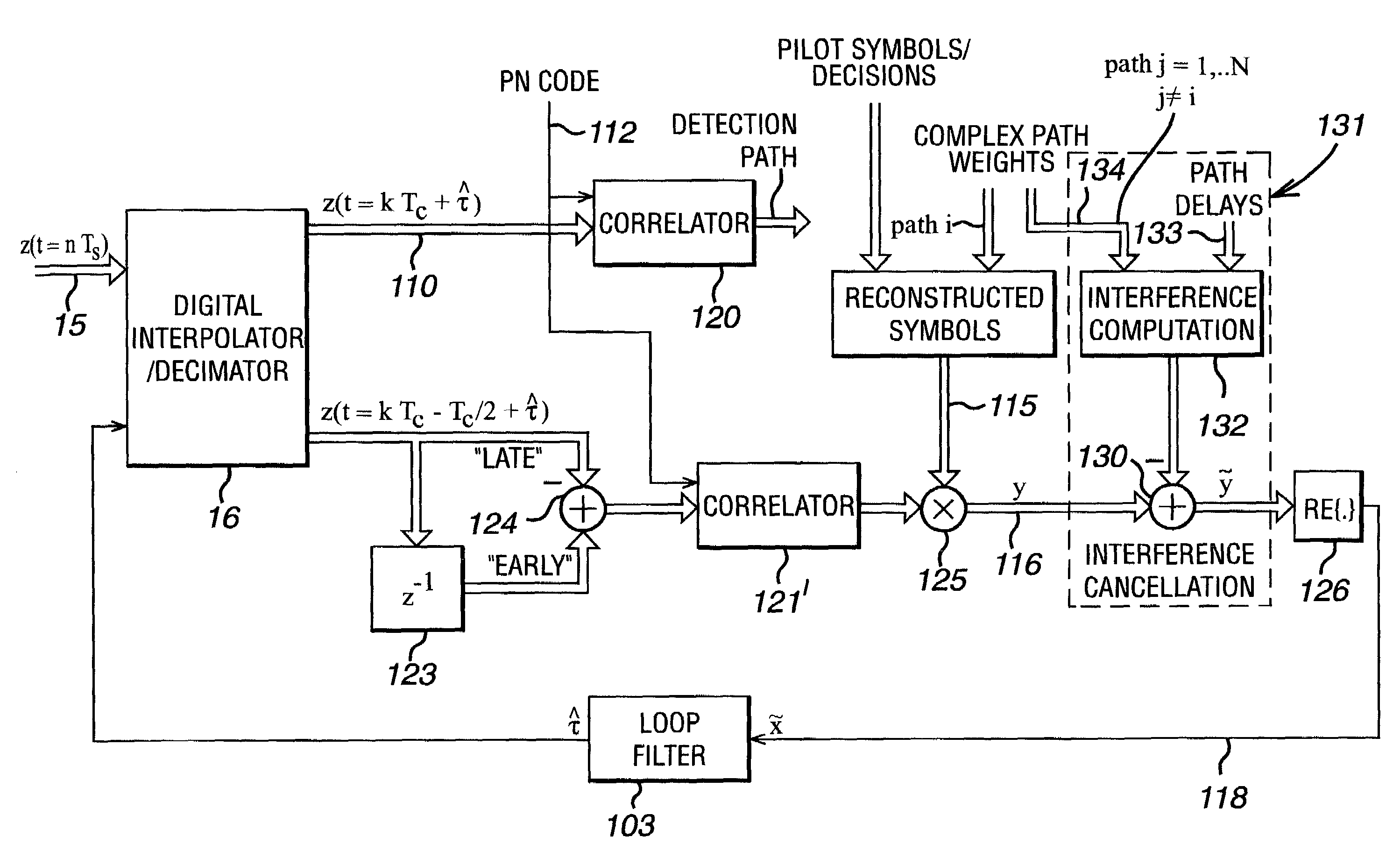
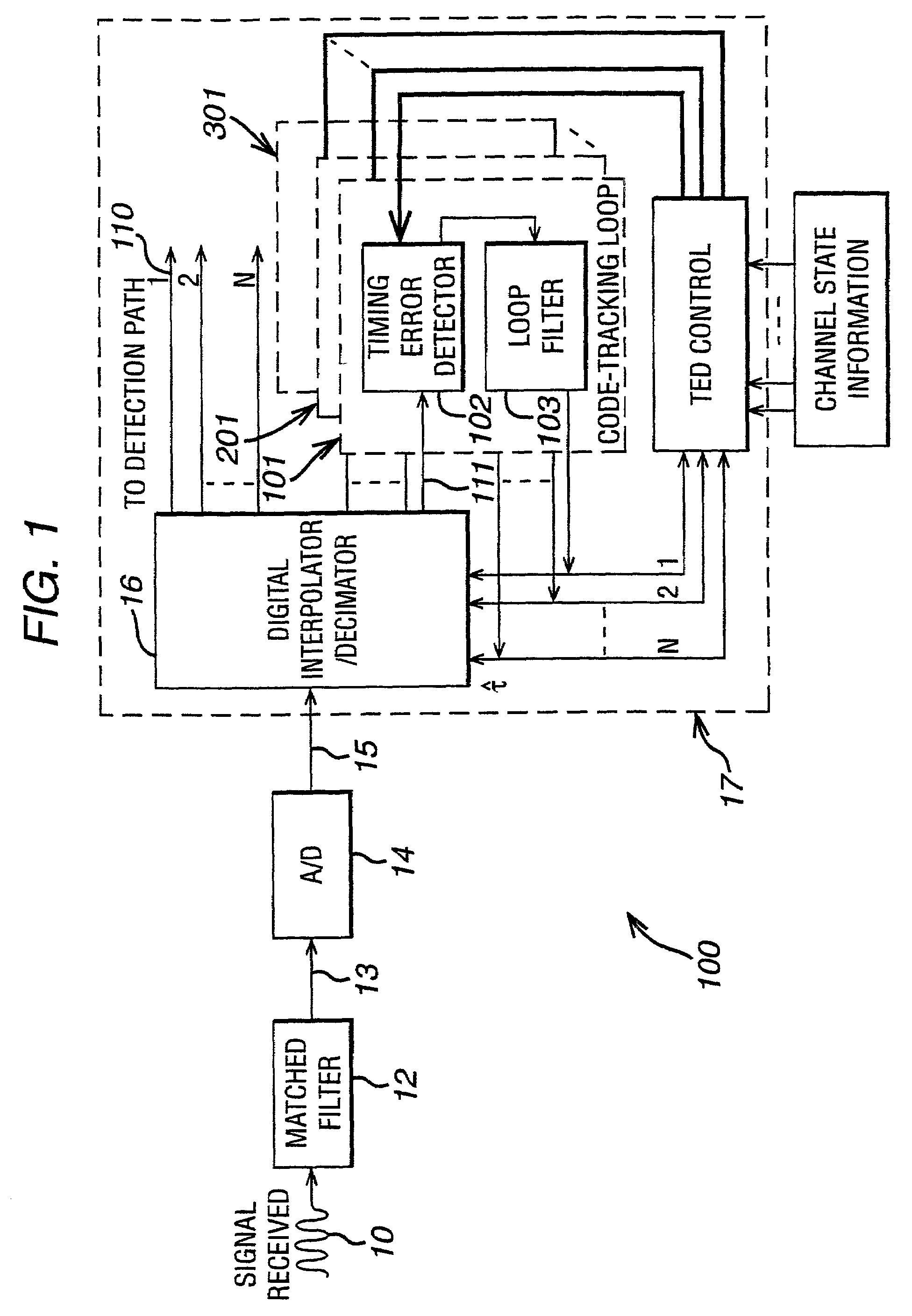
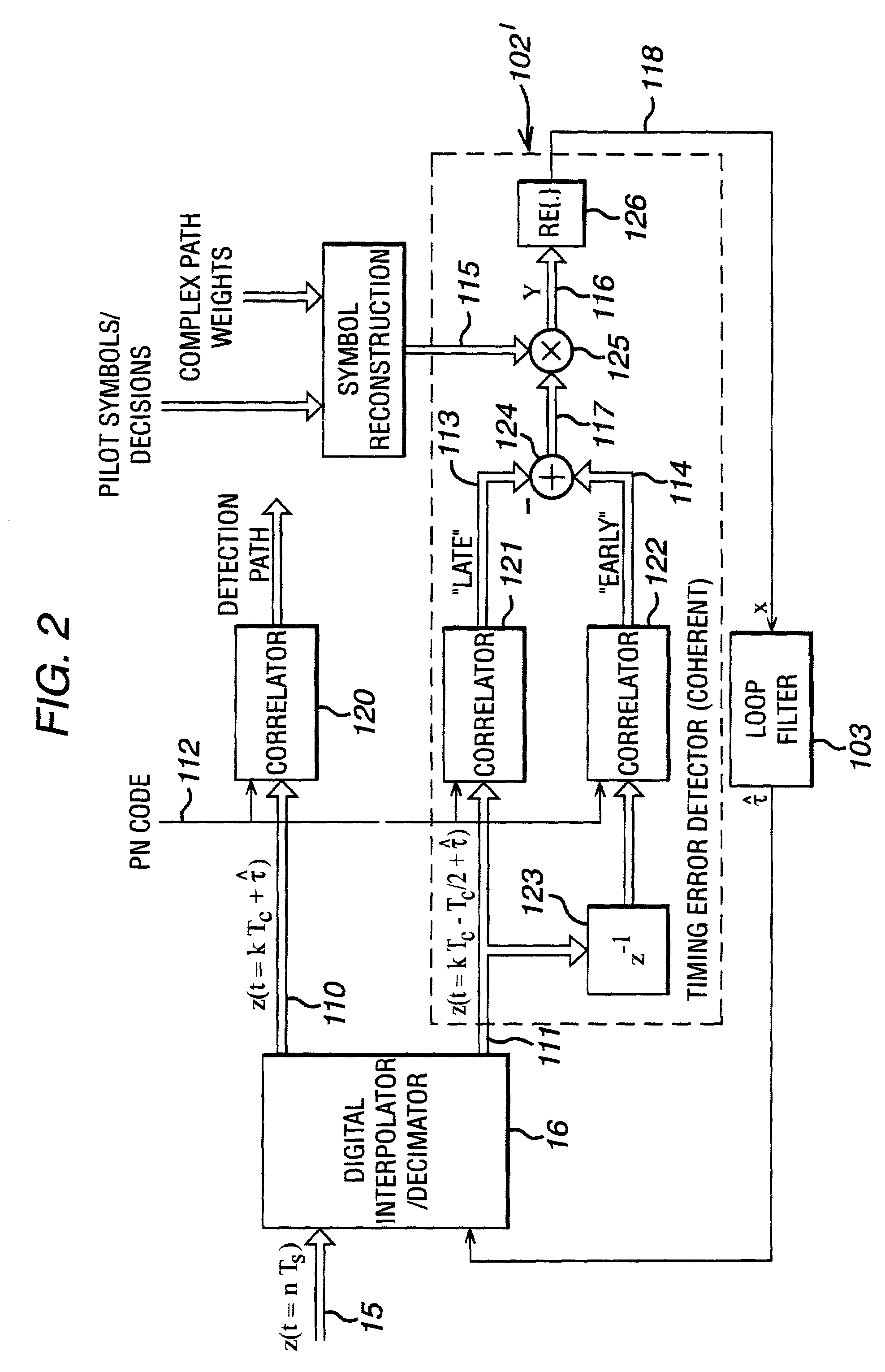
Method and rake receiver for code-tracking in communication systems
InactiveUS7203220B2Reduce distractionsHigh sensitivity to multipath fadingTransmissionPhase shiftedCommunications system
The invention relates to a code-tracking method and a rake receiver for CDMA communication systems of low complexity yielding stable tracking. Received signal are distributed to a plurality of receiver fingers of a rake receiver. Each receiver finger i is assigned to a signal path of the transmitted signal which is subject to phase shift and power dissipation due to reflection, diffraction and scattering. According to the invention in each receiver finger i an estimation of the timing delay {circumflex over (τ)}(i) is provided and interference from other signal components j are subtracted from signal components of the current signal path i (i≠j) yielding a reliable estimated timing delay {circumflex over (τ)}.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
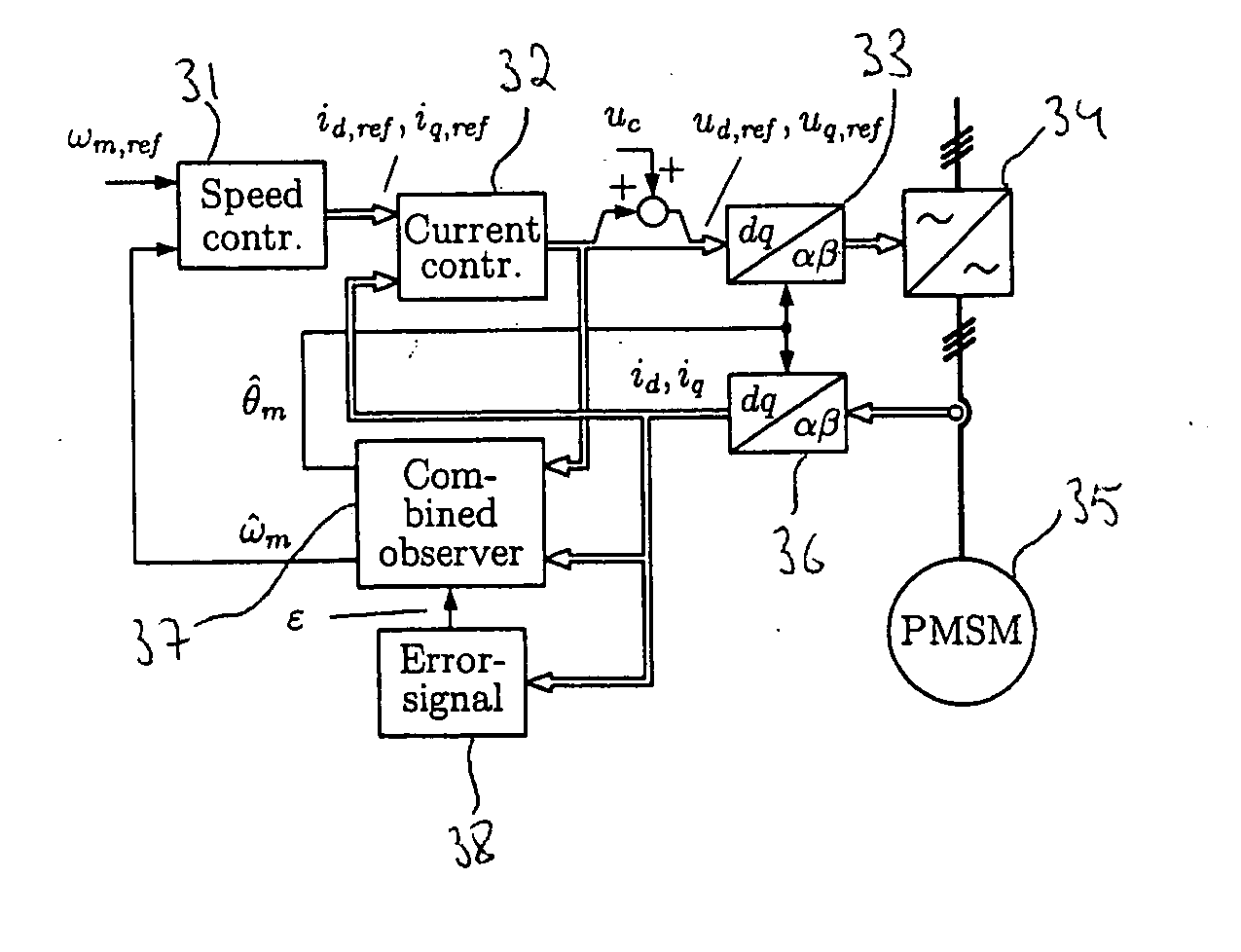
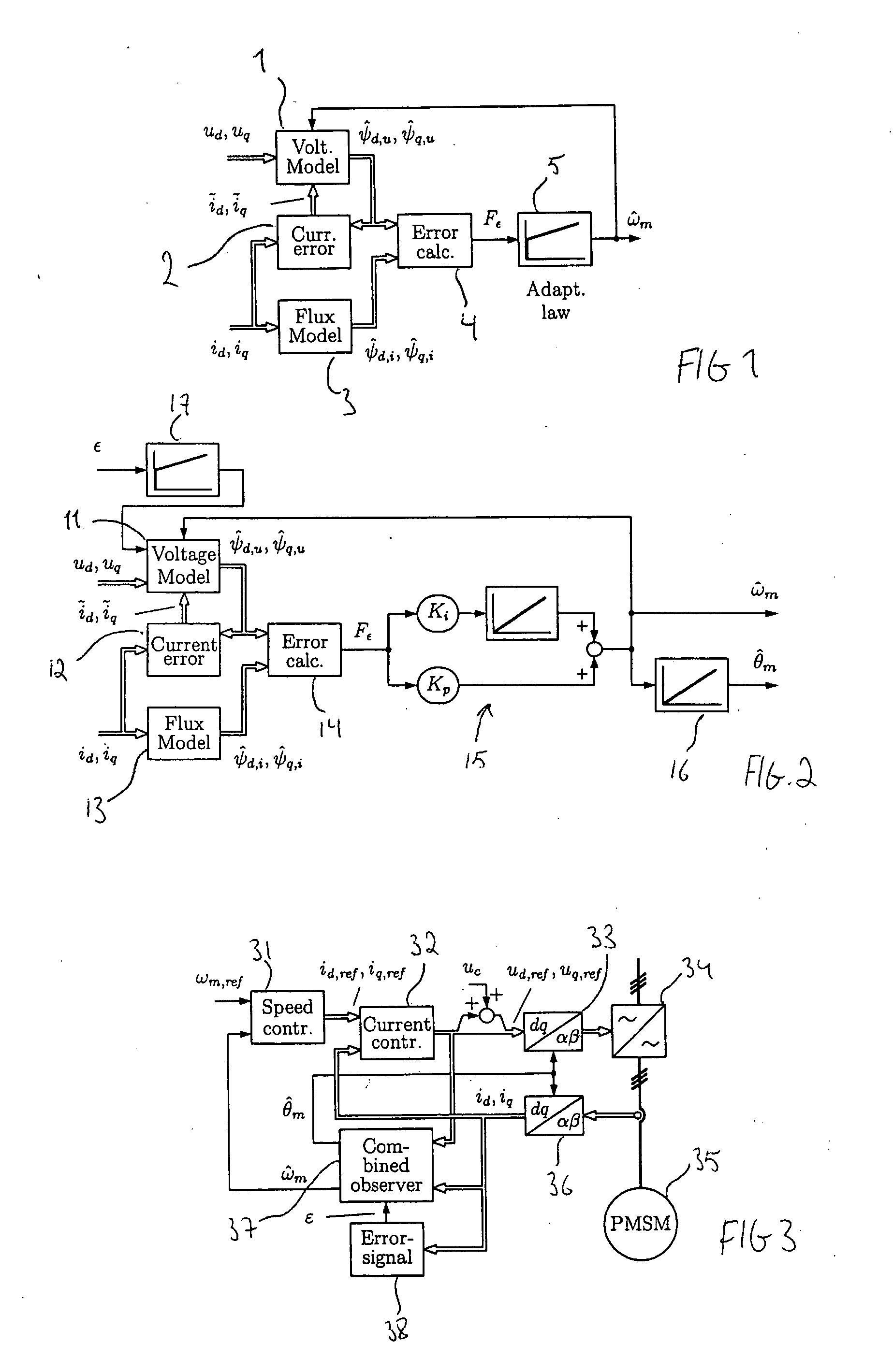
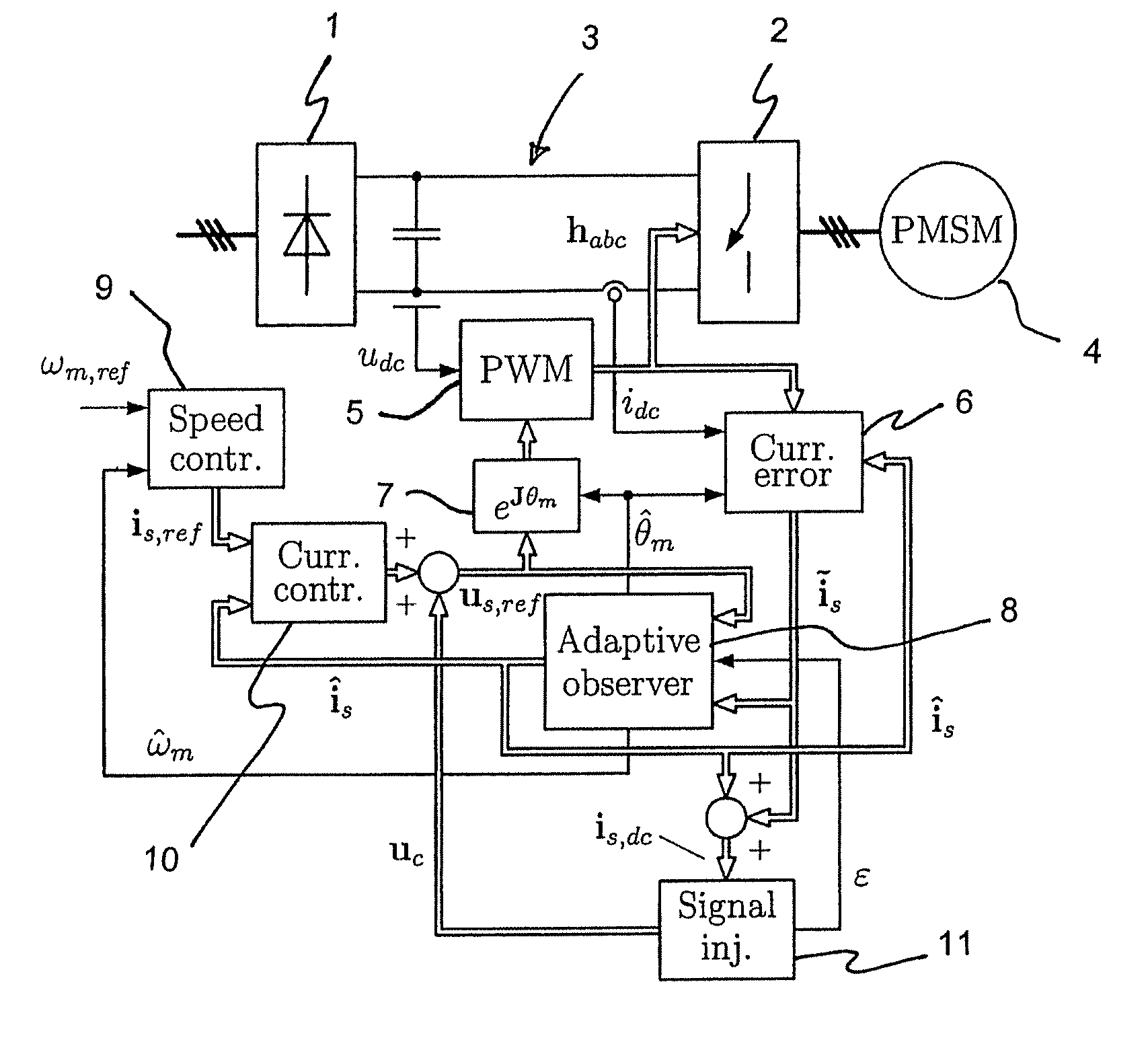
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS20060091847A1Small speedSmall position estimation errorSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
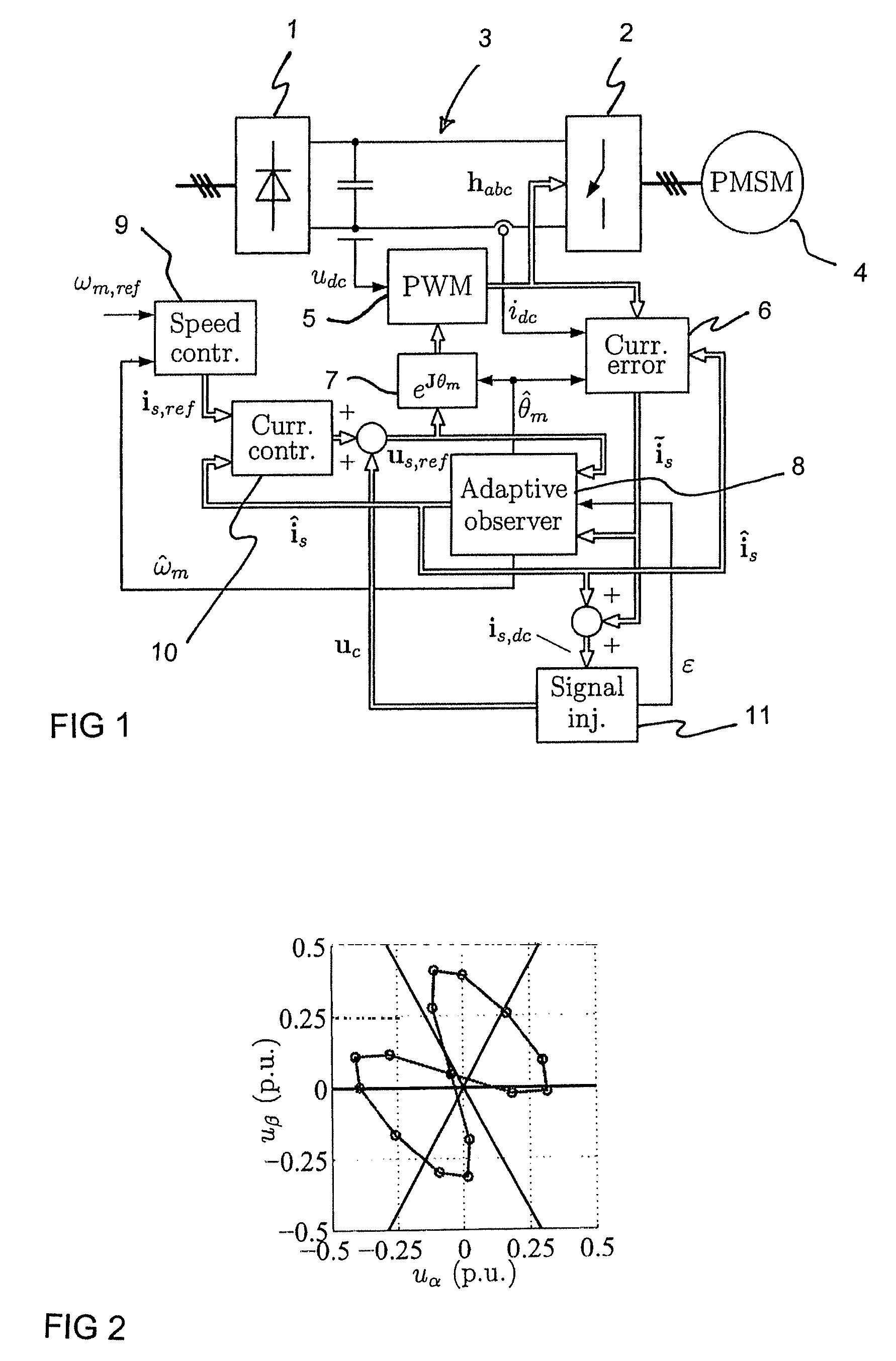
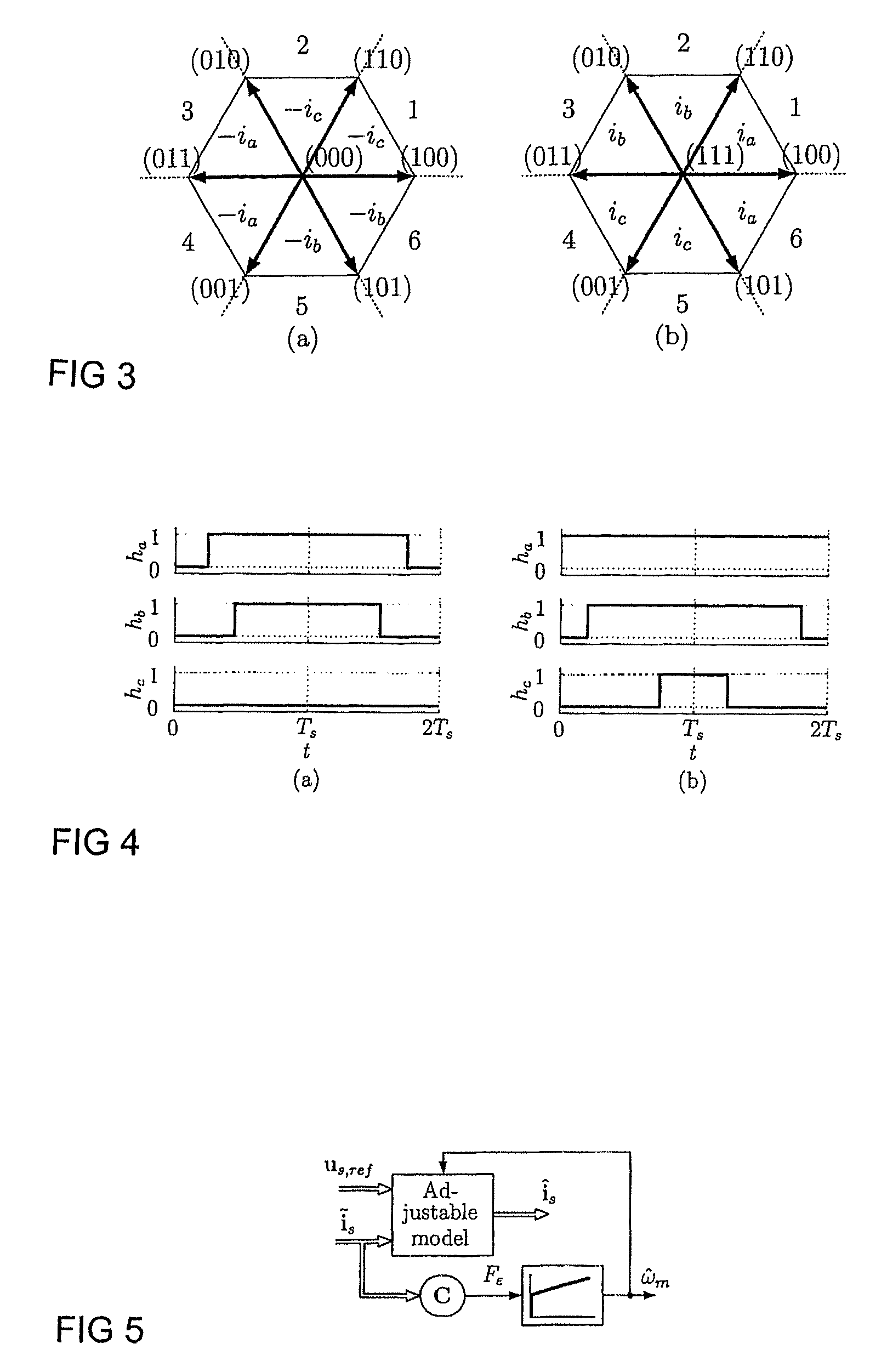
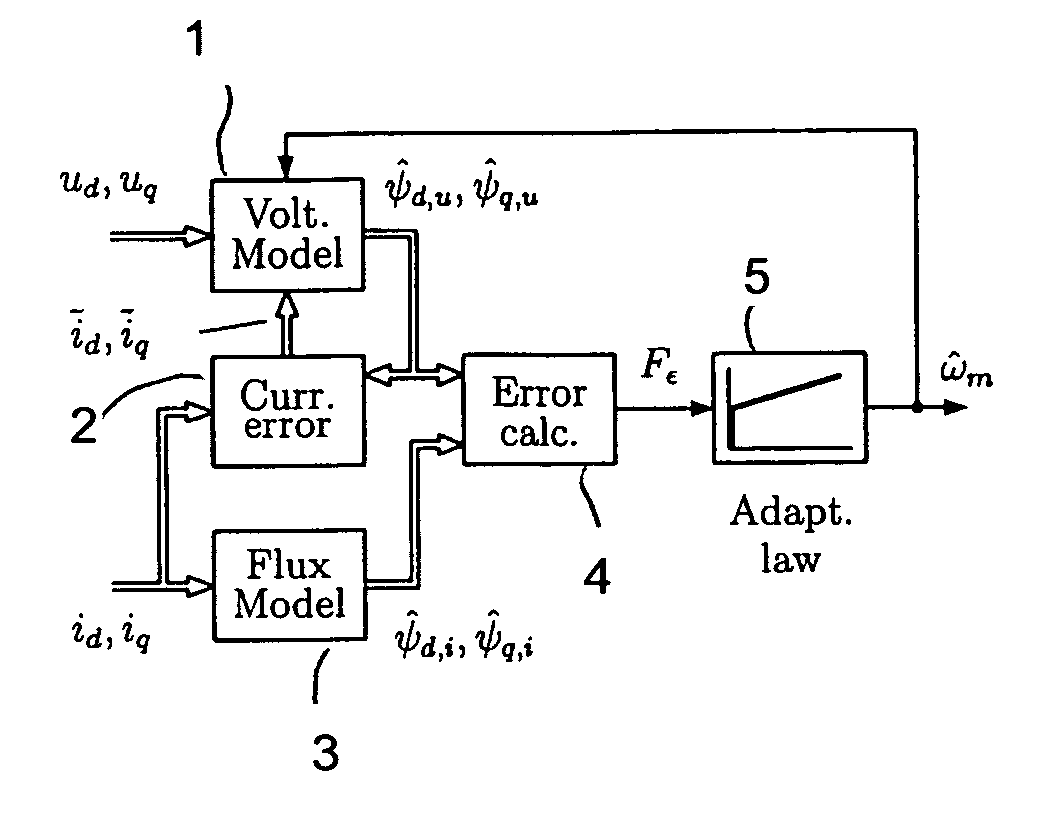
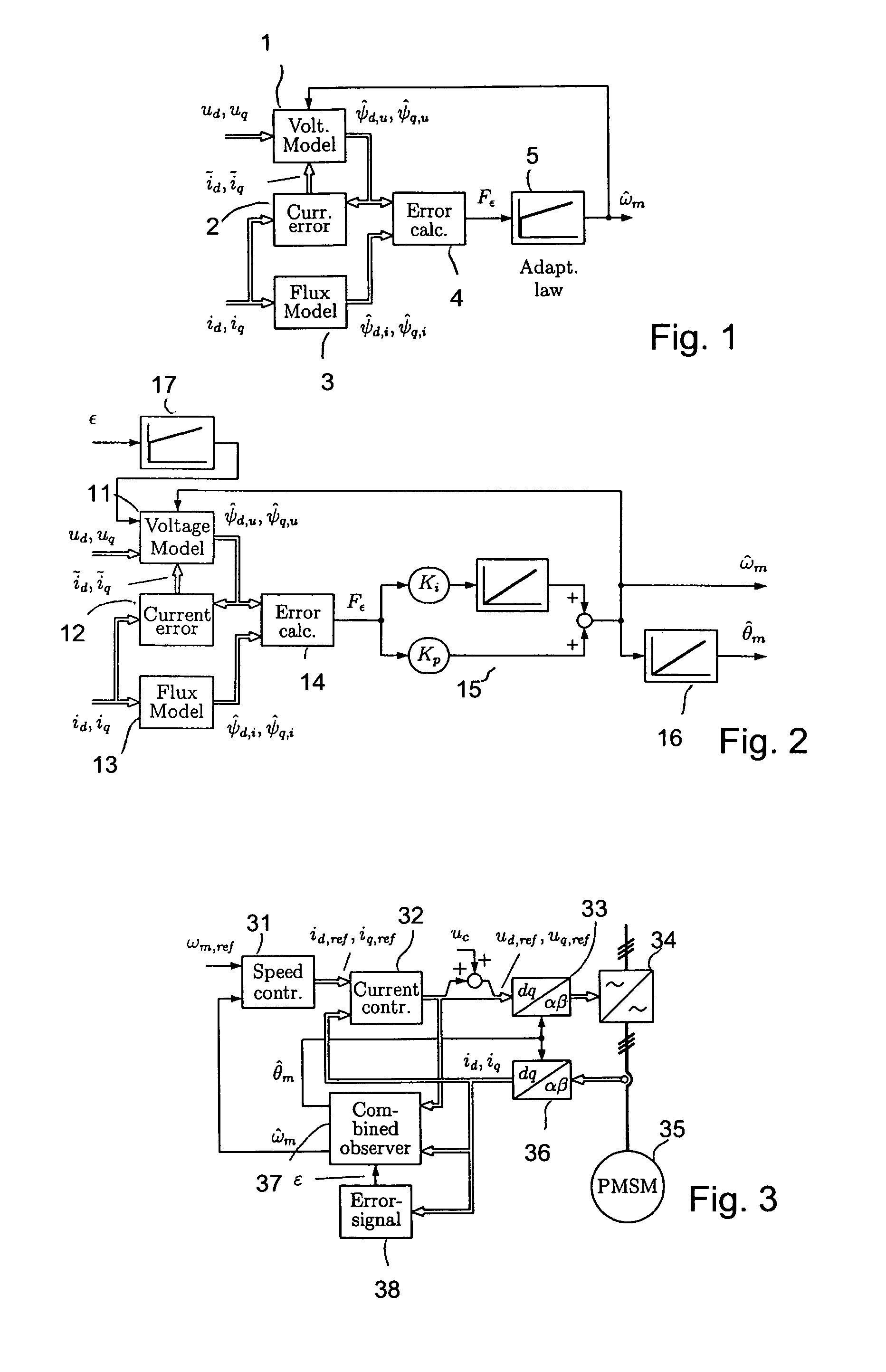
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
Imaging system with multi-state zoom and associated methods
An image capturing device may include a detector including a plurality of sensing pixels, and an optical system adapted to project a distorted image of an object within a field of view onto the sensing pixels, wherein the optical system expands the image in a center of the field of view and compresses the image in a periphery of the field of view, wherein a first number of sensing pixels required to realize a maximal zoom magnification {circumflex over (Z)} at a minimum resolution of the image capturing device is less than a square of the maximal zoom magnification times a second number of sensing pixels required for the minimum resolution.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS EURO
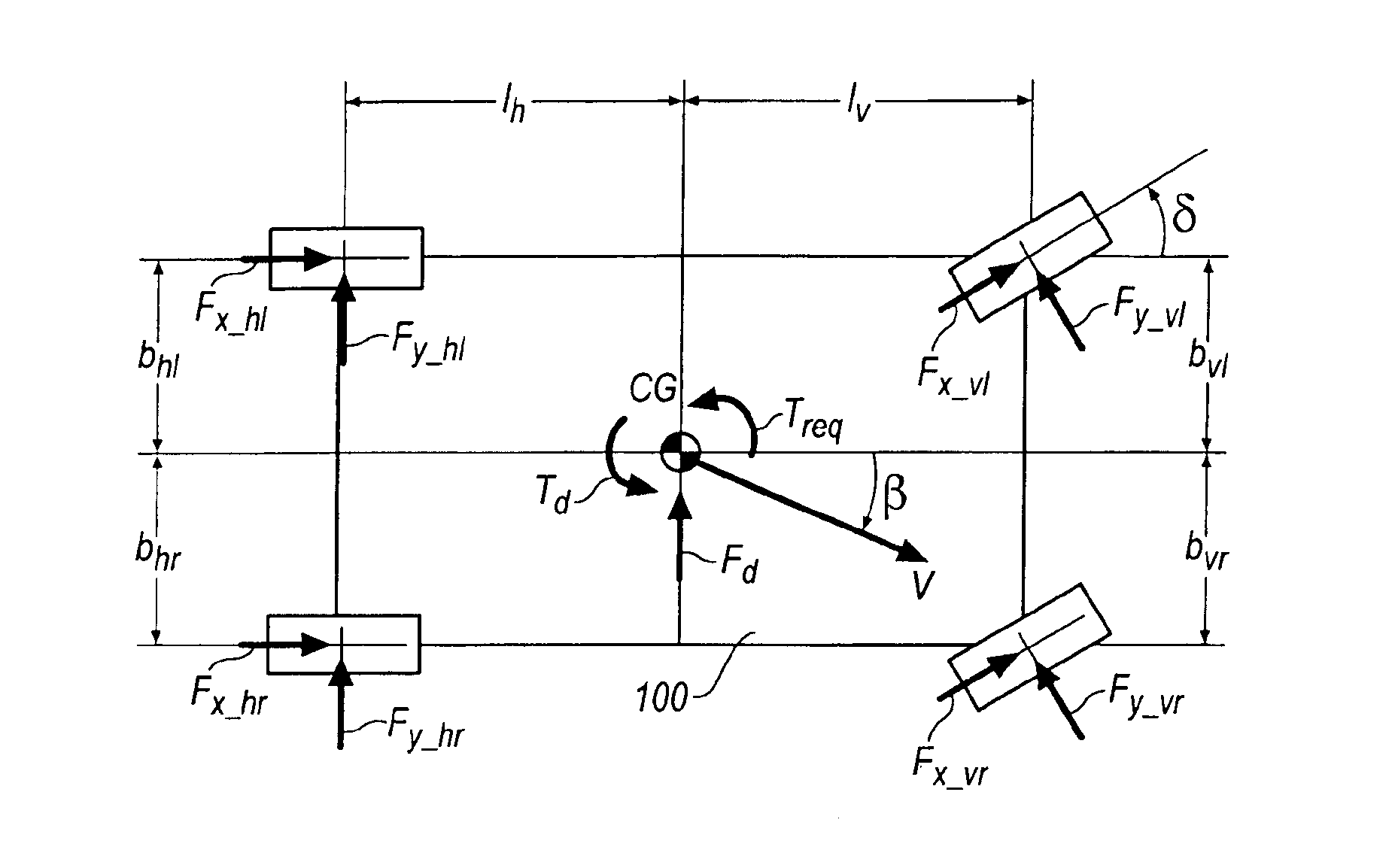
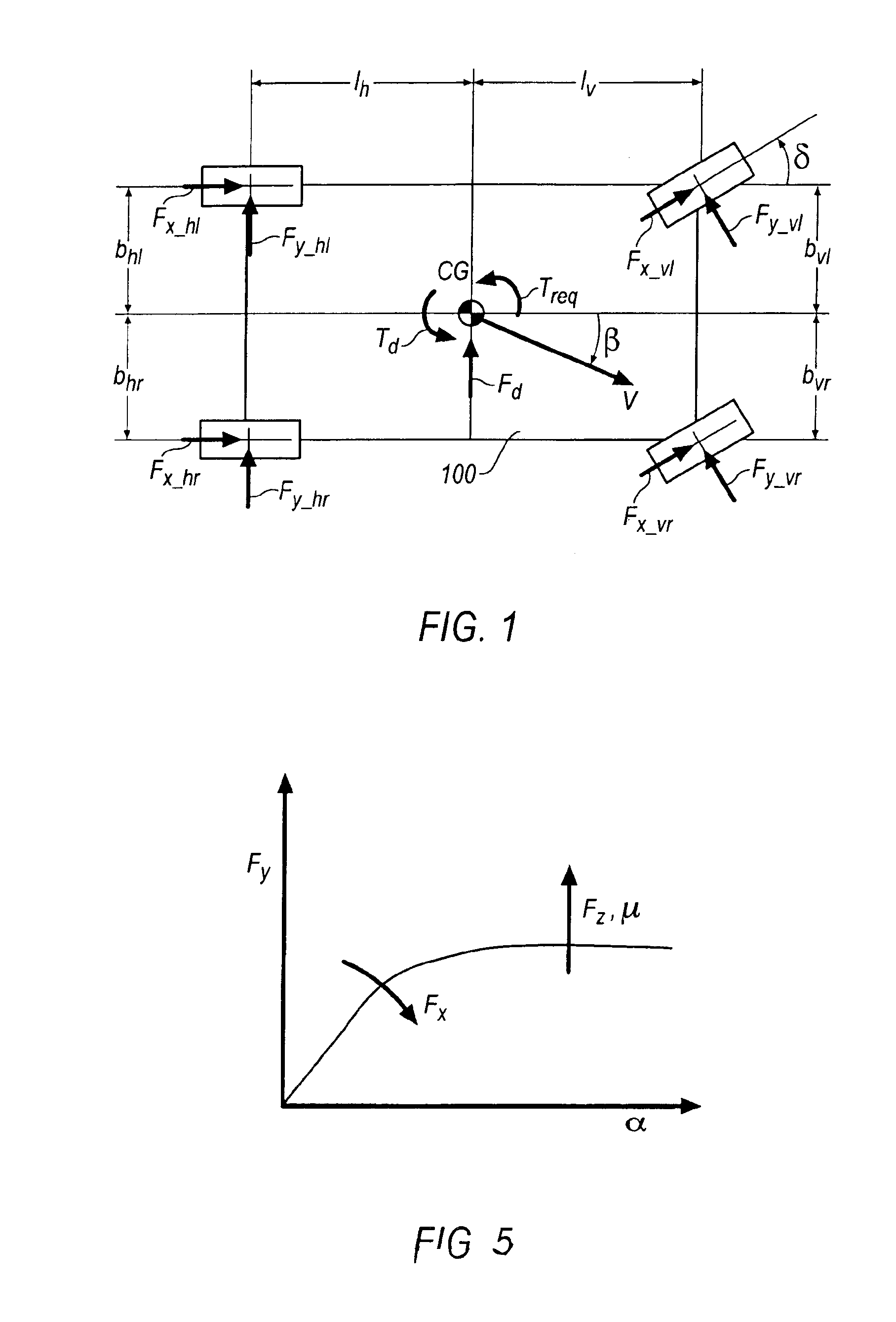
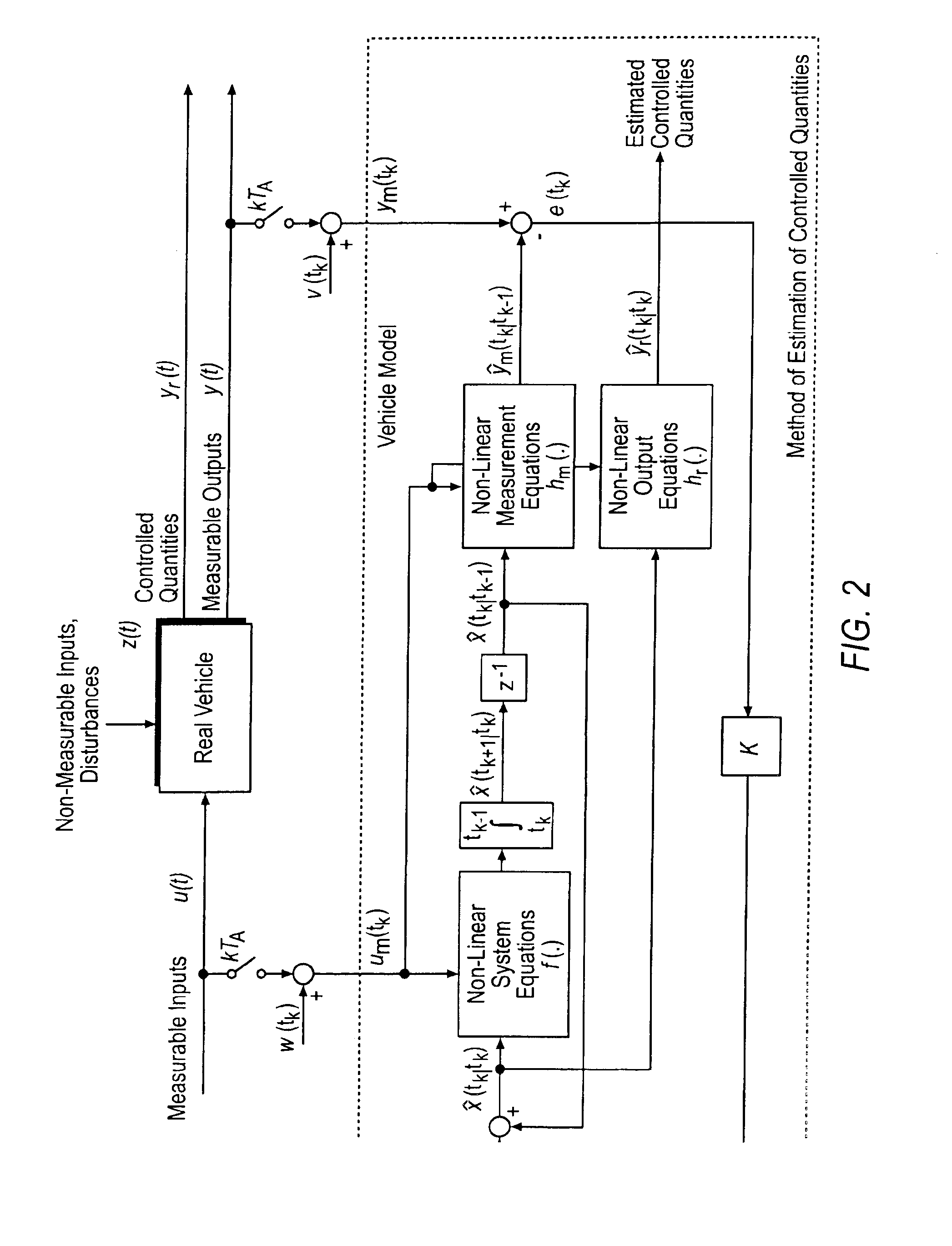
Method for determining the dynamics of vehicle movement
InactiveUS6954691B2Hand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleState variable
A method for the online determination of values of driving dynamics for a motor vehicle. To improve the quality of the control of a motor vehicle and to reduce the demands placed on the driver, the invention discloses a driving dynamics control including the (1) estimated output quantities ŷm in dependence on determined or estimated input quantities u and predetermined or predicted vehicle state variables {circumflex over (x)} and optionally further quantities, (2) comparing the estimated output quantities ŷm with measured output quantities ym, and (3) determining the estimated driving dynamics quantities {circumflex over (x)}(tk / tk) in dependence on the measurement result and, as the case may be, further criteria.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine
ActiveUS7759897B2Stabilize estimationGuaranteed uptimeSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltageFrequency changer
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine, when the permanent magnet synchronous machine is fed with a frequency converter, the method comprising the steps of forming a stator voltage reference for the permanent magnet synchronous machine, injecting a high frequency signal (uc) into the stator voltage reference, measuring a DC-link current (idc) of the frequency converter when the permanent magnet synchronous machine (4) is fed with a voltage (us,ref) corresponding to a sum of the stator voltage reference and the injected signal, calculating a stator current estimate (îs), calculating a current error (ĩs) as a difference between the stator current estimate and the measured DC-link current, and estimating a rotor speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) of the permanent synchronous machine based on the current error. The injected high frequency signal (uc) comprises a direct axis component and a quadrature axis component, the direct axis component having a first frequency and the quadrature axis component having a second frequency, the first and second frequencies being different.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS7098623B2Improve dynamic performanceSmaller positionSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
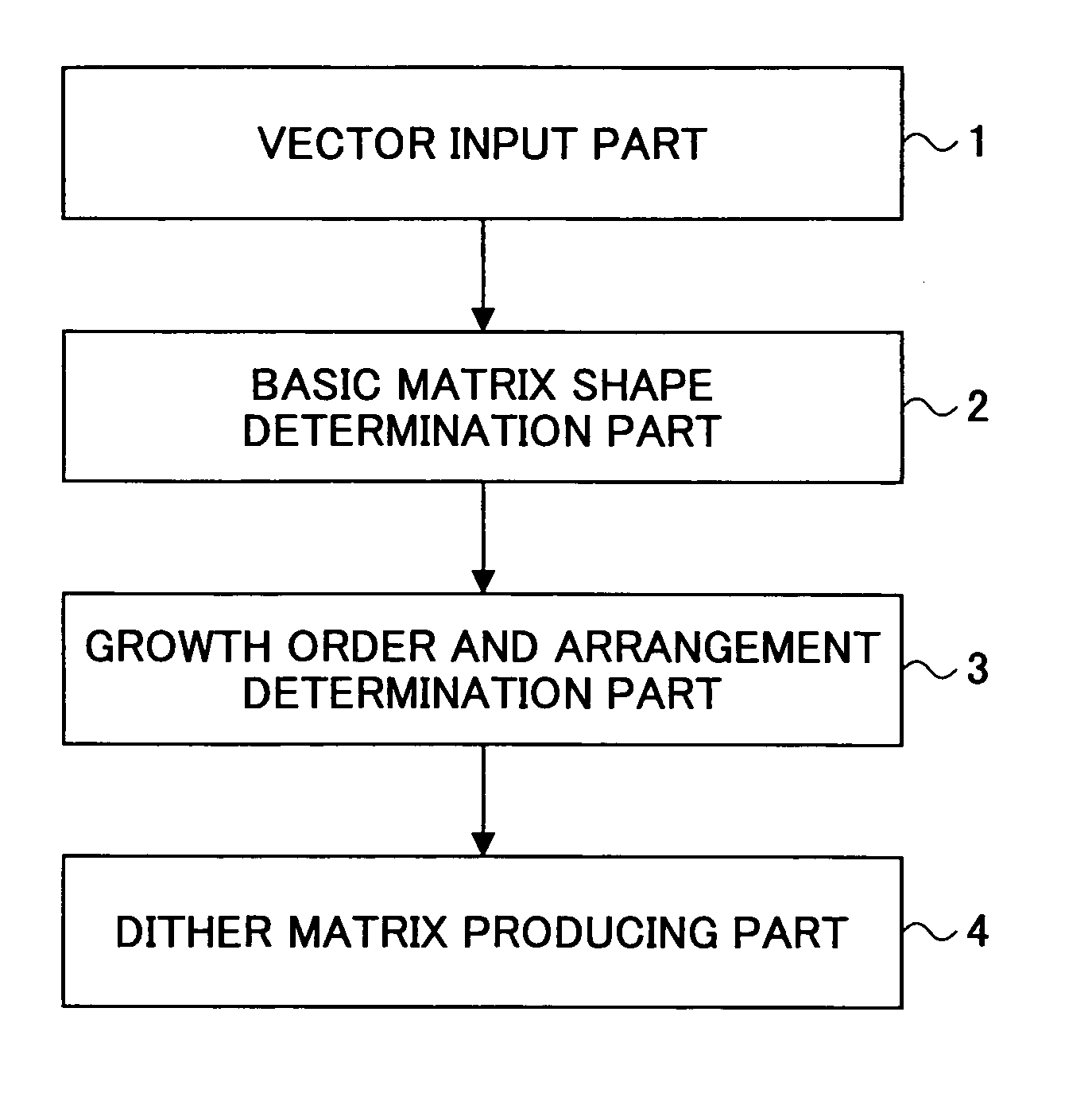
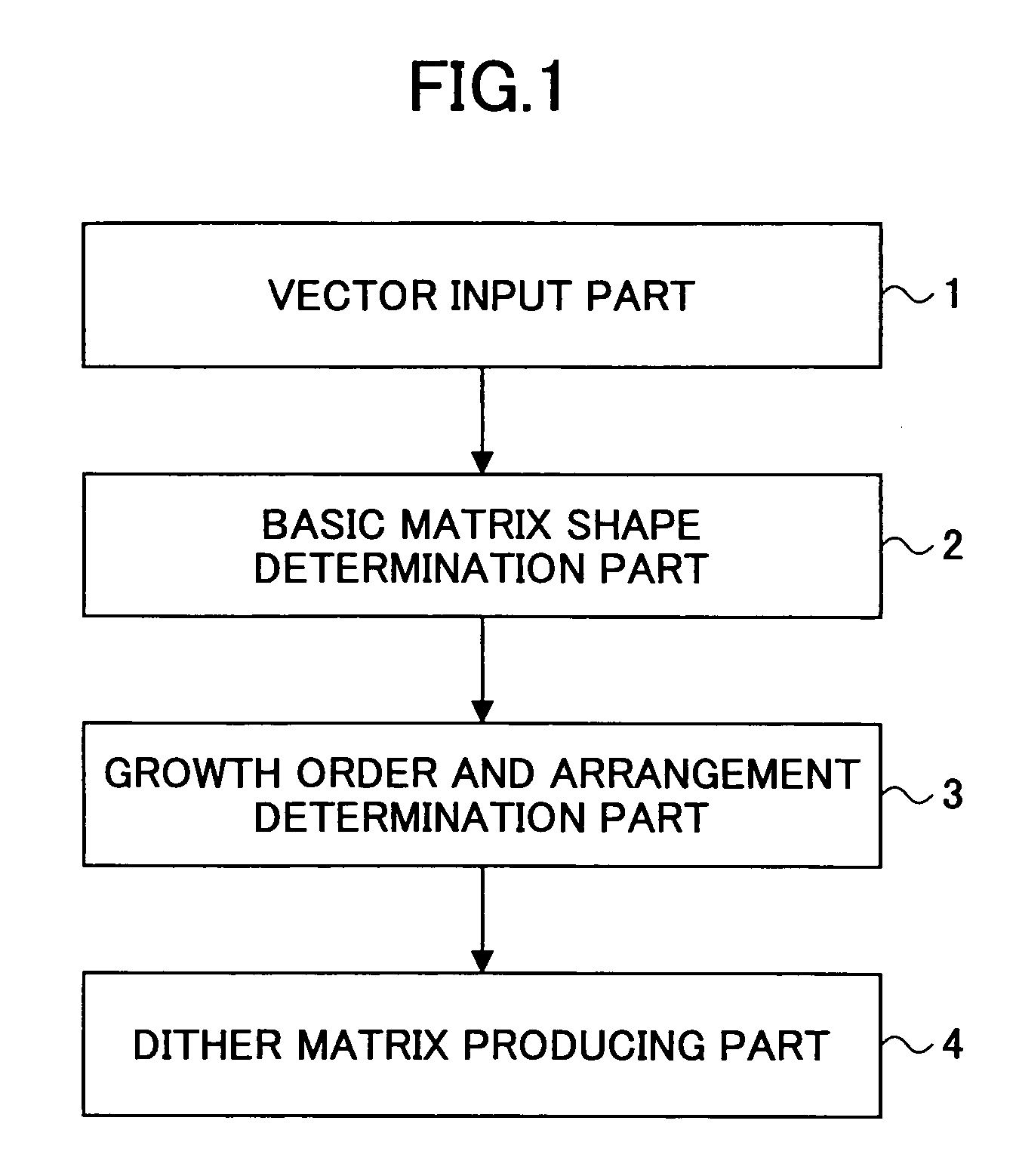
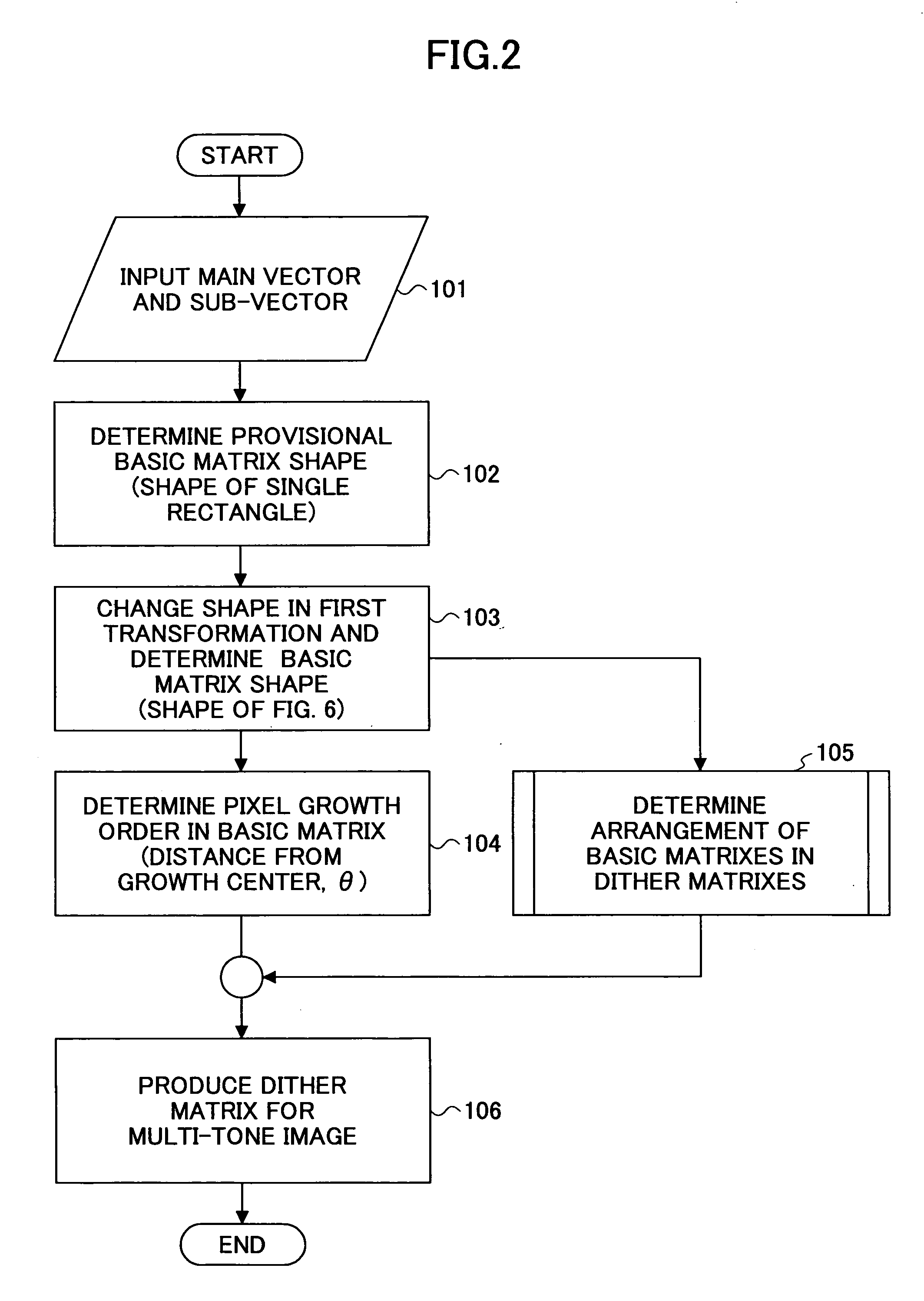
Dither matrix producing method and apparatus, image processing method and apparatus, image forming method and apparatus, program and recording medium
A main vector: m{circumflex over ( )}=(mx, my) and a sub-vector: s{circumflex over ( )}=(sx, sy) determining cyclic structure of a basic matrix are defined, and a positional vector for a pixel configuring the basic matrix Pi{circumflex over ( )}=(Pix, Piy) is defined, where the suffix i denotes an i-th pixel configuring the basic matrix. Then, the pixels configuring the basic matrix are arranged in such a manner as to satisfy the cyclic structure, and transformation of Pi{circumflex over ( )}→Pi{circumflex over ( )}+km{circumflex over ( )}+ls{circumflex over ( )} is carried out where k and l are arbitrary integers, and may be negative values. Then a new shape of the basic matrix is obtained with Pi{circumflex over ( )}+km{circumflex over ( )}+ls{circumflex over ( )} as a new pixel positional vector Pi{circumflex over ( )}.
Owner:RICOH KK
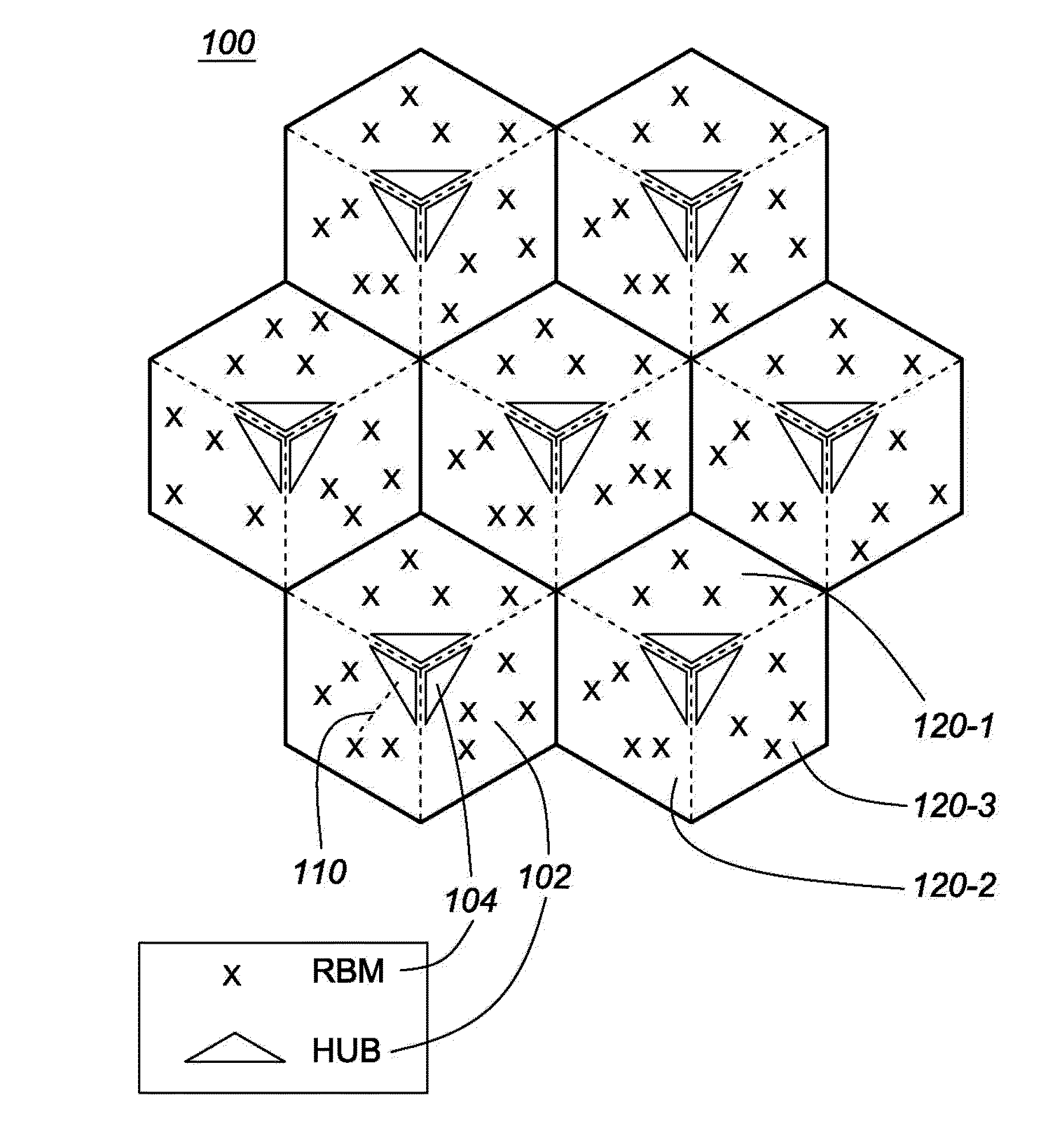
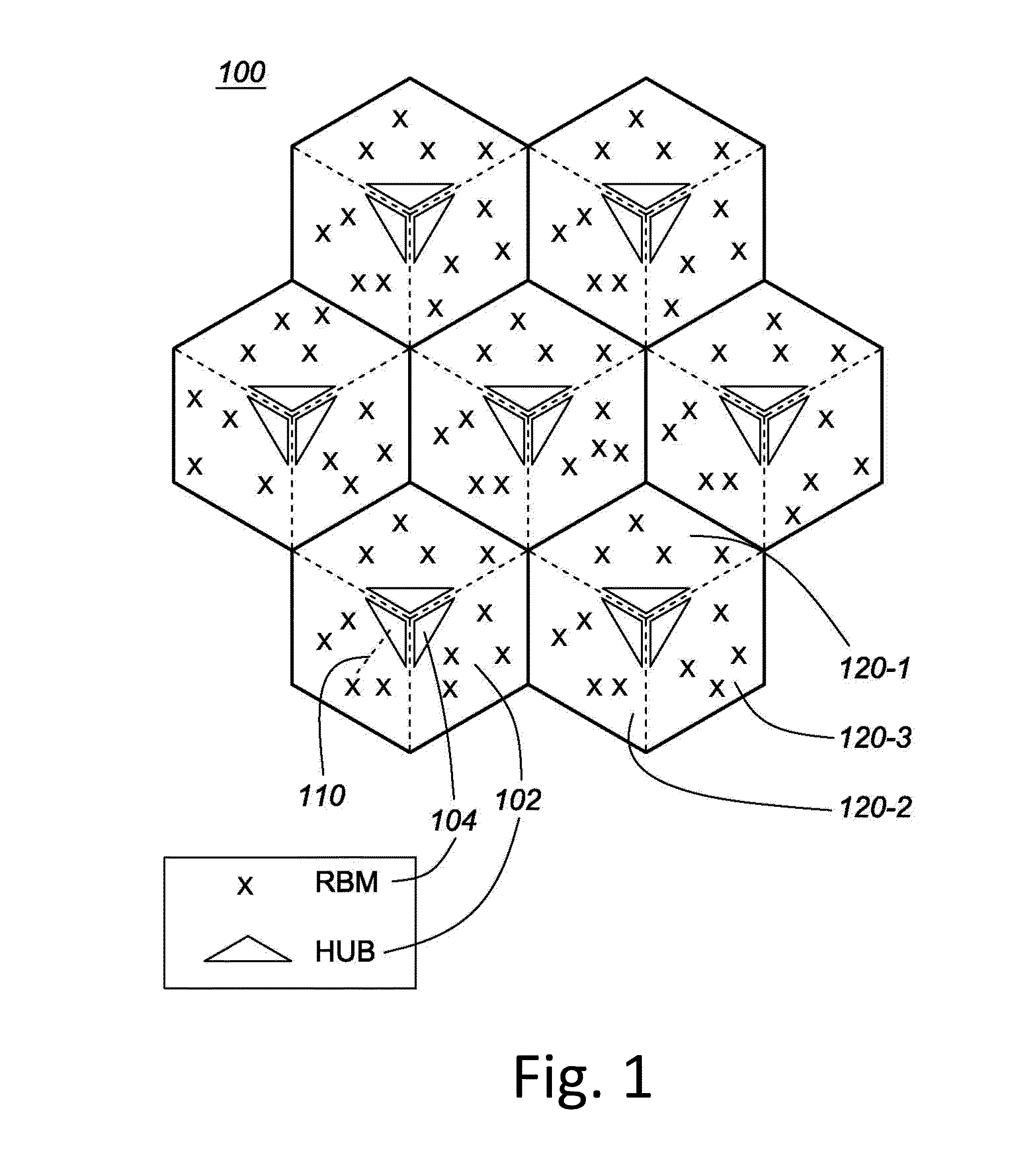
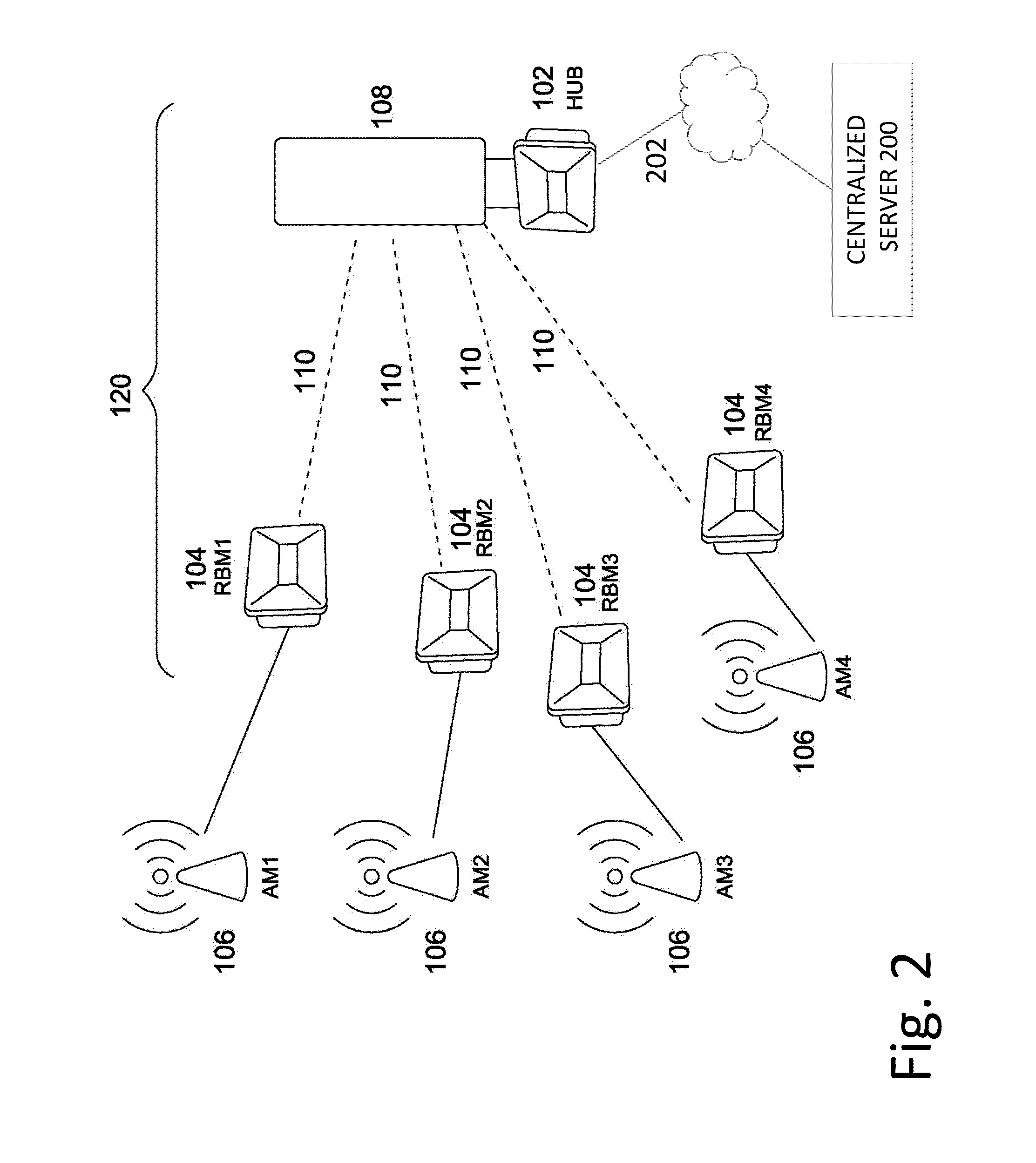
System and method for clock synchronization in a wireless backhaul network using IEEE 1588 precision time protocol
A method and system is disclosed for clock synchronization in a wireless backhaul network, based on the IEEE1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). The network comprises a plurality of hubs, each hub serving one or more remote backhaul modules. Each hub comprises a slave clock, which communicates with a master clock through forward and reverse links. The method comprises, for each hub, estimating the frequency drift {circumflex over (α)} and offset {circumflex over (β)} from the forward and reverse links between the master and slave clock, estimating the accuracy of {circumflex over (α)} and {circumflex over (β)}, determining the least congested link, and adjusting the frequency of the slave clock based on {circumflex over (α)} and {circumflex over (β)} from the least congested link. A fixed or variable time window size is selected to achieve a desired accuracy of {circumflex over (α)} and {circumflex over (β)}. The method may comprise estimating a maximum holdover time for maintaining synchronization with a desired confidence level.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
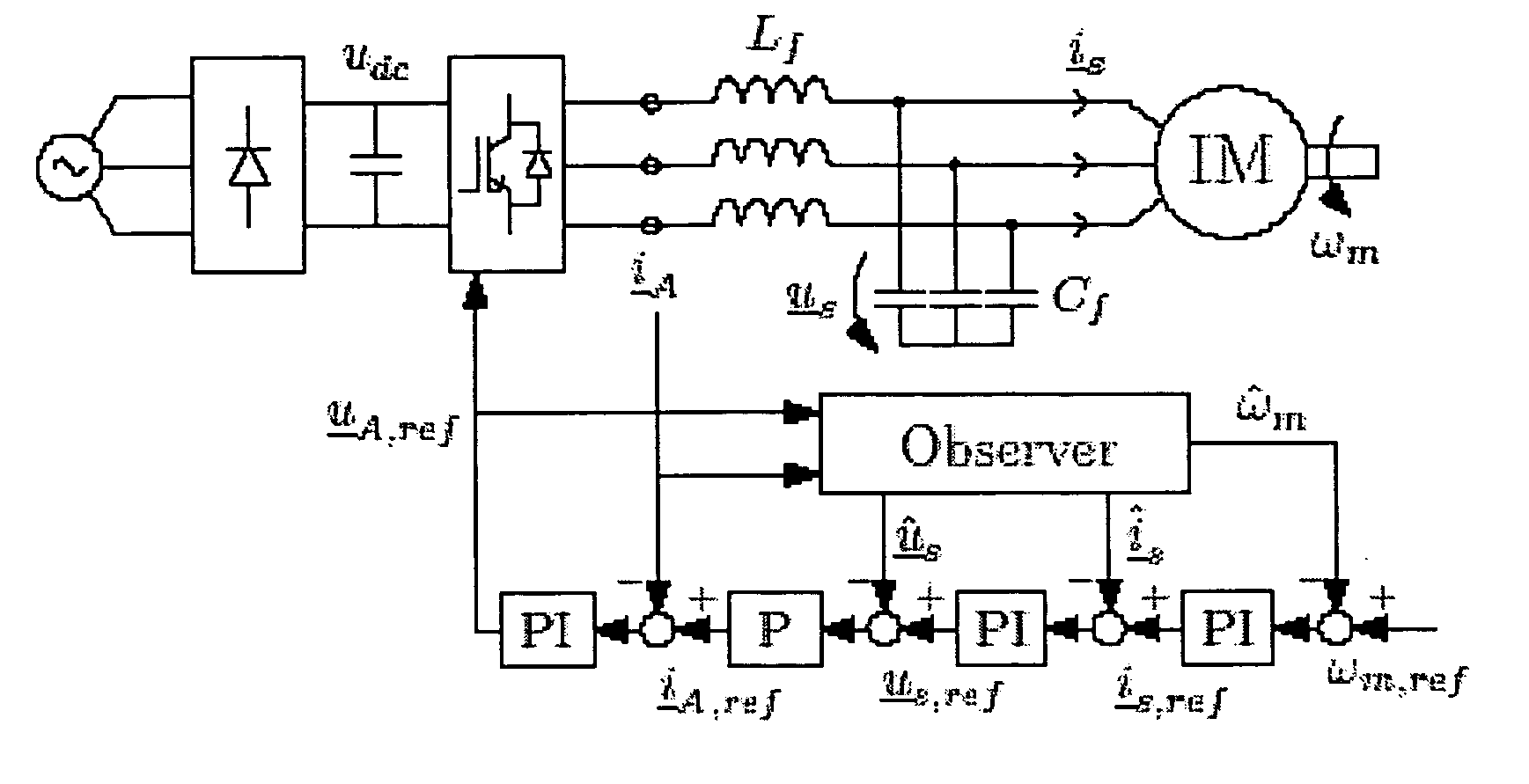
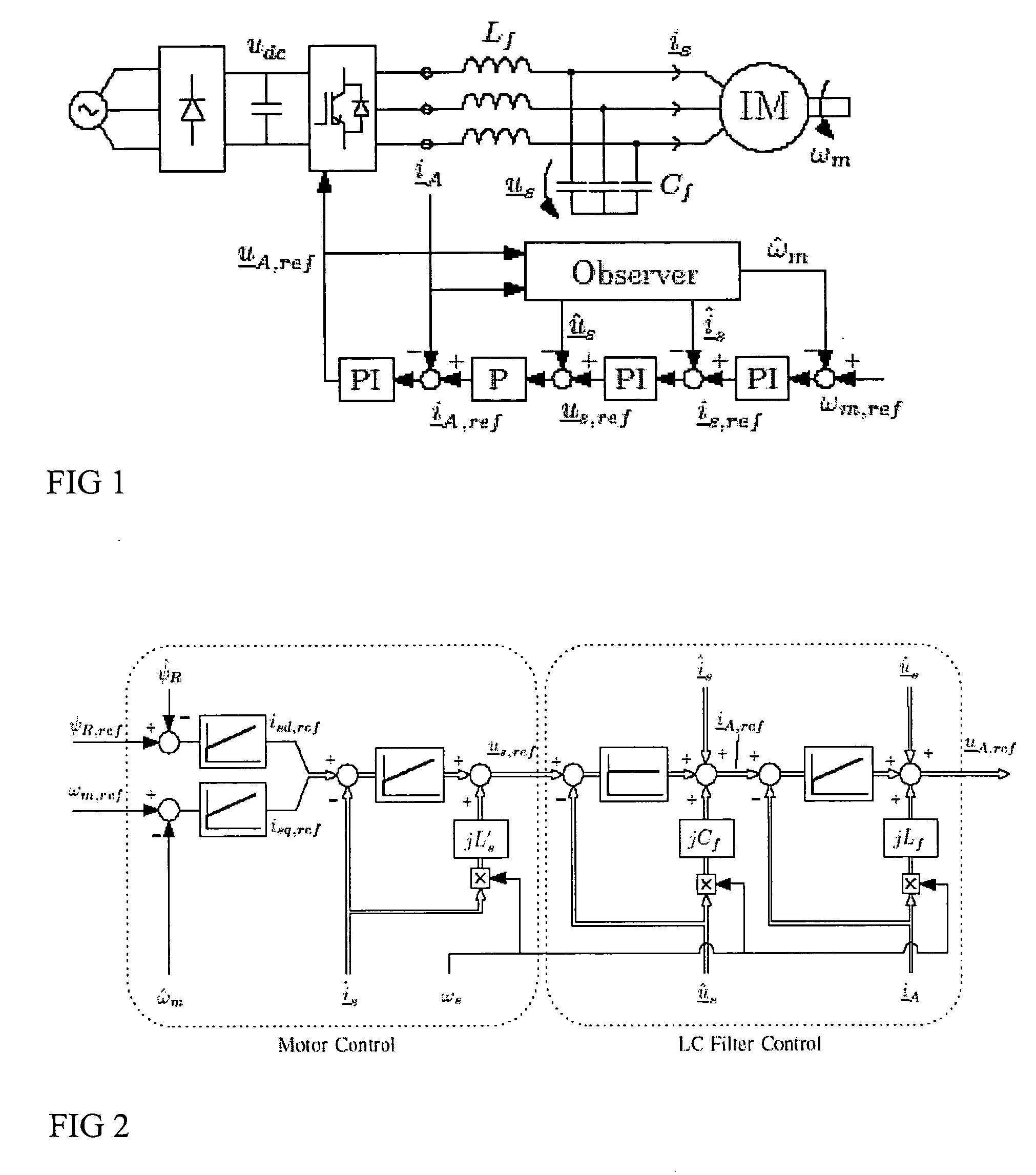
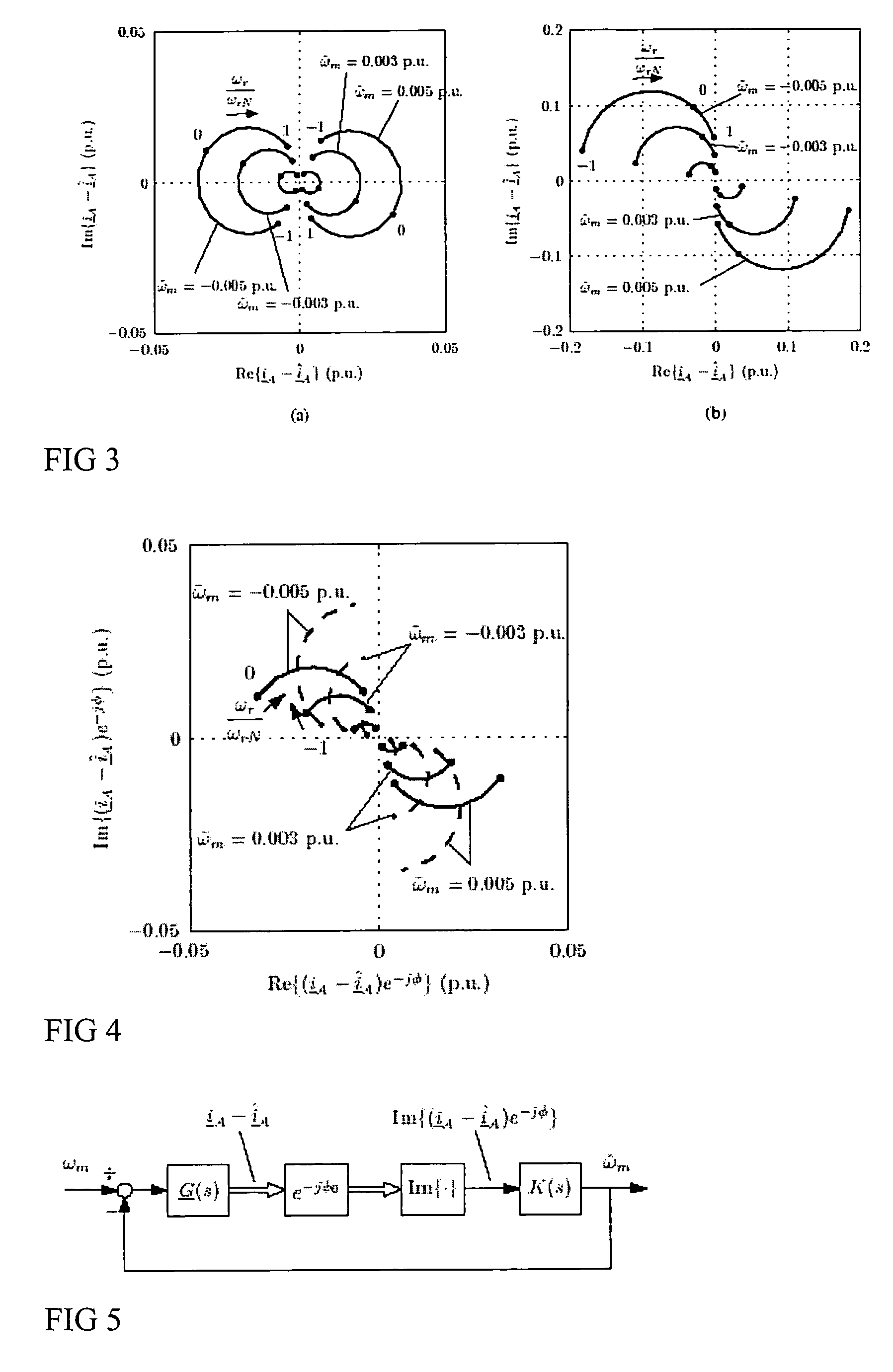
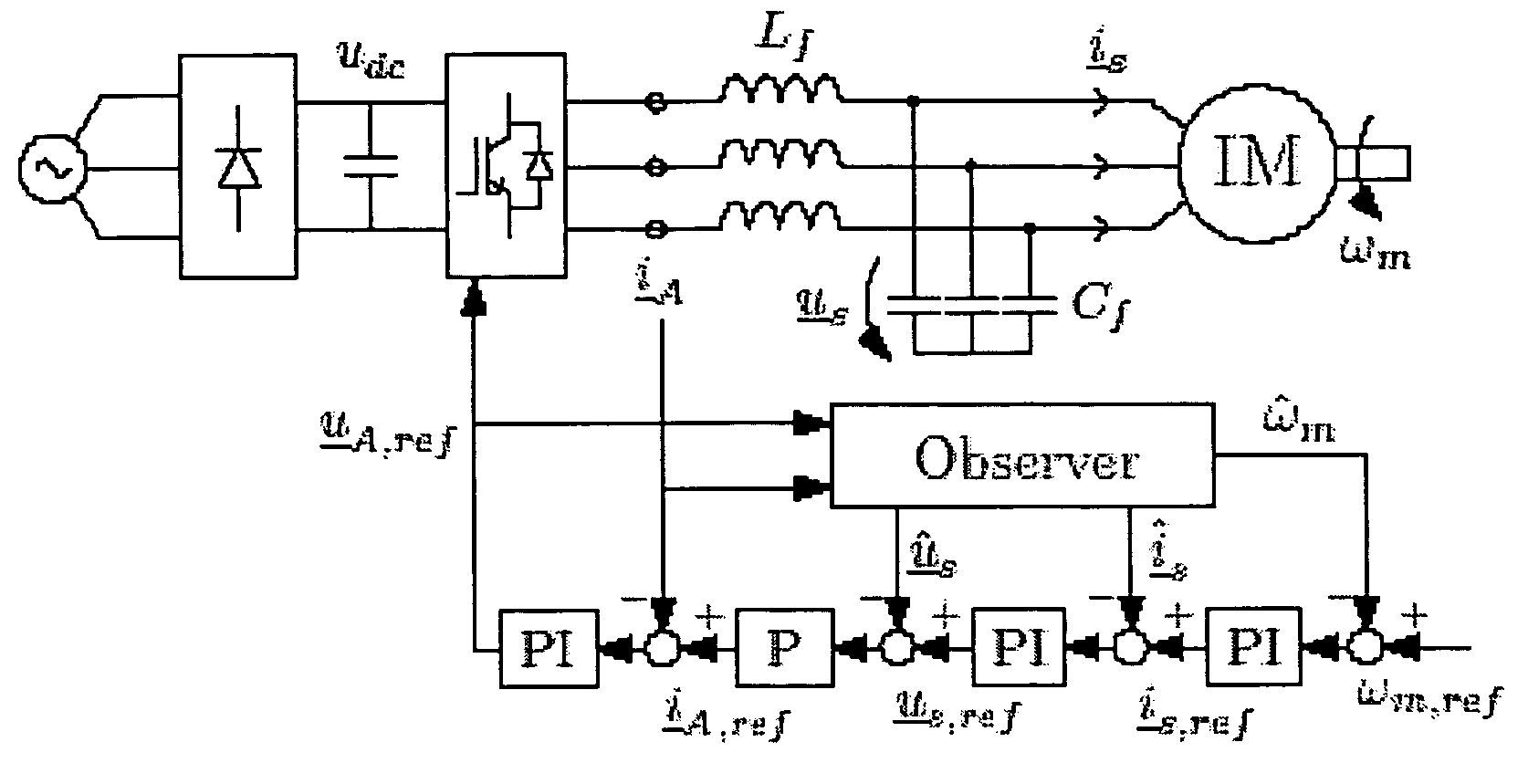
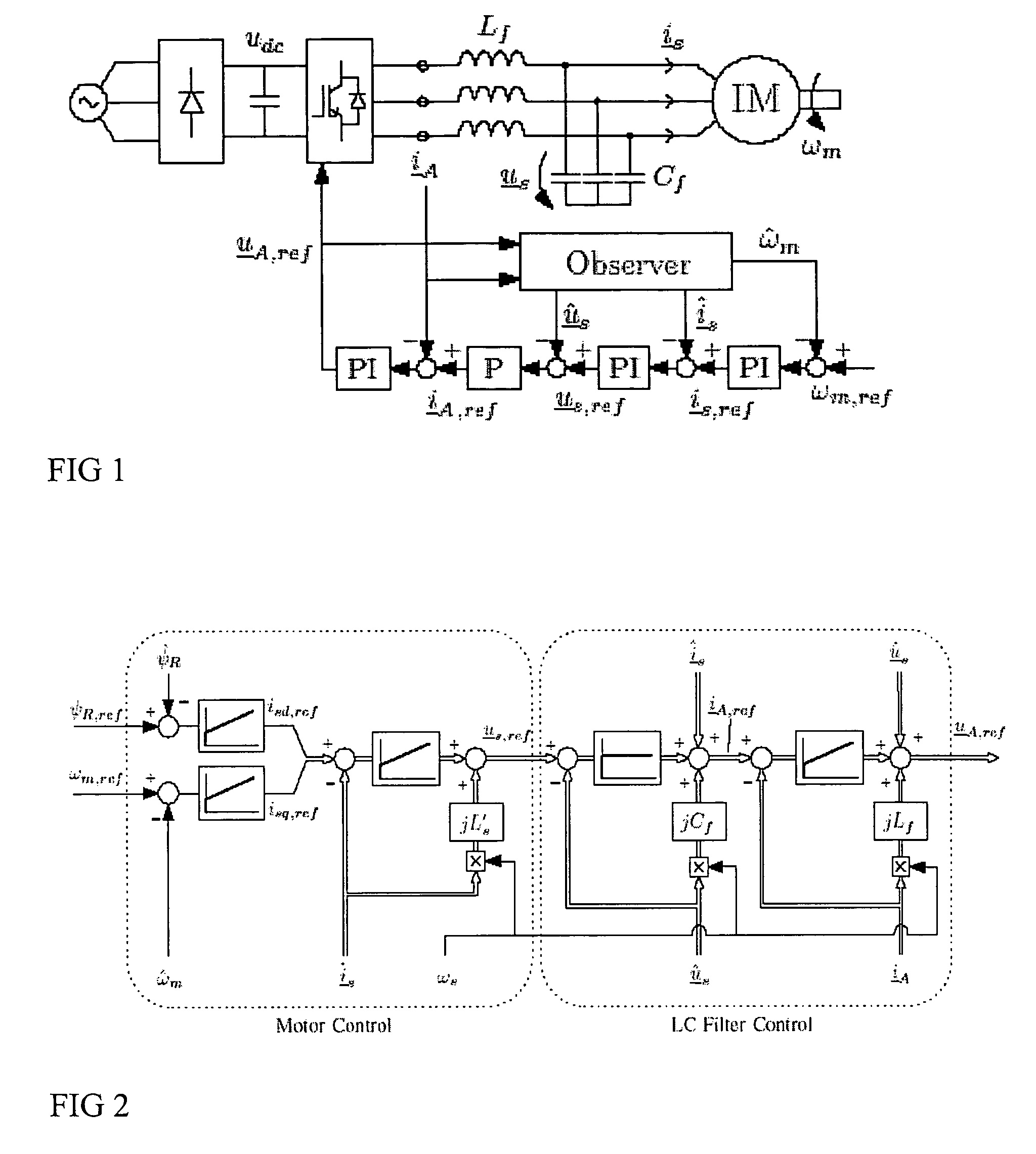
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a PWM inverter with output LC filter
InactiveUS7084604B2Single-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsVoltage vectorSystem matrix
Owner:ABB OY
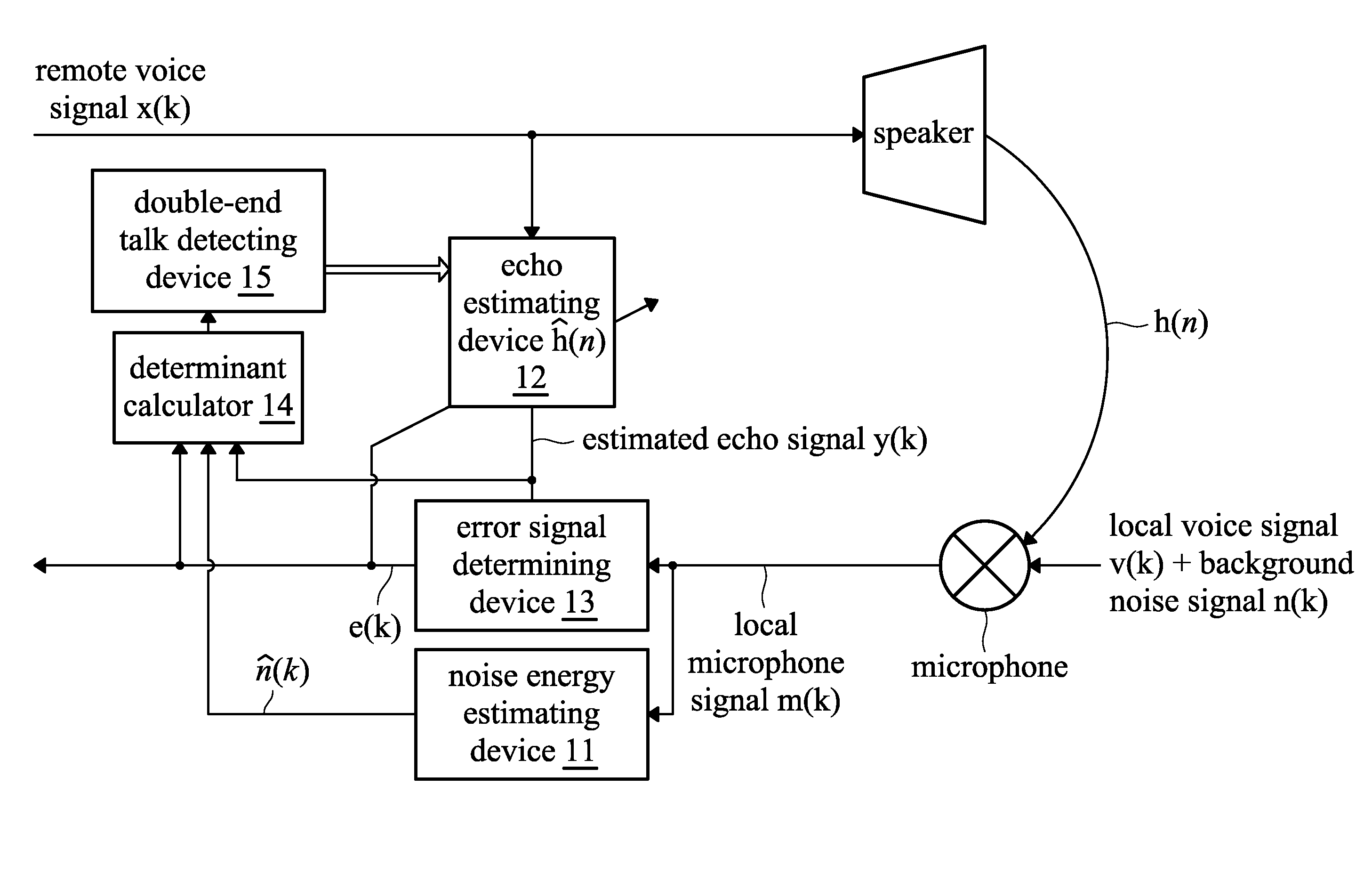
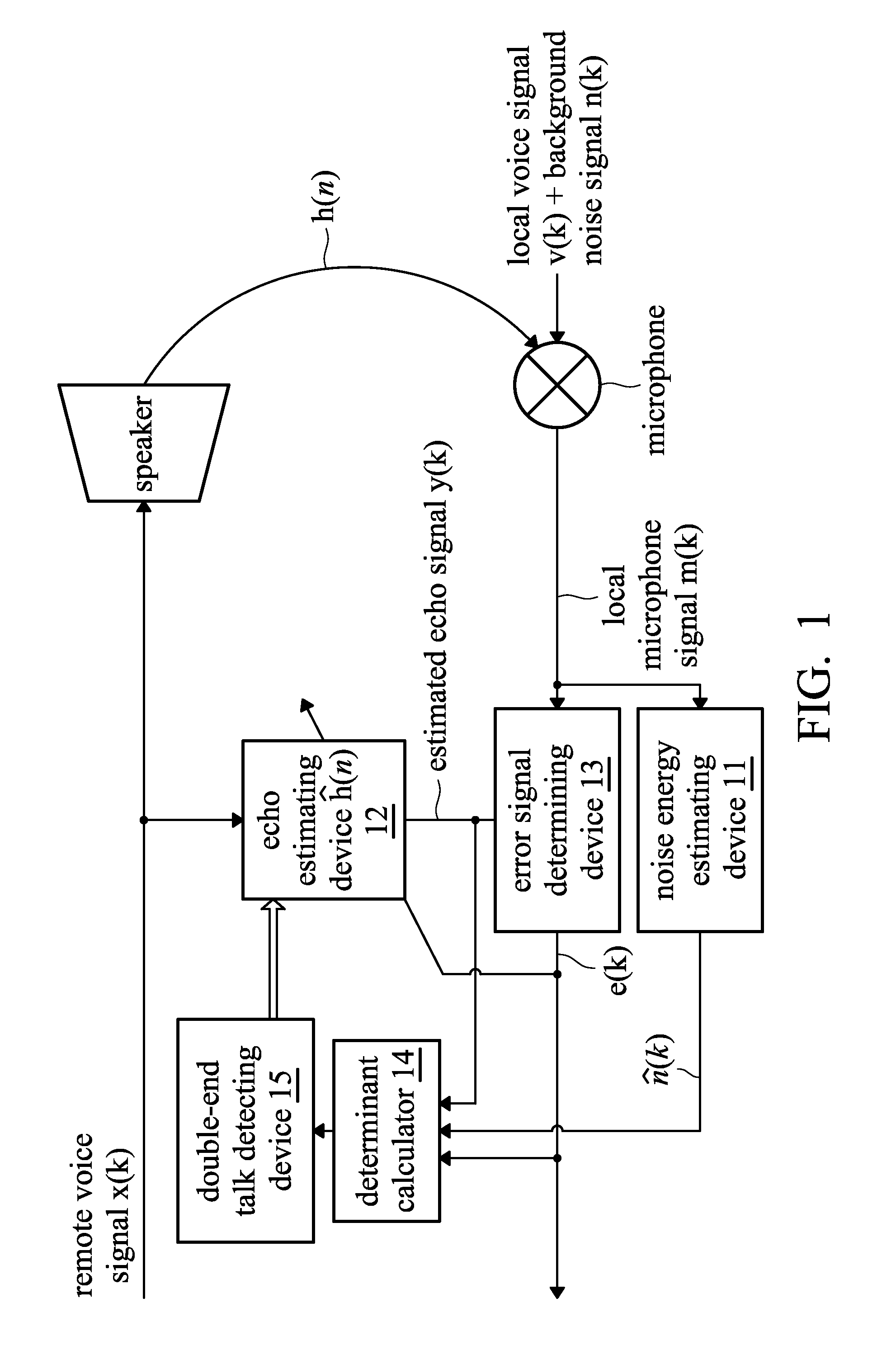
Method and system for double-end talk detection, and method and system for echo elimination
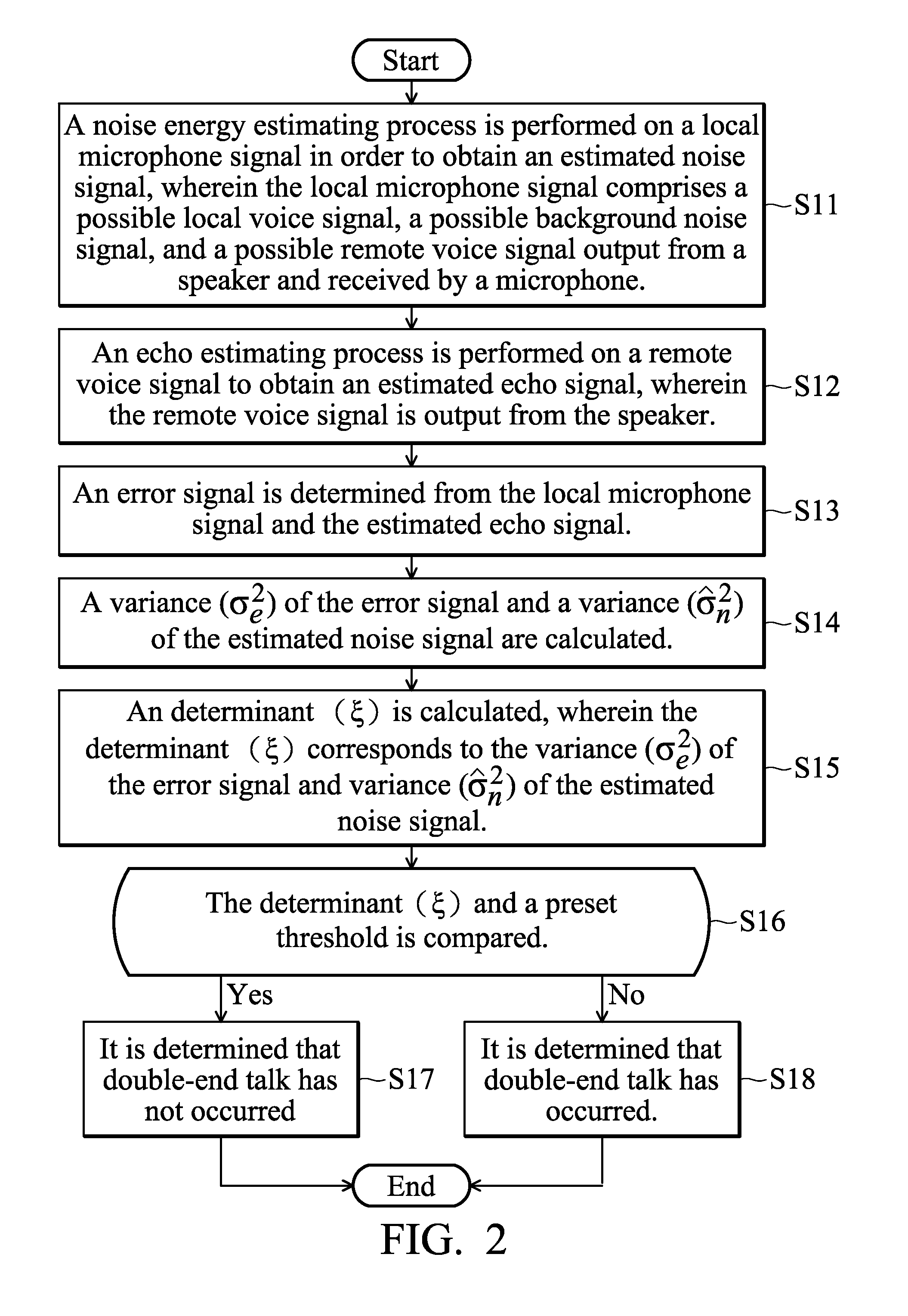
ActiveUS20110124380A1Eliminate effectiveAccurately determineInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemCircumflex
A method and system for eliminating echo in a speaker-microphone communication system are provided. The method includes the steps of: performing a noise energy estimating process on a local microphone signal in order to obtain an estimated noise signal, wherein the local microphone signal includes a local voice signal, possible background noise signal, and possible remote voice signal output from a speaker and received by a microphone; performing an echo estimating process on a remote voice signal to obtain an estimated echo signal, wherein the remote voice signal is output from the speaker; determining an error signal from the local microphone signal and the estimated echo signal; calculating a variance (σe2) of the error signal and a variance ({circumflex over (σ)}n2) of the estimated noise signal; calculating a determinant (ξ), wherein the determinant (ξ) corresponds to the variance (σe2) of the error signal and variance ({circumflex over (σ)}n2) of the estimated noise signal; and comparing the determinant (ξ) and a preset threshold, wherein when the determinant (ξ) is lower than the preset threshold, it is determined that double-end talk has not occurred, otherwise, it is determined that double-end talk has occurred.
Owner:APPLE INC
Robust predictive deconvolution system and method
InactiveUS7106250B2High-fidelity impulse response estimationReduce ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguityCircumflex
Owner:THE U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
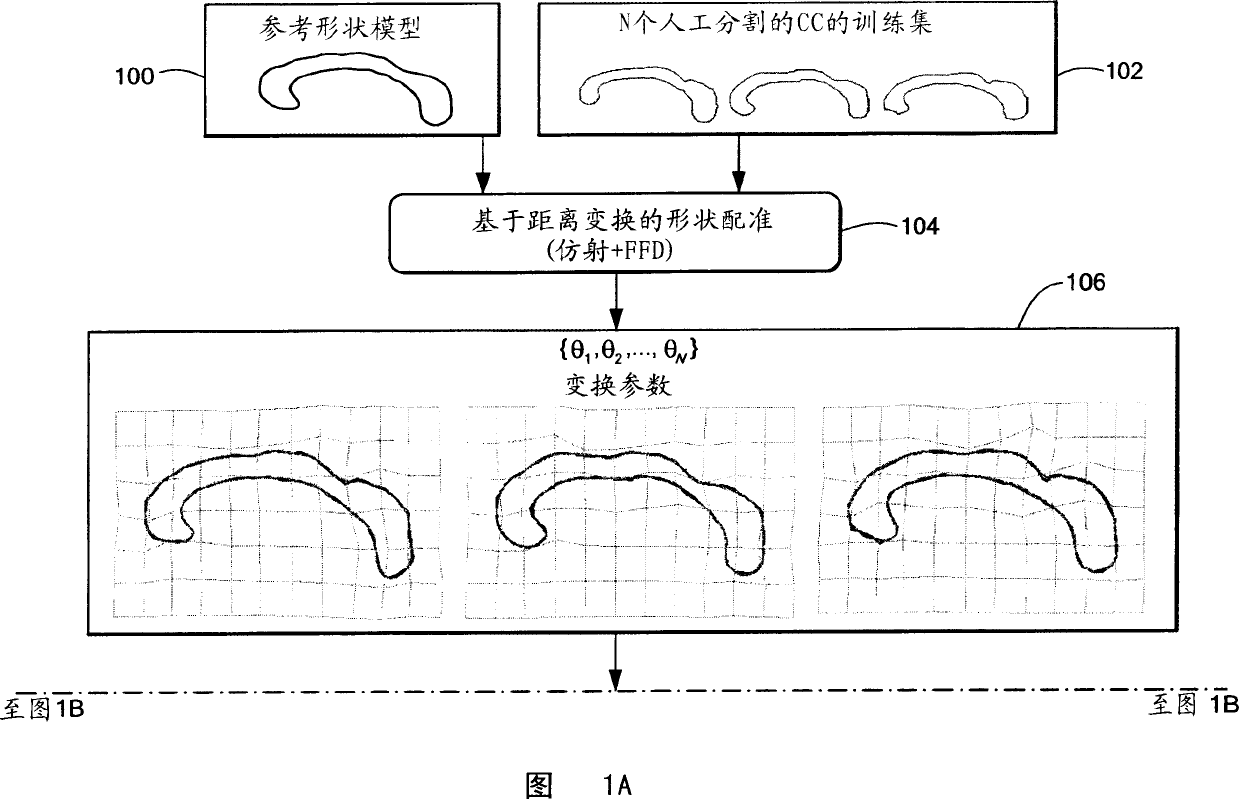
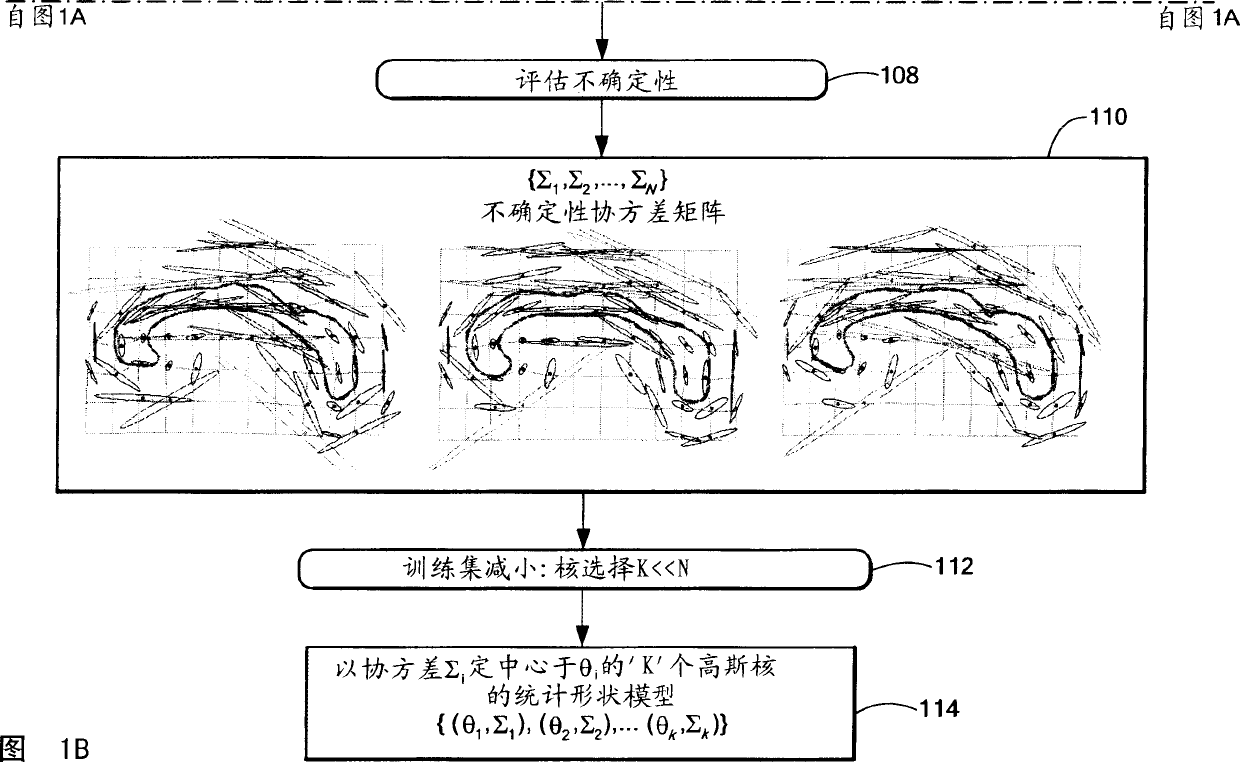
Method for knowledge based image segmentation using shape models
A method for segmenting an object of interest from an image of a patient having such object. Each one of a plurality of training shapes is distorted to overlay a reference shape with a parameter Thetai being a measure of the amount of distortion required to effect the overlay. A vector of the parameters Thetai is obtained for every one of the training shapes through the minimization of a cost function along with an estimate of uncertainty for every one of the obtained vectors of parameters Thetai, such uncertainty being quantified as a covariance matrix Sigmai. A statistical model represented as {circumflex over (f)}H (Theta,Sigma) is generated with the sum of kernels having a mean Thetai and covariance Sigmai . The desired object of interest in the image of the patient is identified by positioning of the reference shape on the image and distorting the reference shape to overlay the obtained image with a parameter Theta being a measure of the amount of distortion required to effect the overlay. An uncertainty is quantified as a covariance matrix Sigma and an energy function E=Eshape+Eimage is computed to obtain the probability of the current shape in the statistical shape model Eshape(Theta,Sigma)=-log({circumflex over (f)}H) and the fit in the image Eimage.
Owner:西门子共同研究公司
Method and apparatus for estimating angles in a synchronous machine
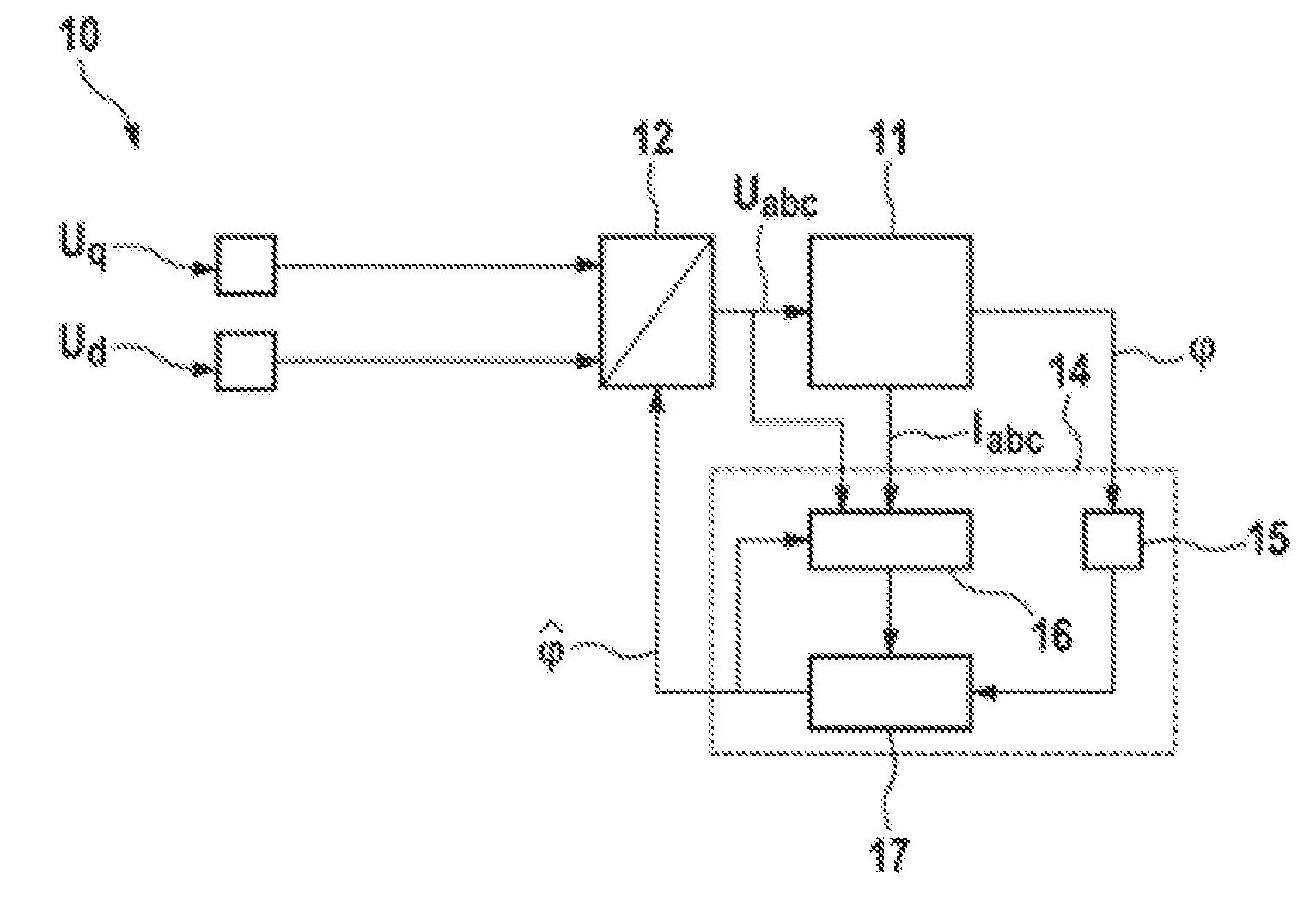
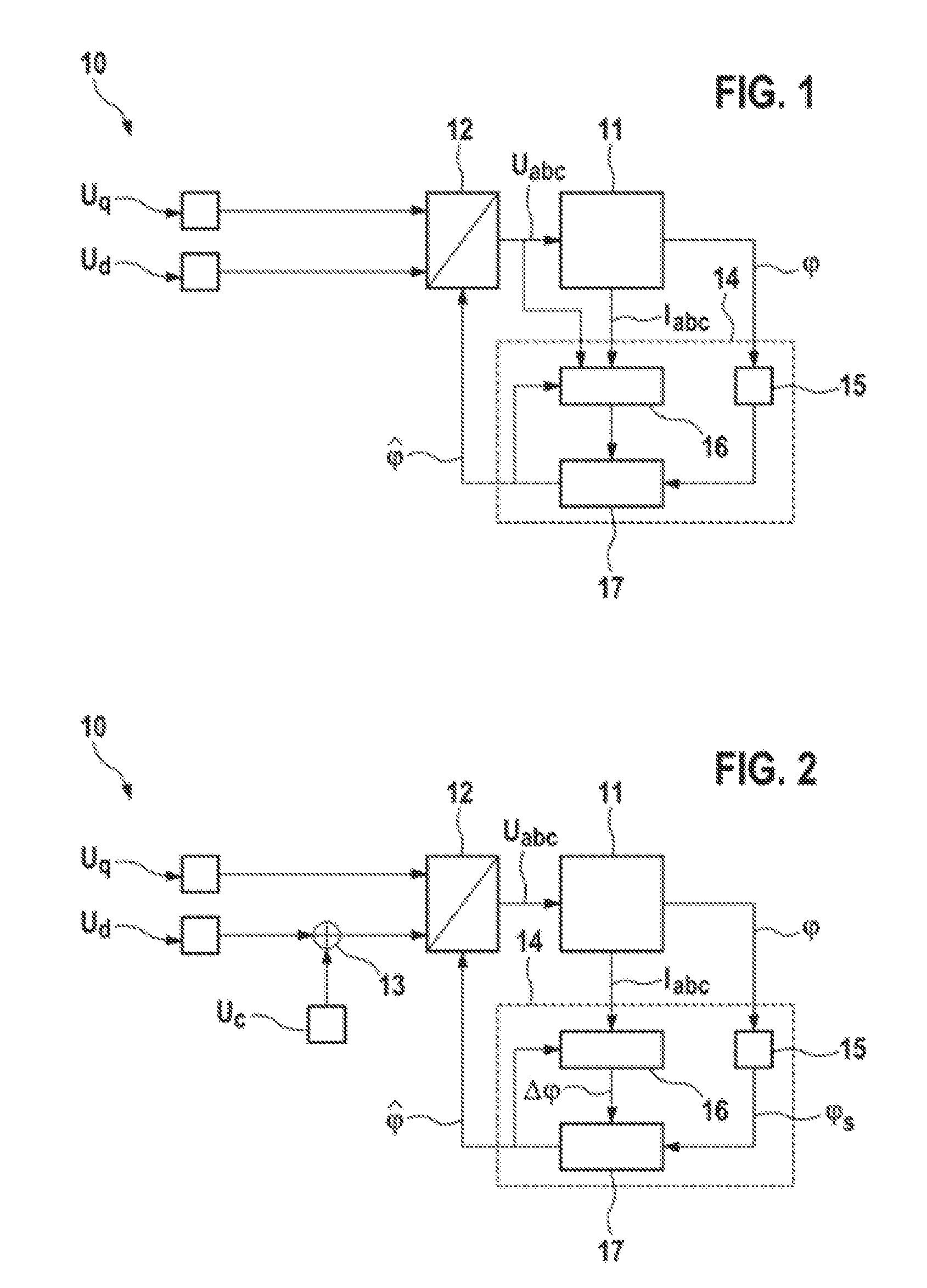
ActiveUS9225274B2Guaranteed uptimeImprove bindingVector control systemsStarter detailsCircumflexRotor angle
The invention relates to an apparatus for estimating angles in a synchronous machine (11), having an angle sensor device (15) which is designed to determine event-discrete measured values for a rotor angle (φ) of a rotor of the synchronous machine (11) and to output a measurement signal dependent on the determined measured values, an estimation device (16) which is designed to record current and / or voltage signals from the synchronous machine (11), to calculate a deviation (Δφ) of the rotor angle (φ) of the rotor of the synchronous machine (11) from an expected rotor angle on the basis of the recorded current and / or voltage signals and to output a deviation signal dependent on the calculated deviation (Δφ), and a combining device (17) which is designed to receive the measurement signal and the deviation signal and to calculate an estimated value ({circumflex over (φ)}) for the rotor angle (φ) of the rotor of the synchronous machine (11) from a combination of the measurement signal and the deviation signal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
[circuit and method for pulse width modulation ]
InactiveUS20050180499A1Improve PWM audio qualityReduce clock frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationElectromagnetic interferencePulse-code modulation
A circuit and a method for performing pulse width modulation are provided. A pulse density modulator (PDM) is applied to receive the least N bits of the input data and to generate a pulse density modulation signal. The number of pulse of the pulse density modulation signal in 2{circumflex over ( )}N frames correspond to a value of the least N bits of the input data. An adder is applied to generate a PWM data by adding a value of the most M bits of the input data to a value of the pulse density modulation signal generated by the PDM. A pulse width modulator is applied to generate a PWM signal dithering in 2{circumflex over ( )}N frames according to the PWM data generated by the adder, so as to improve the audio quality of pulse width modulation and the Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) phenomenon.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
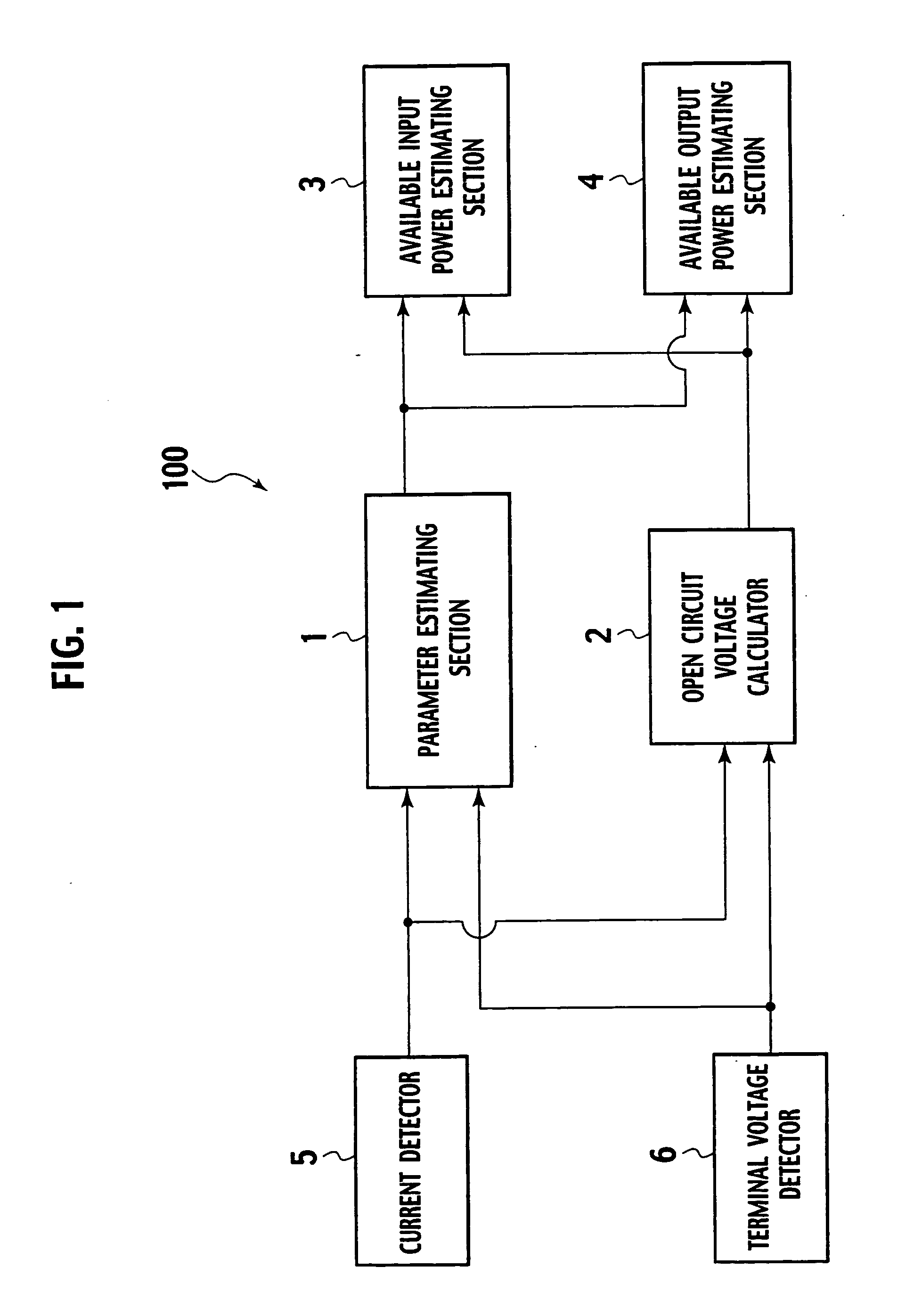
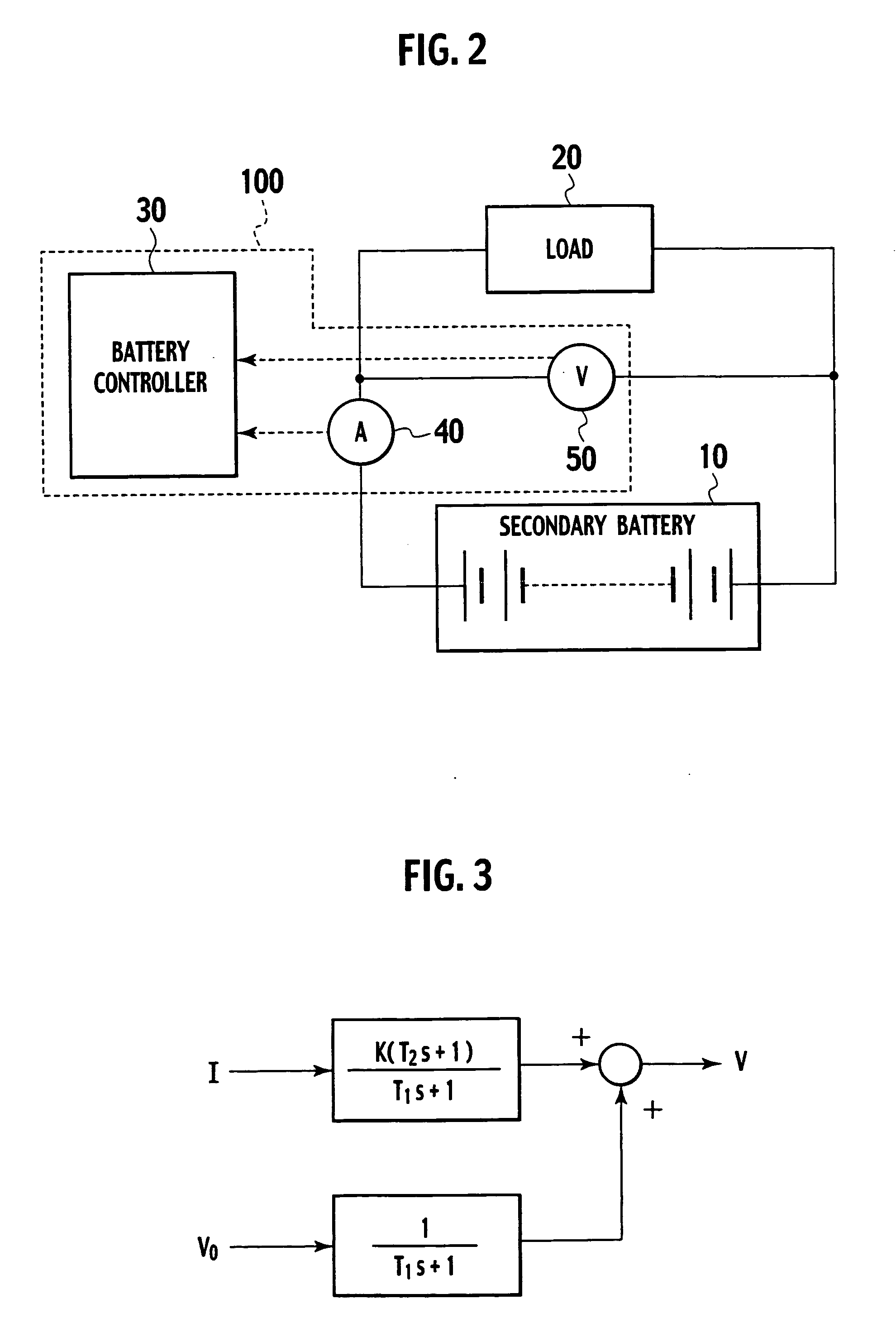
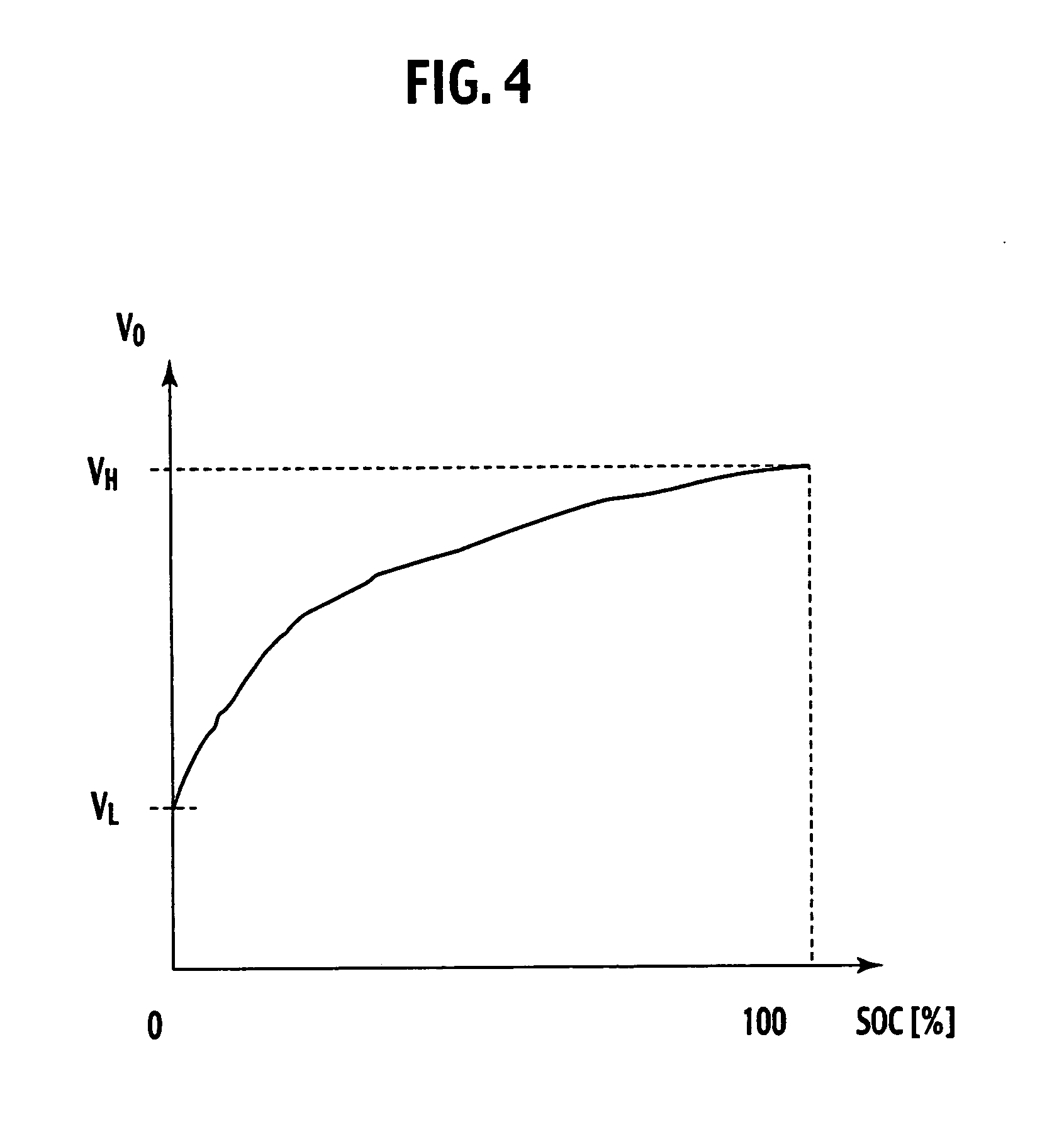
Available input-output power estimating device for secondary battery
ActiveUS20050275407A1Error of estimate valueError minimizationBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLower limitTerminal voltage
An available input-output power estimating device for a secondary battery includes a parameter estimating section substituting a measured current value I and a measured voltage value V into an adaptive digital filter using an equivalent circuit model of the secondary battery for thereby collectively estimating values of parameters in the equivalent circuit model, an open circuit voltage calculator substituting I, V, and the estimated parameter values into the equivalent circuit model for calculating an open circuit voltage {circumflex over (V)}0, an available input power estimating section estimating an available input power Pin of the secondary battery using components (ân,{circumflex over (b)}n), associated with a direct term in the equivalent circuit model, in the estimated parameters, the open circuit voltage estimate value {circumflex over (V)}0 and an upper limit voltage Vmax of the terminal voltage, and an available output power estimating section estimating an available output power Pout for the secondary battery using (ân,{circumflex over (b)}n), {circumflex over (V)}0 and a lower limit voltage {circumflex over (V)}min of the terminal voltage.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
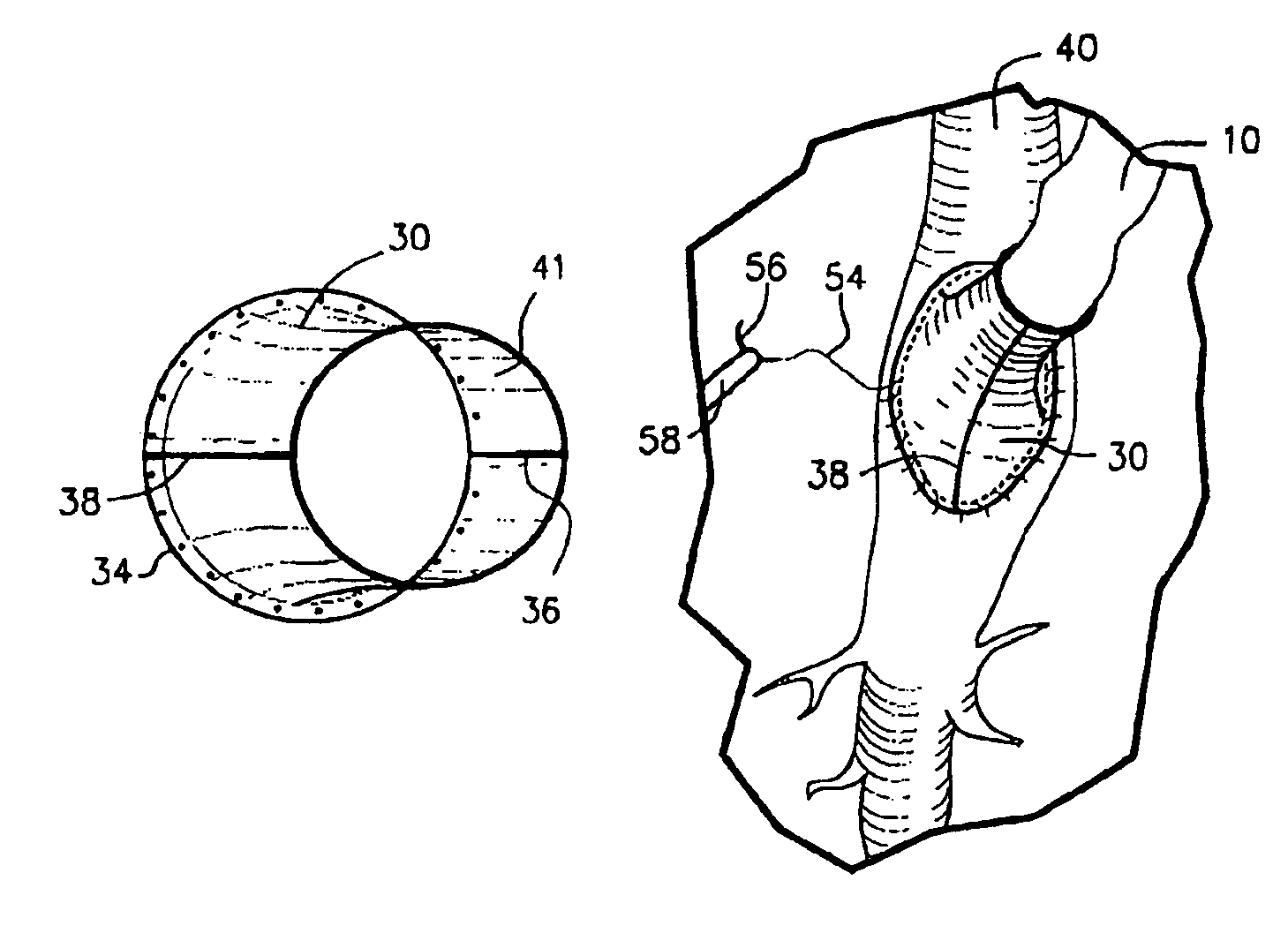
Method and coupling apparatus for facilitating an vascular anastomoses
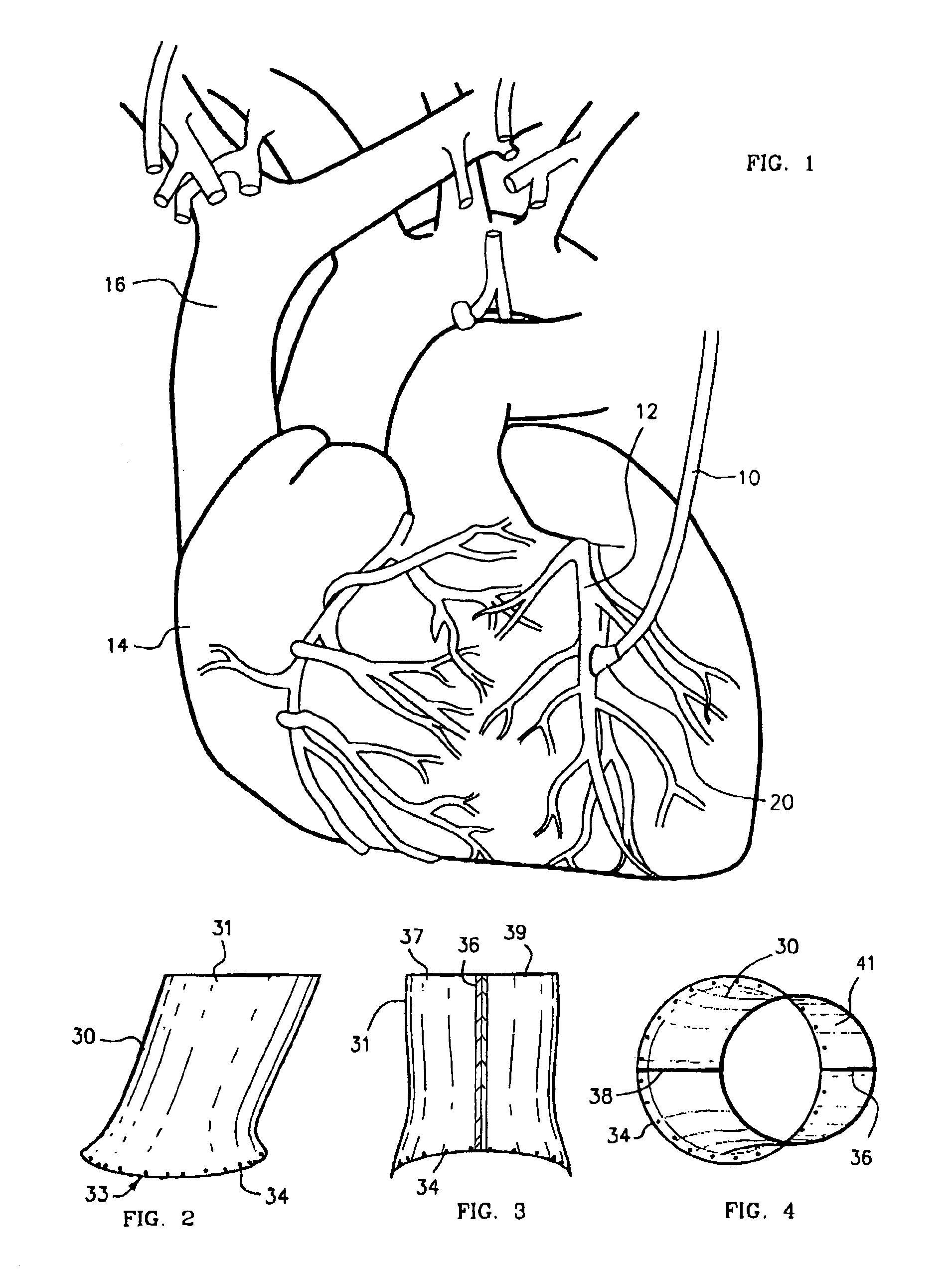
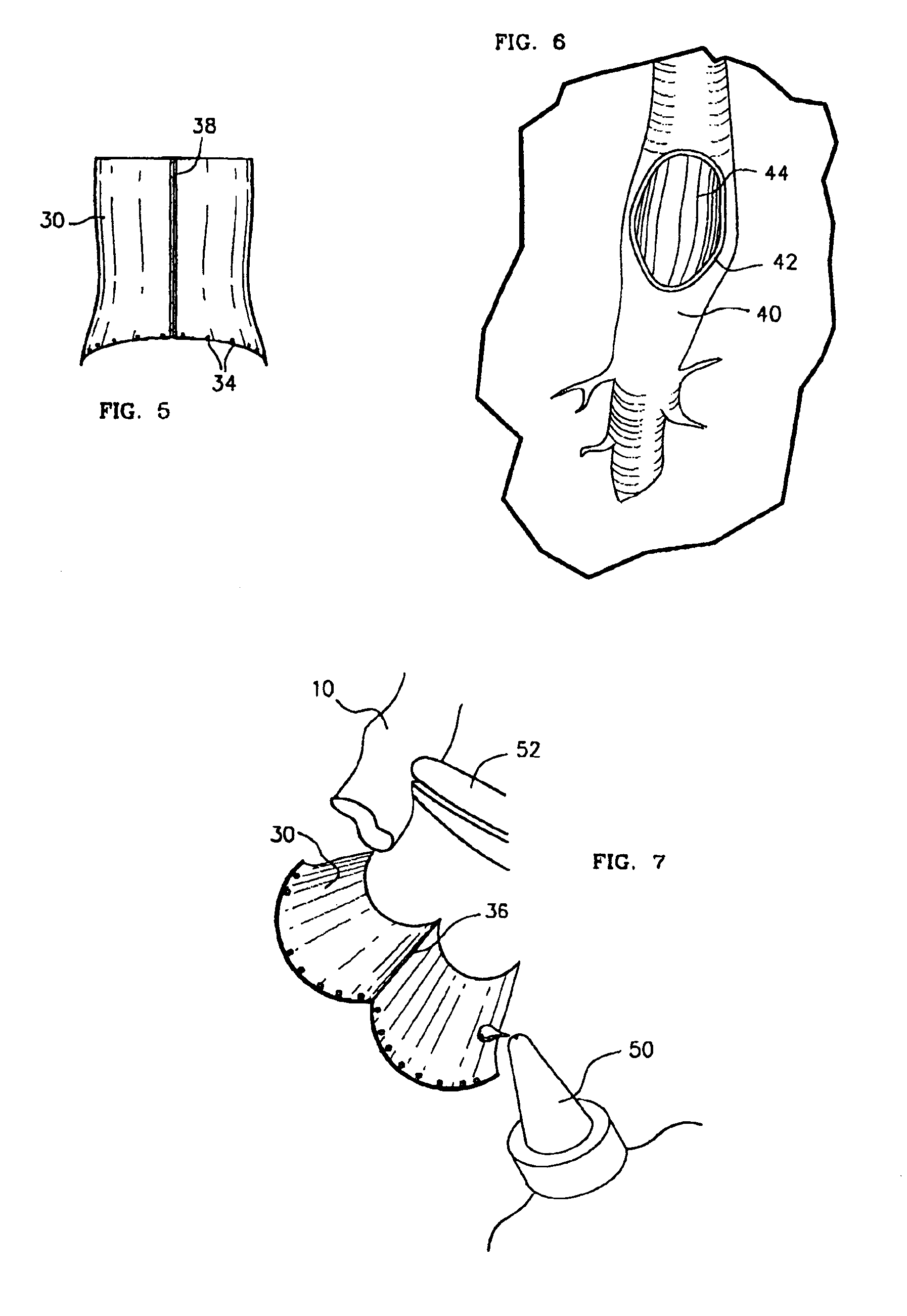
InactiveUS7008436B2Fast and uniform methodTiming inconsistencySuture equipmentsSurgical staplesVascular anastomosisSaphenous veins
The present invention, which addresses the needs described above, resides in an apparatus and method for coupling vascular apertures to a blood supply vessel in a manner that minimizes the time and operator dependent inconsistency in performing vascular anastomoses. In the coronary setting, this concept is fast and can be applied to both conventional and minimally invasive operative techniques. In the preferred embodiment, the present invention relates to an apparatus and method for facilitating end-to-side vascular anastomoses procedure, whereby the present invention acts as a coupling apparatus between a first, blood supplying hollow organ, e.g. the LIMA, radial artery, or a saphenous vein and the side wall of second hollow organ, typically one of the major coronary arteries, such as the left coronary artery (LCA), right coronary artery (RCA) or the circumflex (CX).
Owner:BARATH PETER
Process for providing a pilot aided phase recovery of a carrier
InactiveUS7397869B2Low costReduce jitterColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPhase correctionCarrier signal
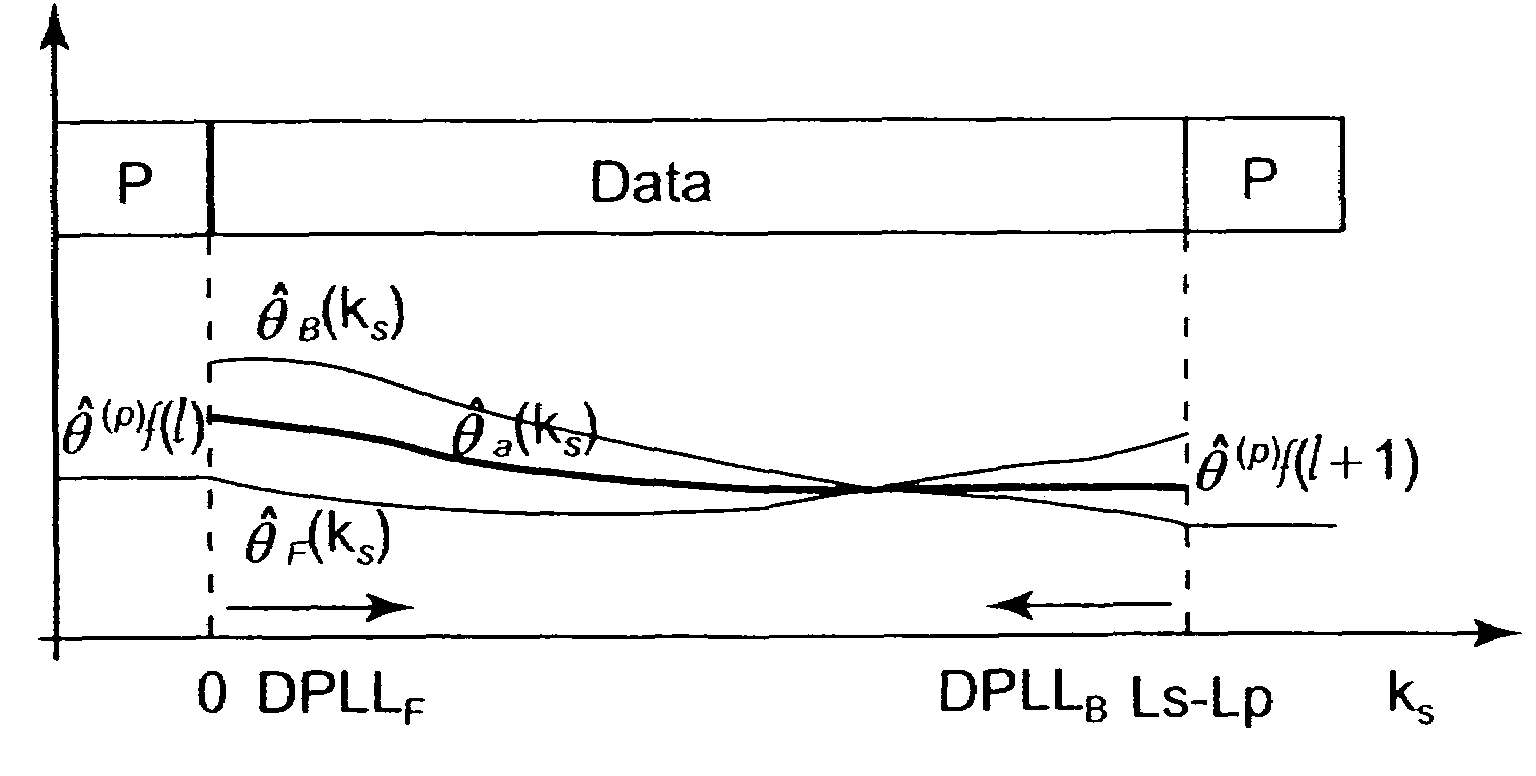
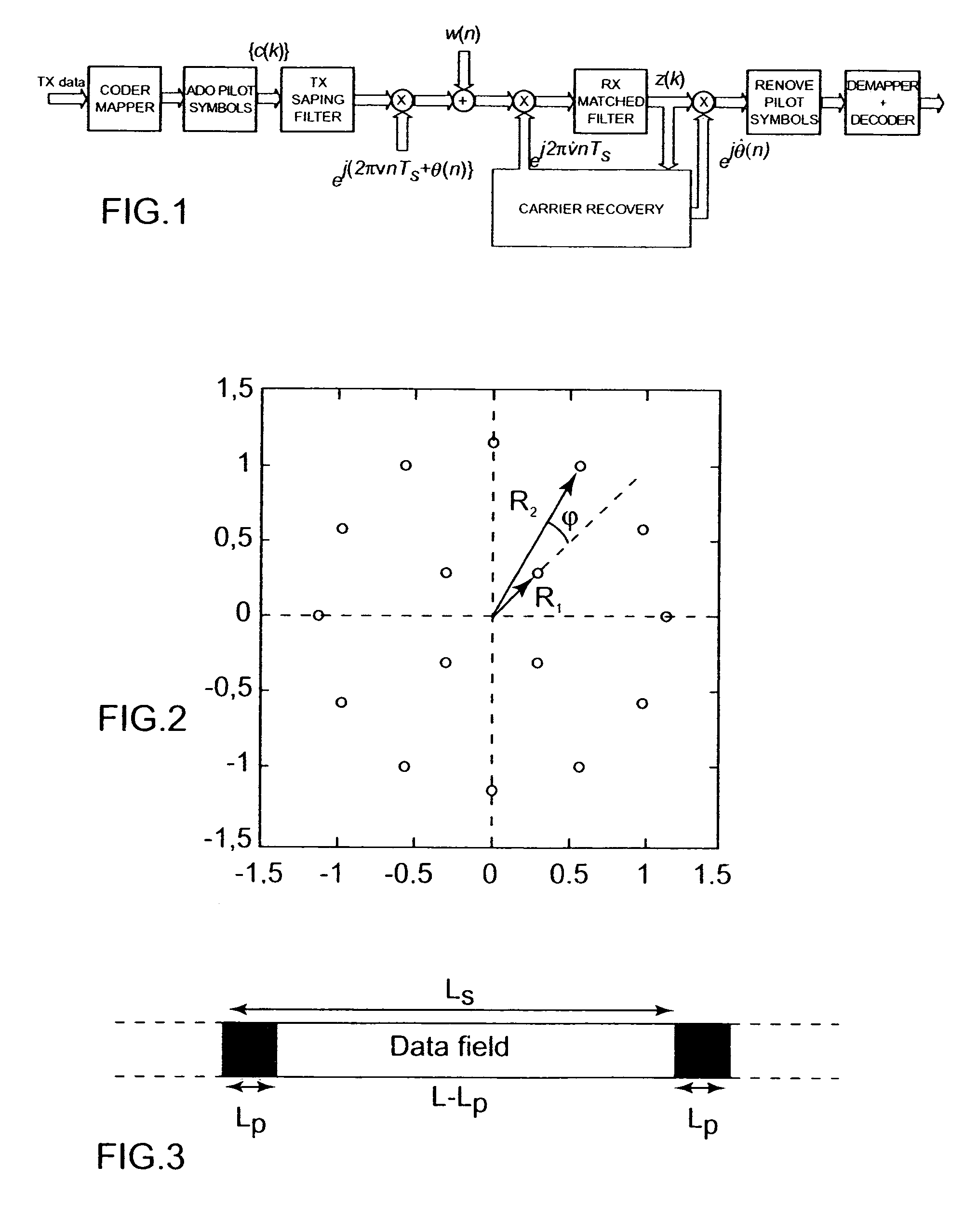
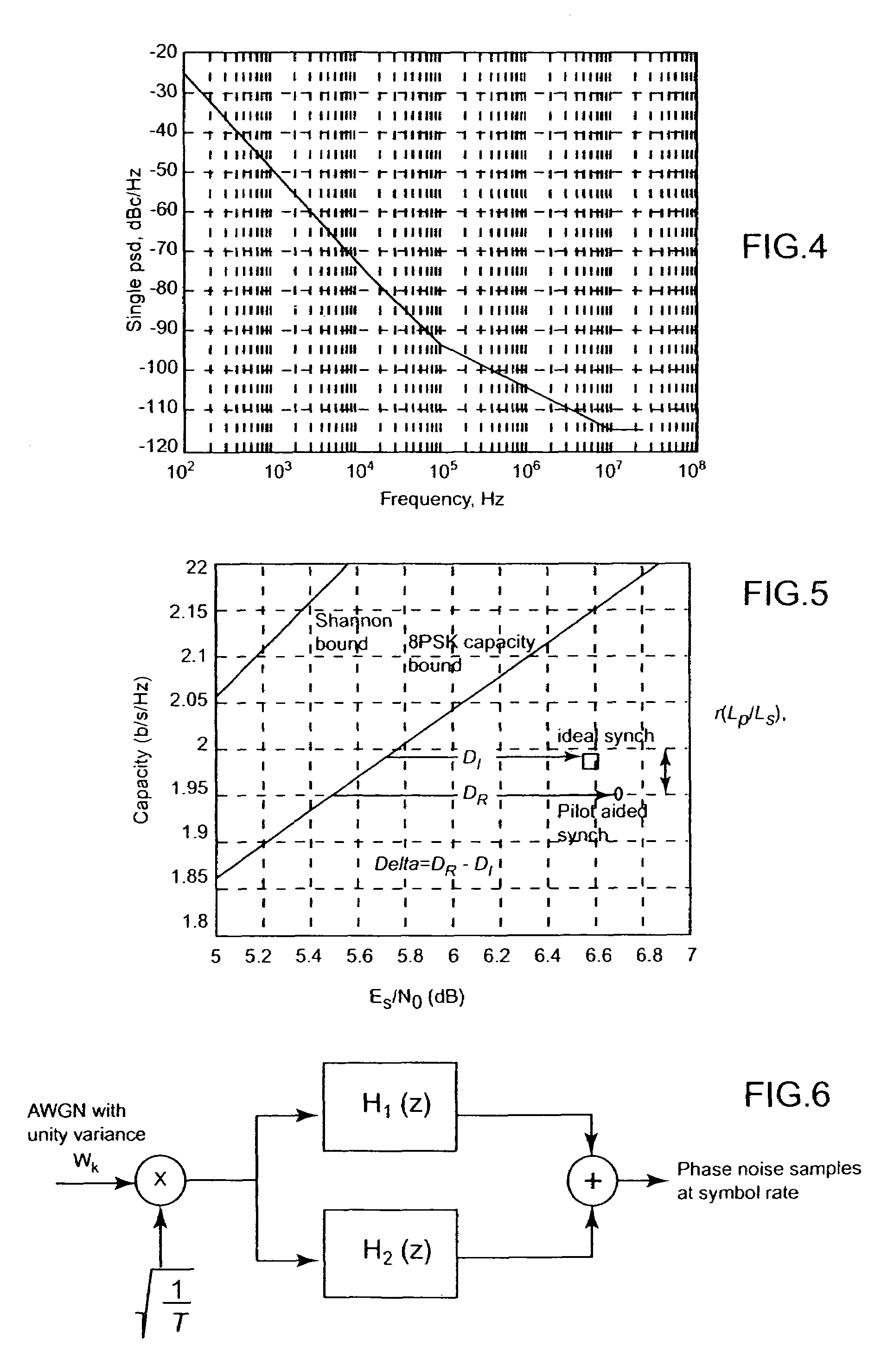
Providing a pilot aided phase recovery of a carrier of an input digital signal Zk having signal fields of Ls symbol signals, LP pilot symbol signals ZP(k) and (Ls−LP) data symbol signals Zd(k), by for each signal field:calculating an unwrapped pilot phase estimate {circumflex over (θ)}f(P)(l);initiating with {circumflex over (θ)}f(P)(l) a first digital phase locked loop implementing a phase estimate algorithm and calculating a forward phase trajectory {circumflex over (θ)}F(k) from Zd(k), ks varying between 1 and Ls−LP over the data field (l), {circumflex over (θ)}F(P)(l) having Ls−LP forward phase estimates {circumflex over (θ)}F(ks);and initiating with {circumflex over (θ)}(P)f(l+1) a second digital phase locked loop, implementing a phase estimate algorithm and calculating a backward phase trajectory {circumflex over (θ)}B(ks) from Zd(k), ks varying between Ls−LP and 1 over said data field (l), {circumflex over (θ)}B(ks) having Ls−LP backward phase estimates {circumflex over (θ)}B(ks); andfrom said phase trajectories calculating a phase correction (e−j{circumflex over (θ)}(ks)).
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
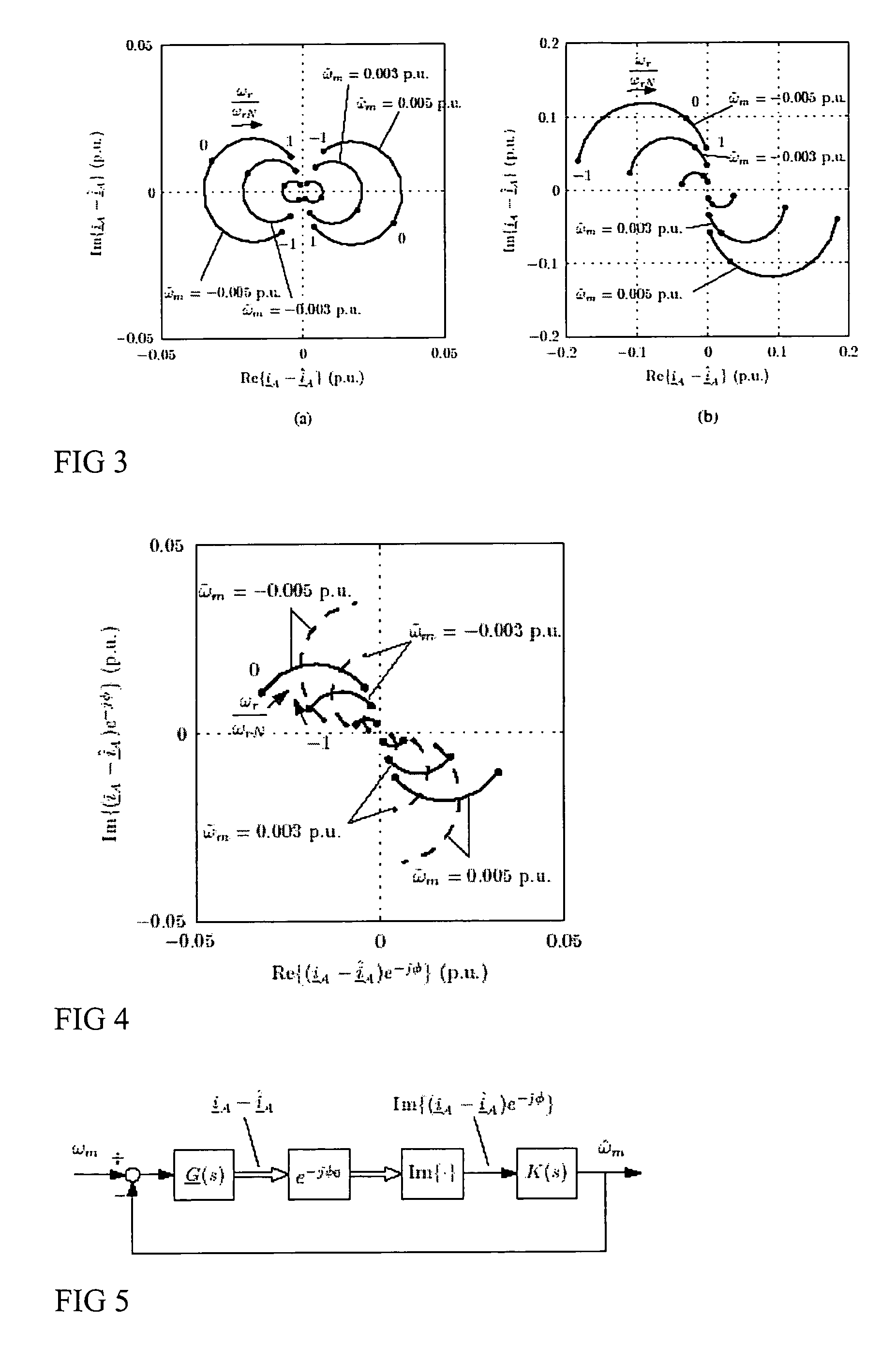
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a pwm inverter with output lc filter
InactiveUS20060145650A1Single-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlVoltage vectorSystem matrix
A method of controlling of an induction machine using an inverter is disclosed with output LC filter. The method includes determining an inverter output current vector (iA), determining an inverter output voltage vector (uA), and forming a full-order observer having a system matrix (Â) and gain vector (K). The observer produces an estimated rotor flux linkage vector ({circumflex over (ψ)}R), an estimated stator current vector (îs), an estimated stator voltage vector (ûs) and an estimated inverter output current vector (îA). An estimation error (iA-îA) of the inverter output current vector is determined, and a speed adaptation law is formed based on the estimation error of the inverter output current vector for determining an estimate for electrical angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) of the induction machine. The induction machine is controlled based on the produced estimates and a measured inverter output current.
Owner:ABB OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
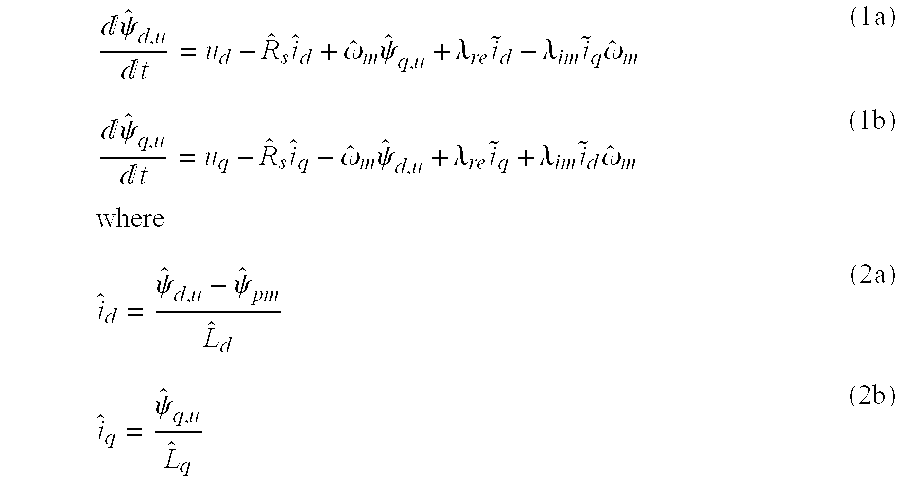
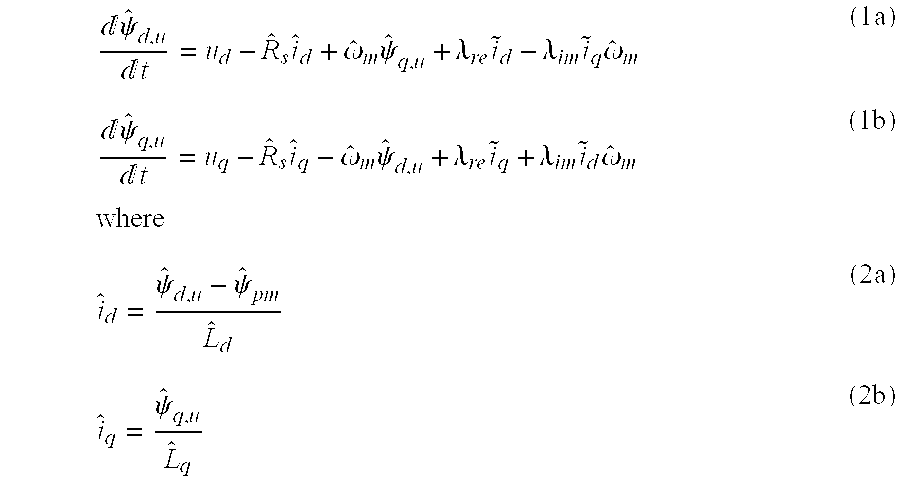
![[circuit and method for pulse width modulation ] [circuit and method for pulse width modulation ]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/61a84826-09ec-4860-9cd9-4fac91c1c63f/US20050180499A1-20050818-D00000.png)
![[circuit and method for pulse width modulation ] [circuit and method for pulse width modulation ]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/61a84826-09ec-4860-9cd9-4fac91c1c63f/US20050180499A1-20050818-D00001.png)
![[circuit and method for pulse width modulation ] [circuit and method for pulse width modulation ]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/61a84826-09ec-4860-9cd9-4fac91c1c63f/US20050180499A1-20050818-D00002.png)