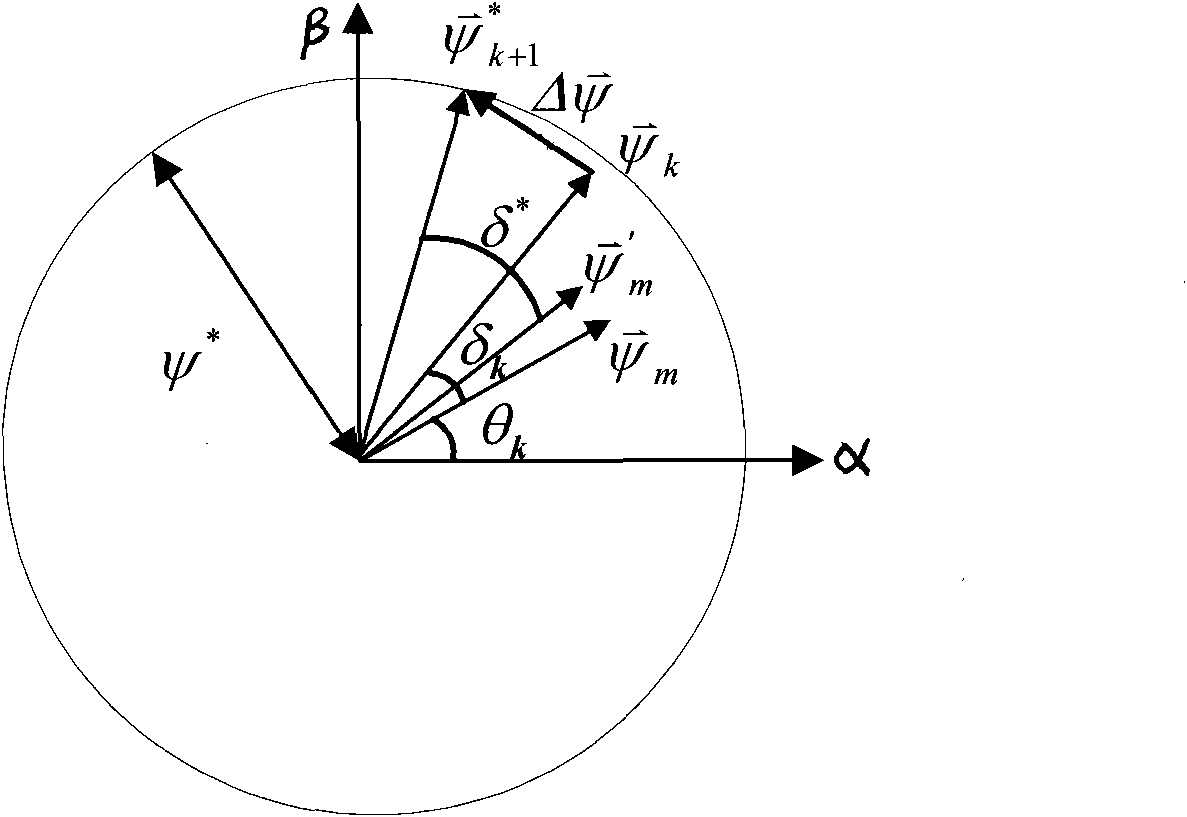
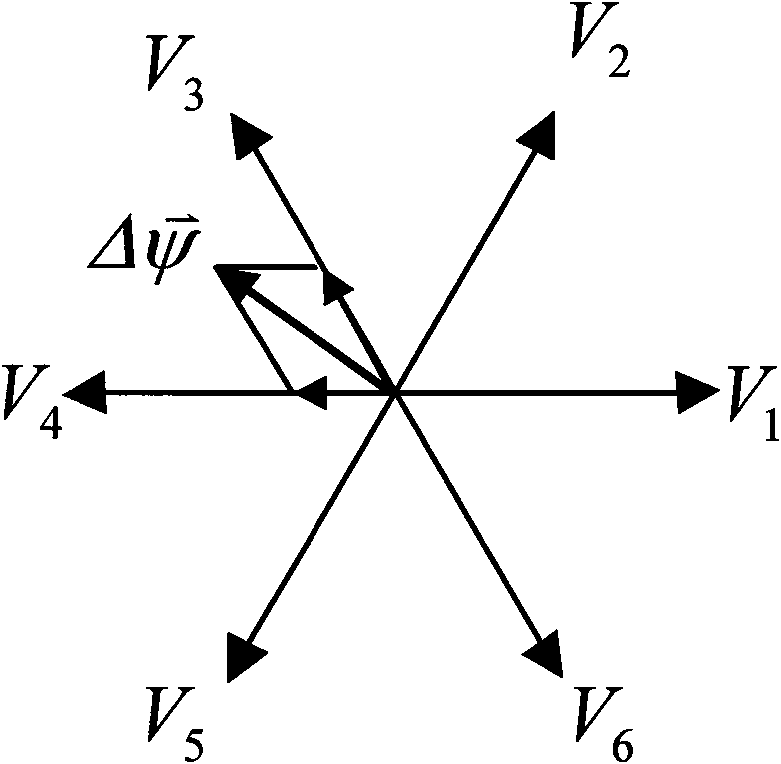
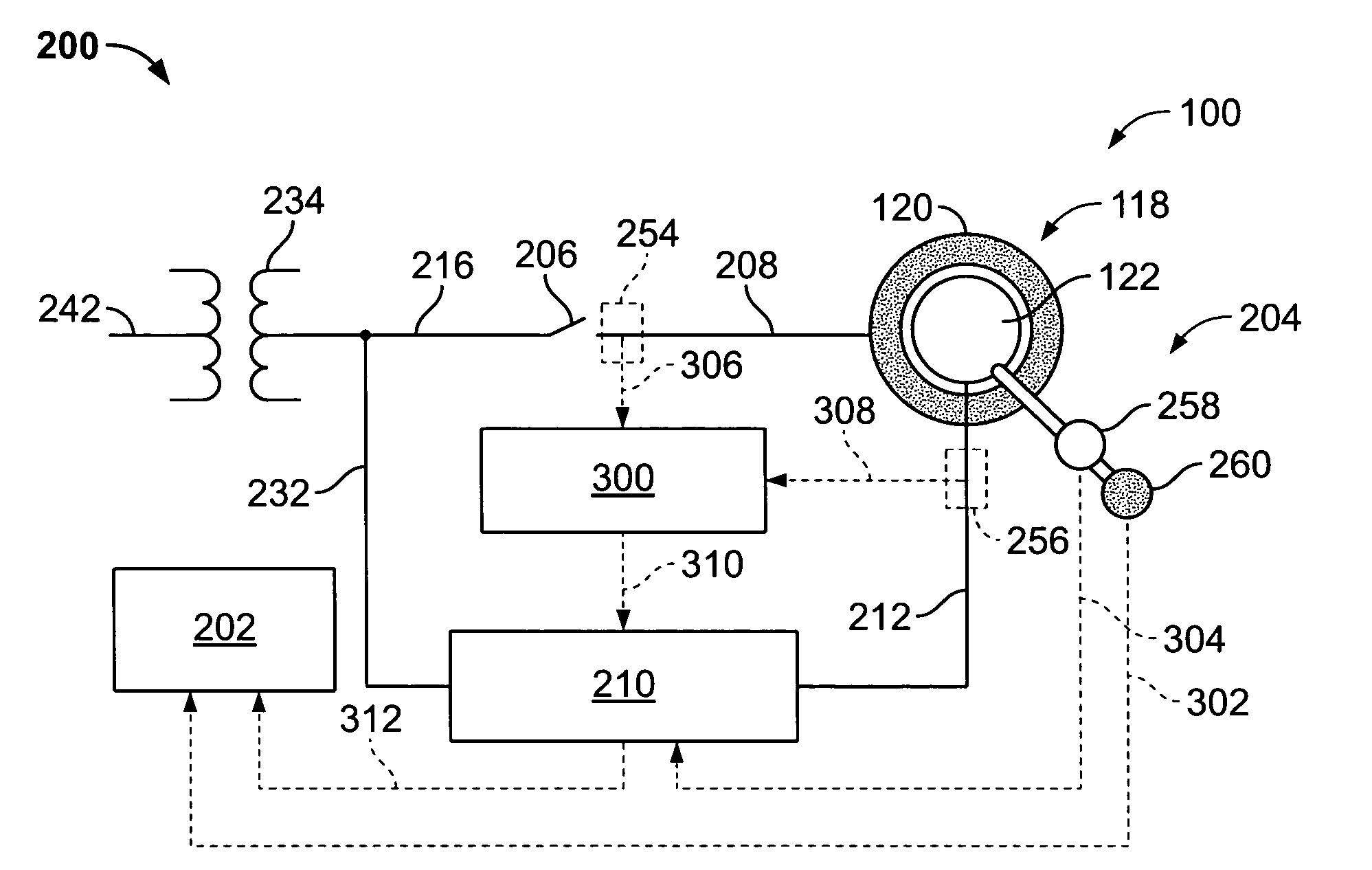
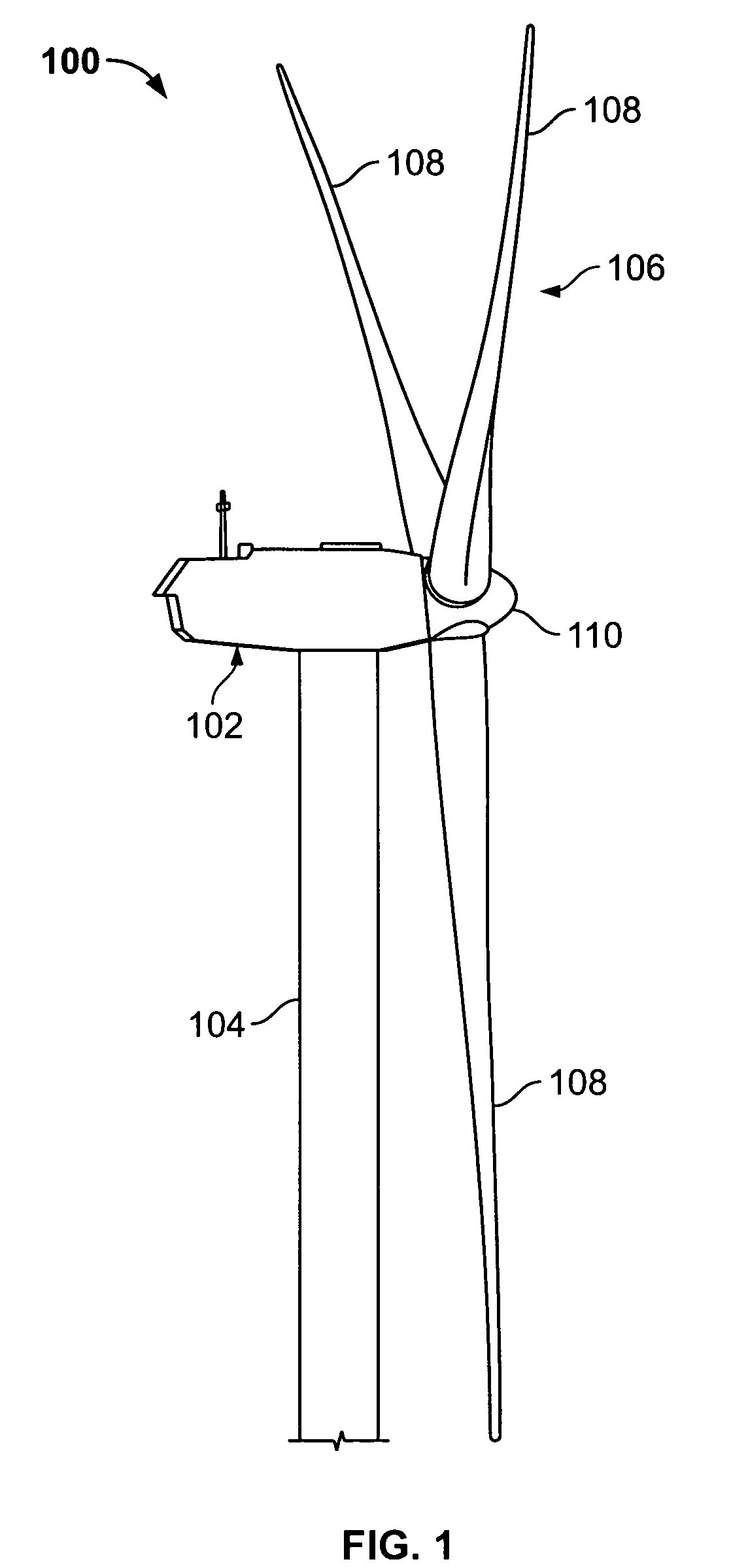
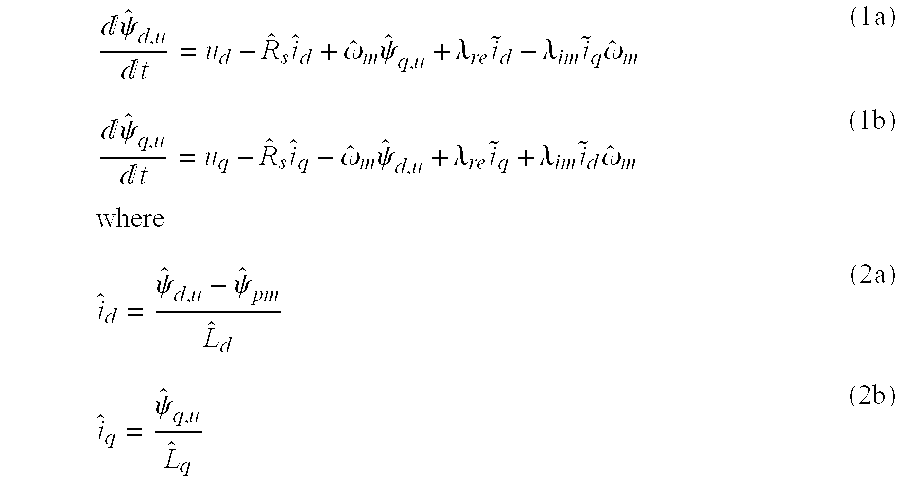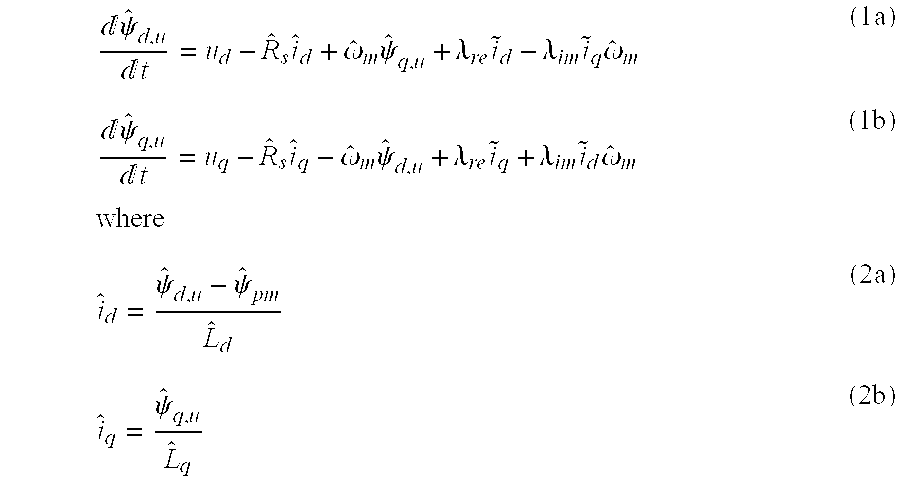Patents
Literature
53 results about "Flux vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multiple label fluorescence polarization assay system and method
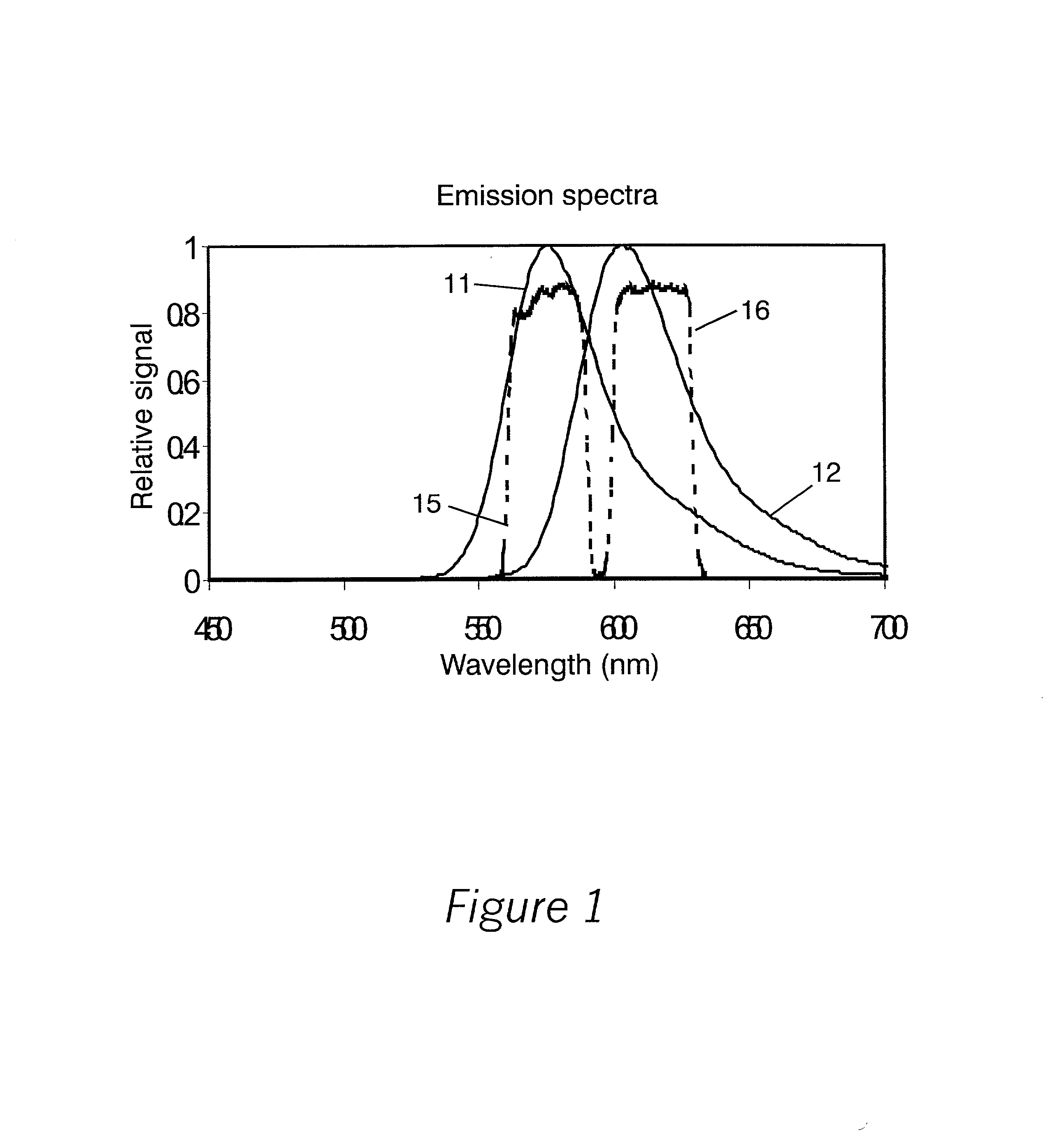
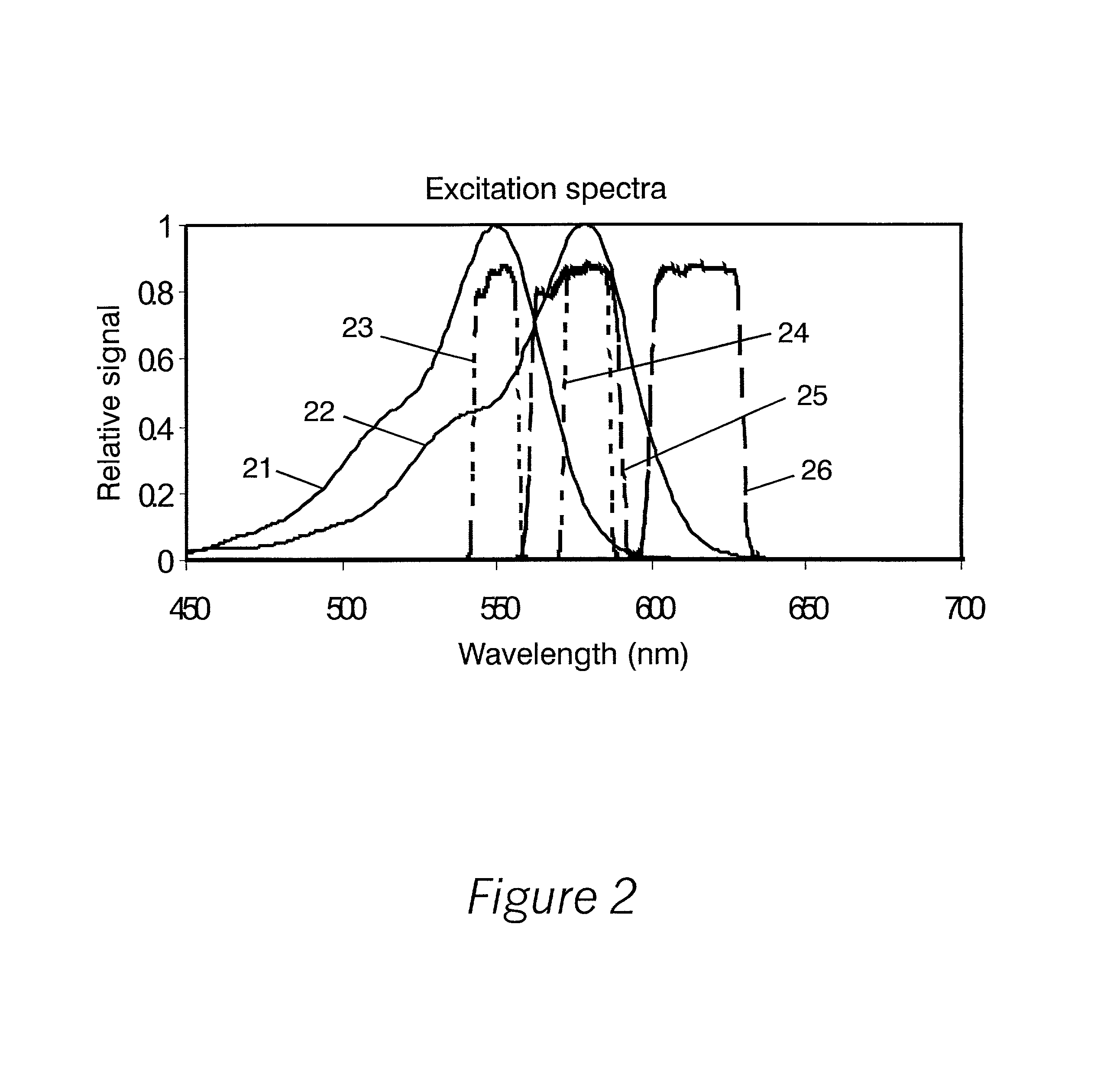
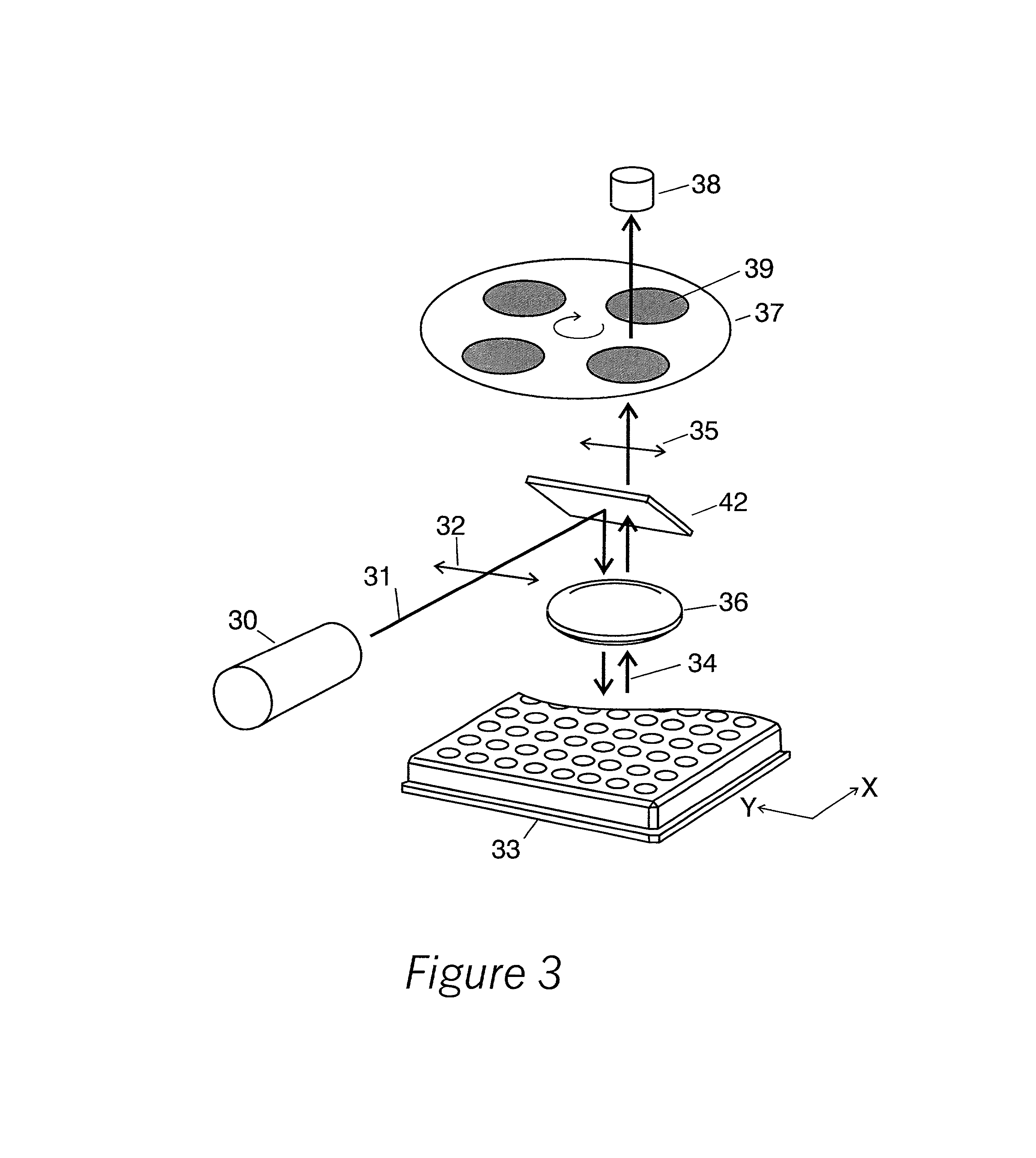
InactiveUS20010033374A1Accurate calculationAccurate valueSpectrum investigationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectral bandsFluorescence
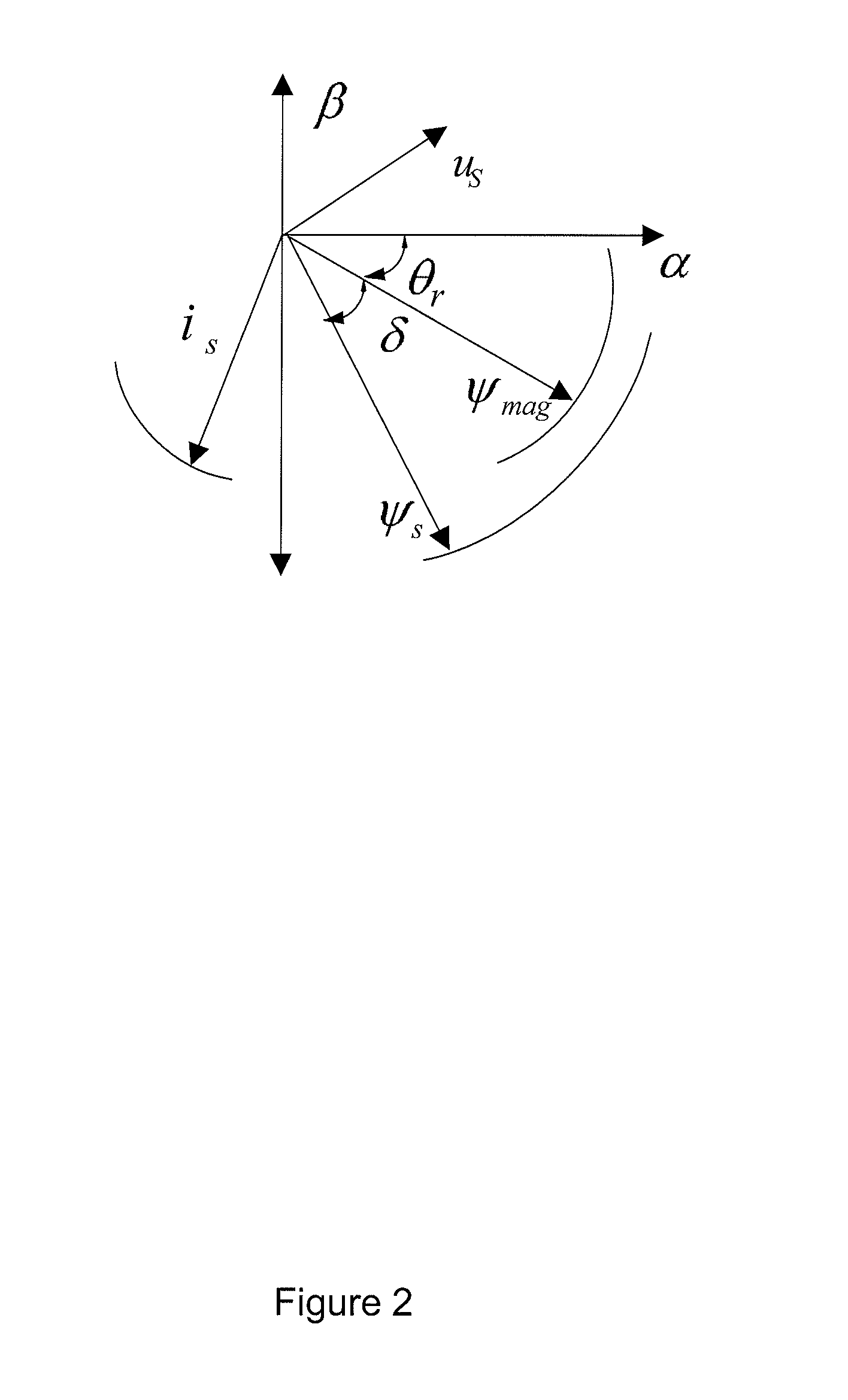
A sample having a plurality of probe molecules is illuminated with at least one beam of excitation light that is linearly polarized along a first axis, thereby effecting fluorescence emission in a plurality of spectral bands. The intensity of a first component of fluorescence emission that is polarized along the first axis, as well as the intensity of a second component of fluorescence emission that is polarized along an orthogonal second axis, is measured for each of said plurality of spectral bands. These measurements are represented as a measurement vector M. Since each probe emits some limited amount of light in the characteristic band of another probe, this results in cross-talk between probes. The measurement vector is therefore corrected using an instrument response matrix A, which is generated by measuring the flux output of control samples which each have only a single probe species. A flux vector S is calculated according to S=A.sup.-1M, and the fluorescence polarization FP is calculated from the S values.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
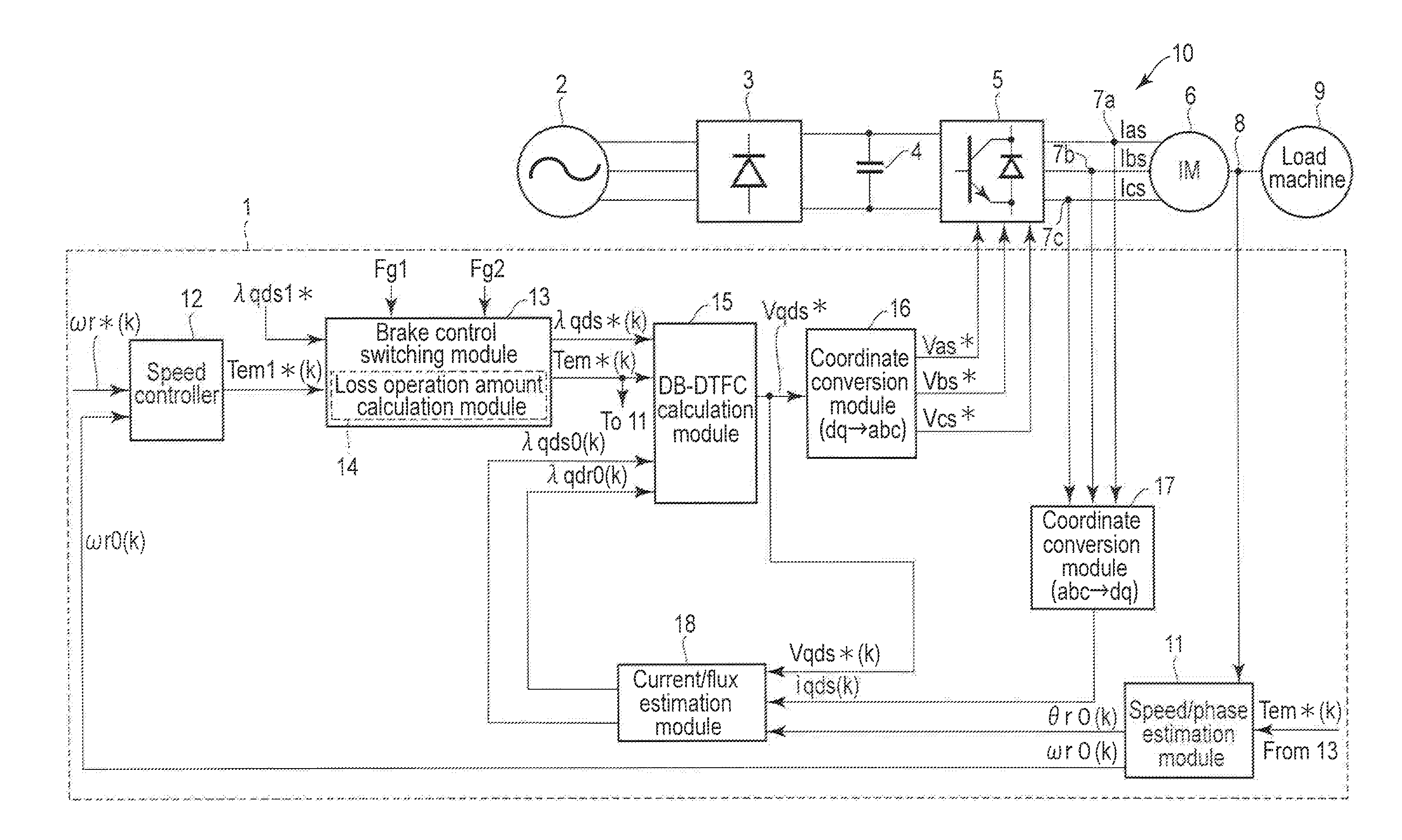
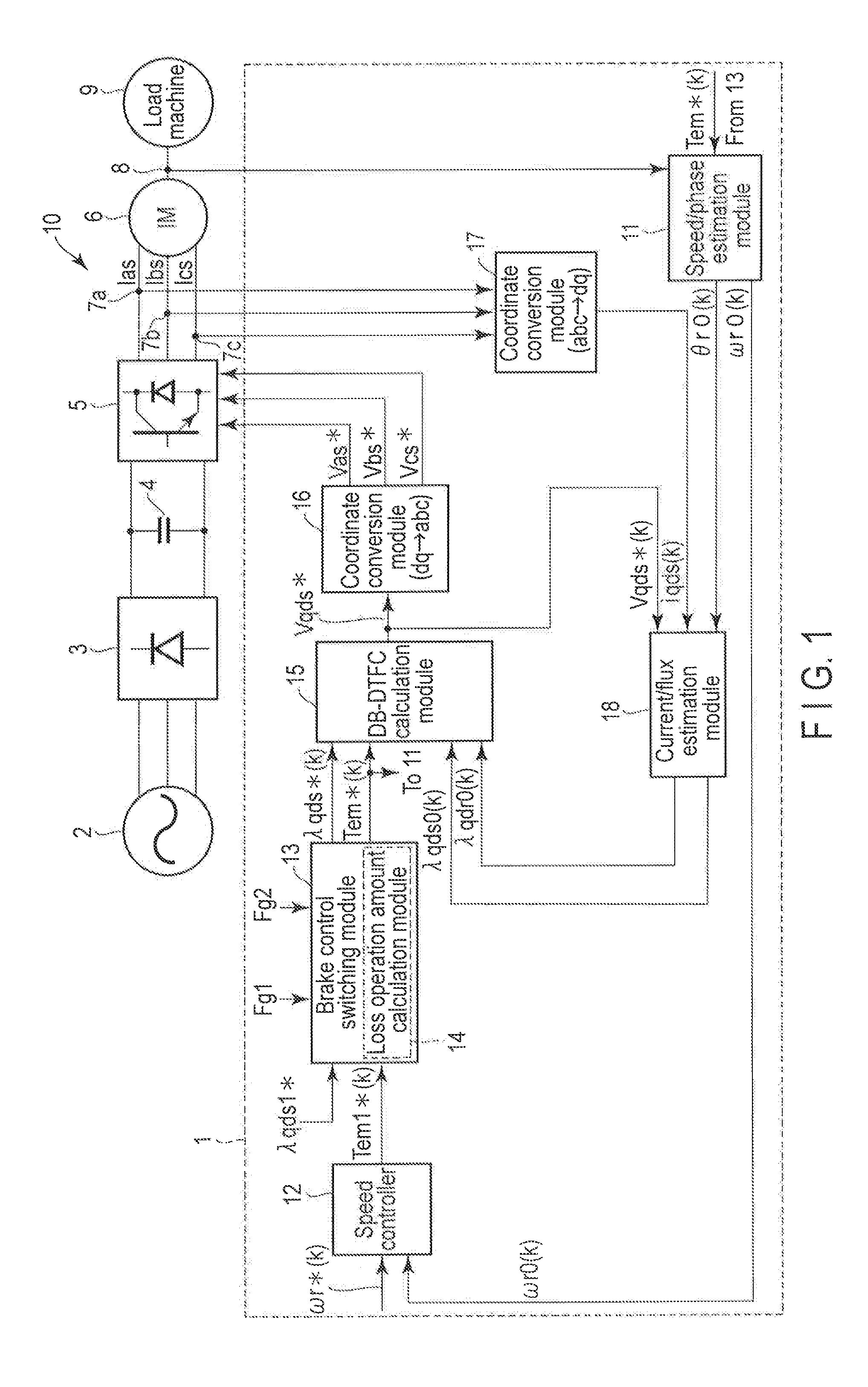
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
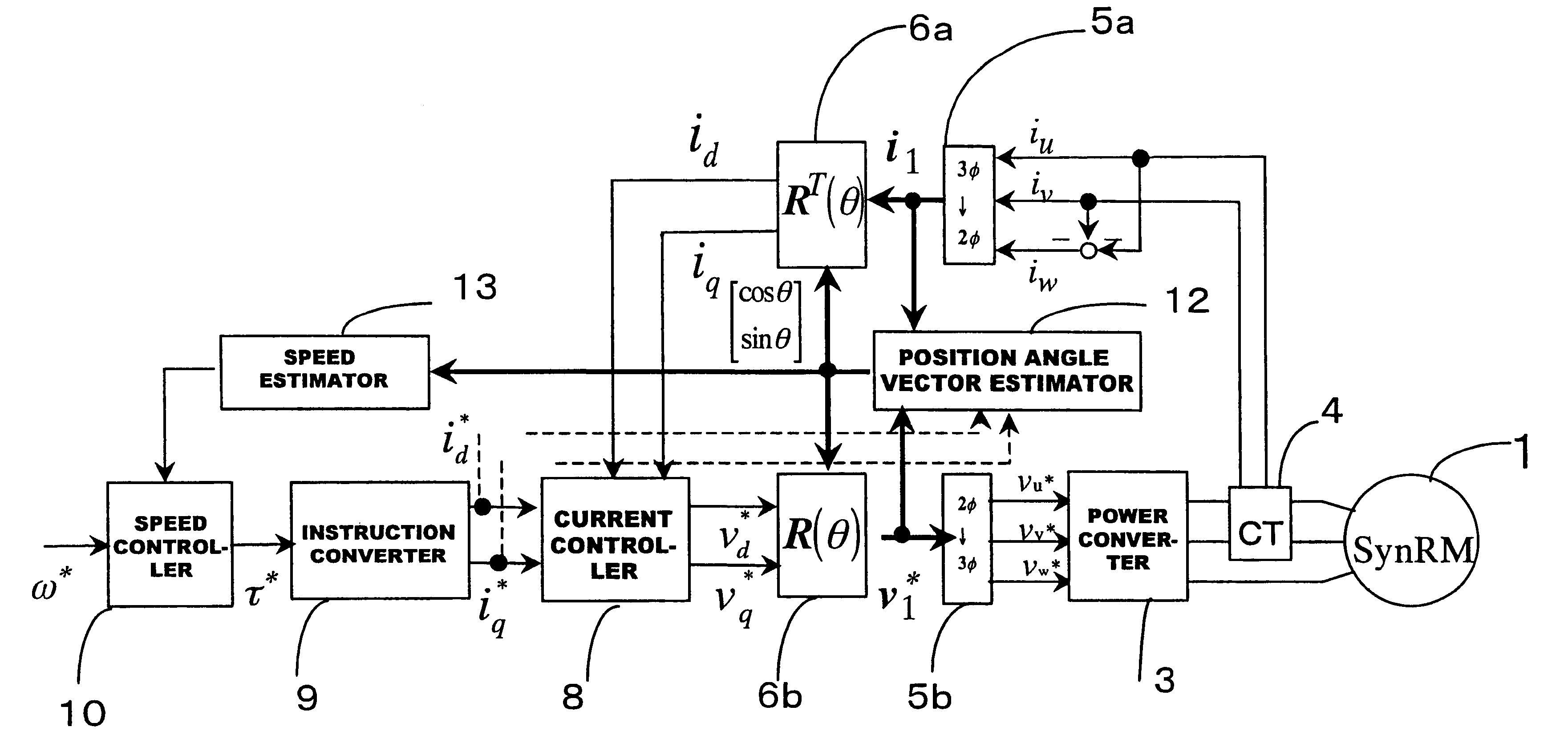
InactiveUS6339308B2Accurate and Efficient EstimationImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous reluctance motorControl vector
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators.A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS20060091847A1Small speedSmall position estimation errorSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
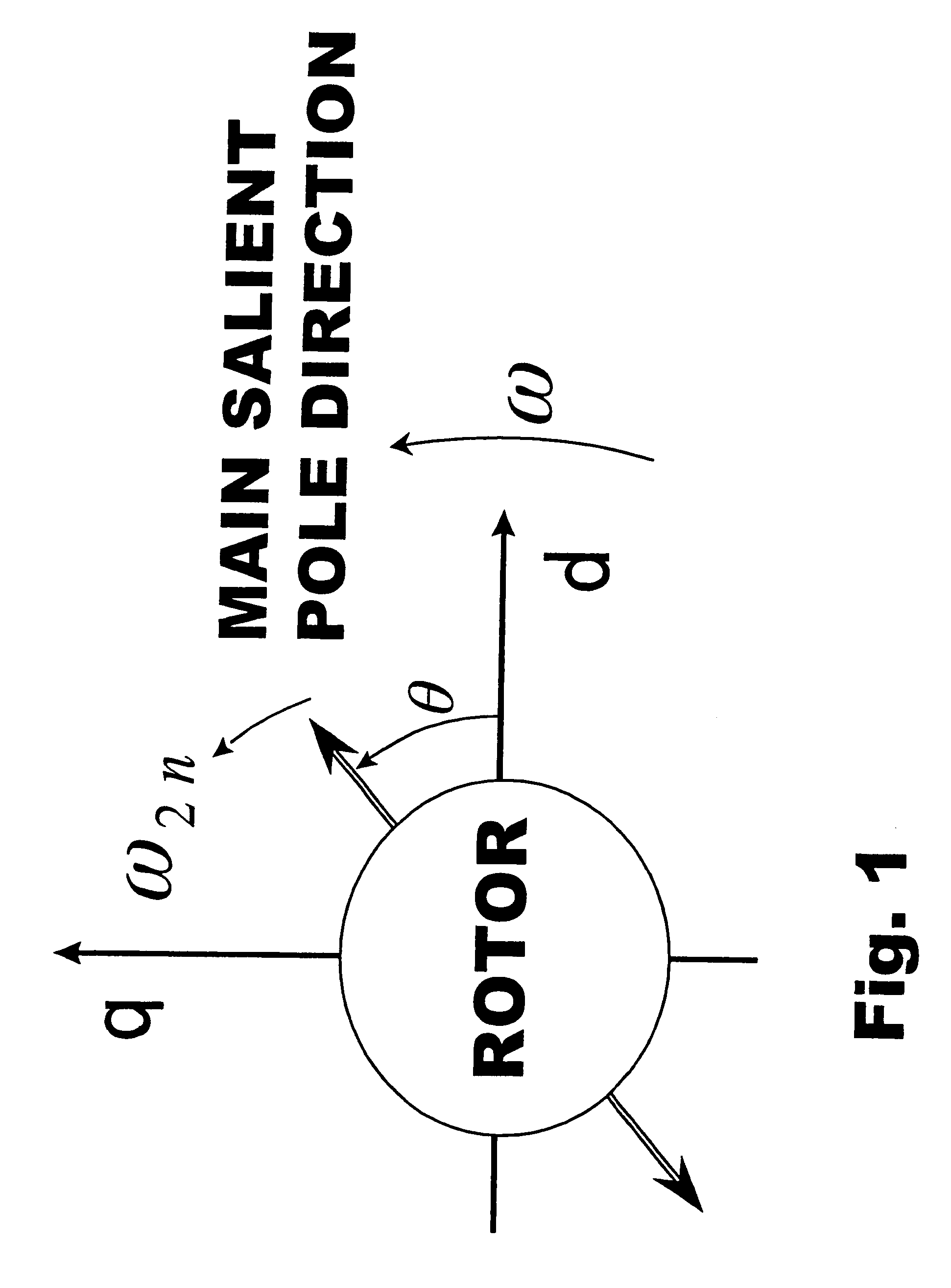
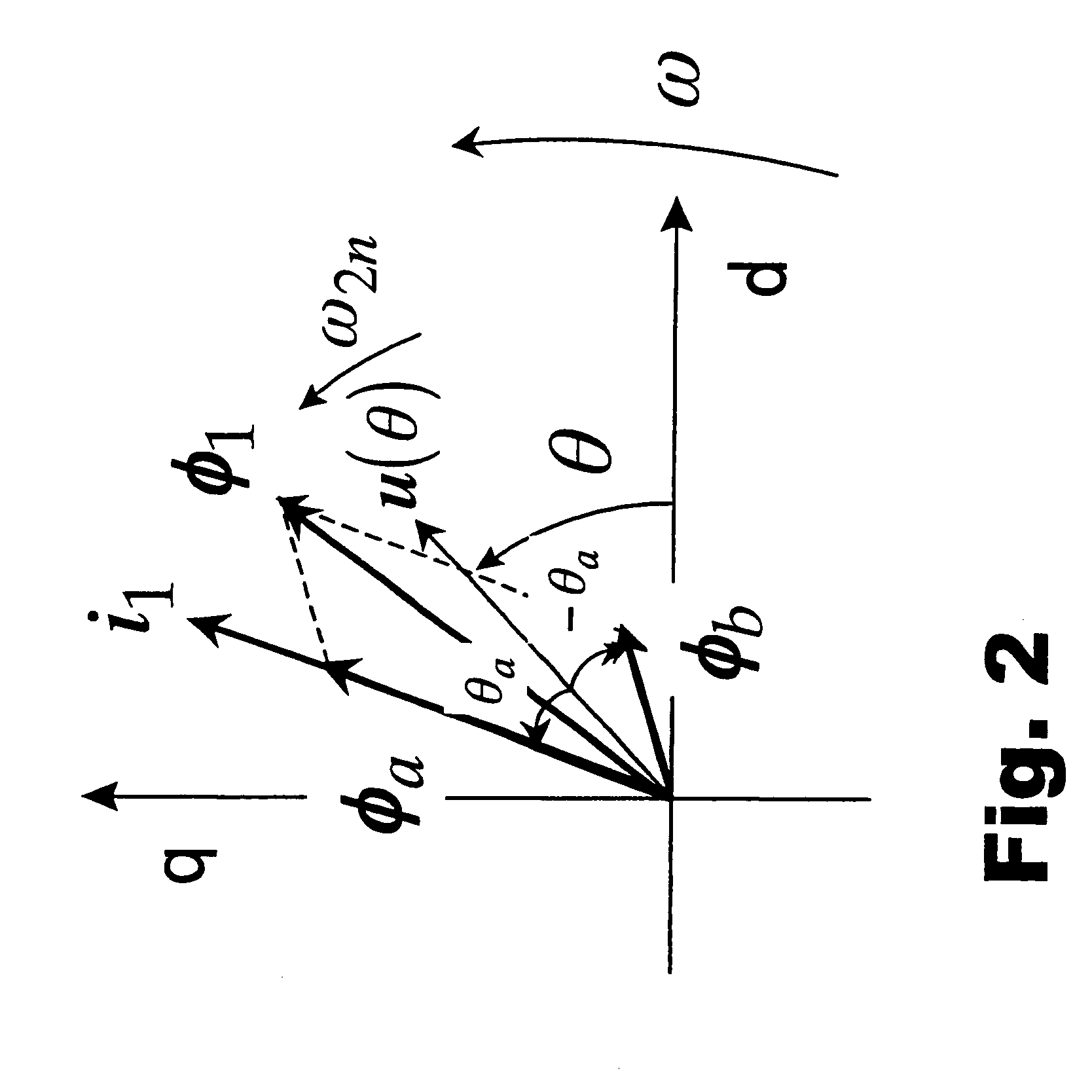
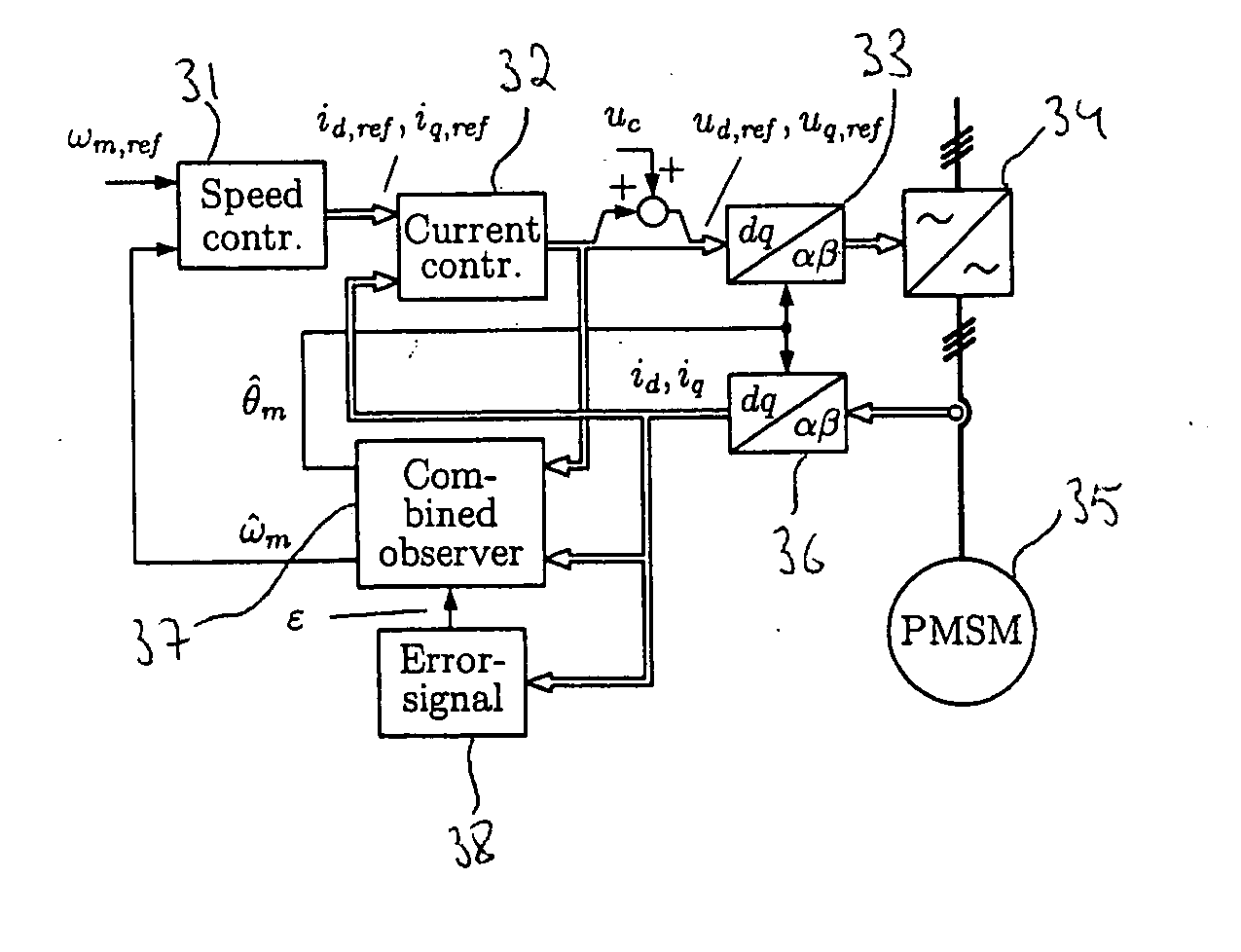
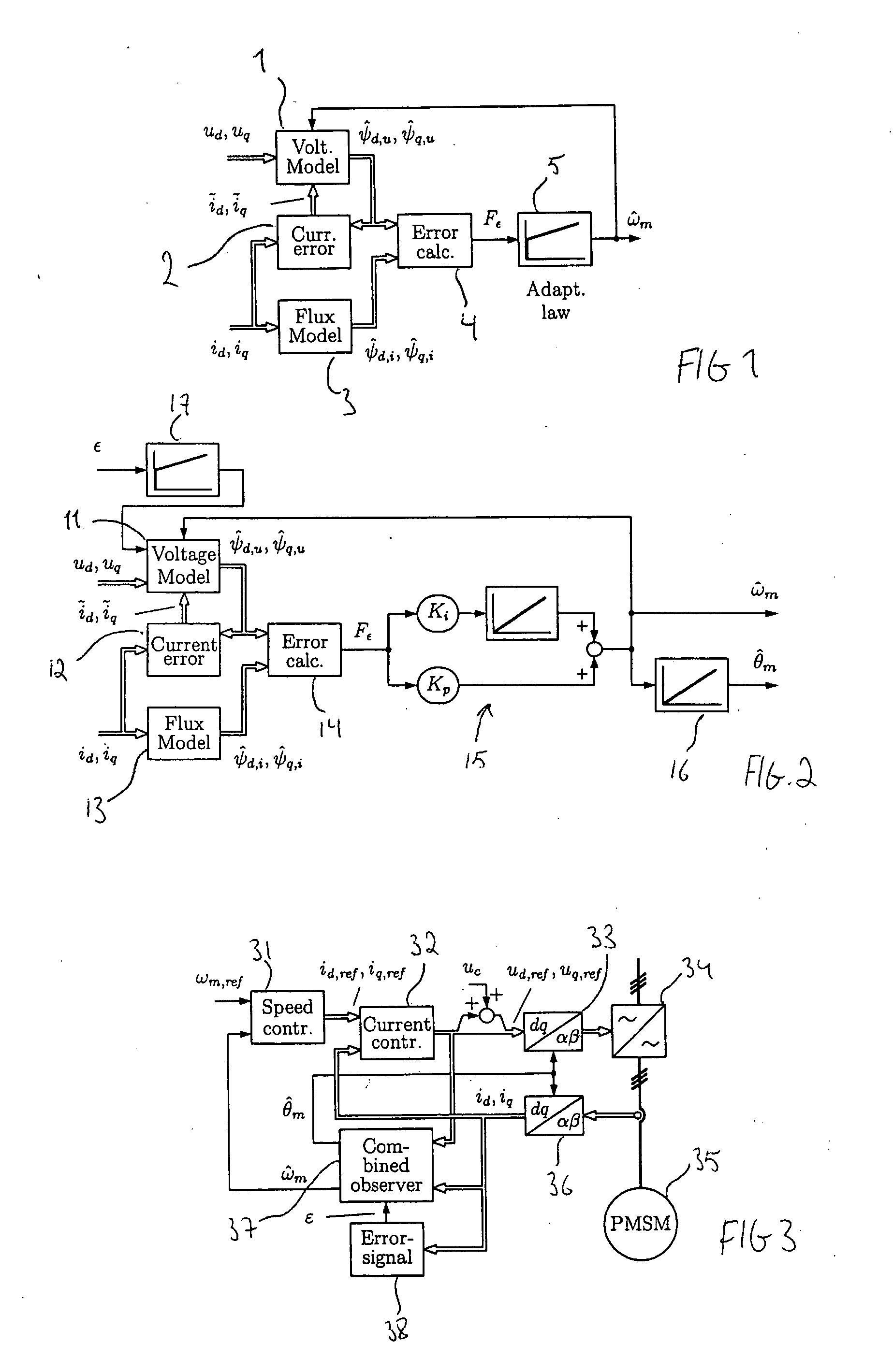
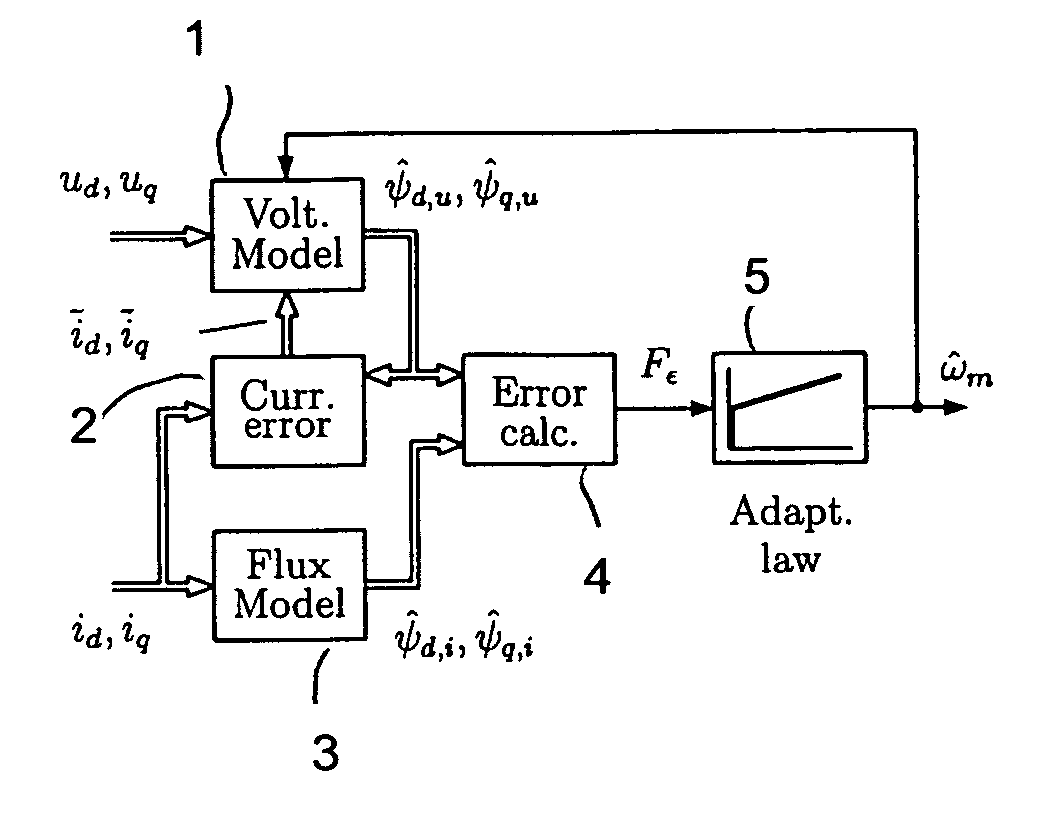
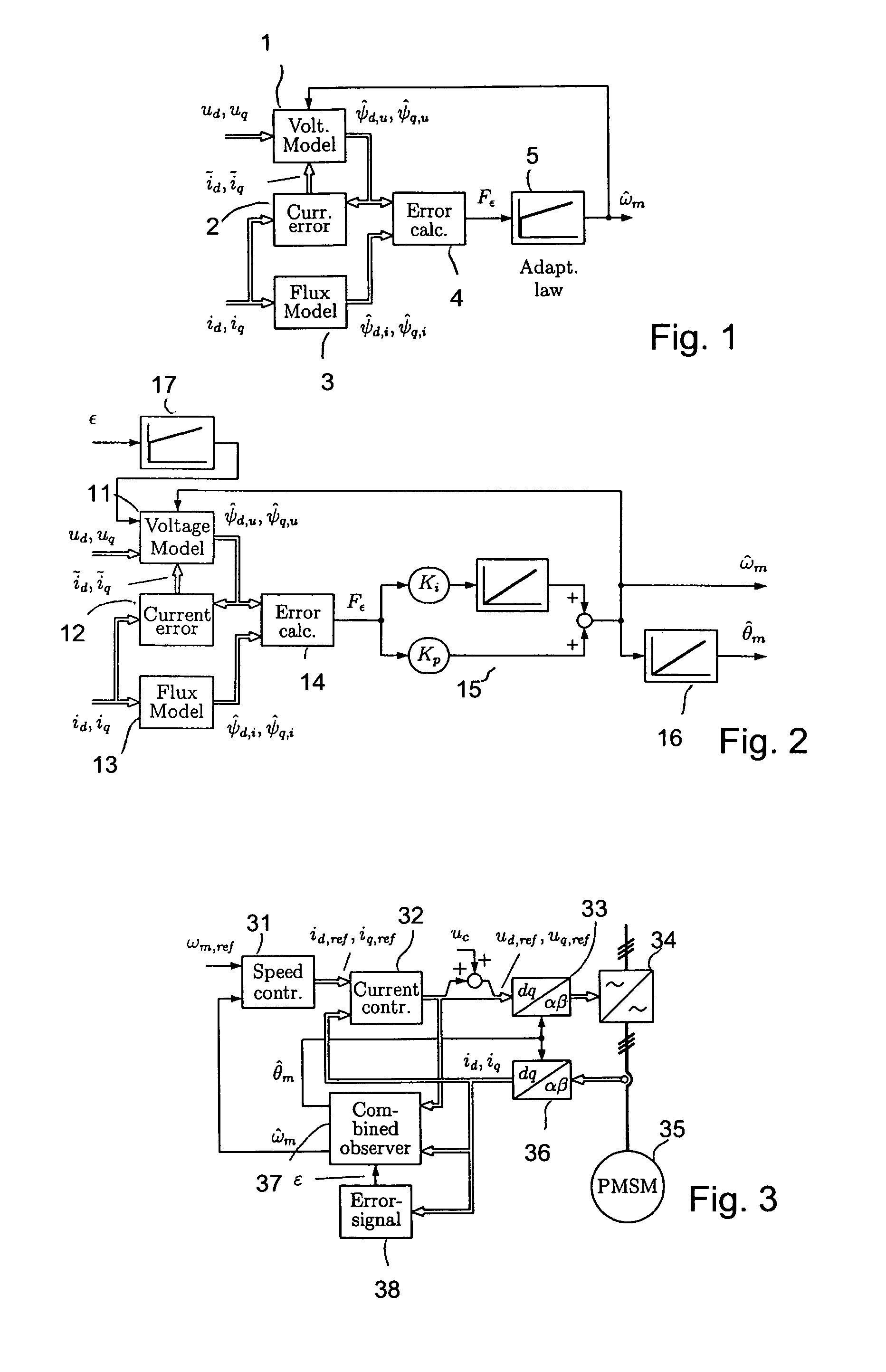
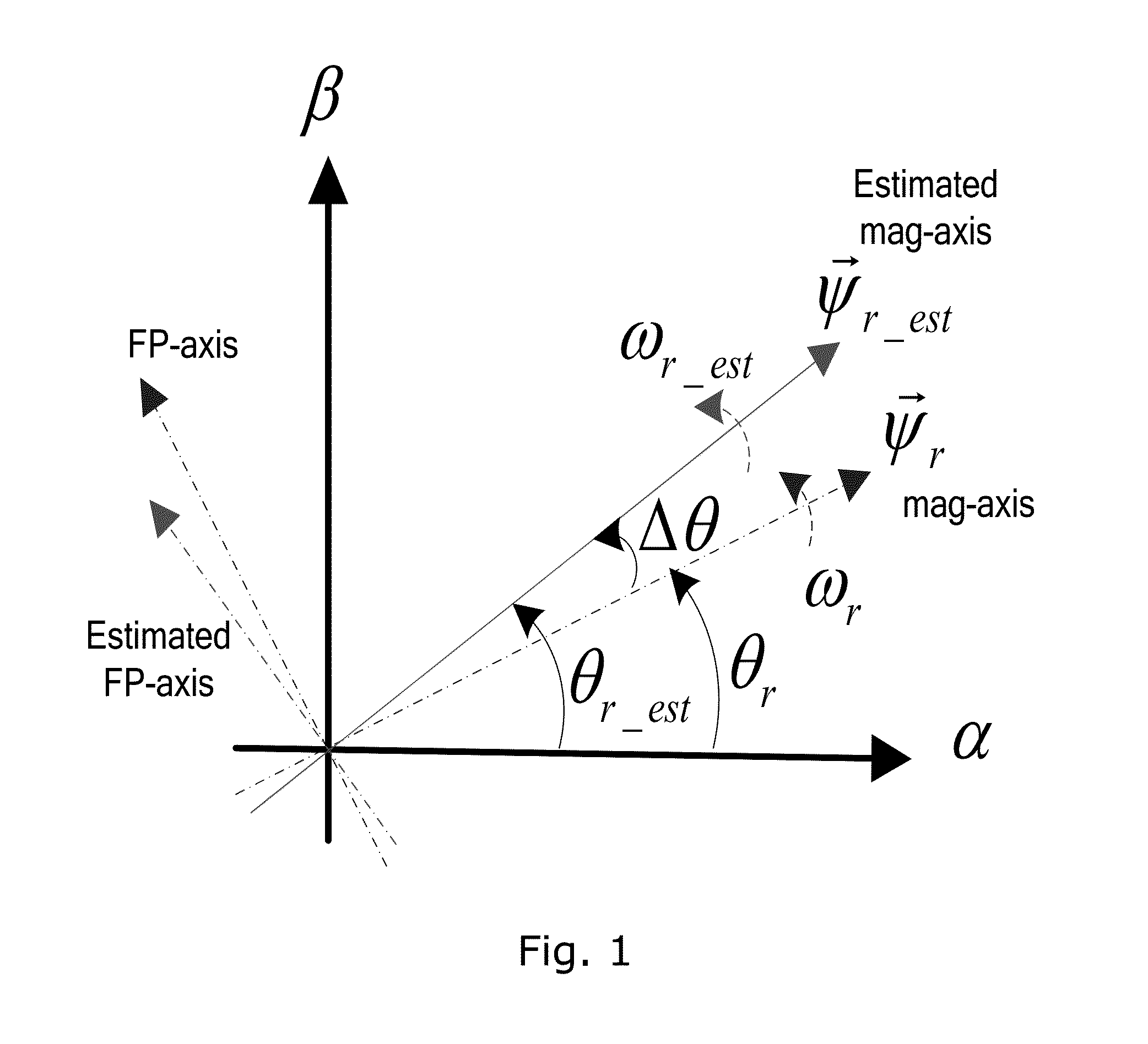
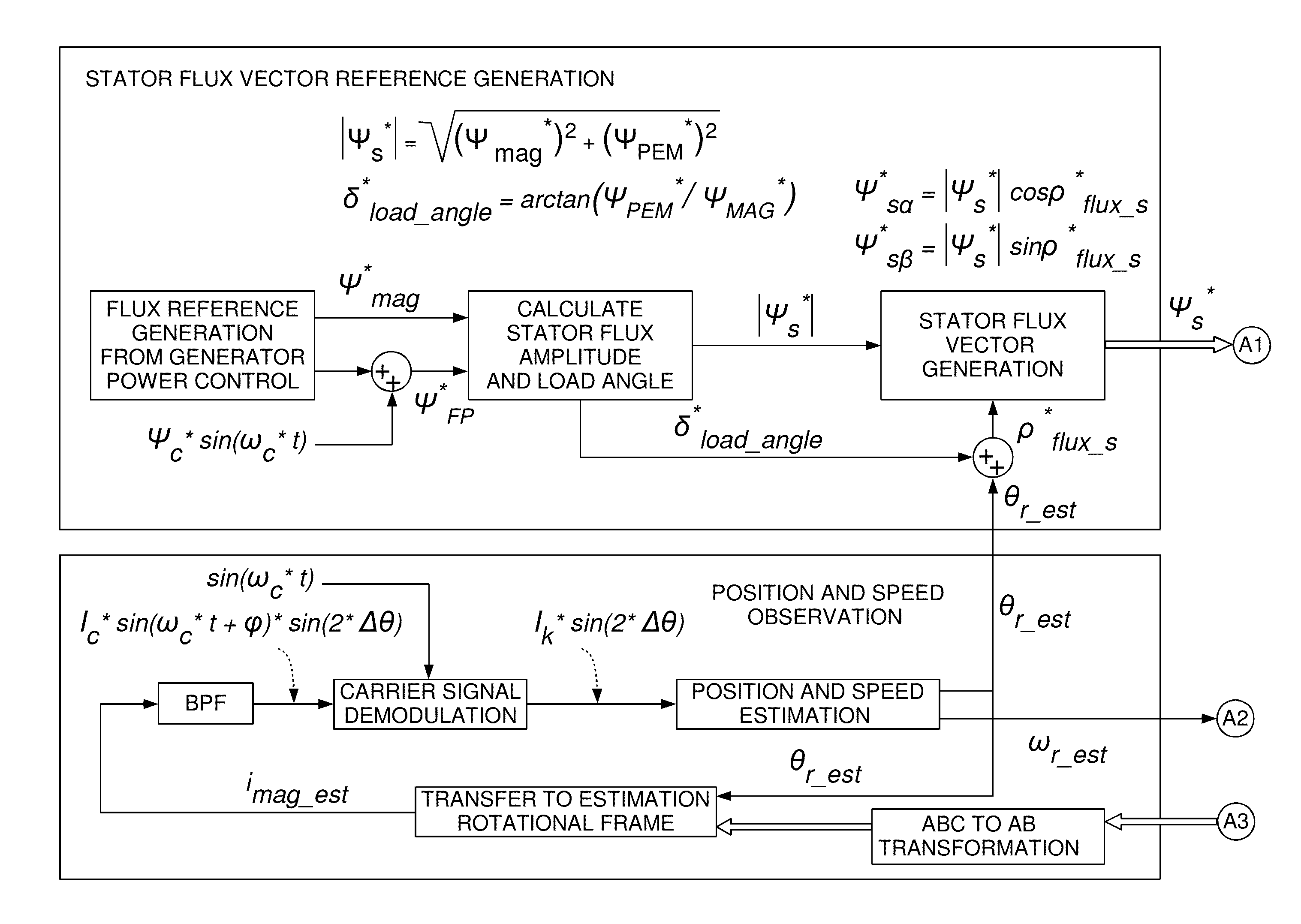
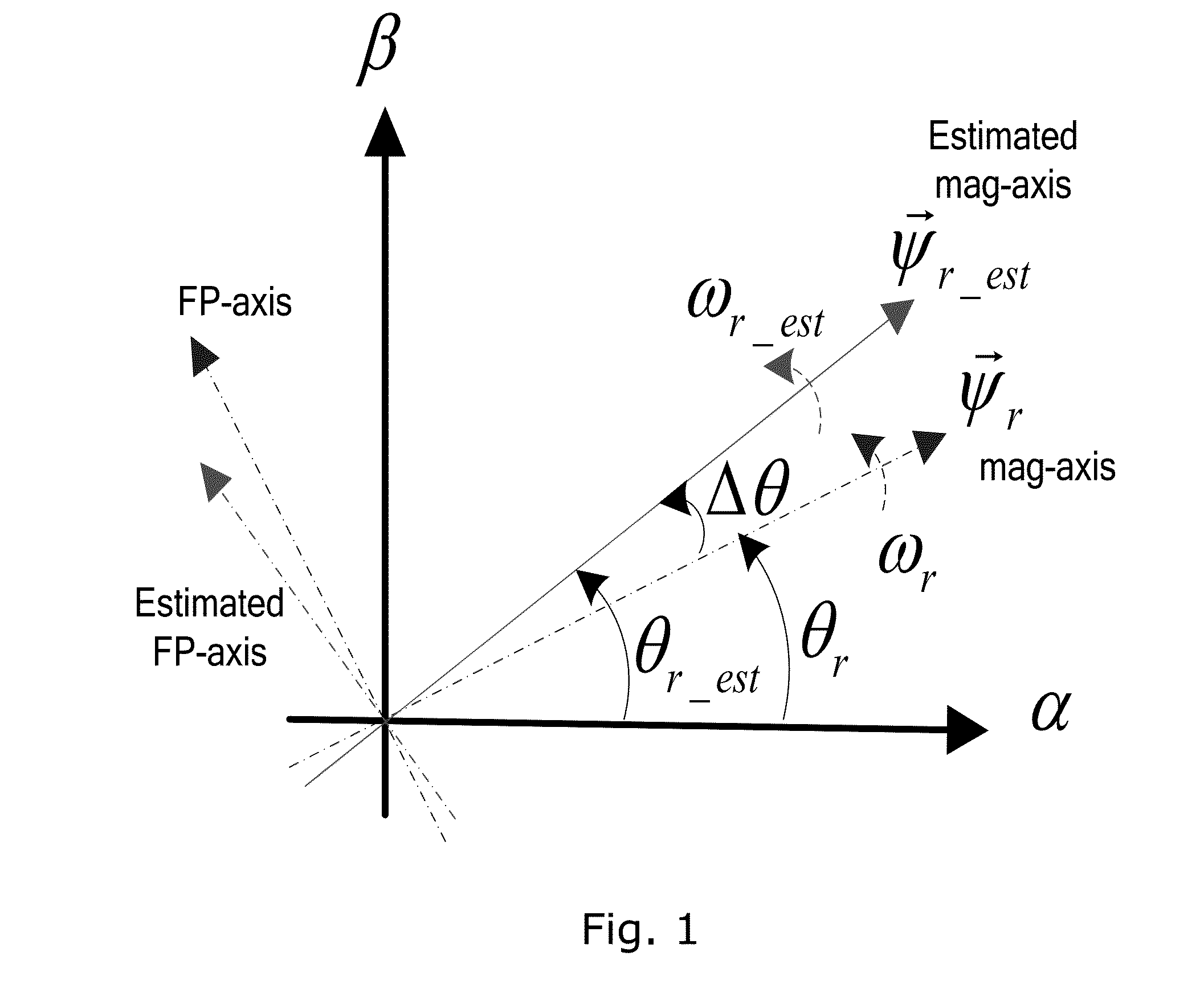
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS7098623B2Improve dynamic performanceSmaller positionSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveUS20010024100A1Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl vectorSynchronous reluctance motor
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators. A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
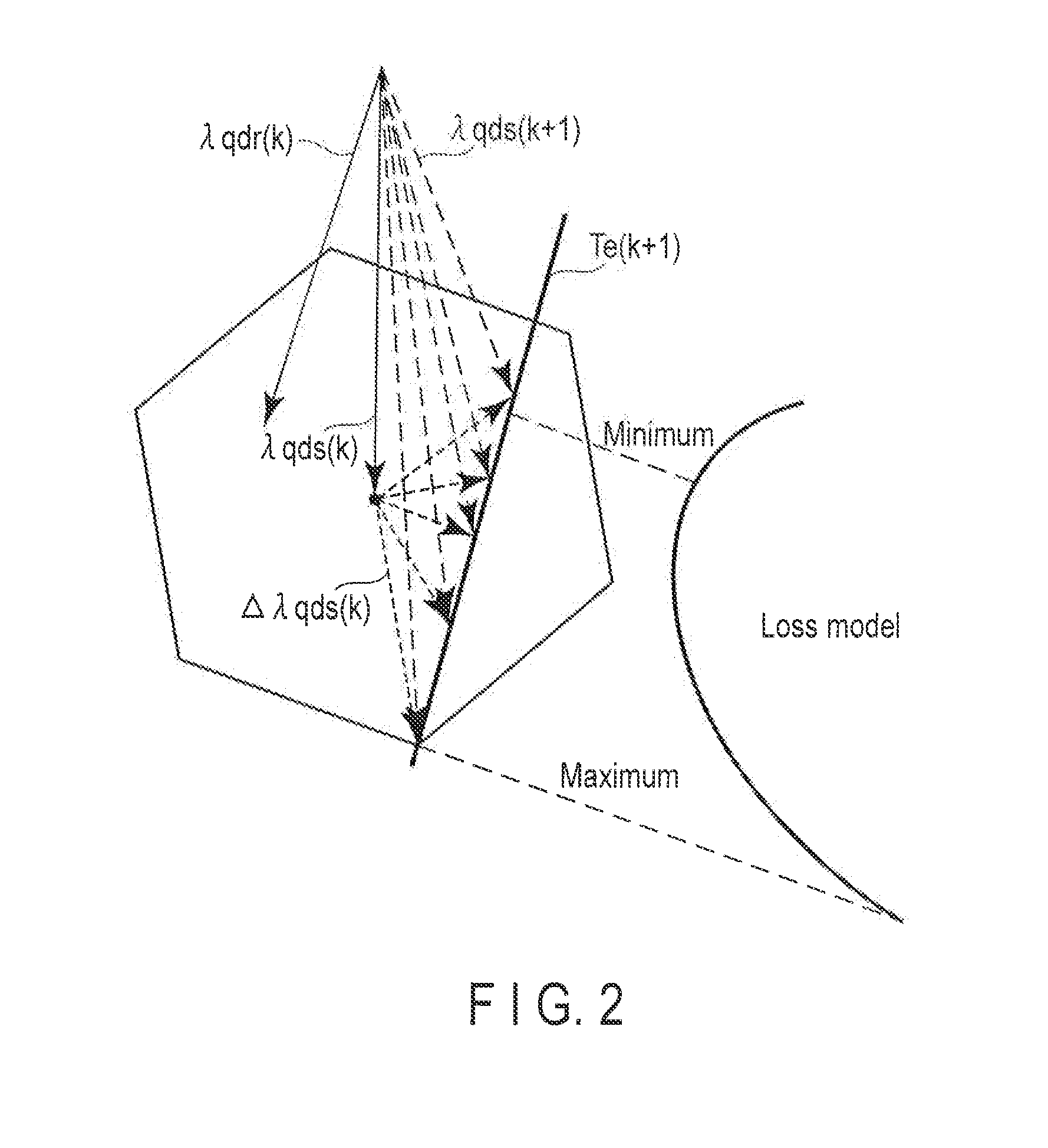
Controller for power converter
ActiveUS9281772B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhysical modelEngineering
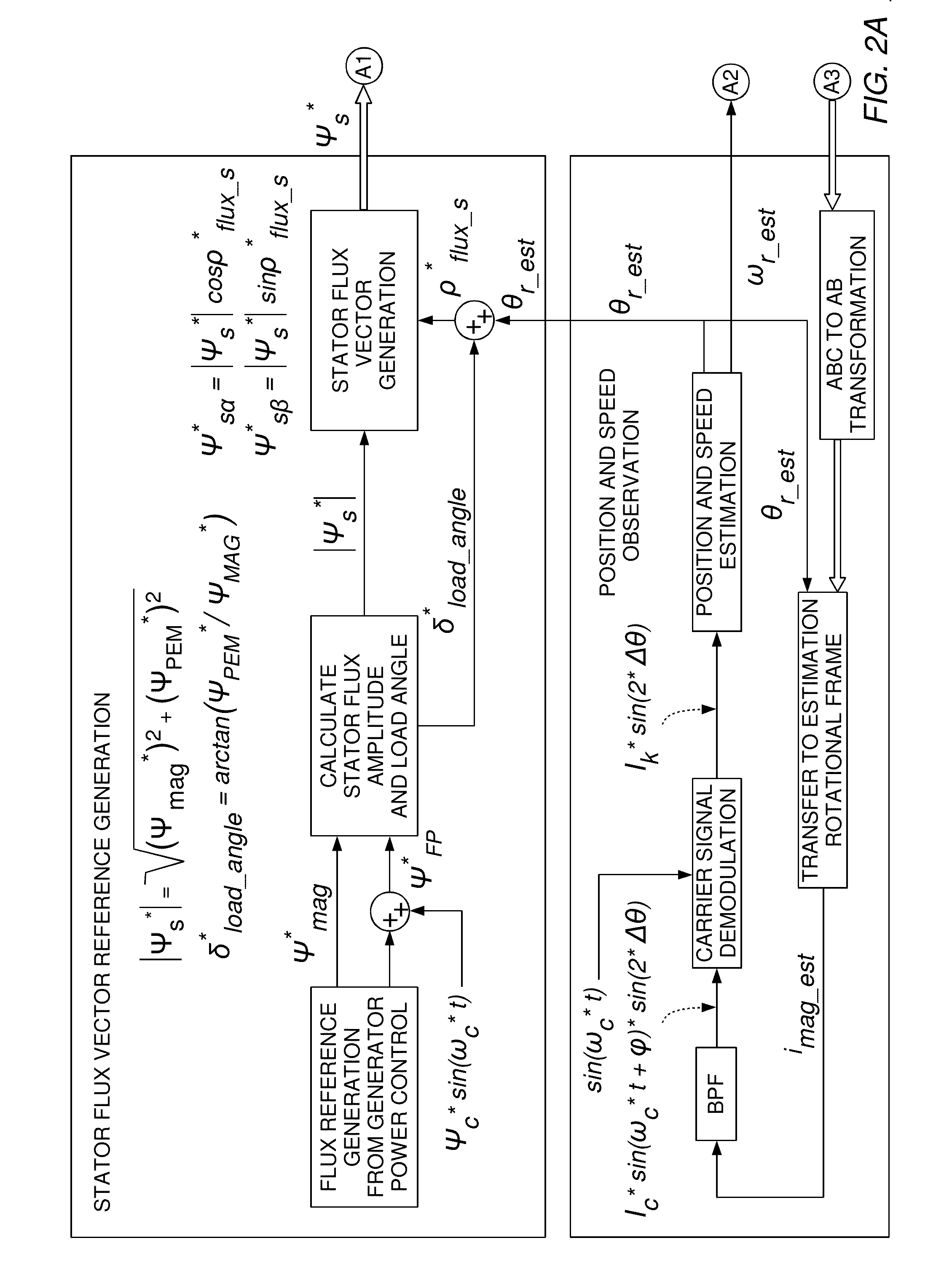
A controller for a power converter detects a current output from the power converter, estimates a flux vector of the motor, and calculates a torque line in a physical model resulting from mathematizing a circuit equivalent to the motor, based on the estimated flux vector. The torque line indicates a line for obtaining a desired torque in a subsequent control period. The controller calculates a stator flux command value in accordance with a loss, calculates a voltage command value based on the torque line and the stator flux command value, and controls an output voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
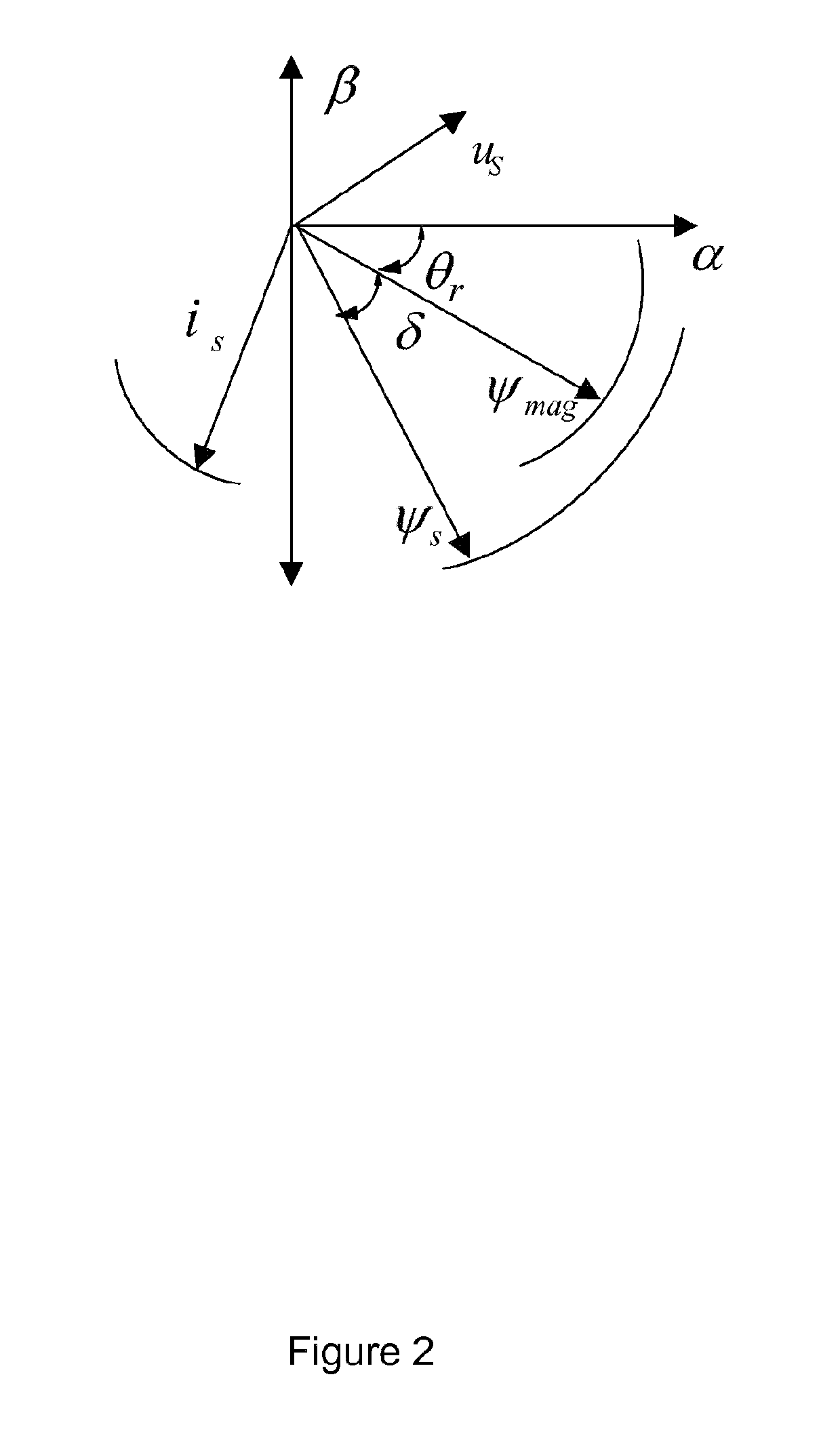
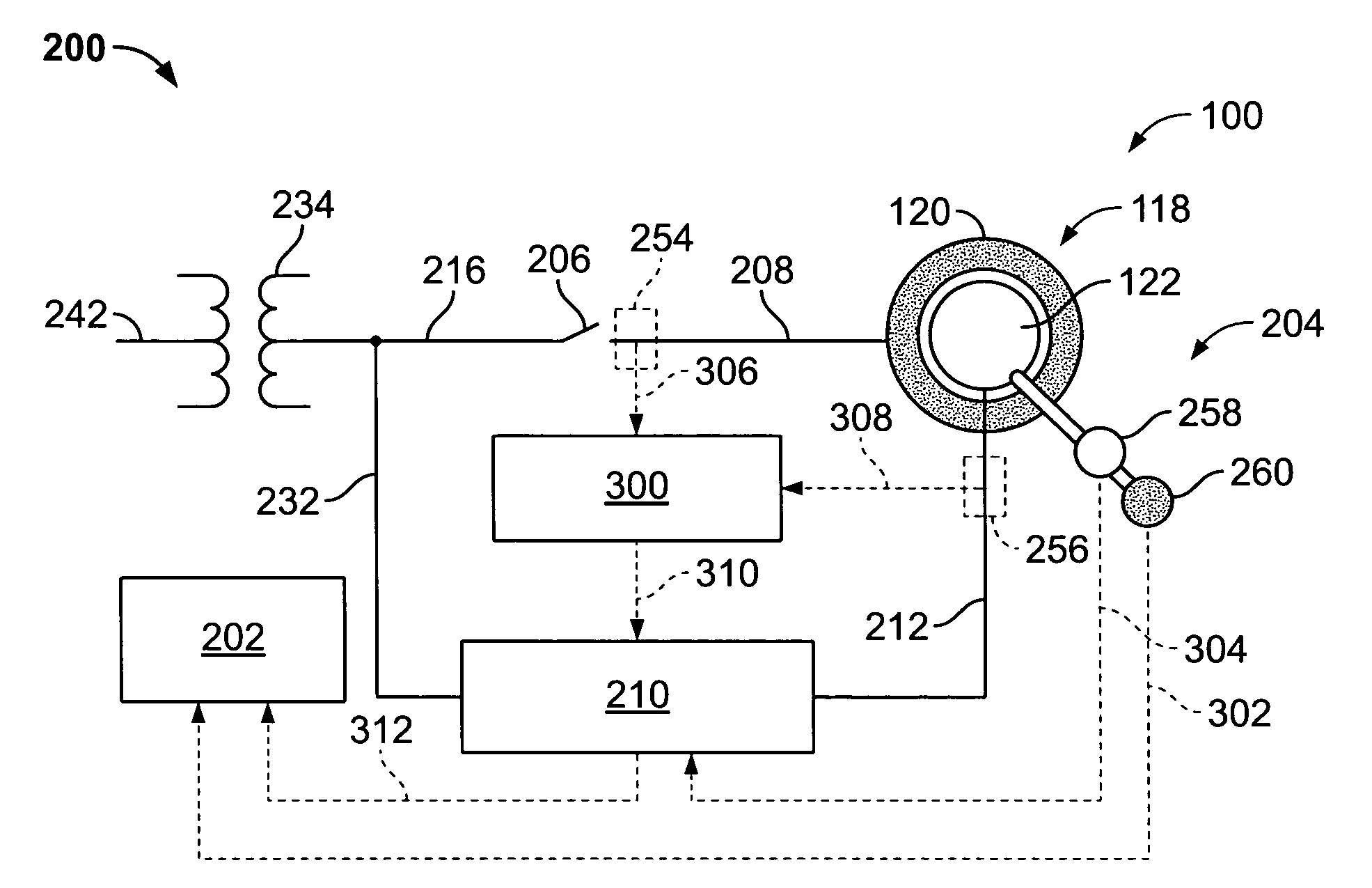
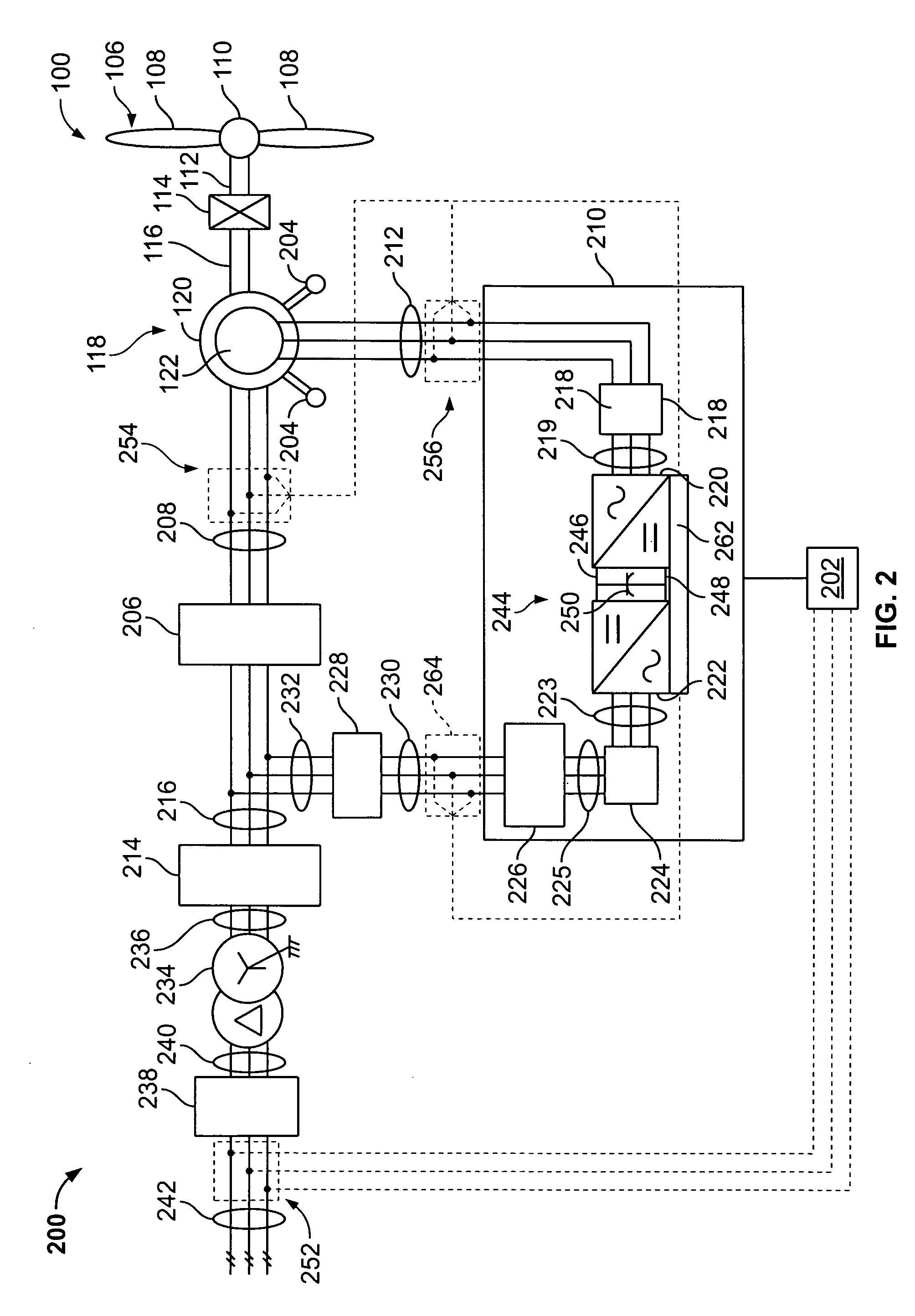
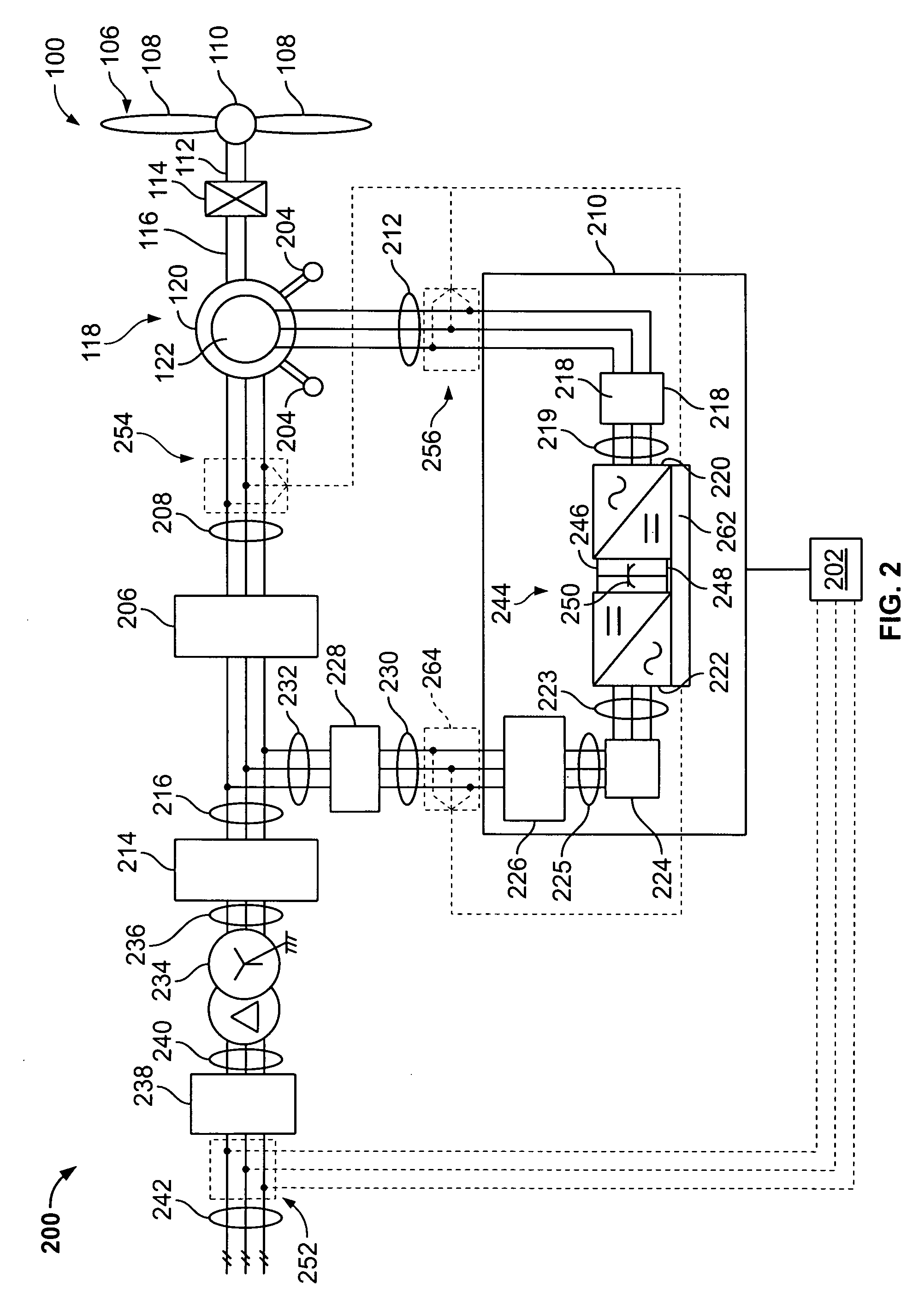
Direct power and stator flux vector control of a generator for wind energy conversion system
InactiveUS8395360B2Lower requirementDirect operationVector control systemsWind motor controlWind energy conversionVariable speed wind turbine
A method for controlling a variable speed wind turbine generator is disclosed. The generator is connected to a power converter comprising switches. The generator comprises a stator and a set of terminals connected to the stator and to the switches of the power converter. The method comprises: determining a stator flux reference value corresponding to a generator power of a desired magnitude, determining an estimated stator flux value corresponding to an actual generator power, determining a difference between the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value, and operating said switches in correspondence to the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value to adapt at least one stator electrical quantity to obtain said desired generator power magnitude.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method and apparatus for assembling electrical machines
ActiveUS20090212564A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric forceElectricity
A method of assembling an electrical machine includes programming at least one processor with a stator flux vector estimation scheme. The electrical machine has a stator at least partially extending around a rotor. The electrical machine is electrically coupled to an electric power system. The electric power system transmits at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine with at least partial power conversion. The stator flux vector estimation scheme is programmed to generate at least one stator back-electromagnetic force (back-EMF) signal and to generate at least one stator flux vector signal using the at least one stator back-EMF signal. The at least one stator flux vector signal at least partially represents an estimated rotor position. The method also includes coupling at least one output device in data communication with the at least one processor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
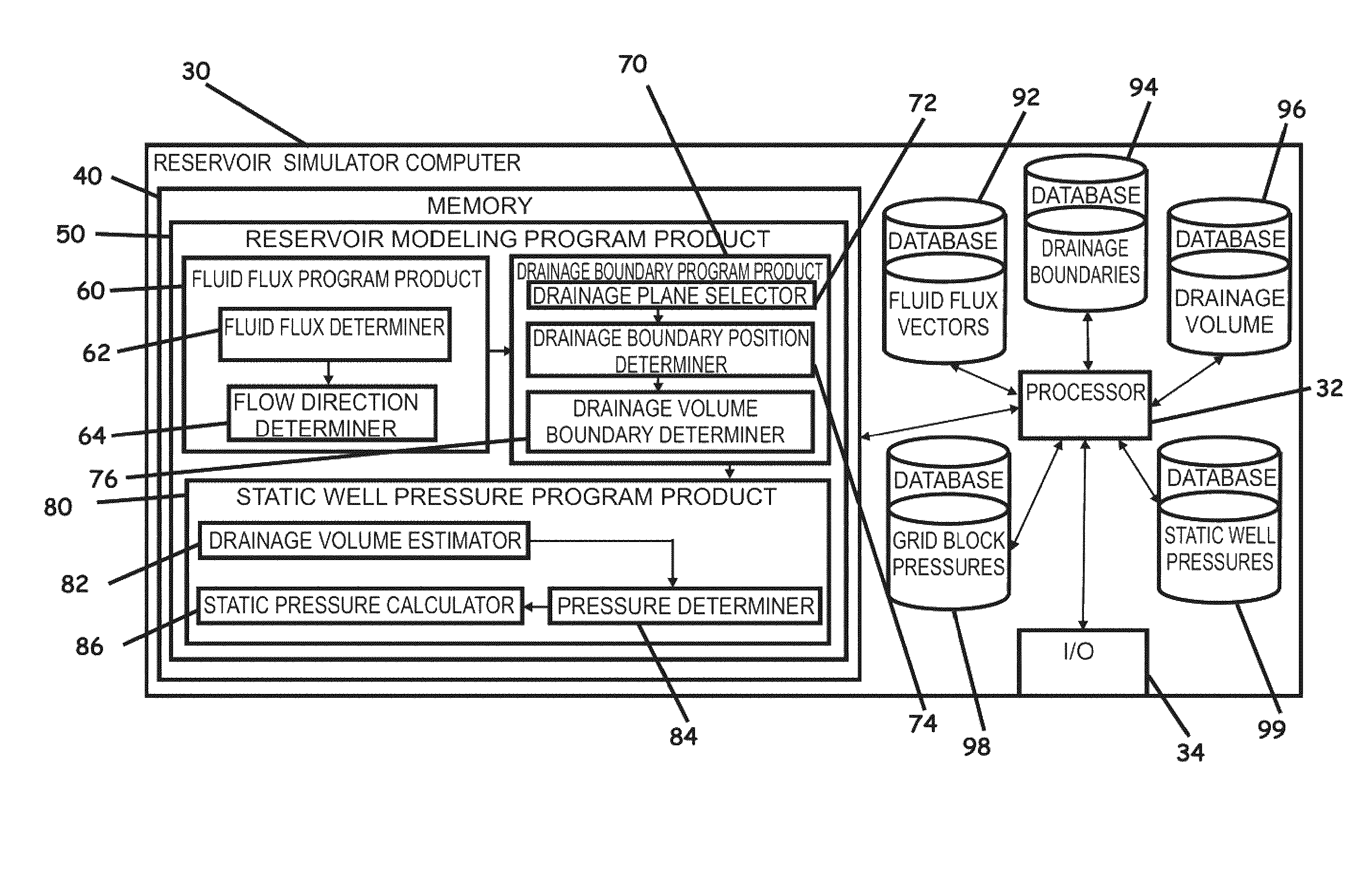
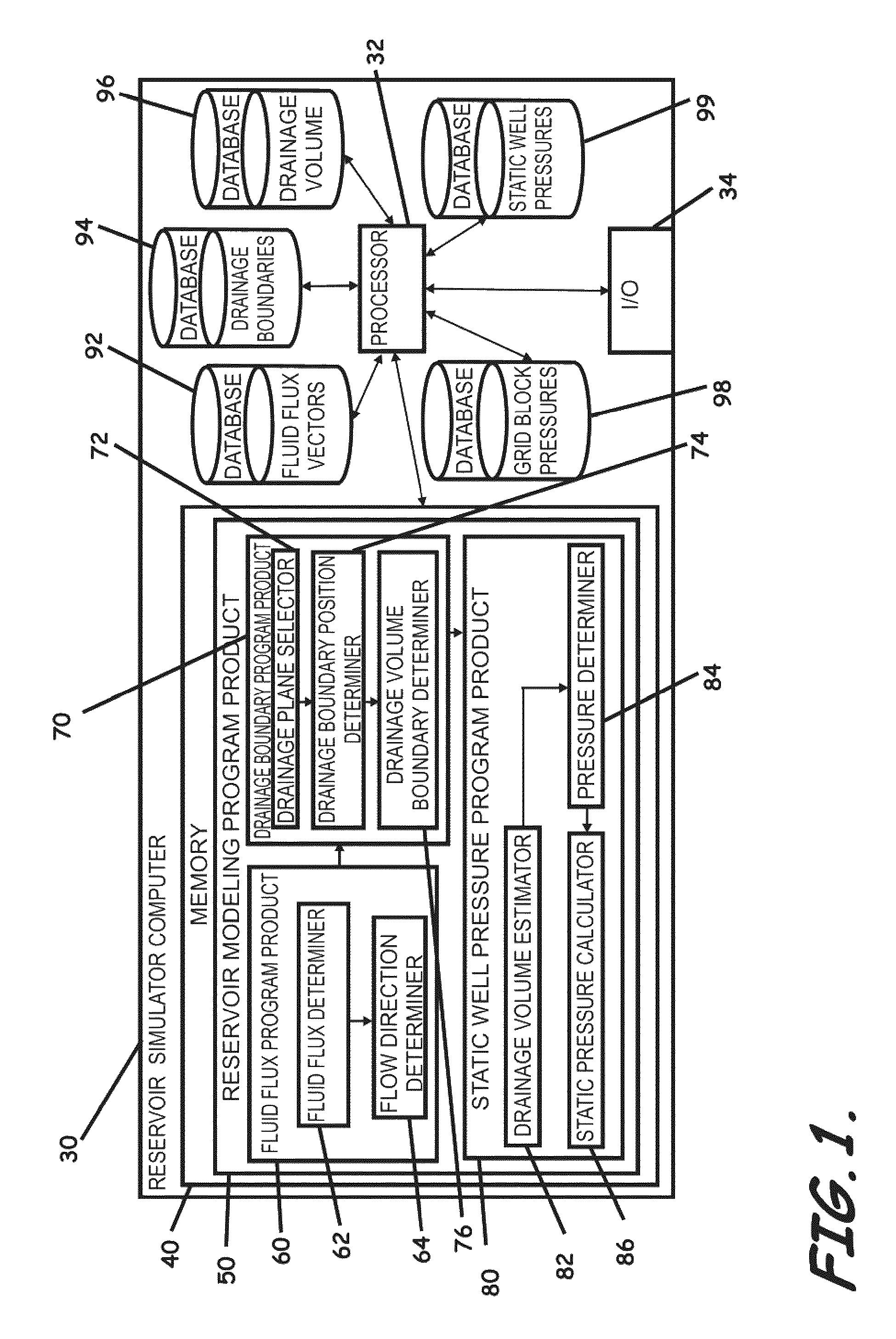
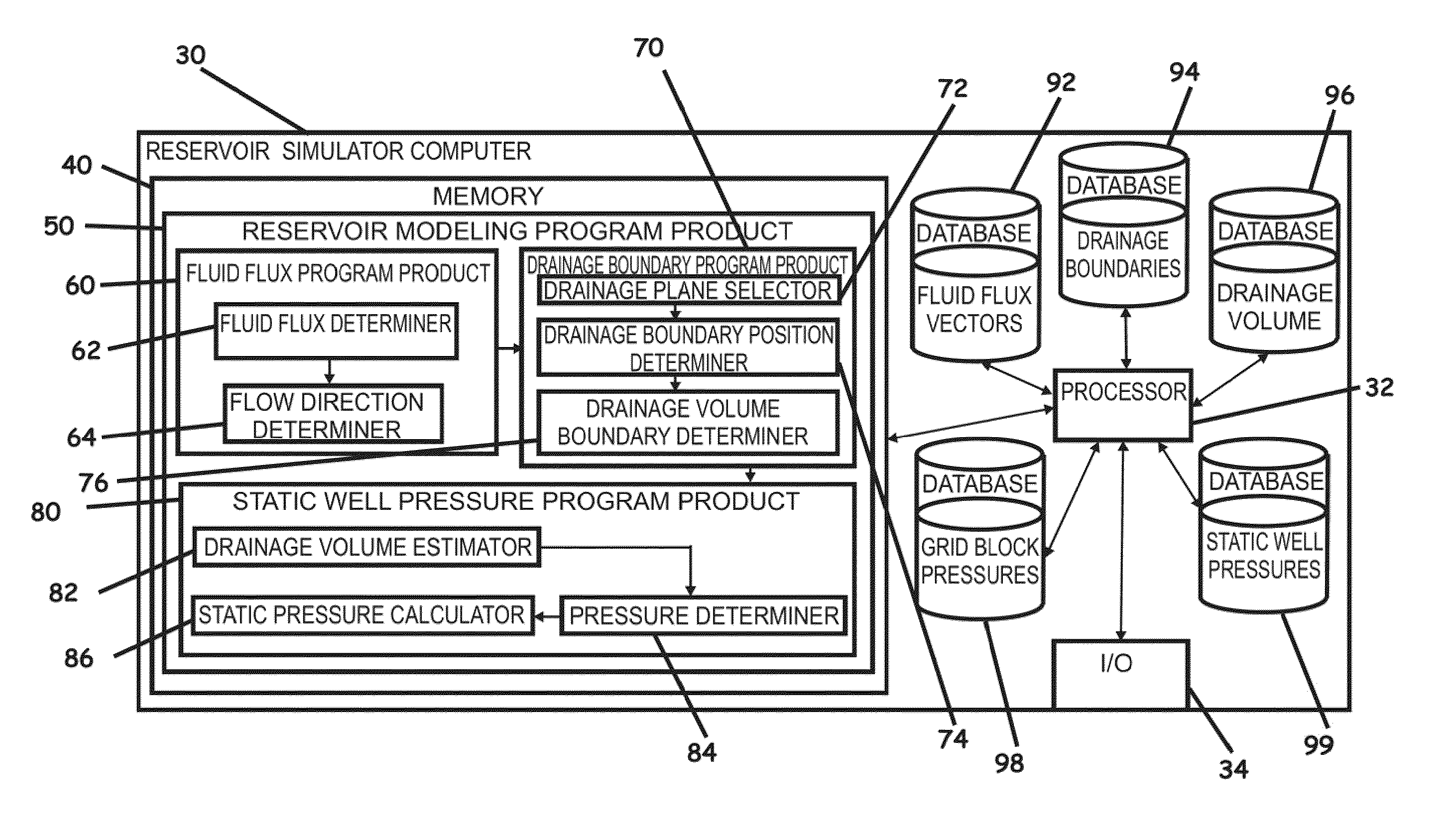
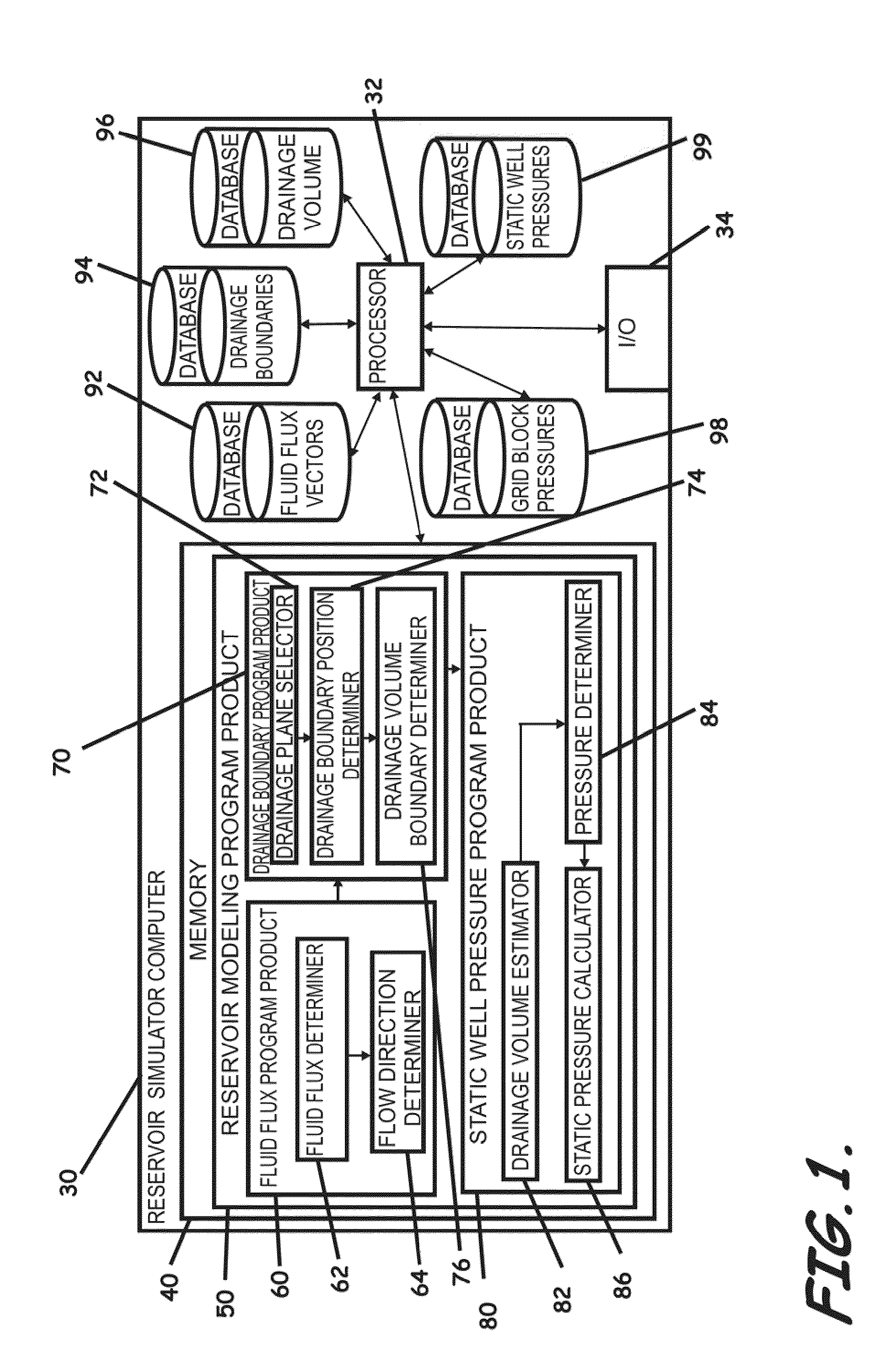
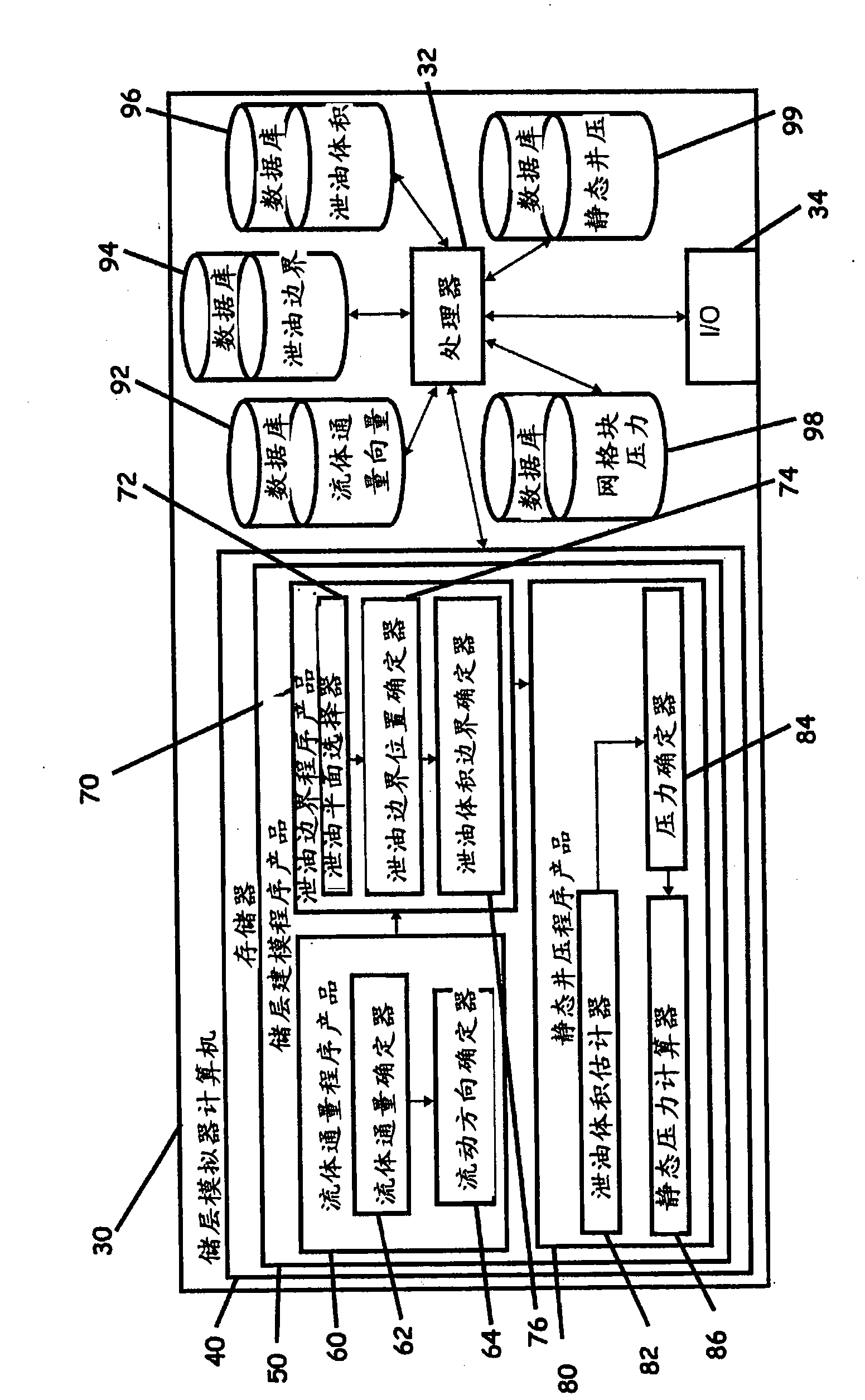
Systems, computer implemented methods, and computer readable program products to compute approximate well drainage pressure for a reservoir simulator
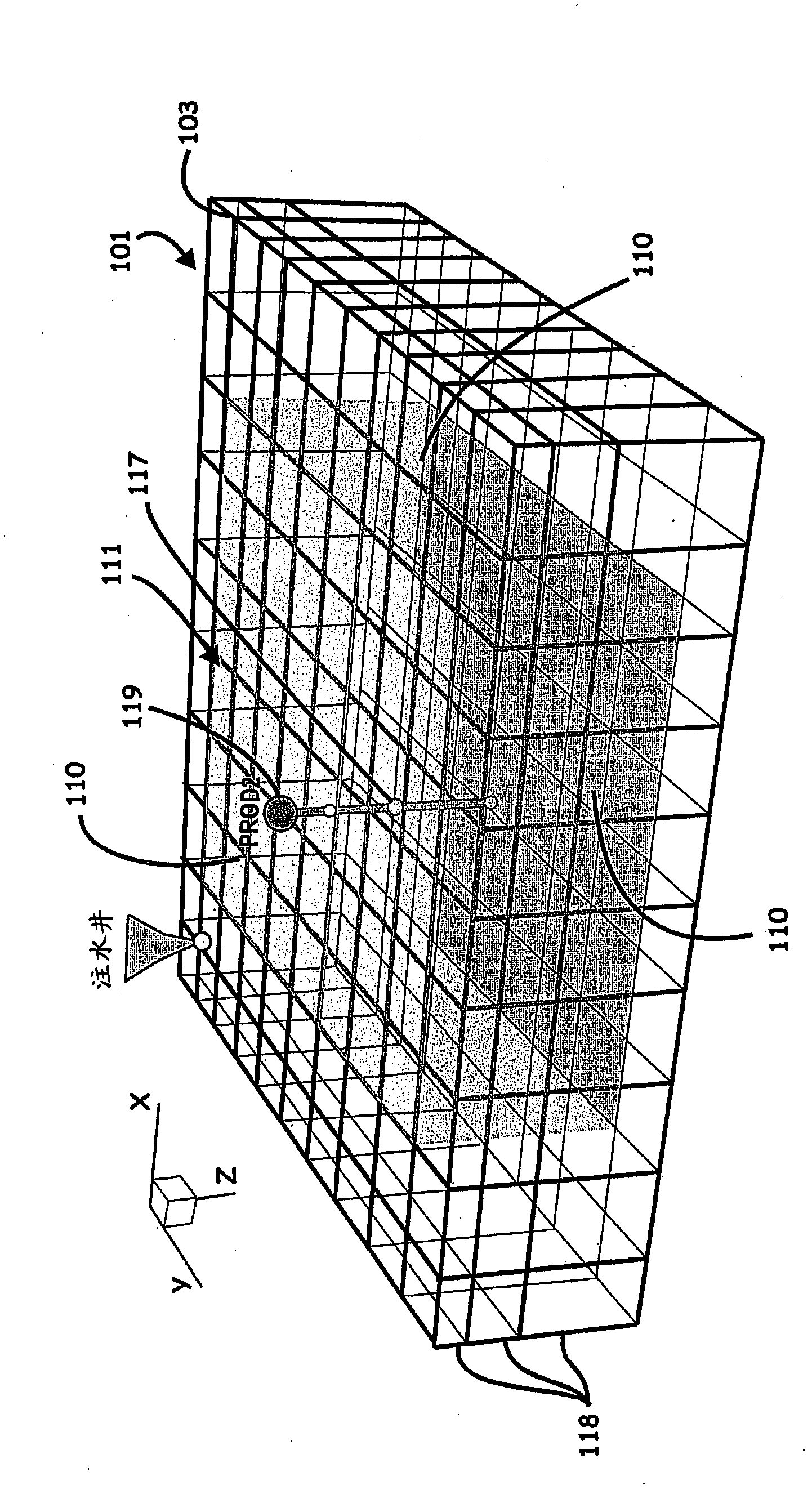
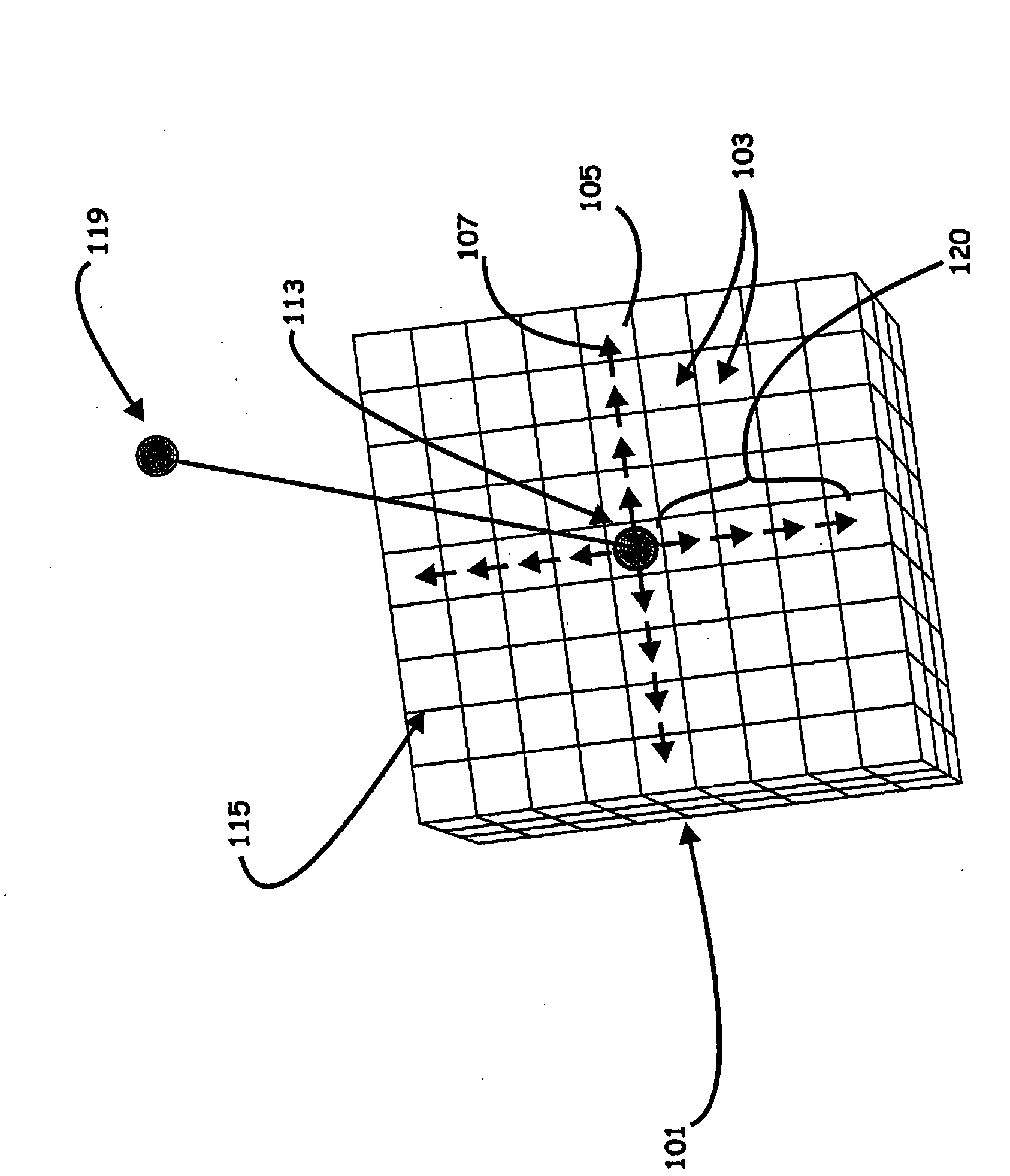
ActiveUS8589135B2Accurately approximatedIncrease pressureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyVolume averageComputer science
Systems, computer implemented methods, and program products to determine approximate static well pressures for one or more arbitrary shaped wells by estimating the drainage volume of the one or more wells, are provided. The drainage volume of the one or more wells, for example, can be estimated from the one or more computed fluid flow flux vectors, and the approximate static well pressures for the one or more wells can be subsequently calculated by taking the pore volume average of the dynamic grid block pressures within the drainage volume of the one or more wells. The one or more fluid flow flux vectors can be calculated at each iteration in a numerical reservoir simulator as a part of standard simulator computations, negating a need for additional, extraneous computations to calculate effective drainage volume of the one or more wells.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Direct power and stator flux vector control of a generator for wind energy conversion system
InactiveUS20120268081A1Lower requirementDirect operationVector control systemsWind motor controlWind energy conversionVariable speed wind turbine
A method for controlling a variable speed wind turbine generator is disclosed. The generator is connected to a power converter comprising switches. The generator comprises a stator and a set of terminals connected to the stator and to the switches of the power converter. The method comprises: determining a stator flux reference value corresponding to a generator power of a desired magnitude, determining an estimated stator flux value corresponding to an actual generator power, determining a difference between the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value, and operating said switches in correspondence to the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value to adapt at least one stator electrical quantity to obtain said desired generator power magnitude.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method for estimating stator flux of motor in vector converter
InactiveCN102340278ASolve DC DriftSolve the shortcomings of poor low-speed performanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageLow speed
The invention discloses a method for estimating a stator flux of a motor in a vector converter, and relates to the method for calculating the stator flux of the motor. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating a back electromotive force of a rotor according to the stator current and stator voltage of the motor; synthesizing a given value of a rotor flux of the motor and the position information of the rotor flux to form a given value of a rotor flux vector; and calculating a pre-estimated value of the rotor flux vector under a two-phase stationary coordinate system (alpha-beta) by adopting a closed loop integration scheme, and calculating a pre-estimated value of a stator flux vector according to relationships between the stator flux vector and rotor flux vector of the motor and the pre-estimated value of the rotor flux vector. The method is applied to a relatively wider speed regulation range; a system is ensured to have relatively higher dynamic performance at low speed, and the influence of an incorrect initial flux value can be eliminated; and the rotating speed of the rotor of the motor can be calculated according to the calculated stator flux and the calculated rotor flux without any speed sensor, so the structure of the motor is simplified and cost is decreased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Systems, Computer Implemented Methods, and Computer Readable Program Products to Compute Approximate Well Drainage Pressure for a Reservoir Simulator
ActiveUS20100286971A1Accurately approximatedIncrease pressureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyVolume averageComputer science
Systems, computer implemented methods, and program products to determine approximate static well pressures for one or more arbitrary shaped wells by estimating the drainage volume of the one or more wells, are provided. The drainage volume of the one or more wells, for example, can be estimated from the one or more computed fluid flow flux vectors, and the approximate static well pressures for the one or more wells can be subsequently calculated by taking the pore volume average of the dynamic grid block pressures within the drainage volume of the one or more wells. The one or more fluid flow flux vectors can be calculated at each iteration in a numerical reservoir simulator as a part of standard simulator computations, negating a need for additional, extraneous computations to calculate effective drainage volume of the one or more wells.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Controller for power converter
ActiveUS20150381092A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl theoryBoost power converter
A controller for a power converter detects a current output from the power converter, estimates a flux vector of the motor, and calculates a torque line in a physical model resulting from mathematizing a circuit equivalent to the motor, based on the estimated flux vector. The torque line indicates a line for obtaining a desired torque in a subsequent control period. The controller calculates a stator flux command value in accordance with a loss, calculates a voltage command value based on the torque line and the stator flux command value, and controls an output voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
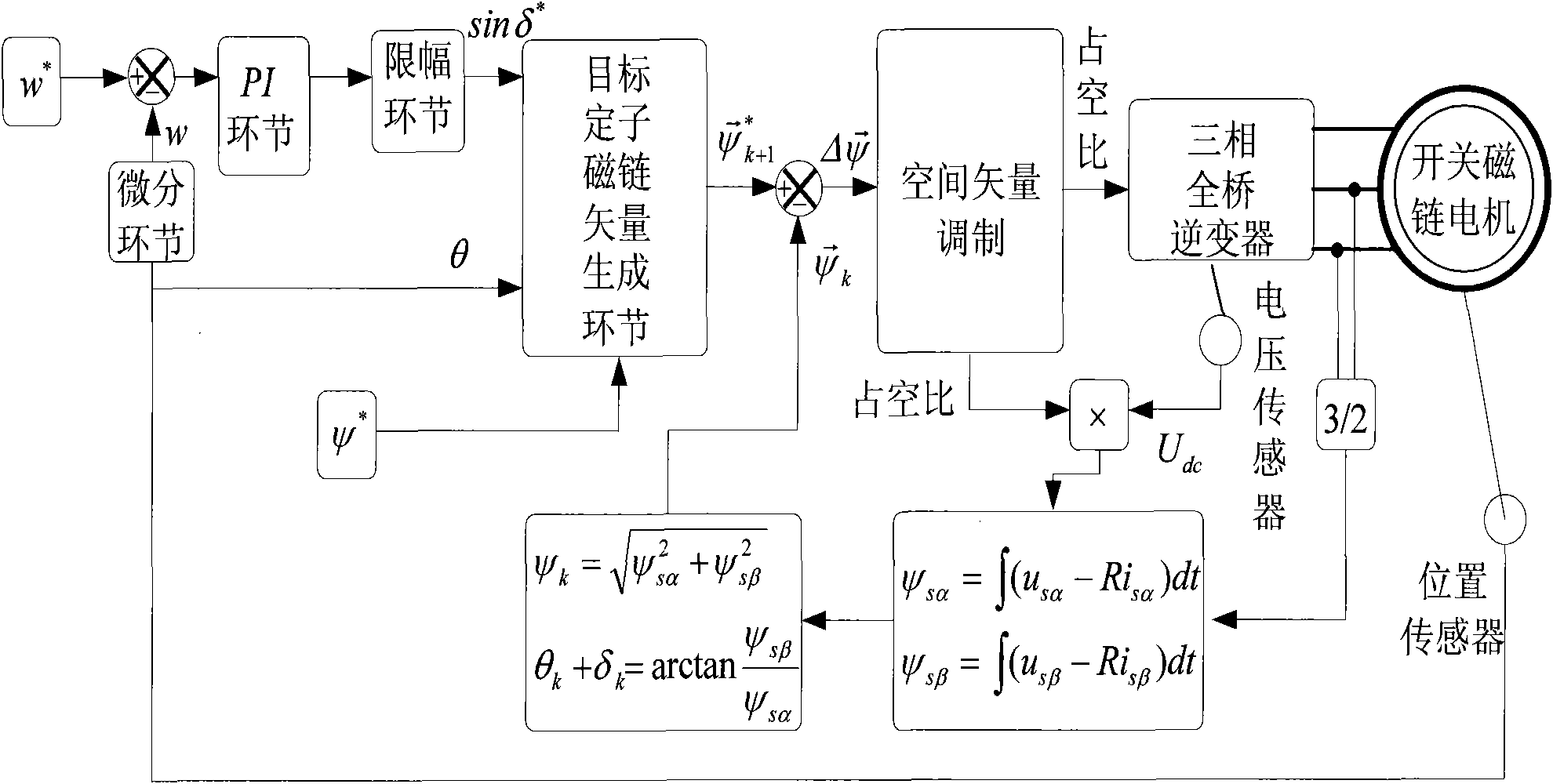
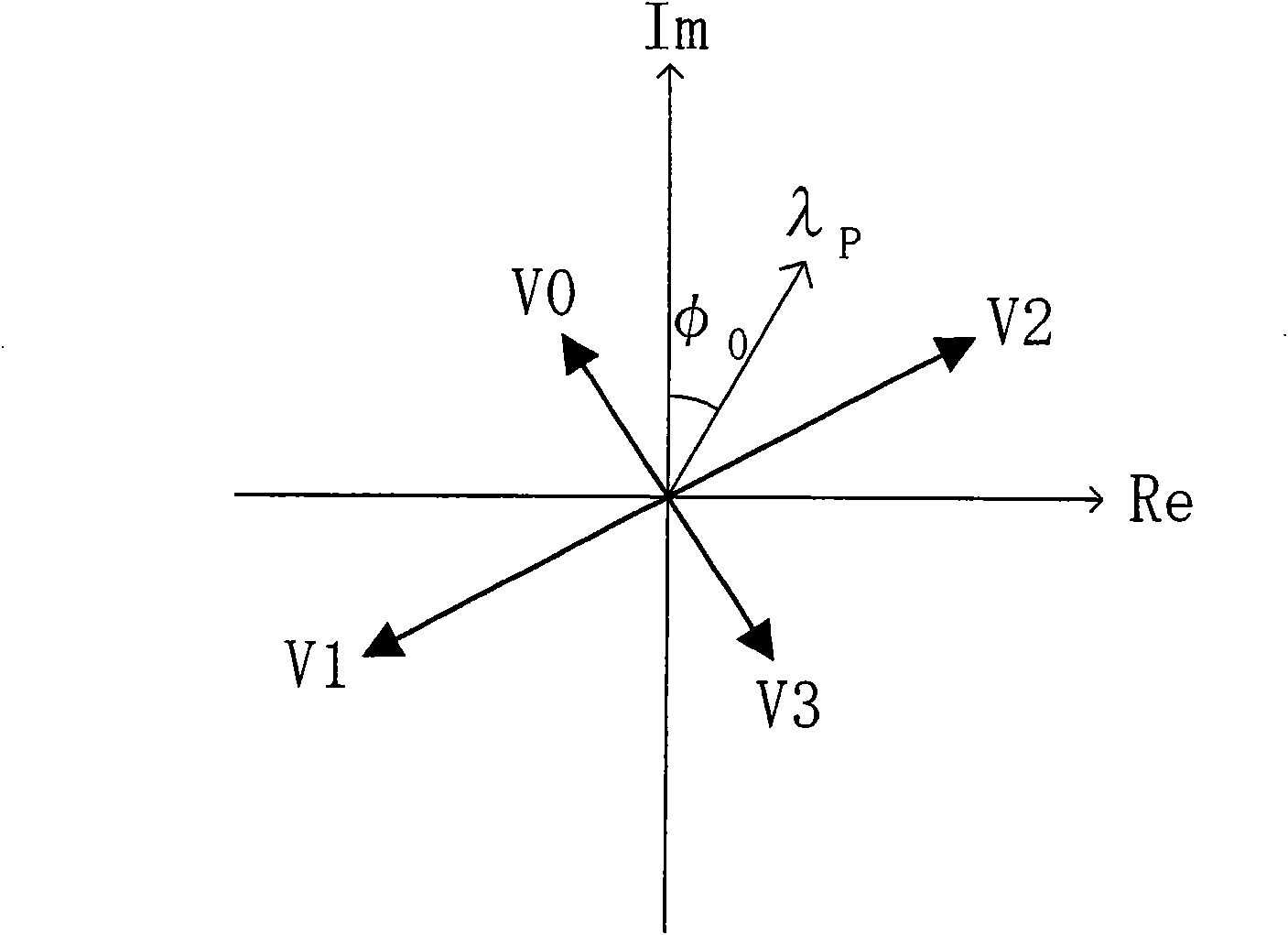
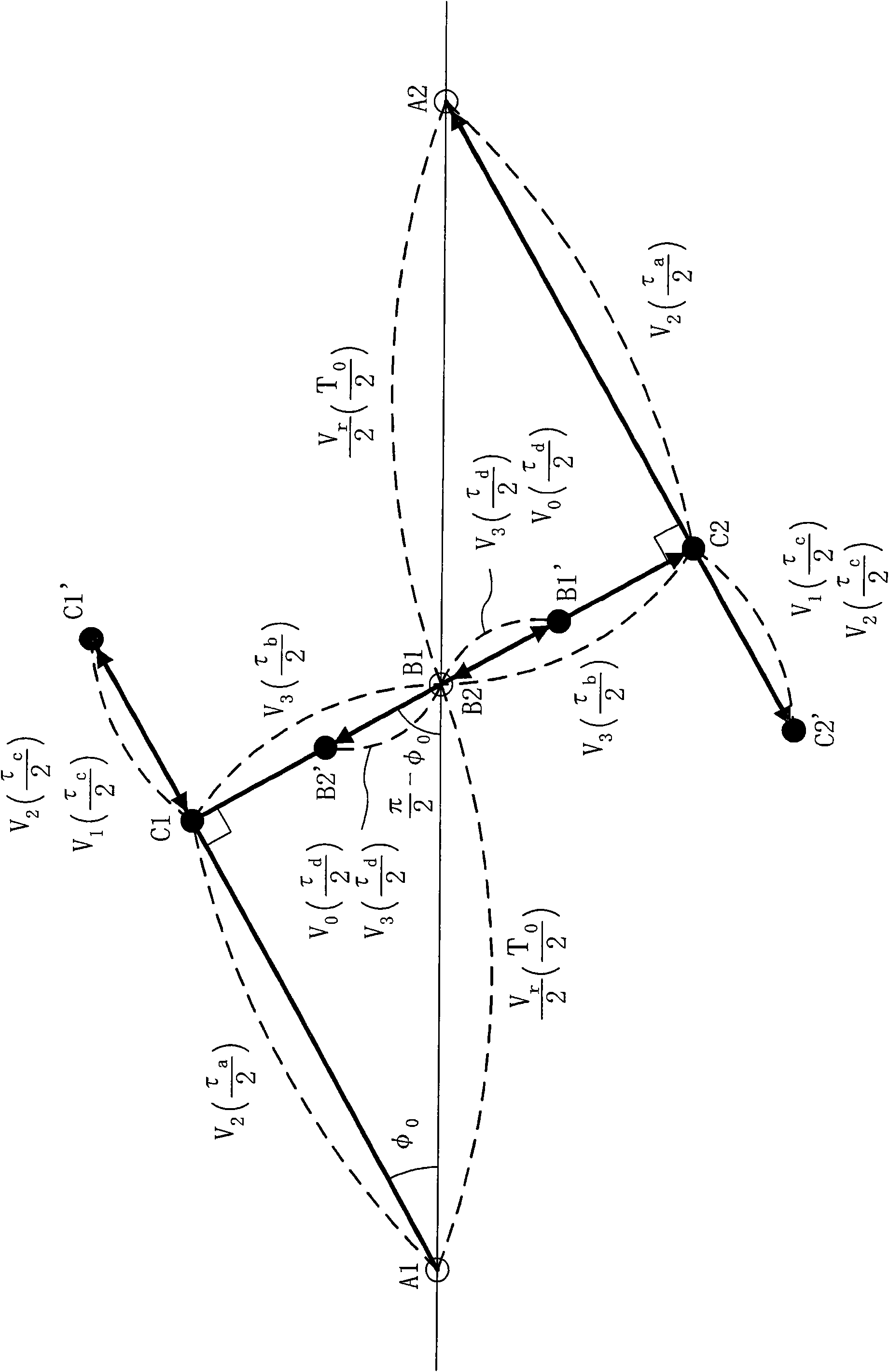
Space vector modulated method for linearly regulating speed of torque angle of permanent magnet flux switching motor
InactiveCN101582675AHarmonic reductionImprove robustnessVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlControl vectorHarmonic
The invention discloses a space vector modulated method for linearly regulating speed of a torque angle of a permanent magnet flux switching motor, and belongs to a method for regulating speed of a stator permanent magnet electrical machine. The speed regulating method defines an included angle between a stator flux vector of the permanent magnet flux switching motor and an unloaded permanent magnet flux vector, establishes a linear relation between a synthesized space vector and the torque angle, and controls torque by selecting the synthesized space vector to directly and linearly regulate a sine value of the torque angle of the permanent magnet flux switching motor. The method combines the characteristics of vector control for linearly regulating the torque and direct torque control for directly regulating the torque angle, no electric current link, and no coordinate conversion, and has simple realization, only identification of stator flux, strong parameter robustness, small current harmonics, torque pulsation and flux fluctuation, and good speed regulating performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and apparatus for assembling electrical machines
ActiveUS7745949B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric power transmissionMagnetic tension force
A method of assembling an electrical machine includes programming at least one processor with a stator flux vector estimation scheme. The electrical machine has a stator at least partially extending around a rotor. The electrical machine is electrically coupled to an electric power system. The electric power system transmits at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine with at least partial power conversion. The stator flux vector estimation scheme is programmed to generate at least one stator back-electromagnetic force (back-EMF) signal and to generate at least one stator flux vector signal using the at least one stator back-EMF signal. The at least one stator flux vector signal at least partially represents an estimated rotor position. The method also includes coupling at least one output device in data communication with the at least one processor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
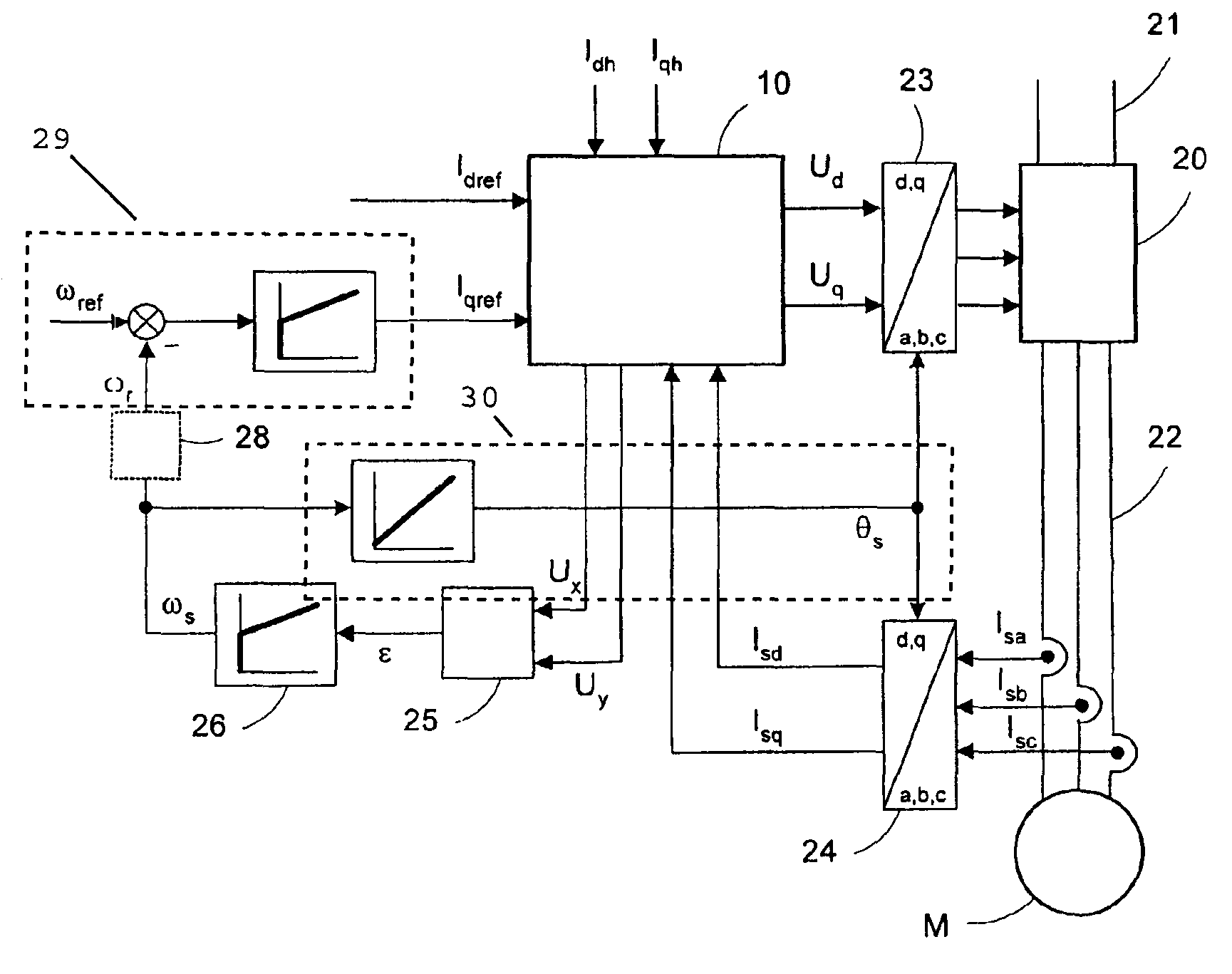
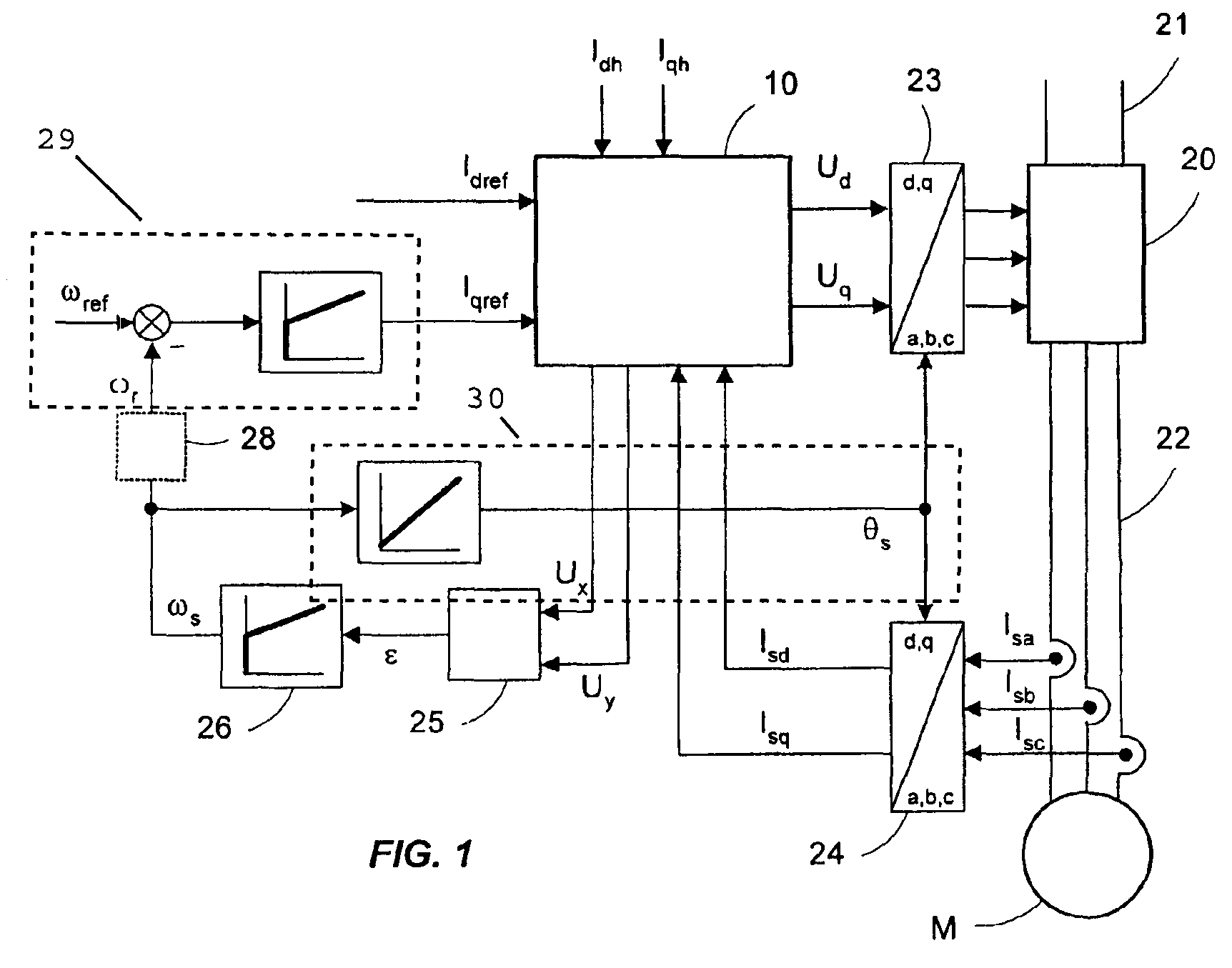
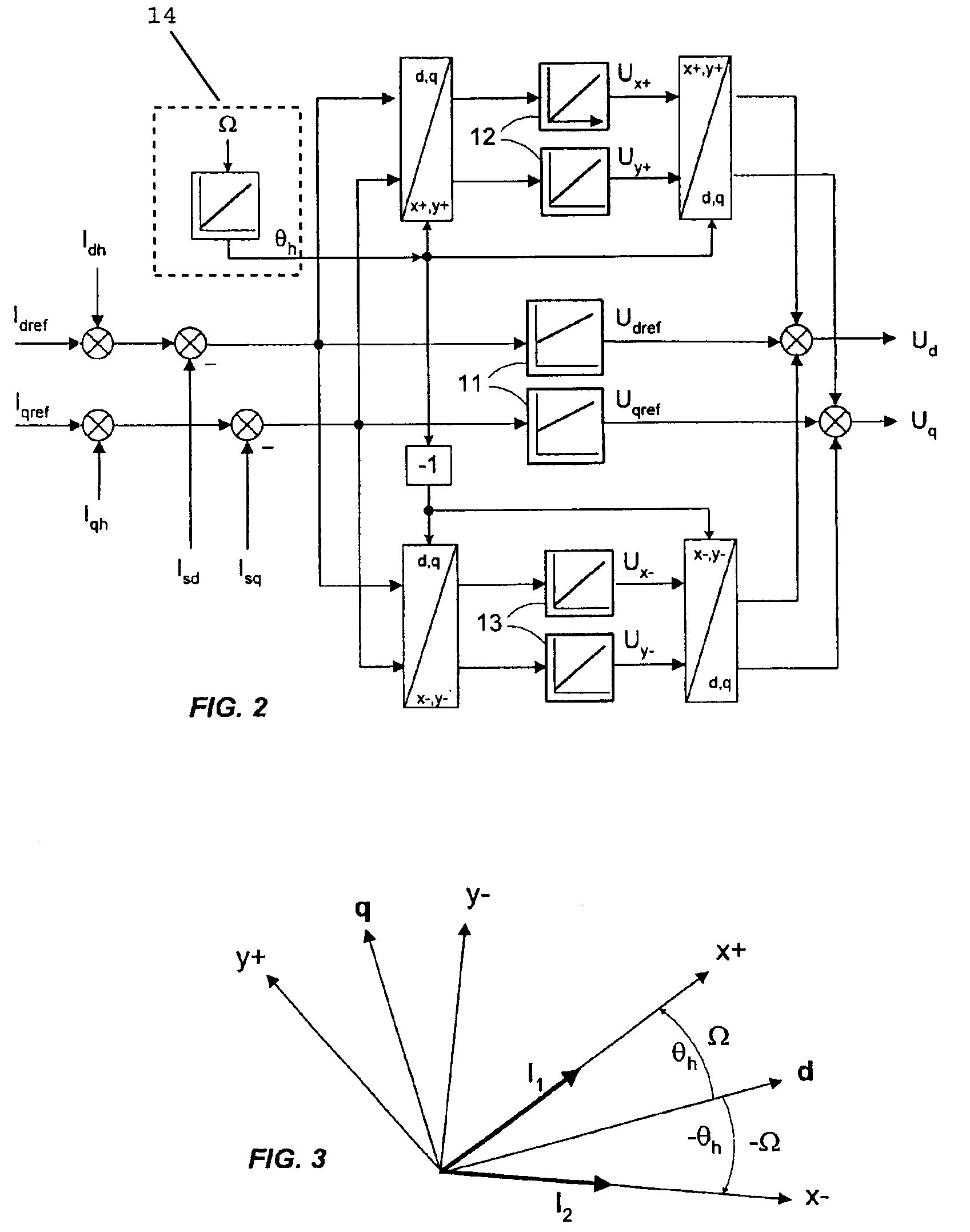
Method for determining the position of the flux vector of a motor
ActiveUS8330403B2Simple and precise and reliableSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlStator voltageIntegrator
The invention relates to a method for determining the position of a rotor flux vector of an electric motor (M), comprising a step of injecting a first current vector into a first reference frame (x+, y+) rotating at a first frequency (Ω) relative to a reference frame (d, q) synchronous with the rotation of the motor, and a second current vector into a second injection reference frame (x−, y−) rotating at a second frequency opposite to the first frequency, a step of determining a first stator flux induced voltage delivered at the output of a first integrator module (12) synchronous with the first reference frame (x+, y+) and a second stator voltage delivered at the output of a second integrator module (13) synchronous with the second reference frame (x−, y−), a step of regulating the position of the rotor flux vector by minimizing the error (ε) between a real position and an estimated position (θS) of the rotor flux vector, the error being determined based on the second induced voltage.
Owner:SCHNEIDER TOSHIBA INVERTER EUROPE SAS
Permanent magnet flux-switching generator voltage control method by space vector modulation
InactiveCN101599737AHarmonic reductionReduce voltage rippleVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlHarmonicVoltage regulation
The invention discloses a permanent magnet flux-switching generator voltage control method by space vector modulation, belonging to stator permanent magnet type generator control method. The voltage regulation method of the invention defines output of a voltage PI loop as given electromagnetic torque, under the condition that the stator flux amplitude of the permanent magnet flux-switching generator is constant, a blended space vector is selected to regulate the included angle of a stator flux vector and a non-load permanent magnet flux vector, so as to realize fast and accurate control on electromagnetic torque and voltage. The invention has no current loop or coordinate transformation link, is simple in realization only by identifying stator flux, and has strong parameter roughness, small current harmonics, small torque pulsation, small voltage ripple, fast dynamic response and favourable voltage control performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of position sensorless control of an electrical machine
ActiveUS20130093375A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineRotor flux
A position sensorless control methodology for electrical machines using high frequency flux vector signal injection in the estimated rotor flux rotational reference frame is provided. In one aspect, the estimated position error function is derived directly from the stator flux equation without any simplification. The method is applicable for electrical generator motoring mode operation from standstill and power generation mode operation.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Direct power and stator flux vector control of a generator for wind energy conversion system
ActiveUS20130009611A1Effective controlConvenient and efficient controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsWind energy conversionVariable speed wind turbine
A method for controlling a variable speed wind turbine generator is disclosed. The generator is connected to a power converter comprising switches. The generator comprises a stator and a set of terminals connected to the stator and to the switches of the power converter. The method comprises: determining a stator flux reference value corresponding to a generator power of a desired magnitude, determining an estimated stator flux value corresponding to an actual generator power, determining a difference between the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value, and operating said switches in correspondence to the determined stator flux reference value and the estimated stator flux value to adapt at least one stator electrical quantity to obtain said desired generator power magnitude.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Electrical hoist drive system
InactiveUS6848675B2Improve performanceProcess controlConveyorsLifting framesMotor driveElectric machinery
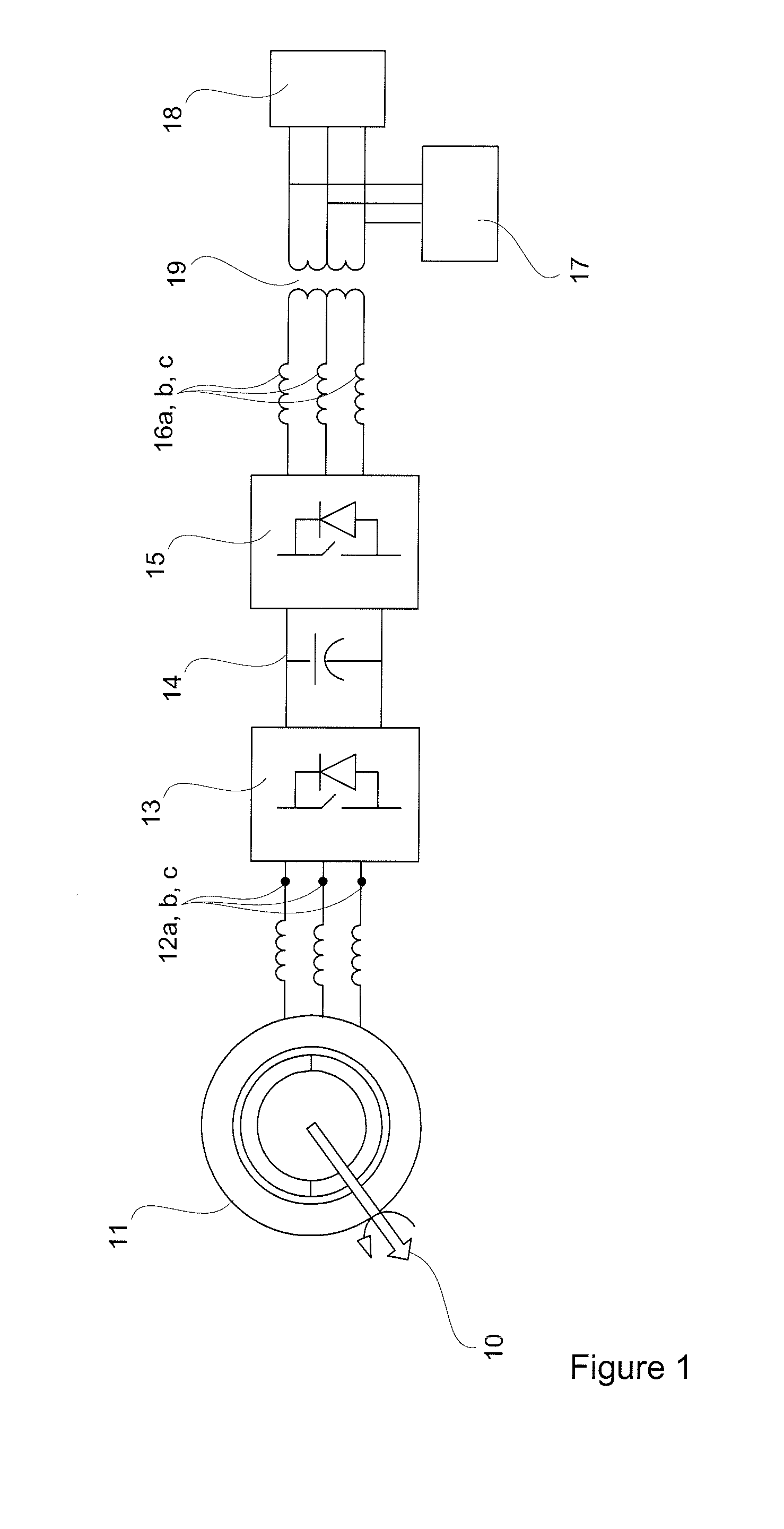
The invention provides a hoist drive system for controlling the position of a hoist platform in a palletizer. In an embodiment of the invention, a hoist drive system comprises two electrical motors with dual output shafts. One motor may have an encoder for taking measurements relating to the rotation of the motor. A common shaft with a spring set safety brake ties the motors together. The two motors may be flux vector motors controlled with input from the encoder. The motors drive two gearboxes, thereby enabling vertical displacement of a hoist platform coupled to the drive system.
Owner:PRODN AUTOMATION
Charge transfer system
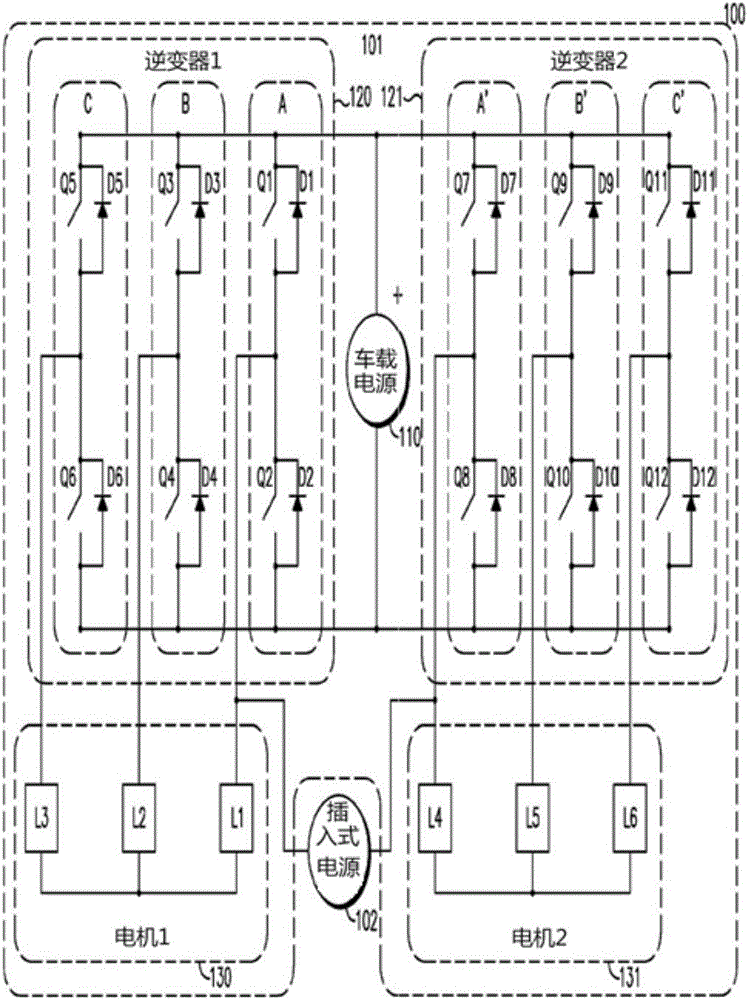
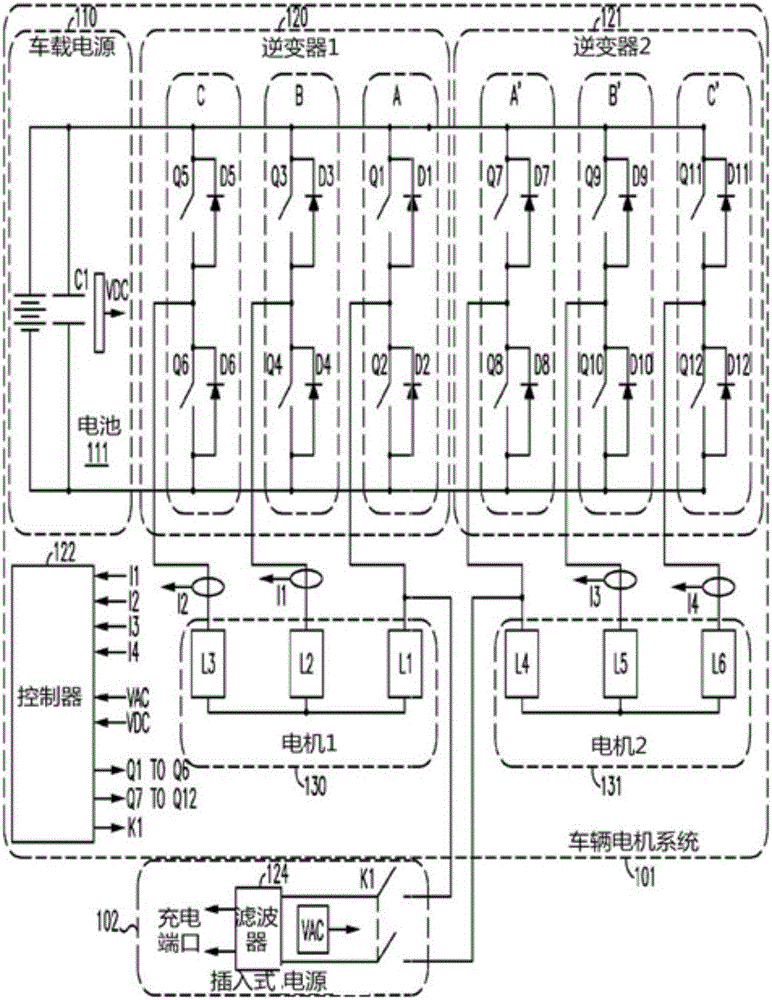
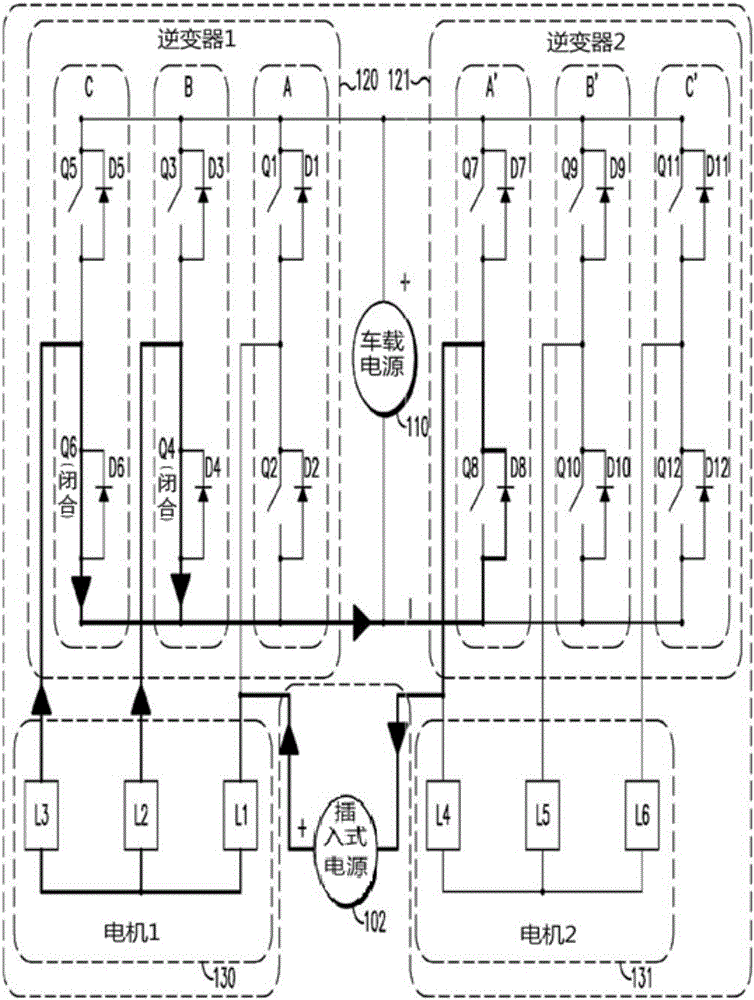
ActiveCN106031016APrevent rotationReduce common mode noiseBatteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlElectric machineOn board
A charge transfer system includes an on-board vehicle motor system and a plug in supply. The on-board vehicle motor system includes a first motor including a plurality of stator windings, a second motor including a plurality of stator windings, a first inverter having a plurality of switch legs, a second inverter having a plurality of switch legs, a controller, and an on-board power supply. The plug-in supply is connected between at least one switch leg of the first inverter and at least one switch leg of the second inverter. The controller modulates the switch legs of the first and second inverters such that electric current flows through at least one stator winding of the first or second motor to charge the on-board power supply. The current flow can also alternate in phase with plug-in supply polarity to produce a stable stator flux vector angle preventing motor rotation during charge transfer.
Owner:JABLIN INC
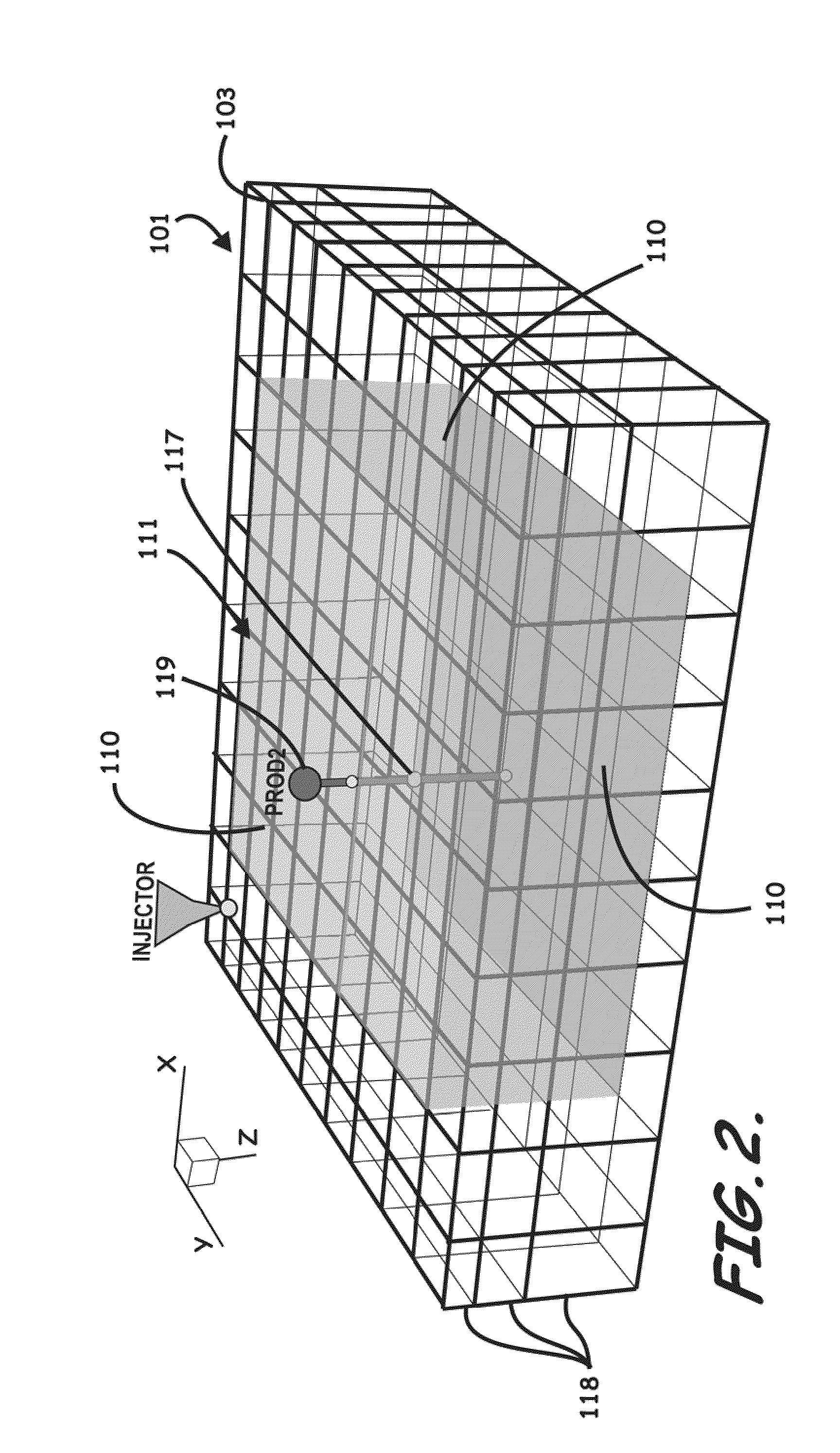
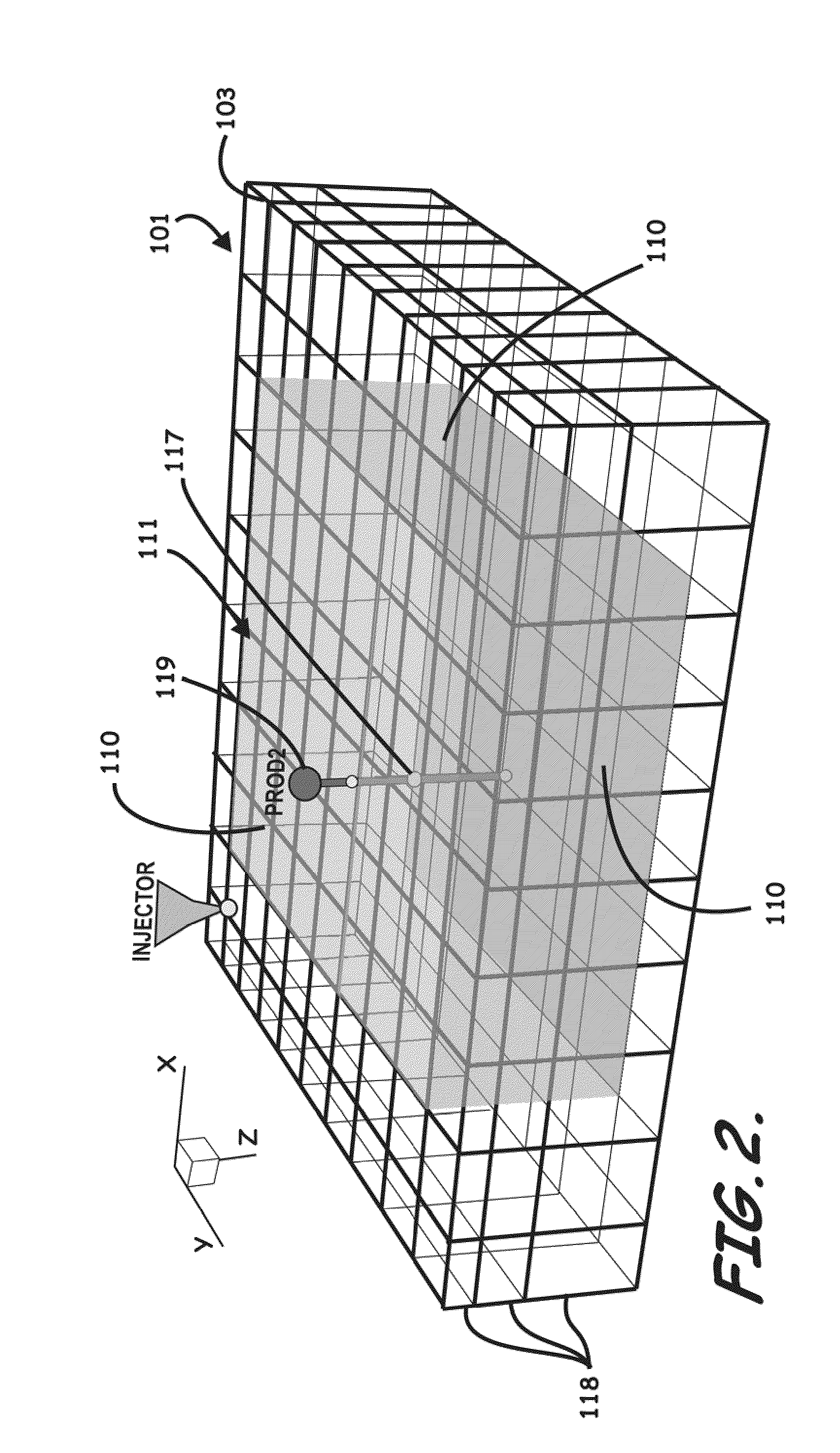
Systems, computer implemented methods, and computer readable program products to compute approximate well drainage pressure for a reservoir simulator
Systems, computer implemented methods, and program products to determine approximate static well pressures for one or more arbitrary shaped wells (119) by estimating the drainage volume (111) of the one or more wells (119), are provided. The drainage volume (111) of the one or more wells (119), for example, can be estimated from the one or more computed fluid flow flux vectors (107), and the approximate static well pressures for the one or more wells (119) can be subsequently calculated by taking the pore volume average of the dynamic grid block pressures within the drainage volume (111) of the one or more wells (119).; The one or more fluid flow flux vectors (107) can be calculated at each iteration in a numerical reservoir simulator as a part of standard simulator computations, negating a need for additional, extraneous computations to calculate effective drainage volume (111) of the one or more wells (119).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method of position sensorless control of an electrical machine
ActiveUS8884566B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersRotor fluxEngineering
A position sensorless control methodology for electrical machines using high frequency flux vector signal injection in the estimated rotor flux rotational reference frame is provided. In one aspect, the estimated position error function is derived directly from the stator flux equation without any simplification. The method is applicable for electrical generator motoring mode operation from standstill and power generation mode operation.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
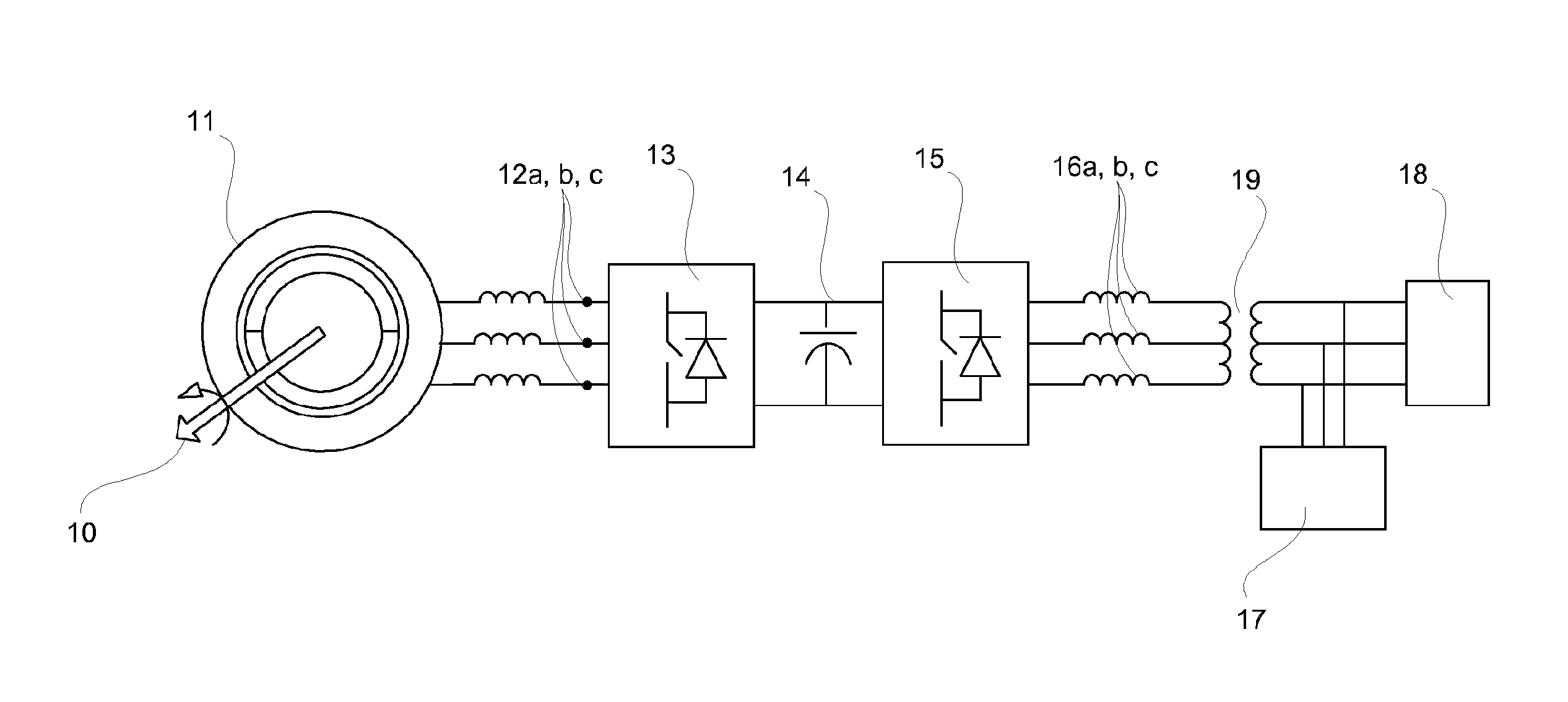
Method for operating a converter circuit, and device for carrying out the method
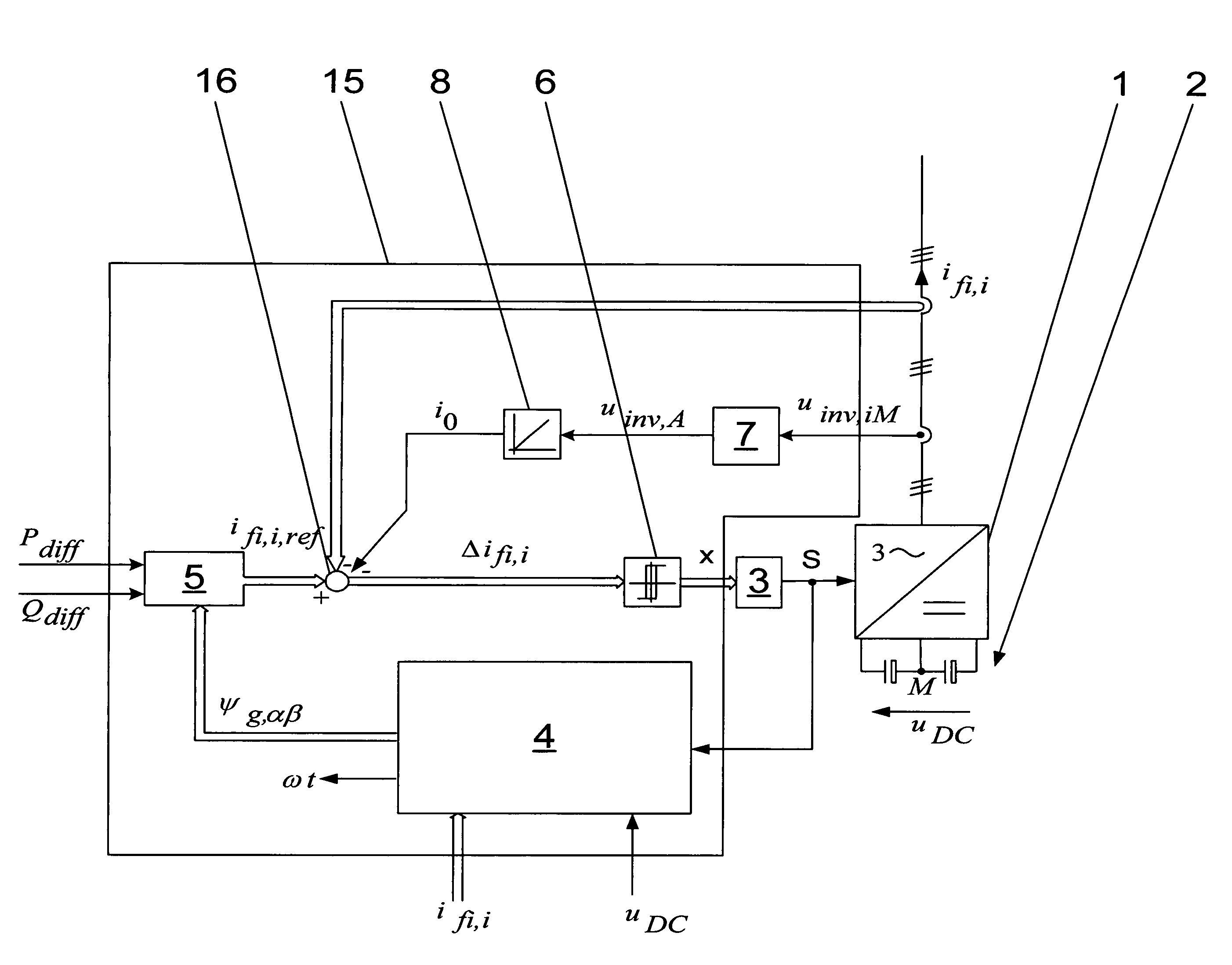
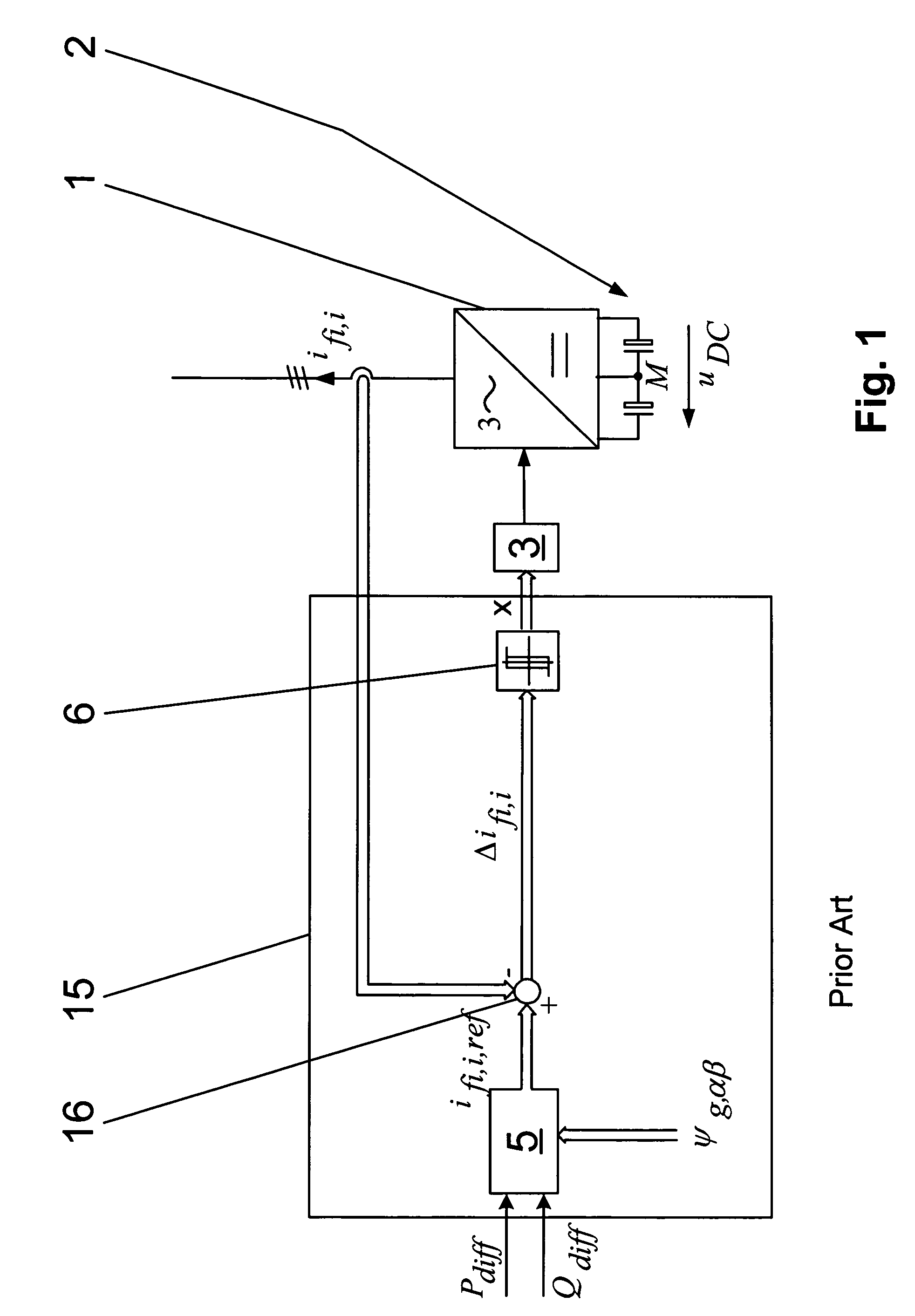
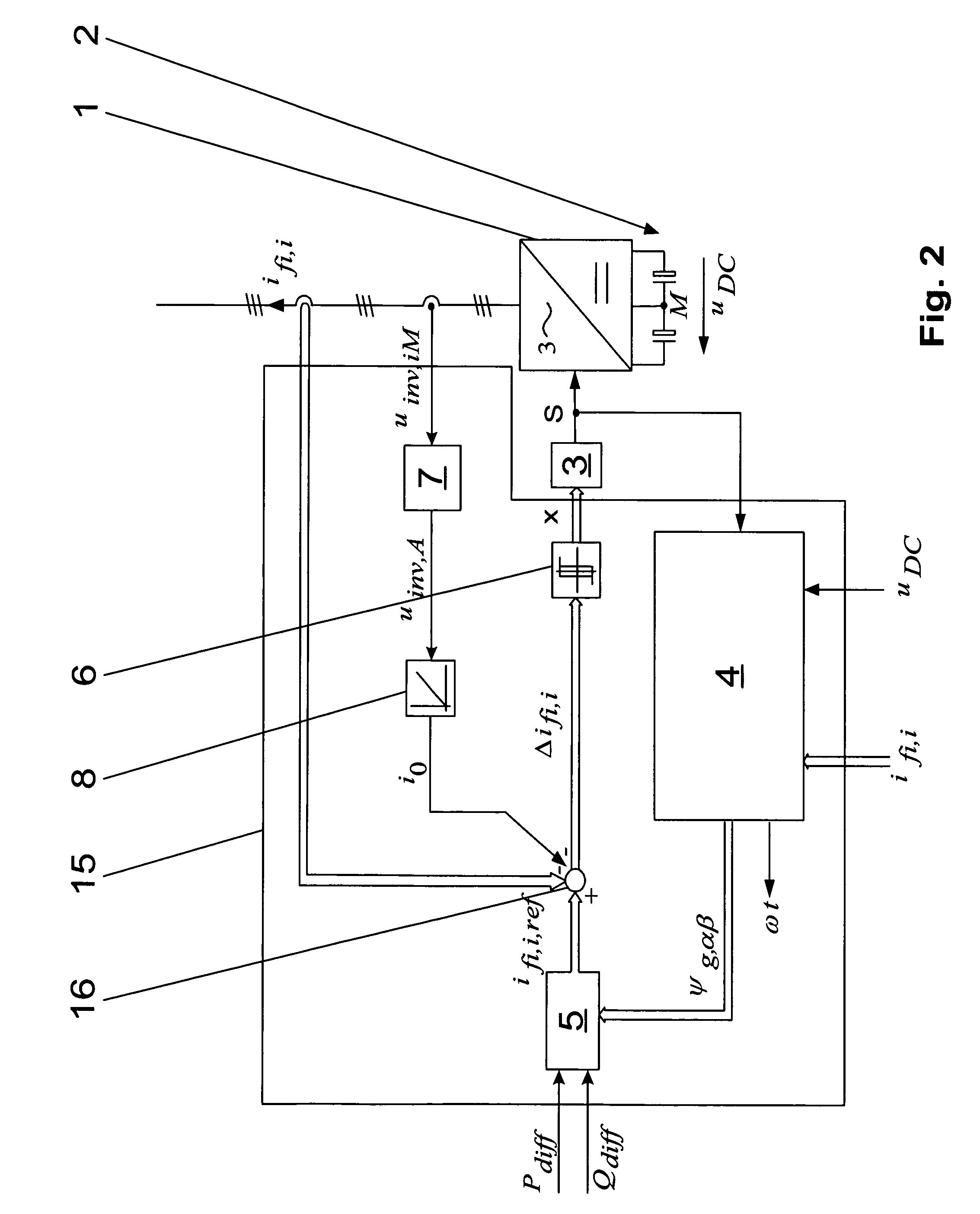
InactiveUS7542311B2Simple wayConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionHysteresisControl signal
A method for operating a converter circuit is specified with the converter circuit having a converter unit with a multiplicity of controllable power semiconductor switches and having an energy storage circuit formed by two series-connected capacitors, in which the controllable power semiconductor switches are controlled by means of a control signal formed from a hysteresis signal vector (x), and the hysteresis signal vector (x) is formed from a difference-phase connection current vector (Δifi,i) by means of a hysteresis regulator, and the difference-phase connection current vector (Δifi,i) is formed from the subtraction of a phase connection current vector (ifi,i) from a reference phase connection current vector (ifi,i,ref), with the reference phase connection current vector (ifi,i,ref) being formed from a difference power value (Pdiff), a difference wattless-component value (Qdiff) and a phase flux vector (ψg,αβ). In order to very largely stabilize the switching frequency of the controllable power semiconductor switches, a current correction value (i0) is additionally subtracted in order to form the difference-phase connection current vector (Δifi,i), with the current correction value (i0) being formed by integration of a phase connection voltage mean value (uinv,A), and the phase connection voltage mean value (uinv,A) being formed by determining the arithmetic mean value of the phase connection voltages (uinv,iM) with the reference point of the connection point of the capacitors in the energy storage circuit. A device is also specified, by means of which the method can be carried out in a particularly simple manner.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Motor control method for predicting voltage vector sequence
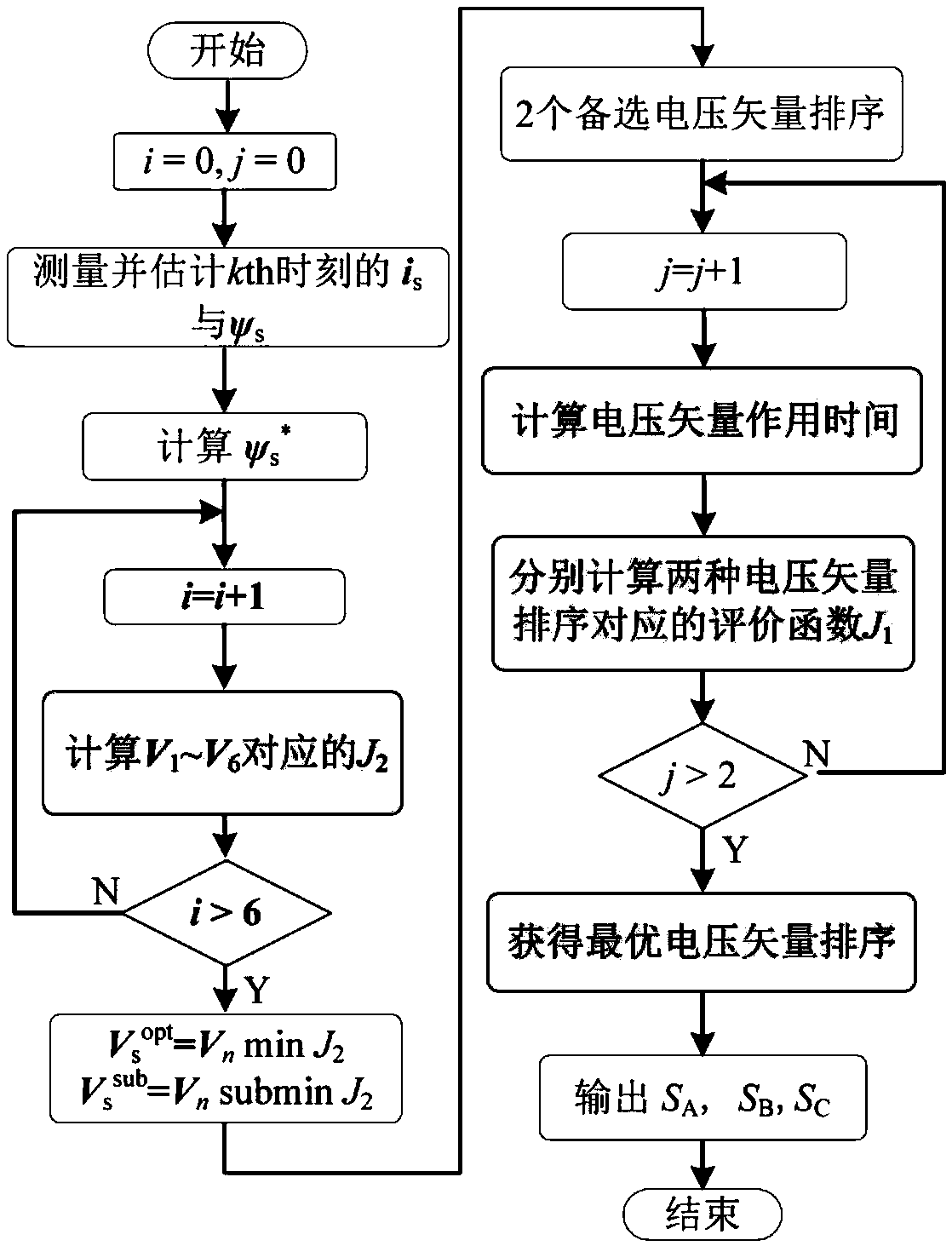
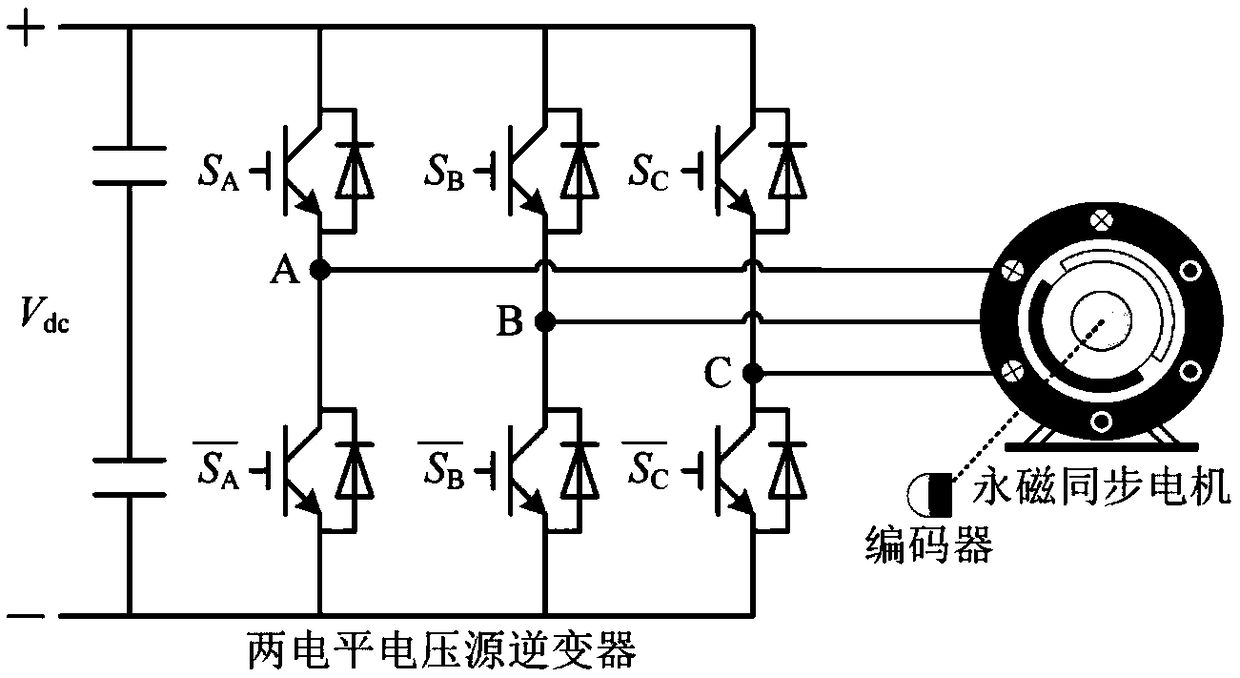
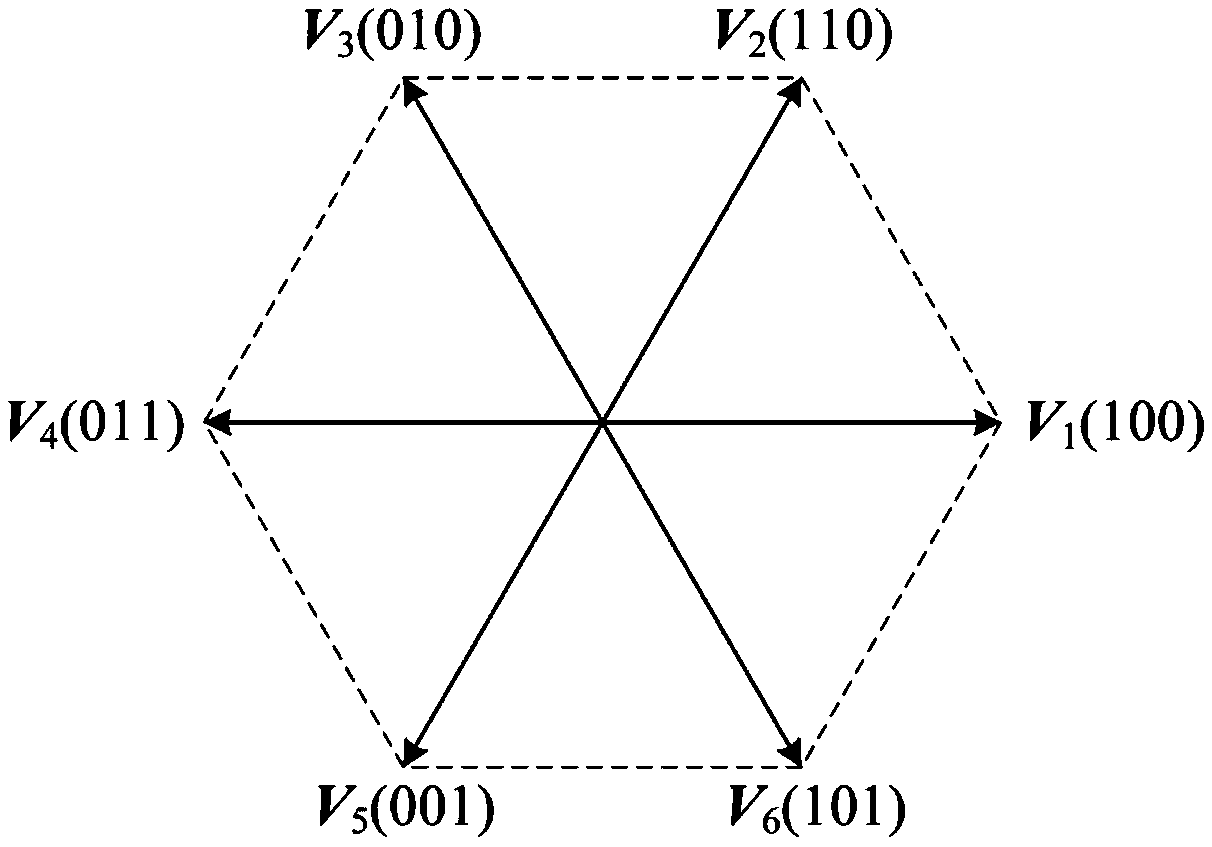
ActiveCN108923698AGuaranteed uptimeReduce lossTorque ripple controlAC motor controlFlux vectorVoltage source inverter
The invention discloses a motor control method for predicting a voltage vector sequence. The motor control method comprises the following steps that by quantitatively analyzing the influence of all voltage vector sequences in a two-level voltage source inverter on fluctuation of a stator flux vector, and 12 kinds of voltage vector sequences favorable for optimizing the control performance of the stator flux vector are screened out; the 12 kinds of voltage vector sequences are incorporated into a control set of predictive control, and a novel voltage vector sequence control set is established;the effective value of fluctuation quantity of the stator flux vector in one control cycle is taken as an evaluation index; the stator flux vector error at each voltage vector switching moment in eachcontrol cycle is evaluated, and an evaluation function is constructed; and the action time of each basic voltage vector is obtained by a two-step method of first confirming a phase angle and then confirming the amplitude. The motor control method reduces torque fluctuation and flux linkage fluctuation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, so that the motor can operate more smoothly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Power conversion device
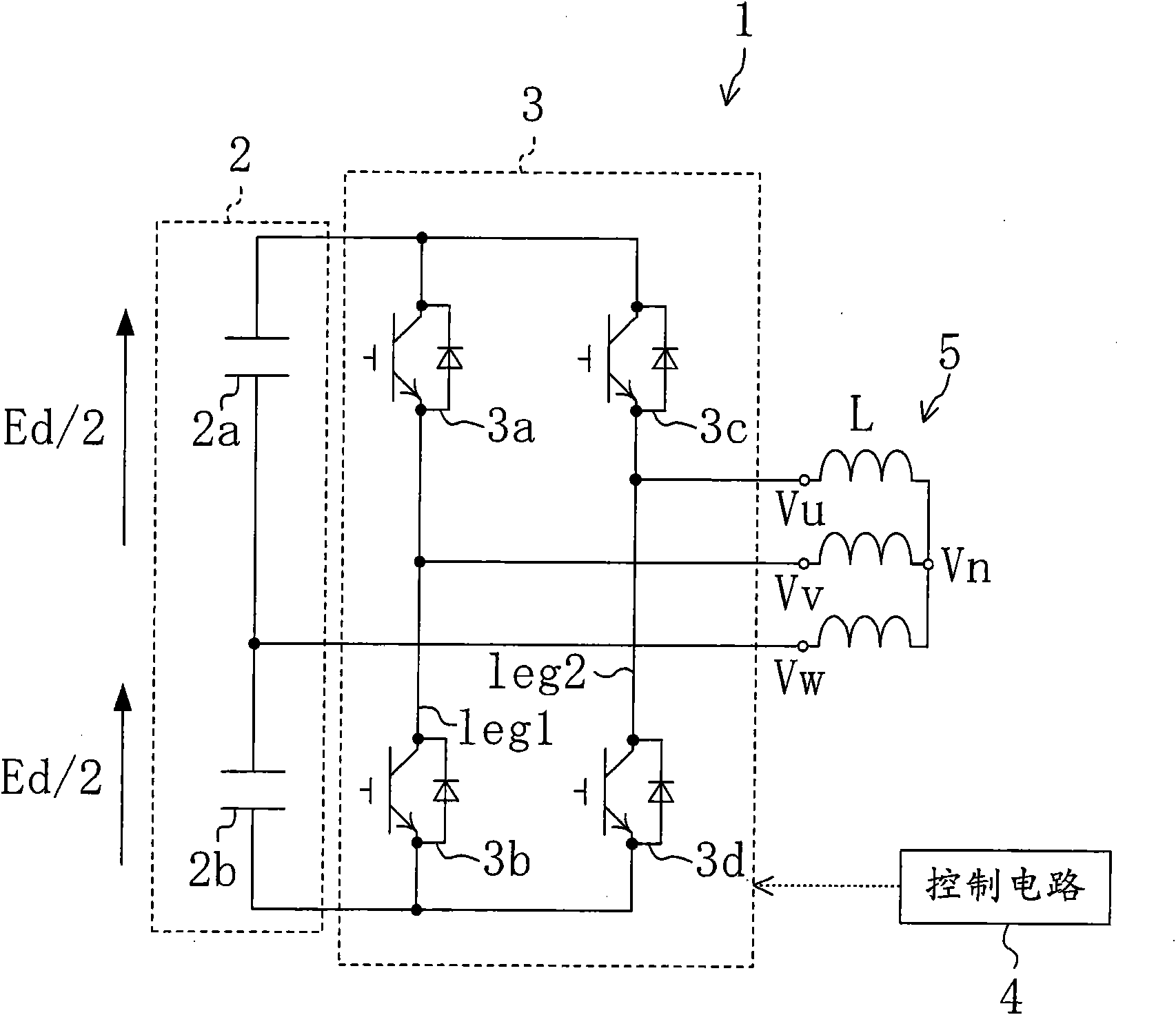
InactiveCN101682269AReduce switching timesReduce lossDc-ac conversion without reversalVoltage vectorHarmonic
The invention provides a power conversion device. In a power converter including a V connection inverter circuit, harmonic components included in output voltage are reduced to achieve a reduction in aloss of a load, such as a motor. Operation of four switching elements (3a, 3b, 3c, 3d) of a V connection inverter circuit (3) is controlled so that the locus of a flux vector p on a complex plane created by using voltage vectors Vp obtained by the operation of the switching elements (3a, 3b, 3c, 3d) approaches to a circle. Specifically, in order to create the locus of the flux vector p close toa circle by using at least three of the four voltage vectors Vp, output sequences and output periods of the voltage vectors Vp are determined.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
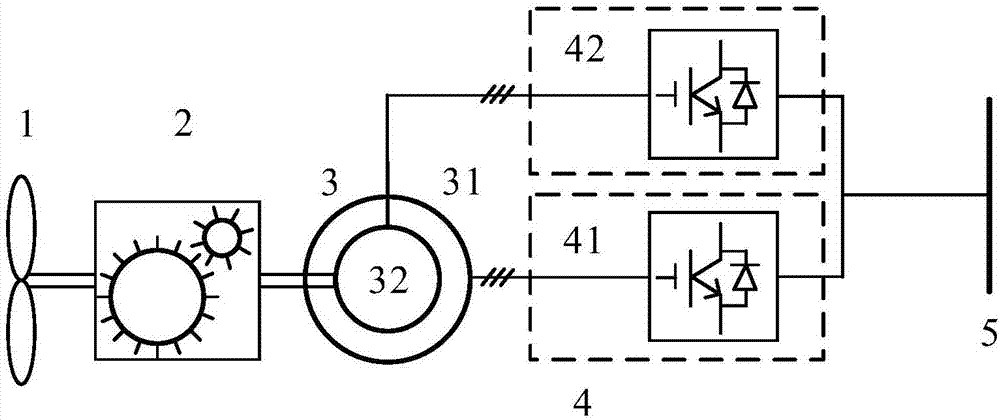
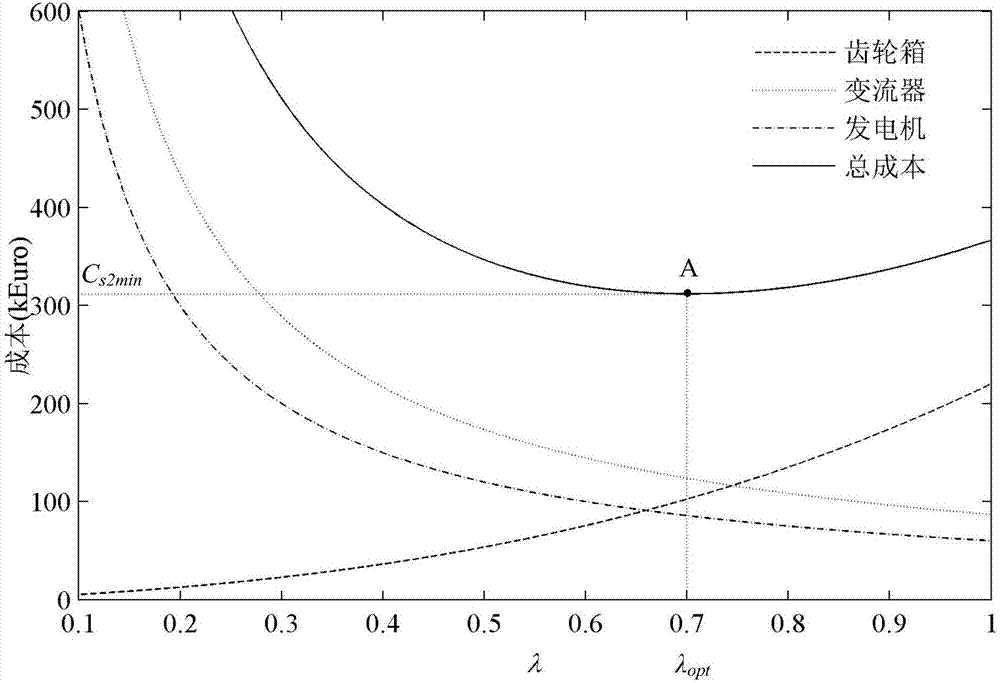
Low-speed gearbox and double-fed wind turbine optimization design method based on direct-current transmission
ActiveCN107273647ALower growth rateReduce volumeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFailure rateLow speed
The invention relates to a low-speed gearbox and double-fed wind turbine optimization design method based on direct-current transmission, and belongs to the field of wind power. According to the method, a double-fed wind power generation system topology structure is adopted to conduct optimization design and control over a double-fed wind turbine comprising a gearbox, a double-fed induction generator (DFIG) and a direct-current transformer. The method comprises the steps that the ratio of the stator current, before optimization, of the DFIG to the stator current, after optimization, of the DFIG, the ratio of the rotor current, before optimization, of the DFIG to the rotor current, after optimization, of the DFIG, the ratio of the total current before optimization to the total current after optimization and the ratio of the total current, before optimization, of the direct-current transformer to the total current, after optimization, of the direct-current transformer are solved by adopting a stator flux vector directional control strategy; the total cost C<s2> of the double-fed wind turbine after optimization is solved; wind turbine optimization design parameters are solved; and a C<s2>-lambda curve is drawn according to a C<s2> formula, a minimum value of C<s2> and an optimum value of lambda are solved, and then the gearbox speed increasing ratio after optimization and the stator current, the rotor current, the synchronous revolving speed and the stator rated frequency of the DFIG are obtained, wherein lambda represents the ratio of the gearbox speed increasing ratio before optimization to the gearbox speed increasing ratio after optimization. According to the method, the gearbox speed increasing ratio is decreased, the failure rate can be decreased, the cost can be reduced, and the system operation reliability can be improved.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
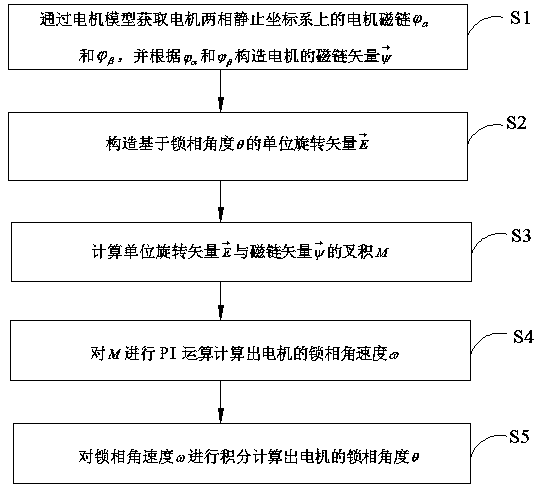
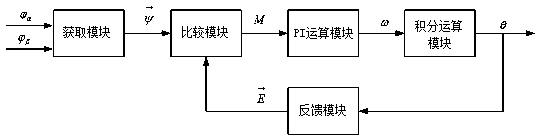
A method and a system for calculating the phase and the speed of a flux linkage of a motor based on a phase-locked loop
InactiveCN109245649ASimple calculationQuick responseElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase differenceAngular velocity
The invention discloses a method and a system for calculating a phase and a speed of a motor flux linkage based on a phase locked loop, wherein the method comprises: obtaining a motor flux linkage ona two-phase stationary coordinate system of a motor through a motor model, and constructing a motor according to and The magnetic chain vector; constructing a unit rotation vector based on the phase locking angle; calculating the cross product of the unit rotation vector and the flux vector; calculating the phase-locked angular velocity of the motor for the PI operation; and integrating the phase-locked angular velocity to calculate the phase lock of the motor angle, in the operation process based on the phase-locked loop, the cross product has the phase difference information of the unit rotation vector and the flux vector, and by determining the phase difference, the flux linkage angle of the motor and the motor magnetic can be accurately calculated. The chain angular velocity, that is,the method and system for calculating the phase and velocity of the motor flux linkage based on the phase-locked loop, has the advantages of simple calculation, fast response, no need to calculate arctangent and differential, high calculation precision, small occupied memory, and no introduction High frequency interference.
Owner:HUNAN VICRUNS ELECTRIC TECH
Optical scanner
An optical scanner comprising stators spaced apart from each other but ferromagnetically coupled together; a magnet positioned relative to the stators such that axis of symmetry of a magnetic field created by the magnet is substantially equidistant from and passes in between ends of the stators; and a flexure element positioned relative to the stators and the magnet such that its center point substantially intersects axis of symmetry of the magnet's magnetic field, wherein the flexure element is not in physical contact with either the stators or the magnet. A method for oscillating an optical scanner's flexure element comprising using a magnet disposed between two stators and beneath the flexure element to create two magnetic circuits that are generally symmetric and coplanar with one another, wherein a portion of the circuits share a common magnetic path through the magnet and remaining, non-common paths of the circuits through the stators are counter-directional relative to each other; applying electromagnetic flux to such circuits via stator electrical coils enhancing flux through one circuit while impeding flux through the other circuit and keeping the stator-induced flux vector through the magnet unchanged; and reversing polarity of the stator-induced electromagnetic flux at a regular frequency in order to oscillate the flexure element.
Owner:LOEBEL NICOLAS G +3
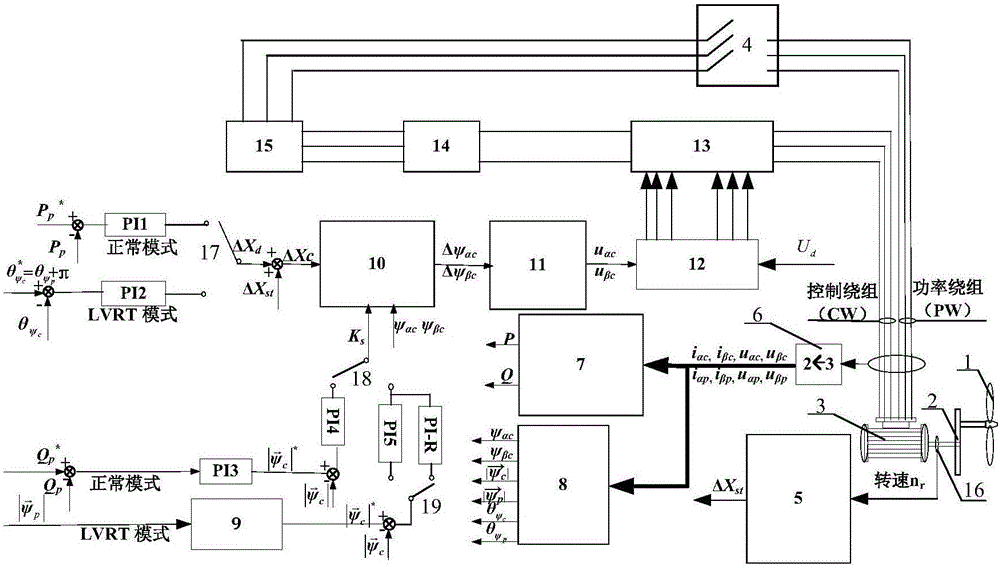
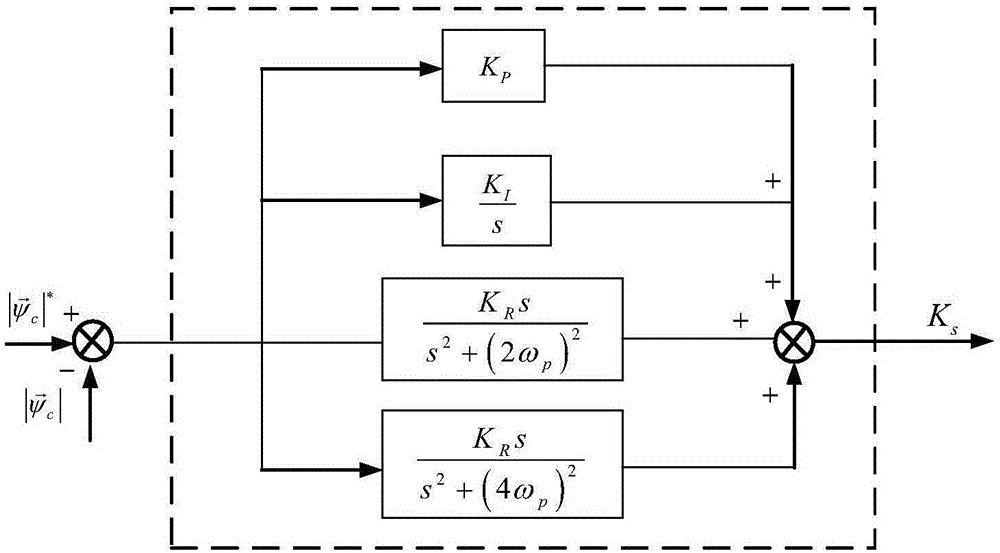
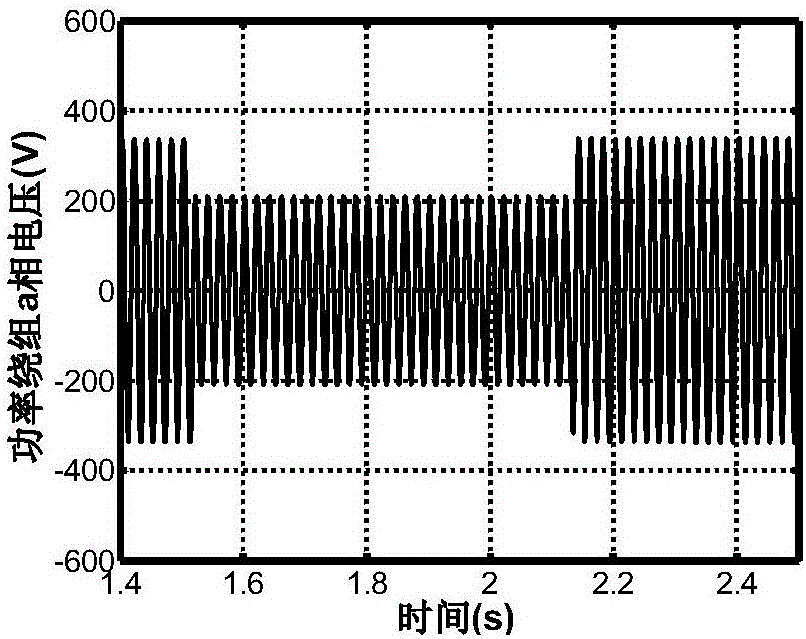
Flux-tracking low voltage ride-through method under asymmetrical voltage faults of brushless doubly-fed wind generator
InactiveCN106786775AAccurate trackingRelieve pressureSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower gridEngineering
The invention relates to a flux-tracking low voltage ride-through method under asymmetrical voltage faults of a brushless doubly-fed wind generator. The method is a flux-tracking-control low voltage ride-through method under three asymmetrical voltage faults, which include phase-to-phase short circuit, phase-to-phase earthing short circuit and single-phase earthing short circuit of the grid connection points of the brushless doubly-fed wind generator. The method has the advantages that a PI-R controller is used as the flux vector amplitude tracking controller of the control windings of the brushless doubly-fed wind generator, a control device and system of the flux-tracking low voltage ride-through operation state under the asymmetrical voltage faults of the brushless doubly-fed wind generator are built, the cage type rotor brushless doubly-fed wind generator can use a software control method to achieve asymmetrical voltage ride through, and the method is low in low-voltage ride through torque ripple, capable of reducing unit transmission chain pressure, simple in system structure and lo in cost; reactive currents can be injected into a power grid to support power grid voltage under the single-phase earthing short circuit fault under a certain condition.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com