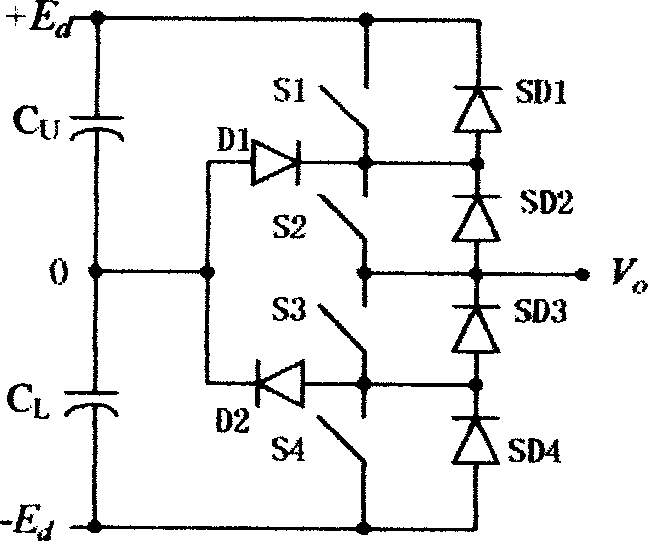
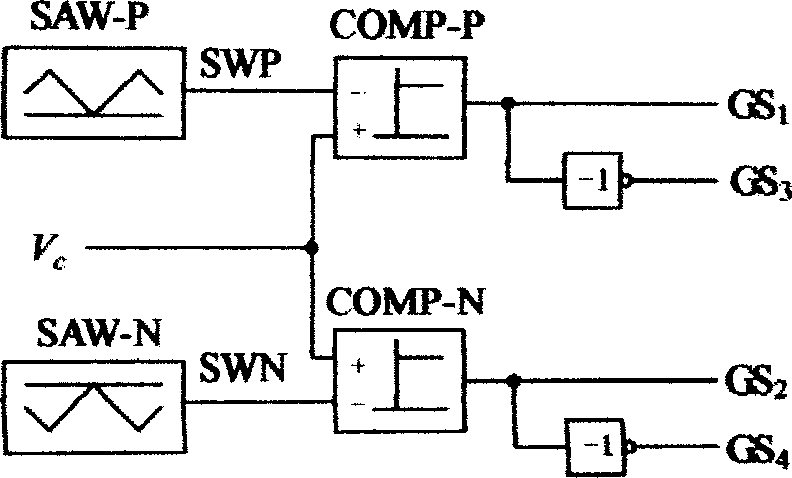
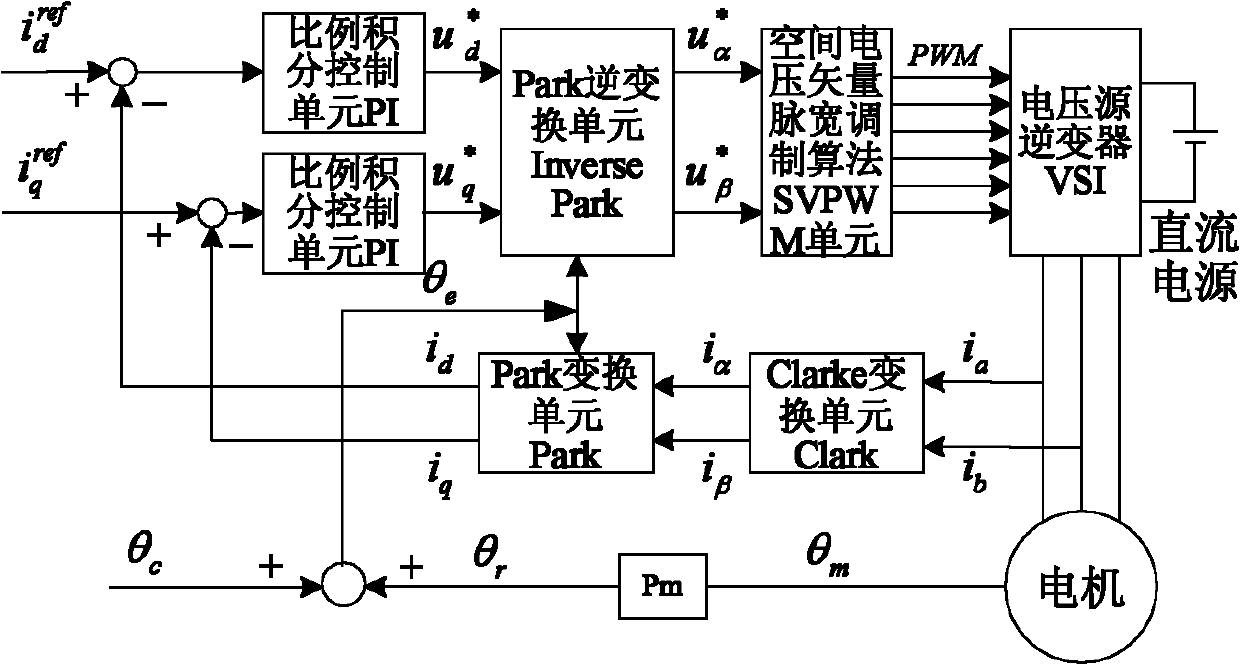
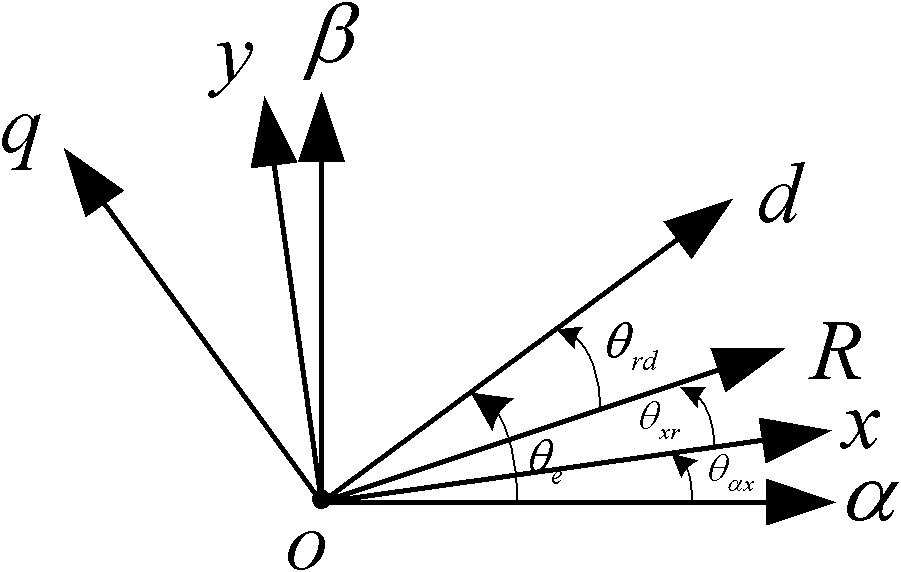
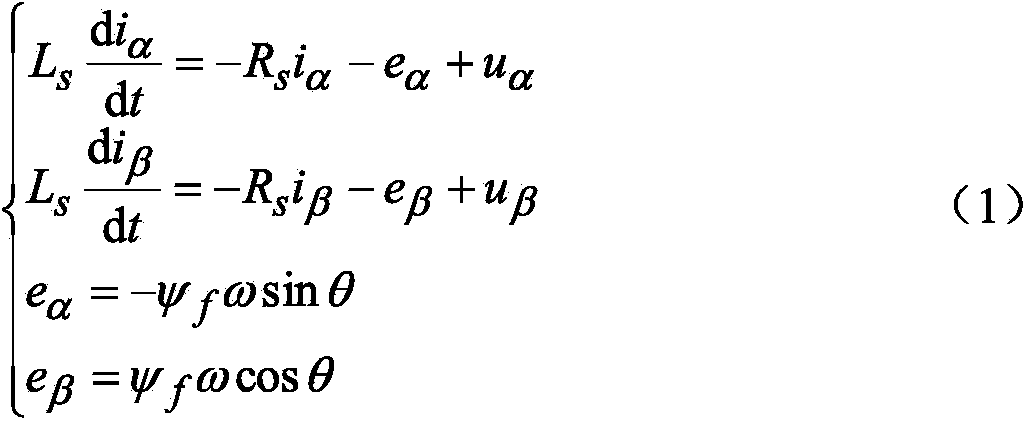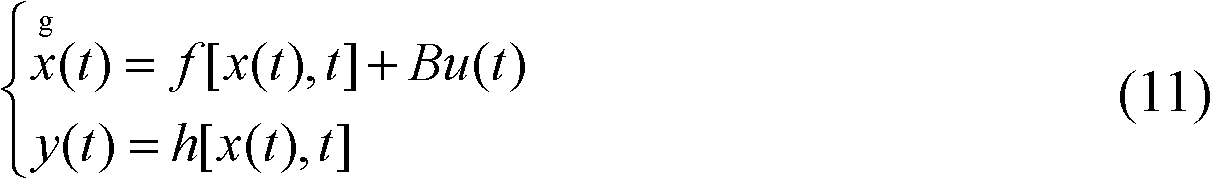Patents
Literature
513 results about "Voltage source inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
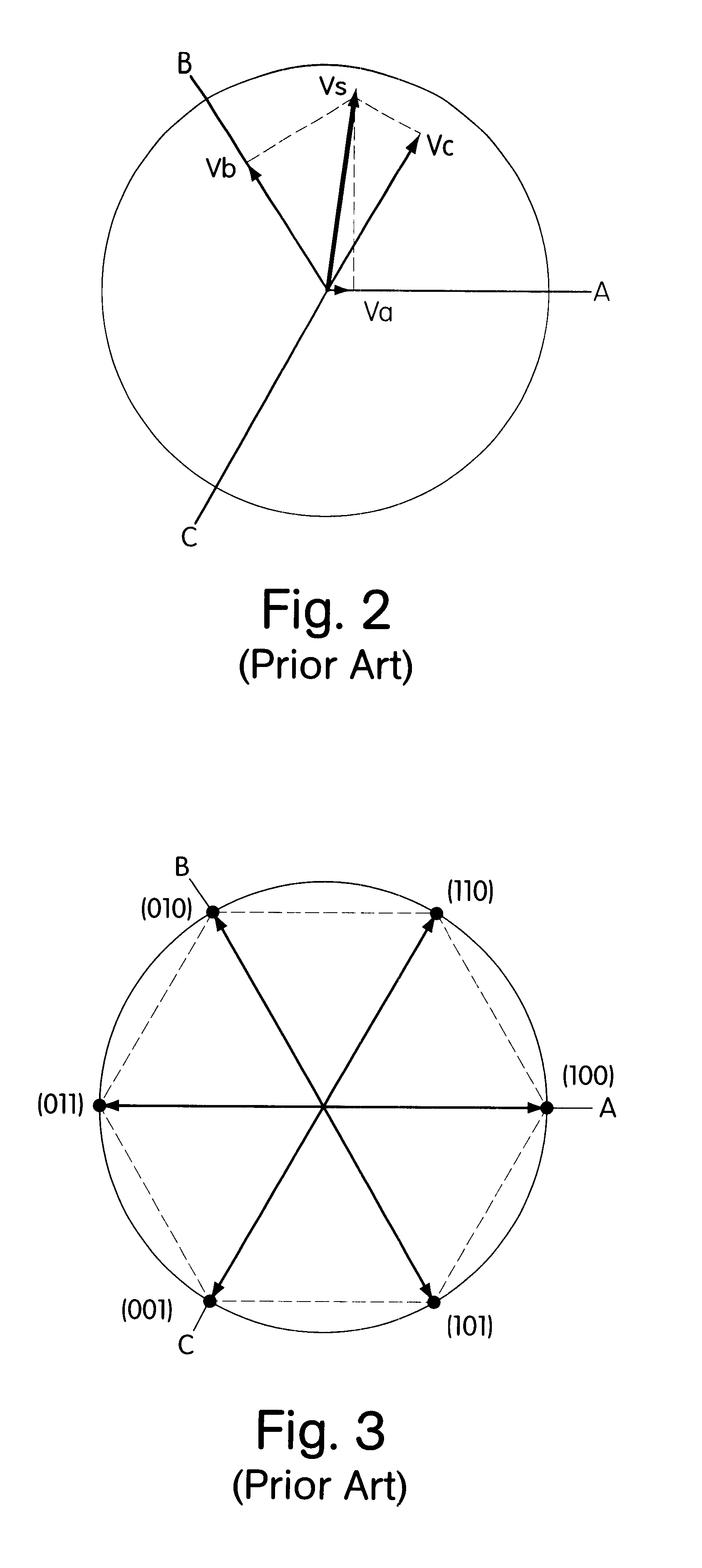
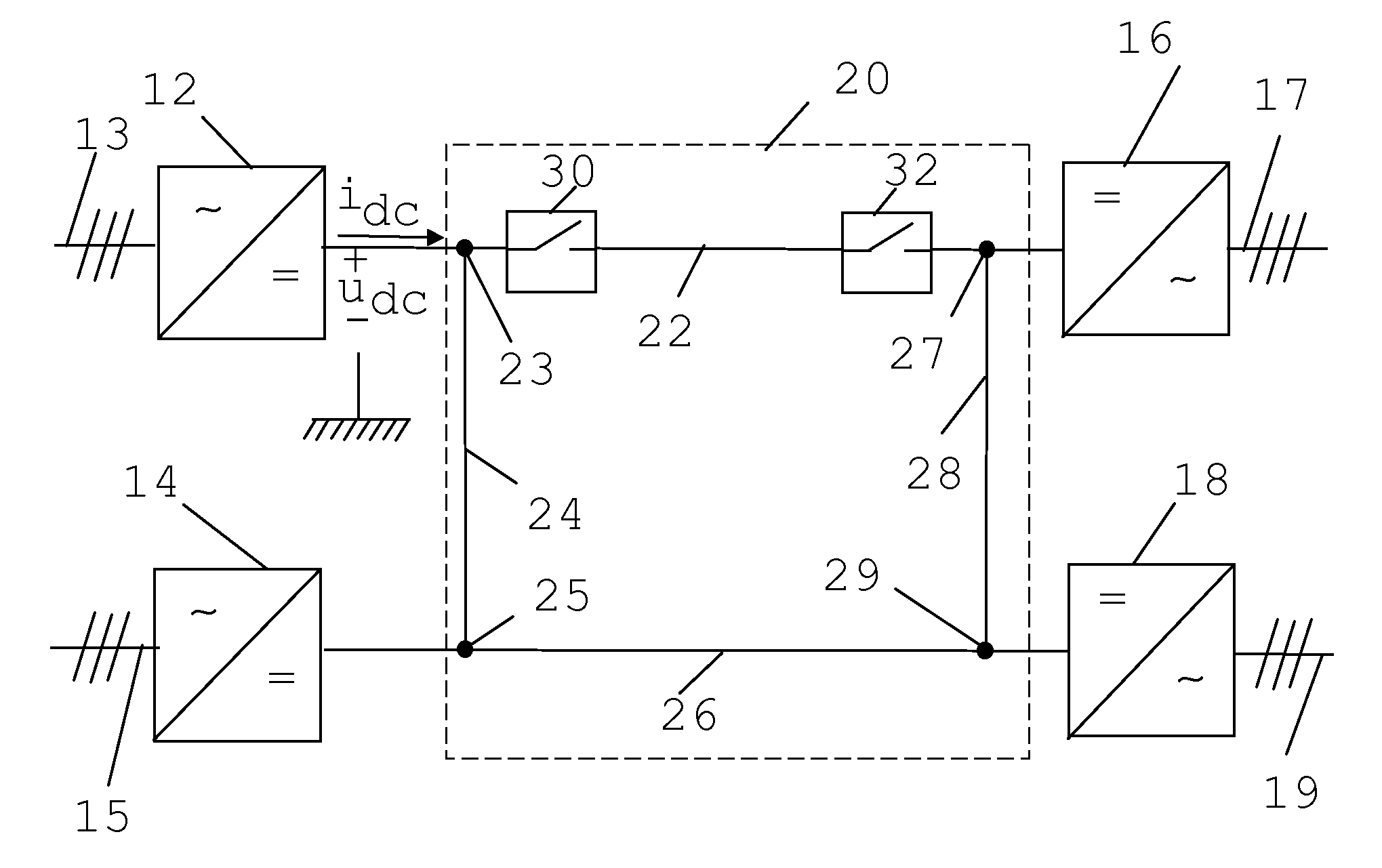
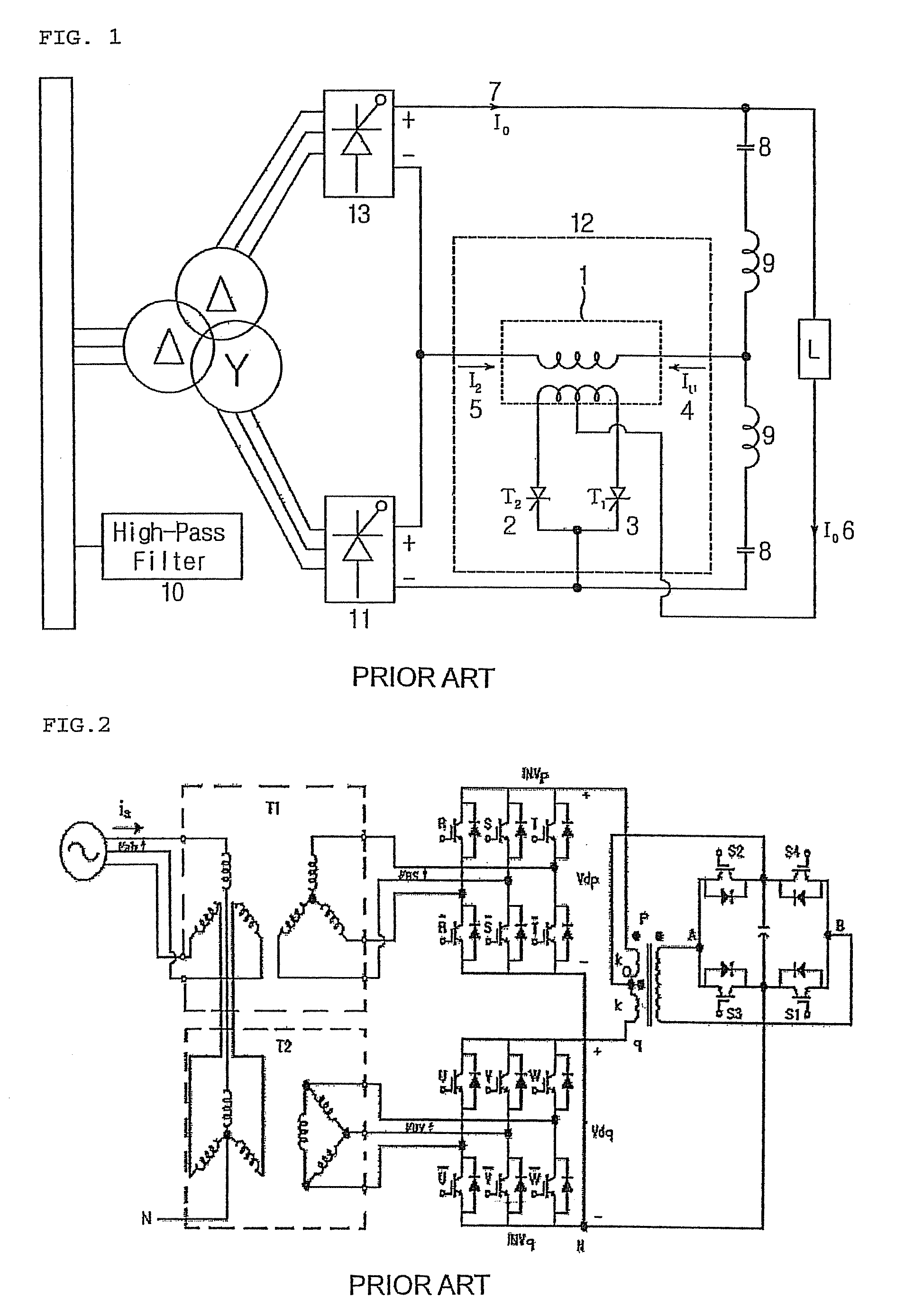
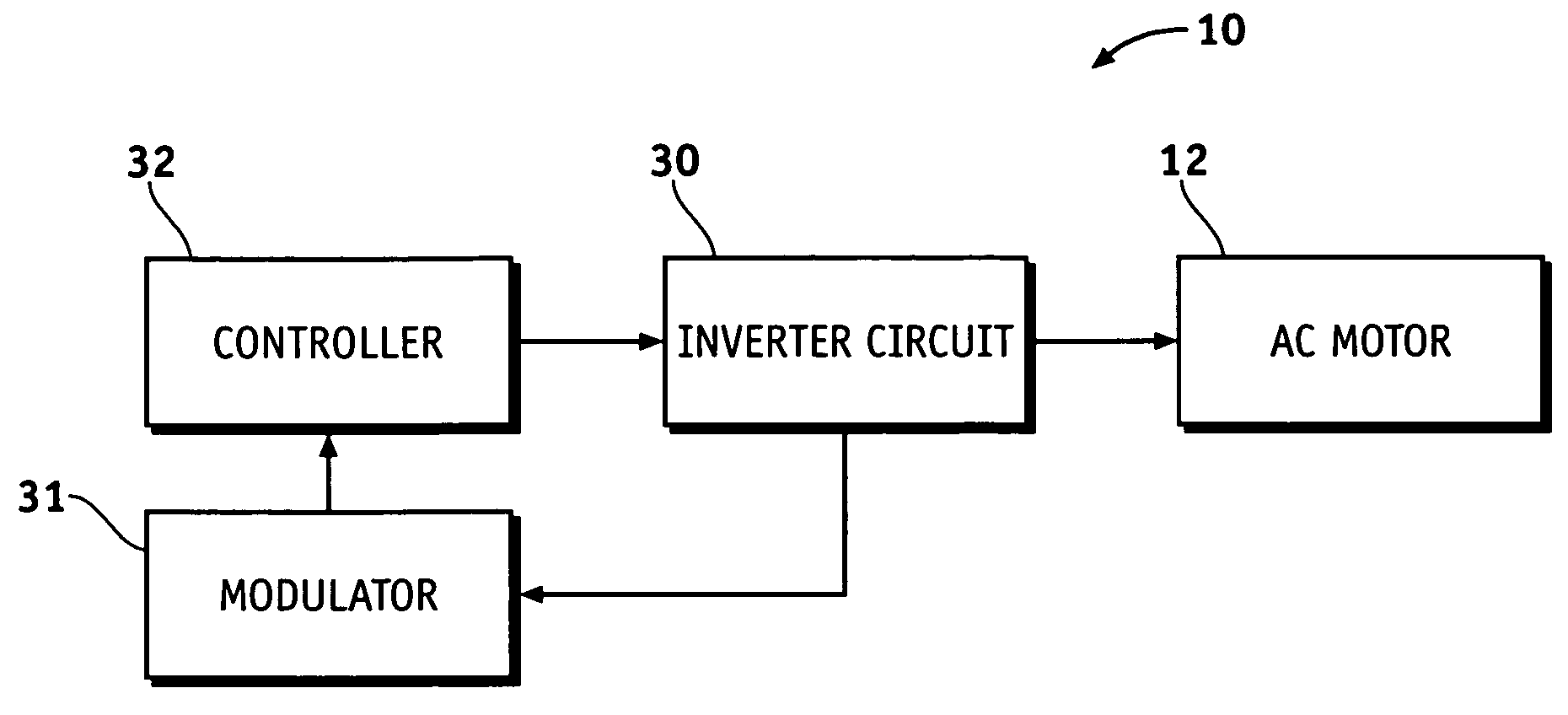
A voltage source inverter(VSI) is fed by a stiff DC voltage, whereas a current source inverter is fed by a stiff current source. A voltage source can be converted to a current source by connecting a series inductance and then varying the voltage to obtain the desired current.
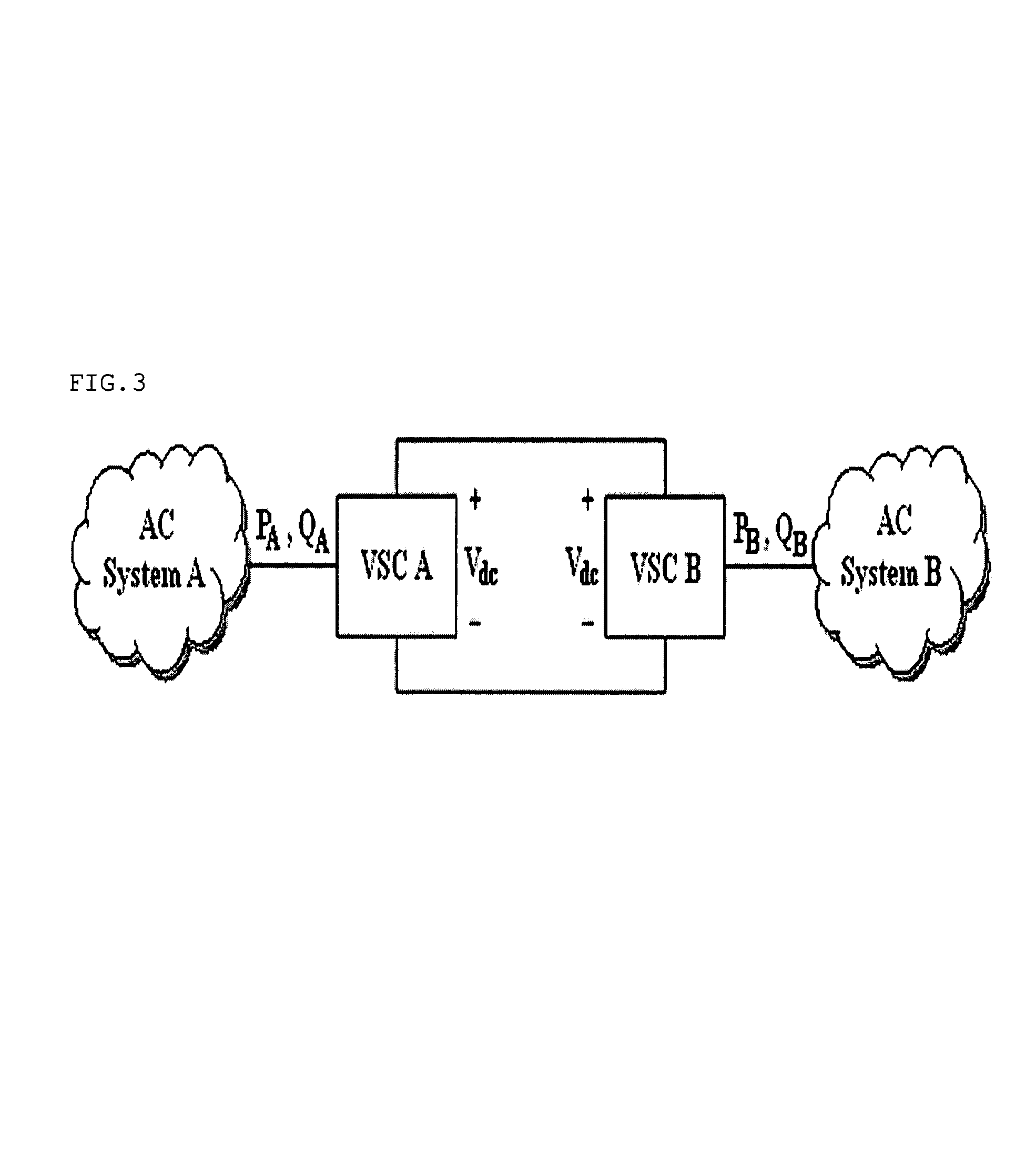
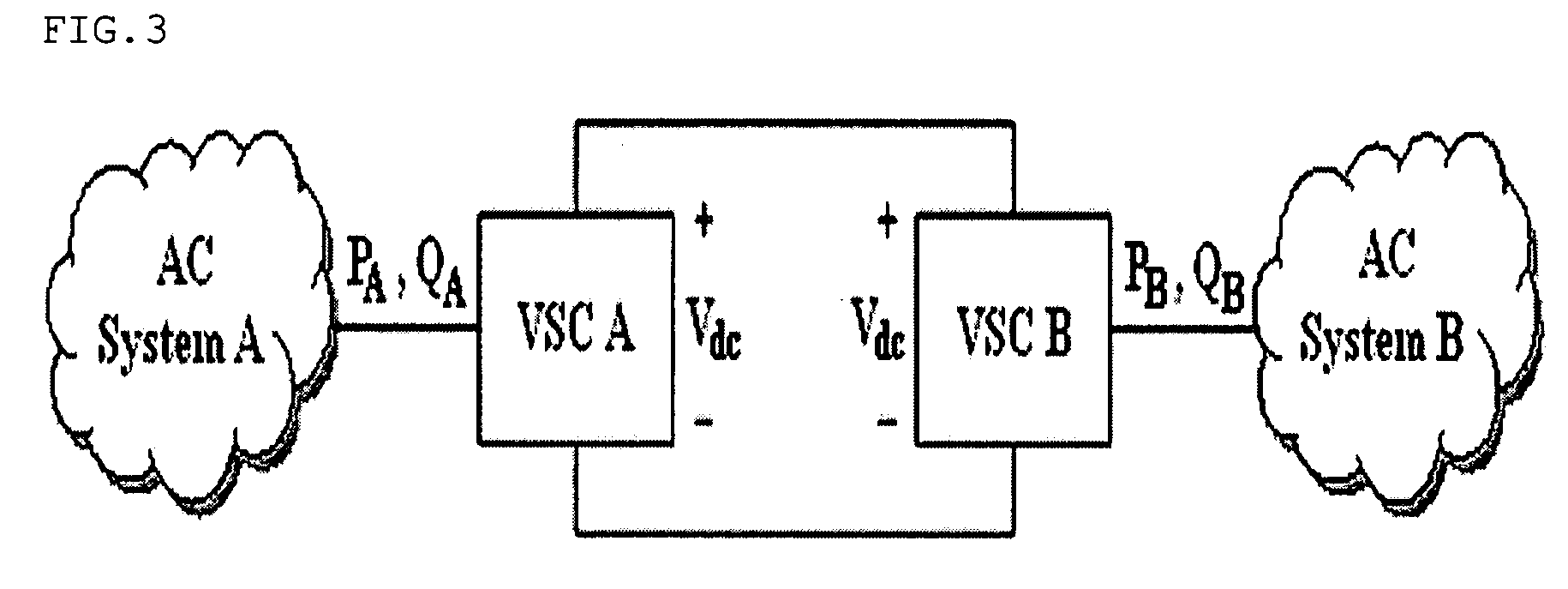
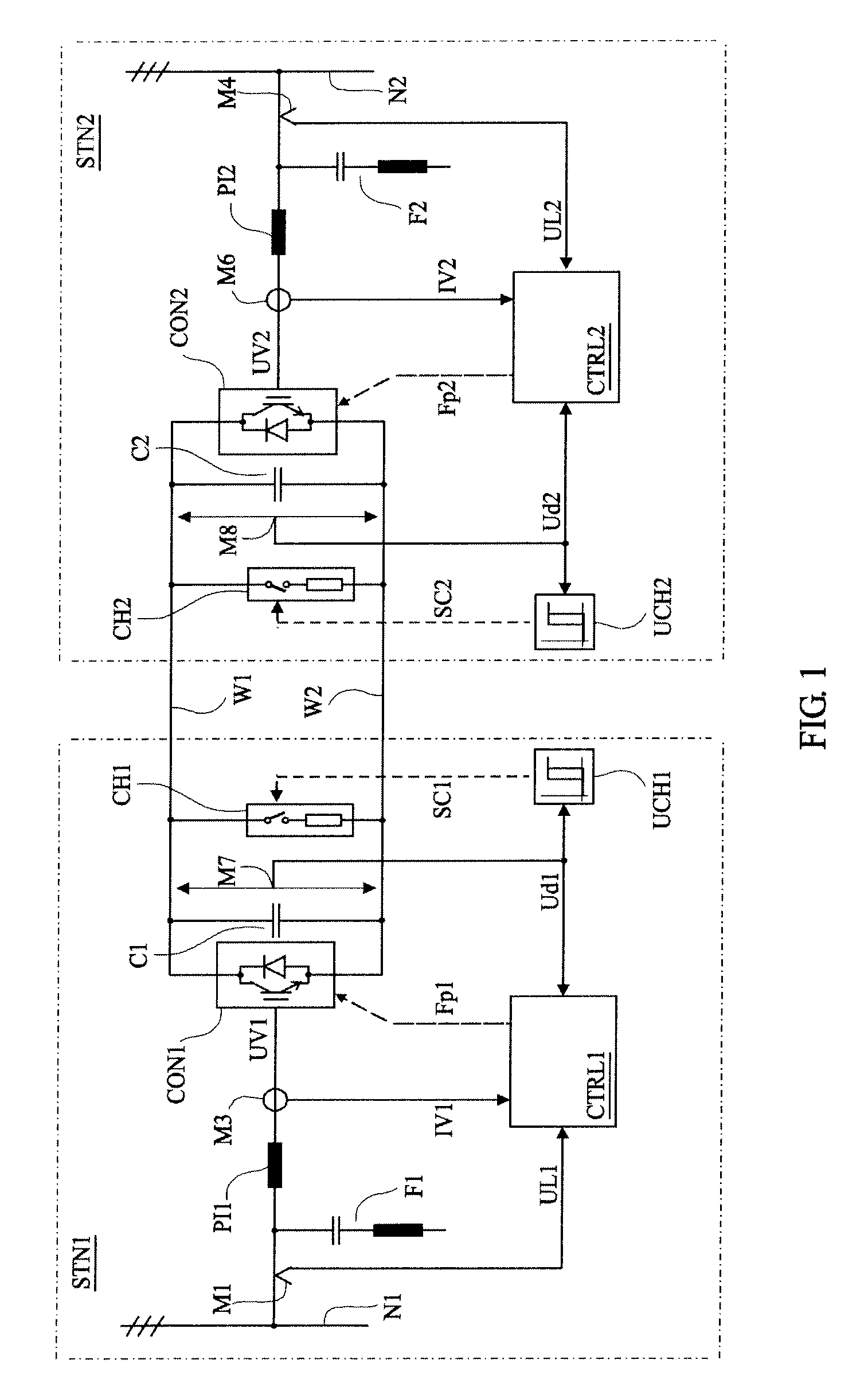
Voltage source converters operating either as back-to-back stations or as parallel static var compensators
InactiveUS6411067B1Powerful control of the flow of electric power in the transmission lineReduce power consumptionFlexible AC transmissionElectric power transfer ac networkBuck converterVoltage source inverter
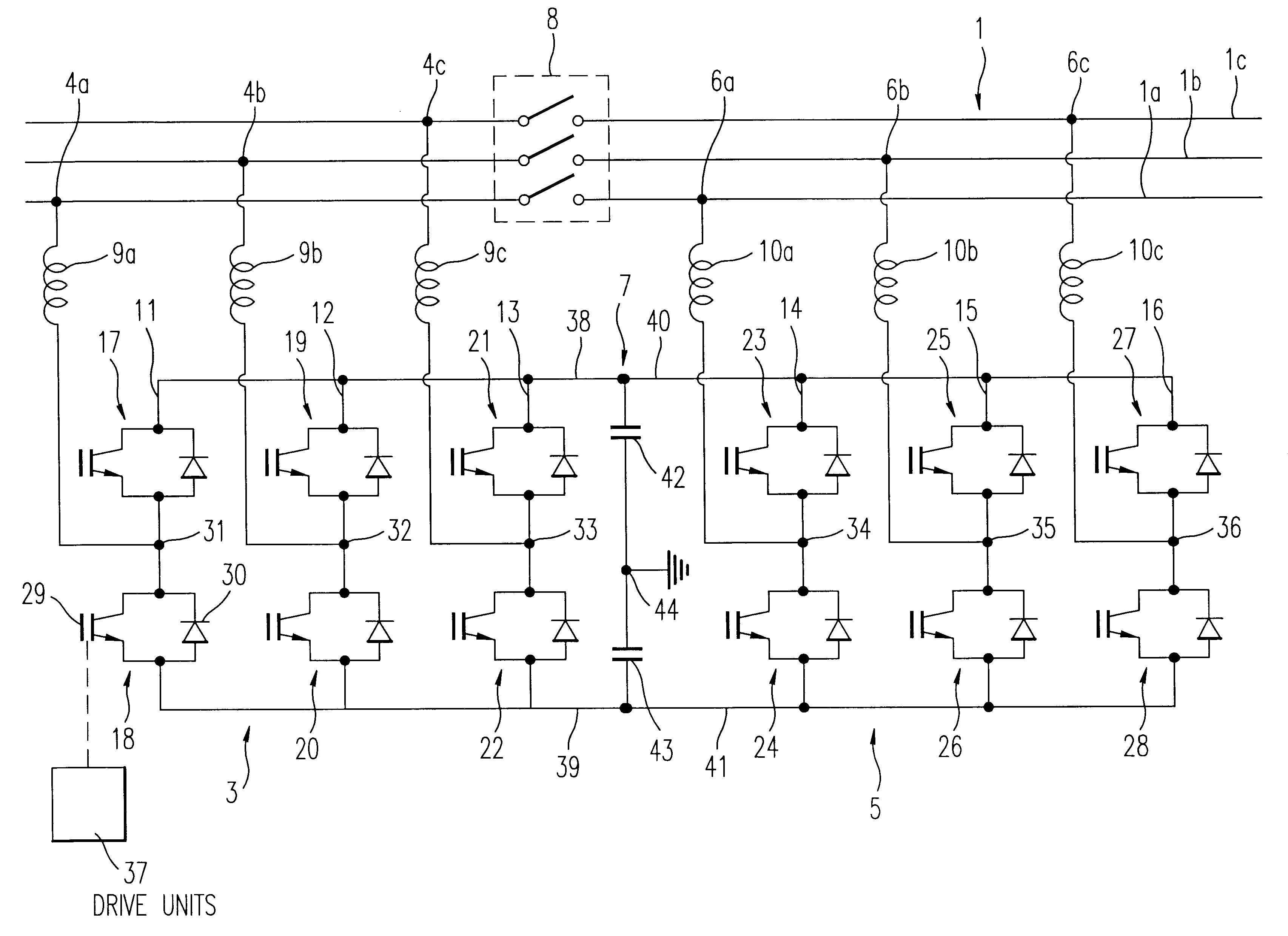
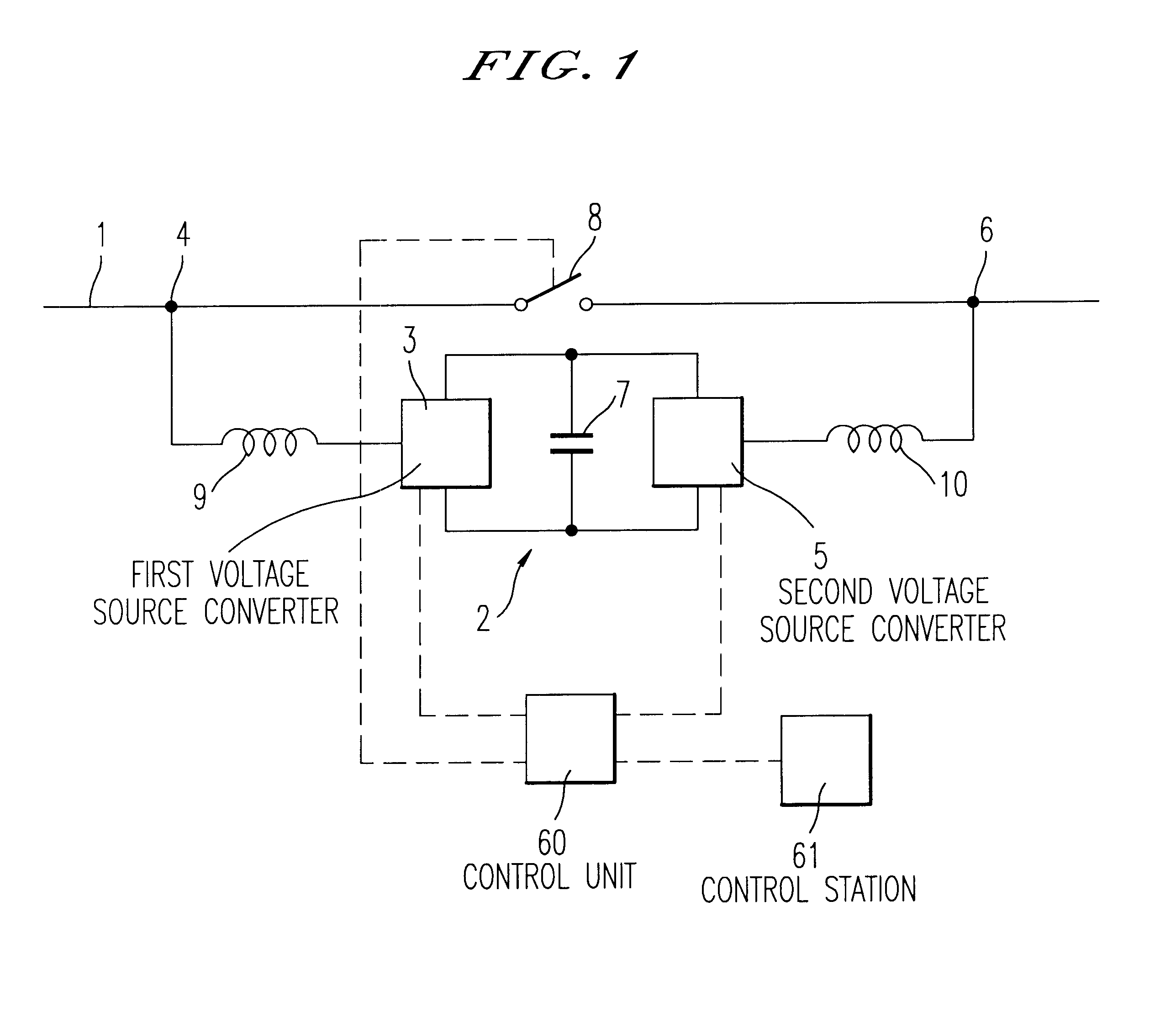
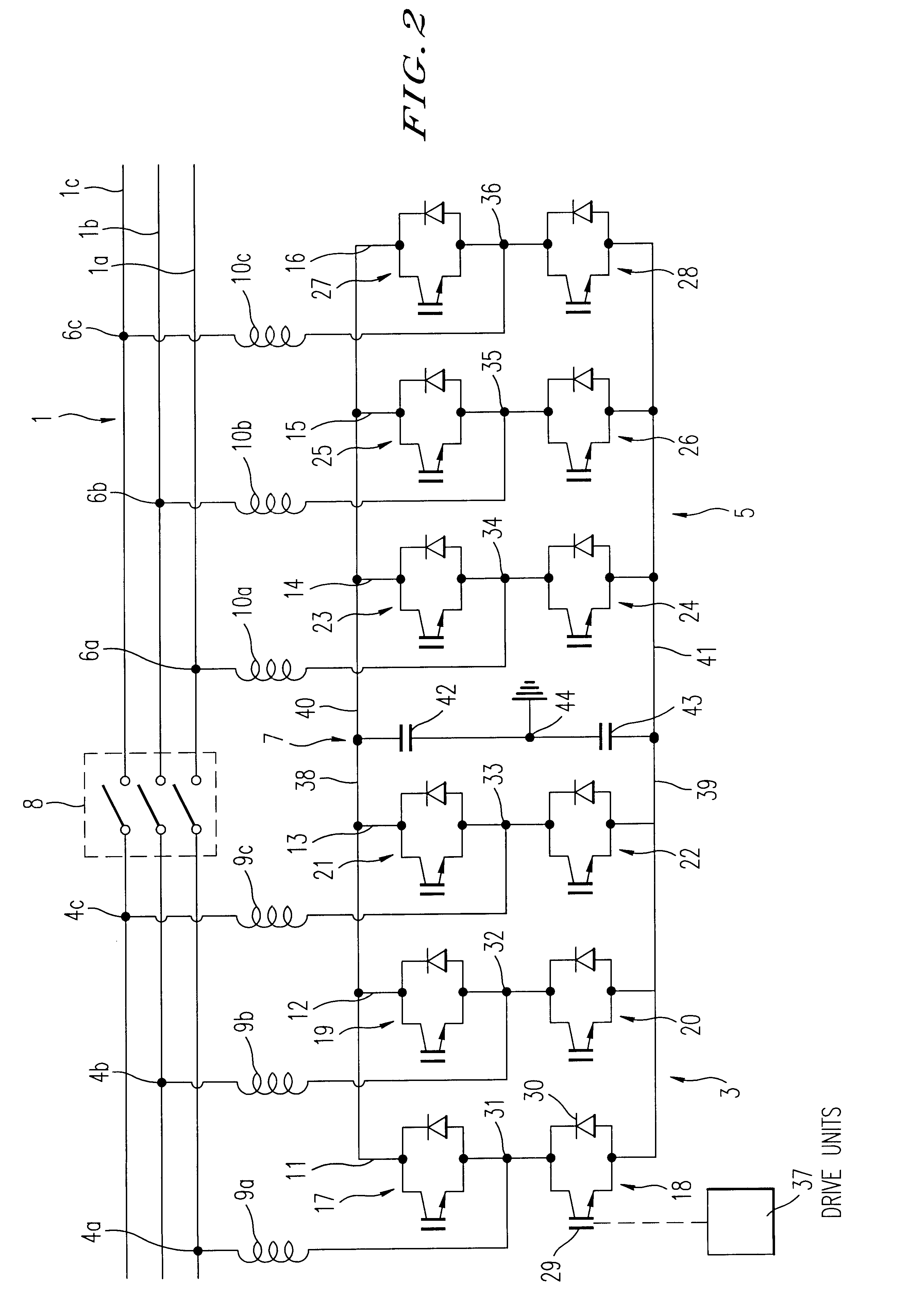
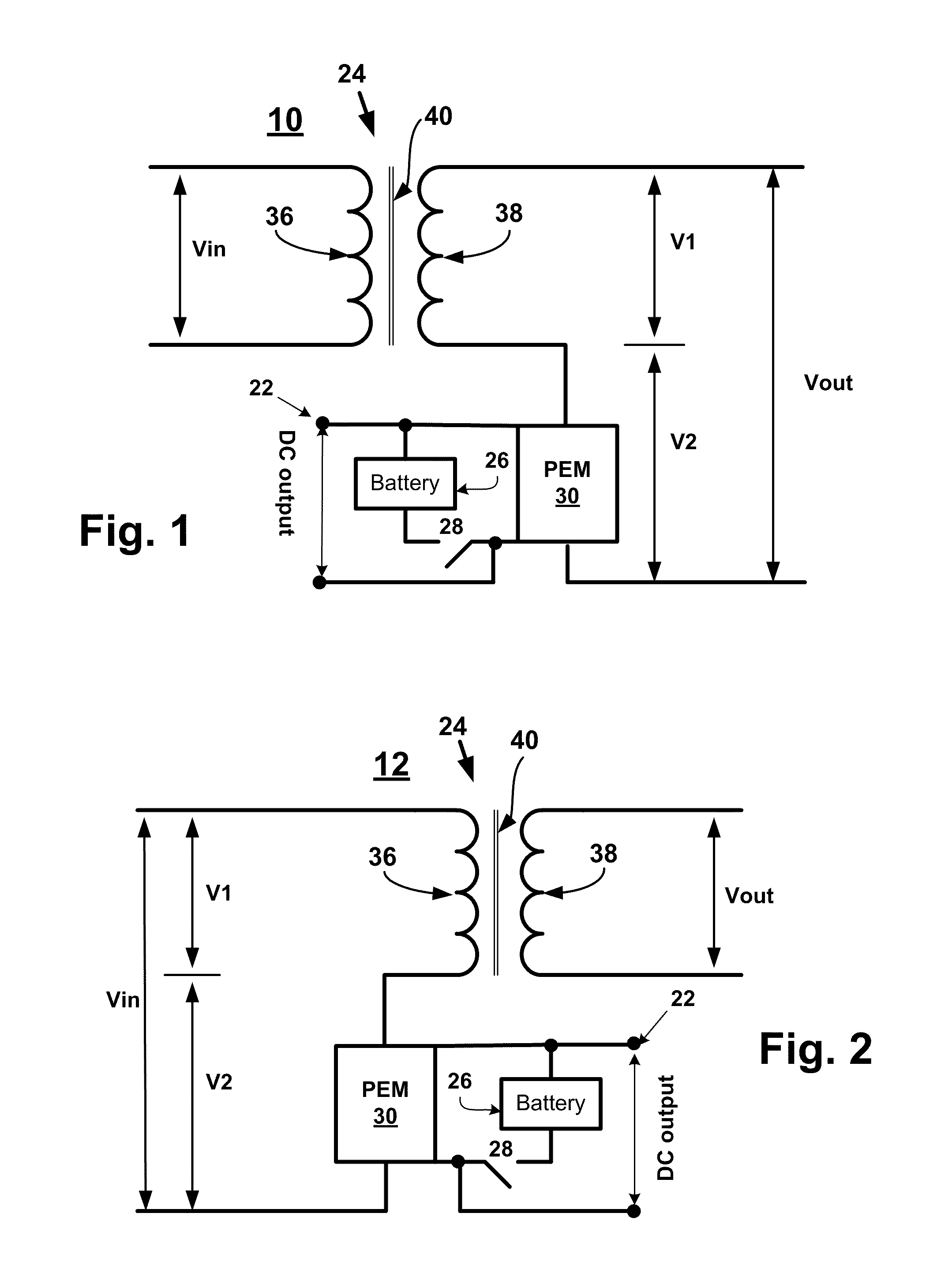
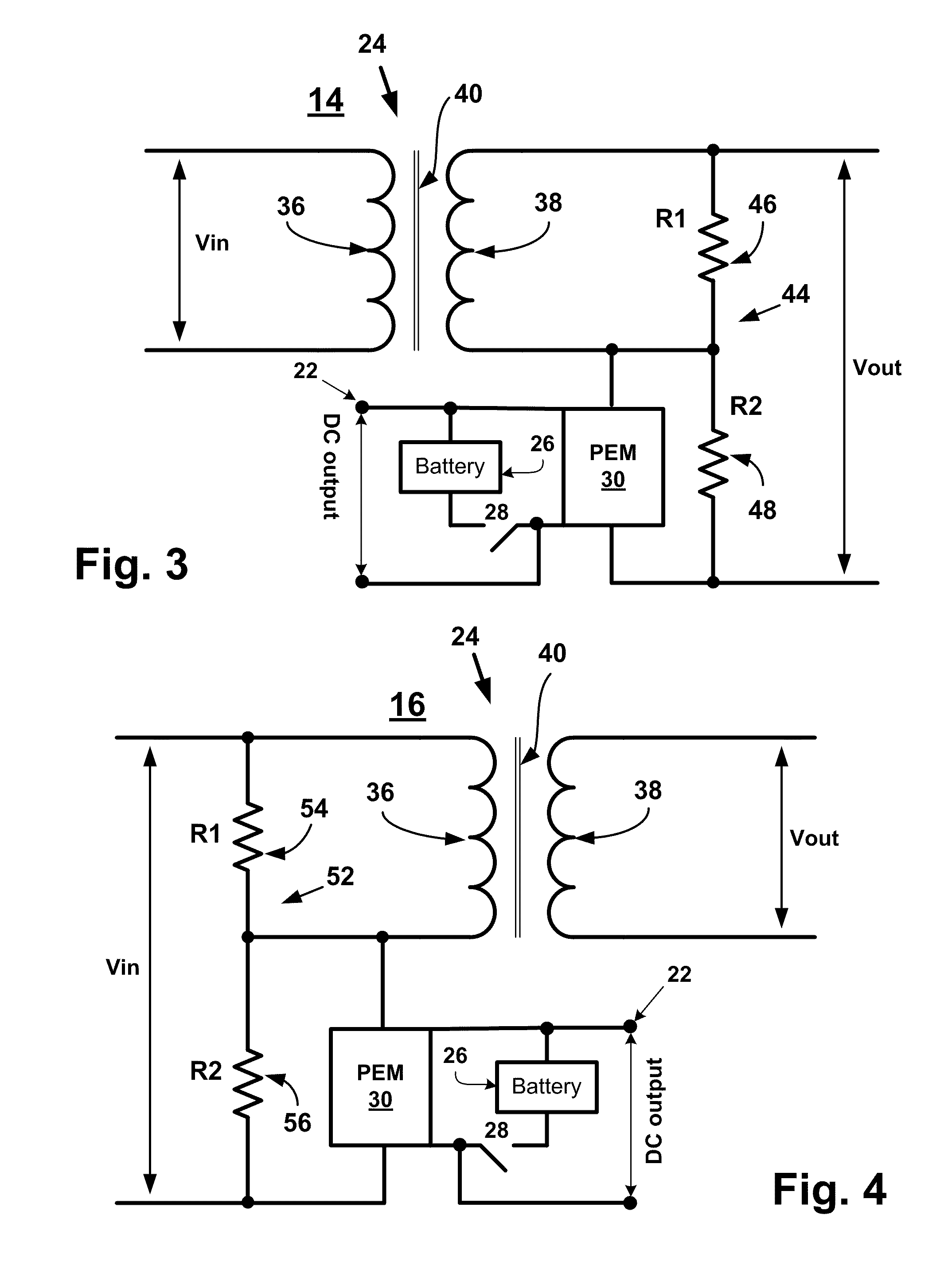
A device and a method for controlling the flow of electric power in a transmission line carrying alternating current, in which a first voltage source converter is connected to the transmission line at a first point and a second voltage source converter is connected to the transmission line at a second point. Further, the first and second voltage source converters have their direct current sides connected to a common capacitor unit. Also included is a by-pass switch connected to the transmission line between the first point and the second point in parallel with the first and second voltage source converters so that the first and second voltage source converters will operate as a back-to-back station when the by-pass switch is open and as two parallel static var compensators when the by-pass switch is closed.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
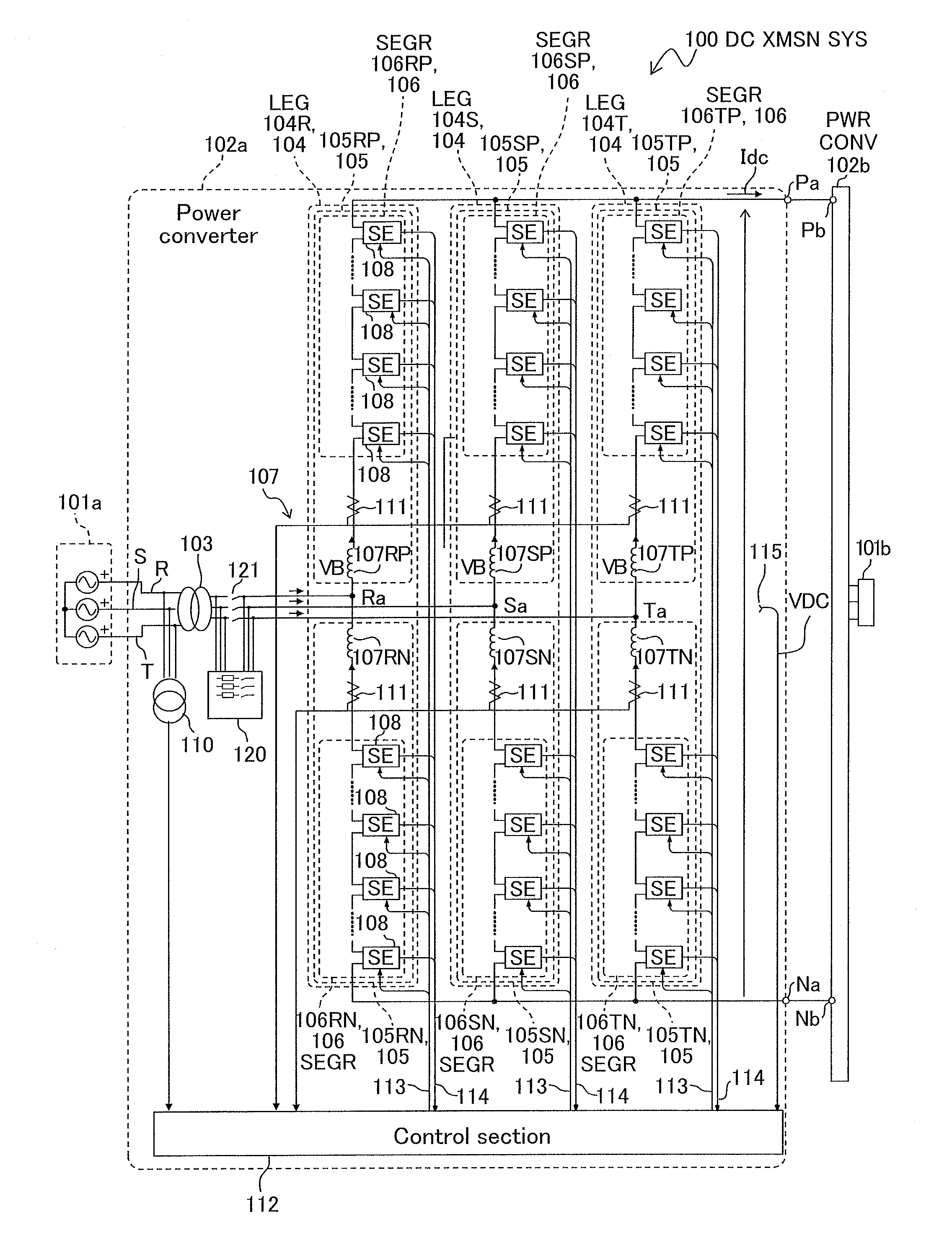
Switching Element, Power Converter, Direct Current Transmission System, Current Control Device, Method of Controlling Power Converter, and Method of Controlling Current in Voltage Source Converter
ActiveUS20130208519A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric forceLow voltage
A switching element of a power converter generates a low voltage, using a current flowing in the power converter, and supplies a power to drive itself. A switching element of a power converter for conversion from direct current into alternate current or from alternate current into direct current includes: a terminal and a terminal which are used in building the switching element itself in the power converter; a capacitor, a high-side controllable switch and a low-side controllable switch enabling outputting the voltage of the capacitor, the voltage being output between the terminal and the terminal, and a self-supply power source for supplying a power to drive the bi-directional chopper switching element itself, using a current flowing in the capacitor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Switching system
A voltage source inverter generating a poly phase AC signal is provided that includes an SVPWM controller. The controller is adapted to modify the switching pattern at low sine-wave frequencies creating a more even distribution of the conduction losses. The switching pattern periodically changes the sequence (or rotational sense) of the space vector components from clock-wise to counter-clock-wise direction, and vice-versa.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
Modular Voltage Source Converter
Voltage source converter based on a chain-link cell topology including one or more phases, each of the phases having one or more series-connected chain-link cell modules connected to each other. The output voltage of the voltage source converter is controlled by control signals applied to the series-connected chain-link cell modules. In case of failure of a chain-link cell module, that module is controlled, by the control signals, such that zero output voltage is provided at its output voltage AC terminal.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Fault current limitation in DC power transmission systems
InactiveUS20120201059A1Simple designGood removal effectEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionTransport systemEngineering
A method, voltage source converter and computer program product for limiting the current in a DC power transmission system are disclosed. The voltage source converter has an AC side and a DC side and a fault current path between these sides. It furthermore includes a control unit and at least one switching unit of a first type provided in the fault current path and that includes a primary switching element together with an anti-parallel secondary controllable rectifying element. Based on a fault being detected in the DC power system when the primary switching elements of the converter are blocked, the control unit changes the control of the controllable rectifying element from acting as a non-controllable rectifying to acting as a controllable rectifying element.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
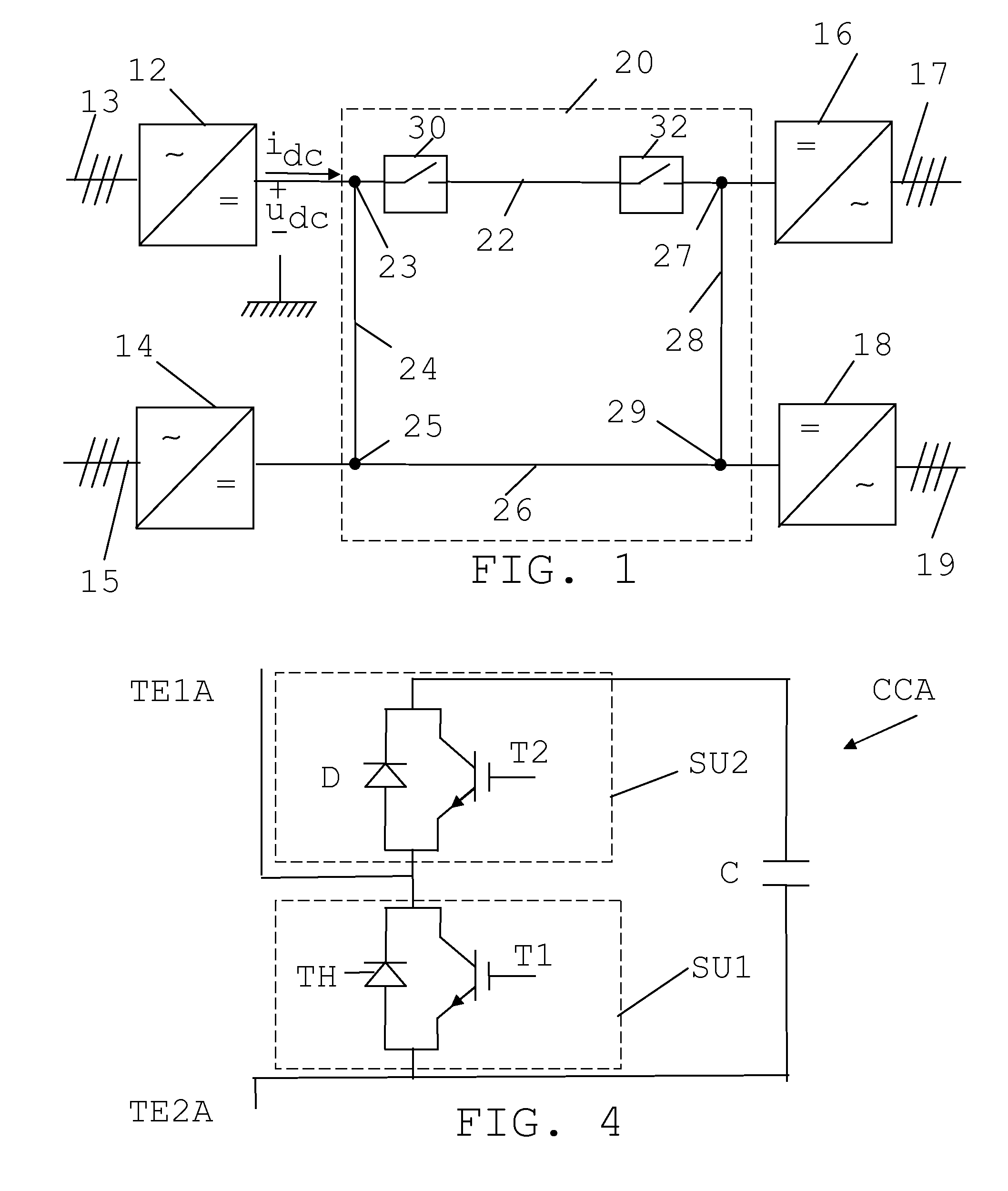
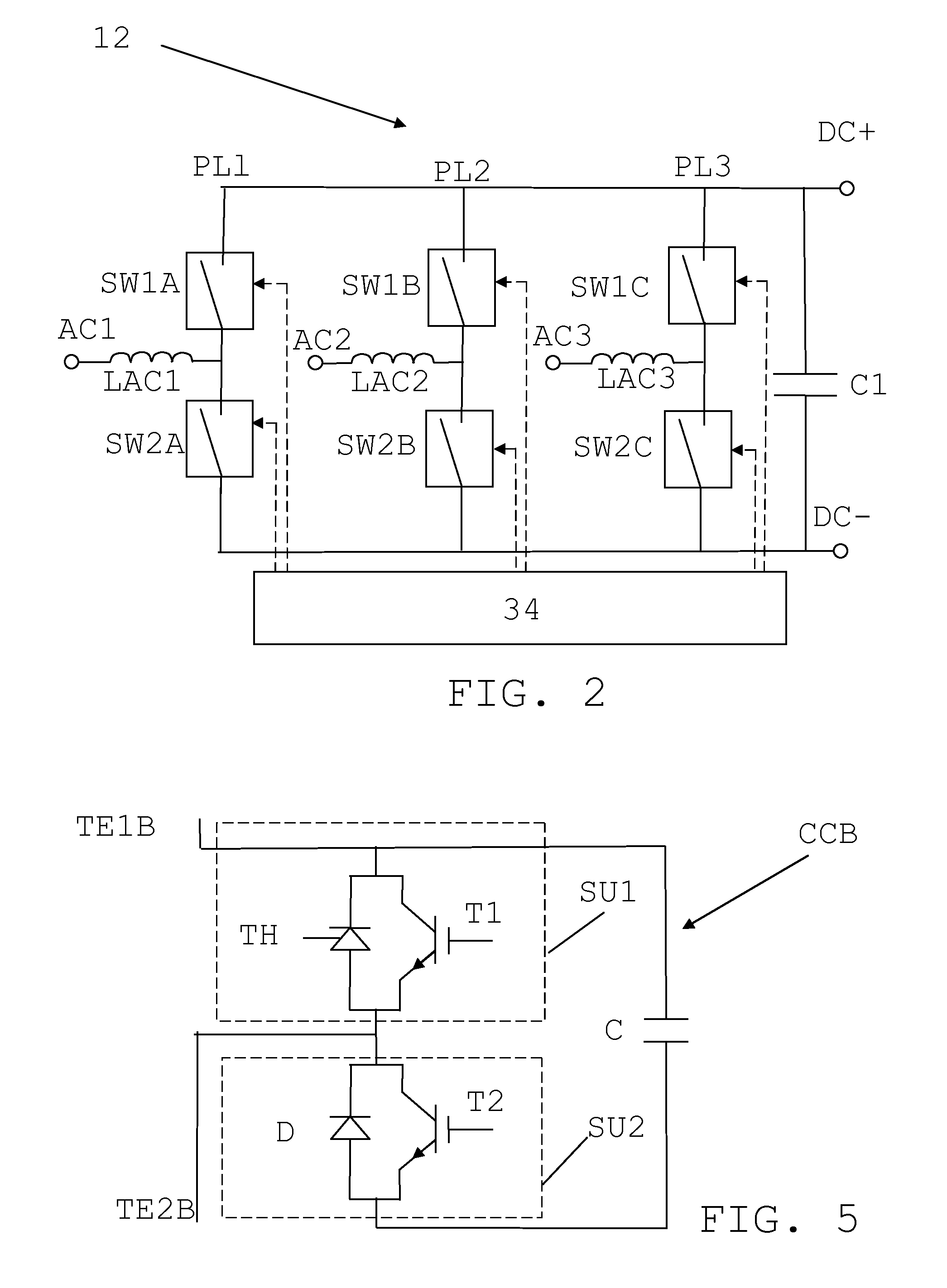
DC power transmission system of voltage source converter using pulse-interleaving auxiliary circuit
InactiveUS7499291B2Increase the number ofAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcTransformerEngineering
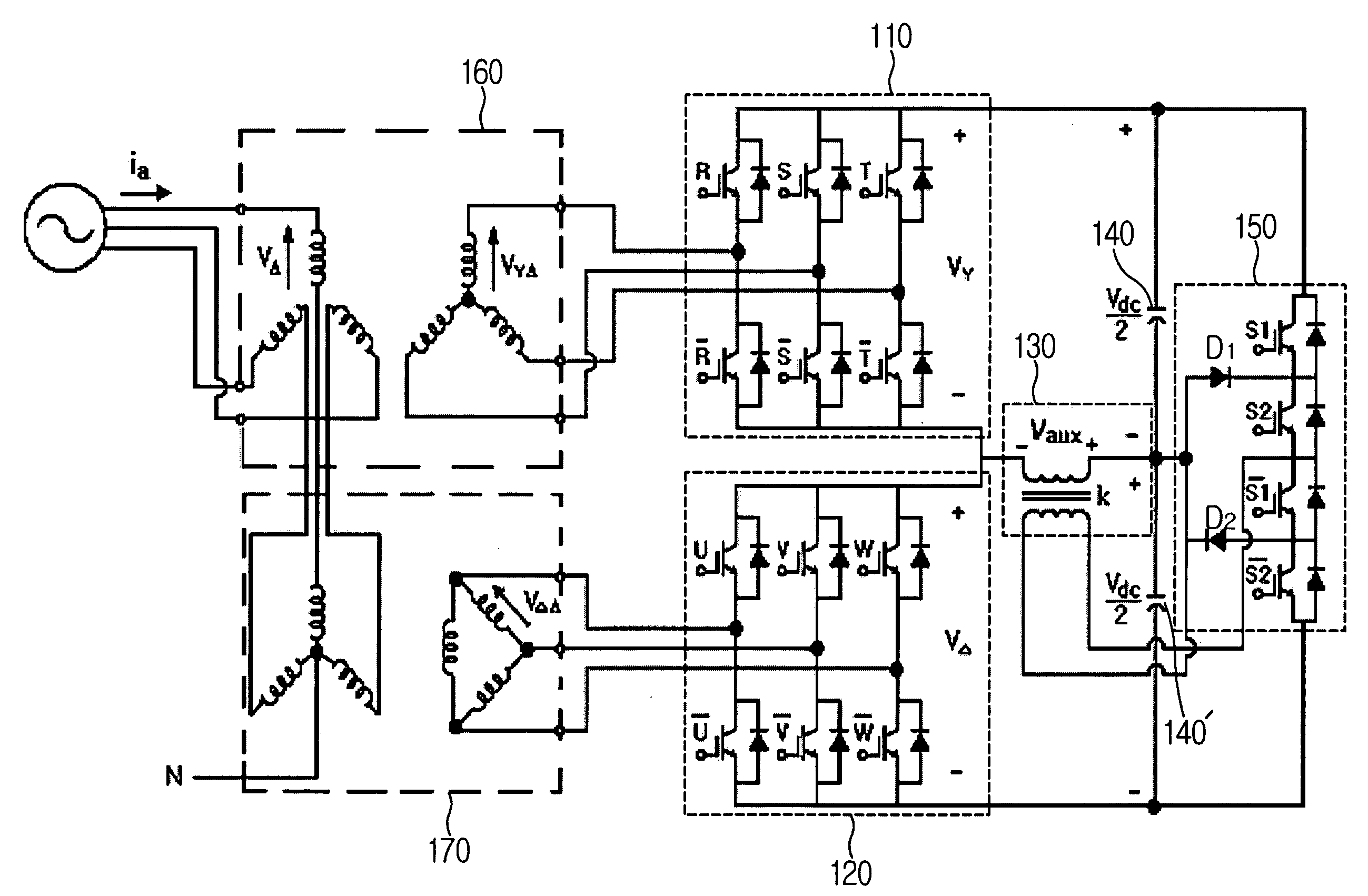
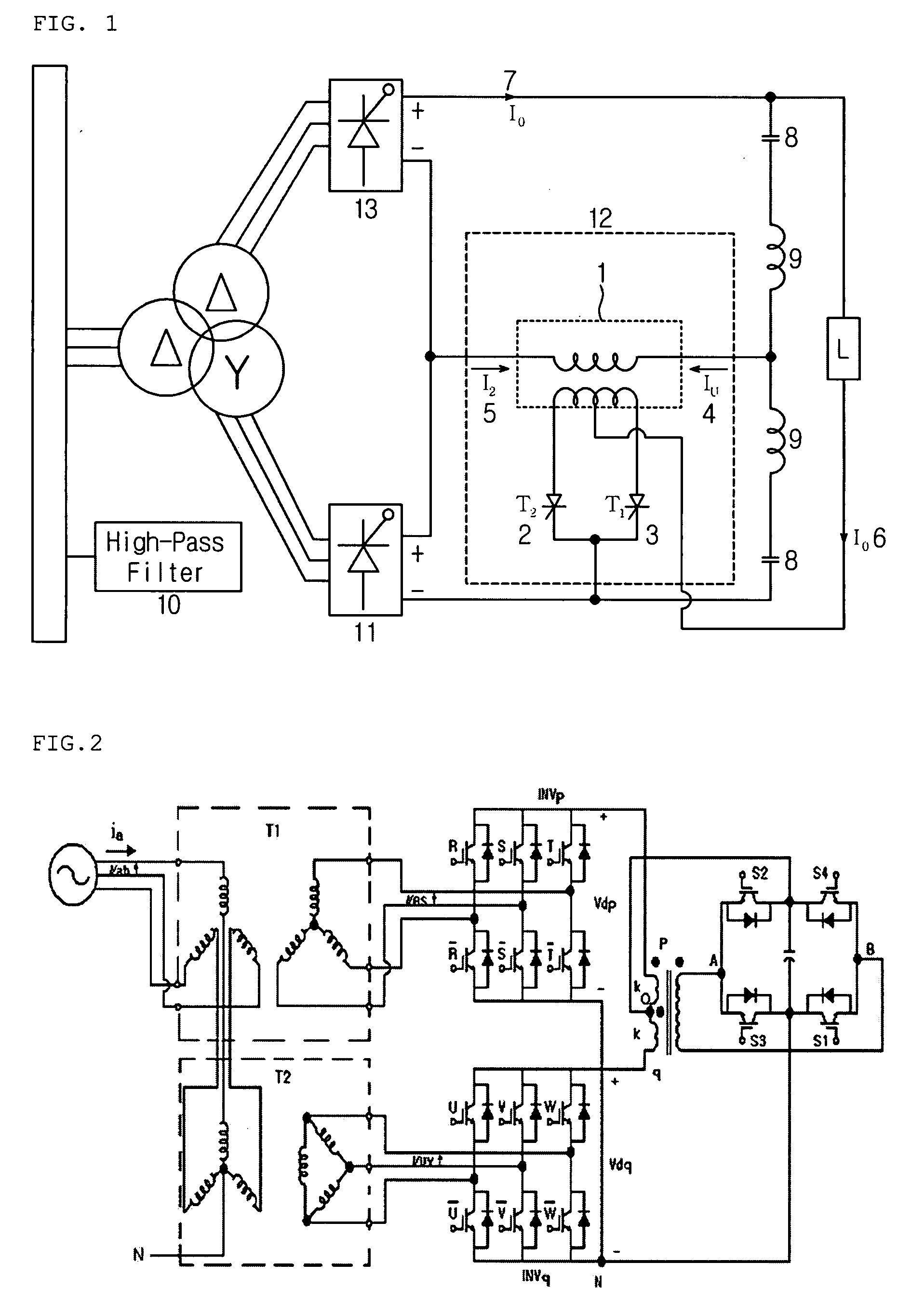
A DC power transmission system of a voltage source converter using a pulse-interleaving auxiliary circuit is disclosed. The converter system comprises an IGBT converter for converting an AC power to a DC power or the DC power to the AC power; an open Y-Y transformer and a Y-Δ transformer for stepping up or stepping down the AC power having a predetermined magnitude; a capacitor for dividing a DC voltage; and a DC Auxiliary circuit composed of a normal transformer and half-bridge for overlapping a pulse type input voltage to increase the number of pulses of an output waveform. In using a DC auxiliary circuit composed of normal transformer and 3-level half-bridge to increase the number of pulses of the output waveform by superposing the voltage in the form of the pulse, a normal transformer may be used instead of the tapped transformer to reduce the size thereof and to obtain an accurate transformer ratio, and a 3-level half-bridge may be used instead of the H-bridge to reduce the switching loss.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
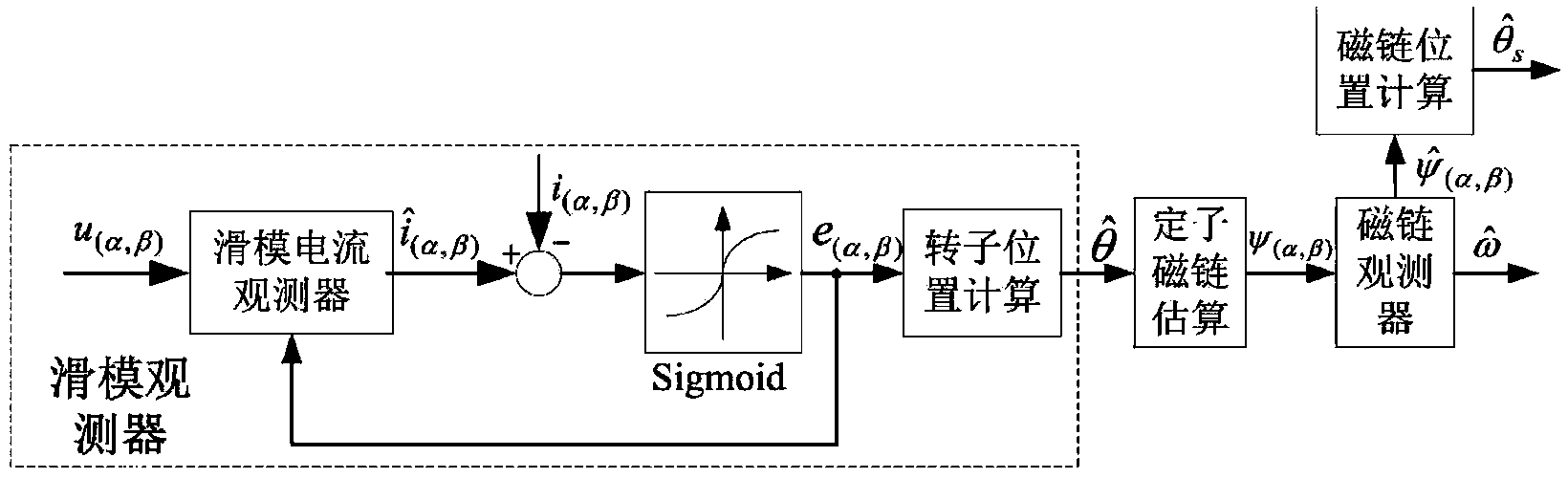
Permanent magnet synchronous motor torque control method based on sliding mode flux linkage observer
ActiveCN103872951AReal-time controlAchieving Direct Torque ControlTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorVoltage reference
The invention discloses a permanent synchronization motor torque control method based on a sliding mode flux linkage observer. Direct torque control is performed on a permanent synchronization motor through a 3 / 2 coordinate conversion module, the sliding mode flux linkage observer, an electromagnetic torque calculation module, a rotating speed PI adjustor, a torque PI adjustor, a flux linkage self-adaptation module, an expected voltage calculation module, an SVPWM module and an inverter. The sliding mode flux linkage observer is adopted for estimating the size, phase and rotator speed of stator flux linkage, and set torque is processed through the flux linkage self-adaptation module to obtain a set value of the stator flux linkage. Expected voltage calculation is performed on size and phase estimation values and the set value of the stator flux linkage and the output quantity of the torque PI adjustor, so that two-phase alternating-current voltage reference values on a two-phase static coordinate system are obtained, and then through SVPWM conversion, a switching signal is obtained to drive the voltage source inverter to achieve direct torque control over the permanent synchronization motor.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Distribution of space-vector PWM conduction losses
InactiveUS20020044472A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionConduction lossEngineering
A voltage source inverter generating a poly phase AC signal is provided that includes an SVPWM controller. The controller is adapted to modify the switching pattern at low sine-wave frequencies creating a more even distribution of the conduction losses. The switching pattern periodically changes the sequence (or rotational sense) of the space vector components from clock-wise to counter-clock-wise direction, and vice-versa.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
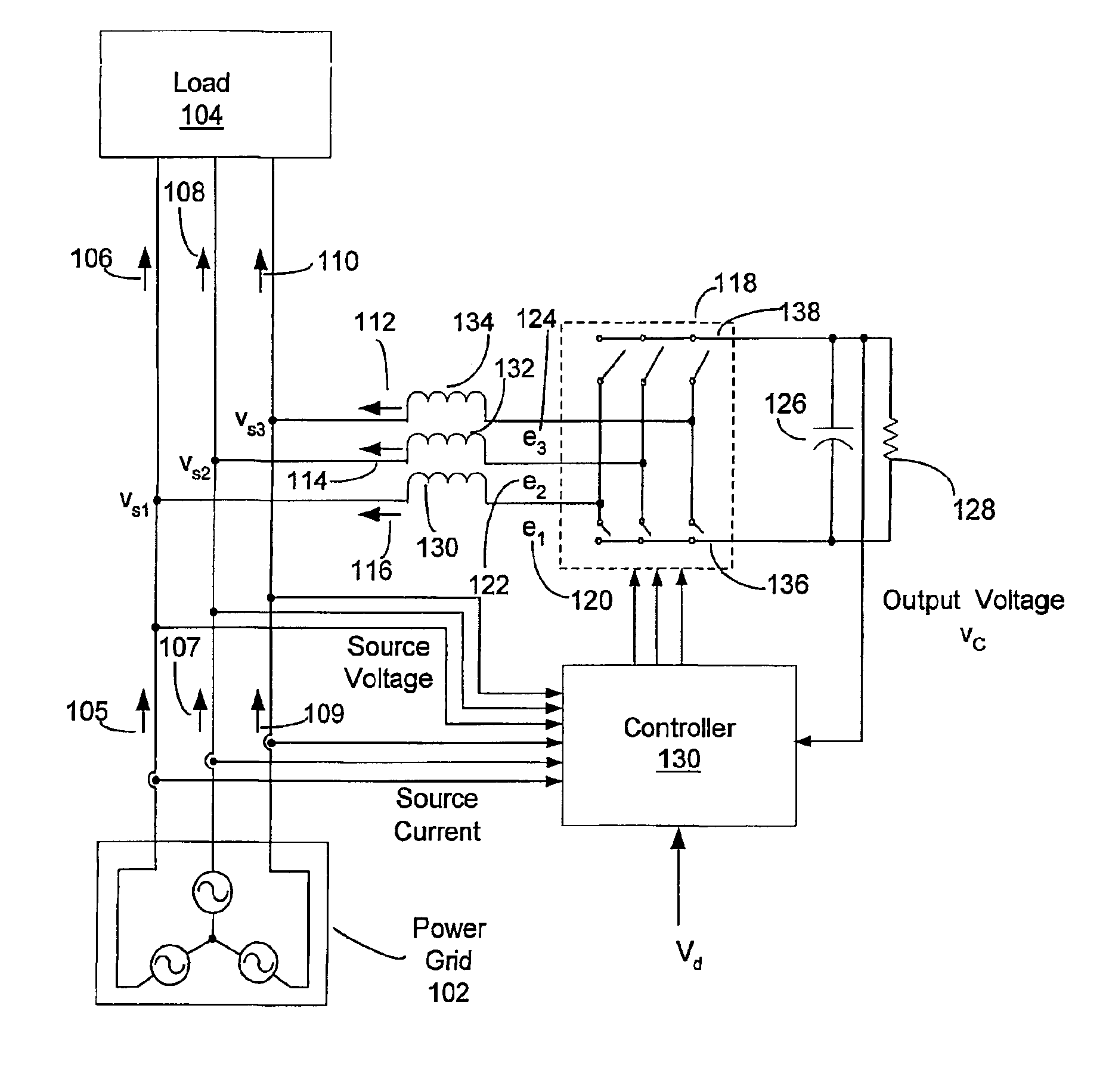
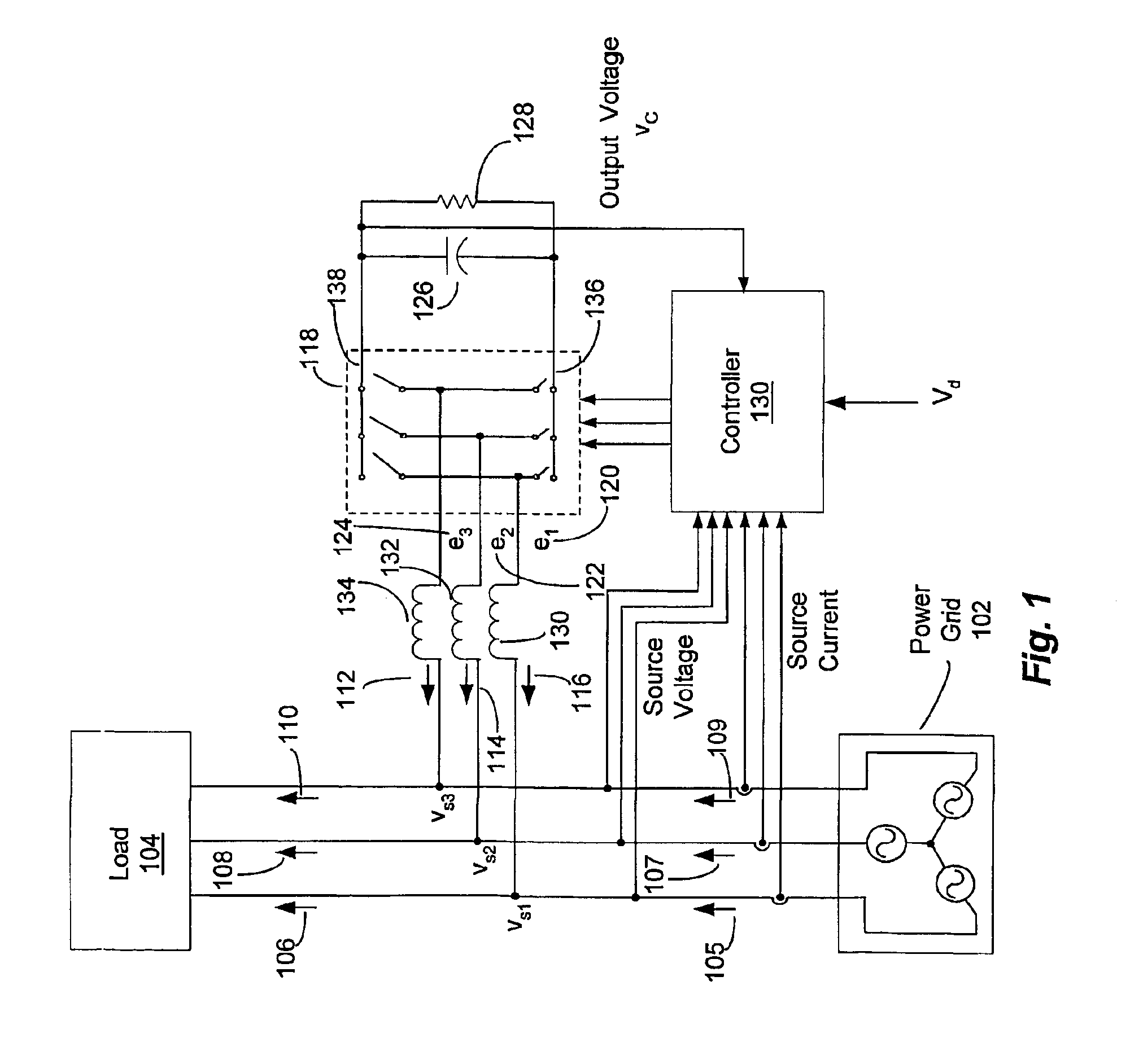
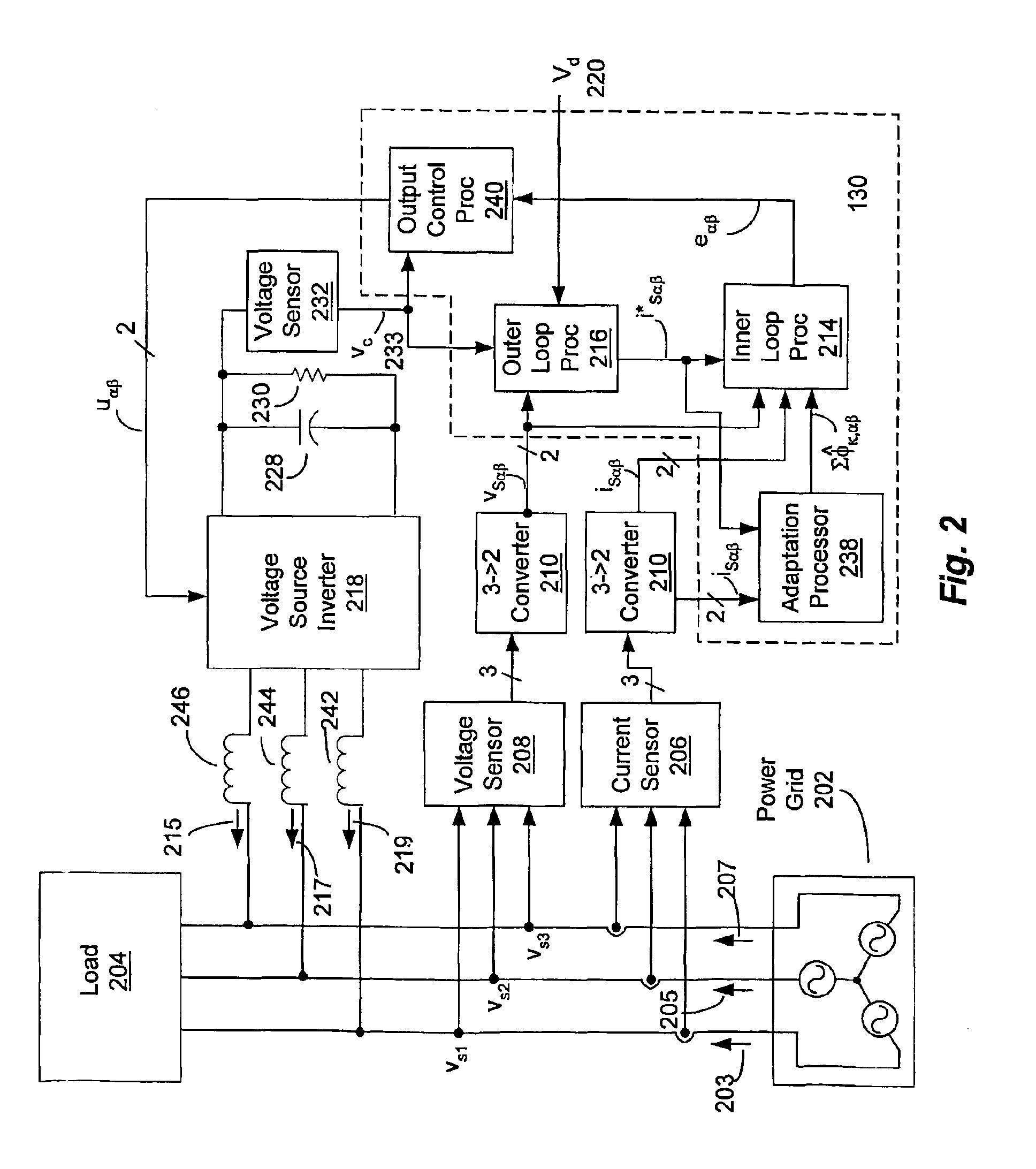
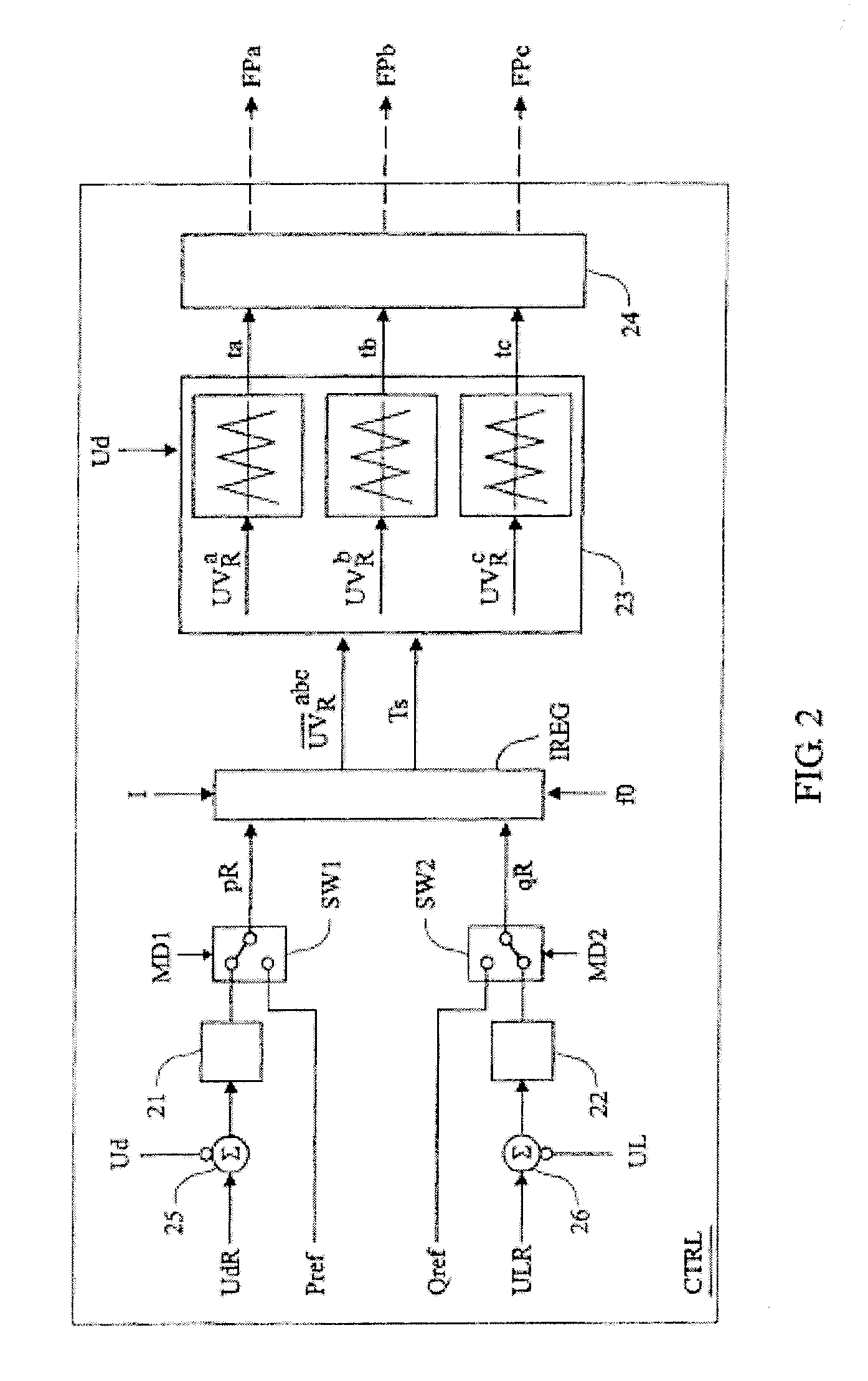
Adaptive controller for d-statcom in the stationary reference frame to compensate for reactive and harmonic distortion under unbalanced conditions
InactiveUS6862199B2Flexible AC transmissionActive power filteringLoop controlTotal harmonic distortion
A controller (130) for compensating reactive power and selected current load harmonics in an unbalanced multi-phase power distribution system. Control current is injected from a multi-phase voltage source inverter (118) into the multi-phase power distribution system as a function of the voltage and current provided by the source inverter 118. The injected current is operative to balance the load seen by the power distribution system including non-linear / distorted and unbalanced loads in each phase. The controller includes an inner loop control processor (216), an outer loop control processor, and an adaptation processor. The adaptation processor (238) is operative to estimate a selected set of predetermined harmonic components in the periodic disturbance which is a function of the unknown system parameters, the source current, the source voltage, and their time derivatives in stationary coordinates.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
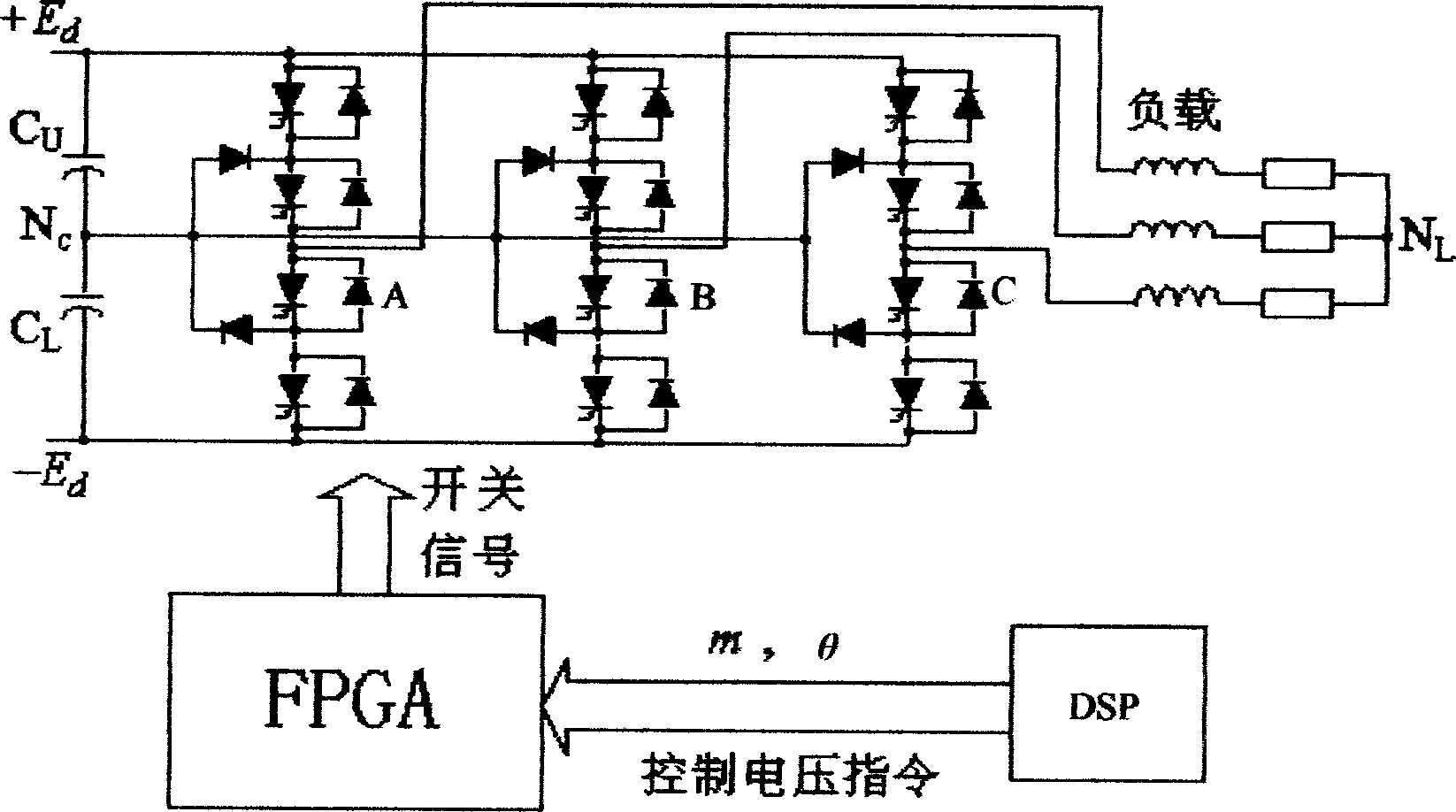
Three level inverter control system and method
InactiveCN1829061AFulfil requirementsImprove real-time performanceDc-ac conversion without reversalFpga field programmable gate arrayVoltage vector
The present invention discloses a three electric level inverter control system. It contains three electric level voltage source inverter (NPC), field programmable gate array (FPGA), digital signal processor (DSP), wherein FPGA field programmable gate array (FPGA) receiving digital signal processor (DSP) sent control voltage instruction generating three electric level voltage source inverter (NPC) control signal. The present invention also discloses three level inverter control method, featuring 1, digital signal processor (DSP) transmitting space voltage vector amplitude value m and argument for controlling three level inverter triphase reference voltage, 2, field programmable gate array (FPGA) receiving DSP sent space voltage vector amplitude value m and argument, generating signal Vca, Vcb, Vcc, through direct current biasing and dead zone compensation techniques processing to generate three-phase voltage modulation signal Vca **, Vcb **, Vcc **, 3, finally respectively comparing with positive triangular wave, negative triangular wave to generate control pulse. The present invention overcomes the insufficiency of current pulse width modulation method (SVPWM) and special harmonic cancellation method (SHE-PWM), provides a fine rapidity, simple controlling, and practical three level inverter control system and method.
Owner:GUANGDONG MINGYANG LONGYUAN POWER ELECTRONICS
Method and system for measuring position compensation angles of permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor
ActiveCN102097988ALow costImprove reliabilityVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlVoltage vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
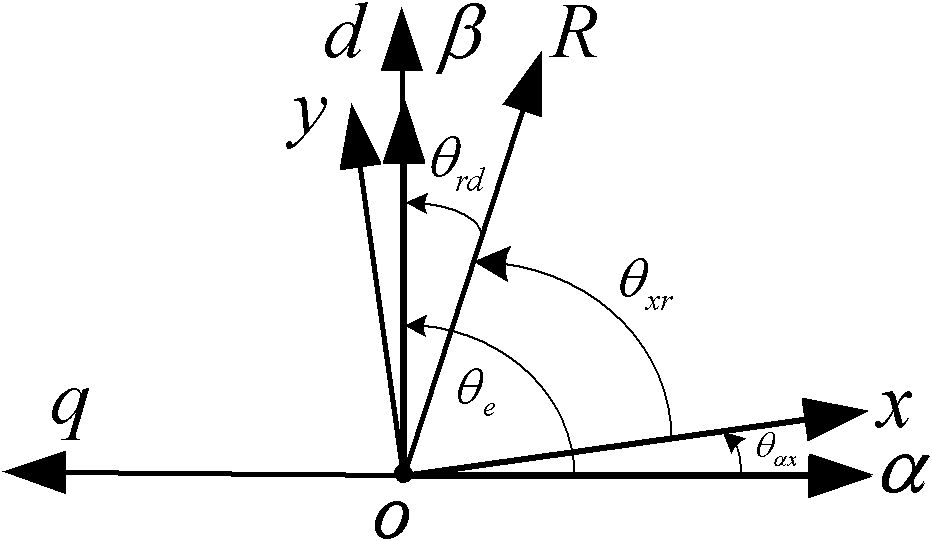
The invention provides a method and device for measuring position compensation angles of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, wherein the method comprises the following steps: setting a forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force; setting component instruction value of a d shaft voltage as u*d=0; inputting the component instruction value u*q of a q shaft voltage which can enable the permanent magnet synchronous motor to enter into a zero speed shaft locking state; according to the forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force, obtaining voltage vectors by virtue of PARK inverse transformation of u*d and u*q; generating a power device pulse-width signal needed by a voltage source inverter by a space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) algorithm; driving the permanent magnet synchronous motor to rote to a position of ThetaForcee+90 DEG by the voltage source inverter; obtaining the angle Theta xr read by an absolute encoder mounted on the rotor; and calculating the compensation angle that Theta c= Theta Force+ 90 DEG-Theta xr. The method provided by the invention can be simply, conveniently and easily realized; a current sensor is unnecessary to work, and the flitter is not existed during initial location.
Owner:北京和利时电机技术有限公司
DC power transmisson system of voltage source converter using pulse-interleaving auxiliary circuit
InactiveUS20080007978A1Increase the number of pulsesAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcTransformerVoltage source inverter
A DC power transmission system of a voltage source converter using a pulse-interleaving auxiliary circuit is disclosed.The converter system of the present invention comprises an IGBT converter for converting an AC power to a DC power or the DC power to the AC power; an open Y-Y transformer and a Y-Δ transformer for stepping up or stepping down the AC power having a predetermined magnitude; a capacitor for dividing a DC voltage; and a transformer and a half-bridge auxiliary circuit for overlapping a pulse type input voltage to increase a number of pulses of an output waveform.In accordance with the present invention, the normal transformer is used instead of a tapped transformer to reduce the size thereof and to obtain an accurate transformer ratio, the 3-level half bridge is used instead of the H-bridge to reduce the switching loss in order to increase the number of pulses of the output waveform by superposing the voltage in the form of the pulse using the auxiliary transformer and the bridge circuit.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
Direct torque control system of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102611381AEmbody practicalityBroaden the field of studyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorSynchronous motor
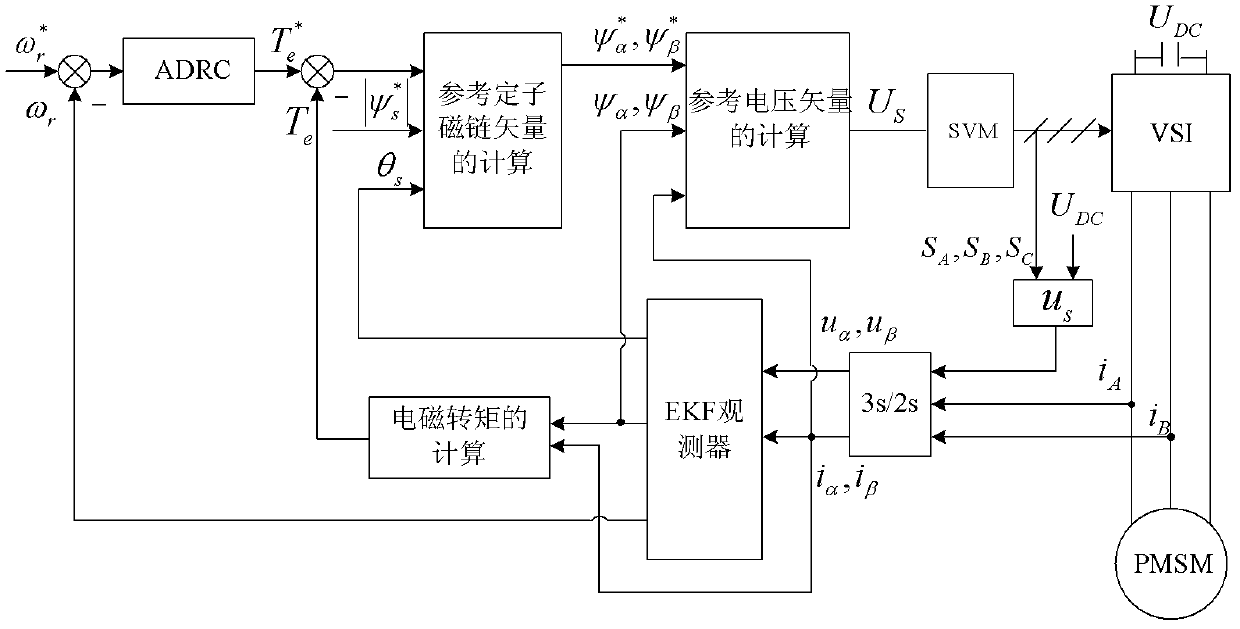
The invention relates to a direct torque control system of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. According to the control system, an extended kalman filter (EKF) observer is adopted for stator magnetic linkage and rotation speed estimation, according to a mathematical model of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor, the state variable x of the system equals to [Psi alpha, Psi beta, Omega gamma, Theta gamma] T, the input variable mu equals to [mu alpha, mu beta] T, the output variable y equals to [Iota alpha, Iota beta ] T, and state equations and output equations (11) of the system are obtained. The motor rotating speed is used as the input of an automatic data rate changer (ADRC) speed controller, the measurement value Te of the electromagnetic torque is calculated through the obtained stator magnetic linkage, in addition, the measurement value Te and electromagnetic torque given signals are compared, comparison results are used as the input of a space voltage vector pulse generator, and the output of the space voltage vector pulse generator is connected with a voltage source inverter of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The direct torque control system has the advantages of good dynamic performance, better stability performance, high robustness and high anti-interference capability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
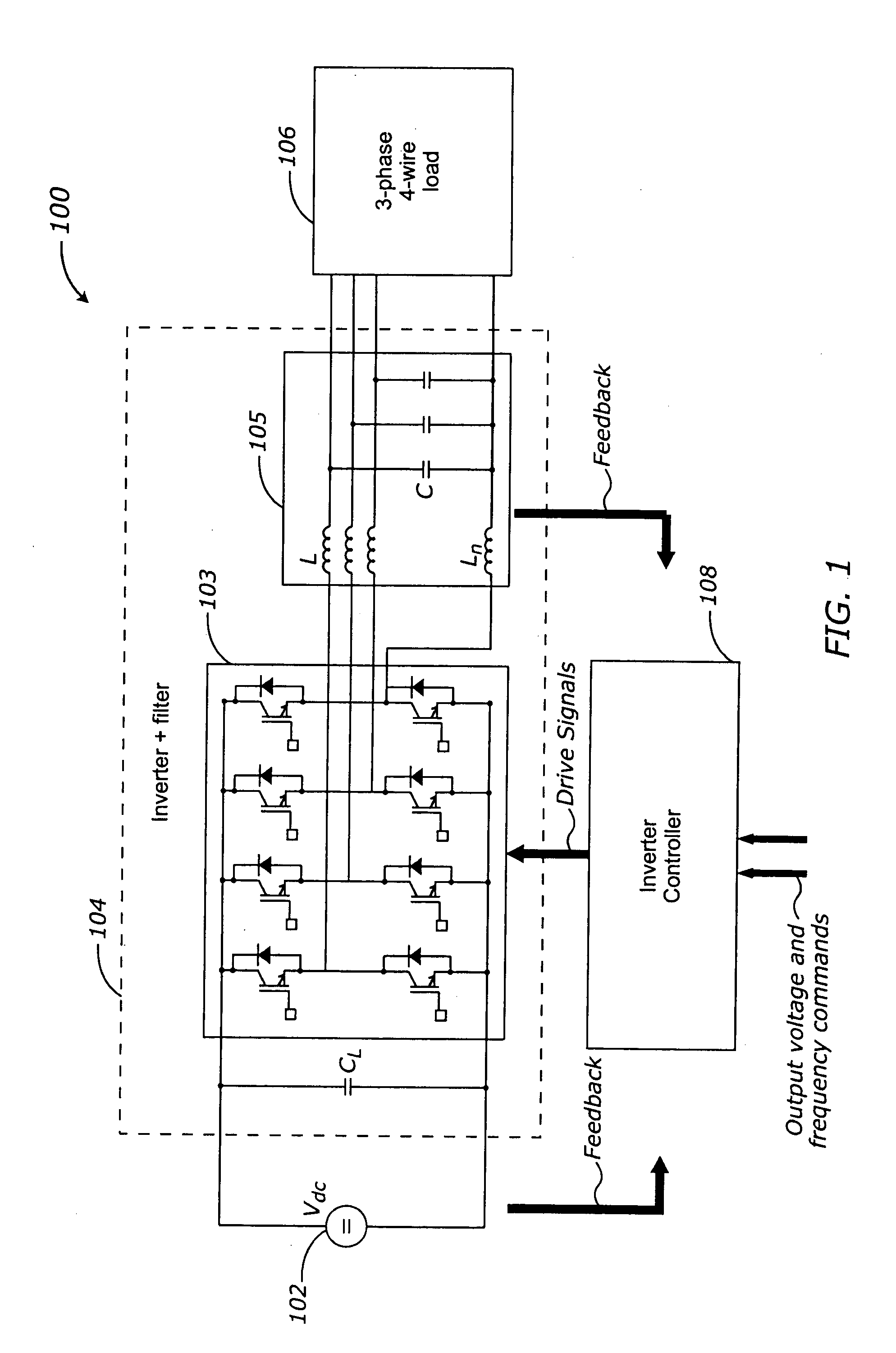
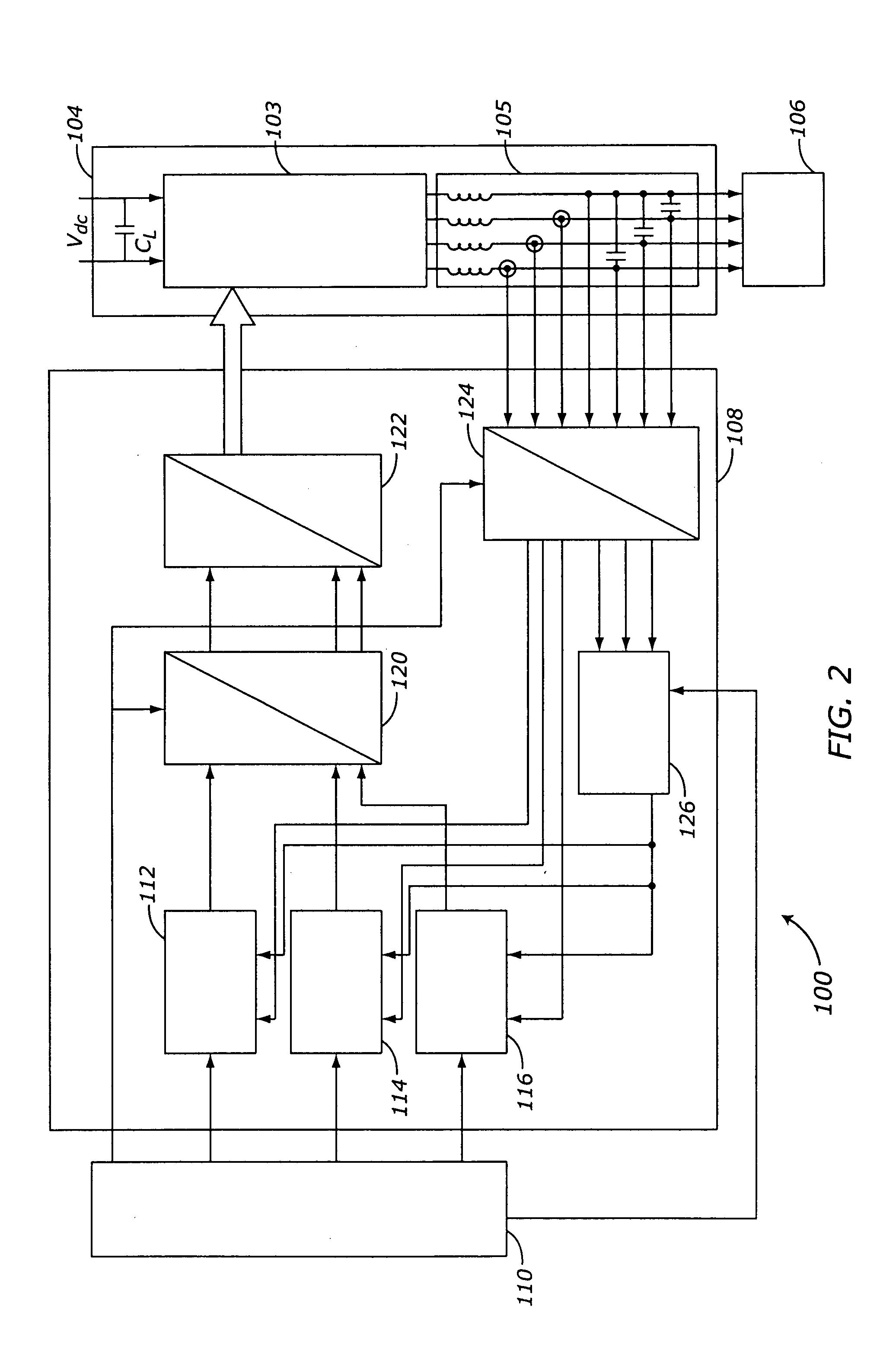
Method and apparatus for controlling a stand-alone 4-leg voltage source inverter
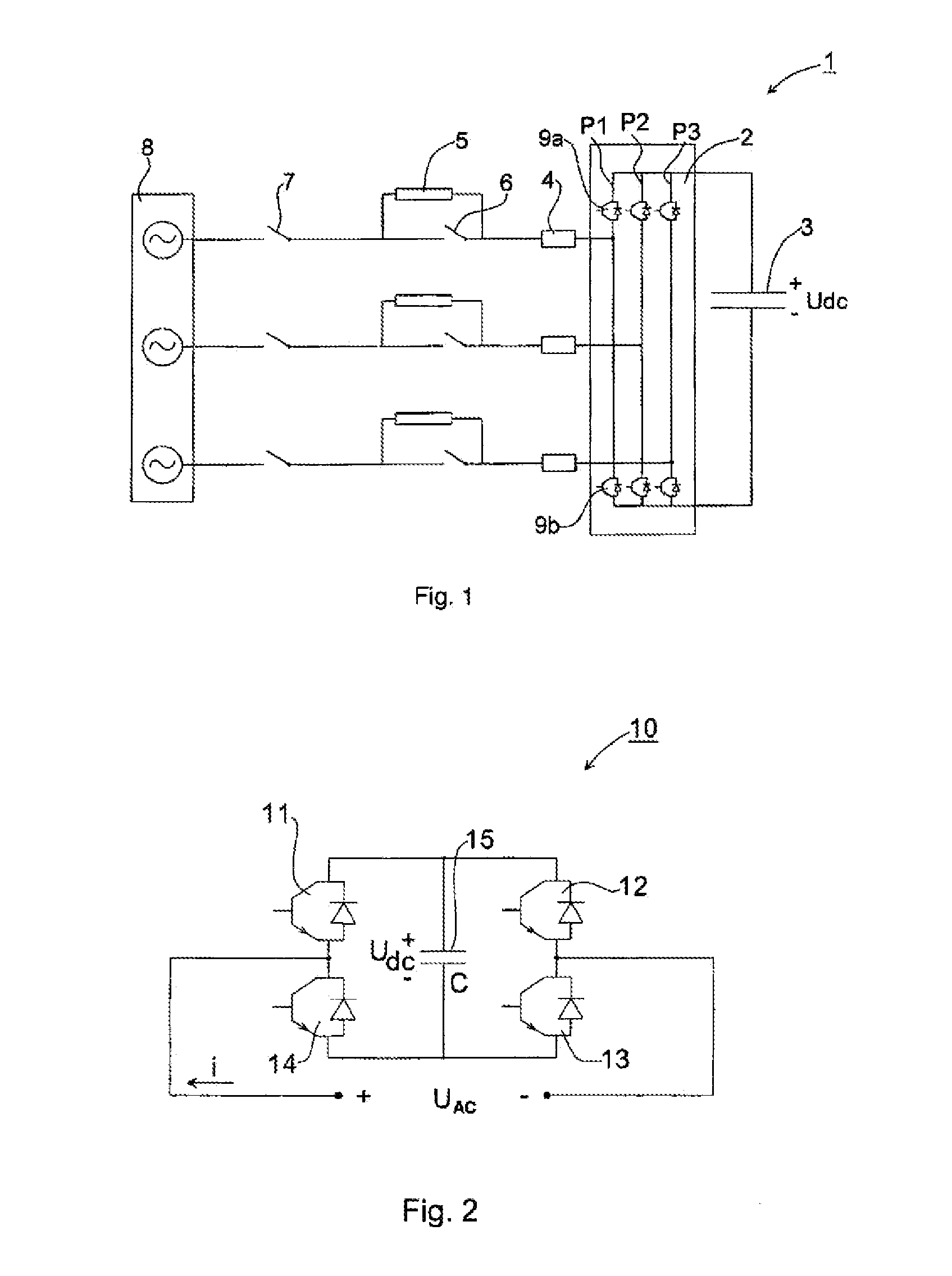
ActiveUS20050063205A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionCurrent limitingEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling a stand-alone four-leg three-phase inverter. The inverter three-phase output is converted from AC domain elements to corresponding DC domain elements. The DC domain elements are processed into combined regulating and imbalance compensating signals, including over-current limiting. The compensating signals are restored to corresponding AC domain signals, and are processed into control inputs for the inverter, in order to stabilize the inverter output when connected to an unbalanced load. The inverter controller can be implemented entirely in software as a control algorithm.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
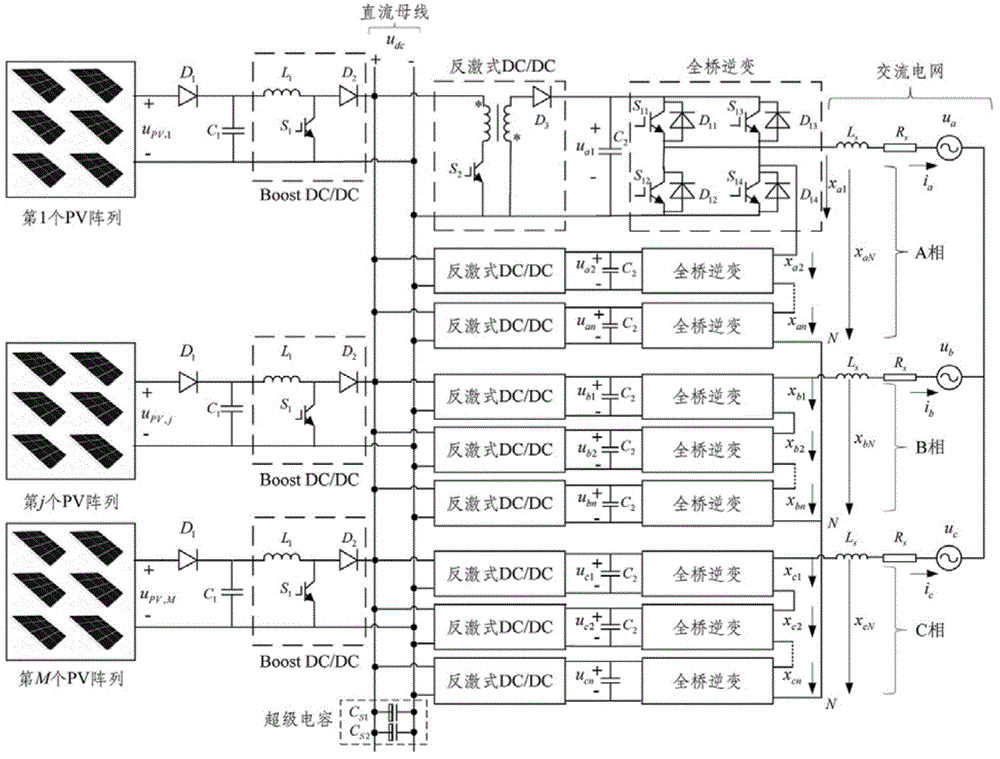
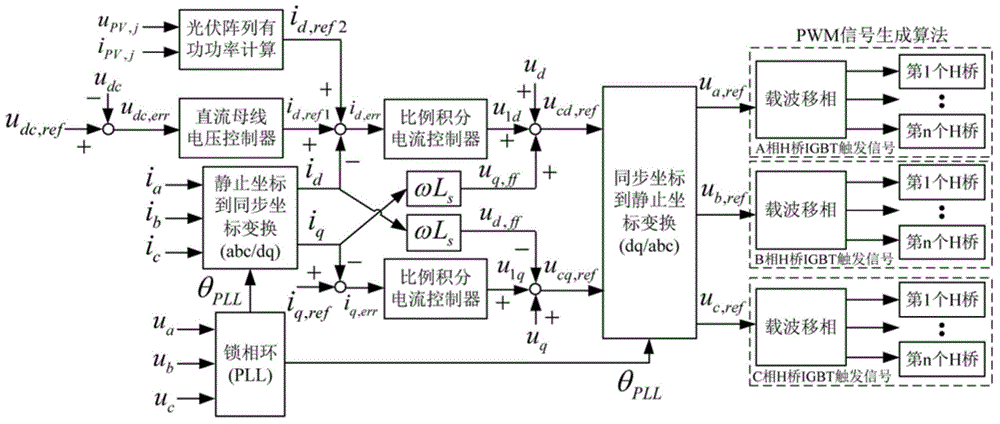
Topological structure of multi-level photovoltaic power generation system and control method of topological structure
InactiveCN104158212AReduce volumeImprove stabilityAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceControl signal
The invention relates to a topological structure of a multi-level photovoltaic power generation system and a control method of the topological structure. The topological structure comprises M photovoltaic arrays, the boost DC / DC (direct current / direct current) converters of the M photovoltaic arrays, 3n isolation flyback DC / DC converters and 3n H-bridge voltage source inverters. The PWM (pulse-width modulation) control signals of the first to nth H-bridge voltage source inverters of the three phases A, B and C of the cascade H-bridge multi-level voltage source inverters are obtained through an active power calculation method of a super-capacitor direct-current bus voltage controller and a photovoltaic array, and current tracking control of a dq synchronous coordinate system; the PWM control signals of the electronic power switches S2 of the wth and kth isolation flyback DC / DC converters are obtained through a control method of the isolation flyback DC / DC converters; the PWM control signals of the electronic power switches S1 of the j boost DC / DC converters are obtained through a control method of the boost DC / DC converters. The topological structure has the benefits that the shortcomings of large volume and high cost of power-frequency boosting transformers used when existing large-scale photovoltaic power generation systems are connected to a power grid are overcome.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
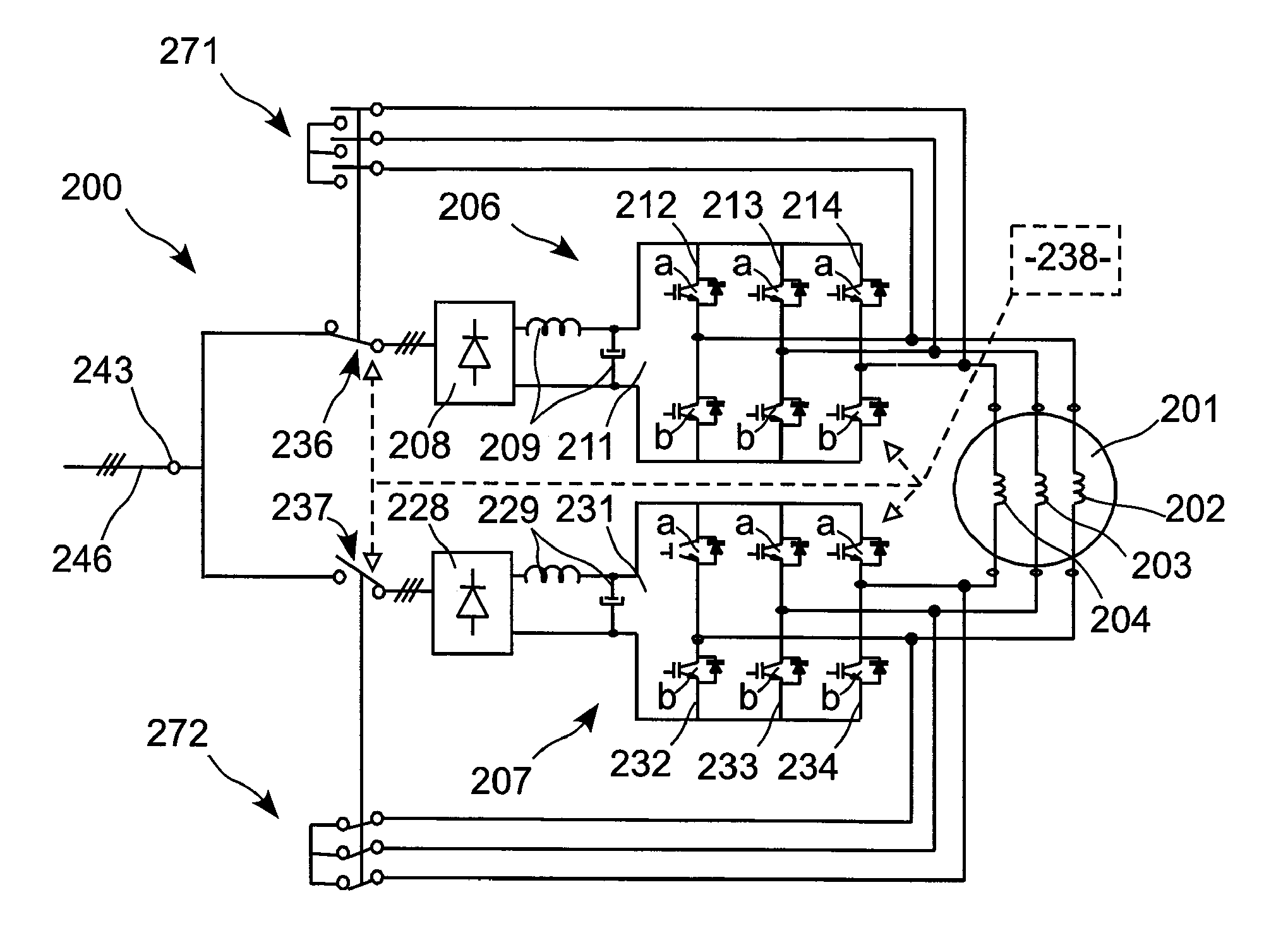
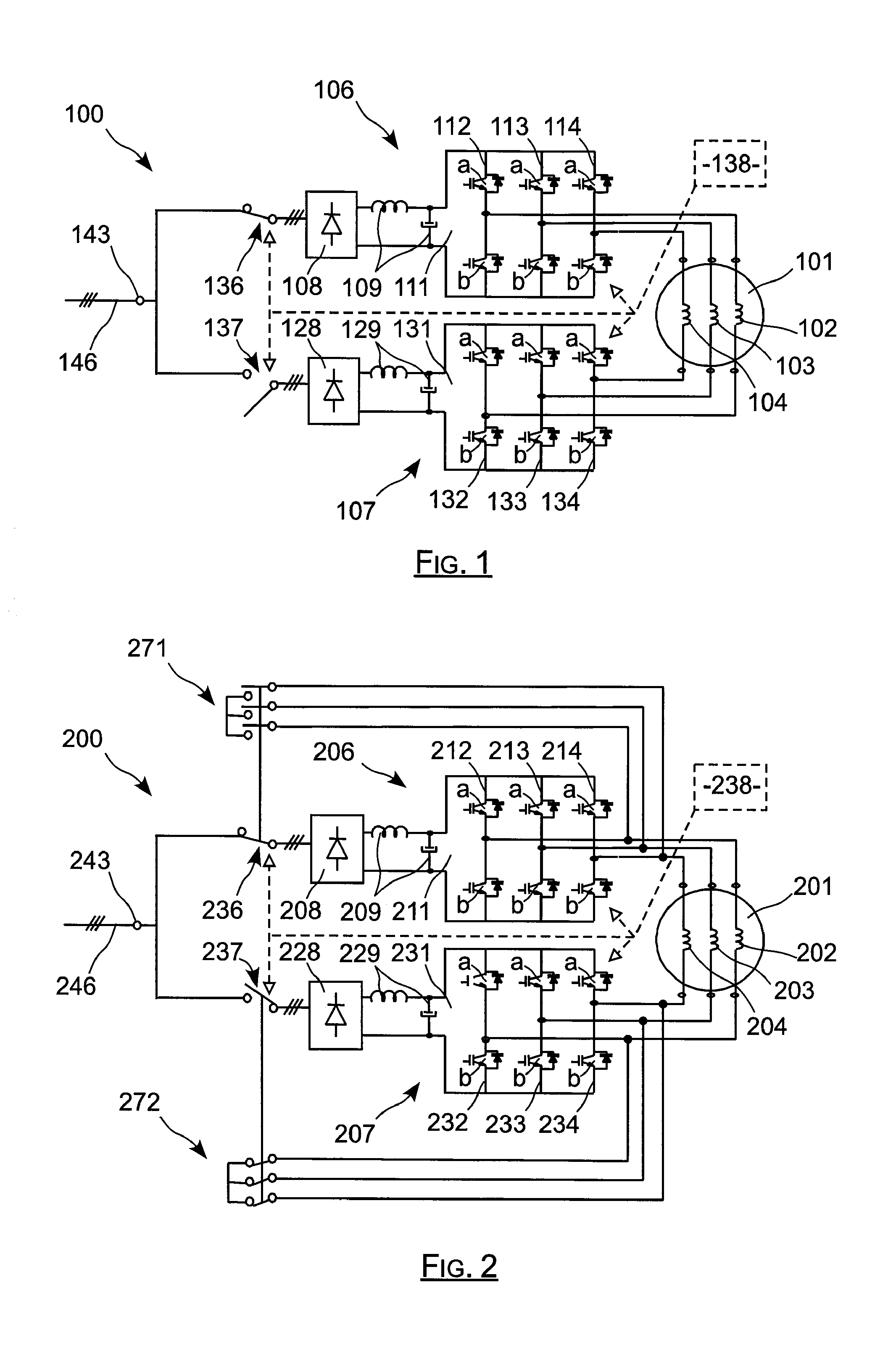
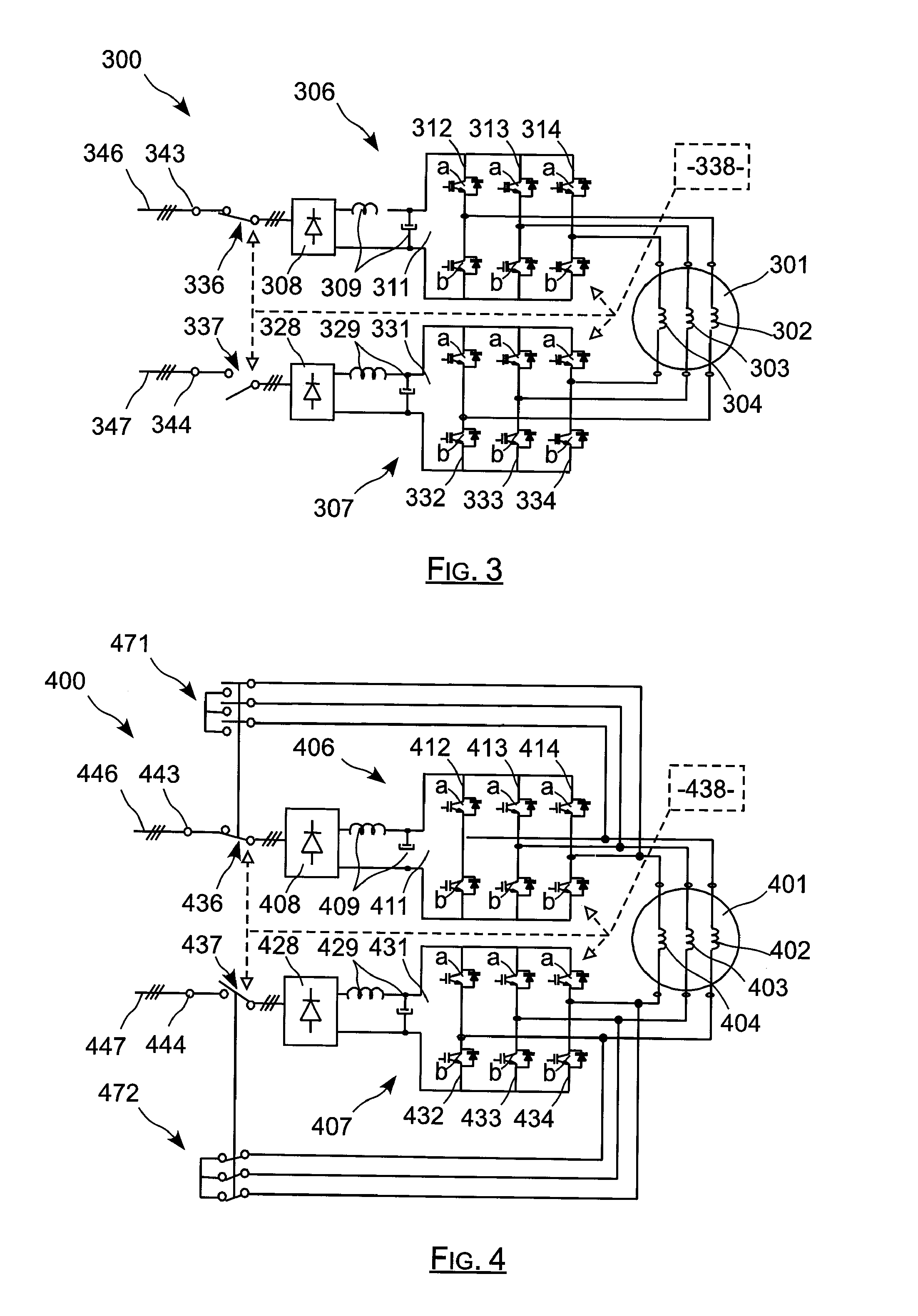
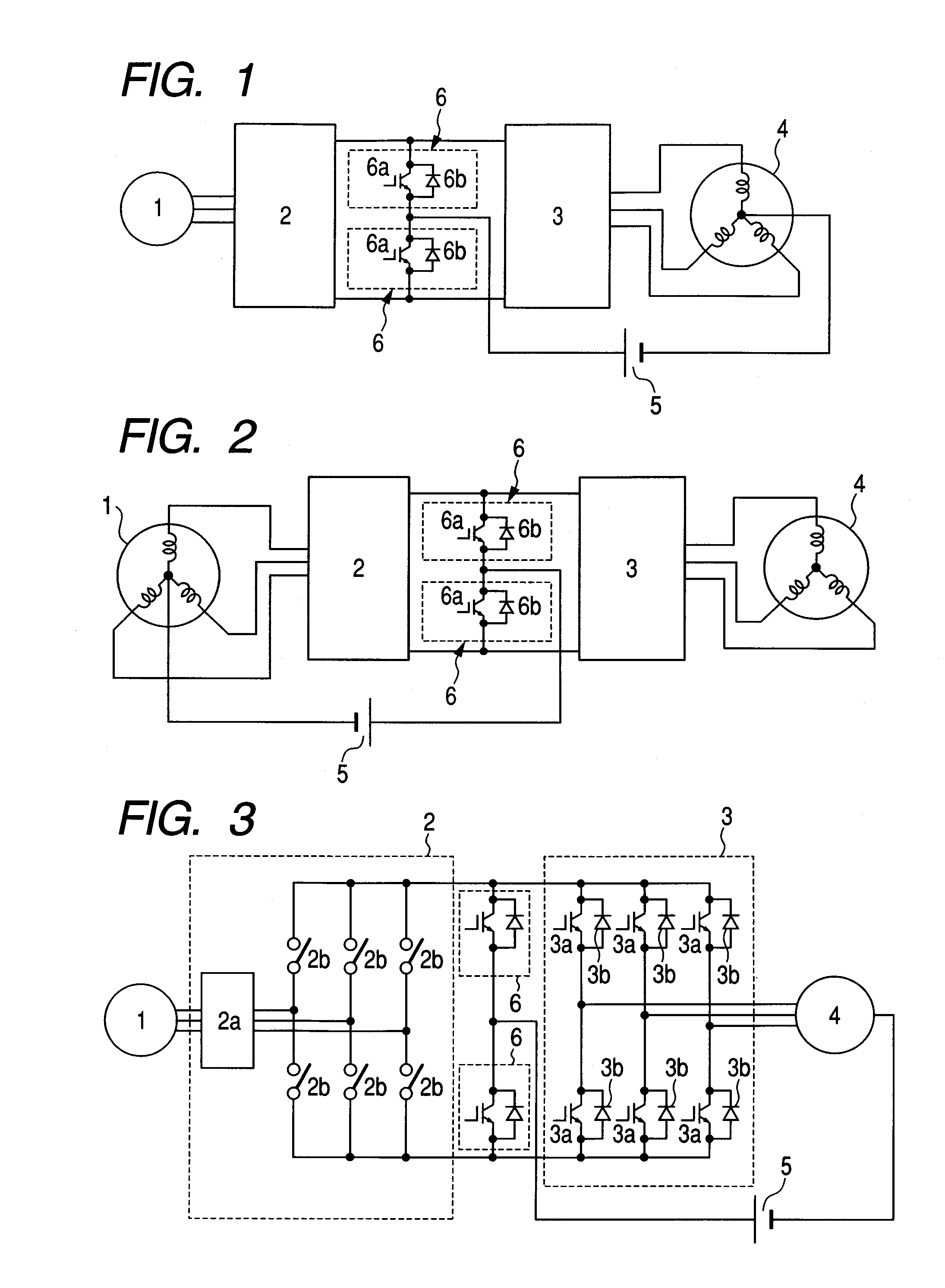
Electric actuator including two current-controlled voltage inverters powering an electric machine, and reconfigurable in the presence of a defect
ActiveUS20110181219A1Control flowMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAviationPower inverter
The invention relates to an actuator including an electrical machine. The electrical actuator (100) comprising: a polyphase machine (101); at least one connection member (143) for powering the actuator from at least one network (146) delivering alternating current; and first and second buses (106, 107) connected in parallel between each connection member (143) and the machine (101) for applying frequency control thereto. Each inverter (111, 131) comprises a plurality of arms each having two controlled switches, each phase of the machine (101) being connected both to the two switches of an arm of the first inverter (111) and also to the two switches of an arm of the second inverter (131). The actuator further comprises controlled connection and disconnection means interposed between each bus (106, 107) and each connection member. The invention is applicable to actuators used in aviation.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS +2
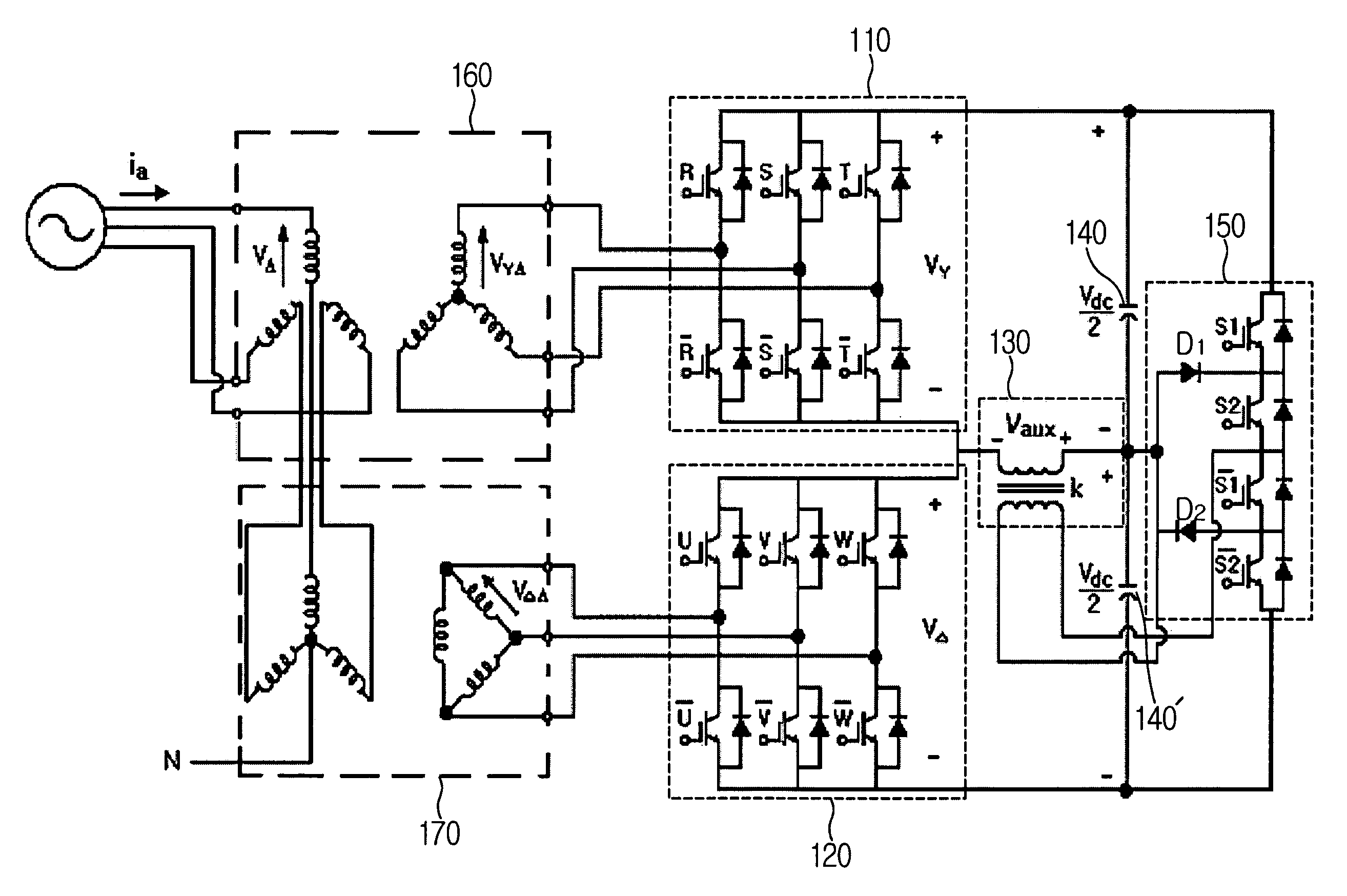
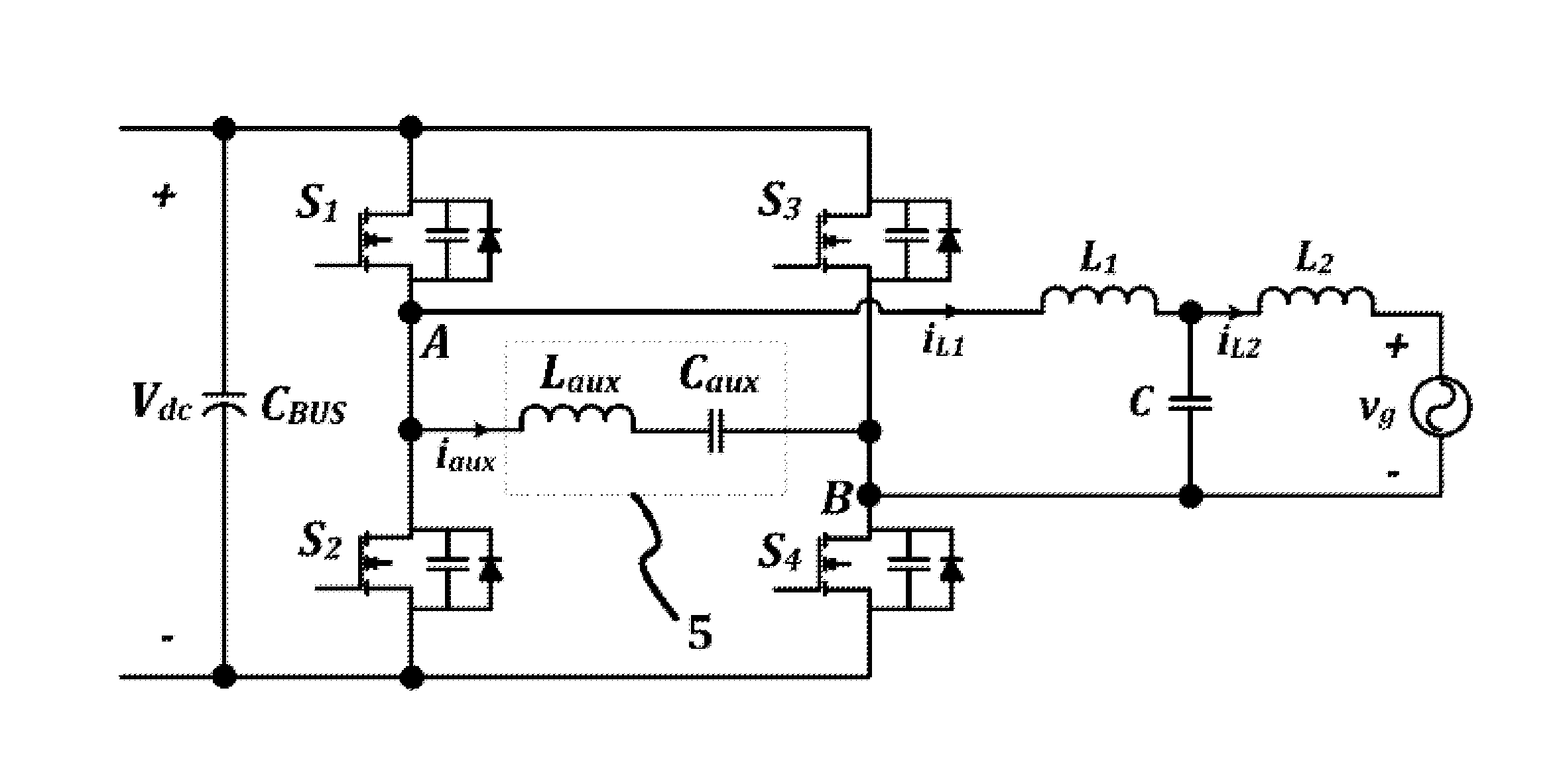
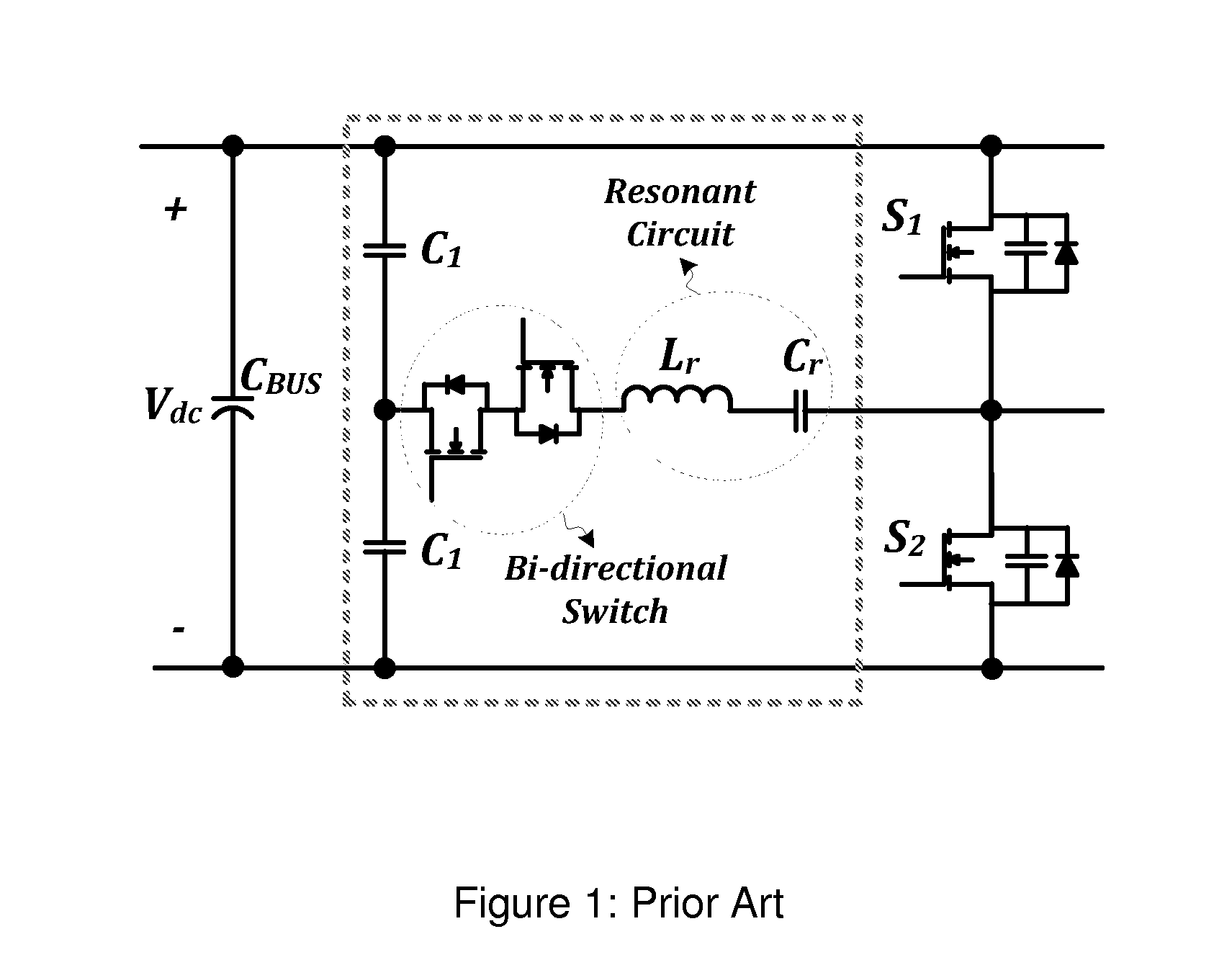
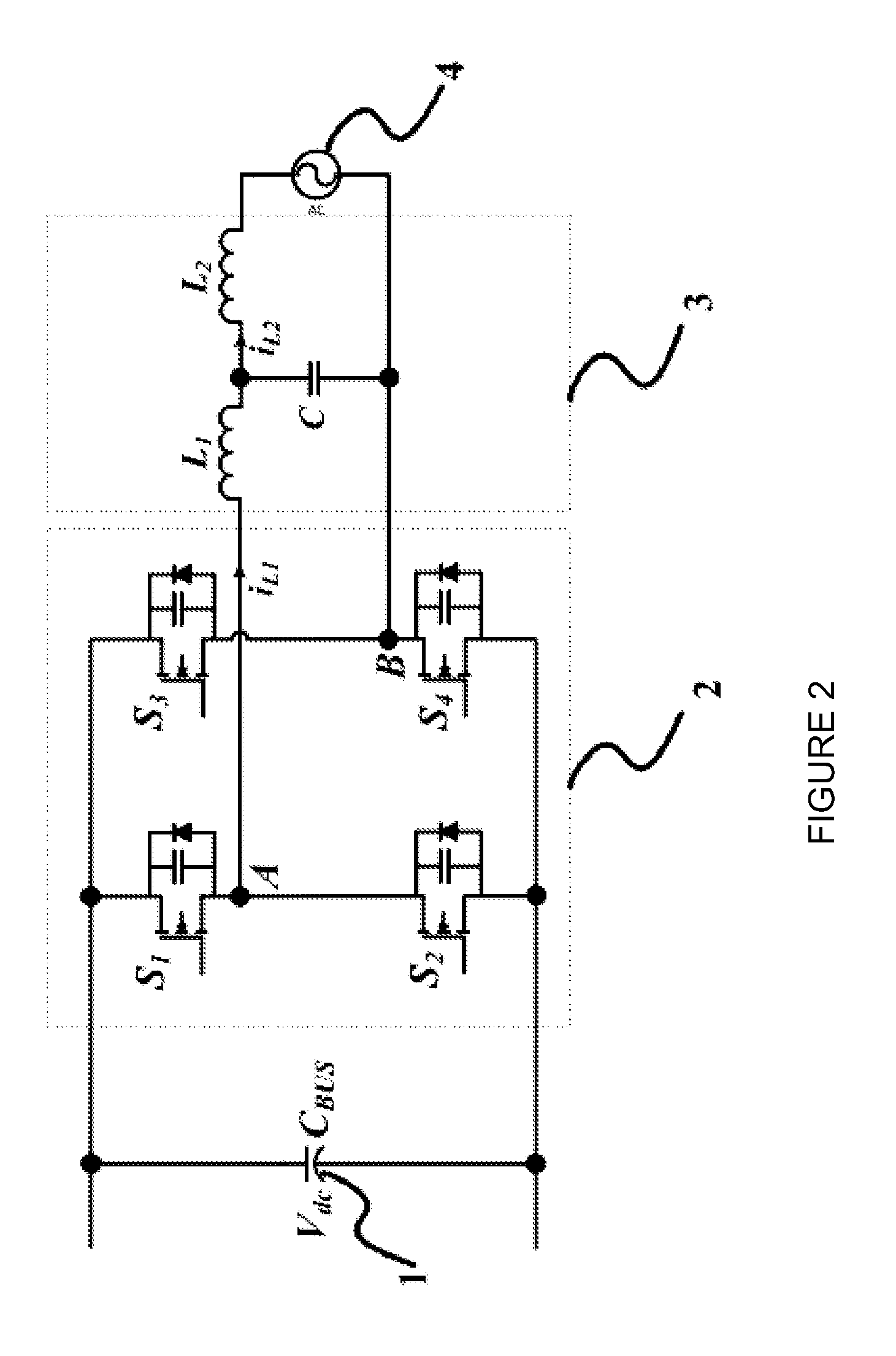
Zvs voltage source inverter
ActiveUS20150194909A1Eliminate switching lossesRemoves reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterFull bridge
Systems and methods relating to zero voltage switching for inverters. A full bridge inverter is used in conjunction with a passive auxiliary circuit and an output filter. A control system controls the current by way of the auxiliary circuit and injects a high quality current to a power grid. The control system adjusts the duty ratio and switching frequency of the gate pulses applied to the power semiconductors in the full-bridge inverter. As well, the control system adjusts the phase shift between gate pulses for both the leading leg and lagging leg power semiconductors to control the current passing through the auxiliary circuit.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
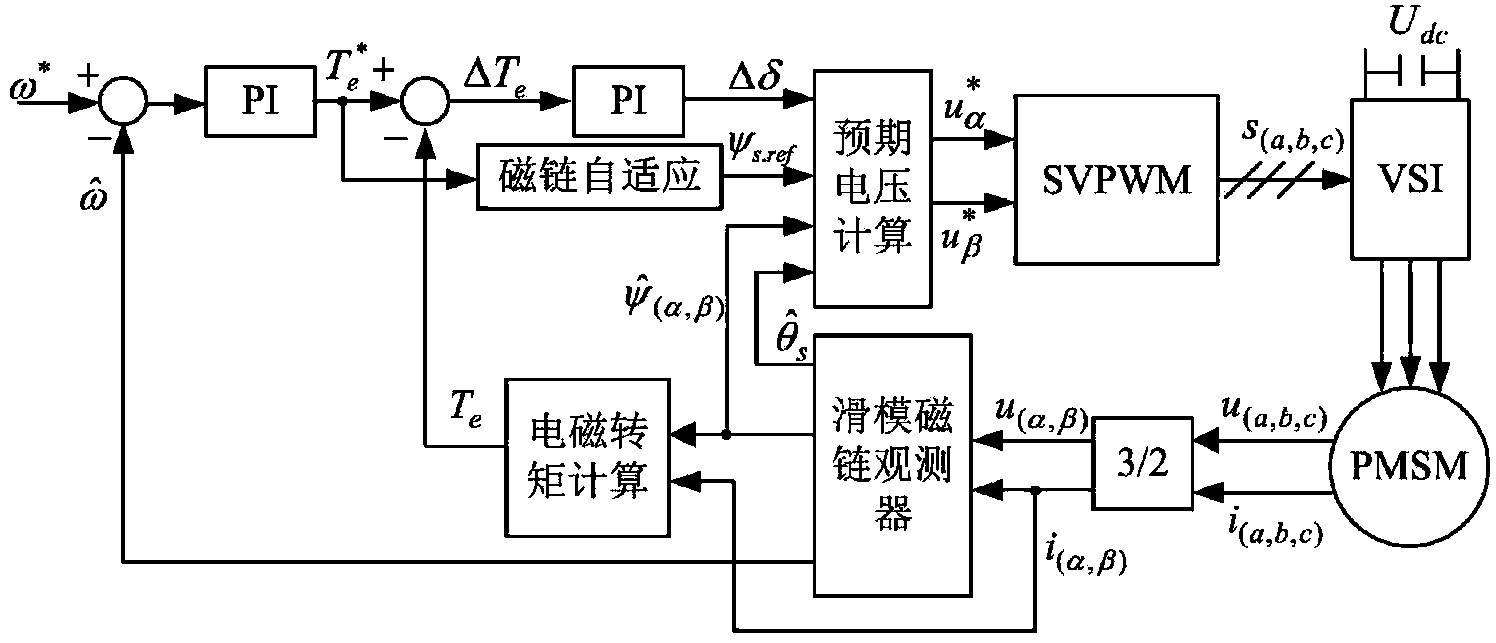
HVDC system and method to control a voltage source converter in a HVDC system
ActiveUS20090279328A1Increase stiffnessPower easy and smoothConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric power transfer ac networkVoltage amplitudeVoltage source inverter
A method to control a voltage source converter in a HVDC system includes controlling a frequency and a voltage amplitude of an AC voltage generated by the voltage source converter independently of the conditions in an AC network connected to the voltage source converter. The method is performed by a control unit of an HVDC system. The method may form a basis of a method to black start an AC network. The AC network includes transmission lines and is connected to at least two AC power stations. One of the at least two AC power stations is connected via a HVDC system to the AC network.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
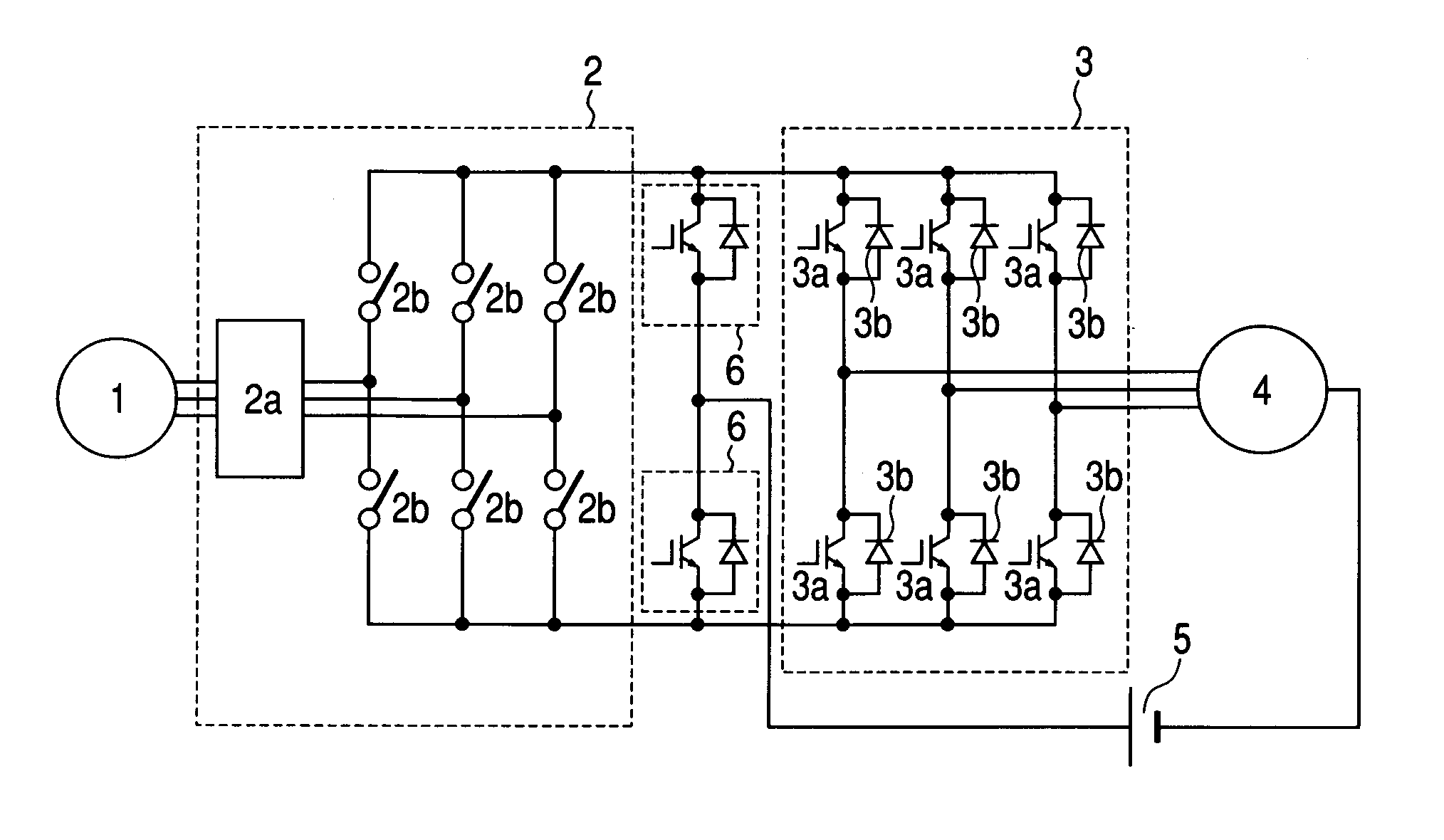
Alternating current motor drive circuit and electric vehicle drive circuit
ActiveUS20090206781A1Reduced weight and size and costSimple circuit configurationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersZ-source inverterEngineering
A current source rectifier is provided at an output of an alternating current generator, an alternating current motor is connected to an output of the rectifier via a voltage source inverter, furthermore, two arms having switching elements connected in inverse parallel to diodes are connected to the output of the rectifier, and one terminal of a direct current power source capable of a power supply and absorption is connected to a midpoint between the arms, while the other terminal thereof is connected to a neutral point of motor coils or generator coils, thereby eliminating a need for a large volumetric reactor in a direct current chopper, achieving a downsizing of the circuit.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP NAGAOKA UNIV TECH +1
Method and apparatus for controlling a stand-alone 4-leg voltage source inverter
ActiveUS6924993B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCurrent limitingEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling a stand-alone four-leg three-phase inverter. The inverter three-phase output is converted from AC domain elements to corresponding DC domain elements. The DC domain elements are processed into combined regulating and imbalance compensating signals, including over-current limiting. The compensating signals are restored to corresponding AC domain signals, and are processed into control inputs for the inverter, in order to stabilize the inverter output when connected to an unbalanced load. The inverter controller can be implemented entirely in software as a control algorithm.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Loss minimized PWM for voltage source inverters taking into account inverter non-linearity
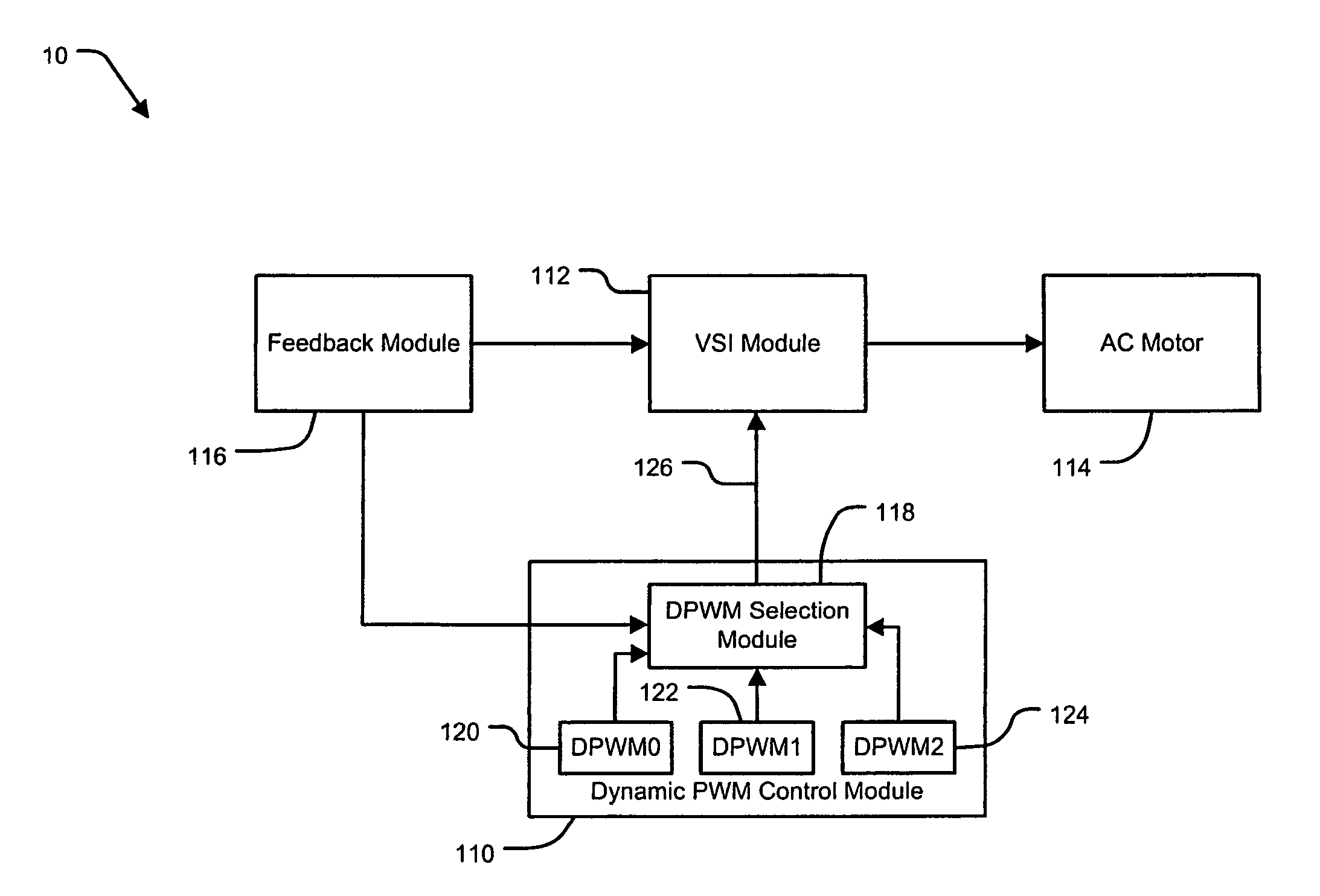
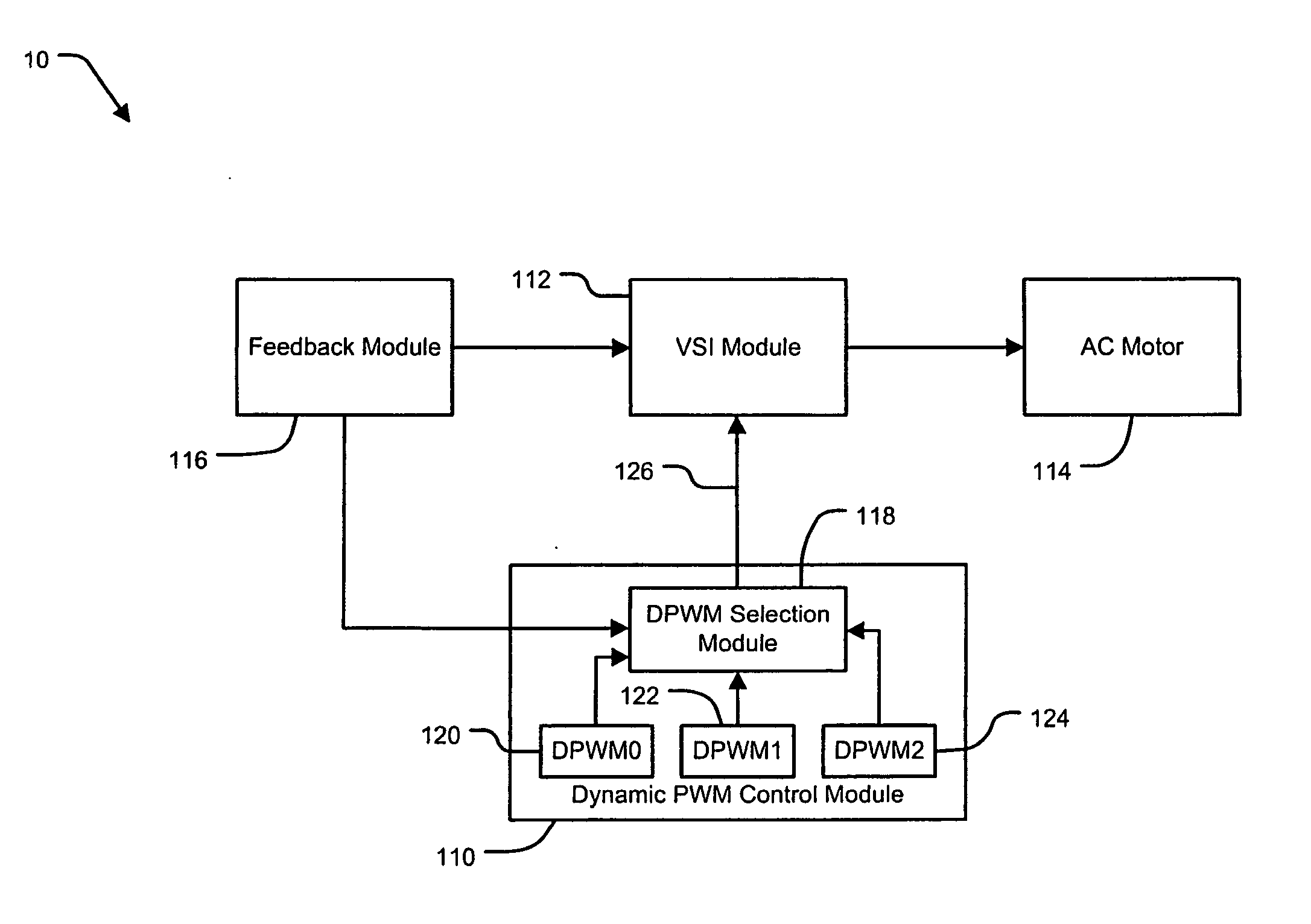
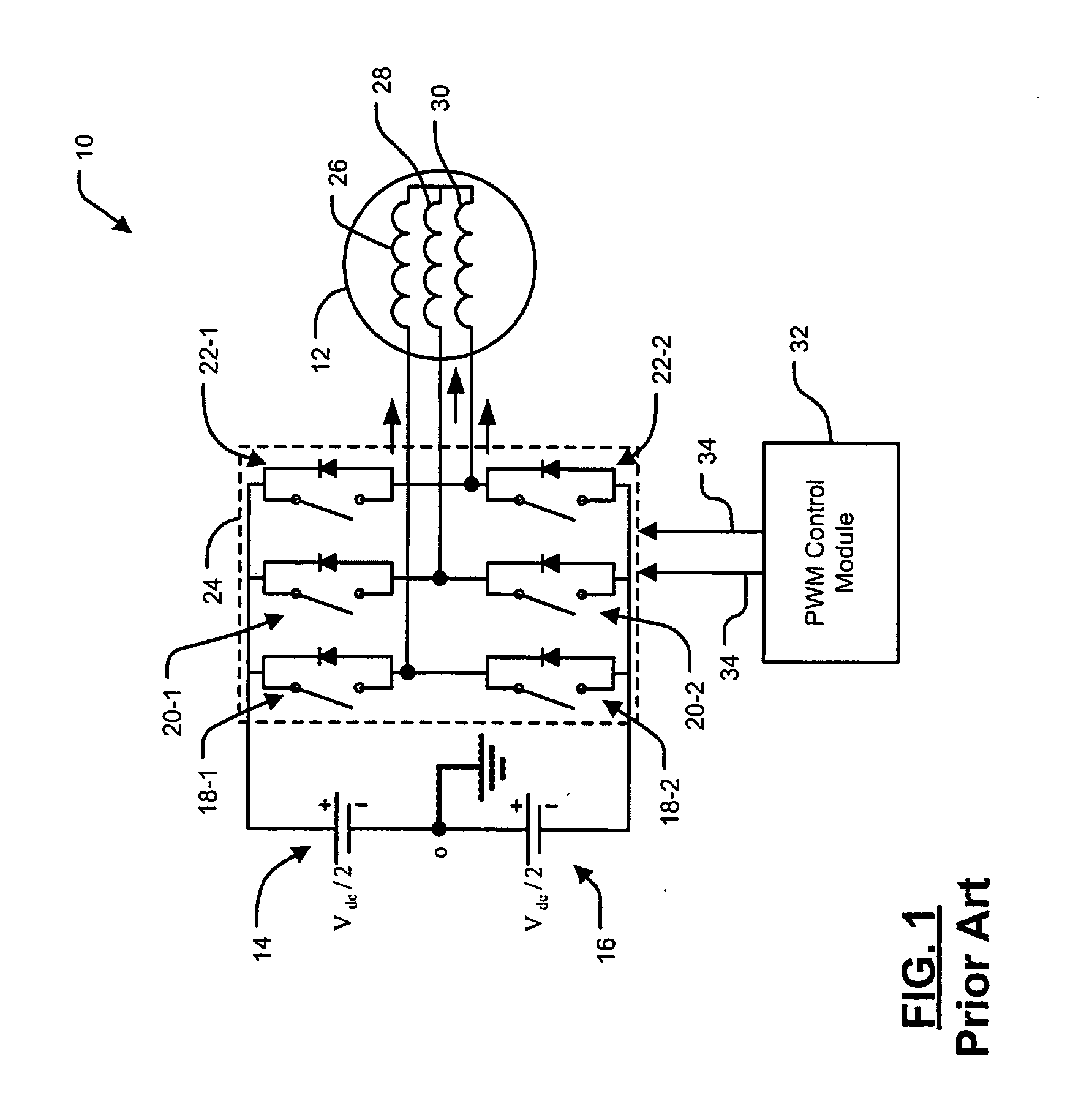
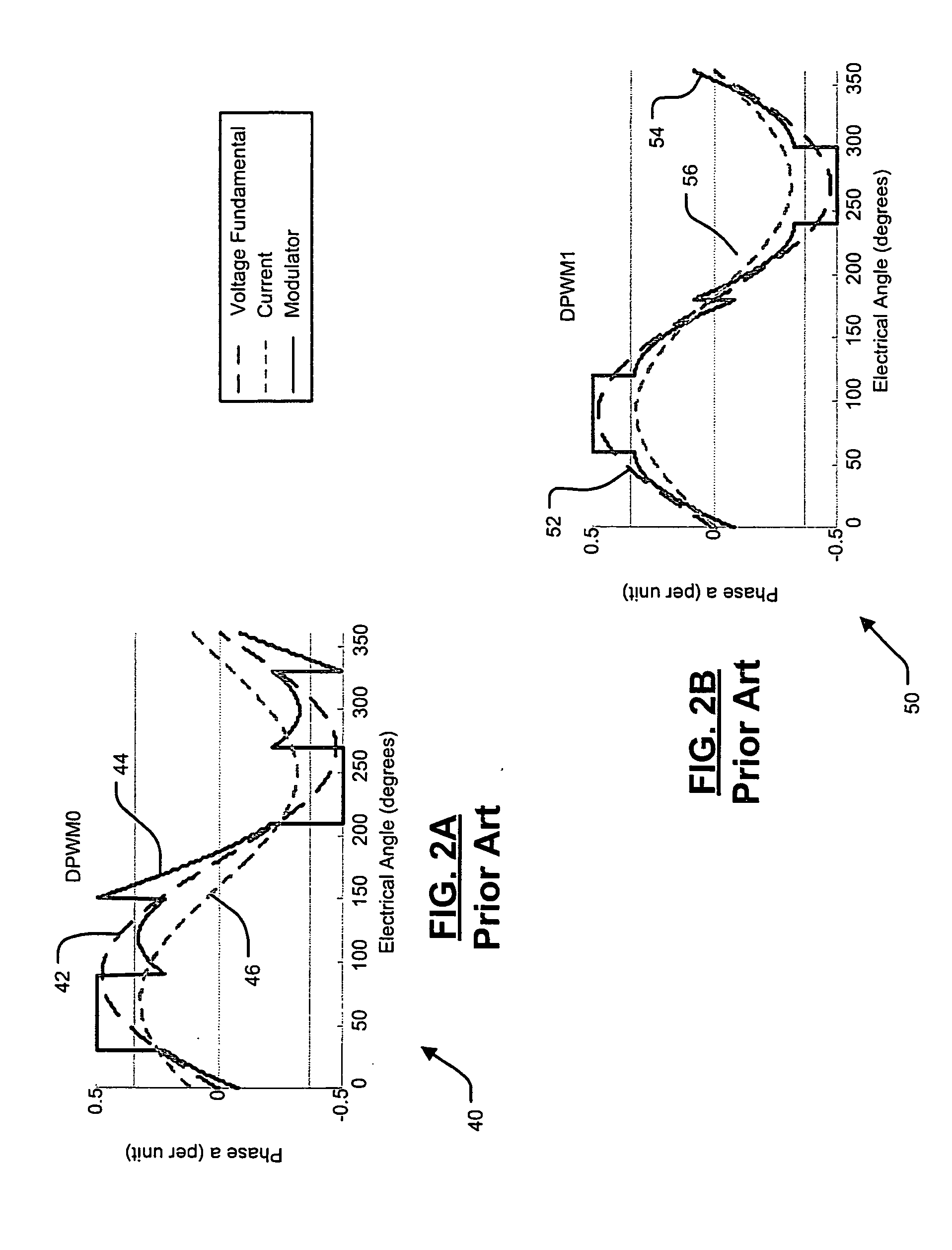
A dynamic pulse width modulation (PWM) selection device automatically switches between discontinuous PWM (DPWM) control methods. The PWM selection device comprises a PWM control module. The PWM control module determines a desired pulse width of a switching control signal according to a desired output signal. The PWM control module controls an actual pulse width of the switching control signal according to the desired pulse width and a first PWM control method. A selection module determines whether the desired pulse width exceeds a pulse width threshold. The selection module selects a second PWM control method when the desired pulse width exceeds the pulse width threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Modulation method for active neutral-point clamp type tri-level inverter
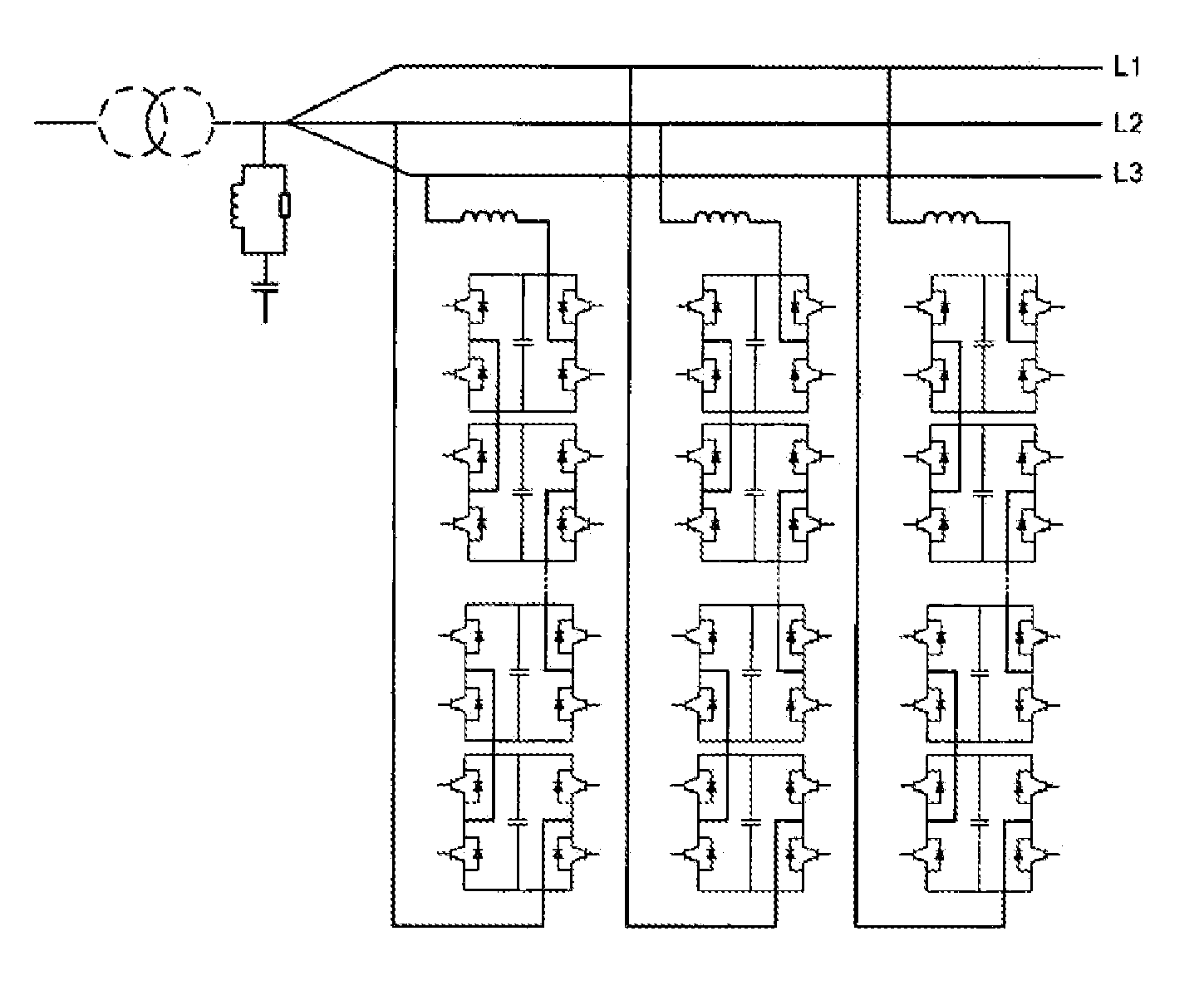
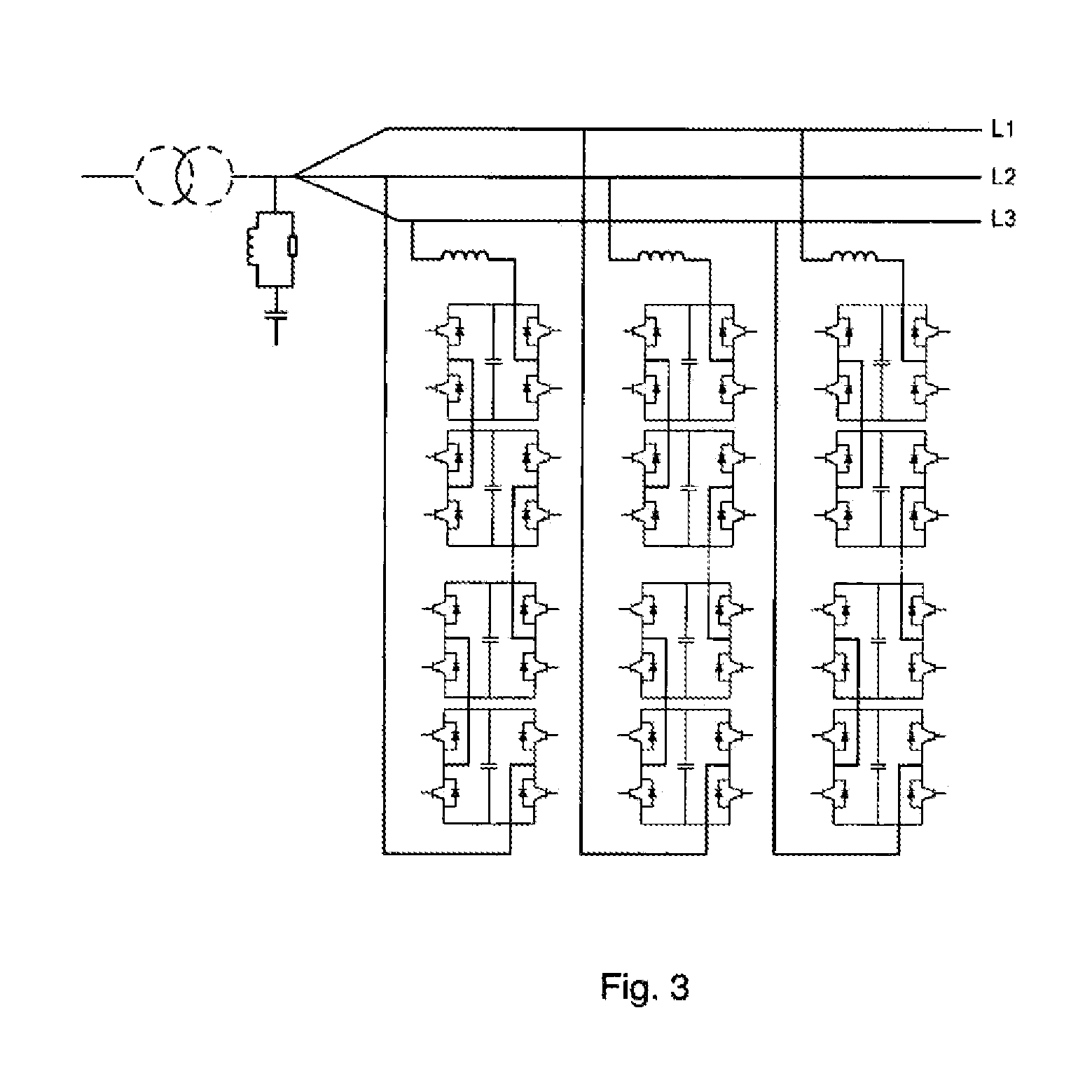
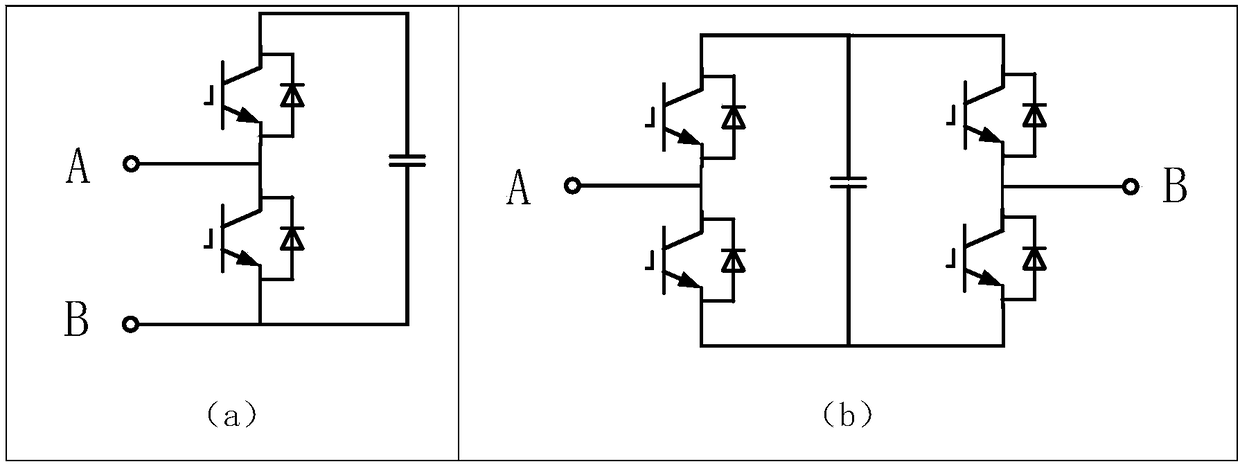
The invention relates to a modulation method for an active neutral-point clamp type tri-level inverter. Based on a tri-level sine pulse-width modulation method, the modulation method of the invention obtains required pulse-width modulation signals by defining level switching manners of the active neutral-point clamp type tri-level voltage-source inverter, and designing conduction sequence of different switching elements according to different influences of the two switching manners on power consumption of the switching elements. The pulse-width modulation signals are used to control switching on / off of each switching element of the active neutral-point clamp type tri-level inverter, so that dc is converted into ac, and ac is provided for a load. The modulation method is suitable for large-power tri-level voltage-source inverters.
Owner:SHANXI LUAN ENVIRONMENTAL ENERGY DEV +1
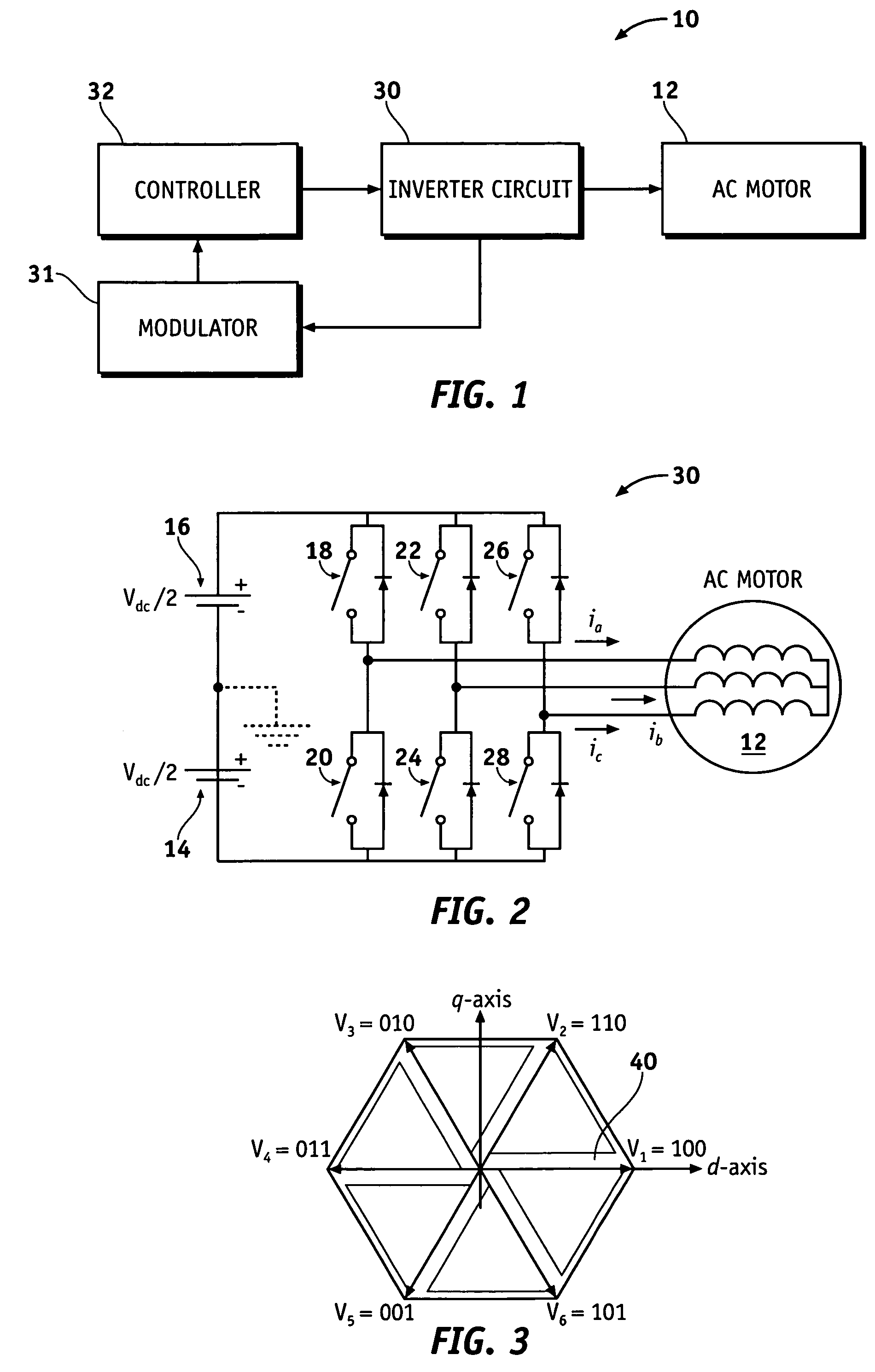
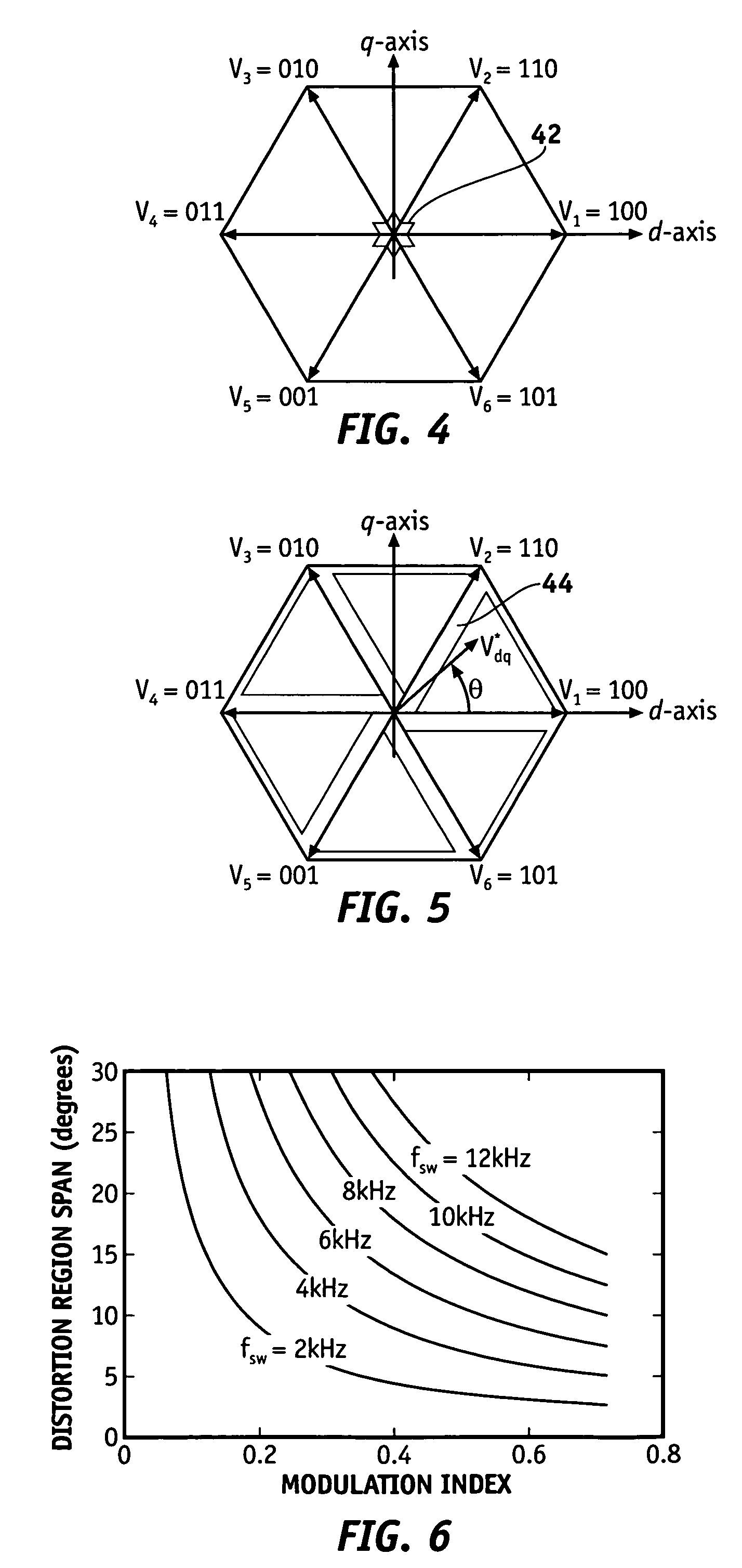
Method and apparatus for PWM control of voltage source inverter
ActiveUS7307401B2Minimize limitationDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlSwitching cycleVoltage source inverter
PWM methods and apparatus are provided for loss minimized control of AC motors taking into consideration inverter non-linear limitations. The method comprises providing a voltage to the AC motor based on a switching cycle, adding a duty cycle of a zero vector to each phase leg of the switching cycle when a duty cycle of a first phase leg of the switching cycle is less than a minimum duty cycle, and subtracting the duty cycle of the zero vector from each phase leg of the switching cycle when a second duty cycle of a second phase leg is greater than a maximum duty cycle. The minimum duty cycle and maximum duty cycle indicate distortion regions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Dead-zone compensation method for voltage source inverter
InactiveCN101917158AZero Current Clamp Effect SuppressionClamp effect suppressionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorDead time
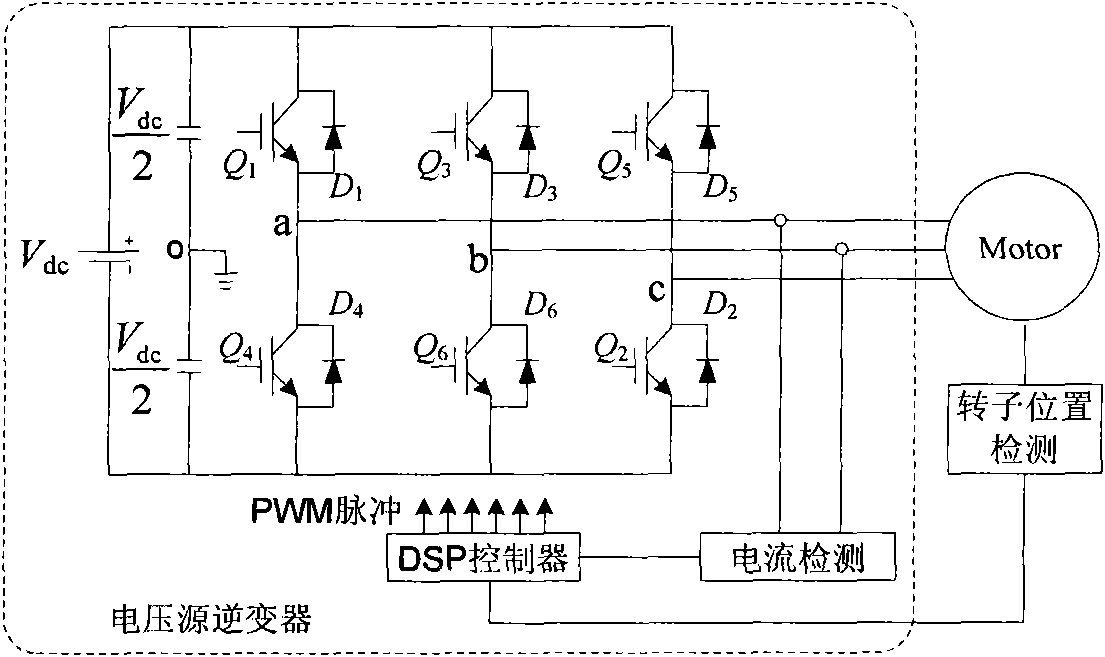
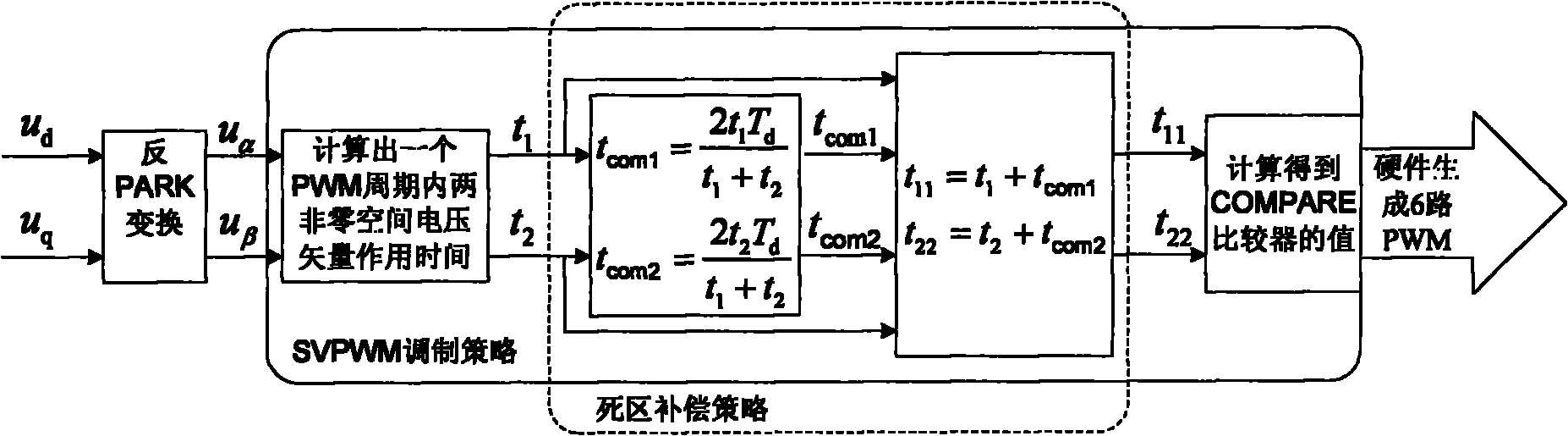
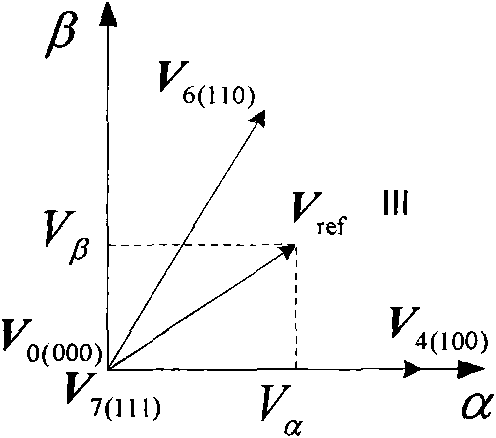
The invention relates to a dead-zone compensation method for a voltage source inverter. The method comprises the following steps of: performing dead-time compensation according to the acting time t1 and t2 of two non-zero base voltage vectors in a pulse-width modulation (PWM) period Ts and the practical dead time Td of the voltage source inverter based on the conventional space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) modulation strategy; adding two dead-time compensation time tcom1 and tcom2 and the acting time t1 and t2 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors to obtain new acting time t11 and t22 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors in the PWM period; and operating the new acting time t11 and t22 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors by using the SVPWM modulation strategy to generate a needed PWM pulse and finally realize deal-time compensation and zero-current clamping effect inhibition.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
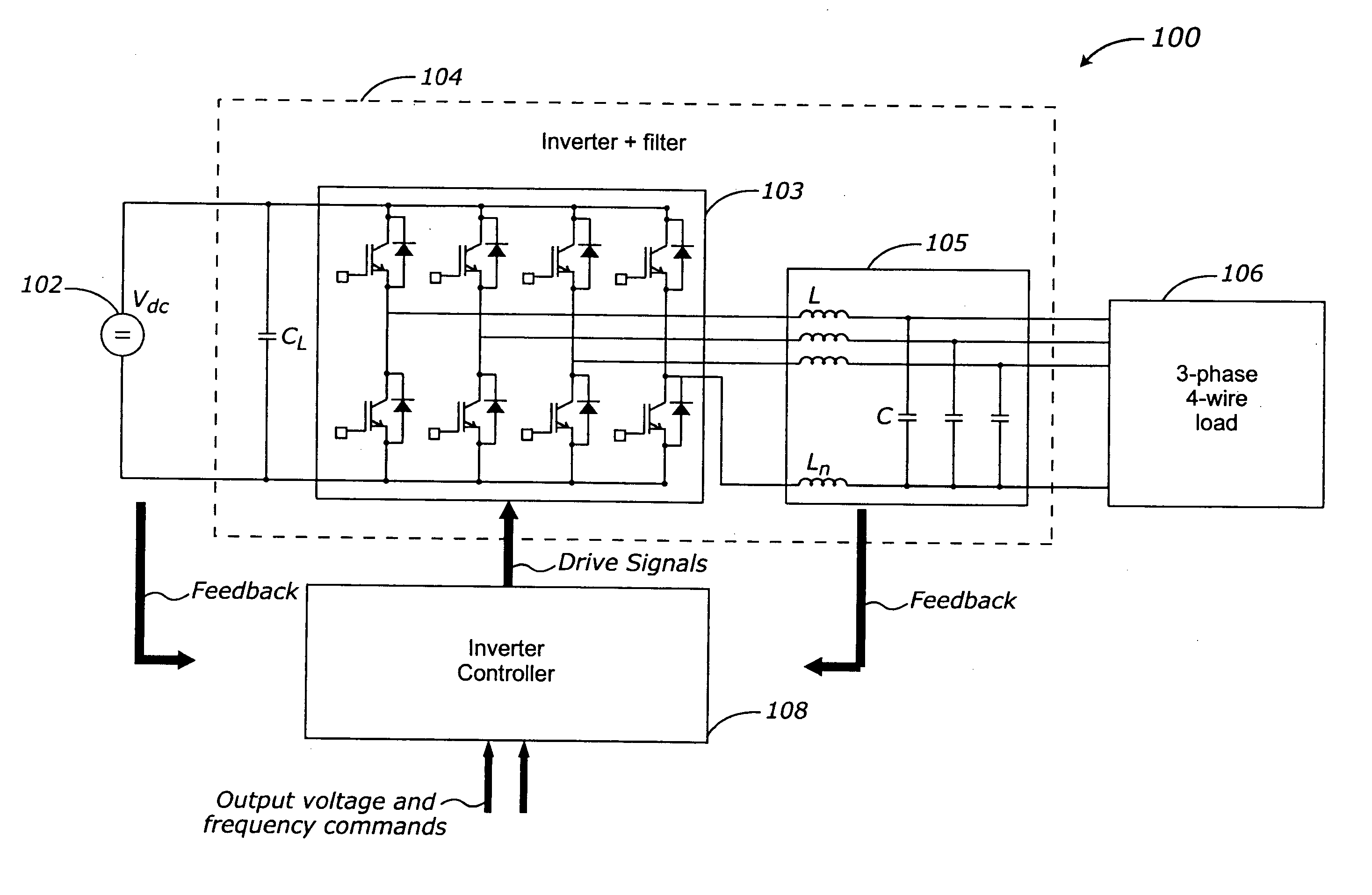
Hybrid distribution transformer with an integrated voltage source converter
ActiveUS20100220499A1Reduce variationEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDistribution transformerVoltage source inverter
A hybrid distribution transformer is provided that includes an electromagnetic transformer and a voltage source converter that is operable to reduce fluctuation in the output voltage of the hybrid distribution transformer in the event of an increase or decrease in the input voltage.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Inverter protection circuit and protection method and device
PendingCN108199571APrevent overpressurePrevent overcurrentElectric power transfer ac networkAc-dc conversionVoltage source inverterZero crossing
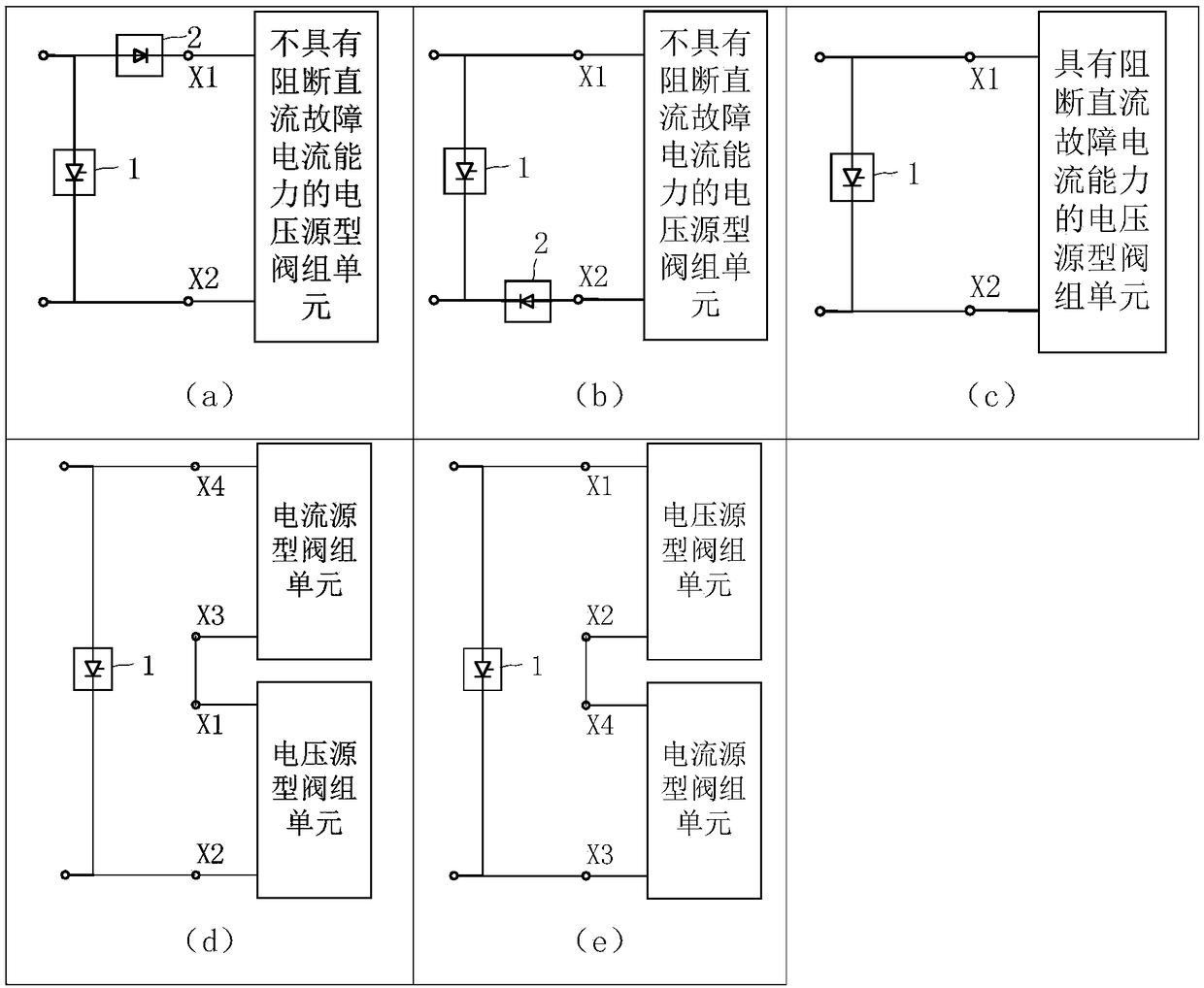
The invention discloses an inverter protection circuit. The circuit is used for protecting a voltage source inverter in an inverter with direct current fault ride-through capability, wherein the inverter is composed of a diode valve group or a current source type valve group unit and a voltage source type valve group unit, and the diode valve group or the current source type valve group unit and the voltage source type valve group unit are connected in series. A bypass thyristor valve group is connected in parallel with both ends of the inverter with direct current fault ride-through capability. The anode and the cathode of the bypass thyristor valve group are connected with the positive pole and the negative pole of the inverter with direct current fault ride-through capability respectively. The invention further discloses an inverter protection method. When the voltage source inverter detects that an alternating current or direct current system is failed and the voltage or current ofthe voltage source inverter exceeds a threshold value, the bypass thyristor valve group is input, and fault information is transmitted to a rectifier station. The rectifier station reduces the directcurrent voltage and reduces the direct current to zero. The bypass thyristor valve group is turned off due to current zero-crossing. The voltage source inverter protection circuit effectively solvesovervoltage and overcurrent problems caused by direct current charging of the voltage source inverter, and ensures the reliable operation of the voltage source inverter.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Hybrid converter and wind power generating system
ActiveUS20150145252A1Increase powerHigh voltageThyristorAc-dc conversion without reversalElectricityVoltage source inverter
The present invention discloses a hybrid converter and a wind power generating system, the hybrid converter comprising a voltage source converter, a line commutated converter and a line commutated converter, a positive DC terminal of the voltage source converter is connected to a negative DC terminal of the line commutated converter, a positive DC terminal of the line commutated converter is connected to a positive DC transmission line, a negative DC terminal of the voltage source converter is connected to a positive DC terminal of the line commutated converter, and a negative DC terminal of the line commutated converter is connected to a negative DC transmission line. The present invention features a self-commutating capability, can be directly connected to a wind farm to convert wind power to DC power, and is able to improve rated voltage and rated power of the hybrid converter, technology of each component thereof is mature, and system reliability thereof is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Loss minimized PWM for voltage source inverters taking into account inverter non-linearity
ActiveUS20070216344A1AC motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalVoltage source inverter
A dynamic pulse width modulation (PWM) selection device automatically switches between discontinuous PWM (DPWM) control methods. The PWM selection device comprises a PWM control module. The PWM control module determines a desired pulse width of a switching control signal according to a desired output signal. The PWM control module controls an actual pulse width of the switching control signal according to the desired pulse width and a first PWM control method. A selection module determines whether the desired pulse width exceeds a pulse width threshold. The selection module selects a second PWM control method when the desired pulse width exceeds the pulse width threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Verification method and experimental device for grid impedance recognition
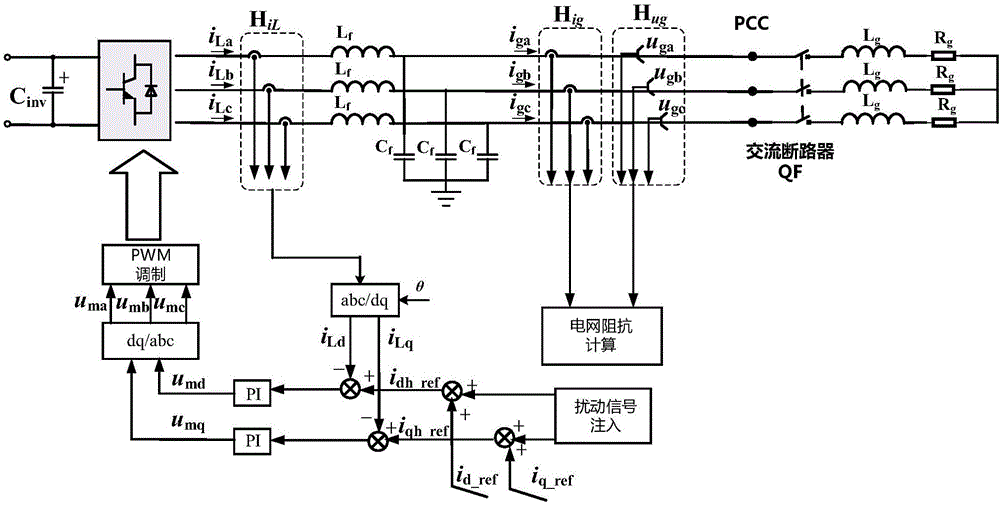
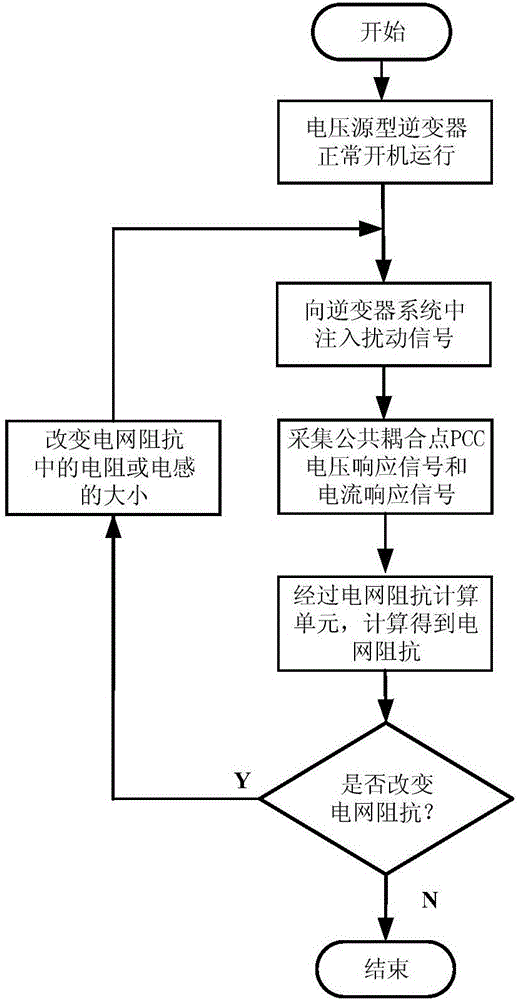
ActiveCN106771786AAvoid the effects of background harmonicsSimplify the extraction processInductance measurementsElectrical testingGrid impedanceValidation methods
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for building simplified self interference rejection controller of permanent magnet synchronous machine
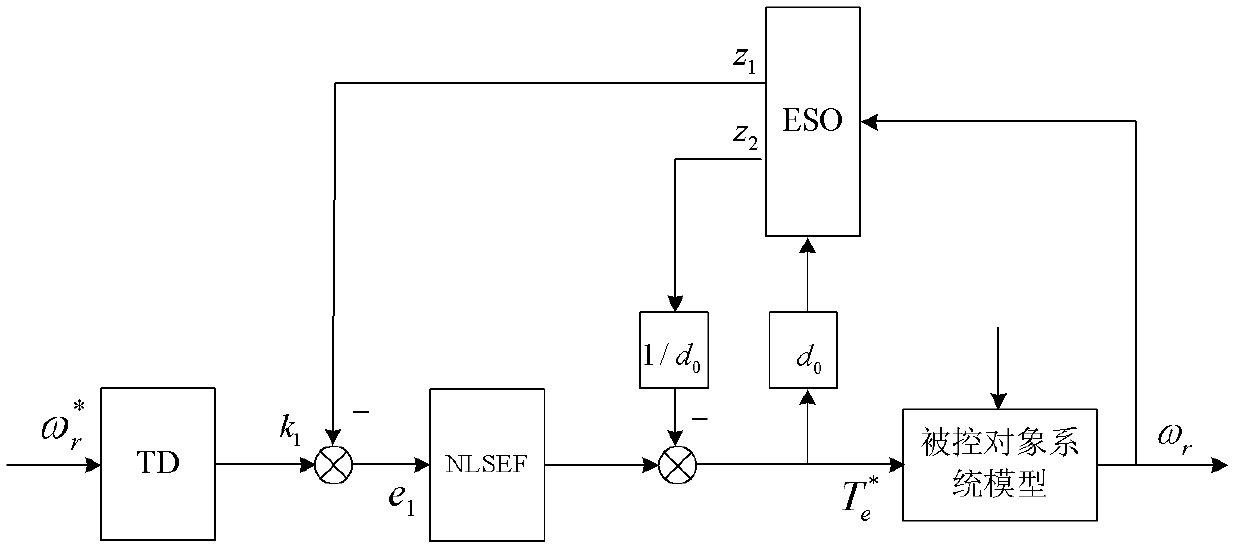
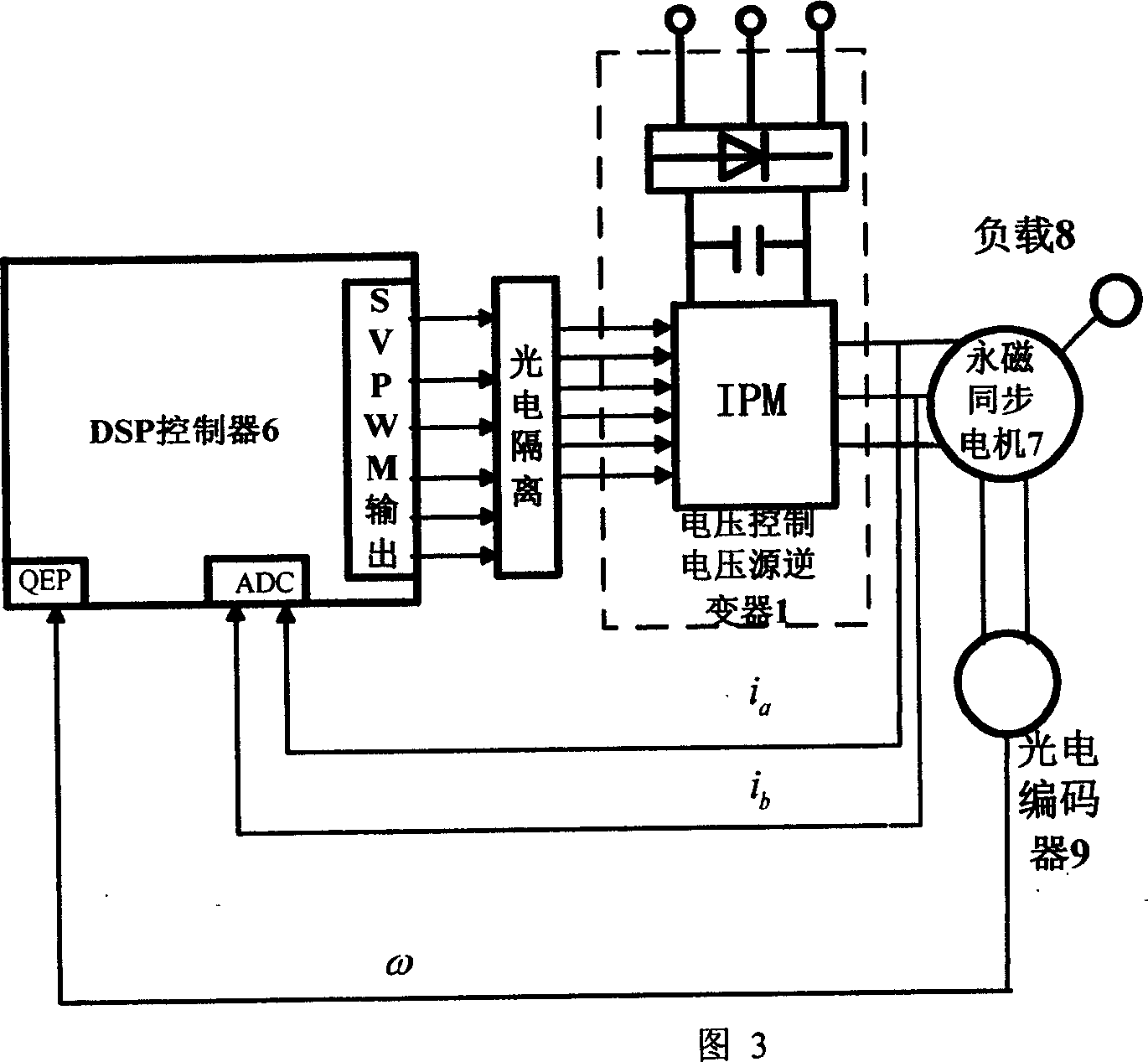
ActiveCN1967414AImprove adaptabilityImprove performanceControllers with discontinuous output signalSelf interferencePermanent magnet synchronous motor
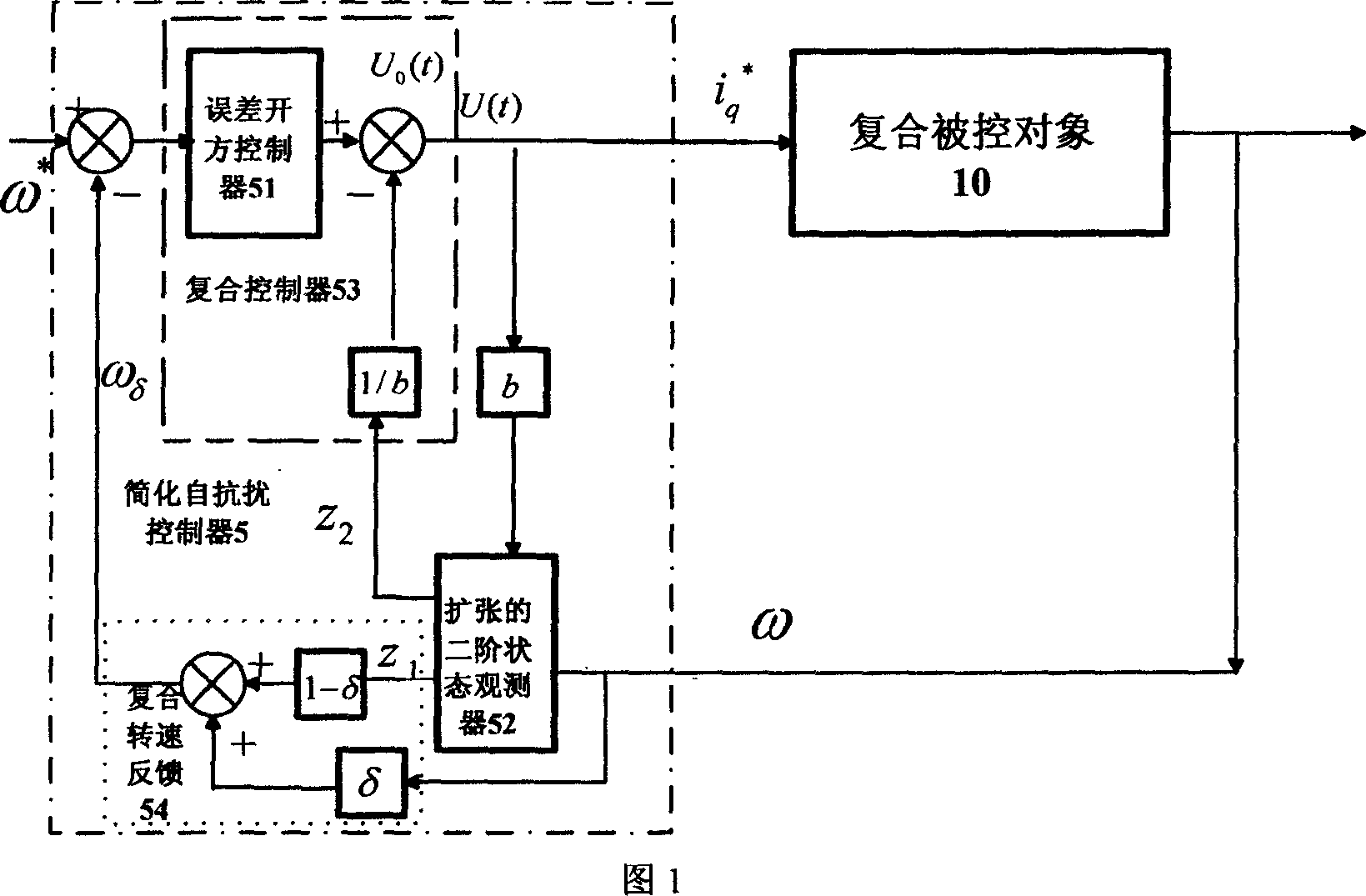
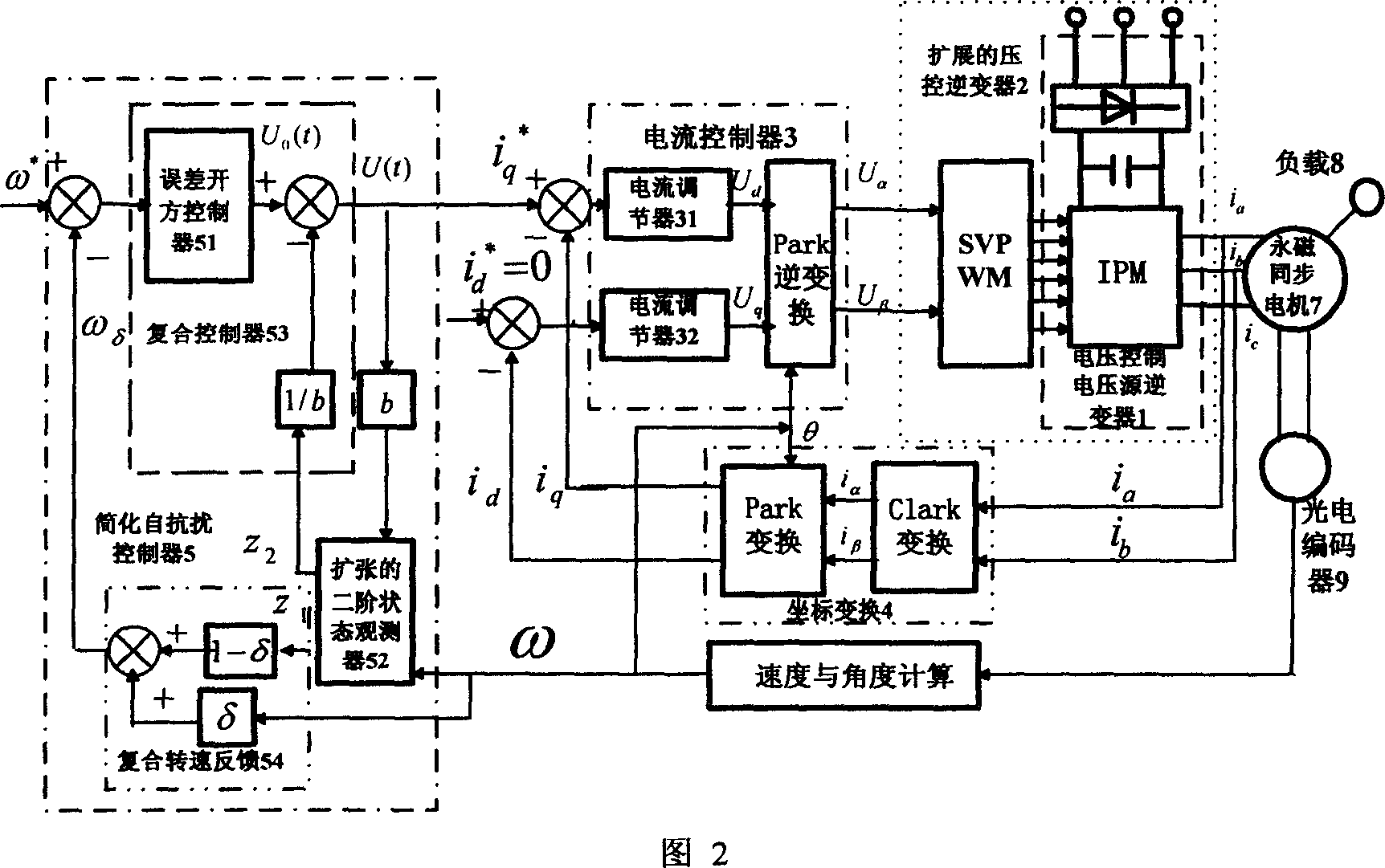
A simplified self noise-immunity controller formation method of PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor) is applicable to the high performance control of PMSM. It constructs the expanding voltage-controlled inverter (2) by the voltage control voltage source inverter (1) and space vector pulse width modulation; it constructs a composite controlled object (10) by the expanding voltage-controlled inverter and current controller (3), the coordinate transformation (4), the permanent magnet synchronous motor (7), the workload (8) and the photoelectric encoder (9); it constructs the second-order state observer (52) by compositing the input and output signals of the controlled object; It constructs the composite speed feedback (54) by the weighted sum of the two speed measurement value; it constructs the composite controller (53) by the superposition of the generalized rate error square controller (51) and the compensation value of the system perturbation (-z2 / b); it series connects the composite controller before the composite controlled object, and finally, it constructs the simplified self noise-immunity controller (5) by the composite controller and the expanding second-order state observer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com