Verification method and experimental device for grid impedance recognition
A technology of grid impedance and voltage source type, applied in the direction of measuring resistance/reactance/impedance, measuring devices, measuring electricity, etc., can solve the difficulty of determining the accuracy of the grid impedance identification method, grid interference, and the complexity of the verification process of the grid impedance identification method and other problems, to achieve the effect of simplifying the extraction process, reducing calculation pressure, and improving security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The preferred modes of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
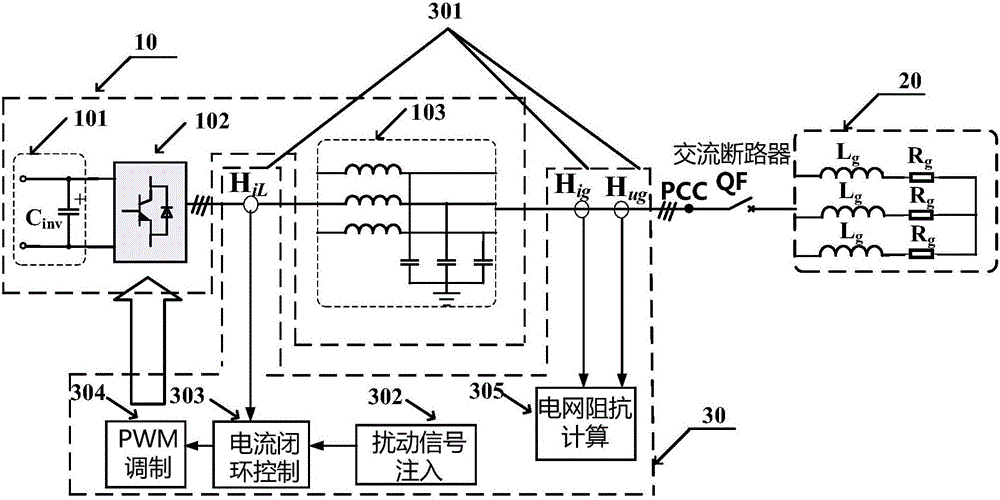
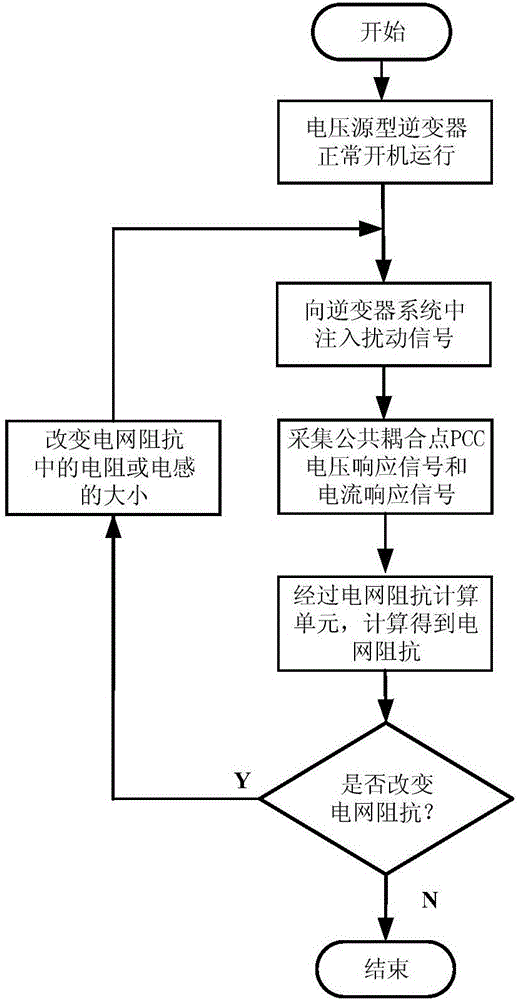
[0047] figure 1 The structural diagram of the experimental device for verifying the grid impedance identification method, as can be seen from the figure, the experimental device structure includes a voltage source inverter 10 , a grid impedance 20 and a grid impedance identification unit 30 .
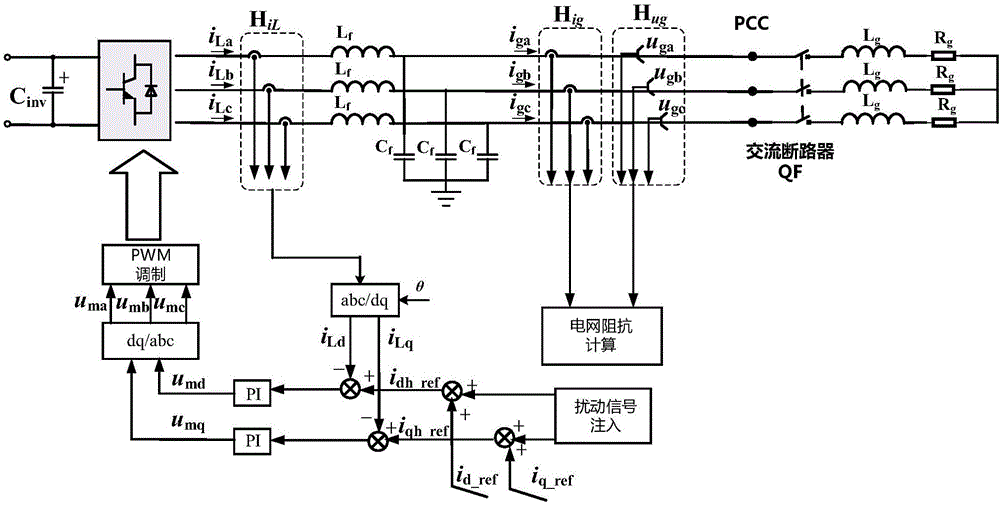
[0048] The voltage source inverter 10 includes a DC side 101, a three-phase full-bridge inverter circuit 102 and an LC filter 103, and the filter capacitor C of the DC side 101 inv The output end of the three-phase full-bridge inverter circuit 102 is connected to the input end, and the output end of the three-phase full-bridge inverter circuit 102 is connected to the input end of the LC filter 103, and the output end of the LC filter 103 is connected to the grid impedance 20 is connected to the input terminal.
[0049] The grid impedance 20 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com