Patents
Literature
600 results about "DNA methylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
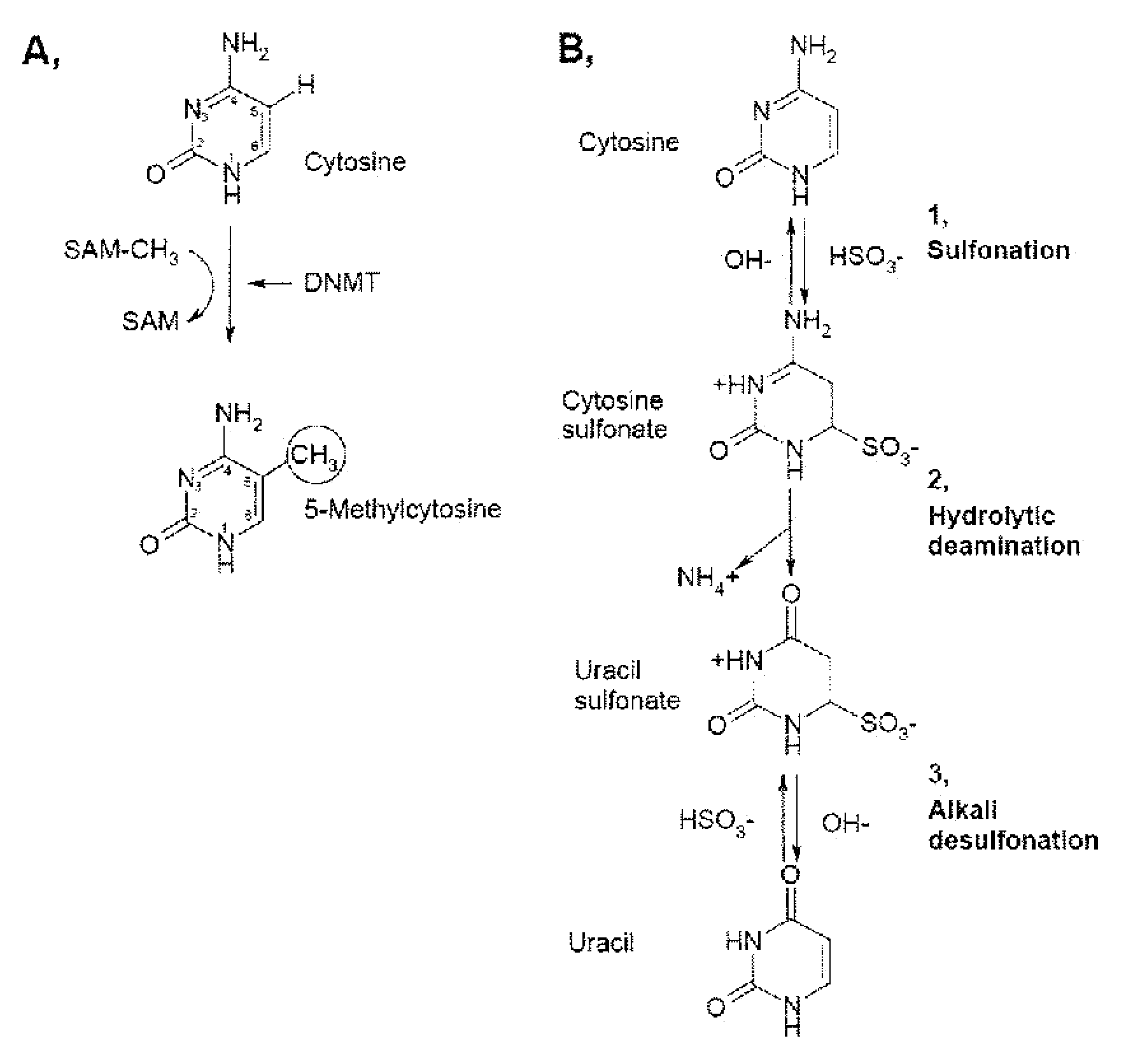
DNA methylation is a process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter, DNA methylation typically acts to repress gene transcription. In mammals DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, repression of transposable elements, aging, and carcinogenesis.
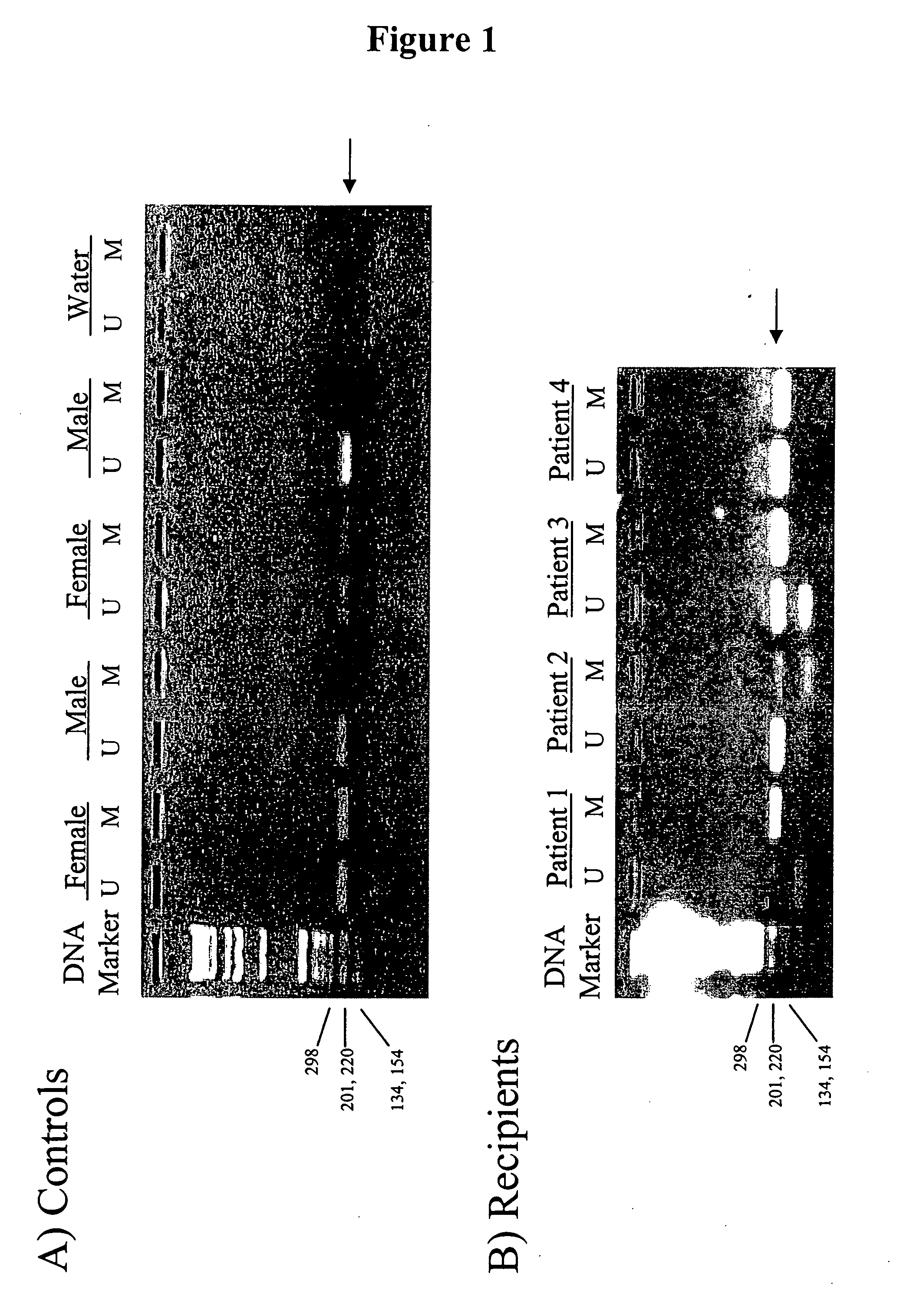
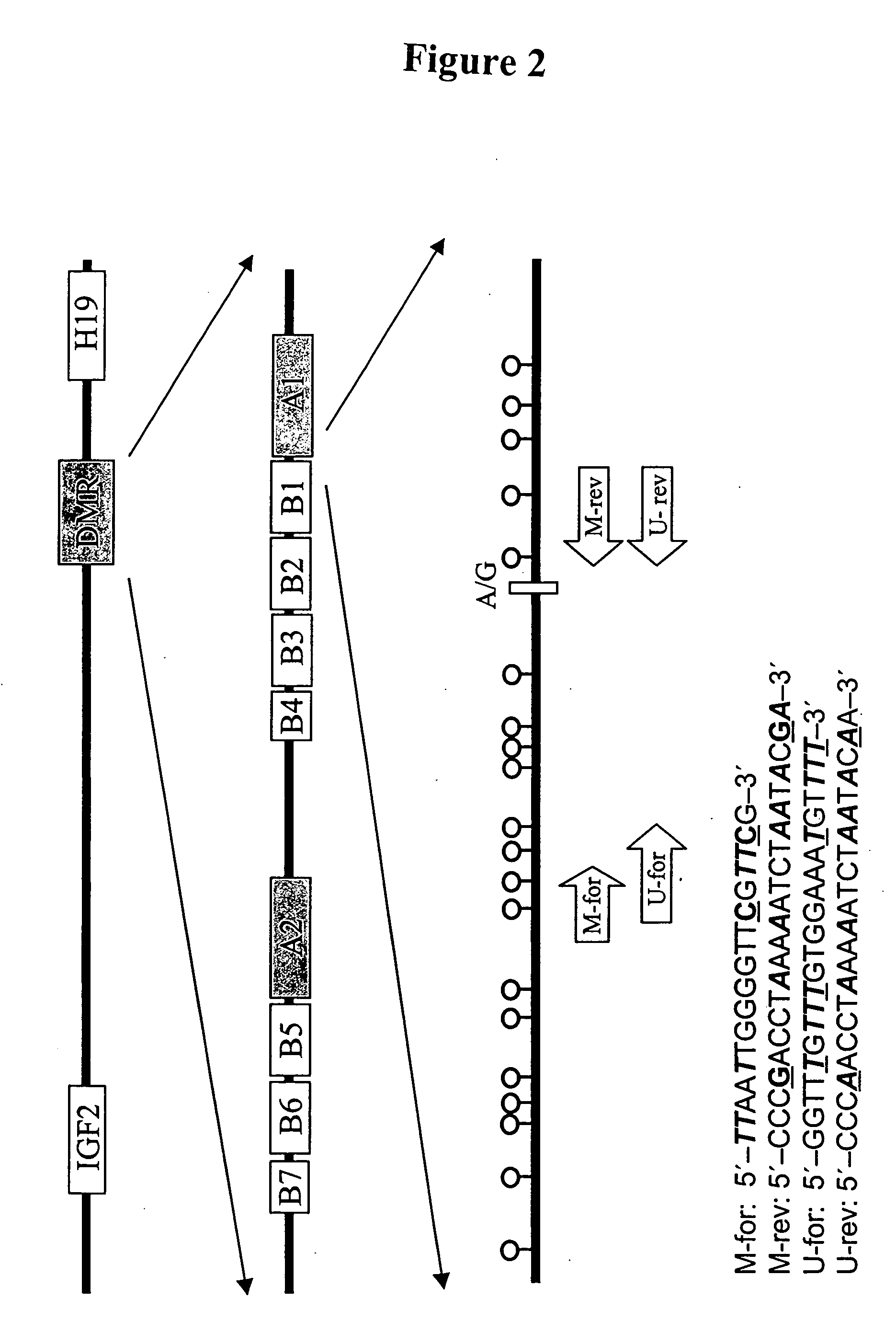
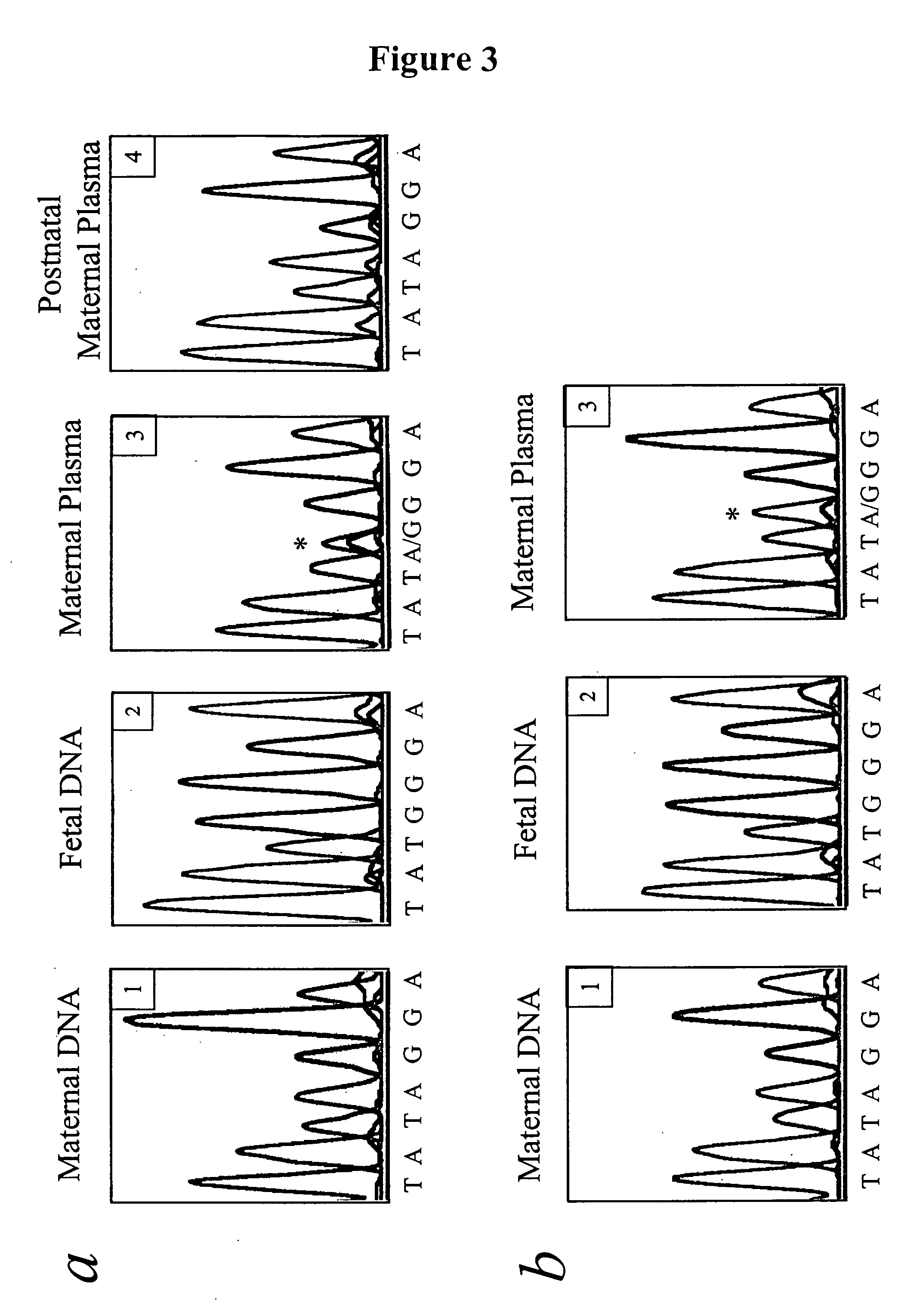
Non-invasive methods for detecting non-host DNA in a host using epigenetic differences between the host and non-host DNA
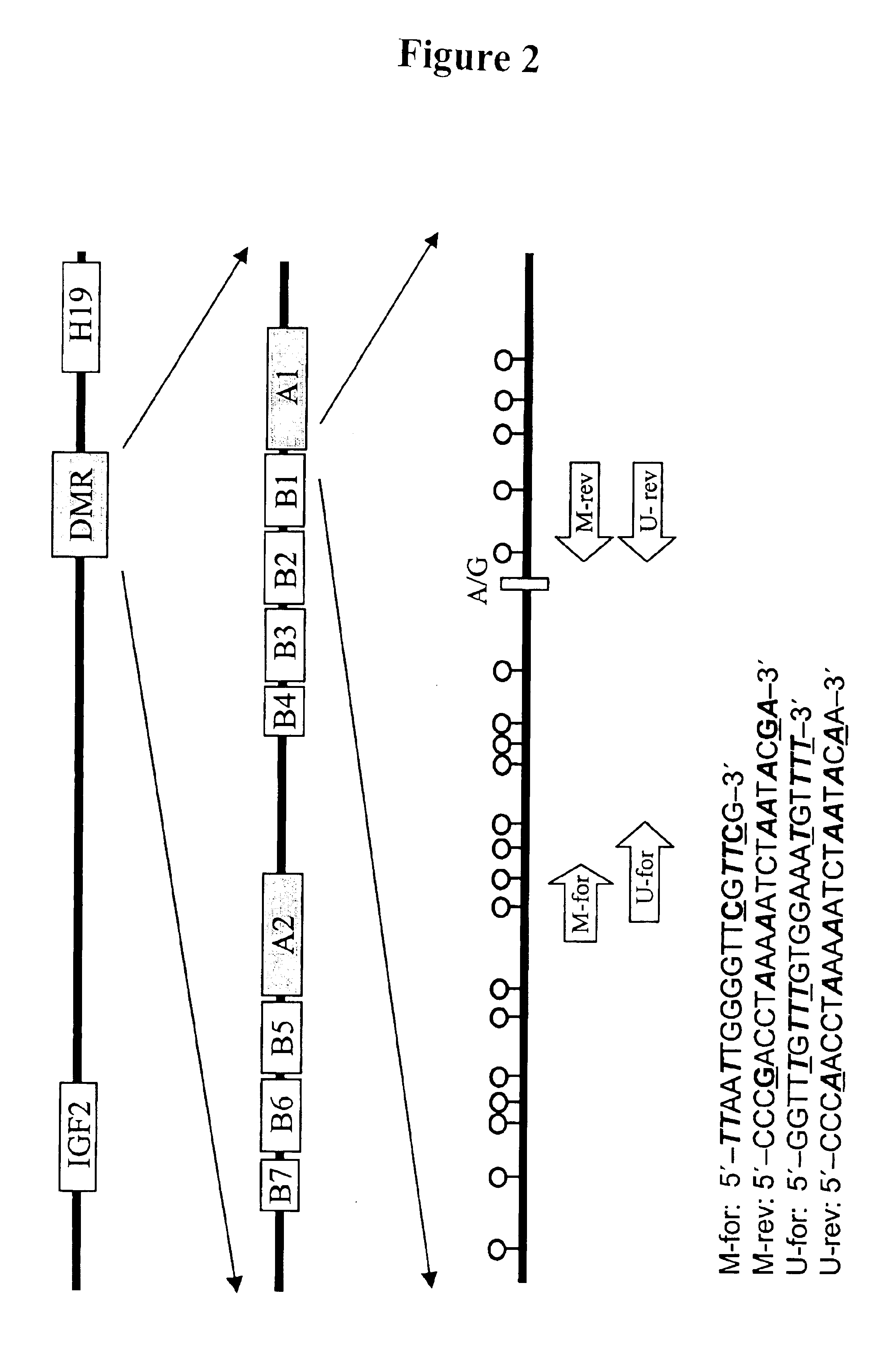
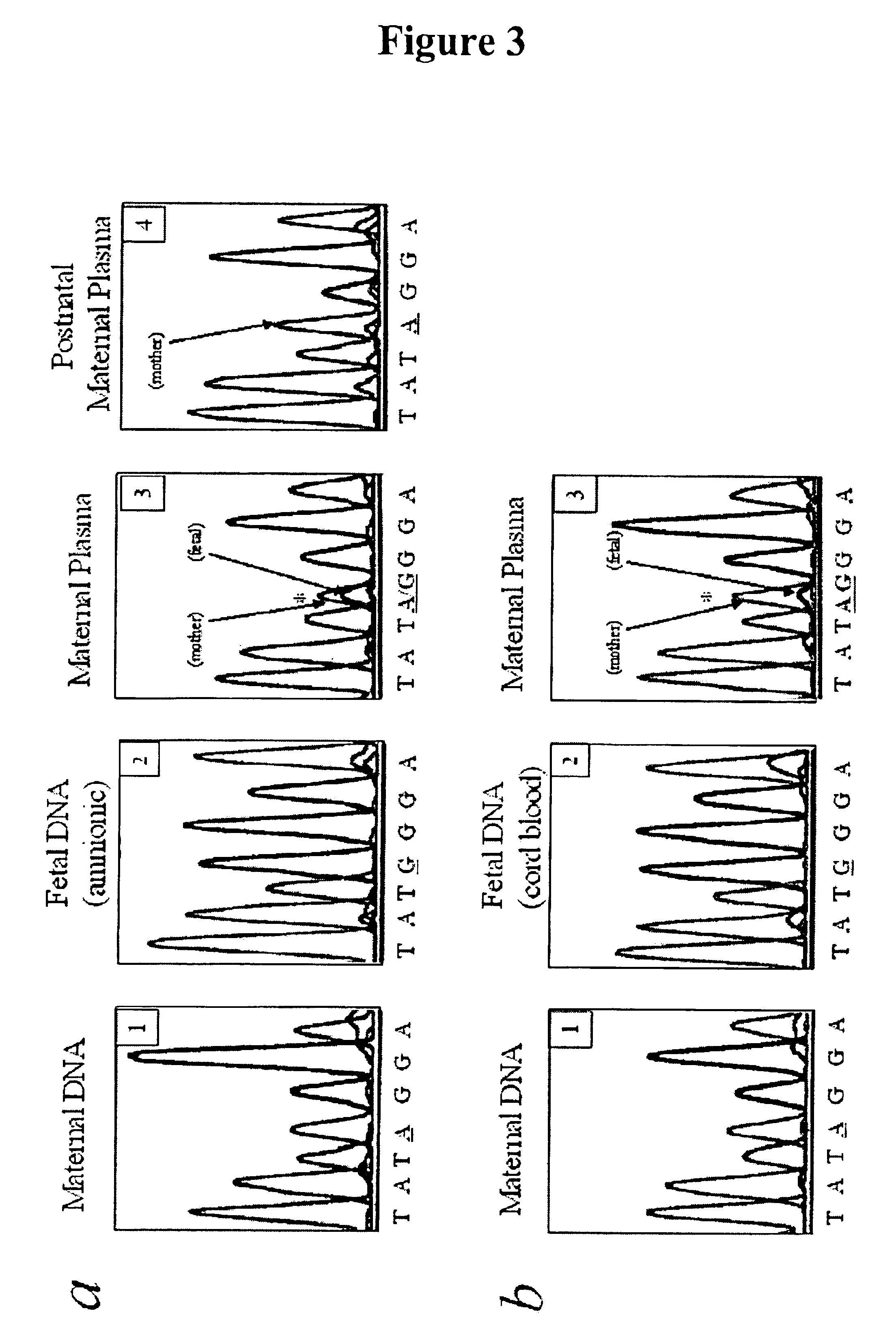
In a first aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample. These methods may be used to differentiate or detect fetal DNA in a maternal sample or to differentiate DNA of an organ donor from DNA of an organ recipient. In preferred embodiments, the DNA species are differentiated by observing epigenetic differences in the DNA species such as differences in DNA methylation. In a second aspect, the present invention features methods of detecting genetic abnormalities in a fetus by detecting fetal DNA in a biological sample obtained from a mother. In a third aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from an organ donor from those of an organ recipient. In a fourth aspect, the present invention features kits for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods and compositions for generating and amplifying DNA libraries for sensitive detection and analysis of DNA methylation
InactiveUS20050202490A1Reduce stepsReduce stretchMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA methylationCell free
The present invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for obtaining epigenetic information, such as DNA methylation patterns, through the preparation, amplification and analysis of Methylome libraries. In several aspects of the present invention, there are methods based on methylation-dependent enrichment or depletion of genomic DNA isolated from cellular and cell-free sources. In additional embodiments, there are methods and compositions for single-step high throughput preparations of Methylome libraries.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
High-throughput methods for detecting DNA methylation
InactiveUS6605432B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationHybridization probe
The present invention provides a method of hybridization, differential methylation hybridization (DMH) for high throughput methylation analysis of multiple CpG island loci. DMH utilizes nucleic acid probes prepared from a cell sample to screen numerous CpG dinucleotide rich fragments affixed on a screening array. Positive hybridization signals indicate the presence of methylated sites. Methods of preparing the hybridization probes and screening array are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
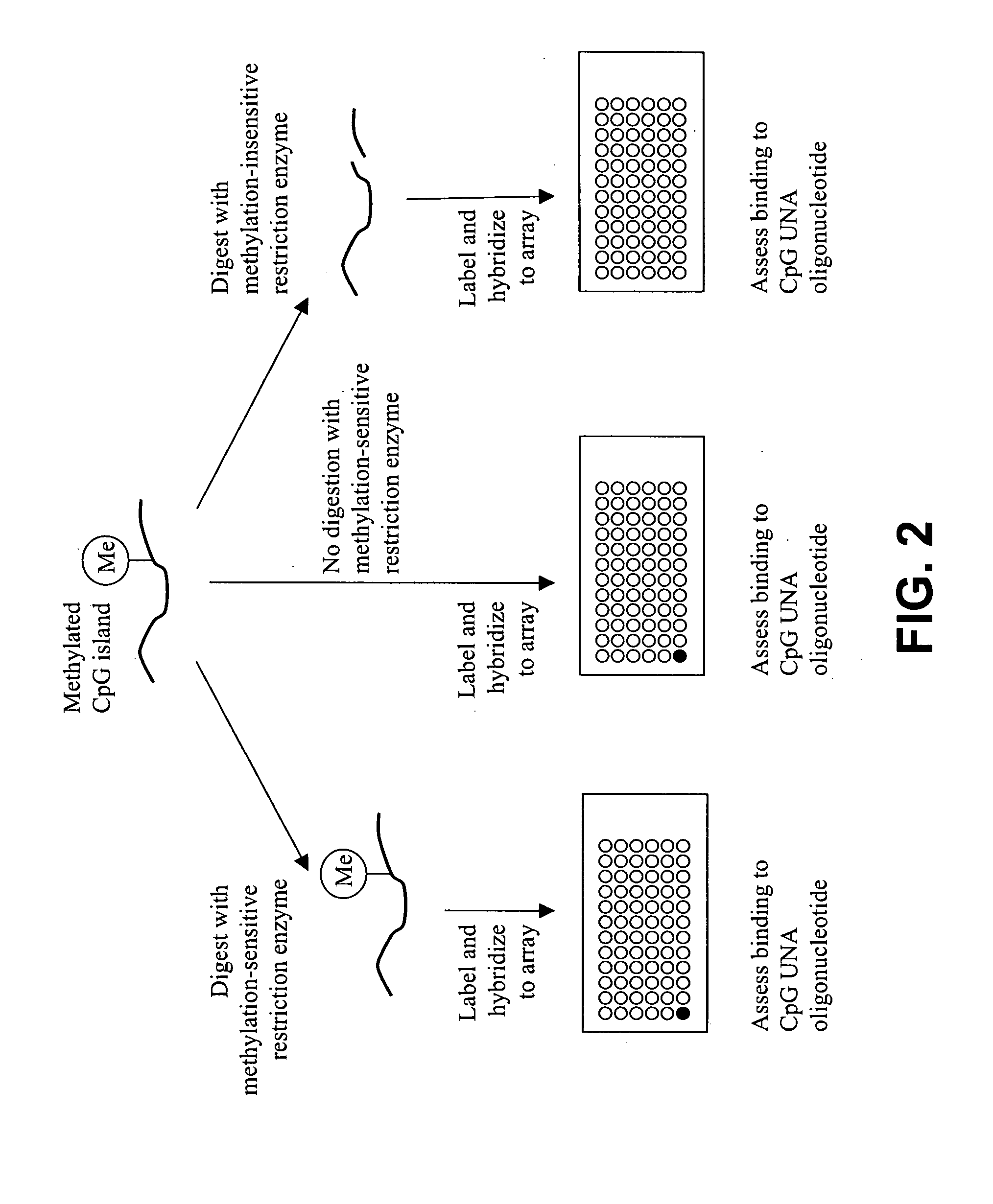
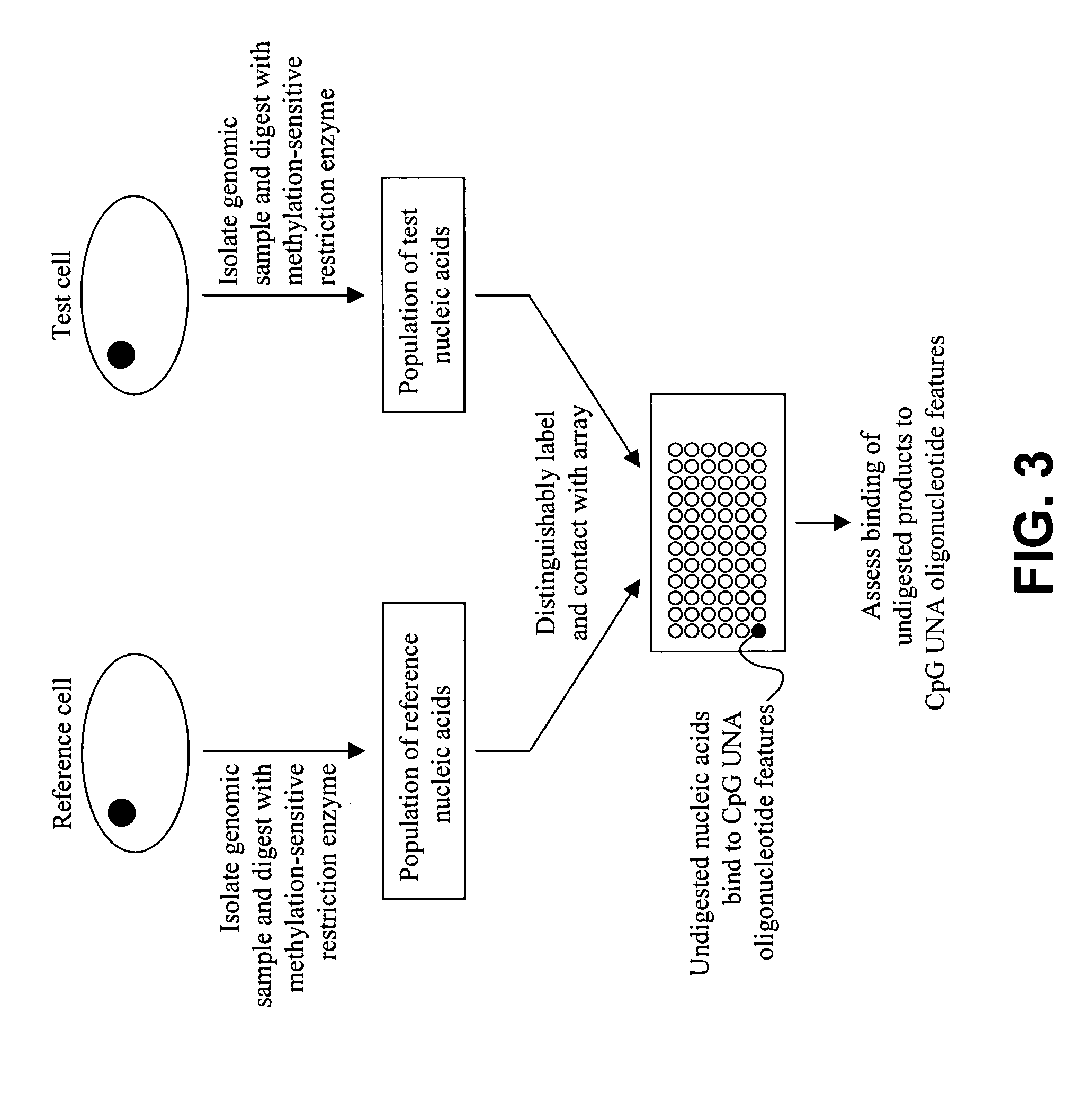
Methods and compositions for assessing CpG methylation
InactiveUS20050233340A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationCpg island methylation
Methods and compositions for assessing CpG island methylation are provided. Specifically, the invention provides an unstructured nucleic acid (UNA) oligonucleotide that base pairs with, i.e., hybridizes to, CpG islands. The subject oligonucleotide may be present in an array, and find use in methods for evaluating methylation of CpG islands in cells. Kits and computer programming for use in practicing the subject methods are also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
High-throughput methods for detecting DNA methylation
InactiveUS20030129602A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationHybridization probe
The present invention provides a method of hybridization, differential methylation hybridization (DMH) for high throughput methylation analysis of multiple CpG island loci. DMH utilizes nucleic acid probes prepared from a cell sample to screen numerous CpG dinucleotide rich fragments affixed on a screening array. Positive hybridization signals indicate the presence of methylated sites. Methods of preparing the hybridization probes and screening array are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
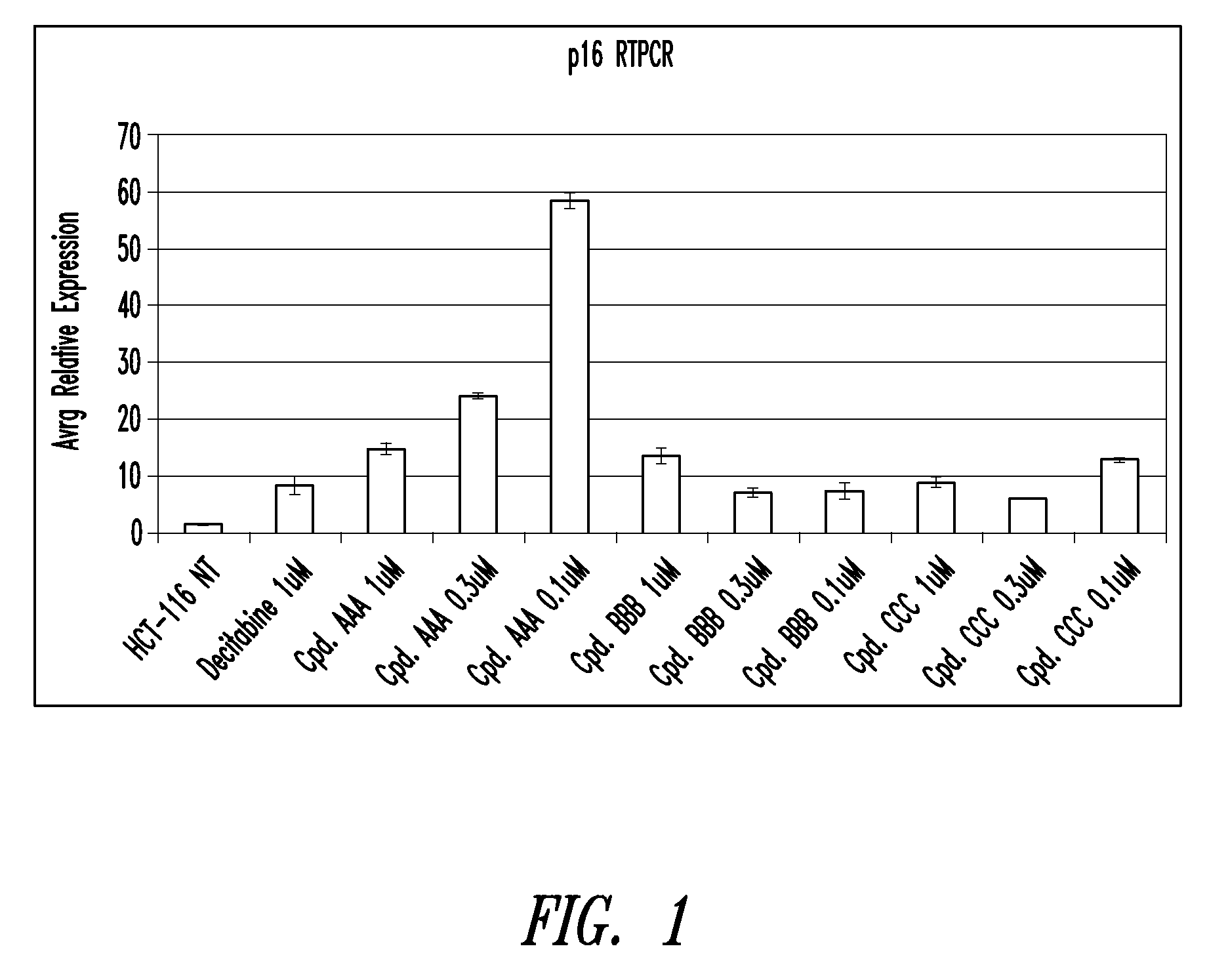
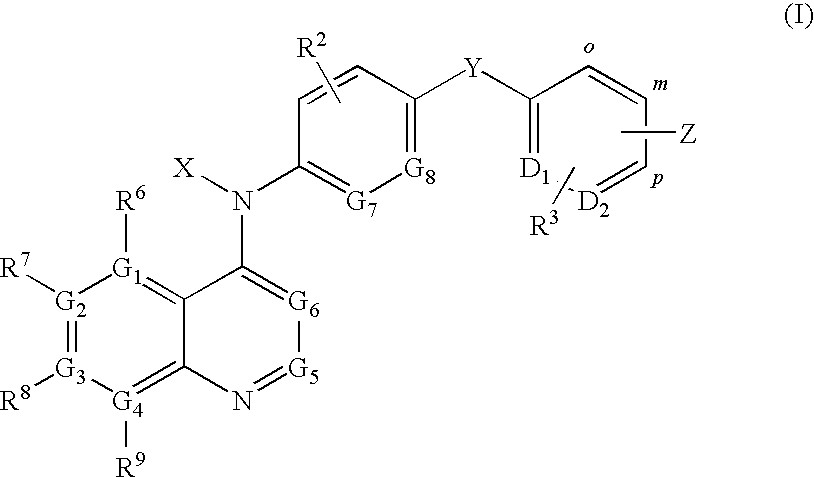
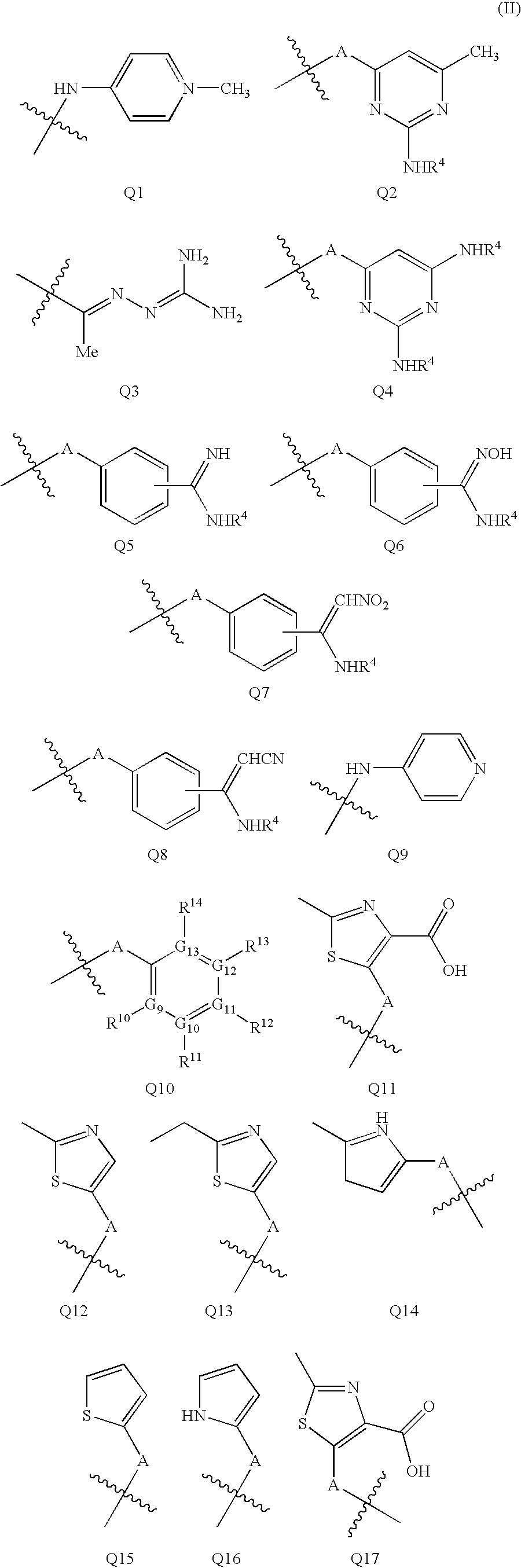
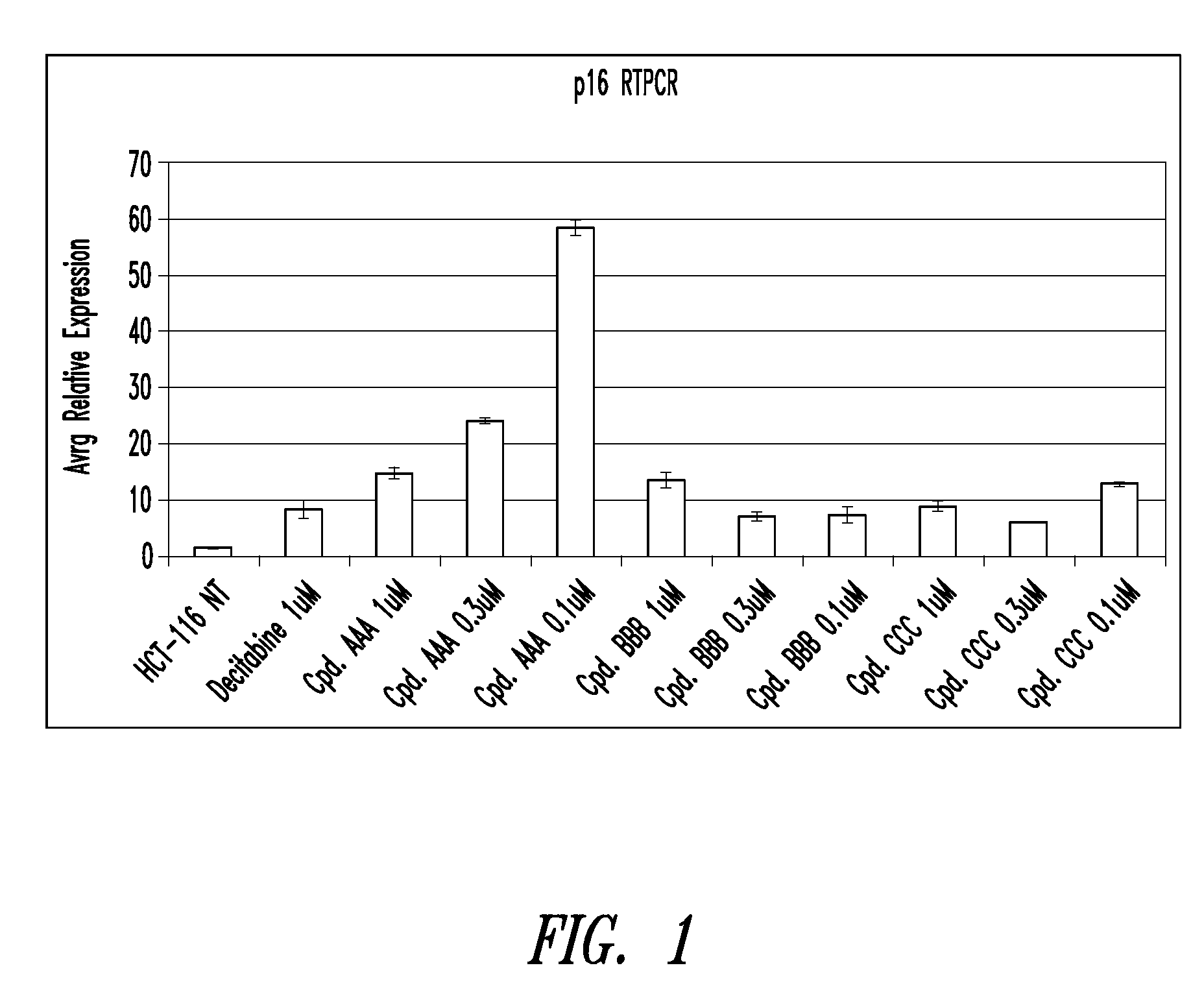
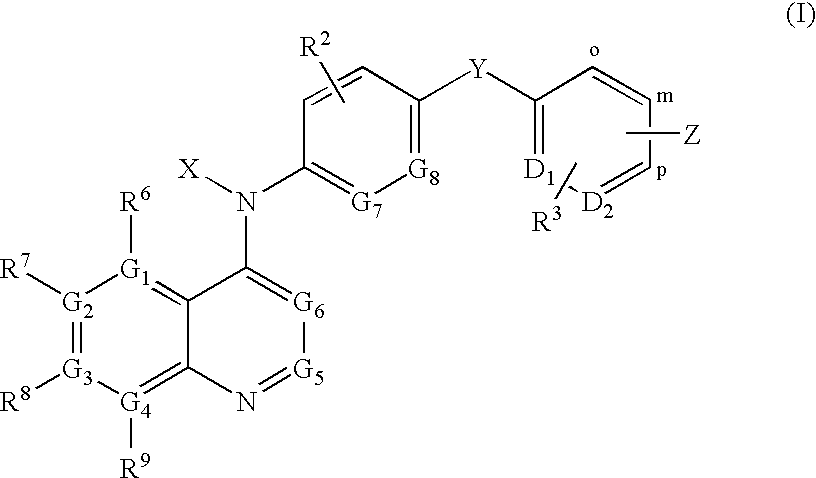
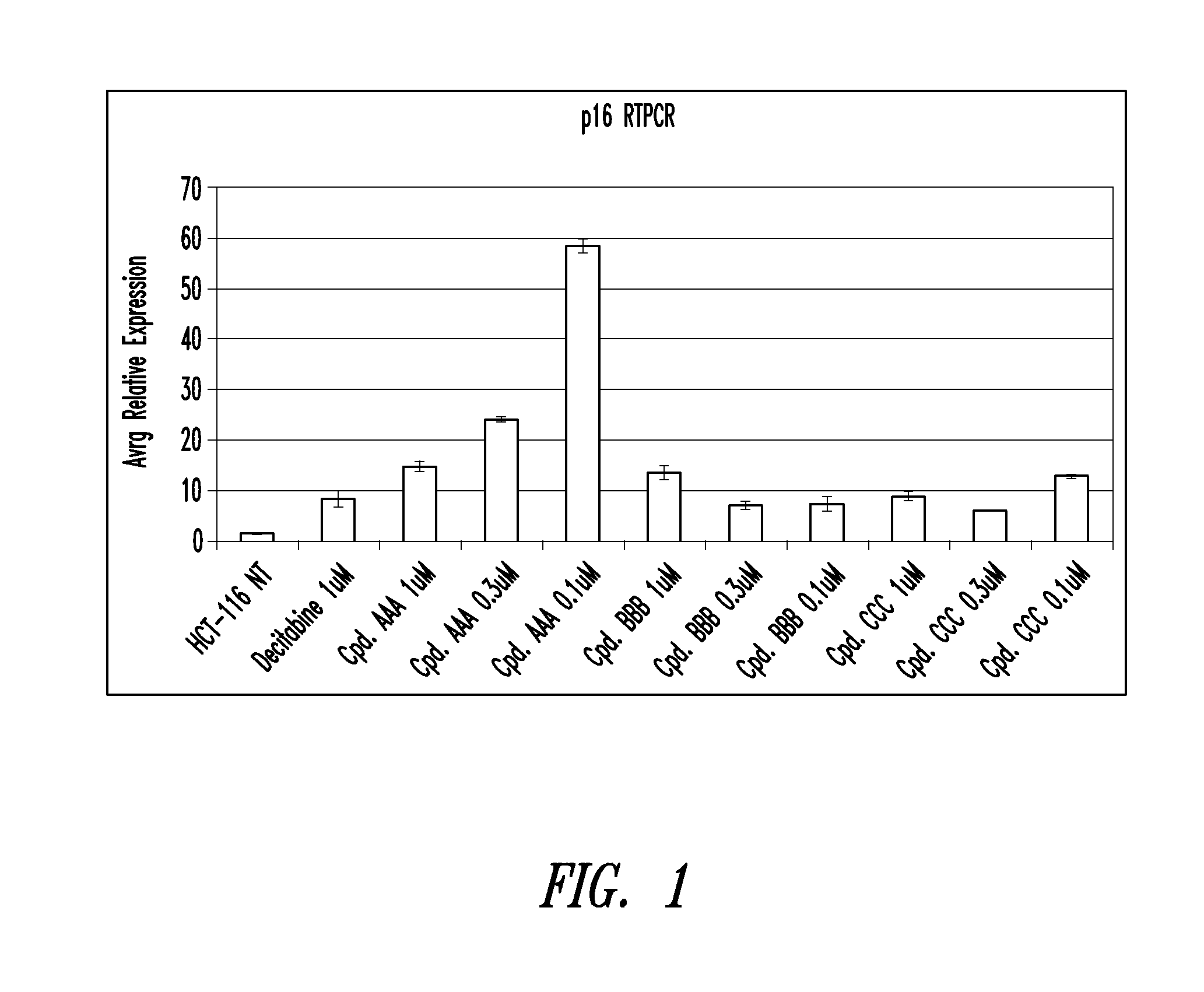
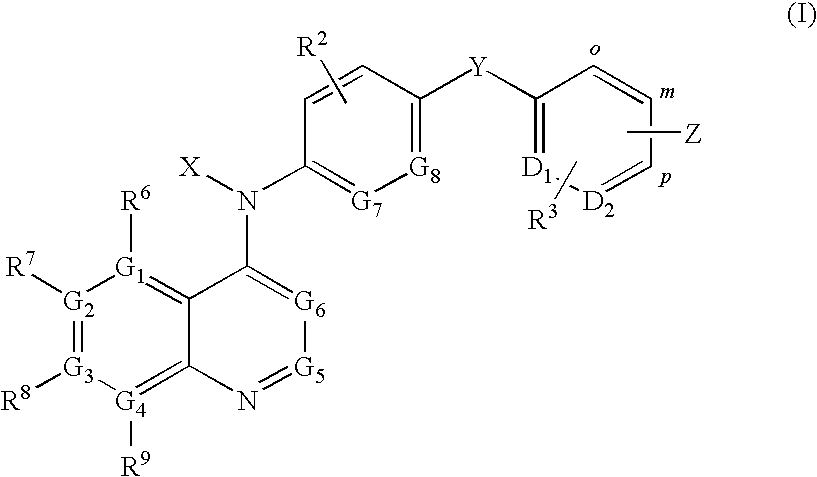
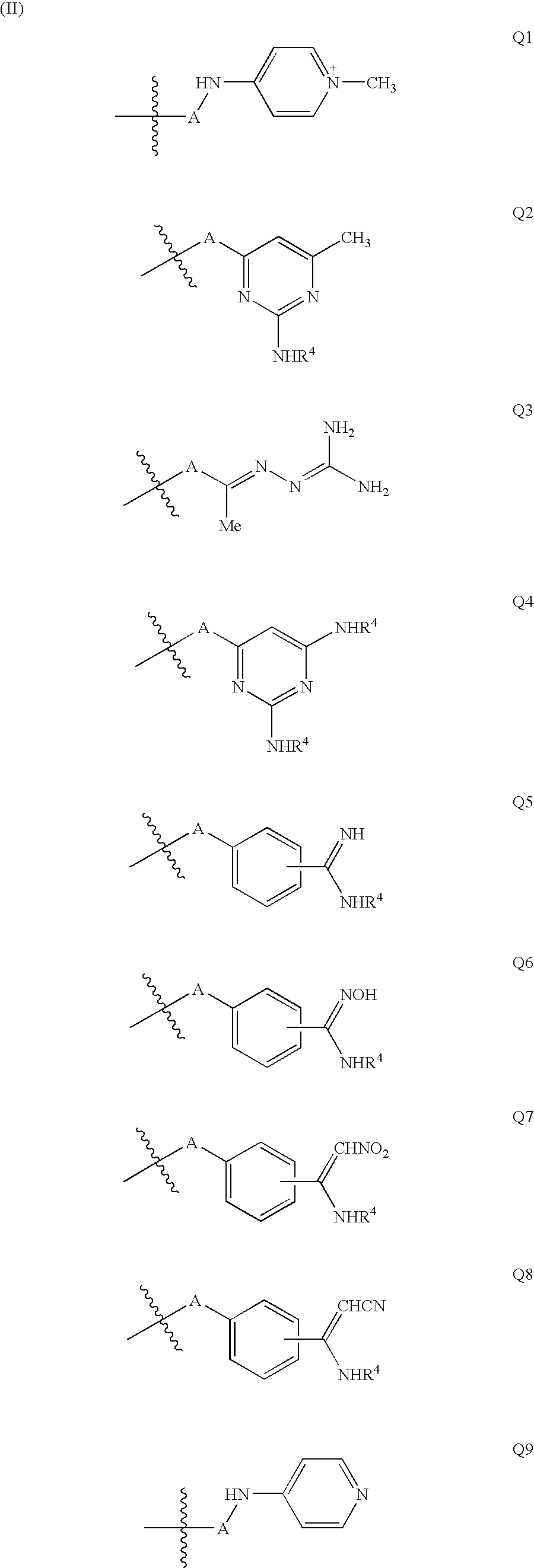
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
InactiveUS20090285772A1Reduction in function/activityReduced activityBiocideOrganic chemistryCytosineDNA methylation
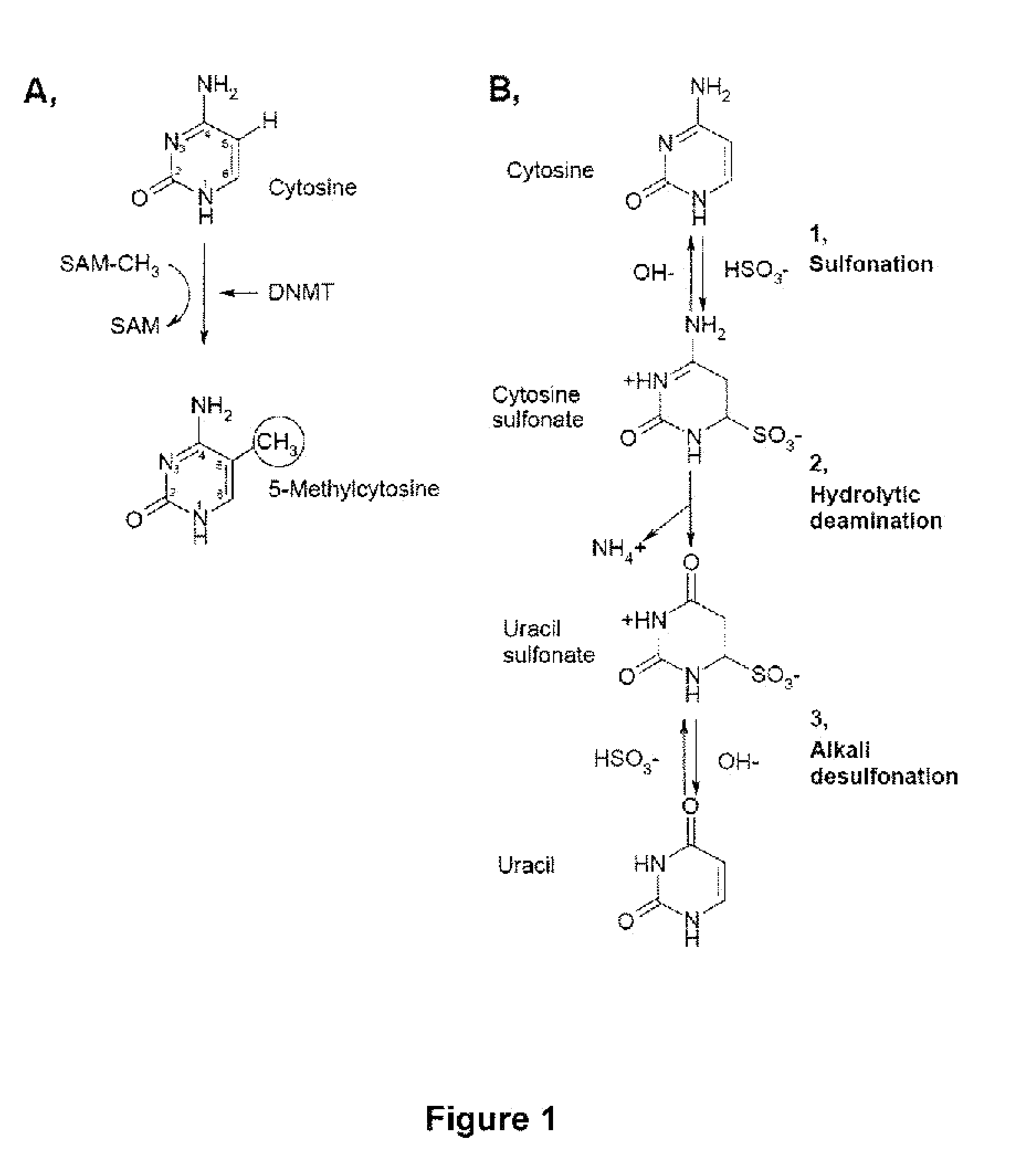
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Methods for detecting DNA originating from different individuals
InactiveUS20050282185A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDNA methylationOrganism
In a first aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample. These methods may be used to differentiate or detect fetal DNA in a maternal sample or to differentiate DNA of an organ donor from DNA of an organ recipient. In preferred embodiments, the DNA species are differentiated by observing epigenetic differences in the DNA species such as differences in DNA methylation. In a second aspect, the present invention features methods of detecting genetic abnormalities in a fetus by detecting fetal DNA in a biological sample obtained from a mother. In a third aspect, the present invention features methods for differentiating DNA species originating from an organ donor from those of an organ recipient. In a fourth aspect, the present invention features kits for differentiating DNA species originating from different individuals in a biological sample.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
InactiveUS20080175814A1Reduction in function/activityReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDNA methylationCytosine
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
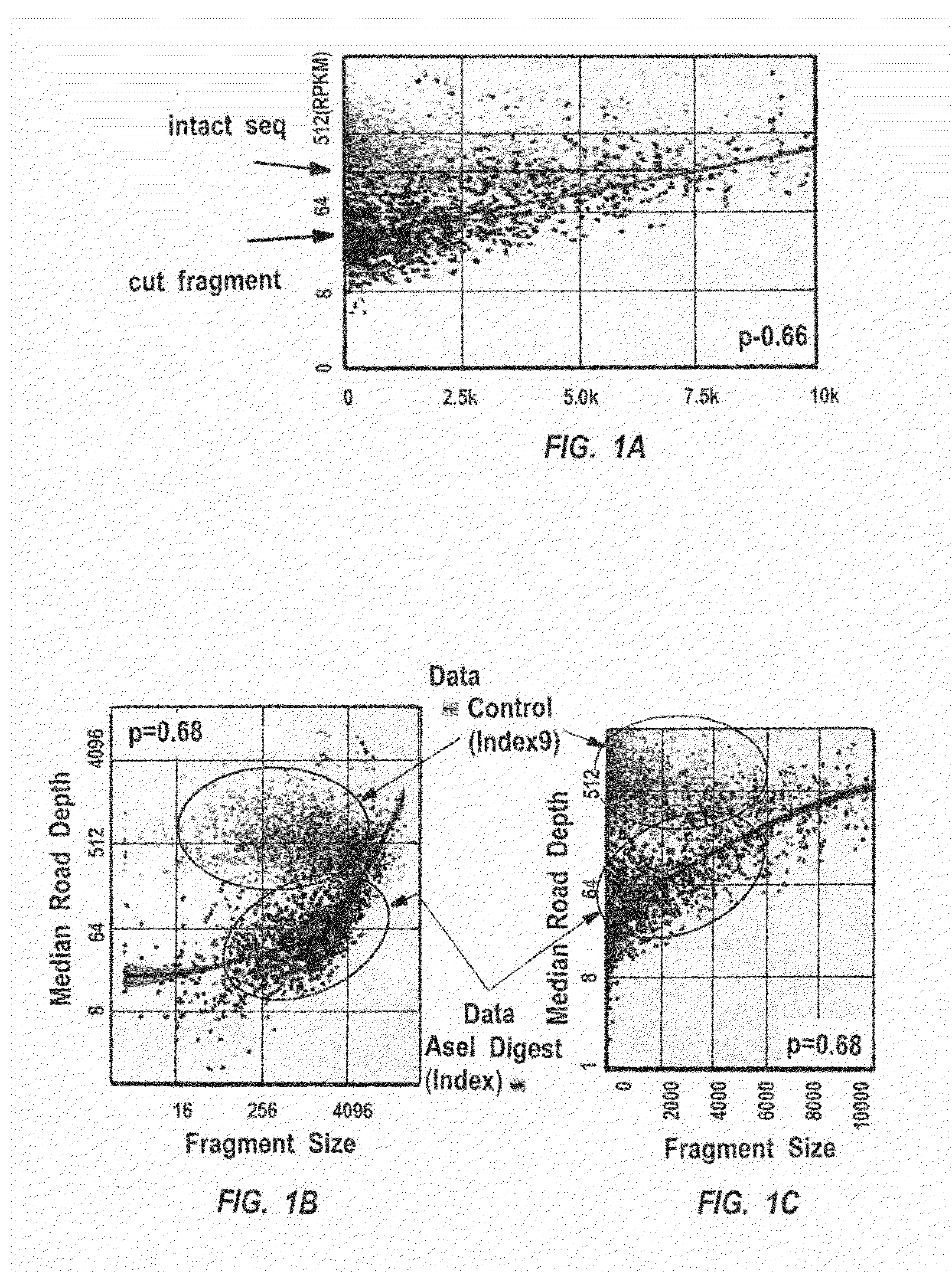
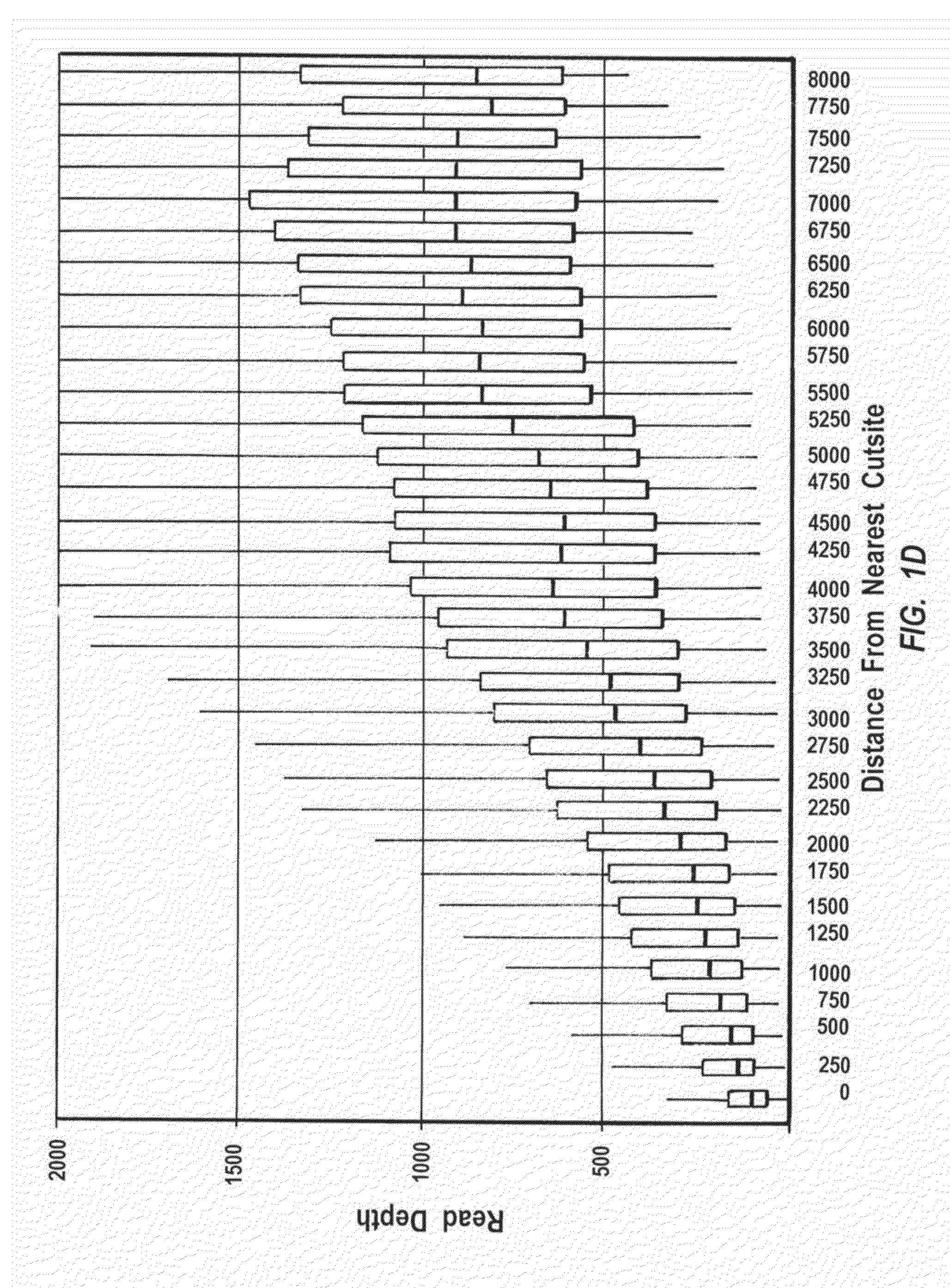
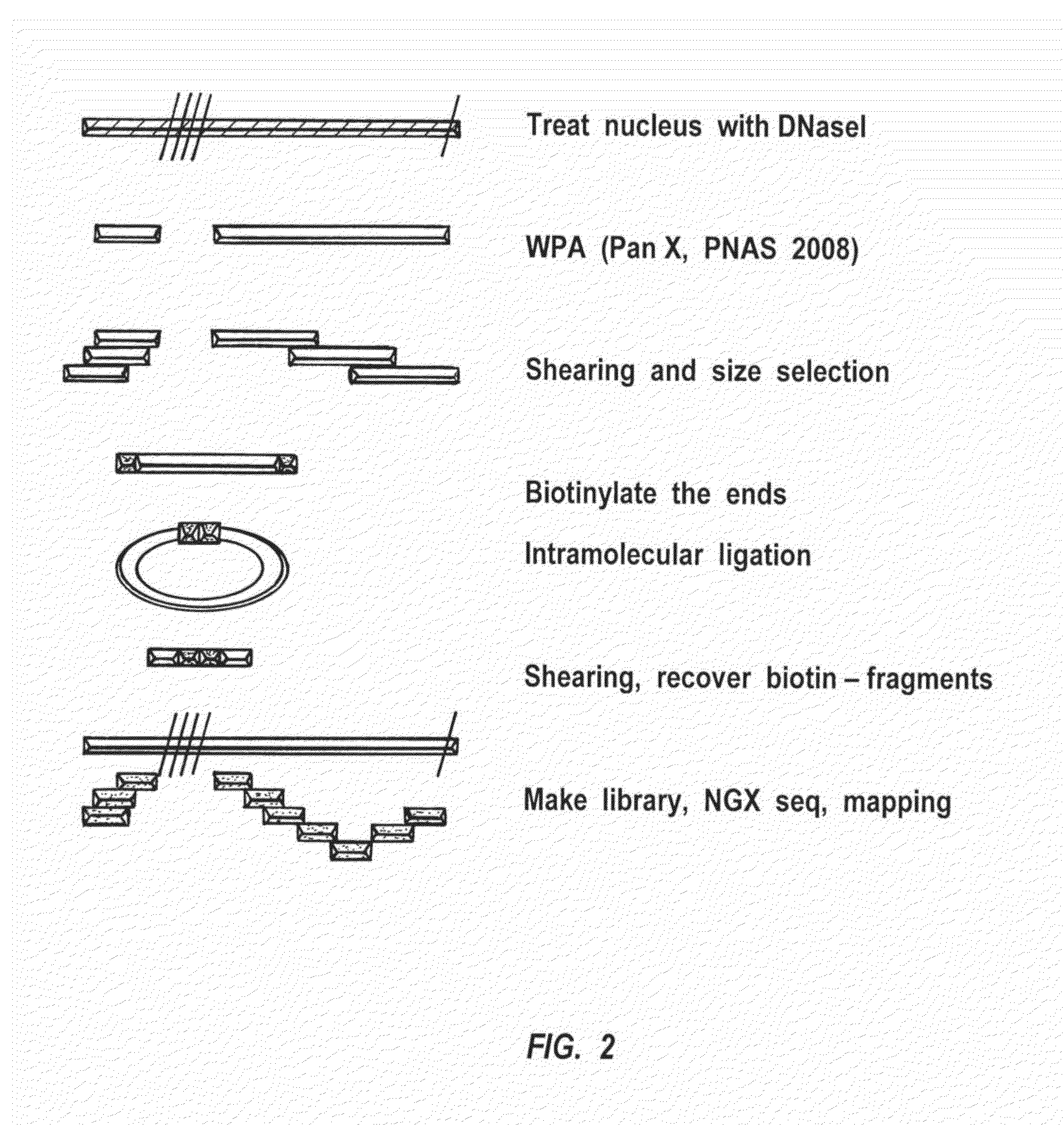
Methods for closed chromatin mapping and DNA methylation analysis for single cells
ActiveUS20150368694A1Reduce and minimize and prevent chanceLess efficiently ligatedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationGenomic DNA
Methods of identifying DNase I Hyper-Resistant Sites (DHRS), or in board sense, highly compact chromatin and characterizing the DNA methylation status of DMRs such as CpG islands and CpG island shores are provided. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of genomic DNA from low quantities of cells, for example, less than 1,000 cells, less than 100 cells, less than 10 cells, or even one cell, and can be used to generate chromatin and methylation profiles. The downstream analyses include in parallel massive sequencing, microarray, PCR and Sanger sequencing, hybridization and other platforms. These methods can be used to generate chromatin and DNA methylation profiles in drug development, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Quinoline derivatives for modulating DNA methylation
Quinoline derivatives, particularly 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives, are provided. Such quinoline derivatives can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position, for example via selective inhibition of DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. Methods for synthesizing numerous 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives and for modulating DNA methylation are provided. Also provided are methods for formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
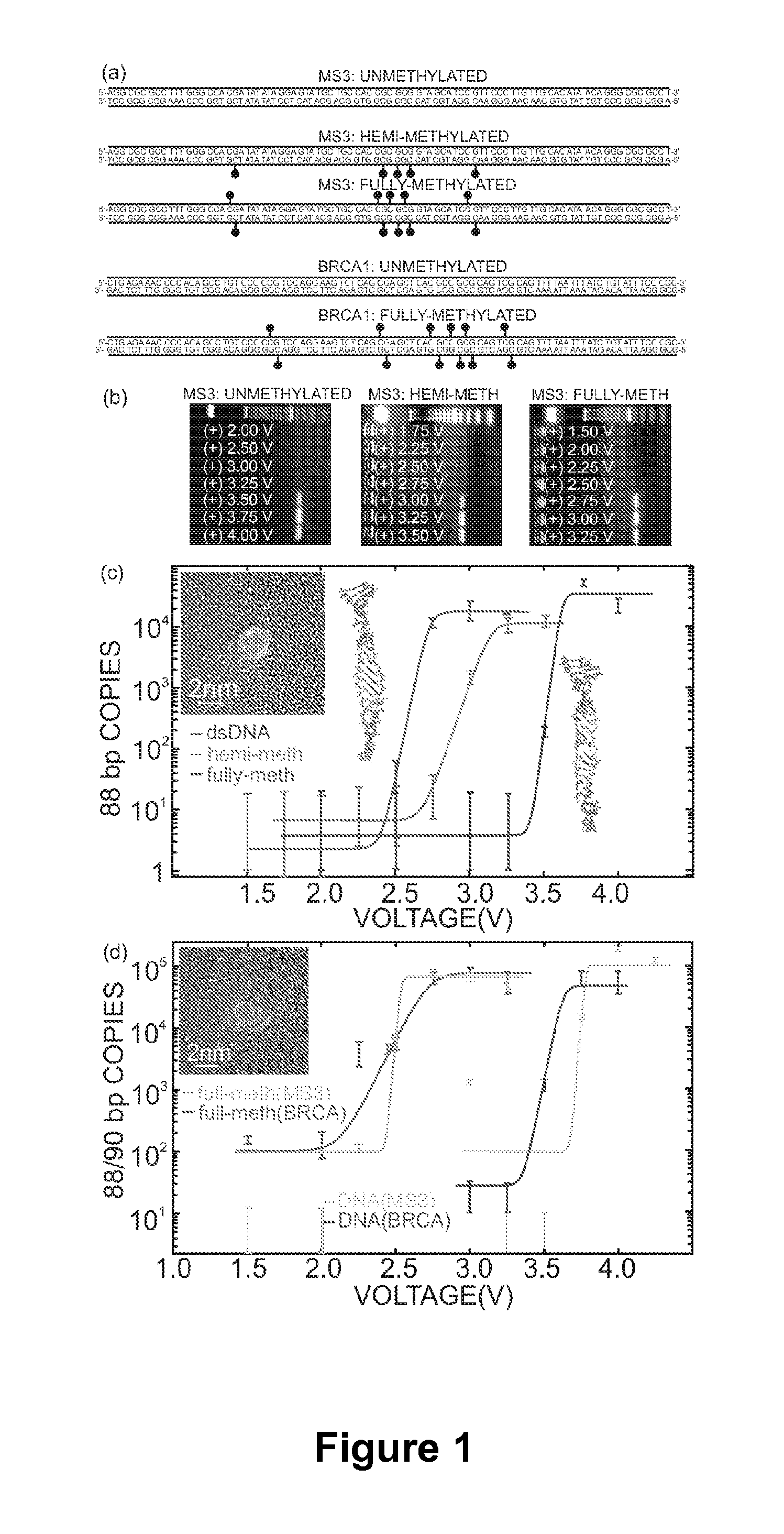
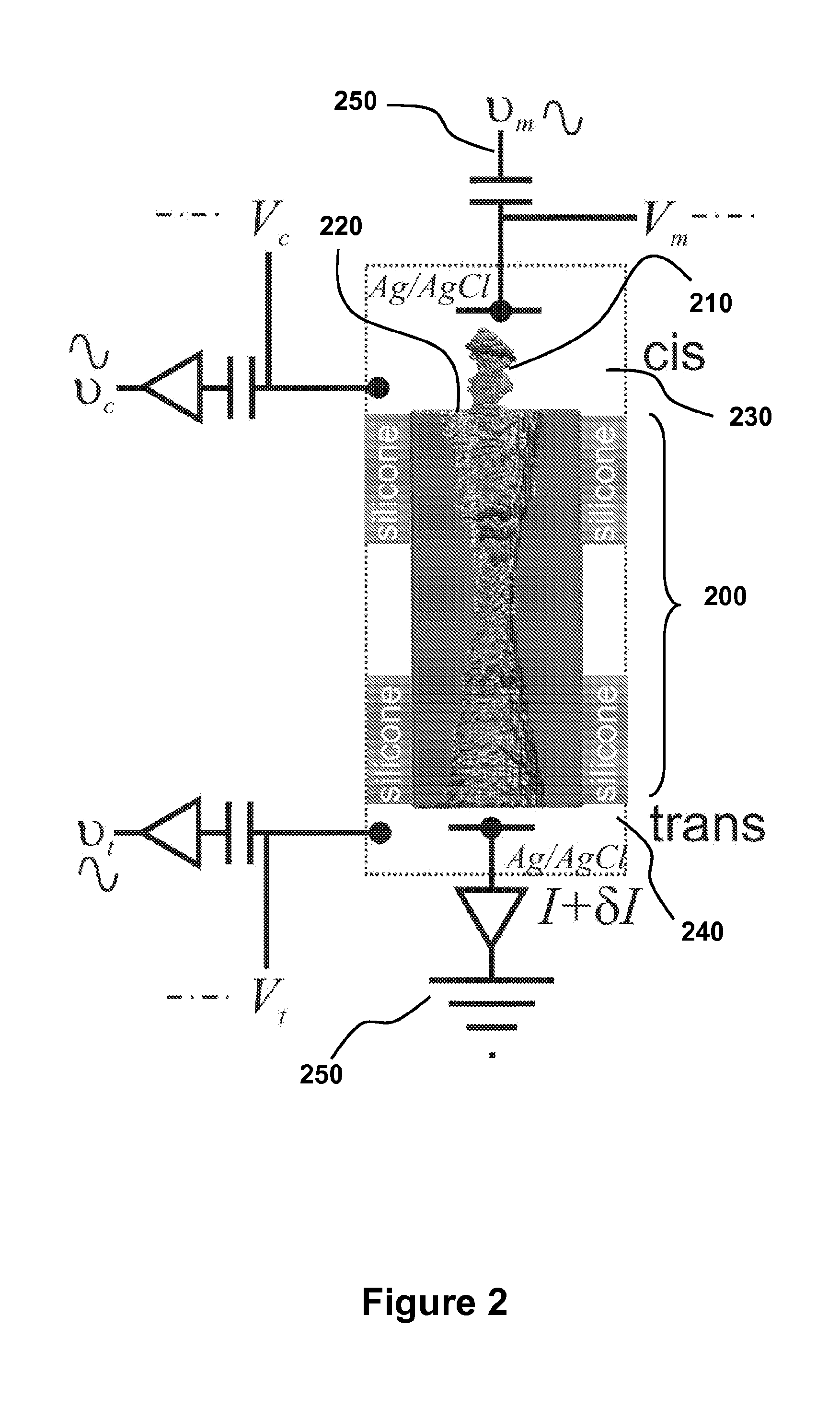
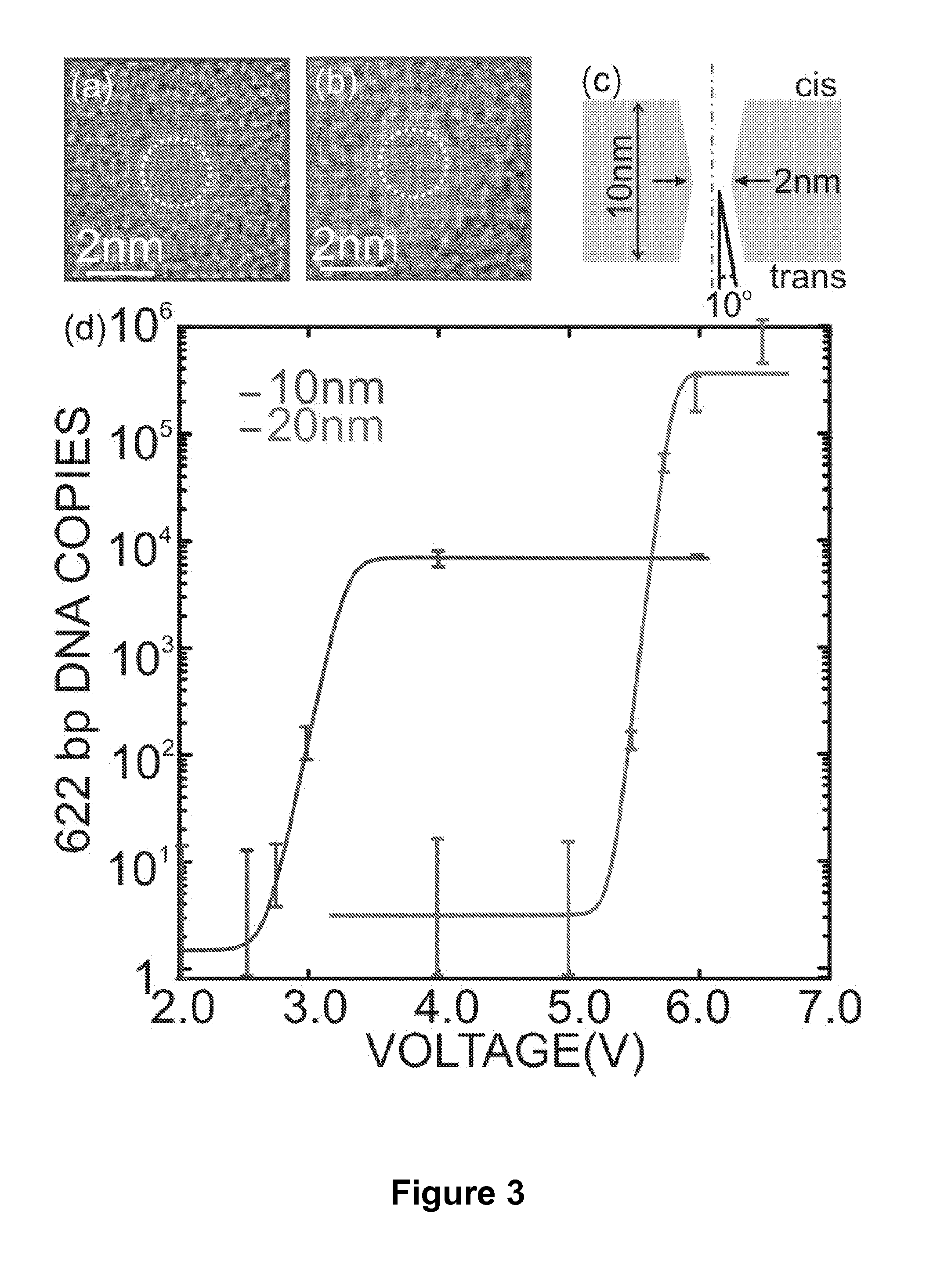
Detecting and Sorting Methylated DNA Using a Synthetic Nanopore
ActiveUS20120040343A1Easy to sortEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsDNA methylationDisease
Provided are methods for detecting, characterizing or separating DNA based on methylation. Heterogeneous DNA populations are separated based on DNA methylation by providing a membrane having a nanopore through which an electric field is applied. DNA of interest is introduced, and for a given threshold voltage across the nanopore, only DNA having a methylation parameter of interest may transit the pore, thereby facilitating detection, characterization, or separation of DNA based on methylation. The methods are optionally used to detect a disease state that is associated with DNA methylation including, but not limited to, cancer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Method and devices for dna methylation analysis
InactiveUS20050153296A1Conserving complex methylation patternBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationDna methylation profiling
The invention outlines a method for the methylation pattern retaining amplification of nucleic acid molecules. Furthermore the invention describes several devices for use in the methylation pattern retaining amplification of nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
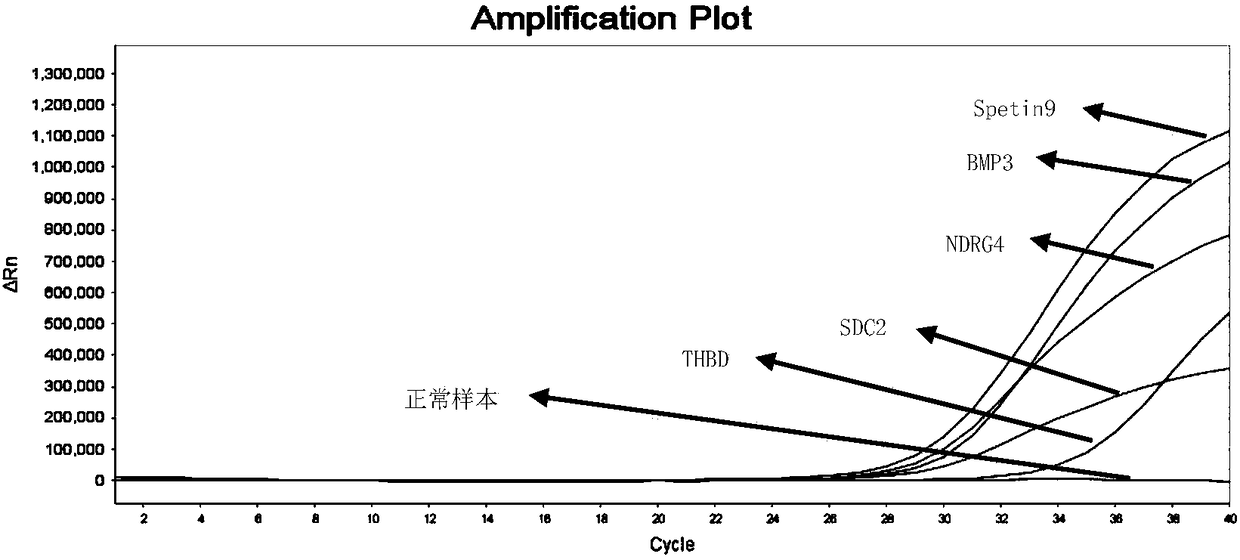
Primer pair, probe and kit used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer and applications thereof
ActiveCN108103195AEasy to sampleSampling non-invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationFluorescence
The invention relates to a primer pair and a probe used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer, and includes the primer pair and the probe used for detecting methylation of genes Spetin9, NDRG4, BMP3, THBD and SDC2 and the primer pair and the probe for internal reference ACTB; the sequences of the primer pair and the probe are represented as the SEQ ID No.1 to the SEQ ID No.18. The invention also provides a kit containing the primer pair and the probe and applications thereof. The application method includes free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, sulfite conversion, PCR amplification reaction, fluorescent signal detection and result determination. The kit and the method are suitable for methylation detection of the five genes Spetin9, THBD, SDC2, NDRG4 and BMP3 in human peripheral blood; compared with a conventional colorectal cancer diagnosis method, the application method fully utilizes the free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, the DNA methylation and QPCR associated technologies, thus developing the kit having high sensitivity and specificity. The primer pair, probe and kit are used for performing early stage noninvasive screening to human colorectal cancer.
Owner:上海酷乐生物科技有限公司
Method for diagnosing bladder cancer by analyzing DNA methylation profiles in urine sediments and its kit
InactiveUS20100317000A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDNA methylationBladder cancer
The present invention provides a method for detecting bladder cancer in a subject, comprising the following steps: (a) providing urine sediment sample from said subject; (b) determining methylation pattern of a given sequence within the promoter CpG islands of one or more genes (known as “gene” infra) in the samples; (c) comparing the methylation pattern from said subject with that from normal subject, wherein the hypermethylation of one or more of genes indicates that said subject is suffering from bladder cancer. The present invention also provides a kit for diagnosing bladder cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Process for high throughput DNA methylation analysis
InactiveUS7112404B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDNA methylationHybridization probe
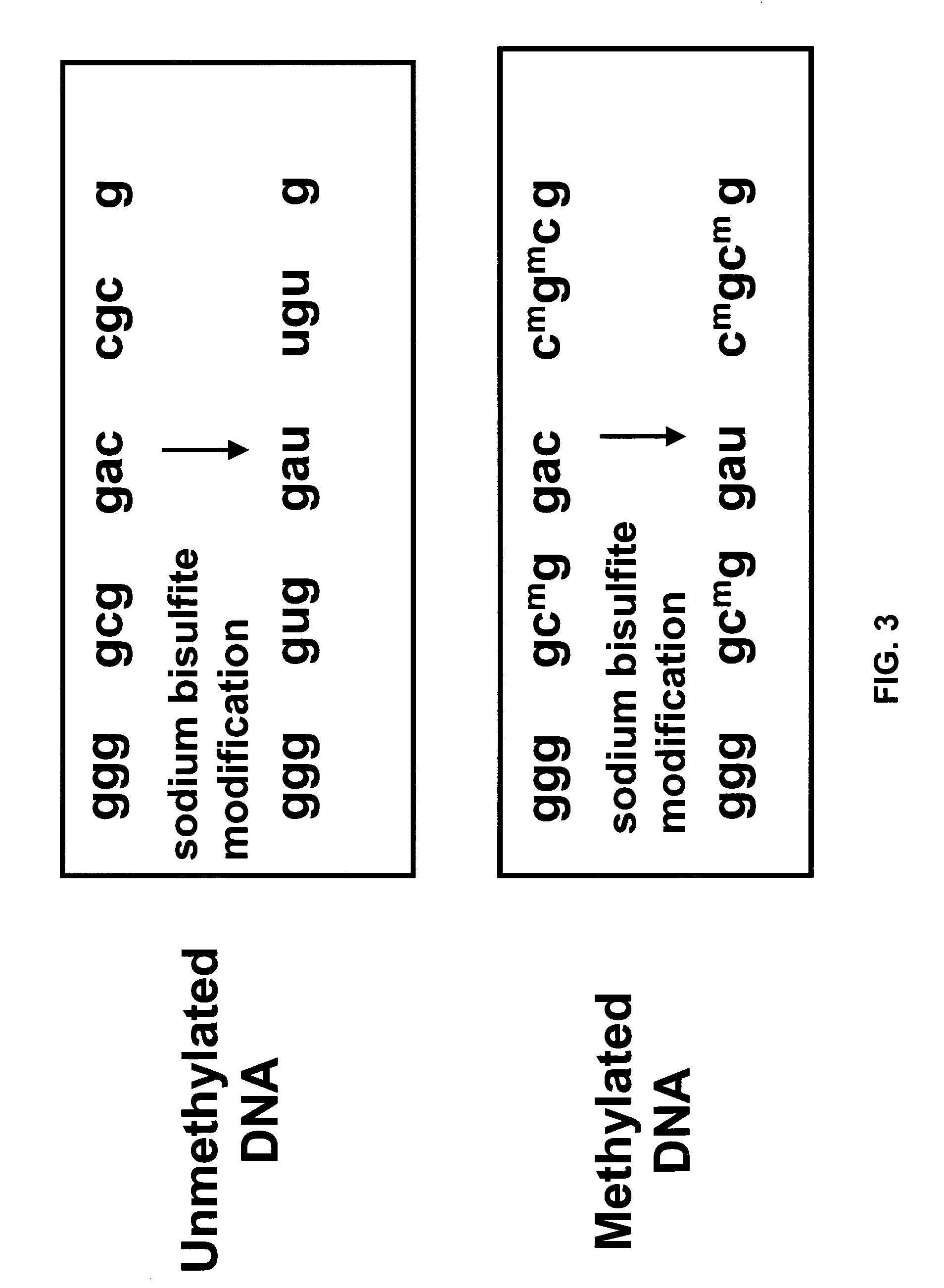
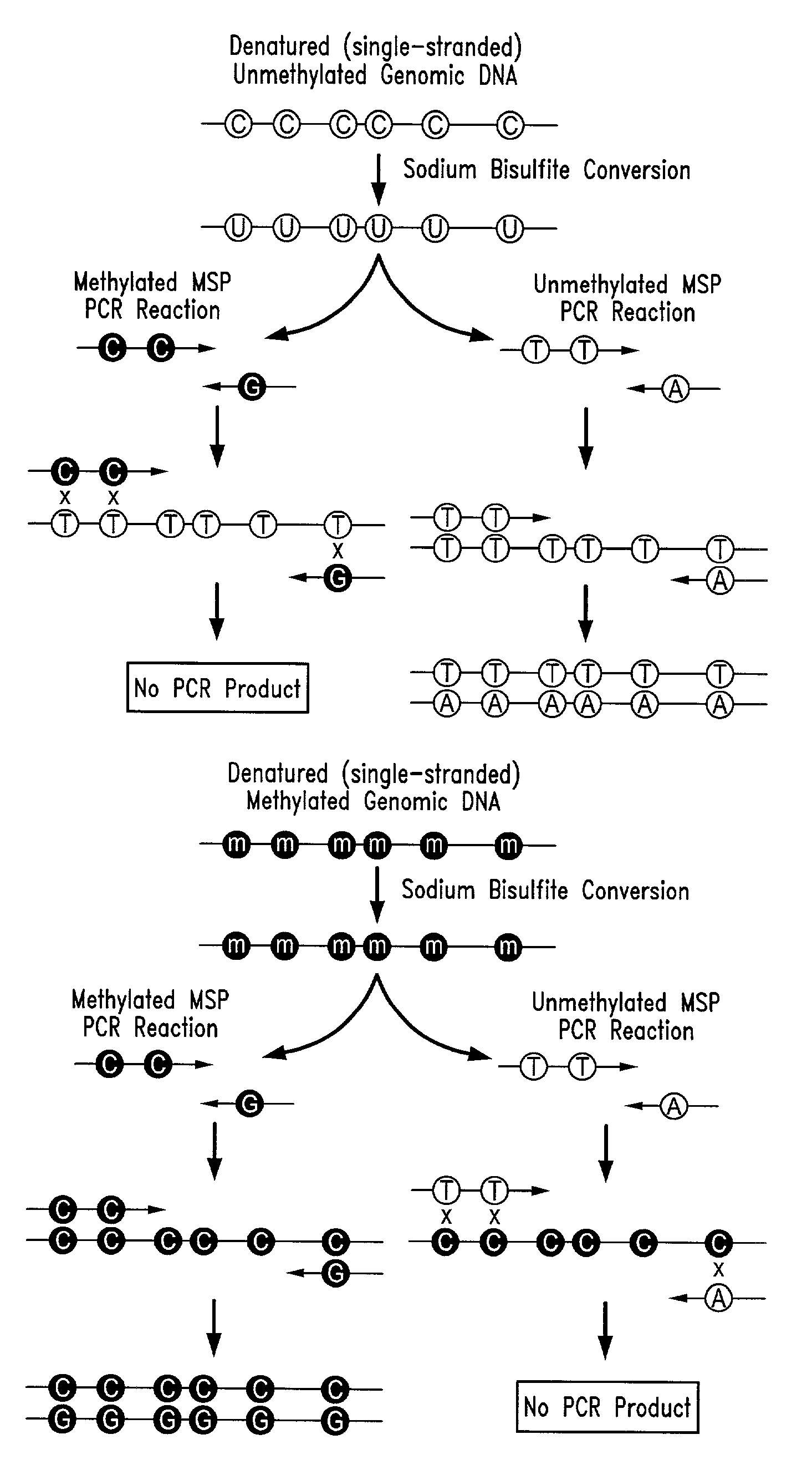
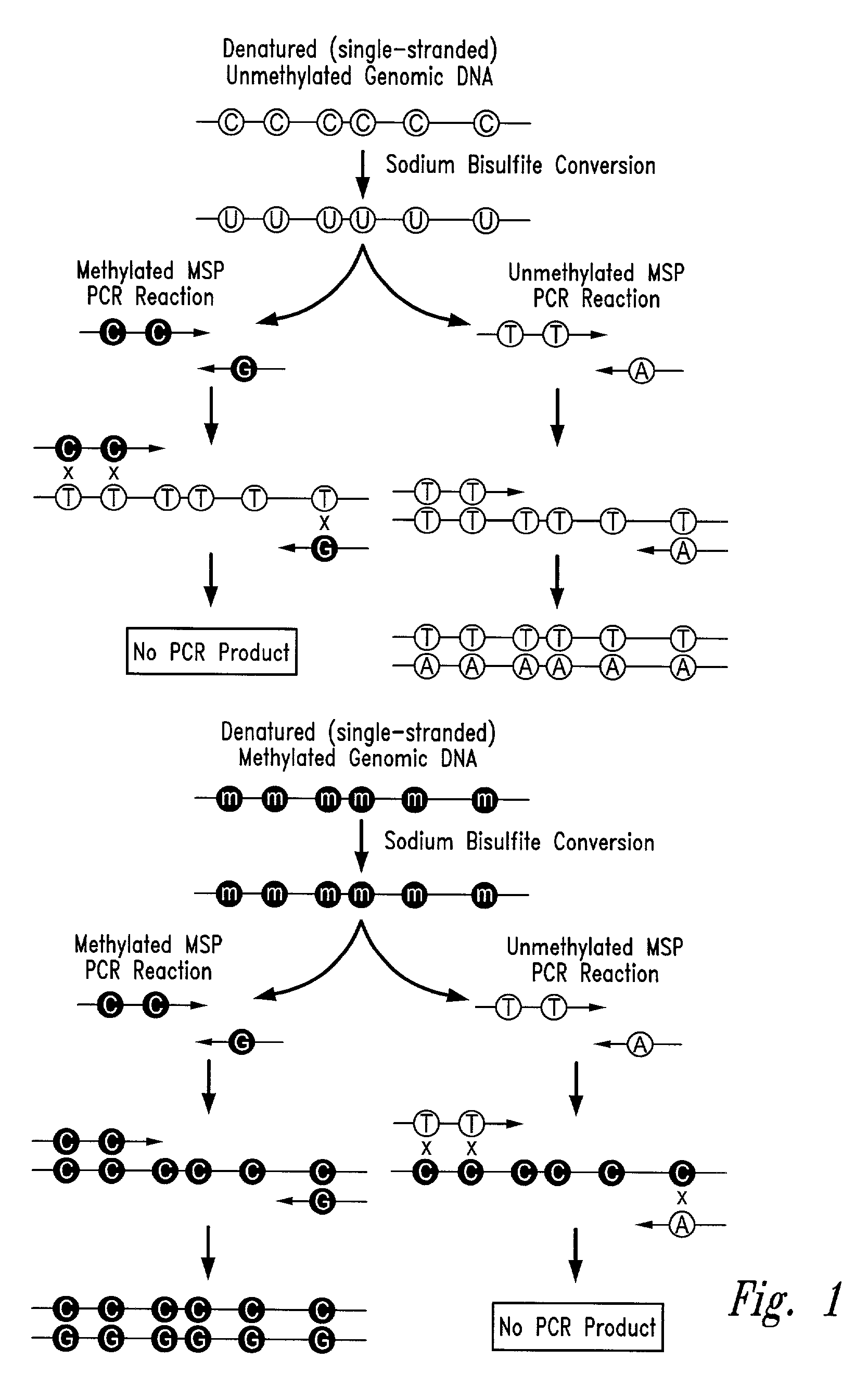
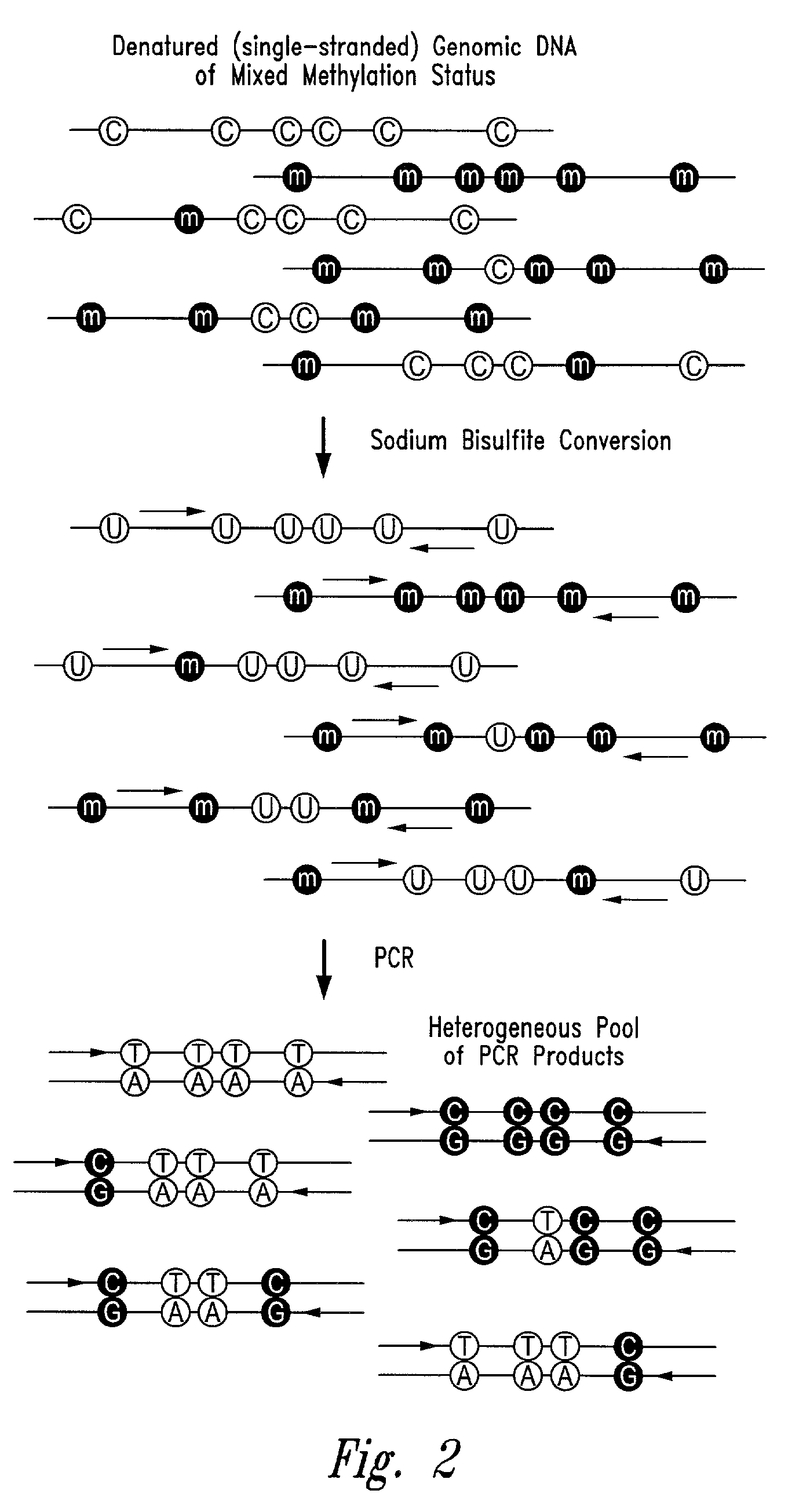
There is disclosed an improved high-throughput and quantitative process for determining methylation patterns in genomic DNA samples based on amplifying modified nucleic acid, and detecting methylated nucleic acid based on amplification-dependent displacement of specifically annealed hybridization probes. Specifically, the inventive process provides for treating genomic DNA samples with sodium bisulfite to create methylation-dependent sequence differences, followed by detection with fluorescence-based quantitative PCR techniques. The process is particularly well suited for the rapid analysis of a large number of nucleic acid samples, such as those from collections of tumor tissues.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Methods of copying the methylation pattern of DNA during isothermal amplification and microarrays
InactiveUS20060257905A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenomic DNA
A method for copying the methylation patterns of molecules of genomic DNA (MGD) during isothermal amplification of the MGD comprising obtaining MGD, copying the methylation patterns of the MGD using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the MGD using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a method for copying the methylation patterns in double-stranded DNA molecules during isothermal amplification of the DNA molecules comprising obtaining DNA molecules, contacting the DNA molecules with transposable elements and an enzyme, which can randomly insert the transposable elements into the DNA molecules, copying the methylation patterns of the DNA molecules using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the DNA molecules using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a buffer comprising a divalent ion, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), primers, and S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM); and a composition comprising a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, and the buffer.
Owner:EUCLID DIAGNOSTICS
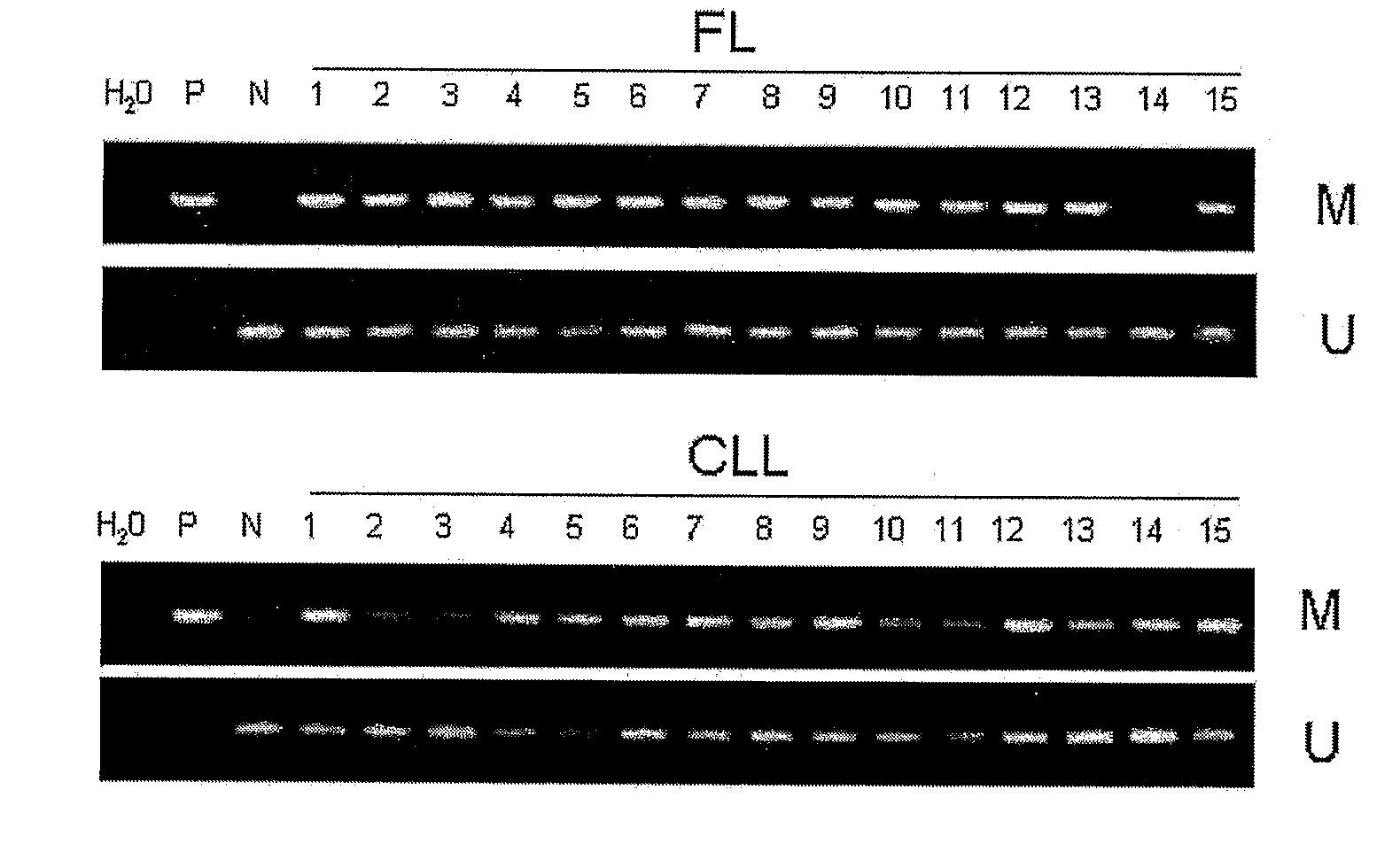
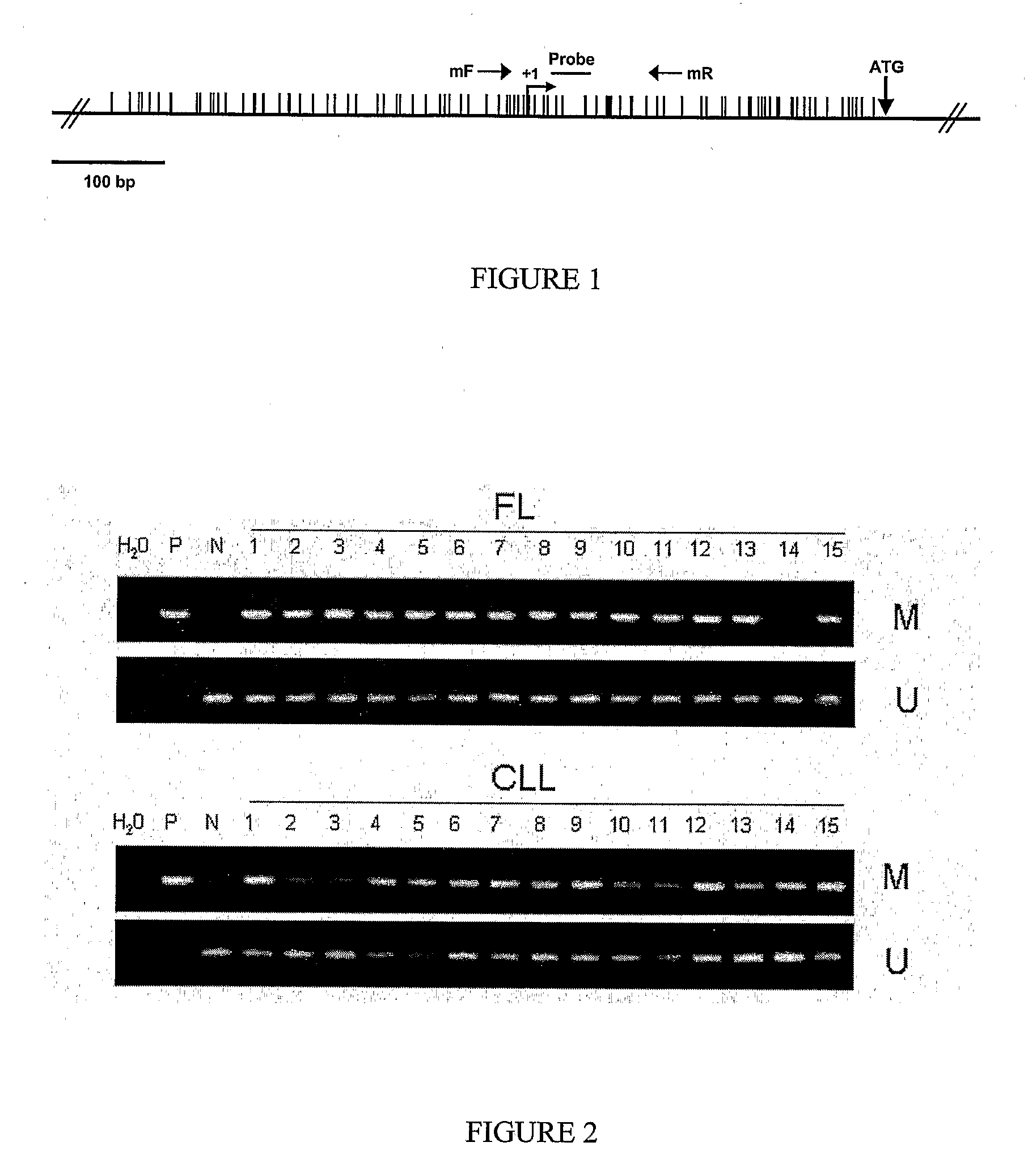
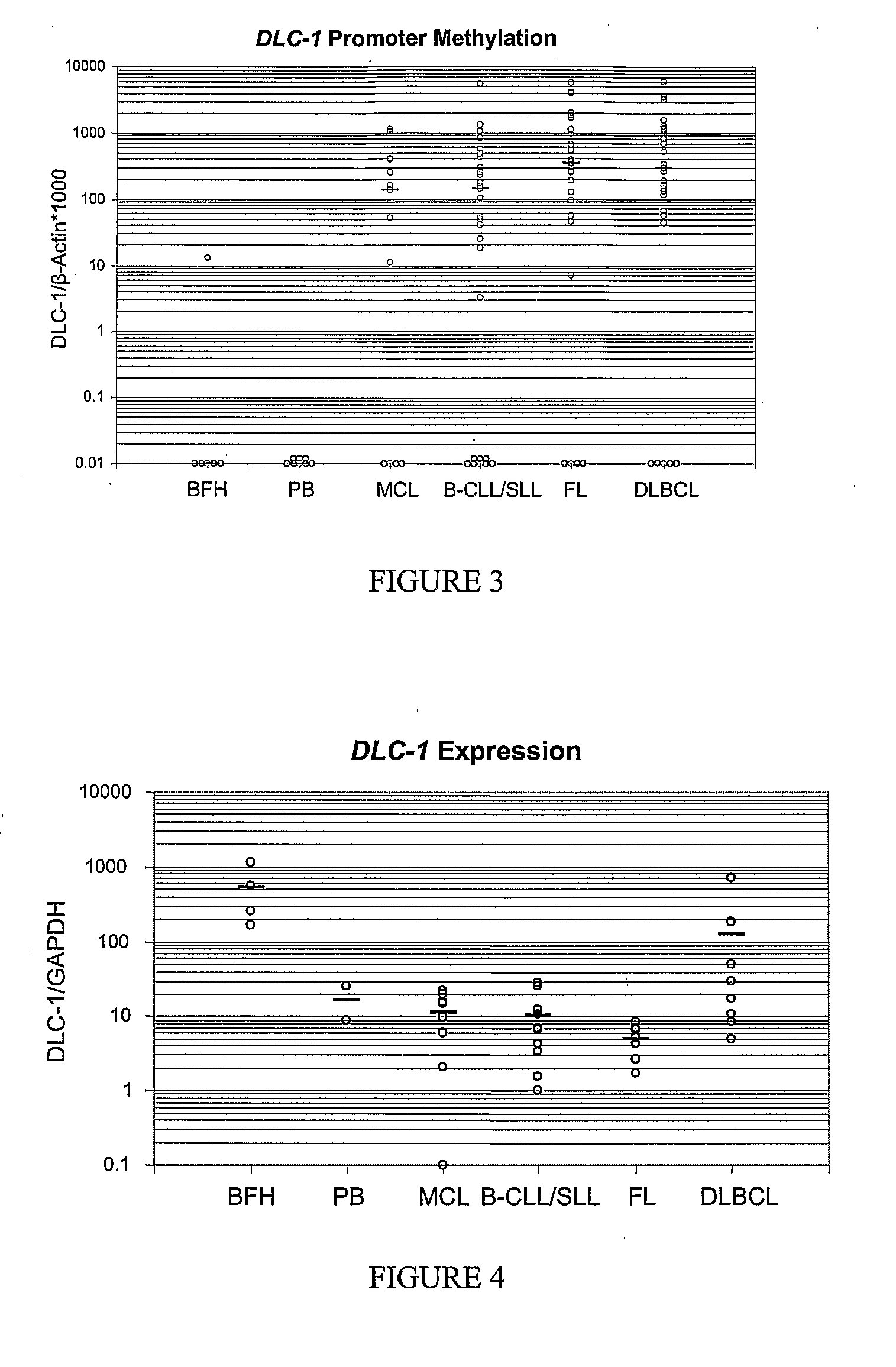
DNA methylation biomarkers in lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies
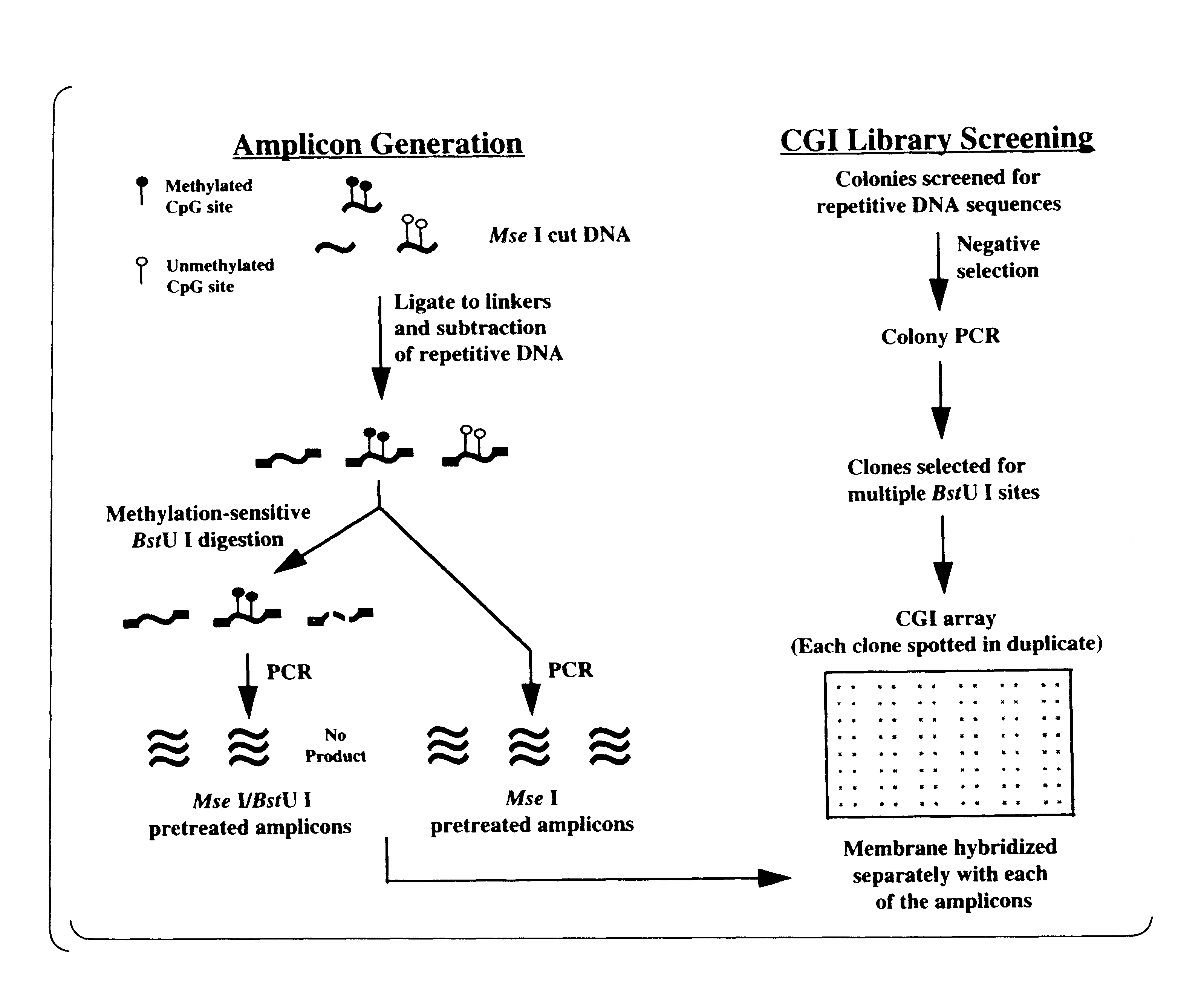
InactiveUS20090264306A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationLymphocytic cell
Differential Methylation Hybridization (DMH) was used to identify novel methylation markers and methylation profiles for hematopoieetic malignancies, leukemia, lymphomas, etc. (e.g., non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL), small B-cell lymphomas (SBCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma (B-CLL / SLL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), multiple myeloma (MM), acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), etc.). Particular aspects provide novel biomarkers for NHL and subtypes thereof (e.g., MCL, B-CLL / SLL, FL, DLBCL, etc.), AML, ALL and MM, and further provide non-invasive tests (e.g. blood tests) for lymphomas and leukemias. Additional aspects provide markers for diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring responses to therapies, relapse, etc., and further provide targets and methods for therapeutic demethylating treatments. Further aspects provide cancer staging markers, and expression assays and approaches comprising idealized methylation and / or patterns” (IMP and / or IEP) and fusion of gene rankings.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Methods and compositions for diagnosing conditions associated with specific DNA methylation patterns
InactiveUS20050026183A1Improve the level ofMany applicationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenomic DNA
The present invention provides a method for identification of differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer in an individual by obtaining a biological sample comprising genomic DNA from the individual measuring the level or pattern of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences for two or more of the genomic targets in the sample, and comparing the level of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences in the sample to a reference level of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences, wherein a difference in the level or pattern of methylation of the genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences in the sample compared to the reference level identifies differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer. As disclosed herein, the methods of the invention have numerous diagnostic and prognostic applications. The methods of the invention can be combined with a miniaturized array platform that allows for a high level of assay multiplexing and scalable automation for sample handling and data processing. Also provided by the invention are genomic targets and corresponding nucleic acid probes that are useful in the methods of the invention as they enable detection of differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer, for example, adenocarcenomas and sqamous cell carcinomas of the lung.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
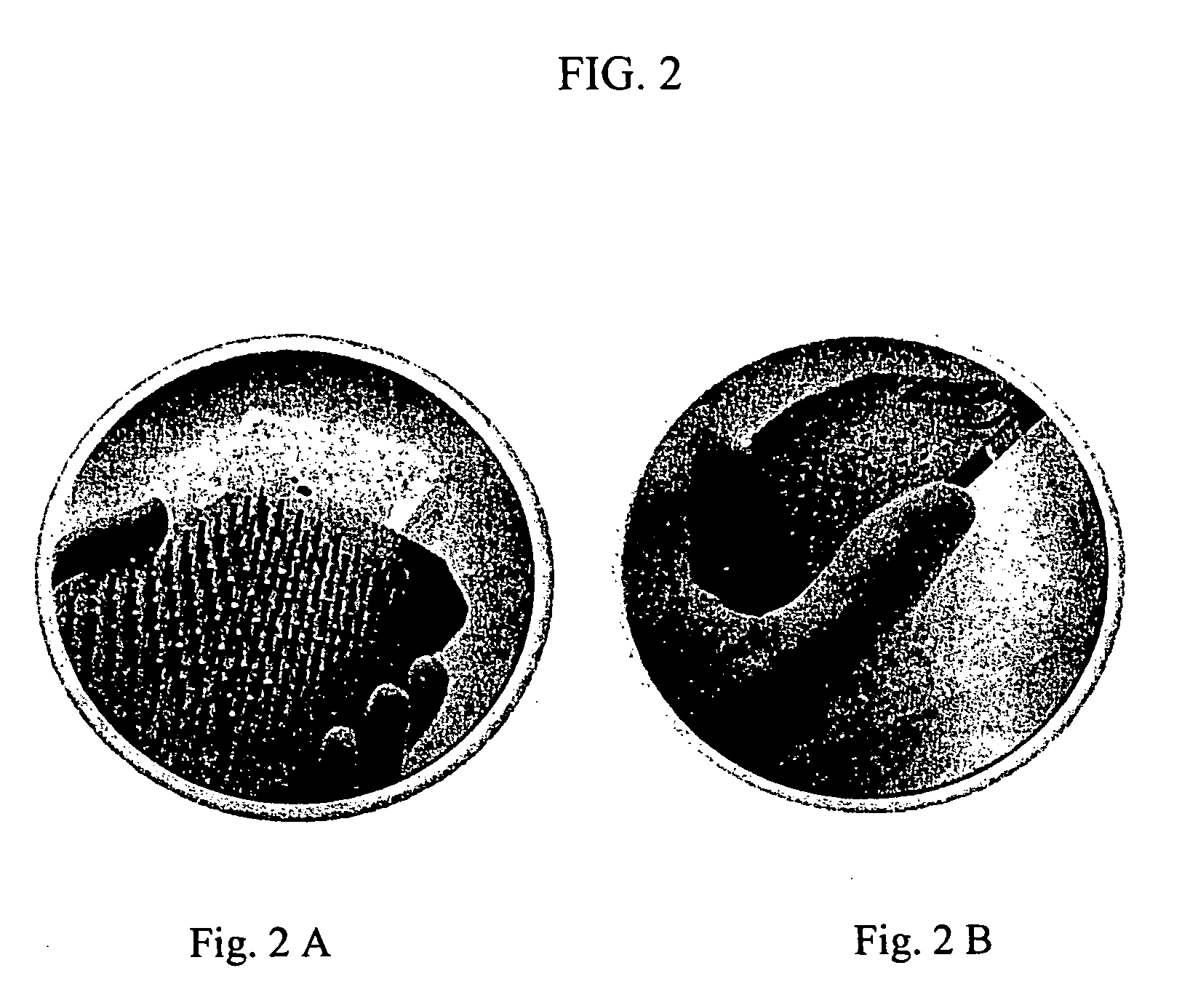
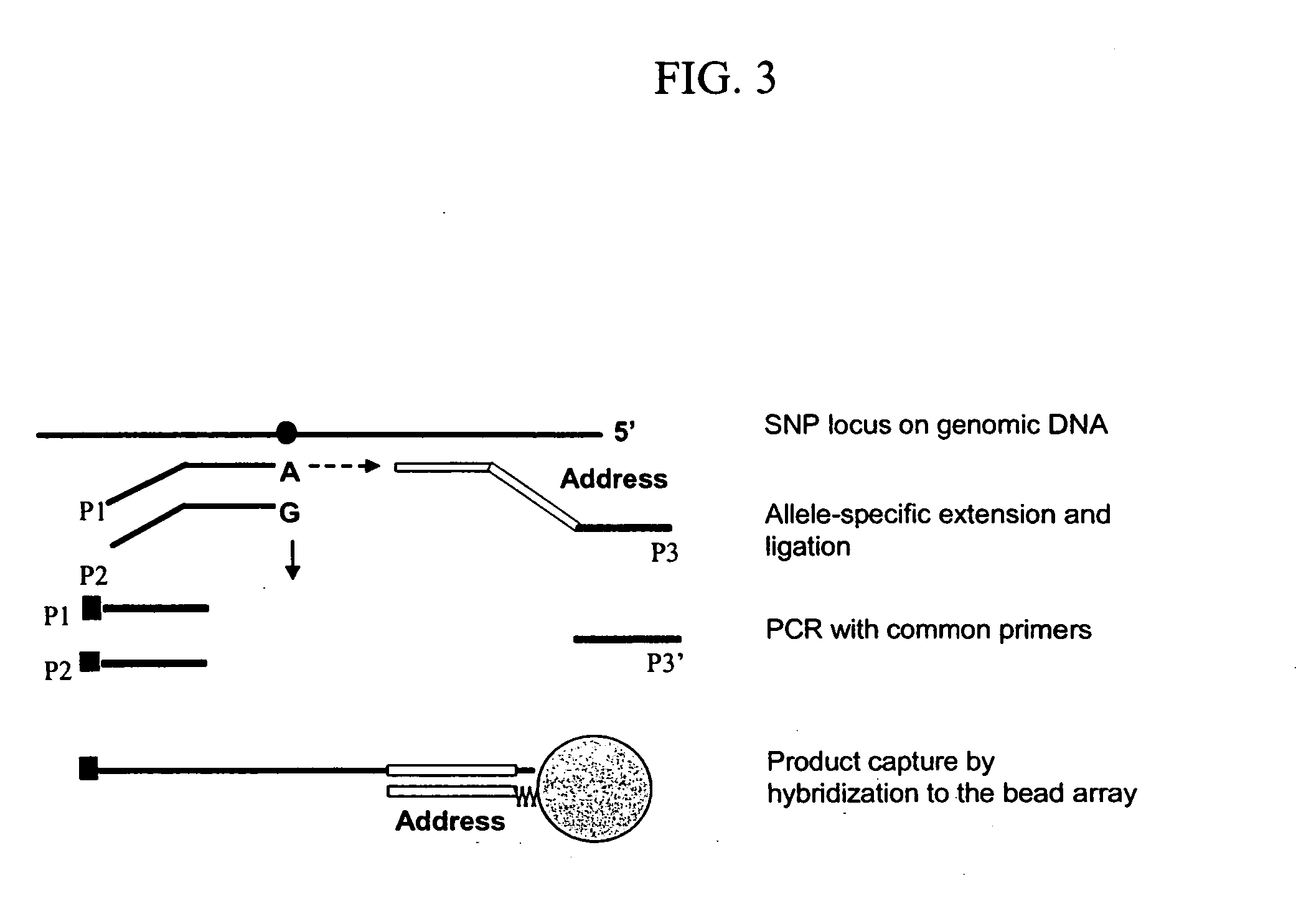
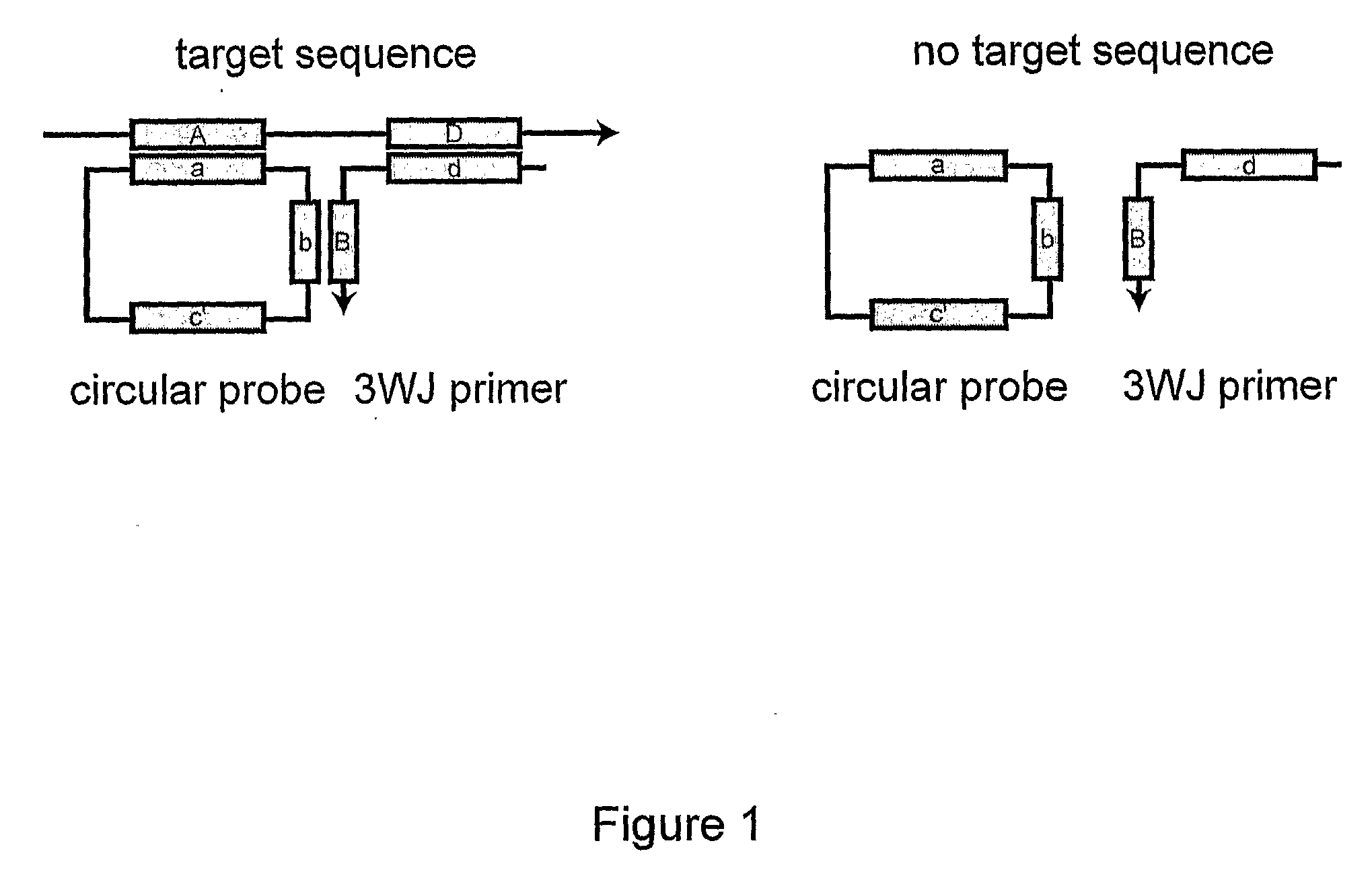
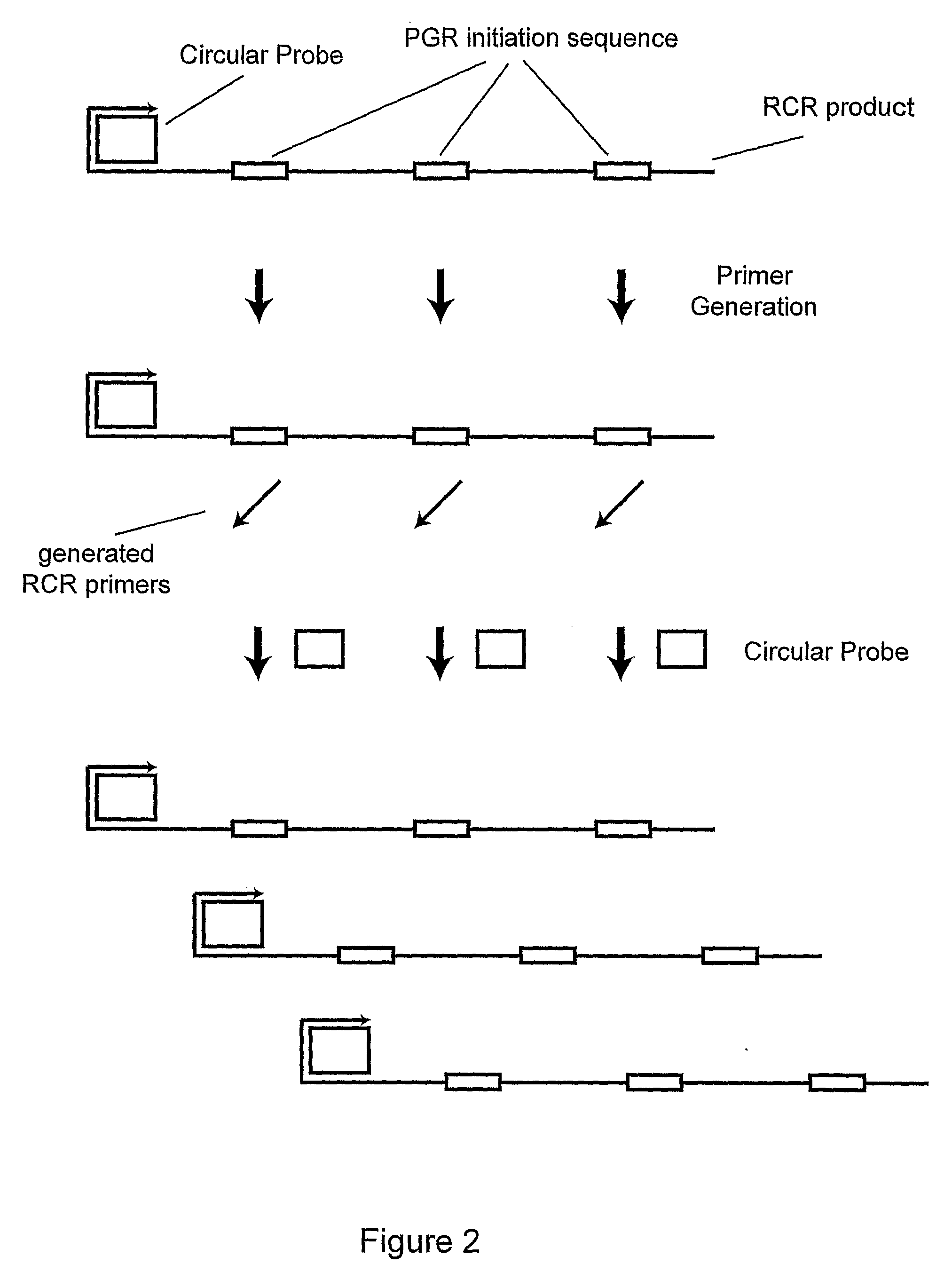
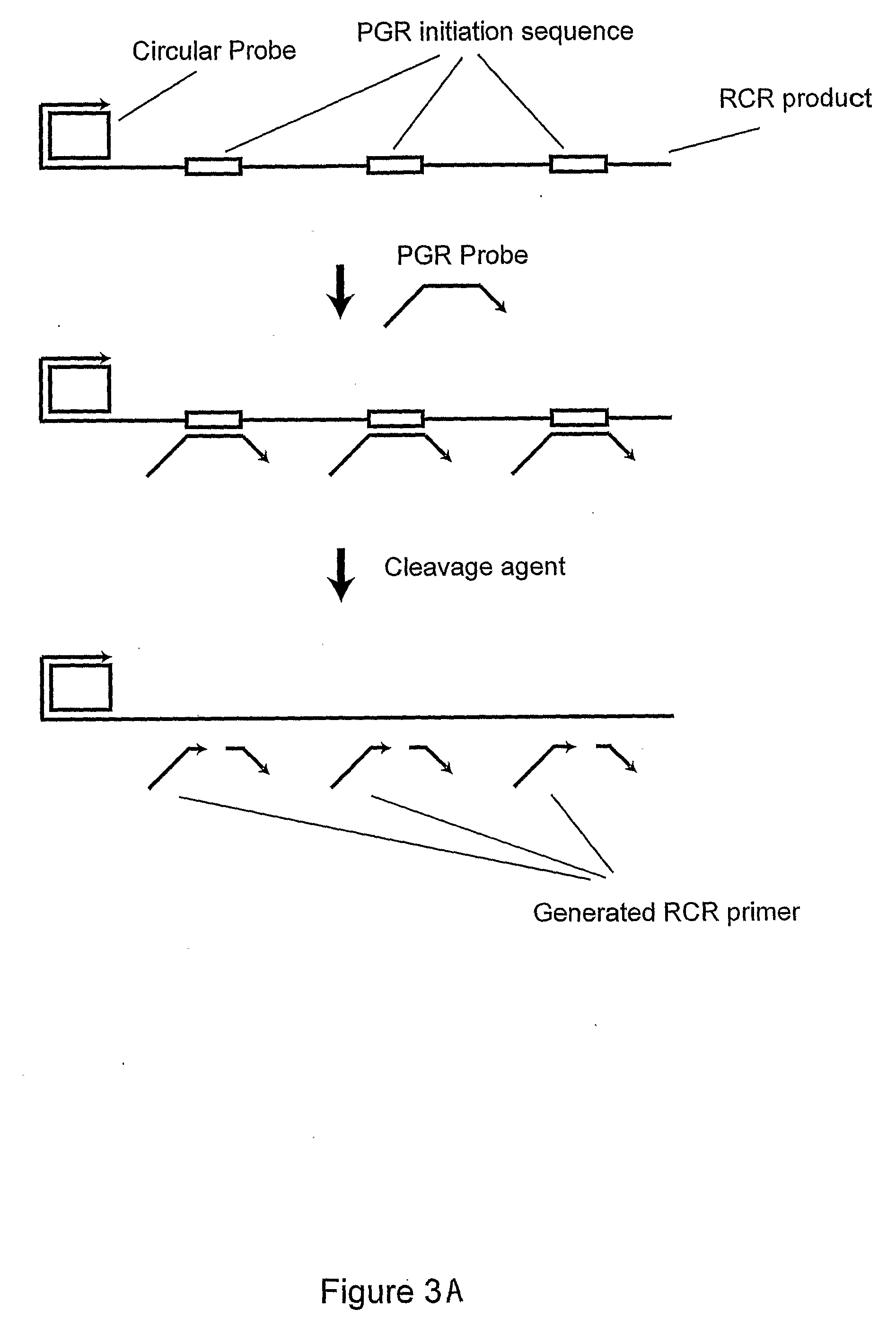
Primer generation rolling circle amplification
InactiveUS20090233277A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationNucleotide
A method of amplifying a nucleic acid is provided which comprises: generating a first nucleic acid primer from a first nucleic acid sequence; combining the first nucleic acid primer with a first polymerase and a first circular nucleic acid probe, wherein the first circular nucleic acid probe contains at least one antisense sequence to a second nucleic acid sequence and at least one antisense sequence to the first nucleic acid primer; producing at least one repeat of a sequence copy of the first circular nucleic acid probe by rolling circle amplification using the first polymerase, wherein the sequence copy contains at least the second nucleic acid sequence; generating a second nucleic acid primer from the second nucleic acid sequence; combining the second nucleic acid primer with a second polymerase and a second circular nucleic acid probe, where the second circular nucleic acid probe contains at least one antisense sequence to the second nucleic acid primer; and producing at least one repeat of a sequence copy of the second circular nucleic acid probe by rolling circle amplification using the second polymerase. The method may be employed to detect molecules of interest such as nucleic acid sequences, DNA methylation, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), proteins and posttranslational modifications. Furthermore, a ribbon probe is provided that comprises a circular nucleic acid probe and a nucleic acid lock probe, wherein: the nucleic acid lock probe contains at least a cleavable linker, and the circular nucleic acid probe and the lock probe are unable to dissociate without cleaving the cleavable linker.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
Method of analysis allowing avoidance of surgery
ActiveUS20170275702A1Prevent removalAvoid surgeryMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisDNA methylationCervix
A multi-gene-based assay for analysis of the following: (a) oncogene expression; (b) DNA methylation of tumor suppressor genes; (c) non-coding RNA expression (microRNA profiling); and (d) long non-coding RNA expression in cancer samples is disclosed. The assay method and device for conducting the assay are applicable to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various cancers such as lung, breast, colorectal, prostate, liver, bladder; kidney, cervix, pancreatic, gastric, brain, oral, endometrium, and ovary. The assay methods allow avoidance of surgery to remove cancerous tissue.
Owner:GENEVERIFY INC
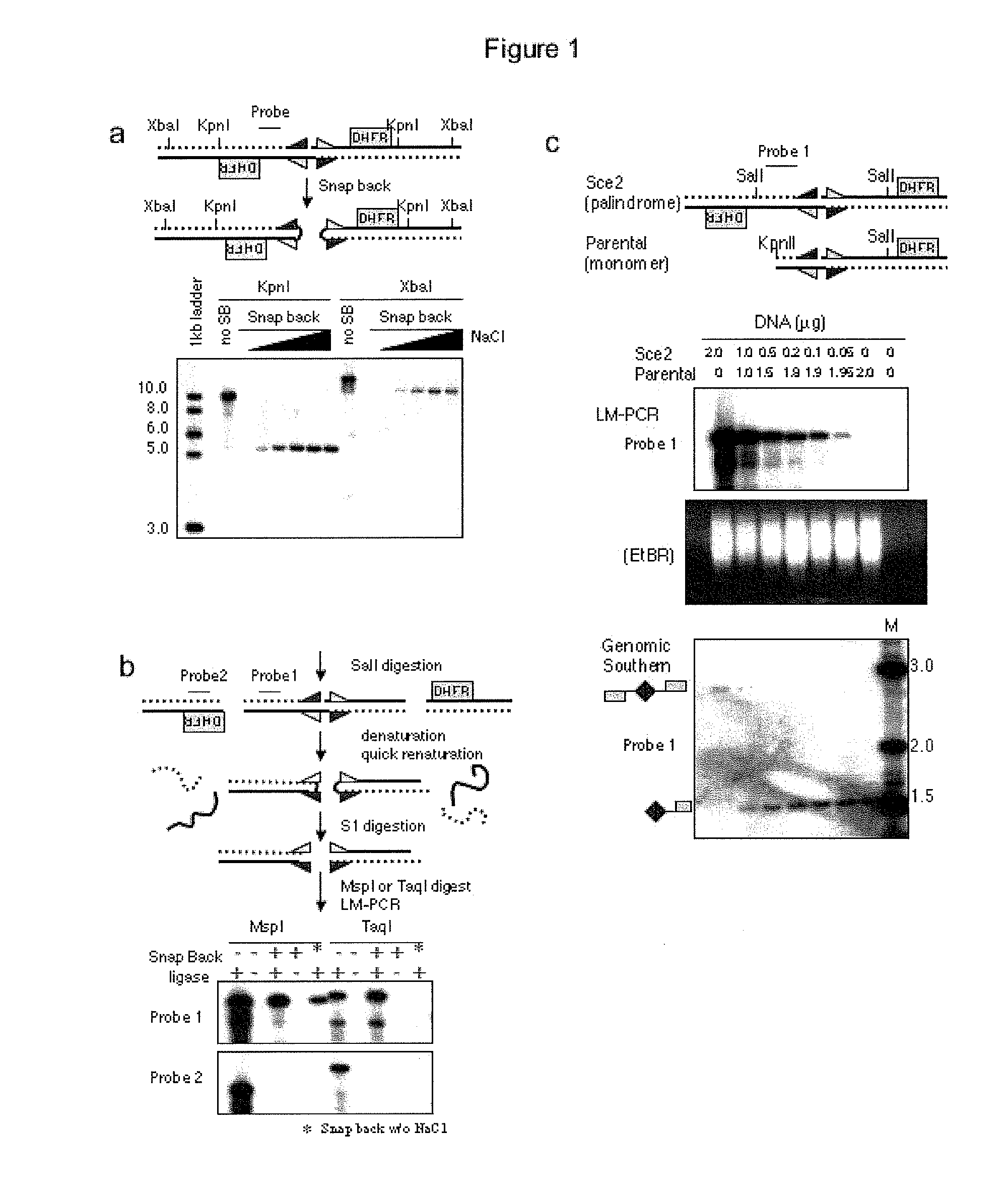
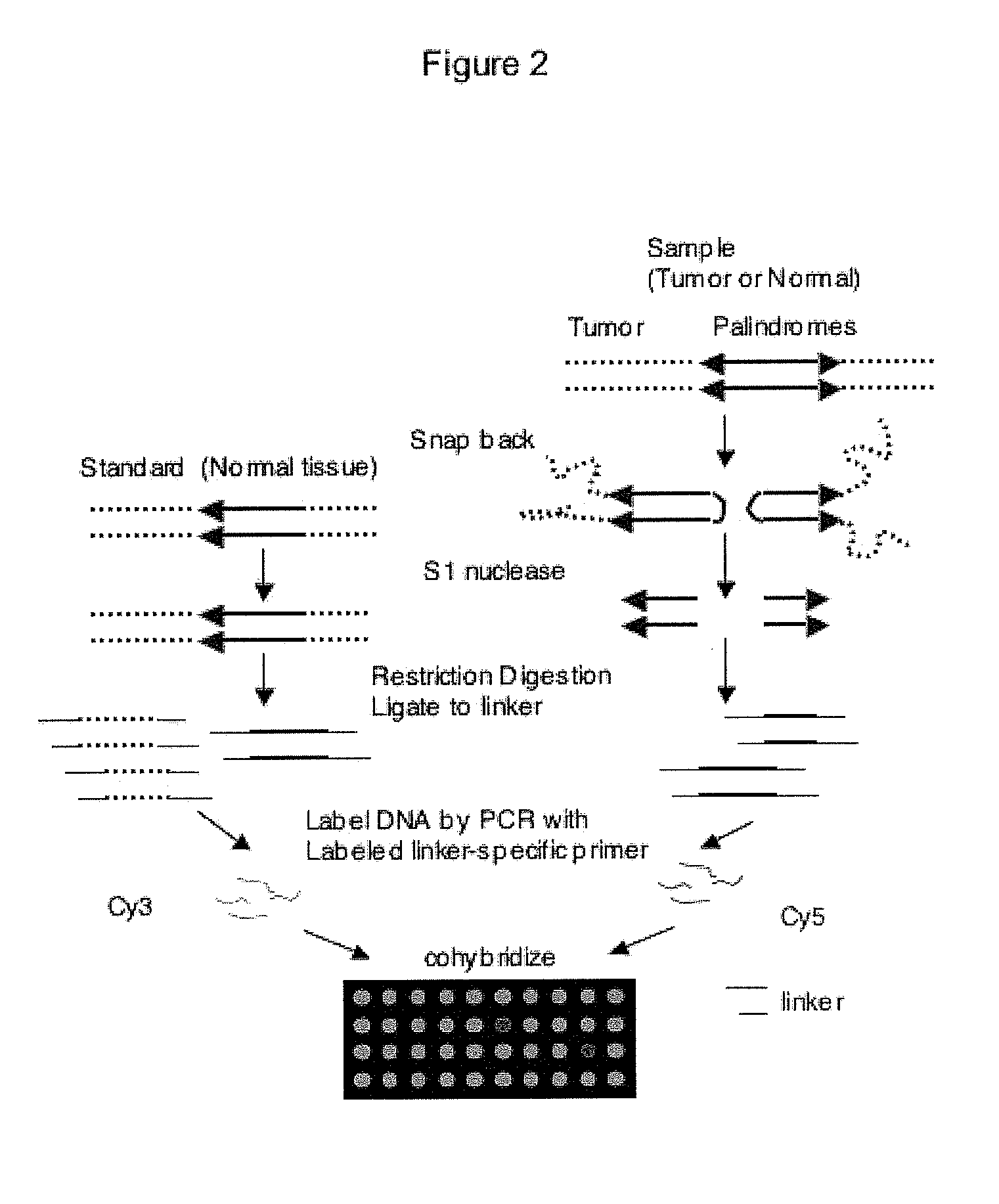
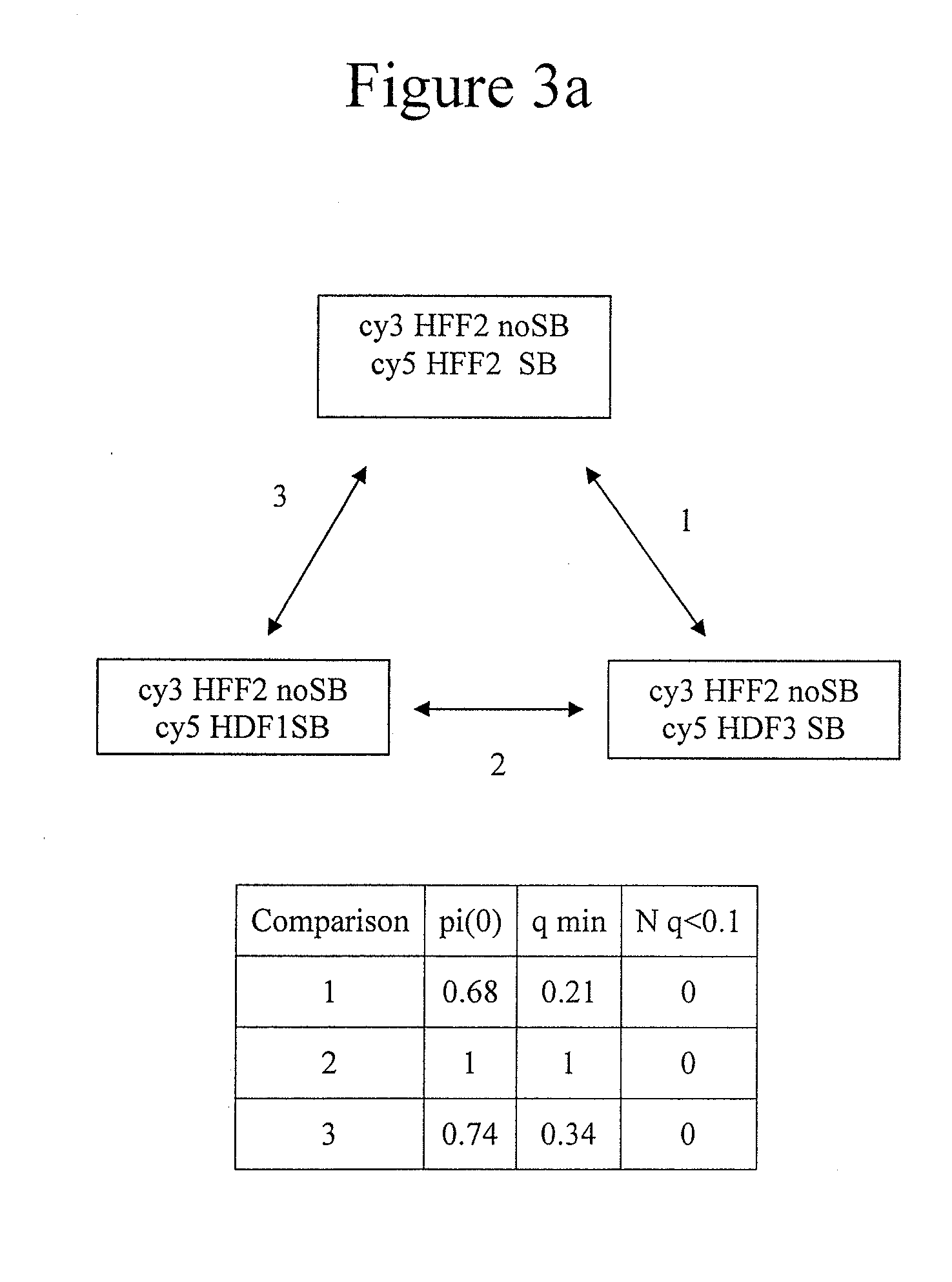
Genome-wide analysis of palindrome formation and DNA methylation
The present disclosure provides methods for detecting the genome-wide presence of methylated DNA and palindrome formation. The present disclosure also provides methods for specific enrichment of methylated DNA or DNA having a DNA palindrome. These methods have demonstrated that somatic palindromes and methylated DNA occur frequently and are widespread in human cancers. Individual tumor types have a characteristic non-random distribution of palindromes in their genome and a small subset of the palindromic loci are associate with gene amplification. The disclosed method can be used to define the plurality of genomic DNA palindromes and regions having methylated DNA associated with various tumor types and can provide methods for the classification of tumors, and the diagnosis, early detection of cancer as well as the monitoring of disease recurrence and assessment of residual disease.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Methods and materials for noninvasive detection of colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease
InactiveUS20130244235A1Improve discriminationSensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationMammal
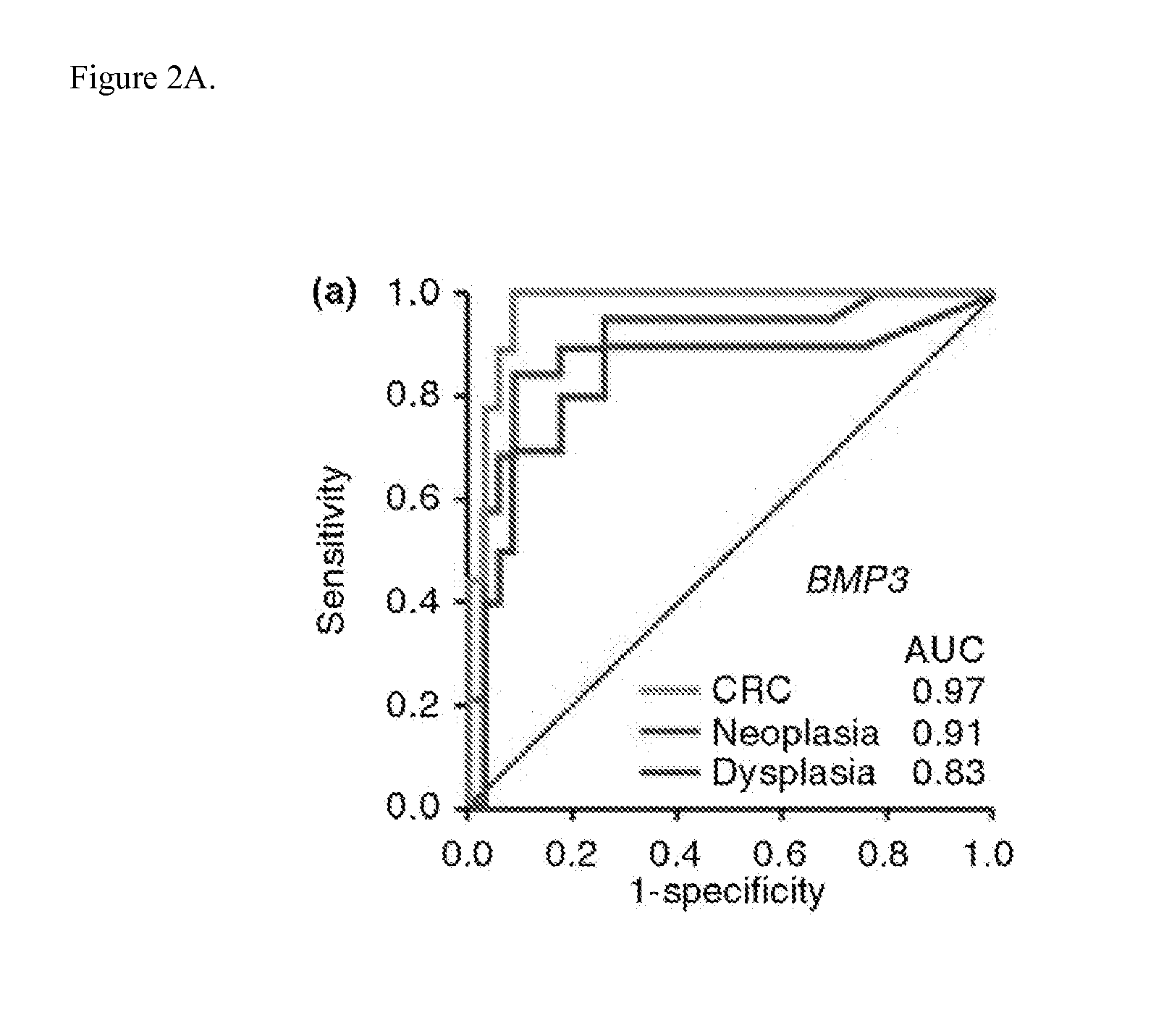
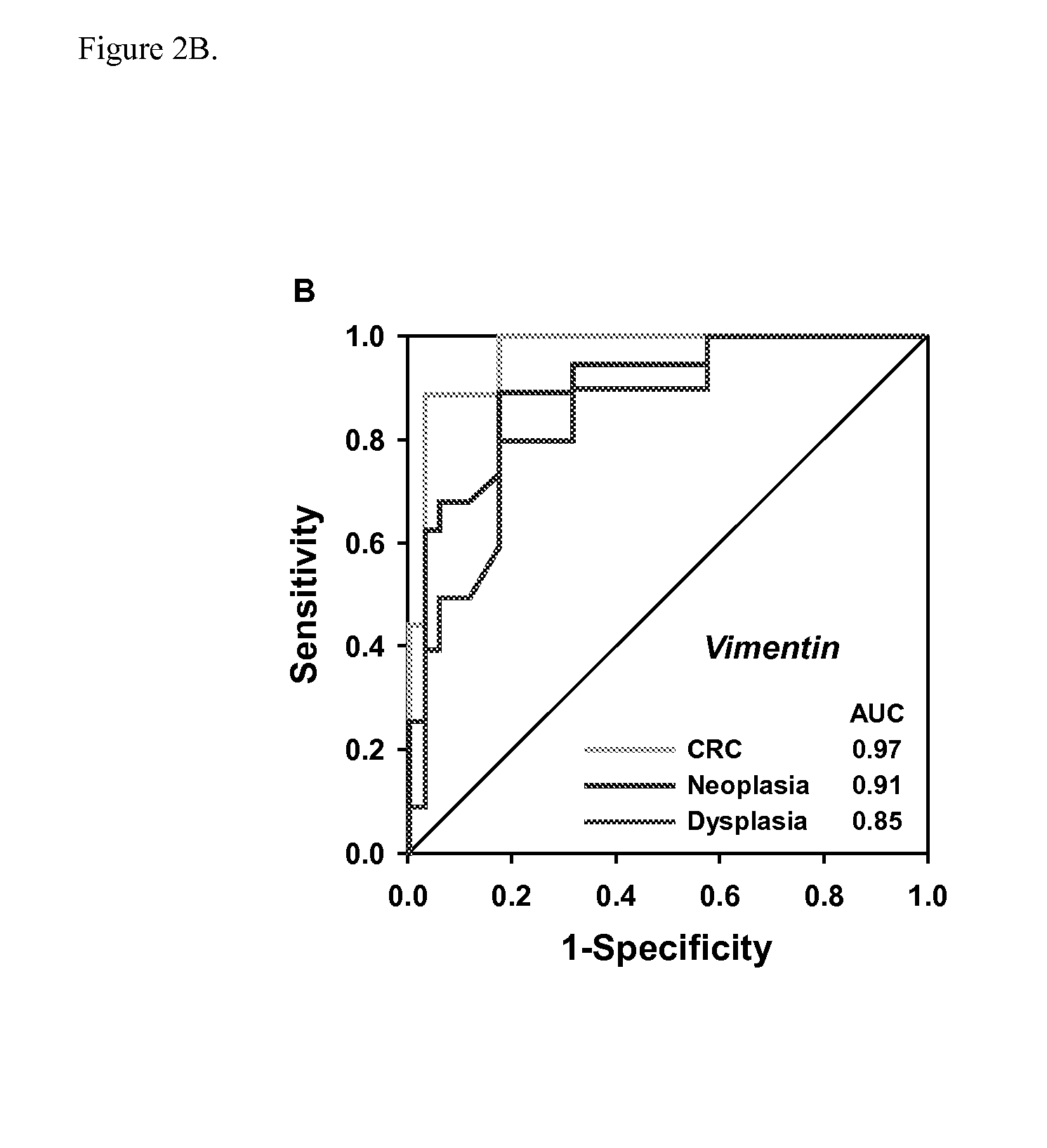
The present invention provides methods and materials related to the detection of colorectal neoplasia (CRN) associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The present invention provides markers specific for colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease in or associated with a subject's stool sample. In particular, the present invention provides methods and materials for identifying mammals (e.g., humans) having colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease by detecting the presence and level of indicators of colorectal neoplasia such as, for example, epigenetic alterations (e.g., DNA methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation in coding or regulatory regions of BMP3, NDRG4, vimentin, EYA4) in DNA from a stool sample obtained from the mammal.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
DNA methylation markers for metastatic prostate cancer
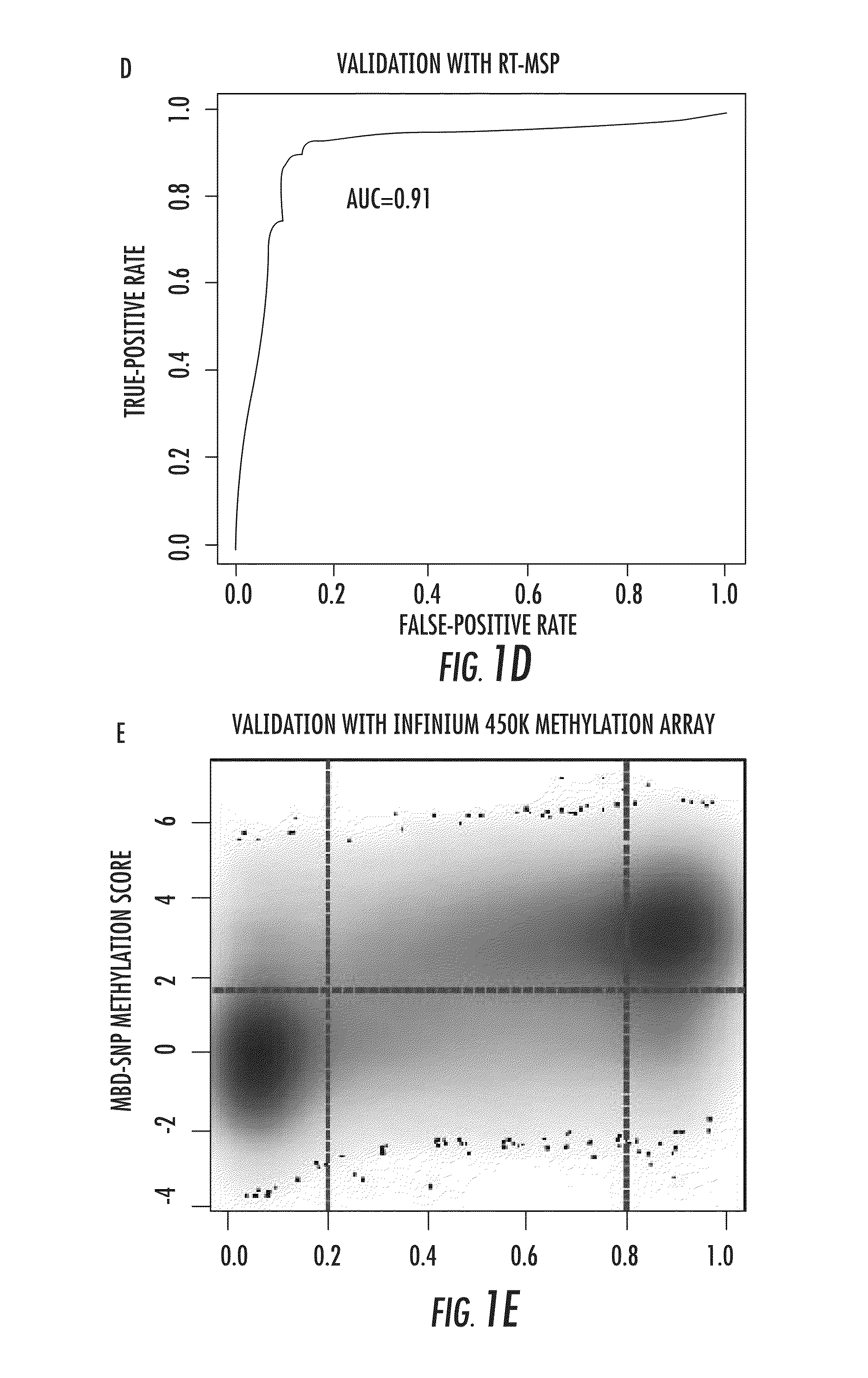
InactiveUS20140274767A1Rapid and cost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationGenome scale
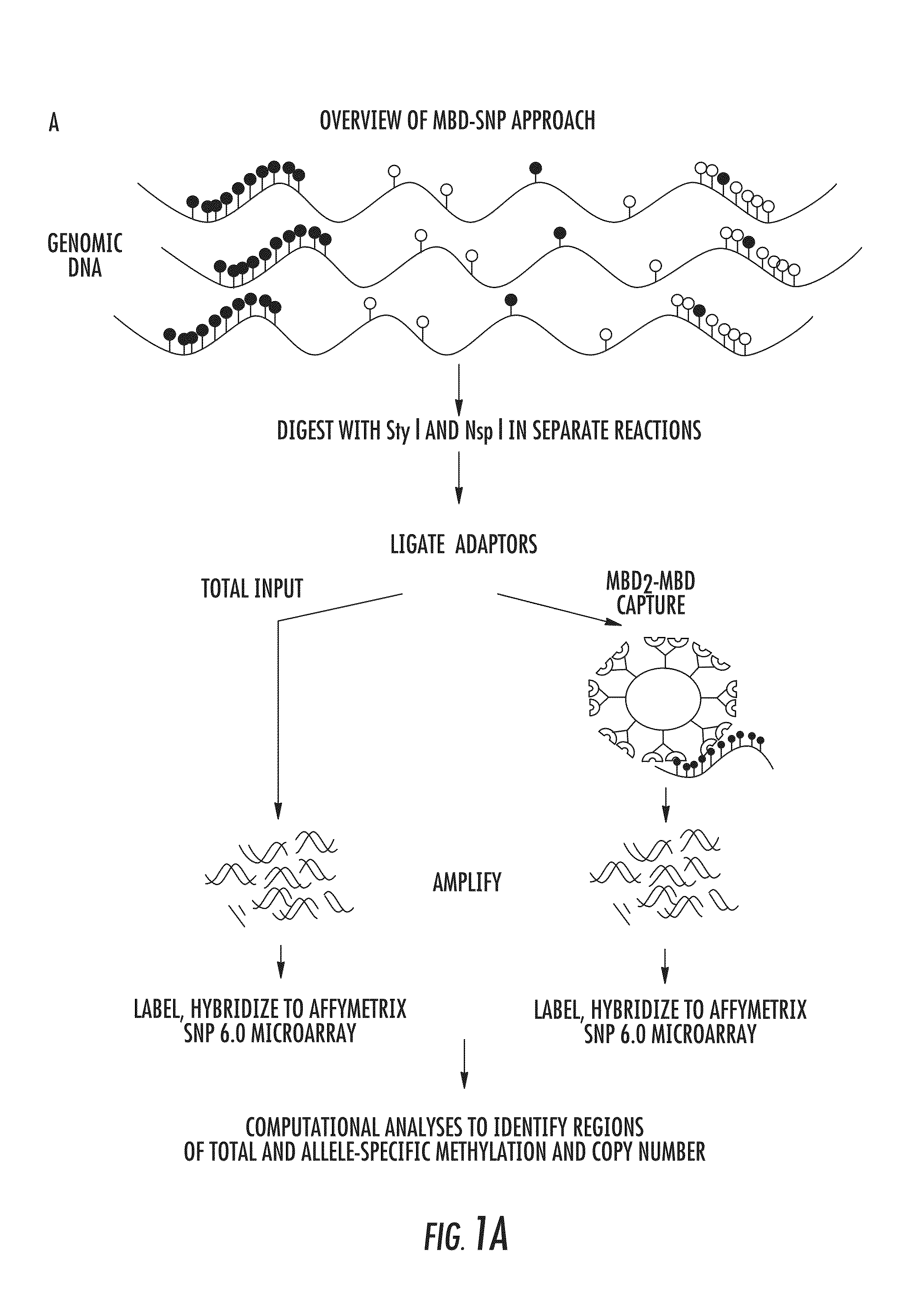
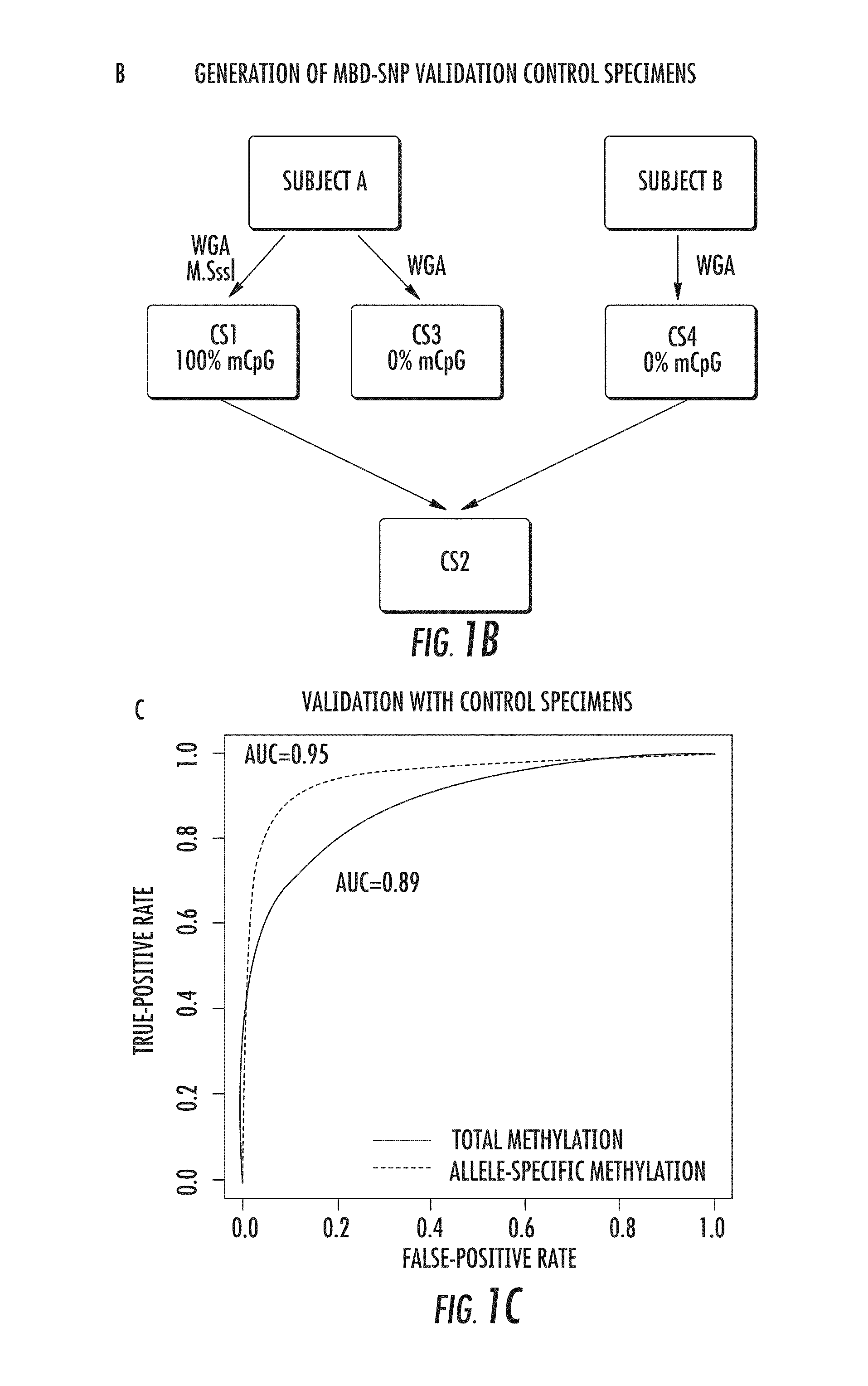
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods and compositions useful for assessing prostate cancer. In a specific embodiment, present inventors have developed and applied a new technology and associated computation methods enabling simultaneous genome-scale analysis of genetic (copy number) and epigenetic (total methylation (TM) and allele-specific methylation (ASM) alternation, This method, called MBD-SNP, features affinity enrichment or methylated genomic DNA fragments using a methyl-binding domain polypeptide.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of copying the methylation pattern of DNA during isothermal amplification and microarrays
InactiveUS7449297B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
A method for copying the methylation patterns of molecules of genomic DNA (MGD) during isothermal amplification of the MGD comprising obtaining MGD, copying the methylation patterns of the MGD using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the MGD using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a method for copying the methylation patterns in double-stranded DNA molecules during isothermal amplification of the DNA molecules comprising obtaining DNA molecules, contacting the DNA molecules with transposable elements and an enzyme, which can randomly insert the transposable elements into the DNA molecules, copying the methylation patterns of the DNA molecules using a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, while isothermally amplifying the DNA molecules using a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, under conditions that simultaneously promote activity of the DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme and the DNA polymerase; a buffer comprising a divalent ion, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), primers, and S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM); and a composition comprising a DNA methylation-maintenance enzyme, a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, and the buffer.
Owner:EUCLID DIAGNOSTICS
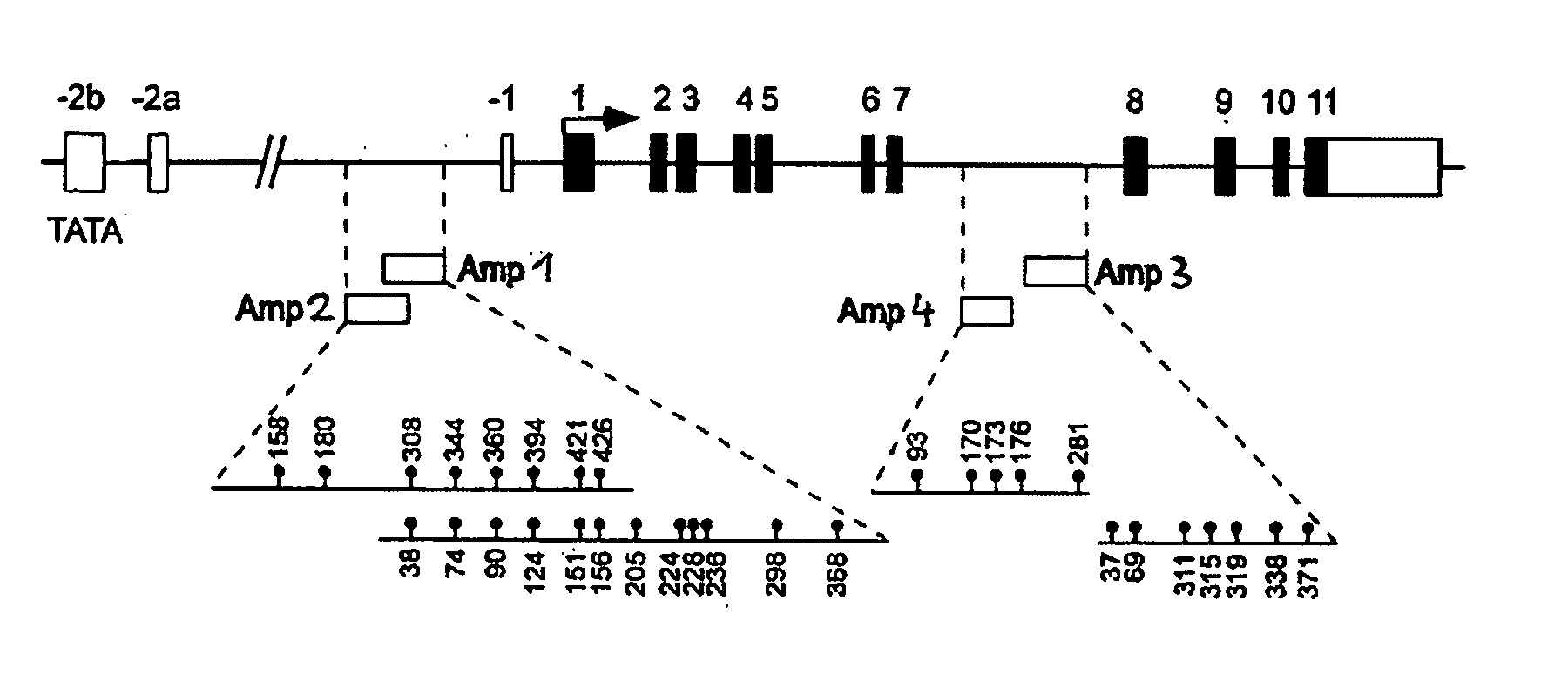
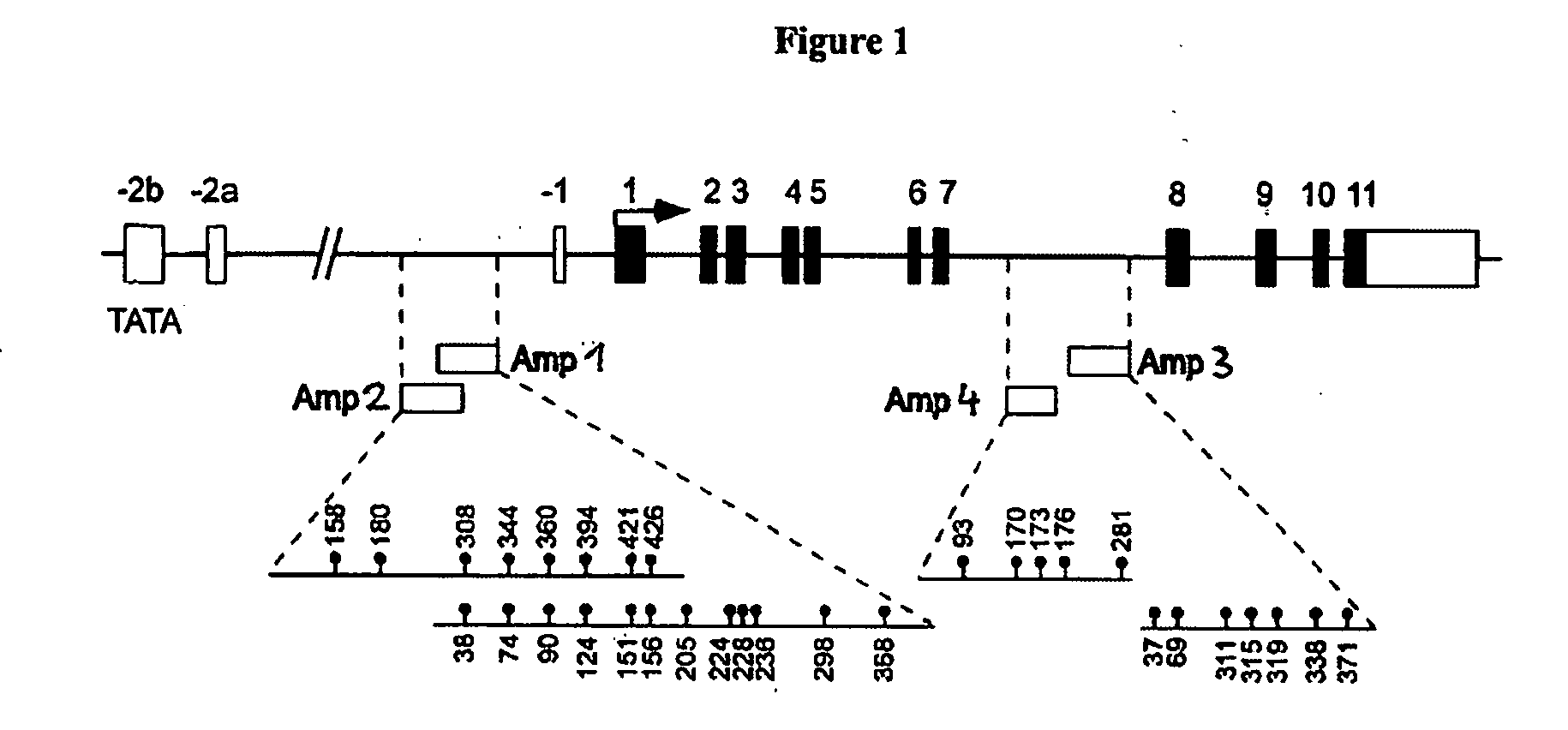
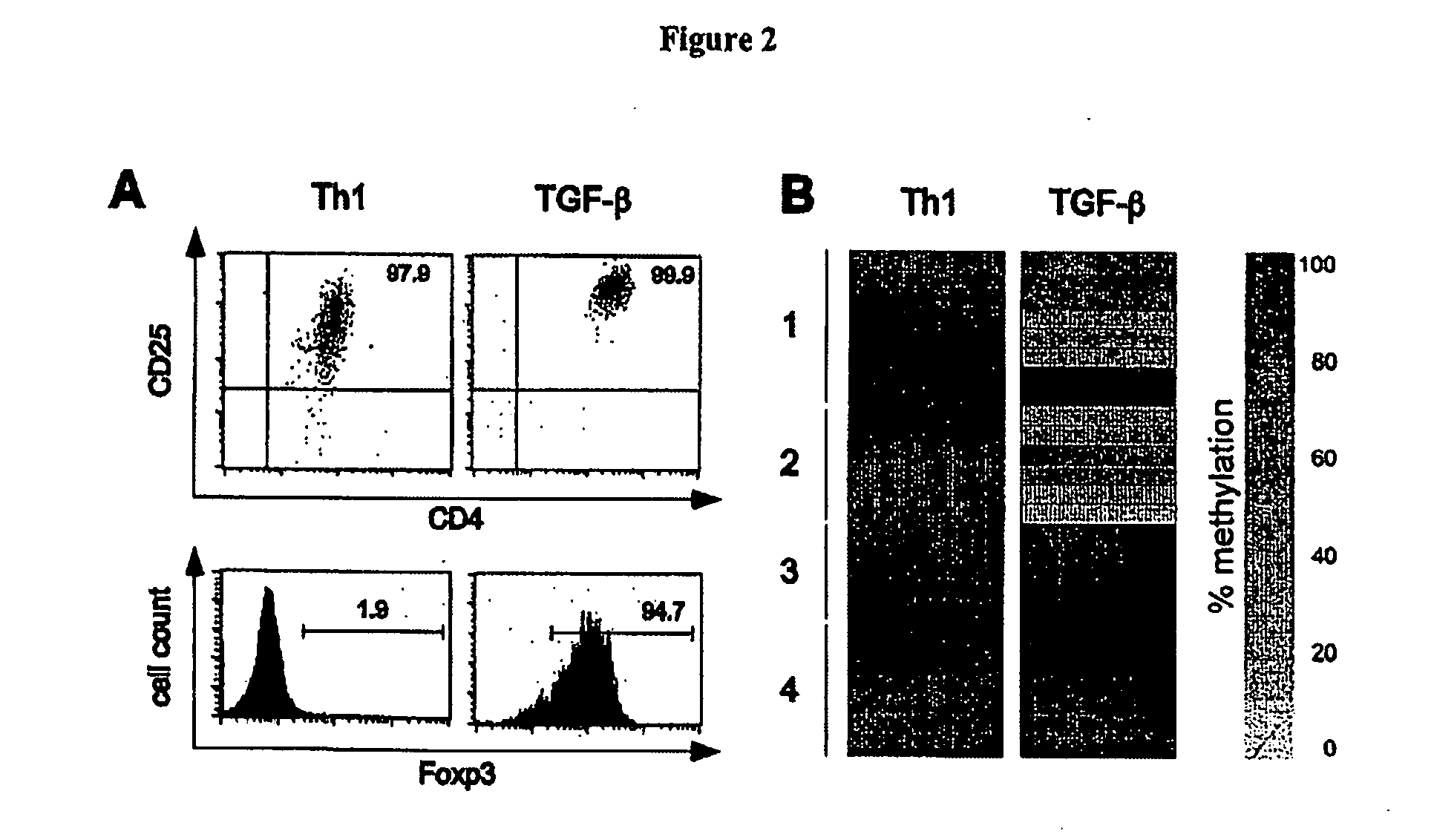
Detection and quality control of regulatory T cells through DNA-methylation analysis of the Foxp3 gene
ActiveUS20070269823A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a method, in particular an in vitro method for identifying FoxP3-positive regulatory T cells, preferably CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells of a mammal, comprising analysing the methylation status of at least one CpG position in the gene foxp3 or an orthologous or paralogous gene thereof, and the use of DNA-methylation analysis of the gene of the transcription factor FoxP3 for a detection and quality assurance and control of regulatory T cells. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a kit for performing the above methods as well as respective uses.
Owner:PRECISION FOR MEDICINE GMBH +1
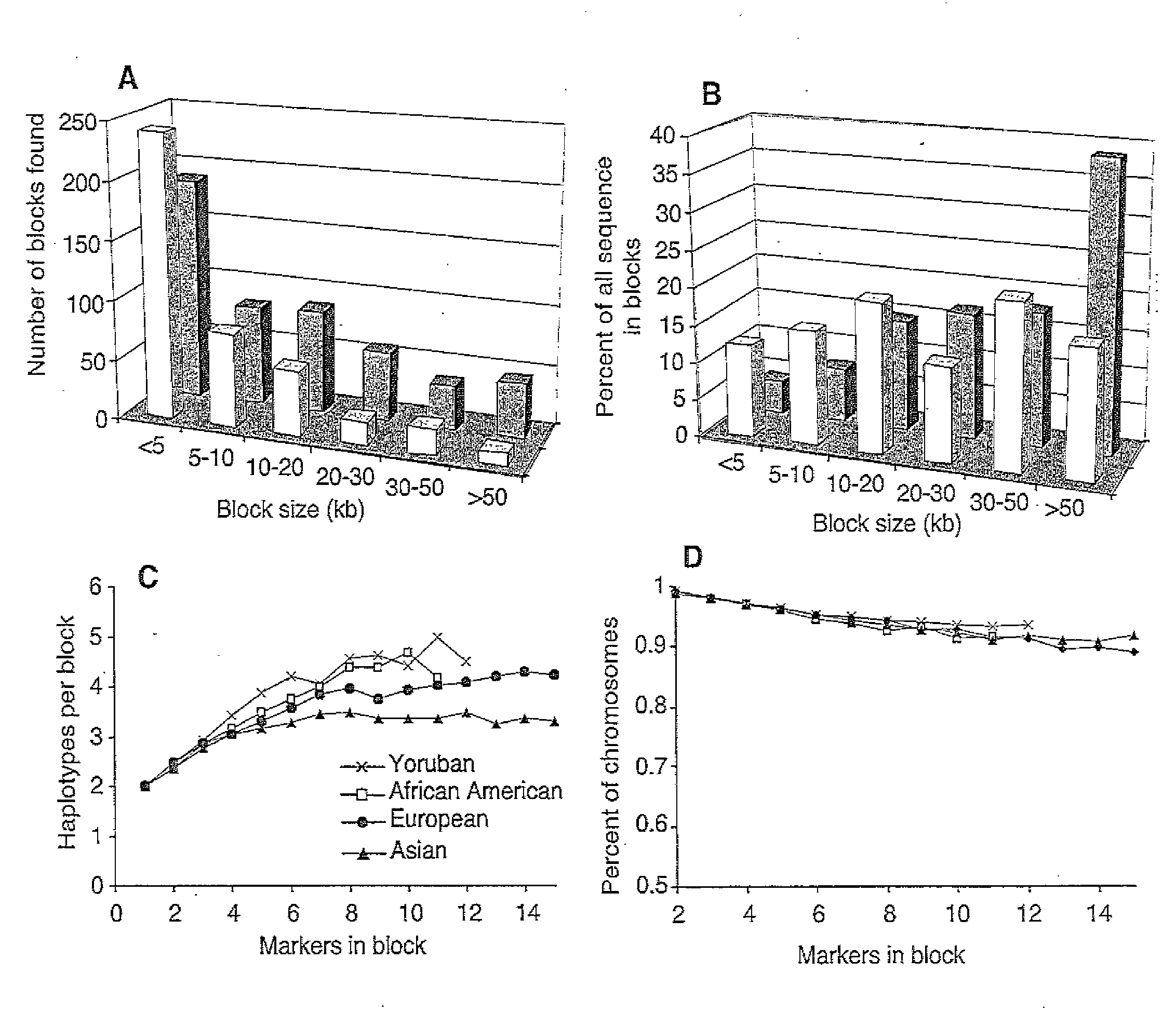
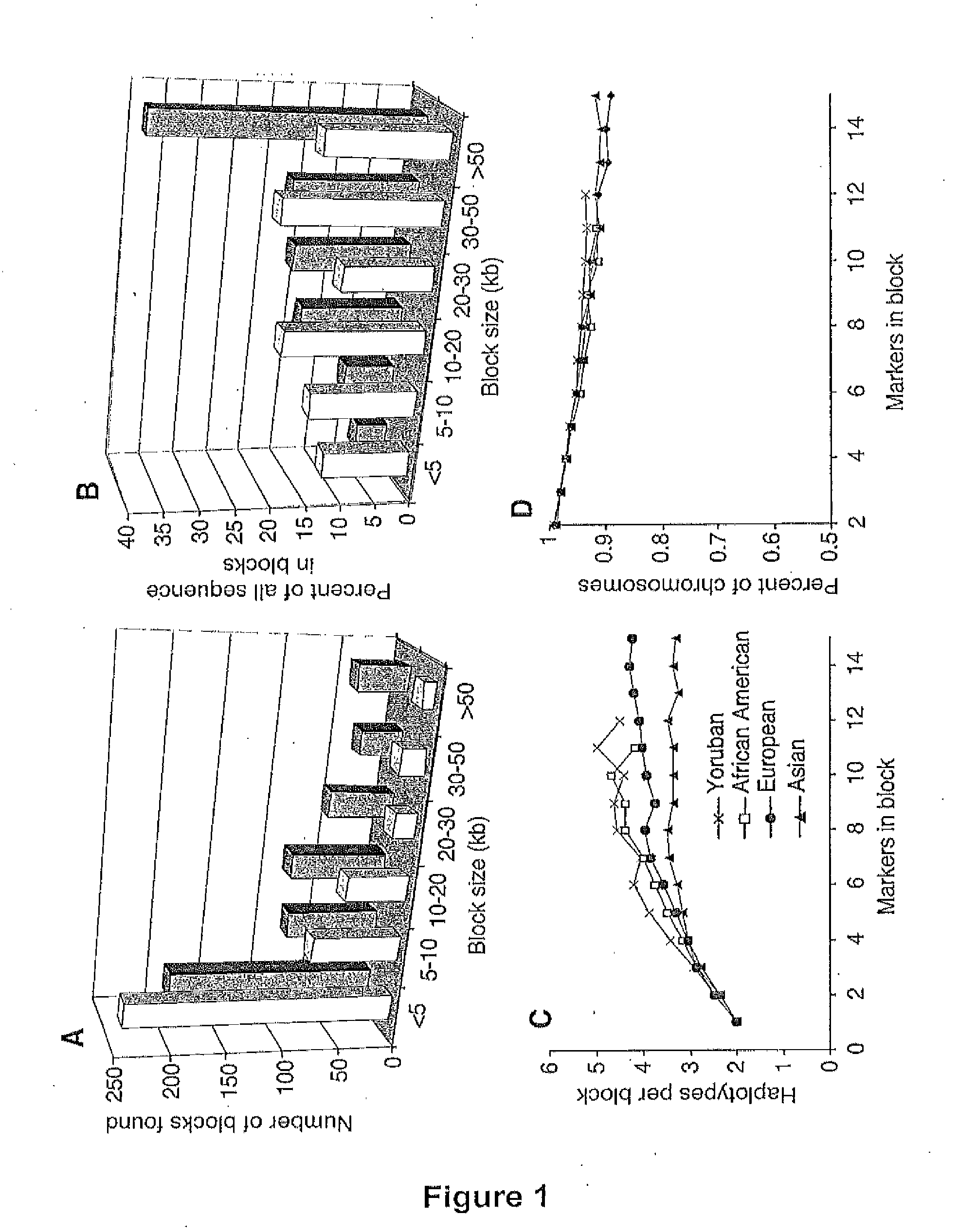
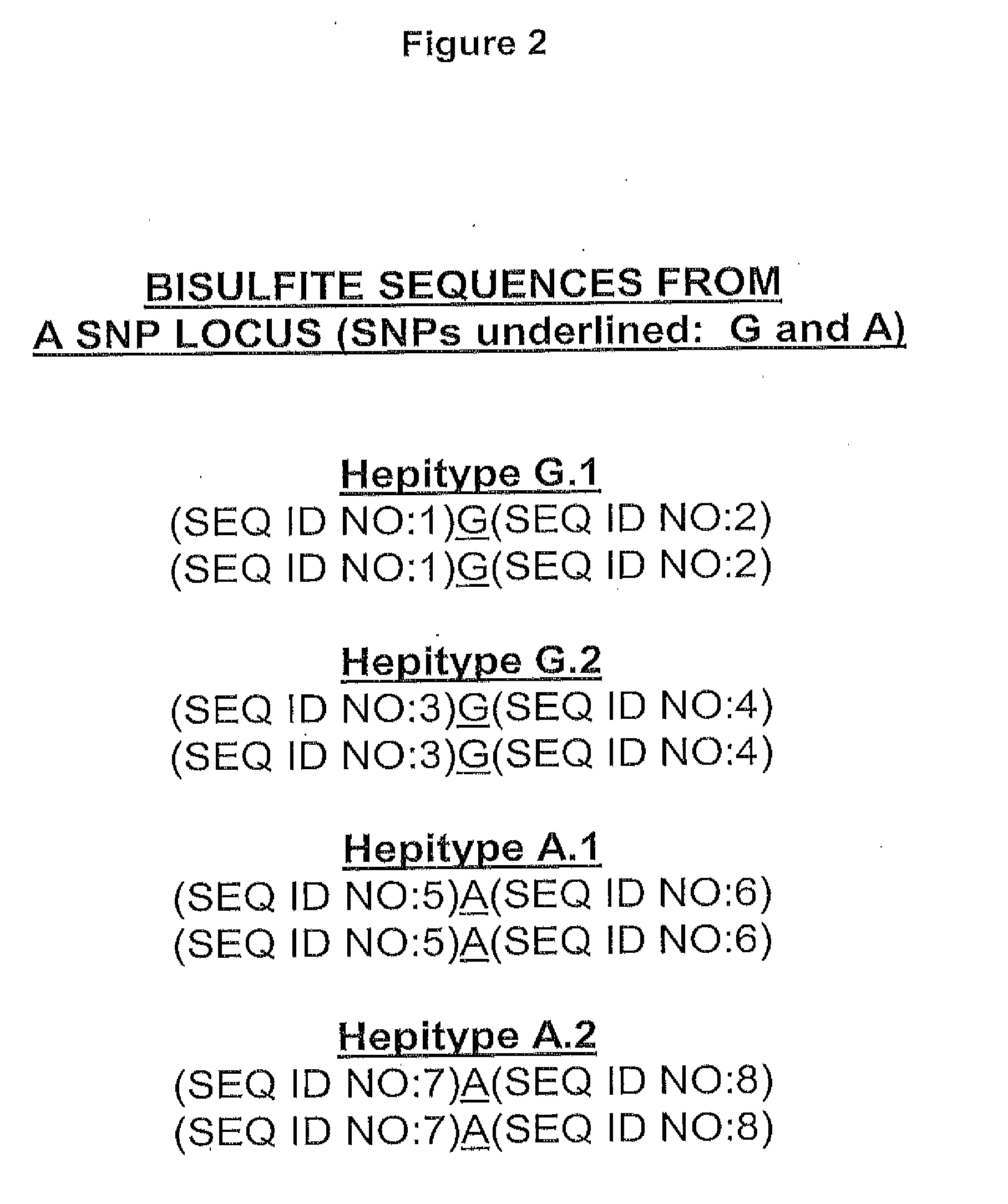
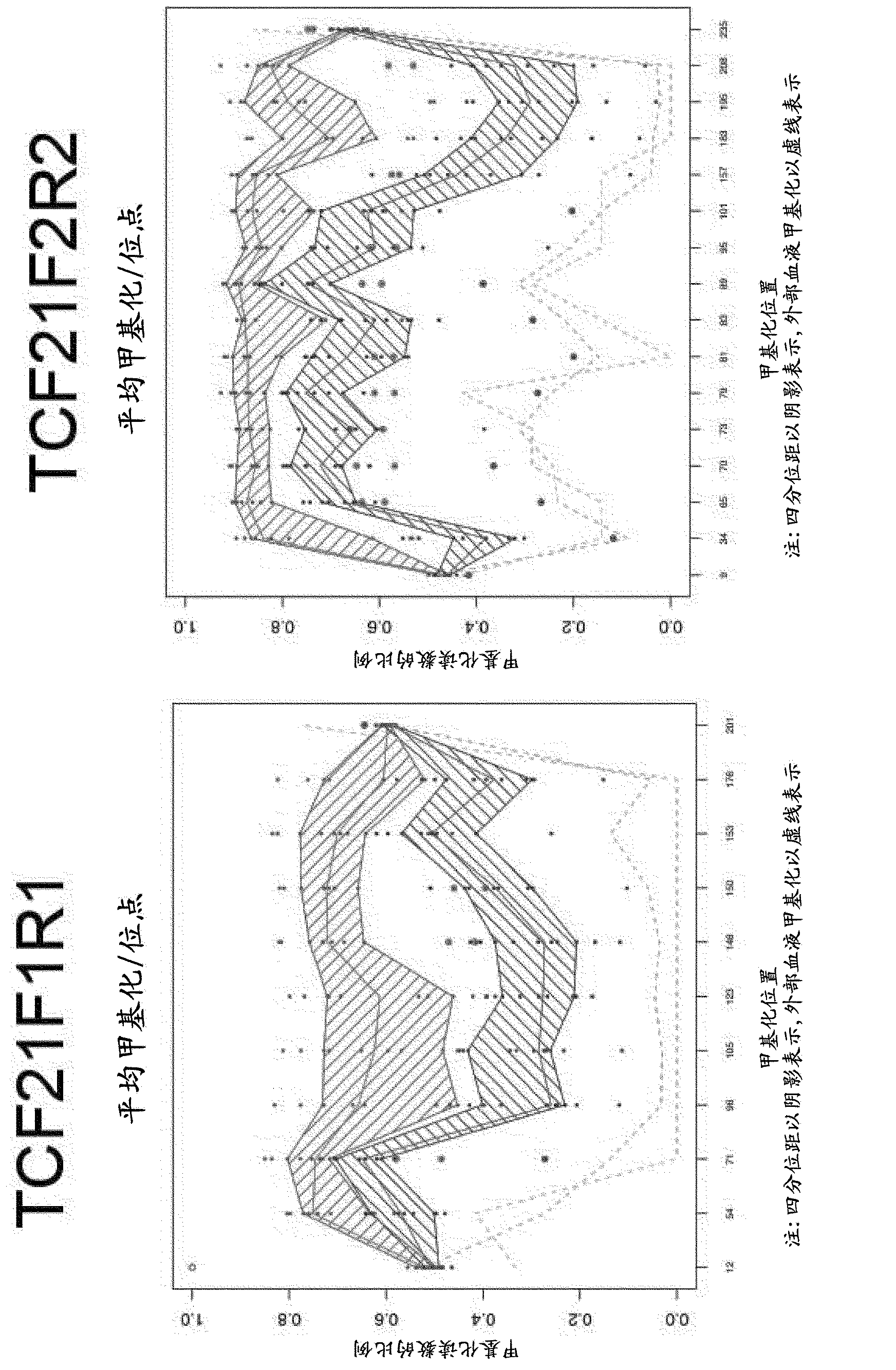
Long Hepitype Distribution (LHD)
The invention includes a method of creating a sequence information framework that defines the range of epigenetic configurations of individual DNA strands in any diploid organism in which DNA methylation is prevalent. The invention also includes a method of generating DNA descriptors referred to as long hepitype distributions (LHDs).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
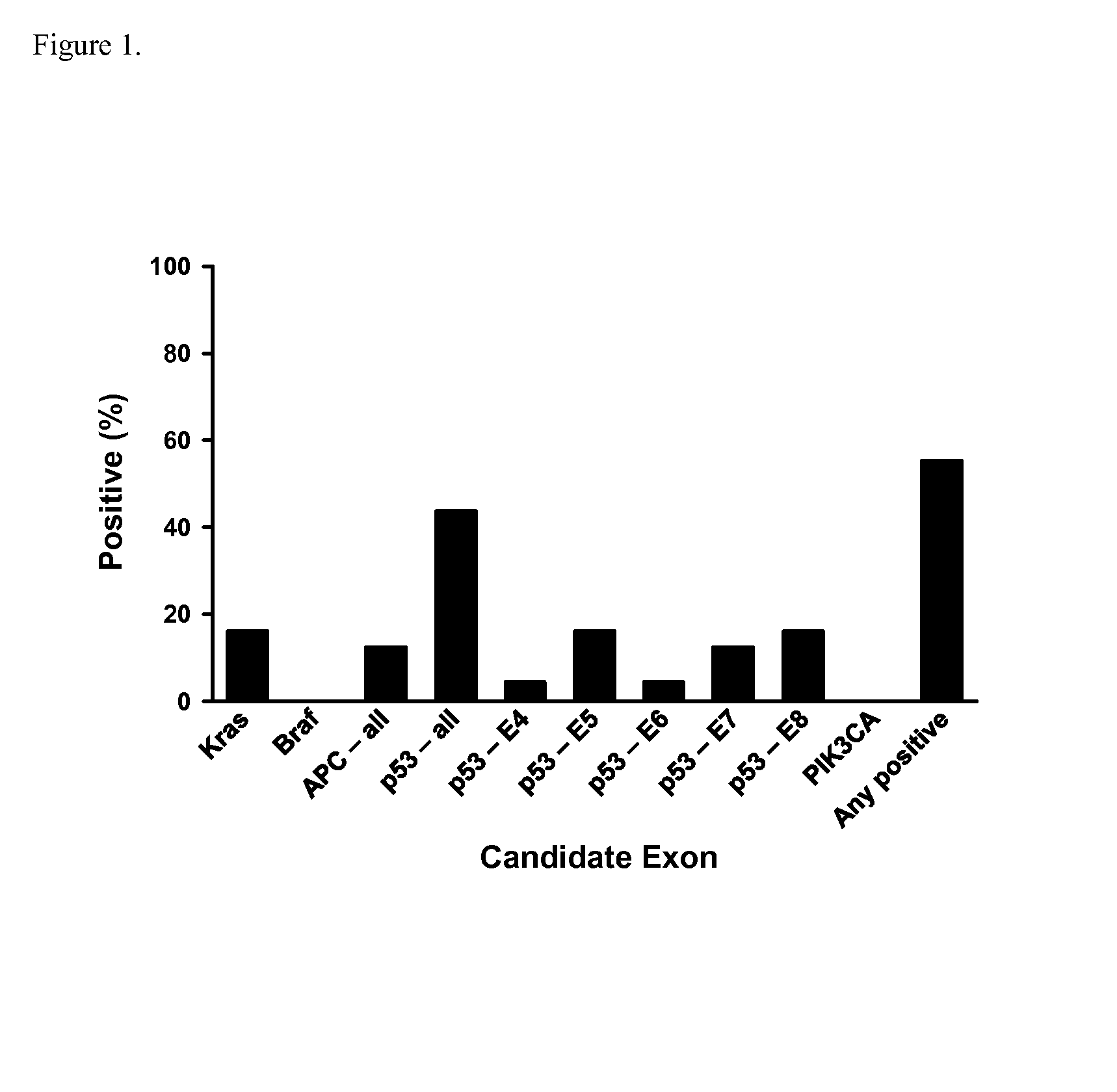
Epigenetic markers of colorectal cancers and diagnostic methods using the same
ActiveCN103314114ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationAdenocarcinoma
The present invention relates generally to nucleic acid molecules in respect of which changes to DNA methylation levels are indicative of the onset or predisposition to the onset of a neoplasm. More particularly, the present invention is directed to nucleic acid molecules in respect of which changes to DNA methylation levels are indicative of the onset and / or progression of a large intestine neoplasm, such as an adenoma or adenocarcinoma. The DNA methylation status of the present invention is useful in a range of applications including, but not limited to, those relating to the diagnosis and / or monitoring of colorectal neoplasms, such as colorectal adenocarcinomas. Accordingly, in a related aspect the present invention is directed to a method of screening for the onset, predisposition to the onset and / or progression of a neoplasm by screening for modulation in DNA methylation of one or more nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:CLINICAL GENOMICS PTY LTD +1
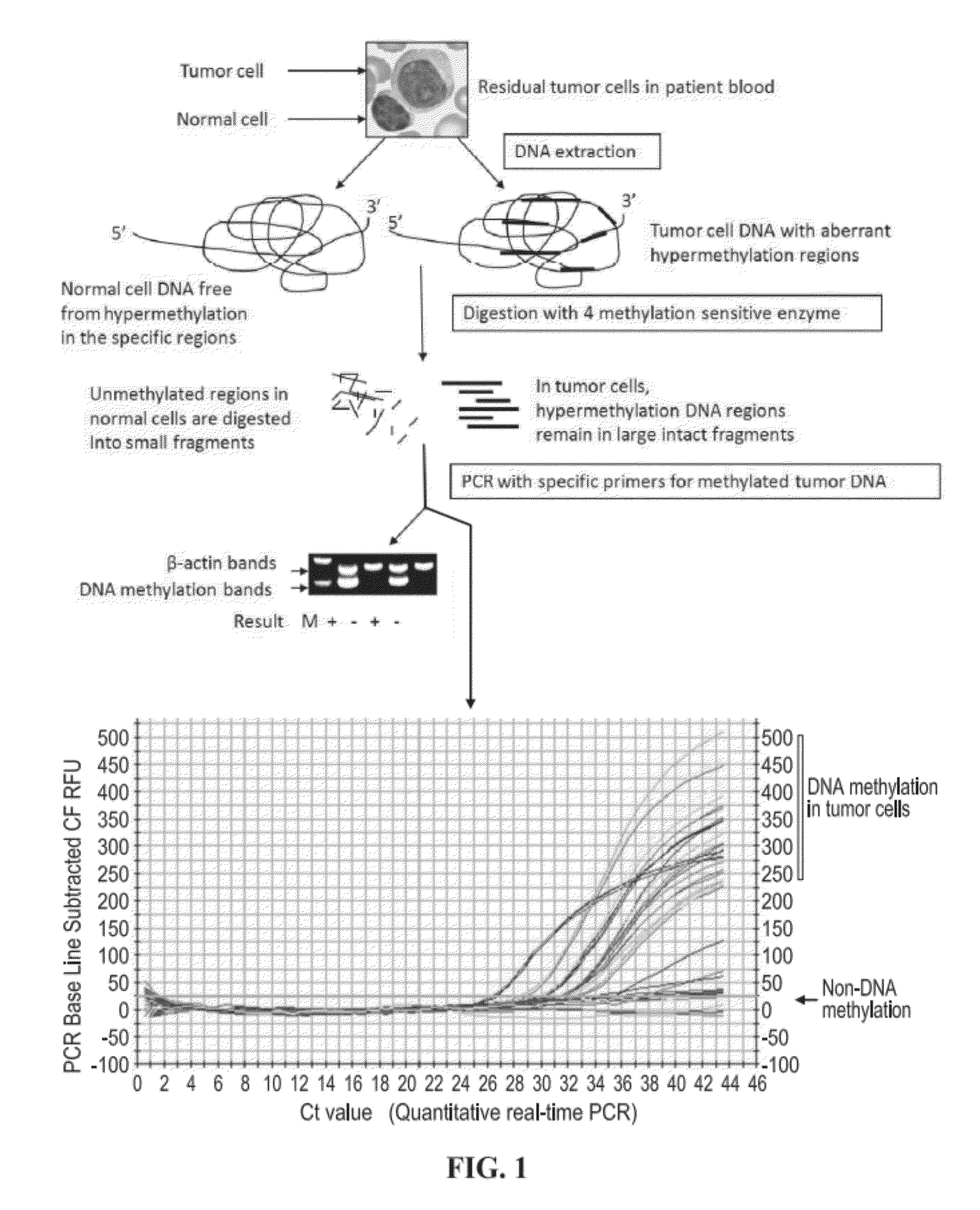
Methods for detecting rare circulating cancer cells using DNA methylation biomarkers
Provided are new and improved methods for detecting circulating tumor cells and tumor cell DNA in patient blood or other biofluid samples. Particular aspects comprise three steps: DNA extraction from patient samples, DNA digestion with multiple selected methylation-sensitive enzymes, and target amplification by a conventional or a real-time PCR with specific probe and / or primers. Also provided are a total of 40 tumor-specific DNA methylation loci as biomarkers having substantial utility and specificity in major types of human malignancies including hematopoietic and solid tumors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
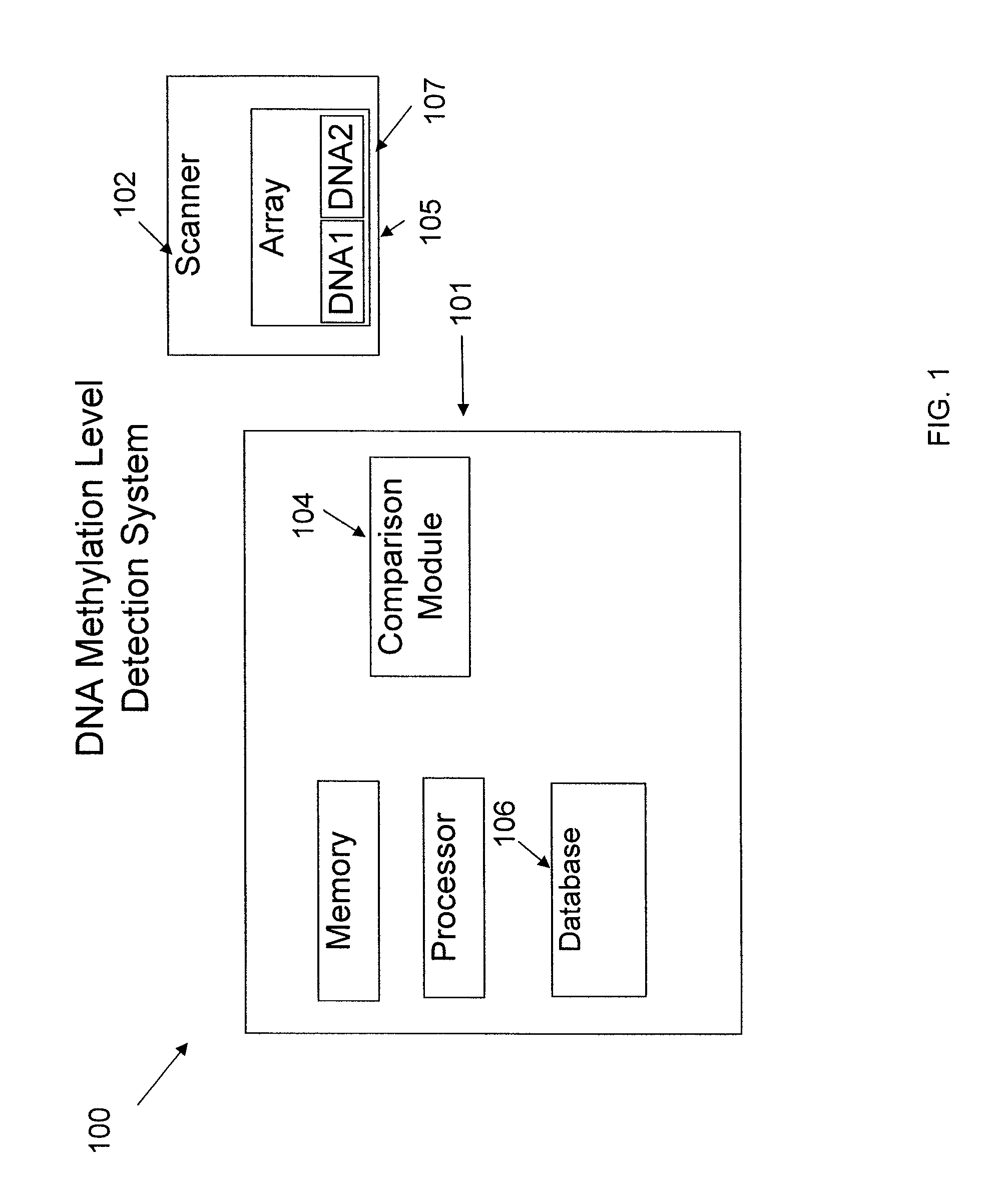
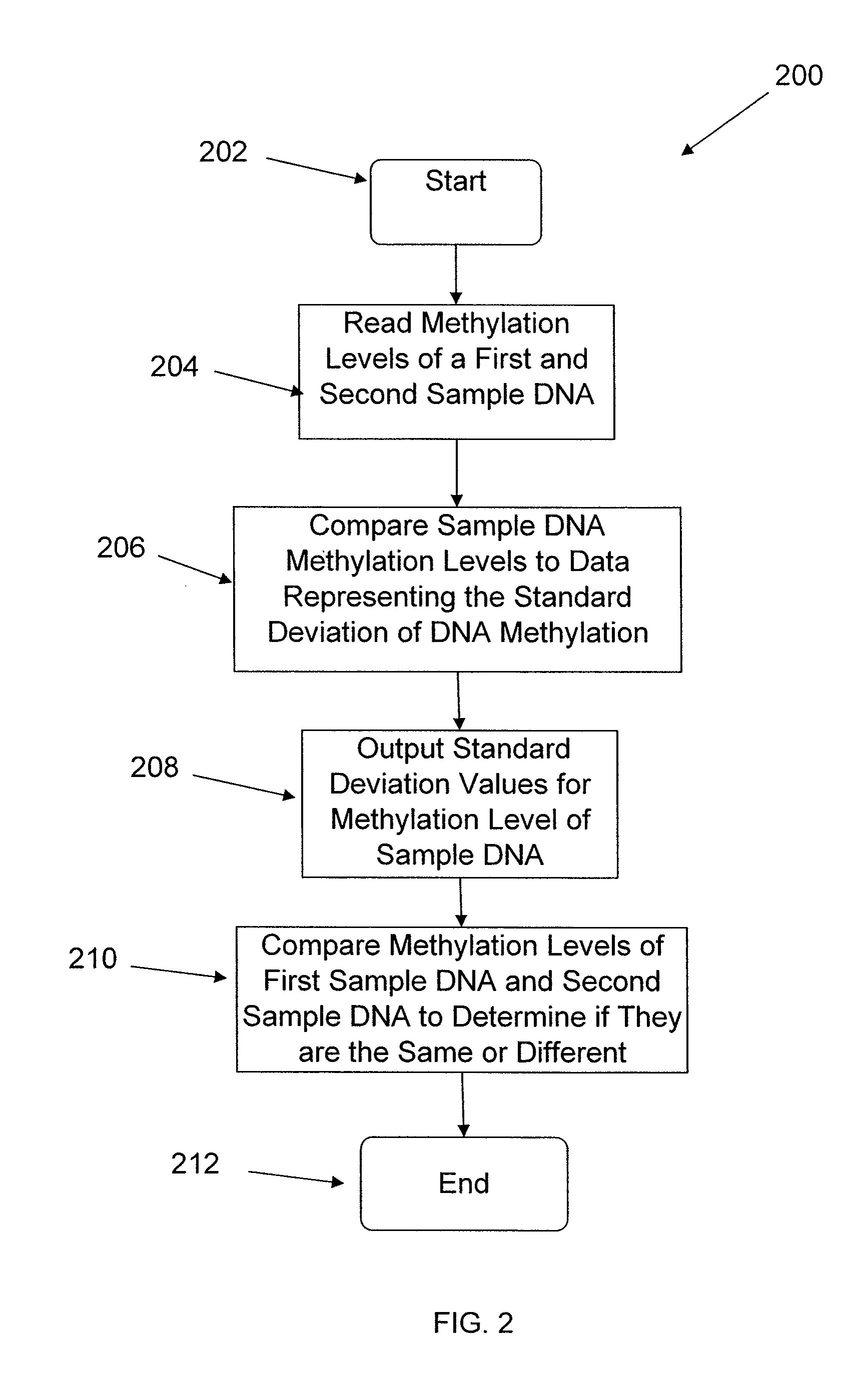
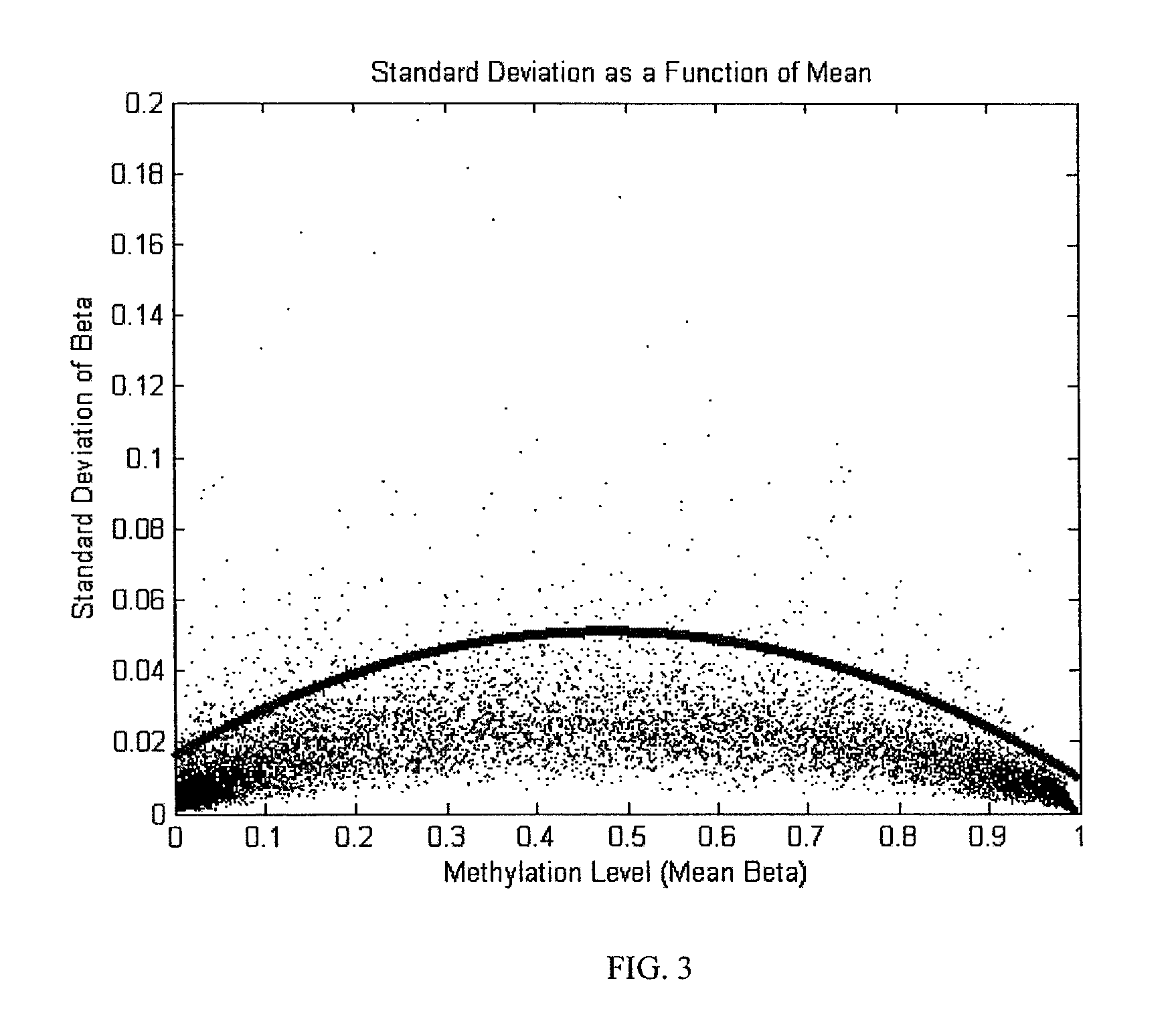
System and method of measuring methylation of nucleic acids
ActiveUS7899626B2Microbiological testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsDNA methylationDNA
The present embodiments relate to a system and method of measuring the methylation level of DNA. Some embodiments relate to a system and method of measuring methylation level of DNA with a gene array.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com