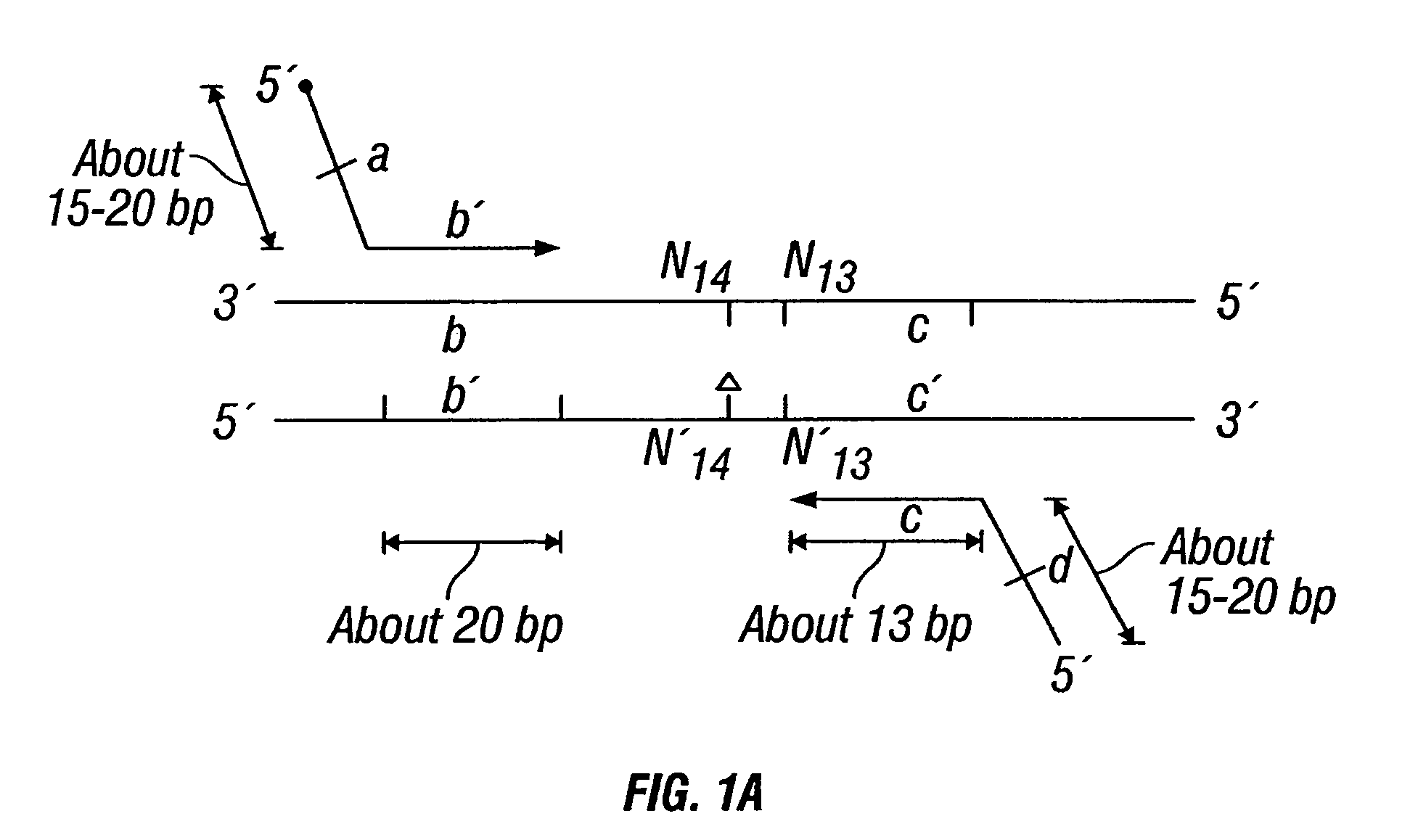
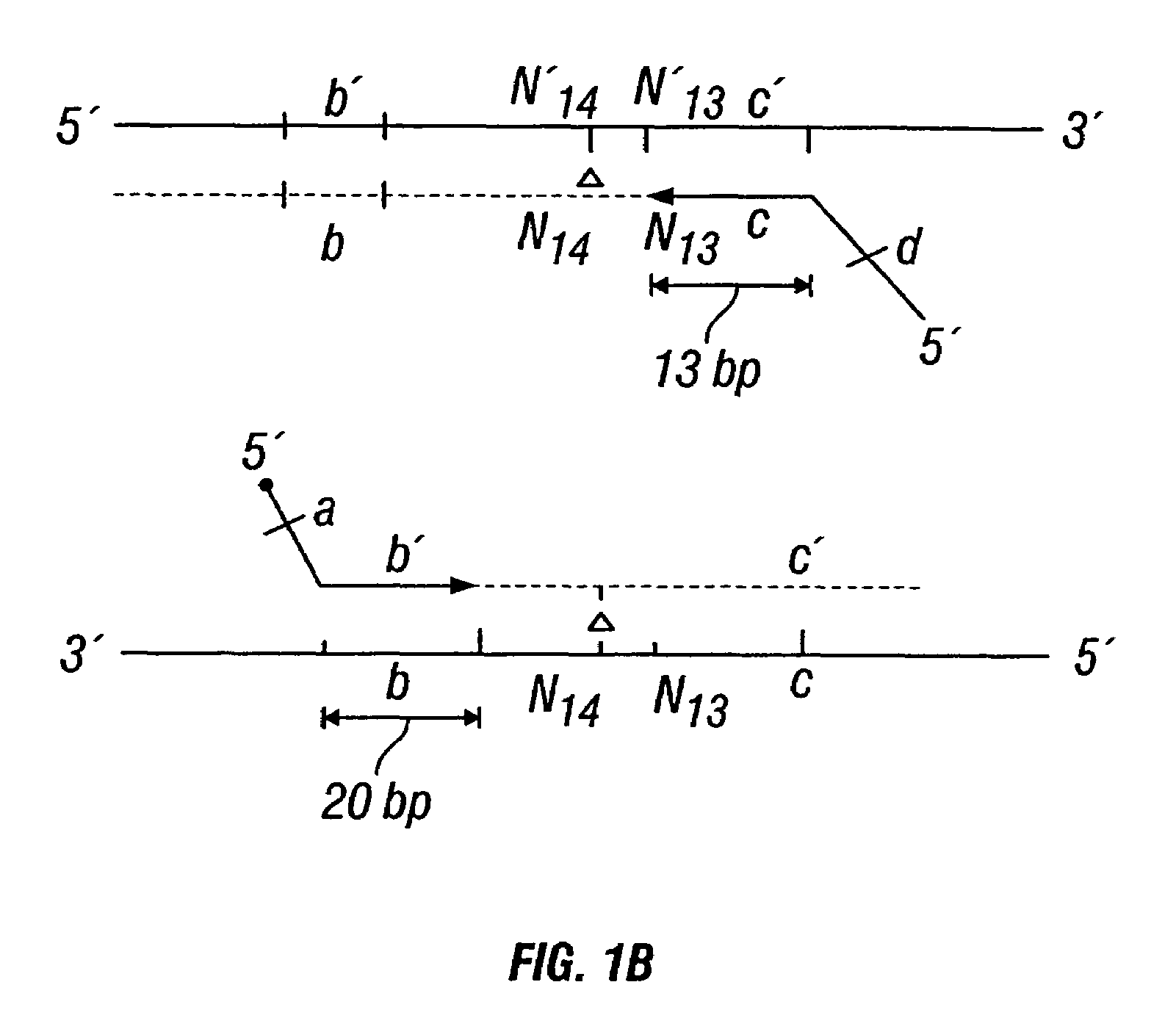
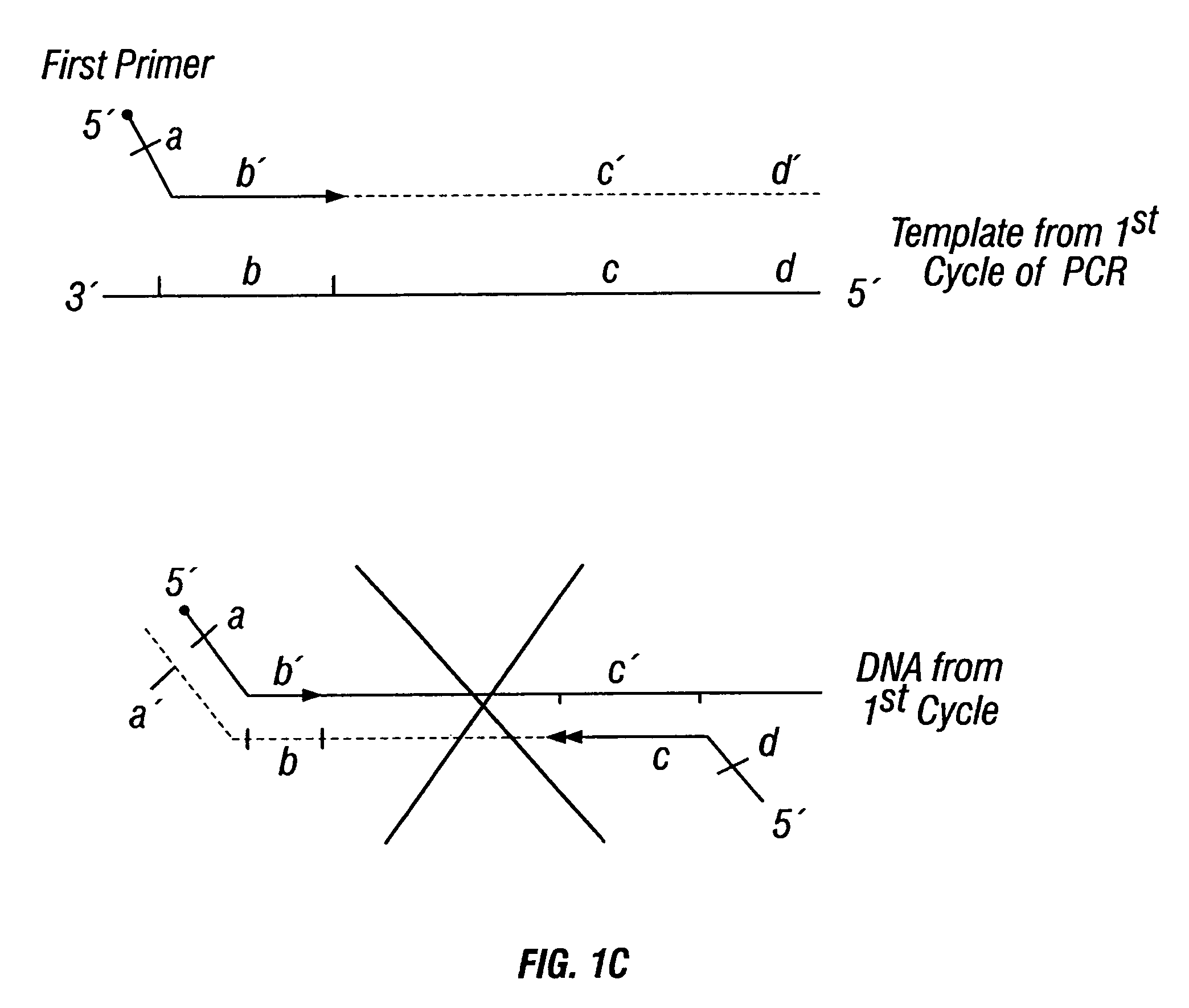
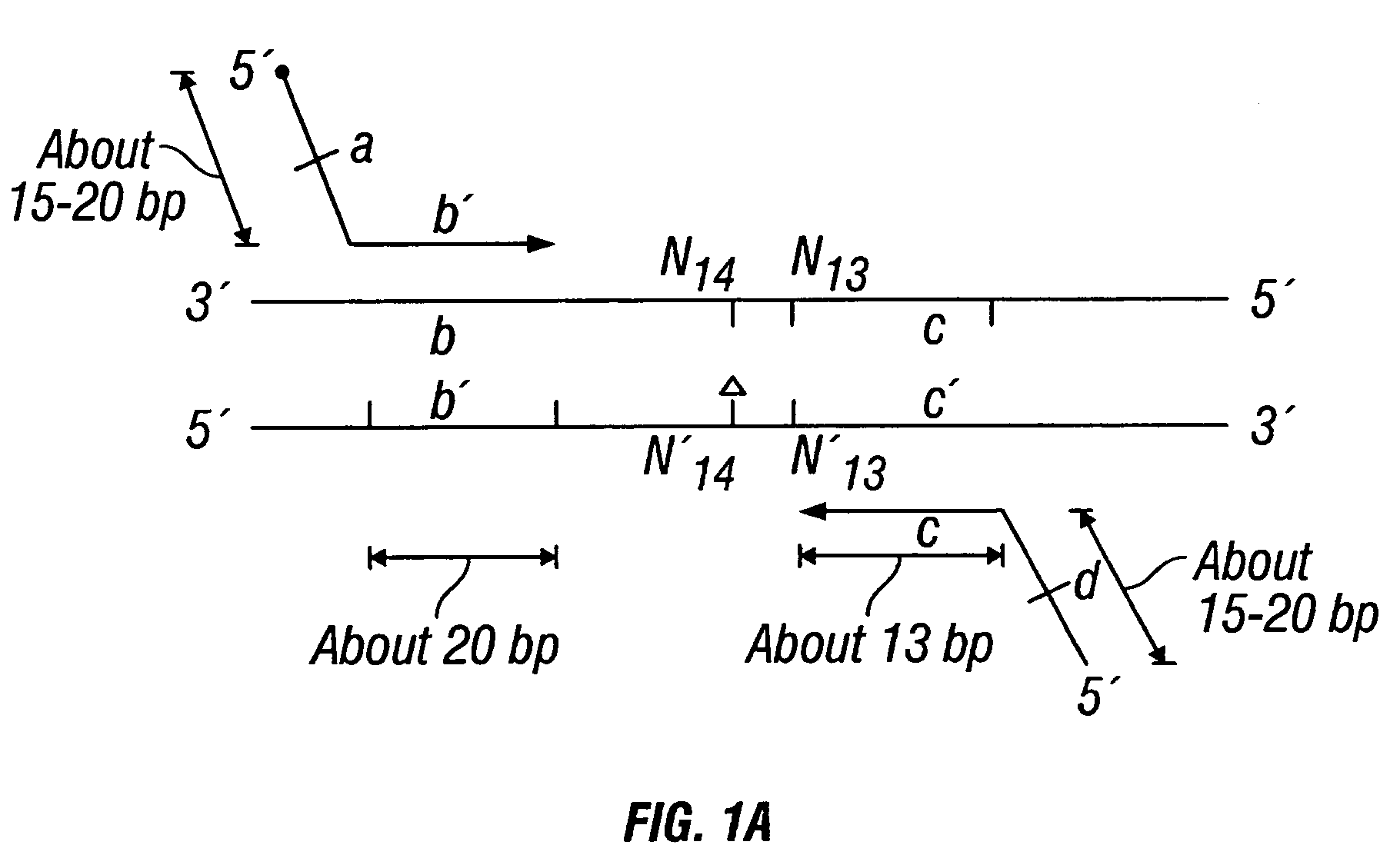
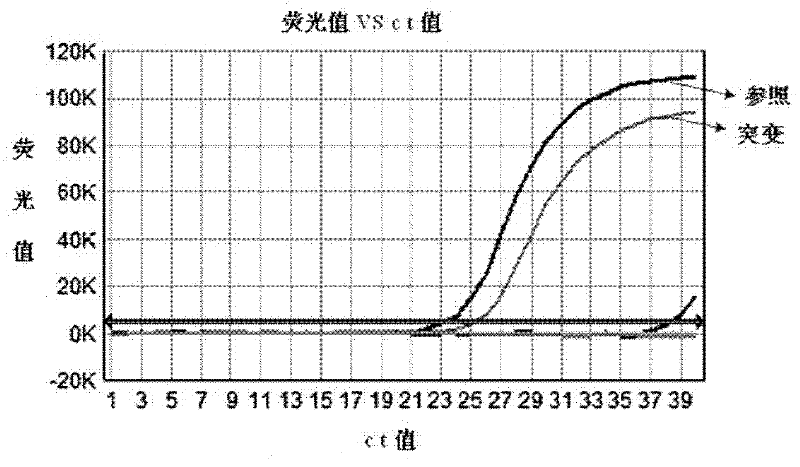
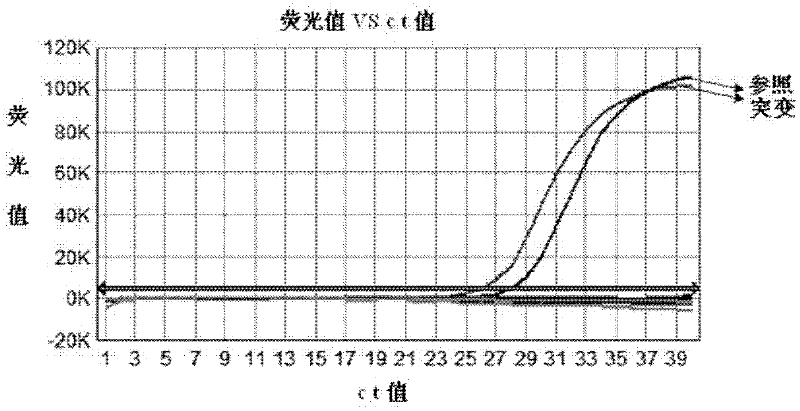
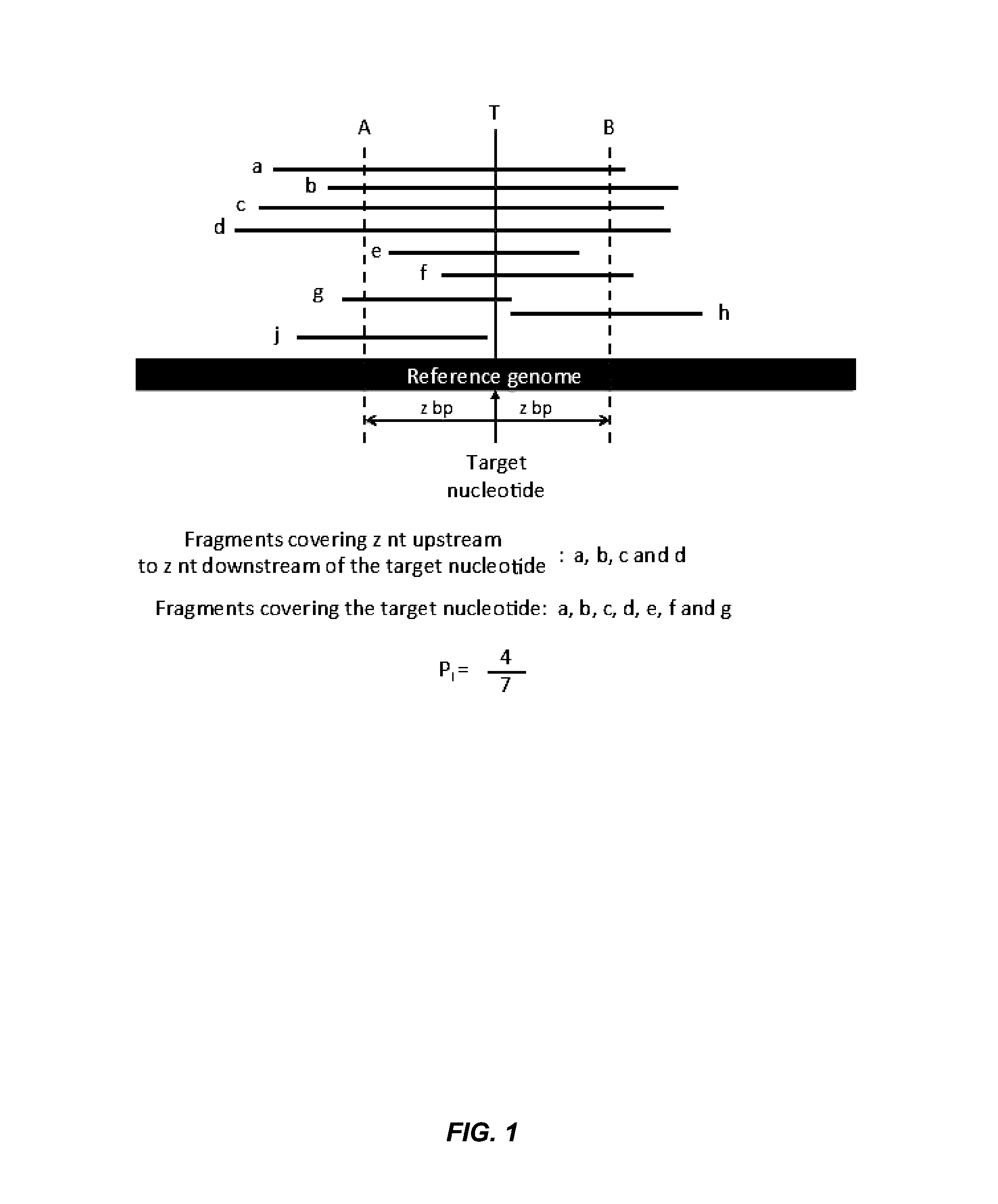
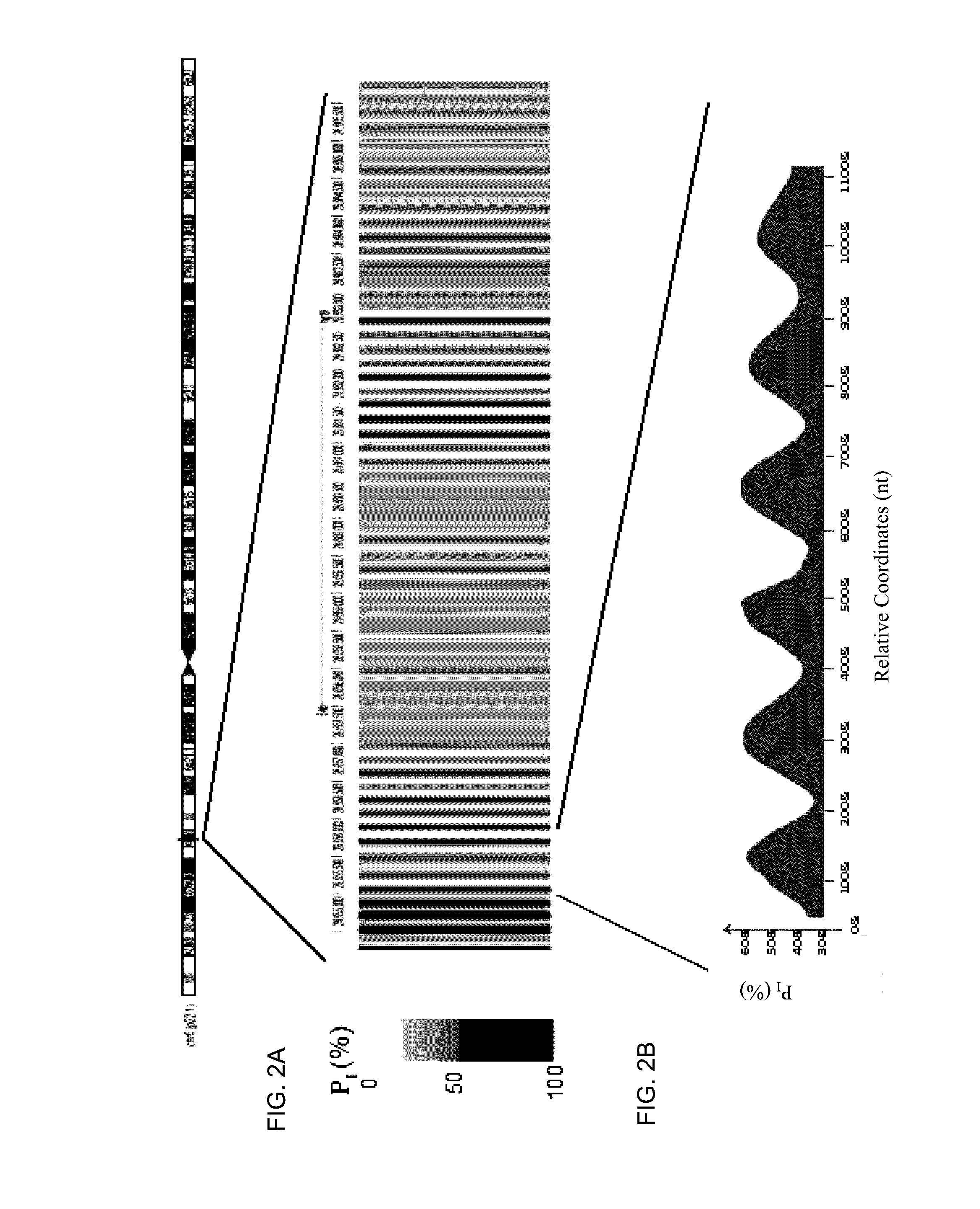
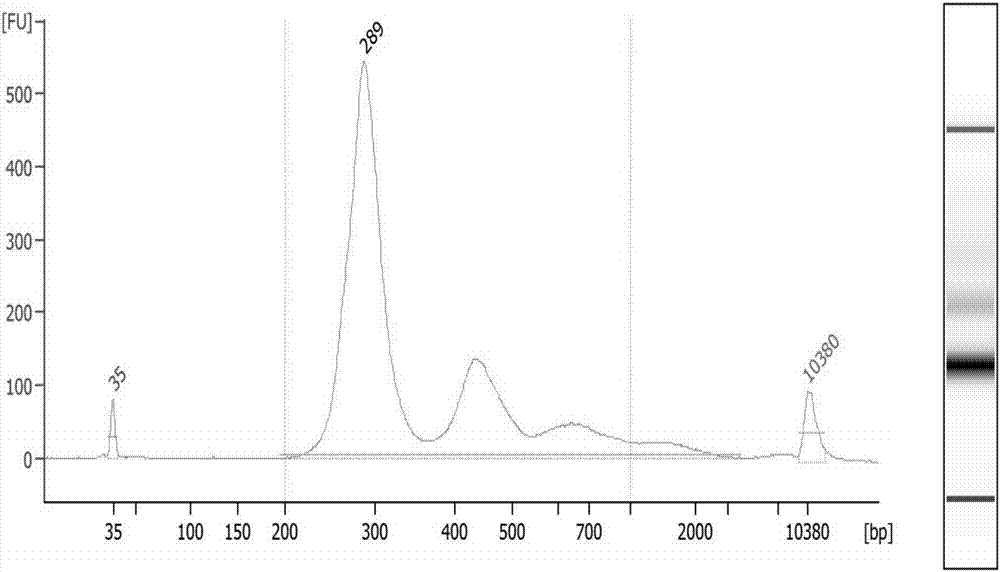
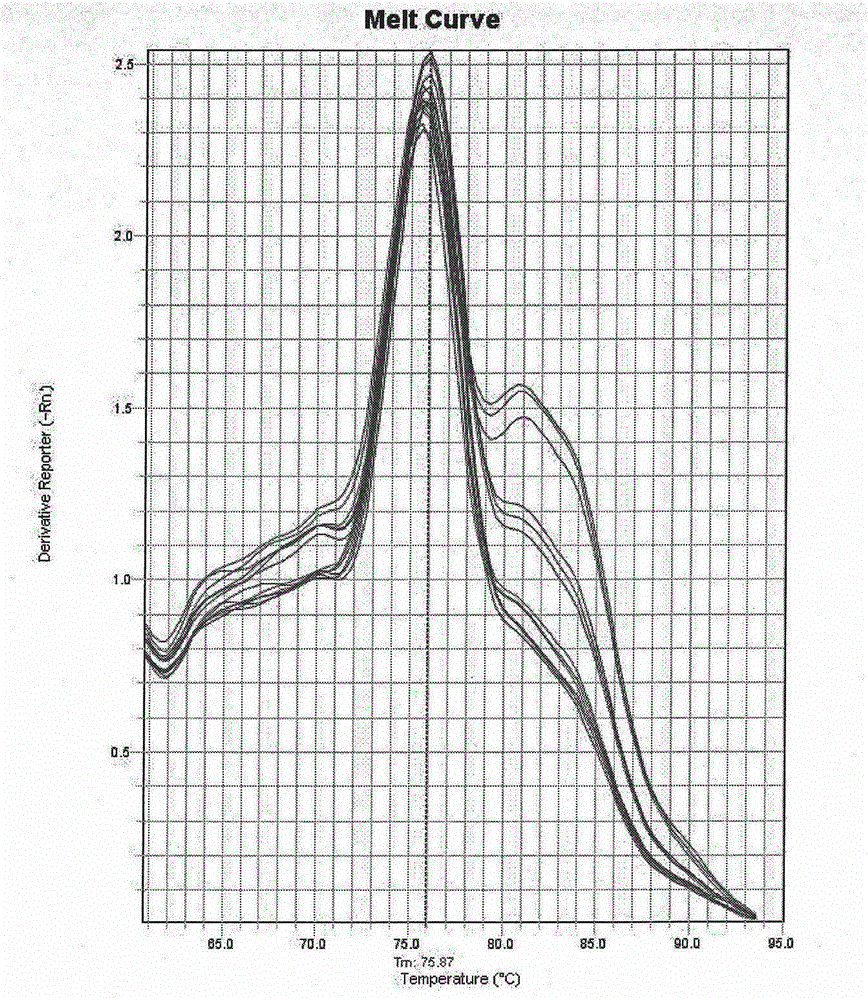
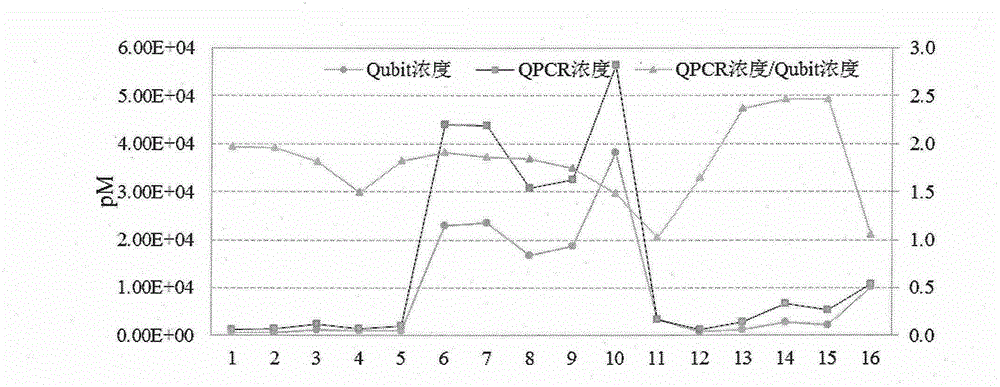
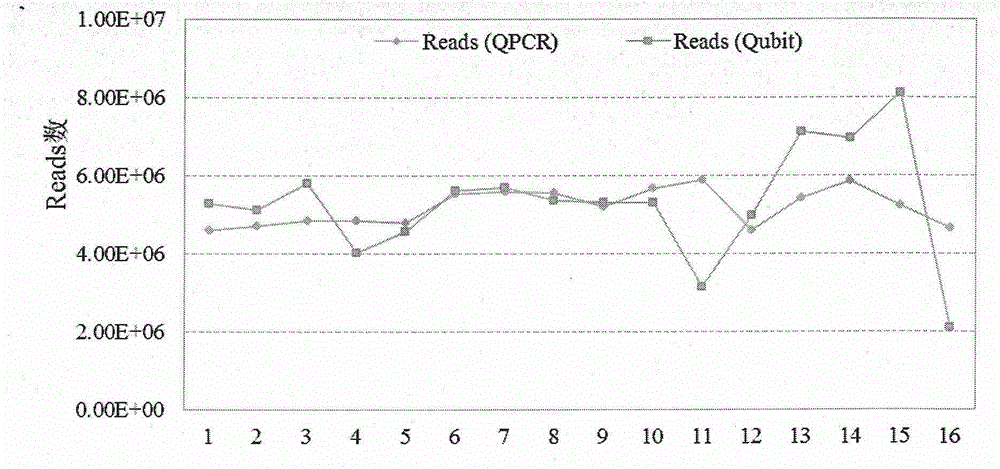
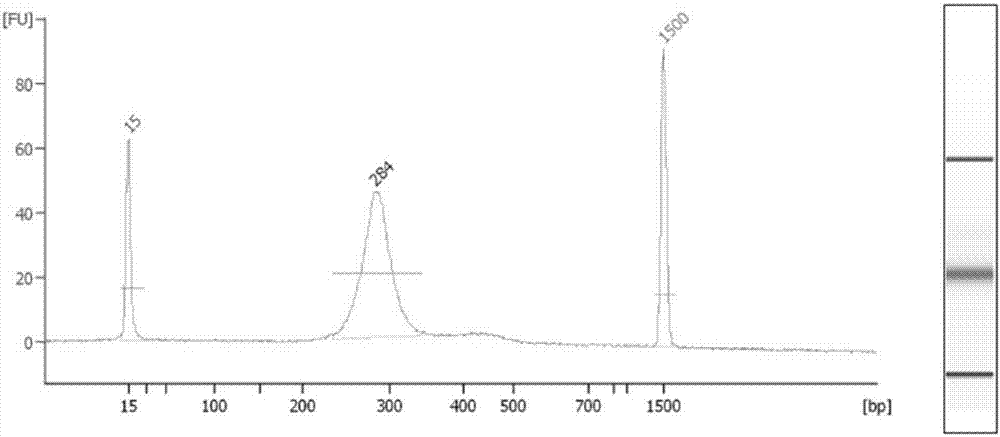
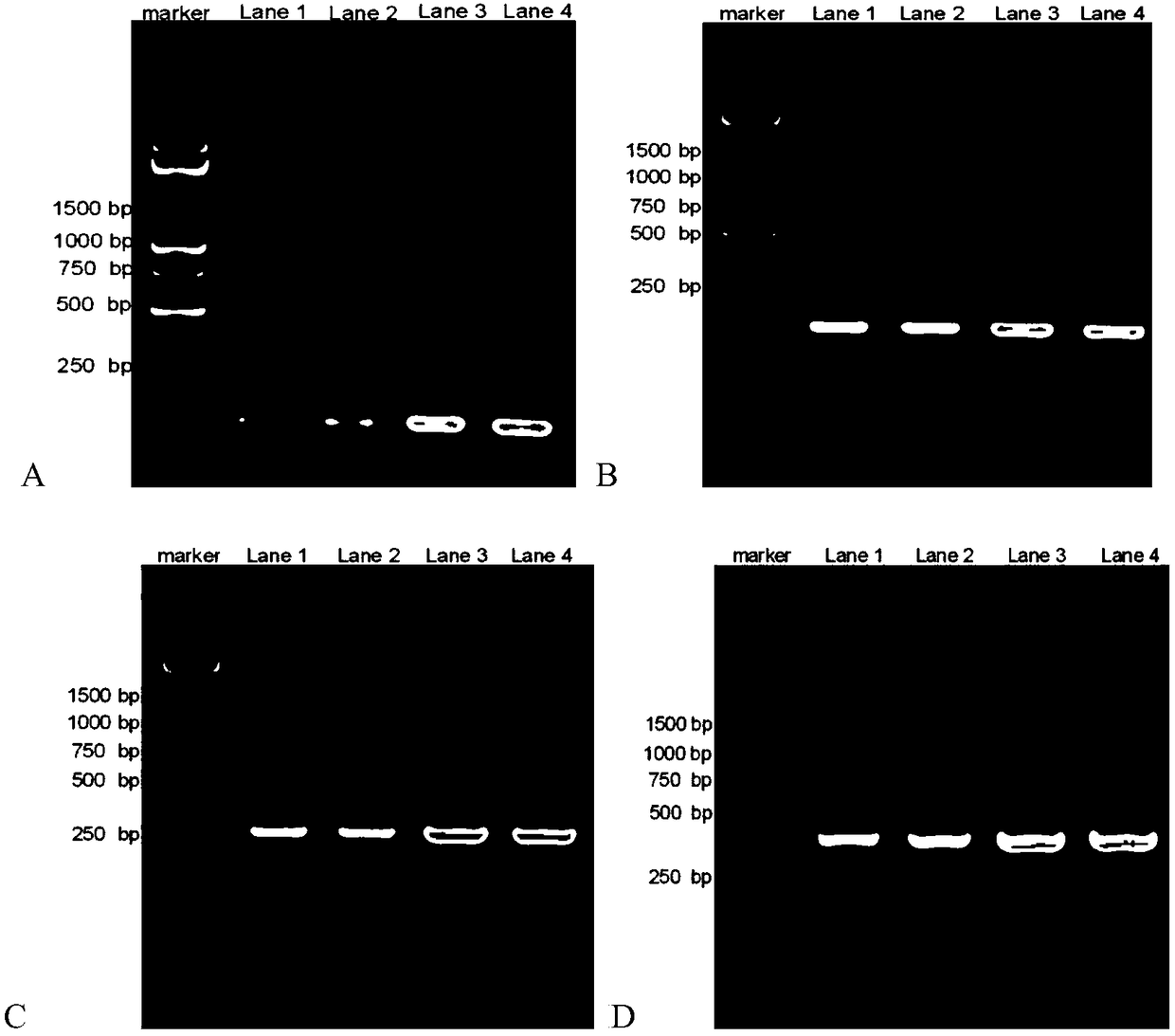
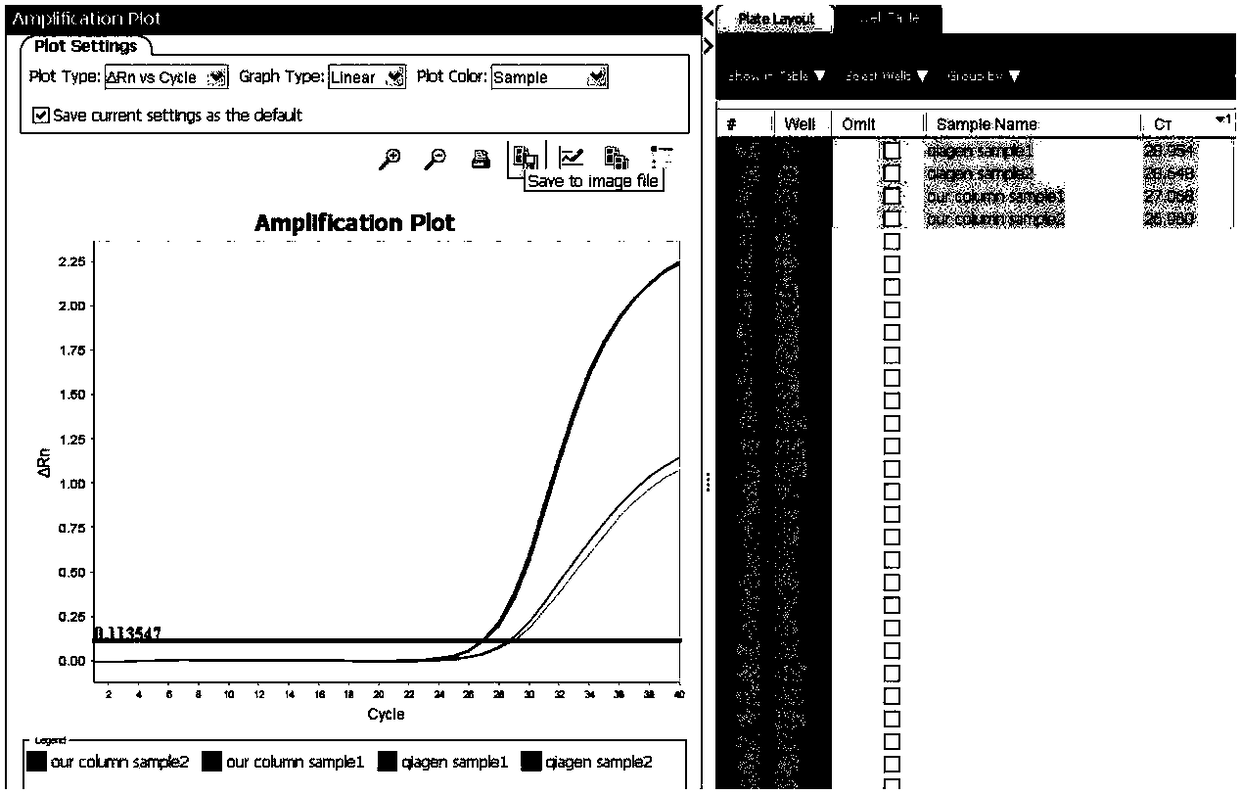
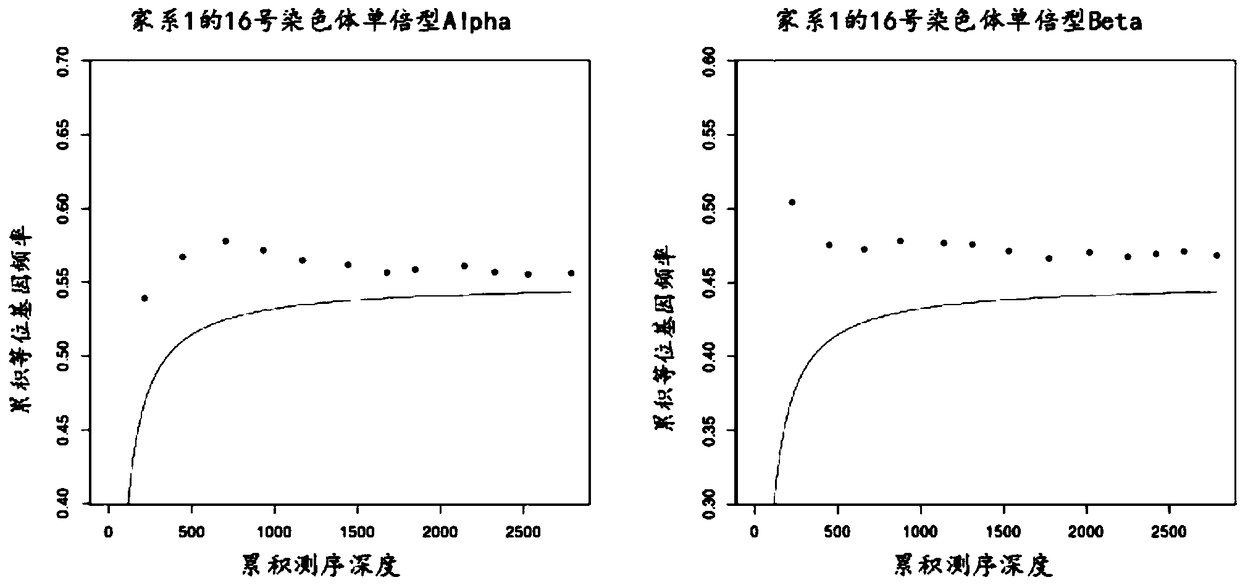
Patents
Literature
500 results about "Free dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
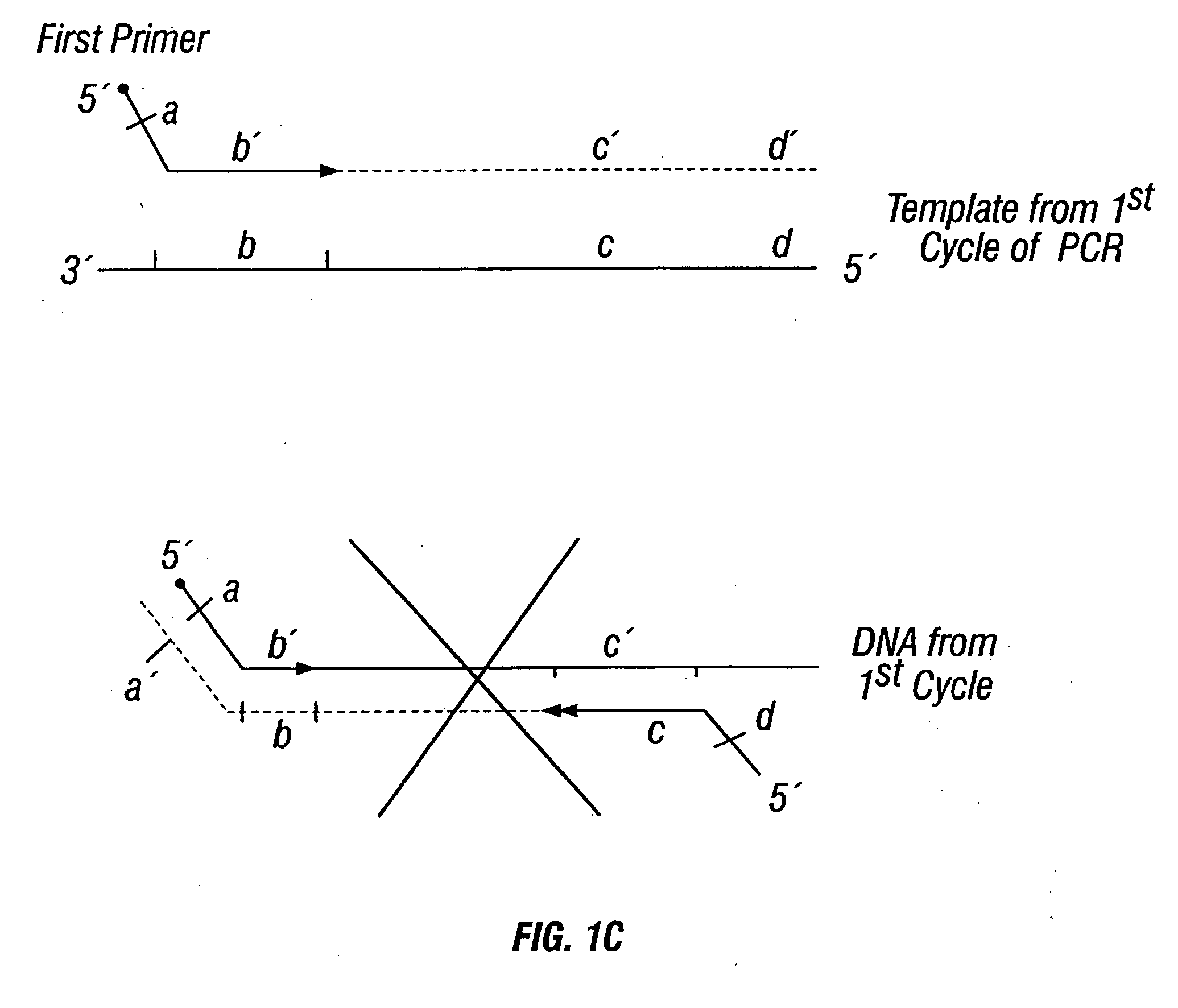
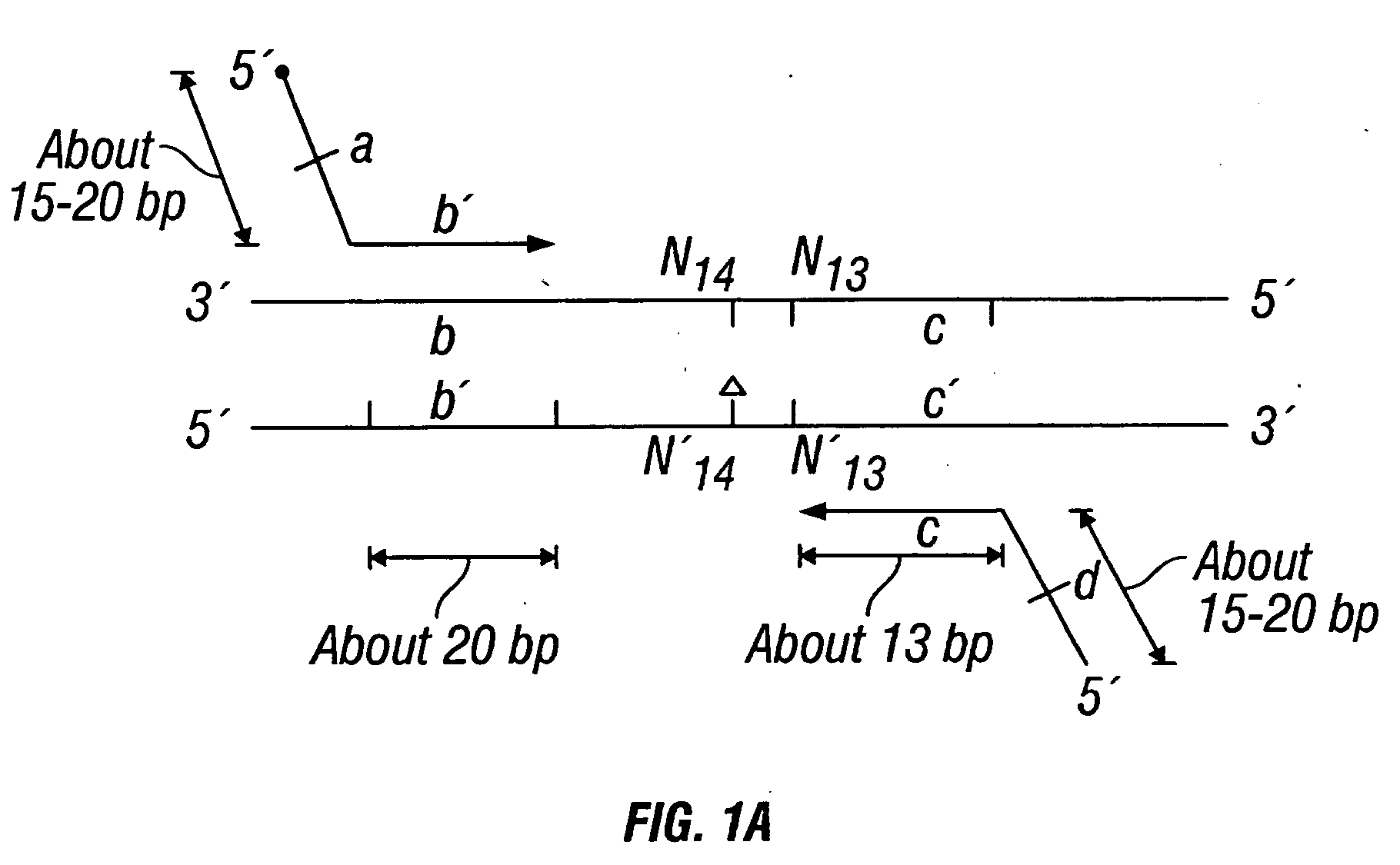
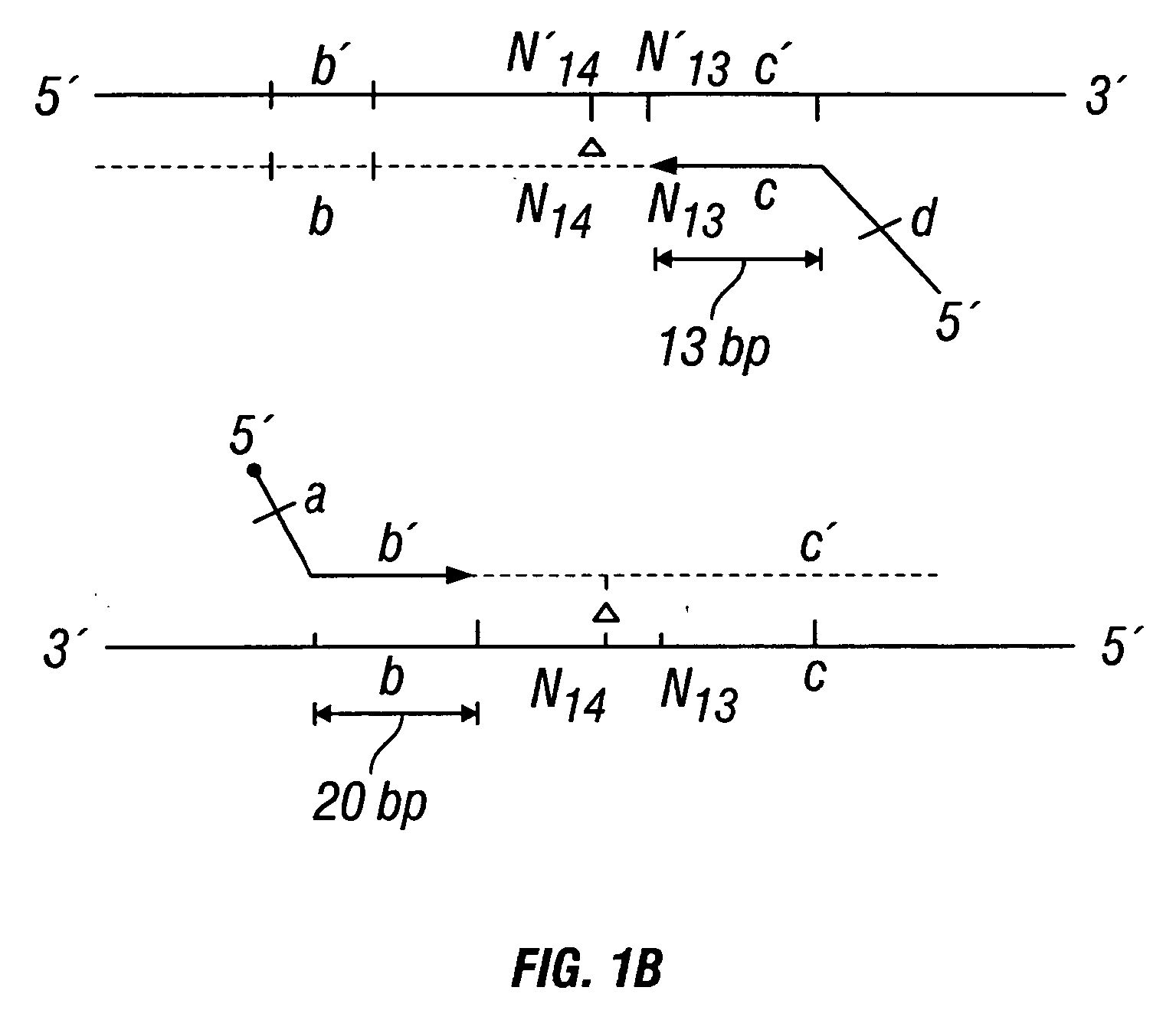
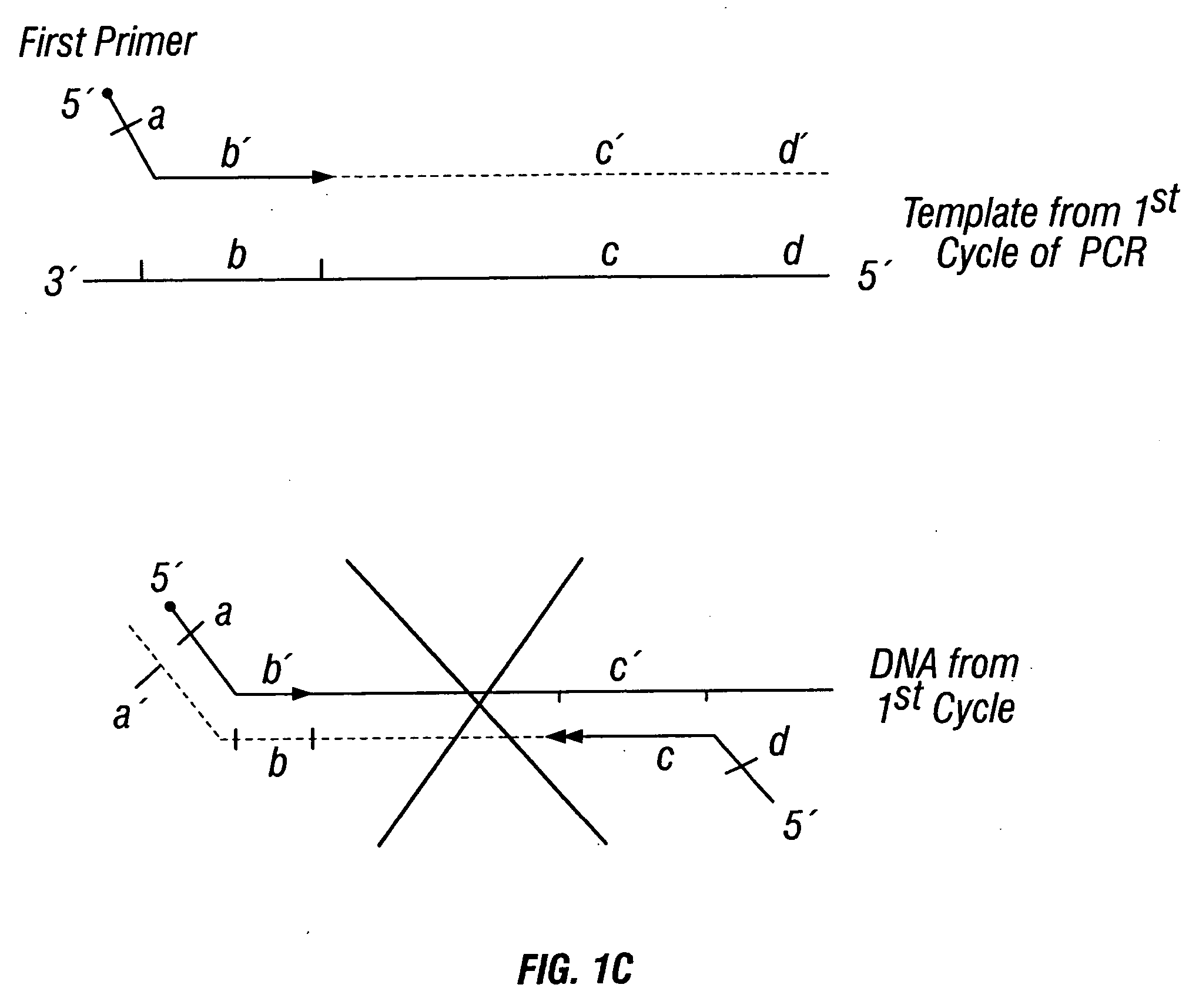
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7727720B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
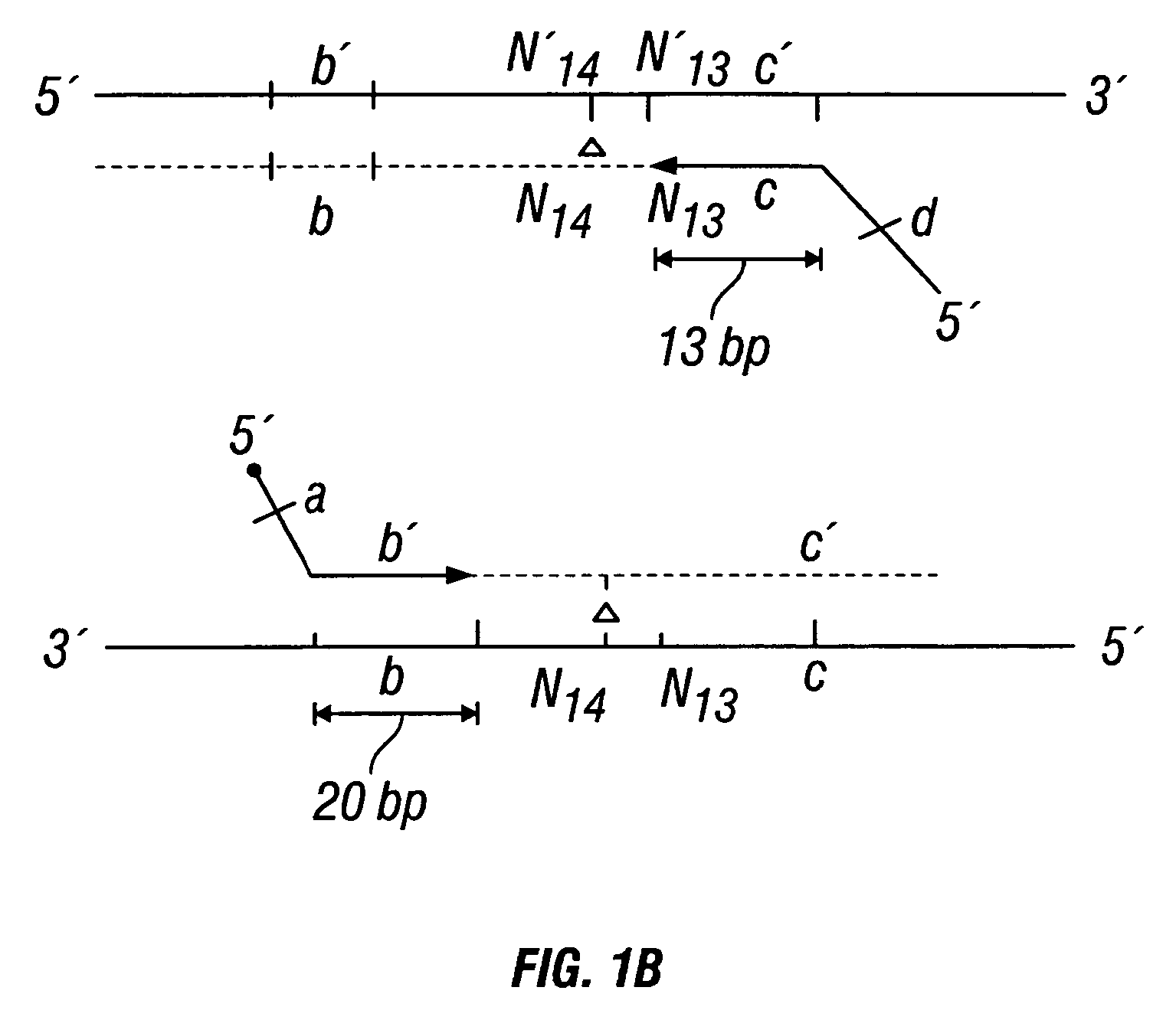
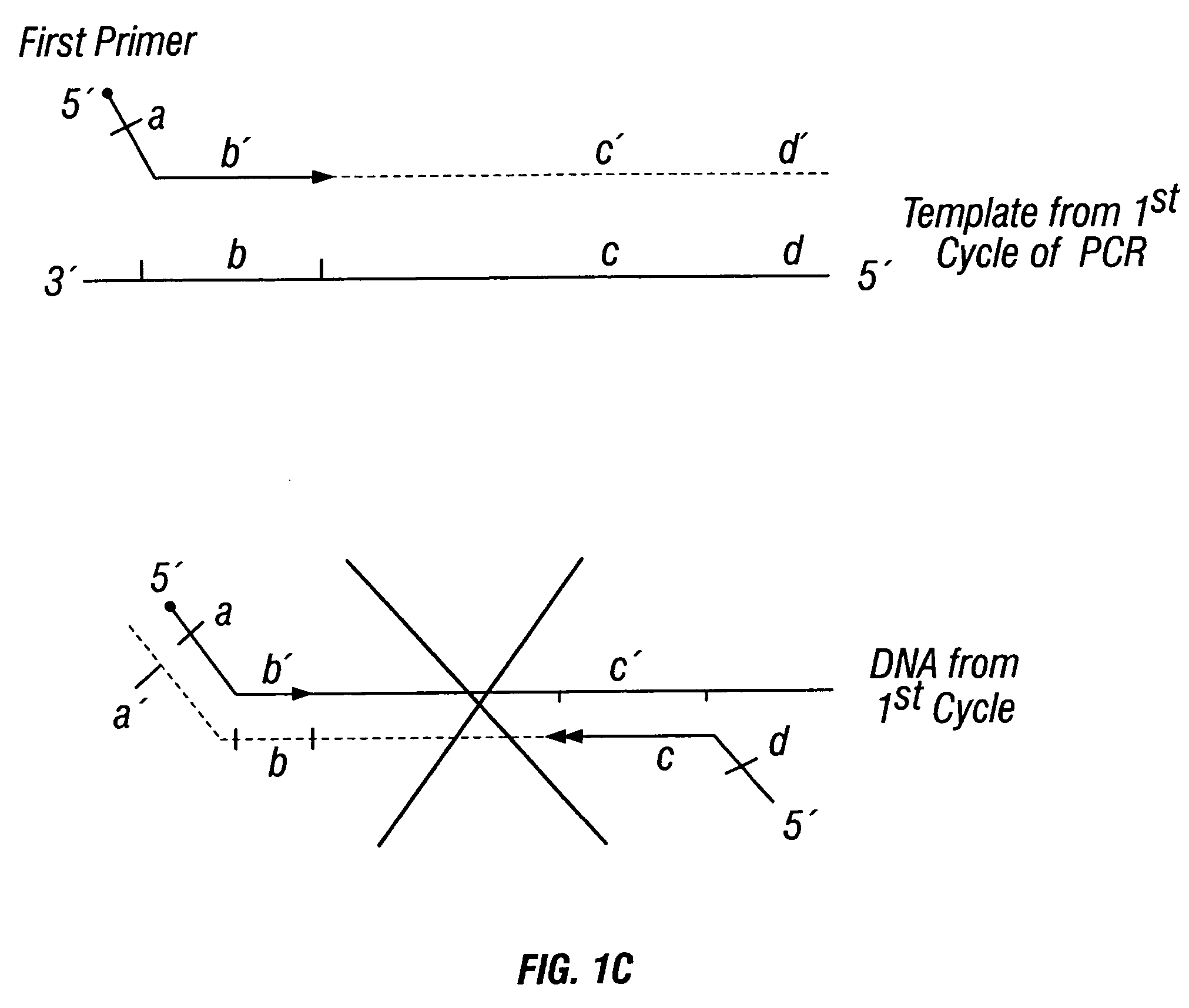
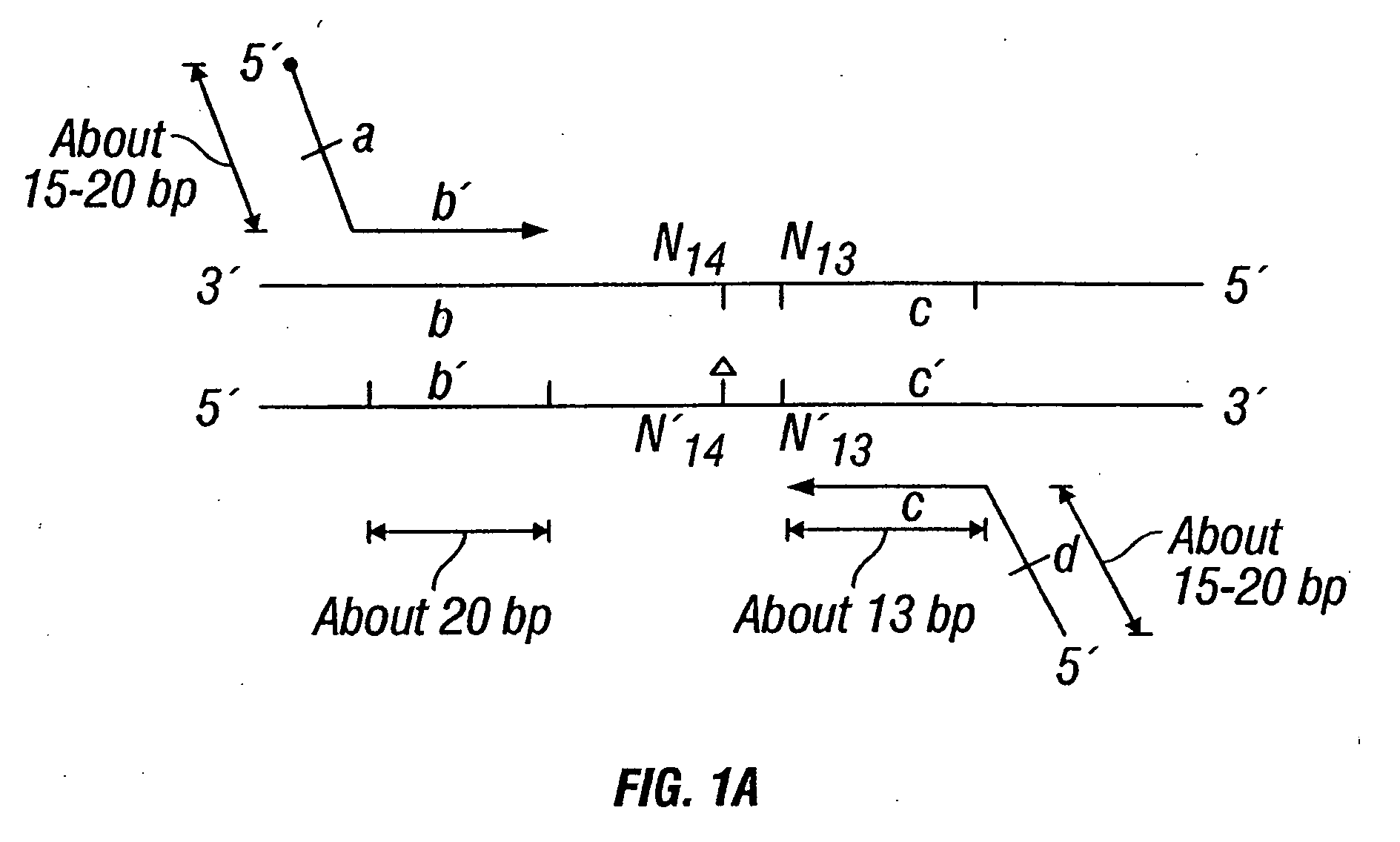
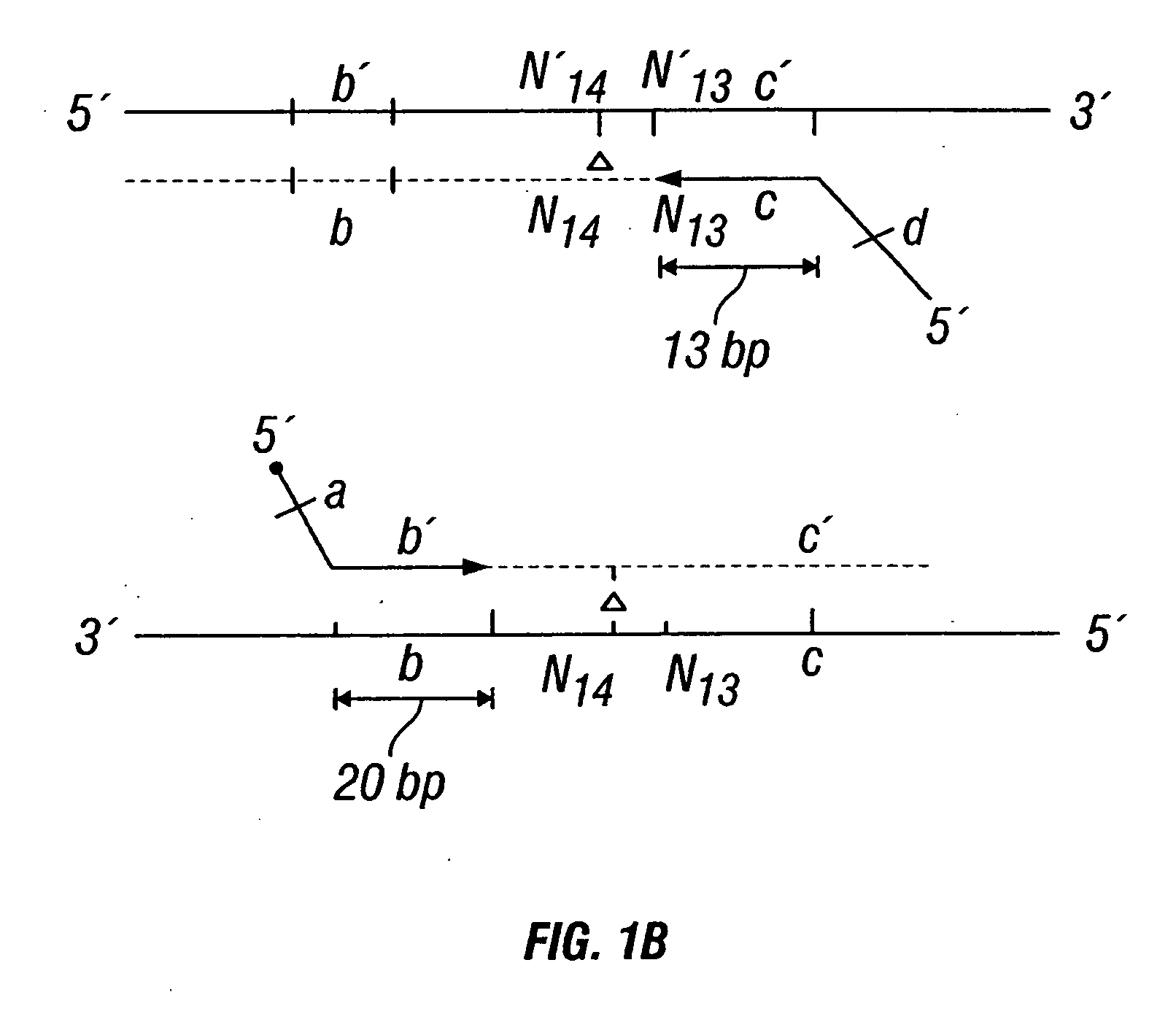
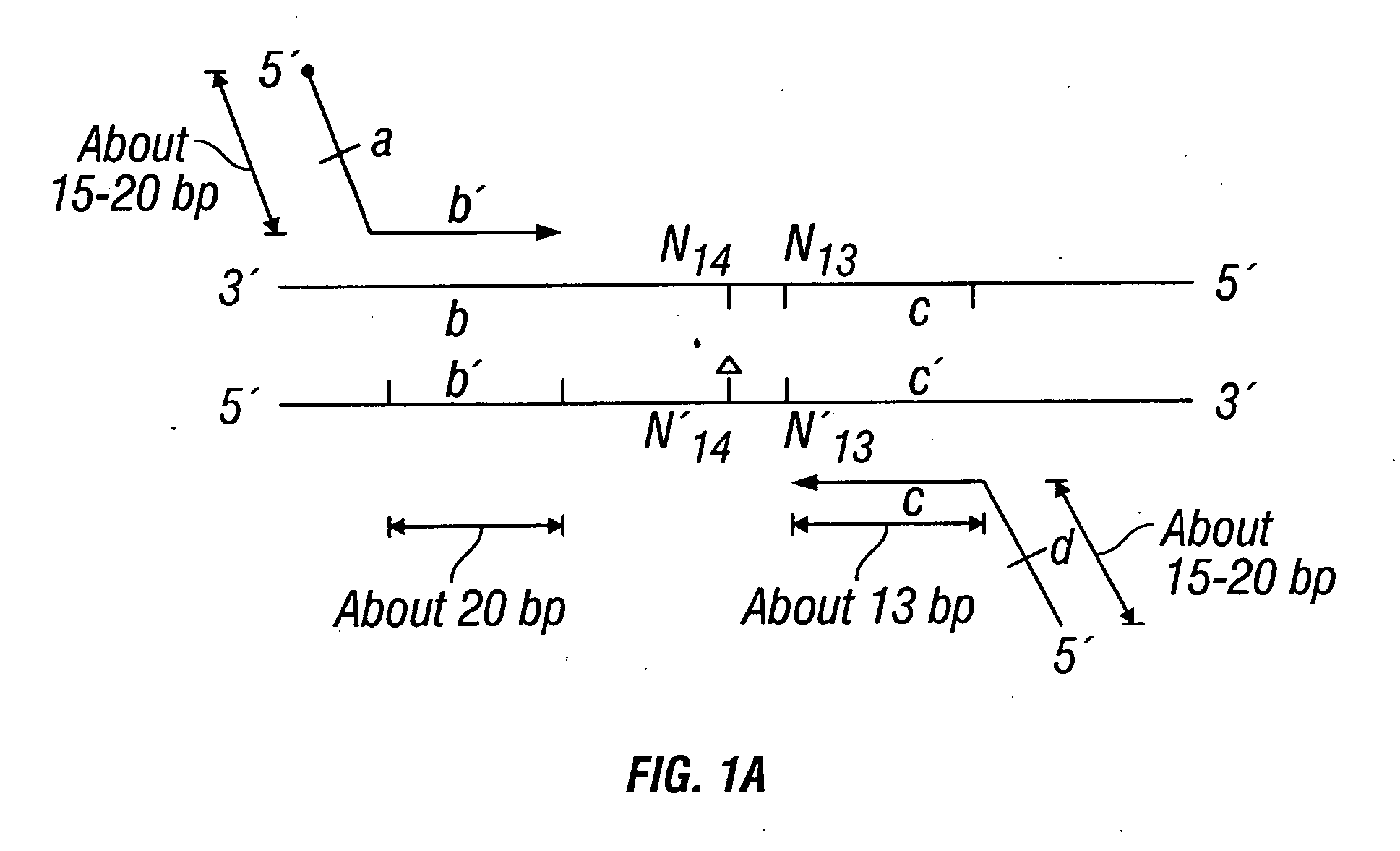
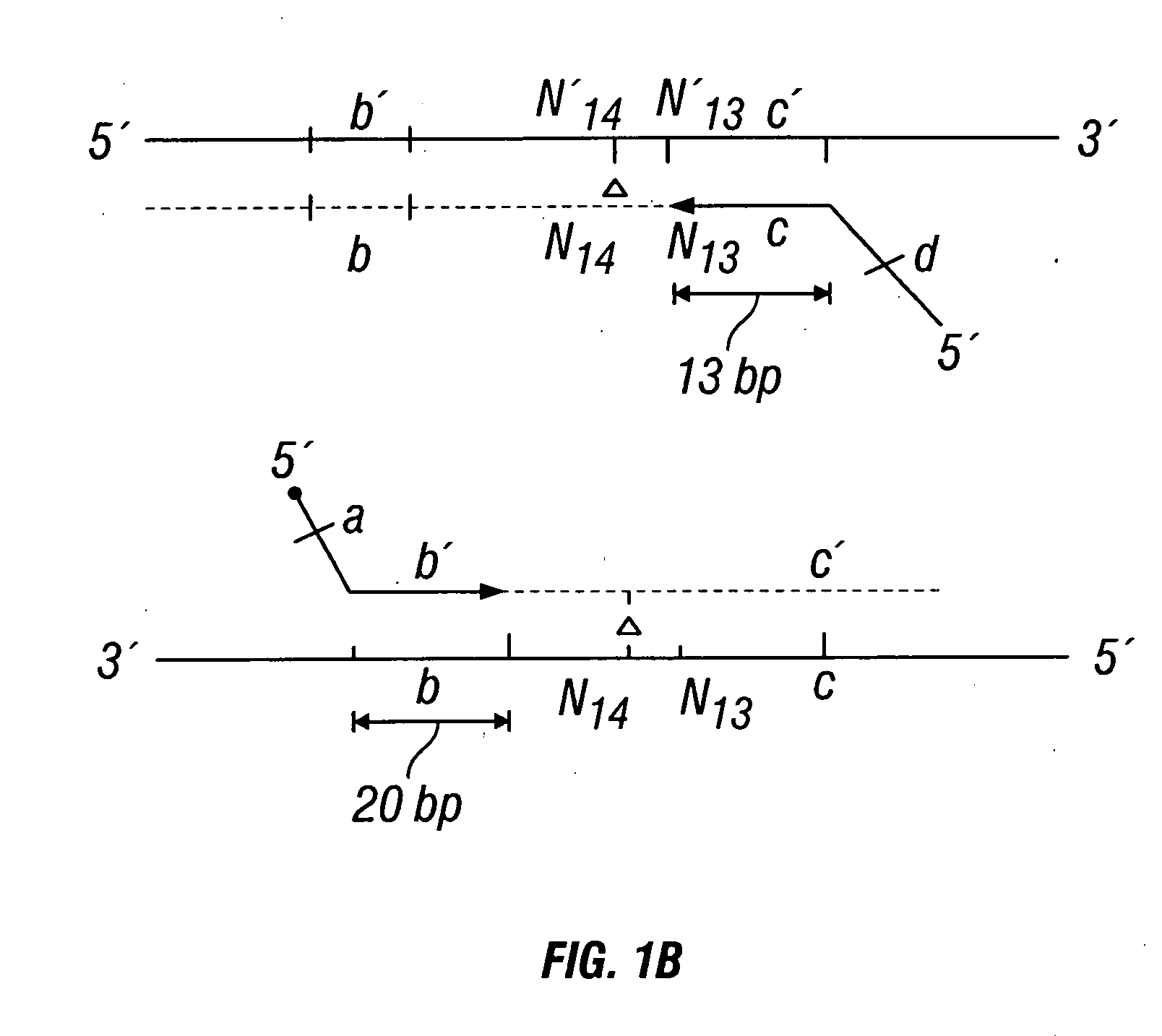
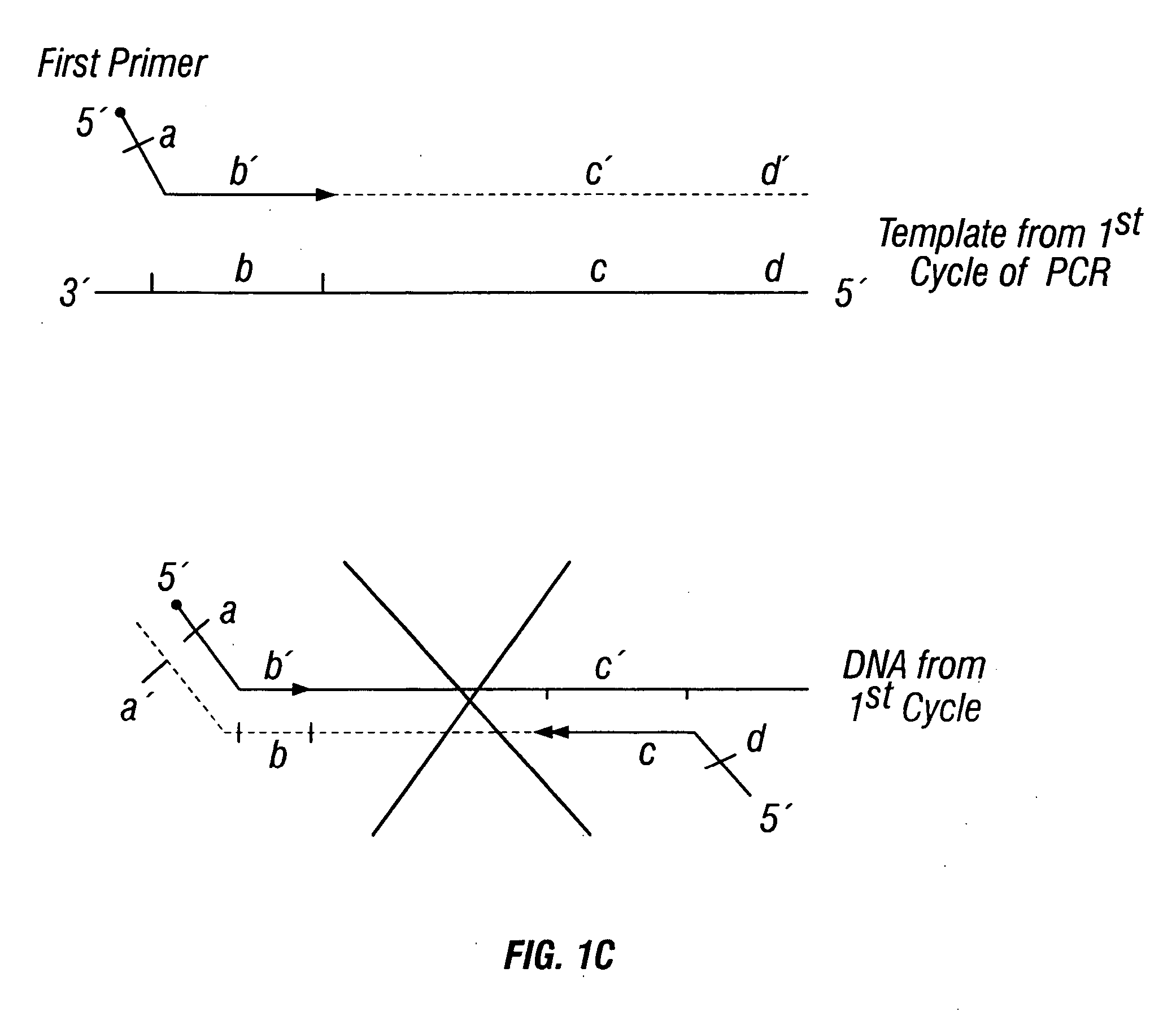
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7442506B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20070178478A1Minimize disruptionMaximize efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20060160105A1Minimize disruptionMaximize efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
Owner:RAVGEN INC
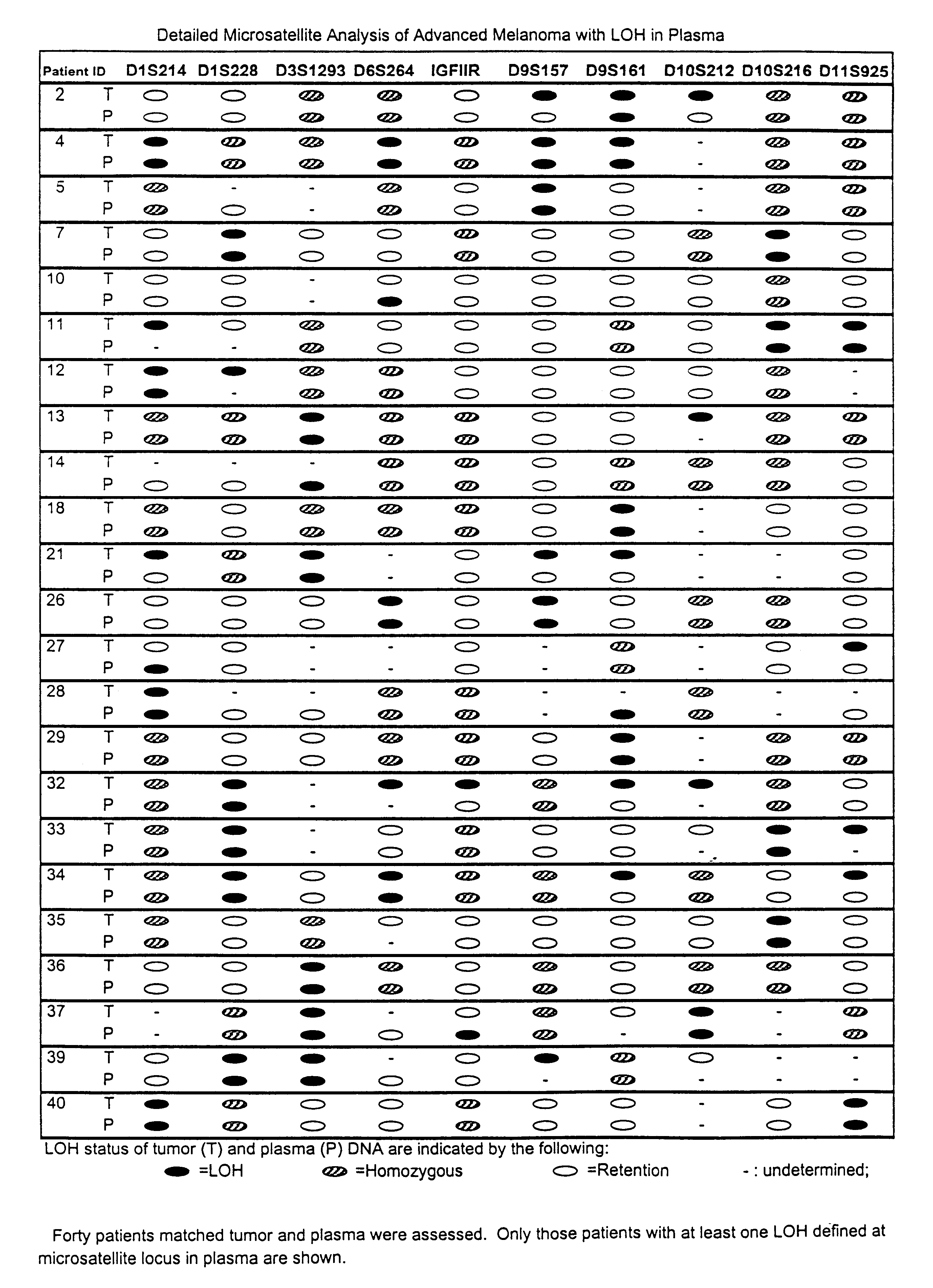
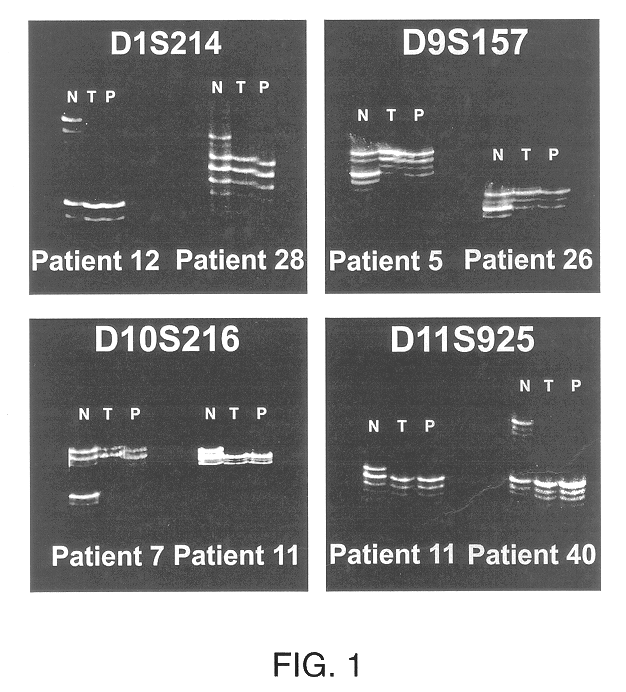
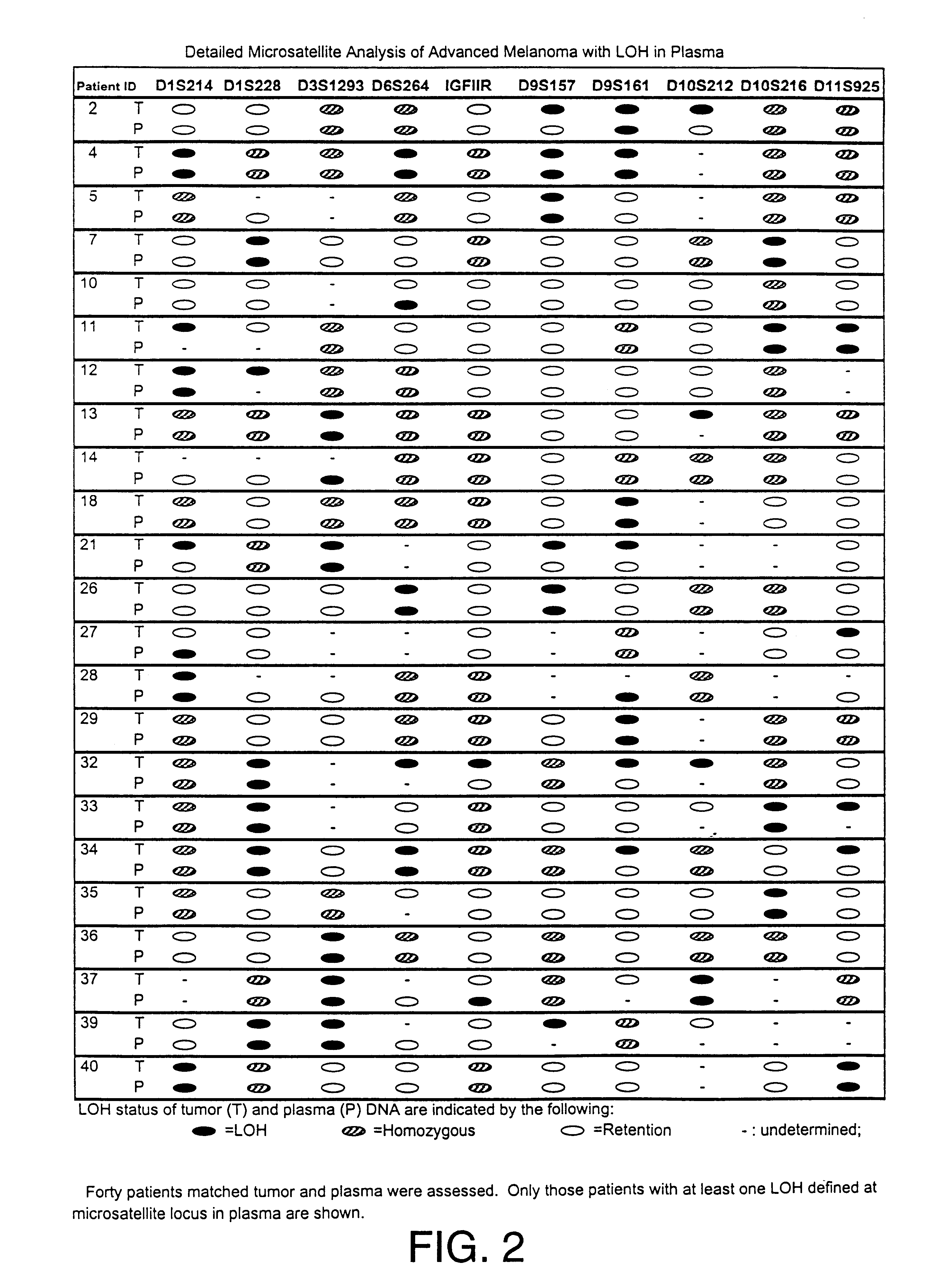
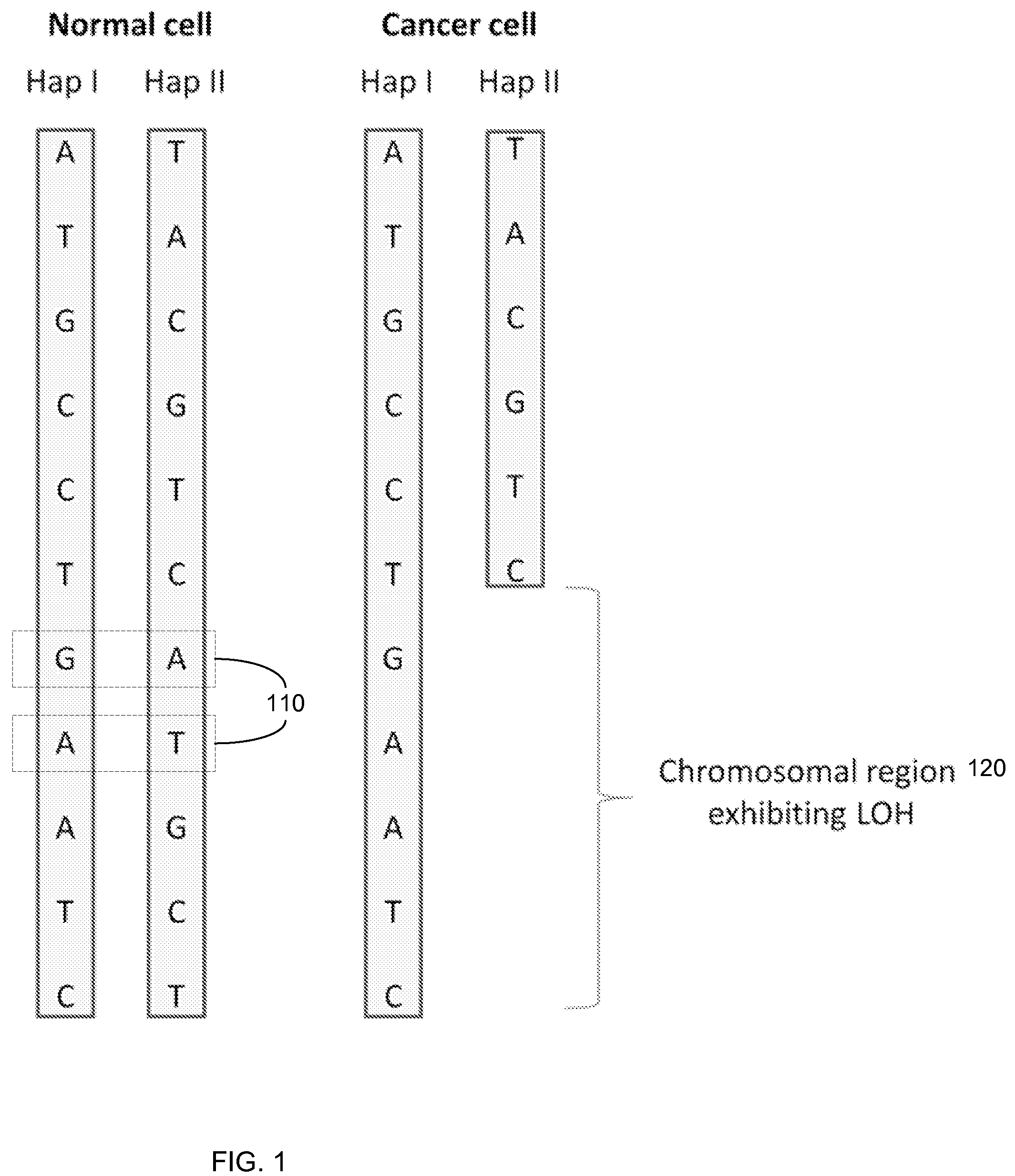
Detection of loss of heterozygosity in tumor and serum of melanoma patients
A method is provided for assessing allelic losses on specific chromosomal regions in melanoma patents. The method relies on the evidence that free DNA may be released in the plasma / serum of cancer patients allowing the detection of DNA with LOH in the plasma / serum of cancer patients by analysis for microsatellite markers. The amount of and specific allelic loss allows a prognosis to be made regarding tumor diagnosis and progression, tumor metastasis, tumor recurrence, and mortality.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
Assay for localized detection of analytes
InactiveUS20110223585A1Efficient localizationSimple and convenient visualizationMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayAnalyte
The present invention relates to a method for detecting an analyte in a sample, said method comprising: (a) contacting said sample with at least one set of at least first and second proximity probes, wherein said probes each comprise an analyte-binding moiety and can simultaneously bind to the analyte, and wherein (i) said first proximity probe comprises a nucleic acid moiety attached at one end to the analyte-binding moiety, wherein a circular or circularizable oligonucleotide is hybridized to said nucleic acid moiety before, during or after said contacting step; and (ii) said second proximity probe comprises an enzyme moiety, attached to the analyte-binding moiety, capable of directly or indirectly enabling rolling circle amplification (RCA) of the circular or, when it is circularized, of the circularizable oligonucleotide hybridized to the nucleic acid moiety of the first proximity probe, wherein said RCA is primed by said nucleic acid moiety of said first proximity probe; (b) if necessary, circularizing said oligonucleotide, to produce a circularized template for RCA; (c) subjecting said circular or circularized template to RCA, wherein if the enzyme moiety of the second proximity probe in step (a)(ii) is a DNA polymerase, this step does not utilize a free DNA polymerase; and (d) detecting a product of said RCA.
Owner:OLINK AB
Method of detecting tumour recurrence
PendingUS20200248266A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsMultiplexCell free
The invention relates to subject-specific methods for detecting recurrence of tumours based on an understanding of the clonal / subclonal mutation profile of the subject's tumour and detection of the mutations in their cell-free DNA (cfDNA), typically by multiplex PCR of tumour mutations such as single nucleotide variants (SNVs).
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Detection of genetic or molecular aberrations associated with cancer
ActiveUS8741811B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell freeAfter treatment
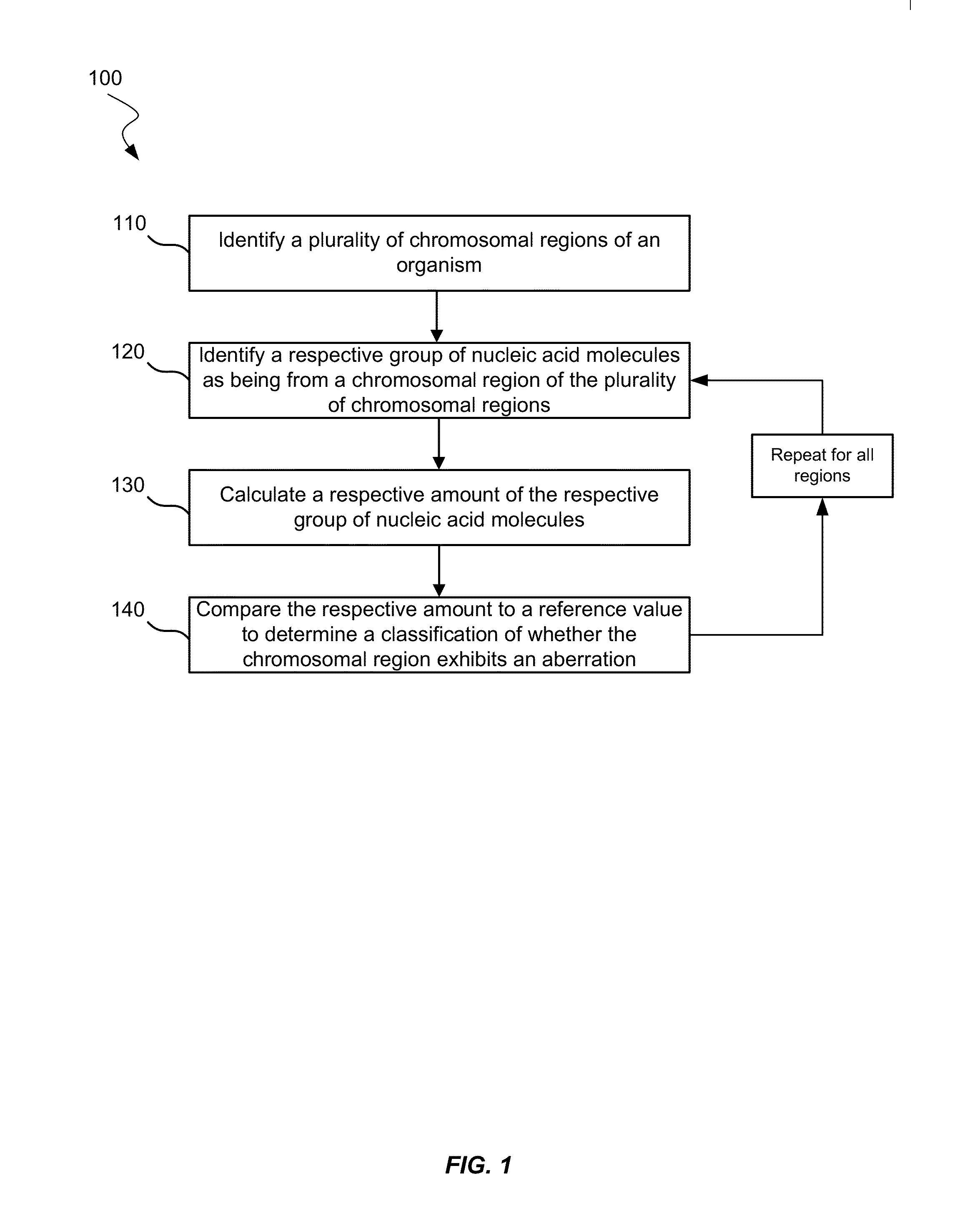
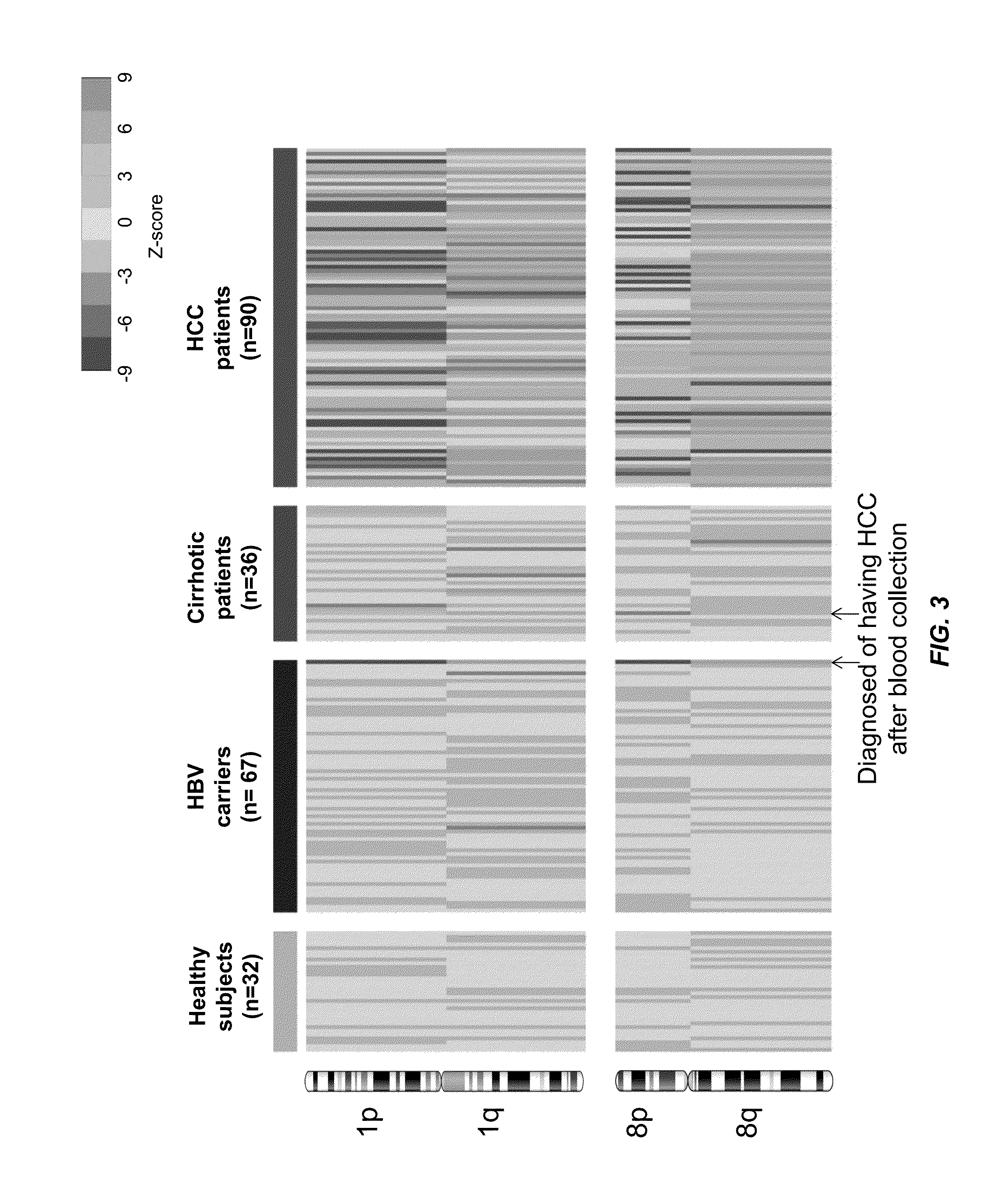
Biological samples including cell-free DNA fragments are analyzed to identify imbalances in chromosomal regions, e.g., due to deletions and / or amplifications in a tumor. Multiple loci are used for each chromosomal region. Such imbalances can then be used to diagnose (screen) a patient for cancer, as well as prognosticate a patient with cancer, or to detect the presence or to monitor the progress of a premalignant condition in a patient. The severity of an imbalance as well as the number of regions exhibiting an imbalance can be used. A systematic analysis of non-overlapping segments of a genome can provide a general screening tool for a sample. Additionally, a patient can be tested over time to track severity of each of one or more chromosomal regions and a number of chromosomal regions to enable screening and prognosticating, as well as monitoring of progress (e.g. after treatment).
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
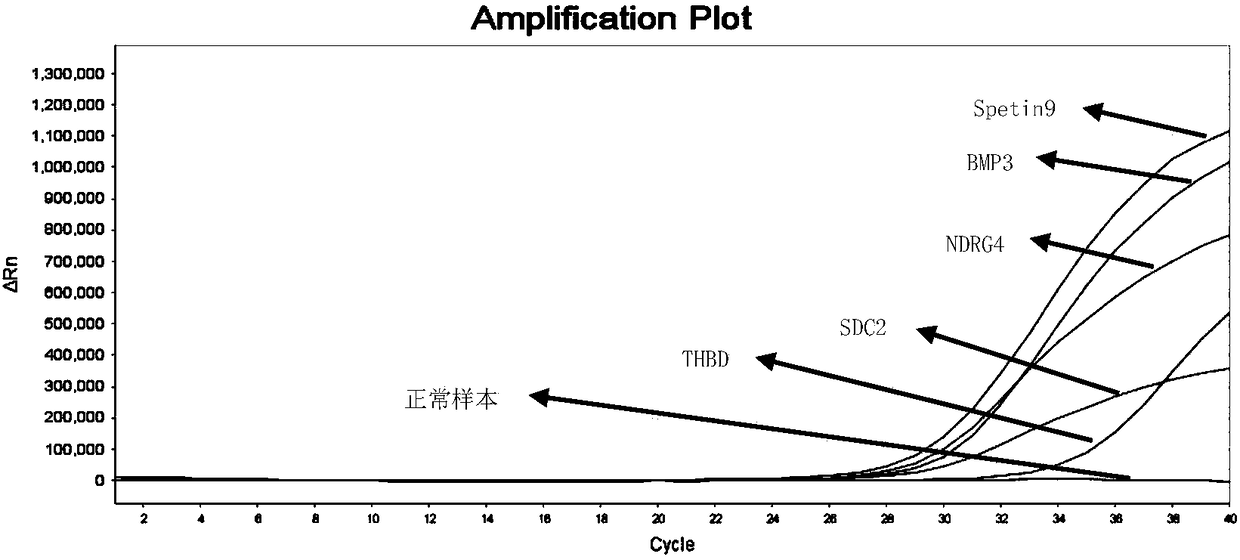
Primer pair, probe and kit used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer and applications thereof
ActiveCN108103195AEasy to sampleSampling non-invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationFluorescence
The invention relates to a primer pair and a probe used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer, and includes the primer pair and the probe used for detecting methylation of genes Spetin9, NDRG4, BMP3, THBD and SDC2 and the primer pair and the probe for internal reference ACTB; the sequences of the primer pair and the probe are represented as the SEQ ID No.1 to the SEQ ID No.18. The invention also provides a kit containing the primer pair and the probe and applications thereof. The application method includes free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, sulfite conversion, PCR amplification reaction, fluorescent signal detection and result determination. The kit and the method are suitable for methylation detection of the five genes Spetin9, THBD, SDC2, NDRG4 and BMP3 in human peripheral blood; compared with a conventional colorectal cancer diagnosis method, the application method fully utilizes the free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, the DNA methylation and QPCR associated technologies, thus developing the kit having high sensitivity and specificity. The primer pair, probe and kit are used for performing early stage noninvasive screening to human colorectal cancer.
Owner:上海酷乐生物科技有限公司
Using size and number aberrations in plasma DNA for detecting cancer
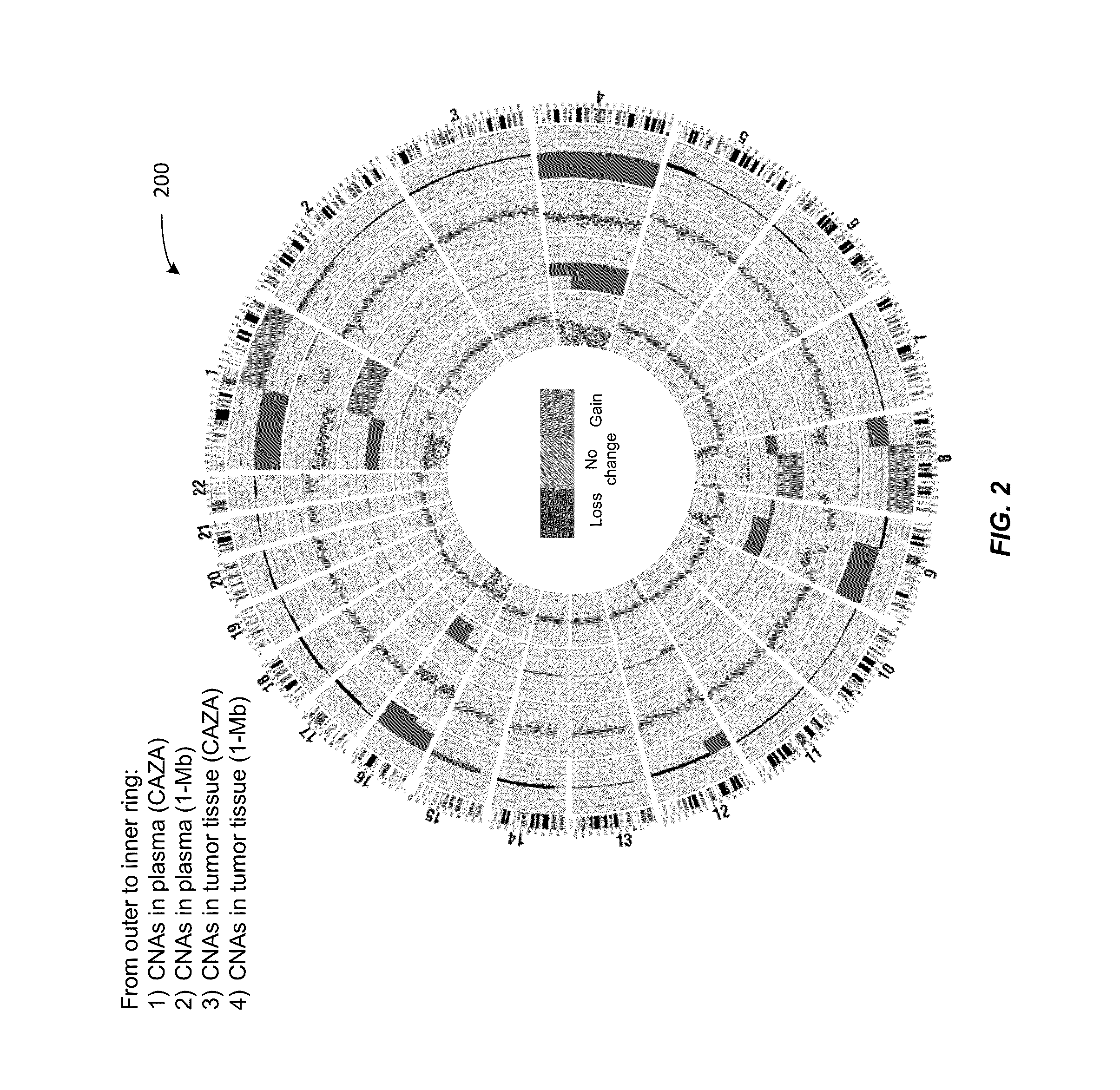
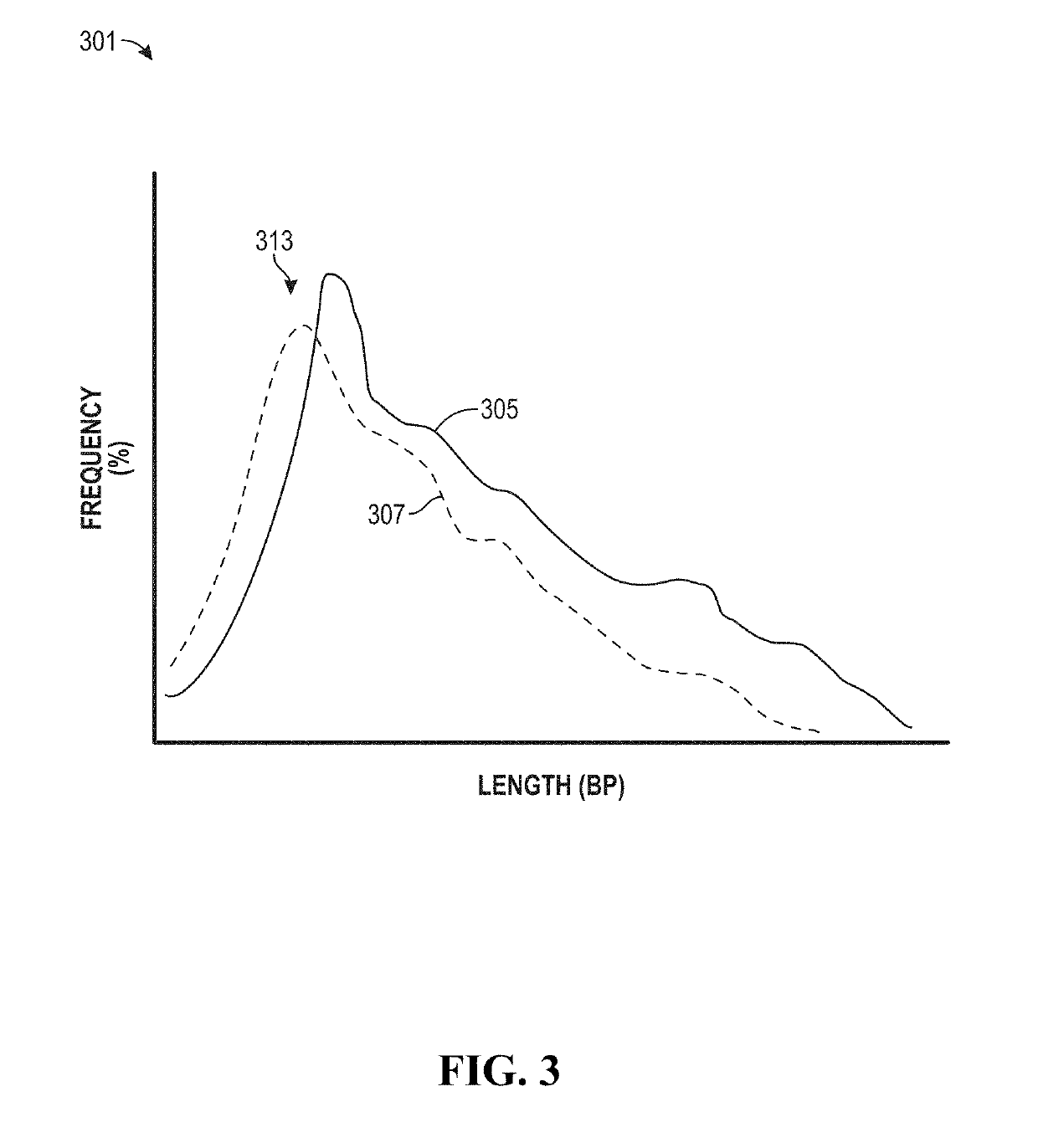
Analysis of tumor-derived circulating cell-free DNA opens up new possibilities for performing liquid biopsies for solid tumor assessment or cancer screening. However, many aspects of the biological characteristics of tumor-derived cell-free DNA remain unclear. Regarding the size profile of plasma DNA molecules, some studies reported increased integrity of tumor-derived plasma DNA while others reported shorter tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules. We performed an analysis of the size profiles of plasma DNA in patients with cancer using massively parallel sequencing at single base resolution and in a genomewide manner. Tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules were further identified using chromosome arm-level z-score analysis (CAZA). We showed that populations of aberrantly short and long DNA molecules co-existed in the plasma of patients with cancer. The short ones preferentially carried the tumor-associated copy number aberrations. These results show the ability to use plasma DNA as a molecular diagnostic tool.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and detection method
InactiveCN102367478AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogenePositive control
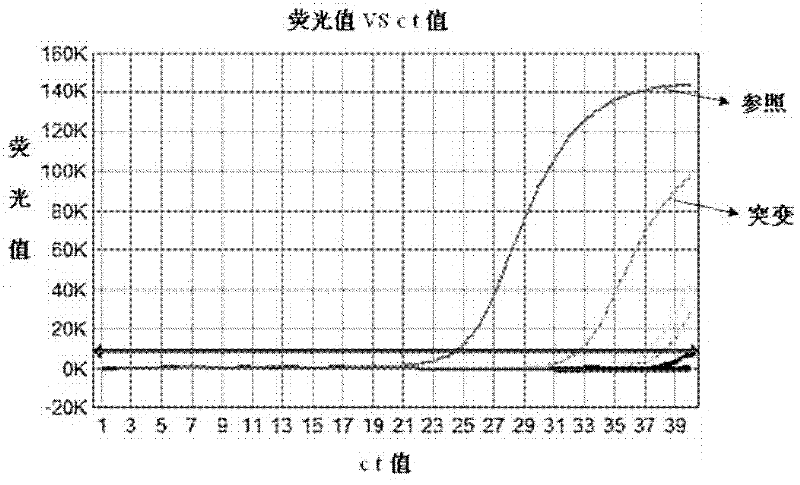
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and aims to provide an ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and a detection method. The kit comprises a qPCR hybrid reaction solution, a locked nucleic acid retardant probe, a reference primer, an ARMS primer and a positive control sample, wherein the qPCR hybrid reaction solution comprises a PCR buffer solution, dNTPs (Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates), MgCl2, GoldStarbest Taq enzyme, a universal PCR reverse primer and a universal TaqMan probe. The kit provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting specific locus mutation of KRAS genes in various cancer tissues with high sensitivity, has high sensitivity, and can be used for detecting genome DNA with various tissue origins, specially free DNA segments adopting cell-free systems, such as blood serum and blood plasma, orother body fluid origins, wherein the genome DNA is derived from cell systems. Compared with direct sequencing and other mutation detection technologies, the kit and the detection method thereof havethe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high throughput, safety, definiteness and objectivity in result identification and the like for detecting the KRAS gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
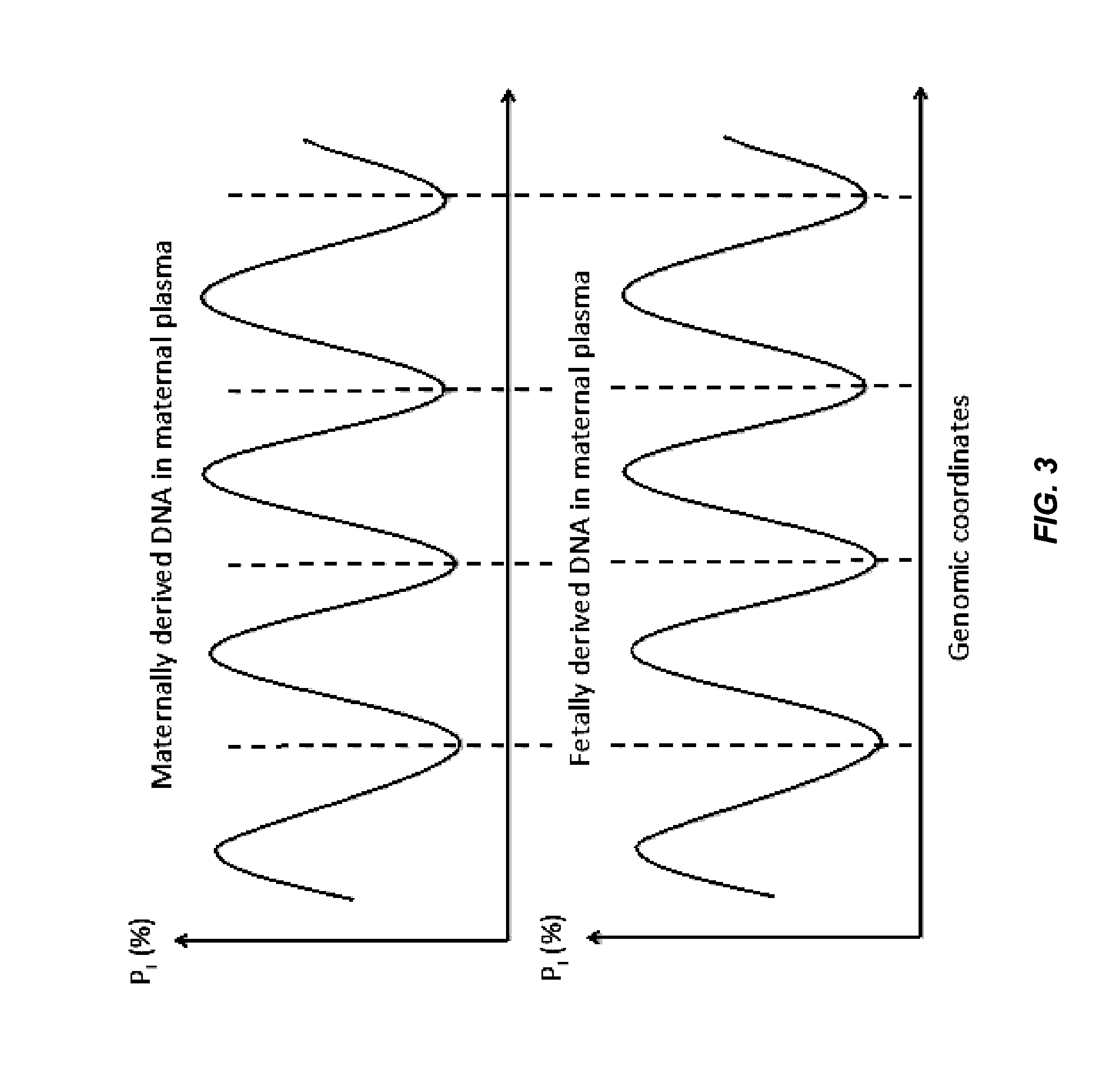
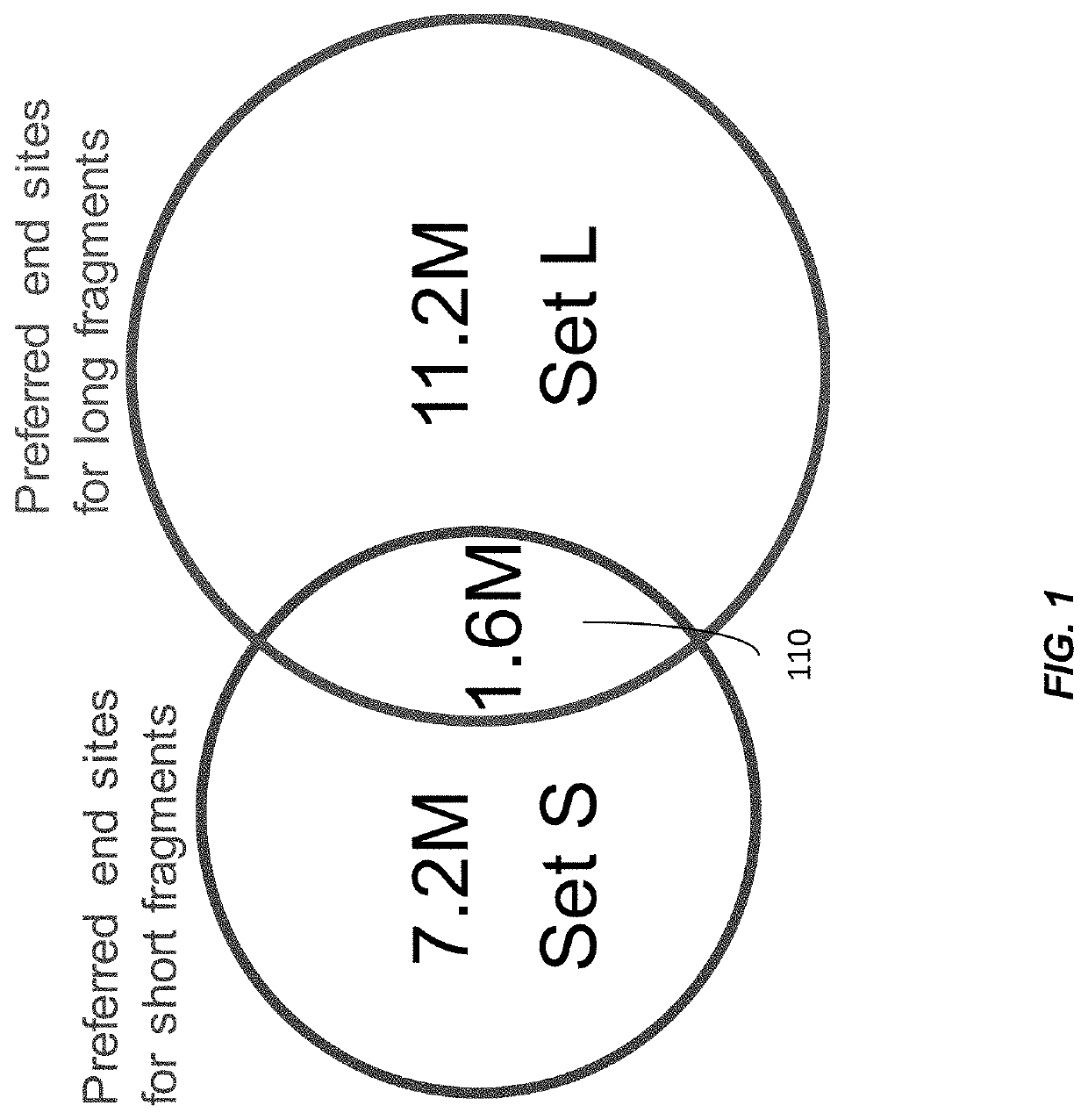
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Non-invasive determination of methylome of fetus or tumor from plasma
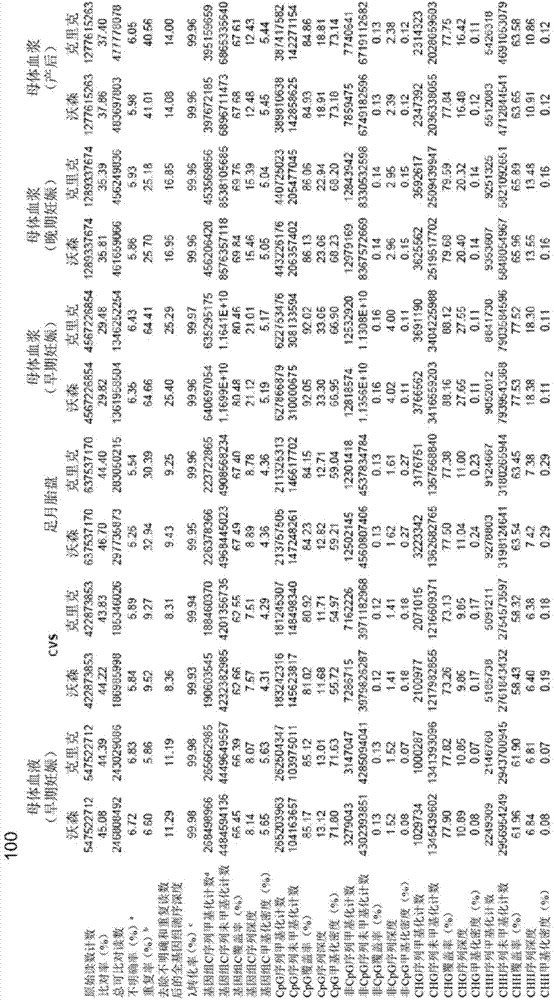
Systems, methods, and apparatuses can determine and use methylation profiles of various tissues and samples. Examples are provided. A methylation profile can be deduced for fetal / tumor tissue based on a comparison of plasma methylation (or other sample with cell-free DNA) to a methylation profile of the mother / patient. A methylation profile can be determined for fetal / tumor tissue using tissue-specific alleles to identify DNA from the fetus / tumor when the sample has a mixture of DNA. A methylation profile can be used to determine copy number variations in genome of a fetus / tumor. Methylation markers for a fetus have been identified via various techniques. The methylation profile can be determined by determining a size parameter of a size distribution of DNA fragments, where reference values for the size parameter can be used to determine methylation levels. Additionally, a methylation level can be used to determine a level of cancer.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
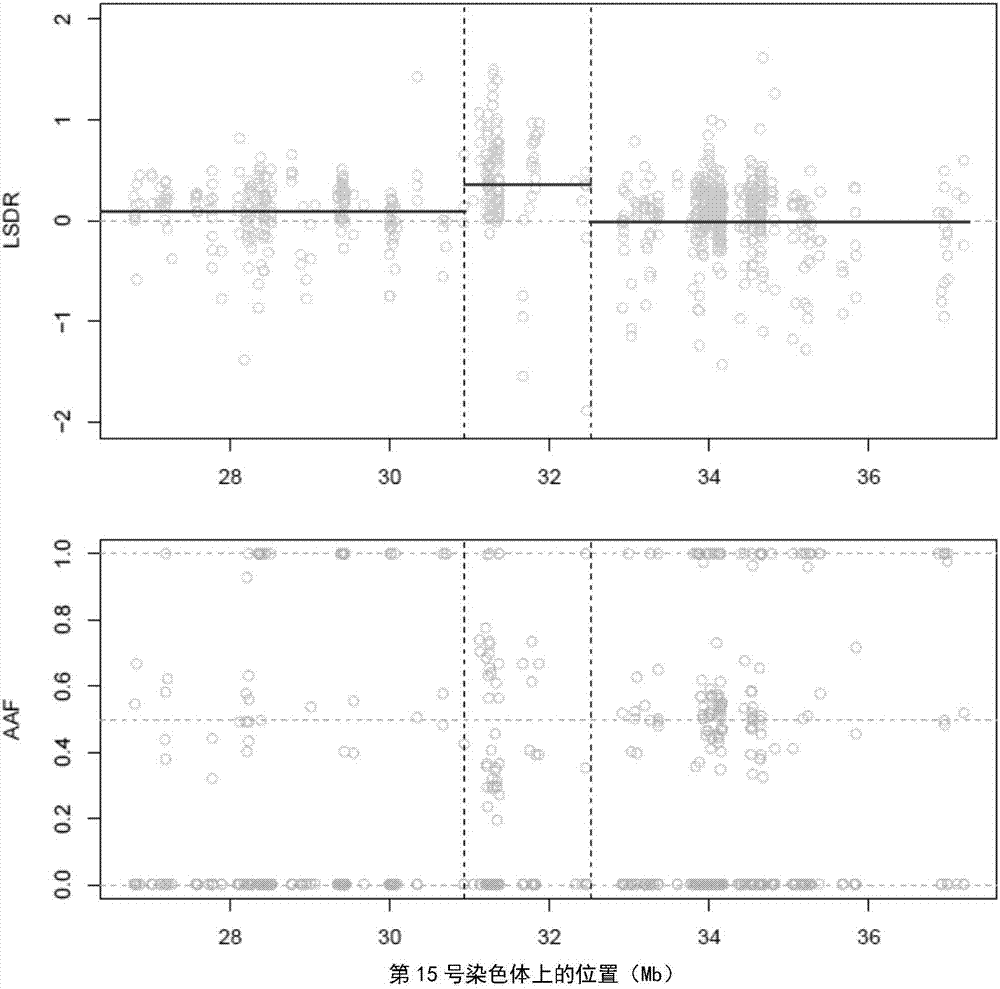
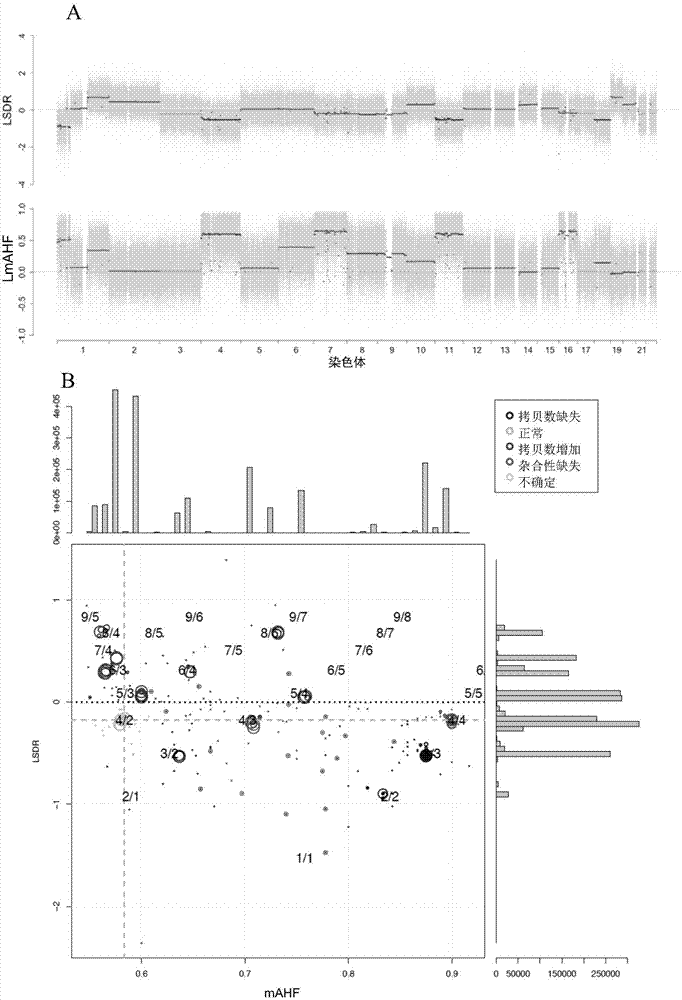
Detection method and system for copy number variation in genome
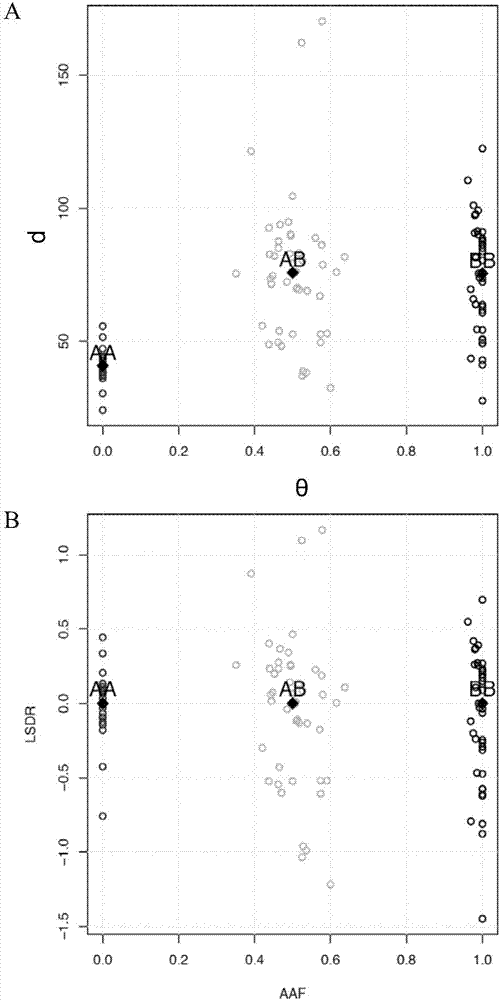
The invention provides a method for analyzing copy number variation in a genome of a testee. According to the method, mathematical manipulation is creatively performed on variables extracted from sequencing data, new two-dimensional variables, namely a sequencing depth ratio (SDR) and alternate allele frequency (AAF) or alternate allelic haploid frequency (AHF) are derived, the signal / noise ratio is further increased, detection sensitivity and precision are improved, and information contained in the high-throughput DNA sequencing data is utilized more fully. Besides, the method is used for processing free DNA in a body fluid sample of the testee, wherein when a CNV feature signal of a certain locus of the genome is extracted from the sequencing data, the information close to the locus is introduced, so that signal strength is greatly improved, and the copy number variation in the free DNA in urine or serum can be effectively detected. The invention furthermore provides a system for implementing the method.
Owner:郝柯 +1
Preservative for preserving free DNA in peripheral blood
The invention discloses a preservative for preserving free DNA in peripheral blood. The preservative is composed of the following components in percentage by weight: 60 to 80% of ultrapure sterile water, 5 to 8% of anti-coagulant, 10 to 25% of antiseptic, 1 to 5% of metabolic inhibitor, and 0.5 to 3% of nuclease inhibitor. The provided preservative can preserve peripheral blood for at least 7 days at a normal temperature, 14 days at most, the blood can be transported at a normal temperature for 72 hours or more under the assistance of the preservative, 96 hours at most; and the free DNA amount is basically not affected during the period.
Owner:厦门万基生物科技有限公司 +1
Removal of DNA fragments in mRNA production process
The present invention describes methods of removing DNA from an RNA transcript during the mRNA production process. The method embodies procedures for obtaining an in vitro transcription product, and removing any DNA from the product. The DNA can be removed by adding either free DNase or a resin containing immobilized DNase to the product, and recovering the RNA transcript. Alternatively, the DNA template used in the in vitro transcription reaction is labeled. After transcription, the product is applied to a resin that is configured to bind the label, and the RNA transcript is recovered. To detect whether any residual impurities are left in the RNA transcript product, the product is subjected to nuclease digestion and subsequently to liquid chromato graphy-tandem mass spectrometry analysis to quantitate any residual DNA. The present invention demonstrates efficient and effective methods of isolating an RNA transcript from an in vitro transcription product.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Process for microsatellite instability detection
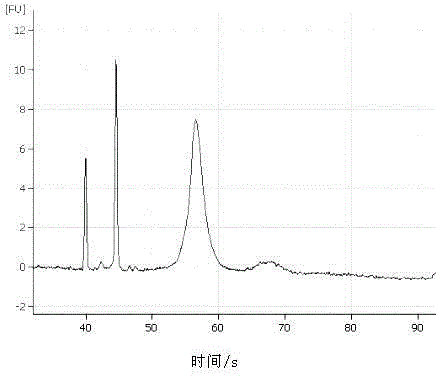
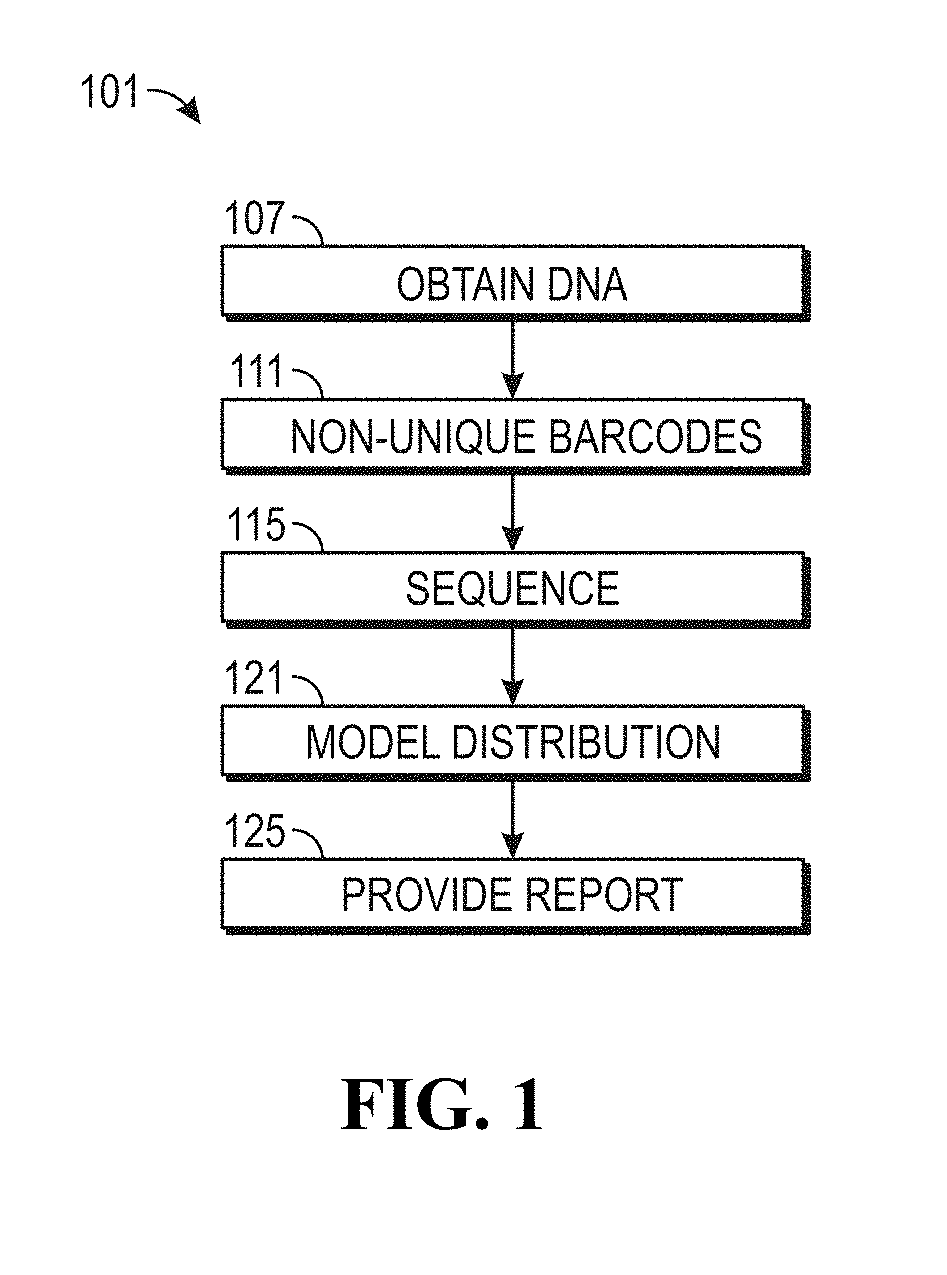
ActiveUS20190169685A1Useful in detectionIncrease the burdenTherapiesHealth-index calculationCell freeNucleotide
The invention provides methods for determining the MSI status of a patient by liquid biopsy with sample preparation using hybrid capture and non-unique barcodes. In certain aspects, the invention provides a method of detecting microsatellite instability (MSI). The method includes obtaining cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from a sample of blood or plasma from a patient and sequencing portions of the cfDNA to obtain sequences of a plurality of tracts of nucleotide repeats in the cfDNA. A report is provided describing an MSI status in the patient when a distribution of lengths of the plurality of tracts has peaks that deviate significantly from peaks in a reference distribution.
Owner:PERSONAL GENOME DIAGNOSTICS INC
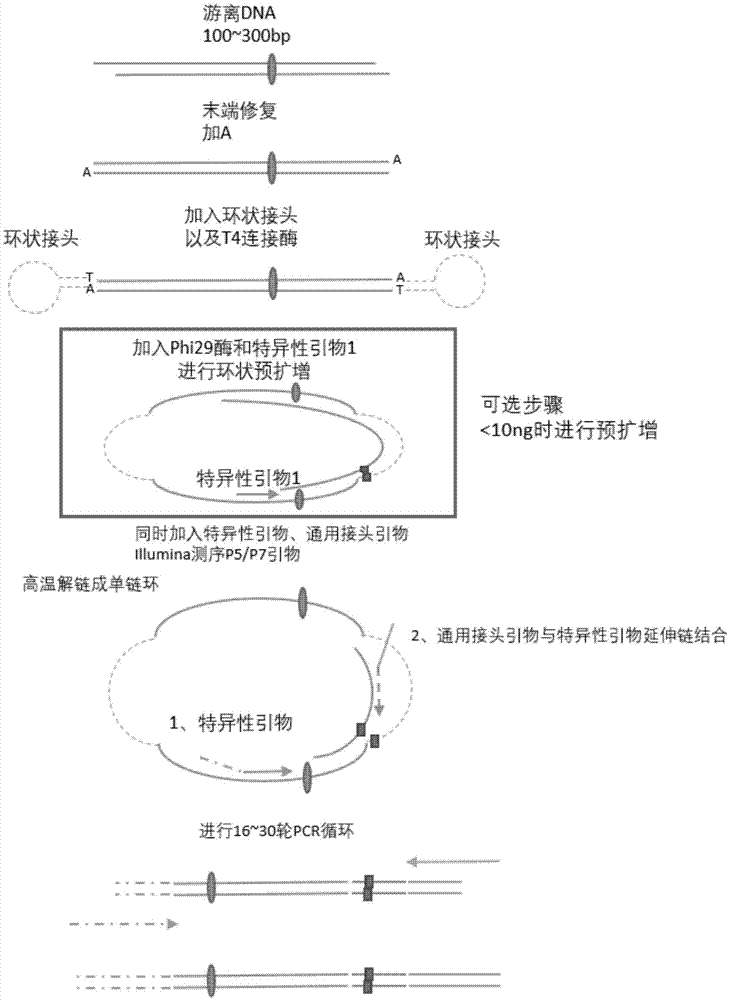
Method for performing multi-target-site amplification library construction on plasma free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The invention discloses a method for performing multi-target-site amplification library construction on plasma free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The method sequentially comprises steps as follows: 1), tail end repairing and A addition are performed; 2), linker connection is performed: a linker DNA with an annular hairpin structure formed through annealing is added to a DNA fragment with A addition at the tail end in the step 1), so that double-stranded DNA after being combined with annular hairpin linkers on two sides is obtained; when the amount of plasma free DNA extracted and purified in the step 1) is smaller than or equal to 10 ng, a step 3) is performed; otherwise, when the amount of plasma free DNA extracted and purified in the step 1) is larger than 10 ng, a step 4) is performed; step 3), a specific primer I, Phi29 enzyme and a buffer solution are added to DNA with linker addition in the step 2), and linear amplification is performed; step 4), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed: amplification products constitute a free DNA mutation site enrichment sequencing library.
Owner:HANGZHOU GUKUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Size-tagged preferred ends and orientation-aware analysis for measuring properties of cell-free mixtures
Various applications can use fragmentation patterns related of cell-free DNA, e.g., plasma DNA and serum DNA. For example, the end positions of DNA fragments can be used for various applications. The fragmentation patterns of short and long DNA molecules can be associated with different preferred DNA end positions, referred to as size-tagged preferred ends. In another example, the fragmentation patterns relating to tissue-specific open chromatin regions were analyzed. A classification of a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type can be determined in a mixture of cell-free DNA from different tissue types. Additionally, a property of a particular tissue type can be determined, e.g., whether a sequence imbalance exists in a particular region for a tissue type or whether a pathology exists for the tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
Gene group and kit for diagnosing lung caner, and diagnosis method thereof
InactiveCN107475370AExcellent detection depthExcellent detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationA-DNABlood plasma
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering and biotechnologic detection, and concretely relates to a gene group and a kit for diagnosing lung cancer, and a diagnosis method thereof. The gene group for diagnosing the lung cancer includes ABCB1, AKT1, ALK, APC, ATIC and other 63 genes. The method using the gene group to diagnose the lung cancer comprises the following steps: (1) extracting free DNA and genome DNA from the plasma of a sample to be detected; and (2) breaking the genome DNA into fragments with the length of 150-250 bp, carrying out hybrid capture on the broken genome DNA and the free DNA to construct a DNA library, carrying out online sequencing, and analyzing the obtained sequencing result. Exon and partial intron regions of the 68 genes of the free DNA are enriched at one time by a probe capture technology to realize multi-gene and multi-target parallel deep high-throughput sequencing with high accuracy, optimize the detection flow and improve the detection precision, so liquid biopsy, low-frequency detection and tumor diagnosis become possible.
Owner:天津脉络医学检验有限公司
Fetal free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library quantitative standard and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105239164ACoefficient of variation between differences is smallEasy to storeNucleotide librariesLibrary creationIon semiconductor sequencingQuality control
The invention discloses a qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) quantitative standard for detecting library DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) concentration of aneuploids, i.e., 21 trisome, 18 trisome and 13 trisome of fetal chromosomes based on a semiconductor sequencing method and a preparation method therefor and belongs to the field of noninvasive prenatal detection on fetal aneuploids. The standard is used for carrying out quality control on detection concentration of detected samples. The preparation method for the qPCR quantitative standard disclosed by the invention comprises five steps: (1) synthesizing joint sequences and primers; (2) preparing simulated fetal free DNA libraries; (3) amplifying and purifying the libraries; (4) producing a library standard curve; and (5) carrying out sample detection. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the DNA concentration of sample libraries can be rapidly determined, and a guarantee of accuracy and validity of noninvasive prenatal detection on the aneuploids, i.e., the 21 trisome, the 18 trisome and the 13 trisome of the fetal chromosomes is provided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH +1
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20070122835A1Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
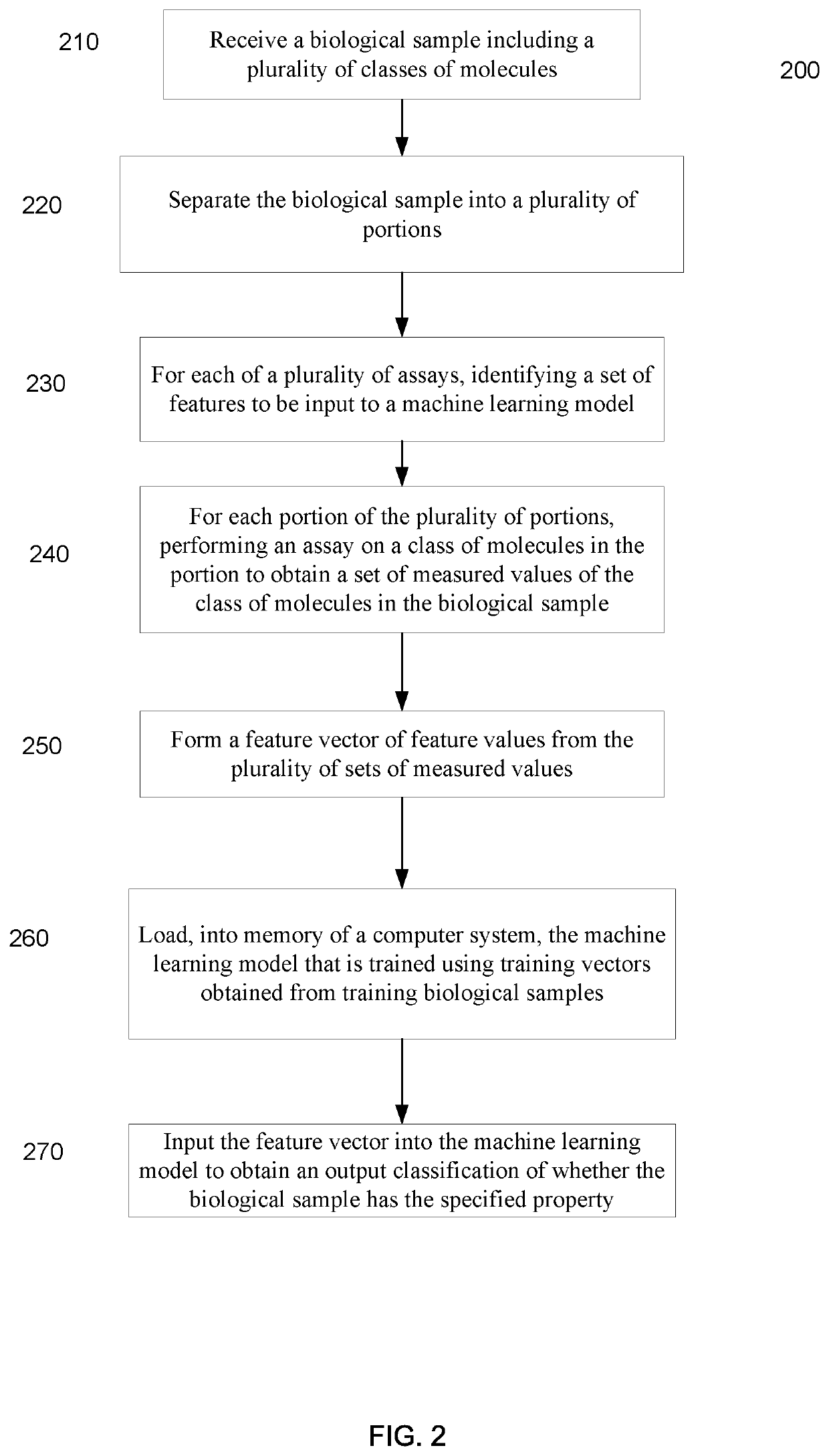
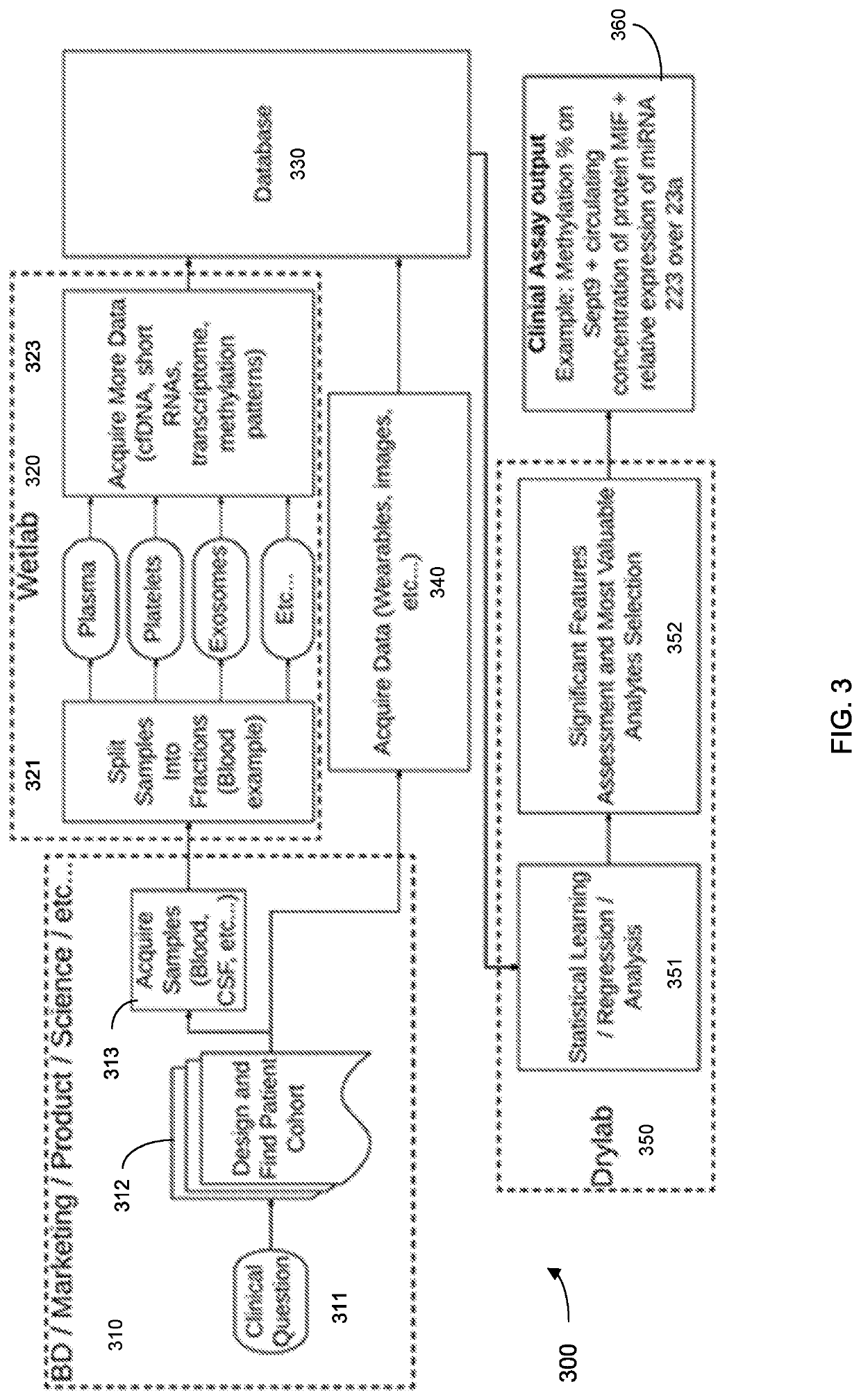
Machine learning implementation for multi-analyte assay development and testing
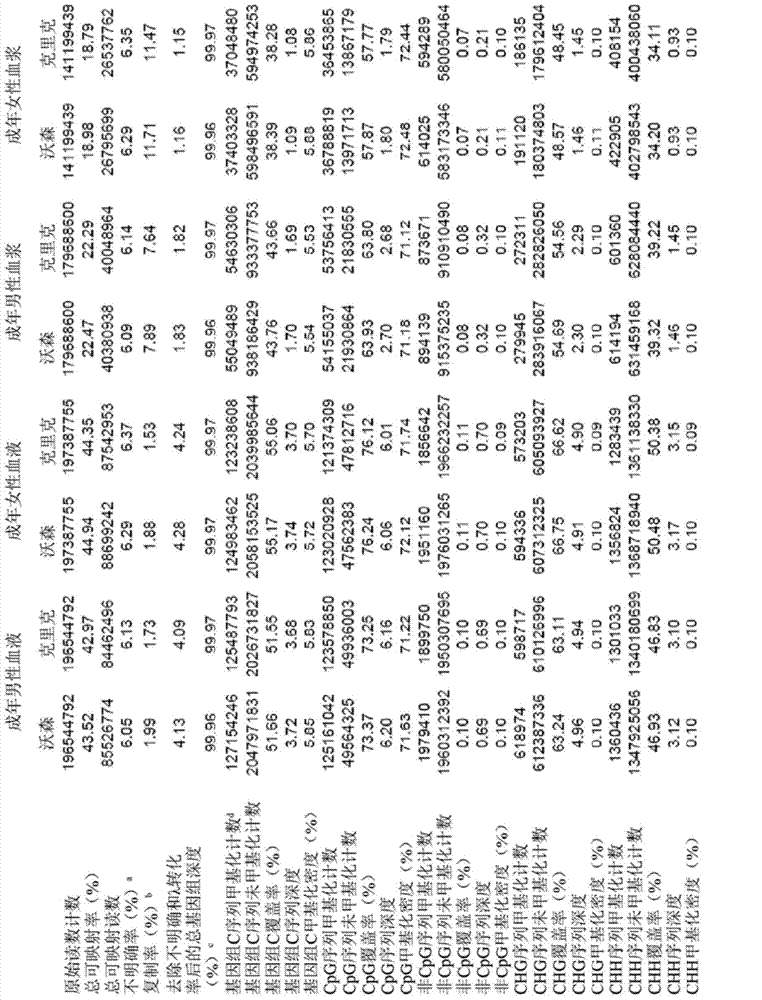
Systems and methods that analyze blood-based cancer diagnostic tests using multiple classes of molecules are described. The system uses machine learning (ML) to analyze multiple analytes, for example cell-free DNA, cell-free microRNA, and circulating proteins, from a biological sample. The system can use multiple assays, e.g., whole-genome sequencing, whole-genome bisulfite sequencing or EM-seq, small-RNA sequencing, and quantitative immunoassay. This can increase the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostics by exploiting independent information between signals. During operation, the system receives a biological sample, and separates a plurality of molecule classes from the sample. For a plurality of assays, the system identifies feature sets to input to a machine learning model. The system performs an assay on each molecule class and forms a feature vector from the measured values. The system inputs the feature vector into the machine learning model and obtains an output classification of whether the sample has a specified property.
Owner:FREENOME HLDG INC
Methods of quantifying cell-free DNA
Owner:CHRONIX BIOMEDICAL
Construction method of small-fragment DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library based on Illumina Hiseq 2500 sequencing platform
InactiveCN104946623AReduce dosageReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMagnetic beadBioinformatics
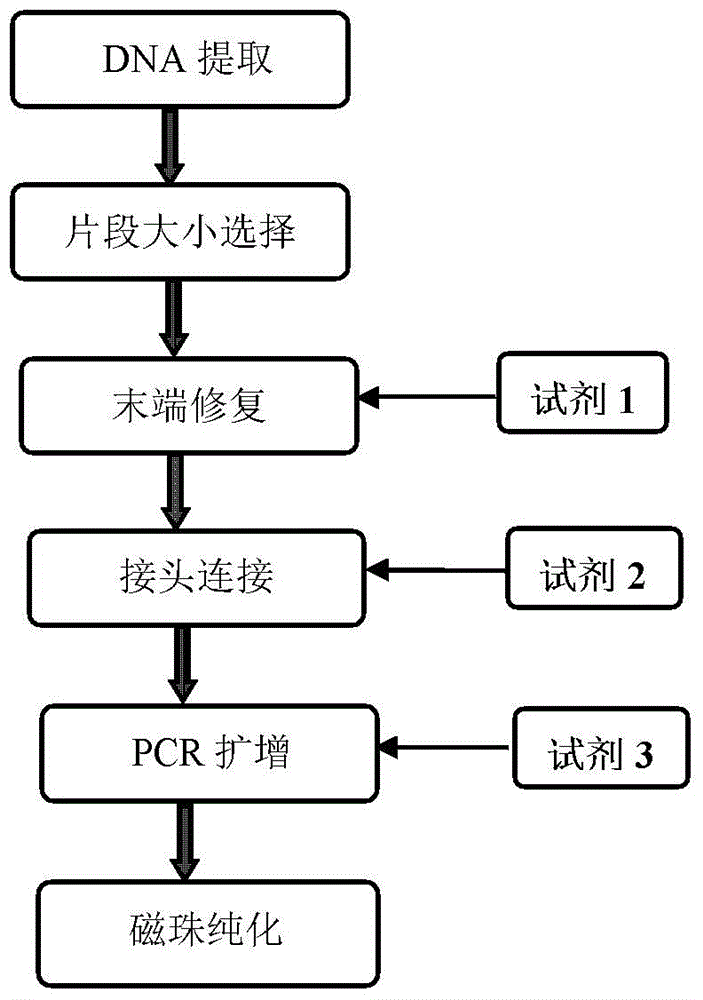
The invention discloses a construction method of a small-fragment DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library based on an Illumina Hiseq 2500 sequencing platform, which comprises the following steps: blood free DNA extraction, fragment size screening, terminal repair, 3' terminal linker addition, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, magnetic bead purification and the like. Compared with the library construction process based on a sequencing platform in the past, the method disclosed by the invention simplifies the experiment process, shortens the library construction time, optimizes the reaction system, greatly reduces the reagent consumption, lowers the library construction cost, lowers the library loss, and is suitable for constructing an artificially-fragmented small DNA library.
Owner:浙江圣庭医学检验实验室有限公司
Kit for detecting nucleic acid of mycobacterium tuberculosis and method thereof
ActiveCN102373273AStrong specificityGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlContamination
The invention relates to a rapid detecting technology for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis through nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification and a kit for qualitative detection. The kit comprises an instrument-free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction kit, a mycobacterium tuberculosis nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification reaction liquid, a contamination-prevention nucleic acid amplification product detecting device, mycobacterium tuberculosis positive control, and mycobacterium tuberculosis negative control. The kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity and high reaction speed, wherein 1-1.5 hours are only needed from the step of processing a single sample to the step of completing the detection; and the kit can simultaneously meet requirements on sample detection of medium flux and low flux and is particularly suitable for being used in field detection and primary hospitals, and one constant-temperature instrument is only needed in the entire reaction process.
Owner:USTAR BIOTECHNOLOGIES (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Construction method of plasma free DNA library
The invention discloses a 'construction method for a small amount of DNA library'. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out end repairing on plasma free DNA or fragmented DNA and simultaneously carrying out phosphorylation modifying on 5' terminal to obtain modified DNA; later, implementing blunt end linking directly to an artificial linker and purifying to obtain relatively pure linker-containing DNA having a gap on joint; then repairing the gap by virtue of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) polymerase before PCR amplification to obtain repaired complete linker-containing DNA; and carrying out PCR amplification reaction and purifying a finished product to obtain a final high-throughput sequencing library. The method is not only simple, convenient and efficient, and is capable of avoiding a purification step and reducing DNA loss in a library construction process, but also can effectively solve a problem of linker self-linking which is easy to occur in a micro-DNA library construction process by virtue of a special linker and blunt end linking way; and meanwhile, by repairing the gap before amplification, sufficient complete templates are provided before amplification for the amplification reaction.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Construction method, kit and application of plasma free DNA methylation detection library
InactiveCN107541791AImprove recycling efficiencyReduce the initial amount of conventional trace methylation library constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMagnetic beadSmall fragment
The invention discloses a construction method, a kit and application of a plasma free DNA methylation detection library. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1 of extracting plasmafree DNA from a blood sample; S2 of performing tail end repair and 3' terminal A base addition on the plasma free DNA; S3 of connecting the tail ends of the plasma free DNA obtained in the S2 with C methylation modified connectors; S4 of performing bisulfite conversion on a product obtained in S3 and performing PCR expansion; S5 of performing magnetic bead purification on the PCR product of S4 andremoving small-fragment DNA which is not amplified in a non-specific mode and primer dimer; S6 of performing PCR amplification on a product of S5 and performing magnetic bead purification to obtain aplasma free DNA methylation detection library. By means of the technical scheme of the construction method disclosed by the invention, an initial amount of general microscale methylation library construction is reduced, library construction steps are simplified, library recycling efficiency is improved, and a foundation is established for sequentially screening tumor diagnosis markers through plasma free DNA methylation difference locus.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Silica gel absorption column extraction kit and method for free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of blood plasma or blood serum
InactiveCN108070584AGuaranteed unobstructedGuaranteed to dissolveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAbsorption columnBlood plasma
The invention discloses a silica gel absorption column extraction kit and method for free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of blood plasma or blood serum and relates to the fieldof molecular biology. The kit comprises proteinase K, isopropyl alcohol, absolute ethyl alcohol and threefold-distilled water, and further comprises a lysis solution containing a nucleic acid separation accelerant, an adsorption solution containing a nucleic acid adsorption accelerant and a washing solution; the method is mainly carried out by utilizing the kit. By adopting the kit provided by the invention, the free DNA and RNA in the blood plasma or the blood serum can be rapidly and completely released, and denatured protein keeps a dissolved state; under the action of the adsorption solution, the free DNA and RNA are efficiently adsorbed on a silica gel absorption column; after the silica gel absorption column is washed by the washing solution, the free DNA and RNA with relatively high purity and concentration are obtained.
Owner:江苏然科生物技术有限公司
Method for detecting fetal thalassemia pathogenic gene and kit
ActiveCN108642160AEnable prenatal testingSmall sample sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementThalassemiaGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fetal thalassemia pathogenic gene, which comprises the following steps of: (1) screening SNP sites, wherein the SNP sites are used for designing a primer pool of the thalassemia gene in an amplification genome and for capturing the probe of the thalassemia gene of the free DNA in the plasma of a pregnant woman; (2) extracting the free DNA in the plasma of the pregnant woman and the whole blood genomic DNA of the father, the mother and a born sibling and constructing a corresponding DNA library, and carrying out template preparation and enrichment; (3) sequencing the free DNA and the whole blood genomic DNA library in step (2); (4) constructing the haploid genotype of the SNP sites on the thalassemia gene, combining the sequencing informationof the free DNA and the whole blood genomic DNA library, analyzing the genetic condition of the parent source and the genetic condition of the parent source, so as to determine the corresponding genotype of the SNP sites of the fetal. According to the method, target area capture and high-throughput sequencing technology are used, so that the noninvasive antepartum detection of the thalassemia isrealized; the required sample amount is small; on the basis of detecting the mutation of the parent source, the method can realize the detection of the gene mutation of the maternal source of the fetal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com