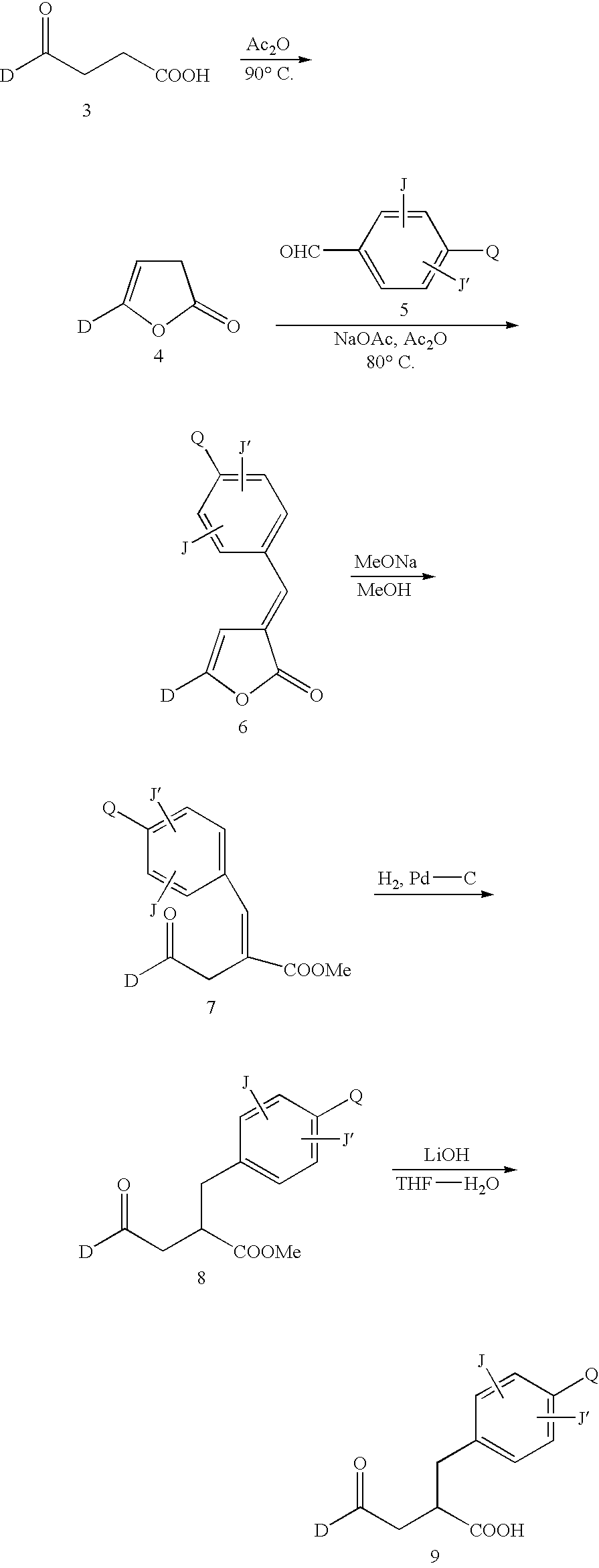
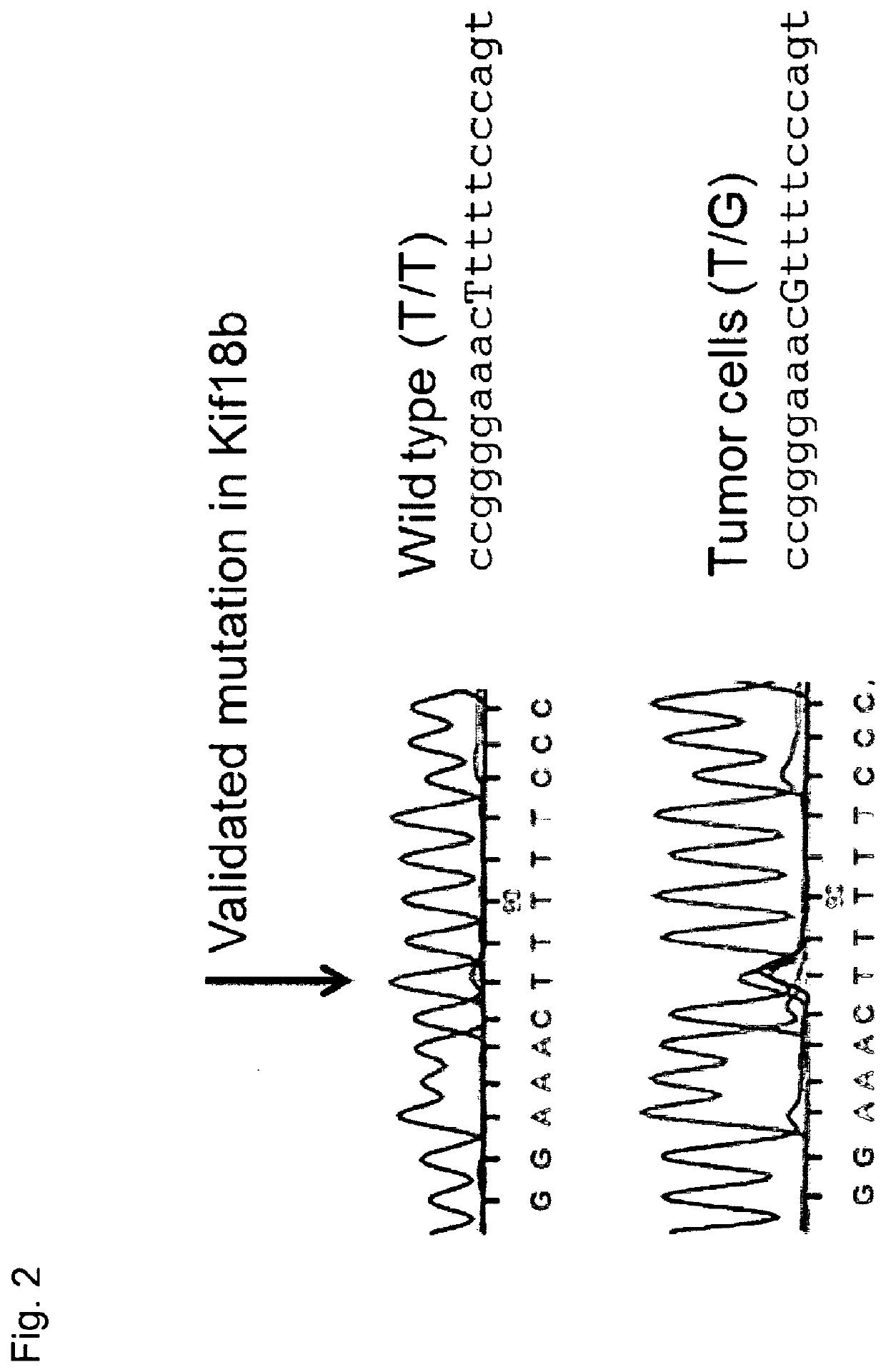
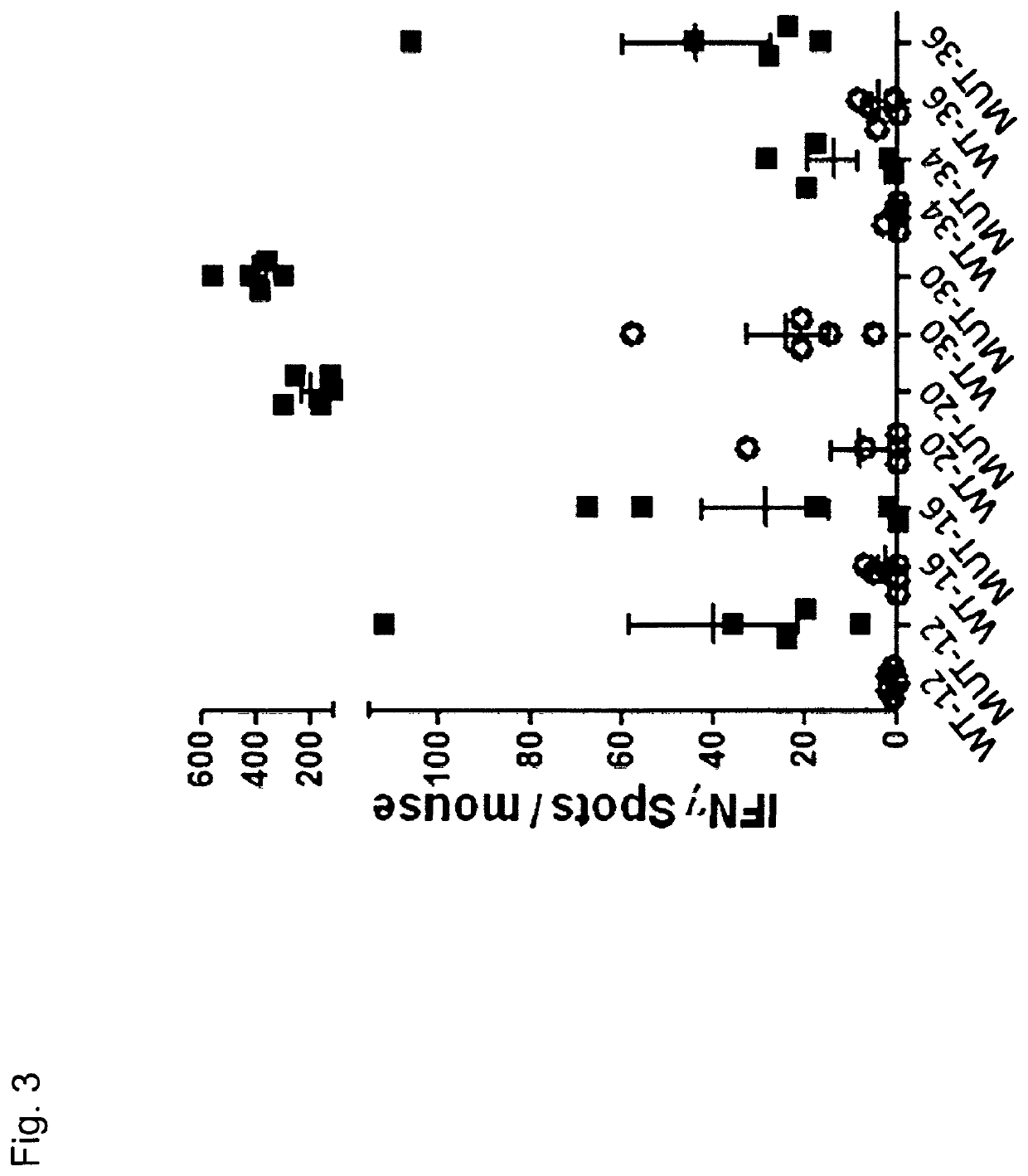
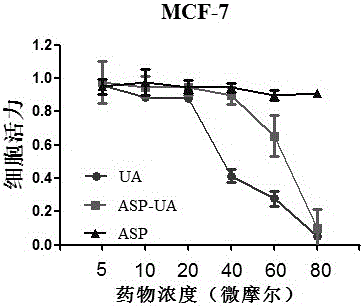
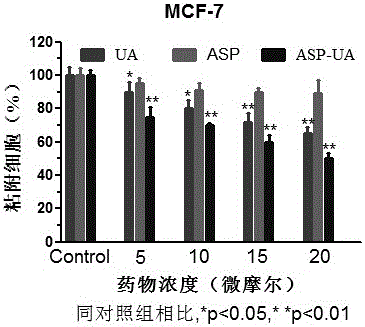
Patents
Literature
367 results about "Tumour metastasis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Individualized vaccines for cancer
ActiveUS20140178438A1Reduces steric hindranceImprove translationVaccinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
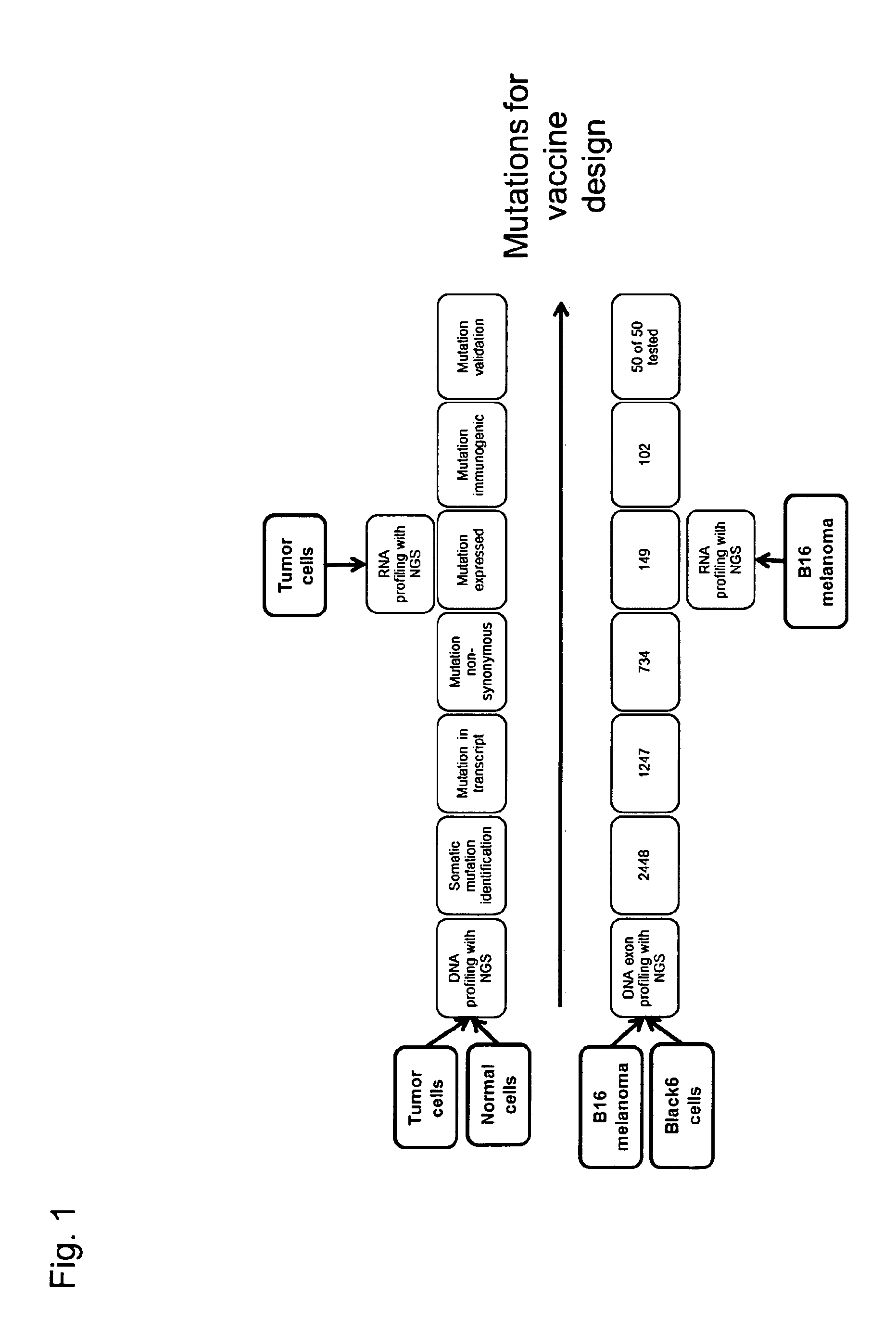
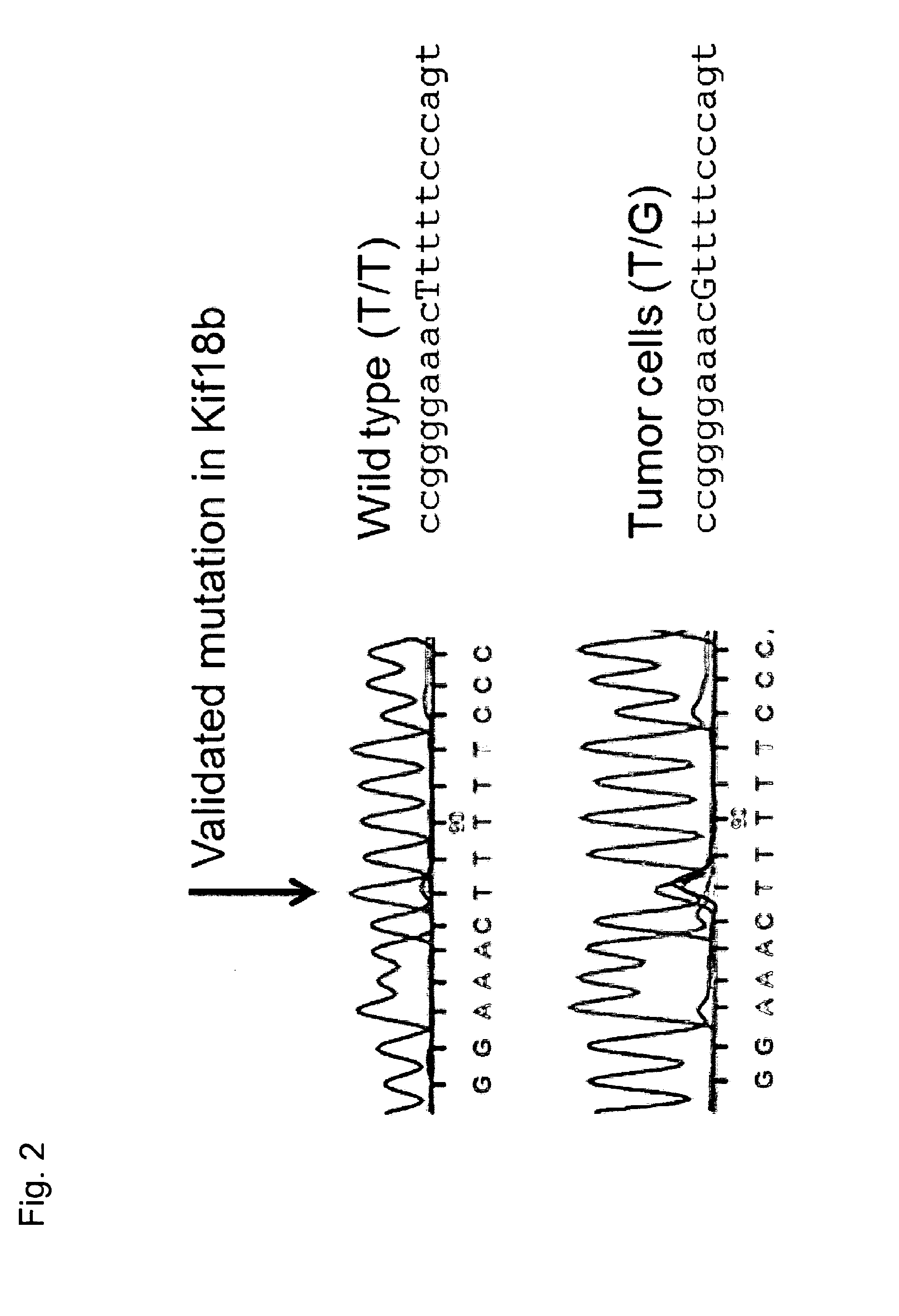
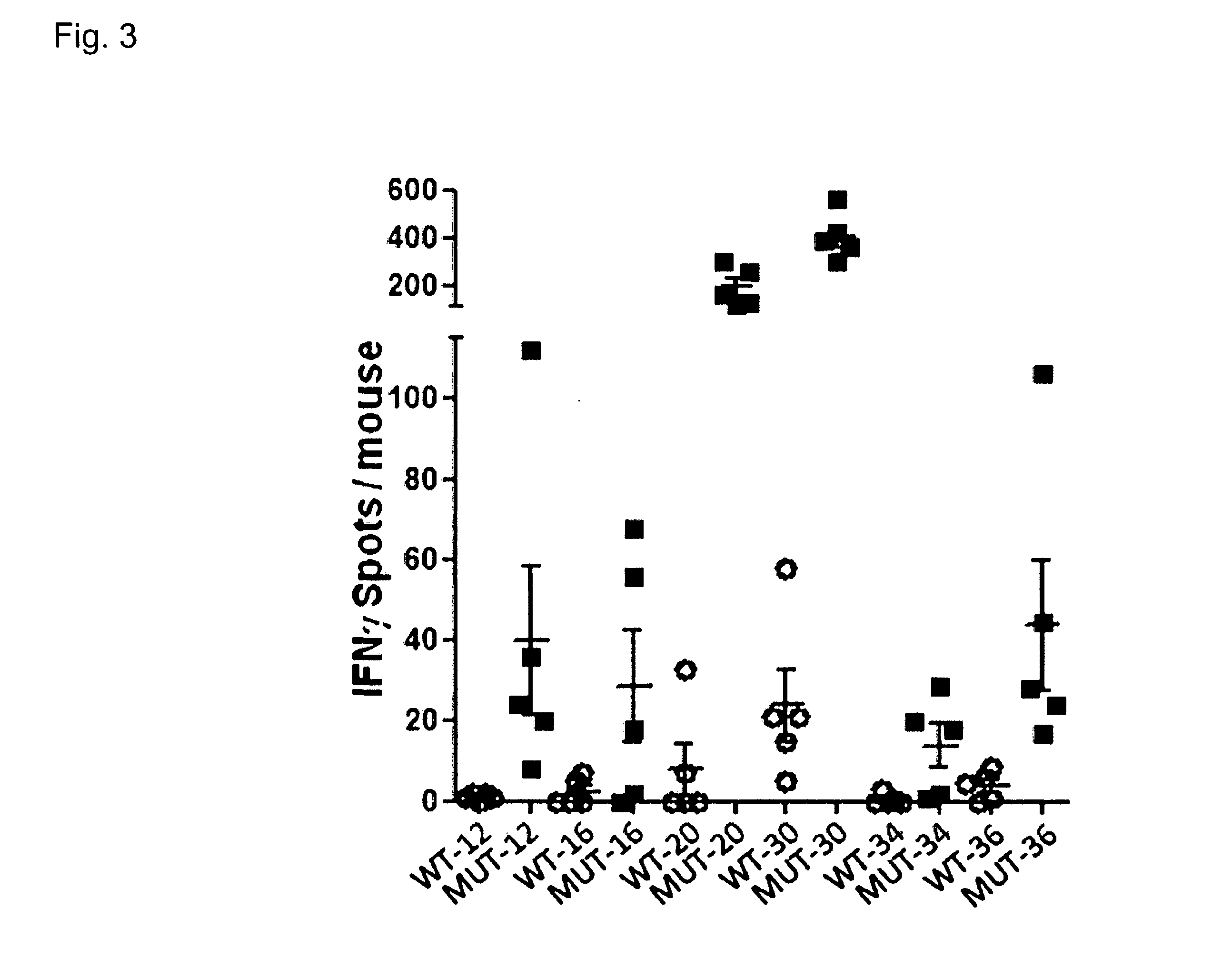
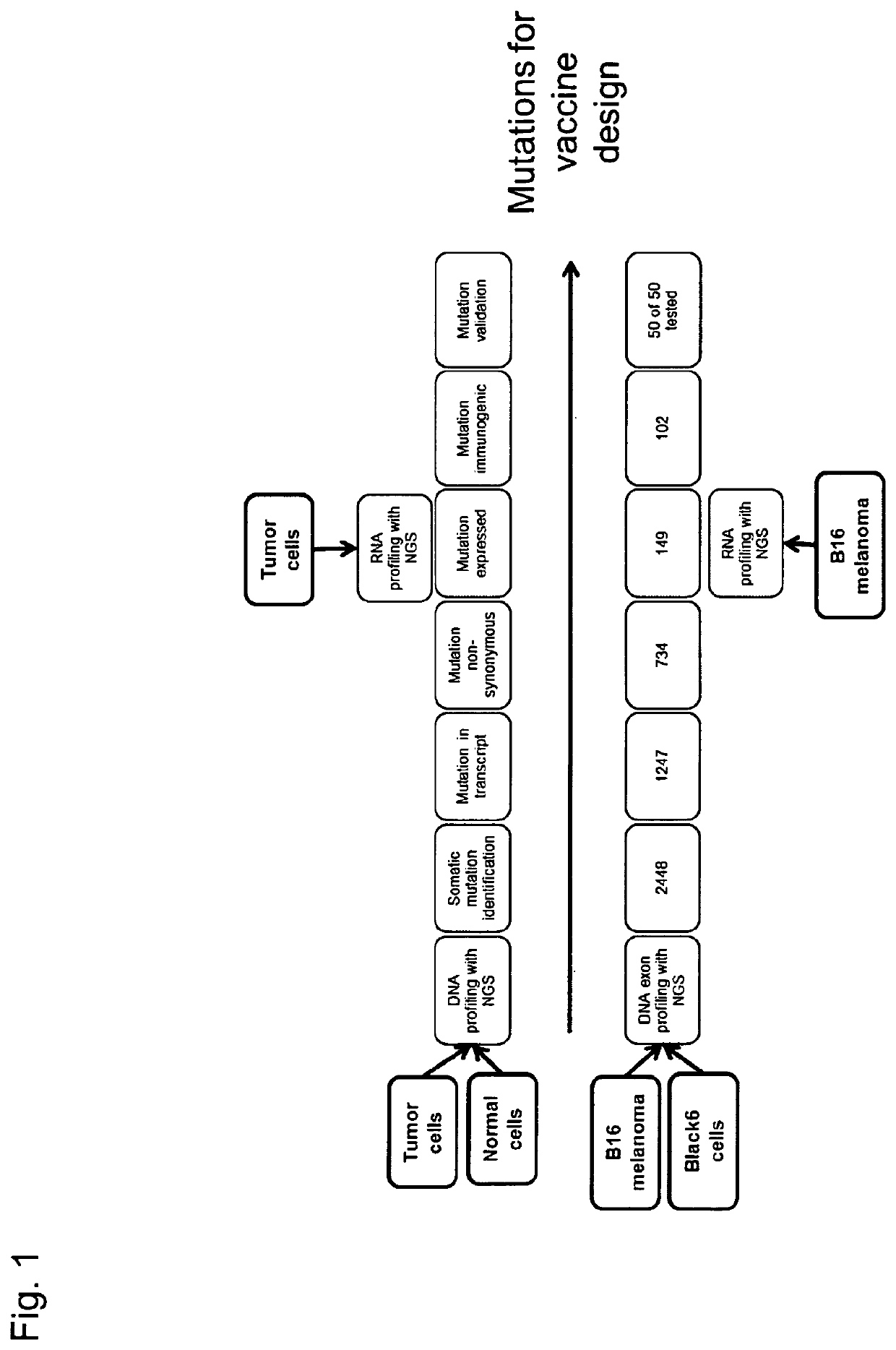
The present invention relates to the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and are potentially useful for immunotherapy of the primary tumor as well as tumor metastases. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for providing an individualized cancer vaccine comprising the steps: (a) identifying cancer specific somatic mutations in a tumor specimen of a cancer patient to provide a cancer mutation signature of the patient; and (b) providing a vaccine featuring the cancer mutation signature obtained in step (a). In a further aspect, the present invention relates to vaccines which are obtainable by said method.
Owner:TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GGMBH +1
Cytotoxicity mediation of cells evidencing surface expression of TROP-2
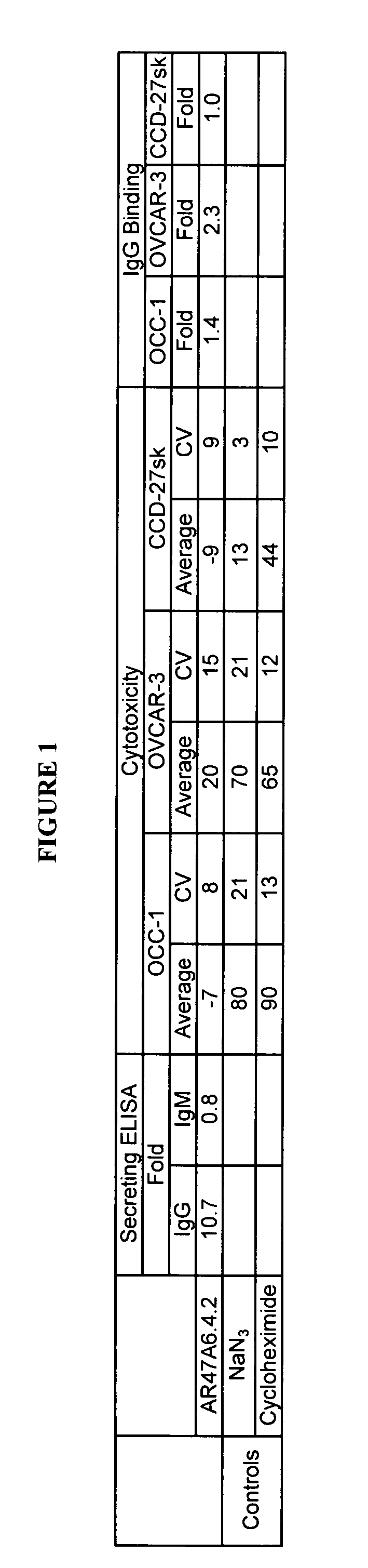
InactiveUS7420040B2Reduce the likelihood of problemsProlong survival timeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationDiseaseHematopoietic cell
The present invention relates to a method for producing cancerous disease modifying antibodies using a novel paradigm of screening. By segregating the anti-cancer antibodies using cancer cell cytotoxicity as an end point, the process makes possible the production of anti-cancer antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The antibodies can be used in aid of staging and diagnosis of a cancer, and can be used to treat primary tumors and tumor metastases. The anti-cancer antibodies can be conjugated to toxins, enzymes, radioactive compounds, cytokines, interferons, target or reporter moieties and hematogenous cells.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
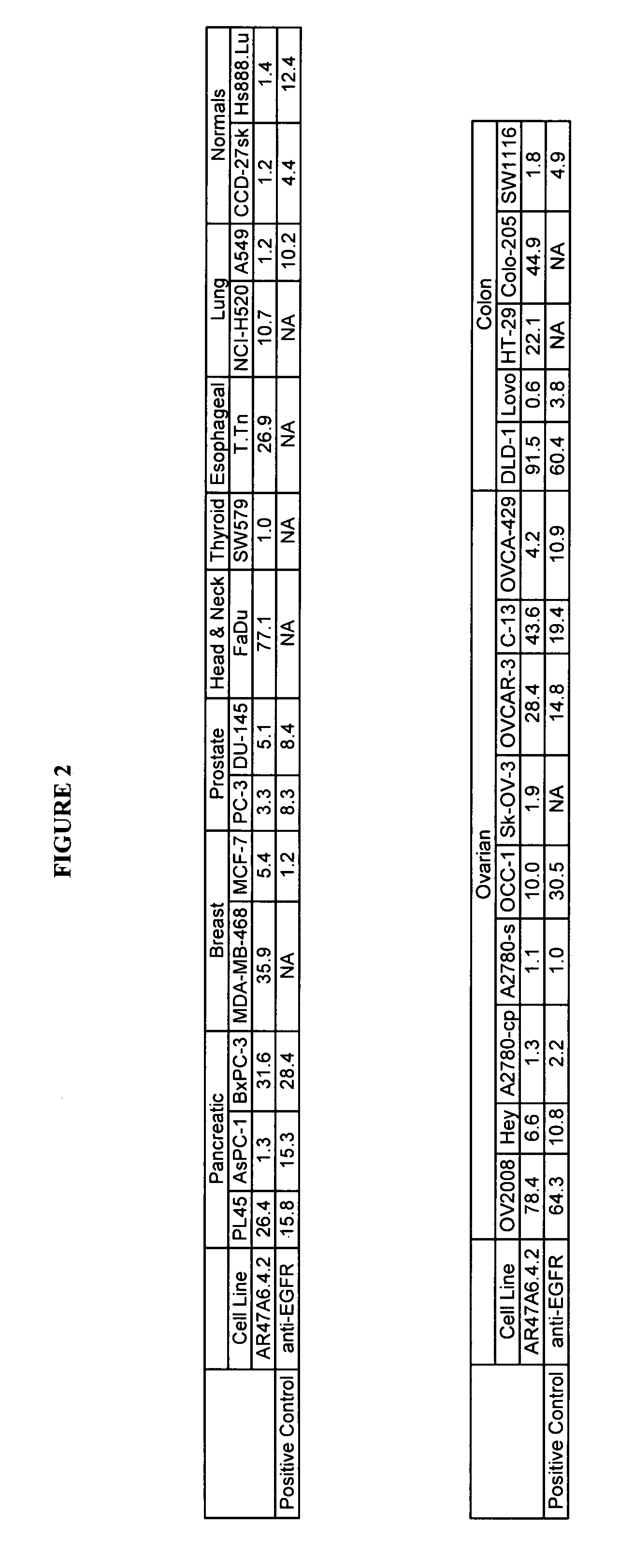
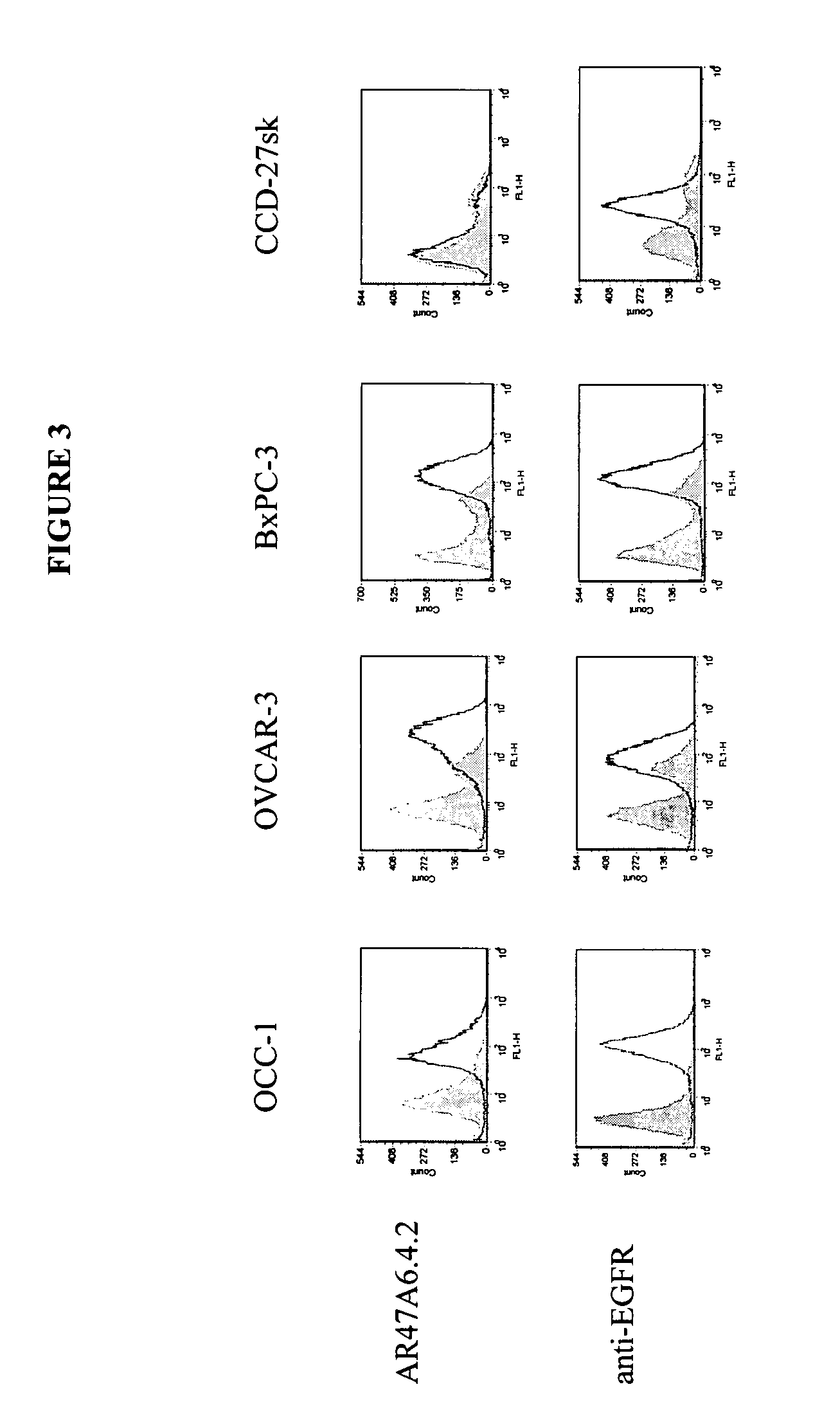
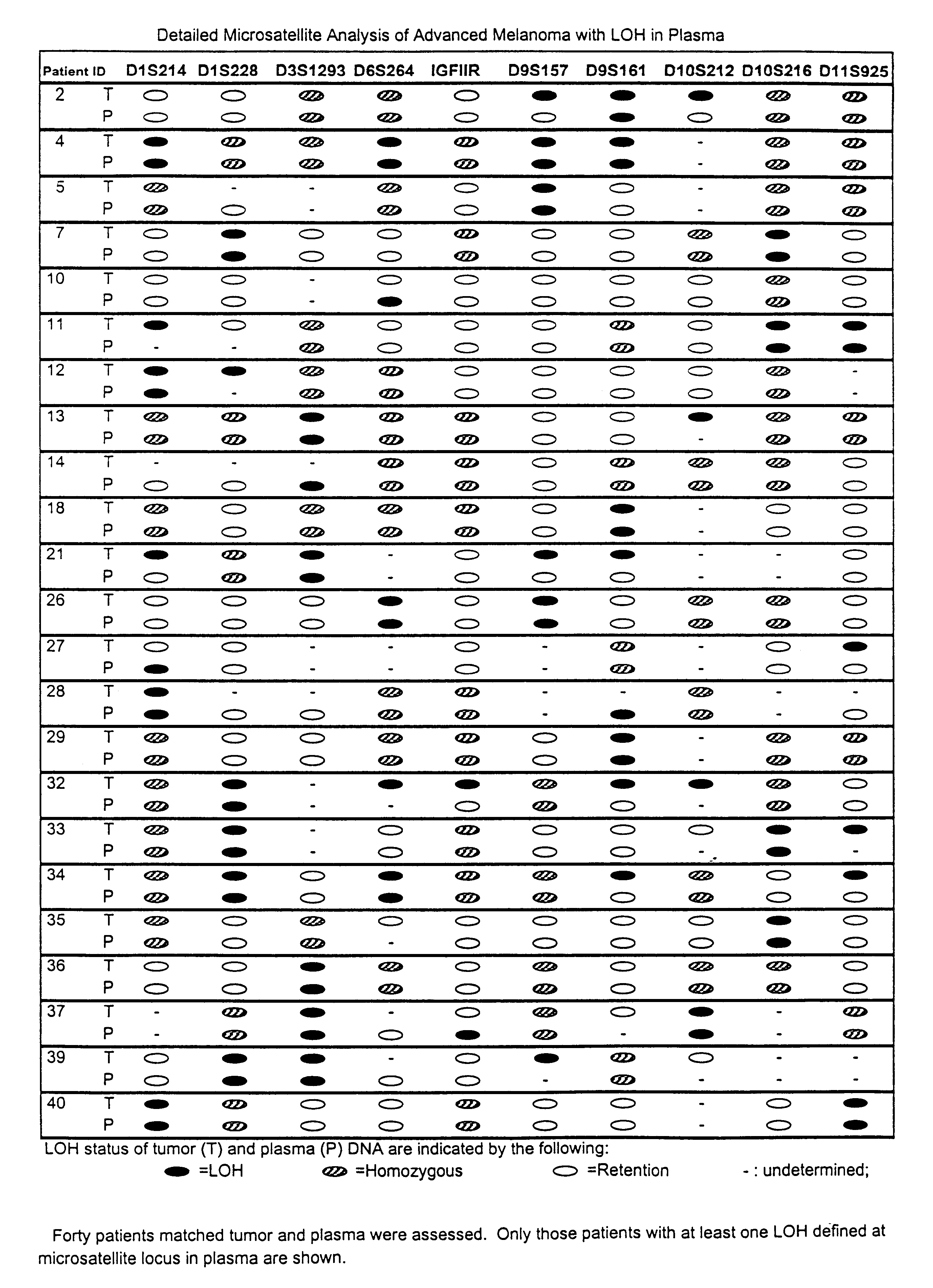
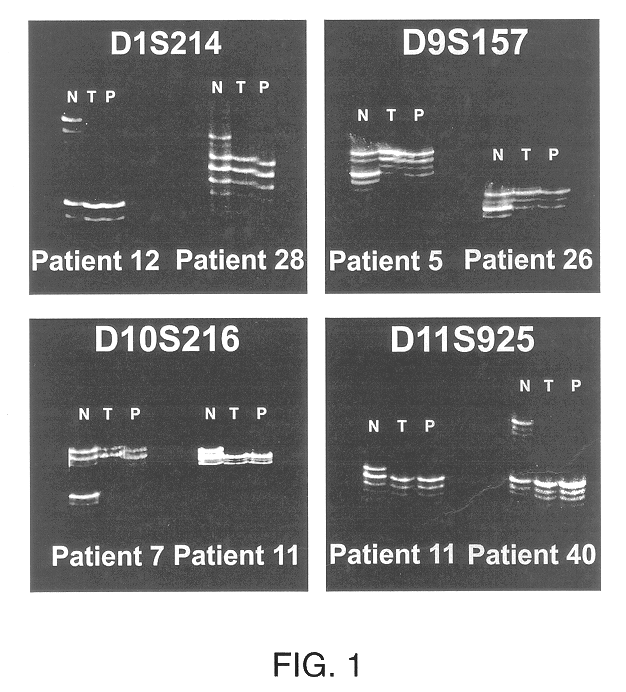
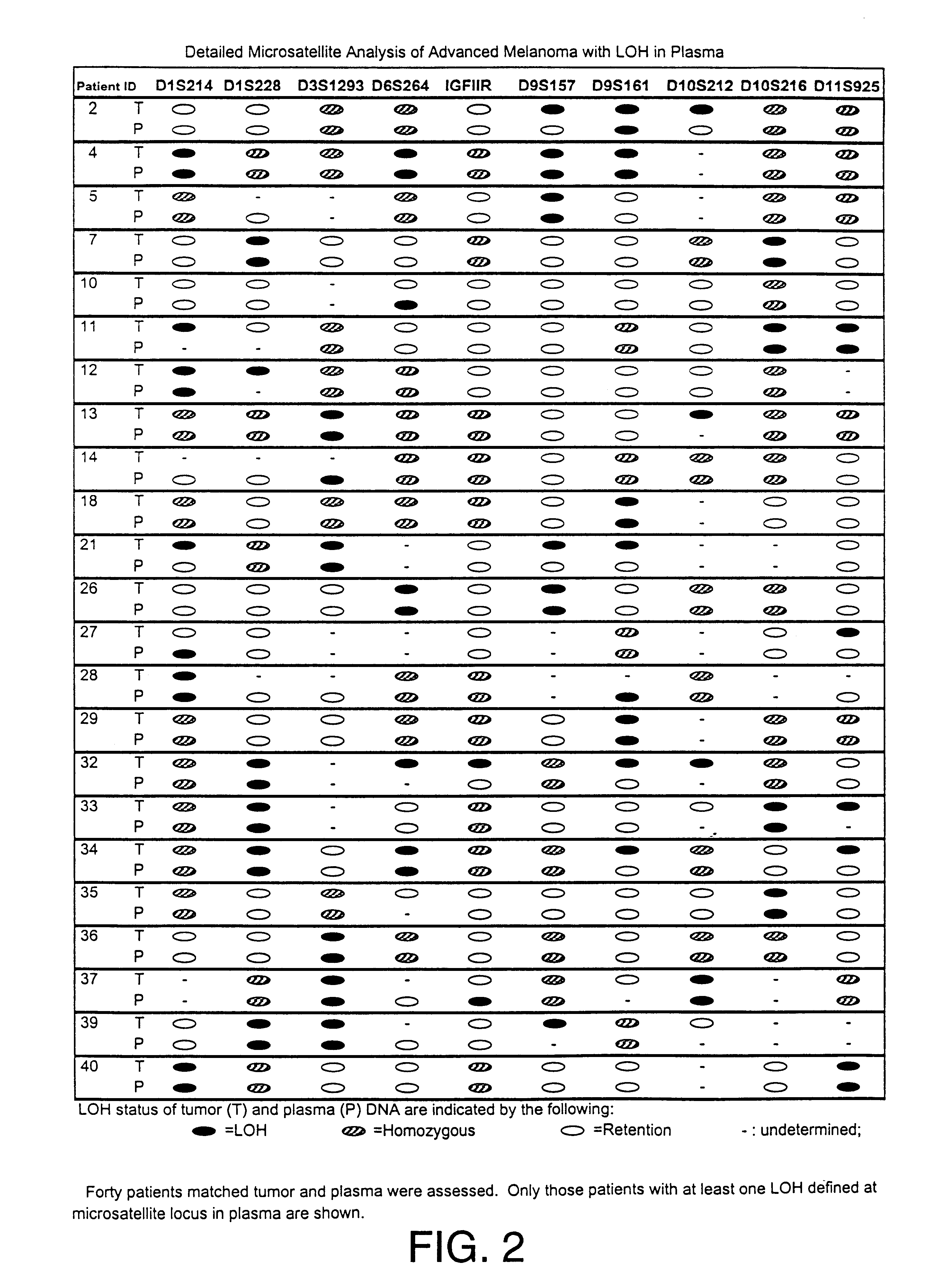
Detection of loss of heterozygosity in tumor and serum of melanoma patients
A method is provided for assessing allelic losses on specific chromosomal regions in melanoma patents. The method relies on the evidence that free DNA may be released in the plasma / serum of cancer patients allowing the detection of DNA with LOH in the plasma / serum of cancer patients by analysis for microsatellite markers. The amount of and specific allelic loss allows a prognosis to be made regarding tumor diagnosis and progression, tumor metastasis, tumor recurrence, and mortality.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
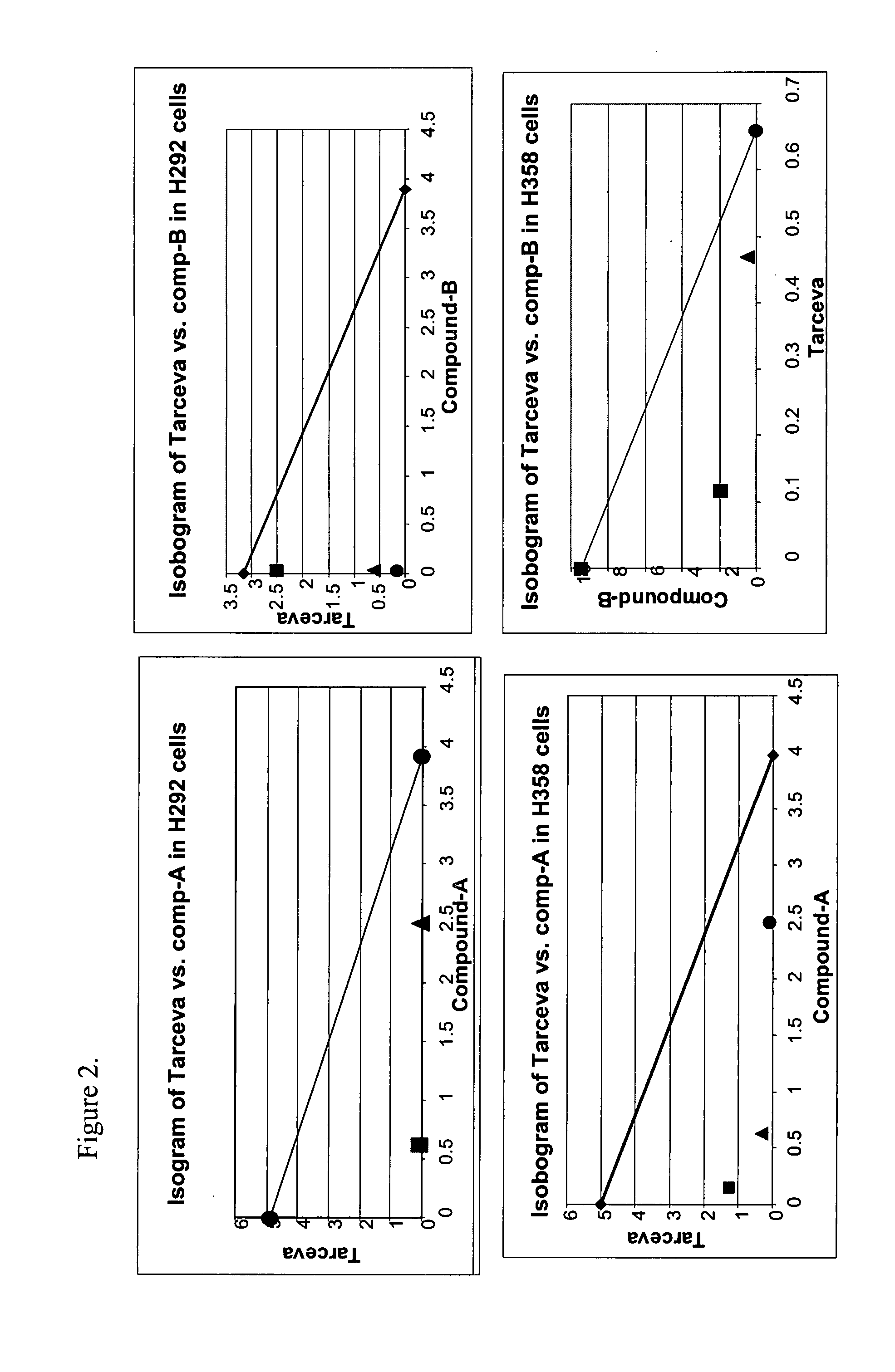
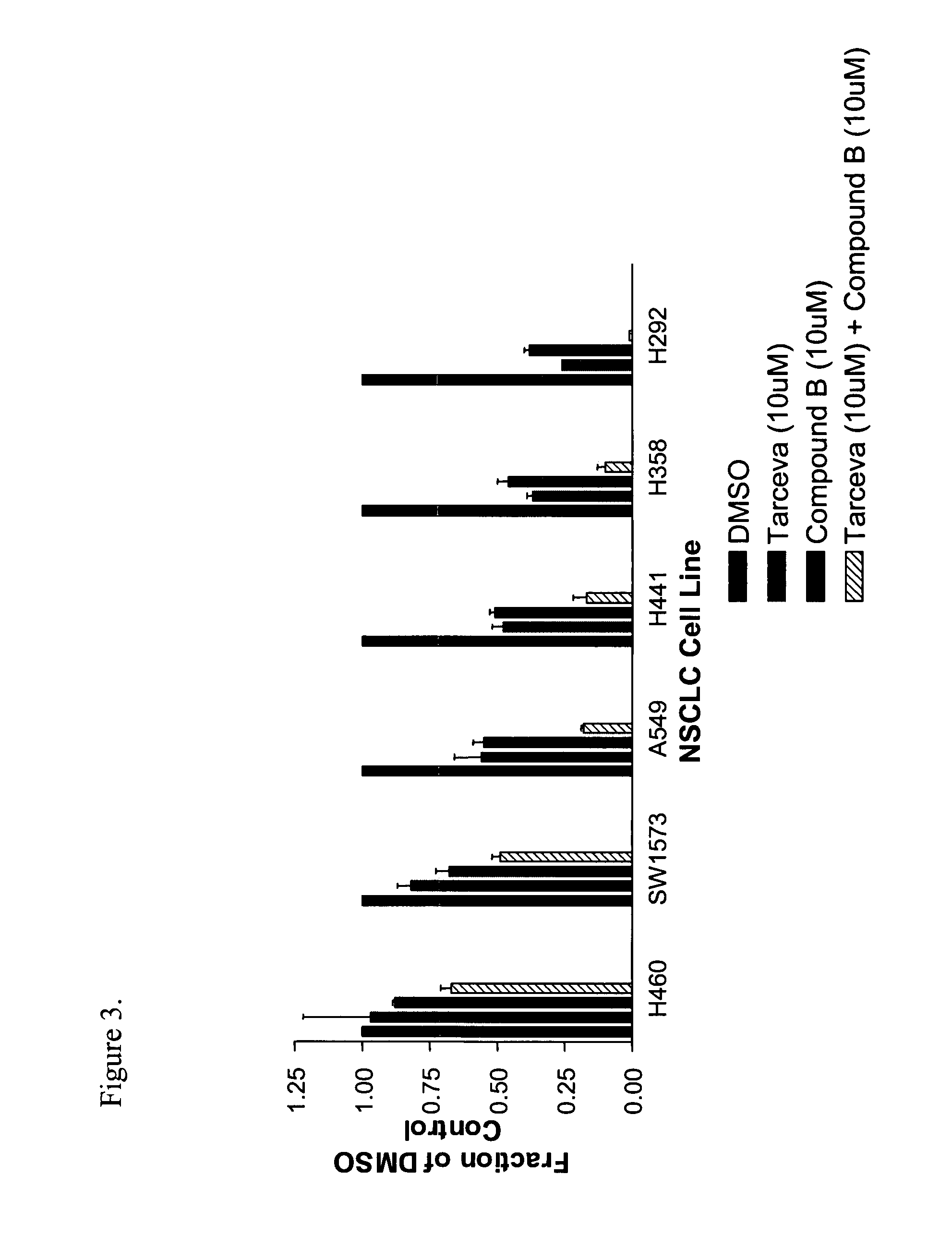
Methods and Therapeutic Compositions Comprising Plant Extracts for the Treatment of Cancer
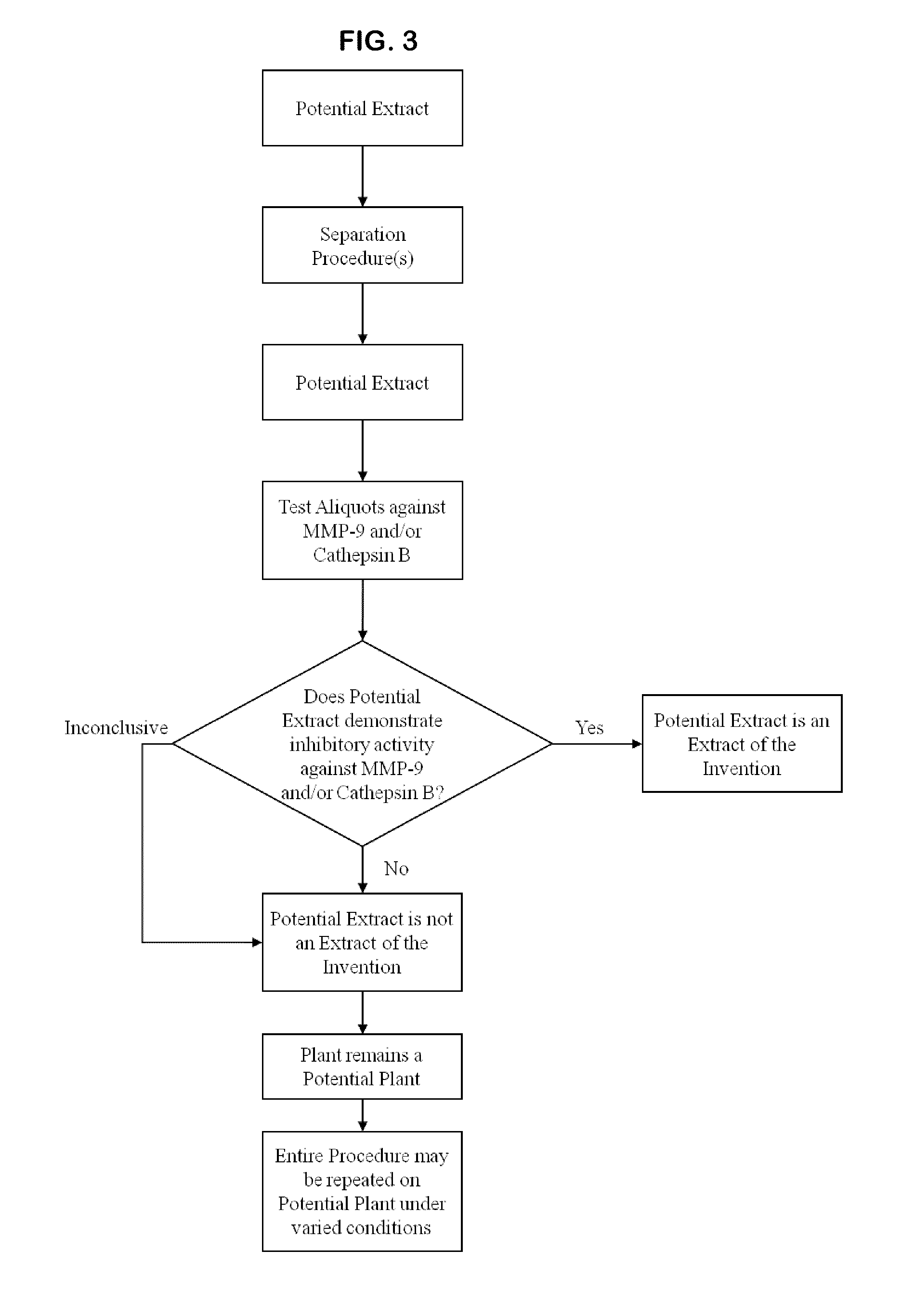
A method of treating cancer by targeting two proteases, MMP-9 and cathepsin B is provided. Therapeutic compositions comprising one or more plant extracts that inhibit MMP-9 and / or cathepsin B, which are capable of inhibiting neoplastic and / or endothelial cell migration, tumour growth, tumour-induced angiogenesis and / or metastasis are also provided. The therapeutic compositions of the invention can be used in the treatment of cancer, and, methods of inhibiting tumour growth, tumour metastasis, and / or tumour-induced angiogenesis using the therapeutic compositions alone or in combination with an anti-cancer agent are, therefore, also provided.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
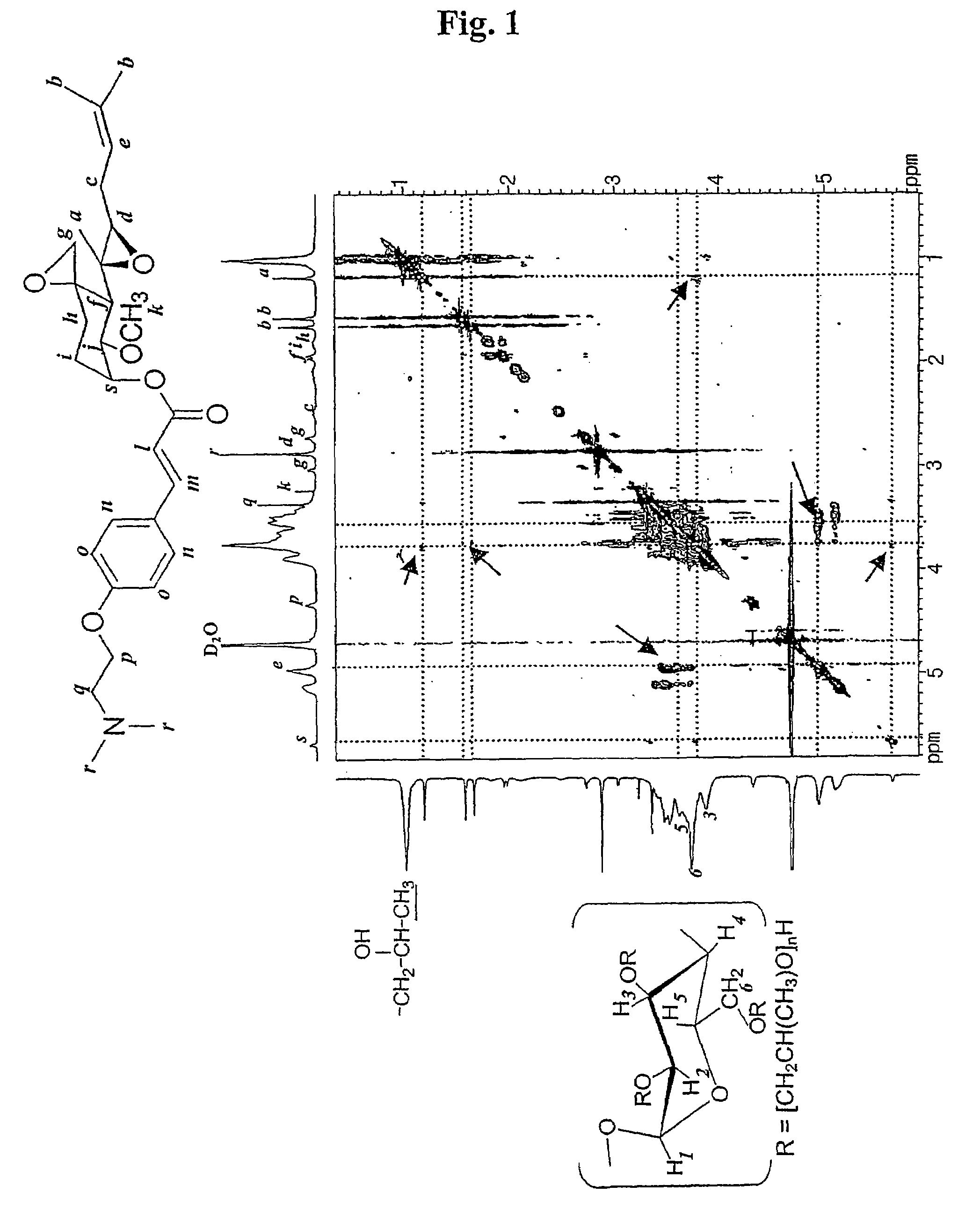
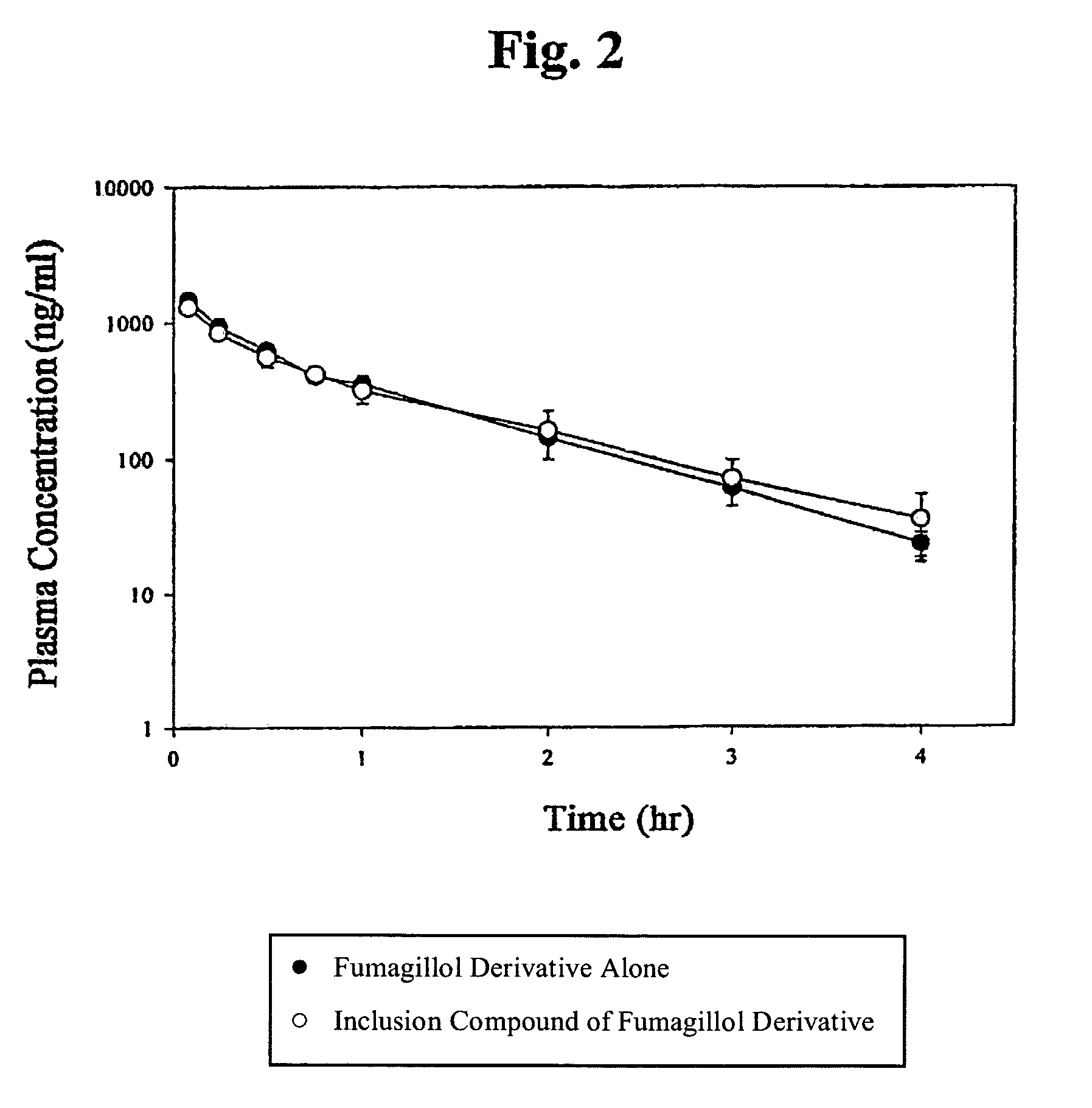
Inclusion compounds of fumagillol derivative or its salt, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
InactiveUS7718695B2Improve solubilityEliminate disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAnticarcinogenTumour metastasis
Owner:CHONG KUN DANG PHARMA CORP
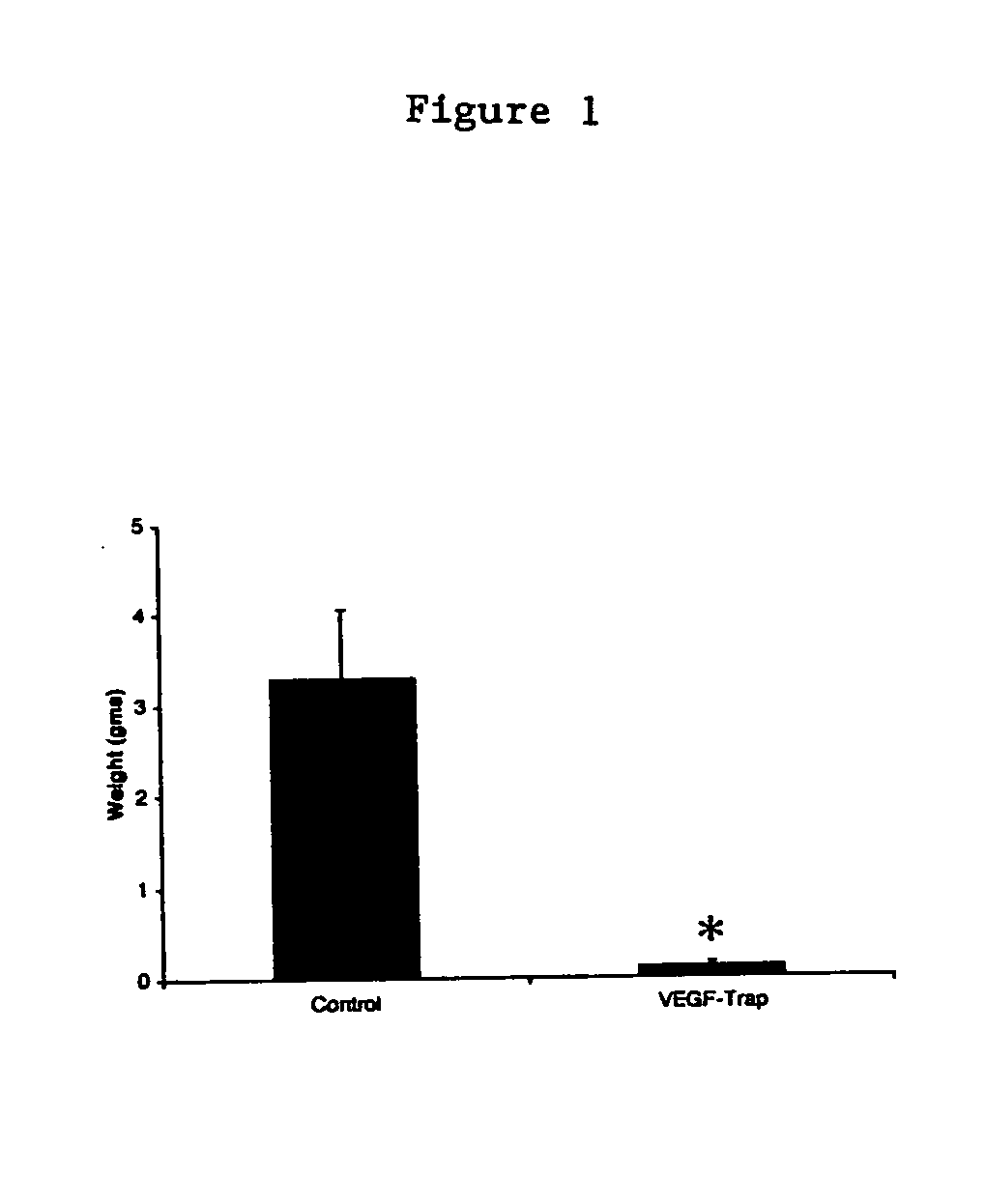
Method of tumor regression with VEGF inhibitors
ActiveUS20040265309A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLymphatic SpreadFactor ii
Methods of regressing or inhibiting a tumor in a subject by administering an agent capable of blocking, inhibiting, or ameliorating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated activity to a subject in need thereof such that the tumor is regressed or inhibited. The method of the invention results in a reduction of tumor size and inhibition of tumor metastases. This method is particularly useful for patients suffering from bulky, metastatic cancers.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +1
Phenylpropionic acid derivatives
Specified phenylpropionic acid derivatives and analogues thereof have an antagonistic activity to α 4 integrin. They are used as therapeutic agents or preventive agents for various diseases concerning α 4 integrin, such as inflammatory diseases in which α 4 integrin-depending adhesion process participates in the pathology, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, Sjögren's syndrome, asthma, psoriasis, allergy, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, arterial sclerosis, restenosis, tumor proliferation, tumor metastasis and transplantation rejection.
Owner:EA PHARMA CO LTD
Radiolabeled peptides for the diagnosis and treatment of breast and prostate tumors and metastases of such tumors
InactiveUS20030224998A1Conveniently providedShort half-lifeCosmetic preparationsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBombesinReceptor
Compounds and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, including breast and prostate tumors and metastases thereof using radiolabelled peptides that bind to GRP receptors. The peptides are Bombesin analogs wherein the first and optionally the third amino acid are modified.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Methods for preparing and analyzing tumor tissue samples for detection and monitoring of cancers
The present invention provides methods for processing and analyzing large intact biological samples, including tumor tissue samples. The methods have a variety of uses, including for the diagnosis and monitoring of tumors and tumor metastasis.
Owner:CLEARLIGHT DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Combined treatment with 6,6-bicyclic ring substituted heterobicyclic protein kinase inhibitor and anti-cancer agents
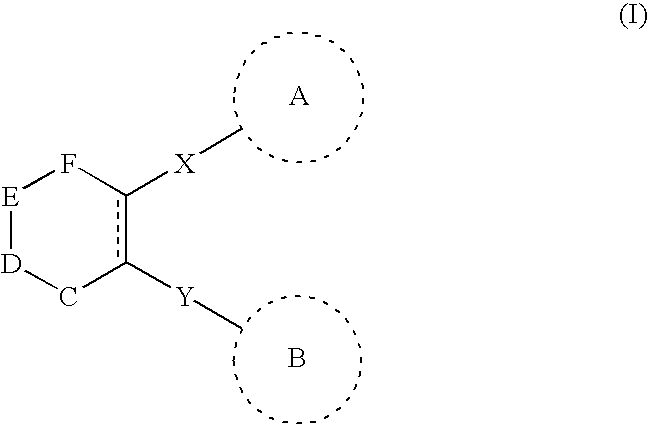
The present invention provides a method for treating tumors or tumor metastases in a patient, comprising administering to the patient simultaneously or sequentially a therapeutically effective amount of an anti-cancer agent and an IGF1R inhibitor compound of Formula I combination, with or without additional agents or treatments, such as other anti-cancer drugs or radiation therapy. The IGF1R inhibitor is represented by Formula I: wherein X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X7, R1, and Q1 are defined herein.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
Methods and therapeutic compositions comprising plant extracts for the treatment of cancer
A method of treating cancer by targeting two proteases, MMP-9 and cathepsin B is provided. Therapeutic compositions comprising one or more plant extracts that inhibit MMP-9 and / or cathepsin B, which are capable of inhibiting neoplastic and / or endothelial cell migration, tumor growth, tumor-induced angiogenesis and / or metastasis are also provided. The therapeutic compositions of the invention can be used in the treatment of cancer, and methods of inhibiting tumor growth, tumor metastasis, and / or tumor-induced angiogenesis using the therapeutic compositions alone or in combination with an anti-cancer agent are, therefore, also provided.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
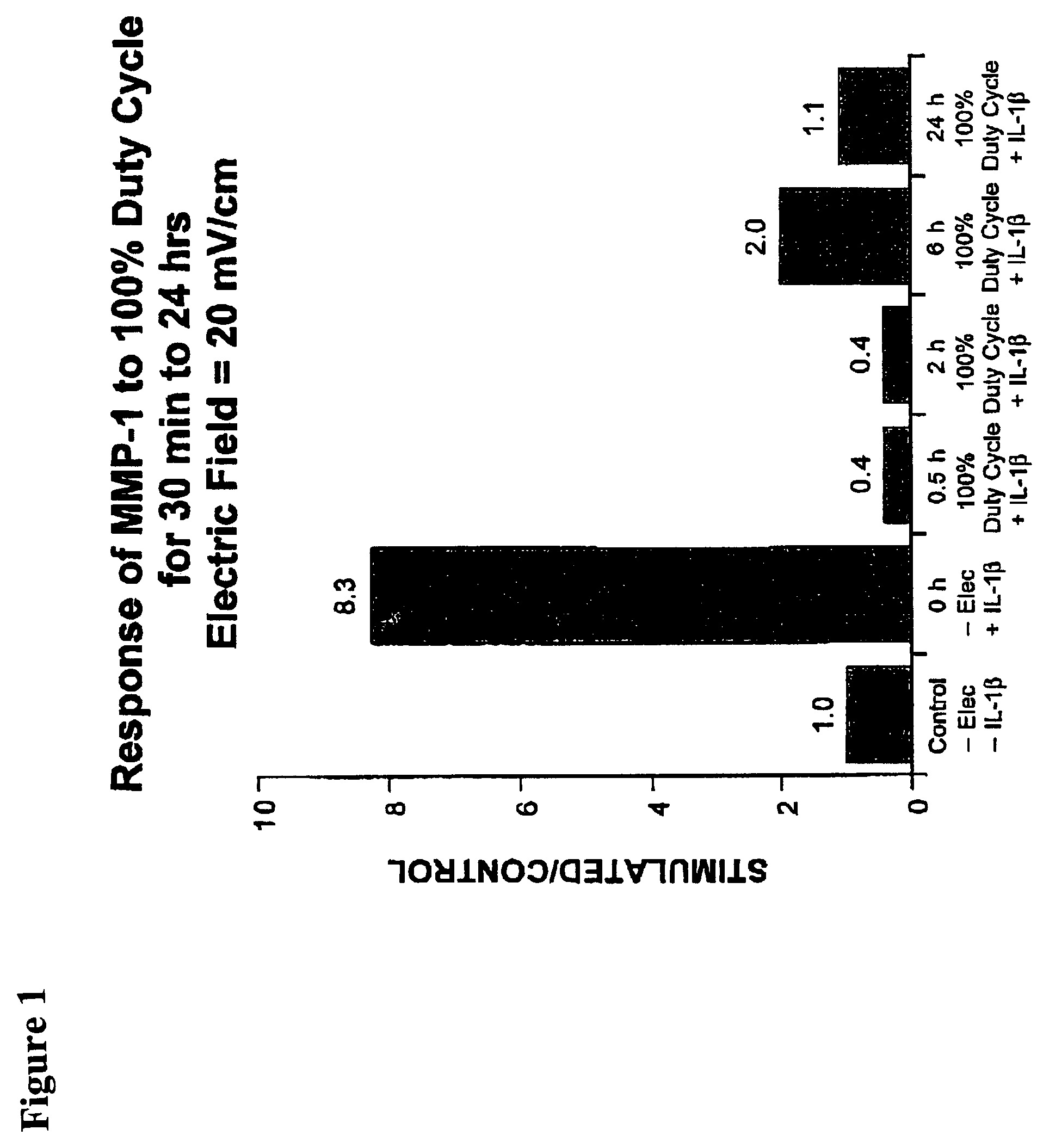
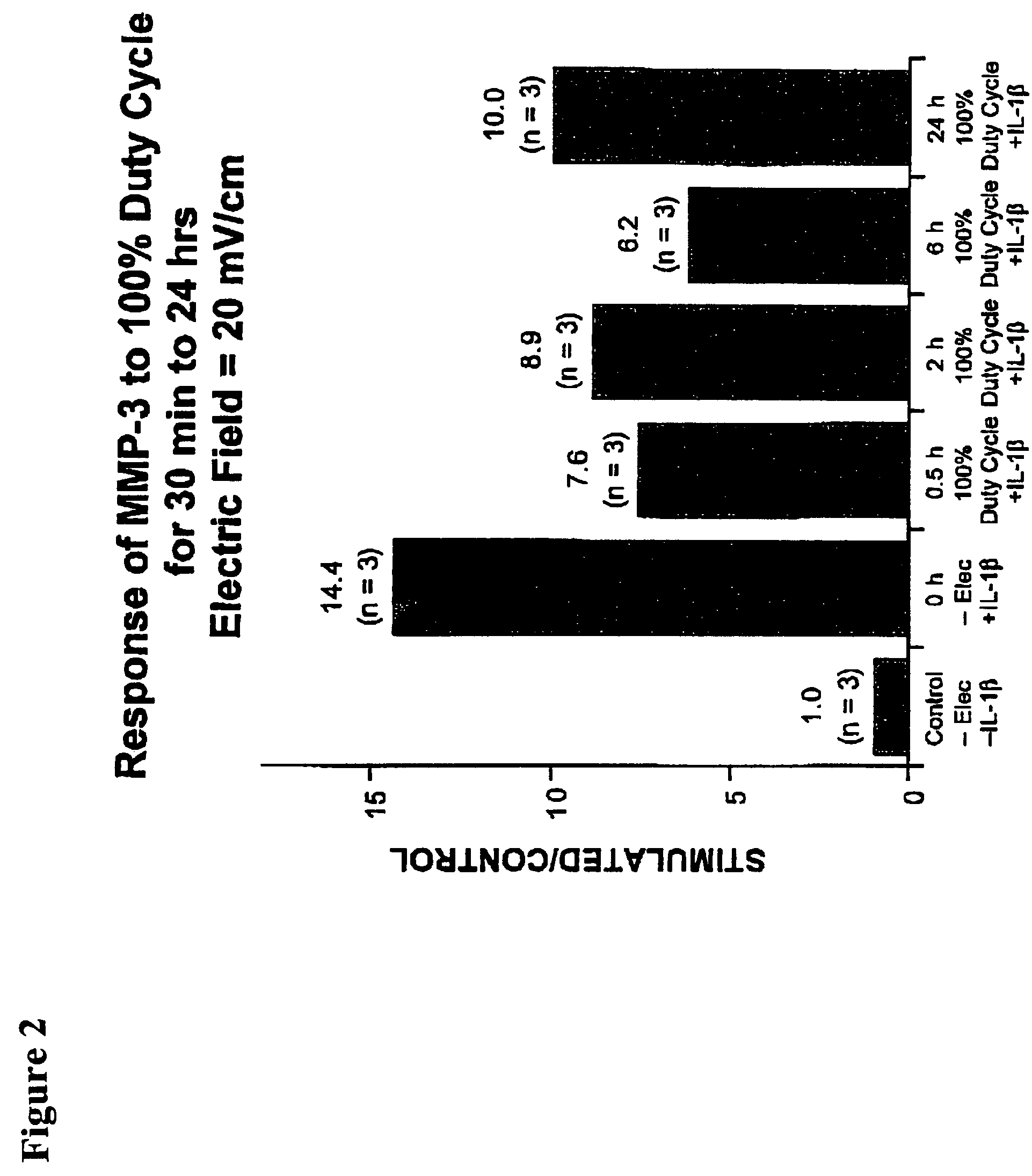
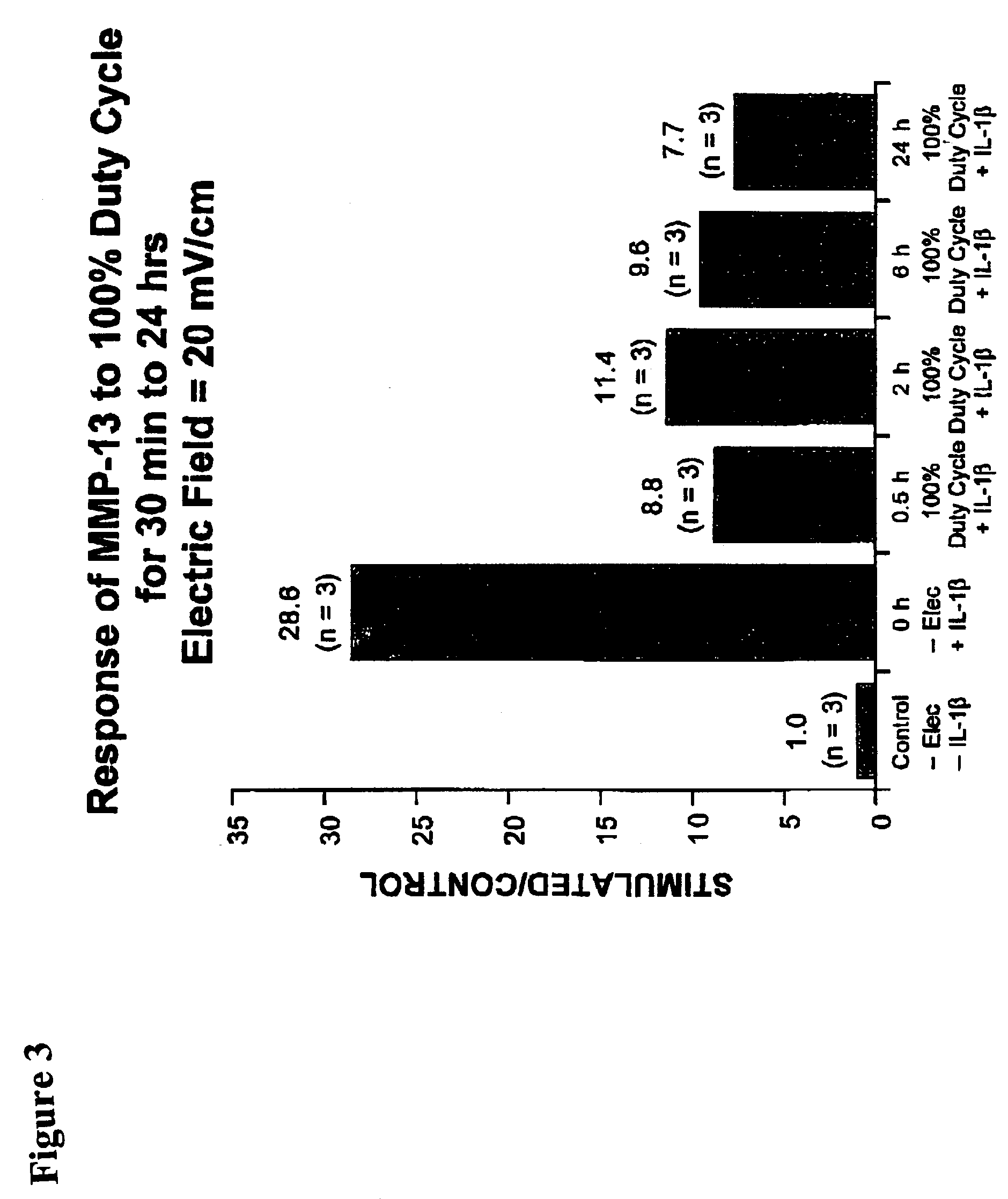
Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression using specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
Methods and devices for the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in cartilage cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured articular cartilage. By gene expression is meant the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased cartilage tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields optimized for reduction of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression and exposing cartilage tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in such cartilage tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, cartilage injury, cartilage defects, and tumor metastasis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Functional nano material drug delivery system for identifying, capturing and restraining circulating tumor cells
InactiveCN104353082AEasy to prepareEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancer preventionCancer metastasis
The invention belongs to the field of application of a nano material coating technology in identifying, capturing and activity regulating of circulating tumor cells. For pre-warning and preventing of cancer metastasis, particularly, the invention relates to a functional nano material drug delivery system for identifying, capturing and restraining circulating tumor cells. The functional nano material drug delivery system consists of a central nano material carrier, a surface targeted antibody or an aptamer, and a drug for resisting cancers or preventing the cancer metastasis. The functional nano material drug delivery system disclosed by the invention can be used for in-vitro simulation or specific identification and capturing research of trace circulating tumor cells of a blood sample of a clinical patient, and also can be used for regulating the activities of the captured circulating tumor cells, so that the application prospect in pre-warning and preventing of the cancer metastasis is expanded.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Individualized vaccines for cancer
ActiveUS10738355B2Reduces steric hindranceImprove translationVaccinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
The present invention relates to the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and are potentially useful for immunotherapy of the primary tumor as well as tumor metastases. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for providing an individualized cancer vaccine comprising the steps: (a) identifying cancer specific somatic mutations in a tumor specimen of a cancer patient to provide a cancer mutation signature of the patient; and (b) providing a vaccine featuring the cancer mutation signature obtained in step (a). In a further aspect, the present invention relates to vaccines which are obtainable by said method.
Owner:TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GGMBH +1
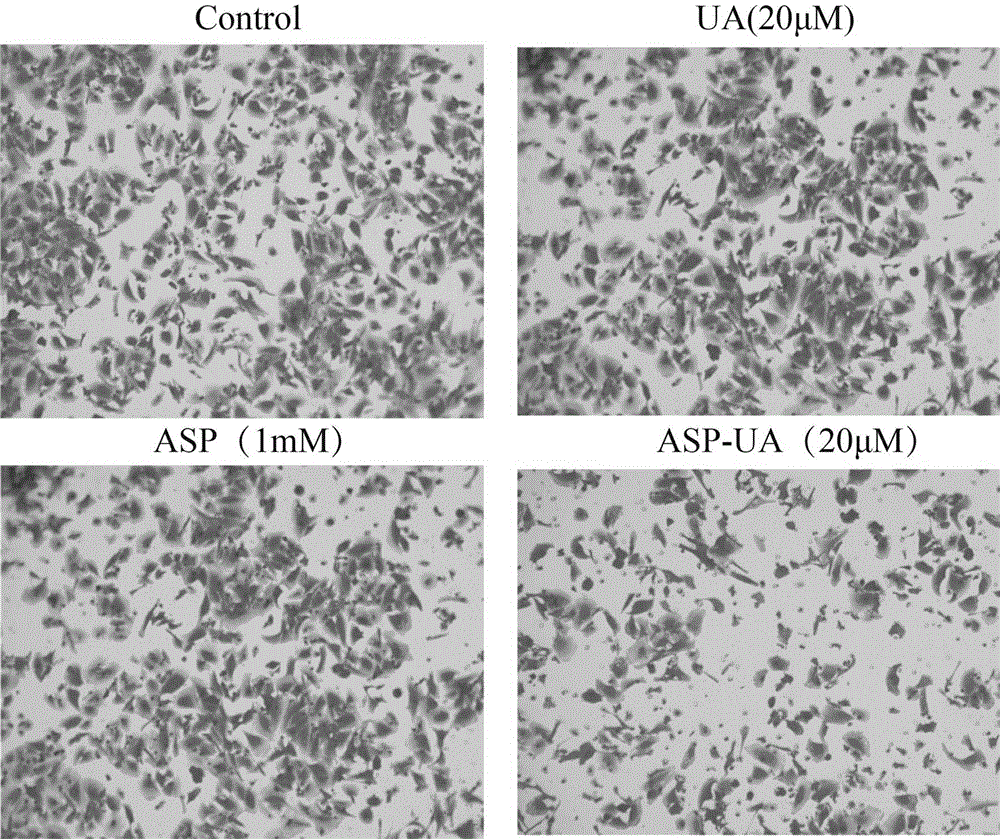
Ursolic acid-aspirin conjugate and application thereof in preparing drugs for preventing tumor metastasis
InactiveCN105111271ALow toxicityAvoid stickingOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsUrsolic acidTumour metastasis
The invention relates to a ursolic acid-aspirin conjugate shown in a formula (I) and application thereof in preparing drugs for preventing tumor metastasis. In vivo experiments verify that the ursolic acid-aspirin conjugate provided by the invention has a remarkable inhibitory effect on adhesion, migration, invasion and the like of tumor cells. in vivo animal experiments verify that the ursolic acid-aspirin conjugate can be used for reducing experimental pulmonary metastasis of 4T1 breast cancer of a rat and showing a relatively good tumor metastasis resisting effect. The ursolic acid-aspirin conjugate provided by the invention can be applied to preventive drugs for tumor metastasis, thereby providing novel selection for developing new drugs for tumor metastasis and preventing postoperative retransfer of malignant tumors. The formula (I) is shown in the description.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
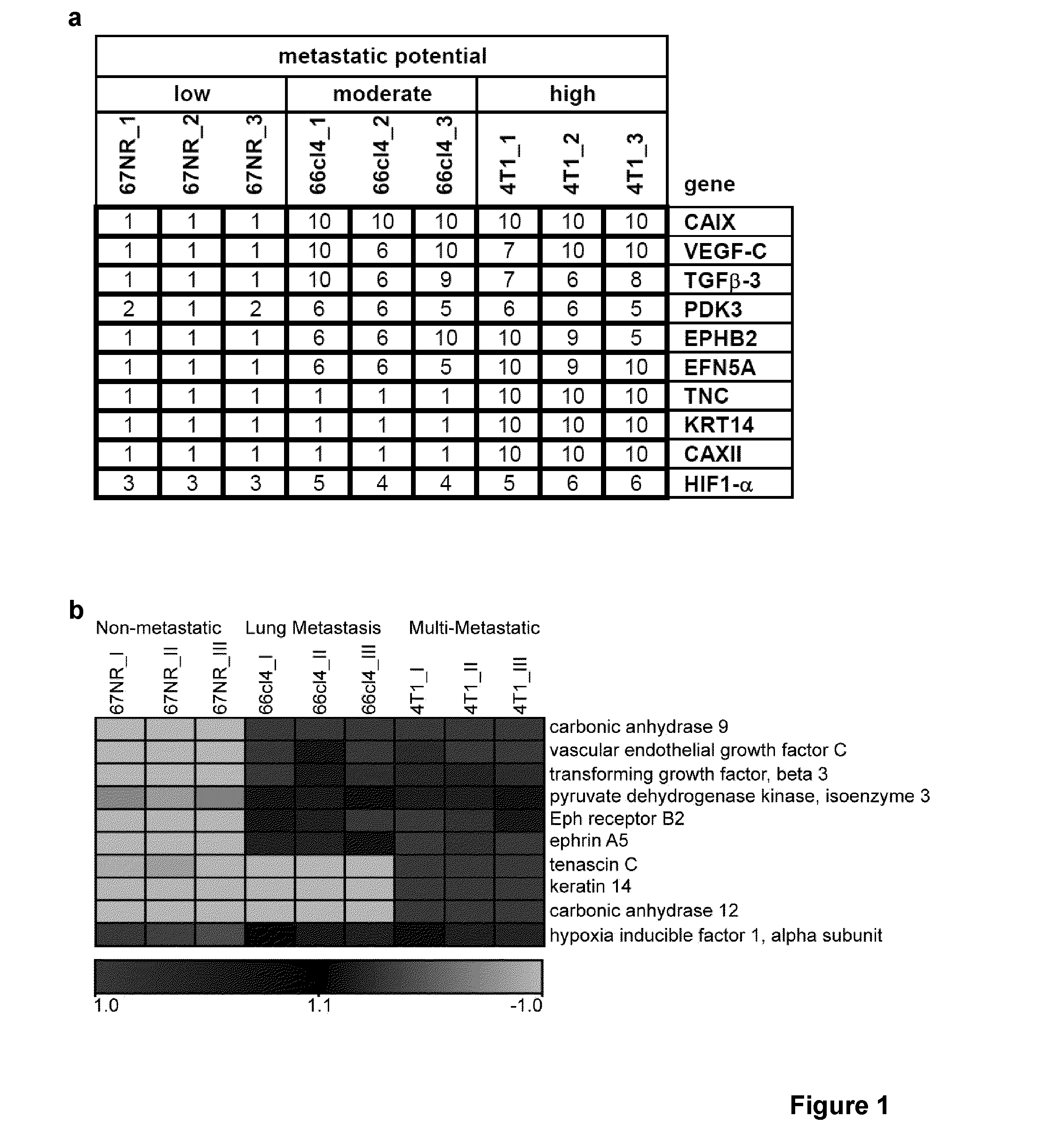
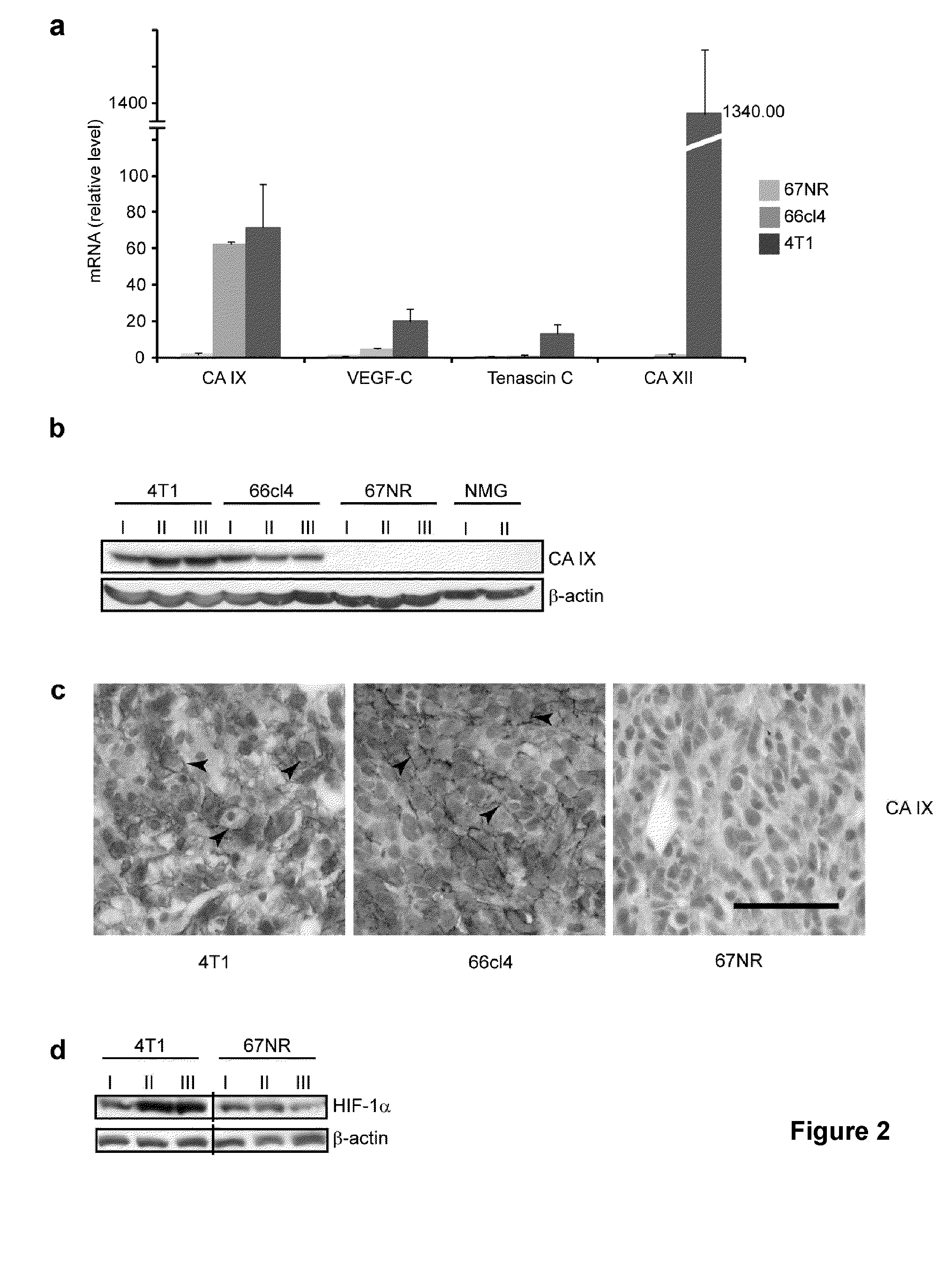
Biomarkers of cancer metastasis
InactiveUS20100317533A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-AlphaCancer metastasis
There is provided a panel of biomarkers of tumour metastasis comprising any two of carbonic anhydrase-9 (CAIX), vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C), ephrin A5 (EFNA5), eph receptor B2 (EPHB2), transforming growth factor beta 3 (TGF-β3), pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoenzyme-3 (PDK3), carbonic anhydrase-12 (CAXII), keratin 14 (KRT14), hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit (HIF-1α), or tenascin C (TNC). CAIX, VEGF-C, EFNA5, EPHB2, TGF-β3 or PDK3 may be indicators of moderate metastatic potential, while CAXII, KRT14, HIF-1α, or TNC may be indicators of high metastatic potential. There is also provided a method of determining risk of tumour metastasis using the aforementioned biomarkers is also provided. The biomarkers may be used in diagnosis, prognosis, treatment selection, or to test putative therapeutics. The biomarkers may be used to assess malignancies or cancers having hypoxic regions, such as breast cancer.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
Animal models of tumor metastasis and toxicity
InactiveUS20070283453A1Promote repairPromote structural and functional repairDisease diagnosisAnimal husbandryHuman environmentHuman tumor
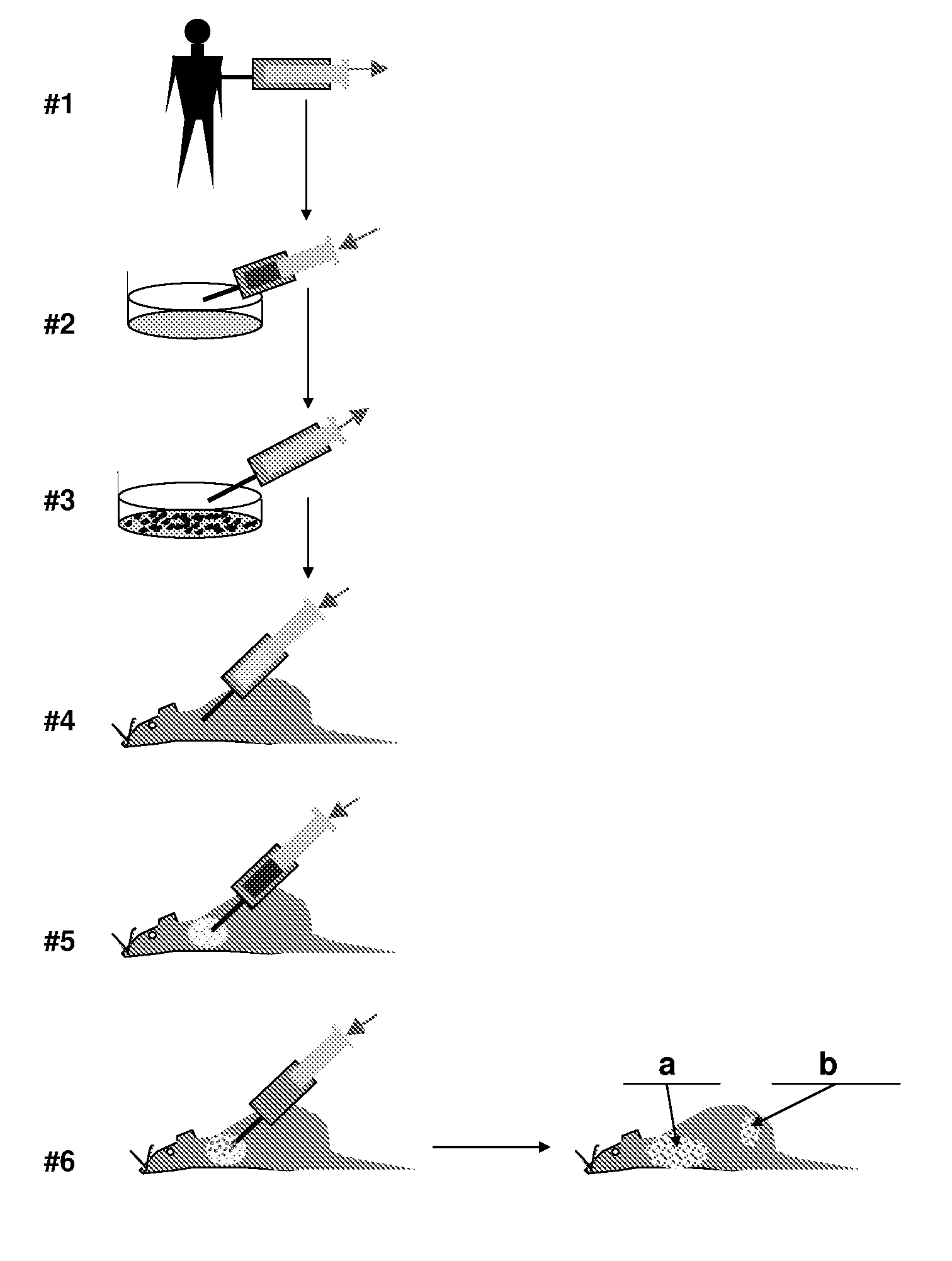
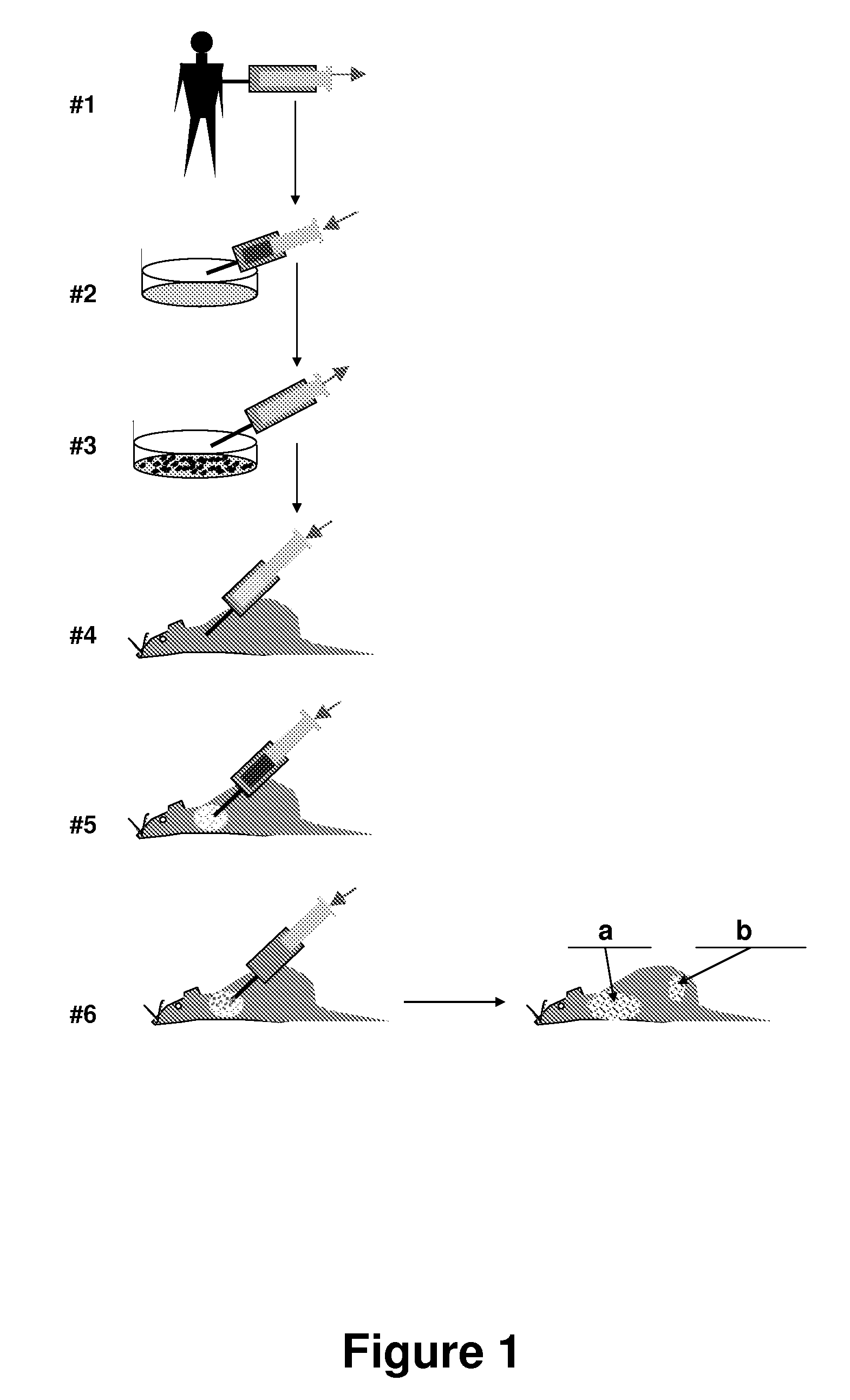
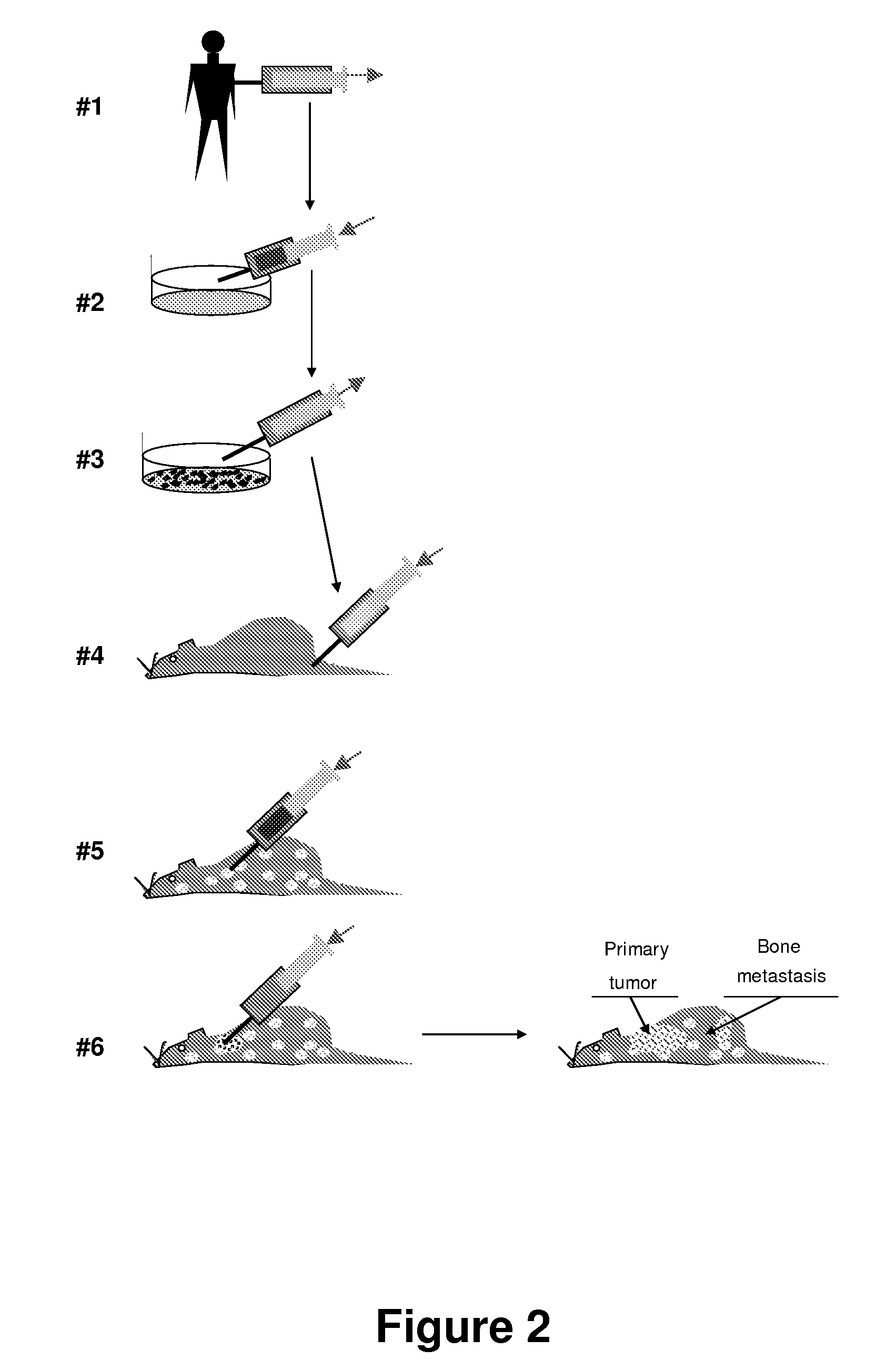
A method for conversion of an animal into an appropriate recipient of tumor cells derived from a different species. Animals for such purpose can be immuno-incompetent animals that are doubly grafted with orthotopic tissues, in which one grafted tissue (i.e., breast) is from an organ of the same class as the tumor of origin (graft A), and the second grafted tissue (i.e., bone) is from a organ of the same class as a target organ for metastasis (graft B). These dual grafted animals can be used to model human diseases. In one implementation, human tumor cells are orthotopically seeded in graft A in order to analyze the occurrence of metastasis in graft B. Methods and compositions are described for creating a multiorgan human environment in mice, by grafting human stem cells (mesenchymal, embryonic or others) into mice, e.g., injured to enhance specific tissue engraftment. Such chimeric mice can be used to grow human tumors and to study the occurrence of metastasis.
Owner:PROJECH SCI TO TECH
Chemotherapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050038248A1Organic chemistryOrganic compound preparationAngiogenesis growth factorTumour metastasis
The invention provides 1,2-substituted cyclic compounds useful for treatment of diseases or disorders arising from abnormal or inappropriate cell proliferation, such as tumour growth, tumour metastasis and associated angiogenesis, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and their use in methods of treatment.
Owner:STARPHARMA PTY LTD
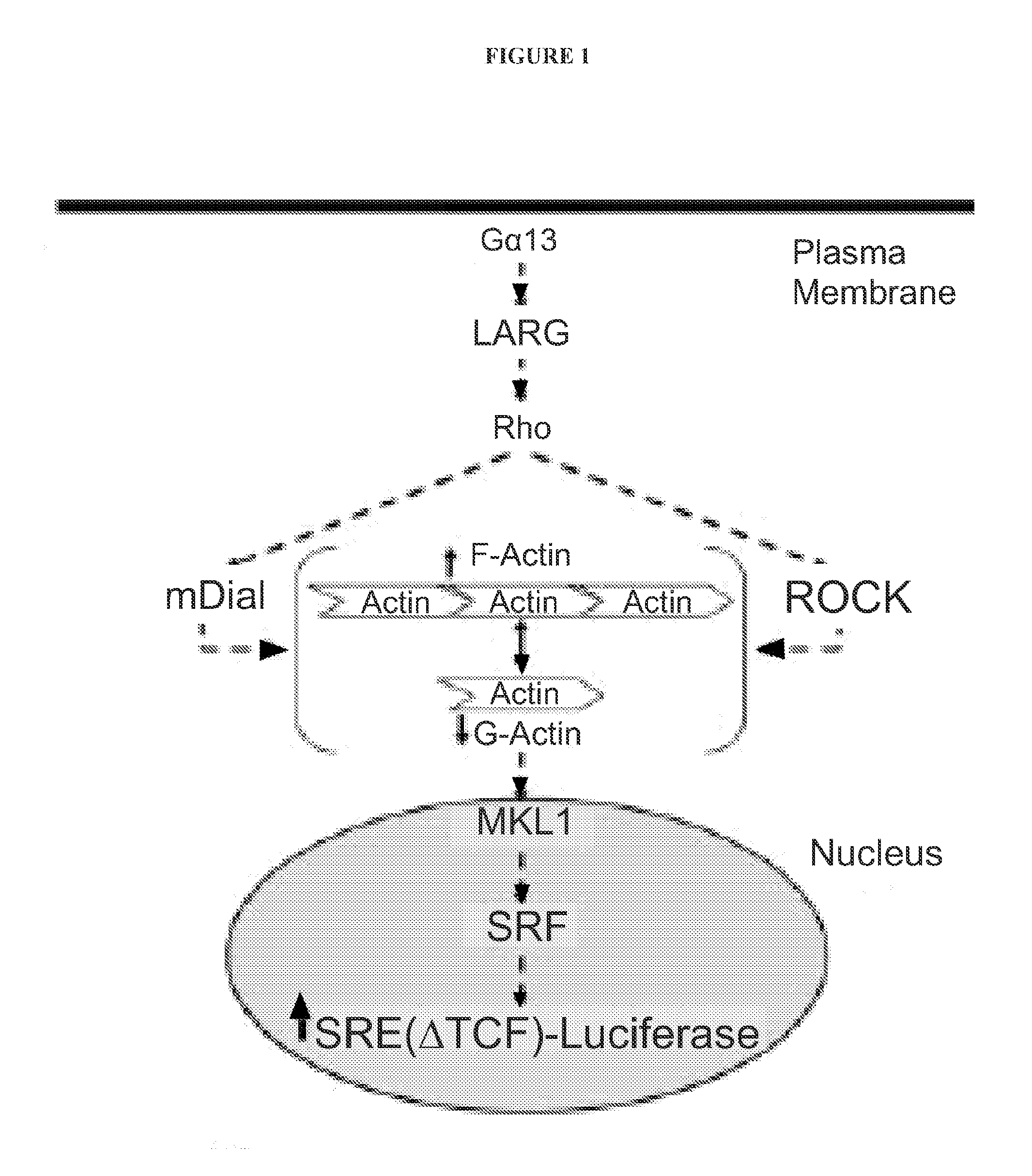
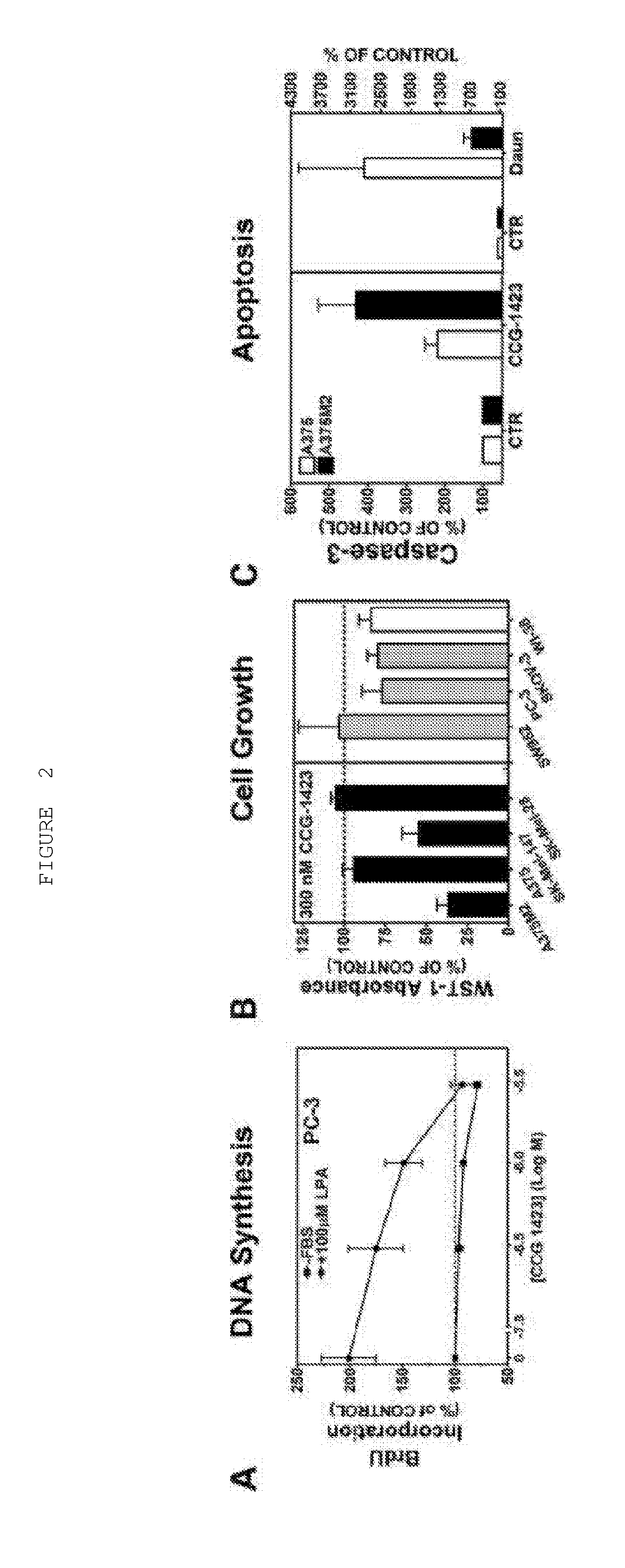
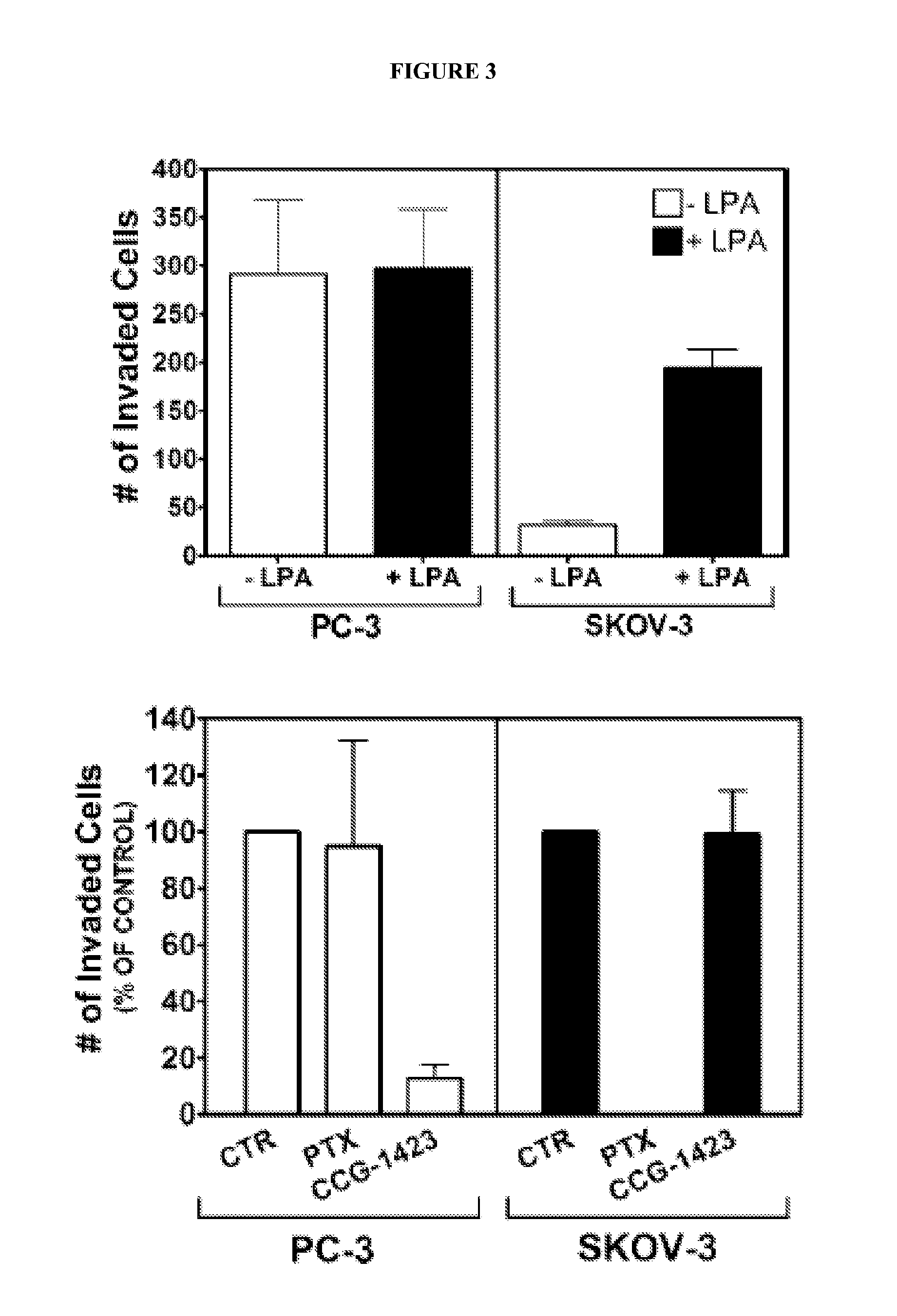
Methods and compositions for modulating rho-mediated gene transcription
InactiveUS20120252792A1Easy to identifyReduce spreadBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseBiological condition
The invention provides methods, compositions, and kits for the inhibition of members of the Rho GTPase family. Specifically, the invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the inhibition of RhoA and / or RhoC transcriptional signalling. The invention finds use in treatment of Rho-mediated disease states (e.g., tumor metastasis, inflammation, inflammatory disease), Rho-mediated biological conditions, and in cell signaling research.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
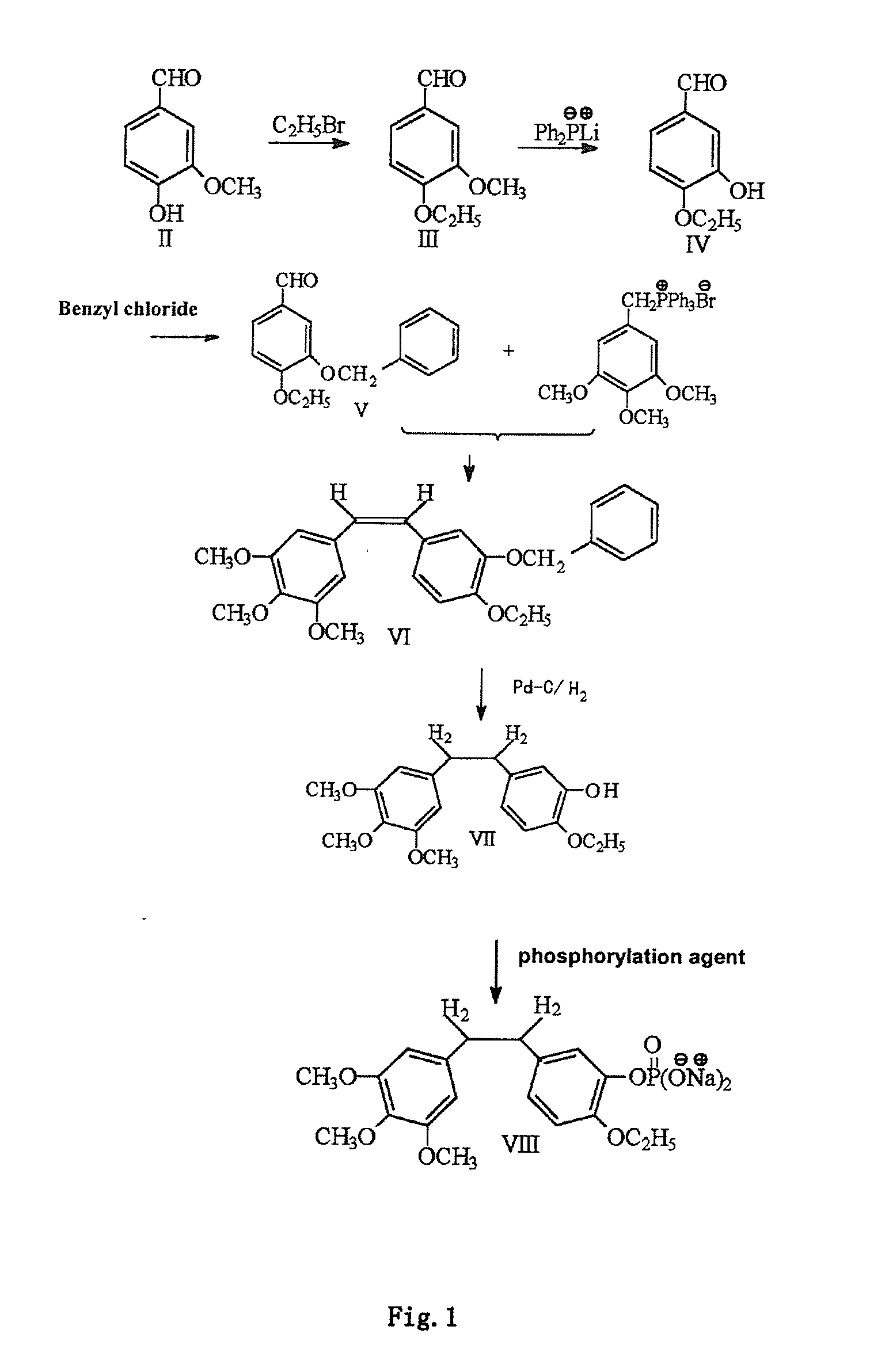
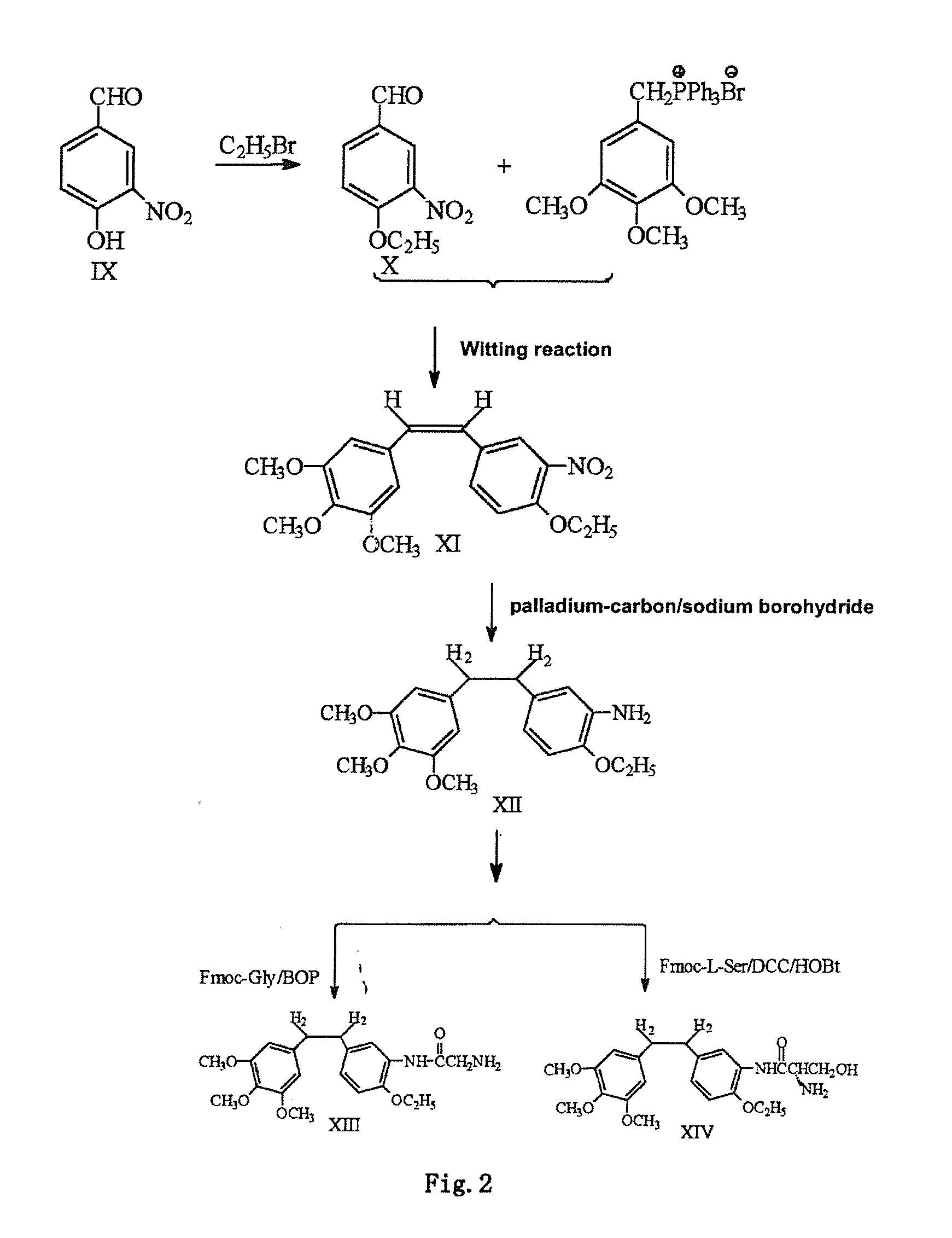
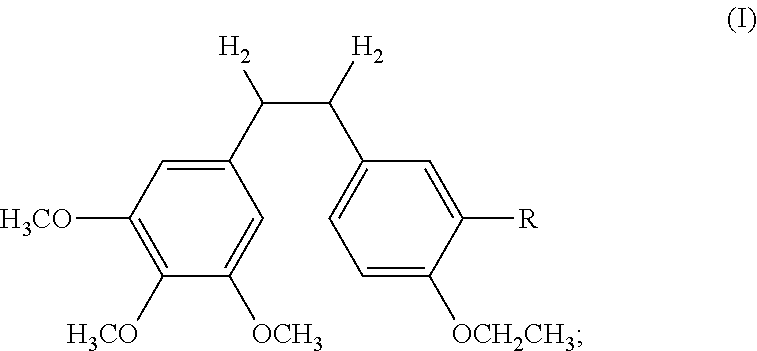
Ethoxy Diphenyl Ethane Derivatives, Preparation Processes and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20120046492A1Improve drug stabilityLow toxicityOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAmino acid side chainVascular endothelium
The invention discloses an ethoxydiphenylethane derivative and a synthetic method and uses thereof 4′ position of phenylethane B aromatic ring is chemically modified by ethoxy and hydroxy at position 3′ thereof is simultaneously modified to water soluble prodrug such as phosphate, and similarly, amino acid side chain is introduced to amino at position 3′ to form amino acid amide water soluble prodrug having the structure shown as formula (I)the ethoxydiphenylethane derivative and the prodrug thereof include strong tubulin aggregation inhibiting ability and obvious target damage effect for tumor vessels, selectively cause dysfunction and structural damage of tumor vessels and induce apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells in order to play the role of killing tumor cells or inhibiting tumor metastasis in case that the tumor cells are free from the support of nutrition and oxygen.
Owner:SHANGHAI ECUST BIOMEDICINE CO LTD +1
Acyl-tetrahydro-beta-carboline compound as well as derivatives, application and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102424681AGrowth inhibitionNo toxicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydrogenStructural formula
The invention discloses an acyl-tetrahydro-beta-carboline micro-molecular organic compound shown as a structural formula (I) or a hydrate thereof or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, application of a compound containing the acyl-tetrahydro-beta-carboline micro-molecular organic compound provided by the invention or a medical composition thereof to the preparation of medicaments for treating various diseases such as cancer, tumor metastasis and the like, and a preparation method of the acyl-tetrahydro-beta-carboline micro-molecular organic compound provided by the invention and derivatives thereof.
Owner:BIORAY LABORATORIES INC
Human tumor invasion and metastasis histioid in vitro three-dimensional model and construction and evaluation thereof
InactiveCN103160468AKeep aliveSimulation excellentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsHuman tumorHydrogel scaffold
The invention discloses an in vitro model simulating human tumor metastasis. Cells in the model have a tumor high metastasis character. The model is constructed by building of a micro spherical hydrogel support frame by tumor high metastasis cells, building of a tumor cell in vitro metastasis model and identifying of the constructed tumor cell in vitro metastasis model. The model can grow in a three-dimensional culturing cell in a clustering mode, and tumor cell biological behaviors in metastasis can be detected. The model has important value in studying of a clinical tumor metastasis mechanism and controlling of screening of metastasis medicine and can be taken as a technical platform for manufacturing anti-tumor metastasis gene vaccines and building screening of anti-tumor metastasis medicine.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
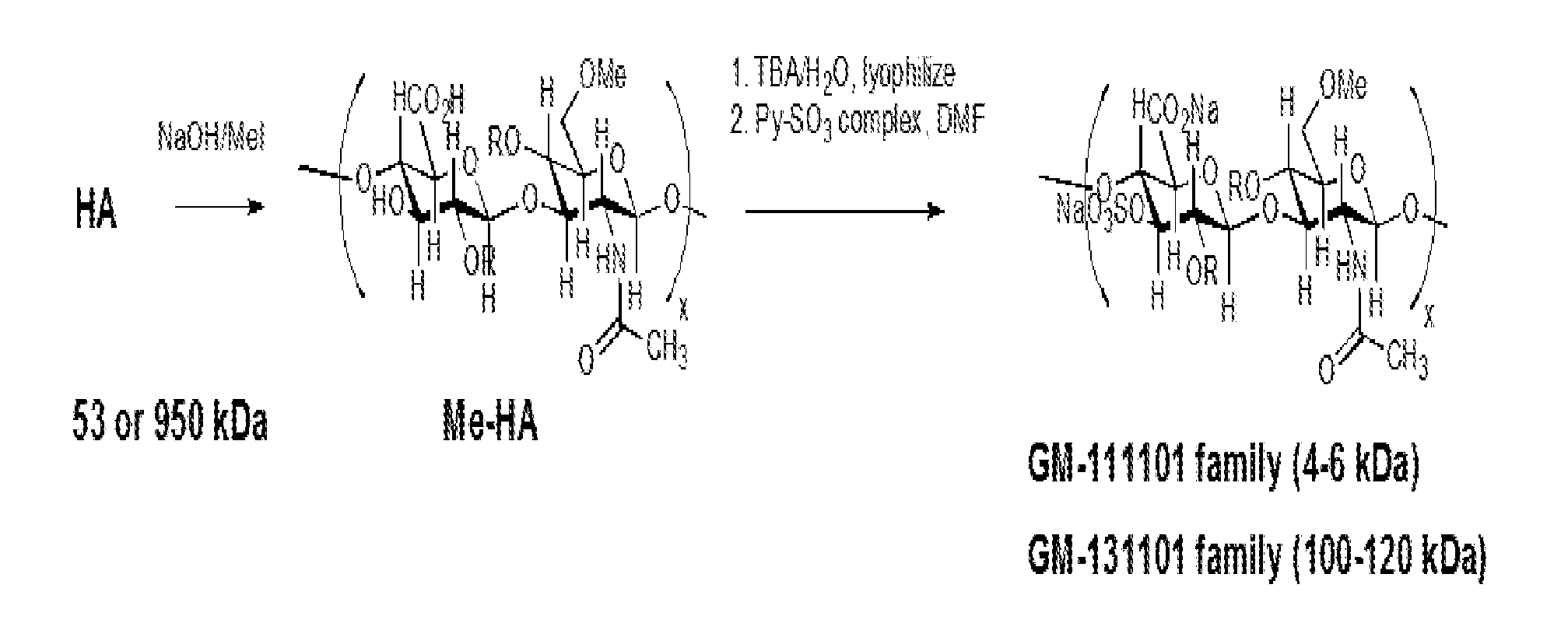
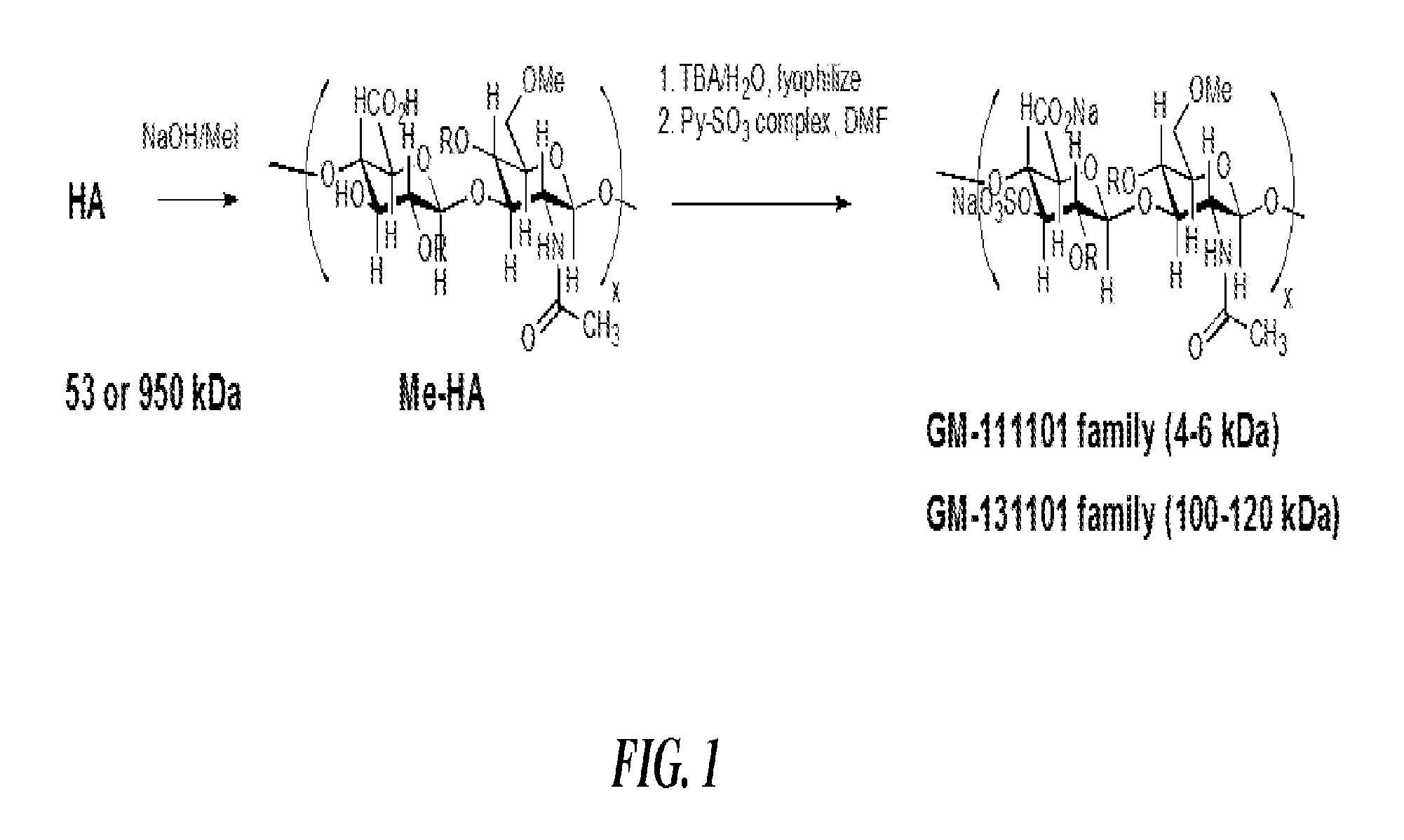
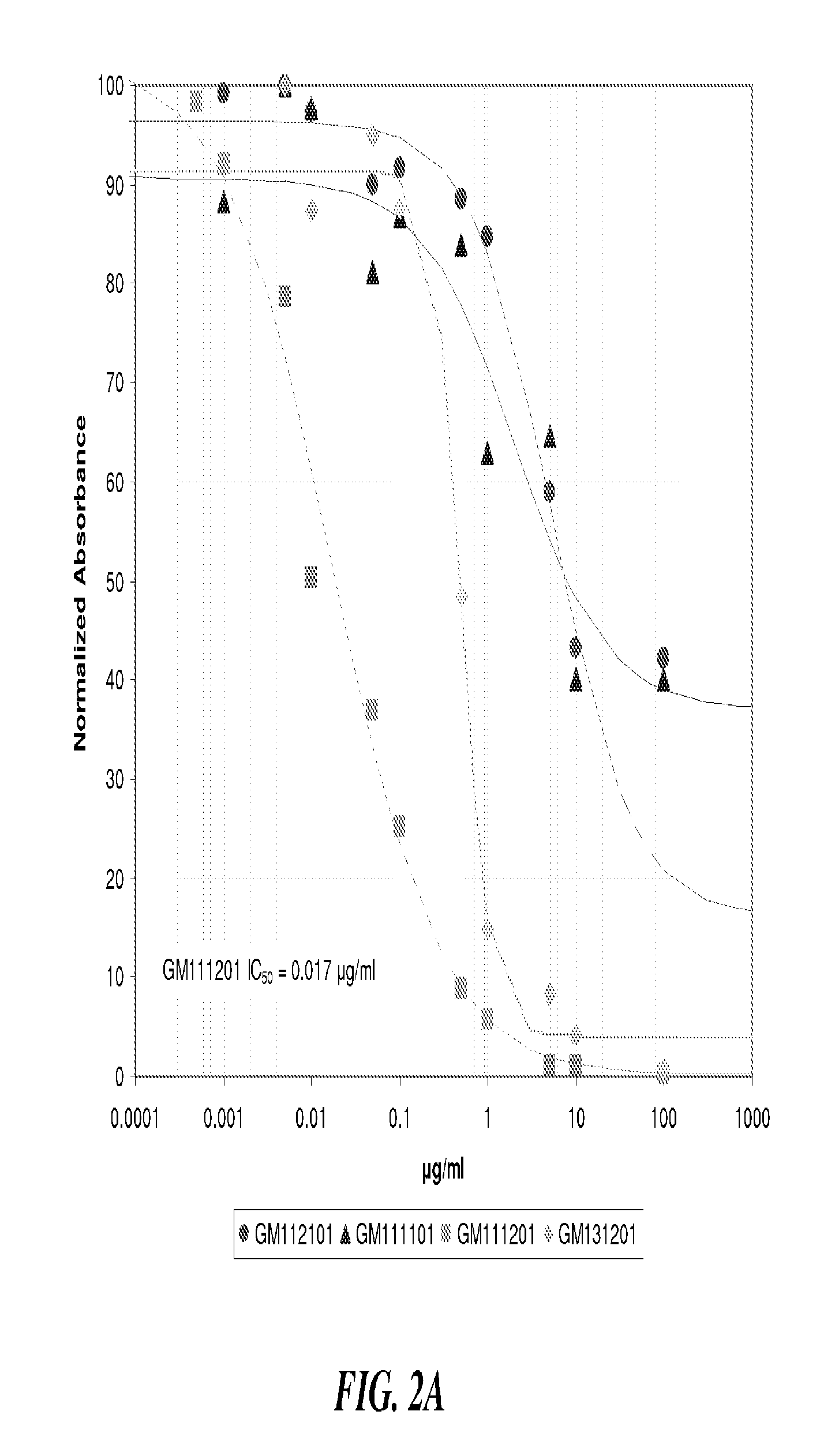
Methods for treating or preventing the spread of cancer using semi-synthetic glycosaminoglycosan ethers
Described herein are methods for the treatment and prevention of tumor metastasis using alkylated and fluoroalkylated semi-synthetic glycosaminoglycan ethers (“SAGEs”). The synthesis of sulfated alkylated and fluoroalkylated SAGEs is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Medicine carrier, micelle, anti-tumor and anti-tumor cell metastasis pharmaceutical preparation, and preparation method and use thereof
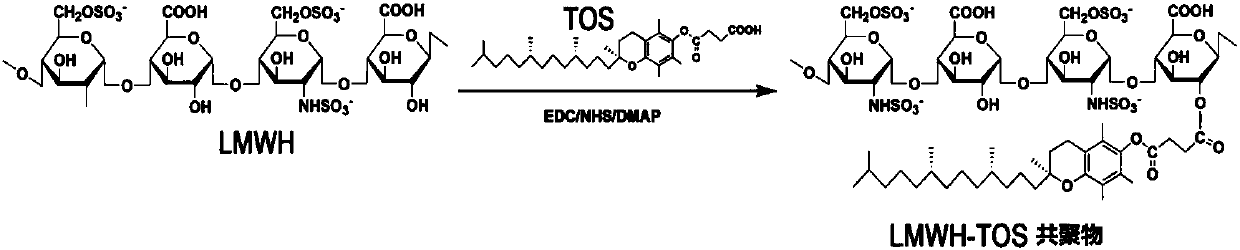
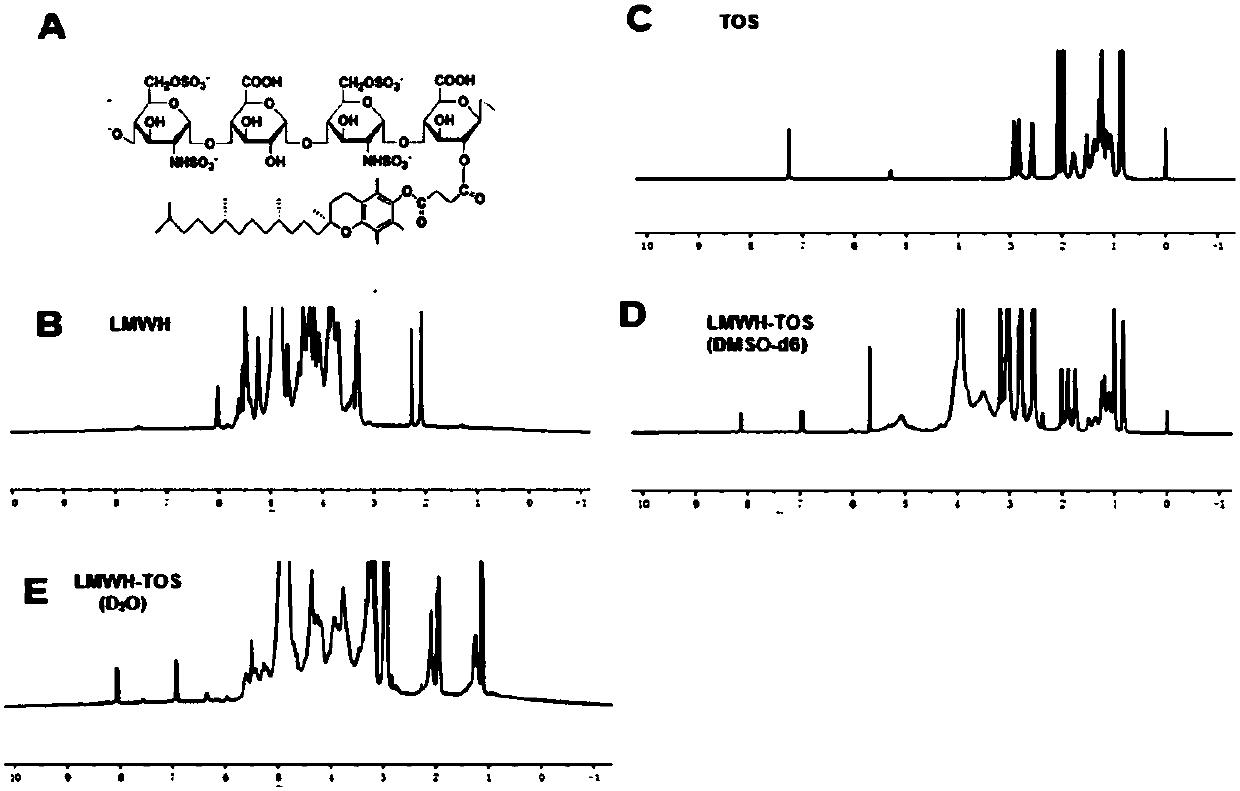
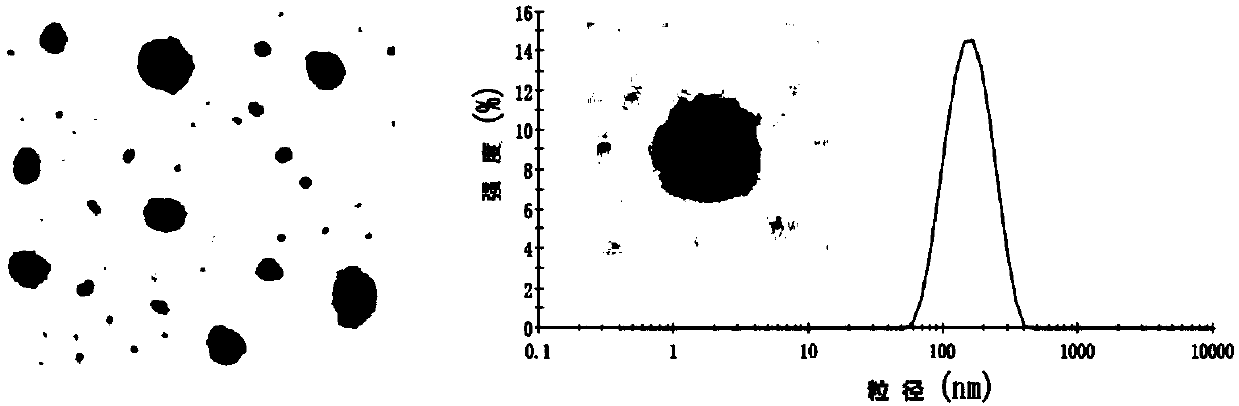
ActiveCN107669632AStrong anti-transfer effectOptimize build stepsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryLymphatic SpreadMedicine
Provided are a medicine carrier, a micelle, an anti-tumor and anti-tumor cell metastasis pharmaceutical preparation, and a preparation method and use thereof. The medicine carrier and the micelle include a) a hydrophilic part and b) a hydrophobic part, wherein the hydrophilic part includes hydrophilic heparin compounds; and the hydrophobic part includes hydrophobic vitamin E compounds. The hydrophilic heparin compounds are connected with the hydrophobic vitamin E compounds in a specific mode. The medicine carrier and the micelle not only have an effect of anti-tumor metastasis, but also can achieve excellent effects of inhibiting tumor and tumor metastasis simultaneously by further coating anti-cancer drugs. In addition, the medicine carrier and the micelle are high in stability, and the preparation method is simple and convenient and facilitates industrial production.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Antibody coupled mesoporous silica/mifepristone nanometer preparation
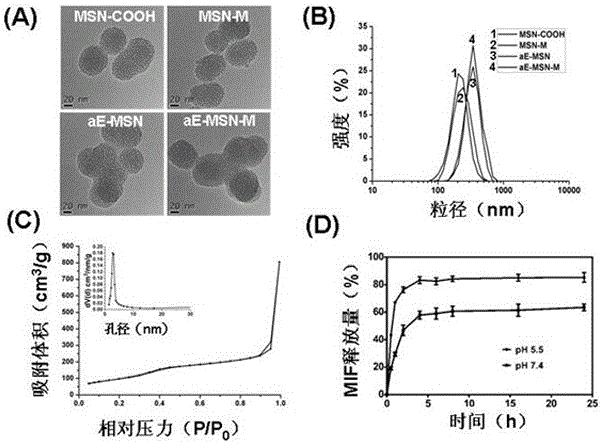
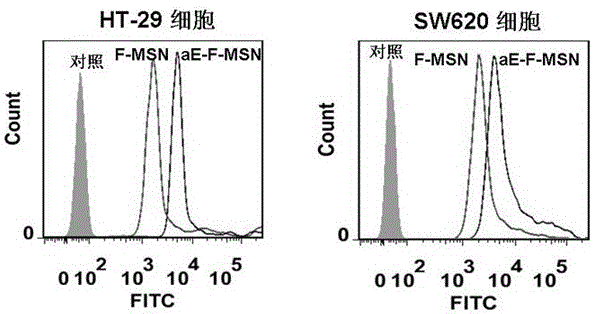
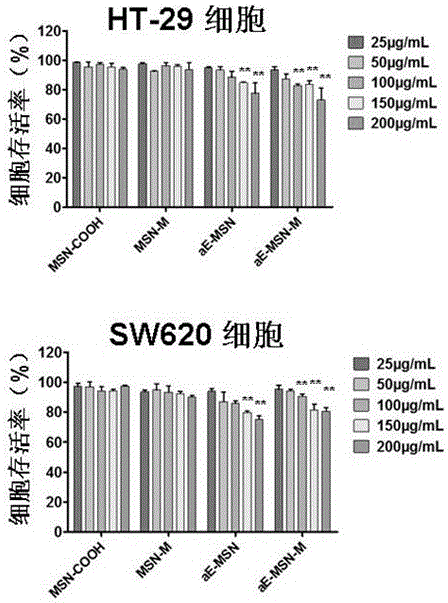
ActiveCN105125510AAvoid stickingInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryEngineeringMesoporous silica
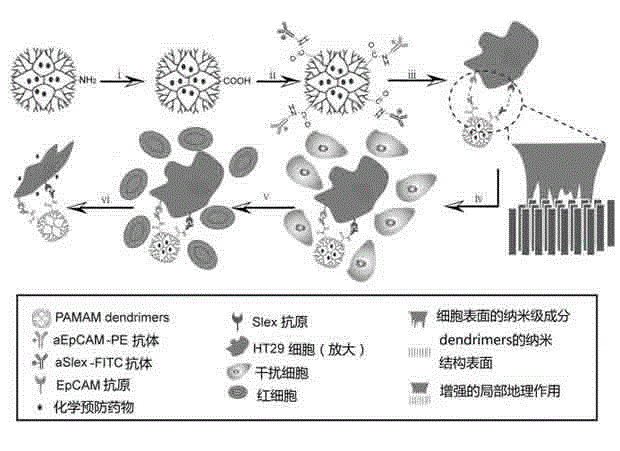
The invention discloses an antibody coupled mesoporous silica / mifepristone nanometer preparation and a preparing method and application thereof. The preparation is prepared from mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN), mifepristone (MIF) and epithelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies (anti-EpCAM, aE), MIF is carried by MSN, and the surface of the MSN is covalently modified by aE. The ntibody coupled mesoporous silica / mifepristone nanometer preparation can recognize in a targeting mode, restrain activity of circular tumor cells (CTCs), restrain adhesion between the CTCs and endangium, disturb a tumor metastasis process and remarkably restrain tumor metastasis.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Novel tumor marker
ActiveCN101942017APrevent invasionInhibit transferMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to the field of diagnosis and treatment of tumors, in particular to a polypeptide in plasma, which has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1, wherein the polypeptide can be used as a tumor marker used in a method and a kit for diagnosing the generation and the metastasis of the tumors. The invention also relates to a method and a medicament for treating tumors and metastasis of tumors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
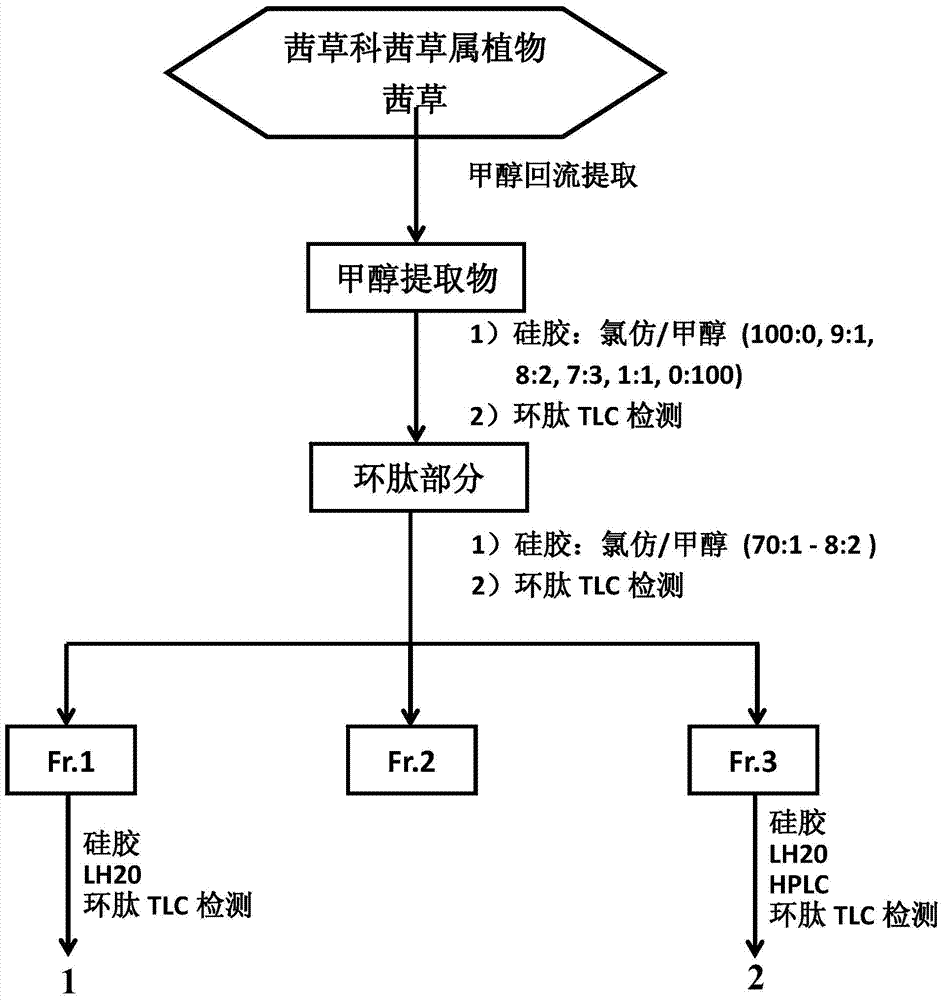
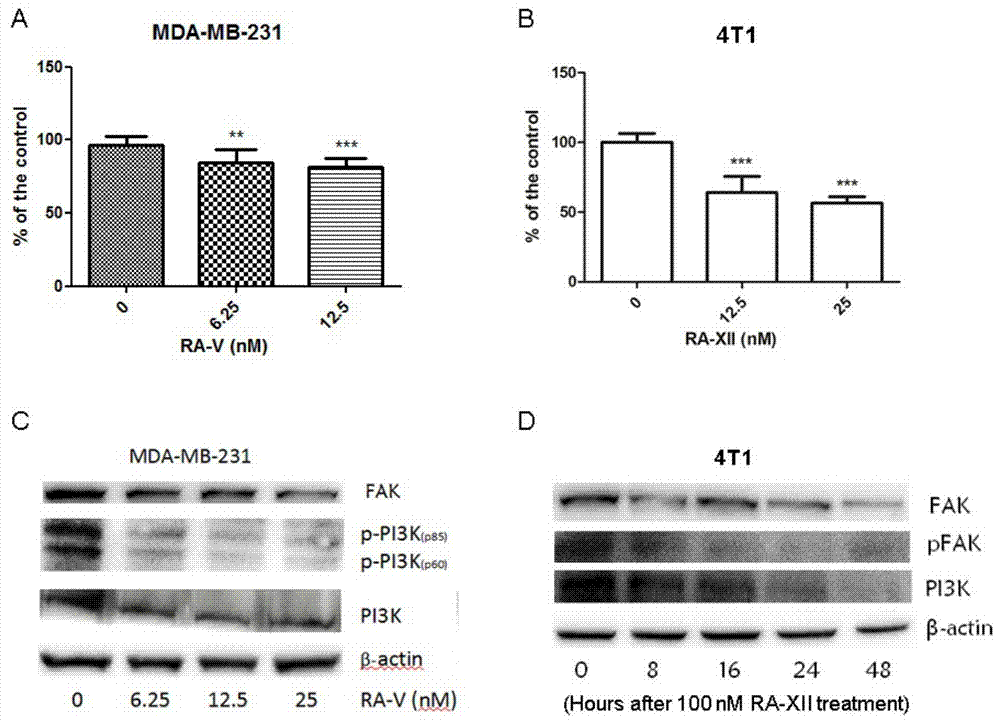
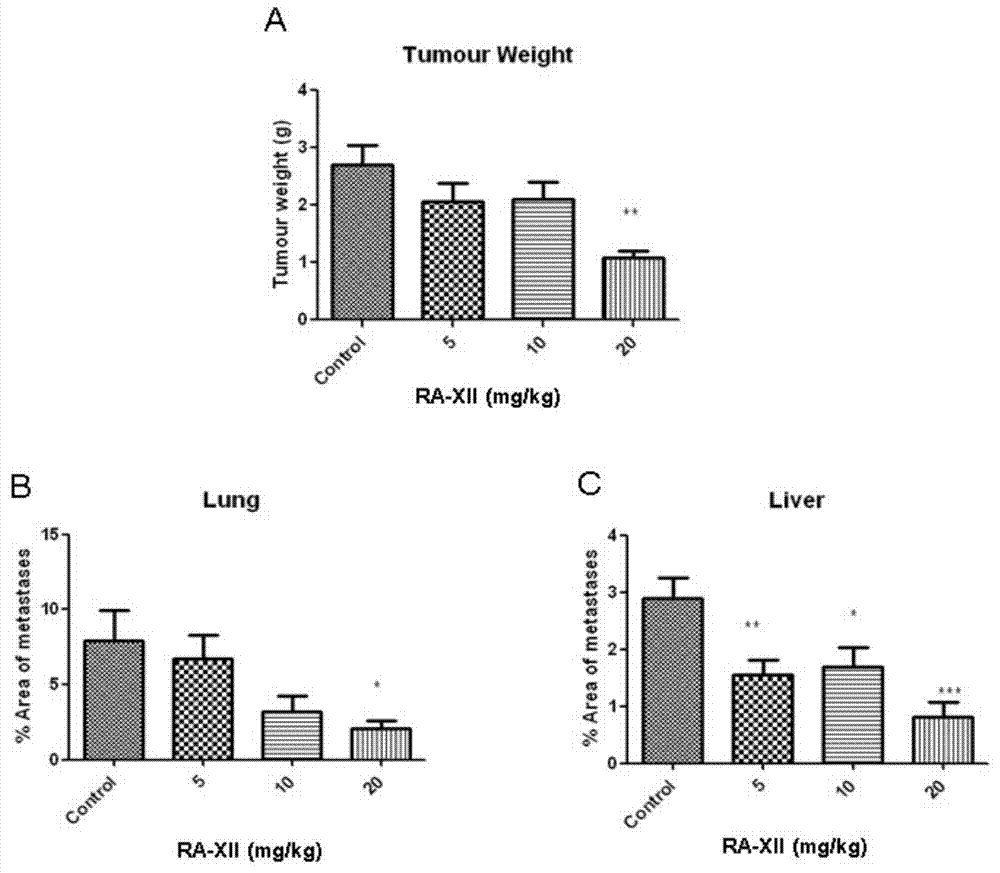
Rubiaceae type cyclopeptide used as tumor metastasis inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103880929ARapid enrichmentReduce lossesSaccharide peptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsLymphatic SpreadGlycoside formation
The invention provides a rubiaceae type cyclopeptide compound RA-V (1) and a glycoside RA-XII (2) thereof as a tumor metastasis inhibitor, a drug composition with the rubiaceae type cyclopeptide compound and the glycoside as active ingredients, a preparation method of the compound and an application of the compound to preparation of anti-tumor metastasis drugs. The method can be used for obtaining cyclopeptide through rapid separation, is less in sample loss, relatively low in cost and convenient to operate, has good controllability and repeatability, ensures that solvents can be recycled, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Establishment of human cancer cell lines with metastatic potential using NOD/SCID
The invention provides a new reproducible transgenic mouse model for the study of tumor metastasis. In particular, the invention concerns the study of tumor metastasis in a NOD / SCID / γcnull transgenic mouse model.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS +1
New drug
InactiveUS20050054593A1Growth inhibitionKeep for a long timePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLymphatic SpreadMurine fibrosarcoma
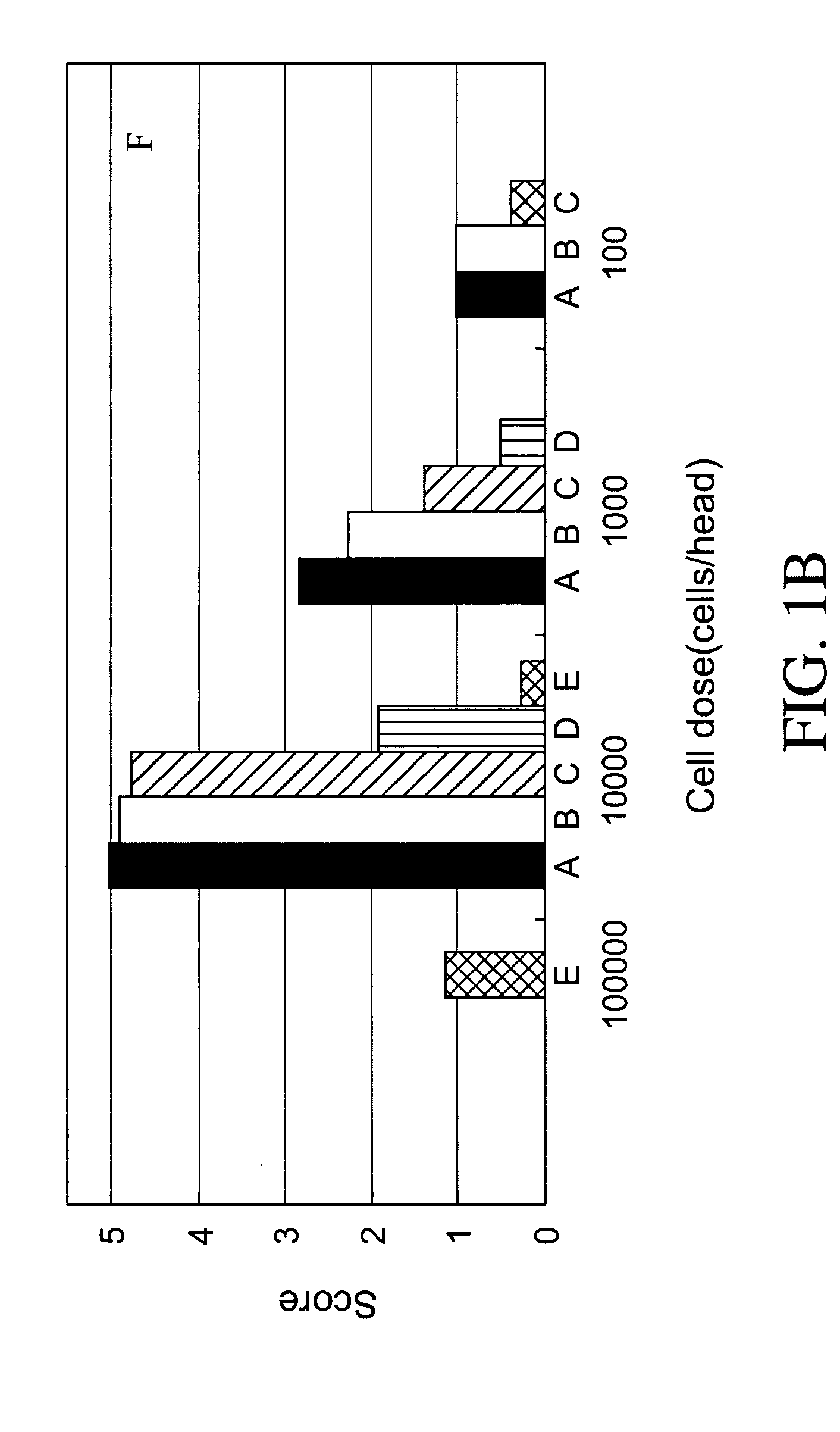
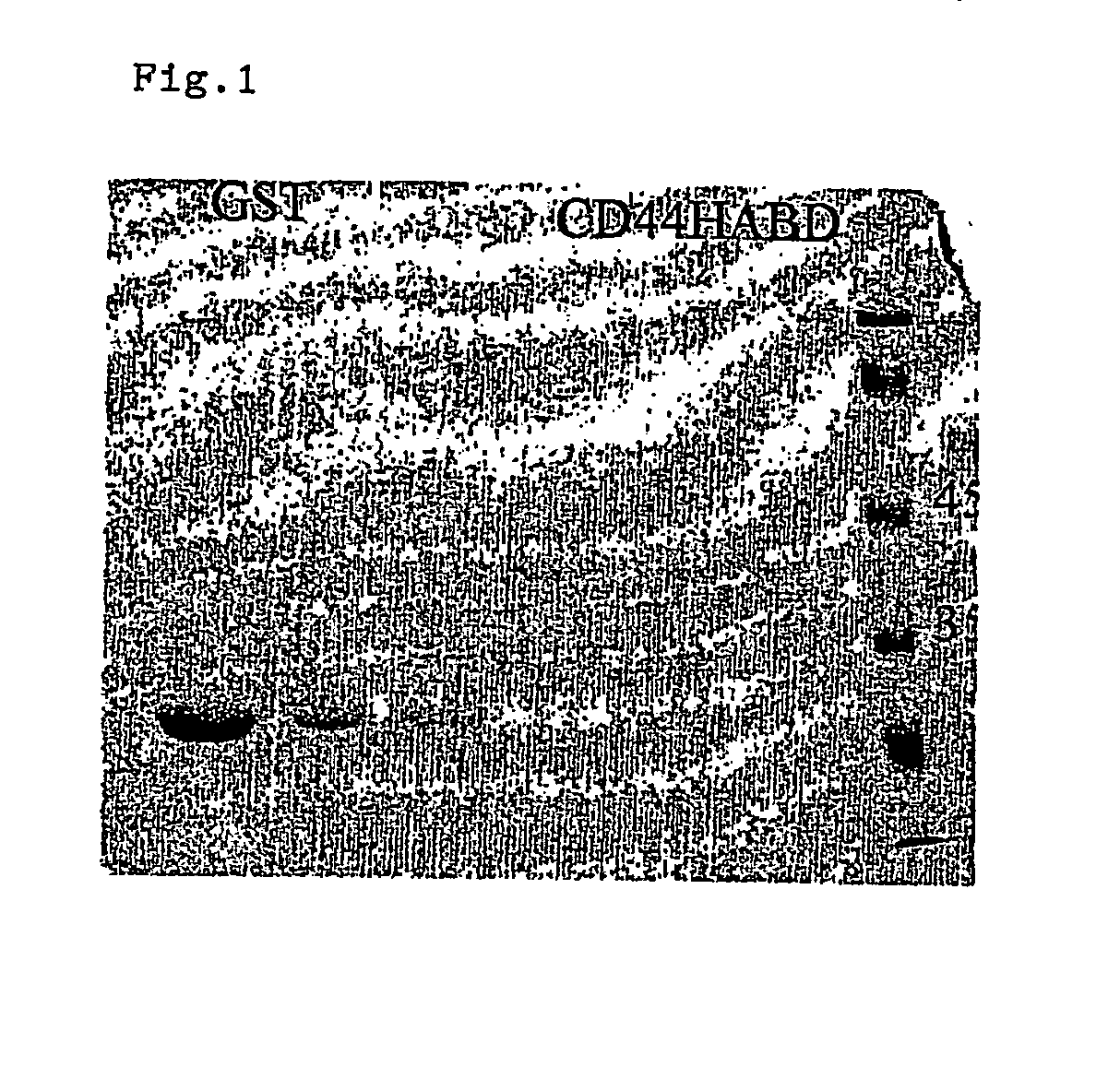
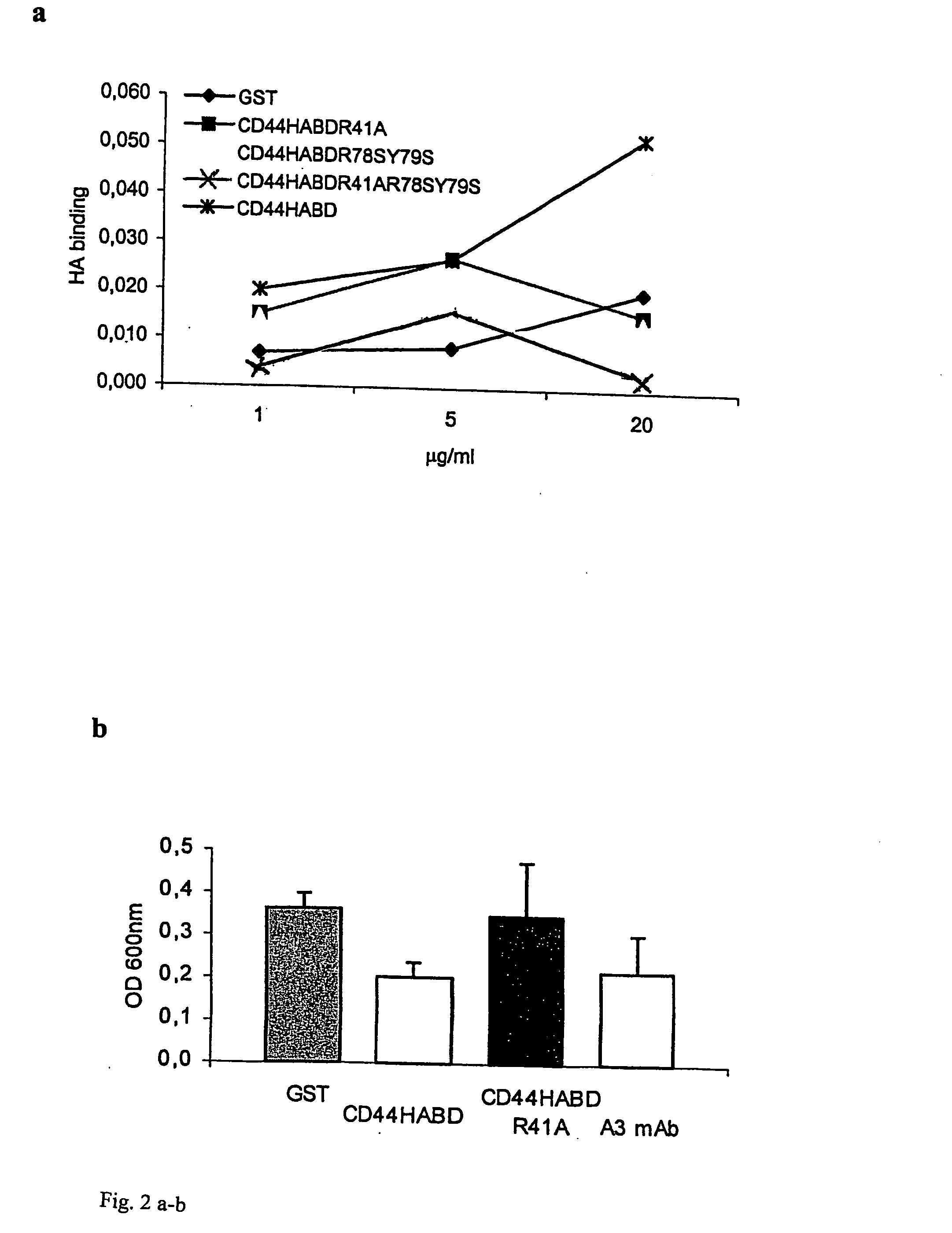
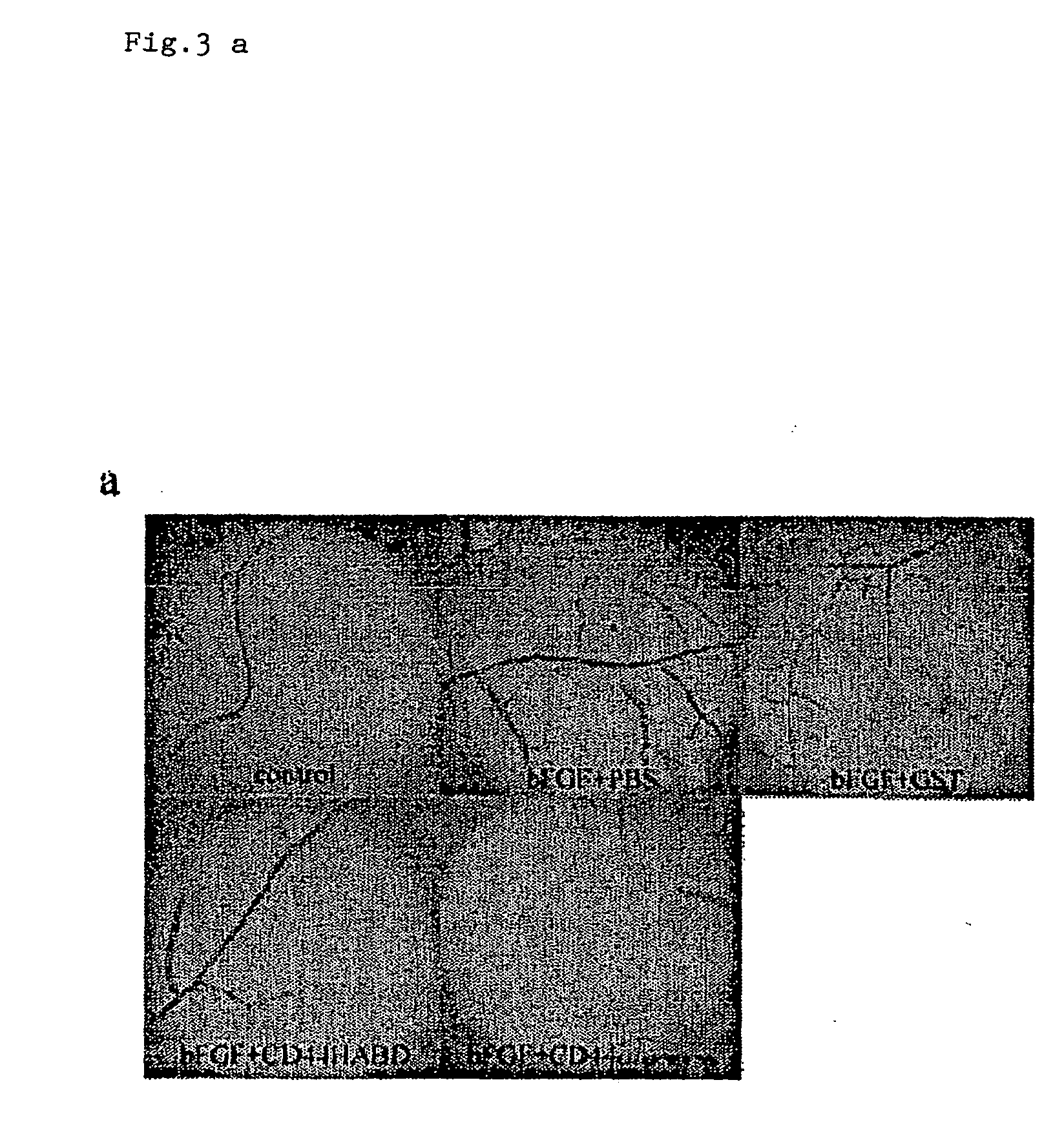
CD44, the receptor for hyaluronic acid, has complex functions in cellular physiology, cell migration and tumour metastasis. The inventors have previously found that human CD44 receptor overexpression in mouse fibrosarcoma cells inhibits subcutaneous tumour growth in mice [Kogerman et al., Oncogene 1997; 15:1407-16; Kogerman et al., Clin Exp Metastasis 1998; 16:83-93]. Here it is demonstrated that a tumour growth inhibitory effect of CD44 is caused by block of angiogenesis. Furthermore, the inventors have found that soluble recombinant CD44 hyaluronic acid binding domain (CD44HABD) inhibits angiogenesis in vivo in cLick and mouse and thereby inhibits human tumour growth of various origins. The anti-angiogenic effect of CD44-HABD is independent of hyaluronic acid (HA) binding, since non-HA-binding mutants of CD44HABD still maintain anti-angiogenic properties. The invention discloses soluble CD44 recombinant proteins as a novel class of angiogenesis inhibitors based on targeting of vascular cell surface receptor. A method of block of angiogenesis and treatment of human tumours using recombinant CD44 proteins as well as their analogues is disclosed. As a further embodiment of the invention, methods for screening for new drug targets using CD44 recombinant proteins and their analogues is presented.
Owner:CELECURE
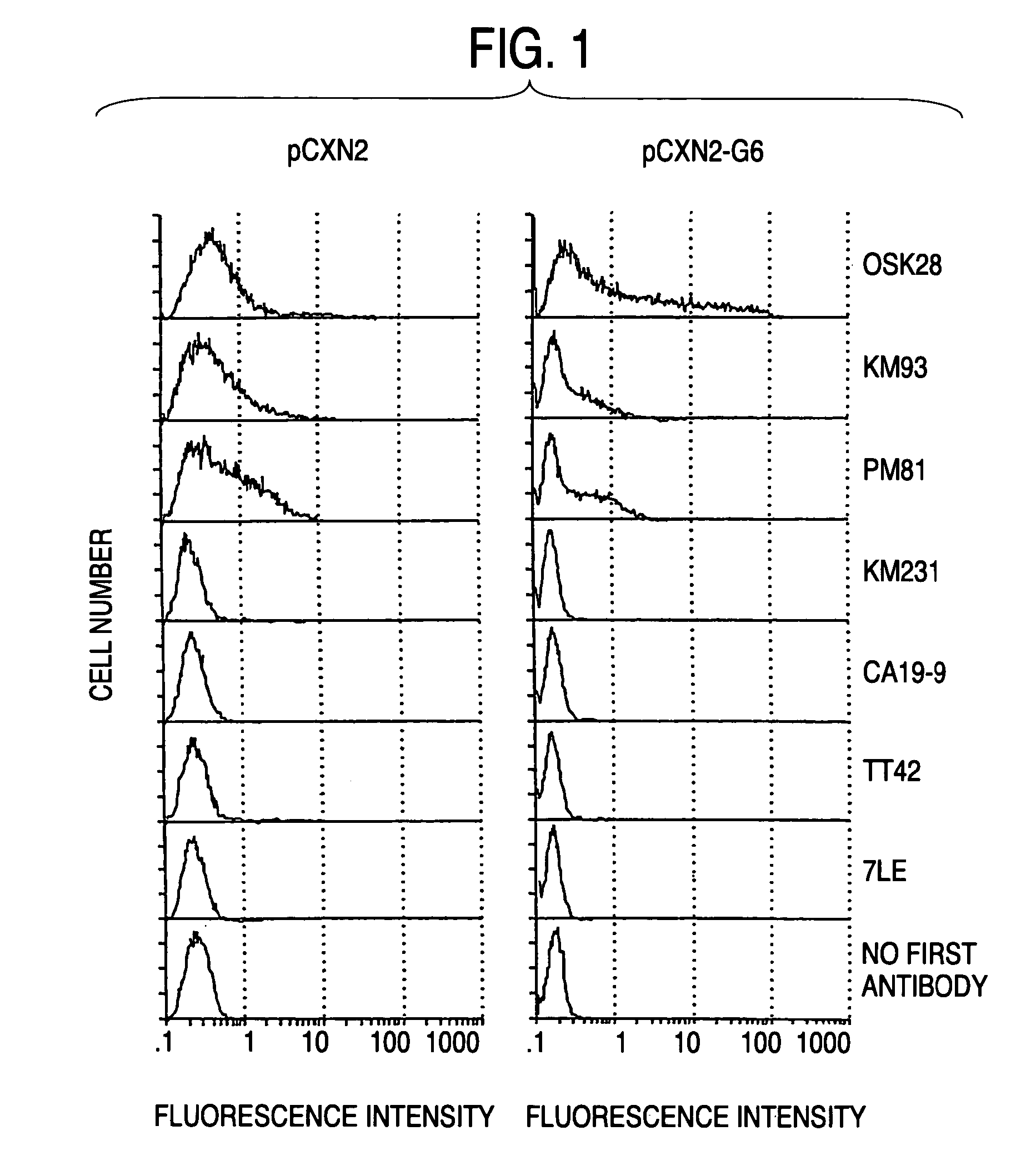
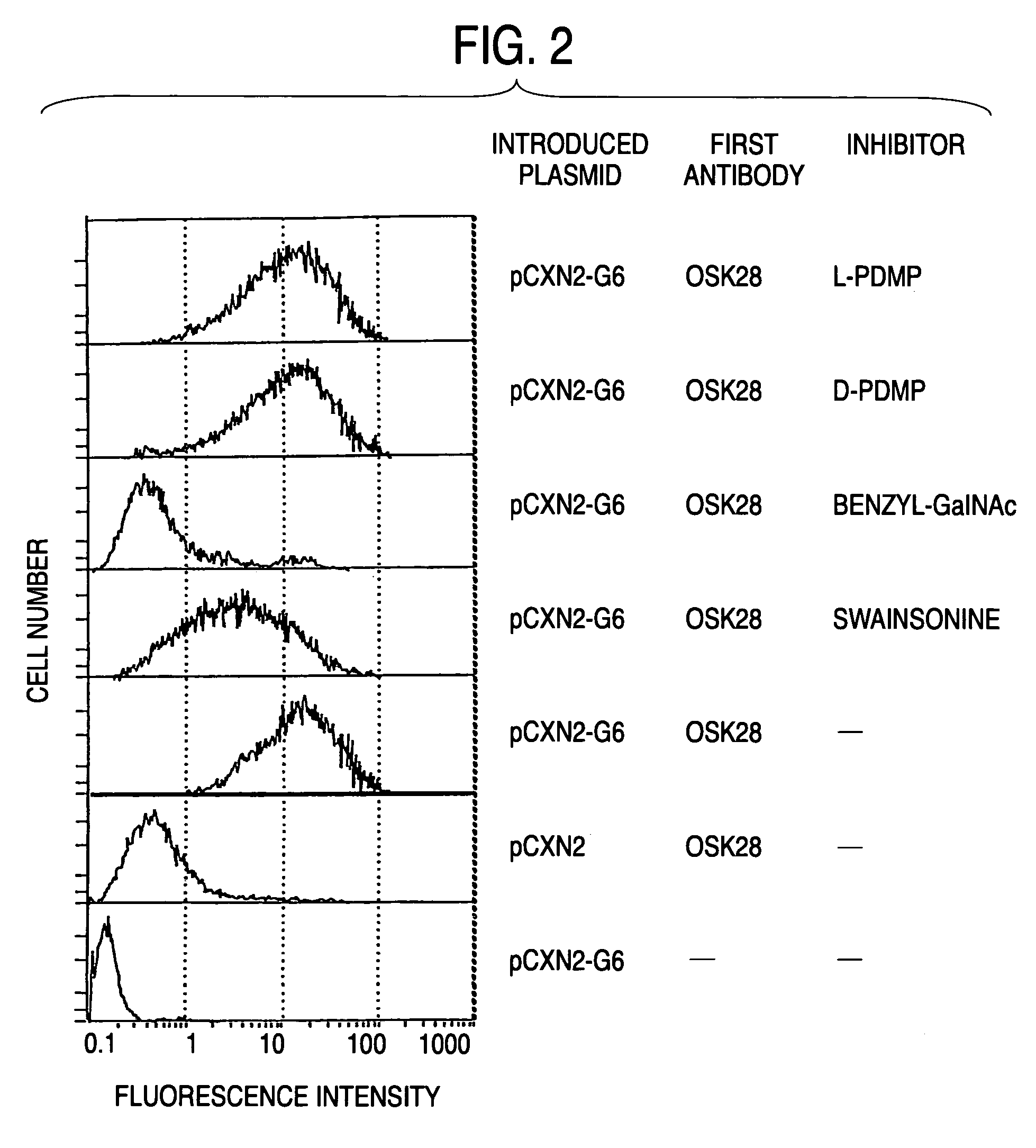
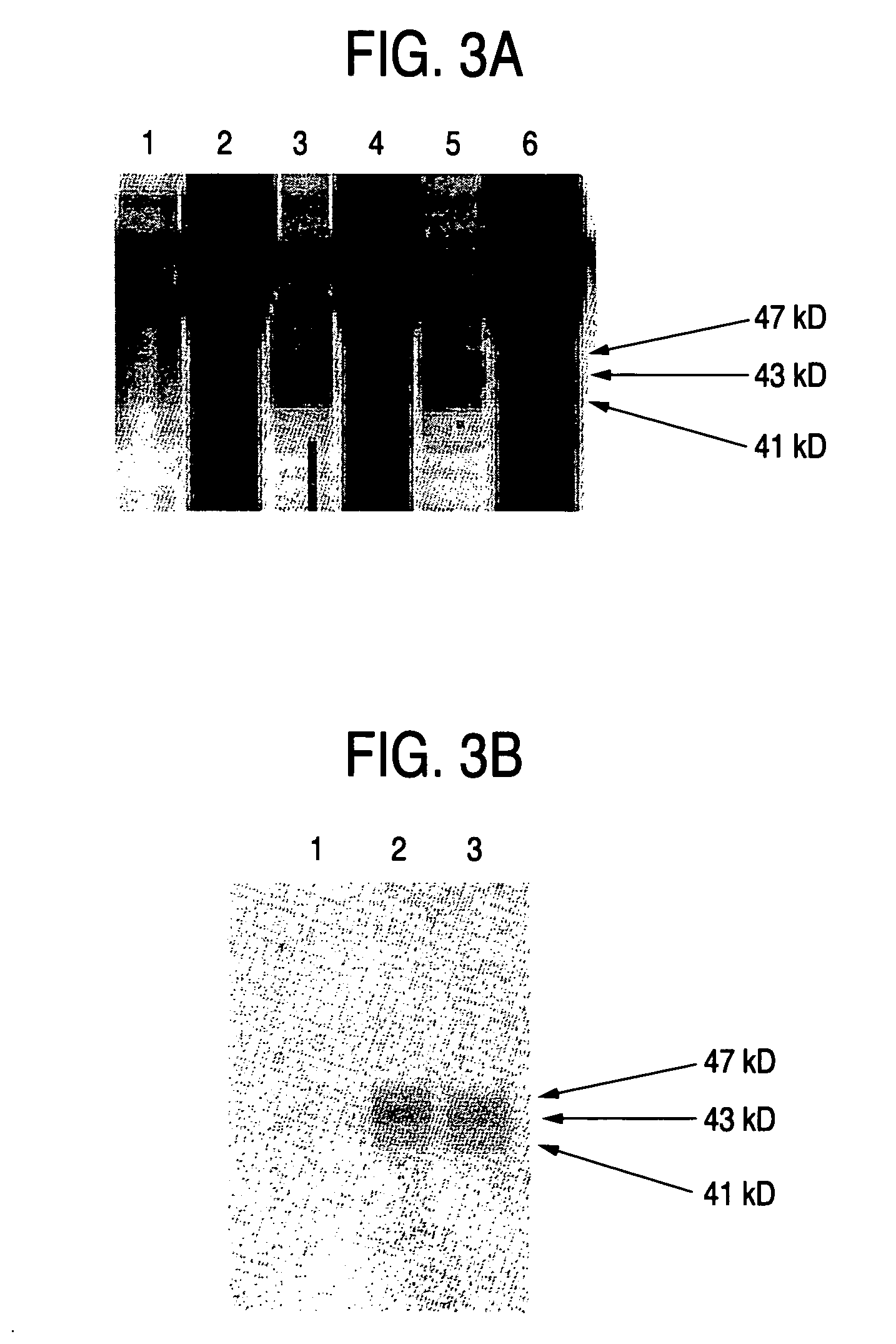
Process for producing sugar chains using beta1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
The present invention provides a novel polypeptide having a β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity, an agent for synthesizing a sugar chain comprising the polypeptide, a process for producing a sugar chain or a complex carbohydrate using the agent for synthesizing a sugar chain, DNA encoding the polypeptide, a process for producing the polypeptide, an antibody against the polypeptide, and a diagnosis method and a medicament for treatment for inflammation, cancer or tumor metastasis using the DNA or the antibody. The present invention is useful for synthesis of a useful sugar chain and diagnosis and treatment for inflammatory diseases, cancer or tumor metastasis.
Owner:HISASHI NARIMATSU +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com