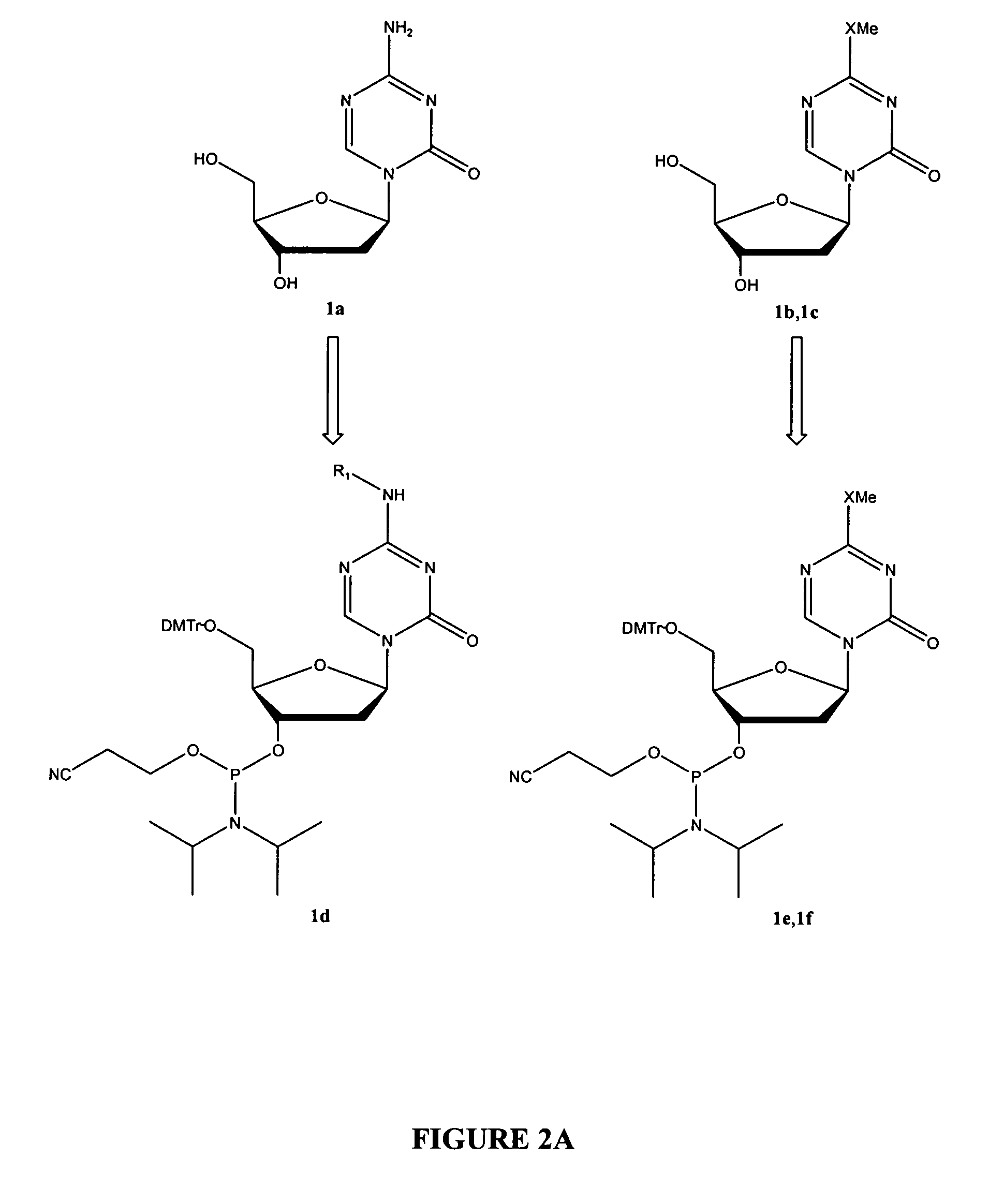
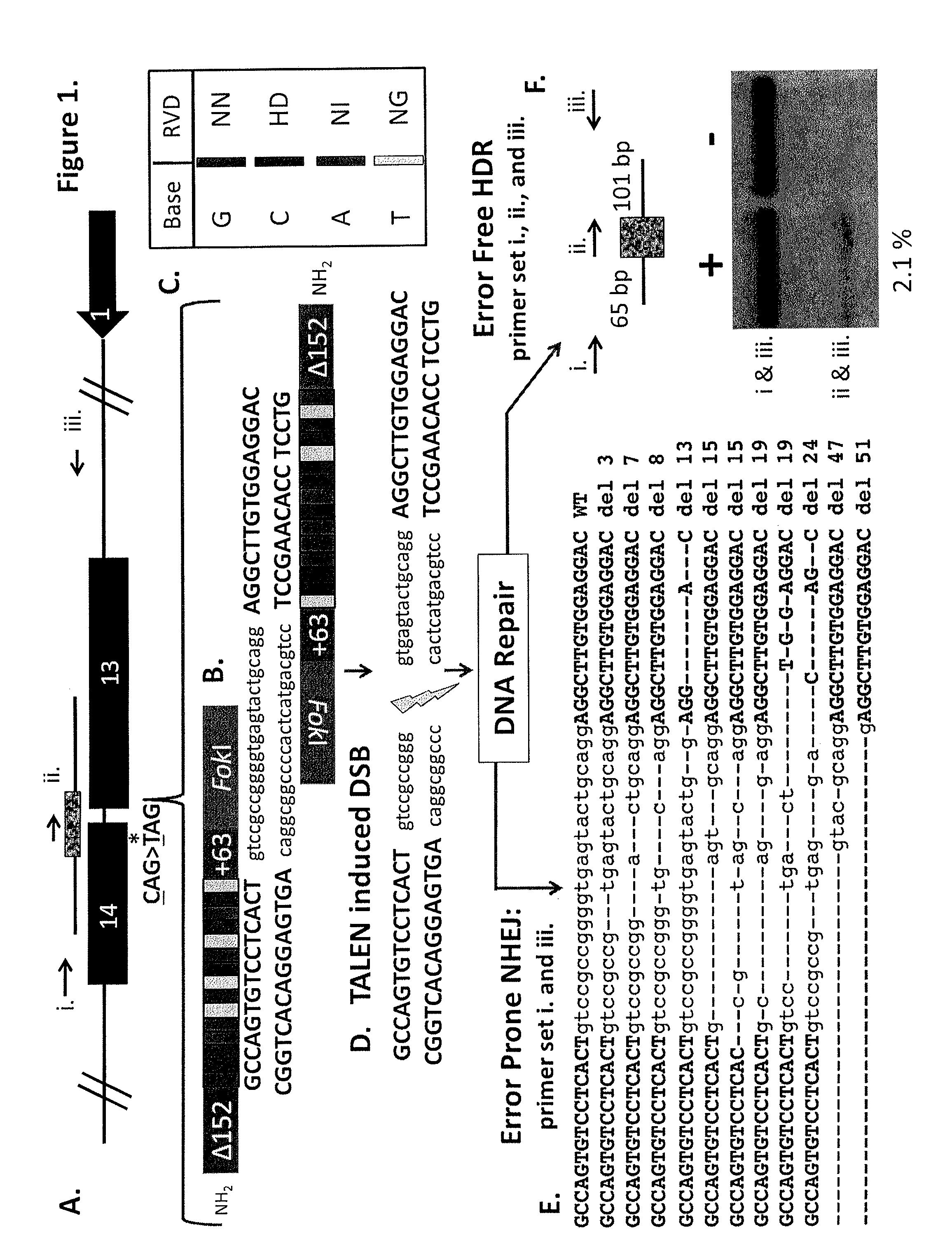
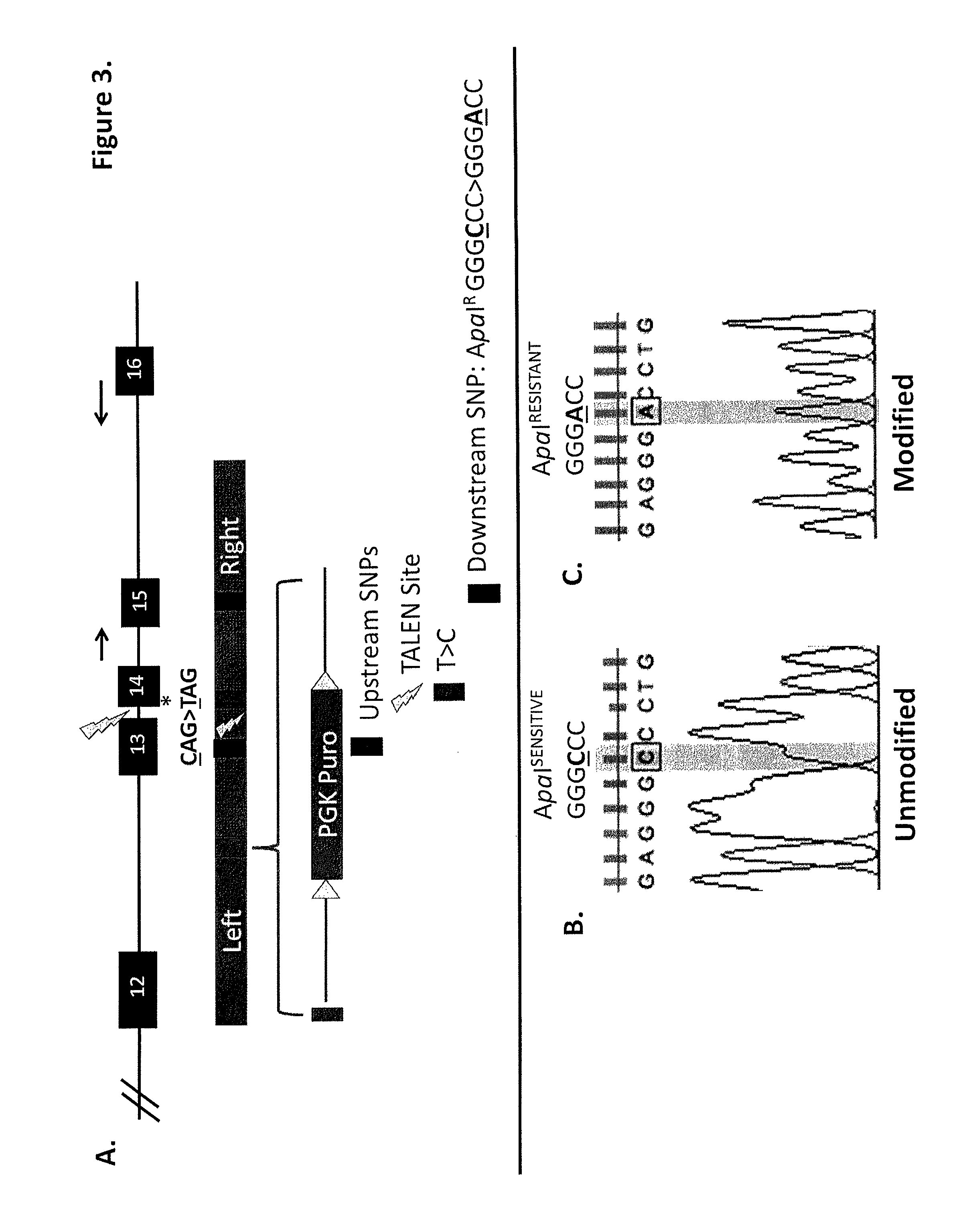
Patents
Literature
605 results about "Human DNA sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The human genome is the complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria.
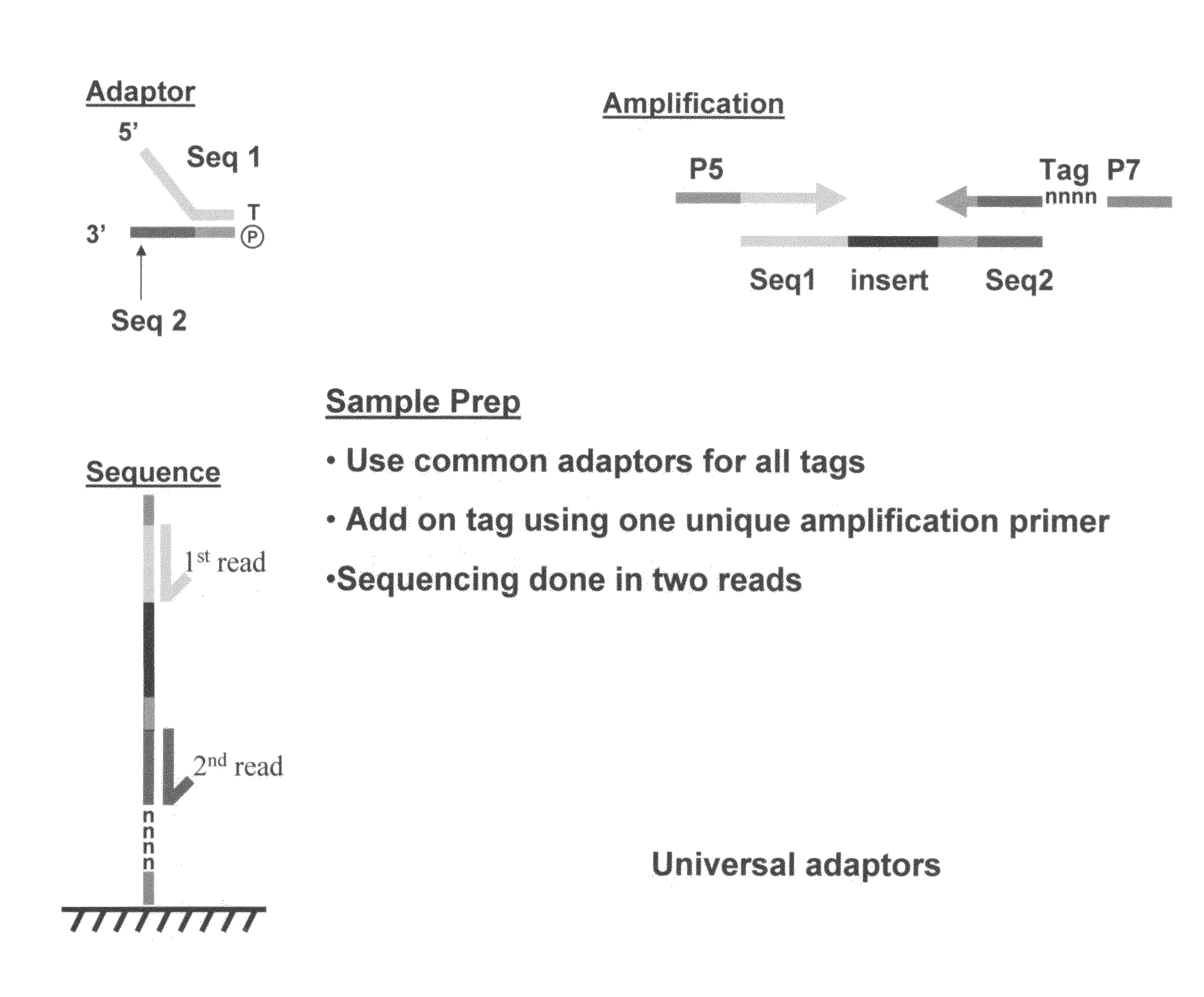
Methods for indexing samples and sequencing multiple polynucleotide templates
The invention relates to methods for indexing samples during the sequencing of polynucleotide templates, resulting in the attachment of tags specific to the source of each nucleic acid sample such that after a sequencing run, both the source and sequence of each polynucleotide can be determined. Thus, the present invention pertains to analysis of complex genomes (e.g., human genomes), as well as multiplexing less complex genomes, such as those of bacteria, viruses, mitochondria, and the like.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
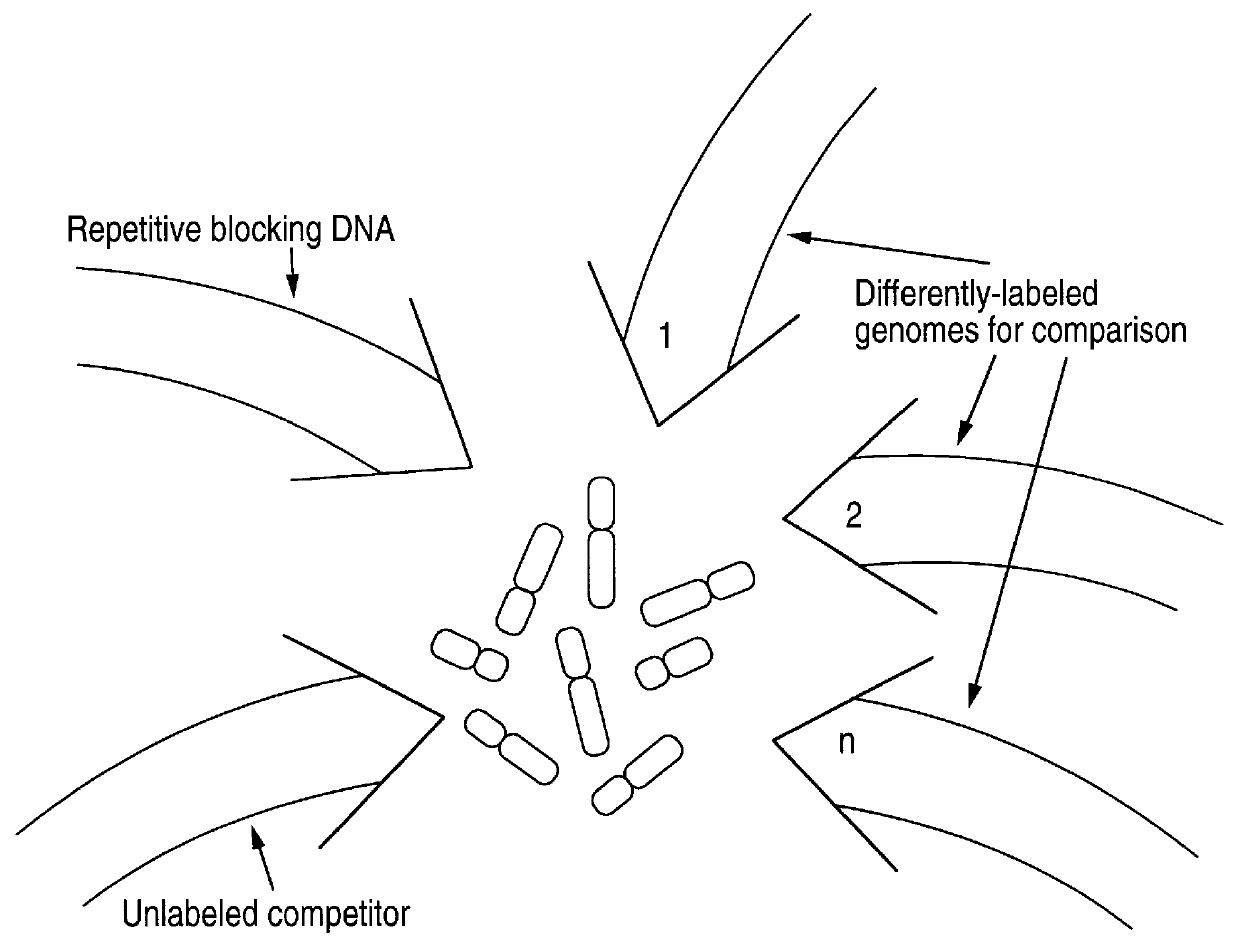
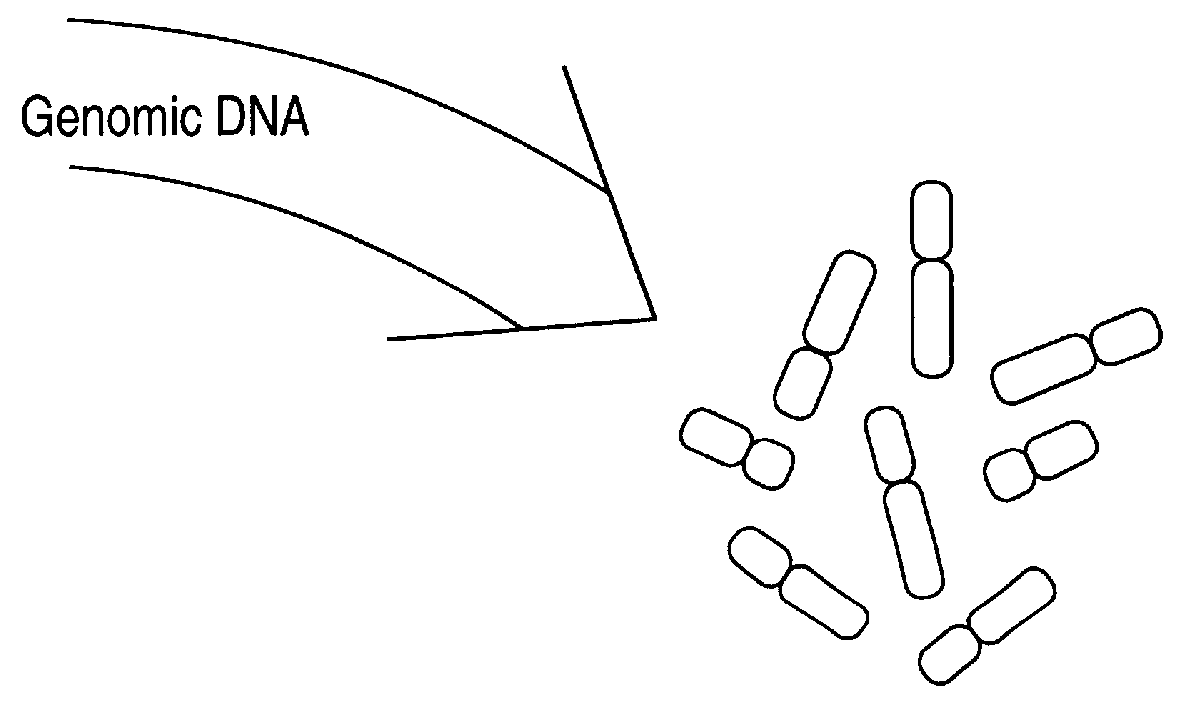
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
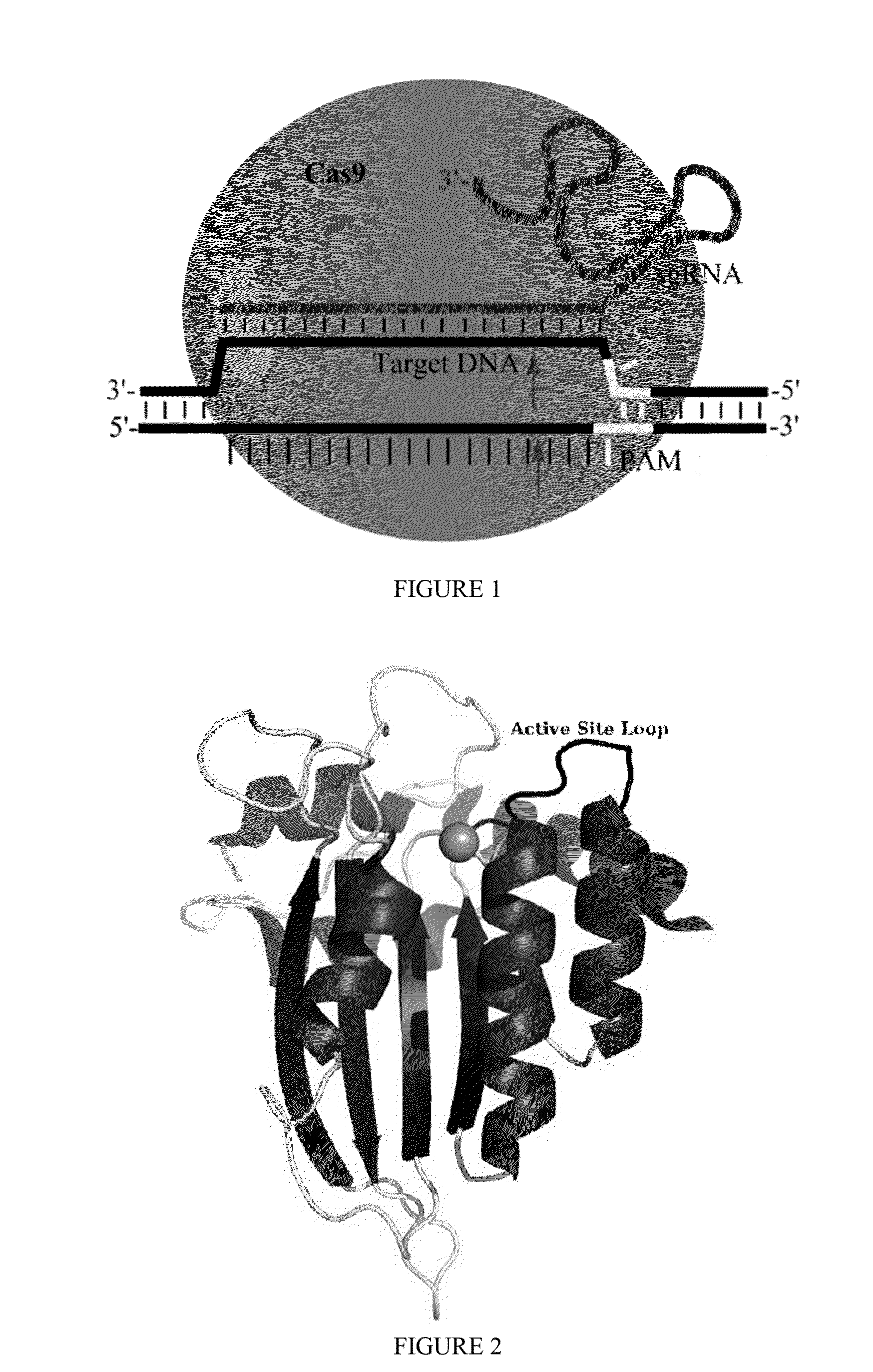
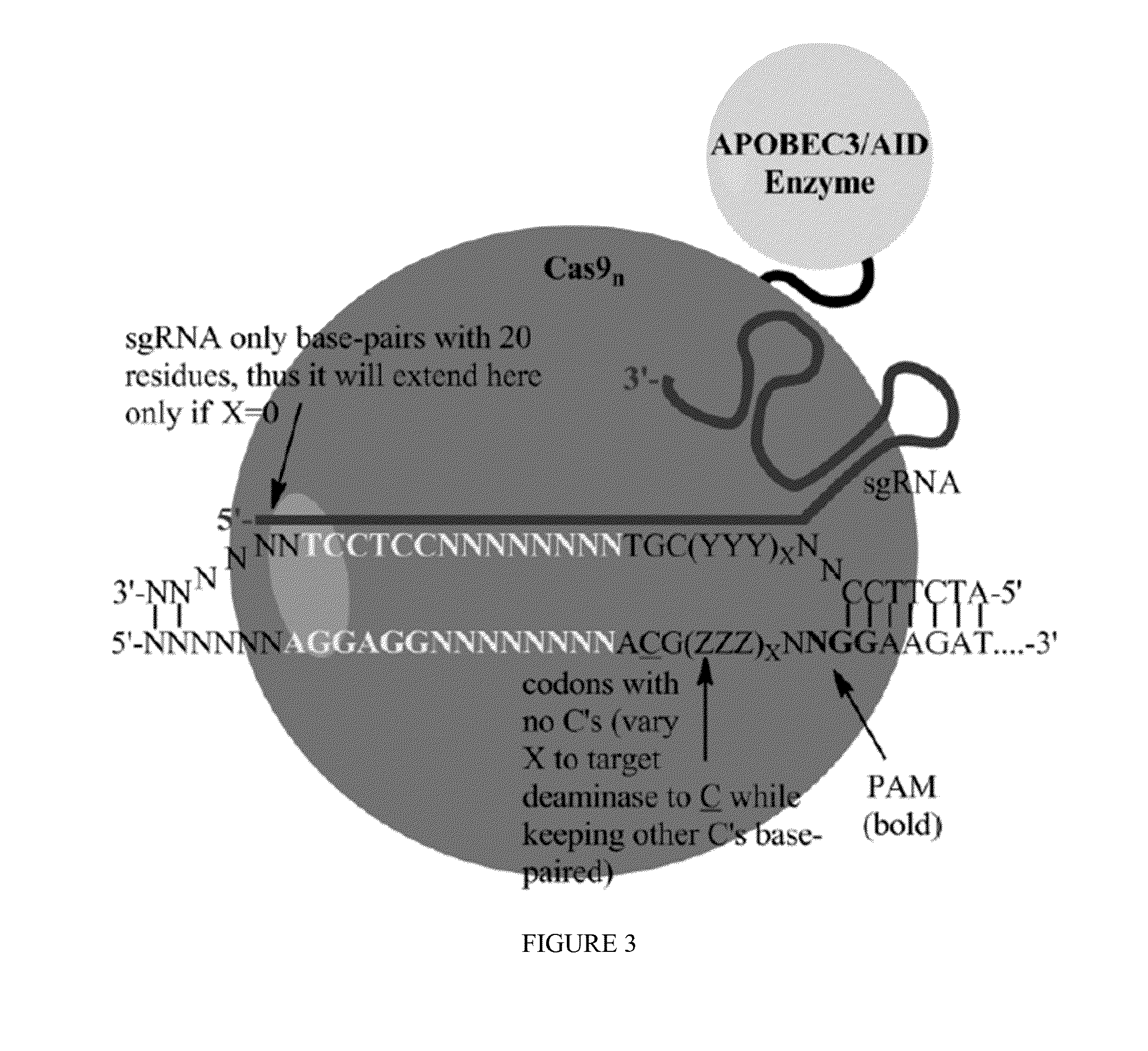
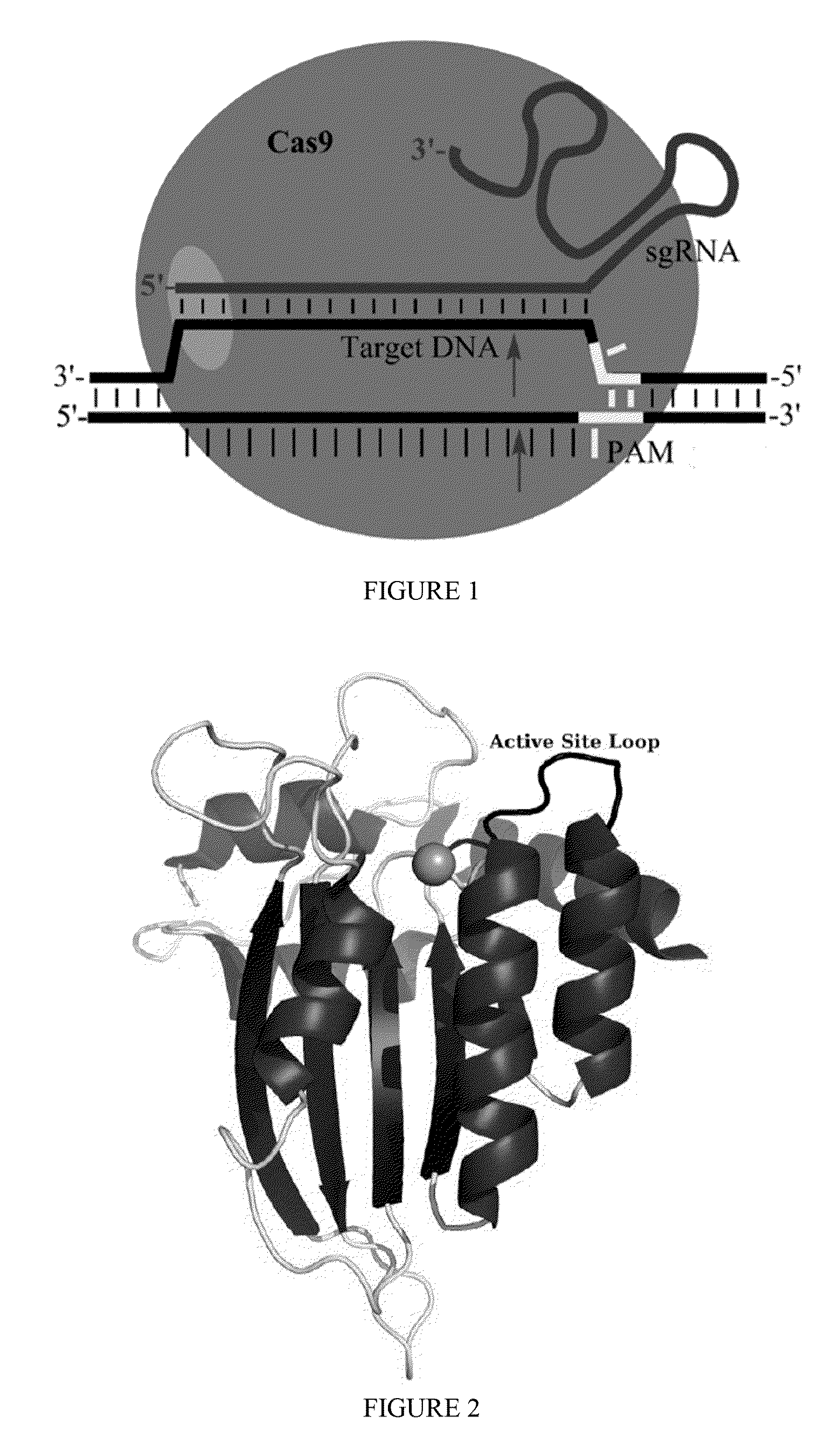
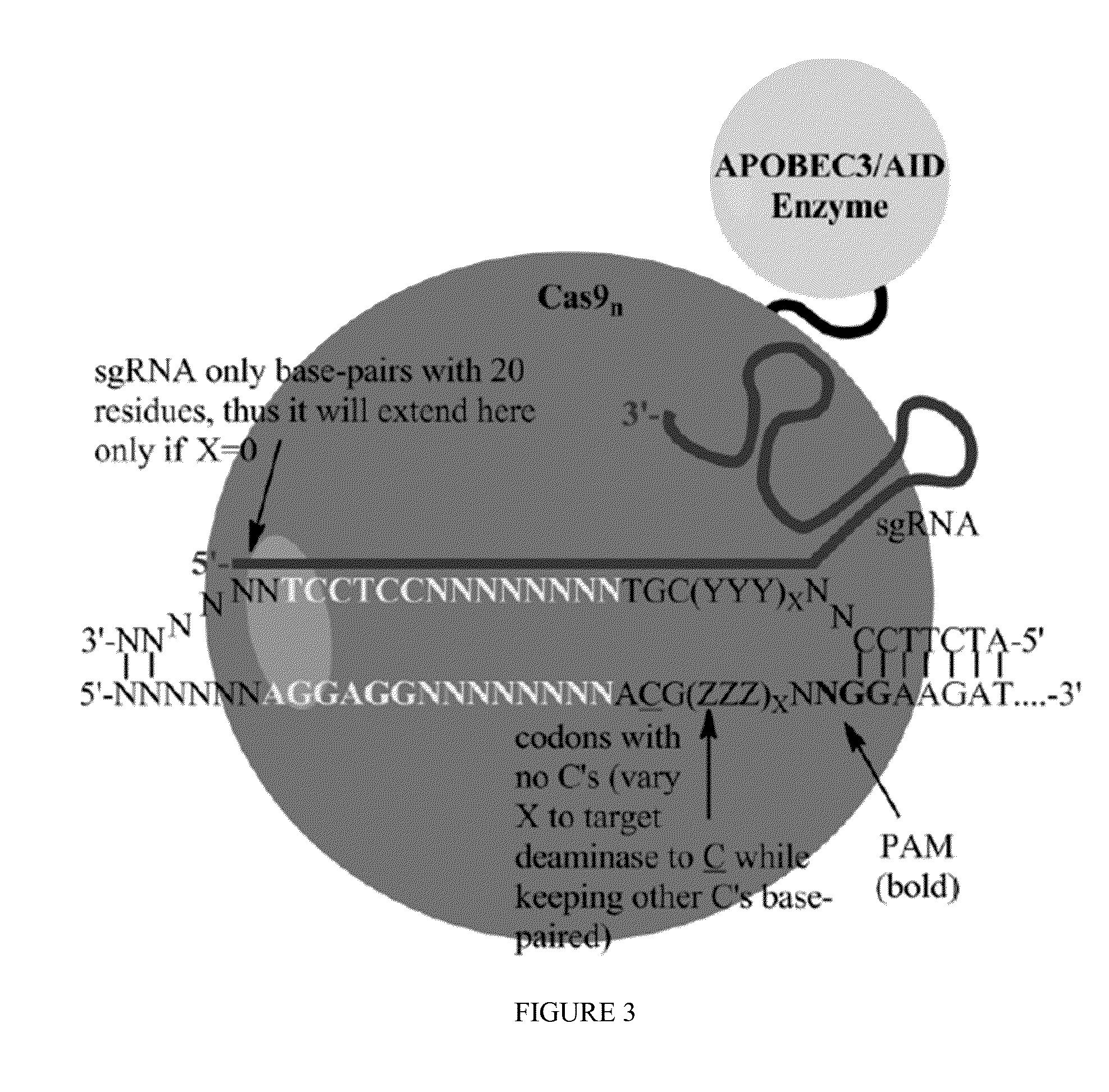
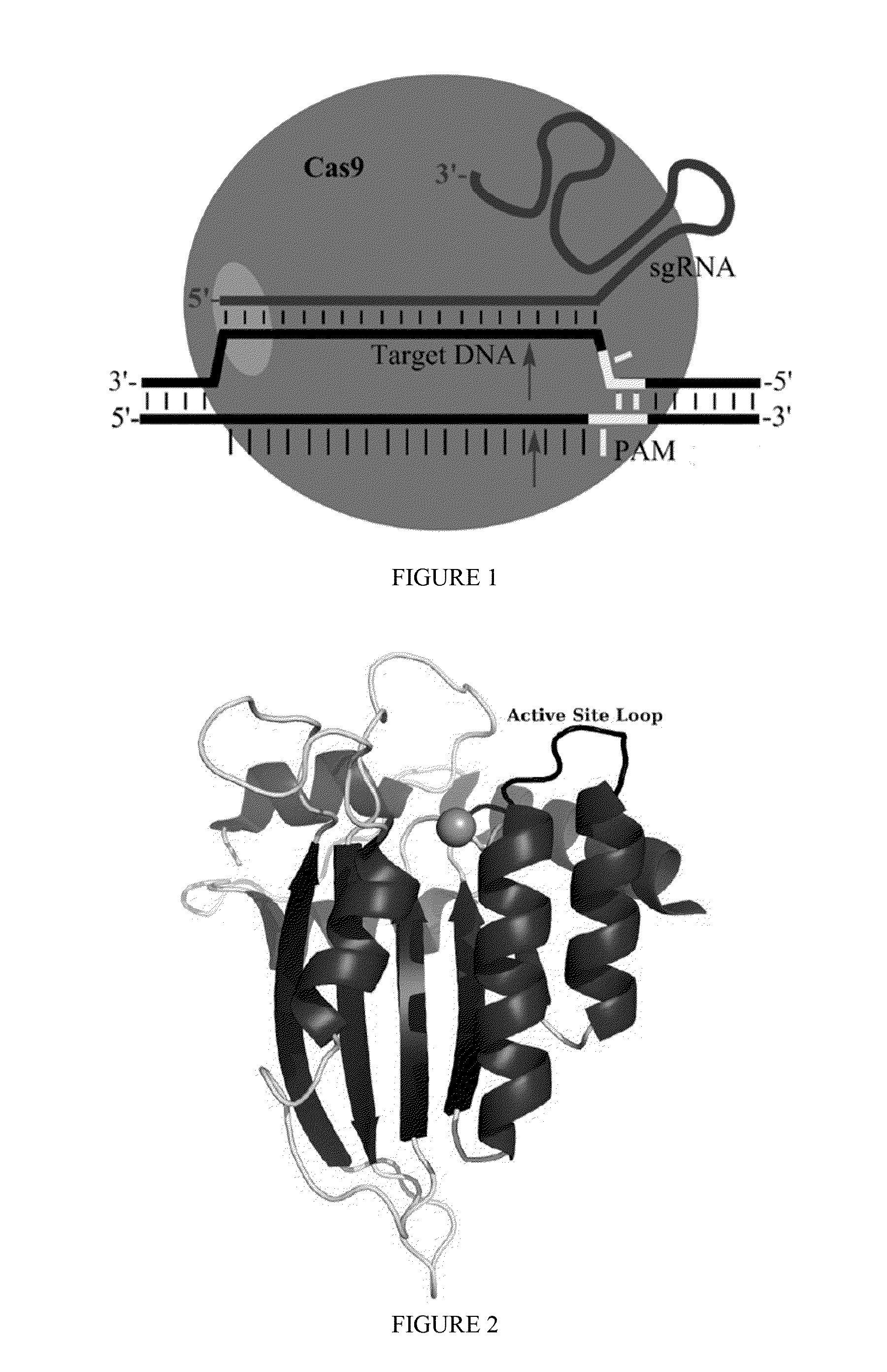
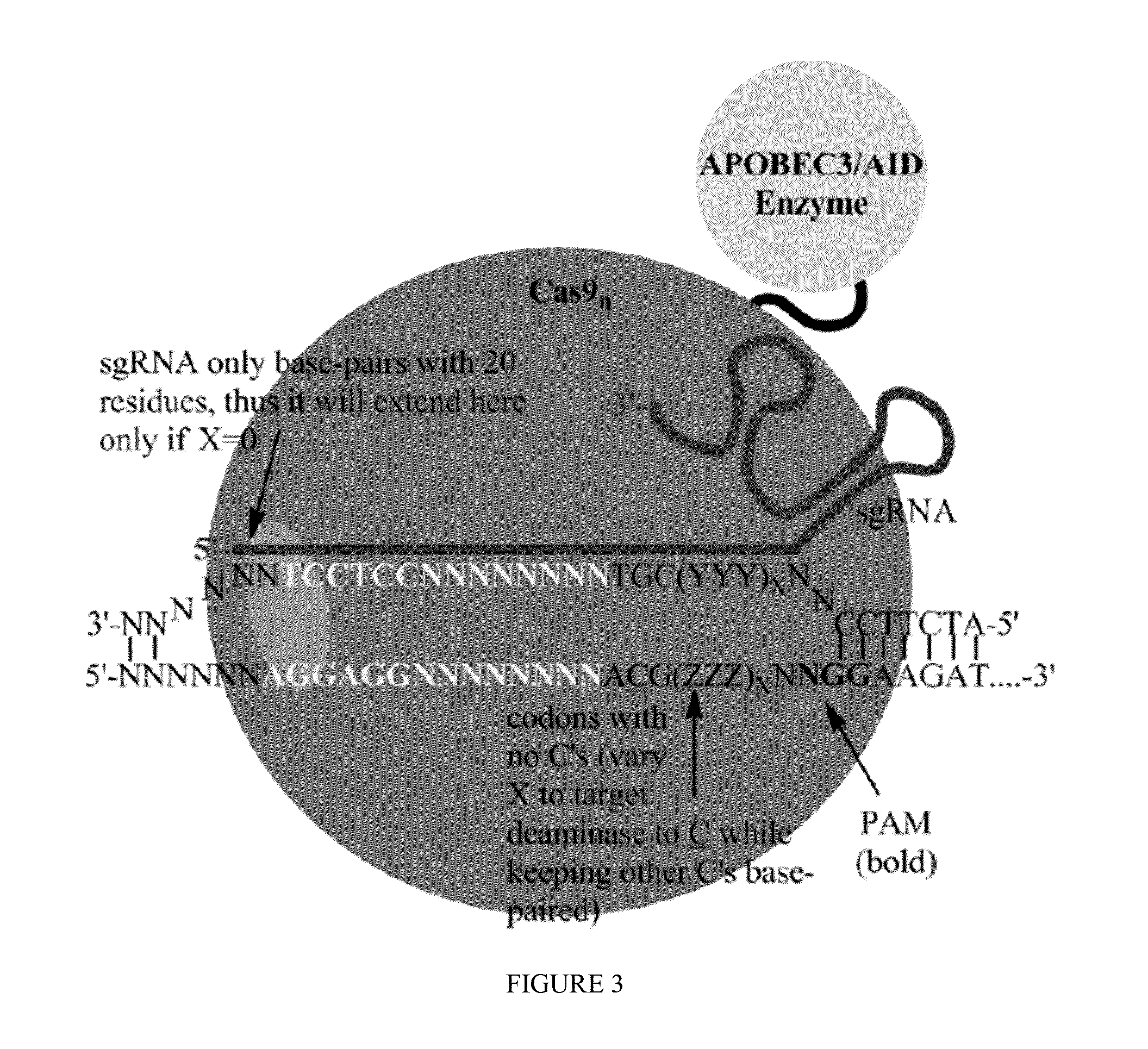
Fusions of cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains
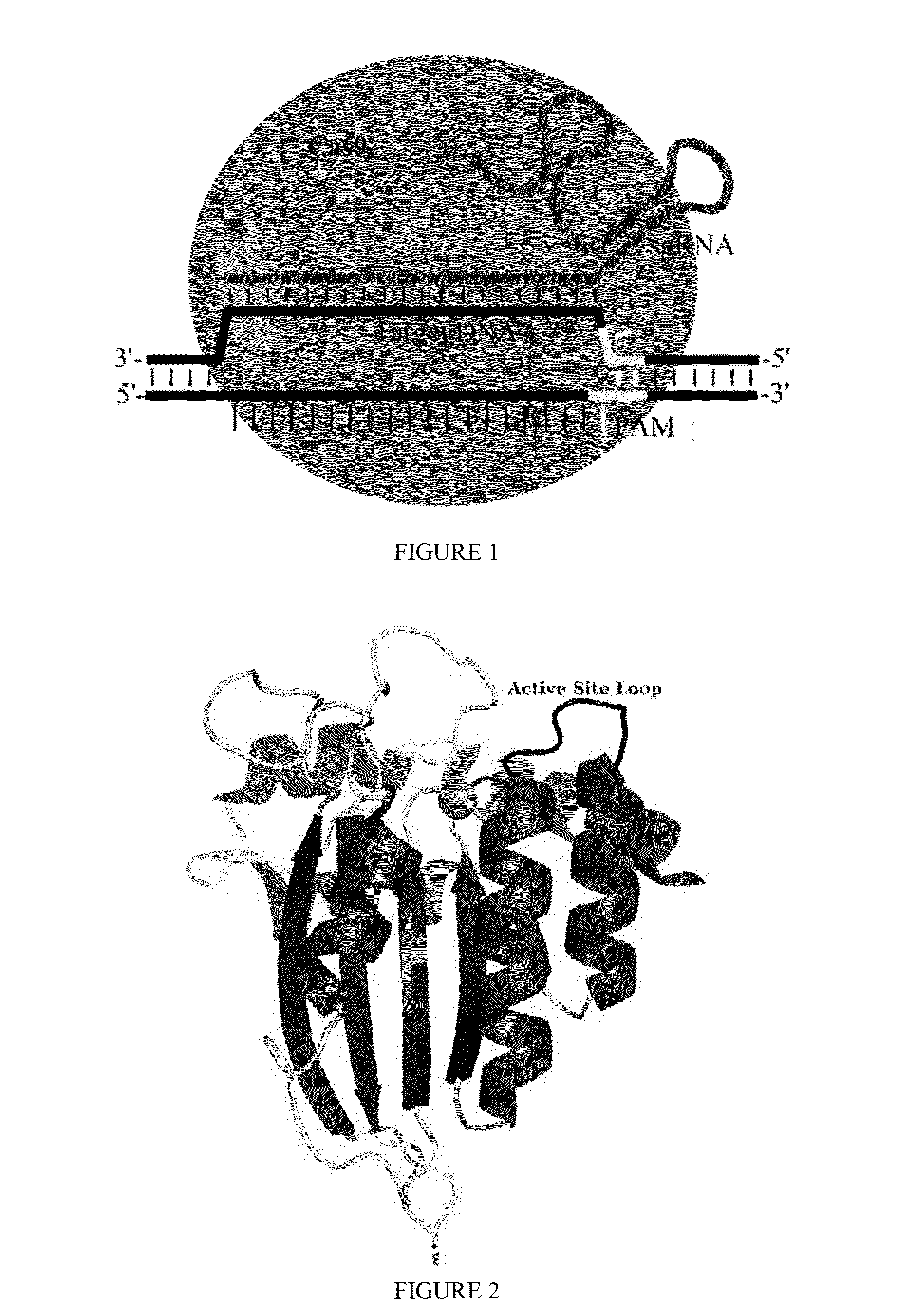
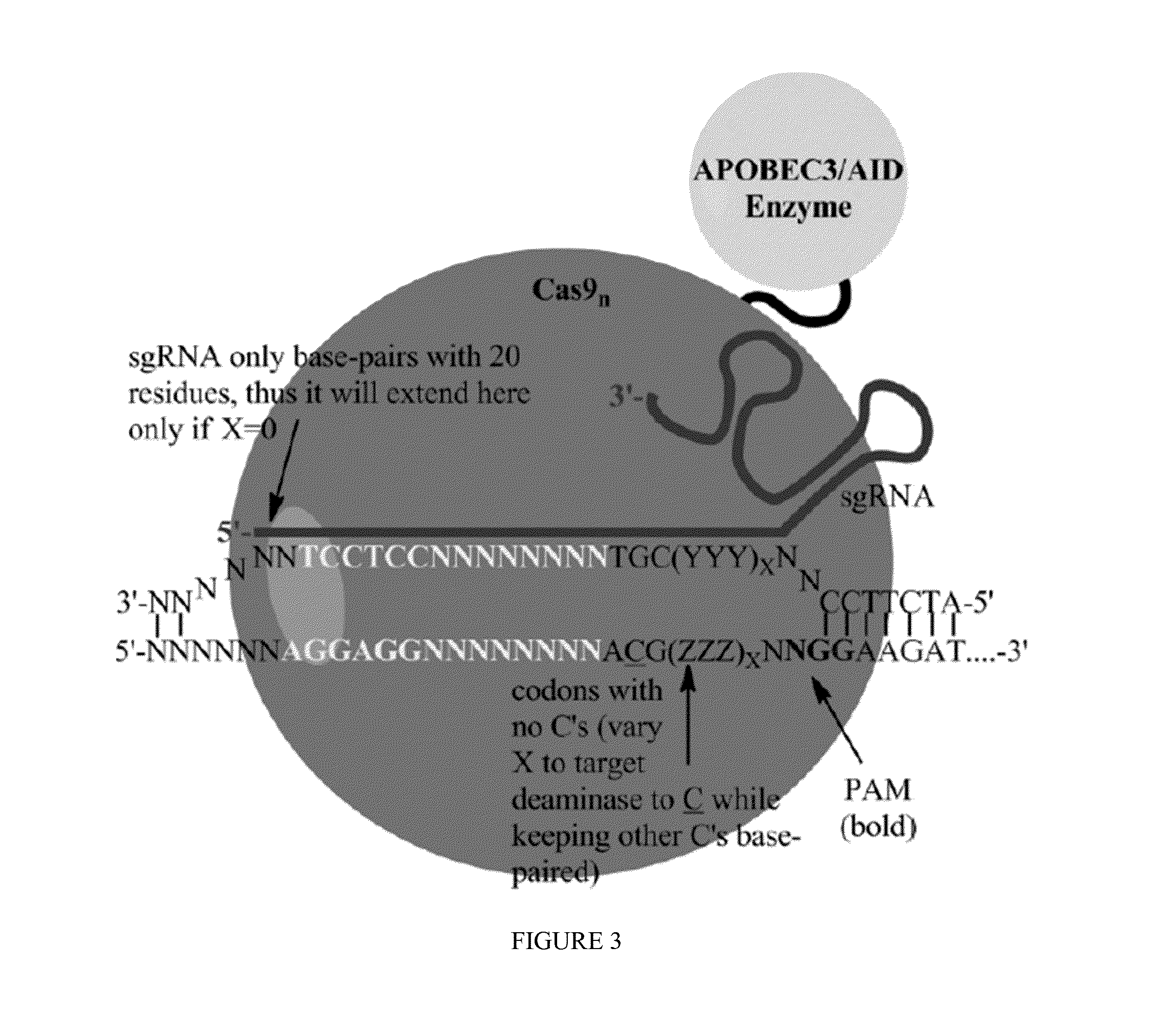
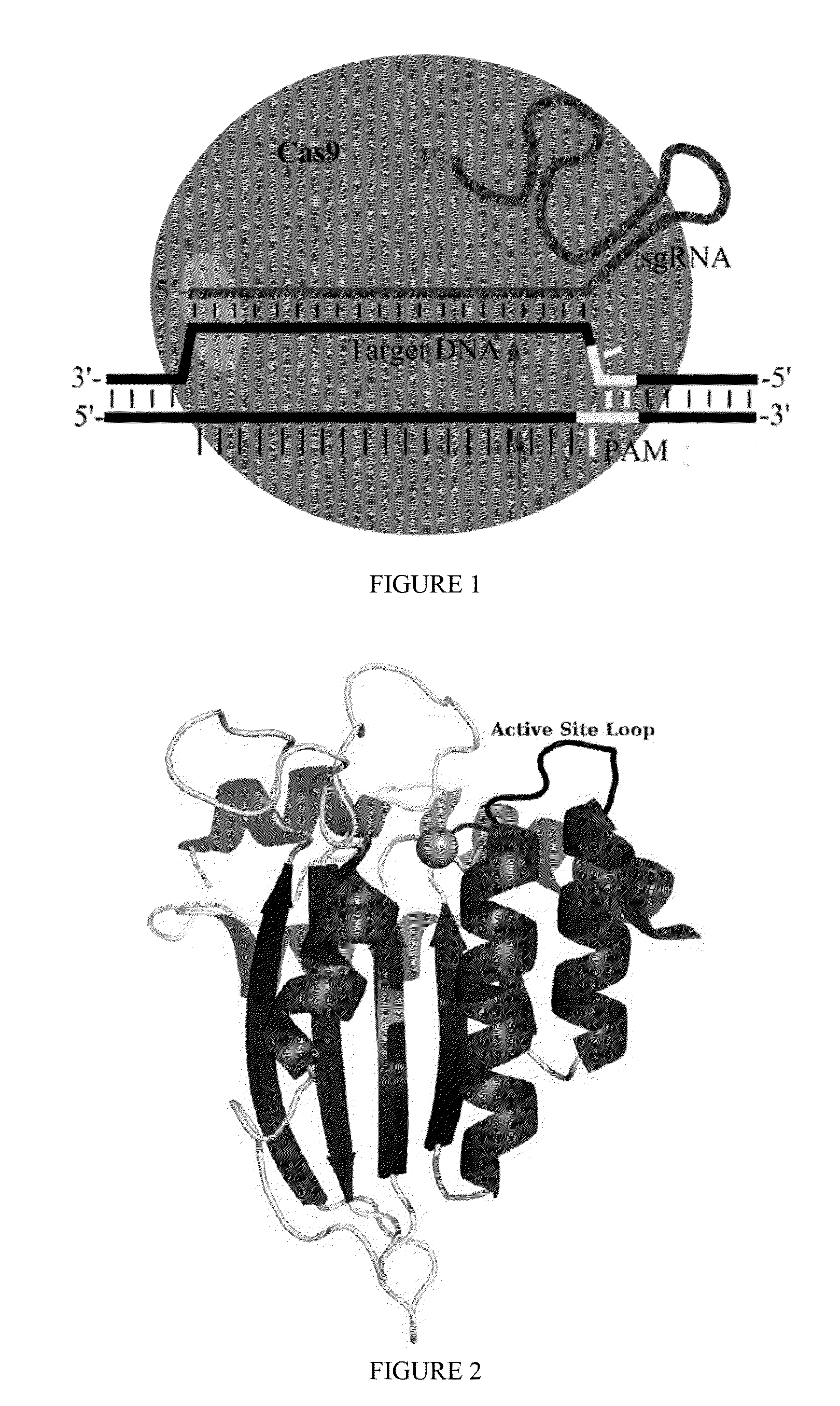
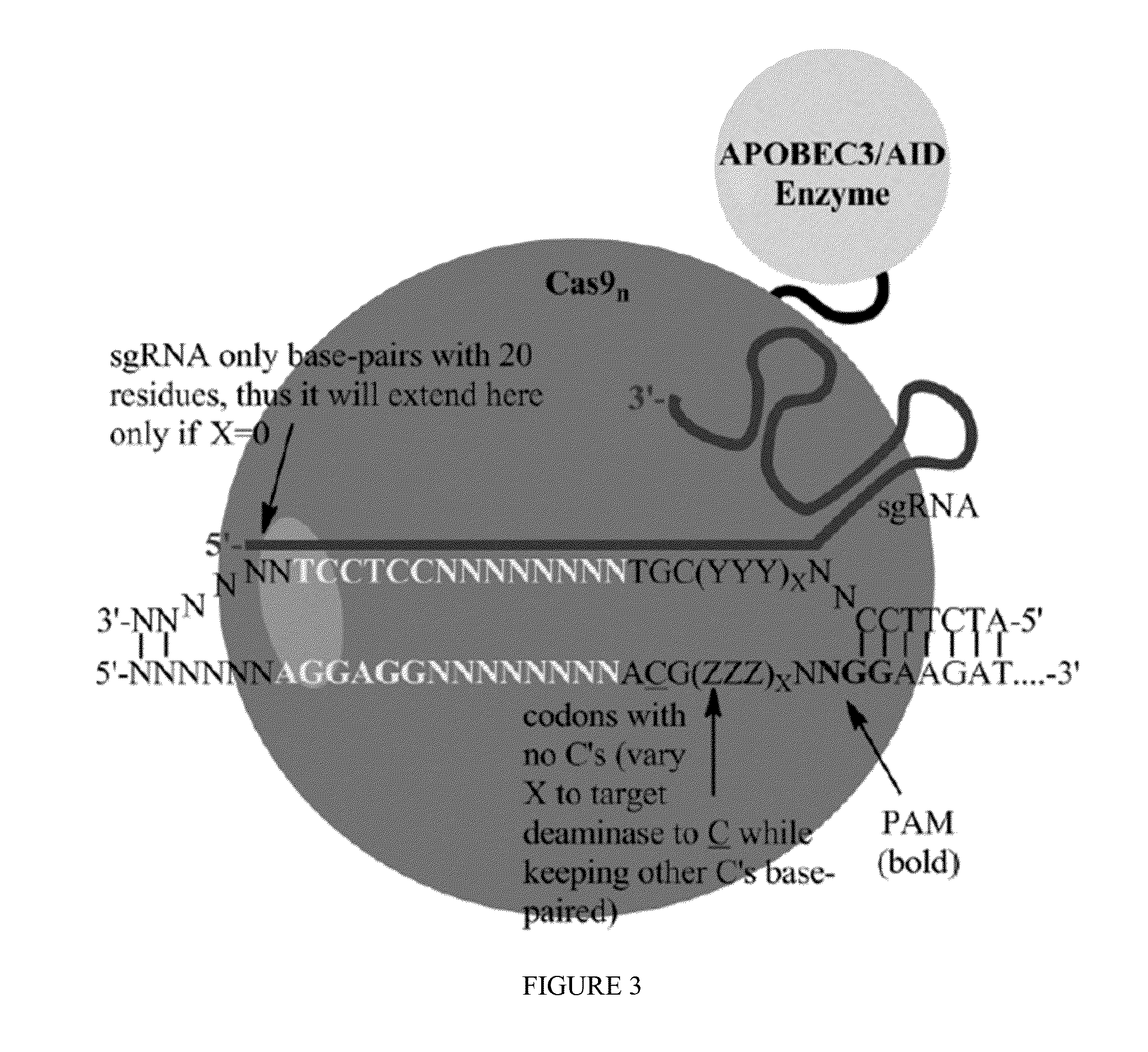
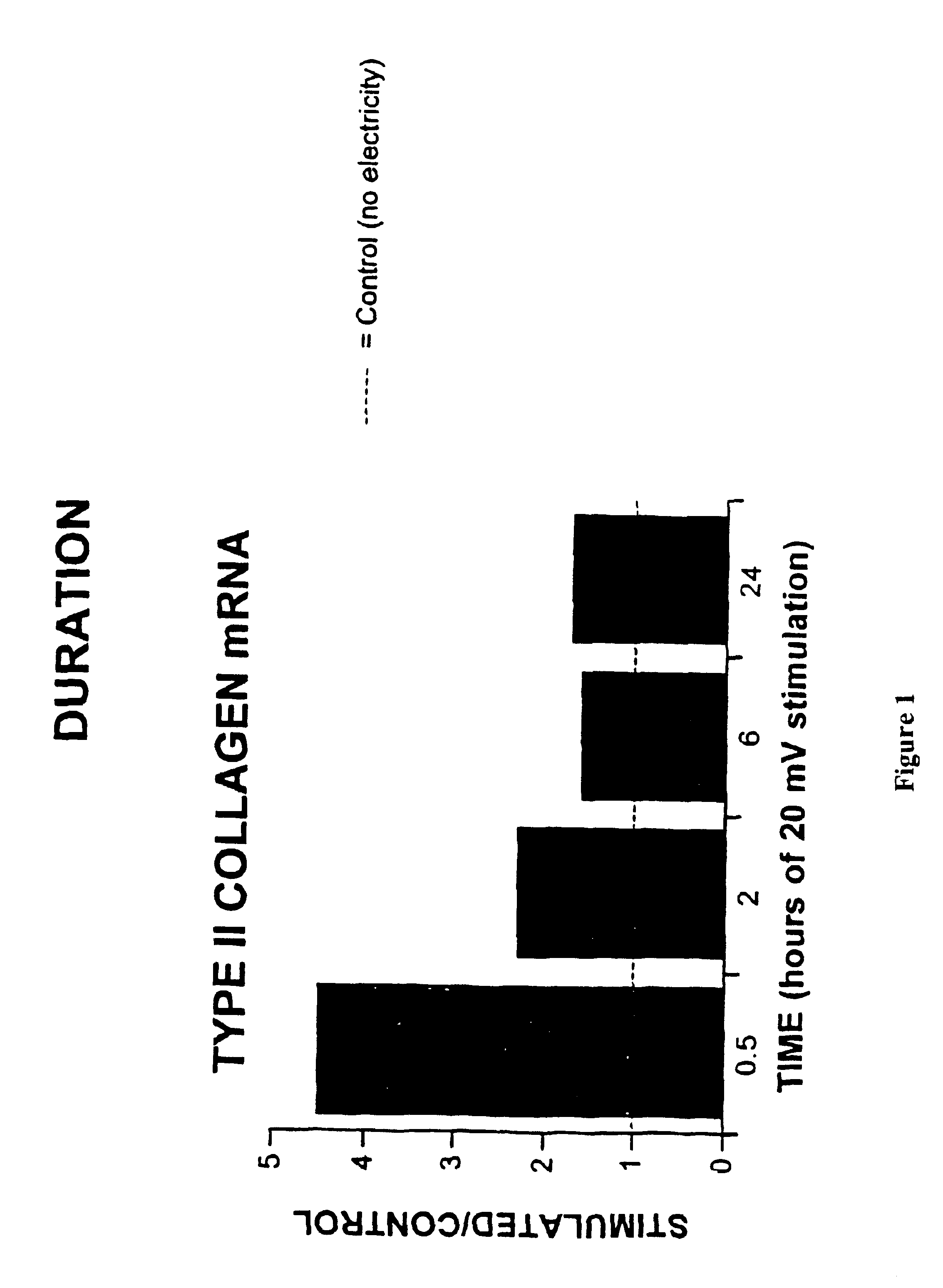
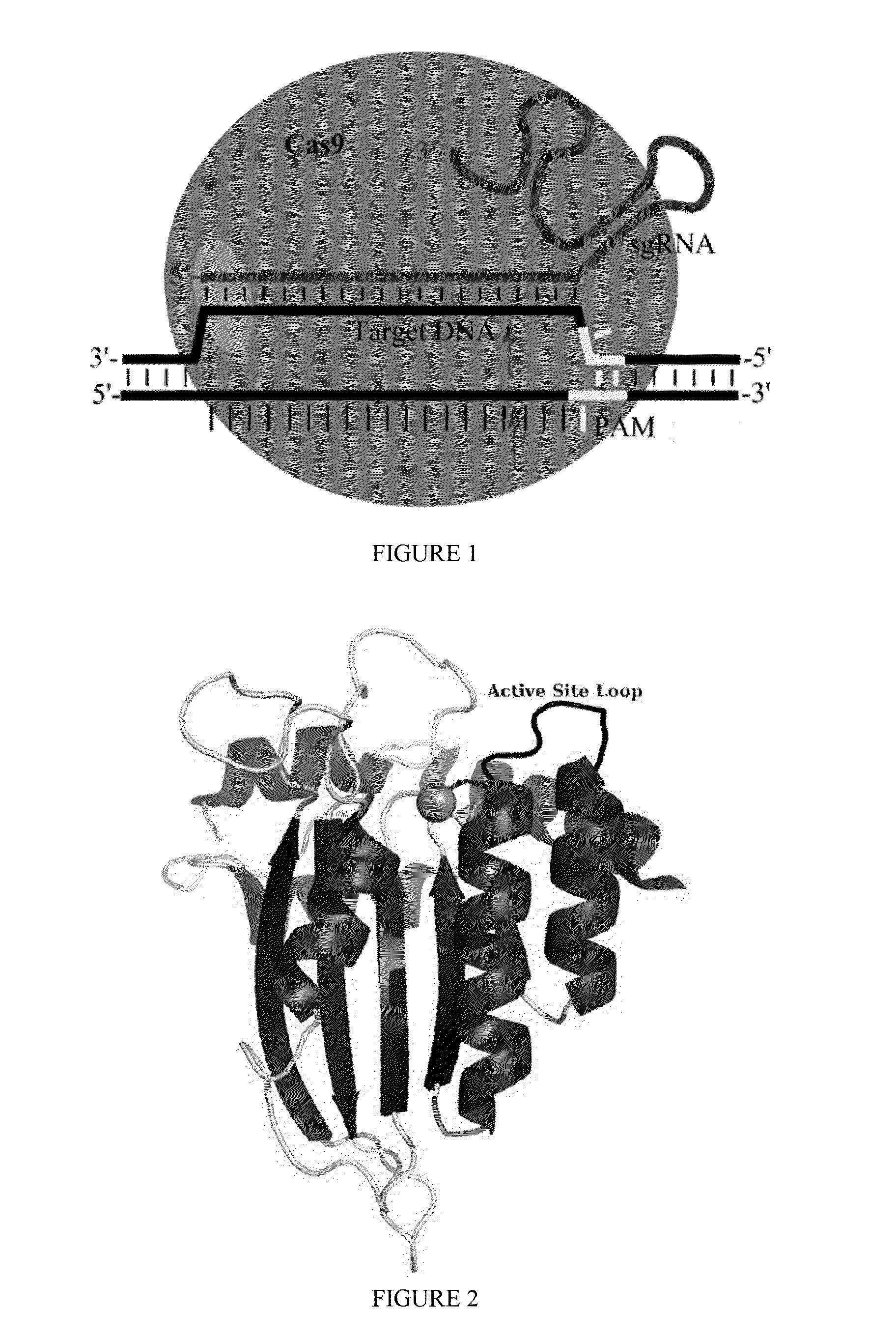
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for indexing samples and sequencing multiple polynucleotide templates
ActiveUS20090233802A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHuman DNA sequencingPolynucleotide
The invention relates to methods for indexing samples during the sequencing of polynucleotide templates, resulting in the attachment of tags specific to the source of each nucleic acid sample such that after a sequencing run, both the source and sequence of each polynucleotide can be determined. Thus, the present invention pertains to analysis of complex genomes (e.g., human genomes), as well as multiplexing less complex genomes, such as those of bacteria, viruses, mitochondria, and the like.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Massively parallel contiguity mapping
ActiveUS20130203605A1Reducing sequenceLimited to sequenceLibrary member identificationChemical recyclingHuman DNA sequencingMammalian genome
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
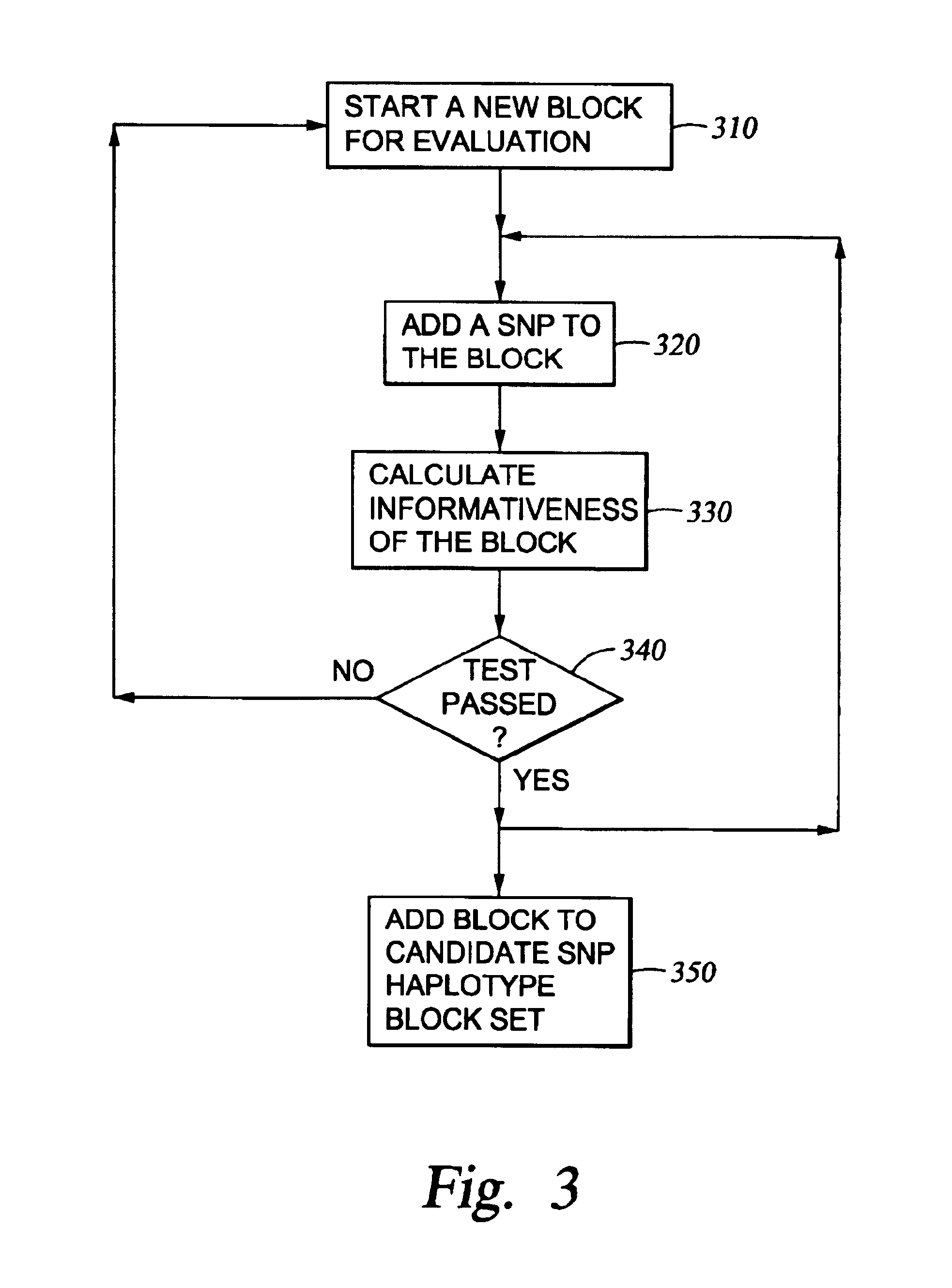
Methods for genomic analysis
InactiveUS6969589B2Quick scanSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenetics
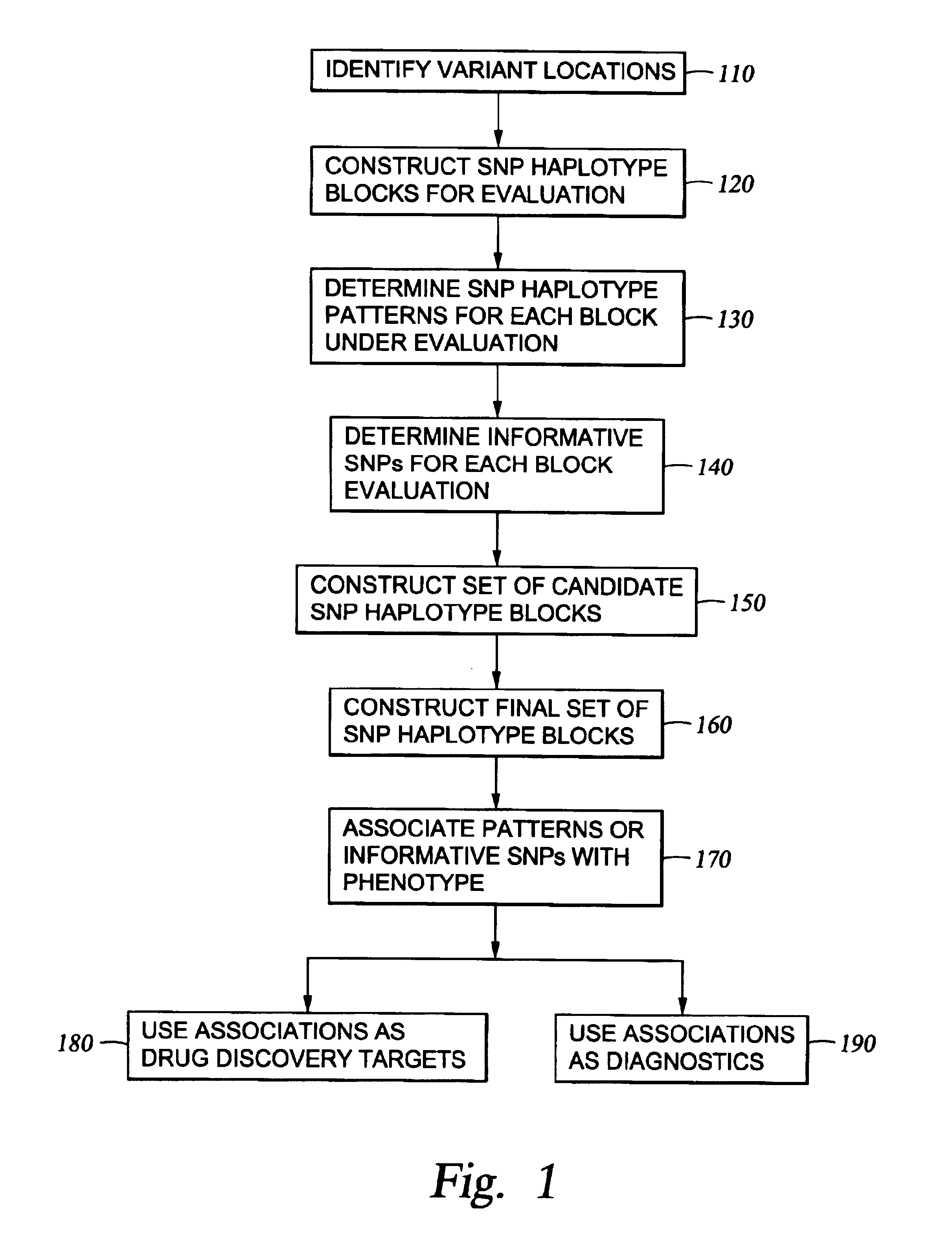
The present invention relates to methods for identifying variations that occur in the human genome and relating these variations to the genetic basis of disease and drug response. In particular, the present invention relates to identifying individual SNPs, determining SNP haplotype blocks and patterns, and, further, using the SNP haplotype blocks and patterns to dissect the genetic bases of disease and drug response. The methods of the present invention are useful in whole genome analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC +1
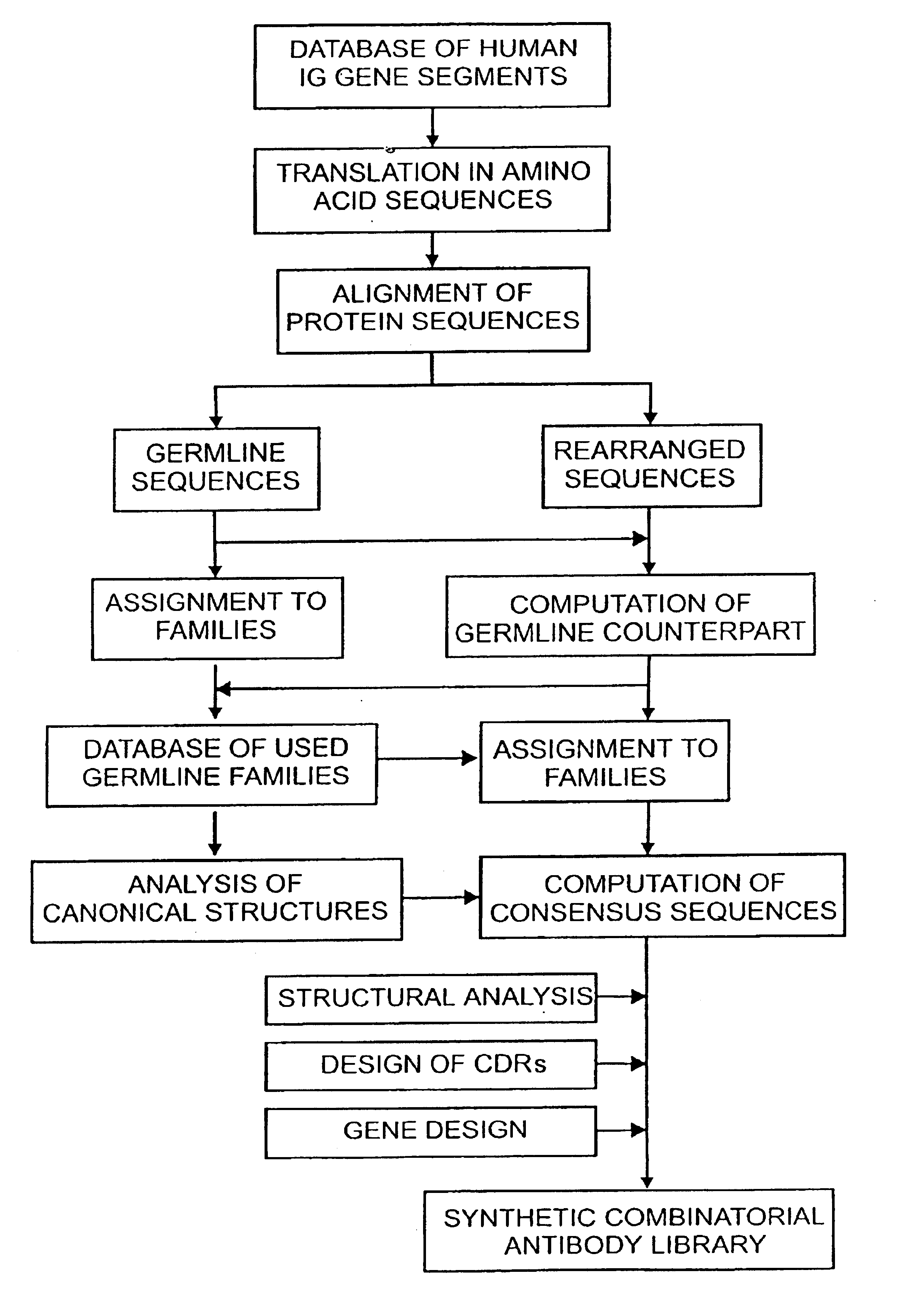
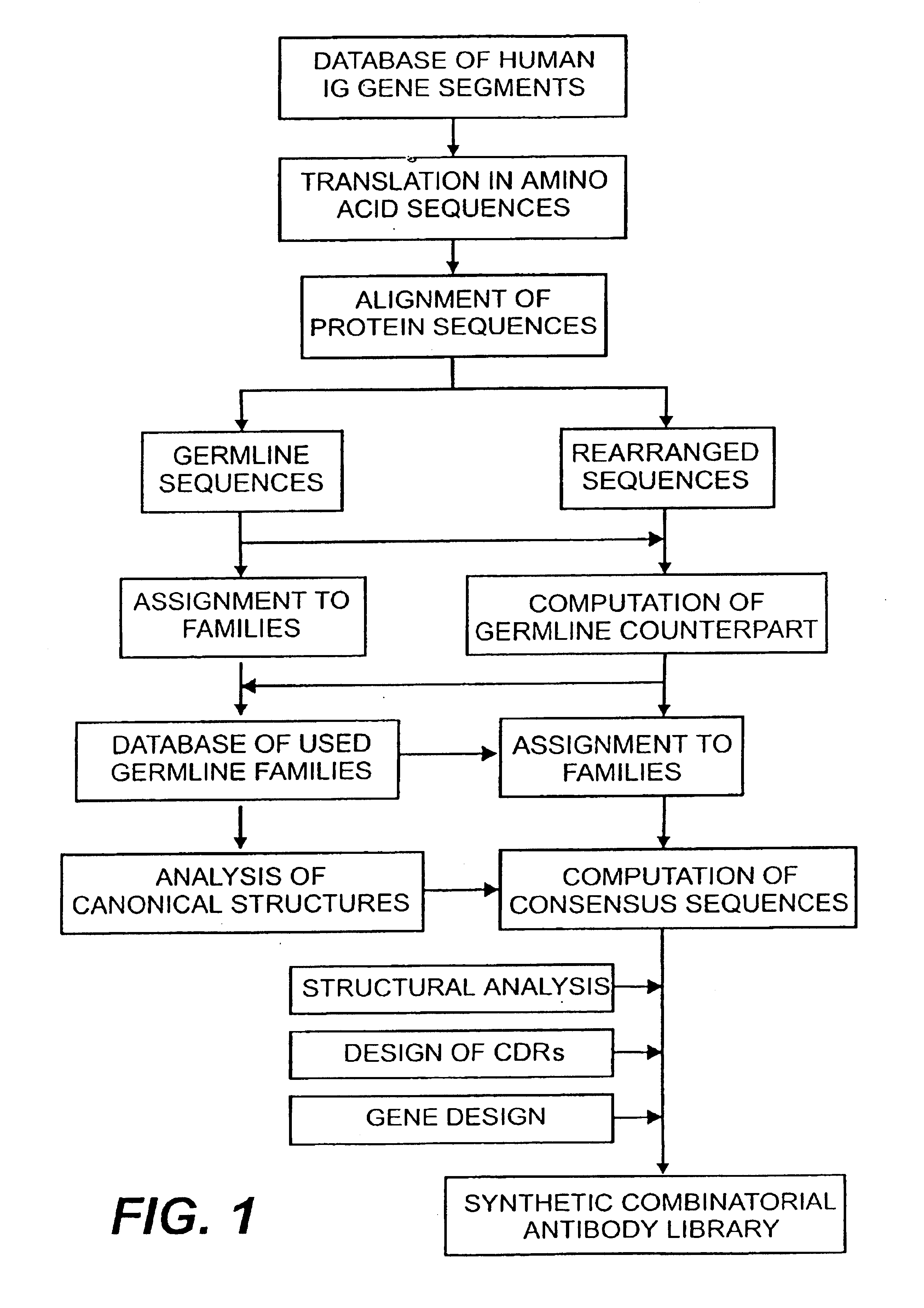
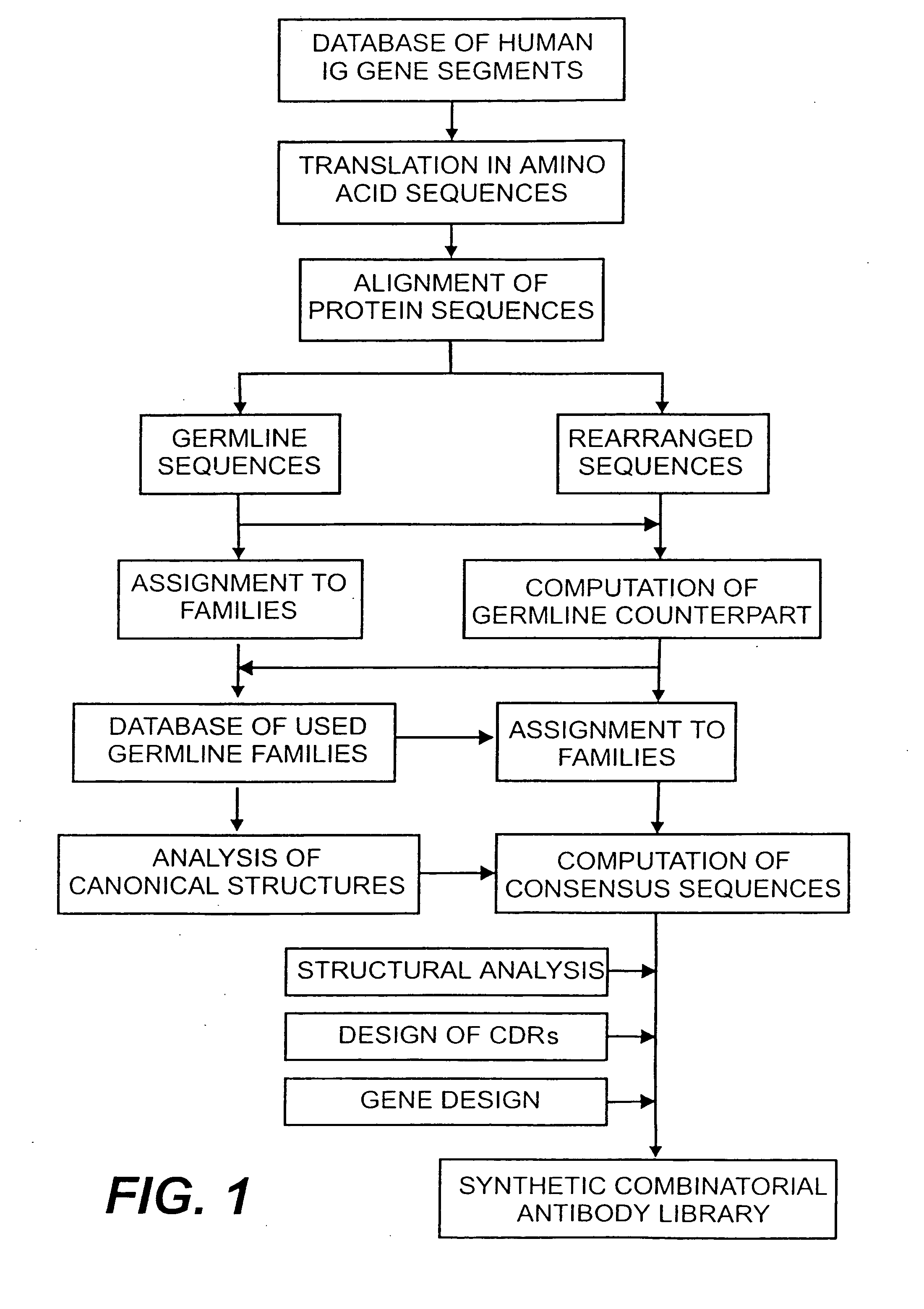
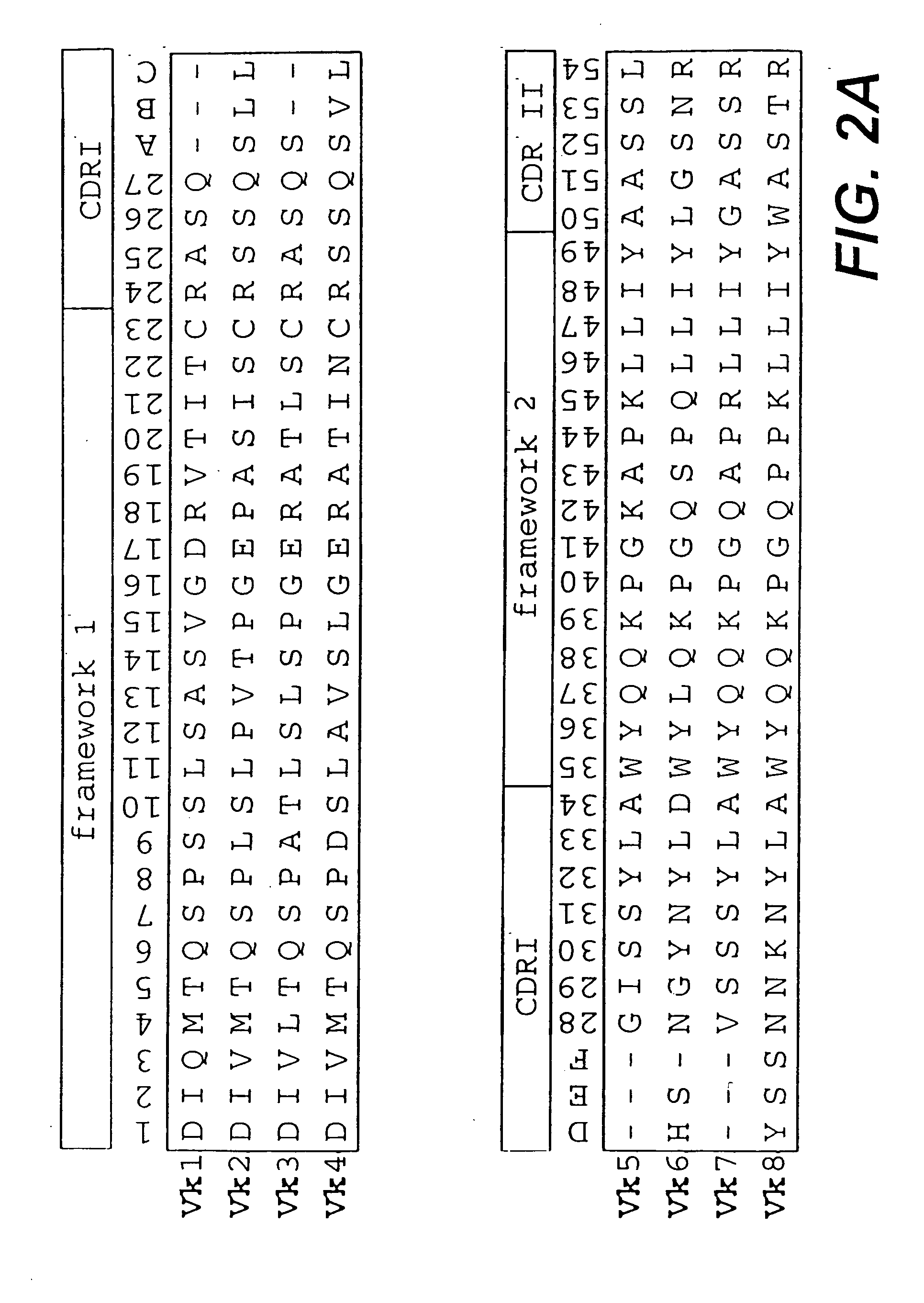
Protein/(poly)peptide libraries
InactiveUS6828422B1Reduce in quantityRemoving unwanted cleavages sitesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman DNA sequencingSynthetic DNA
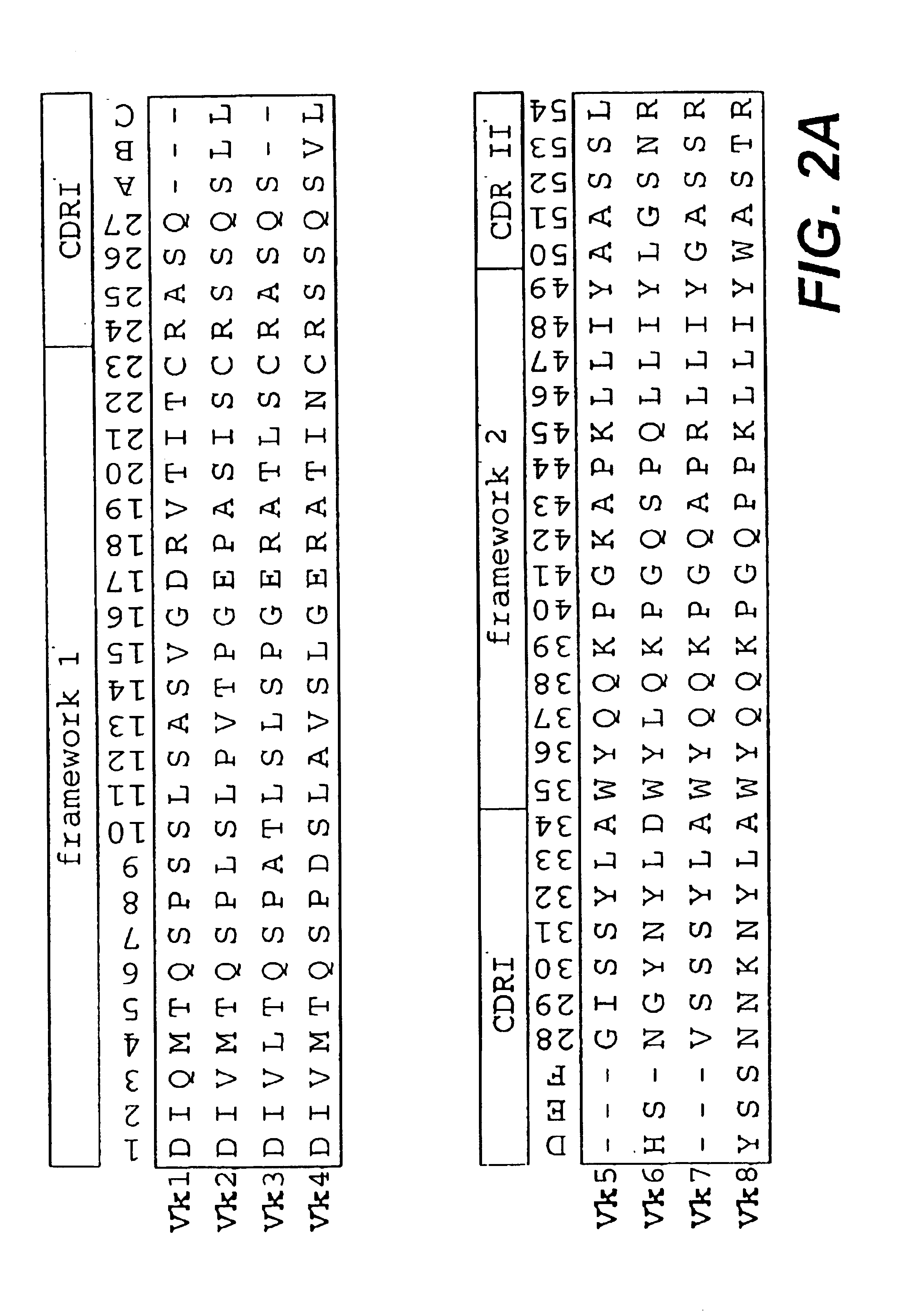
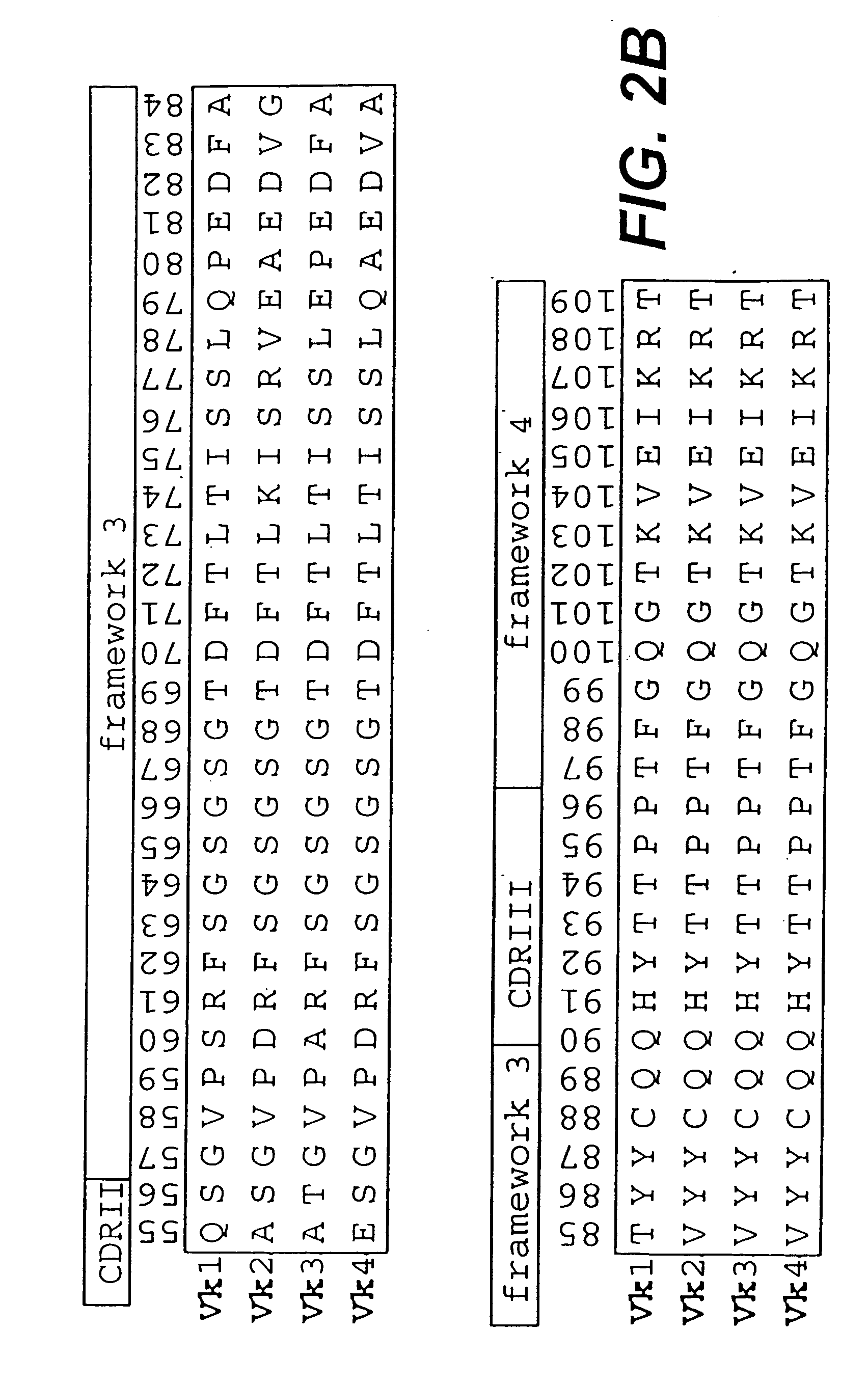
The present invention relates to synthetic DNA sequences which encode one or more collections of homologous proteins / (poly)peptides, and methods for generating and applying libraries of these DNA sequences. In particular, the invention relates to the preparation of a library of human-derived antibody genes by the use of synthetic consensus sequences which cover the structural repertoire of antibodies encoded in the human genome. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of a single consensus antibody gene as a universal framework for highly diverse antibody libraries.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
Method for storing information in DNA
InactiveUS20050053968A1Microbiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHuman DNA sequencingPresent method
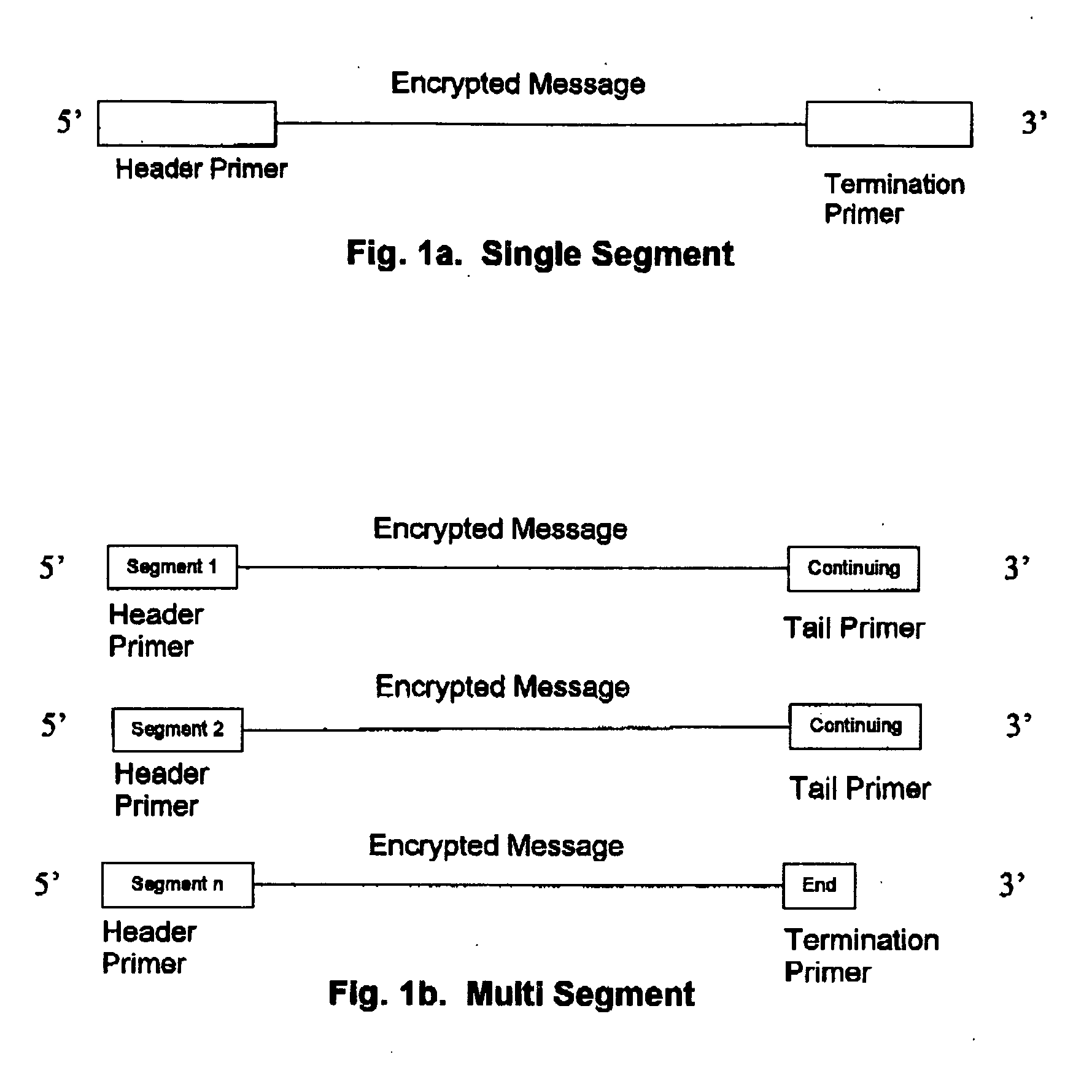
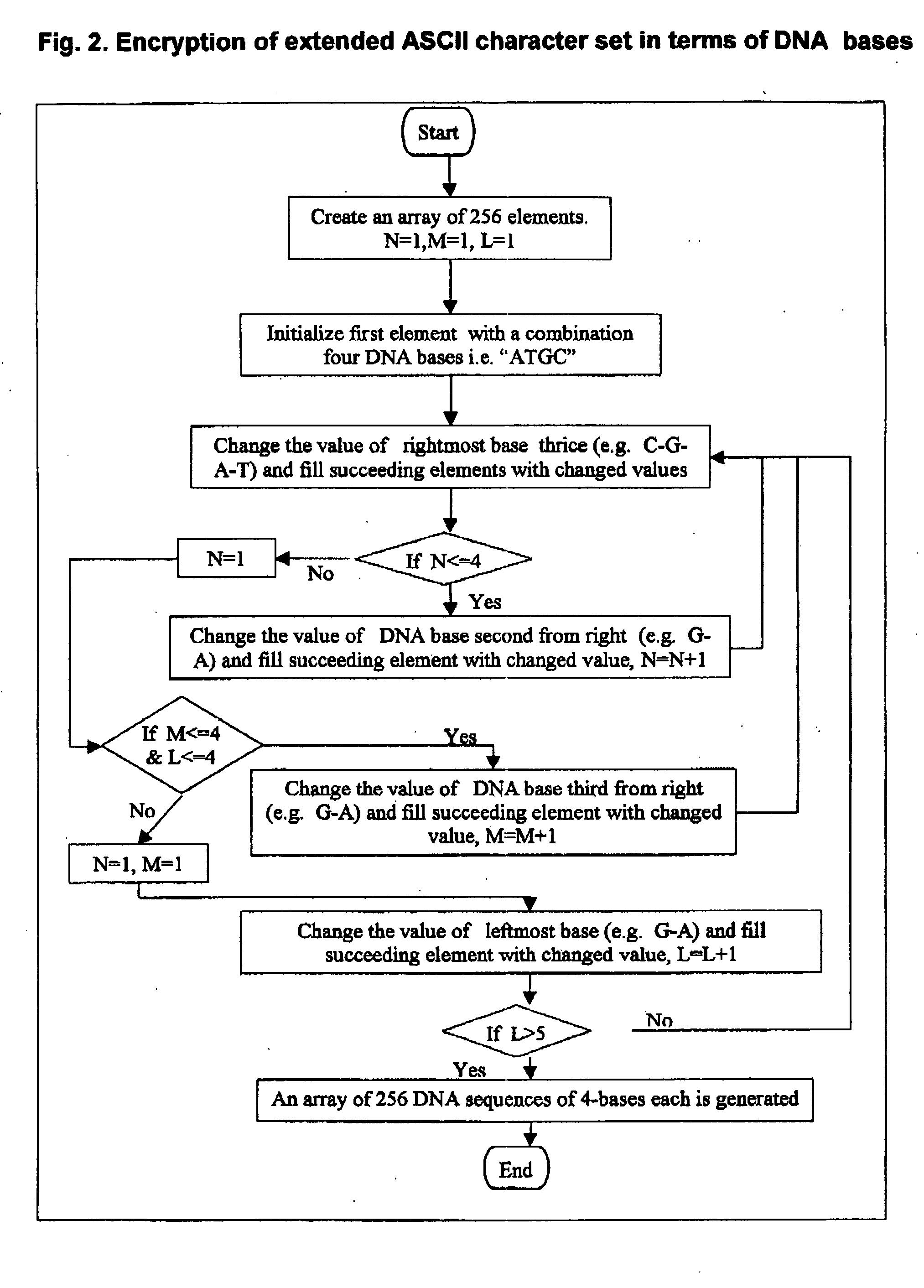
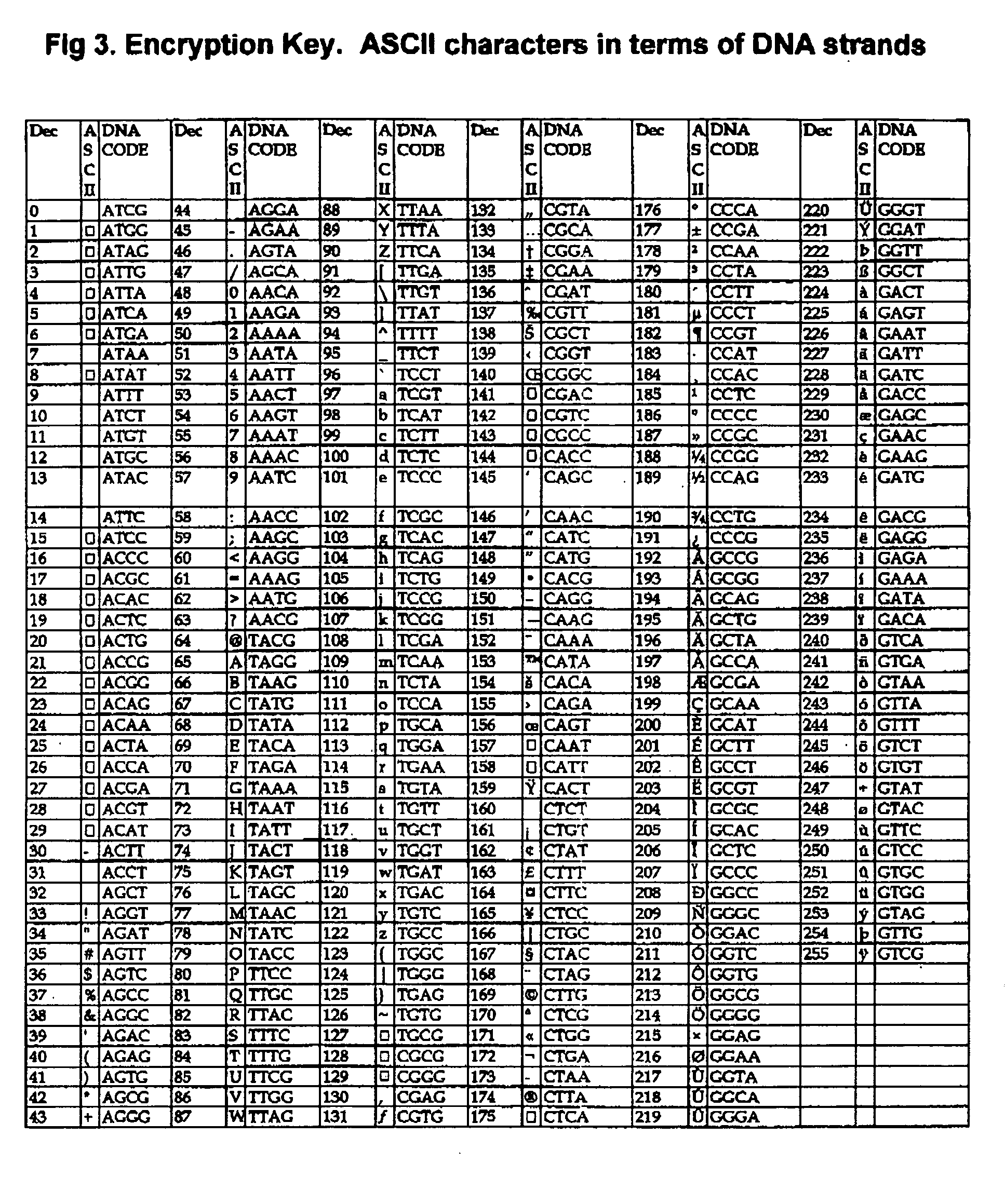
DNA is a natural molecular level storage device. Molecular storage devices use each molecule or part of it for storing a character. Thus it is possible to store information million of times than presently used storage devices. For example a JPEG image (i.e. flag of India) having file size of 1981 Bytes can be encrypted using 7924 DNA bases which occupies about 2694.16 nanometers In other words flag of India can be encrypted 8.07×105 times in human genome which comprises 6.4×109 DNA bases and occupy a tiny volume of about 0.02 μm3. A method for storing information in DNA has been developed which includes software and a set of schemes to encrypt, store and decrypt information in terms of DNA bases. The main advantages of the present method over exiting art is that it addresses complete set of extended ASCII characters set and thereby, encryption of all kind of digital information (text, image, audio etc.). First of all, information is, encrypted along with carefully designed sequences known as header and tail primers at both the ends of actual encrypted information. This encrypted sequence is then synthesized and mixed up with the enormous complex denatured DNA strands of genomic DNA of human or other organism.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
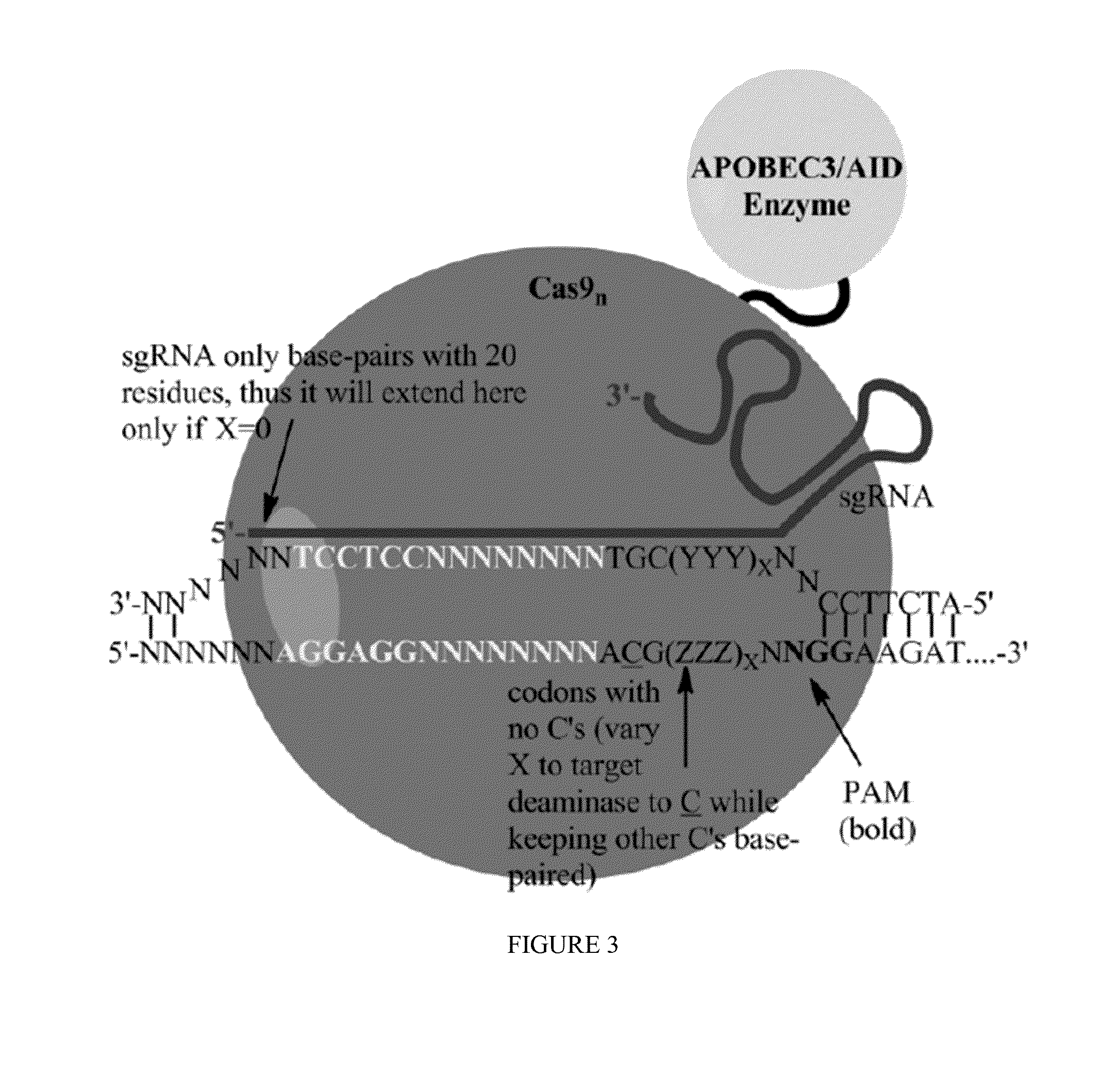
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
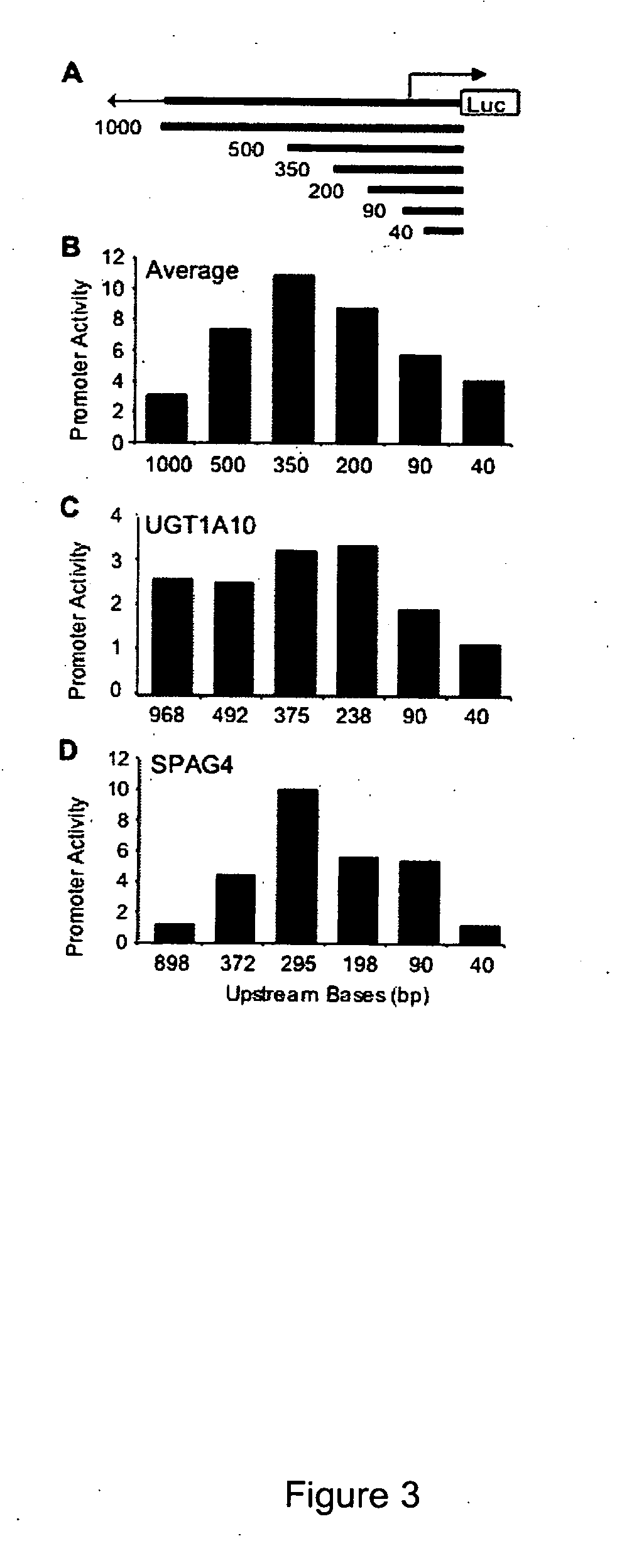
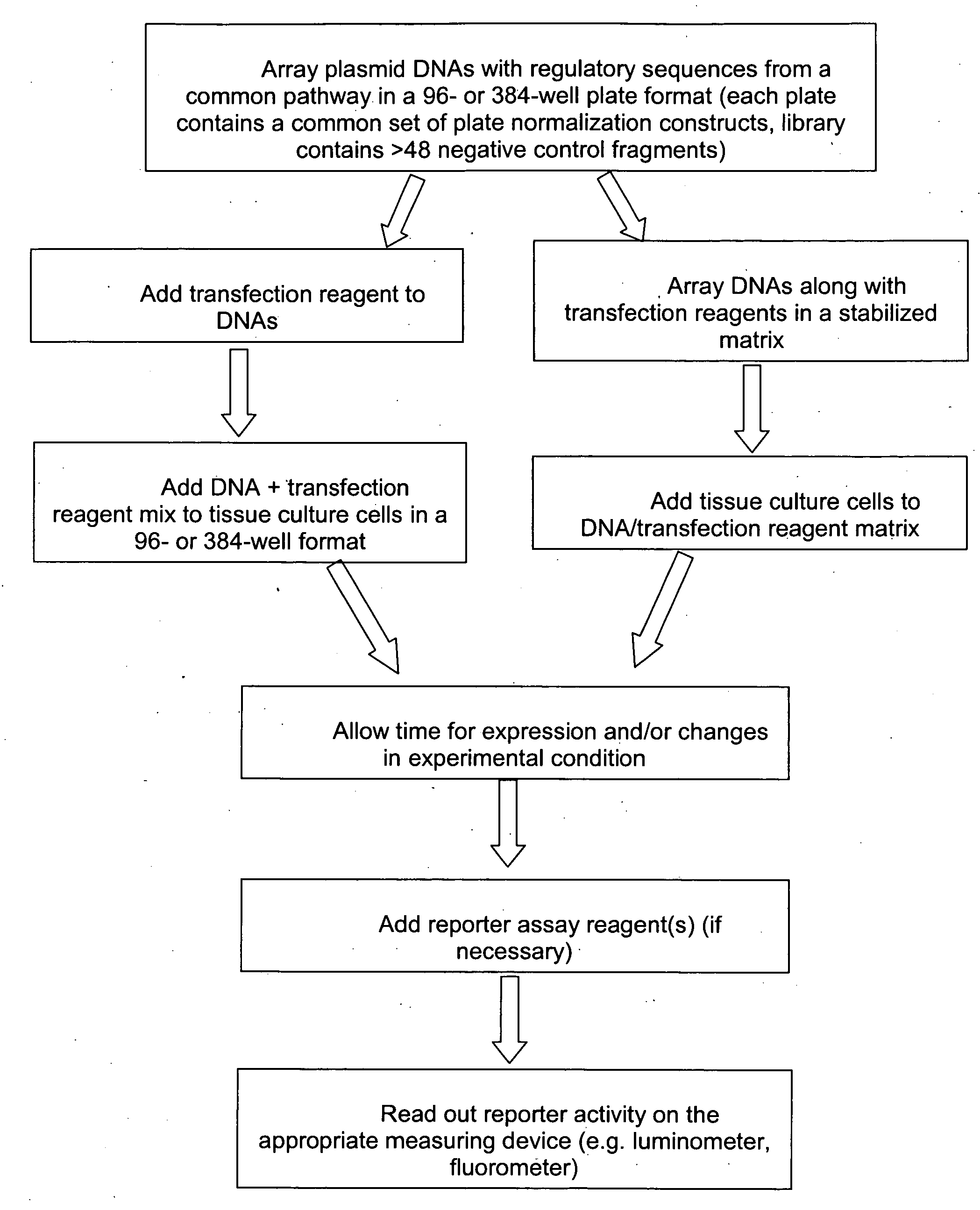
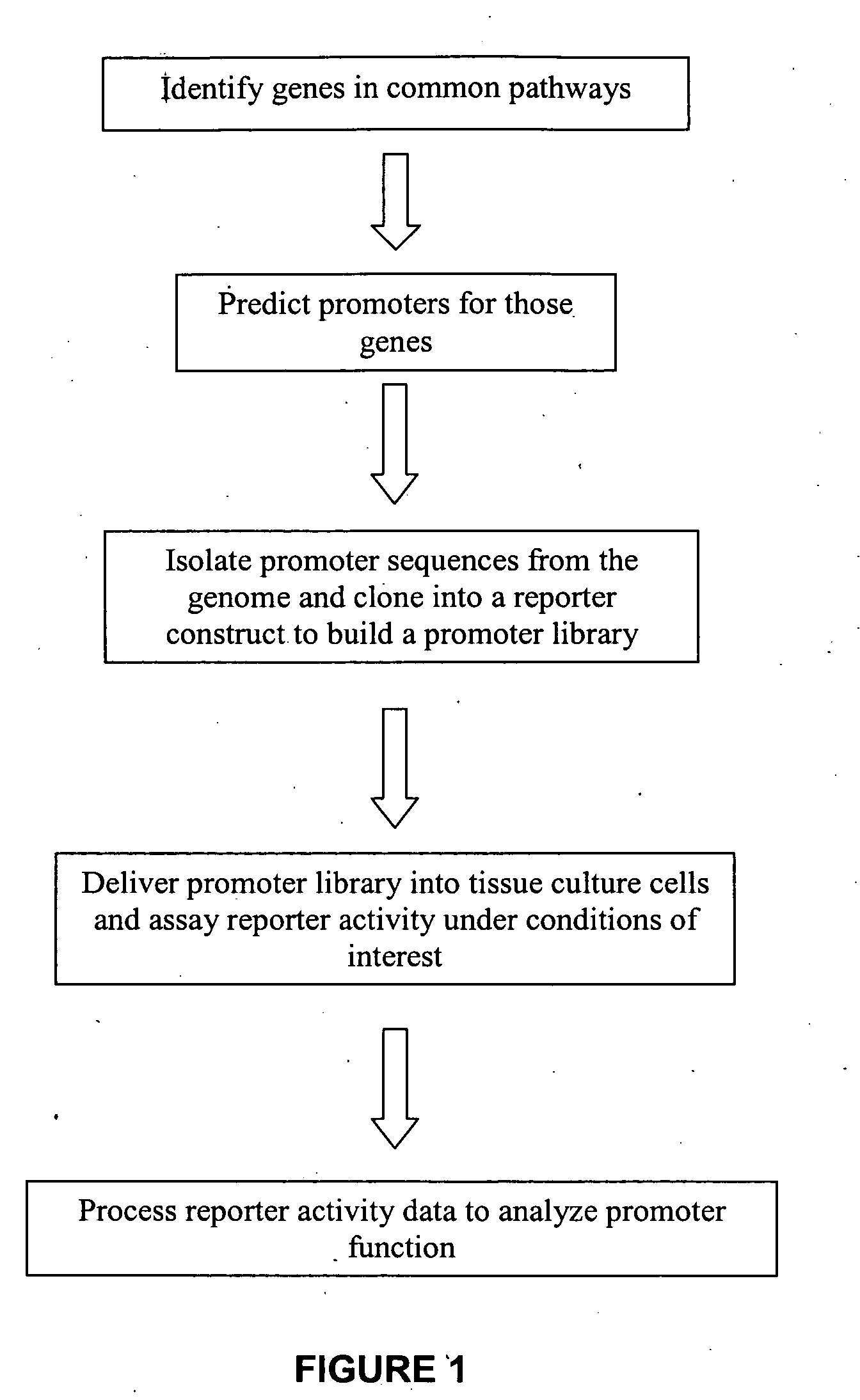
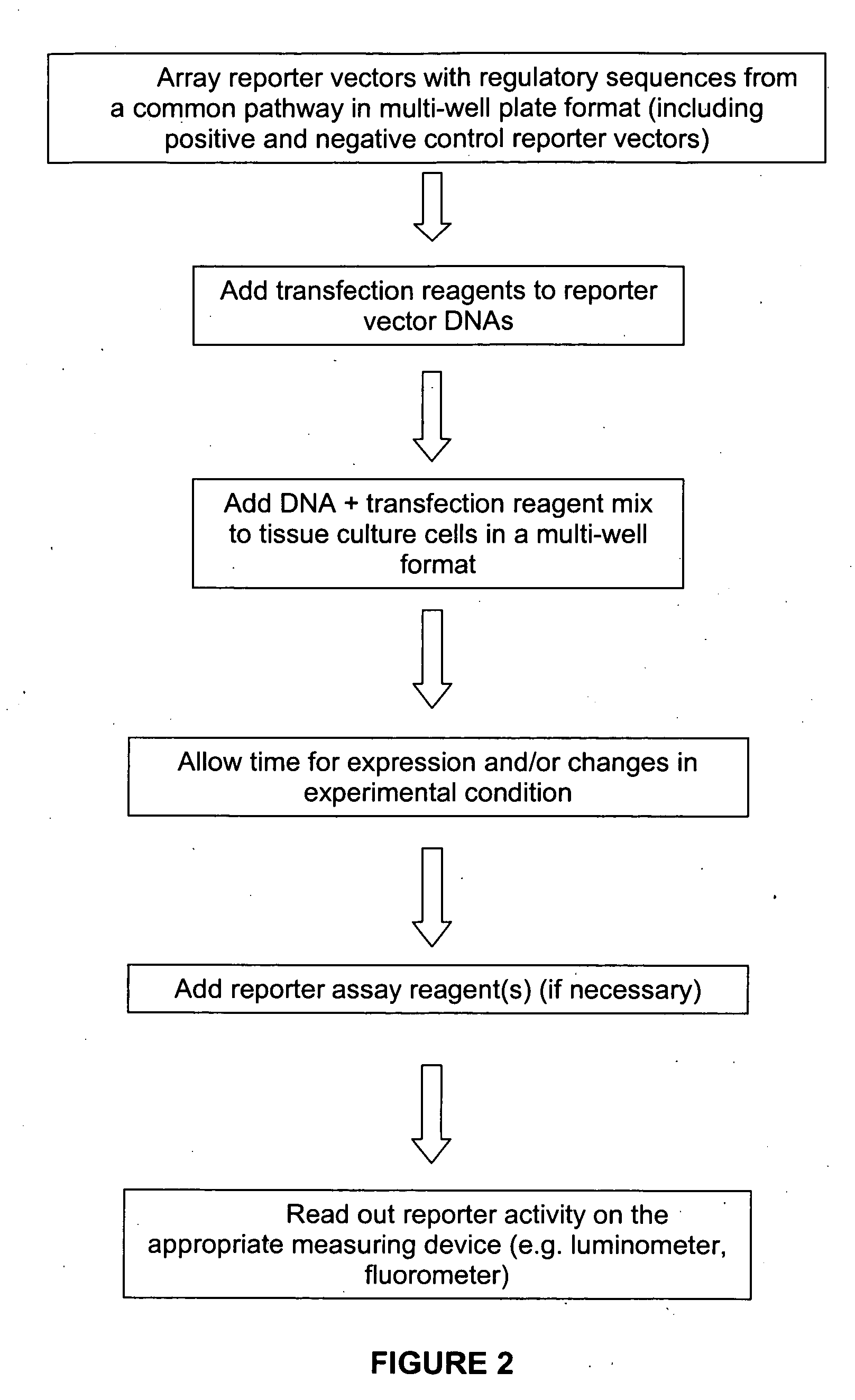
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of gene expression regulatory elements
InactiveUS20070161031A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment, the nucleic acid segment varying in the library and having a diversity of at least 50. The nucleic acid segments can be a large library of gene expression regulatory elements such as transcriptional promoters. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for correcting caspase-9 point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant Caspase-9 protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with neuroblastoma. The methods provided are useful for correcting a Caspase-9 point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
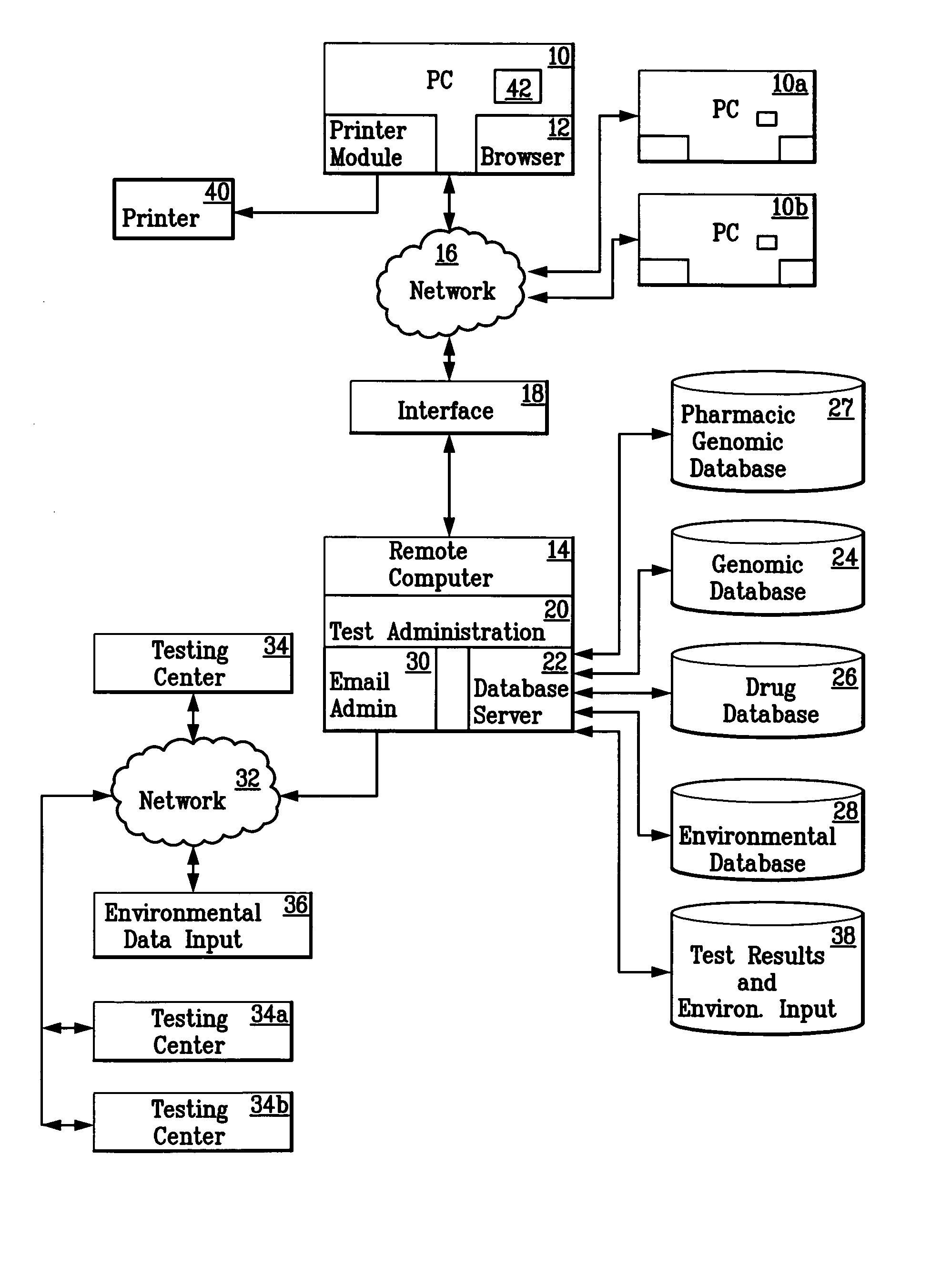
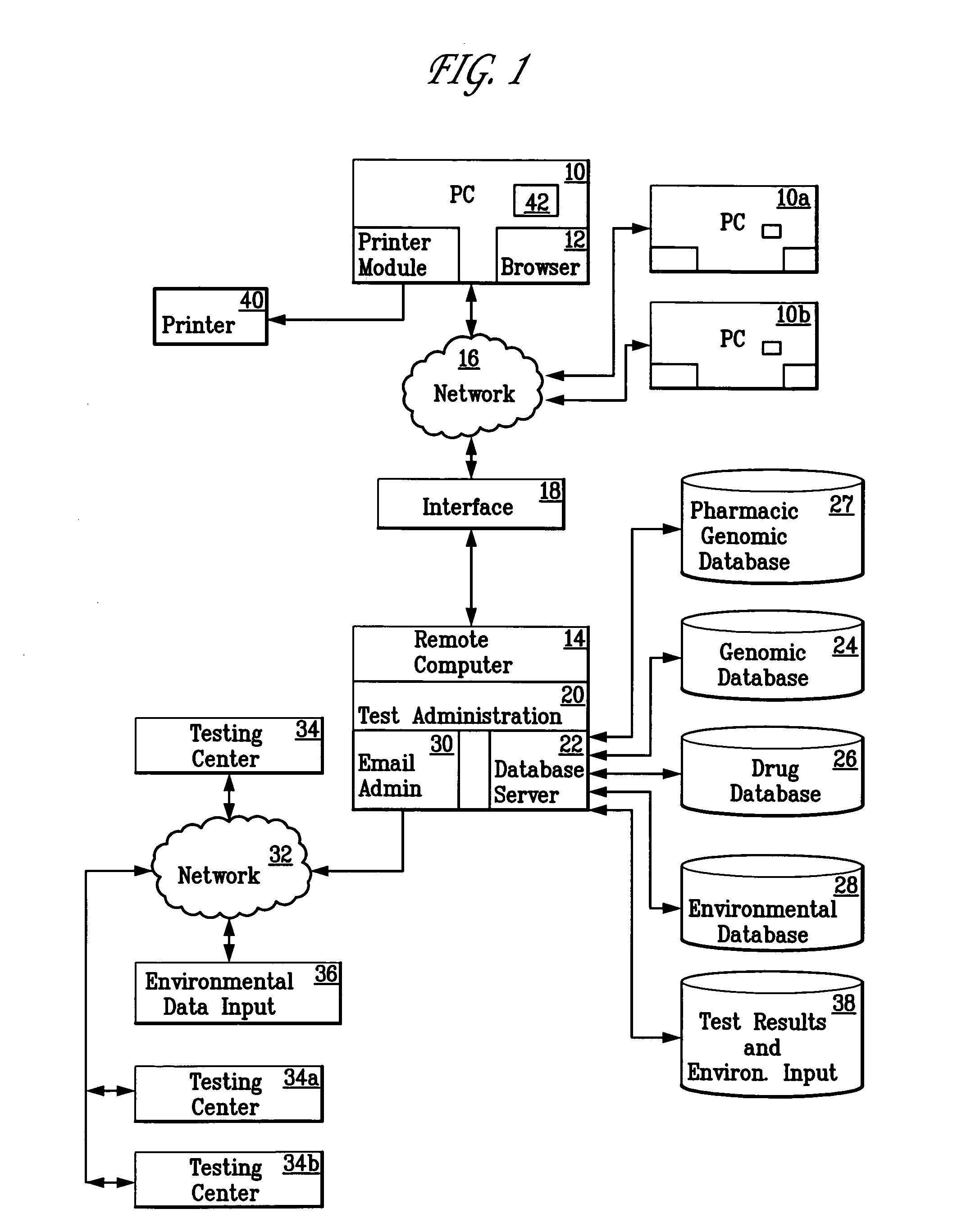
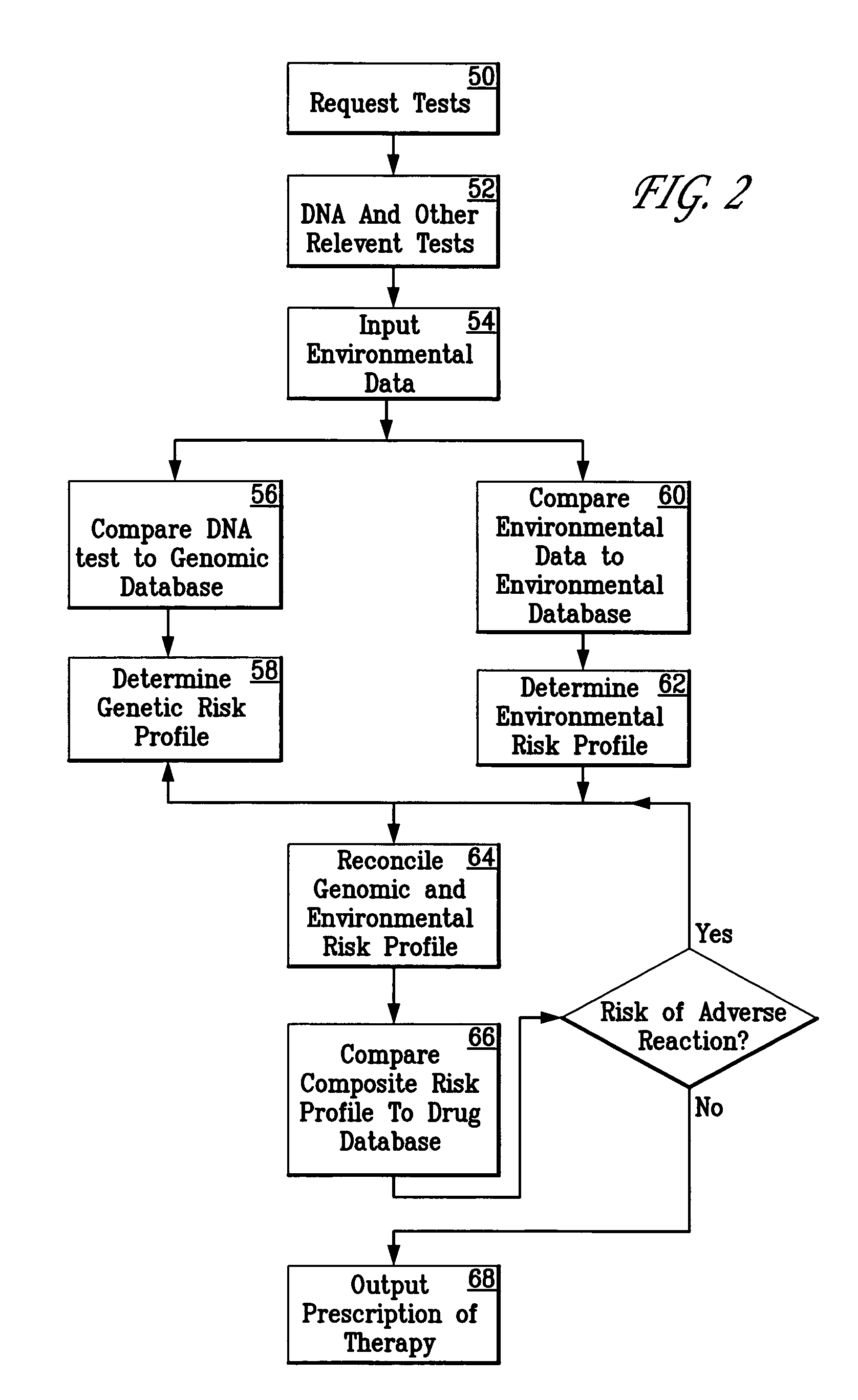
Method for diagnosing and prescribing a regimen of therapy for human health risk
InactiveUS20050260610A1Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingRegimen
A patient is diagnosed and a regimen of treatment is prescribed in a system which tests the patients, receives test results from a patient, including DNA test results. A database of human genome data correlating human health disorder with DNA genetic tests is accessed. A database of environmental factors which correlate known human health disorders with environmental conditions is accessed. Risk factors including genetic risk and environmental risk are developed, and from these, a composite risk factor is developed. This is used to access a database of prescribed drug therapy.
Owner:KLIMANJARO PARTNERSHIP
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Transcriptional regulatory elements of biological pathways tools, and methods
InactiveUS20090018031A1Determine effectNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningHuman DNA sequencingRegulation of gene expression
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome, that are part of a common pathway. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
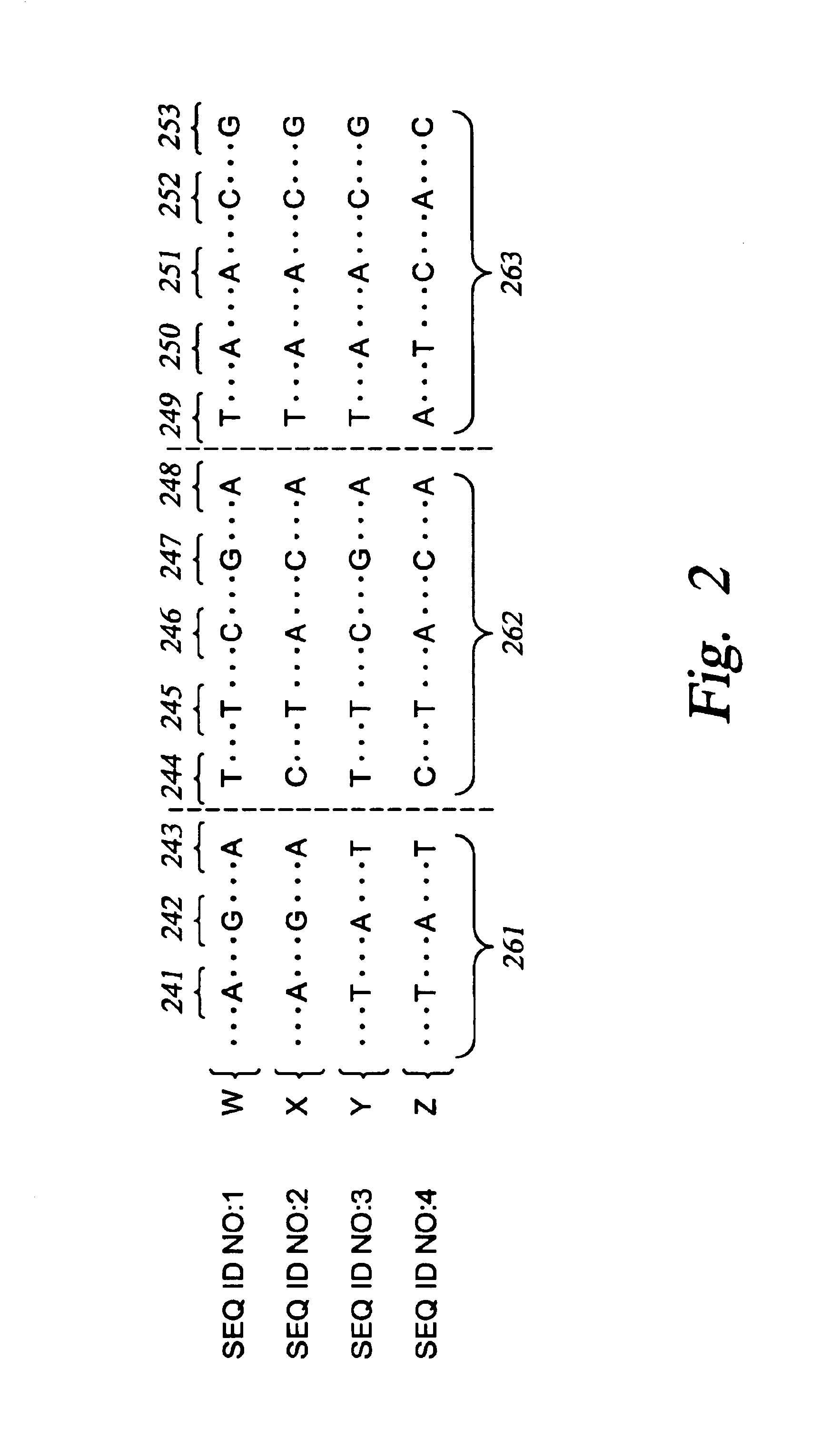
Human genomic polymorphisms
InactiveUS20060188875A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingInformative snps
The invention provides nucleic acid segments of the human genome including polymorphic sites, SNP haplotype blocks, SNP haplotype patterns for each block and informative SNPs for each pattern. Allele-specific primers and probes hybridizing to regions flanking these sites are also provided. The nucleic acids, primers and probes are used in applications such as association studies and other genetic analyses.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Digital karyotyping
ActiveUS7704687B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHuman DNA sequencingHuman cancer
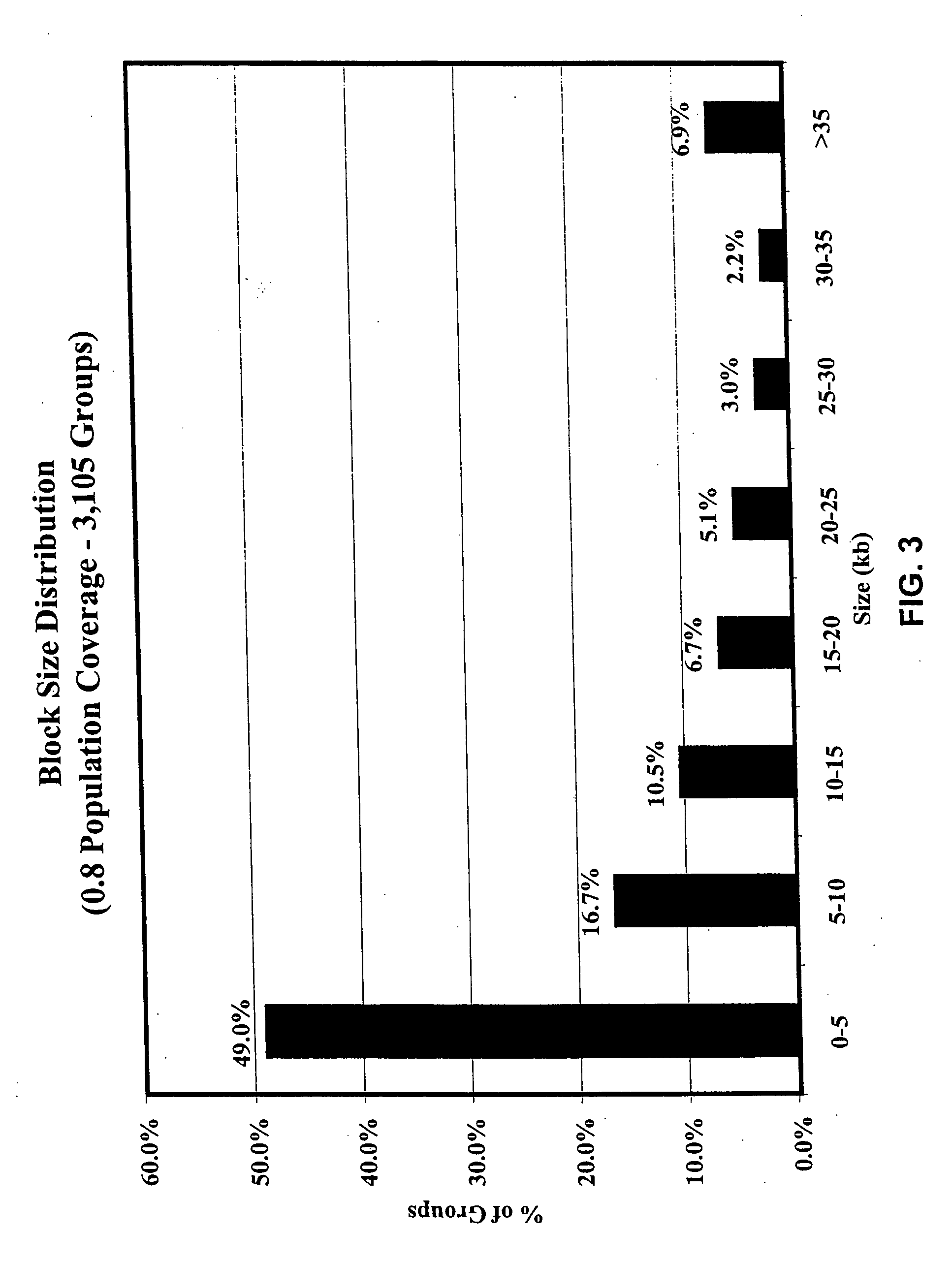
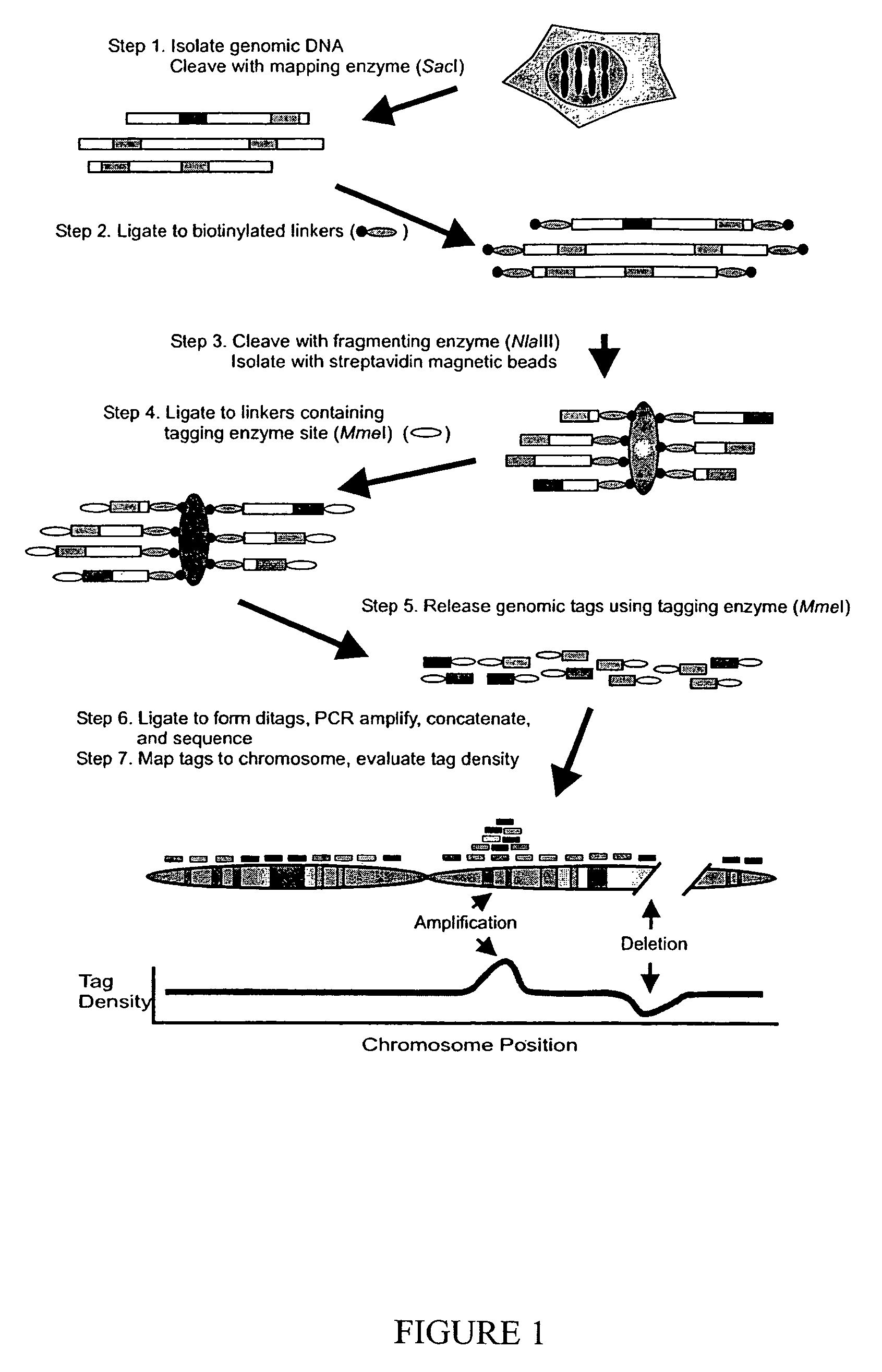
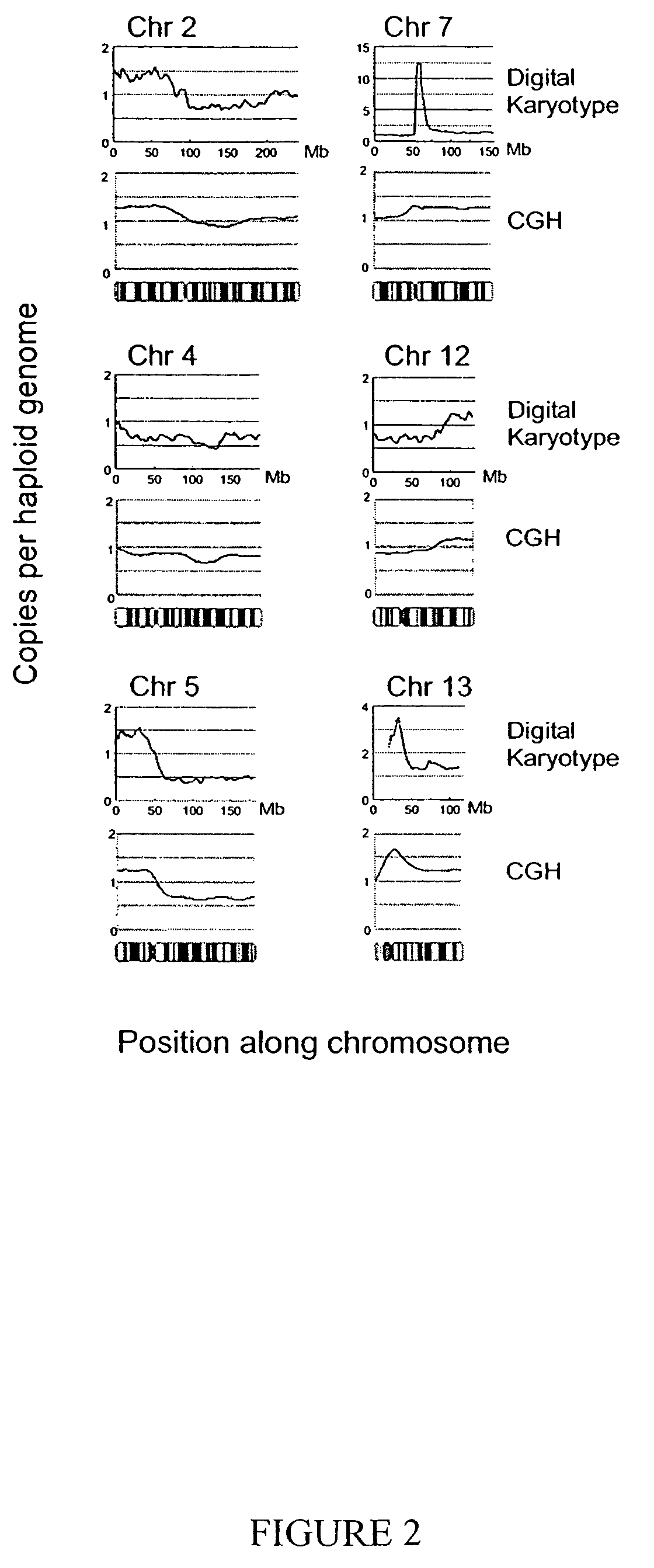
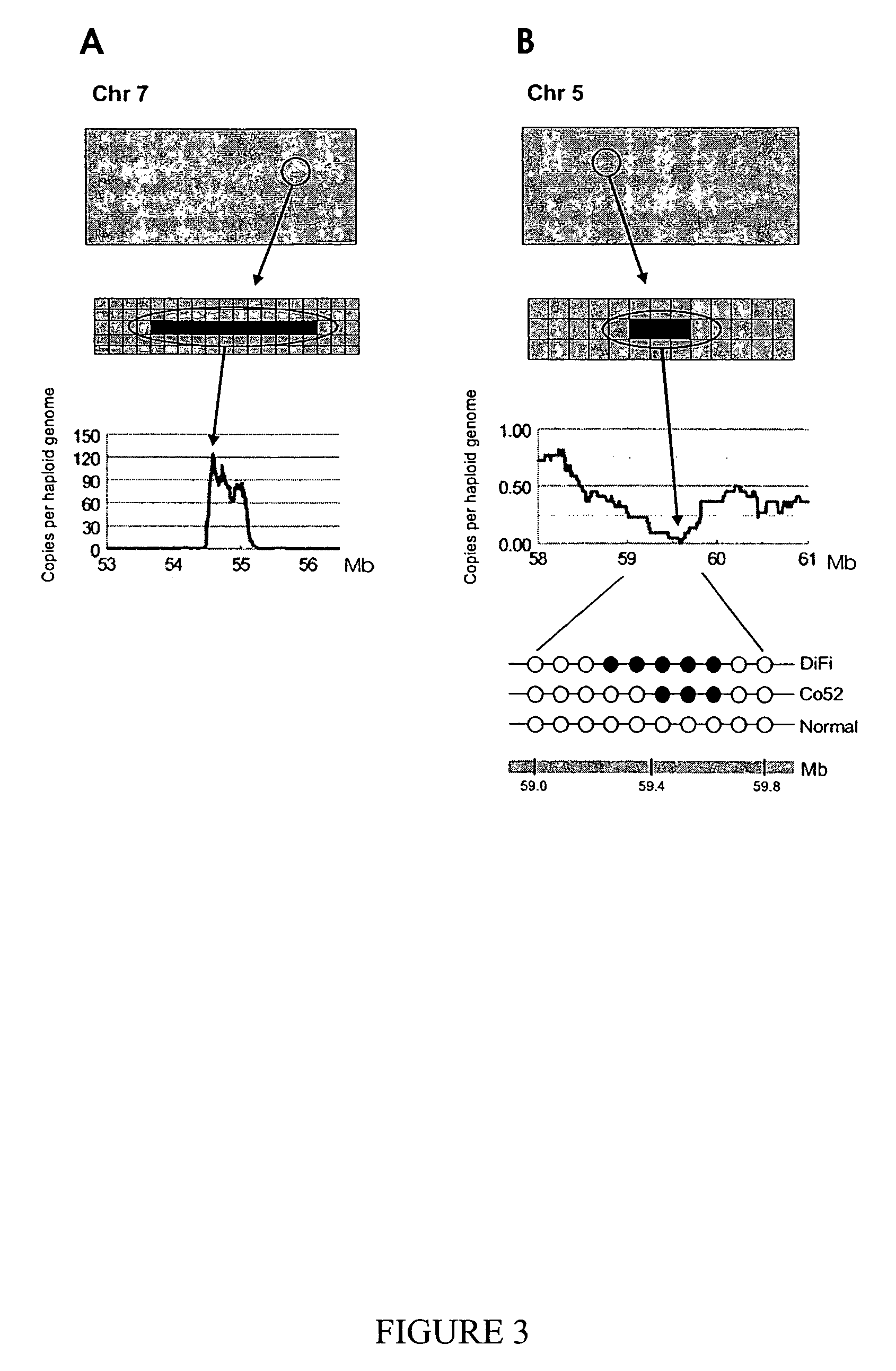
Alterations in the genetic content of a cell underlie many human diseases, including cancers. A method called Digital Karyotyping provides quantitative analysis of DNA copy number at high resolution. This approach involves the isolation and enumeration of short sequence tags from specific genomic loci. Analysis of human cancer cells using this method identified gross chromosomal changes as well as amplifications and deletions, including regions not previously known to be altered. Foreign DNA sequences not present in the normal human genome could also be readily identified. Digital Karyotyping provides a broadly applicable means for systematic detection of DNA copy number changes on a genomic scale.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for correcting pi3k point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant PI3KCA protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with a neoplastic disorder. The methods provided are useful for correcting a PI3KCA point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
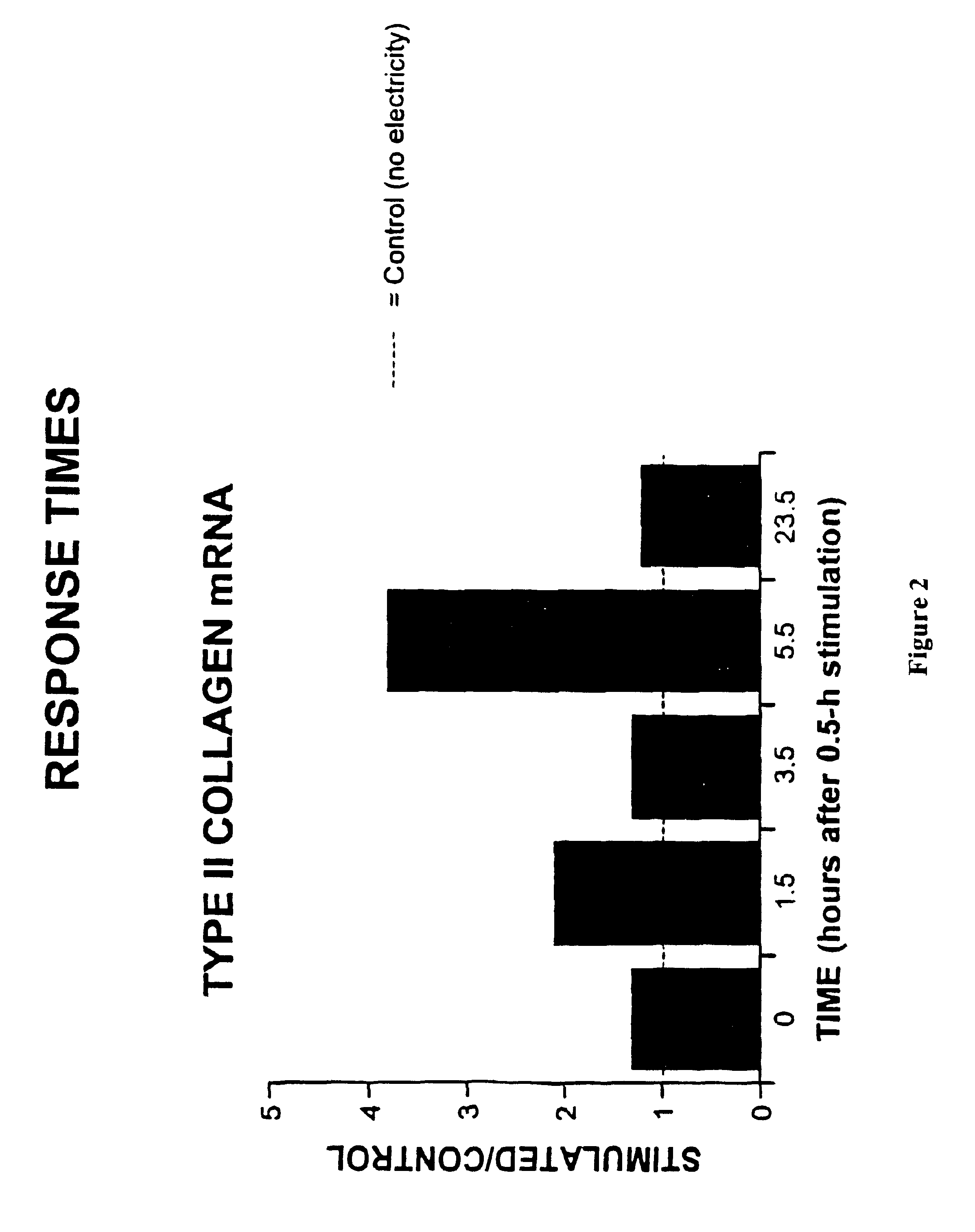
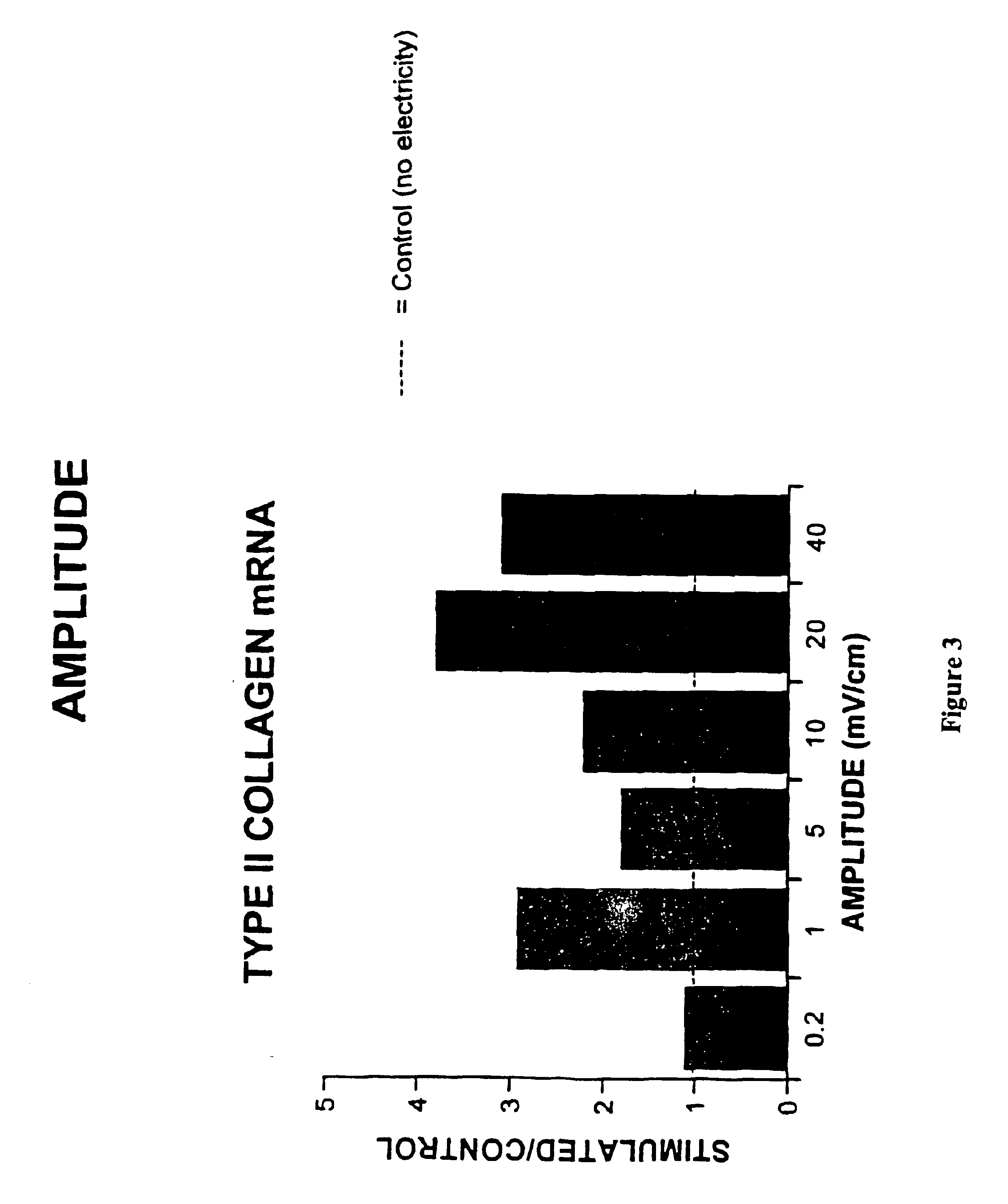
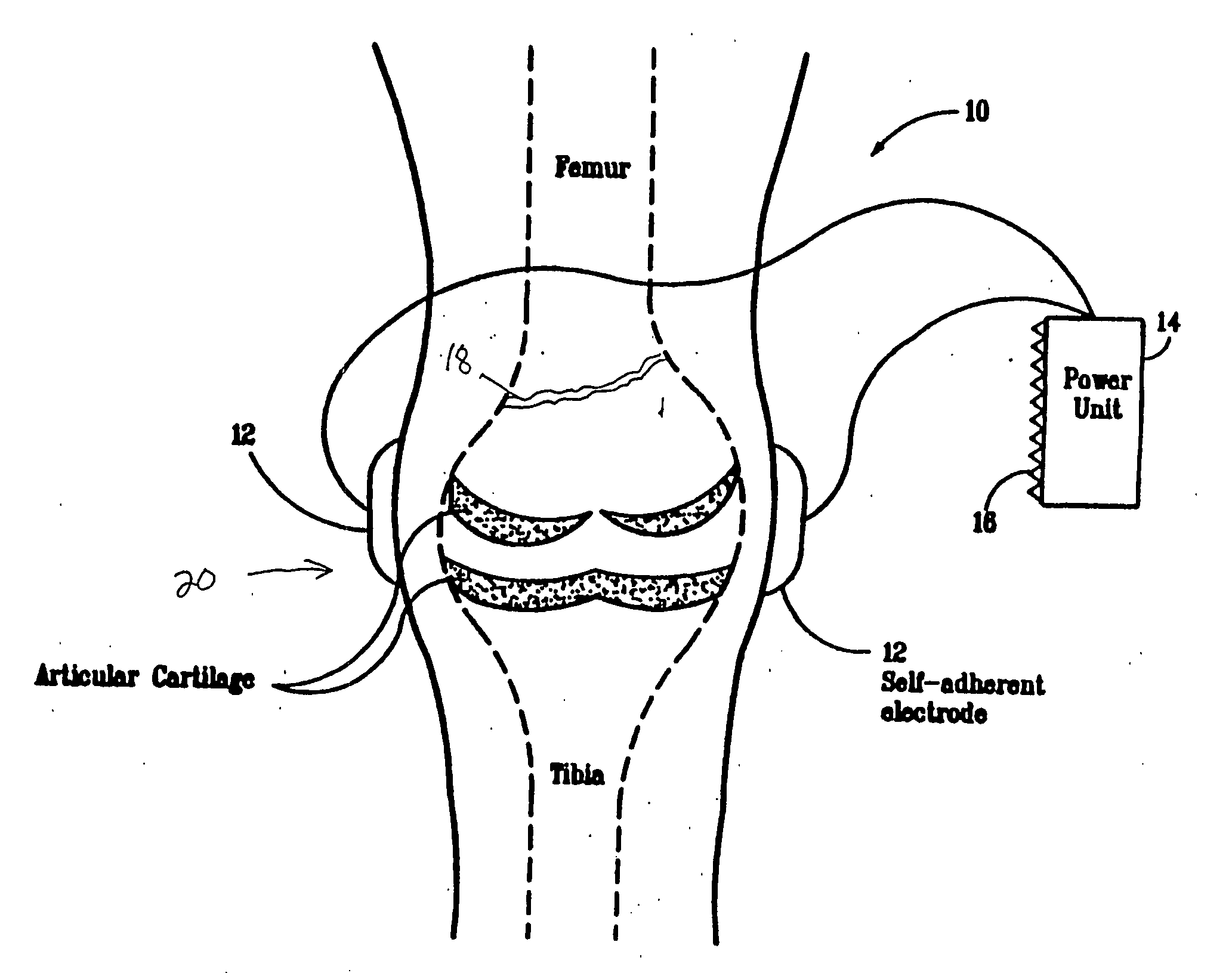
Regulation of type II collagen gene expression using specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
InactiveUS6919205B2Increase typeElectrotherapySkeletal/connective tissue cellsCartilage cellsHuman DNA sequencing
Methods and devices for the regulation of type II collagen gene expression in cartilage cells via the application of specific and selective fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured articular cartilage. By gene expression is meant the up regulation or down regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased cartilage tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate specific and selective fields optimized for type II collagen gene expression and exposing cartilage tissue to the specific and selective fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate type II collagen gene expression in such cartilage tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, cartilage injury, and cartilage defects.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
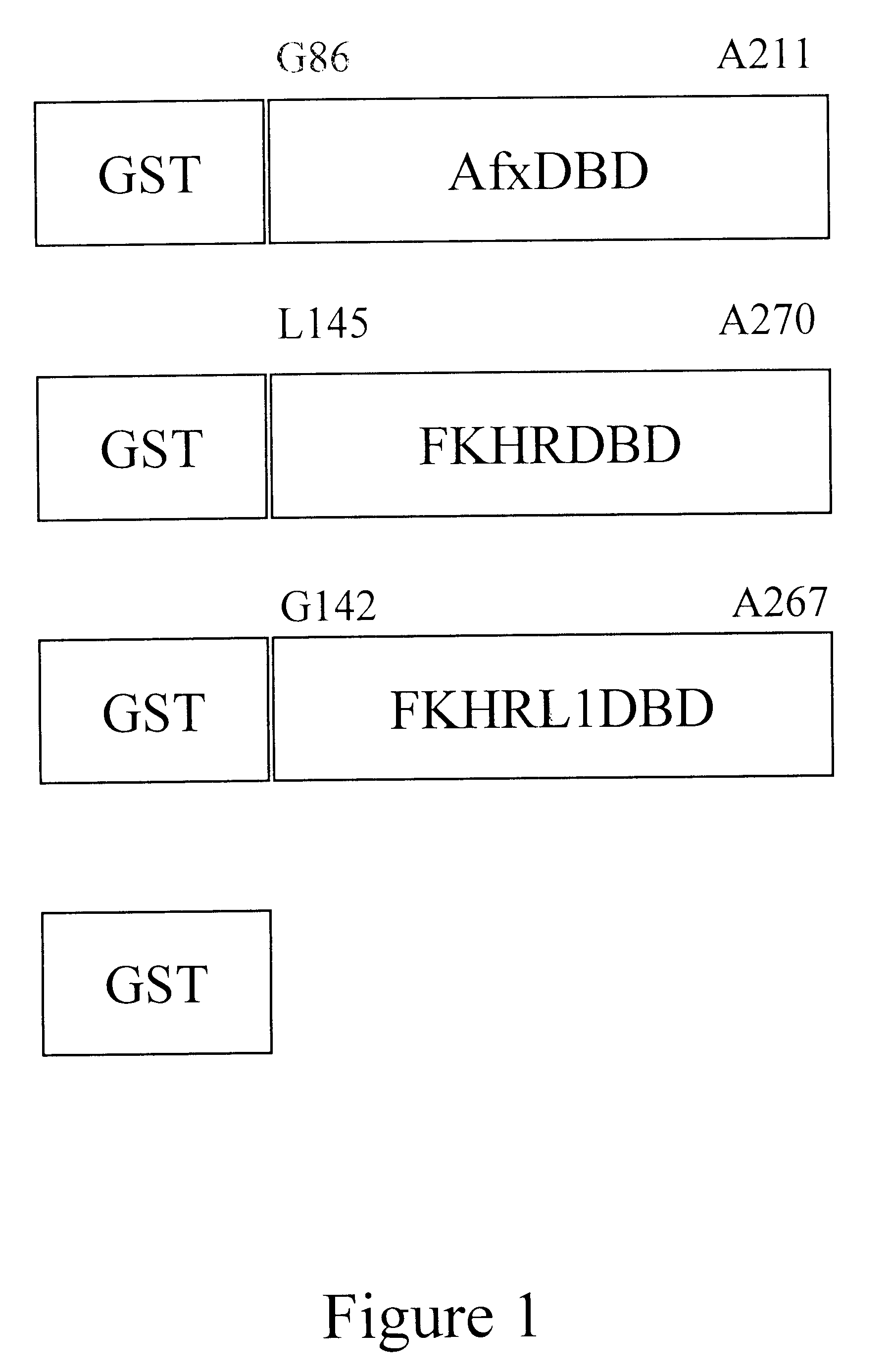
Response element
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
Methods for correcting von willebrand factor point mutations
InactiveUS20150166985A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingFactor VIII vWF
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant von Willebrand Factor protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with von Willebrand disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting a vWF point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for nucleic acid editing
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
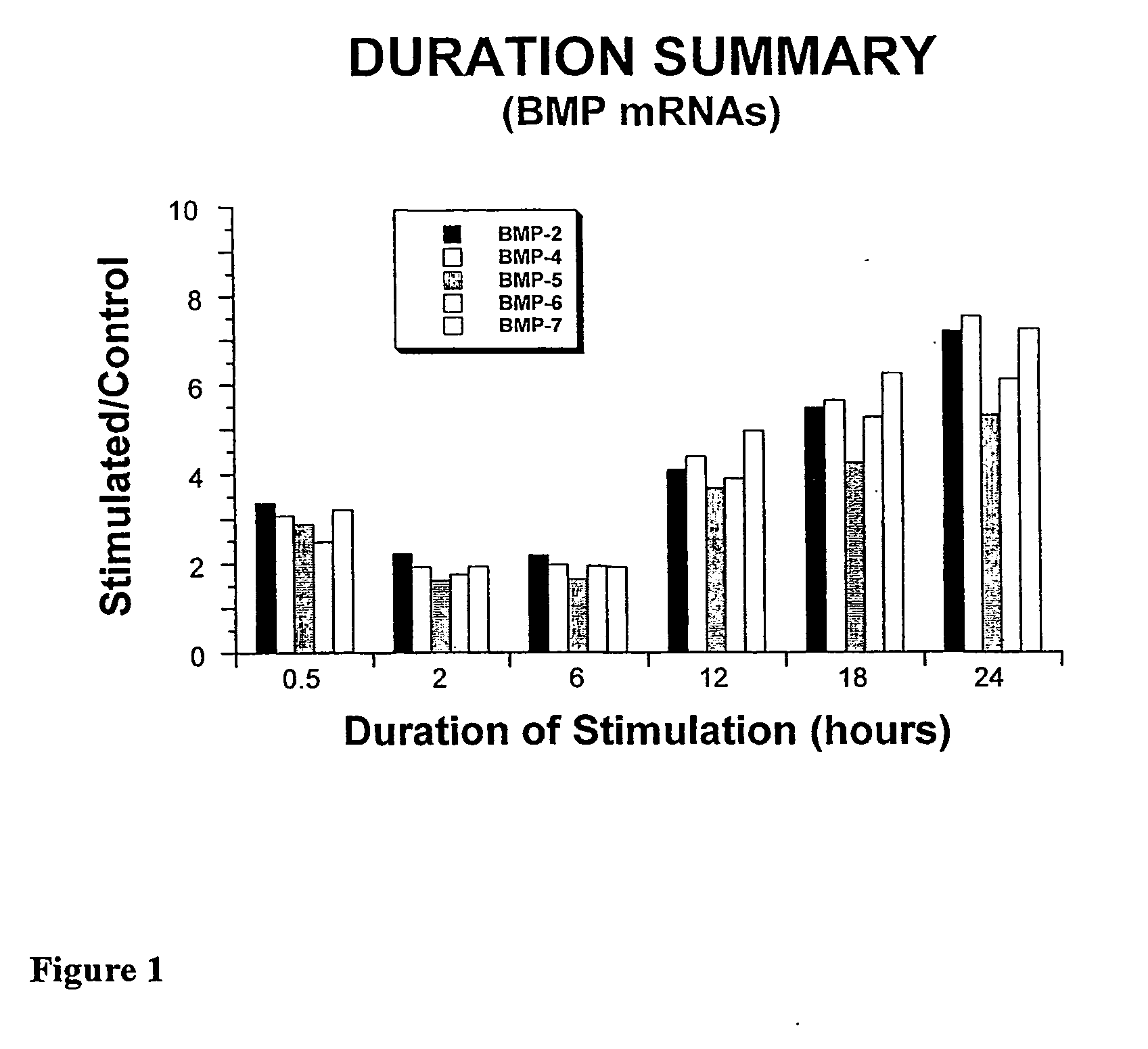
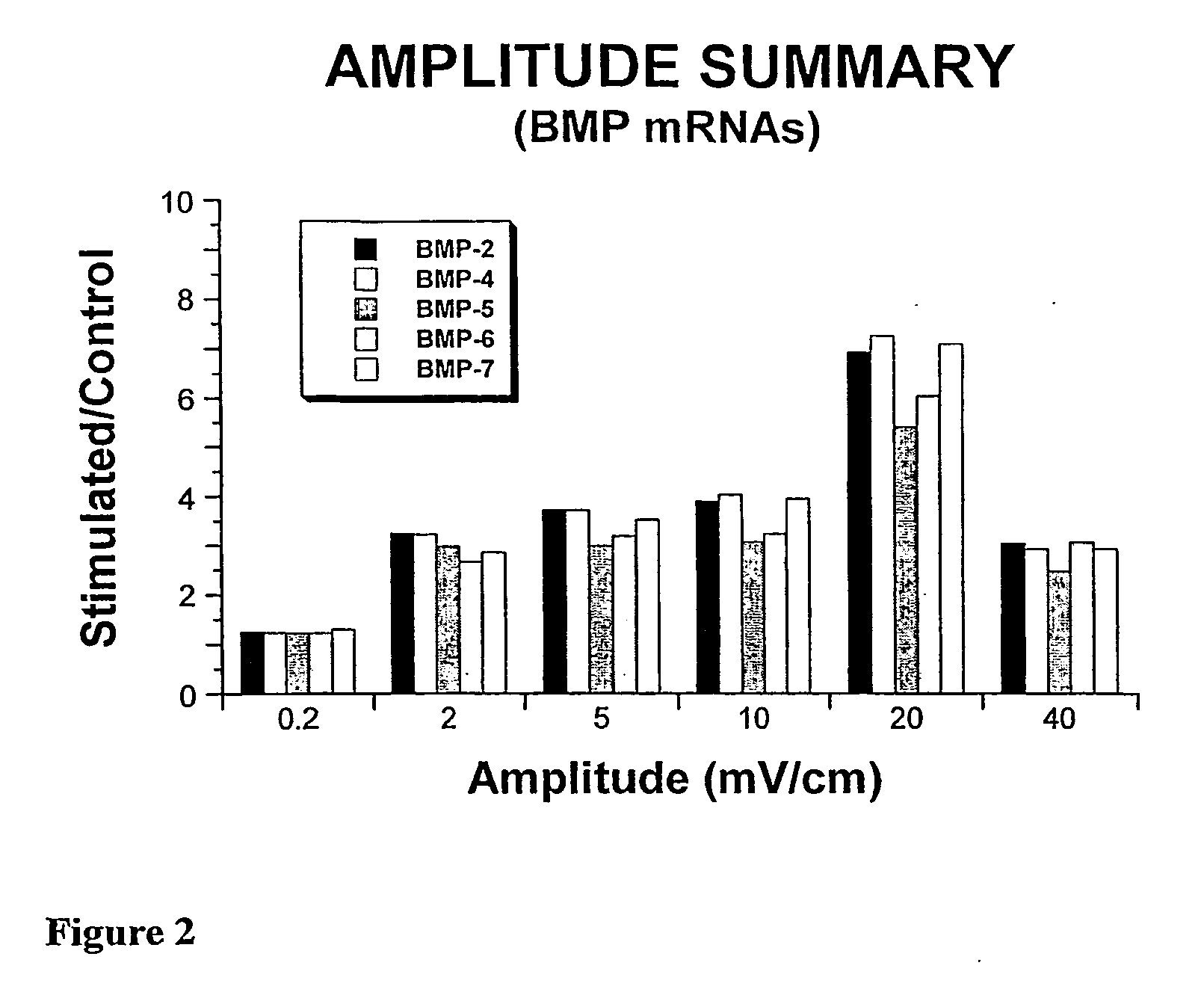
System and Method of Up-Regulating Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (Bmp) Gene Expression in Bone Cells Via the Application of Fields Generated by Specific and Selective Electric and Electromagnetic Signals
InactiveUS20070299472A1High expressionBiocideElectrotherapyHuman DNA sequencingBone Morphogenetic Protein Gene
Methods and devices are described for the regulation of bone morphogenetic protein gene expression in bone cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured bone. By gene expression is meant the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased bone tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields optimized for increase of bone morphogenetic protein gene expression and exposing bone to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate bone morphogenetic protein gene expression in such bone tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of bone fractures, fractures at risk, delayed unions, nonunion of fractures, bone defects, spine fusions, osteonecrosis or avascular necrosis, as an adjunct to other therapies in the treatment of one or all of the above, and in the treatment of osteoporosis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Identification and mapping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human genome
InactiveUS20060057564A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to the role of genes in human diseases. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying genes that are involved in human disease conditions. The invention provides identification and mapping of a very large number of SNPs throughout the entire human genome. This contribution allows scientists to isolate and identify genes that are relevant to the prevention, causation, or treatment of human disease conditions.
Owner:SNP CONSORTIUM
Protein (poly)peptides libraries
InactiveUS20060003334A1High expressionMaximizes correspondenceFungiBacteriaHuman DNA sequencingSynthetic DNA
The present invention relates to synthetic DNA sequences which encode one or more collections of homologous proteins / (poly)peptides, and methods for generating and applying libraries of these DNA sequences. In particular, the invention relates to the preparation of a library of human-derived antibody genes by the use of synthetic consensus sequences which cover the structural repertoire of antibodies encoded in the human genome. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of a single consensus antibody gene as a universal framework for highly diverse antibody libraries.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
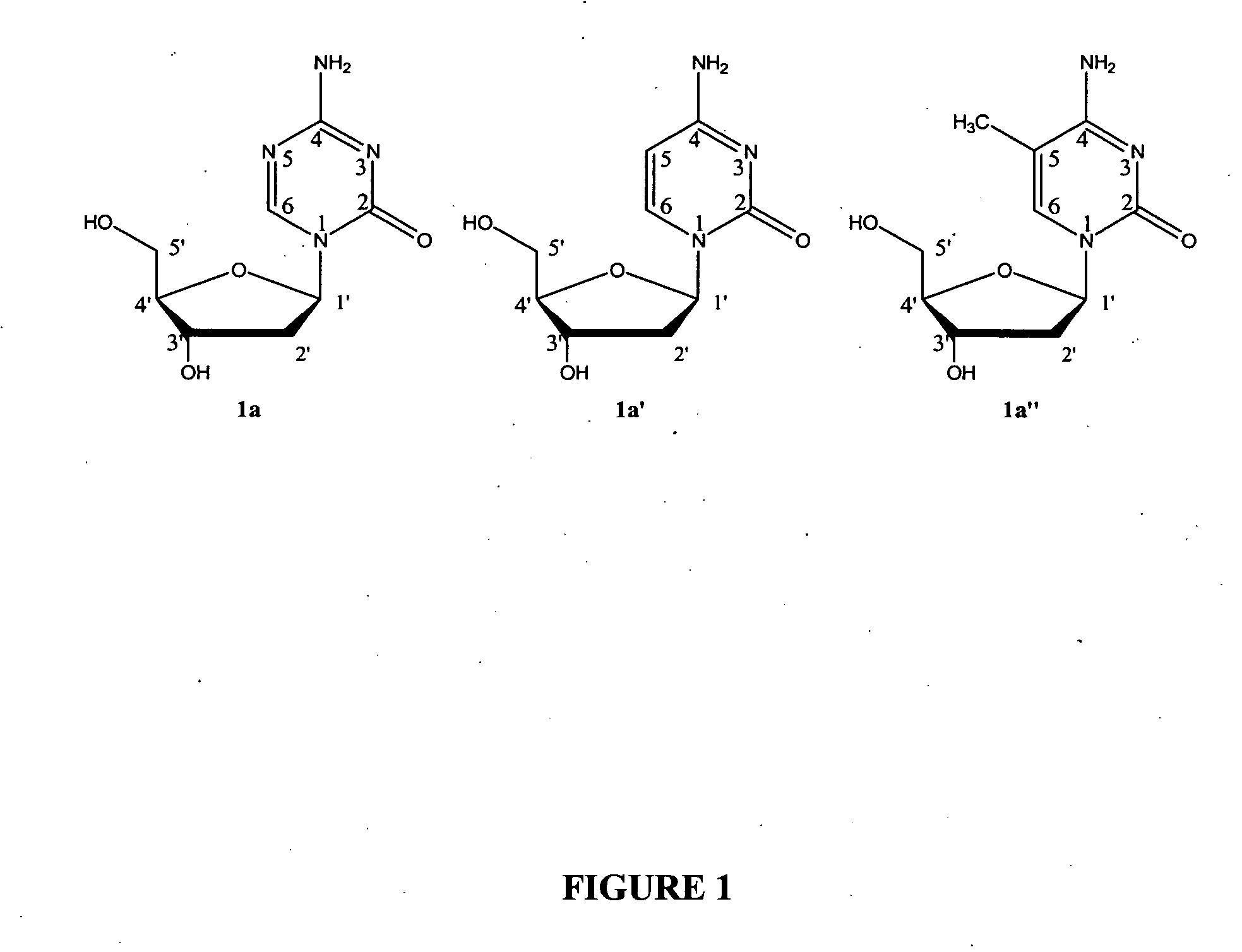
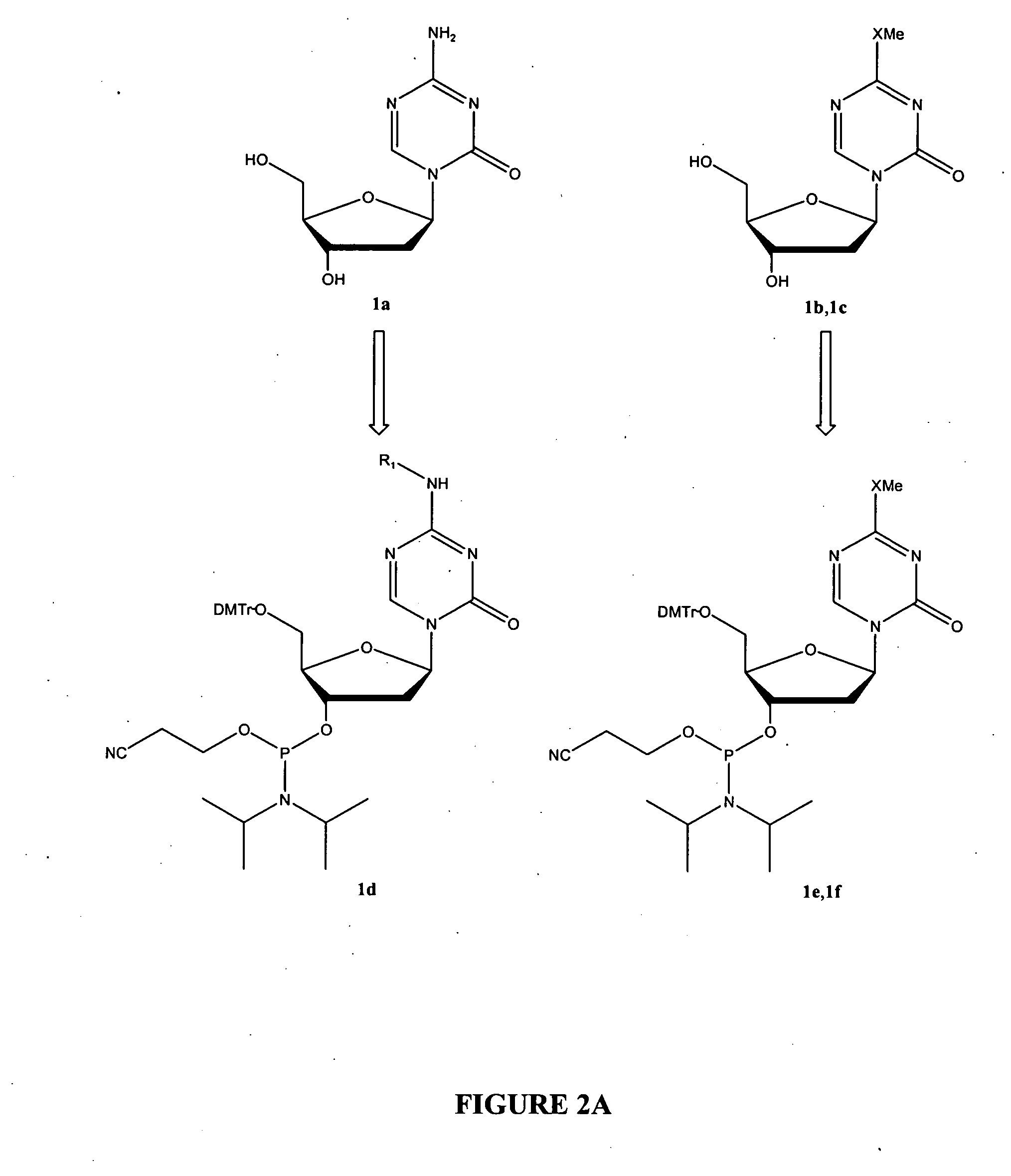
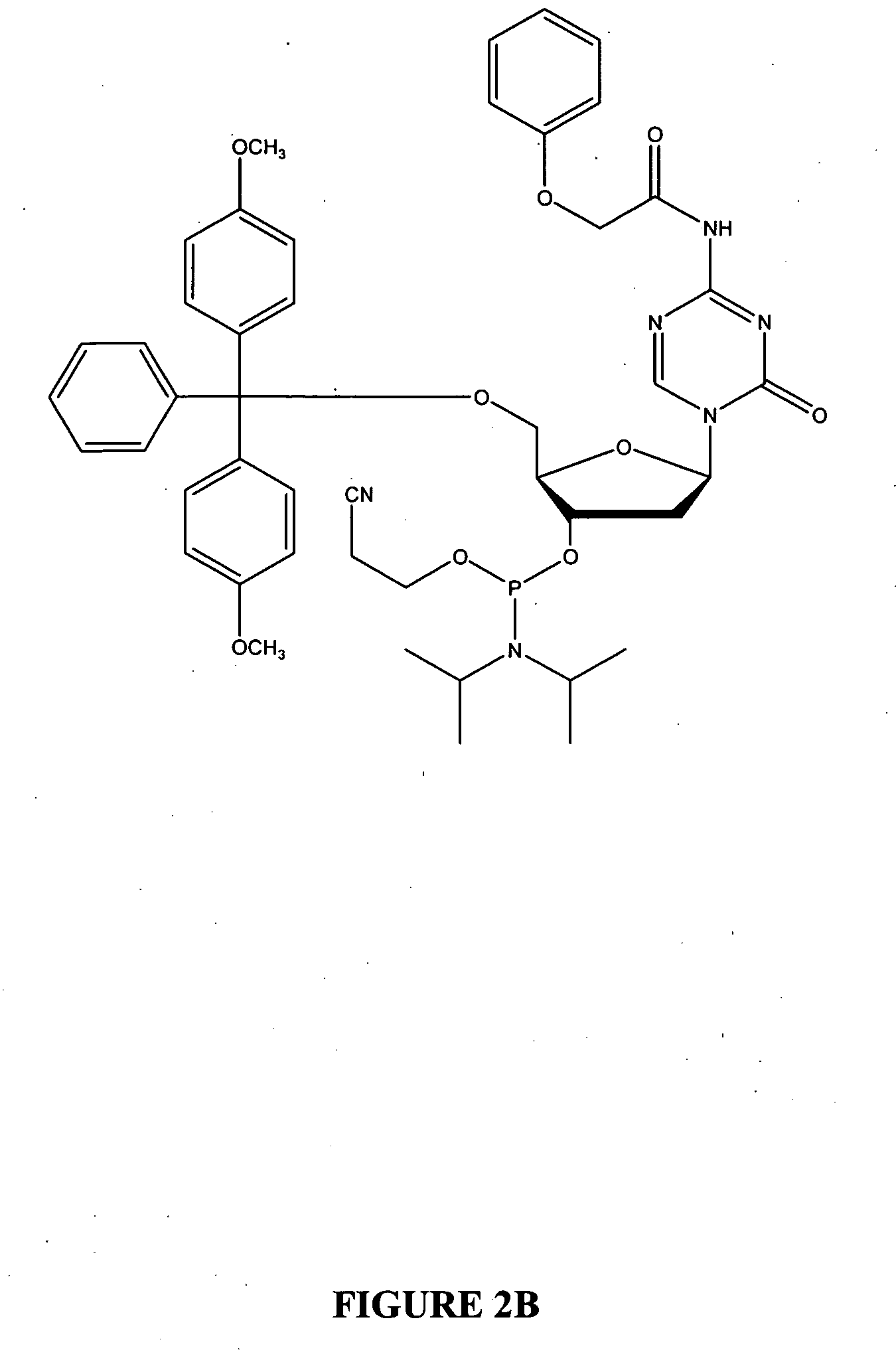
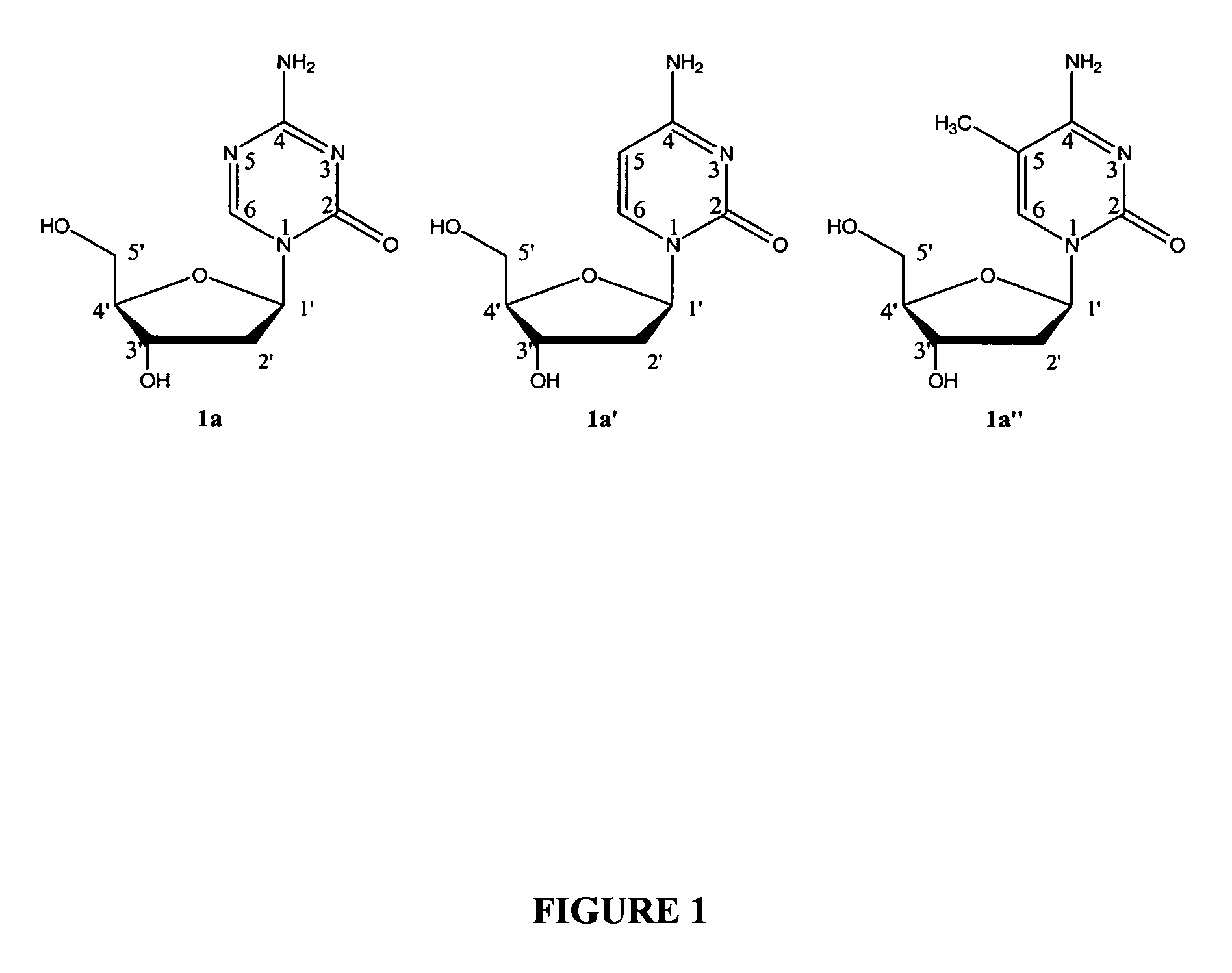
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
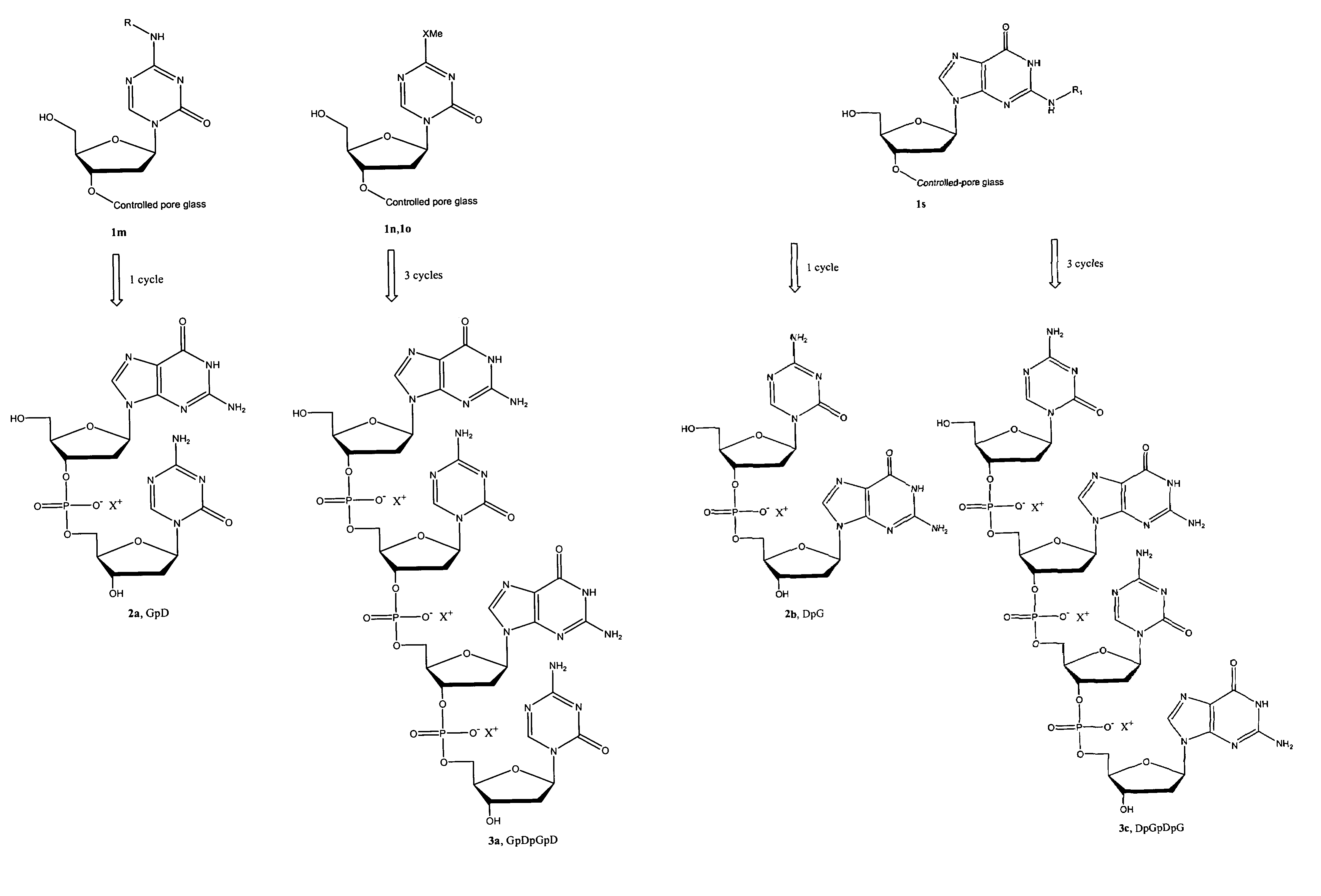
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
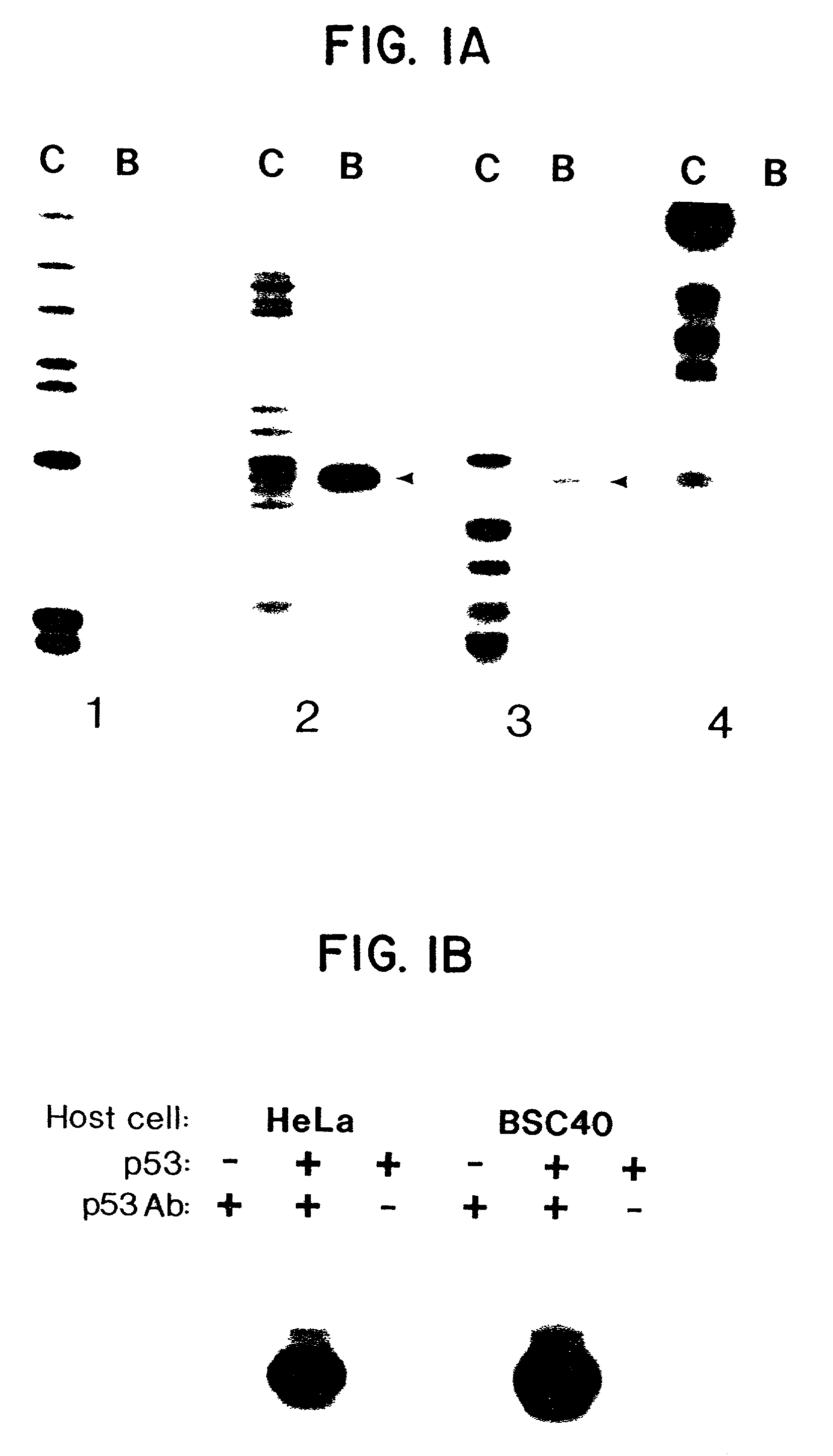
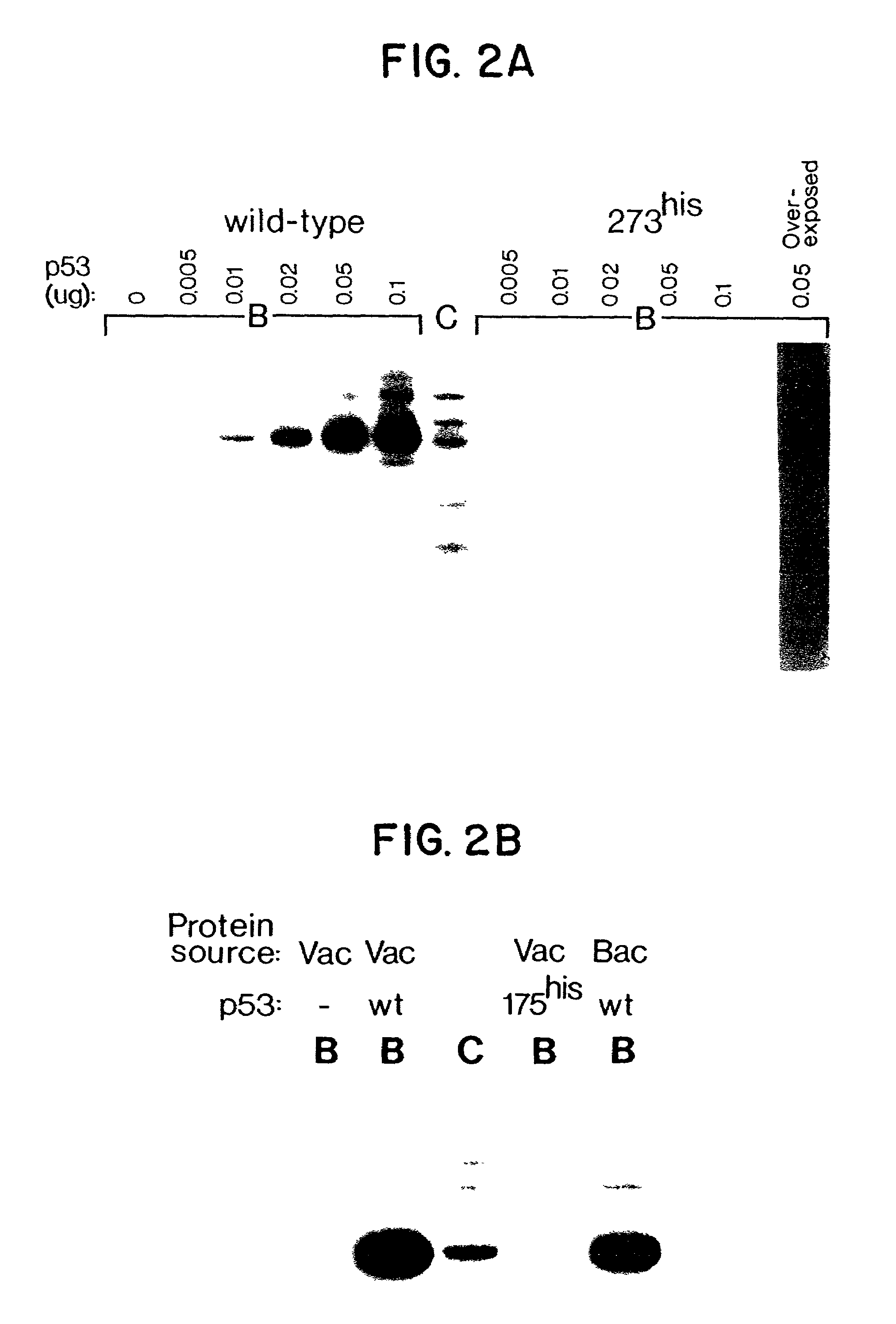
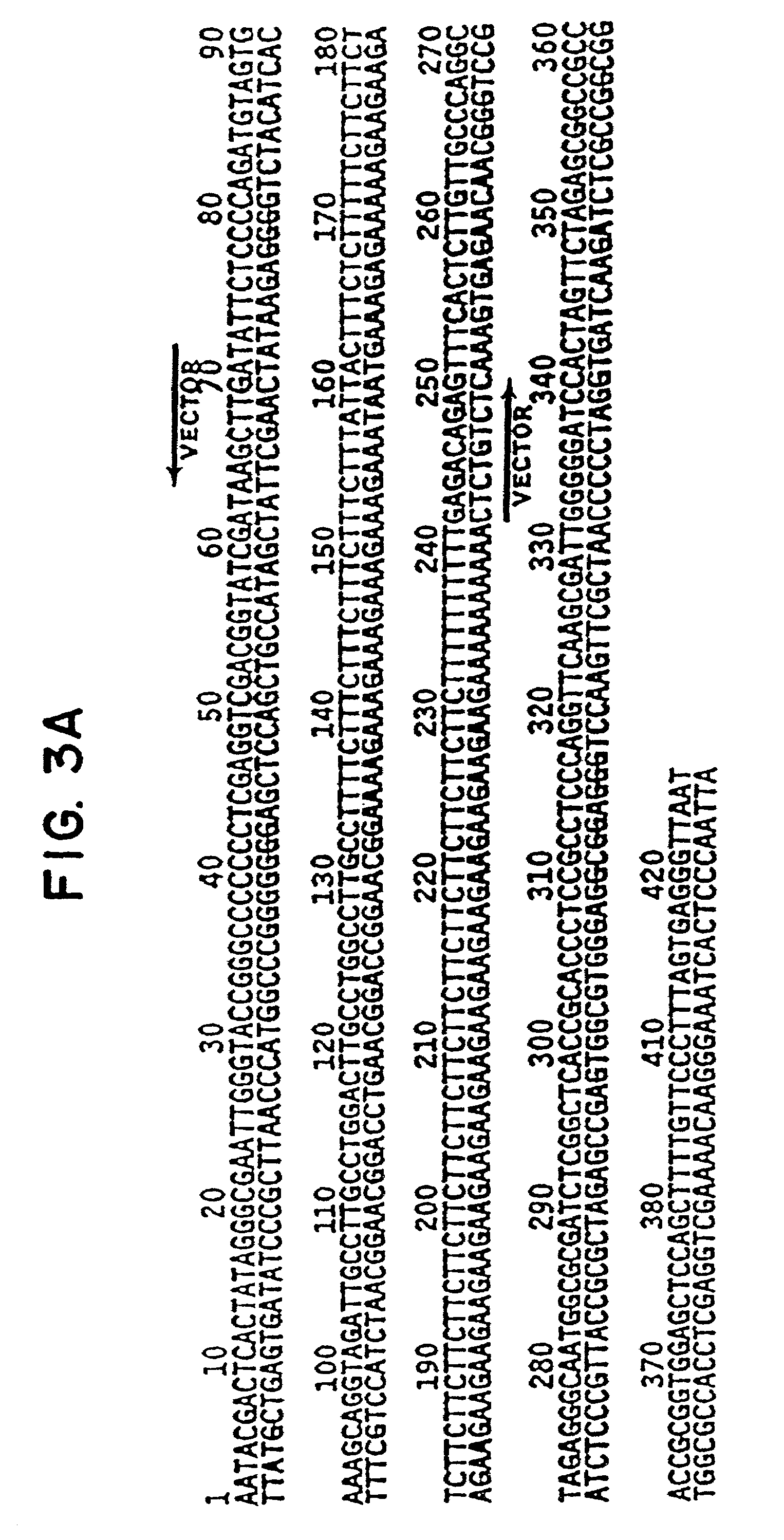
Sequence specific DNA binding by p53
InactiveUS7087583B2Inhibit tumor growthLoss of functionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingCancer cell
Specific sequences in the human genome are the sites of strong binding of wild-type p53 protein, but not mutant forms of the protein. These sequences are used diagnostically to detect cells in which the amount of wild-type p53 is diminished. The sequences can also be used to screen for agents which correct for loss of wild-type p53 to DNA in cancer cells.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
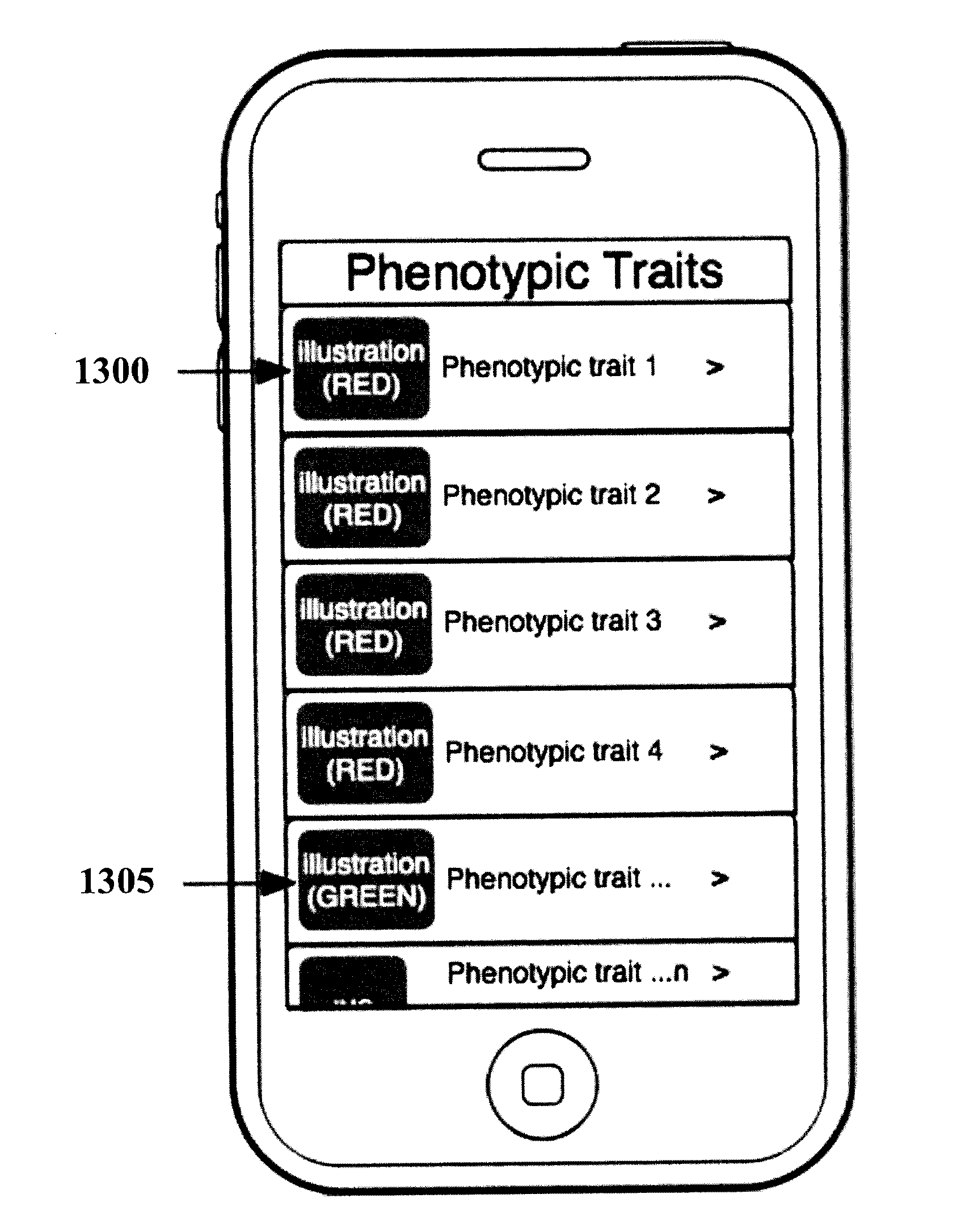
Organization, visualization and utilization of genomic data on electronic devices
InactiveUS20140033125A1Simple organization and visualization and useData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman DNA sequencingPersonalization
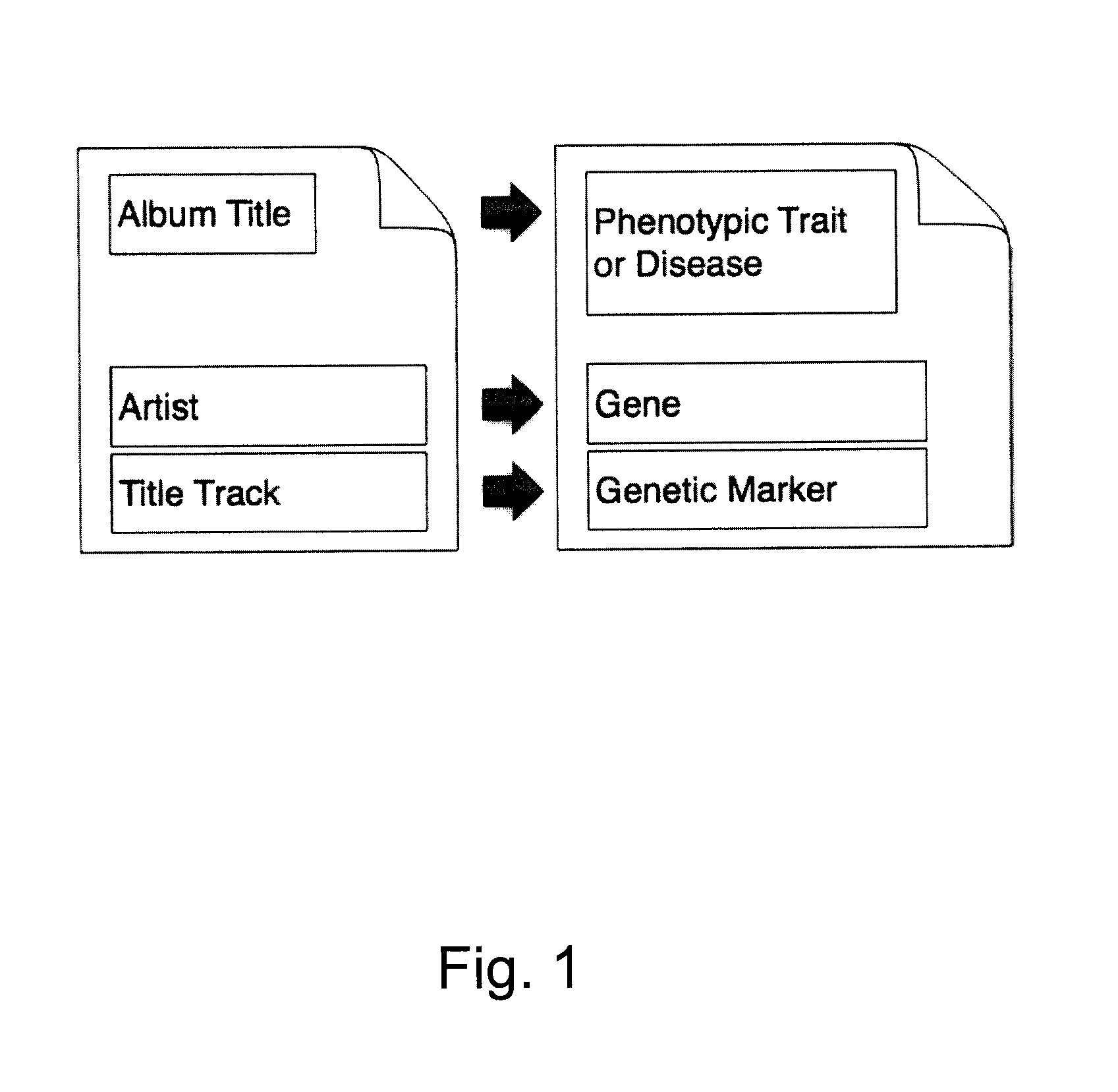
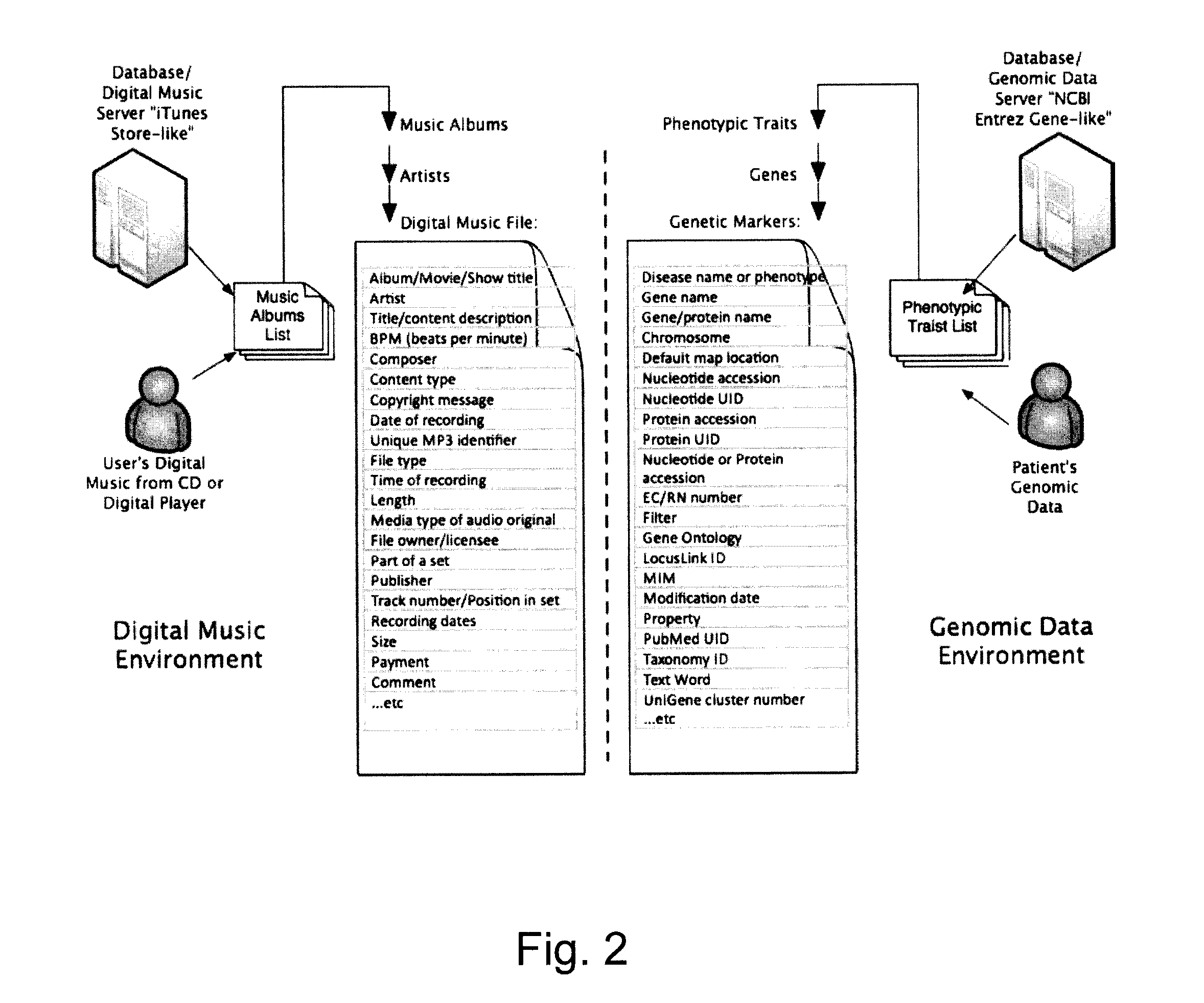
Described herein are methods, devices and systems for simple organization, visualization and use of genome data (e.g. human genome data) on electronic devices (e.g. portable devices). In some embodiments, the data are organized and / or visualized according to phenotype traits, genes, and / or markers in a similar manner to the organization and / or visualization of digital music contents. This concept allows a new procedure for genomic data organization and facilitates the development of genomic data visualization tools. The methods described herein can be implemented with consumer-oriented software on electronic devices, computers, and portable devices, for the use of genomic related data in the field of personalized medicine for predictive, preventive and participative wireless healthcare.
Owner:PORTABLE GENOMICS
Oligonucleotide analogues incorporating 5-aza-cytosine therein
Oligonucleotide analogues are provided that incorporate 5-aza-cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence, e.g., in the form of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) or 5-aza-cytidine. In particular, oligonucleotide analogues rich in decitabine-deoxyguanosine islets (DpG and GpD) are provided to target the CpG islets in the human genome, especially in the promoter regions of genes susceptible to aberrant hypermethylation. Such analogues can be used for modulation of DNA methylation, such as effective inhibition of methylation of cytosine at the C-5 position. Methods for synthesizing these oligonucleotide analogues and for modulating nucleic acid methylation are provided. Also provided are phosphoramidite building blocks for synthesizing the oligonucleotide analogues, methods for synthesizing, formulating and administering these compounds or compositions to treat conditions, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
TALEN-based gene correction
ActiveUS9393257B2Accurate expressionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingHuman cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion
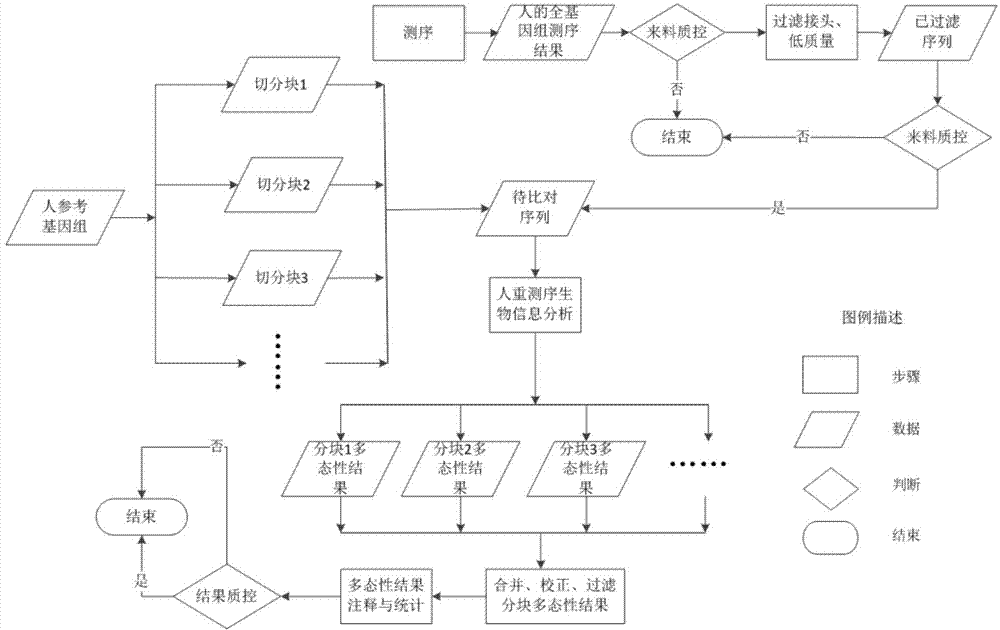
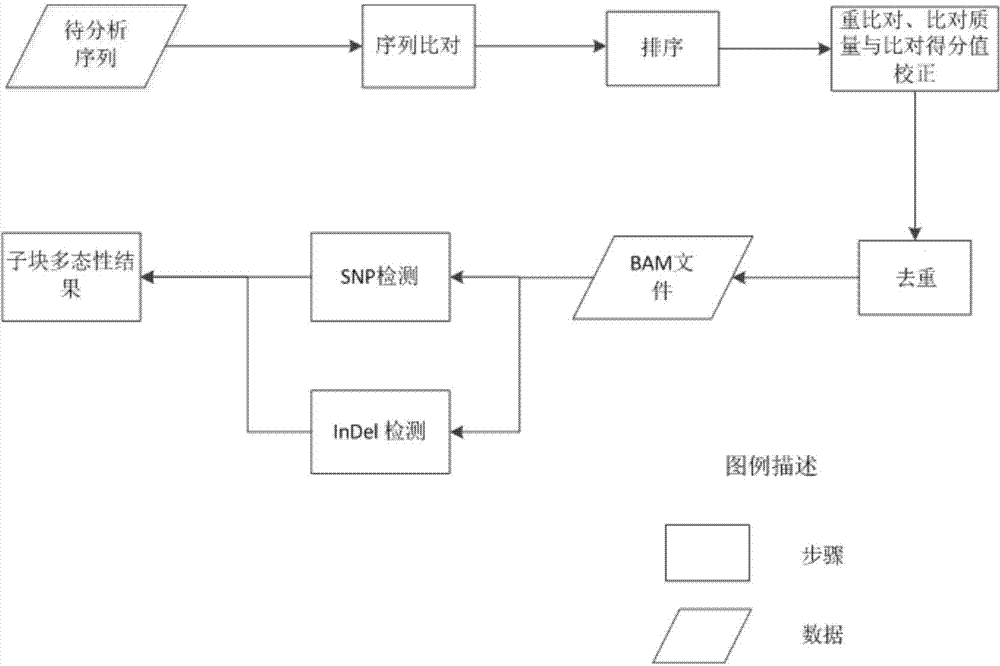
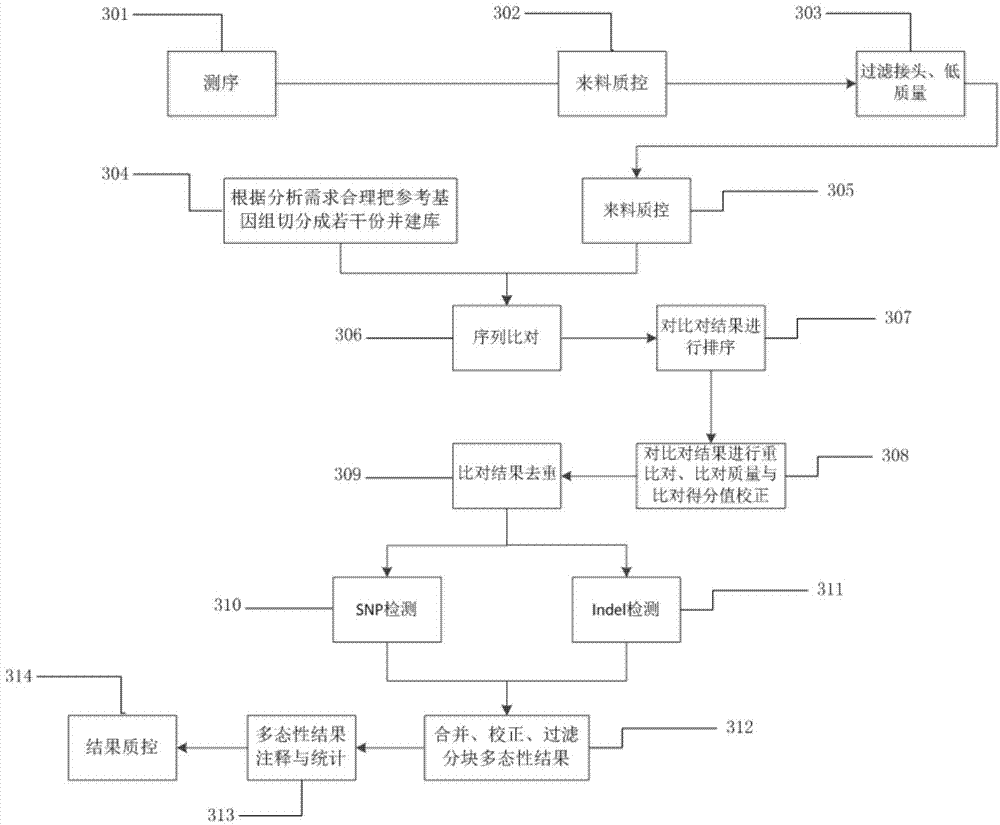
ActiveCN104762402AReduce memory requirementsShort analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsInsertion deletionHuman DNA sequencing
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting human genome single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion. The method is a feasible method for rapidly detecting single base mutation and micro-insertion deletion from a human genome DNA sequencing result. According to the invention, a human reference genome sequence is scientifically and effectively split into small sub reference sequence blocks; almost all steps (including steps with relatively long analysis time) of human resequencing are divided into sub task blocks with greatly reduced computational complexity, wherein the sub task blocks do not influence each other; polymorphism information obtained from the sub reference sequence blocks is subjected to redundancy-removing, correction and filtering, such that the polymorphism information needed by an original human resequencing process is obtained. With the method provided by the invention, a problem of long human resequencing biological information analysis time is solved, and a novel analysis mode is created.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGDING INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com