Patents
Literature
500 results about "In situ hybridisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In situ hybridization indicates the localization of gene expression in their cellular environment. A labeled RNA or DNA probe can be used to hybridize to a known target mRNA or DNA sequence within a sample.
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20060246524A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryIn situ hybridisationOrganic chemistry
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
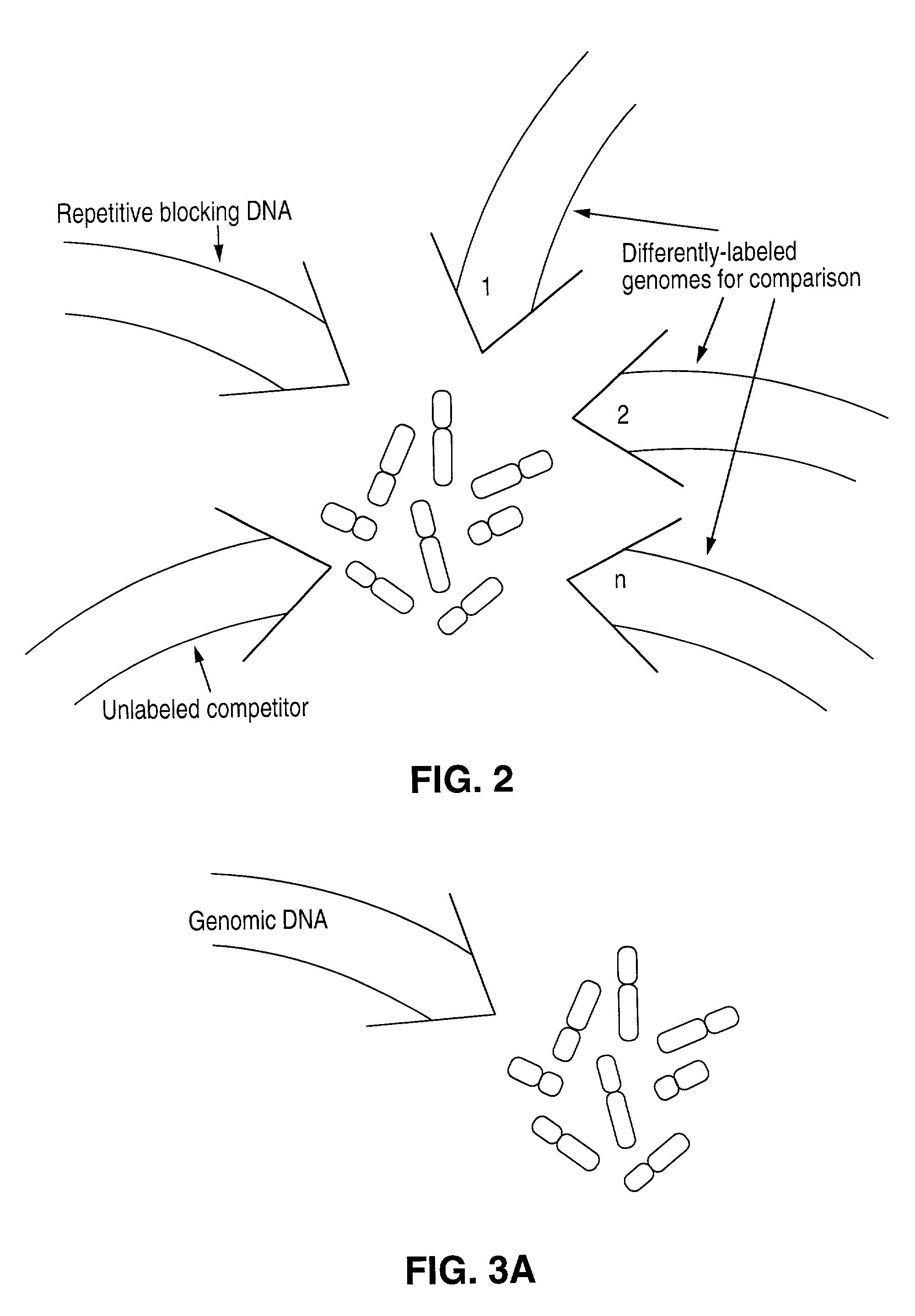
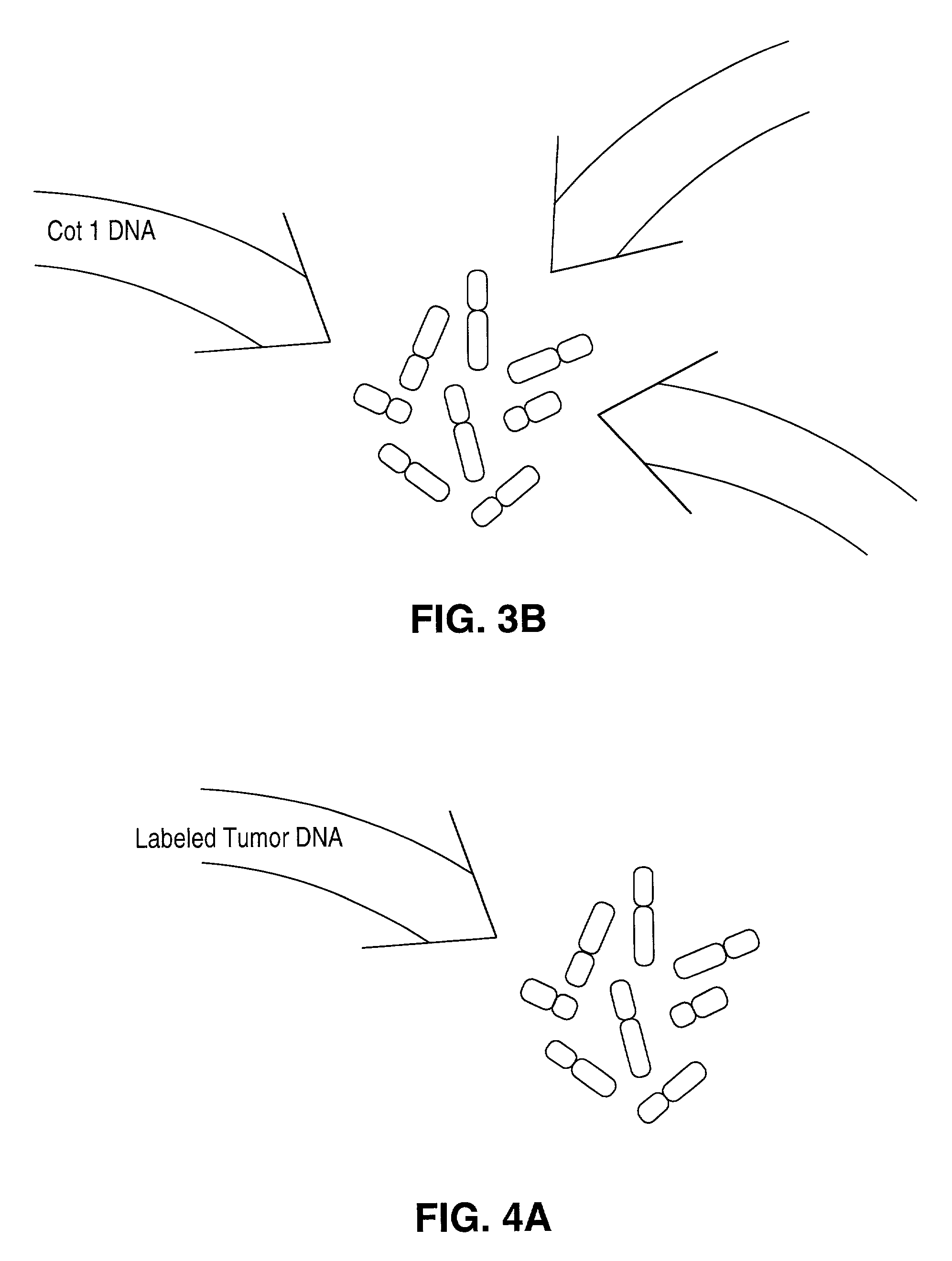
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
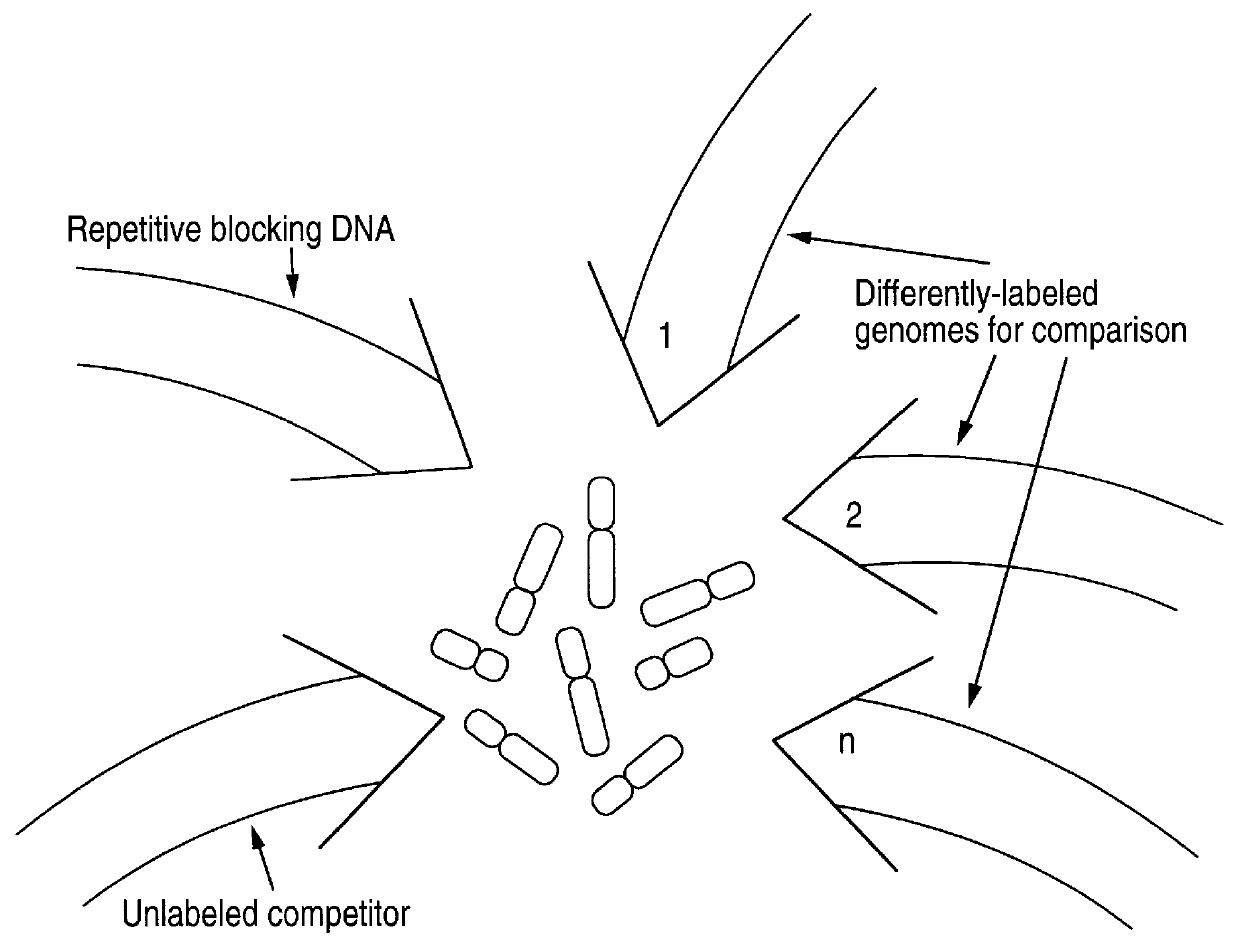
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and compositions for identifying a fetal cell
InactiveUS20100304978A1High expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCandidate Gene Association StudyTrophoblast
The present invention provides methods and compositions for specifically identifying a fetal cell. An initial screening of approximately 400 candidate genes by digital PCR in different fetal and adult tissues identified a subset of 24 gene markers specific for fetal nucleated RBC and trophoblasts. The specific expression of those genes was further evaluated and verified in more defined tissues and isolated cells through quantitative RT-PCR using custom Taqman probes specific for each gene. A subset of fetal cell specific markers (FCM) was tested and validated by RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in blood samples from non-pregnant women, and pre-termination and post-termination pregnant women. Applications of these gene markers include, but are not limited to, distinguishing a fetal cell from a maternal cell for fetal cell identification and genetic diagnosis, identifying circulating fetal cell types in maternal blood, purifying or enriching one or more fetal cells, and enumerating one or more fetal cells during fetal cell enrichment.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Antibody conjugates
InactiveUS20060246523A1Easy to detectIntense stainingHybrid immunoglobulinsHydrolasesIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
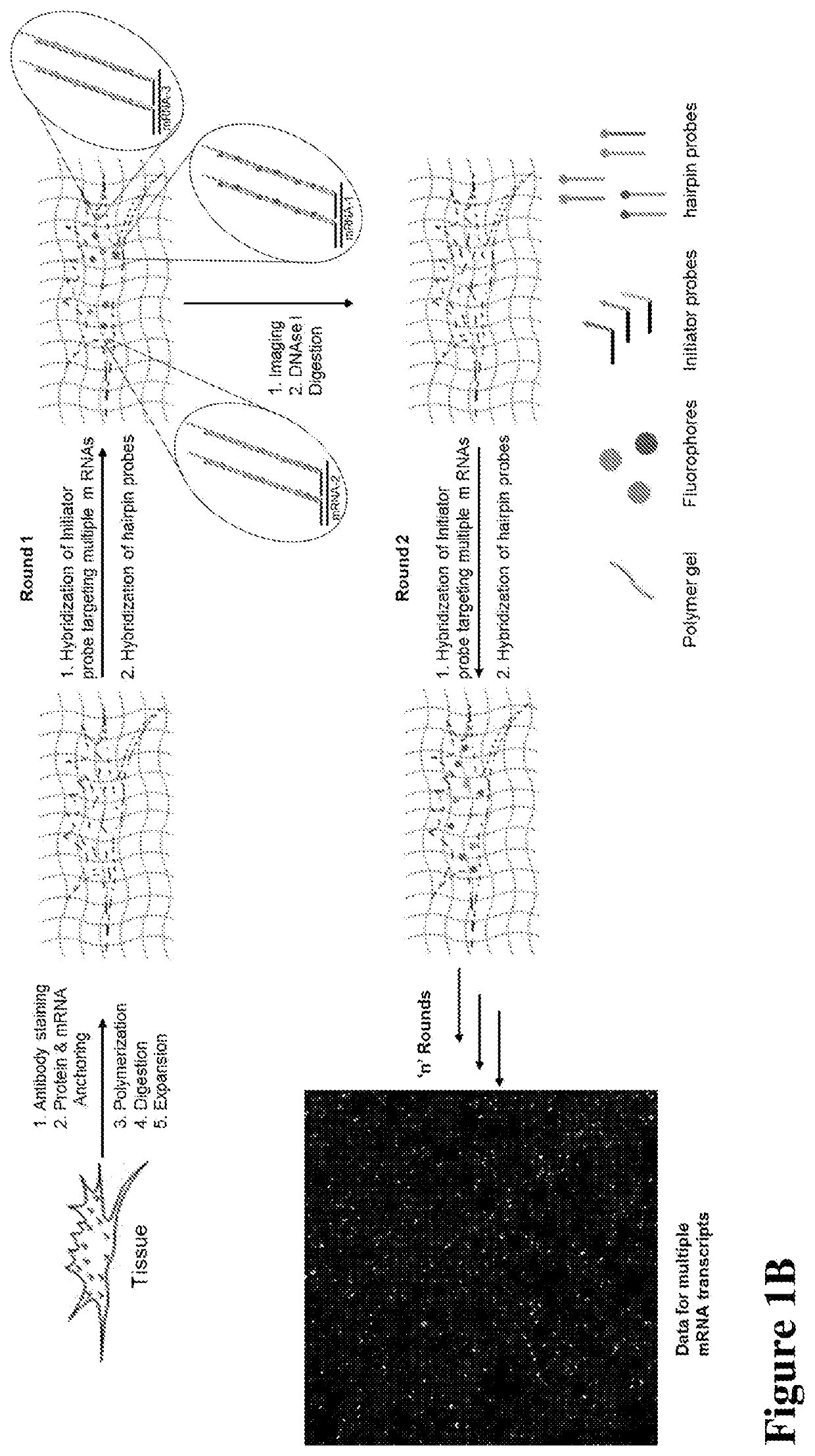
Multiplexed in situ hybridization of tissue sections for spatially resolved transcriptomics with expansion microscopy
This invention relates to imaging, such as by expansion microscopy, labelling, and analyzing biological samples, such as cells and tissues, as well as reagents and kits for doing so.
Owner:EXPANSION TECH
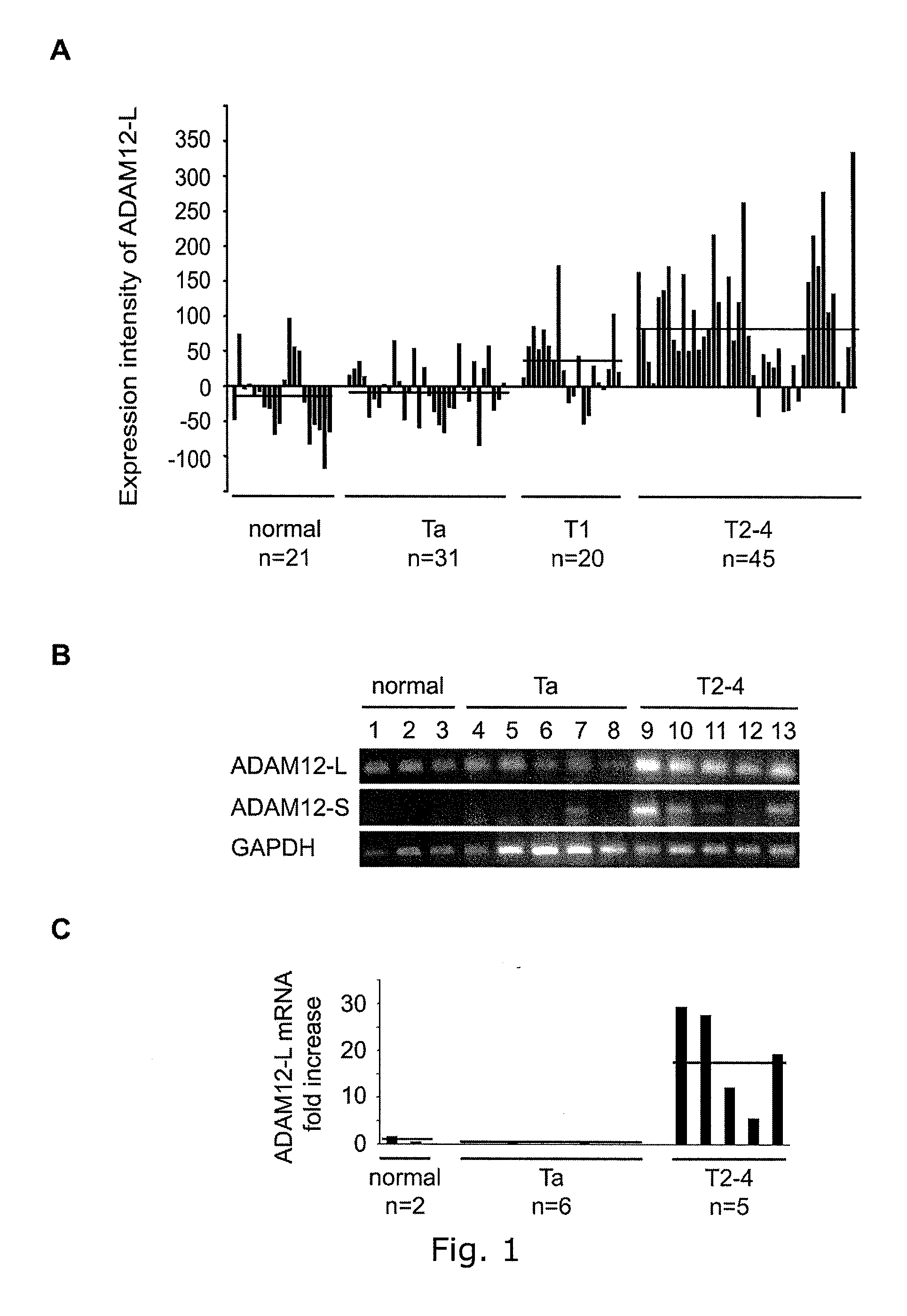
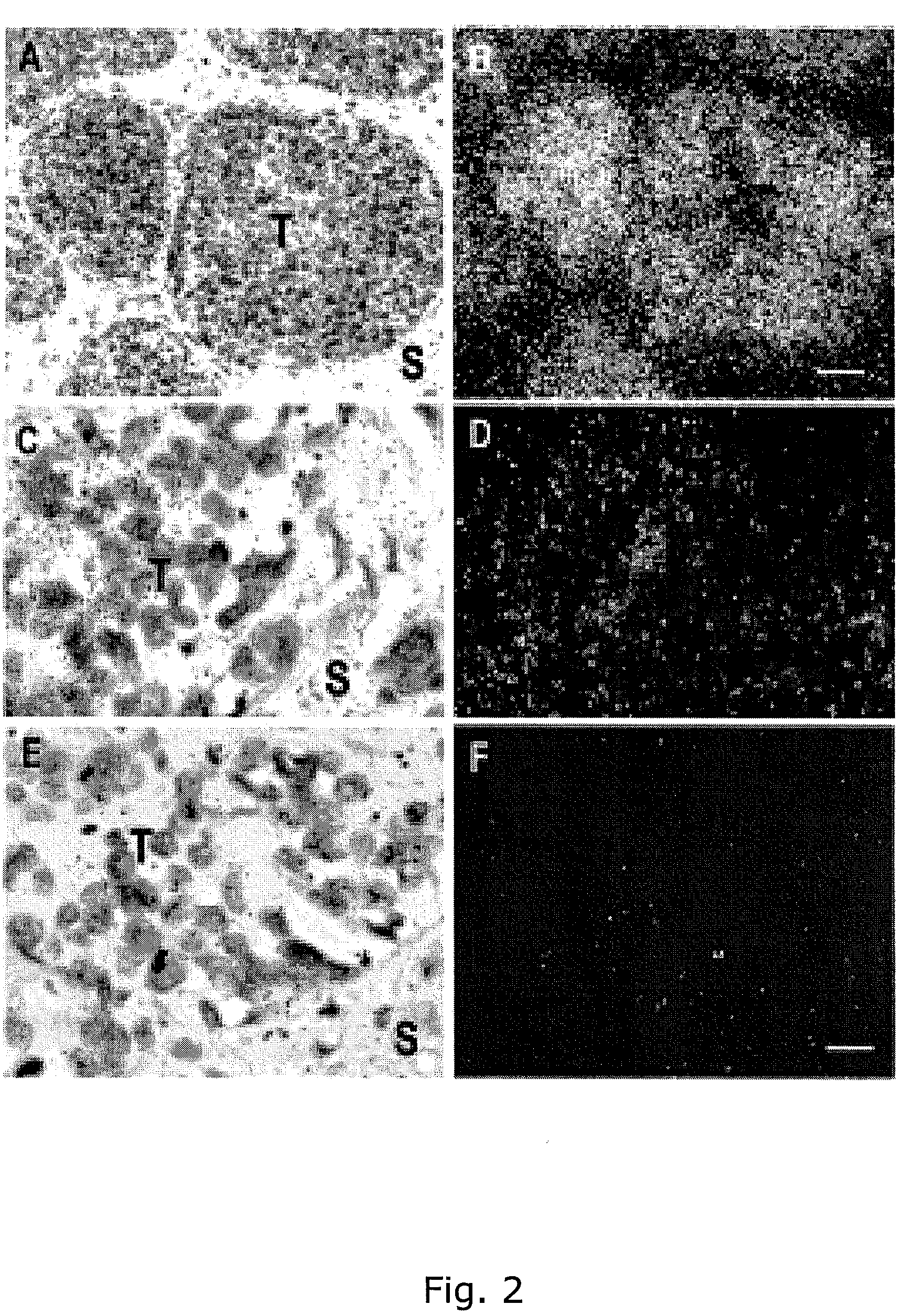
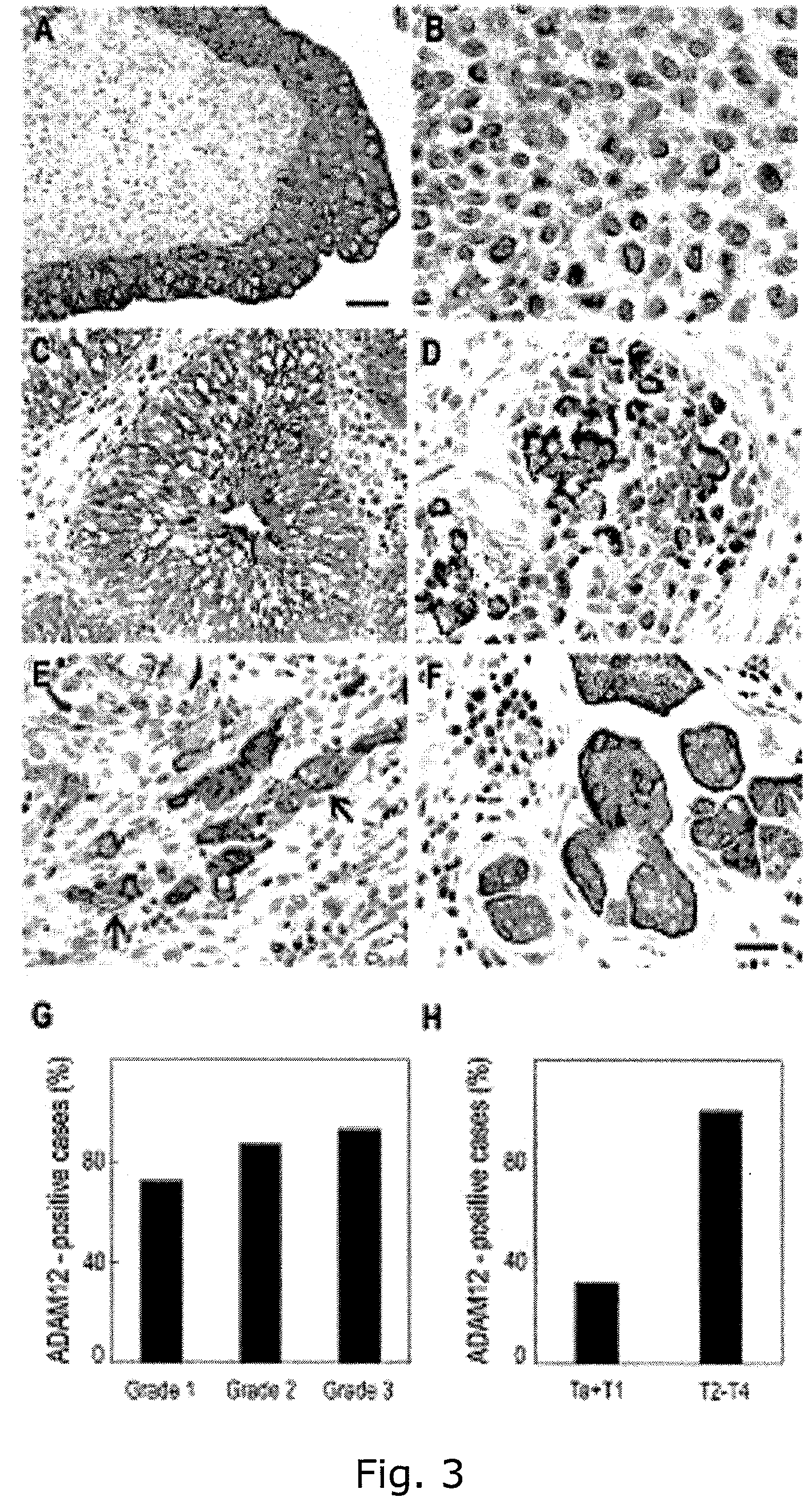
Adam12 as a biomarker for bladder cancer
InactiveUS20090029372A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTissue ArraysAffymetrix genechip
The present inventors have shown that the gene and protein expression profiles of ADAM8, ADAM10 and ADAM12 in different grades and stages of bladder cancer.ADAM12 gene expression was evaluated in tumors from 96 patients with bladder cancer using a customized Affymetrix GeneChip. Gene expression in bladder cancer was validated using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), quantitative PCR, and in situ hybridization. Protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining on tissue arrays of bladder cancers.The presence and relative amount of ADAM12 in the urine of cancer patients were determined by Western blotting and densitometric measurements, respectively.Particularly ADAM12 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in bladder cancer, as determined by microarray analysis, and the level of ADAM12 mRNA correlated with disease stage. ADAM12 protein expression correlated with tumor stage and grade. ADAM12 was present in higher levels in the urine from bladder cancer patients than in urine from healthy individuals. Significantly, following removal of tumor by surgery, in most bladder cancer cases examined the level of ADAM12 in the urine decreased and, upon recurrence of tumor, increased.
Owner:PHYSICIANS CHOICE LAB SERVICES +1
Tissue analysis and kits therefor
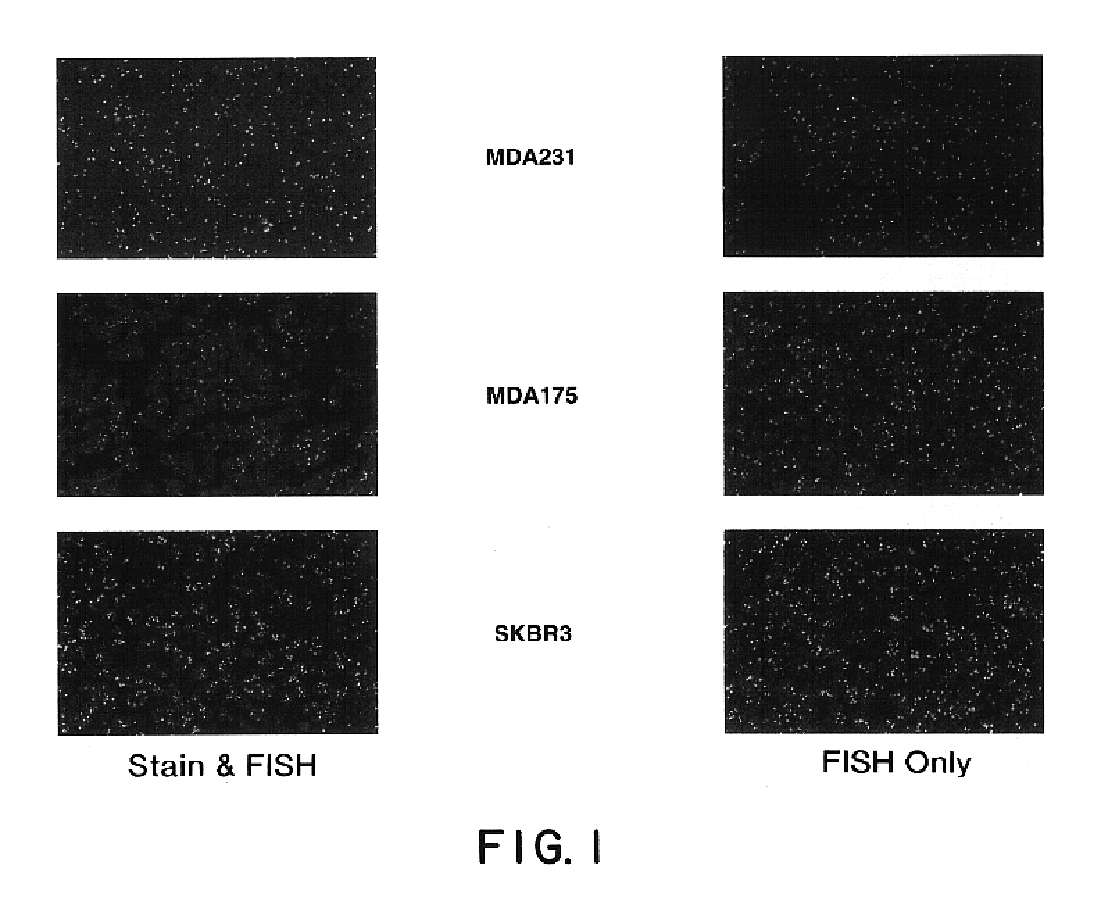
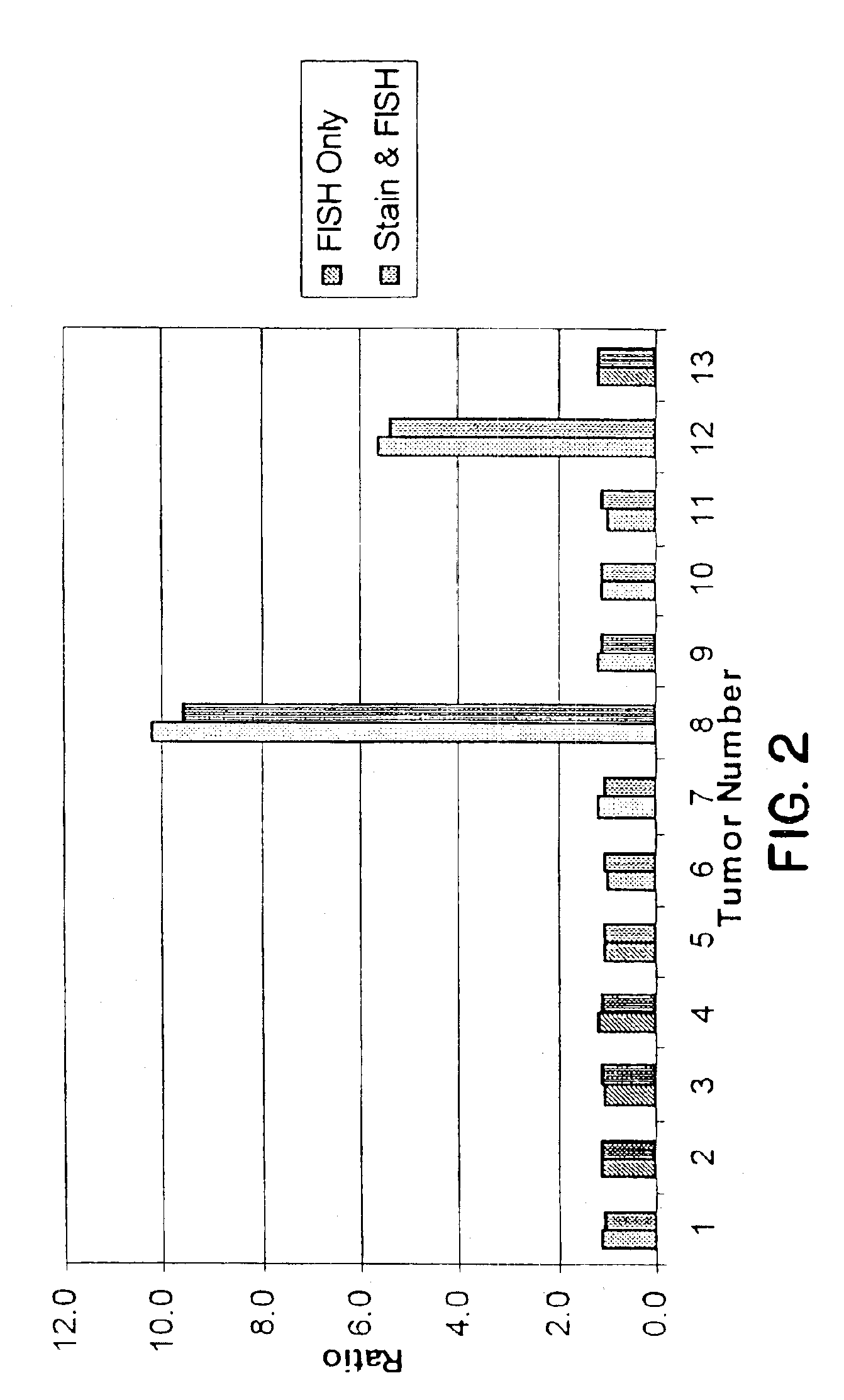
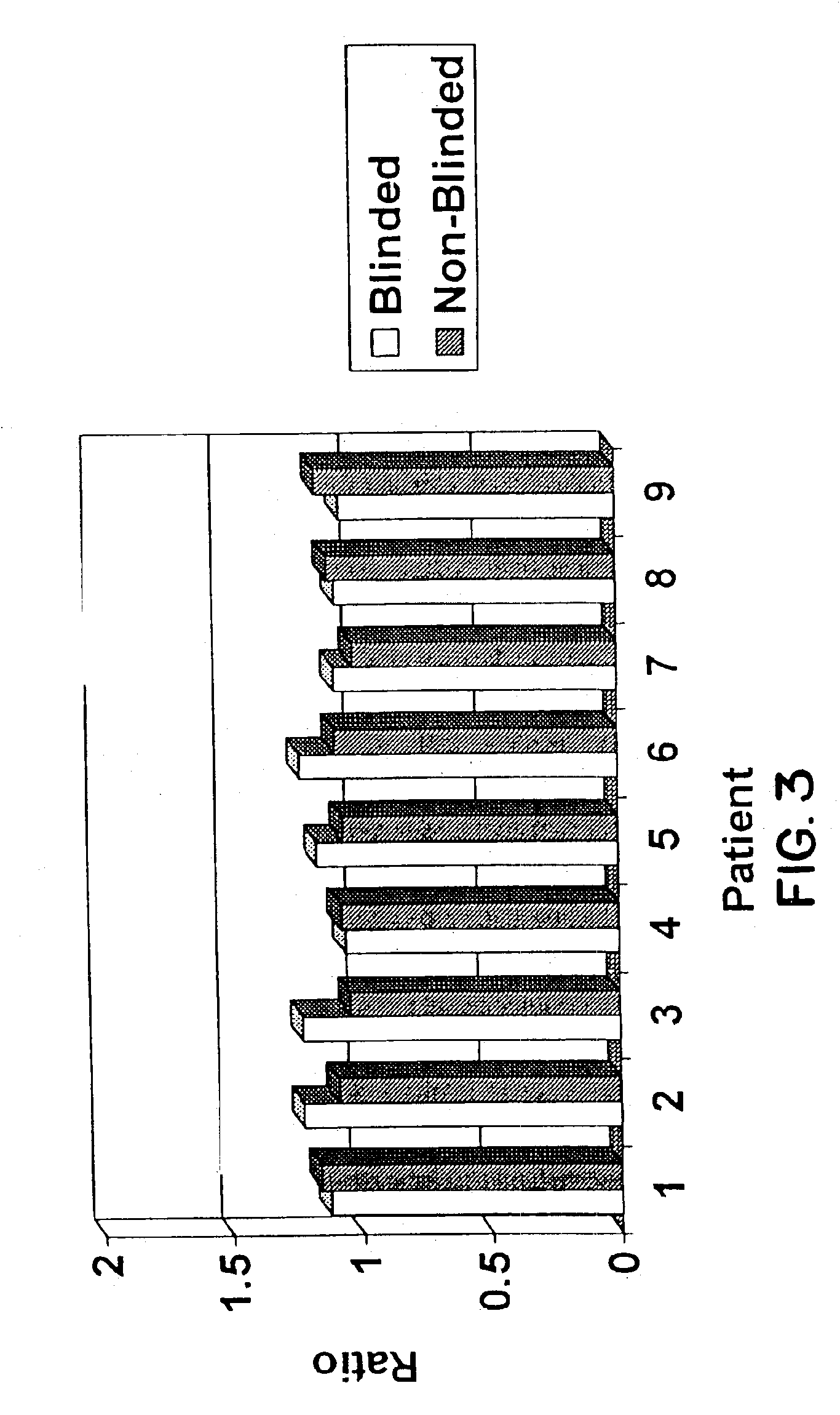
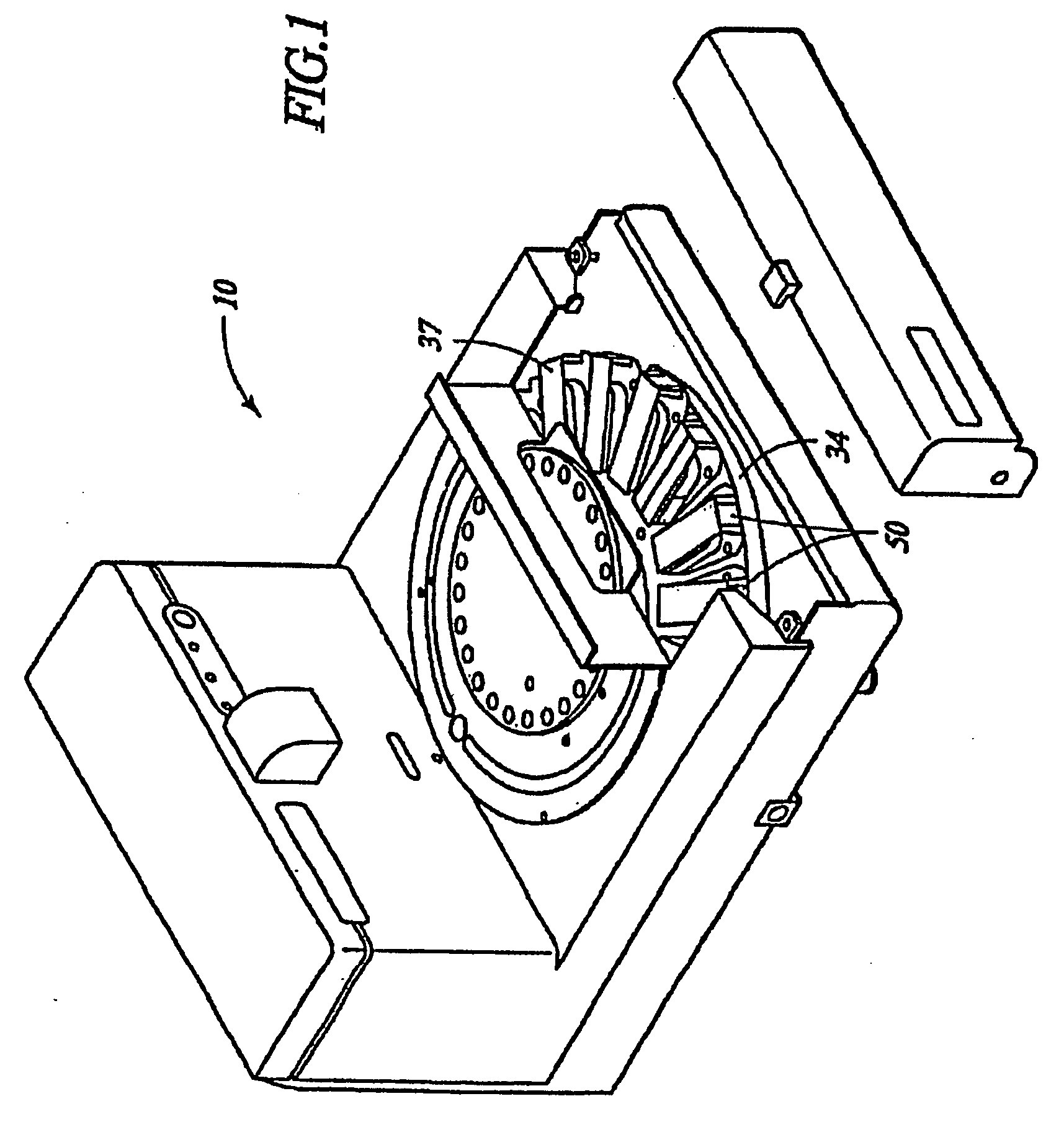
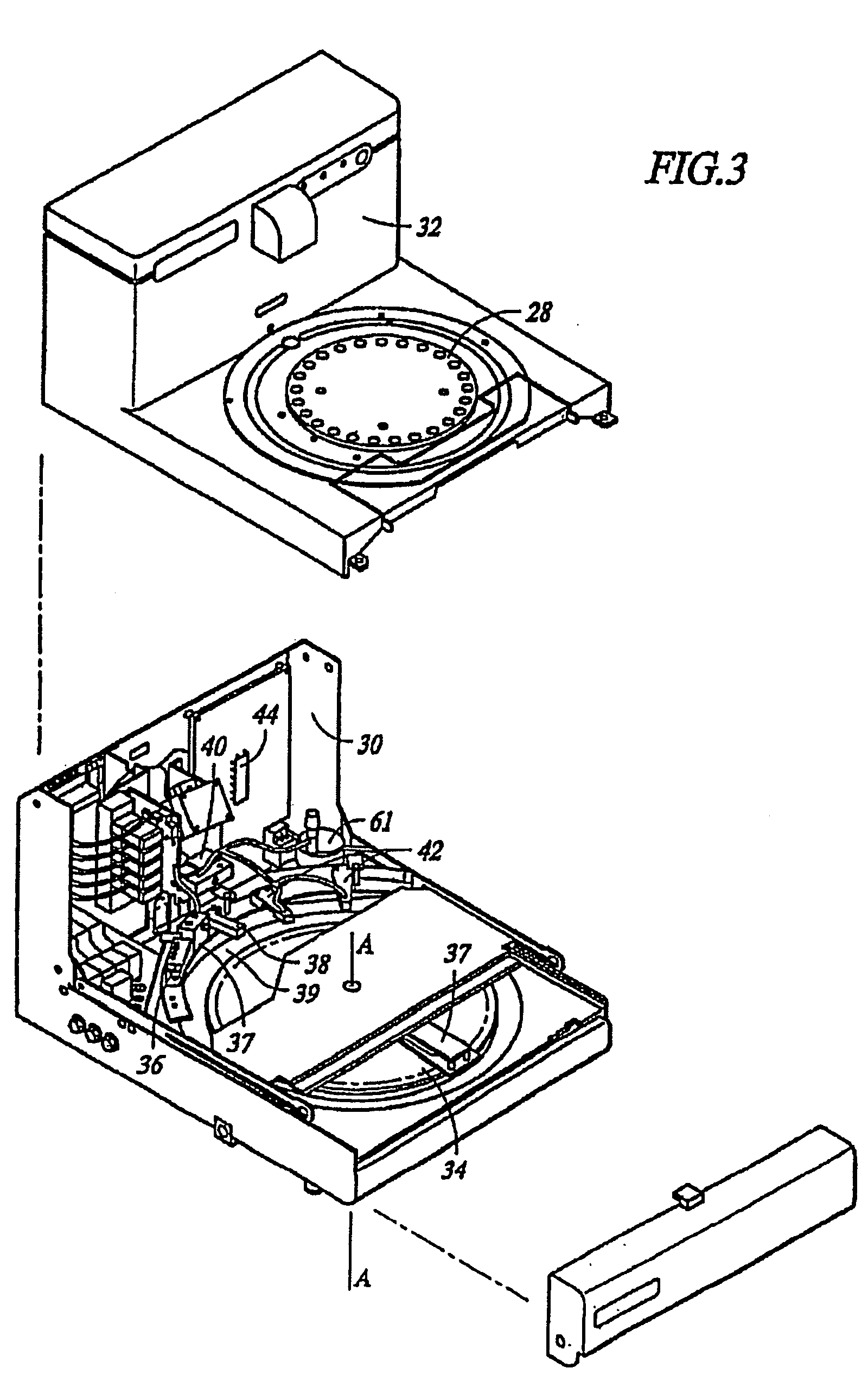
InactiveUS6905830B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationIn situ hybridisationStaining
This invention relates to methods of analyzing a tissue sample from a subject. In particular, the invention combines morphological staining and / or immunohistochemistry (IHC) with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) within the same section of a tissue sample. The analysis can be automated or manual. The invention also relates to kits for use in the above methods.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Blood test to monitor the genetic changes of progressive cancer using immunomagnetic enrichment and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
InactiveUS20080113350A1Accurate measurementEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadGenetic Change
Amplification and overexpression of theHER-2 oncogene in breast cancer is felt to be stable over the course of disease and concordant between the primary tumor and metastases. Therefore, patients with HER-2 negative primary tumors will rarely receive anti-HER-2 antibody therapy. A very sensitive blood test is used to capture circulating tumor cells (CTC's) and evaluate their HER-2 gene status by FISH evaluation. The HER-2 status of the primary tumor and corresponding CTC's is used to assess the ratio of CTC's as a reliable surrogate marker. HER-2 expression of 10 CTC's is sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of the HER-2 gene status for the whole population of CTC's in patients with recurrent breast cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Automated scanning method for pathology samples
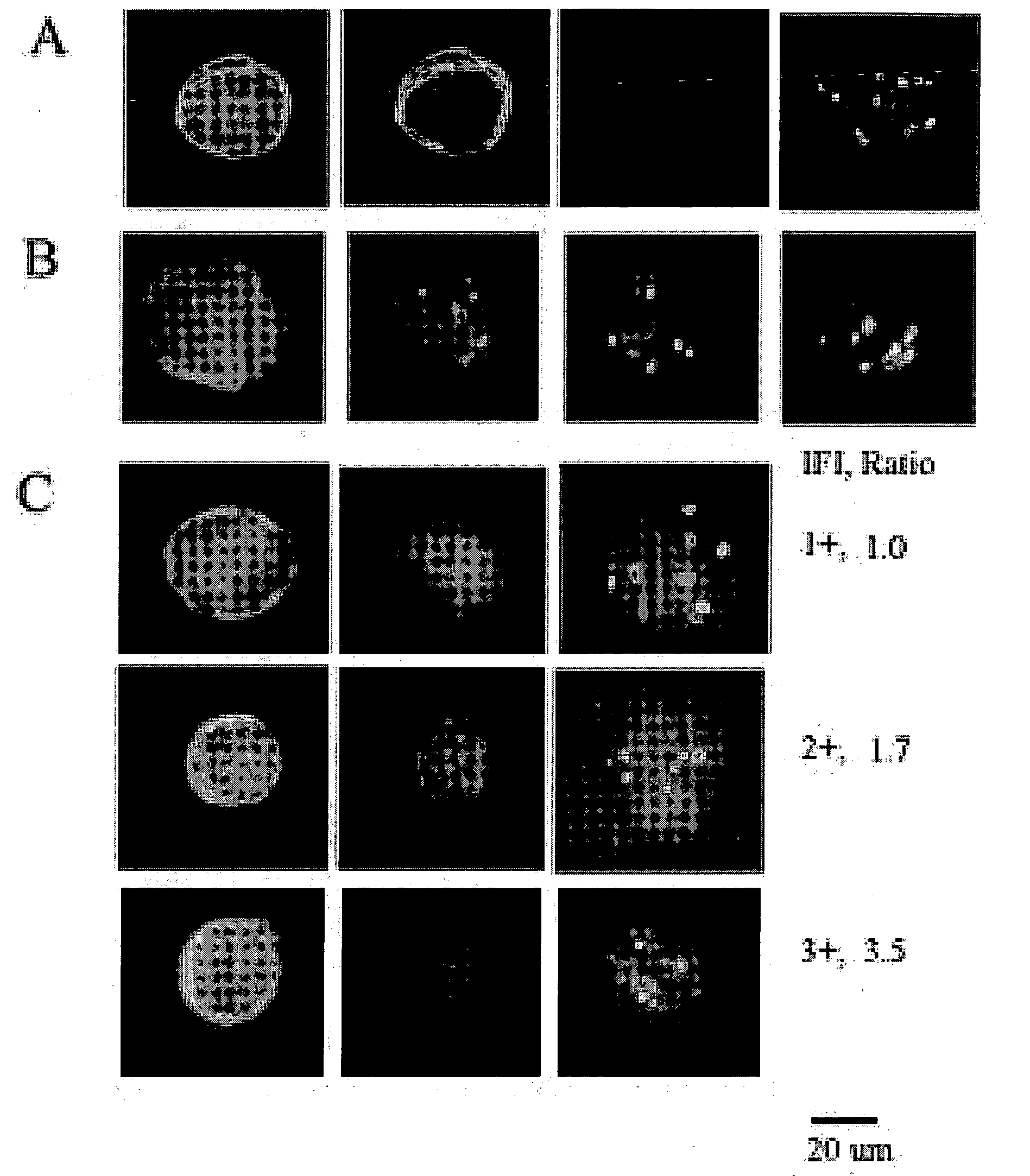
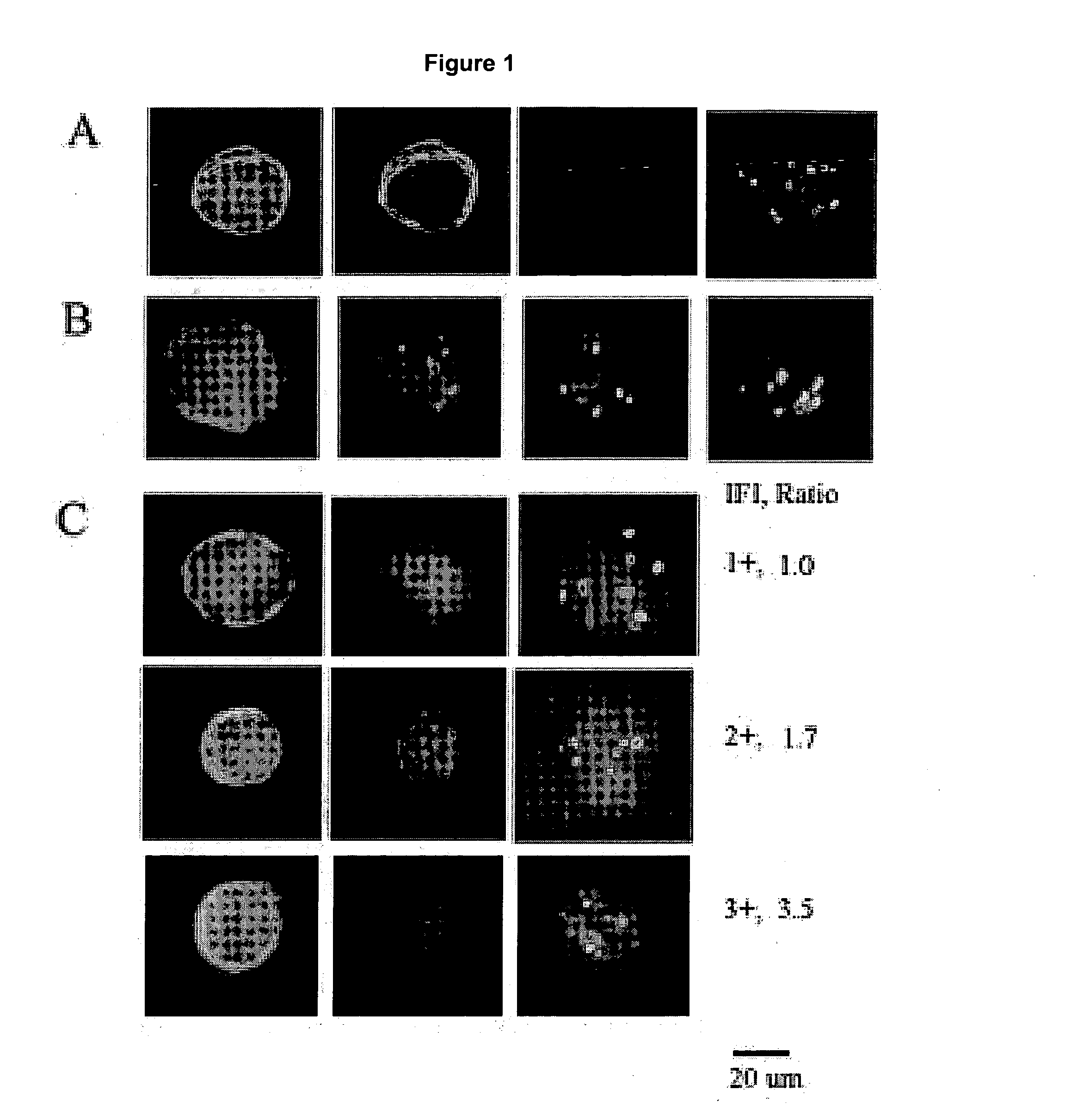
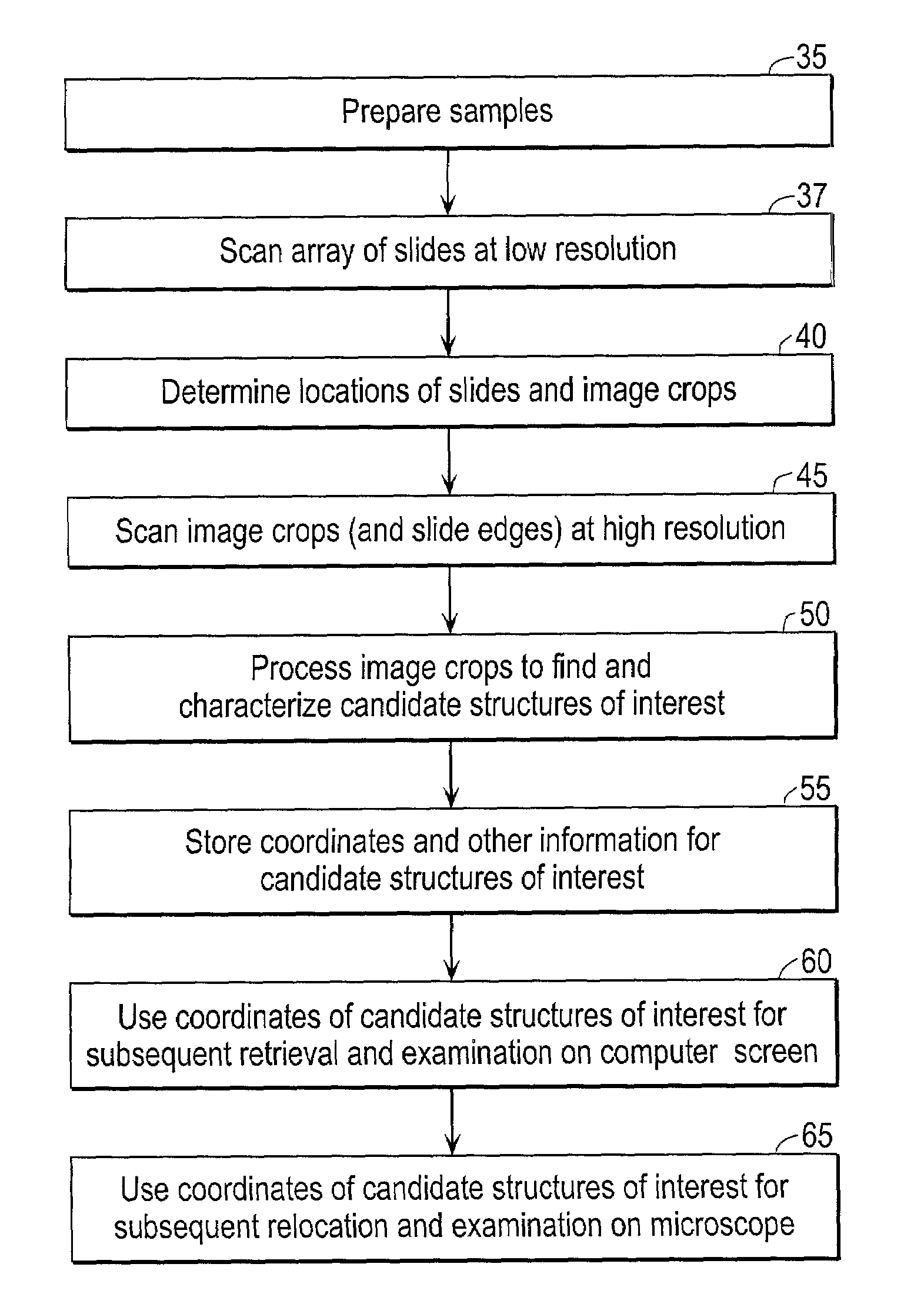
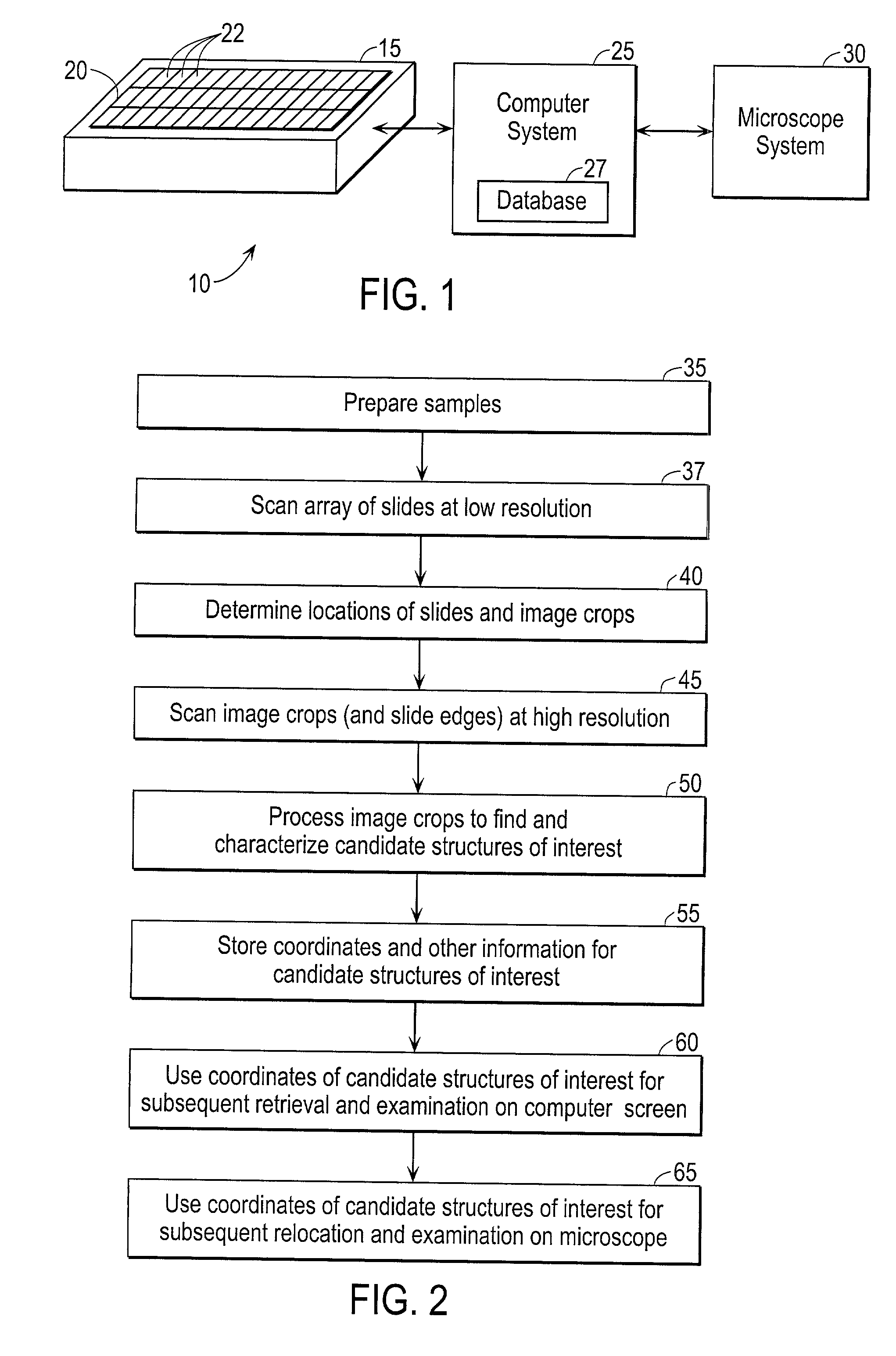
Scanning and analysis of cytology and histology samples uses a flatbed scanner to capture images of the structures of interest such as tumor cells in a manner that results in sufficient image resolution to allow for the analysis of such common pathology staining techniques as ICC (immunocytochemistry), IHC (immunohistochemistry) or in situ hybridization. Very large volumes of such material are scanned in order to identify cells or clusters of cells which are positive or warrant more detailed examination, and if analysis at higher resolution is necessary, information regarding these positive events is transferred to a secondary microscope, such as a conventional scanning microscope, to allow further analysis and review of the selected regions of the slide containing the sample.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Method and probes for the detection of chromosome aberrations
InactiveUS7105294B2Lower melting temperatureRaise the ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationHybridization probe
A novel method for detecting chromosome aberrations is disclosed. More specifically, chromosome aberrations are detected by in situ hybridisation using at least two sets of hybridisation probes, at least one set comprising one or more peptide nucleic acid probes capable of hybridising to specific nucleic acid sequences related to a potential aberration in a chromosome, and at least one set comprising two or more peptide nucleic acid probes capable of hybridising to specific nucleic acid sequences related to another potential aberration in a chromosome. In particular, the method may be used for detecting chromosome aberrations in the form of breakpoints.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Low temperature deparaffinization
InactiveUS20060252025A1Easy to explainImproving stainability and readabilityPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationCytochemistryBatch processing
Methods and apparatuses for gently removing embedding media from biological samples at temperatures below the embedding medium melting point with liquid composition using batch methods or automated instruments prior to immunohistochemical (IHC), in situ hybridization (ISH) or other special staining or histochemical or cytochemical manipulations.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
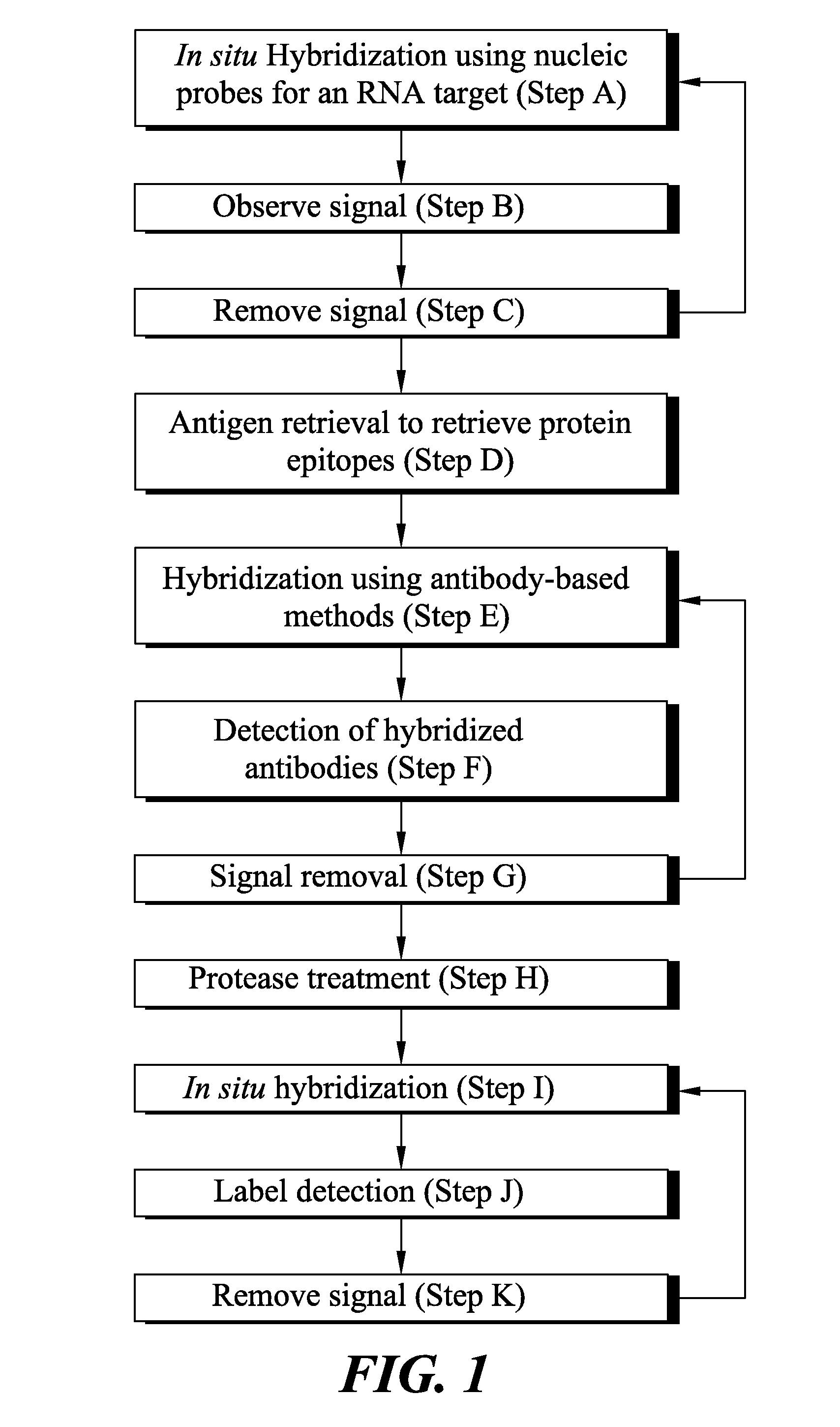
Methods of detecting dna, RNA and protein in biological samples
InactiveUS20140024024A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingIn situ hybridisationProteinase activity
Novel methods of probing multiple targets in a biological sample are provide whereby the targets are DNA, RNA and protein. The method comprises subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe that binds an RNA target, observing a signal, and optionally removing the signal. The method further comprises an antigen retrieval protocol, observing a signal, removing the signal, and optionally applying a protease treatment to access the sample's DNA targets by subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe, observing a signal from the labeled DNA targets, and optionally removing the signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Antibody conjugates
ActiveUS20090176253A1Easy to detectHigh activityHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
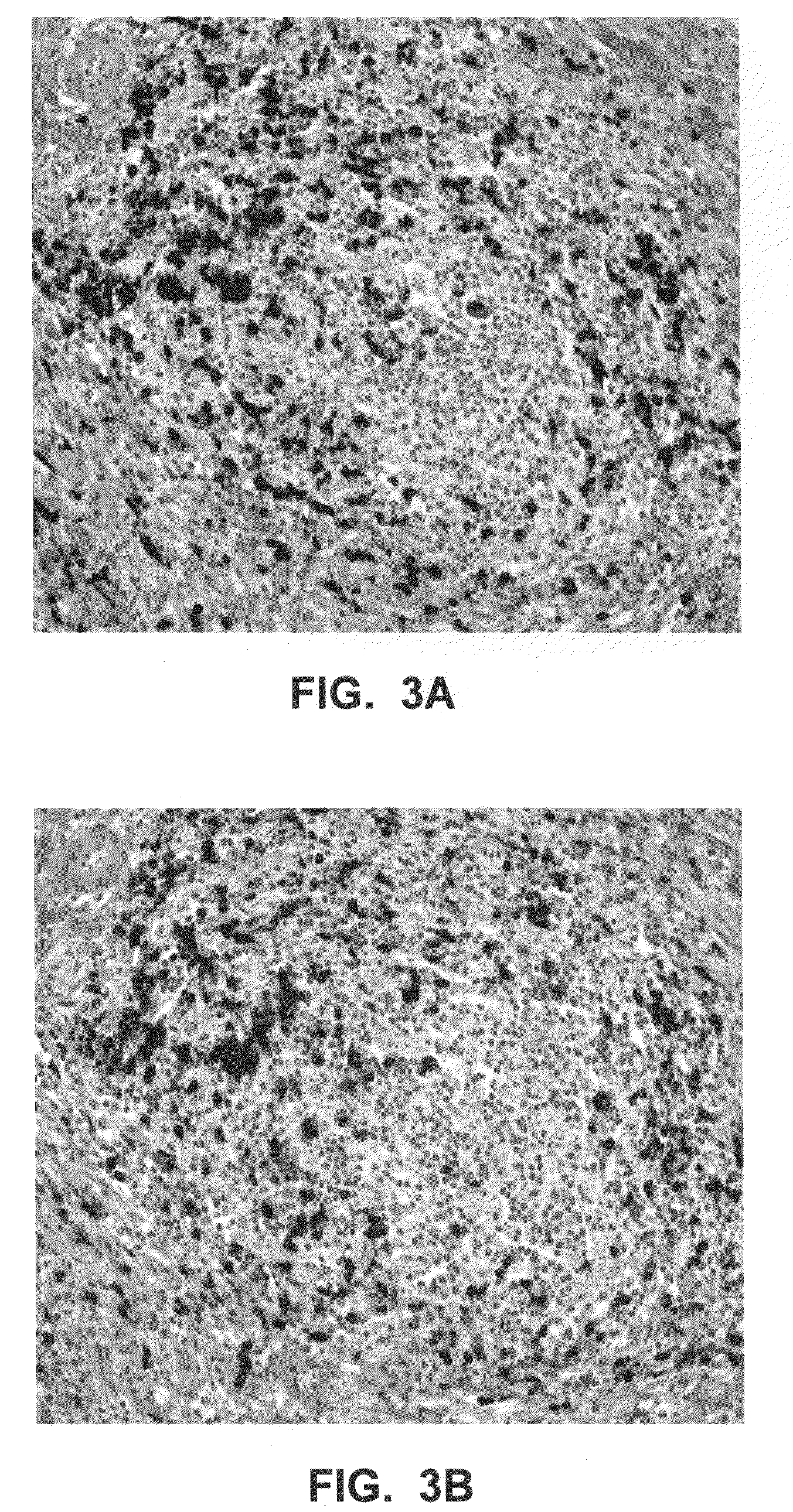
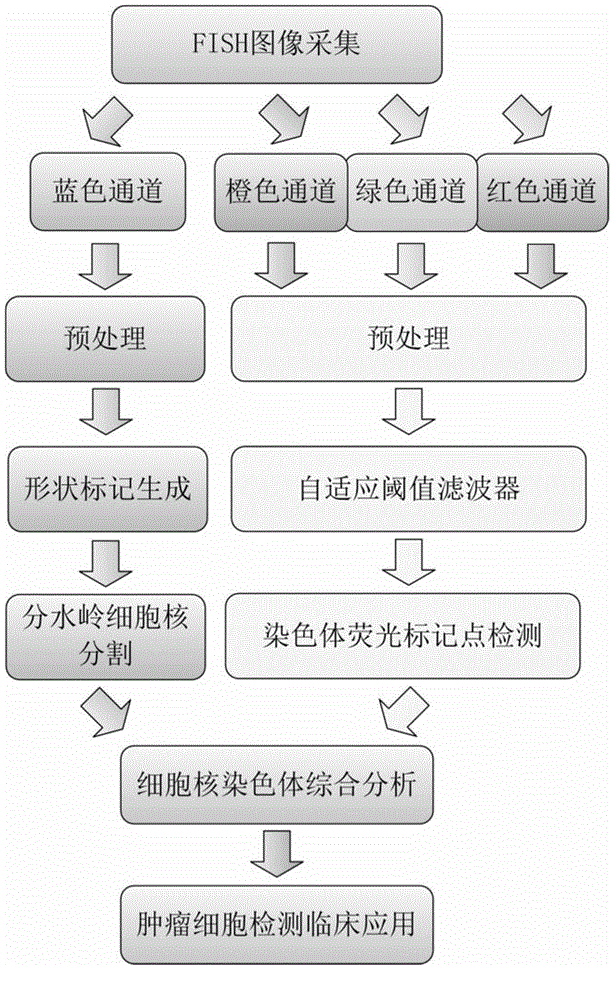
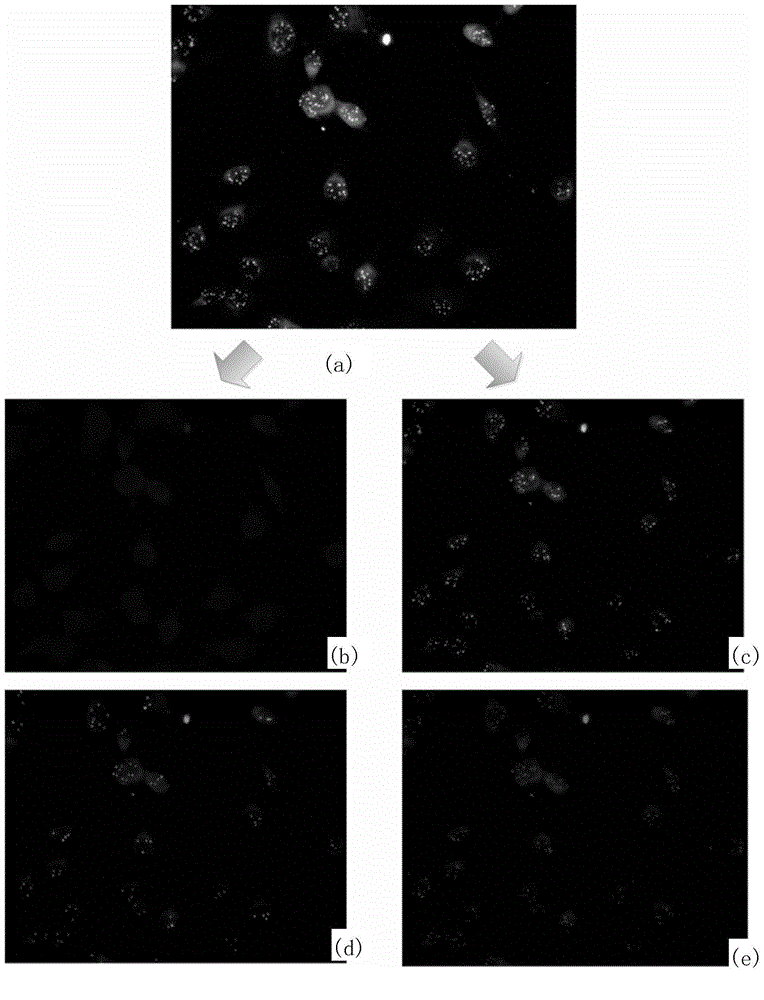
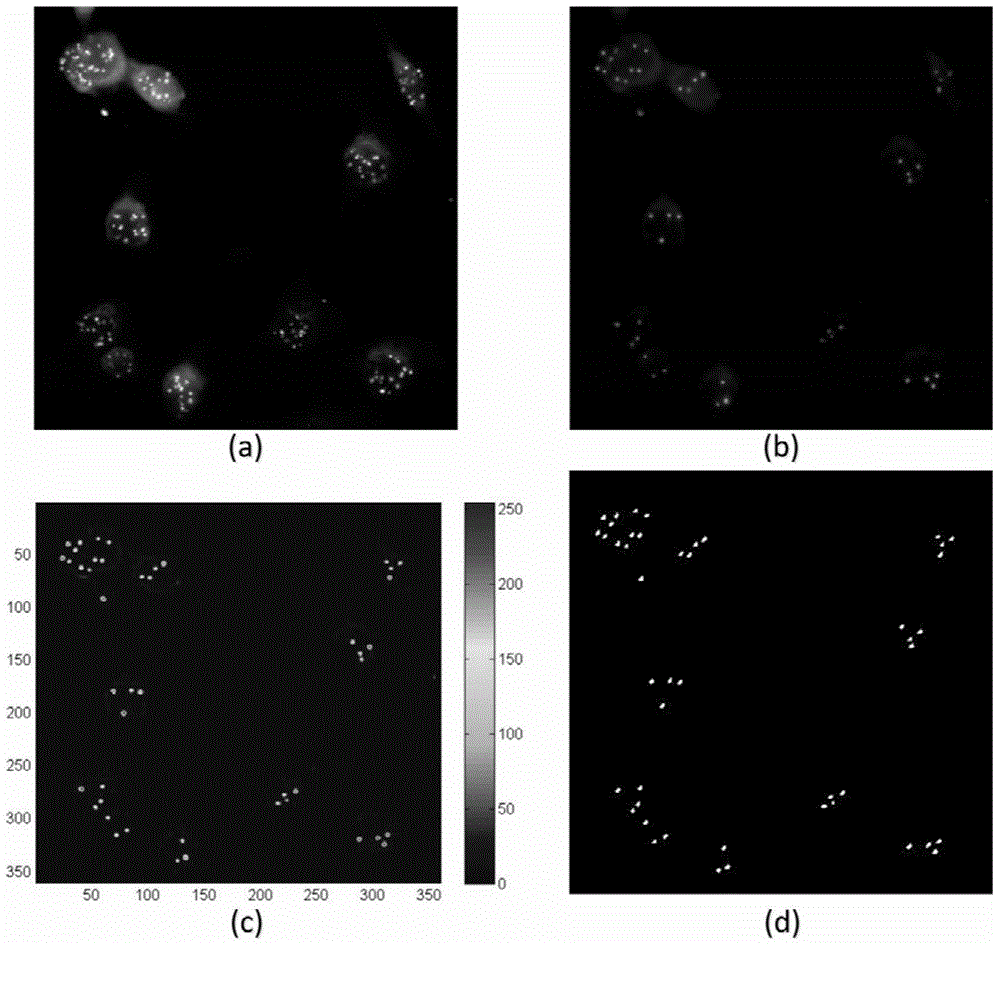
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image parallel processing and analysis method
ActiveCN106296635AReduce running timeImprove image processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceAlgorithm
The invention provides a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image parallel processing and analysis method. The method employs parallel processing, detection of chromosome fluorescent labeling points and edge detection and segmentation of nucleuses can be performed simultaneously, and the processing time is reduced; and a watershed algorithm based on adaptive shape labels is employed so that the segmentation precision of the adhered nucleuses in FISH images is substantially improved, the detection accuracy of relative positions of the nucleuses in tumor cells and the chromosome fluorescent label points is improved, and online real-time detection of the tumor cells can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN LUJIA BIOTECH
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
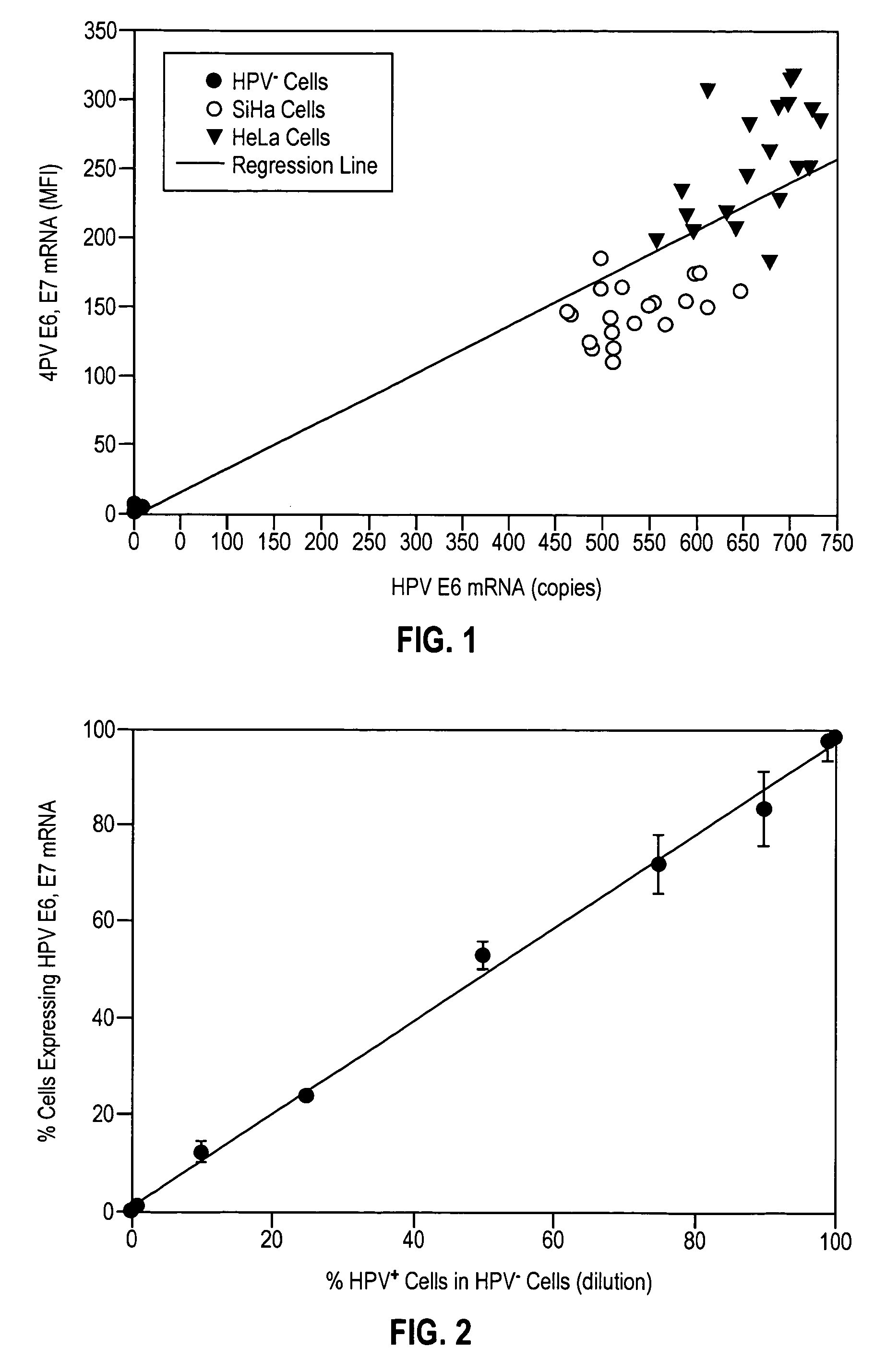
HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay and methods of use thereof
Provided is an HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay, referenced herein as the “In Cell HPV Assay,” that is capable of sensitive and specific detection of normal cervical cells undergoing malignant transformation as well as abnormal cervical cells with pre-malignant or malignant lesions. The In Cell HPV Assay identifies HPV E6, E7 mRNA via in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for HPV E6, E7 mRNA and quantitates the HPV E6, E7 mRNA via flow cytometry. The In Cell HPV Assay can be carried out in less than three hours directly from liquid-based cervical (“LBC”) cytology specimens. The In Cell HPV Assay provides an efficient and highly sensitive alternative to the Pap smear for determining abnormal cervical cytology.
Owner:INCELLDX
Methods for preparing and analyzing cells having chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20060257884A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescenceFluorescence in situ hybridization
The present invention provides methods for preparing cells with highly condensed chromosomes, such as sperm, and methods for detecting and quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. Specifically, methods are provided for detecting chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, in intact cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization of cells in suspension, such as sperm cells.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and application method thereof
ActiveCN103146693ADeep meaningFar-reaching promotionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExpression vectorRNA interference
The invention relates to a newly cloned full-length sequence of a long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and an application method thereof. The gene can be detected in a separation sample by methods including a hybrid method or an amplification method; and the gene can be used as a tumor marker, in particular a marker of liver cancer. According to the gene sequence, a real-time quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and an in situ hybridization probe are designed and synthesized; and by detecting the expression level of the long chain non-coding RNA in a liver cancer clinical case sample, expression of the long chain non-coding RNA in liver cancer is up-regulated remarkably, and prognosis of patients with liver caner with high expression of long chain non-coding RNA is poorer. According to the gene sequence, a RNA eukaryotic expression vector in a short hairpin structure for closing the expression of the long chain non-coding RNA by RNA interference is designed and synthesized; and the expression of the long chain non-coding RN in a liver cancer cell line A is inhibited successfully by using the vector.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of identifying cellular target molecules
InactiveUS20060246481A1Easy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionFlow cytometryIntact cell
The present invention provides methods of detecting and / or quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. The present invention further provides methods of processing an intact cell to facilitate in situ hybridization for use in flow cytometry.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Preparation method for probes related to breast cancer molecular markers and application of same
ActiveCN102399772AImprove the detection rateAccurate typingMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMortality rate
The invention relates to a preparation method for probes related to breast cancer molecular markers and to preparation of a breast cancer fluorescence in situ hybridization detection kit by using the probes. The breast cancer fluorescence in situ hybridization detection kit can be prepared from HER2, TOP2A and AGTR1 gene probes prepared by using the method provided in the invention, human chromosome 17 counting probe, hybridization buffer, unlabelled competitive DNA and DAPI counter strain; application of the kit enables the detection rate of breast cancers to be substantially improved and type sorting of breast cancers to be more accurate and provides guidance to formulation of an individual therapeutic schedule and selection of proper therapeutic drugs, thereby lowering down mortality, reducing recurrence risk and achieving the goal of optimizing the effect of diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
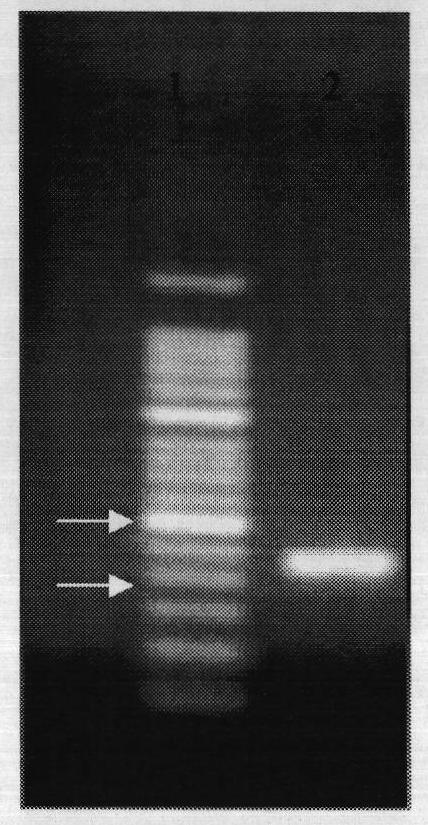
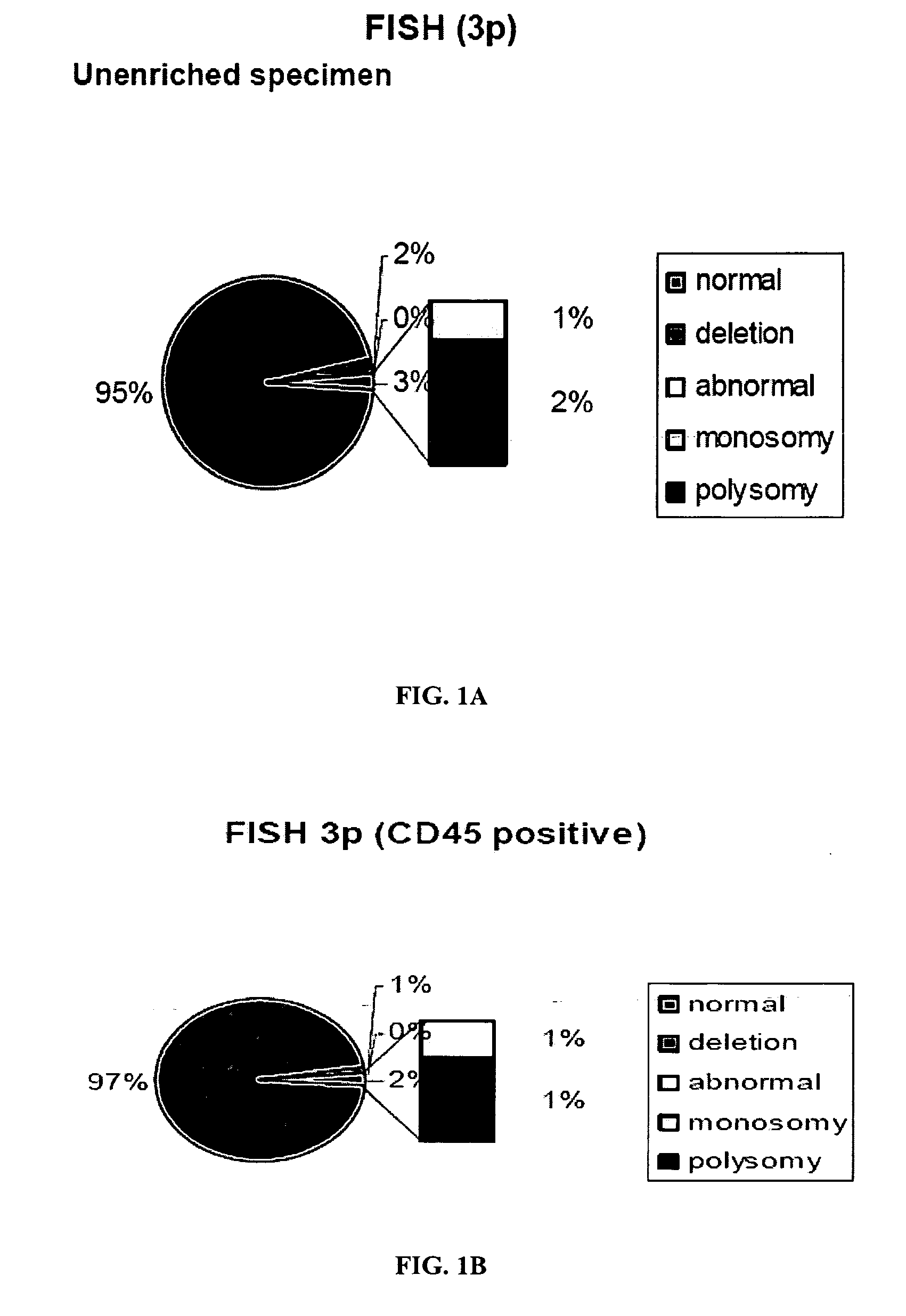
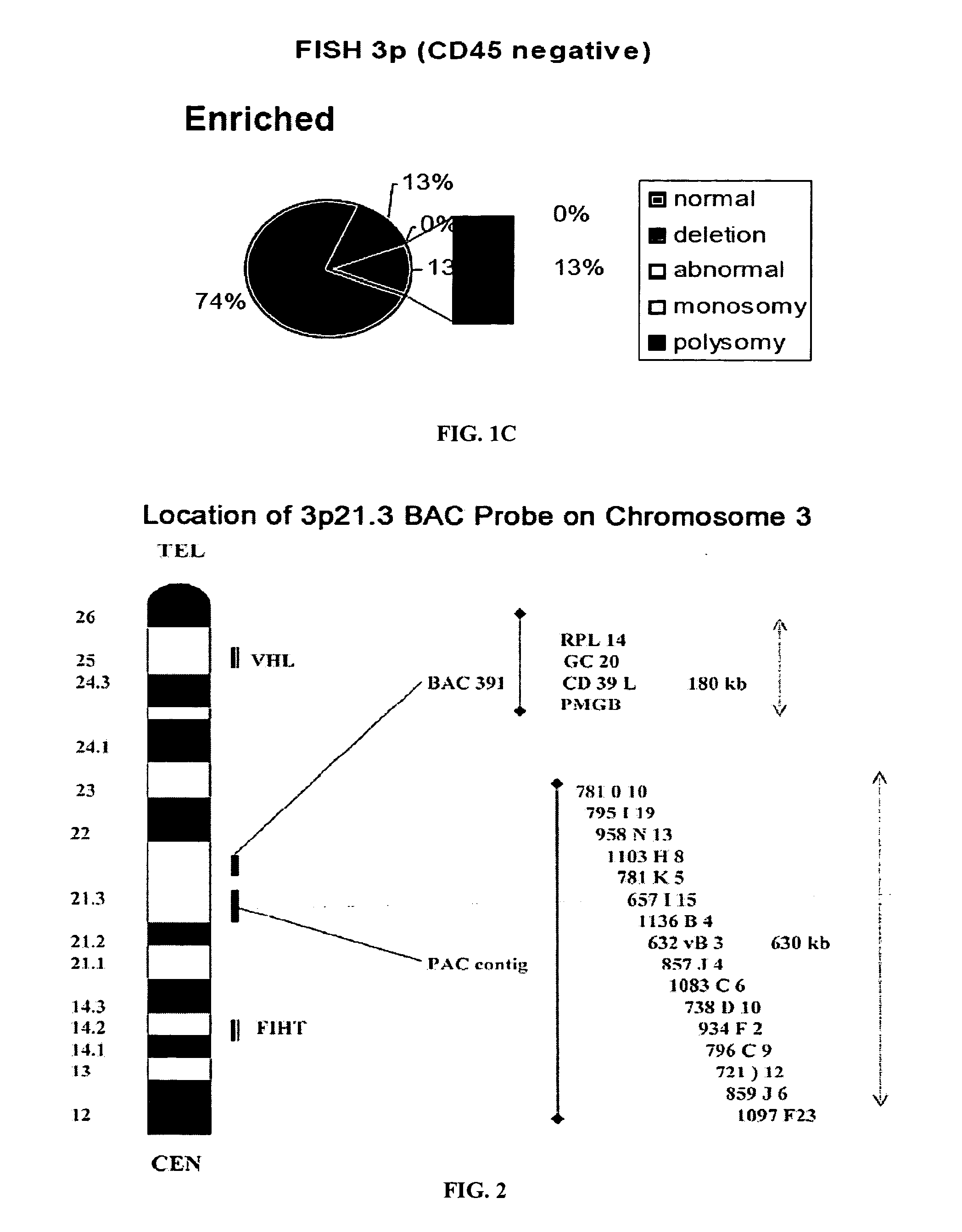
Circulating Tumor and Tumor Stem Cell Detection Using Genomic Specific Probes
InactiveUS20110189670A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisStainingFluorescence
The present invention comprises a method of detecting circular tumor cells and methods of detecting, evaluating, or staging cancer in a patient, as well as a method of monitoring treatment of cancer in a patient using the claimed method. The method comprises contacting a sample with a CD45 binding agent; selecting the cells based on positive or negative CD45 staining; contacting the selected cells with a labeled nucleic acid probe, and detecting hybridized cells by fluorescence in situ hybridization; and analyzing a signal produced by the labels on the hybridized cells to detect the CTCs. In other embodiments, the method provides for directed to a method of determining the level of CTCs in a sample having blood cells from a patient by contacting a sample having blood cells from a patient, wherein the sample has not been pre-sorted into CD45-positive and CD45-negative cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for chromogenic detection of two or more target molecules in a single sample
ActiveUS20110136130A1Low backgroundReduce and preventMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSingle sampleTissue sample
The present invention provides a method and kit for detection of two or more target molecules in a single tissue sample, such as for gene and protein dual detection in a single tissue sample. Methods comprise treating a tissue sample with a first binding moiety that specifically binds a first target molecule. Methods further comprise treating the tissue sample with a solution containing a soluble electron-rich aromatic compound prior to or concomitantly with contacting the tissue sample with a hapten-labeled binding moiety and detecting a second target molecule. In one example, the first target molecule is a protein and the second is a nucleic acid sequence, the first target molecule being detected by immunohistochemistry and the second by in situ hybridization. The disclosed method reduces background due to non-specific binding of the hapten-labeled specific binding moiety to an insoluble electron rich compound deposited near the first target molecule.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
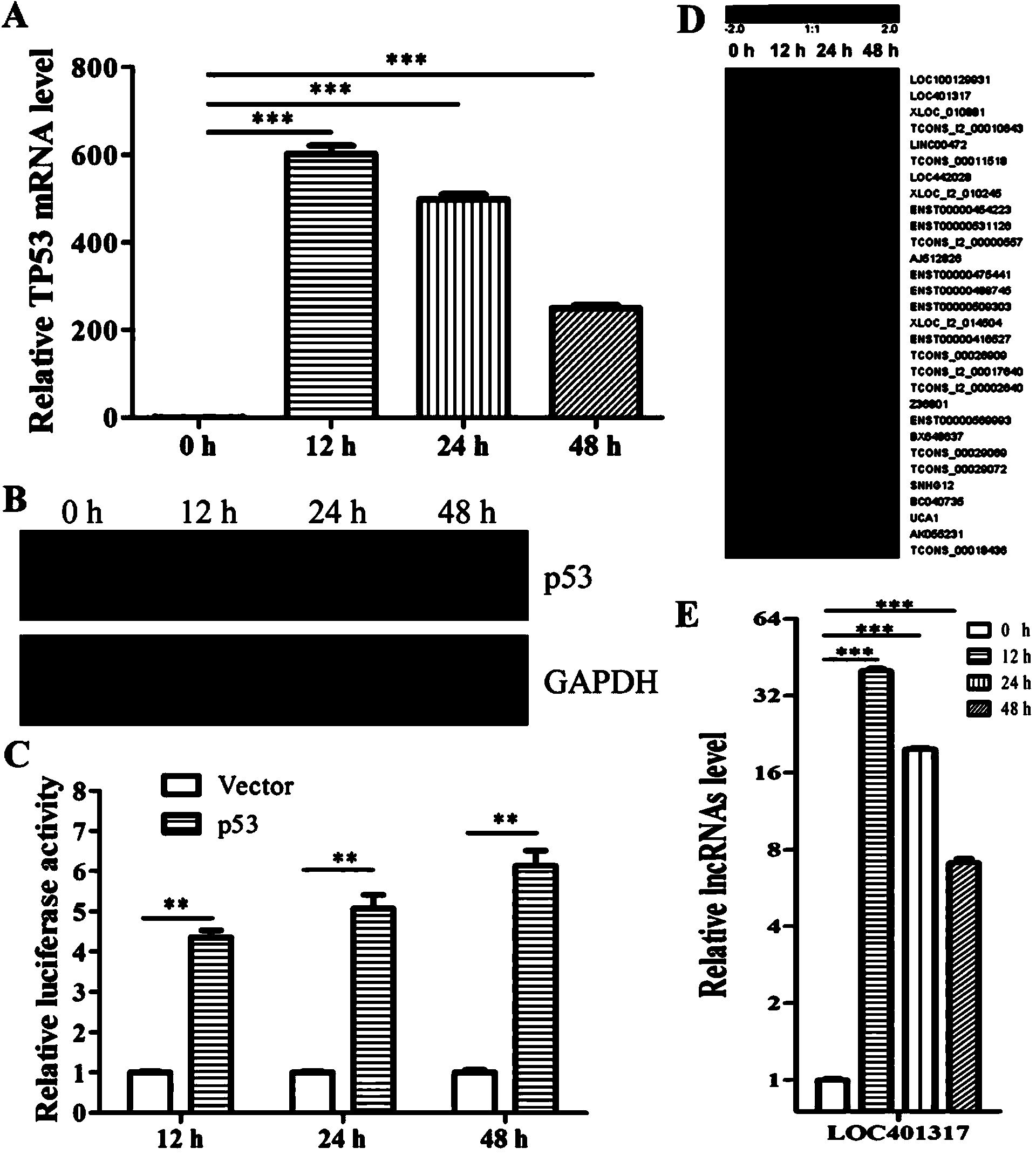
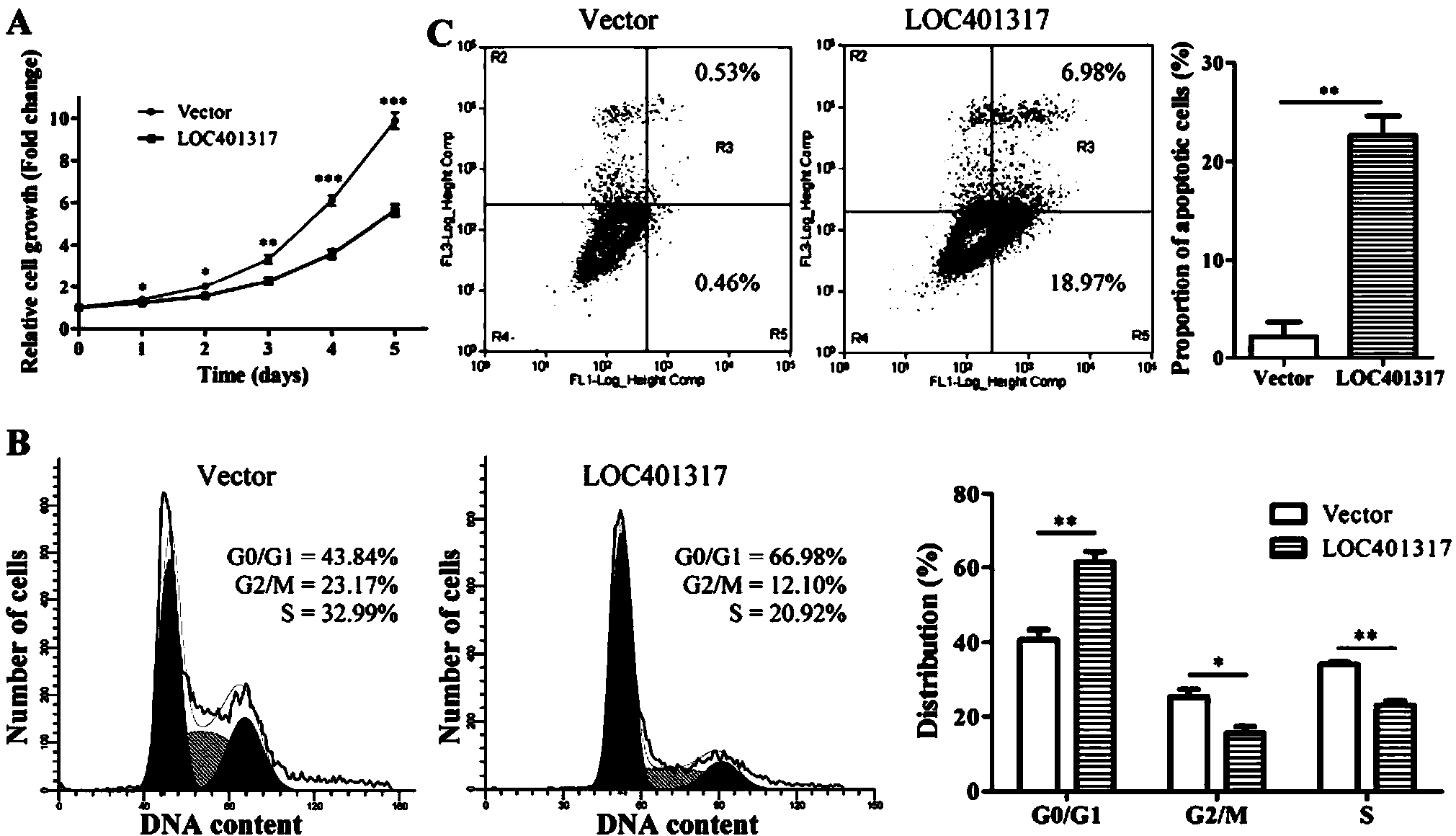
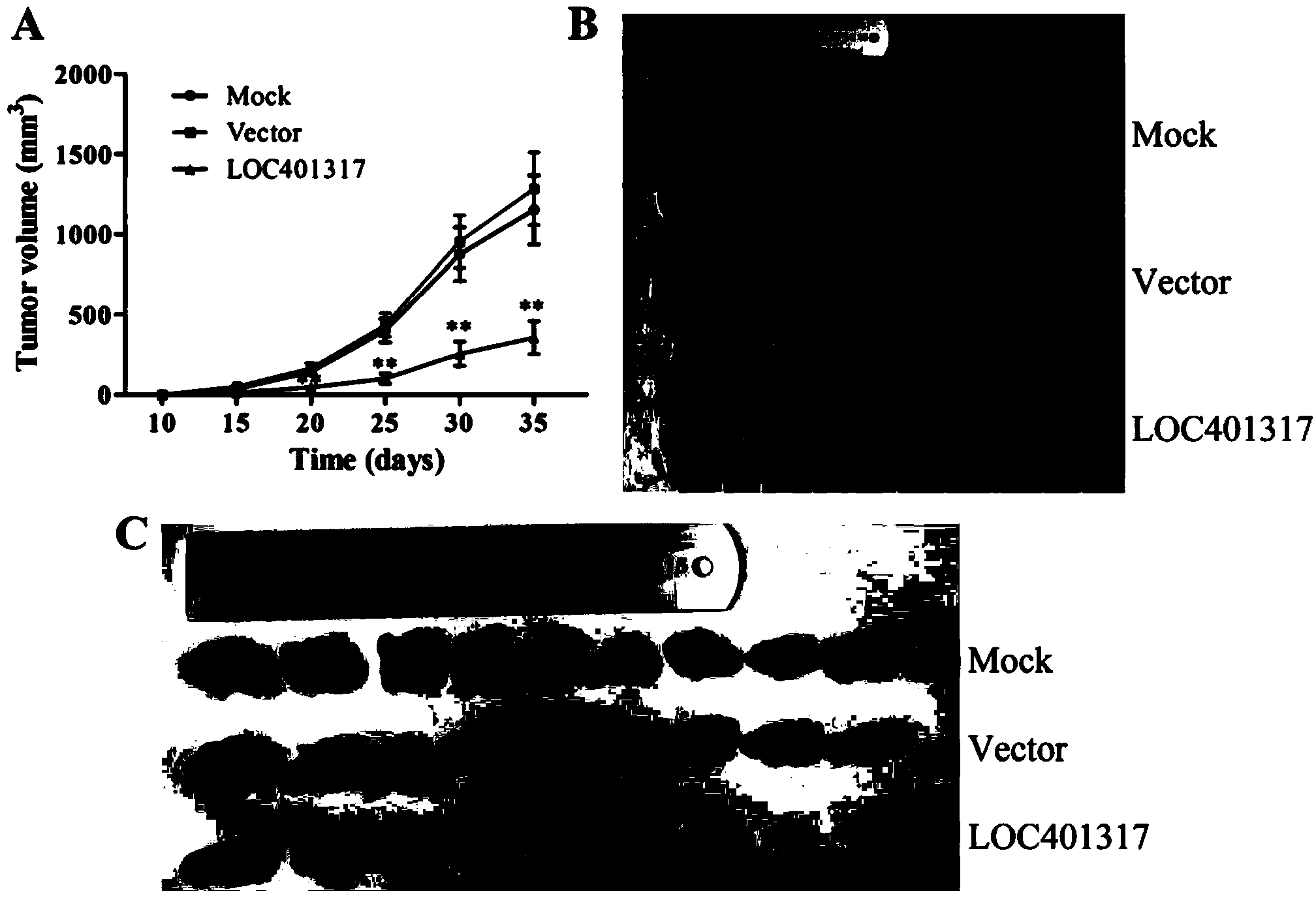
In situ hybridization probe, reagent and application of long non-coding RNA LOC401317
ActiveCN104388543ADyingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIn situ hybridisationHybridization probe
The invention discloses an in situ hybridization probe, a reagent and an application of long non-coding RNA LOC401317. The long non-coding RNA LOC401317 can be used for preparing a prognosis preparation for a patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and particularly a kit for predicting prognosis of the patient with the nasopharyngeal carcinoma employing an in situ hybridization detection method is prepared. A research proves that expression of the LOC401317 in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissue is lowered, and the patient with the nasopharyngeal carcinoma in low-expression LOC401317 is worse than the patient with the nasopharyngeal carcinoma in high-expression LOC401317 in prognosis, therefore, expression of the LOC401317 is applied to prognosis prediction of the patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma; a powerful molecular biology basis can be provided for prognosis of the patient with the nasopharyngeal carcinoma; and the long non-coding RNA LOC401317 has profound clinical significance and important popularization and application prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for specific fast detection of relevant bacteria in drinking water
InactiveUS20050064444A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria in drinking water and surface water, especially a method for simultaneous specific detection of bacteria from the Legionella species and the Legionella pneumophila species by in situ hybridization. The invention also relates to a method for specific detection of faecal streptococci by in situ-hybridization and a method for simultaneous specific detection of coliform bacteria and bacteria of the Escherichia coli species, in addition to corresponding oligonucleotide probes and kits enabling said inventive method to be carried out.
Owner:VERMICON
Tissue chip used for tumour early stage diagnosis and preparation device
Three kinds of tissues including cancer tissue, precancerosis and corresponding normal tissue are sliced up, dyed, marked, and positioned. Receptor holes are prepared by leading designed lattice array mould paper to paste on surface of wax block of receptor. Wax block with tissue core bar is prepared by using perforating needle and puncture needle for tissue. Common cancer such as lung cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, oesophagus cancer etc. and having integrated clinical data and pathology features are selected. Through in situ hybridization, testing mRNA of relevant gene and expression of protein on tissue chip, consistent result between the invented product and traditional test is validated. In the product, cellular morphology is clear and even, and there is no fallen off tissue point. The invention is applicable to filter cancers, early diagnosis and forecasting prognosis.
Owner:中南大学湘雅医学院肿瘤研究所
Methods and compounds for detection of molecular targets
ActiveUS8435735B2Faster and more sensitive and precise detectionEasy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationChemical compound
The present invention relates to methods and compounds for detection of molecular targets, such as biological or chemical molecules, or molecular structures, in samples using a host of experimental schemes for detecting and visualizing such targets, e.g. immunohistochemistry (IHC), in situ hybridization (ISH), ELISA, Southern, Northern, and Western blotting, etc.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
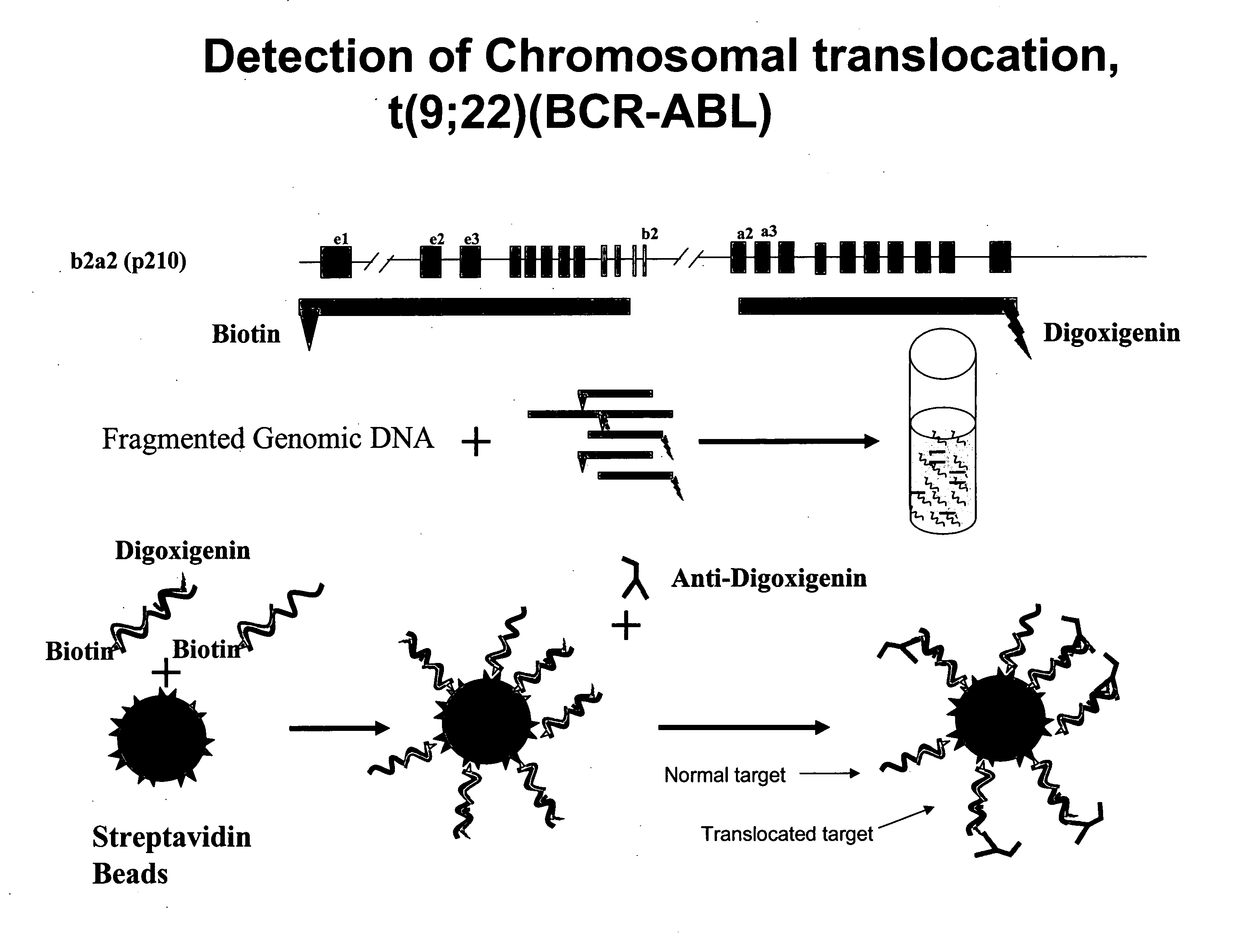
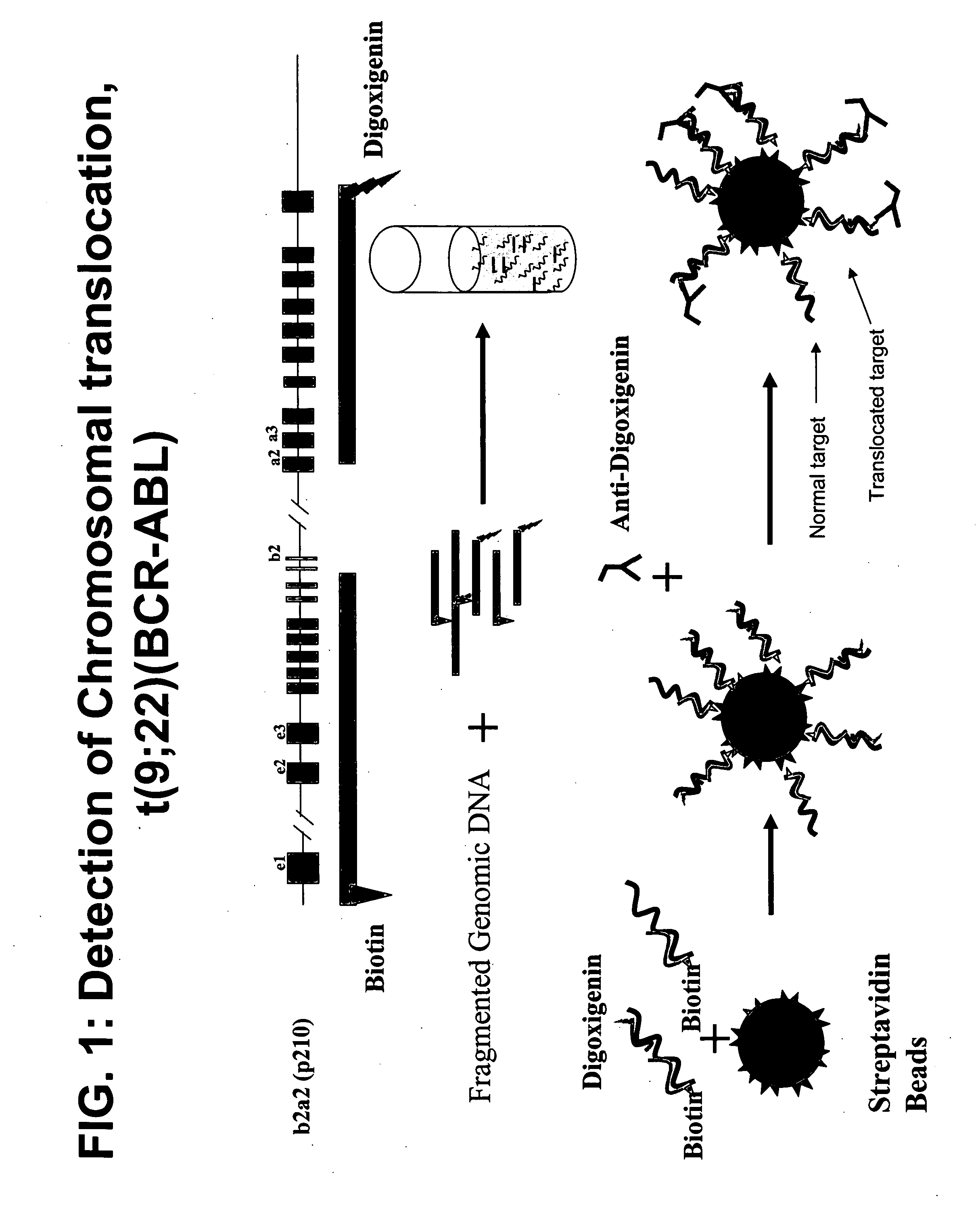
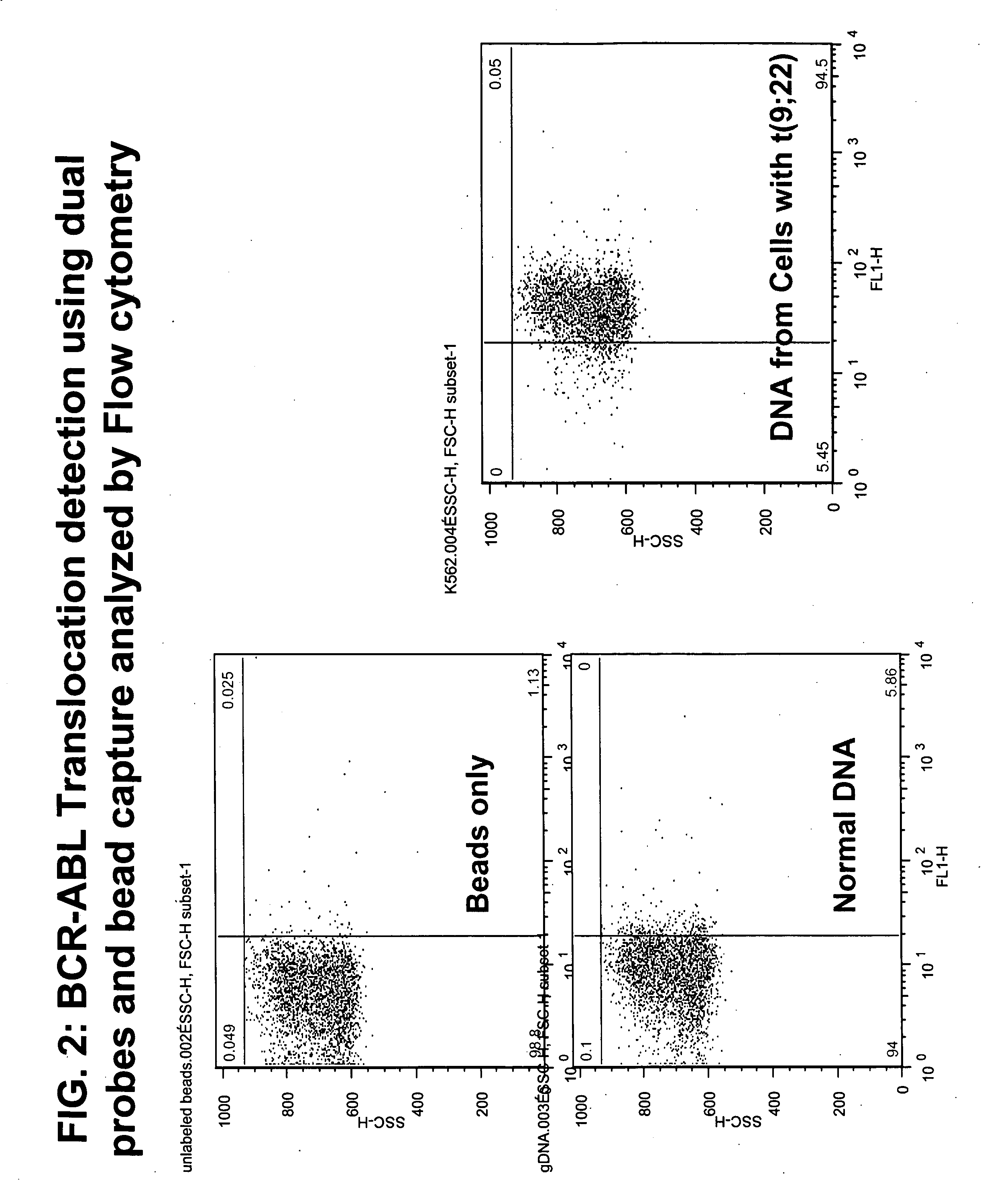
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, kit and detection method for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence
InactiveCN103409505AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, a kit and a detection method for detecting BCR / ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence. A BCR gene and ABL gene are used as templates to perform polymerase chain reaction on non-repetitive sequence in the BCR gene and ABL gene, the amplification product is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments with 350-800 different base-pairs, the repetitive sequences in the BCR gene and ABL gene are eliminated so as to form the product free from repetitive sequence; after the product is in fluorescence labeling, the BCR gene and ABL gene free from repetitive FISH are obtained for the BCR gene and ABL gene FISH detection. The BCR / ABL fusion gene FISH probe obtained by the invention can be used for eliminating the repetitive sequence, the non-specific background signal of the FISH probe can be obviously reduced, and the specificity of the FISH probe is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation method for gill tissue paraffin section
InactiveCN103940648AImprove the effect of dipping waxFull penetrationPreparing sample for investigationAntigenIn situ hybridisation
The invention discloses a preparation method for a gill tissue paraffin section. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fixing, decalcifying, dehydrating, transparentizing, carrying out paraffin permeation, embedding, slicing, sticking sections, expanding the sections, de-waxing and rehydrating, staining, re-staining, sealing and the like. Compared with an existing paraffin section manufacturing method, an operation process of dehydrating, transparentizing and immersing by wax is improved; the preparation fixing and tissue wax immersing effects of gill tissue paraffin are improved; a slicing problem when the gill tissue paraffin section is prepared is improved; the structure definition of the gill tissue section is greatly improved; a plurality of problems in a gill tissue manufacturing process in the prior art are solved. The preparation method is good for antigen positioning of immunocytochemical staining, so that when experiments including in-situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and the like are carried out on the gill tissue paraffin section, tissue distribution and cell positioning of some genes and proteins can be displayed, and further feasible conditions are provided for carrying out gill research on levels of cells, genes and proteins.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
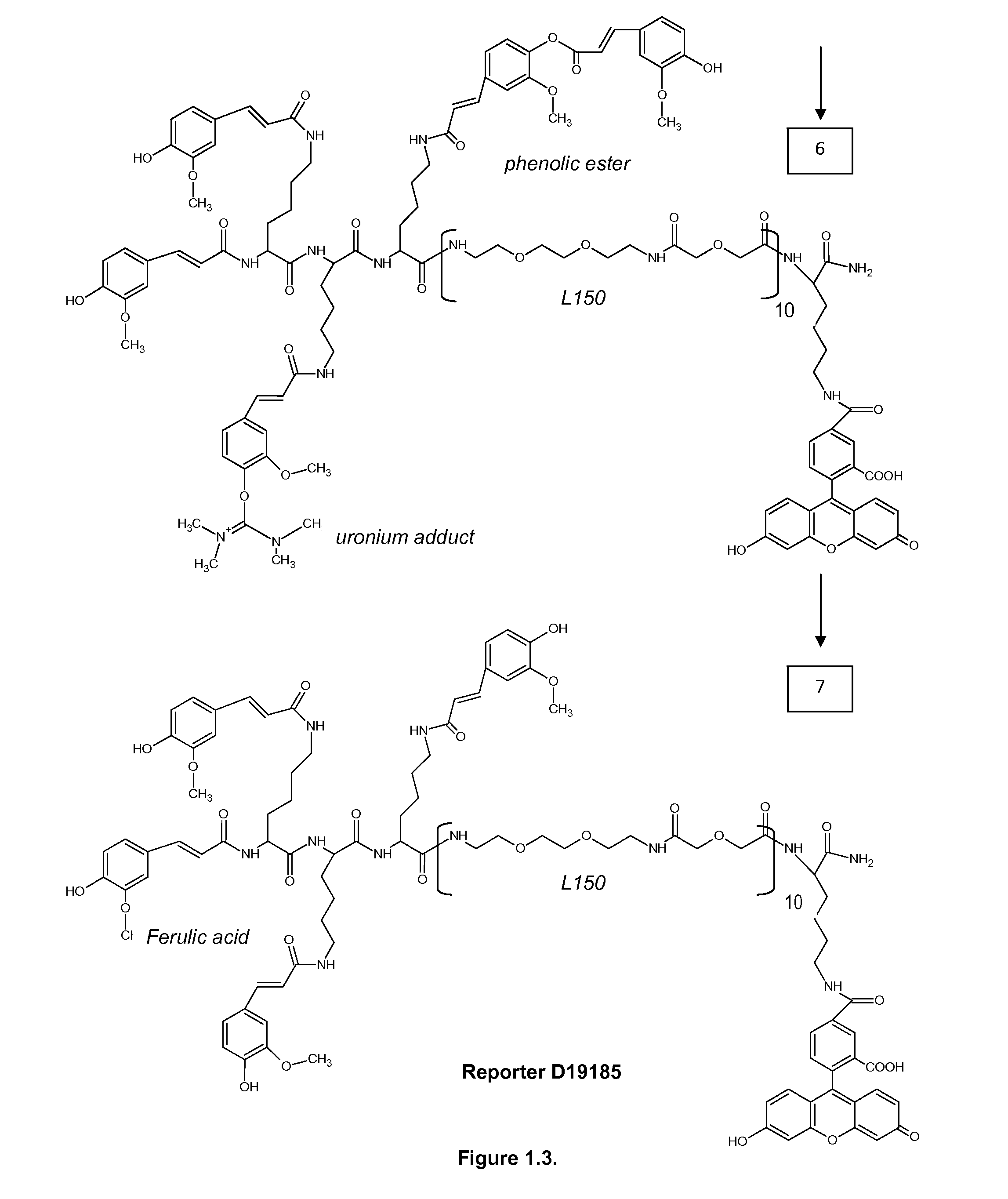
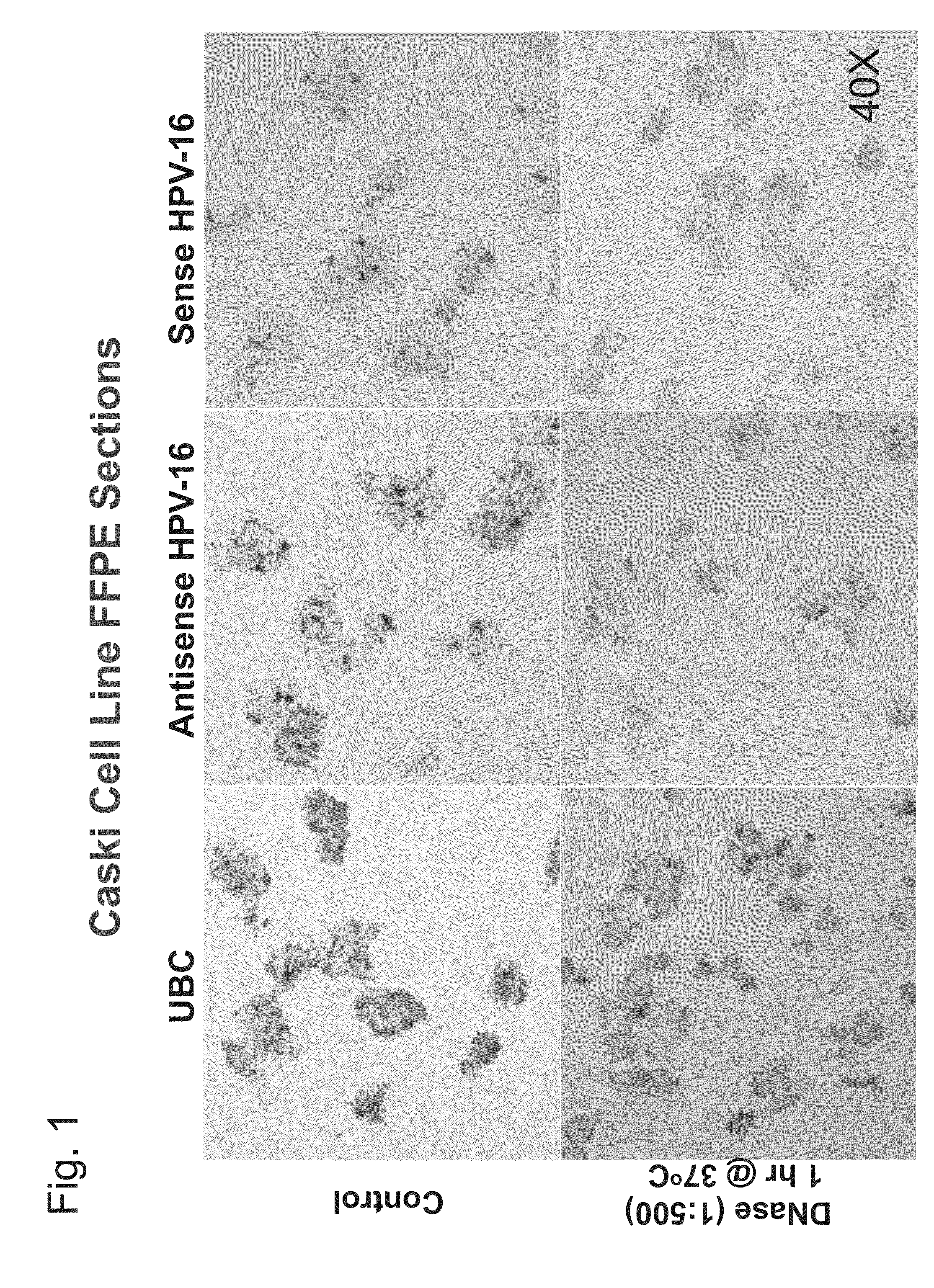
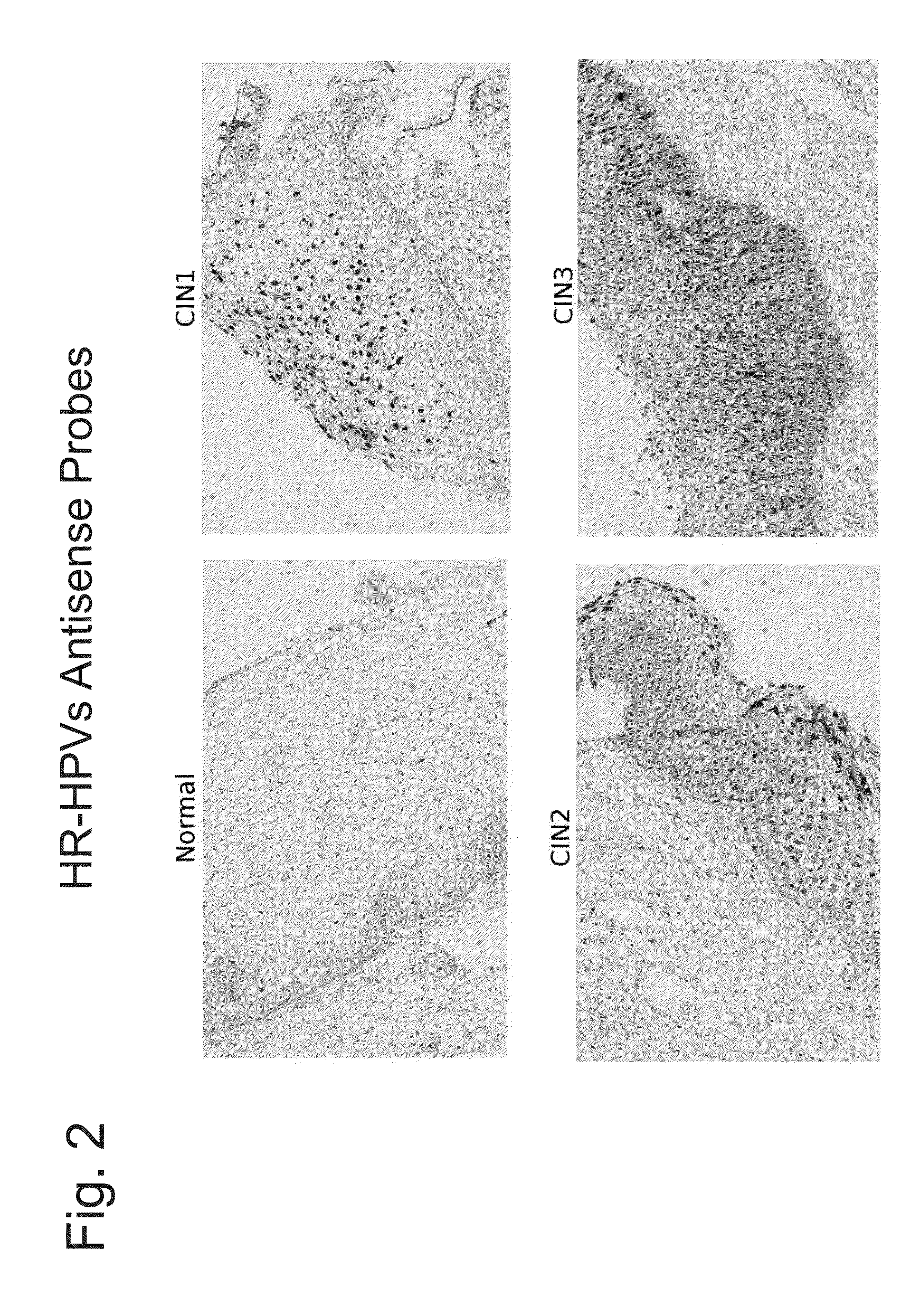
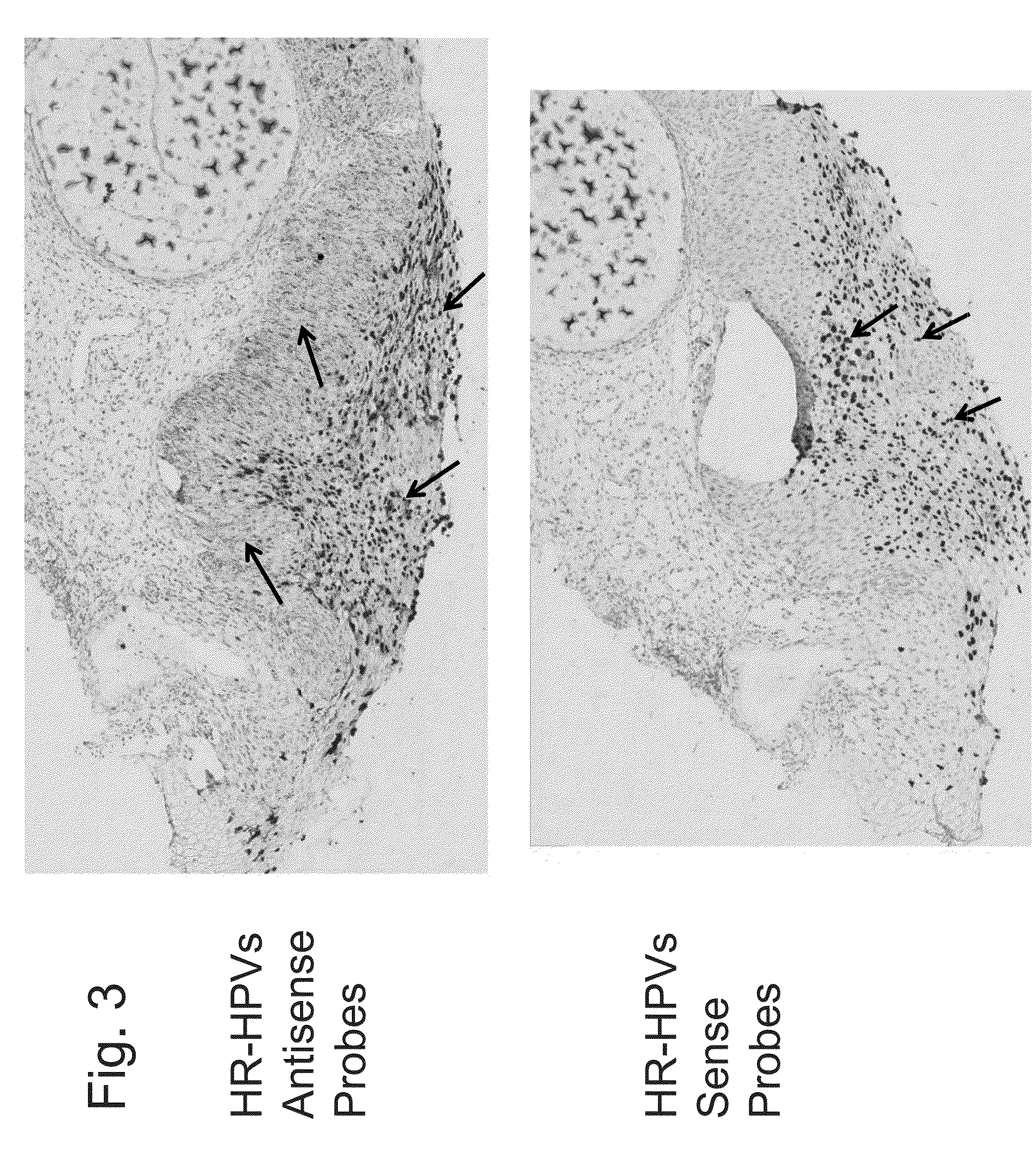
Differentiation between transient and persistent high-risk HPV infection by in situ hybridization
InactiveUS20140357509A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningIn situ hybridisationCervical tissue
The invention relates to methods of categorizing a cervical tissue or cytology sample by performing an in situ hybridization assay using an antisense E6 or E7 probe on a cervical tissue sample, wherein the antisense E6 or E7 probe can simultaneously detect HPV DNA and HPV RNA; detecting the presence of HPV nucleic acid; and categorizing the cervical tissue sample based on HPV nucleic acid expression.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com