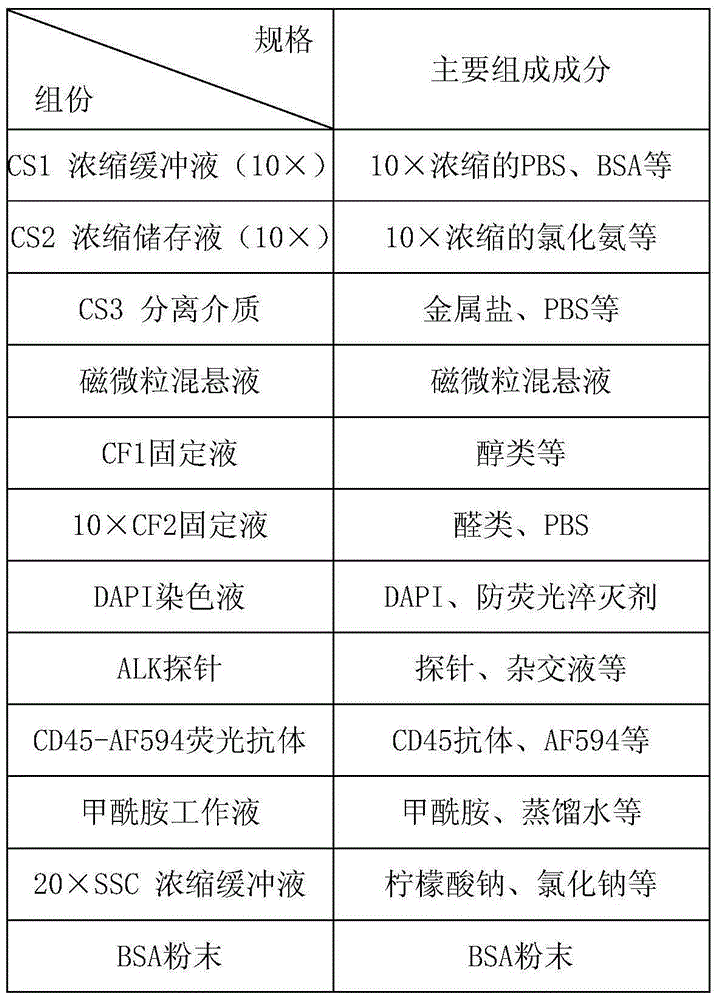
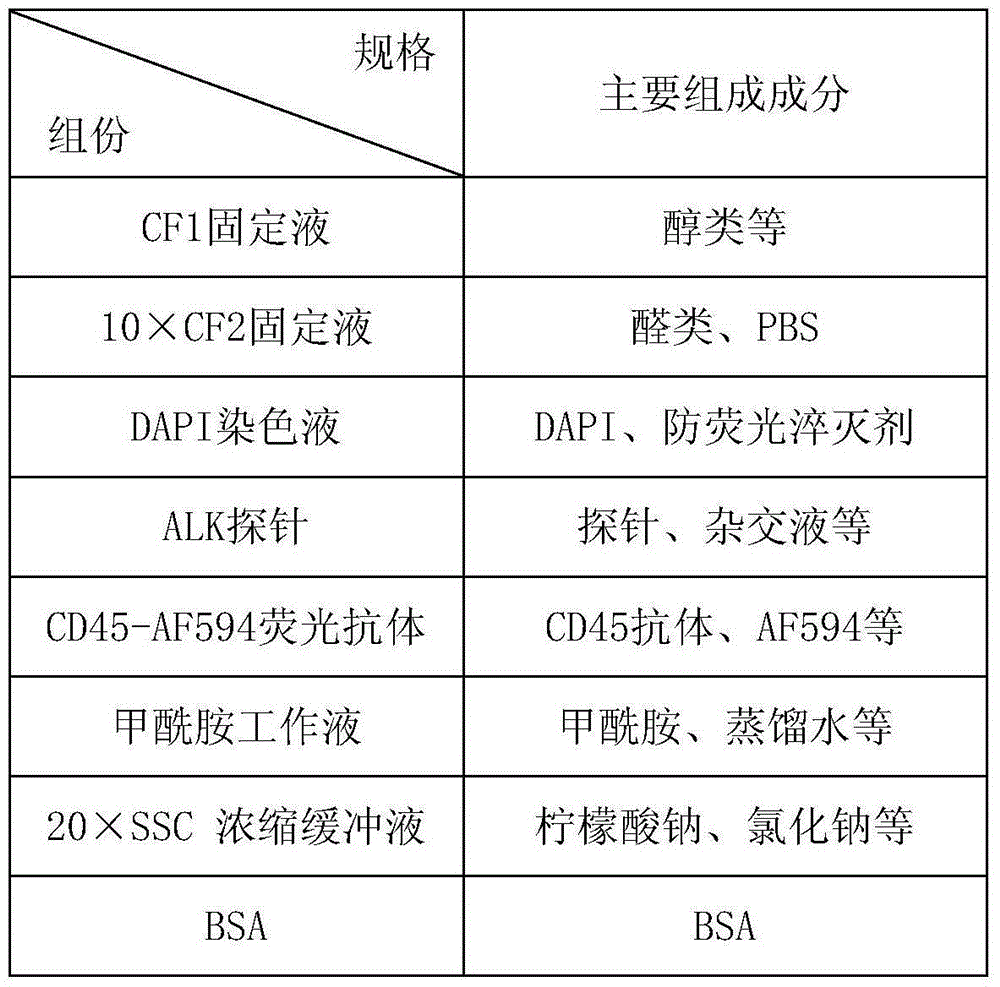
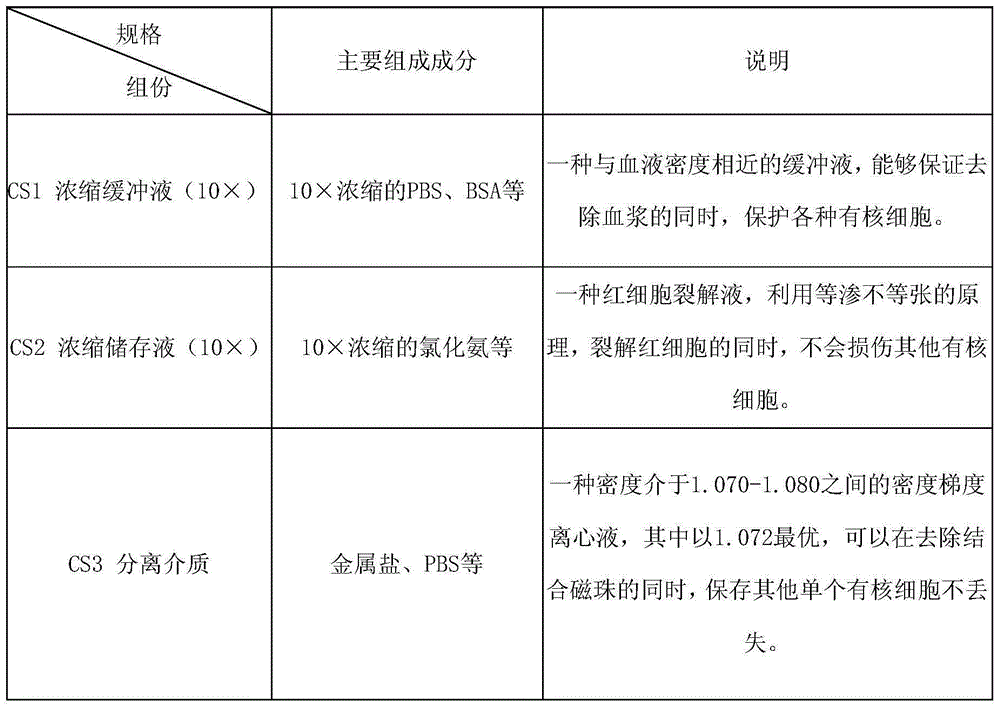
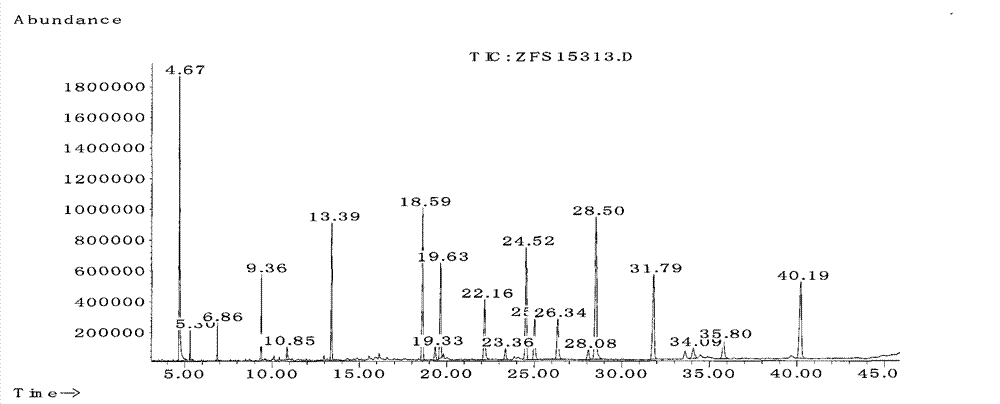
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Cytochemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytochemistry is the biochemistry of cells, especially that of the macromolecules responsible for cell structure and function. The term is also used to describe a process of identification of the biochemical content of cells. Cytochemistry is a science of localizing chemical components of cells and cell organelles on thin histological sections by using several techniques like enzyme localization, micro-incineration, micro-spectrophotometry, radioautography, cryo-electron microscopy, X-ray microanalysis by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, immunohistochemistry and cytochemistry, etc.
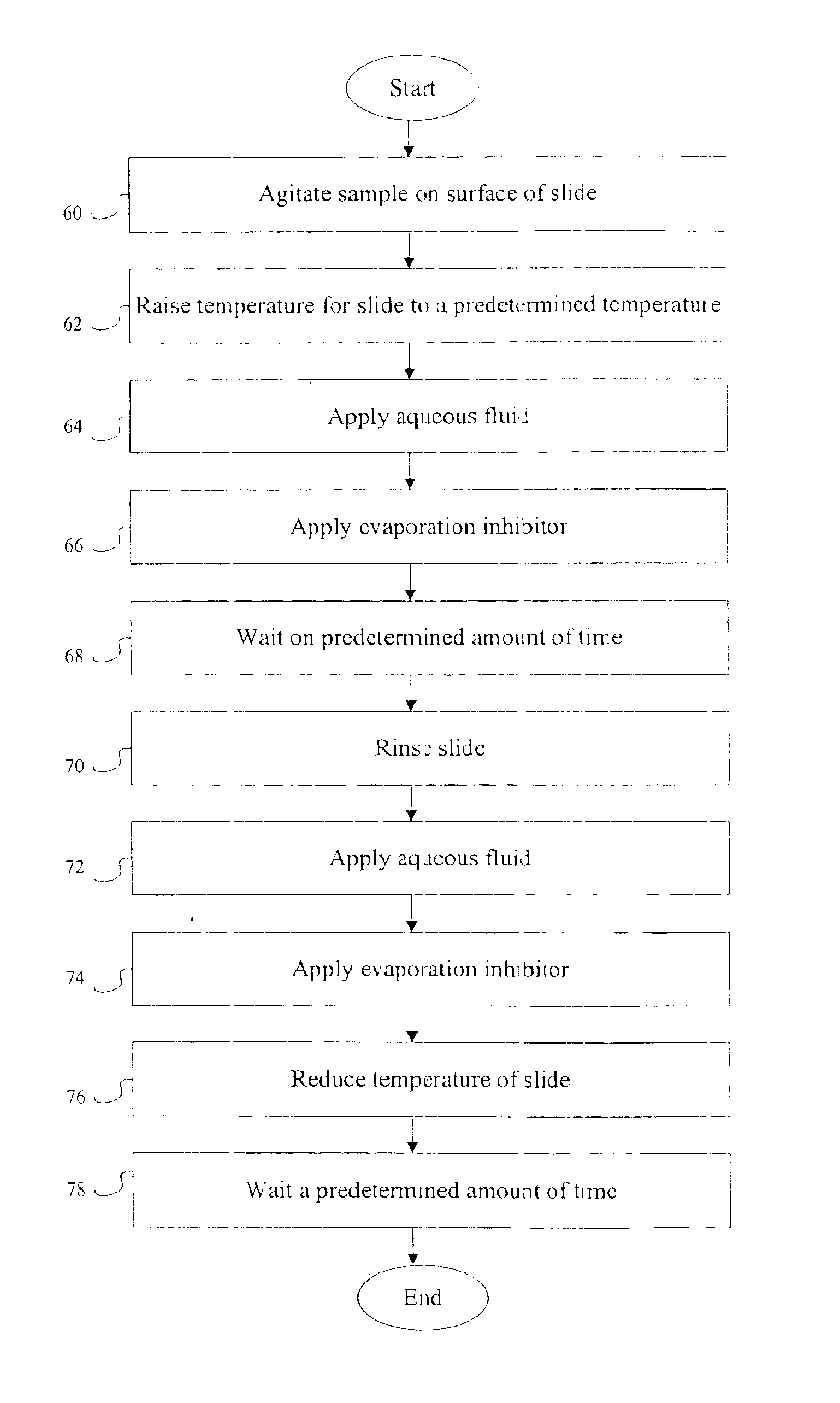
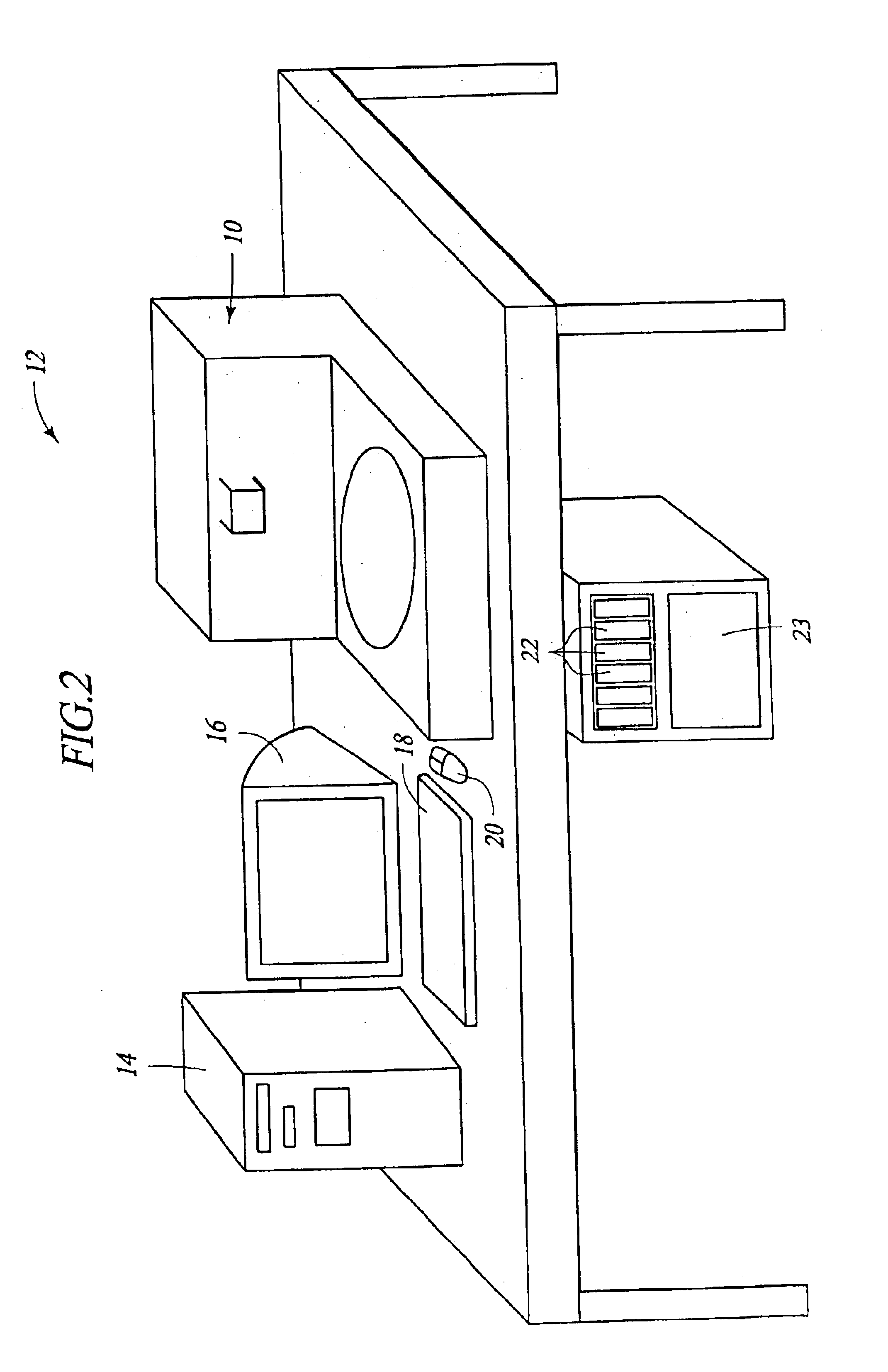
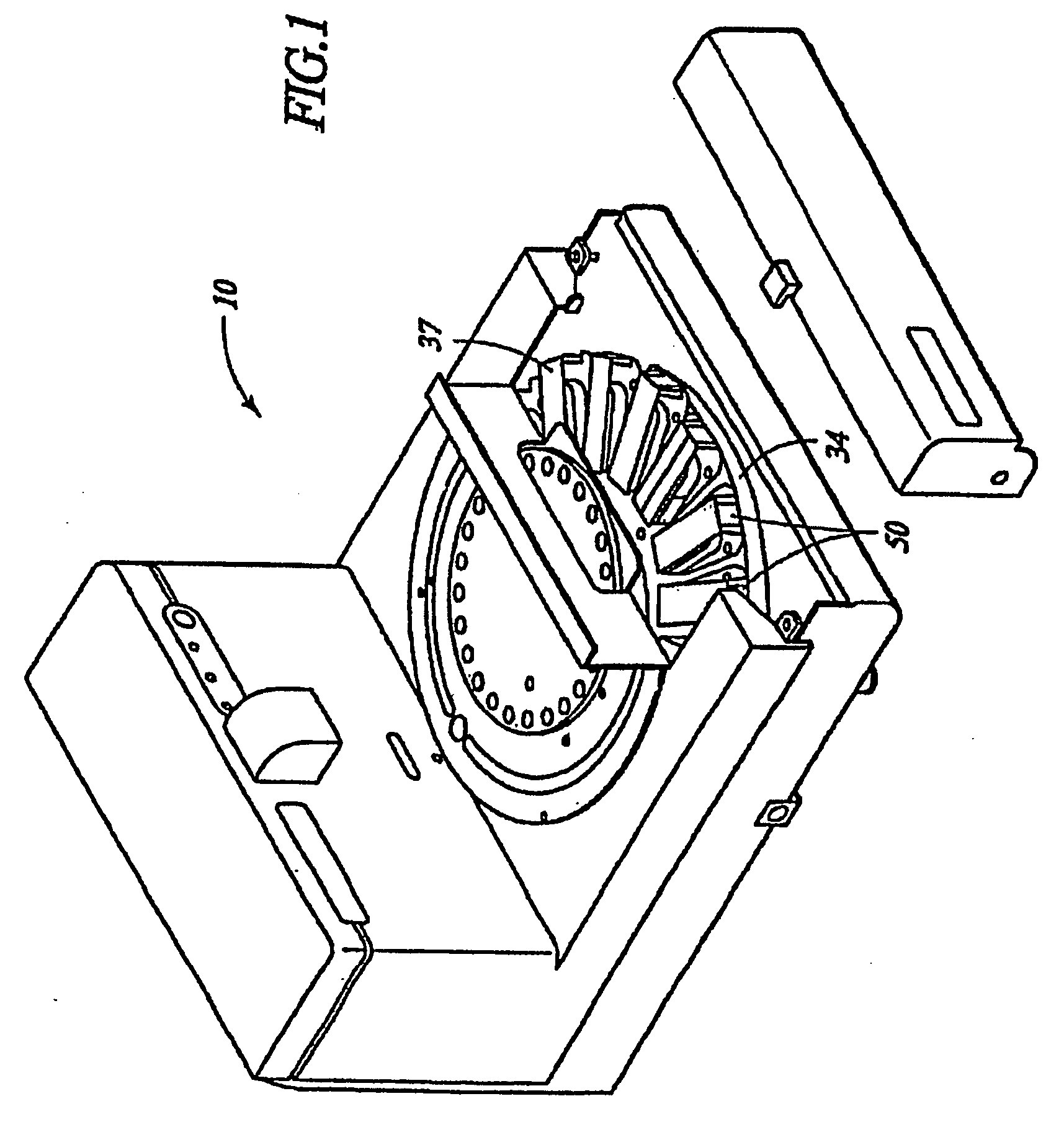
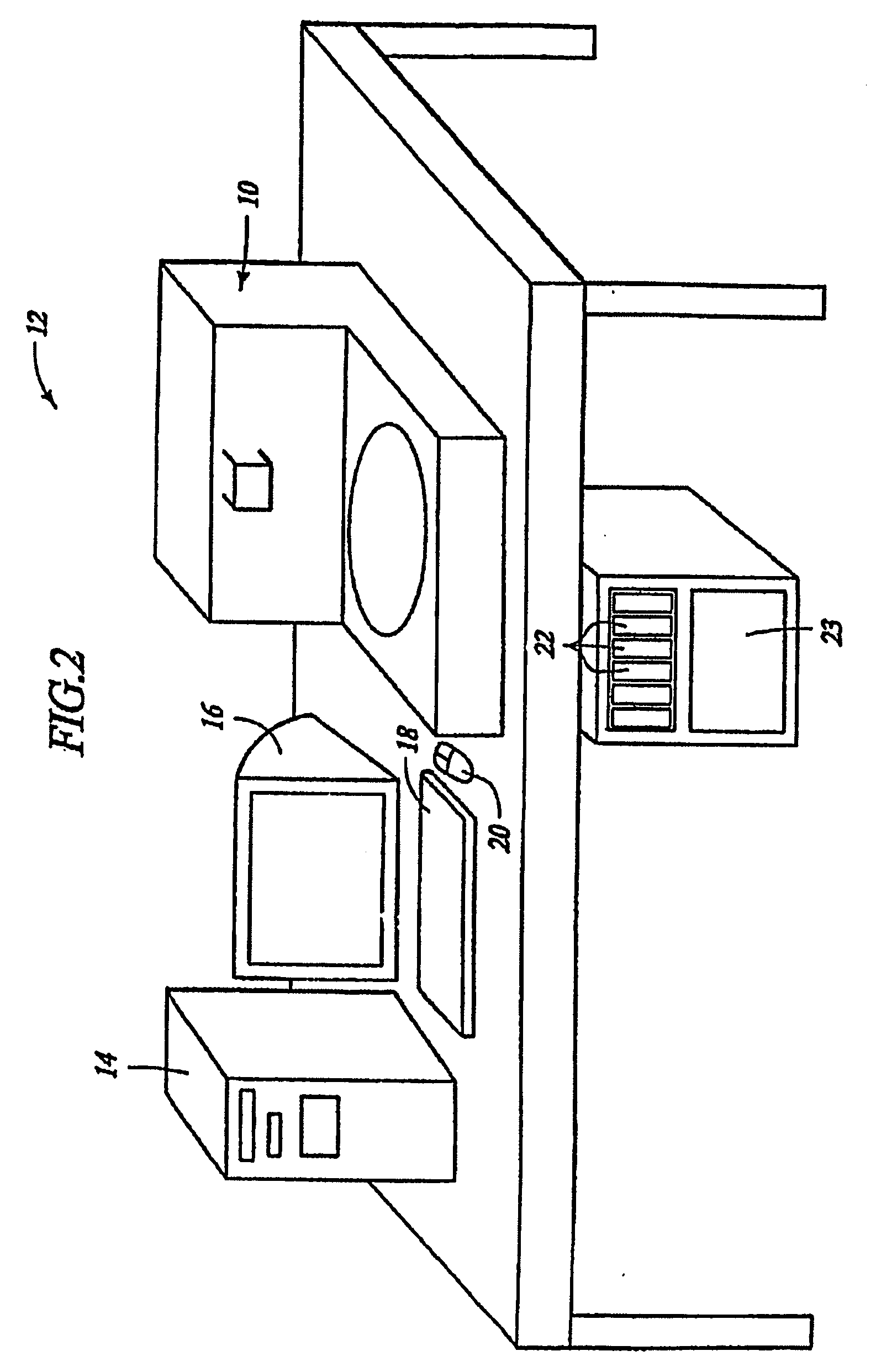
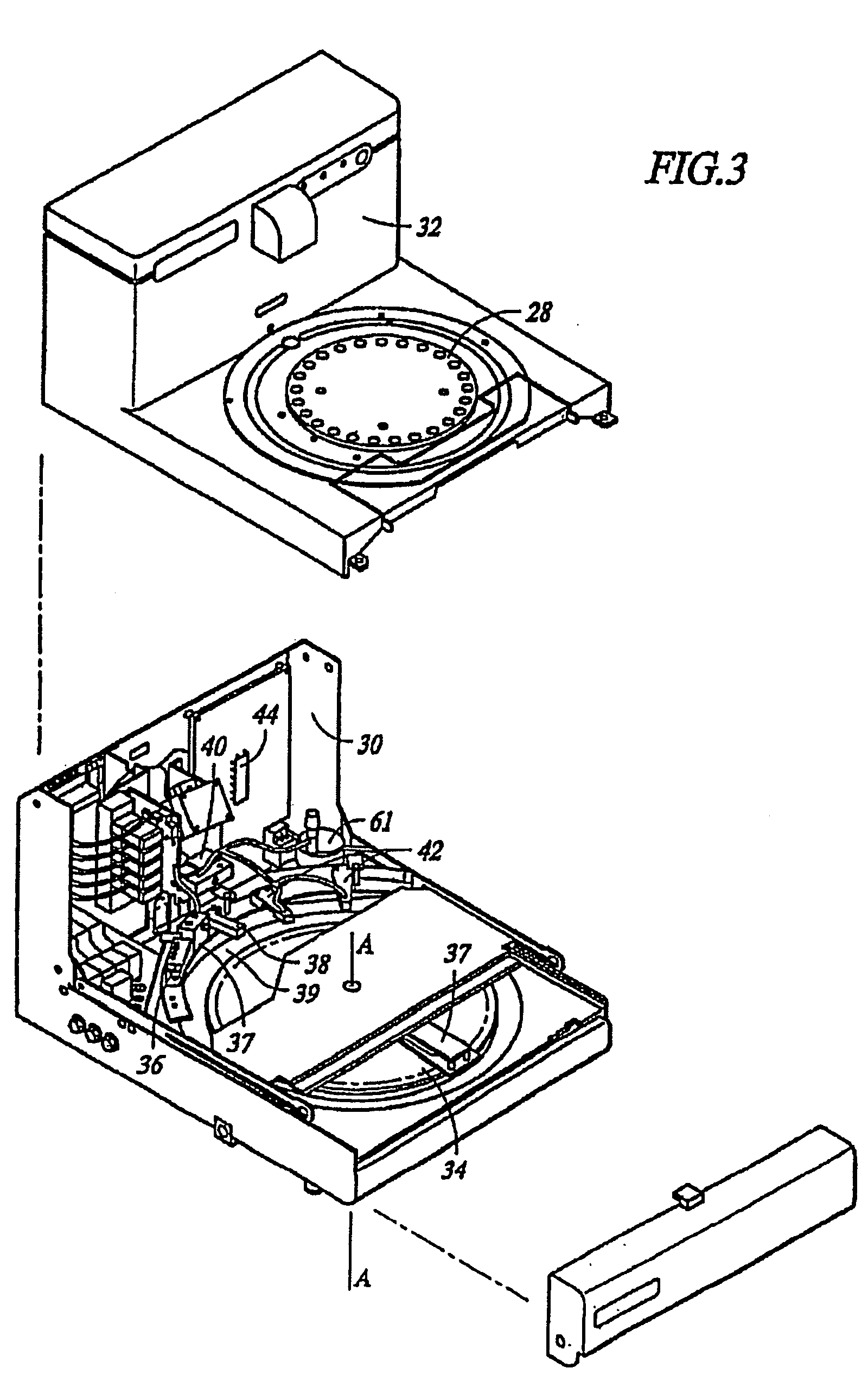
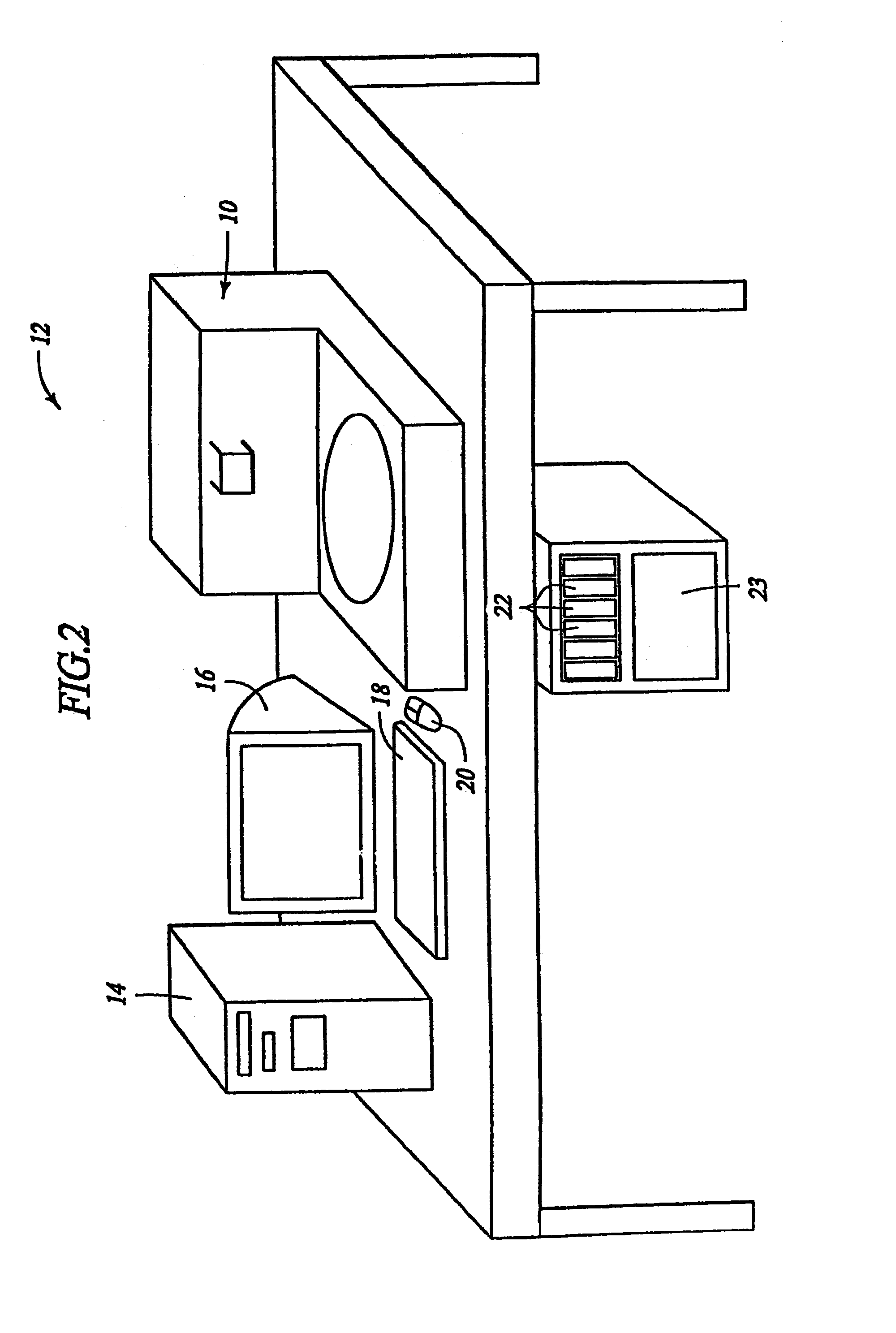
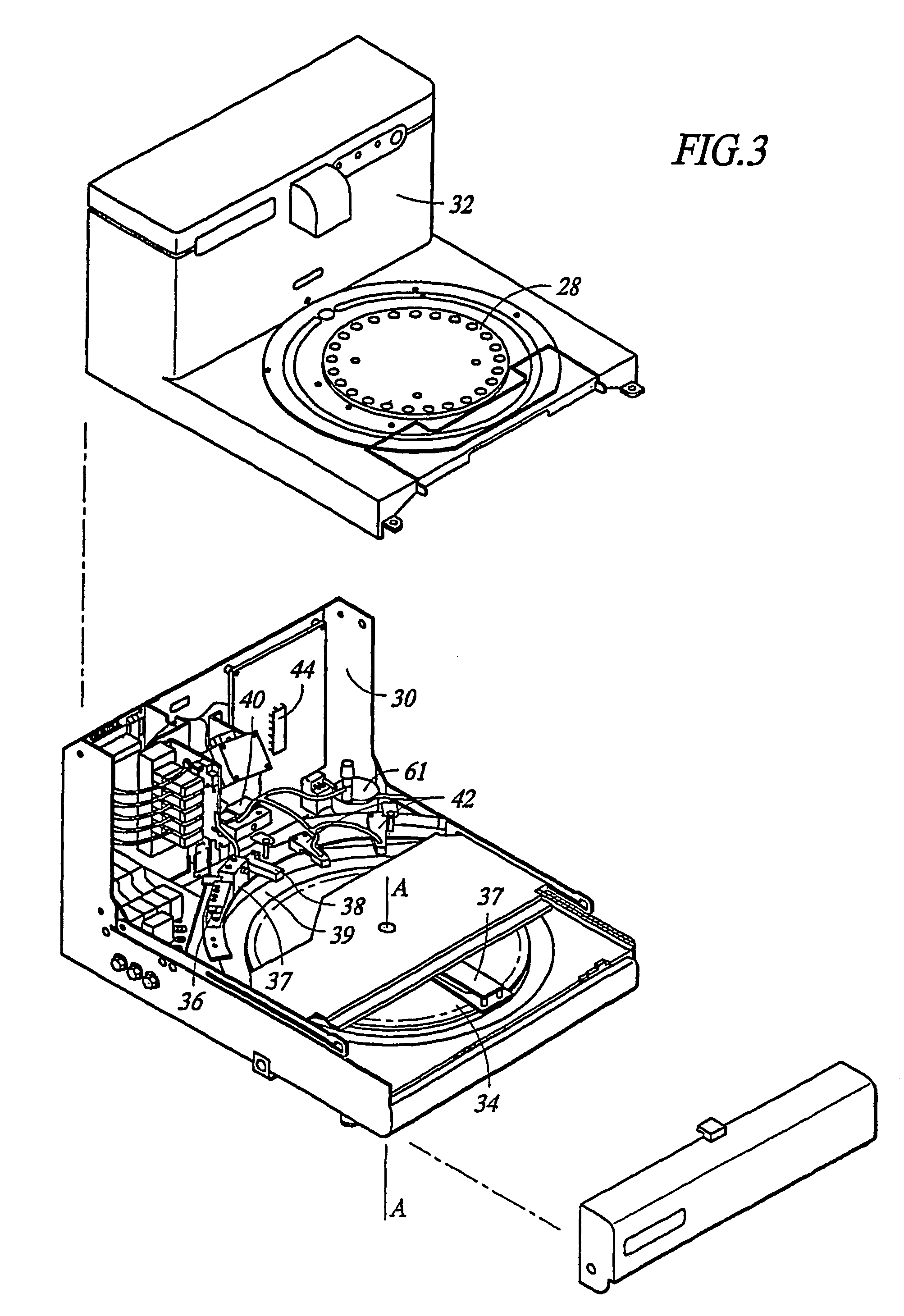
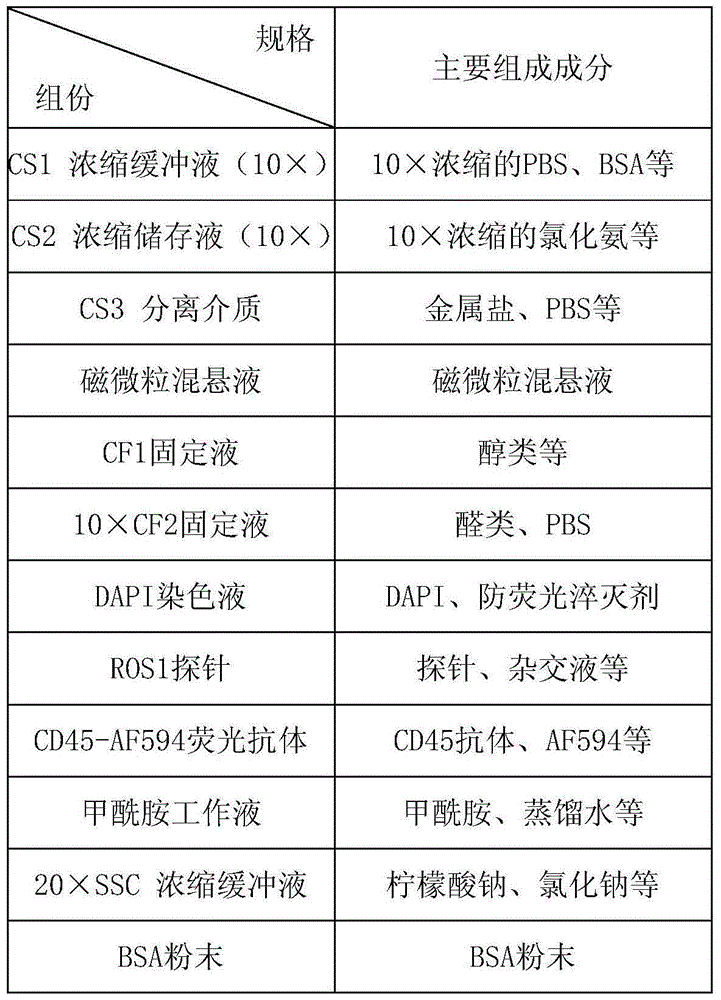
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
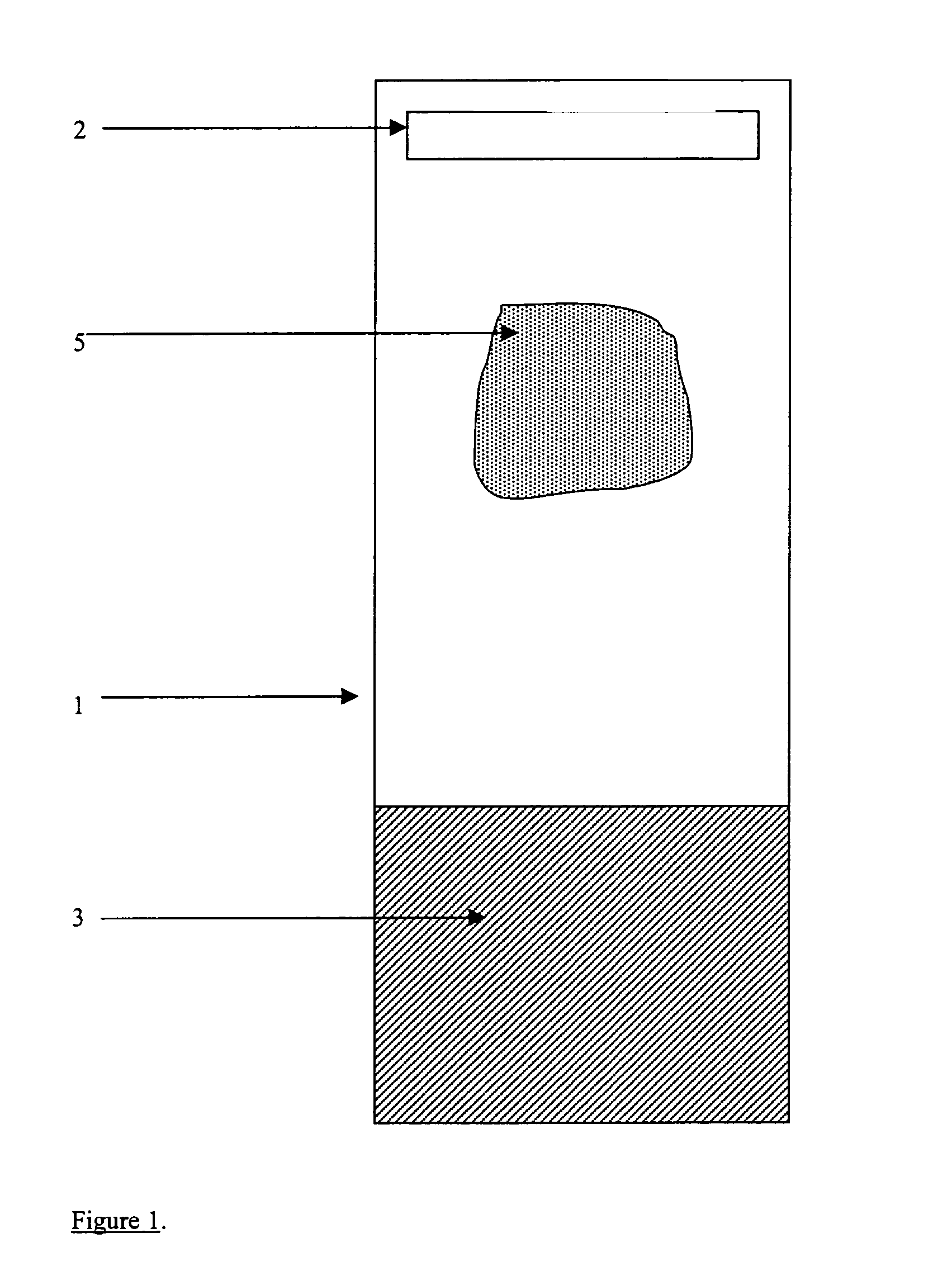
InactiveUS6855559B1Increase semaphoreAccurate interpretationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
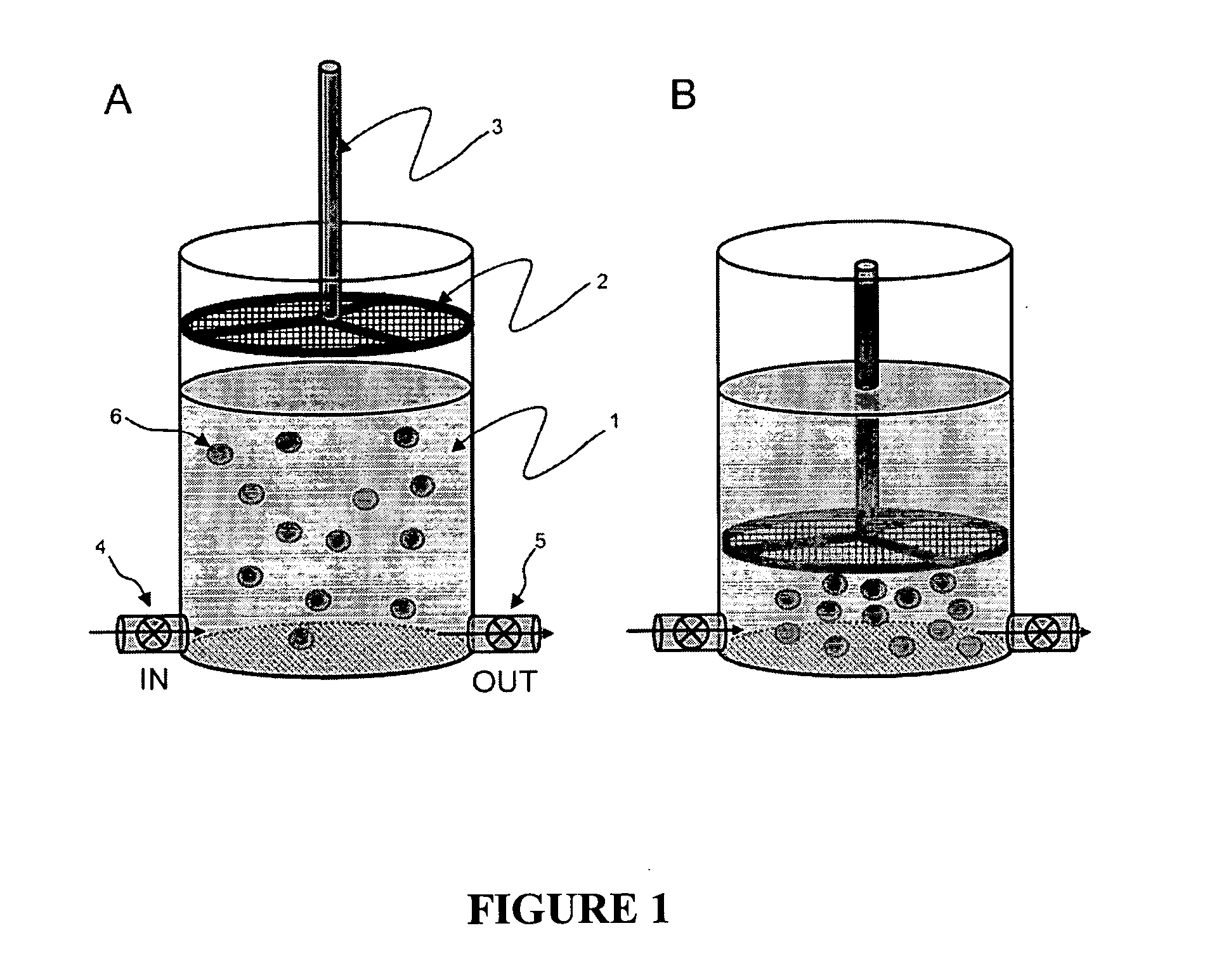
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning biological samples wherein the cells are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods and compositions for detecting rare cells from a biological sample
InactiveUS20080057505A1Strong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentHematopoietic cellWhite blood cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for isolating and detecting rare cells from a biological sample containing other types of cells. In particular, the present invention includes a debulking step that uses a microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and the enriched rare cells can be used in a downstream process such as identifies, characterizes or even grown in culture or used in other ways. The invention also include a method of determining the aggressiveness of the tumor or of the number or proportion of cancer cells in the enriched sample by detecting the presence or amount of telomerase activity or telomerase nucleic acid or telomerase expression after enrichment of rare cells. This invention further provides an efficient and rapid method to specifically remove red blood cells as well as white blood cells from a biological sample containing at least one of each of red blood cells and white blood cells, resulting in the enrichment of rare target cells including circulating tumor cells (CTC), stromal cells, mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells, fetal cells, stem cells, non-hematopoietic cells etc from a blood sample. The method is based upon combination of immuno-microparticles (antibody coated microparticles) and density-based separation. The final enriched target cells can be subjected to a variety of analysis and manipulations, such as flowcytometry, PCR, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, image analysis, enzymatic assays, gene expression profiling analysis, efficacy tests of therapeutics, culturing of enriched rare cells, and therapeutic use of enriched rare cells. In addition, depleted plasma protein and white blood cells can be optionally recovered, and subjected to other analysis such as inflammation studies, gene expression profiling, etc.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
InactiveUS7067325B2Improve accessibilityPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingCytochemistryEtching
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
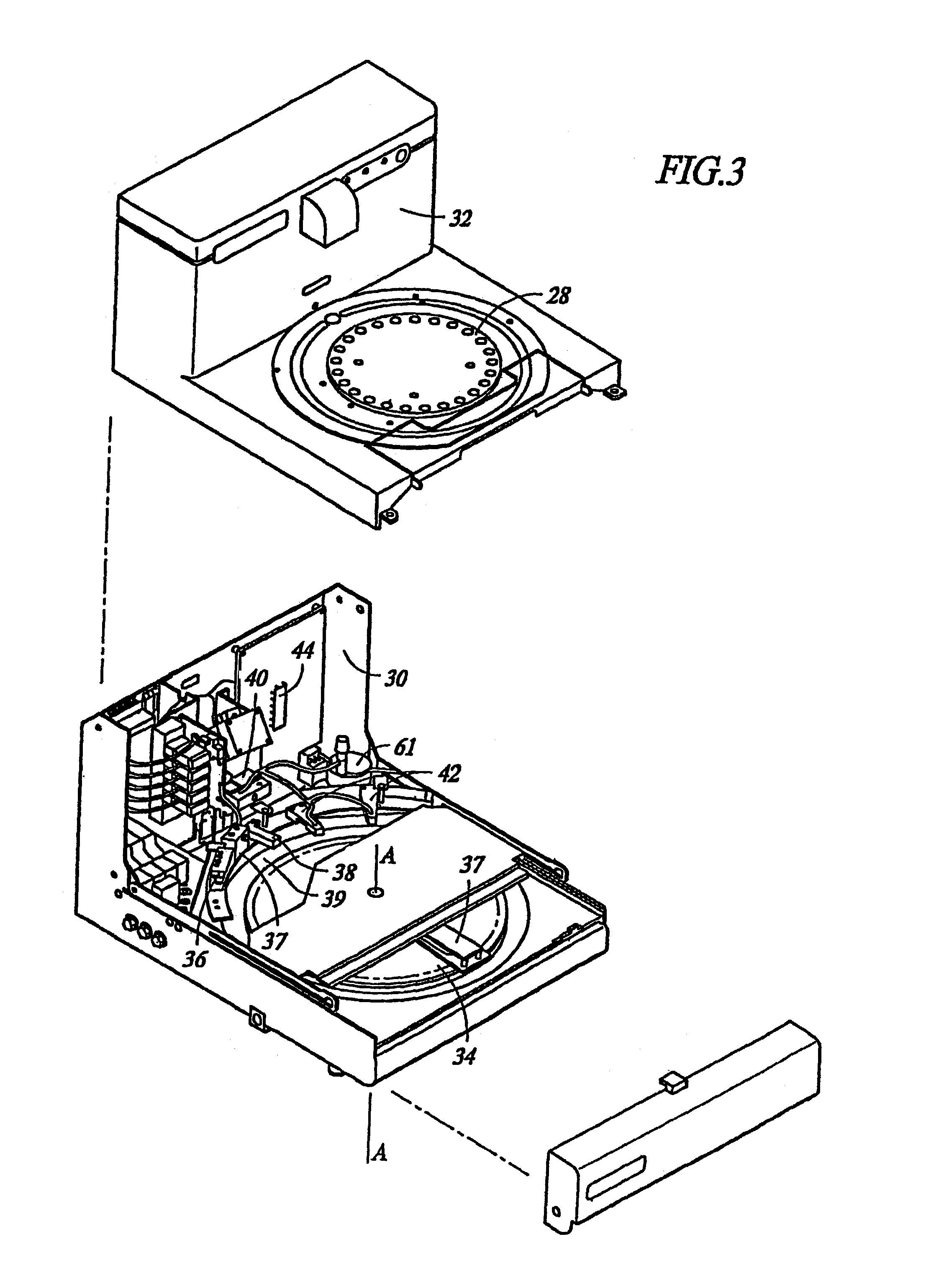
Low temperature deparaffinization
InactiveUS20060252025A1Easy to explainImproving stainability and readabilityPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationCytochemistryBatch processing
Methods and apparatuses for gently removing embedding media from biological samples at temperatures below the embedding medium melting point with liquid composition using batch methods or automated instruments prior to immunohistochemical (IHC), in situ hybridization (ISH) or other special staining or histochemical or cytochemical manipulations.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Automated immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assay formulations
InactiveUS20050118725A1Shorten the timeLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning of biological samples wherein the cells or tissues are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to faciliate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Removal of embedding media from biological samples and cell conditioning on automated staining instruments
InactiveUS7410753B2Increase semaphoreAccurate interpretationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning biological samples wherein the cells are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
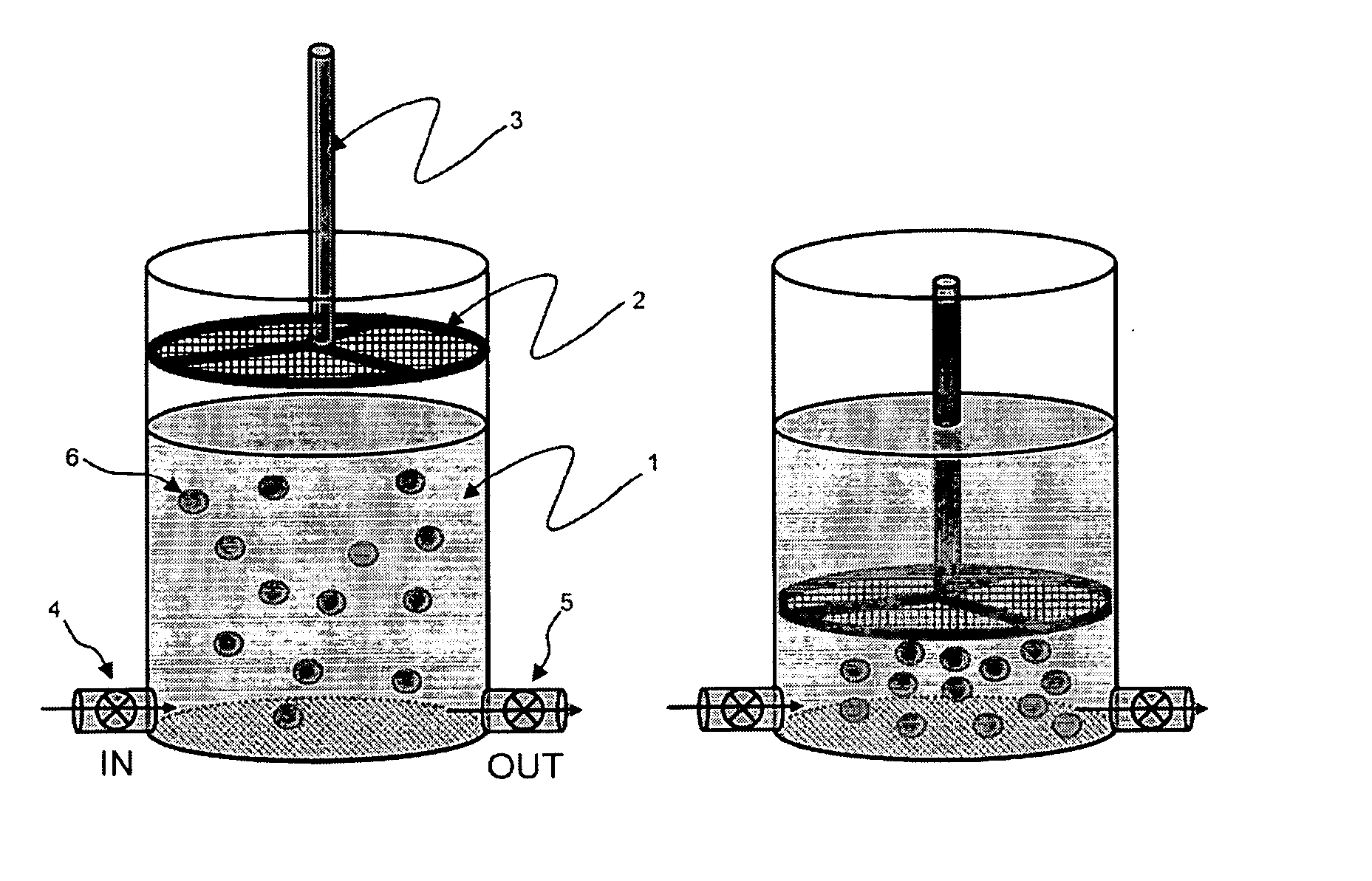
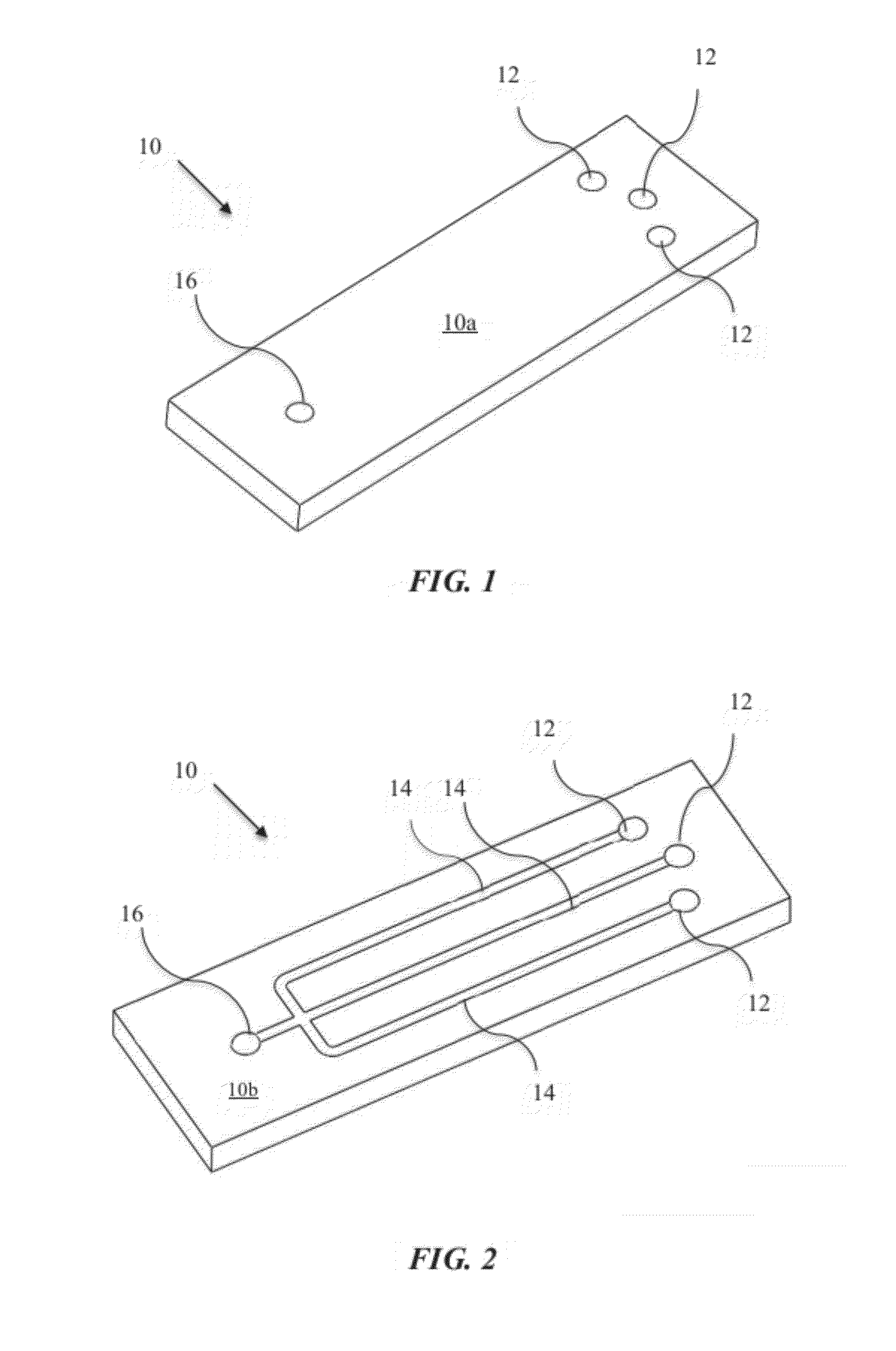
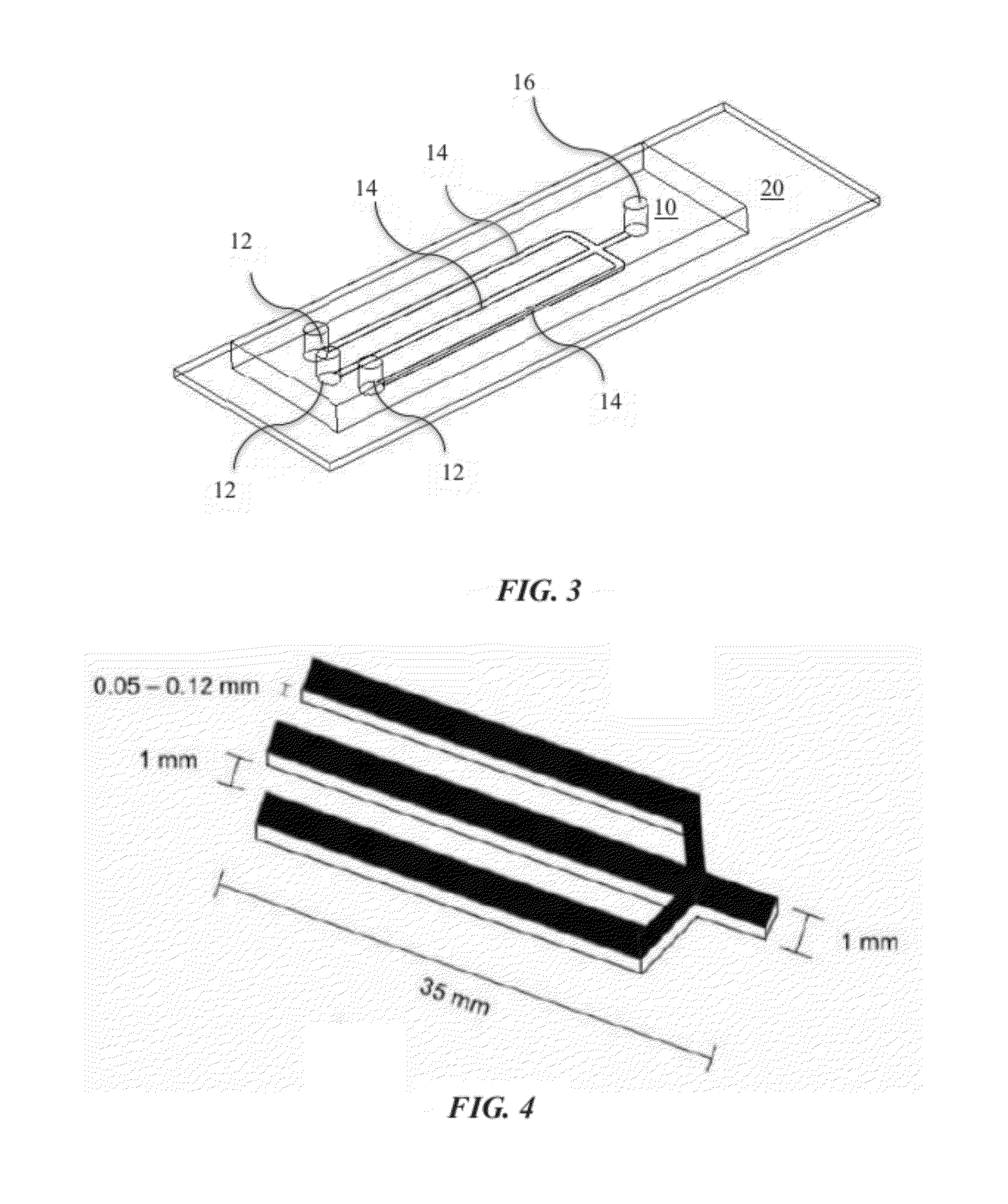
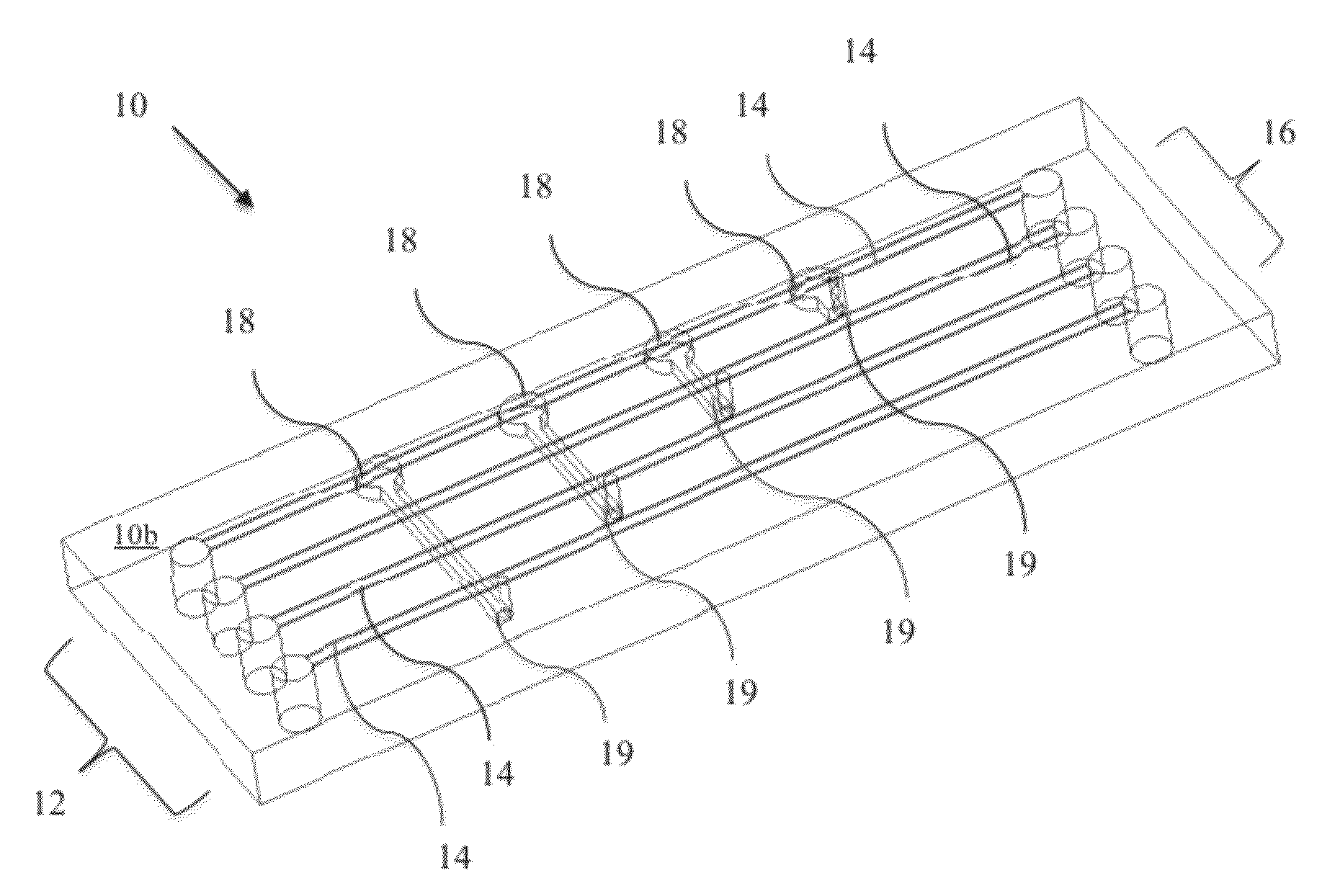
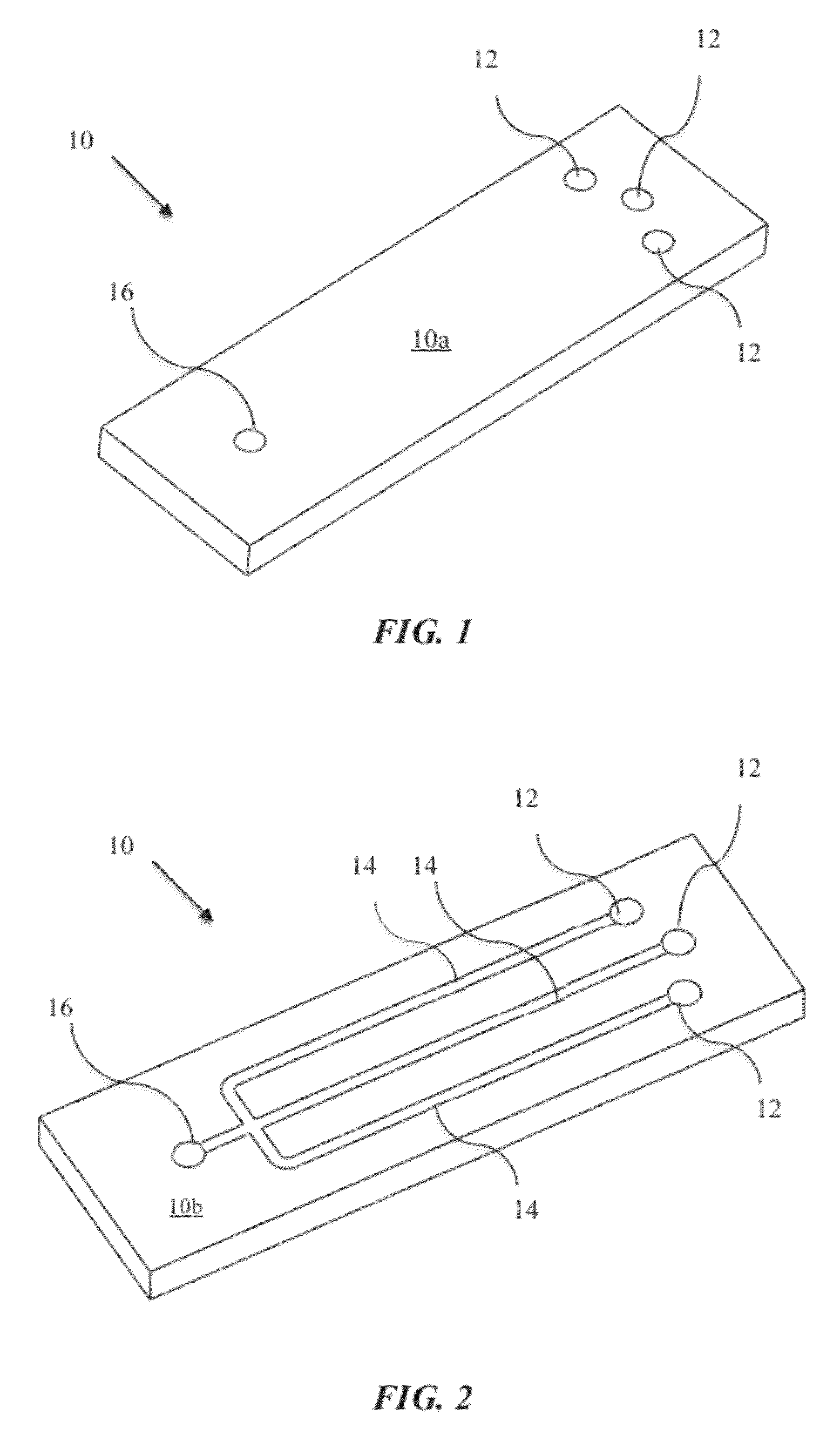
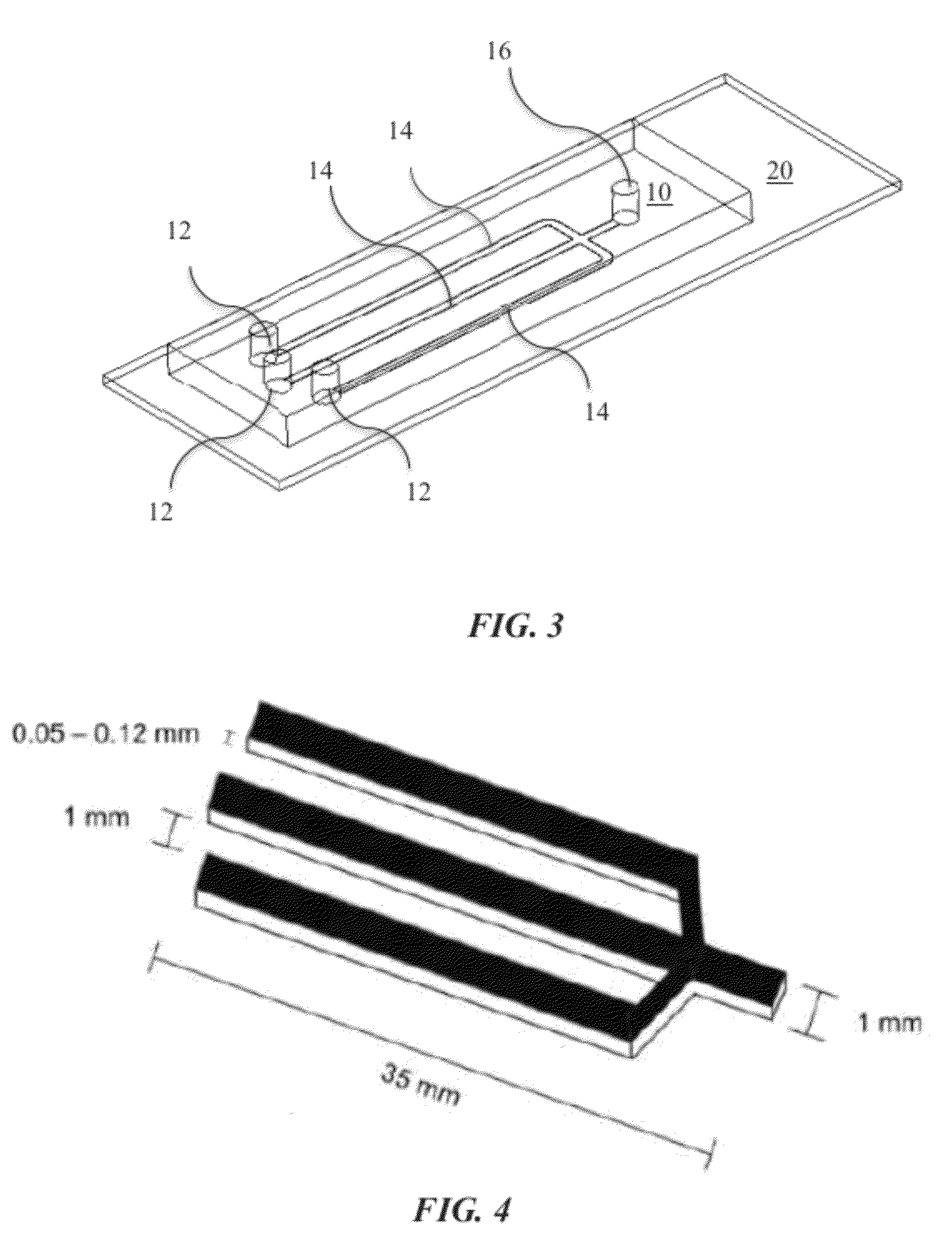
Microfluidic Cytochemical Staining System
ActiveUS20120230886A1Accurate disease diagnosisGood curative effectSamplingLaboratory glasswaresCytochemistryDisease
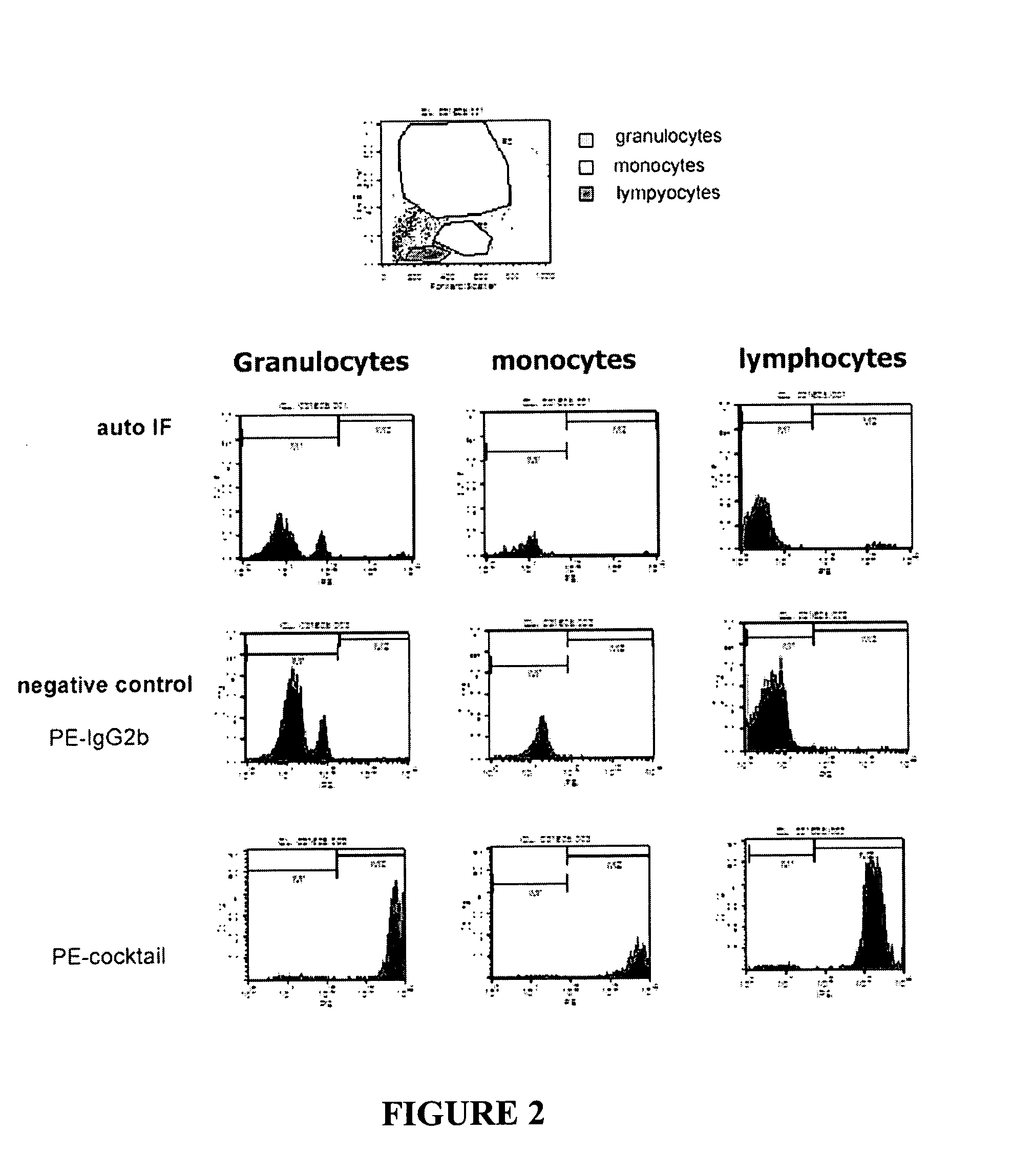
The present invention provides devices and associated methods to facilitate multiplexed staining on a slide. The use of multiplexed staining on a single slide allows for more accurate disease diagnosis while also conserving sample. A PDMS based cytology overlay was created that is capable of coupling on-chip morphological, cytochemical, and immunological staining. Morphological and cytochemical staining of blood smears, along with immunostaining of lymph node imprints, was carried out to demonstrate the application of this microfluidic cytology chip (μCC) device.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
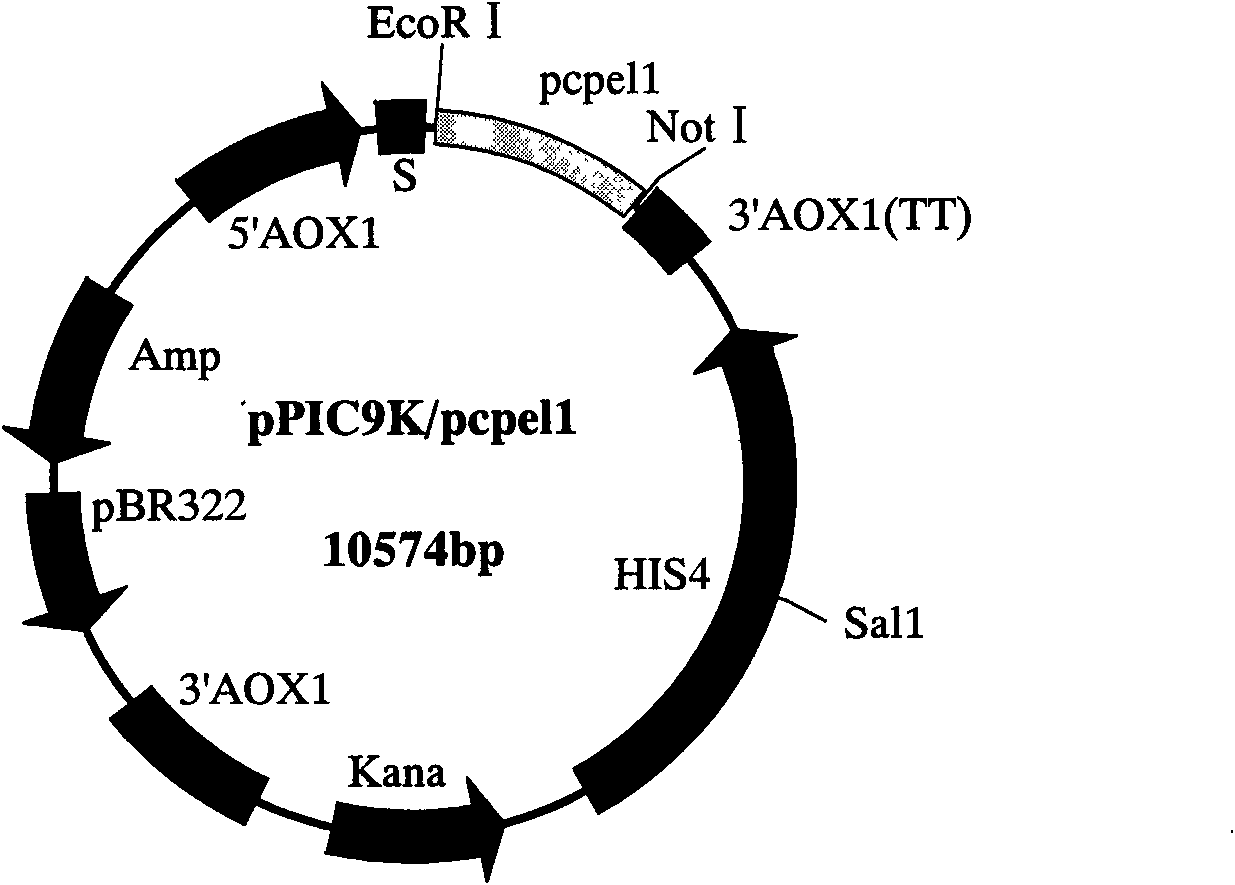
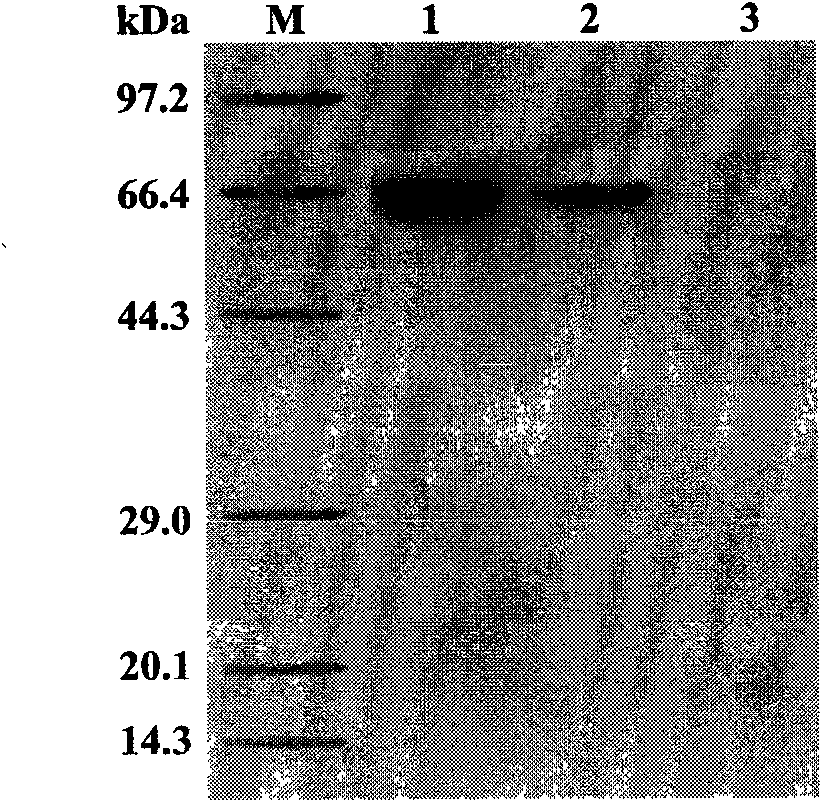
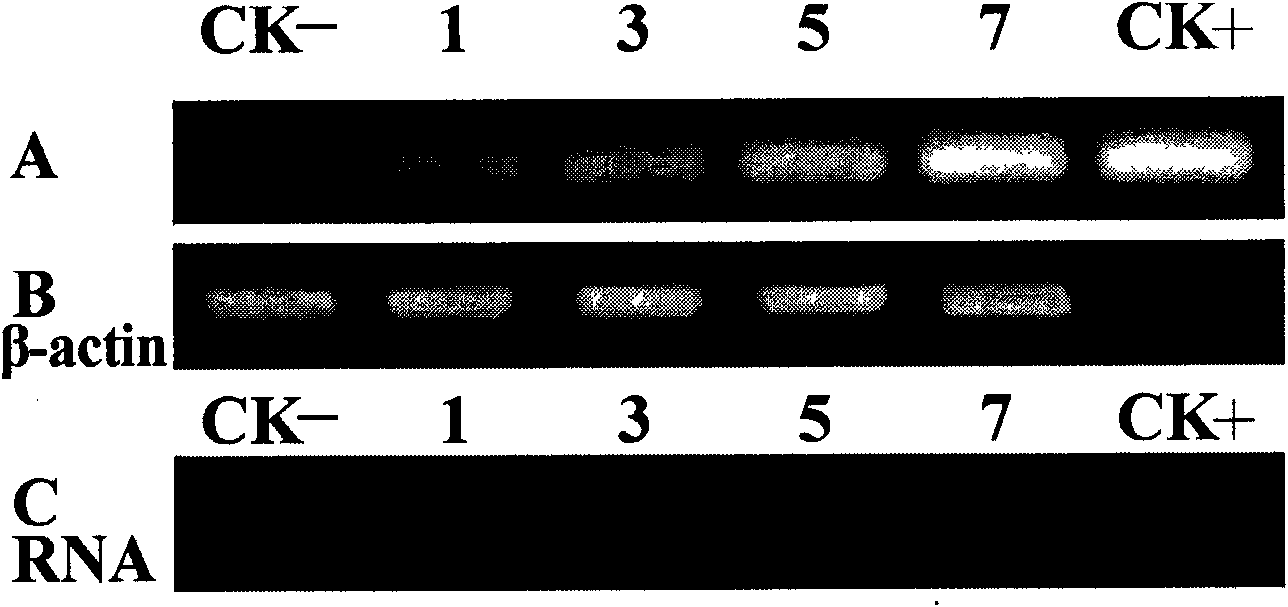
Phytophthora capsici pectate lyase (PL) Pcpel1 gene, protein preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101638663AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytochemistryPlant pathology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular provides a pectate lyase (PL) gene Pcpel1 which is cloned from phytophthora capsici and protein preparation technology thereof. Gene and protein levels prove that the gene is effectively involved in the process that the phytophthora capsici infects hot pepper hosts and results in occurrence of the course of diseases on hot pepper leaves. Plant pathology and cytochemistry technology further prove that after the protein coded by the gene is inoculated onto the hot pepper leaves, obvious withering and shrinking occur on theinoculated parts of the leaves and the cell walls on the affected parts of the leaves are obviously degraded, namely the gene code is an important protein related to the course of diseases or is possibly an important target pathogenic gene of a phytophthora capsici PL gene cluster. The invention provides important technical reserve for further developing phytophthora capsici molecule detection technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
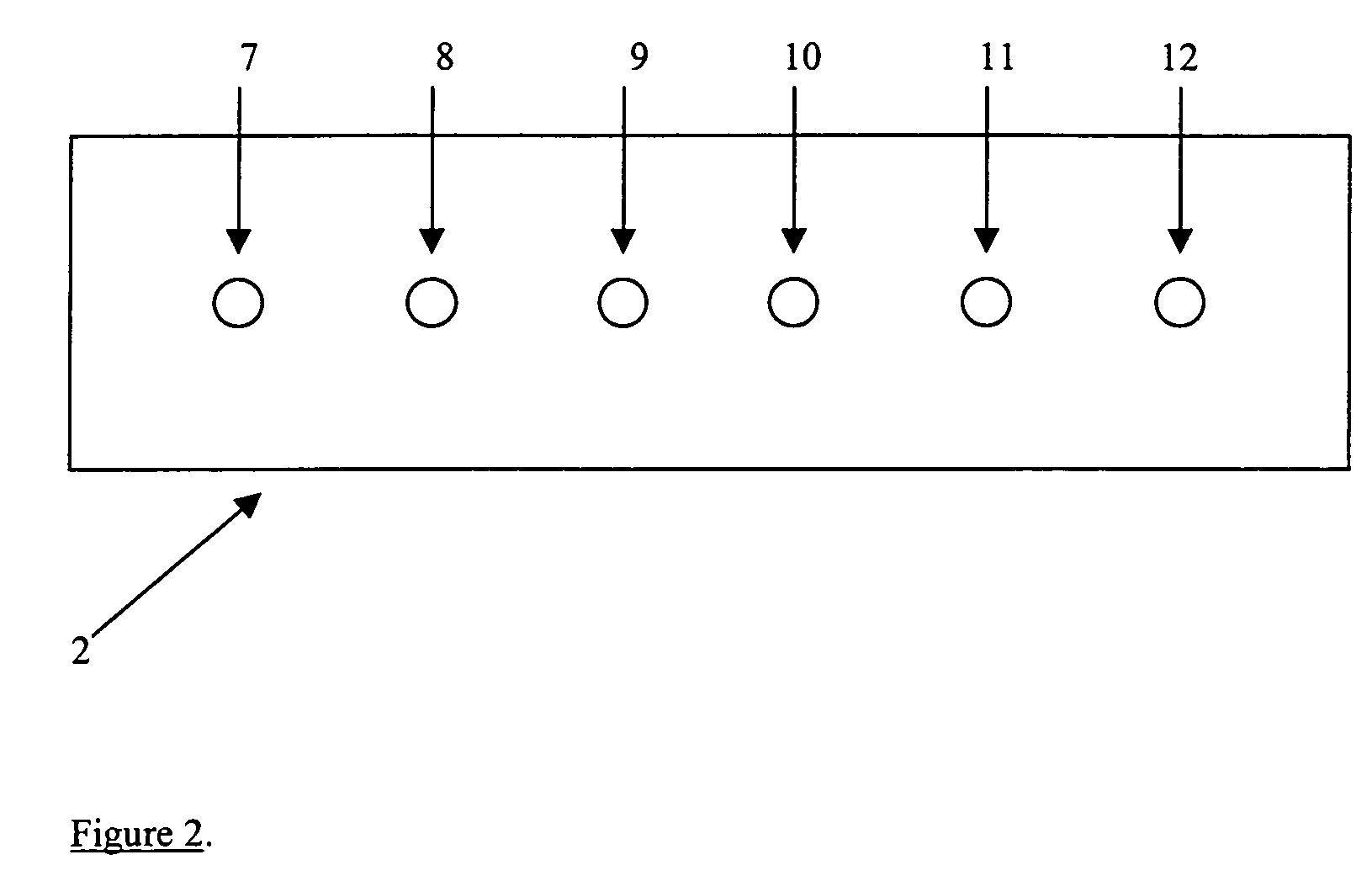
Quality control for cytochemical assays
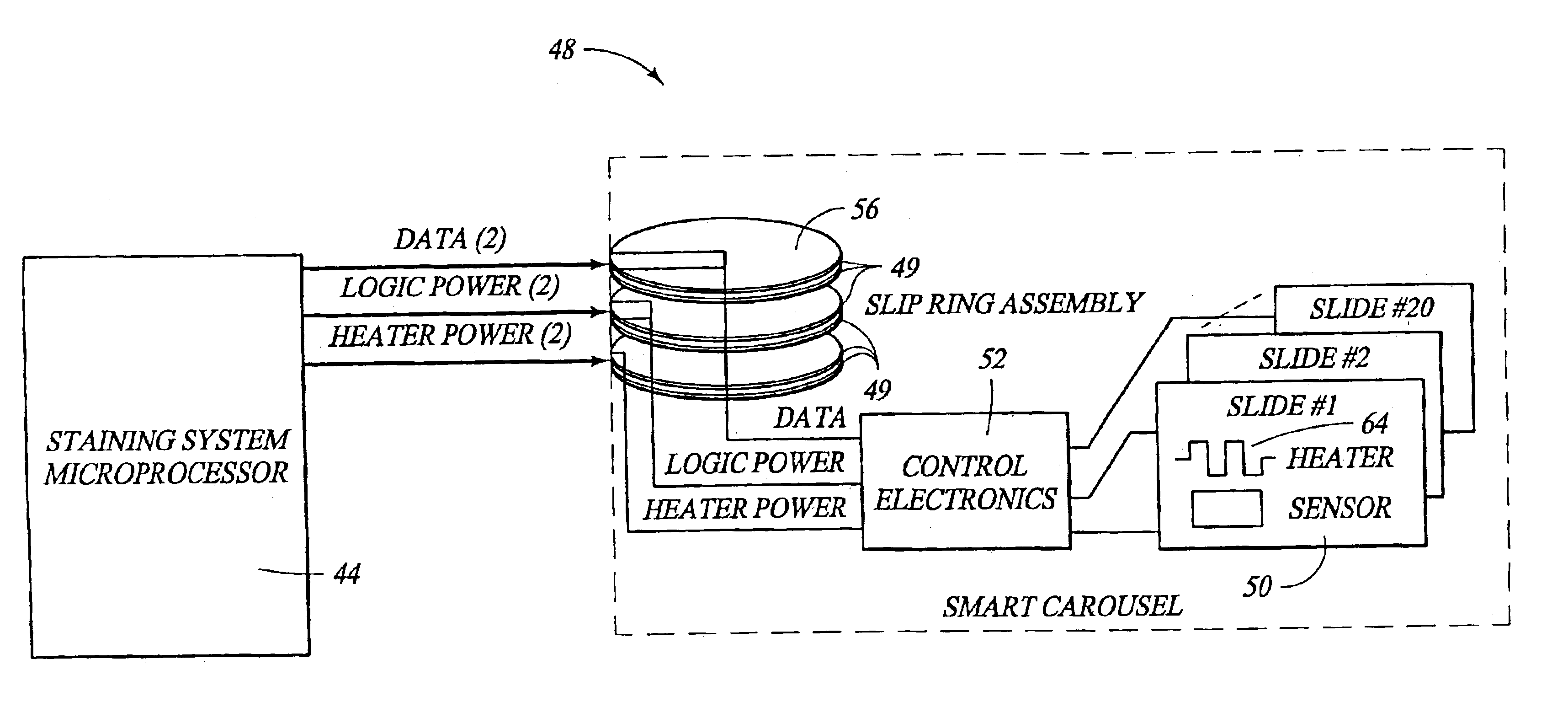
InactiveUS7011940B1Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytochemistryMicroscope slide
The invention describes quality control devices for assays that measure analytes in cells and tissue samples, and methods of use thereof. In particular, the quality control device comprises a matrix affixed with synthetic controls in different concentrations, or different synthetic controls. The quality control device can be adhered to a microscope slide via an adhesive or chemically attached to a microscope slide and processed simultaneously with a tissue sample.
Owner:LAB VISION CORP
Analytical method of components of fatty acid contained in listeria cells
InactiveCN101936960ABreaking the limits of taxonomyBreak the limitsComponent separationCytochemistryFatty acid
The invention relates to an analytical method of components of fatty acids contained in listeria cells, in particular to a method for carrying out bacteria classification by adopting a cell chemical analysis method, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: rejuvenating listeria; respectively separating and purifying the listeria by using an OXA agar plate and a trypticase soy yeast extract agar plate; culturing the listeria of a single typical colony, and preparing into a bacterial suspension; carrying out inactivation processing by using formaldehyde; averagely filling the bacterial suspension processed by the formaldehyde into centrifuge tubes for washing; carrying out methyl esterification by using a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and the formaldehyde; and carrying out GC-MS (Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer) analysis on the prepared fatty acids. The method can not only break through the limit of the traditional bacterial taxonomy and reduce the errors brought about by anthropic factors on the traditional morphological taxonomy, but also provide a strong and powerful tool for the classification and the identification of new strains and virus types; and in addition, the method can be used for identifying the listeria from other bacteria and foods.
Owner:HUBEI INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT
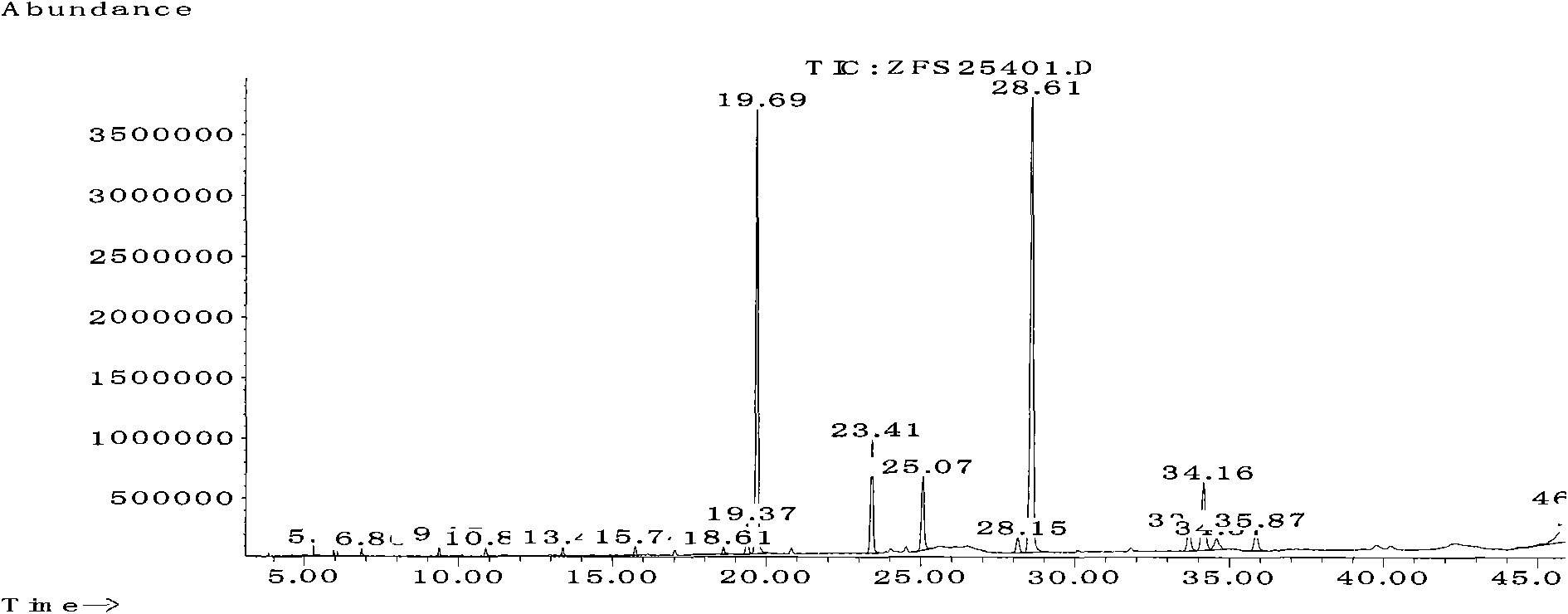
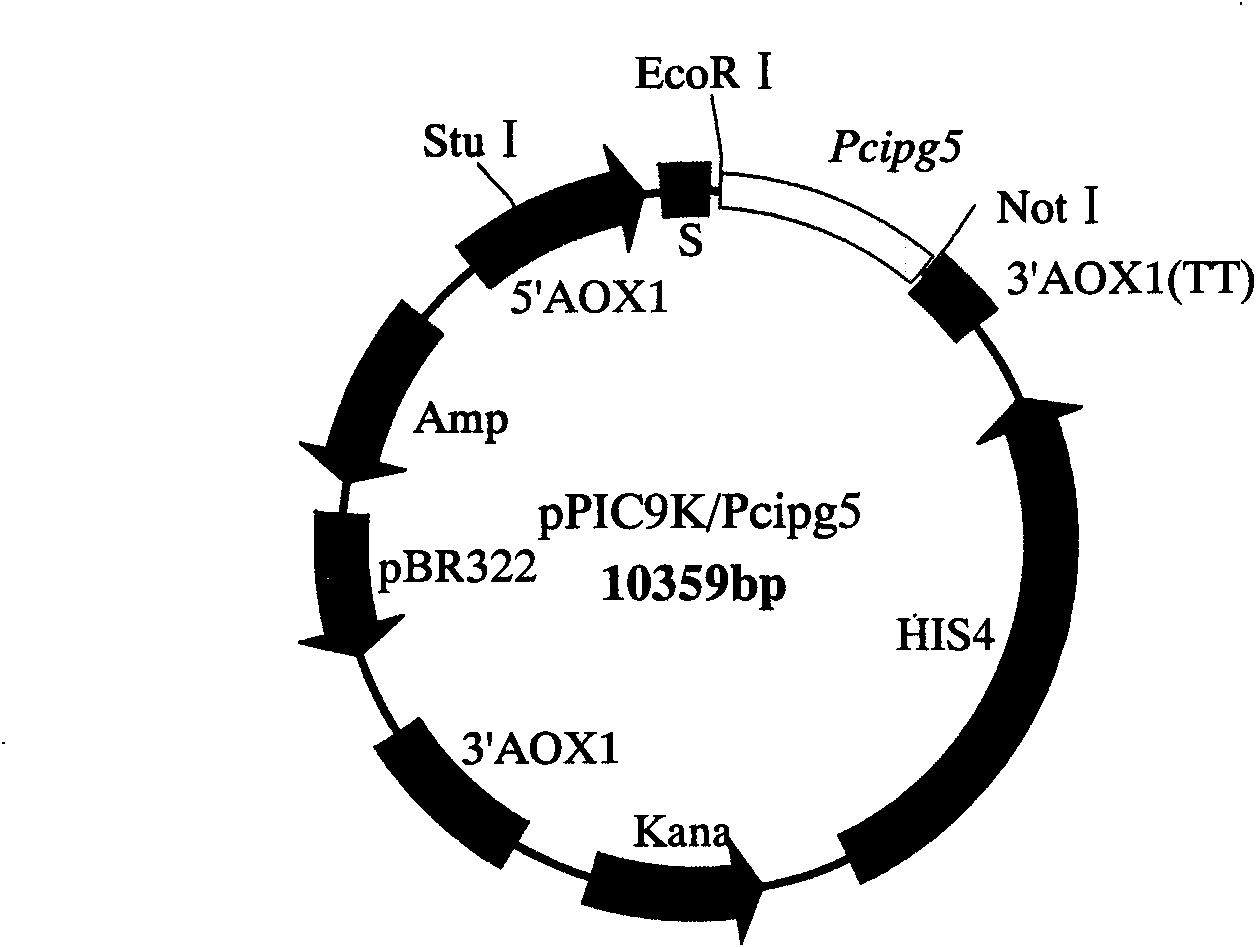
Phytophthora capsici polygalacturonase (PG) Pcipg5 gene, protein preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101638662ASufficient technical reservesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytochemistryPentagalacturonic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular provides a polygalacturonase (PG) gene Pcipg5 which is cloned from phytophthora capsici and protein preparation technology thereof. Gene and protein levels prove that the gene is effectively involved in the process that the phytophthora capsici infects hot pepper hosts and results in occurrence of the course of diseases on hot pepper leaves. Plant pathology and cytochemistry technology further prove that after the protein coded by the gene is inoculated onto the hot pepper leaves, obvious withering and shrinking occur on the inoculated parts of the leaves and the cell walls on the affected parts of the leaves are obviously degraded, namely the gene code is an important protein related to the course of diseases or is possibly an important target pathogenic gene of a phytophthora capsici PG gene cluster. The invention provides important technical reserve for further developing phytophthora capsici molecule detection technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Automated immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assay formulations
InactiveUS7550298B2Improve accessibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
Provided herein are reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning of biological samples wherein the cells or tissues are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents include, but are not limited to, components optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample. Also provided herein are reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents include, but are not limited to, components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method and related kit for detecting c-MET/CEP7 gene status based on rare cells
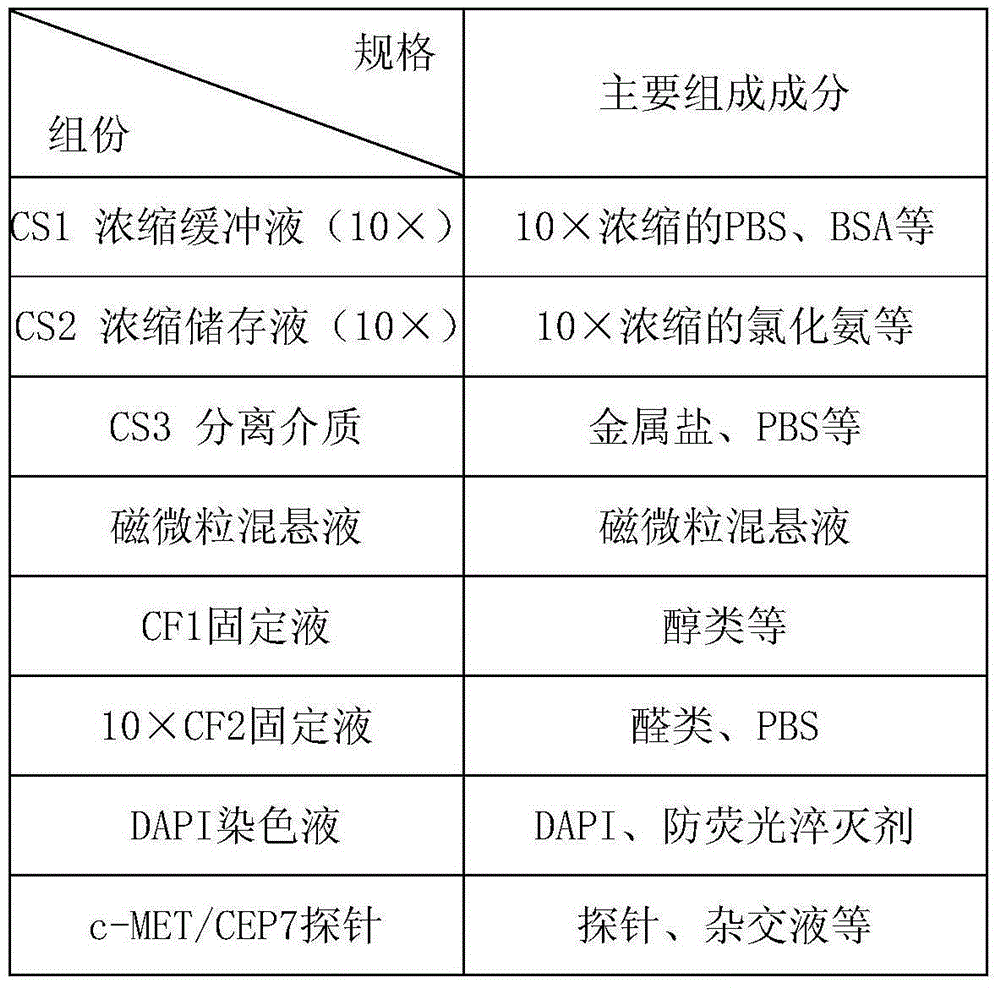
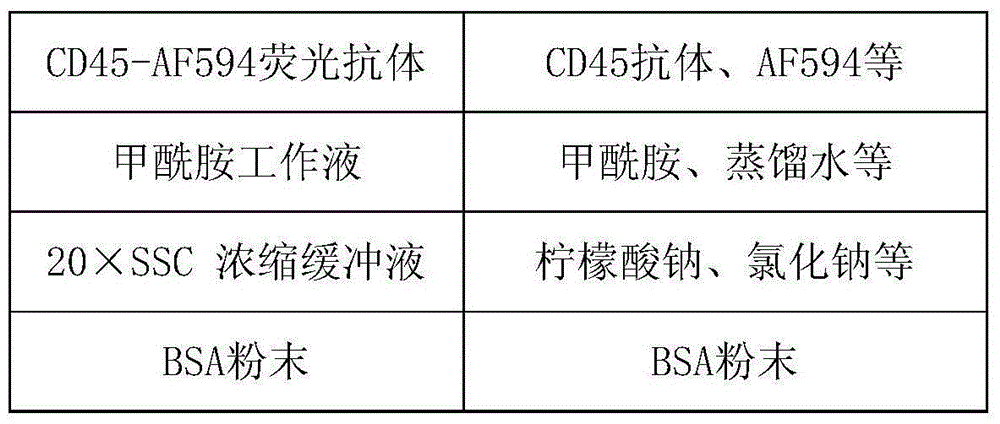
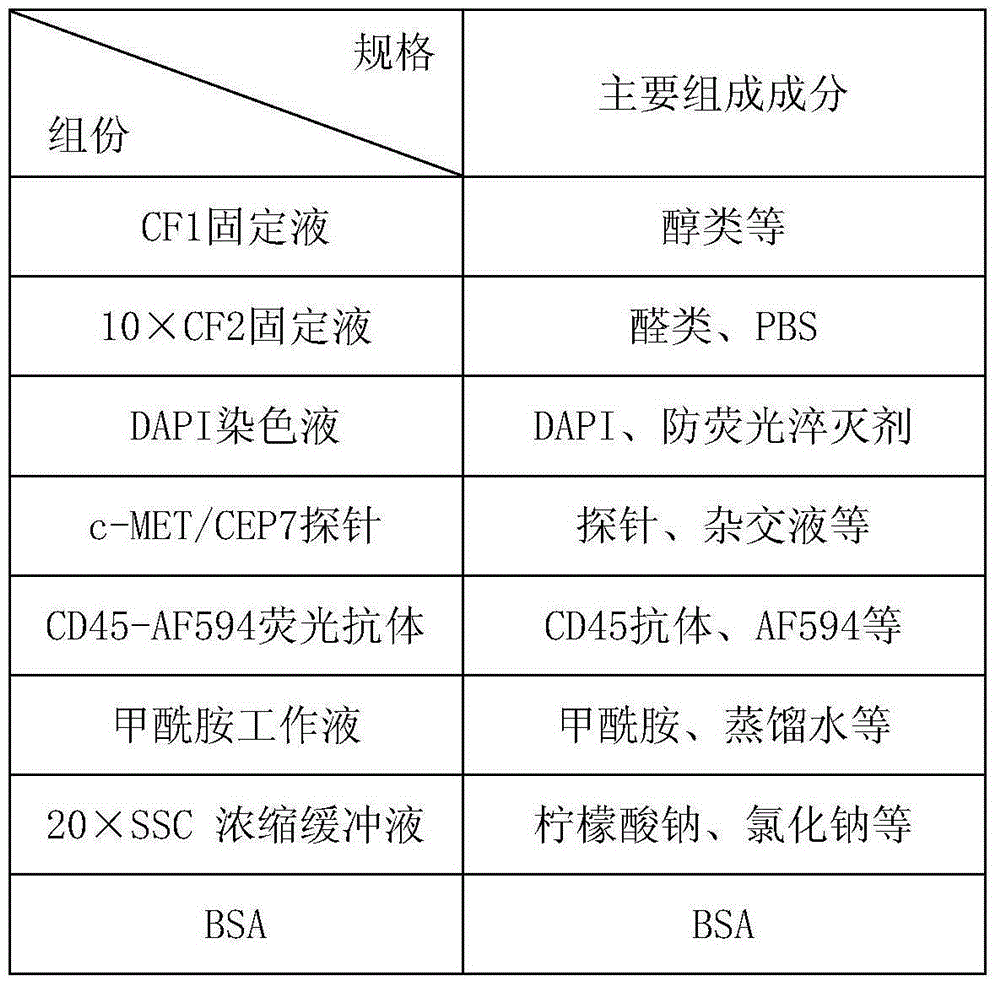
The invention relates to a method and a related kit for detecting c-MET / CEP7 gene status based on rare cells, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1. acquiring a blood sample or a body fluid sample, wherein the sample includes a mixed cell population of circulating tumor cells or other rare cells and white blood cells; 2. diluting the sample by virtue of a buffer solution, removing plasma and recovering CTC or other rare cells; 3. cracking by virtue of a red blood cell lysis buffer, removing red blood cells and recovering CTC or other rare cells; 4. recovering cells with magnetic particles coated with related anti-human leucocyte antigens and antibodies, uniformly mixing and breeding, and fully combining so as to form a magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture; 5. isolating the magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture from other cells so as to obtain a mixed cell population containing CTC or other rare cells and a few of white blood cells; and 6. by virtue of a method combining immunofluorescence cytochemistry and fluorescence in-situ hybridization, determining the status of c-MET / CEP7, and simultaneously identifying CTC or other rare cells.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
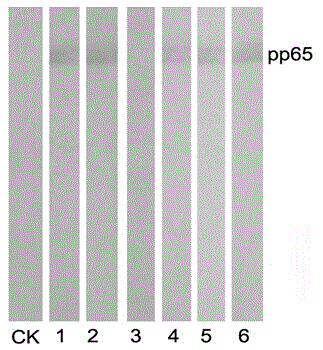
Preparation method and application of anti-HCMV (human cytomegalovirus) Pp65 protein monoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a high-specificity and high-affinity anti-Pp65 monoclonal antibody which is generated by a hybridoma cell strain 8D6 of the anti-Pp65 monoclonal antibody, wherein the cell strain 8D6 is collected in China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) and has a collection number of CCTCC NO:C201476. The monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain has good affinity and specificity, and the immunoreactivity and the specificity of the antibody are superior to those of domestic and imported monoclonal antibodies. The anti-Pp65 monoclonal antibody can serve as a key raw material for blood white cell immunofluorescent cytochemical diagnosis and immunofluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of HCMV (human cytomegalovirus) infection, also can serve as a key raw material for detecting HCMV by using a double antibody sandwich method, has important meaning for establishment of a quick and sensitive clinical diagnosis reagent to HCMV infection, and has important application prospects.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
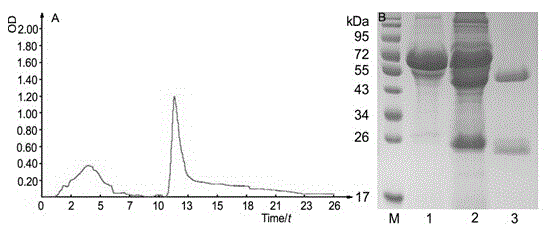
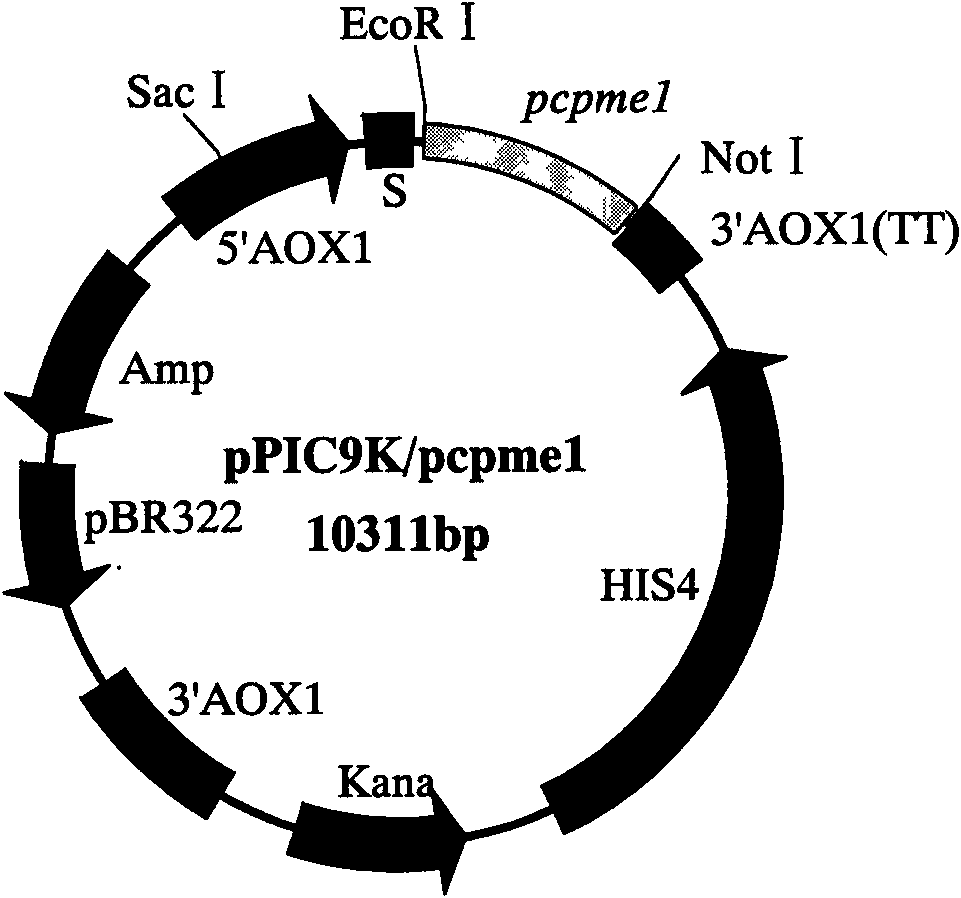
Phytophthora capsici pectin methylesterase Pcpme l gene as well as preparation method of protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101671684AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease courseCell wall
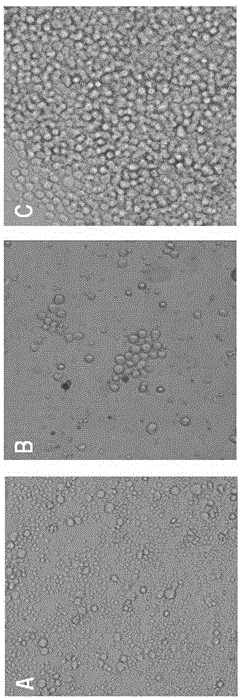
The invention provides a pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l cloned from phytophthora capsici and a preparation technique of a protein thereof, belonging to the technical field of biology. The invention proves that the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l effectively participates in the processes of infecting a host by the phytophthora capsici and causing the disease course of phytophthora capsici leonian on the basis of gene and protein levels and also proves that the protein coded by the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l has property of destroying leaf tissue cells and cell wall structures thereof to enable destroyed parts to generate obvious symptoms on the basis of a cell chemistry technique, thus the pectin methylesterase gene Pcpme l is an important target pathogenic gene of a coded phytophthora capsici pectin methylesterase gene cluster. The invention provides sufficient technical reserve for further researching a germ molecule detection technique.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Immunofluorescence microscopy observation method for marine bivalve meiosis device
InactiveCN101639441AEasy to operateOperation time savingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytochemistryFluorescence
The invention relates to cytochemistry and cellular immunology, which are particularly used for observing a marine bivalve meiosis device through immunofluorescence microscopy. A sample can be observed after pre-treatment of fixing and the like, dyeing and flaking. The sample is fixed by phosphate buffered saline (PBS) of paraformaldehyde at a mass percentage concentration of 2 to 6 percent; then,permeabilization treatment and sealing treatment are performed sequentially; immunofluorescence dyeing is performed on sample spindle bodies, and fluorescence dyeing is performed on chromosomes withthe phosphate buffered saline containing propidium iodide of which the concentration is 5 to 20 mg of per liter; and the sample is flaked after dyeing for observation through fluorescence microscopy.The cytological immunofluorescence observation method is suitable for observing the spindle bodies and the chromosomes of the marine bivalve meiosis device synchronously, has the advantages of simpleand direct operation, high definition and high study efficiency, and is a qualitative, positioning and quantitative cytological immunofluorescence observation method which inosculates forms and functions.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and related kit for detecting HER-2/CEP17 gene status based on rare cells
InactiveCN105087778AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCytochemistryWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a method and a related kit for detecting HER-2 / CEP17 gene status based on rare cells, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1. acquiring a blood sample or a body fluid sample, wherein the sample includes a mixed cell population of circulating tumor cells or other rare cells and white blood cells; 2. diluting the sample by virtue of a buffer solution, removing plasma and recovering CTC or other rare cells; 3. cracking by virtue of a red blood cell lysis buffer, removing red blood cells and recovering CTC or other rare cells; 4. uniformly mixing and breeding magnetic particles coated with related anti-human leucocyte antigens and antibodies with the recovered cells, and combining so as to form a magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture; 5. isolating the magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture from other cells so as to obtain a mixed cell population containing CTC or other rare cells and a few of white blood cells; and 6. by virtue of a method combining immunofluorescence cytochemistry and fluorescence in-situ hybridization, determining the status of HER-2 / CEP17, and simultaneously identifying CTC or other rare cells.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
Microfluidic cytochemical staining system
ActiveUS9295988B2Facilitate multiplexed staining of a biological sampleGood curative effectPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresCytochemistryCytology
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
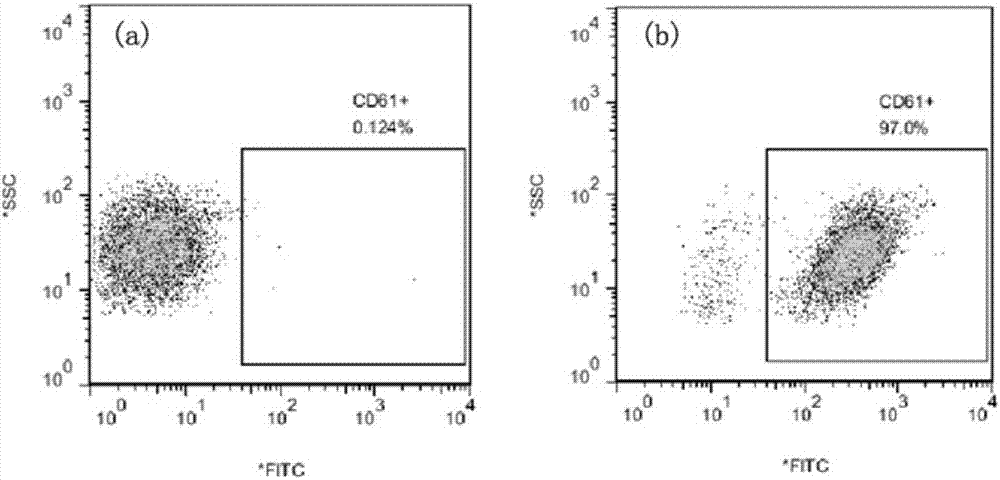
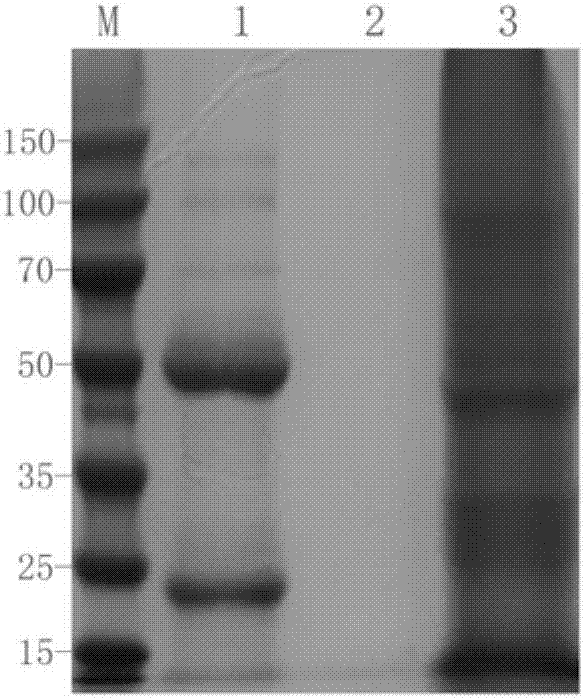
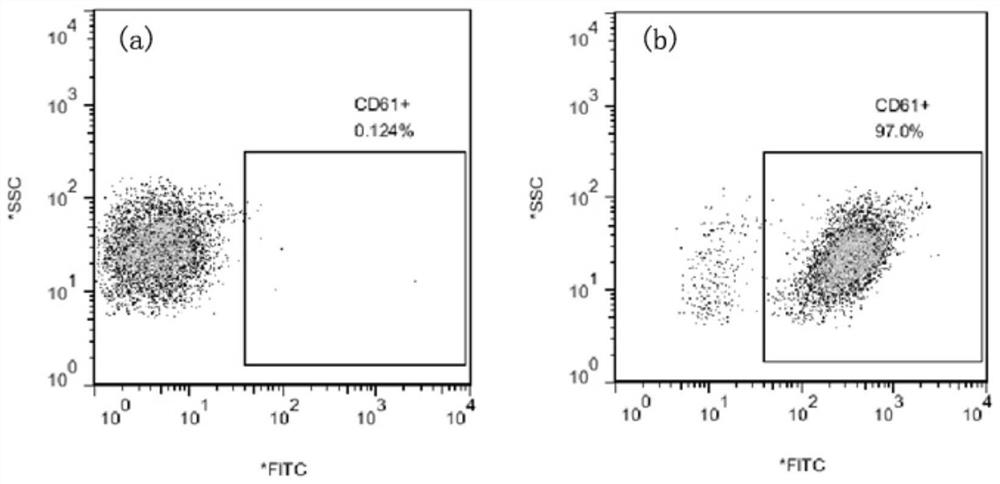
Mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof and flow cytometry detection reagent
ActiveCN107058242AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureAntigenBALB/c
The invention discloses a mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, a monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and application thereof and a flow cytometry detection reagent, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, human peripheral blood leukocytes are used as an immunogen for immunizing Balb / c mice; a cell fusion technology is adopted and hybridoma cells are screened by utilizing an immunocytochemistry and a flow cytometry indirect immunofluorescent method; an antibody generated by monoclonal hybridoma cells is subjected to specific identification by applying an immunoprecipitation-mass-spectrometric method; Western Blot proves that one hybridoma cell line IID5G8 capable of stably secreting a mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody is obtained and a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 13300. The monoclonal antibody is prepared by adopting an animal in-vivo induction method; a heavy chain of the antibody is identified to be IgG1 and a light chain is identified to be kappa type; after the antibody is purified, an FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate) label can be used for detecting antigen expression of human peripheral blood platelets CD61 by utilizing flow cytometry direct-labeling immunofluorescence.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
P16 immune cell chemical labeling color-developing kit
PendingCN110501497APrecise positioningGood colorColor/spectral properties measurementsCytochemistryChemical labeling
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology, and specifically relates to a p16 immune cell chemical labeling color-developing kit. The detection kit comprises the following reagents:0.5-1.0 ml of a p16 immune cell standard substance with the concentration of 81 pg / mL, 1.5 to 2.0 ml of a standard substance diluent, 2-4 ml of horseradish peroxidase, 2-4 ml of a sample diluent, 2-4ml of a color-developing agent solution A, 2-4 ml of a color-developing agent solution B, 2-4 ml of a stop solution, and 20ml of 20 times of concentrated washing solution. The method comprises the steps of coating a microporous plate with a purified human p16 antibody to prepare a solid-phase antibody, adding p16 into micropores coated with a monoclonal antibody, combining with a horseradish peroxidase-labeled p16 antibody to form an antibody-antigen-enzyme-labeled antibody compound, thoroughly washing, and then adding a color-developing agent A substrate for color development. The color-developing agents A and B are converted into blue under the catalysis of horseradish peroxidase and converted into final yellow under the action of acid, the positioning effect and the color-developing effect are good, the labeling is more obvious, the color depth is in positive correlation with p16 in a sample, and the absorbance is measured by using a microplate reader at the wavelength of 450 nm.
Owner:深圳市森盈生物科技有限公司
Device and method for detecting blood leukocytes
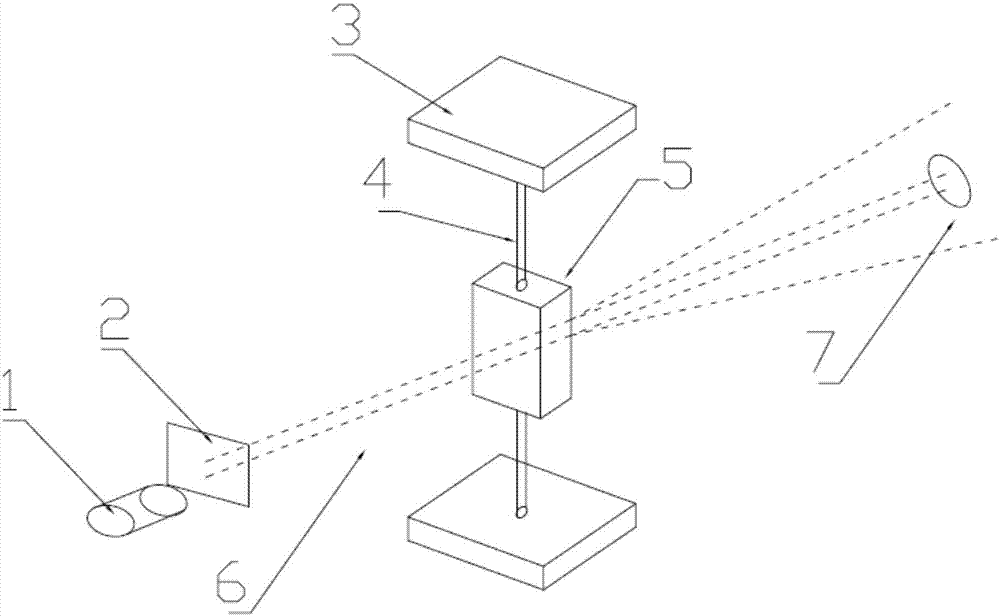
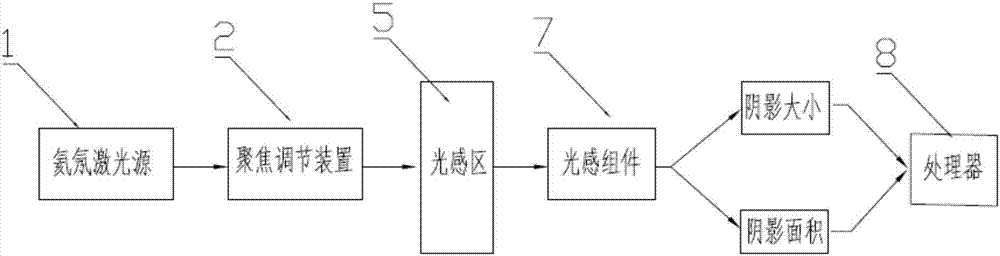
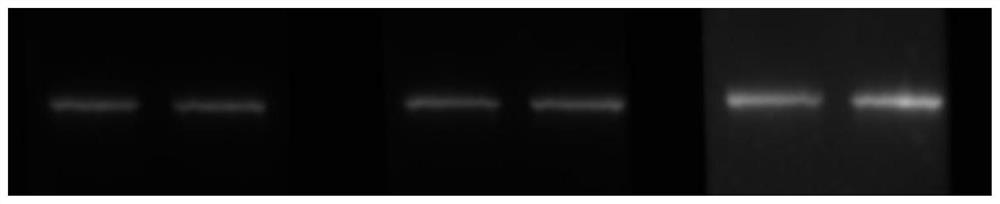
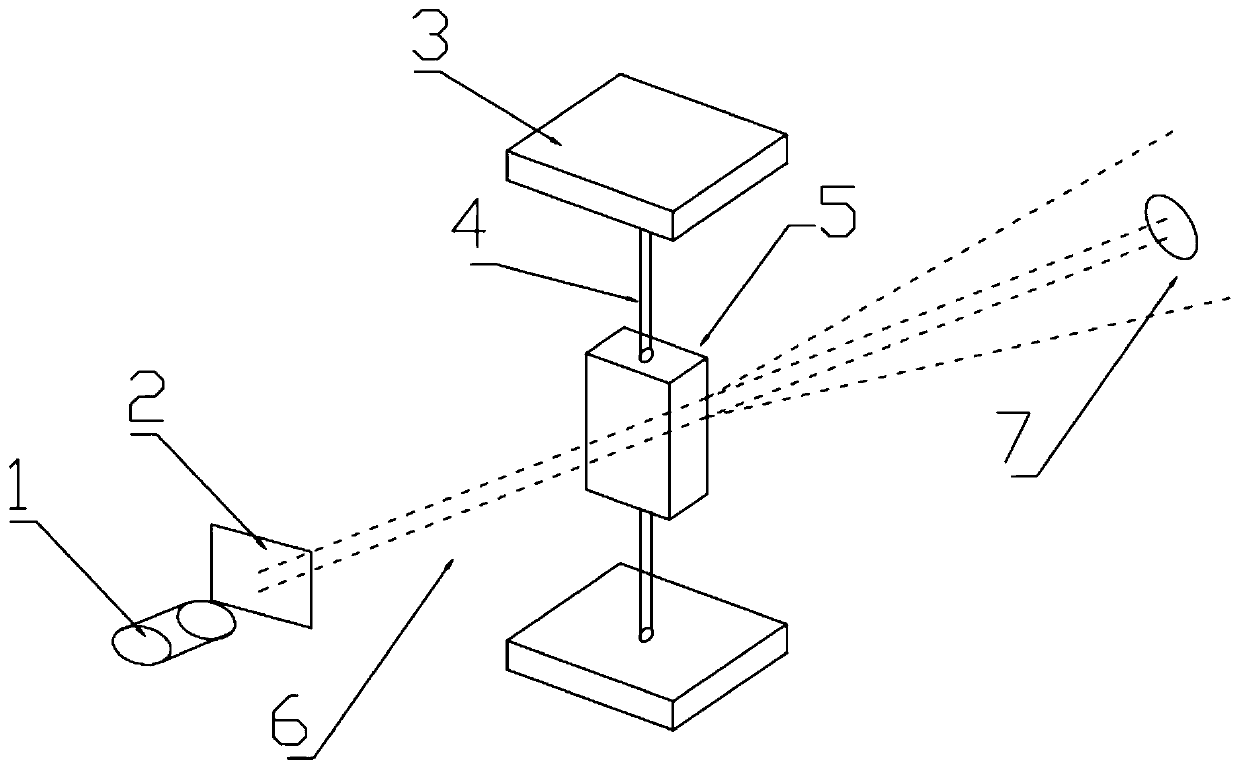
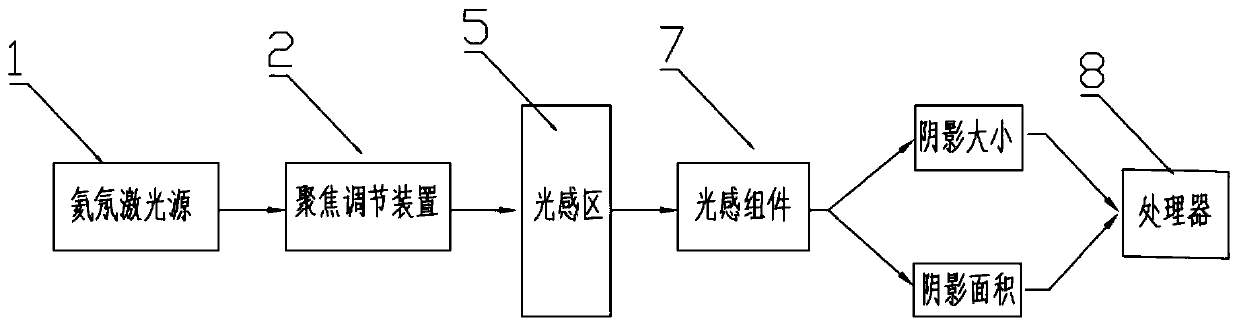
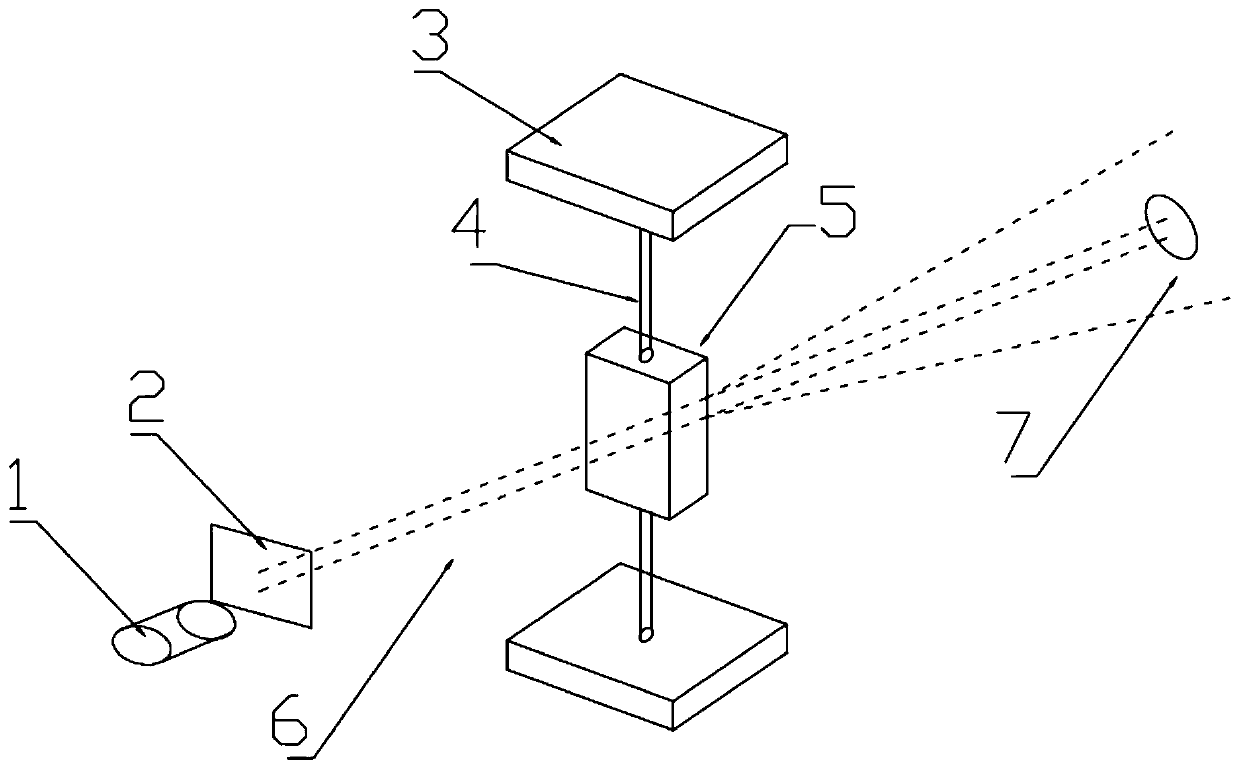
InactiveCN107219195ASimplify the inspection processScattering properties measurementsCytochemistryDisease
The invention relates to a device and method for detecting blood leukocytes. Leukocytes play an important role in a human body. Total amount and differential counting of the leukocytes have certain significance in diagnosing various diseases. The conventional method for detecting the leukocytes always combines with two or more detection principles, combines with the techniques, such as, electrics, optics and cytochemistry, and is complex in the detection process. The invention provides the device and method for detecting blood leukocytes in a simple process, for achieving the purpose of analyzing the total amount of the leukocytes. A user can judge if the quantity and size of the leukocytes are abnormal in the manner of adopting laser light for scattering the blood diluted with sheath fluid, collecting the scattering light along the direction at 0 degree and analyzing and comparing the light shadow after scattering.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV OF TCM
Method for detecting ROS1 gene status based on rare cell and correlated kit
The invention relates to a method for detecting ROS1 gene status based on a rare cell and a correlated kit. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring a blood sample or a body fluid sample, wherein the sample contains a mixed cell population of circulating tumor cell (CTC) or other rare cells and leukocyte; step 2, using a buffer to dilute the sample, removing blood plasma, and recovering CTC or other rare cells; step 3, performing lysis by using a erythrocyte lysate, removing erythrocyte, and recovering CTC or other rare cells; step 4, uniformly mixing a magnetic particle coated with an anti-human-leucocyte correlated antigen-antibody with the recovered cell and performing incubation, so as to form a magnetic particle-leucocyte mixture through combination; step 5, centrifuging to separate the magnetic particle-leucocyte mixture from other cells, so as to obtain a mixed cell population containing CTC or other rare cells and a few of leucocytes; and setp 6, using immunofluorescence cytochemistry and fluorescence in-situ hybridization combined method to determine the ROS1 gene rearrangement state of CTC or other rare cells.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
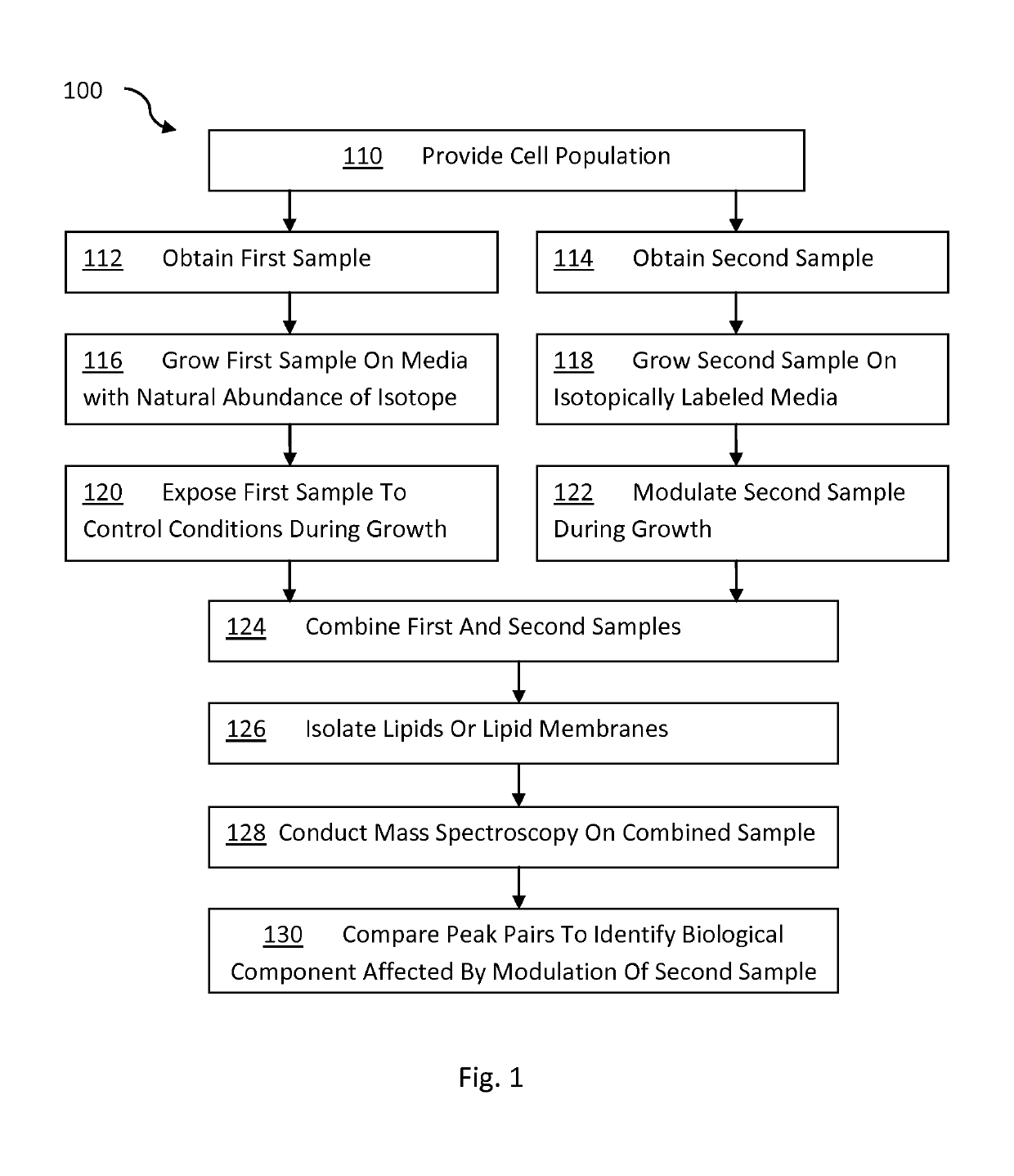
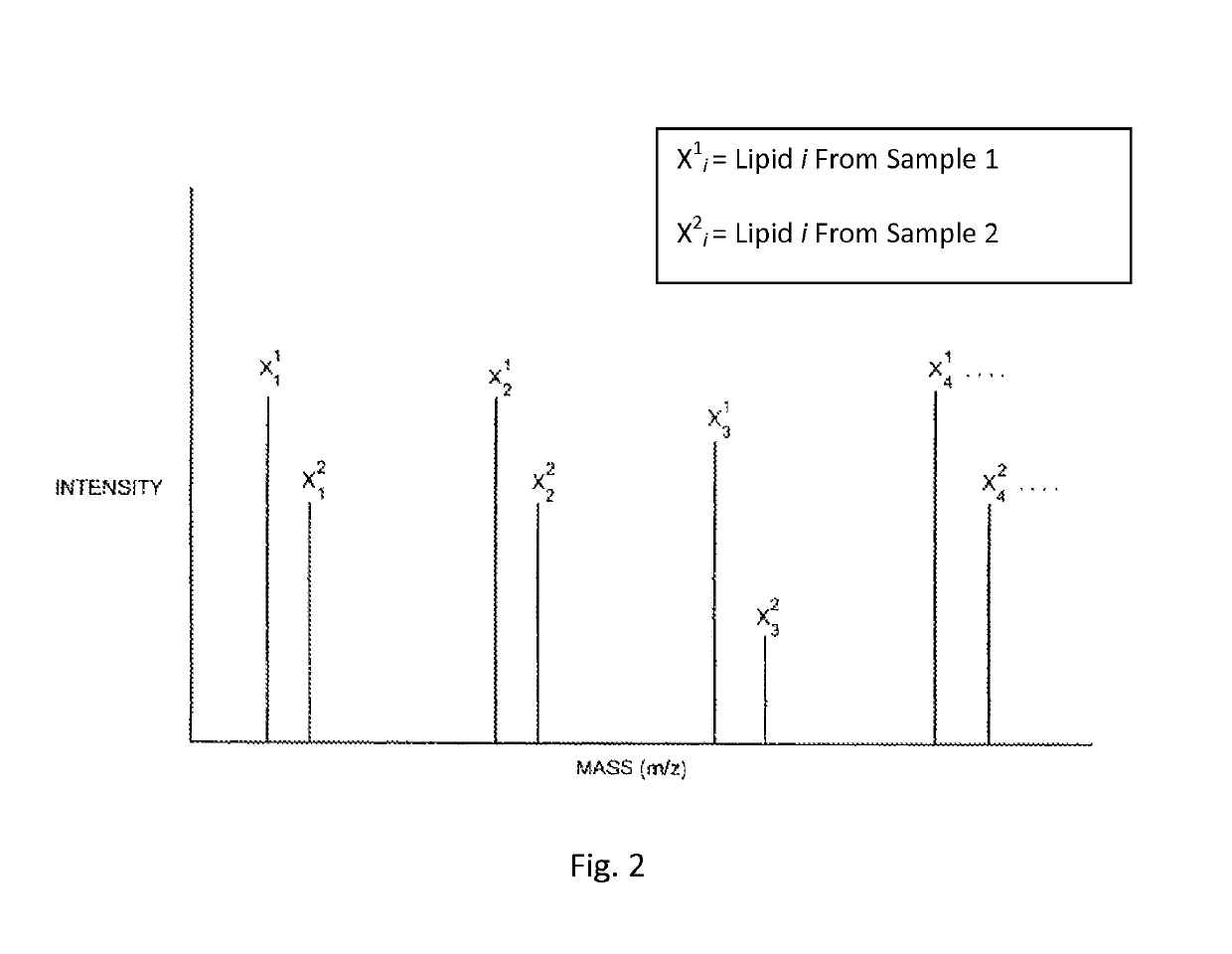
Methods for analyzing lipids and membrane proteins in biological matter using stable isotopes and mass spectrometry
ActiveUS10705100B1Accurate comparisonMass spectrometric analysisBiological testingCytochemistryIsotopic labeling
Methods for accurately comparing the levels of ionizable lipids in two cell populations that differ in some respect from each other using mass spectroscopy and isotopic labeling are provided. The methods can be used to identify a change in a lipid of interest in response to a cellular, chemical, genetic, or environmental change to the cell population (i.e., a lipid response to a cell perturbation). The change in the lipid of interest can be a change in composition, rate of synthesis, and / or location of the lipid.
Owner:HB BIOTECH LLC
Method for detecting ERCC1/CEP19 gene status based on rare cell and correlated kit
The invention relates to a method for detecting ERCC1 / CEP19 (excision repair cross-complementing 1) gene status based on a rare cell and a correlated kit. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring a blood sample or a body fluid sample, wherein the sample contains a mixed cell population of circulating tumor cell (CTC) or other rare cells and leukocyte; step 2, using a buffer to dilute the sample, removing blood plasma, and recovering CTC or other rare cells; step 3, performing lysis by using a erythrocyte lysate, removing erythrocyte, and recovering CTC or other rare cells; step 4, uniformly mixing a magnetic particle coated with an anti-human-leucocyte correlated antigen-antibody with the recovered cell and performing incubation, so as to form a magnetic particle-leucocyte mixture through combination; step 5, centrifuging to separate the magnetic particle-leucocyte mixture from other cells, so as to obtain a mixed cell population containing CTC or other rare cells and a few of leucocytes; and step 6, using immunofluorescence cytochemistry and fluorescence in-situ hybridization combined method to determine the state of ERCC1 / CEP19 and also identify CTC and other rare cells.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
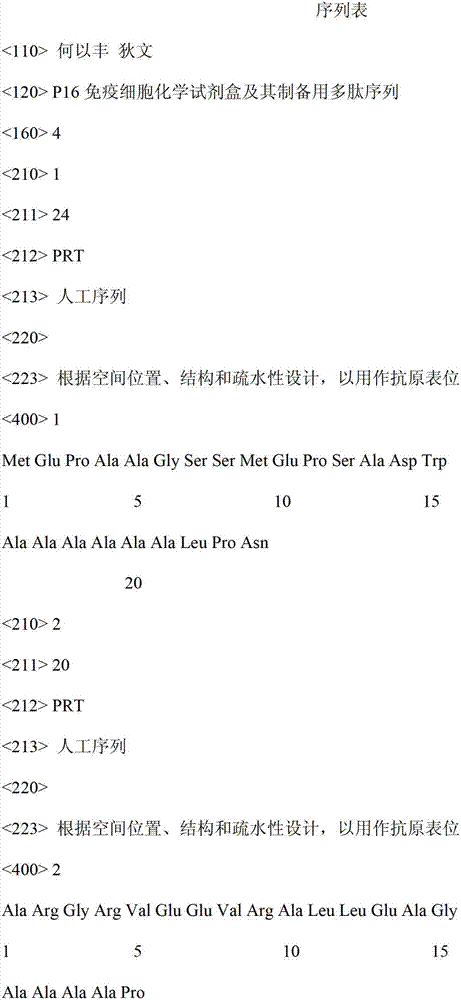
P16 immune cell chemical reagent kit and polypeptide sequence in preparing same
ActiveCN103076453BCombined detection (immunolabeling) with high efficiencyHelp anti-counterfeitingBiological testingAnimals/human peptidesCytochemistryPositive control
Owner:何以丰 +1
Mouse anti-human cd61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody and its preparation method and application, flow detection reagent
ActiveCN107058242BImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureBALB/cCytochemistry
The invention discloses a mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, a monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and application thereof and a flow cytometry detection reagent, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, human peripheral blood leukocytes are used as an immunogen for immunizing Balb / c mice; a cell fusion technology is adopted and hybridoma cells are screened by utilizing an immunocytochemistry and a flow cytometry indirect immunofluorescent method; an antibody generated by monoclonal hybridoma cells is subjected to specific identification by applying an immunoprecipitation-mass-spectrometric method; Western Blot proves that one hybridoma cell line IID5G8 capable of stably secreting a mouse anti-human CD61 monoclonal antibody is obtained and a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 13300. The monoclonal antibody is prepared by adopting an animal in-vivo induction method; a heavy chain of the antibody is identified to be IgG1 and a light chain is identified to be kappa type; after the antibody is purified, an FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate) label can be used for detecting antigen expression of human peripheral blood platelets CD61 by utilizing flow cytometry direct-labeling immunofluorescence.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
An immunochemical staining kit for cervical cancer auxiliary diagnosis
ActiveCN109856383BLess componentsEasy to useBiological testingLiquid base cytologyAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to the field of liquid-based cytology immunocytochemistry, in particular to an immunohistochemistry kit for auxiliary diagnosis of cervical cancer. The present invention provides a ready-to-use antibody working solution, including antibody reagents, bovine serum albumin, non-reducing sugars, betaine, cyclodextrin, neutral inorganic salts, surfactants, and preservatives; wherein the The antibody reagent is reagent A or reagent B; the reagent A is p16 INK4a The PBS buffer solution of monoclonal antibody and Ki-67 monoclonal antibody; The reagent B is the PBS buffer solution of the goat anti-mouse secondary antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase and the goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody labeled with alkaline phosphatase; The pH value of the PBS buffer solution is 7.2-7.8.
Owner:肖国林
A blood leukocyte detection device and method
InactiveCN107219195BSimplify the inspection processScattering properties measurementsDiseaseCytochemistry
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV OF TCM
Method and relevant kit for detecting ALK gene status based on rare cells
The invention relates to a method and a relevant kit for detecting ALK gene status based on rare cells. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, taking a blood sample or a body fluid sample, wherein the sample contains a mixed cell population comprising circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or other rare cells, and white blood cells; step 2, diluting the sample by adopting a buffer solution, so as to remove plasma and recover the CTCs or the other rare cells; step 3, splitting by adopting red blood cell splitting solution, so as to remove red blood cells and recover the CTCs or the other rare cells; step 4, uniformly mixing magnetic particles coated by relevant human-leukocyte-resisting antigen-antibodies and the recovered cells obtained in the step 3 for incubation, and mixing to form a magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture; step 5, separating the magnetic particle-white blood cell mixture from other cells through centrifugation, and thus obtaining the mixed cell population containing CTCs or other rare cells, and small quantity of white blood cells; and step 6, determining the ALK gene rearrangement state of CTCs or other rare cells by adopting a method of combining the immunofluorescence cytochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Owner:北京莱尔生物医药科技有限公司
Analytical method of components of fatty acid contained in listeria cells
InactiveCN101936960BBreaking the limits of taxonomyBreak the limitsComponent separationBacteroidesCytochemistry
The invention relates to an analytical method of components of fatty acids contained in listeria cells, in particular to a method for carrying out bacteria classification by adopting a cell chemical analysis method, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: rejuvenating listeria; respectively separating and purifying the listeria by using an OXA agar plate and a trypticase soy yeast extract agar plate; culturing the listeria of a single typical colony, and preparing into a bacterial suspension; carrying out inactivation processing by using formaldehyde; averagely filling the bacterial suspension processed by the formaldehyde into centrifuge tubes for washing; carrying out methyl esterification by using a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and the formaldehyde; and carrying out GC-MS (Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer) analysis on the prepared fatty acids. The method can not only break through the limit of the traditional bacterial taxonomy and reduce the errors brought about by anthropic factors on the traditional morphological taxonomy, but also provide a strong and powerful tool for the classification and the identification of new strains and virus types; and in addition, the method can be used for identifying the listeria from other bacteria and foods.
Owner:HUBEI INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com