Patents
Literature
165 results about "Liter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric system unit of volume which is a non-SI unit mentioned in the SI. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm³), 1,000 cubic centimetres (cm³) or 1/1,000 cubic metre. A cubic decimetre (or litre) occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm (see figure) and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.
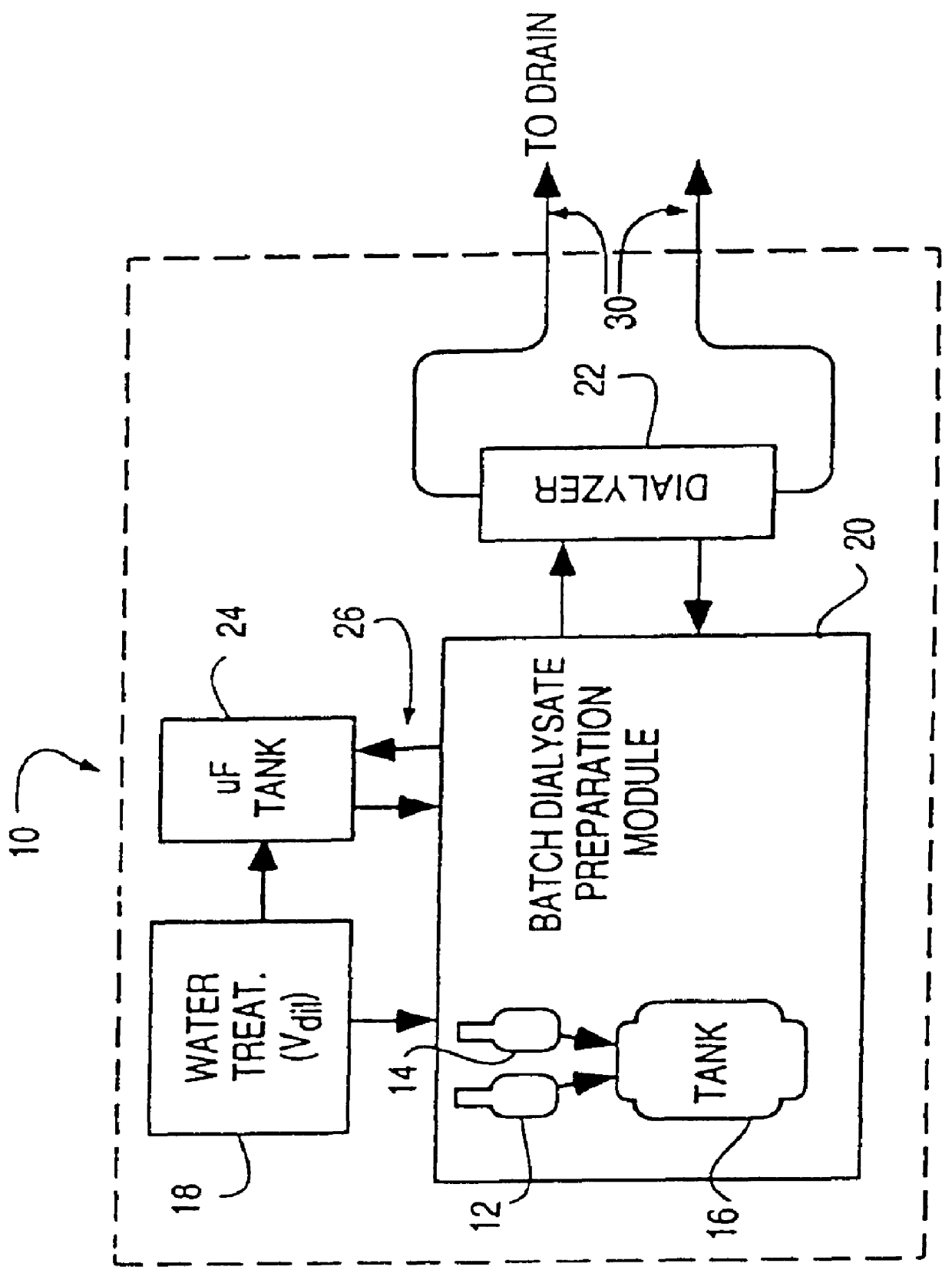
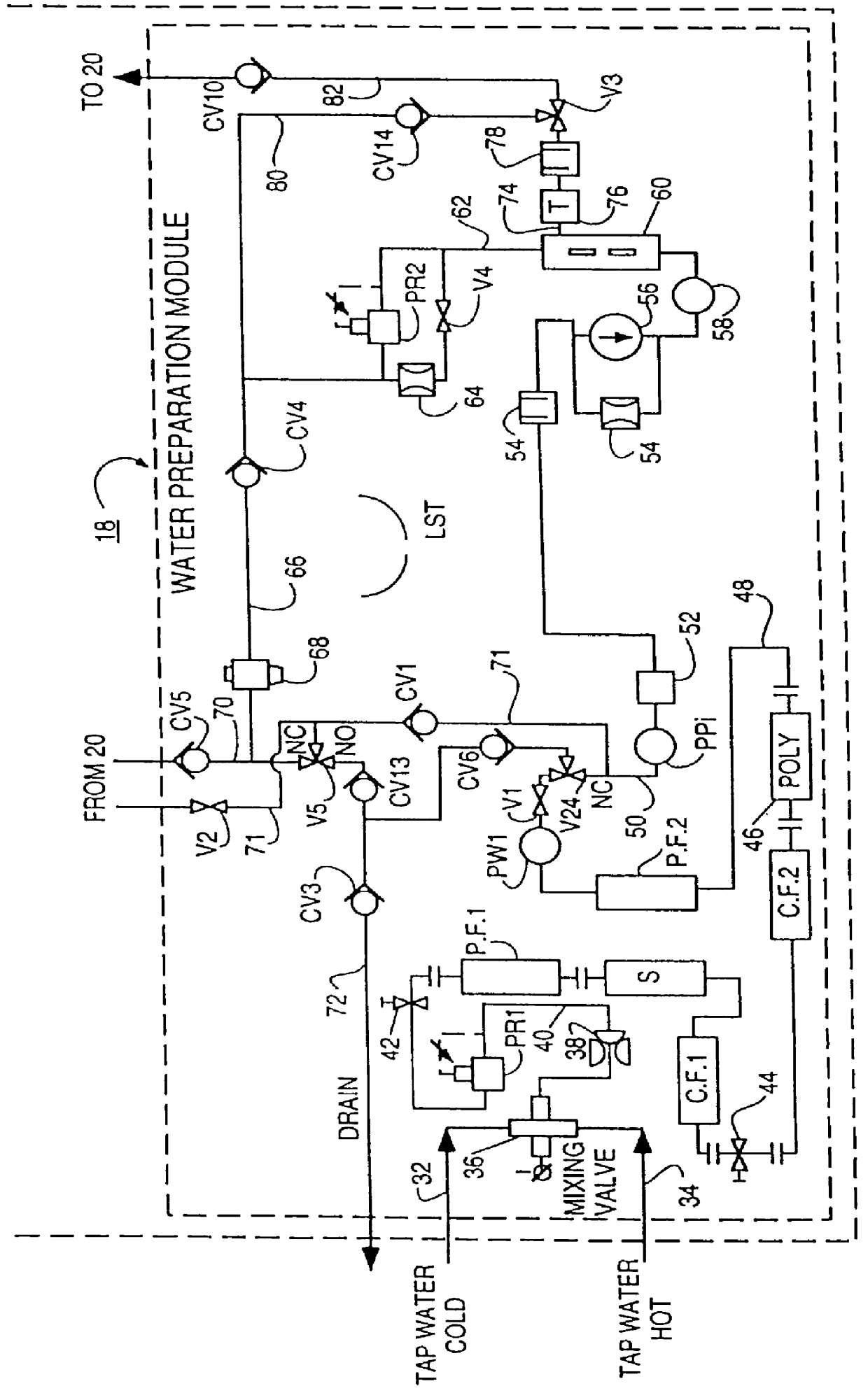
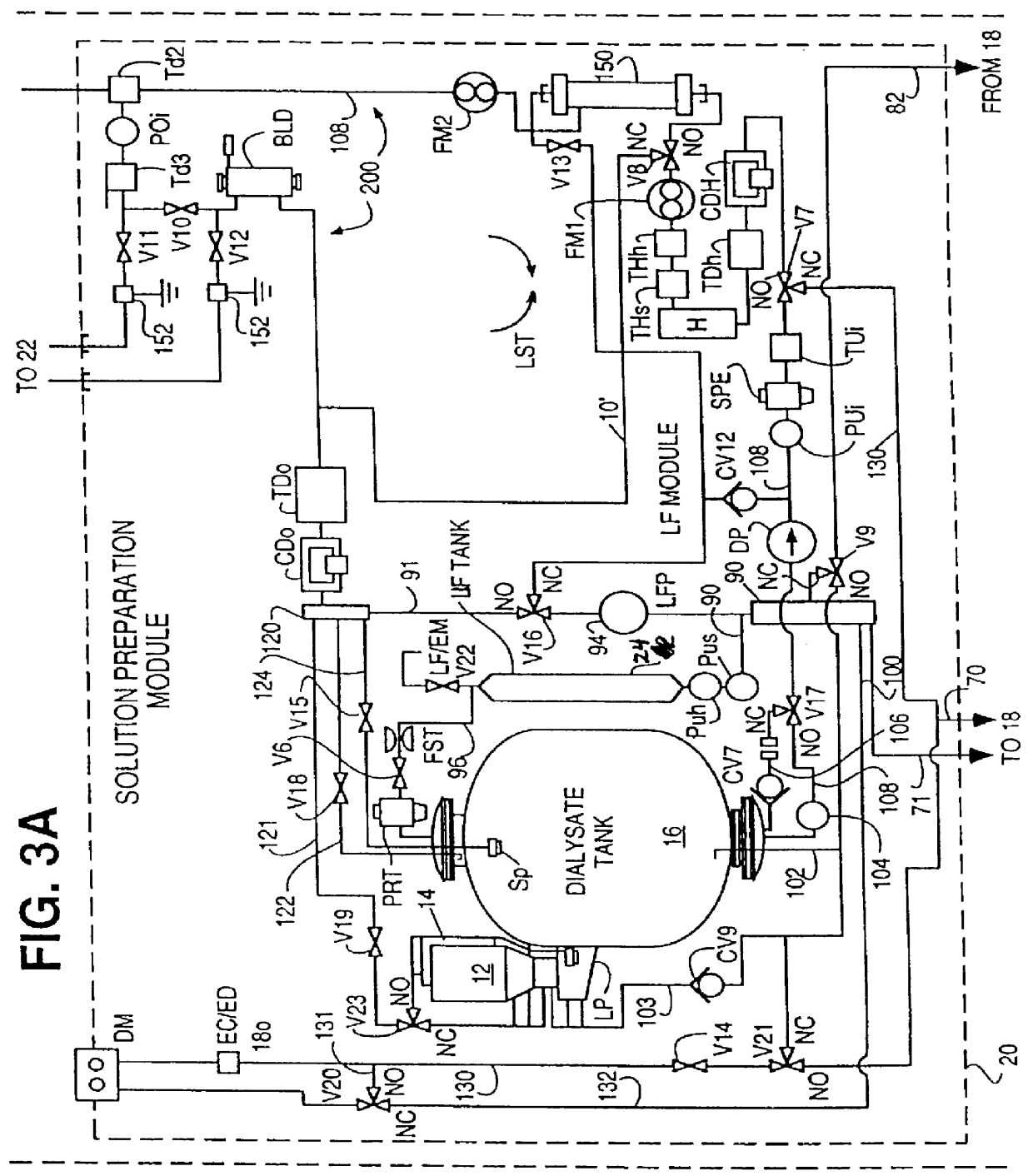
Method of preparation of batch of physiologic solution
A batch of dialysate solution is made from a mixture of bicarbonate formulation and a liquid acid formulation. The liquid acid formulation is introduced into a dialysate tank and then removed from the tank and stored elsewhere, such as in an ultrafiltration tank, where it is diluted with a few litres of water. The dialysate tank is then filled with water and the bicarbonate formulation is added to the dialysate tank. The bicarbonate formulation is mixed and dissolved by circulation in a closed loop, with the liquid acid formulation kept separate. When the bicarbonate solution has been prepared, the liquid acid solution and the bicarbonate solution are mixed together and stored in the dialysate preparation tank. An additional quantity of dilution water is introduced into the dialysate system to bring the final conductivity down to the desired range. The excess dialysate solution can be used for several purposes, such as an endotoxin flush of the blood tubing set or a dialyzer clearance test.
Owner:HHD LLC A DELAWARE LLC +2
Nutritional composition
ActiveUS20100092610A1Sufficient quantityReduce riskMilk preparationVitamin food ingredientsBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
A nutritional composition for infants at risk of developing obesity later in life comprises a protein source, a lipid source and a carbohydrate source and has a protein content of less than 1.8 g / 100 kcal and an energy density of less than 650 kcal / litre.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
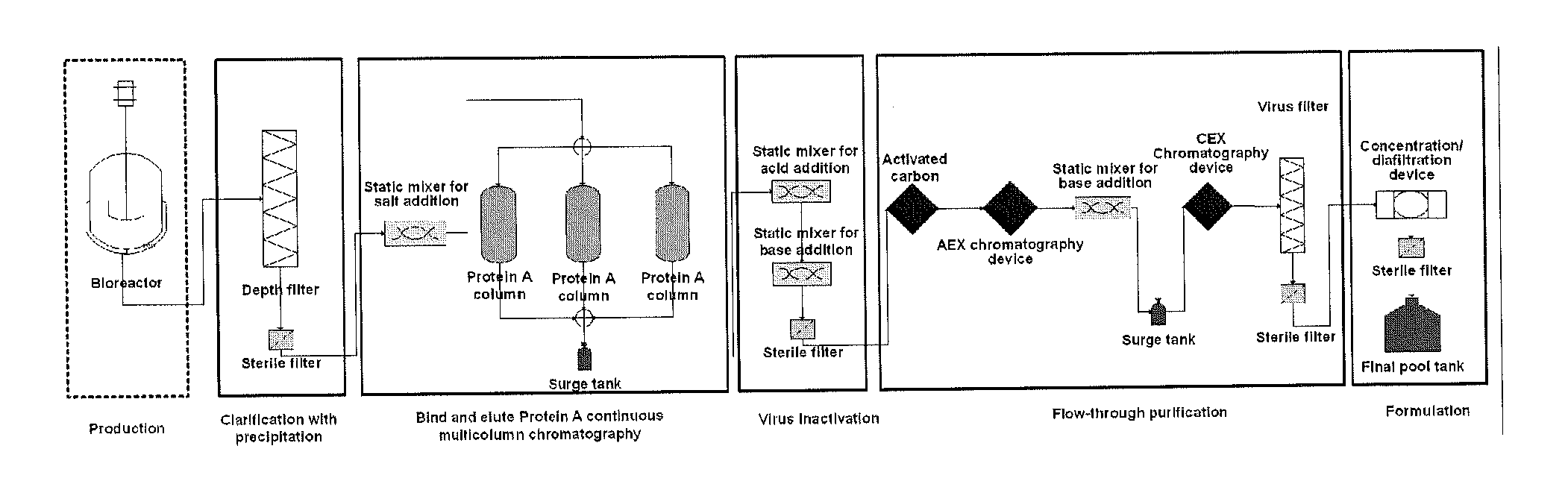
Depth Filters For Disposable Biotechnological Processes
InactiveUS20130012689A1Avoid concentrationEfficient separationIon-exchanger regenerationUltrafiltrationChemical treatmentColloidal particle
A process for the primary clarification of feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds, containing the target biomolecules of interest such as mAbs, mammalian cell cultures, or bacterial cell cultures, using a primary clarification depth filtration device without the use of a primary clarification centrifugation step or a primary clarification tangential flow microfiltration step. The primary clarification depth filtration device contains a porous depth filter having graded porous layers of varying pore ratings. The primary clarification depth filtration device filters fluid feeds, including chemically treated flocculated feeds containing flocculated cellular debris and colloidal particulates having a particle size distribution of approximately about 0.5 μm to 200 μm, at a flow rate of about 10 litres / m2 / hr to about 100 litres / m2 / hr. Kits and methods of using and making the same are also provided.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylaldehyde azomethine, synthesizing process and application in measuring content of copper ion
InactiveCN101270121AAccurate quantitative analysisHigh sensitivityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistrySodium acetateSodium acetrizoate
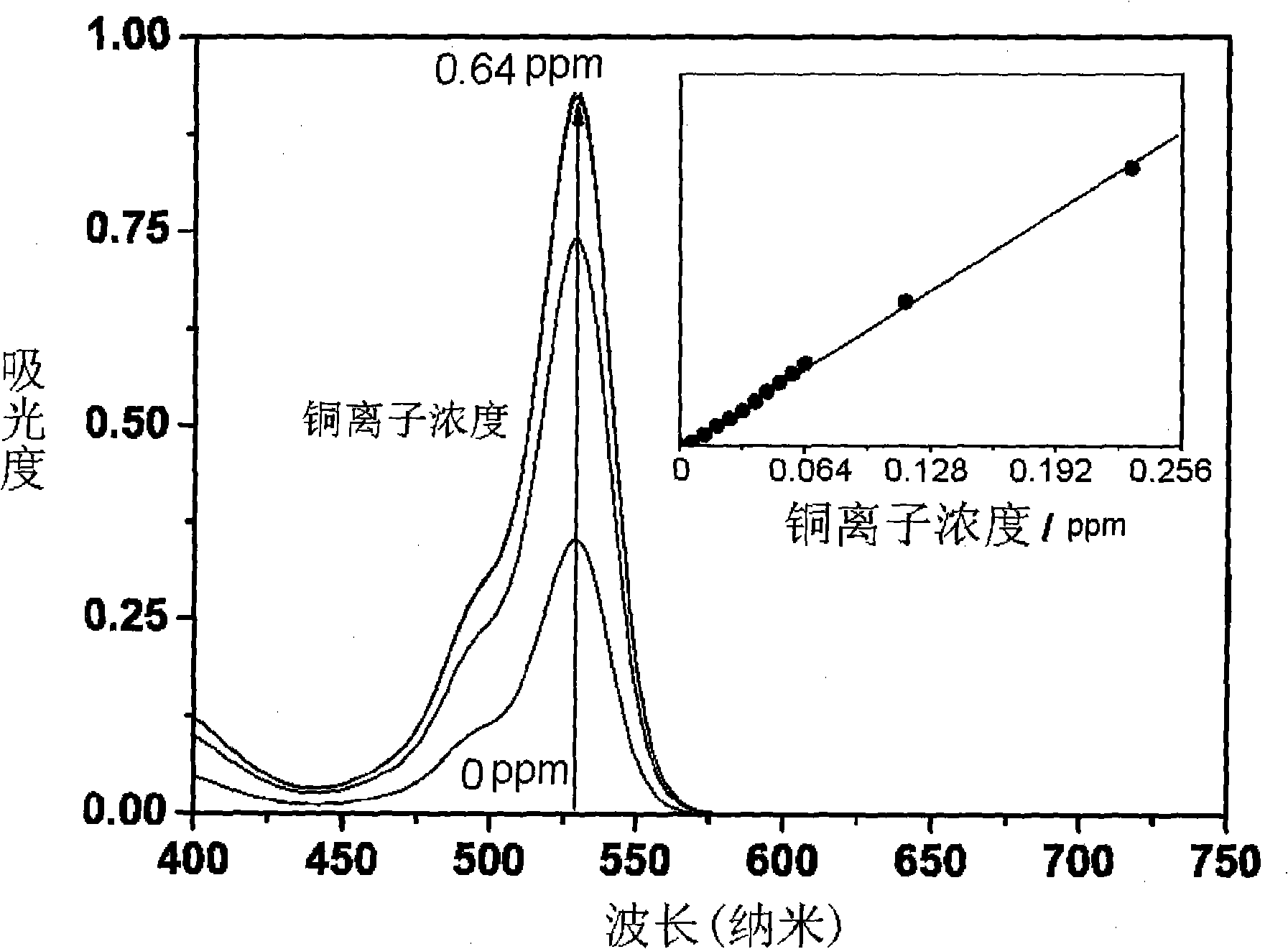
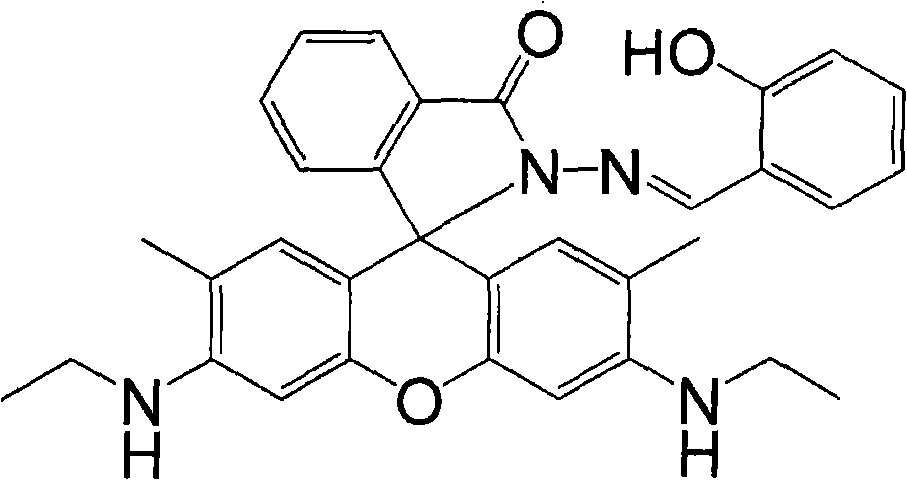
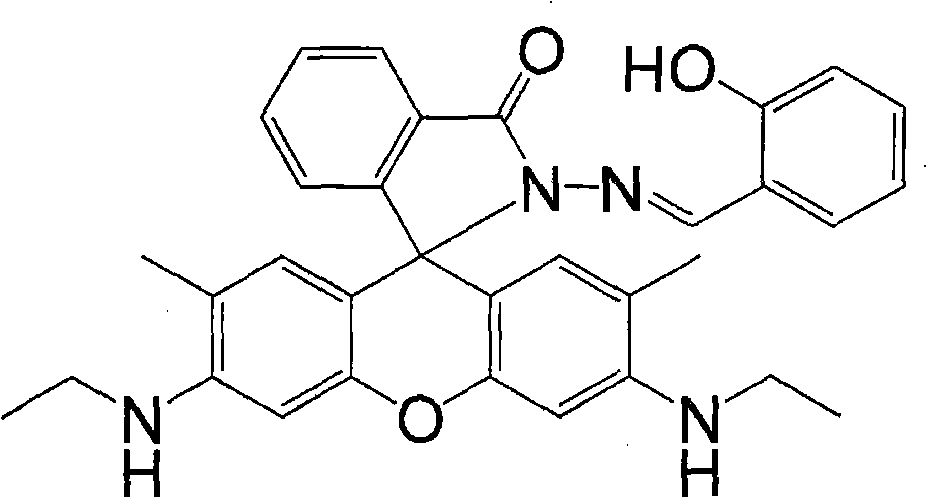
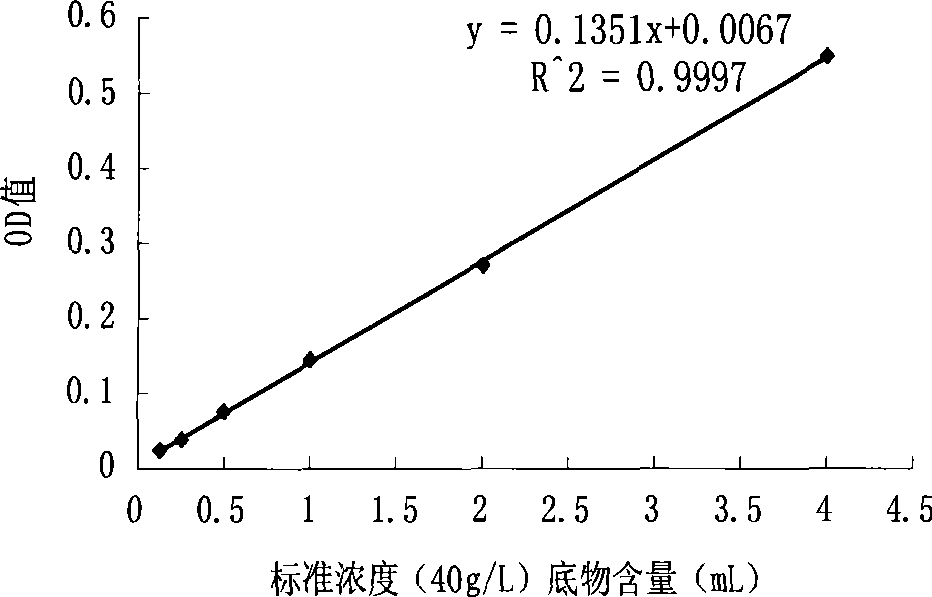
The present invention relates to rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylal azomethine, a synthesization method and an application in the content determination of cupric ions, which belong to the field of the analysis and determination of cupric ions in water sample. The molecular structural formula of the rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylal azomethine is shown on the right, and the present invention discloses the synthesization method of the rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylal azomethine and rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylal azomethine solution used for the content determination of a small amount of cupric ions in water sample: 0 percent to 98.99 percent of ethanol, 99.99 percent to 1 percent of acetic acid / sodium acetate buffer solution with the pH value of 5 to 9, in which the total concentration of acetic acid is 1 to 100 millimoles per litre, 0.01 percent of N, N-dimethylformamide and 1ppm to 100ppm of rhodamine 6G hydrazide salicylal azomethine, all measured in mass percentage. By a spectrophotometer, the solution can be used for the accurate quantitative determination of 0.005ppm to 0.256ppm of cupric ions in water sample as well as the semiquantitative determination of no less than 0.075ppm of cupric ions in water sample by direct naked-eye observation on the change of colors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cultivation method for north America rhododendron
InactiveCN101292628AImprove featuresRealize factory breedingCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsMixed materialsBud
Disclosed is a method for tissue culture of rhododendron. The tissue culture method comprises the steps that: step 1: rhododendron explant material is collected, and placed on a supper-clean bench after being treated; the rhododendron explant material is disinfected by alcohol with a concentration of 75 percent for 6 to 8 seconds, washed by sterile water for three times, disinfected by 0.001 litre of mercury for 6 to 8 minutes, and washed by sterile water for three times in order; step 2: the material after being disinfected and cut is implanted into bud induce culture medium for thirty days; 30 days later, the obtained material is then implanted into proliferation culture medium for 60 days; step 3: healthy and strong rhododendron seedlings cut with 2 to 3cm by height are implanted into a rooting culture medium for 45 days; step 4: after the newborn root of rhododendron is about 0.5 cm long, the culture medium attached to the root is cleaned and newborn root is moved into sterile thick sand, the air humidity of which is kept ranging from 75 percent to 85 percent; one week later, the newborn root is moved into the mixed material of turfy soil and perlite; 45 days later, the treated root is moved into the field where the root is under the shade for one week. The method can realize industrial culture of seedling within 6 to 7 mouths and mass production of shipshape nursery stock of rhododendron.
Owner:CHINA PAULOWNIA RES CENT
Method for curing soil by using carbonate mineralized bacterium
ActiveCN101368384AHigh compressive strengthHigh strengthSoil preservationCompressive resistanceHigh concentration
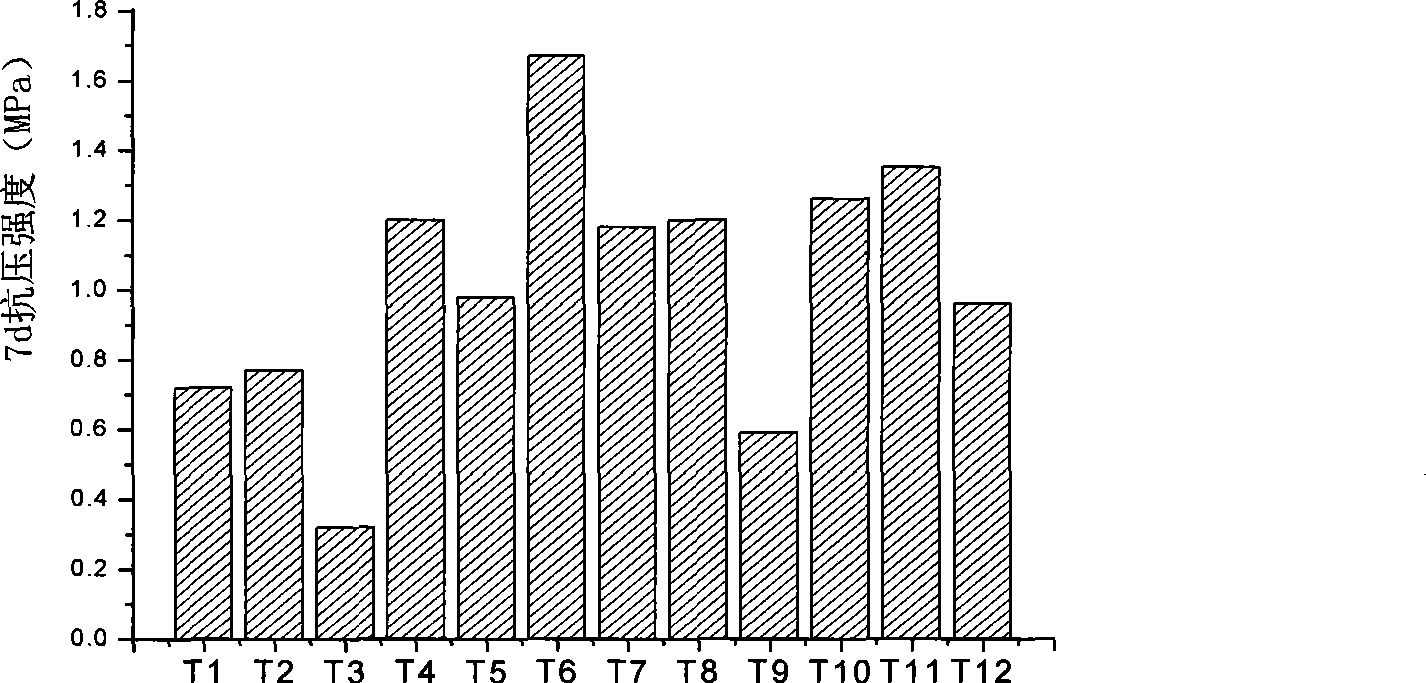
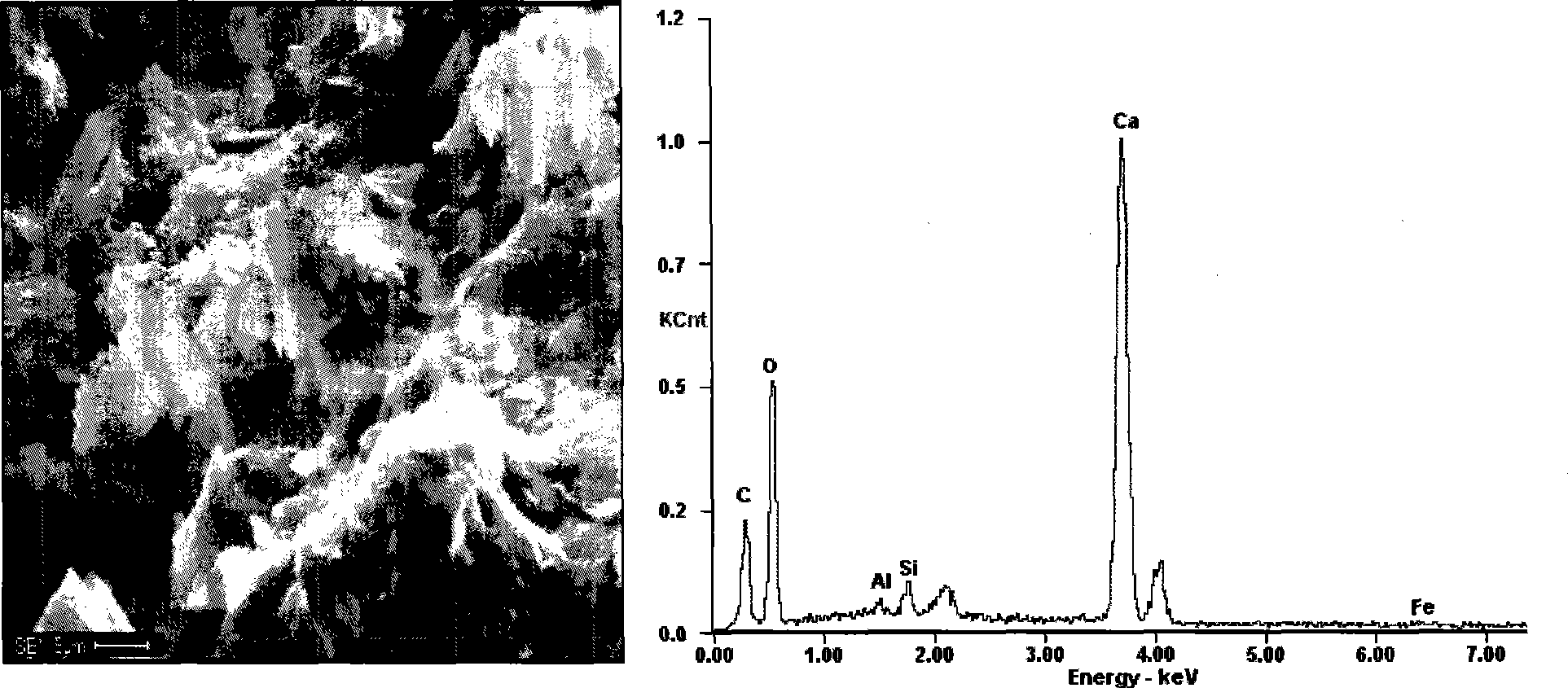
The invention discloses a soil curing method through carbonate-mineralization microbes, including the following steps: first, preparing high concentration microbe liquid: inoculating Bacillus pasteurii strain into the culture fluid of beef extract and peptone; wherein each litre of culture fluid contains 4-6g peptone and 2-4g beef extract; cultivating for16-24h under30DEG C with the pH value controlled at 6-8, then getting out the mixture and centrifuging for 5-8min under the speed of 5000-8000rpm, thus getting high-concentration microbe liquid at concentration of 2 X 10<9>-2 X 10<11>cell / ml; second, mixing the soil: mixing the high-concentration microbe liquid prepared in the first step and the newly prepared culture fluid into the dried soil sample through lime(3%-7% the weight of the dry soil) and carbamide(2%-6% the weight of the dry soil) according the proportioning of 100g dry soil per 2-3mL high-concentration microbe liquid and 0-50mL newly prepared culture fluid, blending to be even and then cultivating for 0.5-8days; third; molding through a die: molding the soil mixture cultivated in second step in a die when the mixture reaches the optimal water ratio, then demoulding and conserving in constant temperature of 20 DEG C. Seven days later, the soil will be cured, with the compressive resistance reaching above 1.0MPa, up by 38% as compared with pure soil.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Kettle
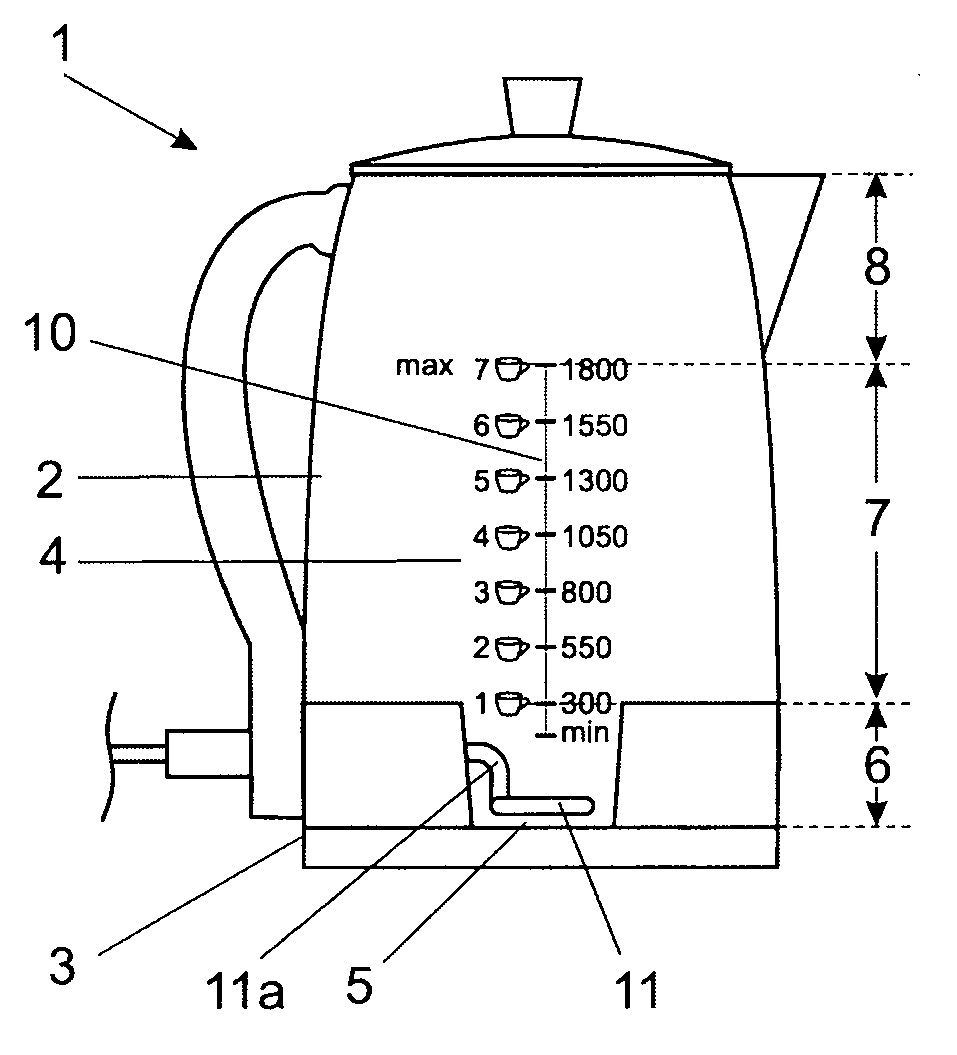
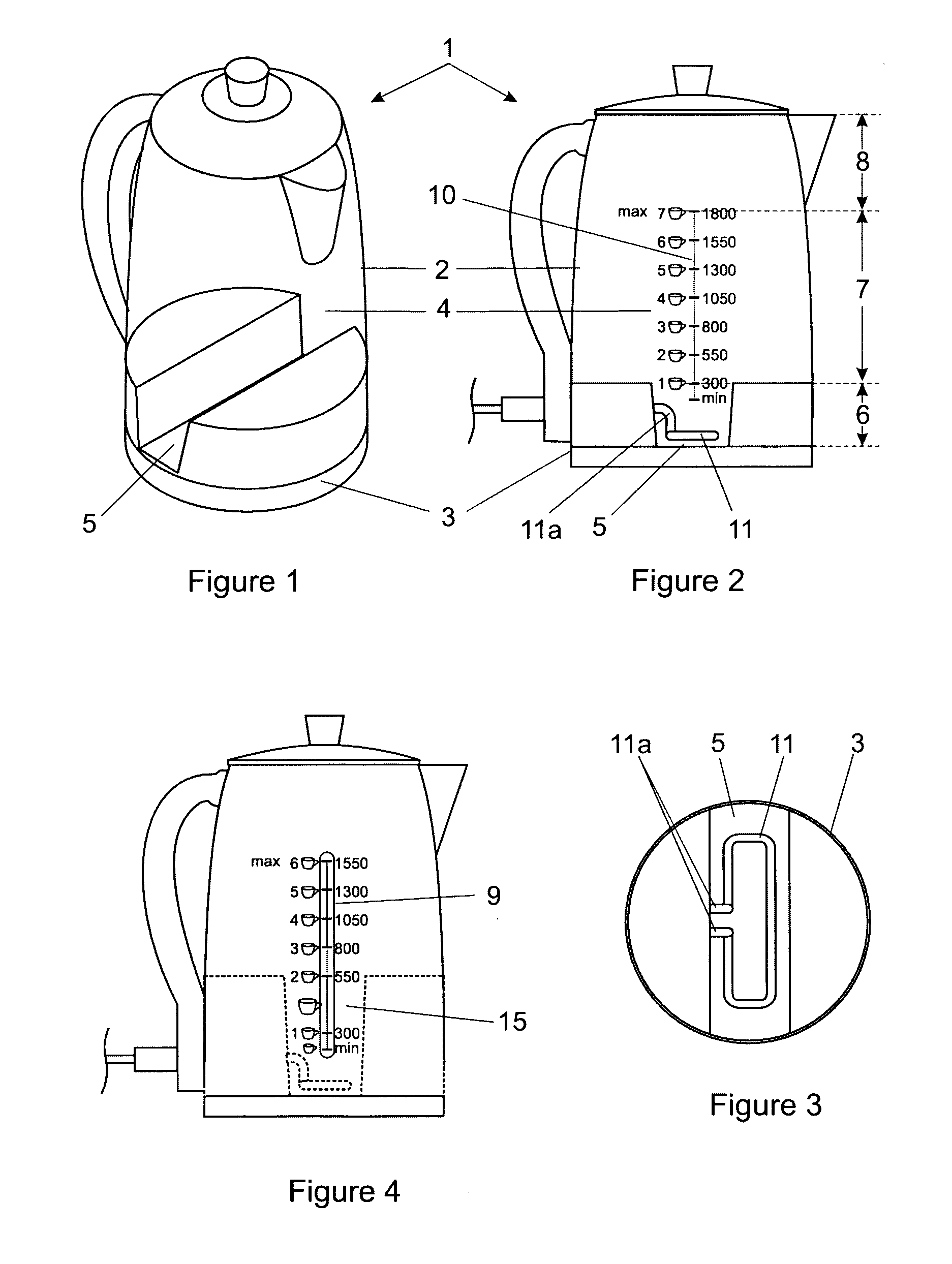
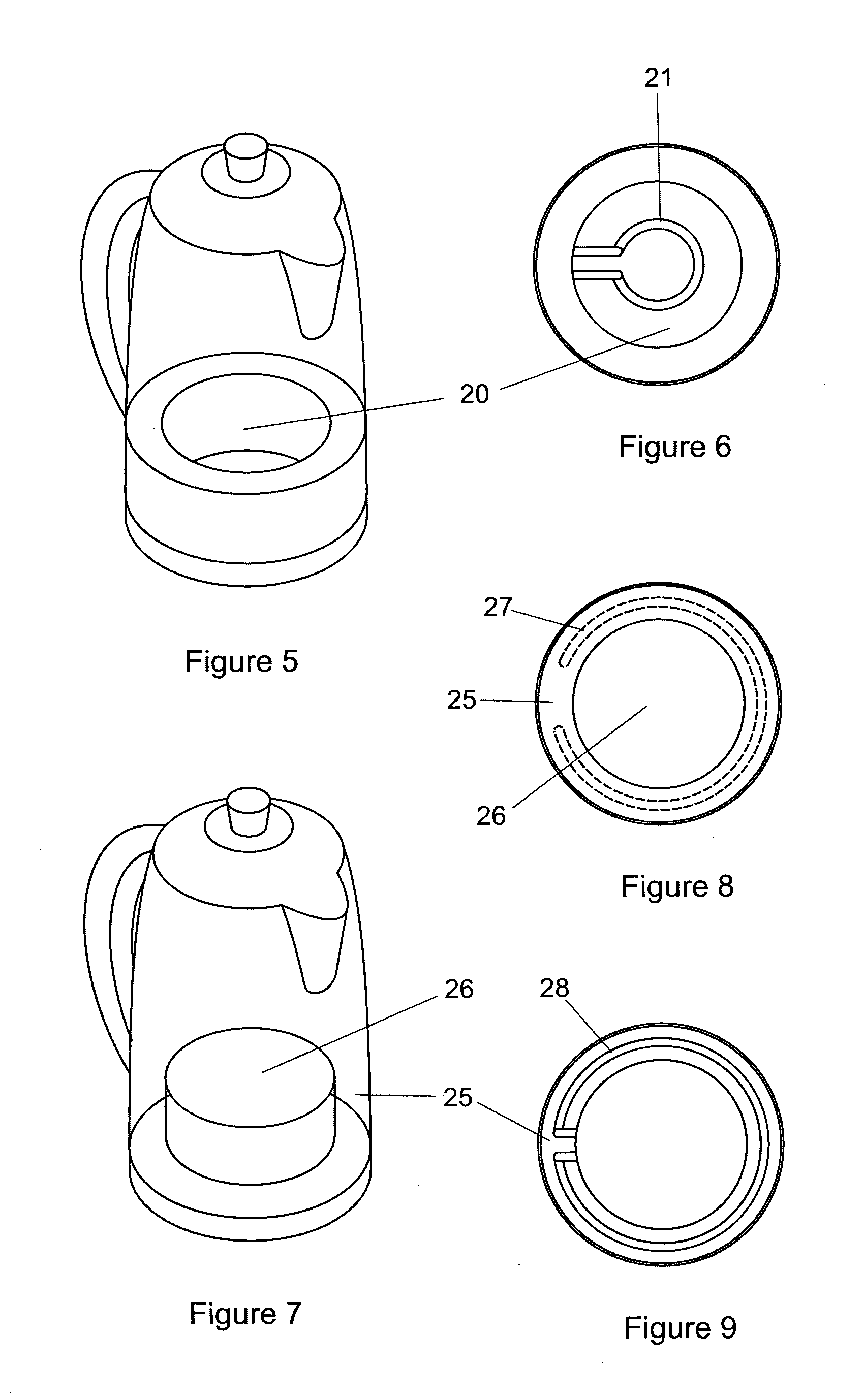
InactiveUS20120145698A1Increase in sizeImprove accuracyWater-boiling vesselsElectric heating for furnacesVisual observationEngineering
A kettle (1) is provided having a body (2) with a lowermost outer periphery (3), a water chamber (4) inside the body wherein the water chamber has a bottom (5), a lower region (6) immediately above the bottom and a central region (7) that together define a maximum volume of water of at least 1 litre, and typically from 1.4 to 1.8 litres. A transparent wall section or window (9) enables visual observation of the water level. Electrical heating means (11, 21, 27, 28) are provided for heating the water. The lower region of the water chamber has an average horizontal sectional area that is not more than 75%, and preferably not more than 50% of the area enclosed by the lowermost outer periphery. This enables one or 2 cups of water to occupy a greater vertical height in the water chamber and a minimum volume of water of 400 millilitres, and preferably 300 millilitres or less to be visible through the transparent wall section or window. The arrangement greatly facilitates introducing only one or two cups of water into the kettle.
Owner:VON SEIDEL MICHAEL
Drying method
ActiveUS20130305560A1Keep dryExtended drying timeDrying solid materials with heatTextiles and paperSolid particleEngineering
The invention provides a method for the drying of a wet substrate, the method comprising treating the substrate with a solid particulate material at ambient or elevated temperature, the treatment being carried out in an apparatus comprising a drum comprising perforated side walls, wherein the drum comprising perforated side walls is rotated so as to facilitate increased mechanical action between the substrate and the particulate material. Preferably, the drum comprising perforated side walls has a capacity of between 5 and 50 litres for each kg of fabric in the load and is rotated at a speed which generates G forces in the range of from 0.05 to 0.99 G, and the method is carried out at a temperature of between 5° and 120° C. Preferably, the solid particulate material comprises a multiplicity of particles at a particle to fabric addition level of 0.1:1-10:1 by mass, wherein the particles comprise polymeric particles, non-polymeric particles, or mixtures of polymeric and non-polymeric particles. All particles may be solid or hollow in their structure, have smooth or irregular surface features, and are of such a shape and size as to allow for good flowability and intimate contact with the wet substrate. The invention provides optimum drying performance as a result of improved mechanical interaction between substrate and particulate media and is preferably used for the drying of textile fabrics. The method allows for significant reduction in the consumption of energy when compared with the conventional tumble drying of textile fabrics, and also facilitates reduced textile fabric damage.
Owner:XEROS LTD
Food composition for prodromal dementia patients
ActiveUS20100323982A1High probability to developReduce developmentBiocideNervous disorderMedicinePhospho tau
A composition comprising (a) one or more ω-3 fatty acids selected from DHA, DPA and EPA, (b) uridine or its equivalent, and (c) a methyl donor, useful in the treatment of a person having characteristics of a prodromal dementia patient. The characteristics include e.g. a level of more than 350 ng Total-tau per litre cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and a weight ratio of abeta-42 / Phospho-tau-181 of less than 6.5 in CSF.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
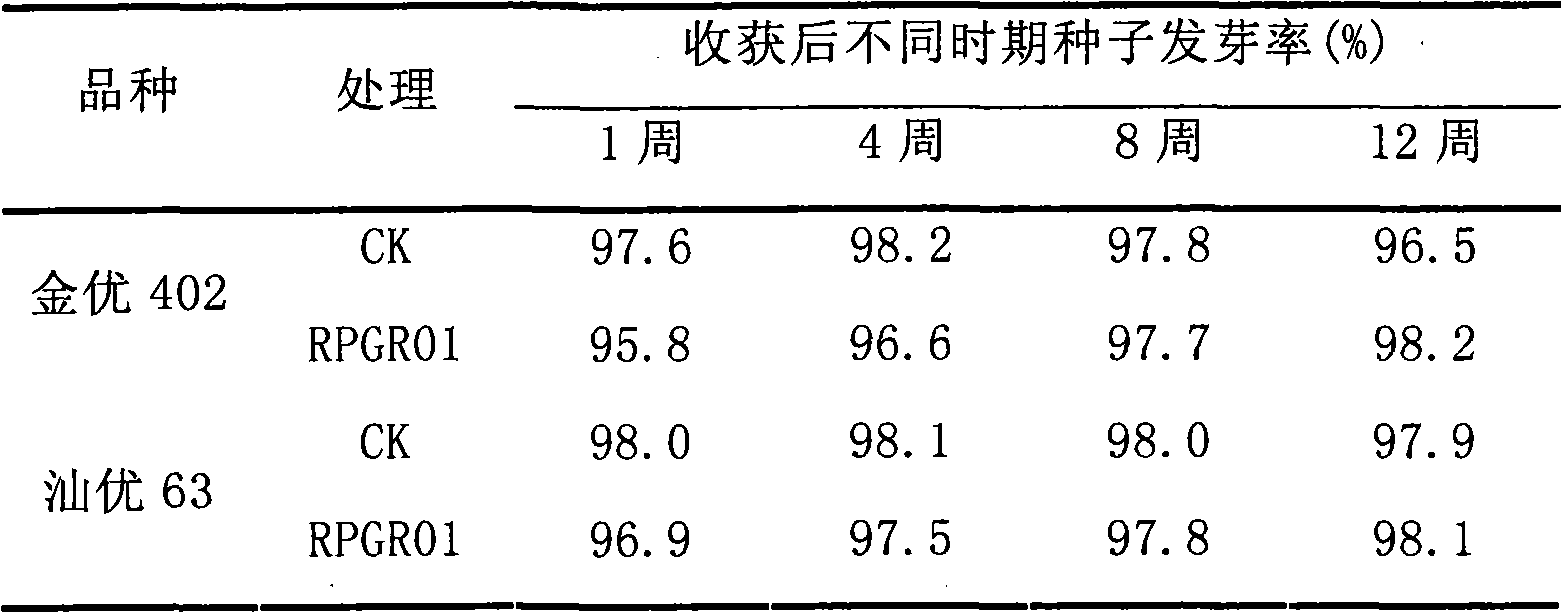
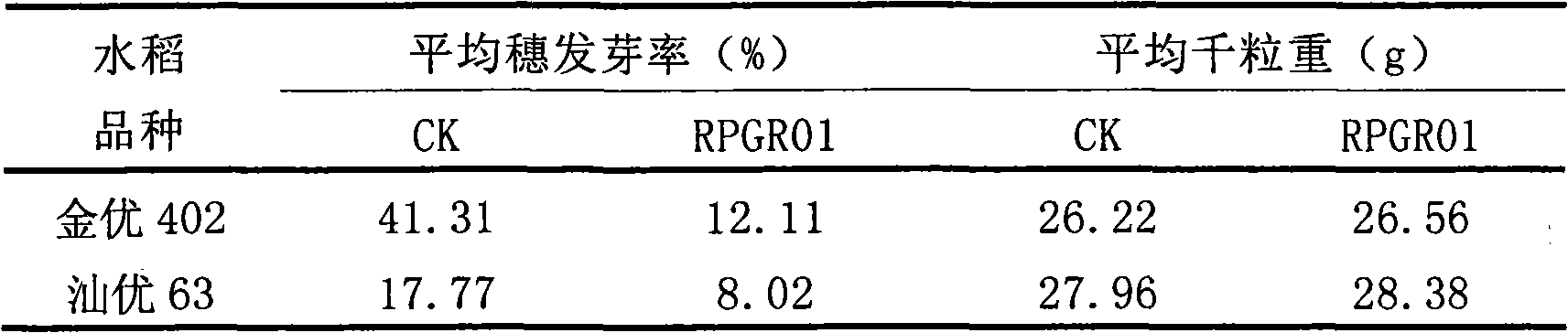
Hybrid rice pre-harvest sprouting inhibitor
InactiveCN101773137AReduce dosageNo worries about damaging the ecological environmentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPhytic acidSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a hybrid rice pre-harvest sprouting inhibitor, which belongs to the technical field of agricultural production. In the process of hybrid rice seed production and cultivation, the pre-harvest sprouting phenomenon can easily occur due to high temperature and high humidity. The pre-harvest sprouting not only has a strong impact on yield, but also reduces the quality of rice and brings difficulty to harvesting as well. The inhibitor comprises the following main active components weighted in gram (in 1 litre of aqueous solution): 2.200 to 5.900 grams of phytic acid, 0.120 to 0.850 grams of abscisic acid, 6.520 to 9.400 grams of calcium chloride, 7.500 to 10.200 grams of boric acid, 0.100 to 0.800 grams of paclobutrazol and 0.001 to 0.010 grams of salicylic acid. The inhibitor has a good effect in inhibiting the pre-harvest sprouting of hybrid rice, the pre-harvest sprouting-inhibiting percentage can be up to 75 percent, the thousand kernel weight can be increased by 0.32 to 0.55 grams, and the seed vigor cannot be affected. The inhibitor has the advantages of convenient use, tiny dosage, low cost, no toxicity and no harm, and has a broad popularization and application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Process for the hydrolysis of milk proteins
The present invention provides a composition comprising hydrolysed milk casein and, preferably non-hydrolysed whey protein in a ratio from 9:1 to 1:1 (on dry weight), which is a clear liquid at pH 4 when dissolved or present in water in an amount of 40 g / litre at 10° C.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Kiwi fruit suspension liquid atomizing artificial pollination method
The invention relates to a kiwi fruit suspension liquid atomizing artificial pollination method. The kiwi fruit suspension liquid atomizing artificial pollination method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: a. pollen collection, namely selecting and plucking a flower which is about to blossom or early blossoms, taking down an anther, and then screening out pollen; b. preparation of a suspension liquid, namely adding 5g of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 1g of borax, 3g of white granulated sugar and 2g of the pollen into every litre of an aqueous solution; c. pollination, namely placing the prepared solution into an atomizer, and beginning to spray on the kiwi flowers after dew is dry in the morning. According to the cultivation technique of the kiwi fruit suspension liquid atomizing artificial pollination method provided by the invention, kiwi fruits can be well planted, the variety in a park is pure, the male and female proportion is accurately controlled, and the fruit quality is superior to the quality of an existing kiwi fruit.
Owner:恩施州益寿果业股份有限公司 +1
Production method of polishing powder for liquid crystal display device
InactiveCN101381586AHigh crystallinityAccelerated settlementPolishing compositionsNon-linear opticsComing outTunnel kiln
The invention relates to a method for producing polishing powder used for a liquid crystal display device. The method comprises the following steps: at the room temperature, 30 to 40 percent of fluorosilicic acid is added into rare earth chloride solution with REO of between 80 and 100 gram / litre and CeO2 / REO of more than or equal to 70 percent under the stirring; after five minutes, an additive A is added into the mixture, is heated to the temperature of between 70 and 80 DEG C, is kept at the temperature and is added with mixed precipitant solution till the reaction ends; the PH value of the mixture is 7; the mixture is stirred for 10 minutes, is kept stand for 3 to 5 hours and supernatant fluid of the mixture is removed through siphonage; under the stirring, cold water is added to nearly fill a groove fully; before the stirring is stopped, flocculant solution is added till appearing the flocculating effect; the mixture is kept stand, is deposited and the supernatant fluid of the mixture is removed through siphonage for three times; the mixture is washed, is heated up to 98 DEG C, is kept at the temperature for 10 minutes and is discharged to a stainless steel sieve with 120 meshes; the mixture is subjected to solid-liquid separation, vacuum extraction and filtering and dewatering by a centrifuge; a filter cake is transferred to a quartz material sagger; the charging thickness is less than or equal to 9 centimeters; the filter cake is transported to a muffle tunnel kiln at the temperature of 900 DEG C, is subjected to dehydration in a preheating section and decomposition and transformation at certain degree, is roasted for 3 to 4 hours at high temperature of 900 DEG C, is cooled to the temperature of less than 400 DEG C in a cooling section and comes out from the kiln; a roasted material is cooled to the room temperature and is subjected to stage treatment; and a quality part is the product.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIELONG RARE EARTCH FINE ABRASIVE MATERIAL
Mulberry leaf tea beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101558798ASolve the problem of bad taste and difficult to be accepted by the publicChange the single agricultural production modelPre-extraction tea treatmentFood preparationAcute hyperglycaemiaSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a mulberry leaf tea beverage and a preparation method thereof. Each litre of the mulberry leaf tea beverage comprises the following compositions: 4 to 6 grams of mulberry leaf powders, 0.4 to 0.6 gram of tea powders, 0.14 to 0.18 gram of AK sugar, 0.14 to 0.18 gram of aspartame, 2.0 to 2.2 grams of citric acid, 0.5 to 0.7 gram of sodium citrate, 0.06 to 0.1 gram of sodium erythorbate, 0.15 to 0.25 gram of salt, 0.15 to 0.25 milliliter of citric acid black tea flavor and 0.15 to 0.25 milliliter of black tea flavor. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: the mulberry leaf powders are extracted by 95 percent ethanol; the residue is extracted by water; an extraction solution is subjected to vacuum condensation at a temperature of 60 DEG C; each litre of the extraction solution is subjected to adsorption treatment by 0.2 gram of bentonite; mulberry leaf juice and tea juice are mixed in volume ratio of 10:1, added with an auxiliary material and homogenized; and the mixture is subjected to short-time sterilization for 4 seconds at high temperature of 105 DEG C and heat exchange to quickly cool to a temperature of 65 DEG C, and canned. The test proves that the beverage taking mulberry leaf as a main material can effectively prevent hyperglycemia and hyperlipemia and has safe edibility and good mouthfeel.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Pond polyculture method for Yangtze-river two-year-old coilia ectenes fingerlings and scatophagus argus
ActiveCN103960174AImprove water qualityHigh outputClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPolycultureScatophagus argus
The invention discloses a pond polyculture method for Yangtze-river two-year-old coilia ectenes fingerlings and scatophagus argus. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, an estuary-area pond and natural brackish water with an inflow salinity of 0.5-1.5% are chosen, and food organism is inoculated in the pond; secondly, fingerlings are put in the pond in winter or in early spring, wherein the stocking size of Yangtze-river two-year-old coilia ectenes fingerlings is a total length of 10 to 12 cm, and the stocking density thereof is 500 to 600 fishes per mu; thirdly, the scatophagus argus is put in the pond from the end of April to the beginning of May, wherein the stocking density is 150 to 250 fishes per mu,and the stocking size is 20 to 30 gram per fish; fourthly, 1 / 3 of water is changed each month from January to June, 1 / 3 of water is changed each half month from July to September, and 1 / 3 of water is changed each month from October to December; fifthly, food organism is supplemented timely when the density of the food organism is lower than 1 per litre; sixthly, during a cultivation period, artificial pellet feed is supplemented as the feed for the scatophagus argus, opossum shrimp and crustacean 1 to 2 jin per mu and 1 time per day; finally, fishes are captured with nets in early winter, wherein the specification of captured coilia ectenes is 16 to 20 gram per fish while the specification of the scatophagus argus is 110 to 130 gram per fish.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Green and environment-friendly sealing method for surface anode oxidization of aluminum alloy
InactiveCN103305892AComposition is stableFlat surfaceSurface reaction electrolytic coatingEnvironmental resistanceCerium nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal surface treatment, and particularly relates to a green and environment-friendly sealing method for an anode oxidization membrane of aluminum alloy. The sealing fluid used in the sealing method is aqueous solution cerium nitrate, and the cerium nitrate content per litre aqueous solution is 3-10g. With the sealing fluid, the defect that the existing sealing fluid contains toxic and harmful substances can be solved, the use of chromate and nickel salt in the sealing process can be avoided by sealing the anode oxide membrane of the aluminum alloy through the sealing fluid, so that the sealing method is a green and environment-friendly sealing method for the anode oxidization membrane of the aluminum alloy. The method is stable in technique, and the sealing fluid is easy to prepare, and low in cost, does not contain fluorine ions and hexavalent chromium ions, thus being green and safe sealing fluid which meets environment-friendly requirement. Compared with the traditional technology, the equivalent aluminum and aluminum alloy anode oxidization membrane corrosion resistance can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
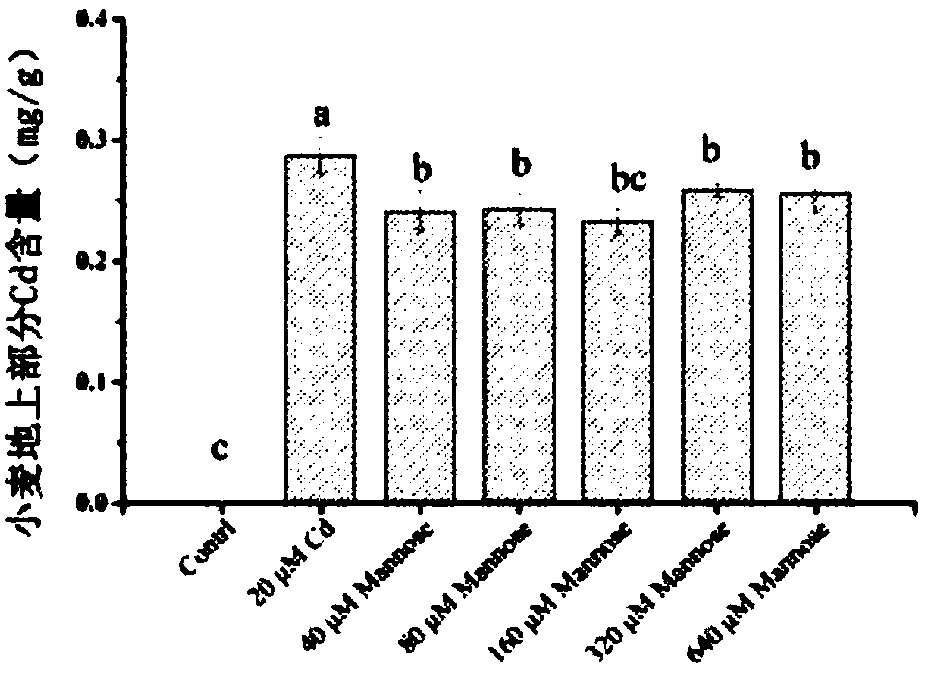
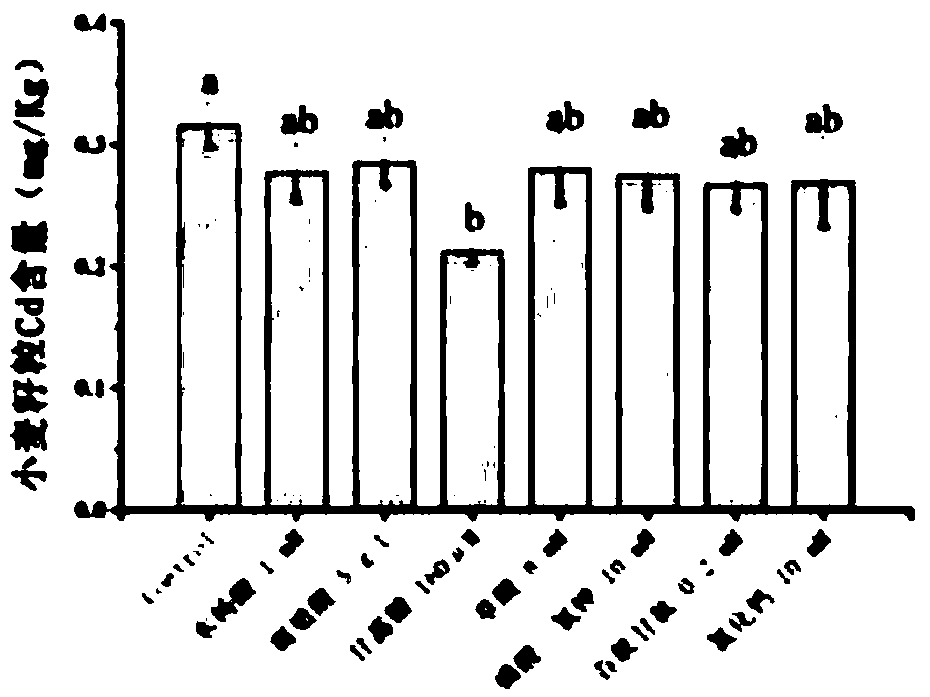
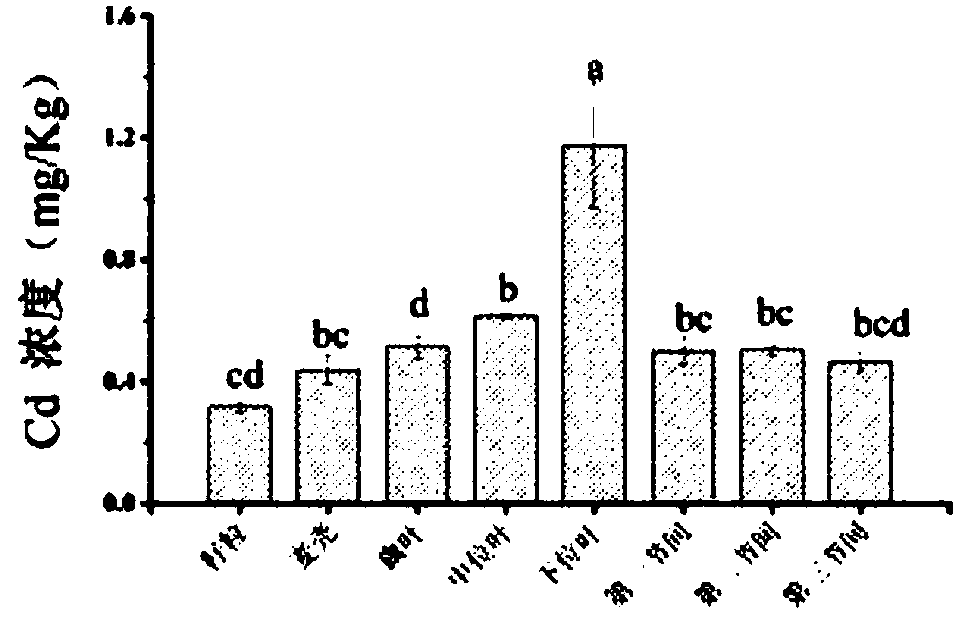
Leaf surface obstructing agent capable of inhibiting wheat grains from cadmium absorption and accumulation and using method thereof
ActiveCN108739165AReduce cadmium contentCause secondary pollutionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsWheat grainContamination
The invention discloses a leaf surface obstructing agent capable of inhibiting wheat grains from cadmium absorption and transferring. The main effective component of the leaf surface obstructing agentis mannose, and the concentration of the mannose is 40 micromoles per litre-320 micromoles per litre. The invention further discloses a using method of the leaf surface obstructing agent. The using method of the leaf surface obstructing agent comprises the steps that the spraying period of the leaf surface obstructing agent is the growing and developing period of wheat, the mist spraying mode isadopted to make the leaf surface spraying agent sprayed to wheat leaves contaminated by cadmium, and the leaf surface obstructing agent is sprayed at regular intervals. According to the leaf surface obstructing agent, the cadmium content contained in the wheat grains can be effectively reduced by 32.93%-33.52%, the operations are simple, secondary contamination on soil cannot be caused, and good solving ways are provided for the cadmium contamination problem of the wheat grains.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
High-content camptothecine camplotheca acuminata callus culture method
The invention is a high-content camptothecin callus cultivating method of camptotheca acuminata, its steps including: (1) prepare outer plant body; (2) induce the callus; cut the happy-tree laminae into blocks of 0.5X0.5-1.0 cm2, and the leafstalk cut into 0.5-1.0 cm segments inserted in the callus-inducing culture medium for inducing. The above culture medium is prepared by adding sucrose, 20-40g, agar powder, 5.4-7.2g, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 0.25-3.0 mg, and 6-(benzyl amino) purine, 0.5-3.0 mg in 1 litre of MS basic culture medium, pH 6.0. Hold the prepared culture medium in the nutritious bottles, 25ml / bottle, then sterilize for 25 minutes under a 0.1-0.15 MPa pressure, then place the bottles in the hothouse for cultivating, temperature 22-26 deg.C and luminous intensity 2000-3000 lx.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Casing preservation method
InactiveCN103461458AIncrease elasticityImprove toughnessMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsSODIUM METAPHOSPHATEPhosphate
The invention relates to a casing preservation method and a preparation method for a fresh-retaining solution. The method solves difficult problems of a conventional casing preservation method is high in casing breakage ratio and wastes water source because of requiring a great amount of water to wash before use, and the casing is poor in elasticity and toughness. The method comprises the steps of preparing the fresh-retaining solution according to the following components: 0.05% of nisin : 0.03% of natamycin : 1% of ascorbic acid : 3.5% of a phosphate combination (including 29% of sodium tripolyphosphate, 55% of sodium metaphosphate, 3% of sodium pyrophosphate, 13% of sodium dihydrogen phosphate) : 95.42% of oxygen-enriched water; immsersing the casing in the fresh-retaining solution for 6 hours according to a proportion of 200 per litre; fishing the casing out, draining off and packaging for use, or immersing the fresh-retaining solution in the casing for a long time, or immersing the fresh-retaining solution in the casing for a long time; and keeping the casing in a sealed container in a normal temperature. The casing preservation method is advantageous in that the fresh-retaining solution and the preservation method which are prepared by the invention, can be preserved for six months without deteriorating or decoloring and can be preserved for 24 months to the longest; the fresh-retaining solution is natural and non-toxic and has high security of biological preservation; breakage rate of the casing is zero; a processing process of washing with a great amount of water; no water resource is wasted; and elasticity and toughness of the casing are increased.
Owner:山东省蓝源生物工程有限公司
Method for treating diseases associated with changes of qualitative and/quantitative composition of blood extracellular dna
The invention relates to medicine and veterinary science and can be used for treating diseases associated with changes of the qualitative and / quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations. The inventive method for treating diseases associated with modifications of the qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations consists in injecting an agent destroying blood extracellular DNA. DNAse enzyme injected into a systemic blood circulation in doses which modify the electrophoretic profile of the blood extracellular DNA definable by pulse-electrophoresis can be used in the form of an agent destroying said blood extracellular DNA. Said DNAse enzyme can be injected in doses and at regimes ensuring the level of a blood plasma DNA-hydrolytic activity which is measured in the blood plasma and is higher than 150 Kunz units per litre of plasma during a total time higher than 12 hours a day. The inventive method makes it possible to develop a high-efficient and low-toxic method for treating diseases associated with modifications of qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA individually or in combination thereof.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Blood cell analyzer cleaning fluid
InactiveCN101281194ANot affected by the surrounding environmentGrowth inhibitionIndividual particle analysisBiological testingCyanide compoundNon toxicity
A blood cell analyzer cleaning fluid is characterized in that one litre of cleaning fluid is provided with 10.0-4.0g of sodium chloride, 0-6.0g of sodium sulfate, 16.0-23.0g of plant prolease, 0.4-1.2g of complex enzyme stabilizer, 0.17-0.2g of sodium hypochlorite, 2.0-6.0g of anionic surfactant, a phosphate buffer toning the ph value to 8.0-9.0, and the balance is water, wherein, the adding amounts of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate are complementary, the sum of the two adding amounts is no more than 10g. The invention does not contain cyanide, azide, and has non-toxicity, which can effective improve working atmosphere of operating staff, and can reduce harm of toxicant to personal health; the physical chemistry characters of the reagent are stable, and the reagent can be stored in the room temperature for more than one year. The invention can not only secure testing result accuracy, but also can secure non-corrosiveness to the blood cell analyzer; and hs no pollution to the environment.
Owner:南昌百特生物高新技术股份有限公司
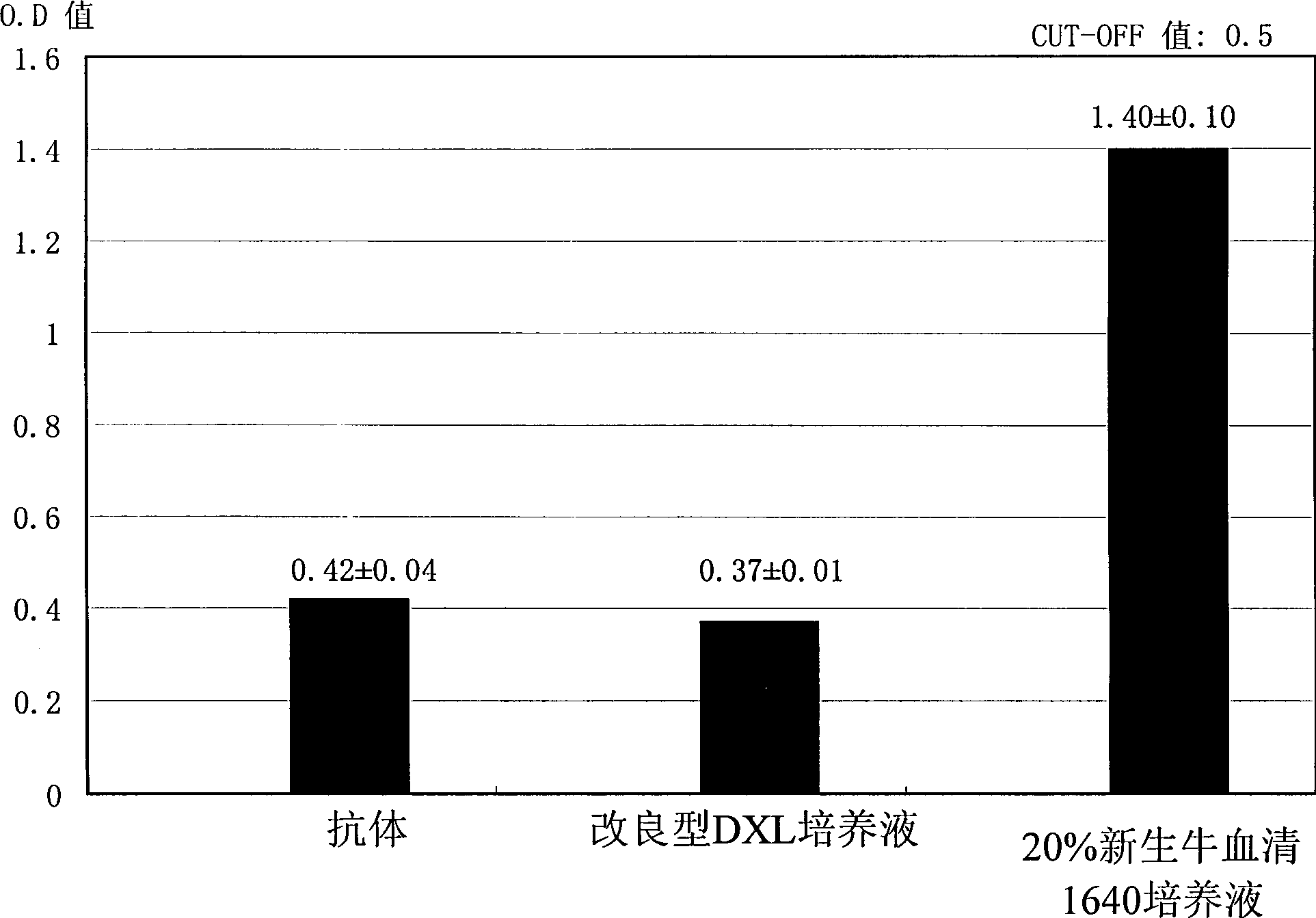
Preprartion method of improved hepatoma murine monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN1367258AReduce slow growthReduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureSerum free mediaNeural cell
The present invention relates to an improved preparation method of hepatoma murine monoclonal antibody. This invented method uses the improved DXL serum-free medium as culture medium, i.e. various growth factors, such as neural cell growth factor, epidermal growth factor, fibroblast grwoth factor or embyro growth factor are added in the DXL serum-free proteinless medium, and the content is 0.01-0mg / L. This invention adopts packed bed bioreactor to make high-density hybridoma cell continuous culture, and its technological conditions are as follows: temp. is 30-40 deg.c, rotating speed is 300-480 rpm, pH is 6.8-7.25, PO2 is 0.5-1.95 bar, PCO2 is 0.5-1.95 bar, PN2 is 0.5-1.95 bar, air flow rate is 0.1-2 hr. and pressure is 2-5 bar. Its cell density is upt o 10 to the eight power / ml, and theyield of monoclonal antibody of each litre of culture medium can be up to 1000-1500 mg.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Counter for metal nano particles in solution
InactiveCN101581655ASensitive detectionRaise the ratioIndividual particle analysisData acquisitionMetal particle
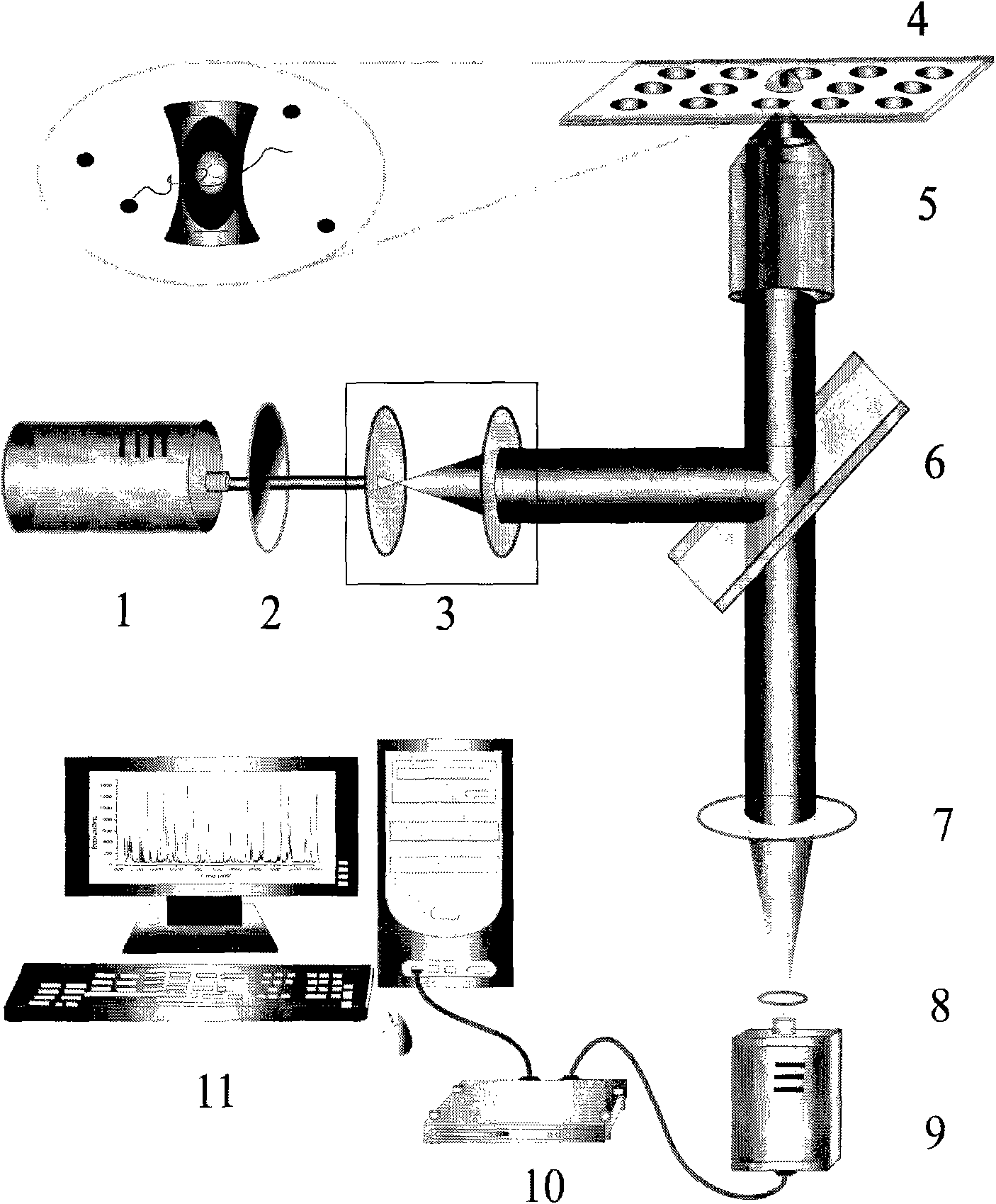
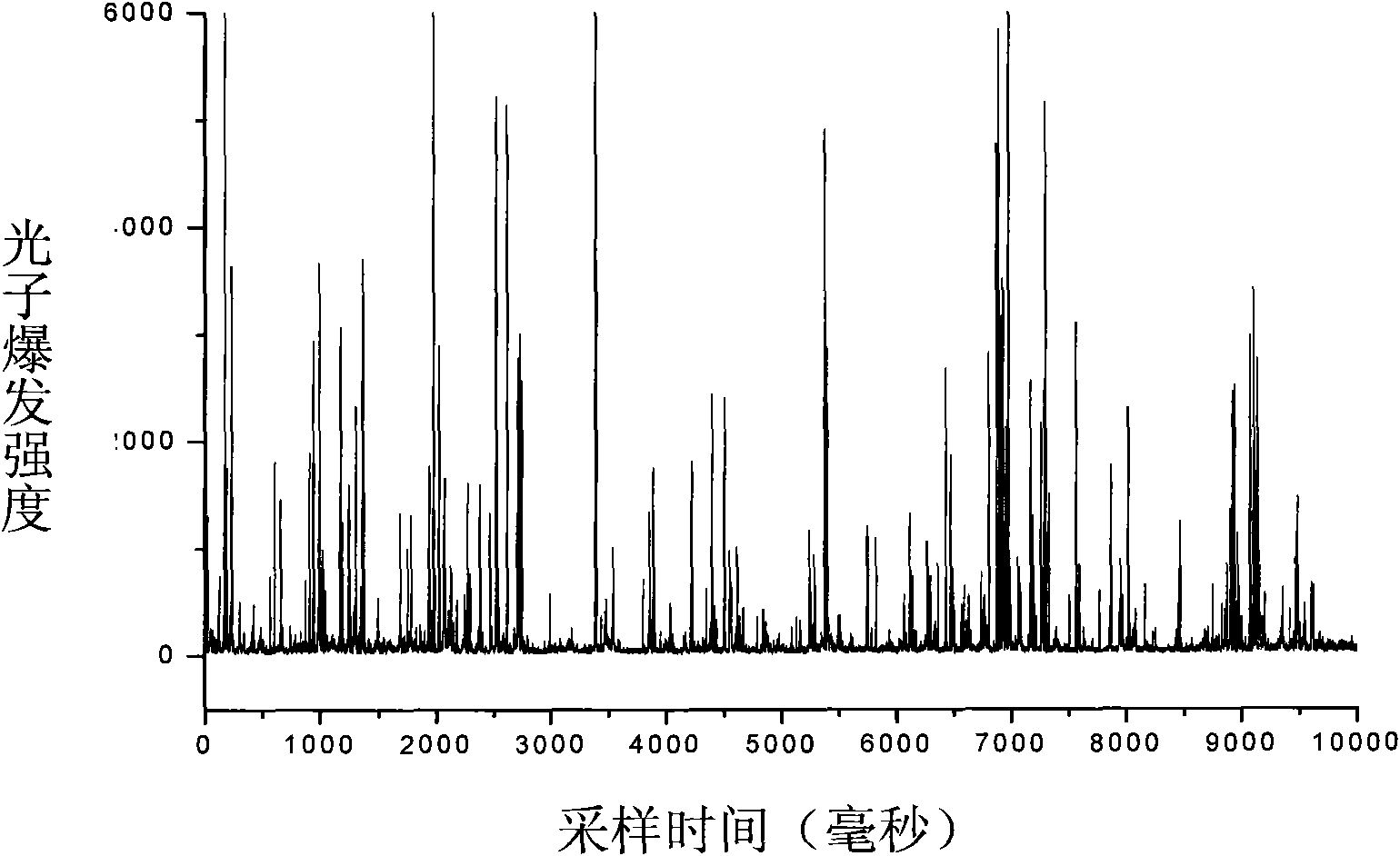
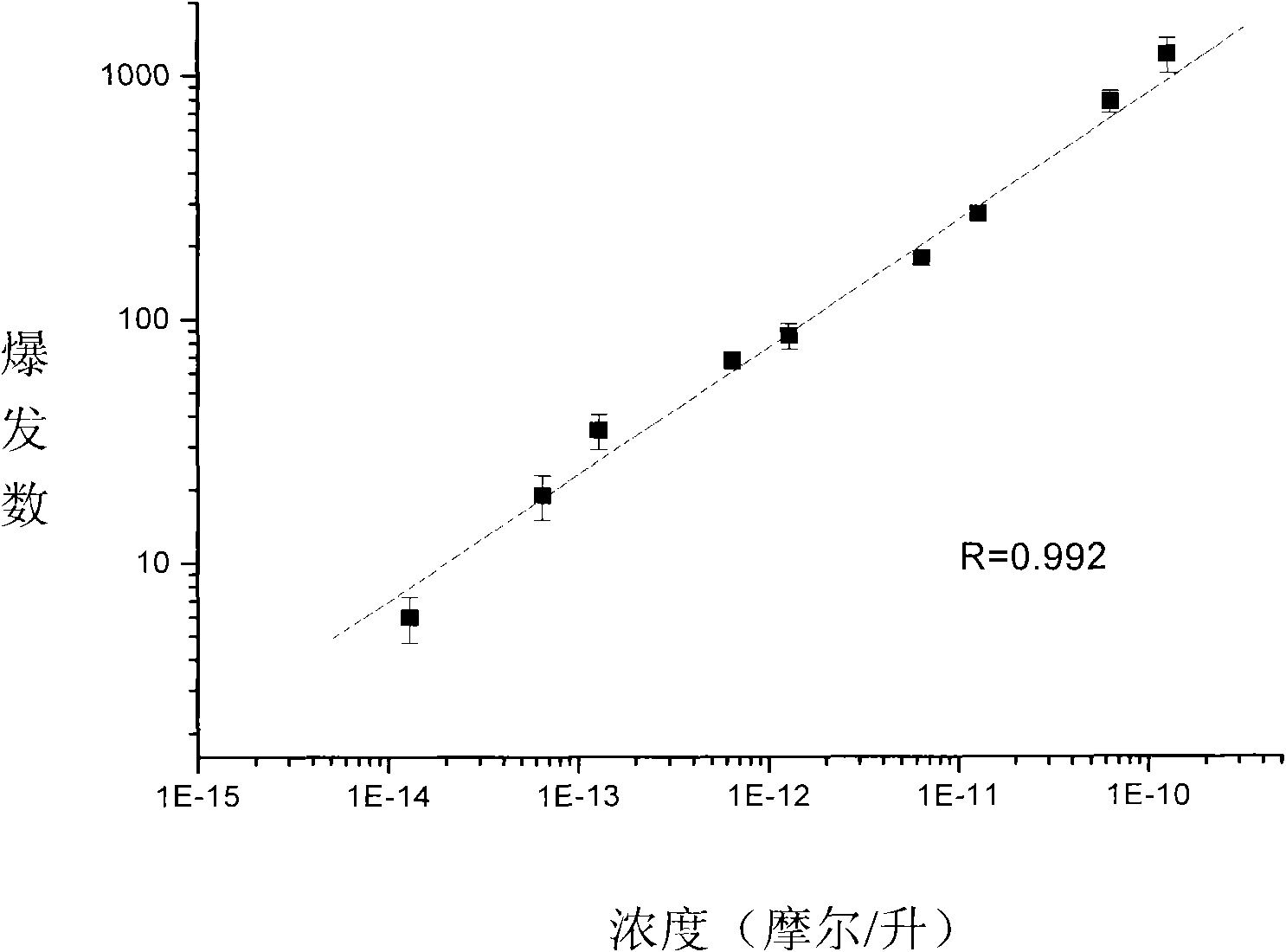
The invention relates to a counter for metal nano particles in solution, which is used for measuring relative concentration of metal nano particles in solution. The counter comprises a laser, a neutral attenuator, a beam expanding lens, a cover glass or a sample cell, a micro objective, a dichroic mirror, a lens, a pinhole, a single photon detector, a data collection card and a computer. Sample solution is placed on the cover glass or on the sample cell, the laser irradiates the metal nano particles in the solution, the produced scattered light is focused on the pinhole by the lens after being collected by the objective lens and the pinhole is coupled with the single photon detector. Signals generated by the single photon detector are output by the computer via the data collection card. The operating principle of the invention is based on a very small laser confocal irradiation micro-area (-10 litre), photon burst occurs when the metal particles enter or leave the micro-area due to Brownian movement, the number of the photon burst is proportional to concentration thereof. The counter of the invention can be applied to researches and clinical detection in fields such as biomedicine, chemistry, physics and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Vacuumable gel for decontaminating surfaces and use thereof
ActiveCN101278358AGood removal effectAvoid washing with waterAqueous liquid non-soap compositionsDetergent compounding agentsStrong acidsRadioactive decontamination
The invention relates to a vacuumable gel for decontaminating surfaces and to the use of said gel, whereby the decontamination can, for example, take the form of radioactive decontamination. The inventive gel comprises a colloidal solution and contains: between 5 and 25 wt.- % of an inorganic viscosifier in relation to the total weight of the gel; between 0.01 and 0.2 wt.- % of a surfactant in relation to the total weight of the gel and preferably less than 0.1 wt.- % of a surfactant in relation to the total weight of the gel; between 0.5 and 7 mol, per litre of gel, of an acid or an inorganic base; and, optionally, between 0.05 and 1 mol, per litre of gel, of an oxidising agent having a normal oxidation-reduction power E0 of greater than 1.4 V in a strong acid medium or of the reduced form of said oxidising agent, the remainder being water. The invention can be sprayed onto a surface that is to be decontaminated and removed in the form of dry residues by means of vacuuming or brushing after drying.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Vacuumable Gel for Decontaminating Surfaces and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080228022A1Accelerated dryingPromote recoveryAqueous liquid non-soap compositionsDetergent compounding agentsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The present invention relates to a vacuumable gel that can be used for decontaminating surfaces, and also to the use of this gel. The decontamination may be, for example, a radioactive decontamination. The gel of the present invention is composed of a colloidal solution. It comprises from 5 to 25 wt % of an inorganic viscosity modifier relative to the total weight of the gel; from 0.01 to 0.2 wt % of a surfactant relative to the total weight of the gel, and, particularly preferably, a surfactant in an amount strictly below 0.1 wt % relative to the total weight of the gel; from 0.5 to 7 mol, per litre of gel, of an inorganic acid or base; and optionally from 0.05 to 1 mol, per litre of gel, of an oxidizer having a standard redox potential E0 greater than 1.4 V in a strong acid medium or of the reduced form of this oxidizer; the remainder being water. It may be applied, by spraying, to a surface to be decontaminated, and removed in the form of dry residues by suction or brushing after drying.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Solar water heater with heat exchange function
InactiveCN102954604AOccupies less space and resourcesSolar heating energySolar heat devicesThermal energySolar water
The invention relates to a solar water heater with heat exchange function which belongs to the technical field of solar energy utilization. The solar water heater with heat exchange comprises a solar water heater and solar heat pipes, wherein the solar water heater and the solar heat pipes form the solar water heater with heat exchange. The solar water heater with heat exchange has the characteristics that a coil pipe is twined in the solar water heater, the coil pipe has a hot water outlet and a cold water inlet, and the volume of the solar water heater is 2 litres to 8 litres; the volume of the solar water heater is fitted with the solar water heater with heat exchange so that when the solar water heater with heat exchange operates at night, the supplied heat ranges from 15 DEG C to 25 DEG C. The solar water heater with heat exchange function can be used for bath with hot water and heat supply during season change.
Owner:XIAN XINWEI INFORMATION TECH
Colon cleansing compositions and methods
InactiveUS20070098764A1Great tasteLower the volumePowder deliveryBiocideSodium bicarbonateTolerability
A composition comprising, per litre of aqueous solution, from 30 to 350 g polyethylene glycol, from 3 to 20 g of an ascorbic acid component selected form the group consisting of ascorbic acid, a salt of ascorbic acid, or a mixture thereof, an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal sulphate, preferably from 1 to 15 g thereof, and optionally one or more electrolytes selected from sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and sodium hydrogen carbonate, and preferably also comprising flavourings, is effective in cleansing the gut in preparation for a endoscopy, especially colonoscopy. It is safer than conventional sodium phosphate-based gut cleansing compositions, and hence can be used for patients who would be at risk with sodium phosphate-based compositions, and is better tolerated than conventional PEG-based compositions, leading to better patient compliance and enabling effective out-patient use.
Owner:NORGINE BV
Method for preventing loquat fruits from splitting
InactiveCN103141357APrevent cracking at maturityAvoid harmCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsMonopotassium phosphateBran
The invention relates to a method for preventing loquat fruits from splitting. At the full-bloom stage of a loquat garden, 70 milligrams / litre of gibberellin is sprayed on leaf surfaces, 0.05% borax is added, and then a peanut bran liquid fertilizer is added; at the stage of young fruits, the fruits are thinned, and three to four young fruits are left for each fringe; after the fruits are thinned, 0.5% monopotassium phosphate is sprayed once, and the peanut bran liquid fertilizer is added; and after the fruits are thinned, the whole fruit fringe is sheathed into a paper bag made of old newspaper until the fruit is ripe. By using the method, the problems of splitting of the loquat fruits, rusty spots on fruit surfaces and the like can be prevented, so that the fruits have good appearance.
Owner:韦尚仁
First flush water diverter
InactiveUS20050081926A1Lower the volumeGeneral water supply conservationPipeline systemsCarrying capacityCollection system
A first flush water diverter for use with domestic rainwater collection systems. The diverter comprises a T-piece (13) and a collection chamber (14), with an outlet (15) connectable to a hose by way of a flow control valve (24) and hose connector (25). The collection chamber (14) is variable in length to suit the environment and size of the roof from which the rainwater flows. The carrying capacity of the collection chamber (14), and have its length, is determined from the formula: DF=RA×PF×1000 where DF is the rainwater carrying capacity, or diversion factor, measured in litres, RA is the associated roof area measured in square metres, PF is the Pollution Factor for the roof location which is determined on site and varies between 0.0005 for light pollution locations and 0.002 for heavy pollution locations, and wherein said collection chamber includes an outlet and associated flow control valve to regulate the flow of diverted rainwater from the collection chamber.
Owner:WADE RODNEY GEORGE
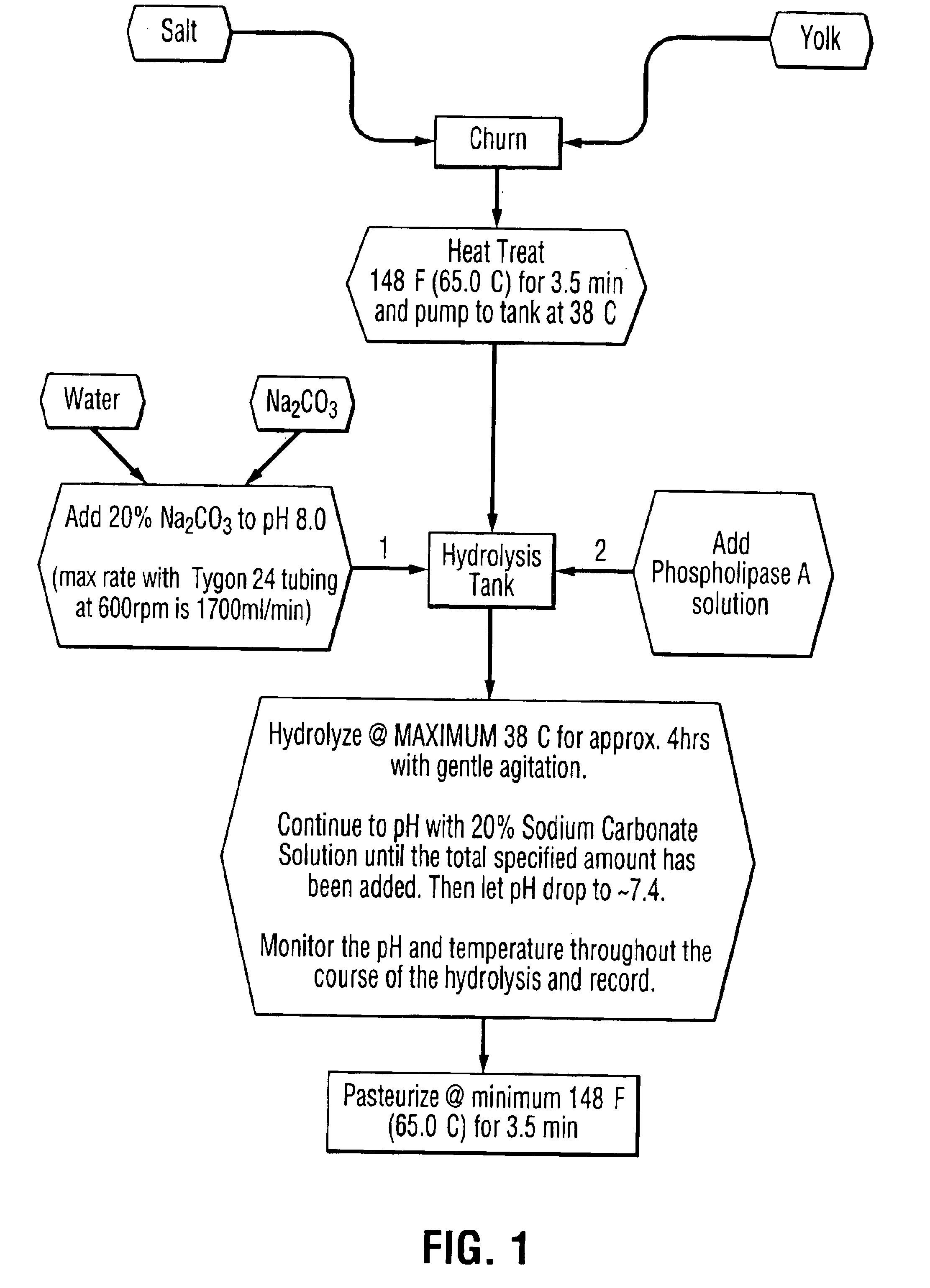
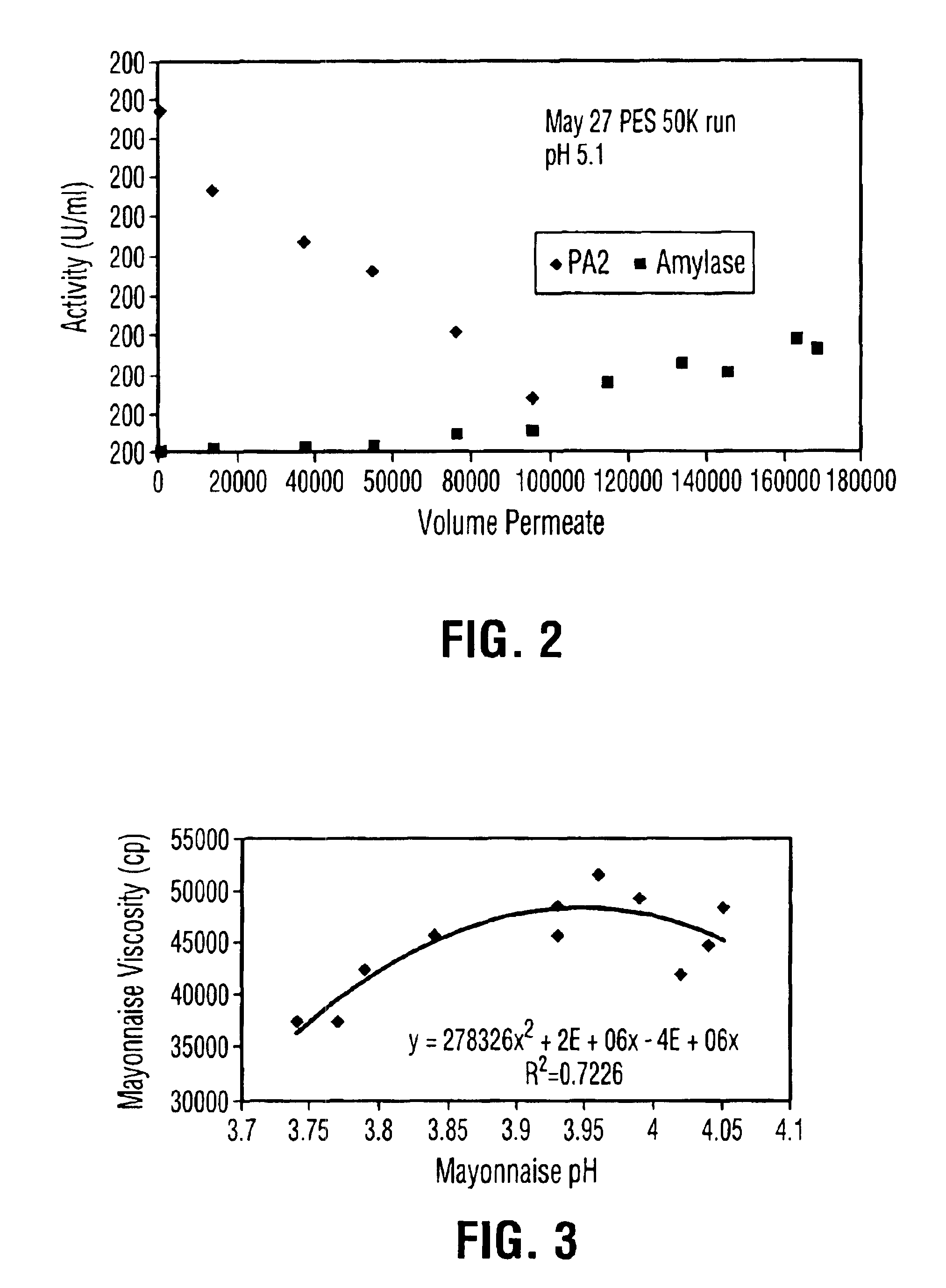
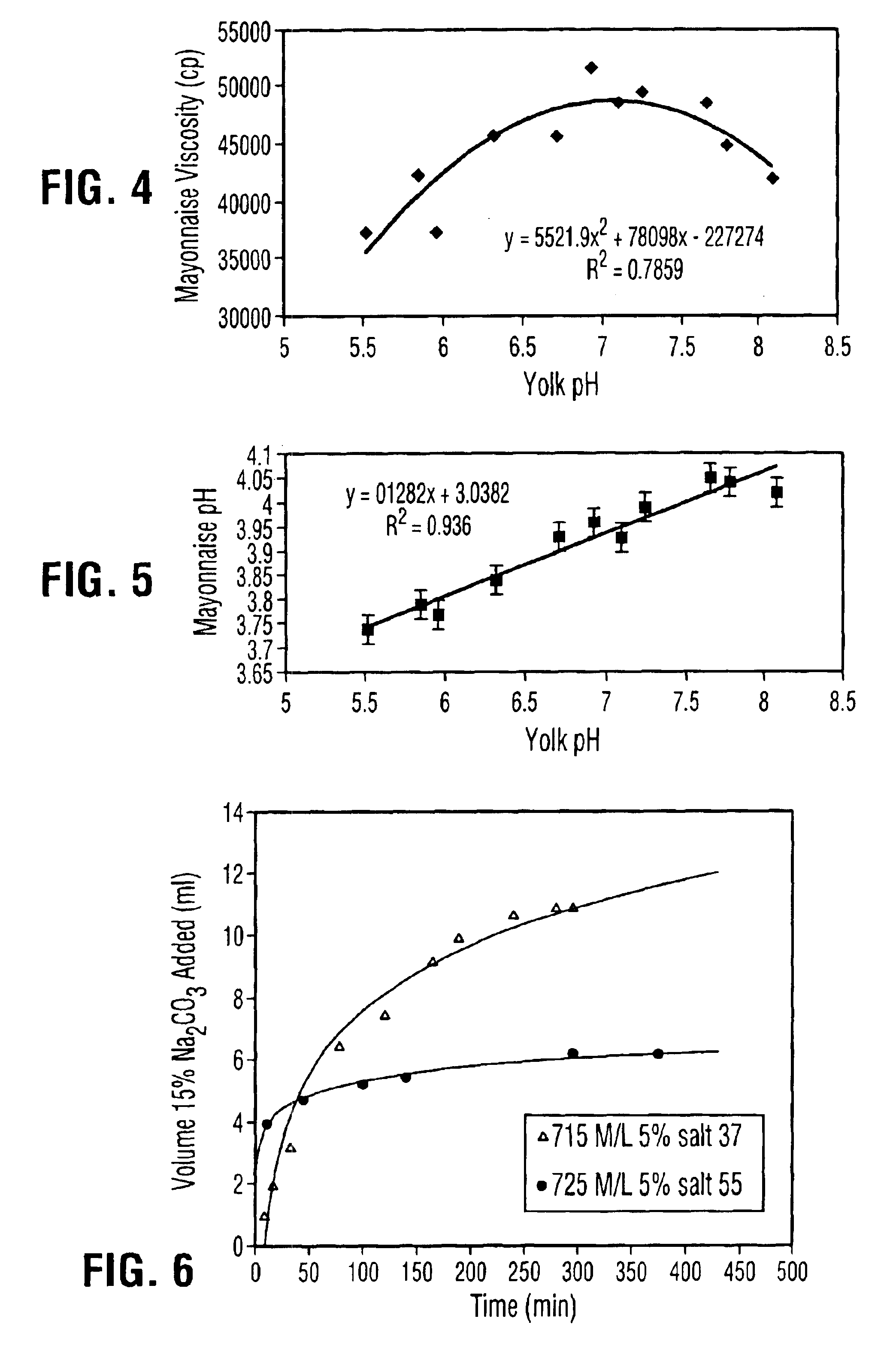
Liquid egg yolk product comprising lysophospholipoprotein
Owner:M G WALDBAUM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com