Patents
Literature
12819results about "Soil preservation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isolation of soil with a low temperature barrier prior to conductive thermal treatment of the soil
InactiveUS6854929B2Low costAvoid flowSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSoil remediationEngineering
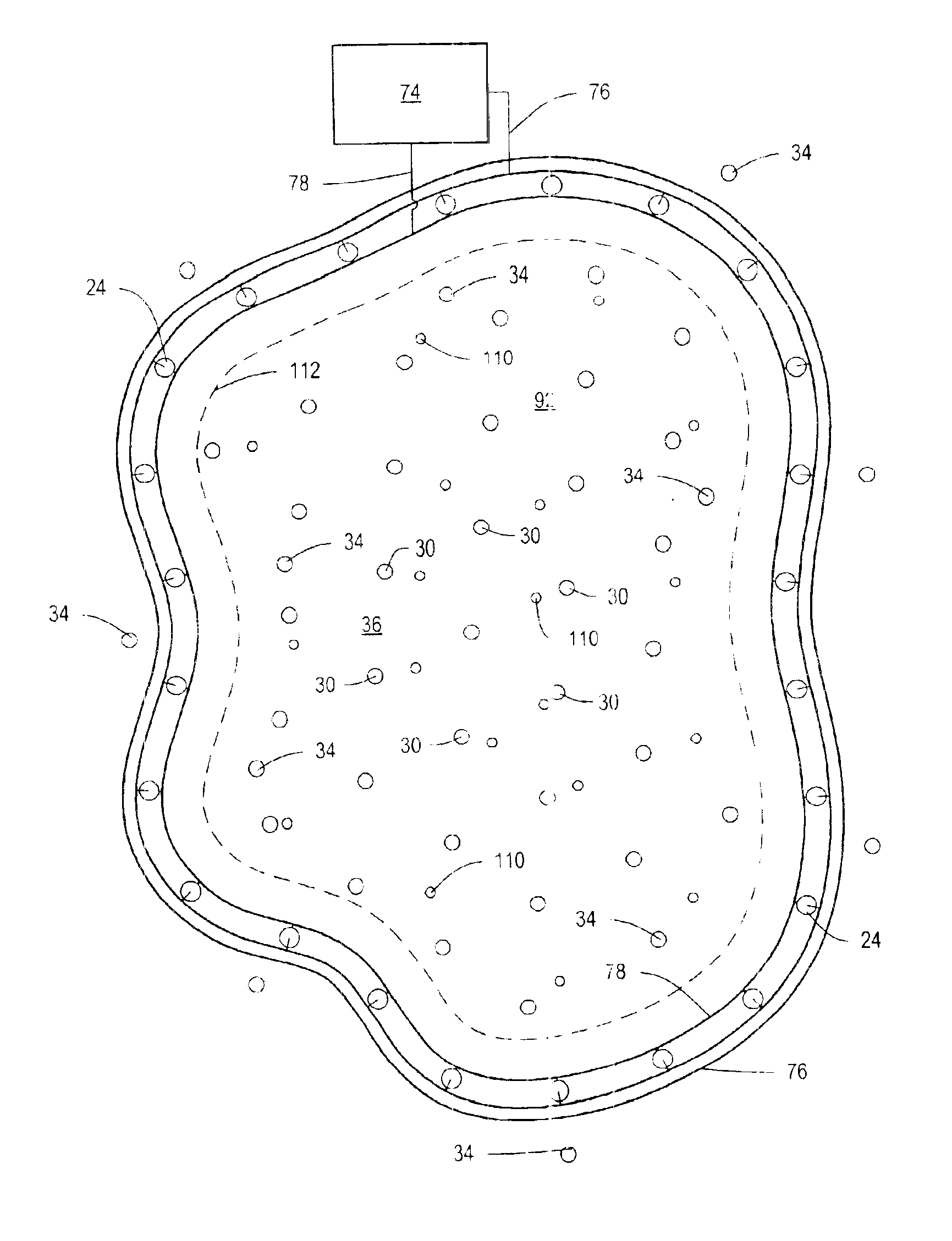
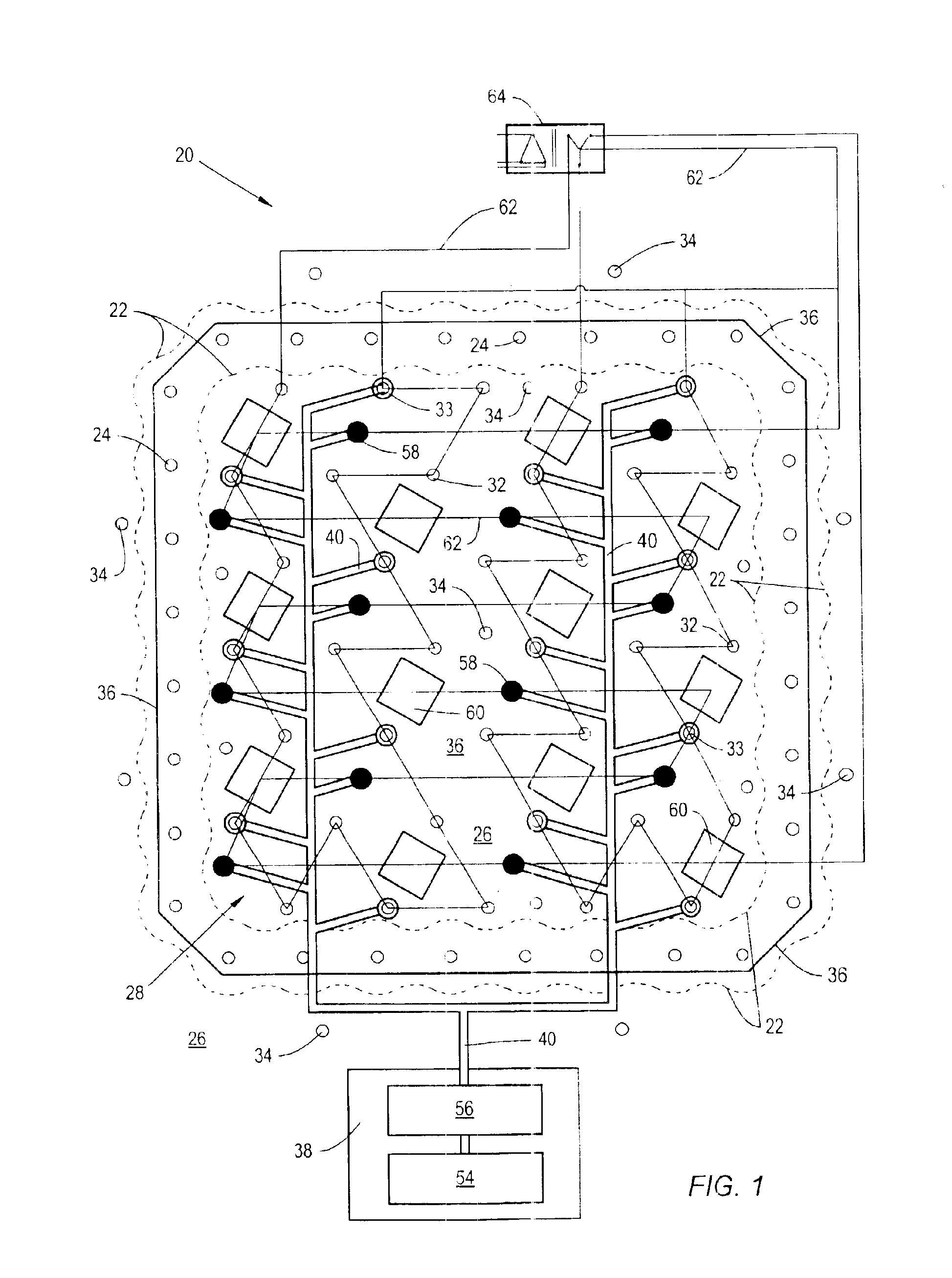
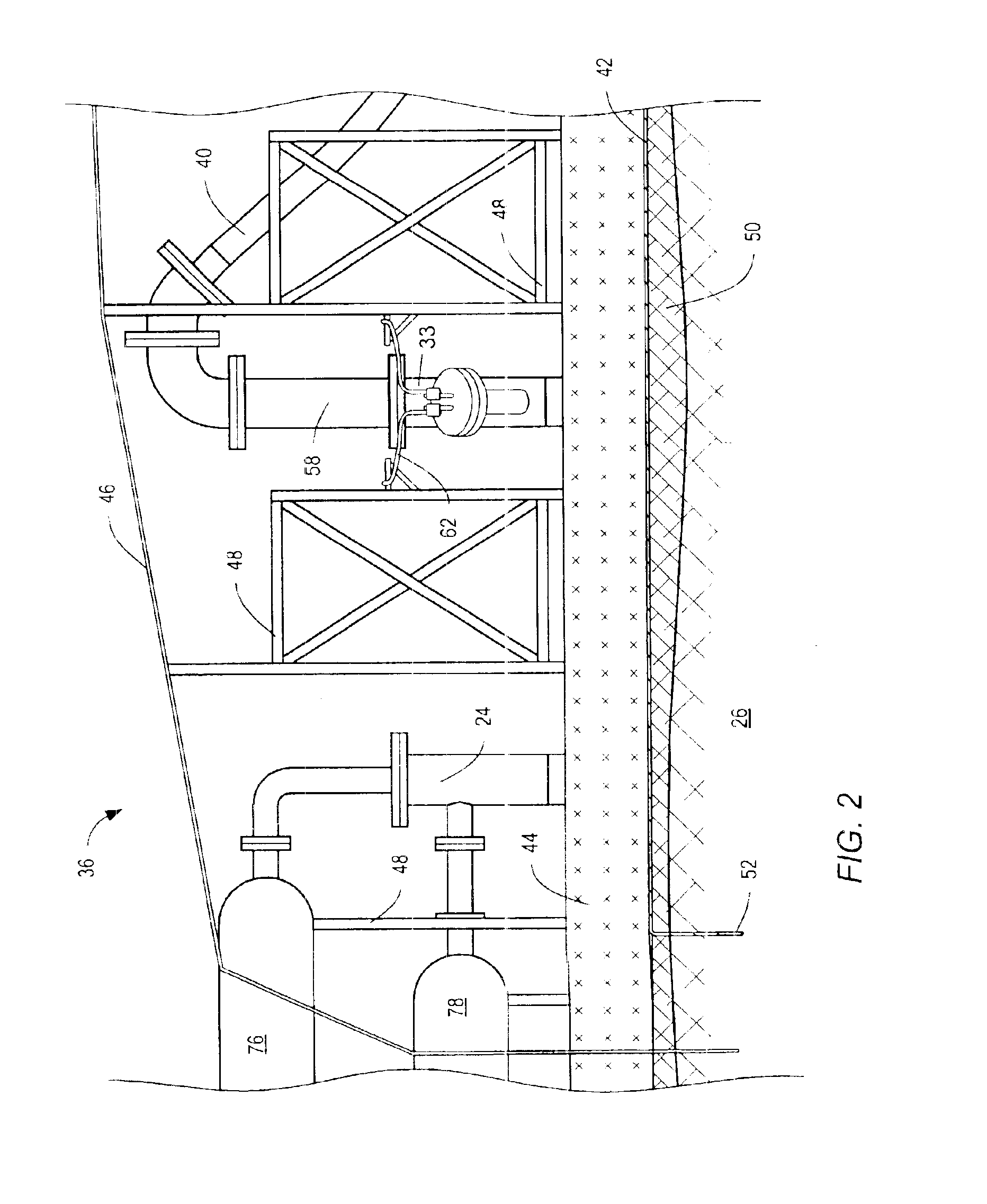
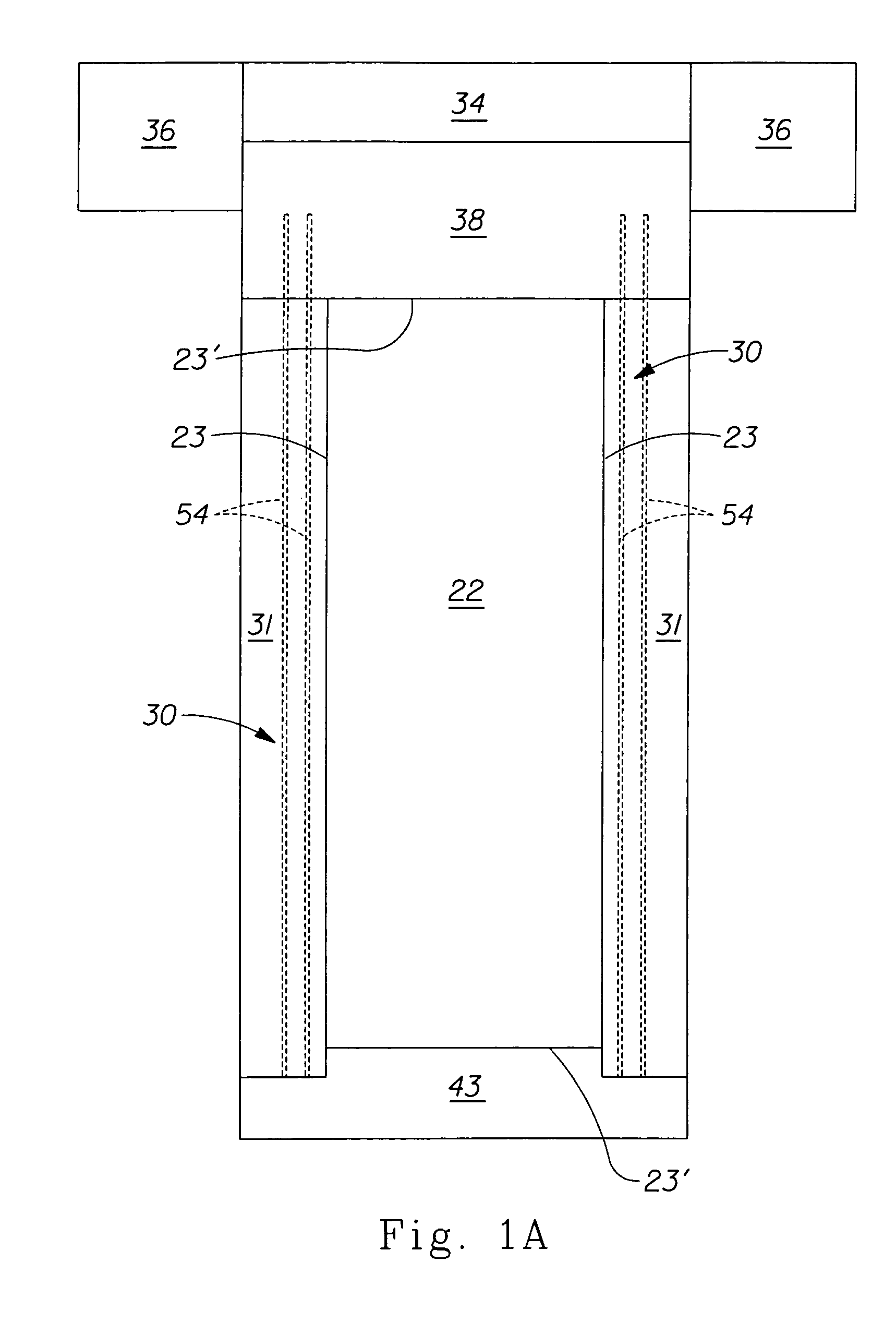
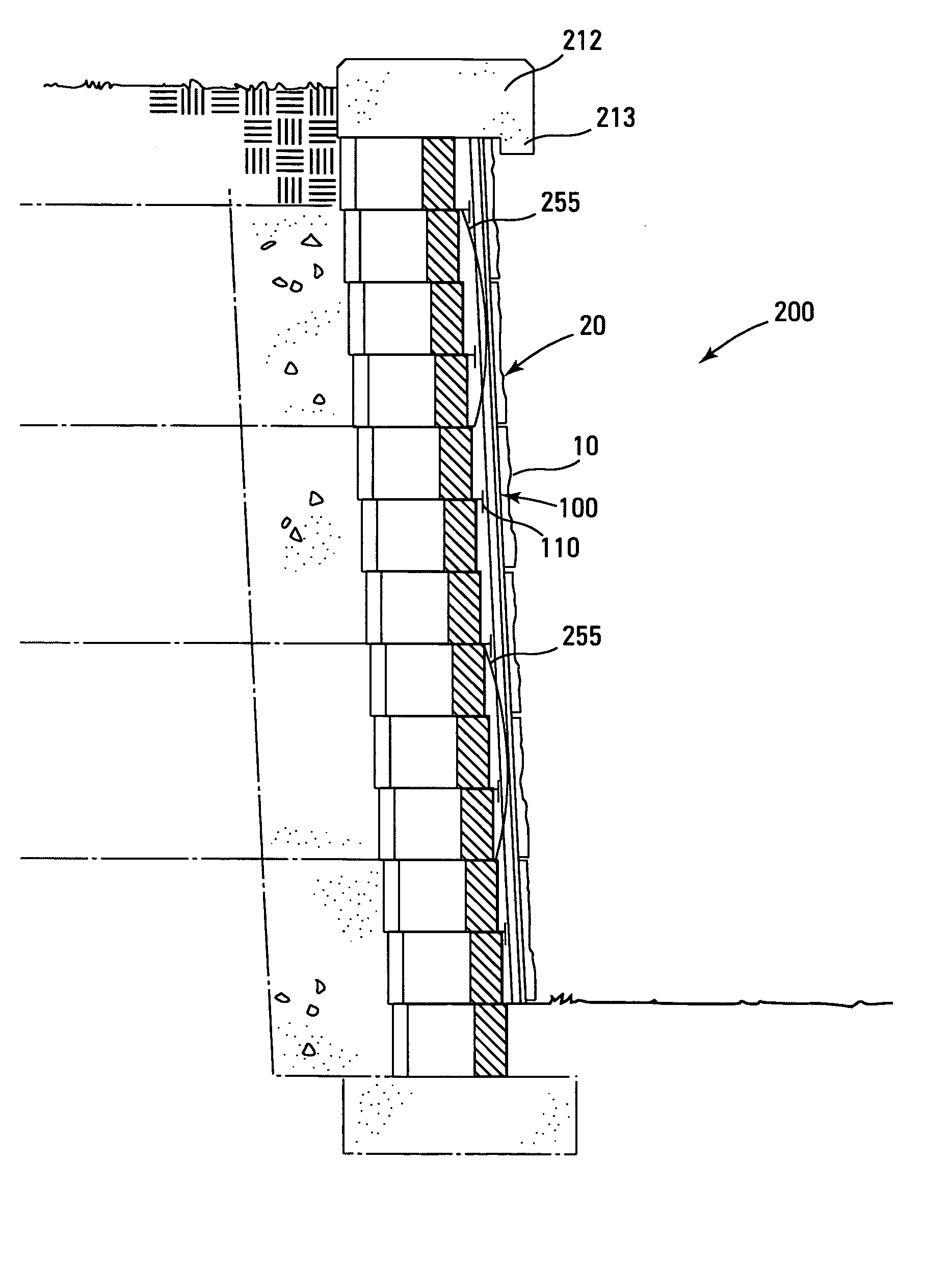
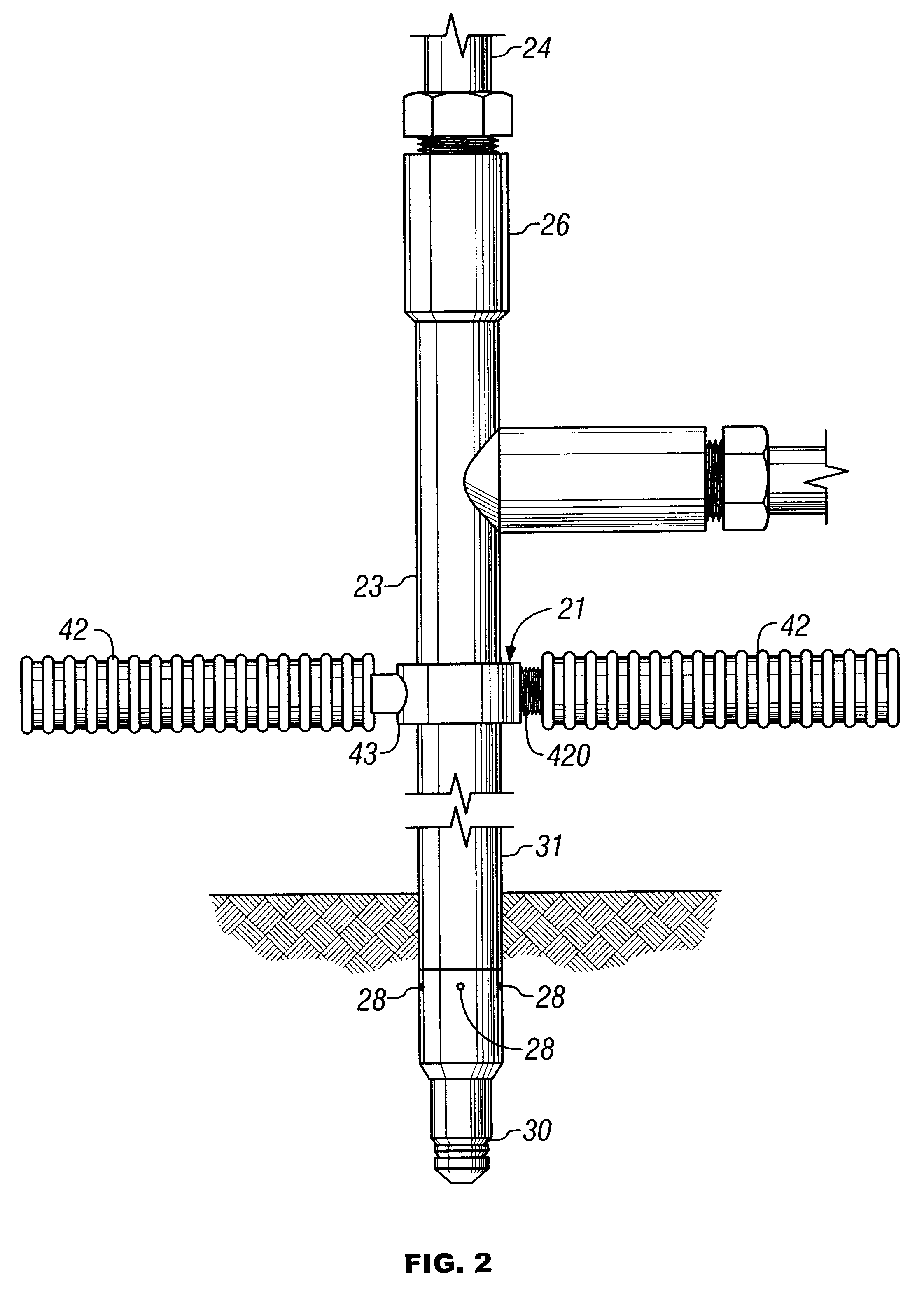
Freeze wells may be used to isolate an area for soil remediation. Freeze wells may form a frozen barrier around a treatment area. The frozen barrier may inhibit fluid from entering into the treatment area. The frozen barrier may also inhibit migration of contamination out of the treatment area. The frozen barrier may be used to surround all of the perimeter of the treatment area. A frozen barrier may also be formed above or below a treatment area. Freeze wells may be activated in advance of soil remediation so that a frozen barrier is formed when soil remediation is begun. The soil remediation may be accomplished by any type of soil remediation system, including a thermal soil remediation system. Heaters of a thermal soil remediation system may be may be placed close to the frozen barrier without the barrier being broken through during remediation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
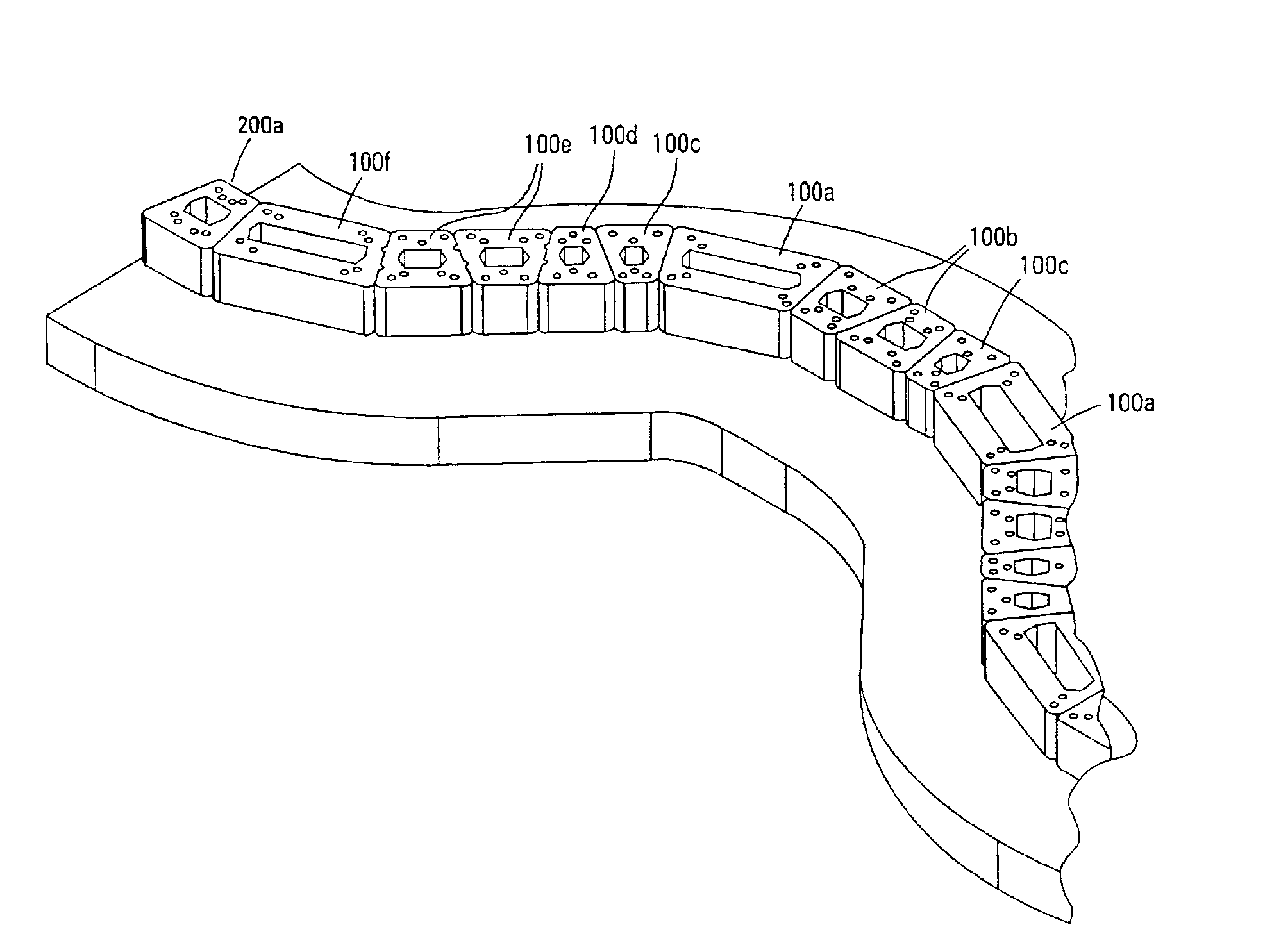
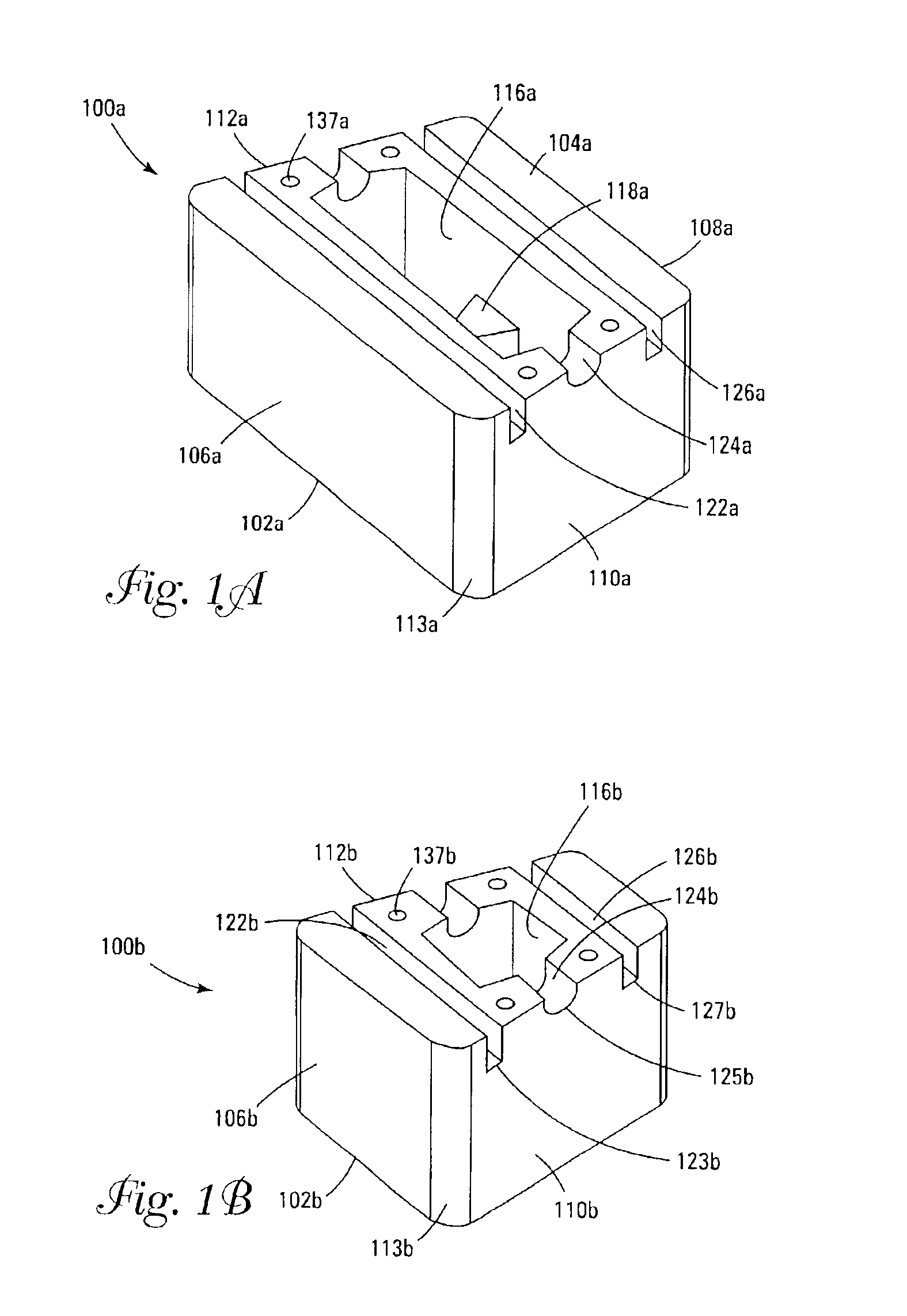
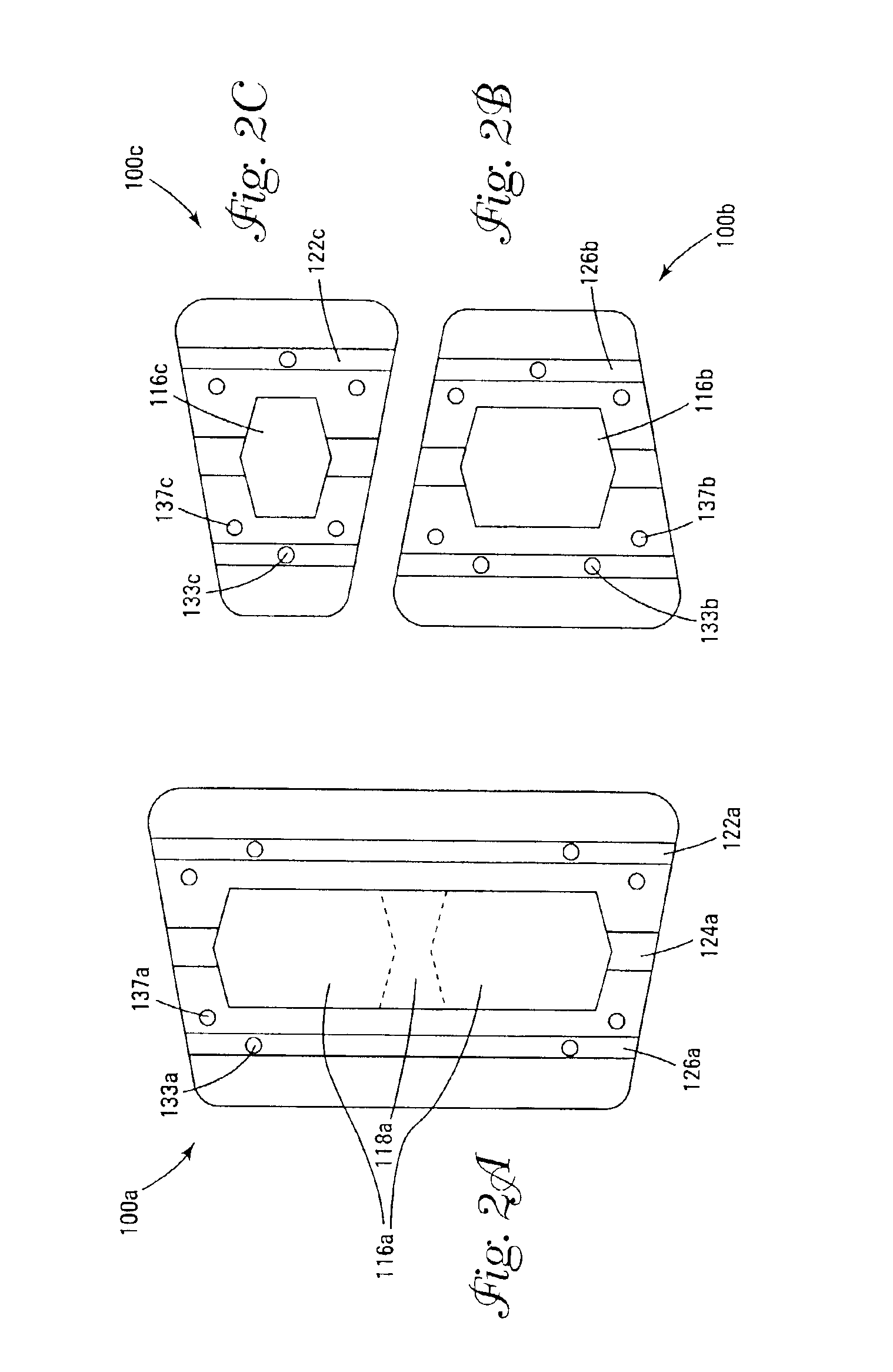
Retaining wall block with face connection
Single and multiple retaining wall blocks and block systems are disclosed. The blocks are provided with a face connection system which includes at least one front lip extending from a top surface of the block and a bottom channel formed into a front face and bottom surface of the block. The front lips have a length which is less than the width of the blocks.
Owner:CONTECH TECH
Structural elastic-like nonwoven web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Settable fluids and methods for use in subterranean formations
The present invention relates to subterranean operations, and more particularly, to settable fluids comprising vitrified shale and hydrated lime and methods of using such settable fluids in subterranean applications. In an exemplary embodiment, the settable fluids of the present invention may be used as a displacement fluid. In another exemplary embodiment, the settable fluids of the present invention may be used as a drilling fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
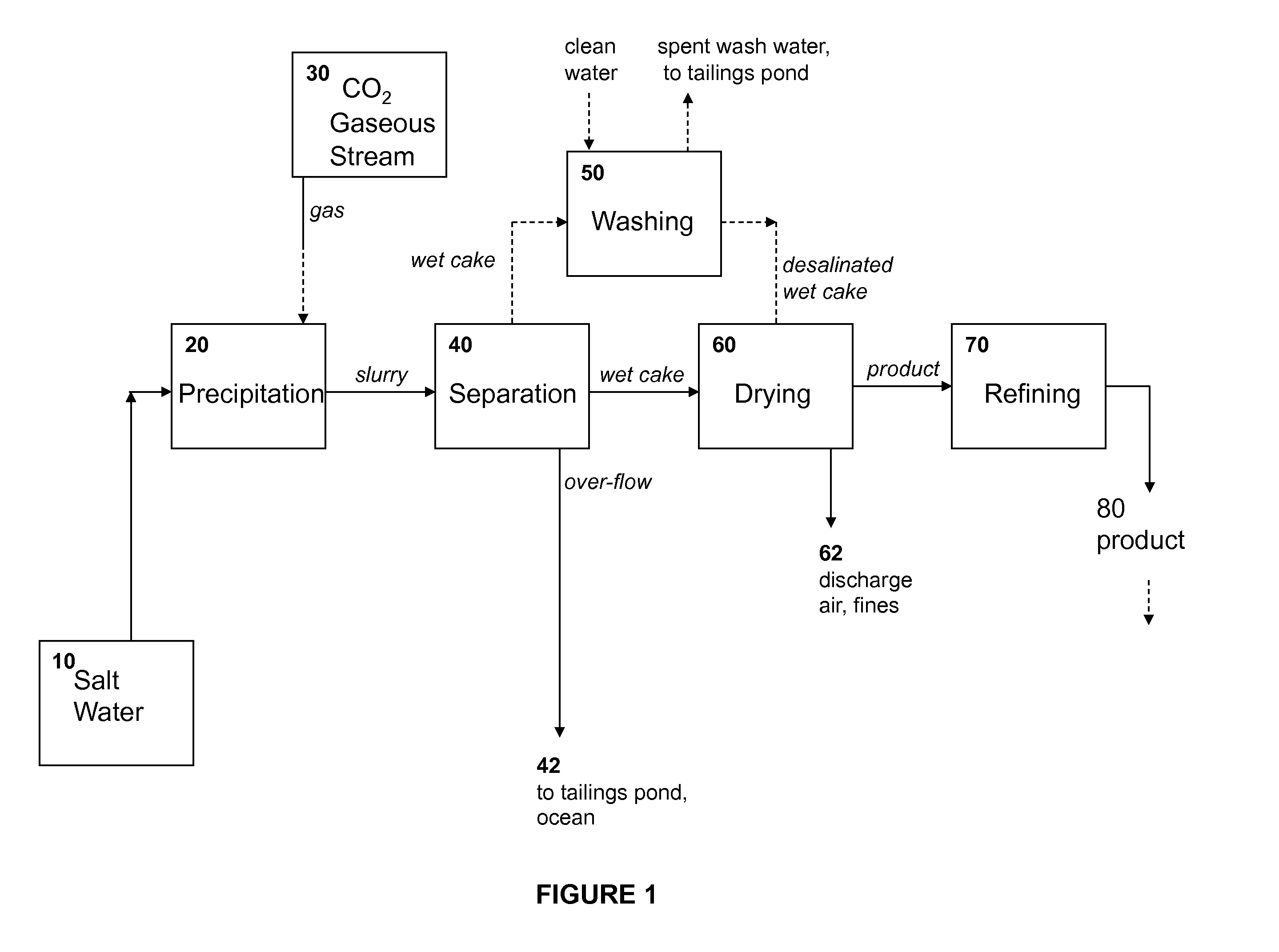
Co2 sequestering soil stabilization composition
InactiveUS20100196104A1Reduce carbon footprintComposition is stableOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersSoil stabilizationCarbonate
CO2 sequestering soil stabilization compositions are provided. The soil stabilization compositions of the invention include a CO2 sequestering component, e.g., a CO2 sequestering carbonate composition. Additional aspects of the invention include methods of making and using the CO2 sequestering soil stabilization composition. The invention also comprises the method of stabilizing soil and producing a soil stabilized structure utilizing such compositions.
Owner:CALERA CORP
Improved soil matrix and remediation method for green mine
InactiveCN109534737AFull of nutritionSuitable for growthGrowth substratesCulture mediaWater storageFriction angle
The invention provides an improved soil matrix and a remediation method for a green mine. According to the improved soil matrix and the remediation method for the green mine, a certain gradient of a mountain is formed by trimming a cliff of the mine, a hard material is laid in a certain mode, then a plastic-coated metal net covers the hard material, and finally, the novel improved soil matrix covers the plastic-coated metal net with a certain thickness so as to realize the effective remediation of the mine. The improved soil matrix and the remediation method for the green mine have the beneficial effects that the improved soil matrix can stably float on the surface of the mine with the gradient of less than 80 degrees, the adhesive force is greater than 20 Kpa, the inner friction angle isgreater than 18 degrees, the anti-corrosion index is greater than 99.1%, the anti-scouring index is greater than 2.0 L.min / g, the structure is high, and scouring of heavy rainfall or heavier can be effectively resisted after three days of spraying; the improved soil matrix is rich in nutrition, loose and breathable, and is suitable for growth of plants; and lots of organic matter such as agricultural and forestry leftovers are adopted, so that the water storage performance is high, and the construction cost and the maintenance cost are greatly saved.
Owner:杰瑞(莱州)矿山治理有限公司
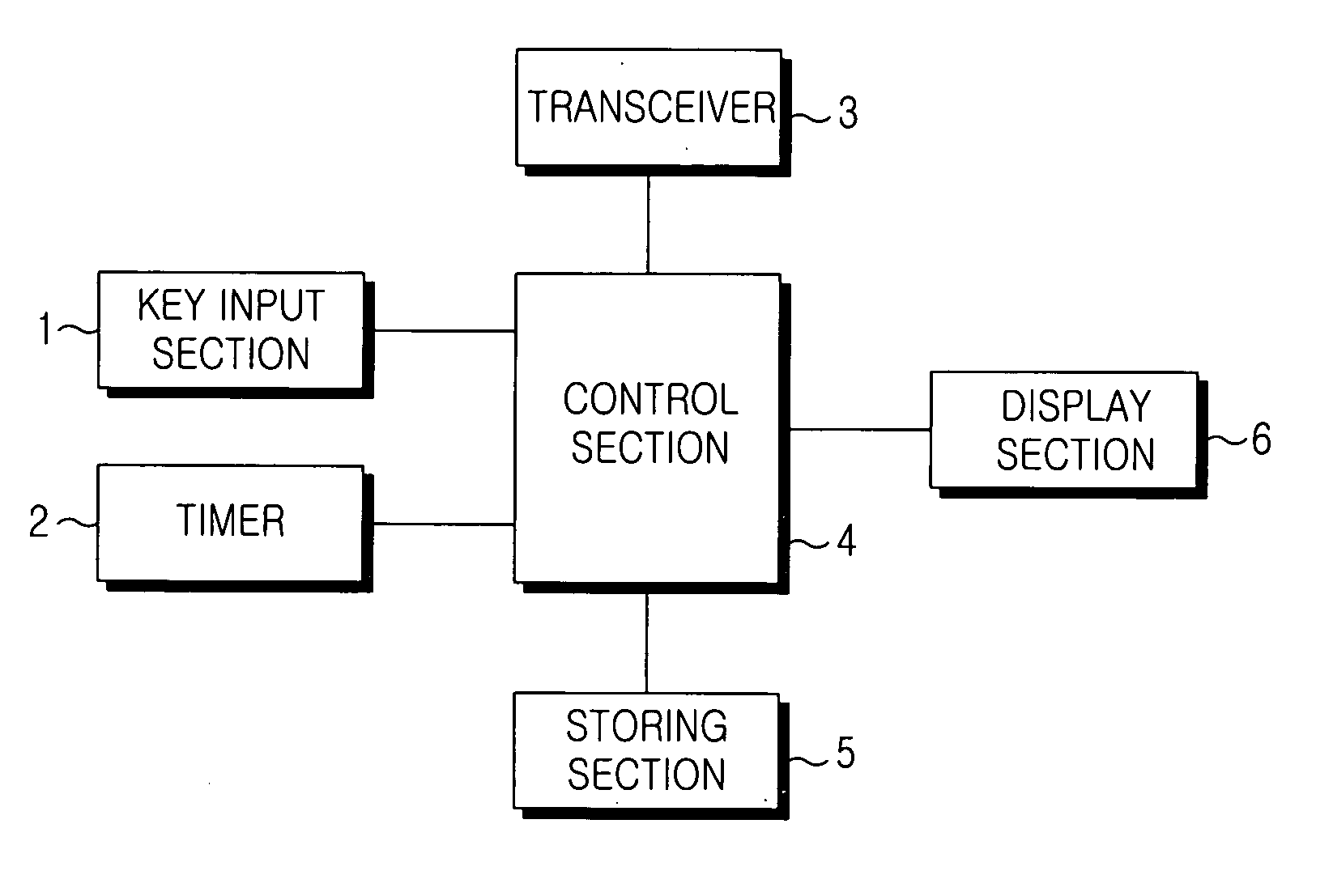
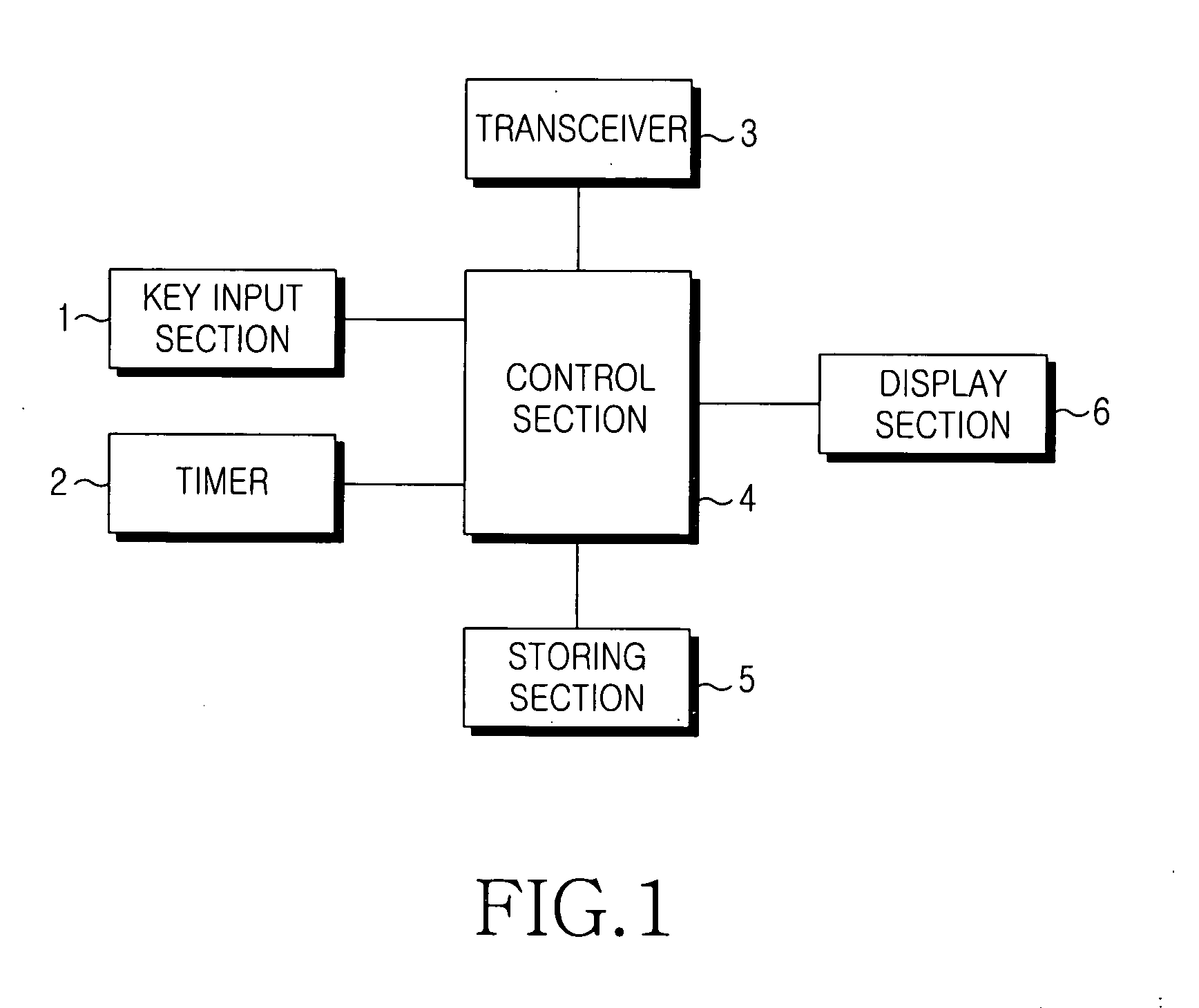
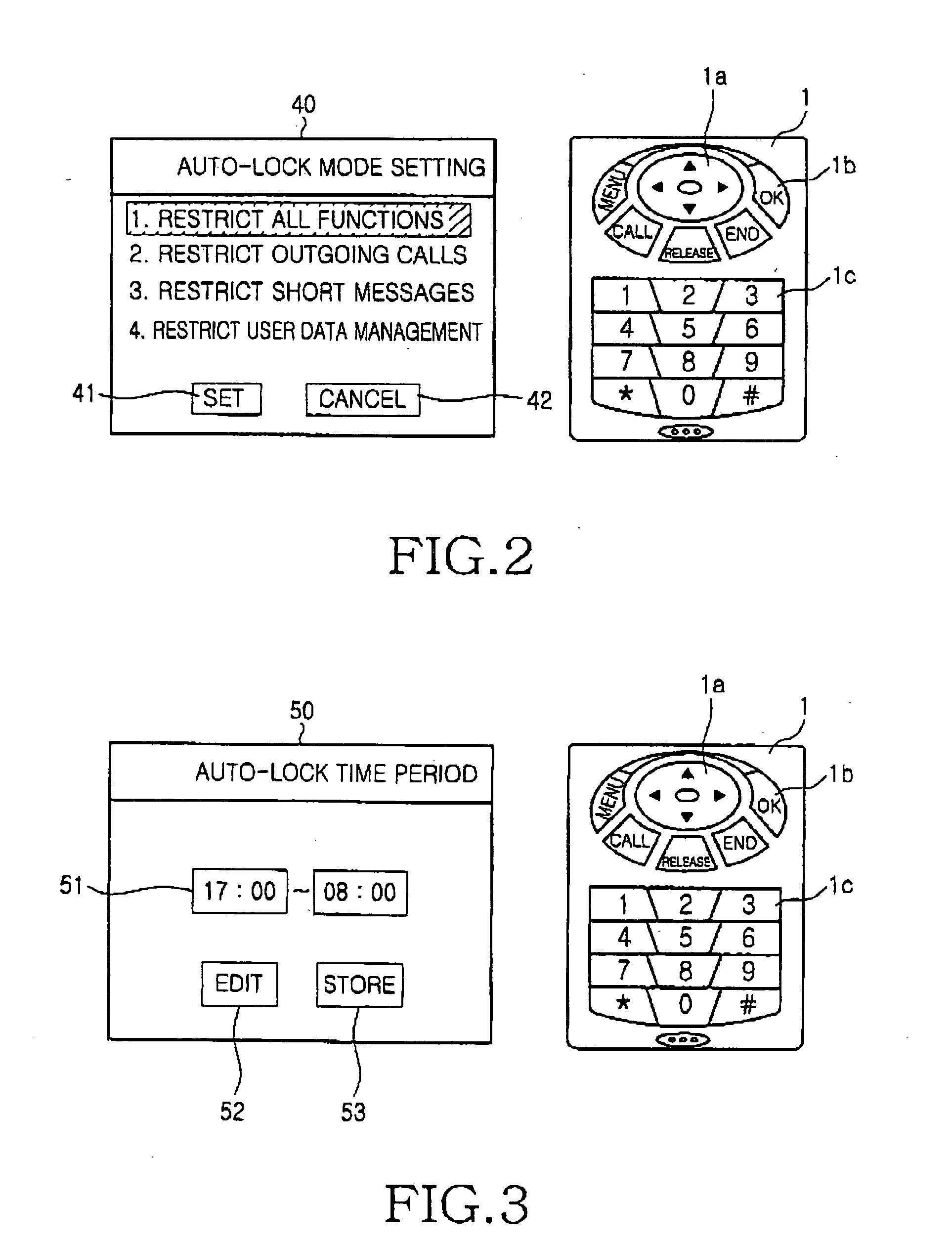
Mobile terminal and method for auto-locking thereof
InactiveUS20050154935A1Prevent illegal useAutomatically locking a mobile terminalUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsTime segmentComputer science
Disclosed is a method for automatically locking a mobile terminal having functions, such as incoming and outgoing calls. The method includes the steps of setting an auto-lock time period to restrict the use of one or more predetermined functions; activating an auto-lock mode to restrict the use of the predetermined functions during the auto-lock time period; and inactivating the auto-lock mode after the auto-lock time period. The auto-lock mode for automatically locking functions of the mobile terminal can be set to be activated only during specified time or during all other times of the day according to the spatial and temporal patterns of the user's daily routine.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Modular building materials
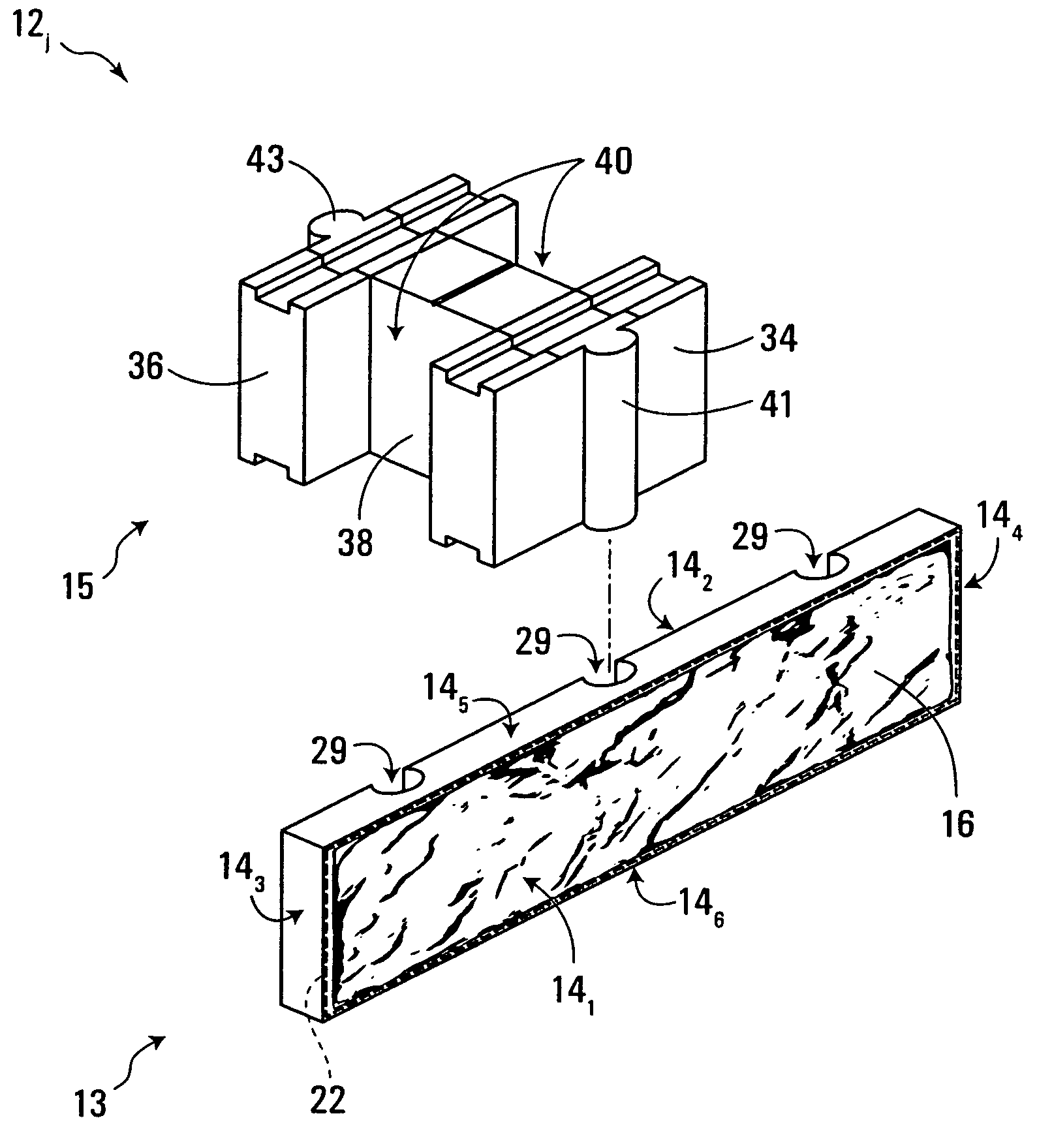
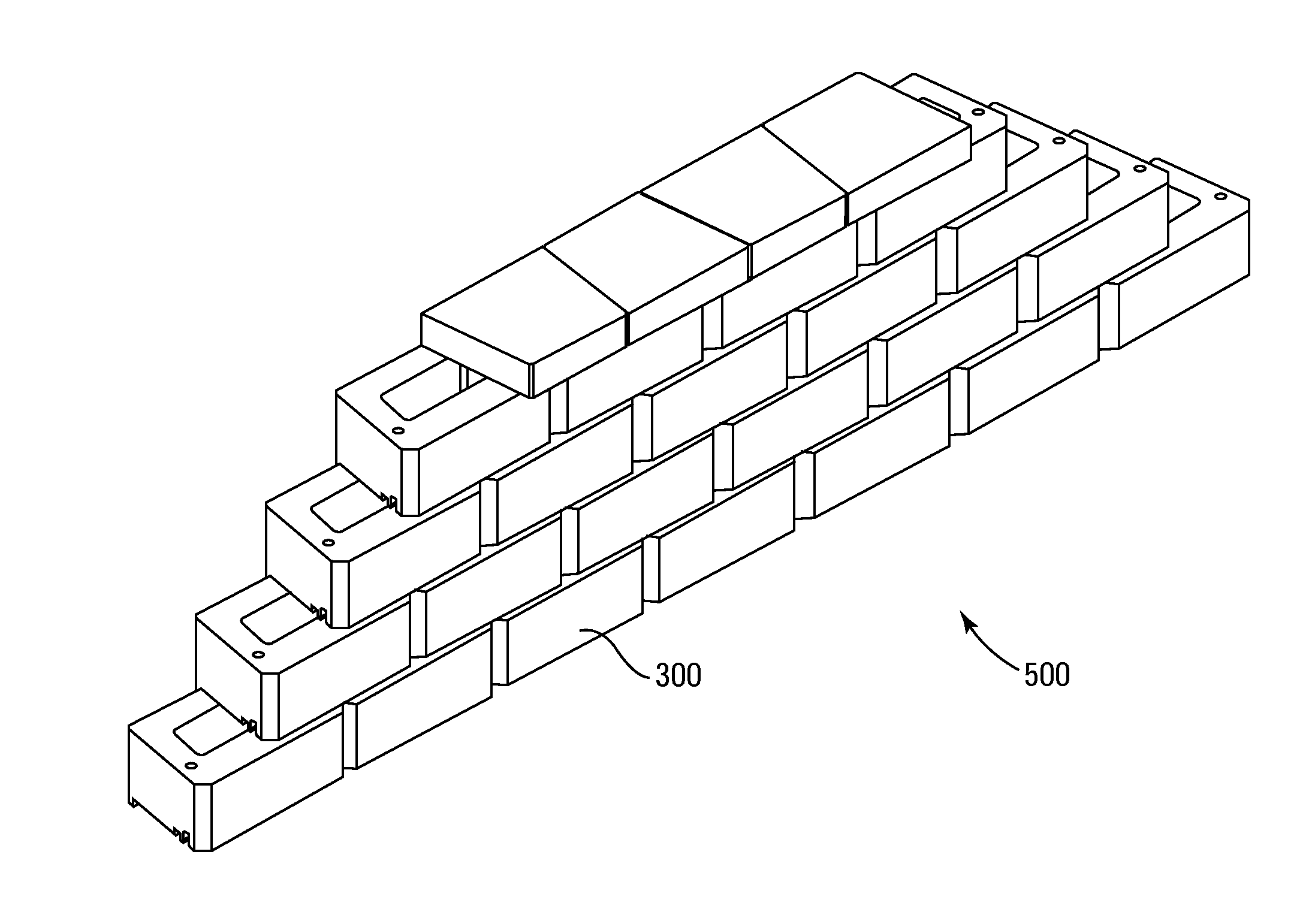
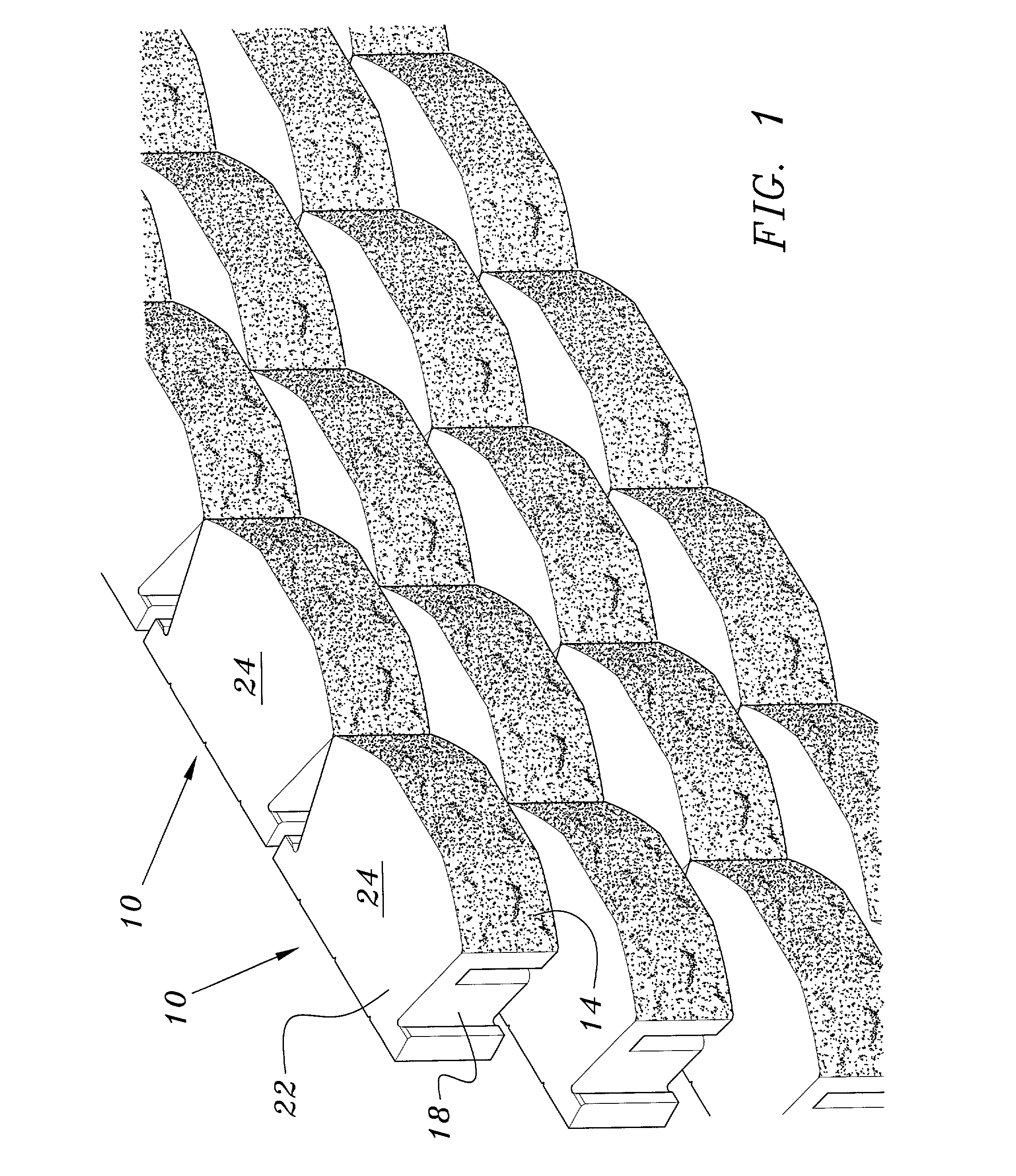
Building materials of modules of at least one mortise and tenon and either a curvilinear side face or joinder of the modules at angles other than zero and ninety degrees. Lateral ends of the modules are flush with lateral ends of adjacent modules. Preferably, the modules are: (1) of a low density aggregate cementitious mix; and / or (2) have a hollow space extending from the mortise to the tenon and include a structural support member passing through the hollow space and a compression retainer securing the structural support member to the modules; and / or (3) have grooves circumscribing the modules and which are proximate corresponding grooves on modules placed on top or below. The modules are preferably sealed to one another with sealant placed in the grooves.
Owner:SIMMONS SCOTT +1
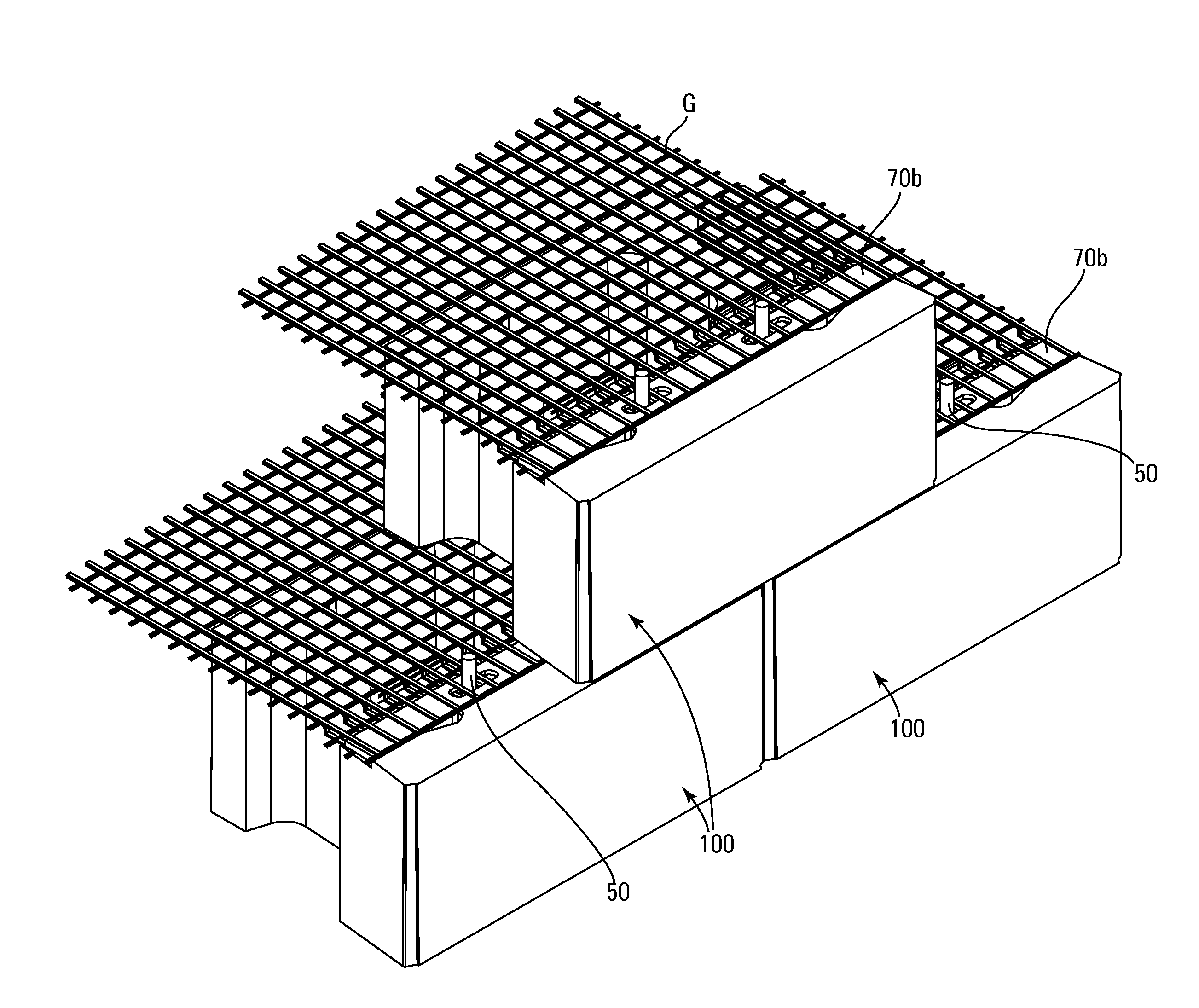
Multi-channel retaining wall block and system
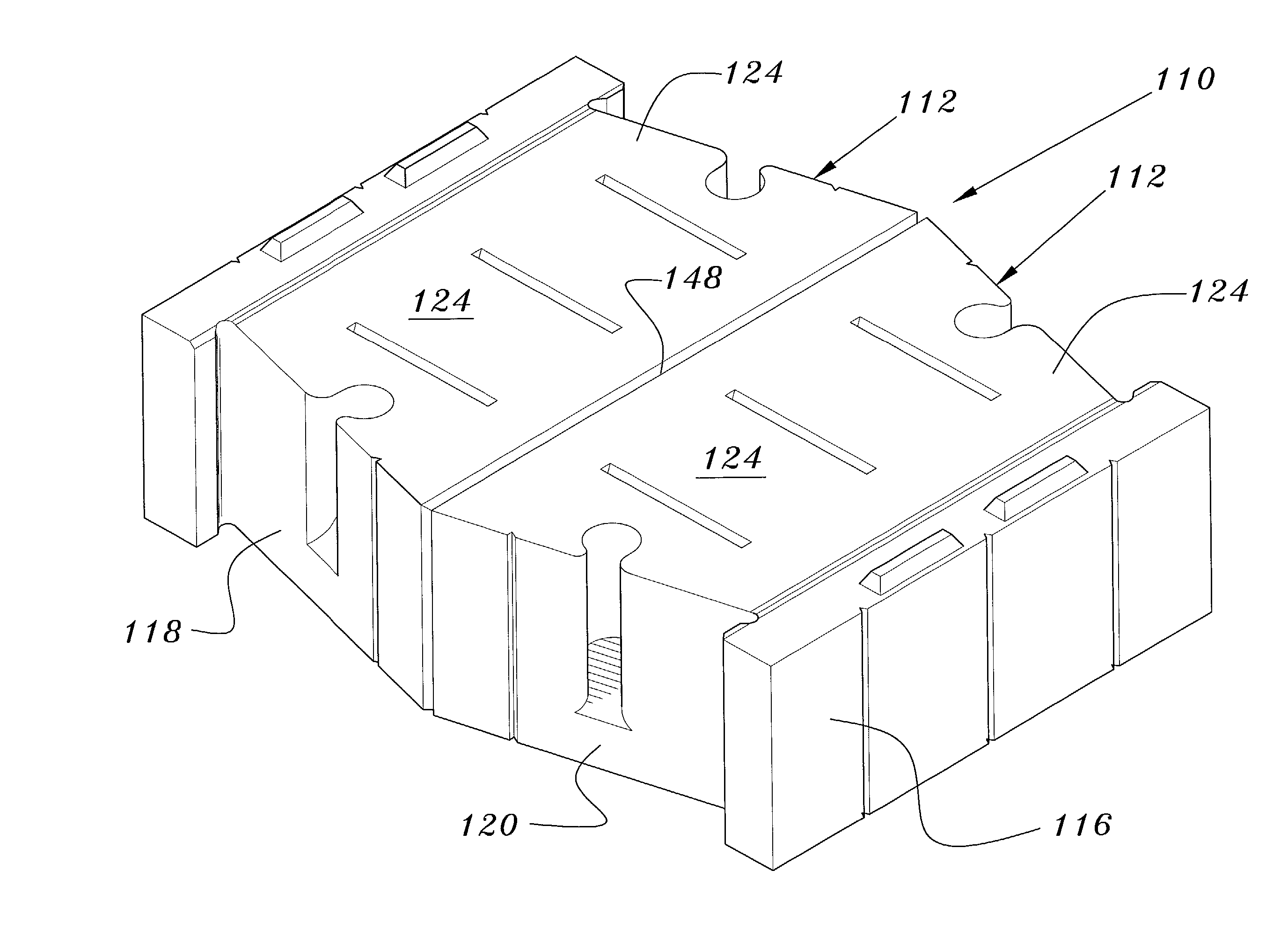
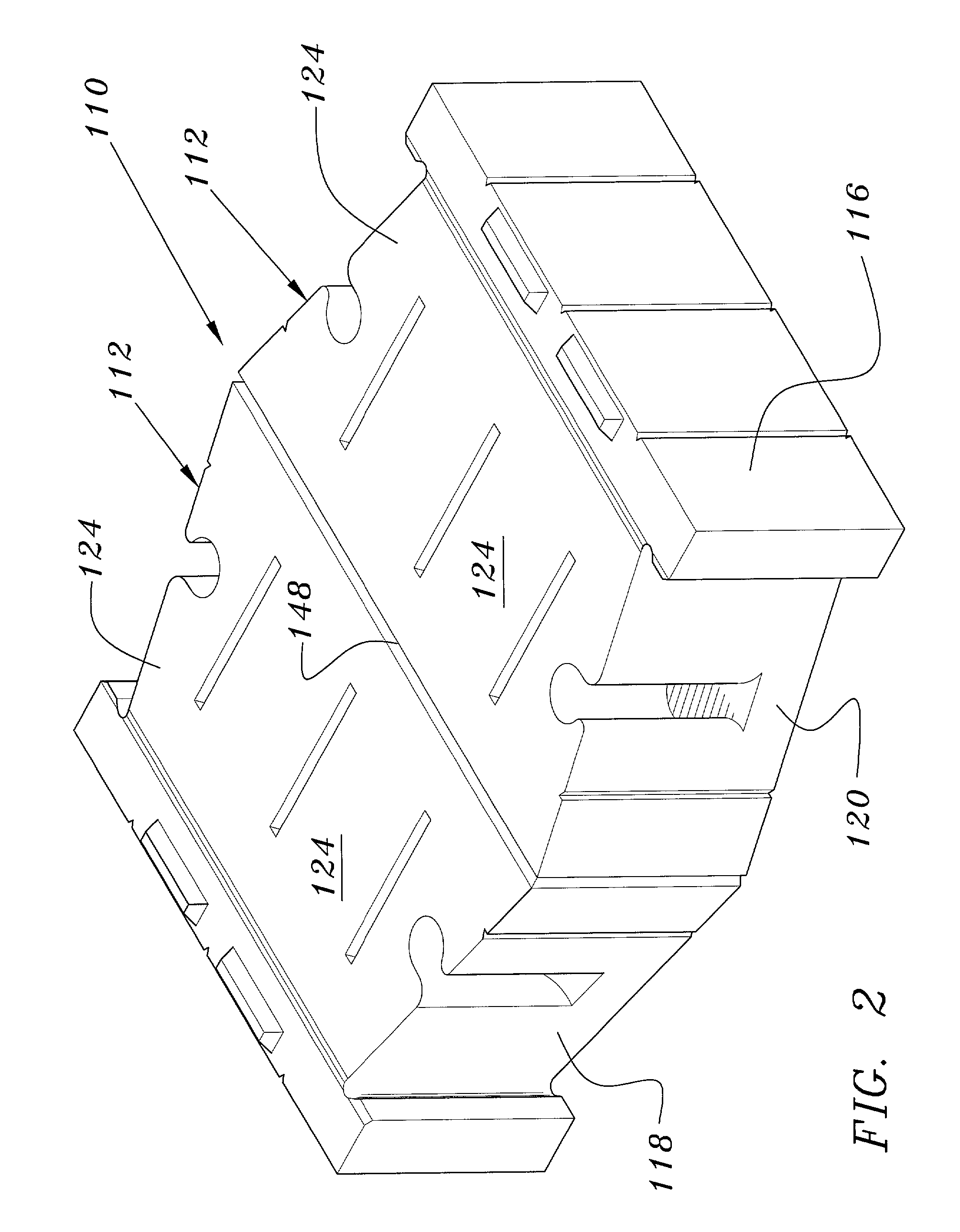
A retaining wall block system having multiple sizes and shapes of blocks with differently dimensioned, interchangeable front and back faces. The blocks are used to construct an irregularly textured wall having a weathered, natural appearance. Multiple channels in the lower face of the block are used to engage pins in pin-receiving apertures to form an attachment system. A side connection system is particularly useful for stabilizing free-standing walls. Horizontal reinforcing members are also used in the channels and vertical reinforcing members are used in cores of adjacent blocks for reinforcing a wall. Reinforcing geosynthetic materials can also be firmly held in a wall by means of the pins or by connectors adapted to fit in the block channels.
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
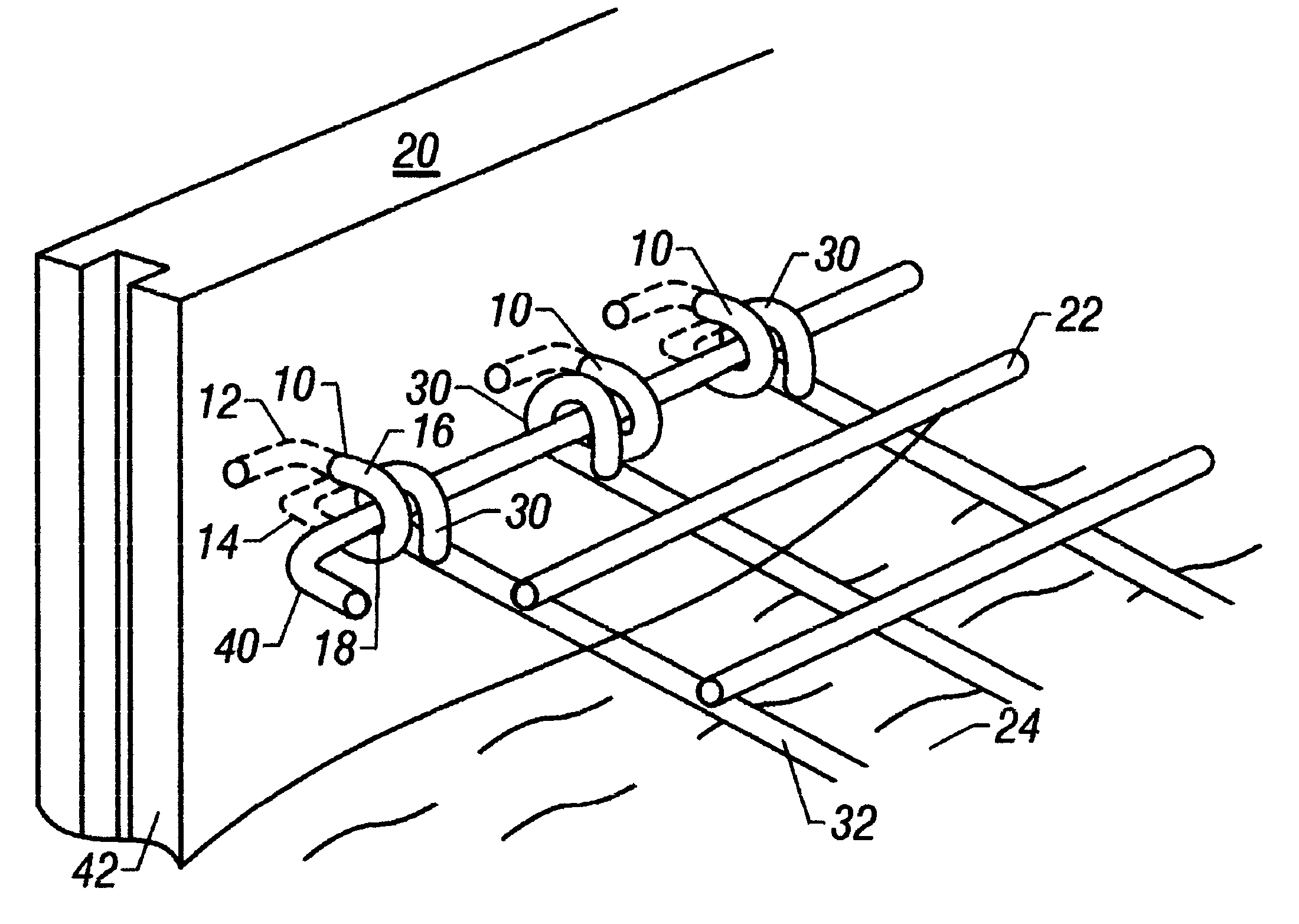
Mechanical interlocking means for retaining wall
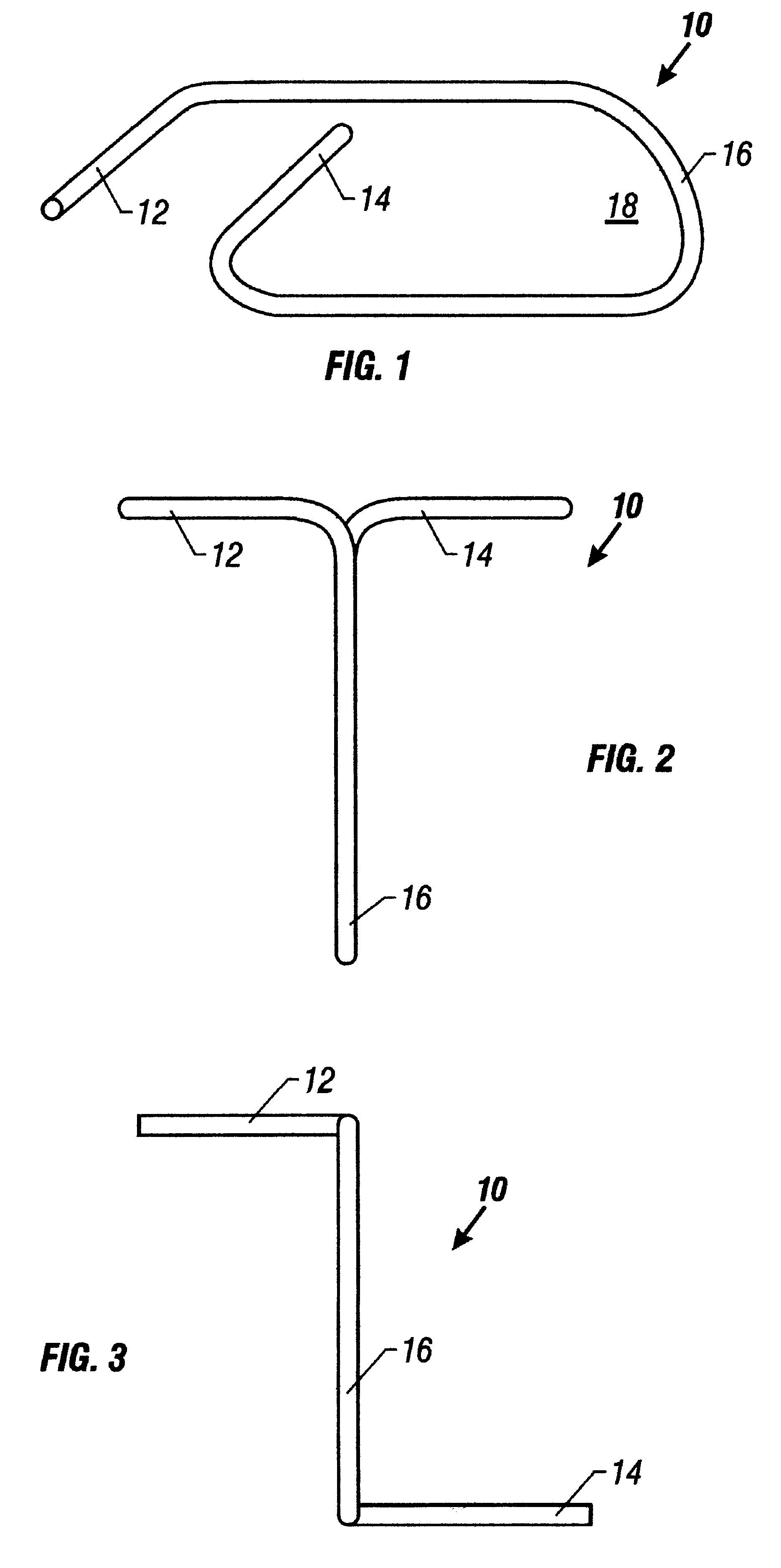
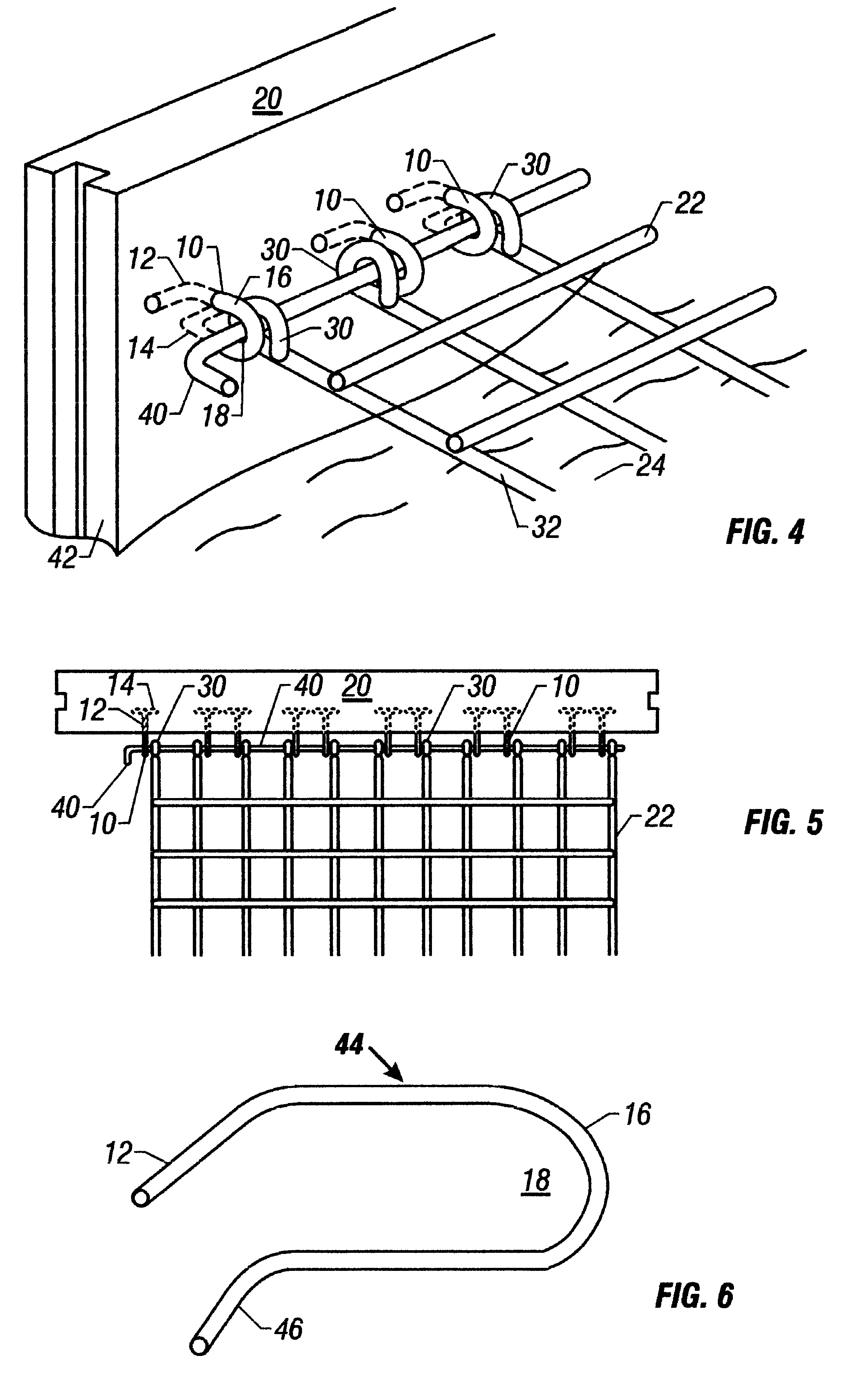
An improved method and system for attaching a welded wire grid-work panel to a plurality of face panels of a retaining wall. The method first begins by providing a plurality of stackable face panels, each face panel having a plurality of anchor links fixed within a back portion of the face panels. Each of the anchor links forms a vertical loop extending outwardly generally perpendicular to the back portion of the face panels. Additionally, each anchor link includes two legs extending laterally from each anchor link within the face panel. Next, a first tier of the face panels is disposed at the bottom of the embankment being erected. Soil is then back-filled behind the first tier of panels to a level of the anchor links disposed within the first tier of face panels. A welded wire grid-work panel, which extends perpendicularly from the back portion of the face panels into a soil embankment, is positioned so that a plurality of wire loops at the edge of the grid-work panel aligns with the vertical loops. A connector rod is extended through the vertical loops of the anchor links and the wire loops of the grid-work panel. Next, additional soil is back-filled behind the first tier of face panels and over the anchor links, vertical loops, wire loops, and grid-work panel to a level at a top edge of the first tier of face panels. The method is repeated until the desired height of the embankment is attained.
Owner:SCR STI LLC
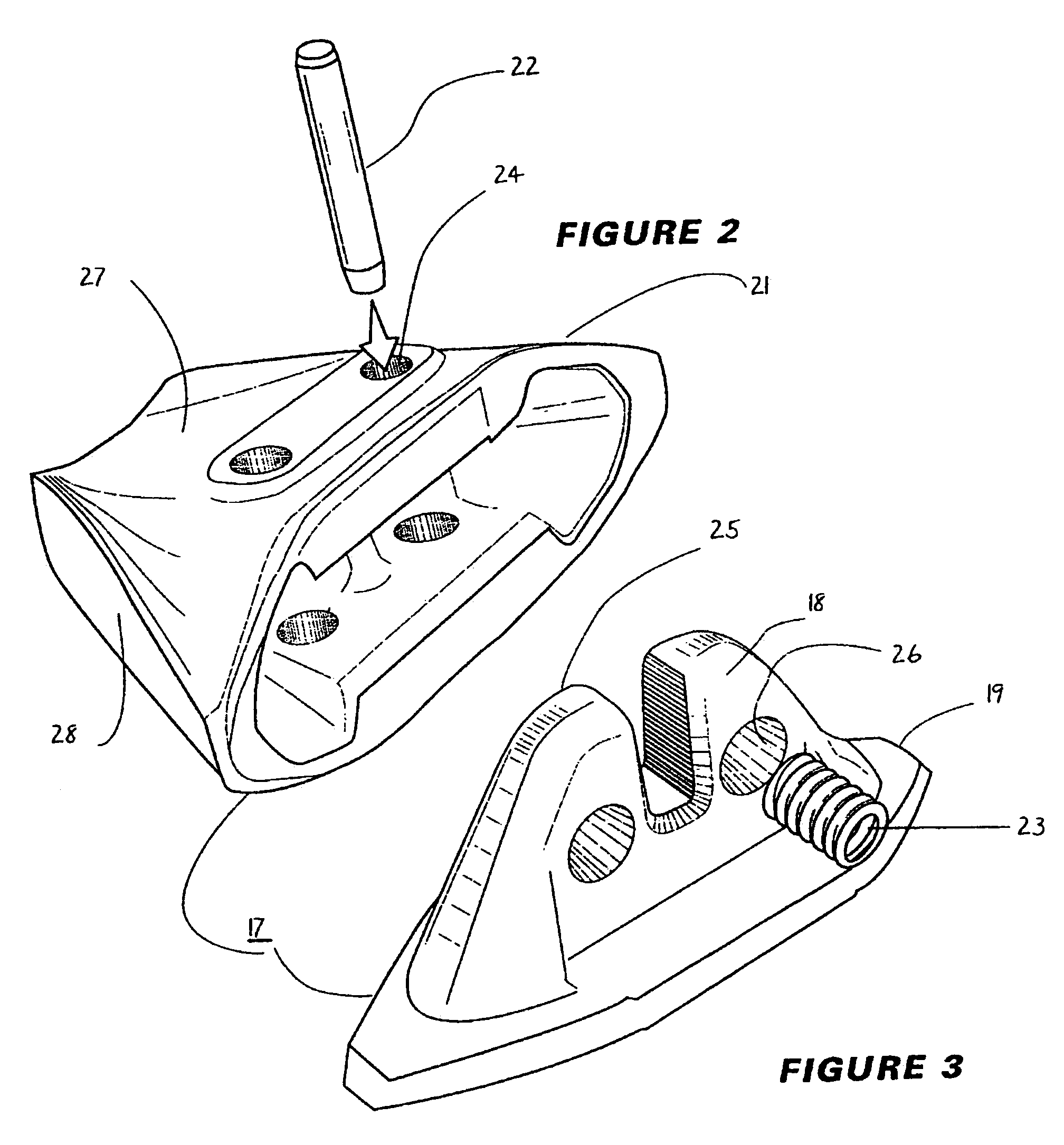
Retaining wall block
InactiveUS7168892B1Reduced and zero predetermined setbackArtificial islandsCoastlines protectionVertical planeEngineering
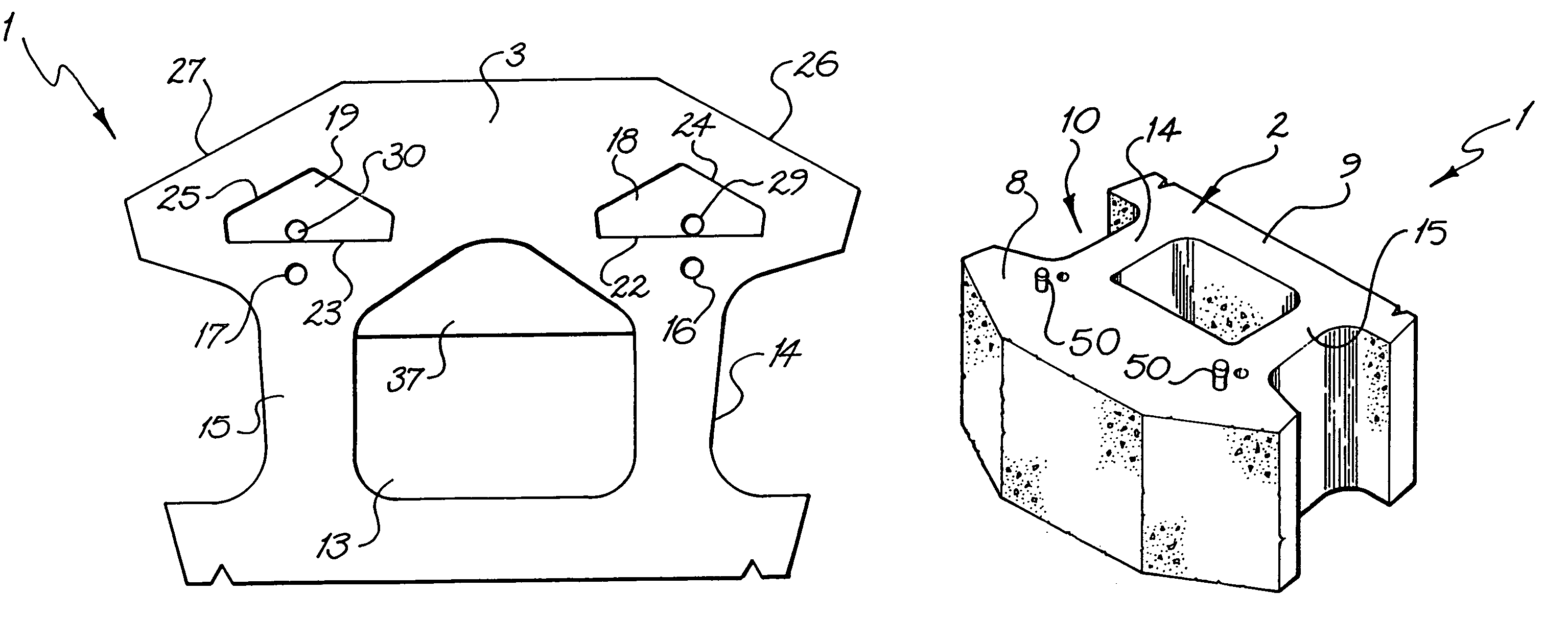
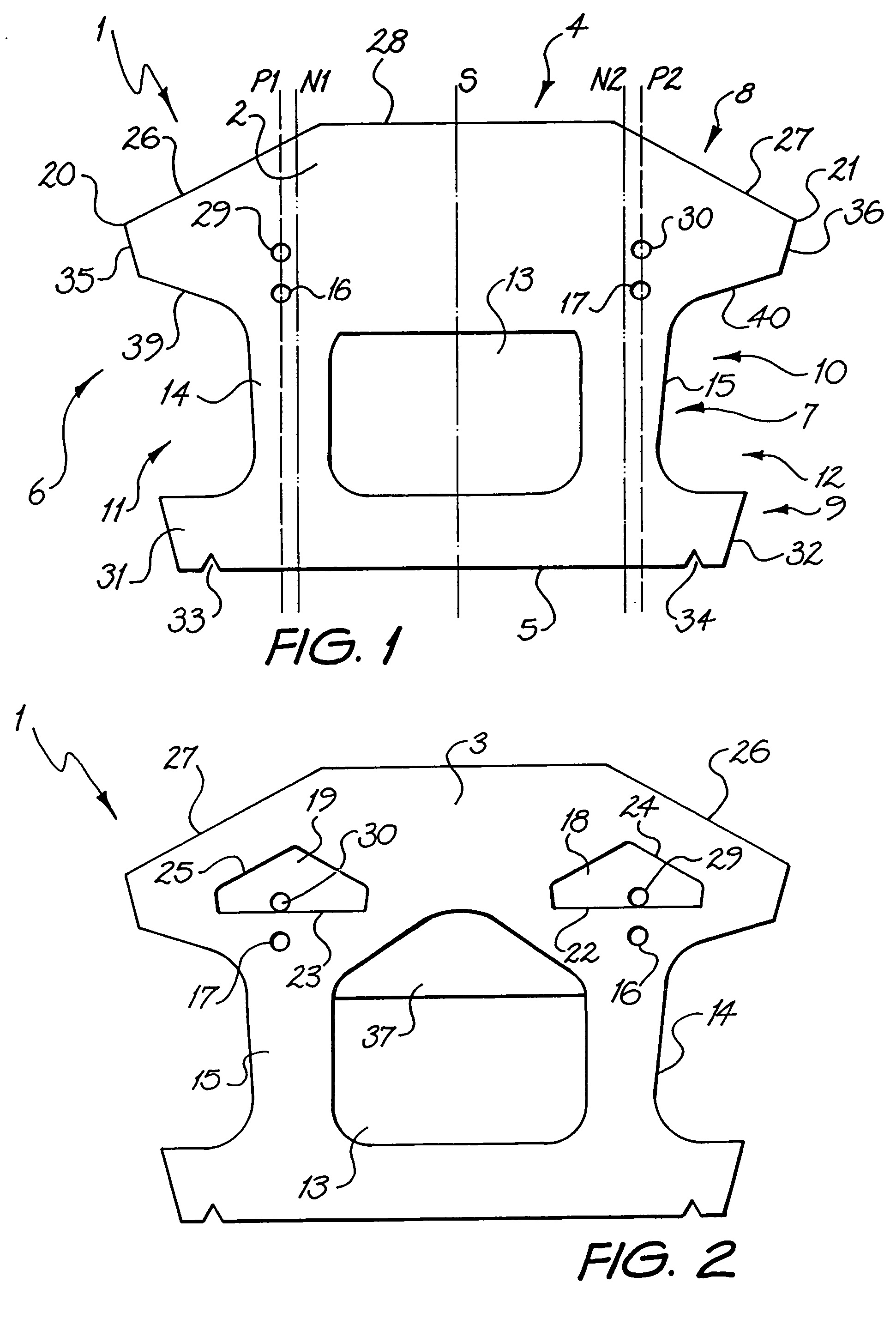
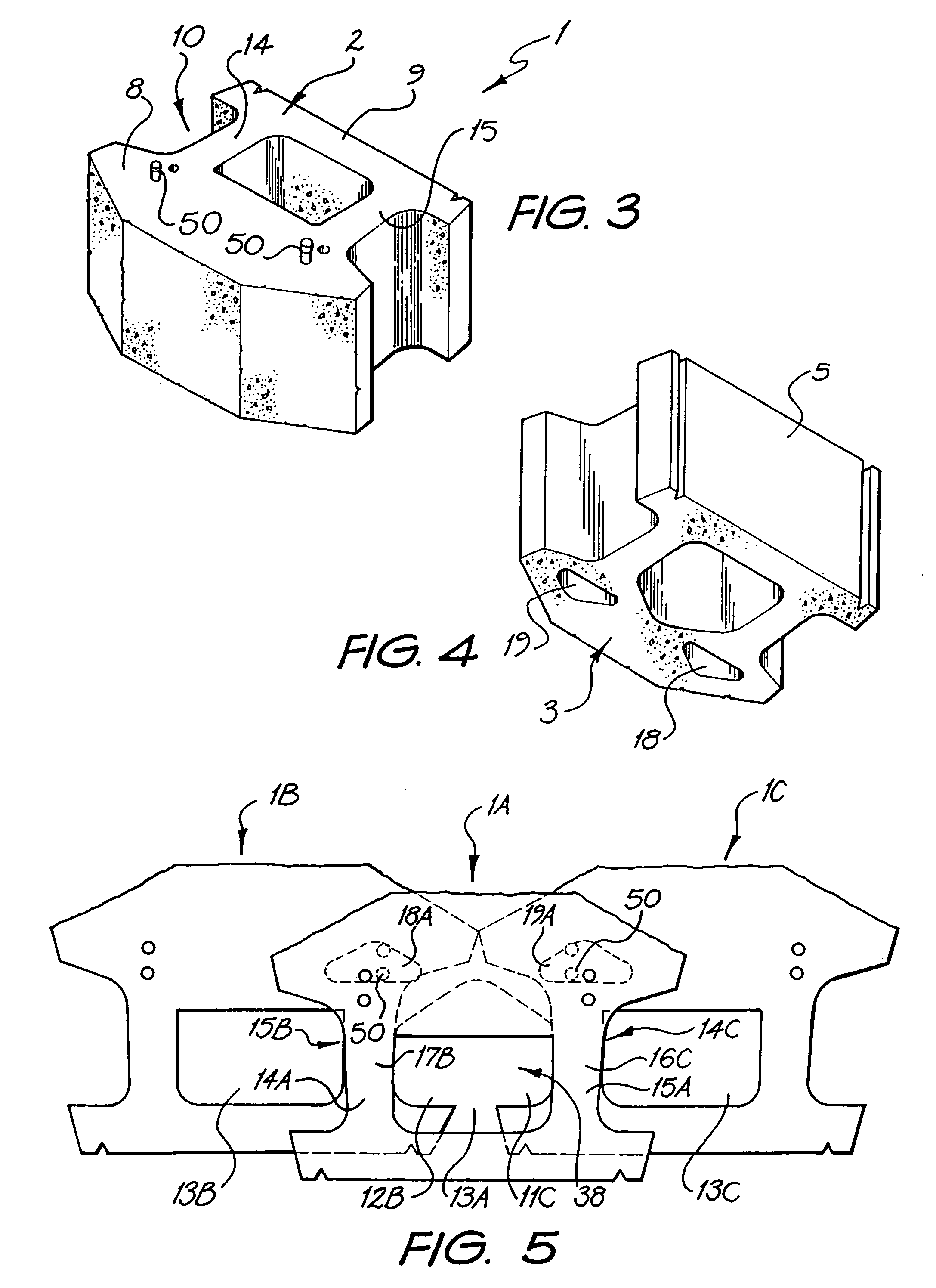
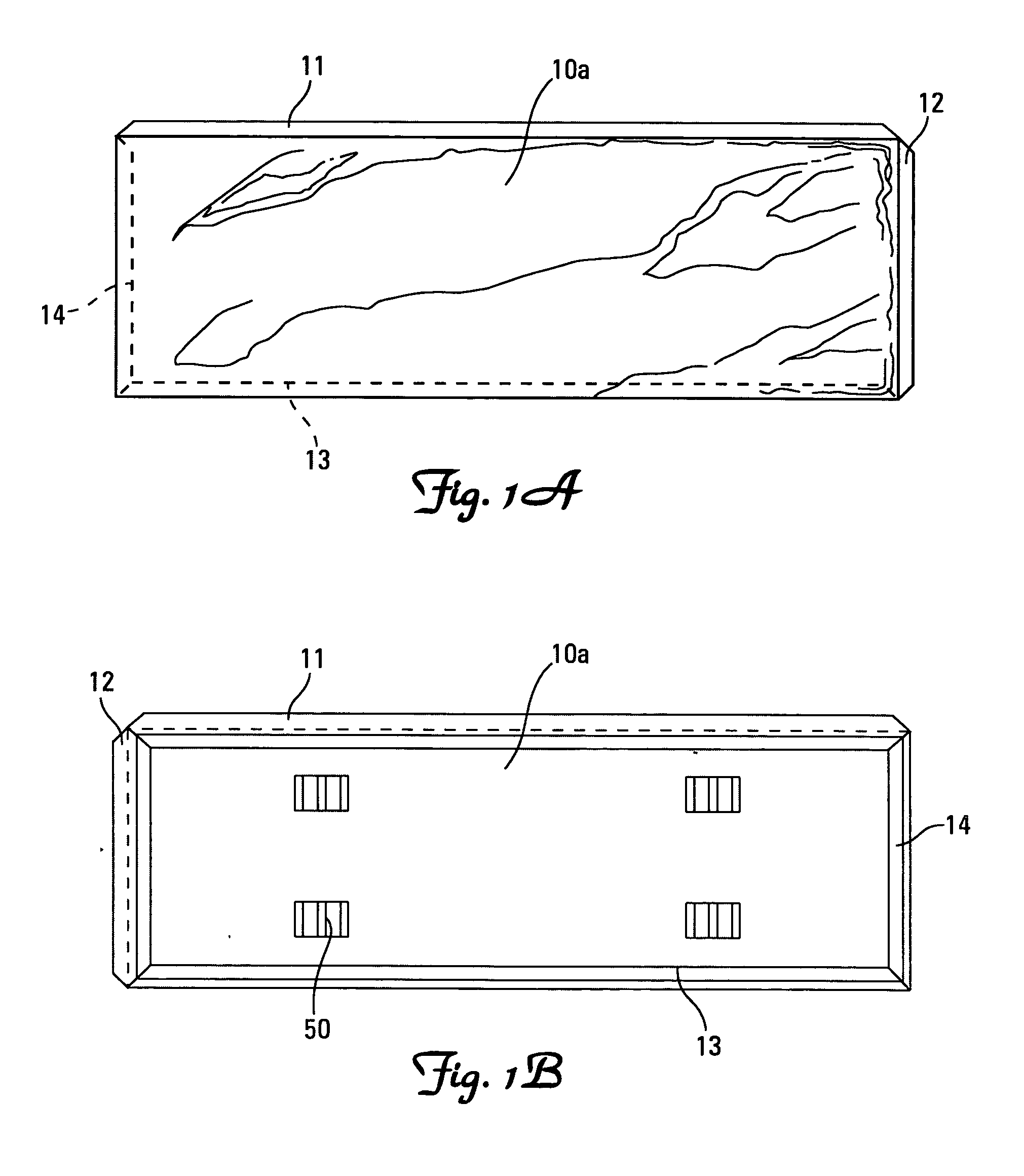
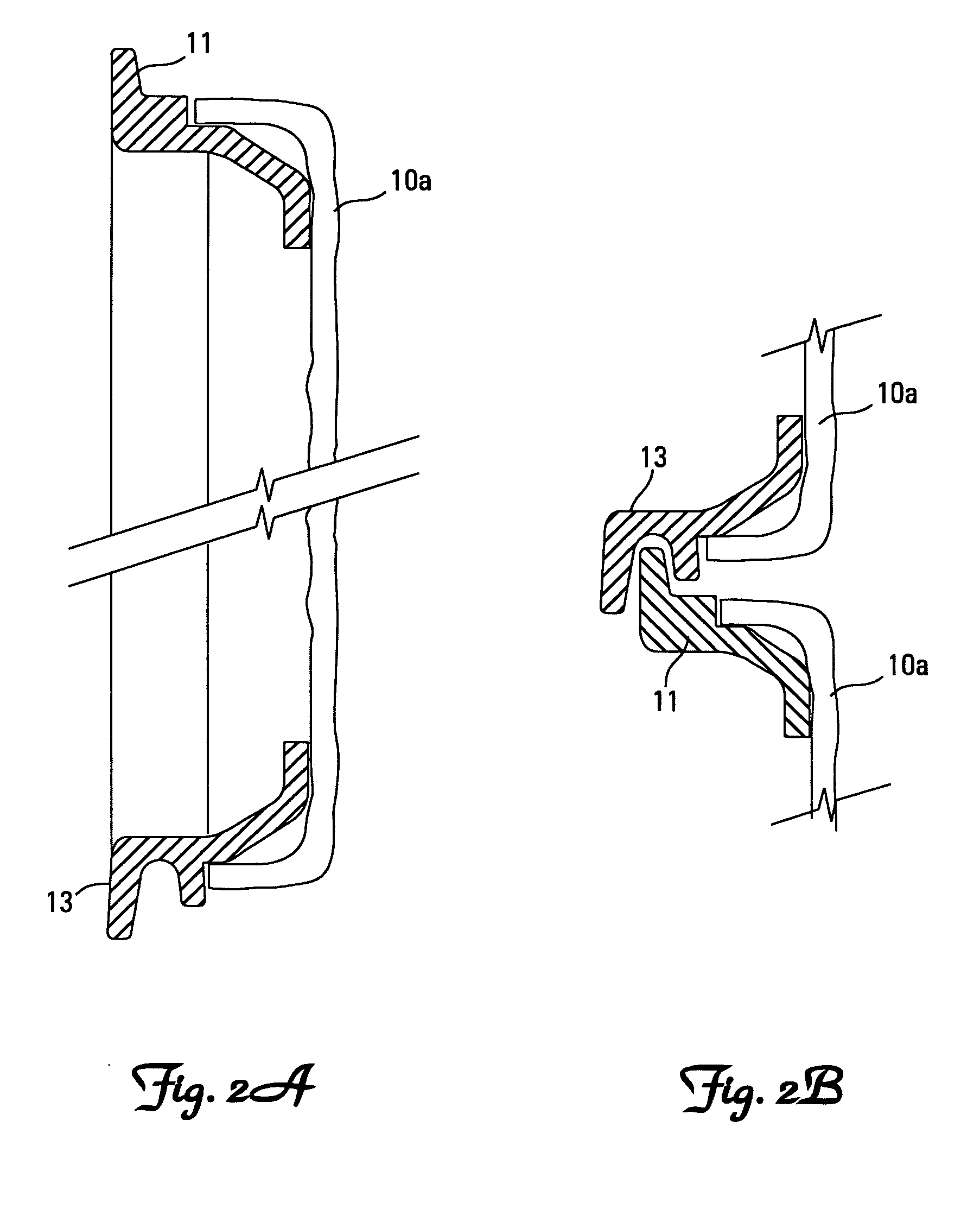
A retaining wall block (1) has parallel top and bottom faces (2, 3), a front face (4), a rear face (5), first and second side wall faces (6, 7) and a vertical plane of symmetry (S) extending between the front and rear faces (4, 5). The block (1) is formed as a body portion (8) including the front face (4), a head portion (9) including the rear face (5) and a neck portion (10) connecting the body portion (8) and the head portion (9). The body, head and neck portions (8, 9, 10) each extend between the top and bottom faces (2, 3) and between the first and second side wall faces (6, 7). An opening (13)′ extends through the neck portion (10) from the top face (2) to the bottom face (3), dividing the neck portion (10) into first and second neck wall members (14, 15) extending rearwardly from the body portion (8) to the head portion (9). First and second pin holes (16 and 17) are each disposed in the body portion (8) and open onto the top face (2) for receiving a pin (50, 51) with a free end of the pin protruding beyond the top face. First and second pin receiving cavities (18, 19) are each disposed in the body portion (8) and open onto the bottom face (3) for receiving the free end of a pin (50, 51) received in a pin hole (16 and 17) of an adjacent block (1) disposed therebeneath so as to interlock the blocks (1) with a predetermined setback. The neck wall members (14, 15), pin holes (16 and 17) and pin receiving cavities (18, 19) are positioned such that a first plane (P1) extending parallel to the plane of symmetry (5) passes through the first pin receiving cavity (18), first pin hole (16) and first neck wall member (14) and a second plane (P2) extending parallel to the plane of symmetry (5) passes through the second pin receiving cavity (19), second pin hole (17) and second neck wall member (15).
Owner:MELLON BANK N A
Multi-channel retaining wall block and system
A retaining wall block system having multiple sizes and shapes of blocks with differently dimensioned, interchangeable front and back faces. The blocks are used to construct an irregularly textured wall having a weathered, natural appearance. Multiple channels in the lower face of the block are used to engage pins in pin-receiving apertures to form an attachment system. Horizontal reinforcing members are also used in the channels and vertical reinforcing members are used in cores of adjacent blocks for reinforcing a wall. Reinforcing geosynthetic materials can also be firmly held in a wall by means of the pins or by connectors adapted to fit in the block channels.
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
Concrete block system
A dry-cast concrete block system for use in a structure. The dry-cast concrete block system comprises a support block comprising a first coupling part and a face block comprising a second coupling part. The first coupling part and the second coupling part enable the face block to be coupled to the support block. The face block comprises a surface adapted to be exposed when the face block is coupled to the support block and the dry-cast concrete block system is positioned in the structure. In one embodiment, at least a portion of the surface has a cast texture with a natural stone appearance. In one embodiment, the structure is a wall and the concrete block system is a wall block system. For example, the wall may be a retaining wall and the wall block system may be a retaining wall block system. In another embodiment, the structure is a column and the concrete block system is a column block system. In yet another embodiment, the structure is steps and the concrete block system is a steps block system.
Owner:OLDCASTLE BUILDING PROD CANADA INC
Retaining wall block system
InactiveUS20110217127A1Improves Structural IntegrityAvoid displacementArtificial islandsStrutsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A wall block having a block body having opposed front and rear faces, opposed first and second side walls, and opposed and substantially parallel top and bottom faces, one or more pin holes that open onto the top face of the block, and one or more lugs that extend from the bottom face, each lug having a back surface that extends contiguously from the rear face of the block. A corner block for use with the wall block. A retaining wall comprising a plurality of wall blocks including at least one lower course and at least one upper course.
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
Methods for controlling water and particulate production
The present invention provides methods of reducing the production of both water and particulates from subterranean formations; the methods are particularly useful in conjunction with subterranean formations surrounding wellbores and fractures. The methods comprise the steps of applying to a subterranean formation a pre-flush fluid, applying aqueous surfactant fluid, applying a low-viscosity consolidating fluid, and applying an after-flush fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
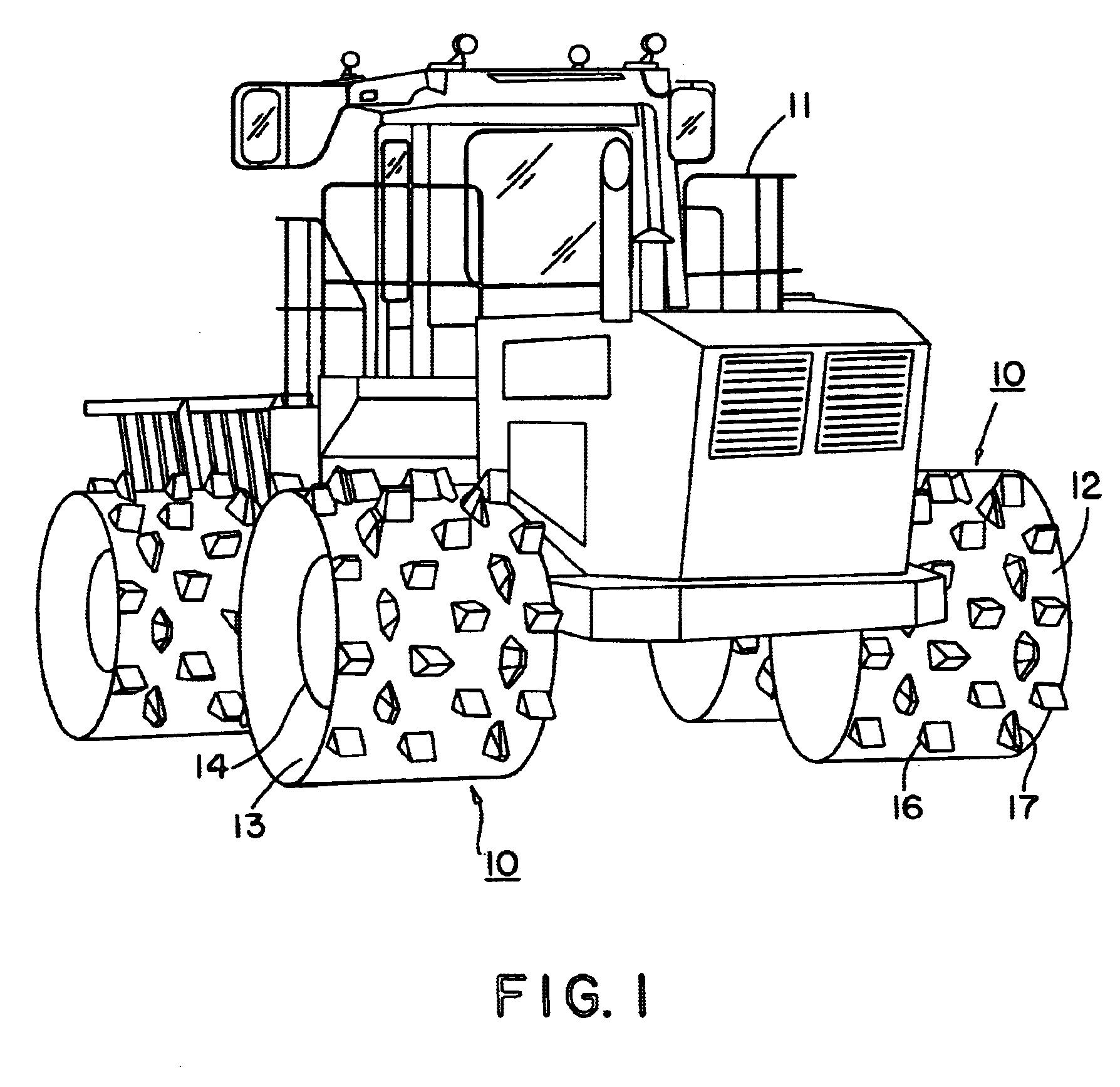
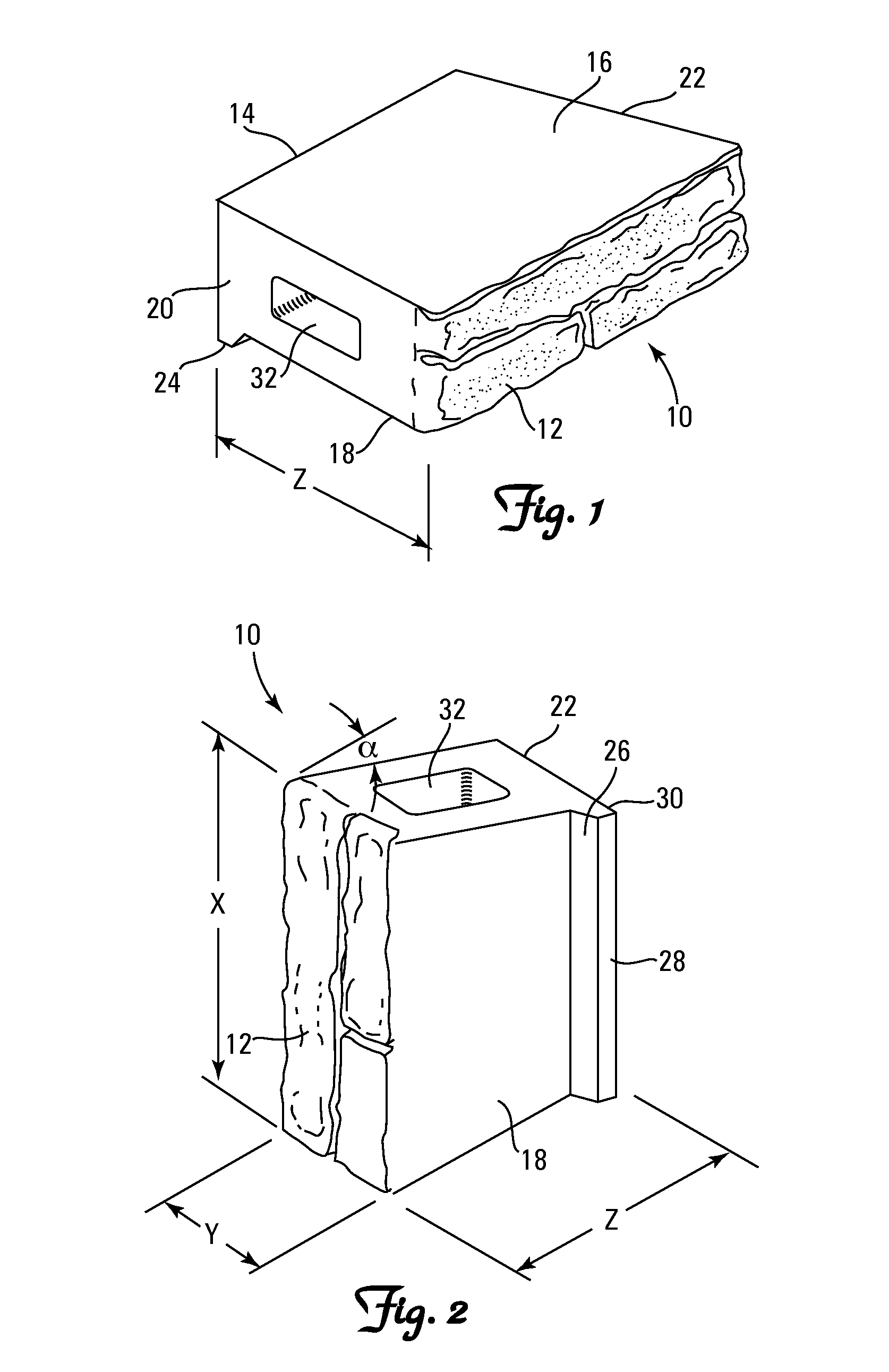
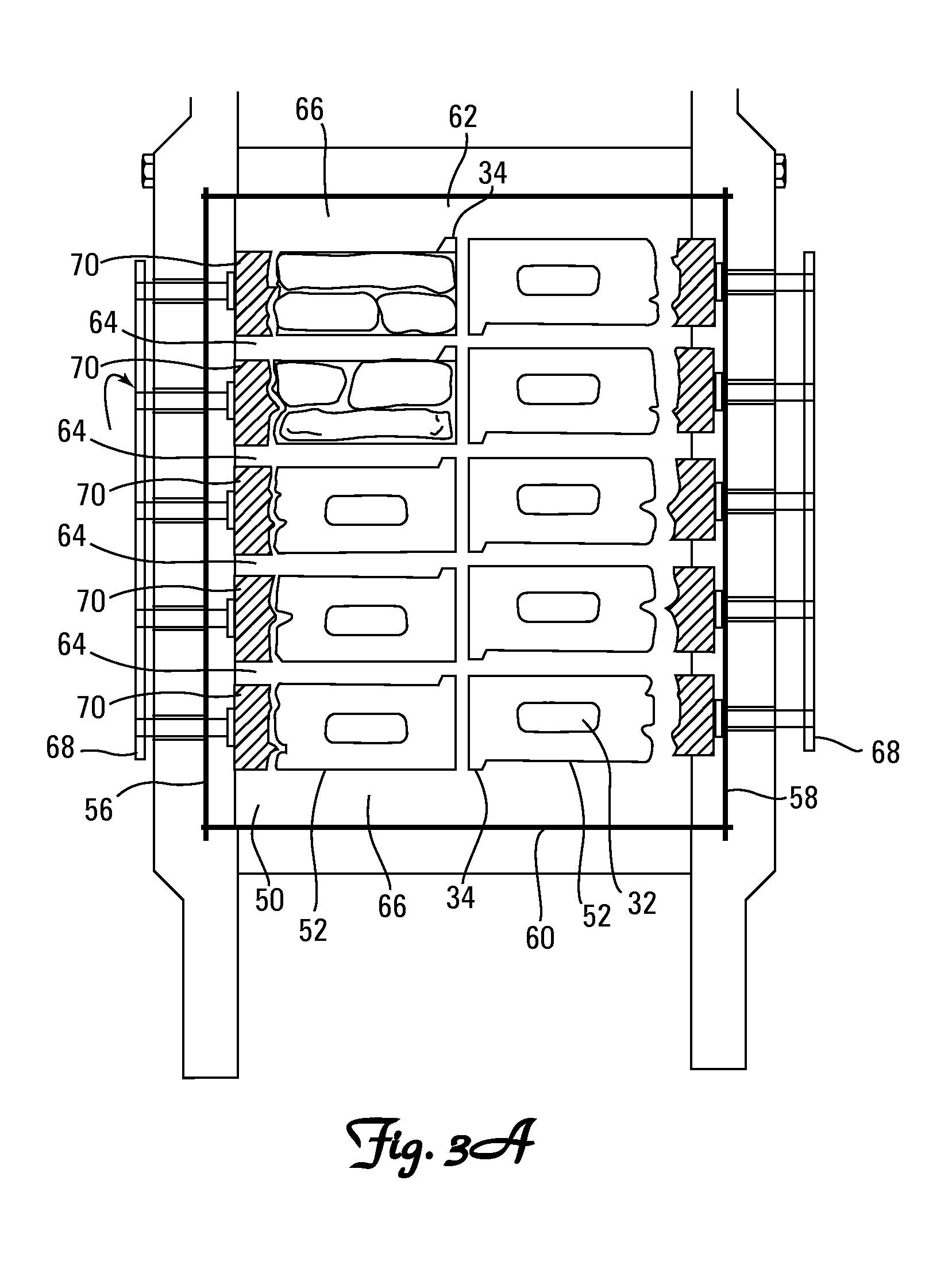
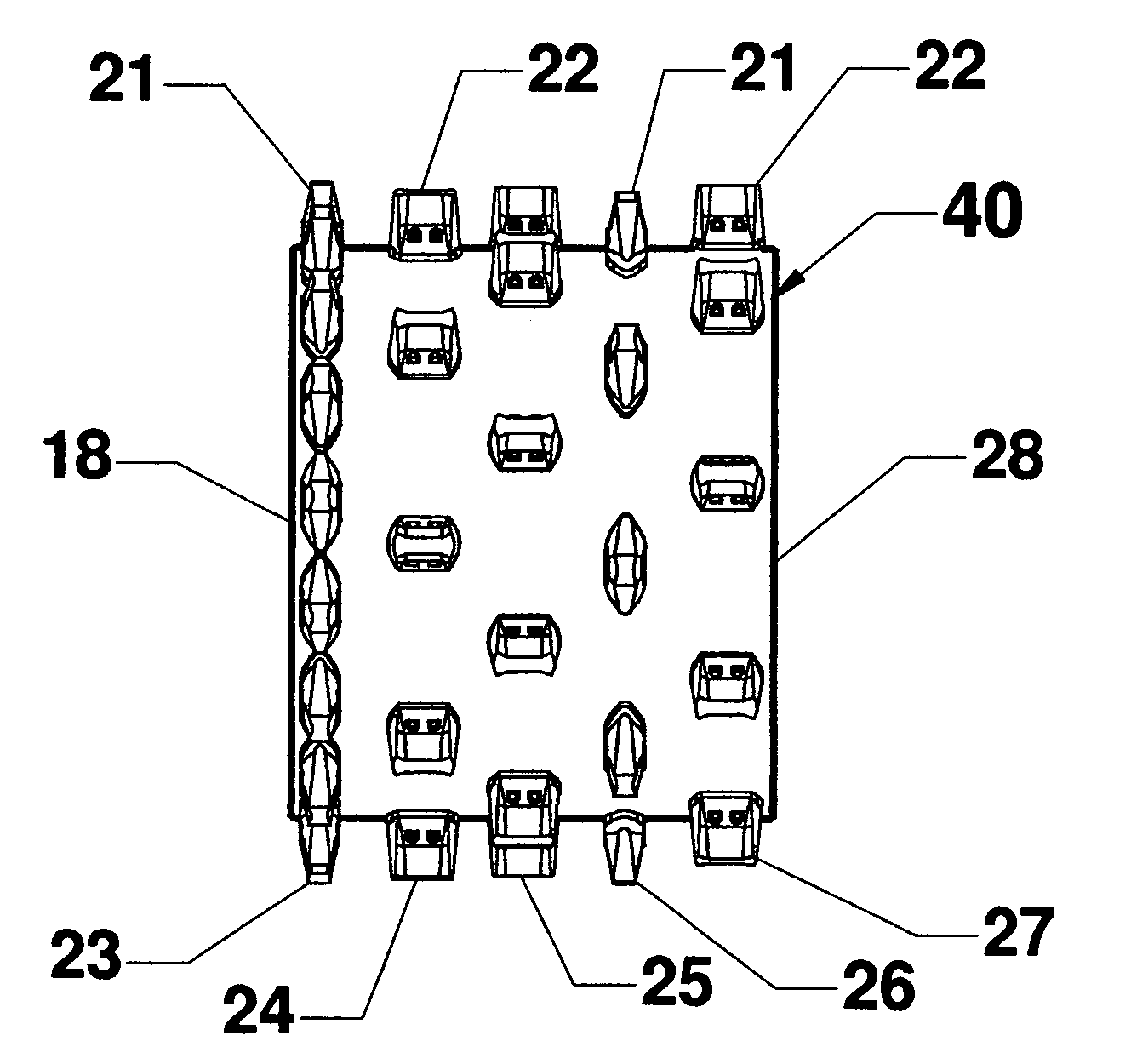
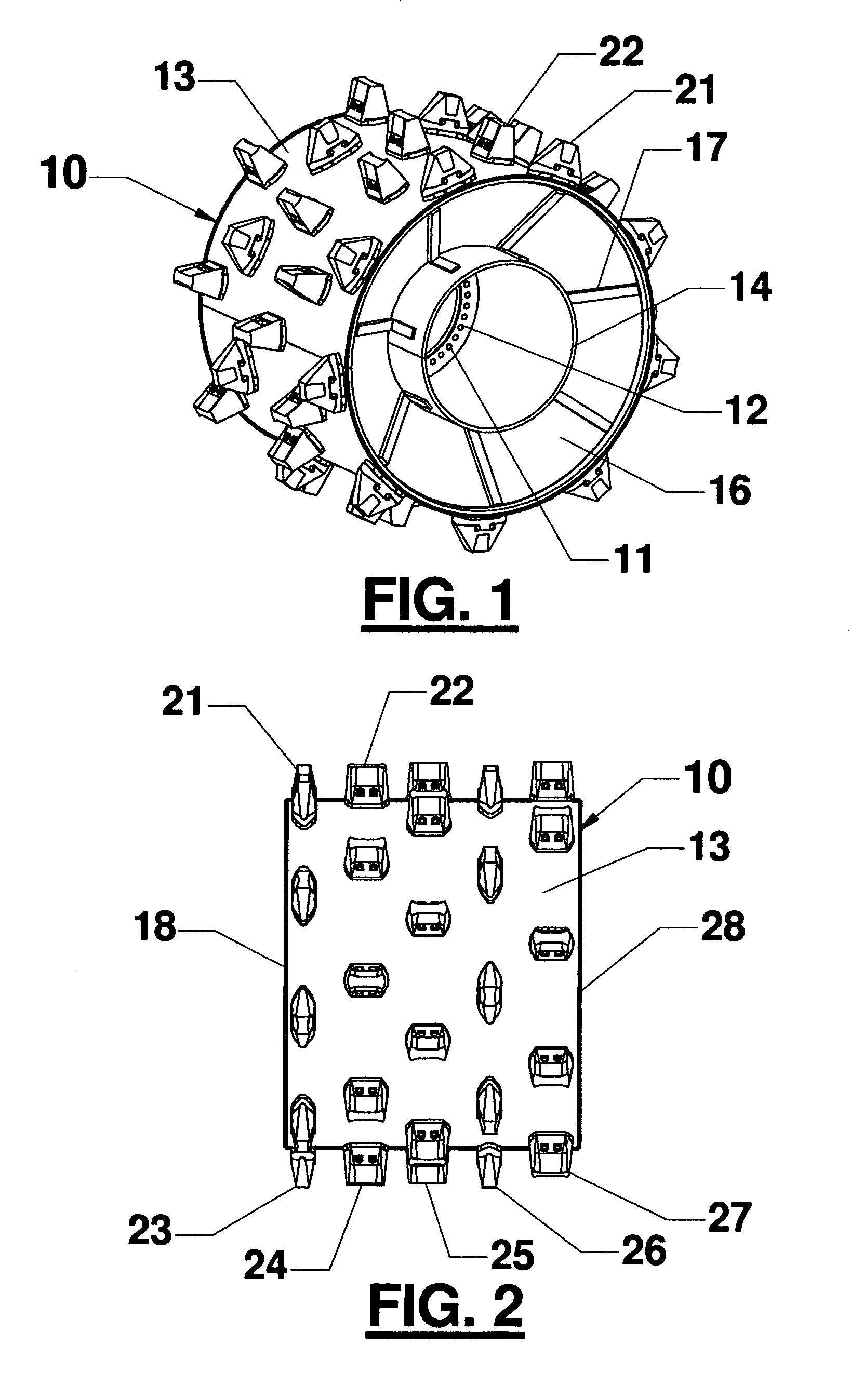
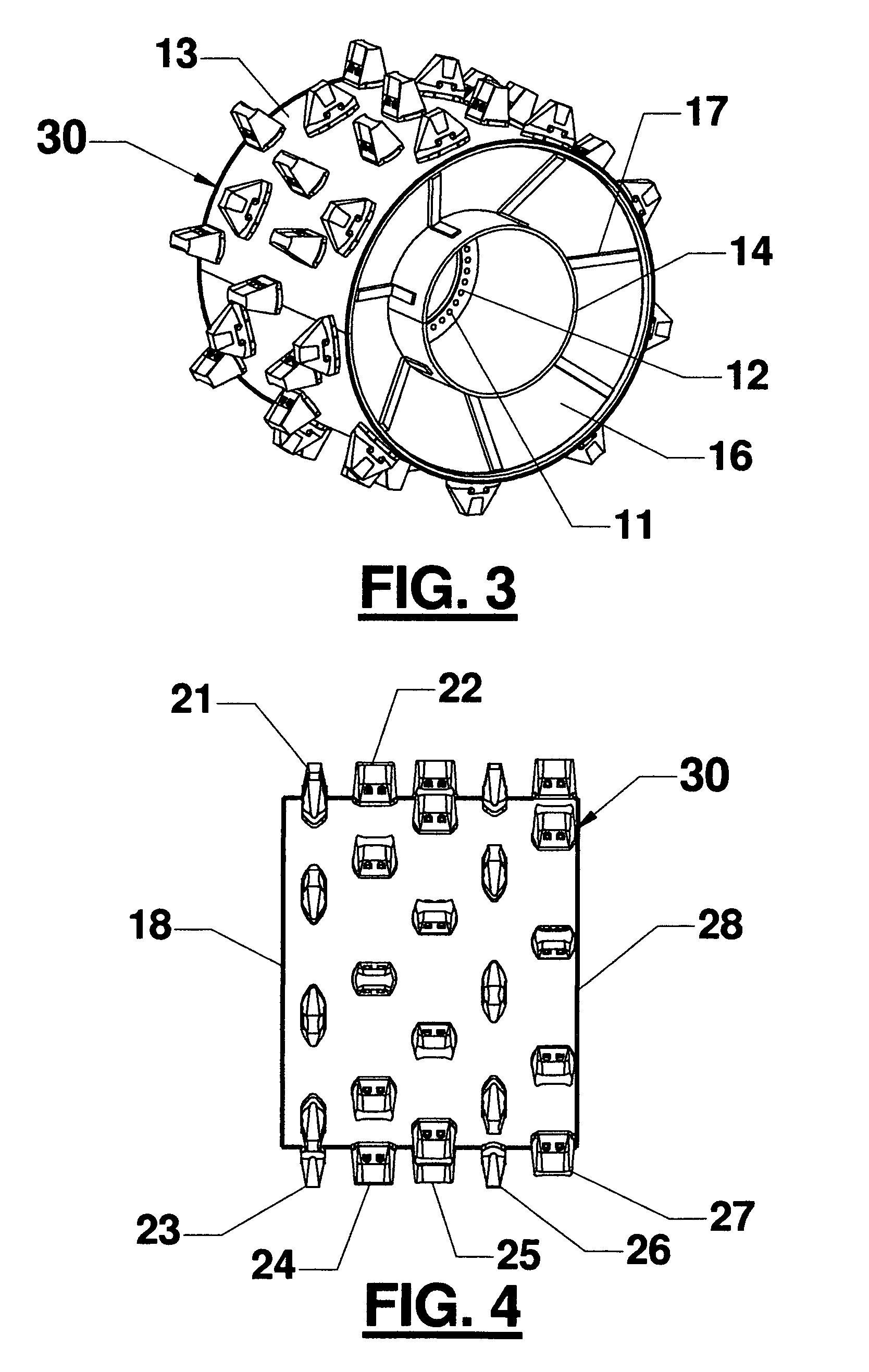
Fill and compaction roller using replaceable cleat assemblies with extended service life
InactiveUS6682262B2Easy to replaceInhibit wearRoads maintainenceSoil preservationWear resistantEngineering
Owner:CARON COMPACTOR
Methods for controlling water and particulate production
The present invention provides methods of reducing the production of both water and particulates from subterranean formations; the methods are particularly useful in conjunction with subterranean formations surrounding wellbores and fractures. The methods comprise the steps of applying to a subterranean formation a pre-flush fluid, applying aqueous surfactant fluid, applying a low-viscosity consolidating fluid, and applying an after-flush fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method for soft soil foundation treatment through microorganism grouting sand drain
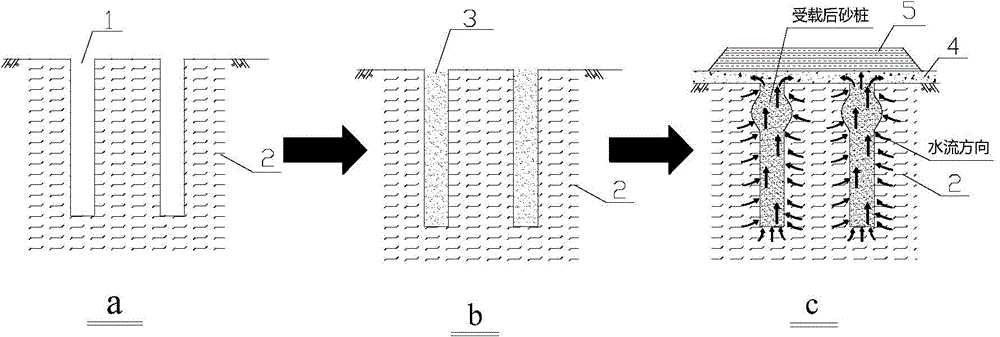
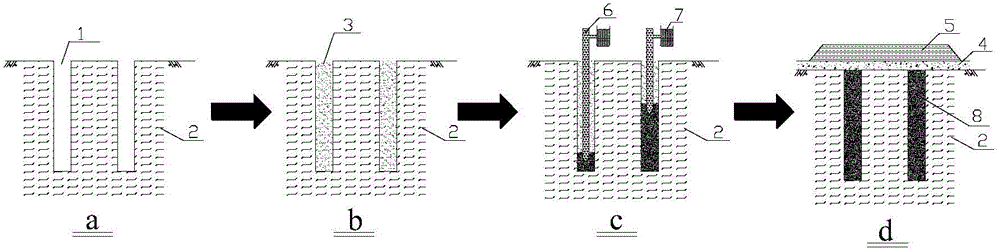
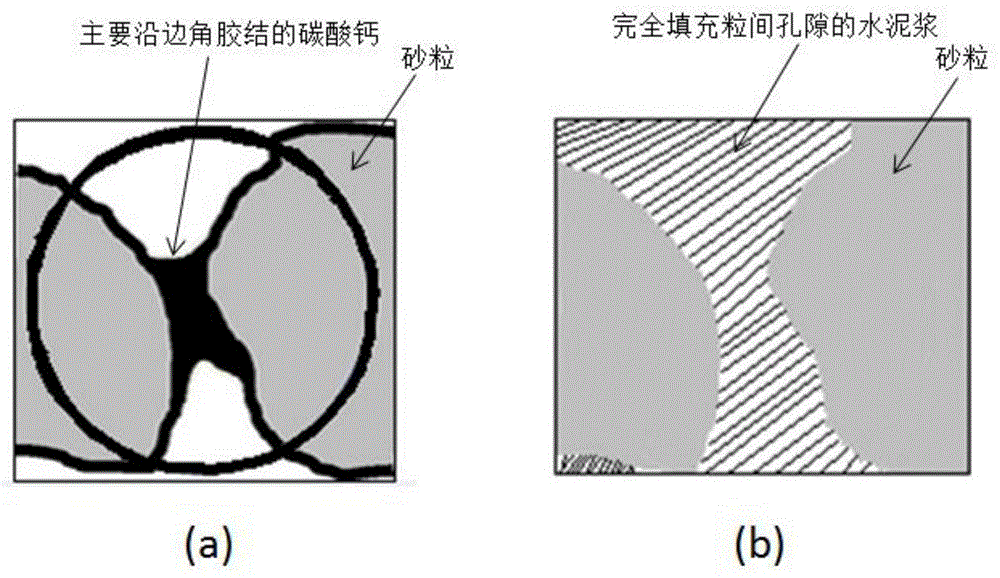
InactiveCN104631430AImprove vertical load carrying capacityPermeability changeOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsSoil scienceSalt solution
Disclosed is a method for soft soil foundation treatment through microorganism grouting sand drain. The method comprises the steps that a, a pile hole 1 is formed in a soft soil foundation to be treated, and sand is poured into the pile hole 1 to form a sand pile; b, a urease-producing microorganism solution 9 and a nutritive salt solution 10 are sequentially and evenly injected into the sand pile through a grouting tube 6, sand cementation is achieved through the microorganism induction calcium carbonate crystal technology, the concentration of the urease-producing microorganism solution 9 and the concentration of the nutritive salt solution 10 are controlled, sand in the pile body forms a specific cementation mode, and the good water permeable characteristic is ensured; c, after the microorganism grouting solidification sand pile is formed, a flexible water permeable sand cushion 4 is laid on the top of the foundation jointly formed by the sand oil and pile space soil 2, prepressing loads 5 are exerted on the top of the flexible water permeable sand cushion 4, pore water in the pile space soil 2 is made to be drained along a drainage channel formed by the sand pile and the sand cushion, the pile space soil is solidified, and the composite foundation with the high bearing capacity is formed jointly through the soft soil obtained after drainage and solidification are carried out on the microorganism grouting sand pile and the flexible water permeable sand cushion covering the soft soil.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
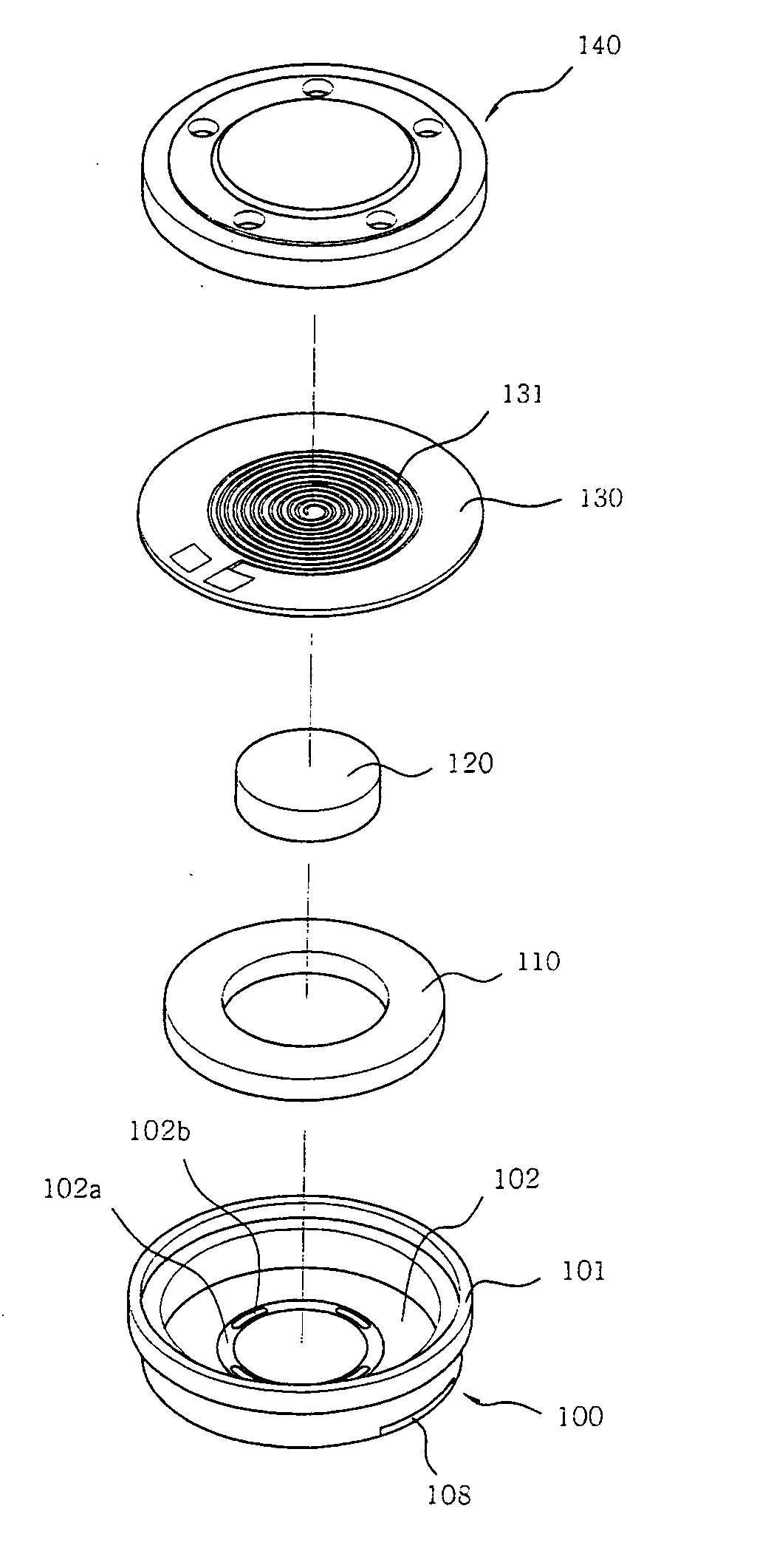
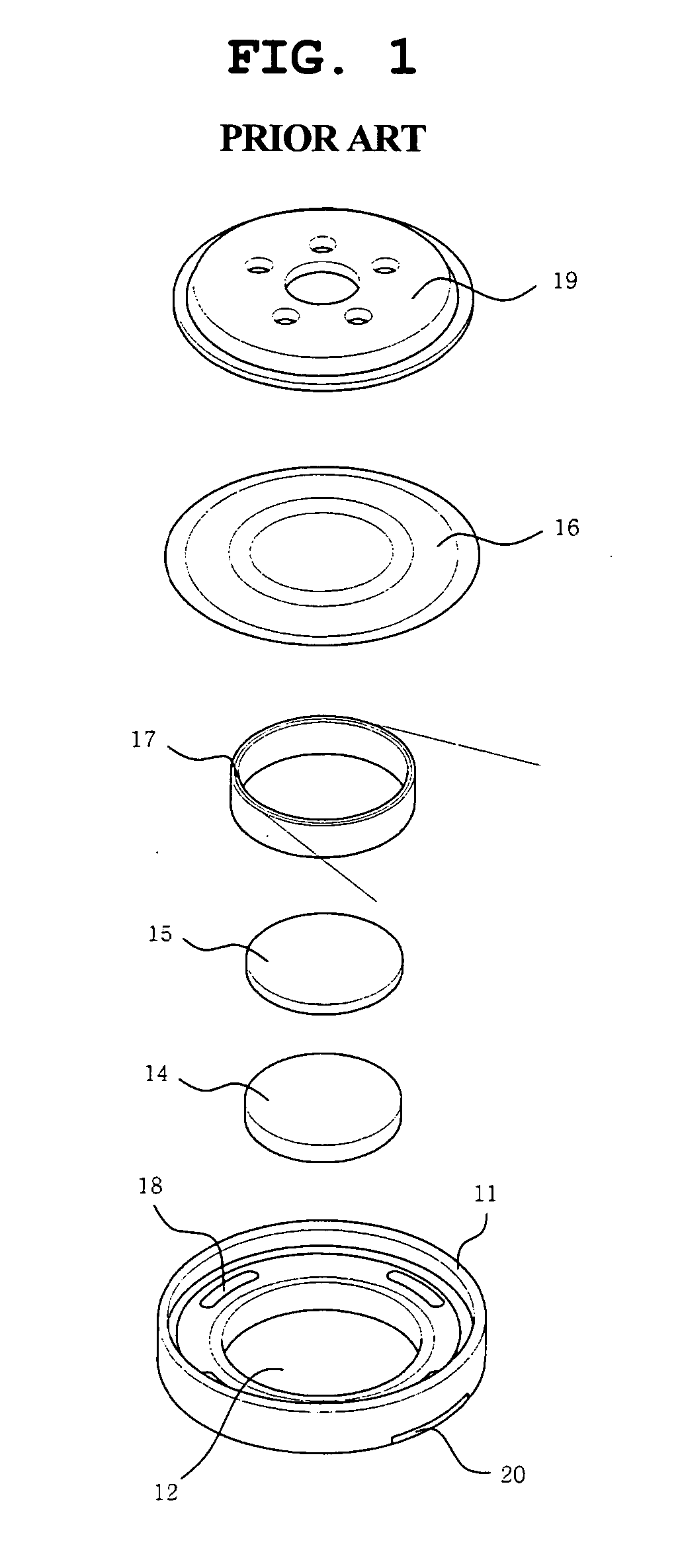
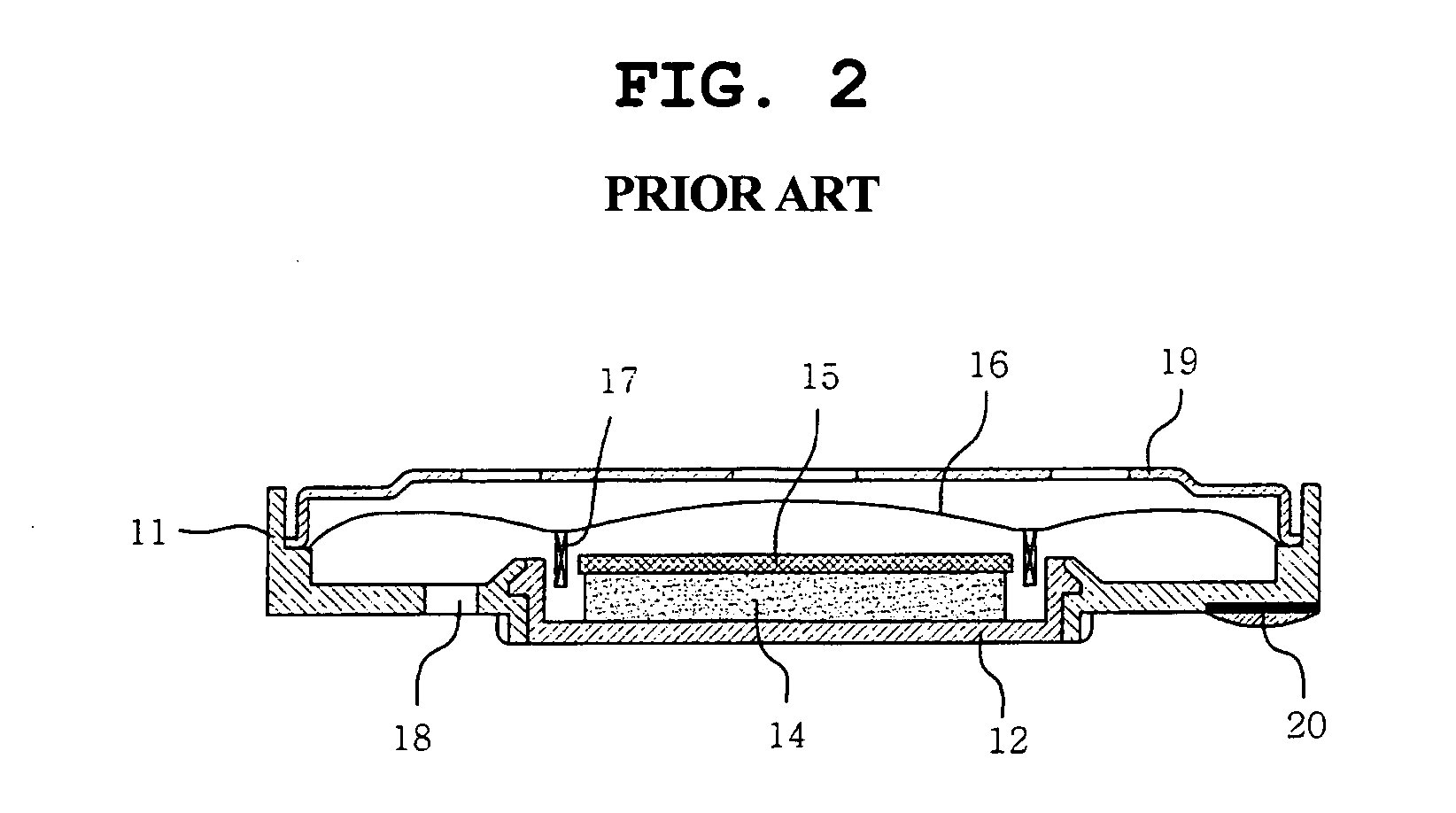
Speaker for mobile terminals and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050220320A1Thin structureWide frequency characteristicTransducer detailsGeotextilesEngineeringSound quality
Disclosed herein are a speaker for mobile terminals which has a slim structure and has a wide frequency characteristic and an excellent high frequency distortion characteristic, thus accomplishing an excellent sound quality, and a method of manufacturing the speaker.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for retroactively installing sensors on marine elements
Sensors, including fiber optic sensors and their umbilicals, are mounted on support structures designed to be retro-fitted to in-place structures, including subsea structures. The sensor support structures are designed to monitor structure conditions, including strain, temperature, and in the instance of pipelines, the existence of production slugs. Moreover the support structures are designed for installation in harsh environments, such as deep water conditions using remotely operated vehicles.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method of vegetation restoration and reconstruction of bare rock slope in East China
InactiveCN101748719APromote growthGuaranteed uptimeWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsRevegetationEcological environment
The invention belongs to the technical field of ecological engineering and particularly relates to a method of vegetation restoration and reconstruction of a bare rock slope in East China. the engineering materials such as active plant material and synthetic geonet are utilized, a plant-growing substrate (plant tool species seed, nutritional soil and binder) is uniformly mixed according to a certain proportion and injected on the rock slope according to the design thickness by a special injection device for the plant-growing substrate, an ecological environment which can ensure normal growth of the plant is created on the rock slope, the slope reinforcement and vegetation restoration are realized through the growth of the plant and other auxiliary functions, and the purpose of vegetation reconstruction of the bare rock slope is achieved. The method is applicable to the vegetation restoration and reconstruction of the bare rock slope in East China with respects to plant tool species and medium formulation and obtains obvious ecological benefits after several years of implementation and popularization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Retaining wall block
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
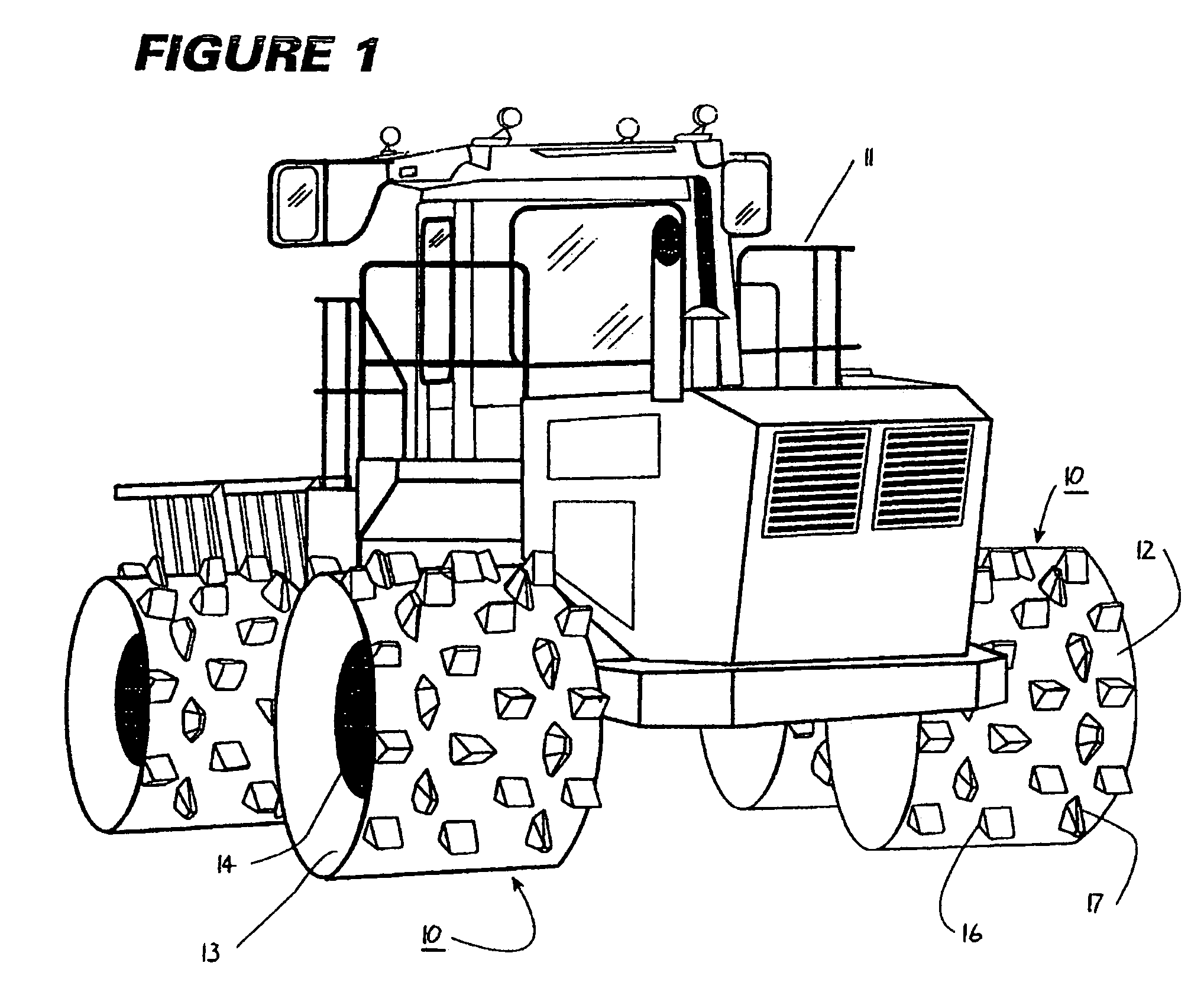
Fill and compaction roller using replaceable cleat assemblies with extended service life
InactiveUS7108452B2Easy to replaceAvoid wear and tearRoads maintainenceSoil preservationMortise and tenonWear resistant
A compaction roller for mounting on a driven compaction vehicle is equipped with both destructive and tractive, highly wear-resistant cleat assemblies. These include readily removable wear caps and supporting bases which have continuous side walls across the parting lines between the parts. Inset in the outer sidewalls are exposed mortise and tenon Jock joints serving to reduce relative movements between the parts under sever working forces. Pins extending radially between the wear caps and supporting bases further enhance the anti-twist resistance between the parts.
Owner:CARON COMPACTOR
Retaining wall block system
A wall block having a block body having opposed front and back faces, opposed first and second side walls, and opposed and substantially parallel top and bottom faces, the top face having a receiving channel, and the receiving channel opening onto one or more pin holes. The wall block can be used in a retaining wall made of (i) a plurality of blocks including at least one lower course and at least one upper course, at least one block comprising a block body having opposed front and back faces, opposed first and second side walls, and opposed and substantially parallel top and bottom faces, the top face having a receiving channel, and the receiving channel opening onto one or more pin holes; (ii) a soil retaining material; and (iii) a channel bar.
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
Veneers for walls, retaining walls and the like
InactiveUS20050252144A1Good lookingCost effectiveArtificial islandsConstruction materialEngineeringNatural stone
A veneer panel system is used with a wall or a retaining wall to provide a natural stone appearance and / or to improve the appearance of an existing wall. Panels can be interlocked to form a stable veneer structure. The structure is attached to a wall by various attachment means.
Owner:KEYSTONE RETAINING WALL SYST
Drifting sand layer and gravel stratum water-moving double-liquid high pressure slip-casting water-blocking construction method
InactiveCN101255698AHigh strengthImprove water stabilitySolid waste managementUnderground chambersWater blockCement slurry
The present invention discloses a running sand layer and sandy gravel layer dynamic-water double-liquid high-pressure slurry-injecting water-shutoff construction method which comprises the following construction steps: drilling a hole, flushing the hole, executing double-liquid high-pressure slurry-injecting operation and sealing the hole. The running sand layer and sandy gravel layer slurry-injecting liquid adopts an ordinary portland cement (P.O.42.5) and 40''Be sodium silicate as material for preparing the slurry, according to the weight proportion of water: cement, namely the cement slurry is prepared with the water cement ratio for 0.5-1.2:1. Then the slurry-injecting liquid is prepared with the volume ratio of cement slurry: sodium silicate for 1:0.08-0.15. The sodium silicate is taken as additive for regulating the initial setting time of the slurry-injecting liquid. The cement slurry can also be doped with fly-ash with cement consumption (weight proportion) for 10%-15%. The invention executes water-insulating construction aiming at the characteristics of large pressure of the underground dynamic water and high flowing velocity in the running sand layer and sandy gravel layer, and can obtain the maximal application sphere and optimum water-shutoff effect.
Owner:HUNAN CONSTR ENG GRP COR
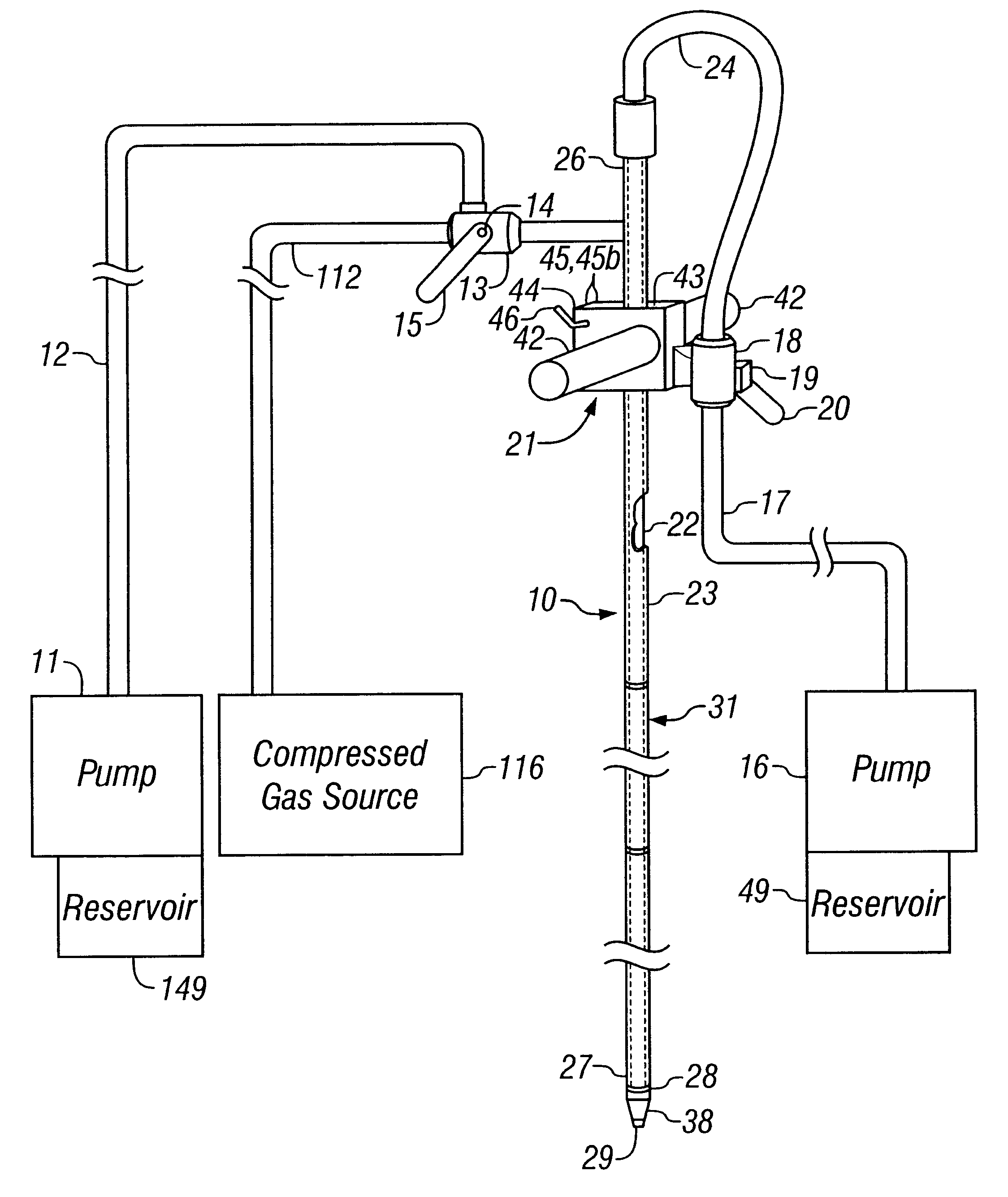
In-situ deep remediation injection system and method
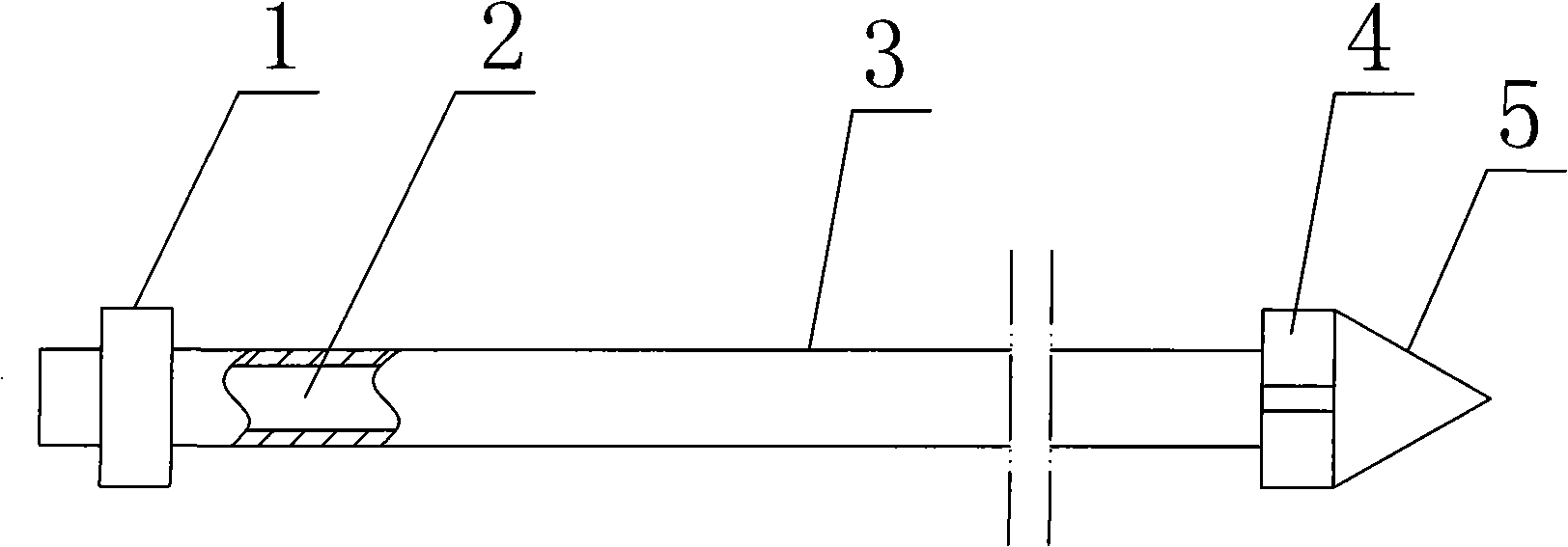
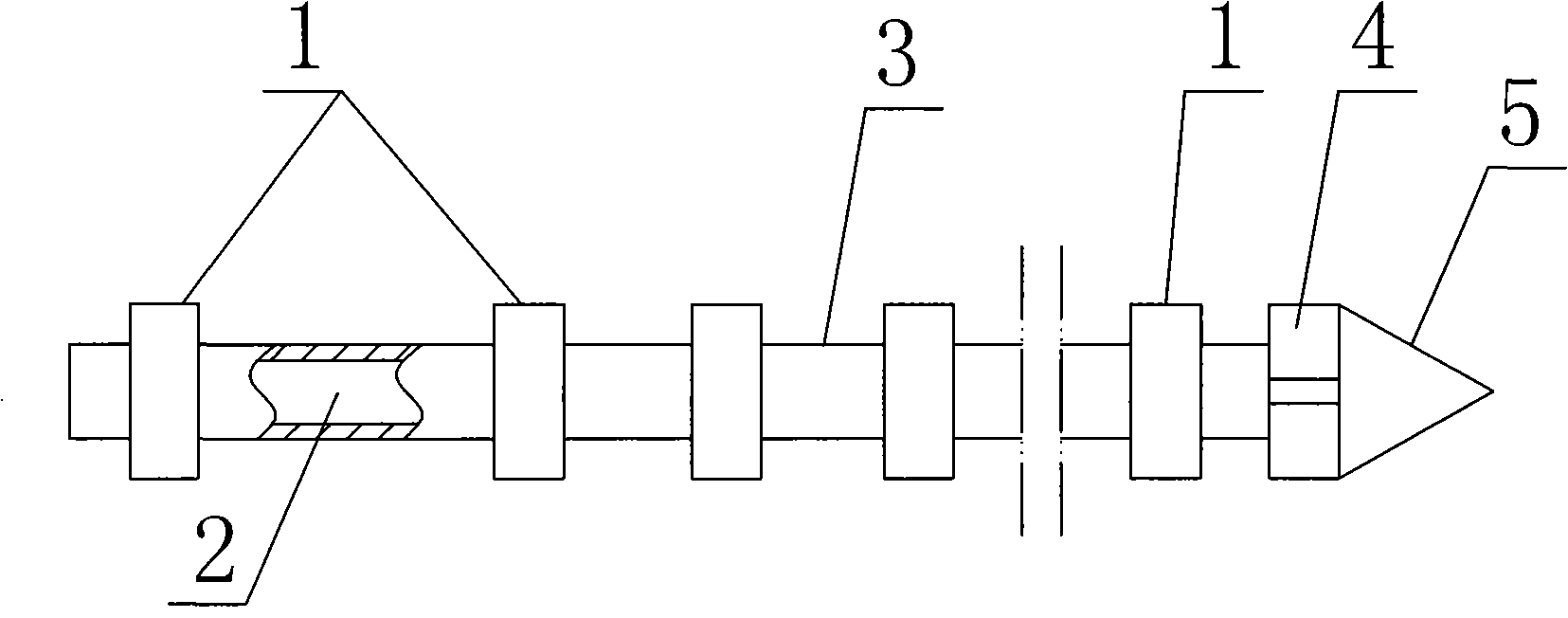
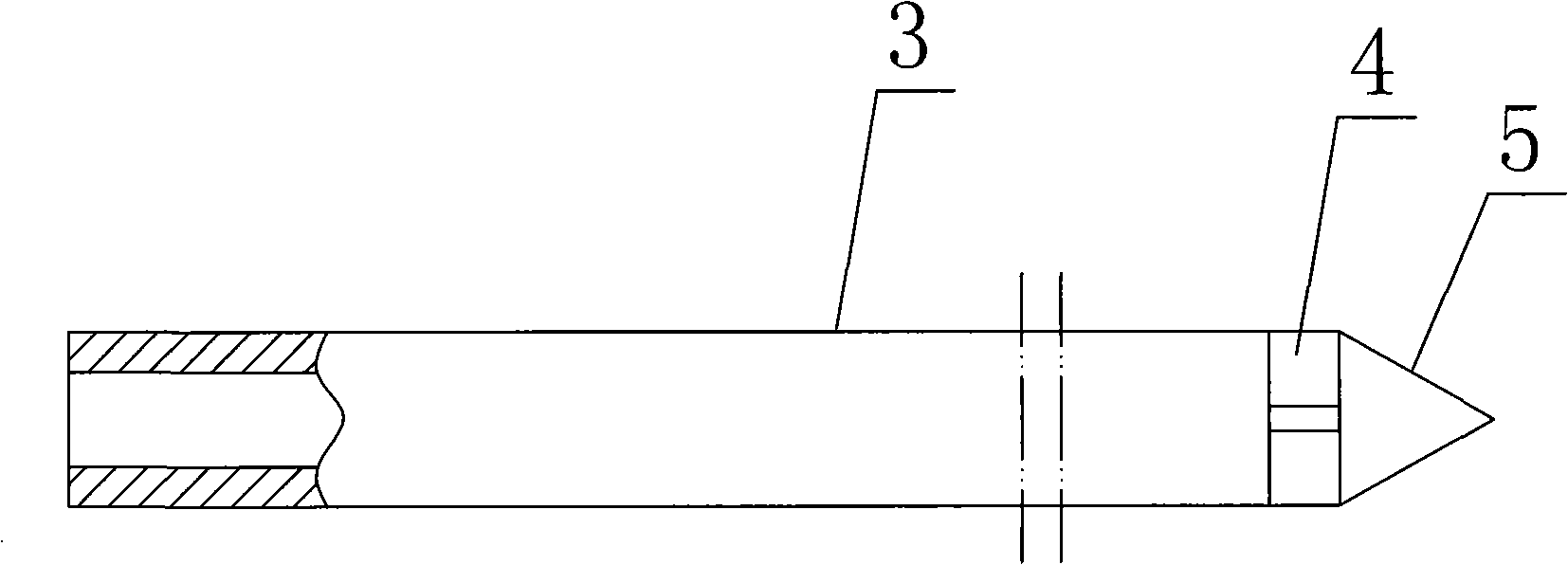
An improved deep remediation injection system for in-situ remediation of contaminated soil and ground water. The system includes a soil penetrating lance for injecting at least two different highly-pressurized fluids taken from the group of air, gaseous oxygen, ozone, oxygenated liquid, hydrogen peroxide, surfactant-containing liquid, catalyst-containing liquid and suspended biologicals-containing liquids, or a liquid containing other chemicals, into said contaminated soil as said soil penetrating lance is inserted for penetration therein. The soil penetrating lance has at least an upper set of injection ports, the upper set of injection ports being generally radially spaced-apart on said lance, and at least one lower set of injection ports, the lance having an average width in the vicinity of the upper set of injection ports. The lance further includes substantially fluidically-independent first and second conduits leading, respectively, to the lower set of injection ports and the upper set of injection ports so as to permit delivery of separate pressurized fluid streams to the upper and lower sets of injection ports and then into the soil. The upper and lower sets of injection ports are spaced apart from each other on said lance a distance no farther than about three times the average width of said lance in the vicinity of the upper set of injection ports.
Owner:NICKELL JERRY D
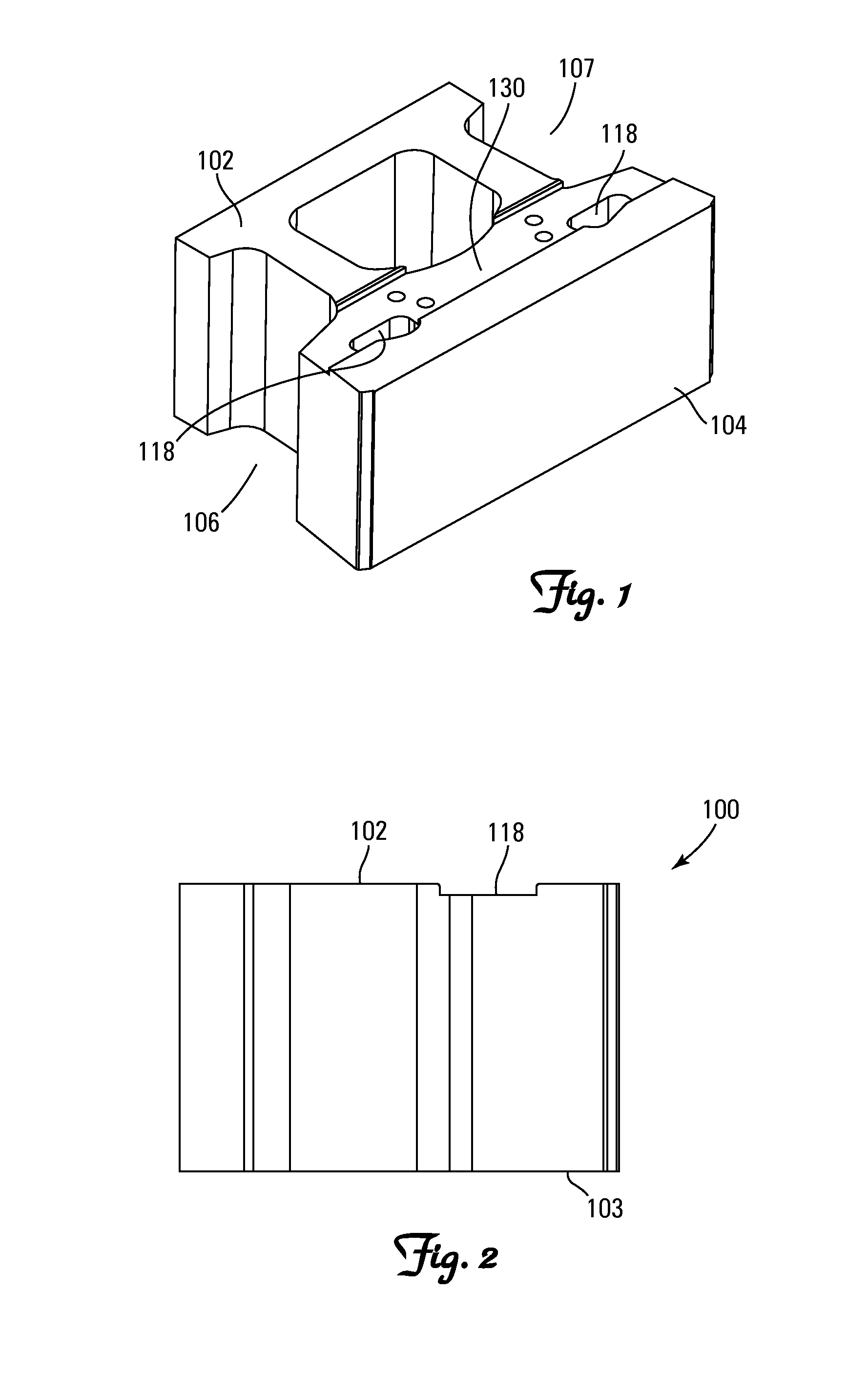
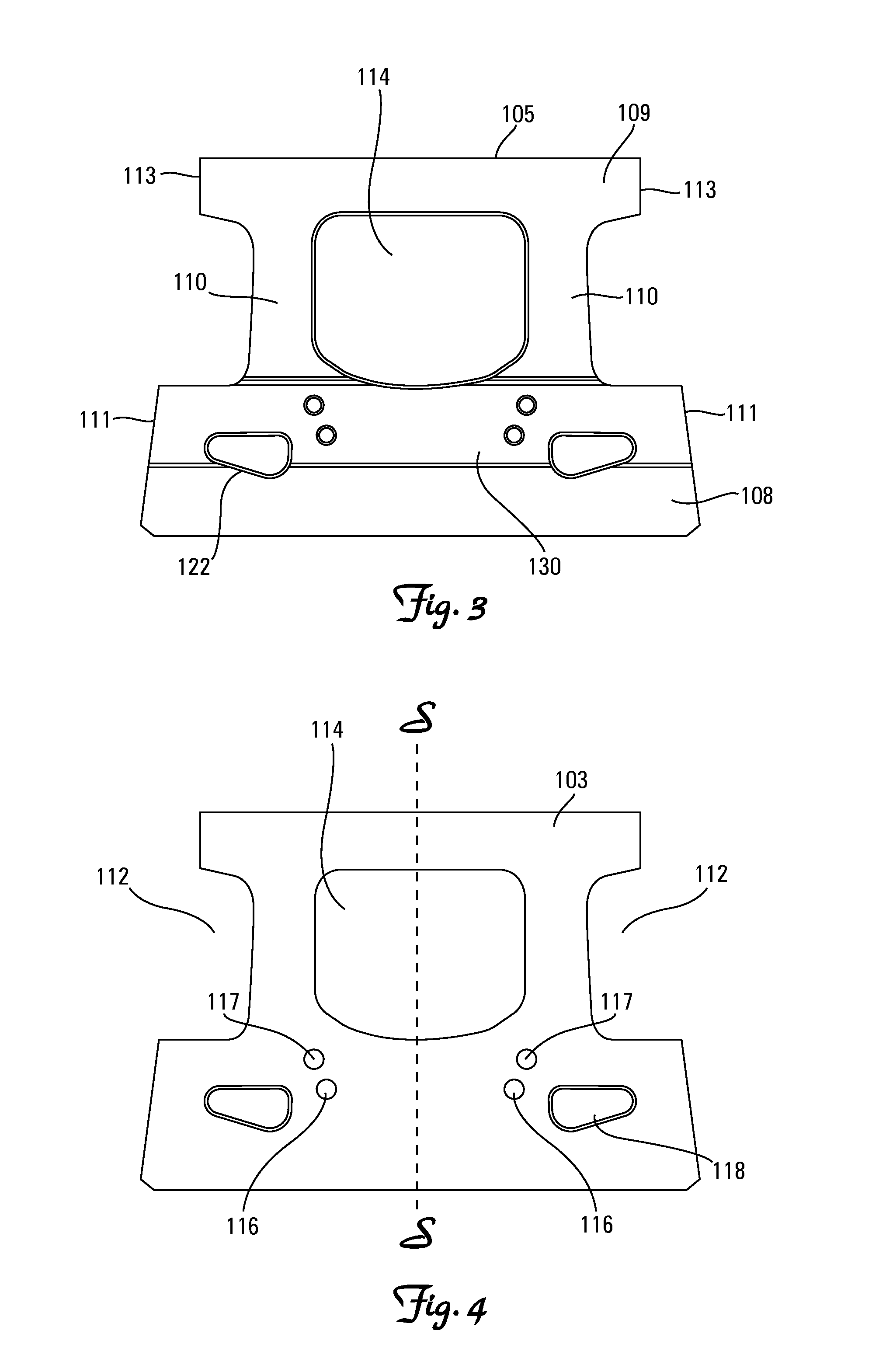
Retaining wall masonry block
A masonry block that may be used in construction of block walls particularly retaining walls for retaining soil and preventing soil erosion. A masonry block having at least one body with a front face, back face, a pair of sides extending therebetween a top face and a bottom face, defining a block having six major surfaces. One of the sides has an opening therethrough that is in communication with a cavity extending inwardly in relation to the body. The cavity is sized and configured to receive at least a portion of a hand therein to provide structure for easily grasping and lifting the block. The centerline of the cavity extends from the opening inwardly so that the angle between the centerline and the portion of the side adjacent to the opening is less than 90 degrees, so that the cupped fingers of a user may be received therein.
Owner:MATT STONE
Compactor wheel with trash exclusion properties
Landfill compactor vehicles having wheels equipped with wedge shaped cleats tend to accumulate about the vehicle's axle trash such as cable, wire, rope and the like debris requiring daily removal to permit unobstructed axle rotation. The wheel construction of this invention provides compaction cleats of two types, contour and traction, in rows positioned across the width of the wheel with substantially no cleat free zone adjacent the wheel edges but with a row of contour teeth arranged adjacent the wheel's inner edge thus affording trash exclusion properties to the compactor wheel.
Owner:CARON COMPACTOR
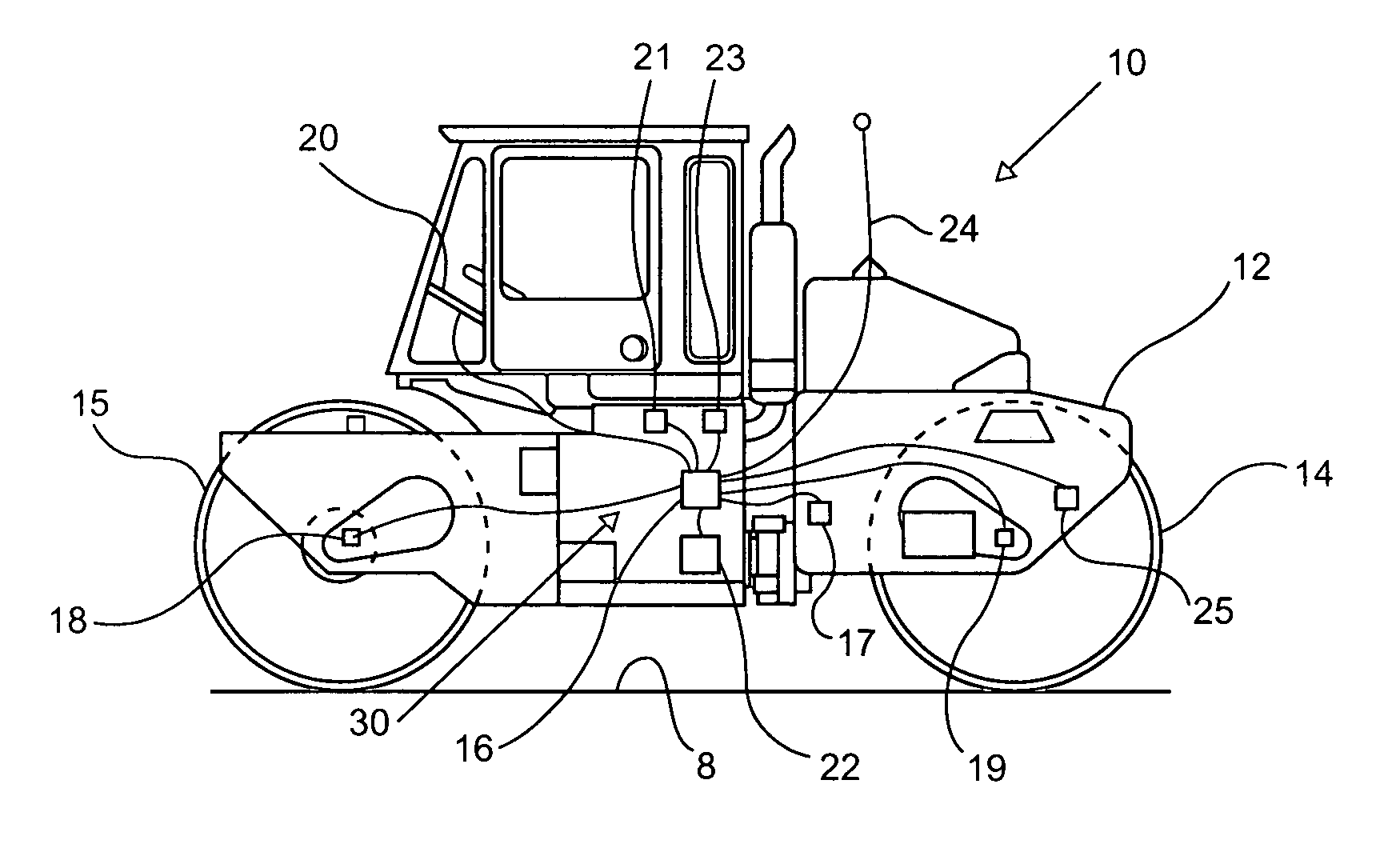
Compaction quality assurance based upon quantifying compactor interaction with base material
InactiveUS6973821B2Material strength using tensile/compressive forcesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEnergy transferDowntime
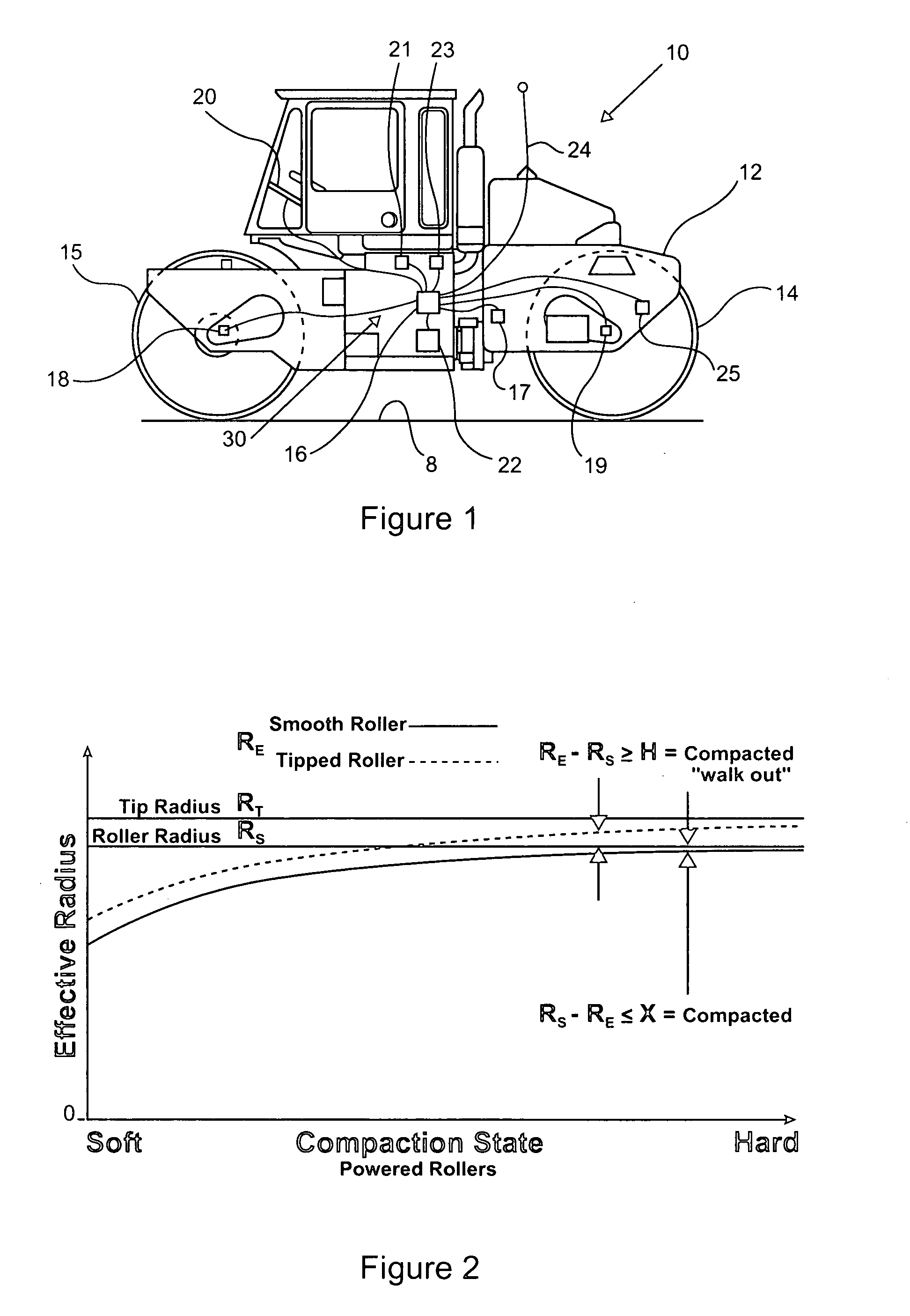
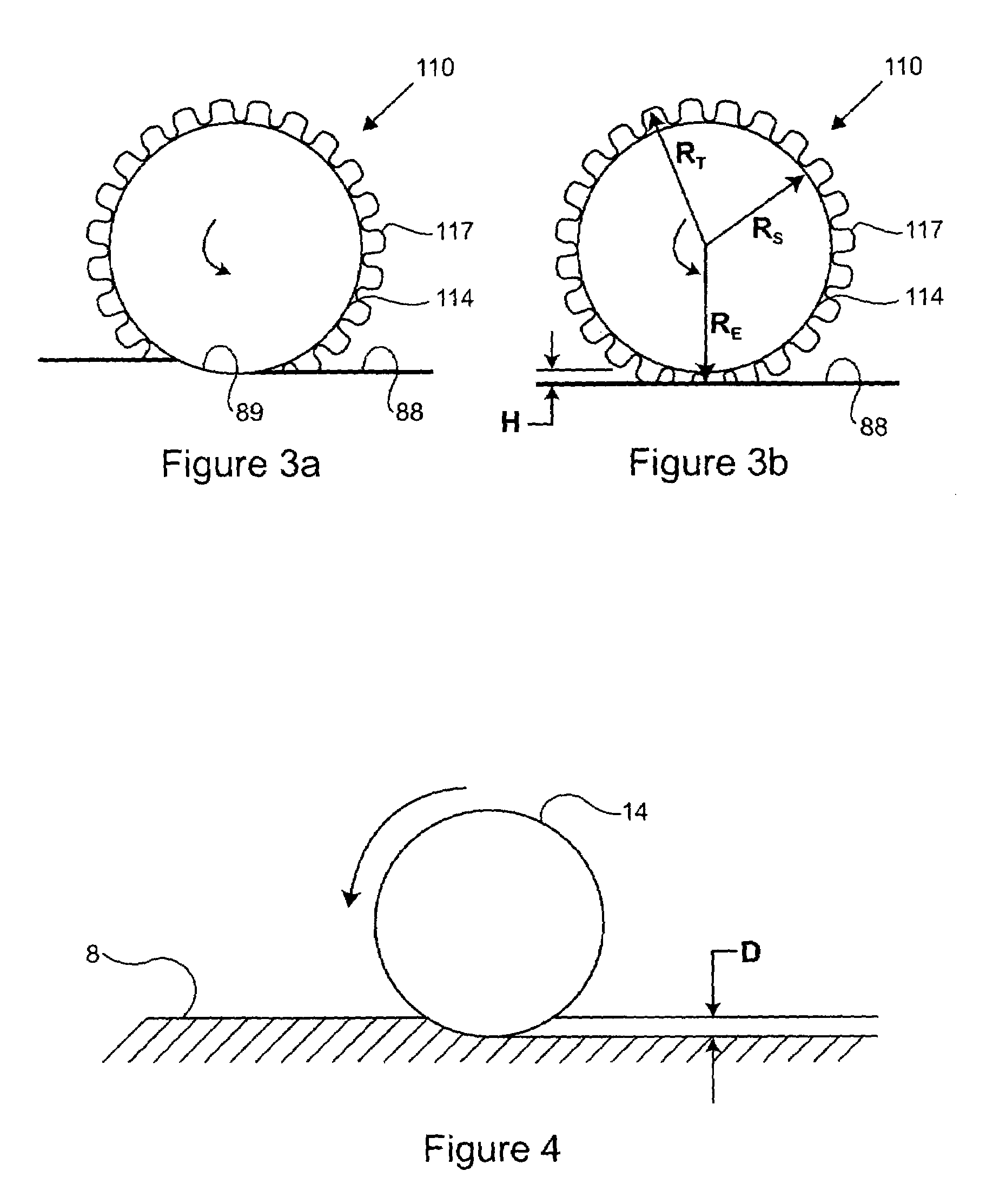
In most construction processes, some quality assurance compaction test must be performed on a base material before further construction can take place on or relative to the compacted base material. In order to avoid costly downtime associated with waiting for a quality assurance test to be performed, the present invention contemplates generating compaction quality assurance data using on-board generated compaction quality control data. The quality control compaction data is based upon quantifying a sinkage deformation interaction between the compactor and the base material. The interaction might include monitoring an effective roller radius of the compactor, or an amount of energy transferred or consumed when the compactor moves over the base material, or even measuring a rut depth caused by the compactor. The compaction quality assurance data can be indicative of a proof rolling test result, a walk out test result, a penetrometer test result, a base material density test result, or possibly even a compactor sinkage into the base material.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com