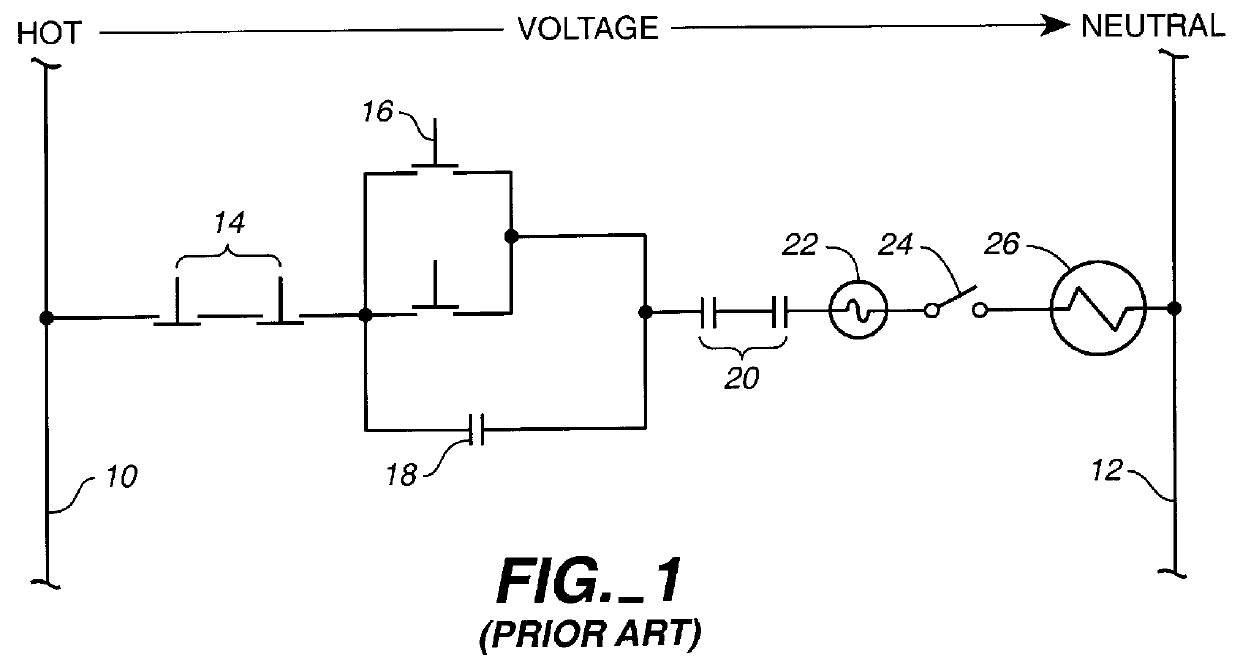
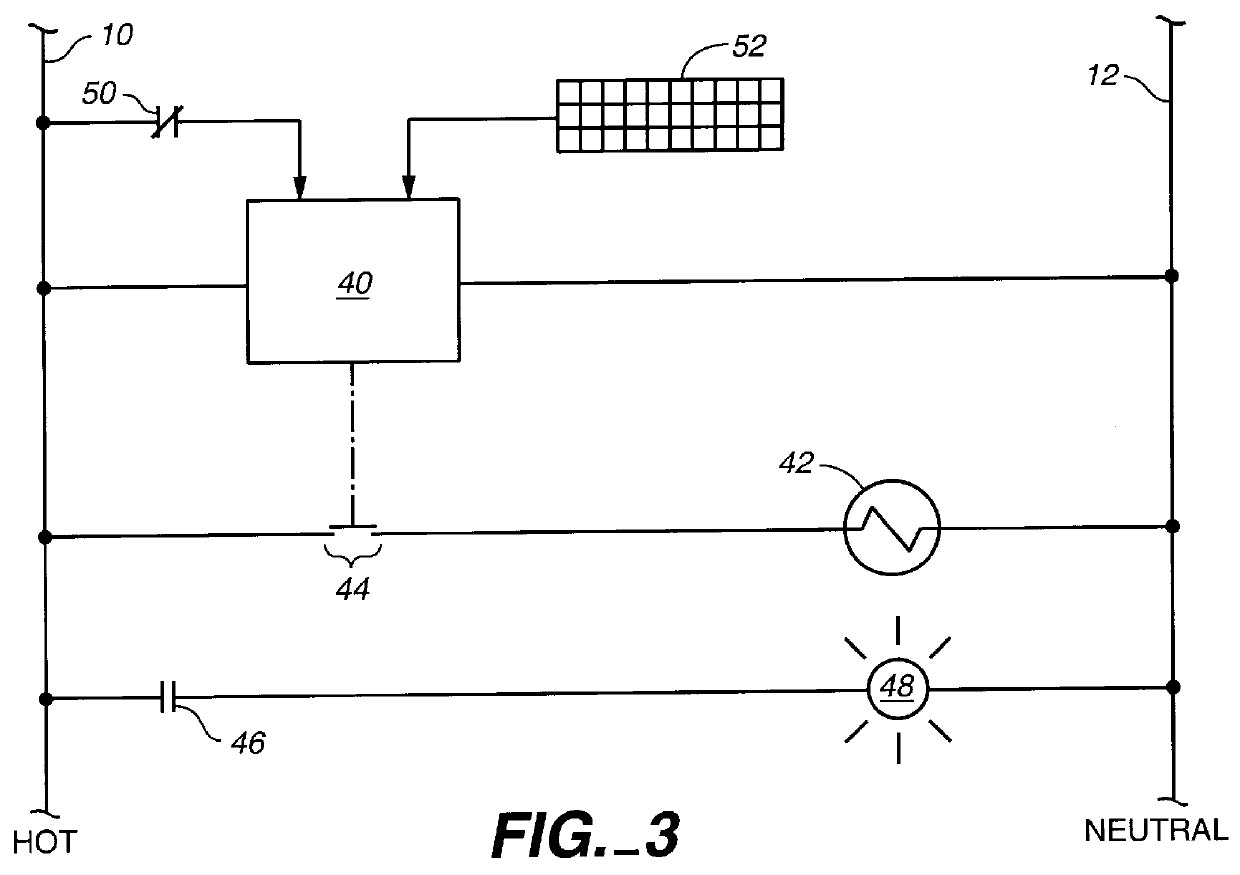
Patents
Literature
1611 results about "Downtime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term downtime is used to refer to periods when a system is unavailable. Downtime or outage duration refers to a period of time that a system fails to provide or perform its primary function. Reliability, availability, recovery, and unavailability are related concepts. The unavailability is the proportion of a time-span that a system is unavailable or offline. This is usually a result of the system failing to function because of an unplanned event, or because of routine maintenance (a planned event).
Method of cleaning a semiconductor device processing chamber after a copper etch process
The present invention is a method for removing deposited etch byproducts from surfaces of a semiconductor processing chamber after a copper etch process. The method of the invention comprises the following general steps: (a) an oxidation step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with an oxidizing plasma; (b) a first non-plasma cleaning step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with an H+hfac-comprising gas; and (c) a second cleaning step, in which interior surfaces of the processing chamber are contacted with a plasma containing reactive fluorine species, whereby at least a portion of the copper etch byproducts remaining after step (b) are volatilized into gaseous species, which are removed from the processing chamber. The method of the invention is preferably performed at a chamber wall temperature of at least 150° C. in order to achieve optimum cleaning of the chamber at the chamber operating pressures typically used during the cleaning process. The dry cleaning method of the invention can be performed between wafer processing runs without opening the processing chamber, thereby minimizing potential contamination to the chamber as well as chamber downtime.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
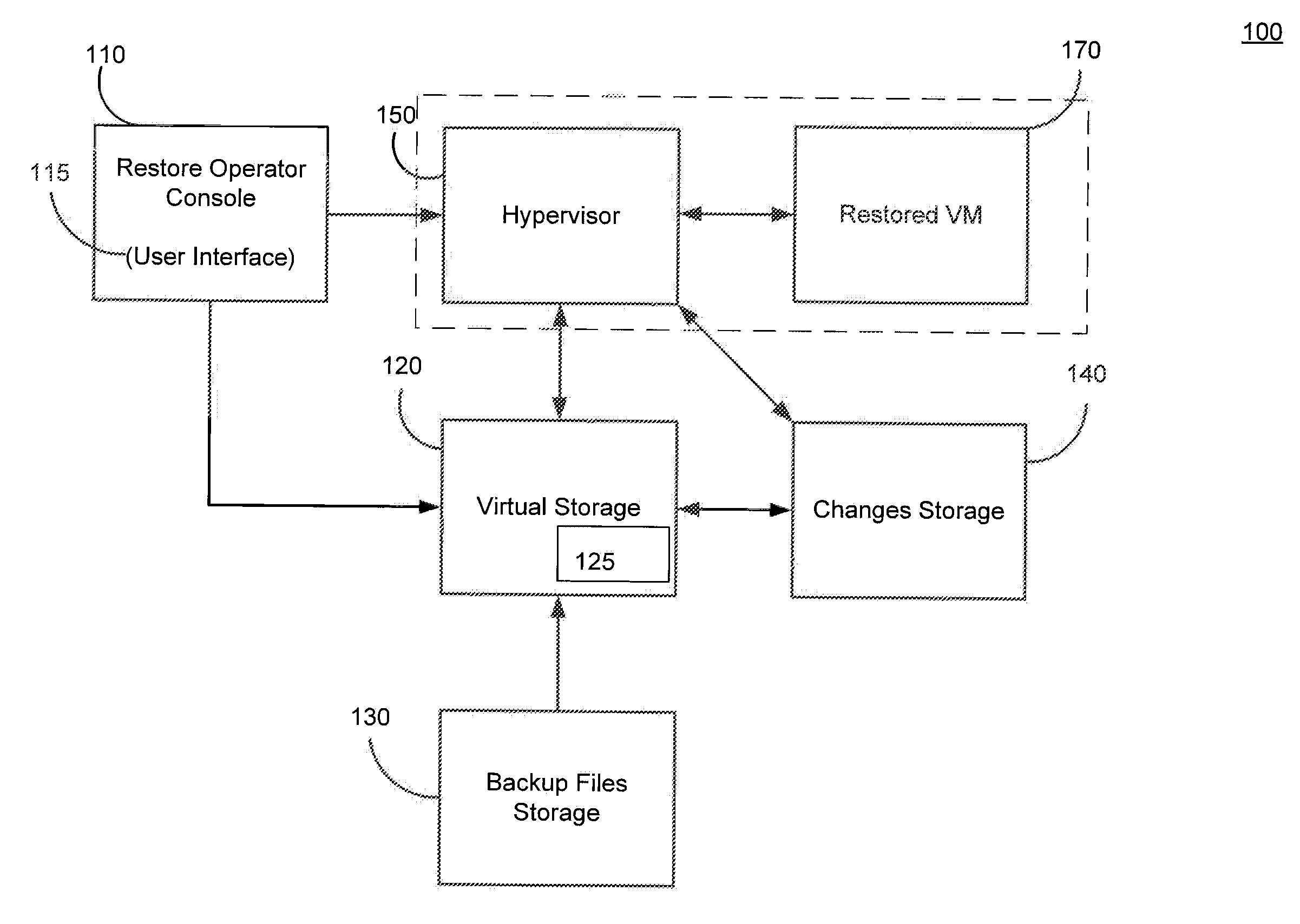
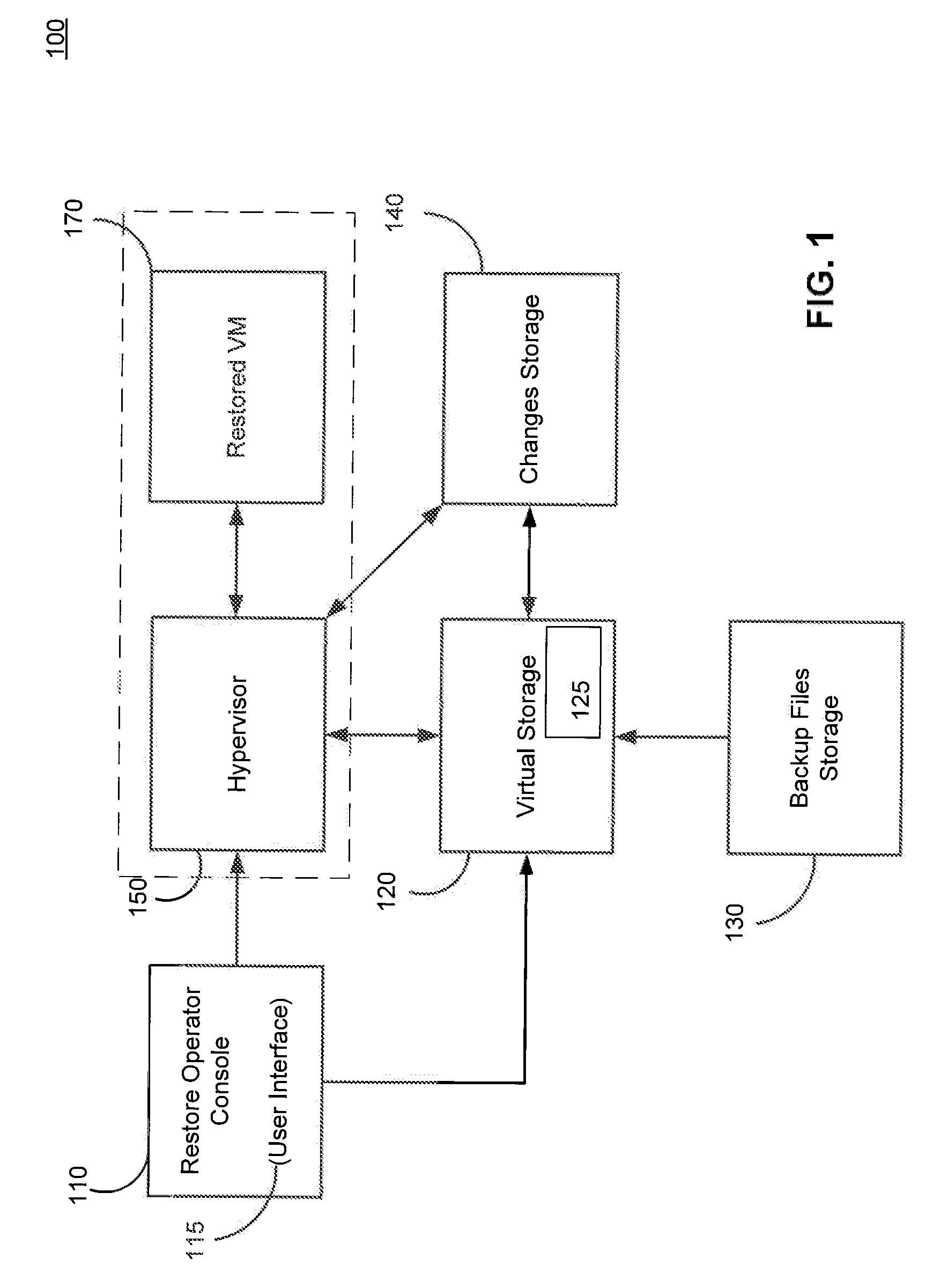
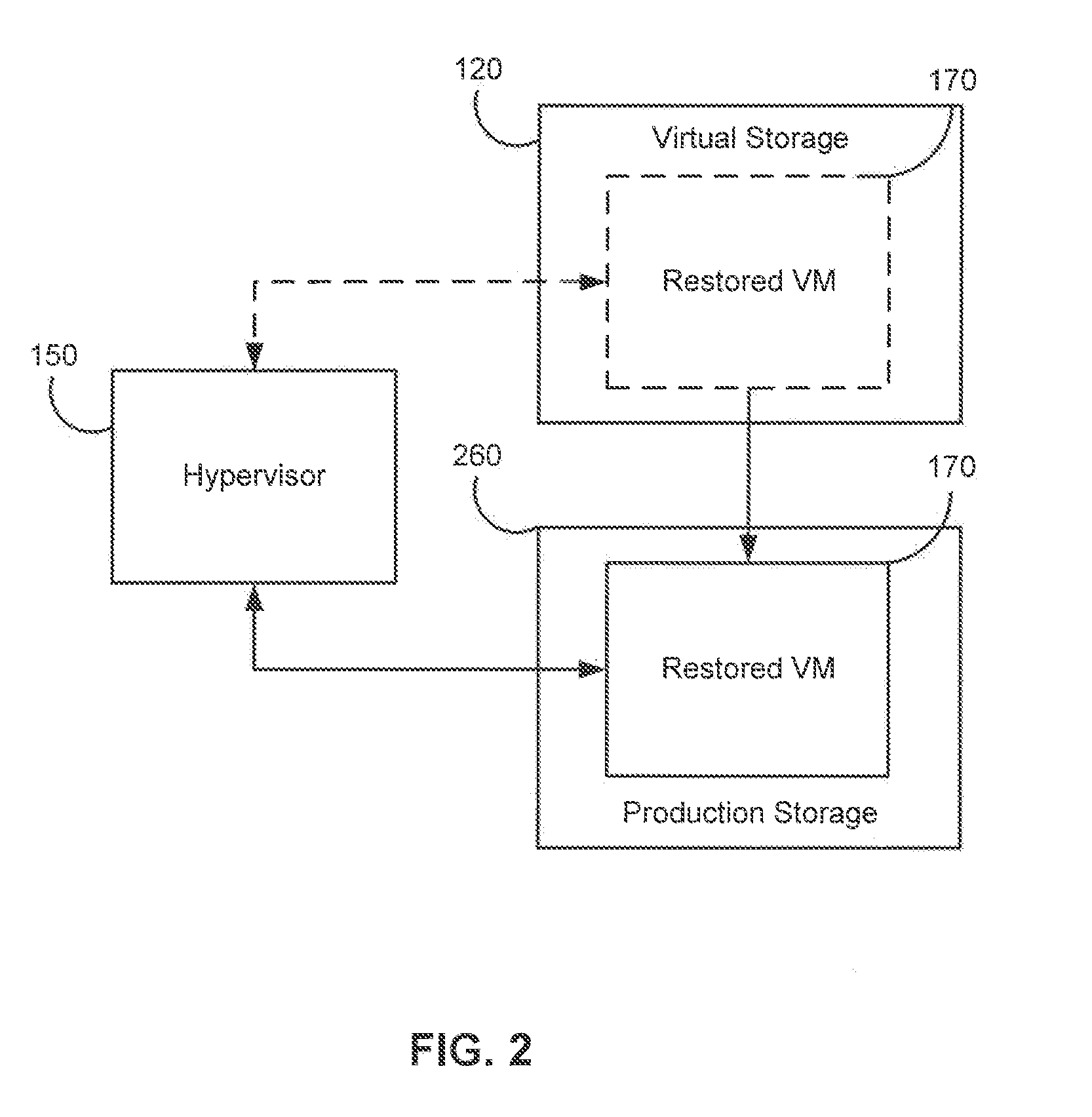
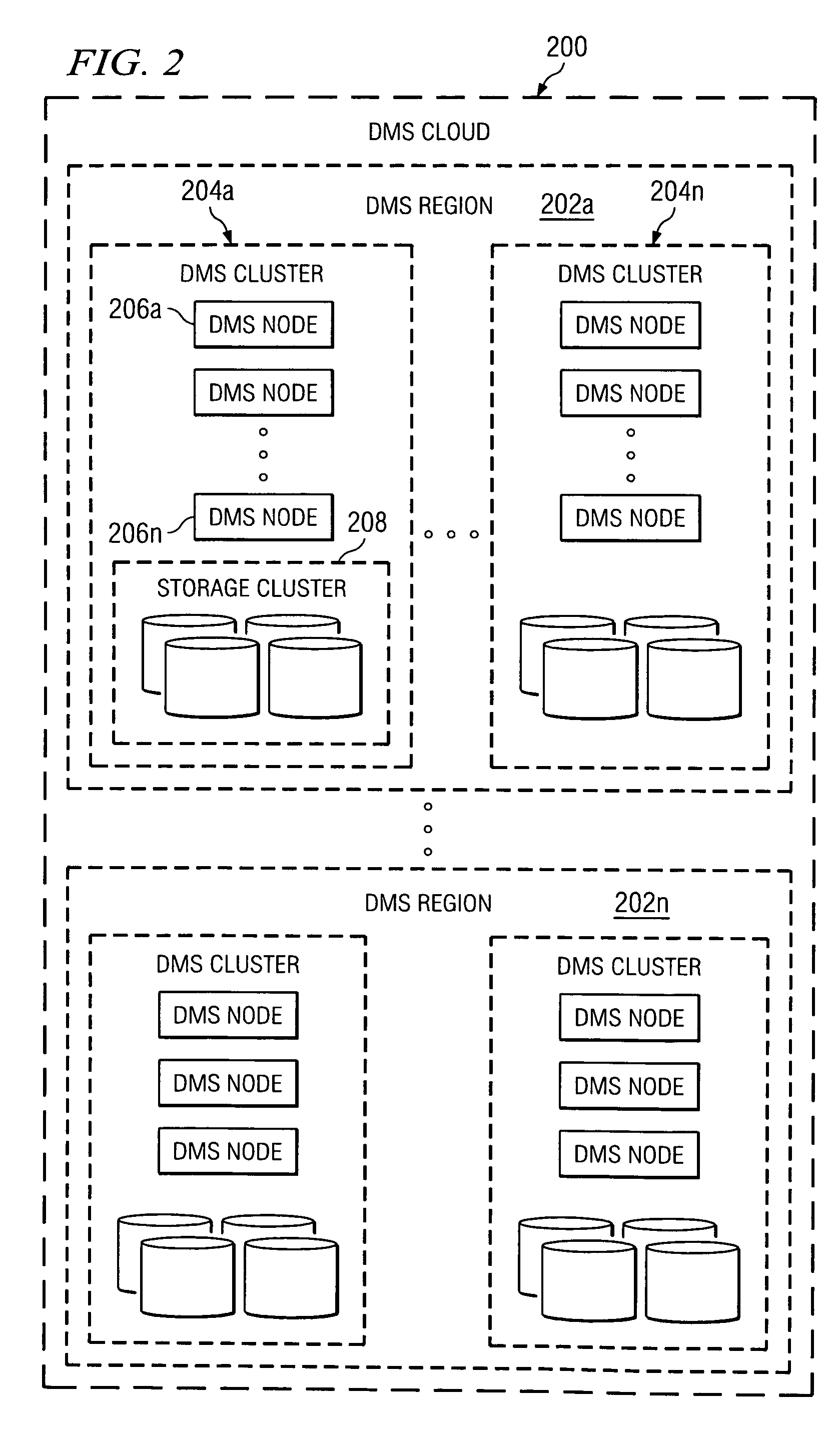
Systems, Methods, and Computer Program Products for Instant Recovery of Image Level Backups
ActiveUS20120017114A1Fault responseSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemDowntime
Systems, methods, and computer program products are provided for instant recovery of a virtual machine (VM) from a compressed image level backup without fully extracting the image level backup file's contents to production storage. The method receives restore parameters and initializes a virtual storage. The method attaches the virtual storage to a hypervisor configured to launch a recovered VM. The method stores virtual disk data changes inflicted by a running operating system (OS), applications, and users in a changes storage. The method provides the ability to migrate the actual VM disk state (taking into account changed disk data blocks accumulated in changes storage) so as to prevent data loss resulting from the VM running during the recovery and accessing virtual storage, to production storage without downtime. In embodiments, the method displays receives restore parameters in an interactive interface and delivers the recovery results via an automated message, such as an email message.
Owner:VEEAM SOFTWARE GROUP GMBH
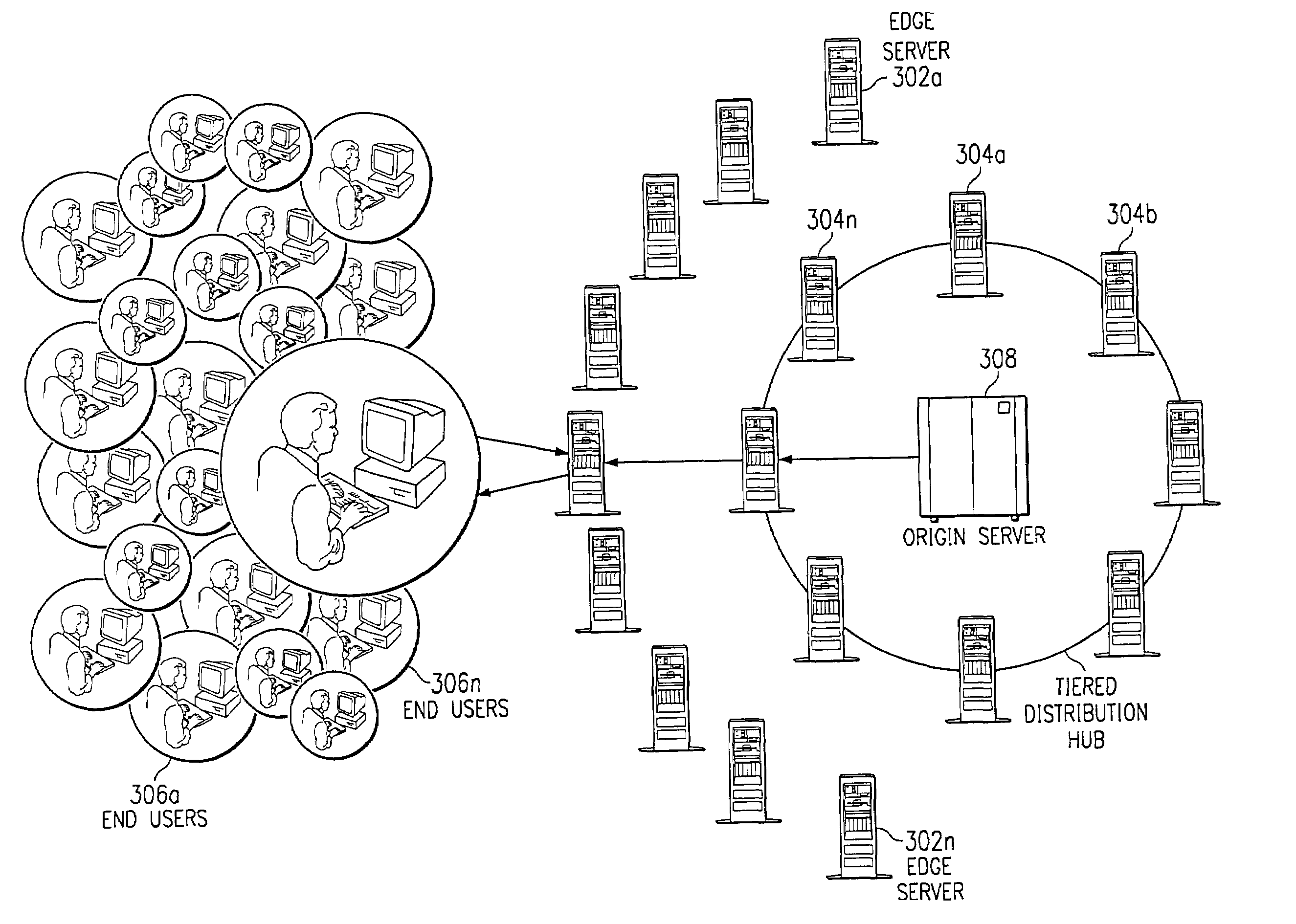
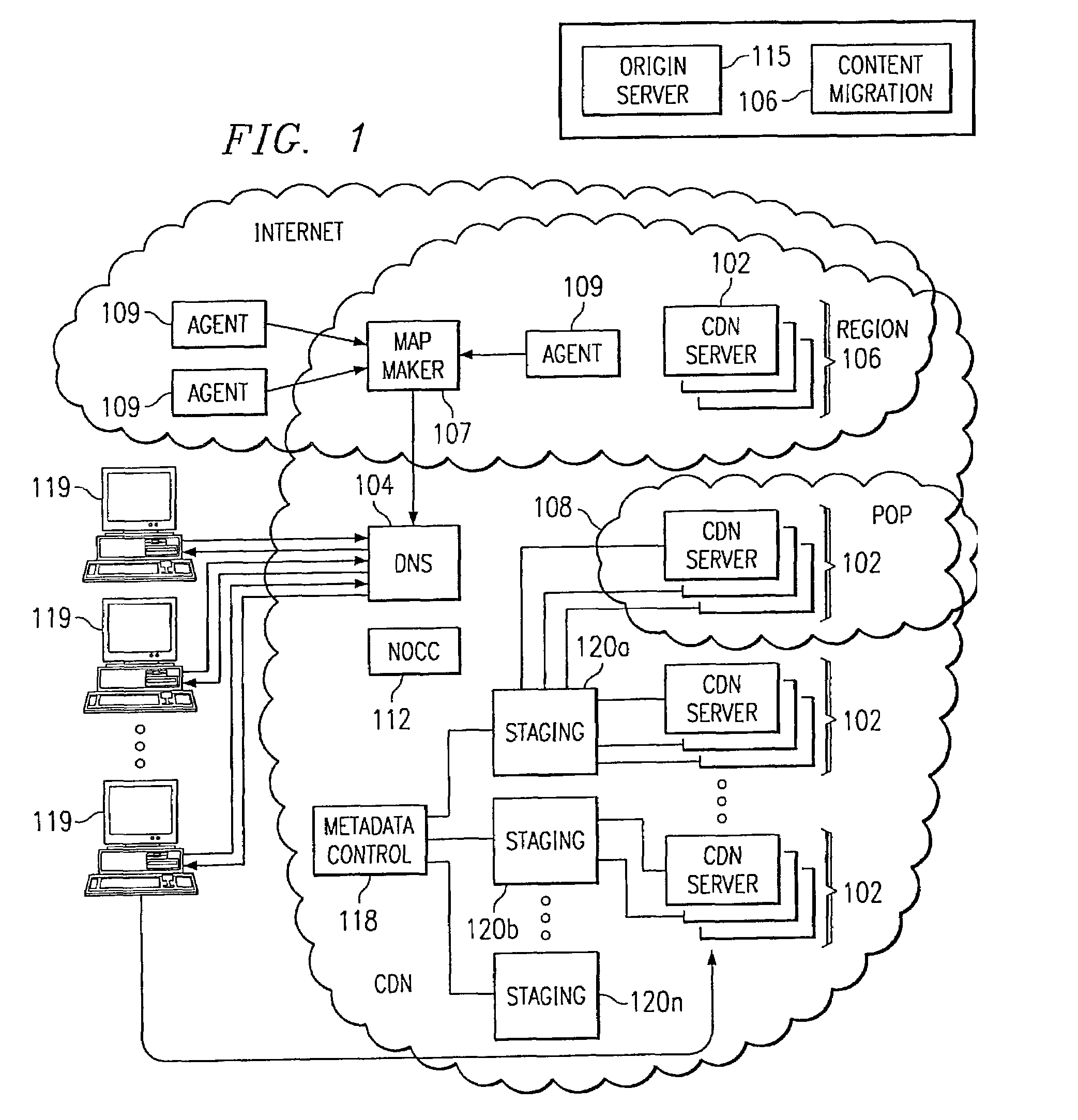
Method and system for protecting web sites from public internet threats
ActiveUS7260639B2Delivered quickly and without failEfficient removalMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionWeb serviceIp address
The present invention addresses the known vulnerabilities of Web site infrastructure by making an origin server substantially inaccessible via Internet Protocol traffic. In particular, according to a preferred embodiment, the origin server is “shielded” from the publicly-routable IP address space. Preferably, only given machines (acting as clients) can access the origin server, and then only under restricted, secure circumstances. In a preferred embodiment, these clients are the servers located in a “parent” region of a content delivery network (CDN) tiered distribution hierarchy. The invention implements an origin server shield that protects a site against security breaches and the high cost of Web site downtime by ensuring that the only traffic sent to an enterprise's origin infrastructure preferably originates from CDN servers. The inventive “shielding” technique protects a site's Web servers (as well as backend infrastructure, such as application servers, databases, and mail servers) from unauthorized intrusion—improving site uptime and in the process, customer loyalty.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
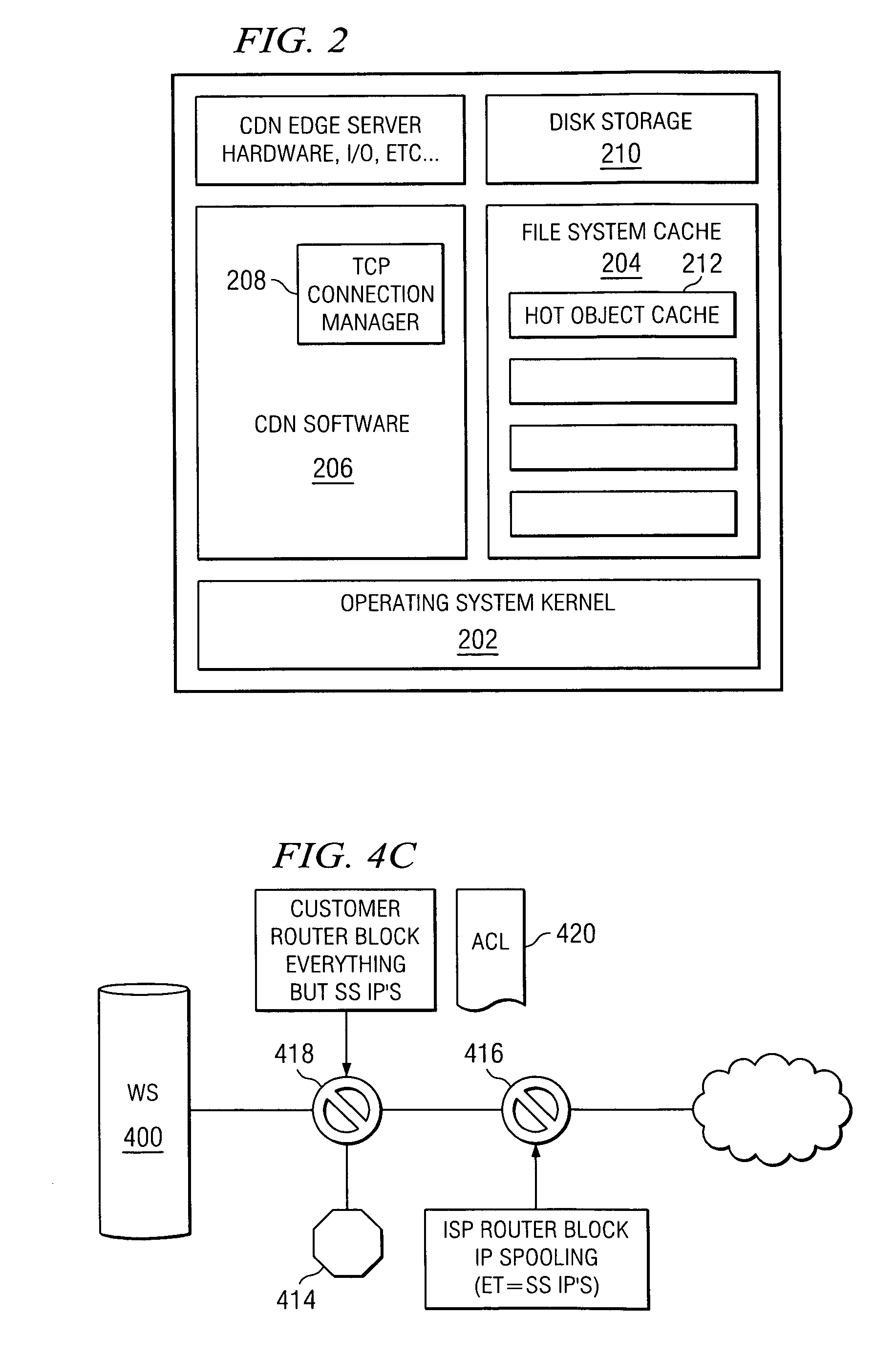
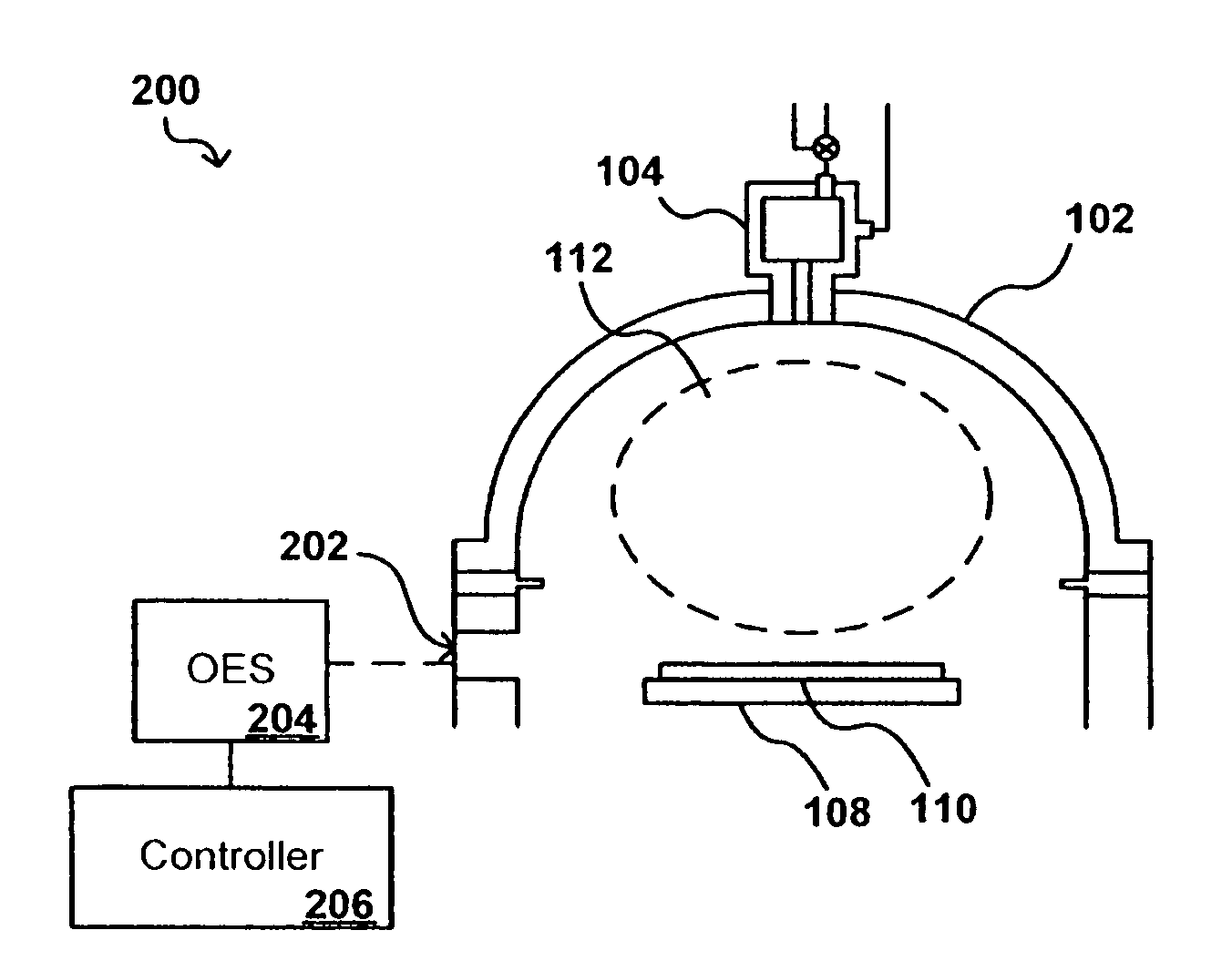
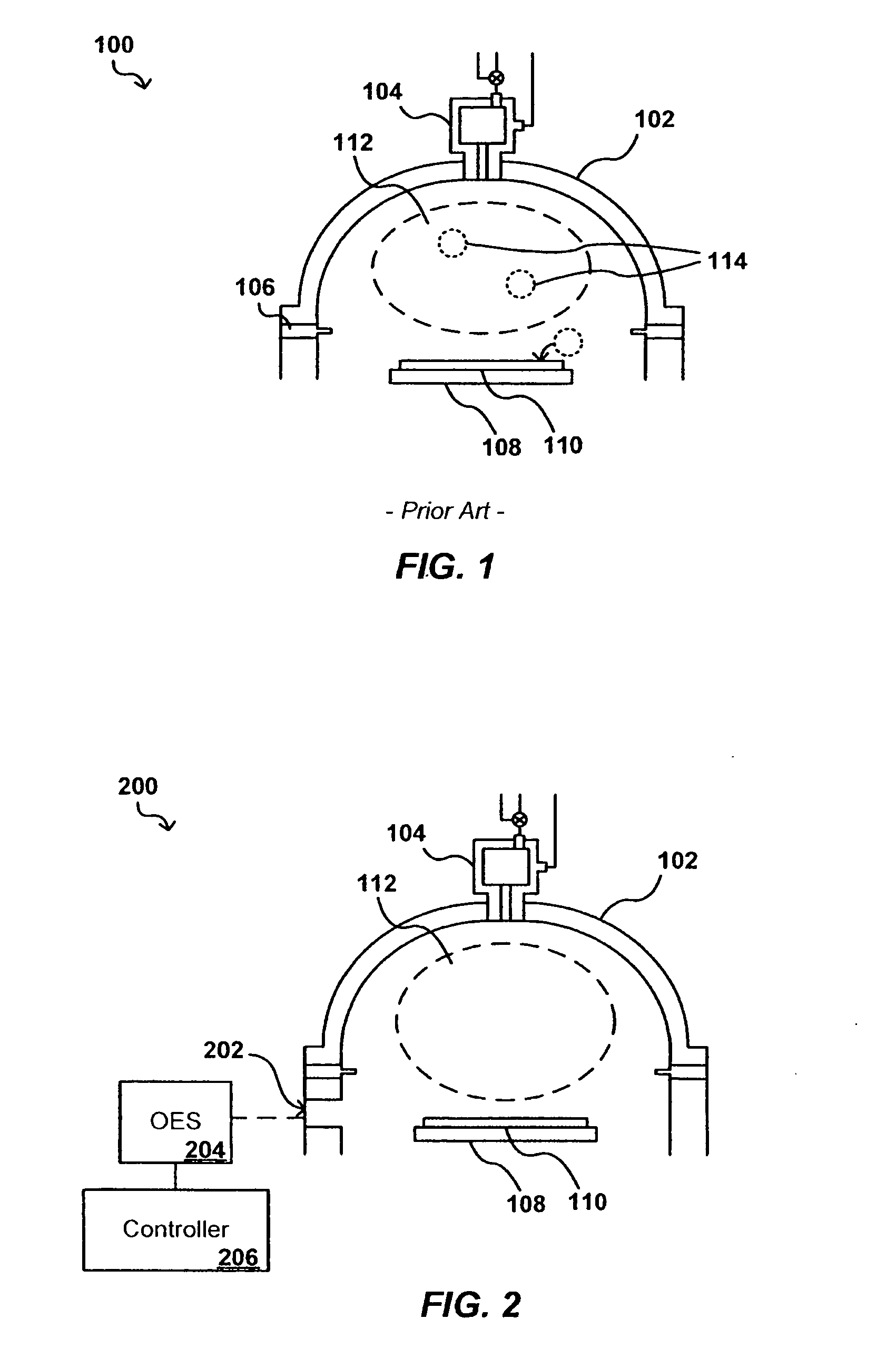
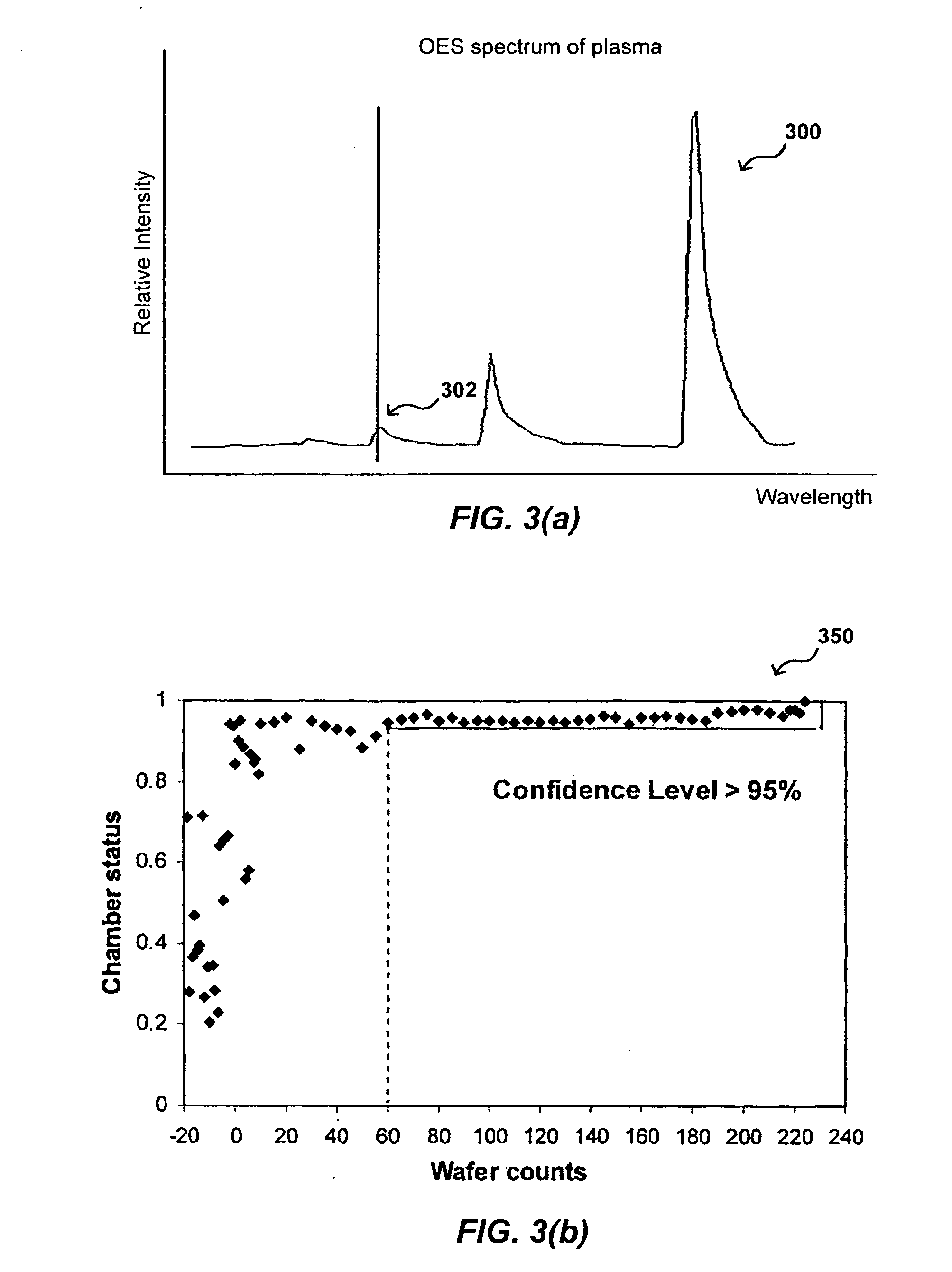
In-situ process state monitoring of chamber
InactiveUS20080063810A1Process be stopElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingDowntimeStatistical analysis
The process state of a chamber after a maintenance procedure can be monitored in-situ in order to ensure that the chamber is ready for processing, while minimizing waste and downtime due to aftereffects of the maintenance procedure. The composition of a bulk plasma in a process chamber can be analyzed using an analytical tool to capture the emission spectrum of the plasma. The spectrum can be analyzed to generate a model of the current chamber conditions, which can be compared to a model of ideal chamber conditions using a statistical analysis approach such as multivariate primary component analysis. If the current and ideal models match to within a set confidence level, the chamber conditions are acceptable for processing devices, and any processing of cycling workpieces or other plasma-cleansing processes can be stopped.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method, system, and program for recovery from a failure in an asynchronous data copying system
InactiveUS20050071708A1Application downtime is minimizedMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionRecovery methodDevice form
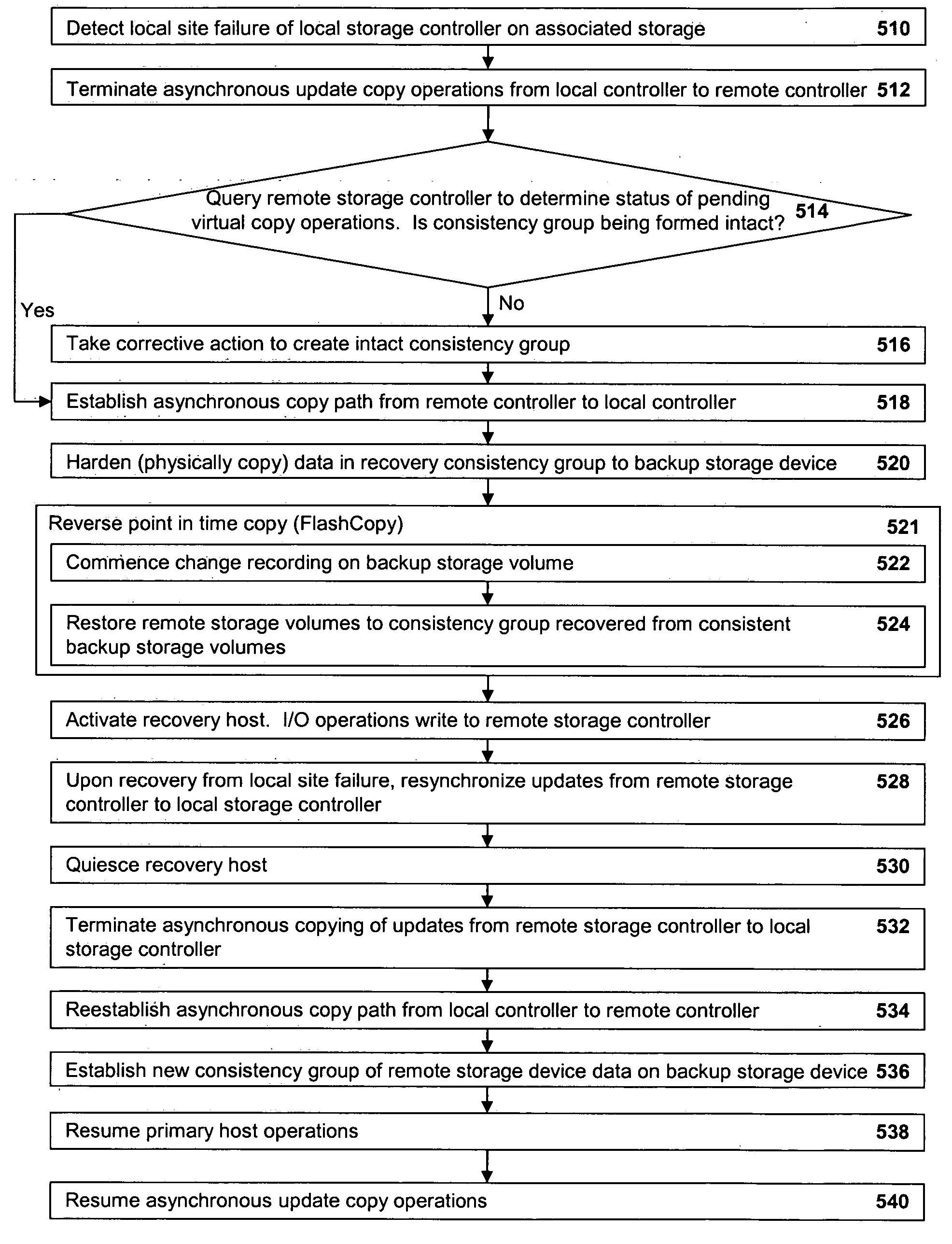
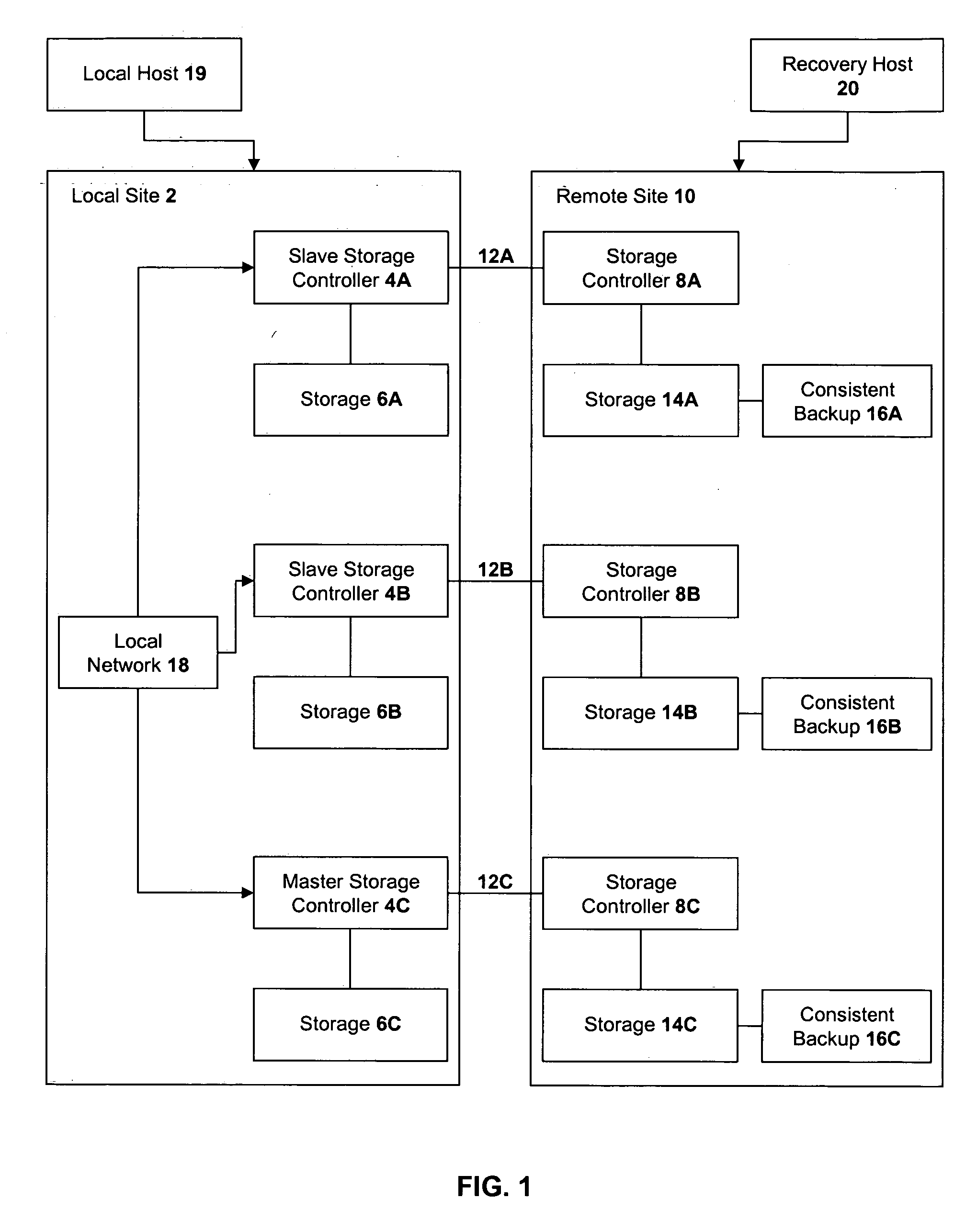
A method of recovery from a data storage system failure in a data storage system having a host computer writing data updates to a local storage controller at a local site. The local controller is associated with a local storage device. The local storage controller is also configured to asynchronously copy the updates to a remote storage controller associated with a remote storage device at a remote site. In addition, the remote storage controller is configured to store a consistent point in time copy of the updates on a backup storage device. The consistent point in time copy is known as a consistency group. Upon detection of a failure associated with the local site, a determination is made whether a group of updates pending for storage on the backup storage device form an intact consistency group. If an intact consistency group has not formed, corrective action may be taken to create an intact consistency group. The recovery method further consists of synchronizing the remote storage device, initiating recovery operations and, upon recovery of the local site, resynchronization of the local storage device and the backup storage device to recovery consistency group without the need for full volume storage copies and while minimizing application downtime.
Owner:IBM CORP
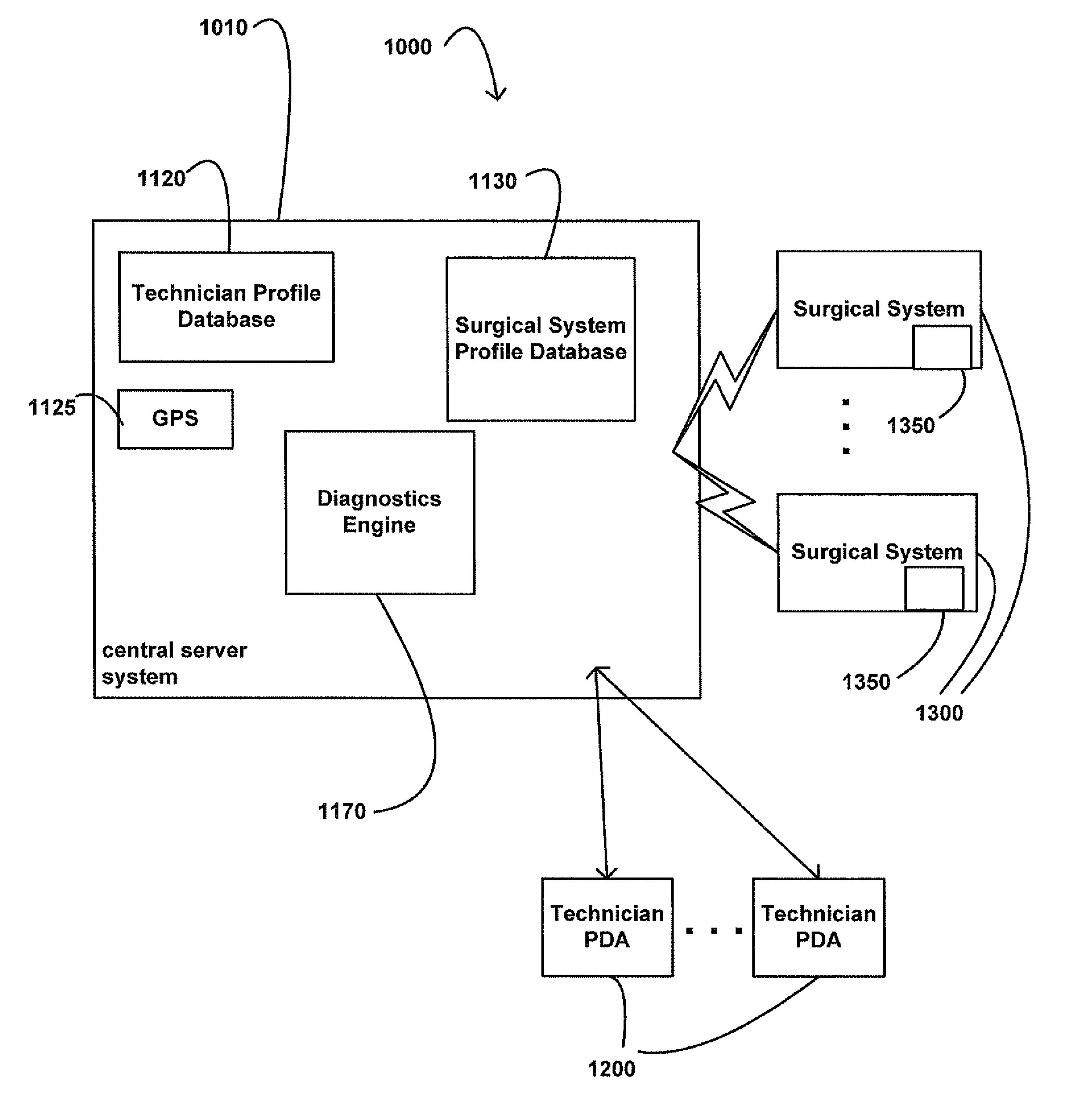
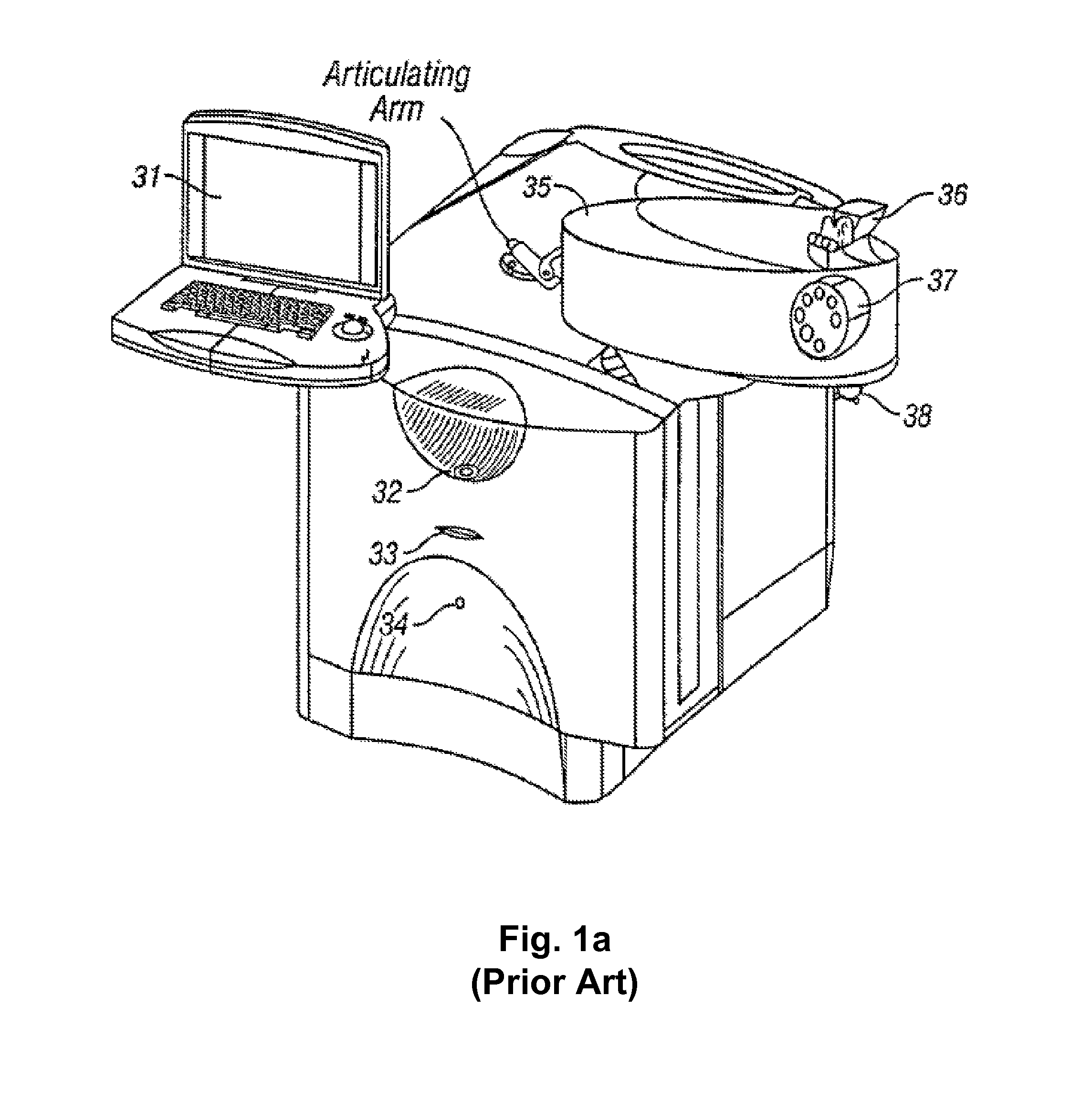
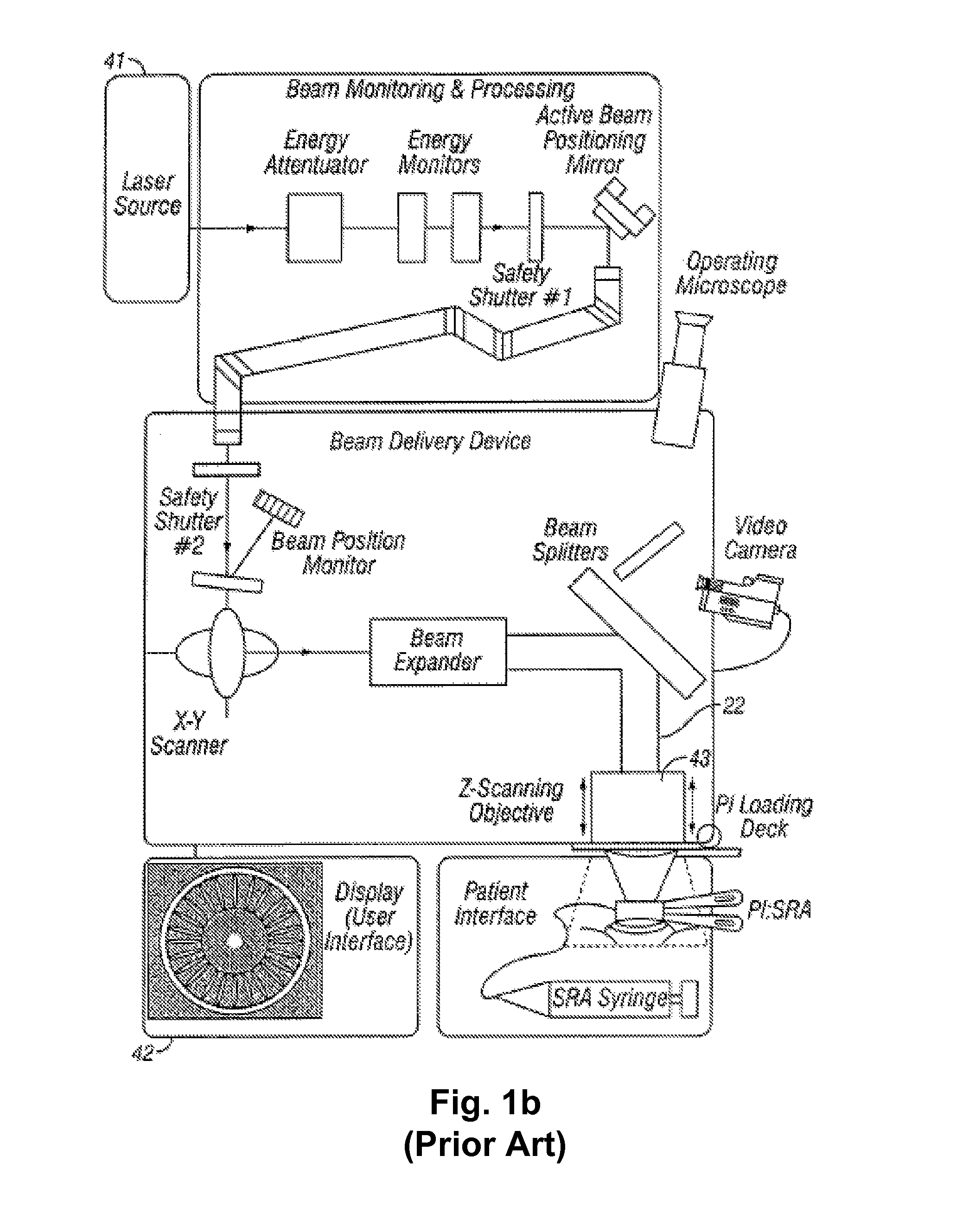
Systems and methods for providing remote diagnostics and support for surgical systems
ActiveUS8005947B2Minimizes any potential undesirable downtime of the surgical machinesLaser surgeryLocal control/monitoringSurgical operationSupporting system
Systems and methods for medical care, and more particularly, systems and methods for providing remote diagnostics and support for surgical systems. A central computer system is communicatively coupled to one or more computer-based surgical machines. The central computer system is programmed to monitor the operation of each of the surgical machines, diagnose any problems that occur with the machines, and notify a technician of potential problems with the machines to provide for an efficient support system that minimizes undesirable downtime of the surgical machines.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
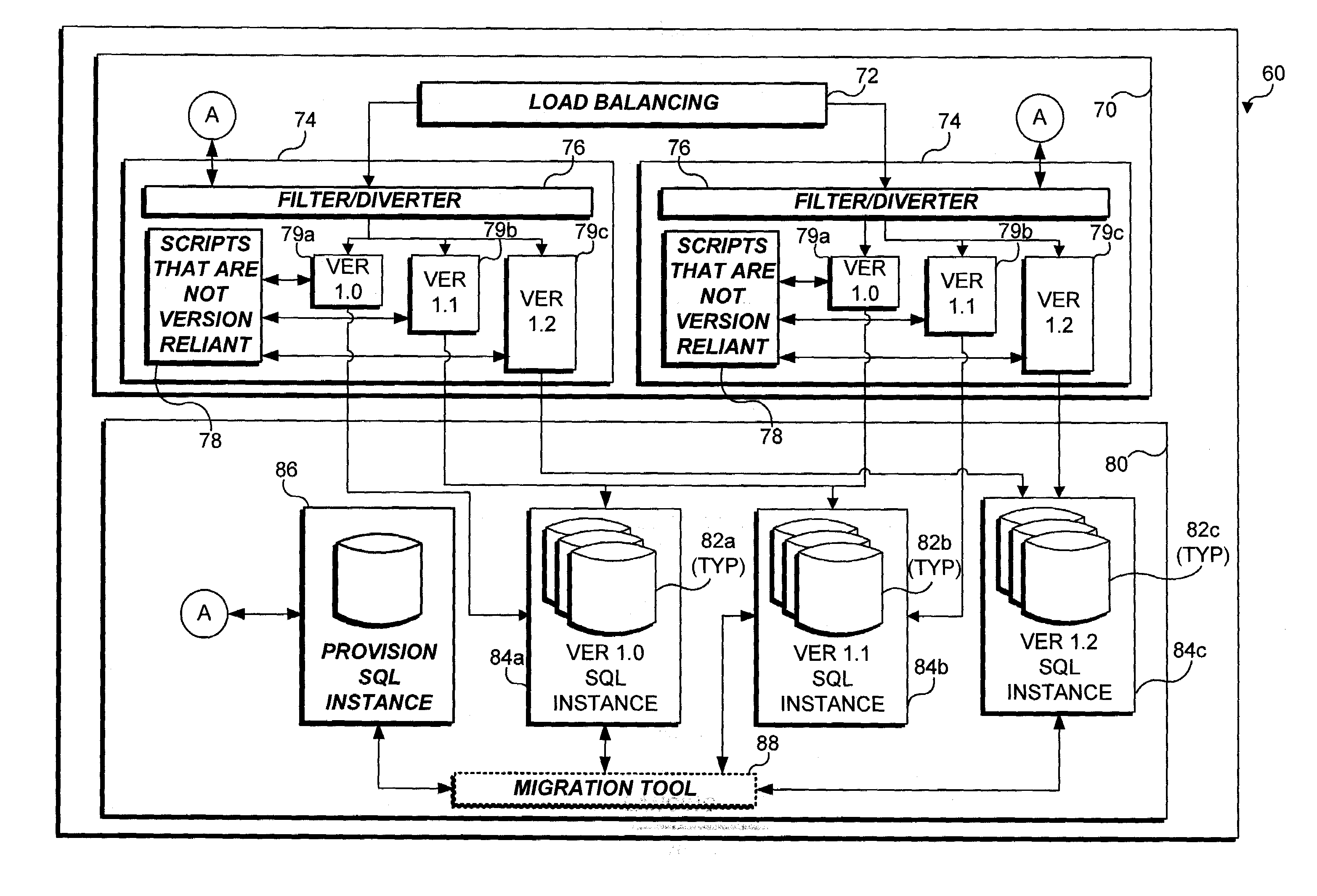
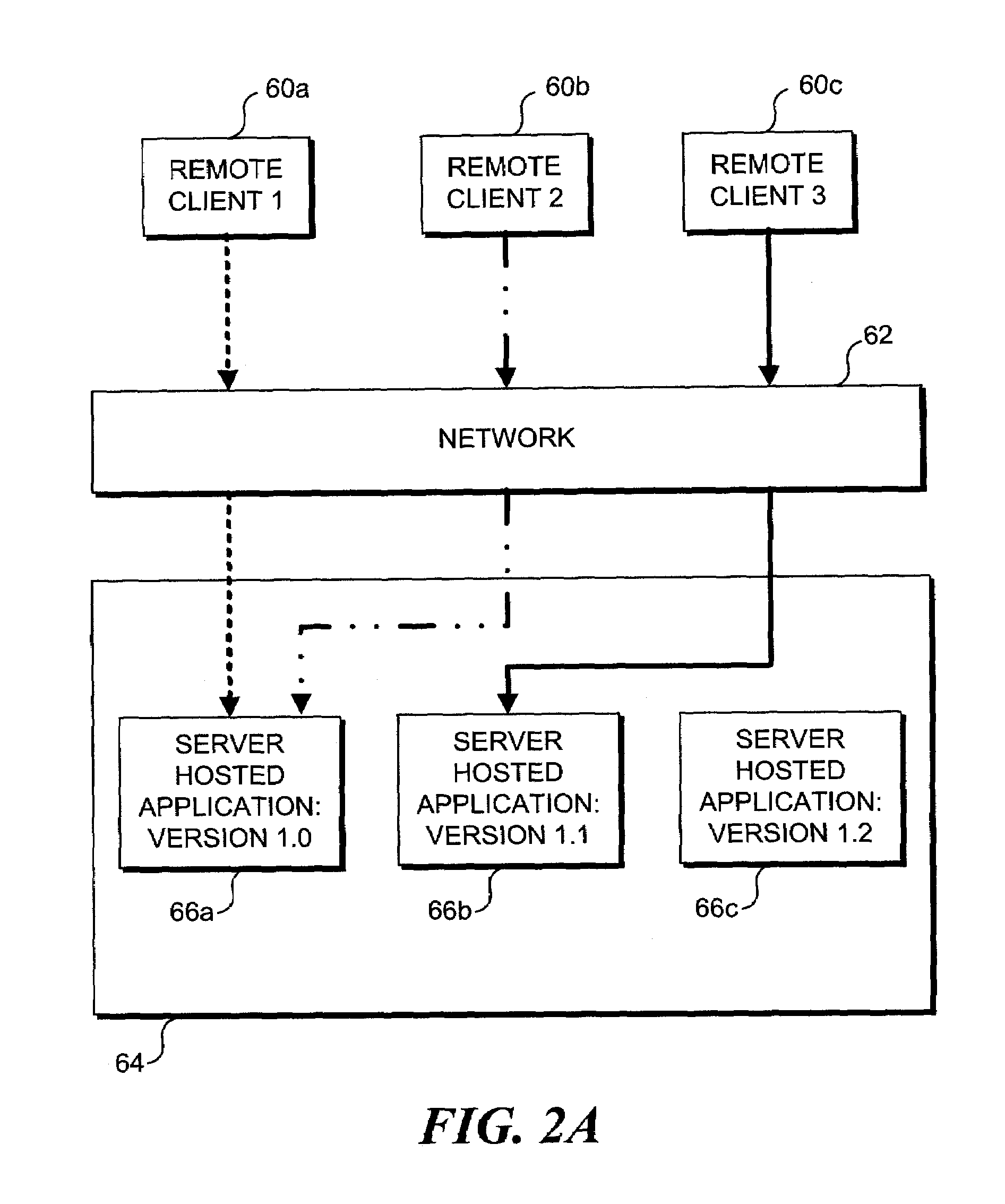
Method and apparatus enabling migration of clients to a specific version of a server-hosted application, where multiple software versions of the server-hosted application are installed on a network
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
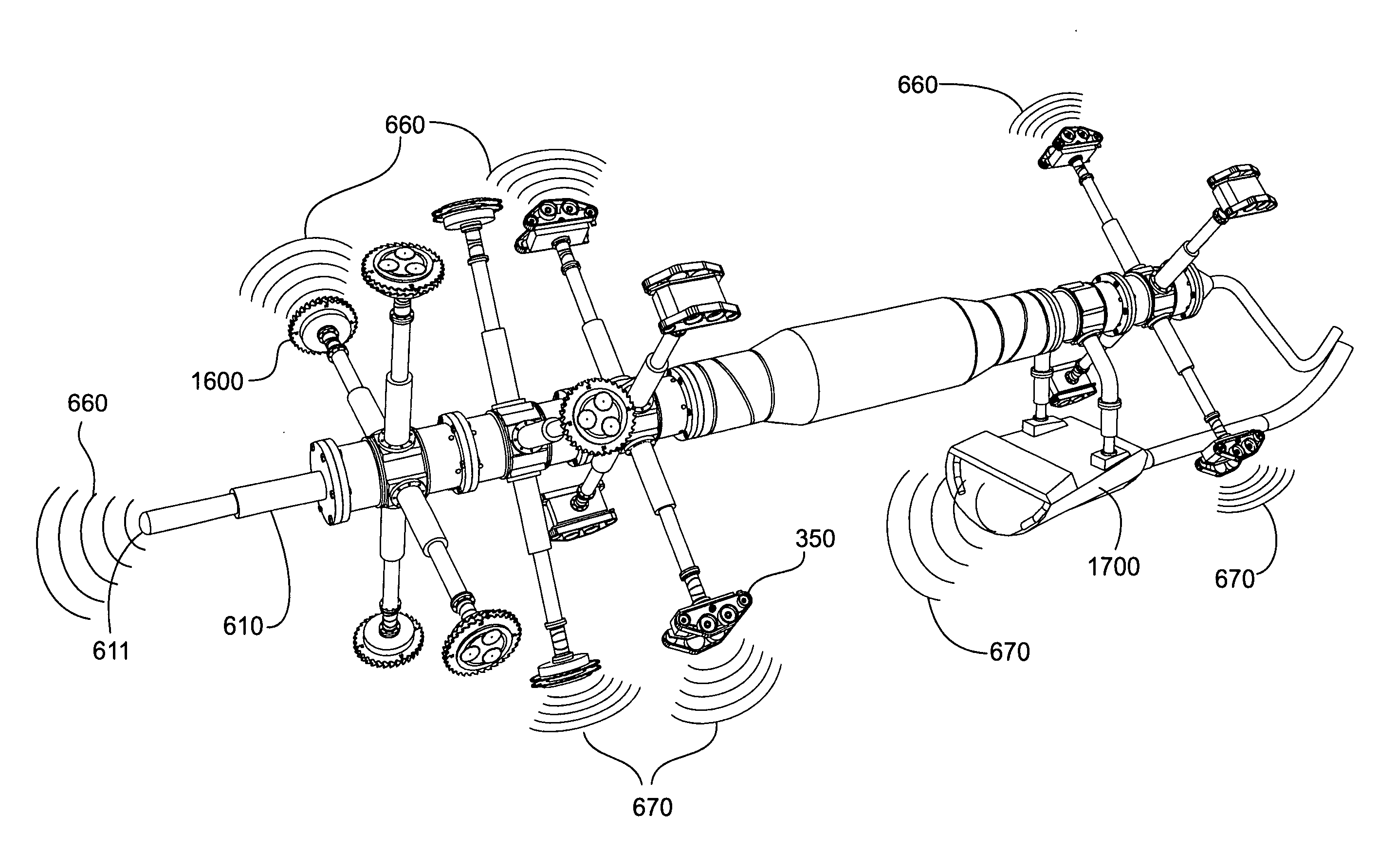
Submersible robotically operable vehicle system for infrastructure maintenance and inspection
InactiveUS20120215348A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsElectric powerInstrumentation
A configurable robotic apparatus and system is disclosed that is remotely operable in difficult, hazardous, subterranean, or submerged environs. The apparatus merges diverse disciplines to effect inspecting, cleaning, treating, repairing or otherwise maintaining a wide variety of materials and conditions. Deployment environments include power, municipal water and wastewater plants, surface and submerged infrastructures (pipes, lines, conduits), and like industrial applications. Extensible and articulating modules, configurable through standardized and interchangeable connectors, provide unique flexibility, scalability and versatility to accommodate a wide range of shapes, surfaces, and obstacles. In-module intelligence and instrumentation eliminates the need for constant manual control through autonomous operation capable of simultaneous optimization and synchronization of multiple work processes, but manual override and remote control is provided to overcome unanticipated limitations. Benefits include improved efficiency, cost, and safety over prior art. High-performance, one-pass operation reduces facility downtime while incorporating environmentally responsible debris recovery.
Owner:SKRINDE RICHARD ARTHUR
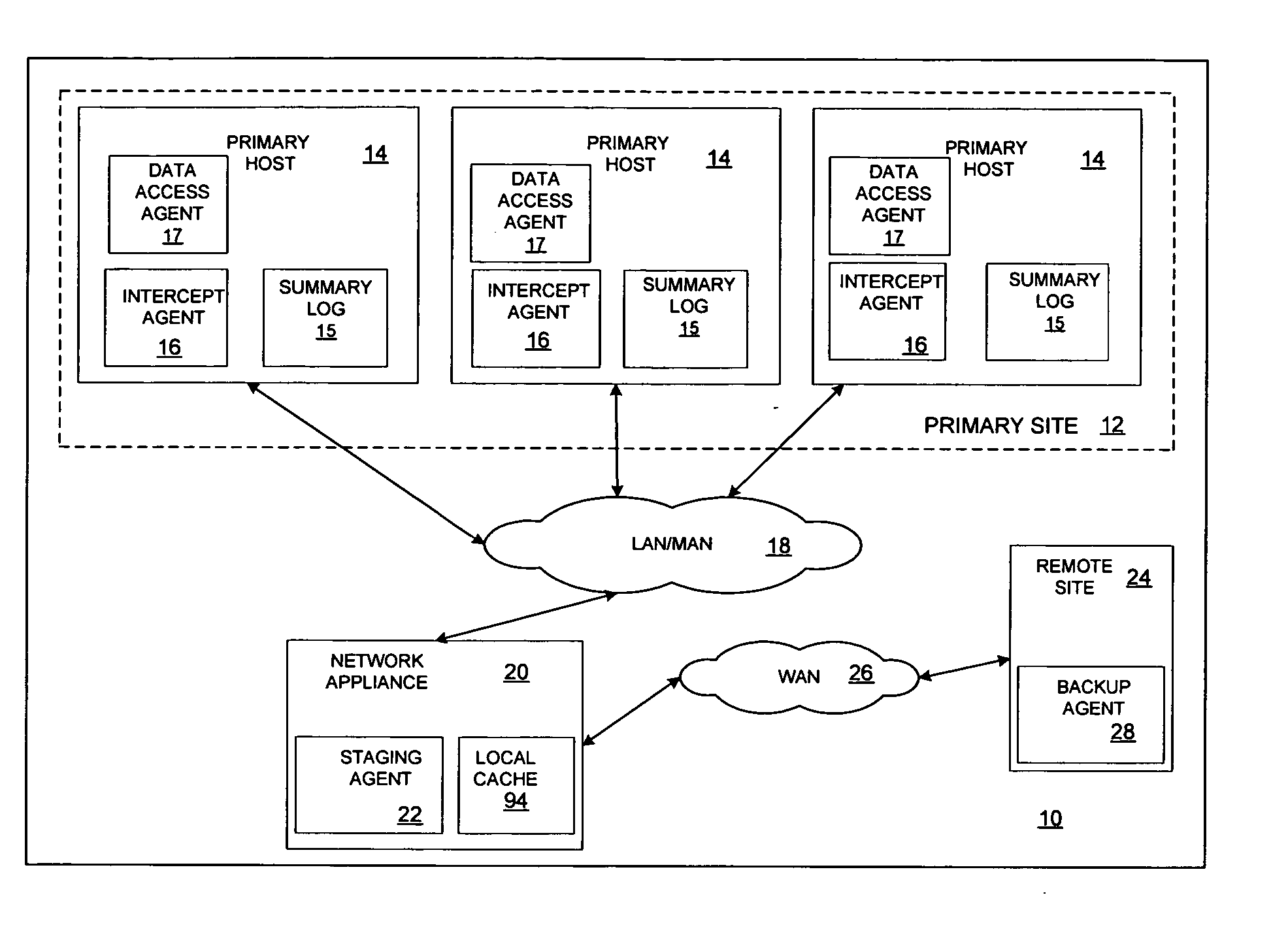
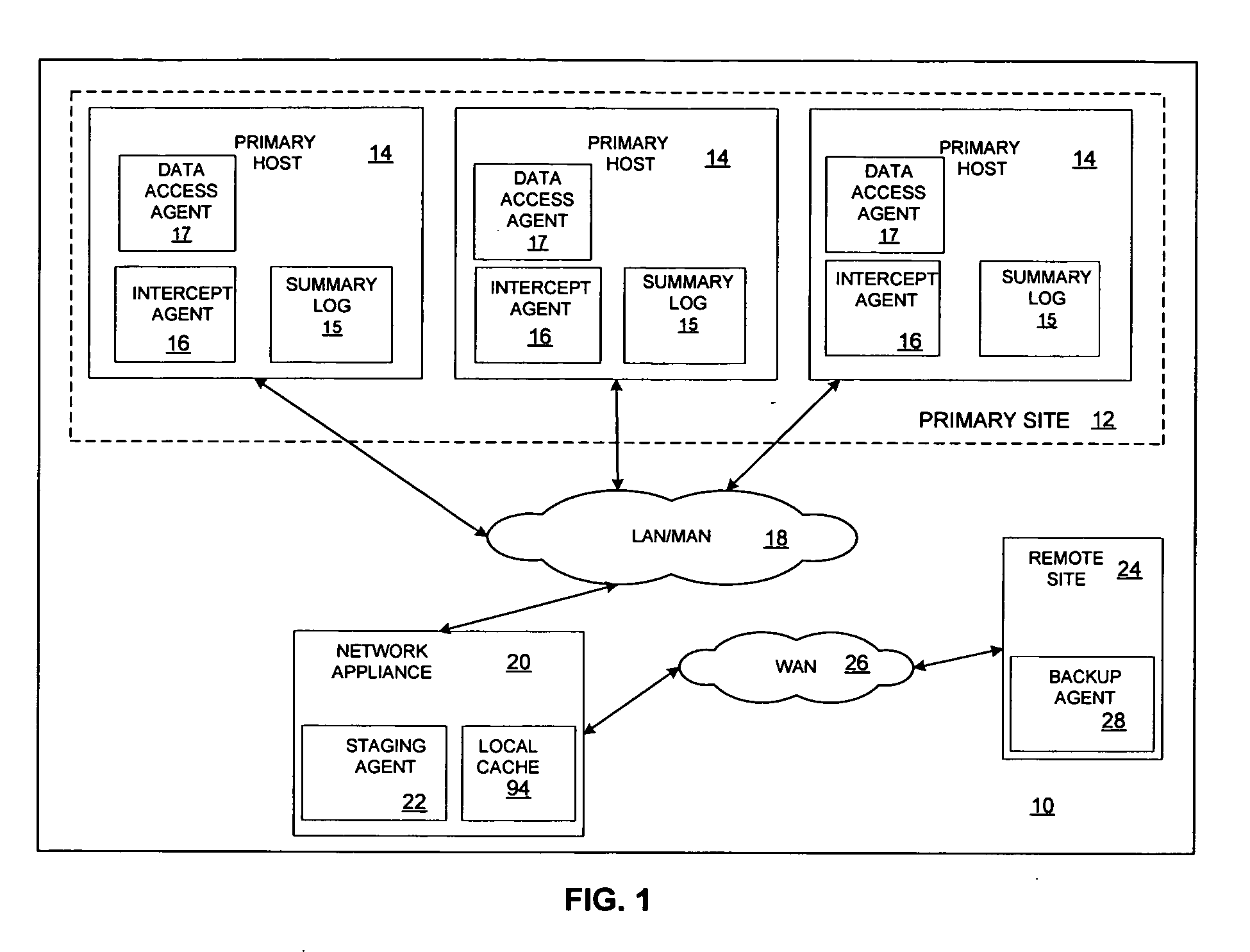
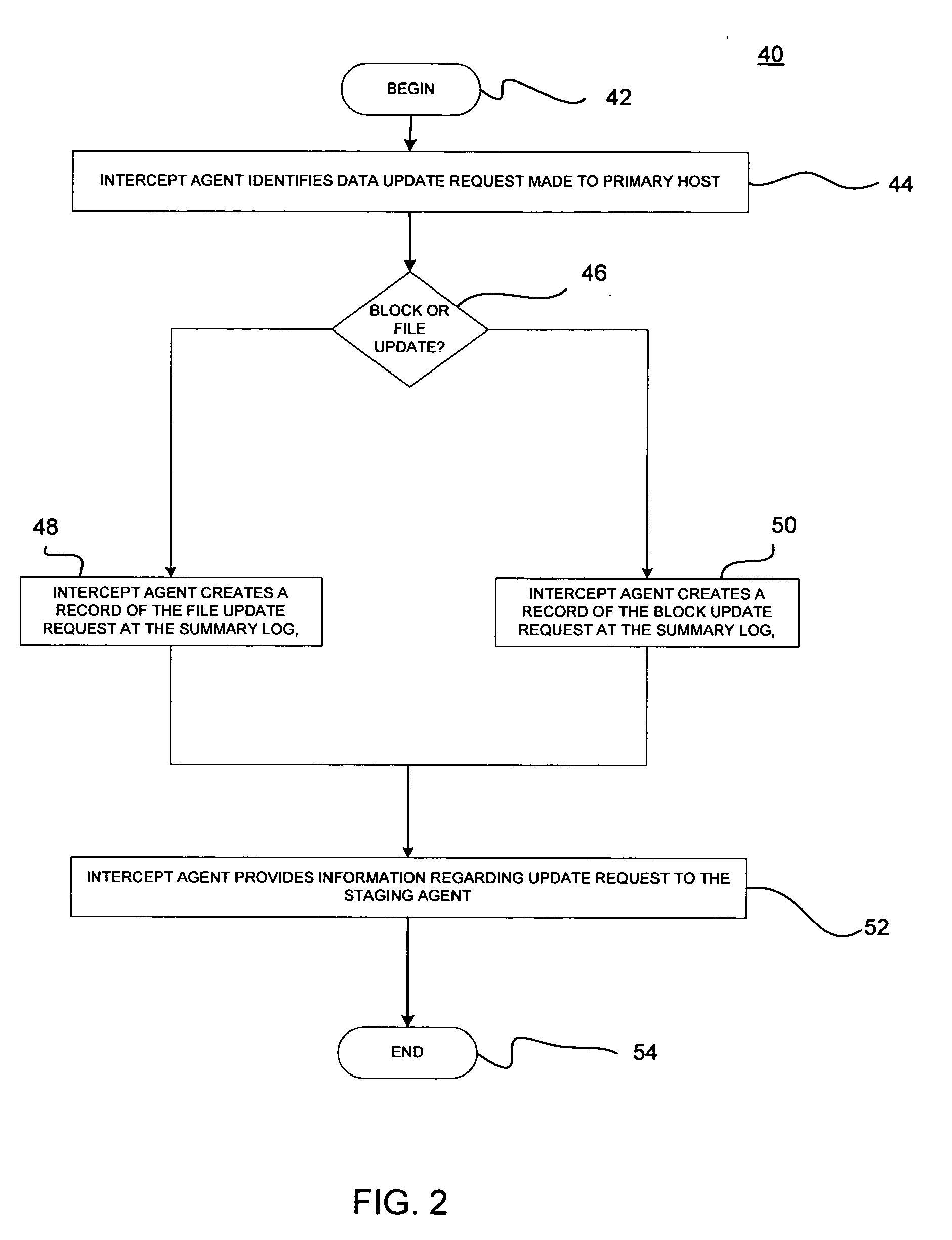
Minimizing resynchronization time after backup system failures in an appliance-based business continuance architecture
ActiveUS20050273654A1Minimize resynchronization timeMinimize timeMemory systemsRedundant hardware error correctionDowntimeSystem failure
A system for minimizing downtime in an appliance-based business continuance architecture is provided. The system includes at least one primary data storage and least one primary host machine. The system includes an intercept agent to intercept primary host machine data requests, and to collect information associated with the intercepted data requests. Moreover, at least one business continuance appliance in communication with the primary host machine and in communication with a remote backup site is provided. The appliance receives information associated with the intercepted data requests from the intercept agent. In addition, a local cache is included within the business continuance appliance. The local cache maintains copies of primary data storage according to the information received. Furthermore, the remote site is provided with the intercepted data requests via the business continuance appliance, wherein the remote site maintains a backup of the primary data storage.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
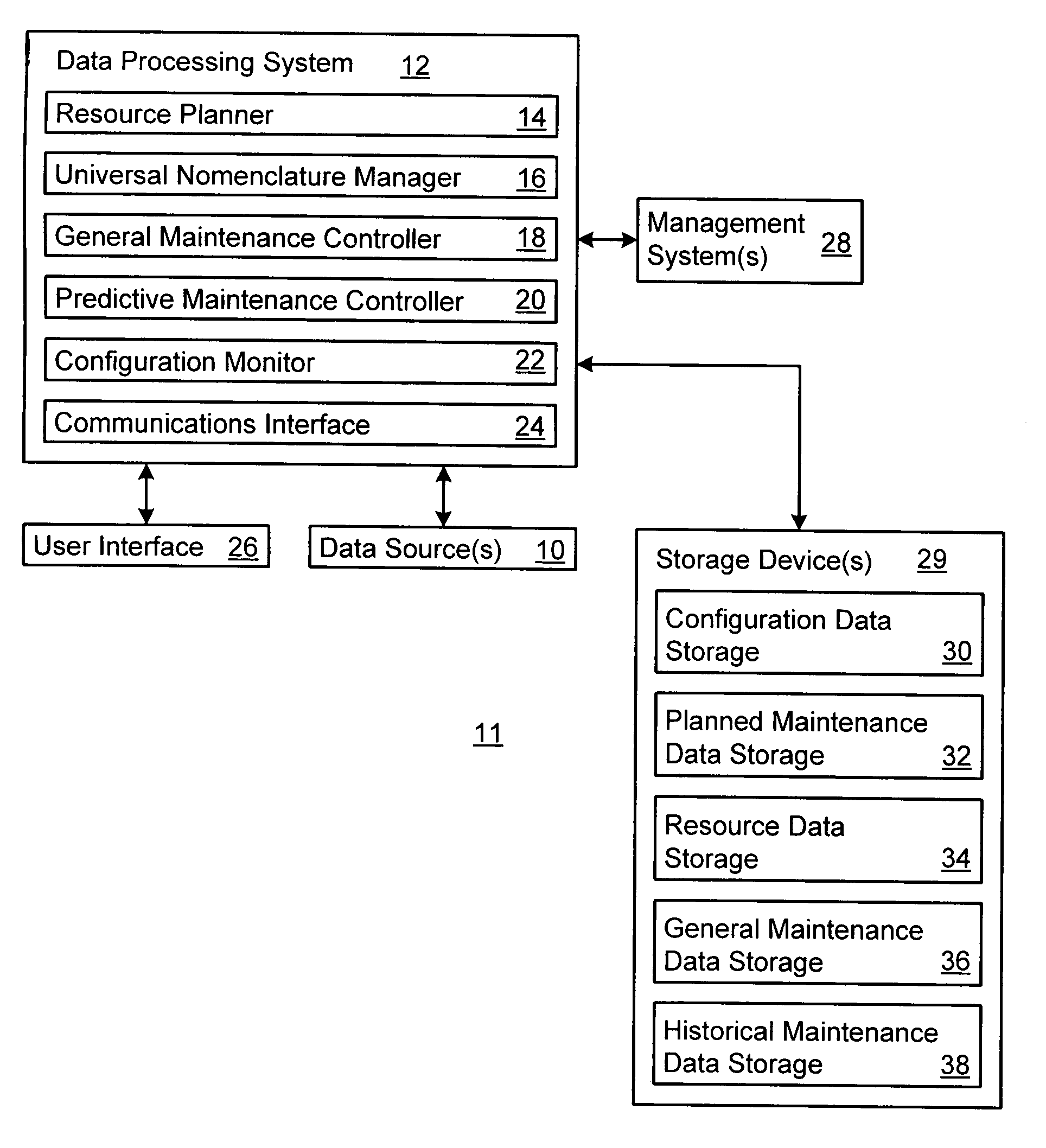
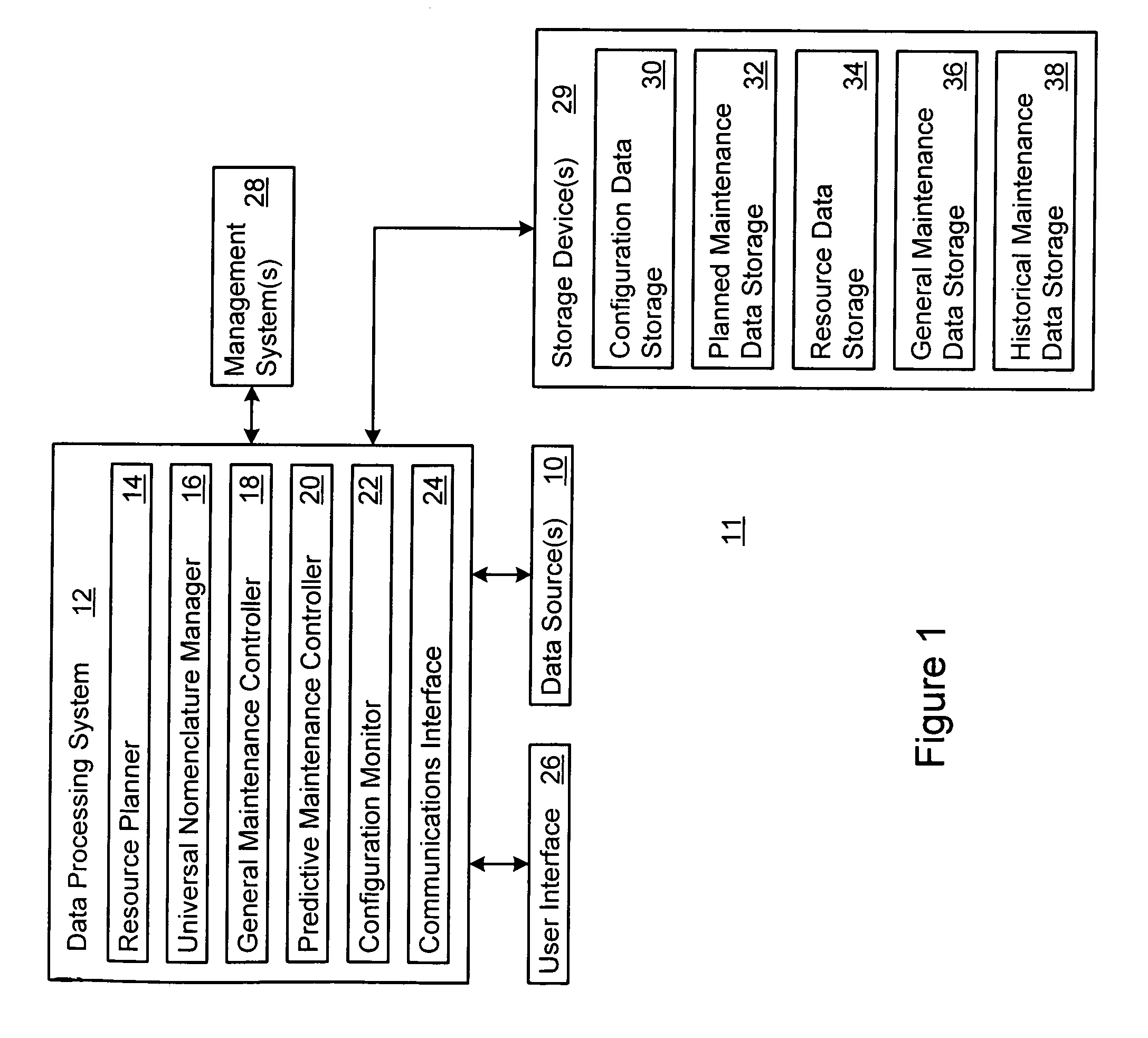
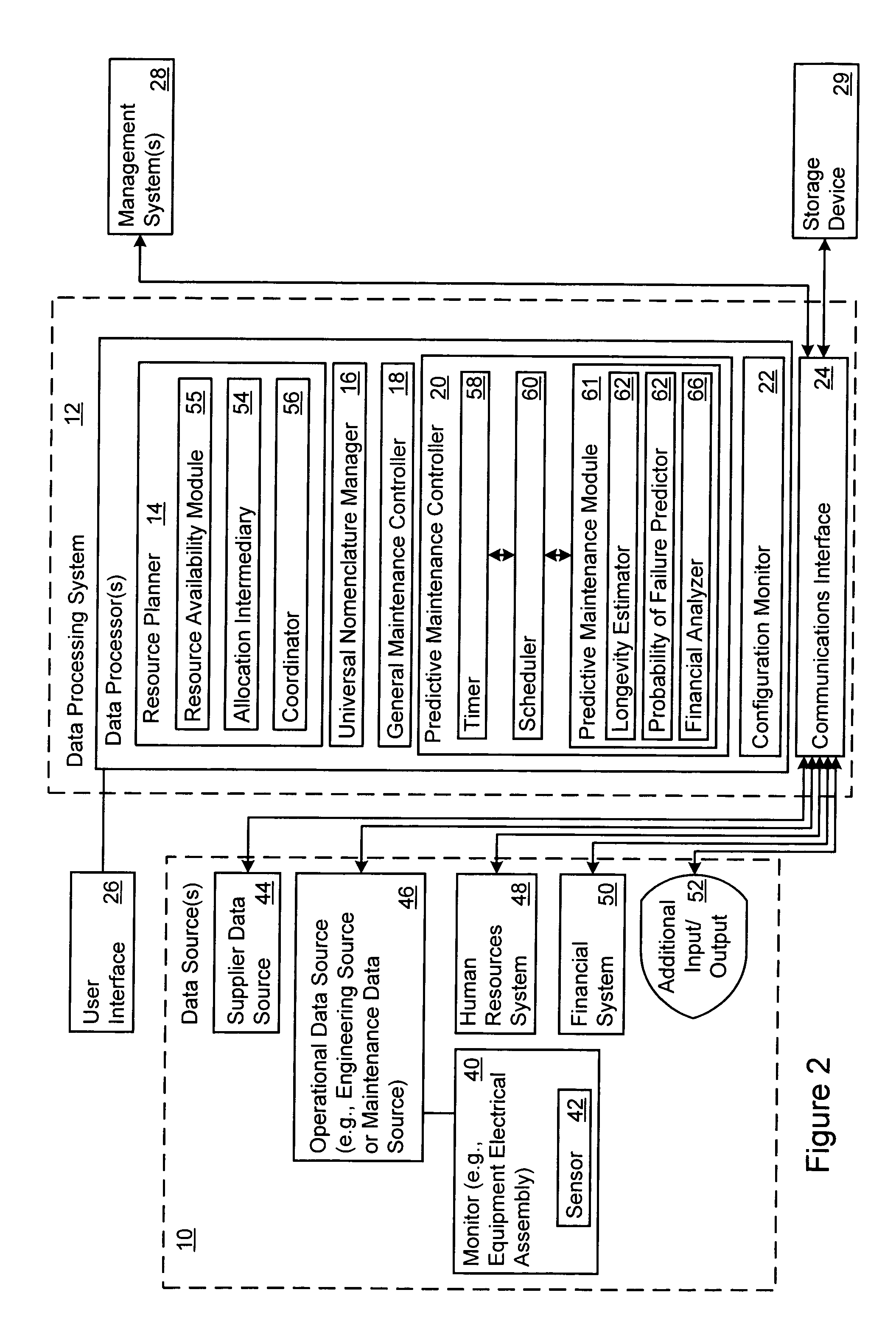
Managing maintenance for an item of equipment
InactiveUS7124059B2Eliminates and reduces downtimeLaser detailsElectric testing/monitoringDowntimePredictive maintenance
A method and system for maintaining an item of equipment supports the provision of predictive maintenance in a manner which eliminates or reduces downtime of the equipment. The method includes tracking performance data on the equipment or a particular component of the equipment. At least one required maintenance activity is predicted based upon the performance data with respect to a defined performance standard. Performance of the required maintenance activity is scheduled at a defined respective time based upon the prediction.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
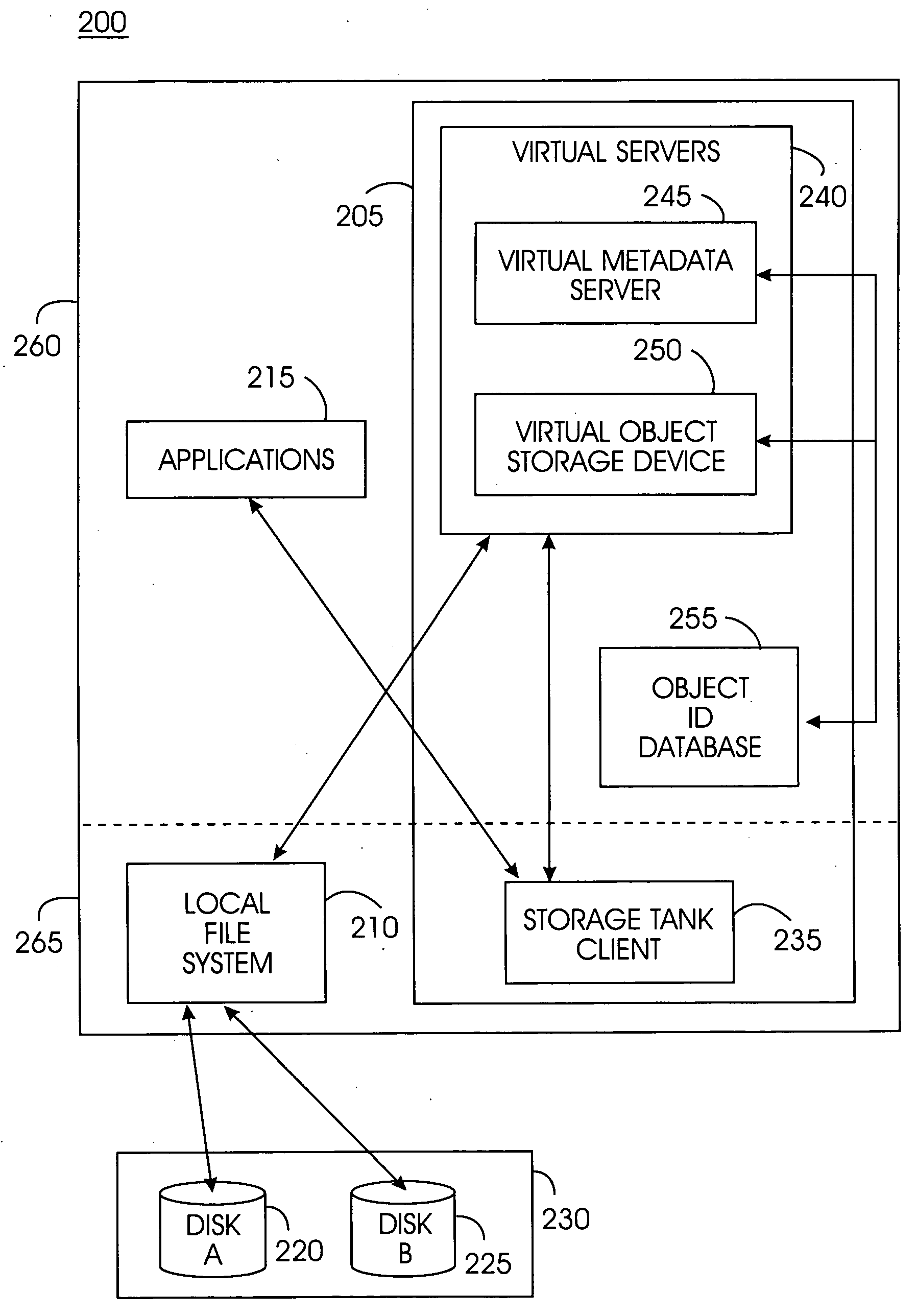
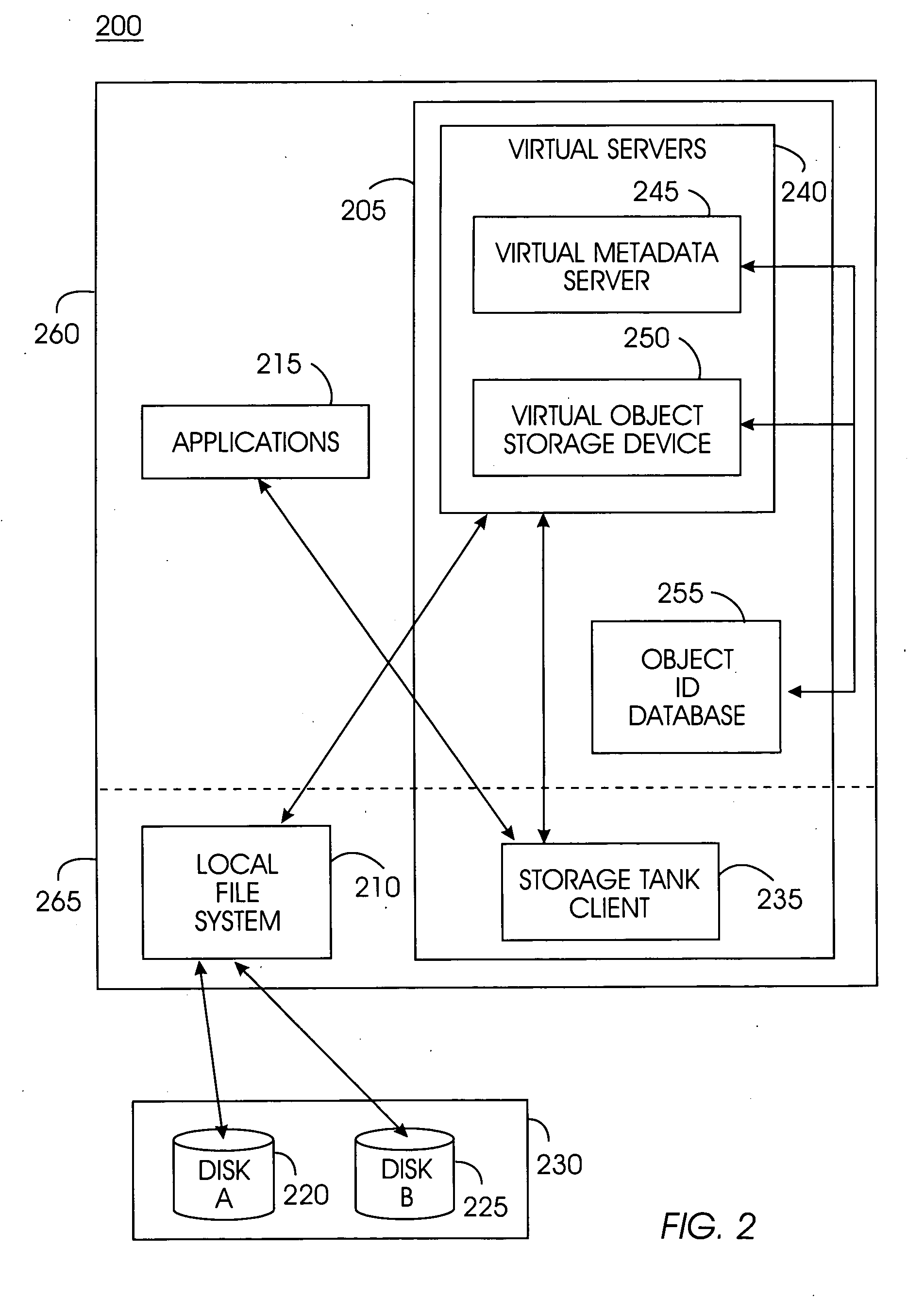
System, method, and service for federating and optionally migrating a local file system into a distributed file system while preserving local access to existing data
ActiveUS20050114291A1Minimal disruptionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemDowntime
Indirect access to local file systems is provided using storage tank protocols, allowing federation of a local file system into a distributed file system while preserving local access to the existing data in the local file system. The goal of the present system is to federate and migrate the data on a computer system with minimum disruption to applications operating on the computer system. Existing applications on a computer system continue to operate during data federation and migration and require little or no reconfiguration either when the data migration starts or when it ends. Data consistency is maintained: existing applications may modify data in the file system during migration or federation. During federation, other computer systems (or hosts) may modify the data in the file system if access control information allows them to do so. All changes in the file system are seen consistently on all hosts. Minimal downtime is required to install the present system and reconfigure the existing applications to communicate with the present system.
Owner:IBM CORP
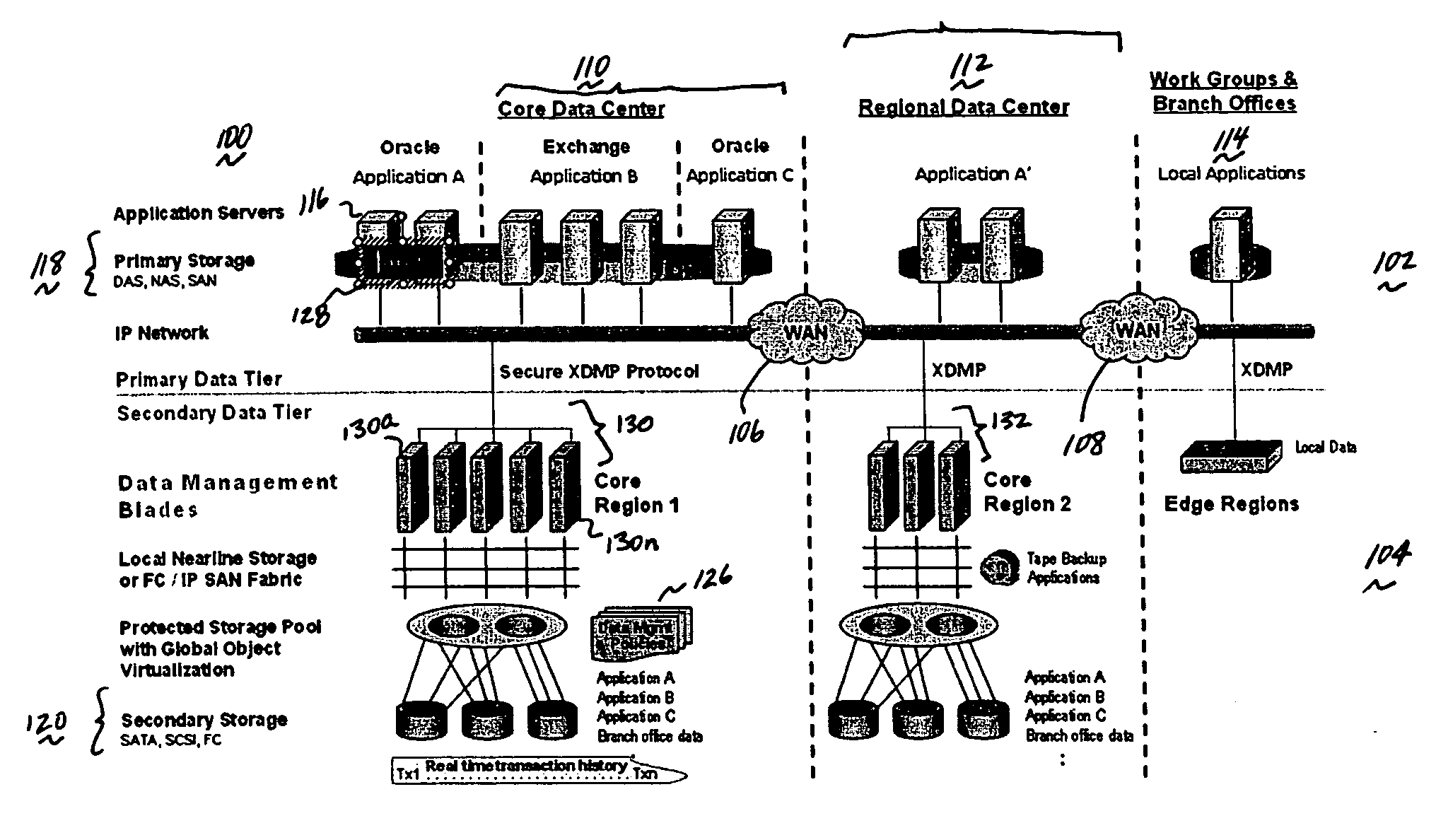
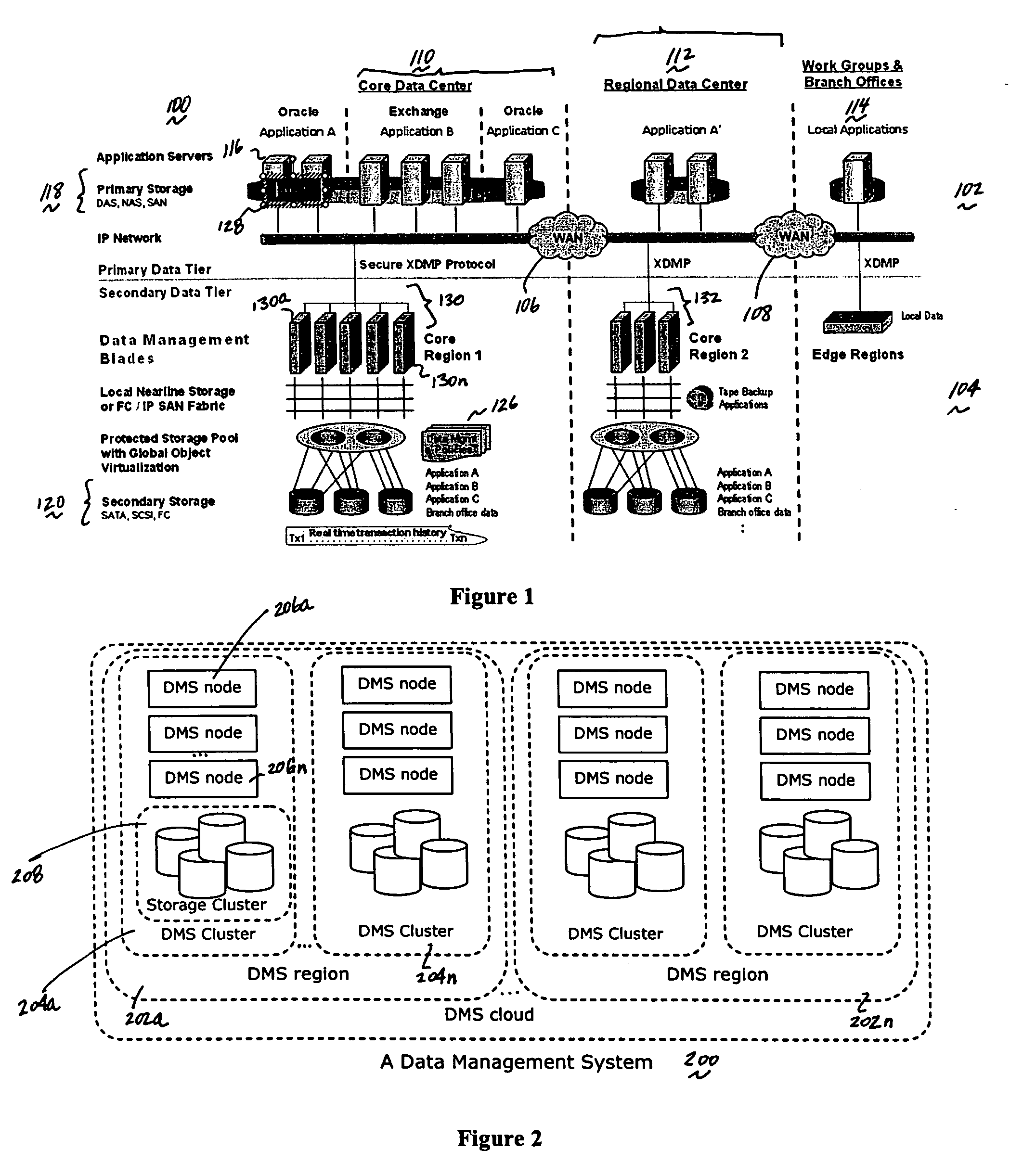
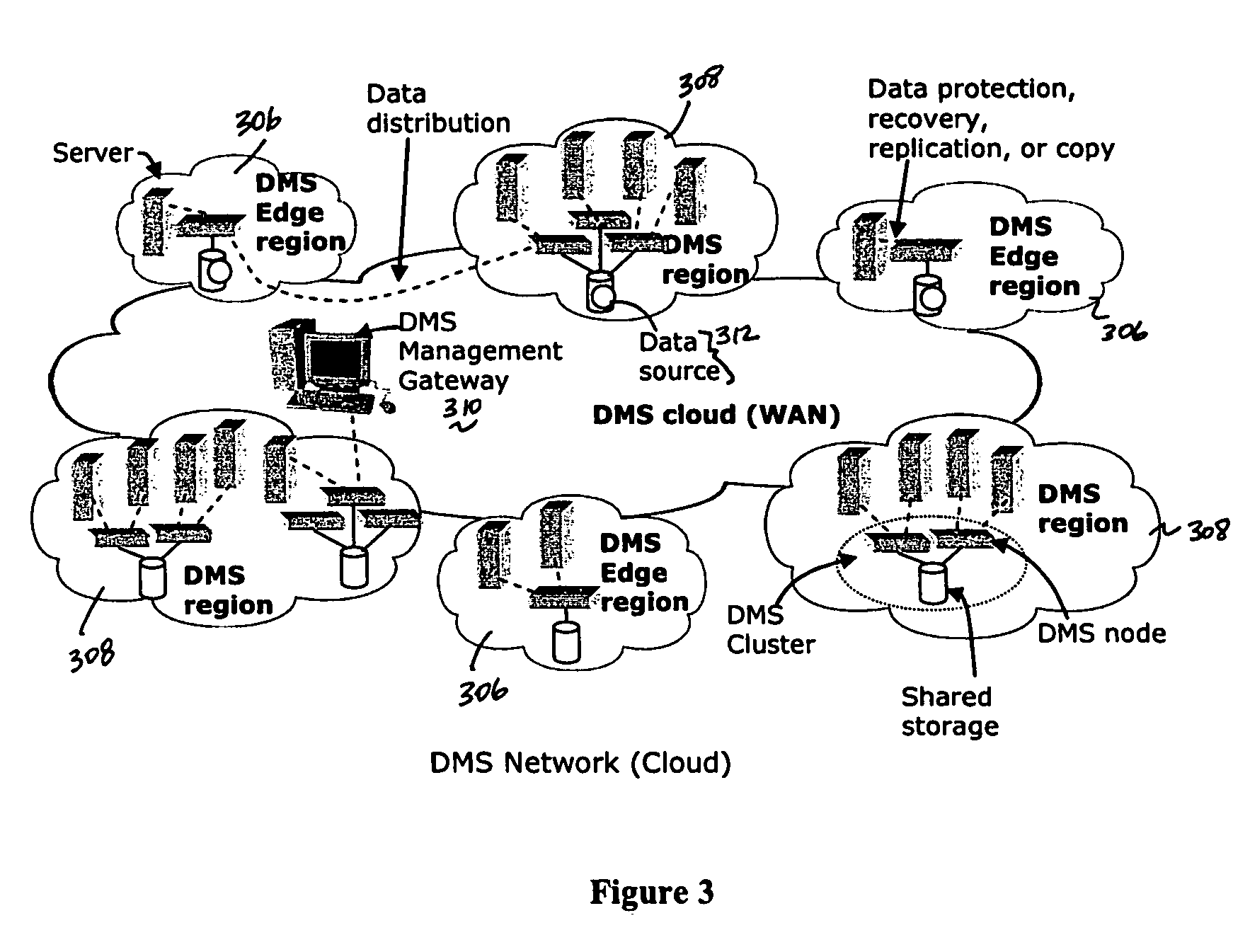
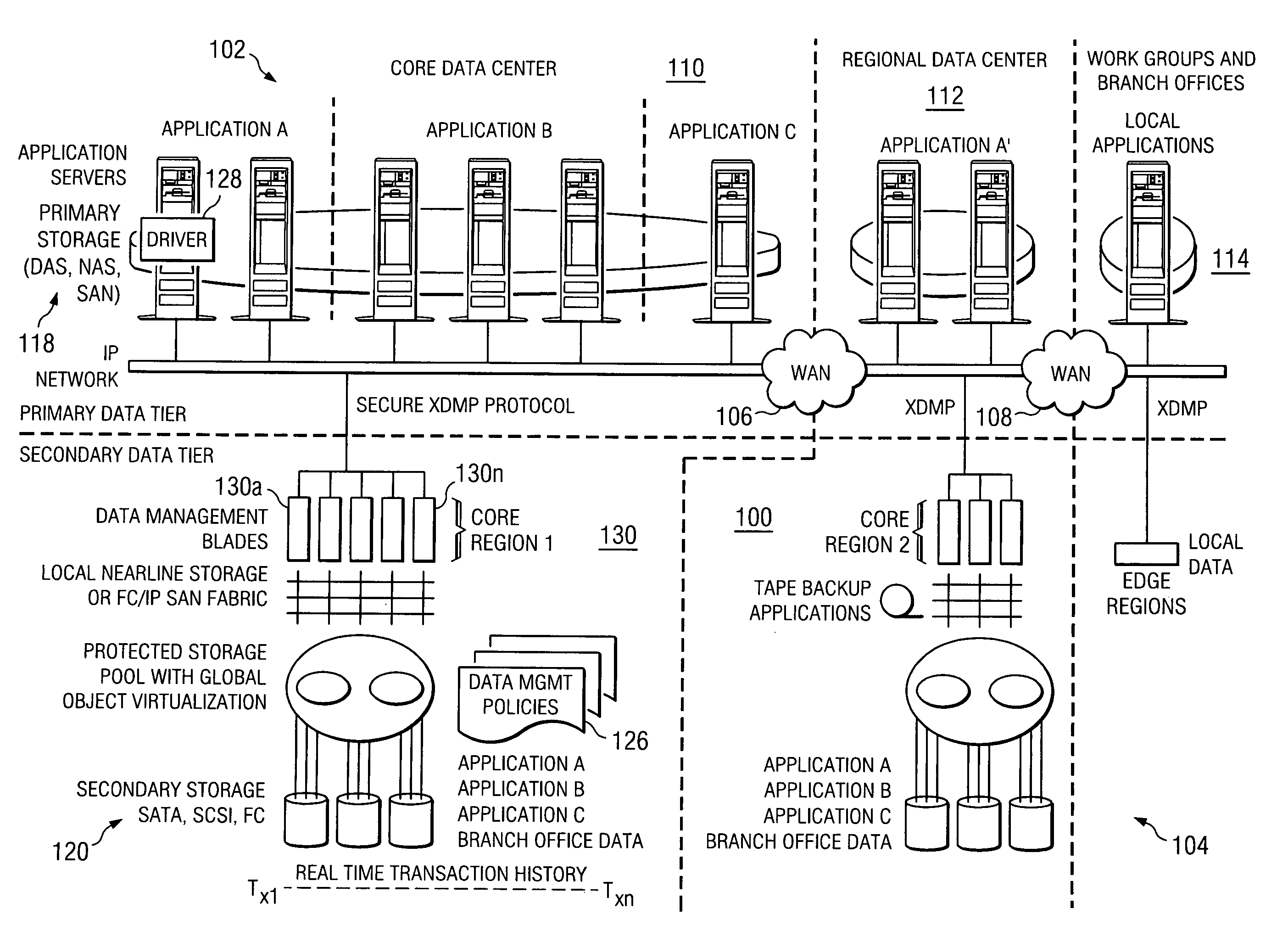
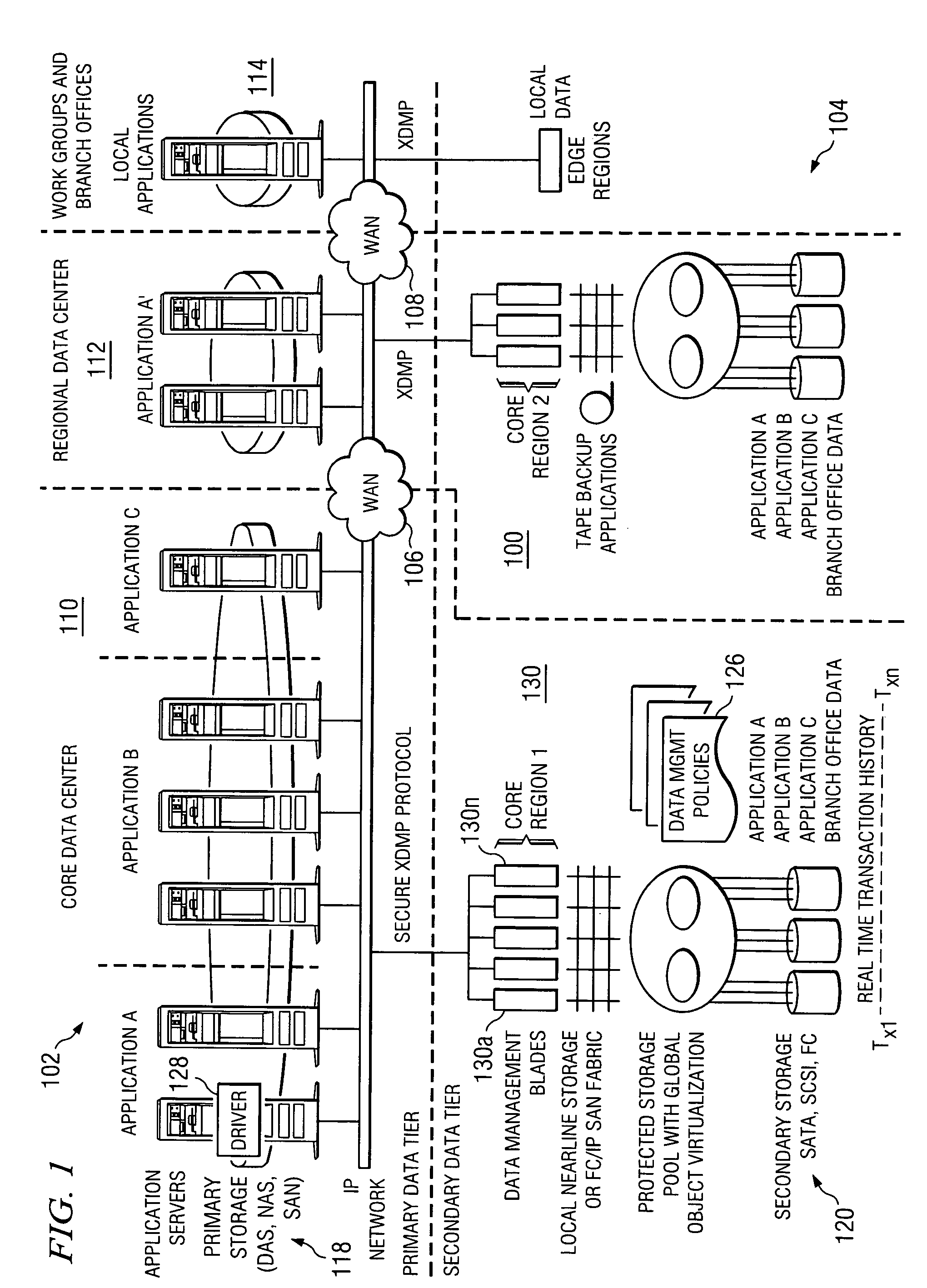
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS20050262377A1Easy to optimizeError detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
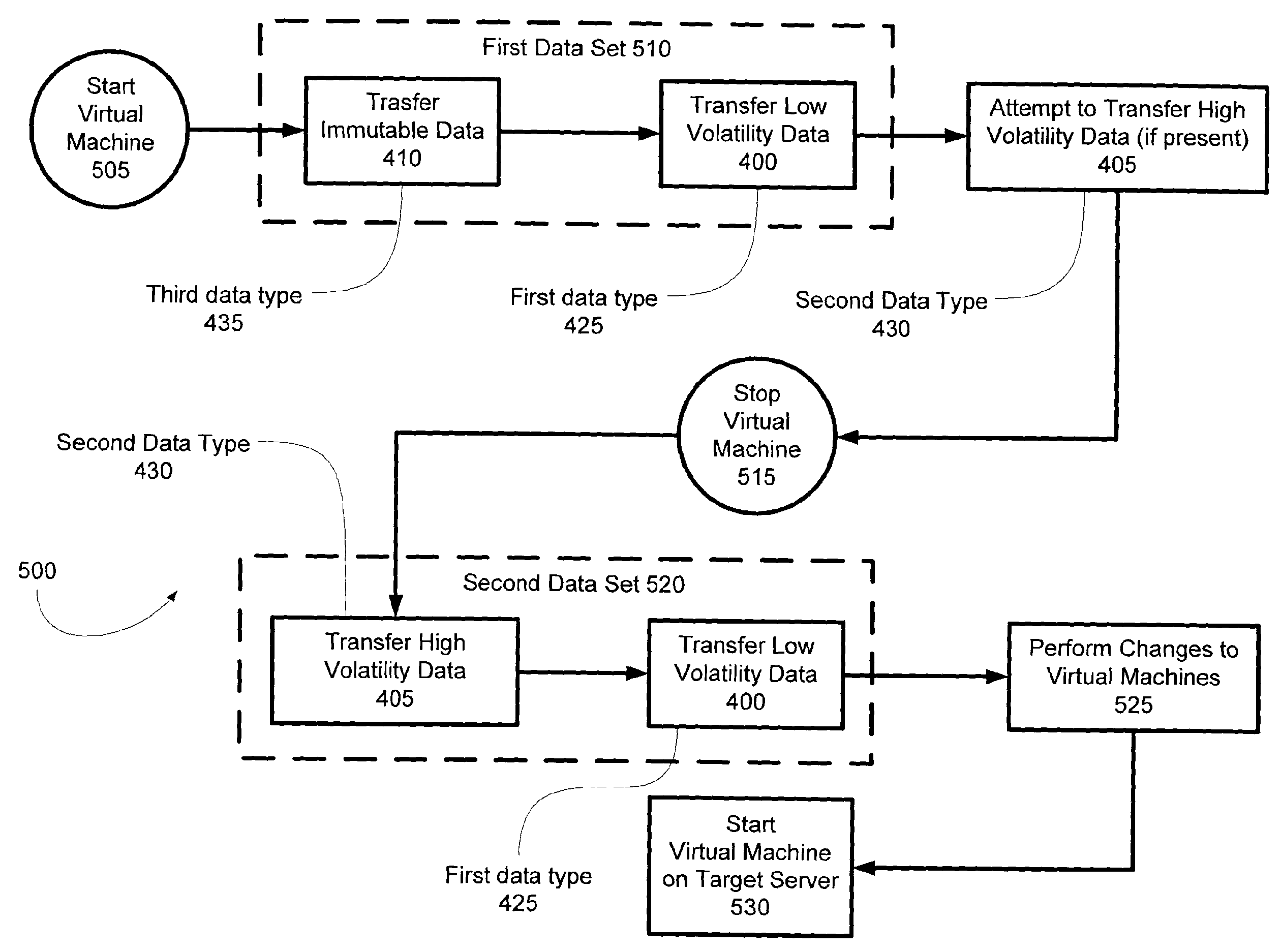
Virtual Machine Smart Migration
ActiveUS20090007106A1Reduce downtimeMaximizing consistent stateInterprogram communicationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationRandom access memoryData storing
Migration mechanisms are disclosed herein that smartly transfer data among virtual machines, minimizing the down time of migration of such machines but maximizing the consistent state of data stored thereon. Specifically, data can be classified into three types: low volatility data (such as hard disk data), high volatility data (such a random access memory data), and immutable data (such as read only data). This data can be migrated from a source virtual machine to a target virtual machine by sending the immutable data along with the low volatility data first—before the source virtual machine has stopped itself for the migration process. Then, after the source virtual machine has stopped, high volatility data and (again) low volatility data can be sent from the source to the target. In this latter case, only differences between the low volatility data may be sent (or alternatively, new low volatility data may be sent).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for automatically and dynamically optimizing application data resources to meet business objectives
ActiveUS20050015641A1Provide flexibilityMinimize impactEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSpecial data processing applicationsQuality of serviceData availability
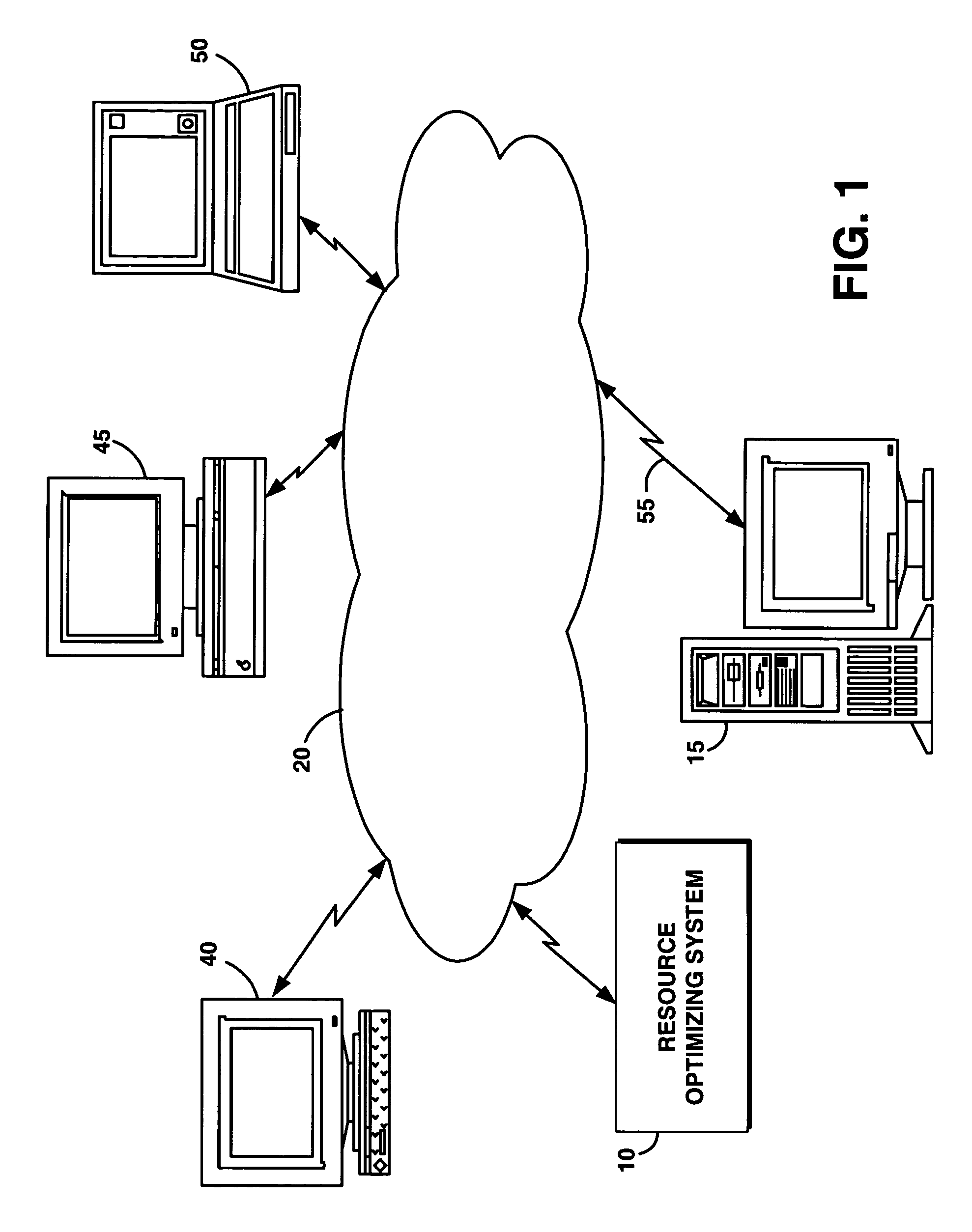
A system and method to automatically and dynamically optimize available resources to meet application data availability and business objectives. In one embodiment, a backup and data recovery system continually and dynamically adjust to the backup and recovery or restore process depending on the customer's environment, workload, and business objectives. Acceptable tolerance of downtime due to recovery and backup impacts the customer's business or system operation. From this high-level business requirement, the present system determines the backup and recovery plan details. The present system accepts application data availability policies based on business objectives, and devises, executes and refines a resource optimal backup and recovery strategy required to deliver the desired quality of service in the environments that have dynamically changing application workloads, business objectives, and hardware / software infrastructure technologies. In addition, the present system performs backups outside blocked windows to minimize the impact on the customer's system.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
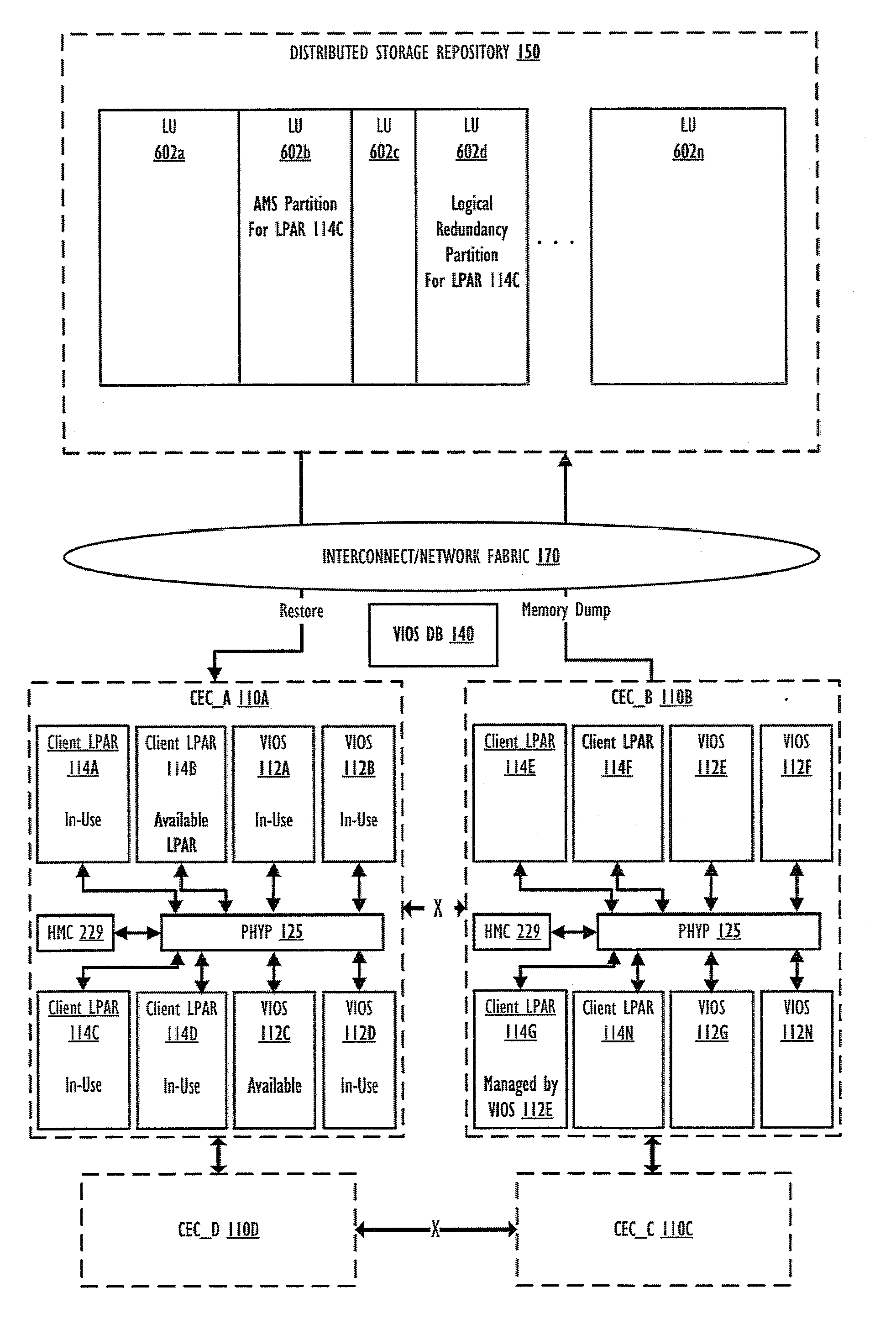
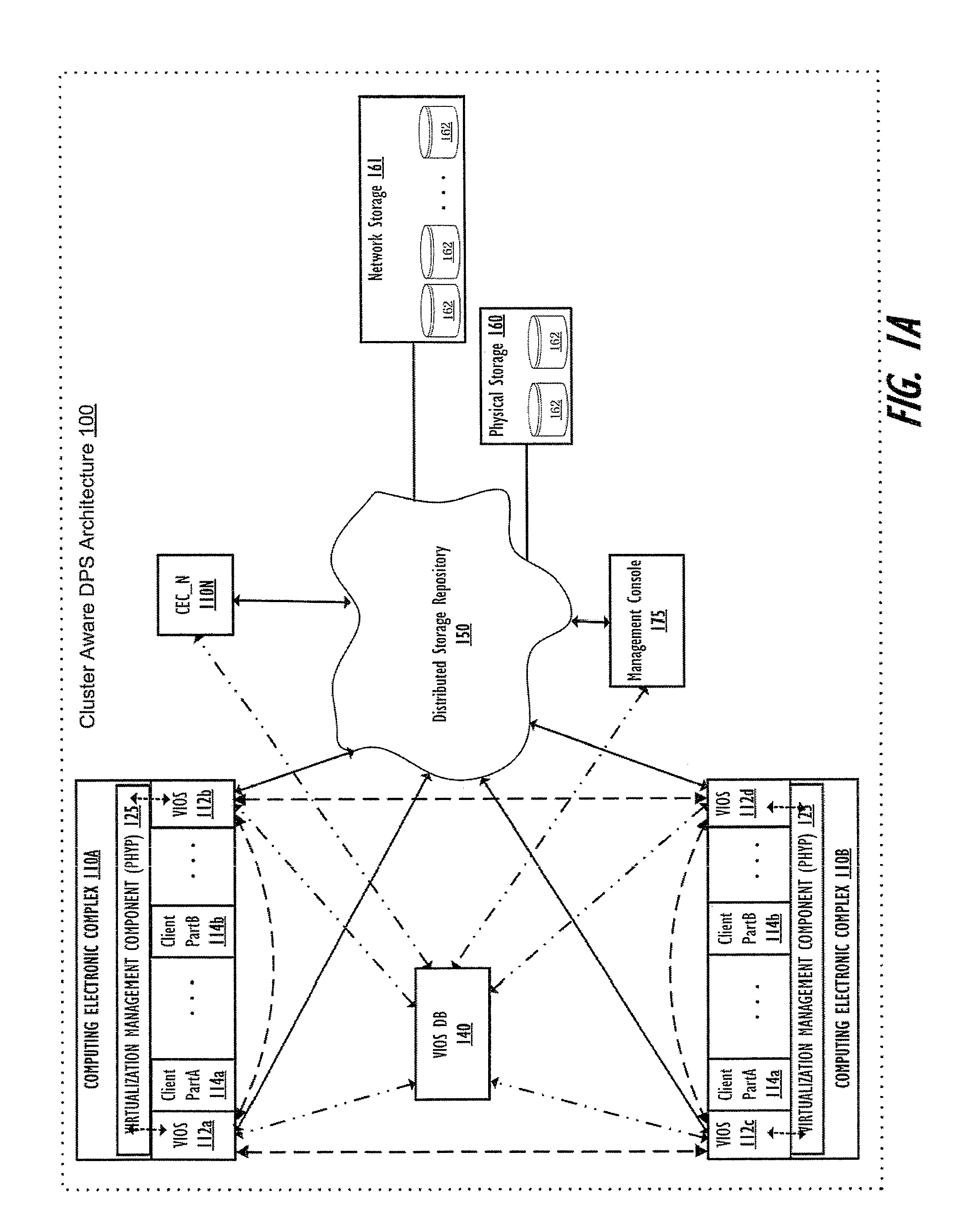
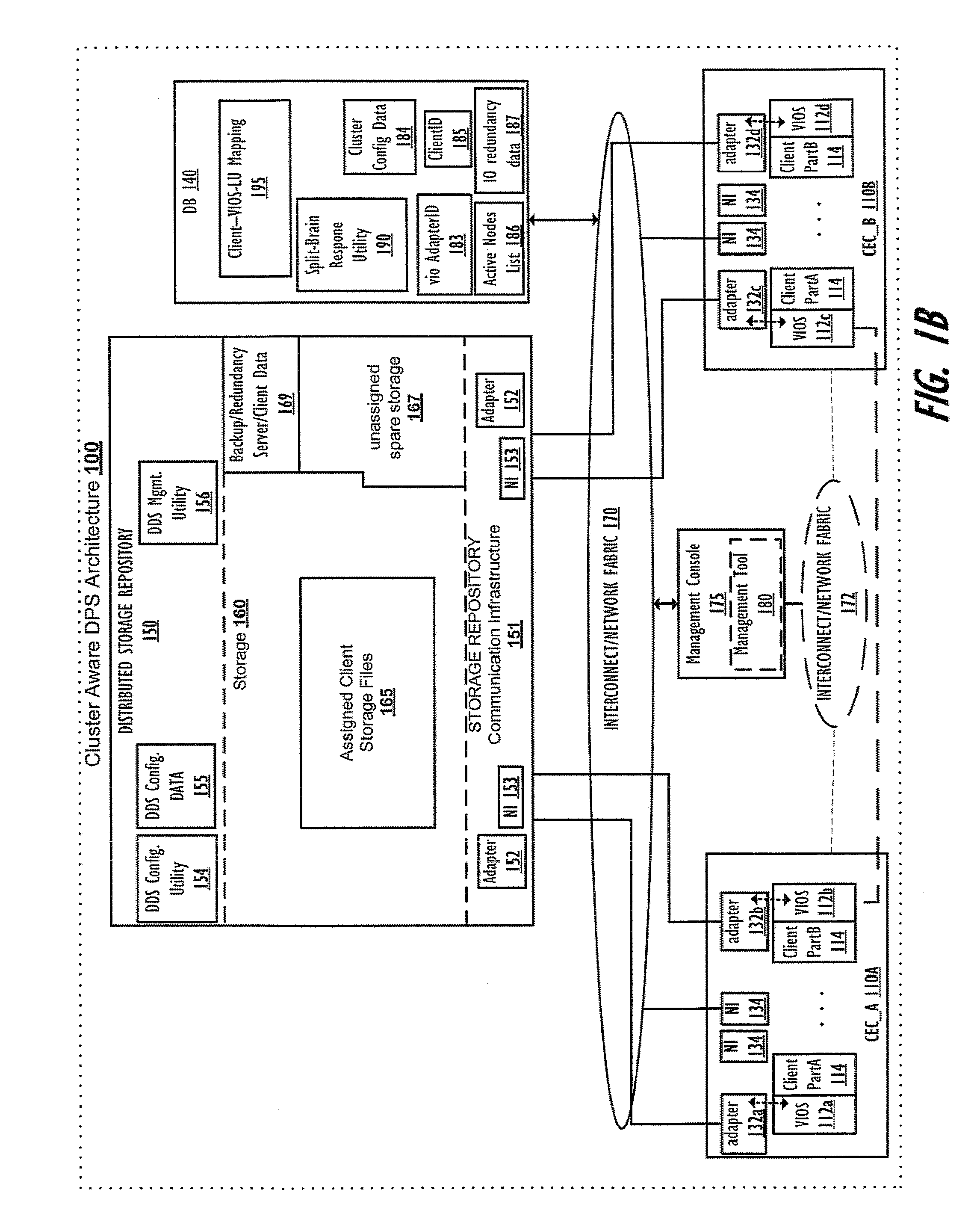
Supporting autonomous live partition mobility during a cluster split-brained condition
InactiveUS20120179771A1Avoiding and minimizing any downtimeError preventionTransmission systemsData processing systemDowntime
A method, data processing system, and computer program product autonomously migrate clients serviced by a first VIOS to other VIOSes in the event of a VIOS cluster “split-brain” scenario generating a primary sub-cluster and a secondary sub-cluster, where the first VIOS is in the secondary sub-cluster. The VIOSes in the cluster continually exchange keep-alive information to provide each VIOS with an up-to-date status of other VIOSes within the cluster and to notify the VIOSes when one or more nodes loose connection to or are no longer communicating with other nodes within the cluster, as occurs with a cluster split-brain event / condition. When this event is detected, a first sub-cluster assumes a primary sub-cluster role and one or more clients served by one or more VIOSes within the secondary sub-cluster are autonomously migrated to other VIOSes in the primary sub-cluster, thus minimizing downtime for clients previously served by the unavailable / uncommunicative VIOSes.
Owner:IBM CORP
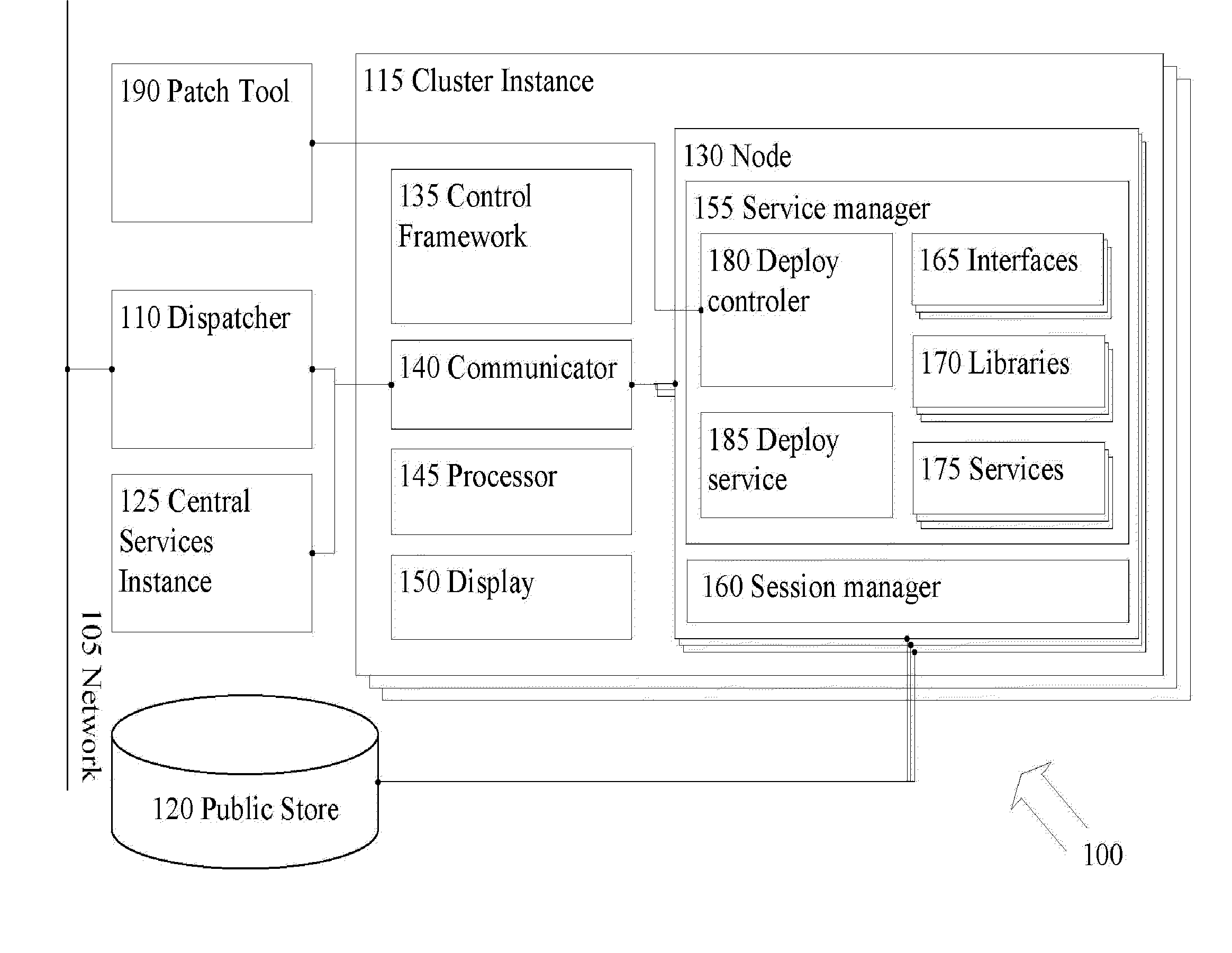
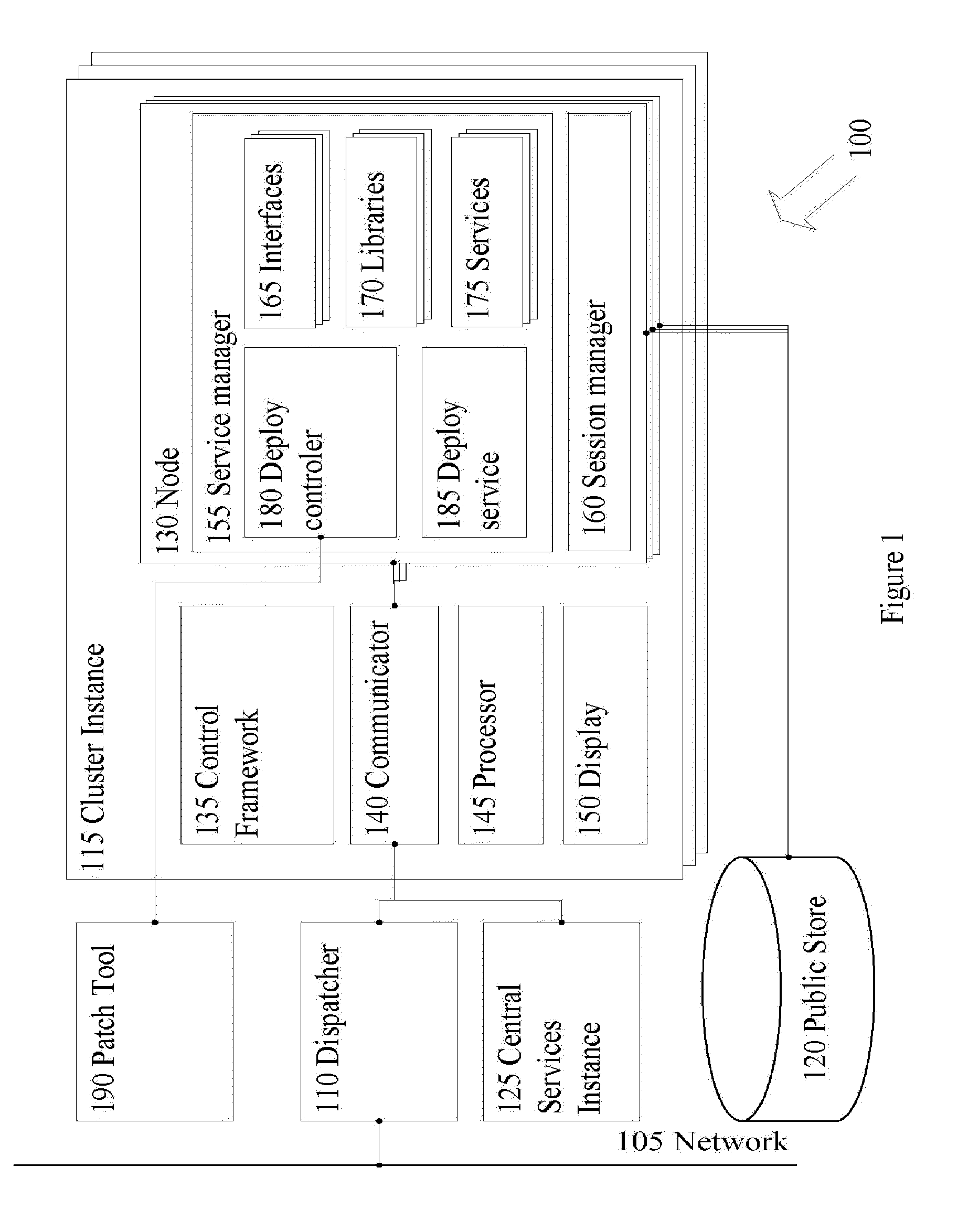
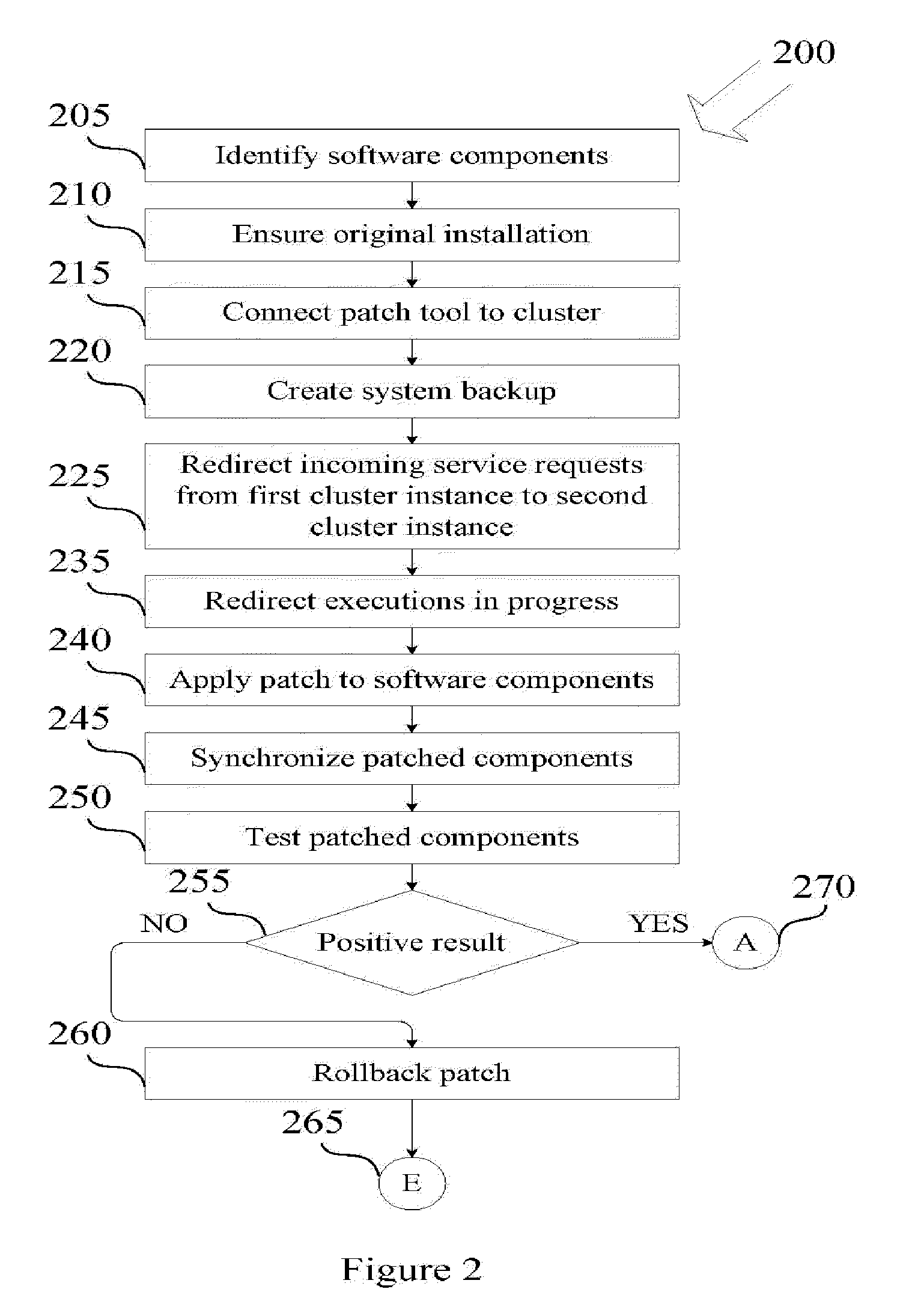
Zero downtime mechanism for software upgrade of a distributed computer system
ActiveUS20100162226A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsApplication serverDowntime
A system and a method for installing software upgrades in a distributed computer system with no downtime. In a distributed computer system with cluster architecture, a number of service requests are redirected from a first instance of the cluster to a second instance of the cluster for execution. An execution in progress of a service request is also redirected from the first instance of the cluster to the second instance of the cluster. The execution in progress proceeds from a state that is saved on a public store by the first instance of the cluster. A software patch is applied to one or more software components running on an application server node of the first instance of the cluster. A number of service requests are redirected from the second instance of the cluster to the first instance of the cluster for execution. An execution in progress of a service request is also redirected from the second instance of the cluster to the upgraded first instance of the cluster. The execution in progress proceeds from a state that is saved on the public store by the second instance of the cluster. The software patch is applies on the one or more software components running on an application server node of the second instance of the cluster. A number of new service requests are directed to the upgraded second instance of the cluster for processing.
Owner:SAP AG
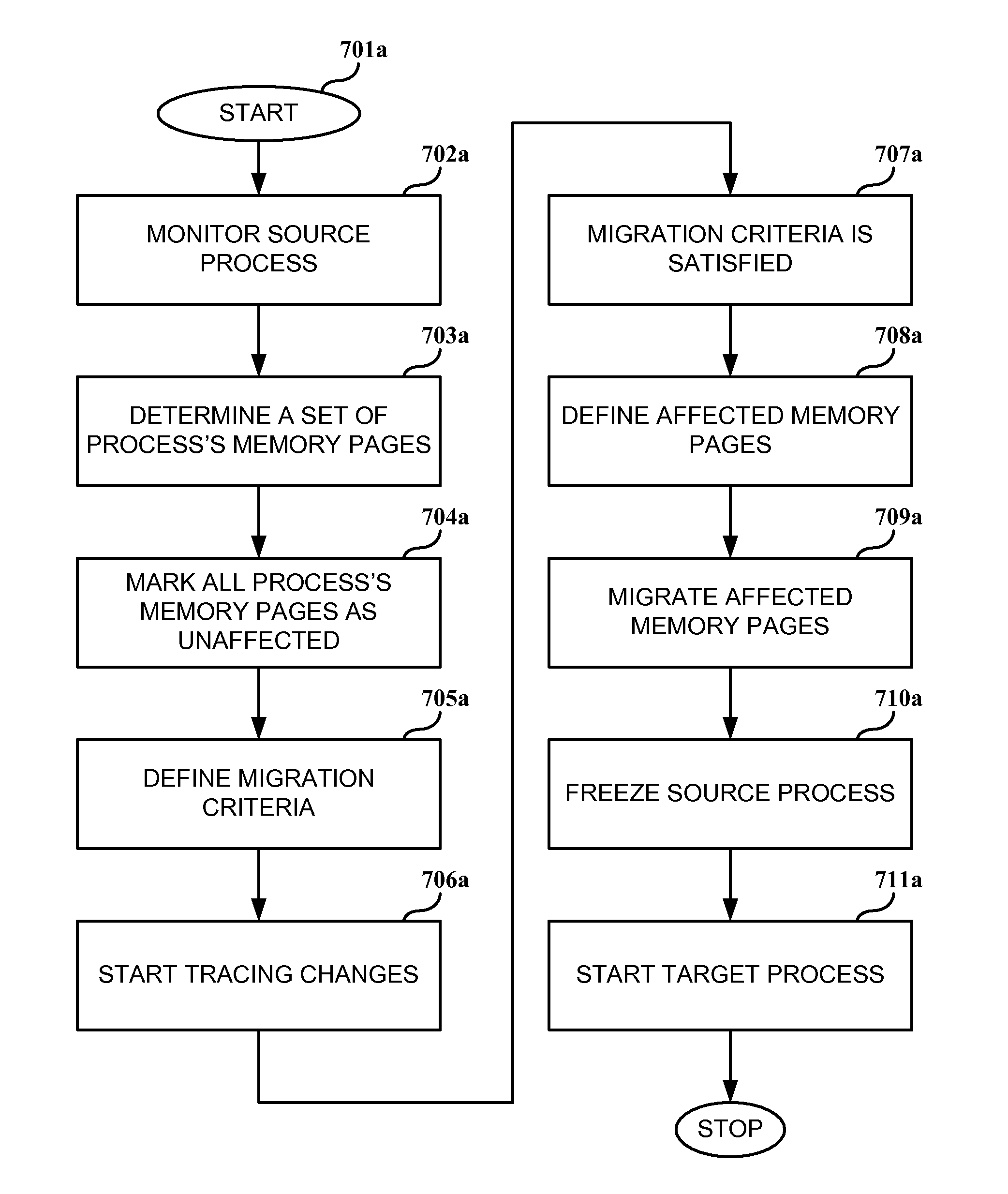
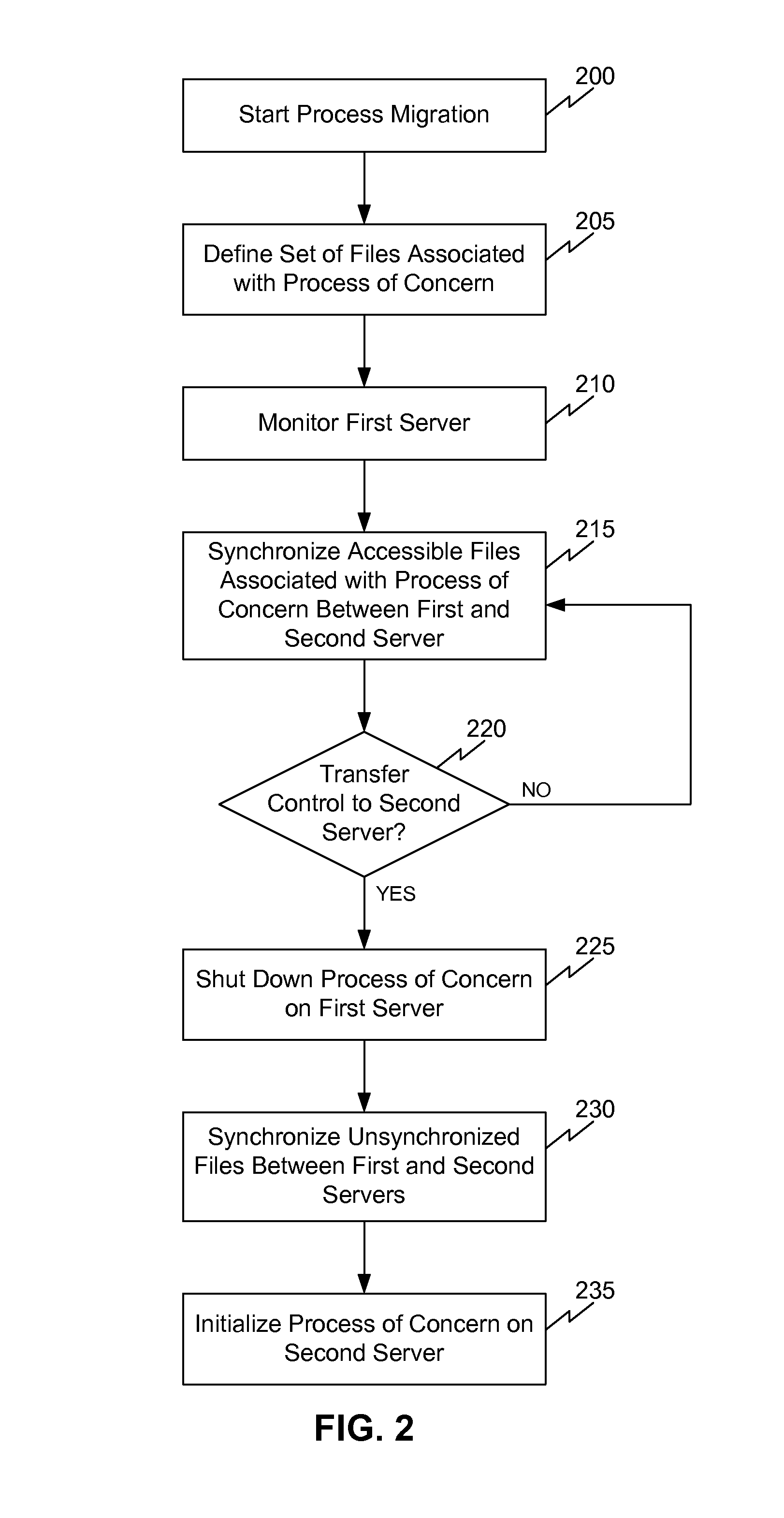
System, method and computer program product for process migration with planned minimized down-time
ActiveUS8069218B1Reduce downtimeGood synchronizationDigital computer detailsProgram controlData synchronizationProgram planning
A system, computer program product and method for a running process migration with planned minimized down-time. The method facilitates fast and efficient process migration by performing background data synchronization prior to actual process migration. The service slowdown is reduced by employing two-stage transfer method. During a first stage the service, being executed on the original machine, does not stop and all the available data required by this process is being copied. After the first stage is completed the service continues to be executed without an interruption, while the most of the data associated with the service process is already transferred to the new machine. During the second stage the execution of the service on the first machine is stopped. The files, which were not available during the first stage, are now copied. Then the execution of service is started on the second machine. The down-time is reduced to the duration of the second stage.
Owner:VIRTUOZZO INT GMBH
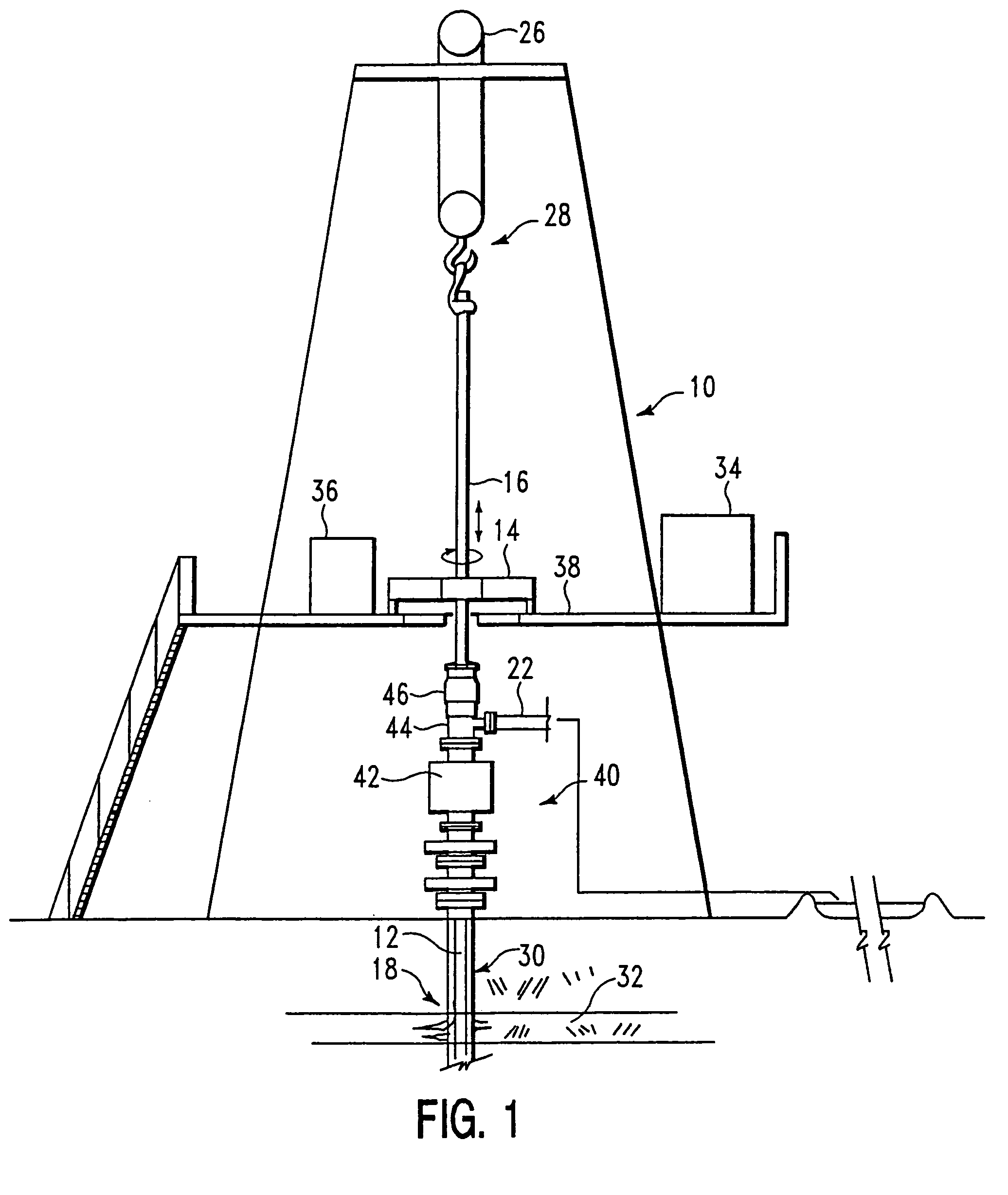
High pressure rotating drilling head assembly with hydraulically removable packer
The present invention generally provides a reduced downtime maintenance apparatus and method for replacing and / or repairing a subassembly in sealing equipment for oil field use. The invention allows the removal of rotating portions of a rotary drilling head without having to remove non-rotating portions. The reduction in weight and size allows a more efficient repair and / or replacement of a principal wear component such as a packer. Specifically, the packer in a rotary drilling head can be removed independent of bearings and other portions of the rotary drilling head. Furthermore, because of the relatively small size and light weight, the packer can be removed typically without having to use a crane to lift a rotary BOP and without disassembling portions of the drilling platform. In some embodiments, the packer can be removed with the drill pipe without additional equipment. Furthermore, the packer can be removed remotely without necessitating manual disengagement typically needed below the platform. The invention also provides a fluid actuated system to maintain a pre-load system on the bearing.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method and system for automated, no downtime, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS7096392B2Error detection/correctionGroup 6/16 element organic compoundsData streamFinite-state machine
A data management system or “DMS” provides an automated, continuous, real-time, substantially no downtime data protection service to one or more data sources associated with a set of application host servers. To facilitate the data protection service, a host driver embedded in an application server captures real-time data transactions, preferably in the form of an event journal that is provided to other DMS components. The driver functions to translate traditional file / database / block I / O and the like into a continuous, application-aware, output data stream. The host driver includes an event processor that provides the data protection service, preferably by implementing a finite state machine (FSM). In particular, the data protection is provided to a given data source in the host server by taking advantage of the continuous, real-time data that the host driver is capturing and providing to other DMS components. The state of the most current data in DMS matches the state of the data in the host server; as a consequence, the data protection is provided under the control of the finite state machine as a set of interconnected phases or “states.” The otherwise separate processes (initial data upload, continuous backup, blackout and data resynchronization, and recovery) are simply phases of the overall data protection cycle. As implemented by the finite state machine, this data protection cycle preferably loops around indefinitely until, for example, a user terminates the service. A given data protection phase (a given state) changes only as the state of the data and the environment change (a given incident).
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Method of Suspending and Resuming Virtual Machines
ActiveUS20110066786A1Minimize downtimeEfficient use ofMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsOperational systemDowntime
A virtual machine is suspended and quickly restarted while maintaining the VM's state. The method is quick enough so that network connections are maintained across the restart and the guest operating system and guest applications running in the VM are not aware of the restart. As a result, users and clients connected to the VM do not notice any downtime or disruption to the VM. After suspension and before the restart, VM configuration changes that would not be possible or be very difficult through code changes alone while the VM was running can be made.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Method and apparatus for efficient software updating
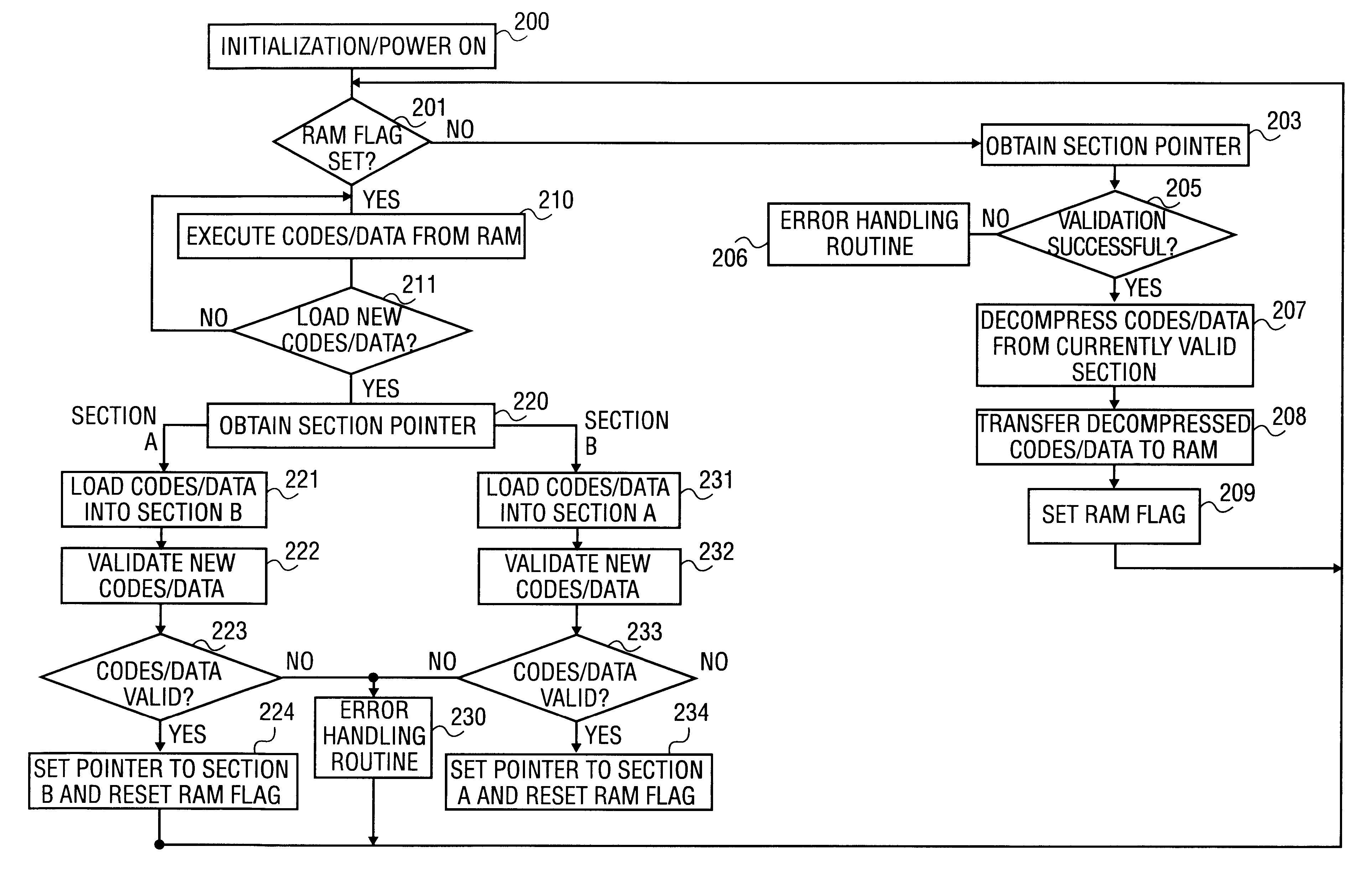
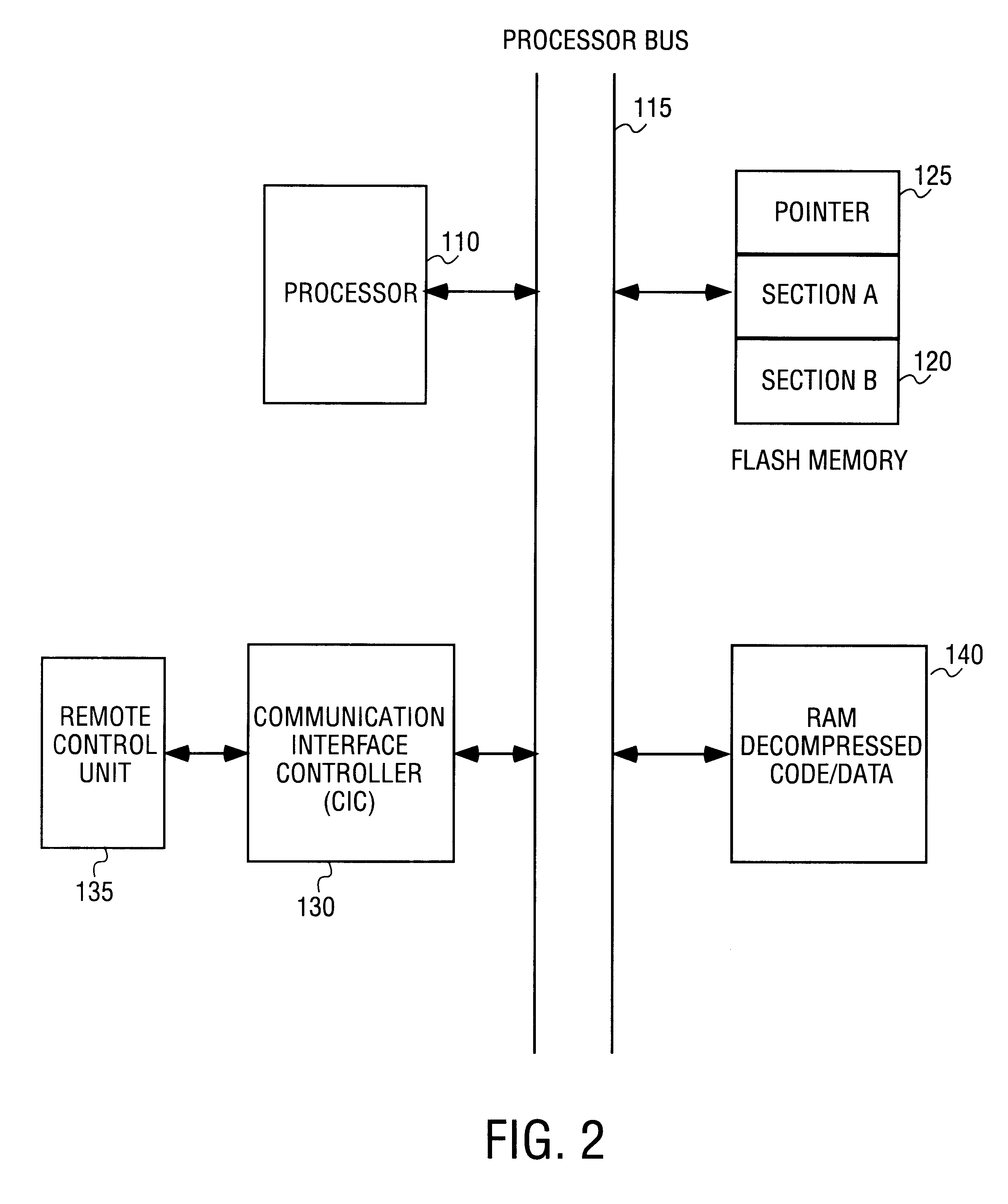
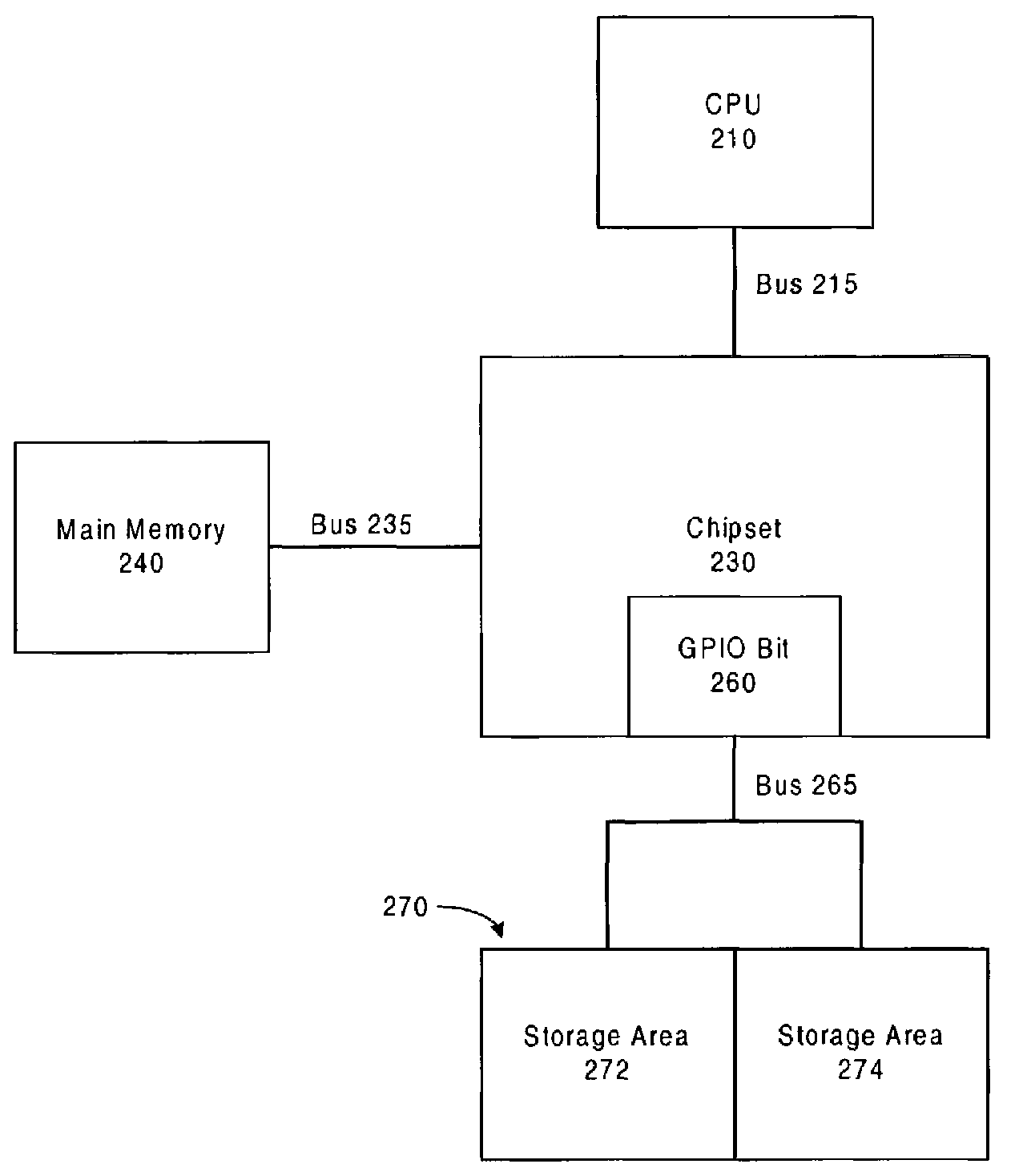
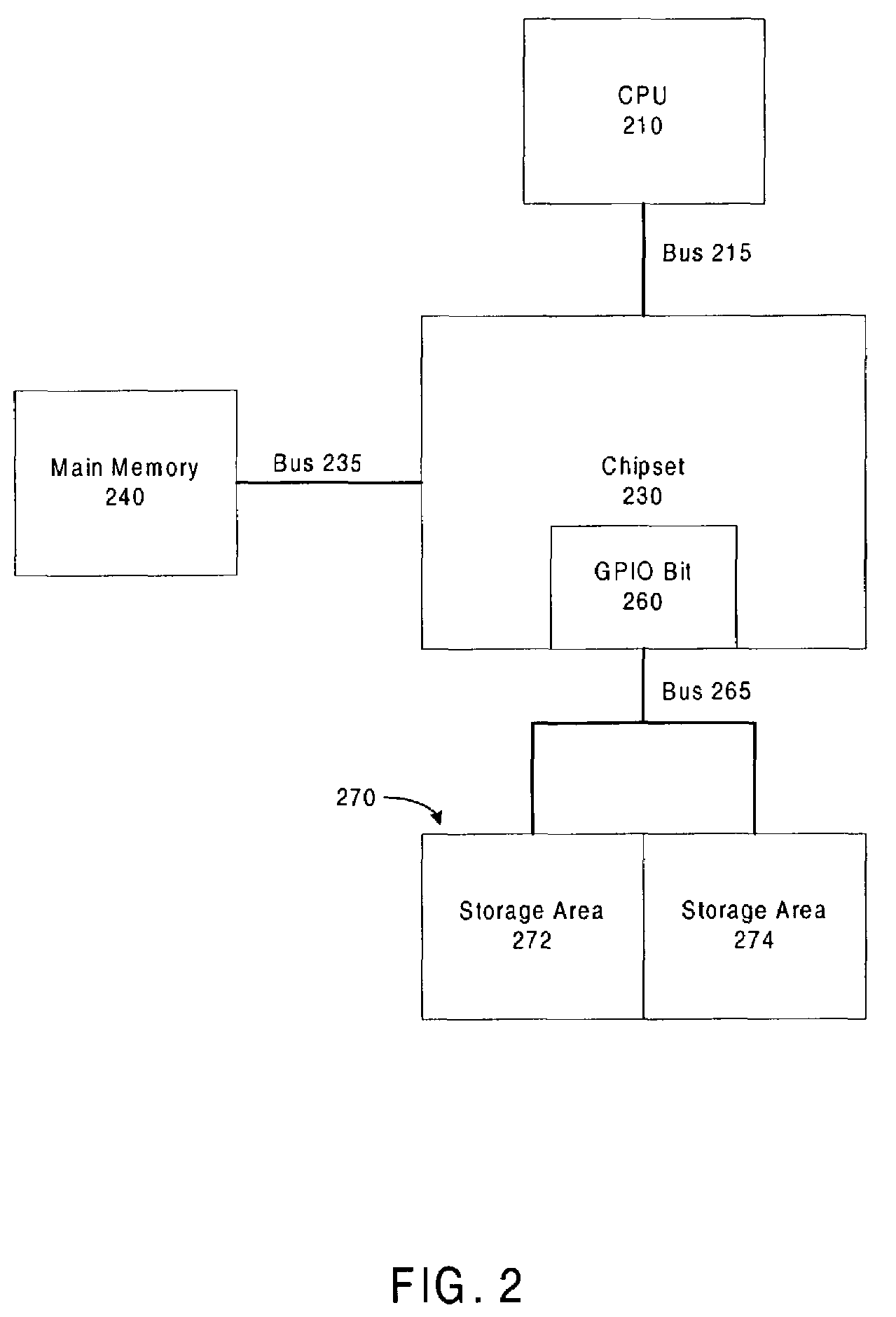
A method to update information including code and data in a non-volatile memory reliably and efficiently to avoid loss of information during the loading process and to minimize aircraft service downtime in an In-Flight Entertainment System (IFES). The non-volatile memory is partitioned into two sections: one section contains the currently valid information and the other is available for loading the new information. A section pointer is used to keep track of the currently valid section and to select the loading section. The new information is loaded to the selected loading section. A validation procedure is performed to determine if the loading is successful. When the loading of the new information is successfully completed, the section pointer is updated to point to the newly loaded section.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
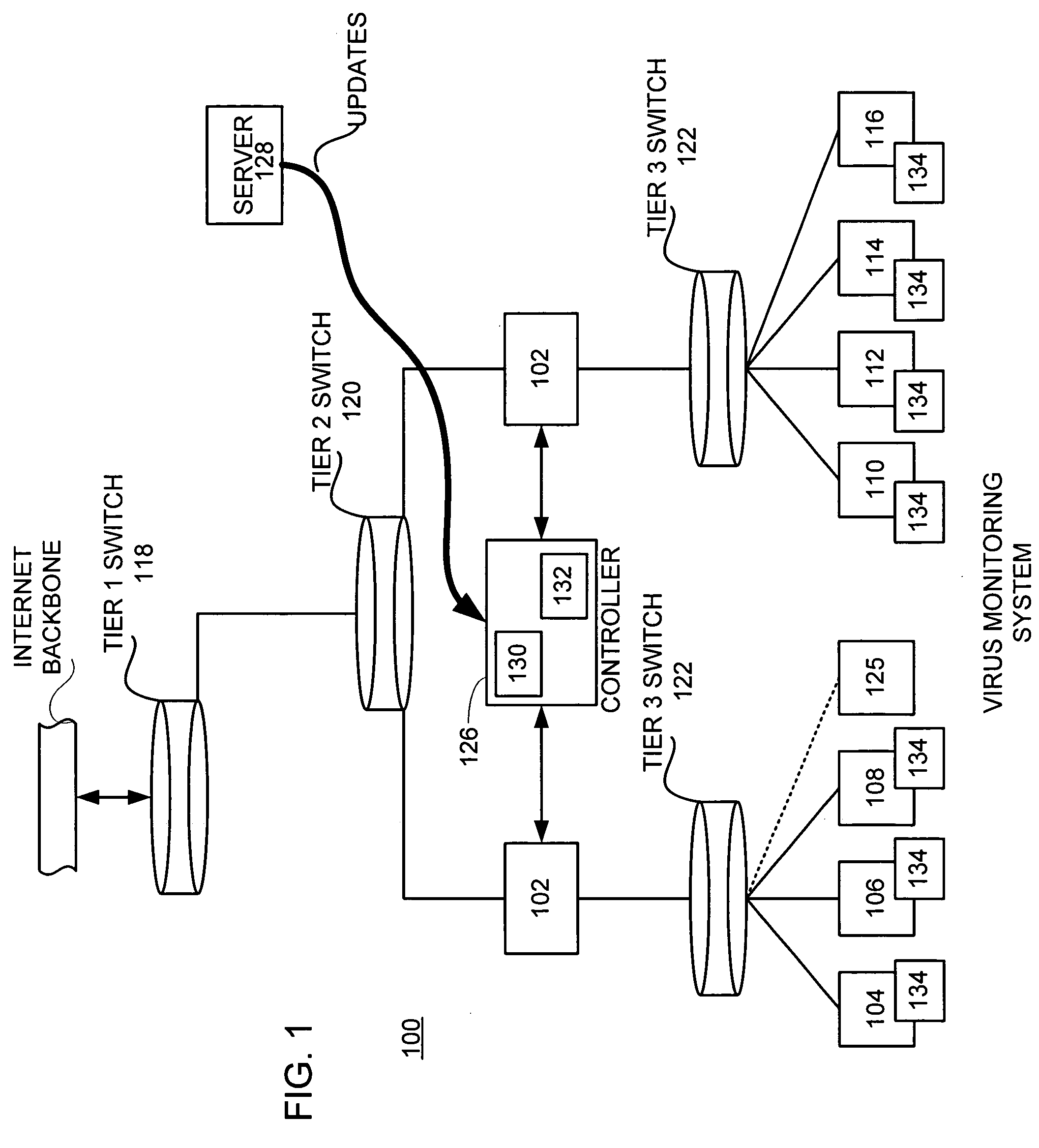
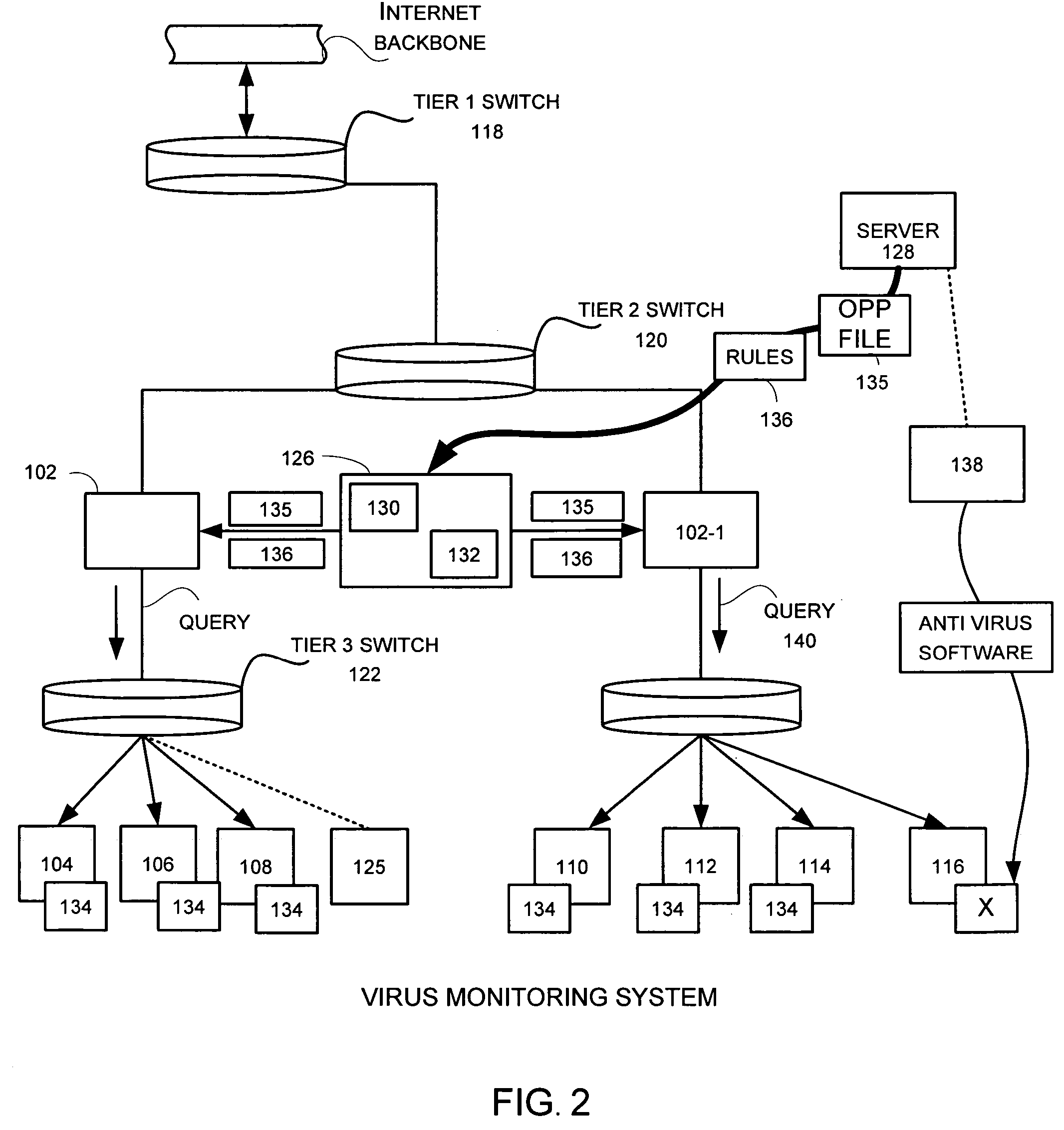
Virus monitor and methods of use thereof
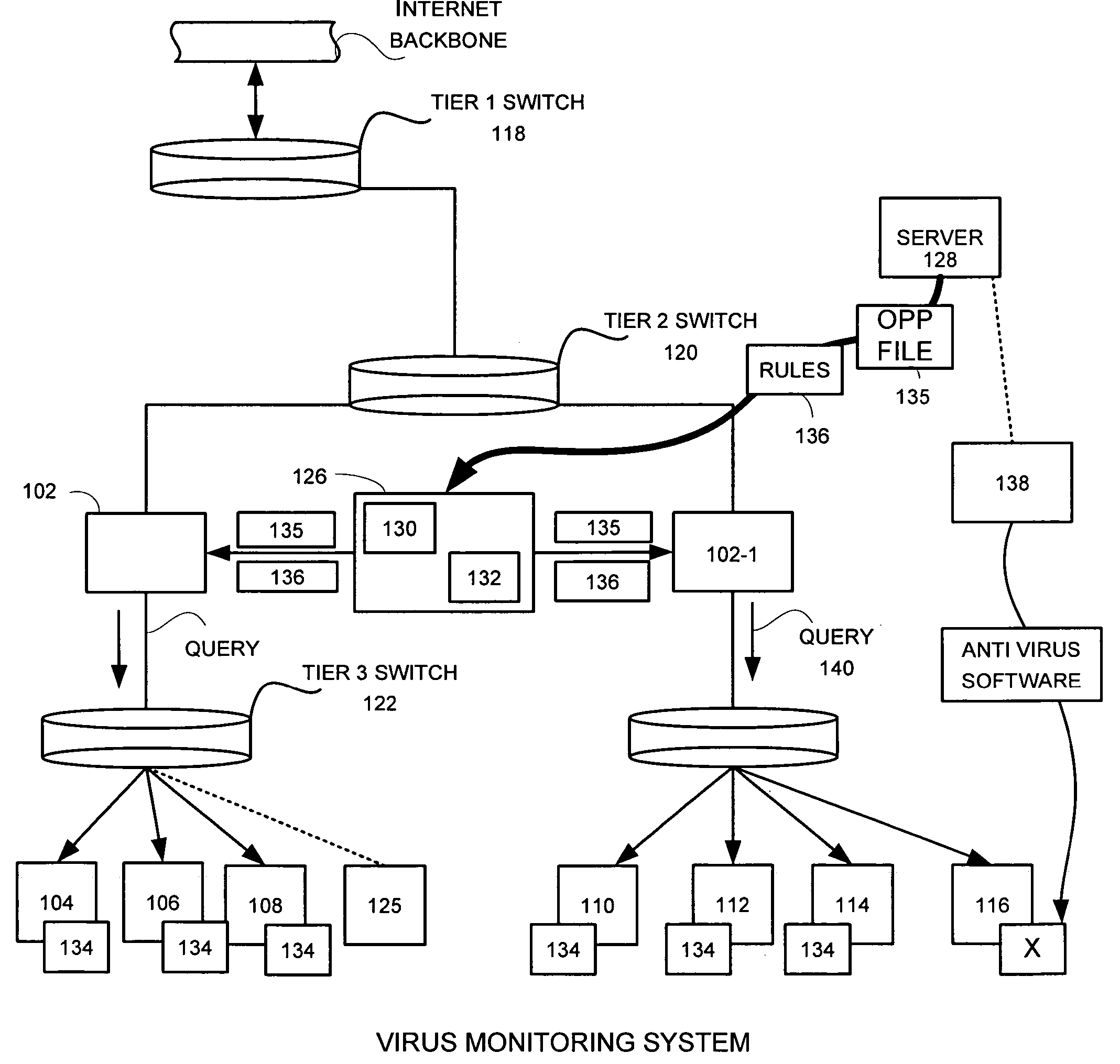
A network level virus monitoring system capable of monitoring a flow of network traffic in any of a number of inspection modes depending upon the particular needs of a system administrator. The monitoring provides an early warning of a virus attack thereby facilitating quarantine procedures directed at containing a virus outbreak. By providing such an early warning, the network virus monitor reduces the number of computers ultimately affected by the virus attack resulting in a concomitant reduction in both the cost of repair to the system and the amount of downtime. In this way, the inventive network virus monitor provides a great improvement in system uptime and reduction in system losses.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
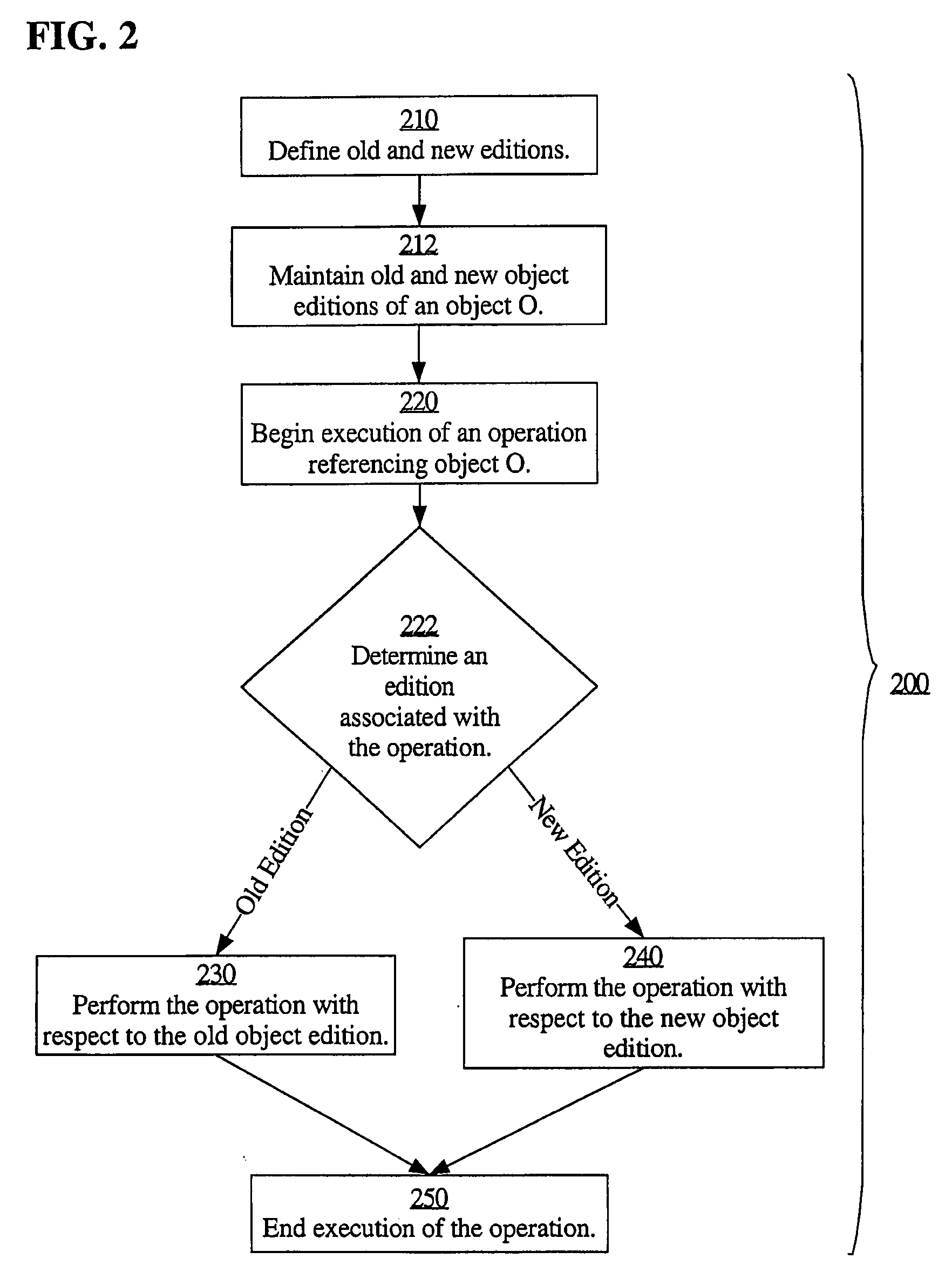
Low-downtime and zero-downtime upgrades of database-centric applications
ActiveUS20080098046A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDowntimeDatabase application
A database may facilitate zero-downtime upgrades by concurrently maintaining multiple editions of database objects for use by both pre-upgrade and post-upgrade clients of a database application. Operations performed within the database are associated with an edition based on, for example, an initiating client or transaction. When an operation references an object or data, the database automatically performs the operation using the object or data associated with the edition with which the operation is itself associated. The database may determine the associated edition without explicit identification of the associated edition in a query or in code. Thus, no client or stored procedure code changes are necessary to reflect a new edition added during an update. Data changes in one edition may be automatically and immediately propagated to the other edition through the use of cross-edition triggers, thereby allowing both pre-upgrade and post-upgrade clients to remain fully functional throughout an upgrade.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
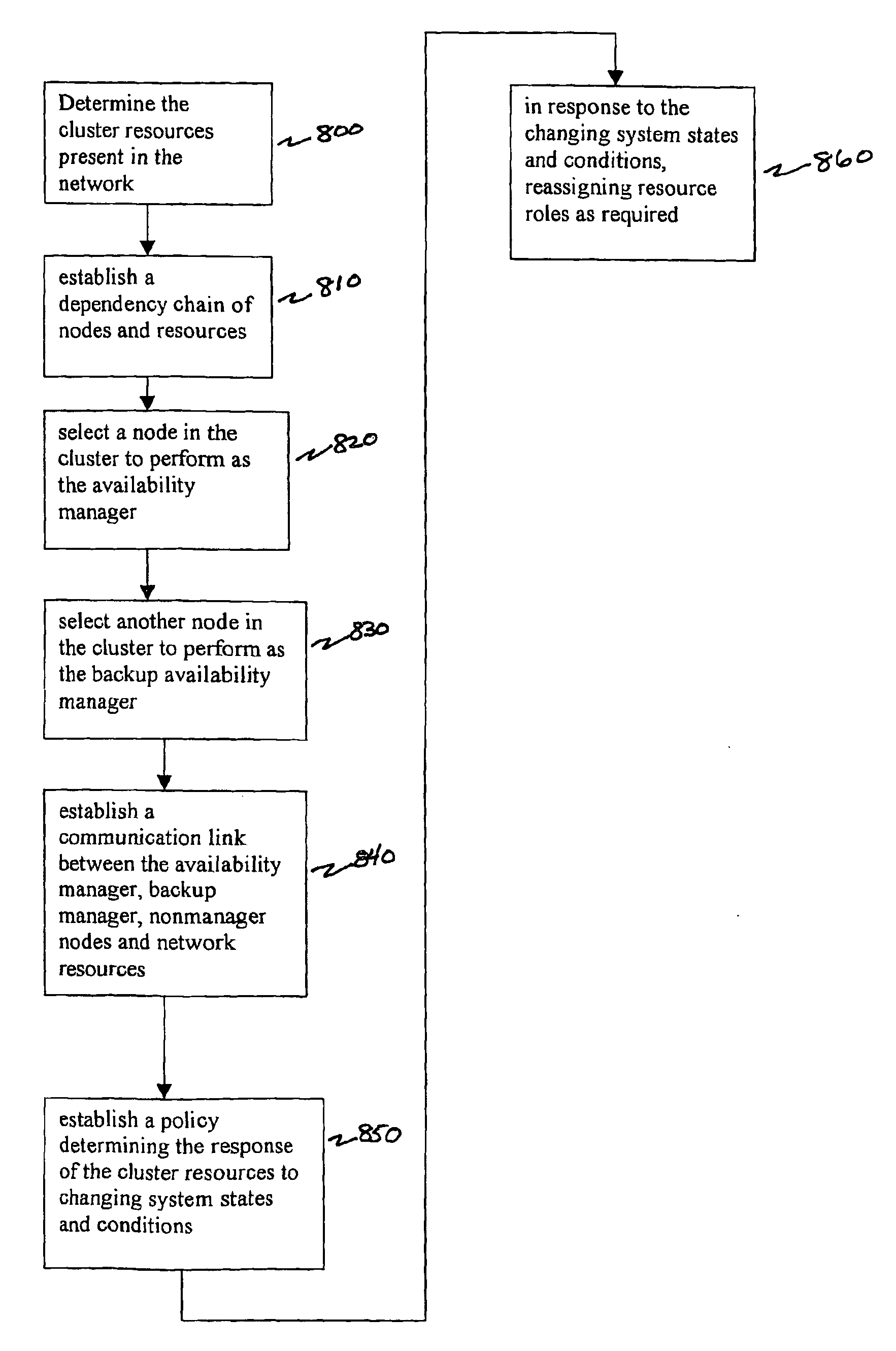
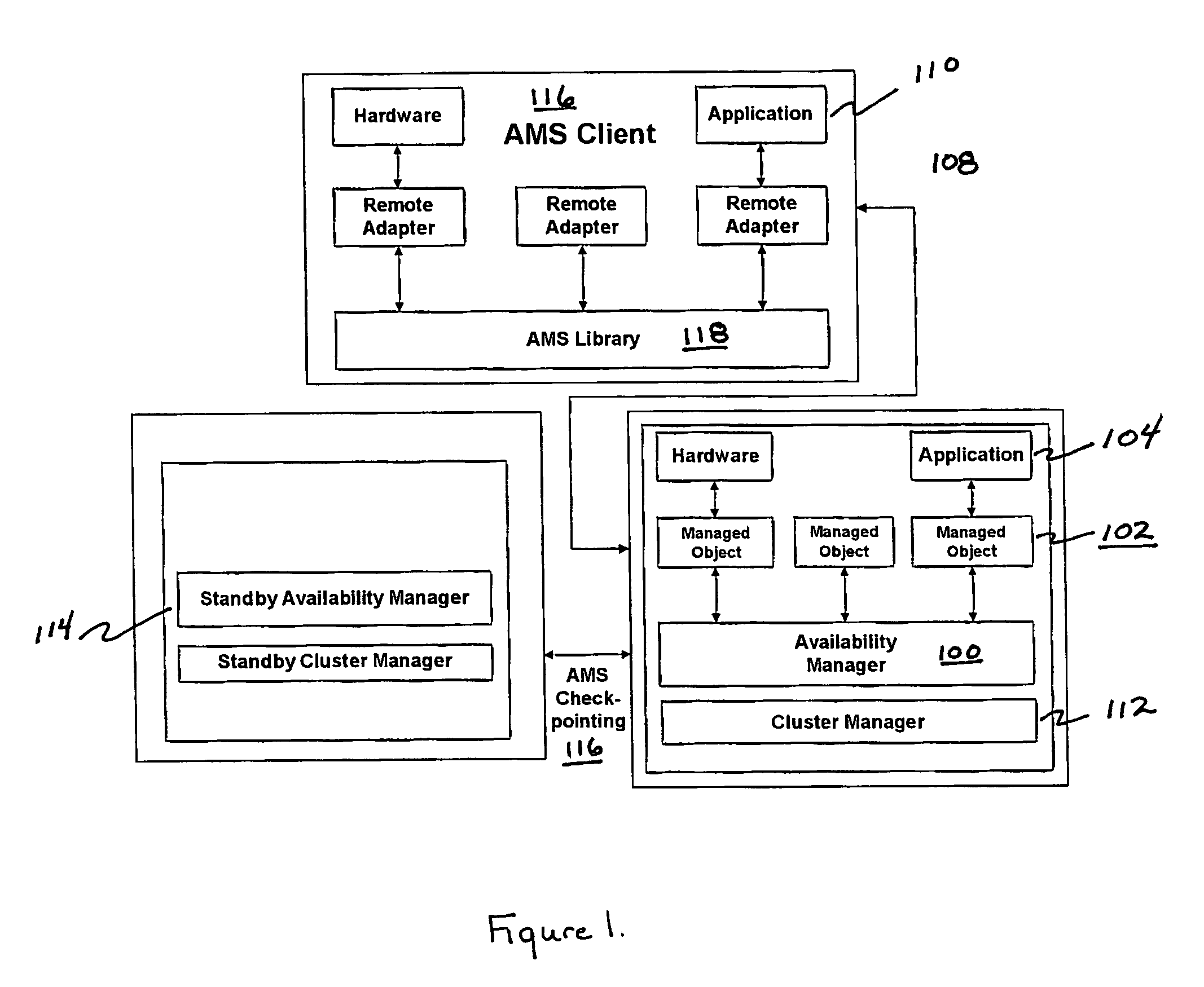
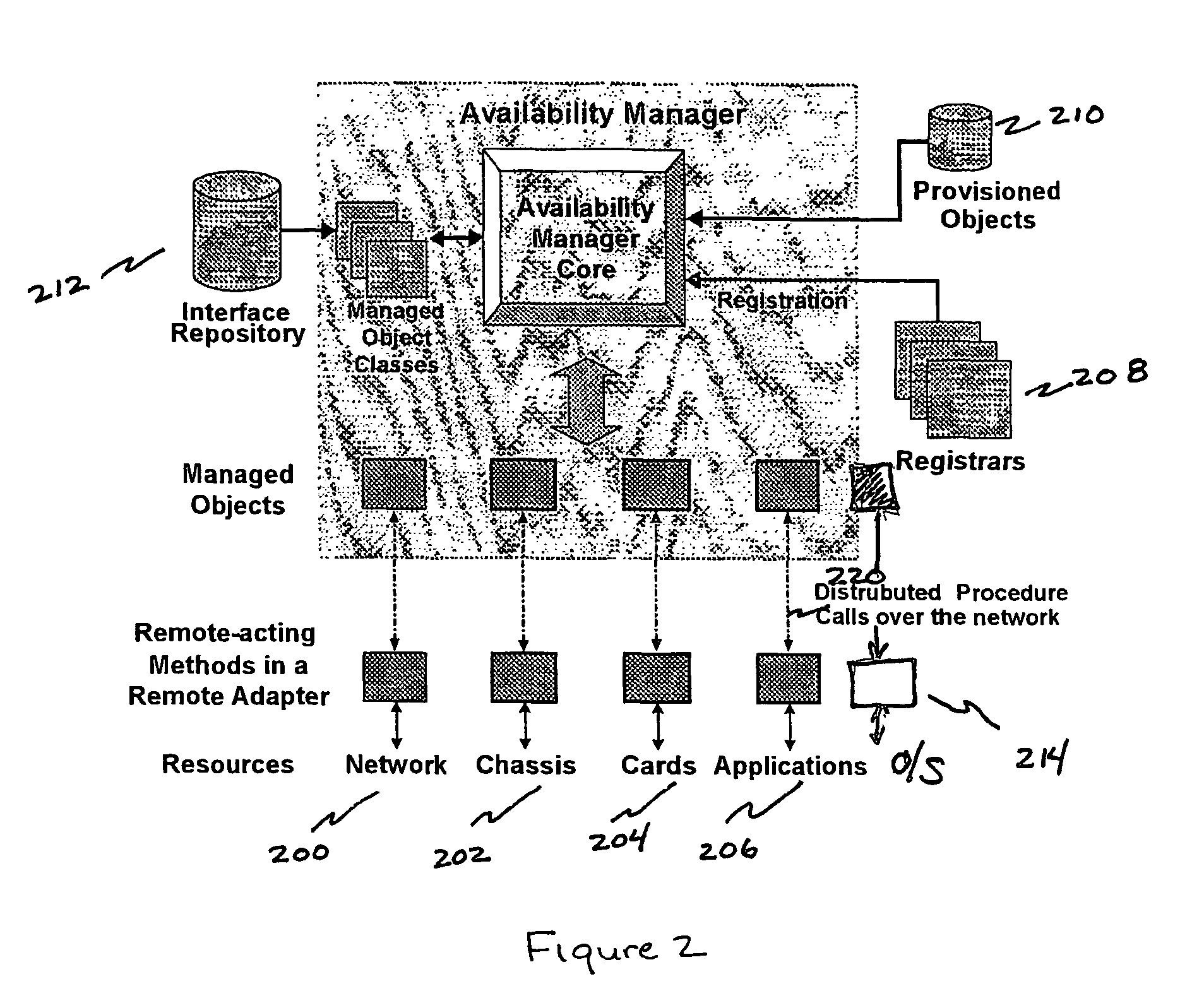
Techniques for maintaining high availability of networked systems
ActiveUS20050071470A1Improve usabilityMaintain availabilityDigital computer detailsData switching networksDowntimeHigh availability
This computer implemented software invention supervises networked system resources with the goal of maximizing service availability, providing on-demand and uninterrupted access to service, and minimizing the down time due to failures. It is a cluster-wide solution that co-ordinates the states and activities of resources, assigns availability roles, implements recovery from failures, and implements overall system policy. To do this, it maintains a system model of the system's physical and logical configuration and models the resources using managed objects that provides an extensive representation of the states, roles, and relationships of the systems resources.
Owner:GOAHEAD SOFTWARE
Offline Upgrades
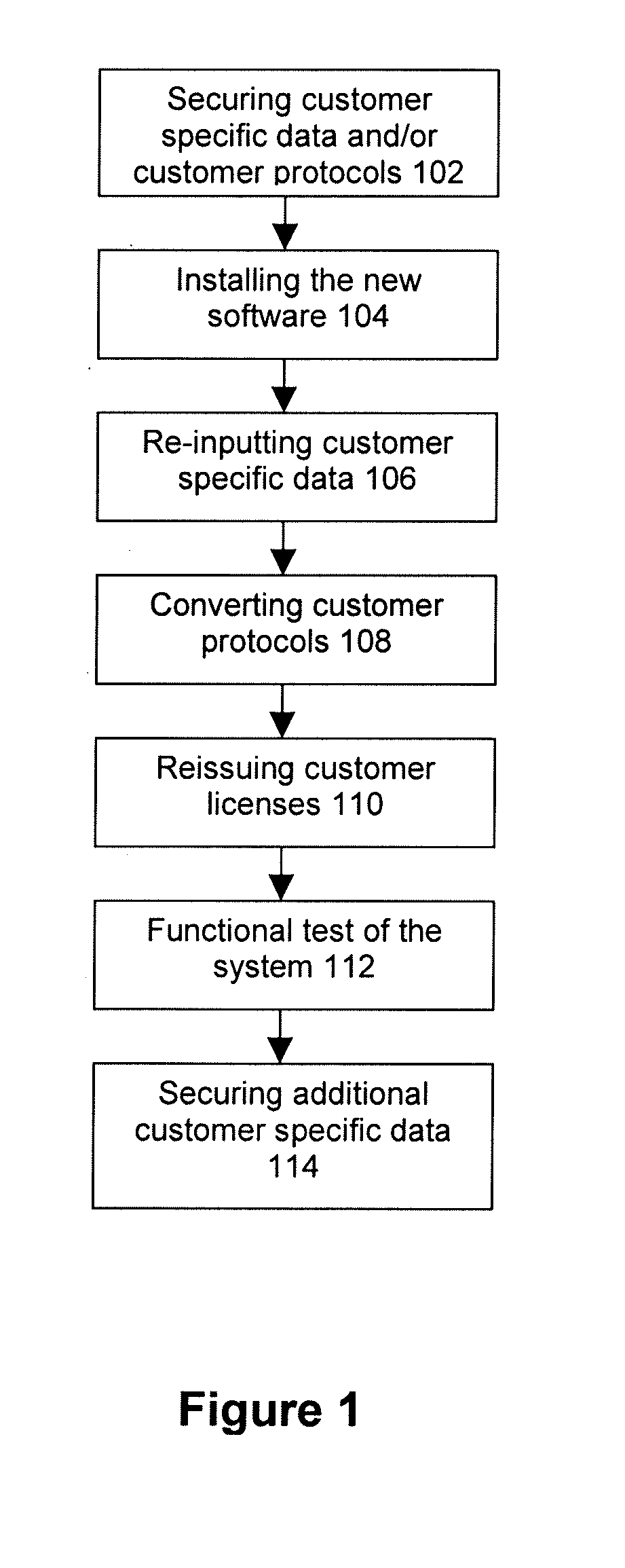
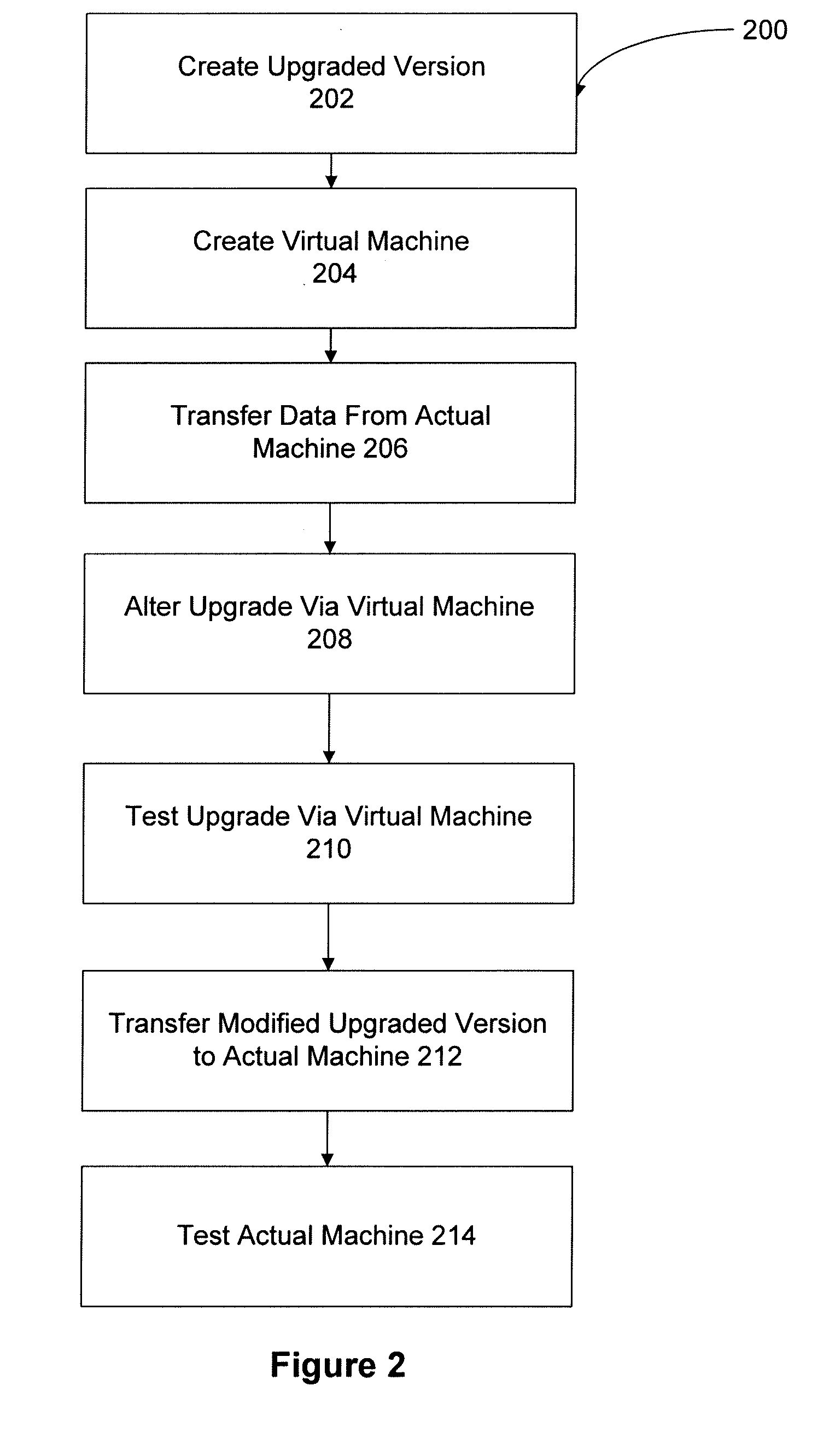
InactiveUS20090113413A1Minimize downtimeCompletely processedLocal control/monitoringSoftware engineeringDowntimeSoftware engineering
A system and method upgrade software applications offline using a virtual machine. Software applications used by actual customer machines may rely upon customer specific data and protocols. An upgraded version of a software application may become available. The upgrade may be loaded onto a virtual machine. Customer specific data or protocols associated with a previous version of the application may be copied to the virtual machine. The upgraded version may be modified on the virtual machine using the data associated with the previous version. The upgrade process using the virtual machine may detect and eliminate problems with the upgrade associated with the customer machine and / or settings. Once modified, the upgraded version may be transferred from the virtual machine to the customer machine. The upgrade process may be performed primarily on the virtual machine. Therefore, the downtime of the customer machine required to complete the upgrade process may be substantially reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for collecting manufacturing equipment downtime data
InactiveUS6128543AAccurate qualityFaster rateSafety arrangmentsTechnology managementDowntimeRunning time
A method and apparatus for collecting manufacturing equipment downtime data which electrically blocks stopped equipment (production) from restarting until an acceptable reason (either by code or direct identification) has been entered and recognized by an electronic logic system. Locking out the restart capability until the downtime cause has been entered ensures that the causes for all downtimes are recorded in a timely fashion. This data is gathered and recorded to measure and define explanations for lost equipment running time. Other related data may also be gathered.
Owner:HITCHNER JIM
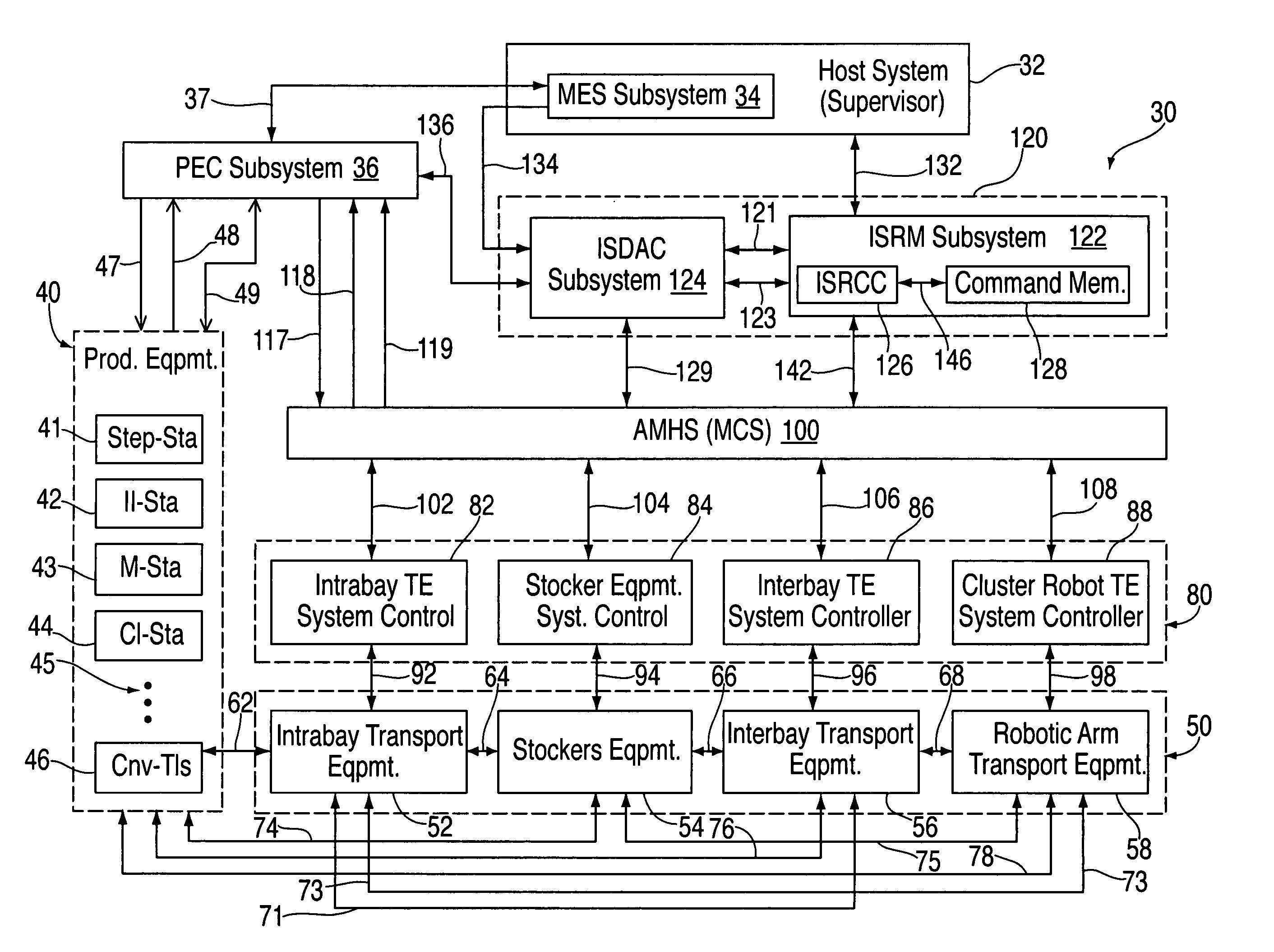
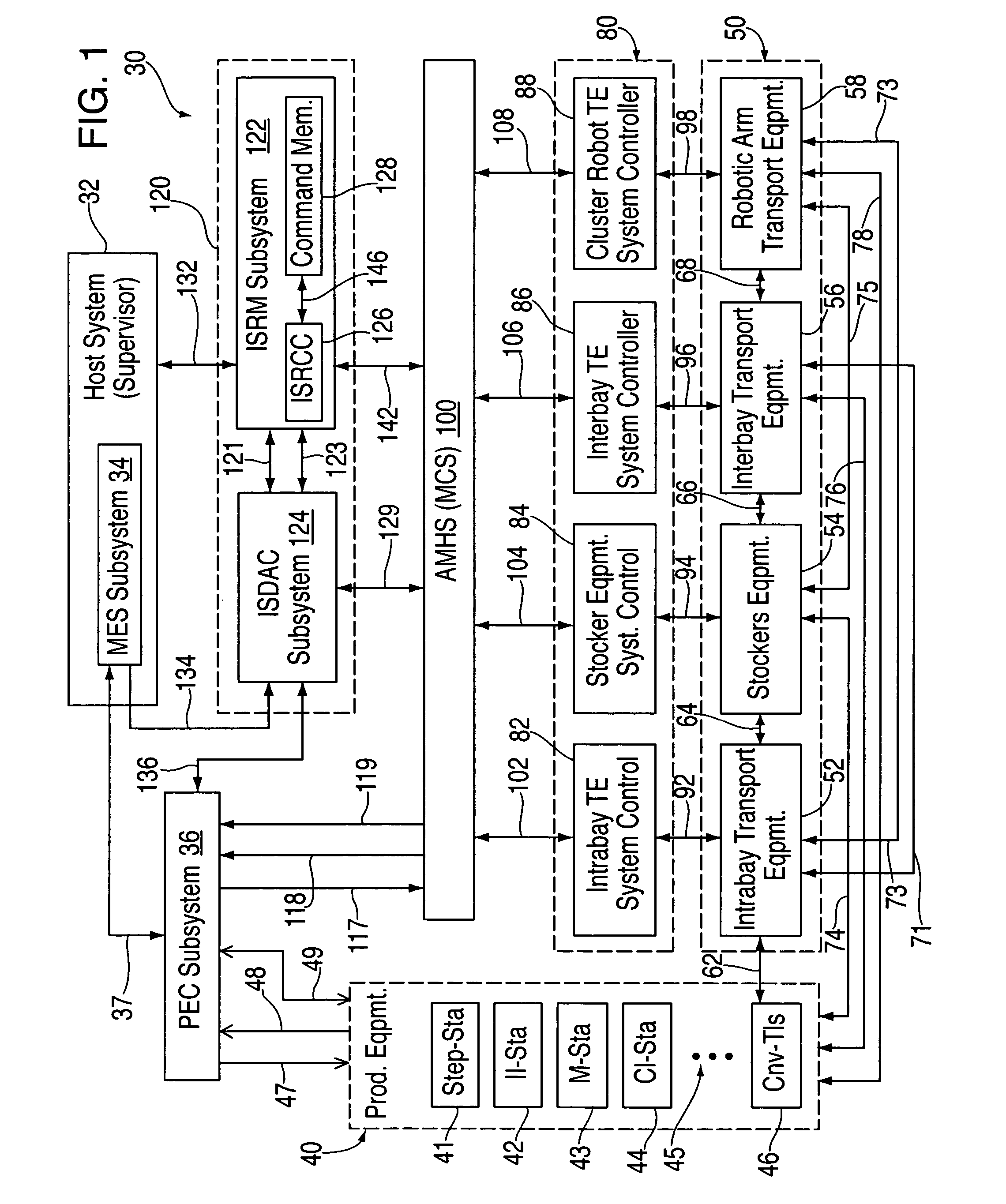
Method and system for automating issue resolution in manufacturing execution and material control systems
InactiveUS20050075748A1Decrease productivityImprove productivitySafety arrangmentsTesting/monitoring control systemsProduction rateImage resolution
Automatic error recovery systems and methods for automated manufacturing plants and factories are disclosed. Such facilities normally have multiple automated control systems, including an automated material handling system (AMHS), all of which run automatically, typically under the control of a computerized manufacturing execution system (MES). The disclosed issue resolution (ISR) systems and methods involve providing components, which may be supervised and operated by an issue resolution management (ISRM) system, if desired, that interfaces with the MES, AMHS, and / or production control system(s) which operate the tools and other stations within the automated factory. The components, which may be considered customized logic cells, may each be written for handling a specific kind of incoming error condition, problem or other issue that might occur and which is amenable to automatic resolution or recovery. These errors often occur between or across the boundaries of the various interactive systems and automated equipment. Each cell may cycle through a sequence of possible error resolution or recovery steps until the specific issue is resolved or until the sequence of steps is exhausted. Other components of the ISR system may provide results-oriented messages and / or facilitate the collection of data as to whether and which corrective commands from the ISR system resolved the reported error conditions automatically. The disclosed ISR systems and methods for resolving errors and other issues automatically helps improve the overall productivity of automated factories by reducing downtime and the need for human intervention to correct problems, thereby increasing factory throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
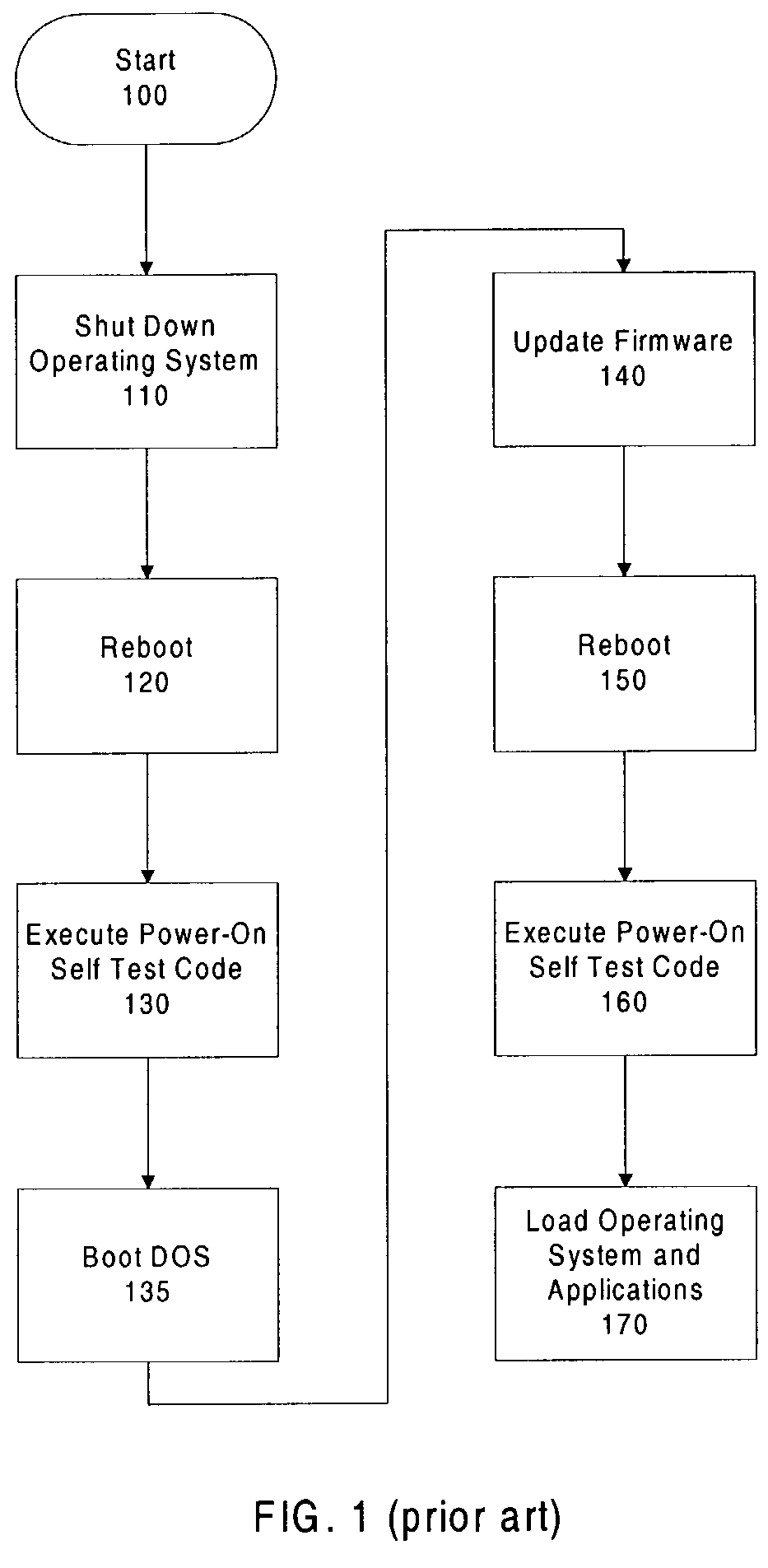
Secure method to perform computer system firmware updates
A secure method for updating computer firmware online is described. The firmware storage locations are write protected prior to loading the operating system. Updating the firmware after loading the operating system helps to reduce downtime.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
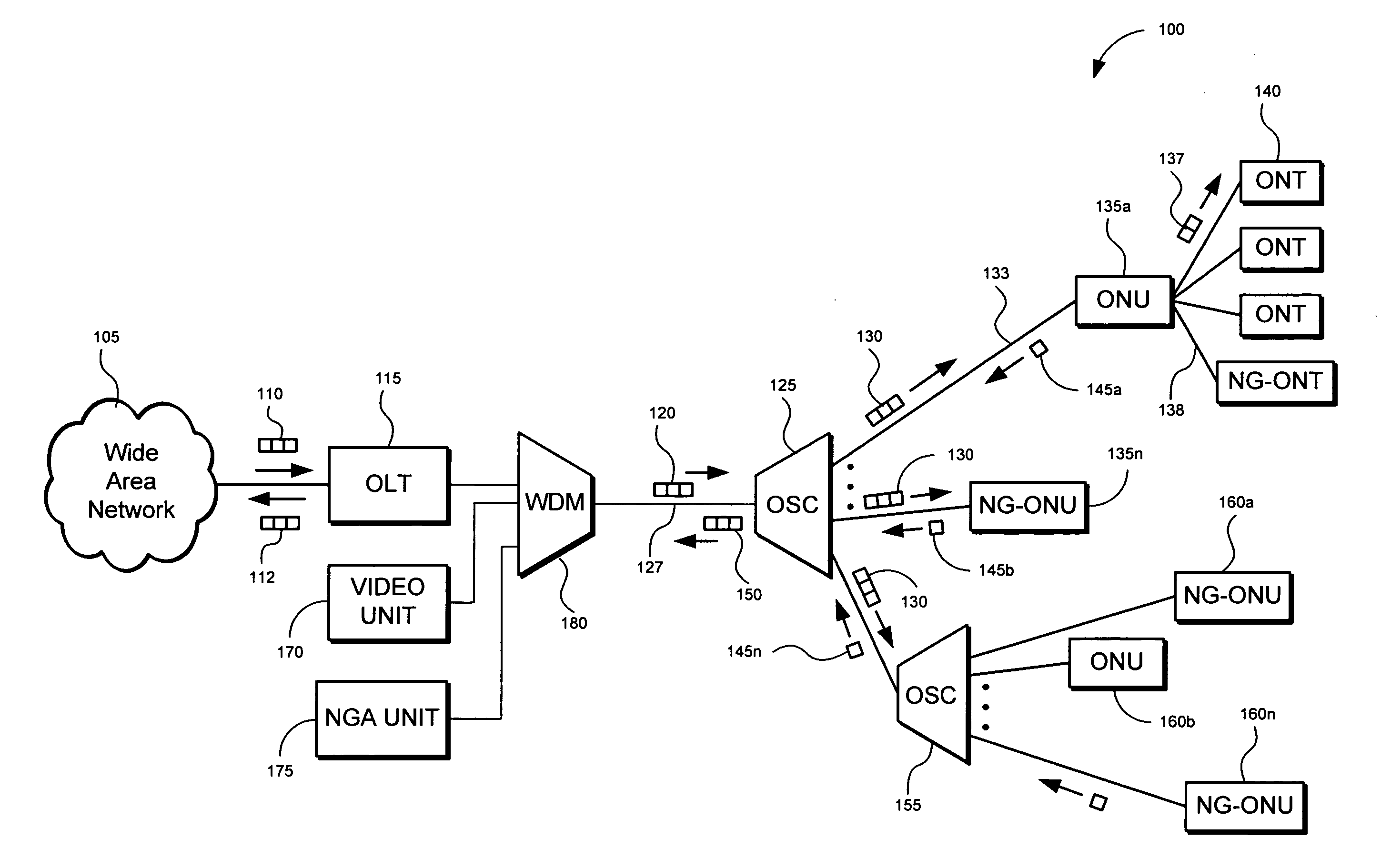
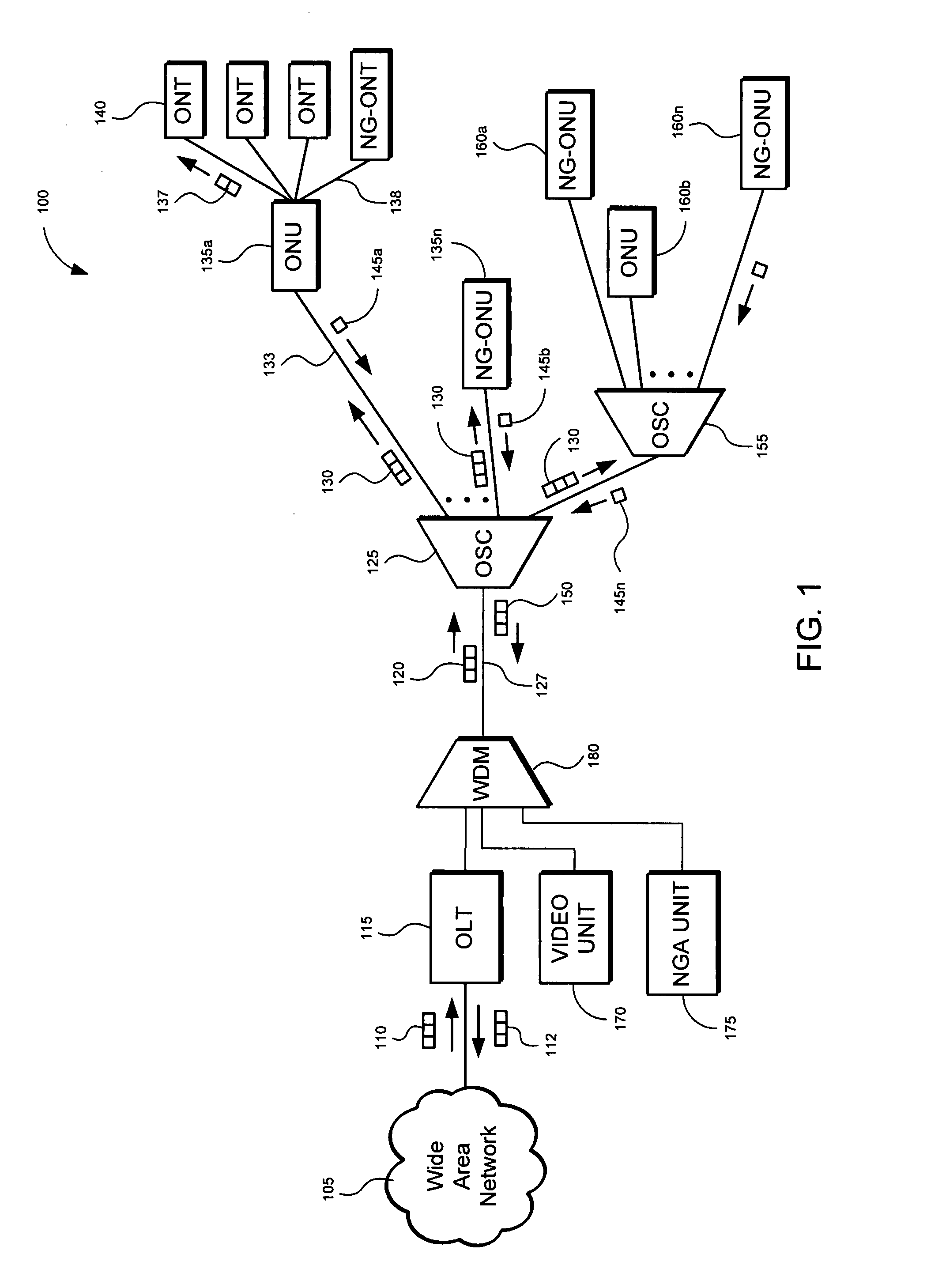
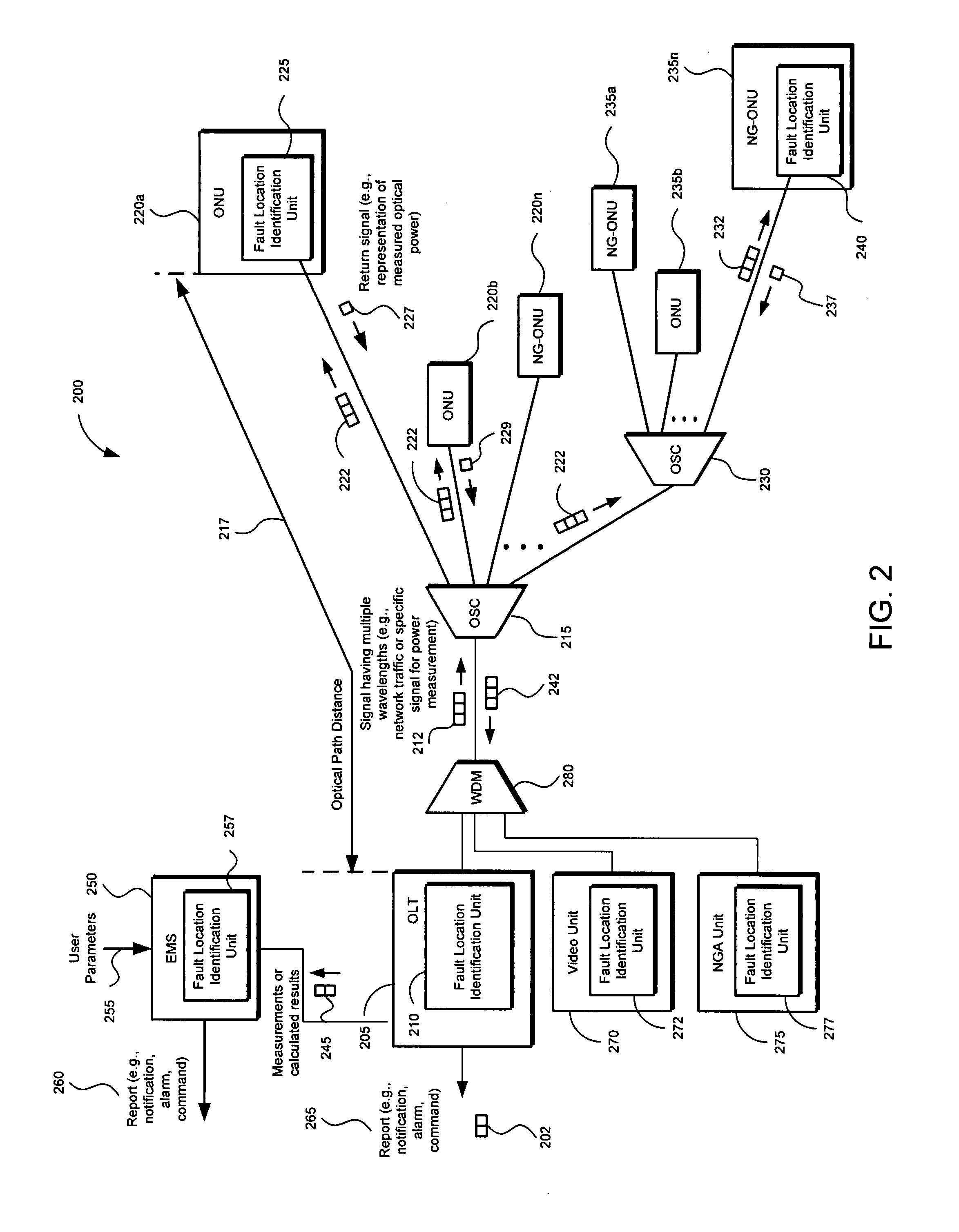
Method and apparatus for isolating a location of a fault in a passive optical network
A method and apparatus of isolating a location of a fault in an optical network may include using communications traffic signals and network nodes to determine excess power losses without interrupting service or requiring additional external test equipment. A transmit optical network node is configured to measure the transmit power of multiple wavelengths of a transmitted optical signal. A receive optical network node is configured to measure the receive power of the same multiple wavelengths. Power differentials of the transmit and receive optical power for each wavelength may be calculated. Optical power losses as a function of the optical path distance between the transmit and receive optical network nodes my be determined. The data may be used to isolate the location of a fault in a passive optical network based on the differences between the optical power losses of the multiple wavelengths thereby reducing troubleshooting time and network downtime.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
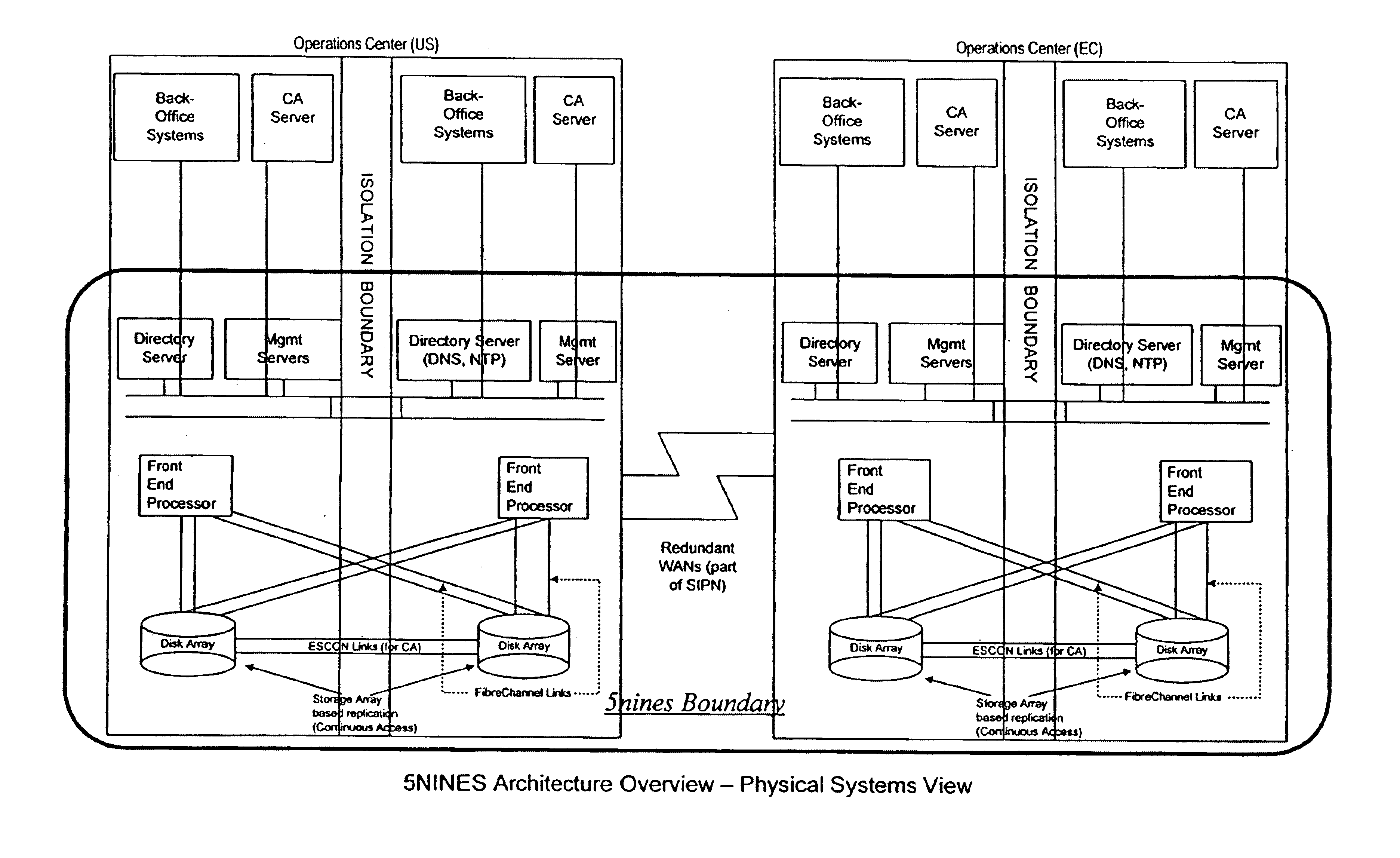
Highly available transaction processing
ActiveUS7058853B1Minimize data lossImprove availabilityError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsHandling systemTransaction processing system
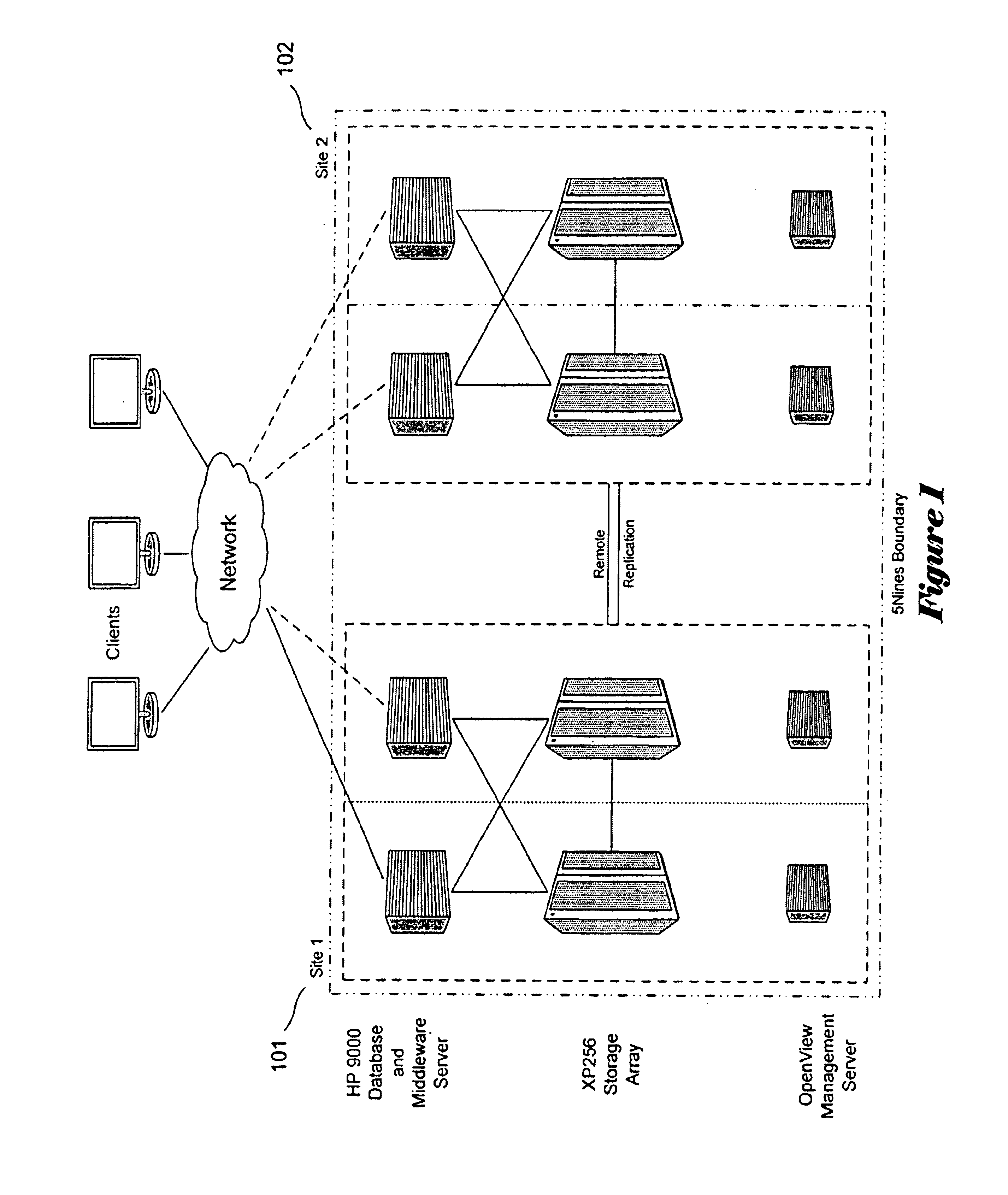
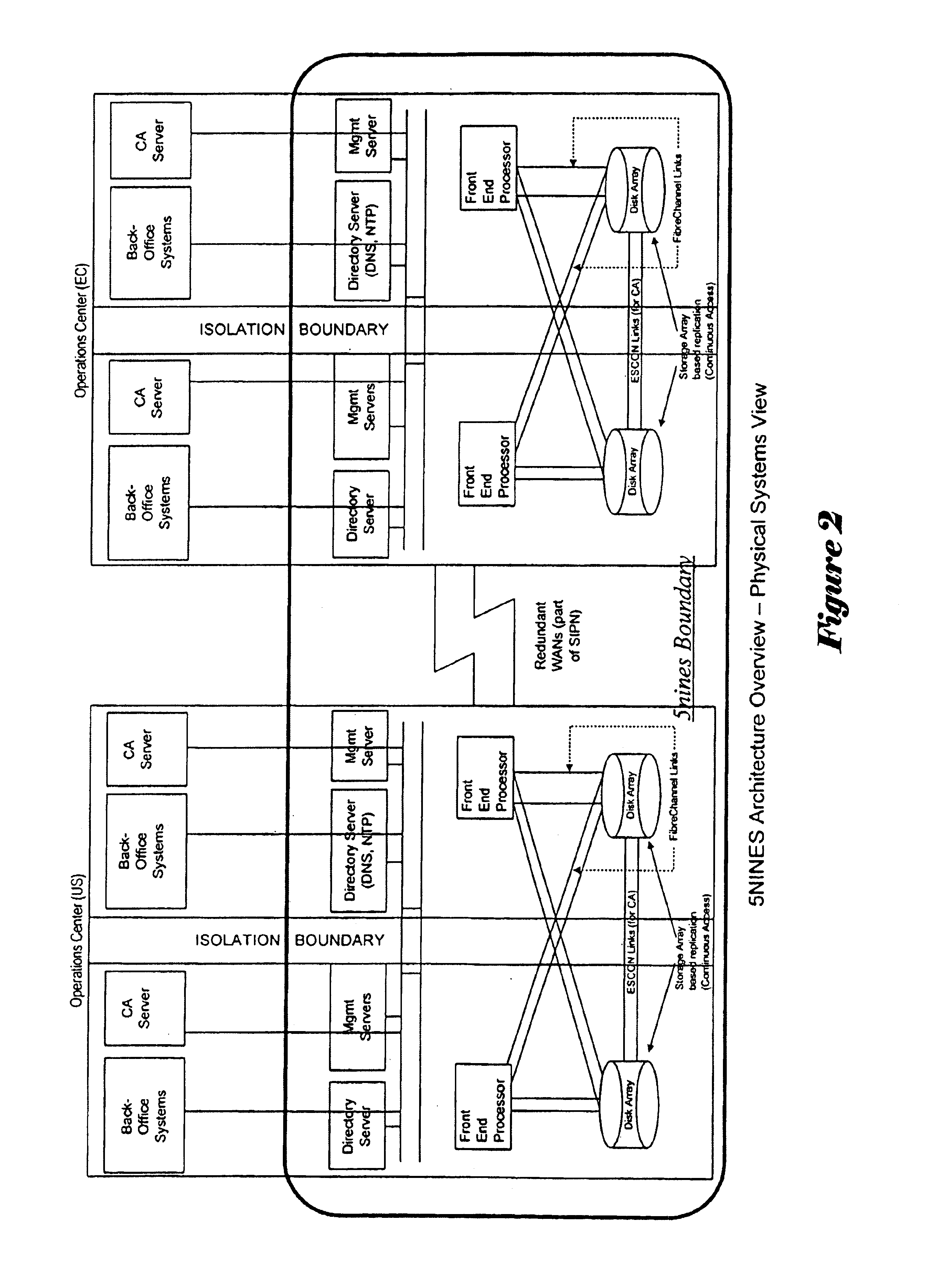
A generalized architecture for a highly available transaction processing system that combines commercially available components and software components specifically developed to implement the architecture into an integrated, highly available transaction processing system that minimizes planned and unplanned downtime, minimizes data loss in the event of failures, provides proactive monitoring of both hardware and software components of the highly available transaction processing system, provides automated recovery actions that involve fast failover, either locally to an Inactive Node, or remotely to a Standby Site, and provides an easy-to-use graphical-user-interface-based management interface that provides service-oriented views of the state of the system, with context-directed commands and meta-commands to guide managers in execution of their tasks.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com