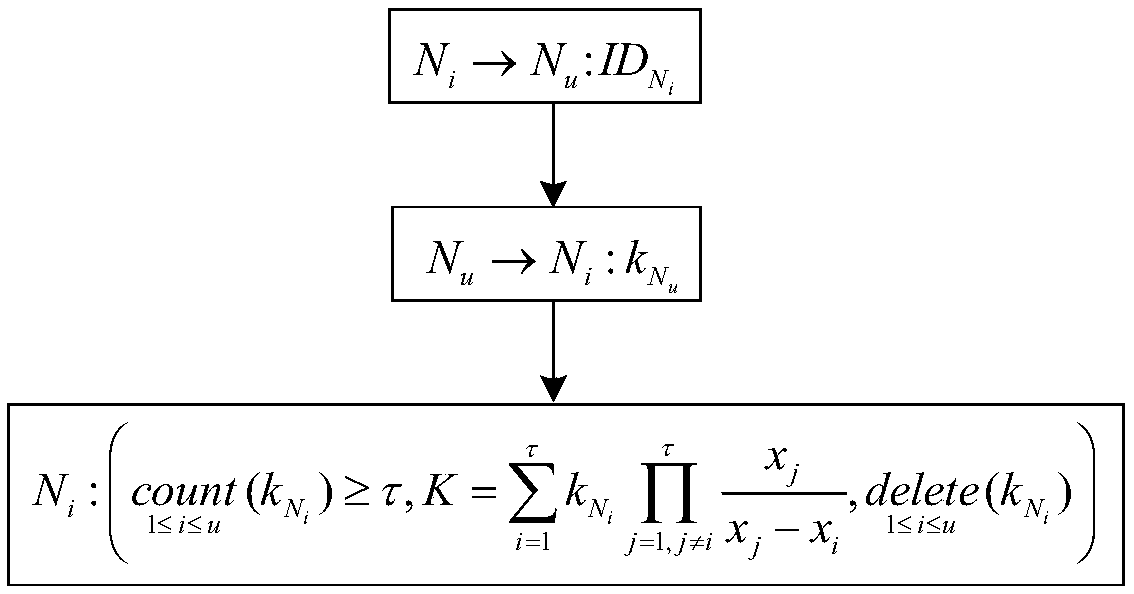
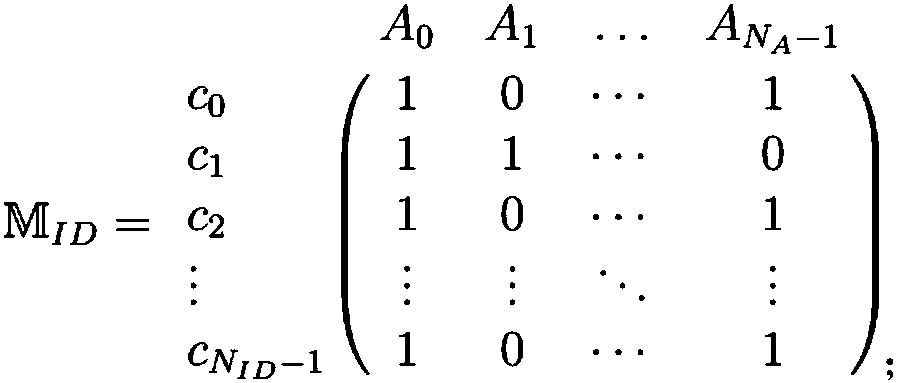
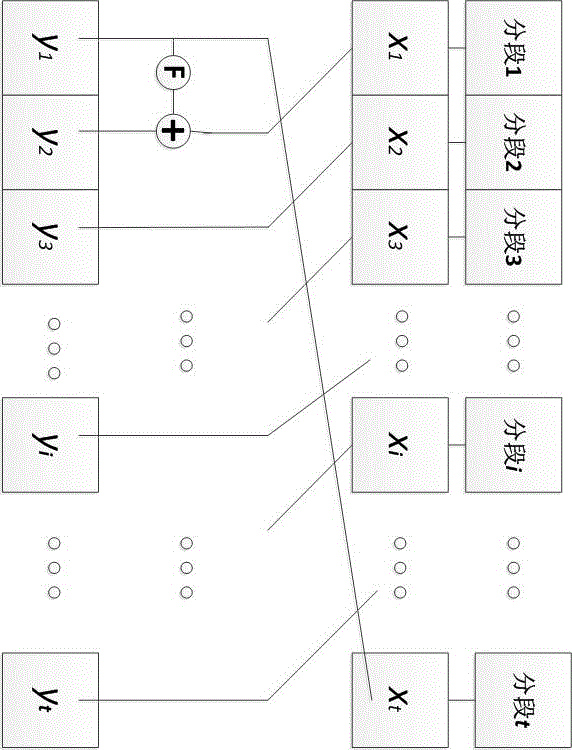
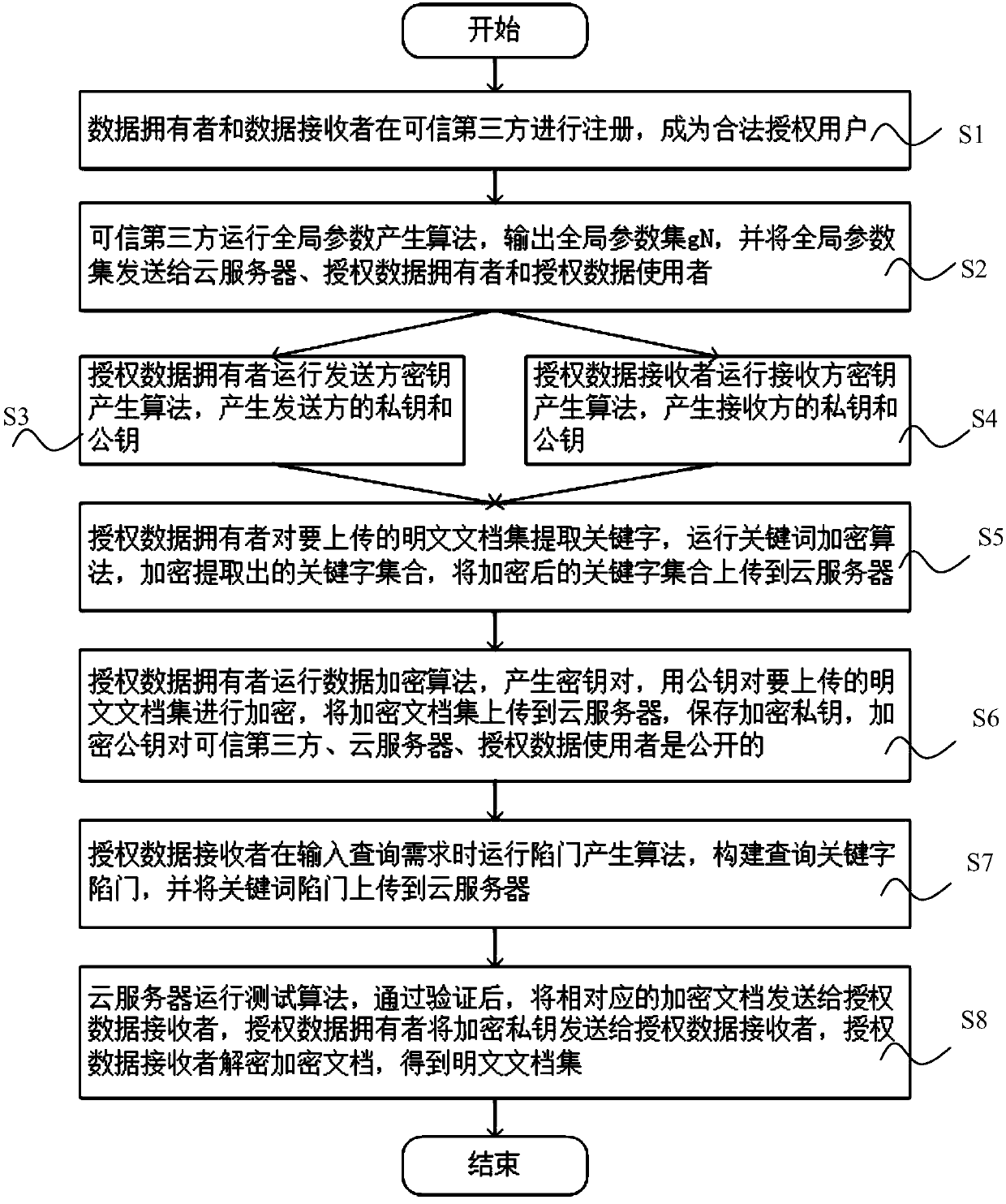
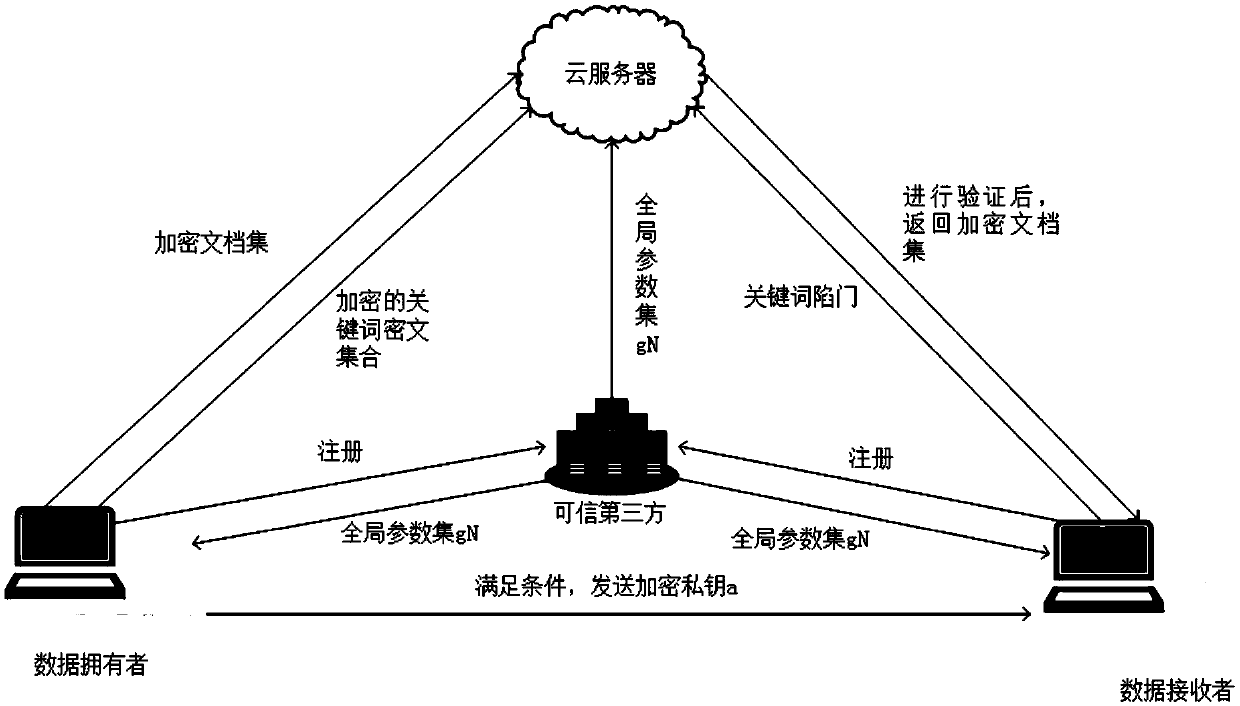
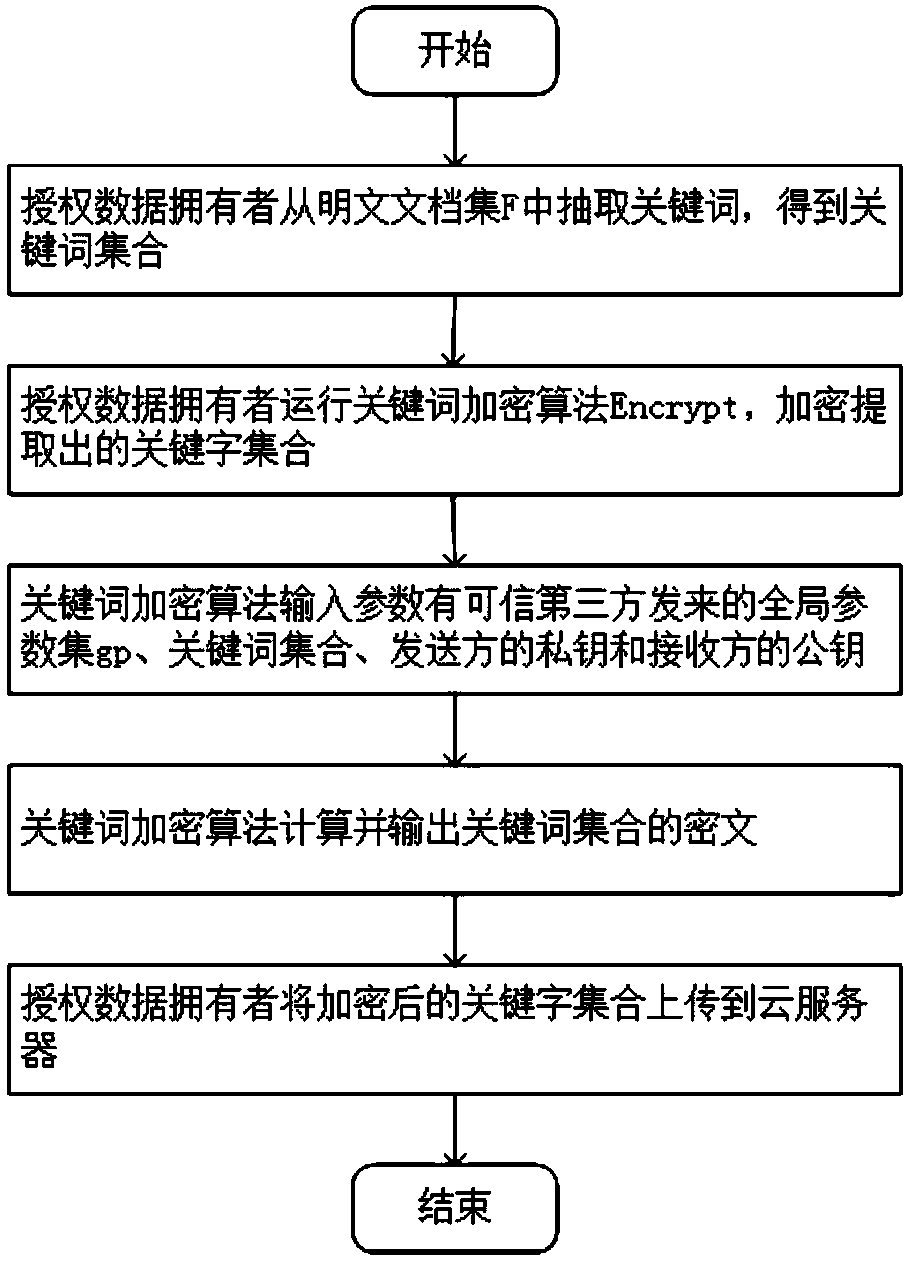
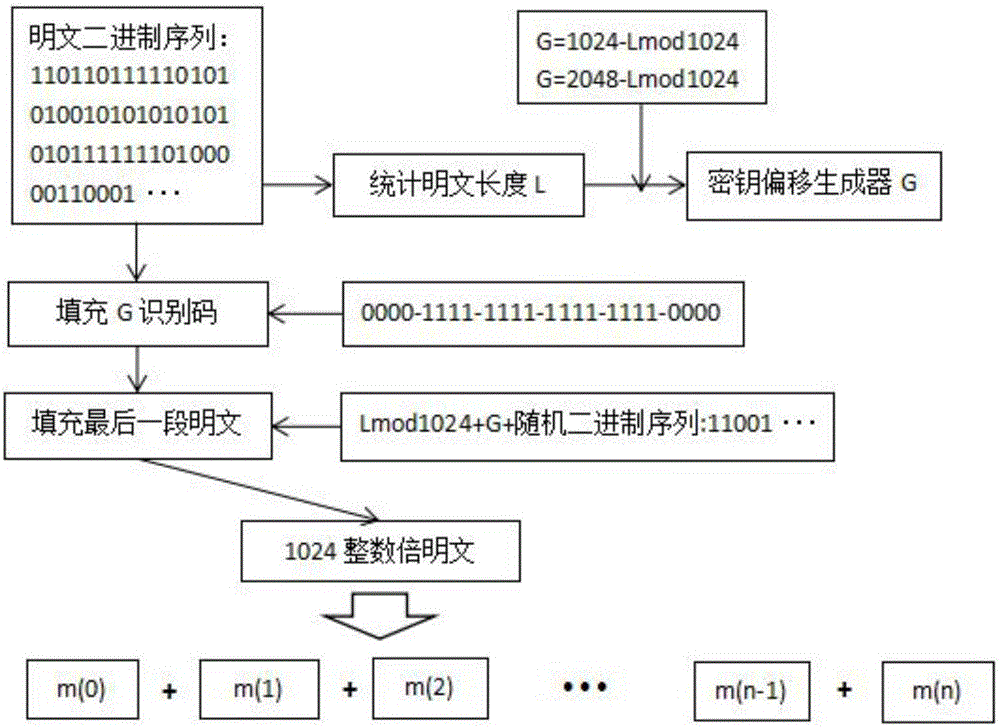
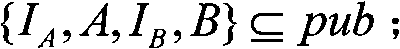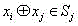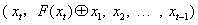Patents
Literature
354 results about "Advantage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, an adversary's advantage is a measure of how successfully it can attack a cryptographic algorithm, by distinguishing it from an idealized version of that type of algorithm. Note that in this context, the "adversary" is itself an algorithm and not a person. A cryptographic algorithm is considered secure if no adversary has a non-negligible advantage, subject to specified bounds on the adversary's computational resources (see concrete security). "Negligible" usually means "within O(2⁻ᵖ)" where p is a security parameter associated with the algorithm. For example, p might be the number of bits in a block cipher's key.
Industrial control identity authentication method and device with state cryptographic algorithms
InactiveCN103490895AAchieve border securityPrevent leakagePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAuthorizationNetwork interface
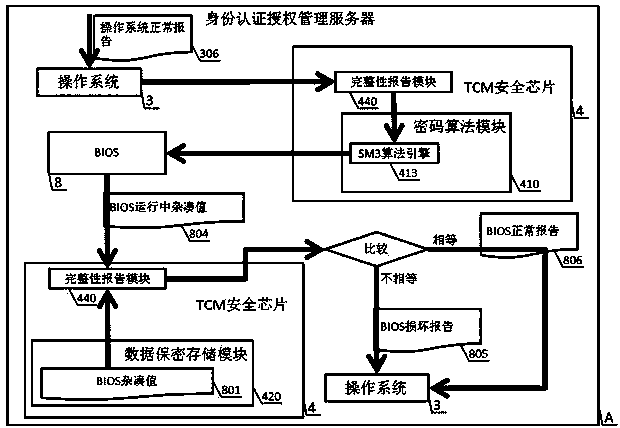
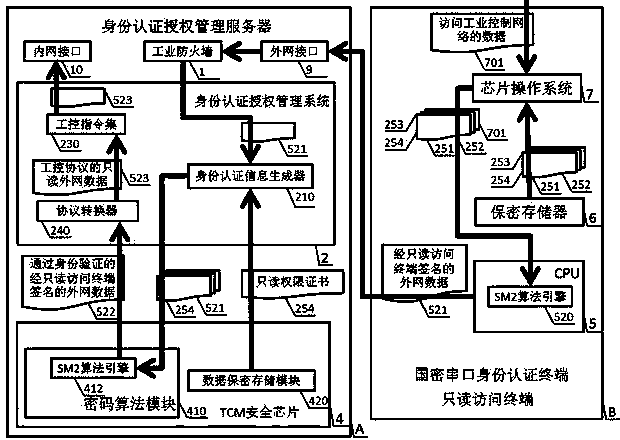
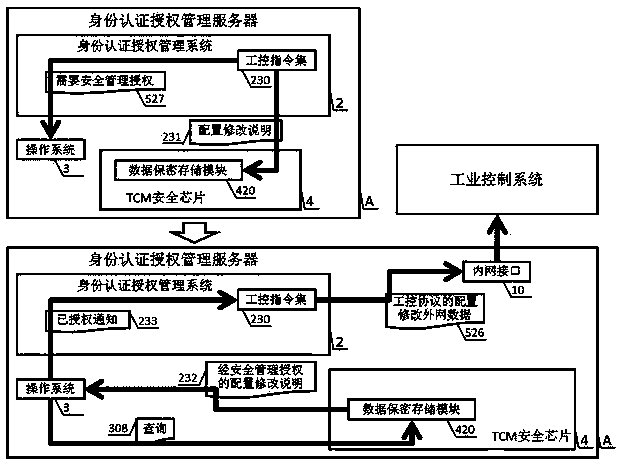
The invention discloses an industrial control identity authentication method and device with state cryptographic algorithms, and relates to the field of industrial control safety. The device is composed of an identity authentication authorization management server and a state cryptographic serial port identity authentication terminal, wherein the identity authentication authorization management server comprises a TCM security chip, an operating system, an identity authentication authorization management system, an industrial firewall, an outer network interface, an inner network interface and a BIOS, and the state cryptographic serial port identity authentication terminal comprises a CPU, a confidentiality memorizer and a chip operating system. The reliable operation of the identity authentication authorization management server, the authorization of different authority limits of a read-only access terminal, a configuration modification terminal and a safety management terminal and the authority limit achieving method of three kinds of state cryptographic serial port identity authentication terminals for accessing an industrial control system through an outer network are achieved through the combining application of the state cryptographic algorithms, SM1, SM2 and SM3. The method and device can effectively and strictly manage the boundary of the industrial control system and the outer network to meet the needs of the industrial control system safety of our country, and the method and device have the advantages of being safe and reliable, fast in promotion, easy and convenient to maintain, low in operating cost and universal in use.
Owner:北京时简科技有限公司
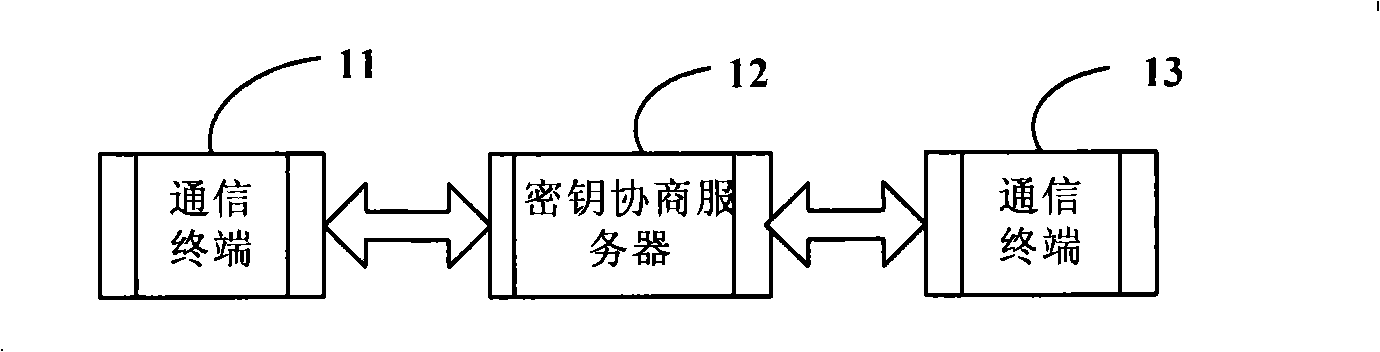
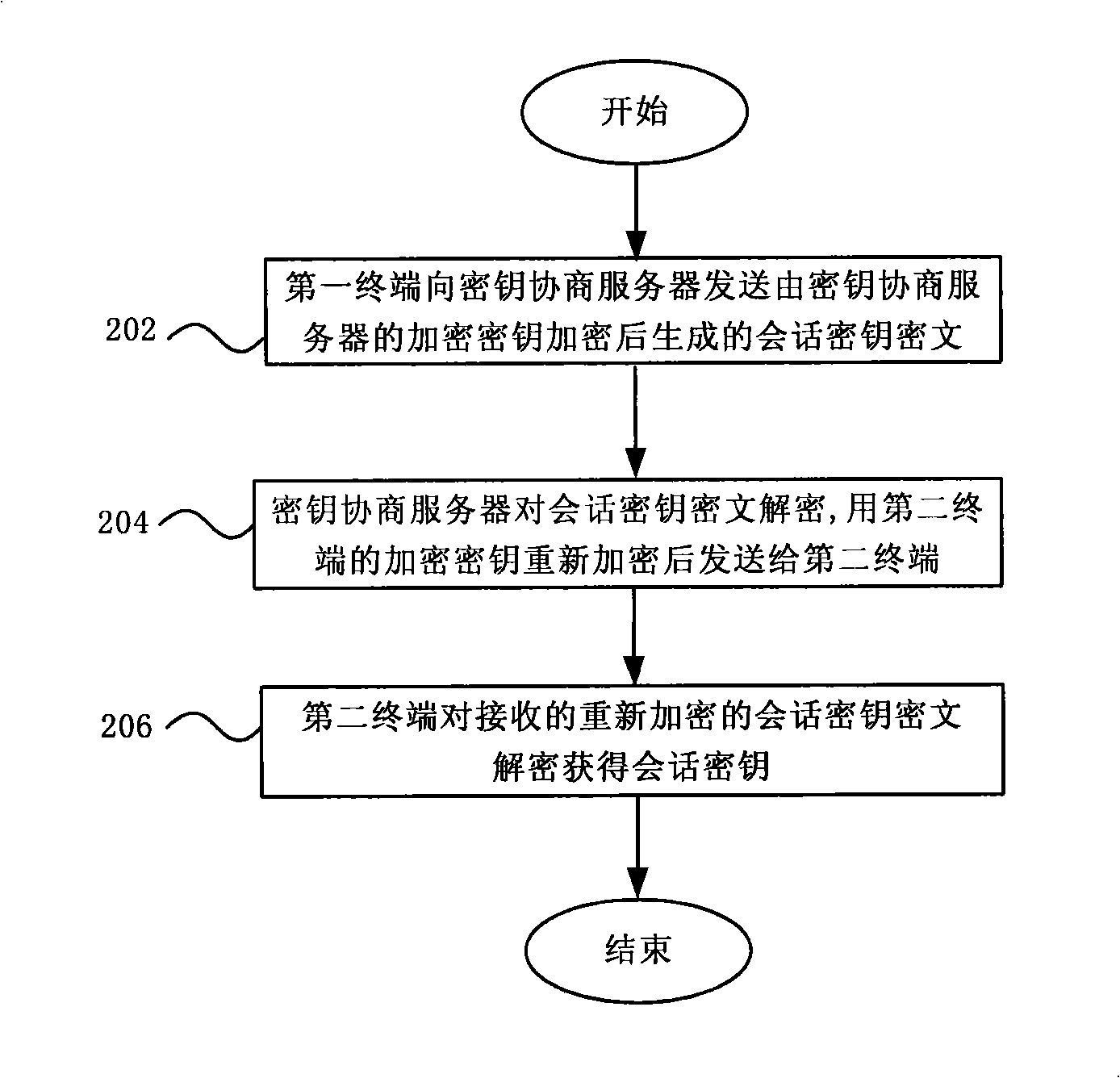
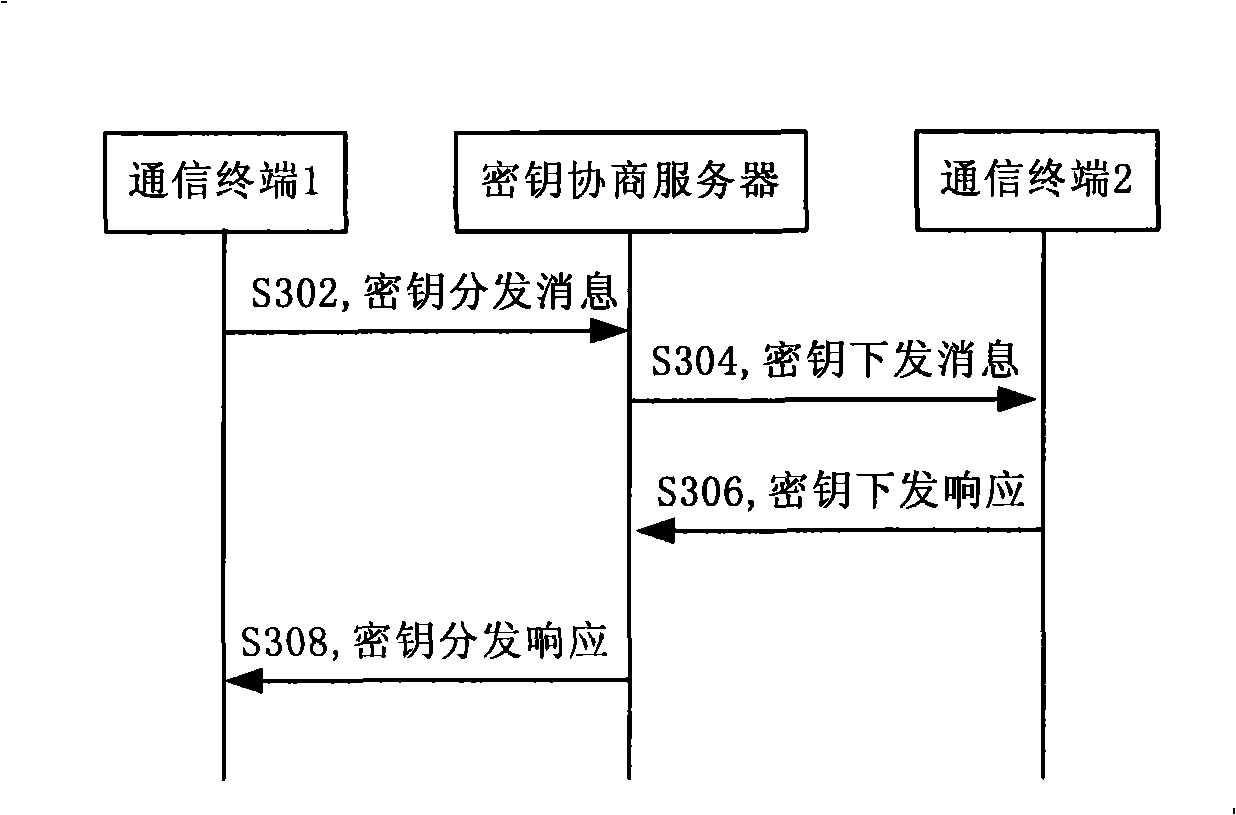
Session key negotiating method, system and server in communication network
ActiveCN101340443ASimple negotiation processImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationNon symmetricCiphertext
The invention discloses a key agreement method, a system and a server of a communication network, the method comprises the following steps: a first terminal sends a conversation key ciphertext which is generated after the encryption of a conversion key by an encryption key of a key agreement server to the key agreement server; the key agreement server obtains the conversation key from the decryption of the conversation key ciphertext, the encryption key of a second terminal re-encrypts to the conversation key for generating the conversation key ciphertext to be sent to the second terminal; and the second terminal obtains the conversation key from the decryption of the obtained conversation key ciphertext and returns a response message to the first terminal. The conversation key agreement method and the system provided by the invention realize the simple process and ensure the safety of the key transmission through the realization of the encryption transmission of the conversation key by the key agreement server. The key agreement is realized by the use of the non-symmetric cryptosystem, and the encryption communication is realized by using the symmetric cryptosystem, thereby fully utilizing the advantages of the symmetric and the non-symmetric cryptosystems.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
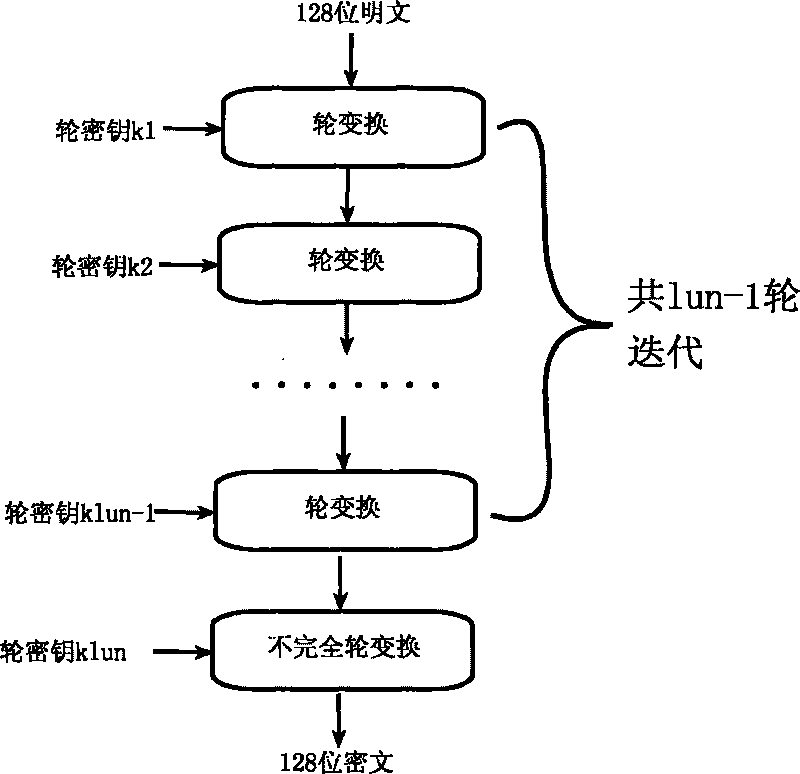
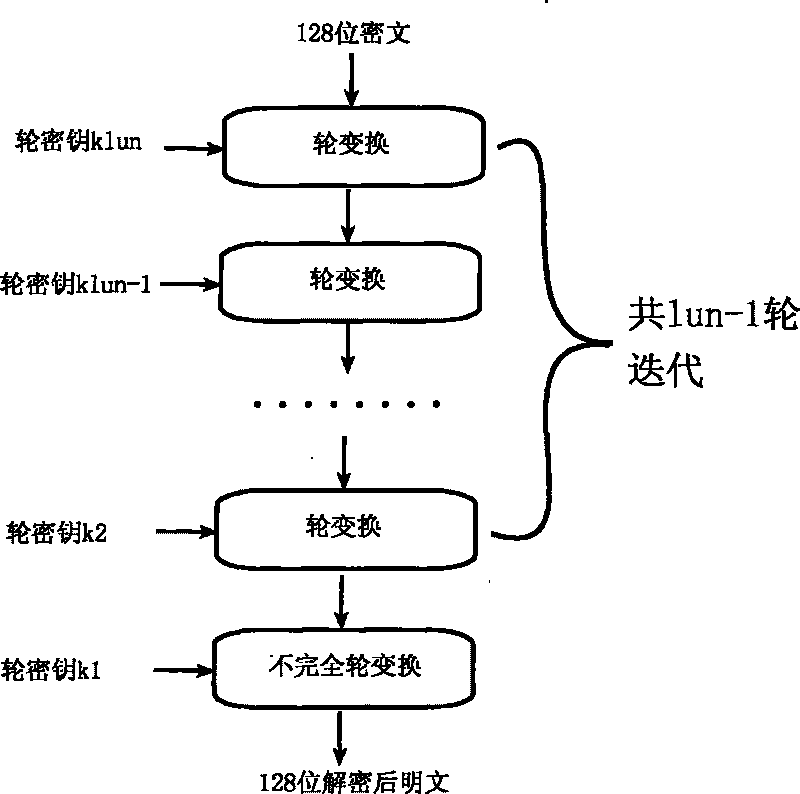
Encryption method for network and information security
ActiveCN101764686AHigh speedDiffusion is fastKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareKey size
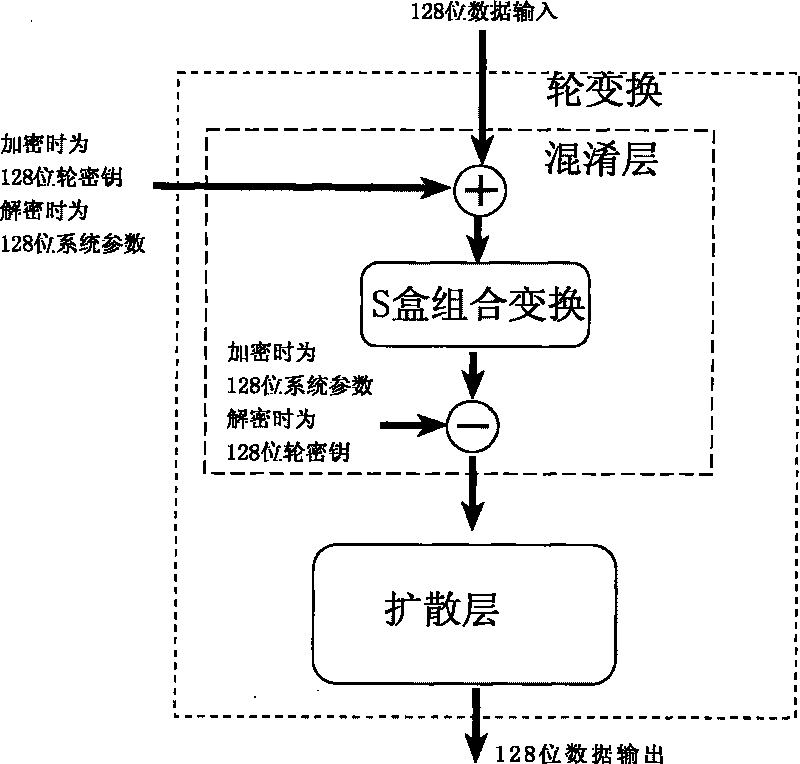
The invention relates to an encryption method for network and information security; the adopted packet length and key length are 128 bits, and a 128-bit system parameter is added; encryption algorithm comprises a plurality of rounds of round transform iteration consisting of mixed layers and diffusion layers, wherein the last round is incomplete round transformation, and the incomplete round transformation consists of the mixed layer; the mixed layer comprises key plus, S box portfolio transform and system parameter minus; the S box portfolio transform comprises 8-input 8-output reversible S box transform and inverse S box transform in the same number which are output by parity exchange; the diffusion layer can construct linear transformation with a reversible re-model polynomial matrix; an encryption round key is generated by an encryption key through encryption round transformation; and decryption algorithm is the inverse transformation of encryption algorithm. The encryption methodfor network and information security has the advantages of high diffusion speed, good security strength, hardware resource saving, and very high speed when being realized by hardware and on a software platform.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS HEBEI ACADEMY OF SCI
Cryptogram-based safe full-text indexing and retrieval system
InactiveCN101520800ASolve search and useFix security issuesDigital data protectionSpecial data processing applicationsPlaintextCiphertext
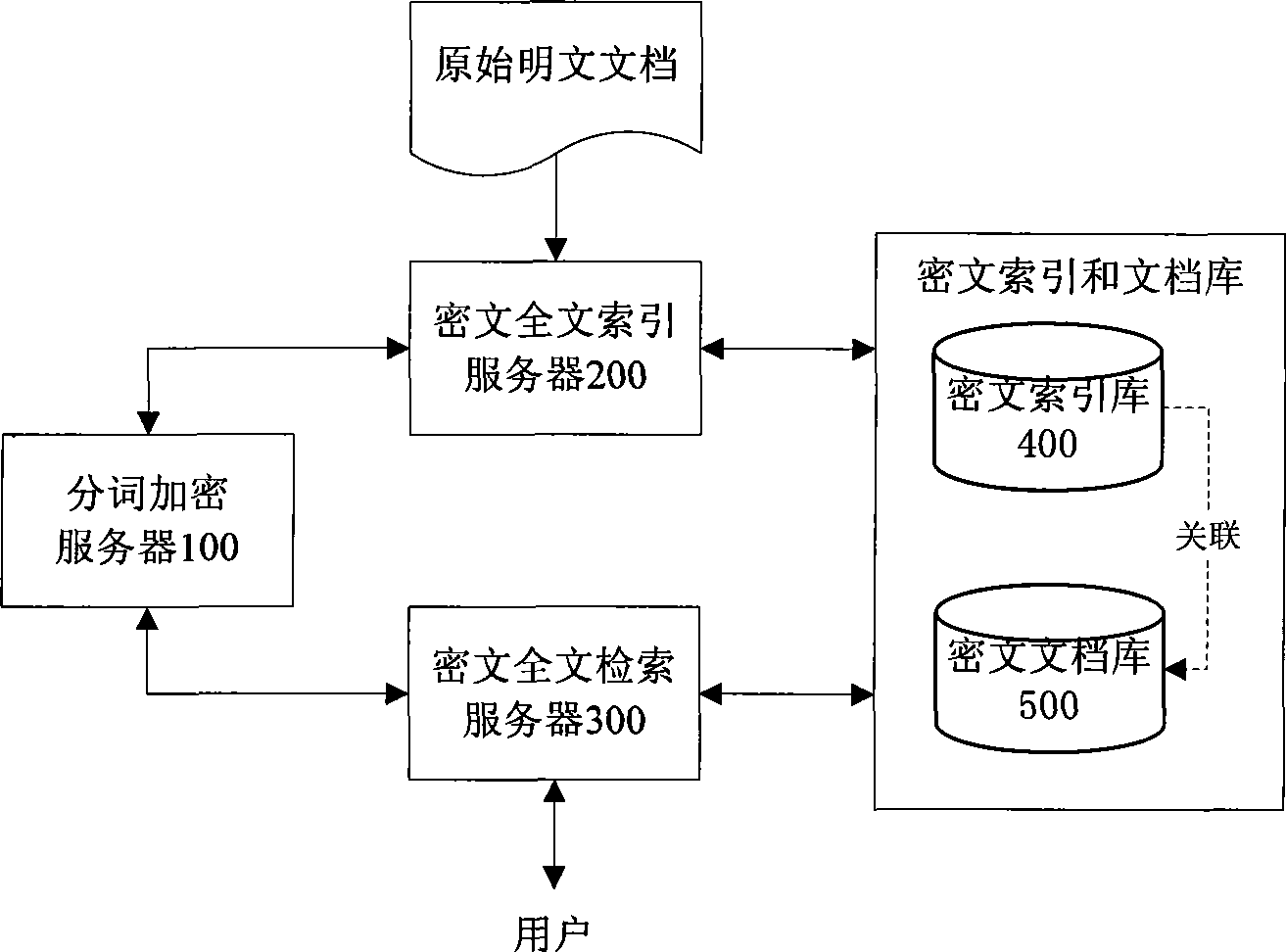
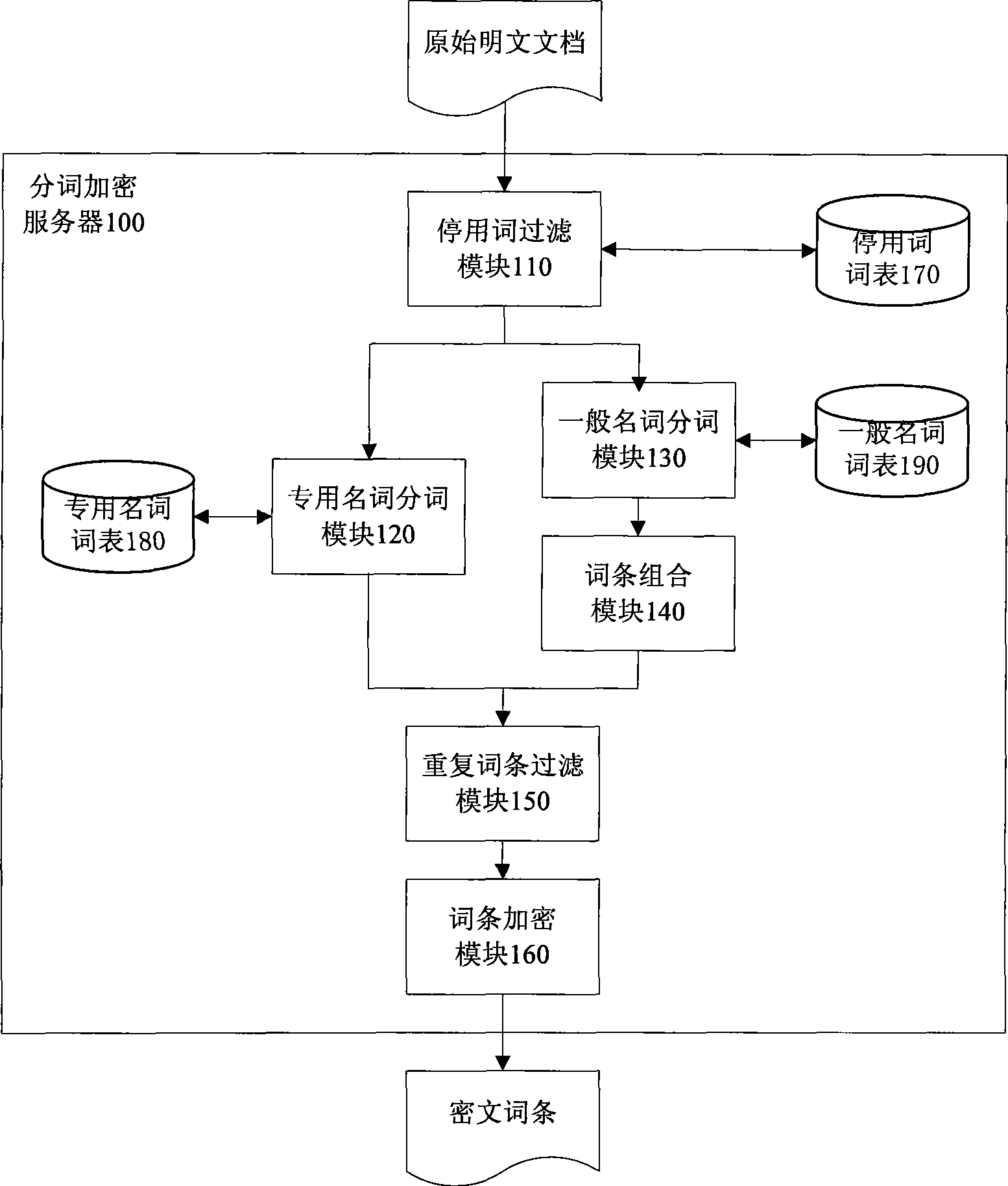
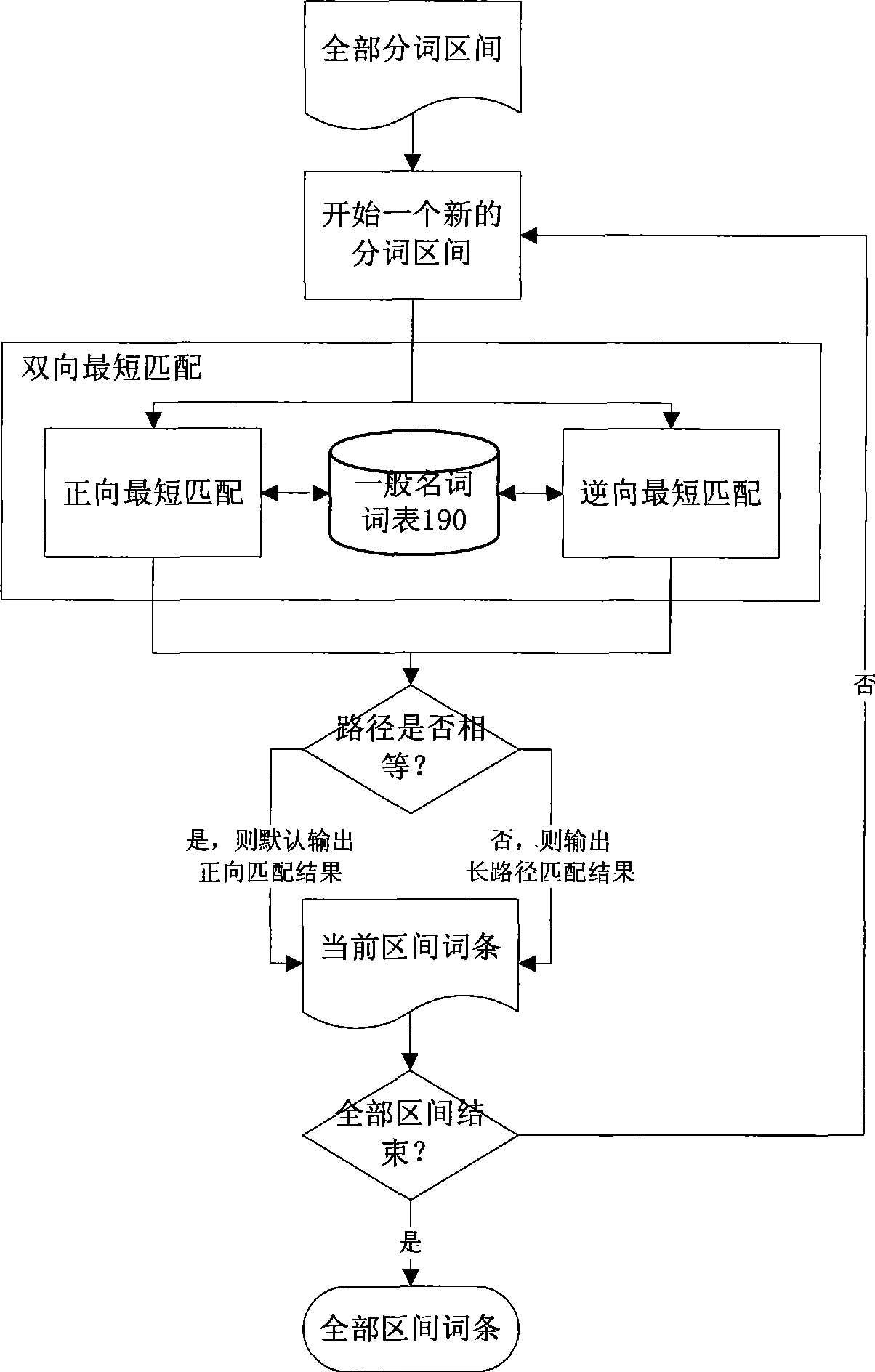
The invention discloses a cryptogram-based safe full-text indexing and retrieval system. In the system, a cryptogram index library comprises a cryptogram entry reverse index and an internal document object set; a cryptogram document library is responsible for storing and managing an encrypted XML document; a word segmentation encryption server carries out Chinese word segmentation on a plaintext document and encrypts the plaintext document item by item; a cryptogram full-text indexing server standardizes an original plaintext document into an XML document, encrypts and stores the XML document in the cryptogram document library, creates a corresponding internal document object in the cryptogram index library by combining document metamessage, and creates a cryptogram reverse index for the XML document through the cryptogram entry; and a cryptogram full-text retrieval server retrieves the cryptogram index library to obtain the internal document object set through user authority information and the cryptogram entry, obtains a corresponding encrypted XML document result set from the cryptogram document library according to a pointer, decrypts the corresponding encrypted XML document result set, and returns the decrypted corresponding encrypted XML document result set to a user. The Chinese word segmentation method, the safe and high-efficiency indexing structure and the retrieval mechanism of the invention based on the special requirements of cryptogram full-text indexing can realize the cryptogram full-text indexing integrated with an access control strategy. The cryptogram-based safe full-text indexing and retrieval system has the advantages of a safe and high-efficiency indexing process, no decrypted docuterms in the indexing process, a high recall ratio and a high precision ratio in a cryptogram environment, and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
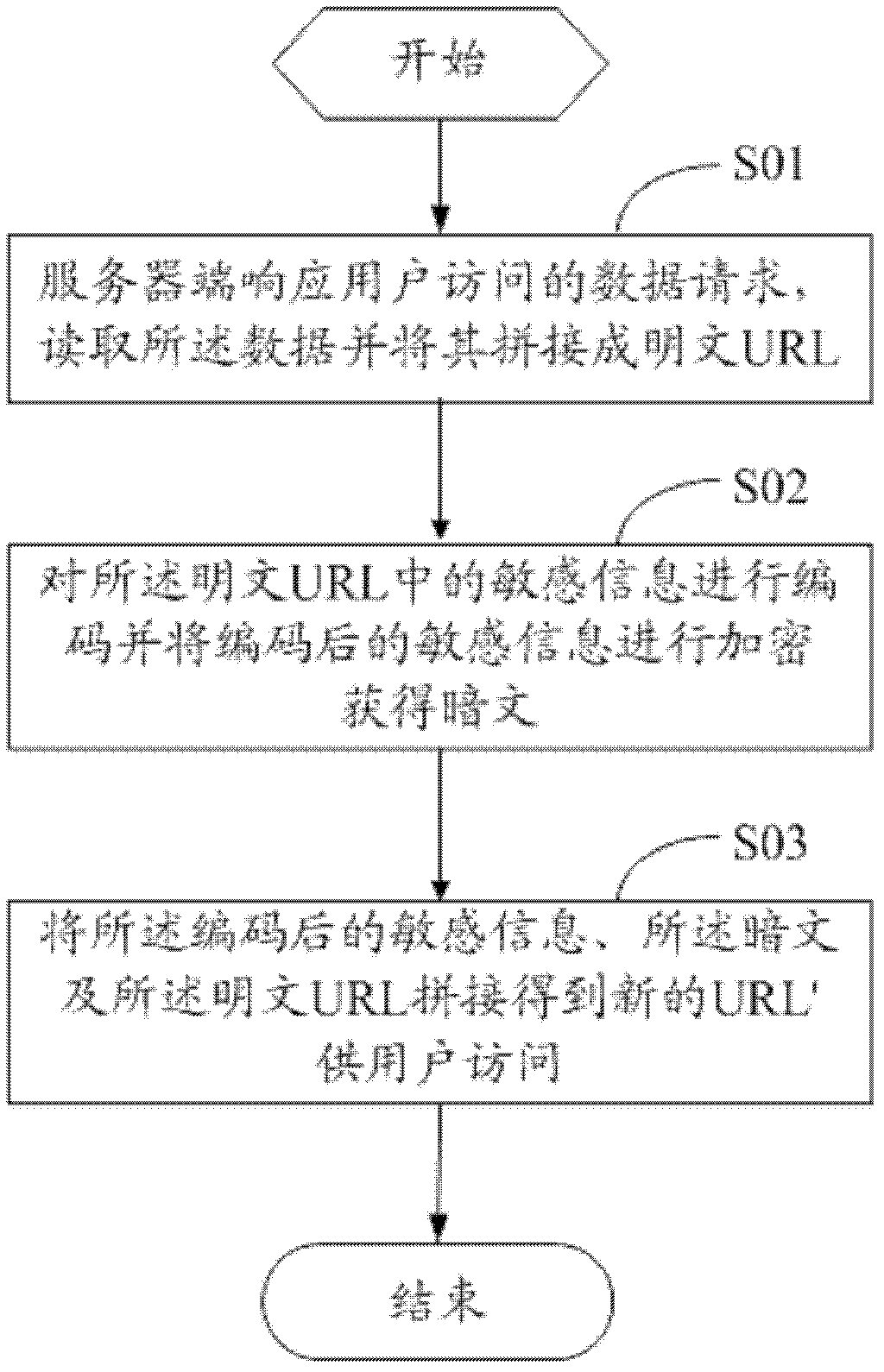
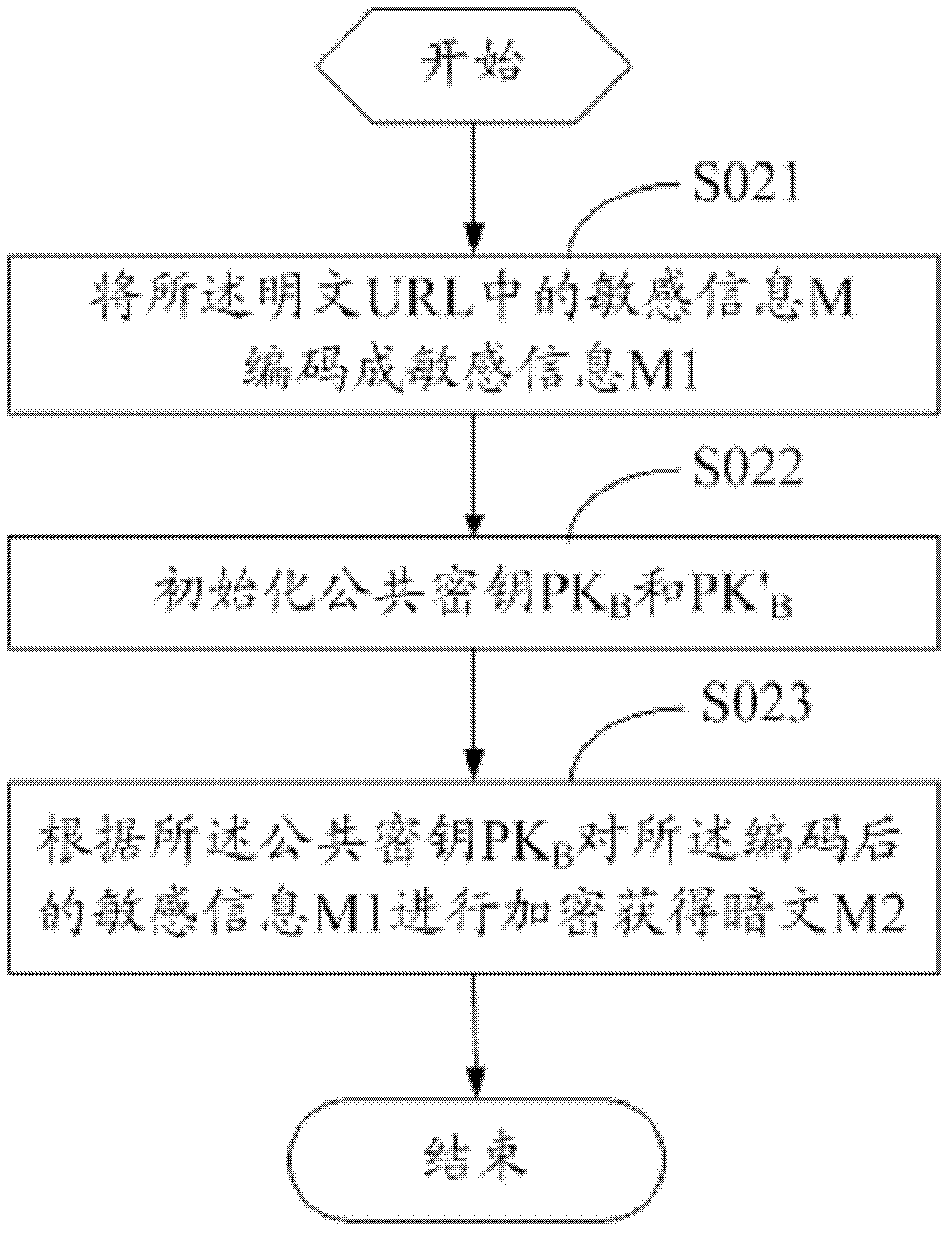
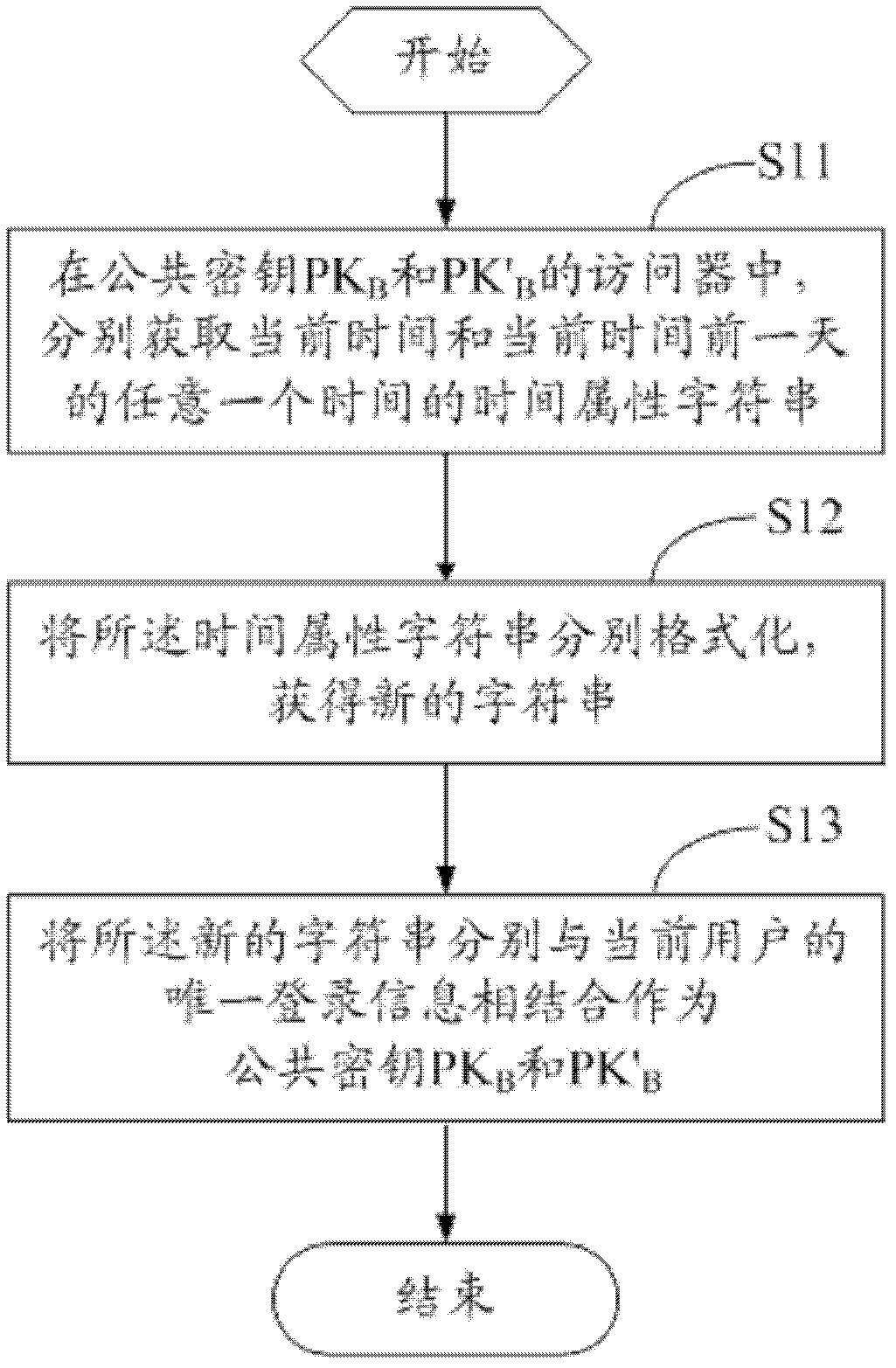
Method and device for encrypting uniform resource locator (URL) and method and device for authenticating URL
InactiveCN102594557ASave resourcesImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextCiphertext
The invention discloses a method and a device for encrypting a uniform resource locator (URL). The method comprises the following steps that: a server responds to a data request of user access, reads data and splices the data into a plaintext URL; sensitive information in the plaintext URL is coded and the coded sensitive information is subjected to encryption to obtain a ciphertext; and a new URL' is obtained by splicing the coded sensitive information, the ciphertext and the plaintext URL and provided for a user to access. The invention also discloses a method and a device for authenticating the URL, and a double-secret-key comparison algorithm is adopted in the method for authenticating the URL. The method and the device for encrypting the URL and the method and the device for authenticating the URL have the advantages that: resources and overhead of the server are saved, the security of the conventional URL encryption algorithm is improved and the timeliness of URL authentication is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAMPOO SCI & TECH
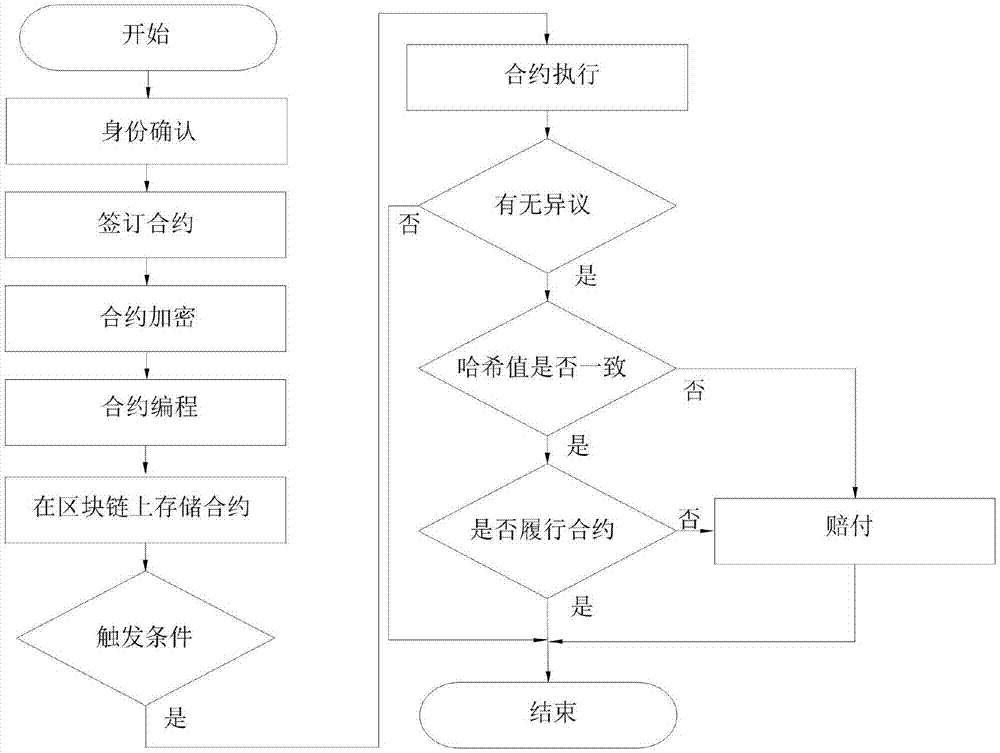
Intelligent contract technology-based medical rescue contract method
InactiveCN107423565AEasy to implementEnsure safetyData processing applicationsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareSmart contract
The invention relates to an intelligent contract technology-based medical rescue contract method. The method comprises the steps of establishing a rescue contract, an RSA encryption algorithm, a block chain storage technology and a protocol execution and punishment mechanism; encrypting the established rescue contract by utilizing the RSA encryption algorithm; storing a programmed intelligent contract by utilizing a block chain; when a patient meets with an accident and triggering conditions of the contract are met, executing contents of the rescue contract; and when a situation of breaking the contract occurs, performing punishment according to regulations of the intelligent contract. The method has the advantages that execution and verification are facilitated; the establishment time can be queried; the security of personal information of the patient can be ensured; the trust degree of both parties of the contract is increased; the contract cannot be tampered; and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
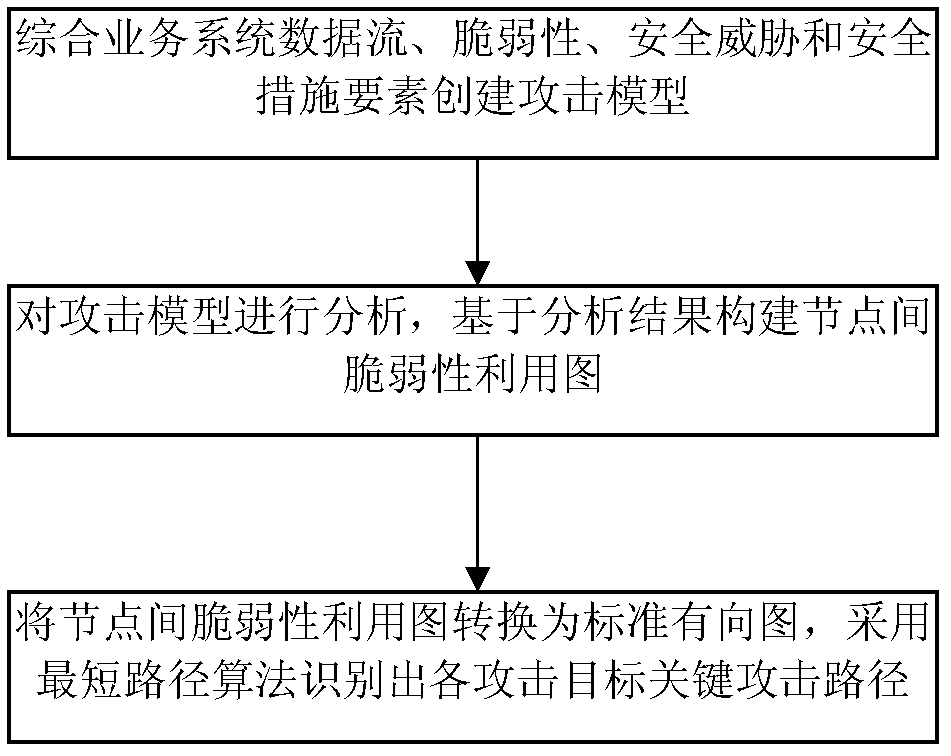
Method for identifying key attack path in service system
InactiveCN102447695AAchieving Unified ModelingAttack graph simplificationTransmissionComputation complexityDirected graph
The invention discloses a method for identifying the key attack path in a service system and belongs to the technical field of network information safety. The method comprising the steps as follows: 1, synthesizing data stream of the service system, vulnerability of the system, security threat, security measures and other factors to establish an attack model of the service system; 2, analyzing the established attack model and building a vulnerability exploitation map comprising all attack paths based on the model analysis result; and 3, converting the vulnerability exploitation map into a standard directed graph and analyzing the standard directed graph through a shortest path method to identify the key attack path that an attacker can reach all targets. The method has the advantages that the expandability is better than that of a traditional attack map, and the computation complexity of identification of the key attack path can be reduced effectively.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
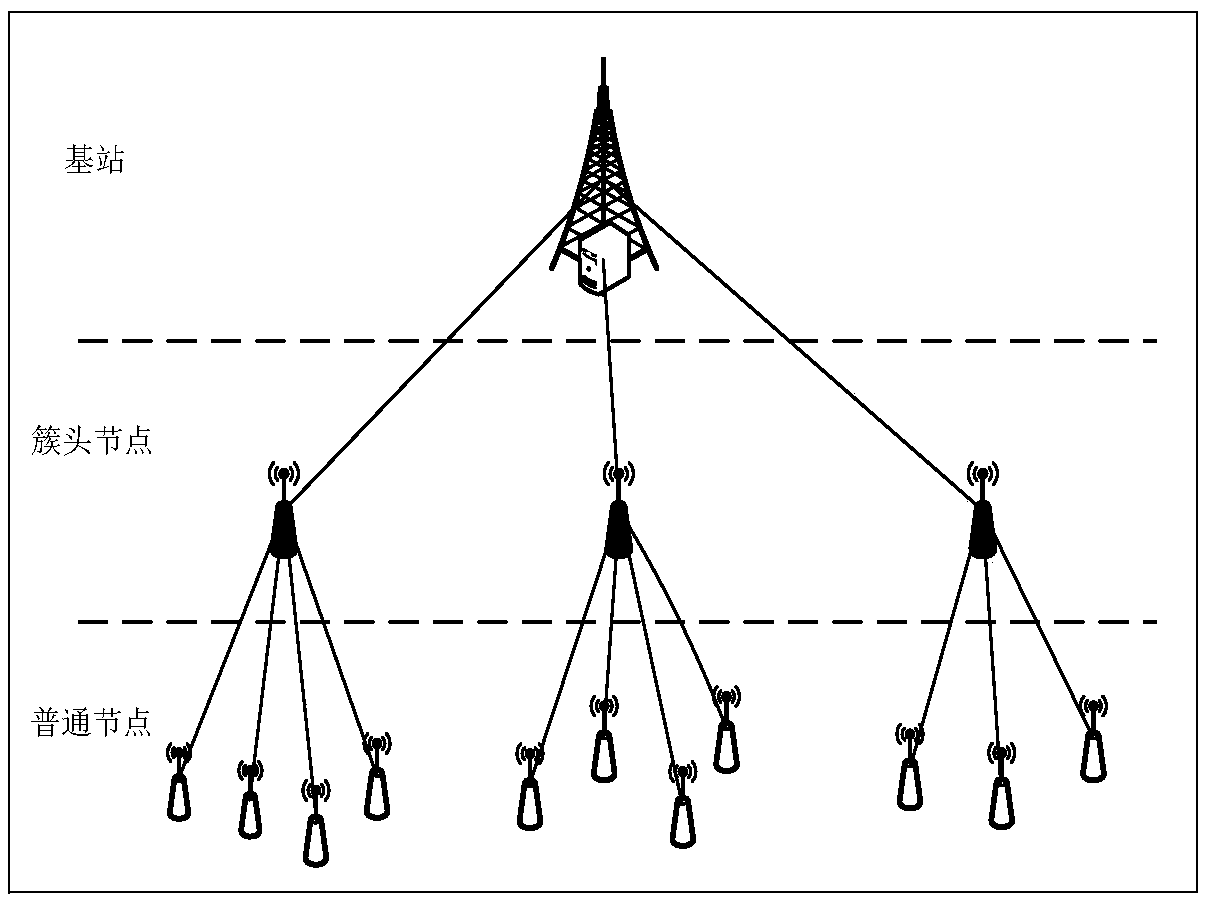
Dynamic clustering wireless sensor network cipher key management method
InactiveCN108880814AImprove securityAvoid breakingKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCluster typeWireless sensor network
The invention discloses a dynamic clustering wireless sensor network cipher key management method. The dynamic clustering wireless sensor network cipher key management method comprises steps that allnodes of a network are divided into three layers such as a base station, a cluster head node, and a common node according to node functions, and then a system network structure model is established; the parameters of the system network structure model are initialized to generate a cipher key, and at last, communication between the base station and the cluster head node, and the communication between the common node and the cluster head node are realized, and when the nodes are captured or energy is exhausted during the operation process of the network, the cipher key in the network is updated.The method provided by the invention is advantageous in that high safety performance is provided, and the common attacks of the wireless sensor network such as node forgery attacks, message replay attacks, and denial of service attacks are resisted, and at the same time, on aspects of network connectivity, storage overhead, and network power consumption, compared to conventional schemes, a largeadvantage is provided, and the method can be used in a large-scale layer cluster type wireless sensor network.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
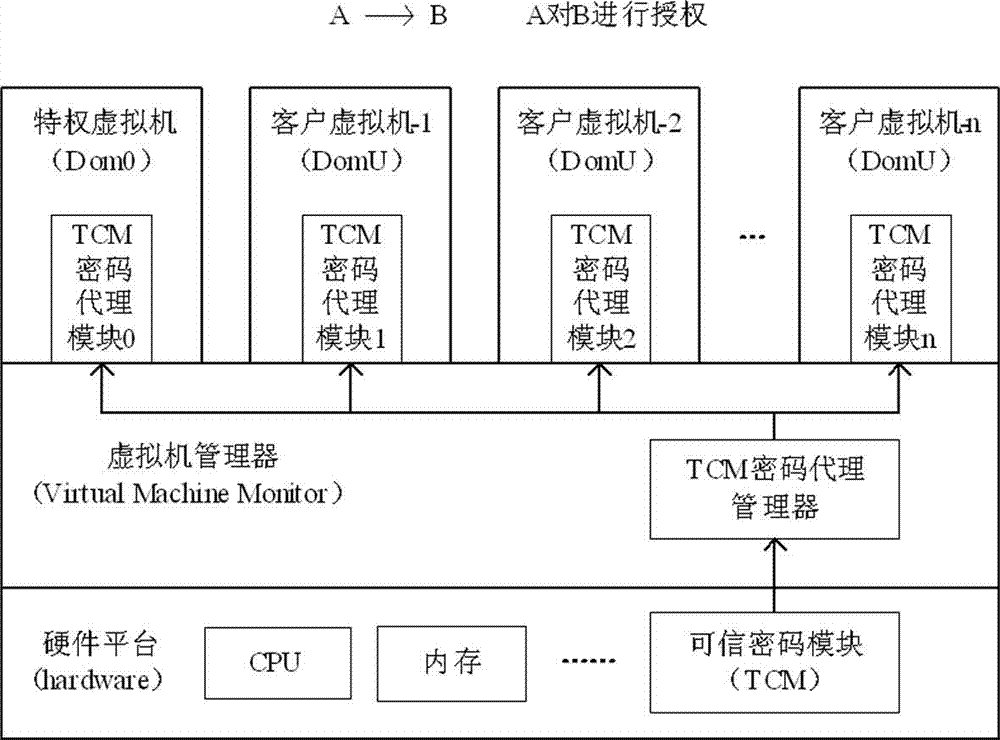
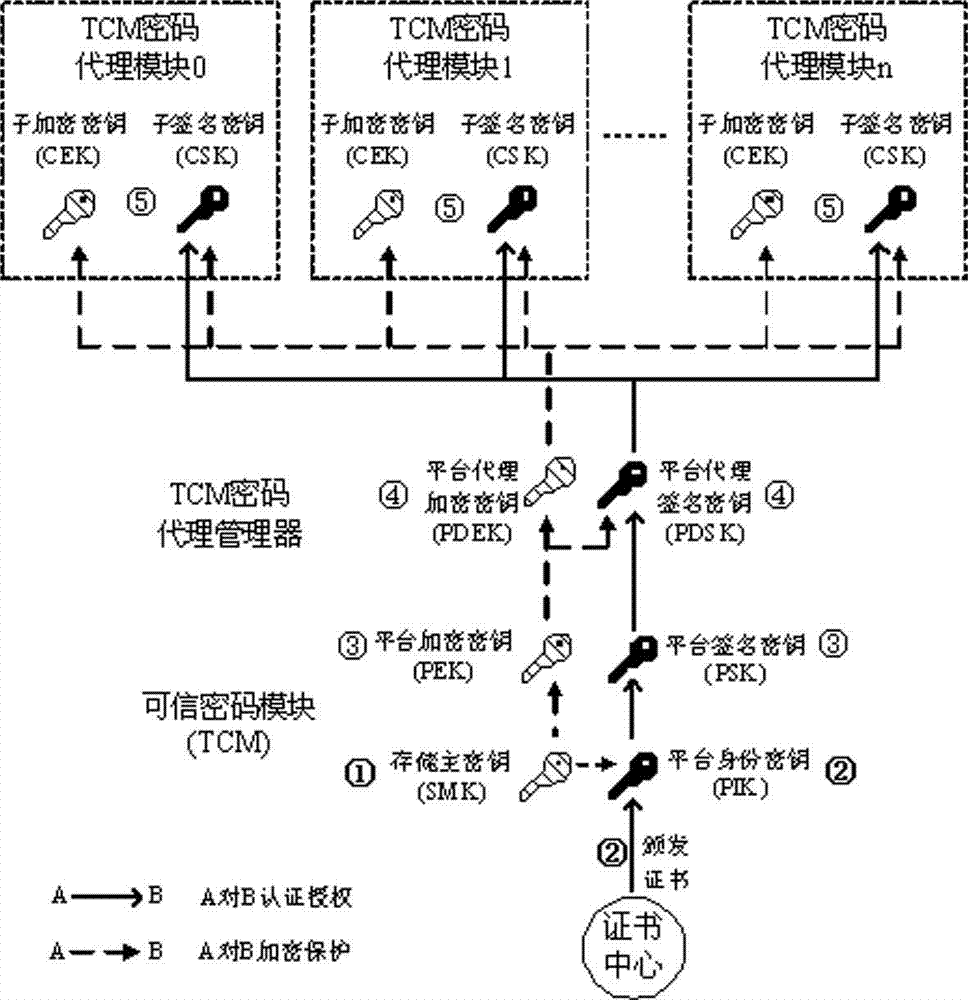
Method for realizing delegation of cipher function of TCM (trusted cryptographic module) under cloud computing environment
InactiveCN103051455AGuaranteed confidentialityIntegrity guaranteedUser identity/authority verificationConfidentialityProcess efficiency
The invention relates to a method for realizing delegation of a cipher function of a TCM (trusted cryptographic module) under a cloud computing environment. The method comprises the following steps that a cipher function of the hardware TCM is sequentially delegated by a TCM cipher delegation manager arranged in a VMM (virtual machine monitor) and a TCM cipher delegation module arranged in a VM (virtual machine), the TCM and each level of agency need to generate corresponding encryption and decryption keys and signing keys, and the delegation of the cipher function of the TCM is realized by a manner of gradual key delegation and encryption protection. The method for realizing the delegation of the cipher function of the TCM (trusted cryptographic module) under the cloud computing environment, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that each VM owns one light-weight TCM cipher delegation module and finishes the cipher function compared with a hardware TCM chip and a virtual TCM; and a plurality of TCM cipher delegation modules can quickly construct and concurrently and efficiently process data, so that the data processing efficiency of a whole platform is improved while the confidentiality, the completeness and the authentication of platform data are ensured, and the concurrent and efficient data process requirements under the cloud computing environment are better met.
Owner:NO 709 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Method for authentication for resisting secrete data disclosure and key exchange based on passwords
InactiveCN101626364AImprove computing efficiencyPrevention analysisPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeCryptographic protocol
The invention belongs to a cryptographic protocol, and in particular relates to a method for authentication for resisting secrete data disclosure and key exchange based on passwords. The method is superior to correlative American or international current standard in the aspects of user password protection, secrete data disclosure resistance, better user privacy protection, better online efficiency calculation, less communication bandwidth and higher security. The method for the authentication and the key exchange comprises sub-methods of an innovative method for public key encryption and signcryption based on passwords, a method for knowledge binding certification, a method for resisting temporary secrete data disclosure, a method for awarding a public key certificate. The method has the advantages of good systematicness, adaptability and compatibility.
Owner:赵运磊 +3
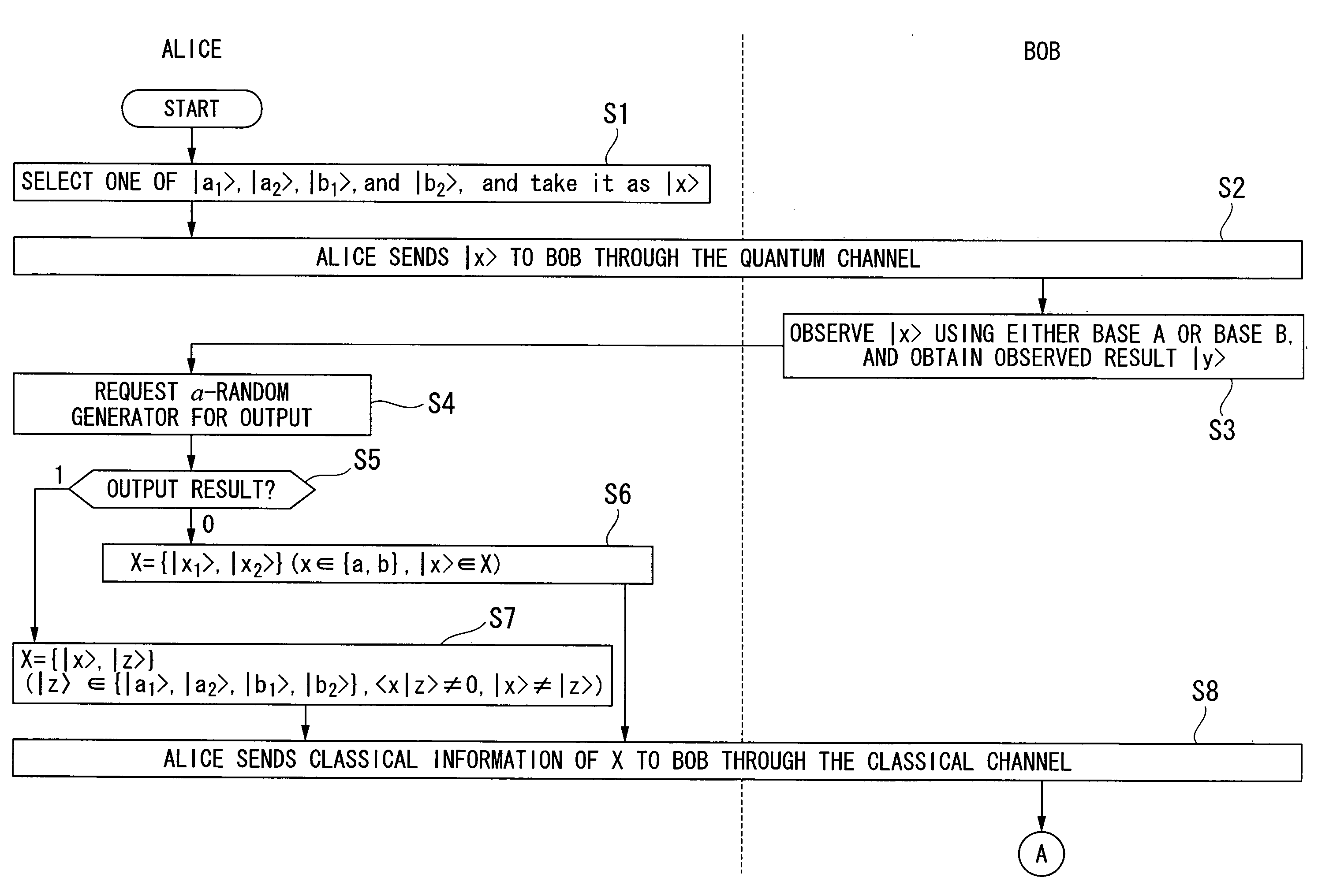
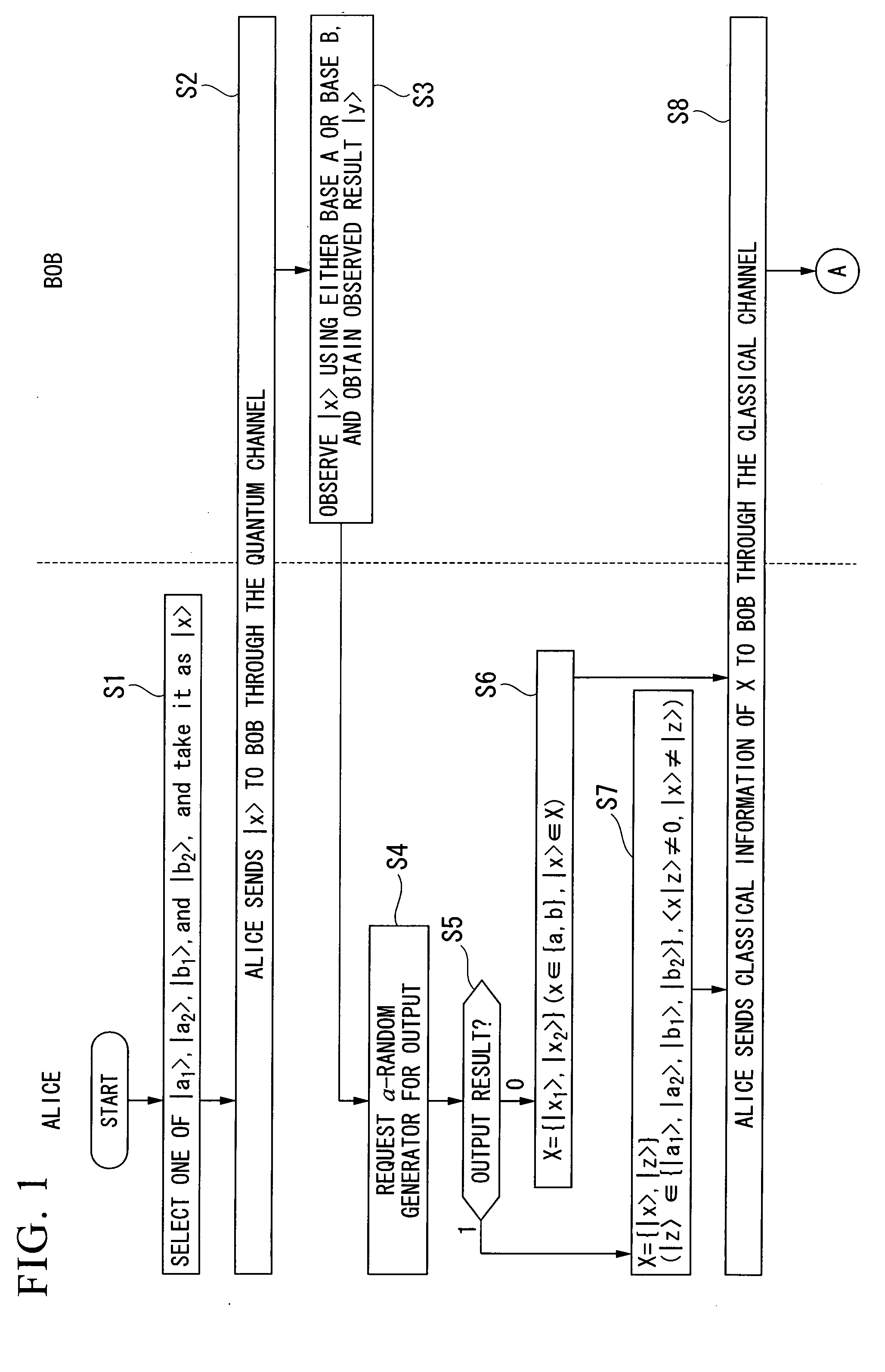
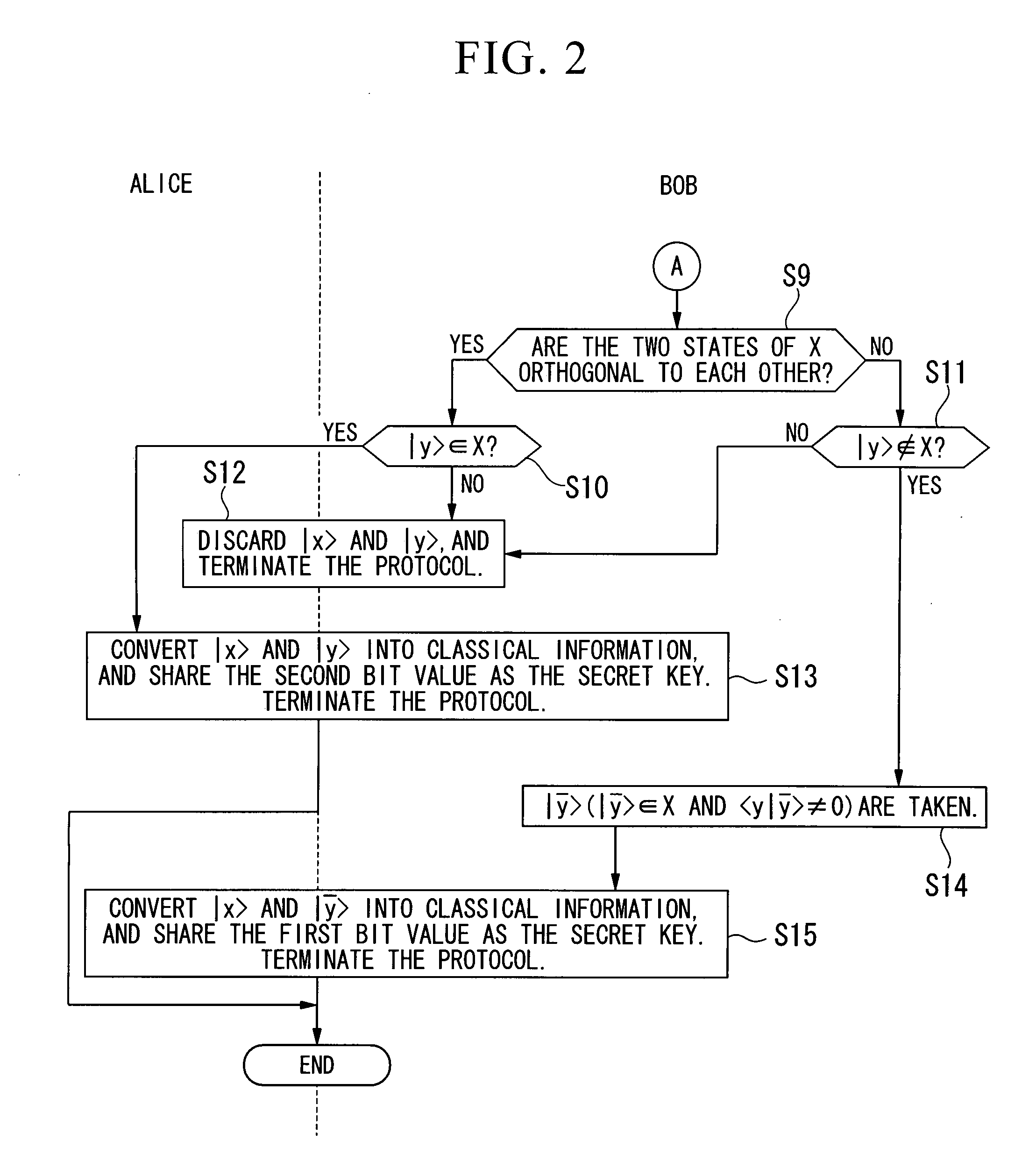
Quantum Key Distribution Protocol
InactiveUS20080101612A1Easily realizedIncrease the number ofKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareTransmitter
A quantum key distribution protocol is provided that reduces the maximum value of the leaked information amount over the same distance when an adversary makes a photon number splitting attack more than the reduction by the BB84 protocol and the SARG protocol, by making use of the advantages of the BB84 protocol and the SARG protocol. By properly proportioning the existing BB84 protocol and the SARG protocol in accordance with the rate determined by the communication distance between the sender and the receiver of the coherent light, a protocol that is more robust against photon number splitting attack than the known existing protocols can be realized, and long distance quantum key distribution, which was not possible until now, becomes possible.
Owner:THE FOUND FOR THE PROMOTION OF IND SCI +1
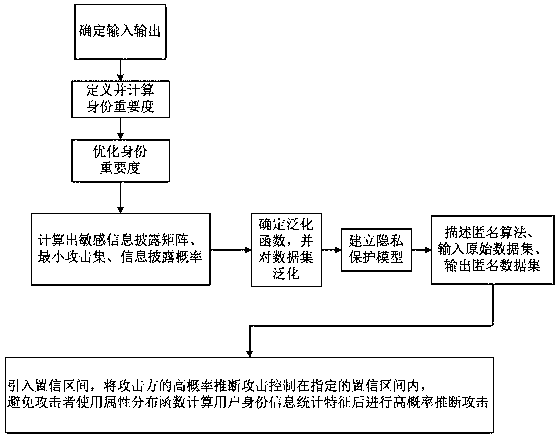
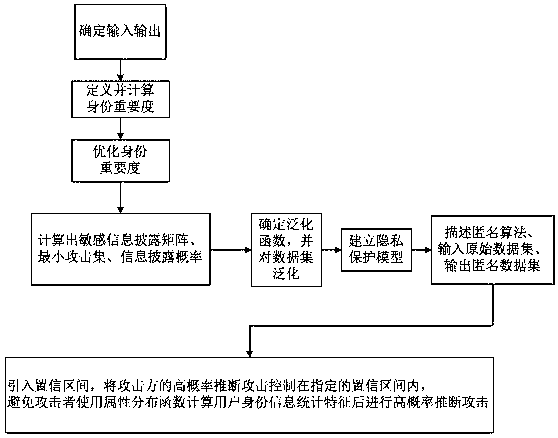
Method for protecting privacy of identity information based on sensitive information measurement
ActiveCN106940777AEffective protectionImprove protectionDigital data protectionData setInference attack
The invention discloses a method for protecting privacy of identity information based on sensitive information measurement. The method comprises the comprises the following steps of S1, determining input and output; S2, defining and calculating identity importance degree; S3, optimizing the identity importance; S4, calculating a sensitive information disclosing matrix, a minimum attack set and an information disclosing probability; S5, determining a generalizing function, and generalizing a dataset; S6, establishing a background knowledge attack-avoidance privacy protection model; S7, describing a (gamma, eta)-Risk anonymity algorithm, inputting an original dataset D, and outputting an anonymity dataset D'; S8, introducing a confidence interval, controlling the high-probability inference attack of an attacking party within the specified confidence interval, so as to avoid a user using an attribute distribution function to calculate the identity information of the user, calculate features, and perform high-probability inference attack. The method has the advantages that the problem of difficulty in effectively treating the privacy information attack based on background knowledge attack in the existing privacy protection method is solved, and the key identity and identity sensitive information are more comprehensively and effectively protected.
Owner:湖南宸瀚科技有限公司
Format-reserved encryption algorithm based on multi-segmented Feistel network
InactiveCN105959098ADoes not affect compatibilityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPlaintextComputer hardware
A format-preserving encryption algorithm based on a multi-segmented Feistel network, the method includes the following steps: S According to its own format, it is divided into t part: S 1 ,S 2 ,…,S t . where set S i is of size n i . Set the number of rounds for the Feistel network r and the key used by the round function k , where the number of rounds r for the number of divisions t associated even numbers; for a given plaintext m , format it as: m=x 1 || x 2 || … || x t ,in: x 1 ∈ S 1 ,x 2 ∈ S 2 ,…,x t ∈ S t ;Will x 1 ,x 2 ,…,x n as t Segmentation of the Feistel network t input, or input as ;Execute r rounds of round operations, and the final output ciphertext is c=y 1 || y 2 || … || y t ,in: y 1 ∈ S 1 ,y 2 ∈ S 2 ,…,y t ∈ S t , the advantages of the present invention are: by segmenting the sensitive data and defining the value domains of different segments, using self-defined pseudo-random functions, modulus addition and modulus subtraction operations, and using Feistel network to perform even-numbered rounds of round operations to achieve Encryption that preserves the format can support numerical data encryption schemes that retain any given format. After encryption, the data and database will not be affected, which provides the possibility for the encryption protection of numerical personal identification information in existing database application systems.
Owner:东港股份有限公司 +1
Encryption and decryption method, and PLC system using the same
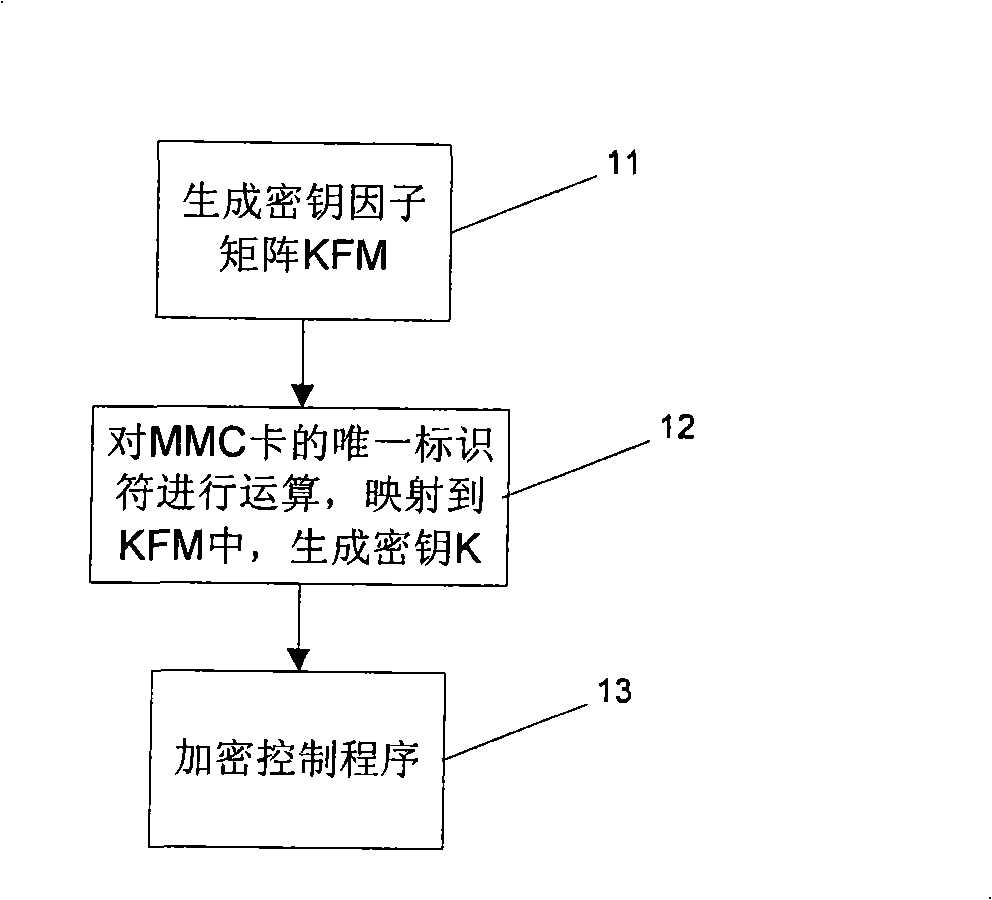
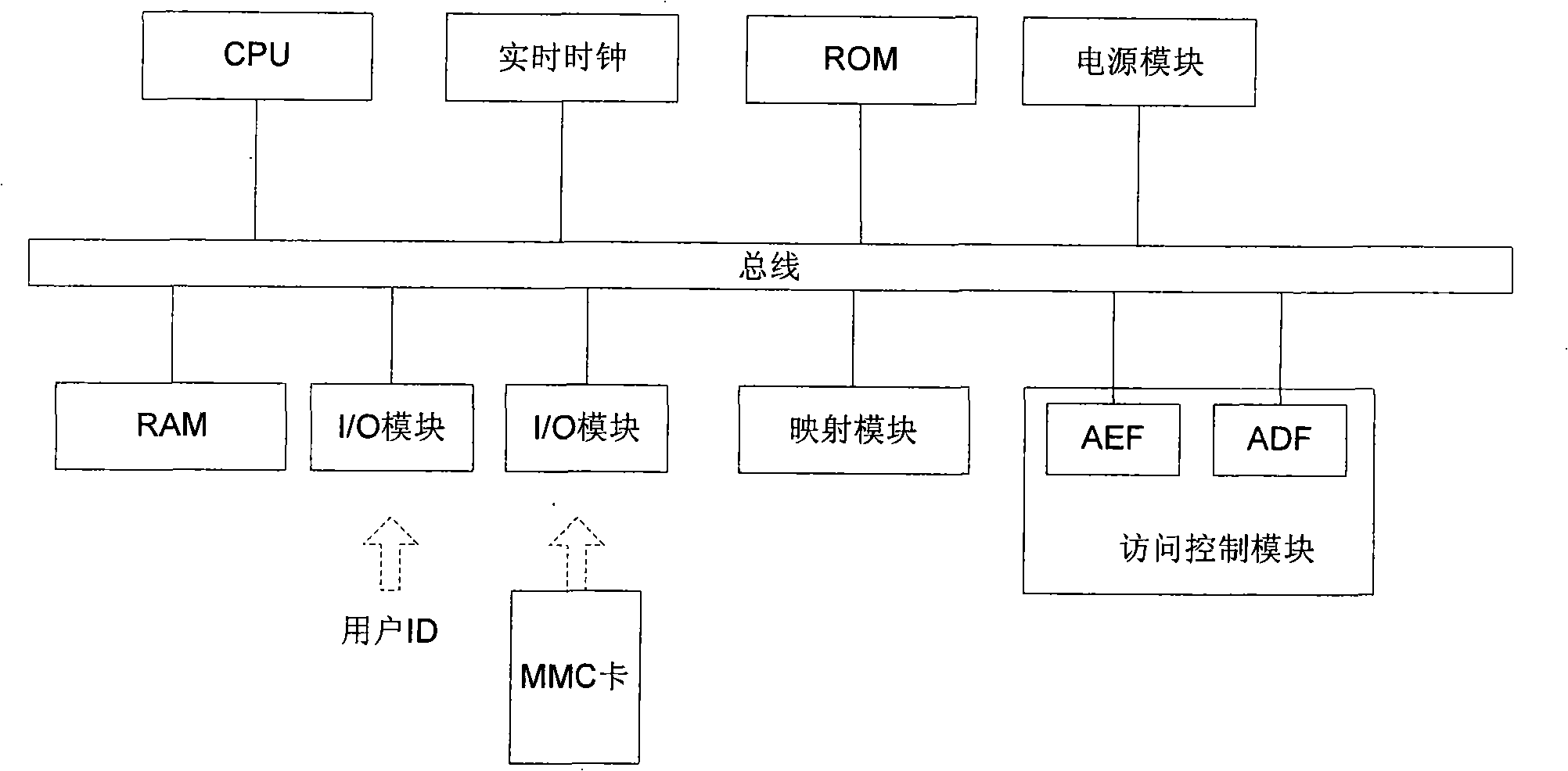
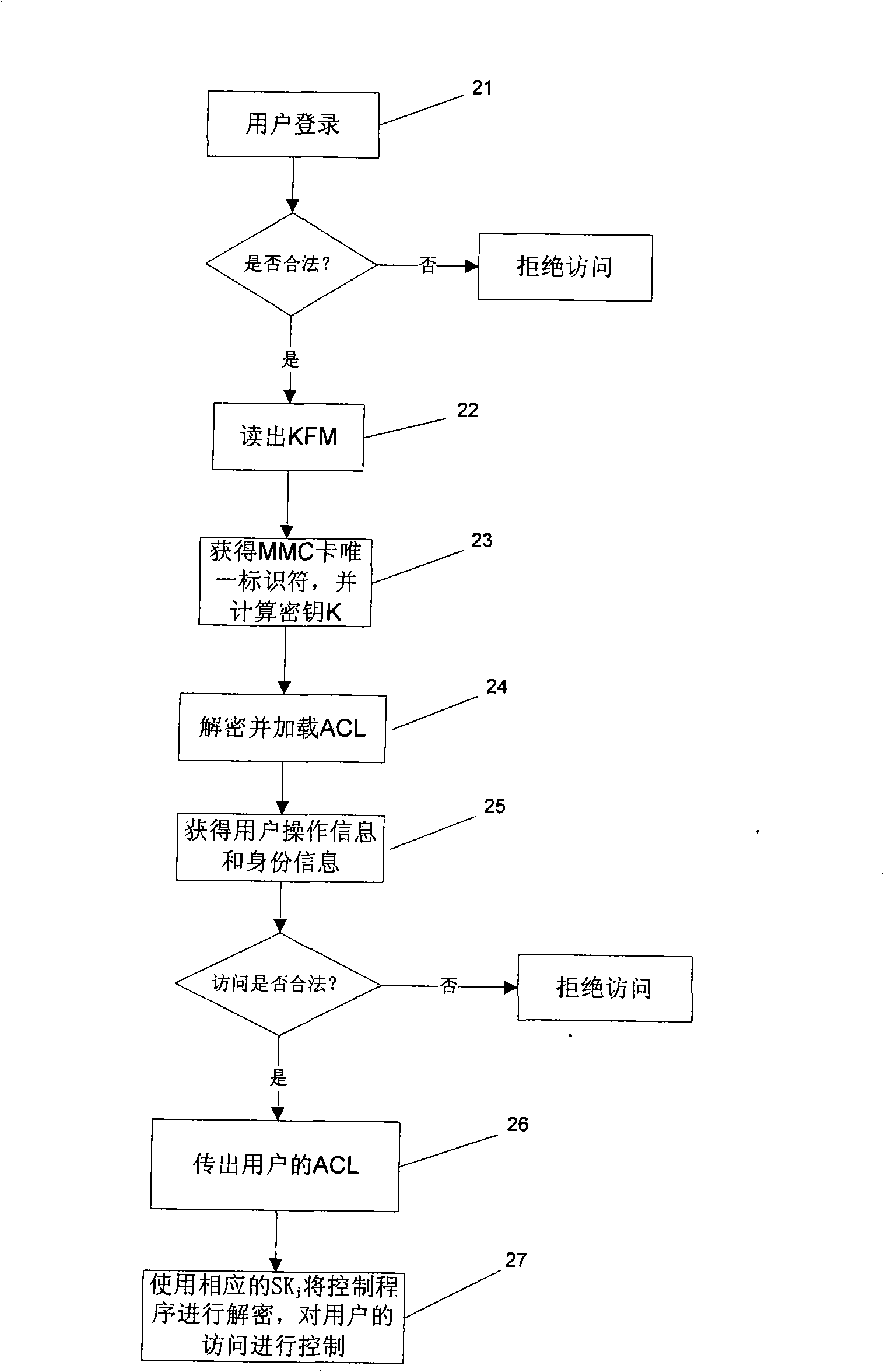
ActiveCN101329658ASafety protectionImprove protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital data protectionUnique identifierComputer software
The invention relates to the field of industrial computer software safety, in particular to a method for encrypting and decrypting information in a memorizer and a PLC system for applying the method. The encrypting method of the invention comprises the following steps of storing an algorithm F()in the system; mapping the unique identifier of the memorizer into a cipher key K; encrypting the information stored in the memorizer by utilizing the cipher key K based on a symmetric encryption algorithm; and predefining the access strategy based on the user identity in order to control the user's access to the information stored in the memorizer; and storing the access strategy in the memorizer by utilizing the cipher key K based on the symmetric encryption algorithm. During the decryption process, decrypting, information stored in the memorizer is decrypted by utilizing the cipher key K based on the symmetric encryption algorithm, and the access strategy is decrypted by utilizing the cipher key K based on the symmetric encryption algorithm. Then the user's access to the information stored in the memorizer is controlled based on the user identity. The method and the system of the invention have the advantage of being capable of enhancing the safety of software codes.
Owner:SIEMENS CHINA
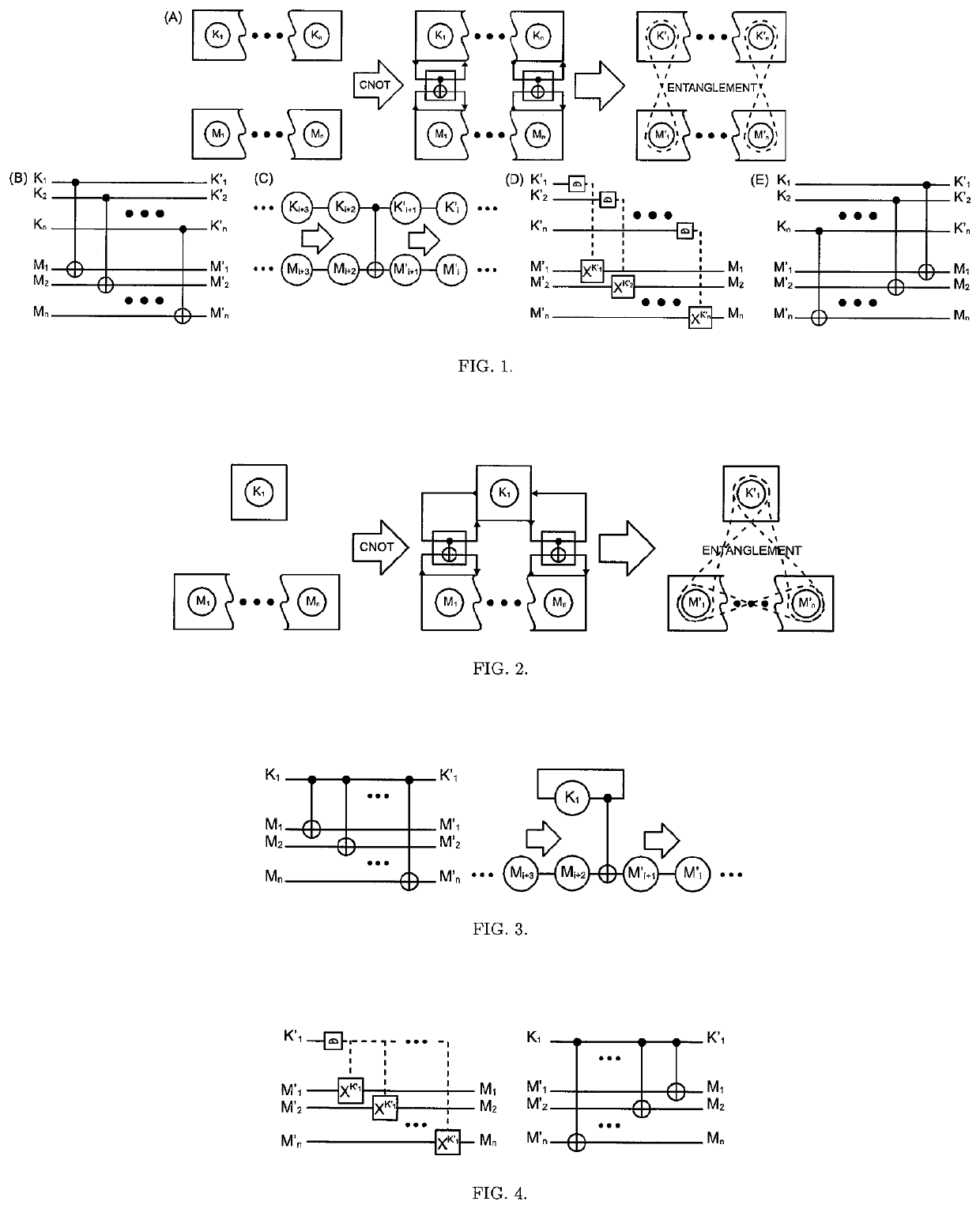
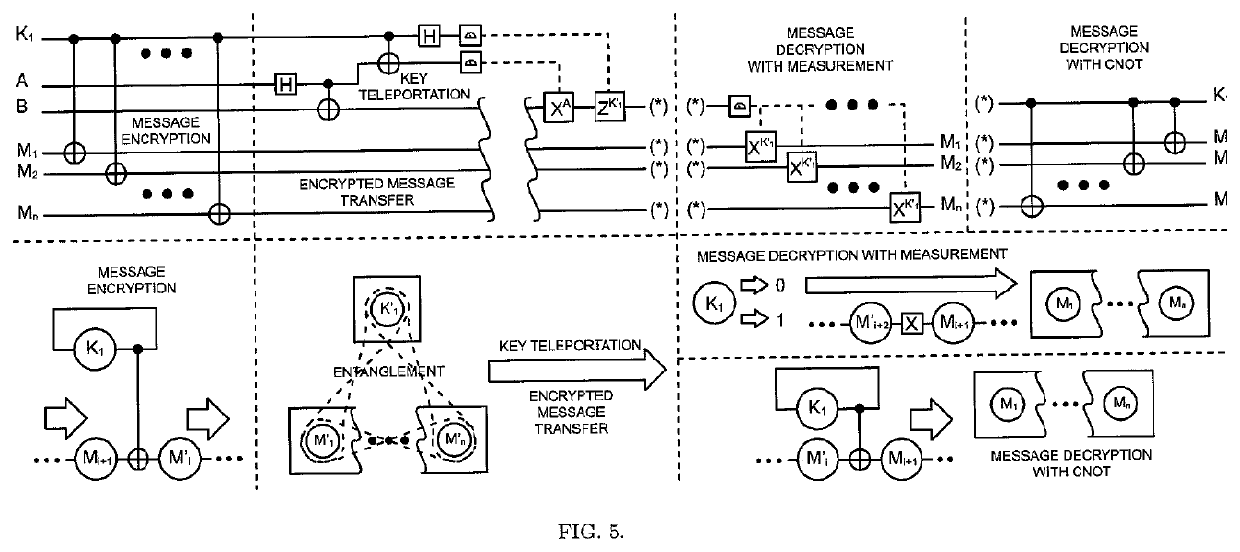
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) for entanglement encryption of quantum information
InactiveUS20210058244A1Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationInformation processingQuantum teleportation
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) protocol and its generic implementing device constitute a novel, maximally efficient scheme for encryption of quantum information with a quantum key of just a single qubit in an arbitrary unknown quantum state. The OQP enables encryption of the quantum information of n qubits register with a single qubit key upon provision of a multi-qubit entanglement between the single qubit key and the n qubits of the quantum message by the iterative application of the CNOT gate on the same key qubit (control input) and subsequent qubits of the message (target input). This results in an entanglement of all n+1 qubits, which locks original quantum information qubits and the single qubit of the key in a jointly entangled state that cannot be disentangled without the single qubit key. In order to decrypt the quantum message (by its disentanglement) one needs to have the qubit key and either reverse the protocol (applying CNOT operations in the reversed order) or simply measure the entangled key qubit and then depending on the outcome either straightforwardly obtain the decrypted quantum message or its quantum negation (dealt with by again applying quantum negation on all of the message qubits thus restoring their original states). The OQP protocol and its implementing device is proposed one hundred years after the classical One-Time Pad (Vernam cipher) was invented in 1917. The main differences between two schemes show how much quantum and clasical information differ. It is of course impossible to unconditionally securely encrypt classical sequence of n bits with just 1 bit of a key or guarantee that the random key that can be used for this purpose of n bits length (same as of the message) could not be copied. In contrast both these features are possible for the quantum information as described upon the proposed invention. The main characteristic of the OQP protocol to use only a single qubit as the key to enable information-theoretic security of n qubits quantum information encryption follows from the introduction in the invention of the multi-qubit entanglement, which is a non-local, topological and non-classical phenomenon giving quantum information significant edge over its classical counterpart. The main application of the OQP protocol and its implementing generic device is to lock quantum information with the single key qubit in order to prevent any unauthorized access to it (not only a classical access upon a measurement, but more importantly a quantum access by a quantum information processing device). This application can be also extended to communication scenario jointly with the Quantum Teleportation, which without OQP requires pre-sharing of n pairs of Bell states between Alice and Bob to securely communicate n qubits long quantum message, whereas in contrast with the OQP protocol just one pair of Bell state is required to securely teleport only the single qubit key for the OQP encrypted quantum message sent through an insecure quantum channel and still be access-protected from Eve (an adversary).
Owner:COMPSECUR SP ZOO
Confounding method of encrypted group signatures
ActiveCN104917617AImplement encryption group signature functionImprove confidentialityUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextEngineering
The invention relates to a confounding method of encrypted group signatures, thereby protecting signature private keys of members in a group. The method comprises the following steps that: (1), a group master constructs a signature group and a group parameter sequence pub, a main private key MK, a tracking private key TK are obtained according to a setup algorithm; (2), an information receiver obtains a respective encrypted public key PKe and decrypted private key SKe based on an EKGen algorithm according to the group parameter sequence pub: (3), according to the group parameter sequence pub, the main private key MK, and IDs of the members in the group, the group master obtains signature tracking information sID and signature private keys KID corresponding to the respective IDs of the members in the group by using an Enroll algorithm, and the signature private keys KID are sent to corresponding members in the group; (4) according to a confounding algorithm Obf, confounding processing is carried out on an initial encryption group signature algorithm EGS of the members in the group and the signature private keys KID of the members in the group, thereby obtaining an encryption group signature algorithm Rpub,z,PKe; and (5), according to the encryption group signature algorithm Rpub,z,PKe, information signature encryption is carried out a to-be-sent message M to generate an encrypted ciphertext C and then the encrypted ciphertext C is sent to the information receiver. Compared with the prior art, the confounding method has advantages of function of private key protection and good secret keeping effect and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A public key encryption method supporting multi-keyword search against keyword guess attack
InactiveCN109086615AUnforgeableOvercoming the Problem of Guessing AttacksDigital data protectionTransmissionThird partyCiphertext
The invention discloses a public key encryption method for supporting multi-keyword search to resist the attack of keyword guess. The method comprises the following steps: a data owner and a data receiver are registered as a legal authorized user in a trusted third party; the trusted third party runs the global parameter generation algorithm, outputs the global parameter set and sends it to the cloud server, the authorized data owner and the authorized data receiver. The data owner receives the global parameter set and sends the encrypted document set and the keyword ciphertext to the cloud server. The data receiver receives the global parameter set, constructs the keyword trap according to the query sentence, and sends the keyword trap to the cloud server. The cloud server receives the global parameter set, encrypts the ciphertext document, the keyword ciphertext and the keyword trap, and returns the satisfied ciphertext document to the authorized data recipient by running the test algorithm verification. The invention effectively solves the problem of keyword guess attack, realizes keyword search, and has obvious advantages in computational efficiency and communication cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Novel symmetric key algorithm for high speed encryption
ActiveCN106656475AReduce repetition rateImprove securityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPlaintextCiphertext
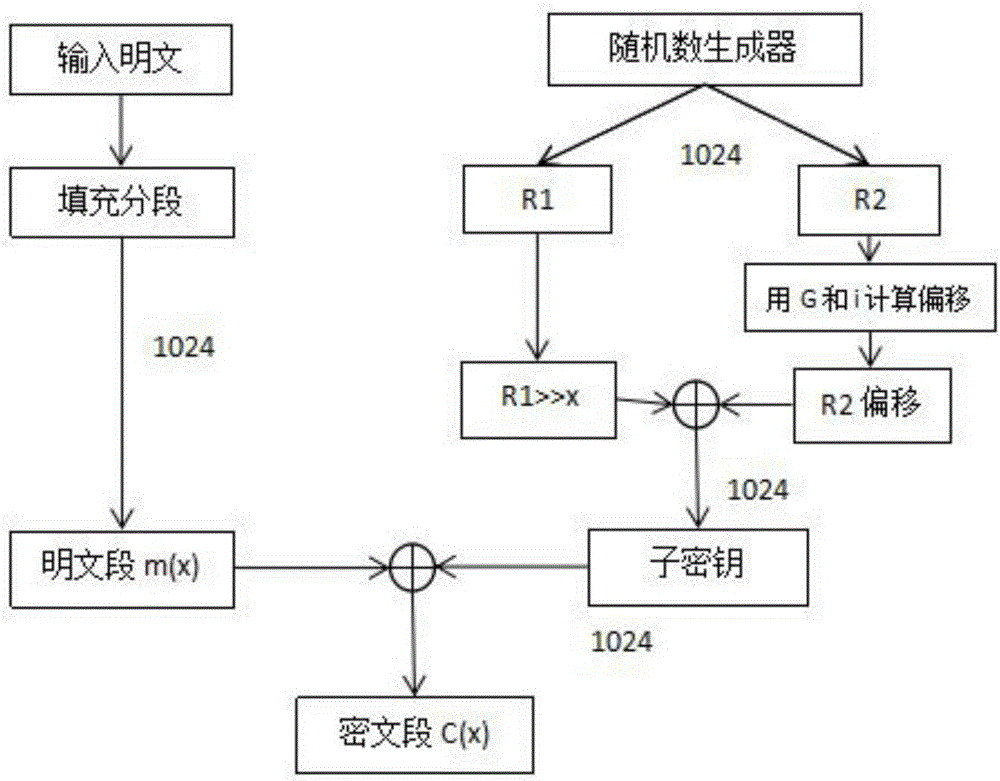
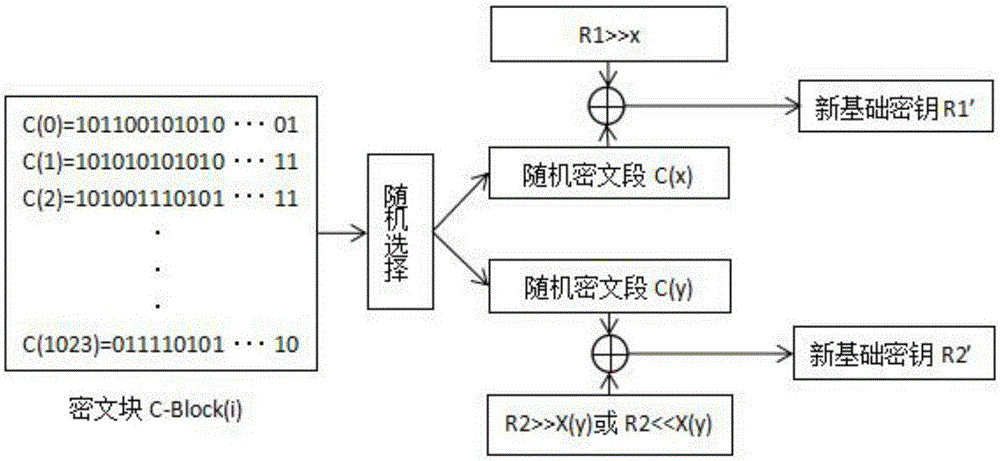
A novel symmetric key algorithm for high speed encryption comprises an encryption algorithm and a decryption algorithm, wherein the encryption algorithm comprises the following steps: grouping plaintexts M to obtain Mi; generating basic keys R1 and R2 by using a random number generator; collecting statistics about a plaintext length L, and filling Mn-1 with plaintext, that is, firstly filling a binary key generator identification code, calculating remaining bits, and filling with random binary code; getting a key offset generator G; encrypting a Mn-1 plaintext group; obtaining an encrypted key Keyi; encrypting all the plaintext groups; encrypting the basic keys R1 and R2, to obtain a cipher key CR; and completing the encryption, and transmitting the obtained ciphertext. The novel symmetric key algorithm has the advantages that the probability of key repetition is zero, and the encryption subkey of each plaintext segment is unique and random, so that the security is high; and the encryption speed is fast, that is, only two offsets, two modular operations, one multiplication, two additions, one judgment, two different or same 10-step basic operations are needed.
Owner:上海同态信息科技有限责任公司
Method for constructing block encryption algorithm based on random function
ActiveCN102571330AImprove securityHeavy calculationKey distribution for secure communicationPlaintextPassword
The invention belongs to the field of information security and relates to construction of encryption algorithm. The password (encryption) algorithm is uncertain and random by using the random function to construct the block encryption method. The uncertainties are determined by partial data in the secret key and some information of plaintext. The encryption method has the advantage that the indeterminacy of the algorithm ensures that the password analysis becomes very difficult as a result of the lack of the information about the algorithm, so that a great amount of known (selected) plaintext ciphertext pair of the same algorithm and the same secret key cannot be acquired, and the condition for password analysis is destroyed to enhance the security. The existing abundant password analysis aims at determined algorithm, and the password analysis is difficult to perform when the algorithm is random. The uncertainty of the password system is increased through multiple ways. The encryption algorithm of the plaintext is uncertain, and the algorithms of different blocks are different, therefore, the secret key space can be increased so as to enhance the safety.
Owner:桂林碧琪信息科技有限公司
One-time password authentication method
InactiveCN101394284AImprove safety performanceReduce operational complexityUser identity/authority verificationHash chainDiscrete logarithm
The invention relates to an encryption and authentication technology and provides a one-off authentication method based on an RSA encryption. The method introduces a uniform random number, has the advantages of a one-off password authentication mechanism, is based on the method of encrypting an asymmetric key of an RSA, has the intractability of a discrete logarithm, can effectively resist replay attack, overcomes the weaknesses of the one-off password authentication mechanism password based on an HASH chain algorithm, and eliminates the need of reinitializing a system at intervals. The technology has the beneficial effects that compared with the one-off password authentication method in the prior art, the safety of the technology is improved, and the complexity of an operation is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Encryption storage method for tampering-resistant files
ActiveCN107220559AIncreased sensitivityMeet storage requirementsPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTree rootIn-memory database
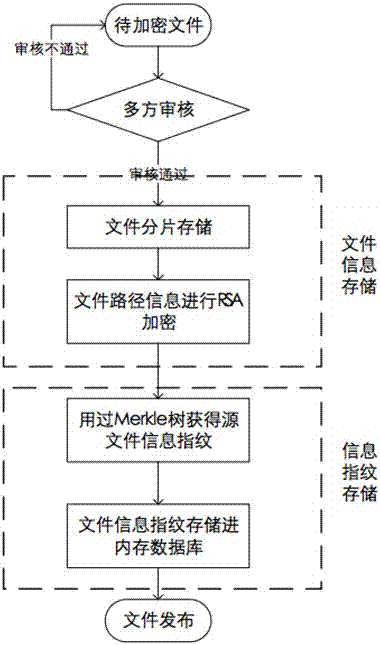
The invention discloses an encryption storage method for tampering-resistant files. The encryption storage method includes carrying out auditing querying in file uploading phases; storing the files which pass auditing in distributed clusters; segmenting and encrypting the files; carrying out Merkle tree Hash computation on the segmented files to obtain information fingerprints of the files; utilizing id (identification) of the files and tree roots hashRoot as key value pairs and storing the key value pairs in memory databases; carrying out decryption by the aid of encryption algorithms in file acquiring phases to obtain segmenting paths so as to obtain the original files. The encryption storage method has the technical advantages that the storage reliability of the distributed files further can be improved, file loss risks can be decentralized to multiple nodes, file management tasks are assigned to multiple users, segmenting information is briefly stored by the aid of structures of Merkle trees, accordingly, the file tampering sensitivity of systems can be improved, and file storage requirements with high safety requirements can be met.
Owner:南京安链数据科技有限公司
Data transmission encryption method of MANET network
InactiveCN101127597AReduce computing loadBalance workloadPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTime delaysConfidentiality
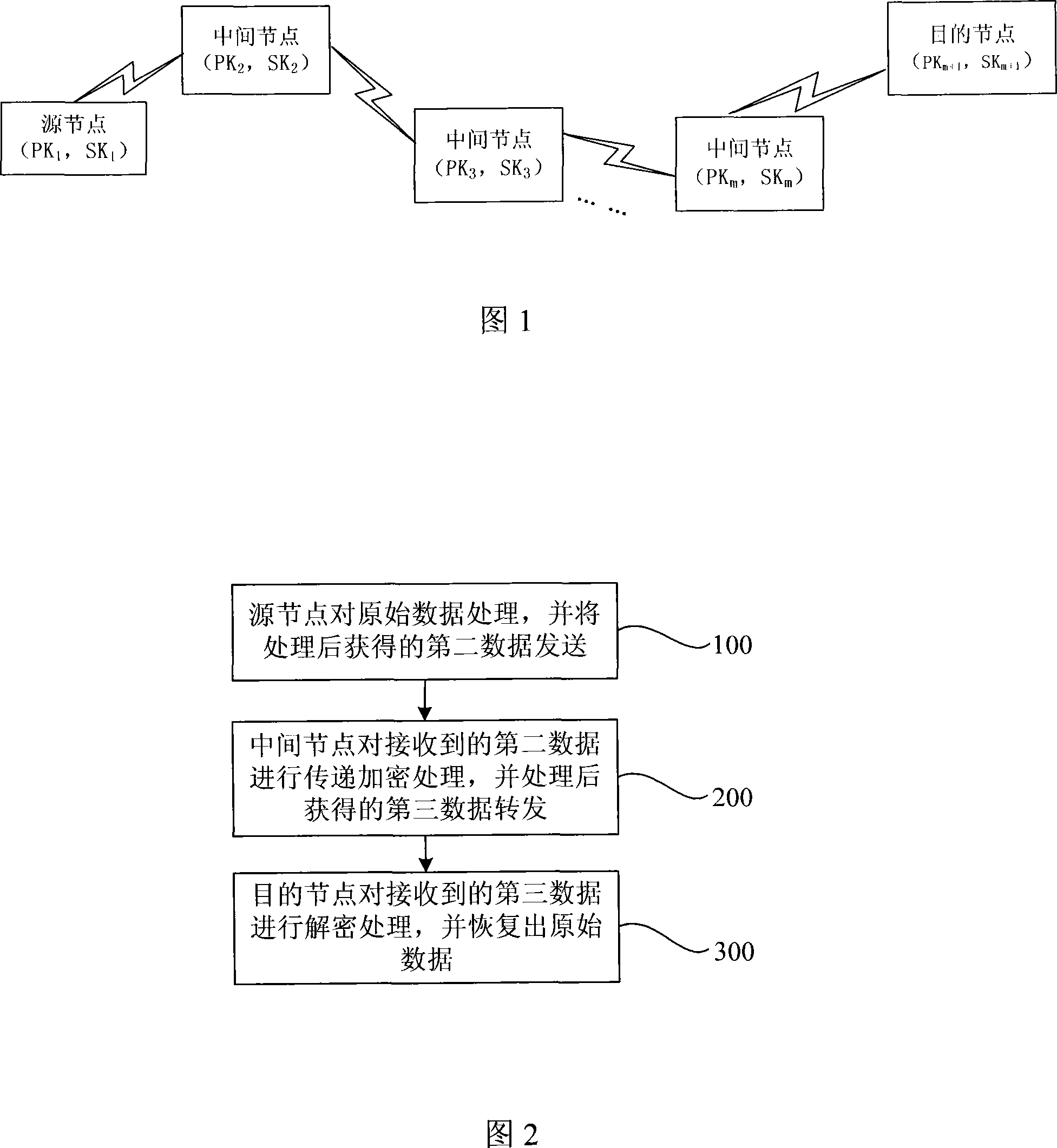
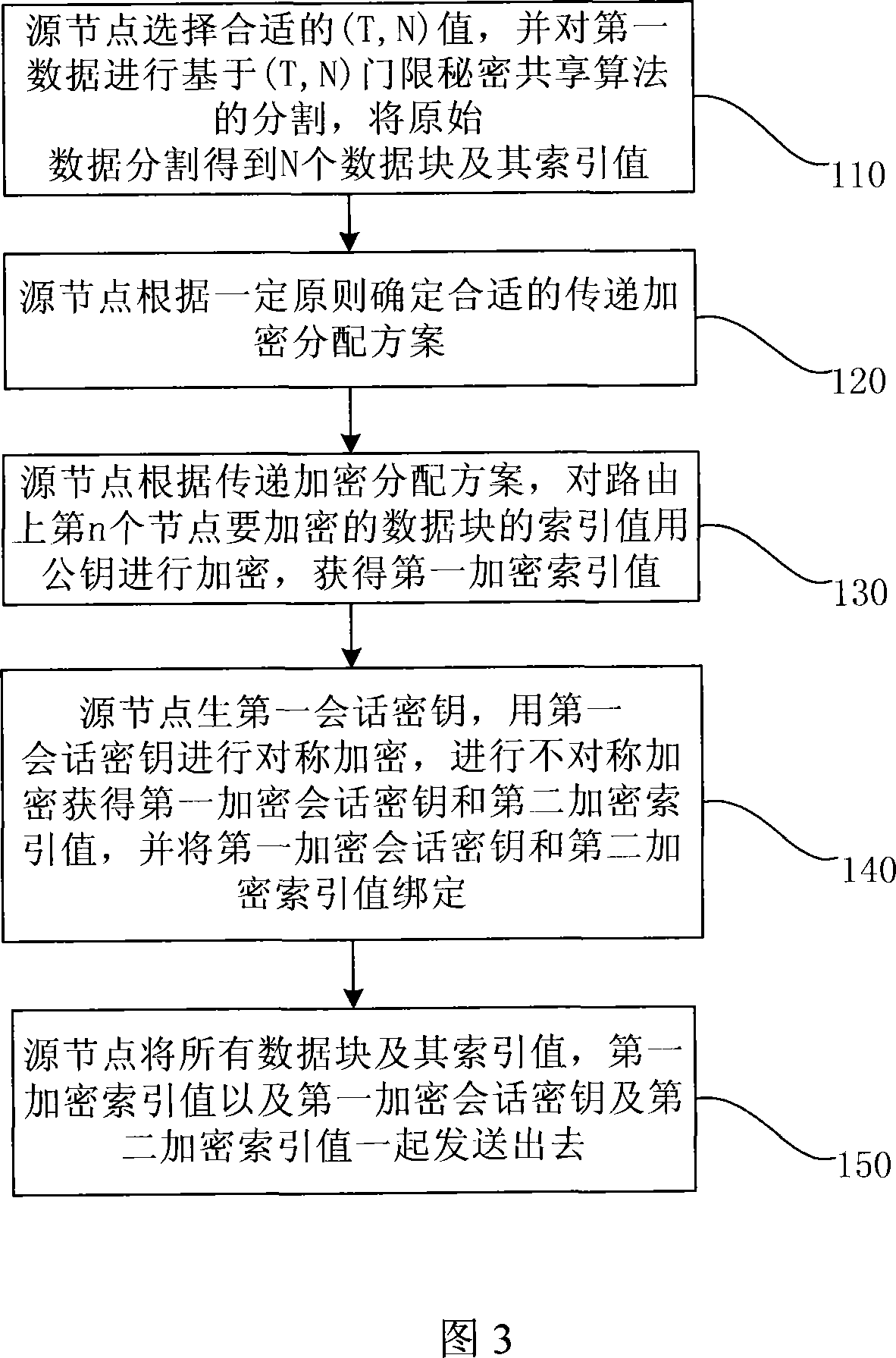
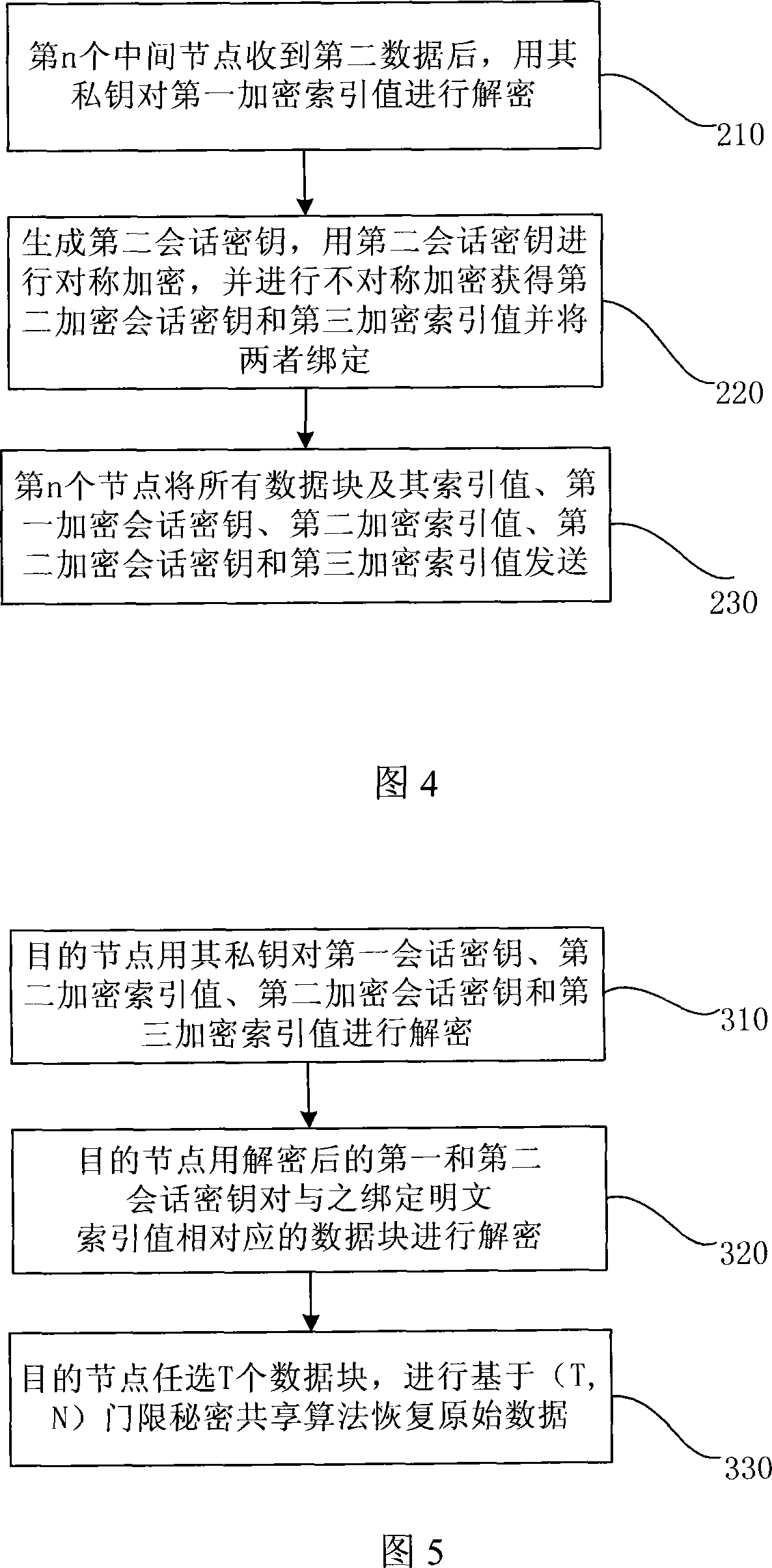
The utility model discloses a data encryption method in the MANET network, comprising: the first pitch point processes the first data and forwards the second data obtained after the process; the intermediate node encrypts the second data received in turn and forwards the third data obtained after the encryption; the second pitch point deciphers the third data received and restores the first data. The utility models has the advantages that the verifying protection of confidentiality, reliability and integrity can be provided to the data transmitted in the MANET network via the encryption method; the computing load of the pitch point is comparatively reduced; the work load of each pitch point on the communication route is balanced, and the communication time delay is shortened.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Safety control system and method applied to smart power grid wireless sensor network and cloud computing
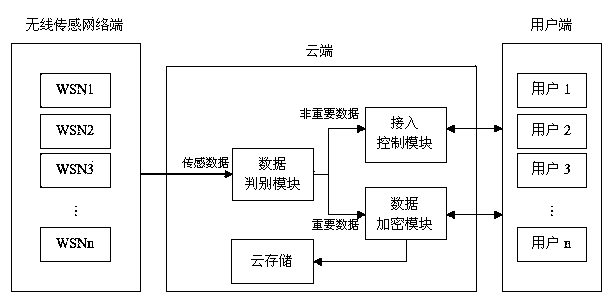
ActiveCN103905469AEnsure correctnessEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationConfidentialitySmart grid
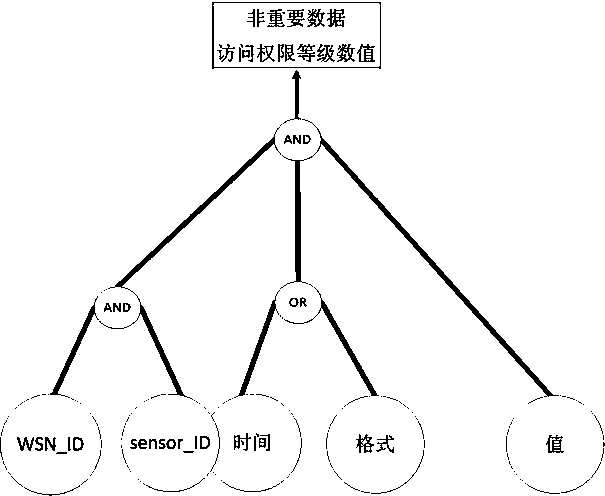
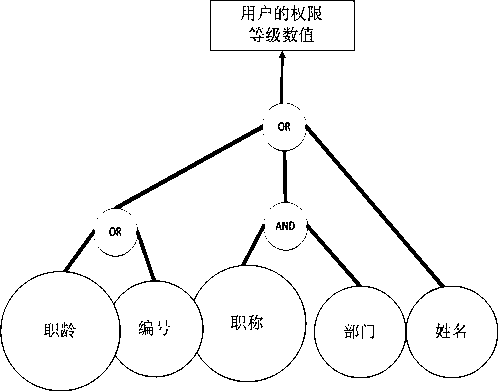
The invention discloses a safety control system and method applied to a smart power grid wireless sensor network and cloud computing. The safety control method comprises the steps that data are collected; whether the data are important data or unimportant data is judged; access control is performed to guarantee that the unimportant data are only transmitted to a user with access right; the important data are encrypted according to an encryption algorithm obtained through search, and therefore it is guaranteed that the important data are not illegally tampered or peeked at. According to the safety control system and method applied to the smart power grid wireless sensor network and cloud computing, an access control module is used for guaranteeing that the unimportant data are transmitted to the user with the access right; an access tree structure is adopted, so that complexity is low; the important data are encrypted through the encryption algorithm obtained through search, as a result, a third party can not know or tamper encrypted data content, it can be effectively avoided that sensing data are tampered and peeked at by the third party in the transmission process, and the integrity and confidentiality of the data are guaranteed. Due to the adoption of two safety strategies, the safety control system and method have the advantages of being high in flexibility and extendibility and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
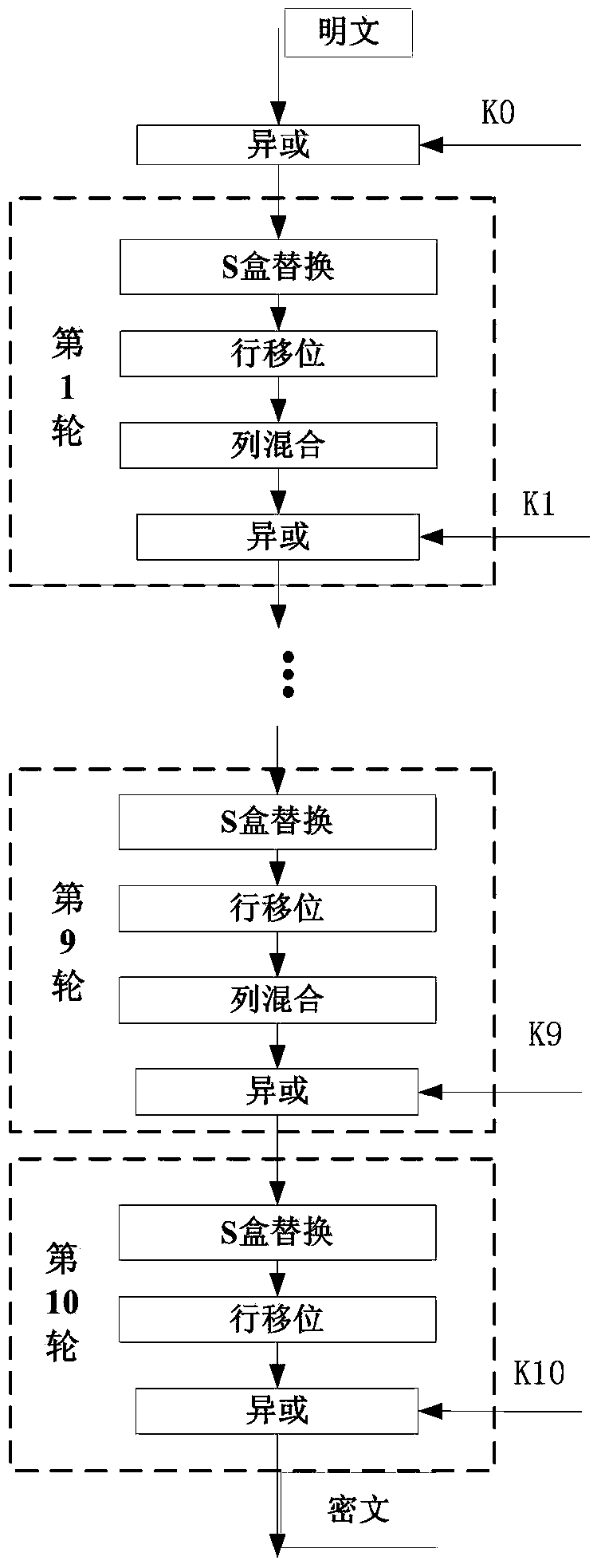
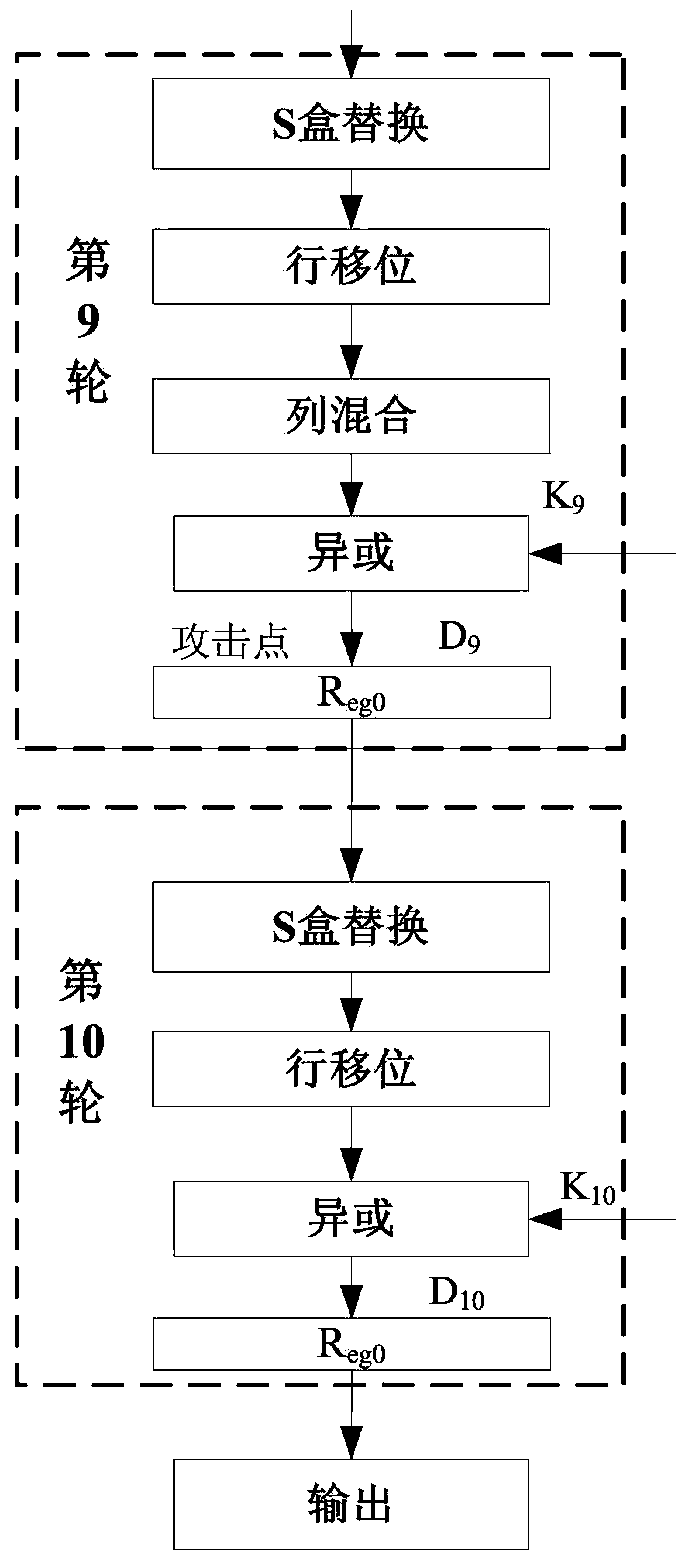
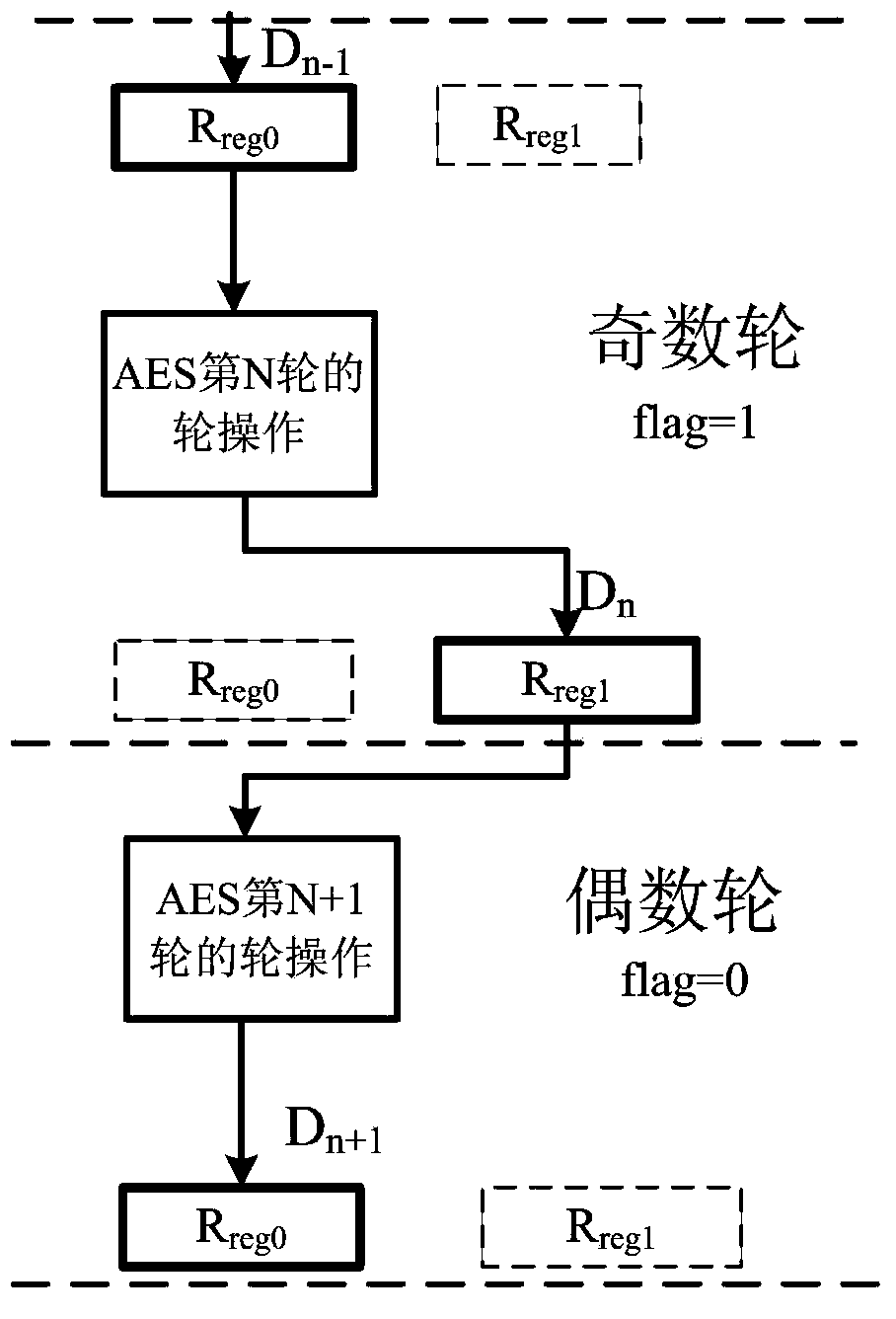
Power attack prevention method oriented at AES algorithm and circuit achieving method thereof
ActiveCN103916236APrevent leakageImprove the ability to resist power consumption attacksEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareProcessor register
The invention provides a power attack prevention method oriented at an AES algorithm and a circuit achieving method of the power attack prevention method oriented at the AES algorithm. According to the basic principle, a control module and redundancy registers are added to an AES algorithm circuit. The AES algorithm selects the position of a register storing middle calculation data in each turn according to a zone bit generated by the control module, so that the middle data of each turn of encryption operation are alternatively stored in the different registers, the Hamming distance of the middle data of the AES algorithm is effectively hidden, and the AES algorithm can resist power analysis attacks based on a Hamming distance model. The power attack prevention method oriented at the AES algorithm and the circuit achieving method of the power attack prevention method oriented at the AES algorithm have the advantages of being high in flexibility, small in area cost, high in power attack resistance and the like, and provide a good resolution scheme for designing safe chips.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
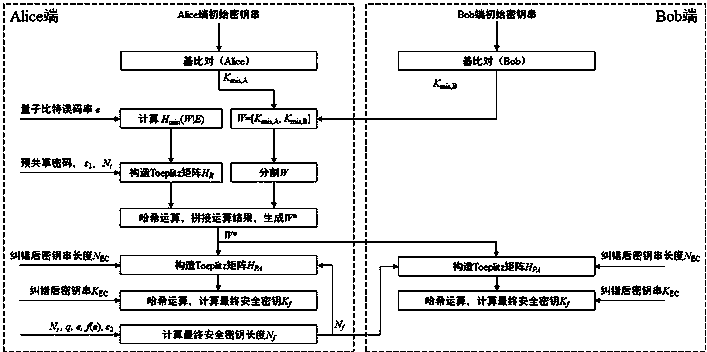
Verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution
ActiveCN108599934AMeet security needsEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobLower limit
The invention discloses a verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution. The method comprises the steps of S1, generating an initial random number string W, respectively generating random number strings K<mis,A> and K<mis,B> by two communication parties (Alice and Bob) in a base comparison process of quantum key distribution, and combining the two random number strings into a random number string W=[<Kmis,A>, K<mis,B>] by the Alice; S2, verifying randomness, after an error correction phase of the quantum key distribution is finished, estimating the minimum entropy lower limit of the W relative to an attacker Eve, wherein H<min>(W|E) is greater than or equal to 1-H<2>(e); S3, calculating a final secure key length N<f>; S4, extracting a perfect random string W*, through adoption of a partial pre-shared secure key of the two communication parties, constructing a Toeplitz matrix H<R>, and extracting the perfect random number string W* from the W according to the H<R>; S5, negotiating a universal hash function H<PA> through a public channel according to the W*; and S6, respectively carrying out hash operation on error corrected key strings by the two communication parties according to the H<PA>, and generating a final secure key. The method has the advantages of verifiability, security, easy realization and simplification of quantum key distribution system design and realization.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
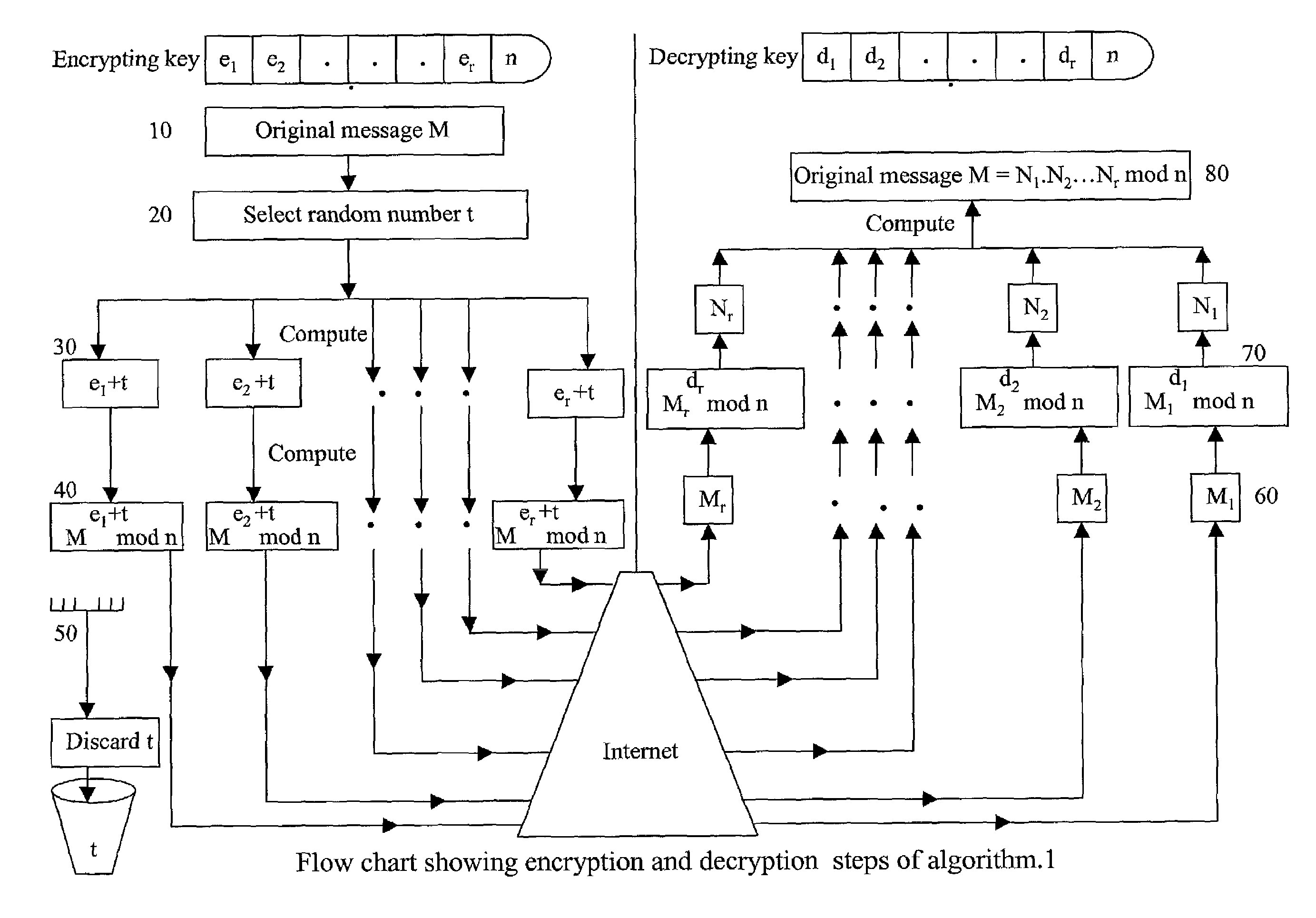
Absolute public key cryptographic system and method surviving private-key compromise with other advantages
InactiveUS7088821B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunications securityKey (cryptography)
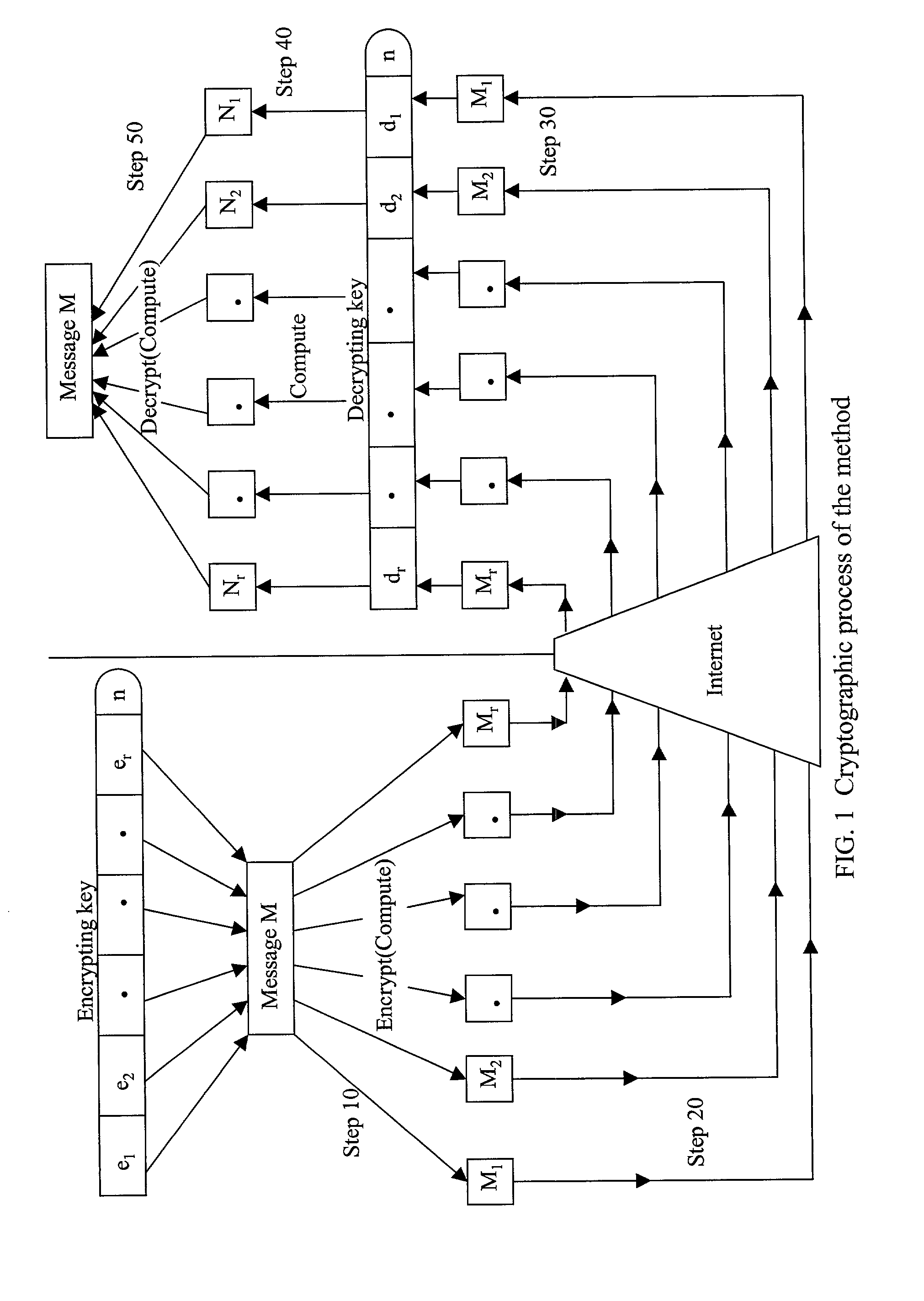
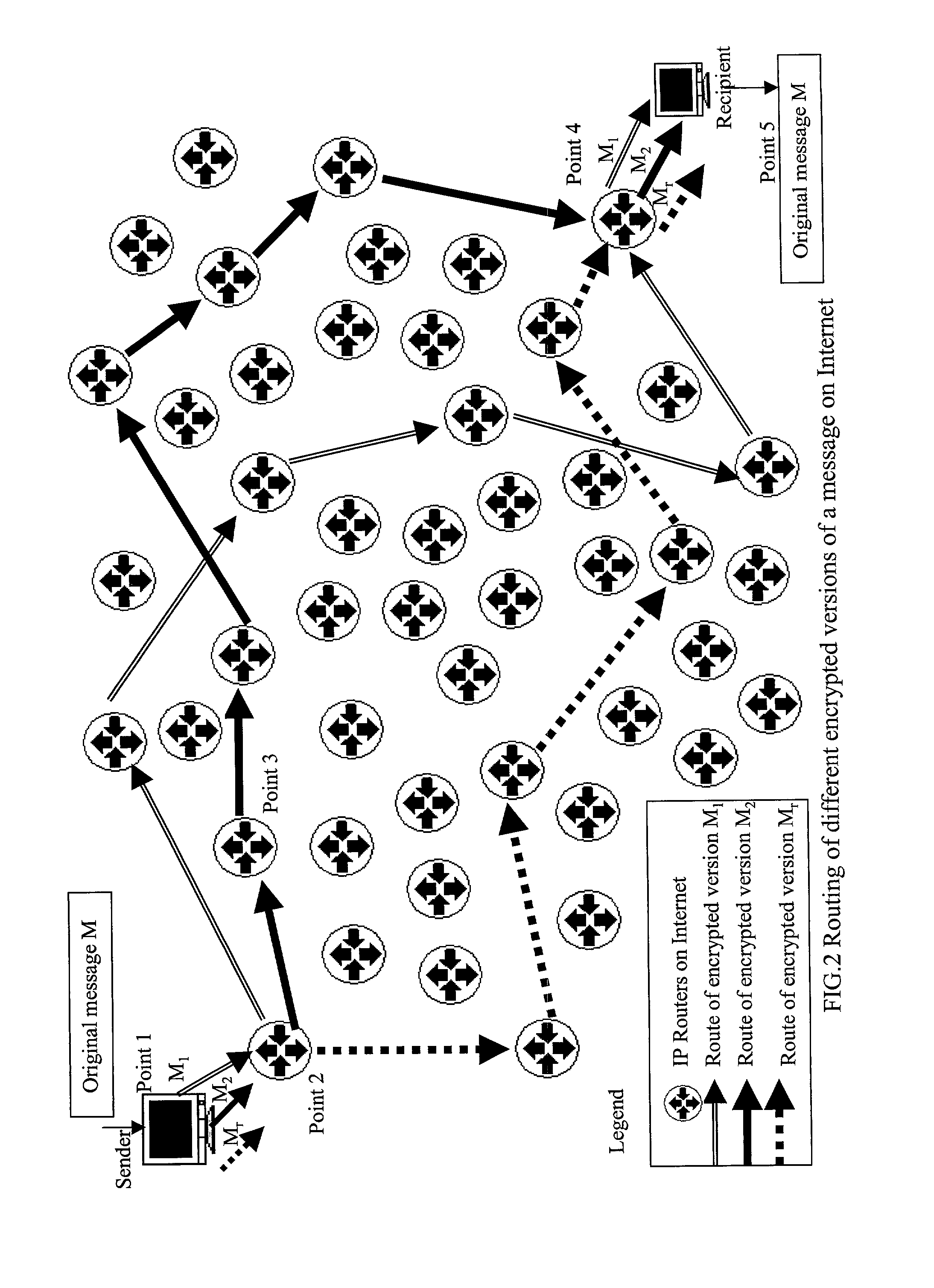
The present invention presents a public key cryptographic system and method called Absolute Public Key Cryptography that survives private key compromise and offers two-way communication security. Communications are secured even when the private key is revealed. It provides security to the private-to-public side communications and also allows short keys to be used with mobile devices that have low processing power. The system uses keys with two or more components and encrypts a message into the same number of cipher versions. The cipher versions are delivered to the destination in source routing mode, or hop-by-hop routing mode with a small time gap. The recipient performs certain mathematical operations on all the cipher versions and obtains the original message. All the versions are necessary for obtaining the original message. Even a single version missing leads to produce a junk for an attacker. As an attacker at an intermediary IP router can not have all the cipher versions available, he can not obtain the original message even when he knows the private key. This is why the system is called Absolute Public Key Cryptography. The robustness against private key compromise is achieved by blinding the public key through adding a random number to each of its components before encryption. When the encryption process is complete, the random number is discarded and the cipher versions are delivered to the recipient. The effect of blinding is made void by the actual intended recipient, who has all the cipher versions available. Robustness is also achieved another way, that is, by choosing the encrypting key such that each of its components has a common factor with Euler Totient Function of the key modulus, and there is no common factor among all the components. This makes it harder for an attacker to decrypt a single cipher version of the message into the original message and thereby allows smaller keys to be used for mobile communications. Communication in both directions is secured by using two different key pairs, one for public-to-private-side and the other for private-to-public-side communications.
Owner:KIOBA PROCESSING LLC
Security Certification Method for Hiding Ultra-High Frequency Electronic Tag Identifier
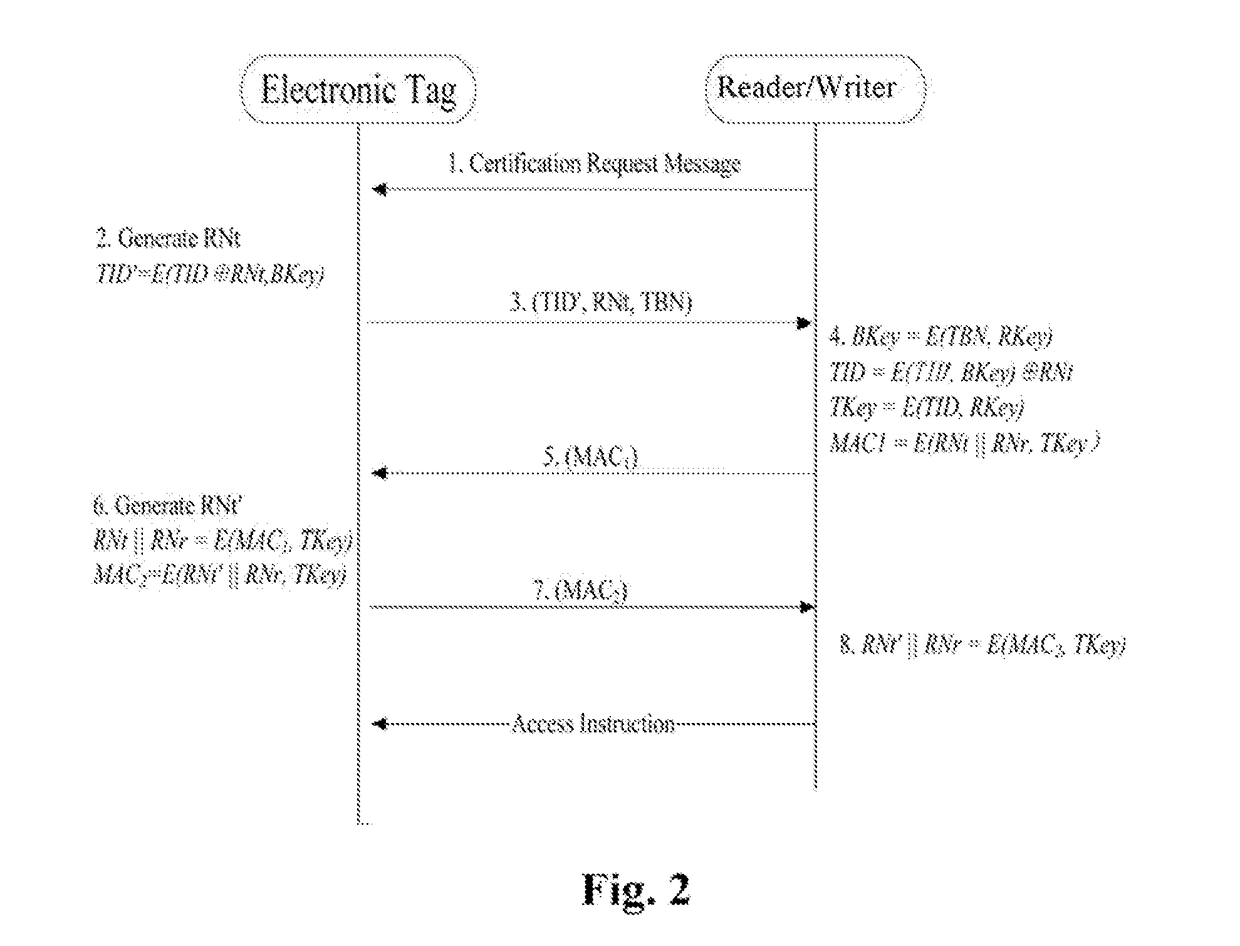
InactiveUS20180196973A1Overcome deficienciesAvoid trackingEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCo-operative working arrangementsIdentity recognitionCiphertext
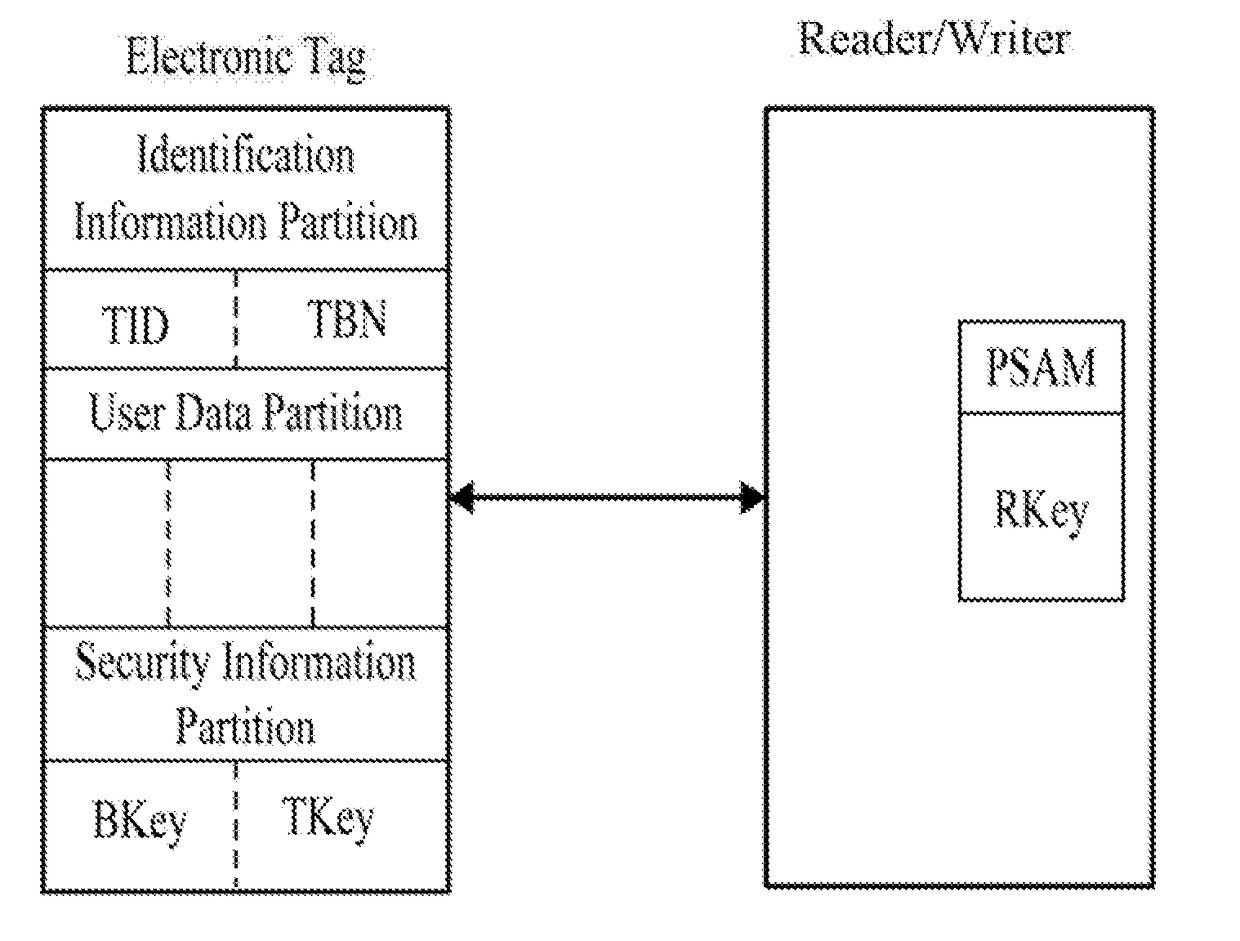
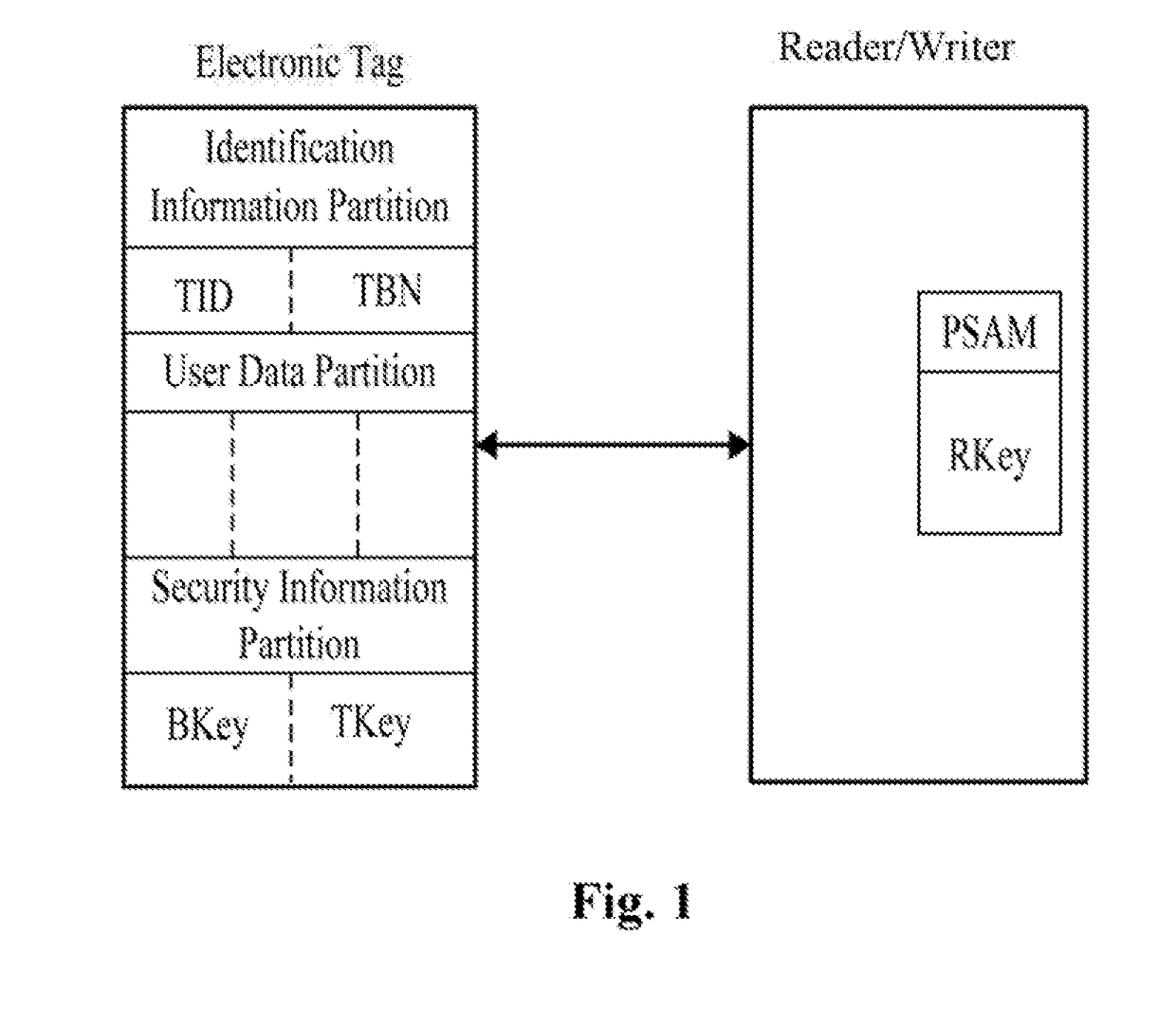
A security certification method for hiding an ultra-high frequency electronic tag identifier. By encrypting the electronic tag identifier (TID) using a random number, and returning it in the cipher text, this certification method can effectively avoid an illegal reading / writing device from acquiring the TID information and from performing illegal tracking and identity recognition on an object identified by the electronic tag. Meanwhile, this certification method can effectively resist attacks, such as eavesdropping, counterfeiting, replaying, and etc. It has the advantages of preventing the electronic tag information from being eavesdropped and counterfeited, and etc. The security certification method uses the symmetric encryption algorithm of the national commercial cryptographic algorithm and the dual-key and the two-step certification mechanism. Thus, the certification of the validity of the electronic tag with the same-key of a batch of cards, and the bidirectional security certification with the single-tag and single-key are achieved.
Owner:TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Chaos message authentication code realization method for wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102594566AImprove securityEasy to implementUser identity/authority verificationWireless mesh networkHash-based message authentication code
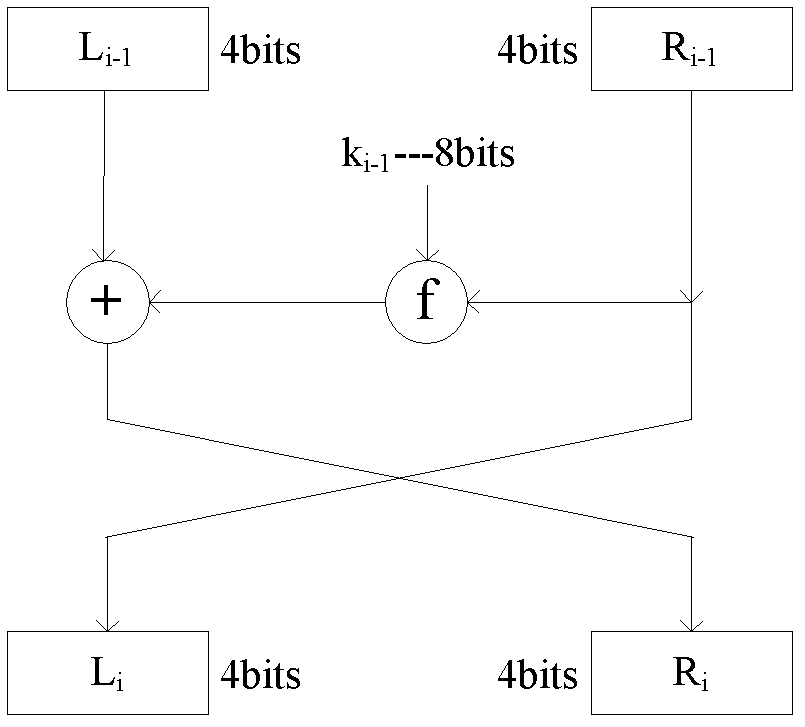
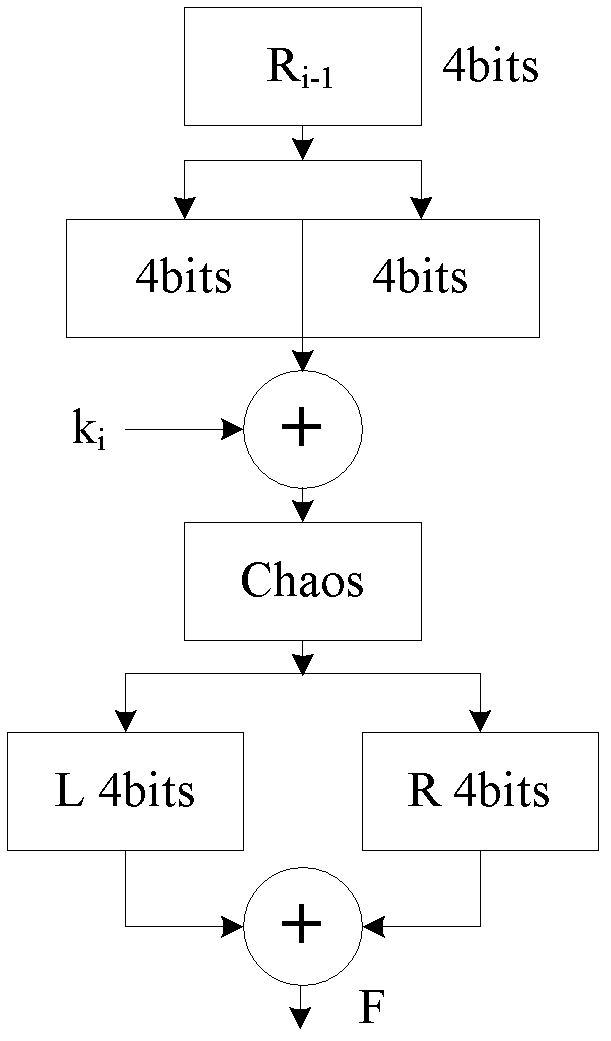
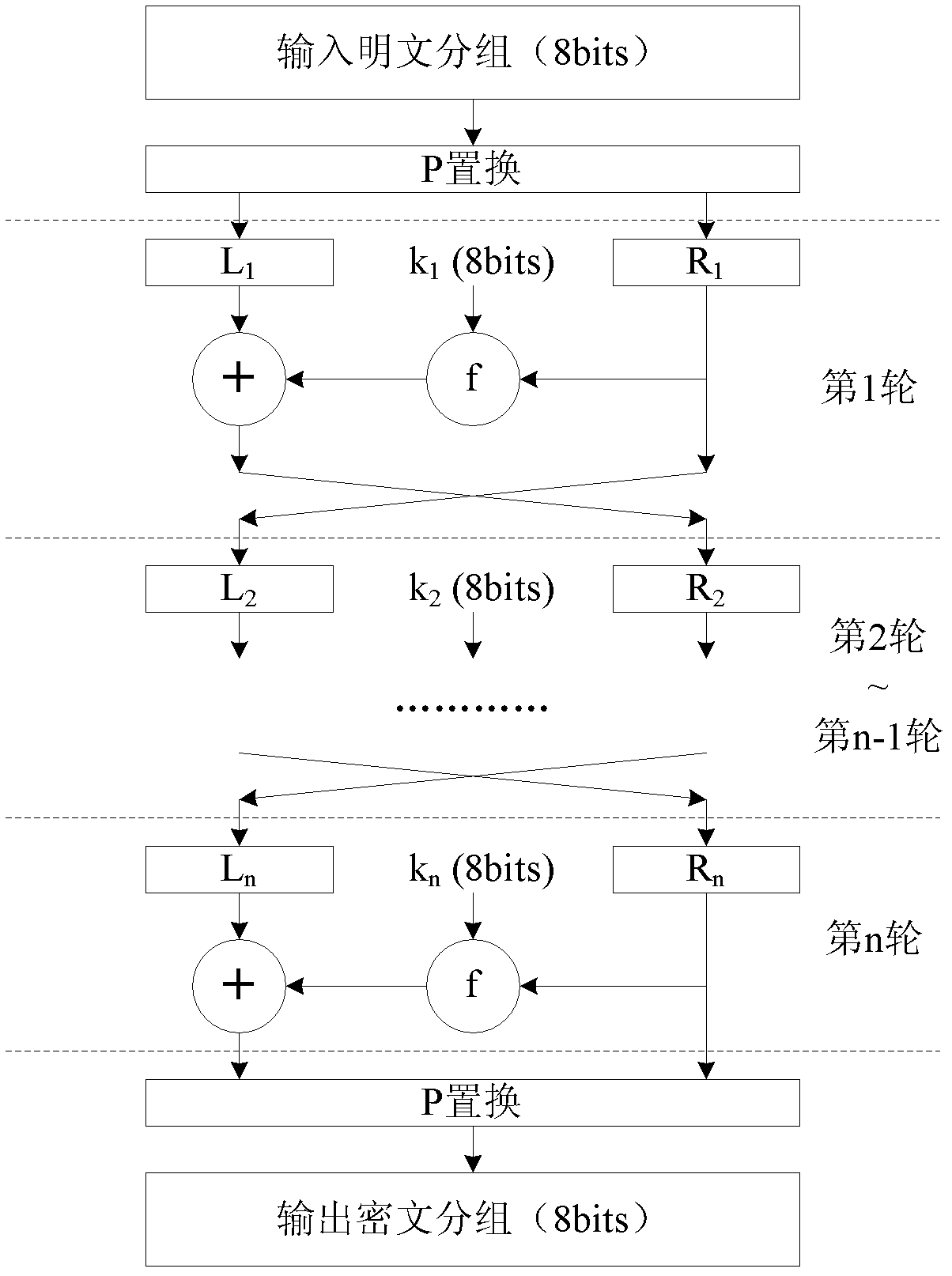
The invention relates to a chaos message authentication code realization method for a radio sensor network, which comprises the following steps: 1) firstly, adopting a Logistic chaotic mapping function calculated based on an integer type for a radio sensor node; 2) adopting a block encryption algorithm which has the dynamic Feistel structural characteristic and has a block length being 8 bits only; and 3) realizing a message authentication code of which the length is 32 bits based on the block encryption algorithm. The invention provides the chaos message authentication code realization method for the radio sensor network, which has the advantages of good safety and higher efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
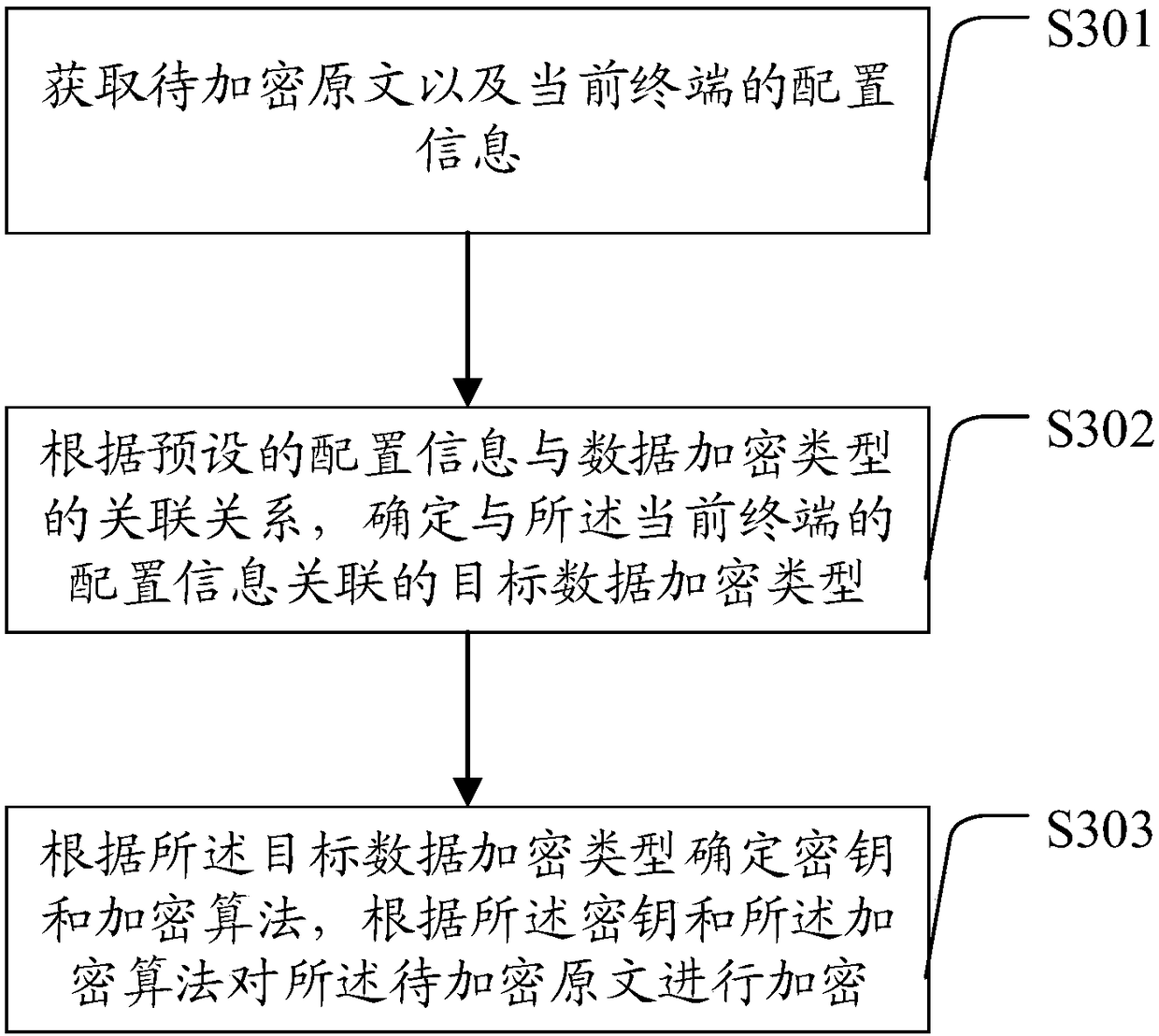
Terminal data encryption method and system and terminal data decryption method and system
ActiveCN108197485AImprove compatibilityImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer compatibilityComputer terminal
The invention relates to a terminal data encryption method and system and a terminal data decryption method and system and relates to the technical field of data encryption. The terminal data encryption method includes: acquiring to-be-encrypted original text and the configuration information of a current terminal, determining a target data encryption type associated with the configuration information of the current terminal according to the preset association relationship of the configuration information and the data encryption type, determining a secrete key and an encryption algorithm according to the target data encryption type, and encrypting the to-be-encrypted original text according to the secrete key and the encryption algorithm. The terminal data encryption method has the advantages that the data encryption type is determined according to the acquired configuration information of the current terminal, the secret key and the encryption algorithm are determined according to thedata encryption type, the to-be-encrypted original text is encrypted by using the secrete key and the encryption algorithm, the cracking difficulty of the secret key and the encryption algorithm is increased, large-scale exposure of the secret key is prevented, terminal encryption compatibility is increased, and terminal data encryption safety is increased.
Owner:E-SURFING DIGITAL LIFE TECH CO LTD
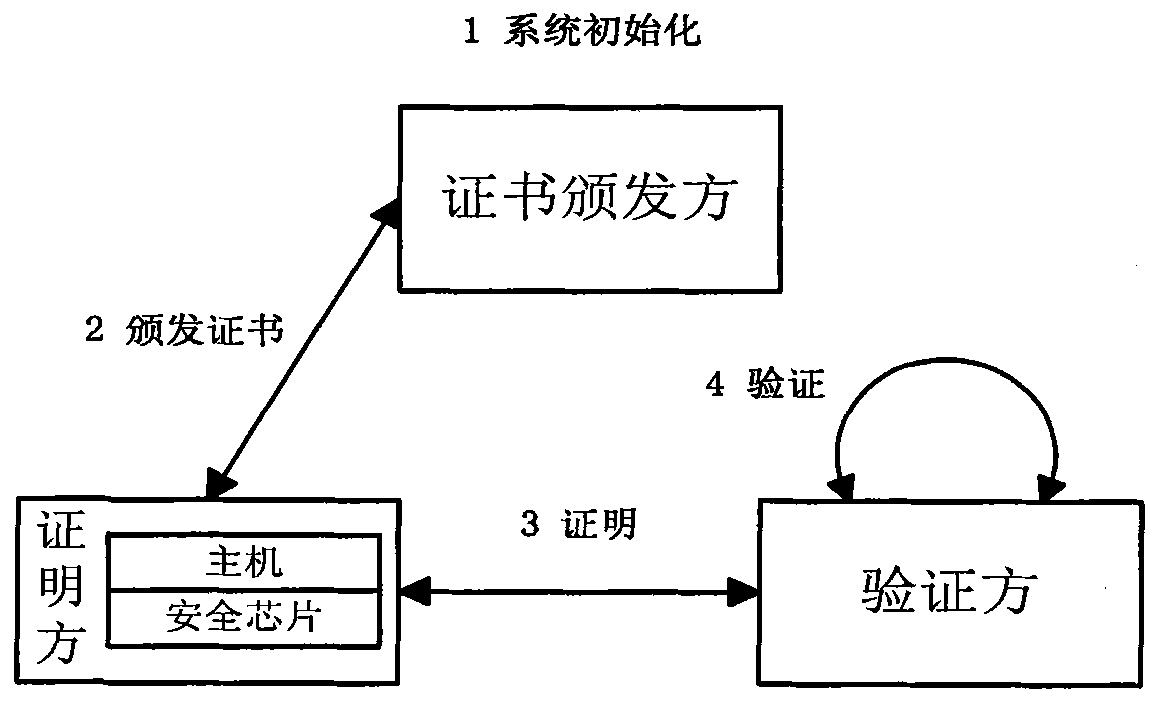
Elliptic curve and bilinear pairing cryptography based direct anonymous proving method
InactiveCN102096778AEnsure safetyHigh degree of anonymityDigital data protectionFinite field arithmeticAnonymity
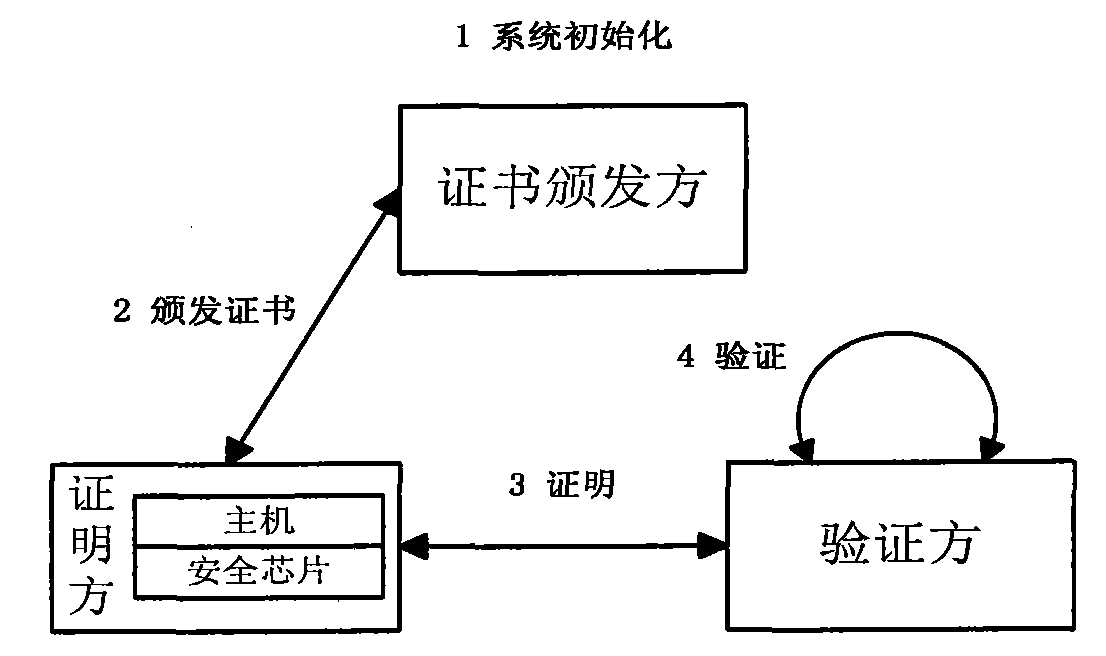
The invention discloses an elliptic curve and bilinear pairing cryptography based direct anonymous proving method, comprising the following steps of: (1) initializing a certificate issuing party system and sending common parameters to a certification party and a verification party; (2) issuing an anonymous certificate; (3) anonymously certifying DAACert (Computer emergency response team) by the certification party; and (4) anonymously verifying the anonymous certificate DAACert of the certification party by the verification party. According to the direct anonymous proving method provided by the invention, when the certification and the verification are carried out on the verification party by the certification party, high anonymity is maintained; the certified information is stored in a security chip and cannot be divulged; even the certified information is divulged, the real but broken certification party can be detected by utilizing the method provided by the invention; therefore, the safety of the certified information can be guaranteed. In the mean time, the method has the advantages of fast arithmetic speed and small traffic; when the security intensity of 128 bit is adopted,the arithmetic speed of the invention is at least 14 times faster than that of a scheme based on finite field arithmetic and the traffic of the invention is not more than 10 % of that of the scheme based on the finite field arithmetic.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com