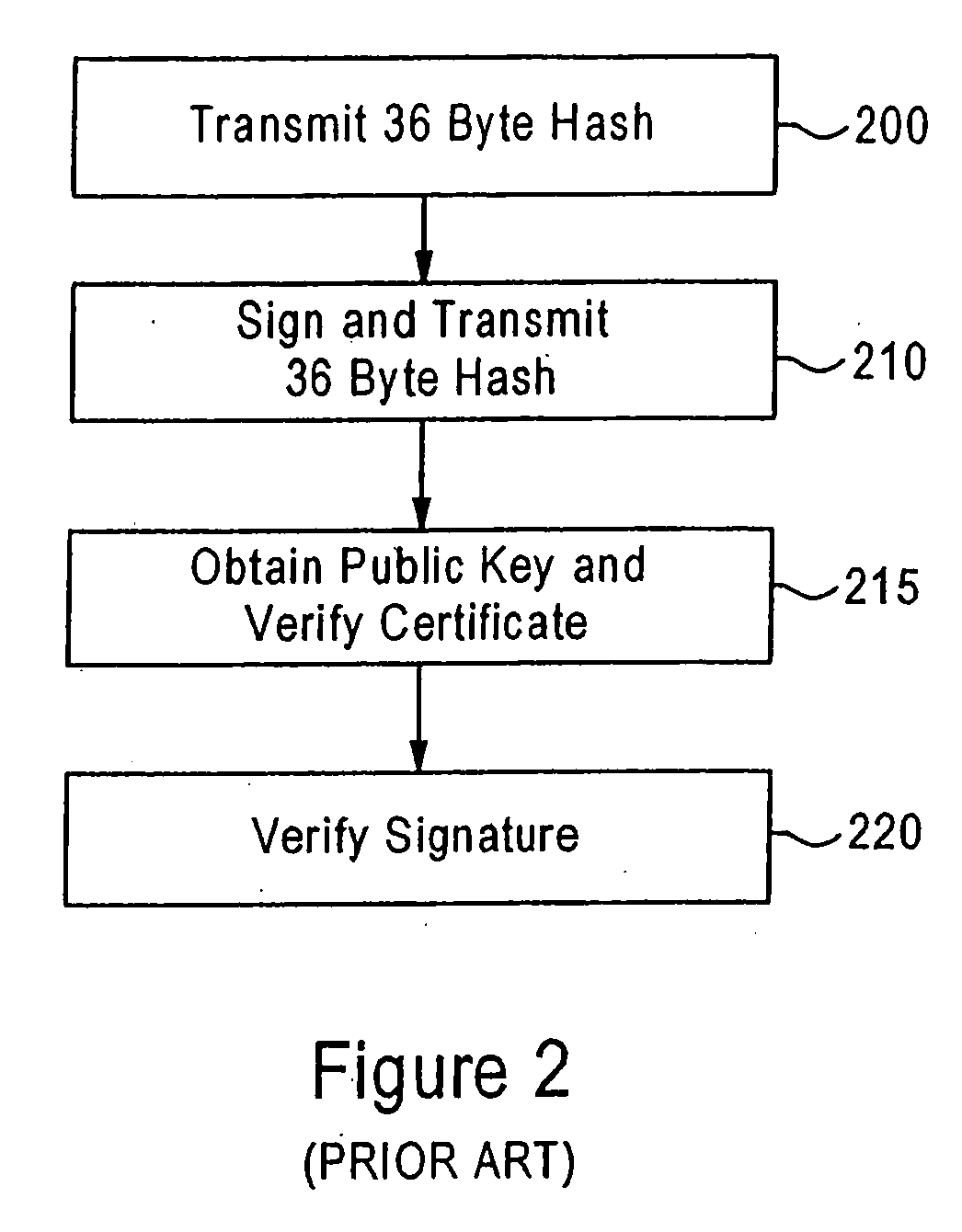
Patents
Literature
415 results about "Key (cryptography)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
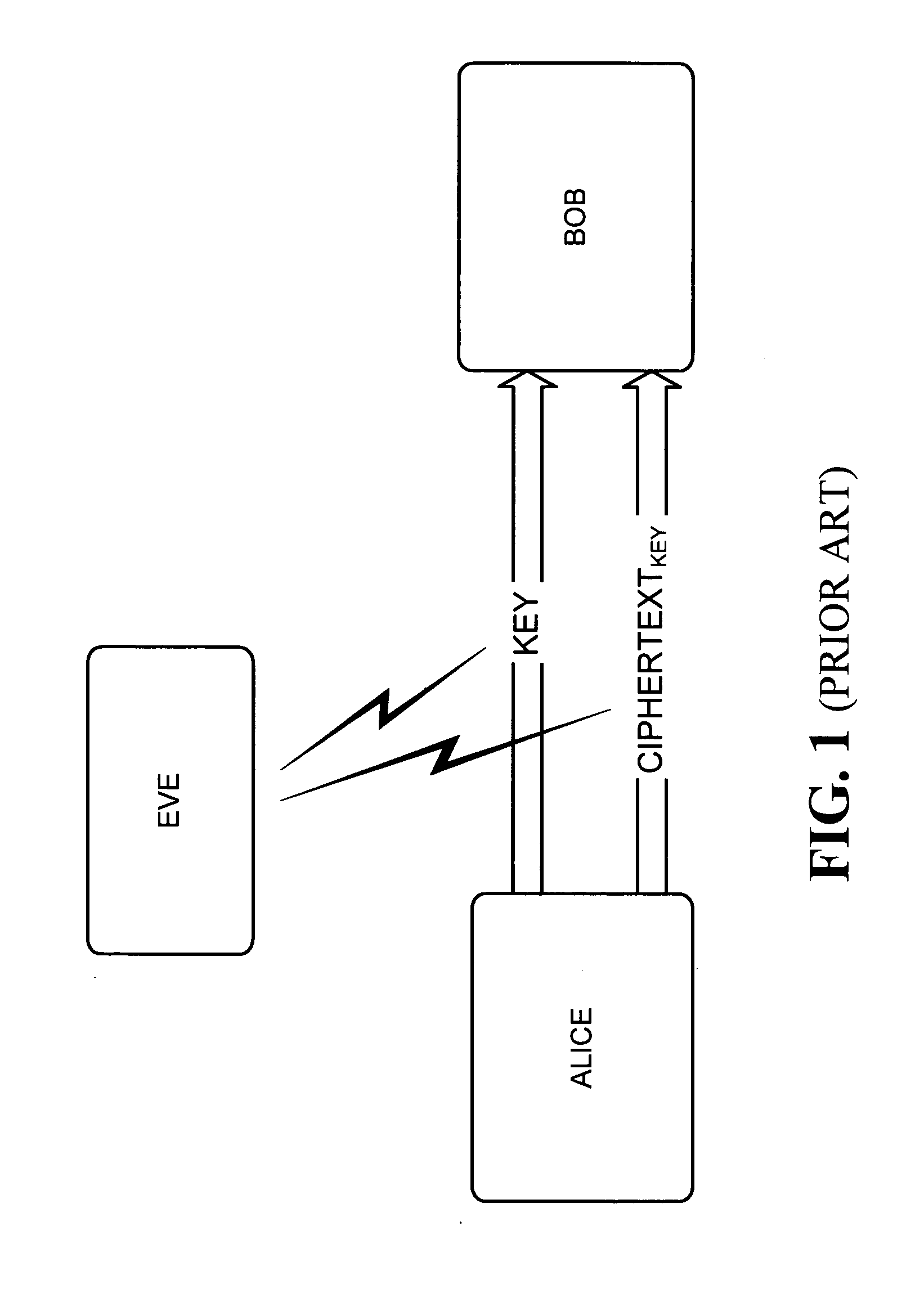
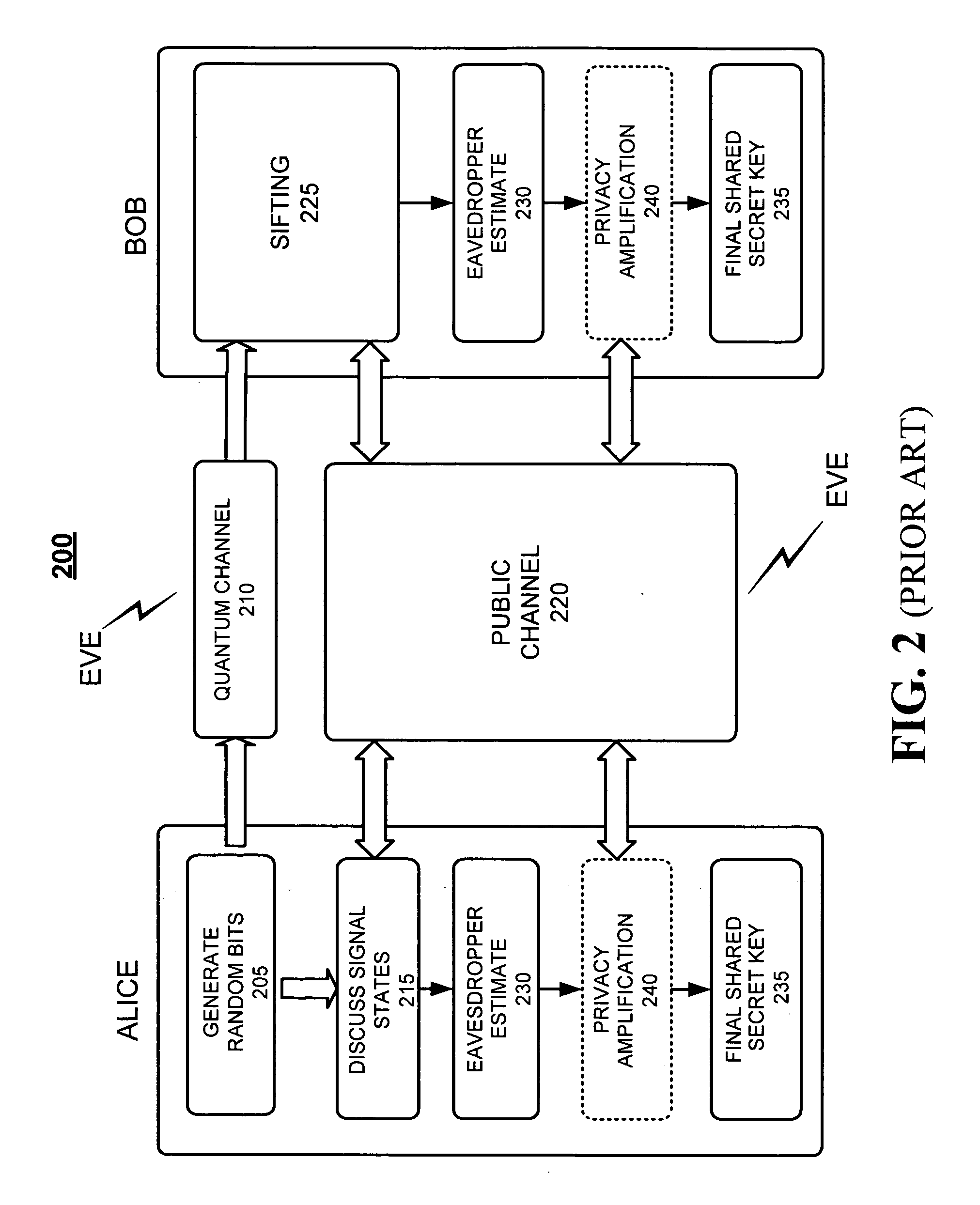
In cryptography, a key is a piece of information (a parameter) that determines the functional output of a cryptographic algorithm. For encryption algorithms, a key specifies the transformation of plaintext into ciphertext, and vice versa for decryption algorithms. Keys also specify transformations in other cryptographic algorithms, such as digital signature schemes and message authentication codes.
Systems and methods using cryptography to protect secure computing environments
InactiveUS6157721AProtection from disclosureSpeeding up digital signature verificationRecording carrier detailsDigital data processing detailsThird partyTamper resistance
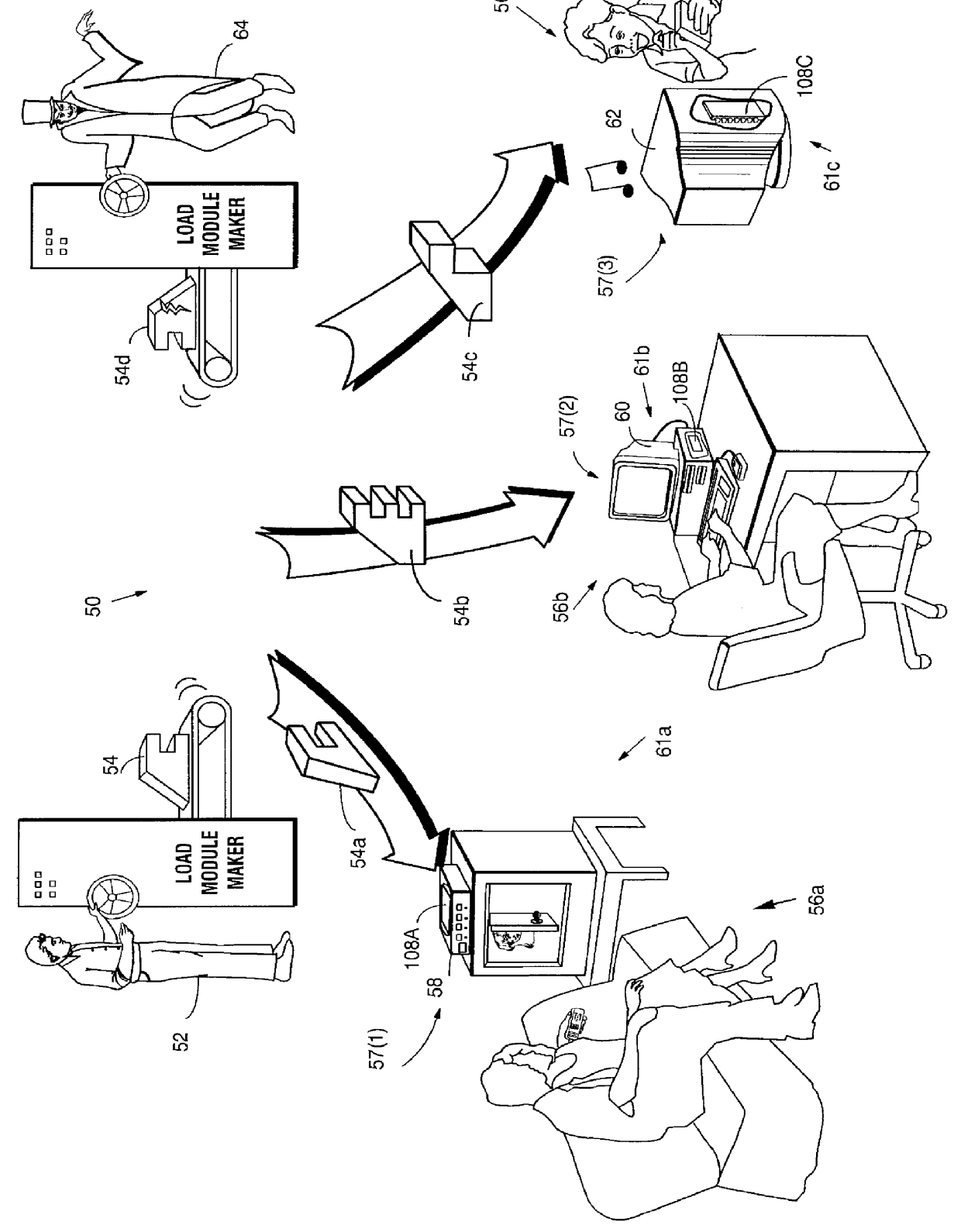
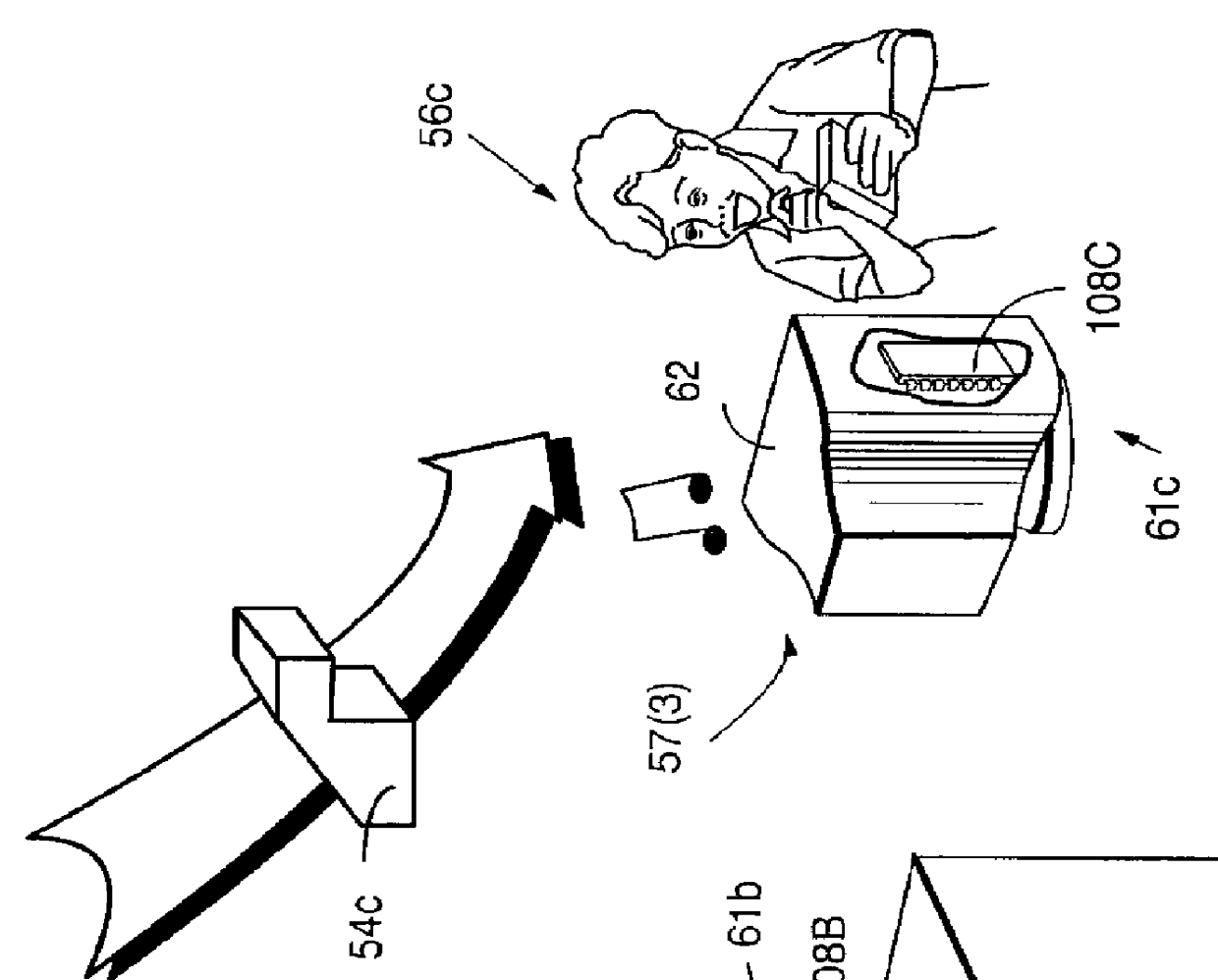
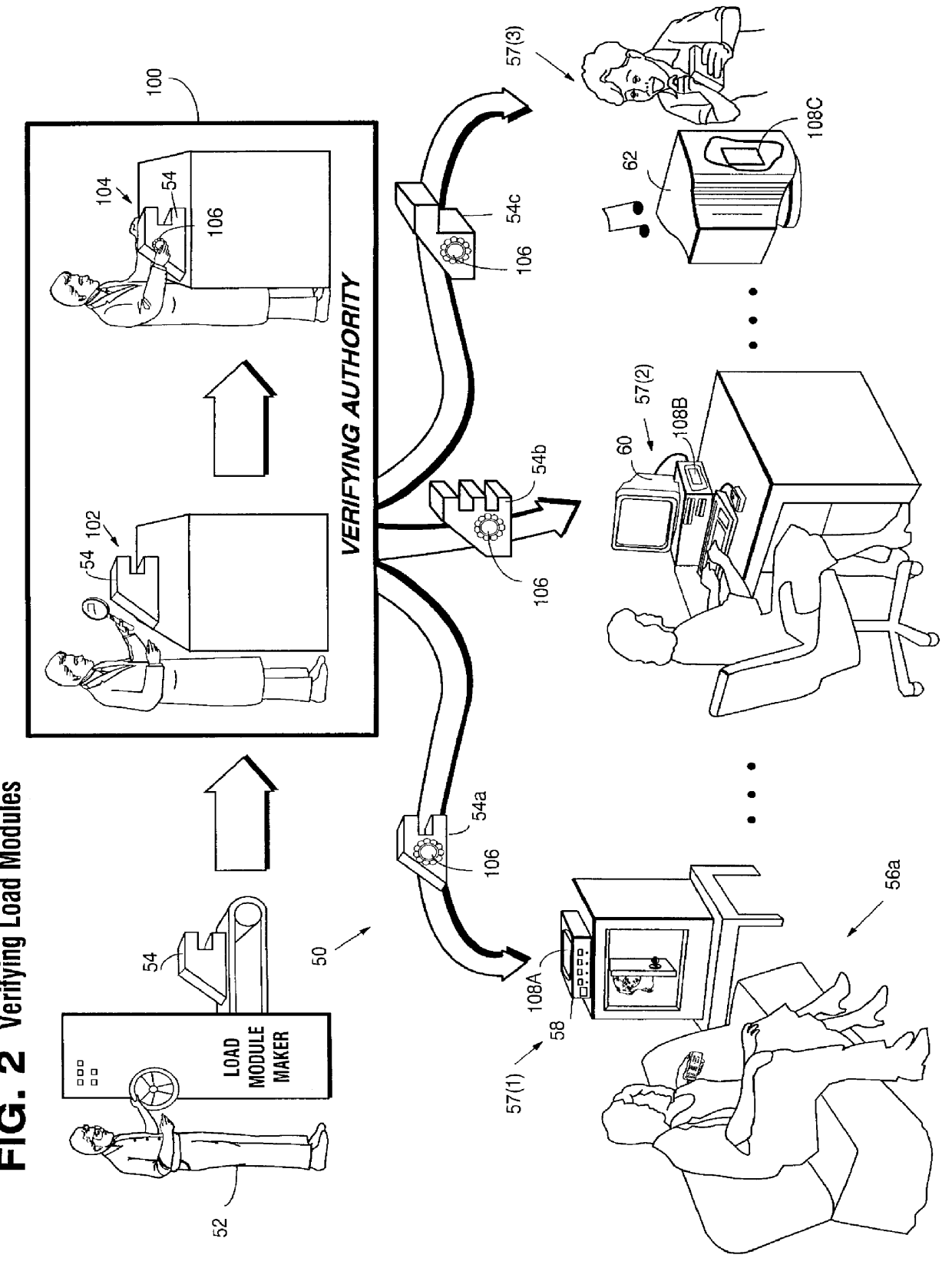
Secure computation environments are protected from bogus or rogue load modules, executables and other data elements through use of digital signatures, seals and certificates issued by a verifying authority. A verifying authority-which may be a trusted independent third party-tests the load modules or other executables to verify that their corresponding specifications are accurate and complete, and then digitally signs the load module or other executable based on tamper resistance work factor classification. Secure computation environments with different tamper resistance work factors use different verification digital signature authentication techniques (e.g., different signature algorithms and / or signature verification keys)-allowing one tamper resistance work factor environment to protect itself against load modules from another, different tamper resistance work factor environment. Several dissimilar digital signature algorithms may be used to reduce vulnerability from algorithm compromise, and subsets of multiple digital signatures may be used to reduce the scope of any specific compromise.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
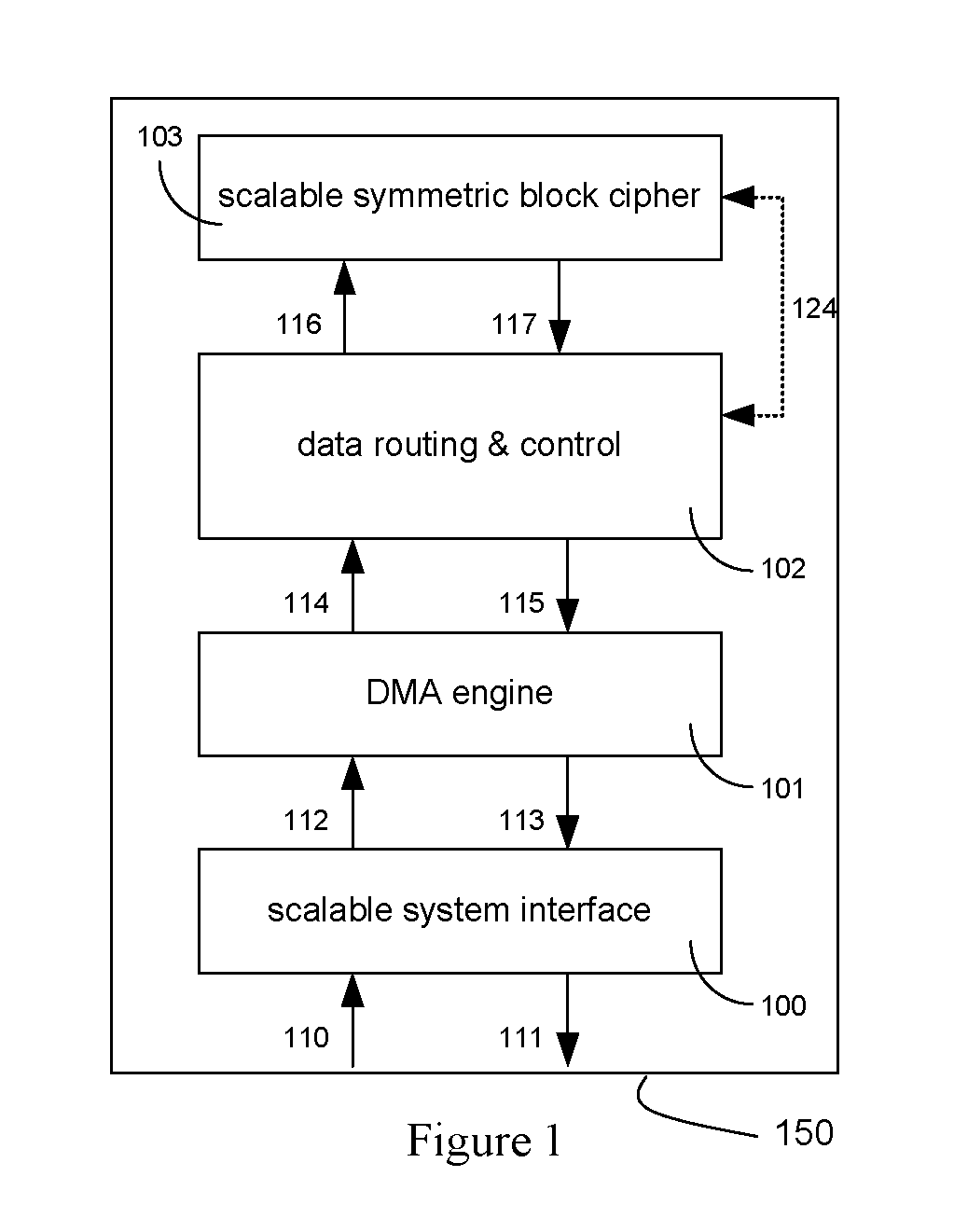
Method and Apparatus for Hardware-Accelerated Encryption/Decryption
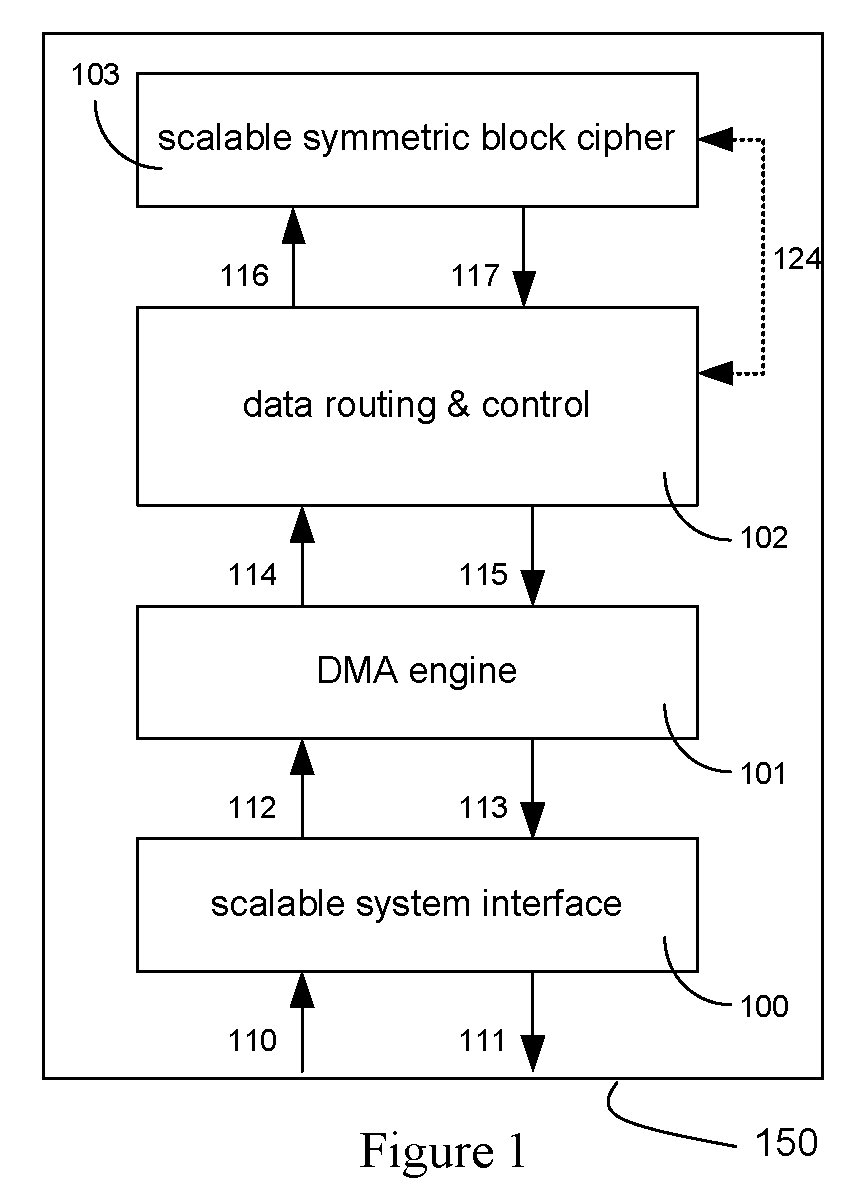
ActiveUS20090060197A1Avoid contactMaximize availabilityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationMultiple encryptionComputer hardware
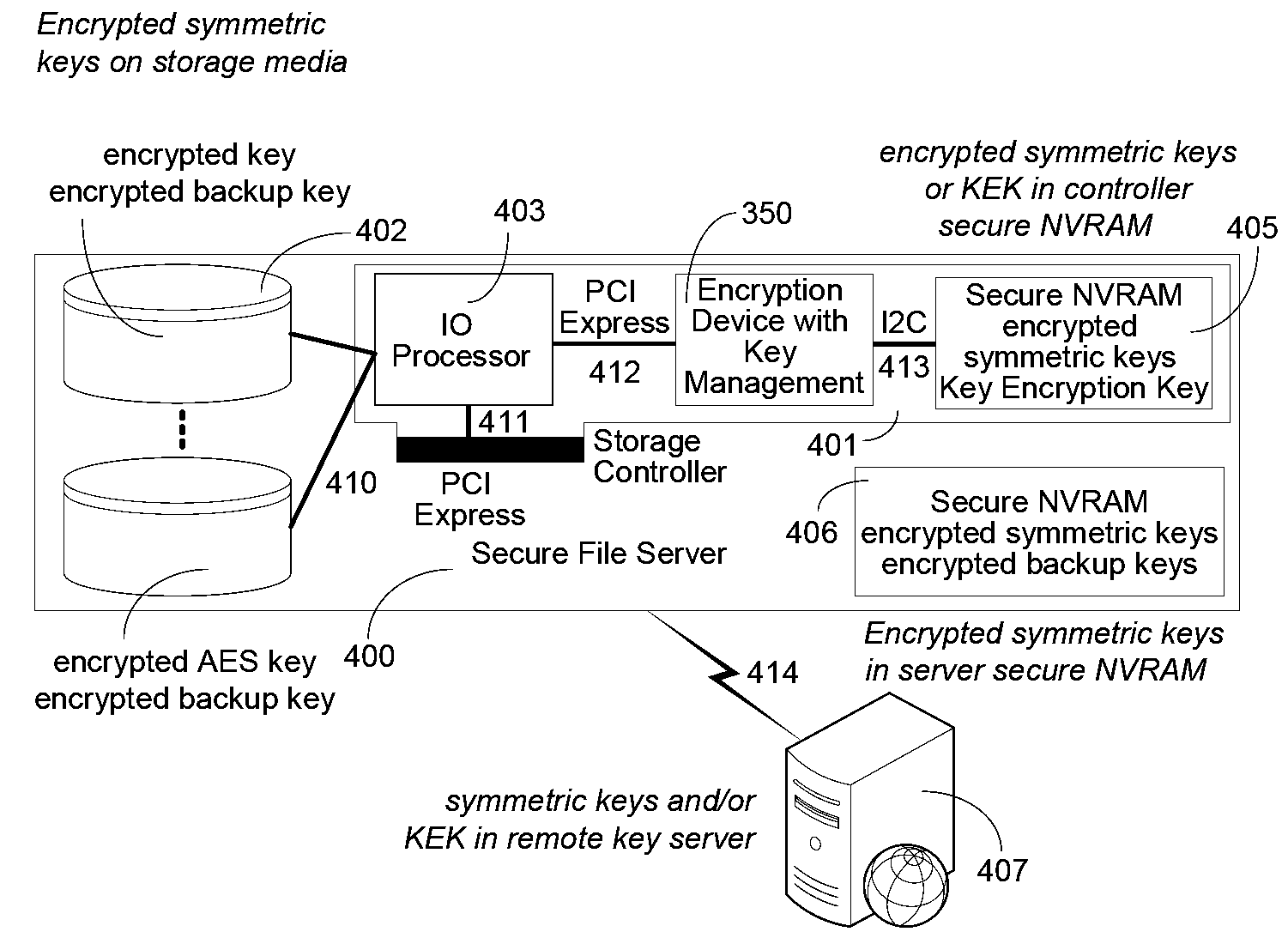
An integrated circuit for data encryption / decryption and secure key management is disclosed. The integrated circuit may be used in conjunction with other integrated circuits, processors, and software to construct a wide variety of secure data processing, storage, and communication systems. A preferred embodiment of the integrated circuit includes a symmetric block cipher that may be scaled to strike a favorable balance among processing throughput and power consumption. The modular architecture also supports multiple encryption modes and key management functions such as one-way cryptographic hash and random number generator functions that leverage the scalable symmetric block cipher. The integrated circuit may also include a key management processor that can be programmed to support a wide variety of asymmetric key cryptography functions for secure key exchange with remote key storage devices and enterprise key management servers. Internal data and key buffers enable the device to re-key encrypted data without exposing data. The key management functions allow the device to function as a cryptographic domain bridge in a federated security architecture.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
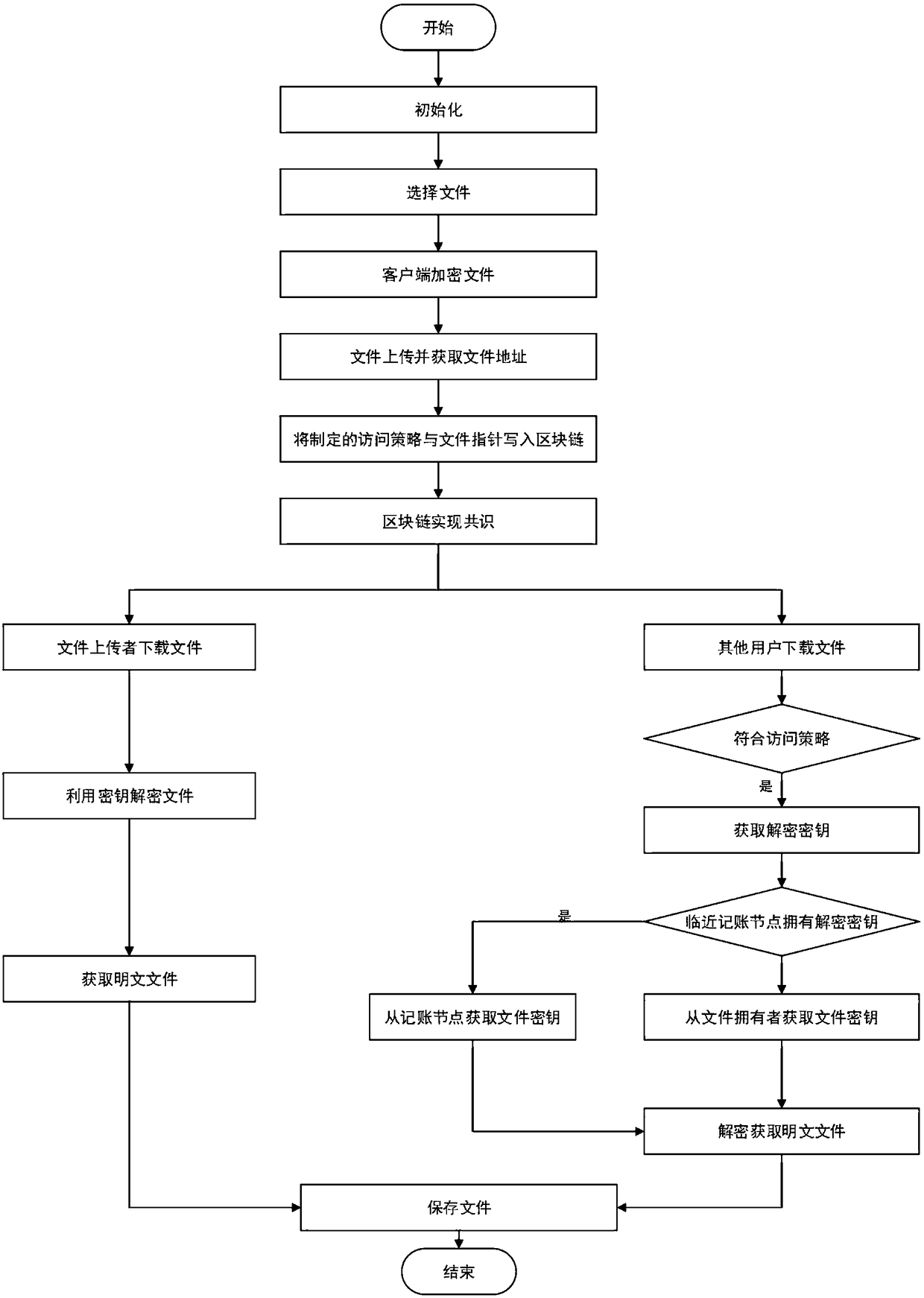
Method for storing and sharing secure files based on blockchain
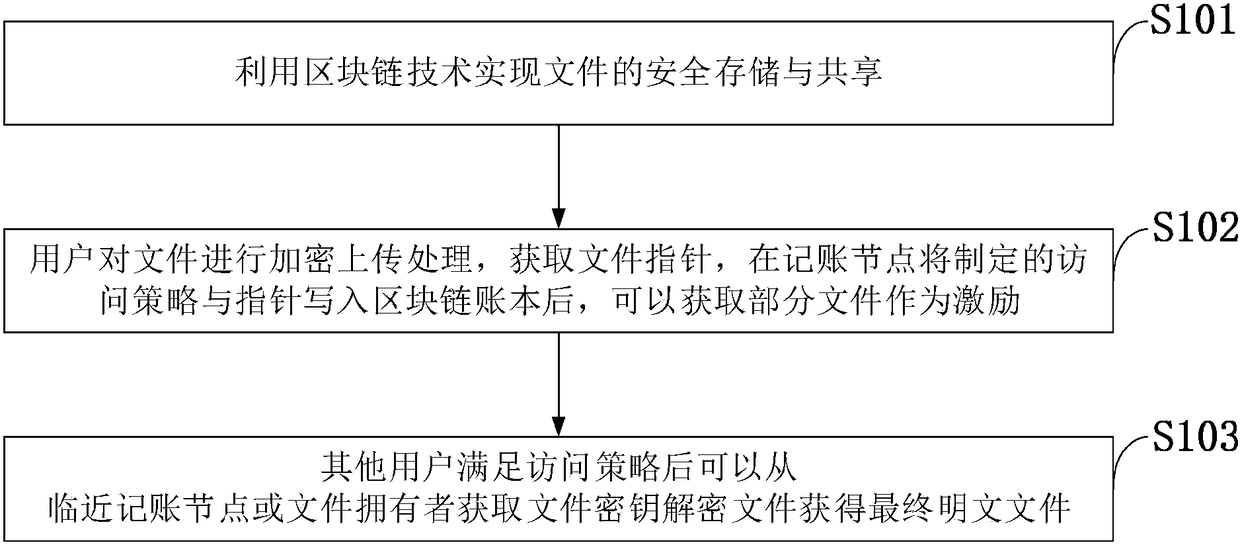
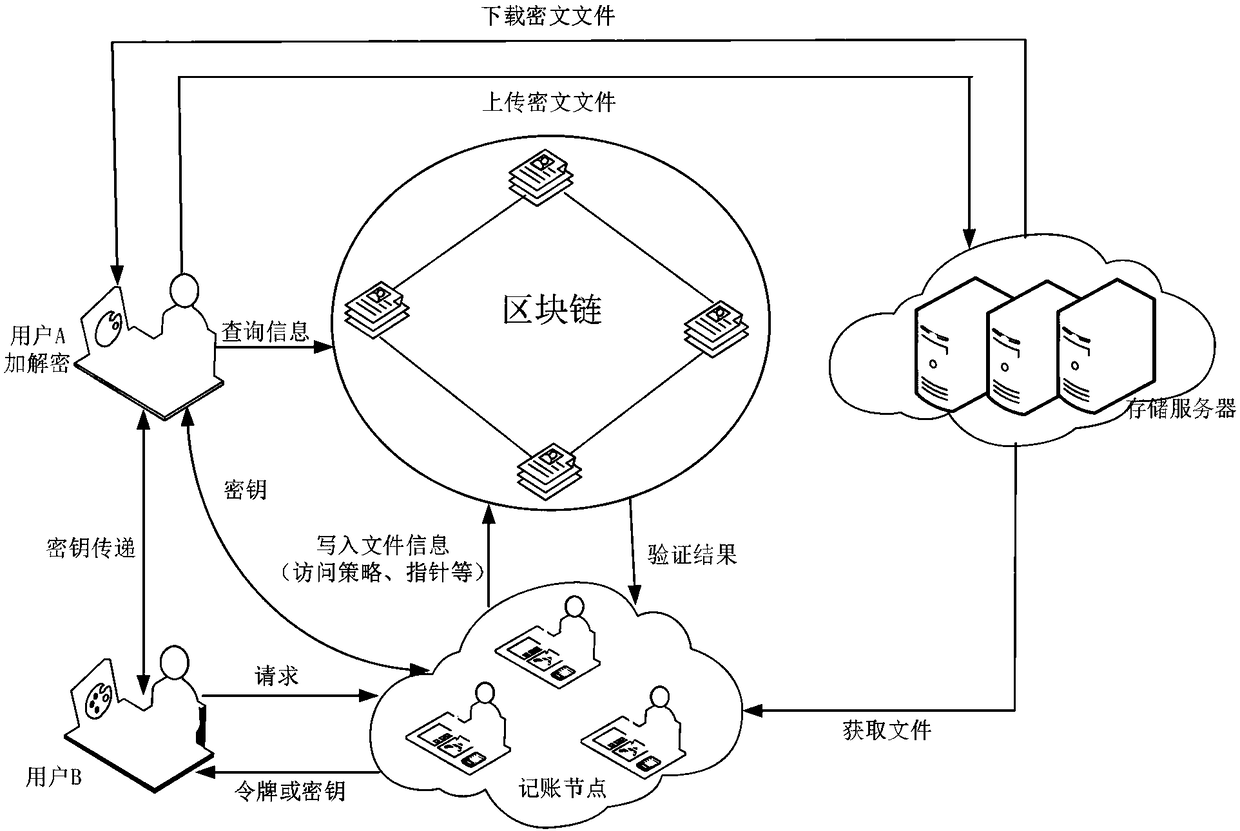
ActiveCN108462568AGuaranteed not to be tampered withIntegrity guaranteedKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPlaintextData library
The invention belongs to the technical field of information retrieval and database structure, discloses a method for storing and sharing secure files based on a blockchain, and uses the blockchain technology to realize secure storage and sharing of files. A user encrypts and uploads the files to obtain a file pointer, and acquires the partial file as the excitation after the accounting node writesthe information such as the formulated access policy and the pointer into a blockchain account. And the other users may acquire a file key from the adjacent accounting node or the file owner after satisfying the access policy to decrypt the files so as to finally obtain a plaintext file. The invention ensures the security of the user data, and is simple and convenient for the user to use, and thepublic key cryptography technology makes the file more secure at the same time. The unchangeable modification progress of the blockchain account further ensures the complete availability of the files, enables the user to formulate different access strategies for different files, and enables full control of the files while sharing the same.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20060023887A1Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityWireless ad hoc network
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
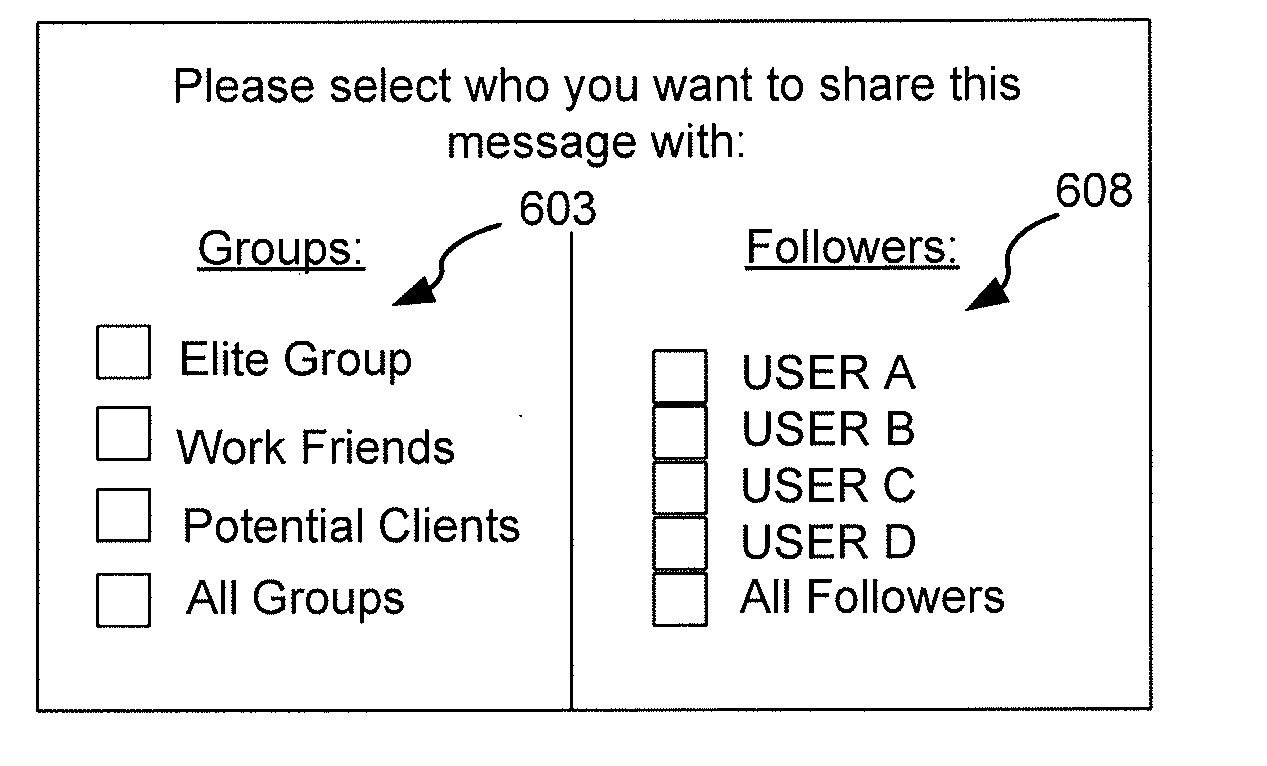
Methods and systems for providing a secure online feed in a multi-tenant database environment
InactiveUS20110307695A1Digital data information retrievalUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyPassword
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems, apparatus, and methods for securing information shared between users of a database system. A message in a feed on a multi-tenant database can be securely shared when a user marks the message as private. Users of the database can selectively decide on which recipient and / or group of recipients have access rights to view the message. The messages are secured through cryptography, such as by a key shared between two or more users. The user can additionally have a private key that is used to decrypt the secure (e.g., encrypted) messages. This private key can be further protected by the user's password used to log into the database system. The secure message can appear in either encrypted form or be absent from the feed to which the secure message is posted. Secure messages can be transparently encrypted and decrypted by the system. In some embodiments, sharing rules can be pre-defined by the user to determine how messages are secured. Furthermore, the secured messages are stored in encrypted fomi on the multi-tenant database and only accessible by users with whom the messages are shared.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
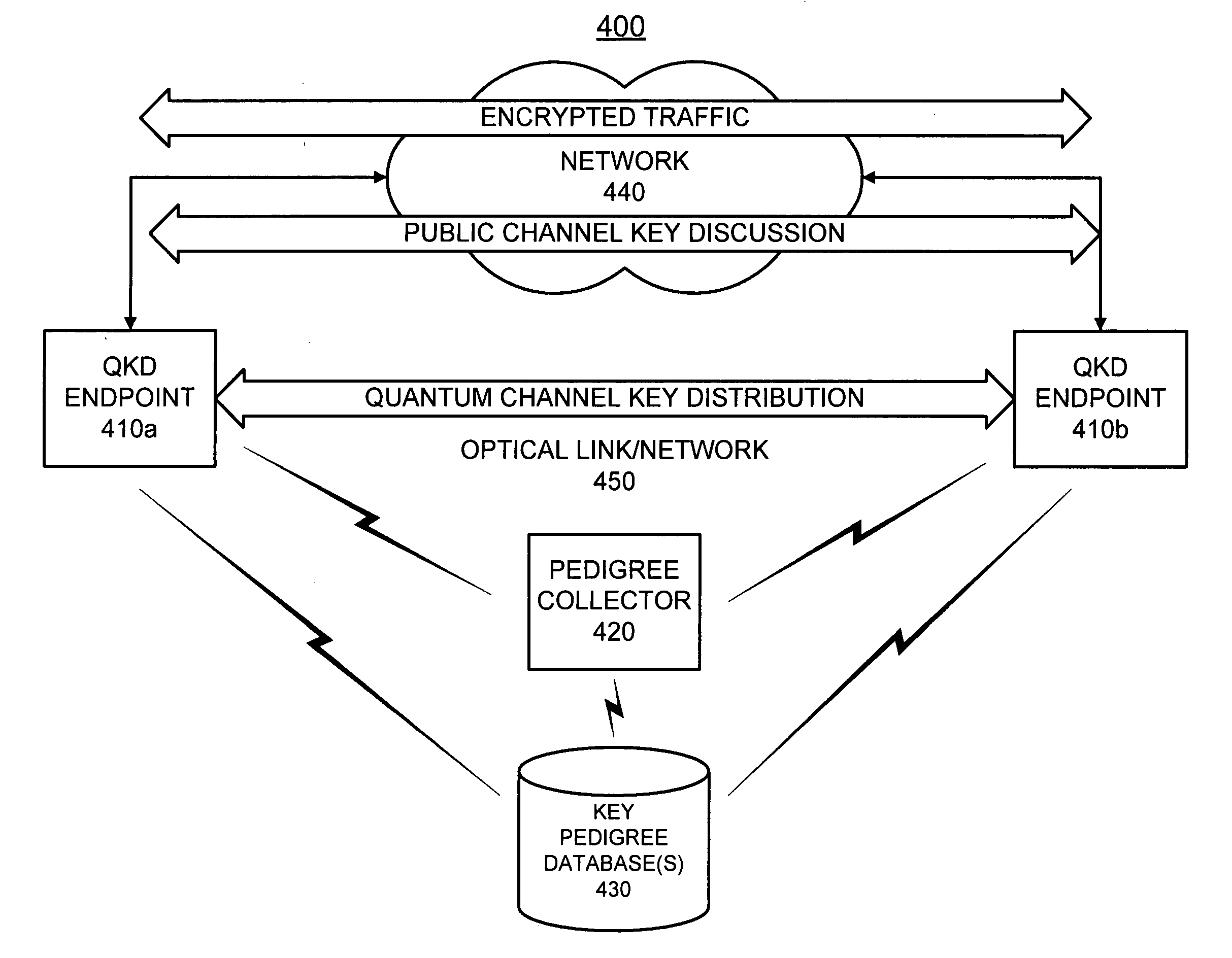
Pedigrees for quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20070192598A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationQuantumInformation system
A system stores pedigrees that include details of how and when each of multiple blocks of encryption key material were distributed between two endpoints using quantum cryptographic techniques. The system receives an indication of a possible quantum cryptographic security violation and accesses the stored pedigrees to identify one or more of the multiple blocks of encryption key material that may have been compromised.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for polarization-insensitive quantum cryptography
InactiveUS6529601B1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCommunications systemSingle polarization
A communication system uses quantum cryptography for the secure distribution of a key. A single-photon signal is phase-modulated and transmitted over a pair of time-multiplexed transmission paths. With each original single-photon signal in a given one of the transmission paths, a duplicate signal is transmitted. The duplicate is identically modulated and orthogonally polarized. At the receiver, the outputs of the two paths are combined interferometrically. A single polarization-insensitive measurement is derived from the combined contributions of the orthogonally polarized signals.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
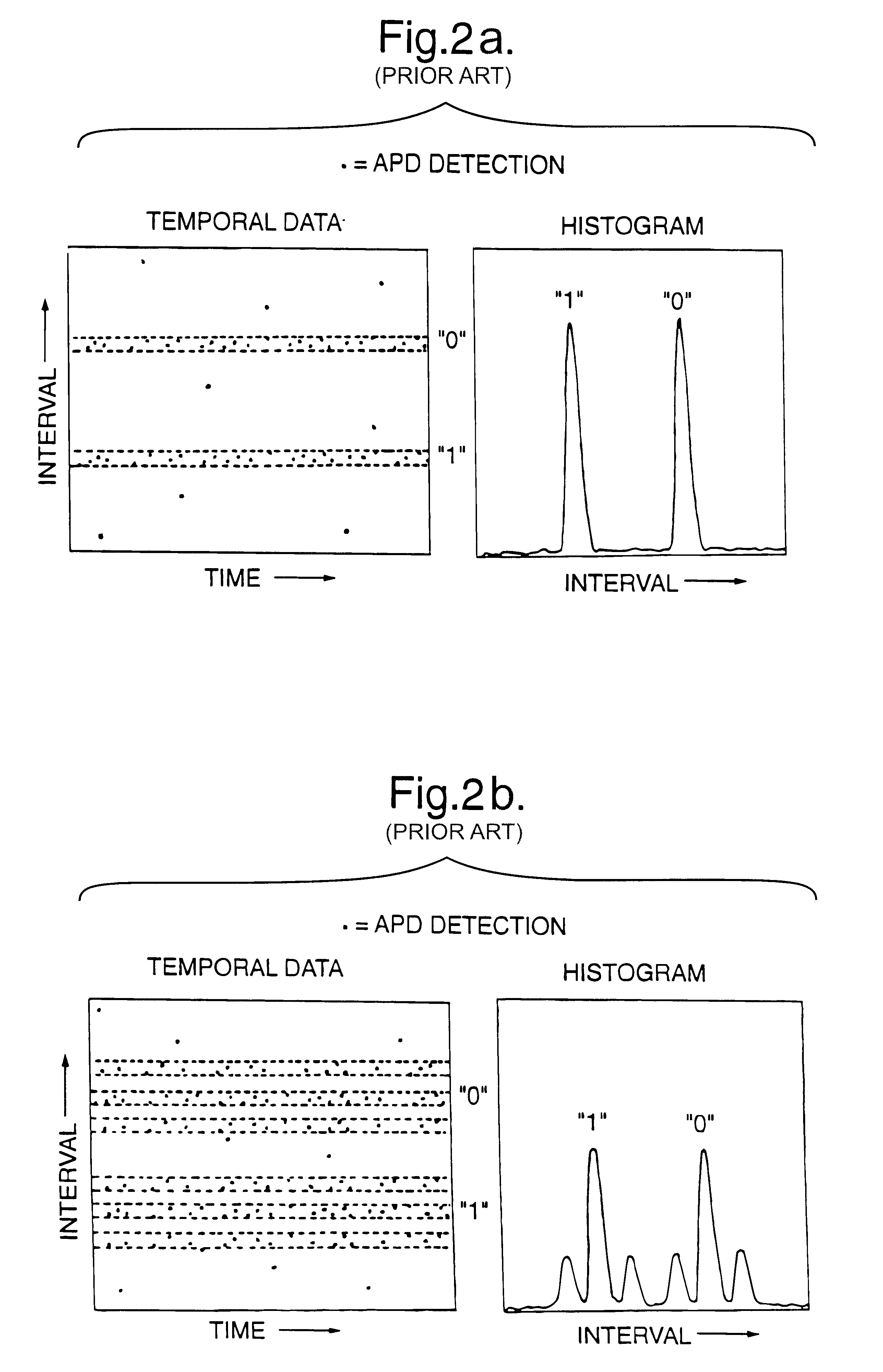
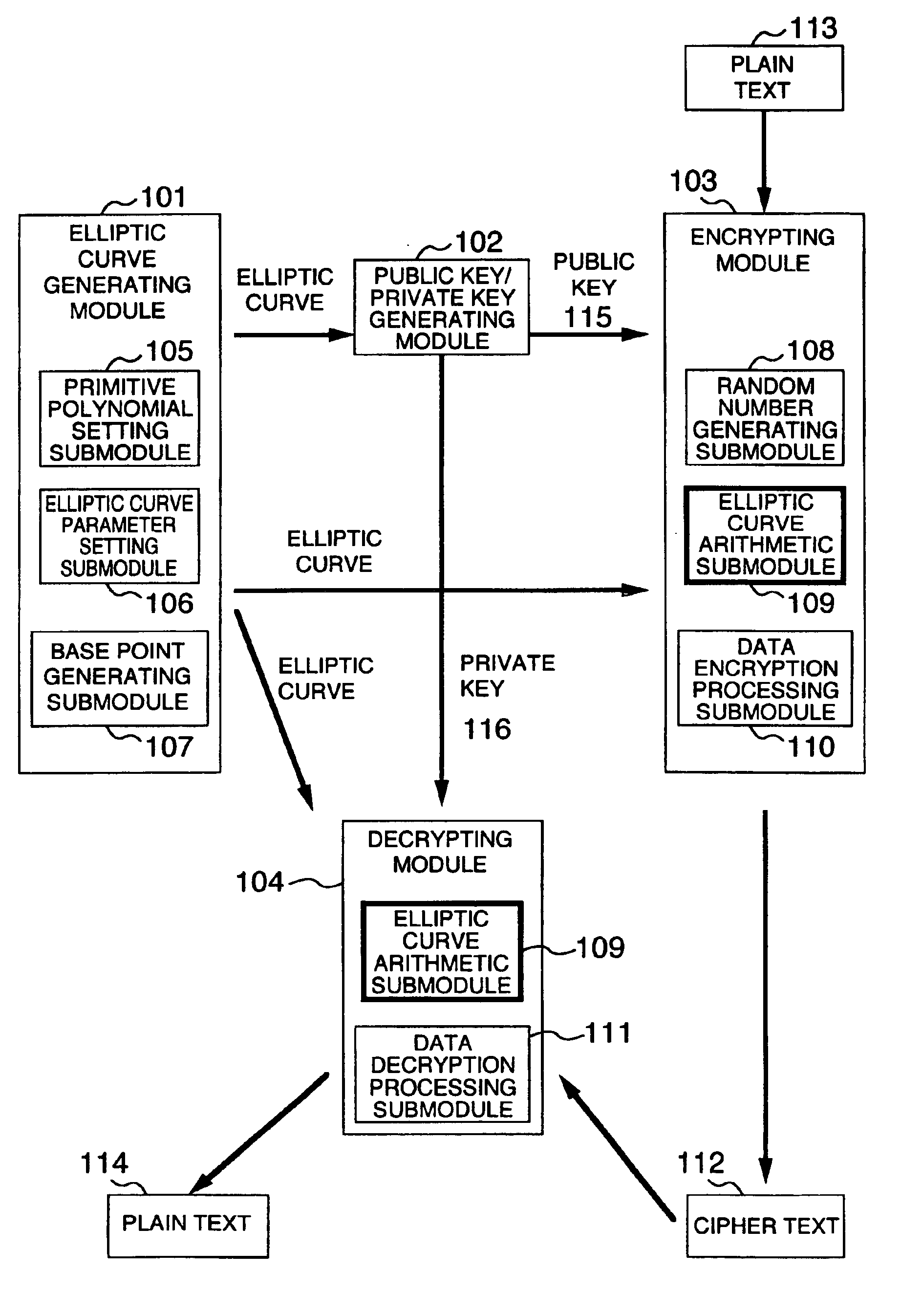
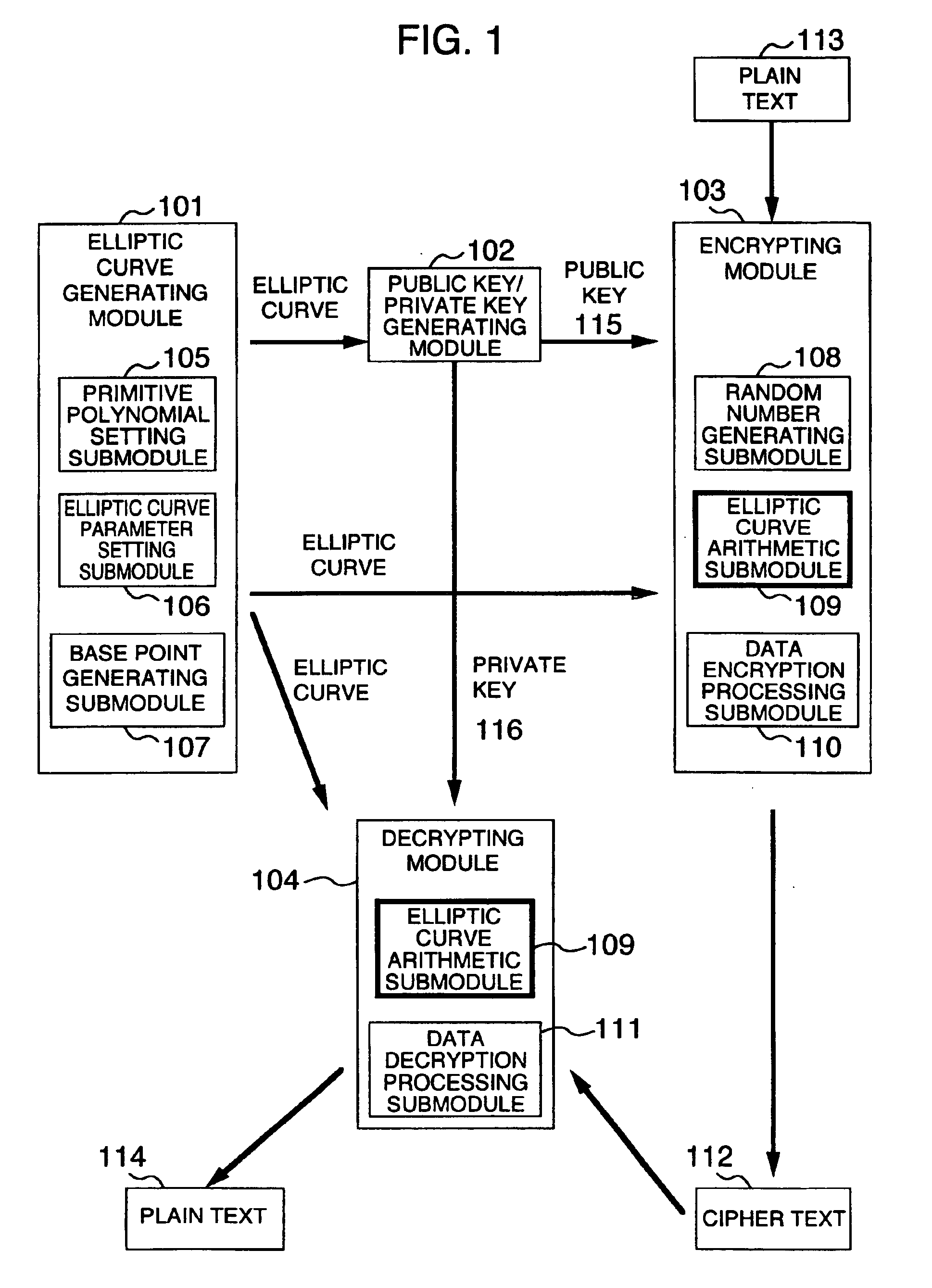
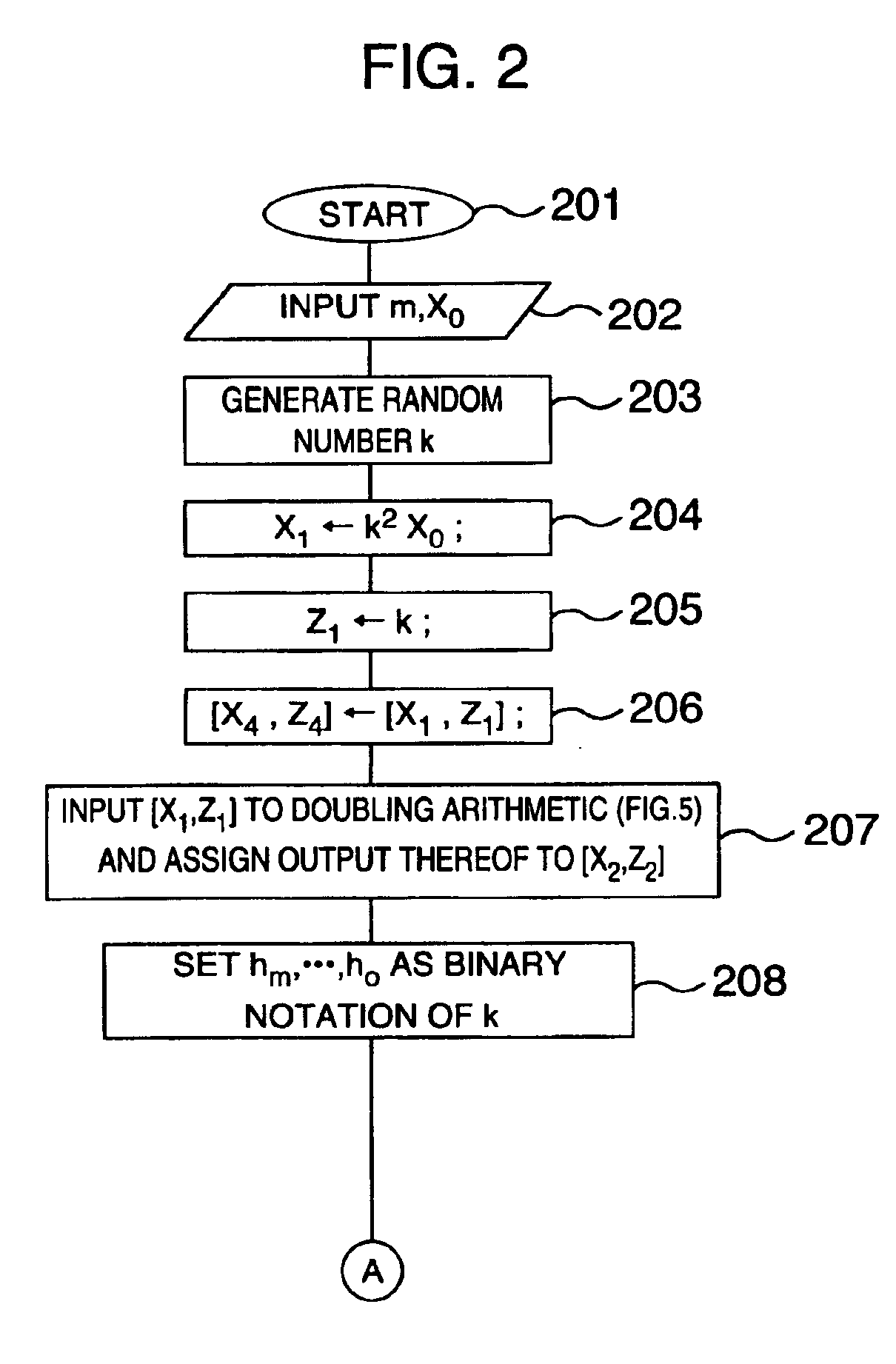
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
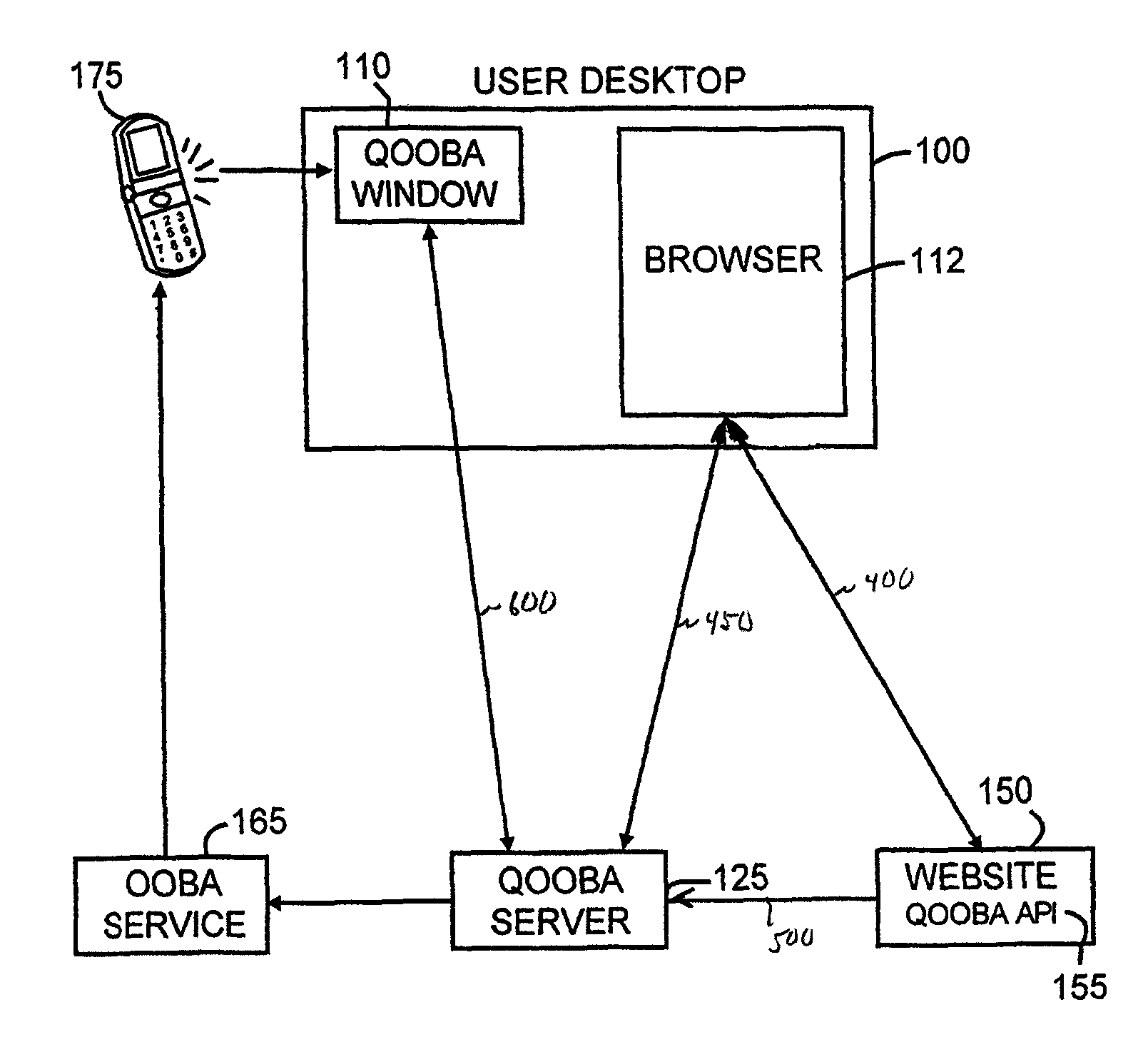
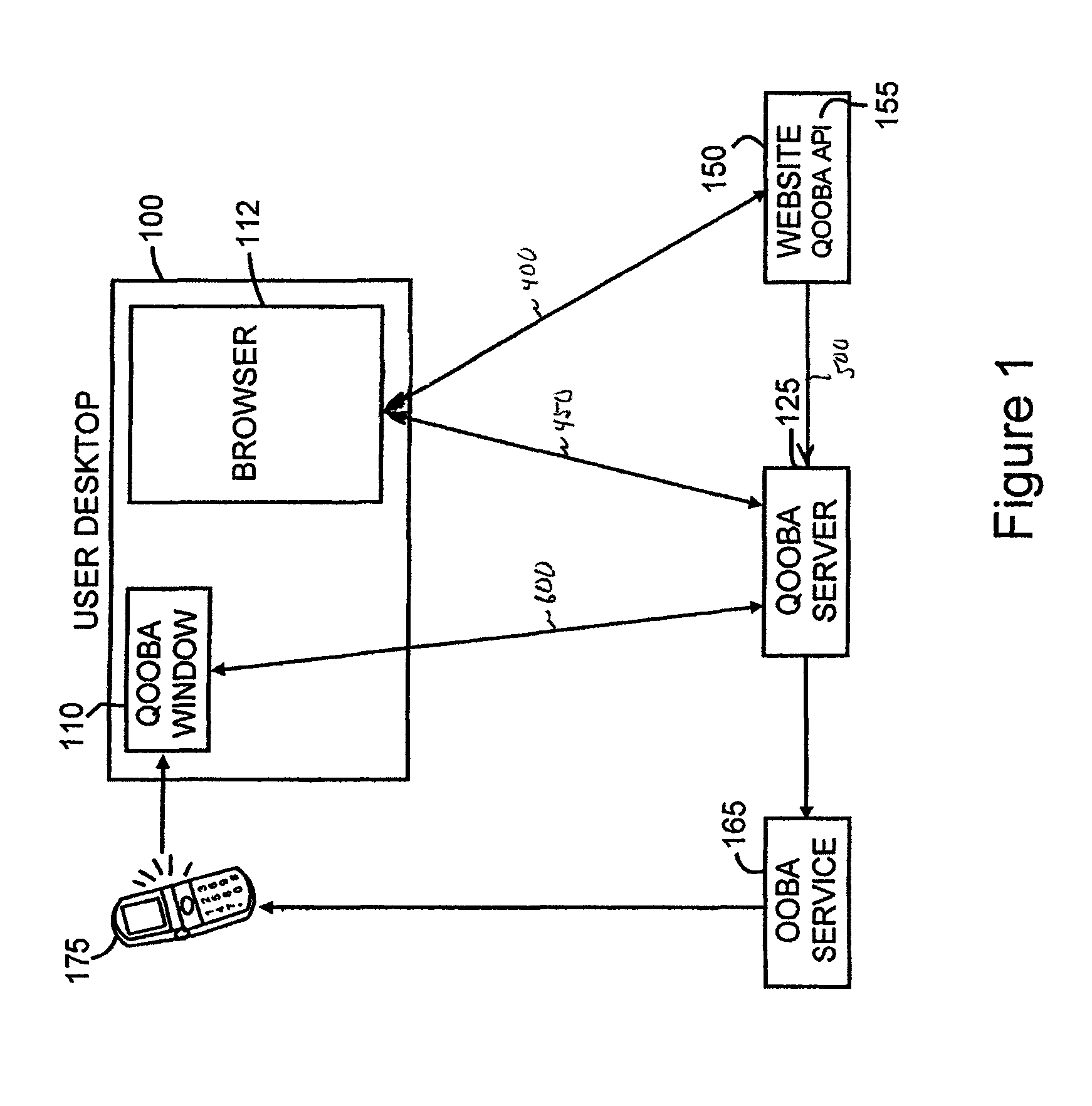
Key management using quasi out of band authentication architecture
ActiveUS8713325B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationKey (cryptography)
Owner:PAYFONE
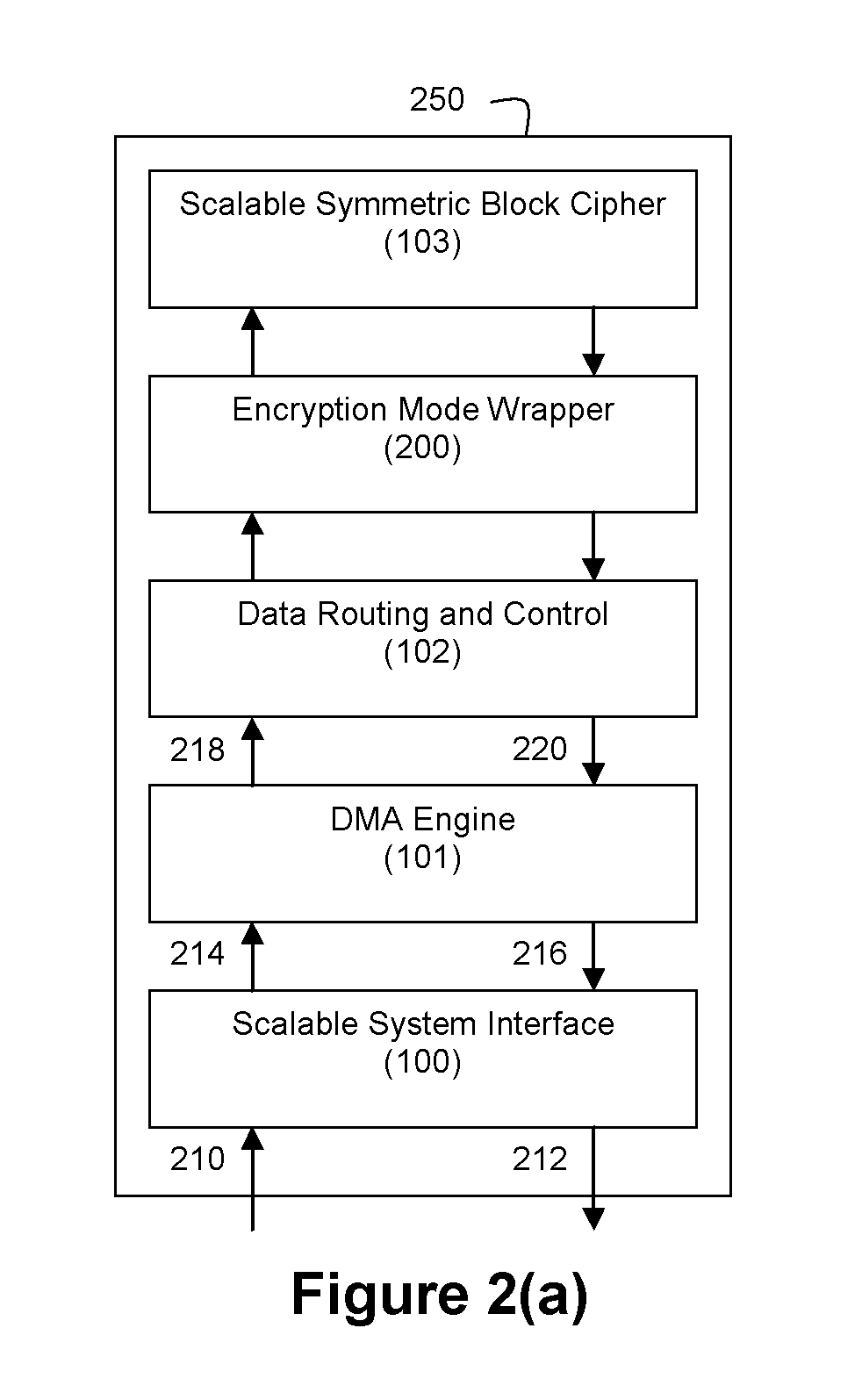
Method and apparatus for hardware-accelerated encryption/decryption
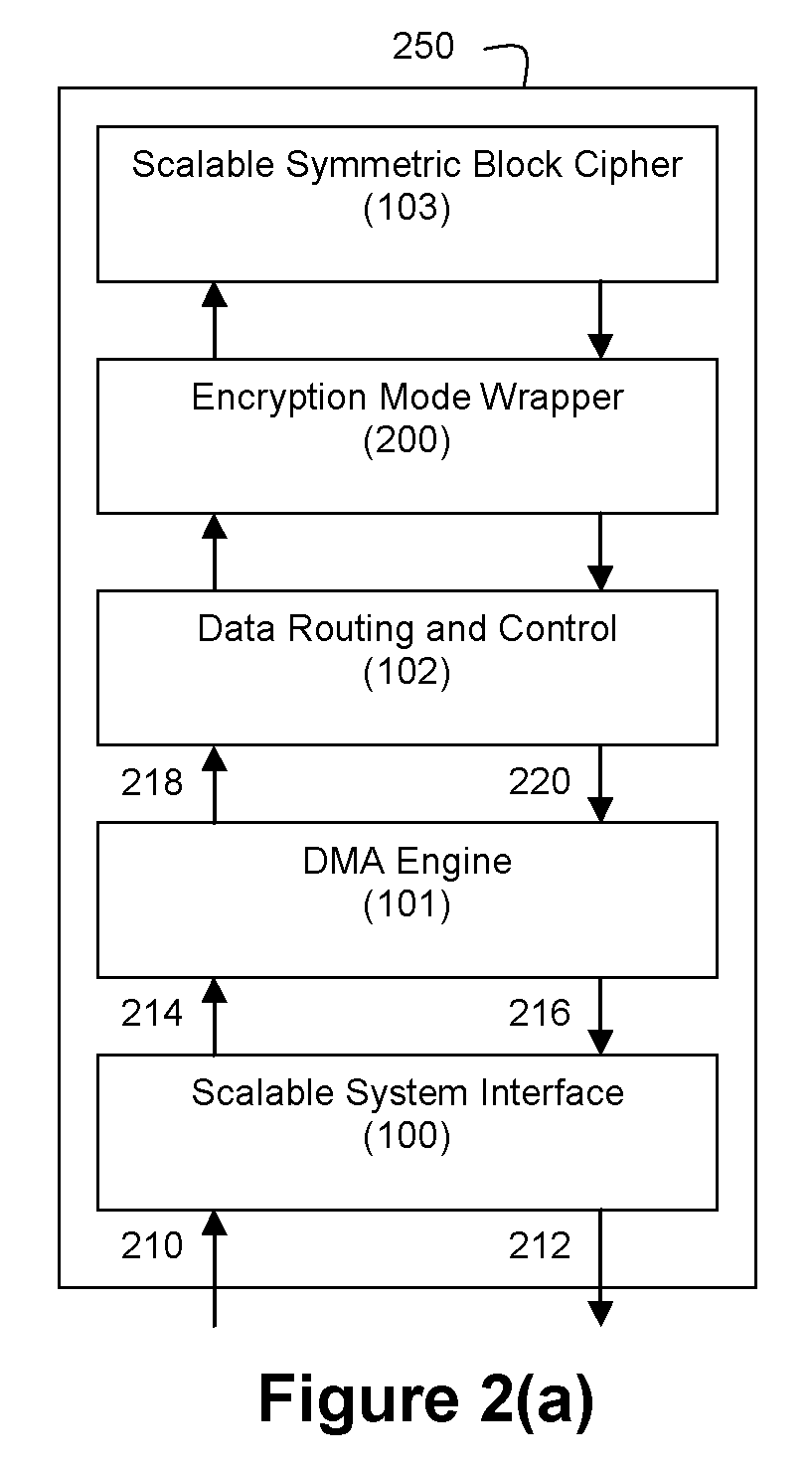
ActiveUS8879727B2Maximize availabilityLimited operating lifeKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMultiple encryptionKey exchange
An integrated circuit for data encryption / decryption and secure key management is disclosed. The integrated circuit may be used in conjunction with other integrated circuits, processors, and software to construct a wide variety of secure data processing, storage, and communication systems. A preferred embodiment of the integrated circuit includes a symmetric block cipher that may be scaled to strike a favorable balance among processing throughput and power consumption. The modular architecture also supports multiple encryption modes and key management functions such as one-way cryptographic hash and random number generator functions that leverage the scalable symmetric block cipher. The integrated circuit may also include a key management processor that can be programmed to support a wide variety of asymmetric key cryptography functions for secure key exchange with remote key storage devices and enterprise key management servers. Internal data and key buffers enable the device to re-key encrypted data without exposing data. The key management functions allow the device to function as a cryptographic domain bridge in a federated security architecture.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
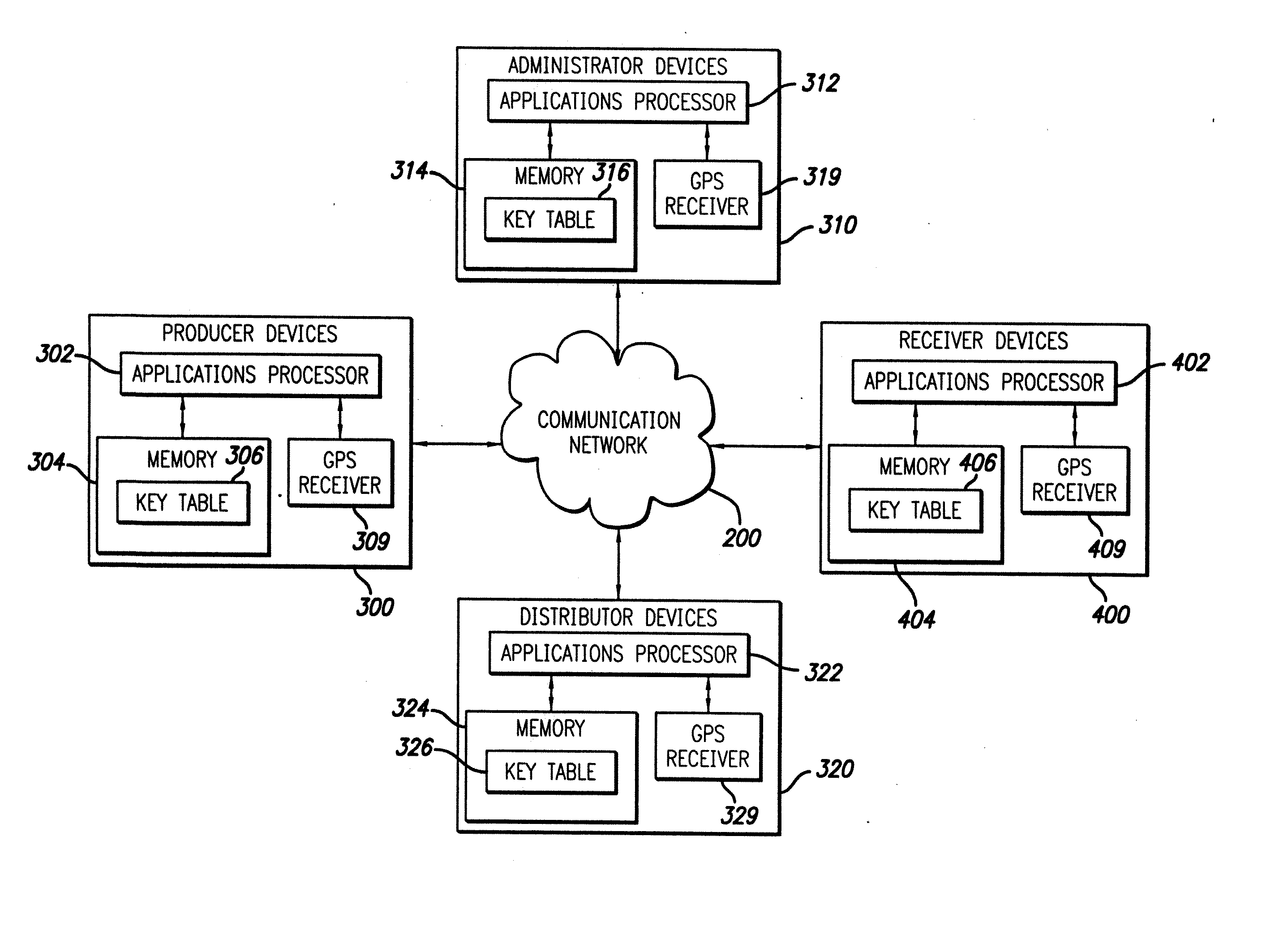
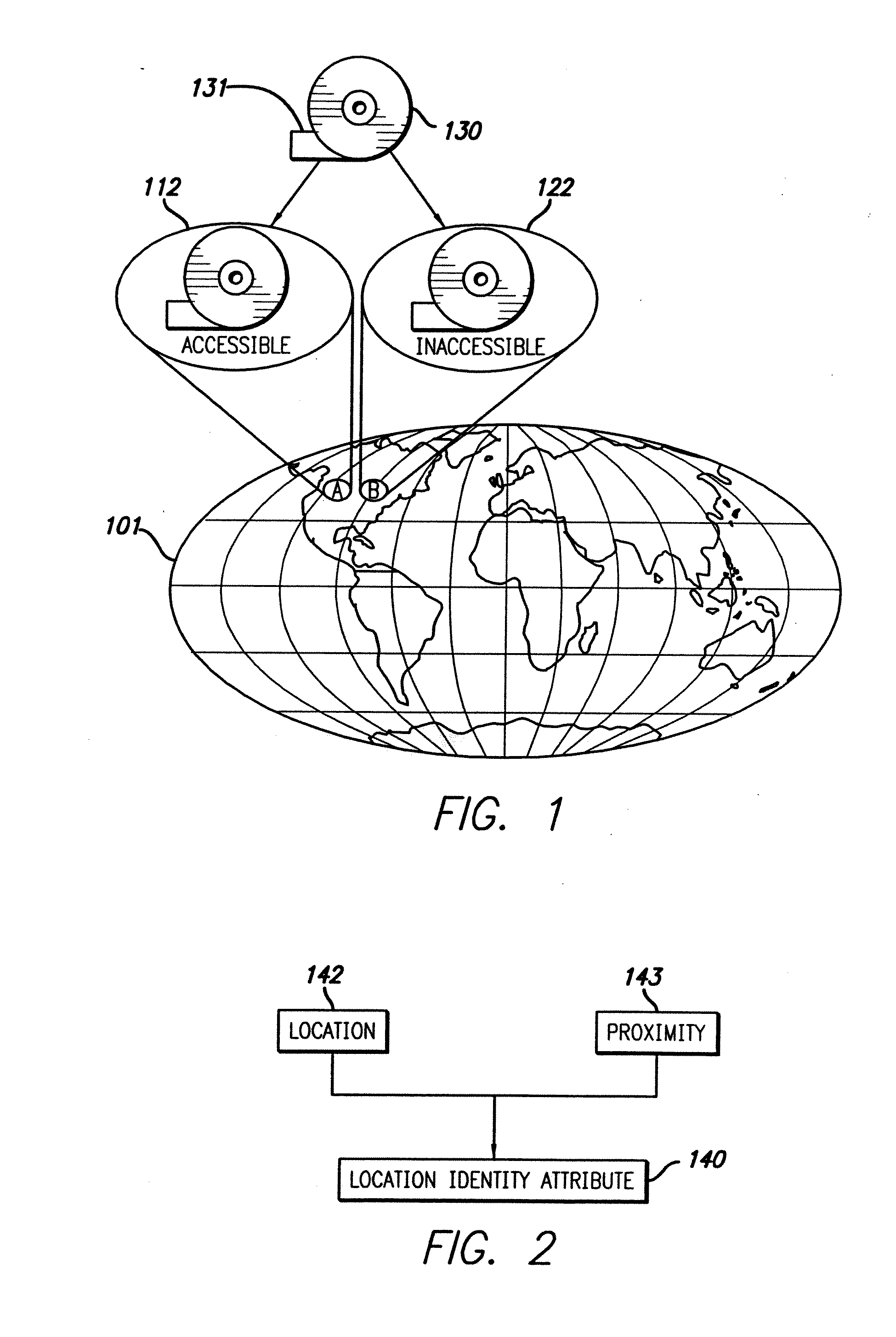
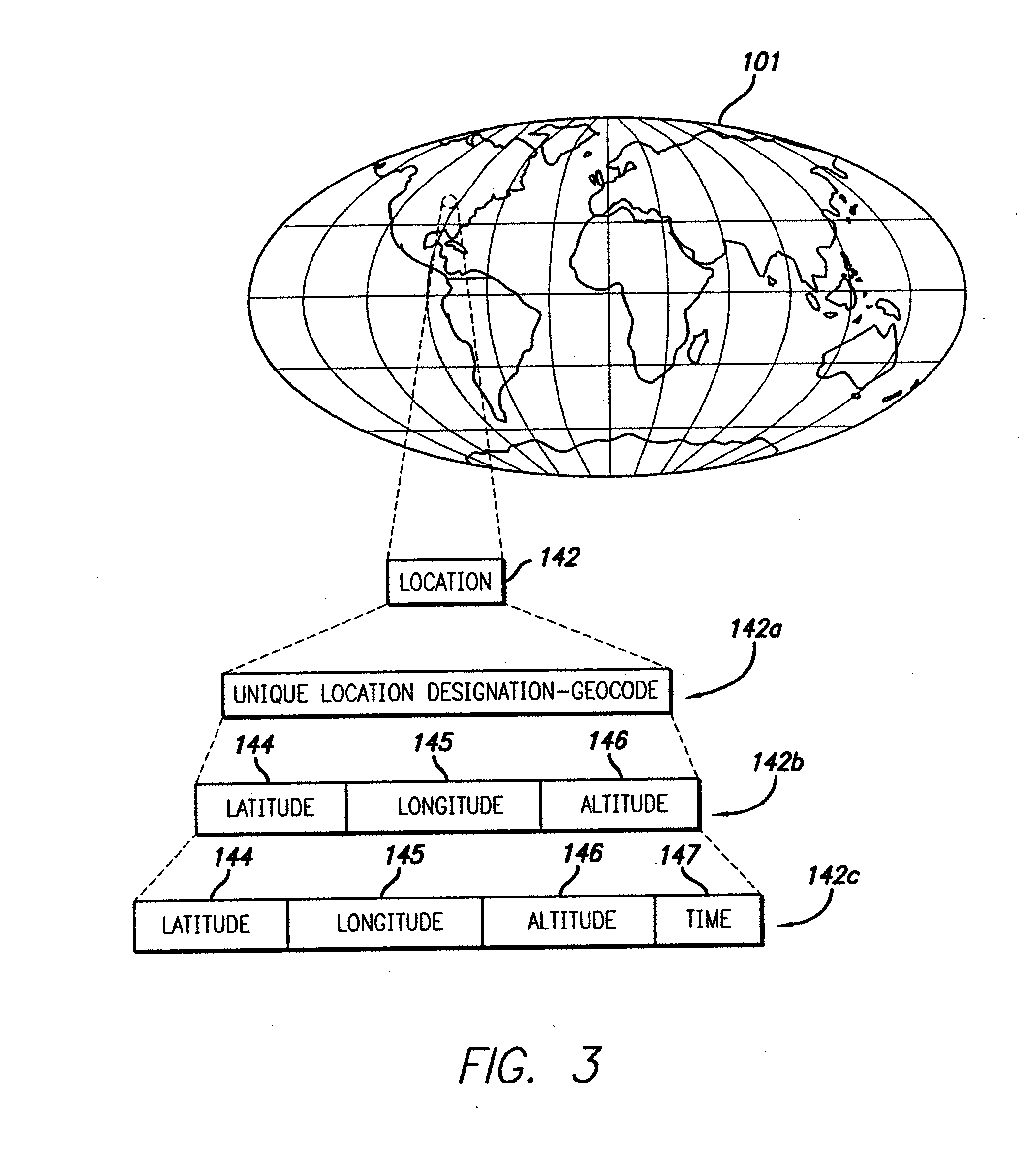
System and method for delivering encrypted information in a communication network using location indentity and key tables
InactiveUS20070086593A1Secure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPlaintextDigital data
Access to digital data is controlled by encrypting the data in such a manner that, in a single digital data acquisition step, it can be decrypted only at a specified location, within a specific time frame, and with a secret key. Data encrypted in such a manner is said to be geo-encrypted. This geo-encryption process comprises a method in which plaintext data is first encrypted using a data encrypting key that is generated at the time of encryption. The data encrypting key is then encrypted (or locked) using a key encrypting key and information derived from the location of the intended receiver. The encrypted data encrypting key is then transmitted to the receiver along with the ciphertext data. The receiver both must be at the correct location and must have a copy of the corresponding key decrypting key in order to derive the location information and decrypt the data encrypting key. After the data encrypting key is decrypted (or unlocked), it is used to decrypt the ciphertext. If an attempt is made to decrypt the data encrypting key at an incorrect location or using an incorrect secret key, the decryption will fail. If the sender so elects, access to digital data also can be controlled by encrypting it in such a manner that it must traverse a specific route from the sender to the recipient in order to enable decryption of the data. Key management can be handled using either private-key or public-key cryptography. If private-key cryptography is used, the sender can manage the secret key decrypting keys required for decryption in a secure manner that is transparent to the recipient. As a consequence of its ability to manipulate the secret keys, the sender of encrypted data retains the ability to control access to its plaintext even after its initial transmission.
Owner:LONGBEAM TECH LLC
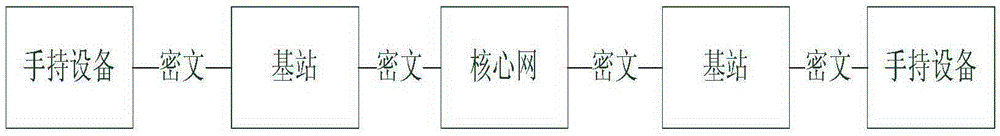
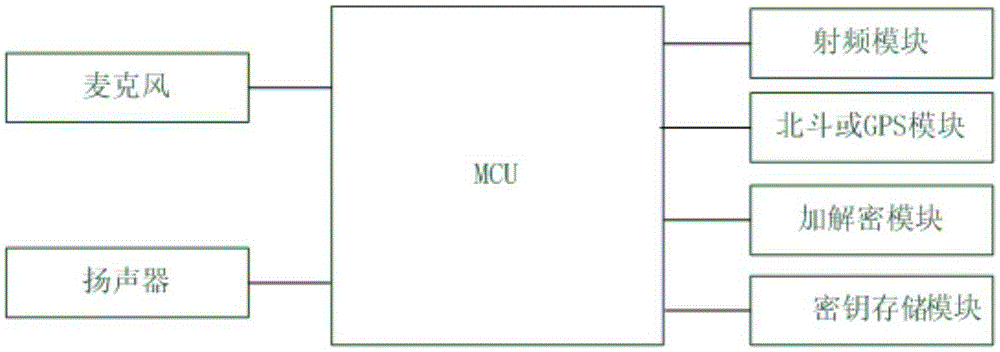
End-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and system
InactiveCN105337726AImprove securityIncrease independenceKey distribution for secure communicationHand heldHand held devices
The invention discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and a system. The encryption method comprises following steps of storing quantum keys; initiating a call; synchronizing the quantum keys; performing synchronous confirmation; answering the call; and performing encryption communication. In the encryption communication, an MCU of a main calling end injects quantum communication keys Ksa into an encryption and decryption model; an MCU of a called end injects the quantum communication keys Ksa into the encryption and decryption model; the MCU of the called end using the quantum communication keys to encrypt the data; the encrypted data is sent out via a radio frequency module of the called end; a radio frequency module of the main calling end injects the received encrypted data into the encryption and decryption model for decryption; and after being decrypted, the data is played by a loudspeaker of the main calling end or displayed via a touch type display. The invention also discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption system based on quantum cryptography. The encryption method and system are highly safe, independent and easy, quick and simple to deploy.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
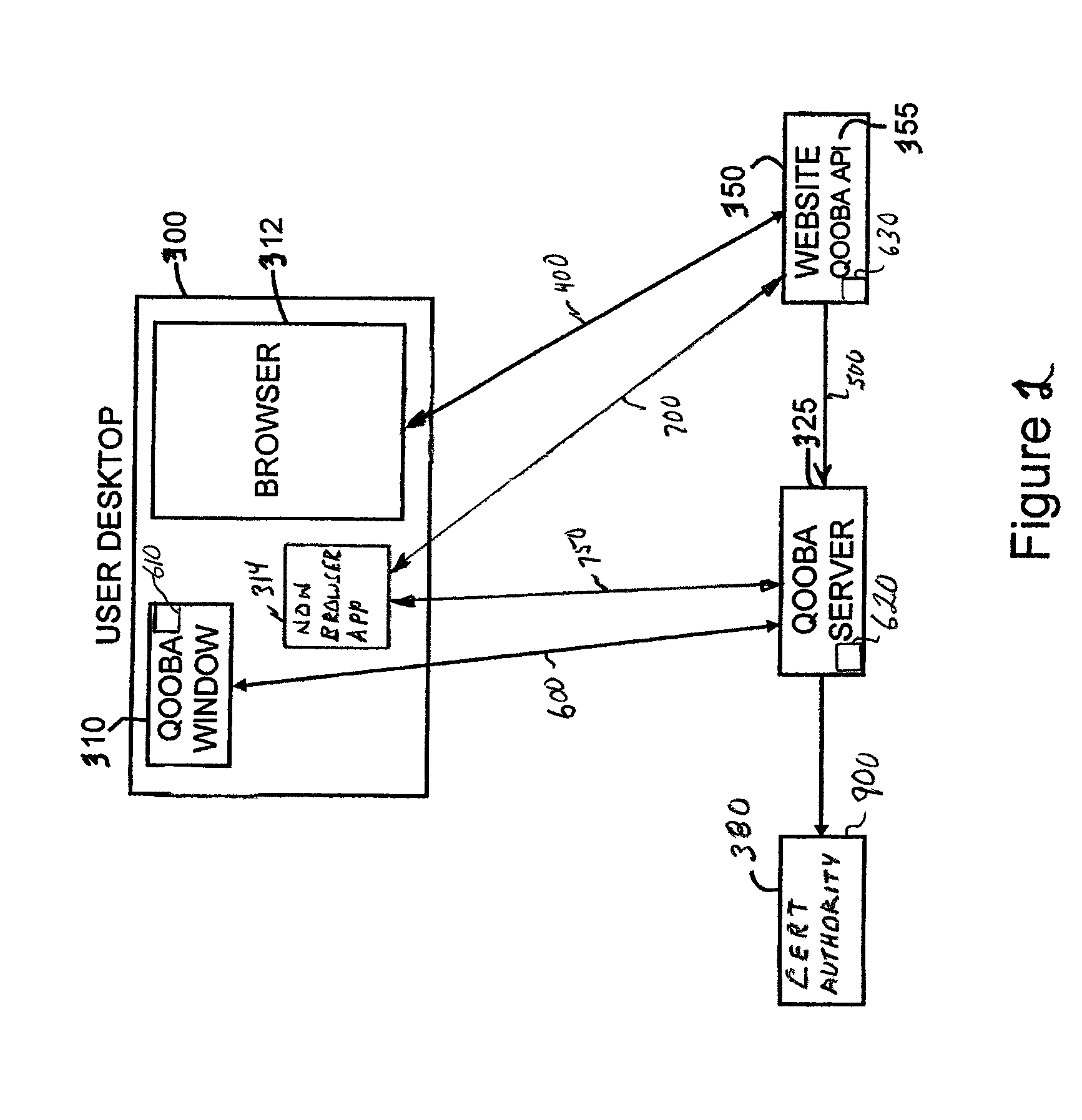
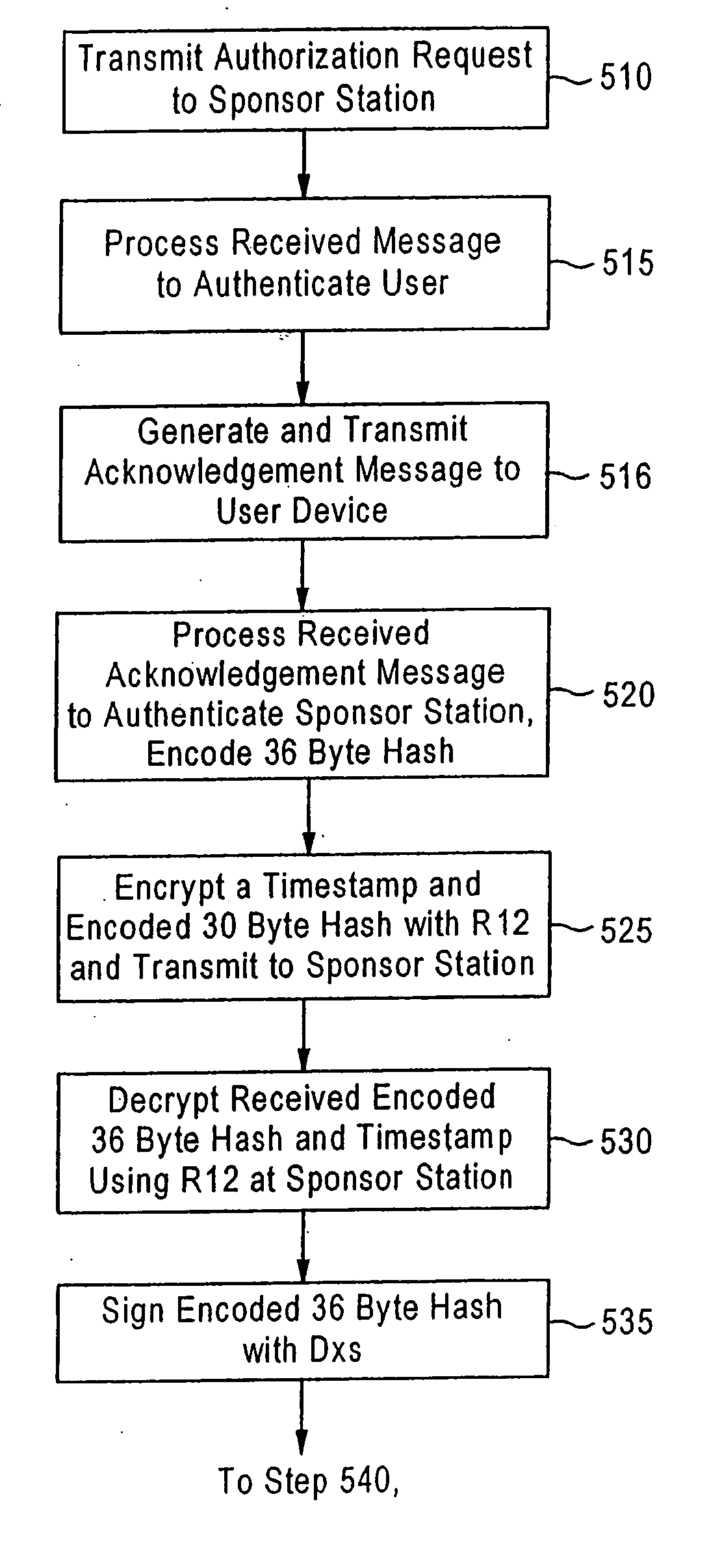
Secure login using augmented single factor split key asymmetric cryptography
A user network station transmits a cookie that includes a user identifier and an augmenting factor transformed with one key of a first asymmetric crypto-key or with a symmetric crypto-key. An authenticating entity network station recovers the augmenting factor from the transformed augmenting factor included in the transmitted cookie, with the other key of the first asymmetric crypto-key or with the symmetric crypto-key, and transmits a customized login page corresponding to the user identifier. The user network station transmits a factor responsive to the transmitted customized login page. The authenticating entity network station generates a first key portion based on the transmitted factor and the recovered augmenting factor, and validates the generated first key portion based on a second key portion of one key of a second asymmetric crypto-key associated with the user and on the other key of the second asymmetric crypto-key, to thereby authenticate the user.
Owner:VMWARE INC
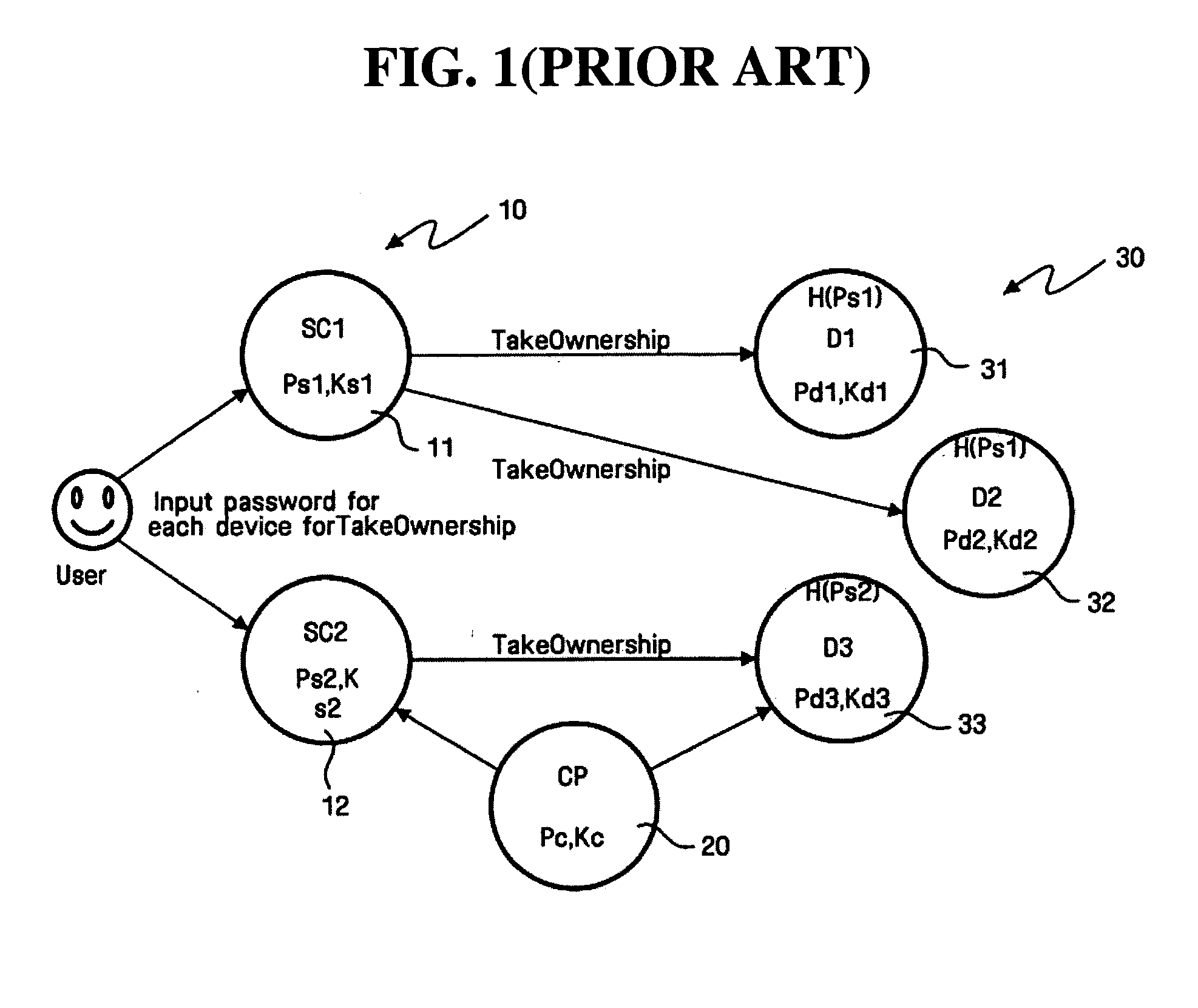
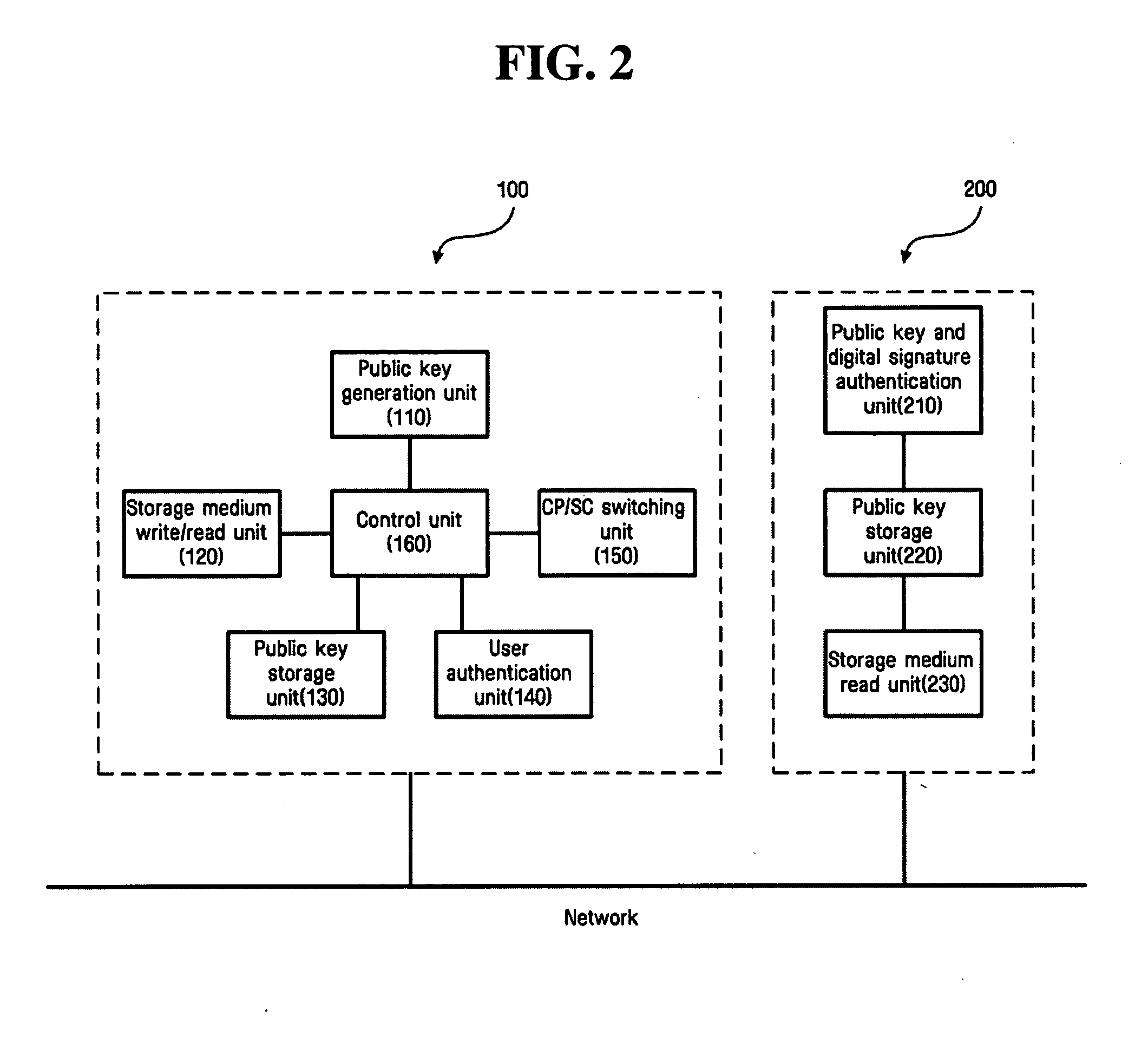
Home network device, home network system and method for automating take ownership process
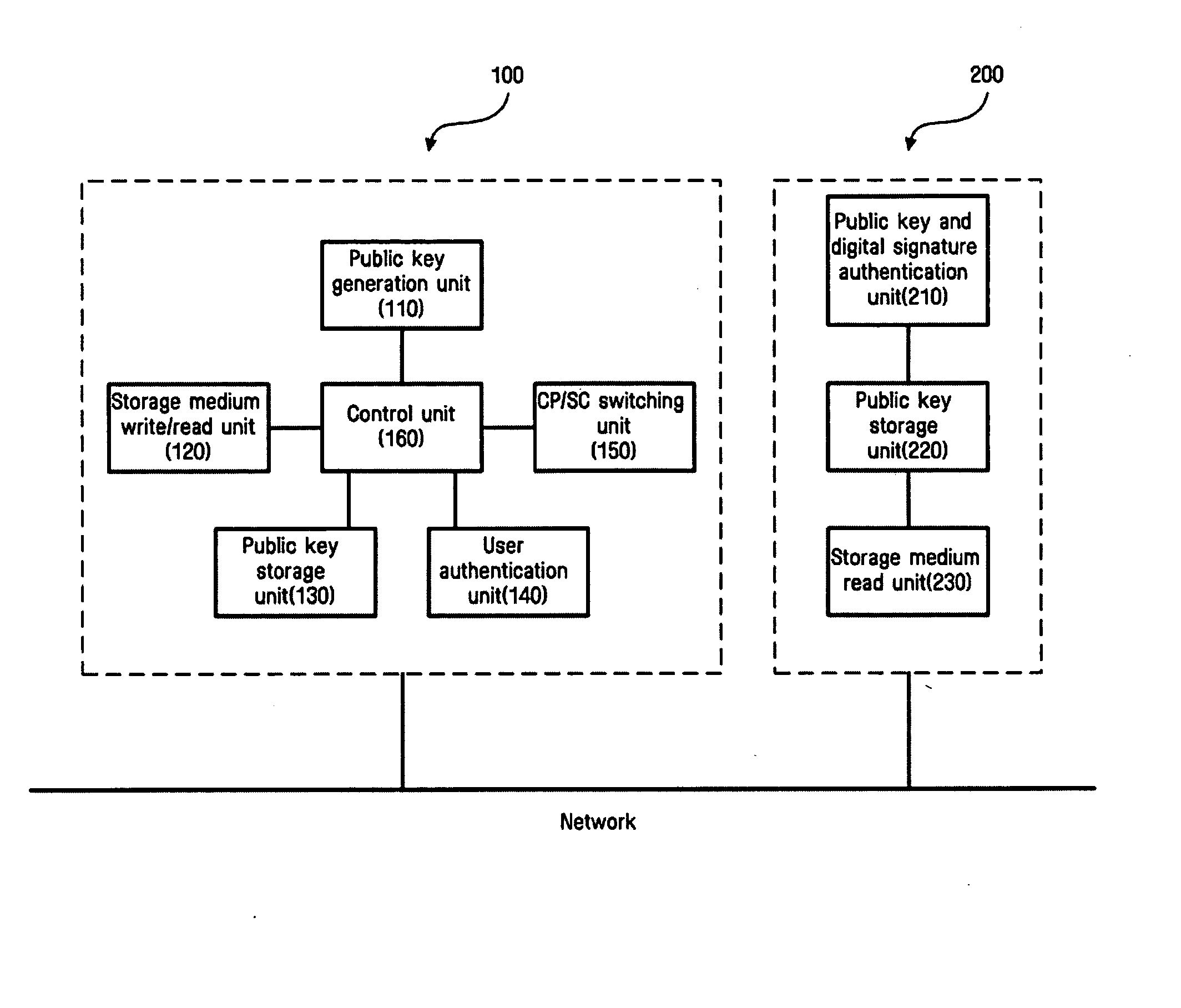
InactiveUS20050071636A1Function is performedOperational securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureSmart card
A network device for automating a TakeOwnership process includes a public key generation unit for generating a public key and a private key by employing public key cryptography, a storage medium write / read unit for writing the generated public and private keys on a storage medium and for reading the public and private keys written on the storage medium, and a control point / security console switching unit for selecting one of a security console function providing an access authority for a predetermined device and a control point function controlling operation of the predetermined device, after authentication of a user using the private key stored on the storage medium. Thus, by employing public key cryptography in which a digital signature is created using the private key stored on the storage medium, such as a smart card, and is verified by the public key, the user can securely operate home network equipment as well as enjoy a convenience in use.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
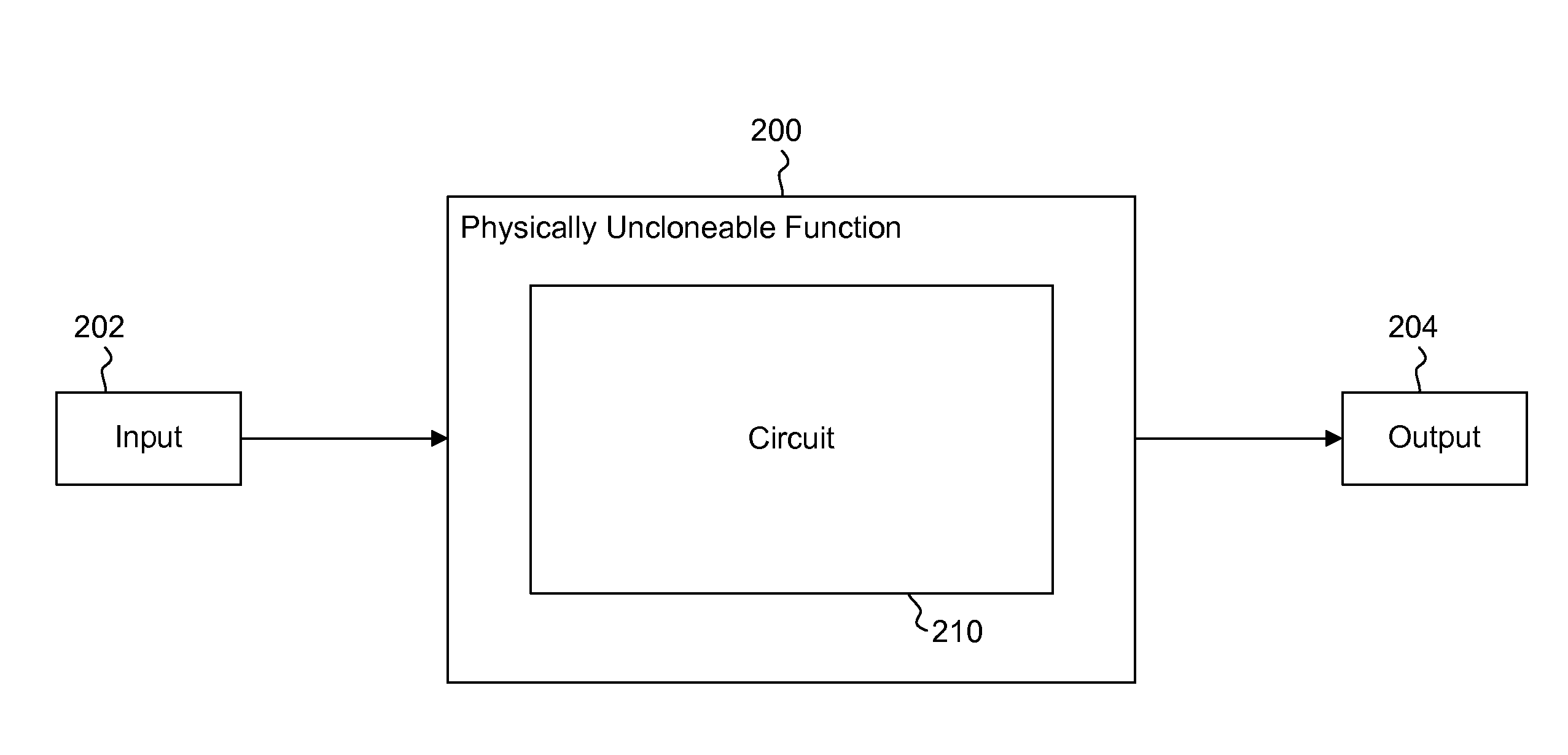
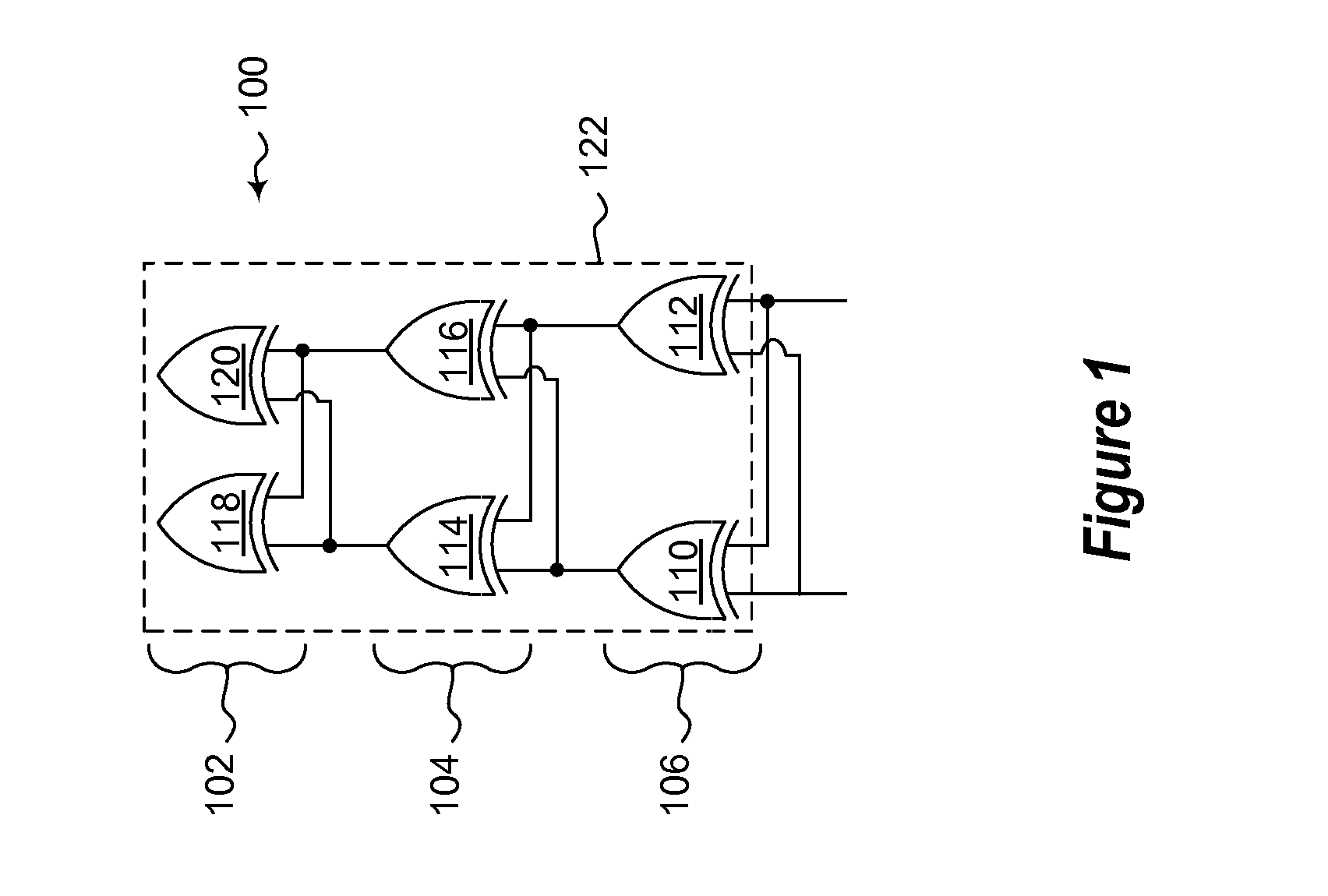
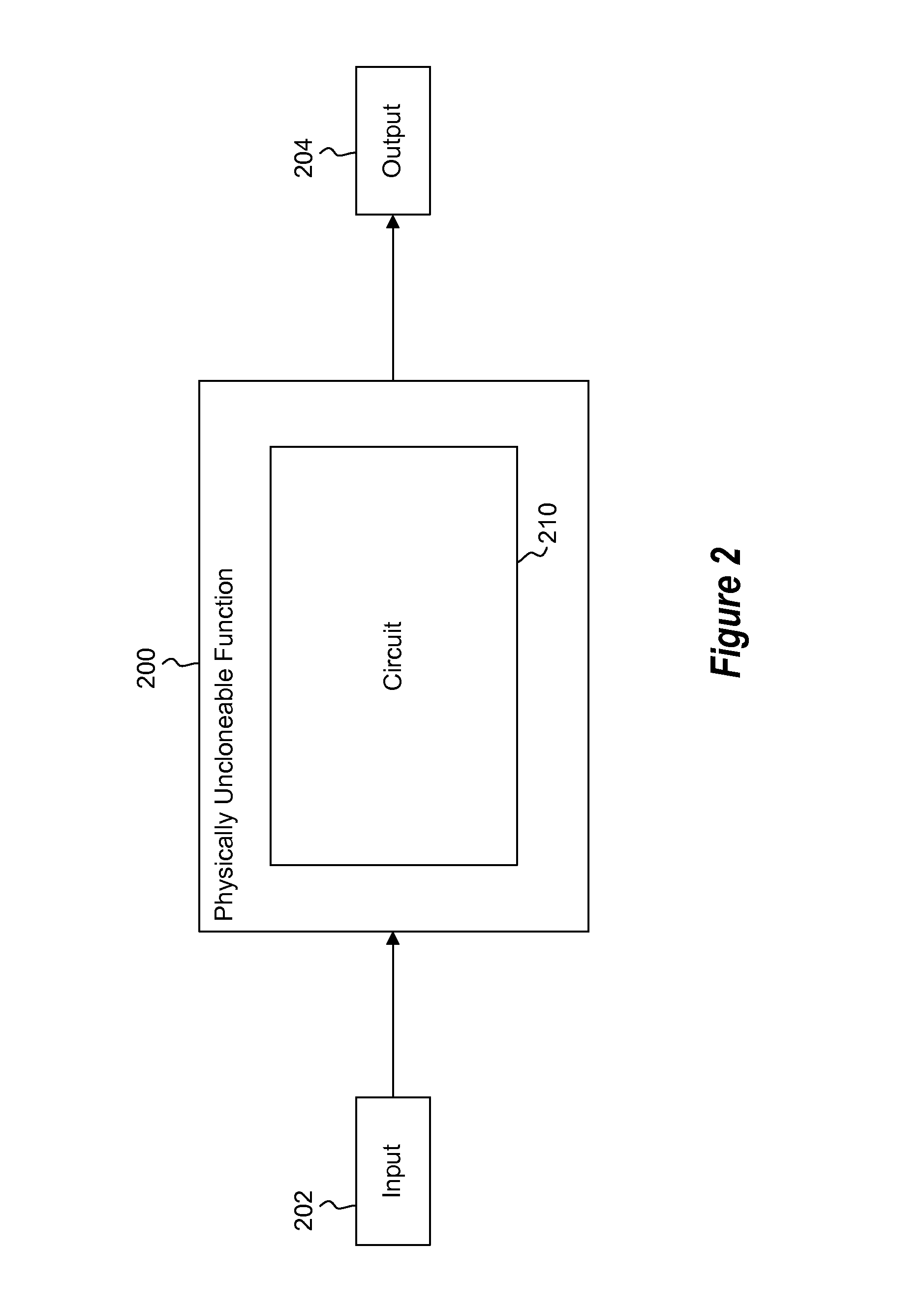
Differential uncloneable variability-based cryptography
InactiveUS20110239002A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringKey (cryptography)Physical unclonable function
Differential uncloneable variability-based cryptography techniques are provided. The differential cryptography includes a hardware based public physically uncloneable function (PPUF) to perform the cryptography. The PPUF includes a first physically uncloneable function (PUF) and a second physically uncloneable function. An arbiter determines the output of the circuit using the outputs of the first and second PUFs. Cryptography can be performed by simulating the PPUF with selected input. The output of the simulation, along with timing information about a set of inputs from where the corresponding input is randomly selected for simulation, is used by the communicating party that has the integrated circuit with the PPUF to search for an input that produces the output. The input can be configured to be the secret key or a part of the secret key.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
Grid-based multi-user fuzzy searchable encryption method in secure multimedia cloud storage
ActiveCN106803784AImplement searchKey distribution for secure communicationSpecial data processing applicationsGrid basedCloud storage
The invention relates to a grid-based multi-user fuzzy searchable encryption method in secure multimedia cloud storage. The semantic information is used to realize the privacy semantic search of encrypted data. The user-selected search keywords do not need to be exactly the same as the keywords in the outsourced encrypted multimedia data. in view of the shortcomings of the existing scheme that only supports single-user application, the scheme introduces the searchable broadcast encryption method; encrypted multimedia files can be shared by a group of users without sharing their own private keys; each authorized user can use his / her unique private key to generate his / her own keyword trap door; and the user can also upload the encrypted multimedia files as a data sender using the group public key. The scheme introduces the concept of post-quantum security and designs a searchable broadcast encryption scheme that supports semantic keyword search, and the scheme is constructed by means of grid-based cryptography and grid-based proxy methods. Based on the difficulty of LWE (error learning) problem, the security of resisting quantum attack can be realized.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Chinese remainder theorem - based computation method for cryptosystems
ActiveUS20080226064A1Less computational intenseSecure against cryptanalysisRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationChinese remainder theoremCryptosystem
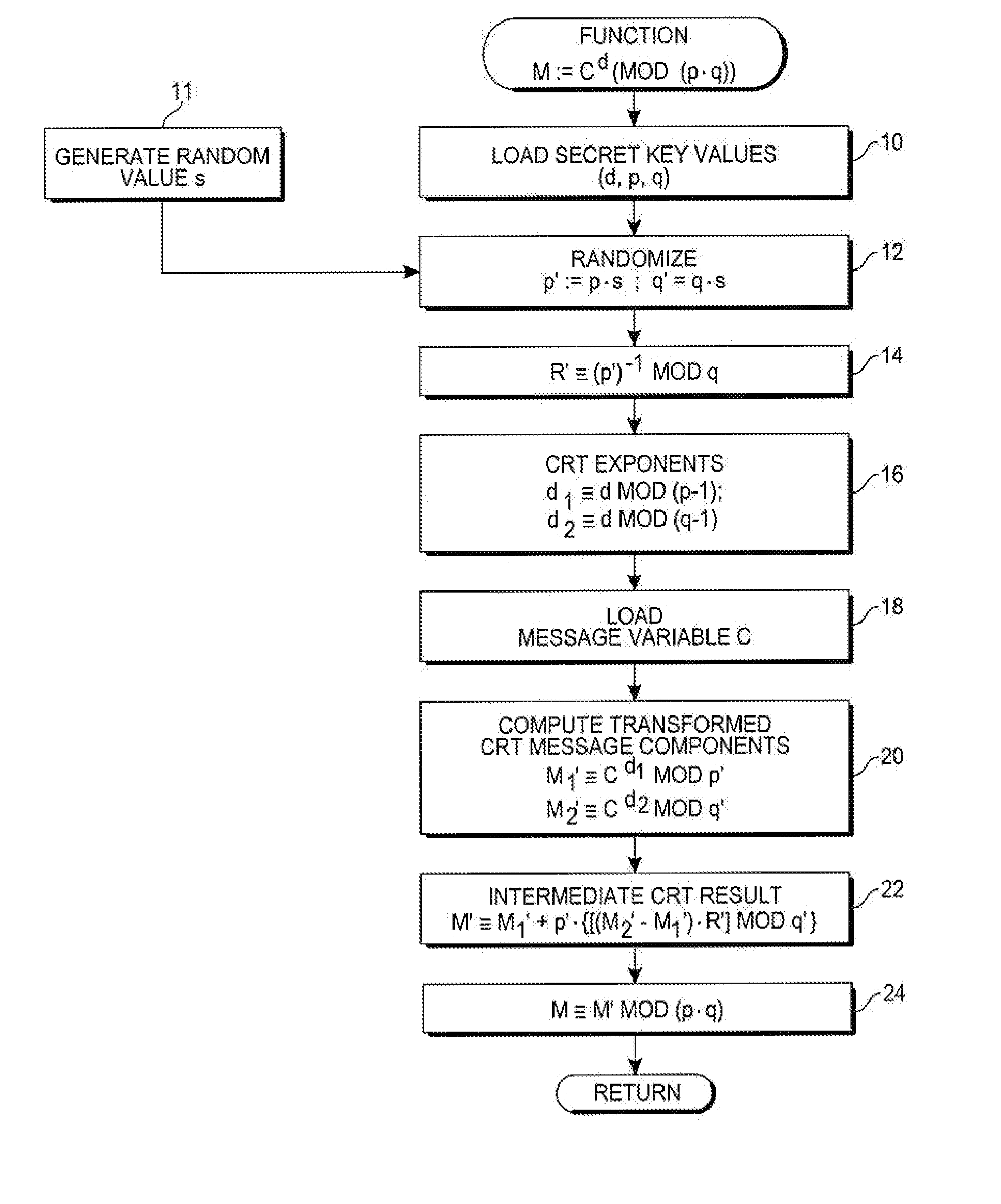
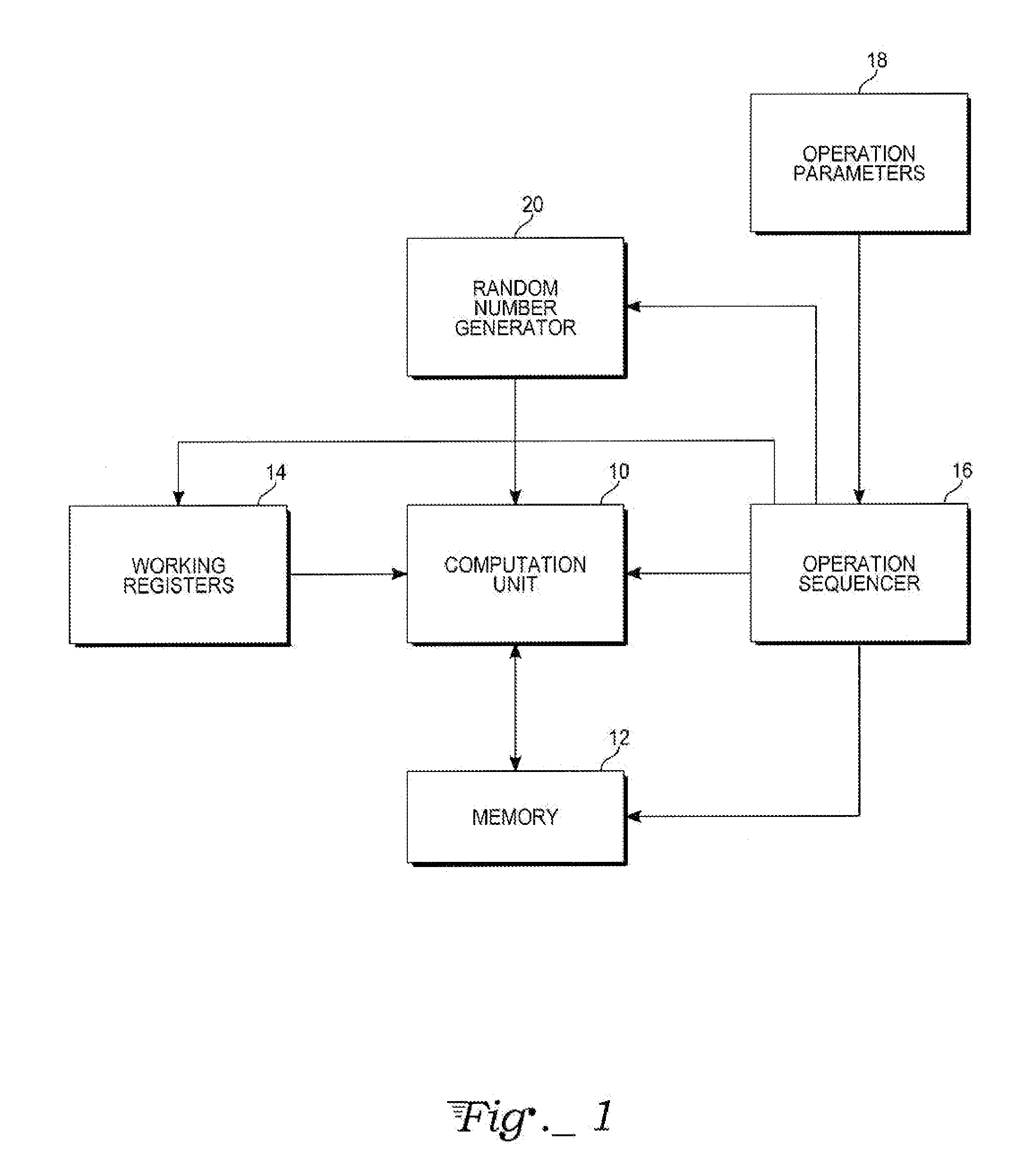
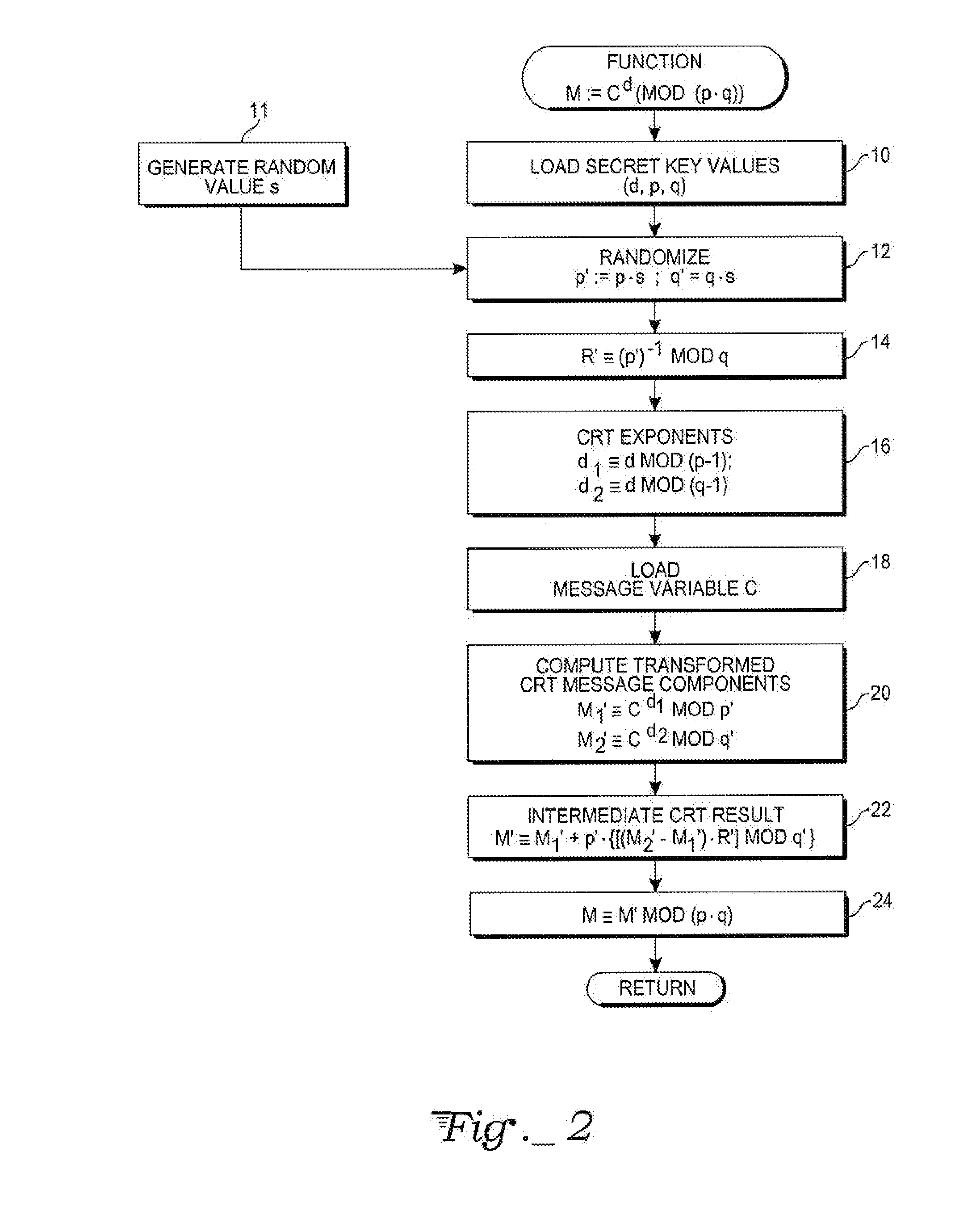
A computer hardware implemented cryptography method computes a modular exponentiation, M:=Cd (mod p·q) upon a message data value C using a Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) based technique. To secure against cryptanalysis,, the private key moduli p and q are transformed by multiplication with a generated random value s, so that p′:=p·s and q′:=q·s. The CRT steps of the modular exponentiation are applied using the transformed moduli p′ and q′ to obtain a random intermediate message data value M′. A final reduction of M′ modulo p·q yields the final message data value M. Values needed for the computation are loaded into data storage and accessed as needed by electronic processing hardware.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
Integrated method and device for storing and sharing data
ActiveUS20200076596A1Simple working processEasy to provide accessKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer networkKey (cryptography)
The present invention relates to a method for sharing secure data between players (5) on a net said method comprising a cryptography step for data using an asymmetrical cryptographic method with double keys, each player (5) having at least one said double key. The method includes a step for initializing (STP1) a blockchain that includes an operation for storing, at least one initialization block (26) in the blockchain by a predetermined authority using at least one computer, said at least one initialization block (26) comprising at least one said transaction (36) that includes an identity record (84) of a major player, said authority no longer intervening at the end of the initialization step (STP1) at least outside a reinitialization step of a player.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Method of authenticating identification based common key cryptosystem and encryption address in network
InactiveCN101162999AImprove security featuresSolve the owner problemPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPublic key cryptosystemAuthentication
The invention provides an identity-based public-key cryptography system (IBC) and the authentication method of CGA (Cryptographically Generated Addresses) in a mobile IPv6 network. In the method, a mobile node obtains owned public and private keys via an identity identifier registered on the identity-based public-key cryptography system (IBC) and configures an IPv6 address via the owned public key. Only by knowing the identifier of a communication peer, the mobile node can use the public parameters of the system to calculate the public key of the communication peer in order to carry out message encryption or signature authentication, whereas the private key of the mobile node can be obtained only by the center of the IBC cryptography system and the mobile node. The method resolves three problems at the same time, the first problem is the ownership of IPv6 addresses, the second problem is the authentication property of message sources, that is, messages come from the owers of addresses, and the third problem is the trust property which is resolved by the IBC, that is, a message source is an authentic entity.
Owner:柏建敏
Method and apparatus for implementing processor instructions for accelerating public-key cryptography
ActiveUS20040267855A1Conditional code generationPublic key for secure communicationParallel computingCarry-save adder
In response to executing an arithmetic instruction, a first number is multiplied by a second number, and a partial result from a previously executed single arithmetic instruction is fed back from a first carry save adder structure generating high order bits of the current arithmetic instruction to a second carry save adder tree structure being utilized to generate low order bits of the current arithmetic instruction to generate a result that represents the first number multiplied by the second number summed with the high order bits from the previously executed arithmetic instruction. Execution of the arithmetic instruction may instead generate a result that represents the first number multiplied by the second number summed with the partial result and also summed with a third number, the third number being fed to the carry save adder tree structure.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
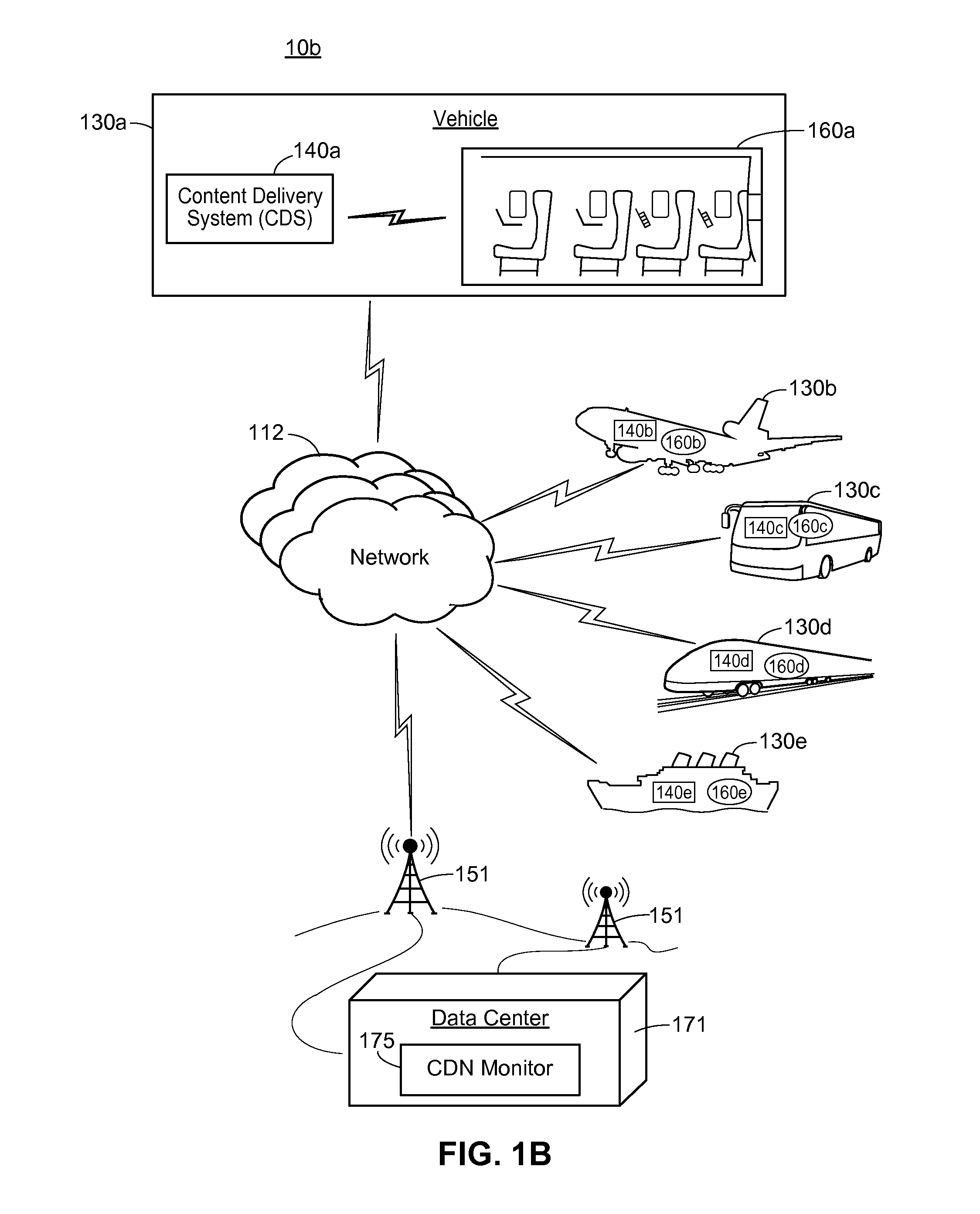
Autonomous-Mode Content Delivery and Key Management
ActiveUS20160127895A1Facilitate secure content-deliveryFacilitate usage trackingKey distribution for secure communicationParticular environment based servicesTelecommunicationsKey (cryptography)
Multimedia content may be delivered to content consumer devices via a content-delivery network. Encrypted content and cryptography keys for decrypting the content may be distributed from a data center to various nodes of the content-delivery network, each node acting as a semi-independent content-delivery system. Each content-delivery system is capable of delivering received content to end-users and implementing a key-management scheme to facilitate secure content-delivery and usage tracking, even when the content-delivery system is disconnected from the data center. In other words, the disclosed systems and methods facilitate the operation of nodes which may operate in “autonomous mode” when disconnected from a larger content-delivery network, thus maintaining content-delivery capabilities despite having little if any connectivity to external networks.
Owner:SORENSON COMM +1
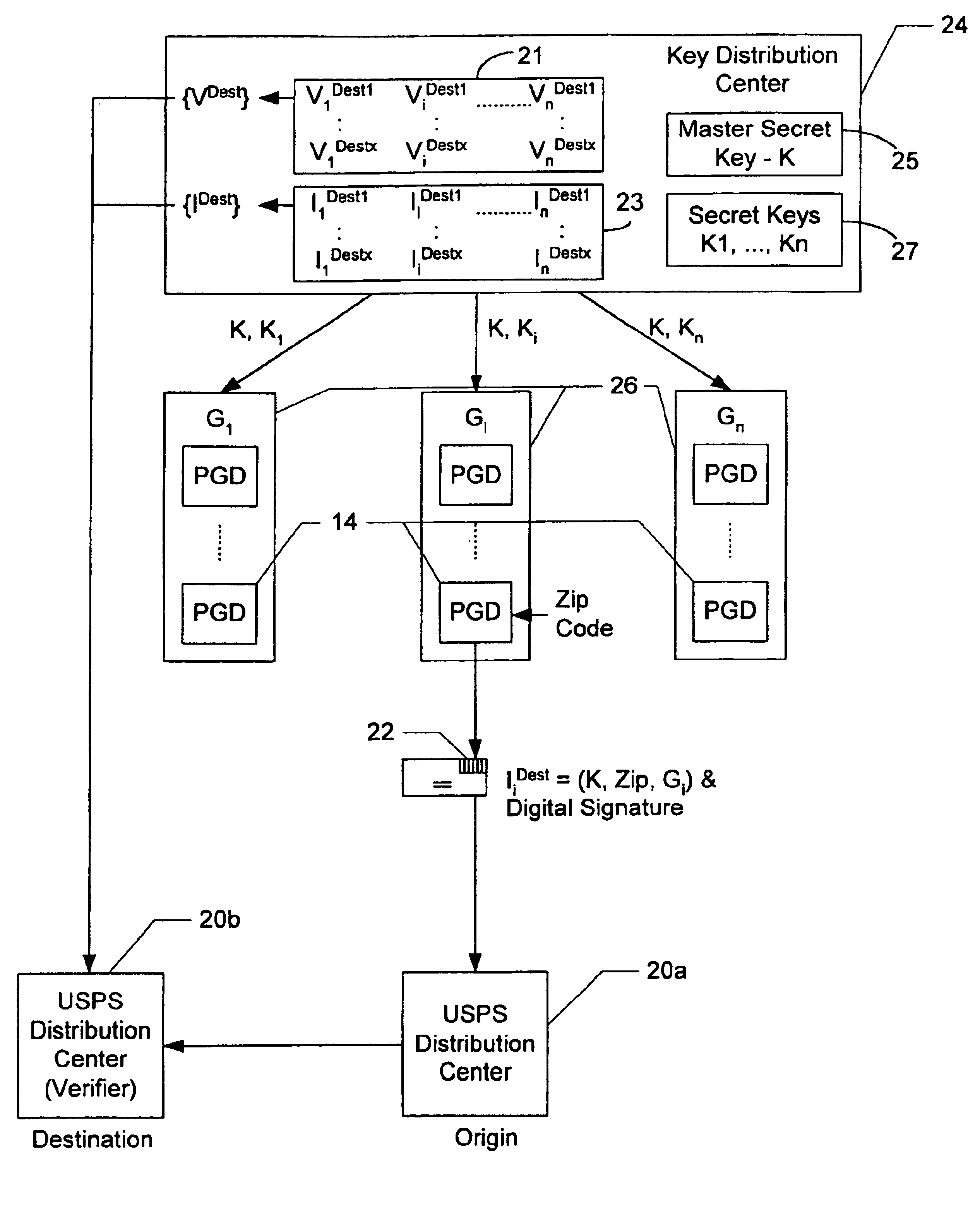
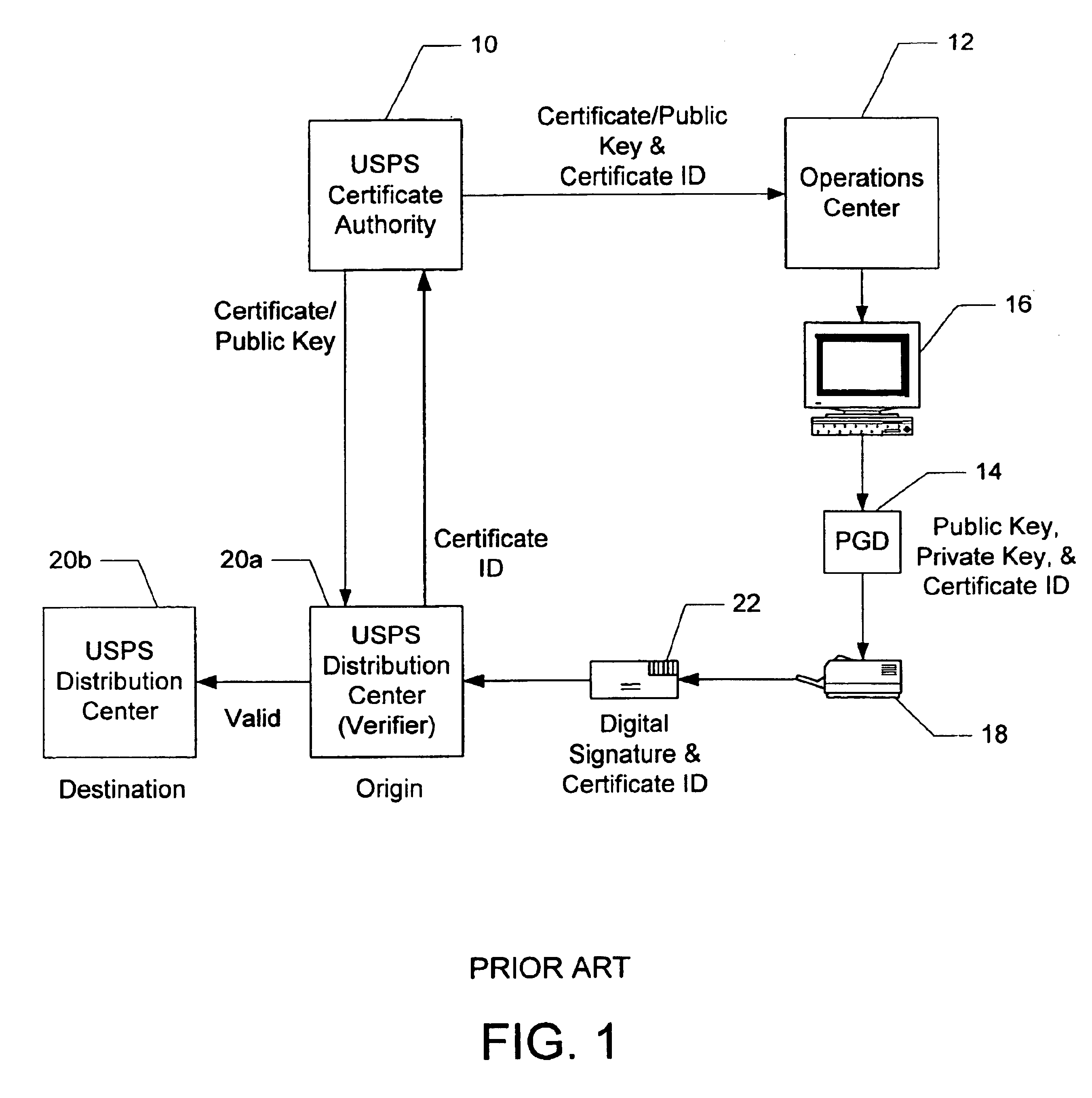
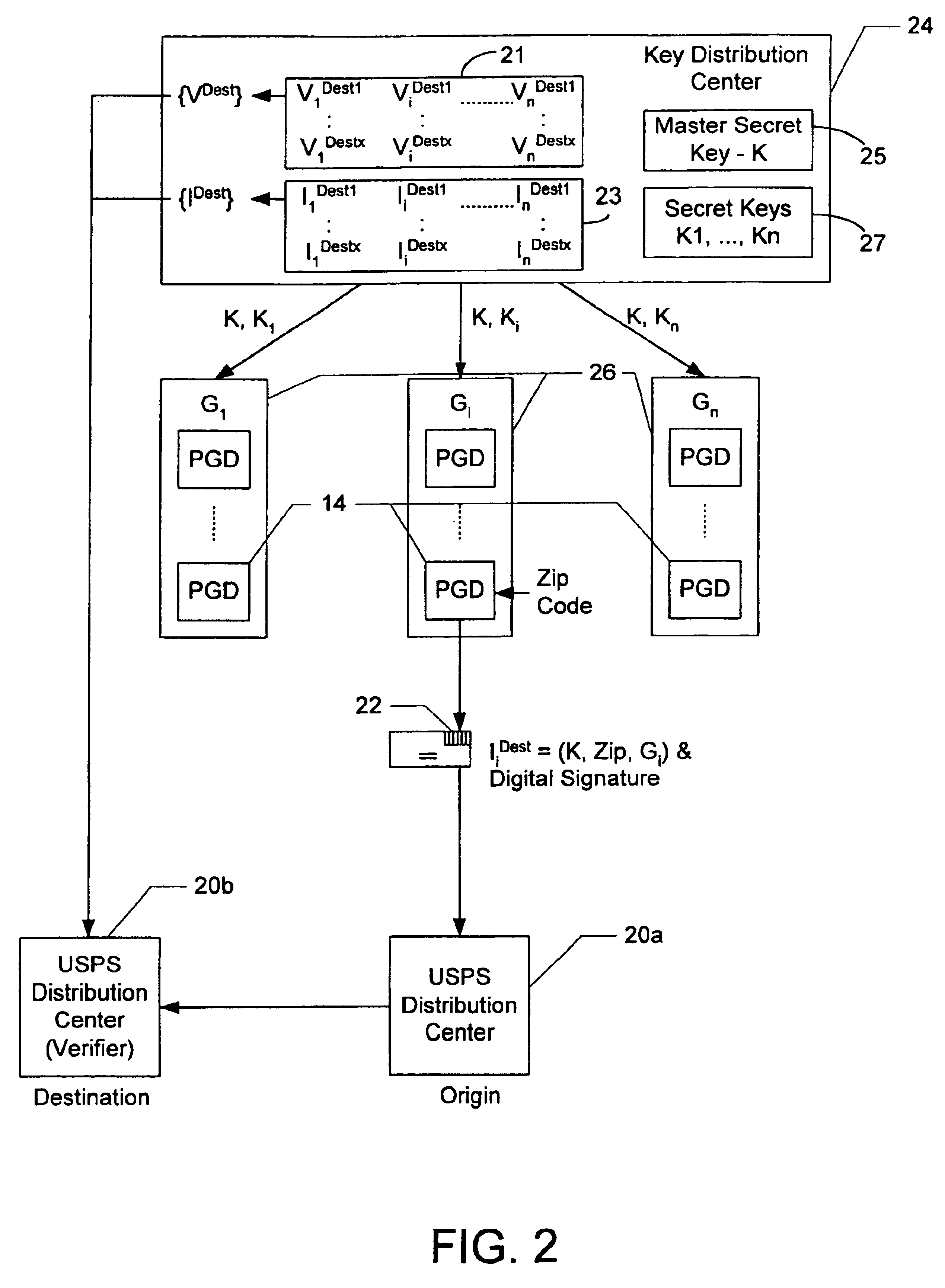
Evidencing and verifying indicia of value using secret key cryptography
InactiveUS6934839B1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPaymentDigital signature
A method and system for evidencing payment of indicia using secret key cryptography is disclosed. The method and system include a plurality of indicia generating devices that are divided into groups for generating and printing indicia on a media that is to be received at a plurality of establishments, wherein the establishments are associated with different geographic designations. The method and system include assigning a plurality of verification keys to each indicia generating device in each of the groups, wherein each of the verification keys assigned to each of the groups is encrypted as a function of a respective geographic designation. A key ID is associated with each of the verification keys and is encrypted as a function of the same geographic designation used to encrypt the corresponding verification key. After the verification keys and key ID's are assigned, each one of the establishments receives the verification keys and the key ID's that were encrypted as a function of the geographic designation associated with the establishment. When generating indicia for media destined for a particular one of the establishments, the indicia generating devices evidence the indicia by generating one of the verification keys and the corresponding key ID assigned to indicia generating device's group based on the geographic designation associated with the particular establishment, and uses the generated verification key to create a digital signature. The indicia generating devices digitally sign the indicia by including the digital signature and the generated key ID in the indicia. Upon receiving the media at the particular establishment, the indicia on the media is verified by using the key ID on the indicia and the distributed verifications keys to compute a digital signature, and comparing the computed digital signature with the digital signature on the indicia.
Owner:STAMPS COM
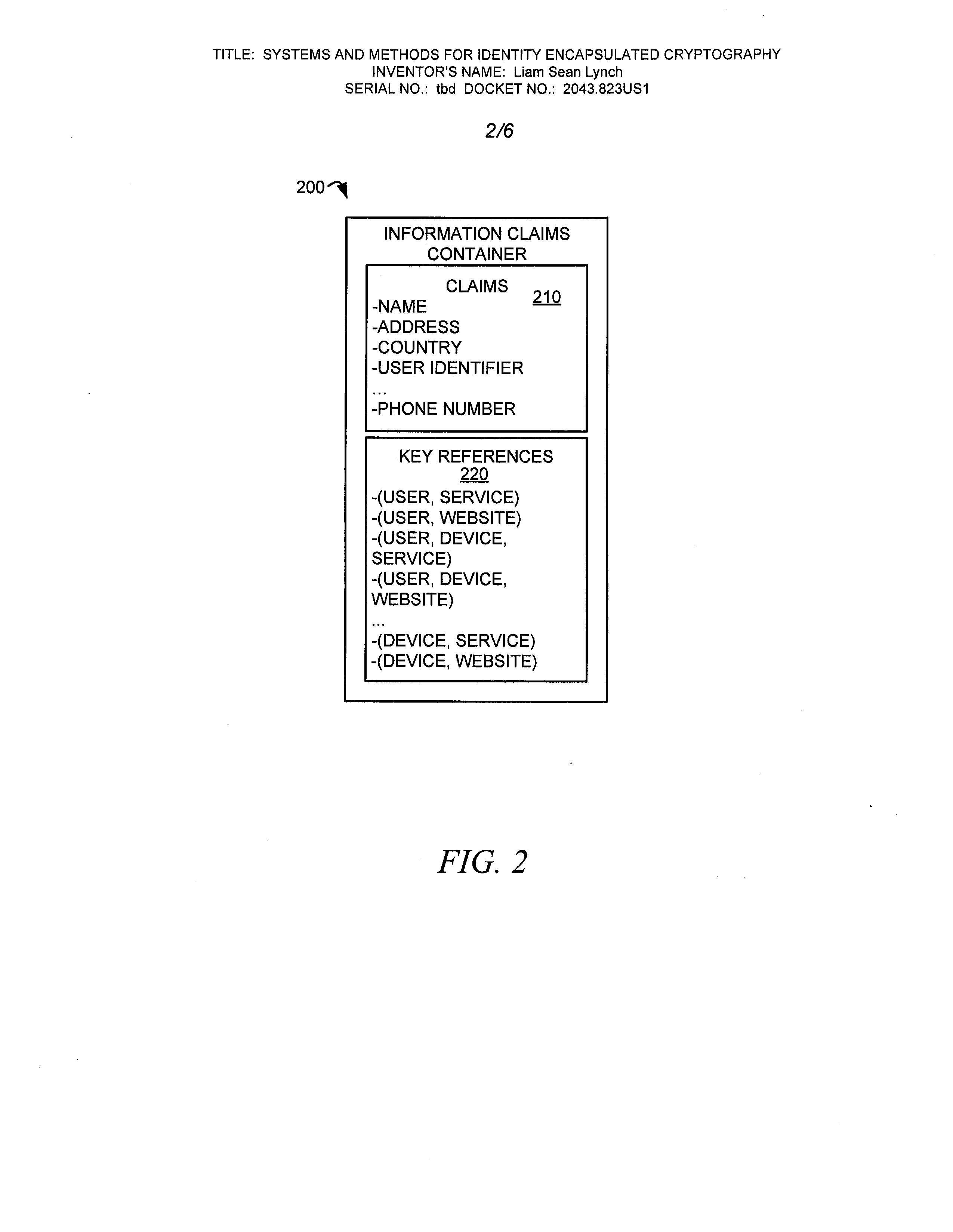
Systems and methods for identity encapsulated cryptograhy
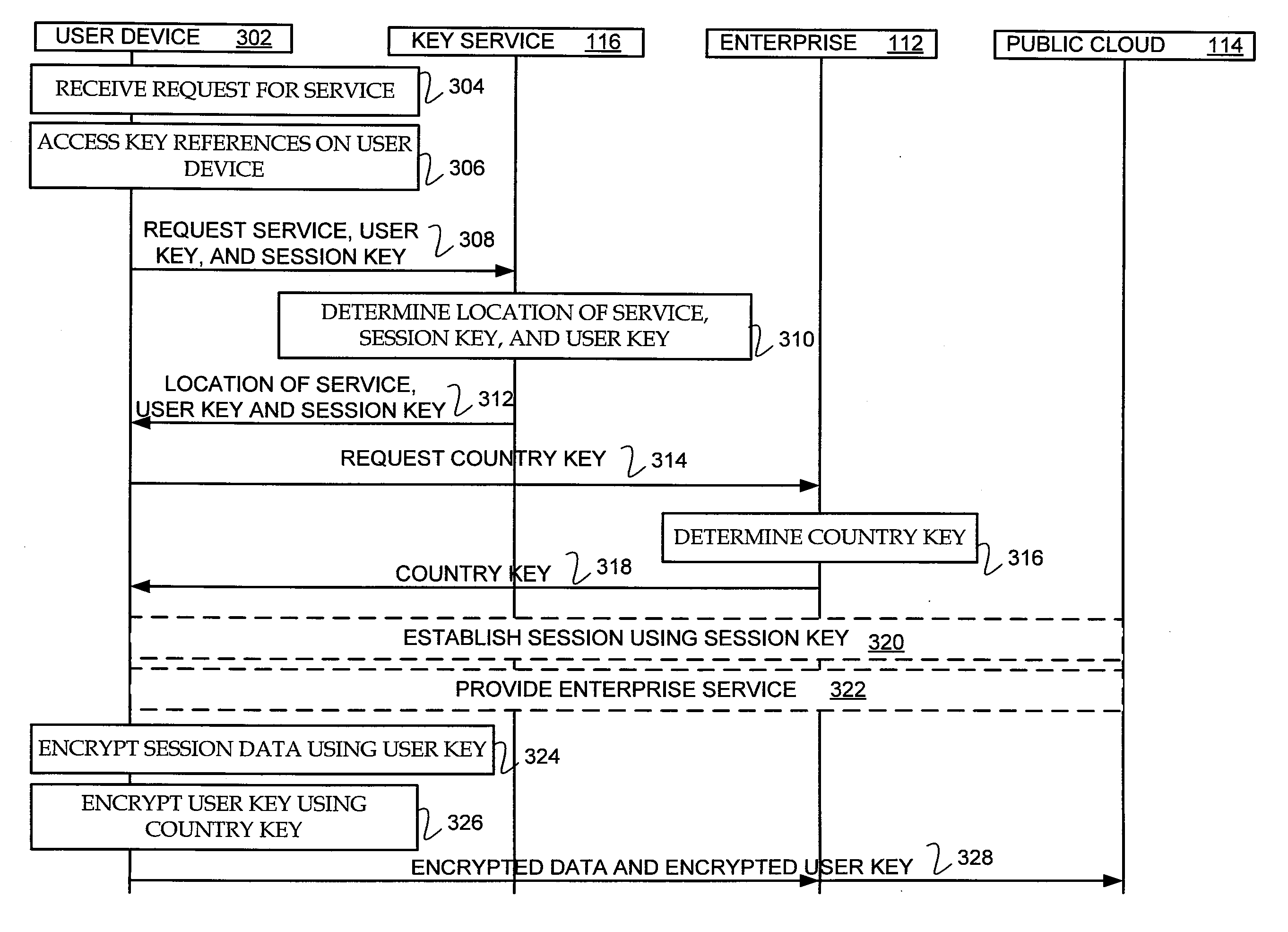
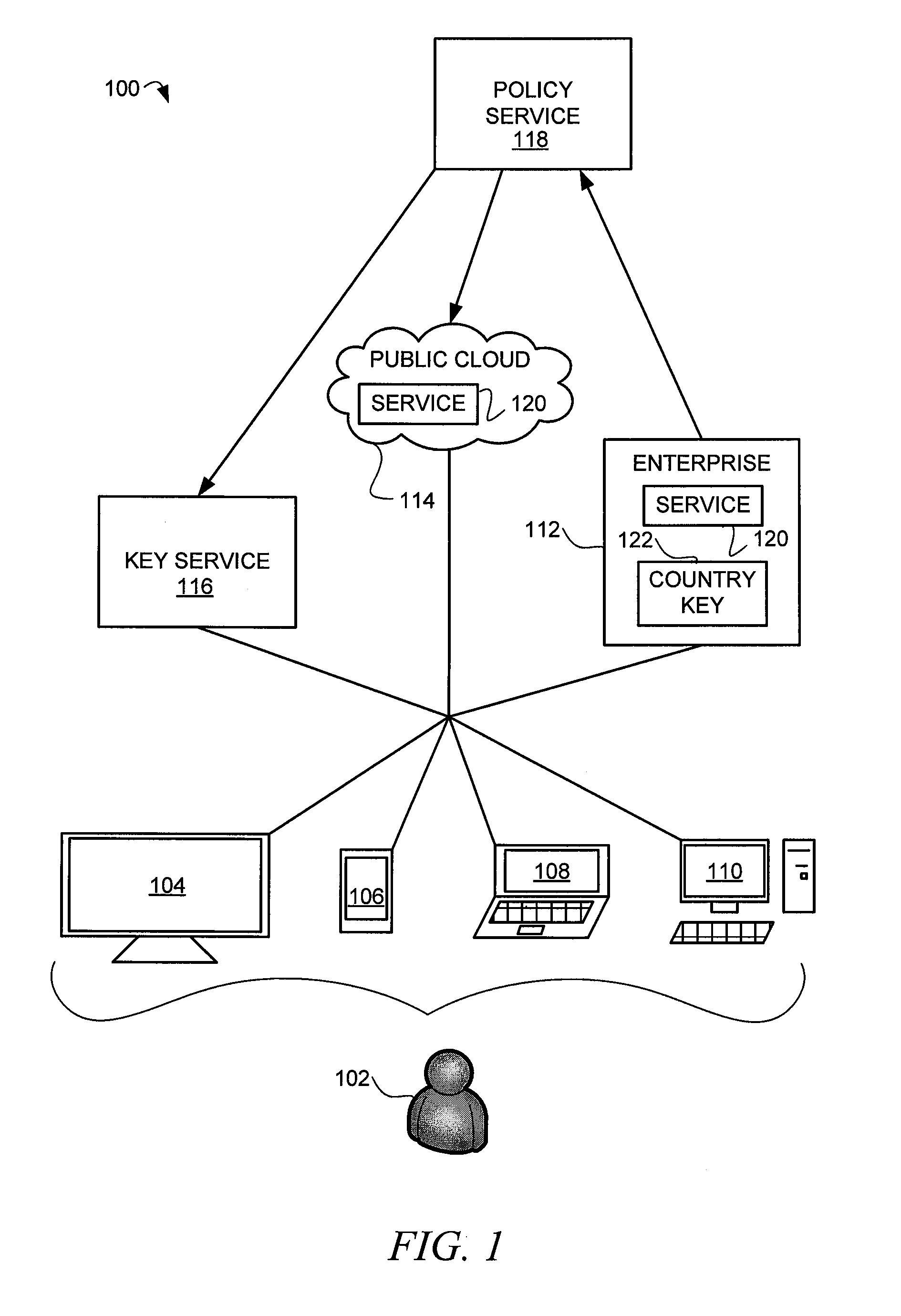
A method and a system to provide identity encapsulated cryptography are provided. A method may comprise receiving a user key to access a service. The service may be provided by an enterprise and hosted within a public cloud. A request for a country key assigned to a country of a user is transmitted and the country key is received. Session data resulting from the use of the service hosted within the public cloud is encrypted using the user key and the user key is encrypted using the country key. The encrypted session data and the encrypted user key are stored in the public cloud. The country key may be provided to a legal agency of the country of the user to decrypt session data of the user and to not decrypt session data of other users of another country.
Owner:EBAY INC
Network real-name system implementing method
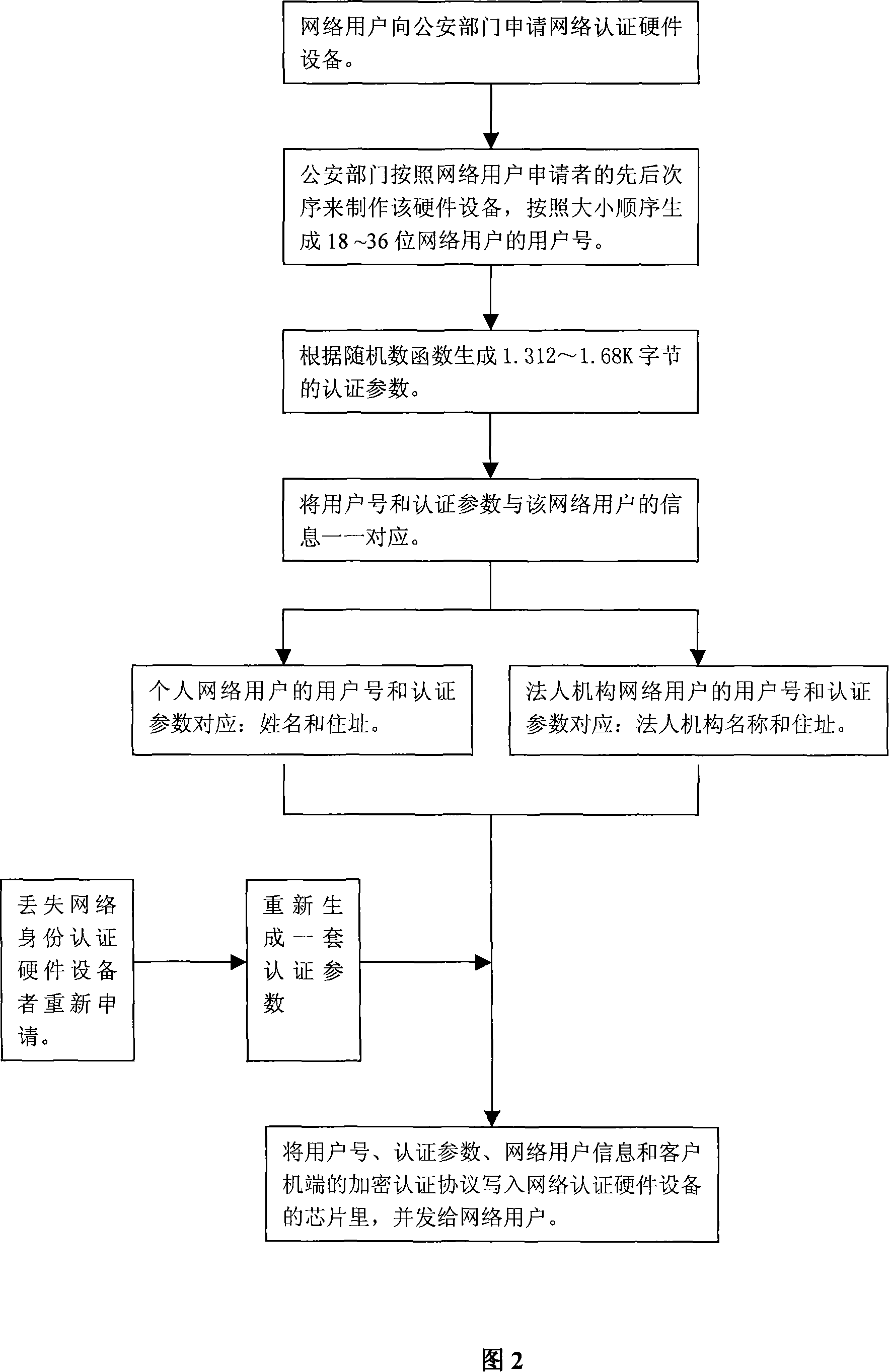
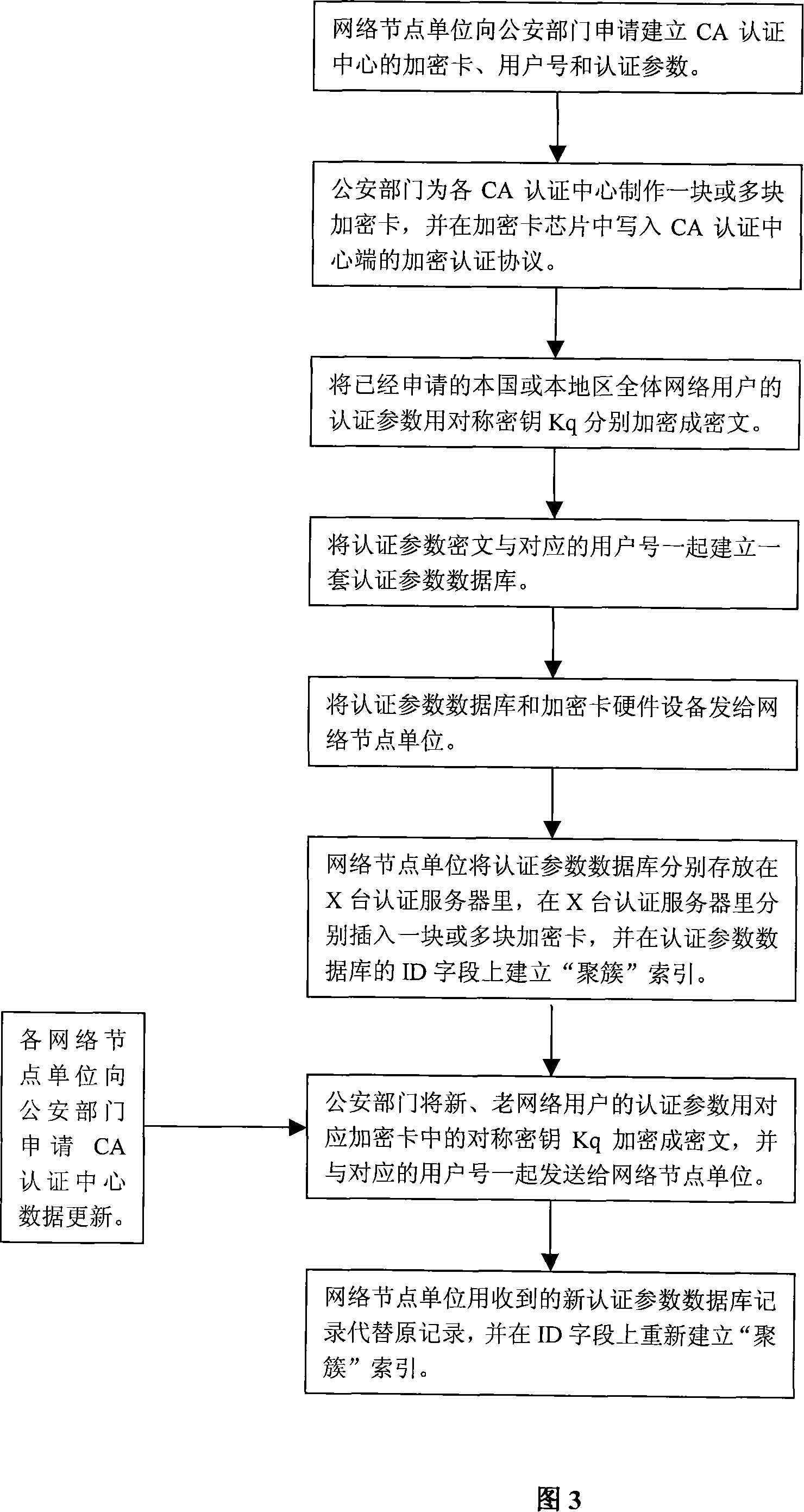
InactiveCN101136750AImprove authentication efficiencyImprove security levelUser identity/authority verificationApplication serverWeb authentication
The implement method for real name system establishes center of authentication (CA) respectively for network nodes i.e. WEB server as unit. The method connects WEB server with CA and network resources or application servers (AS) in series mode. Identifiers and authentication parameters of overall network users in homeland or local area are stored in AS of CA in advance. Protocol of cryptographic authentication based on algorithm of symmetric cryptography and technique of combined symmetric cryptographic key are built in hardware chips at two ends of client and CA. all CAs in each network node can provide authentication of network ID for overall network users in homeland or local area. Each network user holds hardware device for network authentication. Through authentication of CA in each network node, resources or application server in each network node logs on network. Thus, the method implements management on networks in homeland or local government through real name system.
Owner:BEIJING JINAOBO DIGITAL INFORMATION TECH
Laddered authentication security using split key asymmetric cryptography
InactiveUS20060248333A1Improving conventional public key cryptographyLevel of authentication securityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPasswordAuthentication
Owner:VMWARE INC
Public key exchange with authenticated ecdhe and security against quantum computers
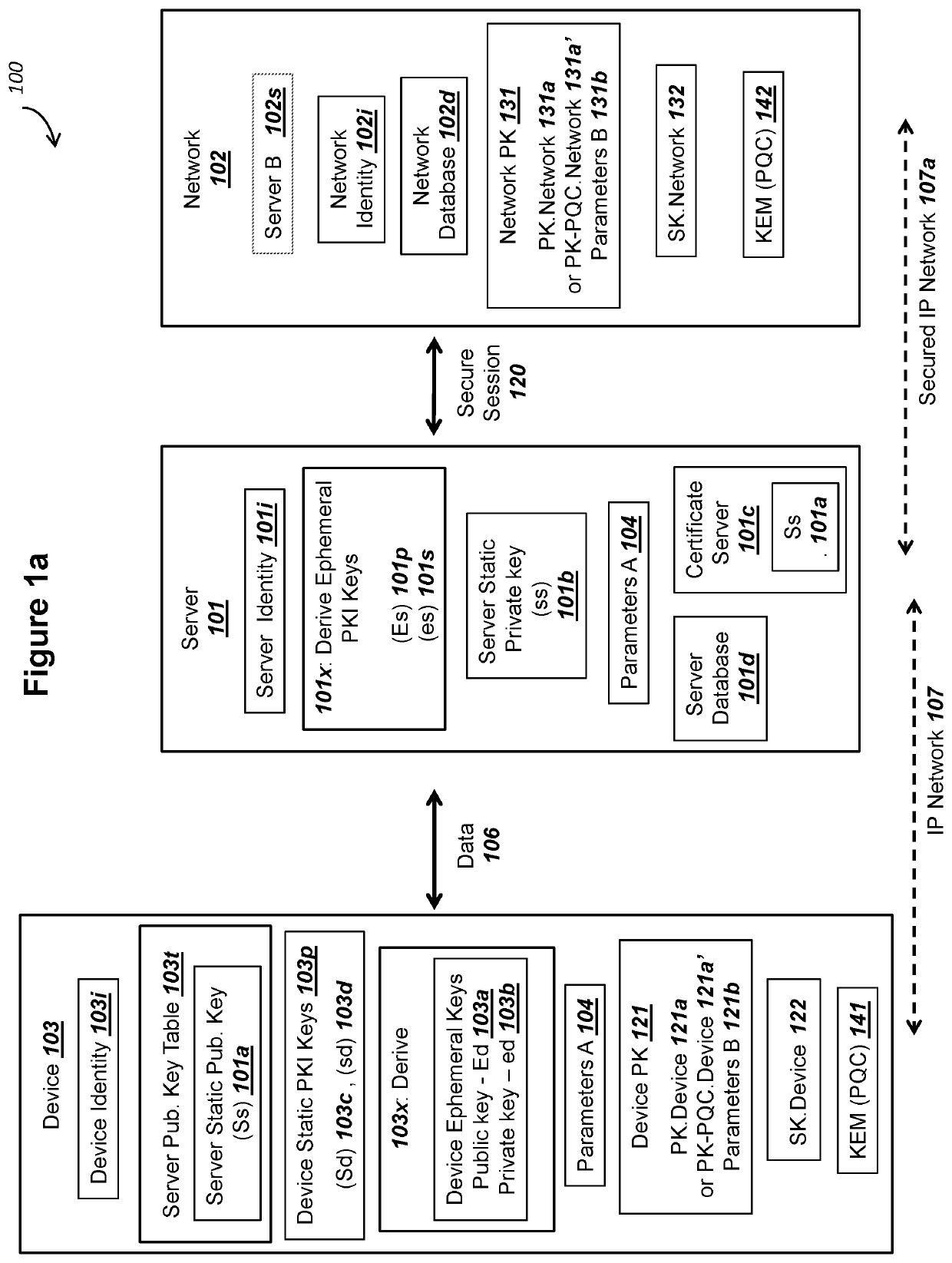
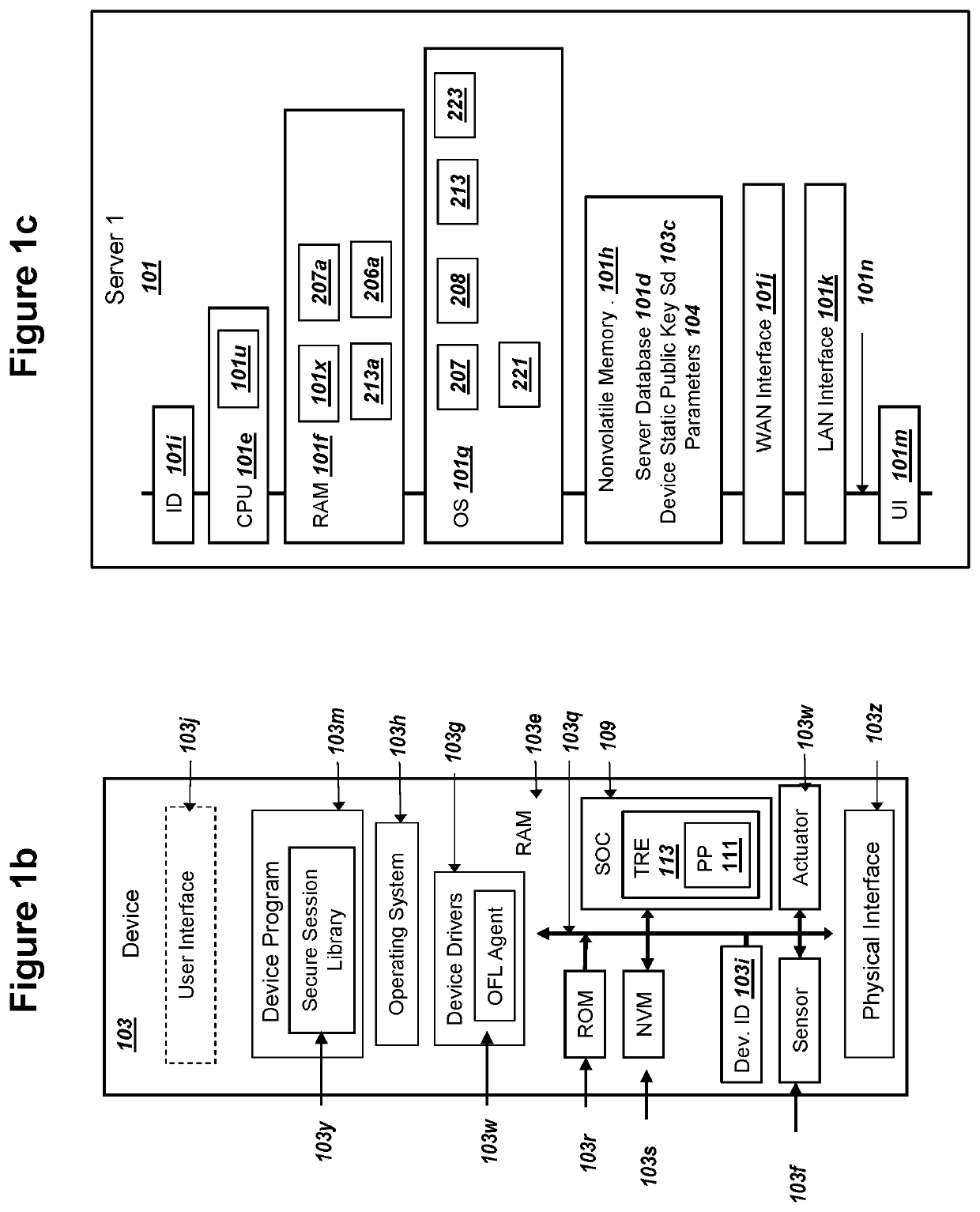
ActiveUS20200280436A1Solve insufficient capacityQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationKey exchangeKey (cryptography)
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) can provide security against quantum computers that could feasibly determine private keys from public keys. A server communicating with a device can store and use PKI keys comprising server private key ss, device public key Sd, and device ephemeral public key Ed. The device can store and use the corresponding PKI keys, such as server public key Ss. The key use can support all of (i) mutual authentication, (ii) forward secrecy, and (iii) shared secret key exchange. The server and the device can conduct an ECDHE key exchange with the PKI keys to mutually derive a symmetric ciphering key K1. The device can encrypt a device public key PK.Device with K1 and send to the server as a first ciphertext. The server can encrypt a server public key PK.Network with at least K1 and send to the device as a second ciphertext.
Owner:IOT & M2M TECH LLC
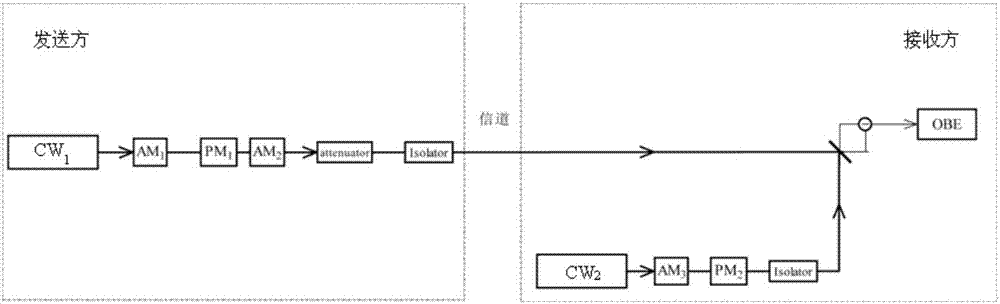
Phase compensation implementation method of continuous variable quantum key distribution system
InactiveCN107086891AAvoid interception and resend attacksKey distribution for secure communicationFibre transmissionCoherent statesConfidentiality
The invention discloses a phase compensation implementation method of a continuous variable quantum key distribution system. A sender performs Gaussian modulation on initial continuous key data by using the coherent state and then sends the modulated signals to a receiver through an optical fiber channel; and the receiver performs preprocessing, error corrosion and confidentiality enhancement on the acquired initial continuous key data by using an algorithm based on orthogonal basis expansion so as to acquire the final security key. According to the method, the practical use of the continuous variable quantum cryptography is prompted, and environmental interference and human attack affected by the quantum signals in the quantum communication process can also be effectively suppressed.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of performing elliptic polynomial cryptography with elliptic polynomial hopping
InactiveUS20110200185A1Solve excessive overheadImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareNumber generator
The method of performing elliptic polynomial cryptography with elliptic polynomial hopping allows for the encryption of messages through elliptic polynomial cryptography, i.e., using elliptic polynomials with multi x-coordinates, and particularly with the utilization of elliptic polynomial hopping based upon both the elliptic polynomial and its twist, regardless of whether the elliptic polynomial and its twist are isomorphic with respect to one another. Each plaintext block is encrypted by a different elliptic polynomial, and the elliptic polynomials used are selected by an initial secret key and a random number generator. The method is particularly useful for symmetric encryption systems, and provides a block cipher fundamentally based upon a computationally hard problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Reconfigurable Free-Space Quantum Cryptography System
ActiveUS20170250805A1Communication securityKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationSecure communicationTransmission protocol
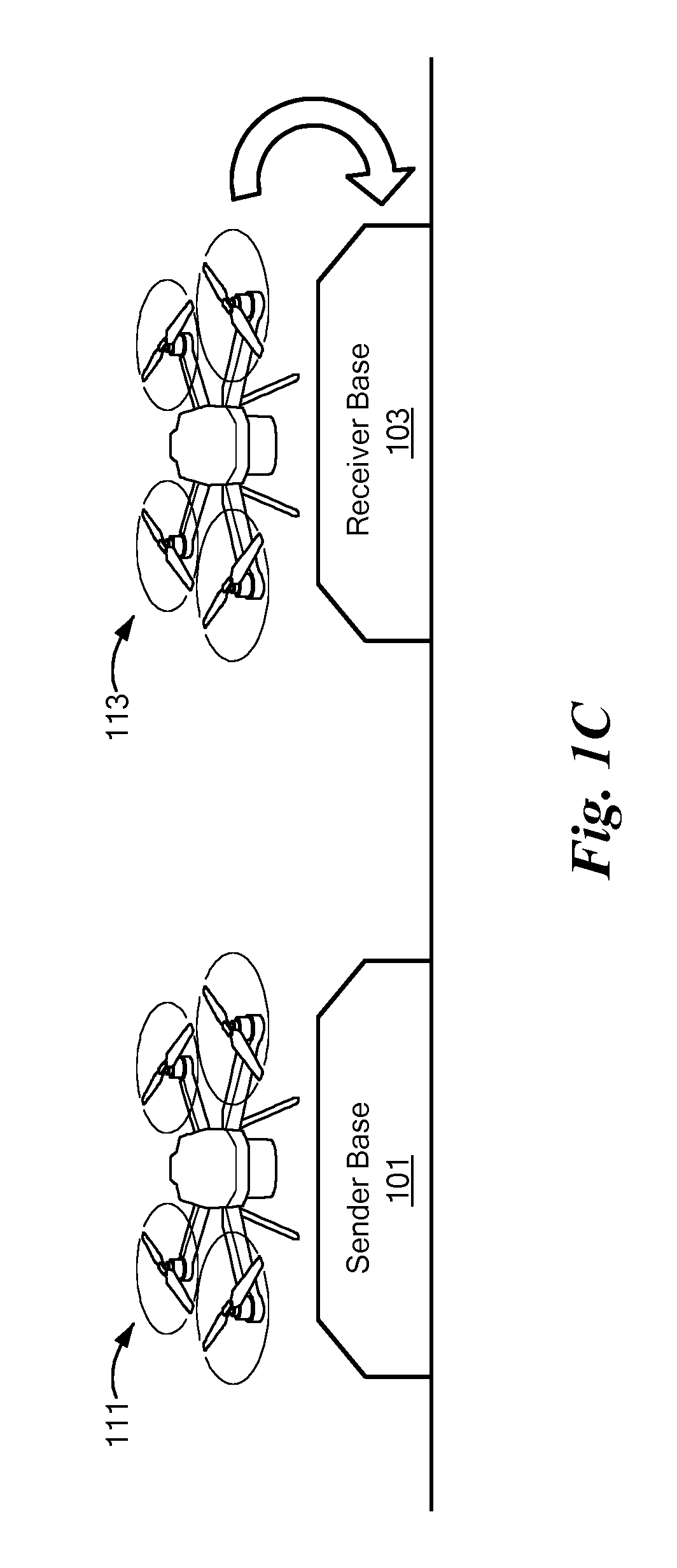
A system, and methods, for transmitting encrypted information as a quantum transmission between a first node and a second node, or among more than two nodes. Each node is characterized by an instantaneous spatial position, and the instantaneous spatial position of the second node is repositionable within a frame of reference associated with the first node. A hovering drone is adapted either for running a quantum key transmission protocol in secure communication with the first node, and / or for running a quantum key reception protocol in secure communication with the second node. Either drone may serve as a relay of optical data between a base station and another drone. Secure communication among more than two nodes may be reconfigured.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Homomorphic white box system and method for using same
ActiveUS20180198613A1Performance maximizationReduce expertiseKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptographyKey (cryptography)
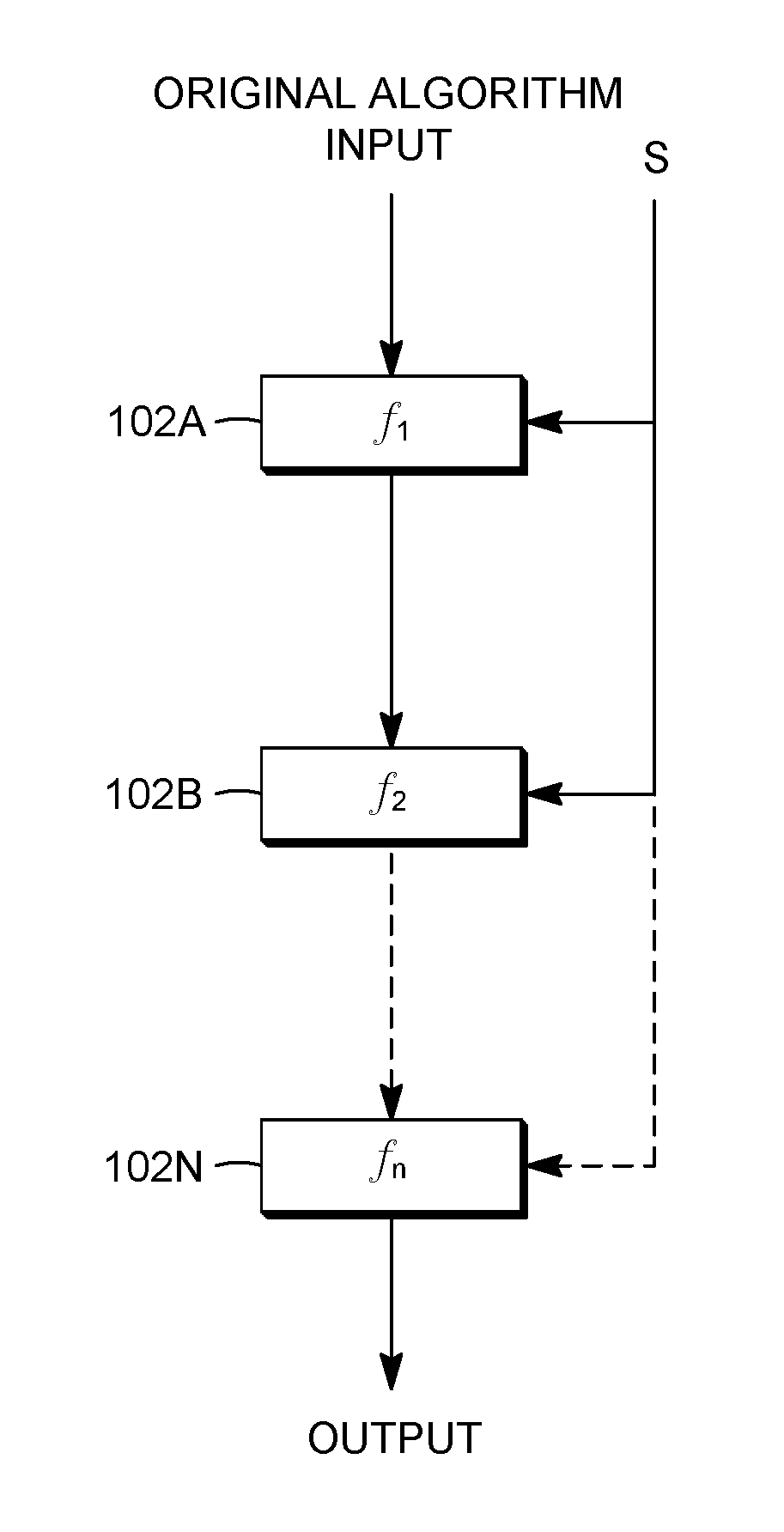
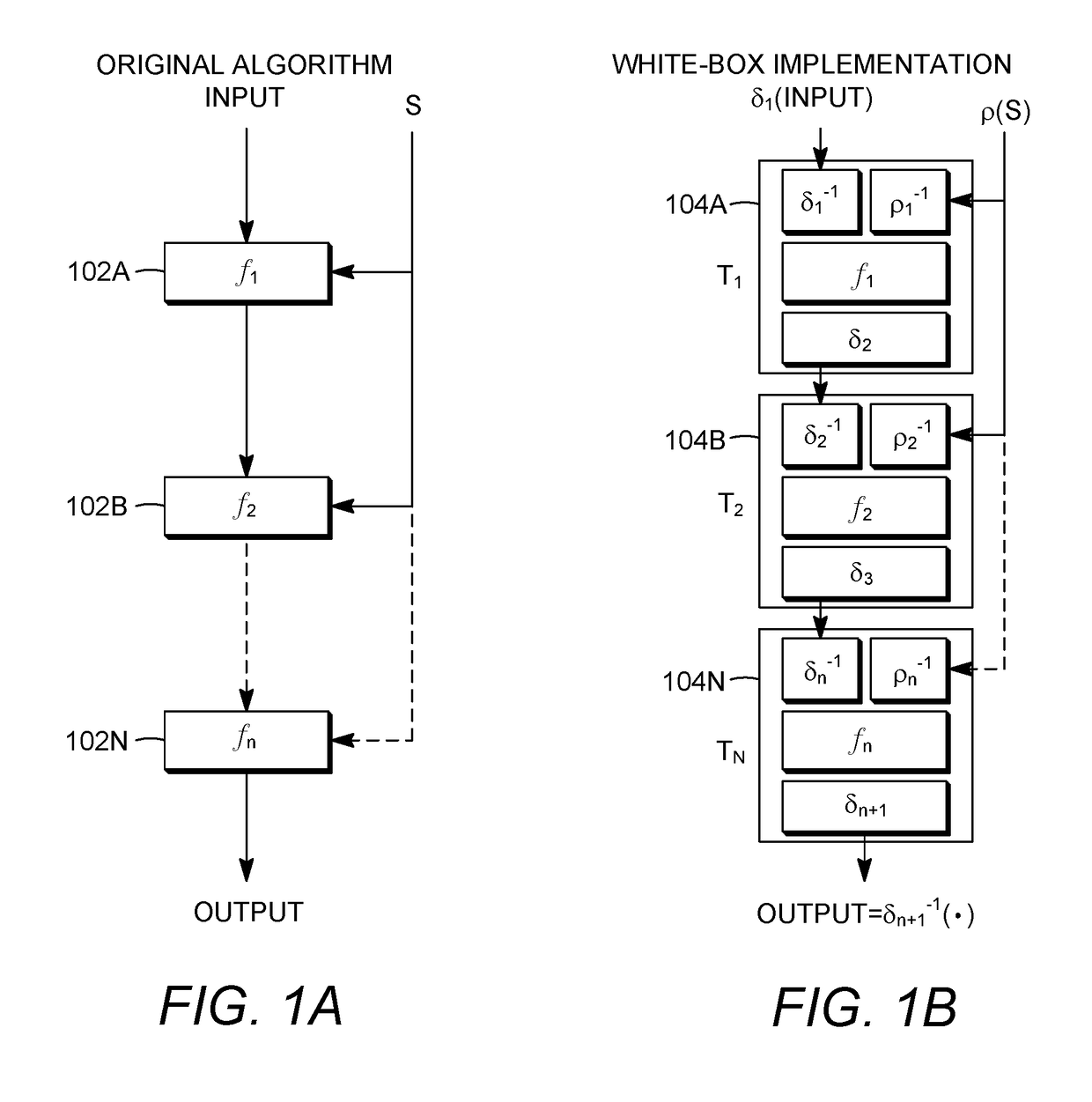
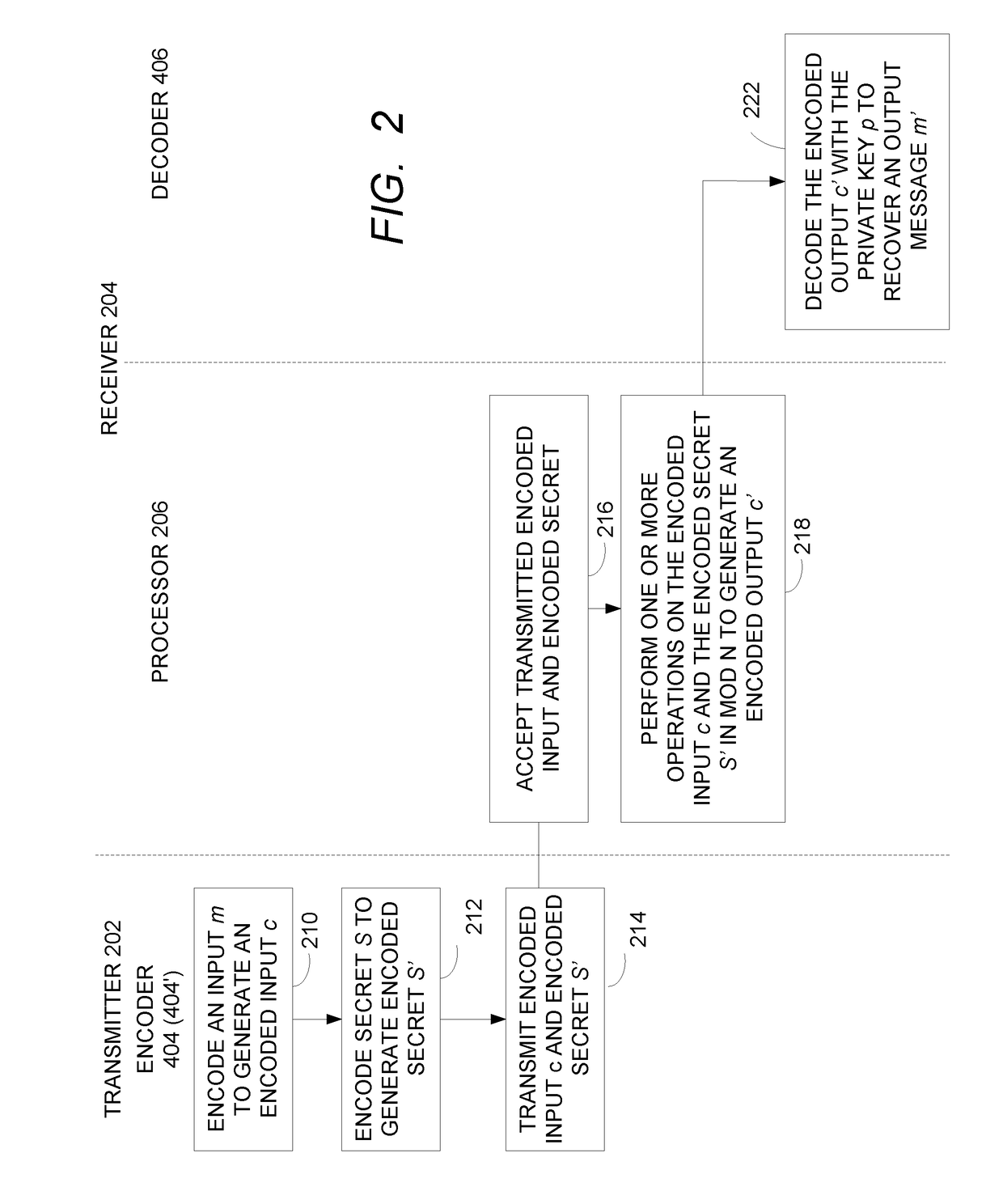
A method for whitebox cryptography is provided for computing an algorithm (m,S) with input m and secret S, using one or more white-box encoded operations. The method includes accepting an encoded input c, where c=Enc(P,m); accepting an encoded secret S′, where S′=Enc(P,S); performing one or more operations on the encoded input c and the encoded secret S′ modulo N to obtain an encoded output c′; and decoding the encoded output c′ with the private key p to recover an output m′ according to m′=Dec(p,c′), such that m′=(m,S).
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com