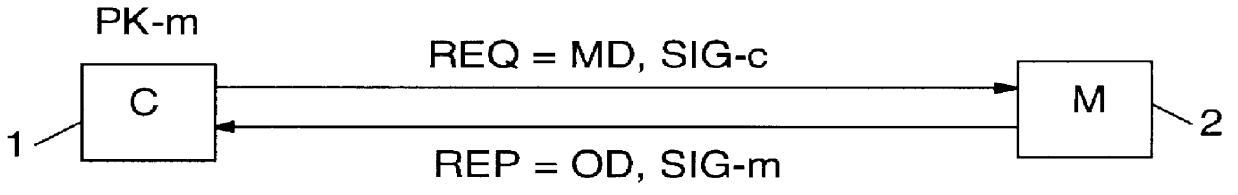Patents
Literature
489 results about "Public key infrastructure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. It is required for activities where simple passwords are an inadequate authentication method and more rigorous proof is required to confirm the identity of the parties involved in the communication and to validate the information being transferred.
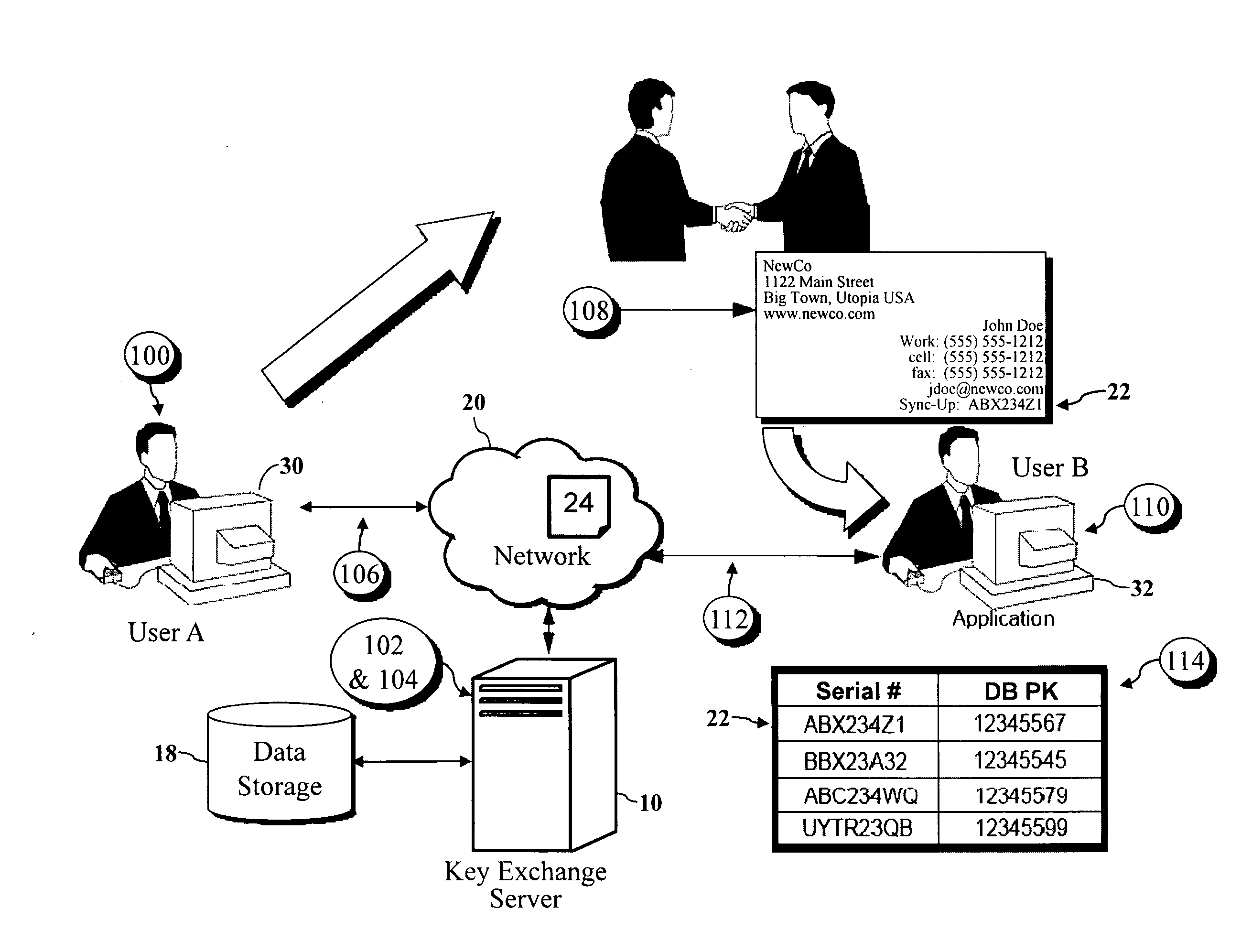
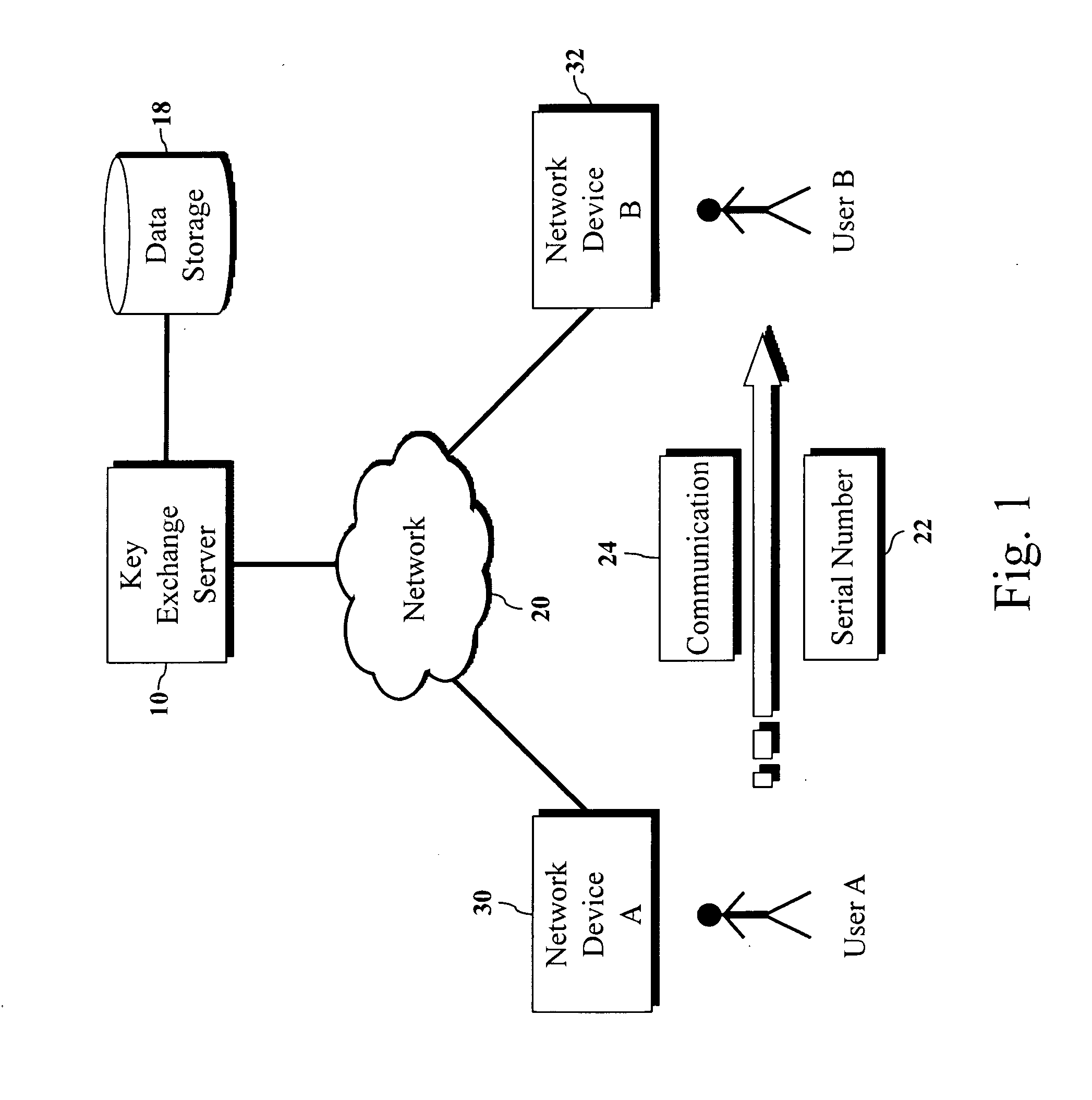
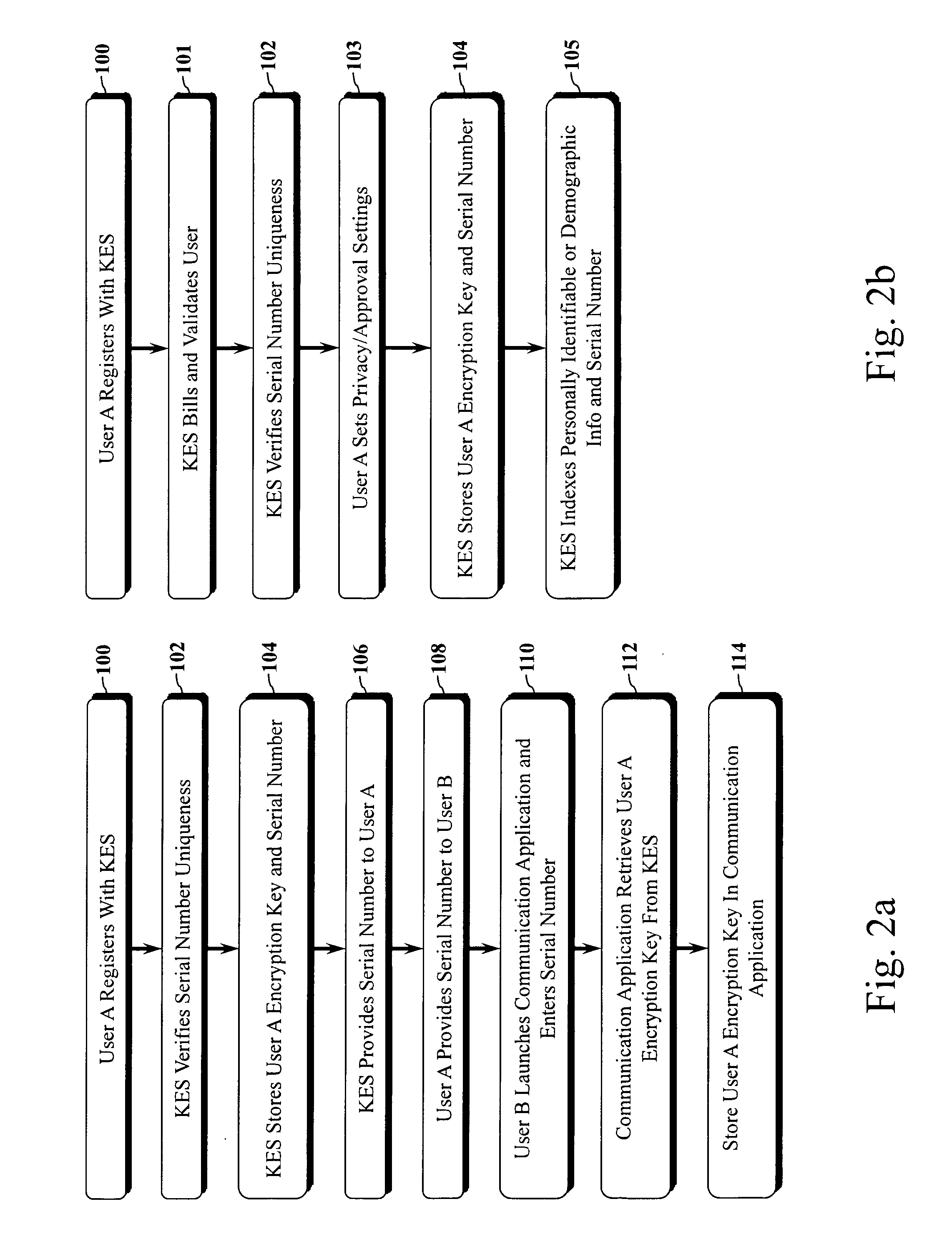
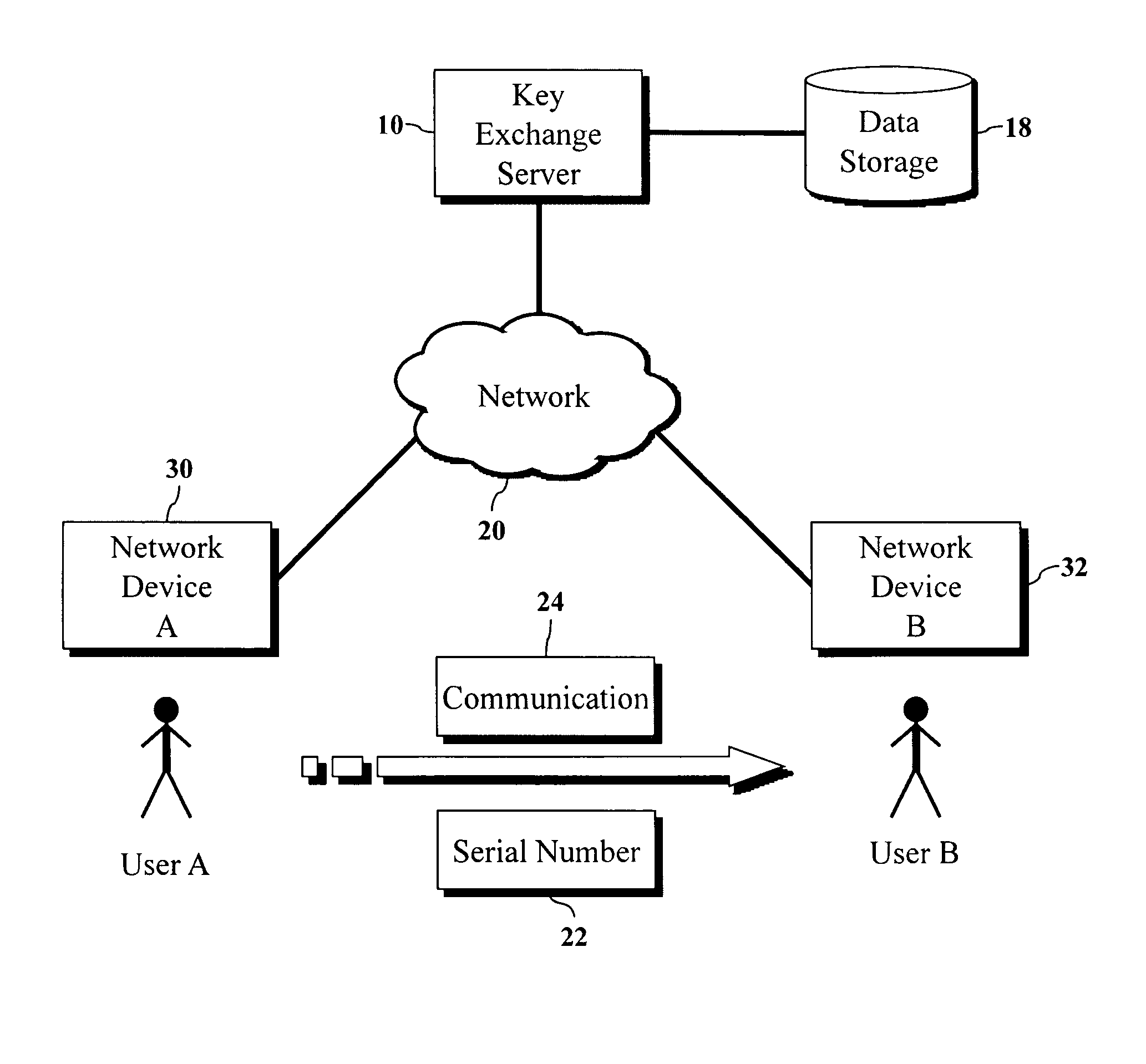
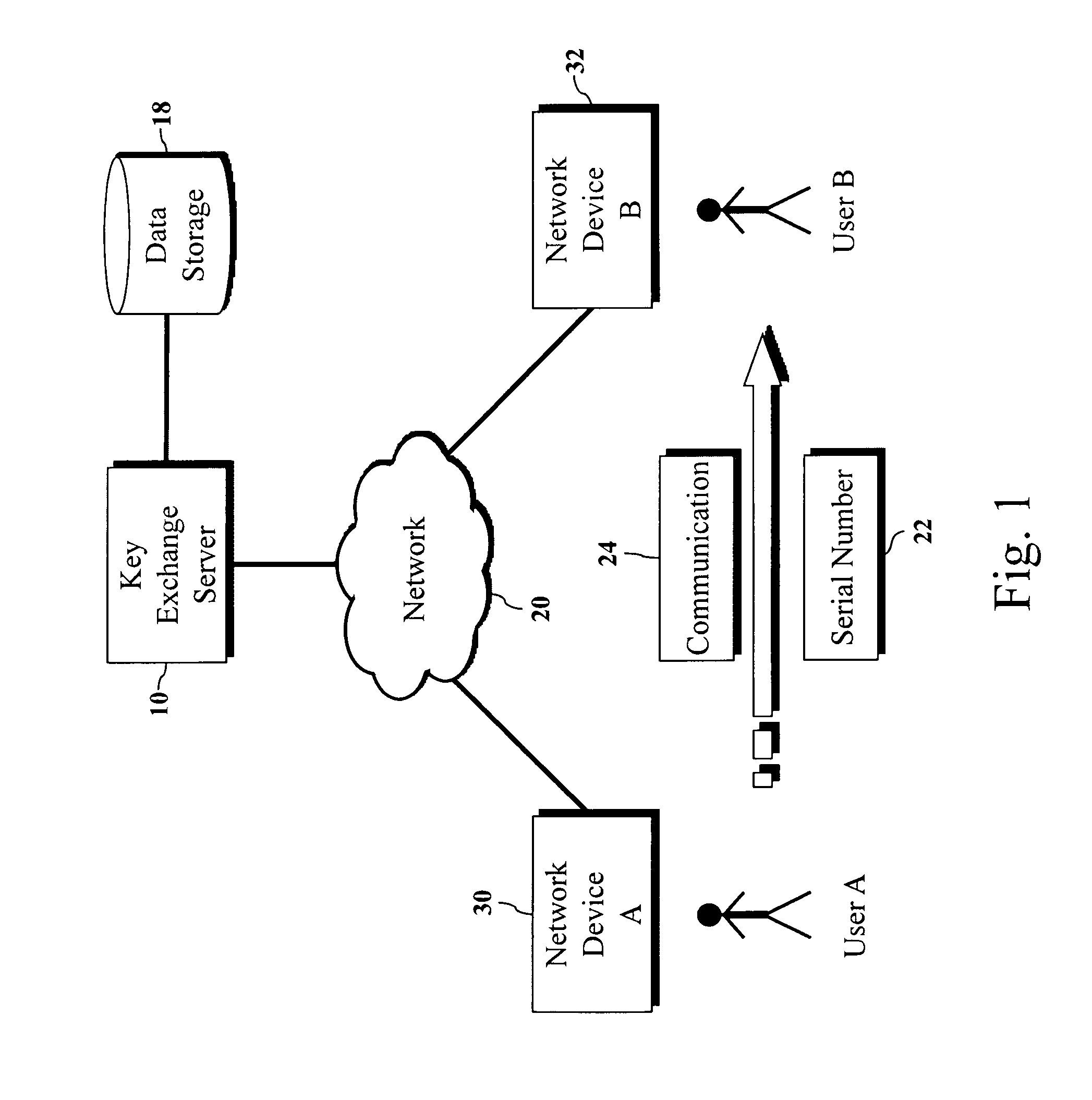
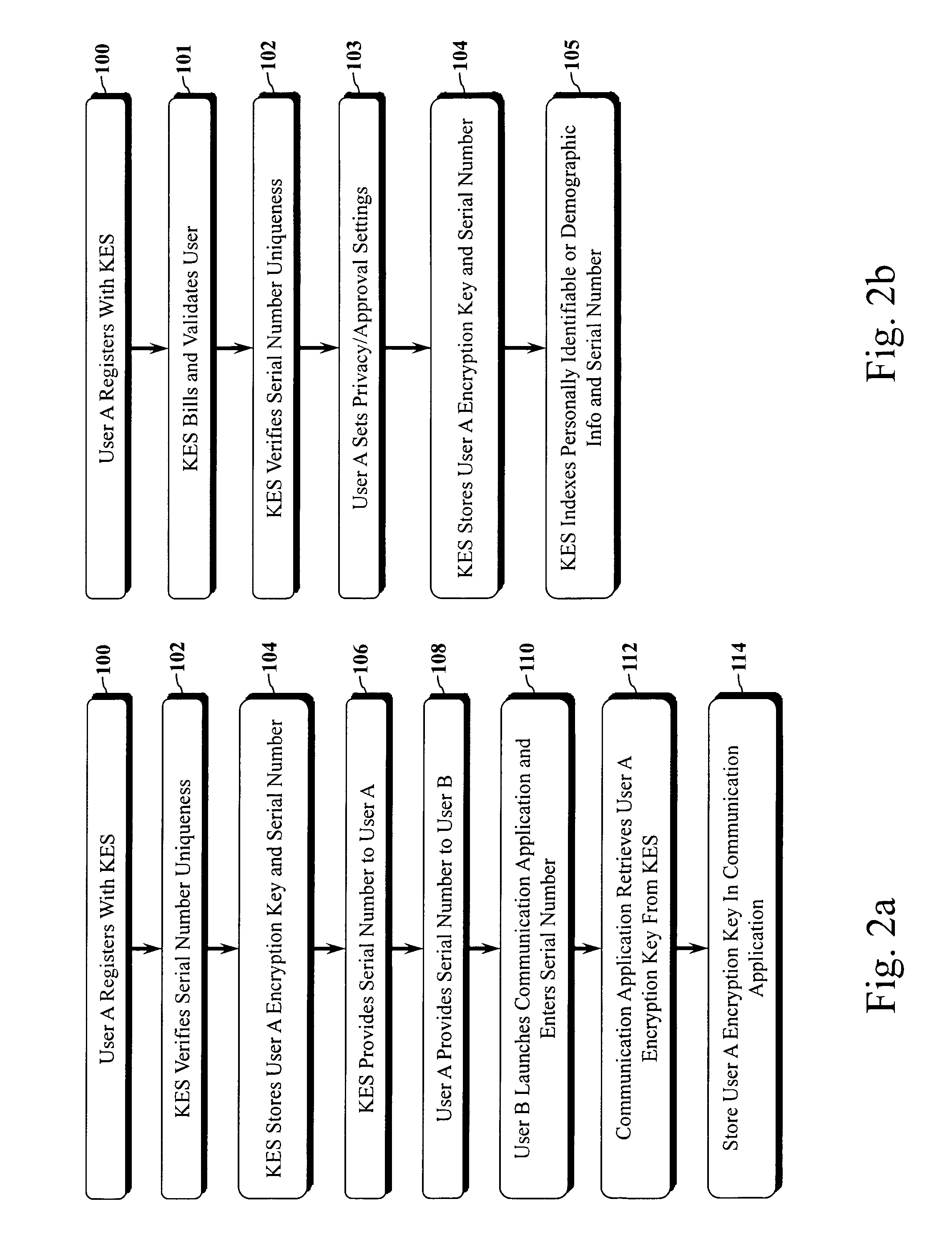
Encryption key exchange system and method
InactiveUS20120204032A1Improve usabilityUser identity/authority verificationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsUsabilityEncryption
The present invention is a computer-implemented key exchange system and methods for improving the usability of encryption technologies such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). One aspect of the present invention includes registering users, verifying user identity, and classifying users such that the users may send a communications such that communication recipients can verify the user identity and classification of the communication sender. Another aspect of the present invention includes users initiating relationships with other users, approving the establishment of relationships, and exchanging encryption keys between users after the establishment of a relationship.
Owner:SYNC UP TECH
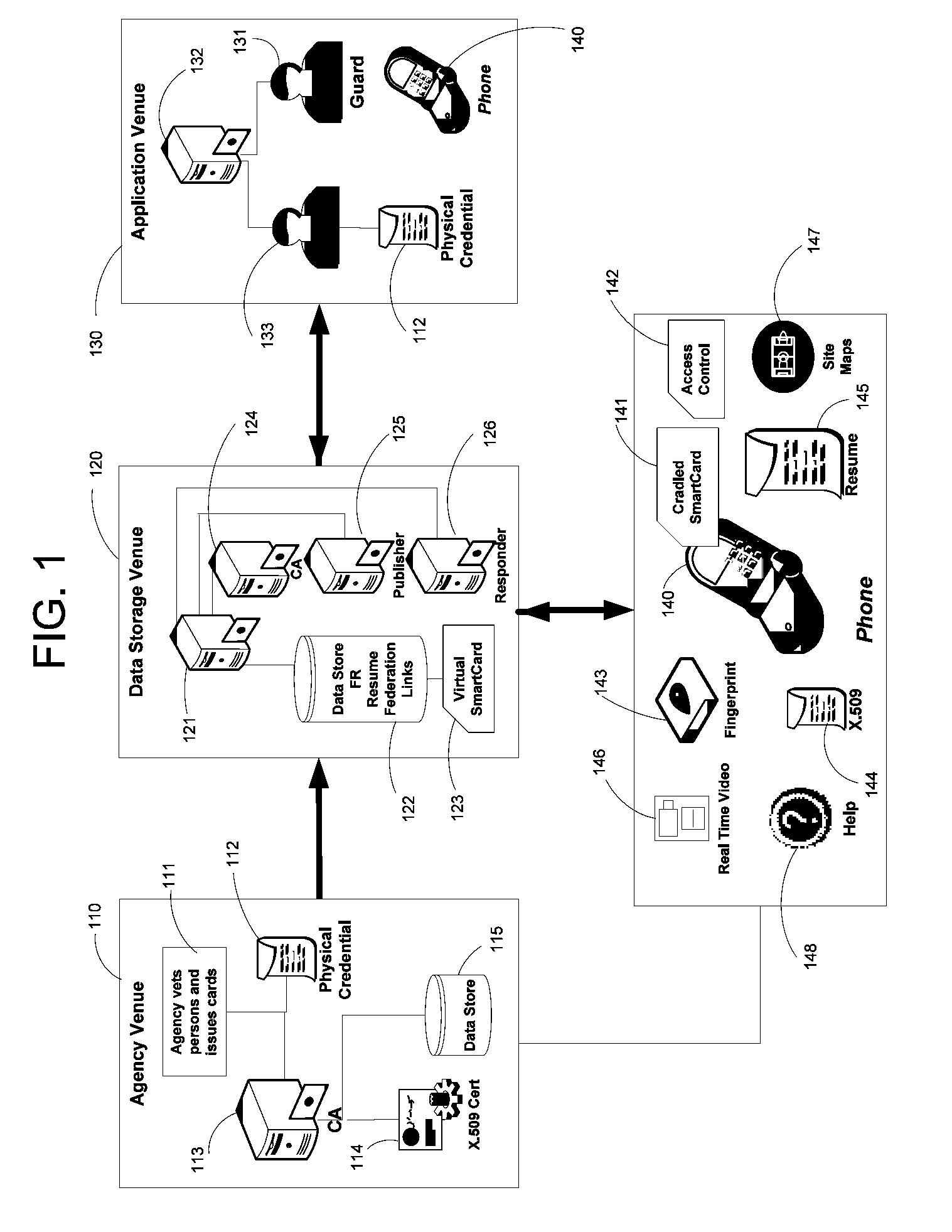
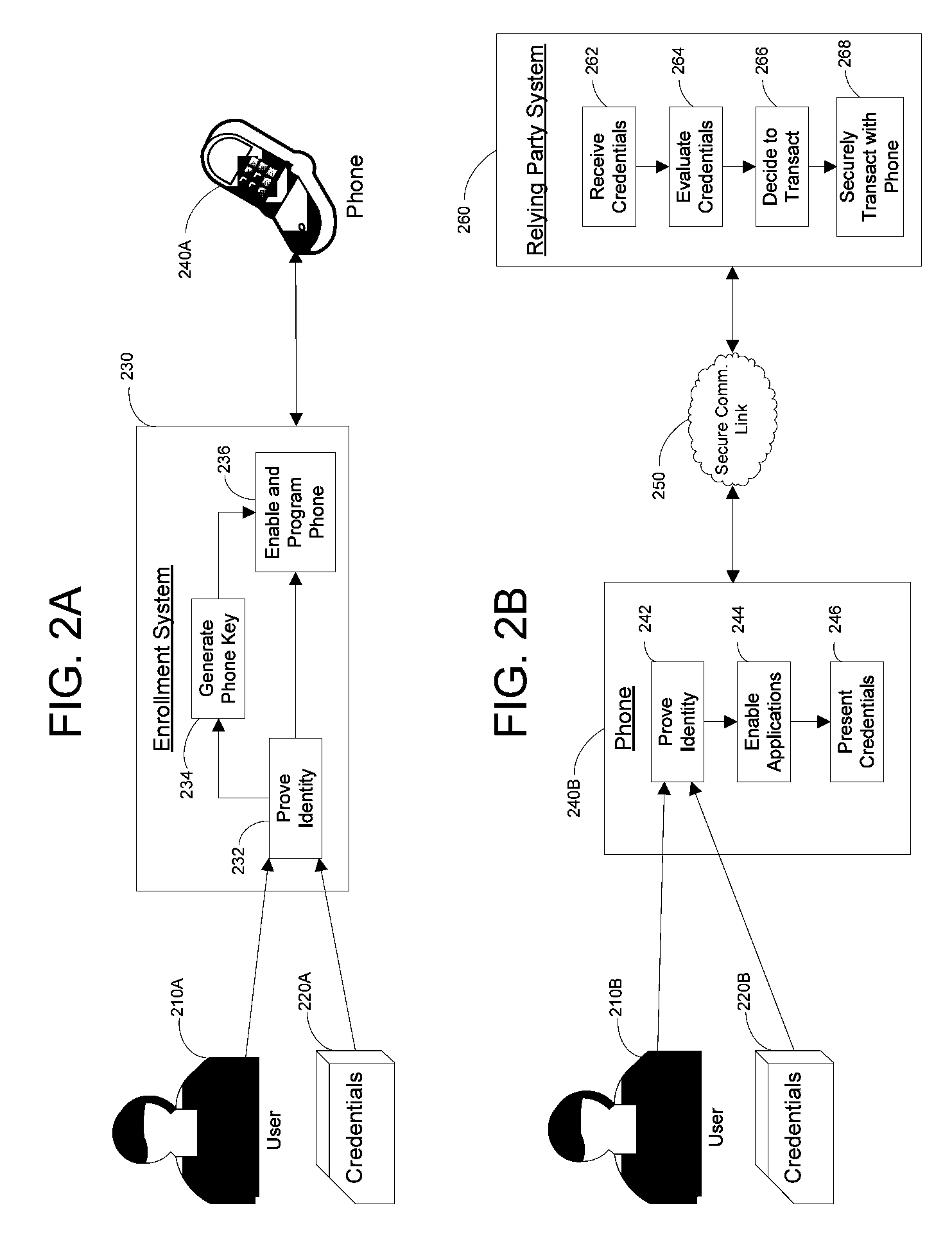
Apparatus and Methods for Providing Scalable, Dynamic, Individualized Credential Services Using Mobile Telephones
InactiveUS20090132813A1Save bandwidthSaving response timeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationElectronic systemsFinancial transaction
Apparatus and methods perform transactions in a secure environment between an individual and another party, such as a merchant, in various embodiments. The individual possesses a mobile electronic device, such as a smartphone, that can encrypt data according to a public key infrastructure. The individual authenticates the individual's identity to the device, thereby unlocking credentials that may be used in a secure transaction. The individual causes the device to communicate the credentials, in a secure fashion, to an electronic system of a relying party, in order to obtain the relying party's authorization to enter the transaction. The relying party system determines whether to grant the authorization, and communicates the grant and the outcome of the transaction to the device using encryption according to the public key infrastructure.
Owner:SURIDX
Secure anonymous information exchange in a network
InactiveUS6061789AMinimize additional effort and expenditureUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionSystems designData set
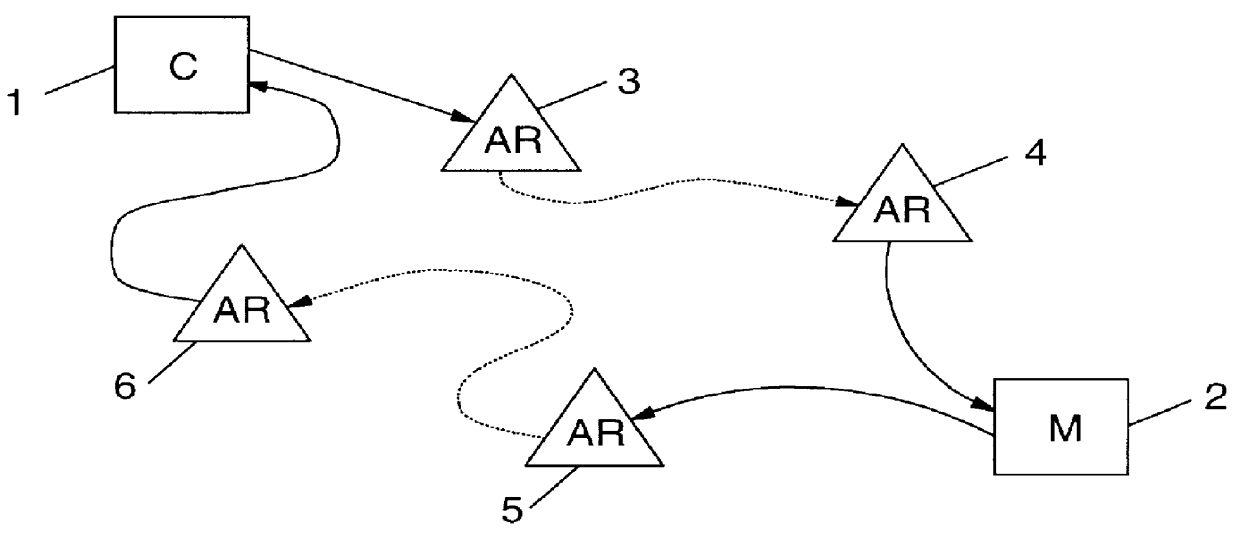
PCT No. PCT / IB96 / 00025 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Jan. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 25801 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 17, 1997Computer network management for electronic commerce requires technical implementations of business processes. The process addressed here is a technical method for a communication in which two or more parties legitimately want to communicate anonymously, often before discussing a deal or closing a business, e.g. for anonymous bidding or auctioning in electronic commerce. Essentially, the invention is a method, described by a protocol, for safely exchanging data in a network that provides a public key infrastructure and an anonymous communication possibility between network users. It consists of a sequence of steps in which both sender (e.g. customer) and addressee (e.g. merchant) compose data sets (i.e., requests and replies) that are based on received data and / or prior knowledge. The data sets are enciphered to provide anonymity, and digitally signed to provide proof of the partner. The invention is also a system designed to implement the invented method.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
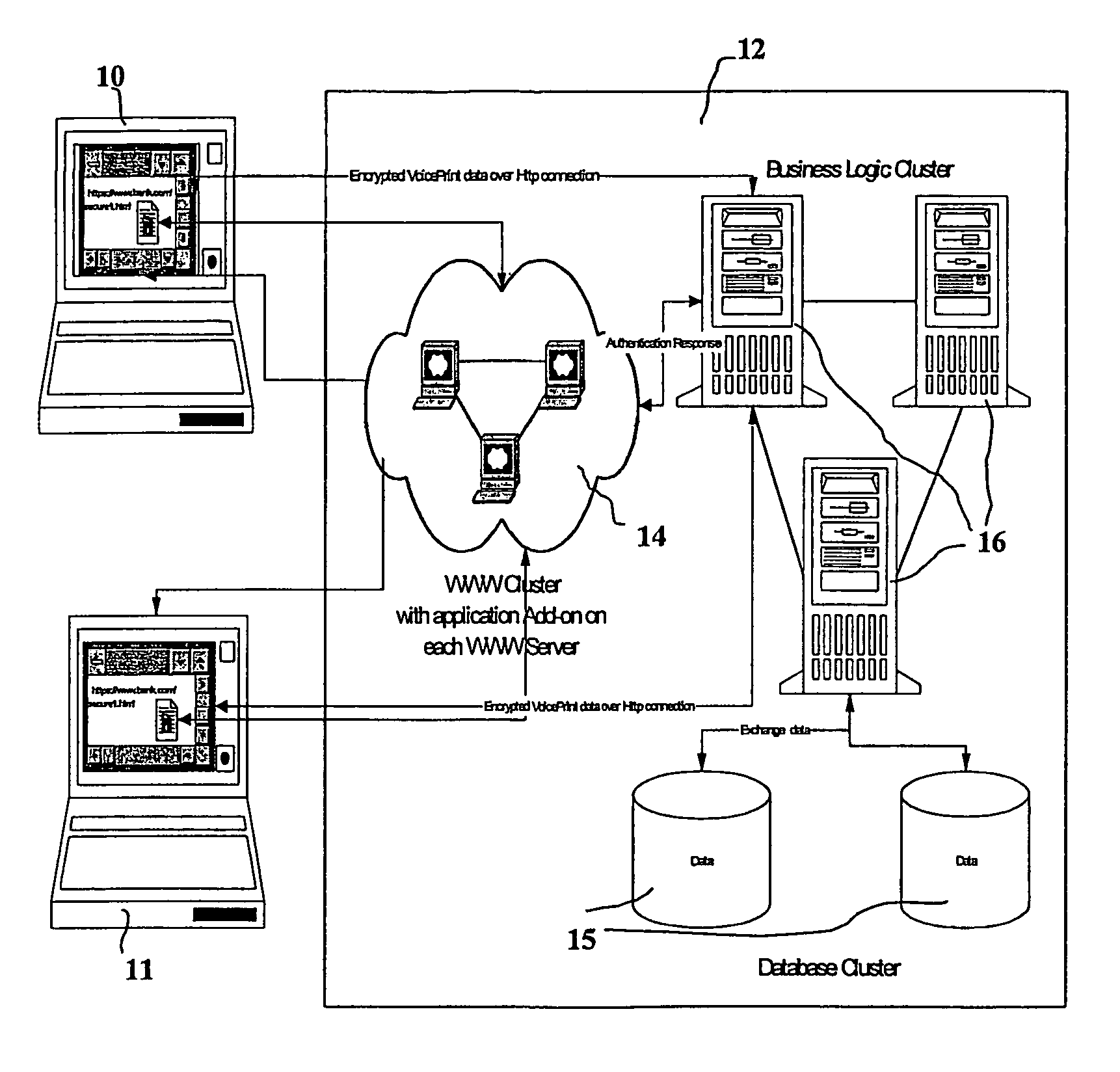
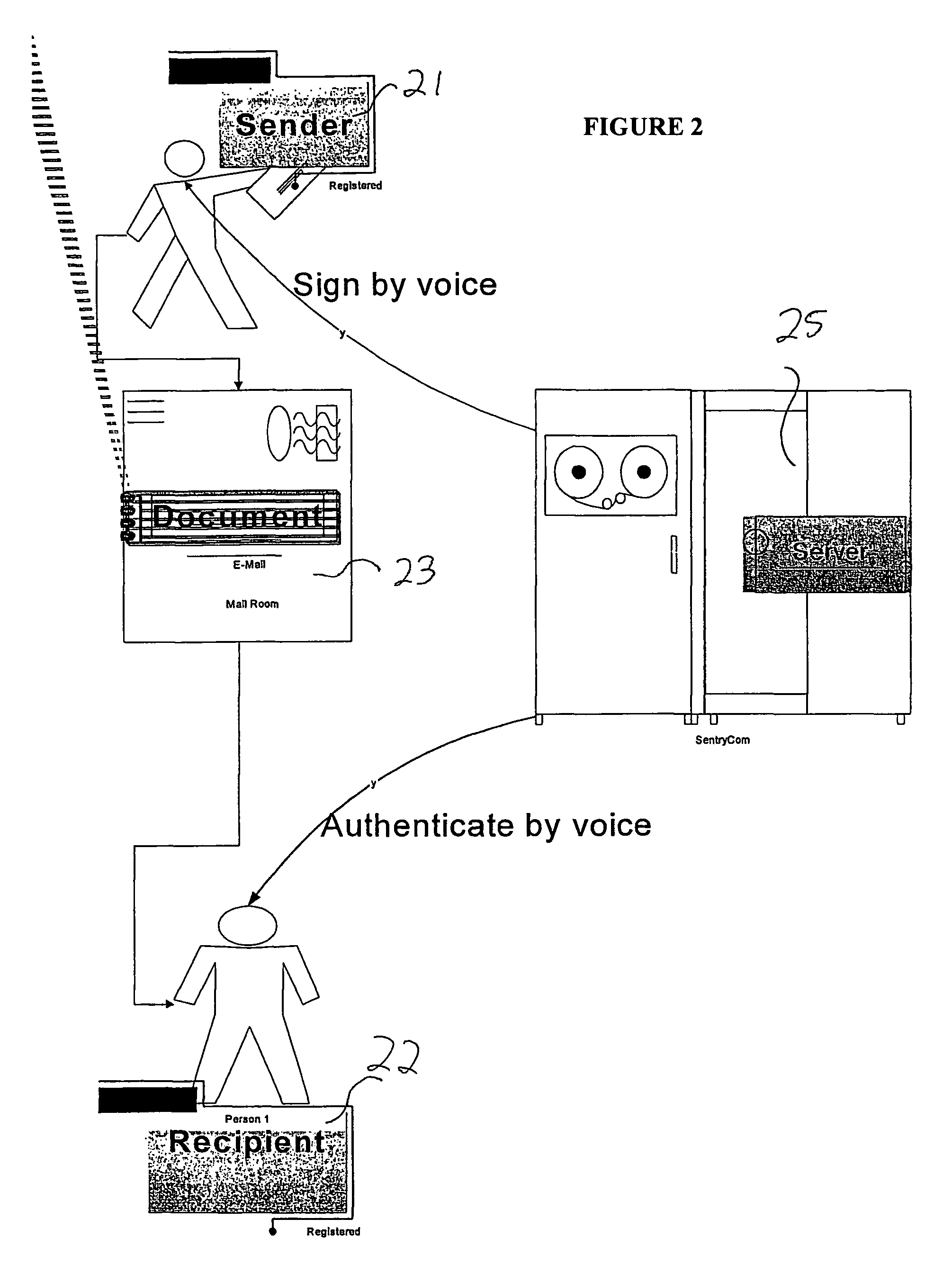
Biometric-based system and method for enabling authentication of electronic messages sent over a network
InactiveUS7689832B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationReal time validationData authenticity
A network based mechanism for real time verification and authentication of data and user identities. The present invention enables a method whereby biometric elements, such as voice prints, are utilized to enhance the Public Key Infrastructure as a means to decrypt data and verify data authenticity, such that the user's private key is authenticated remotely on a one-time basis. The present invention comprises an authentication server (25) with various software modules that enable authentication of user identity, secure user access to data, digital signatures, secure messaging and secure online transactions.
Owner:SENTRYCOM
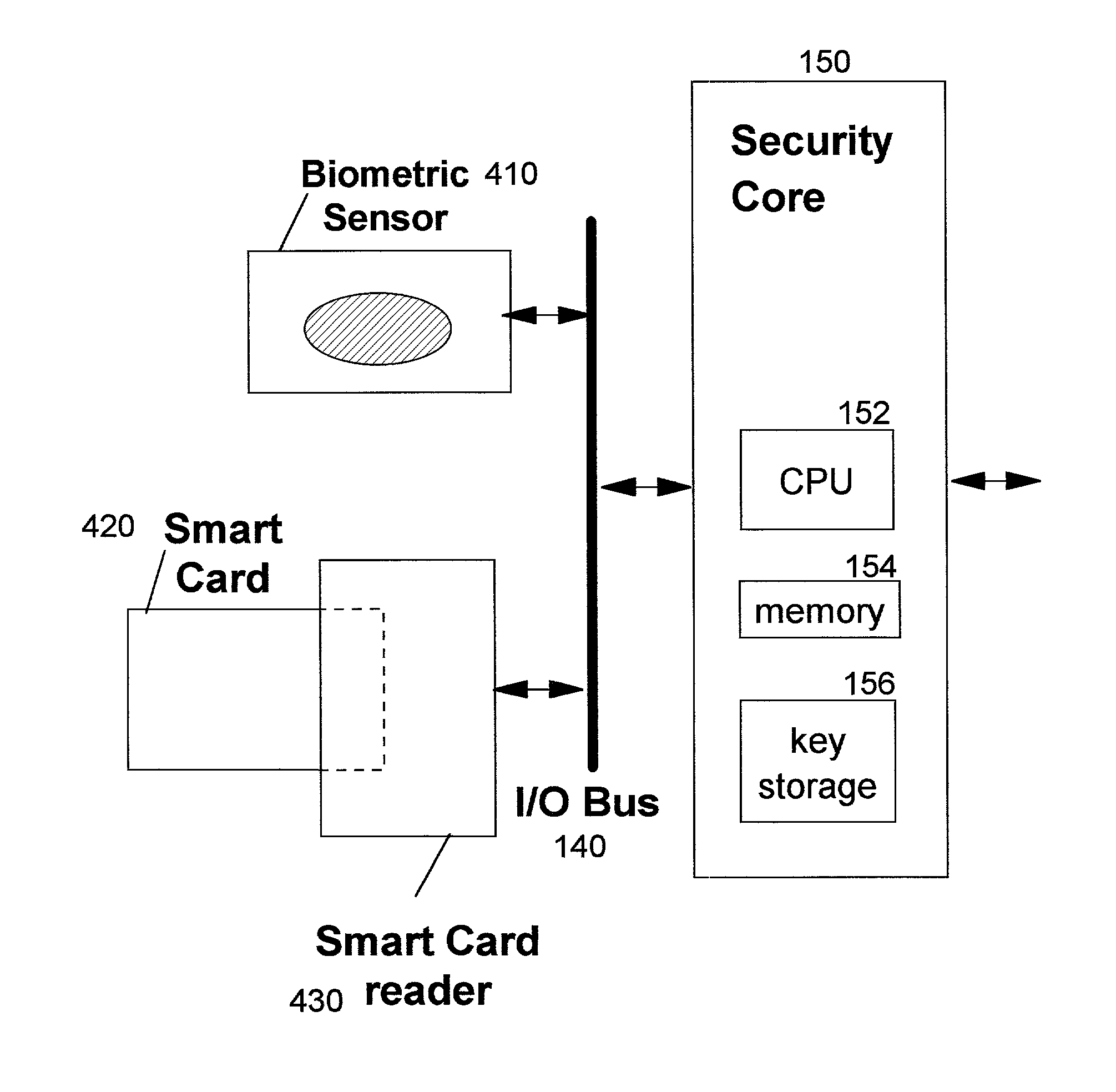
Secure integrated device with secure, dynamically-selectable capabilities
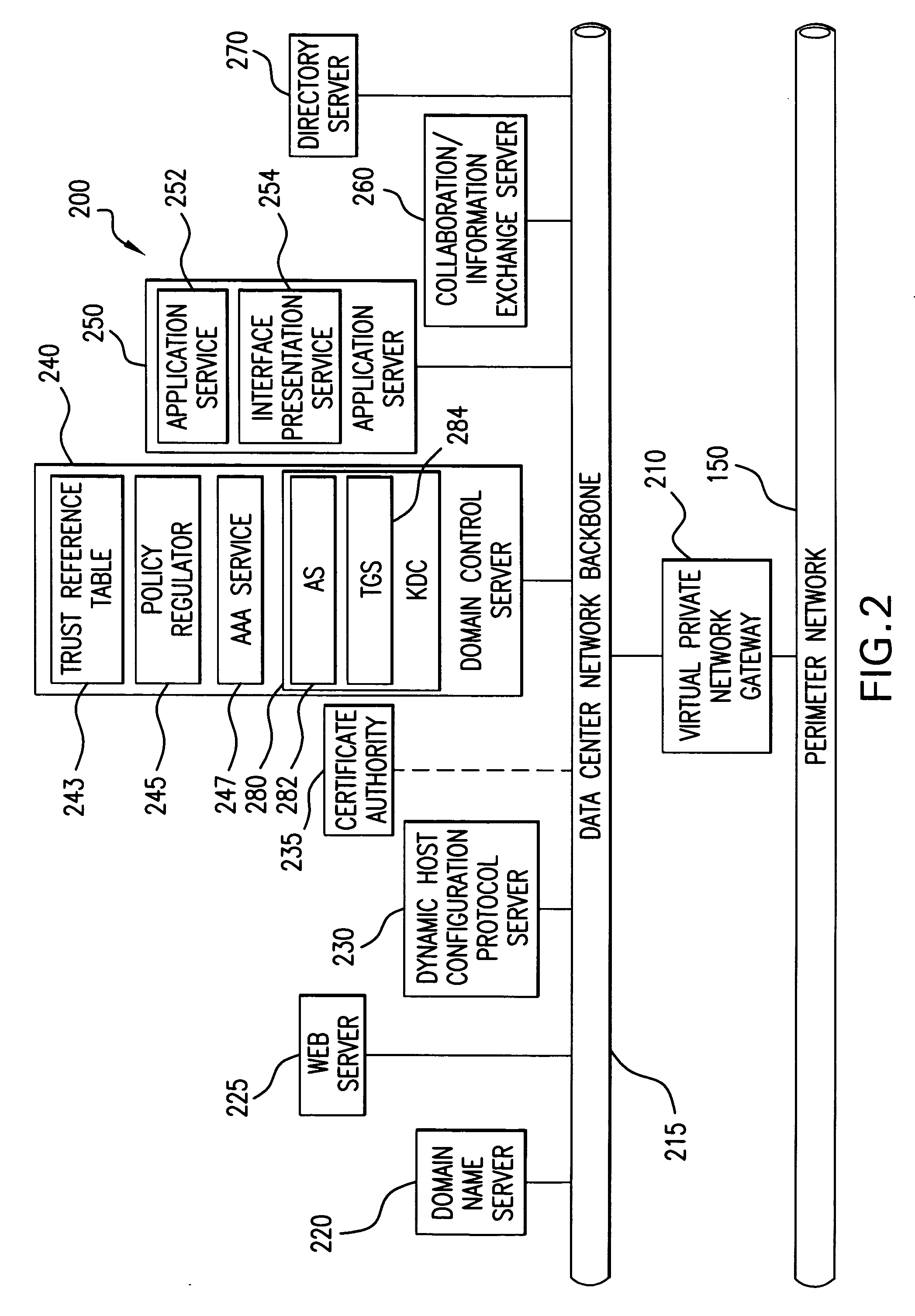
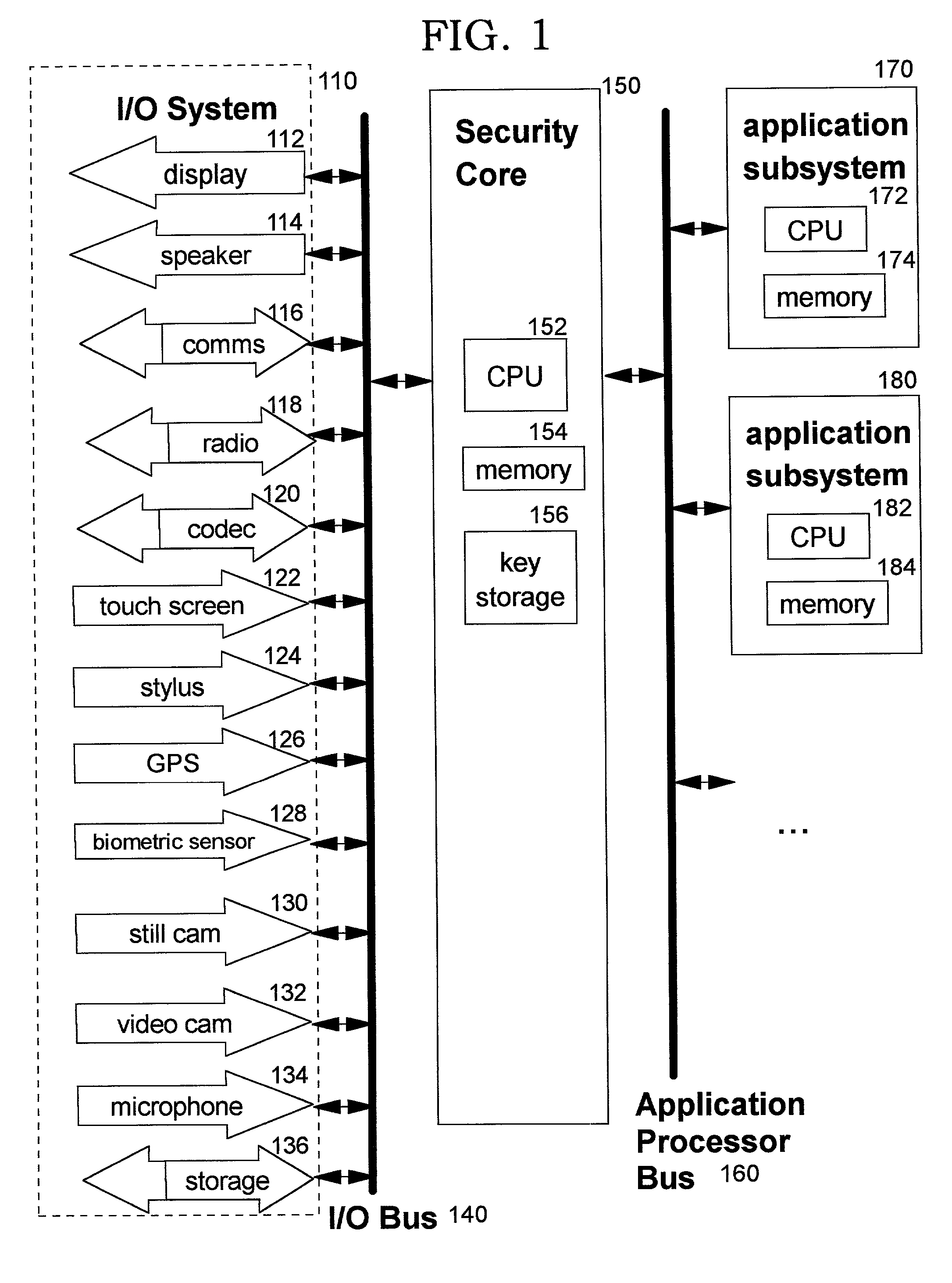
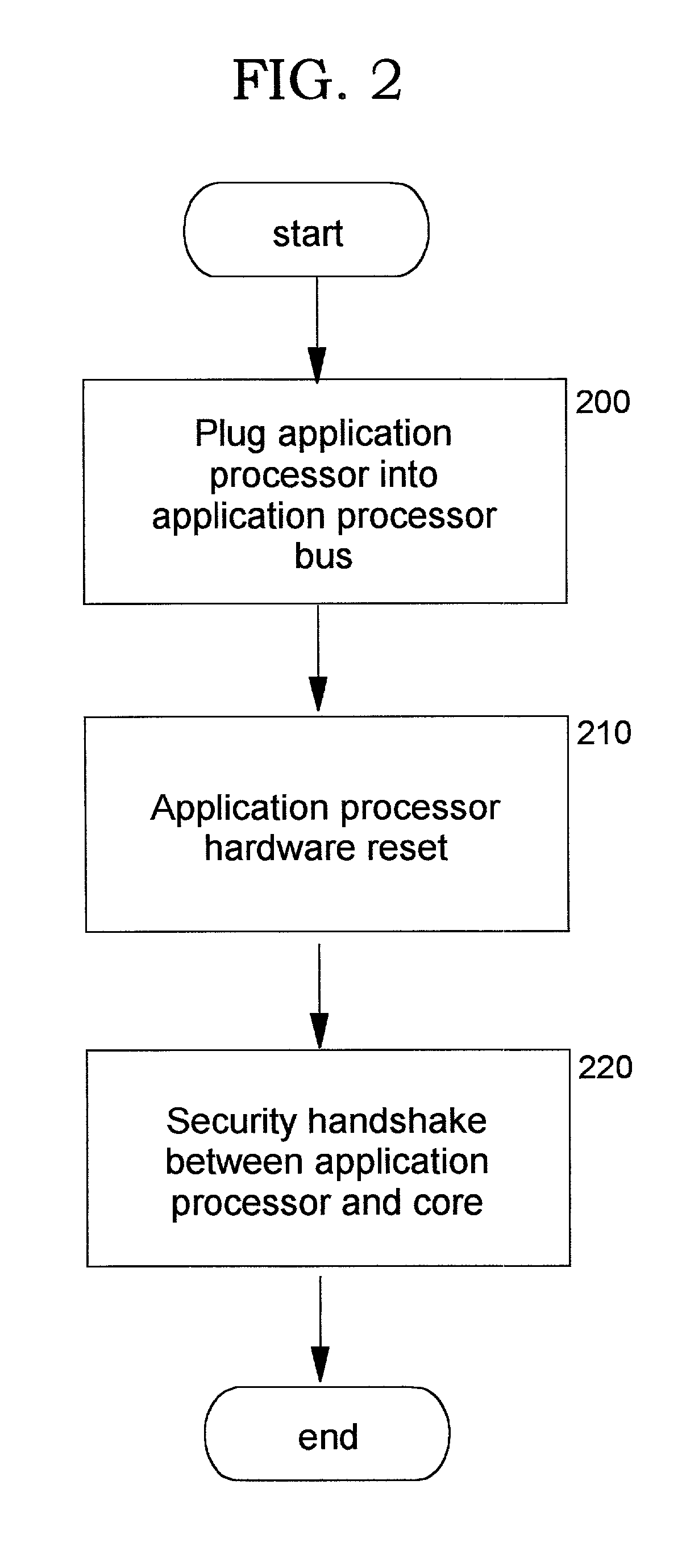
InactiveUS20030159044A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionStructure of Management InformationOutput device
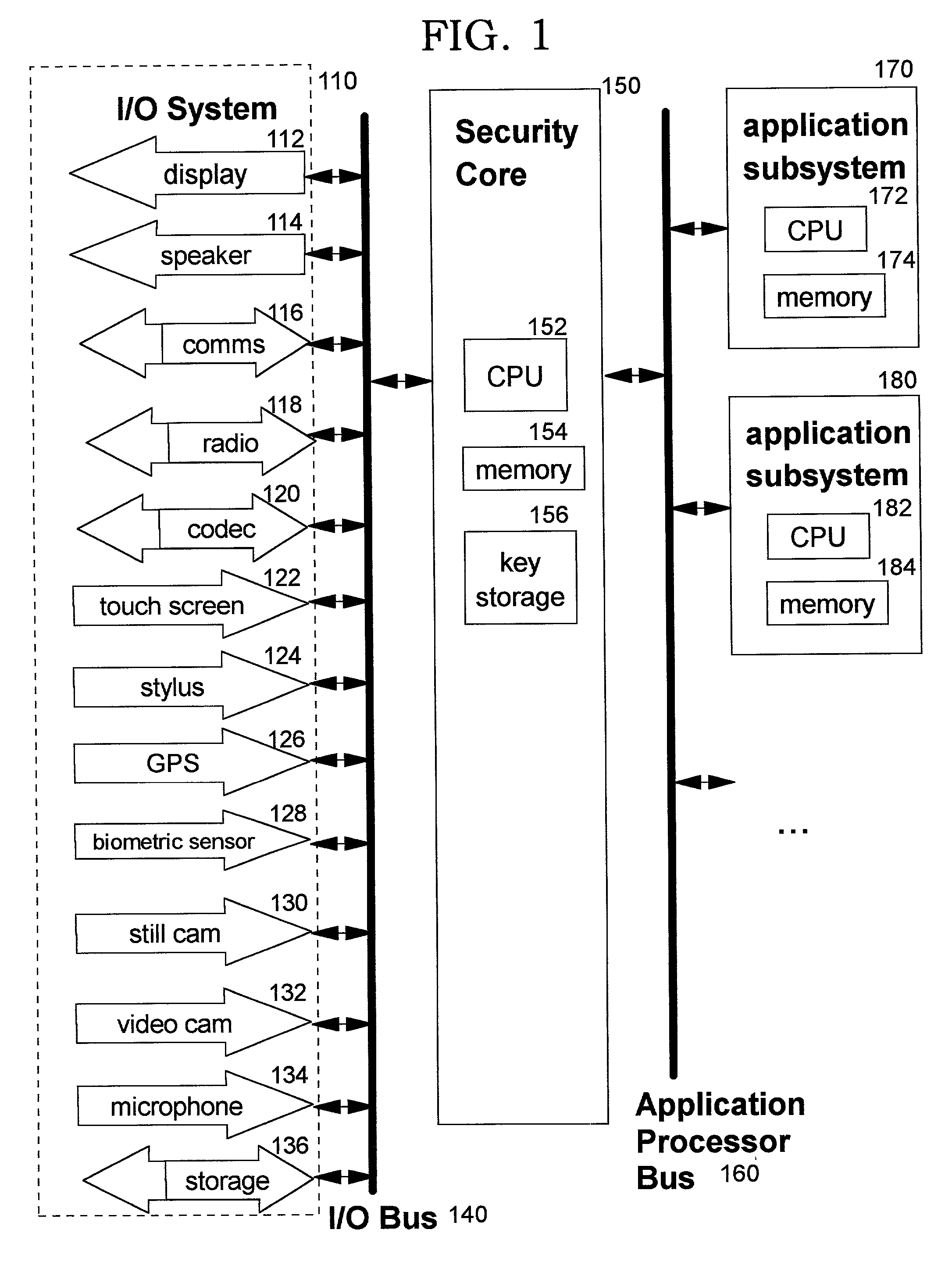
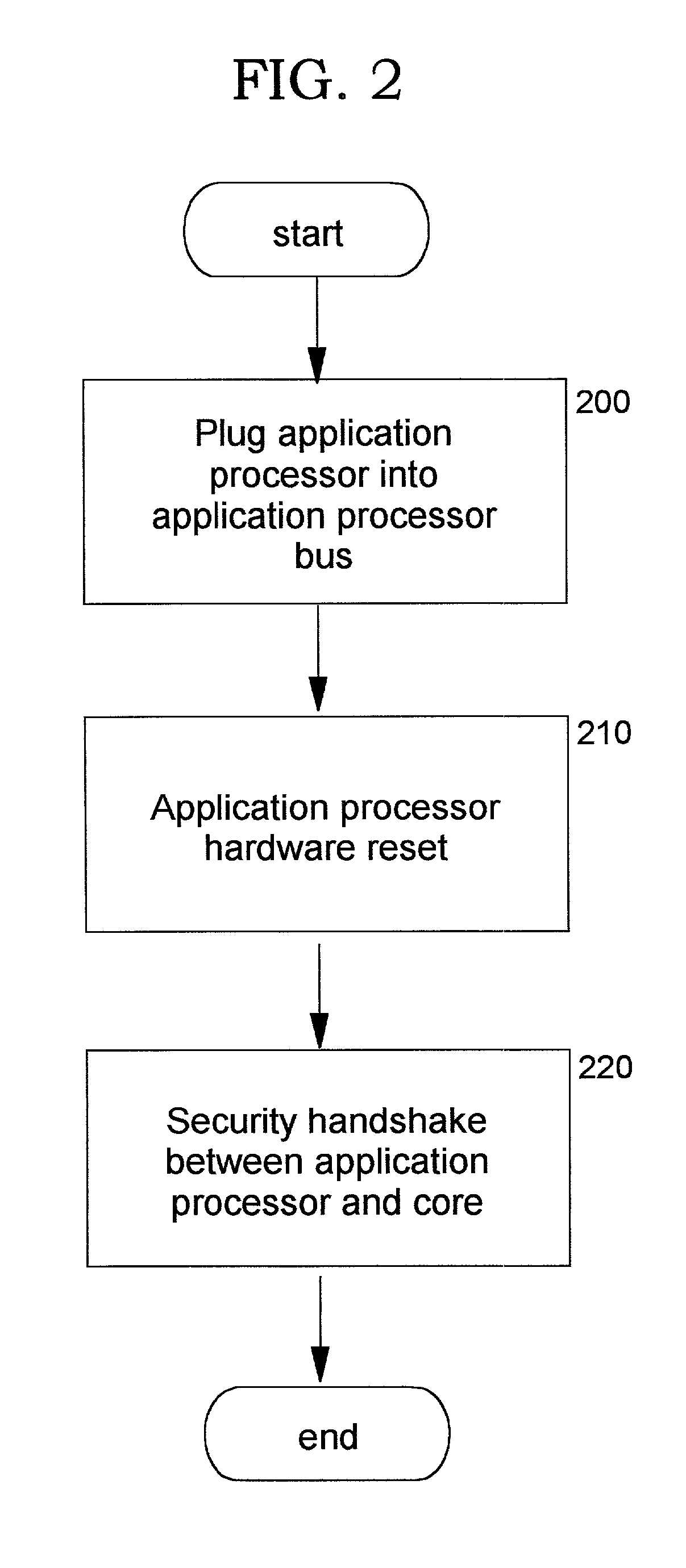
A method, system, computer program product, and method of doing business by providing a secure integrated device (such as a pervasive computing device) for which operating capabilities can be dynamically yet securely selected (including, but not limited to, pluggable connection of input / output devices and / or application processors that provide selected functions). Each input / output (I / O) device and application processor to be used is plugged in to a bus of a security core, and authenticates itself to the security core using public key infrastructure techniques, thereby creating a secure multi-function device. All of the multi-function device's input and output interactions with its environment necessarily traverse an I / O bus under the sole control of the security core. The only communication path between an application processor and the external environment (such as an I / O device) is through an application processor bus, which is likewise under control of the security core. Thus a user may dynamically yet securely select the capabilities of a multi-function device, and because each I / O device and application processor in use by that multi-function device is authenticated, the security of transactions or network services performed when using such devices is improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
System for secure computing using defense-in-depth architecture
ActiveUS20060041761A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionPrivate networkCombined use
A secure computing system is provided which utilizes a unique combination of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), Virtual Private Networking (VPN), and server-based computing on thin client devices. The combination of technology and components provide secure computing through Defense-in-Depth using commercial off-the-shelf components.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Secure integrated device with secure, dynamically-selectable capabilities
InactiveUS6968453B2Conveniently and economically providedEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionStructure of Management InformationOutput device
A method, system, computer program product, and method of doing business by providing a secure integrated device (such as a pervasive computing device) for which operating capabilities can be dynamically yet securely selected (including, but not limited to, pluggable connection of input / output devices and / or application processors that provide selected functions). Each input / output (I / O) device and application processor to be used is plugged in to a bus of a security core, and authenticates itself to the security core using public key infrastructure techniques, thereby creating a secure multi-function device. All of the multi-function device's input and output interactions with its environment necessarily traverse an I / O bus under the sole control of the security core. The only communication path between an application processor and the external environment (such as an I / O device) is through an application processor bus, which is likewise under control of the security core. Thus a user may dynamically yet securely select the capabilities of a multi-function device, and because each I / O device and application processor in use by that multi-function device is authenticated, the security of transactions or network services performed when using such devices is improved.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
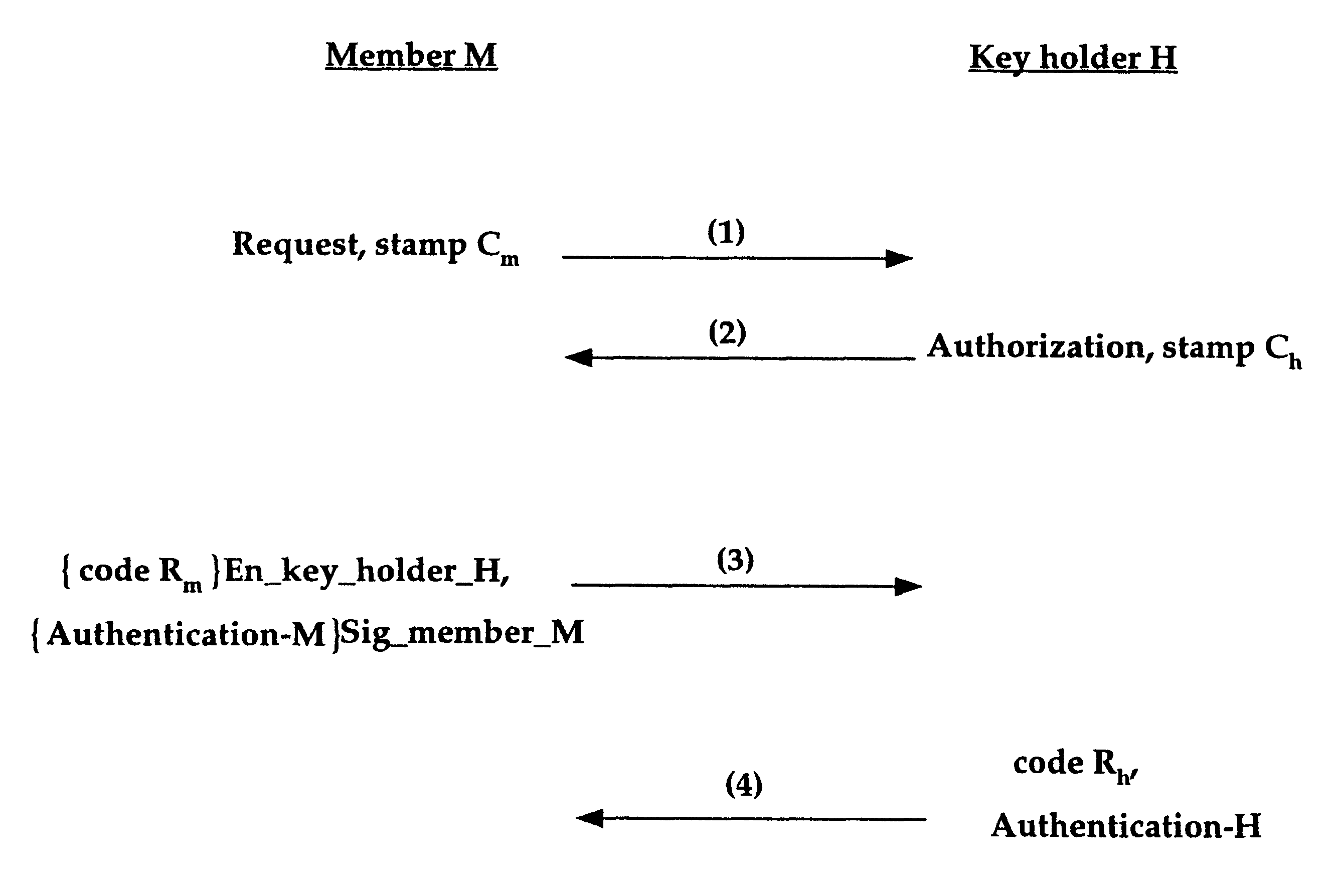
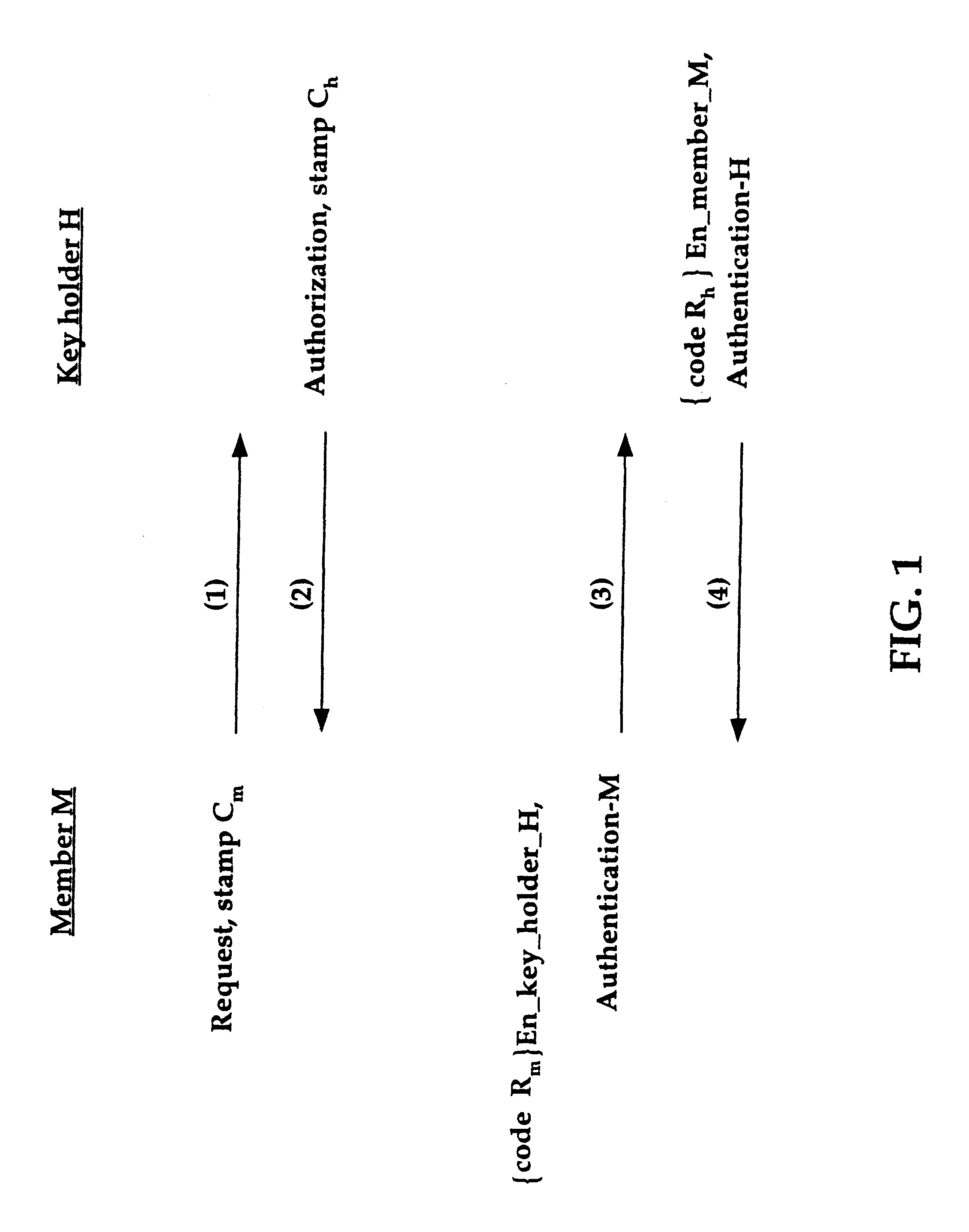
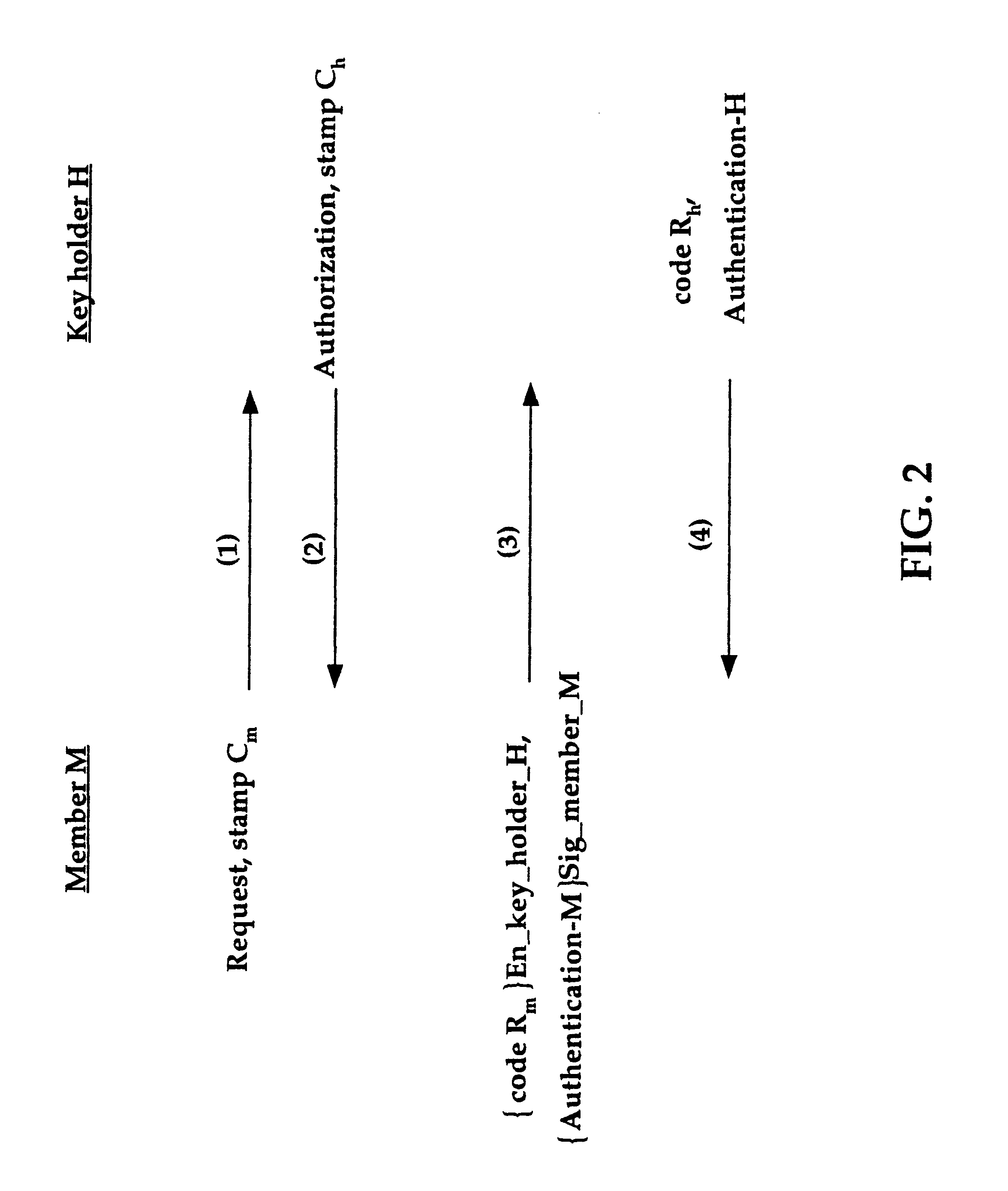
Group key distribution
InactiveUS6038322AEfficient additionLow costKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTimestampNetwork addressing
A method for distributing a secret key from a key holder H to intended group members M. The method assumes that during the distribution process each party, a group member M and the key holder H, can decrypt and encrypt exchanged information such that the encrypter knows that the decrypter will be the intended party. The method preferably uses a public key / private key encryption technique in which, for example, a trusted Certificate Authority in a public key infrastructure signs the certificates to provide the public keys involved in the encryption. Alternatively, the method, together with a symmetric cipher, uses a shared secret, established in an authenticated mechanism that is outside the information exchanges of the invention. Additionally, the method uses a strong mixing function that takes several items of data as input and produces a pseudo-random authentication (or digest). Inputs to the mixing function include identity stamps that are generated by each member M and key holder H. These inputs can be the identity of the stamp generator, such as a network address, port, or protocol, a timestamp, and / or a secret value that is known only to the stamp generator. The stamps include information to bind member M if generated by key holder H, and to bind key holder H if generated by member M. Consequently, the invention authenticates each communication exchange between member M and key holder H.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
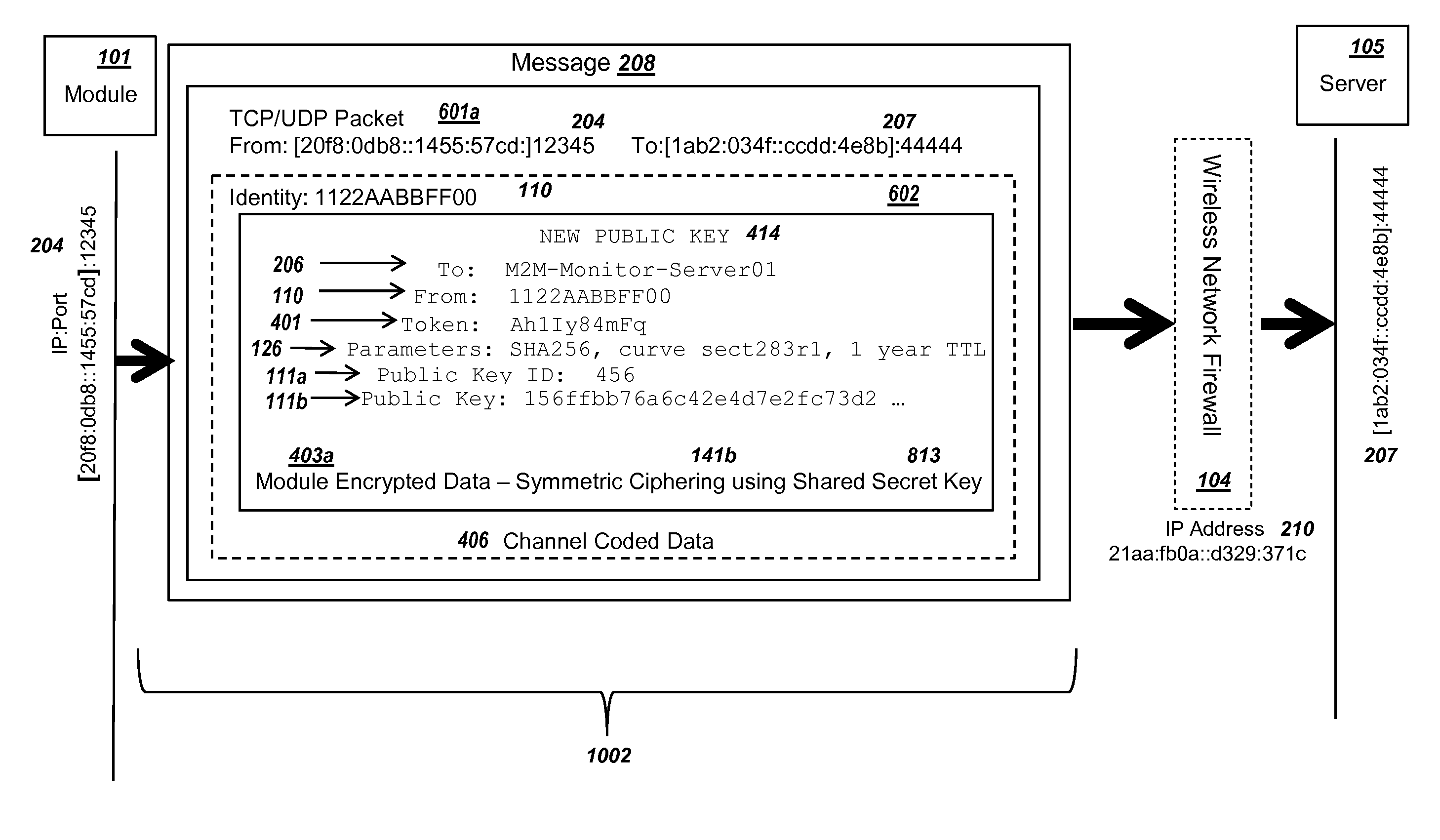
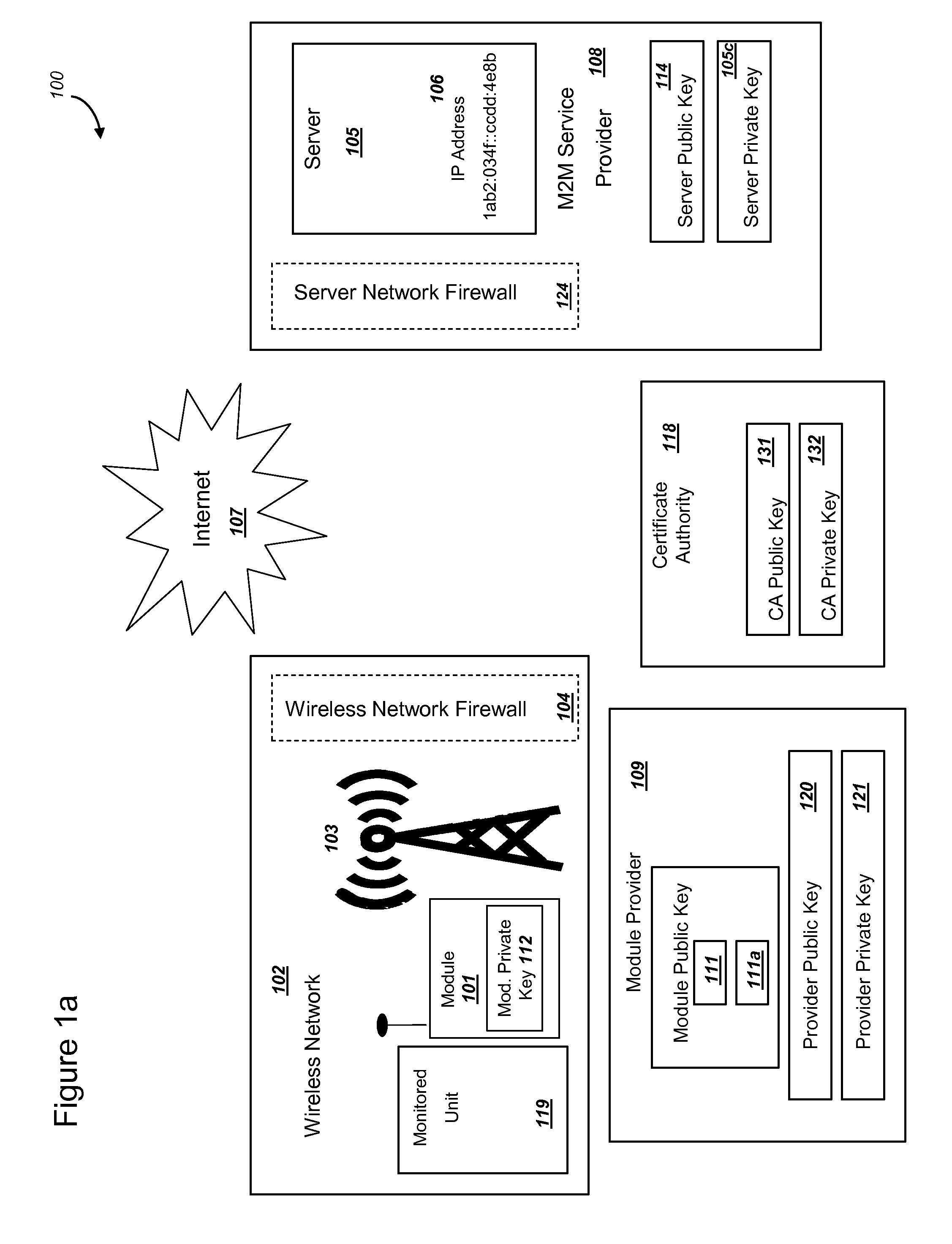
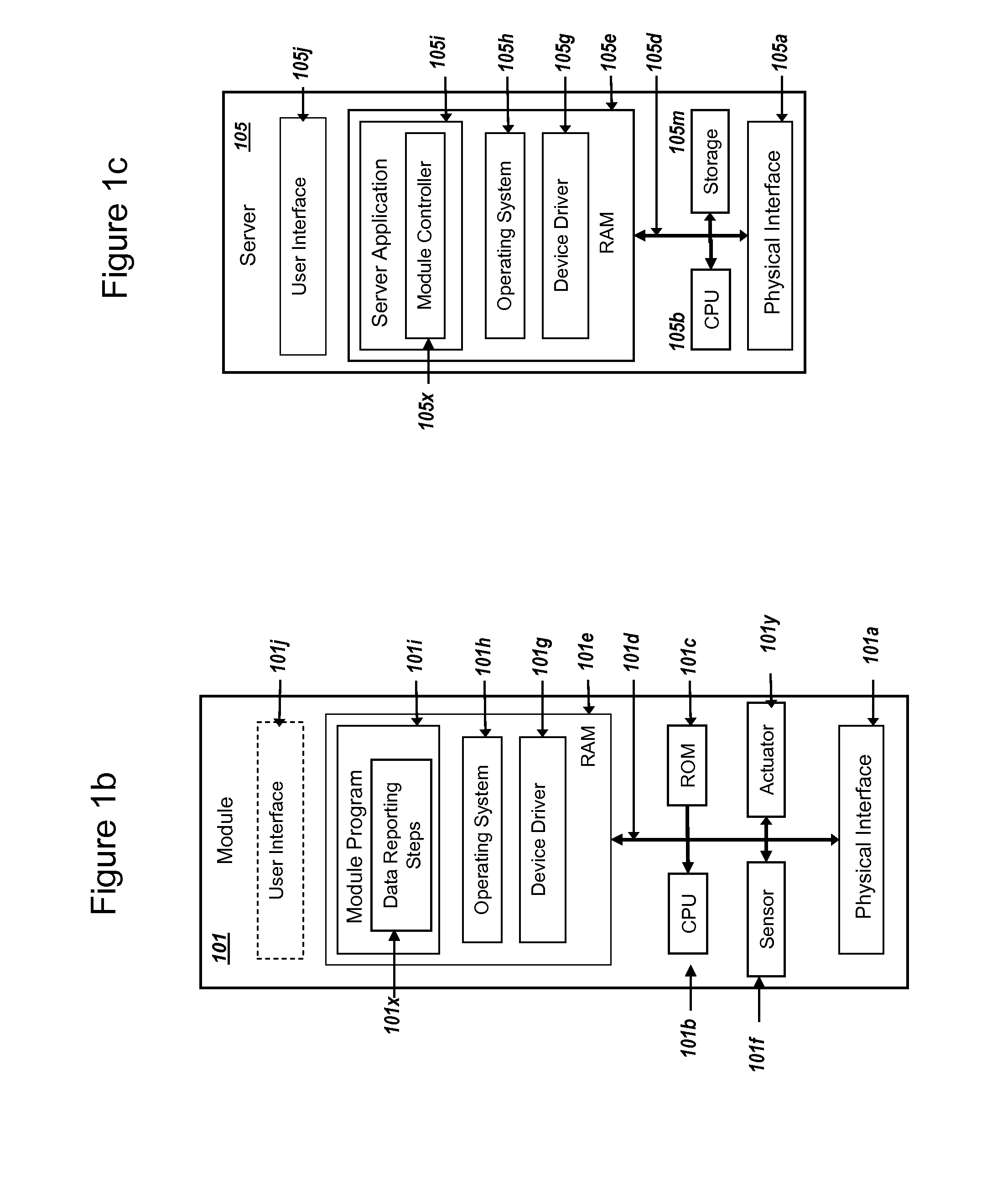
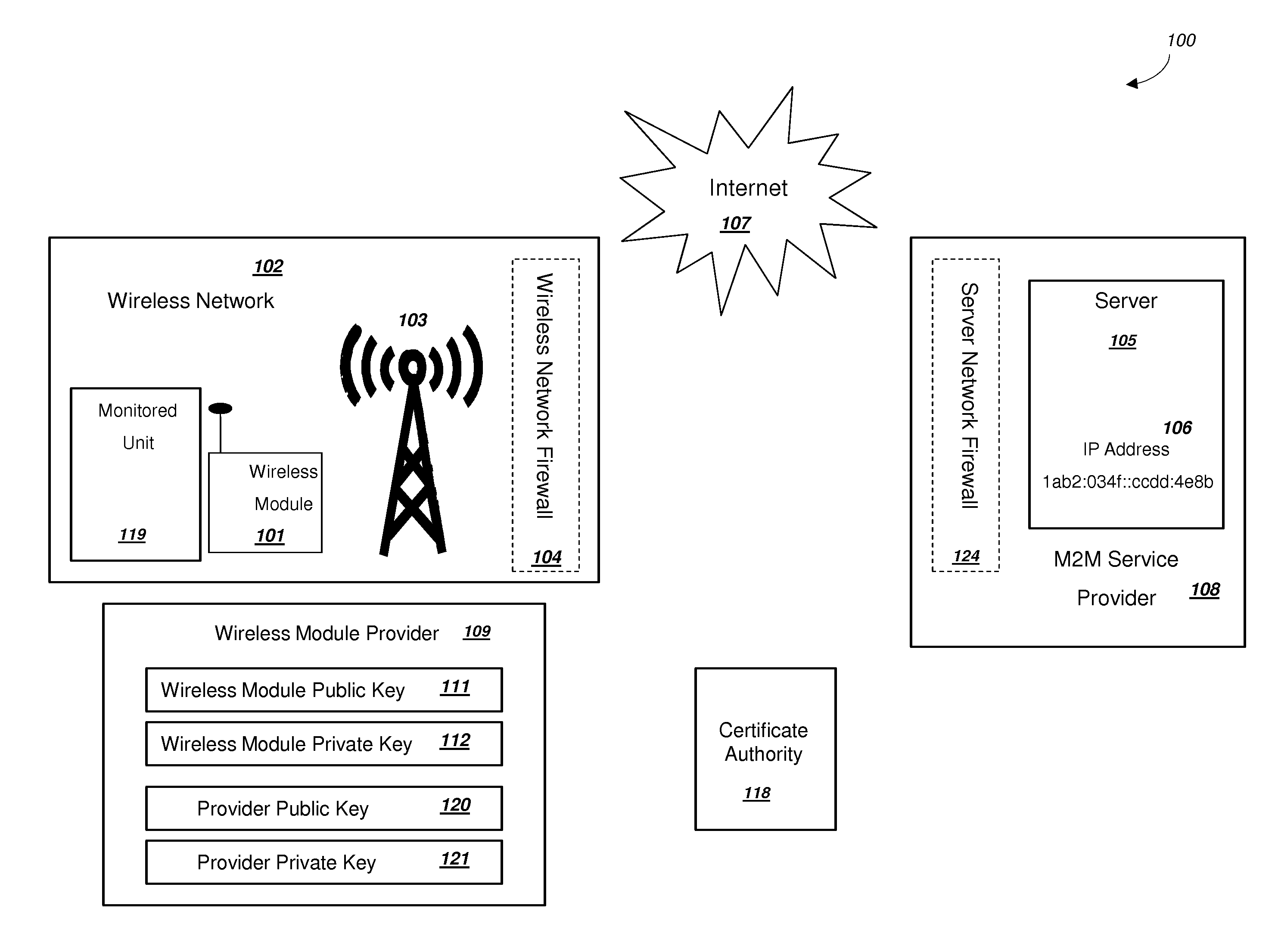
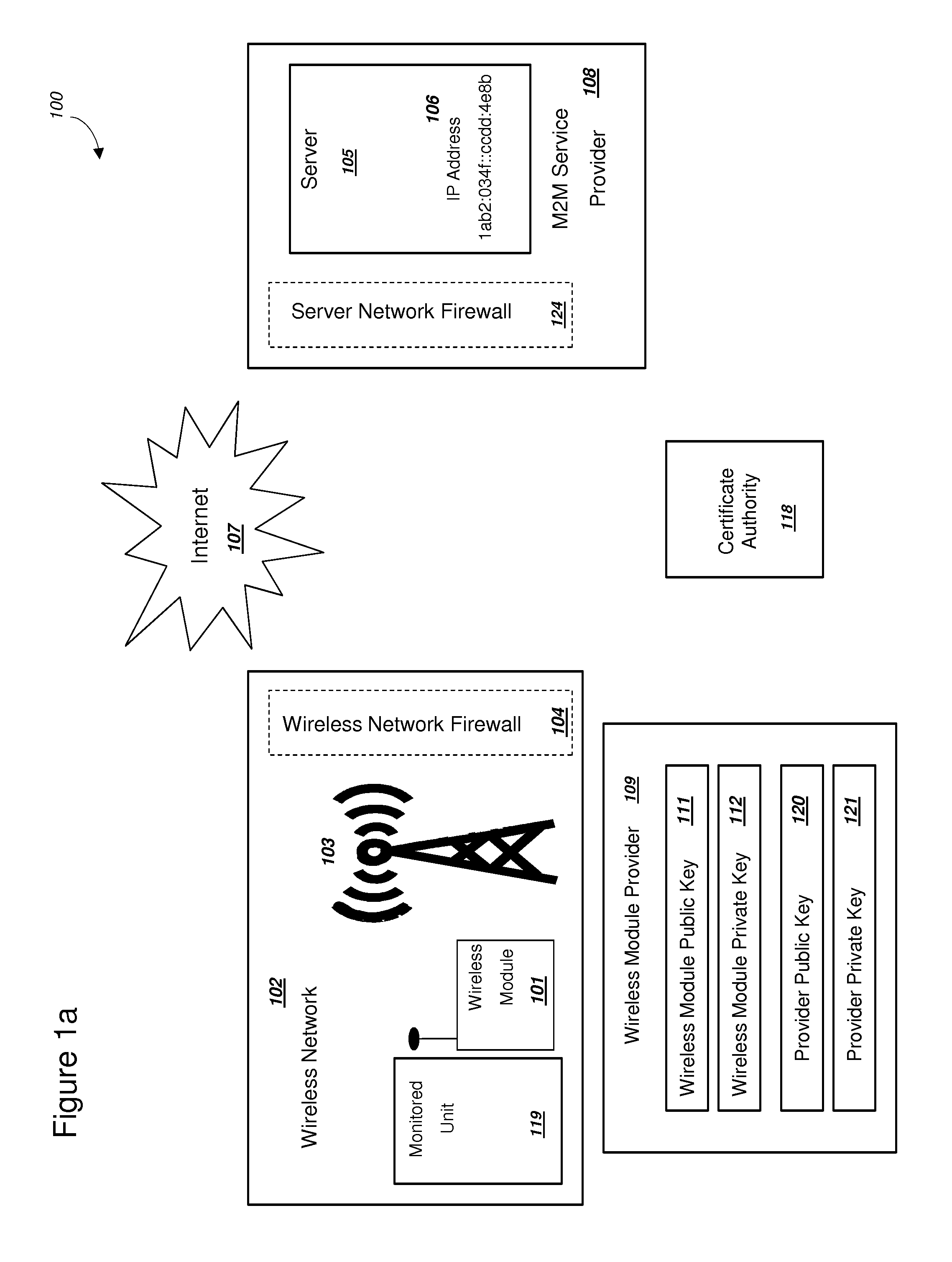
Secure PKI Communications for "Machine-to-Machine" Modules, including Key Derivation by Modules and Authenticating Public Keys
ActiveUS20150095648A1Extend battery lifeImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareDigital signature
Methods and systems are provided for efficient and secure “Machine-to-Machine” (M2M) between modules and servers. A module can communicate with a server by accessing the Internet, and the module can include a sensor and / or actuator. The module and server can utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) such as public keys to encrypt messages. The module and server can use private keys to generate digital signatures for datagrams sent and decrypt messages received. The module can internally derive pairs of private / public keys using cryptographic algorithms and a set of parameters. A server can use a shared secret key to authenticate the submission of derived public keys with an associated module identity. For the very first submission of a public key derived the module, the shared secret key can comprise a pre-shared secret key which can be loaded into the module using a pre-shared secret key code.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH +1
Information security management and control method under cloud manufacturing environment
InactiveCN102710605ASolve the problem of update and maintenanceAvoid complex proceduresPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationConfidentialityPrivate network
The invention discloses an information security management and control method under a cloud manufacturing environment. On the basis of a network security protocol, a password technology and a public key infrastructure (PKI), comprehensive security guarantee is supplied to information interaction among cloud internal networks, between one cloud and another cloud, and between a user and each cloud by using implementation technologies and methods, such as a virtual private network (VPN) based on multiple layers of protocols, a digital envelope and a password algorithm; Intranet, Extranet and Internet of a cloud manufacturing system are covered; comprehensive management and control technical information files are stored and transmitted to each used loop; a session key (SK) which is randomly produced by using a key production protocol is used for symmetrically encrypting the technical information files; and a receiver public key obtained according to a PKI digital certificate asymmetrically encrypts the SK to form the digital envelope for protecting the technical information files and the SK. The information security management and control method has the characteristics of being high in confidentiality, high inefficiency, flexible in arrangement and the like and can be widely applied to the cloud manufacturing system and other network manufacturing systems.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for implementing safe storage system in cloud storage environment
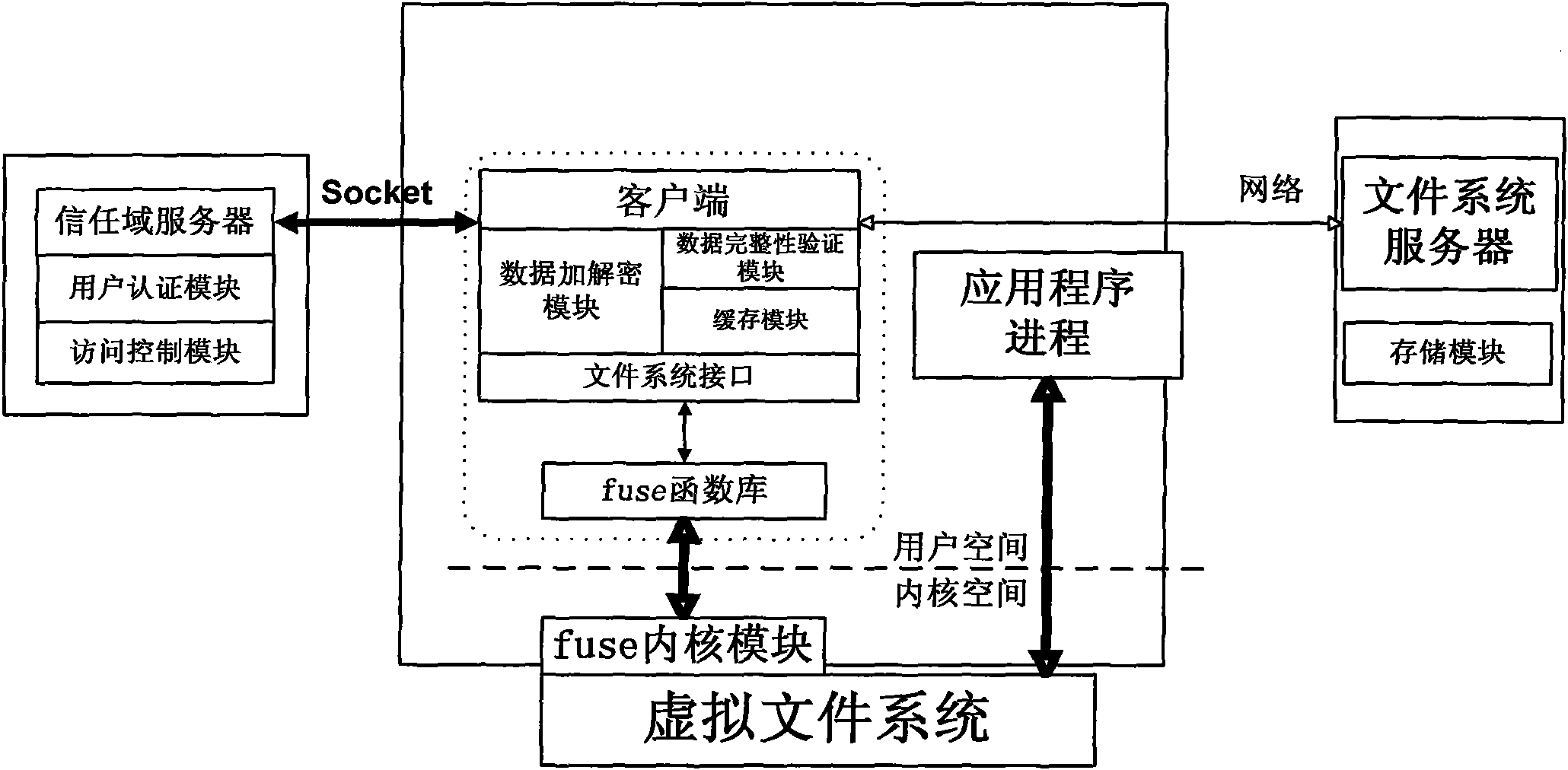
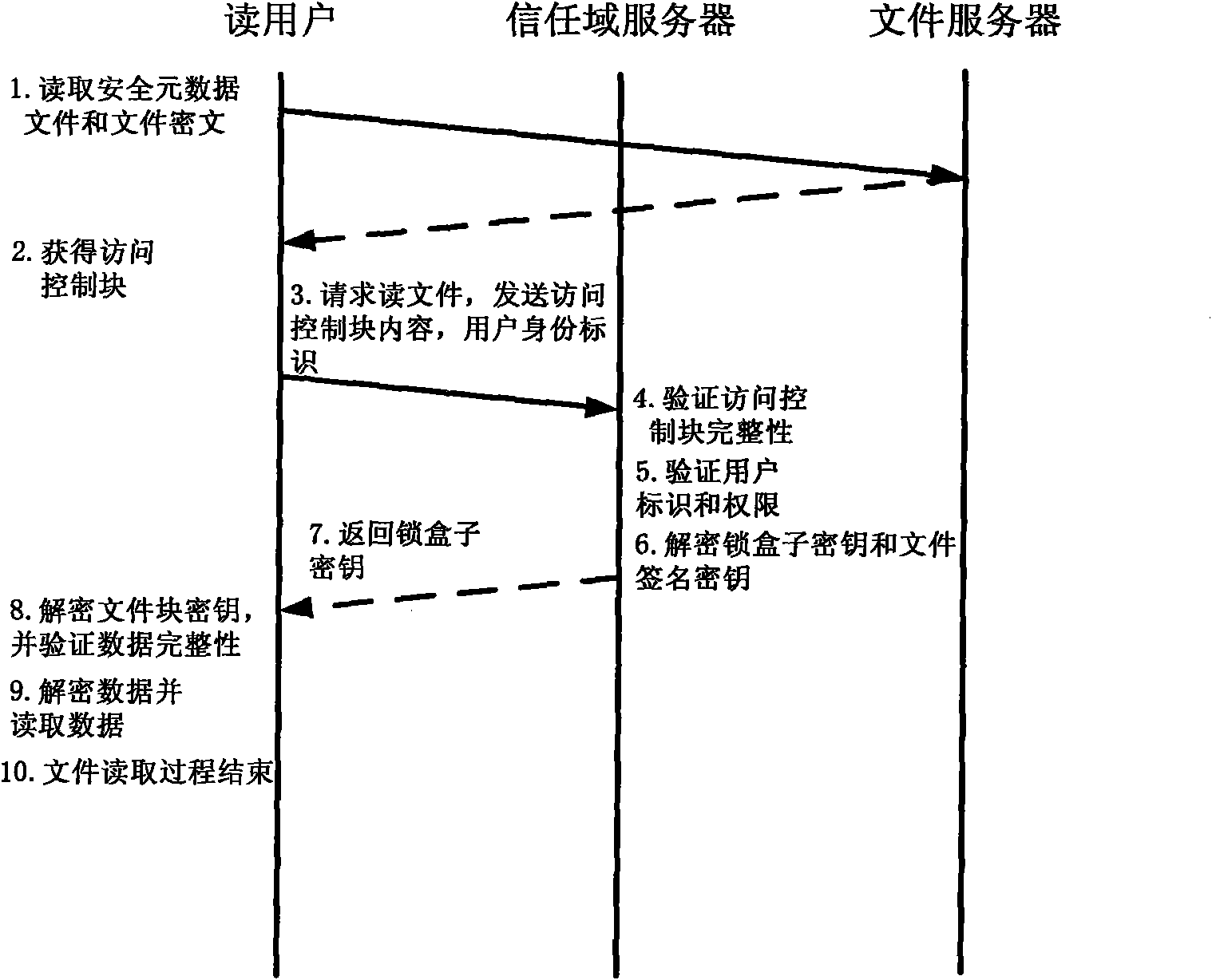
ActiveCN102014133AGuaranteed confidentialityTimely detection of damage, etc.TransmissionConfidentialityCiphertext
The invention relates to a method for implementing a safe storage system in a cloud storage environment and belongs to the technical field of storage safety. The method is characterized in that a trust domain is established in a server according to the requirements of a user; in the trust domain, identity authentication is performed by using an public key infrastructure (PKI); the independence between the storage system and a bottom layer system is realized by utilizing a filesystem in user space (FUSE); a hash value of a file is calculated by utilizing a secure hash algorithm (SHA1) and taking a block as a unit, a file block is encrypted by utilizing a key and an advanced encryption standard (AES) algorithm of a symmetric encipherment algorithm and taking a block as a unit, and a file cipher text is uploaded to a file server in a cloud storage area so as to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the file; a filer owner postpones encrypting the file again when permission is revoked by designating a user with the permission of accessing the file and the permissions thereof in an access control list; and only when the user modifies the content of the file, the user encrypts the file block in which the modified content is positioned again and the system implements three layers of key management, namely a file block key, a safe metadata file key and a trust domain server key so that not only the safety of the file is guaranteed when the permission is revoked, but also the management load of the system is not increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Universal, Biometric, Self-Authenticating Identity Computer Having Multiple Communication Ports
InactiveUS20080148059A1Maintain securityLimited accessUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureSmart cardCard reader
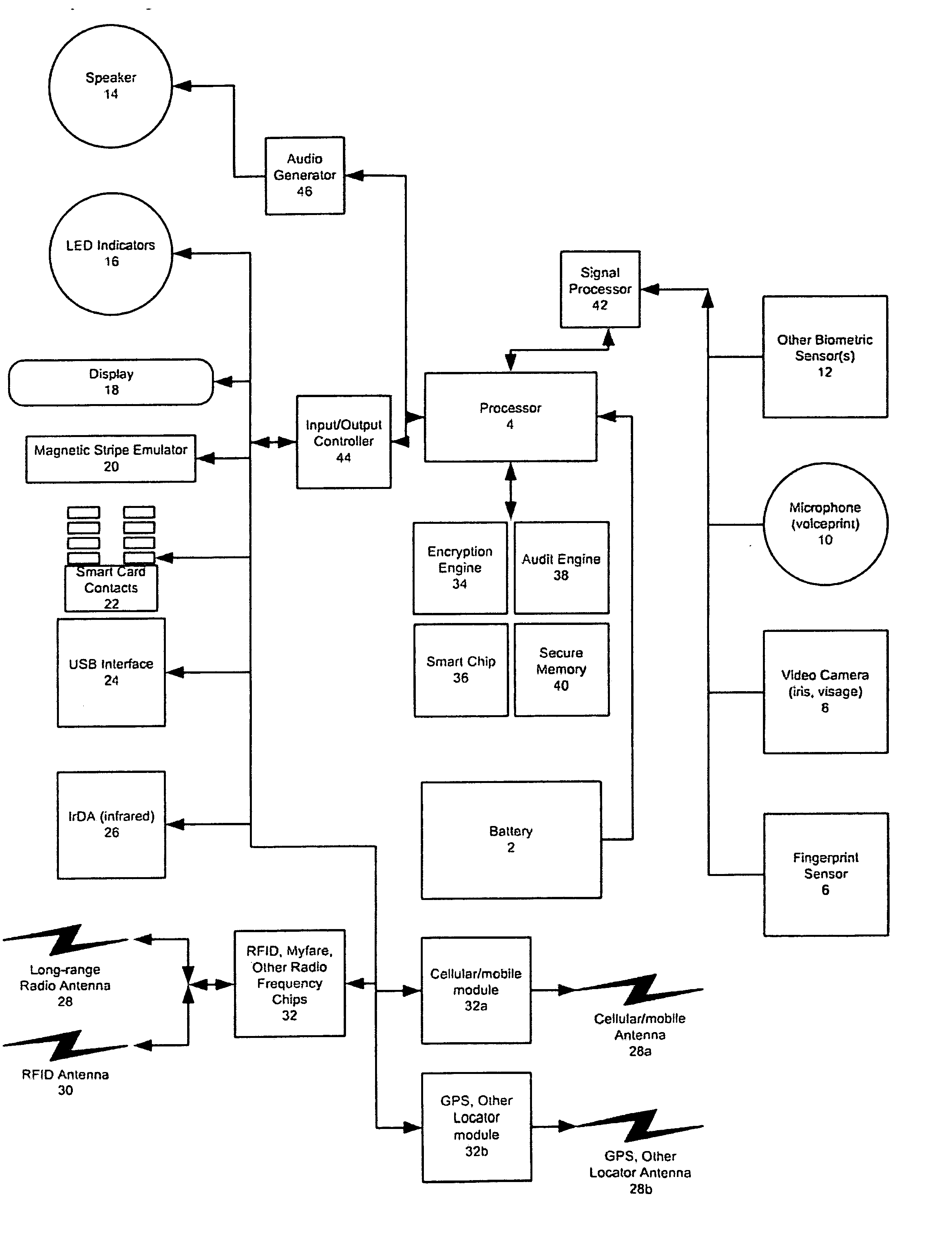
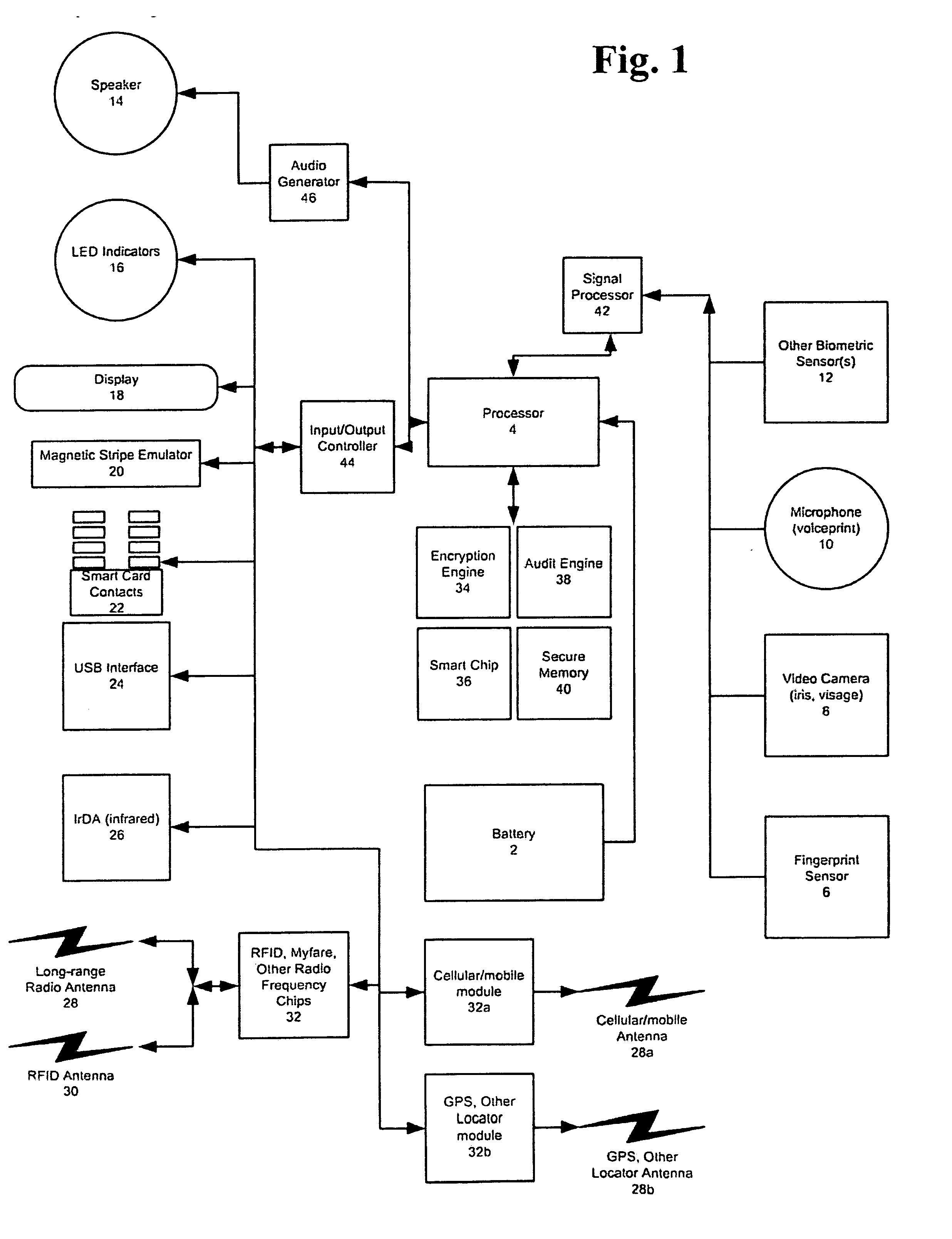
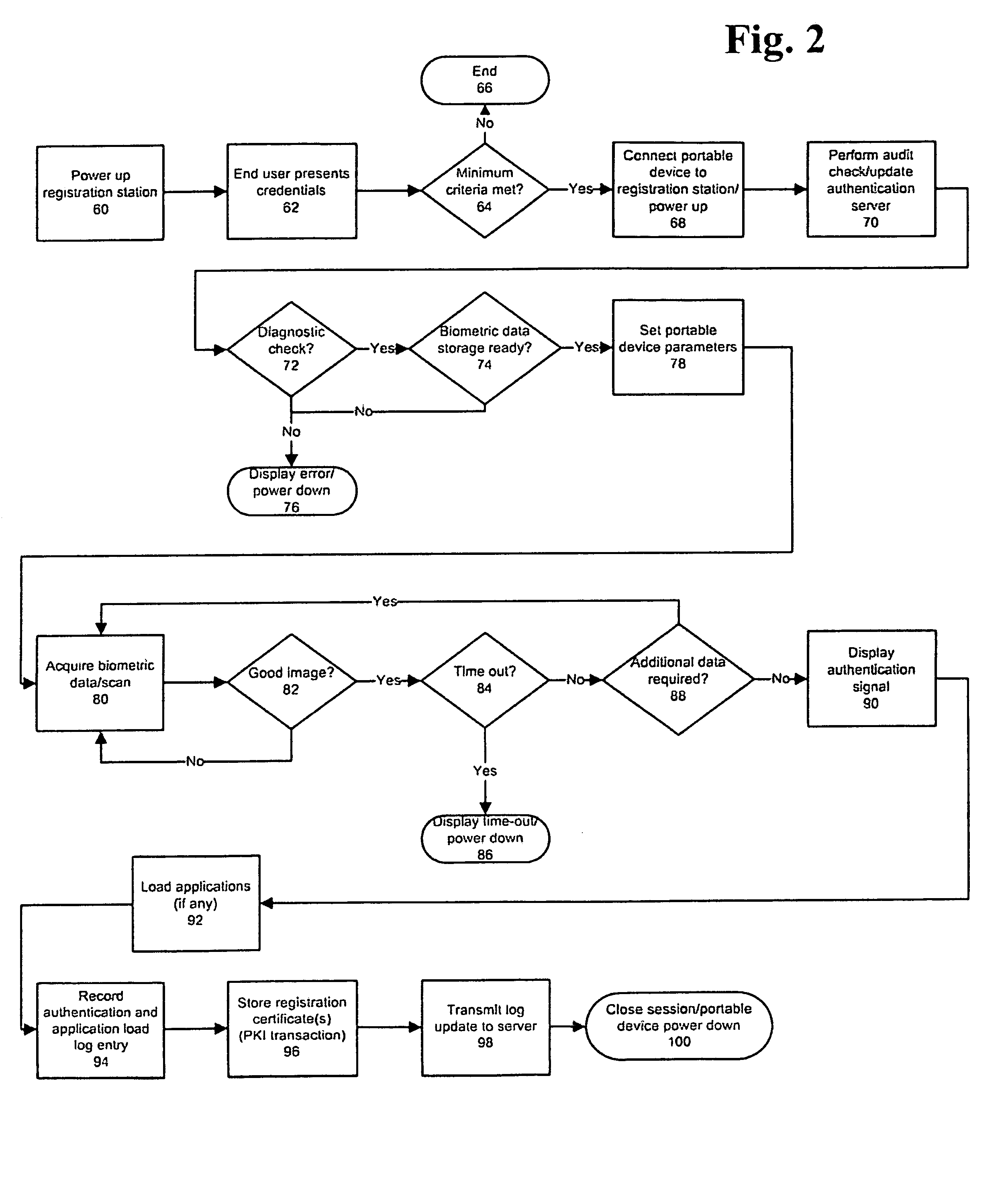
An improved device for use in authorizing transactions, supplying information and performing applications is provided by the present invention, effectively implementing a secured individual and portable Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) terminal. The device uses a local processor and secure data storage in conjunction with a variety of sensors to perform authentication processes that establish an individuals identity and provide authority to perform a desired transaction. The sensors allow the device to directly scan biometric identifying information from an individual. A card swipe interface and a proximity antenna are provided to facilitate communication between the device and remote interface devices such as magnetic swipe card readers, smart card readers, infrared communications ports and proximity and long range radio scanners. In addition, the local processor, memory, display and user inputs allow the device to run applications such as those performed by a traditional computer, gaming device, personal data assistant and smart phone.
Owner:SHAPIRO MICHAEL F
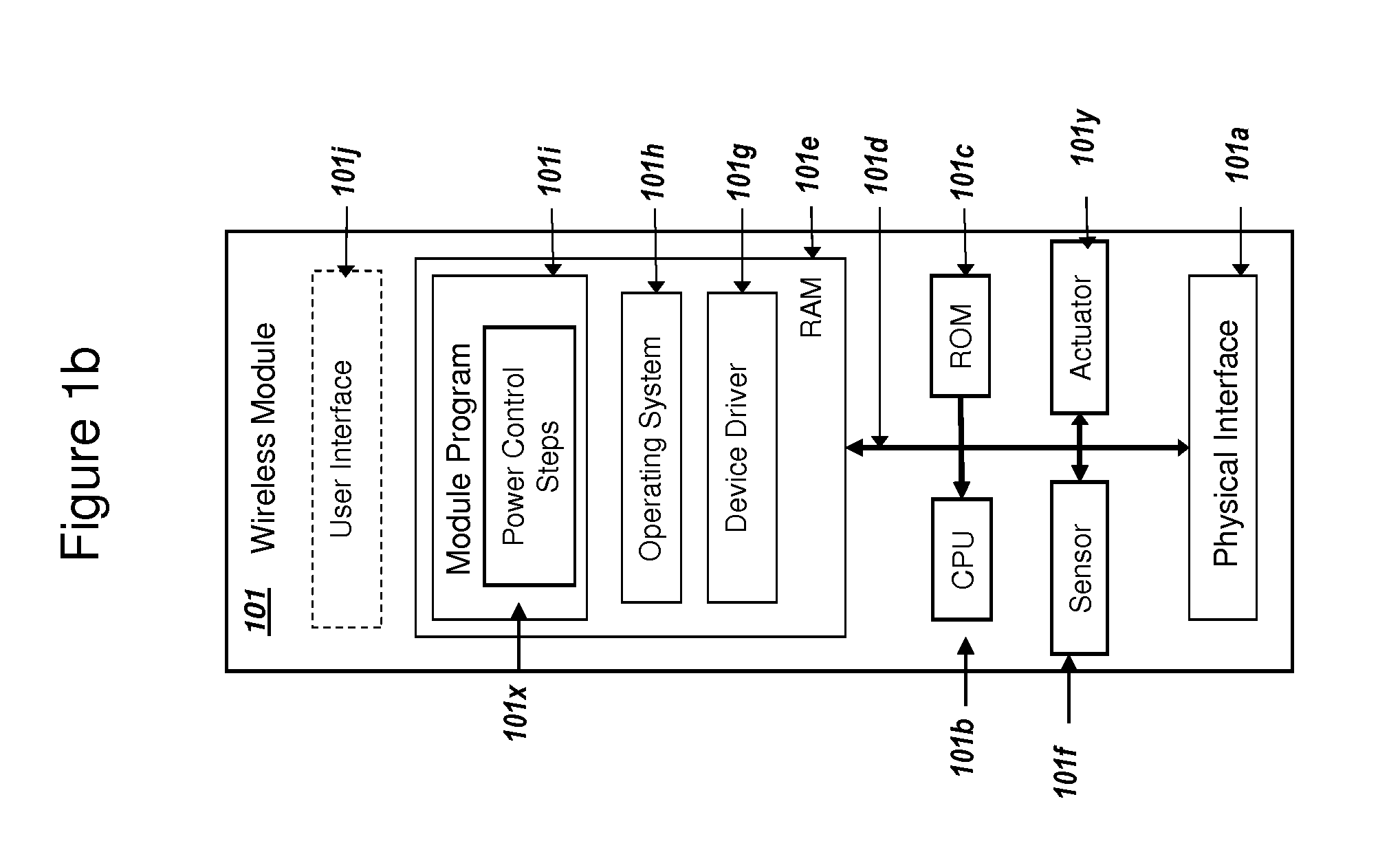
Power Management and Security for Wireless Modules in "Machine-to-Machine" Communications
ActiveUS20150071139A1Efficient power controlExtend battery lifeMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationPublic land mobile networkThe Internet
Methods and systems are provided for power management and security for wireless modules in “Machine-to-Machine” communications. A wireless module operating in a wireless network and with access to the Internet can efficiently and securely communicate with a server. The wireless network can be a public land mobile network (PLMN) or a wireless local area network (LAN). The wireless module may include a sensor and may be installed next to a monitored unit. The wireless module may utilize active states for collecting and sending data, and sleep states at other times to conserve a battery and / or energy usage. The wireless module minimize the time spent in a radio resource control (RRC) connected state. Messages between the wireless module and server can be transmitted according to a user datagram protocol (UDP). The wireless module and server can utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) for encryption and digital signatures.
Owner:NIX JOHN A +1
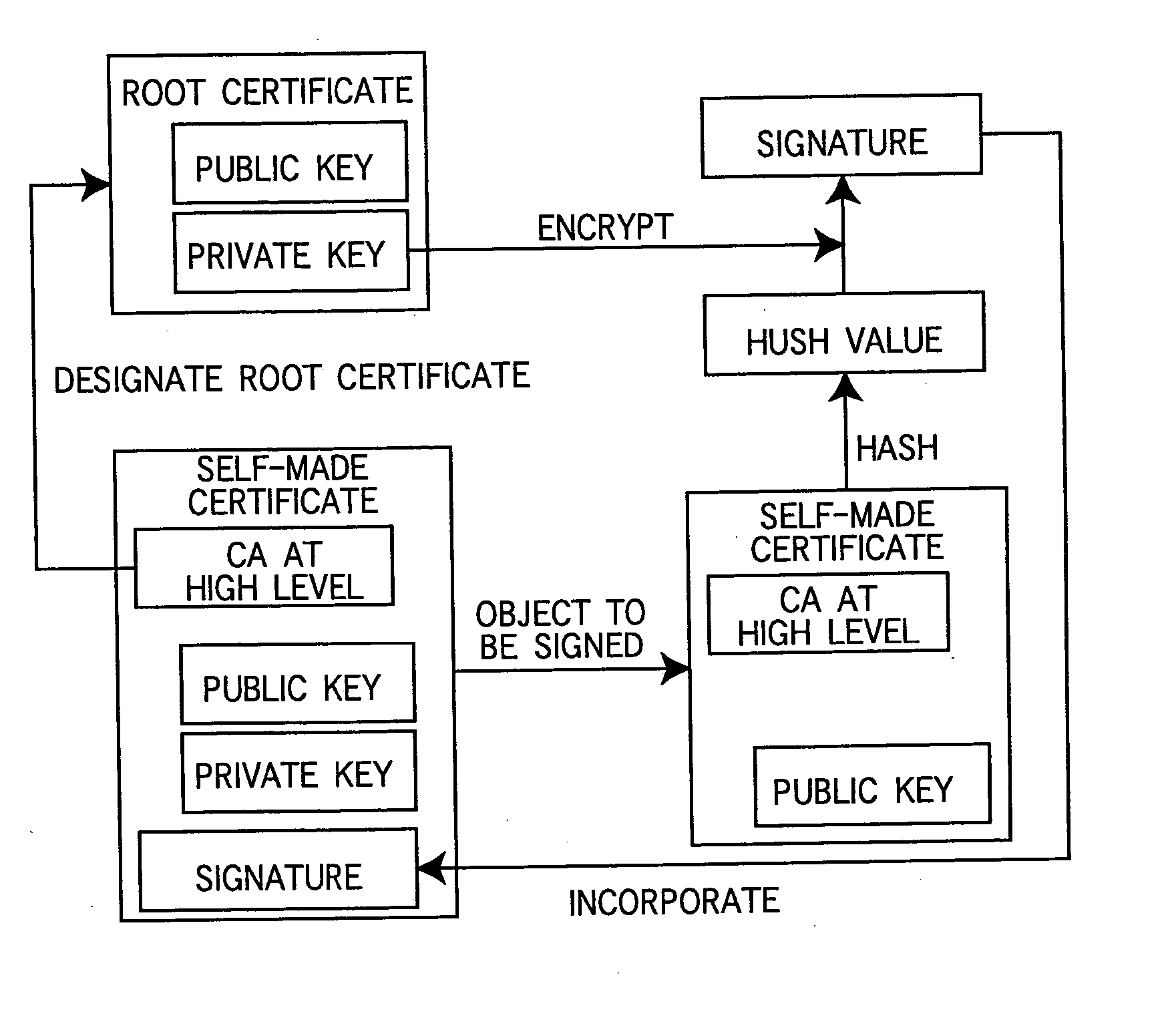
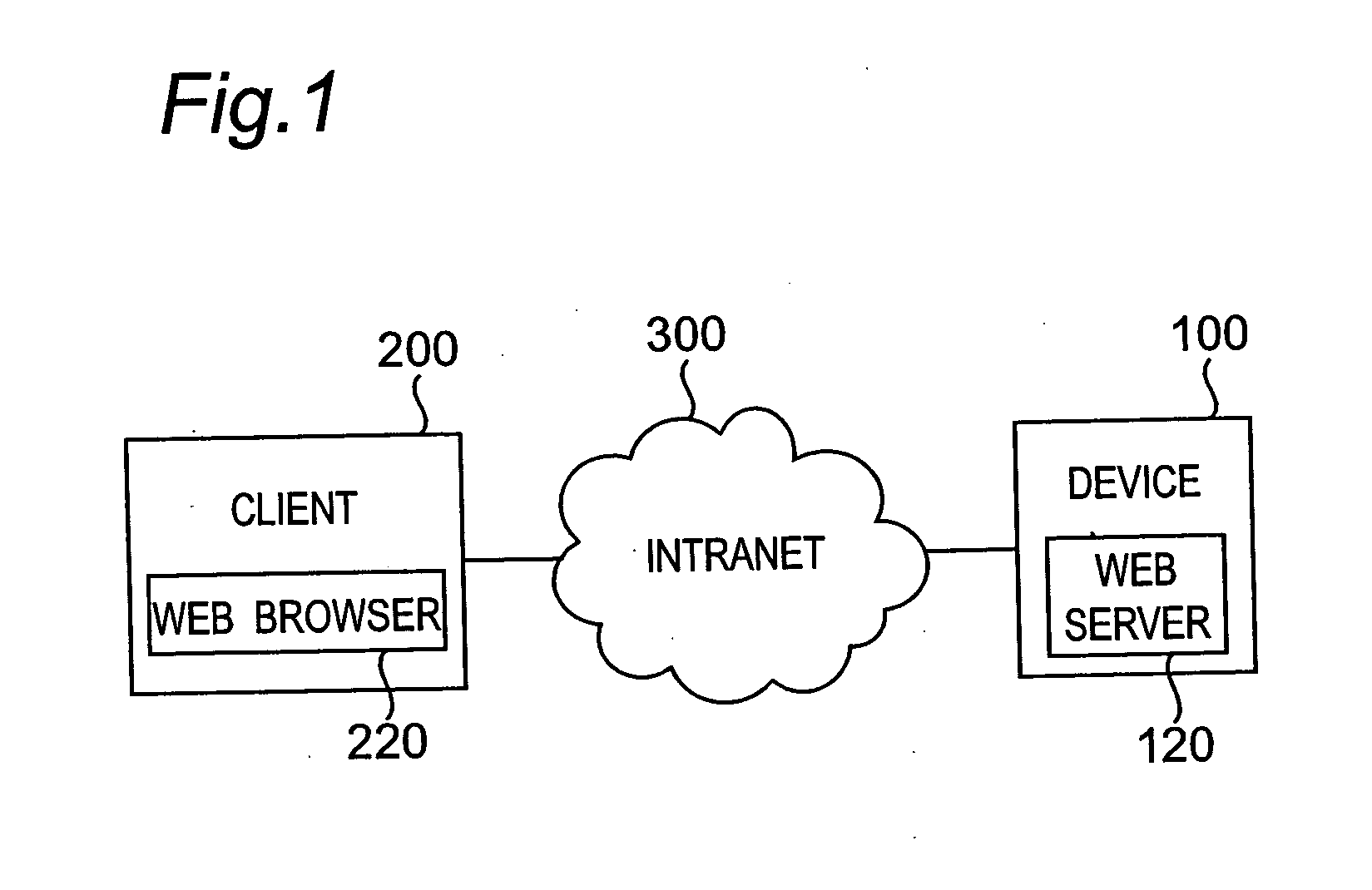
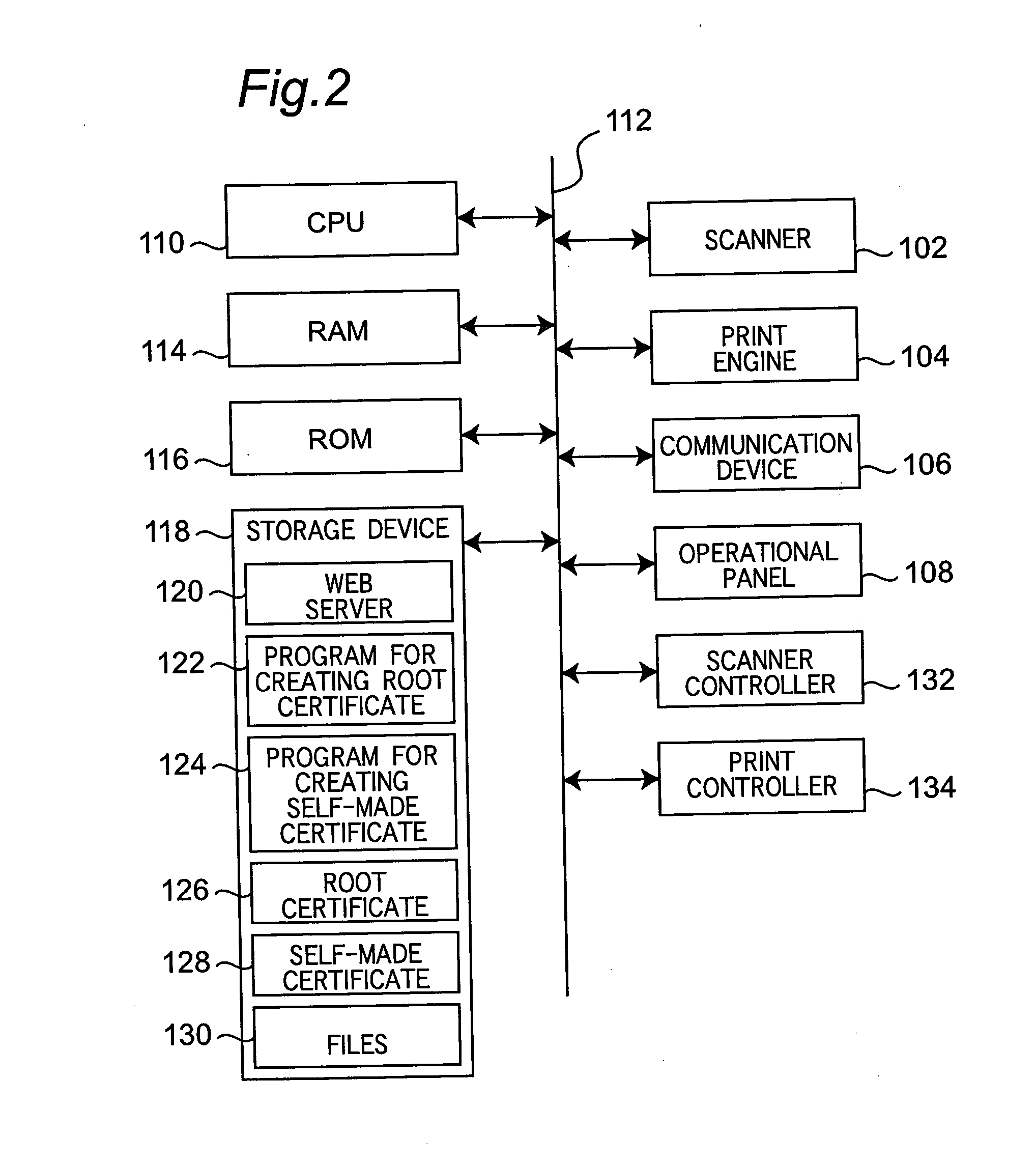
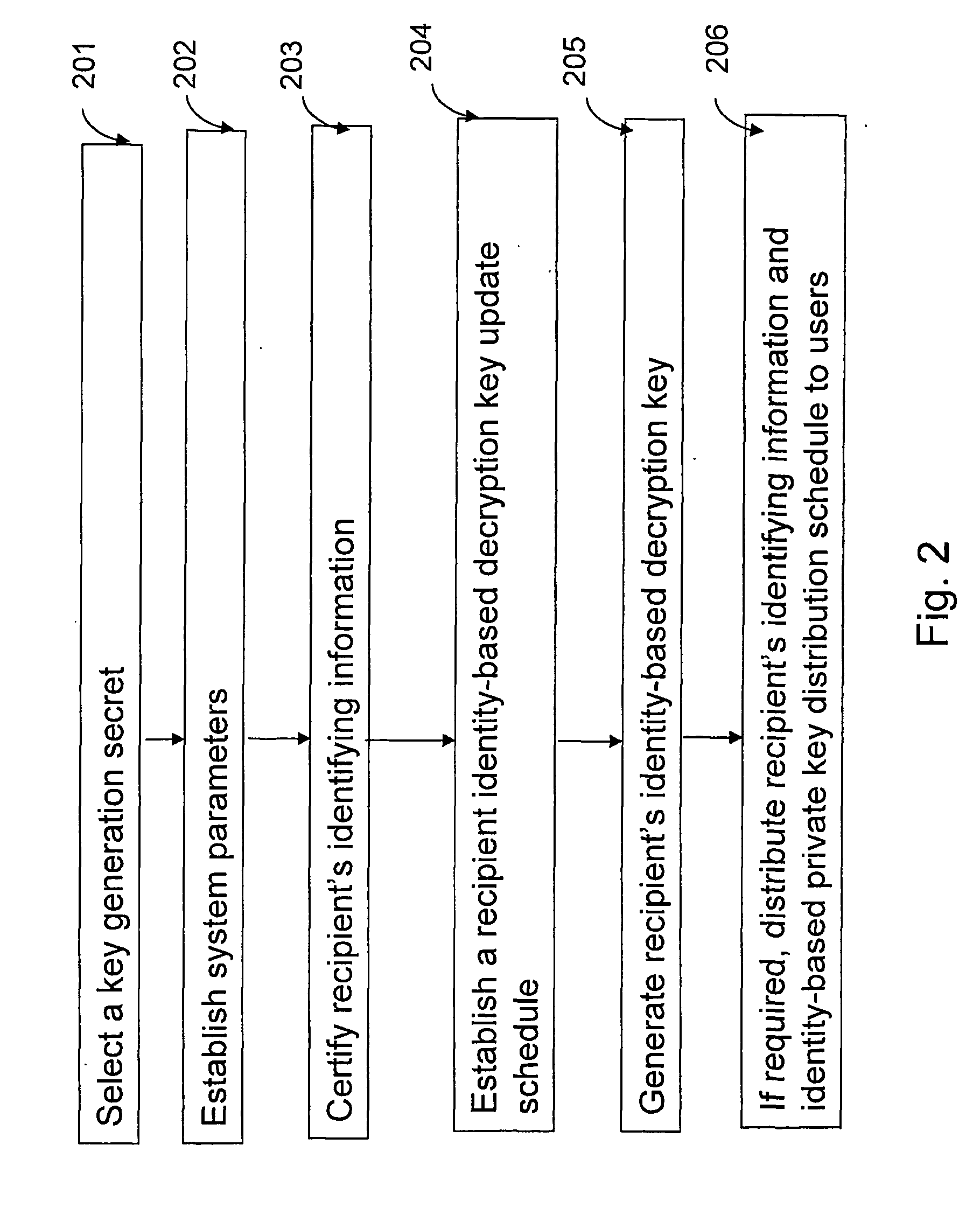
Communication system and method in public key infrastructure
InactiveUS20050005097A1User identity/authority verificationCoding/ciphering apparatusRoot certificateCommunications system
In a communication system wherein a device and a client communicate data with each other through a network, the device holds a root certificate including a public key in a pair of the public key and a private key and signed with the public key. When data is sent, a certificate creator creates a second certificate including the root certificate designated as a certificate authority at a higher level and signed with the root certificate, and the second certificate is sent to the client. In the client, the root certificate has been stored beforehand, and a verifier verifies the signature of the second certificate with the root certificate.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
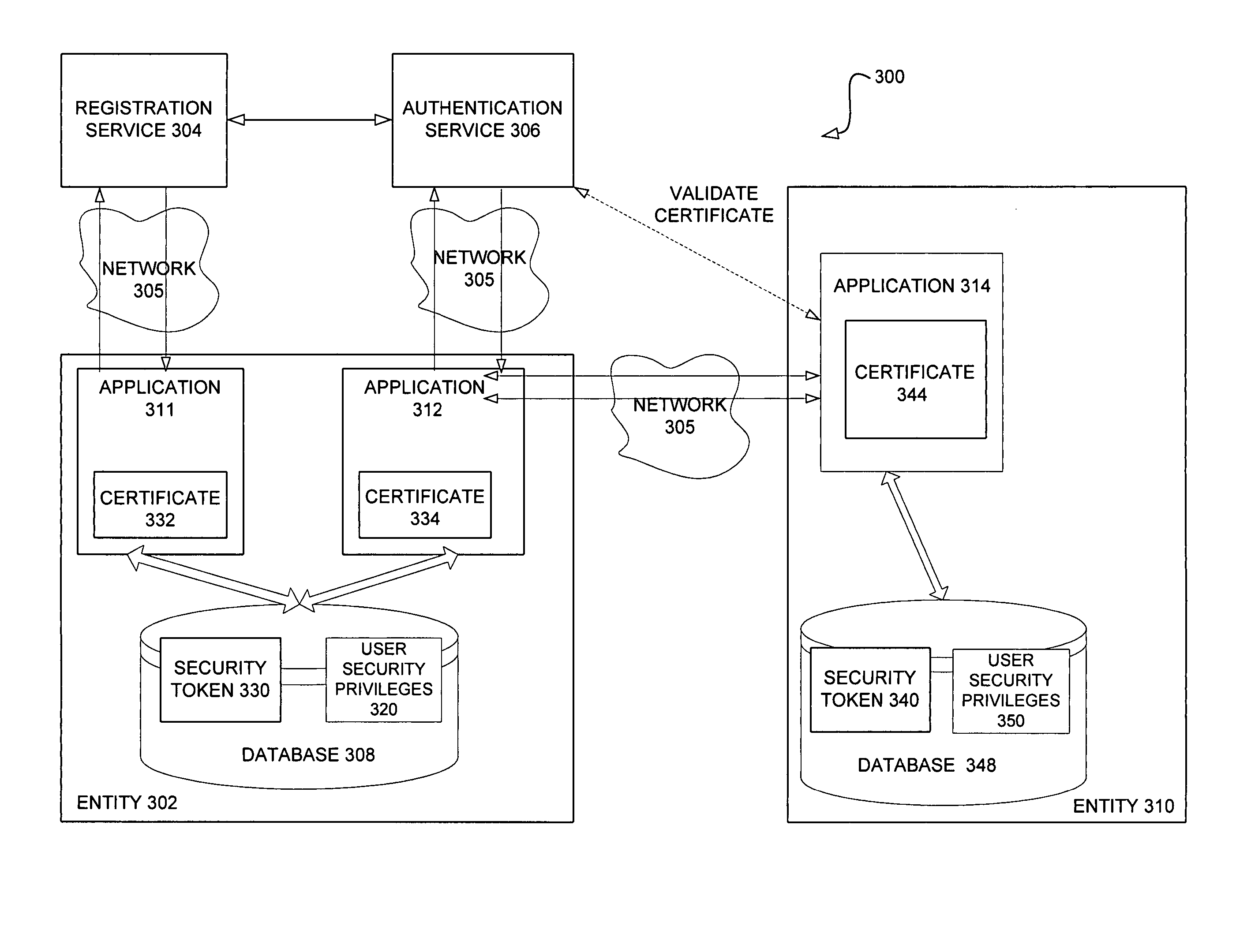
Systems and methods for enhancing security of communication over a public network
InactiveUS20050120214A1Improve securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCommunications securityPublic network
An authentication protocol is disclosed for use in enhancing the security of communications between software applications and Internet-based service providers. The protocol incorporates a two level authentication model based on a distribution of authentication responsibilities, wherein the application authenticates users and the service provider authenticates the application. Embodiments of the protocol incorporate public key infrastructure and digital certificate technology. Other embodiments of the present invention pertain to applying a corresponding protocol to peer-to-peer communication scenarios.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20060023887A1Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityWireless ad hoc network
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Session-based public key infrastructure
ActiveUS20080028206A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSingle sessionSecure communication
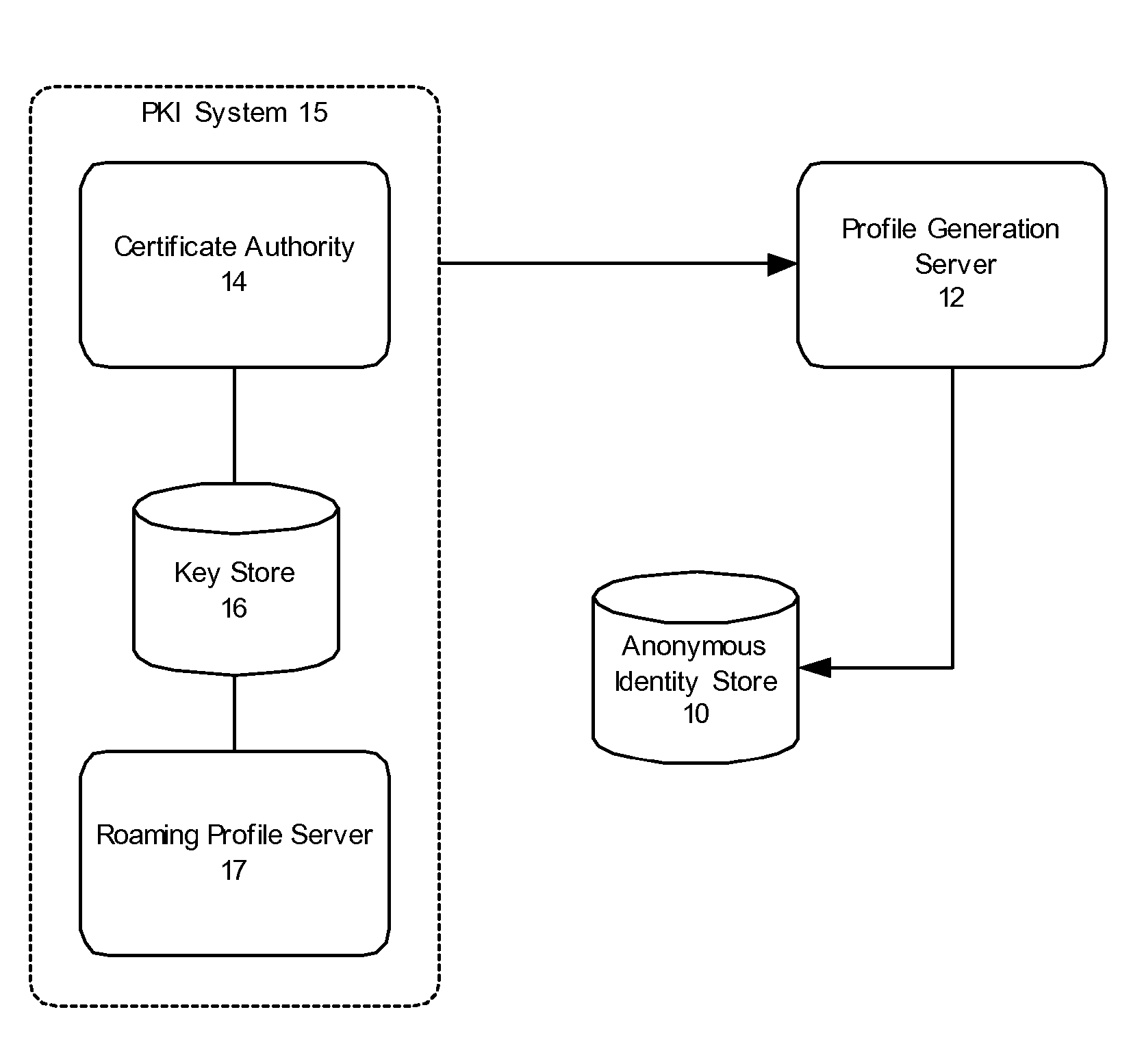
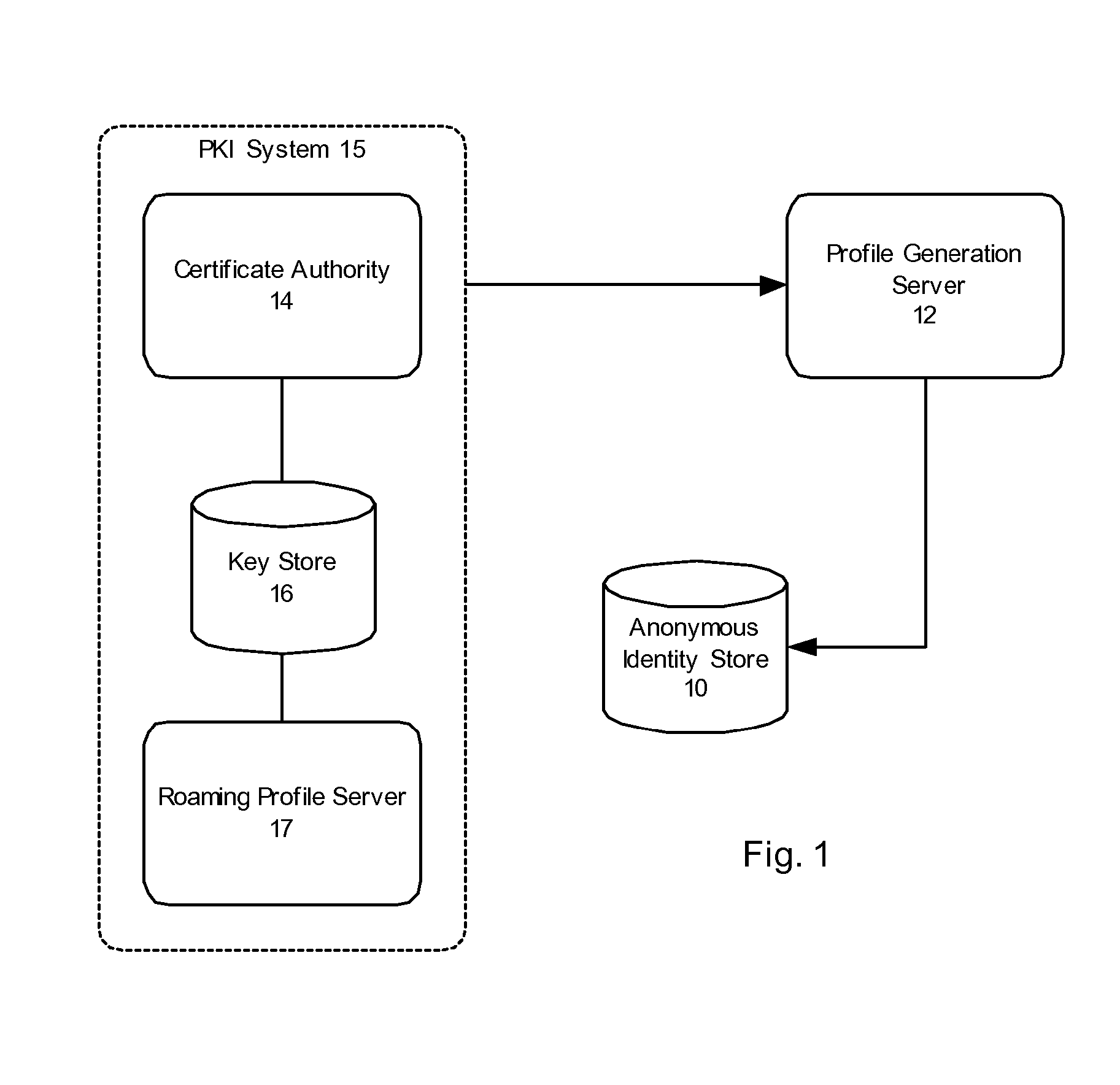
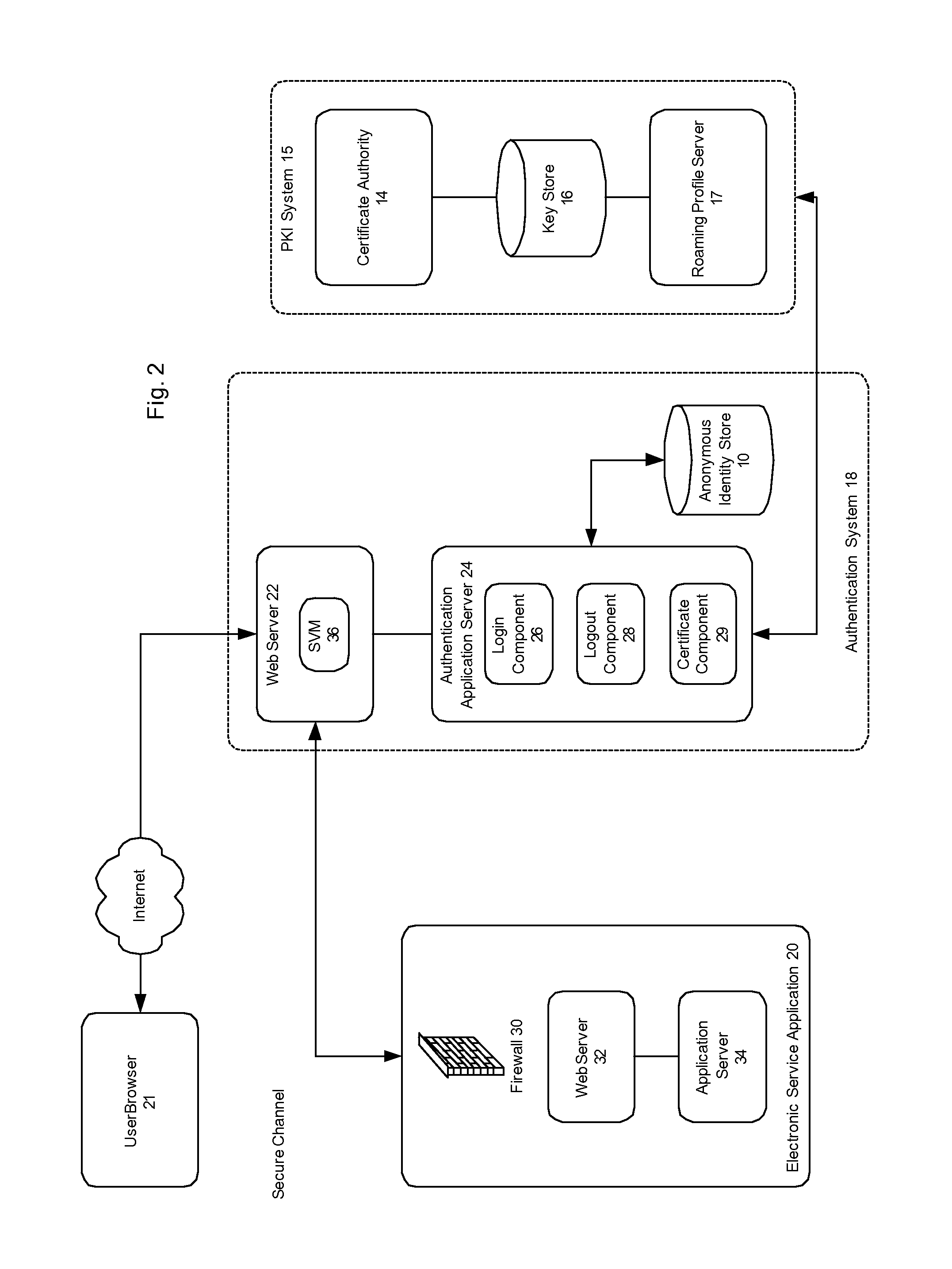
A method and system for issuing anonymous, or user-independent, certificates for secure communication over a network, such as the Internet, to provide authentication and automated login to electronic services. A pool of user-independent certificates is generated. Once the user is identified, a user-independent roaming certificate is automatically transferred to the user's computer for encryption of communications during a single session. Once the user completes the online session or transaction, the issued digital certificate and associated key material is released back to the pool of digital certificates and can be re-used.
Owner:BCE
Method and architecture for security key generation and distribution within optical switched networks
InactiveUS20050177749A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationExchange networkEdge node
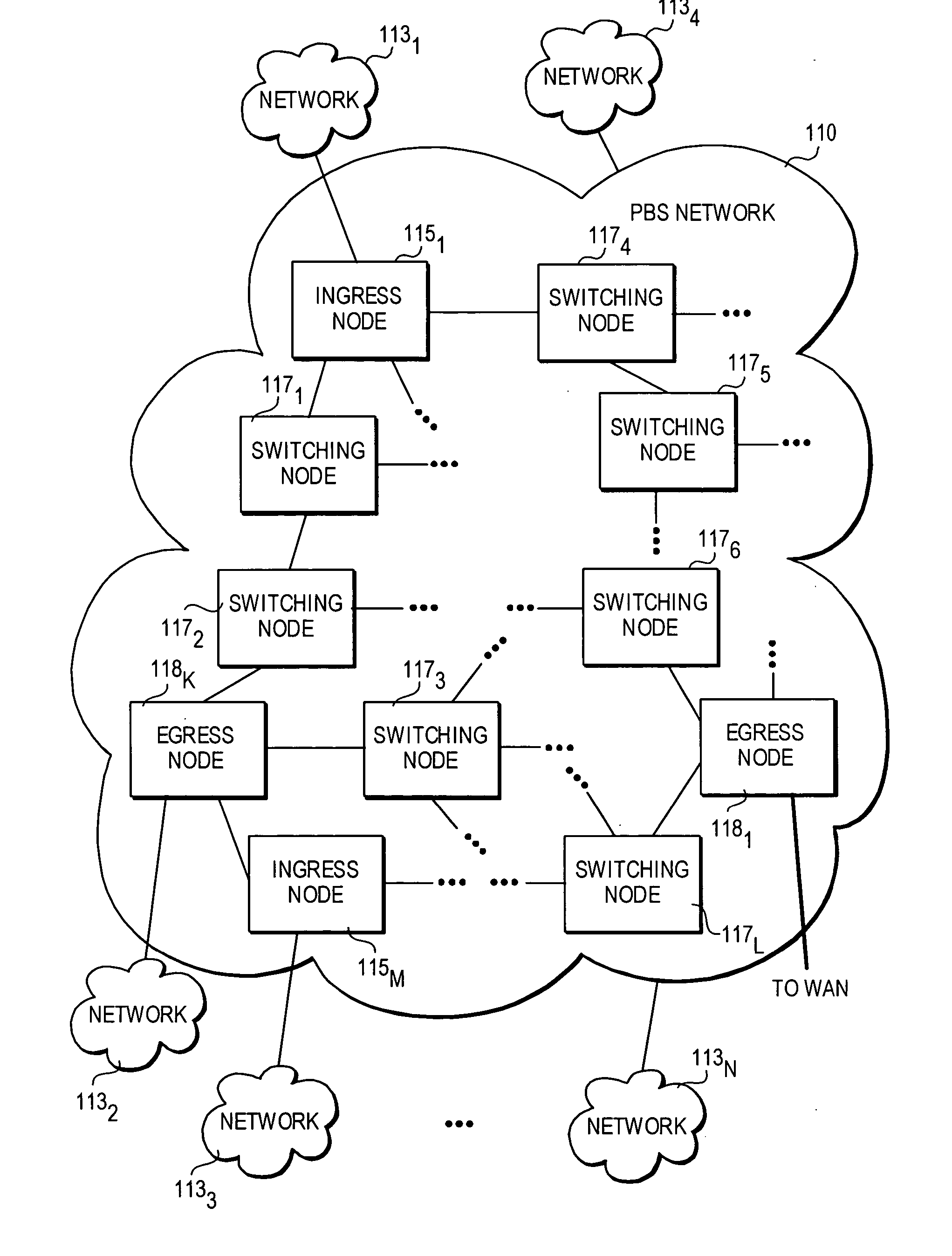
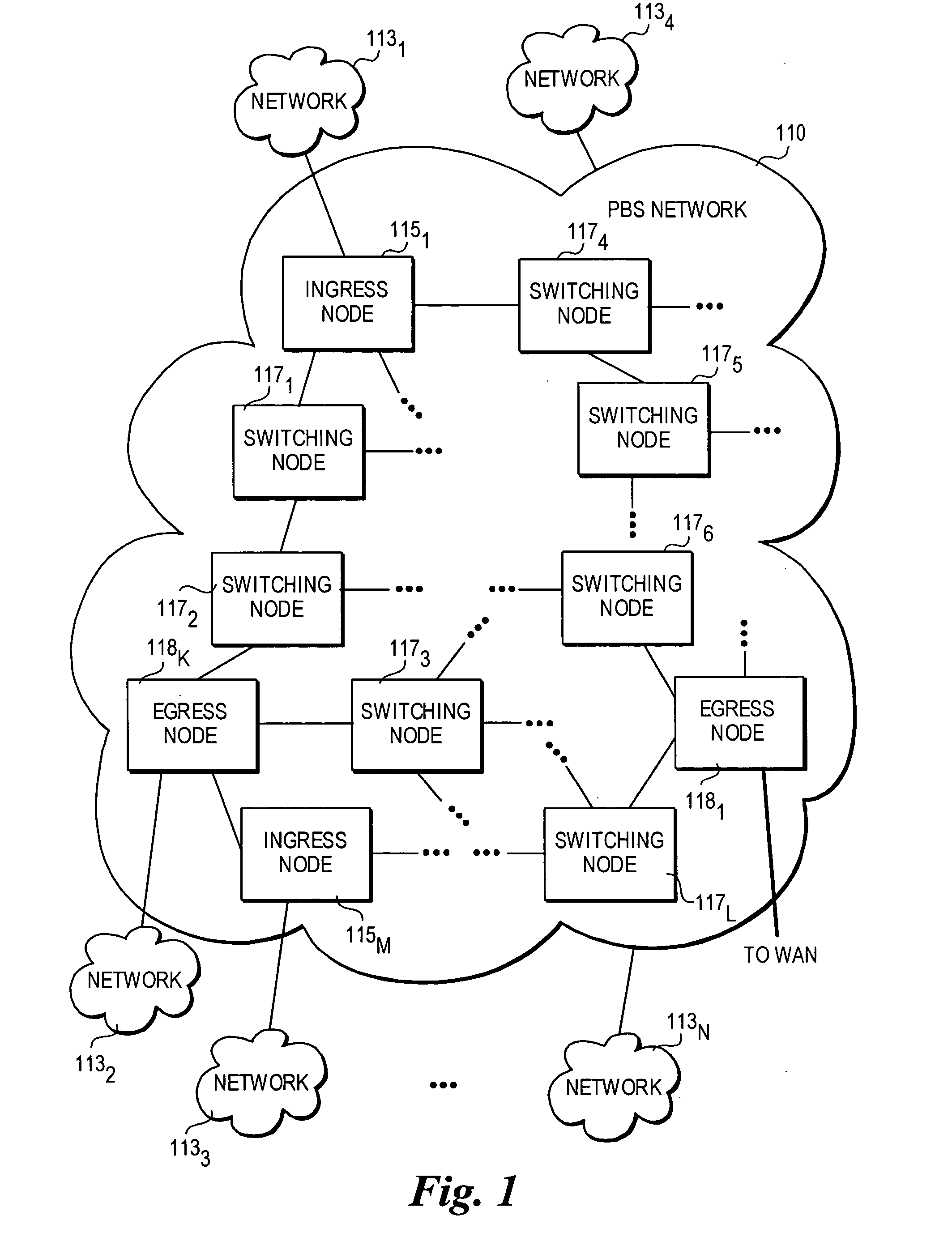
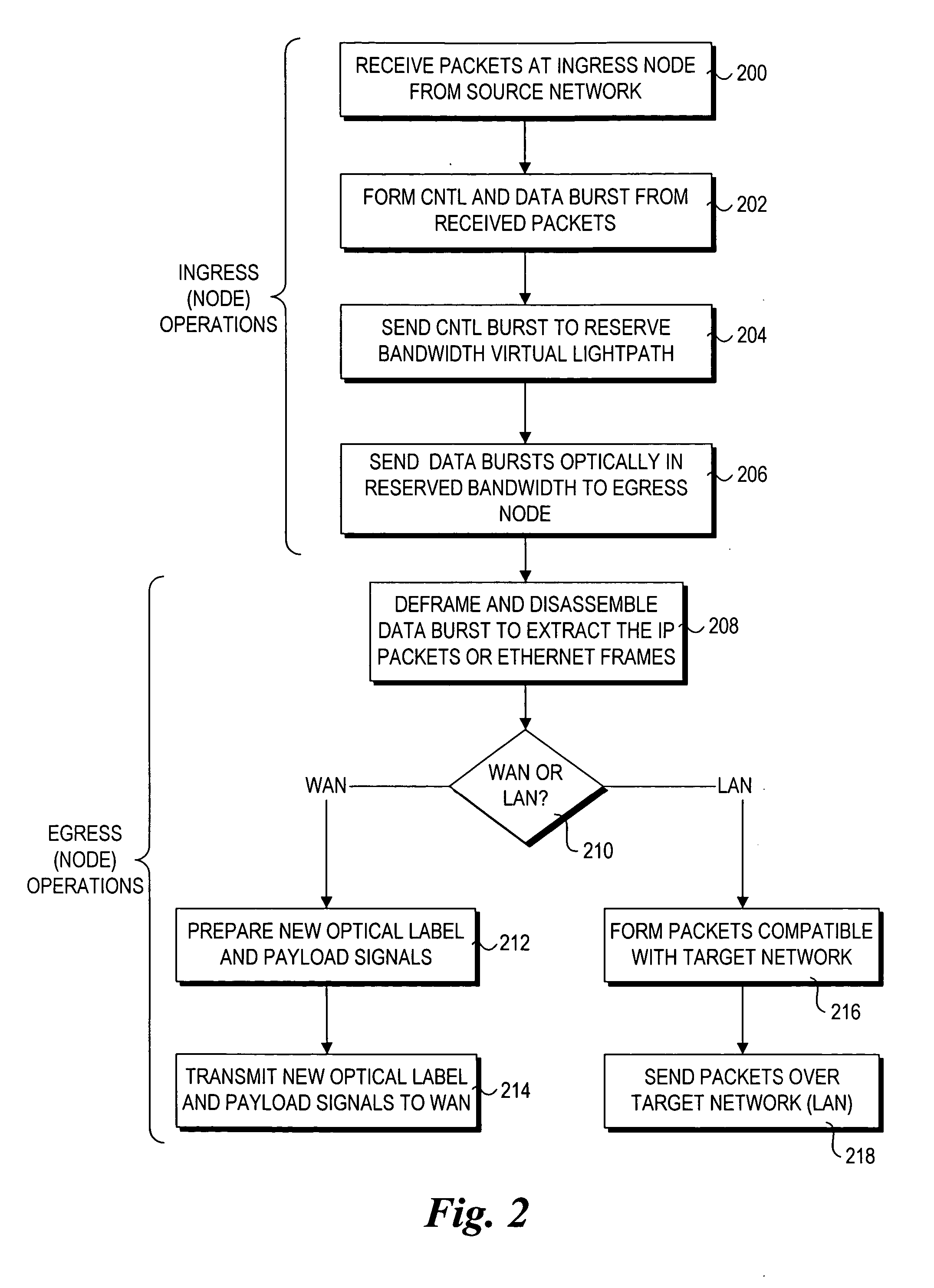
A method and architecture for secure transmission of data within optical-switched networks. In one embodiment, the optical switched network comprises a photonic burst-switched (PBS) network. Under various schemes, security keys including encryption and decryption keys are generated by edge nodes and the decryption keys are distributed to other edge nodes in a PBS network. In one embodiment, the security keys are dynamically generated by a trusted platform module (TPM). A source edge node uses its encryption key to encrypt selected data bursts to be sent to a destination edge node via a virtual lightpath coupling the source and destination edge nodes. Security data are embedded in a control burst header indicates to the destination node whether corresponding data bursts sent via the virtual lightpath are encrypted. The security data also includes the decryption key and may also identify an encryption / decryption algorithm to be used. In some embodiments, public key infrastructure facilities are used in conjunction with employment of private and public keys and digital certificates.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Systems for Securing Control and Data Transfer of Smart Camera
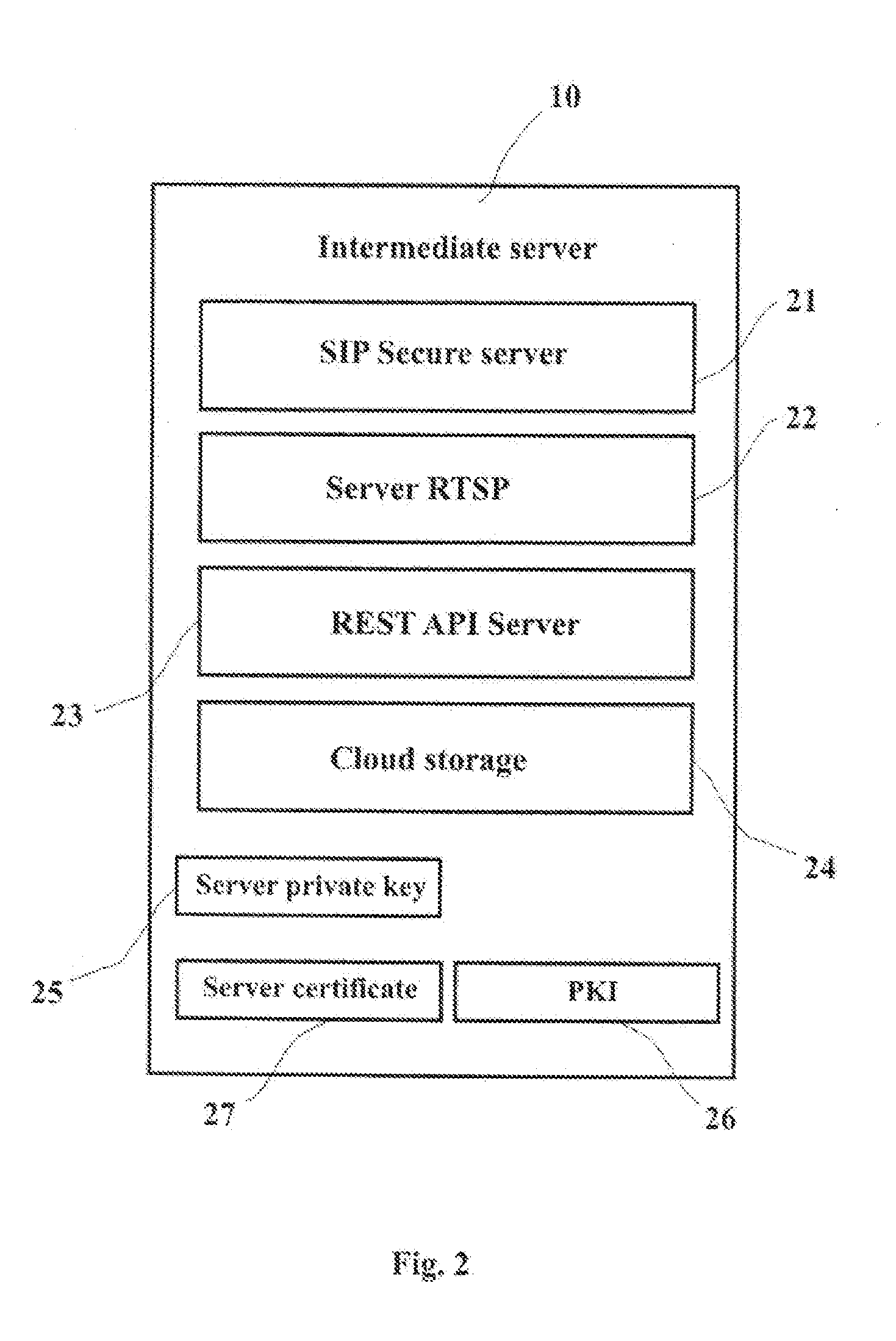
InactiveUS20150222601A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsCloud storageData transmission
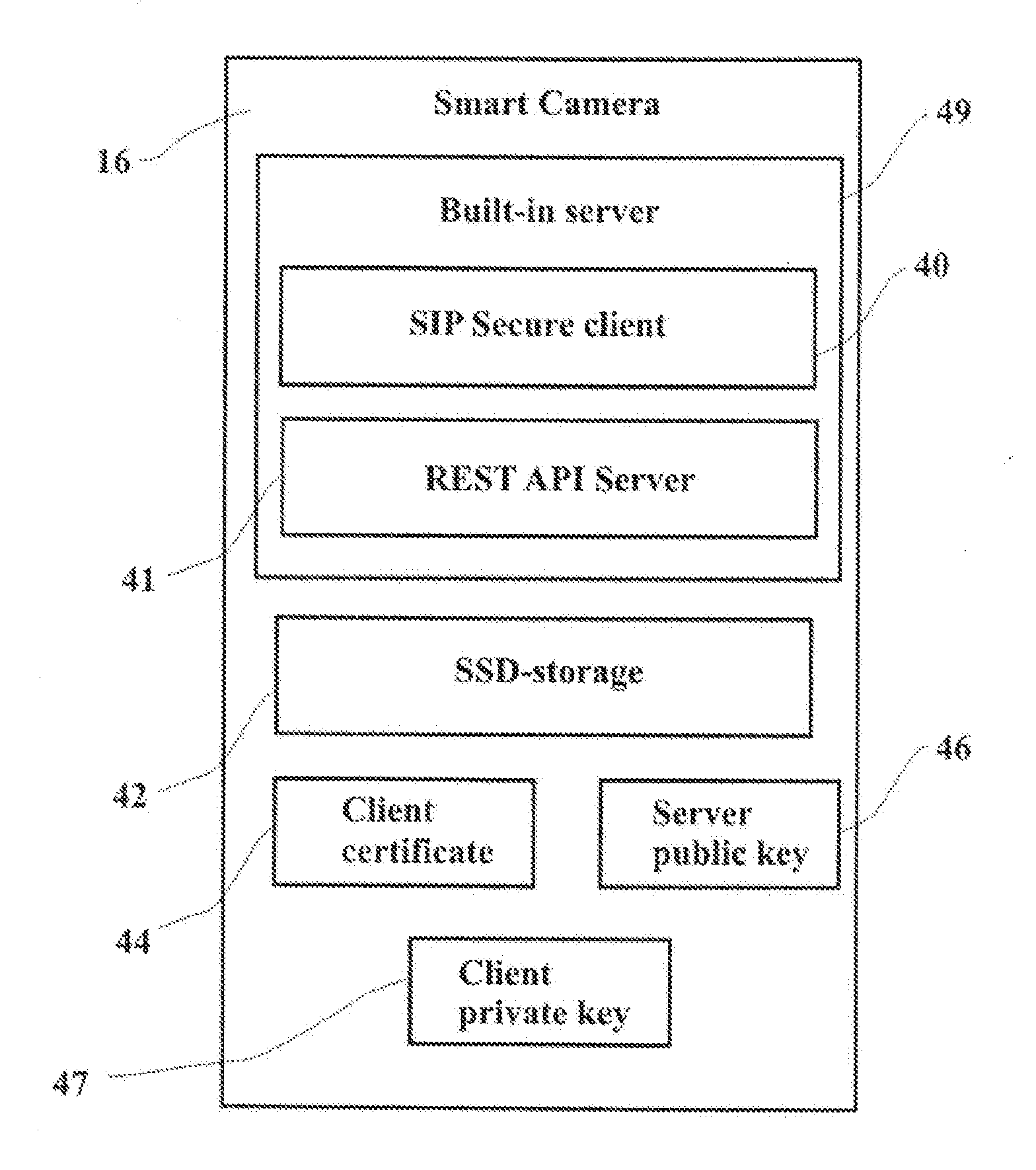
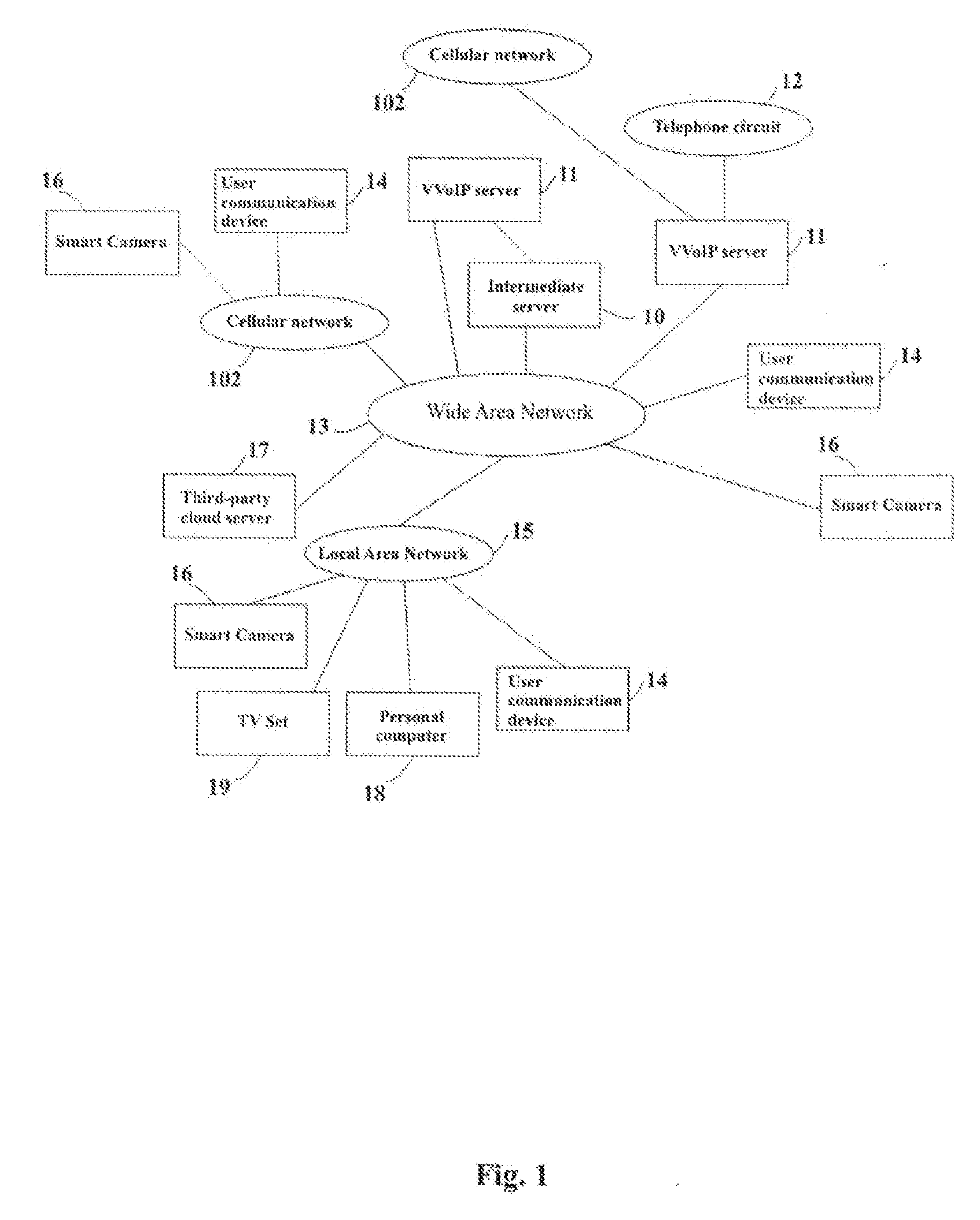
A system of secure control of a smart camera and transfer a media content from and to smart camera by a user communication device and an intermediate server, comprising: a smart camera, intermediate server and user communication device, which are connected to WAN. The intermediate server includes a SIPS-server, REST API Server, cloud storage, Public Key Infrastructure, private key and server certificate. The smart camera includes a built-in server, a SSD-storage, a client certificate, client private key and an intermediate server public key. The built-in server includes a SIPS-client and REST API Server and the user communication device includes a SIPS-client, a REST Client and a public key of said intermediate server. The smart camera and said user communication devices are connected to common local area networks (LAN) with communicating to wide area network (WAN) or cellular networks.
Owner:BRANTO
Encryption key exchange system and method
InactiveUS9002018B2Improve usabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationUsabilityEncryption
Owner:SYNC UP TECH
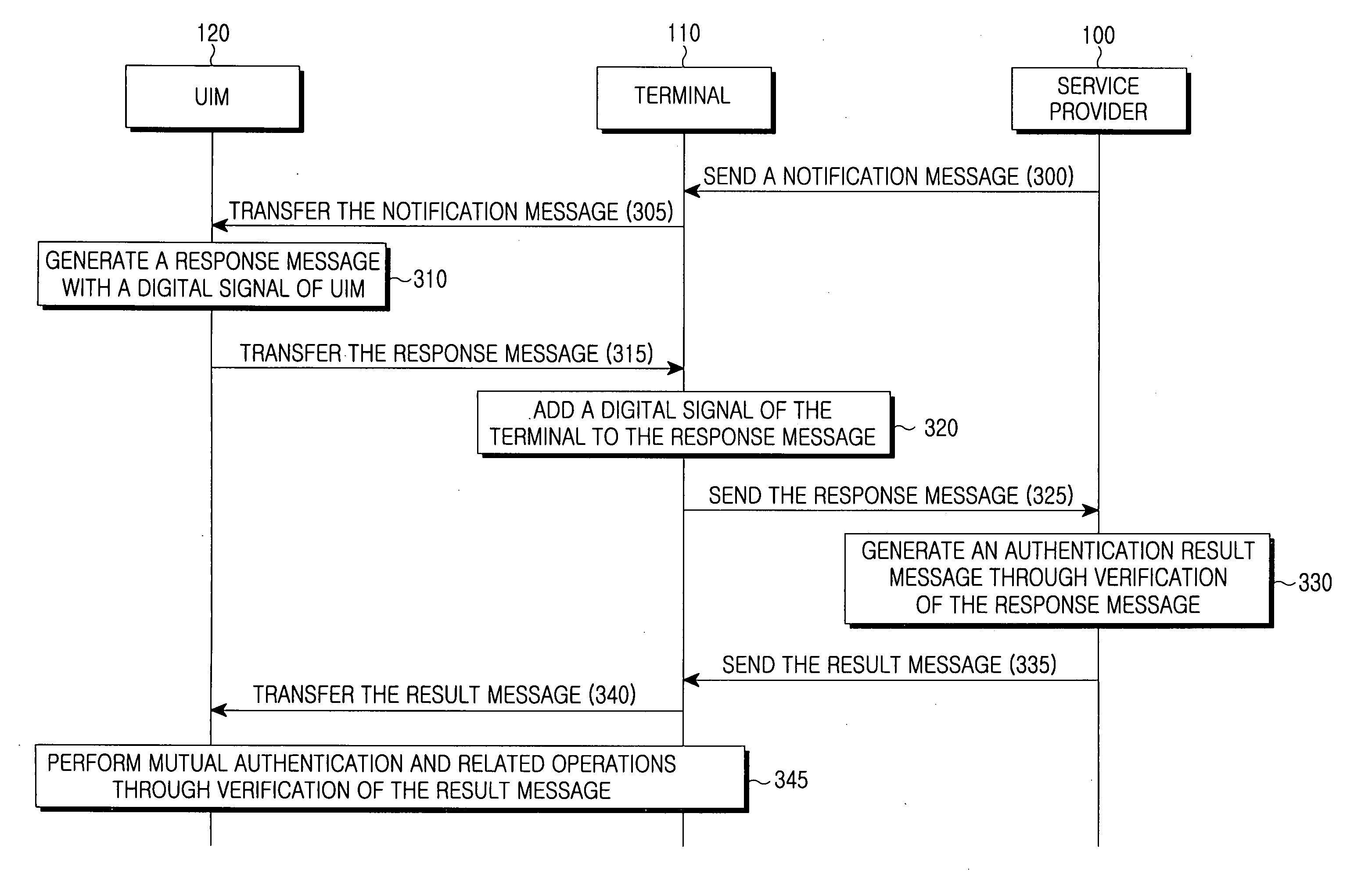
Method for inclusive authentication and management of service provider, terminal and user identity module, and system and terminal device using the method
ActiveUS20060281442A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsPublic key authenticationNetworked system
Disclosed are a method and a system for mutual inclusive authentication between a service provider, a terminal and a user identity module. The authentication system is configured in a structure that can interact with a public key infrastructure of the current network security environment and can be independently used in a specific network system. The inclusive authentication method is divided into public key authentication and symmetric key authentication. Mutual authentication can be made between a service provider, a terminal and a user identity module using any of the two authentication schemes. Then a user can access content on any terminal device using the content license based on the user's identity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
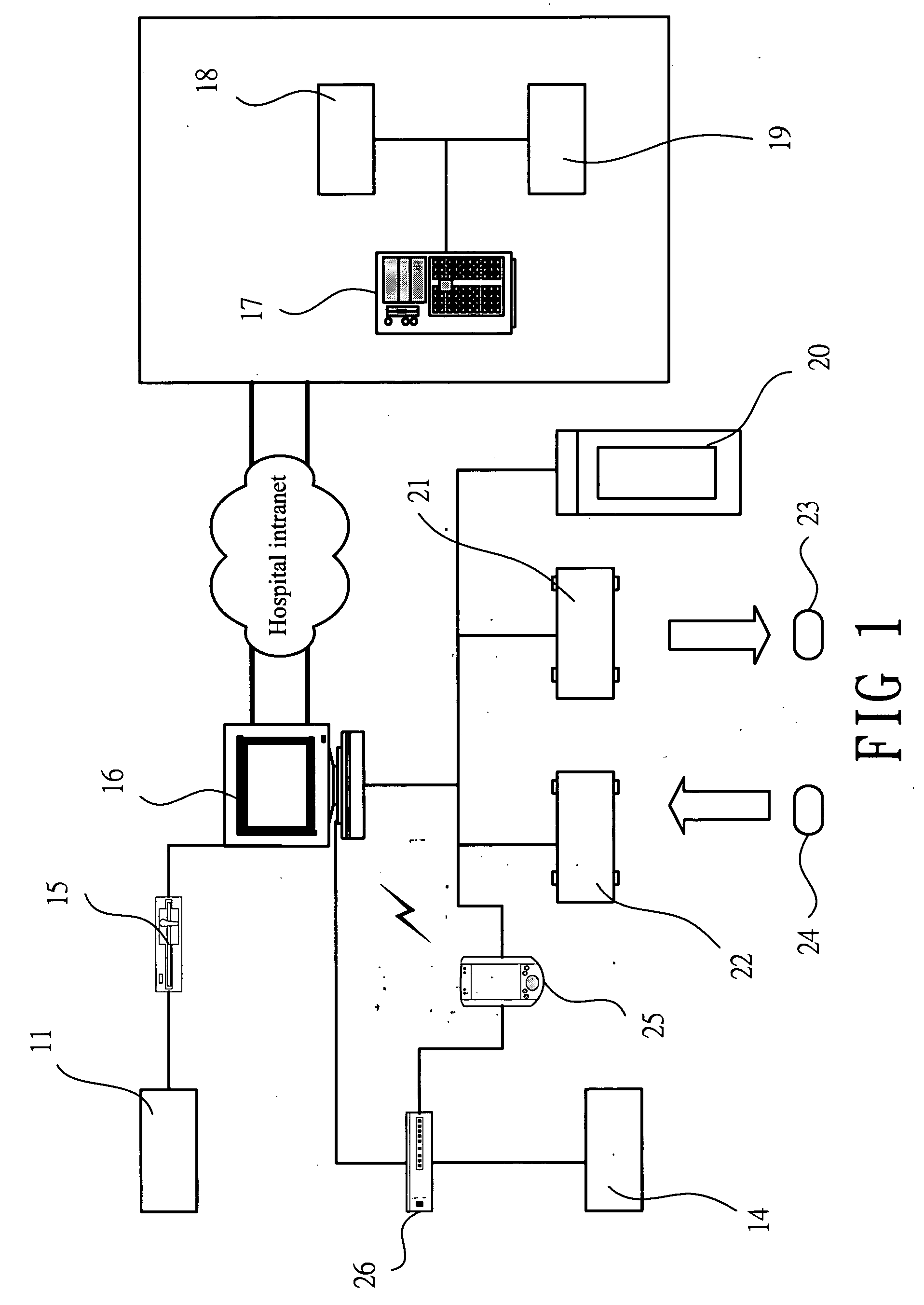
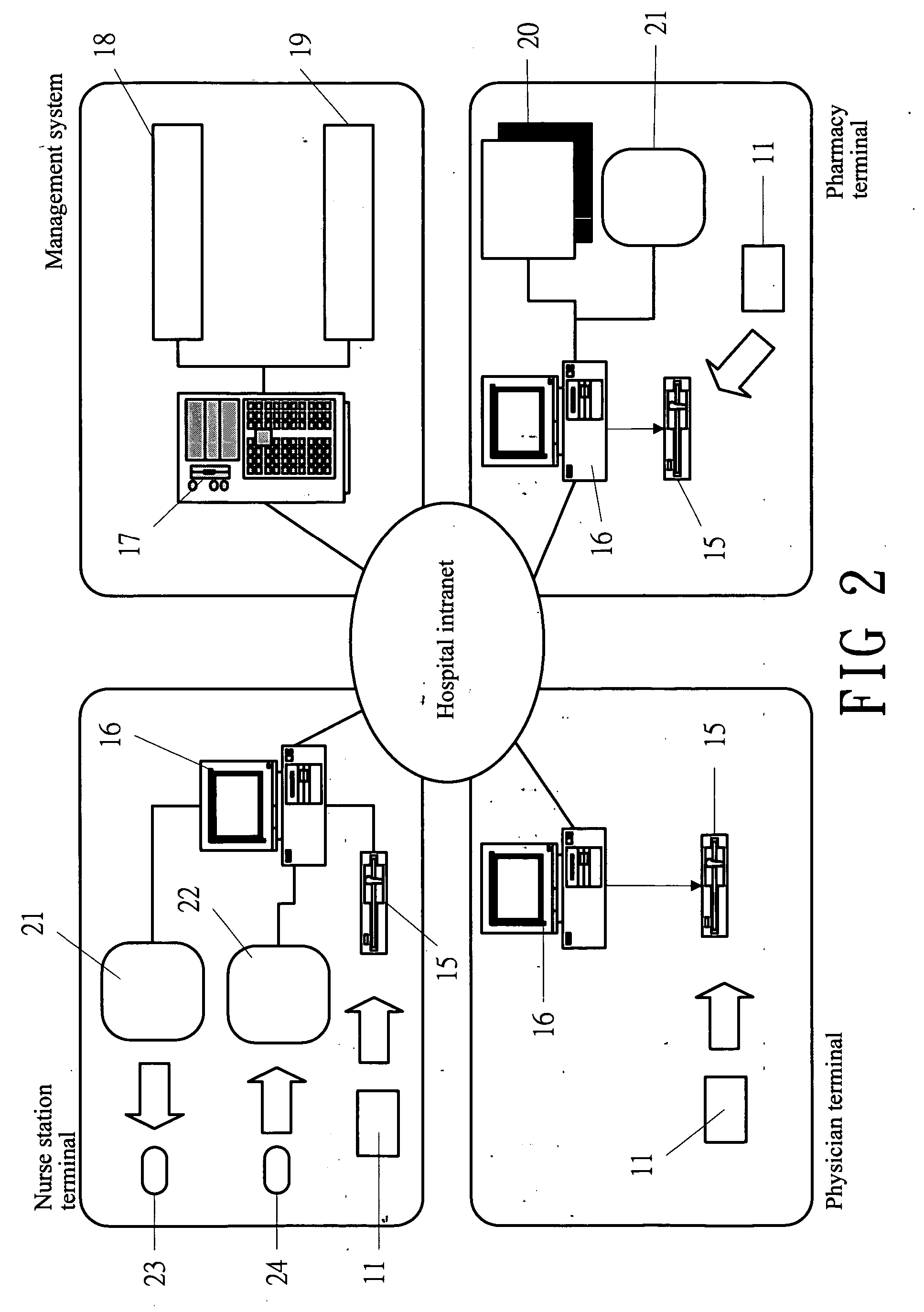
Means and method of applying RFID and PKI technologies for patient safety
InactiveUS20060089858A1Preventing improper useInhibition releaseData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMedical recordMedicine
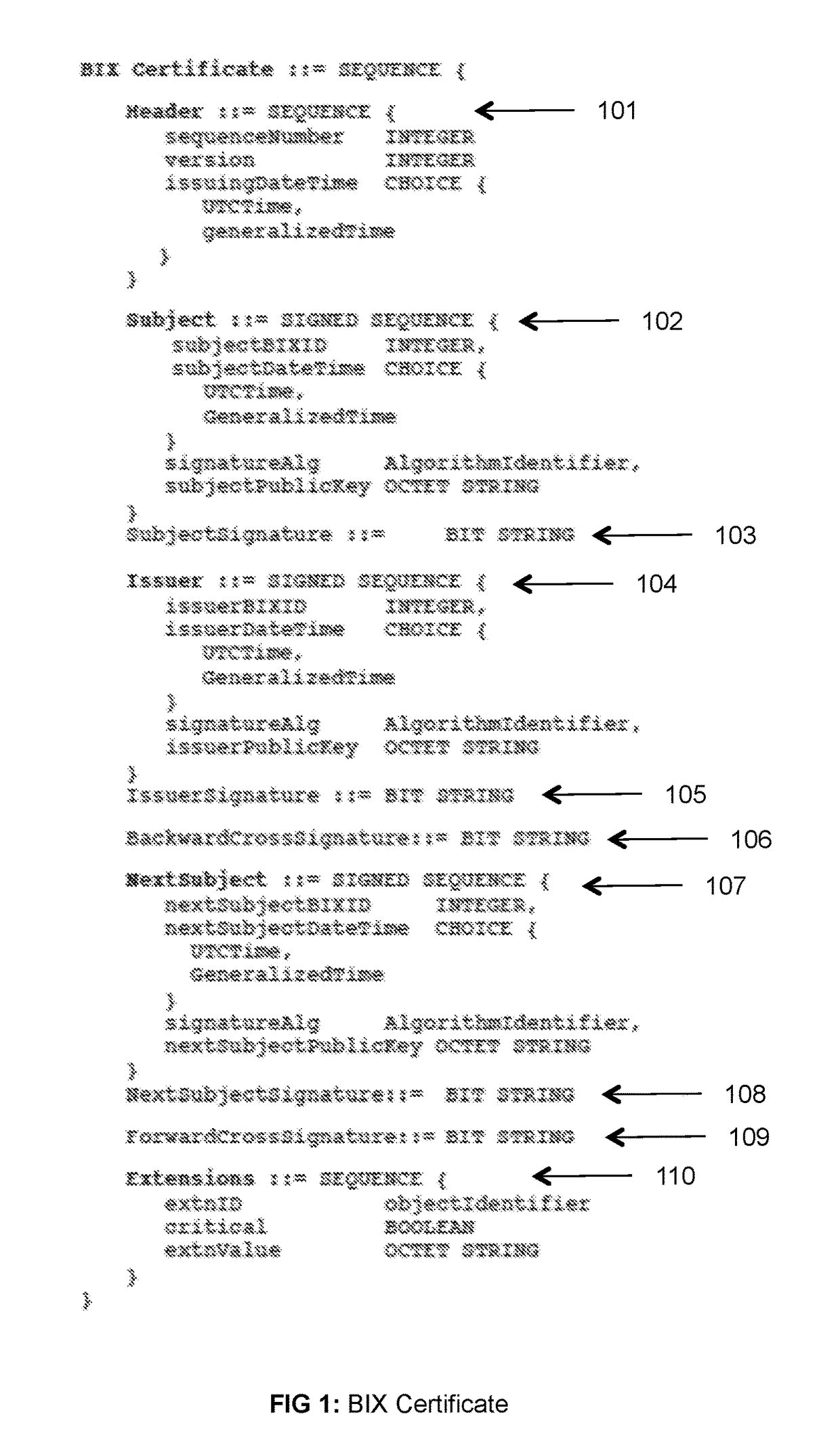
A system and a method for applying RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) technologies for patient health safety to install RFID tag and RFID reader on the medicine-storing appliance. By sensing the RFID tag on medicine, the RFID reader stores the medical records such as medicine usage and movement, and transmit to central database. In this way, the circulation of medicine could be controlled, the improper use and distribution of medicines could be avoided, the medical resource management could be improved, and it could ensure that the correct medicine to enhance the process of five rights (right time, right route, right dose, right patient and right drug) and improve the quality of patient safety.
Owner:LINGANG COMM CORP
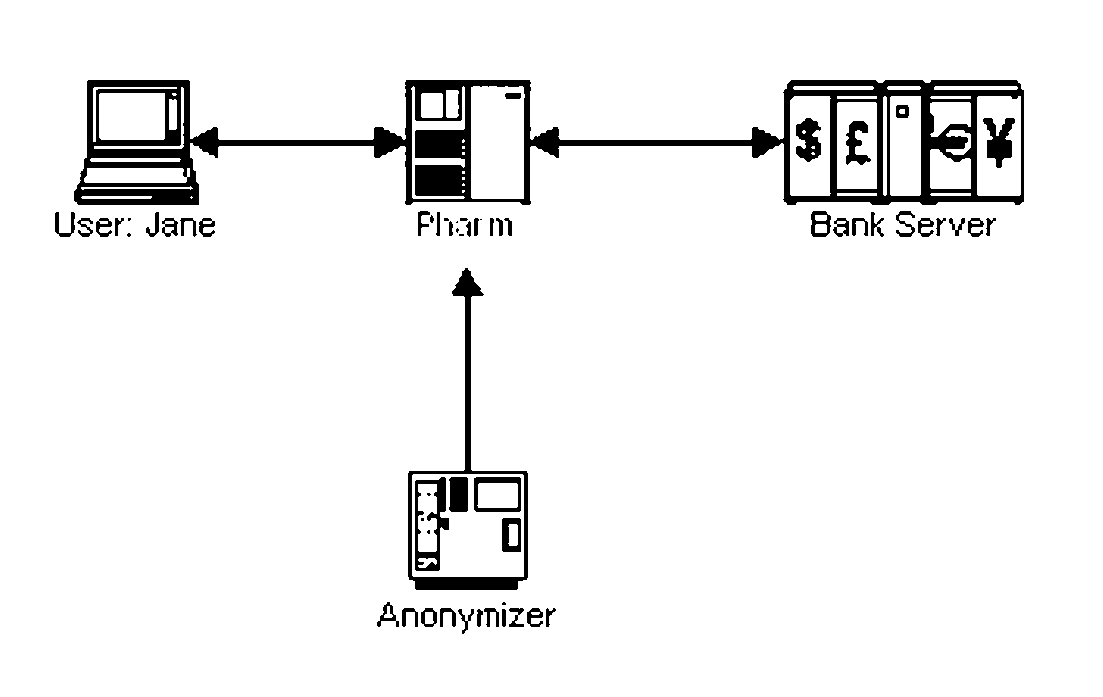
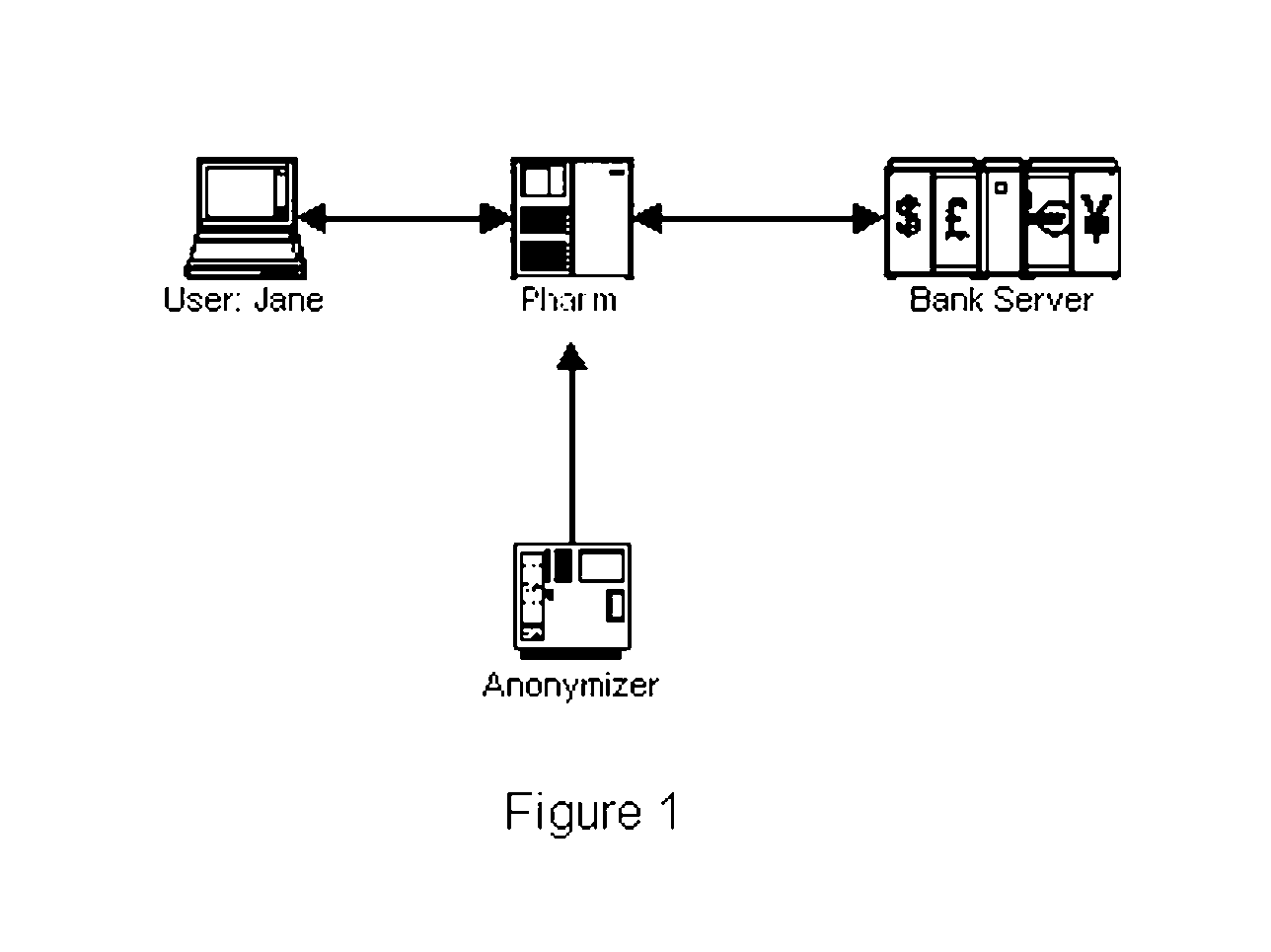
System and Method of Mobile Anti-Pharming and Improving Two Factor Usage
InactiveUS20070174630A1Improve securityLow costRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationPrivate networkSoftware
A variant of phishing involves subverting an Internet access point, often used for mobile computing. Malware can route user requests for bank websites into a phisher's private network, with fake bank websites (pharming). The user can have a “mobile password” at the bank. When she connects from an access point, she sends a hash, found from the password, starting at some position in it. The bank returns a hash, found from the same password, starting at another position in it. Each can verify the other. We protect both from a man in the middle attack. By hashing a web page and the mobile password, and inserting the hash into the page that is sent, the recipient can verify that the page is untampered. We use an anonymizer, external to the access point. A user pre-establishes a password with the anonymizer. At the access point, she and the anonymizer use a zero knowledge protocol to verify each other, based on the password. Then, the password encrypts communication between them. From the anonymizer, she logins elsewhere. The anonymizer is our man in the middle, to defeat a man in the middle attack. W extend earlier antiphishing methods, to attack pharms for non-existent banks, or that are unauthorized websites for actual companies. We show how to use a plug-in to let websites share several two factor implementations. This reduces the cost and inconvenience to consumers, who might otherwise have to carry and use a different two factor gadget, for each of their bank accounts or other corporate websites that mandates the usage of two factor authentication. By expanding the scope of two factor usage, we improve the security of e-commerce, without having to use a public key infrastructure.
Owner:METASWARM INC
Public Key Infrastructure based on the Public Certificates Ledger
InactiveUS20170346639A1Multiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationAs DirectedDigital signature
Systems and methods for managing public key certificates and supporting the users thereof. The certificates are cryptographically encapsulated objects that bind the identities of their owners to public keys and provide digital signature mechanisms for other users to verify the binding and correctness of other attributes of the certificate. Certificates include double links that reflect their validation and position in a public certificates ledger, thereby preventing insertion or removal of certificates in the ledger. Certificate protocols of the system include requesting issuance of certificates, issuing and returning certificates to their requesting users, storing certificates in the certificates ledger, requesting and distributing certificates to transaction partners, verification of certificates by transaction partners, and revoking certificates by their owners. These protocols are performed as direct peer-to-peer transactions between the members of the system.
Owner:MUFTIC SEAD
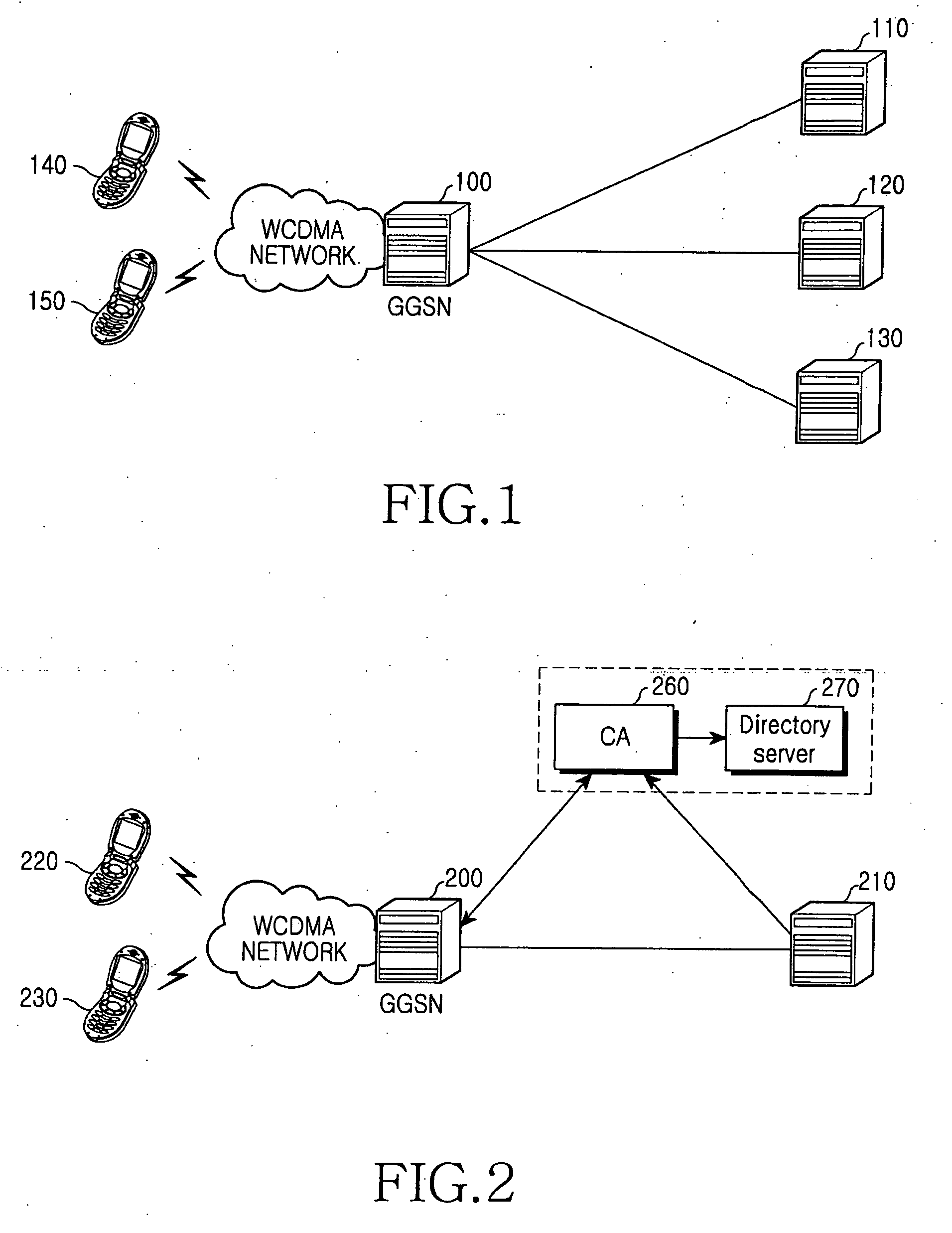
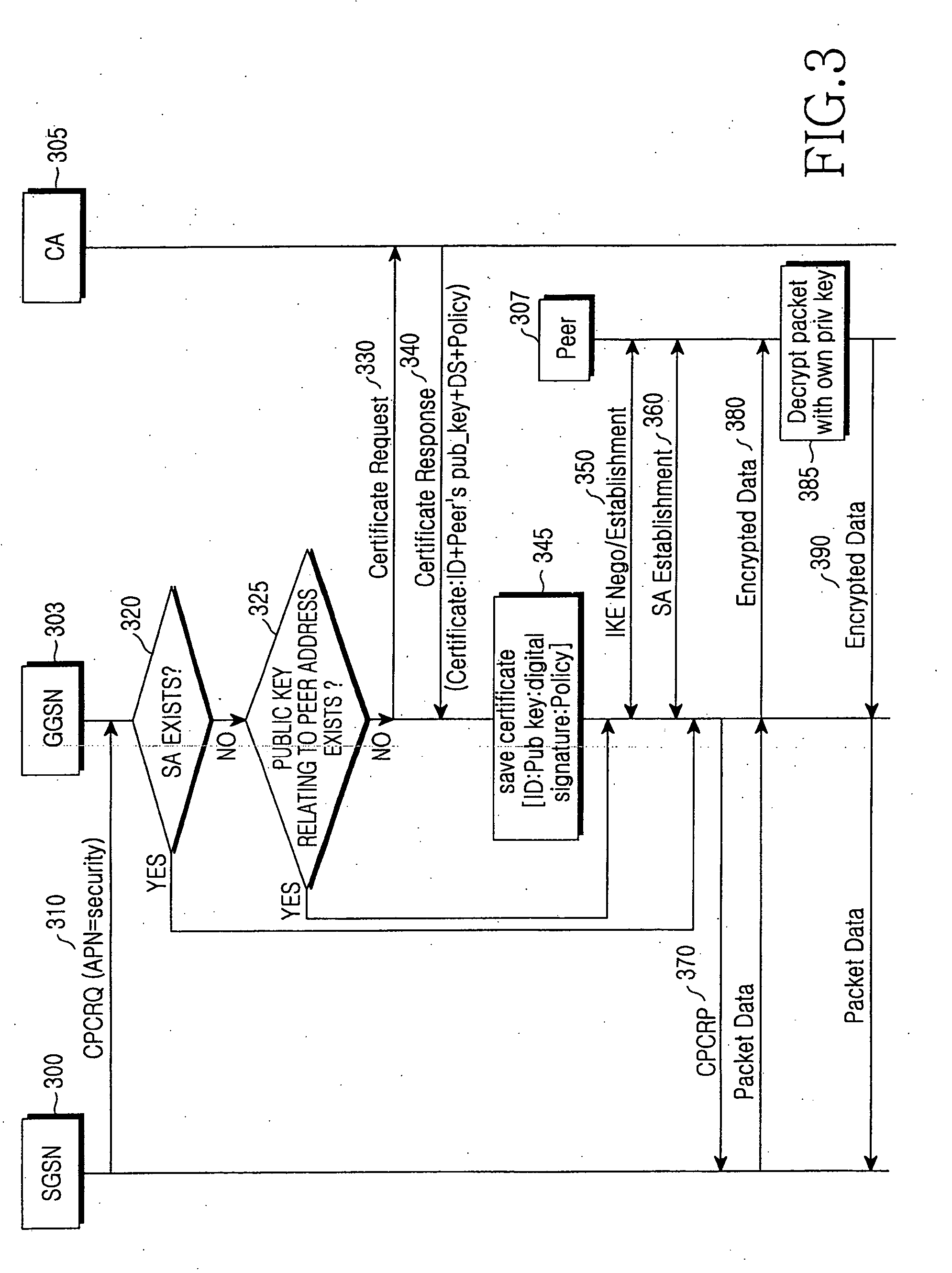
Method and apparatus for security of IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure in mobile communication network
InactiveUS20060105741A1Applied load reductionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
A method and apparatus is provided for security of an IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure, including the steps of receiving a request message which relates to a security service requested by a mobile node, determining if there is security association (SA) for the security service and determining if there is a public key related to a peer address when the SA does not exist, sending a certificate request message to a certificate authority (CA) when the public key does not exist and receiving a certificate response message which has a certificate that includes a public key. The method further includes the steps of performing an internet key exchange and SA establishment procedure with a peer corresponding to the peer address by using the certificate, completing the internet key exchange and the SA establishment, and encrypting a packet received from the mobile node, transmitting the encrypted packet to the peer, decrypting a packet received from the peer, and transmitting the decrypted packet to the mobile node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Certificate-based encryption and public key infrastructure
InactiveUS20050246533A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptosystemSingle entity
The present invention provides methods for sending a digital message from a sender (606) to a recipient (608) in a public-key based cryptosystem comprising an authorizer (606). The authorizer can be a single entity (606) or comprise a hierarchical or distributed entity (602, 604a-604b). The present invention allows communication of messages by an efficient protocol, not involving key status queries or key escrow, where a message recipient (608) can decrypt a message from a message sender (606) only if the recipient (608) possesses up-to-date authority from the authorizer. The invention allows such communication in a system comprising a large number (e.g. millions) of users.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
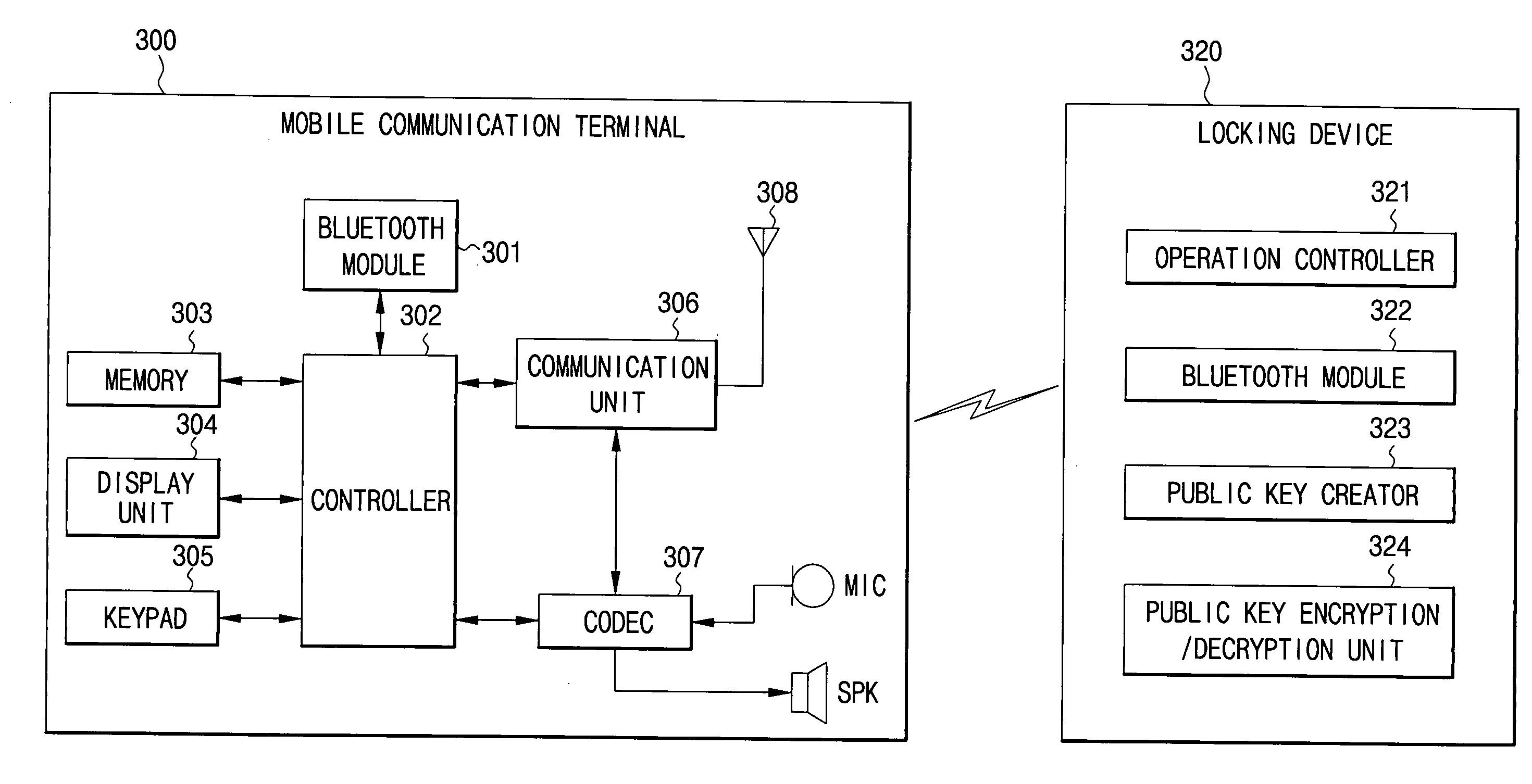
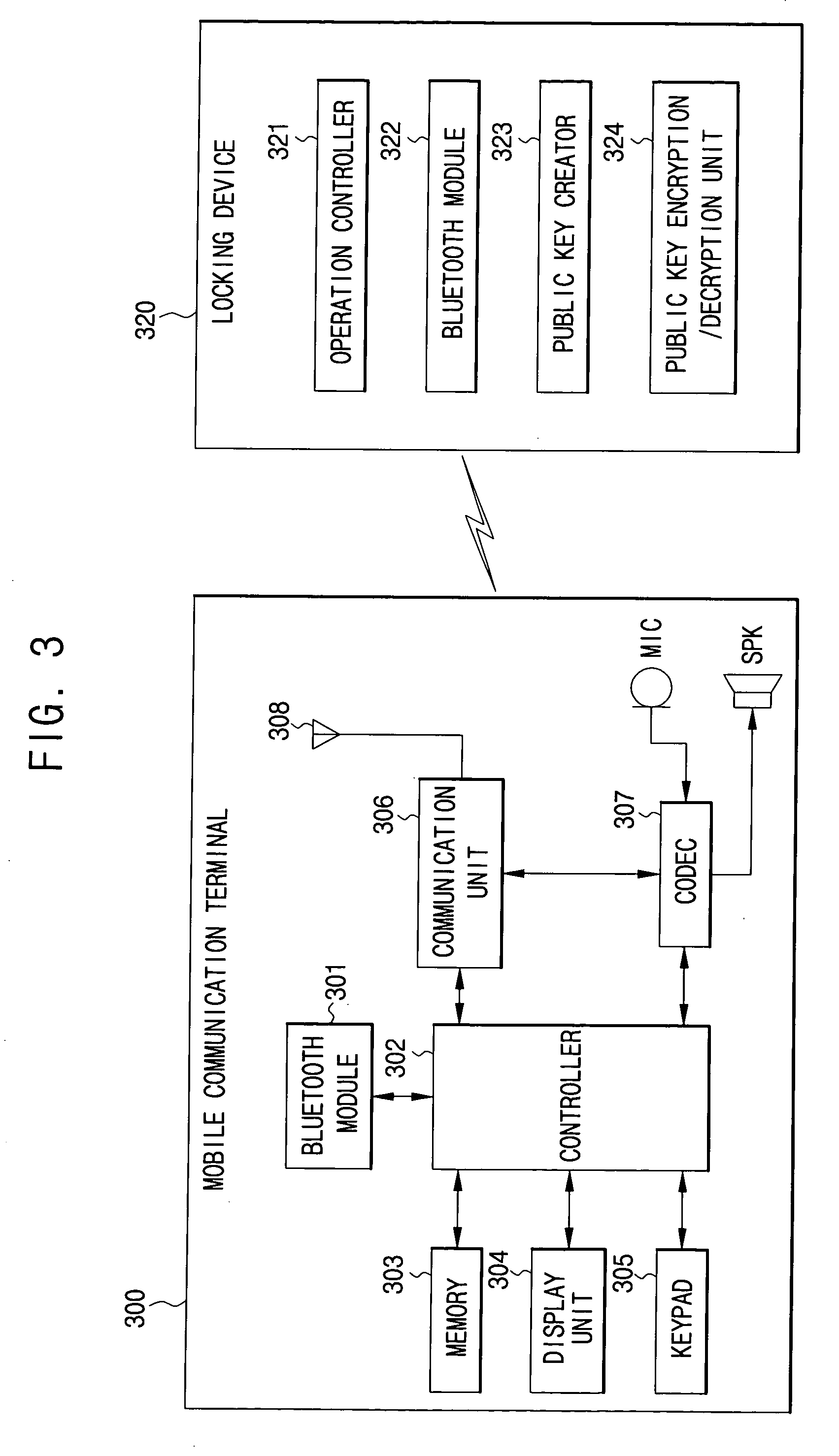
Public key infrastructure-based bluetooth smart-key system and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20090136035A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationData transmissionEmbedded system
A public key infrastructure (PKI)-based Bluetooth smart-key system and operating method thereof. The system includes a locking device and a mobile communication terminal. The locking device enables Bluetooth communication and enables PKI-based data transmission. The mobile communication terminal embedded with a Bluetooth module performs a remote unlocking or keyless entry function through Bluetooth communication with the locking device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Group key distribution
InactiveUS6215878B1Efficient additionLow costKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTimestampNetwork addressing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
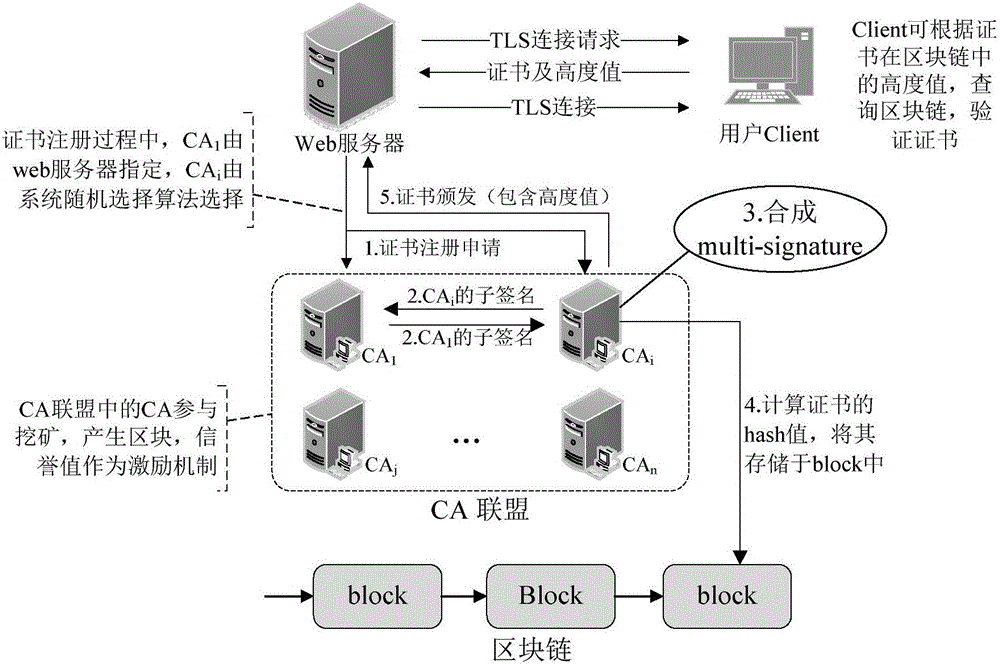
Block chain based PKI (public key infrastructure) system and semi-random joint certificate signature method
ActiveCN106789090ANot tampered withNot forgedUser identity/authority verificationWeb serviceCertificate authority
The invention discloses a block chain based PKI (public key infrastructure) system and a semi-random joint certificate signature method. The system comprises a user Client, a Web server and a plurality of CAs (certificate authorities), wherein the plurality of CAs constitute a CA coalition; the Web server applies to the plurality of CAs for a certificate, the plurality of CAs sign jointly, then the certificate is stored in a block chain, after storage, the CAs issue the certificate to the Web server, and when the user Client and the Web server are in TLS connection, the user Client needs to verify the legitimacy of the certificate of the Web server.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
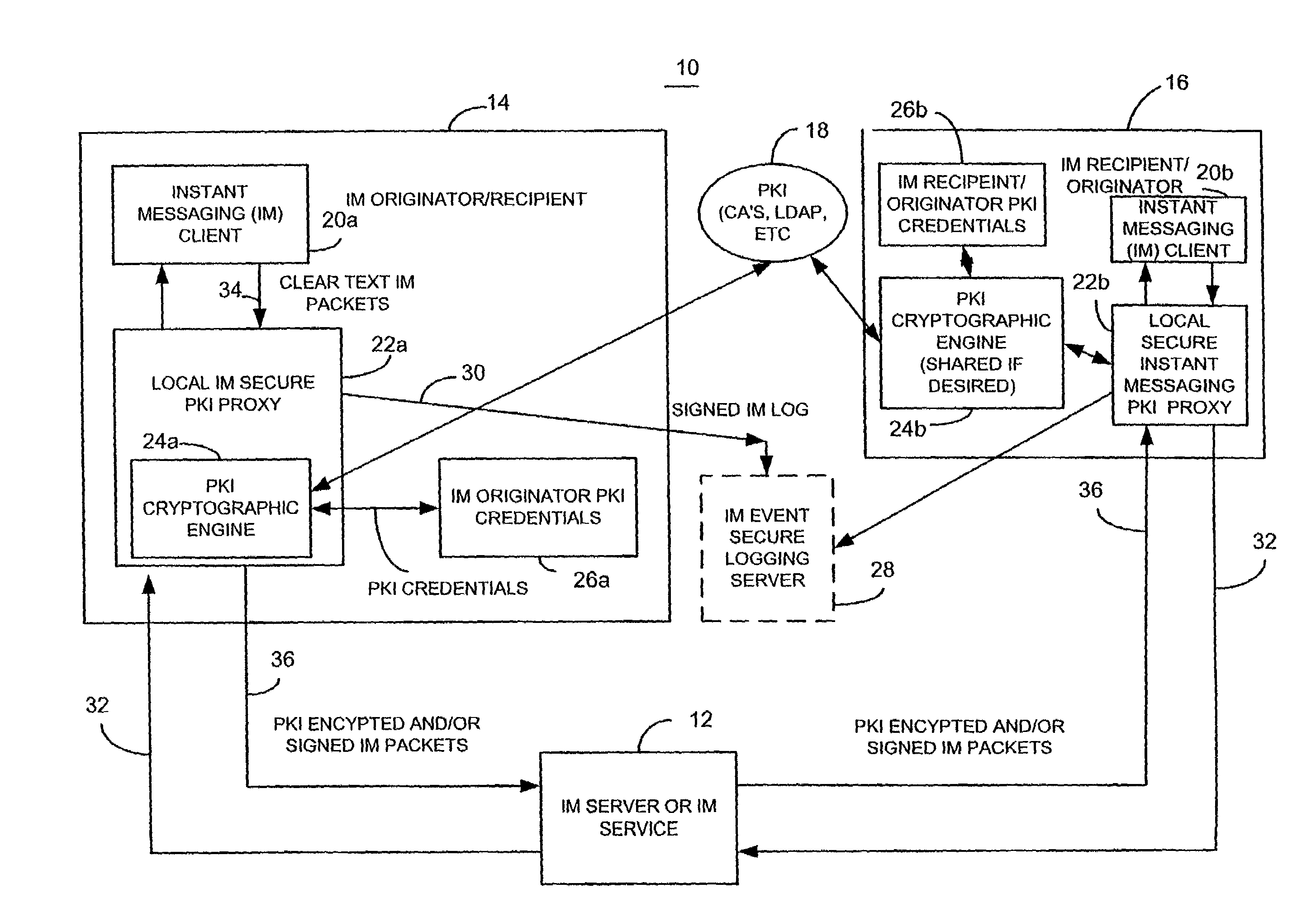
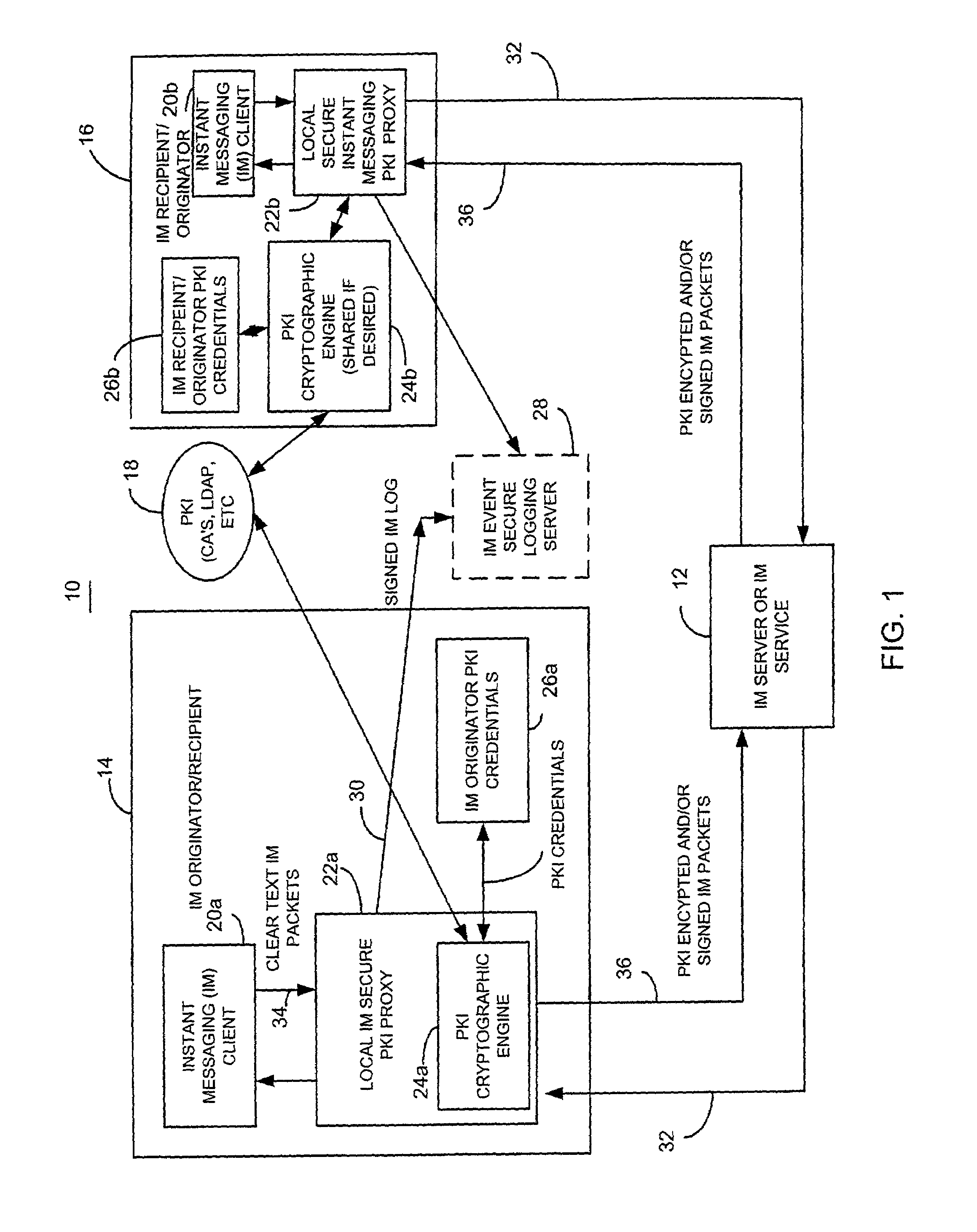
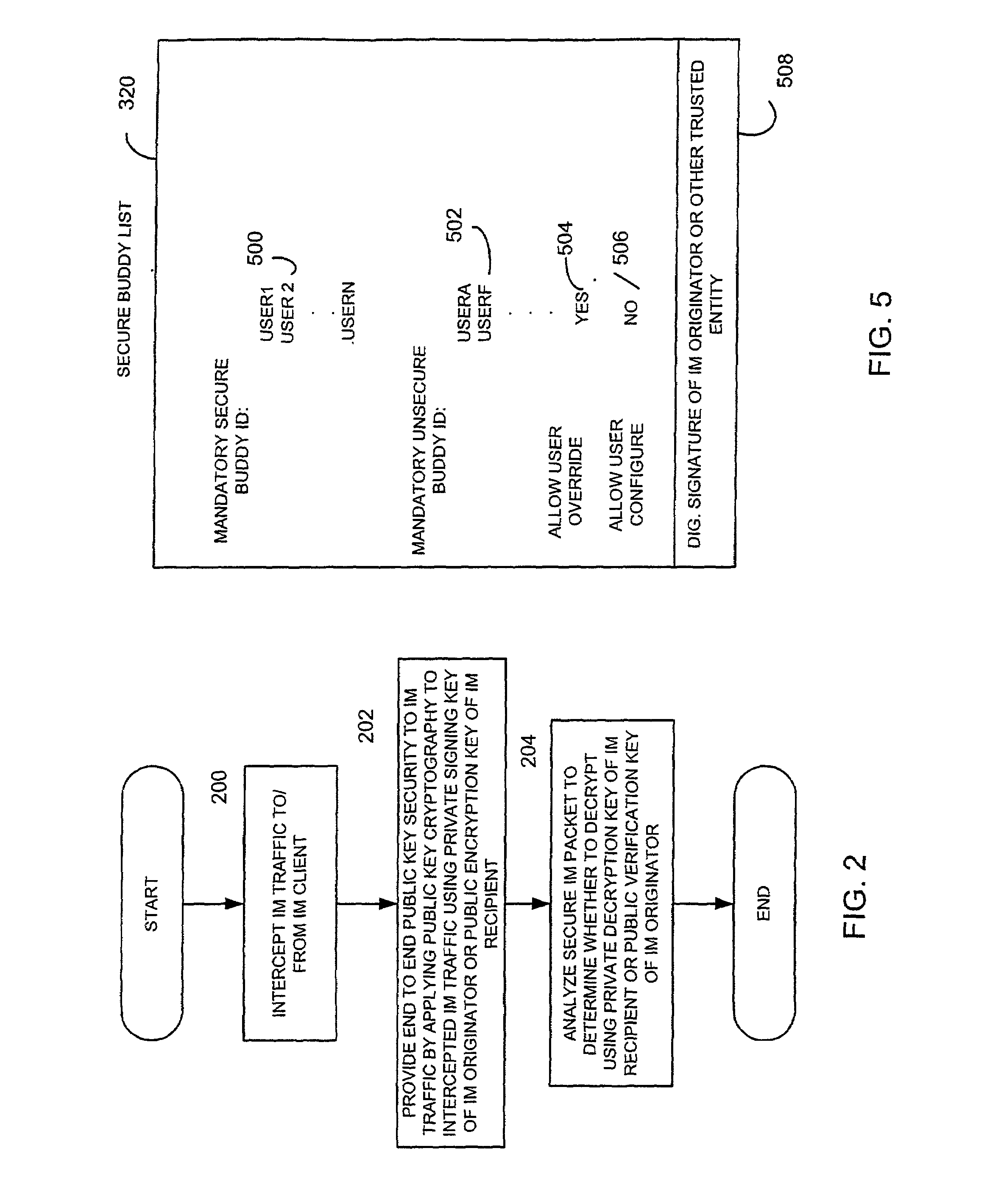
Secure instant messaging system using instant messaging group policy certificates
A method and apparatus for facilitating instant messaging utilizes a secure instant message group policy certificate issued by an instant messaging public key infrastructure policy certificate issuing unit. The secure instant messaging group policy certificate is received, such as through a local instant messaging secure public key infrastructure proxy, and contains data defining the group members, references to other groups, security controls and relevant data such as allowed algorithms. The secure instant messaging group policy certificate defines a plurality of different instant messaging groups, each identified by an instant messaging group identifier. Each instant messaging group identifier is associated with a plurality of instant message group number identifiers.
Owner:CYGNACOM SOLUTION INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com