Patents
Literature
2662 results about "Session key" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A session key is a single-use symmetric key used for encrypting all messages in one communication session. A closely related term is content encryption key (CEK), traffic encryption key (TEK), or multicast key which refers to any key used to encrypt messages, as opposed to other uses, like encrypting other keys (key encryption key (KEK) or key wrapping key).
Methods for secure cryptogram generation
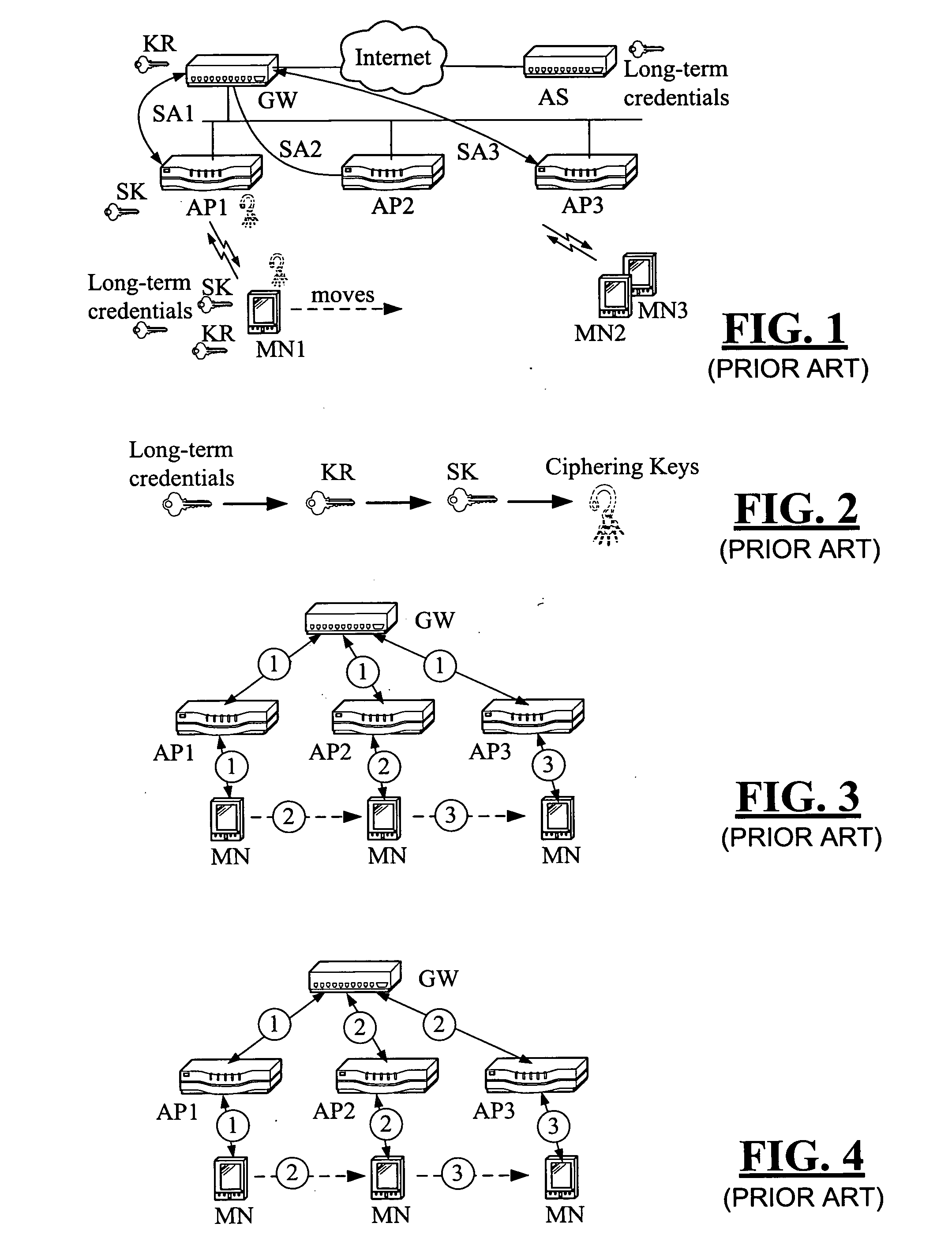
ActiveUS20160065370A1Avoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationUser device
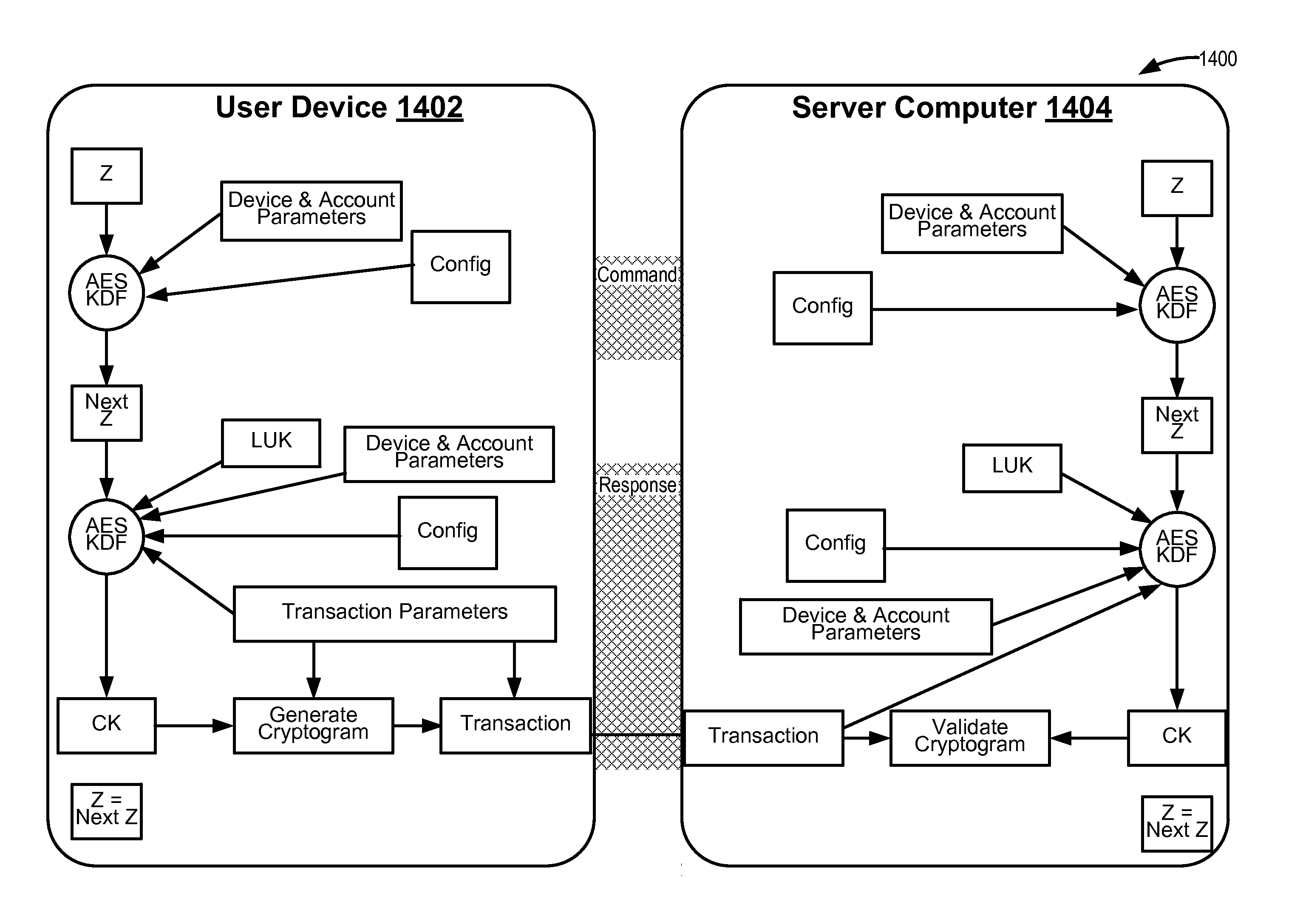
Embodiments of the invention introduce efficient methods for securely generating a cryptogram by a user device, and validating the cryptogram by a server computer. In some embodiments, a secure communication can be conducted whereby a user device provides a cryptogram without requiring the user device to persistently store an encryption key or other sensitive data used to generate the cryptogram. For example, the user device and server computer can mutually authenticate and establish a shared secret. Using the shared secret, the server computer can derive a session key and transmit key derivation parameters encrypted using the session key to the user device. The user device can also derive the session key using the shared secret, decrypt the encrypted key derivation parameters, and store the key derivation parameters. Key derivation parameters and the shared secret can be used to generate a single use cryptogram key. The cryptogram key can be used to generate a cryptogram for conducting secure communications.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
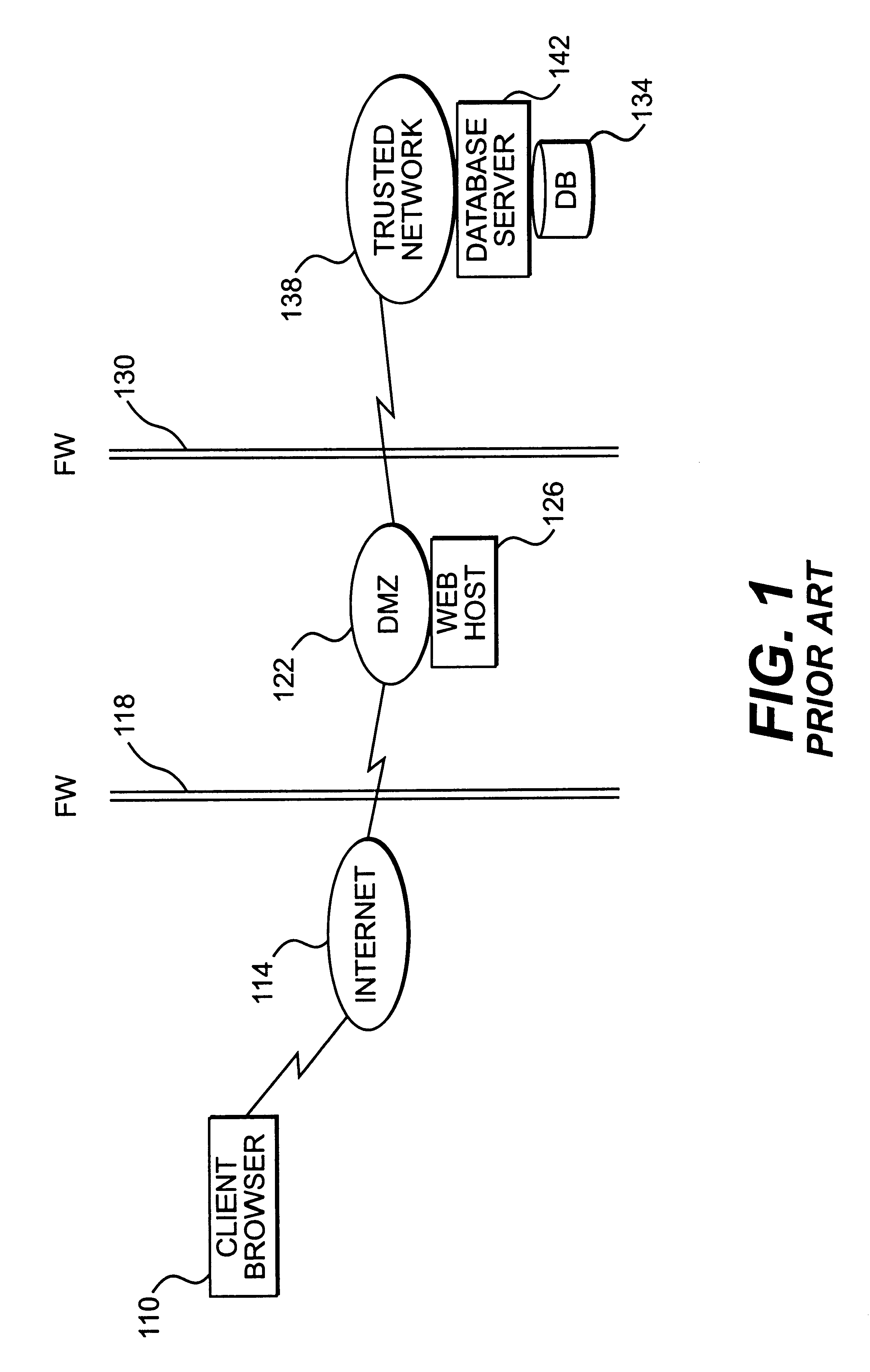
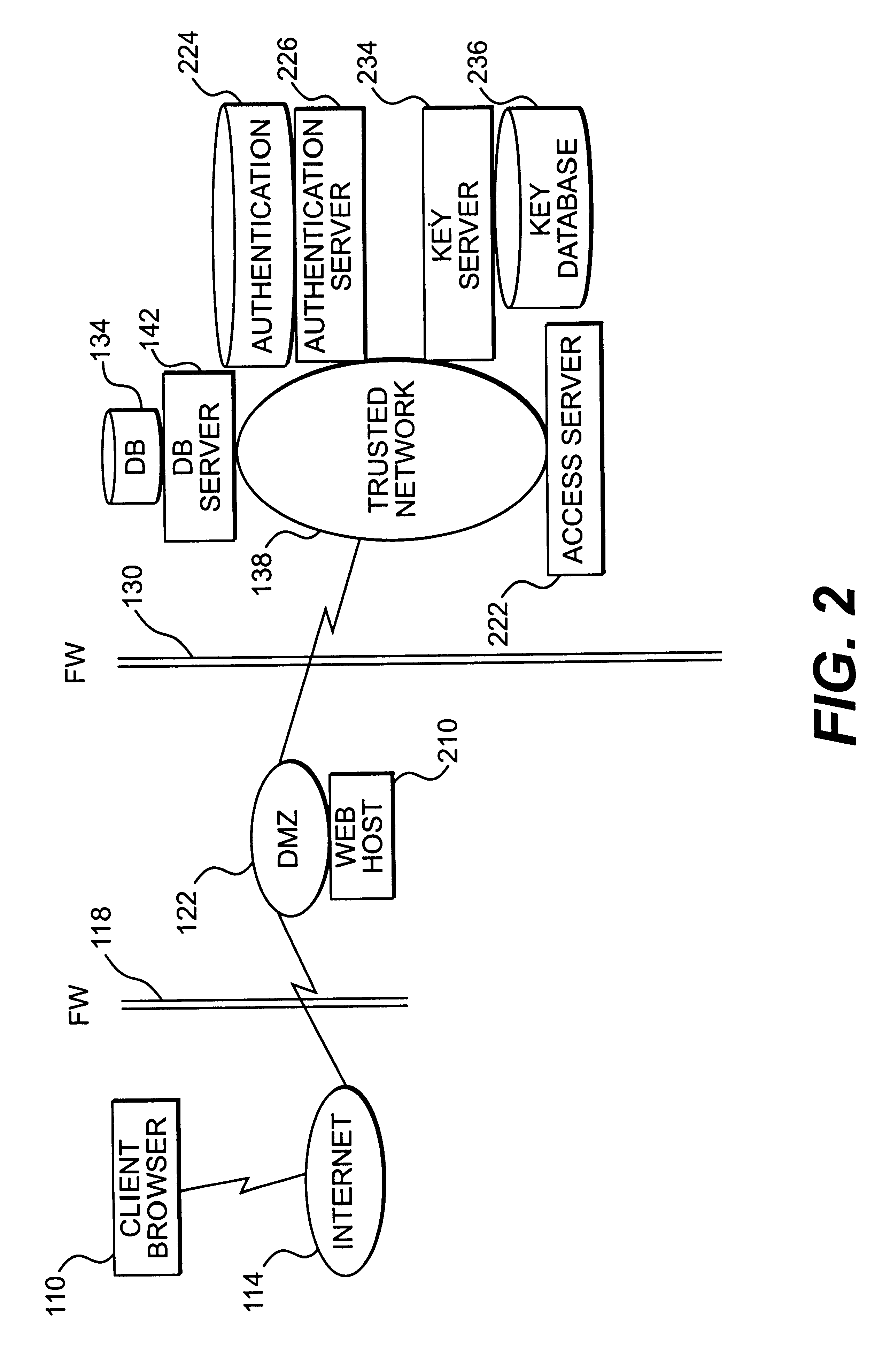
Apparatus and method for providing trusted network security
InactiveUS6199113B1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork packetNetwork security policy
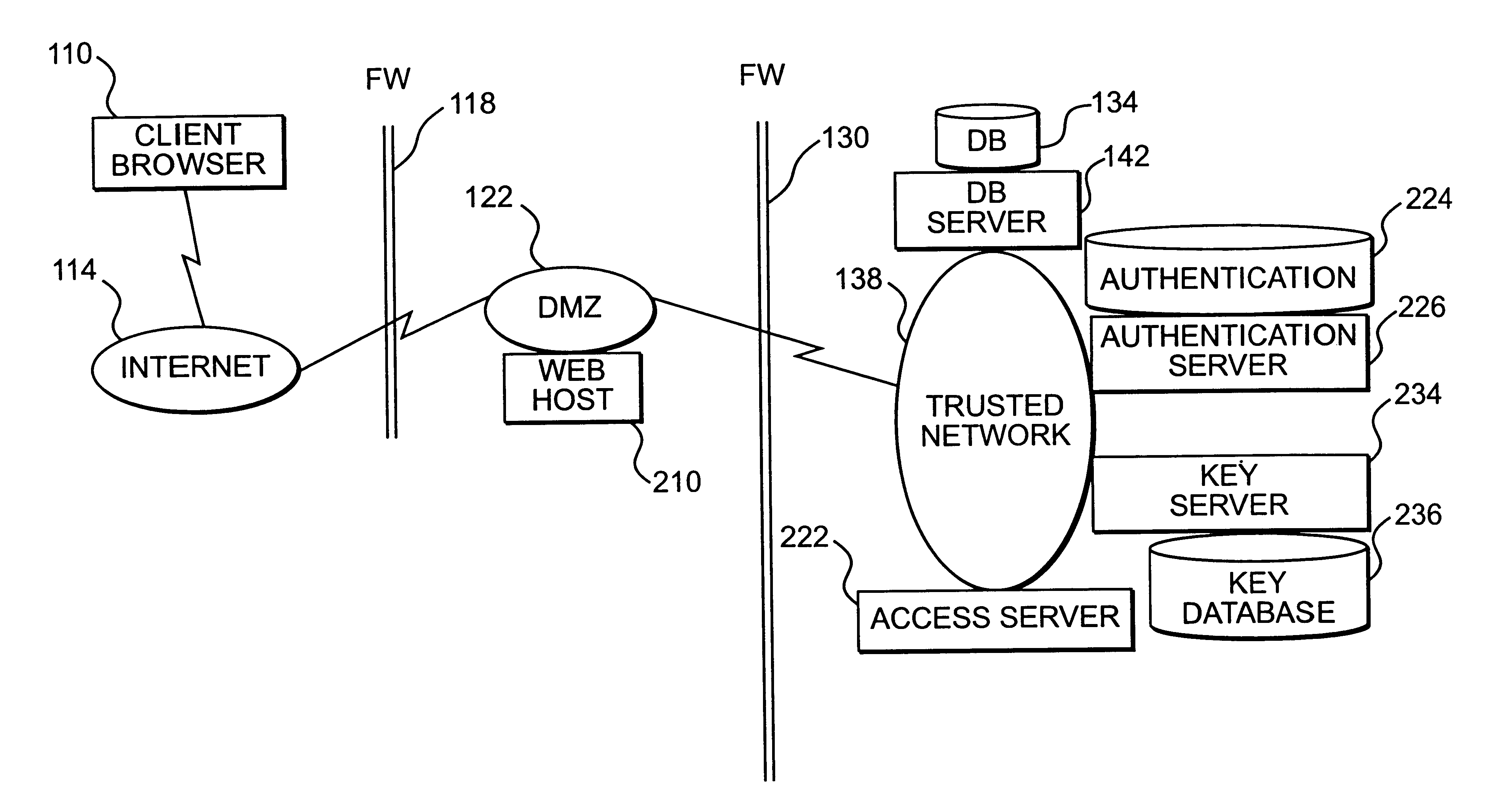
A session key is established for accessing a trusted network from a browser. An authentication process receives identification information from a user at the browser, and authenticates the user by checking the identification information against an authentication database. If the authentication database authenticates the user, a session key is created and stored at the browser. If the user is authenticated, a user profile defining access rights for the user is also retrieved. The user is then presented with access options based on the access rights defined in the user profile. In response to a user selection from the access page, the browser forwards an information request to the trusted network. The request includes a session key. A speaker object processes the information request and session key to form a network request packet. The network request packet is formed in a manner that allows authentication of the speaker object. The session packet is forwarded to a trusted network and processed. The packet is first authenticated to determine if it originated from the speaker object, and then the key is checked for validity at the trusted server. If the key is valid, the information request is processed and the information is returned to the user for display on the browser.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for creating a secure communication channel among multiple event service nodes
InactiveUS7013389B1Easy to scaleUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationGroup session
An approach for establishing secure multicast communication among multiple event service nodes is disclosed. The event service nodes, which can be distributed throughout an enterprise domain, are organized in a logical tree that mimics the logical tree arrangement of domains in a directory server system. The attributes of the event service nodes include the group session key and the private keys of the event service nodes that are members of the multicast or broadcast groups. The private keys provide unique identification values for the event service nodes, thereby facilitating distribution of such keys. Because keys as well as key version information are housed in the directory, multicast security can readily be achieved over any number of network domains across the entire enterprise. Key information is stored in, and the logical tree is supported by, a directory service. Replication of the directory accomplishes distribution of keys. Event service nodes may obtain current key information from a local copy of the replicated directory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Token security on a communication device
ActiveUS20150312038A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureUser authenticationHash table
Techniques for enhancing the security of storing sensitive information or a token on a communication device may include sending a request for the sensitive information or token. The communication device may receive a session key encrypted with a hash value derived from user authentication data that authenticates the user of the communication device, and the sensitive information or token encrypted with the session key. The session key encrypted with the hash value, and the sensitive information or token encrypted with the session key can be stored in a memory of the communication device.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Method and system to securely distribute content via a network
InactiveUS6993137B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSession keyContent delivery
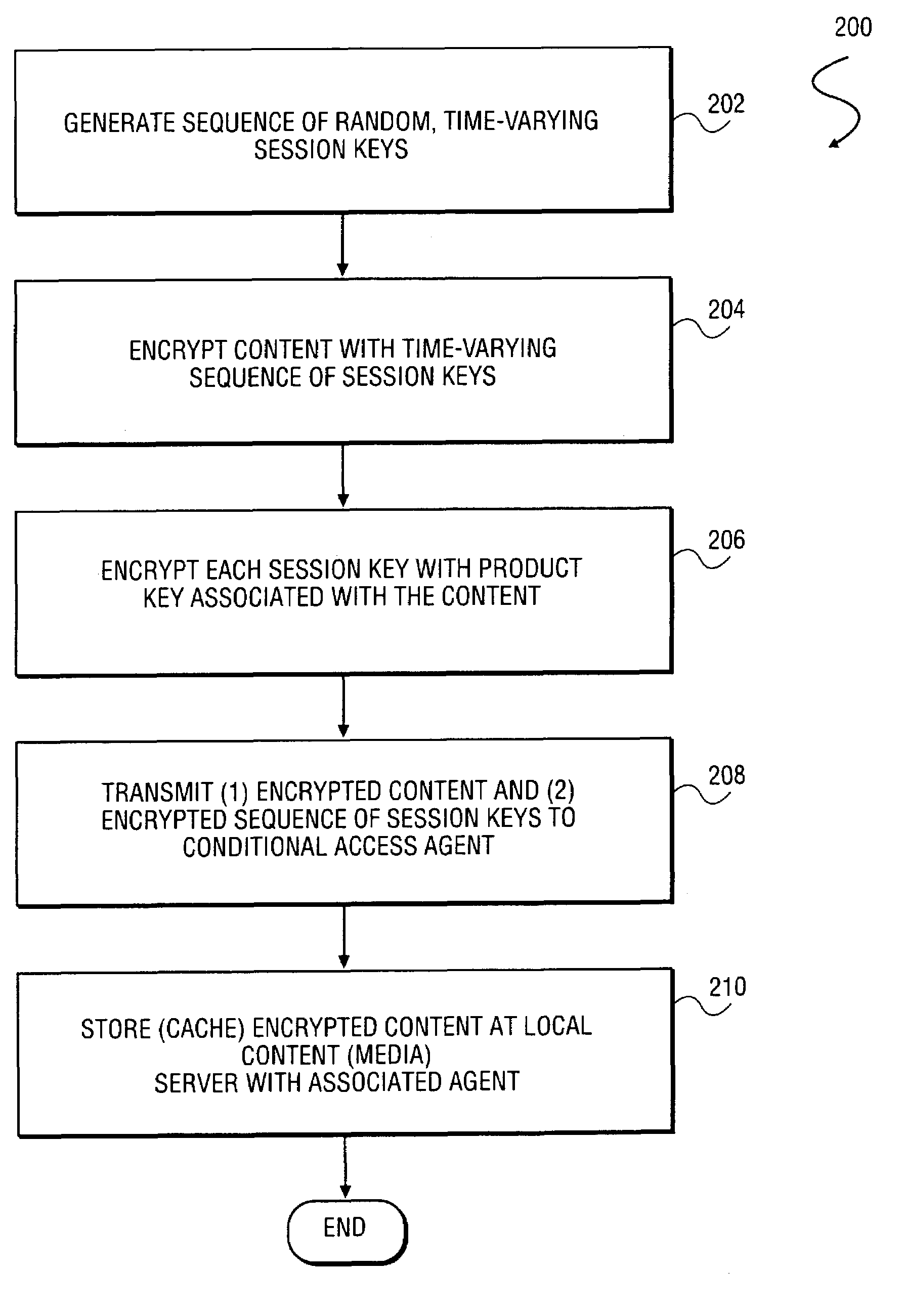
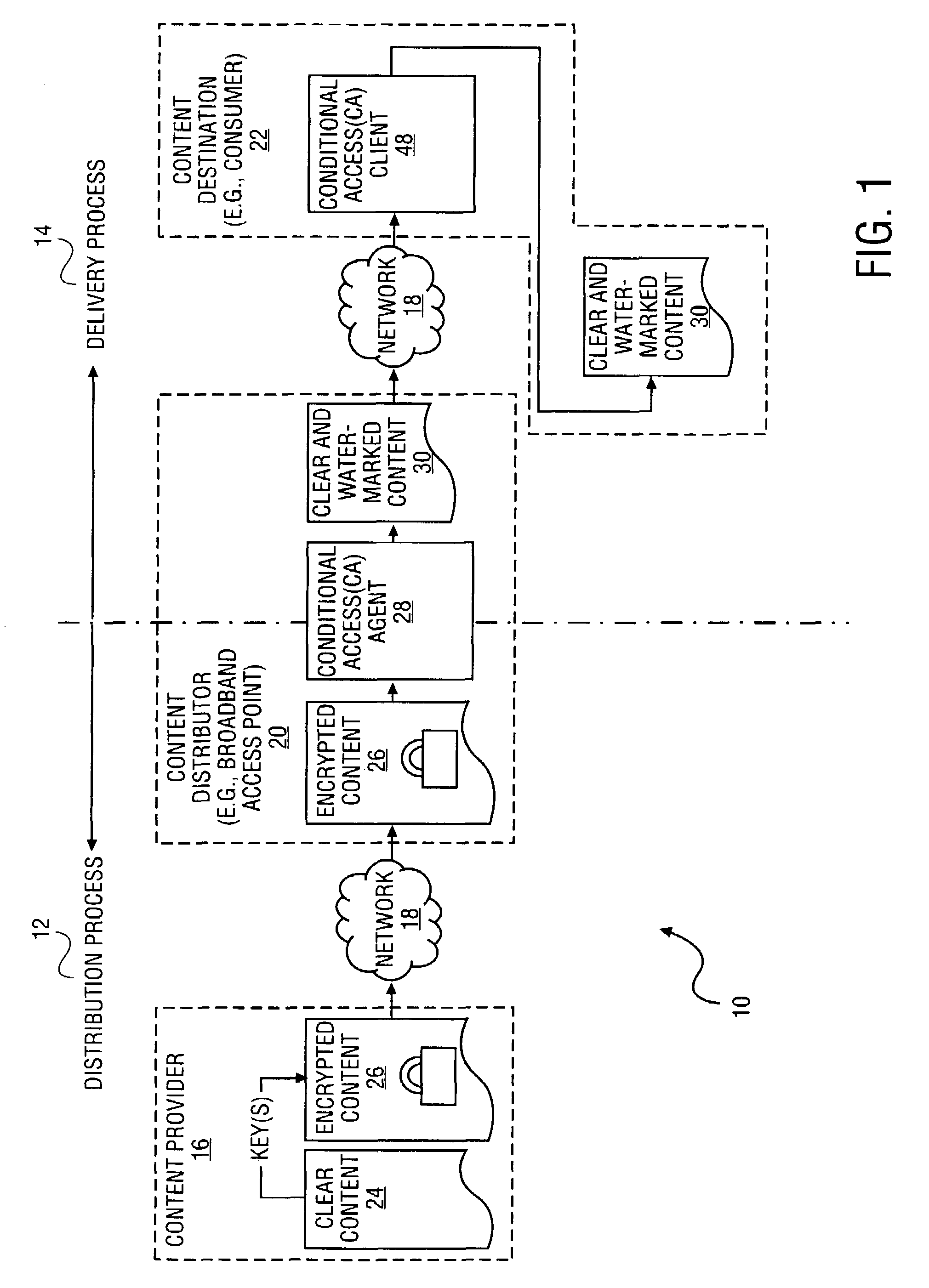
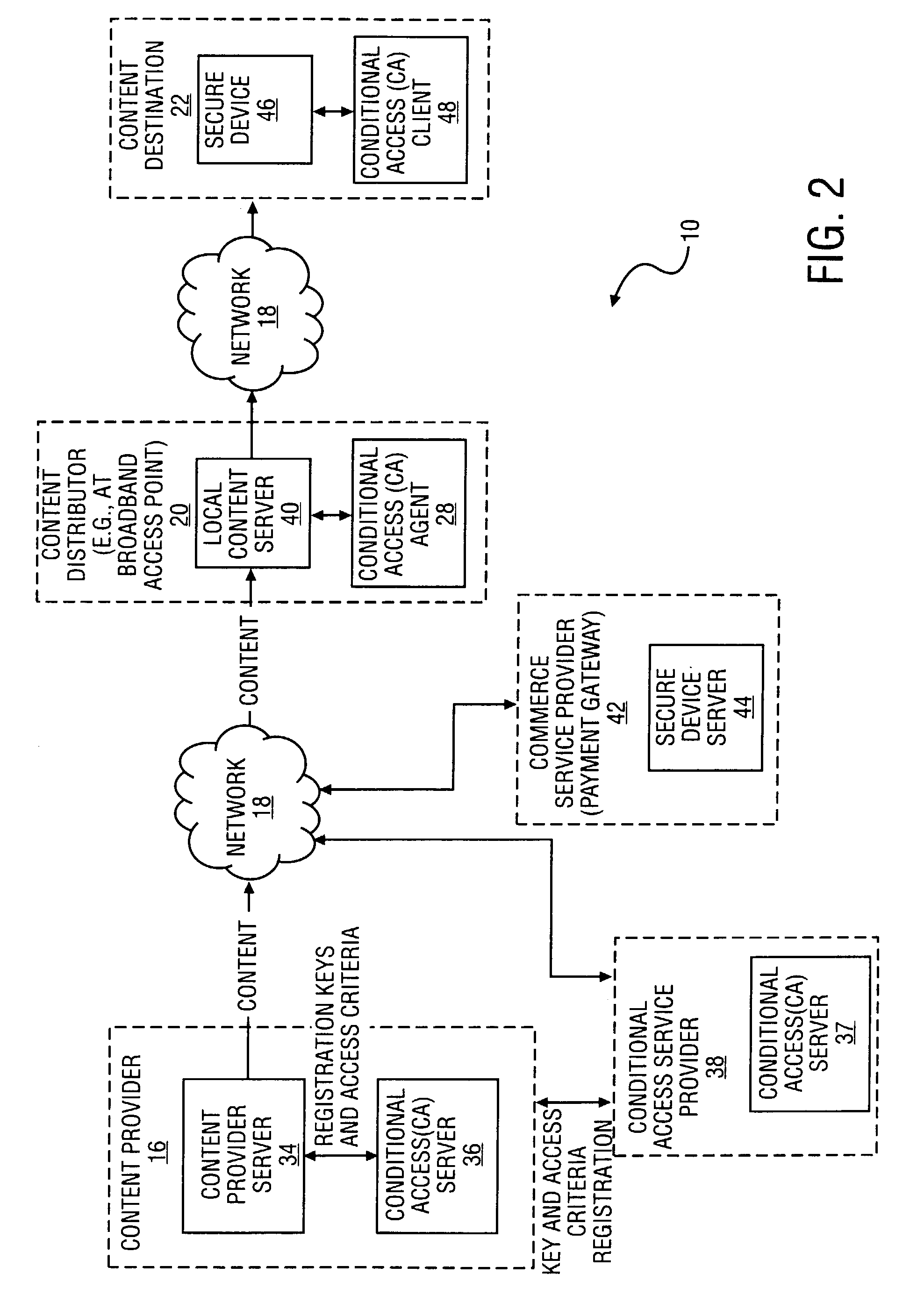
A method and system to distribute encrypted content via a network commences when a content provider generates a set of session keys and encrypts content with the set of session keys. The content provider communicates the set of session keys to a content distributor, which generates a set of encrypted session keys by encrypting the set of session keys with a user key. The content distributor transmits the encrypted content and the encrypted session keys to a content destination. The content distributor also transmits the user key to the content destination, allowing the content destination to decrypt the set of session keys with the user key, and thereby use the set of decrypted session keys to decrypt the content. In a further embodiment of the invention, the session keys are a time-varying sequence of session keys.
Owner:MIH TECH HLDG BV
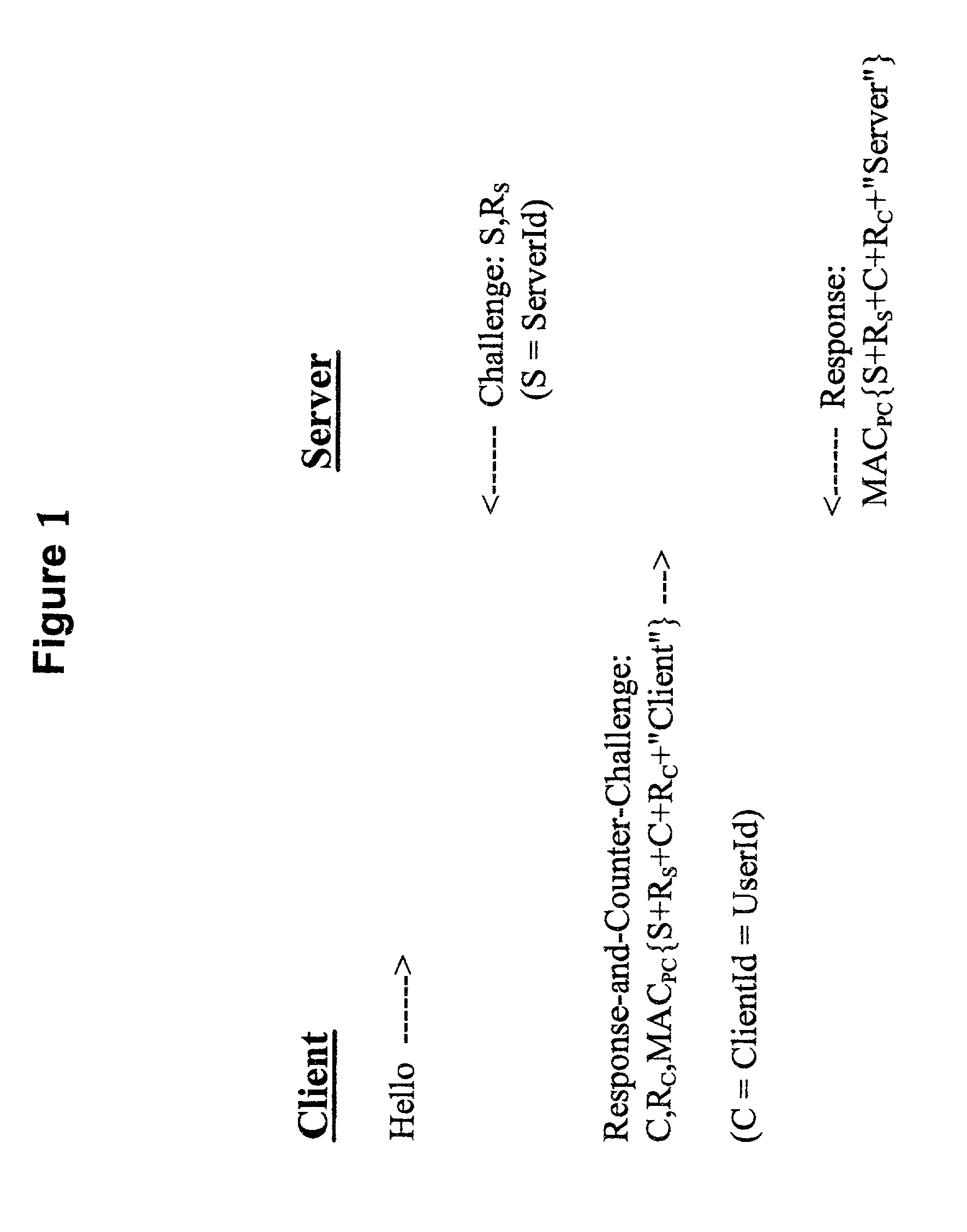
Methods, apparatus and computer programs performing a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol using operating system capabilities
InactiveUS20030093680A1Avoids security exposureMeet growth requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsOperational systemCrypt
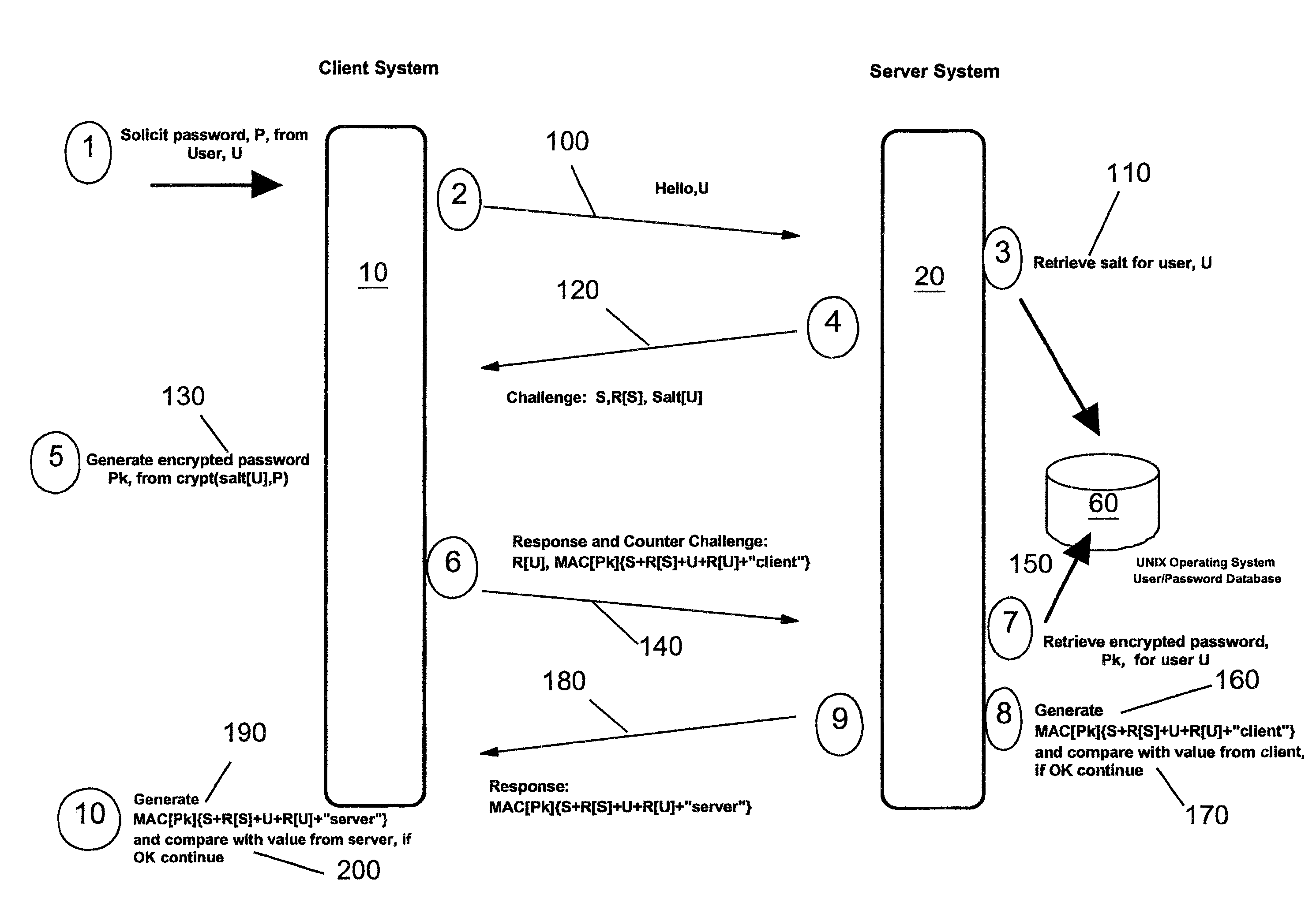
A client-server authentication method for use where a server process has access to a repository storing cipher-protected client passwords. The method includes applying the same cipher function to the client's copy of its password as was previously applied to generate the stored cipher-protected client passwords. This ensures that both the client and server have access to an equivalent cipher-protected client password-providing a shared secret for driving a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol without having to convert the password into cleartext at the server. The invention can be implemented without significant additional software infrastructure in a UNIX environment. Client passwords are typically stored in the UNIX password repository under the protection of the crypt( ) function applied to the combination of the password and a random number (a "salt'). By sending the salt to the client system together with the server's initial challenge of the authentication protocol, a process at the client is able to apply the crypt( ) function to the client password with the same salt such that the client and server have a shared secret for use as, or to generate, a common session key for the authentication.
Owner:IBM CORP
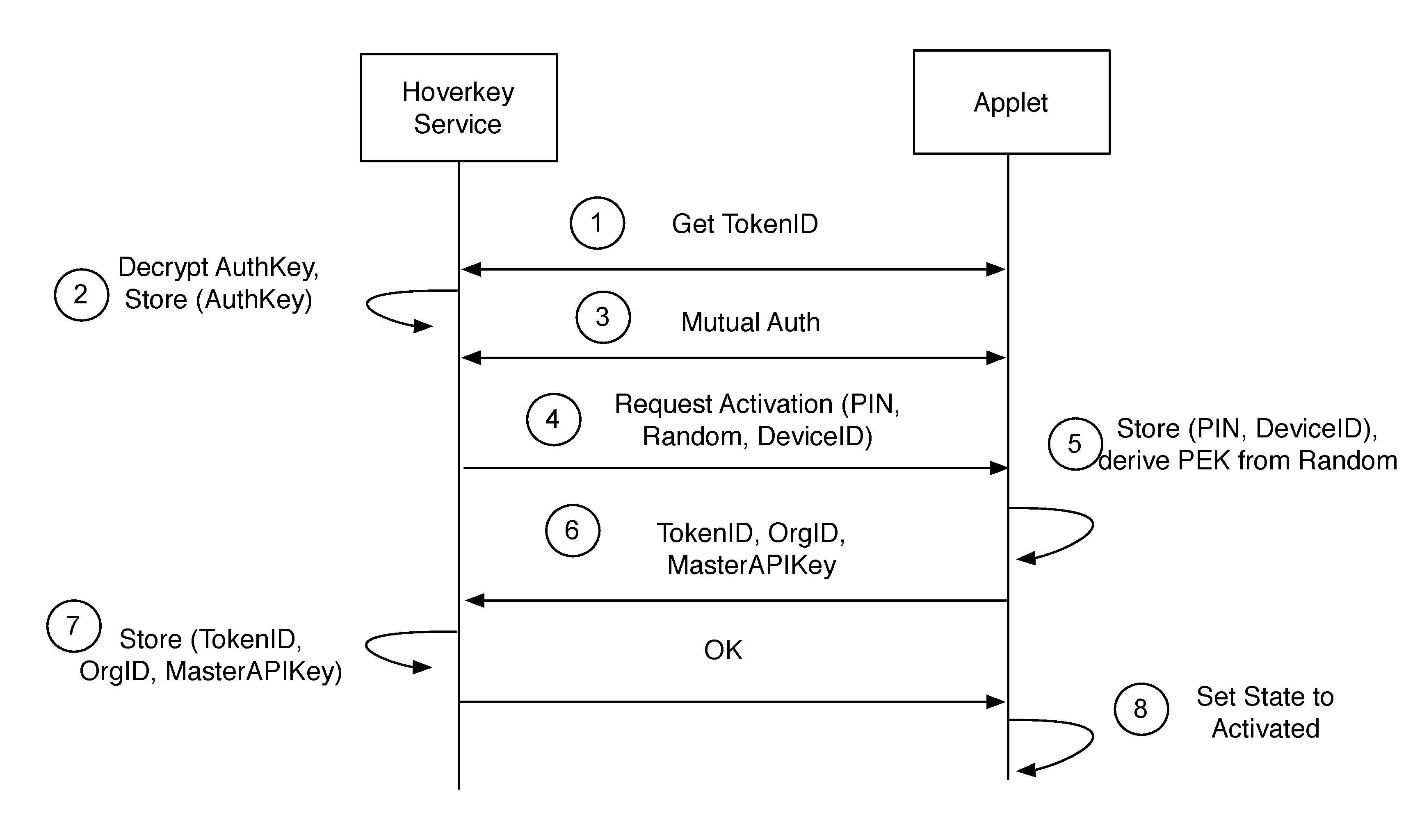
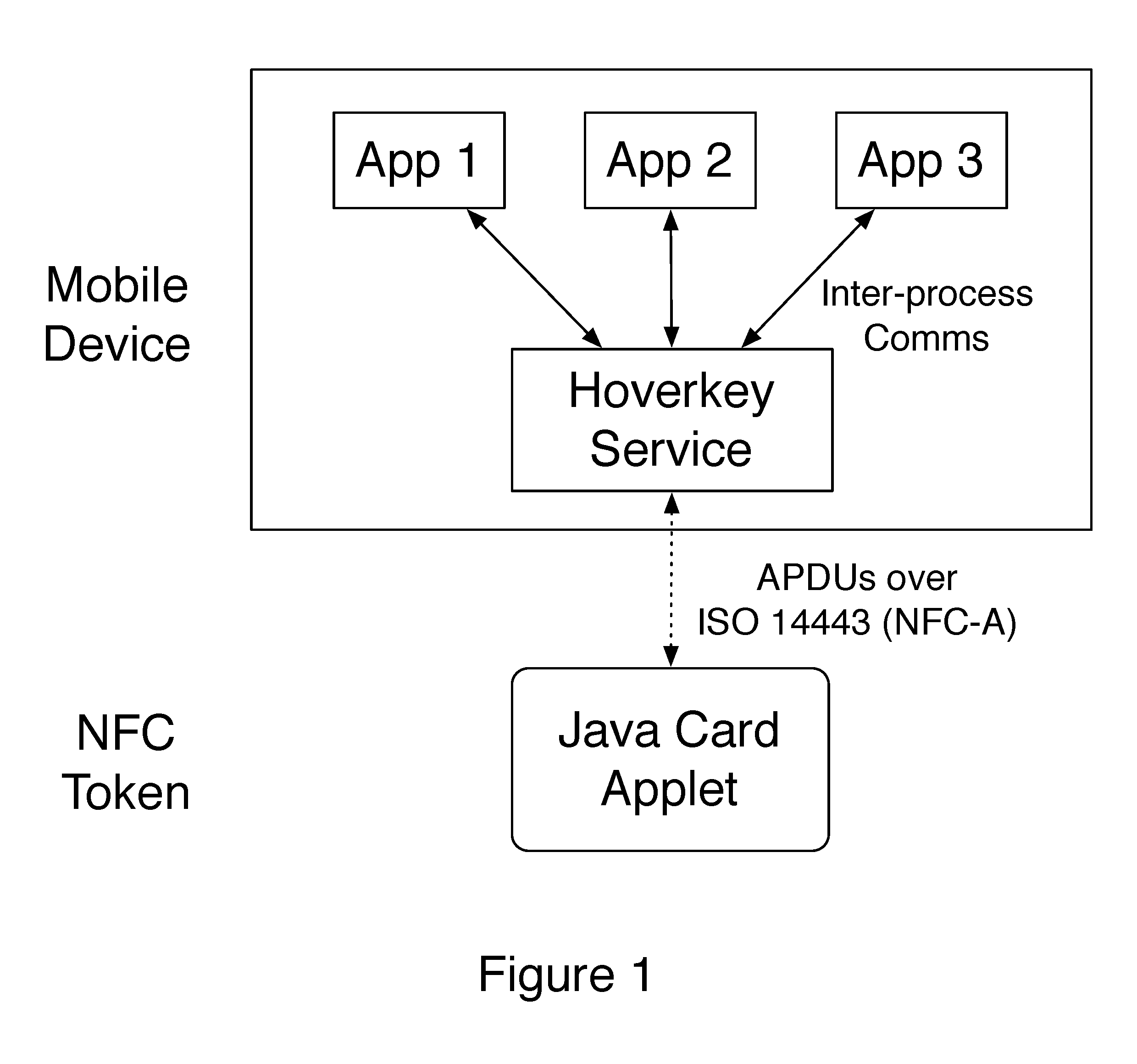
Method and system of providing authentication of user access to a computer resource via a mobile device using multiple separate security factors
ActiveUS20160261411A1Easy to rememberPromote cloningKey distribution for secure communicationCryptography processingComputer resourcesPassword
A method and system of authenticating a computer resource such as an application or data on a mobile device uses a contactless token to provide multi-factor user authentication. User credentials are stored on the token in the form of private keys, and encrypted data and passwords are stored on the device. When an application user requires access to the resource an encrypted password is transmitted to and decrypted on the token using a stored key. An unencrypted data encryption key or password is then transmitted back to the device under the protection of a cryptographic session key which is generated as a result of strong mutual authentication between the device and the token.
Owner:HOVERKEY
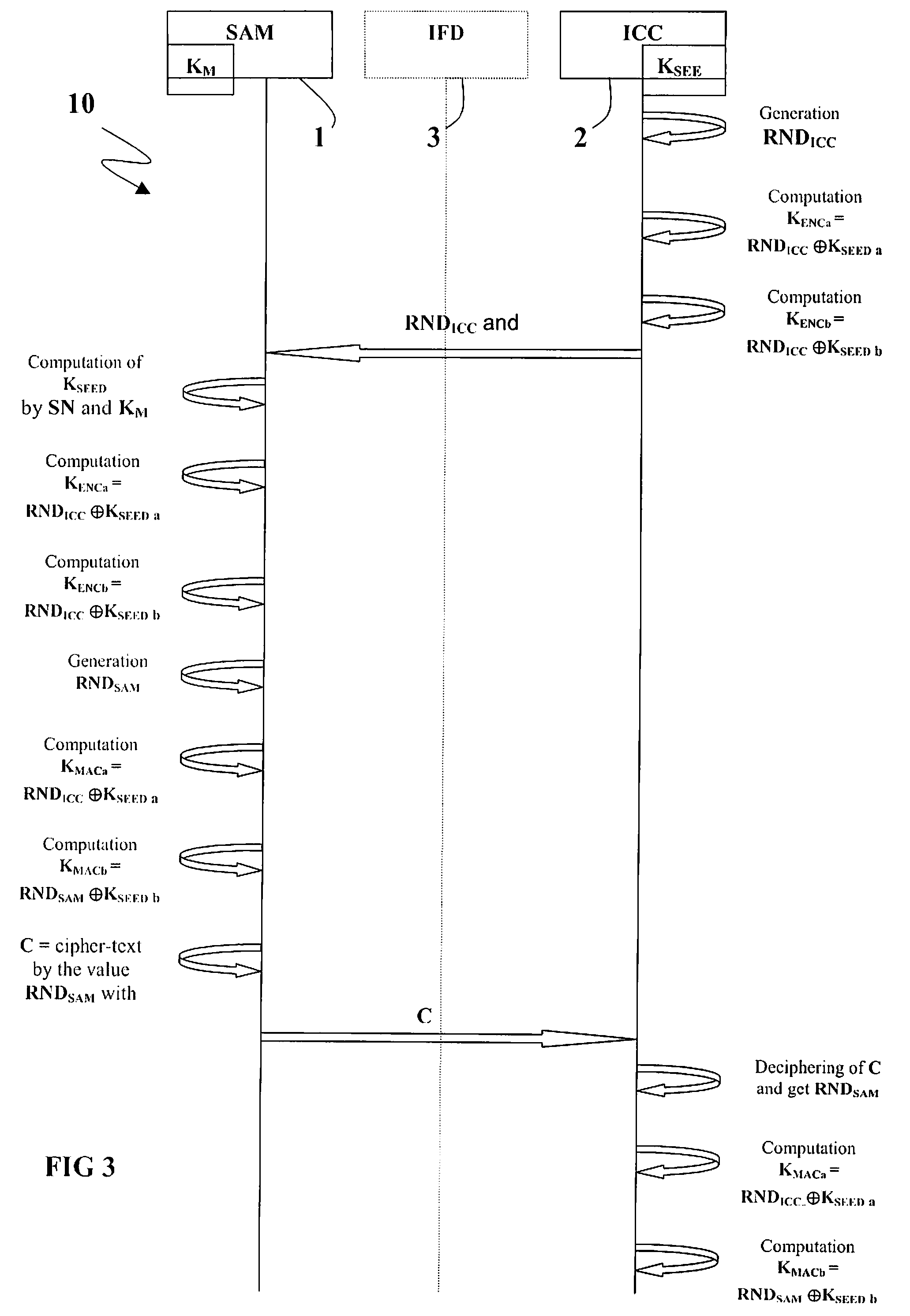
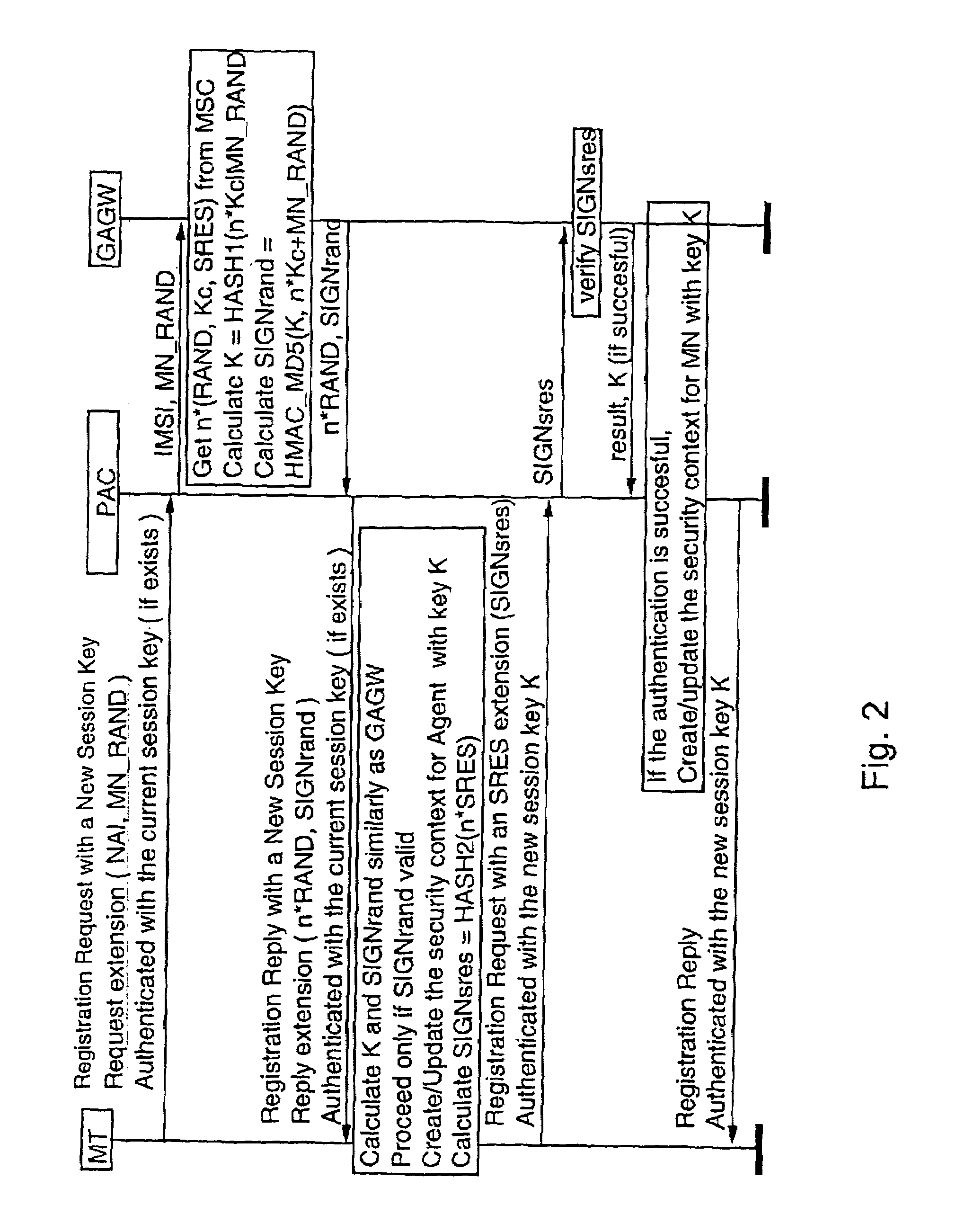
Method for Session Key Derivation in an IC Card
ActiveUS20080008322A1Shorten the timeAcutation objectsKey distribution for secure communicationCommunication interfaceMaster key
A key session derivation is provided during a mutual authentication between a master IC card storing a master key, and a user IC card storing a key-seed. The master IC card and the user IC card are connected through a communication interface for a communication session. A first random number associated to the user IC card is generated. First and second sub keys are derived from the key-seed. First and second session sub keys are respectively derived through the first sub key in combination with the first random number, and through the second sub key in combination with the first random number. The first and second session sub keys are joined in at least a session key for the communication session.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Fast authentication and access control system for mobile networking
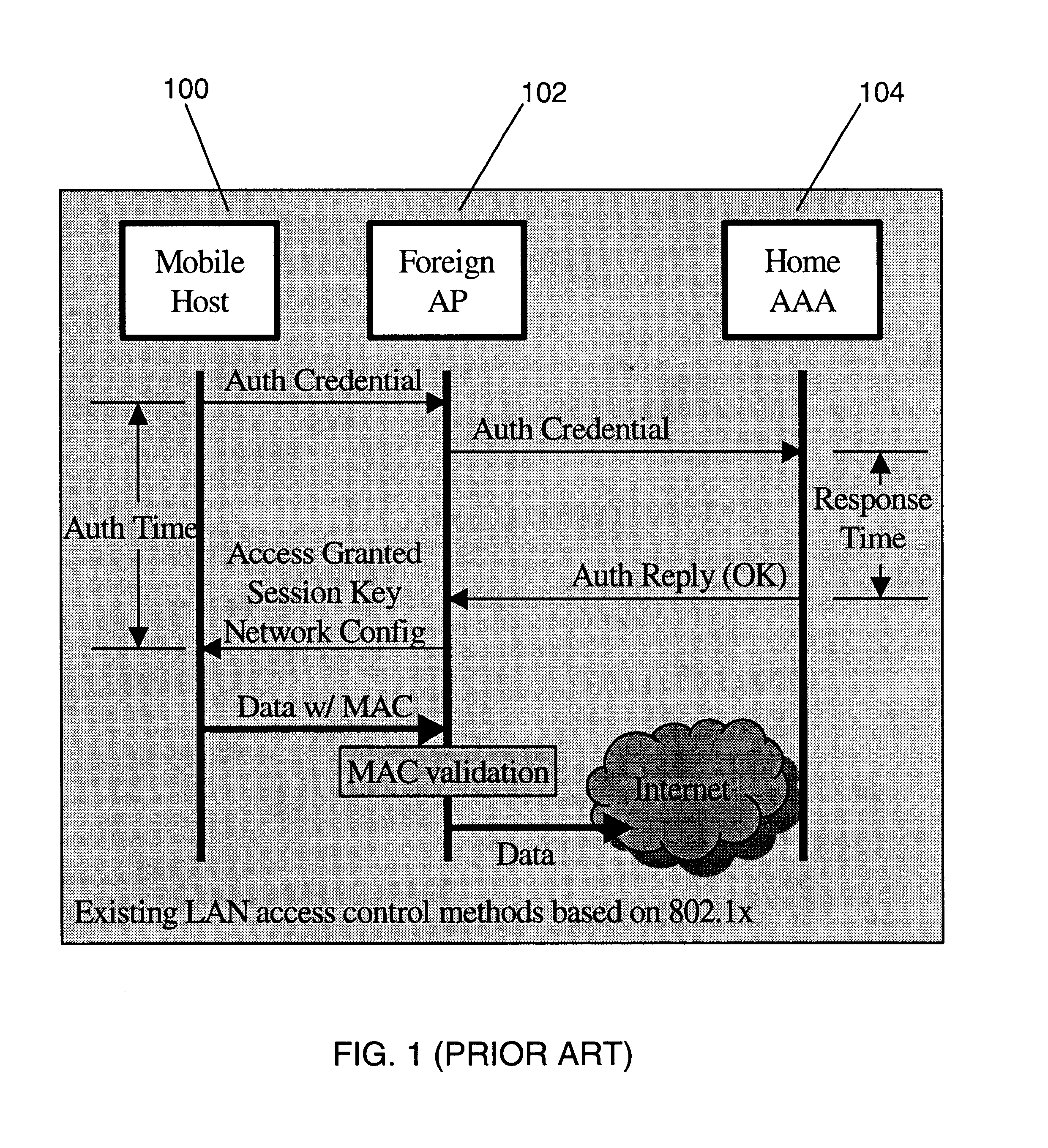
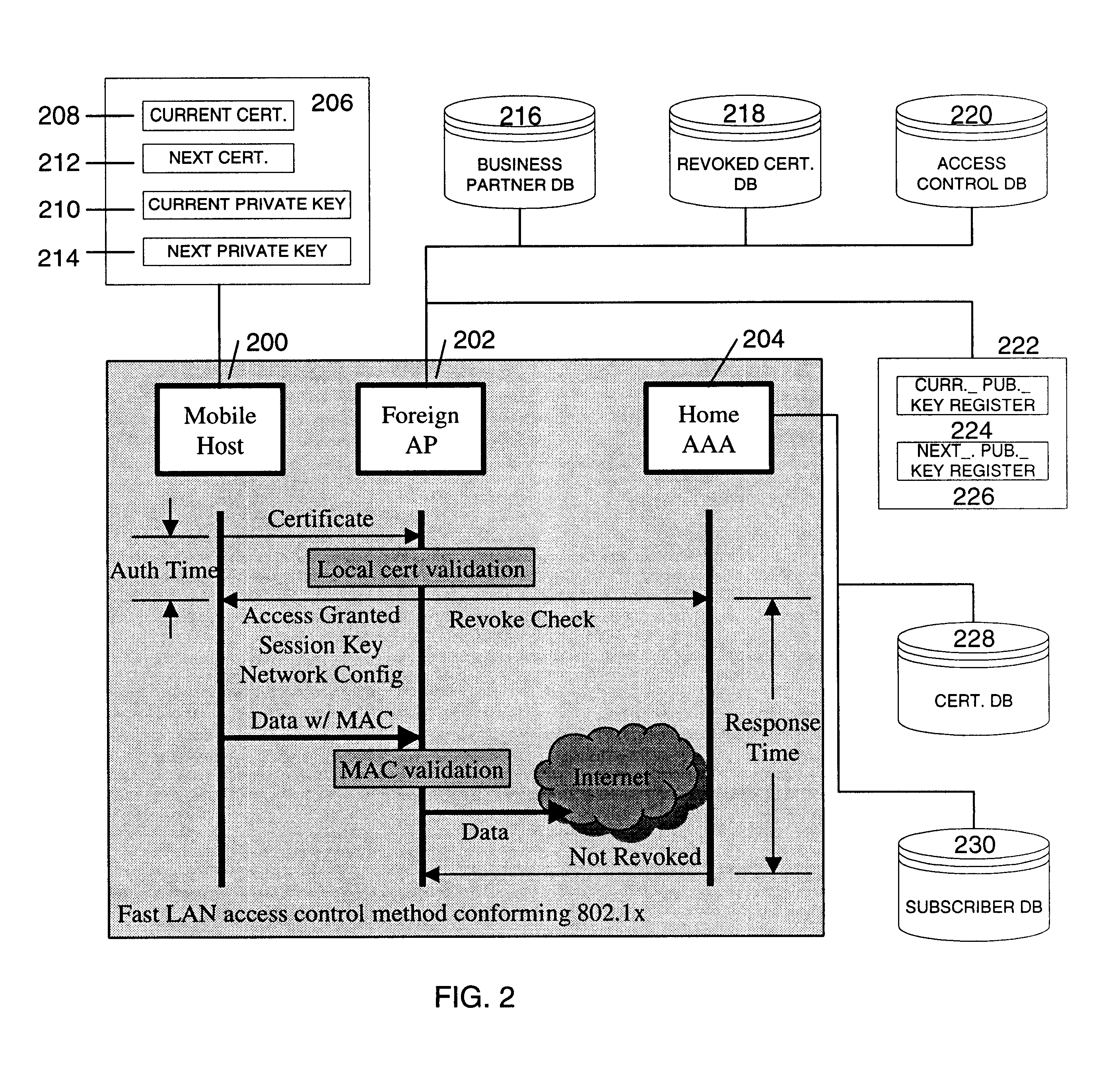
InactiveUS6856800B1Easy to switchReduce certification timeUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsExpiration TimeWeb authentication
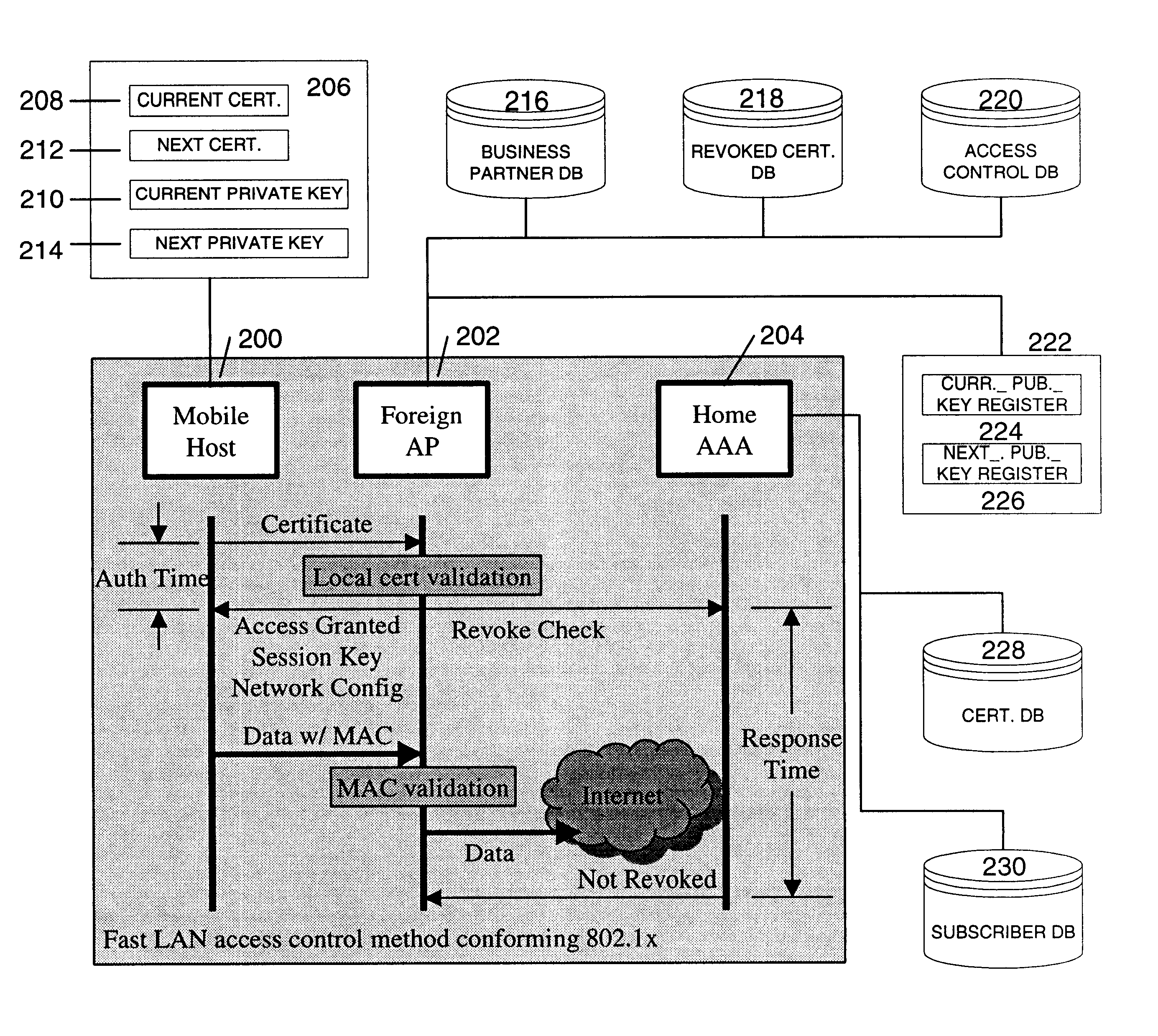
A fast authentication and access control method of authenticating a network access device to a communications network having an access point communicating with a remote authentication (home AAA) server for the network access device. The method includes the step of receiving an access request having an authentication credential from the network access device at the access point. The authentication credential includes a security certificate having a public key for the network access device and an expiration time. The security certificate is signed with a private key for the remote authentication server. The access point locally validates the authentication credential by accessing the public key of the remote authentication server from a local database, and checking the signature and expiration time of the security certificate. If the authentication credential is validated at the access point, the access point grants the network access device conditional access to the network by sending an access granted message to the network access device. The access granted message includes a session key encrypted with a public key for the network access device. The session key is stored in a database associated with the access point. The access point contacts the remote authentication server to check a revocation status of the security certificate for the network access device. If the access point receives a message from the remote authentication server that the authentication credential for the network access device has been revoked, it suspends network access for the network access device.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Protecting one-time-passwords against man-in-the-middle attacks
ActiveUS20070033642A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsMan-in-the-middle attackKey authentication
To authenticate a user having an associated asymmetric crypto-key having a private / public key pair (D,E) based on a one-time-password, the user partially signs a symmetric session key with the first portion D1 of the private key D. The authenticating entity receives the partially signed symmetric session key via the network and completes the signature with the second private key portion D2 to recover the symmetric session key. The user also encrypts a one-time-password with the symmetric session key. The authenticating entity also receives the encrypted one-time-password via the network, and decrypts the received encrypted one-time-password with the recovered symmetric session key to authenticate the user.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Secured peer-to-peer network data exchange
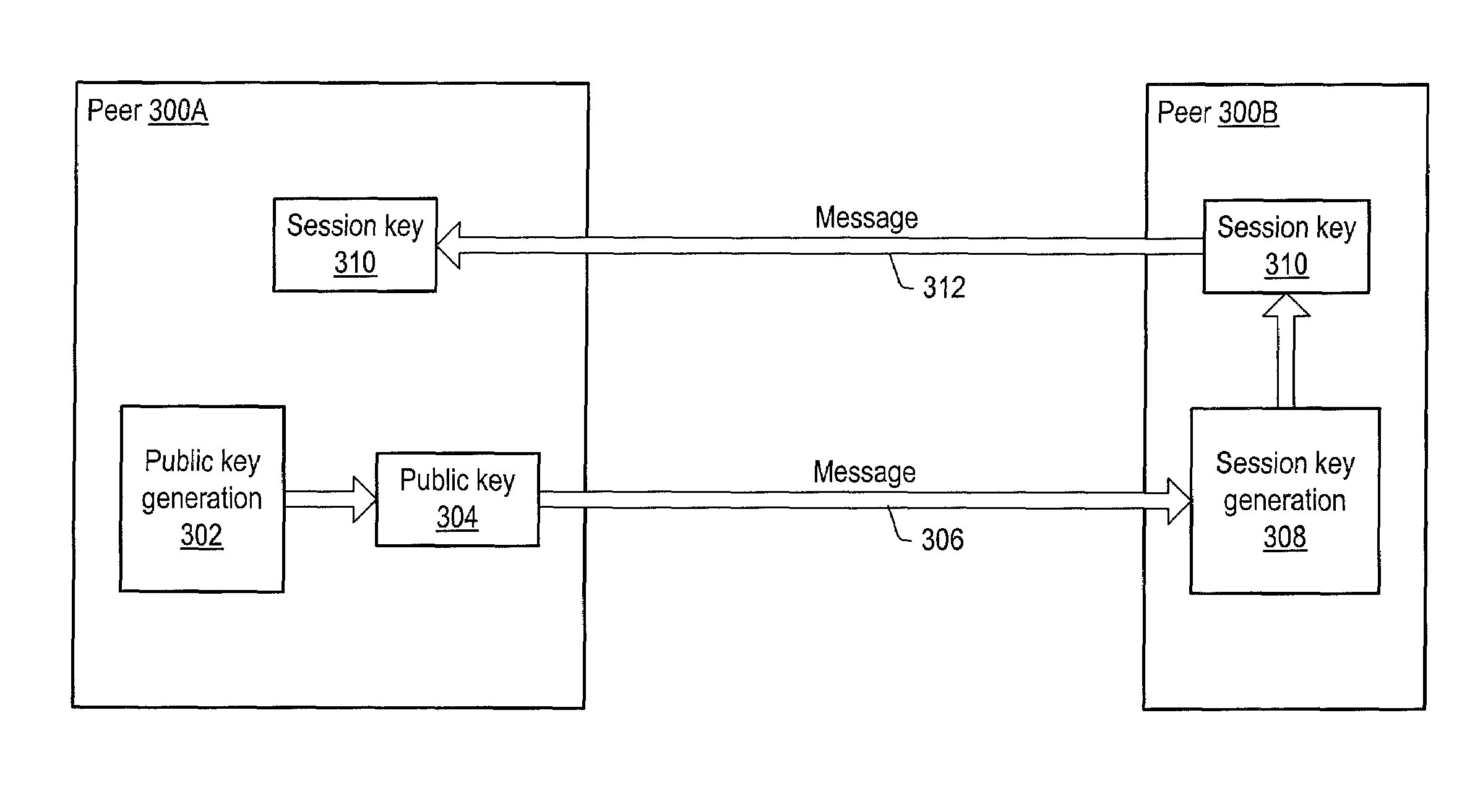
ActiveUS7127613B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGroup sessionMessage switching
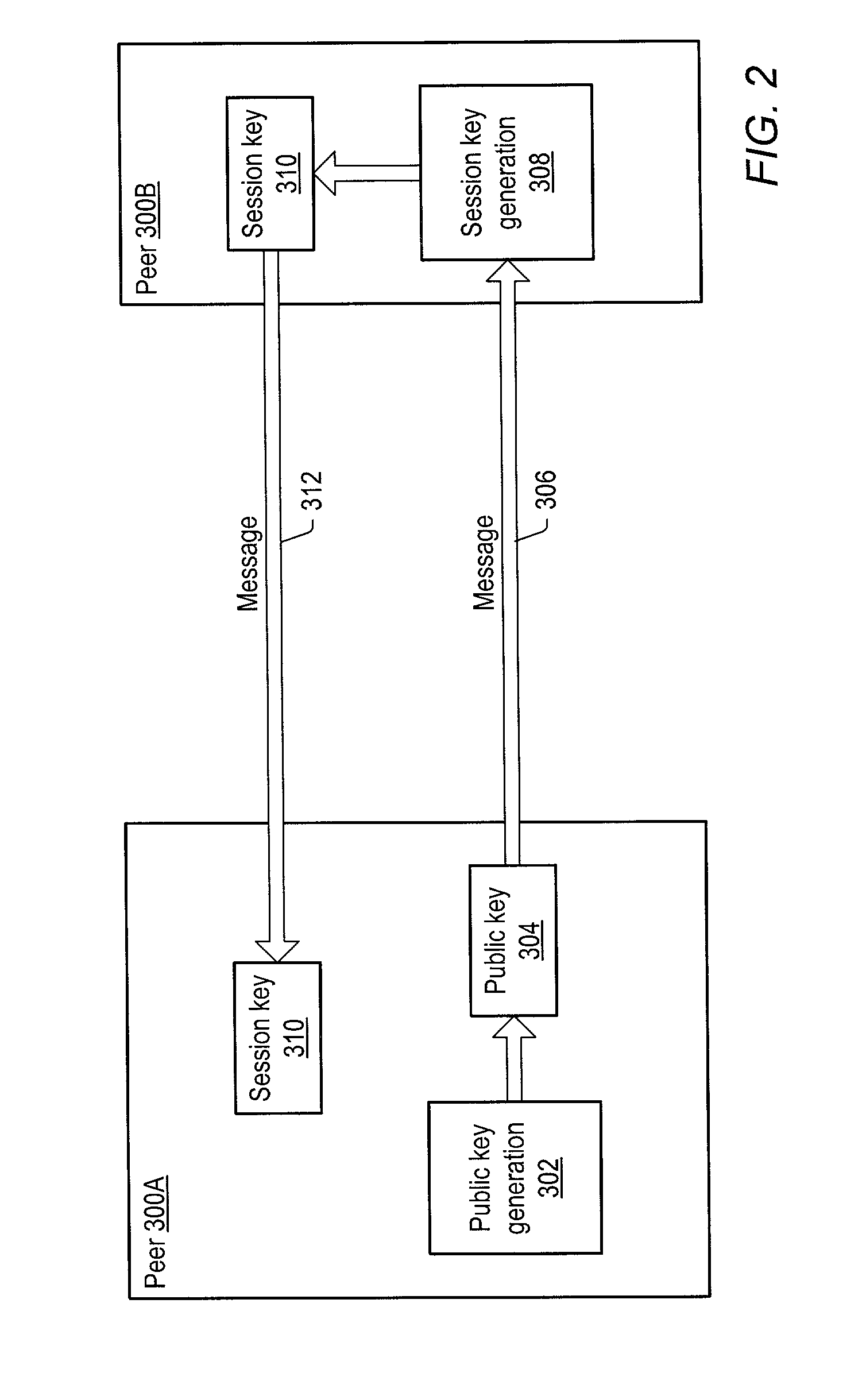
A system and method for providing secure exchange of messages between peers in peer groups. Embodiments may be used to provide secured sessions between peers in the peer-to-peer network. Embodiments may also be used to provide secured group sessions among a plurality of peers. A first peer may generate and send a public key to a second peer. The second peer may generate a session key from the public key. The second peer may send the session key to the first peer, or alternatively to two or more peers in a group session. The session key may be secured when sending. Messages and / or other data exchanged between the two peers may be encrypted and decrypted using the session key.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
802.11 using a compressed reassociation exchange to facilitate fast handoff
ActiveUS7350077B2Reduce the burden onUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesComputer networkRogue access point
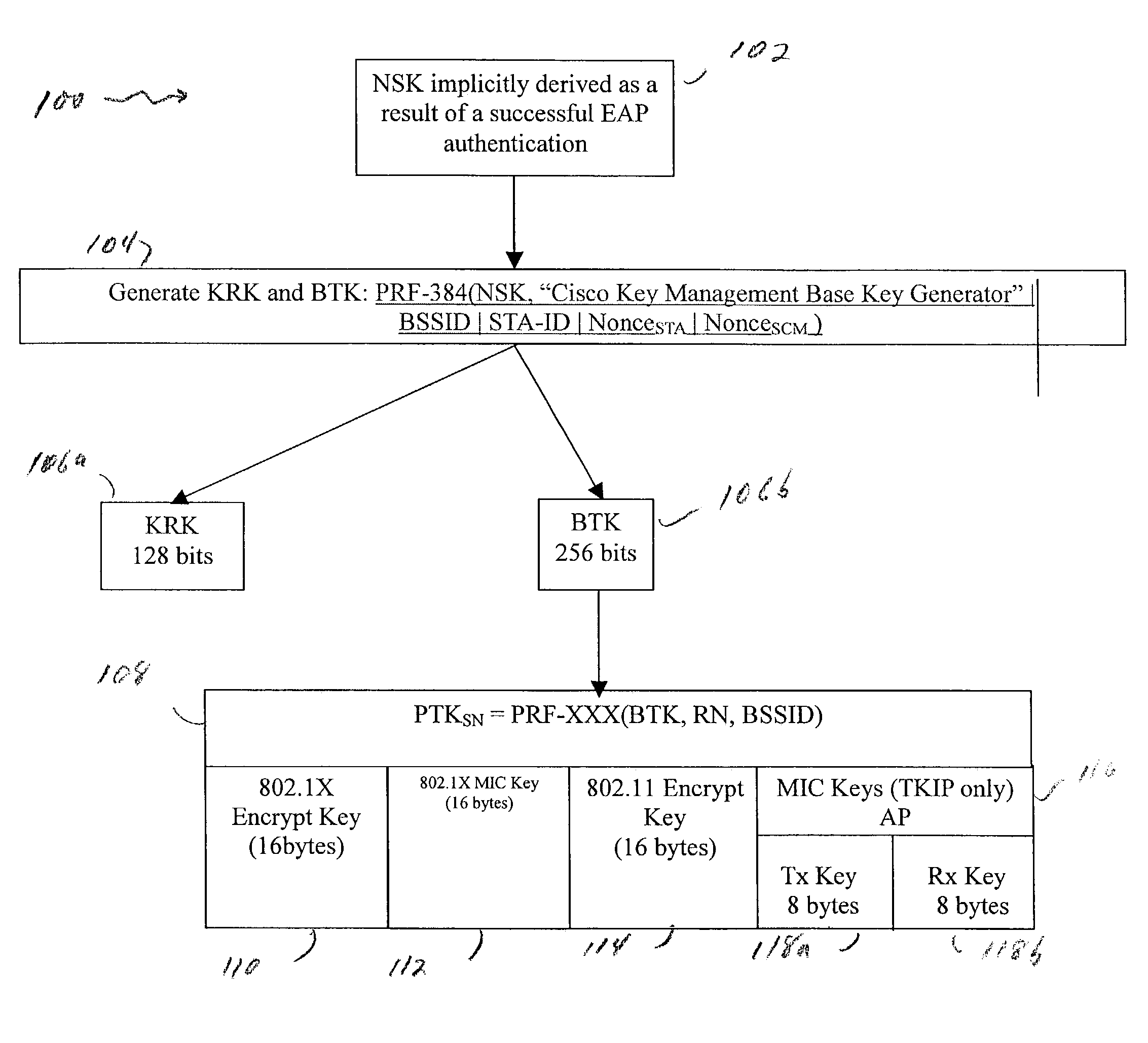
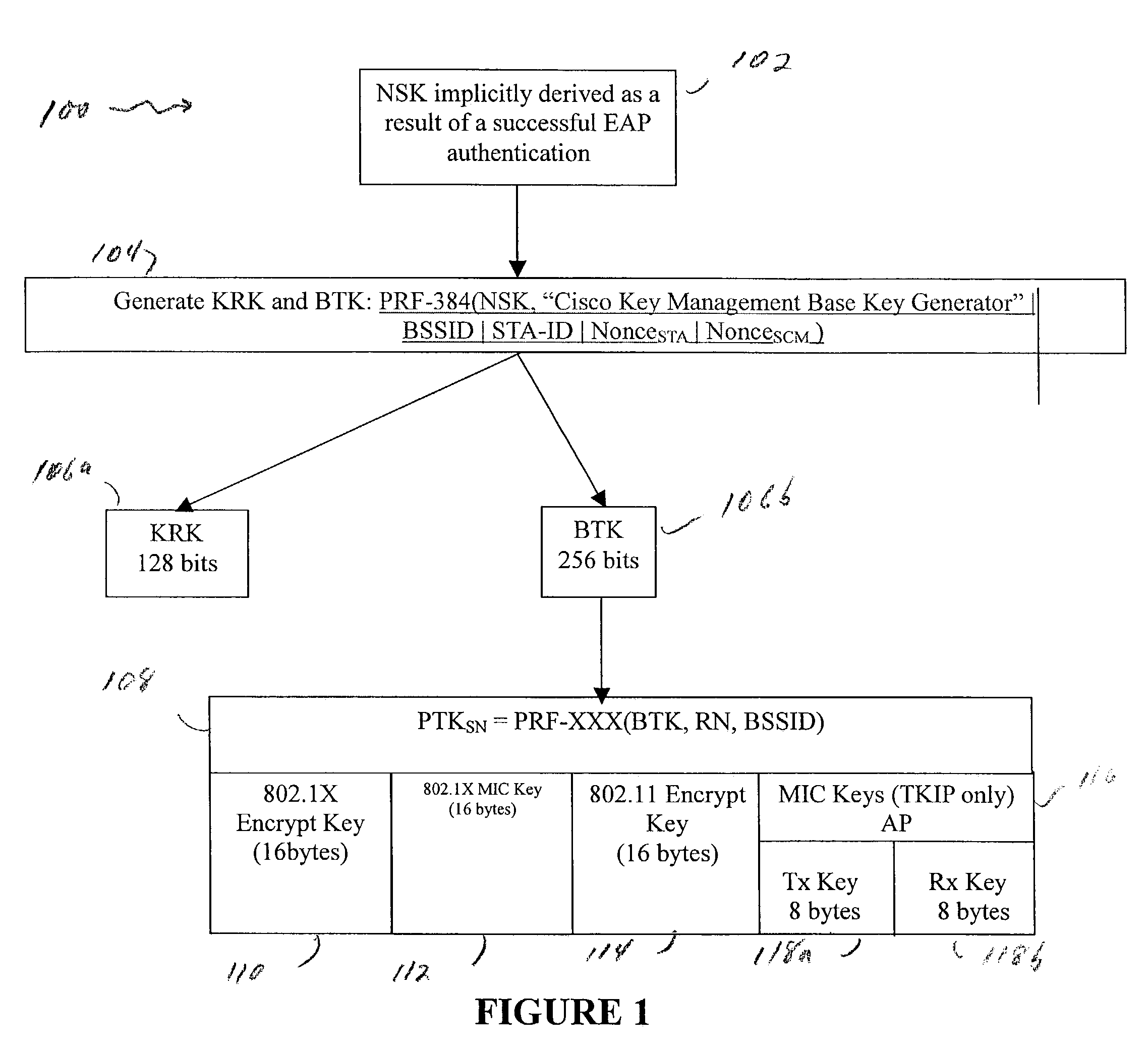
A method and system for handling roaming mobile nodes in a wireless network. The system uses a Subnet Context Manager to store current Network session keys, security policy and duration of the session (e.g. session timeout) for mobile nodes, which is established when the mobile node is initially authenticated. Pairwise transit keys are derived from the network session key. The Subnet Context Manager handles subsequent reassociation requests. When a mobile node roams to a new access point, the access point obtains the network session key from the Subnet Context Manager and validates the mobile node by computing a new pairwise transient key from the network session key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method of exploiting the security of a secure communication channel to secure a non-secure communication channel
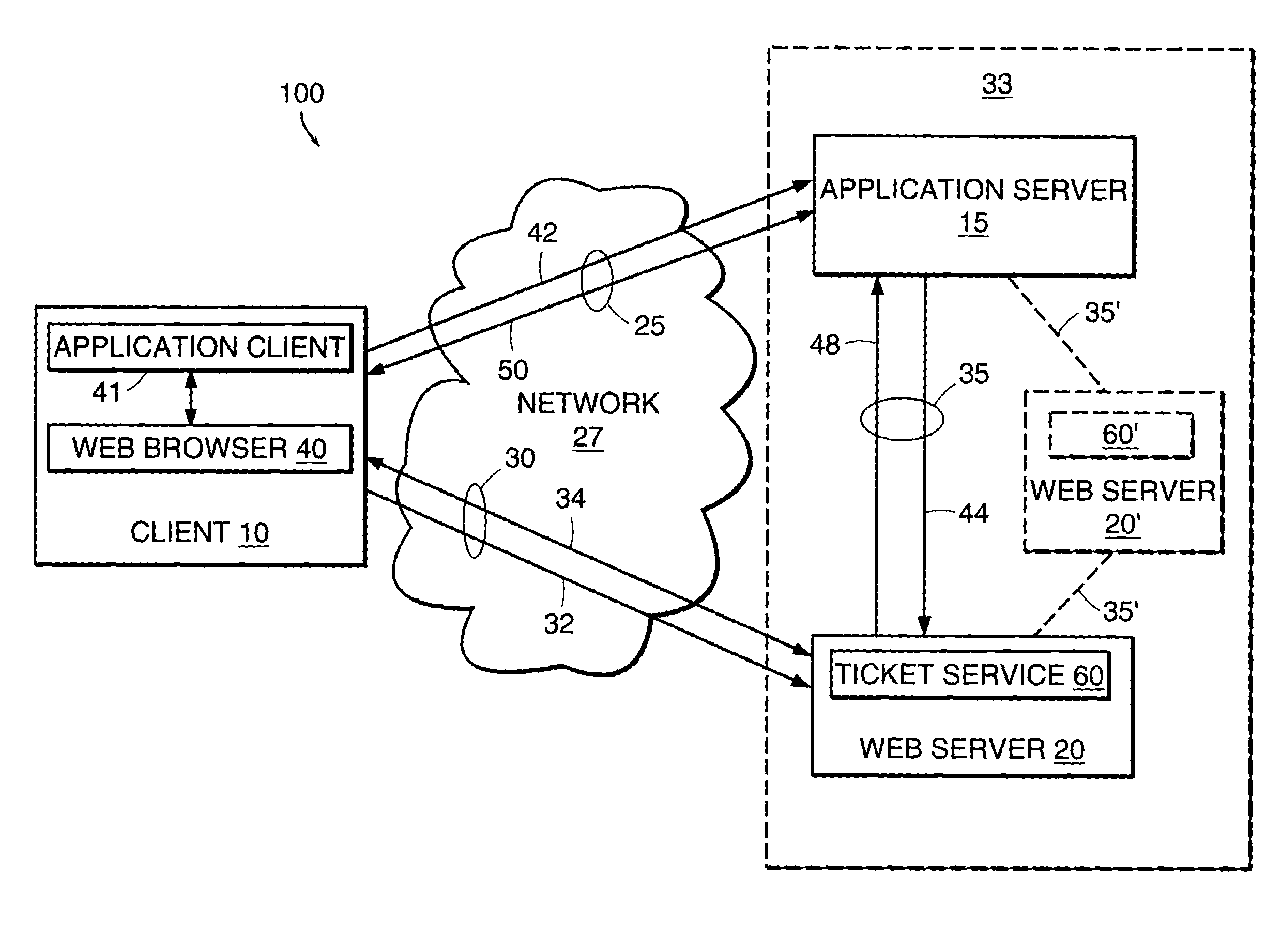
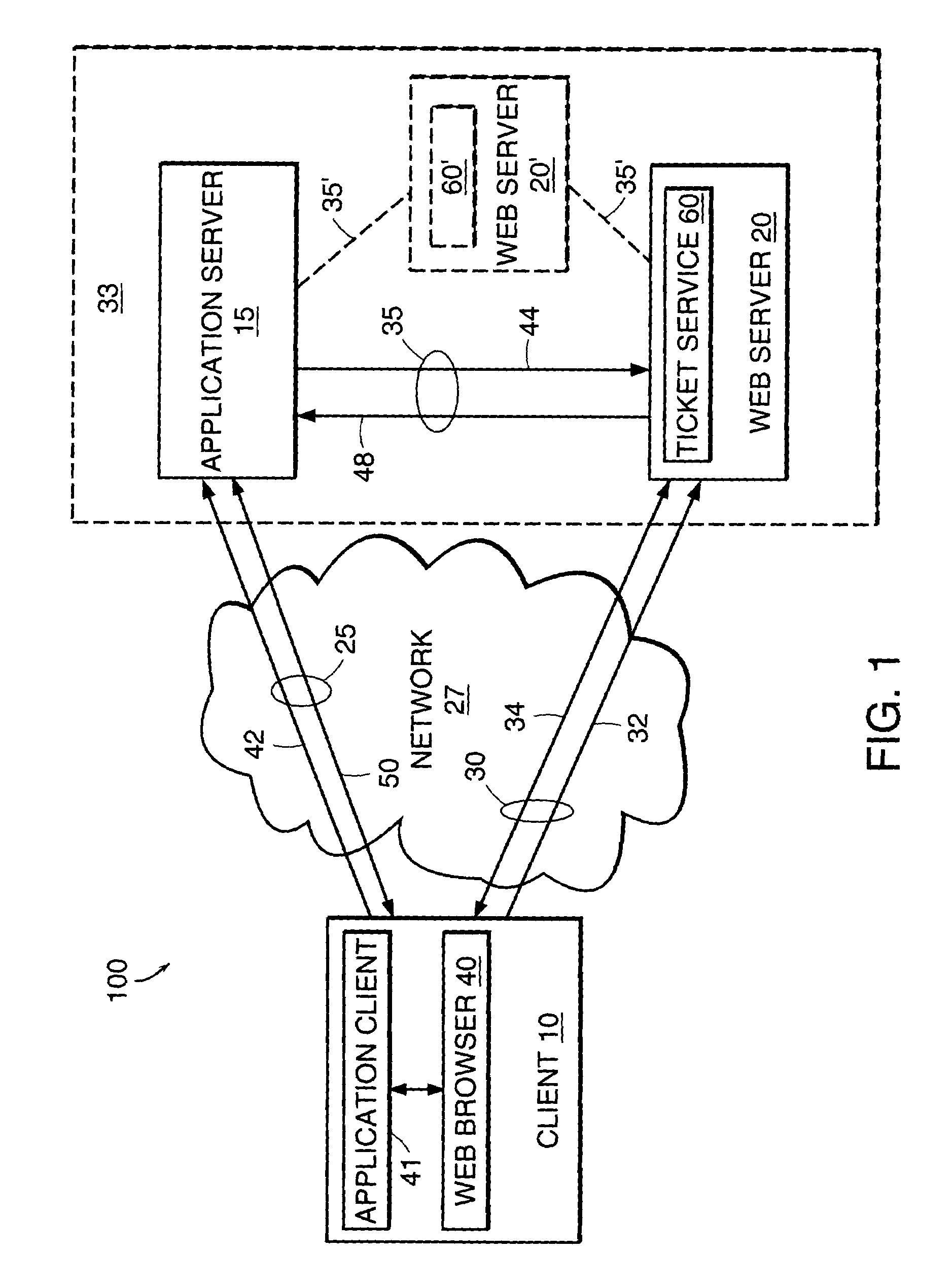
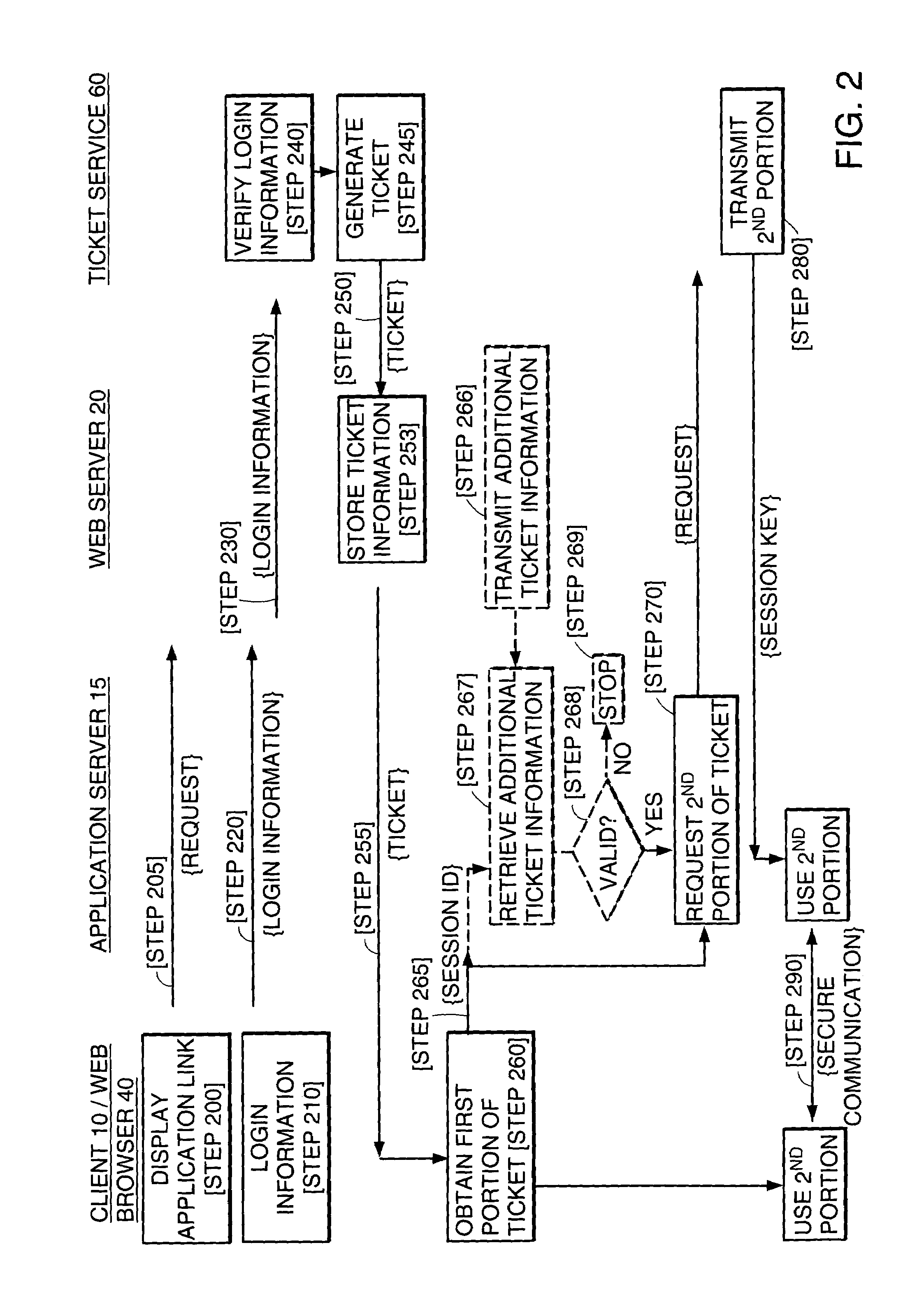
InactiveUS6986040B1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationApplication server
The present invention features a system and method for establishing a secure communication channel between a client and an application server. In one embodiment, a ticket service generates a ticket having an identifier and a session key. A communications device obtains the ticket from the ticket service and transmits the ticket to a client over a secure communication channel. The client transmits the identifier of the ticket to an application server over an application communication channel. The application server then obtains a copy of the session key of the ticket from the ticket service. Communications exchanged between the client and the application server over the application communication channel are then encrypted using the session key to establish the application communication channel as a secure communication channel.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Methods and apparatus for dynamic session key generation and rekeying in mobile IP
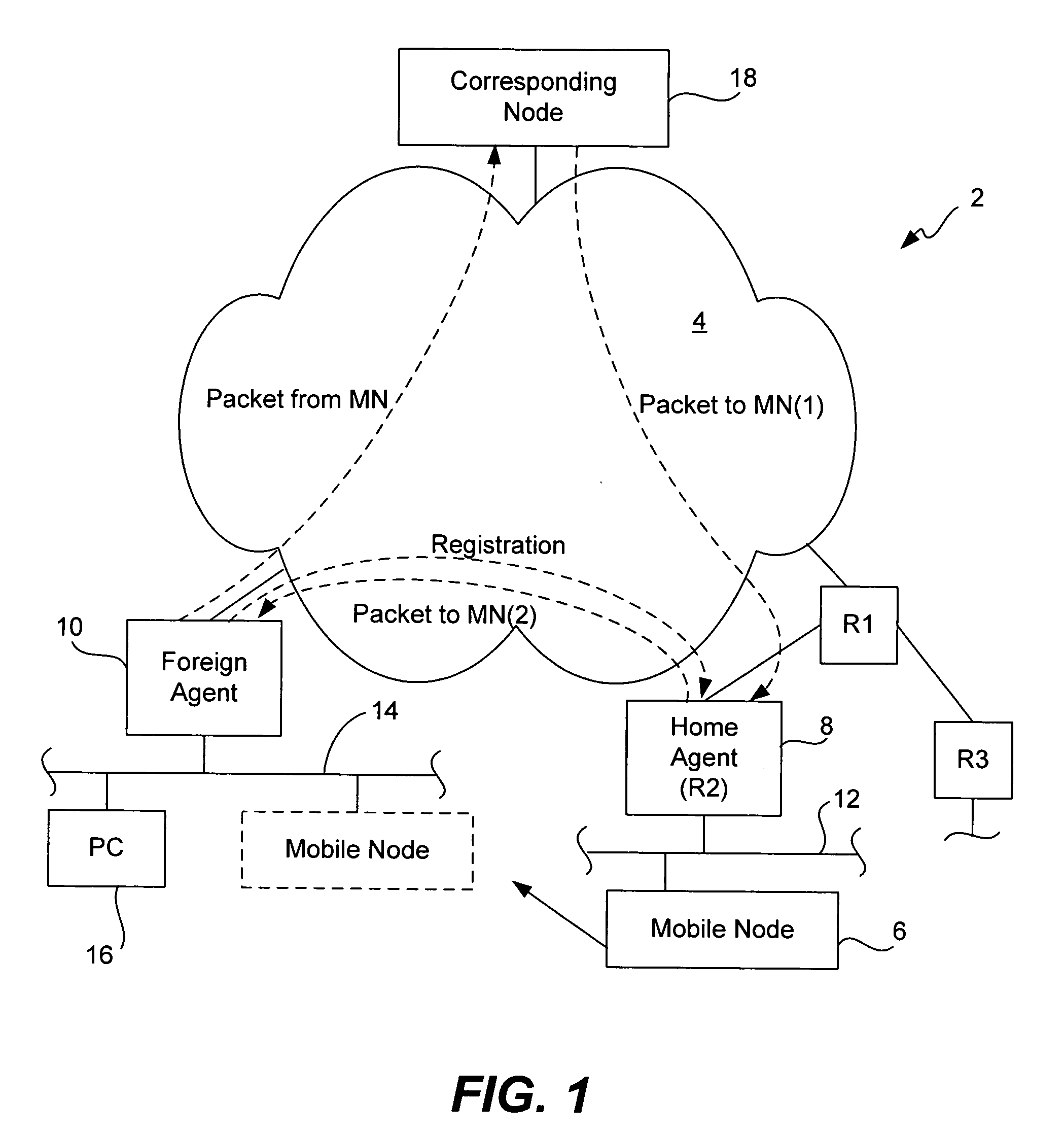
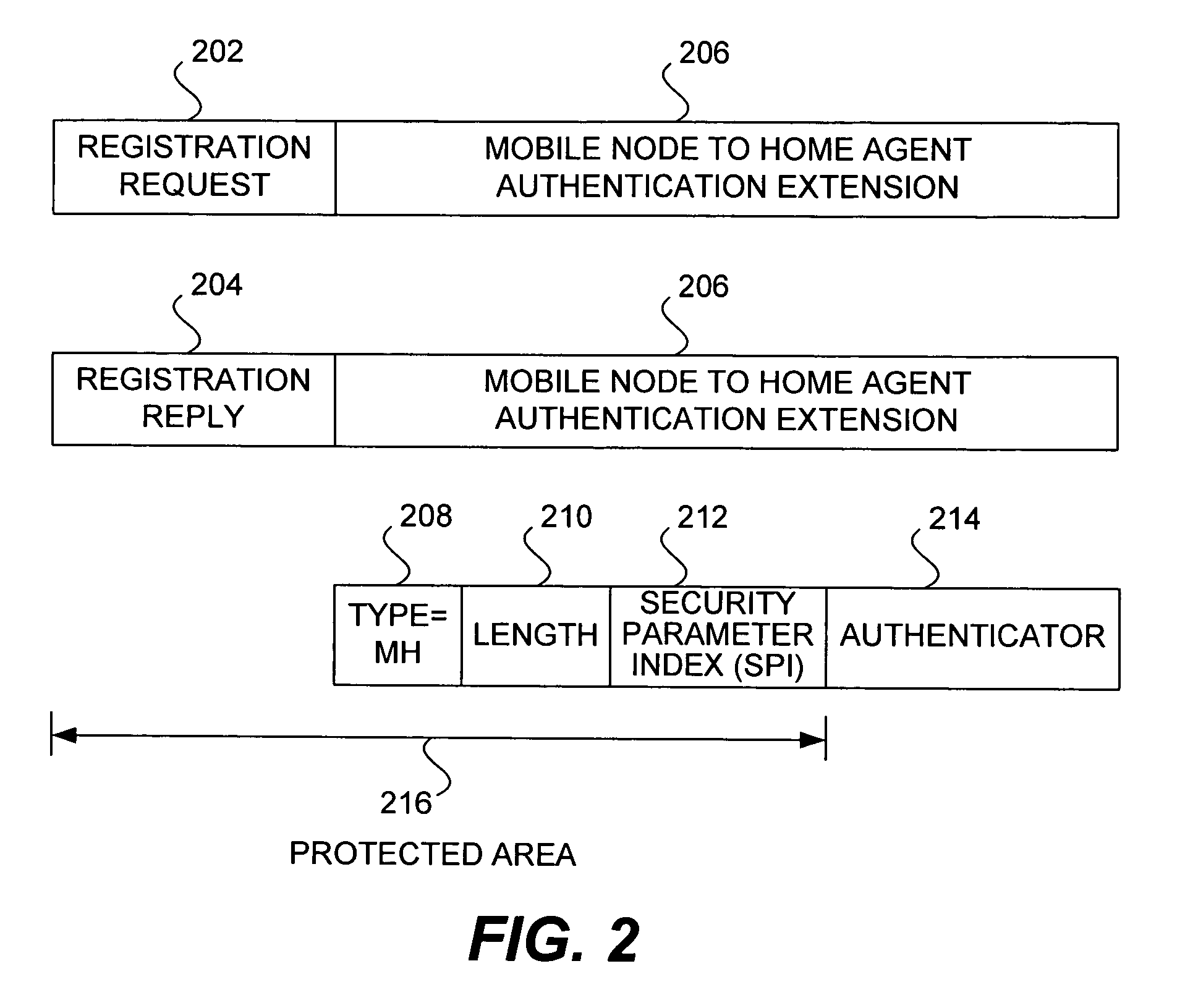
ActiveUS20050025091A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordRe keying
Methods and apparatus for providing a centralized source of session keys to be shared by a Home Agent and a Mobile Node are disclosed. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a Mobile Node registers with a Home Agent supporting Mobile IP by sending a registration request to the Home Agent. The Home Agent sends a request message (e.g., access-request message) to a AAA server, the request message identifying the Mobile Node. The AAA server then derives key information from a key or password associated with the Mobile Node. The AAA server then sends a reply message (e.g., access-reply message) to the Home Agent, the reply message including the key information associated with the Mobile Node, thereby enabling the Home Agent to derive a shared key to be shared between the Mobile Node and the Home Agent from the key information. The Home Agent derives a key from the key information, the key being a shared key between the Mobile Node and the Home Agent. A registration reply is then sent to the Mobile Node. When the Mobile Node receives a registration reply from the Home Agent, the registration reply indicates that the Mobile Node is to derive a key to be shared between the Mobile Node and the Home Agent. The Mobile Node then derives a key to be shared between the Mobile Node and the Home Agent from key information stored at the Mobile Node. The Mobile Node may initiate “re-keying” by sending a subsequent registration request to the Home Agent.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Authentication in a packet data network
InactiveUS7107620B2Strong authenticationKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionTelecommunications networkComputer science
Authentication method for authenticating a mobile node to a packet data network, in which a shared secret for both the mobile node and the packet data network is arranged by using a shared secret of the mobile node and a telecommunications network authentication center. In the method, the mobile node sends its subscriber identity to the packet data network together with a replay attack protector. The packet data network obtains authentication triplets, forms a session key using them, and sends back to the mobile node challenges and a cryptographic authenticator made by using the session key. The mobile node can then form the rest of the authentication triplets using the challenges and then form the session key. With the session key, the mobile node can check the validity of the cryptographic authenticator. If the authenticator is correct, the mobile node sends a cryptographic response formed using the session key to the packet data network for authenticating itself to the packet data network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
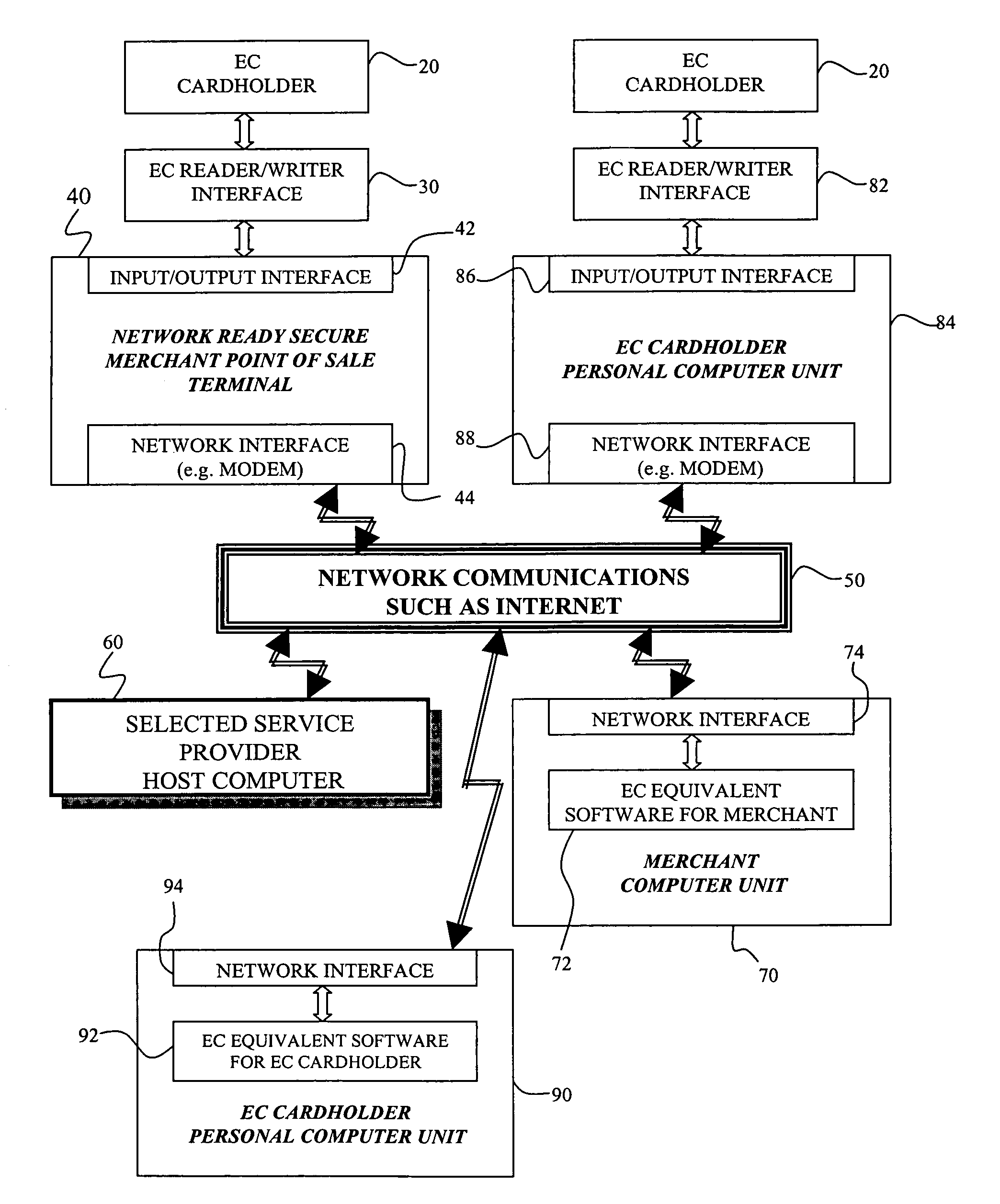
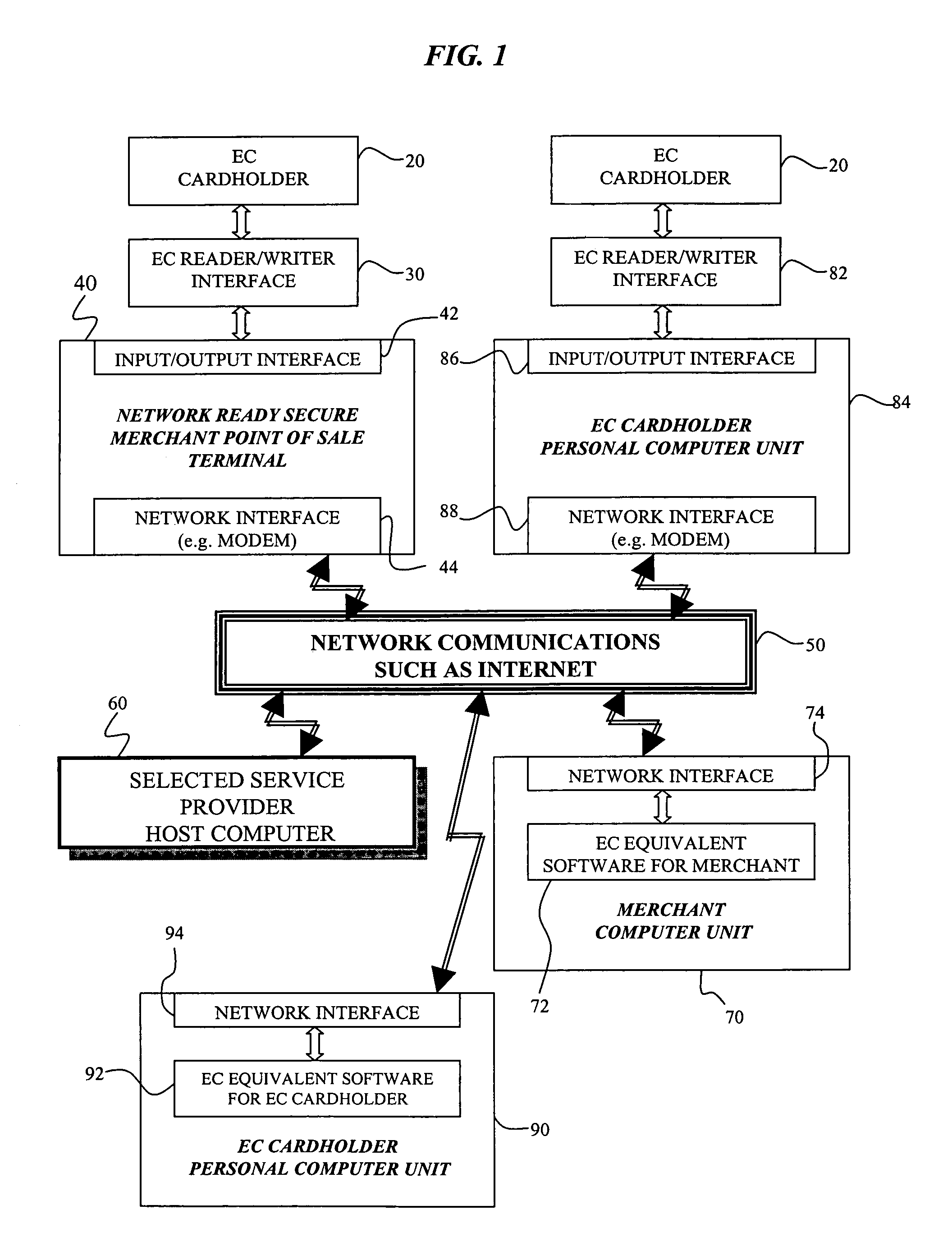
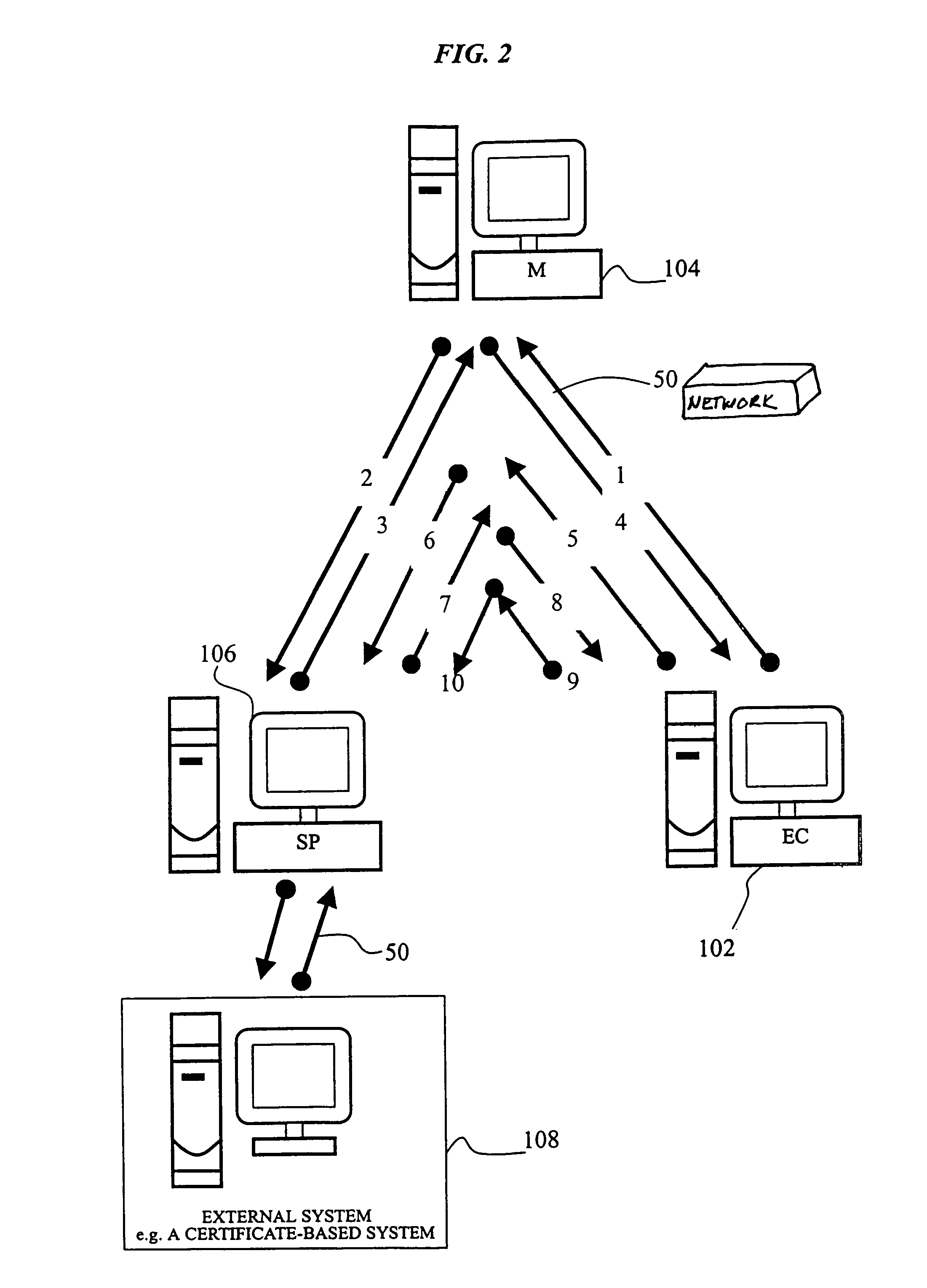
Cryptographic system and method for electronic transactions
InactiveUS7096494B1Key distribution for secure communicationFinanceCredit cardSecure Electronic Transaction
An electronic transaction system, which facilitates secure electronic transactions among multiple parties including cardholders, merchants, and service providers (SP). The system involves electronic cards, commonly known as smart cards, and their equivalent computer software package. The card mimics a real wallet and contains commonly seen financial or non-financial instruments such as a credit card, checkbook, or driver license. A transaction is protected by a hybrid key cryptographic system and is normally carried out on a public network such as the Internet. Digital signatures and challenges-responses are used to ensure integrity and authenticity. The card utilizes secret keys such as session keys assigned by service providers (SPs) to ensure privacy for each transaction. The SP is solely responsible for validating each participant's sensitive information and assigning session keys. The system does not seek to establish a trust relationship between two participants of a transaction. The only trust relationship needed in a transaction is the one that exists between individual participants and the SP. The trust relationship with a participant is established when the SP has received and validated certain established account information from that particular participant. To start a transaction with a selected SP, a participant must have the public key of the intended SP. Since the public key is openly available, its availability can be easily established by the cardholder. The SP also acts as a gateway for the participants when a transaction involves interaction with external systems.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Method and apparatus for privacy and authentication in wireless networks
InactiveUSRE36946E1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTelecommunications linkWireless mesh network
A method and apparatus is disclosed for providing a secure wireless communication link between a mobile nomadic device and a base computing unit. A mobile sends a host certificate (Cert-Mobile) to the base along with a randomly chosen challenge value (CH1) and a list of supported shared key algorithms ("SKCS"). The base determines if the Cert-Mobile is valid. If the Cert-Mobile is not valid, then the base unit rejects the connection attempt. The base then sends a Cert-Base, random number (RN1) encrypted in mobile's public key and an identifier for the chosen SKCS to the mobile. The base saves the RN1 value and adds the CH1 value and the chosen SKCS to messages sent to the base. The mobile unit then validates the Cert-Base, and if the certificate is valid, the mobile verifies under the public key of the base (Pub-Base) the signature on the message. The signature is verified by taking the base message and appending it to CH1 and the list of shared key algorithms that the mobile provided in the first message. If the base signature is not valid, then the communication attempt is aborted. In the event that the base signature is valid, the mobile determines the value of RN1 by decrypting Pub-Mobile, RN1 under the private key of the mobile. The mobile then generates RN2 and the session key, and encrypts RN2 under the Pub-Base. The mobile sends the encrypted RN2 and E(Pub-Mobile, RN1) to the base. The base then verifies the mobile signature using the Pub-Mobile obtained from the Cert-Mobile. If the mobile signature is verified, the base decrypts E(Pub-Base, RN2) using its private key. The base then determines the session key. The mobile and base may then enter a data transfer phase using encrypted data which is decrypted using the session key which is RN1 (+)RN2.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Information security management and control method under cloud manufacturing environment
InactiveCN102710605ASolve the problem of update and maintenanceAvoid complex proceduresPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationConfidentialityPrivate network
The invention discloses an information security management and control method under a cloud manufacturing environment. On the basis of a network security protocol, a password technology and a public key infrastructure (PKI), comprehensive security guarantee is supplied to information interaction among cloud internal networks, between one cloud and another cloud, and between a user and each cloud by using implementation technologies and methods, such as a virtual private network (VPN) based on multiple layers of protocols, a digital envelope and a password algorithm; Intranet, Extranet and Internet of a cloud manufacturing system are covered; comprehensive management and control technical information files are stored and transmitted to each used loop; a session key (SK) which is randomly produced by using a key production protocol is used for symmetrically encrypting the technical information files; and a receiver public key obtained according to a PKI digital certificate asymmetrically encrypts the SK to form the digital envelope for protecting the technical information files and the SK. The information security management and control method has the characteristics of being high in confidentiality, high inefficiency, flexible in arrangement and the like and can be widely applied to the cloud manufacturing system and other network manufacturing systems.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Unique session storage design
A system and method for providing user session state across various networked machines is disclosed. The system encompasses a session saver and a sessions database centrally maintained for access by a plurality of computing devices. The system indexes each stored variant by a user defined key and a descriptive variable name. The session saver is a drop in replacement for the IIS session object that provides session state without using cookies. The session saver is divided into various subcomponents, including Csaver for providing the COM interface, OleDbSessionTable to read and write the data from an OLE database, Cconnection for retrieving a connection string from a UDL file, RegistryInfo that reads the location of the UDL file from the memory, StorageVariant enabling storage of variants in any properly configured OLE DB provider, and CcomVariantEx. Any of the operations servers generates a session key when initially contacted by the user and the session saver stores the session key and variables associated with the particular session, such as account numbers, passwords accepted, and so forth. These session keys and stored variables are available to any of the other operations servers and a procedure for retrieving these keys and variables is performed each time a session is either commenced or resumed. Each generated session key is unique and non predictable such that multiple operation servers can simultaneously generate keys without conflict.
Owner:SENSCOM
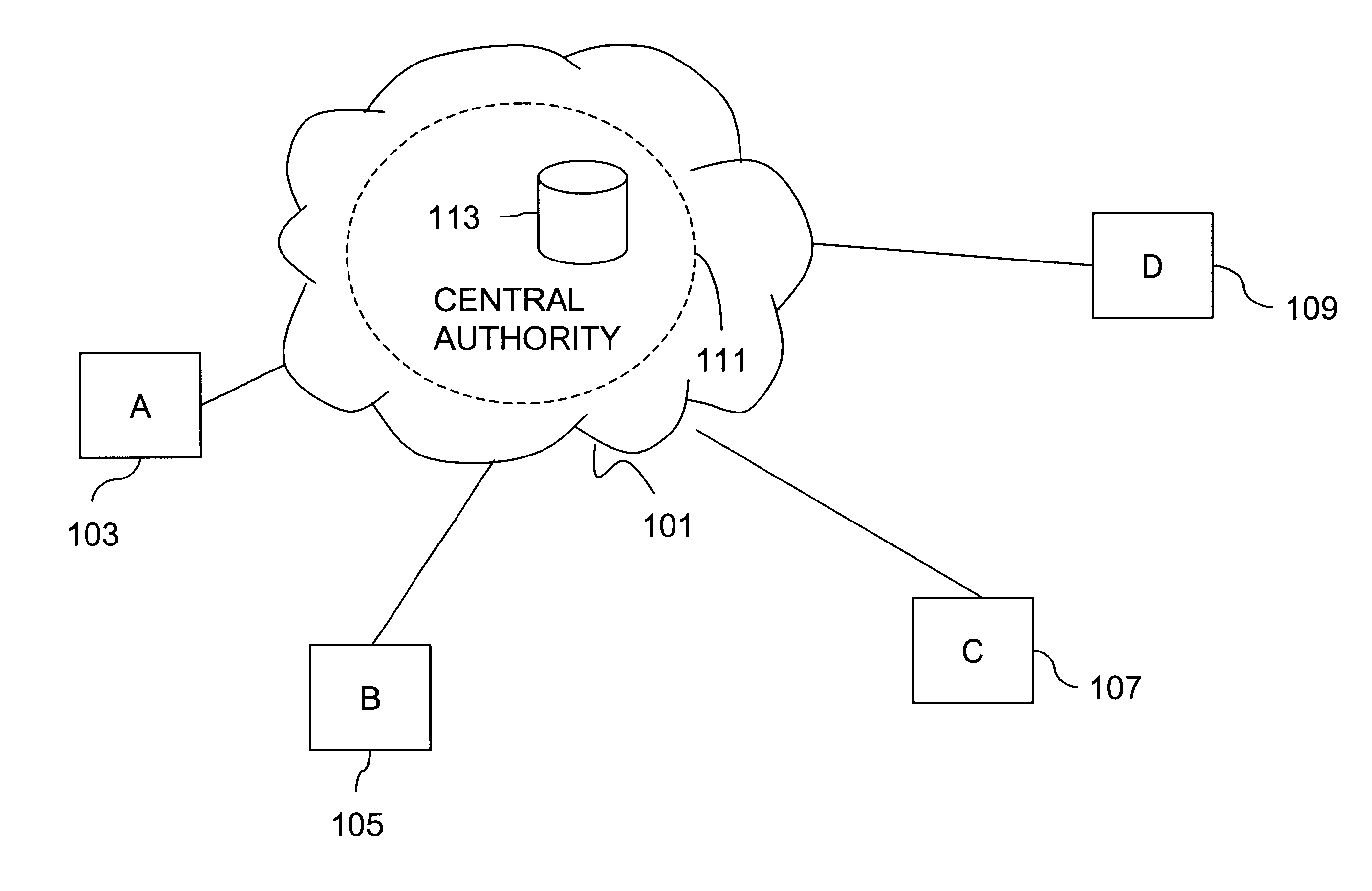
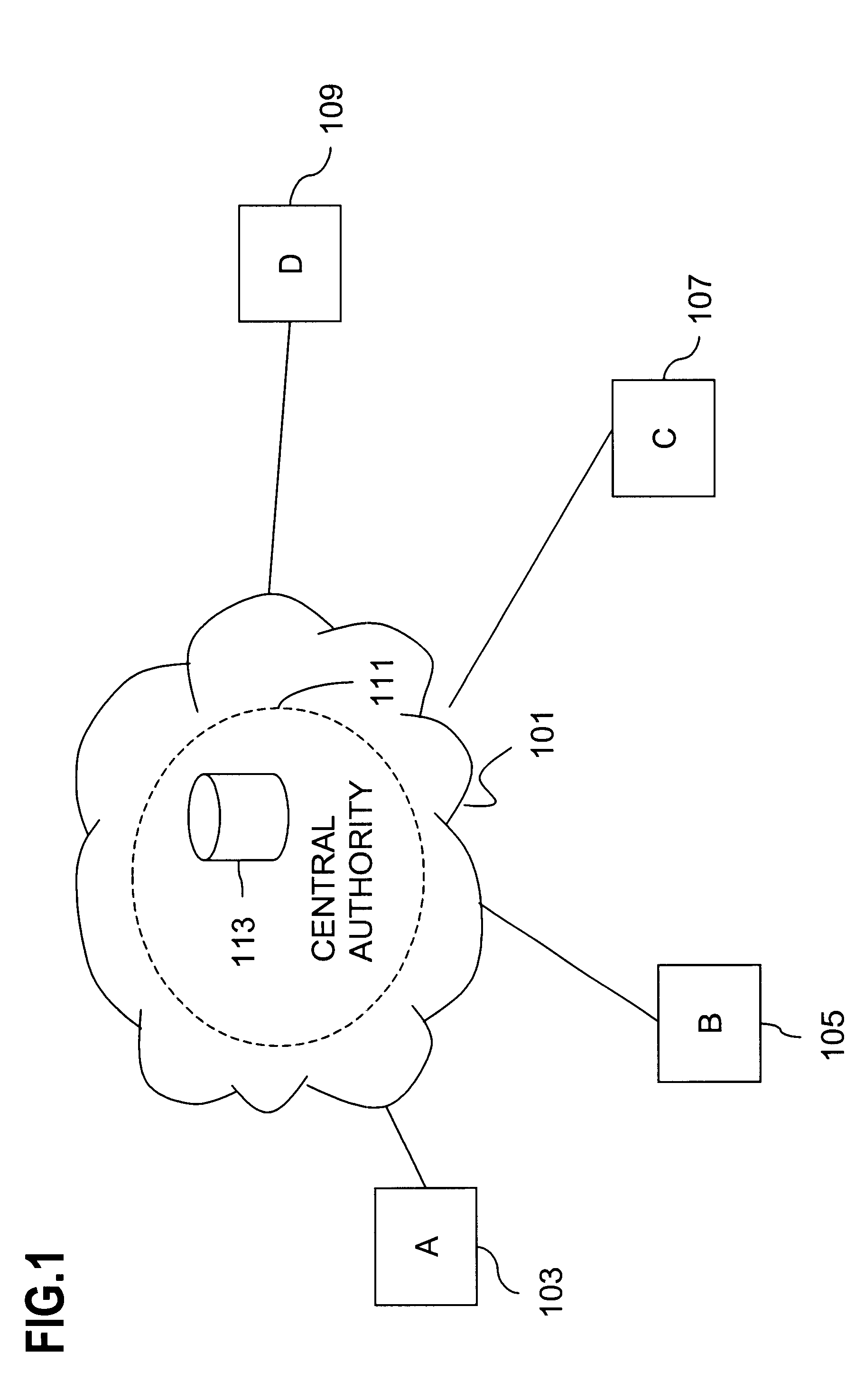
Session key distribution methods using a hierarchy of key servers
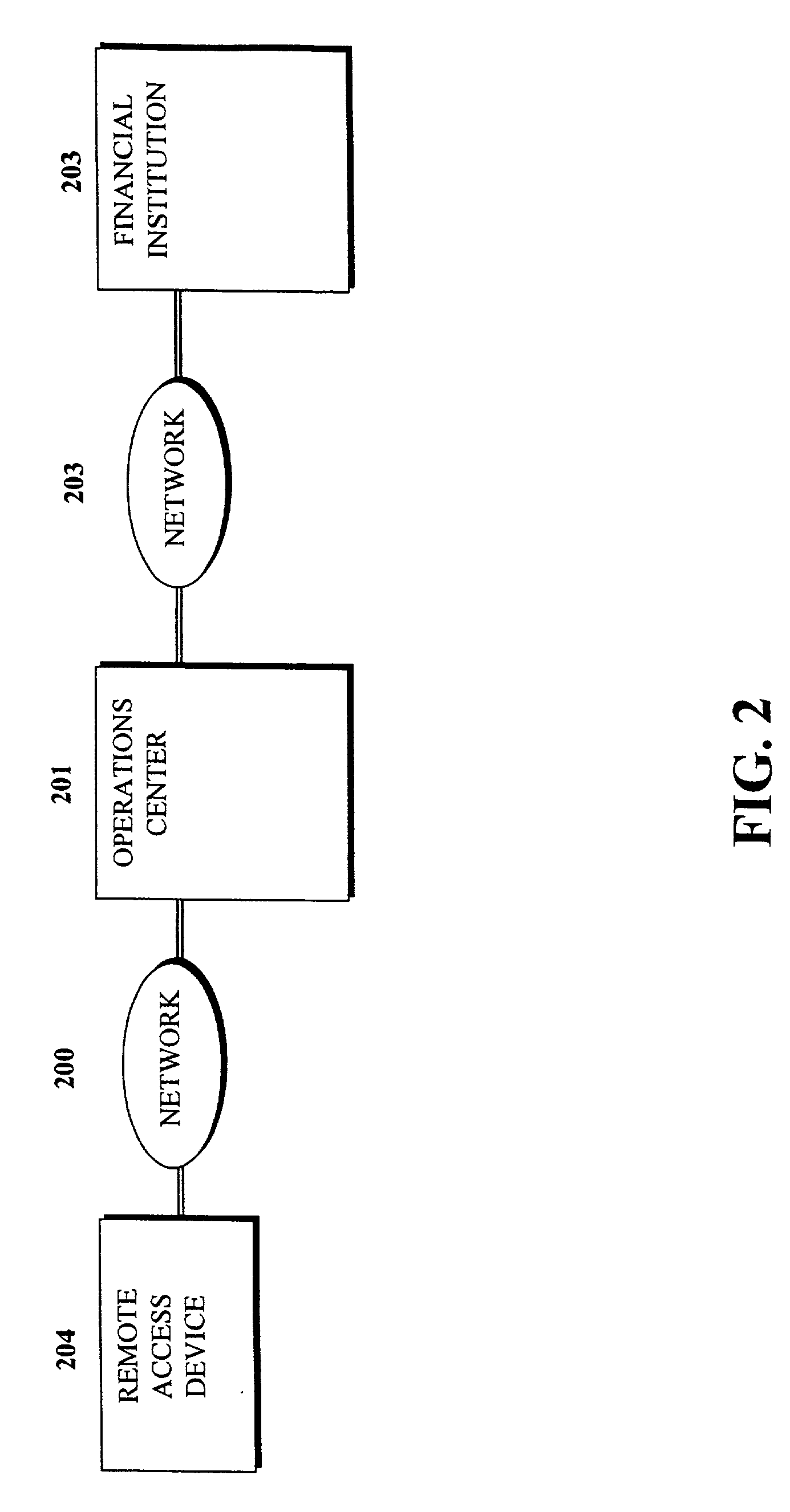
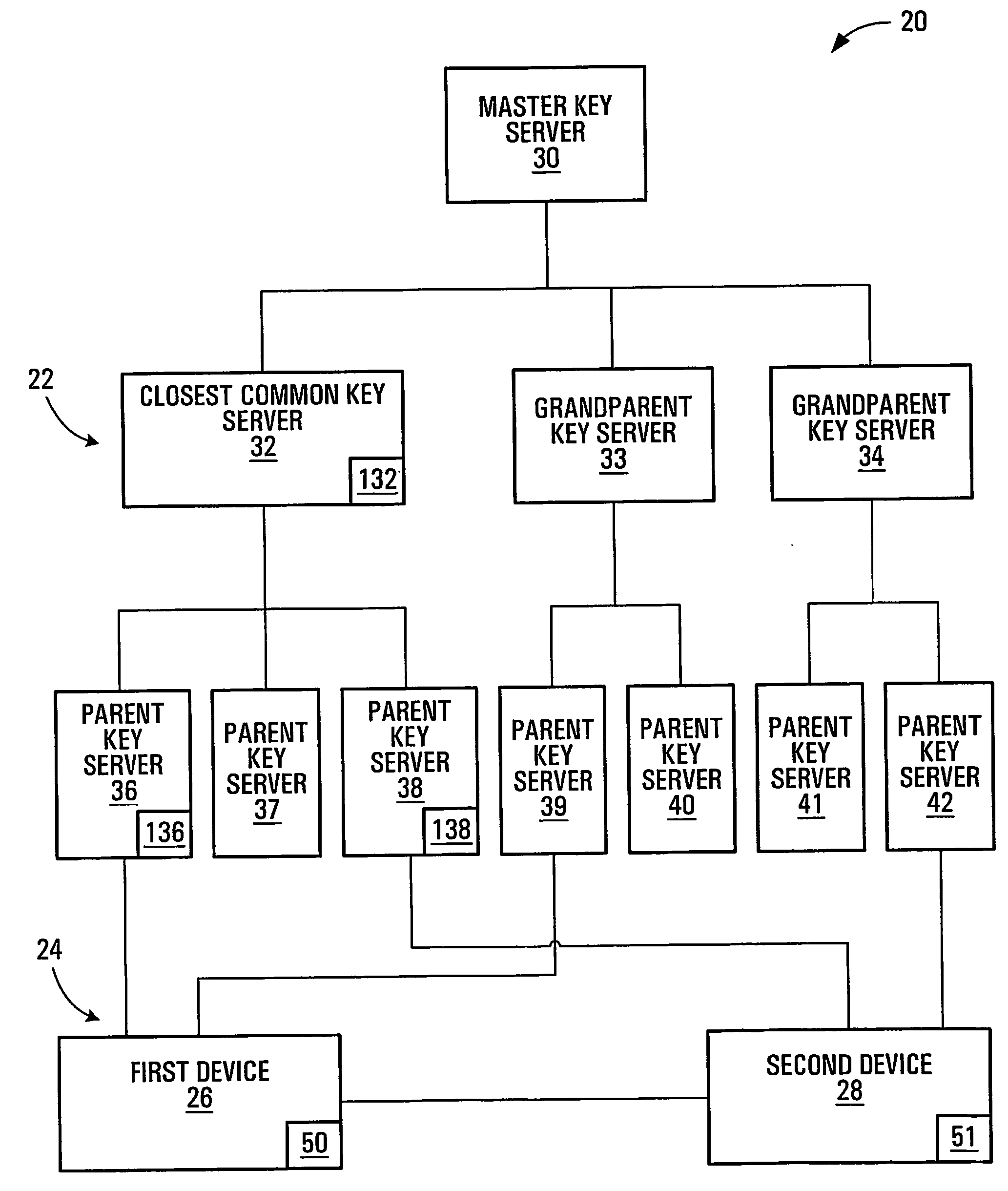
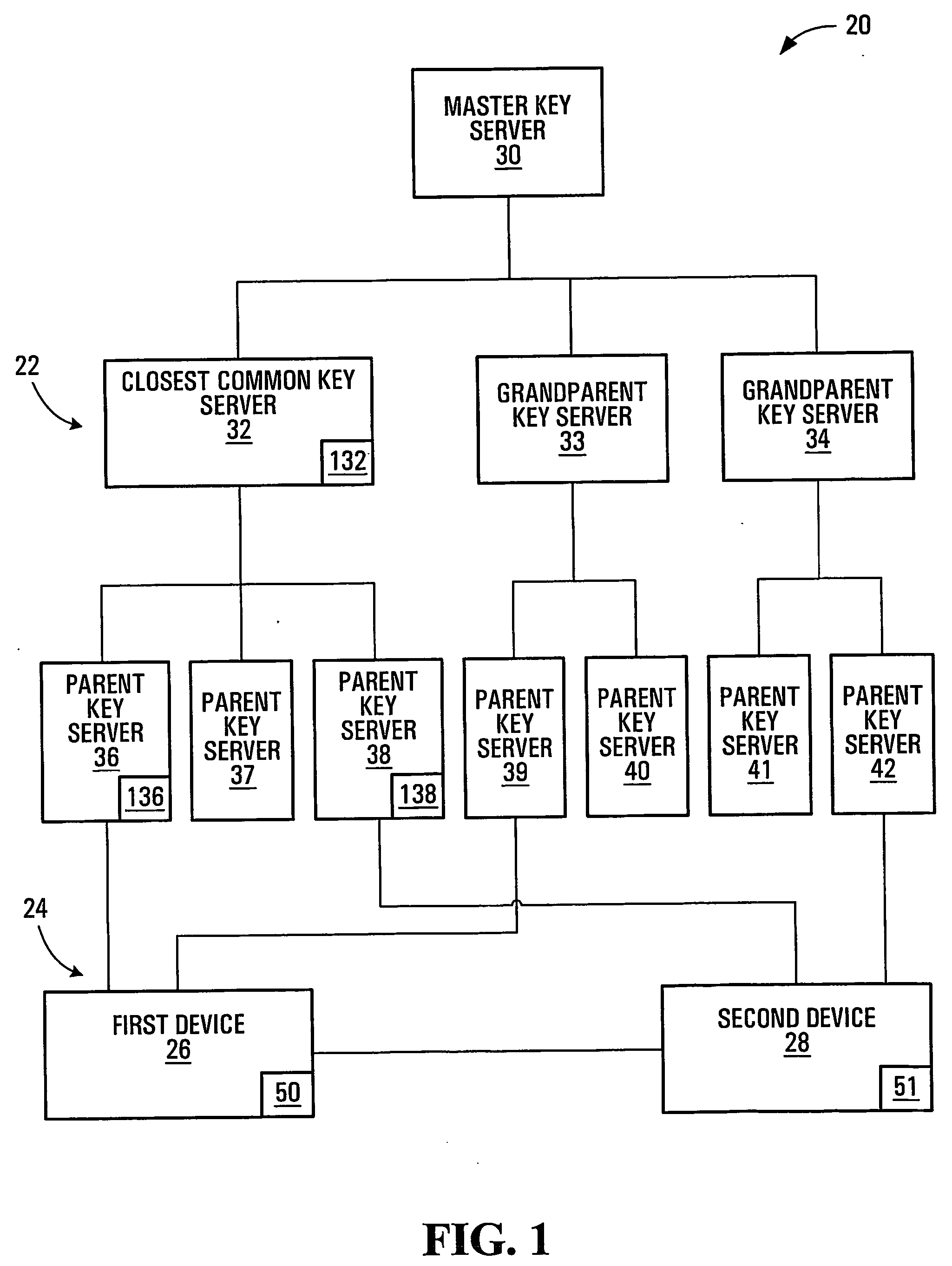
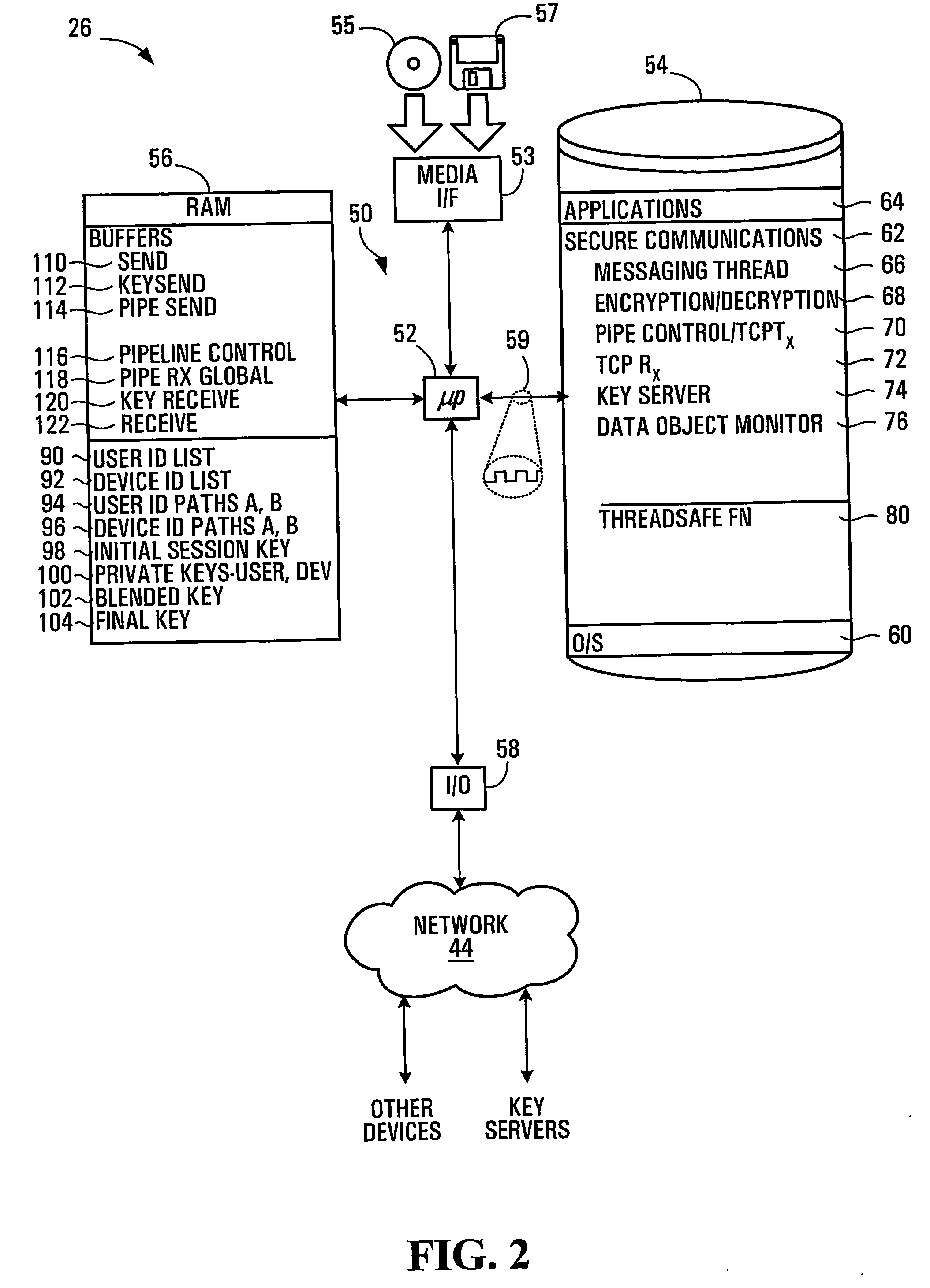
InactiveUS20050125684A1Facilitates secure communicationFacilitate communicationKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationKey server
Methods, apparatuses, media and signals for facilitating secure communication between a first device and a second device are disclosed. One method includes automatically identifying a common key server potentially accessible by both the first and second devices, and obtaining a secure private key from the common key server, for use in encrypting communications between the first and second devices. Identifying may include identifying as the common key server, a key server at an intersection of a first communication path defined between a first key server having a previously established relationship with the first device and a master key server, and a second communication path defined between a second key server having a previously established relationship with the second device and the master key server. Obtaining may include obtaining a plurality of private keys and blending the keys to produce a final private session key.
Owner:SCHMIDT COLIN MARTIN
Transferring a media browsing session from one device to a second device by transferring a session identifier and a session key to the second device
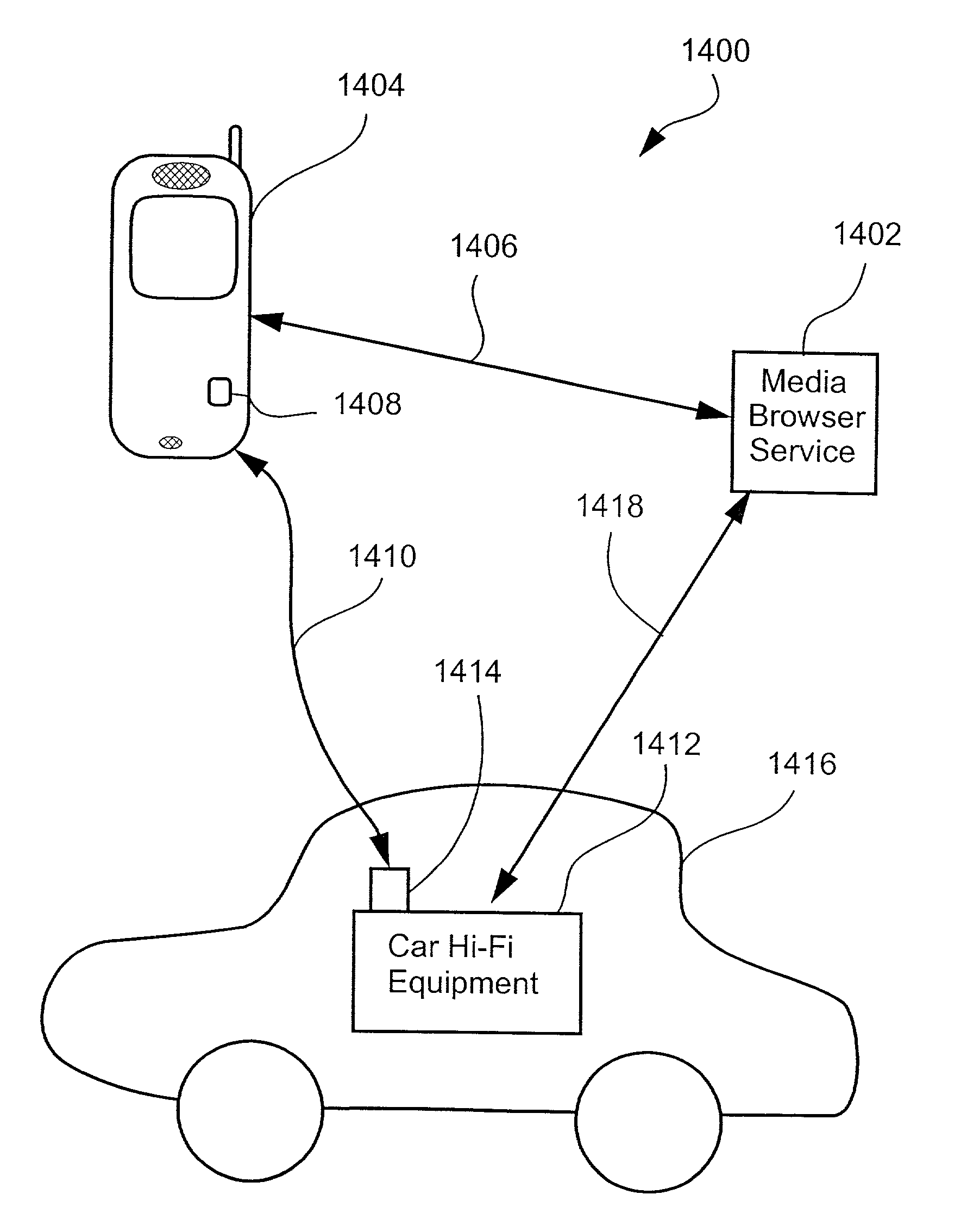
InactiveUS7099946B2Digital data information retrievalRecord information storageQuality of serviceGraphics
A system is described in which a media browser (101), operating as a software application on a user terminal or preferably a server for a number of users, provides a user with a single user interface that facilitates browsing and searching different metadata collections over the Internet (102). A metadata server (212) is associated with each of the metadata collections. When the metadata server (212) receives a request from the media browser (101), the metadata server (212) interprets the request and replies with a description that satisfies the request and according to a predetermined scheme. The description contains at least one link which represents a return link which represents a return request to the metadata server (212). Specifically disclosed are methods of forming a table of contents for a particular user preferably based upon media reproduction attributes, methods of right to use and quality of service control, graphical user interfaces for facilitating the browsing process, methods of interpreting metadata, methods of communicating metadata between users, and method for transferring media sessions between users.
Owner:CANON KK
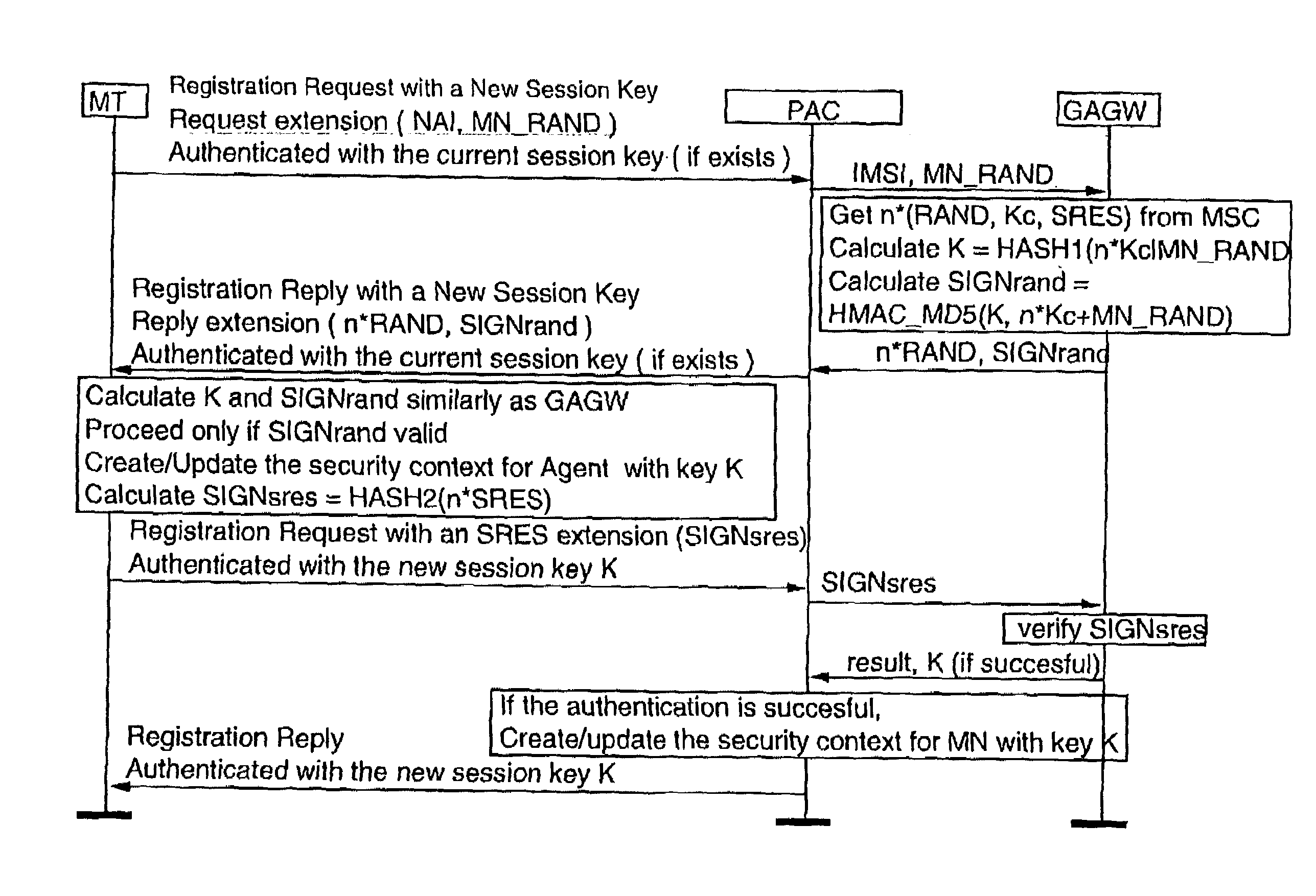
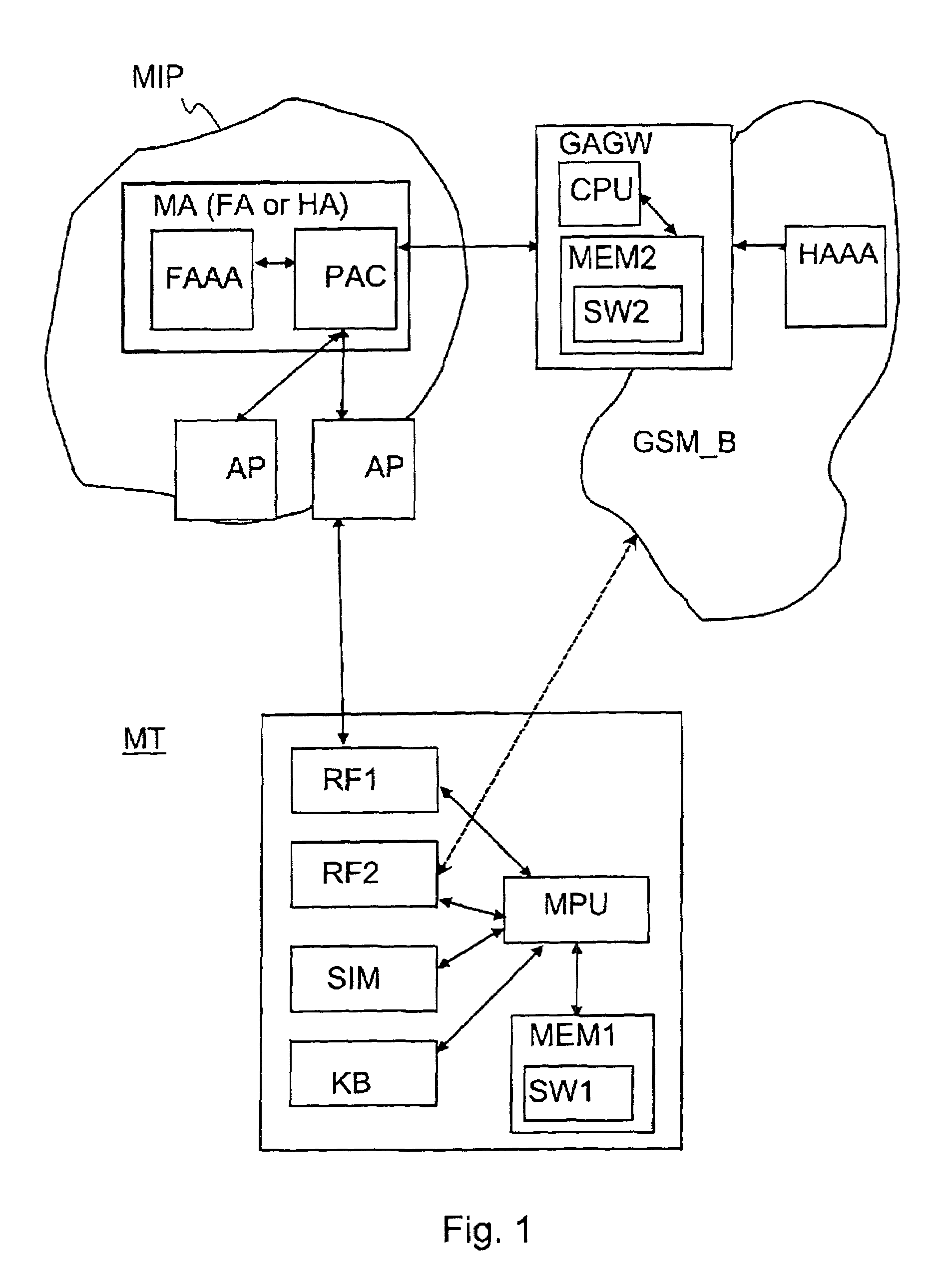
Secure session keys context
InactiveUS20070060127A1Faster and efficient handoffUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsAccess networkExtensibility
Handoffs must be fast for wireless mobile nodes without sacrificing the security between a mobile node and wireless access points in an access network. A secure session keys context approach is shown having all the good features, like mobility and security optimization, of the currently existing proposals of key-request, pre-authentication, and pre-distribution but also providing improved scalability for the access network and for the mobile node. The new approach is compared to the existing proposals including memory requirements and especially how to reduce memory usage using a “just-in-time” transfer of security information between access points and a mobile node during a handover.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
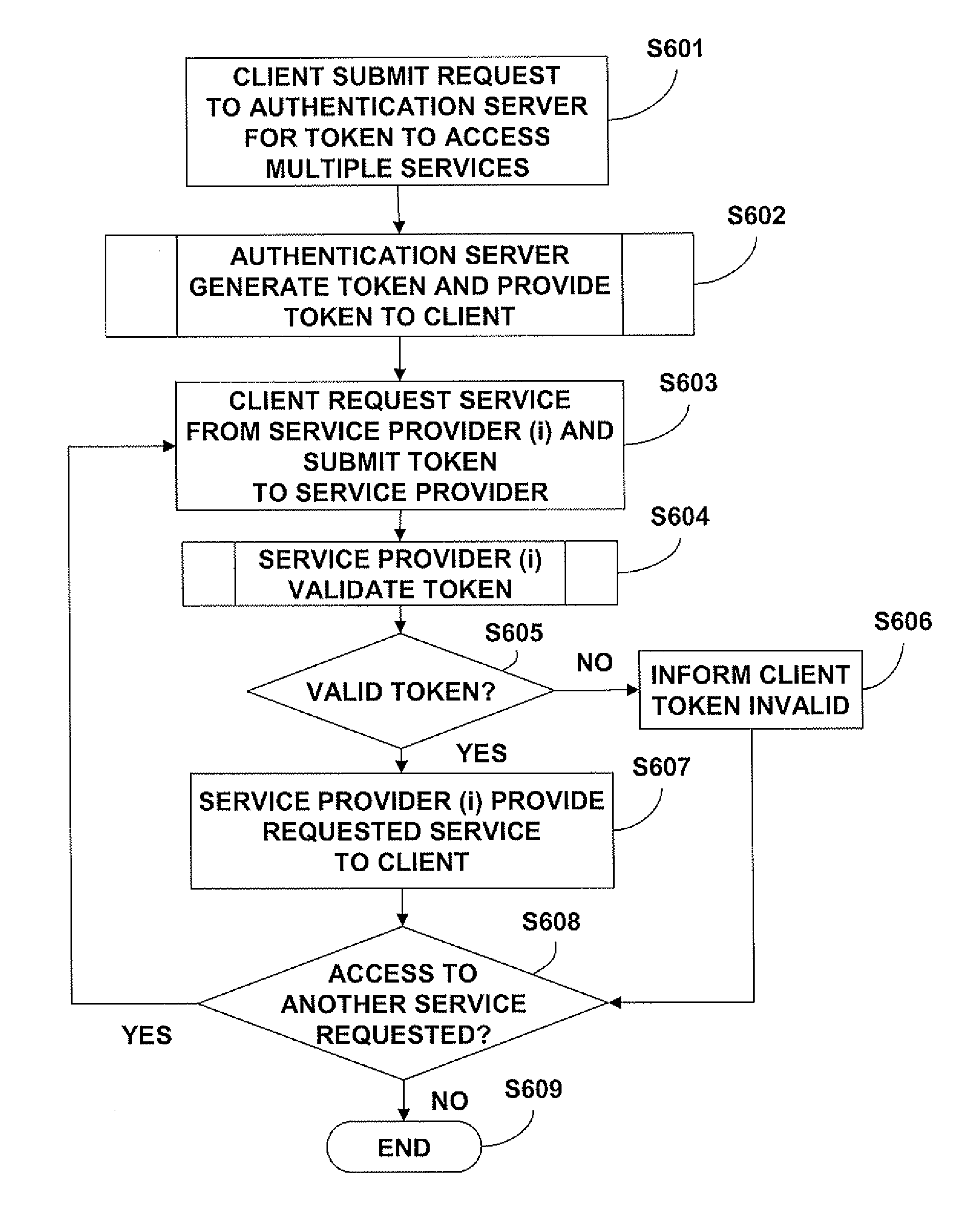
Security token destined for multiple or group of service providers
InactiveUS20110239283A1Easy to useEliminate needDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAuthentication serverWorkstation
An authentication server generates a security token to be used by a client for accessing multiple service providers by obtaining a secret key for each specified service provider, generating a saltbase, generating a salt for each service providers using the saltbase, the secret key, and a hashing algorithm, generating a session key that includes the salt, assigning an order to each of the generated salts, and arranging the salts based on the orders, generating a presalt for each provider using the salt for each previous provider, generating a postsalt for each of the specified service providers using the salt for each following provider, generating a blob for each of the specified service providers using the saltbase, the respective presalt, and the respective postsalt, inserting the generated blobs for the specified service providers in the security token, and providing the generated security token to the client workstation.
Owner:CANON KK
Efficient and secure authentication of computing systems
ActiveUS20050210252A1Efficiently and securely authenticatingKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsClient-sideProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
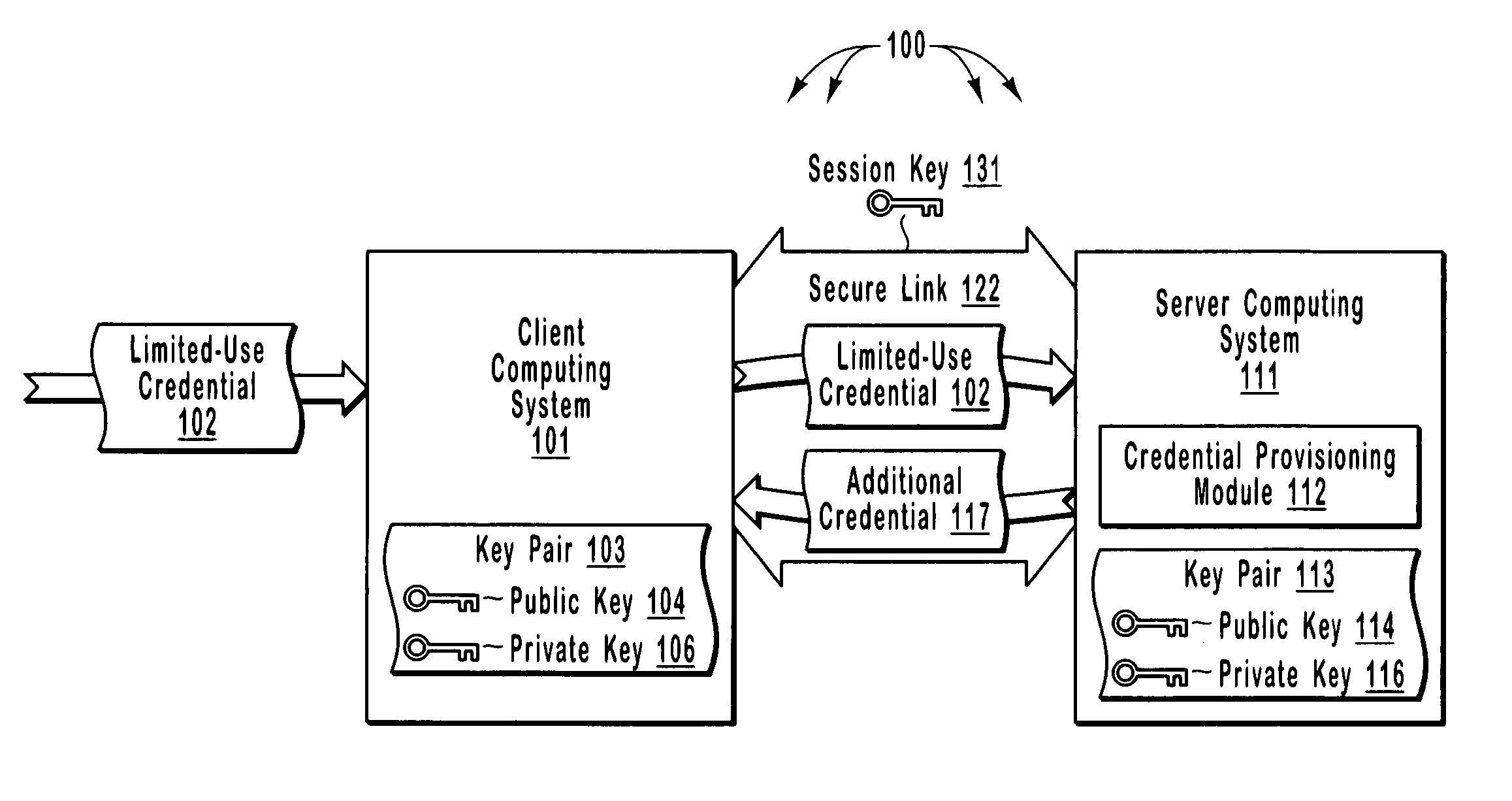
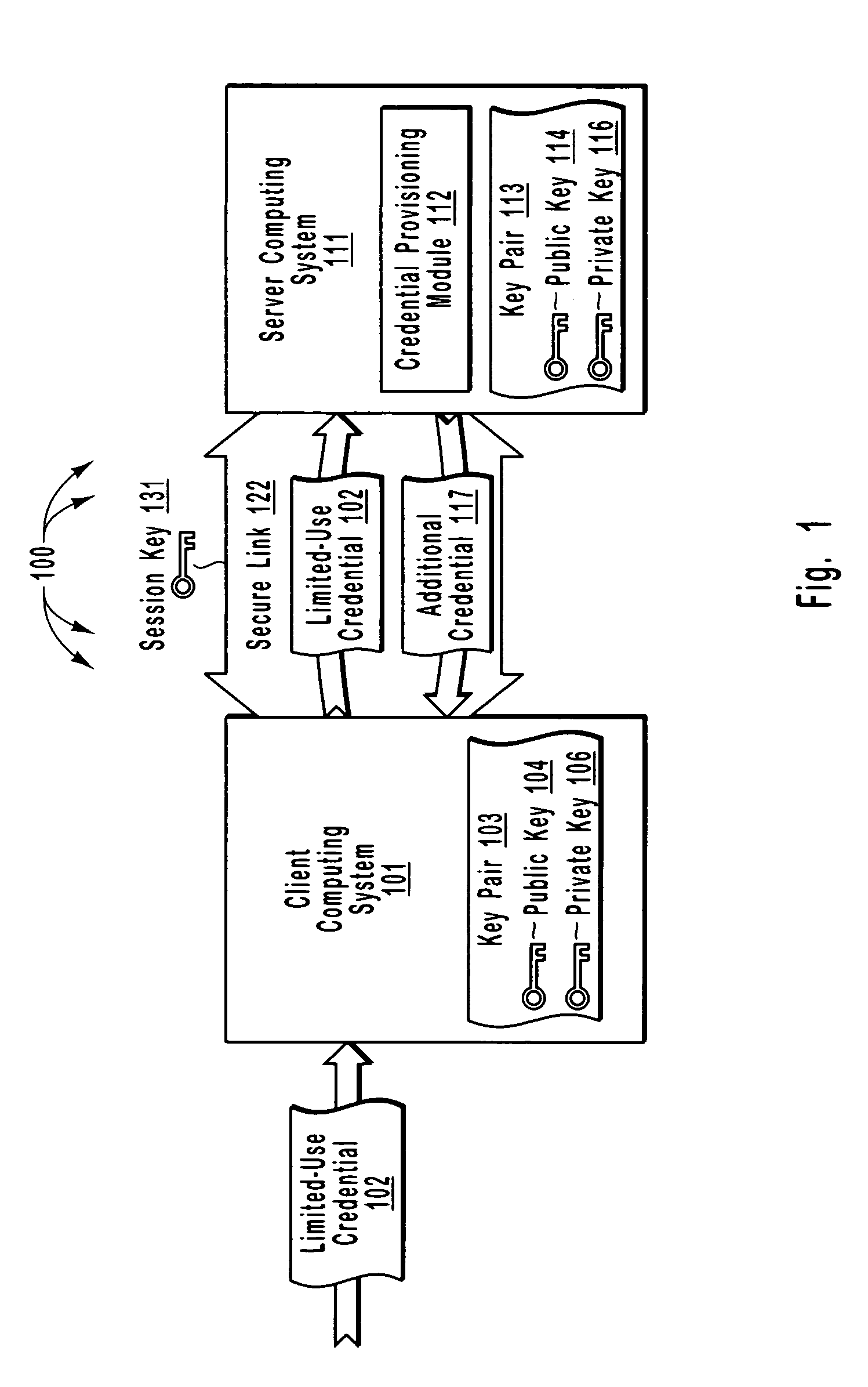
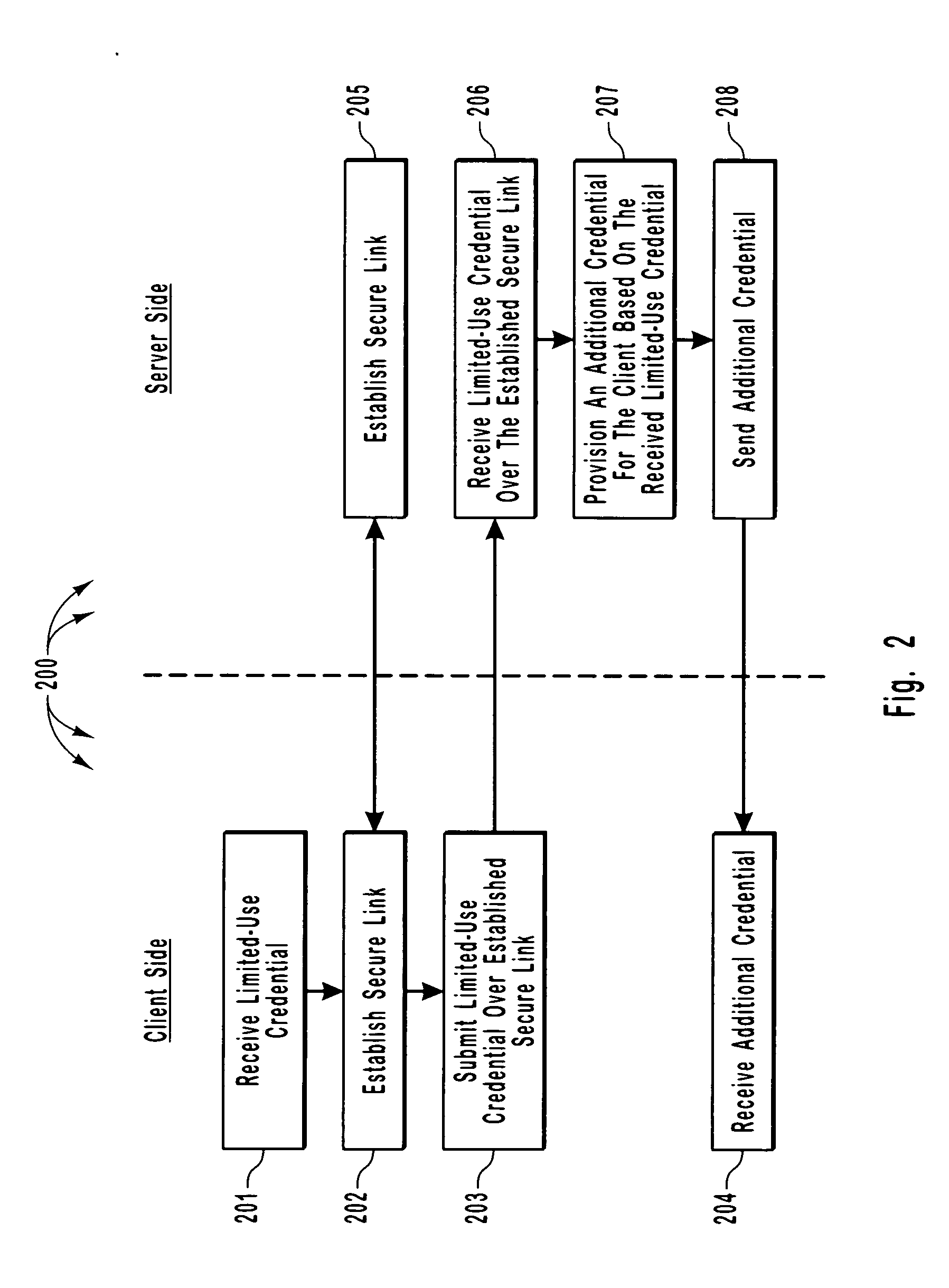
The principles of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and computer program products for more efficiently and securely authenticating computing systems. In some embodiments, a limited use credential is used to provision more permanent credentials. A client receives a limited-use (e.g., a single-use) credential and submits the limited-use credential over a secure link to a server. The server provisions an additional credential (for subsequent authentication) and sends the additional credential to the client over the secure link. In other embodiments, computing systems automatically negotiate authentication methods using an extensible protocol. A mutually deployed authentication method is selected and secure authentication is facilitated with a tunnel key that is used encrypt (and subsequently decrypt) authentication content transferred between a client and a server. The tunnel key is derived from a shared secret (e.g., a session key) and nonces.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
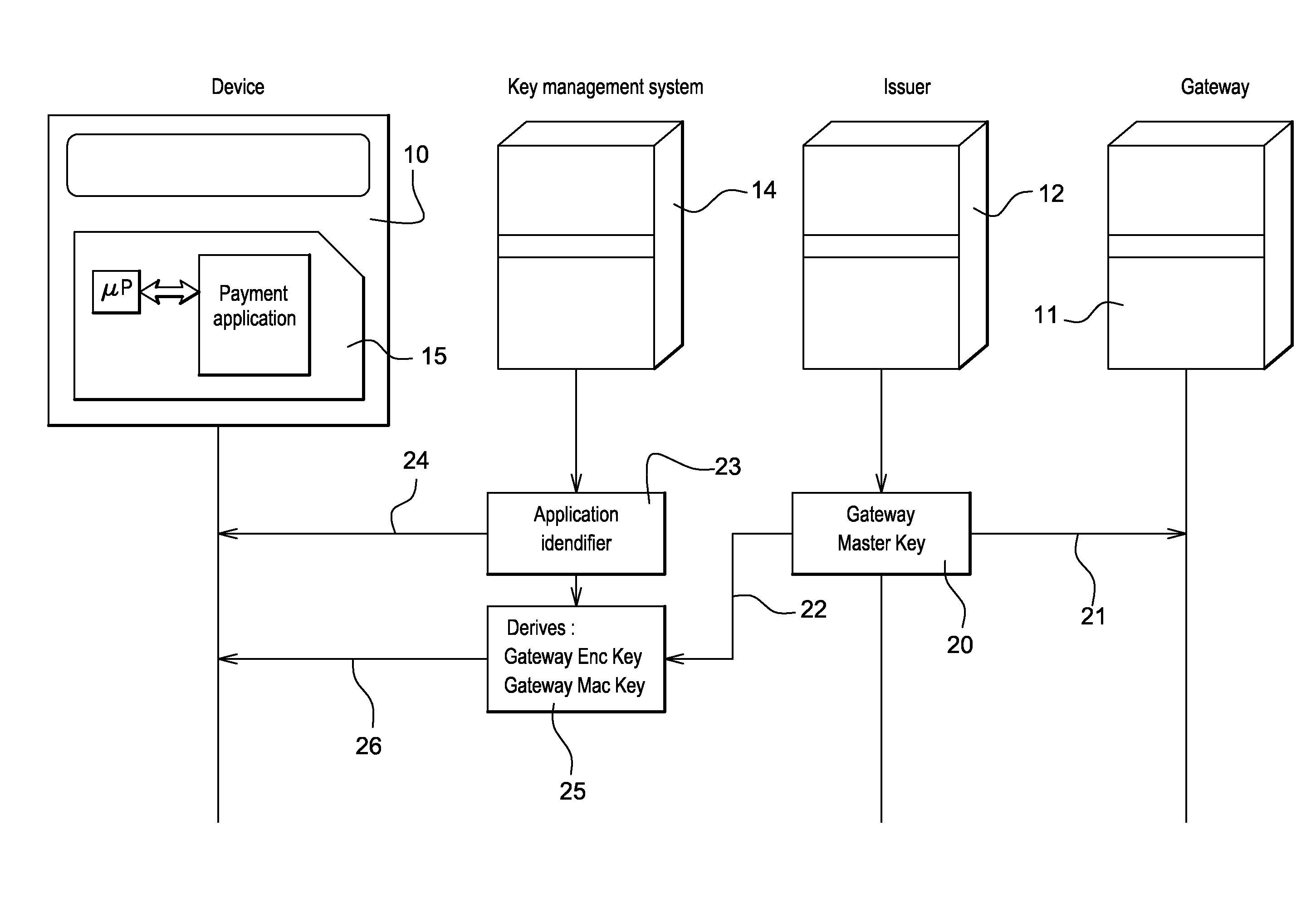
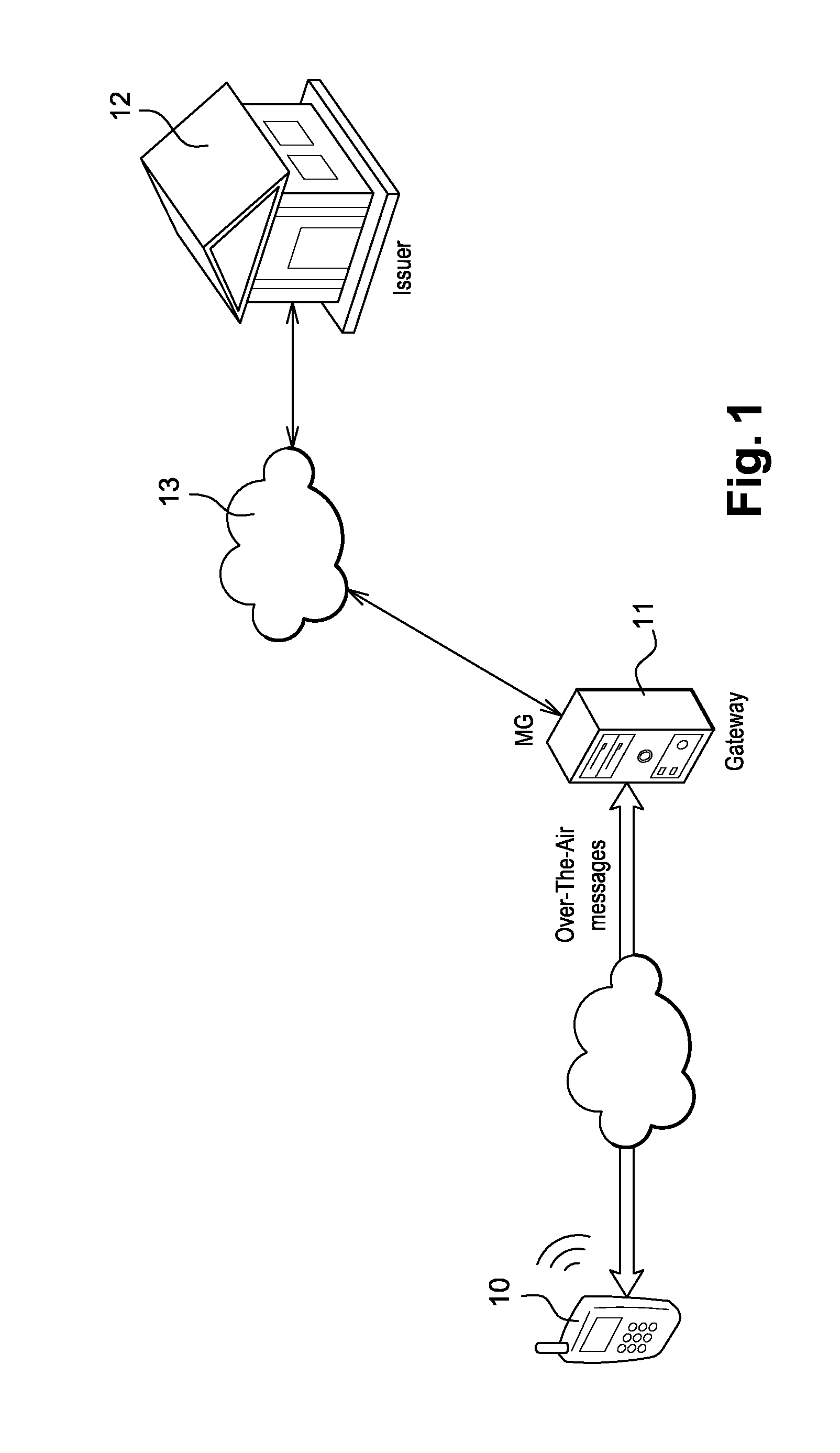
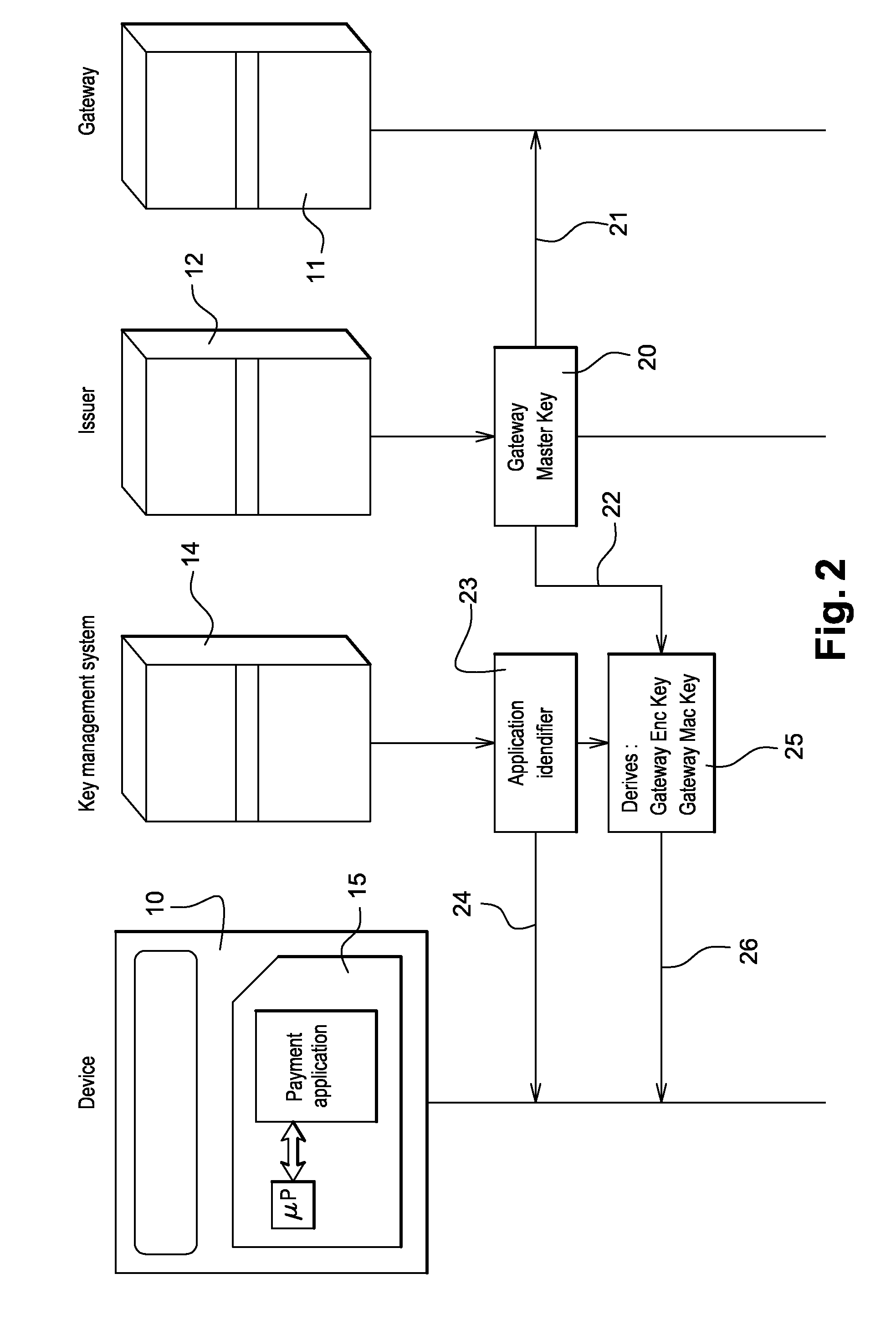
Method for securing over-the-air communication between a mobile application and a gateway
InactiveUS20160232523A1Minimize the numberSimplified generationMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationPayment transactionApplication software
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods for performing issuer updates of data stored in a mobile device, a remote authentication, a remote payment transaction or enable the configuration of mobile application functions or operations. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method and system for securing an issuer updates processing for mobile payment application. When an update transaction is initiated, the payment application increments an Application Transaction Counter ATC and derives from this ATC a session keys. Sensitive user credential data are encrypted with the computed session keys before transmission to a gateway which is configured to compute the session keys for decryption. The decrypted user credential data are forwarded to a payment application issuer for updates.
Owner:GEMPLU
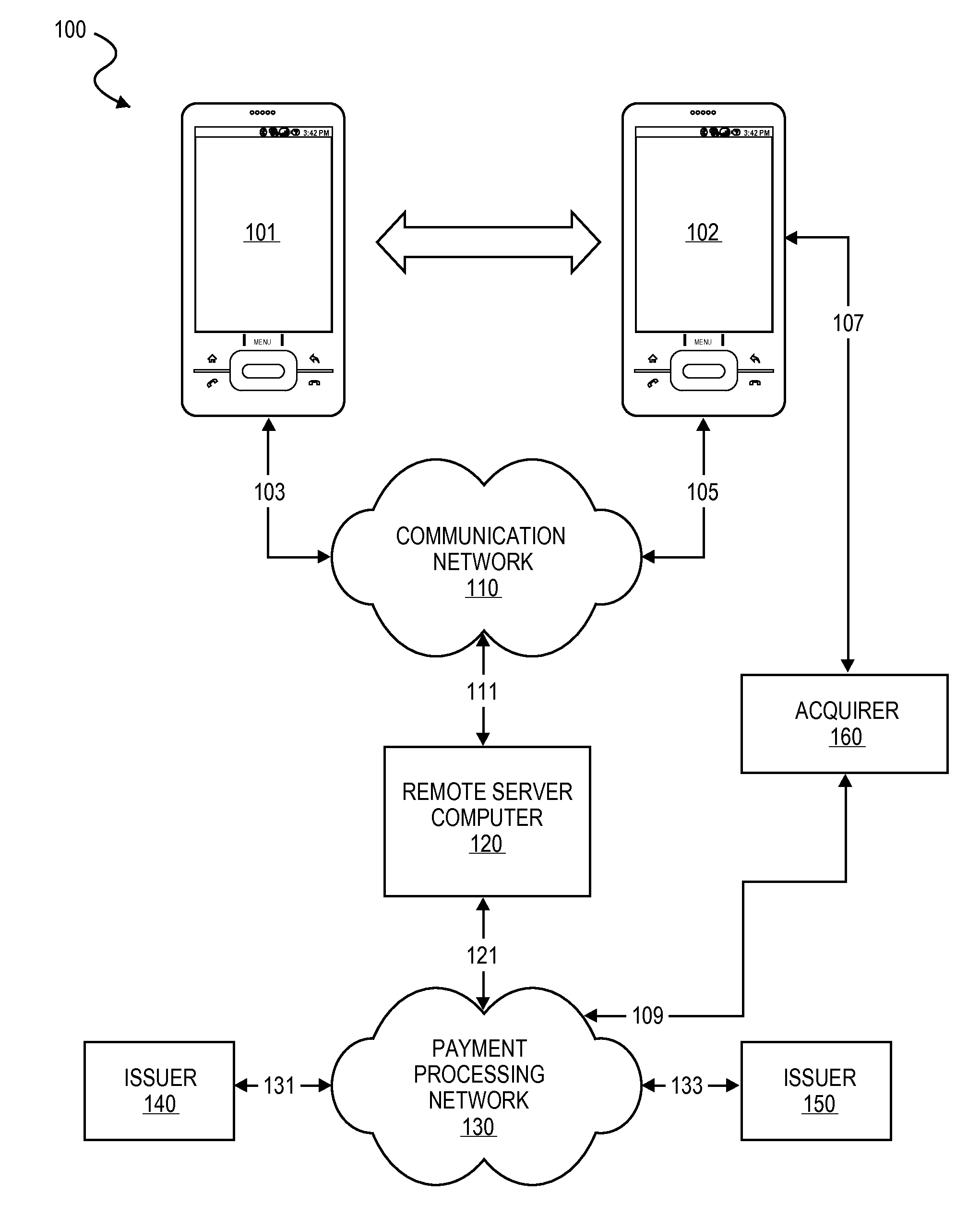
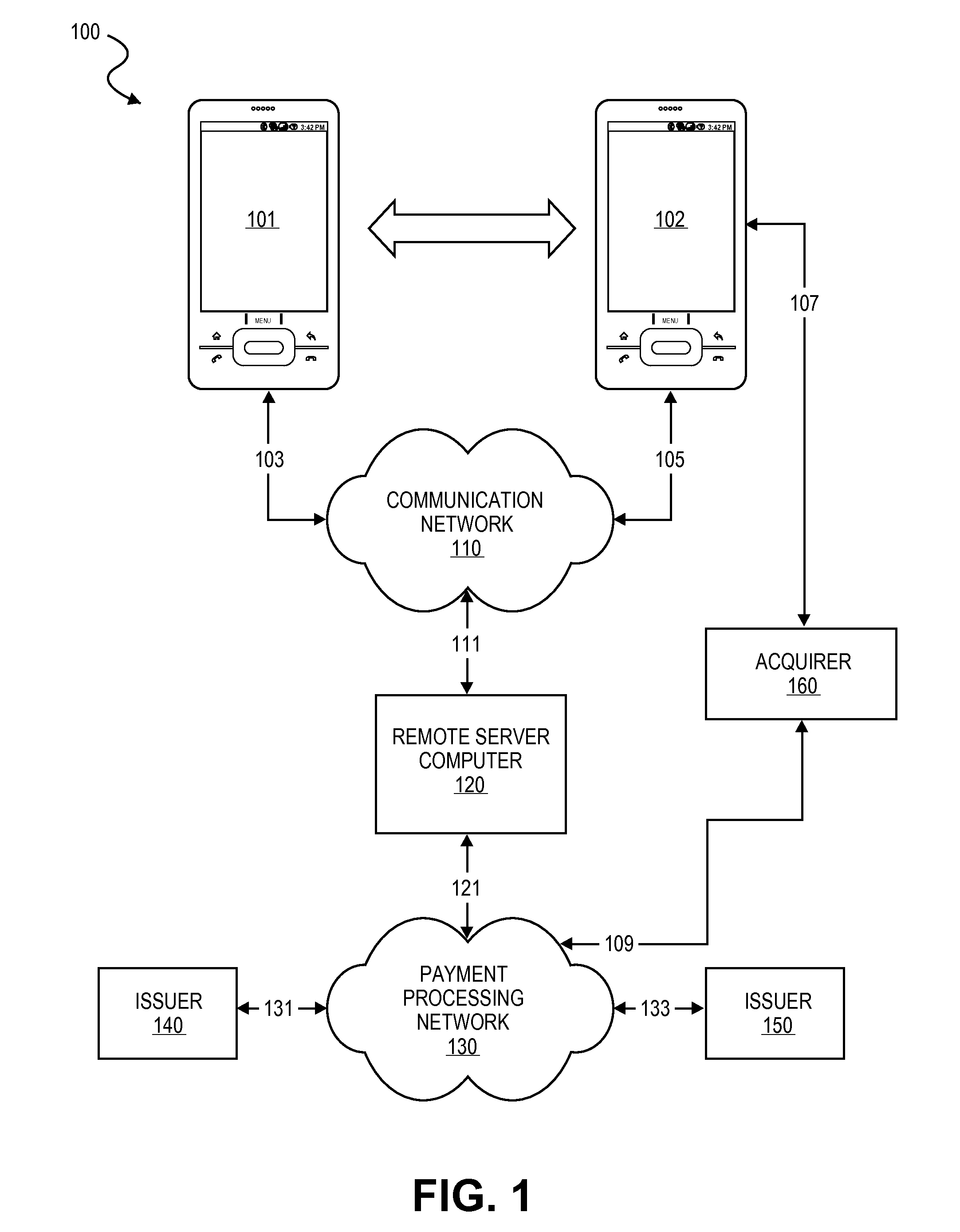
Transaction Using A Mobile Device With An Accelerometer
Embodiments of the invention may use a first accelerometer to measure first acceleration data of a first device. Other interaction data, including time data and geographic location data, generated by the first device may also be recorded. First acceleration data is compared by a remote server computer to second acceleration data generated by a second accelerometer in a second device. If the first and second accelerometer data are substantially equal, it can be determined that the devices have interacted and communications can be initiated. After communications are initiated, a financial transaction is conducted. Accelerometer data may be stored and / or used as part of the authentication process in a payment processing network. Other embodiments of the invention use the accelerometer to generate movement security data to make financial transaction more secure. Accelerometer data is used for authentication, security, encryption, session keys, non-repudiation, or fraud protection.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Method and system for capwap intra-domain authentication using 802.11r
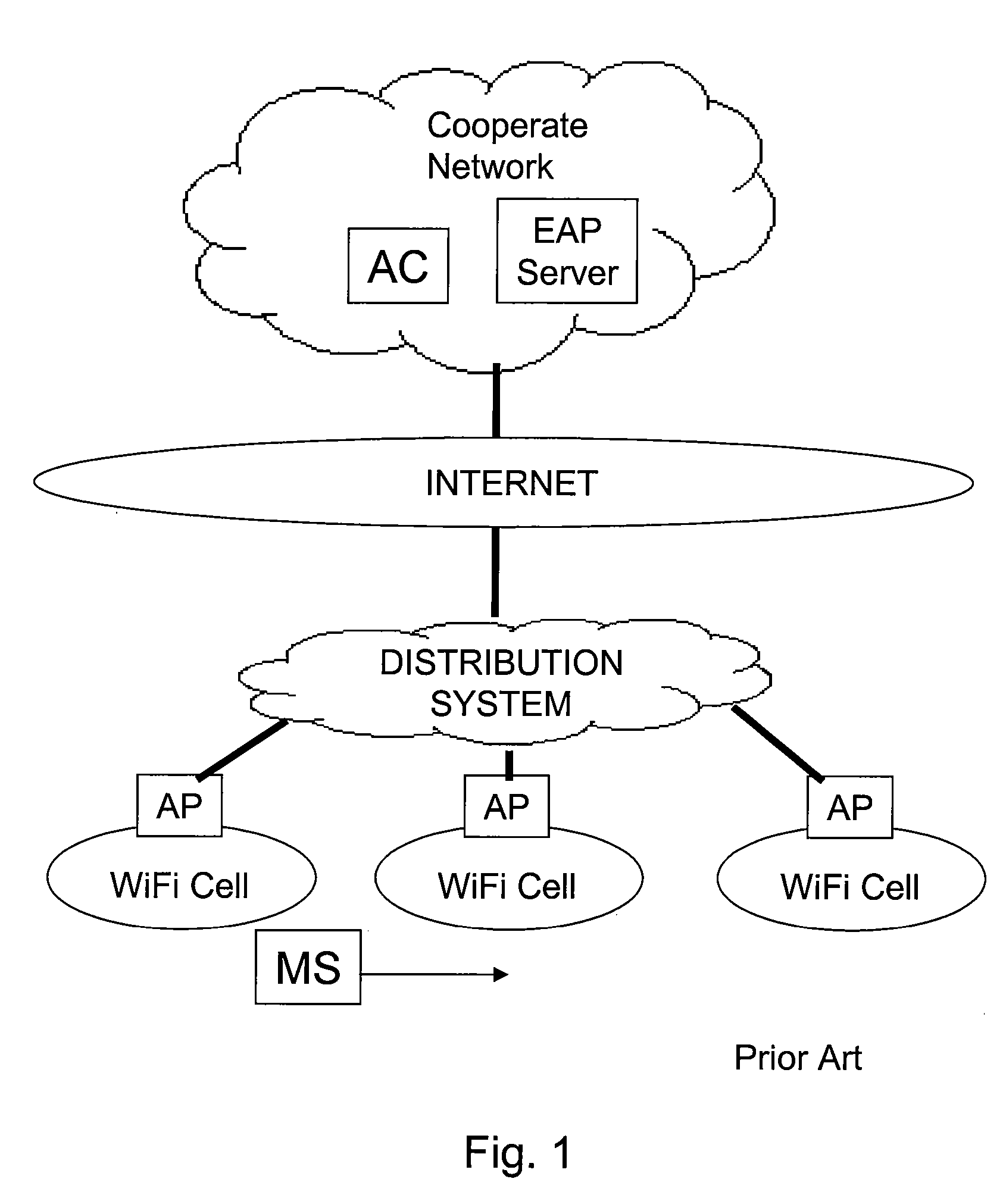
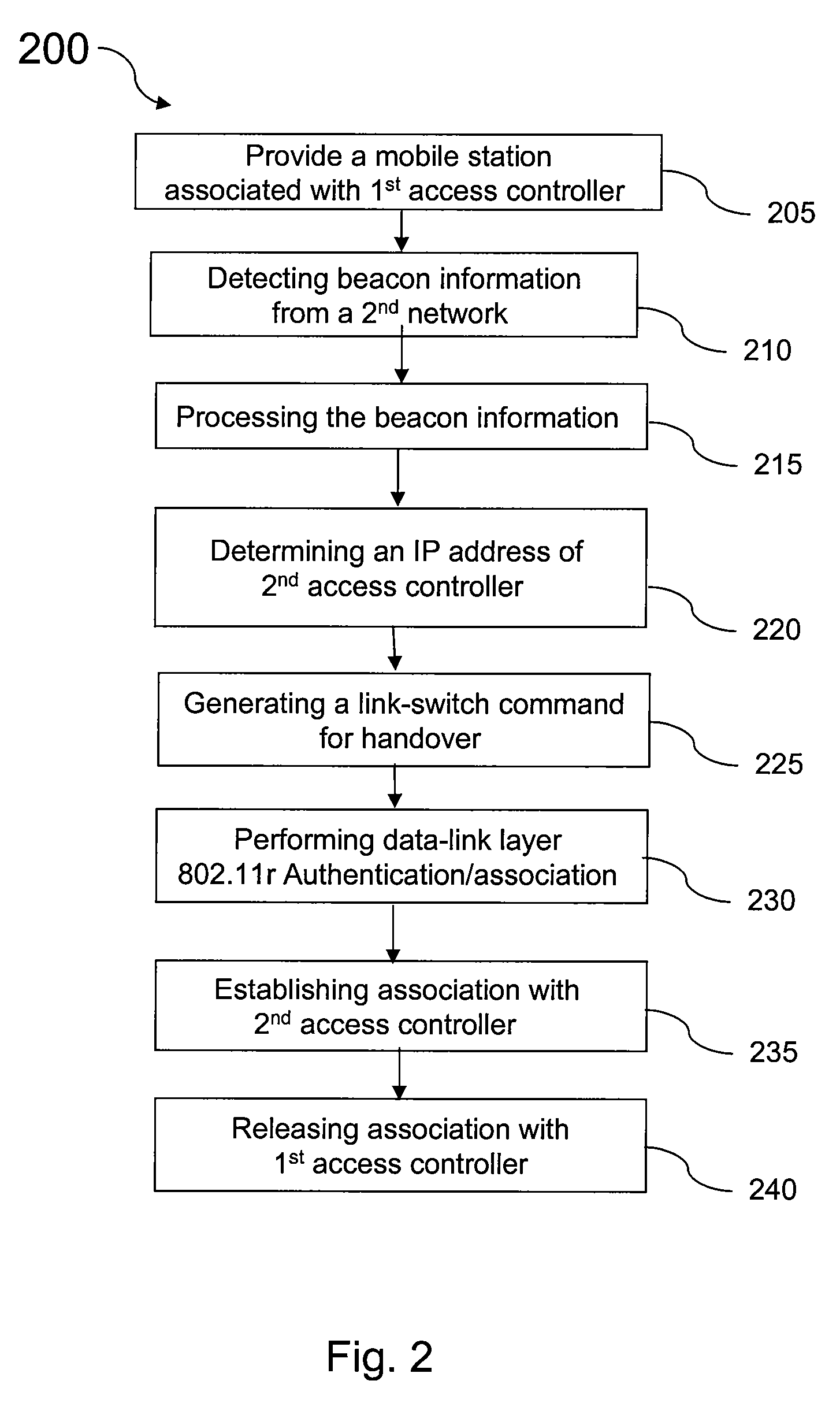
InactiveUS20080072047A1Improve distributionEasy accessNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiple keys/algorithms usageMobile stationCAPWAP
An solution for a mobile station to perform intra-domain inter-access controller authentication using an 802.11r protocol in CAPWAP architecture is presented. The access controller is the authenticator that is configured to store a top-level and second-level shared authentication keys in a key hierarchy defined in 802.11r. The mobile station first-time association and re-association after inter-access-point handoff can be performed through authentication request / response message exchange between the mobile station and the access controller. The new access controller after handoff gets top-level key from the old access controller called an anchor authenticator. The mobile station and the new access controller generate a new second-level key and session key to complete the authentication.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
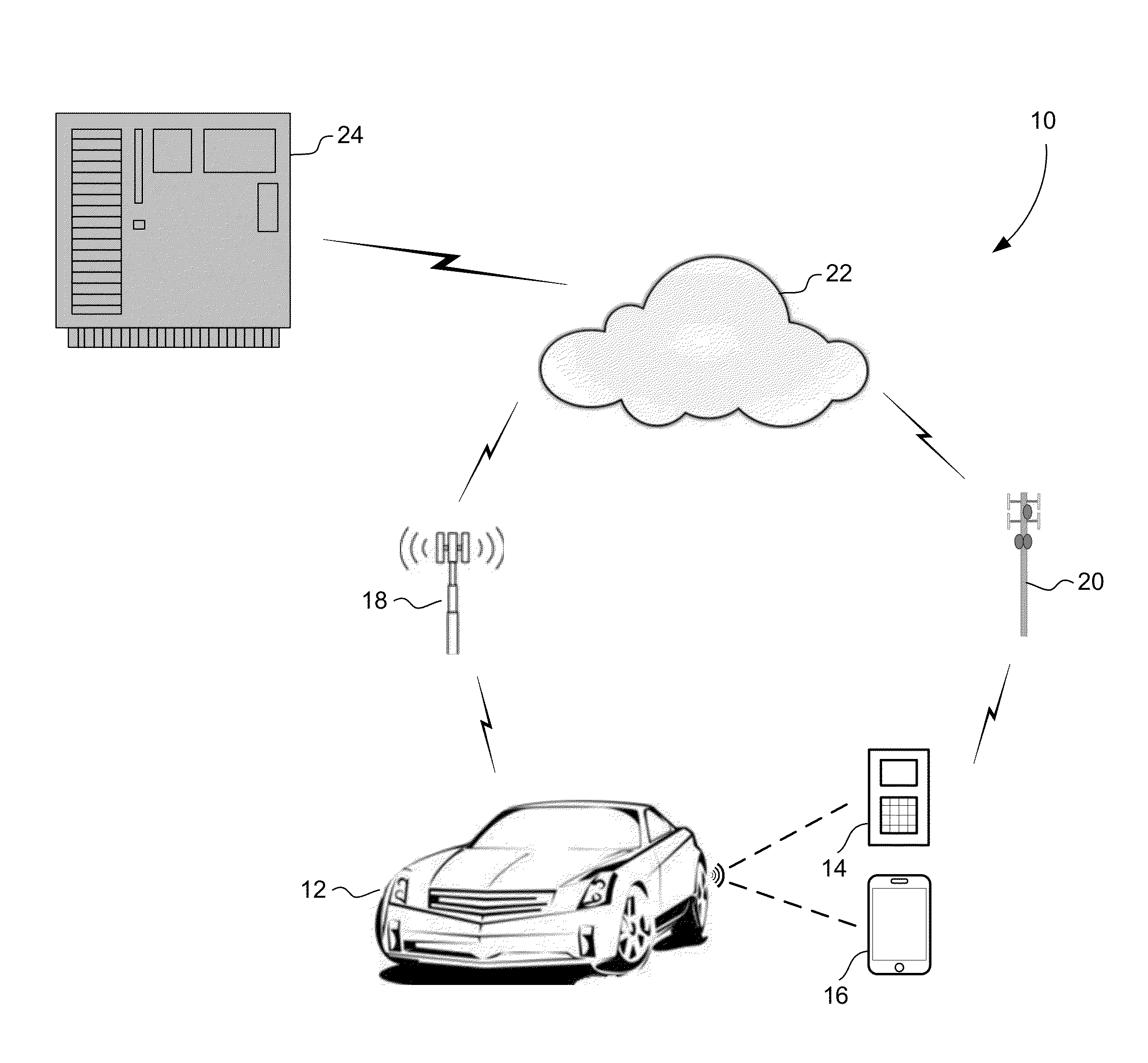
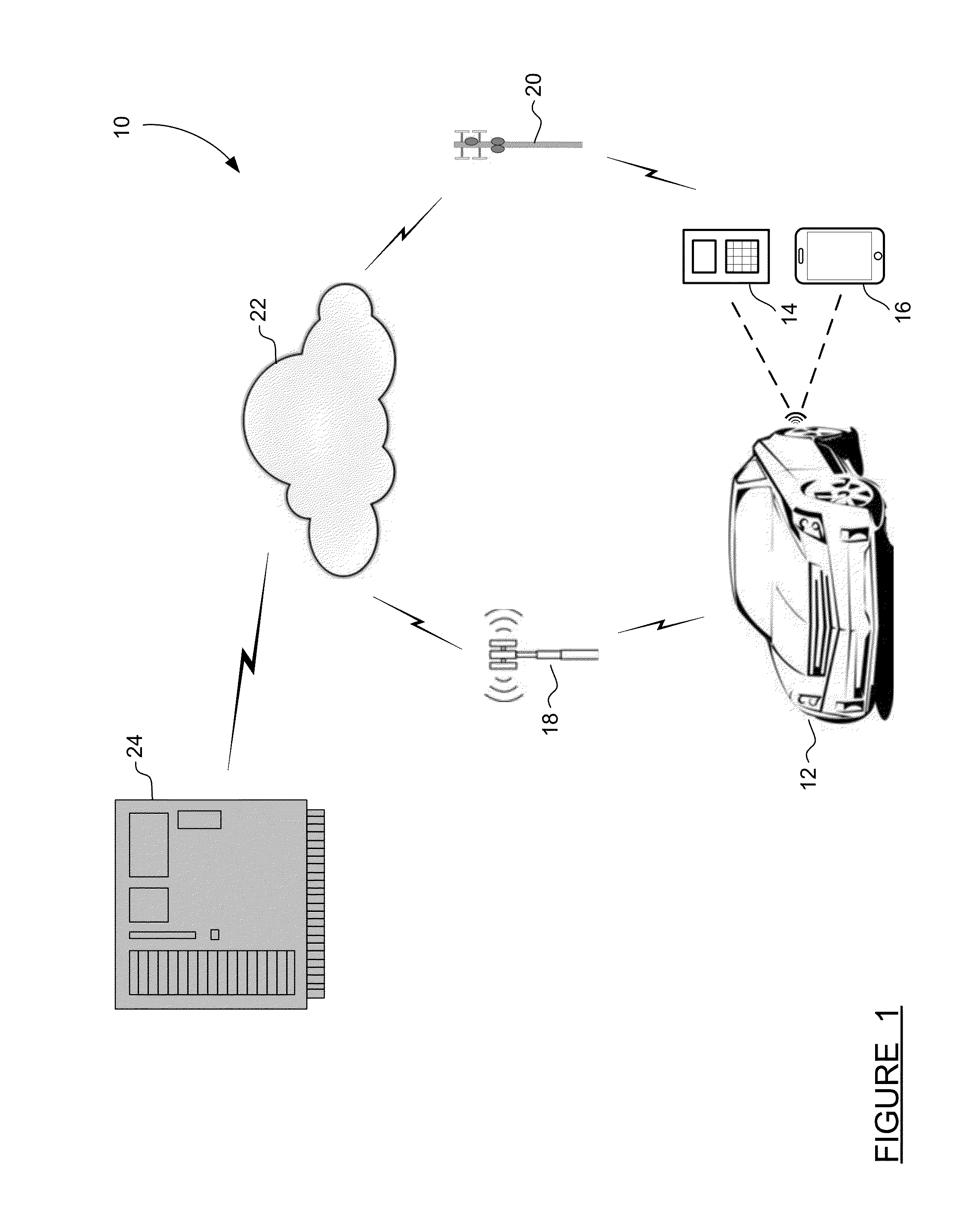
Method and apparatus for secure pairing of mobile devices with vehicles using telematics system
A method for establishing secure wireless communications between a mobile device and a vehicle, where a user is not required to enter a password, but instead the telematics system is used to bootstrap the trust between the mobile device and the vehicle. The user initiates the process by pressing a button on the mobile device to request pairing. The vehicle uses its secure OnStar cellular communication link to verify the mobile device with the OnStar server, which generates and sends a session key to the vehicle via the vehicle-OnStar cellular connection, and also sends the session key to the mobile device via the device's own cellular connection. The session key serves as a shared secret, such that the vehicle can issue a secrecy challenge to the mobile device. When the mobile device responds appropriately, a trusted wireless communications link can be established between the mobile device and the vehicle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
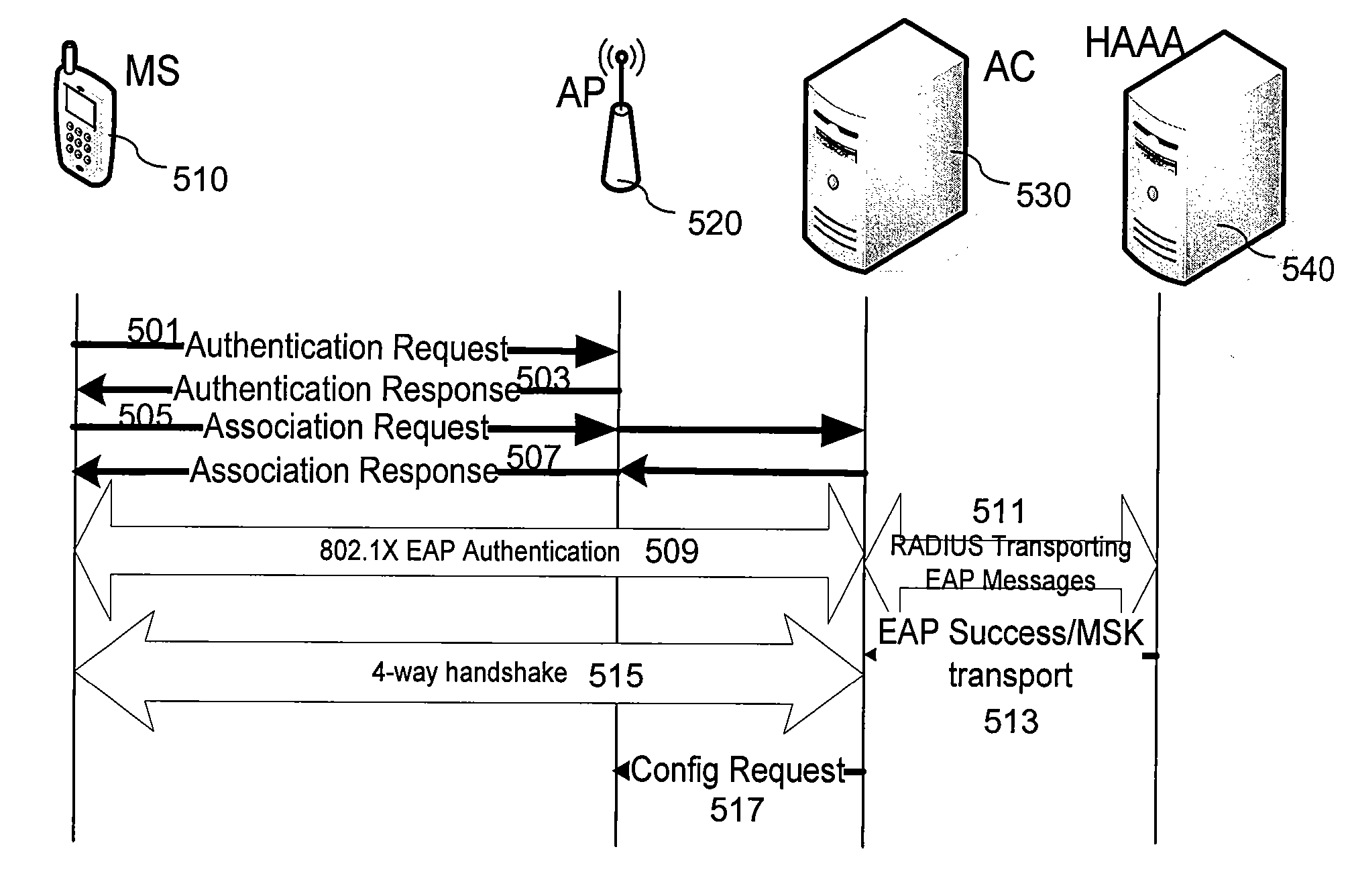
Authentication method for fast handover in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS7158777B2Communication securityIncrease speedUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionData taking preventionSecure communicationFast handover
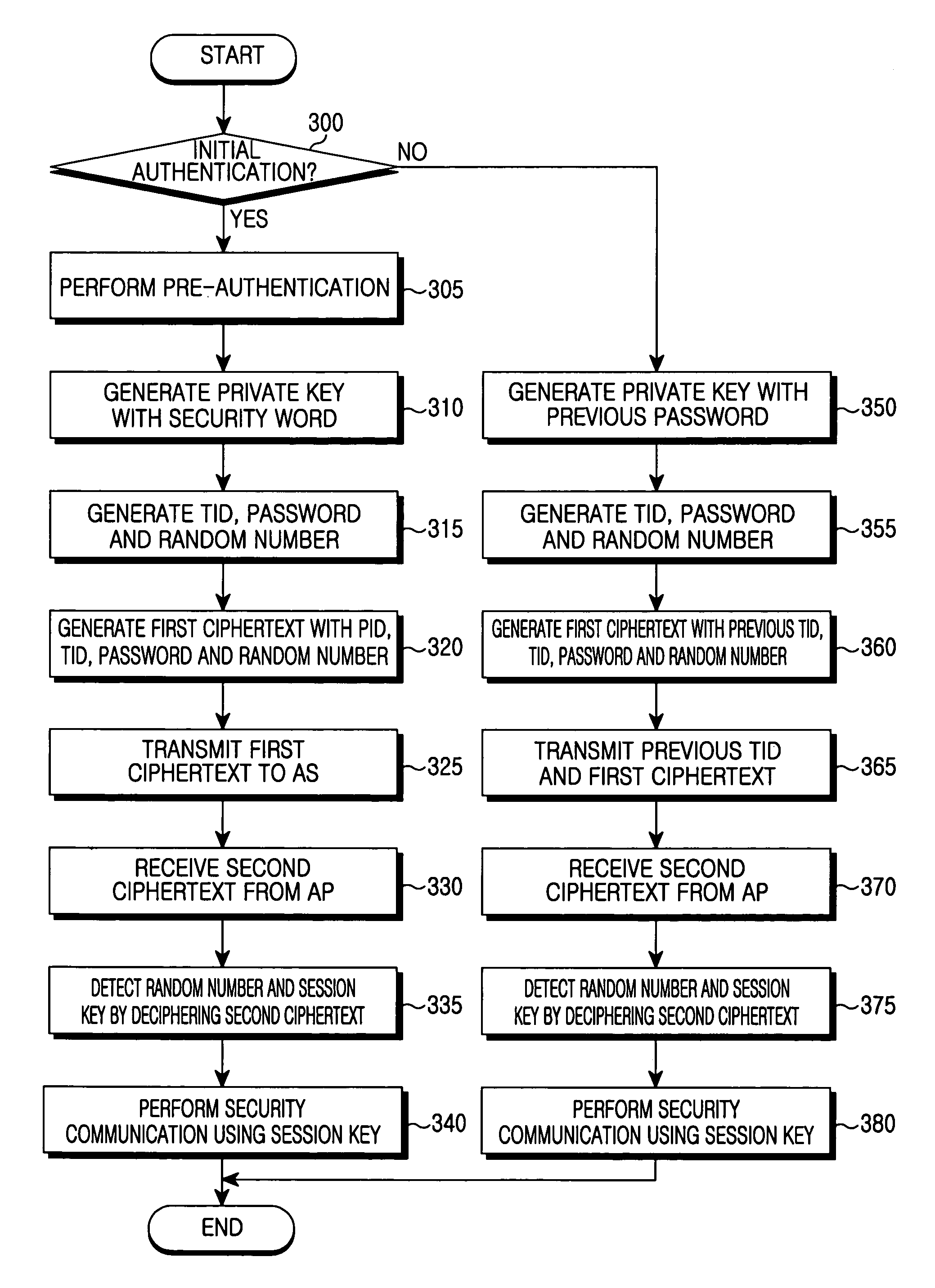
Disclosed is a method for authenticating a mobile node in a wireless local area network including at least two access points and an authentication server. When the mobile node associates with a first access point and performs initial authentication, the mobile node receives a first session key for secure communication from the authentication server by using a first private key generated with a secret previously shared with the authentication server, and the first access point receives the first session key from the authentication server by using a second private key previously shared with the authentication server. When the mobile node is handed over from the first access point to a second access point and performs re-authentication, the mobile node receives a second session key for secure communication from the authentication server by using a third private key generated with authentication information generated during previous authentication and shared with the authentication server and the second access point receives the second session key from the authentication server by using the second private key previously shared with the authentication server.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Secret key negotiation method and device
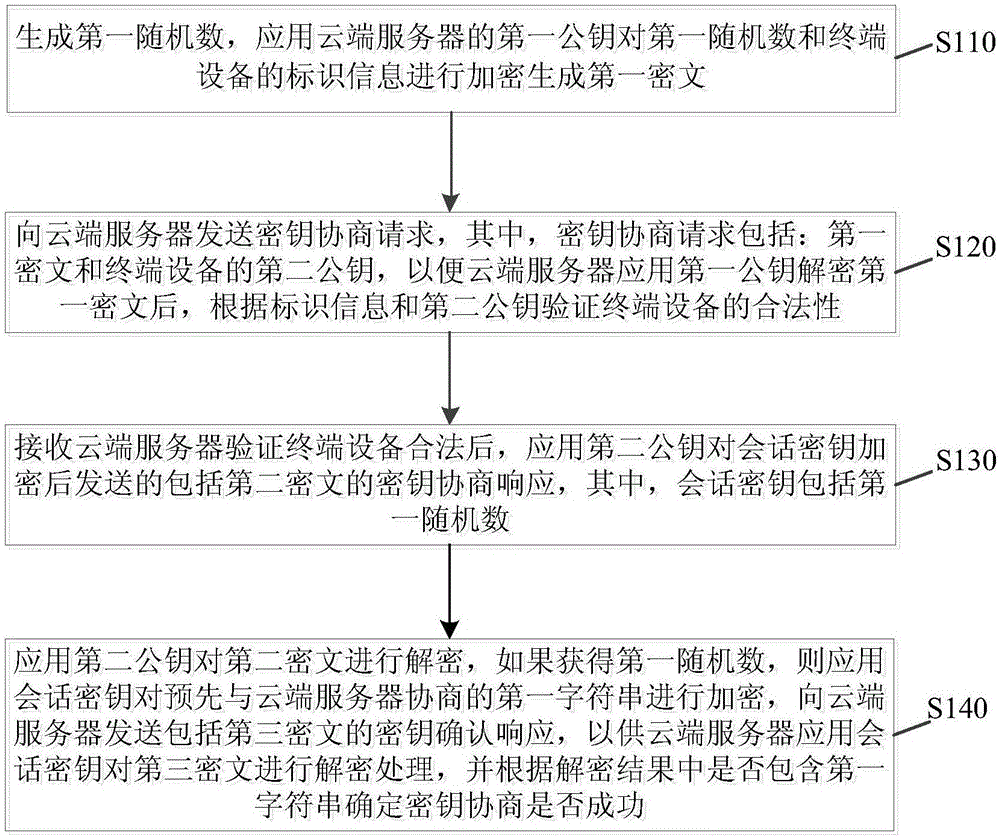
ActiveCN106603485AImprove securityReliable and secure connectionKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextTerminal equipment
The invention discloses a secret key negotiation method and a secret key negotiation device. The secret key negotiation method comprises the steps of: generating a first random number, encrypting the first random number and identification information of terminal equipment by using a first public key of a cloud server to generate a first ciphertext; sending a secret key negotiation request containing the first ciphertext and a second public key of the terminal equipment to the cloud server; receiving a secret key negotiation response containing a second ciphertext sent after the cloud server verifies that the terminal equipment is legal and a session key containing the first random number is encrypted by using the second public key; decrypting the second ciphertext by using a second private key, encrypting a first character string which negotiates with the cloud server in advance by using the session key when the first random number is obtained, and sending a secret key confirmation response containing a third ciphertext to the cloud server. The secret key negotiation method can complete the bidirectional identity authentication of the terminal equipment and the cloud server, establishes reliable and secure connection, reduces cost, improves security of data transmission, and is high in efficiency.
Owner:MIDEA SMART TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com