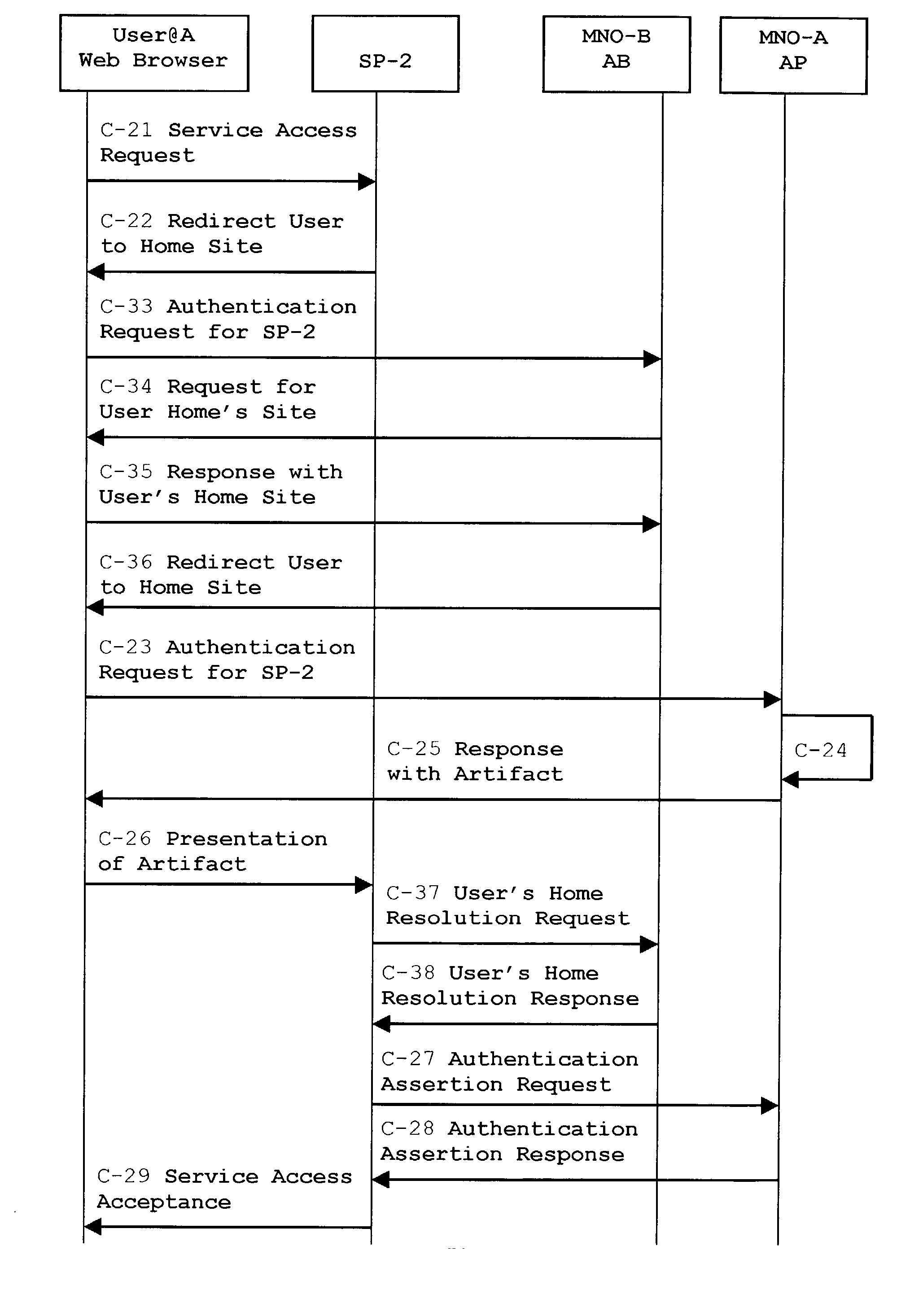
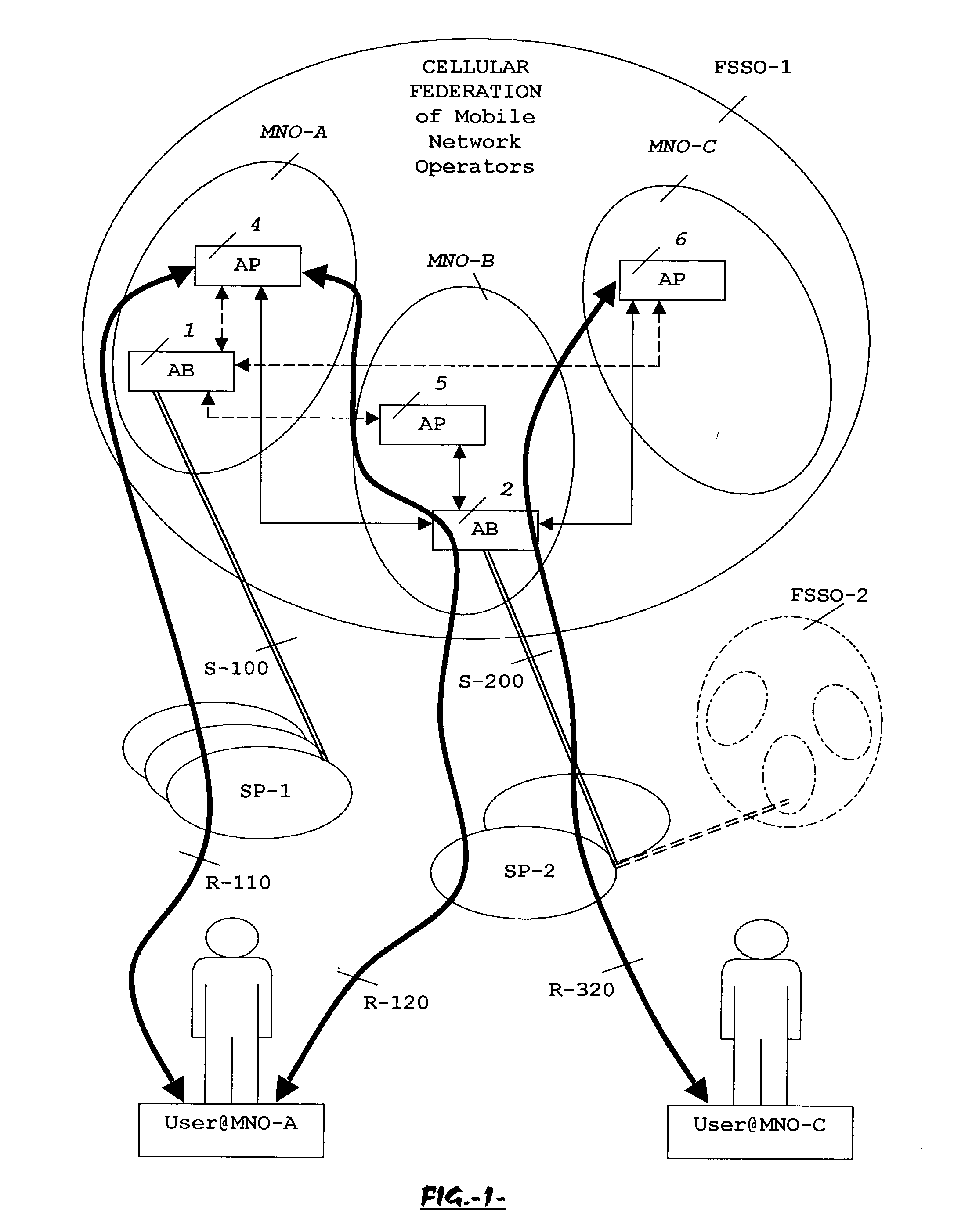
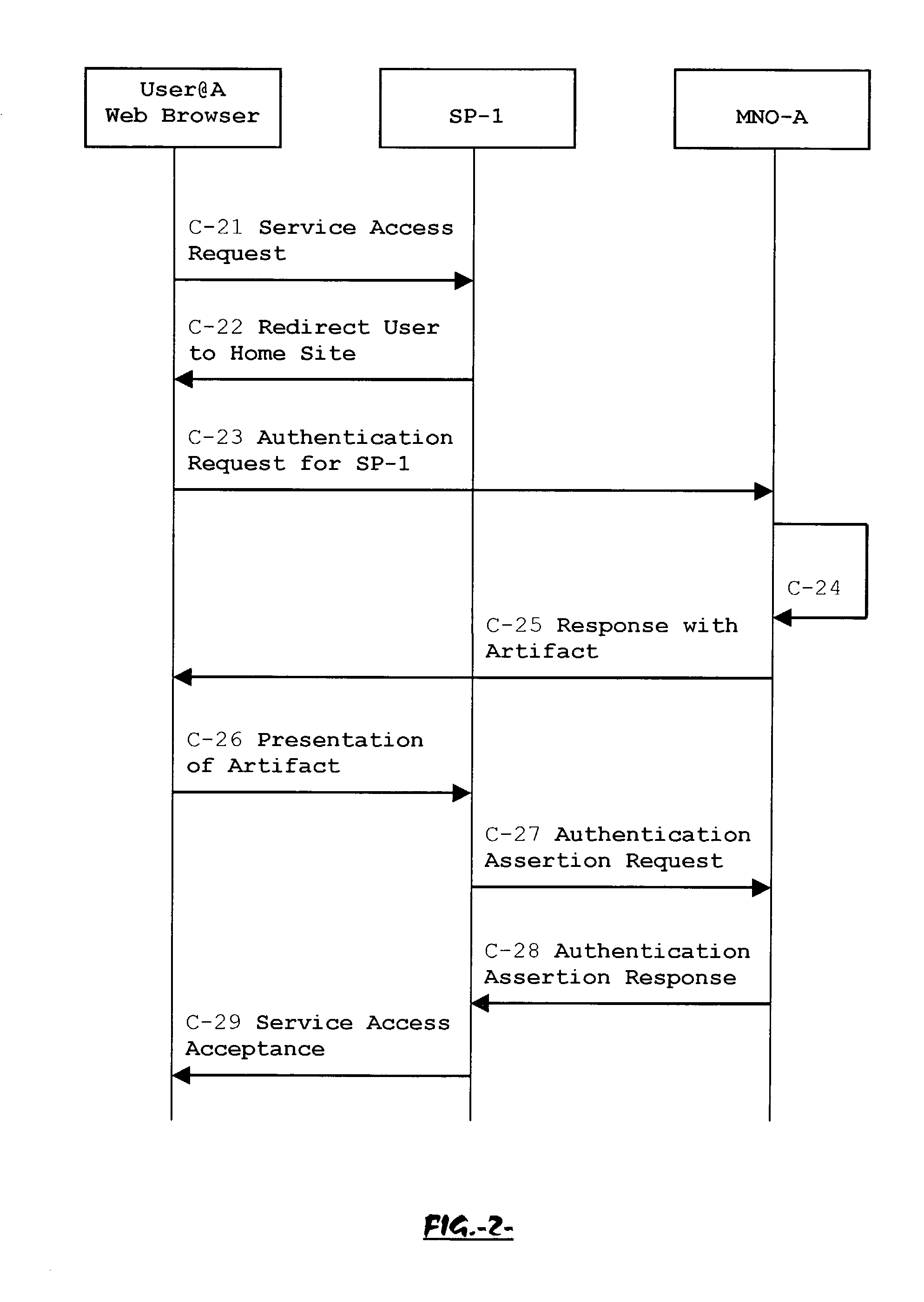
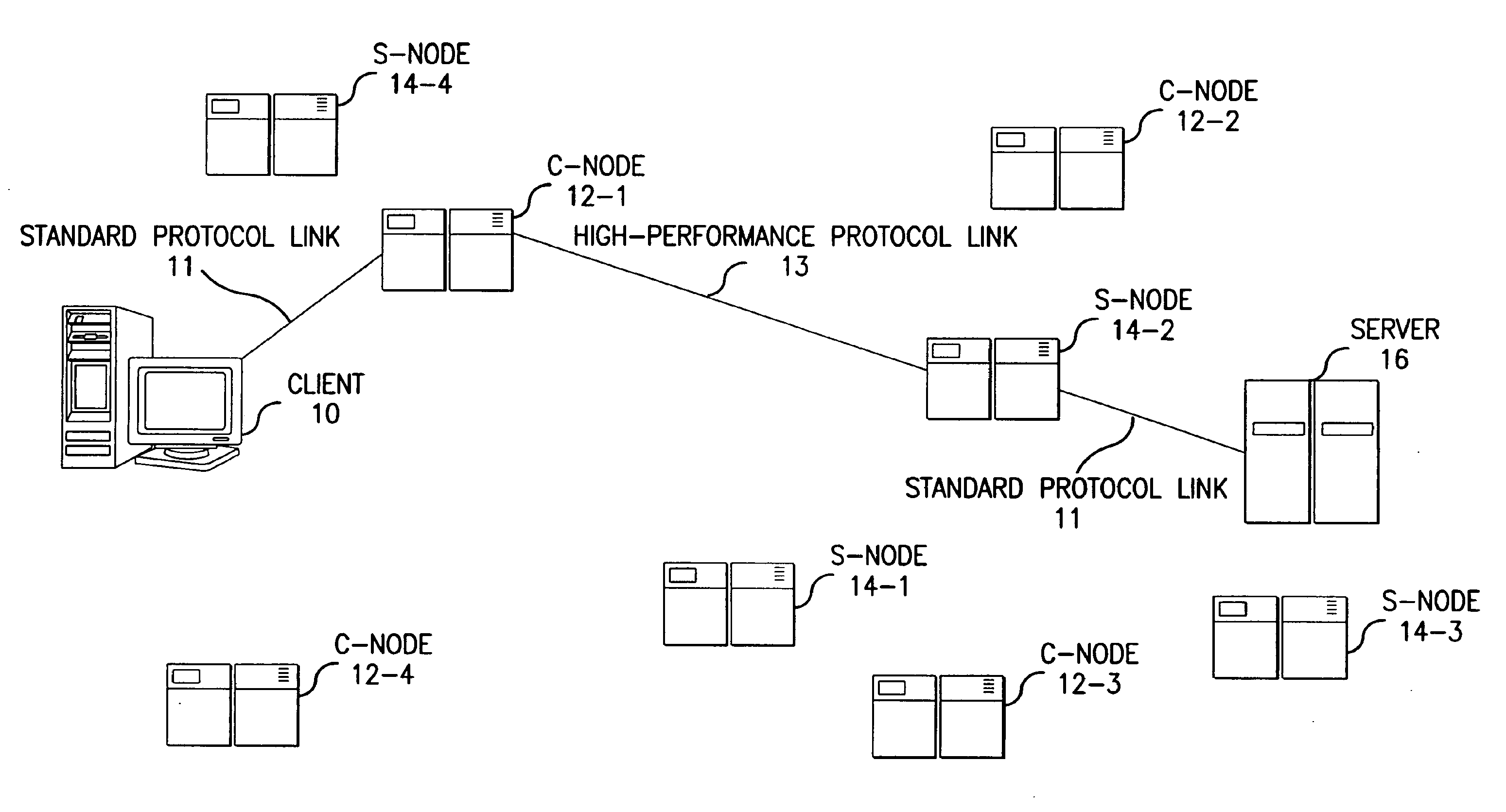
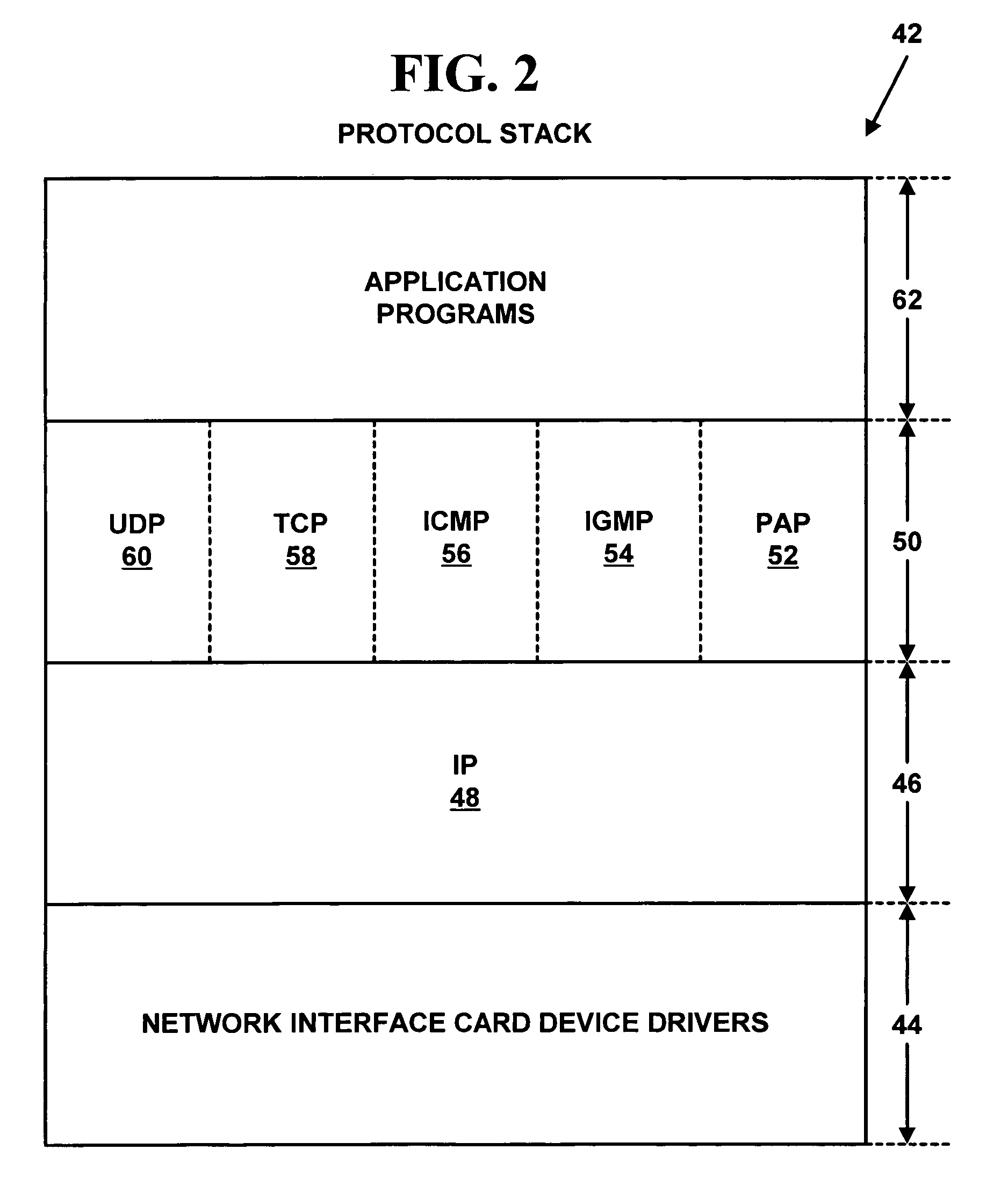
Patents
Literature
14655 results about "Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
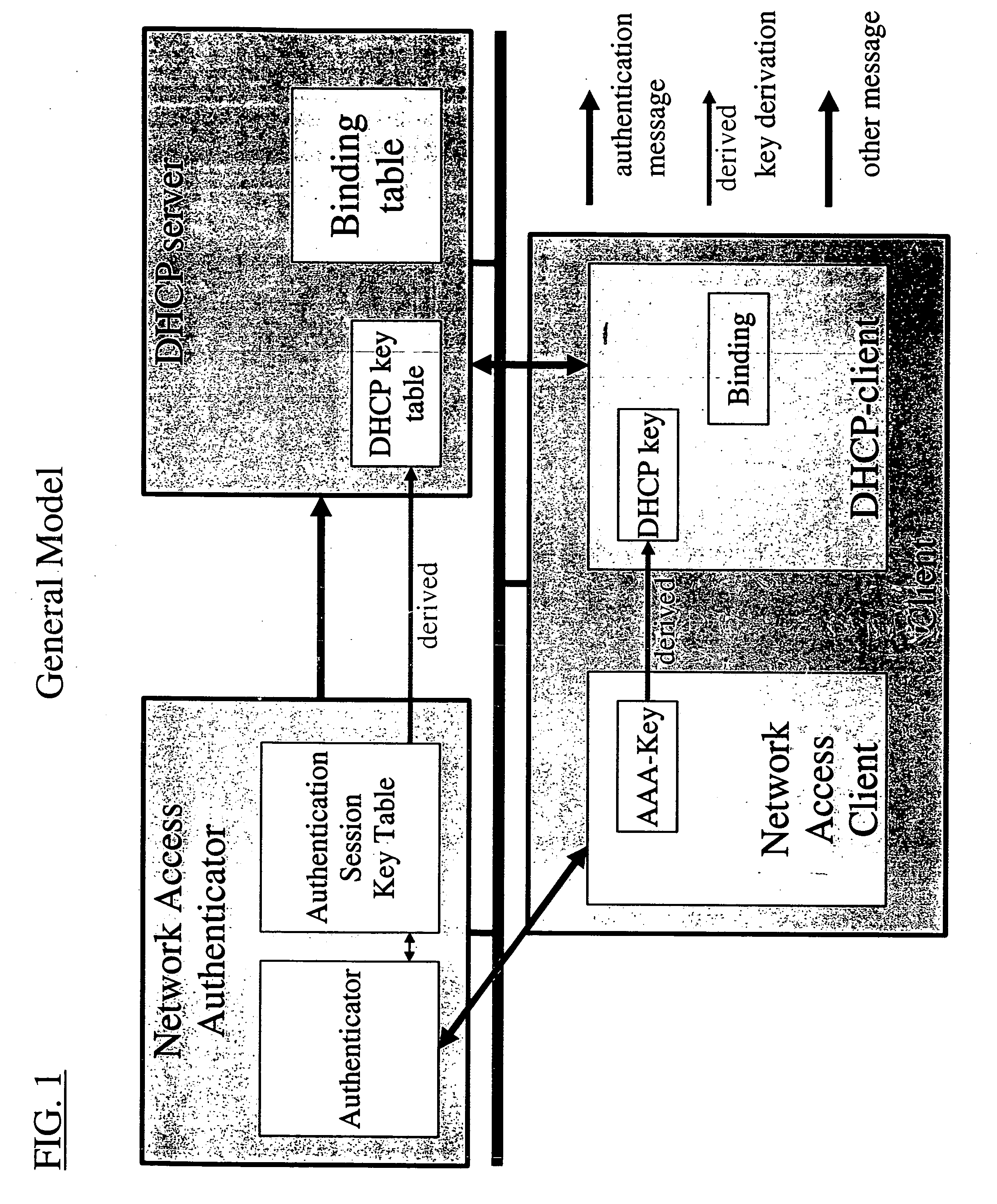
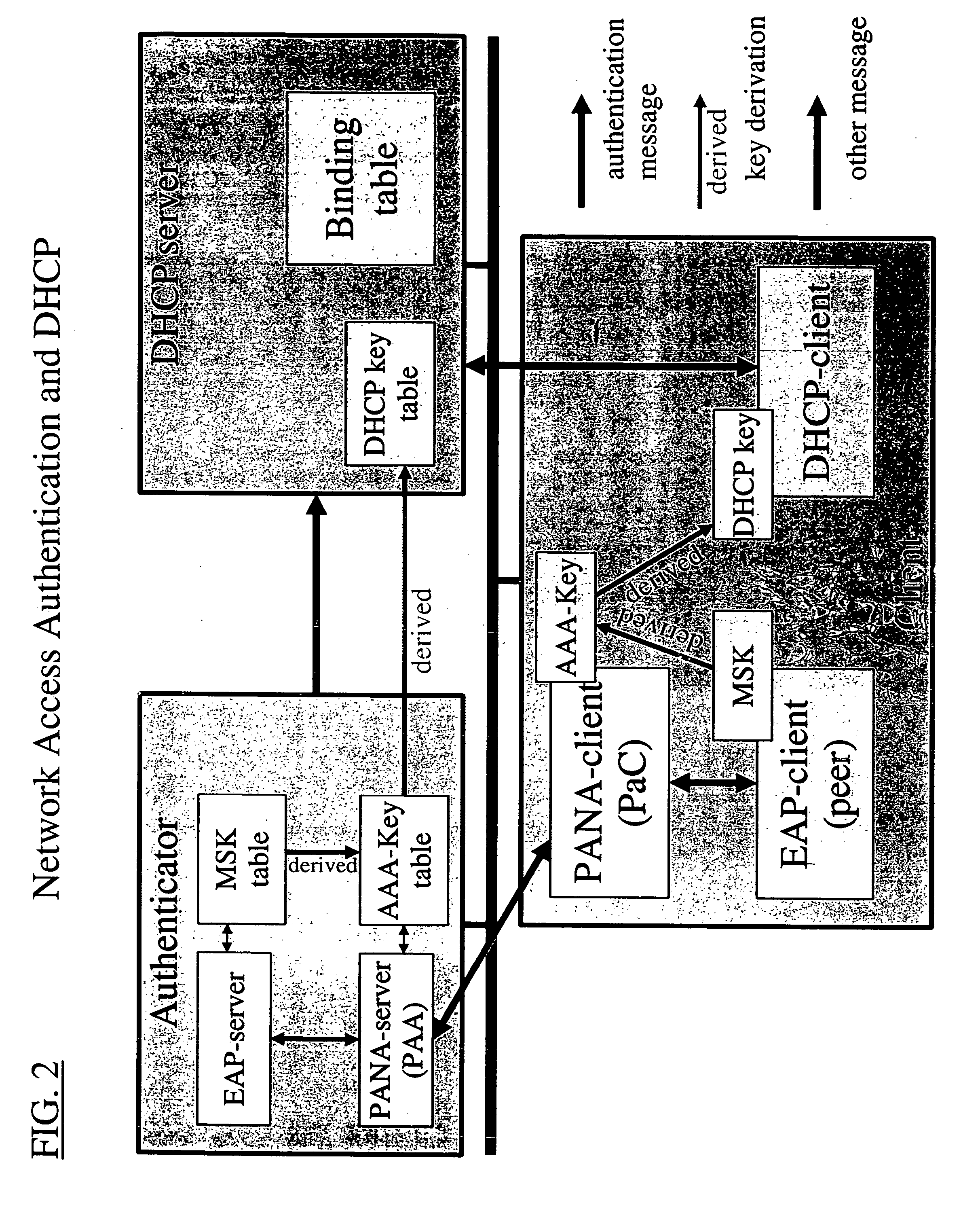
PANA (Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access) is an IP-based protocol that allows a device to authenticate itself with a network to be granted access. PANA will not define any new authentication protocol, key distribution, key agreement or key derivation protocols. For these purposes, the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) will be used, and PANA will carry the EAP payload. PANA allows dynamic service provider selection, supports various authentication methods, is suitable for roaming users, and is independent from the link layer mechanisms.
Audio visual player apparatus and system and method of content distribution using the same
InactiveUS20060008256A1None of methods is secureTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingContent distributionVideo player
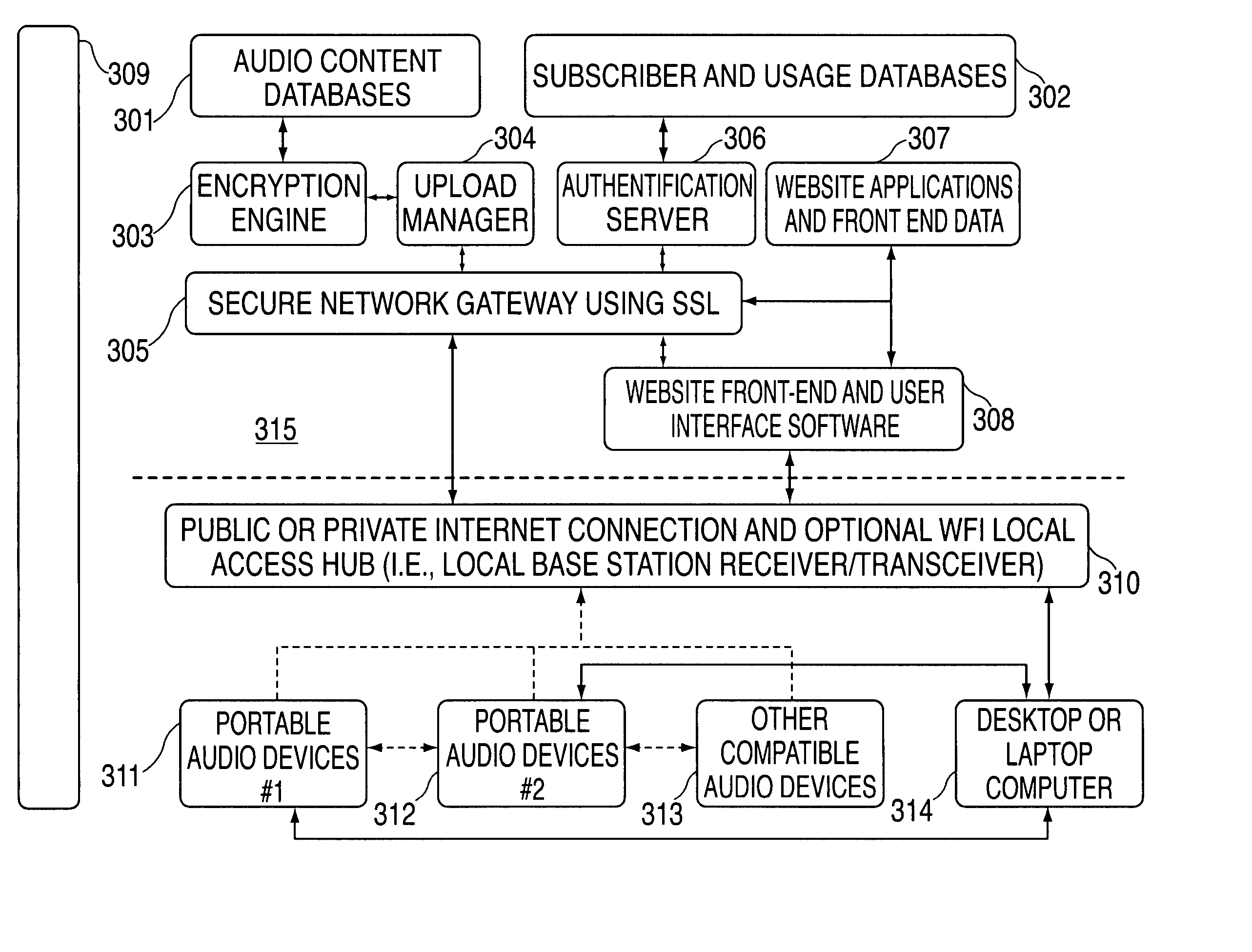
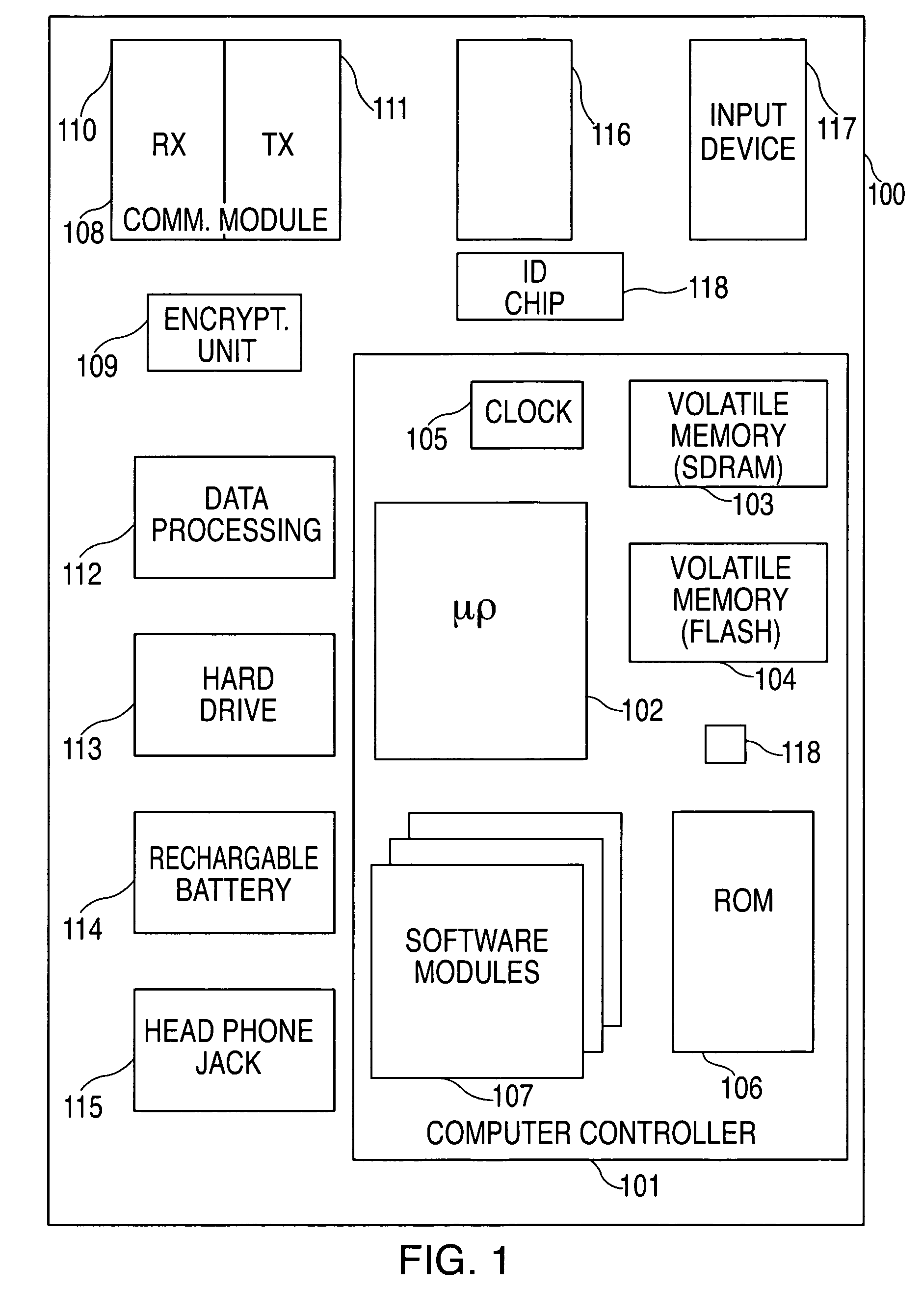
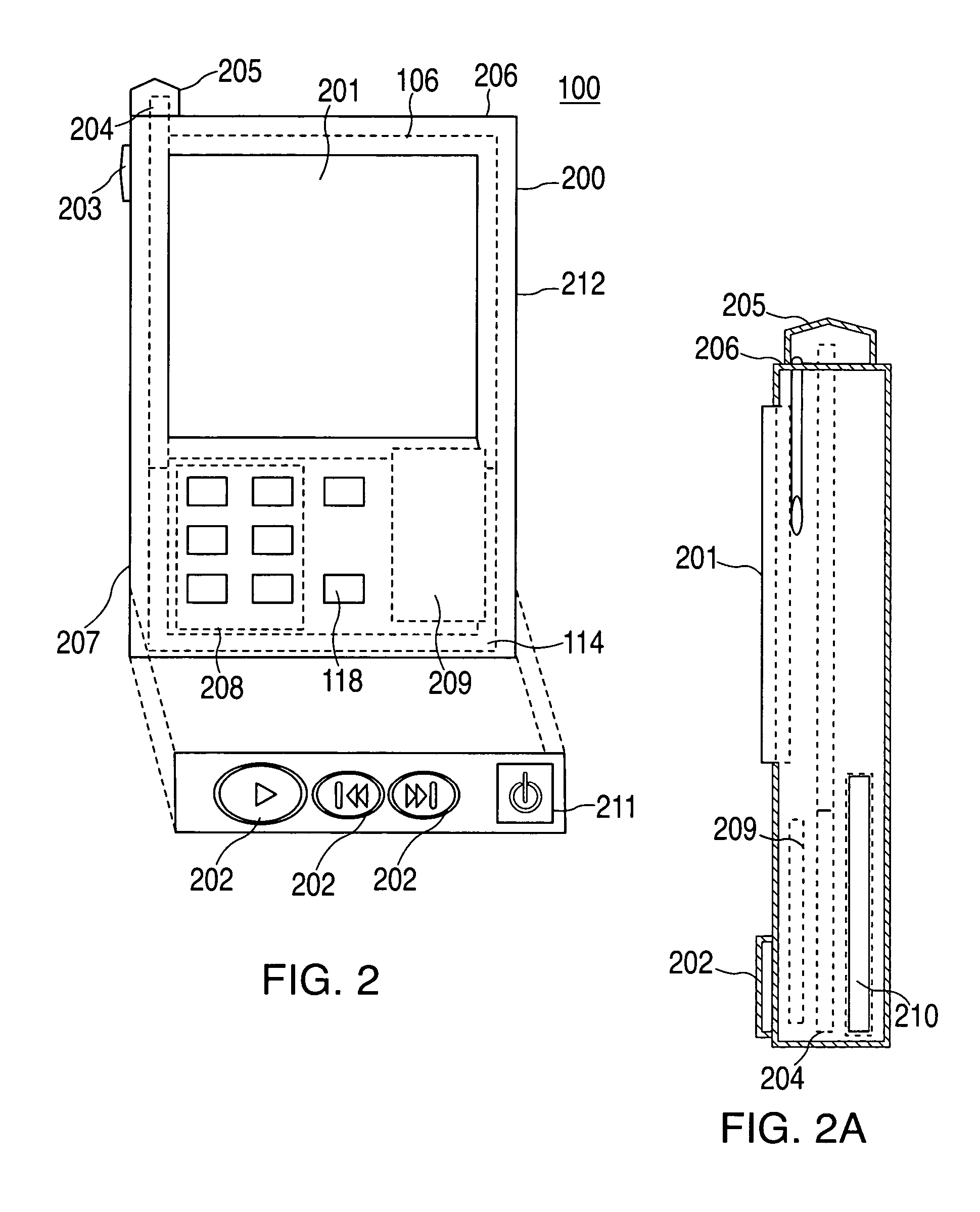
A portable wireless communications subscriber audio and / or video player apparatus and system and method for selecting, requesting, downloading, and playing audio and / or video data content files from an Internet-based database server. The wireless link is preferably implemented in accordance with the WiFi protocol, which allows connectivity to the Internet by being in proximity with a local base station or WiFi hotspot (i.e., publicly available local wireless access hub connected to the Internet). The portable wireless communications subscriber audio and / or video player apparatus and system preferably include a security means for monitoring and blocking unauthorized use of the player apparatus and system. The player apparatus further preferably has the capability to communicate with other neighboring player apparatus for the purpose of exchanging content data files, playlists and personal messages.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
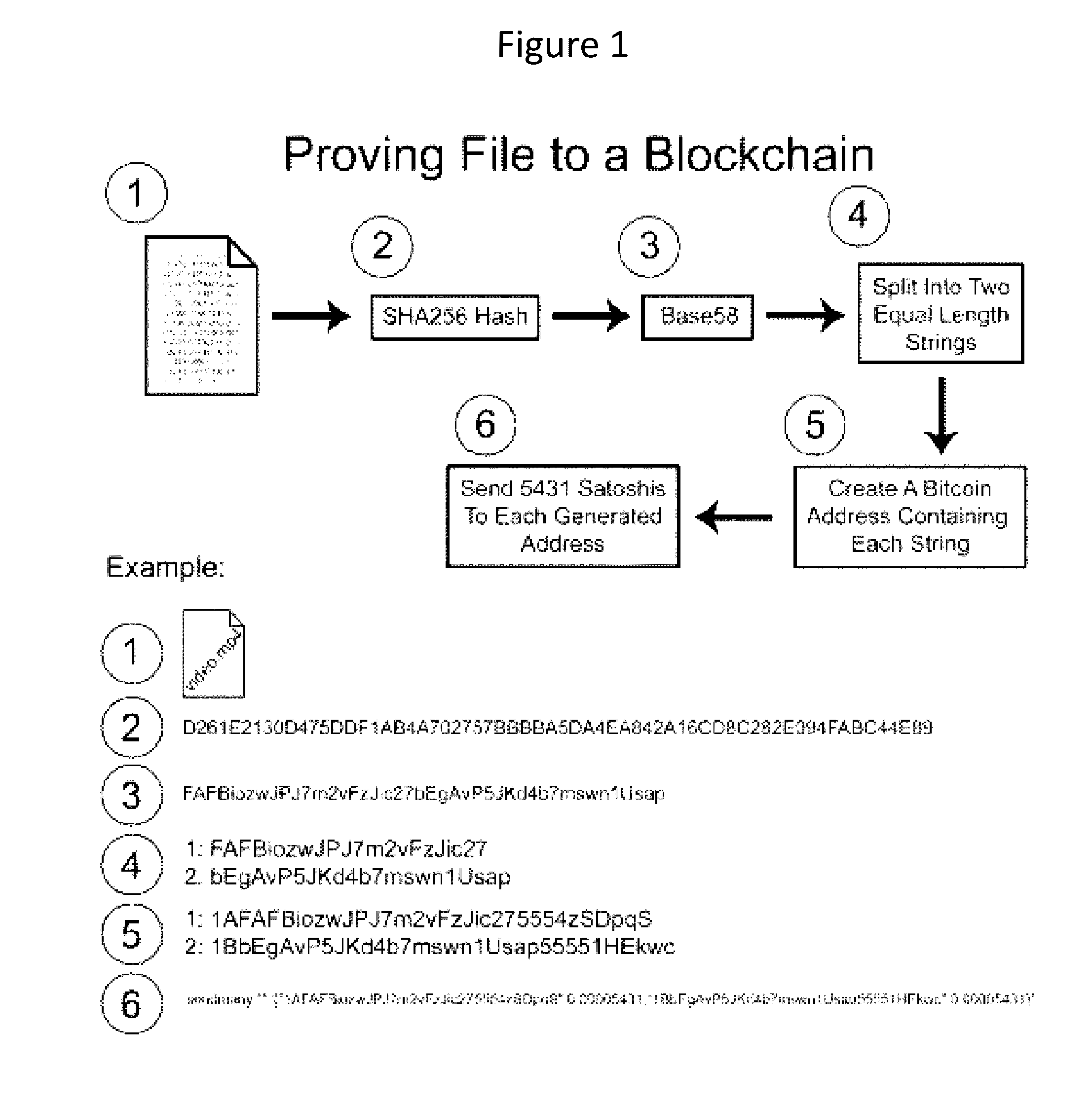
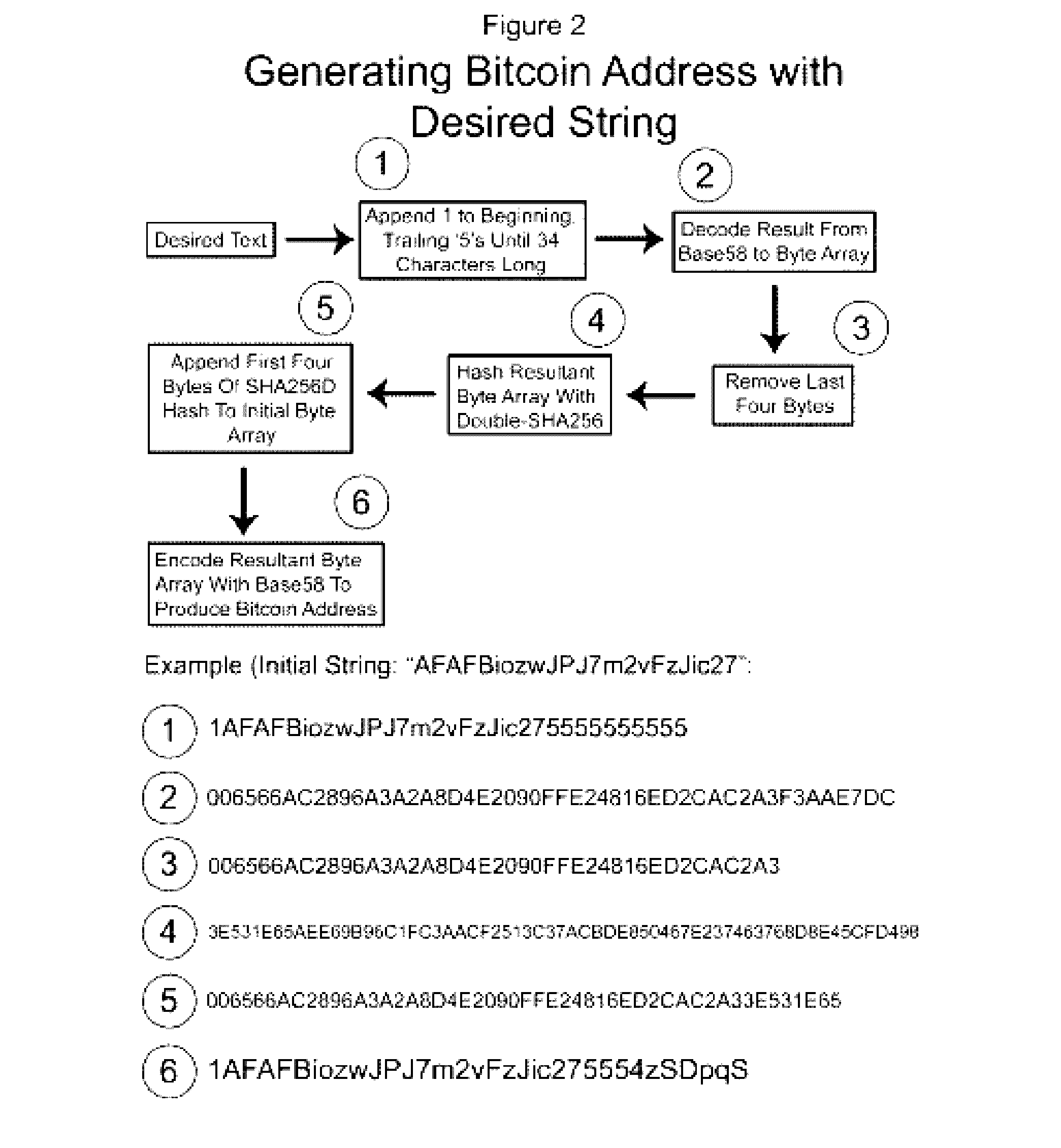
Authentication and verification of digital data utilizing blockchain technology
InactiveUS20160283920A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital dataHuman interaction
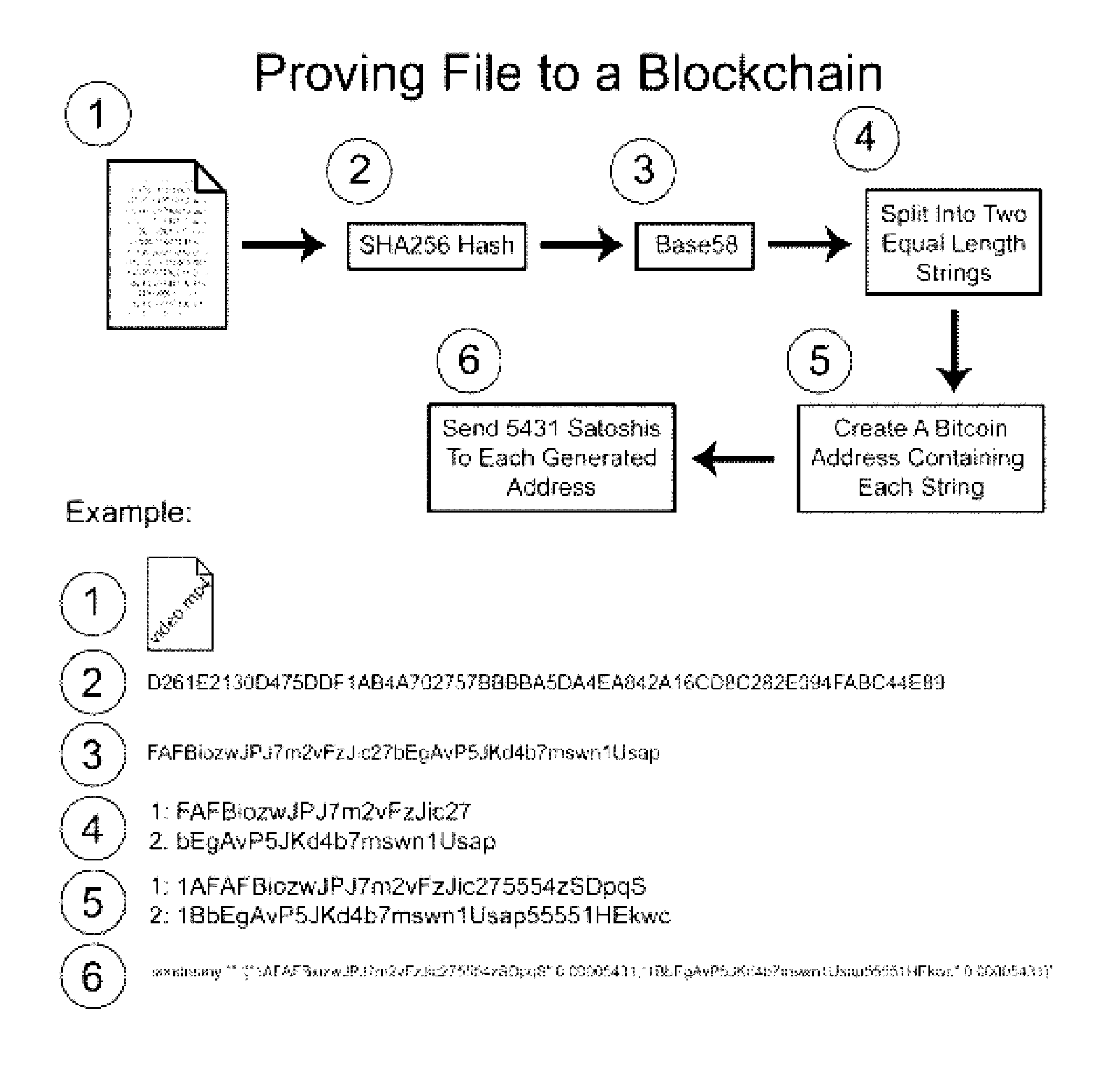
A method for authenticating a chain of custody utilizing blockchain technology, whereby digital evidence or other digital content is acquired and then hashed to produce a hash fingerprint / signature and then immediately or instantly submitting said hash fingerprint / signature to the blockchain using the blockchain network protocol, forming an immediate verifiable chain of custody without human interaction or requiring a trusted third party.
Owner:FISHER JUSTIN +1
Secure Dynamic Communication Network And Protocol
ActiveUS20160219024A1Increase the difficultyUsefulness of their knowledge would be short-livedMultiple keys/algorithms usageData taking preventionDigital dataData segment
In a secure cloud for transmitting packets of digital data, the packets may be repeatedly scrambled (i.e., their data segments reordered) and then unscrambled, split and then mixed, and / or encrypted and then decrypted as they pass through media nodes in the cloud. The methods used to scramble, split, mix and encrypt the packets may be varied in accordance with a state such as time, thereby making the task of a hacker virtually impossible inasmuch as he or she may be viewing only a fragment of a packet and the methods used to disguise the data are constantly changing.
Owner:LISTAT LTD
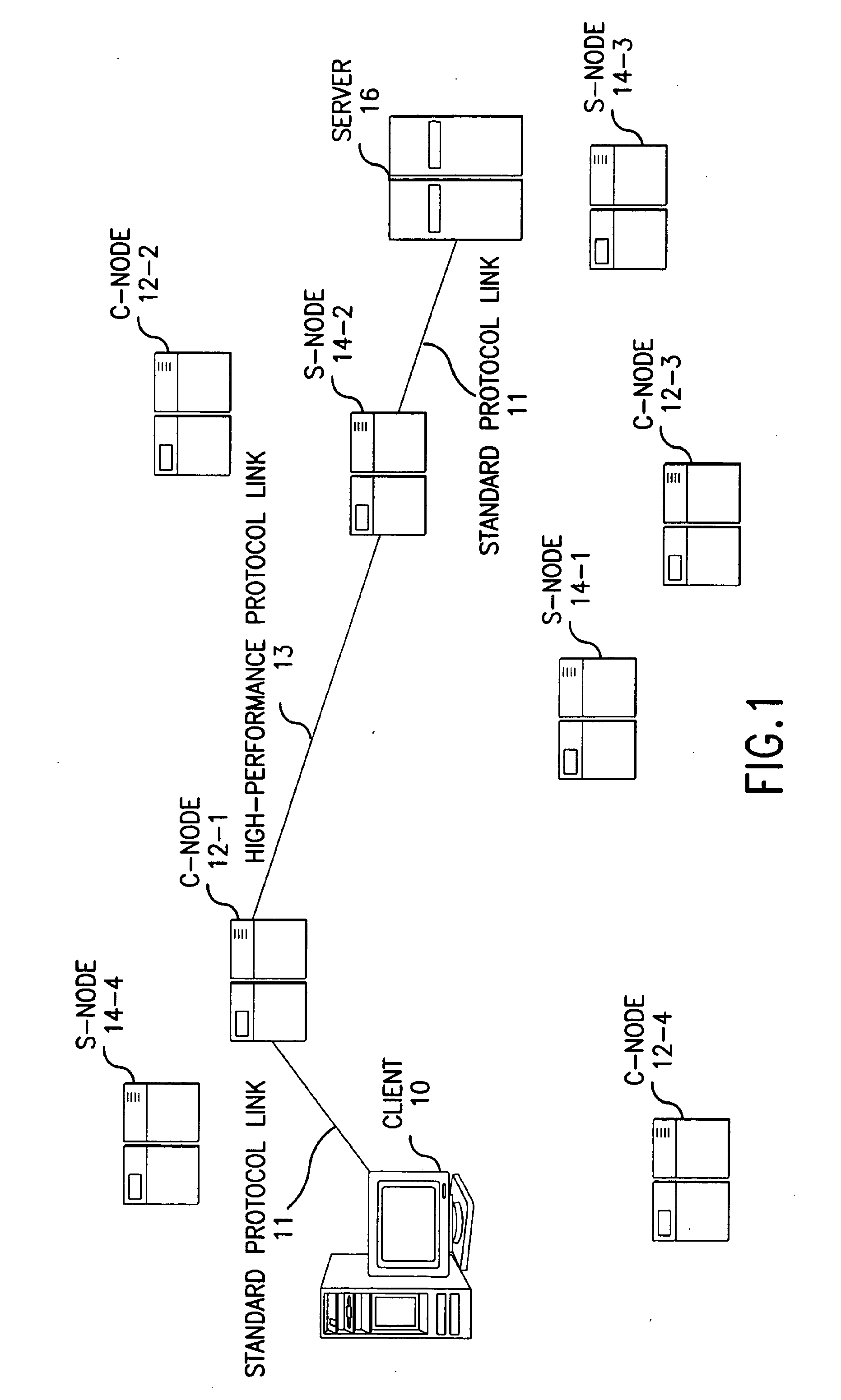
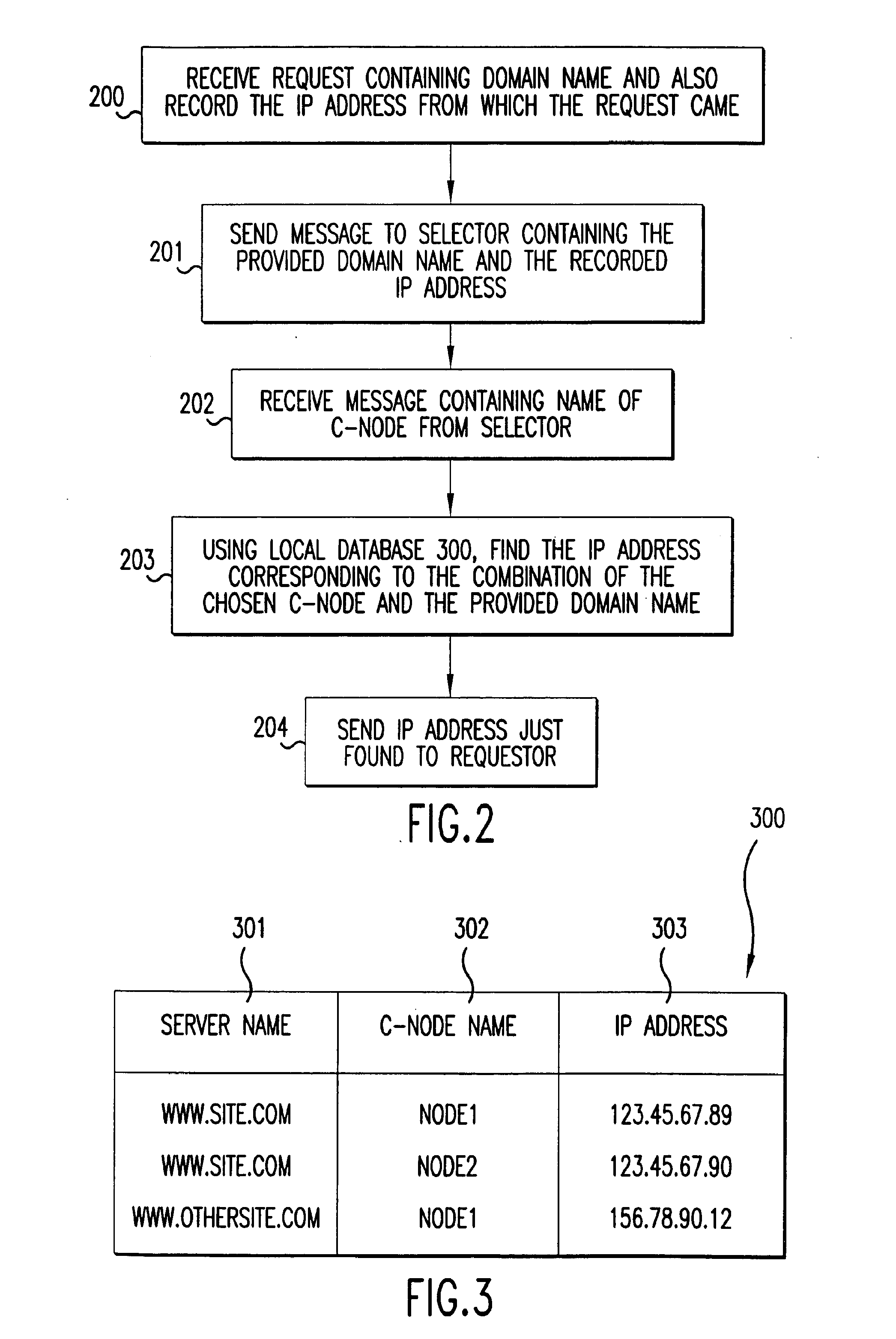
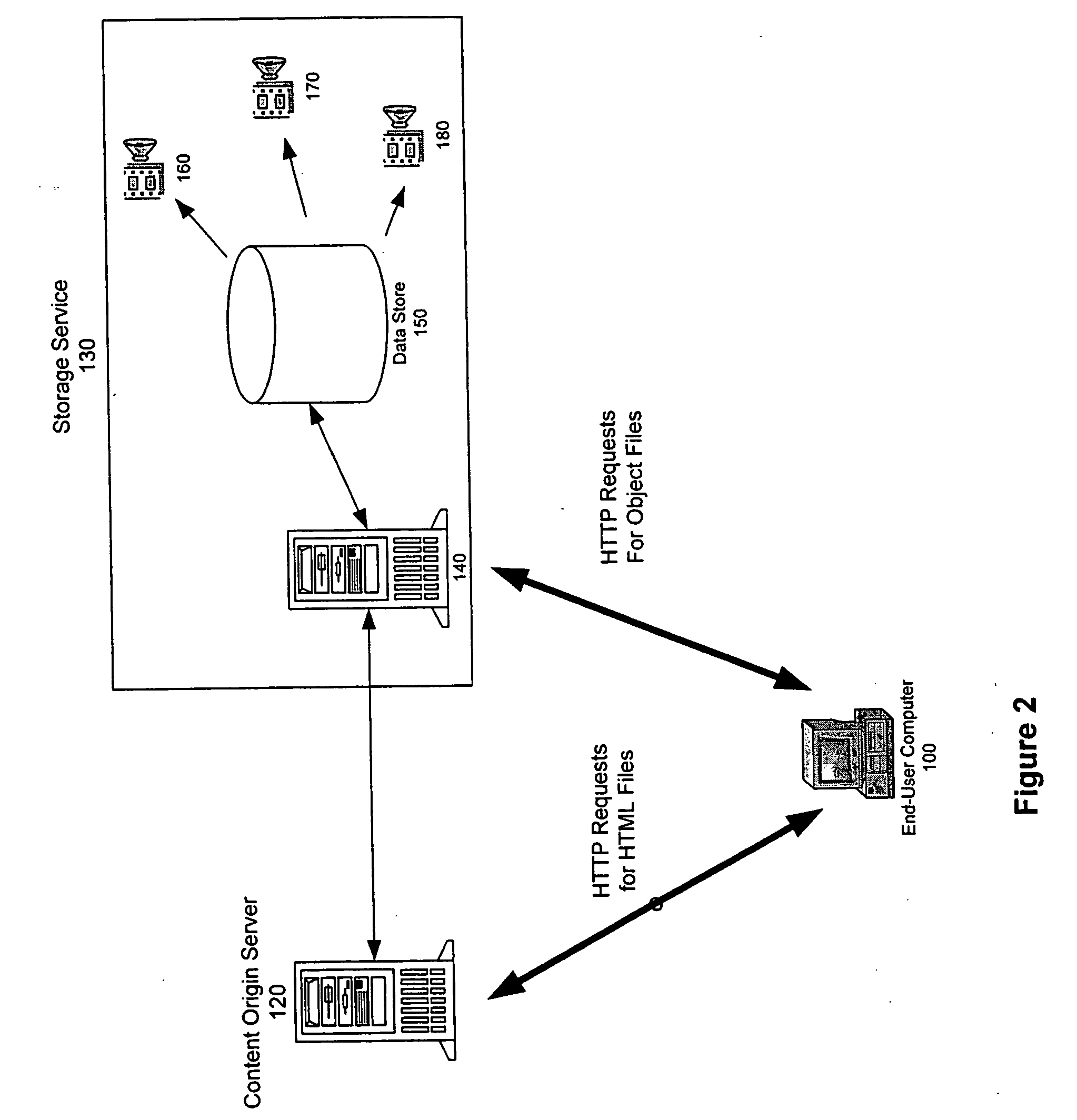
Method for high-performance delivery of web content
InactiveUS20050044270A1Improve performanceReduce deliveryDigital computer detailsData switching networksWeb serviceWeb cache
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for increasing the performance of world-wide-web traffic over the Internet. A distributed network of specialized nodes of two types is dispersed around the Internet. A web client's requests are directed to a node of the first type chosen to be close to the client, and the client communicates with this node using a standard protocol such as HTTP. This first node receives the request, and communicates the request to a node of the second type chosen to be close to the request's ultimate destination (e.g., a web server capable of generating a response to the request.) The first node communicates the request to the second node using a different, specialized, protocol that has been designed for improved performance and specifically to reduce traffic volume and to reduce latency. The second node receives communication from the first node using this specialized protocol, converts it back to a standard protocol such as HTTP, and forwards the request to the destination computer or server. Responses from the destination to the client take the corresponding reverse route, and also are carried over a specialized protocol between the two nodes. In addition, these nodes can employ other techniques such as web caches that avoid or improve some communication steps. Thus, specialized, proprietary, or complex protocols and techniques can be quickly deployed to enhance web performance without requiring significant changes to the clients or servers.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for federated single sign-on services
ActiveUS20030163733A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsCyber operationsService domain
The advent of new and sophisticated web services provided by Service Providers to users, services that individually require authentication of user and authorization of access, brings the needs for a new service to facilitate such authentication and access, a service referred to as Single Sign-On (SSO). The basic principle behind SSO is that users are authenticated once at a particular level, and then access all their subscribed services accepting that level of authentication. The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus wherein a cellular Federation of mobile network operators becomes an SSO authentication authority for subscribers of this Federation accessing Service Providers having such agreement with a mobile network operator of the Federation. In accordance with this invention, mobile network operators can leverage their operator-subscriber trust relationship in order to act as SSO authentication authority for those subscribers accessing Service Providers in a service domain other than the mobile network domain.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for high-performance delivery of web content
InactiveUS20070050522A1Improve performanceReduce deliveryMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksWeb serviceWeb cache
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for increasing the performance of world-wide-web traffic over the Internet. A distributed network of specialized nodes of two types is dispersed around the Internet. A web client's requests are directed to a node of the first type chosen to be close to the client, and the client communicates with this node using a standard protocol such as HTTP. This first node receives the request, and communicates the request to a node of the second type chosen to be close to the request's ultimate destination (e.g., a web server capable of generating a response to the request.) The first node communicates the request to the second node using a different, specialized, protocol that has been designed for improved performance and specifically to reduce traffic volume and to reduce latency. The second node receives communication from the first node using this specialized protocol, converts it back to a standard protocol such as HTTP, and forwards the request to the destination computer or server. Responses from the destination to the client take the corresponding reverse route, and also are carried over a specialized protocol between the two nodes. In addition, these nodes can employ other techniques such as web caches that avoid or improve some communication steps. Thus, specialized, proprietary, or complex protocols and techniques can be quickly deployed to enhance web performance without requiring significant changes to the clients or servers.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
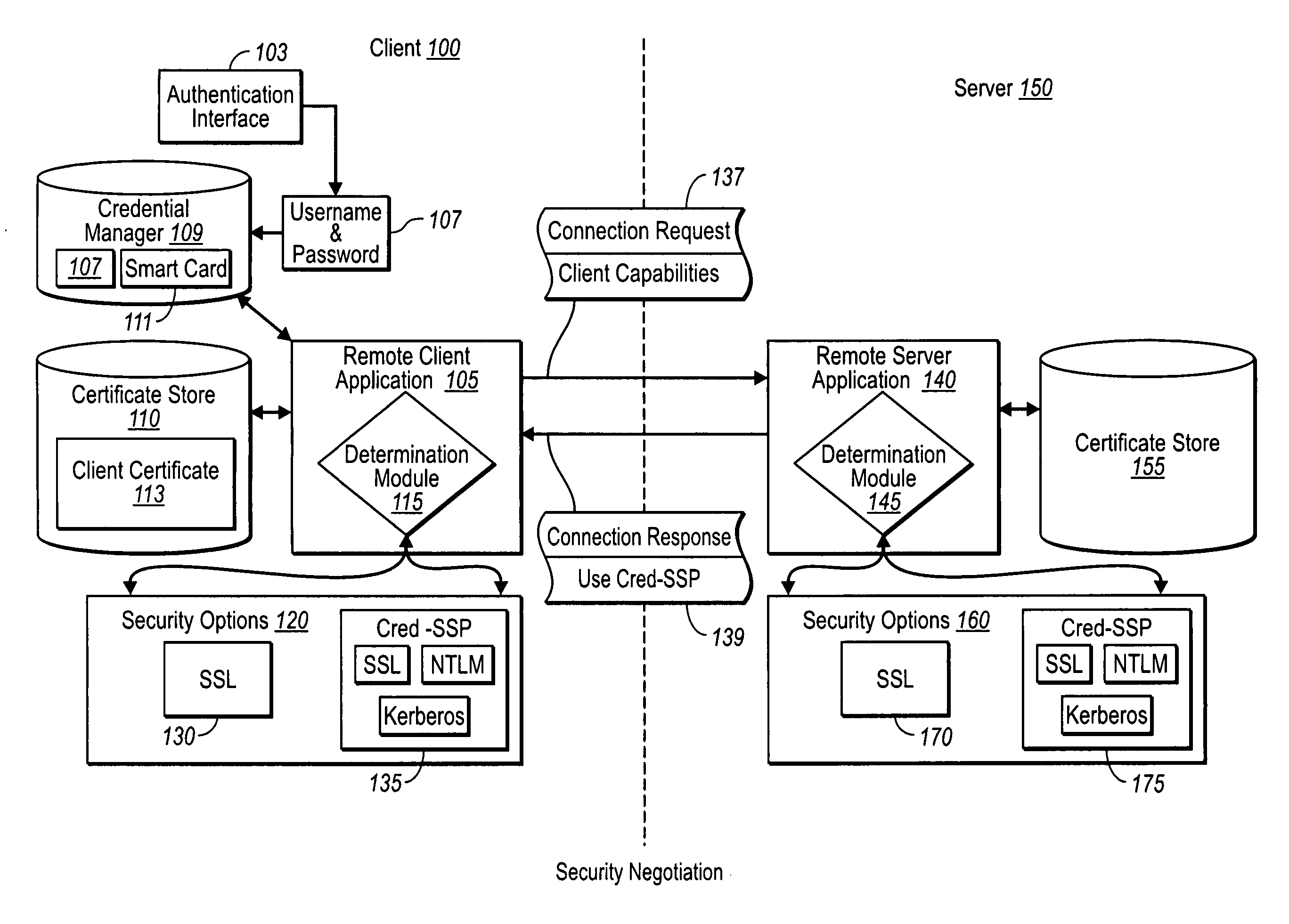
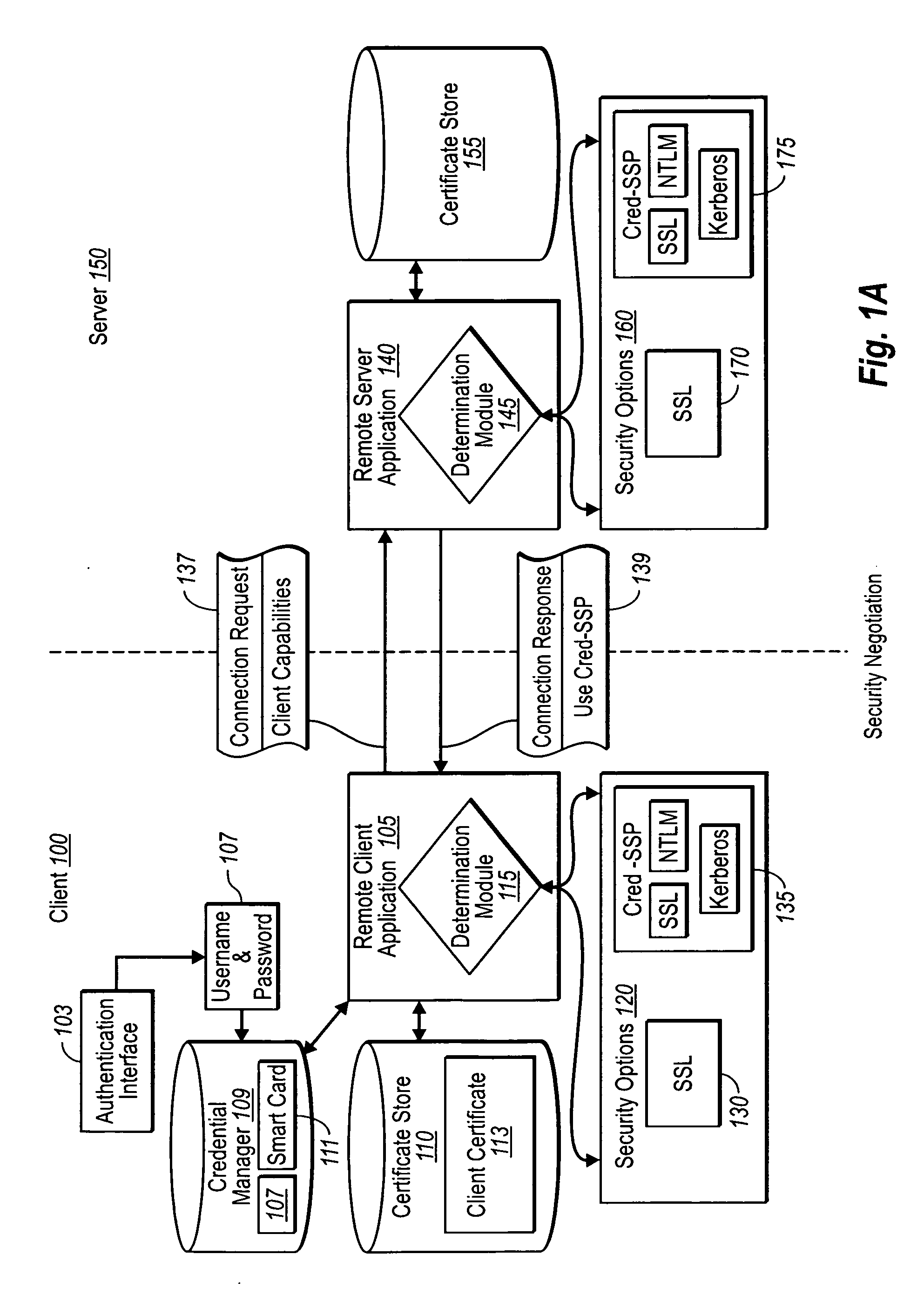
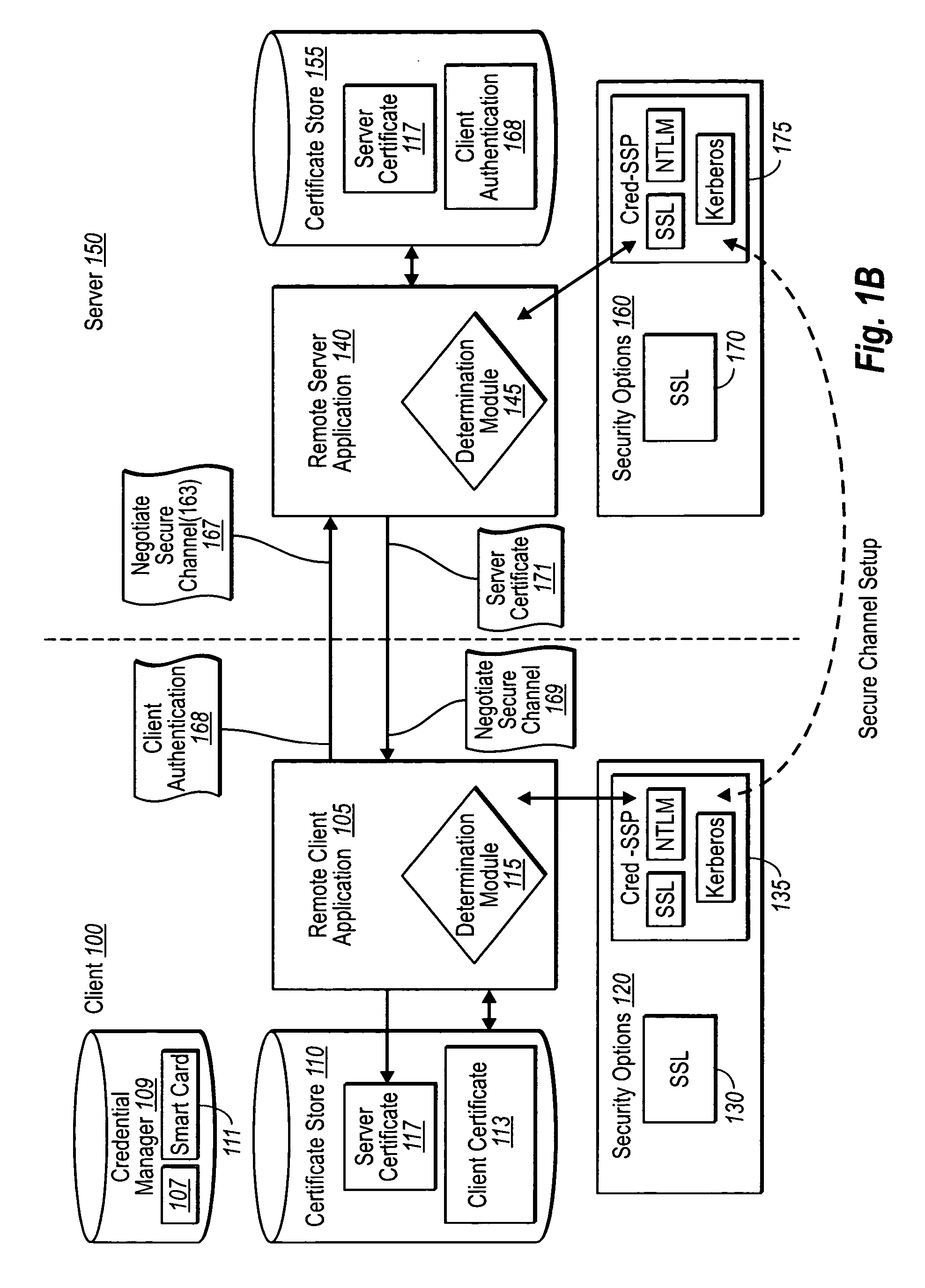
Creating secure interactive connections with remote resources
ActiveUS20070061878A1Easy to adaptDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationClient-side
Implementations of the present invention efficiently establish secure connections between a client and server, at least in part by authenticating the client and server early on in the connection setup phases. A client initiating a connection with a server identifies the secure communication protocols enabled at the client, and identifies these protocols in a connection request it sends to the server. The server processes the message and responds with a communication protocol it deems appropriate for the connection. The client and server then exchange appropriate authentication information, and then establish a connection session that implements the chosen communication protocol, and encrypts messages using the negotiated communication protocol. Additional implementations relate to reestablishing dropped connections behind virtual Internet Protocol addresses, without necessarily having to recommit much connection resource overhead.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
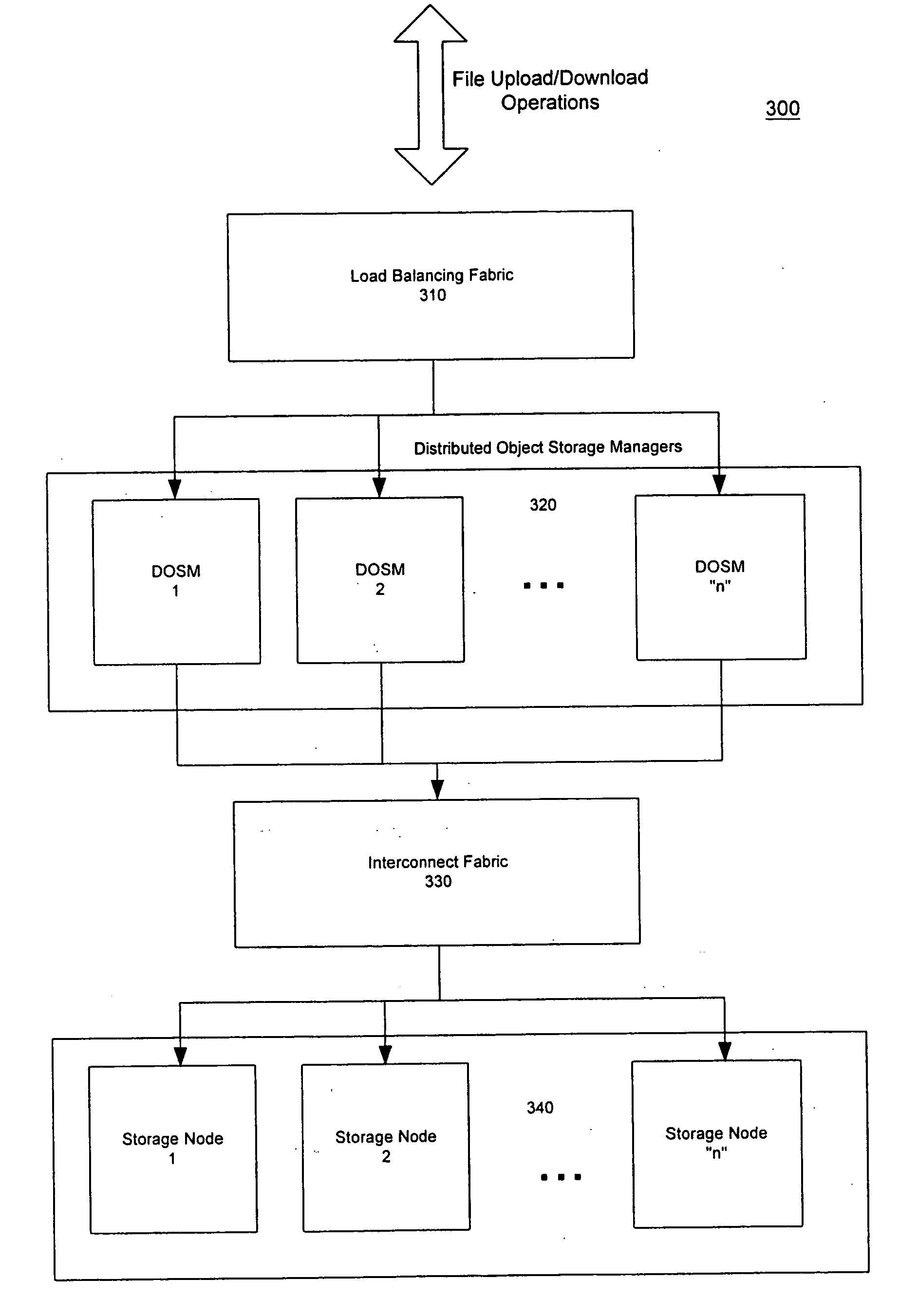
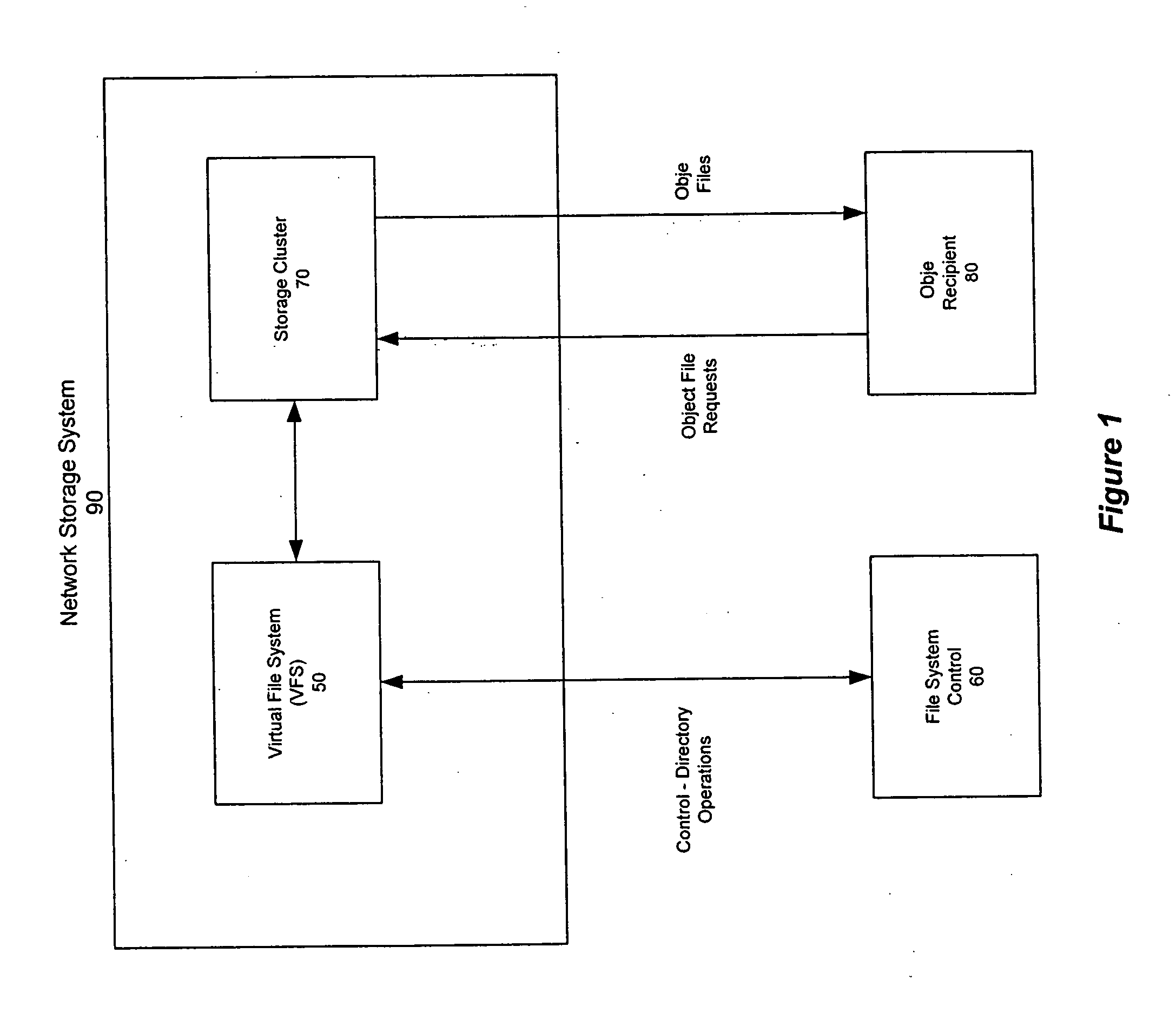
Distributed storage cluster architecture
InactiveUS20050246393A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalVirtual file systemDistributed object
A network storage system includes a virtual file system (“VFS”) that manages the files of the network storage system, and a storage center that stores the files. The VFS and the storage center are separated, such that a client accesses the VFS to conduct file system operations and the client accesses the storage center to upload / download files. The client accesses the network storage system through one or more storage ports. The storage center includes a plurality of distributed object storage managers (DOSMs) and a storage cluster that includes a plurality of intelligent storage nodes. The network storage system includes additional storage centers at geographically disparate locations. The network storage system uses a multi-cast protocol to maintain file information at the DOSMs regarding files stored in the intelligent storage nodes, including files stored in disparate storage centers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for sending a short message containing purchase information to a destination terminal
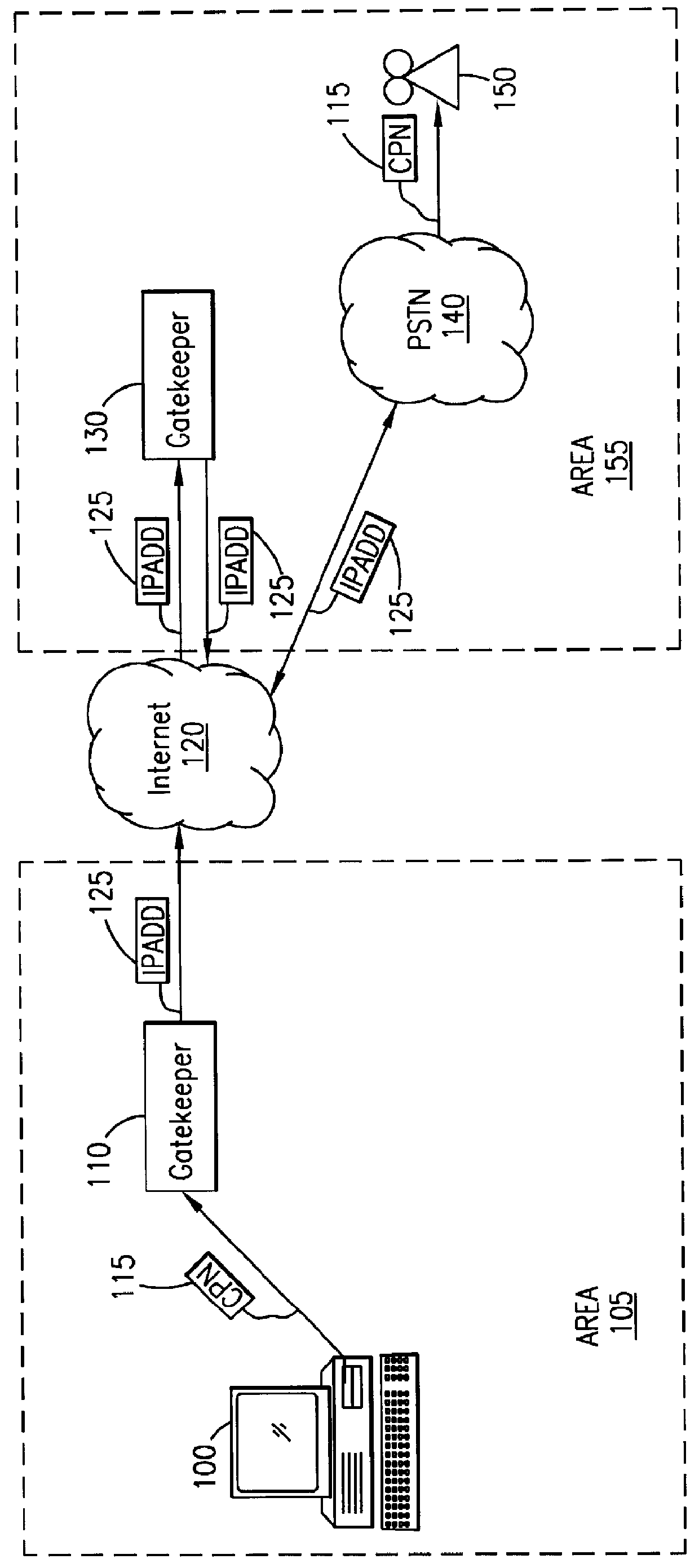
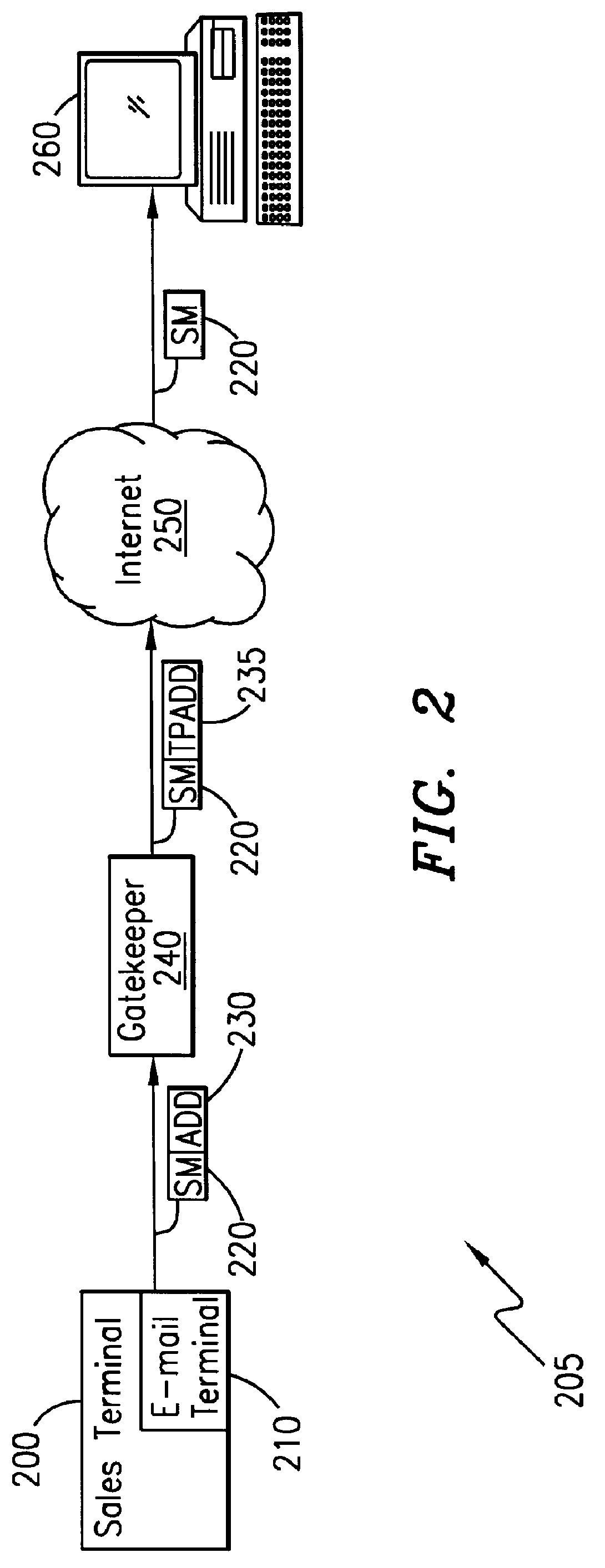
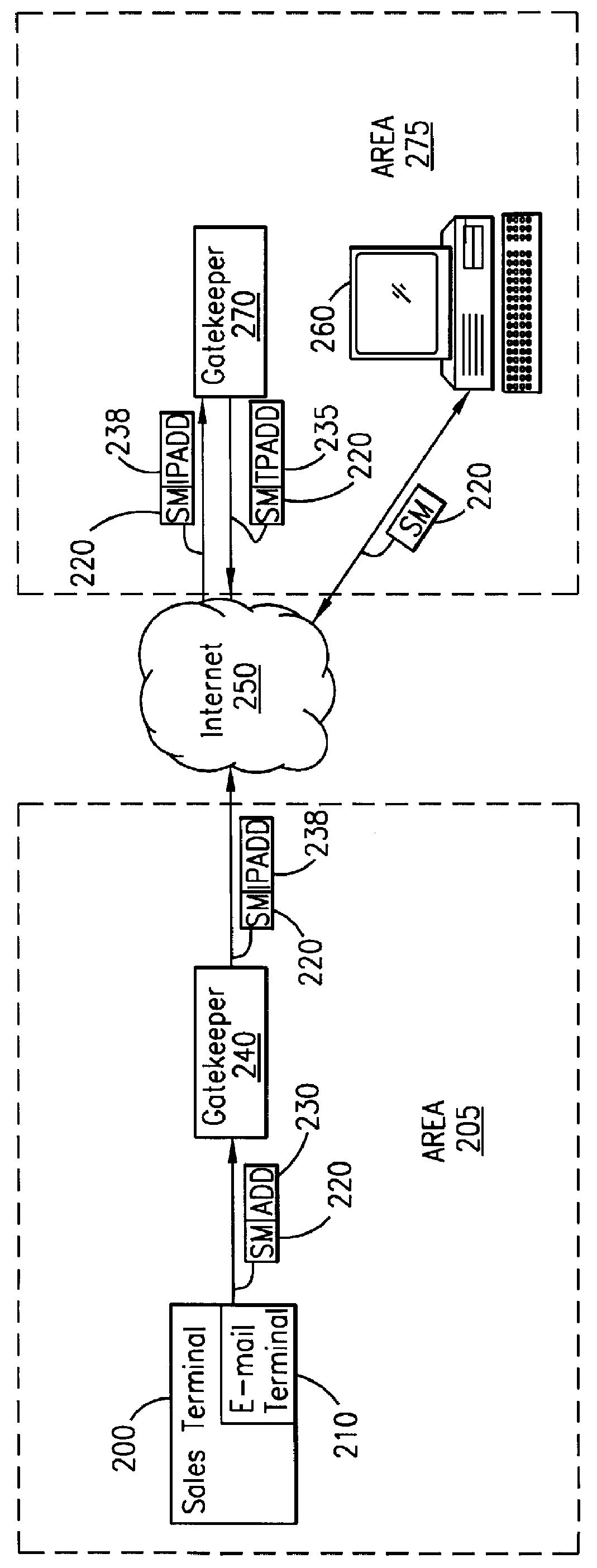
InactiveUS6067529AEfficient and cost-effectiveReliable deliveryComplete banking machinesCash registersMulticast addressComputer terminal
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for providing a substantially immediate electronic receipt after a consumer has made a purchase. When a consumer makes a purchase, the sales terminal, which is attached with a short message / e-mail sending capable terminal, can generate and route a short message along with the detailed purchase information to a transport address or alias address associated with the consumer via a Gatekeeper for the Internet for the area that the sales terminal is located in. Upon receipt of the short message, the Gatekeeper can then convert the alias address to the transport address, if the alias address is given and the consumer does not want the short message sent to the alias address, and forward the short message through the Internet to that transport address (or alias address) as an Internet Protocol datagram for storage and retrieval of the short message by the consumer either immediately or at a later time.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
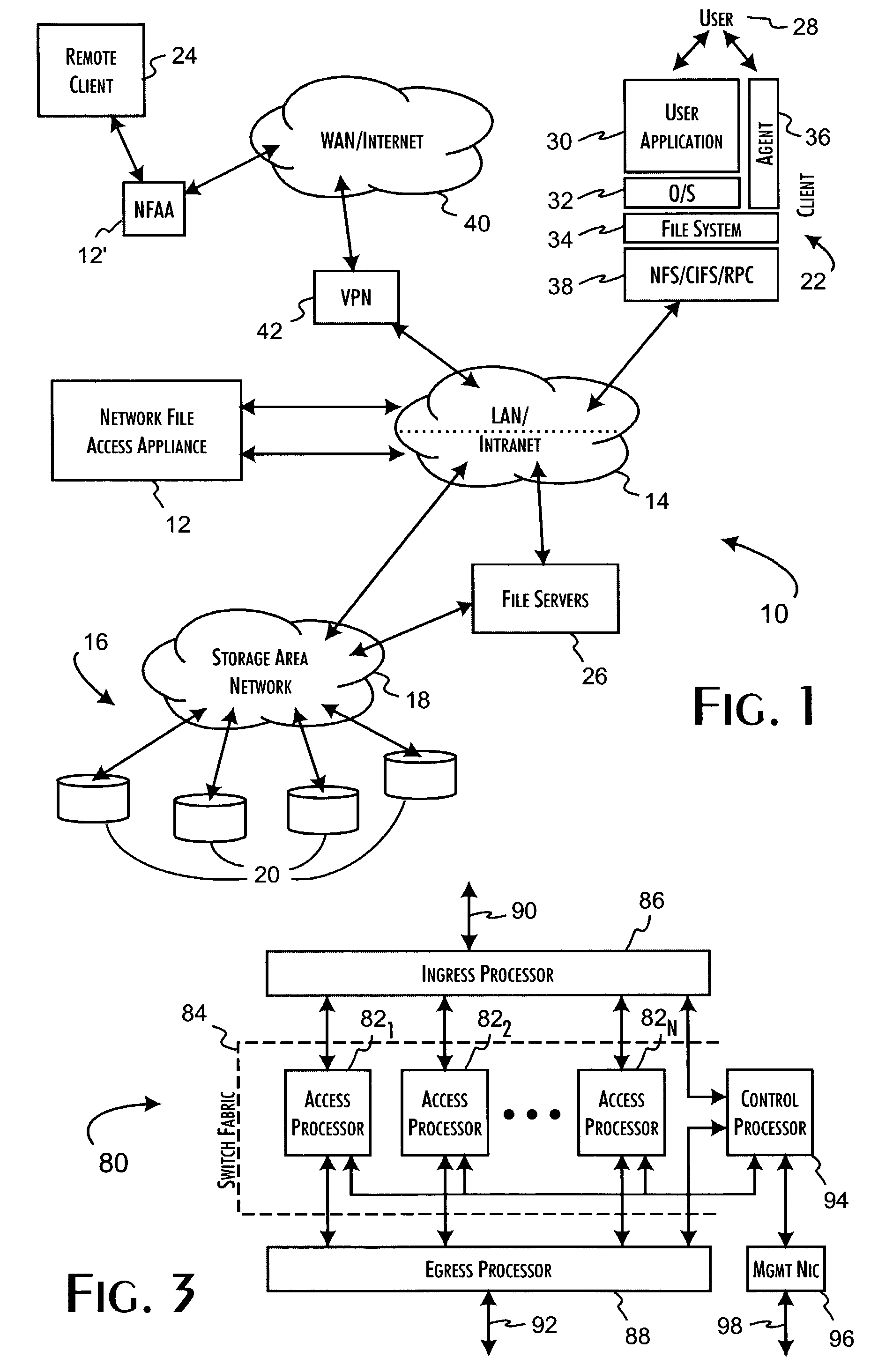
Logical access block processing protocol for transparent secure file storage
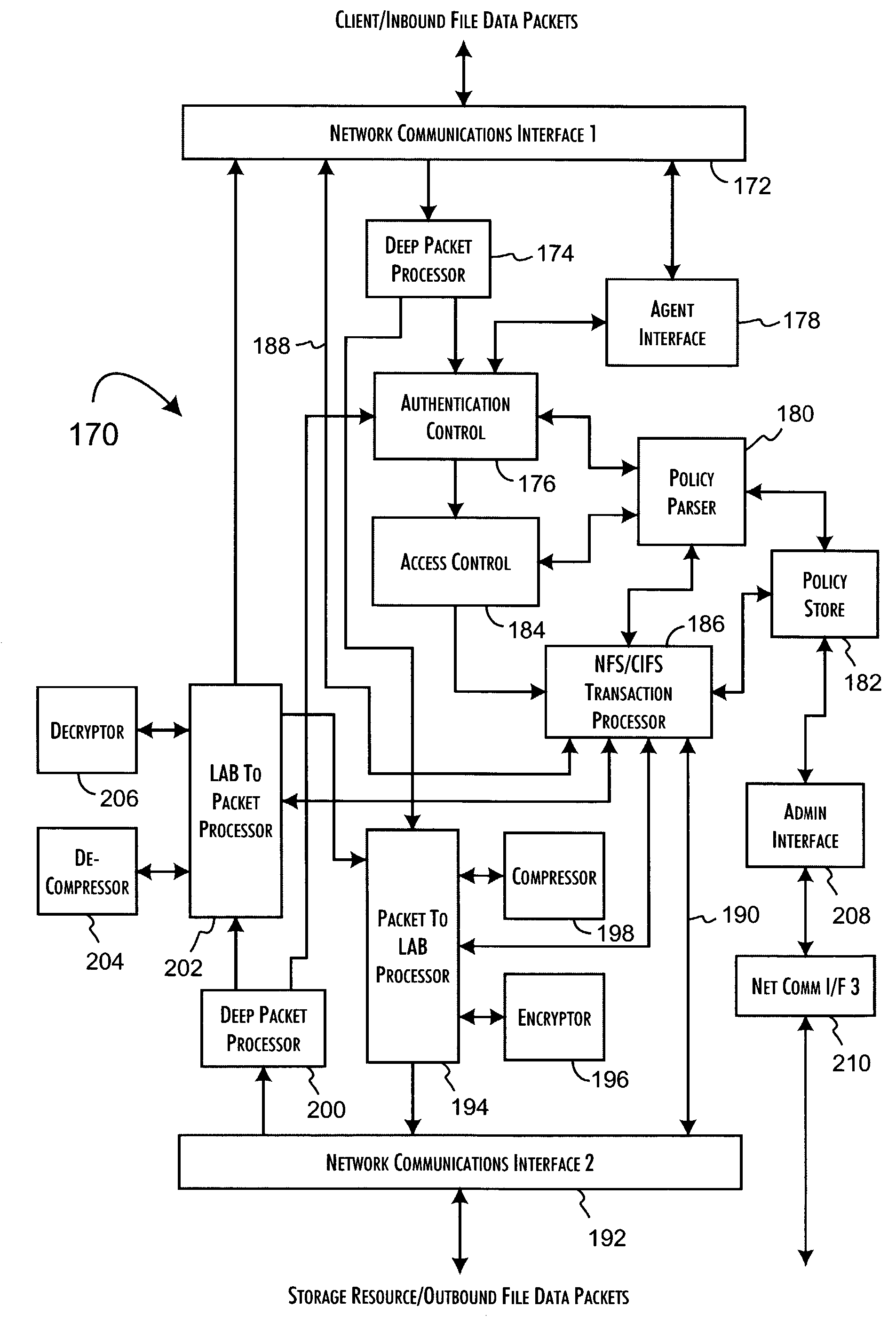
InactiveUS7334124B2Ensure integritySafe storageDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareDigital signature
Network data files are secure through the operation of an infrastructure gateway-based network file access appliance. Network file data, corresponding to network pocket payload data, are further reduced to a sequence of data blocks that are secured through any combination of block encryption, compression, and digital signatures. File meta-data, including encryption, compression and block-level digital signatures are persistently stored with the file data, either in-band in the file as stored or out-of-band key as a separately stored file or file policy record. File meta-data is recovered with accesses of the file data to support bidirectional encryption and compression and to detect tampering with the file data by comparison against block-level digital signatures.
Owner:THALES ESECURITY INC
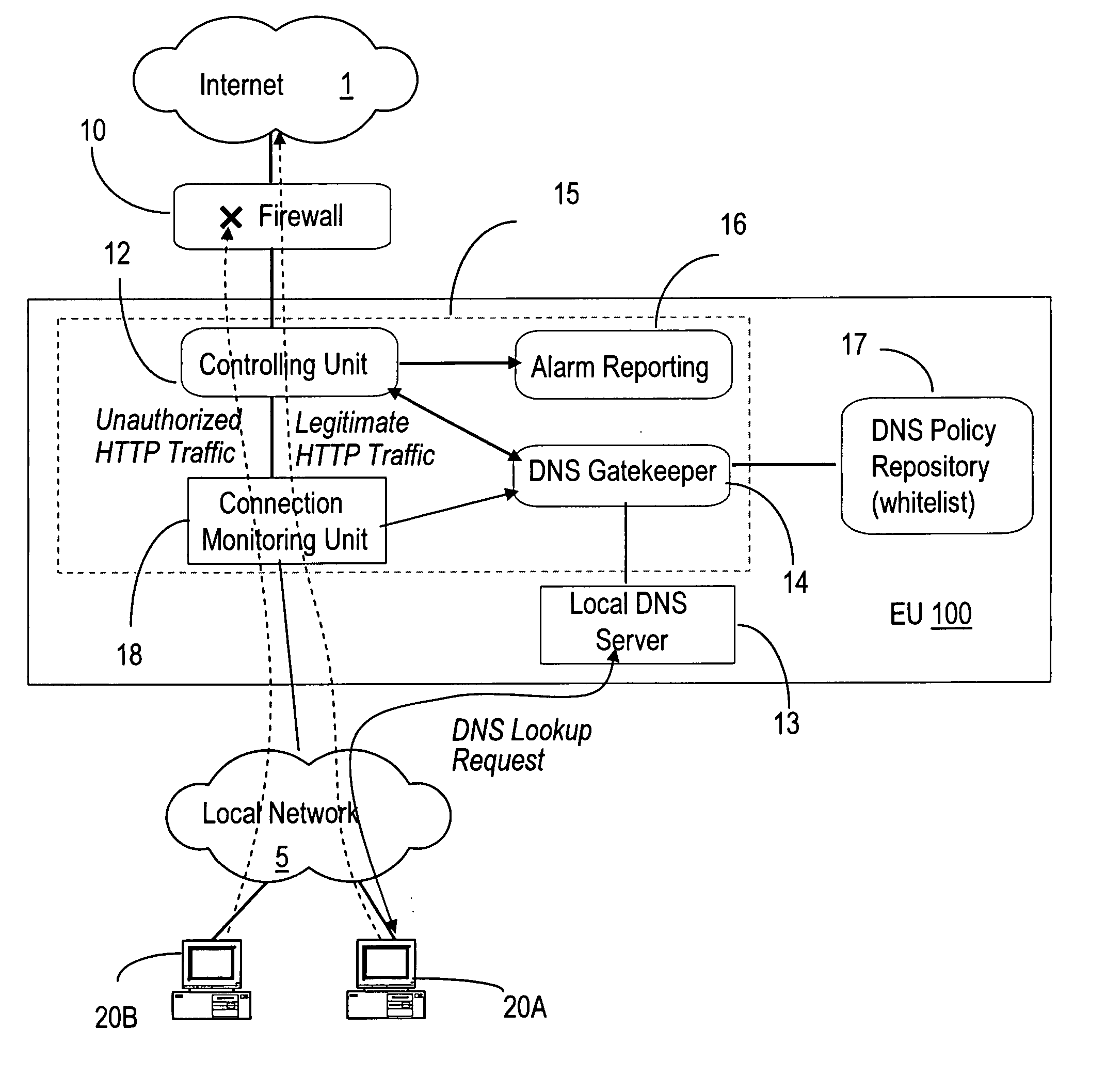
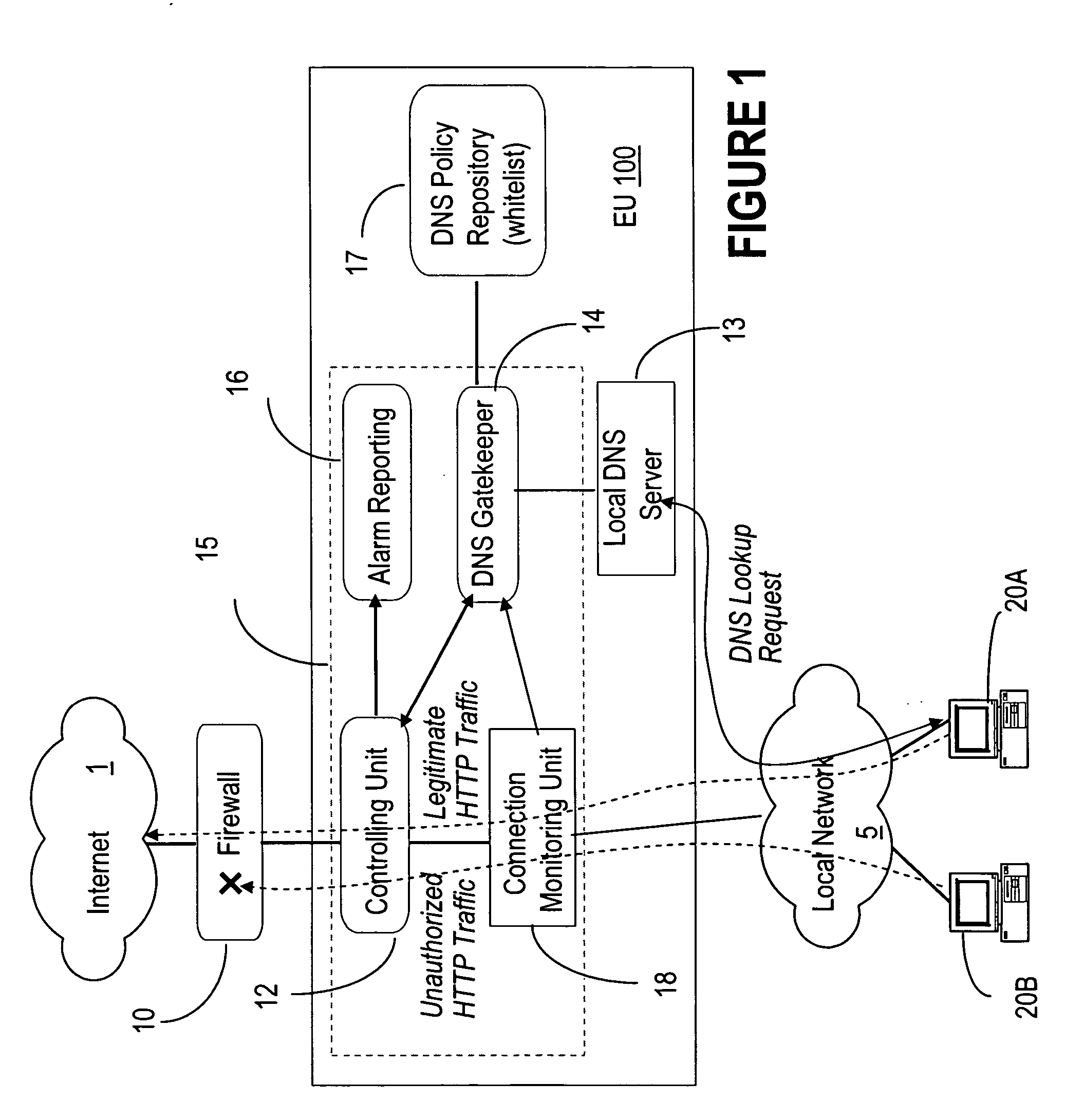
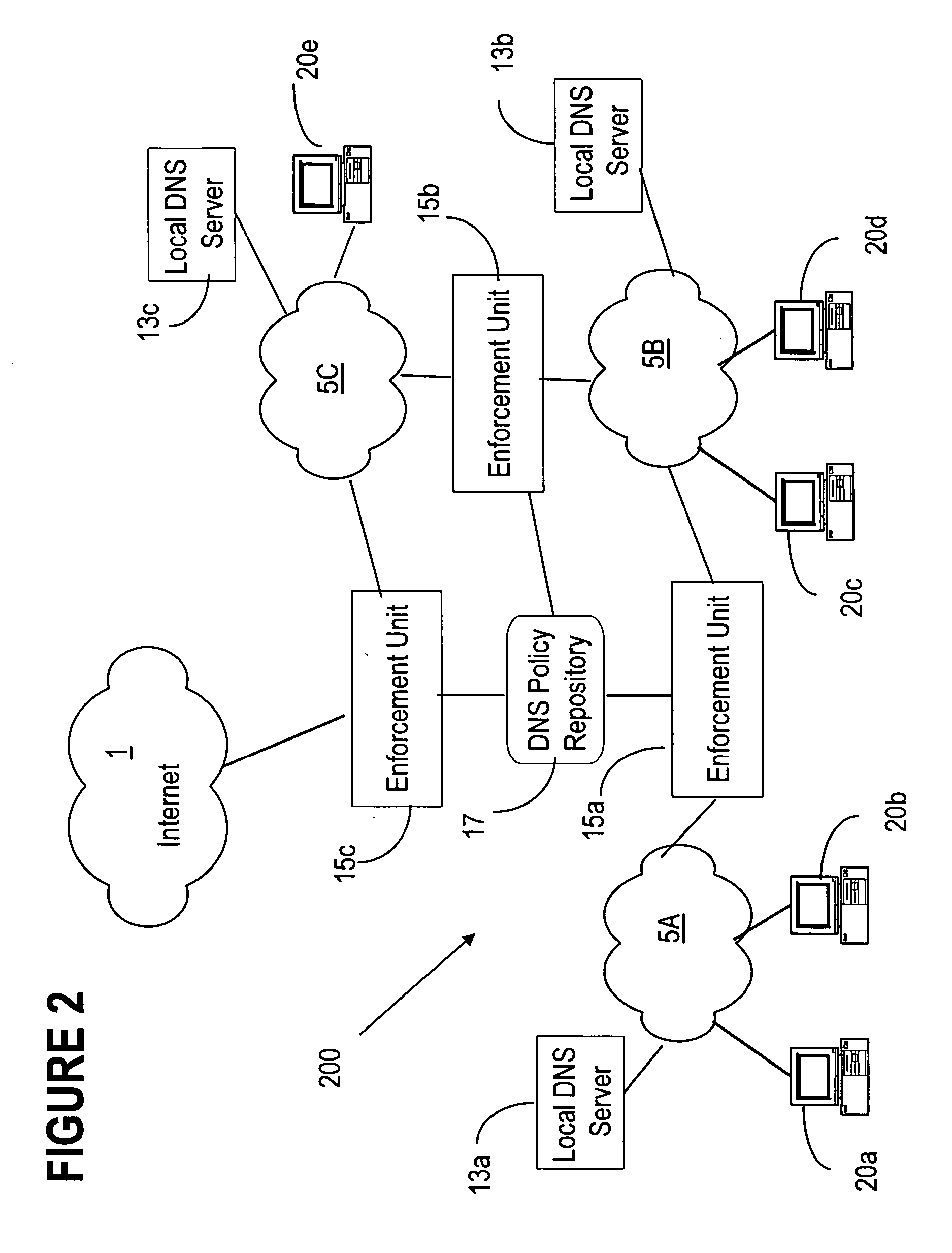
DNS based enforcement for confinement and detection of network malicious activities
InactiveUS20070033645A1Avoid detectionAvoid spreadingDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionDomain nameNetwork activity
Malicious network activities do not make use of the Domain Name System (DNS) protocol to reach remote targets outside a local network. This DNS-based enforcement system for confinement and detection of network malicious activities requires that every connection toward a resource located outside the local network is blocked by default by the local enforcement box, e.g. a firewall or a proxy. Outbound connections are allowed to leave the local network only when authorized directly by an entity called the DNS Gatekeeper.
Owner:RPX CORP
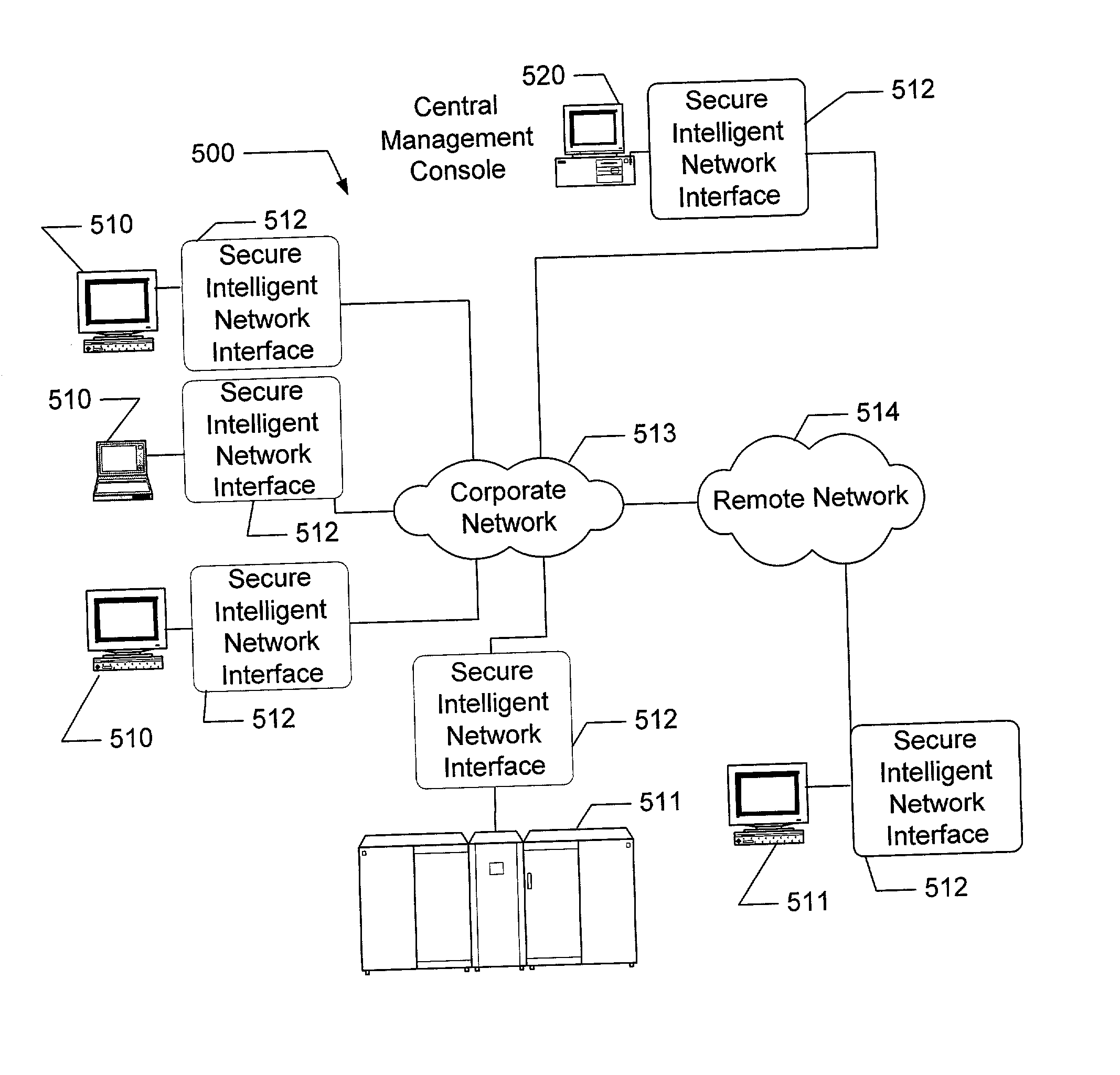
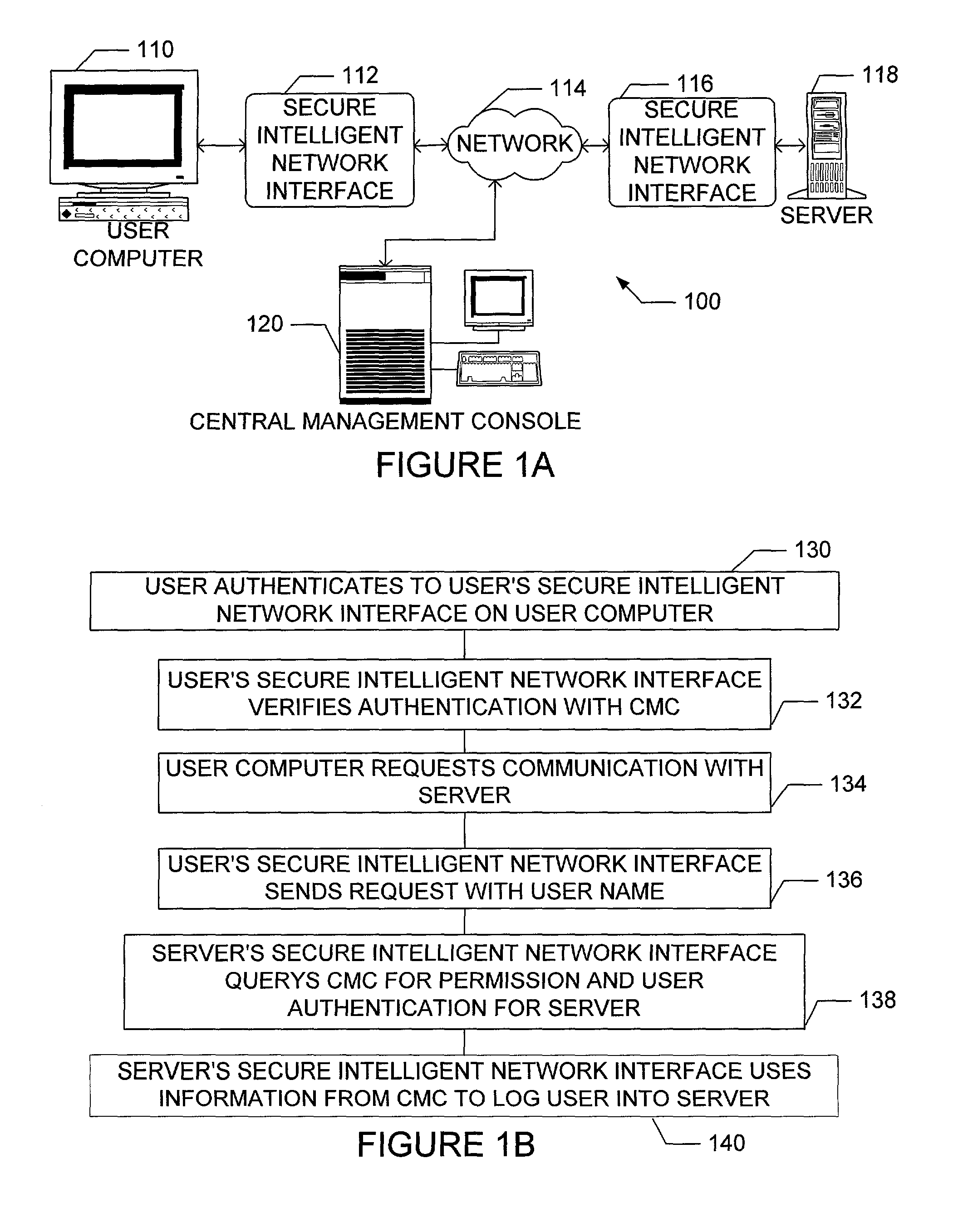
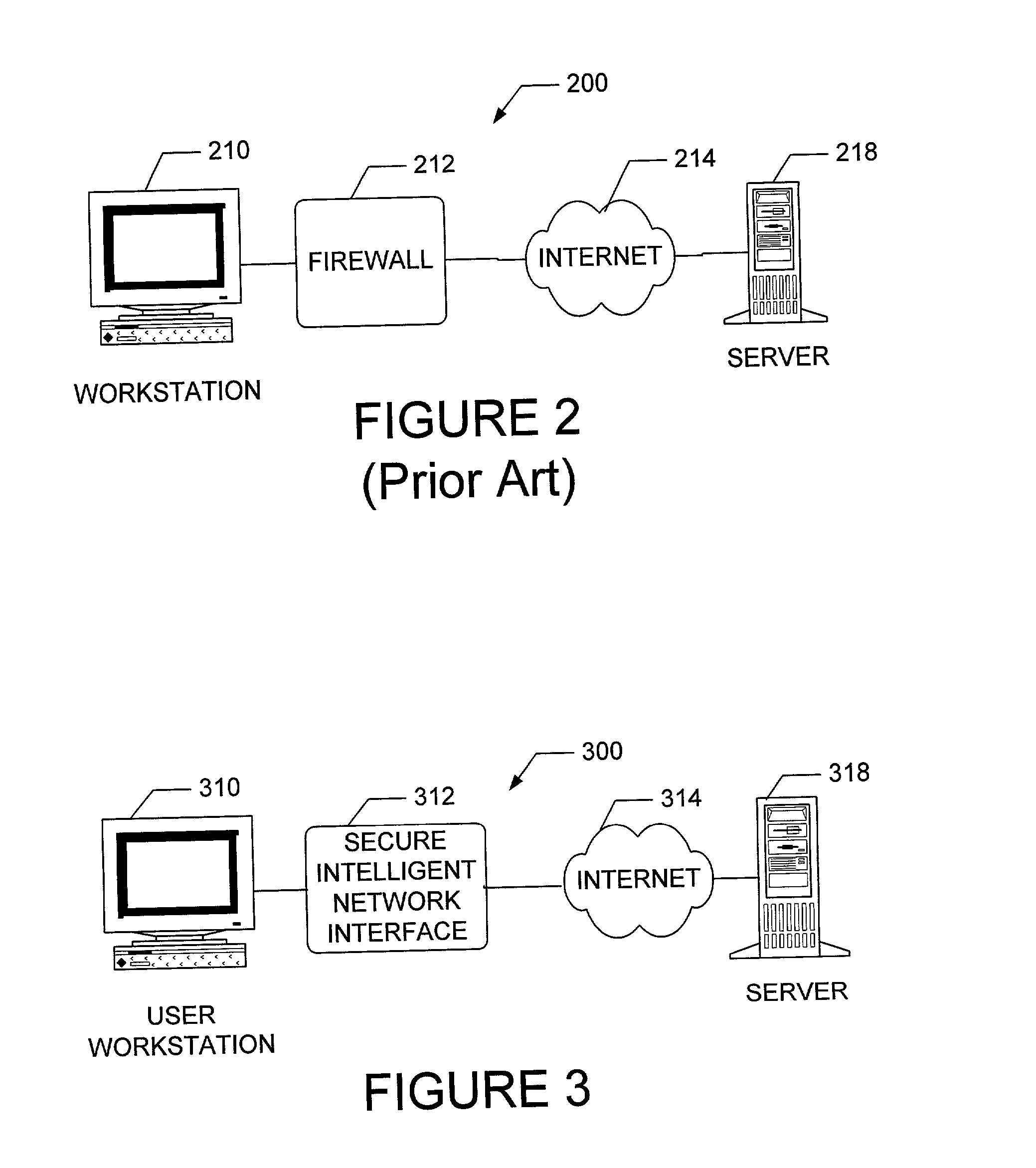
Apparatus and method for providing secure network communication
InactiveUS20020162026A1Eliminate attackEliminate needData taking preventionDigital data processing detailsFault toleranceIntelligent Network
The present invention is drawn to an apparatus and method for providing secure network communication. Each node or computer on the network has a secure, intelligent network interface with a coprocessor that handles all network communication. The intelligent network interface can be built into a network interface card (NIC) or be a separate box between each machine and the network. The intelligent network interface encrypts outgoing packets and decrypts incoming packets from the network based on a key and algorithm managed by a centralized management console (CMC) on the network. The intelligent network interface can also be configured by the CMC with dynamically distributed code to perform authentication functions, protocol translations, single sign-on functions, multi-level firewall functions, distinguished-name based firewall functions, centralized user management functions, machine diagnostics, proxy functions, fault tolerance functions, centralized patching functions, Web-filtering functions, virus-scanning functions, auditing functions, and gateway intrusion detection functions.
Owner:NEUMAN MICHAEL +1
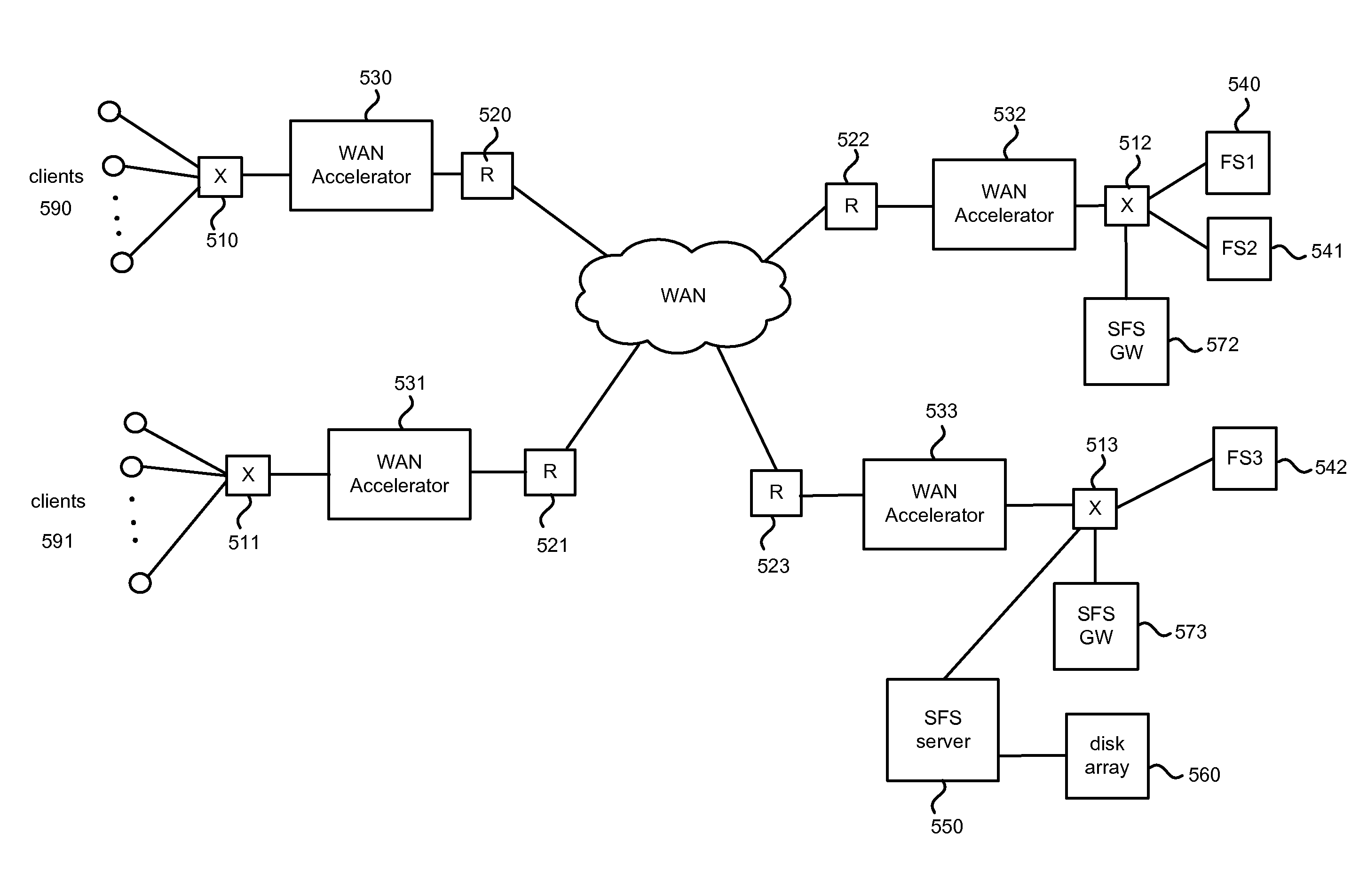
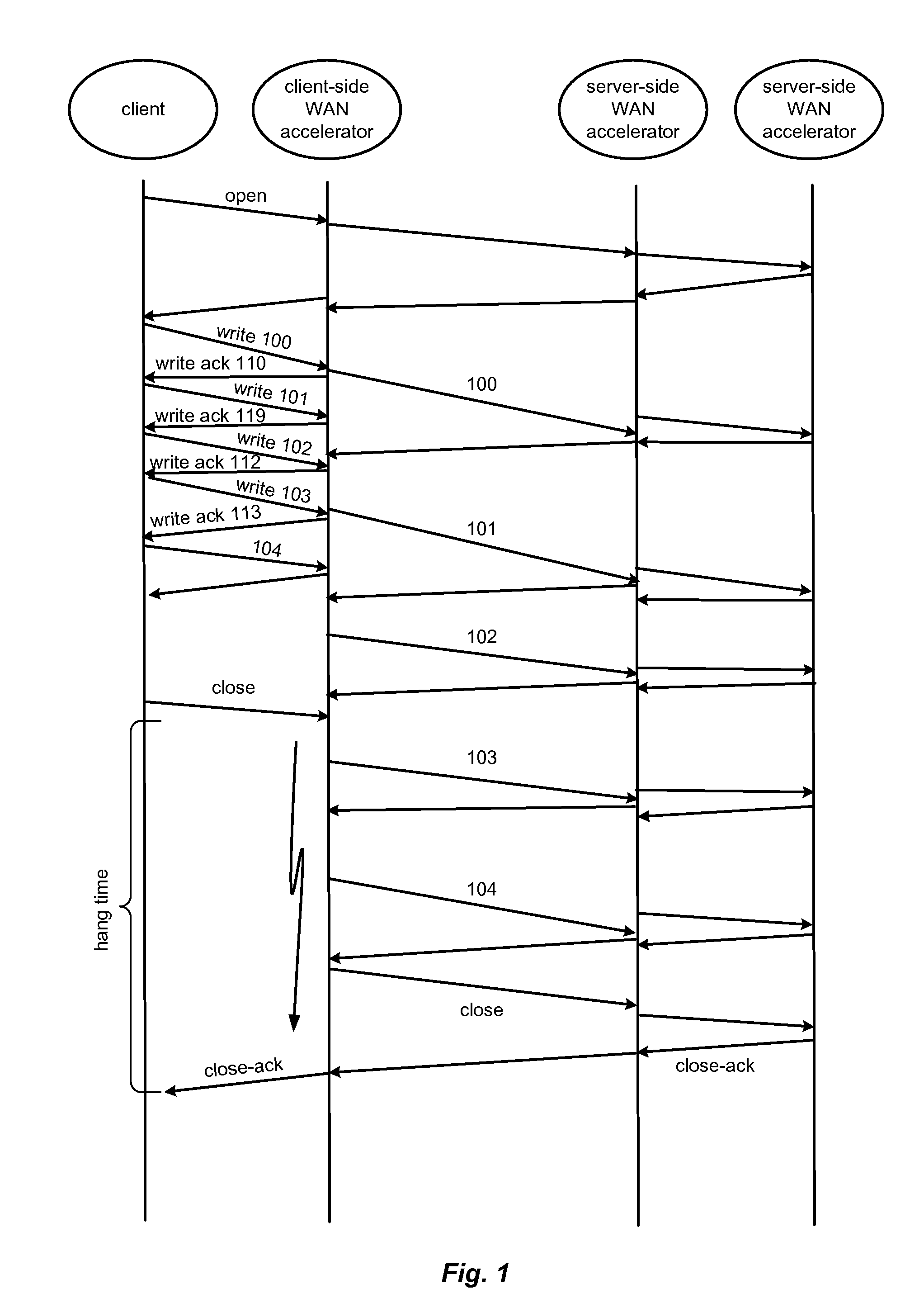
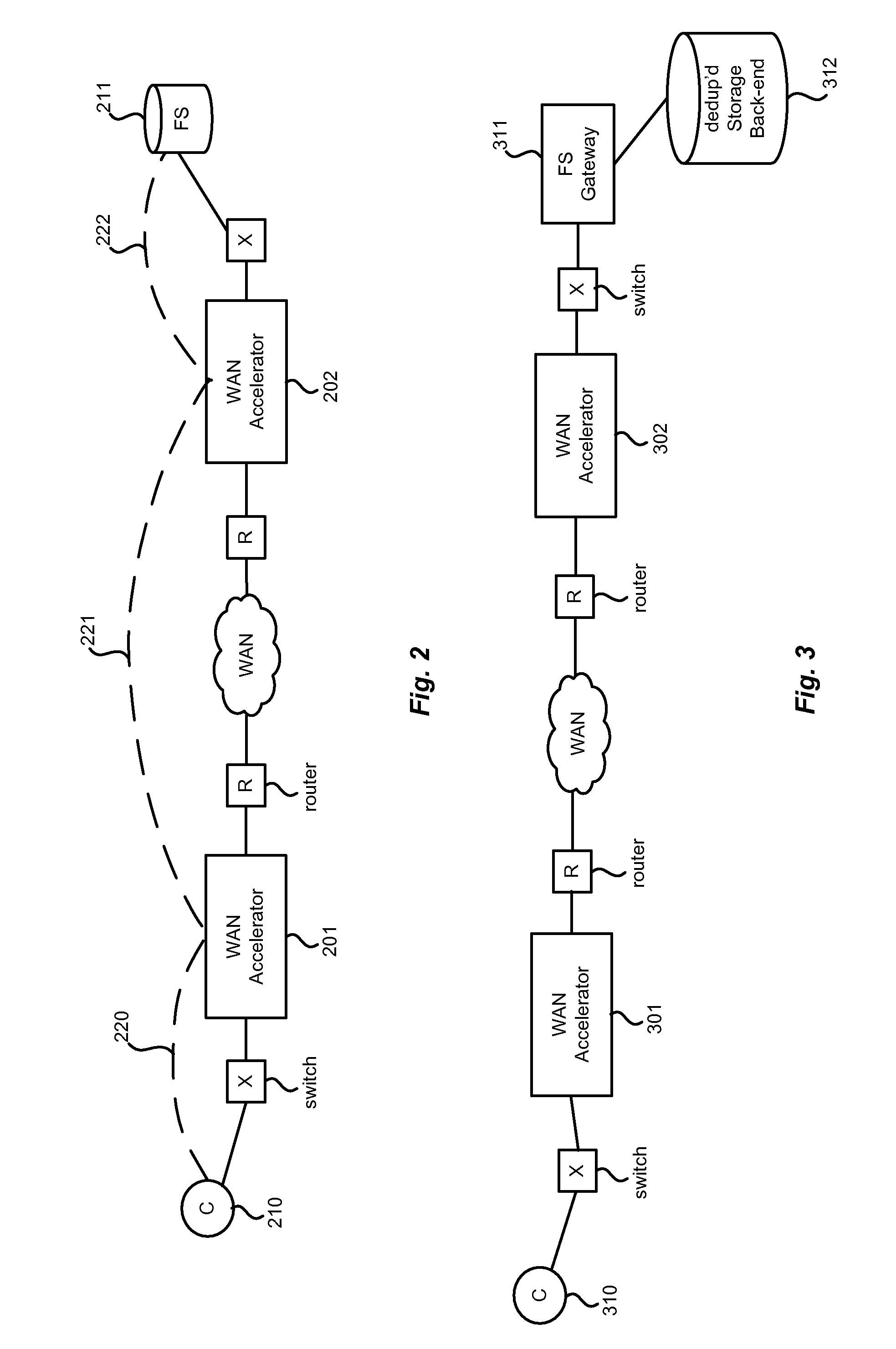
Hybrid segment-oriented file server and wan accelerator
ActiveUS20080281908A1Error detection/correctionComputer security arrangementsFile serverProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
In a network including WAN accelerators and segment-oriented file servers, a method comprises responding to a client request to manipulate a file via a network file protocol by receiving a first request at a first WAN accelerator, wherein the request is a request to open a file located at a file server that is a segment-oriented file server, sending a local request for the file, corresponding to the first request, from the WAN accelerator to the file server, using a segment-aware network request protocol, returning at least a portion of the requested file in the form of a representation of a data map corresponding to the at least a portion of the requested file stored on the file server and using a data map for reconstruction of the requested file.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
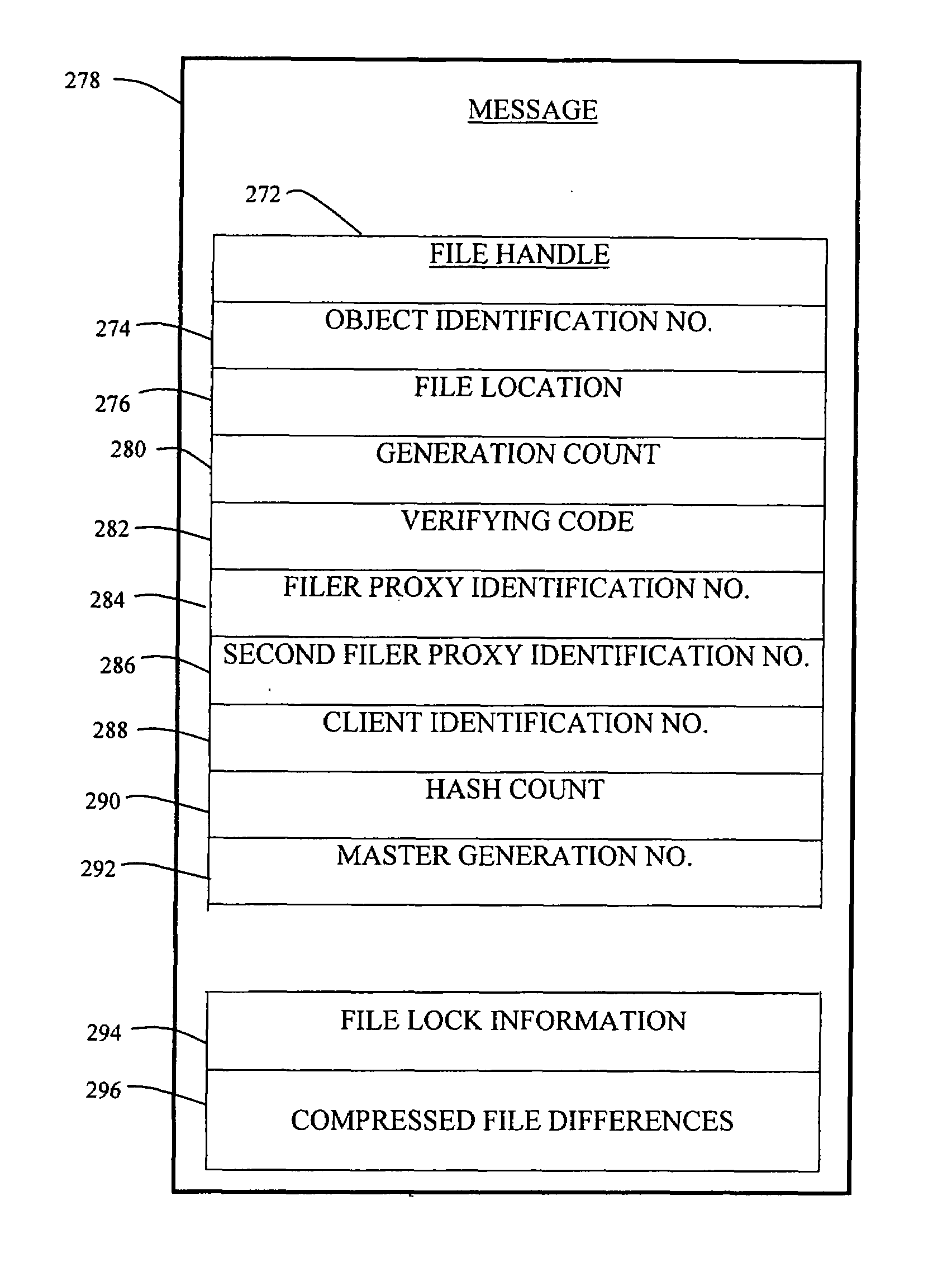
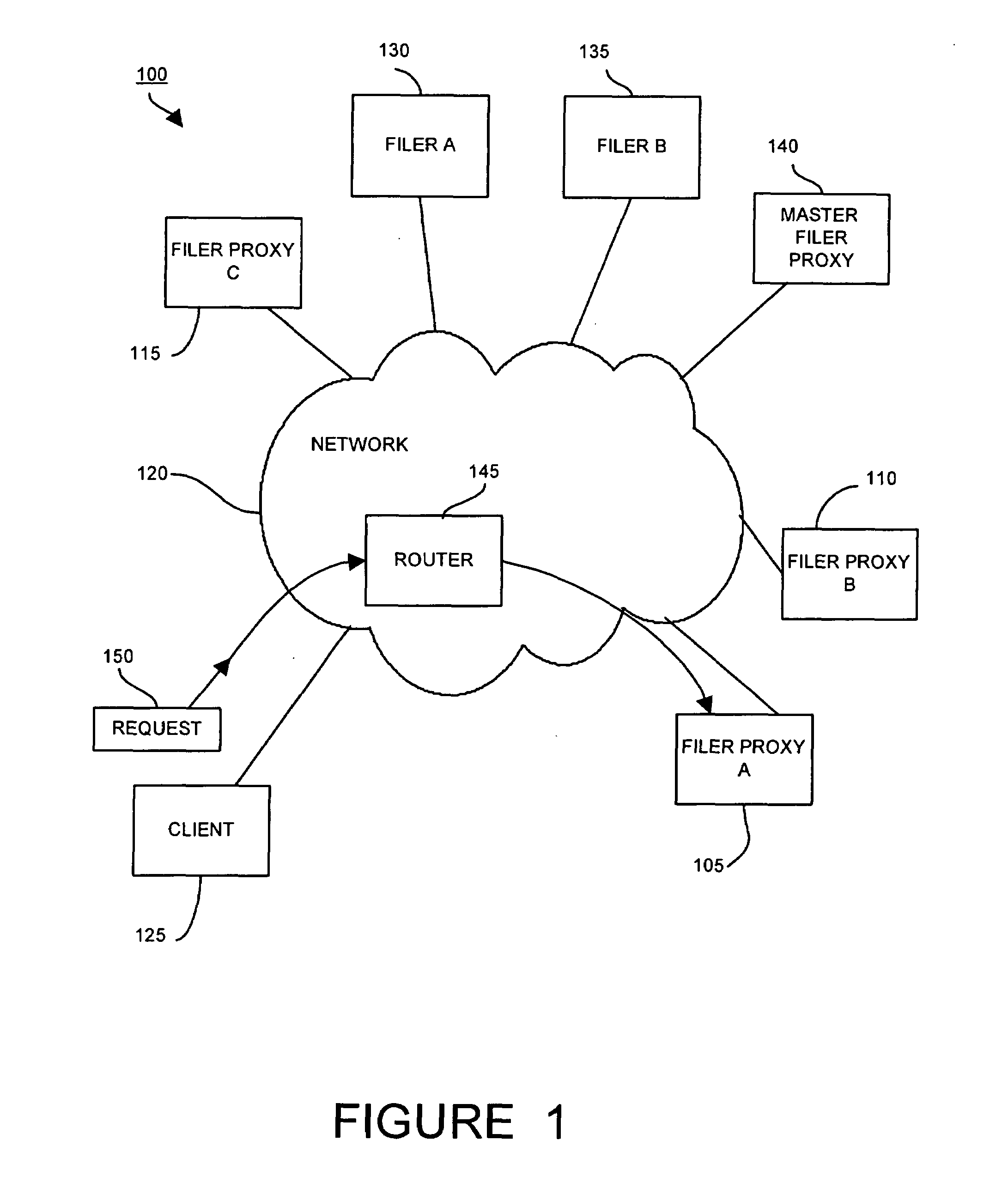
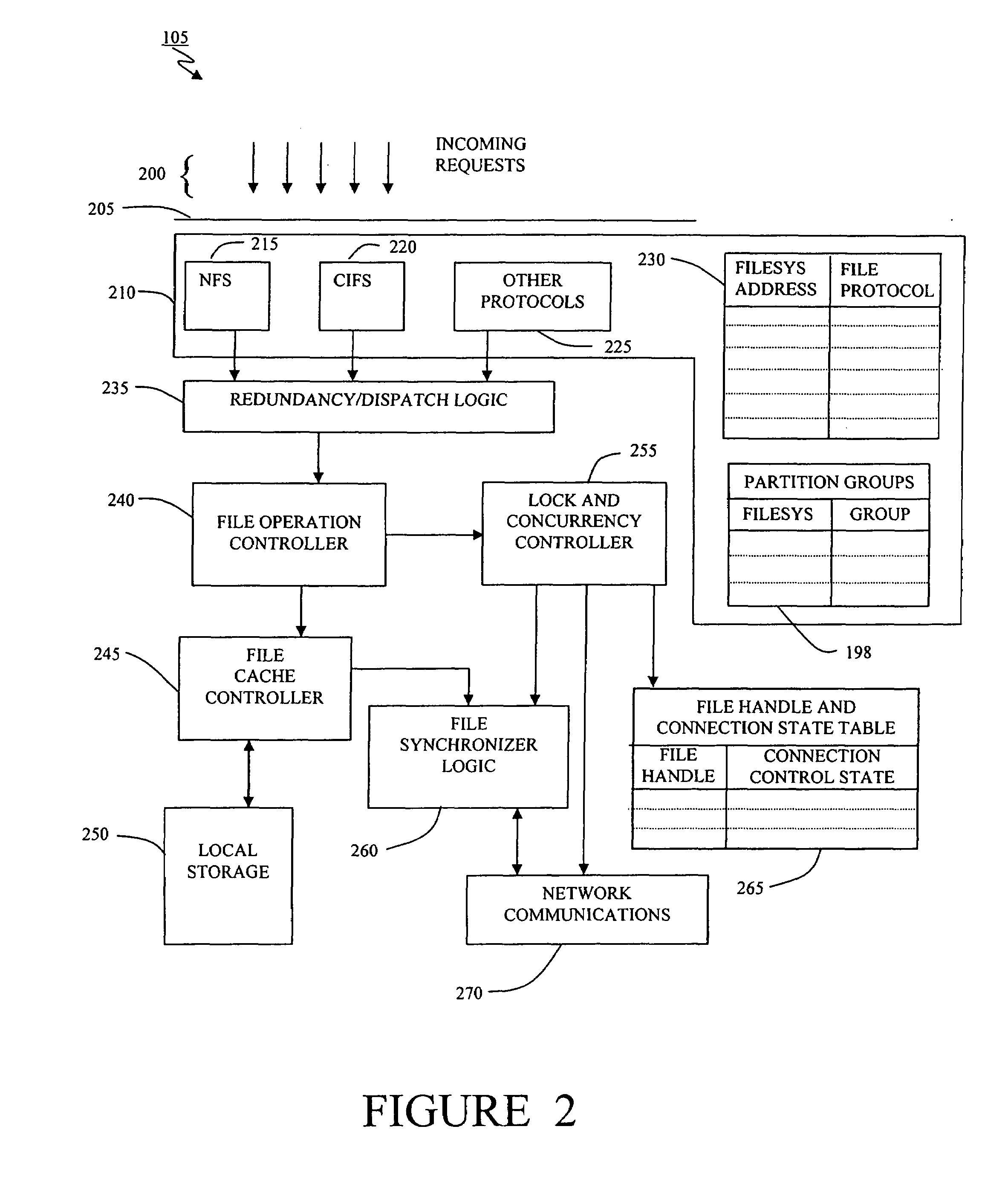
Method and apparatus for transparent distributed network-attached storage with web cache communication protocol/anycast and file handle redundancy
ActiveUS7254636B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsContent distributionNetwork connection
A distributed network-attached storage network provides content distribution using conventional file transfer protocols such as NFS and CIFS. A filer proxy accepts a client request and translates the client request to a file transfer protocol accepted at the file system having the file requested in the client request. The filer proxy generates a file handle for the file containing redundant filer proxy information to be used for failover to a backup filer proxy in the event of a network error or failure of an original filer proxy. The file handle also contains information for network security purposes such as detection of forged file handles.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
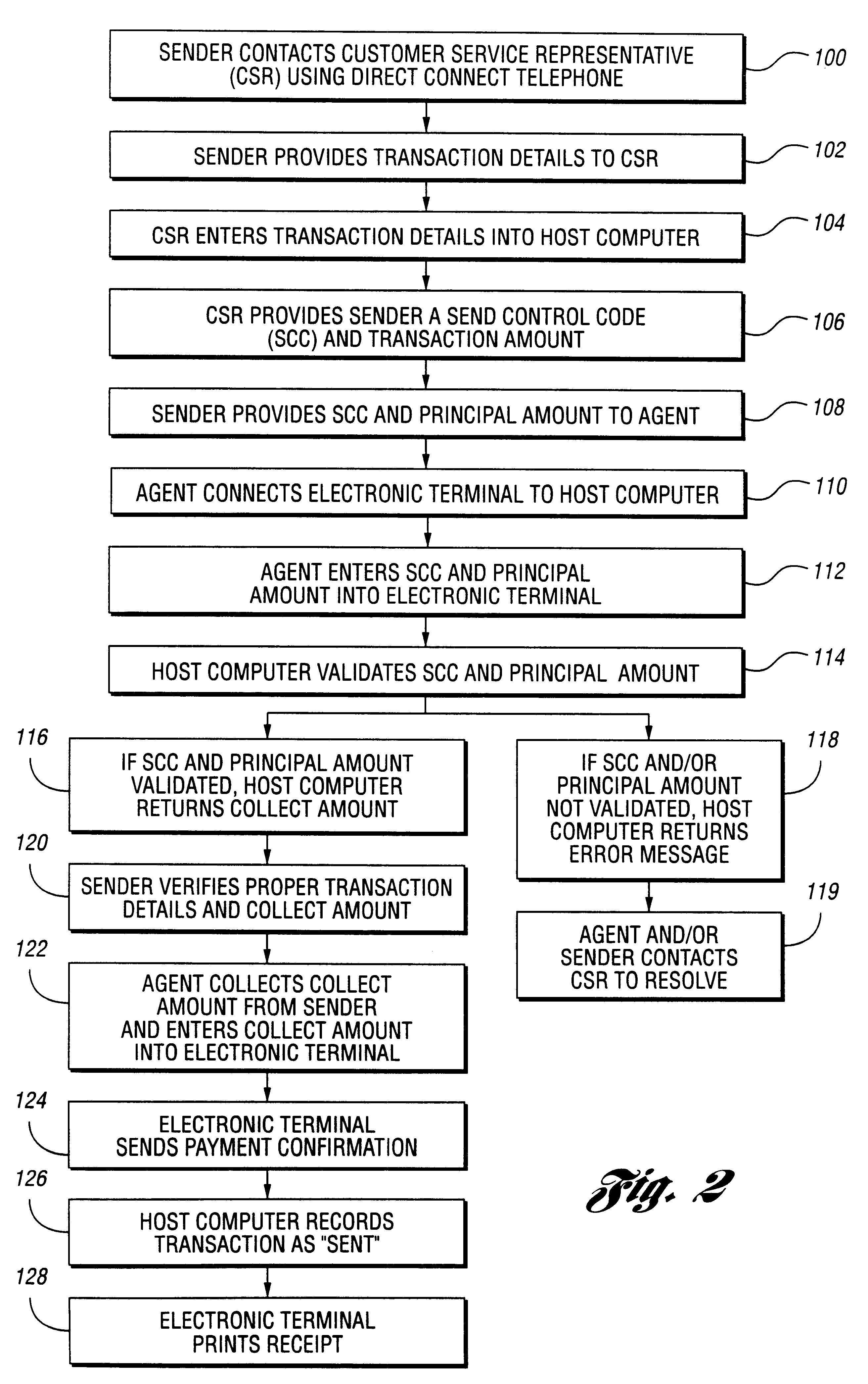
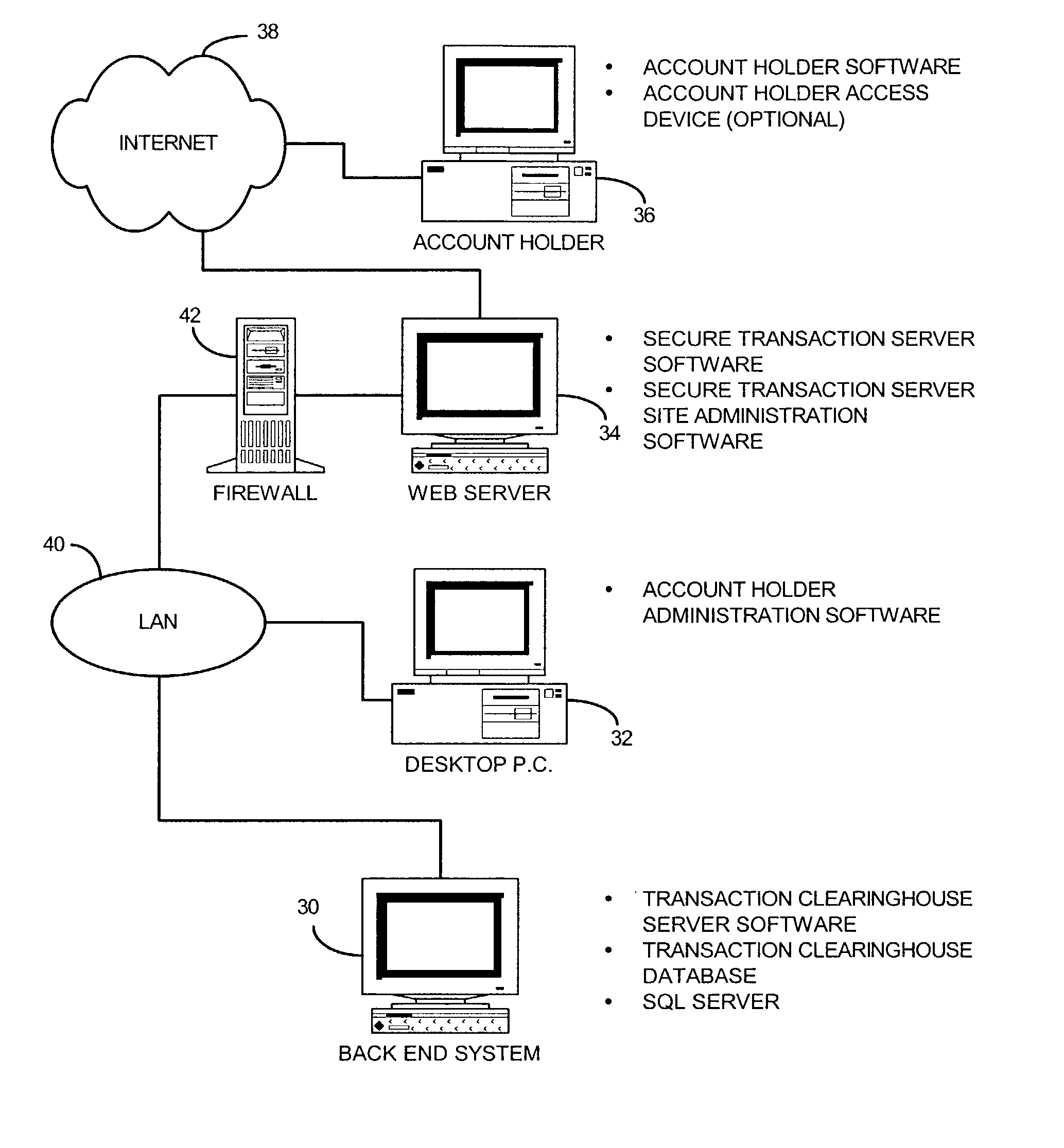
System and method for performing money transfer transaction using TCP/IP
InactiveUS6502747B1Low costShorten the timeComplete banking machinesFinanceInternet protocol suiteProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A method of performing a money transfer transaction through a financial services institution includes receiving information regarding the transaction on a first computer of the financial services institution from a first electronic device using the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol suite (TCP / IP). The method may also include establishing a T1 connection between the first computer and the first electronic device. A system for performing a money transfer transaction using TCP / IP is also disclosed.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
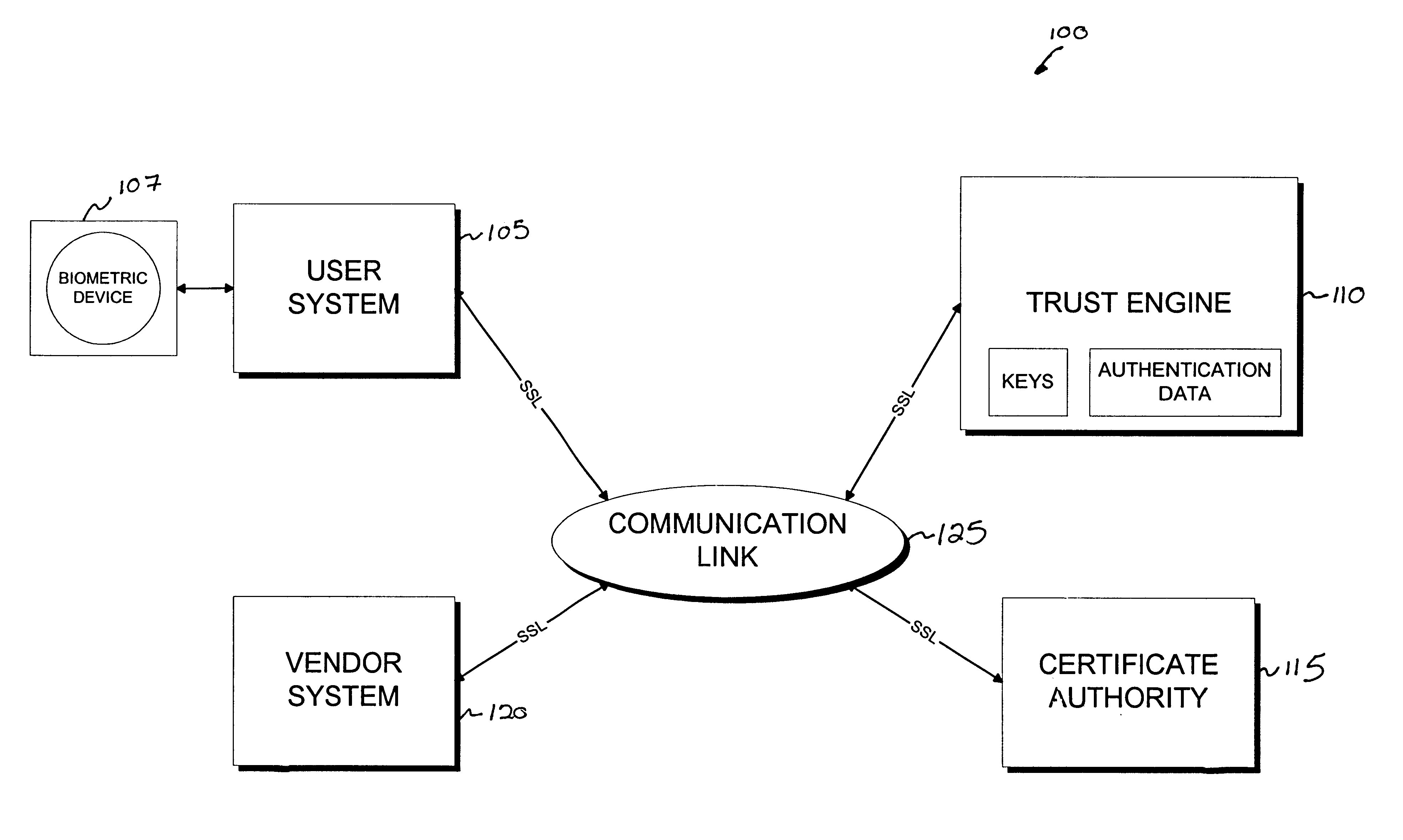
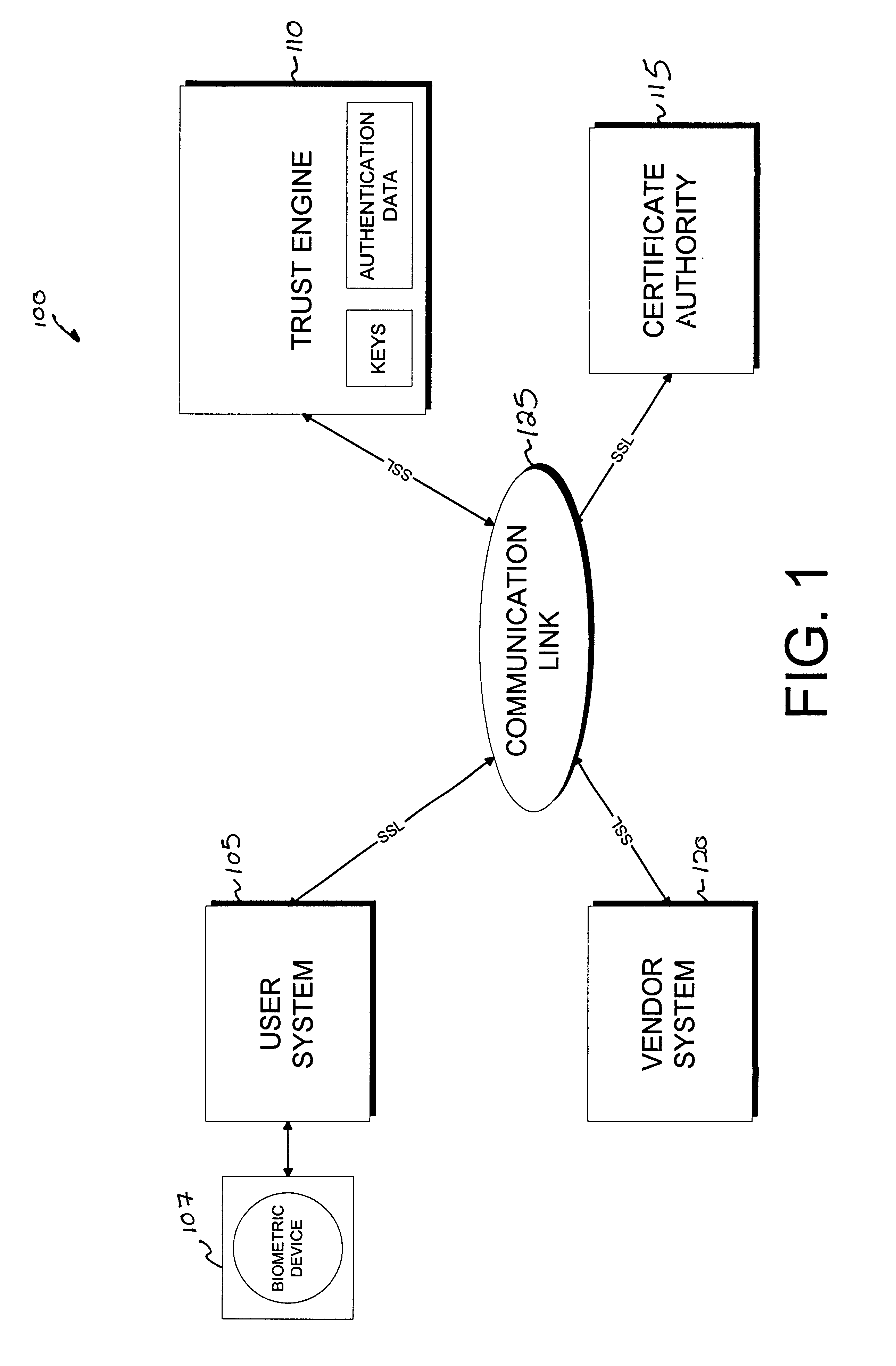
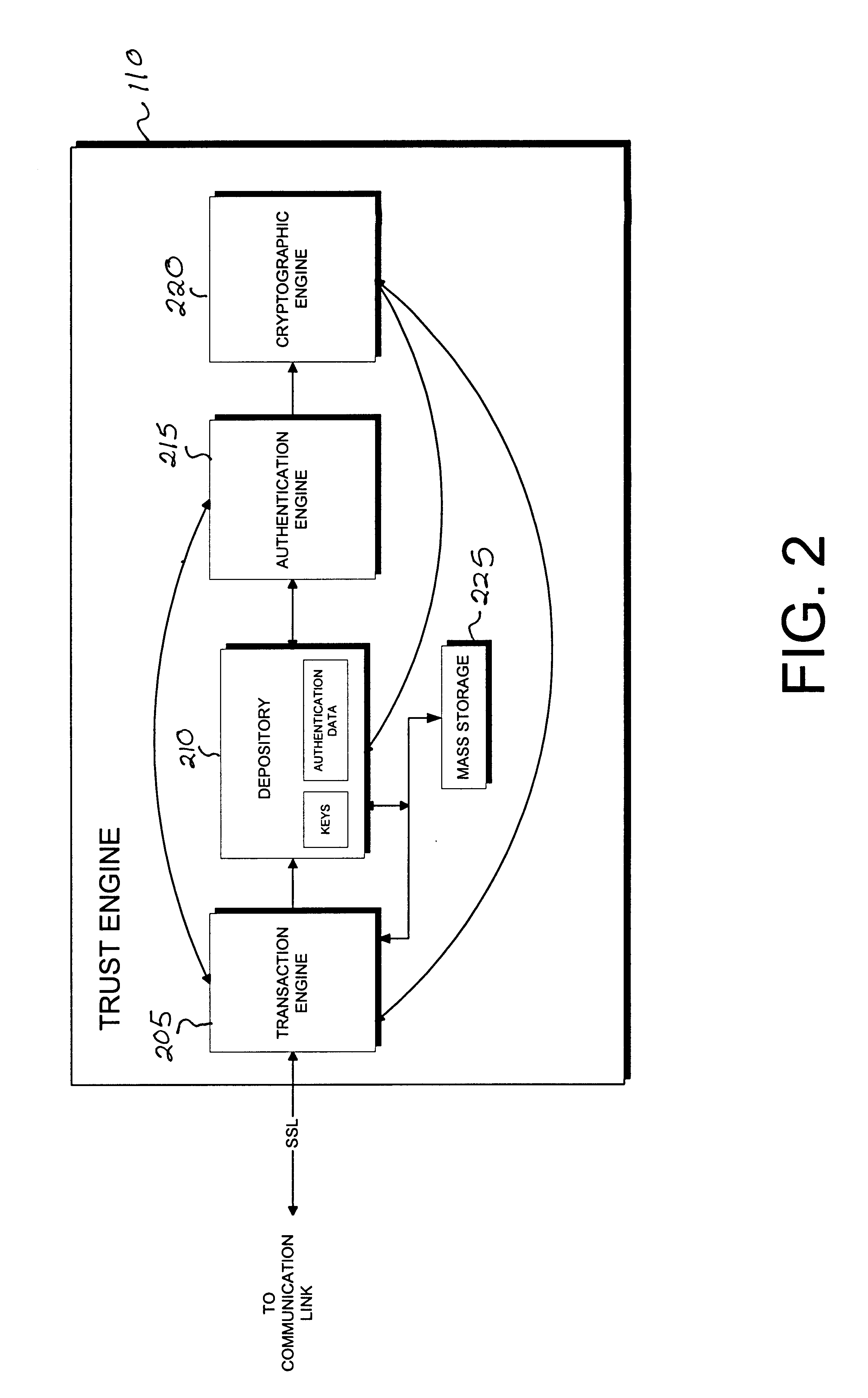
Cryptographic server with provisions for interoperability between cryptographic systems
InactiveUS6853988B1Reduce the number of timesMinimal compute resourceDigital data authenticationBuying/selling/leasing transactionsComputer hardwareKey storage
The invention is a cryptographic server providing interoperability over multiple algorithms, keys, standards, certificate types and issuers, protocols, and the like. Another aspect of the invention is to provide a secure server, or trust engine, having server-centric keys, or in other words, storing cryptographic keys on a server. The server-centric storage of keys provides for user-independent security, portability, availability, and straightforwardness, along with a wide variety of implementation possibilities.
Owner:SECURITY FIRST INNOVATIONS LLC
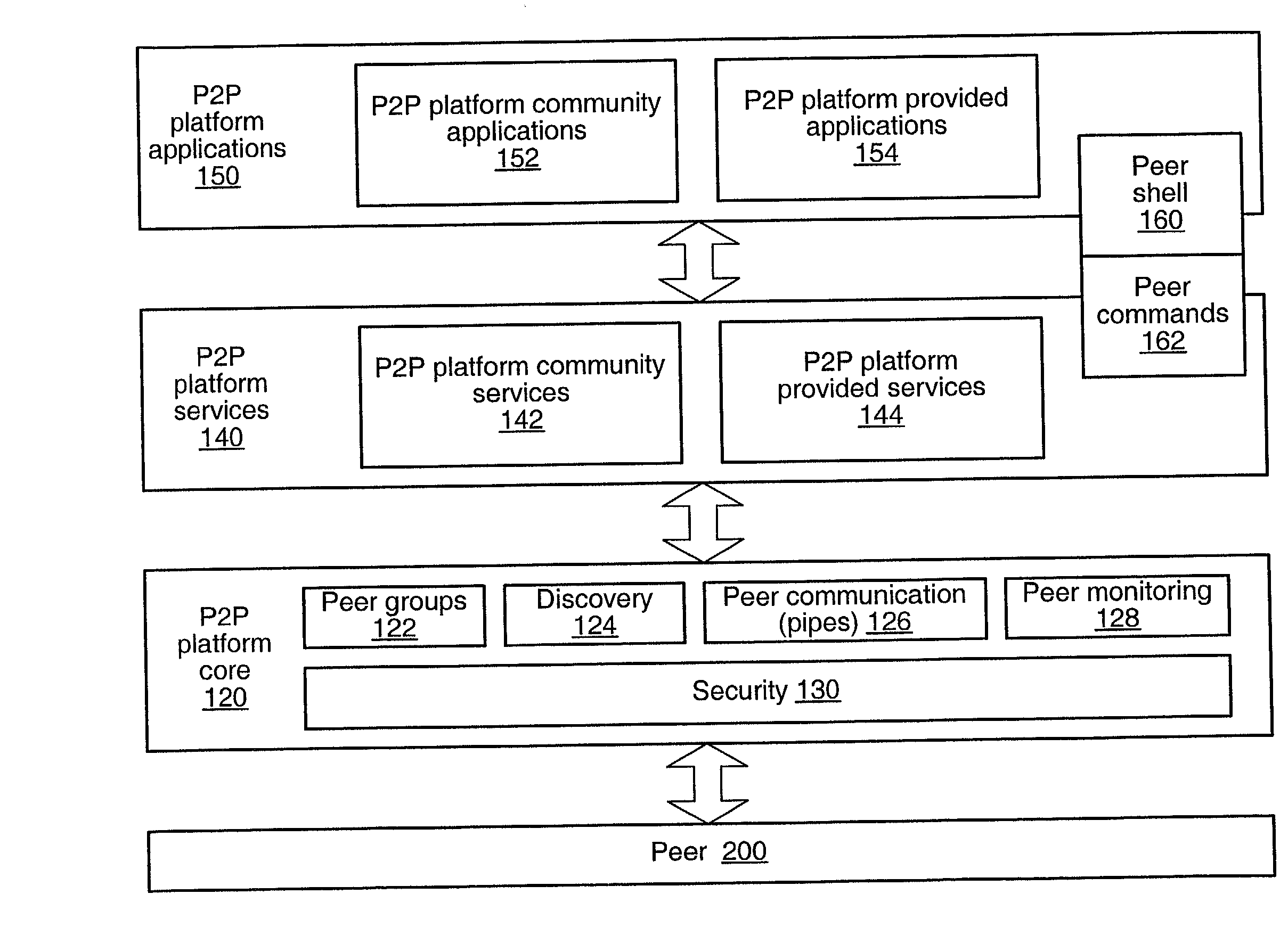
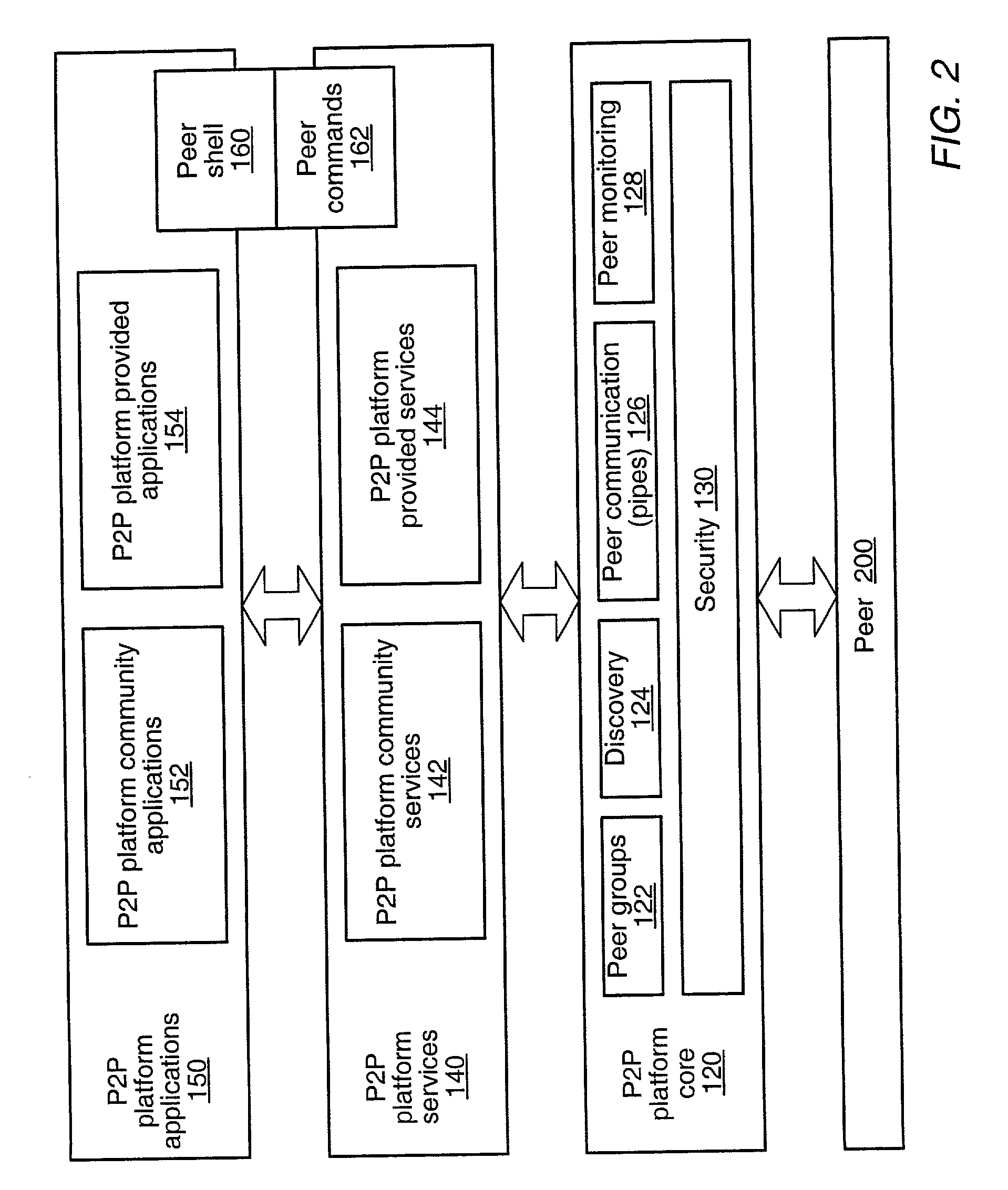
Peer-to-peer computing architecture
ActiveUS20020147771A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPhysical addressProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A system and method for providing an open network computing platform designed for peer-to-peer computing. The peer-to-peer platform may provide protocols for peer-to-peer services and applications that allow peers to discover each other, communicate with each other, and cooperate with each other to form peer groups. The protocols may include a peer membership protocol, a peer discovery protocol, a peer resolver protocol, a peer information protocol, a pipe binding protocol, and a peer endpoint protocol. Services and applications that participate in the protocols may be provided to deal with higher-level concepts. Advertisements may be used to publish peer resources. The peer-to-peer platform provides the ability to replicate information toward end users and may enable peers to find content that is closest to them. The peer-to-peer protocols and unique peer identifiers may allow peer nodes to move to different locations and access services and other content independent of network physical addresses.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for controlling access, by an authentication server, to protected computer resources provided via an internet protocol network
InactiveUS7290288B2Mosaic printer telegraph systemDigital data processing detailsComputer resourcesThe Internet
A method and system for controlling access, by an authentication server, to protected computer resources provided via an Internet Protocol network that includes storing (i) a digital identification associated with at least one client computer device, and (ii) data associated with the protected computer resources in at least one database associated with the authentication server; authenticating, by the authentication server, the digital identification forwarded by at least one access server; authorizing, by the authentication server, the at least one client computer device to receive at least a portion of the protected computer resources requested by the at least one client computer device, based on the stored data associated with the requested protected computer resources; and permitting access, by the authentication server, to the at least the portion of the protected computer resources upon successfully authenticating the digital identification and upon successfully authorizing the at least once client computer device.
Owner:PRISM TECH
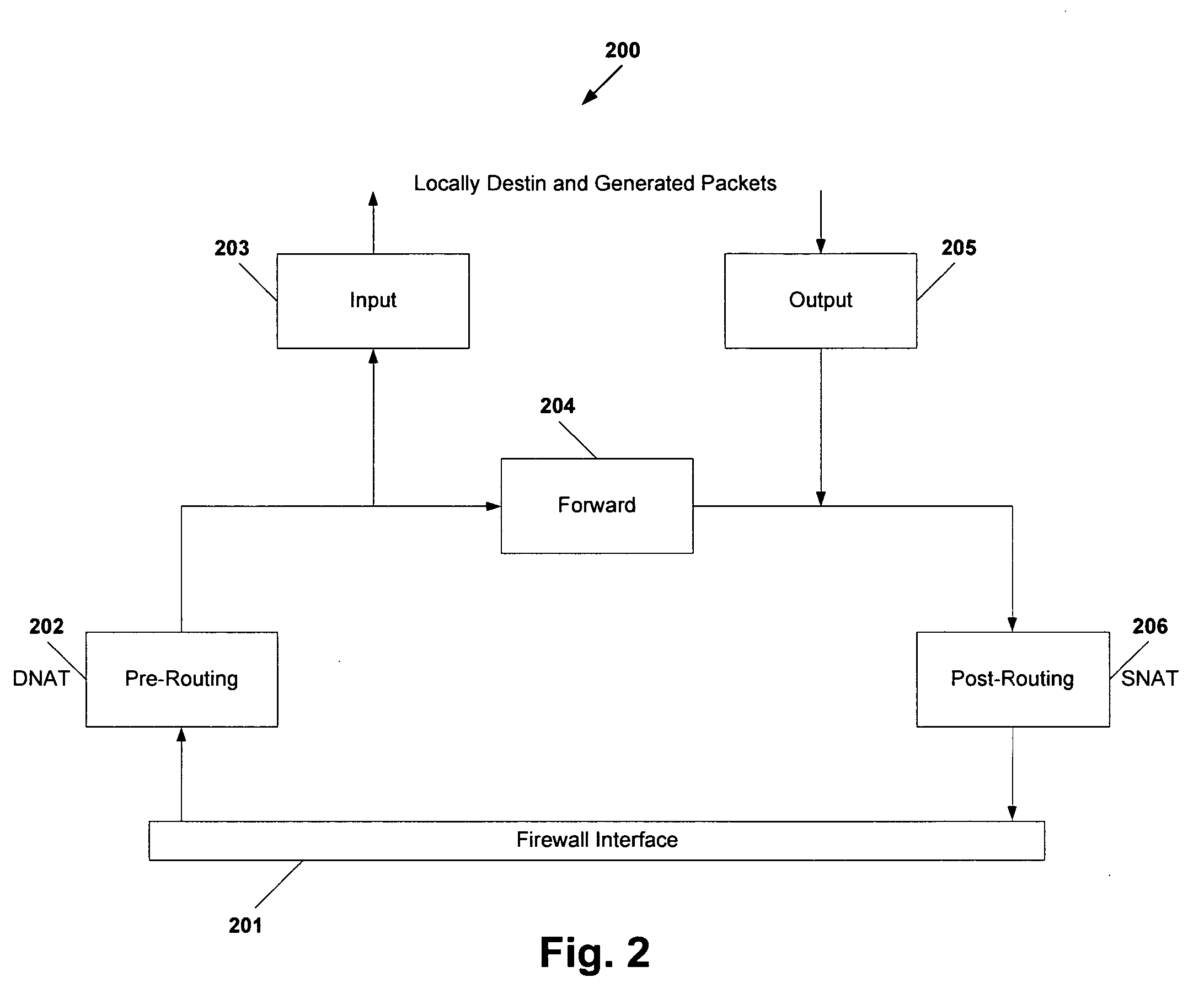
Method and system for distributed network address translation with network security features
InactiveUS7032242B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationIp address
A method and system for distributed network address translation with security features. The method and system allow Internet Protocol security protocol (“IPsec”) to be used with distributed network address translation. The distributed network address translation is accomplished with IPsec by mapping a local Internet Protocol (“IP”) address of a given local network device and a IPsec Security Parameter Index (“SPI”) associated with an inbound IPsec Security Association (“SA”) that terminates at the local network device. A router allocates locally unique security values that are used as the IPsec SPIs. A router used for distributed network address translation is used as a local certificate authority that may vouch for identities of local network devices, allowing local network devices to bind a public key to a security name space that combines a global IP address for the router with a set of locally unique port numbers used for distributed network address translation. The router issues security certificates and may itself be authenticated by a higher certificate authority. Using a security certificate, a local network device may initiate and be a termination point of an IPsec security association to virtually any other network device on an IP network like the Internet or an intranet. The method and system may also allow distributed network address translation with security features to be used with Mobile IP or other protocols in the Internet Protocol suite.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
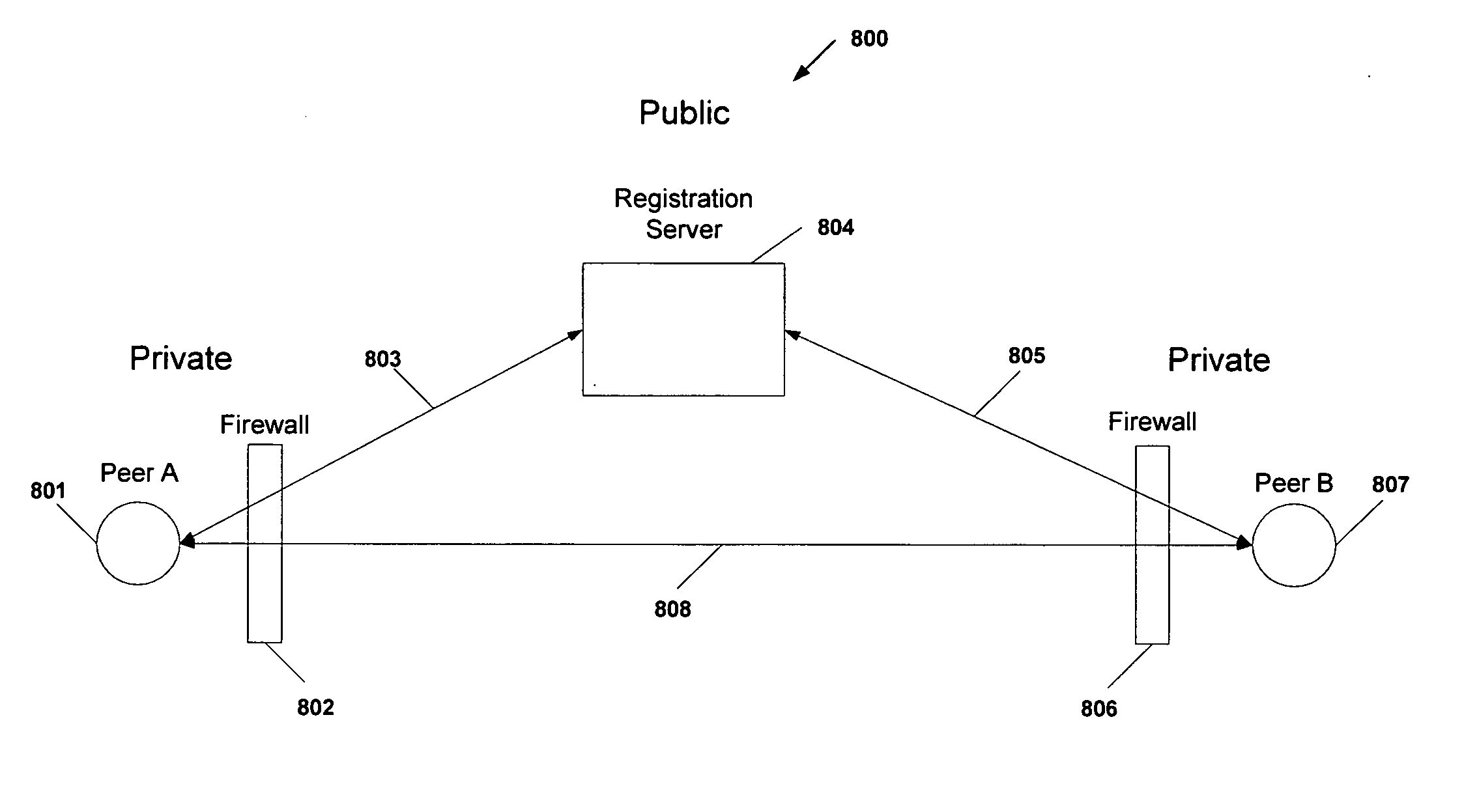
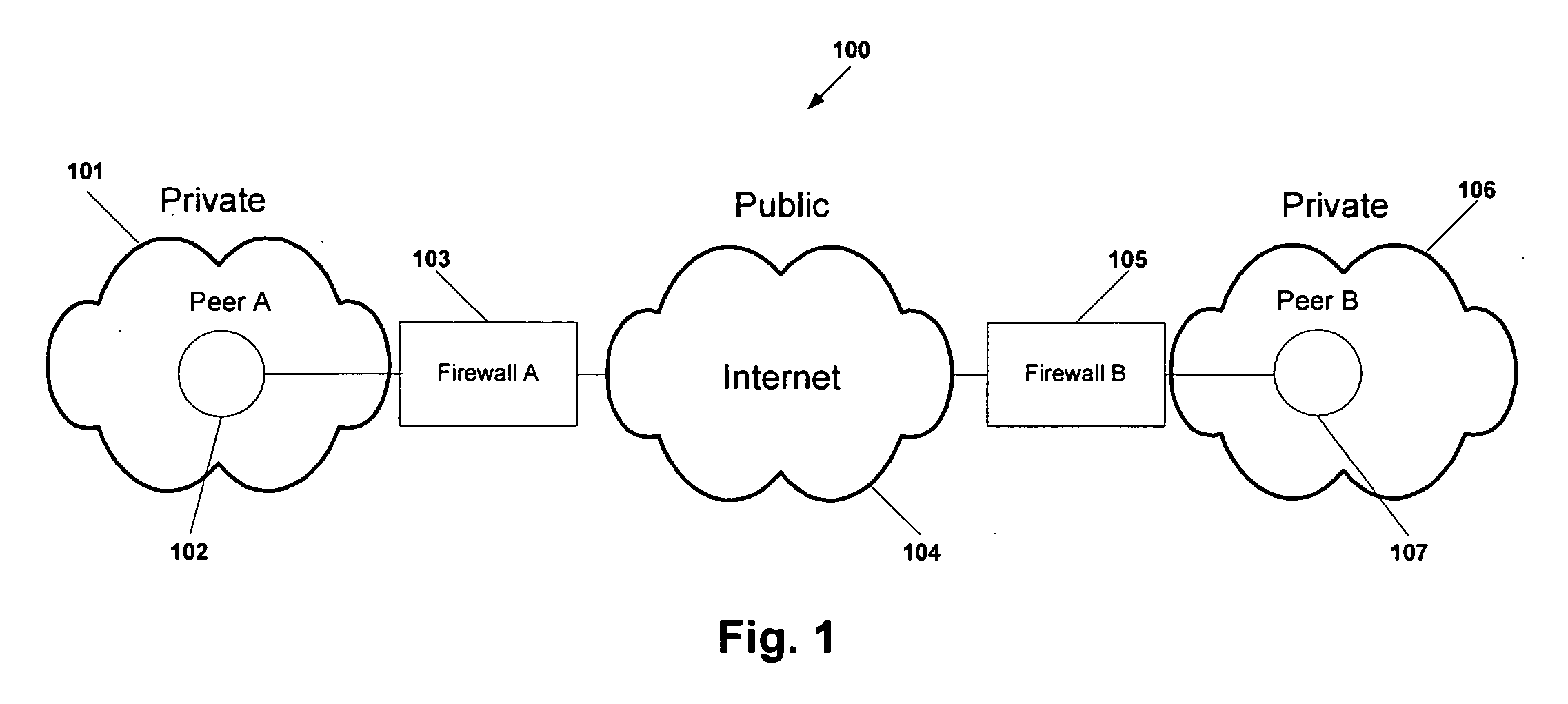
Protocol and system for firewall and NAT traversal for TCP connections
ActiveUS20060215684A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationServer agentNAT traversal
Firewalls and network address translators (NAT) provide many advantages for client and the Internet itself, however, these devices break many existing transmission control protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP) applications, since they conceal the identity of IP clients (i.e., peers) and block transmission control protocol (TCP) call setup requests. Firewalls and NATs make it impossible for one TCP peer to discover another and establish a connection. Embodiments of this invention provides a system and a protocol to enable two TCP peers that exist behind one or more firewalls and NATs to automatically setup a true peer-to-peer TCP connection and exchange data without making changes to the firewall or NAT devices or existing TCP-based applications. In embodiments of this invention, the synchronization between the blind TCP peers is achieved using a system that consists of a registration server, an agent application, and a virtual network interface that together relay and replicate the control signals between the two TCP peers. In addition, embodiments of this invention are also used to traverse the NAT and establish a bi-directional peer-to-peer TCP connection in the firewall.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
Voice over IP architecture
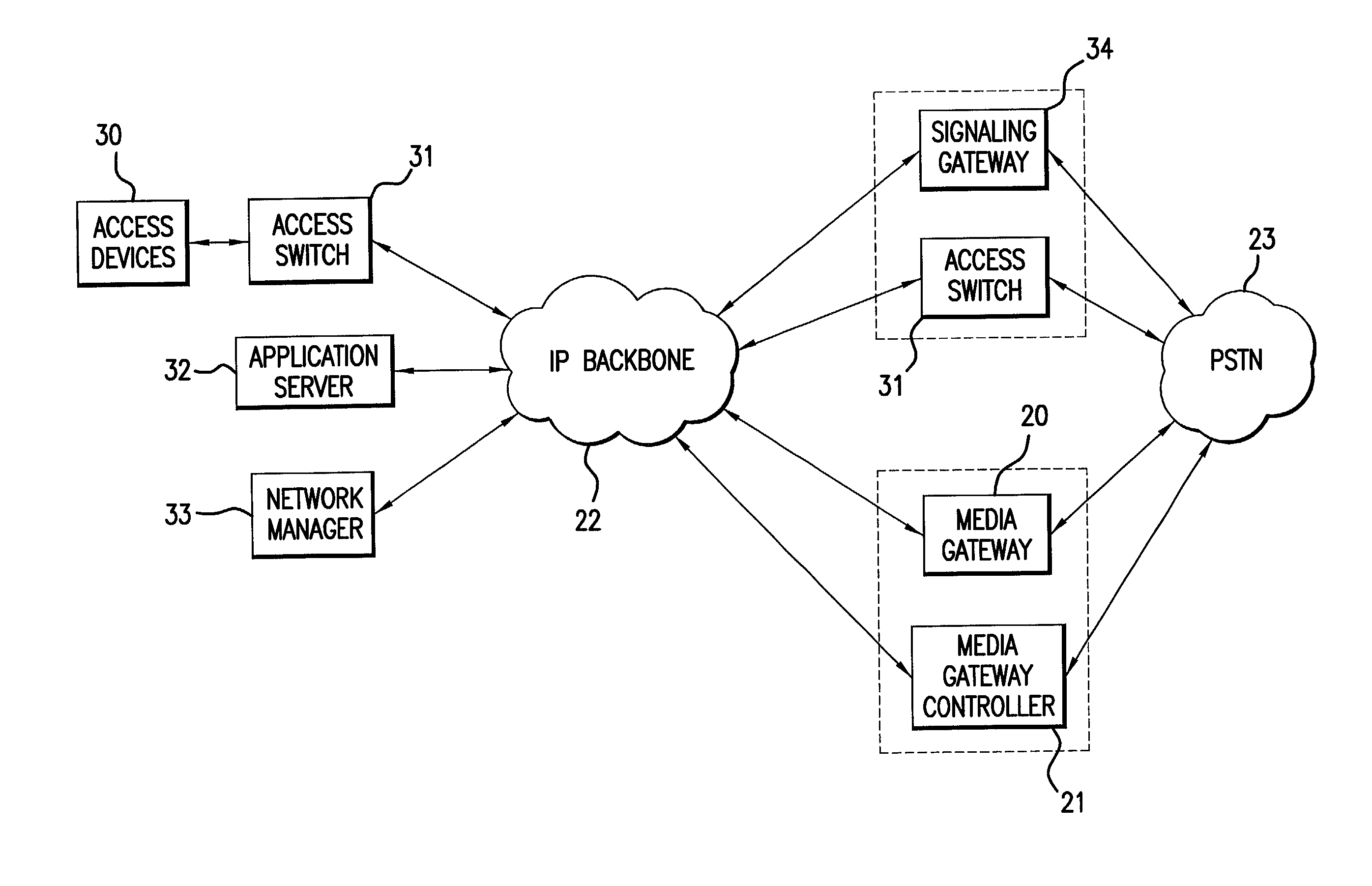
ActiveUS20030076815A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsVoice over IPProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) network is described in which session state is maintained in access switches, but not signaling gateways which maintain transaction state only during pendency of a related transaction. The signaling gateway further provides transparent inter-operation between the VoIP network and non-IP networks, such as the PSTN, by means of a translator which directly translates messages between the networks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
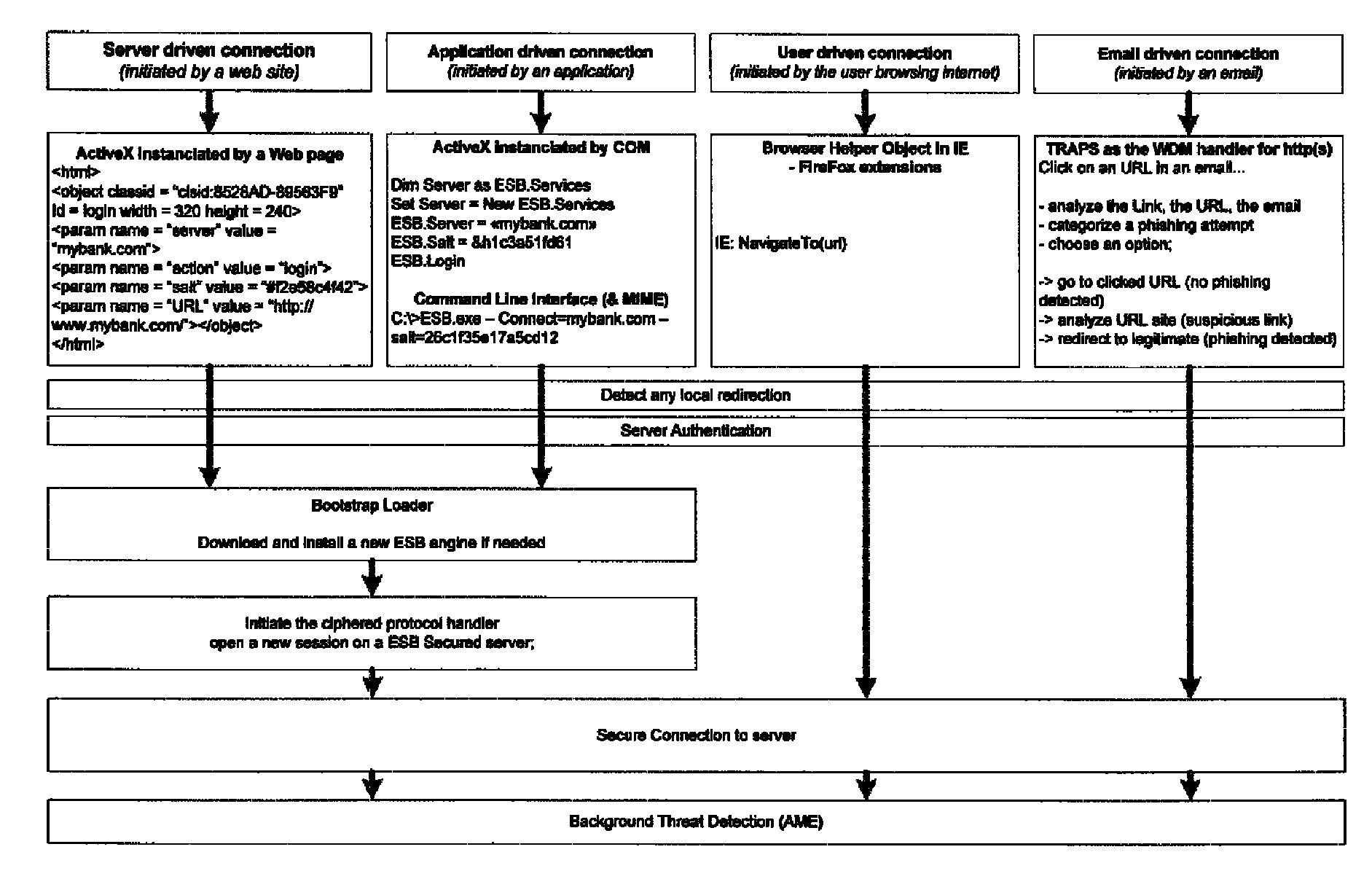
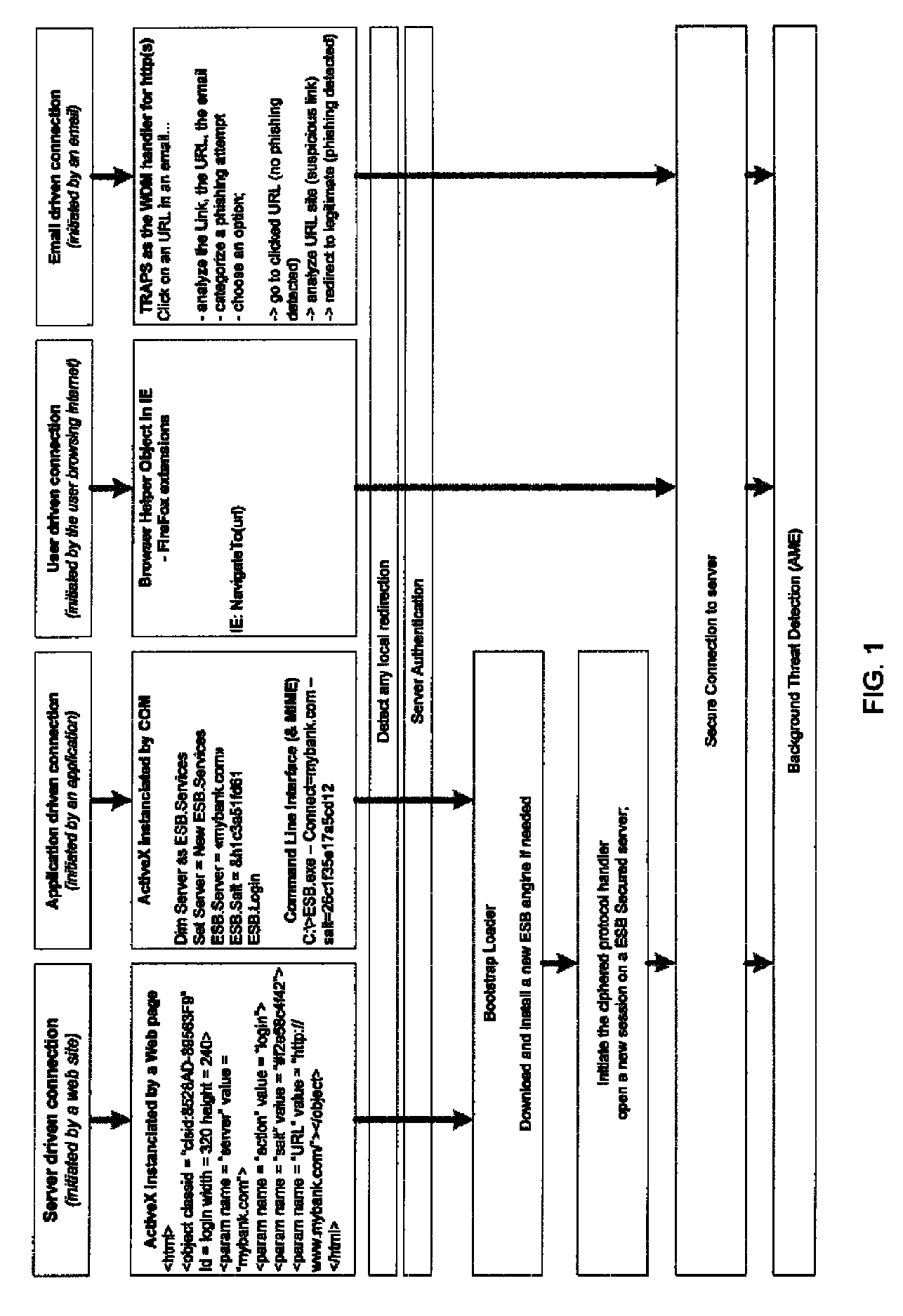
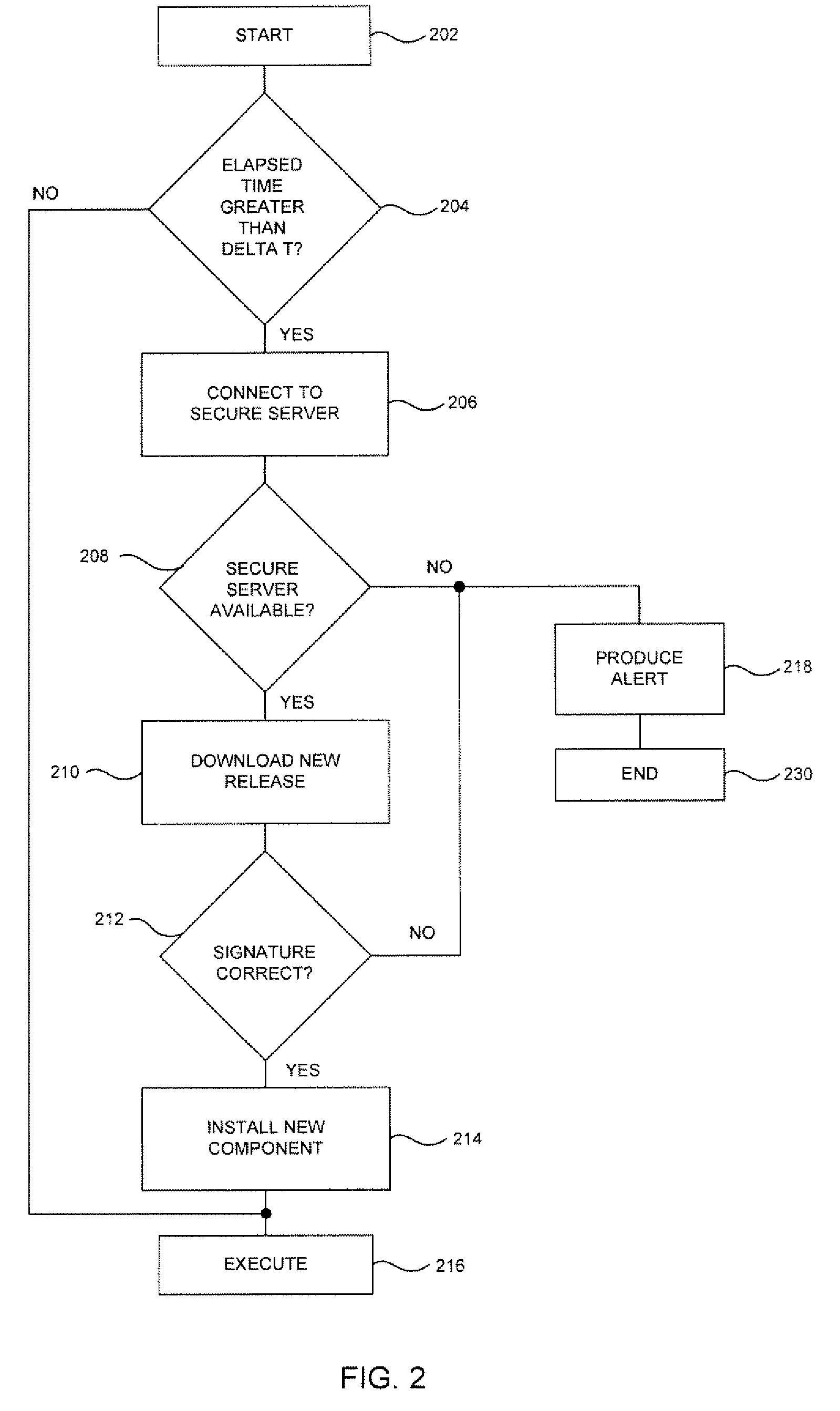
System and method for authentication, data transfer, and protection against phishing
ActiveUS8578166B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsElectronic communicationStructure of Management Information
Methods and systems for secure electronic data communication over public communication networks. A secure data communication component may be utilized to implement a communication protocol. New versions of the data communication component may be generated, with each version containing a different communication protocol. Source code of the data communication component may be modified using a polymorph engine to create a functionally-equivalent component having a different code structure. An anti-phishing component may intercept a link in an electronic communication activated by a user, analyze the link and the electronic communication, determine a phishing risk to the user posed by the link, and direct the user to a location indicated by the link or redirect the user to a valid location. A server authentication component may detect and prevent DNS attacks, injections, and defacing activities.
Owner:MORGAMON
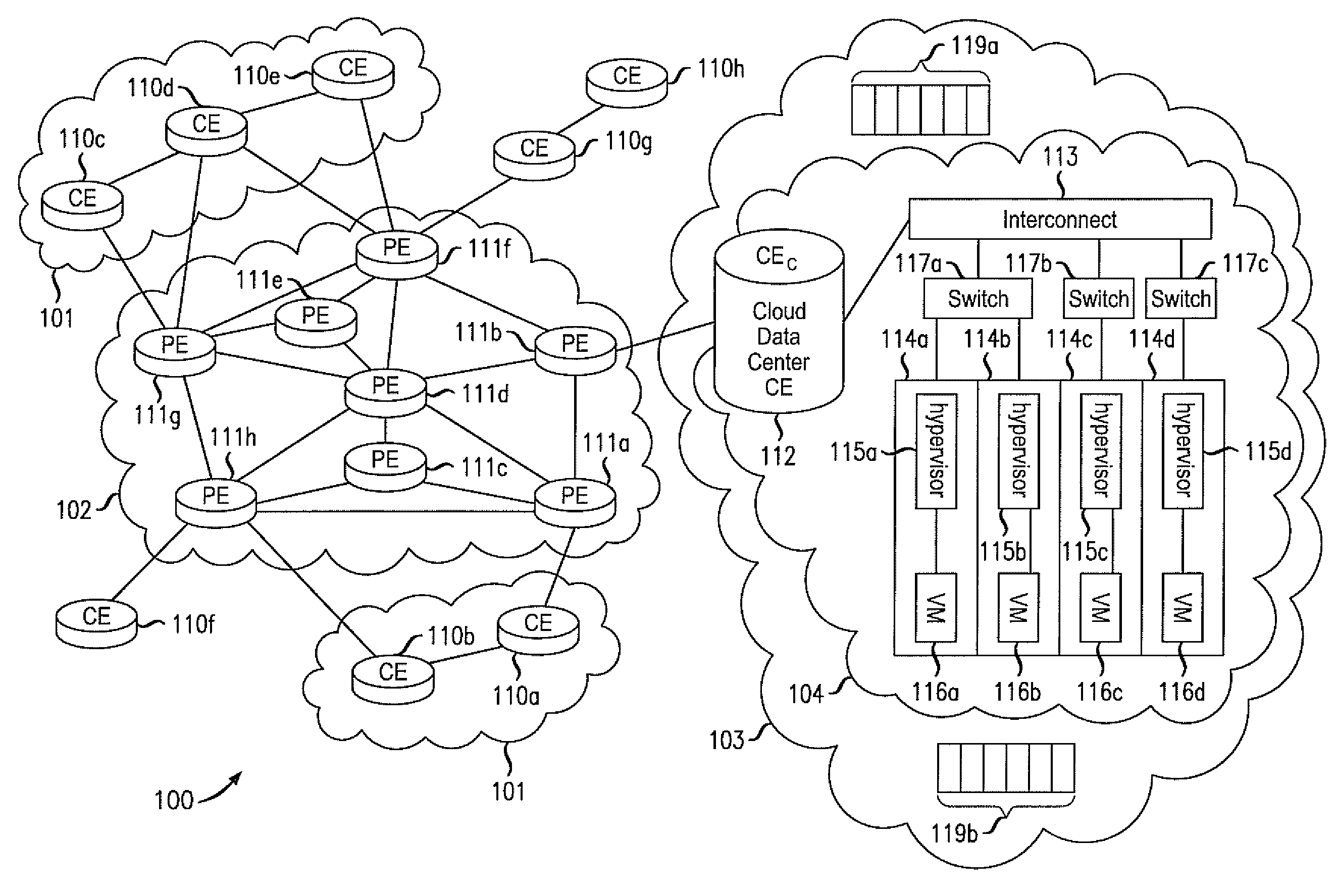
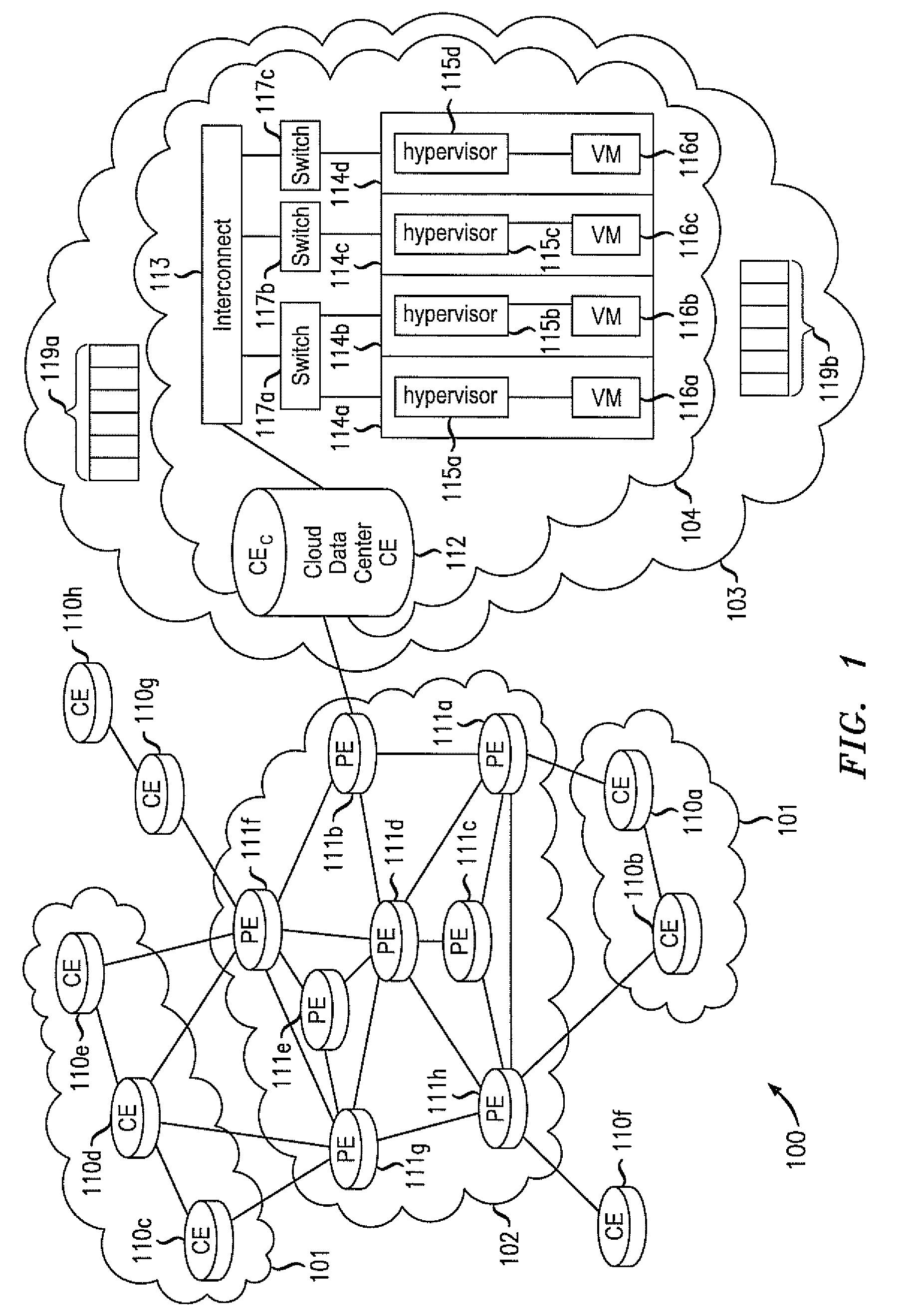
Layer 2 seamless site extension of enterprises in cloud computing
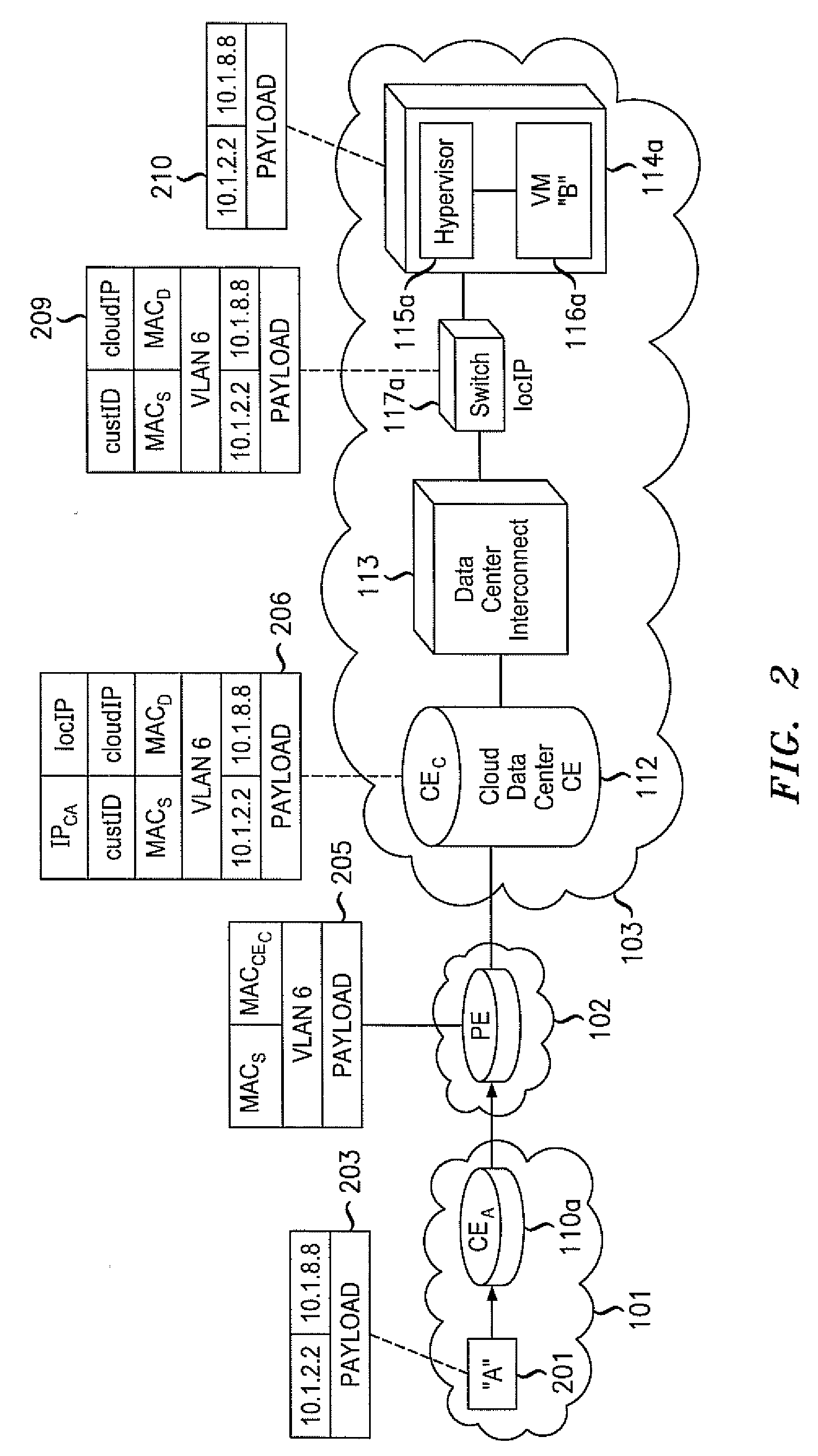
ActiveUS20110075667A1Ensure safetyHighly-dynamic scalability of cloud resourcesMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetIp address
Various embodiments relate to a Cloud Data Center, a system comprising the Cloud Data Center, and a related method. The Cloud Data Center may include a logical customer edge router to send packets between addresses in a private enterprise network and addresses in a logical network within a cloud network using Layer 2 protocol and MAC addressing. The logical network may have resources, known as virtual machines, allocated to the private enterprise network and may share a common IP address space with the private enterprise network. A directory at the Cloud Data Center may correlate the enterprise IP addresses of virtual machines with a MAC address, cloud IP address, and a location IP address within the logical network. The Cloud Data Center may double encapsulate packets with MAC, cloudIP, and locIP headers, when sending a packet to a destination in the logical network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
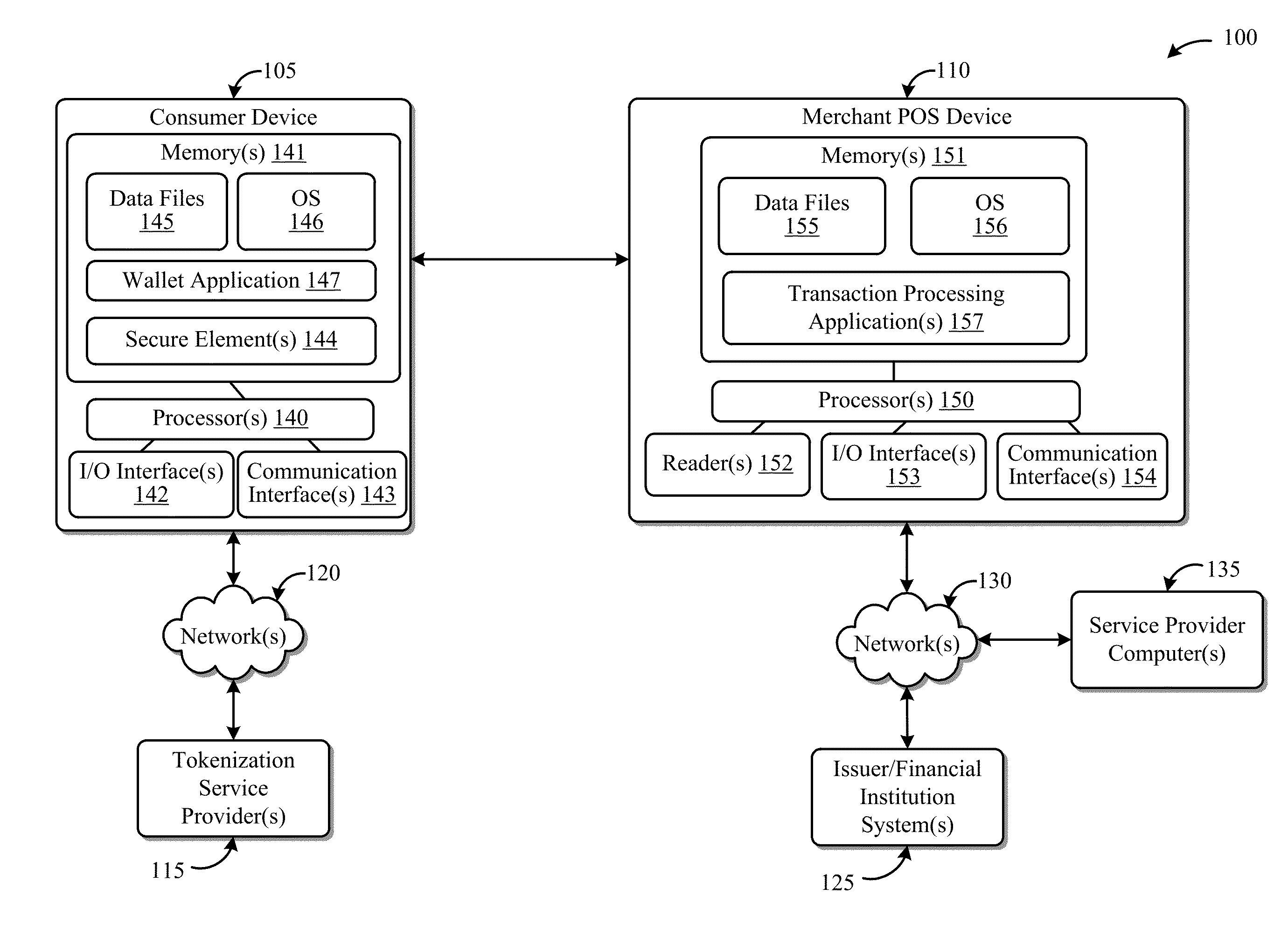
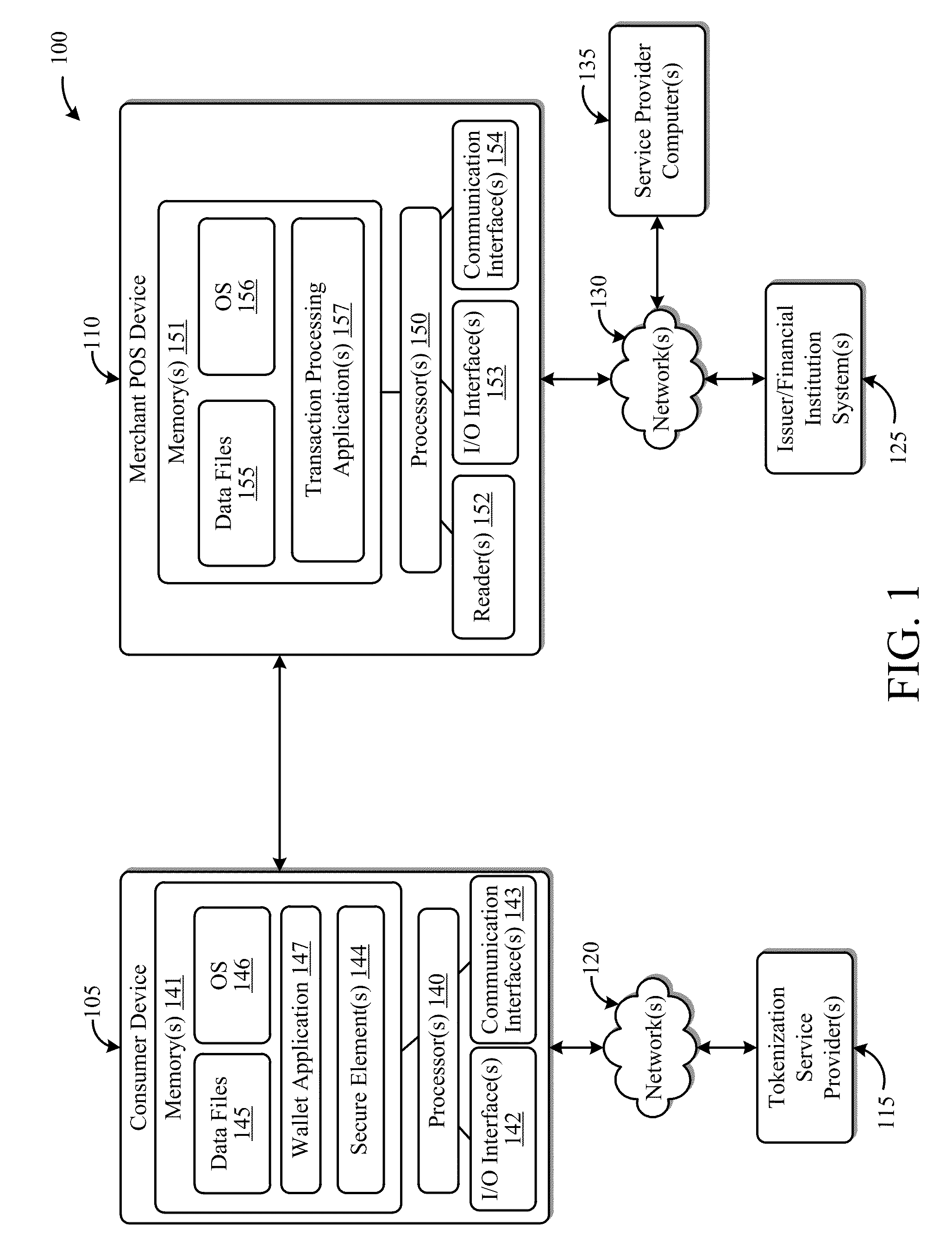
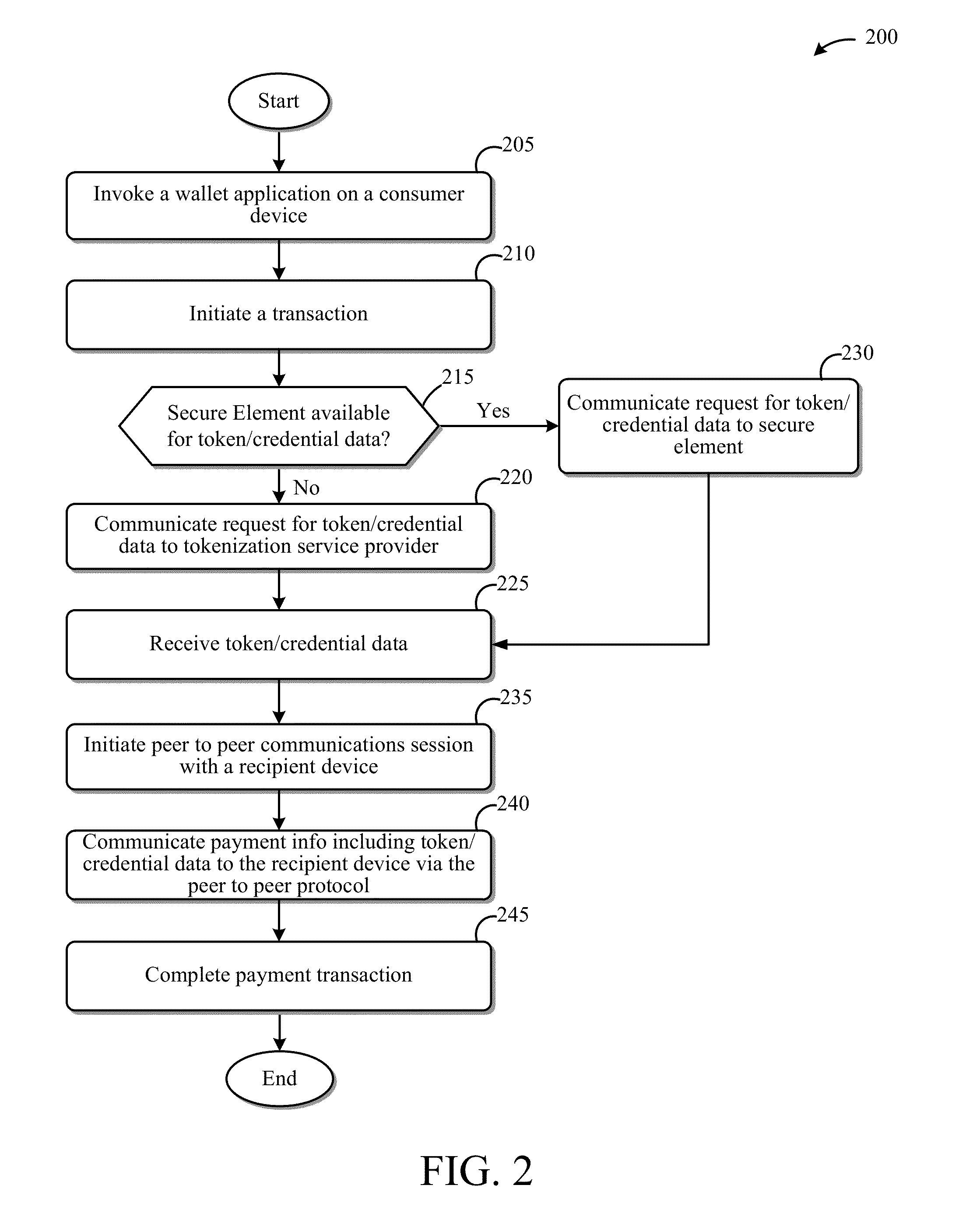
Systems and Methods for Facilitating Payments Via a Peer-to-Peer Protocol
ActiveUS20130254052A1Facilitate peer-to-peer communicationEasy to completeHand manipulated computer devicesFinancePoint-to-Point ProtocolPayment transaction
This disclosure describes systems and methods related to facilitating payments via a peer-to-peer protocol. Tokenized information associated with a payment transaction may be obtained. Establishment of a peer-to-peer communications session with a payment recipient device may be facilitated. The tokenized information to the recipient device via the established peer-to-peer communications session may be communicated in order to facilitate completion of the payment transaction.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Method and apparatus for preventing network traffic analysis
InactiveUS6917974B1Not replace and duplicate and reduce needAugments the protection provided by encryptionHardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
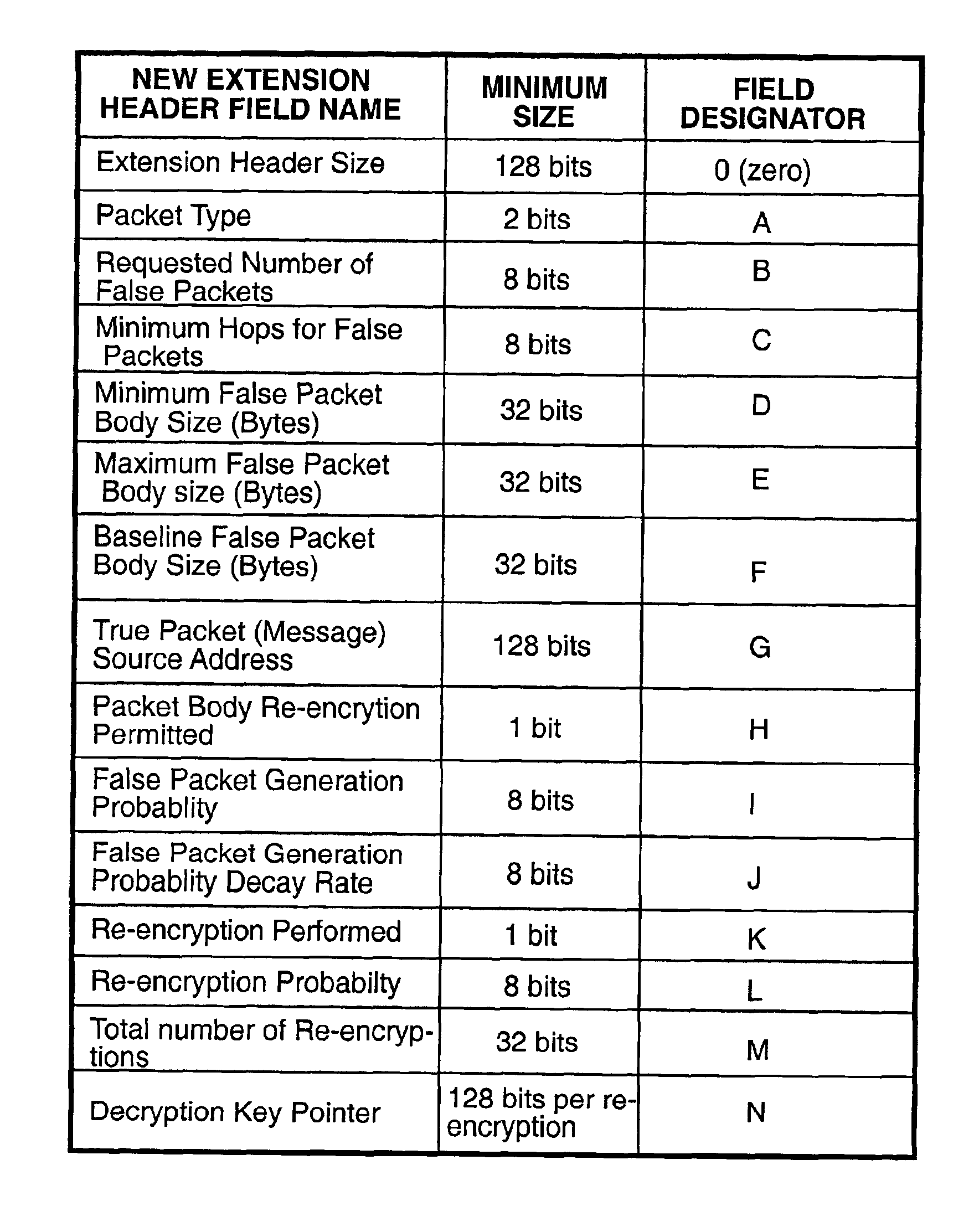
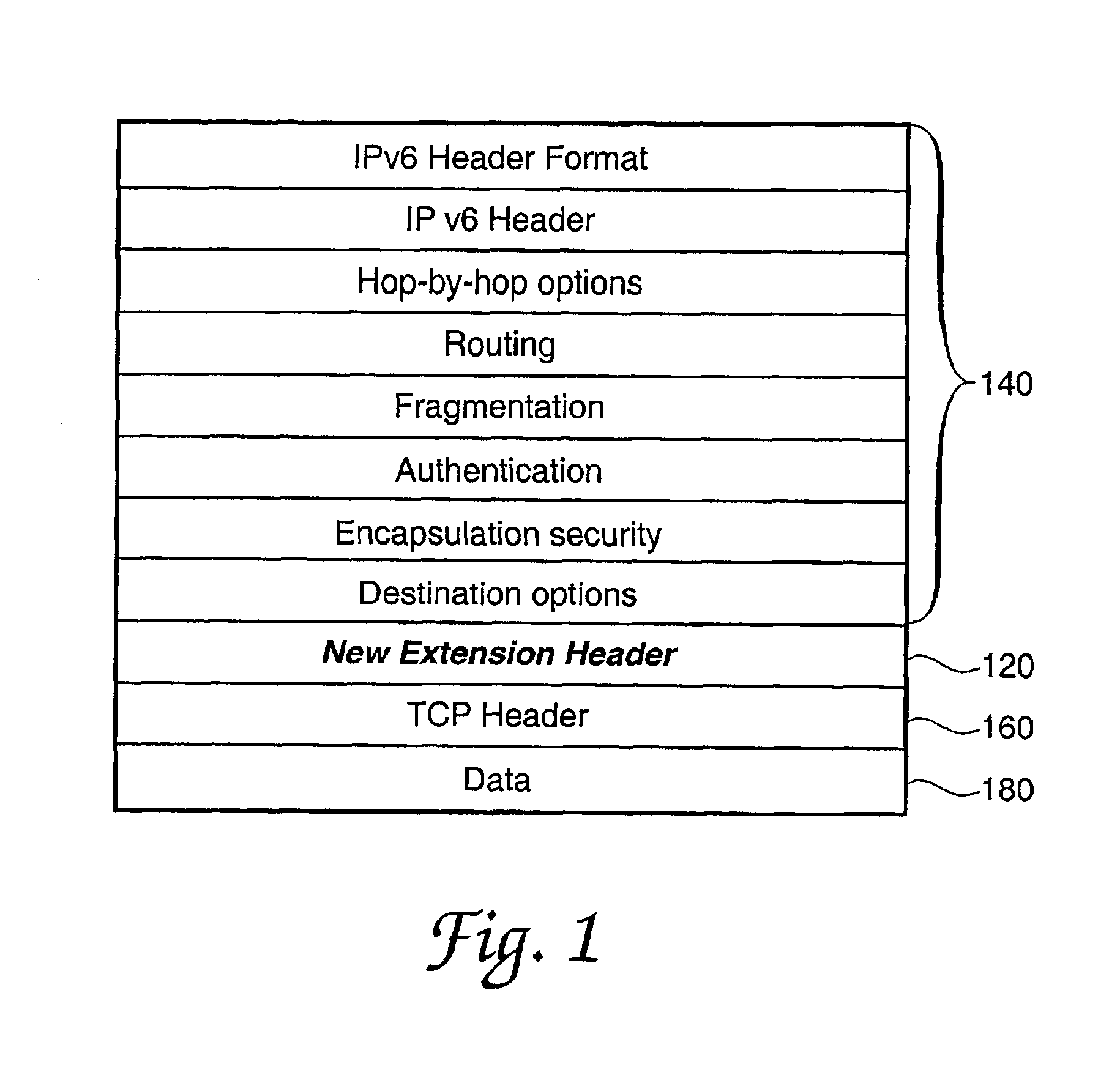
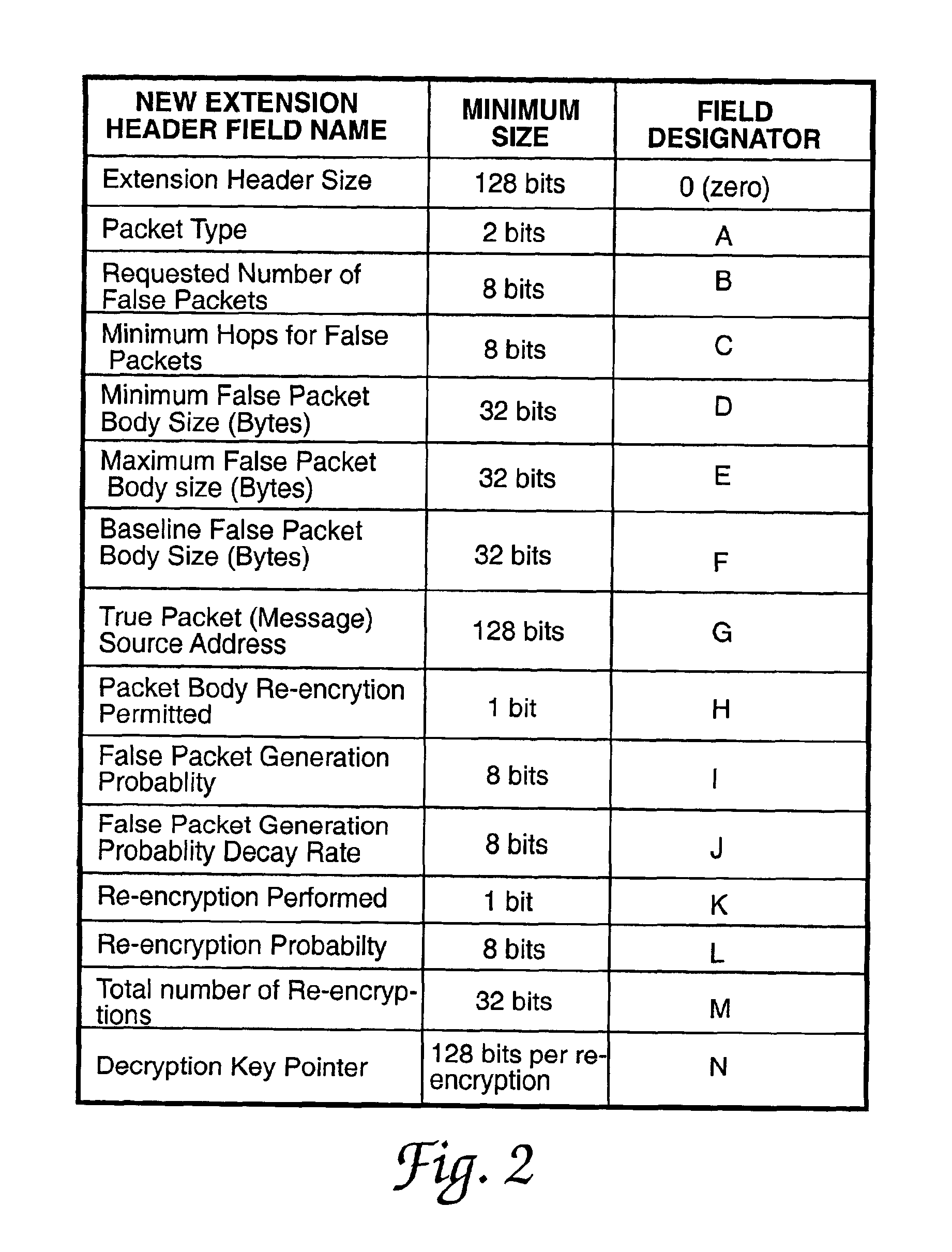
A system and method for generating and transmitting false packets along with a true packet to thereby hide or obscure the actual message traffic. A new extension header having a plurality of fields is positioned in the hierarchy of Internet protocol headers that control passage of the false packets and the true packet through the network. A sending host computer generates a plurality of false packets for each true packet and transmits the false packets and the true packet containing the Internet protocol headers and the extension header over the network. The new extension header is decrypted and re-encrypted each host that handles a message packet that uses the new extension header to control the random re-encryption of the true packet body at random hosts and the random generation of false packets at each host visited by a true packet, at the recipient of the true packet, and at any hosts that receive a false packet.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
Dynamic host configuration and network access authentication
InactiveUS20060036733A1Digital computer detailsTransmissionIP multicastProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC
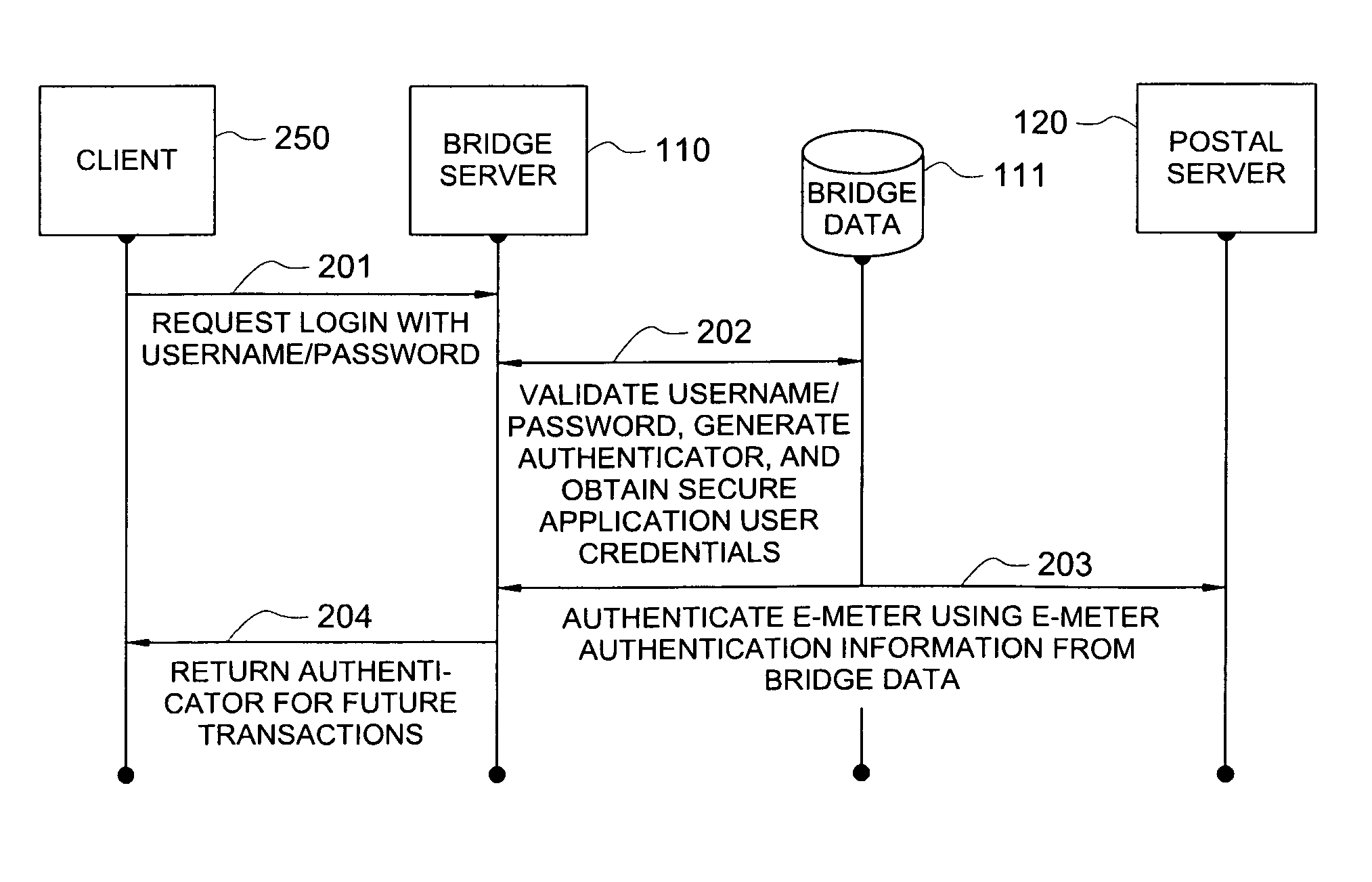
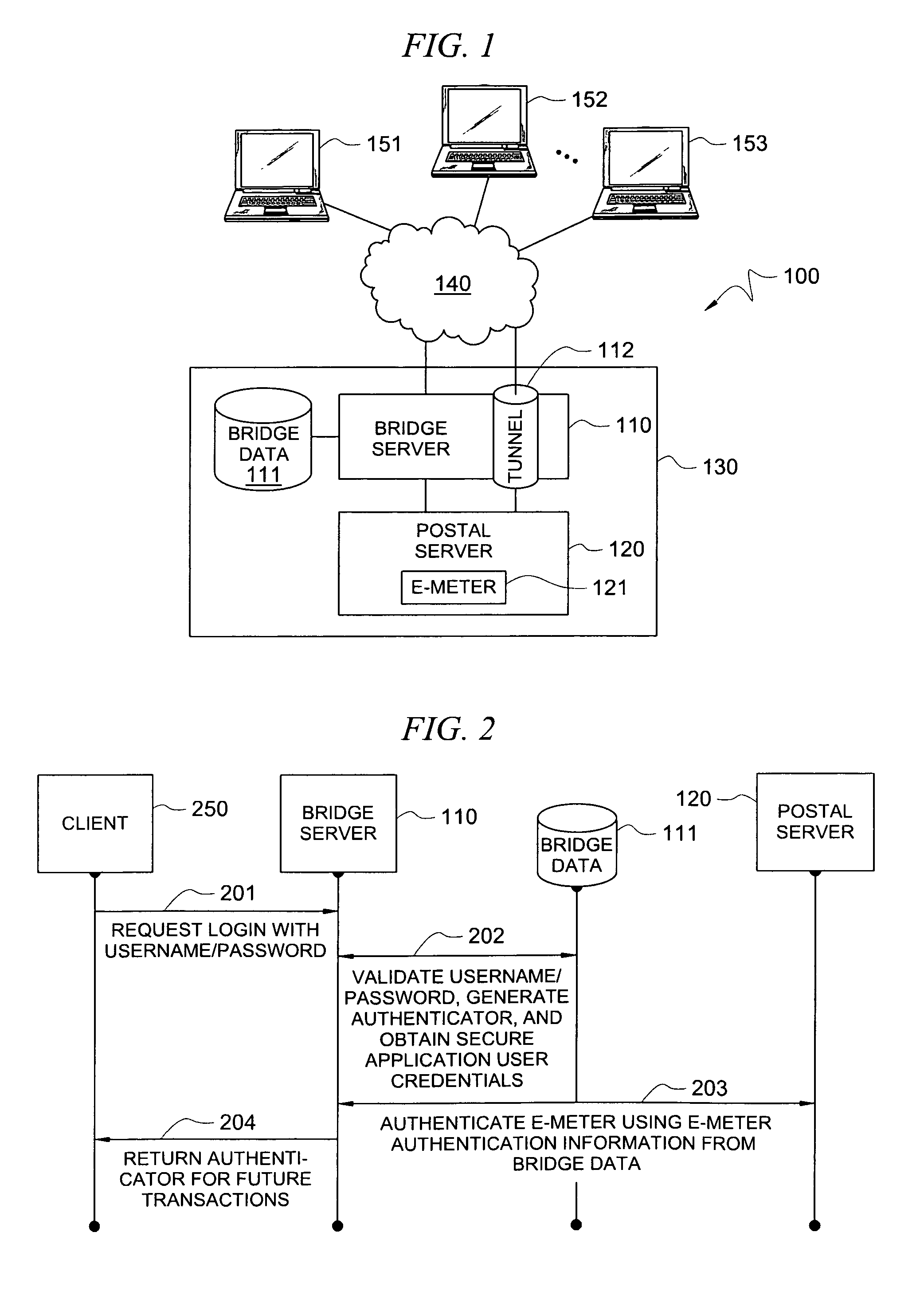
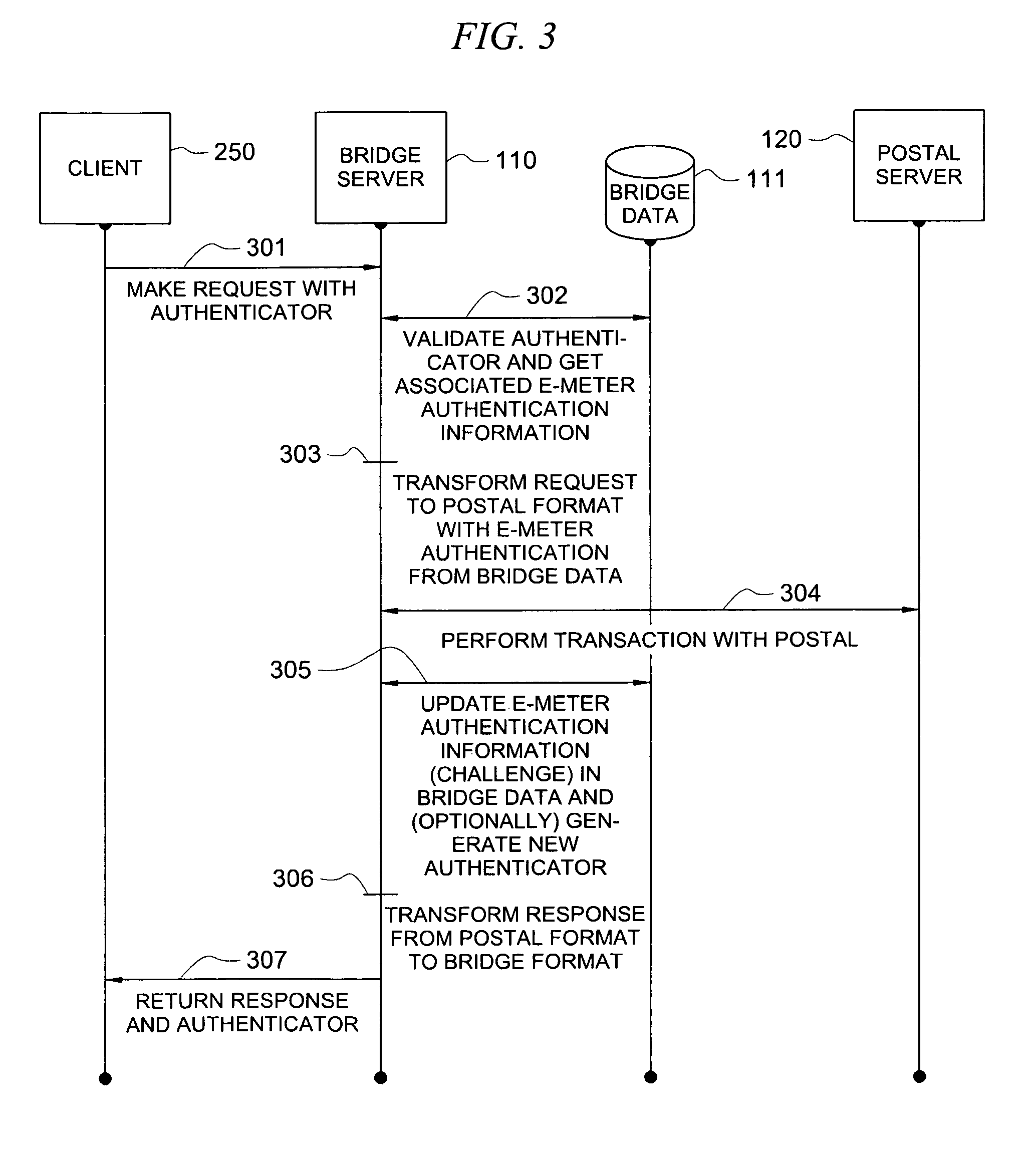
Secure application bridge server
ActiveUS8046823B1Easy to implementConvenient to accommodateDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsApplication serverCryptographic protocol
Systems and methods are provided which implement a bridge server to provide user access to one or more secure applications. A bridge server of embodiments is disposed between a user and a secure application and invokes bridge server security protocols with respect to the user and secure application security protocols with respect to the secure application. In operation according to embodiments, client applications will link into a bridge server, the user will be authenticated by the bridge server, and a valid user will be correlated to an account of the secure application by the bridge server. Bridge servers of embodiments facilitate providing features with respect to secure application user access unavailable using the secure application security protocols.
Owner:AUCTANE INC
Device assisted CDR creation, aggregation, mediation and billing
ActiveUS8275830B2Complete banking machinesMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsNetwork Communication ProtocolsSyntax
Device assisted CDR creation, aggregation, mediation and billing is provided. In some embodiments, device assisted CDR creation, aggregation, mediation and billing for a wireless network includes collecting device generated service usage information for one or more devices in wireless communication on the wireless network; and providing the device generated service usage information in a syntax (e.g., a device assisted charging data record (CDR)) and a communication protocol (e.g., 3GPP, 3GPP2, or other communication protocols) that can be used by other network devices to augment or replace network generated service usage information for the one or more devices in wireless communication on the wireless network.
Owner:HEADWATER RES LLC
Methods, apparatus and computer programs performing a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol using operating system capabilities
InactiveUS20030093680A1Avoids security exposureMeet growth requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsOperational systemCrypt
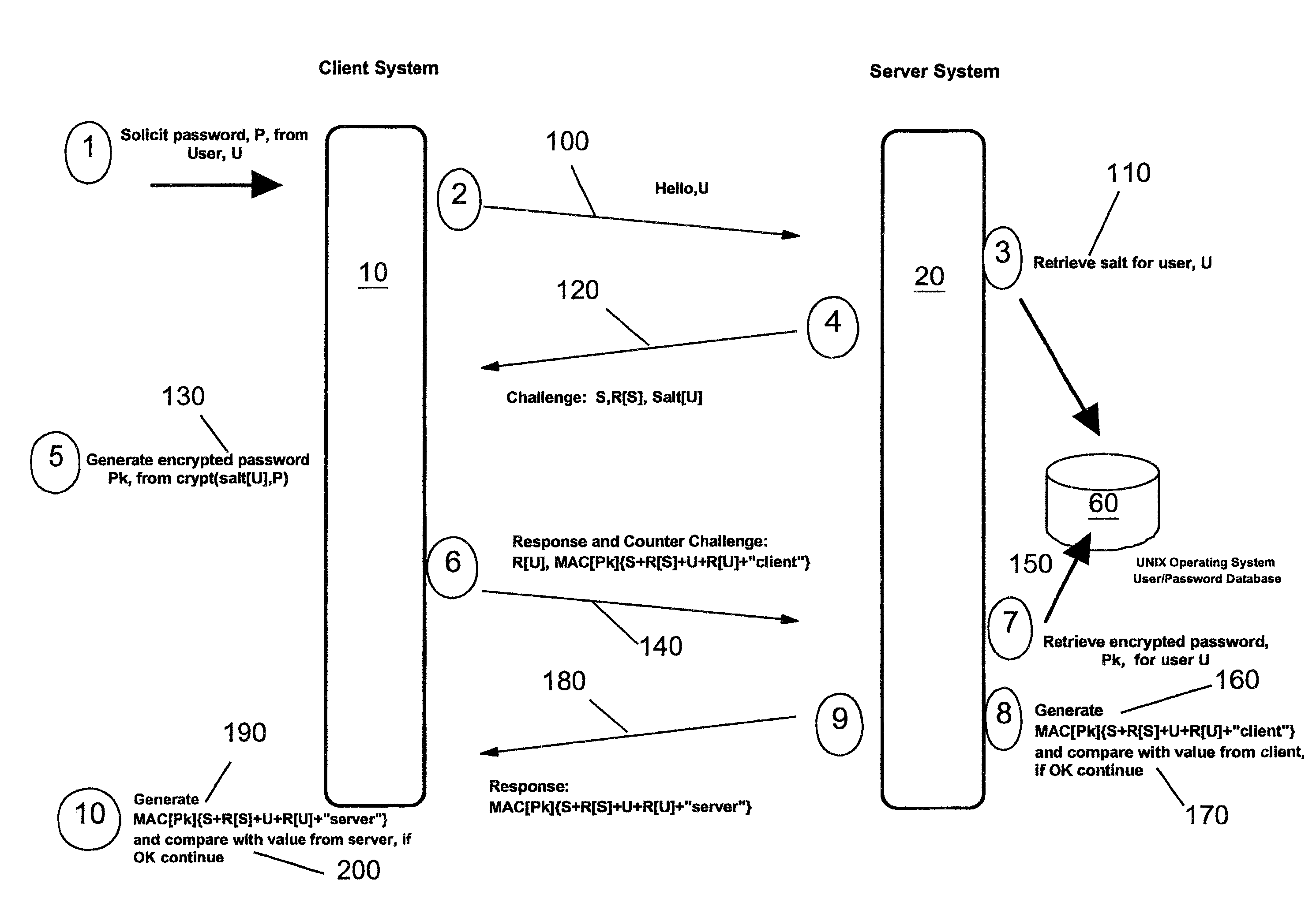
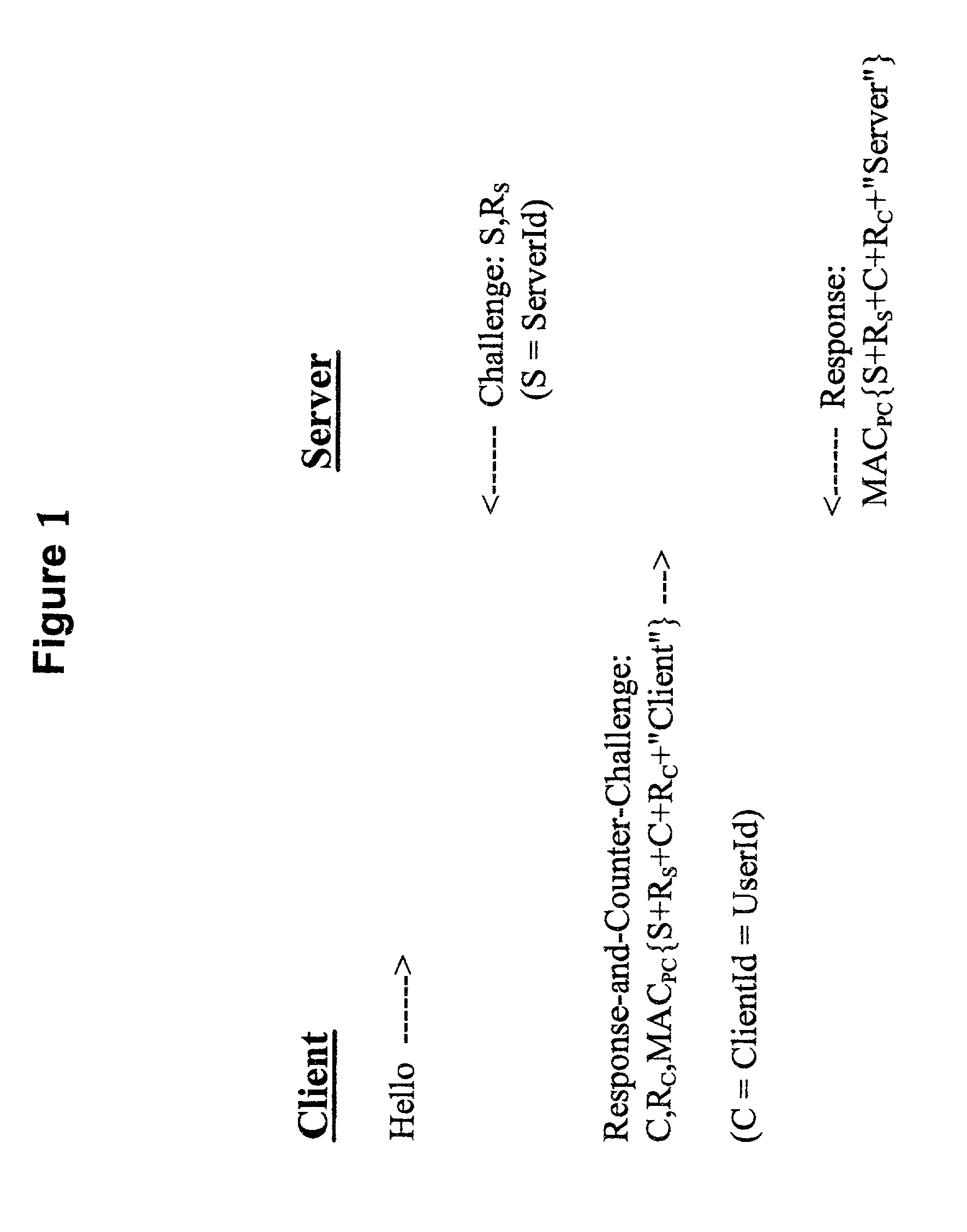
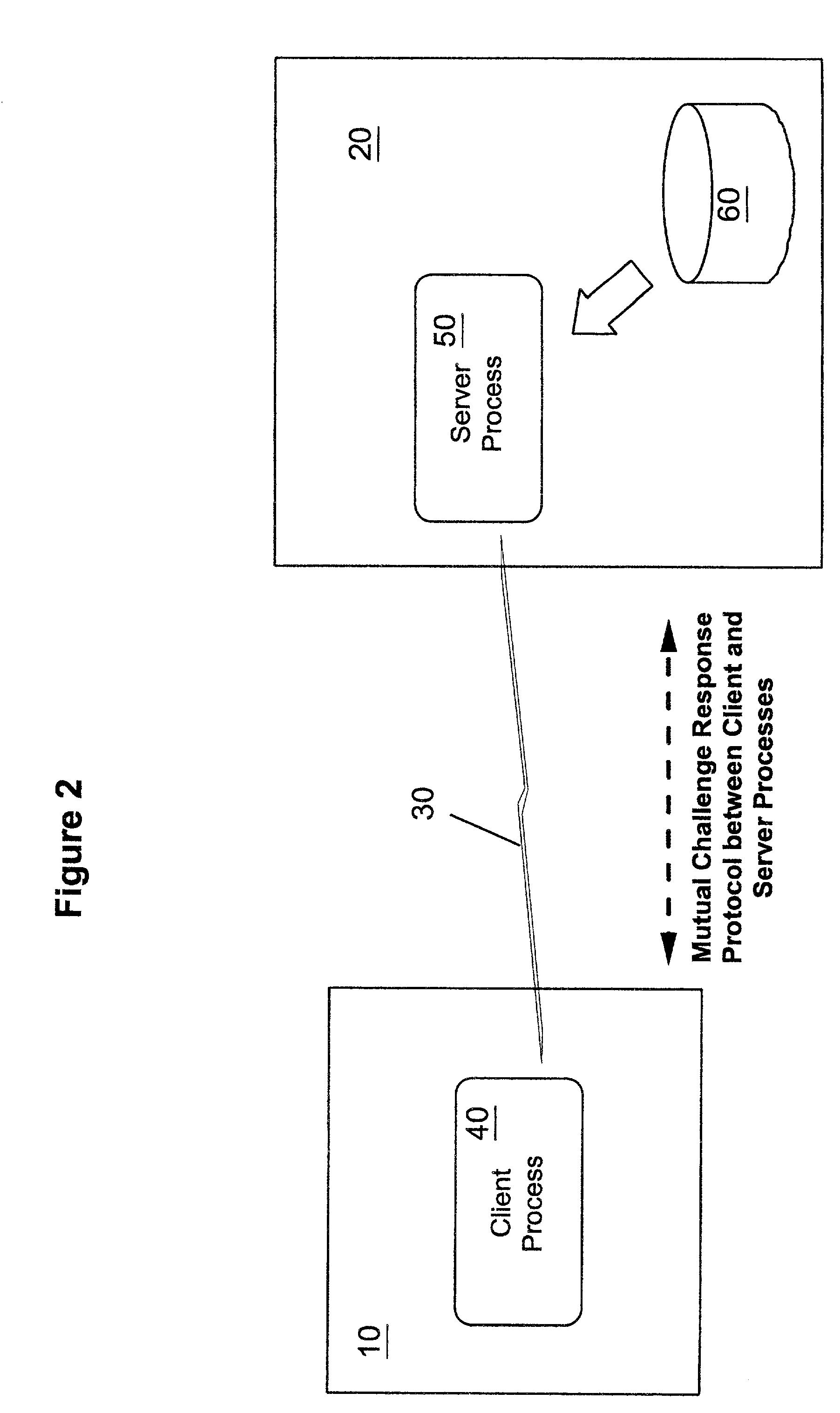
A client-server authentication method for use where a server process has access to a repository storing cipher-protected client passwords. The method includes applying the same cipher function to the client's copy of its password as was previously applied to generate the stored cipher-protected client passwords. This ensures that both the client and server have access to an equivalent cipher-protected client password-providing a shared secret for driving a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol without having to convert the password into cleartext at the server. The invention can be implemented without significant additional software infrastructure in a UNIX environment. Client passwords are typically stored in the UNIX password repository under the protection of the crypt( ) function applied to the combination of the password and a random number (a "salt'). By sending the salt to the client system together with the server's initial challenge of the authentication protocol, a process at the client is able to apply the crypt( ) function to the client password with the same salt such that the client and server have a shared secret for use as, or to generate, a common session key for the authentication.
Owner:IBM CORP
Converged network extension
ActiveUS8625616B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityFiber
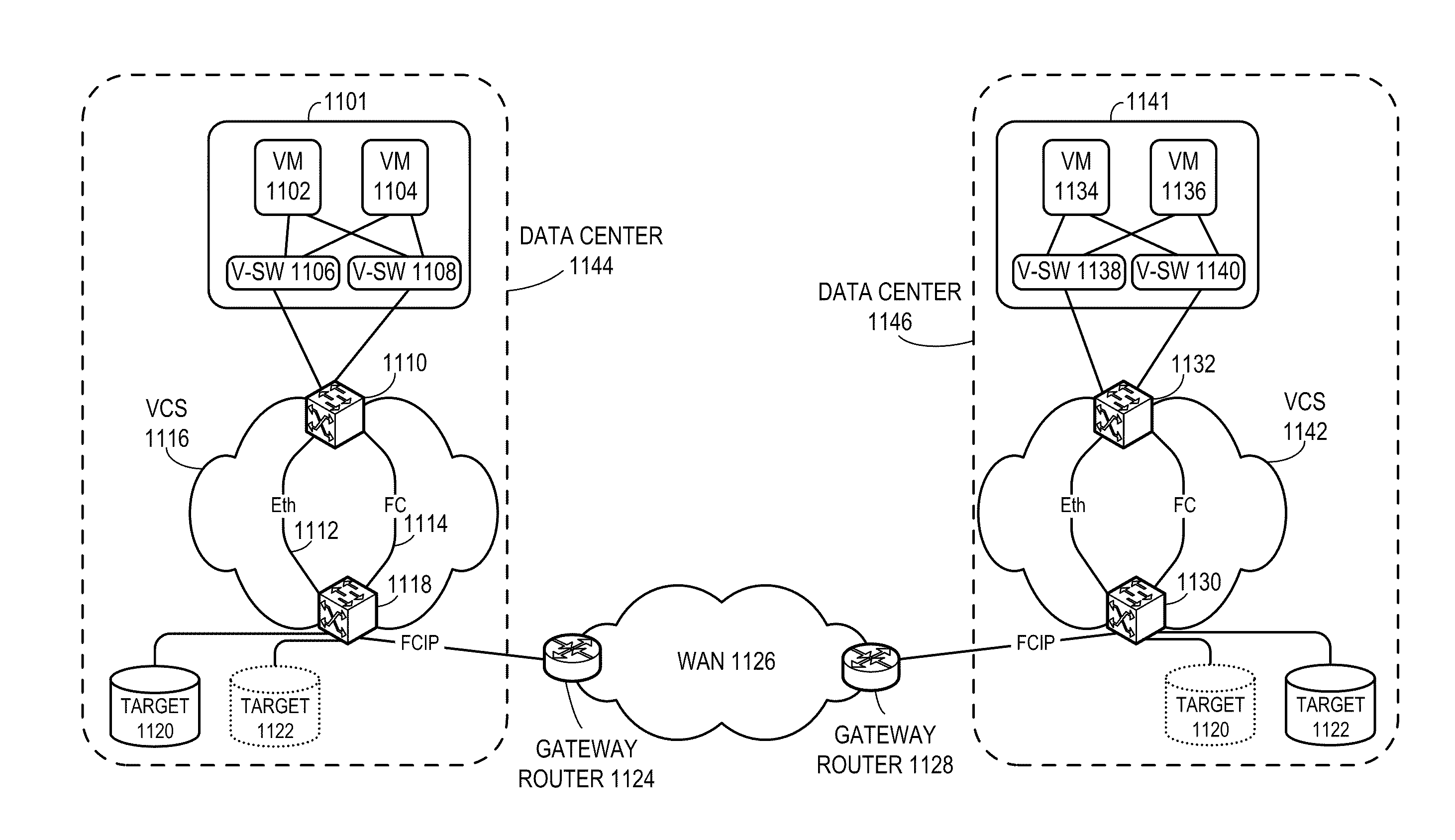
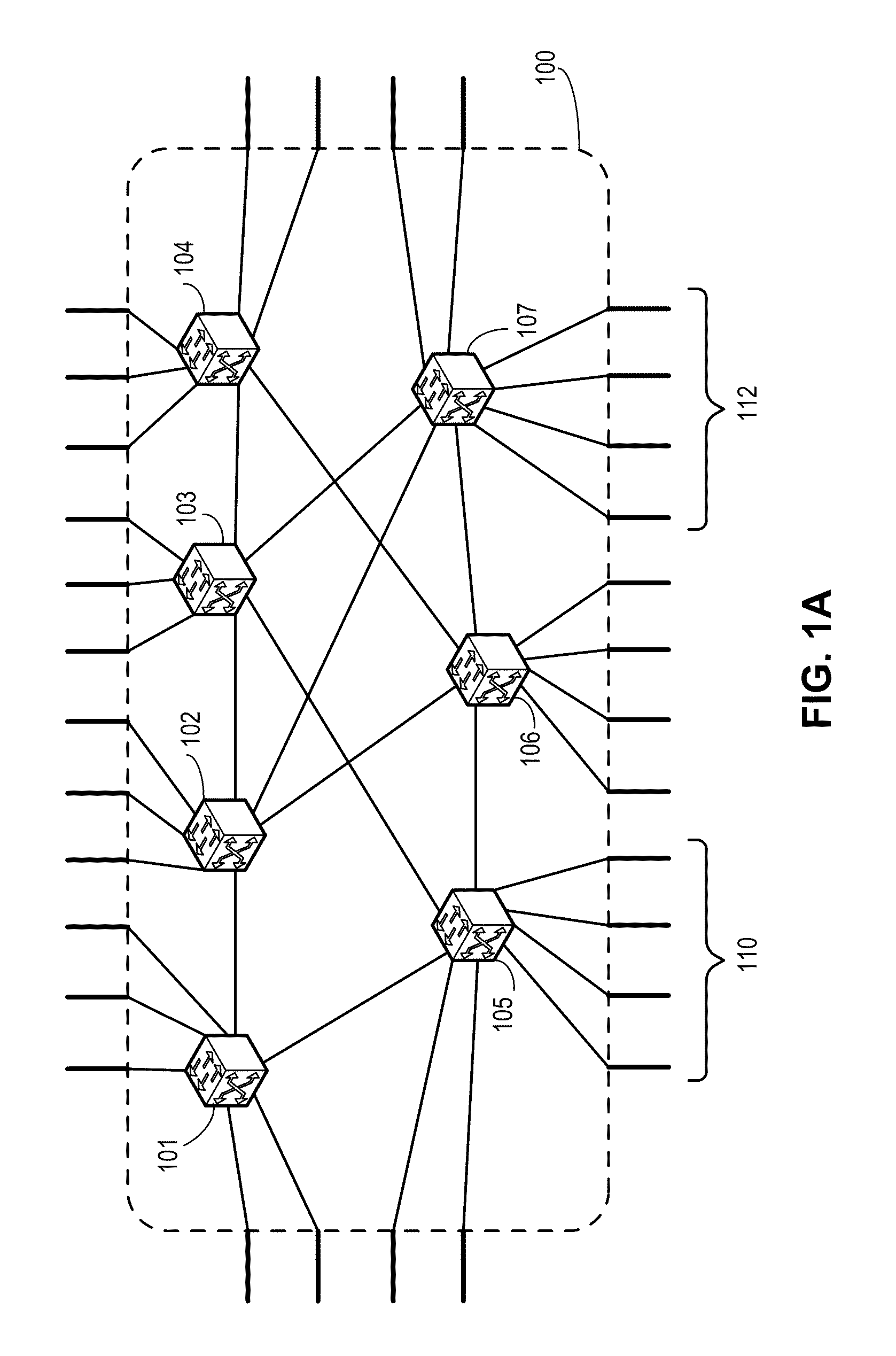
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switch. The switch includes a first port configured to receive Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) traffic; a second port configured to receive Fiber Channel (FC) traffic; and a third port configured to transmit received TRILL or FC traffic based on a Fiber Channel over IP (FCIP) protocol.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com