Patents
Literature
467 results about "IP multicast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
IP multicast is a method of sending Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams to a group of interested receivers in a single transmission. It is the IP-specific form of multicast and is used for streaming media and other network applications. It uses specially reserved multicast address blocks in IPv4 and IPv6.
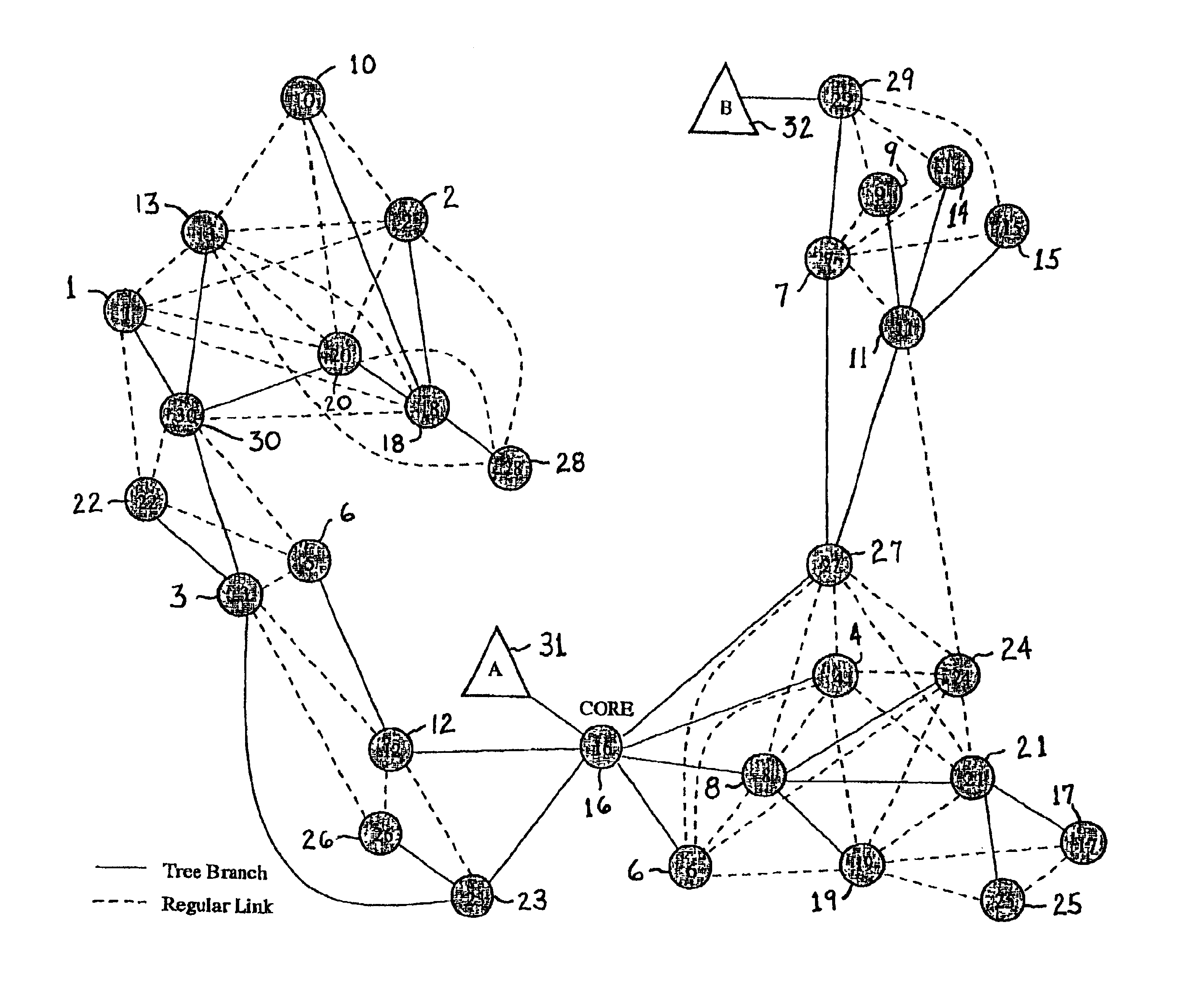
Core assisted mesh protocol for multicast routing in ad-hoc Networks
InactiveUS6917985B2Enrich connectivityStay connectedSpecial service provision for substationError preventionIP multicastBroadcasting
A method of providing multicast routing for use in ad hoc broadcast networks, such as wireless and mobile networks. The method is described within a protocol referred to as core-assisted mesh protocol, or CAMP. The method departs from traditional tree-structured multicast protocols and utilizes multicast meshes in which the network need not be flooded with control or data packets to establish routing paths. Each router configured for CAMP is capable of accepting unique packets arriving from any neighbor in the mesh, wherein packets are forwarded along reverse shortest paths to the receiver. Multiple cores may be defined for a group wherein the loss of a single core does not prevent packet flow. Routers for sender-only hosts are allowed to join the multicast mesh in simplex mode, and in certain cases may join without the sending of a join request.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
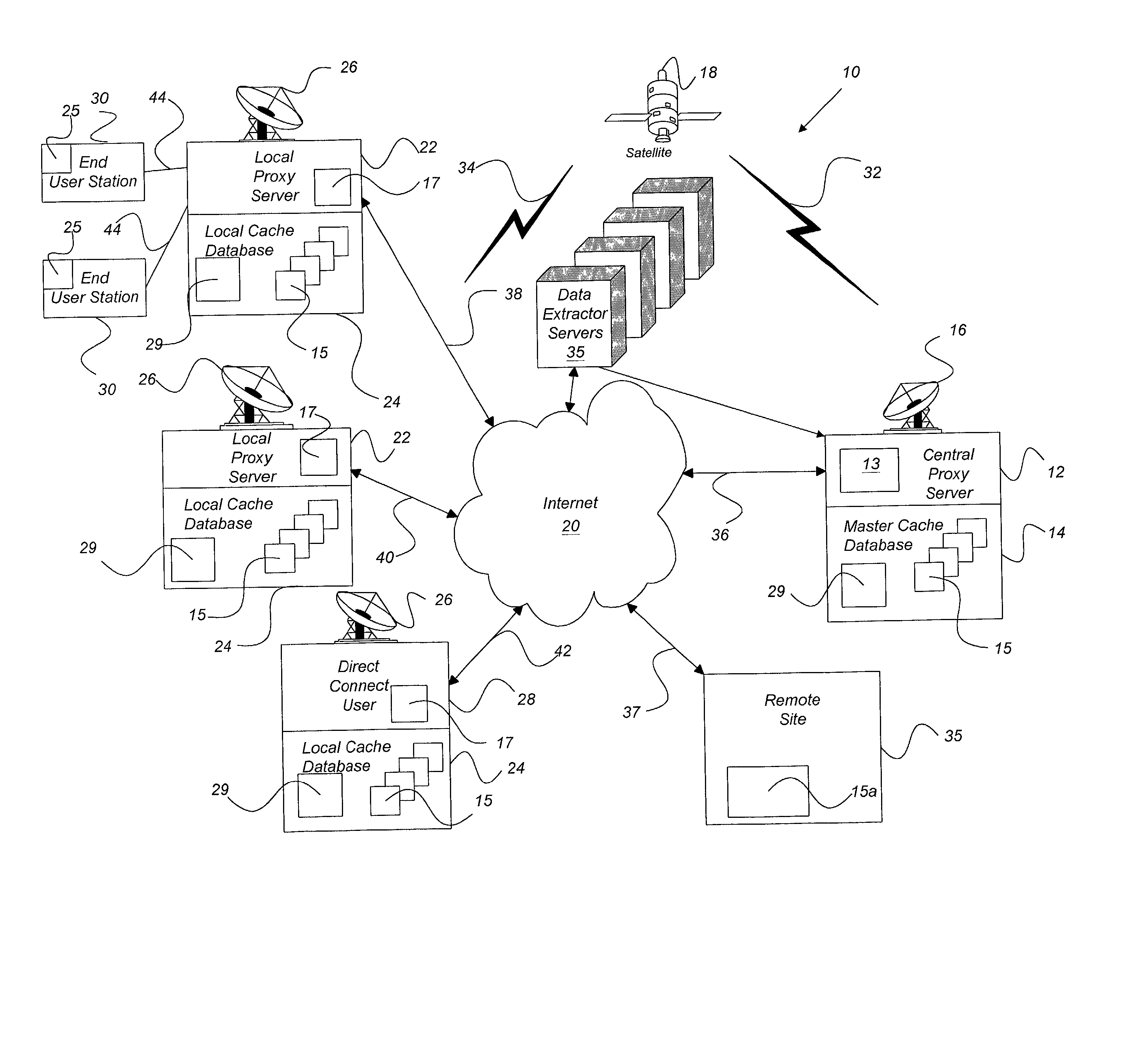
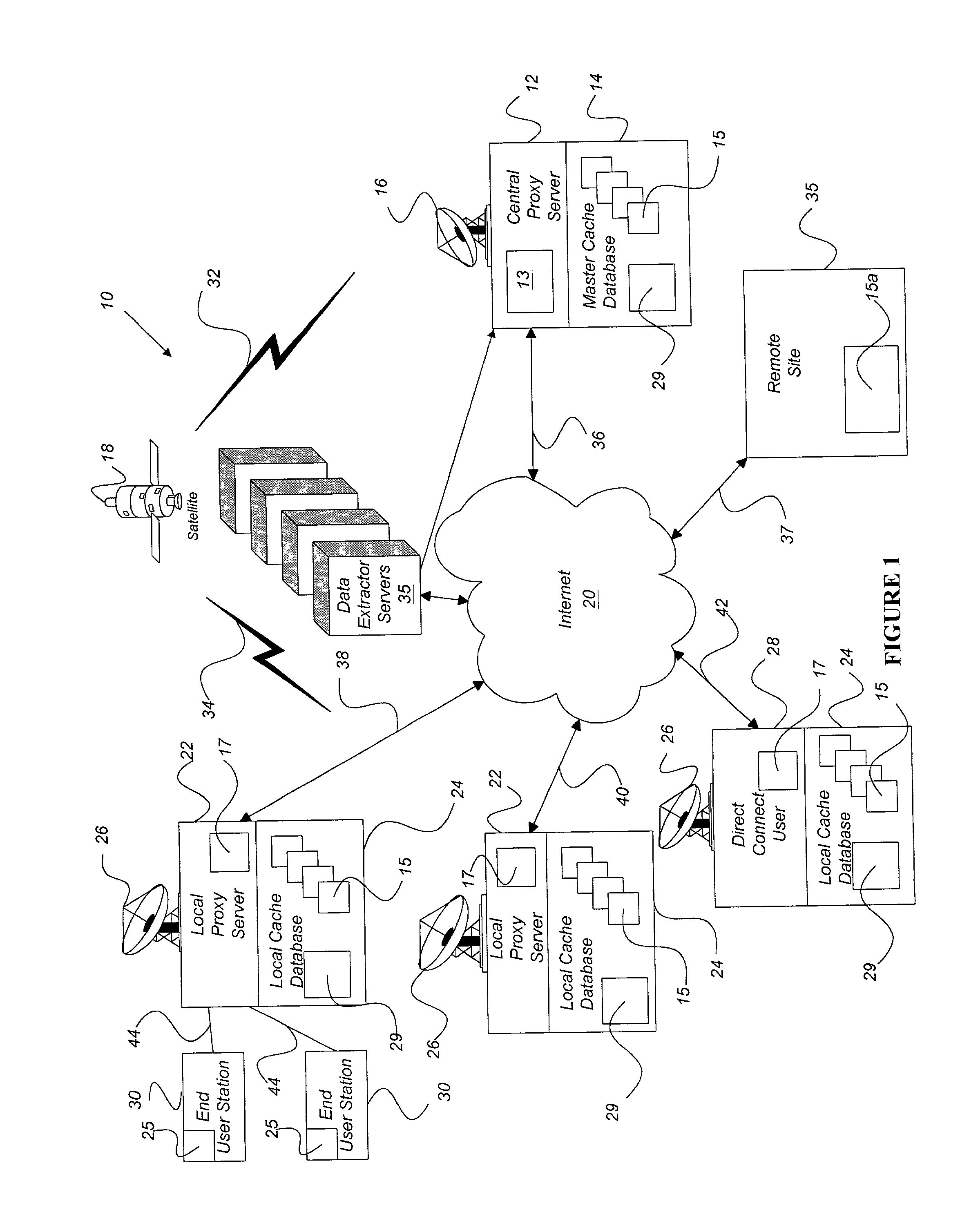
Internet content delivery acceleration system employing a hybrid content selection scheme
InactiveUS20020073167A1Facilitates very efficient reportingMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio transmissionInternet contentHigh rate
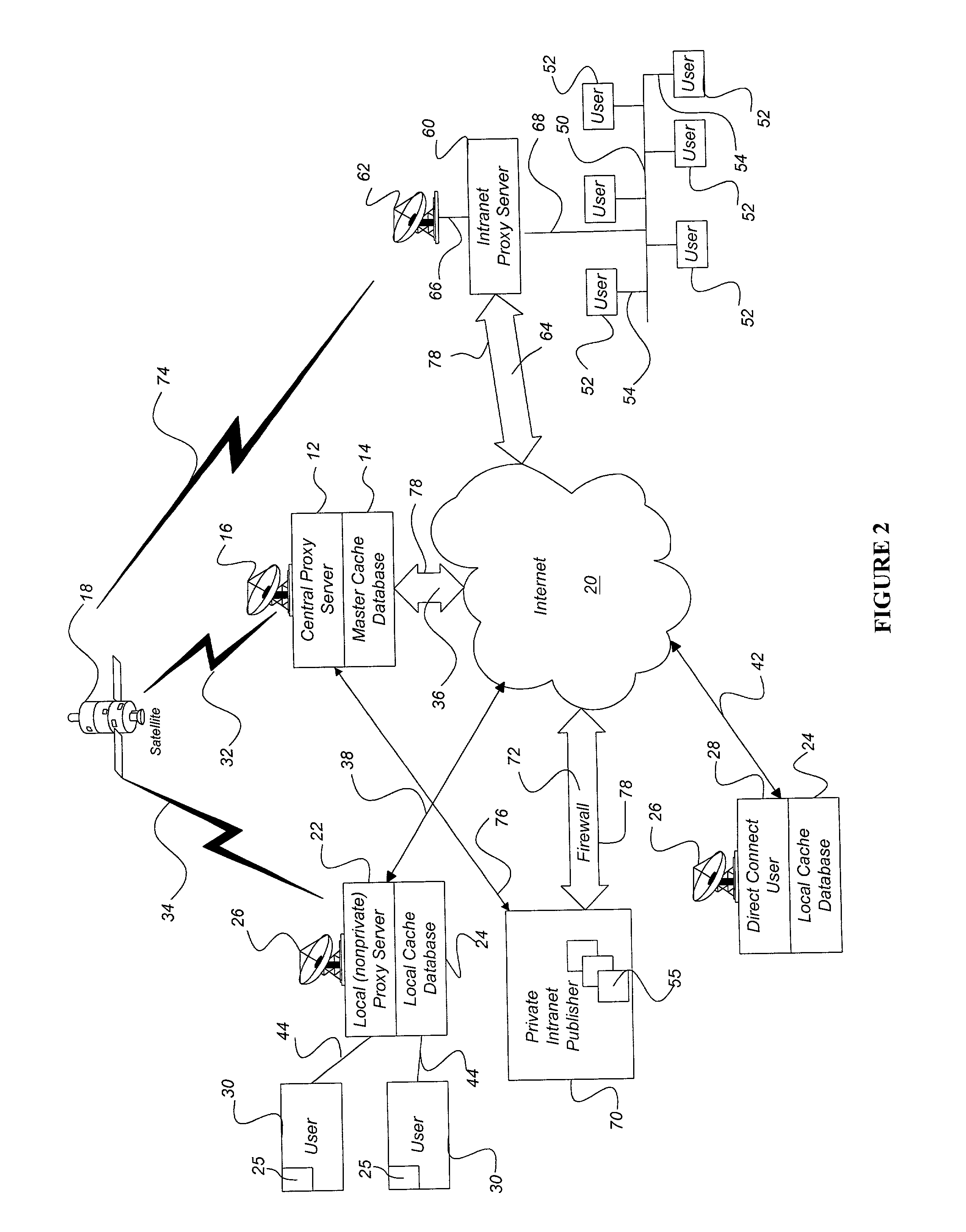
A system and method accelerates the distribution of digital content of a global communications network such as the Internet. A central proxy server selects popular digital objects for transmission over a communication medium to provide content filling of cache databases attendant to local proxy servers. The communication medium may comprise satellite transmission using an IP multicast protocol. The local proxy servers concurrently receive the digital objects at a high rate of speed and store the digital objects in the attendant local cache databases. The local proxy servers may utilize a localized priority determination scheme to determine whether to keep or discard the transmitted digital objects. The priority determination scheme may utilize global demand data and / or local demand data. The demand data may include hits and / or misses on digital objects and may also include quantitative data about the digital objects. The priority determination scheme may be driven by feedback regarding the needs and interests of subscribing users of the local cache database. Consequently, the priority determination scheme and ultimately, the contents of a local cache database, may be unique to that local cache database.
Owner:EDGIX CORP
Digital interactive delivery system for TV/multimedia/internet
InactiveUS20050028206A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSignal onIP multicast
Owner:IMAGICTV
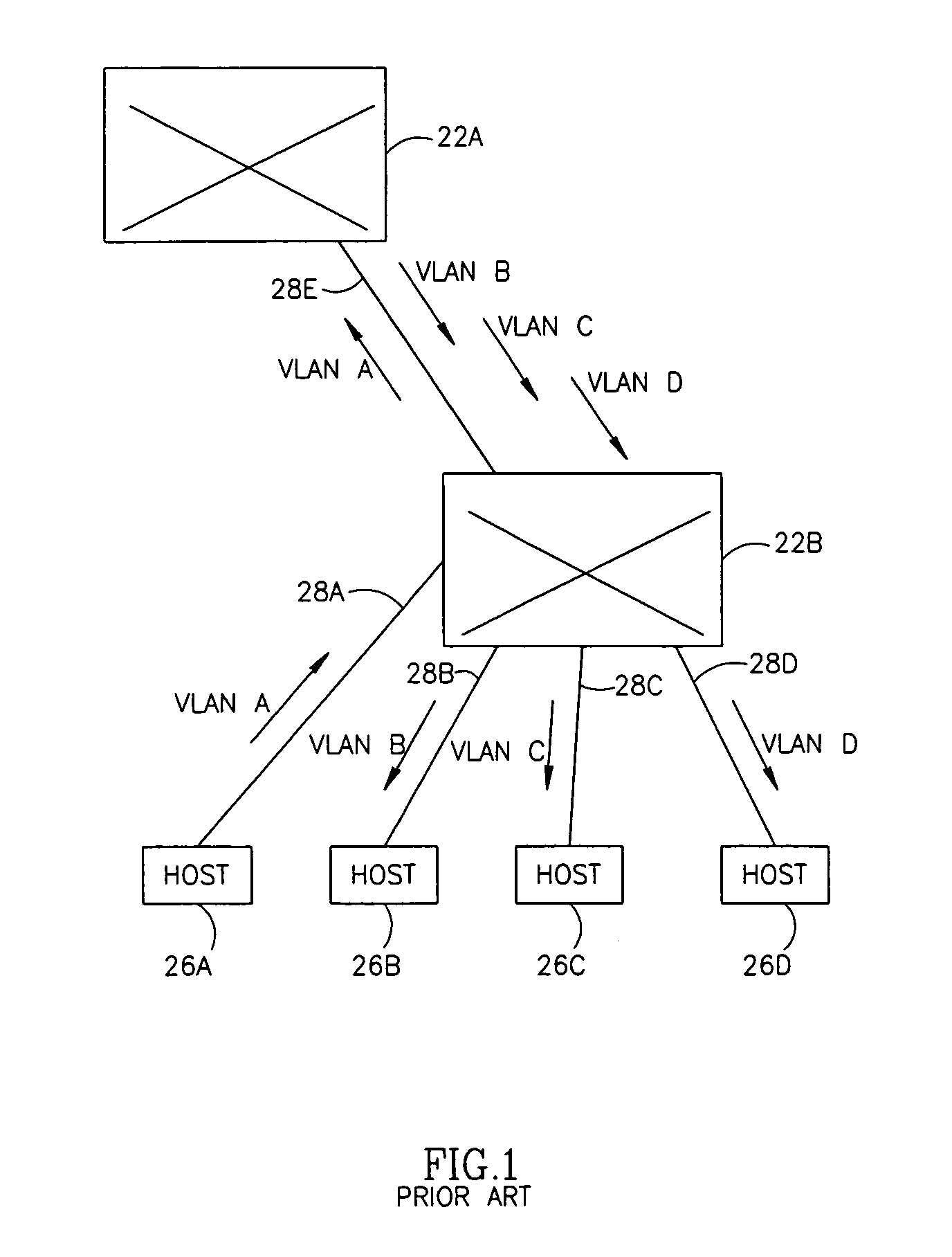
System and method for distributing multicasts in virtual local area networks
InactiveUS6839348B2Effective distributionEfficiently distributedSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexVirtual LANIP multicast
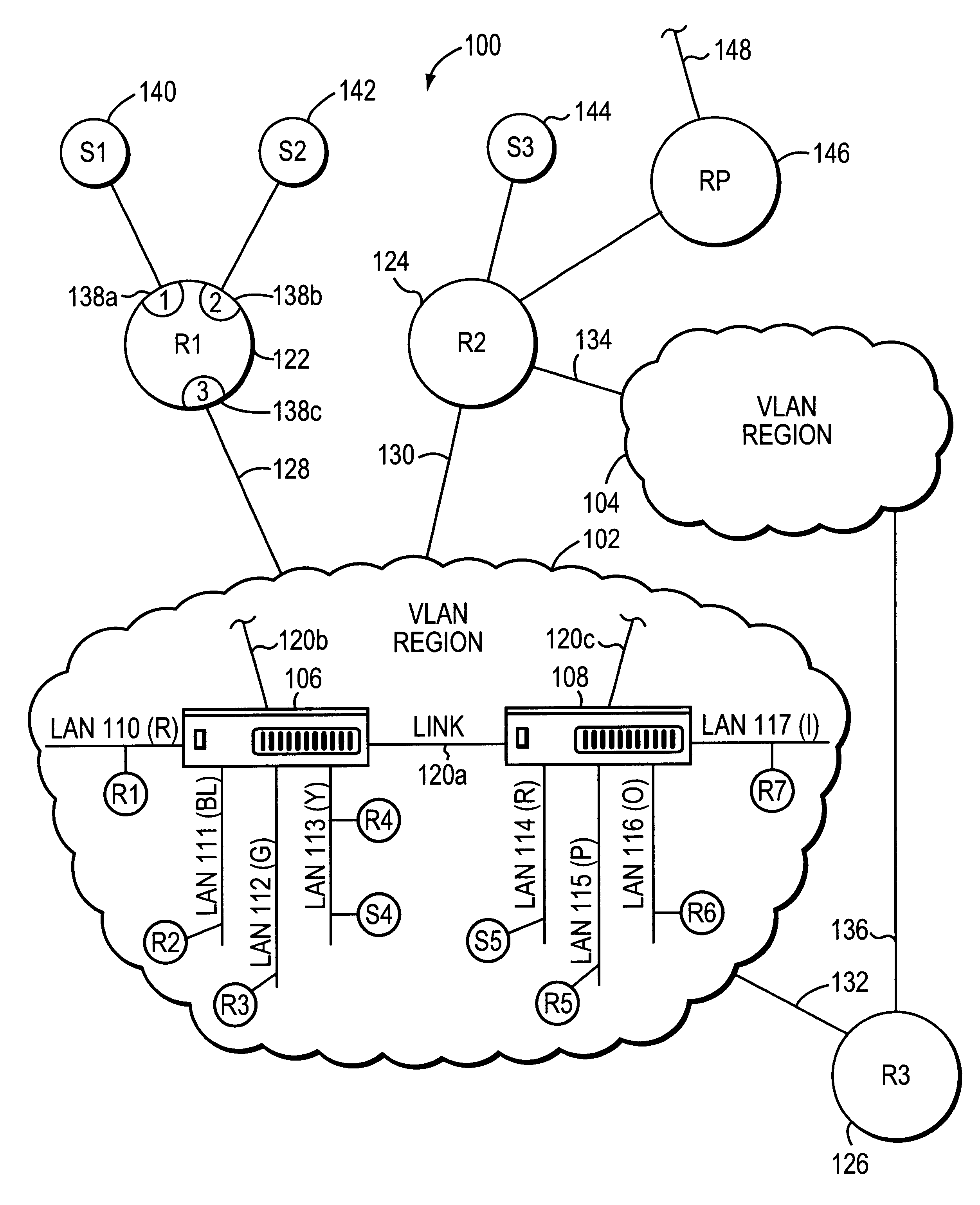
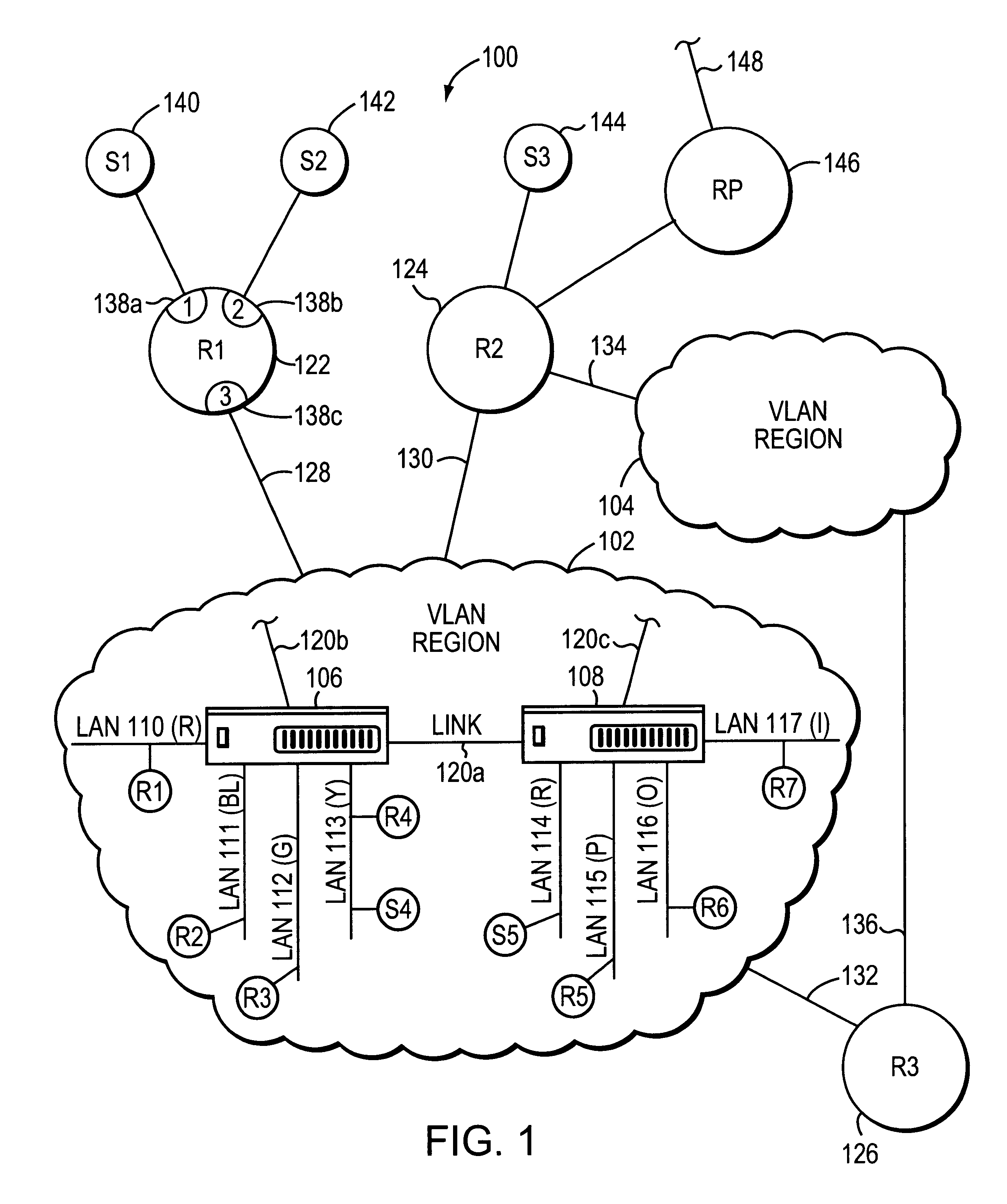
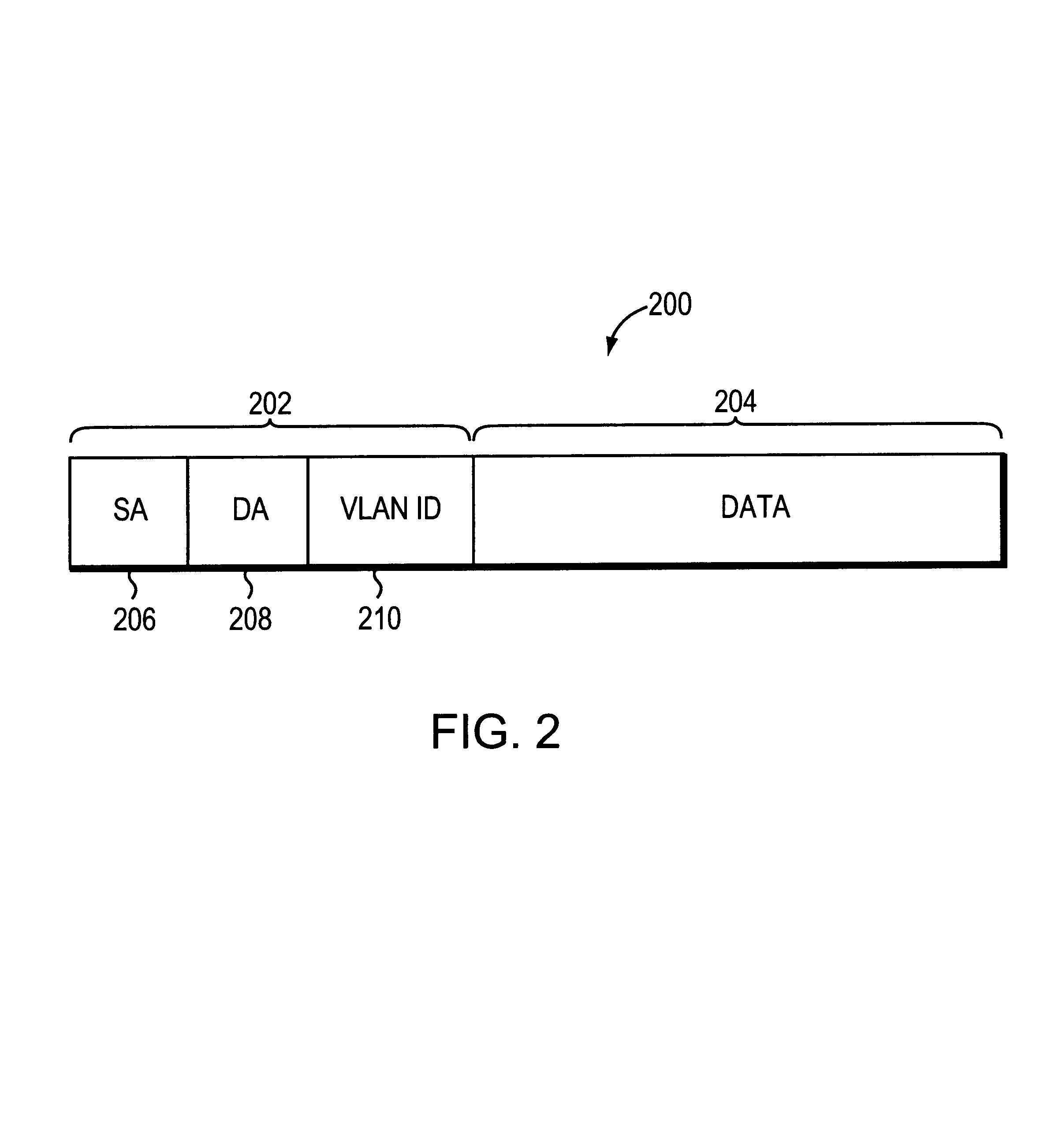
The invention relates to a system and method for efficiently distributing multicast messages within computer networks configured to have one or more virtual local area network (VLAN) domains. A multicast network device (MND), having a plurality of interfaces, includes a multicast controller for efficiently distributing multicast messages among subscribing entities associated with various VLAN domains. The multicast controller, which is in communicating relationship with the interfaces, includes a VLAN assignment engine for assigning responsibility for the VLAN domains to the extent there are multiple MNDs. The multicast controller also accesses a multicast tag source to establish a plurality of novel VLAN tags for efficiently distributing multicast messages, including a sub-regional Multicast VLAN Identifier (MVLAN-ID) that encompasses all of the VLAN domains for which the respective MND is responsible, and one or more color-limited MVLAN-IDs that encompass all of the VLAN domains for which the MND is responsible except for one. The multicast controller then tags multicast messages with its sub-regional or a color-limited MVLAN-ID depending on whether the message is considered internal or external by the respective MND. The tagged messages are then forwarded for distribution to the subscribers associated with the various VLAN domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
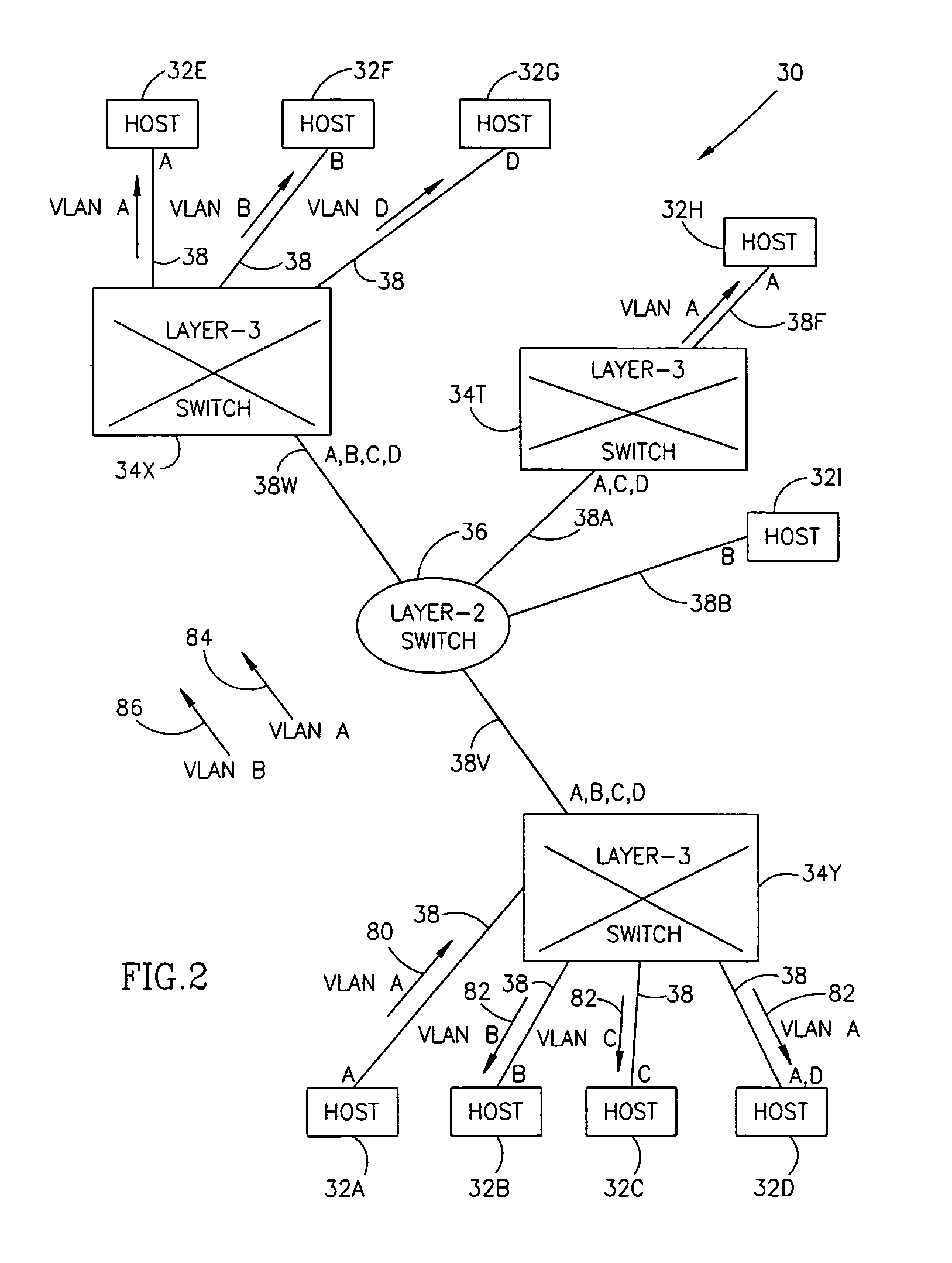
IP multicast in VLAN environment
ActiveUS7924837B1Avoid layeringEasy to implementError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableVirtual LAN
A method of determining local multicast information of a local area network (LAN), comprising dividing the LAN to a number of segments larger than the number of virtual LANs (VLANs) in the network and creating a layer-3 multicast routing table, which relates to each of the segments separately.
Owner:AVAYA TECH CORP +1
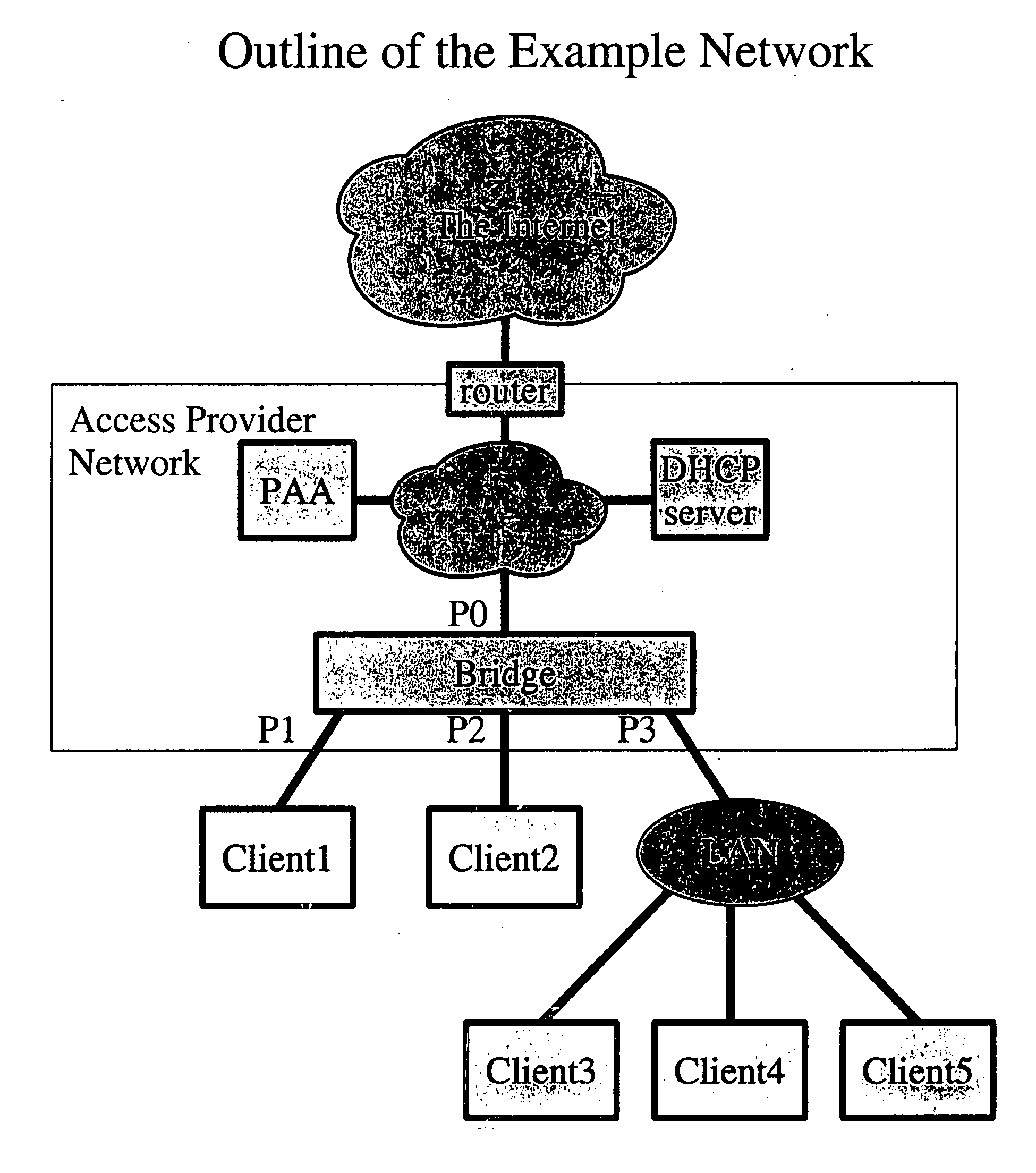
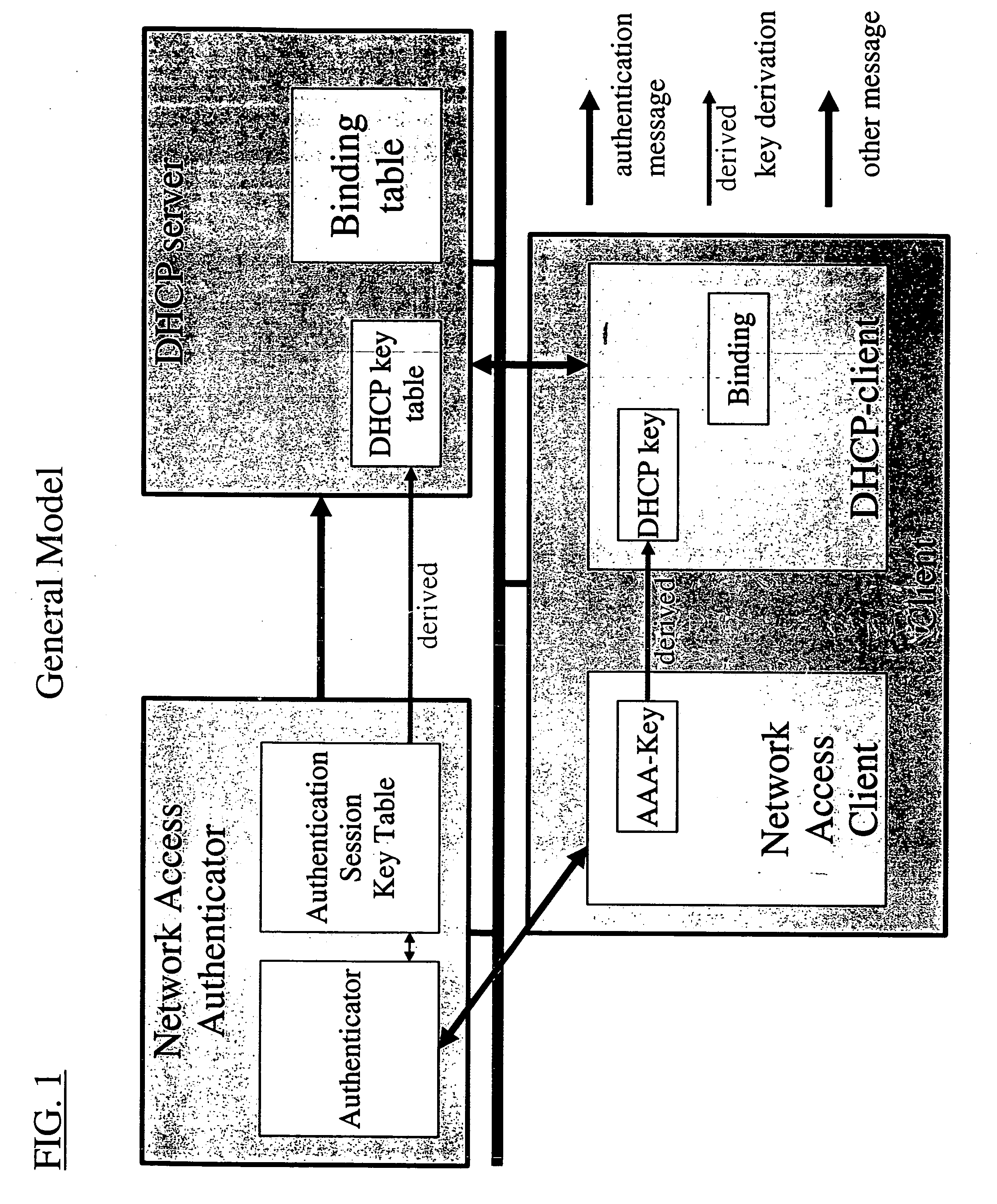
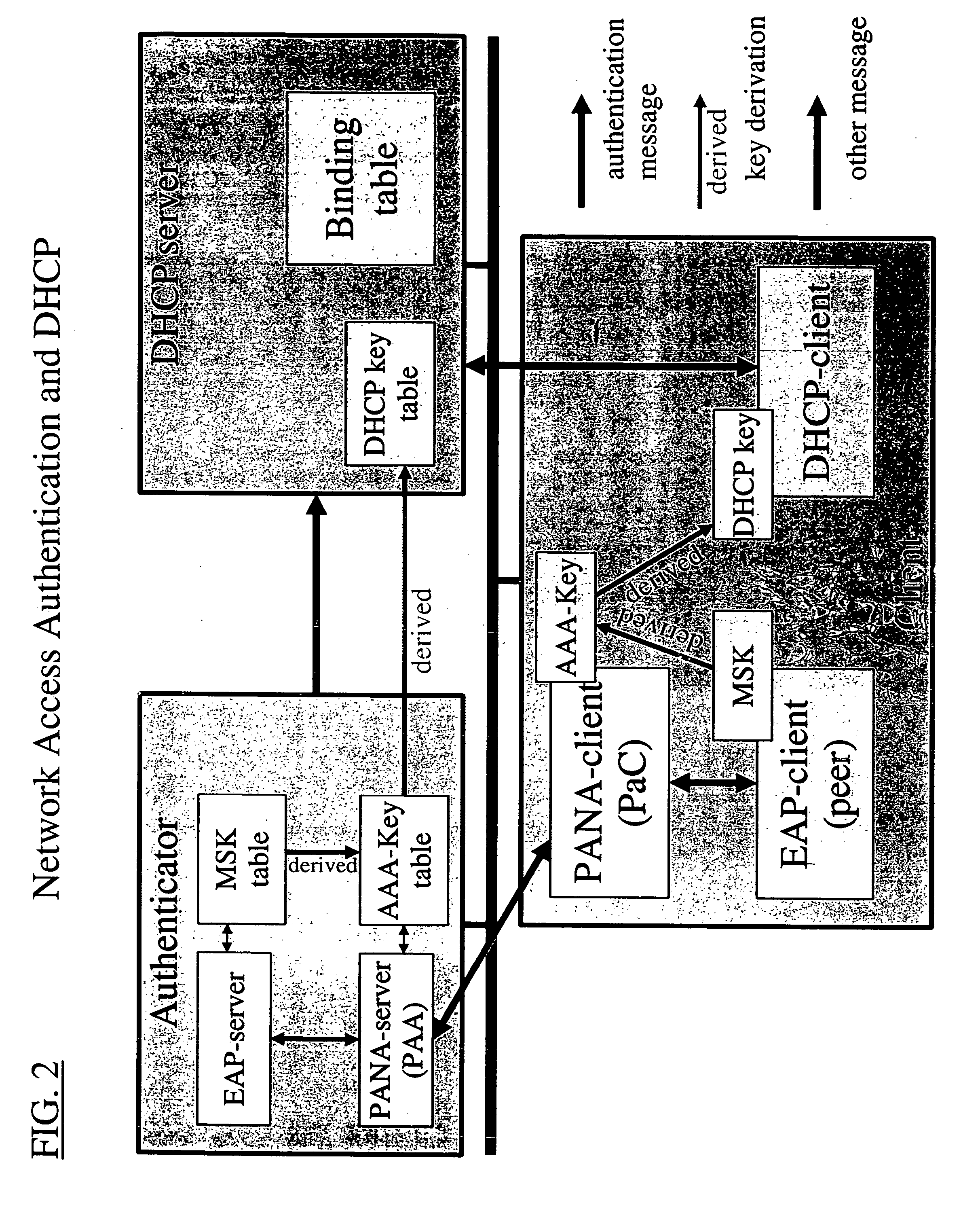
Dynamic host configuration and network access authentication
InactiveUS20060036733A1Digital computer detailsTransmissionIP multicastProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC
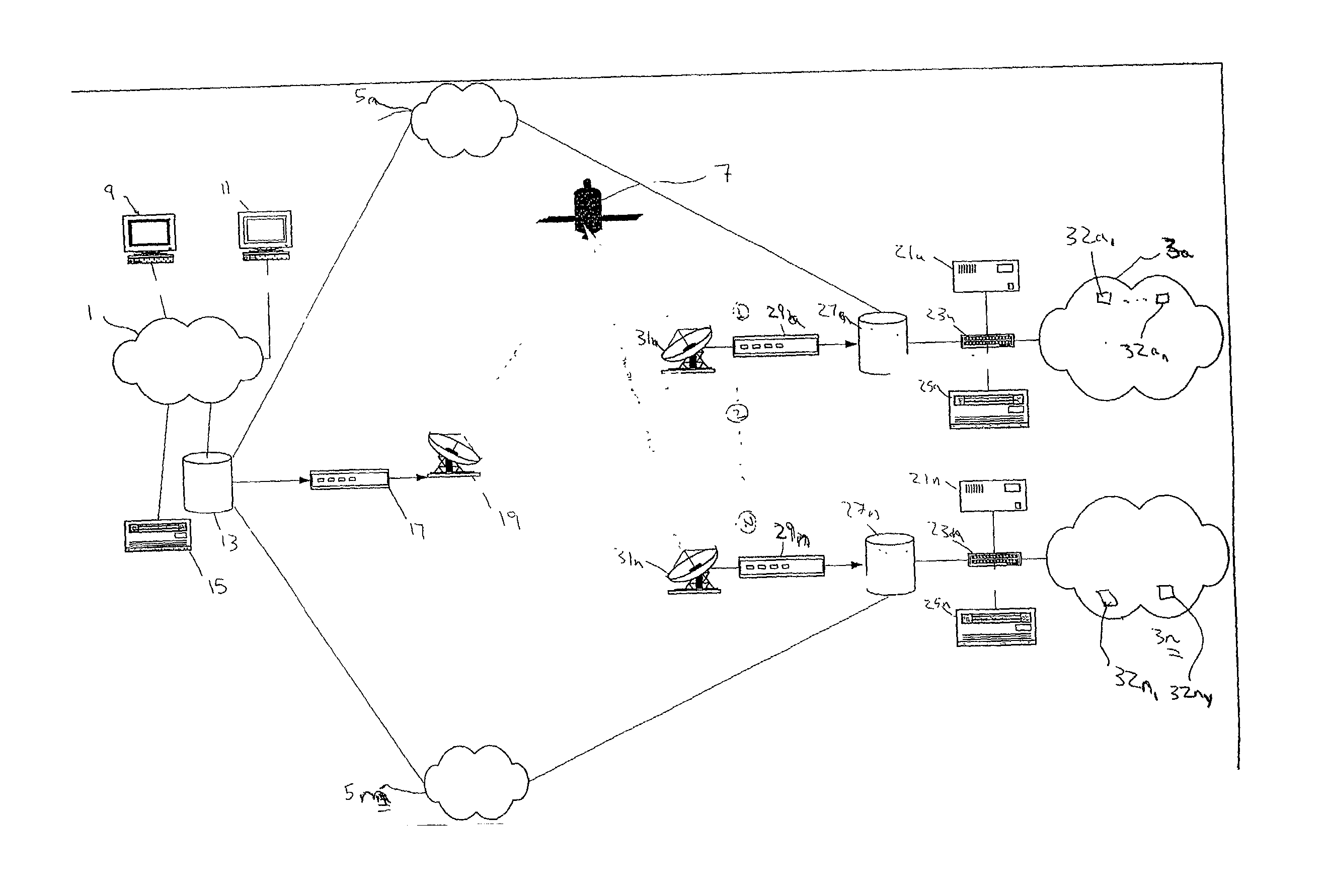
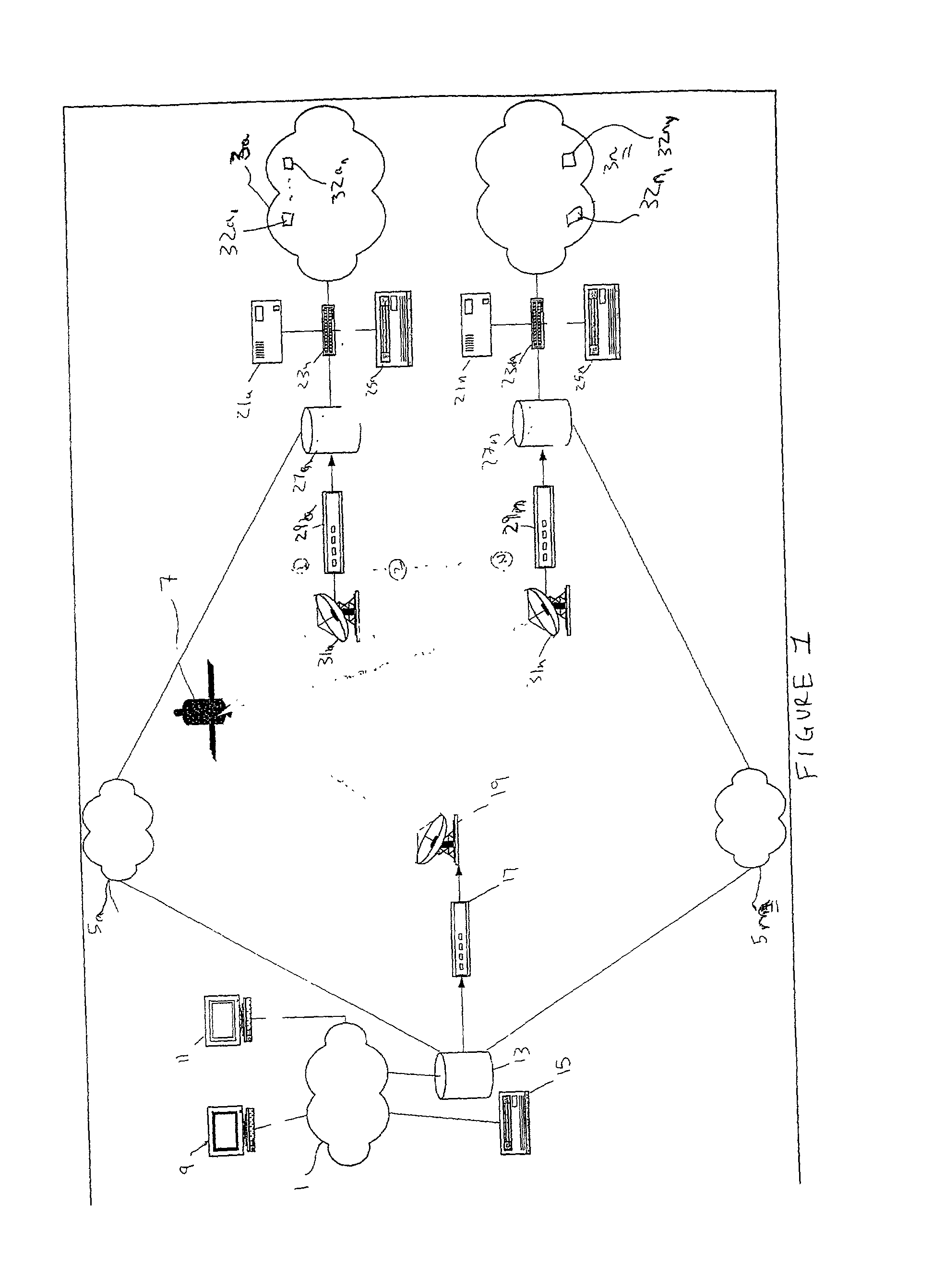
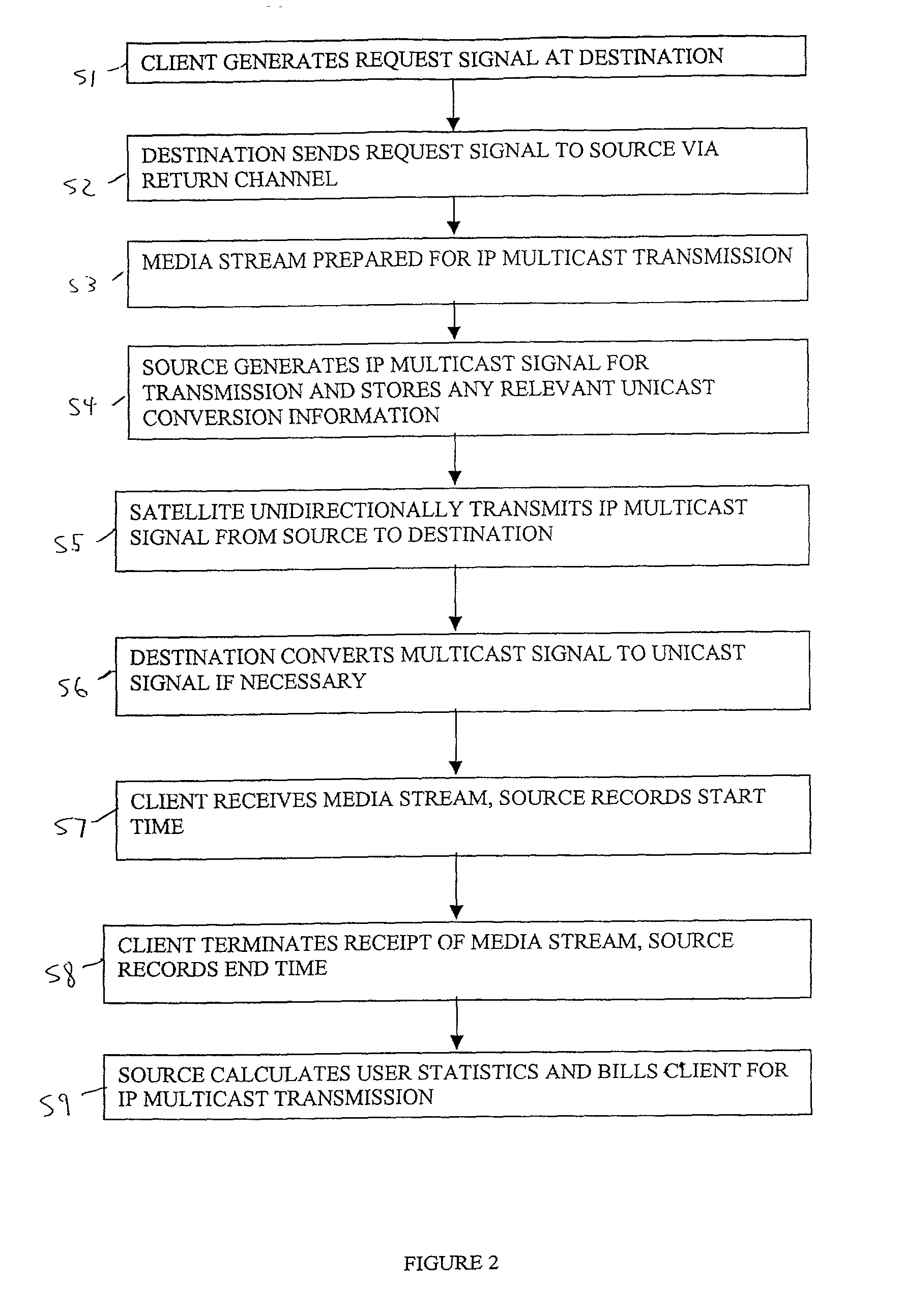
Satellite based content distribution system using IP multicast technology
InactiveUS7161934B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationContent distributionReal-time data
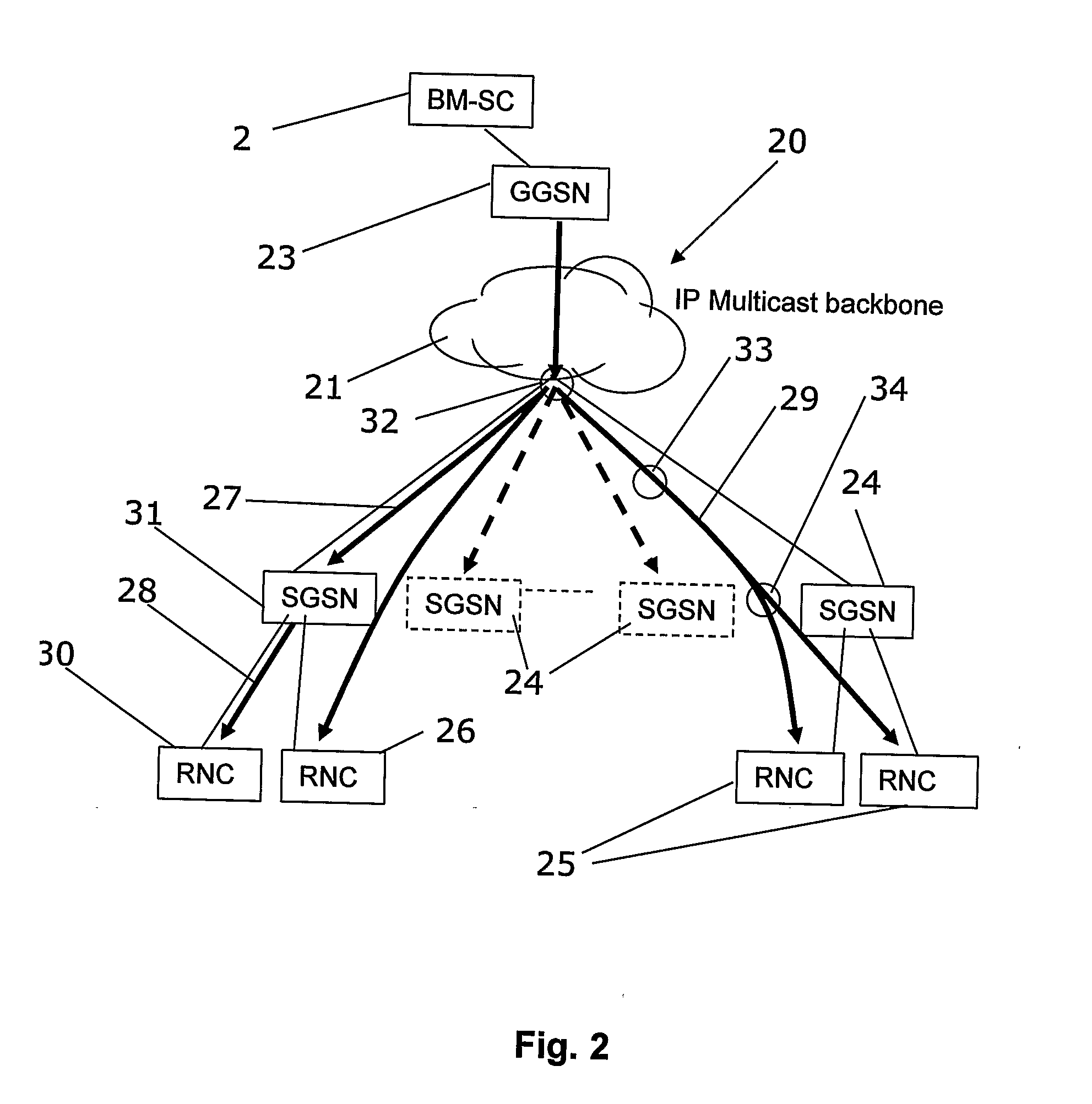
A method and system of performing IP multicast includes a client at one of many downstream networks that sends a request signal to an upstream network via a return channel (e.g., the Internet), and the upstream network sends the request to a media server. The media server, and for live data, a media encoder, processes a media stream to generate a real-time IP multicast communication that is output to a unidirectional satellite that transmits the IP multicast communication to the client without delay via the downstream network, and can convert the IP multicast to unicast. The bidirectional return channel allows the source to calculate billing information based on client usage statistics, and transmits confirmation acknowledgement based on a confirmation request from the upstream network. Because the routing configuration is transparent to the rest of the network, the invention applies to multi-hop networks on both sides of the satellite link.
Owner:INTELSAT SERVICES
Selective tunneling of streaming data
InactiveUS6189039B1Spread the wordImprove bandwidth utilizationSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsStreaming dataData stream
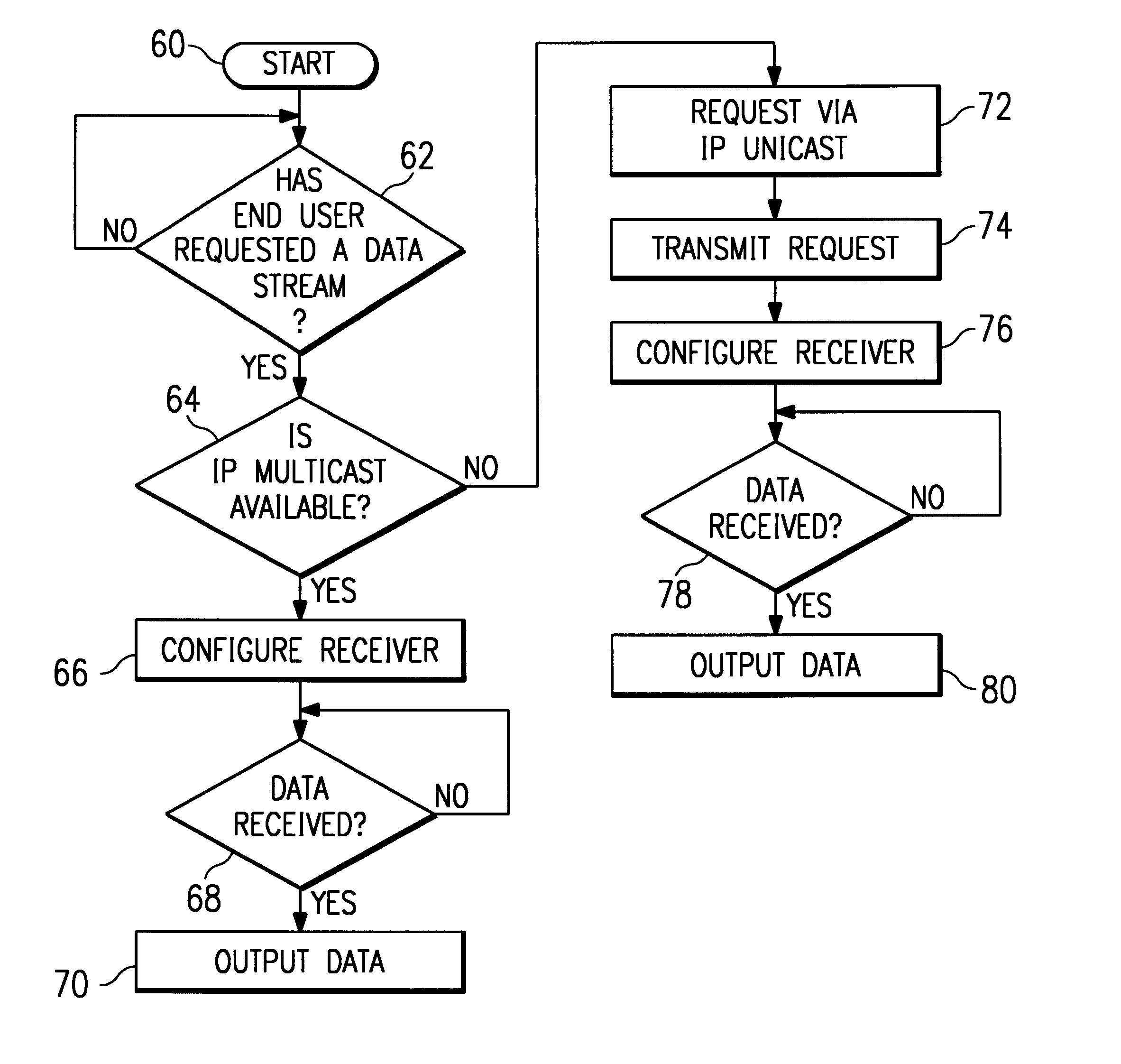
A method and system for "selective" tunneling of streaming data from a server to a client in a computer network having one or more network segments. The server has a tunneler utility, and the client has a receiver utility. The receiver utility first attempts to detect if a given data stream is available via IP multicast on the network segment supporting the client. If not, then the receiver utility issues a request for a IP unicast stream. This request is serviced by the tunneler utility. The tunneler utility re-broadcasts the IP multicast feed using IP unicast to send the data stream directly to the requesting user and / or to a repeater utility. The receiver utility then receives and processes the data stream for output to the end user. Alternatively, the receiver application, or a network administrator, launches the repeater utility, which then converts the IP unicast stream back to IP multicast format for re-broadcast over the network segment to other clients.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
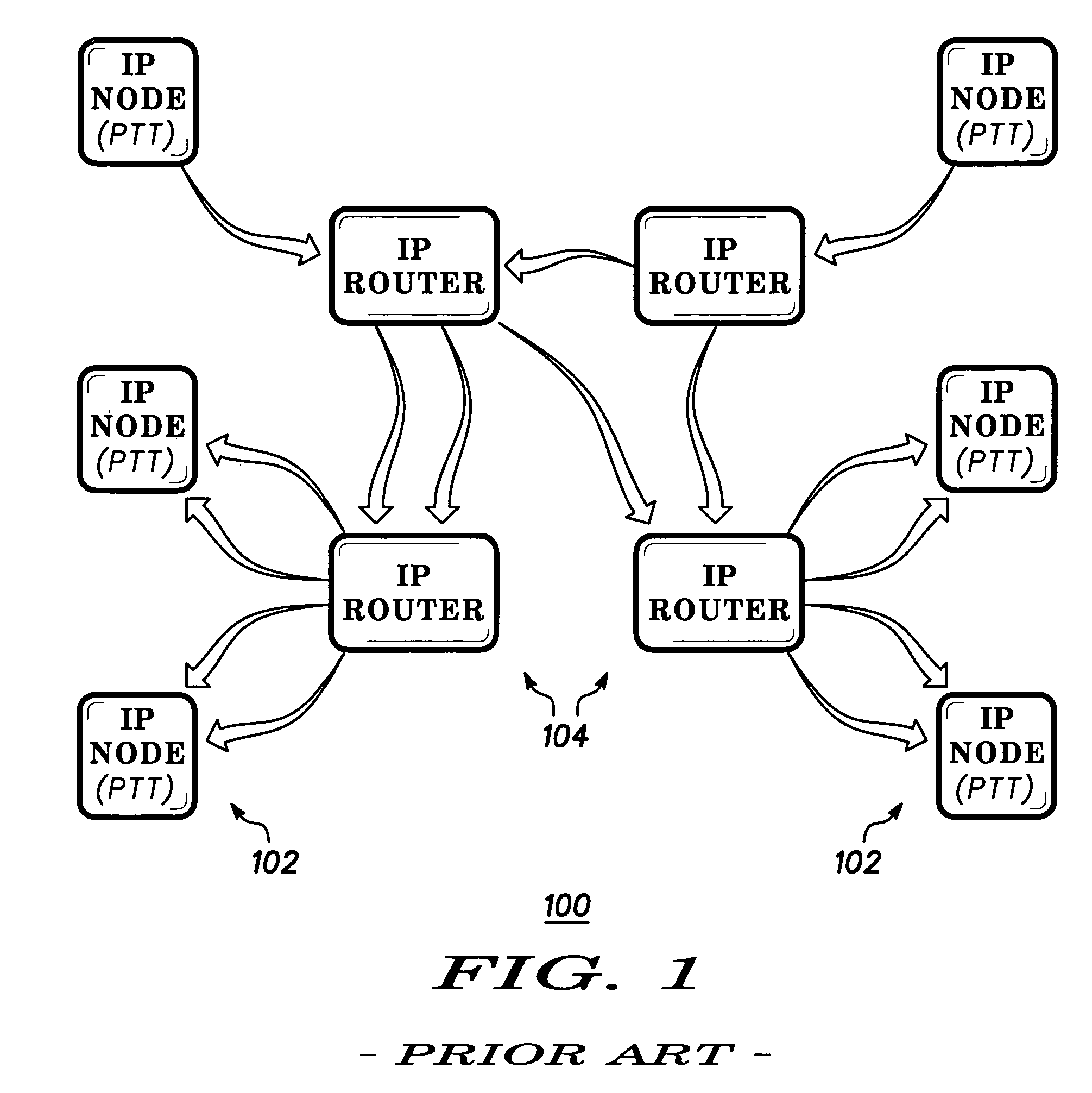
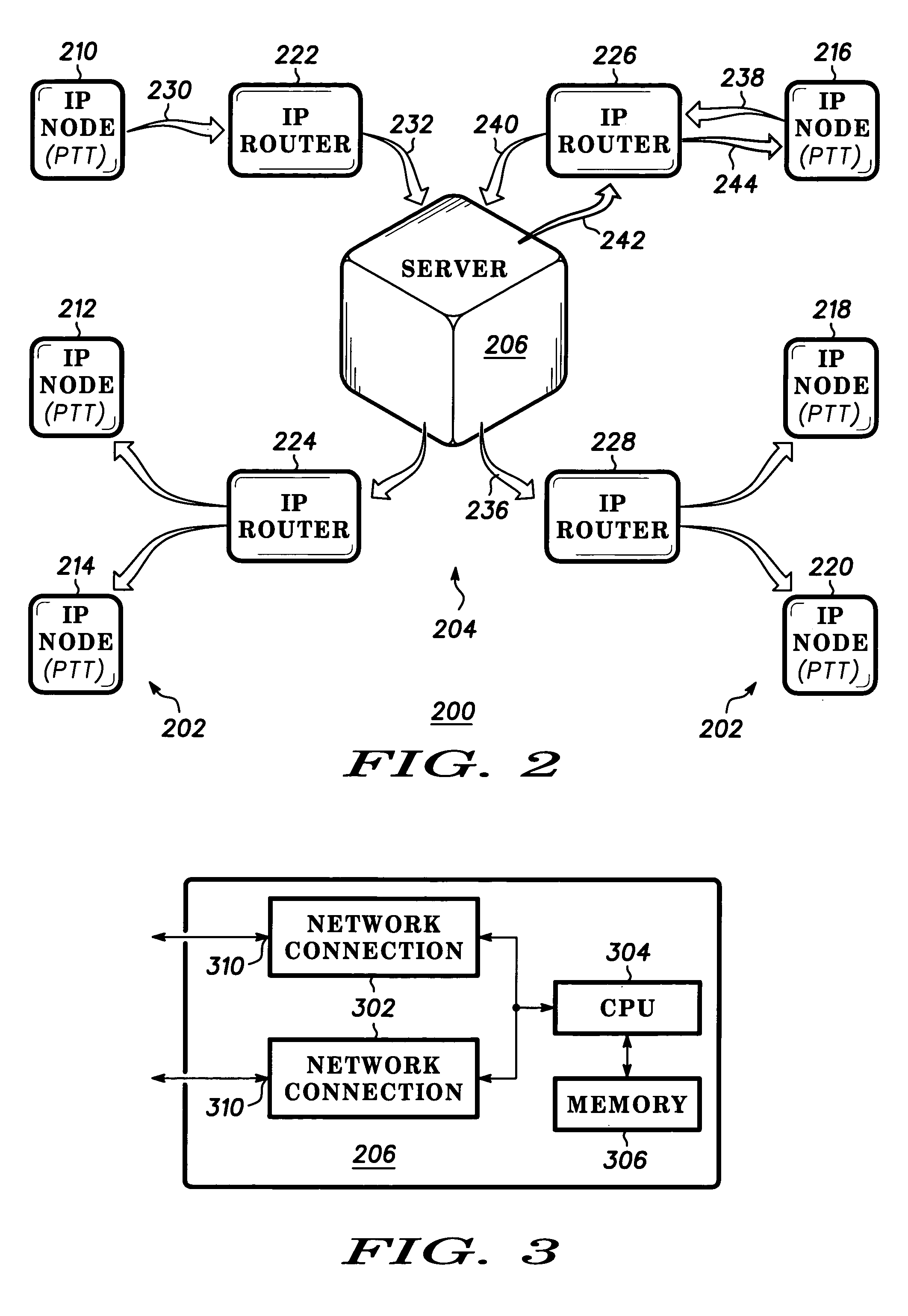
Dispatch call server in a packet based communication network
InactiveUS6970926B1Broadcast transmission systemsDigital computer detailsComputer networkRadio networks
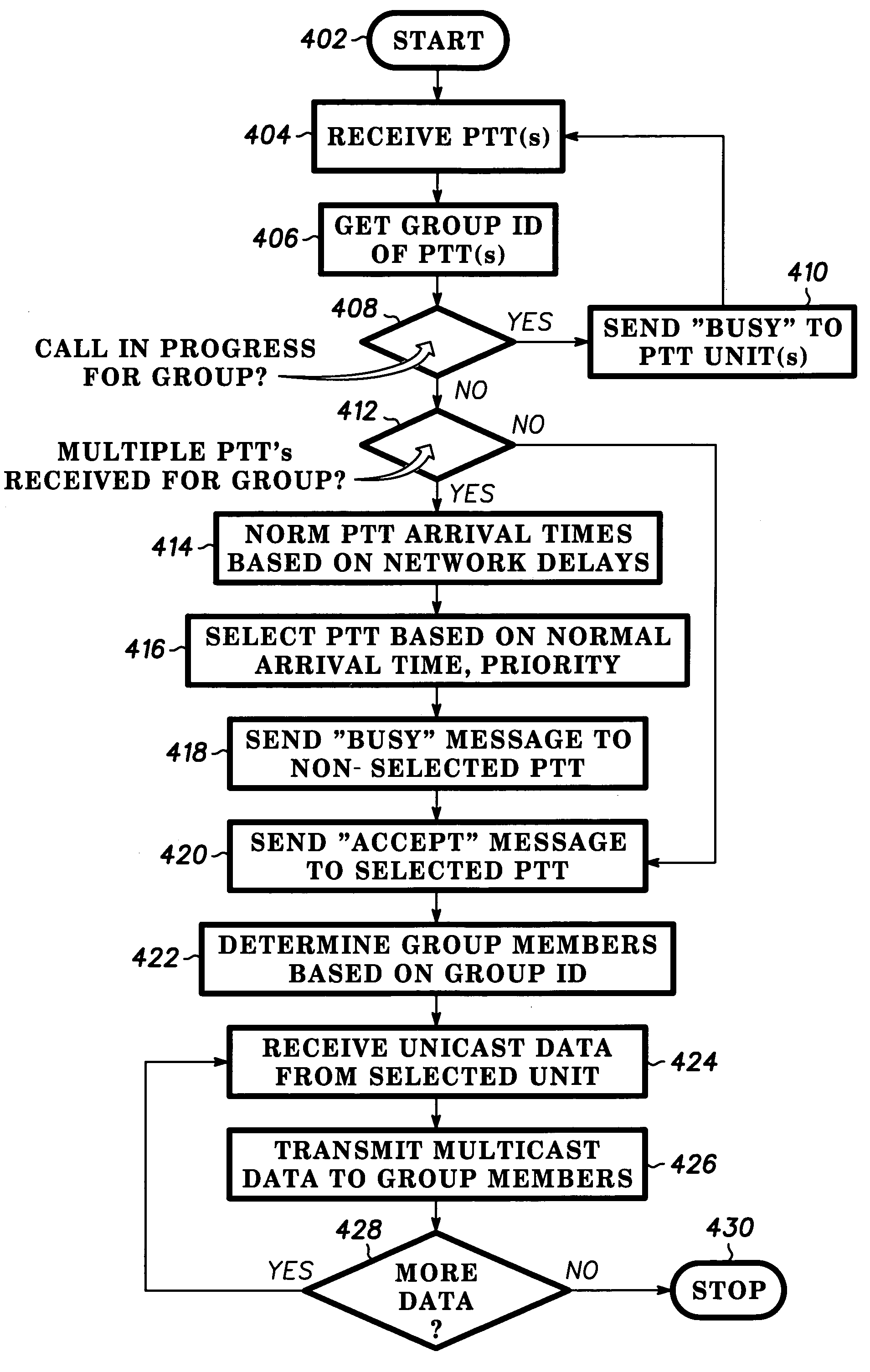
A dispatch server (206) is provided in a packet based dispatch radio network to serve as coordinator and arbitrator for dispatch group calls. Participants in a group call transmit internet protocol (IP) voice packets to the server in unicast fashion. The server receives voice packets from multiple sources (210, 216) and implements a prioritization scheme to select one source to pass on to the group via IP multicast. Various prioritization techniques are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
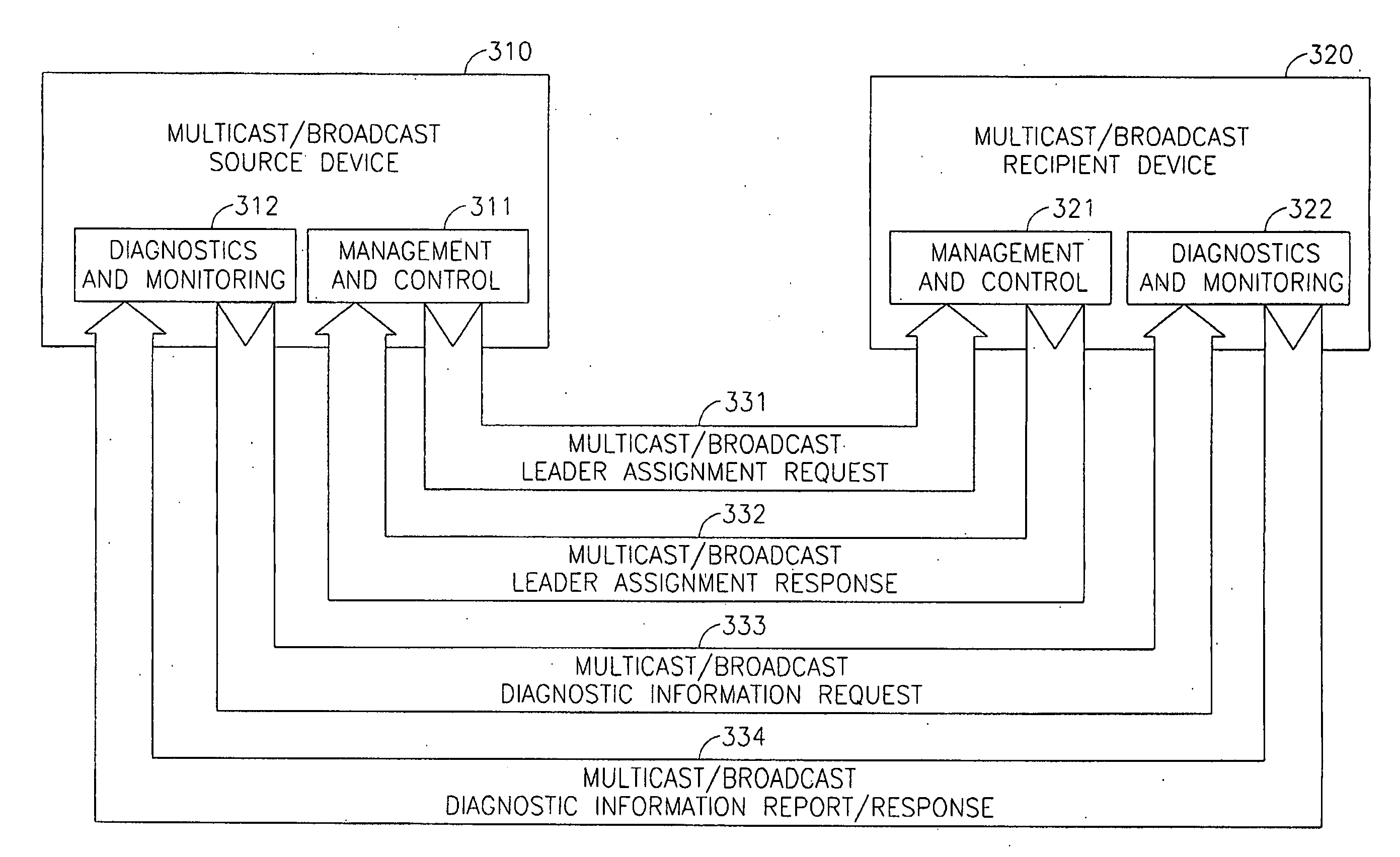
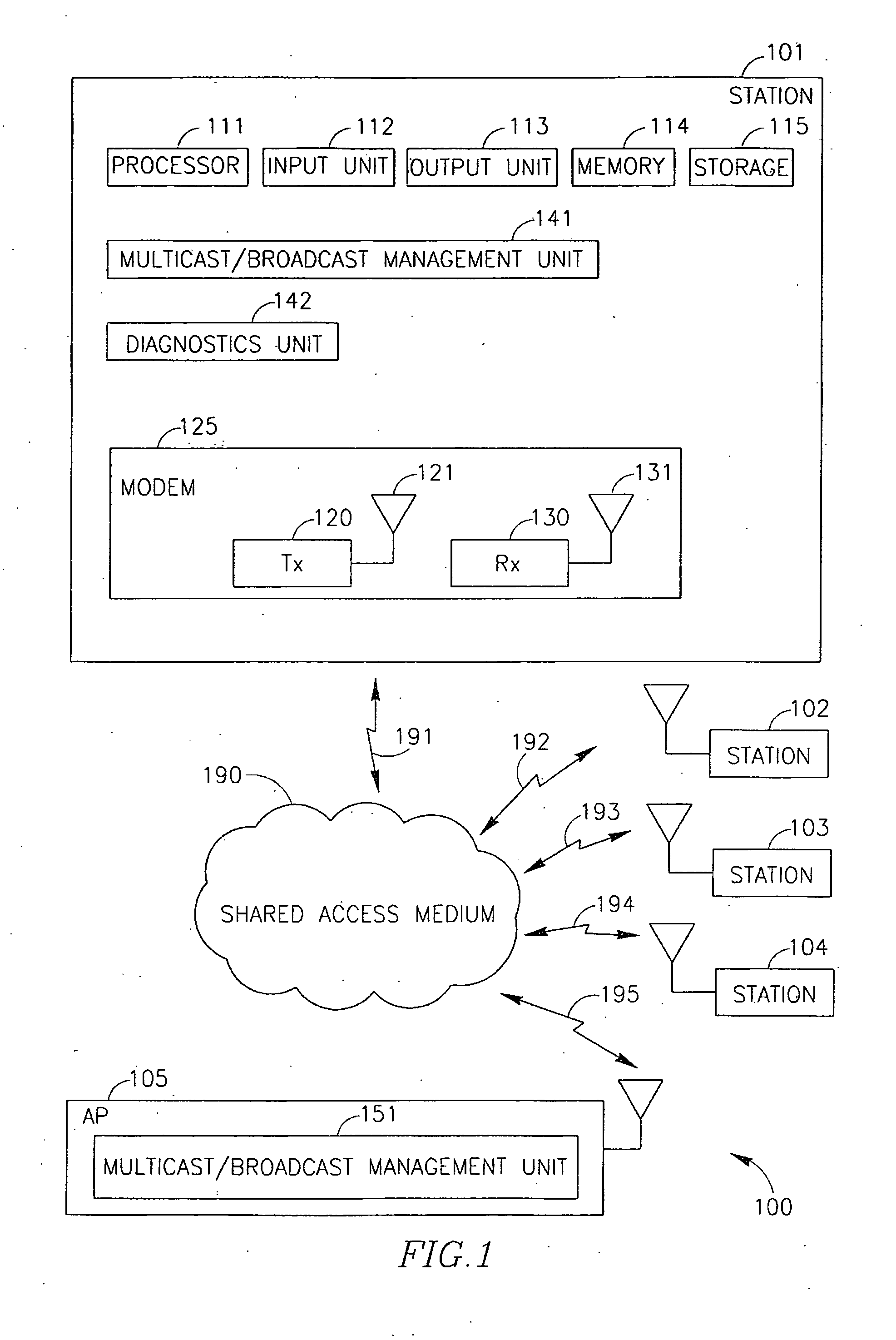
Device, system and method of multicast/broadcast communication
InactiveUS20080002691A1Data switching by path configurationBroadcast service distributionIP multicastMulticast communication
Device, system and method of multicast / broadcast communication. For example, an apparatus in accordance with an embodiment of the invention includes a transmitter to transmit, in response to an incoming multicast communication frame received from a multicast communication source, a multicast acknowledgment frame indicating receipt of the incoming multicast communication frame.
Owner:INTEL CORP
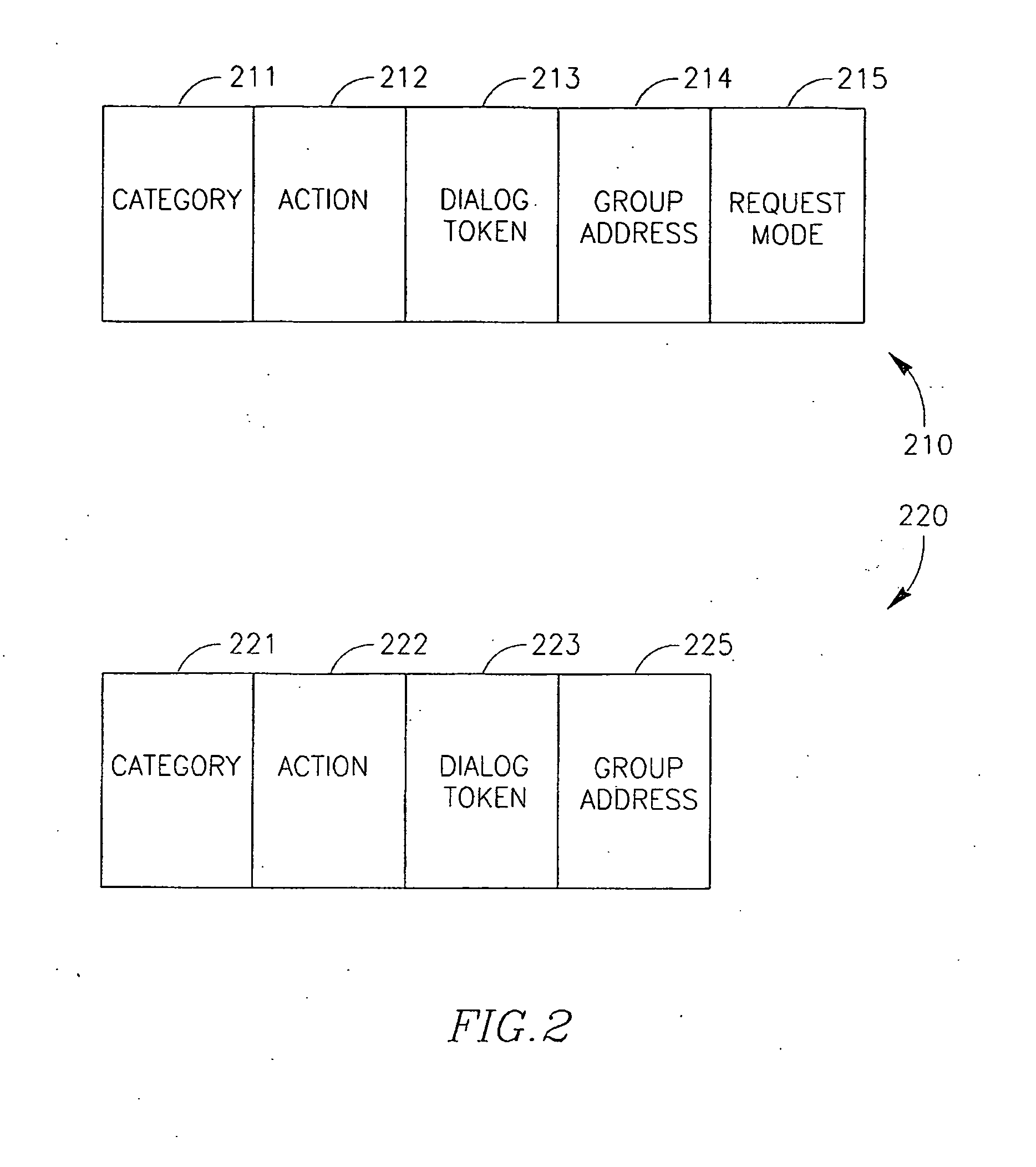
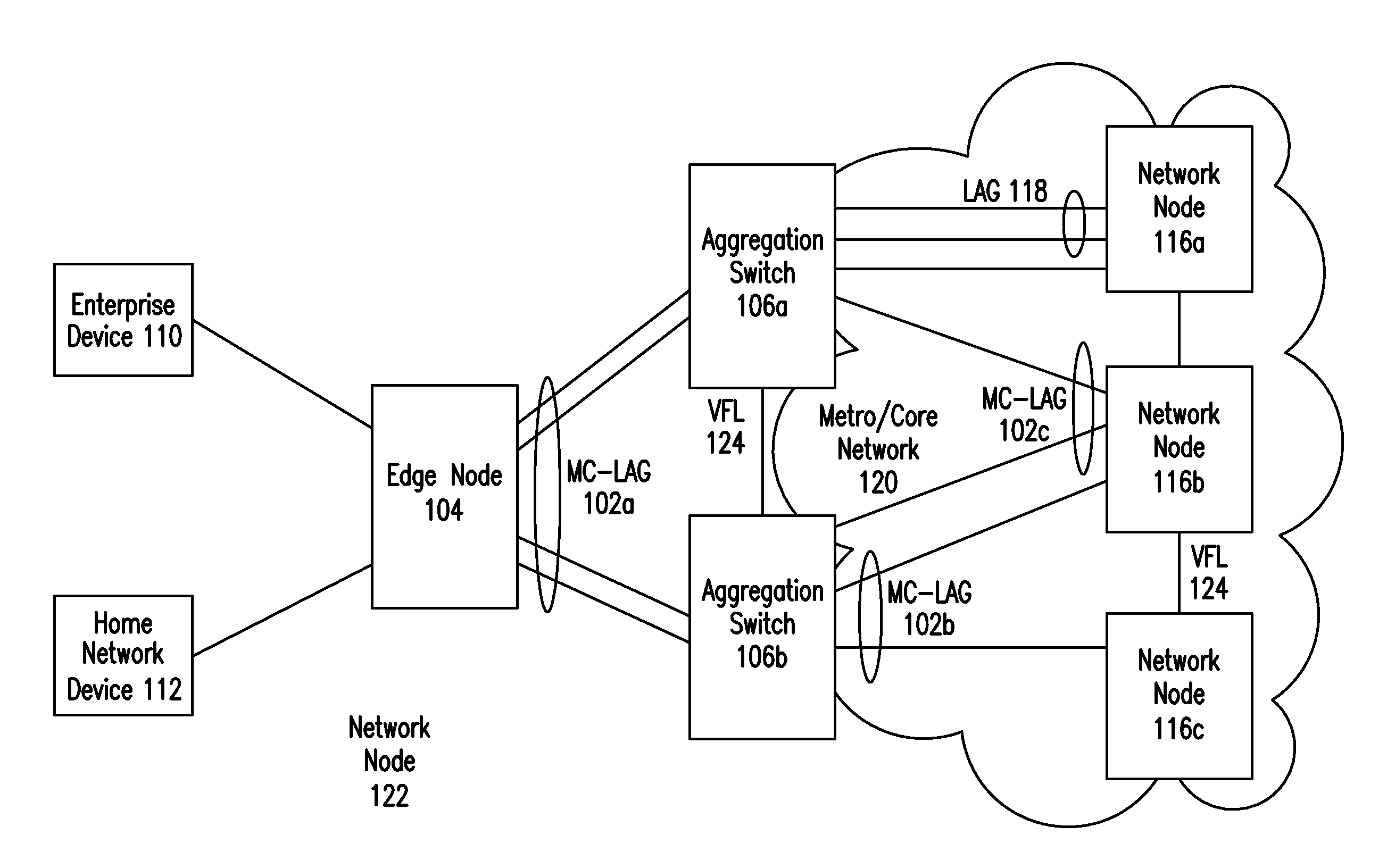
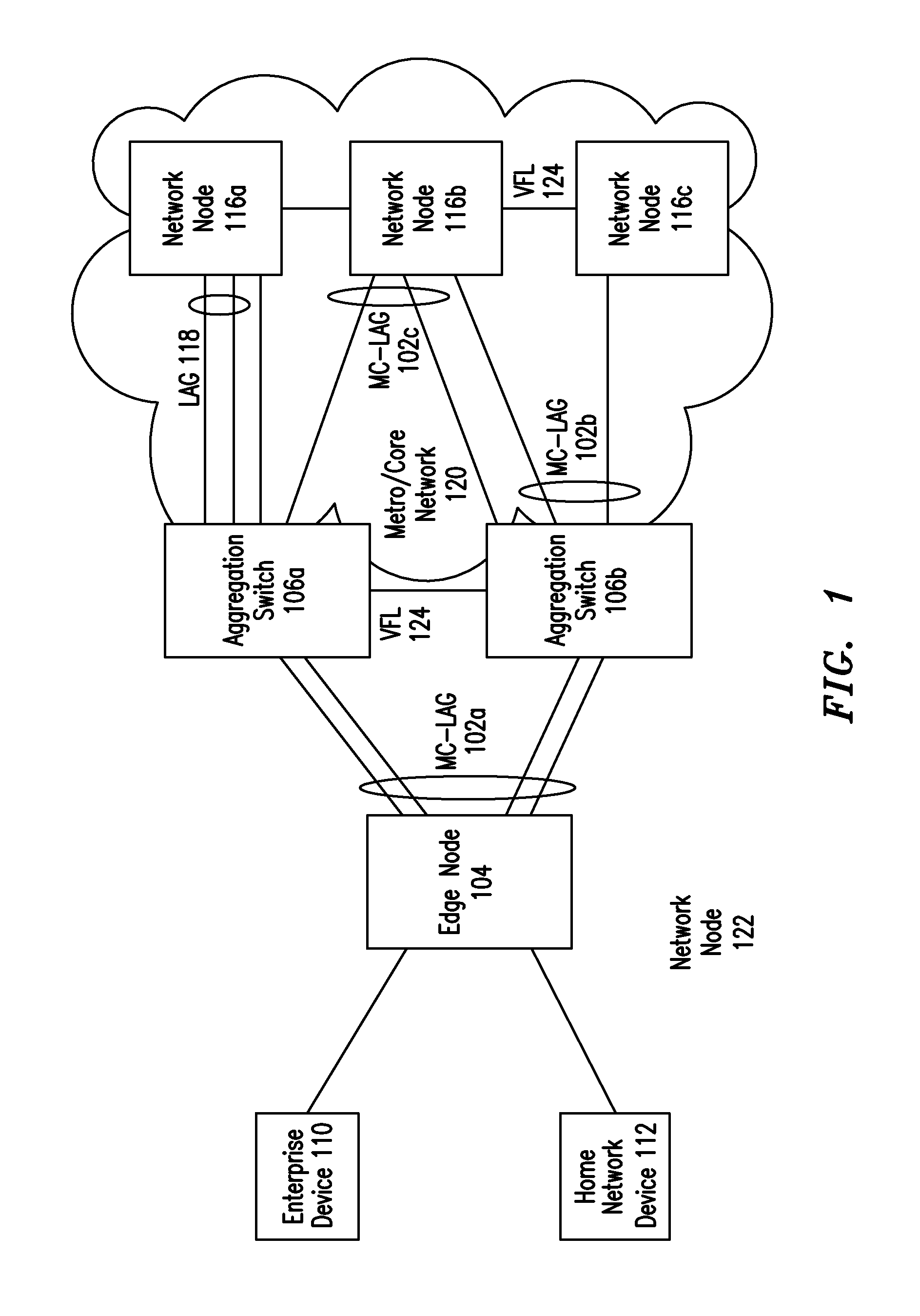
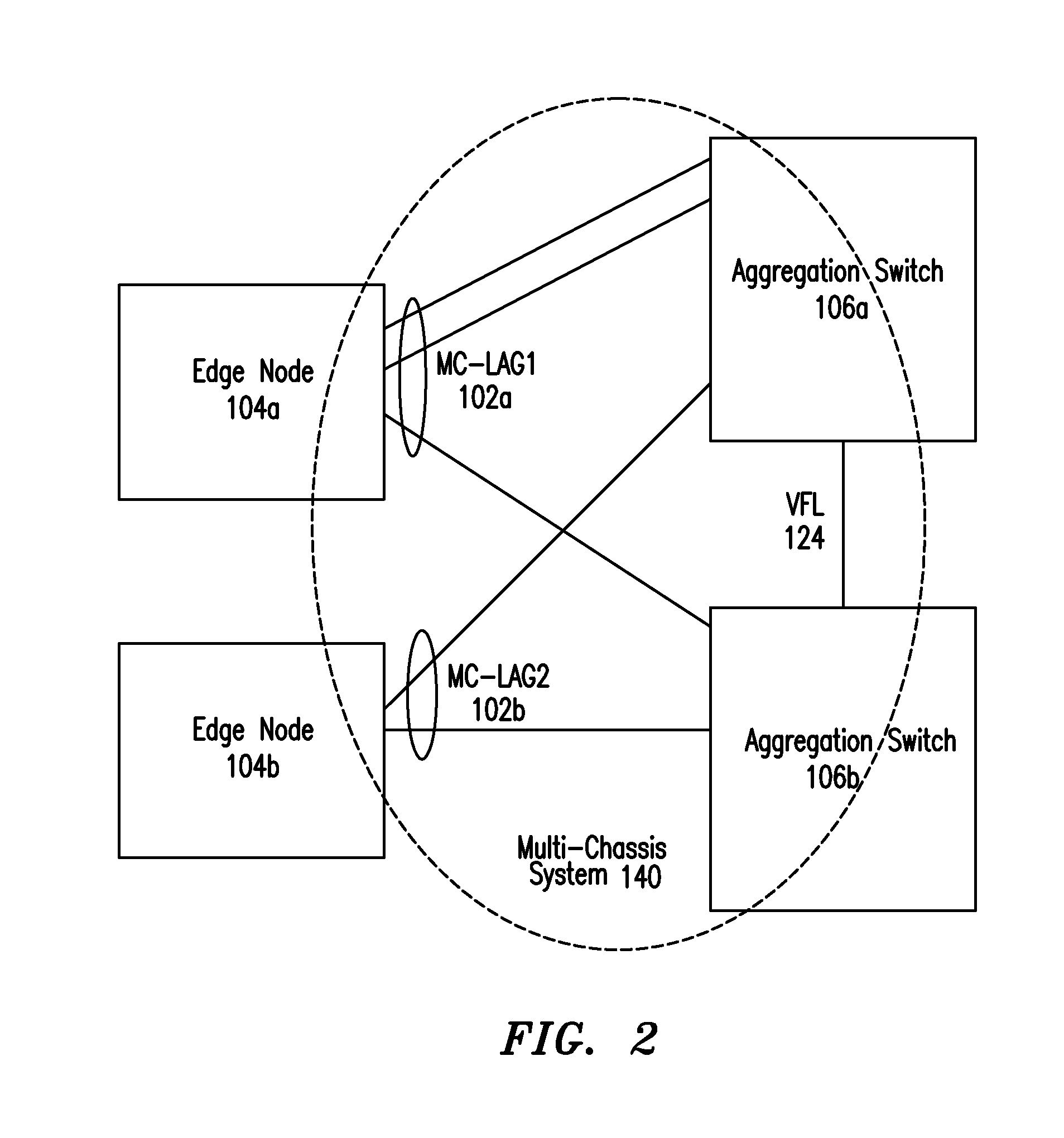
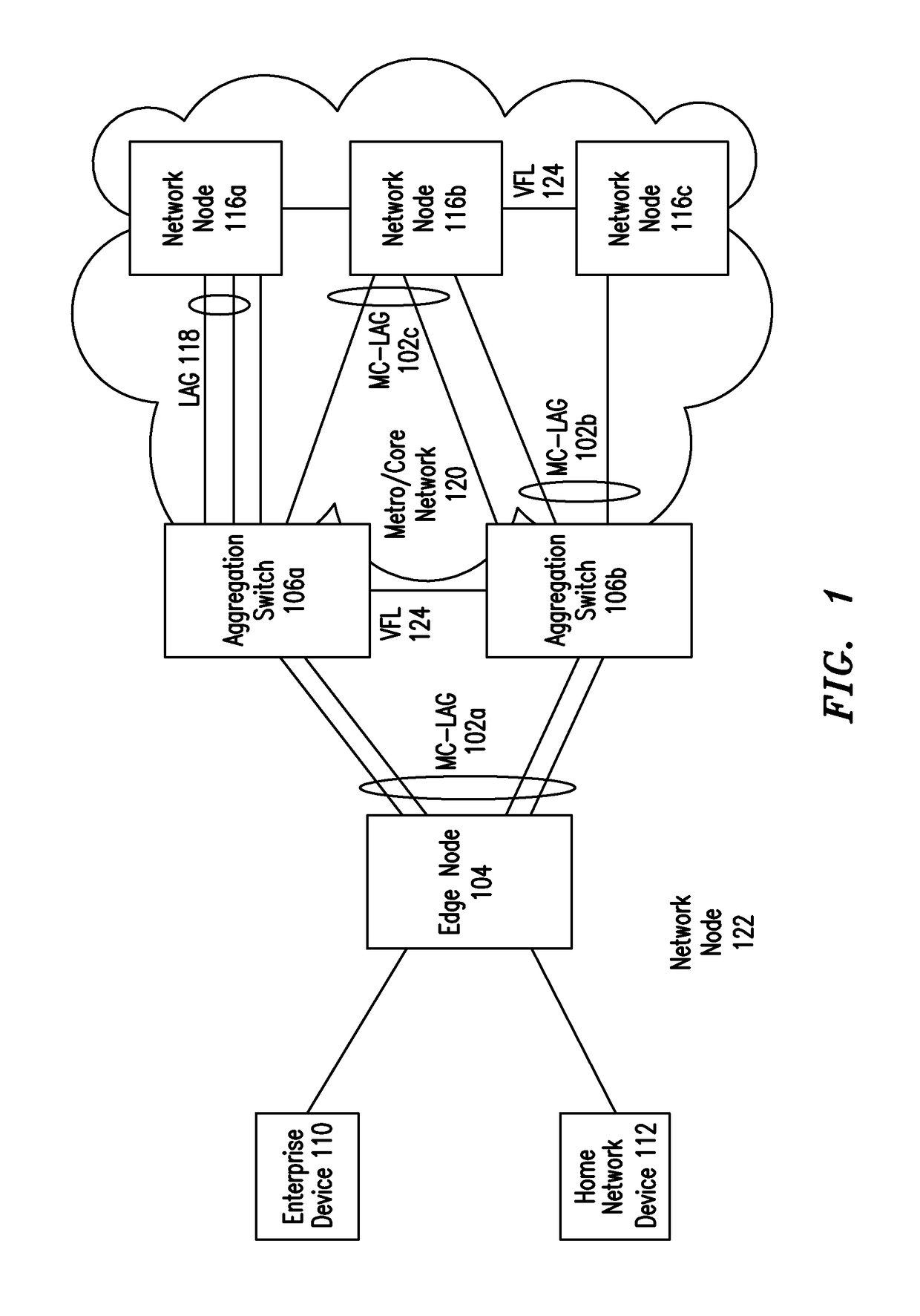
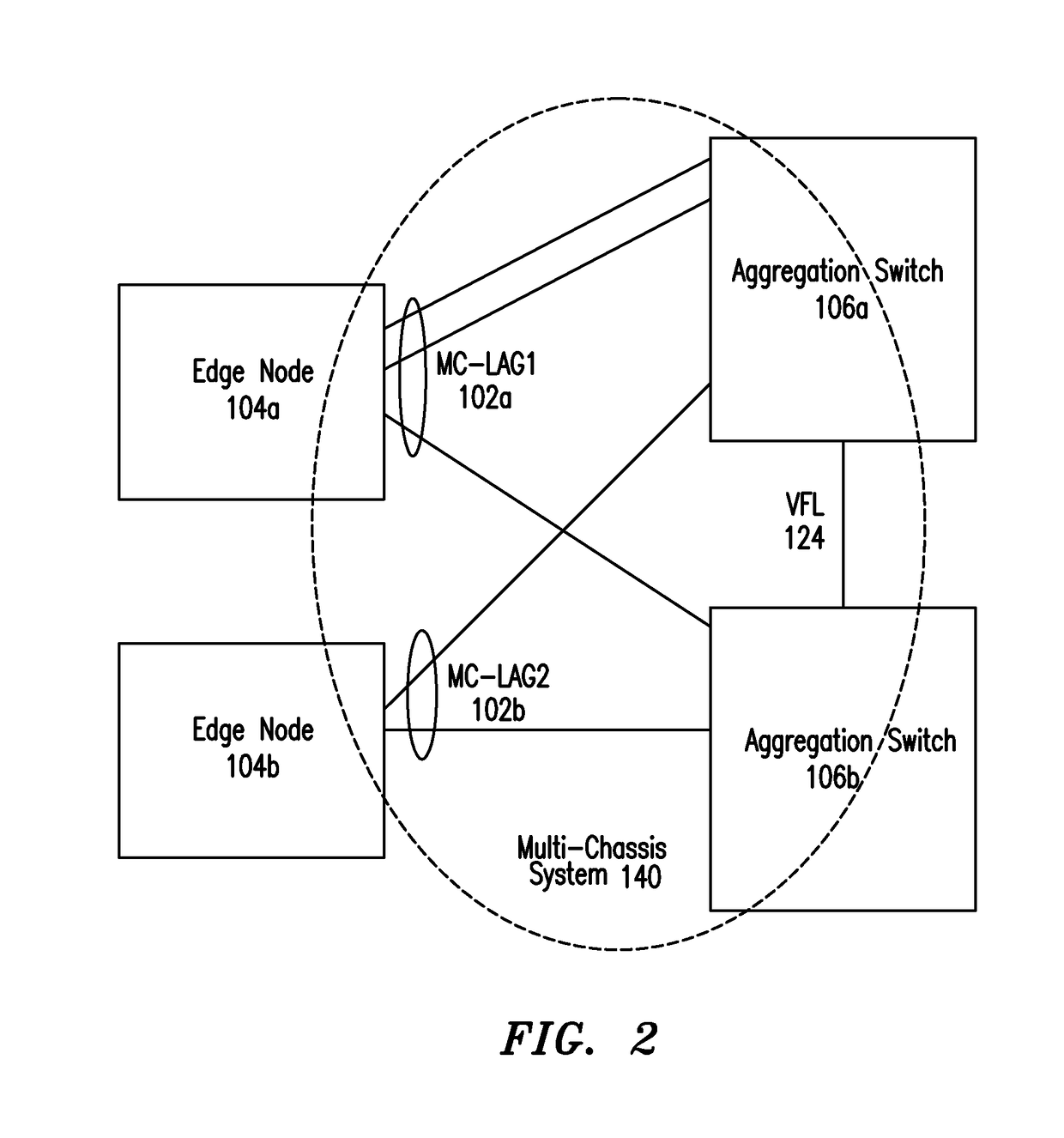
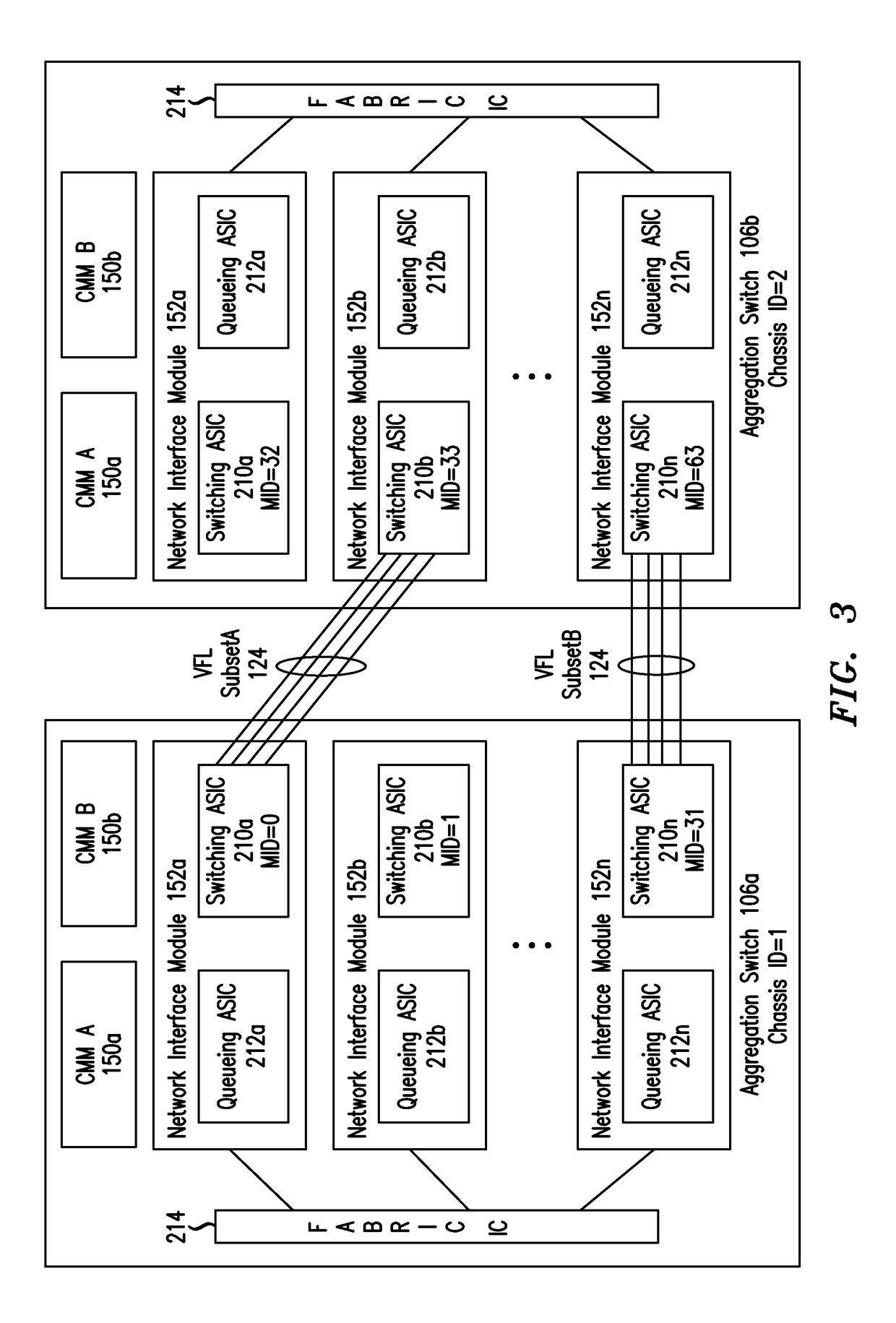
IP Multicast Snooping and Routing with Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation
ActiveUS20120033668A1Energy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationComputer networkIP multicast
Aggregation Switches connected via a virtual fabric link (VFL) are each active and able to perform at least limited IP multicast snooping. The resulting IP multicast snooping information is maintained internally within each Aggregation Switch and shared substantially in real-time therebetween via the VFL.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
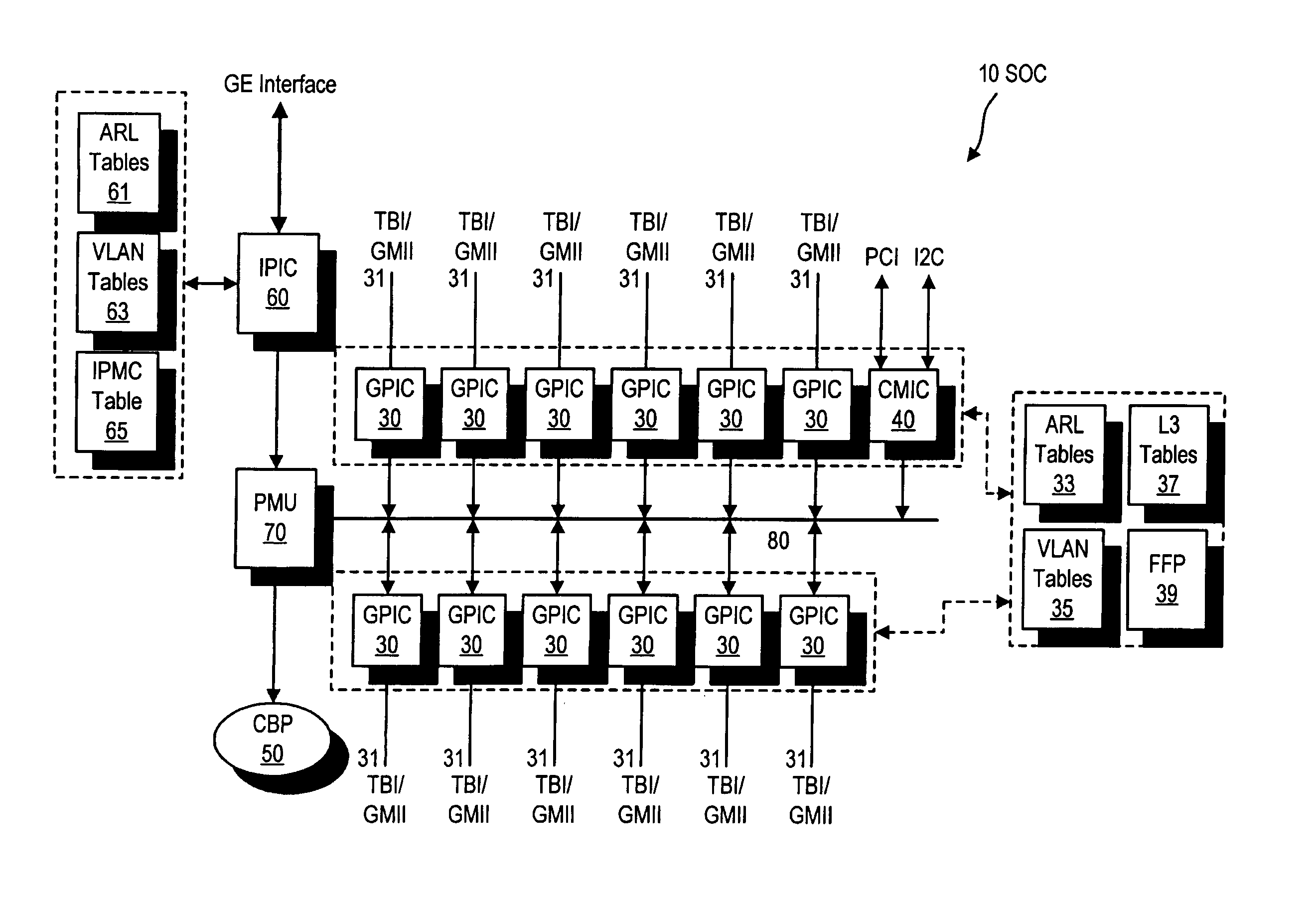
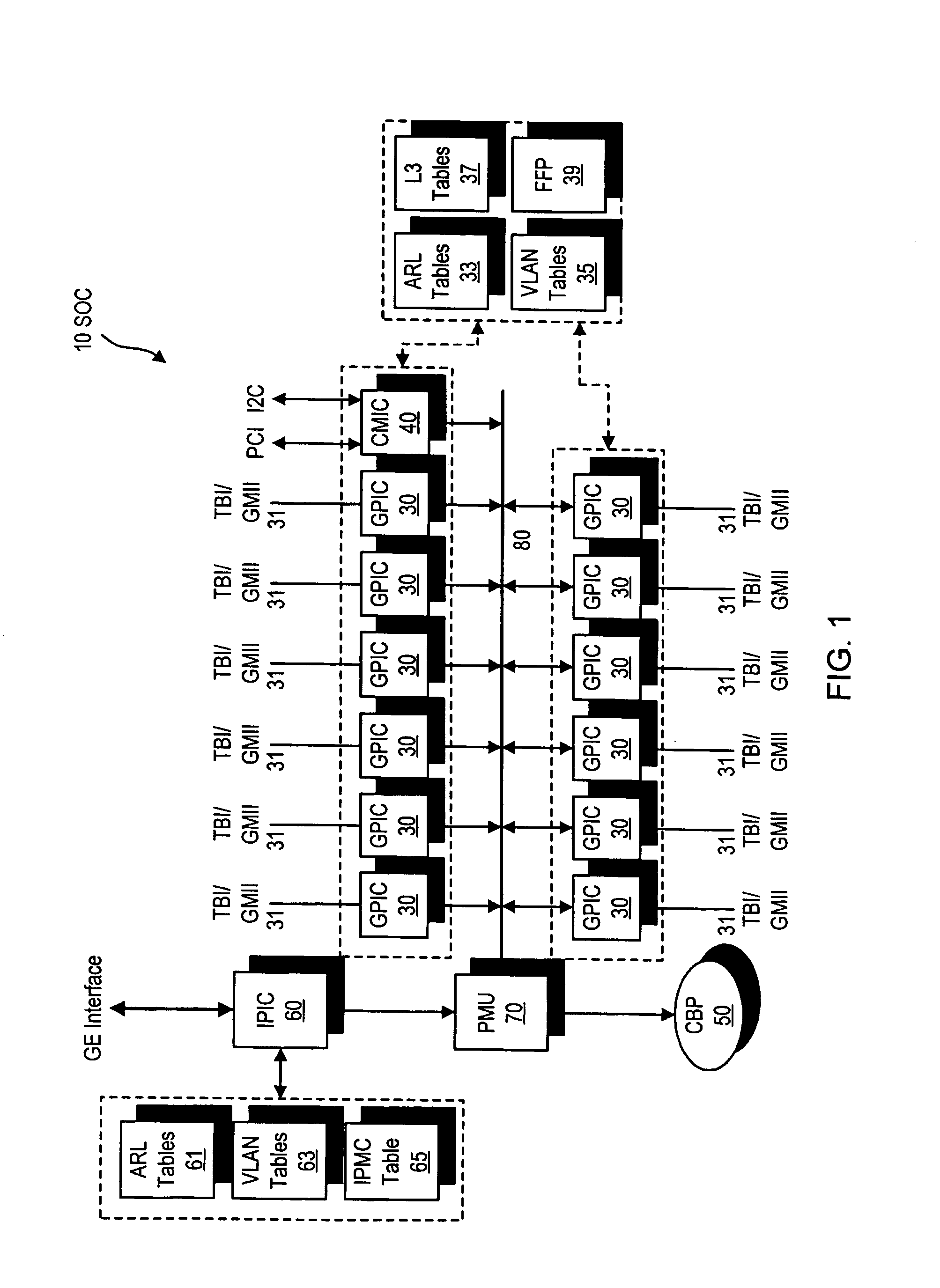
Gigabit switch supporting improved layer 3 switching
ActiveUS7009968B2Improved layer switchingEliminate needSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTIP multicastNetwork communication
A network switch for network communications is disclosed. The switch includes a first data port interface, supporting at least one data port transmitting and receiving data at a first data rate and a second data port interface supporting a at least one data port transmitting and receiving data at a second data rate. The switch also has a CPU interface configured to communicate with a CPU and a memory management unit for communicating data from at least one of the first and second data port interfaces and a memory. It also has a communication channel for communicating data and messaging information between the first and second data port interfaces and the memory management unit and a plurality of semiconductor-implemented lookup tables including an address resolution lookup table, a layer three IP lookup table and VLAN tables. One of the first and second data port interfaces is configured to determine whether an incoming data packet is a unicast packet, a multicast packet or an IP multicast packet; and the address resolution lookup and layer three IP lookup tables are searched to find an egress port for the incoming data packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
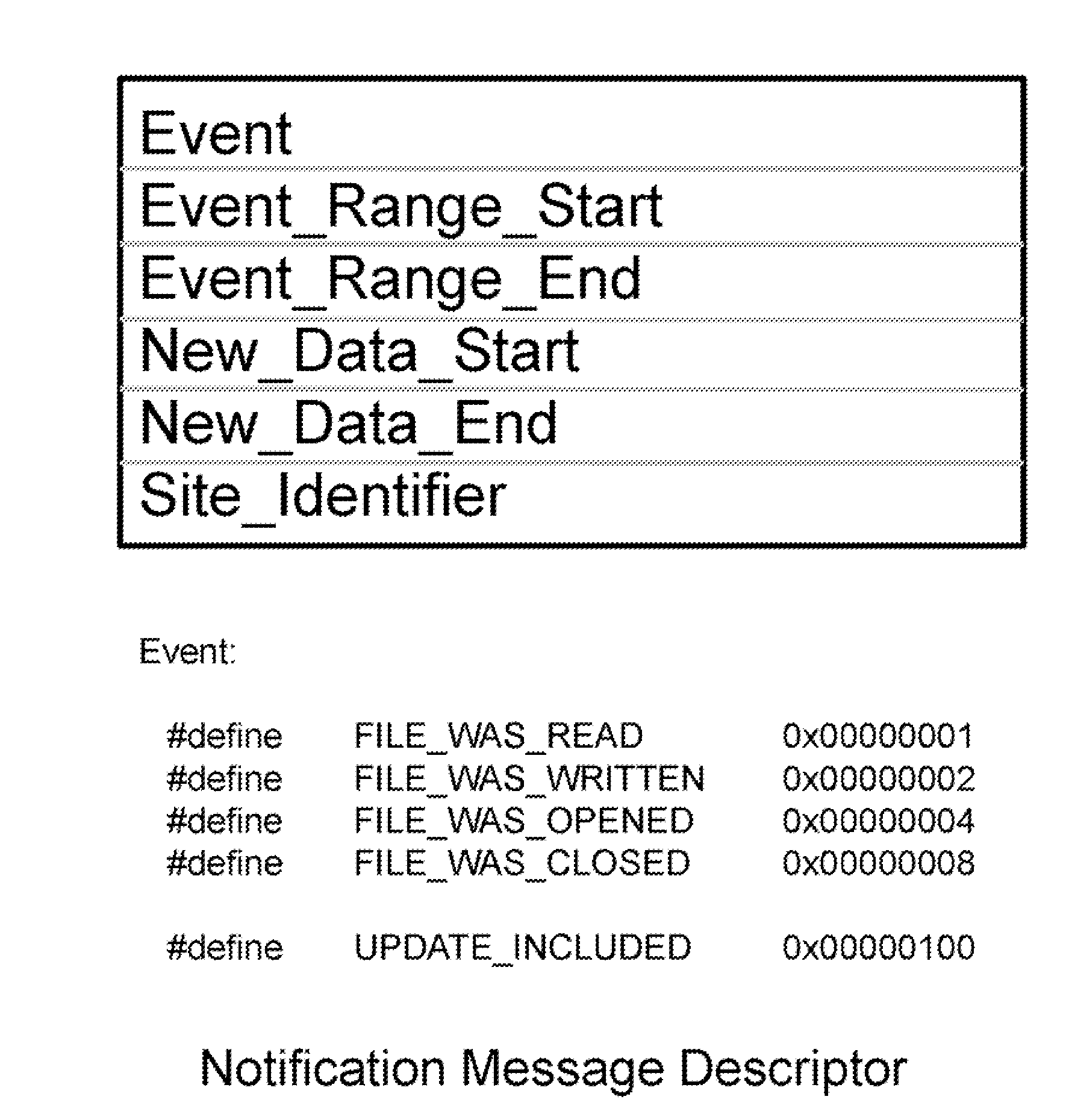
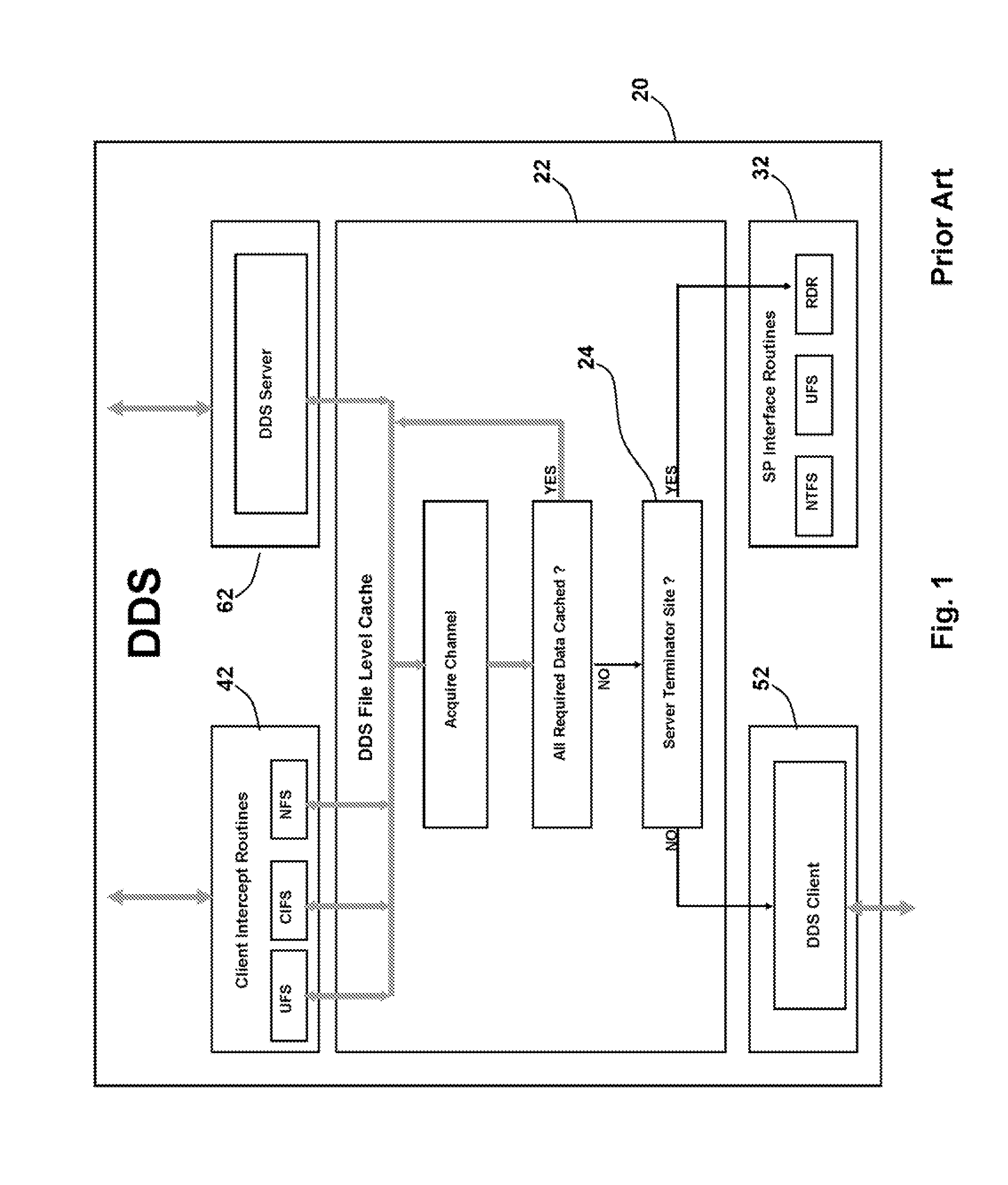
Distributed File System Consistency Mechanism Extension for Enabling Internet Video Broadcasting
ActiveUS20100082774A1Improve scalabilityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGlobal file systemIP multicast
The consistency callback mechanisms employed by local file systems such as NTFS and distributed file systems such as DDS, NFS and CIFS are extended to provide a shared memory foundation for efficiently broadcasting real-time high definition video from a source object to large numbers of viewers via the Internet. Distributed applications such as video viewing client applications establish connections to a common distributed file system object, and then each application registers with the underlying distributed file system to receive notifications whenever the video source modifies the source object. The data required to update images maintained by viewing clients is included in notification messages. The distributed file system employs a network of proxy cache nodes. Proxy cache nodes receive notification messages (complete with image update data) and update their cached images of the source object and then retransmit the notification messages towards the viewing clients using IP multicast techniques. In this manner, the distributed file system's consistency mechanism efficiently employs network resources to enable the real-time distribution of video content streams.
Owner:PITTS WILLIAM M
Multicast system for forwarding desired multicast packets in a computer network
InactiveUS6847638B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationDistribution treeIP multicast
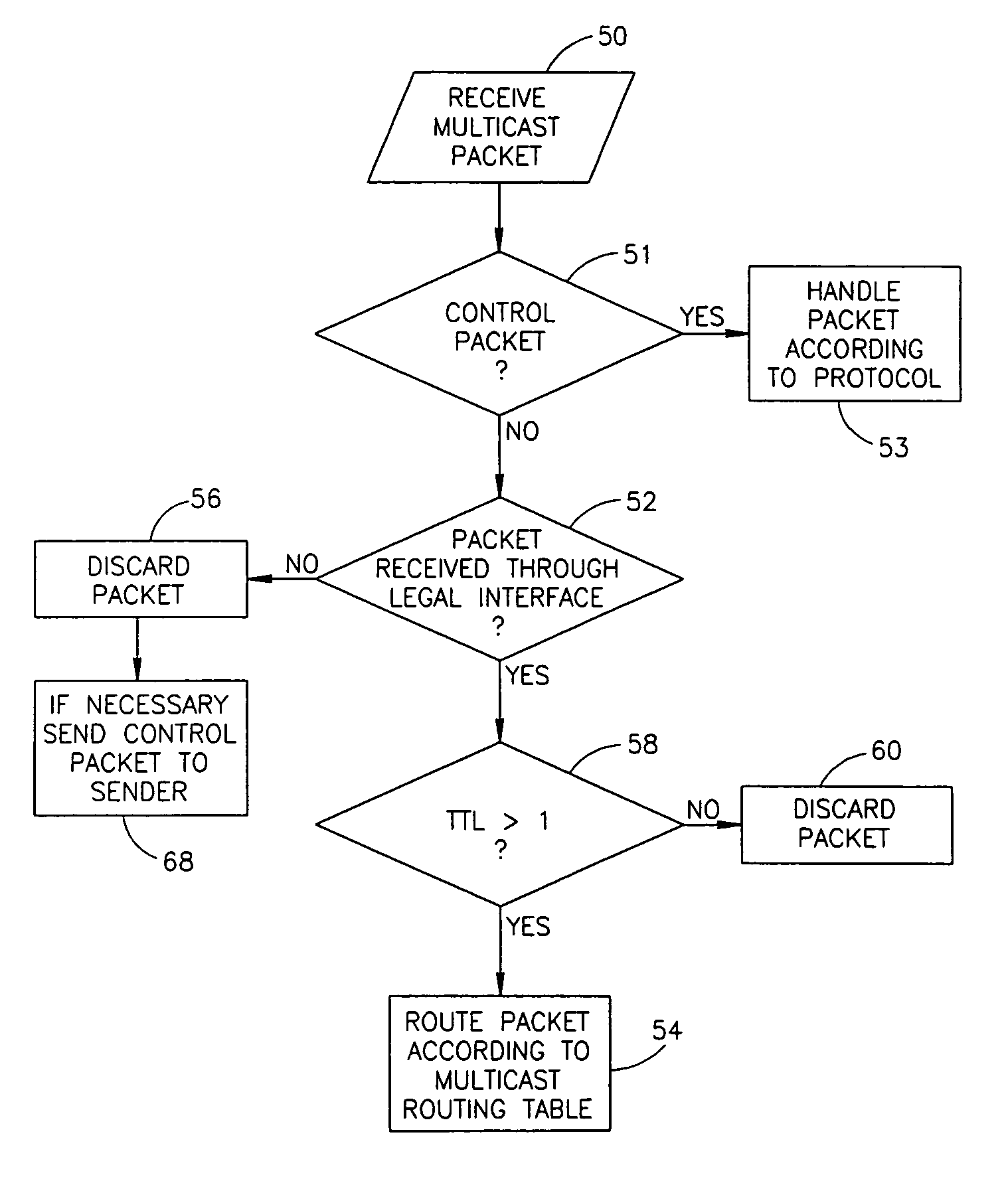
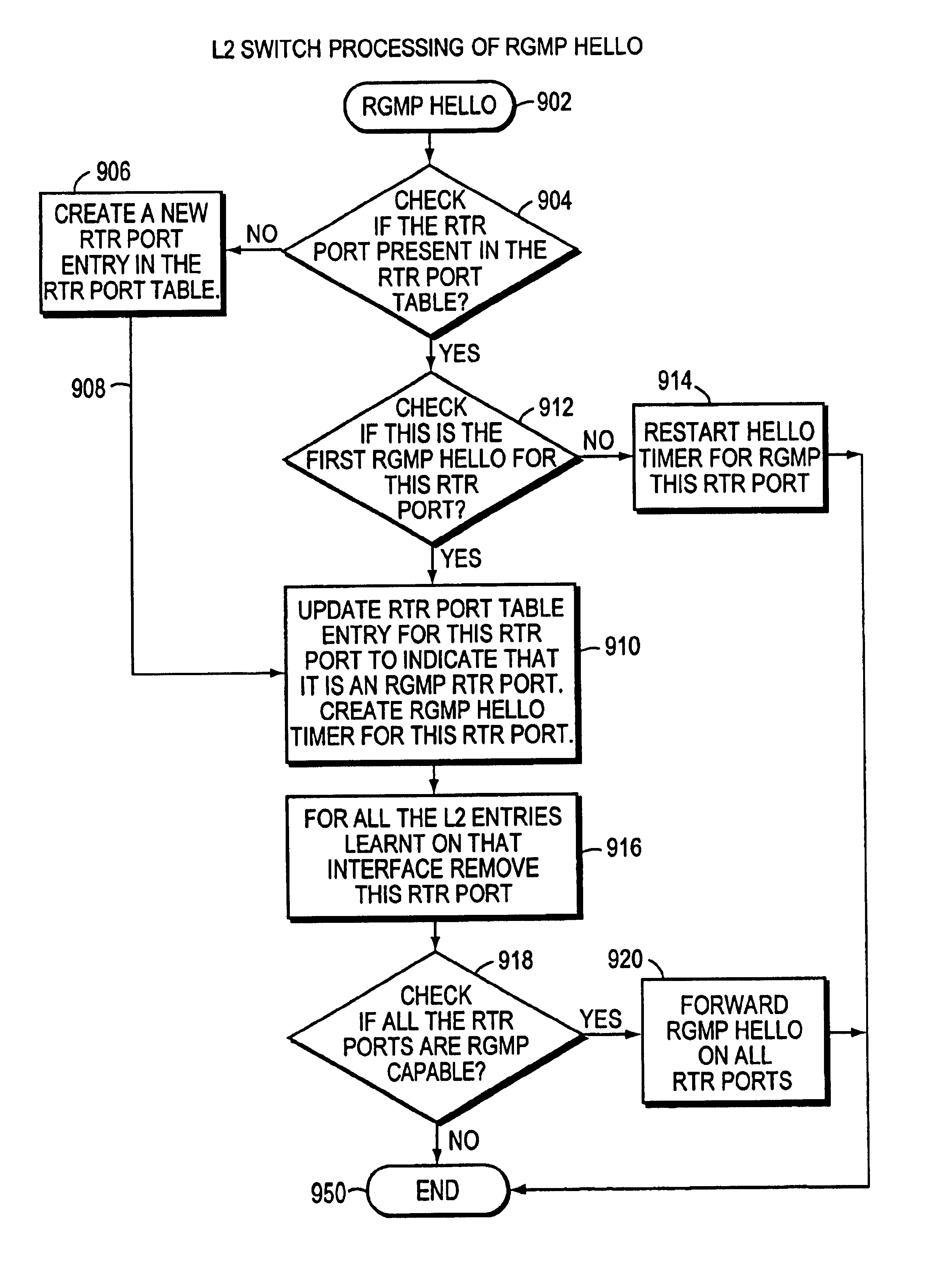
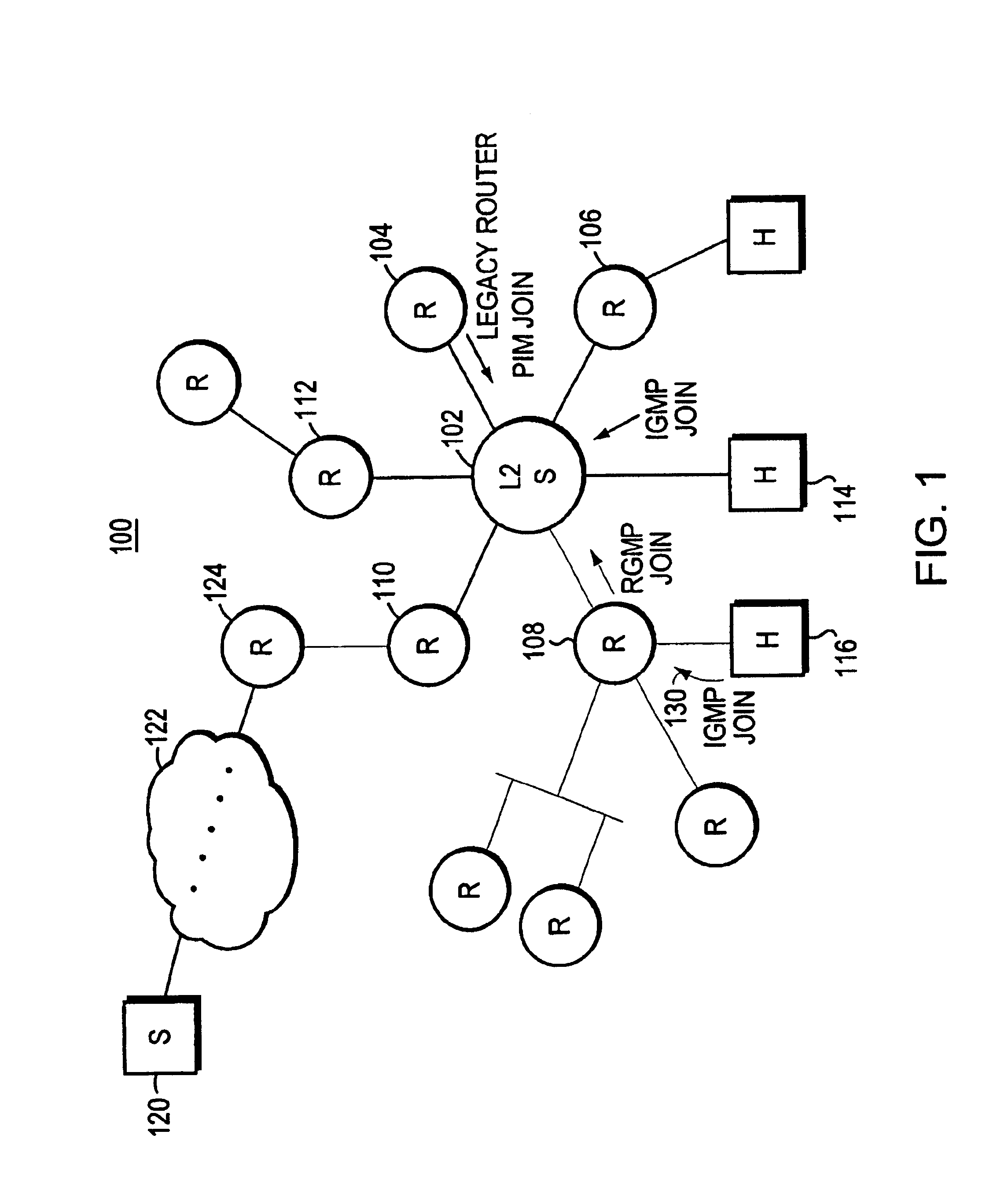
A method and apparatus for a router to inform a Layer 2 switch by use of packets of a new router group port management protocol (RGMP) that the layer 2 switch is to forward multicast packets of a specified group to the router. First the router transmits a RGMP HELLO packet to the layer 2 switch to inform the switch that the router is a multicast router implementing the invention. Then, in the event that the router receives an IGMP packet from an end station requesting multicast packets of a particular group, in response the router sends an RGMP JOIN packet to the layer 2 switch. The RGMP JOIN packet requests that the layer 2 switch forward only multicast group packets, of the group whose group number is written into a field of the RGMP JOIN packet, to the router. Also, the router sends a prior art PIM JOIN packet to other multicast routers in order to be placed on the multicast distribution tree for that group. The layer 2 switch builds a forwarding table for multicast groups listing ports connected to routers having sent a RGMP JOIN for that group. When a multicast group packet arrives at the layer 2 switch, the switch uses the forwarding table to forward the packet only to those routers requesting that group.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for protection of internet sites against denial of service attacks through use of an IP multicast address hopping technique
InactiveUS6880090B1Traffic analysisTimely controlSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressIP multicast
The present invention relates to a method and system for Internet Protocol network communications and a use thereof for protecting Internet sites against denial of service attacks on insecure public networks such as the Internet. The method utilizes a multicast address hopping technique which selectively varies the chosen multicast IP address from a set of available multicast addresses according to a predetermined scheme known to the communicating end stations but not to unauthorized end stations. The packets associated with the multicast stream are then communicated on the chosen multicast address. The set of available multicast IP addresses may also be selectively varied according to a secret predetermined scheme known to the transmitter and subscriber end stations, particularly by adding to and dropping from the set of multicast IP addresses in a seemingly random fashion. Using the method of the present invention, potential attackers are prevented from knowing which address to disrupt or monitor for traffic between end stations.
Owner:SHAWCROSS CHARLES BYRON ALEXANDER
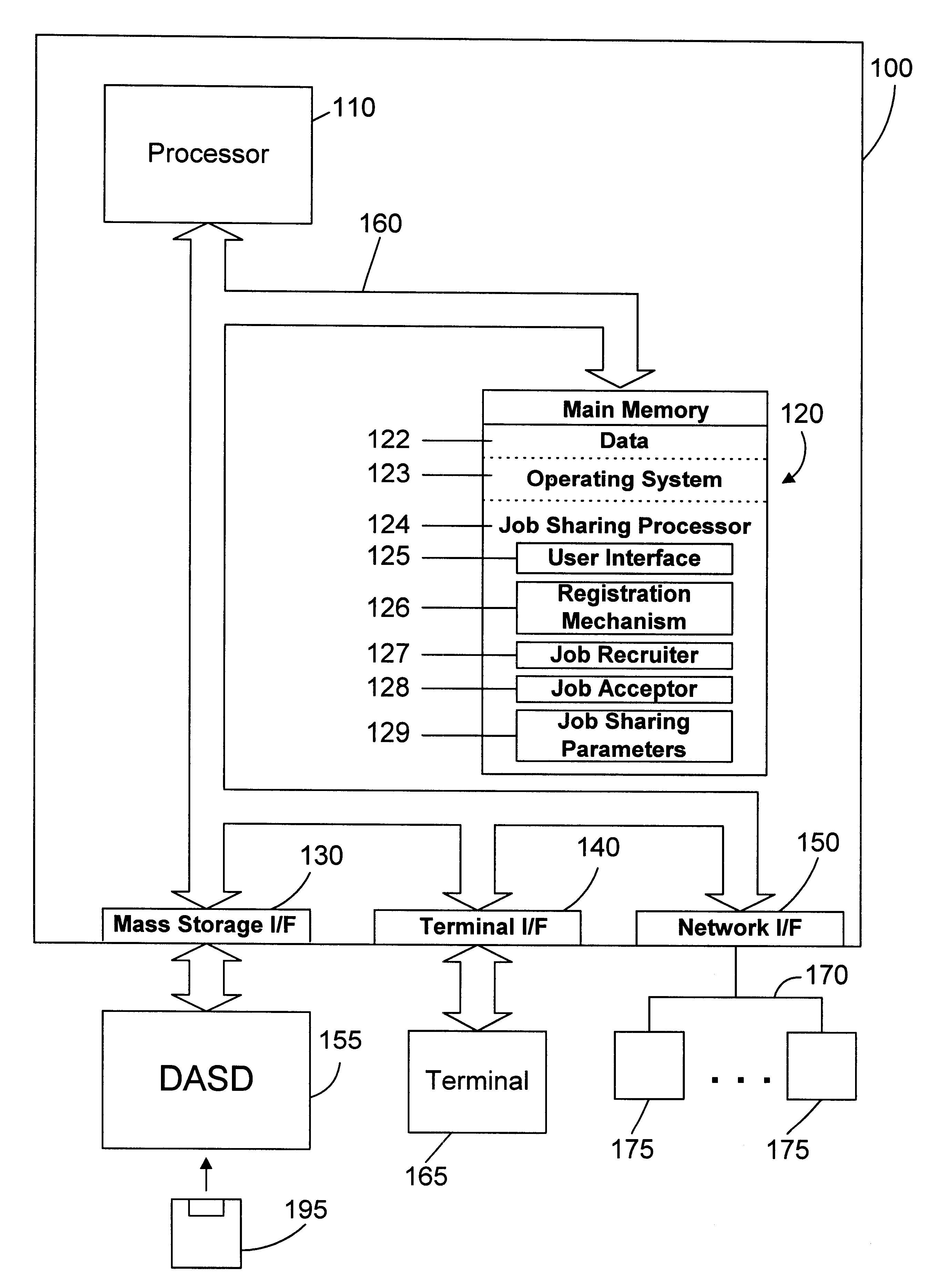
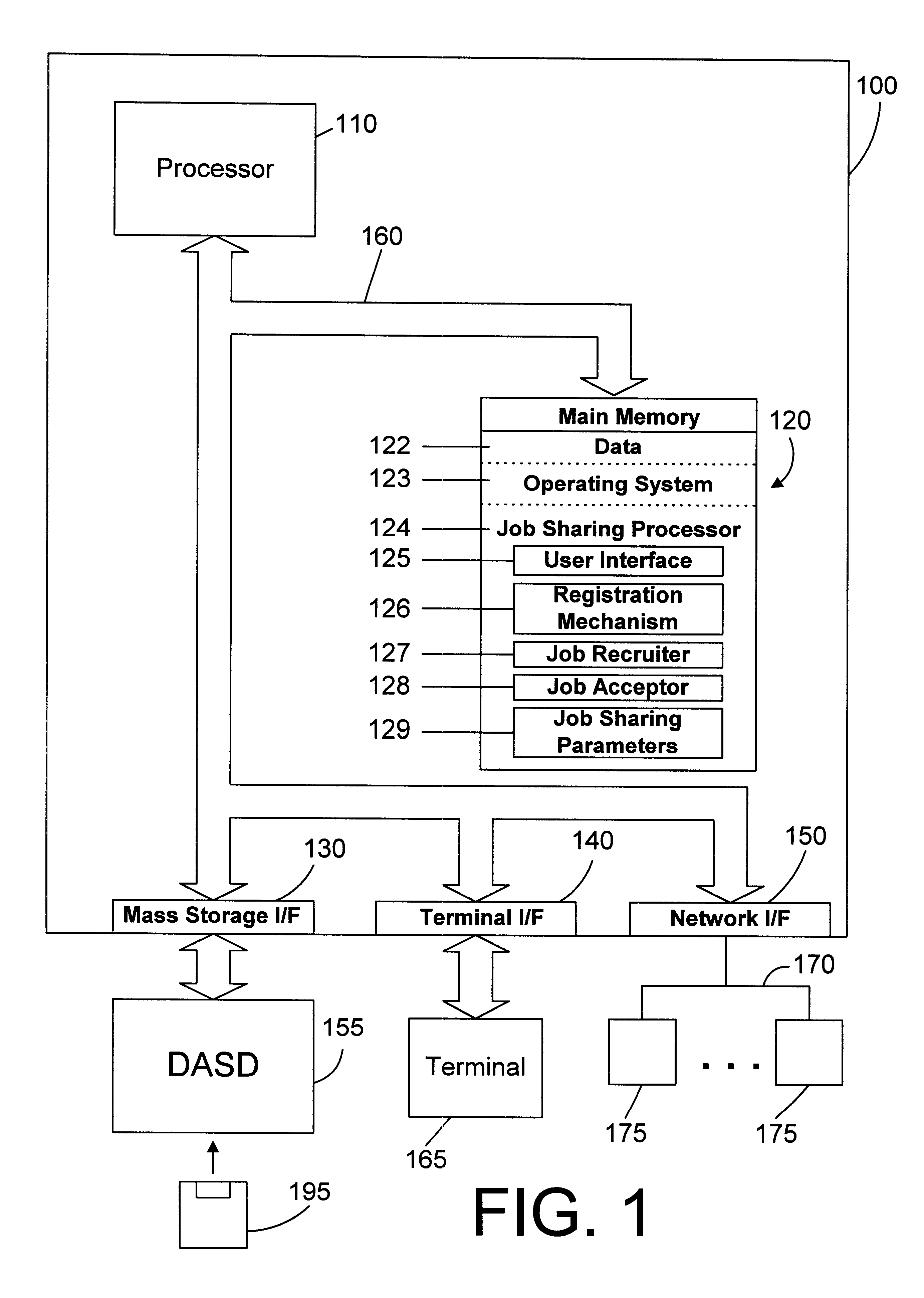
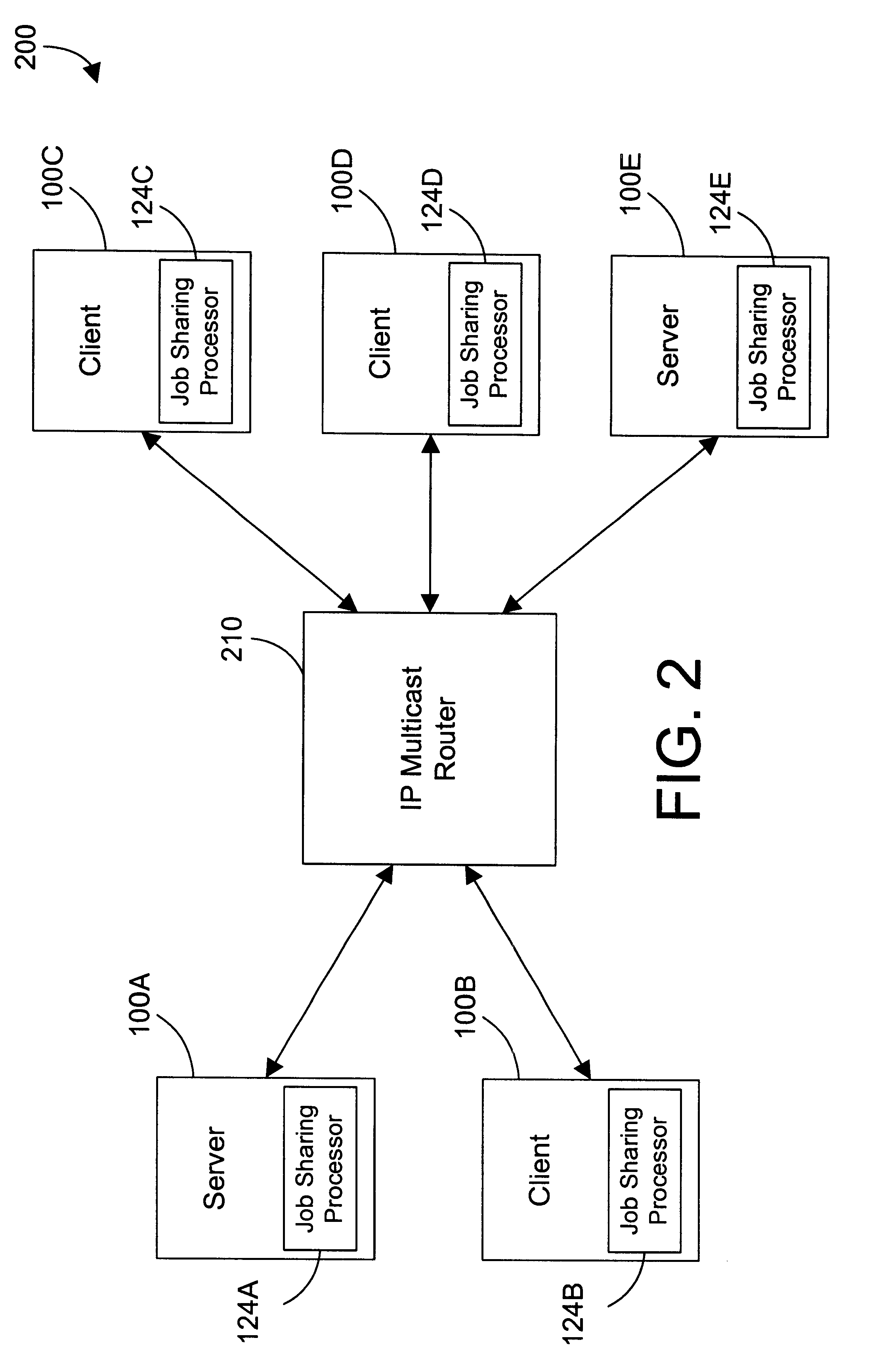
Computer system and method for sharing a job with other computers on a computer network using IP multicast
InactiveUS6356929B1Longer be performedReduce compilation timesMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsJob sharingIp address
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
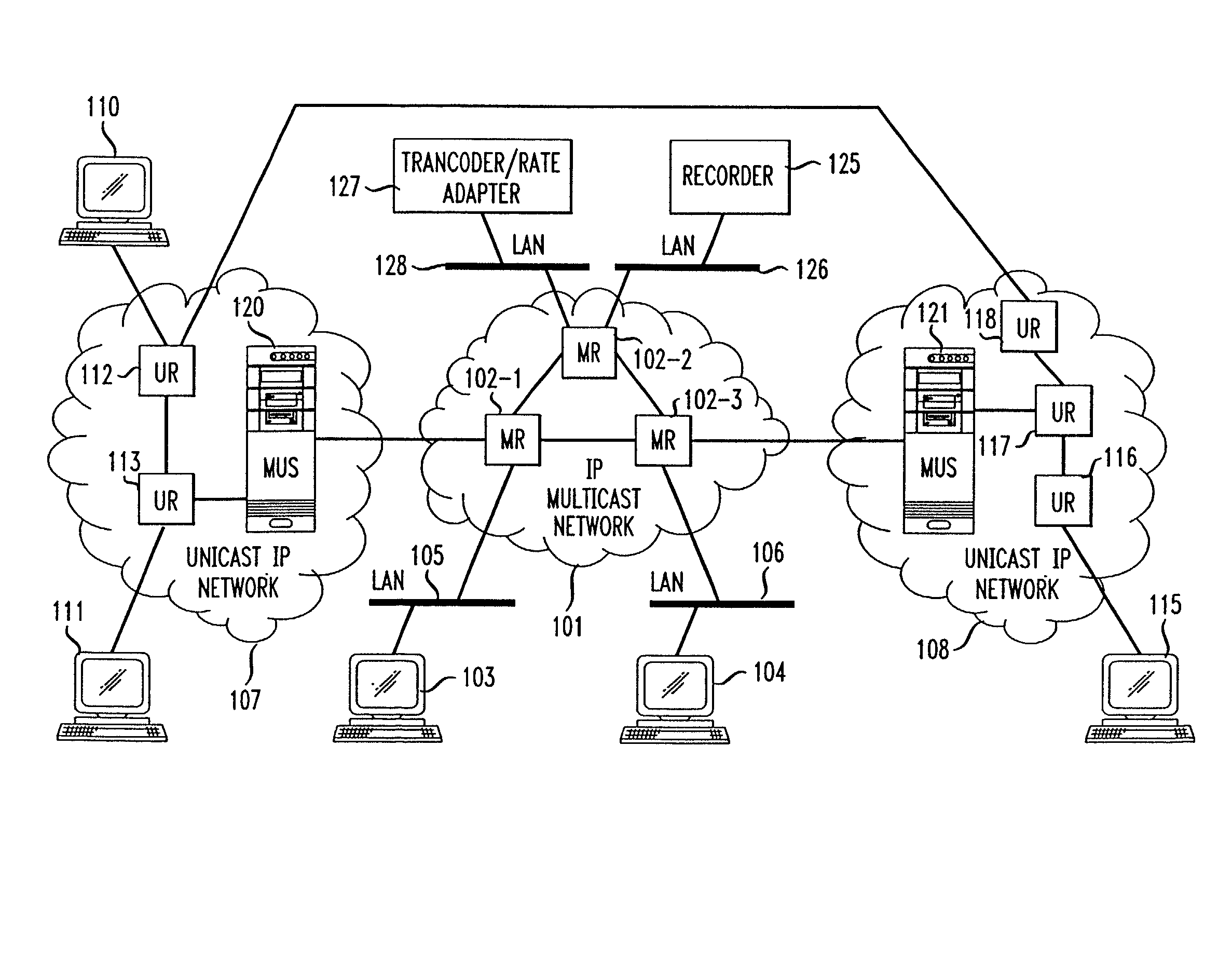
Method and system for a Unicast endpoint client to access a multicast internet protocol (IP) session
InactiveUS7031326B1Information obtainTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMedia typeNetwork packet
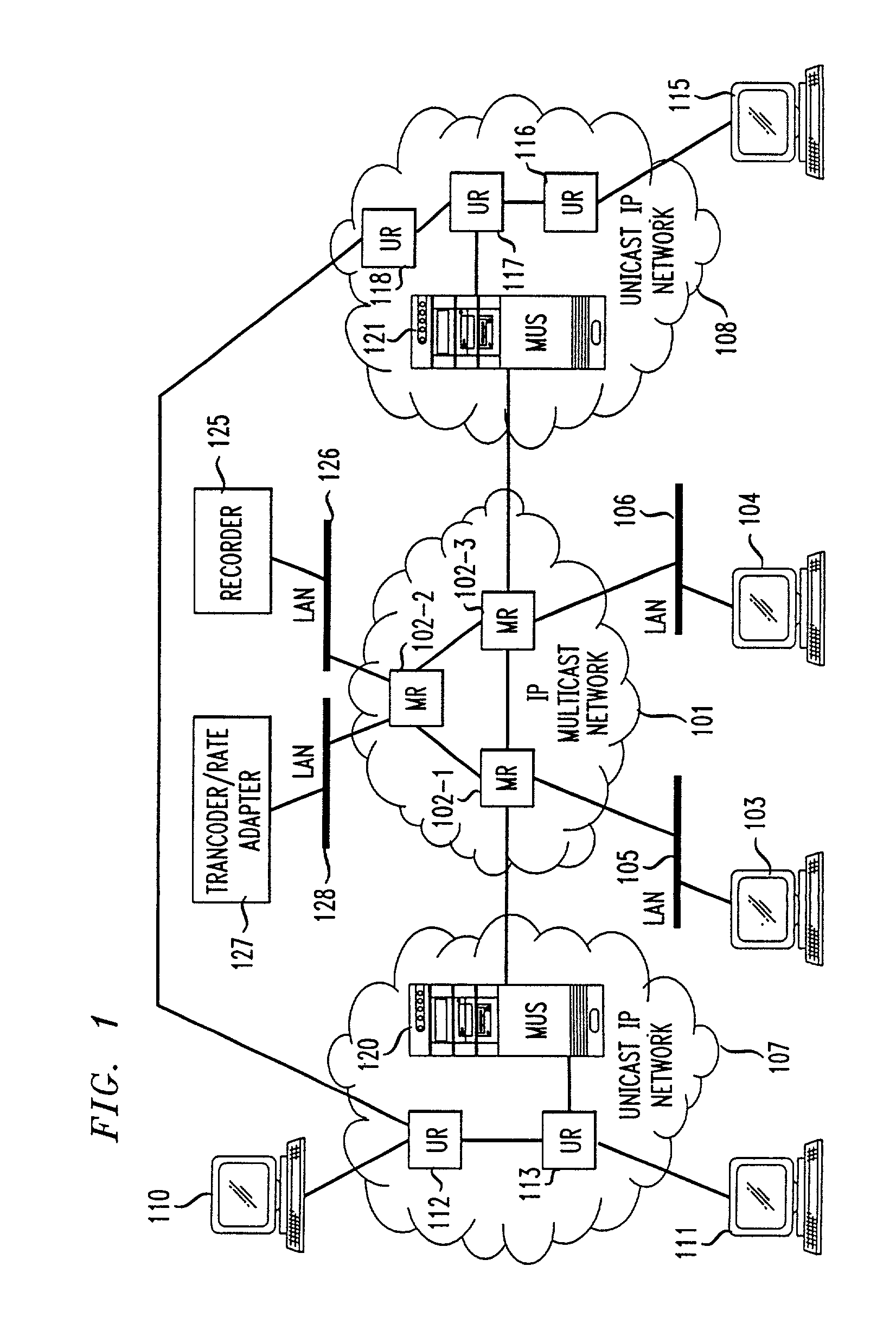
Unicast endpoint clients (110, 111, 115) on an IP Unicast network (107, 108) are provided access to Multicast sessions on an IP Multicast network (101) through a Multicast-Unicast gateway server (120, 121). The server obtains information about sessions on the Multicast network and makes such information available to a Unicast client on the Unicast network upon request by the client. Upon being presented with a list describing the subject matter of each session, the user at the Unicast client selects the session to which he or she wants to join, which causes the Multicast-Unicast server to join the appropriate session on behalf of the requesting client for each media type in which the joining client wants to be a participant. The server then sets a bi-directional Unicast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) stream between itself and the client. All packets then received by the server from the Unicast client are address-translated to the appropriate Multicast session address. In addition, all packets received by the server on the Multicast session address are address-translated and sent to the Unicast client. The Unicast client is then able to participate in the Multicast session as both a sender and a receiver of packets to and from other Unicast and Multicast clients which are active during the session. Further, the Unicast client is capable of creating a new session, recording a session in the network for later retrieval and playback, and creating and accessing low bandwidth versions of existing sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
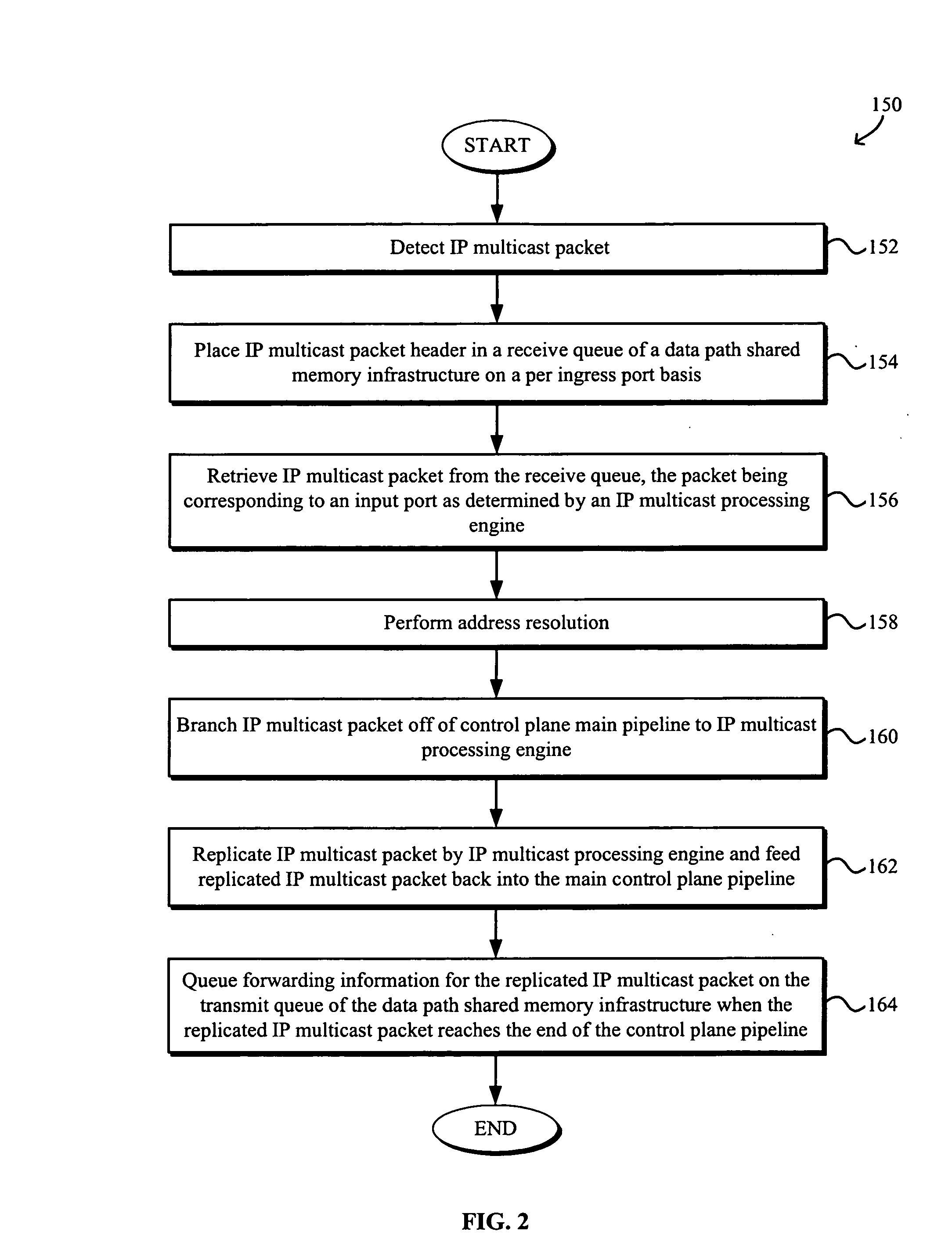
IP multicast packet burst absorption and multithreaded replication architecture
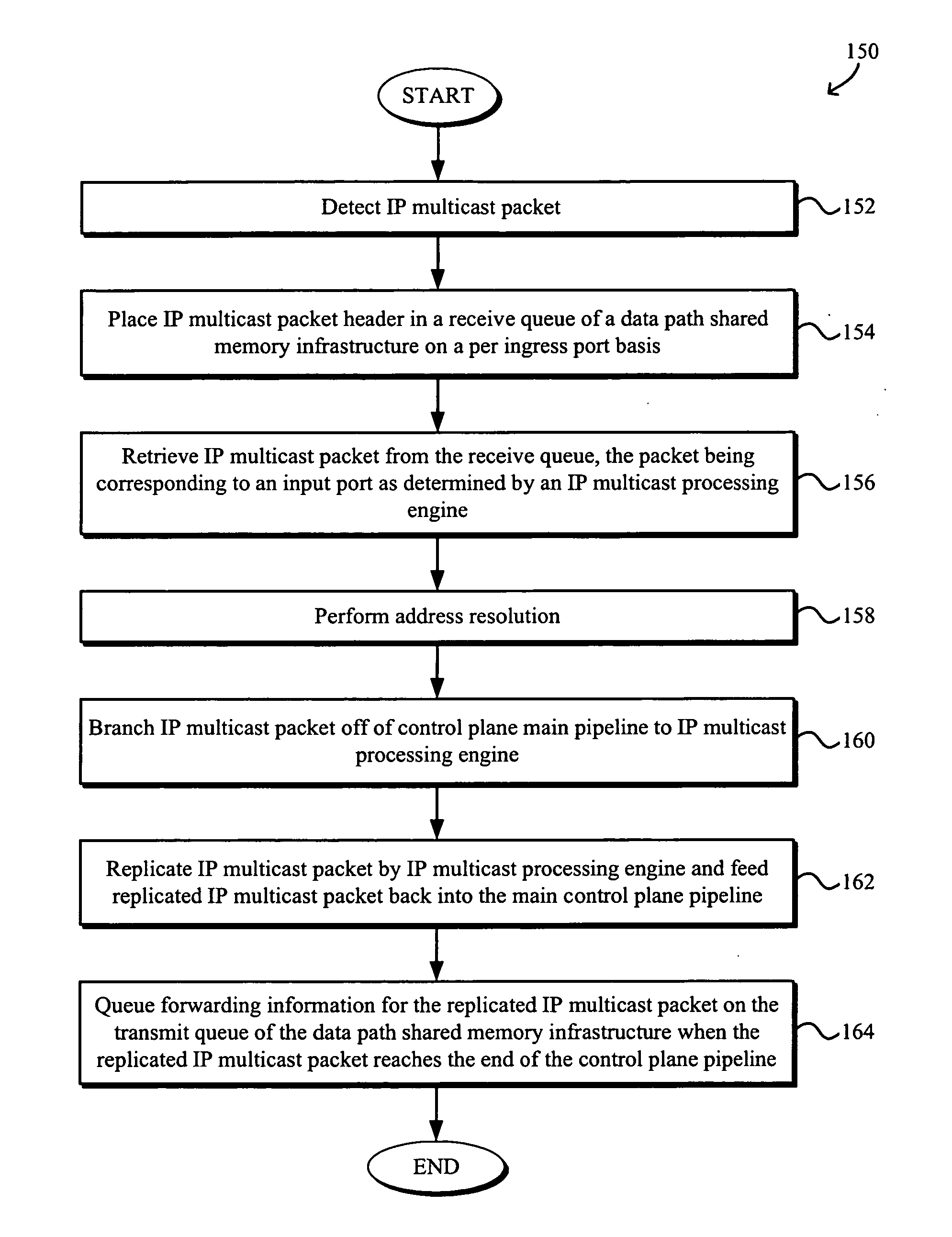
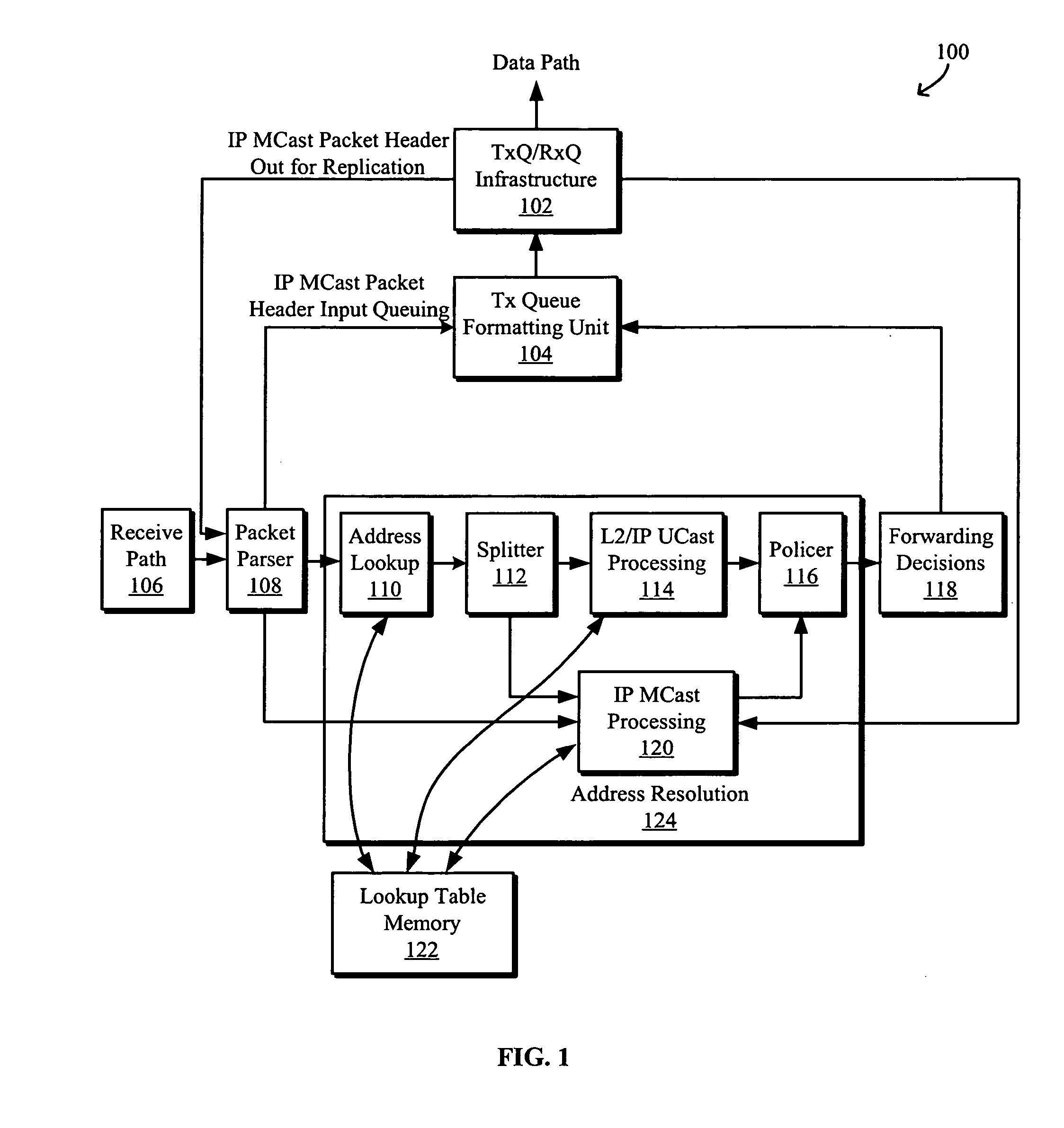
Systems and methods for IP multicast packet burst absorption and multithreaded replication architecture are disclosed. Replications of IP multicast packets are performed in a control plane of a network device. The network device may include a data plane for transmitting data between ingress and egress ports and a control plane including a shared transmit / receive queue infrastructure configured to queue incoming multicast packets to be replicated on a per ingress port basis and to queue transmit packets, and a multicast processing engine in communication with the shared queue infrastructure and including a circular replication buffer to facilitate multithreaded replication of multicast packets on a per egress virtual local area network (VLAN) replication basis. The shared transmit / receive queue infrastructure may dynamically allocate memory between the transmit and receive multicast queues.
Owner:INTEL CORP
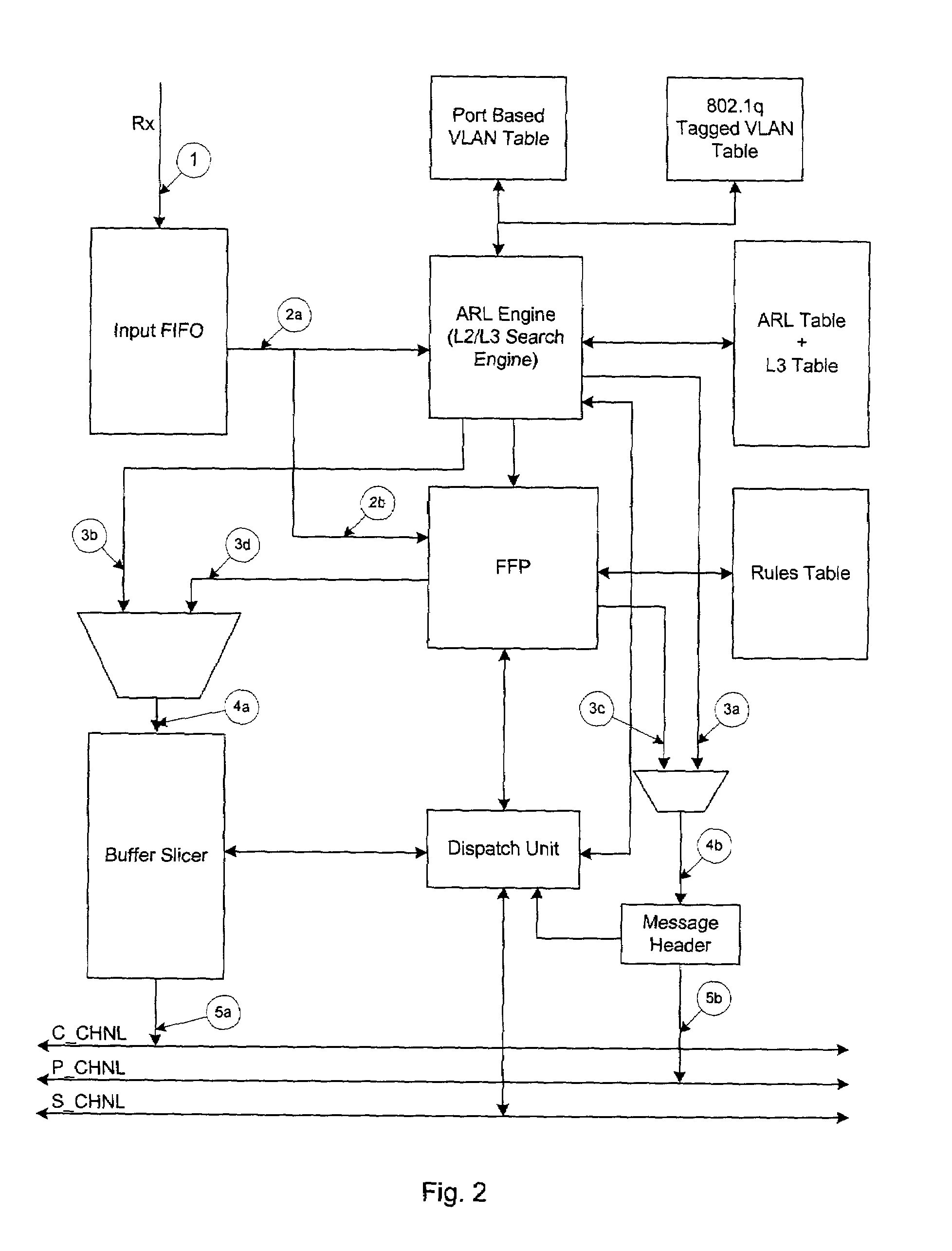
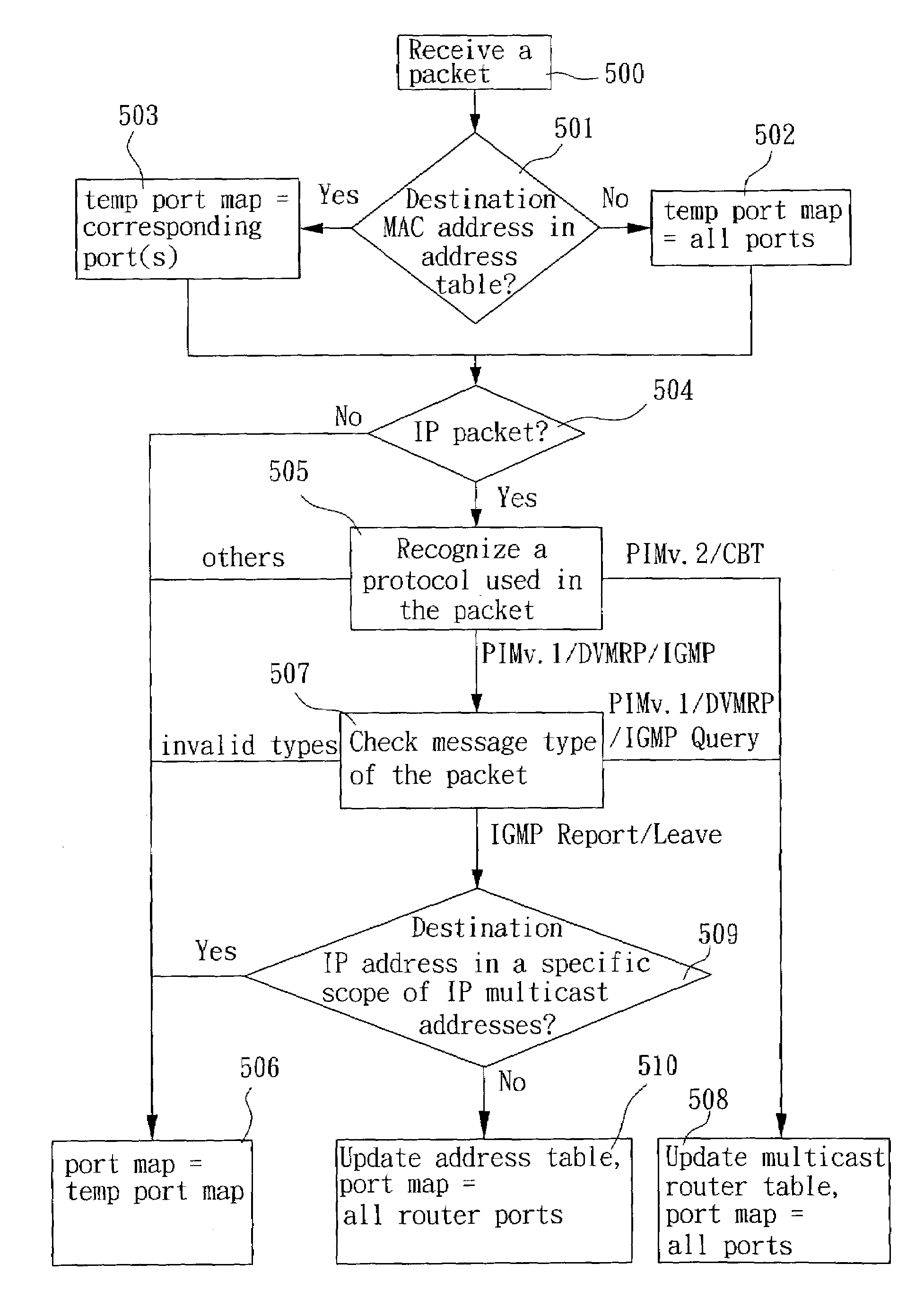
Method and apparatus for packet forwarding in a switch controller
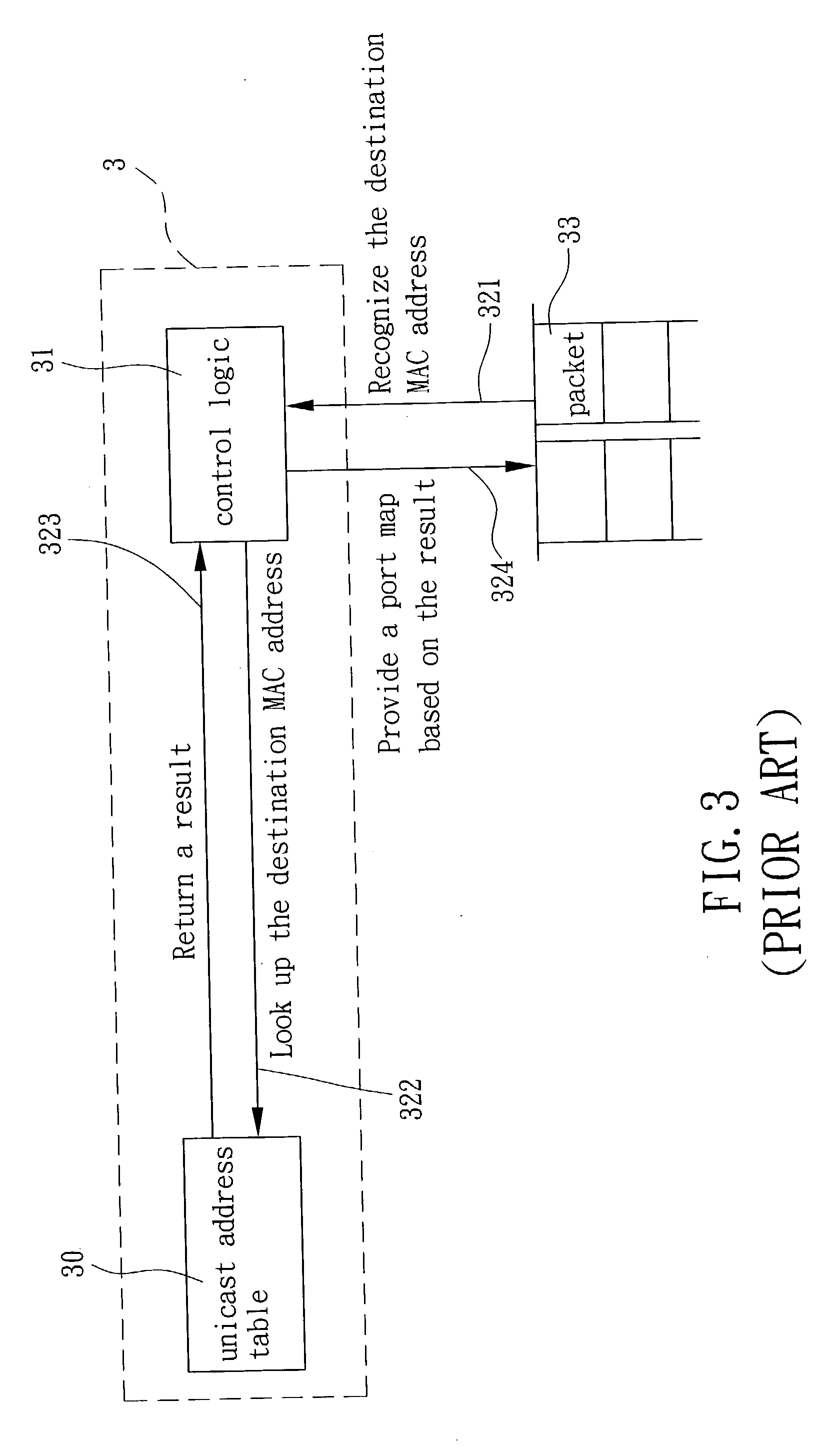
ActiveUS7333491B2Simplify complexityLow costStore-and-forward switching systemsNetworks interconnectionIP multicastMulticast address
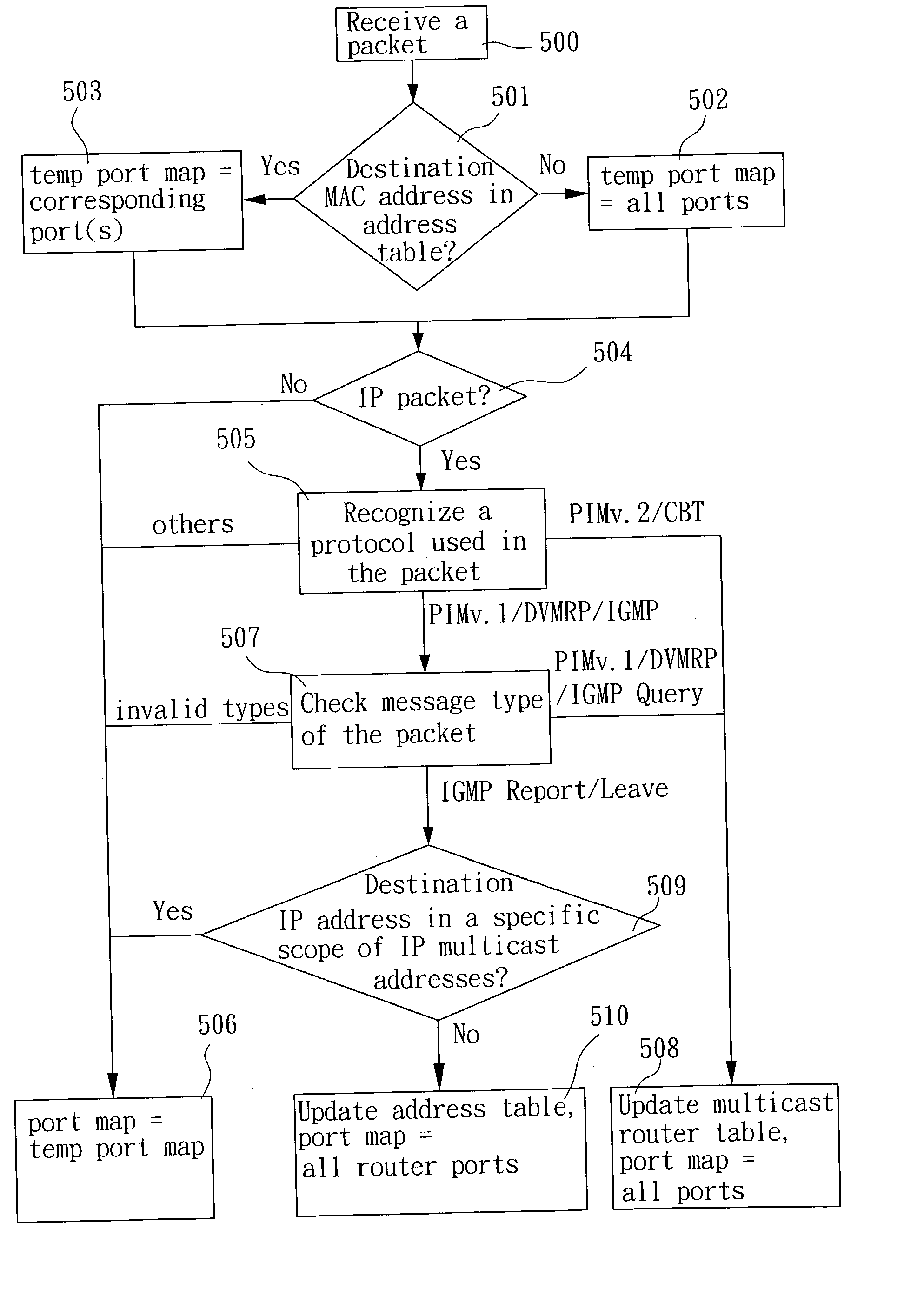
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for packet forwarding within a switch controller. In addition to unicast and broadcast forwarding, the method and apparatus can also analyze and forward IP multicast packets without the need of a CPU and a separate multicast address table, thereby enabling IP multicasting for the switch controller. Wherein, specific packet parsing and updating rules are used to analyze IP multicast control packets, and a multicast router or an address table is updated based on the analyzing result. IP multicast packets is then forwarded according to the updated tables. Moreover, with an extra flag bit set in each address table entry, unicast and multicast forwarding can share the same address table.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method to support multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks
A system and method for supporting multicast in highly dynamic wireless multi-hop networks, such as ad-hoc networks, with good scalability. The system and method provide a multicast routing algorithm to work in wireless ad-hoc networks without any fixed infrastructure nodes present. In doing so, the system and method provide a technique to build a multicast source specific tree on demand, while using a core source node to limit routing overhead. The system and method further provide a repair process to reduce the latency of discovery of topology change, employ a node sequence number mechanism to differentiate between upstream nodes and downstream nodes on the multicast tree in the repair process, and provide an active joining process to reduce the latency of discovery of membership change.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
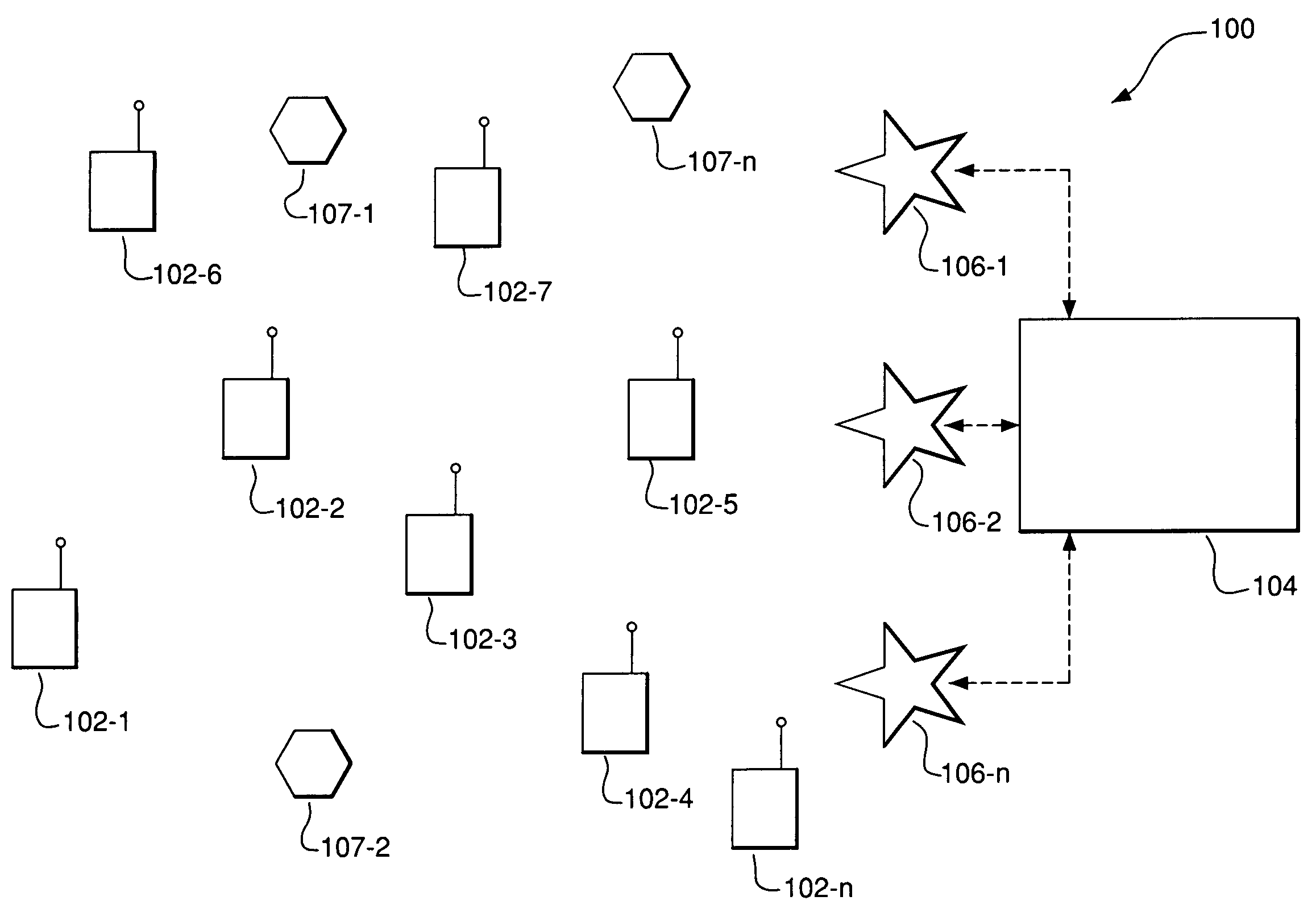
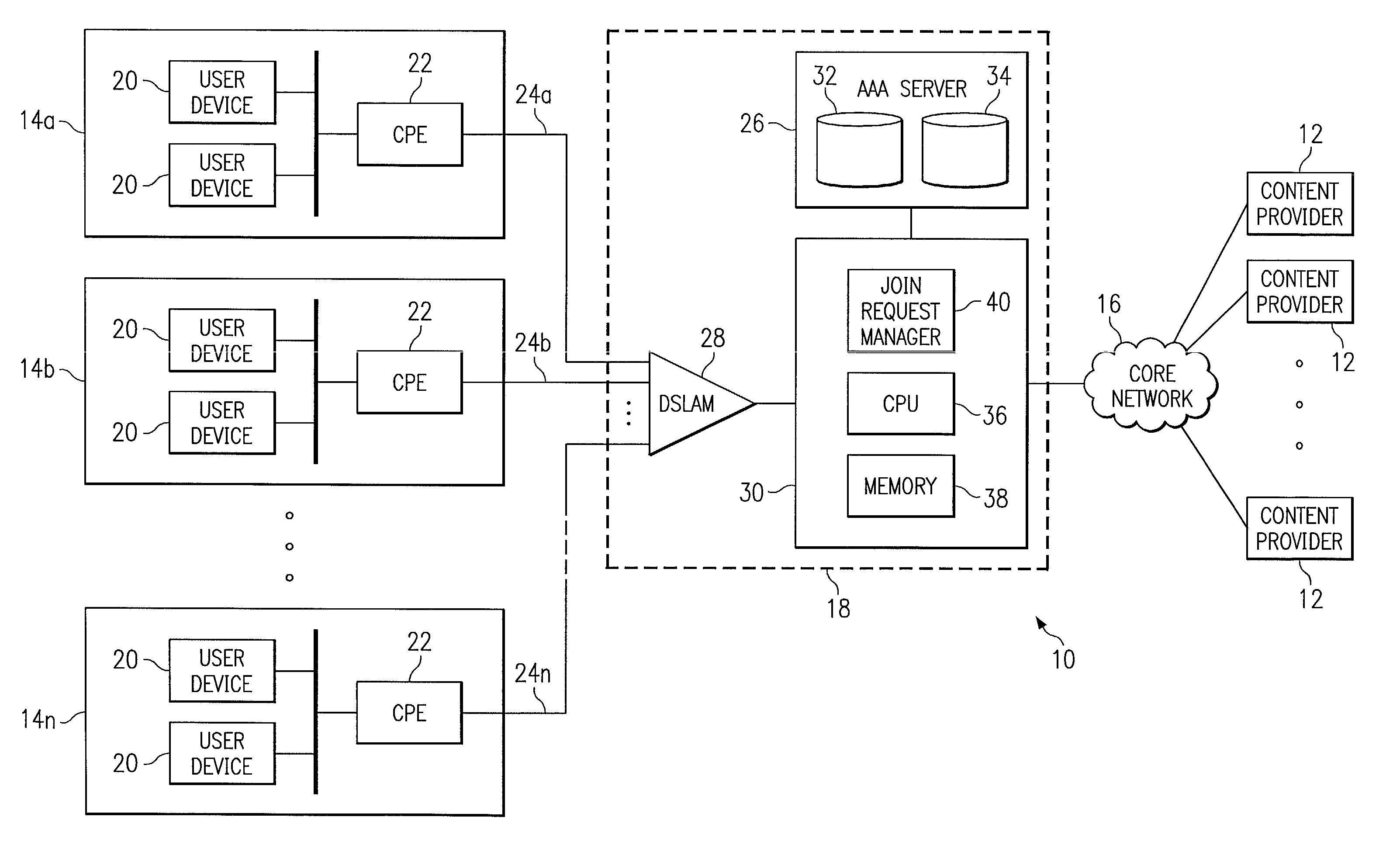
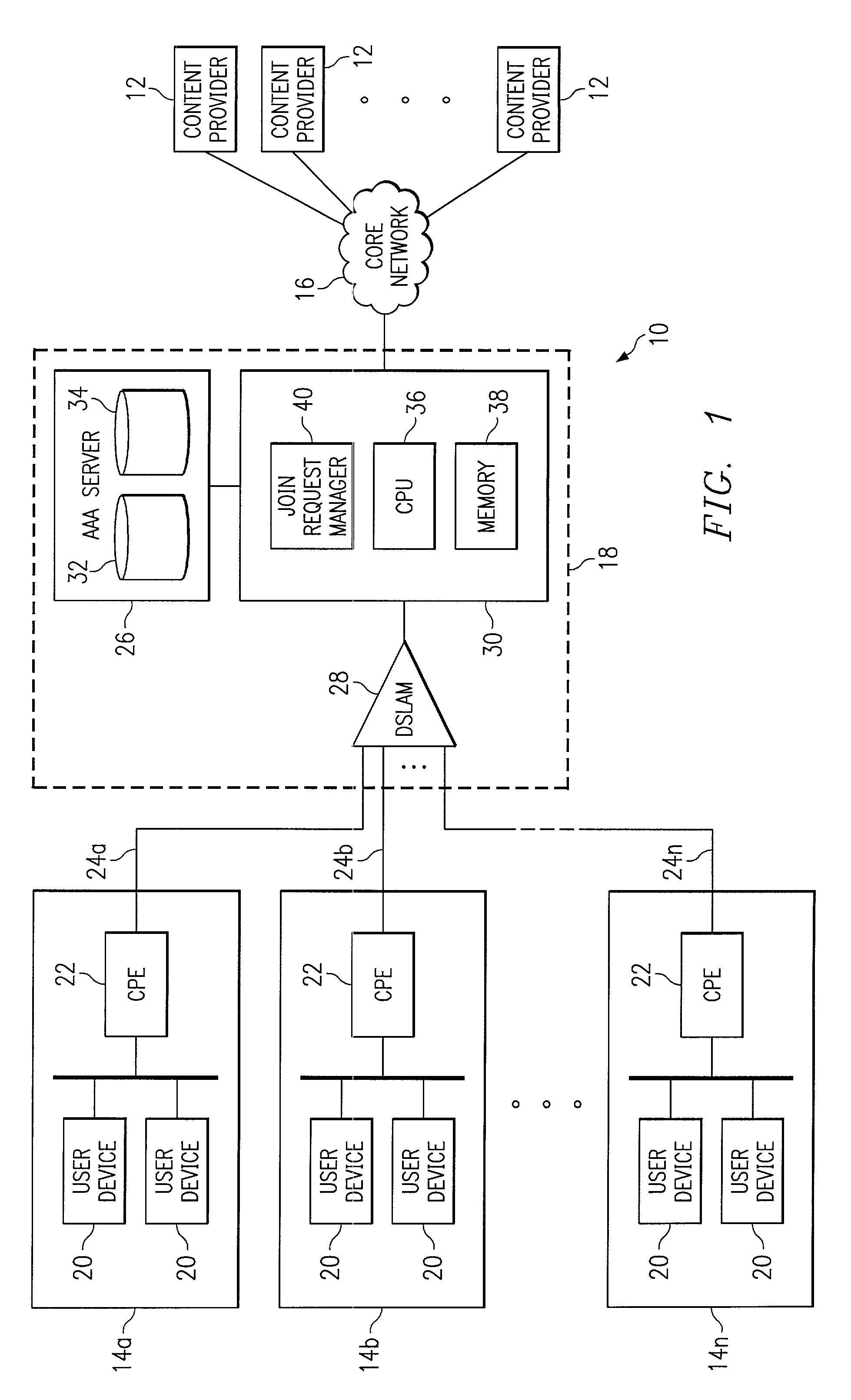
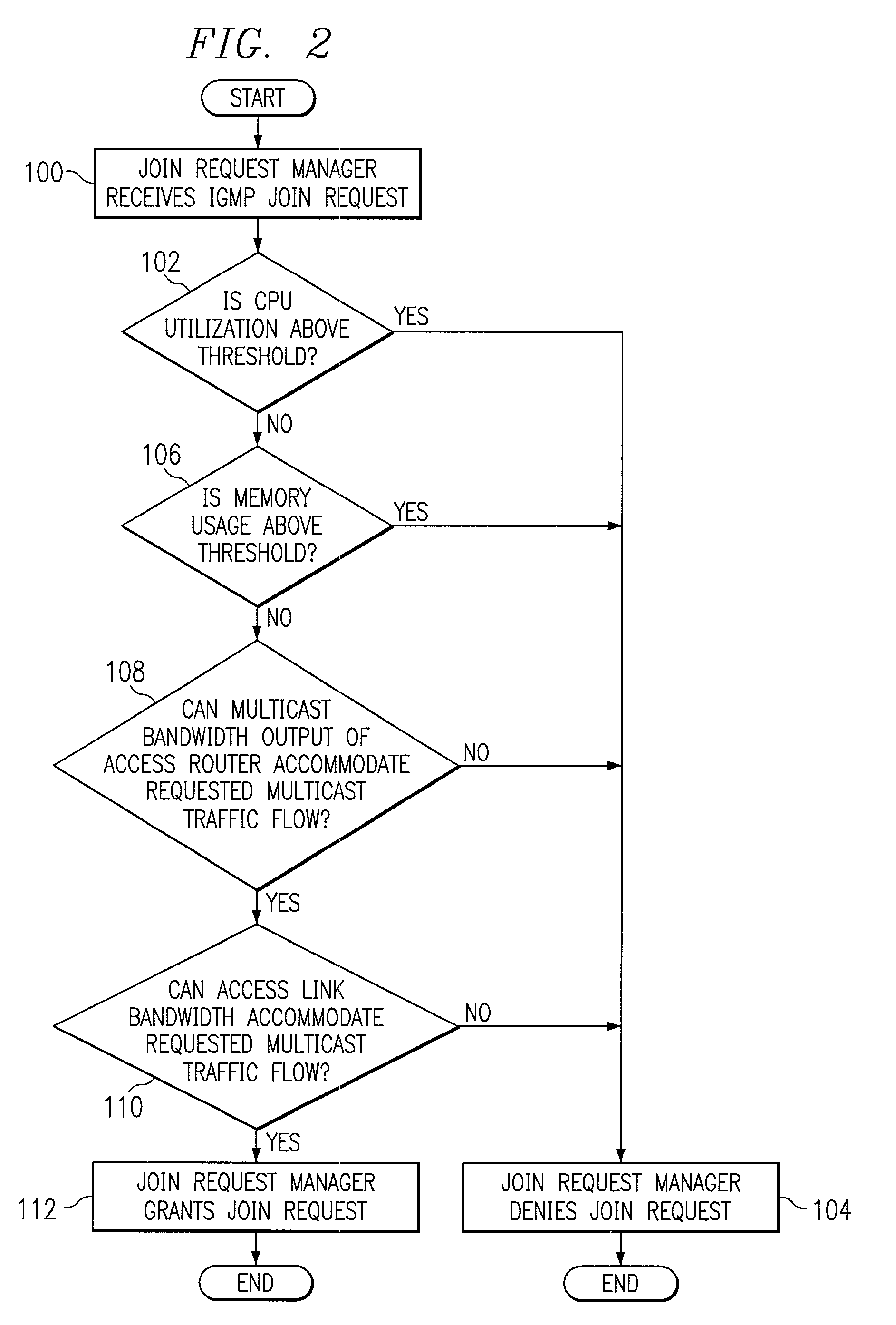
Managing access to internet protocol (IP) multicast traffic
InactiveUS7245614B1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedProblems reduced eliminatedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityUser device
A system for managing access to IP multicast traffic includes a join request manager within an access router. The access router includes a central processing unit (CPU) and a memory unit. The access router replicates multicast traffic flows for communication to one or more user devices within user systems coupled to the access router using a link. The join request manager receives a request to receive a multicast traffic flow, the request being received from one of the user devices within one of the user systems, and denies the request if a system metric is above a threshold.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and systems for automatic device provisioning in an RFID network using IP multicast
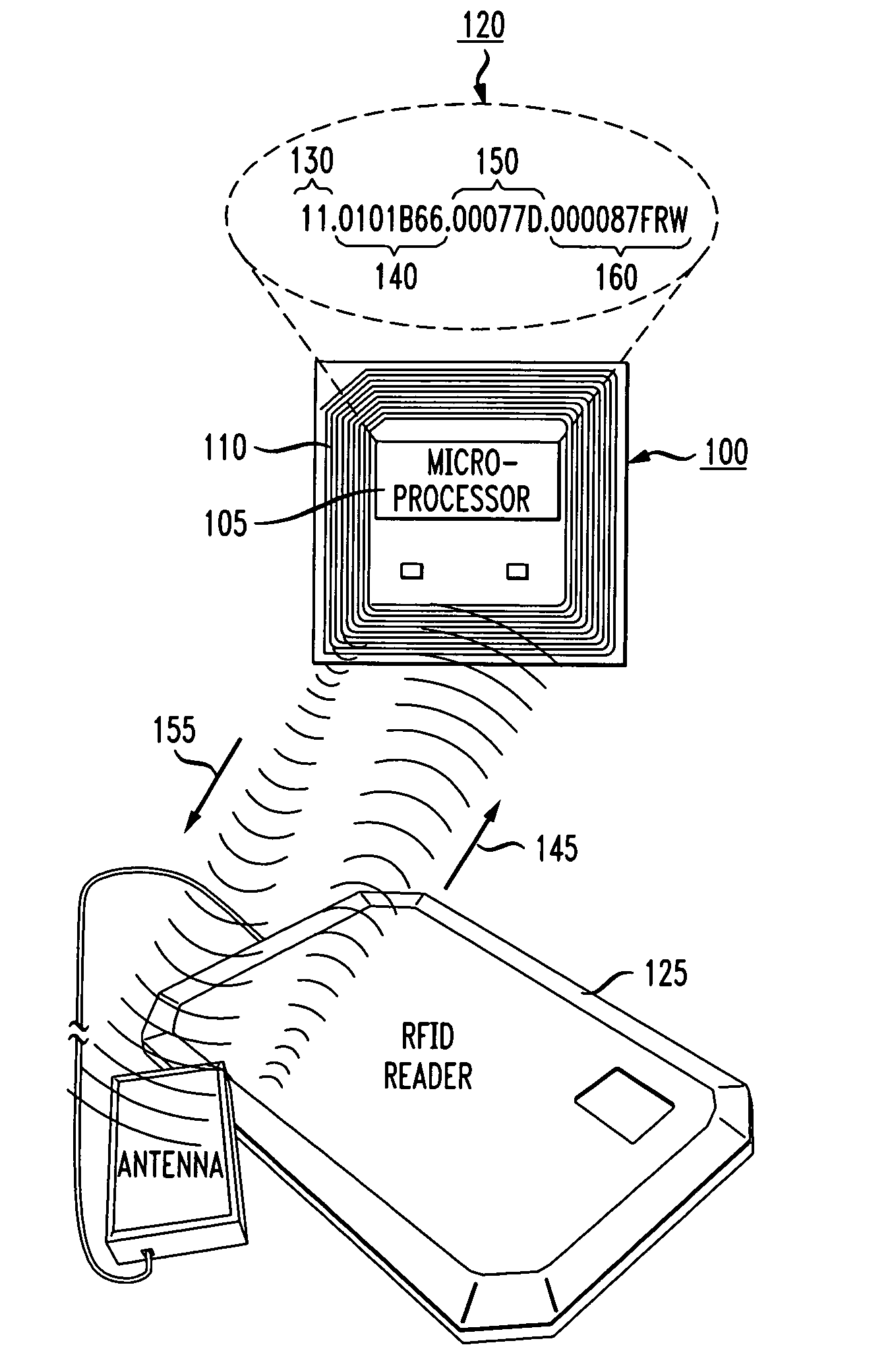
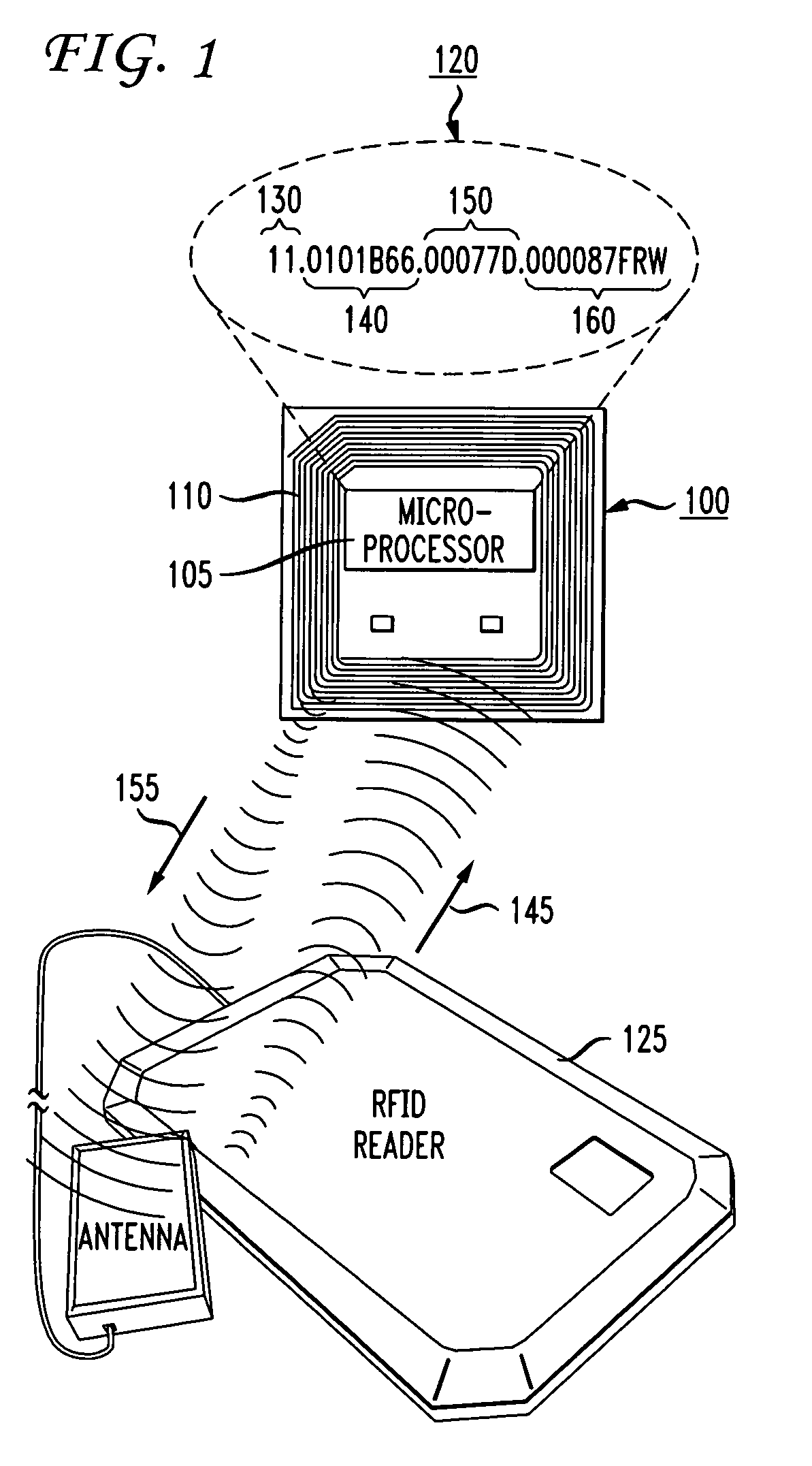
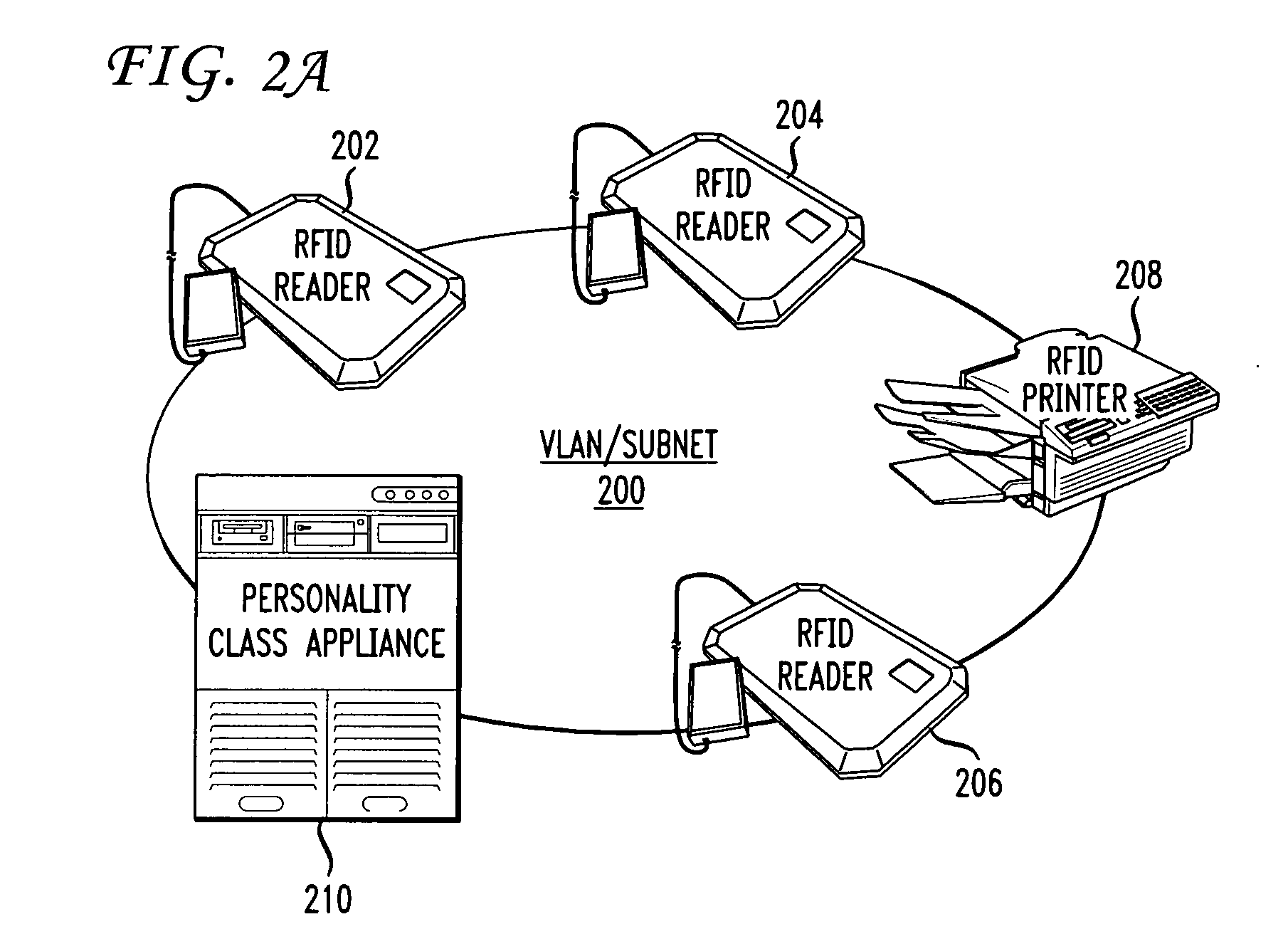
ActiveUS20070109100A1Filter being usedCircuit arrangementsSensing record carriersComputer hardwareAuto-configuration
Methods and systems for automatic provisioning of RFID devices in an RFID network are described. A device, such as a Reader, has within its read field a special EPC Identity (ID) Tag that is specifically encoded for that Reader. When the Reader boots up, it reads the special ID Tag. The Tag has fields formatted according to the EPCglobal standards and certain bits within one of the fields indicates that the Tag is an EPC ID Tag and the data contained in the Tag will be used to provision the Reader. The Reader transmits an IP multicast packet containing data from the Tag to a network device referred to as a personality class appliance which receives the IP multicast packet. Thus, the Reader is an IP multicast sender and the appliance is an IP multicast receiver. Upon receiving the packet, the appliance retrieves configuration parameters for the Reader. These parameters collectively make up a personality class for the Reader. The personality data are transmitted back to the Reader via a unicast message. Once the Reader receives the configuration data, it provisions itself, becomes connected to the RFID network, and is ready for operation. RFID Readers and other devices can be provisioned automatically for a specific role when turned on, without requiring any manual configuration or data entry.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Co-existing static and dynamic IP multicast
InactiveUS20060262792A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAccess timeIp address
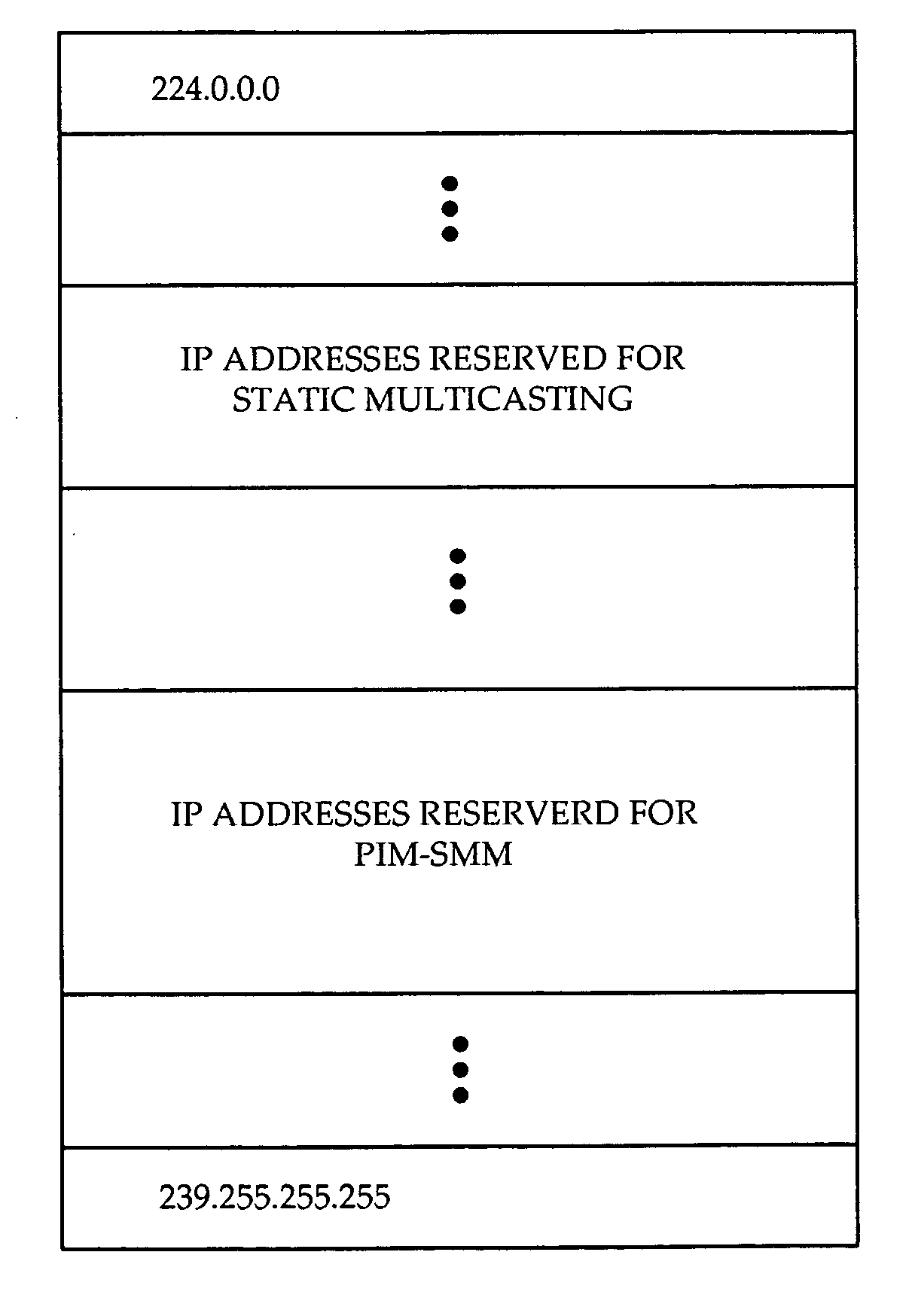
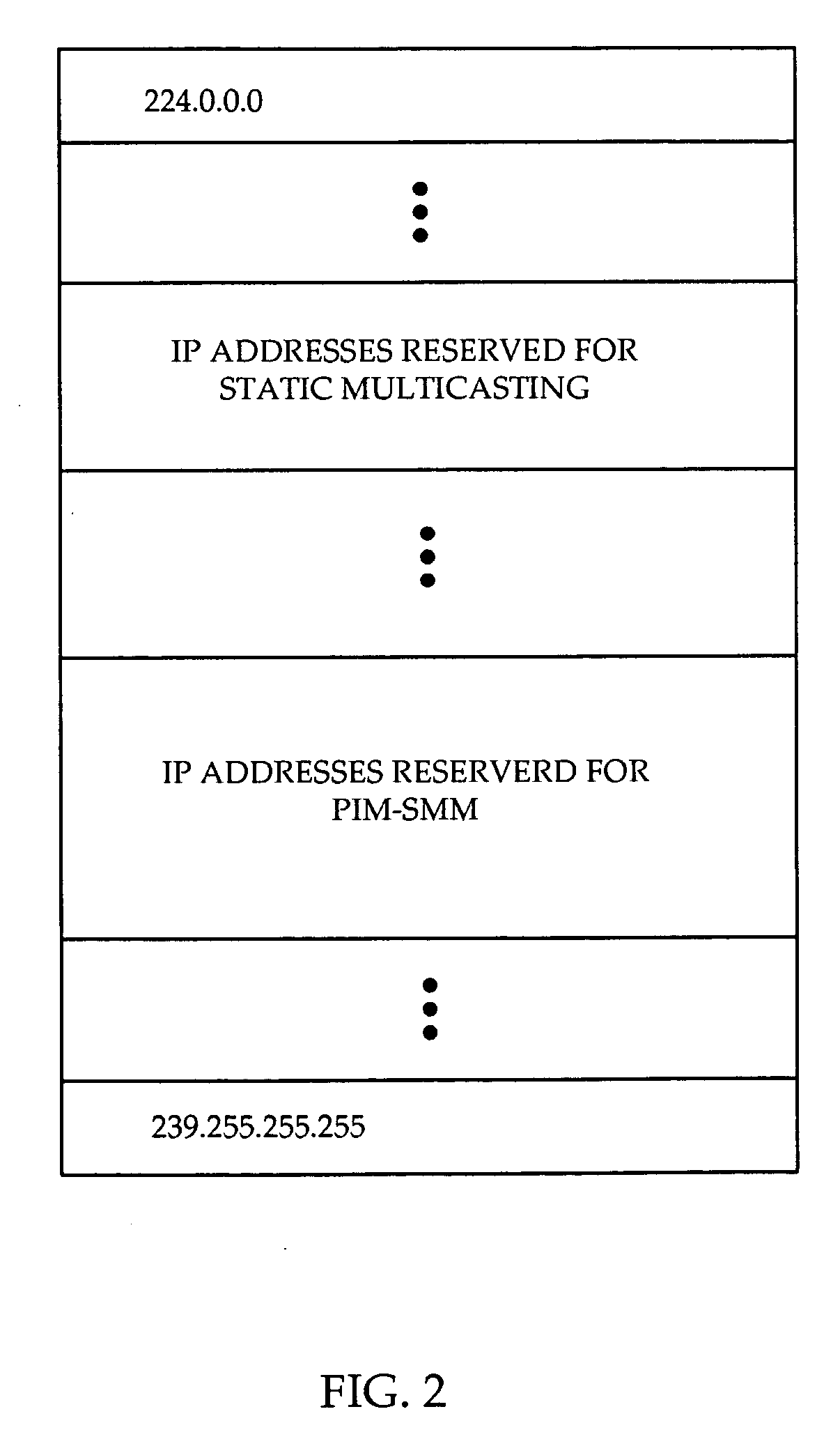
A system and method are provided for providing both static and dynamic IP multicasting. The concept of a multicast Static-Range is introduced which allows the coexistence of static and dynamic IP multicast. The multicast Static-Range is a set of Class D IP addresses which is reserved for static multicasting, and is configured at all routers. When a router receives a PIM message or an IGMP message, the router determines whether the group specified in the message is within the multicast Static-Range. If the group pertains to a static multicasting group, the router does not propagate the message to upstream routers using PIM-SM or PIM-SSM protocols, and only connects or disconnects interfaces internal to the router. If the multicast group address in the message is not within the multicast Static-Range, the router recognizes that the message pertains to a dynamic multicasting group and implements PIM or IGMP protocols as usual. If the invention is used for broadcasting TV, the low end of TB channels or commonly used channels can be created as static IP multicast. This way, a user can access or leave such channels without an entire shortest path tree being created or torn down, improving access time and channel surfing for a user. Also, pay-per-view, digital or less frequently used channels can be created using dynamic IP multicast with traditional PIM-SSM protocol, in order to make efficient use of router resources.
Owner:RPX CORP
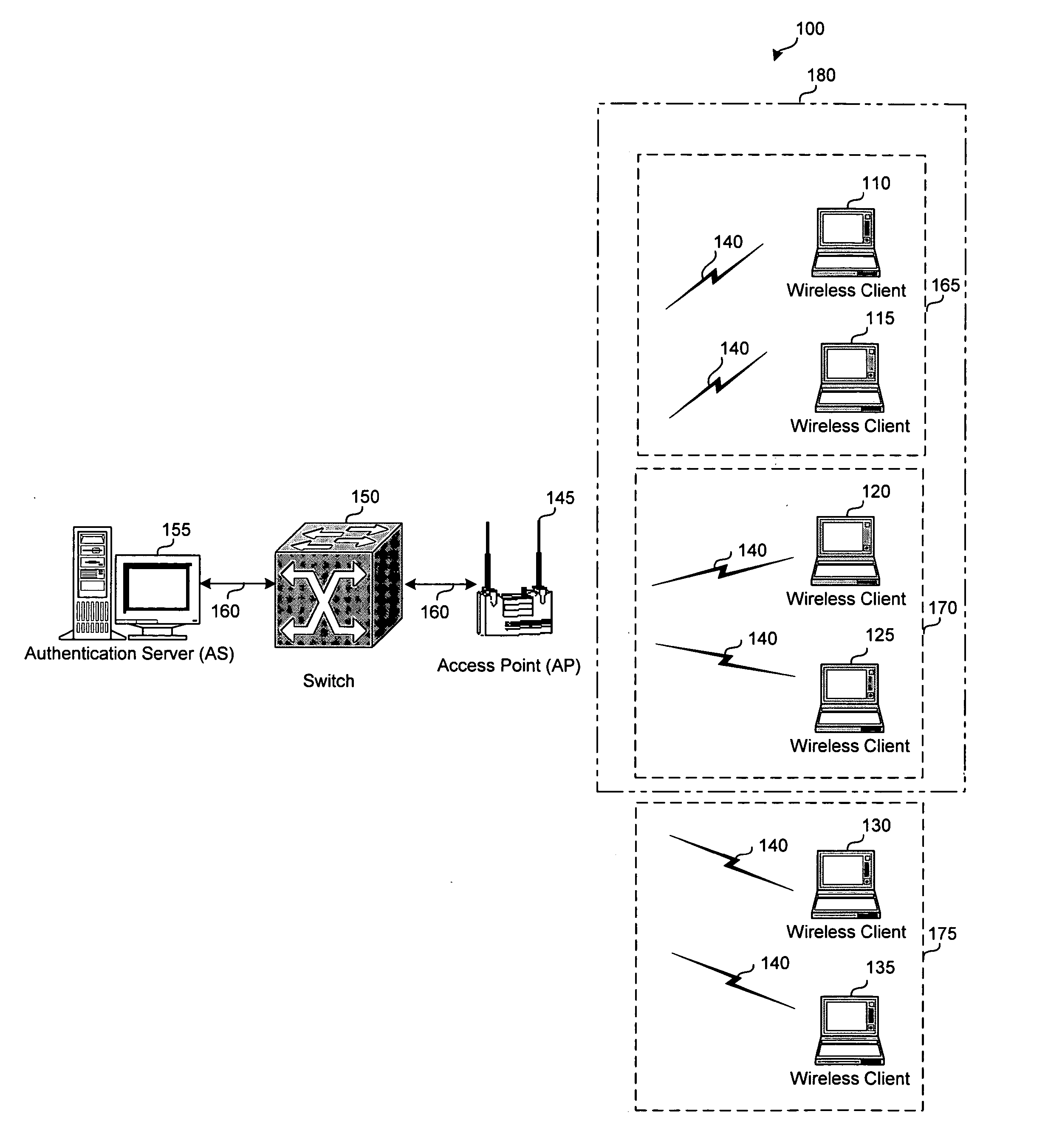
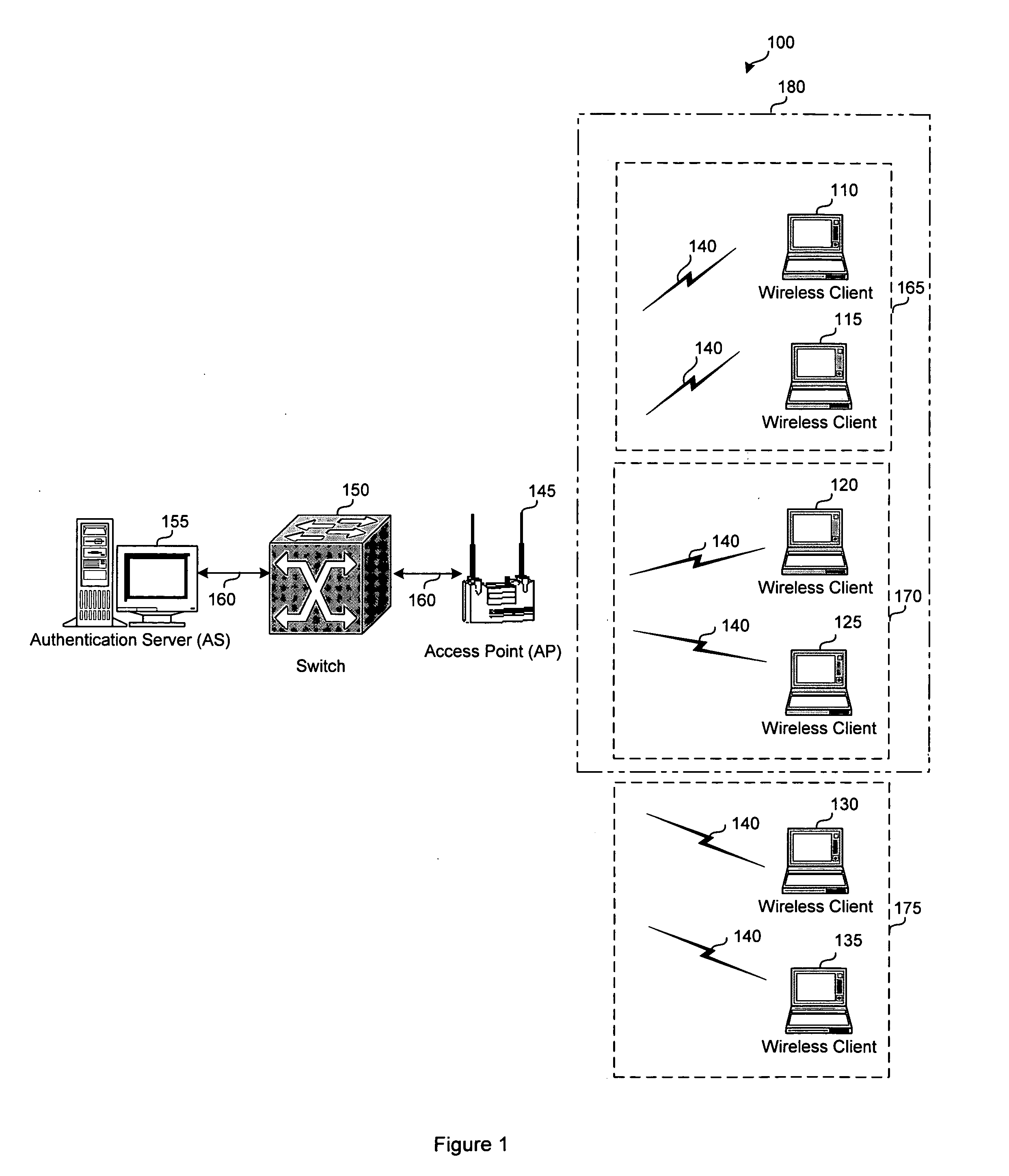
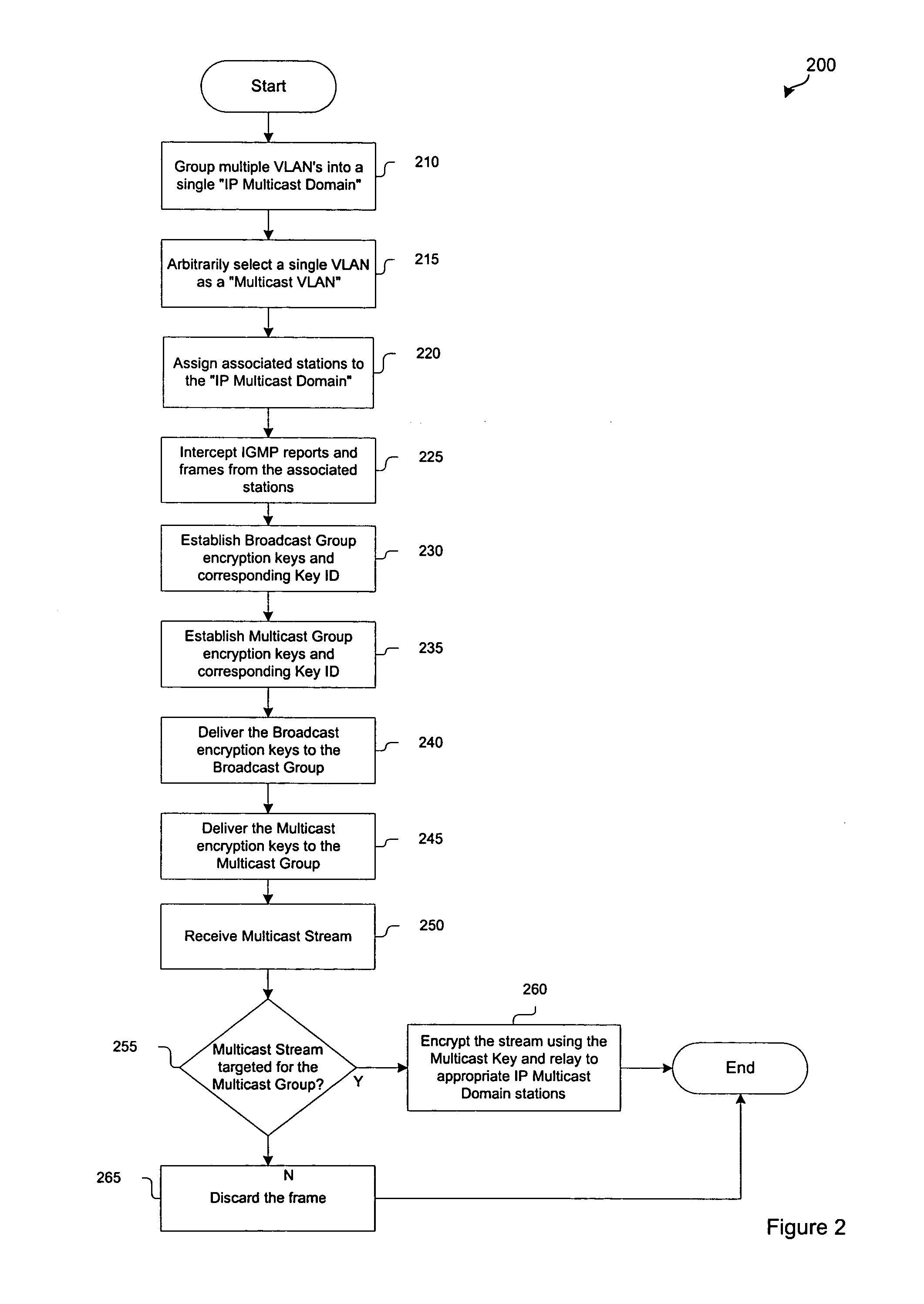
System and method for grouping multiple VLANs into a single 802.11 IP multicast domain
ActiveUS20050025160A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionVirtual LANIP multicast
A system and method for identifying and grouping multiple virtual local area networks into a single multicast domain is provided. The system and method may be configured to designate a virtual local area network within as a multicast virtual local area network to streamline the delivery of multicast messages via a network. A station may be configured with multiple group keys so that it can receive messages from multiple broadcast or multicast domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
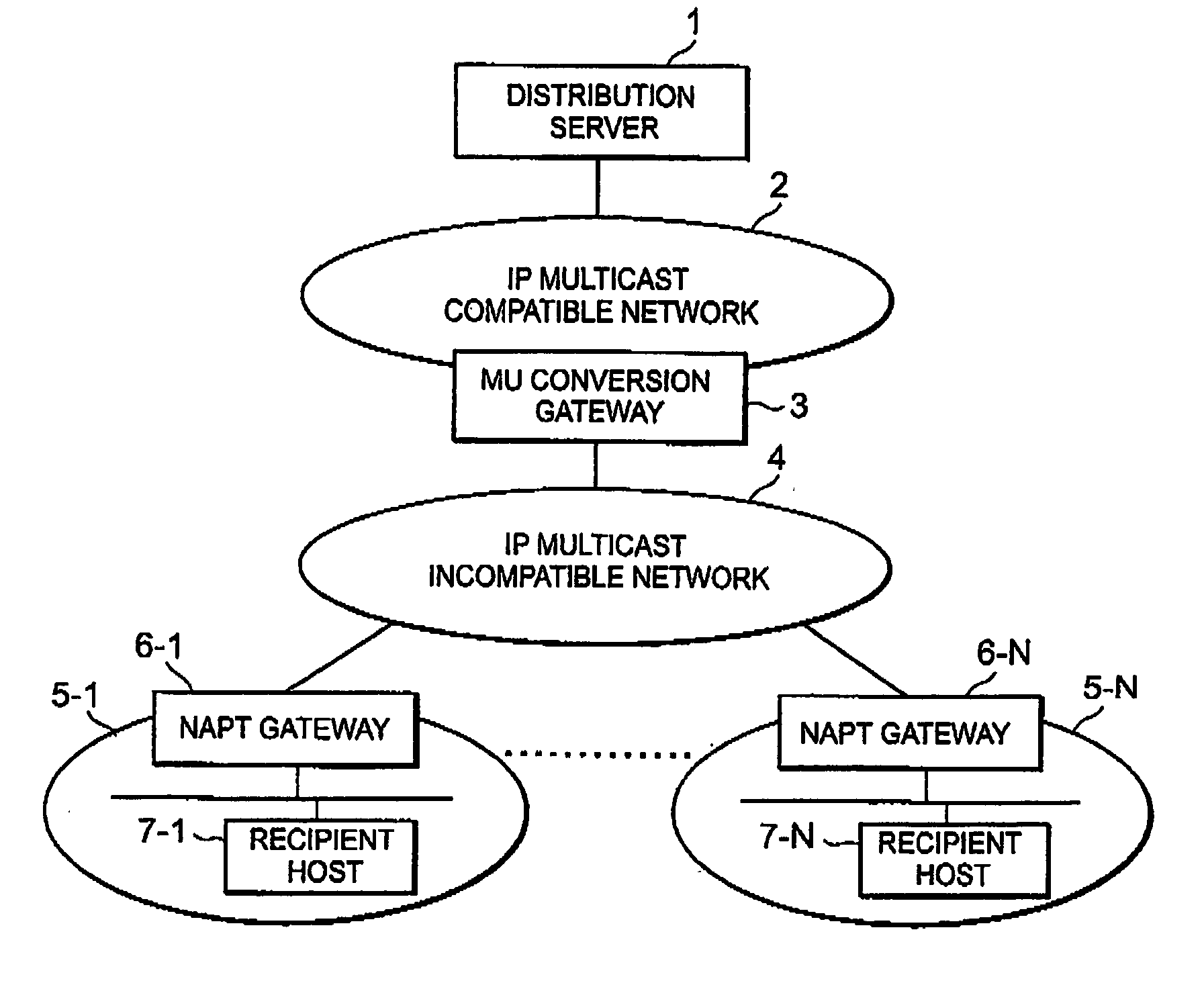
IP multicast distribution system, streaming data distribution system and program therefor
InactiveUS20050002395A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexStreaming dataData pack
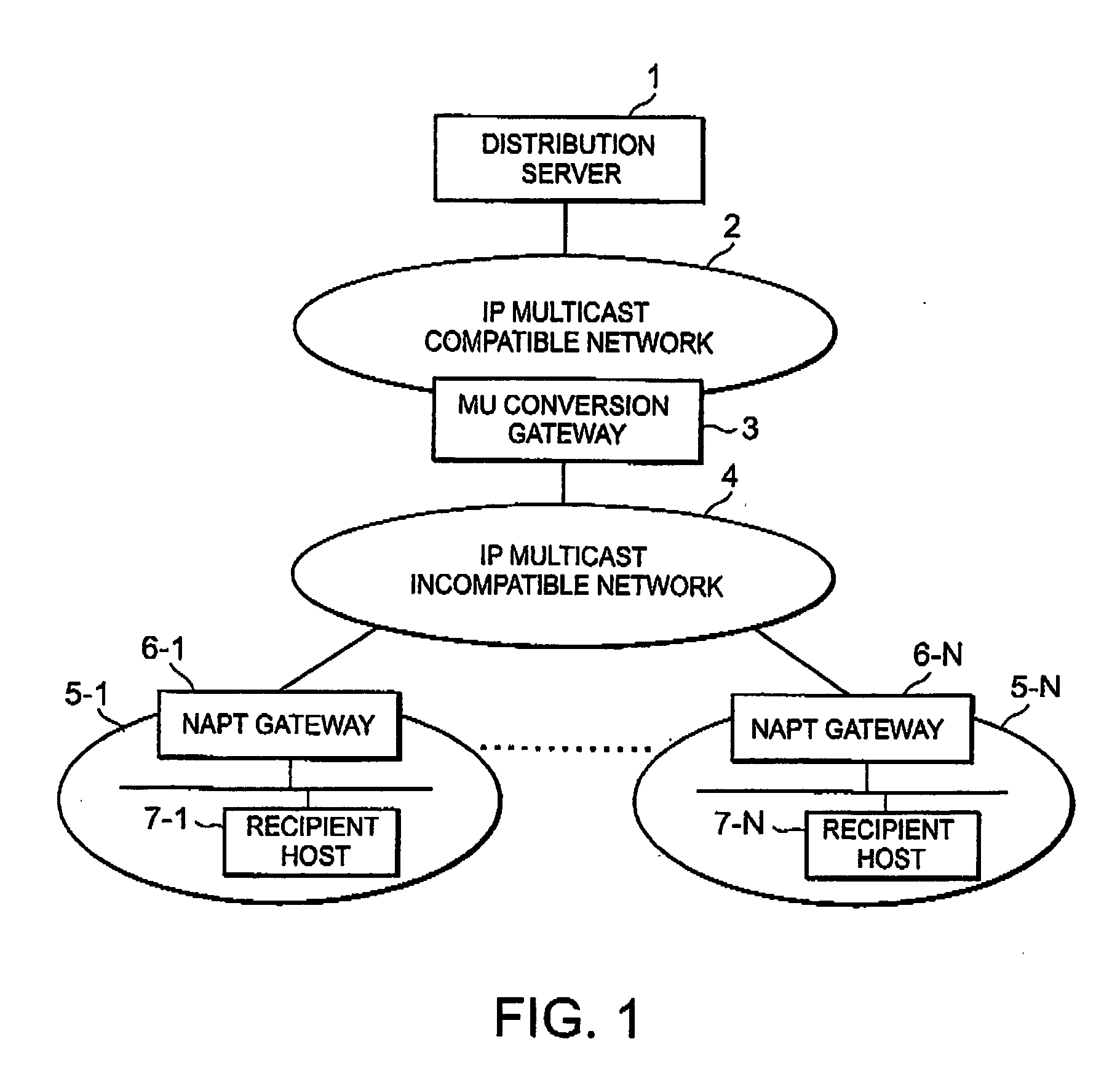
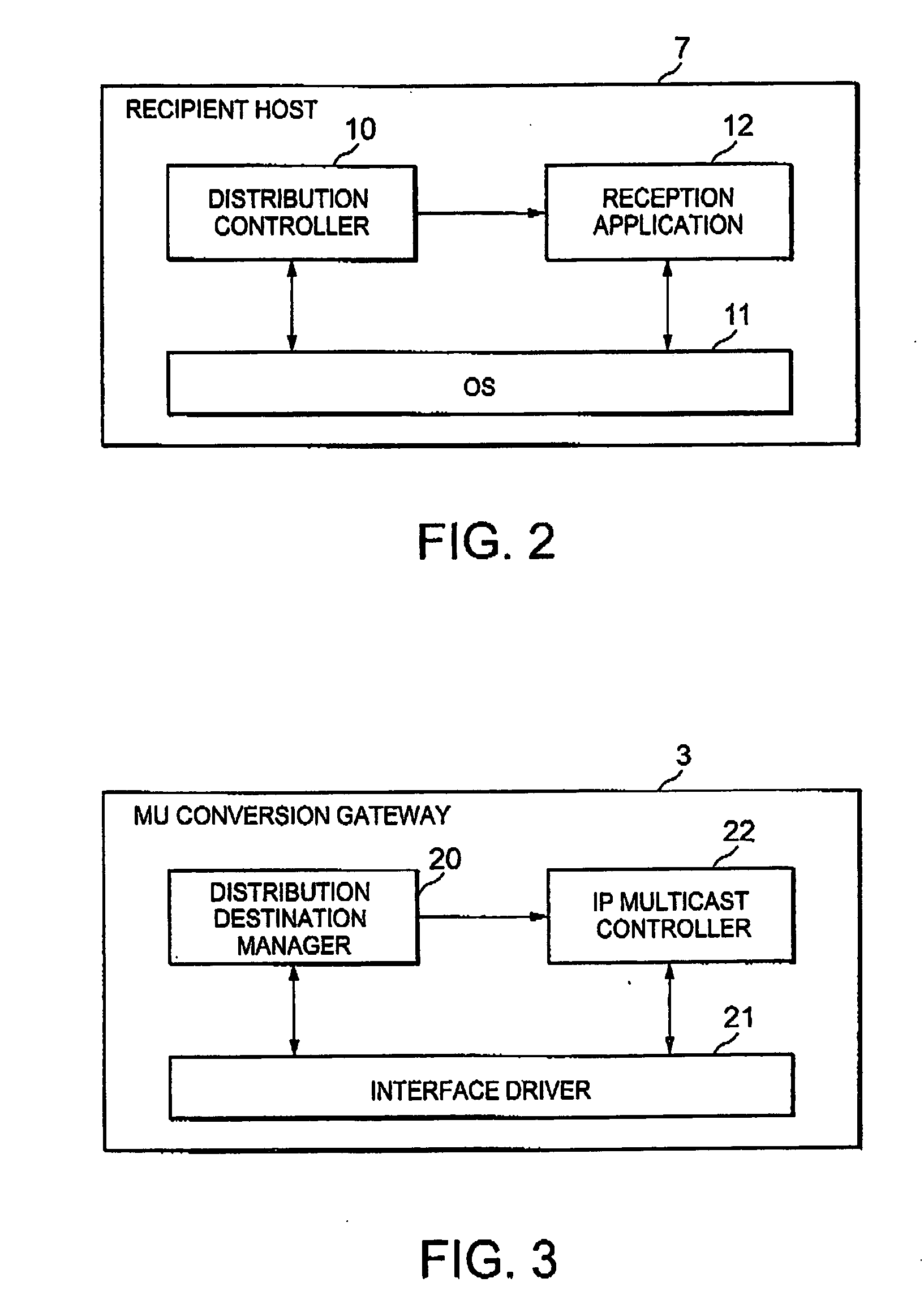
Disclosed is an IP multicast distribution system that can convert IP multicast data into packets for individual unicast addresses and can transmit the data to a recipient host in a private address space. According to the present invention, before accepting streaming distribution from the distribution server, a recipient host transmits, to an NAPT gateway, a distribution request for which the IP address of an MU conversion gateway is designated as a destination address, a source port number is designated a port number, determined in advance by the distribution server, in order to enable the reception of data by a reception application provided for the recipient host, and a destination port number is designated as an acceptance port number for the MU conversion gateway. Upon receiving the distribution request, the NAPT gateway designates a source IP address as the global IP address for the NAPT gateway and the source port number as the predetermined port number, and transfers data to the MU conversion gateway.
Owner:NEC CORP
Efficient MBMS backbone distributionusing one tunnel approach
ActiveUS20100027541A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationTelecommunications networkIP multicast
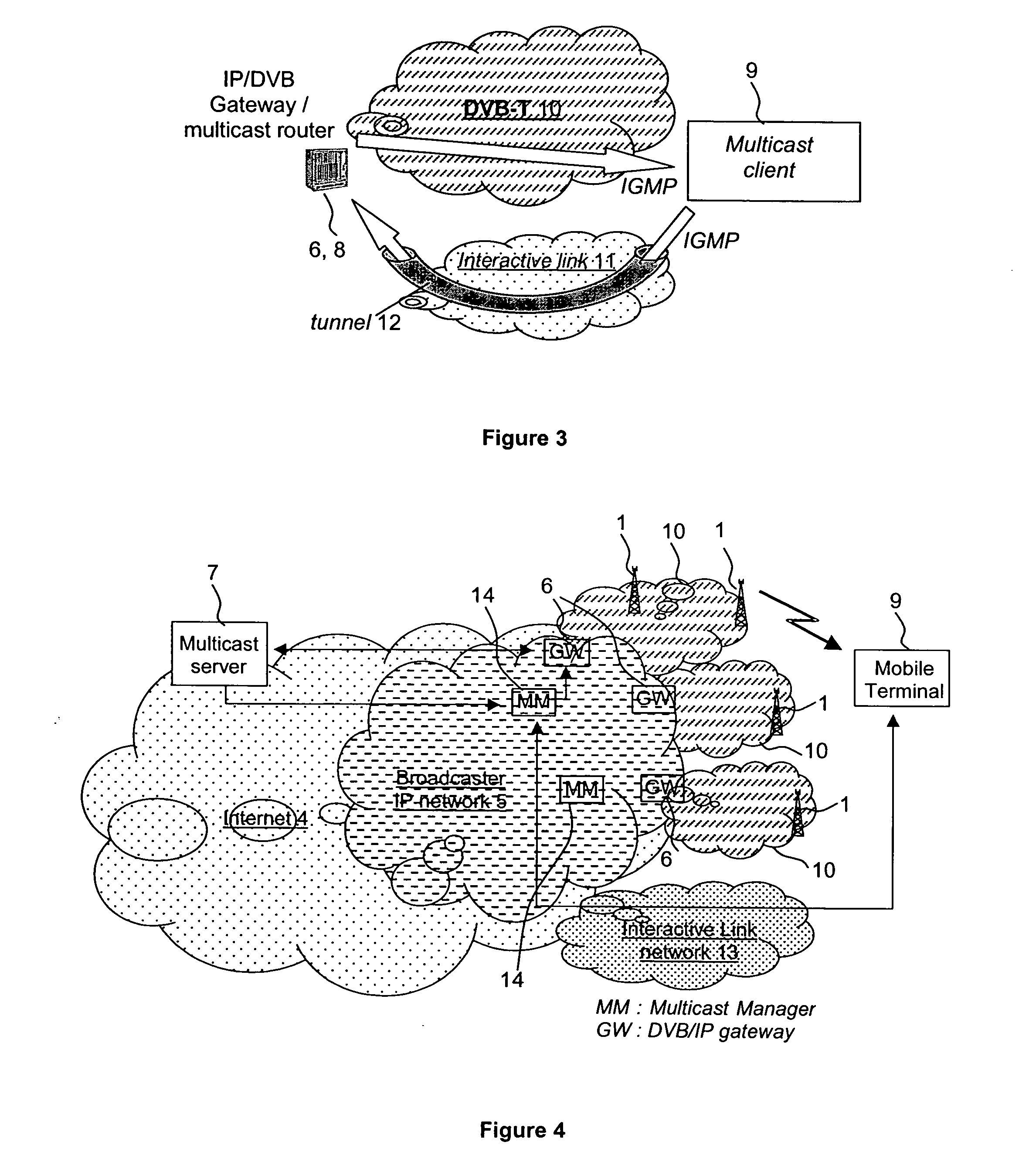
The present invention relates to a method, signal and devices for facilitating distribution of multimedia broadcast multicast services, i.e. MBMS, in a telecommunications network by receiving an MBSM session start message from a broadcast / multicast service center; sending control traffic on a control network; sending as control traffic to a serving node an MBMS session start request message and including a common tunnel end-point identifier, i.e. common TEID, in the MBMS session start request message; receiving information from the serving node indicating the acceptance of using IP multicast; and sending media content on an IP multicast backbone to hosts that have joined the multicast group using the common TEID. If any part of the communication network does not accept the IP multicast backbone as distribution method tunnels will be used between the gateway and serving node and between the serving node and control node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
IP multicast management and service provision system and method
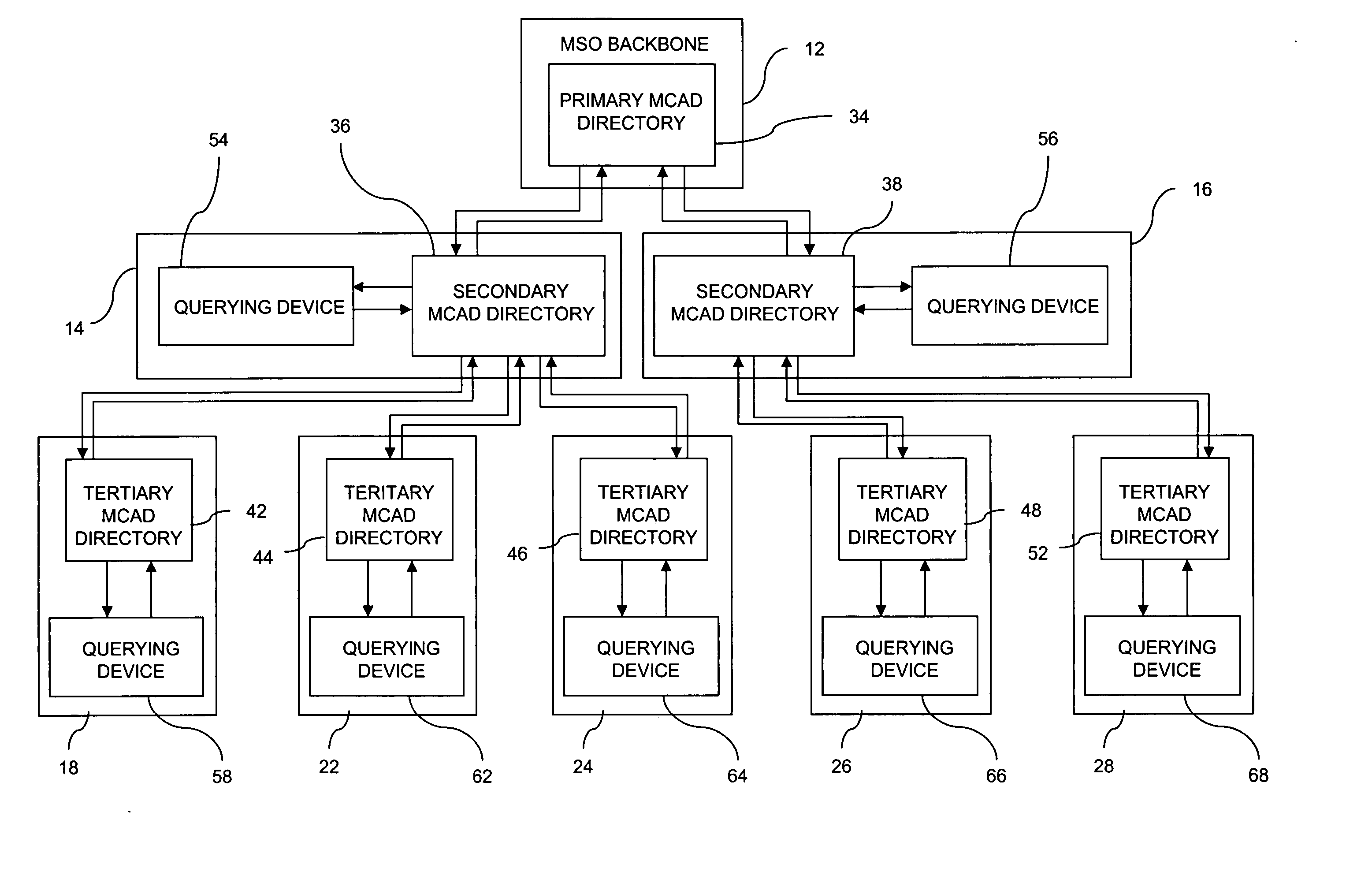
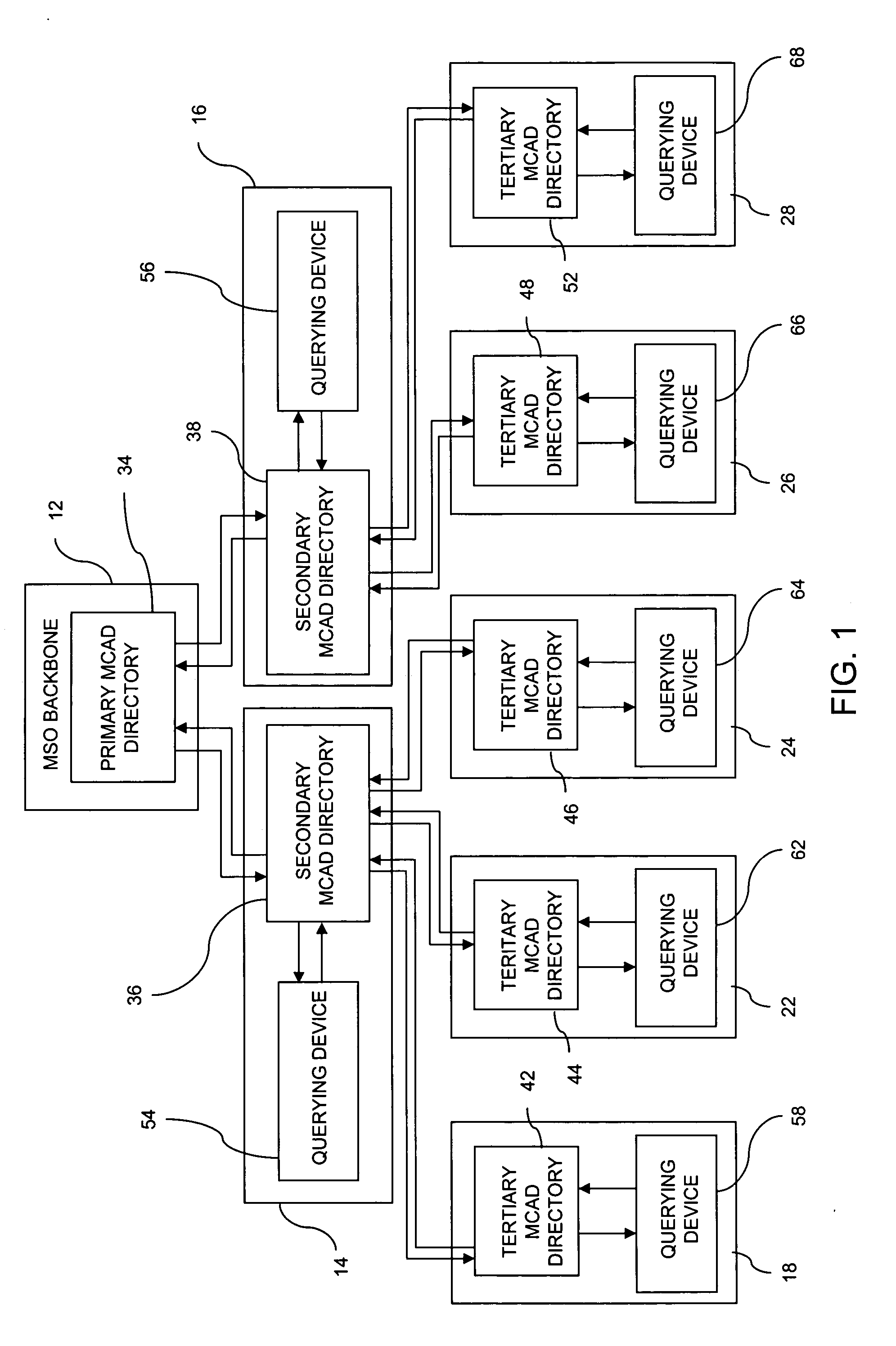
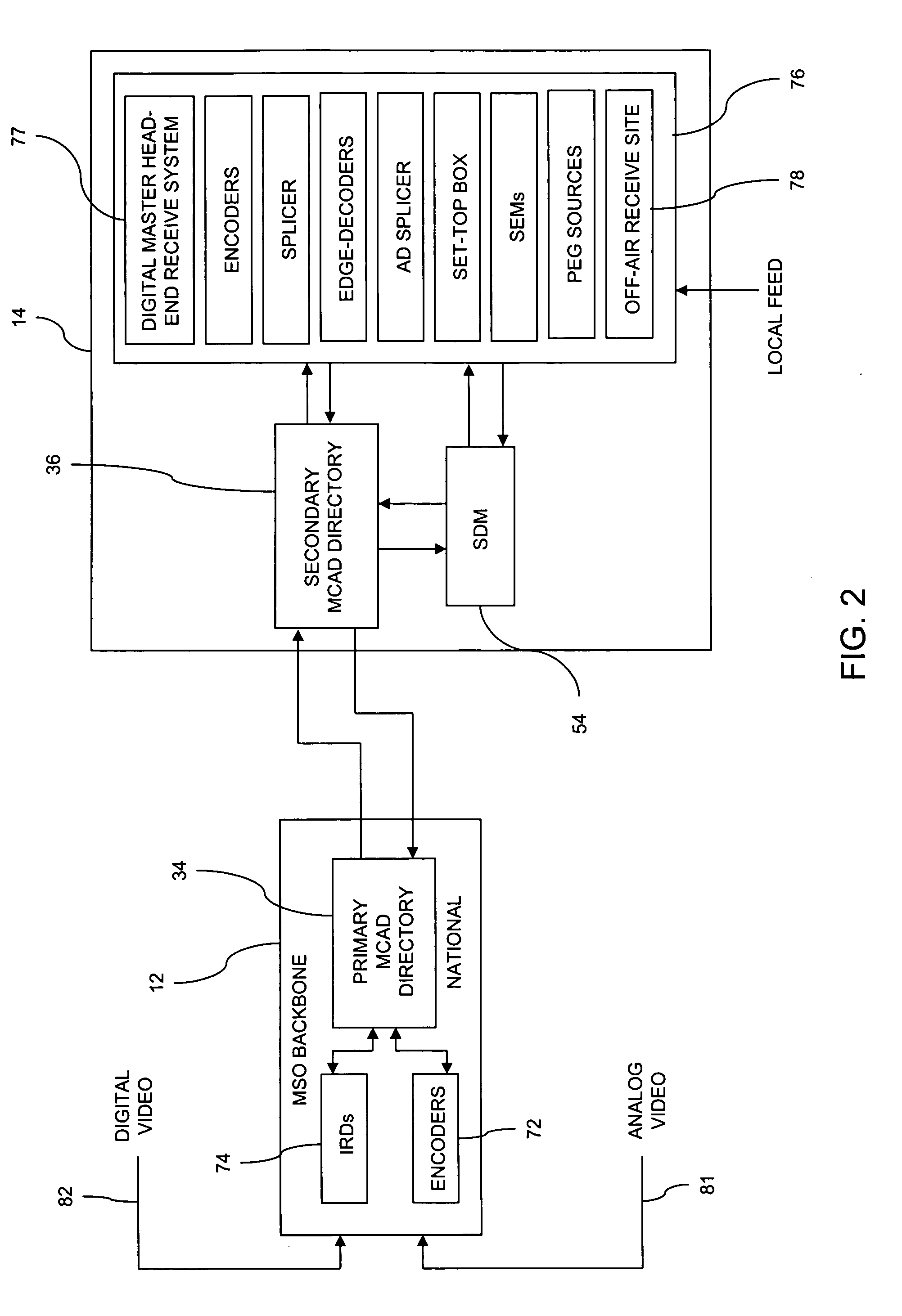
ActiveUS20070030818A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsComputer networkIP multicast
A system (10), method (90) and apparatus (14) are provided for provisioning a multicast stream, such as an IP multicast stream, in a network. The system includes a first tier (12), such as a national backbone, with a first Multicast Address Discovery (MCAD) directory (34), and at least one second tier having a headend, such as a regional headend (14), with a second MCAD directory (36, 38). The system (10) includes a tiered MCAD directory network that allows the assignment of multicast addresses to multicast streams received from an upper tier MCAD directory. The tiered MCAD directory structure allows for requesting and storing stream descriptors and delivering stream descriptors on-demand to MCAD-enabled devices throughout the system. The system (10) also allows for stream provisioning maintenance and validation at lower tier headends via MCAD-enabled device queries or re-queries of upper tier MCAD directories.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
IP multicast snooping and routing with multi-chassis link aggregation
ActiveUS8472447B2Energy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationComputer networkIP multicast
Aggregation Switches connected via a virtual fabric link (VFL) are each active and able to perform at least limited IP multicast snooping. The resulting IP multicast snooping information is maintained internally within each Aggregation Switch and shared substantially in real-time therebetween via the VFL.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Ip multicast service over a broadcast channel
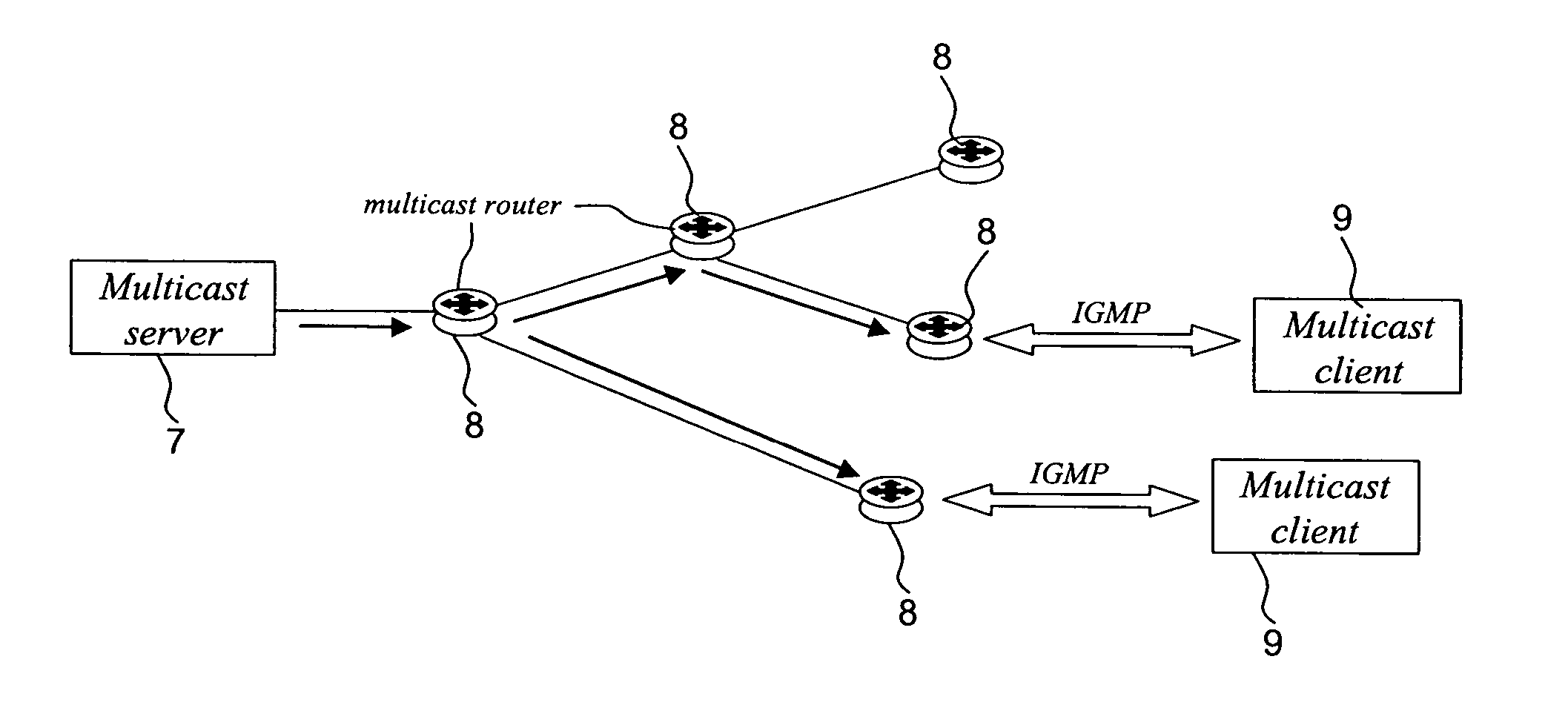
InactiveUS20050044142A1Special service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast channelsIP multicast
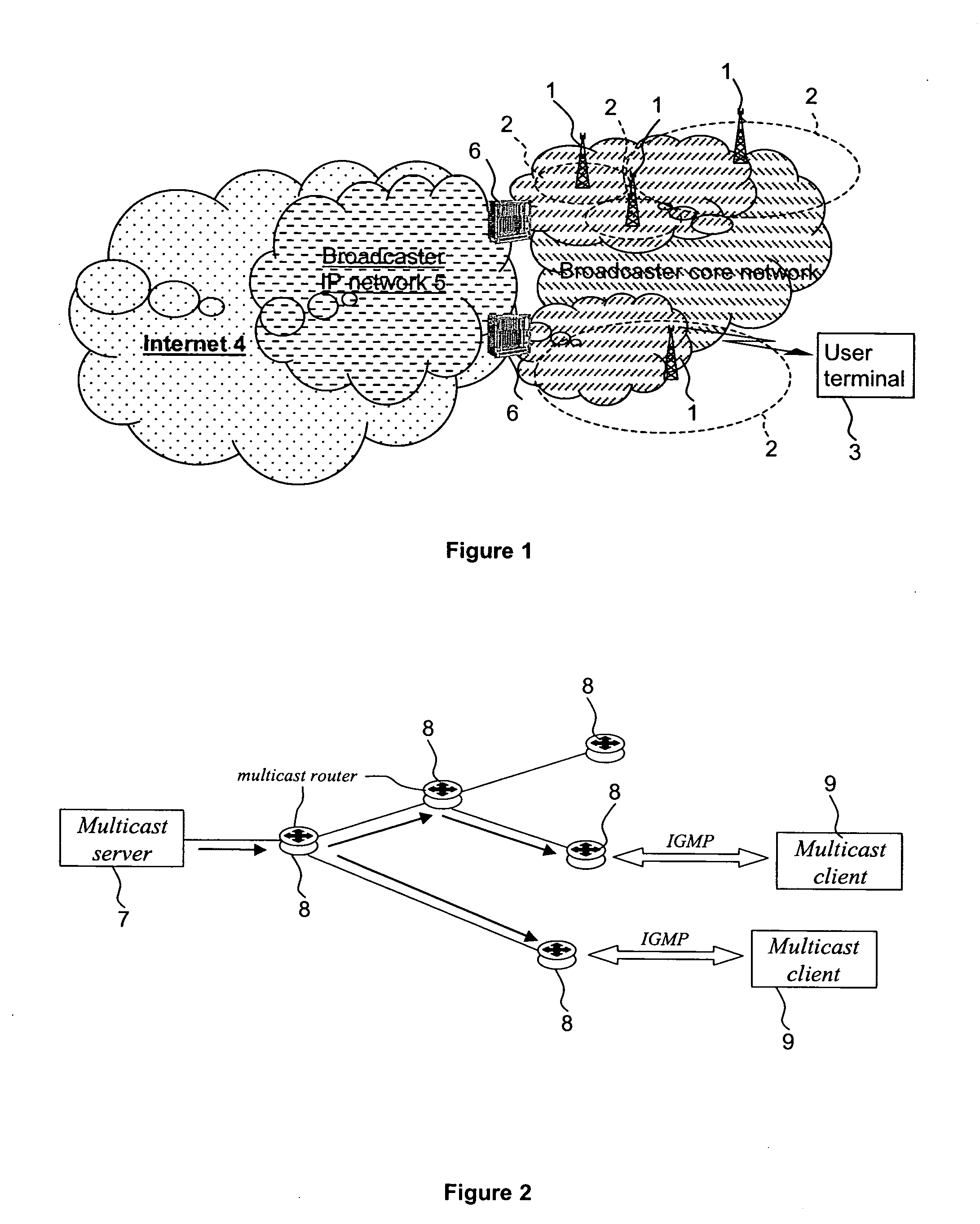
A method of and apparatus for providing an Internet Protocol multicast service wherein multicast data is transmitted through multicast routers (8) to user stations (9) over a digital broadcast channel (especially DVB-T) together with digital broadcast signals, at least if a request has been received from a user station (9) for the multicast data,. The transmission of the multicast data by a multicast router is conditional upon the reception of a request for said multicast data from that multicast router by a plurality of the user stations (9). The number of requests from the user stations (9) has to be greater than a threshold number, which is a function of the available bandwidth for multicast transmission over the broadcast channel. Information concerning the requests for the multicast data by the user stations (9) is unavailable to the other user stations (9).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for packet forwarding in a switch controller
ActiveUS20030202513A1Store-and-forward switching systemsNetworks interconnectionIP multicastMulticast address
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for packet forwarding within a switch controller. In addition to unicast and broadcast forwarding, the method and apparatus can also analyze and forward IP multicast packets without the need of a CPU and a separate multicast address table, thereby enabling IP multicasting for the switch controller. Wherein, specific packet parsing and updating rules are used to analyze IP multicast control packets, and a multicast router or an address table is updated based on the analyzing result. IP multicast packets is then forwarded according to the updated tables. Moreover, with an extra flag bit set in each address table entry, unicast and multicast forwarding can share the same address table.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com