Patents
Literature
2891 results about "Memory management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
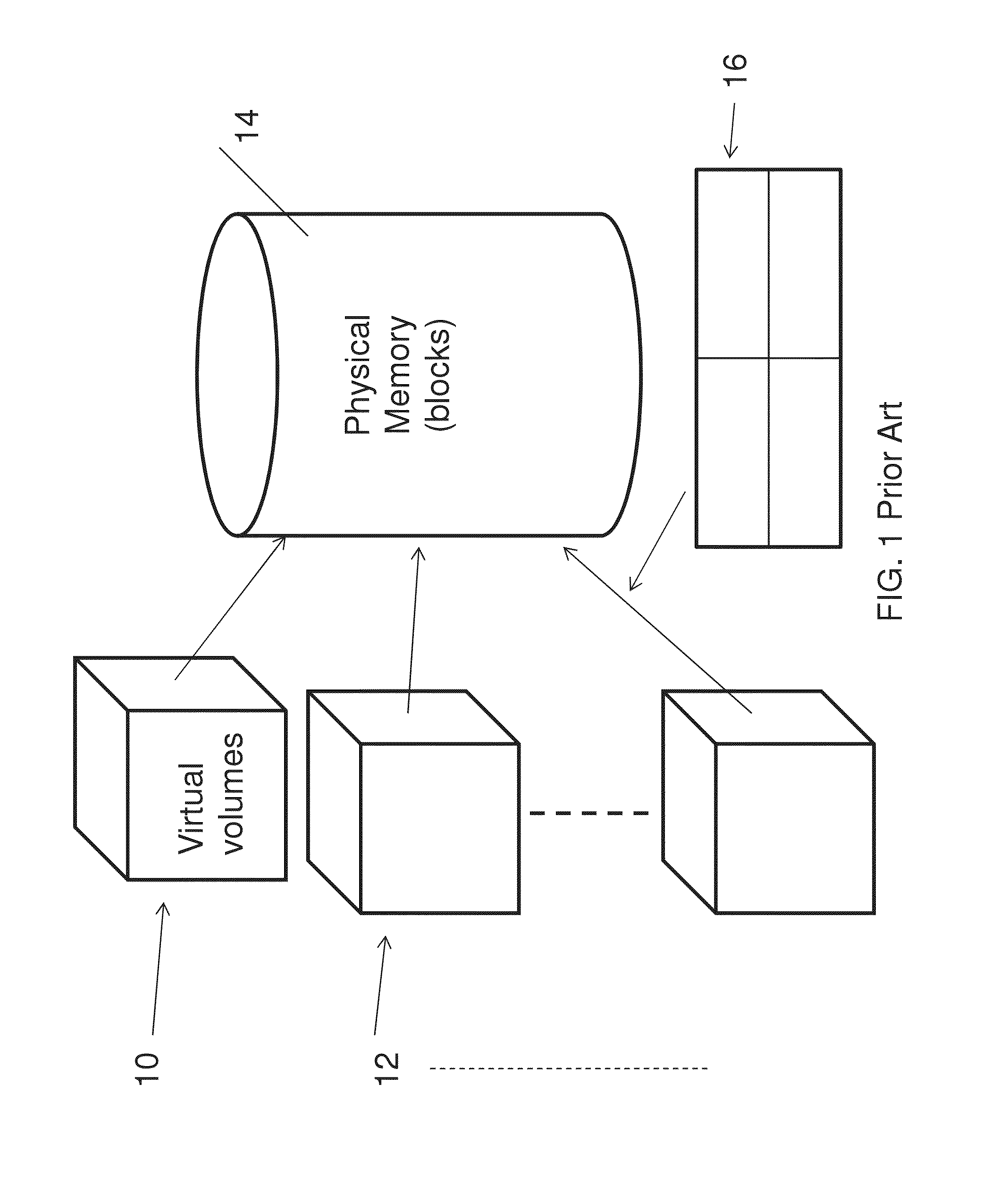
Memory management is a form of resource management applied to computer memory. The essential requirement of memory management is to provide ways to dynamically allocate portions of memory to programs at their request, and free it for reuse when no longer needed. This is critical to any advanced computer system where more than a single process might be underway at any time.
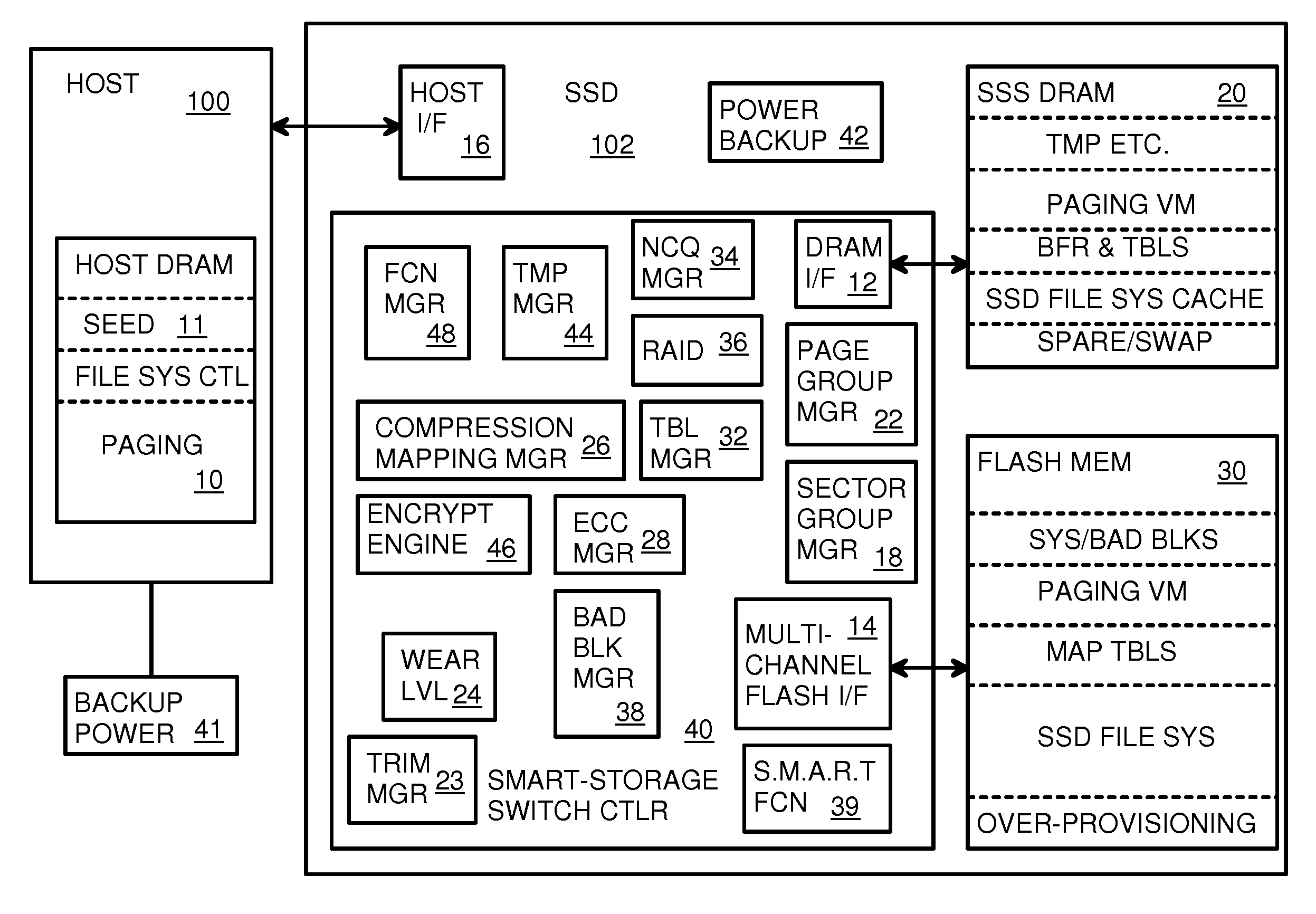
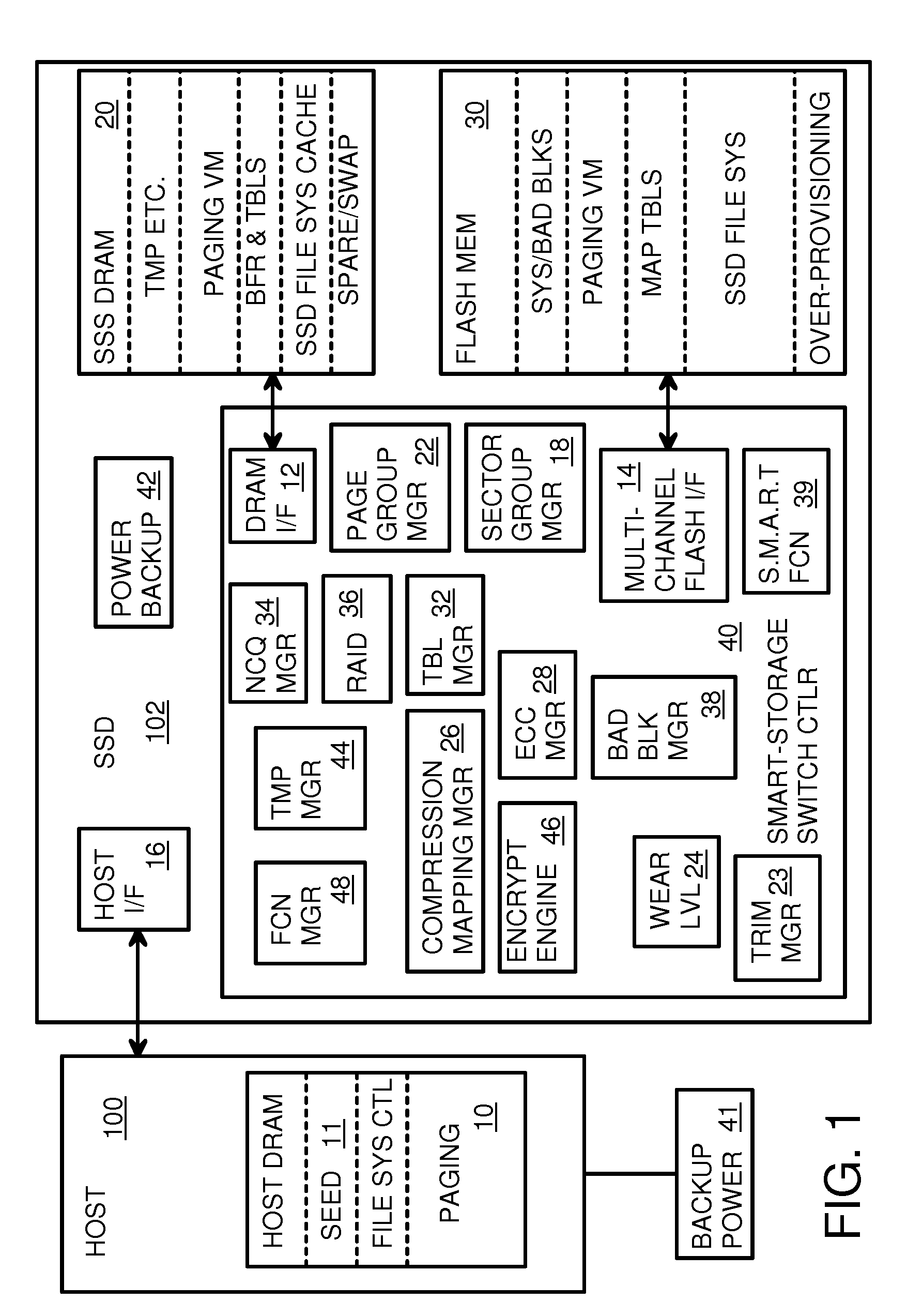
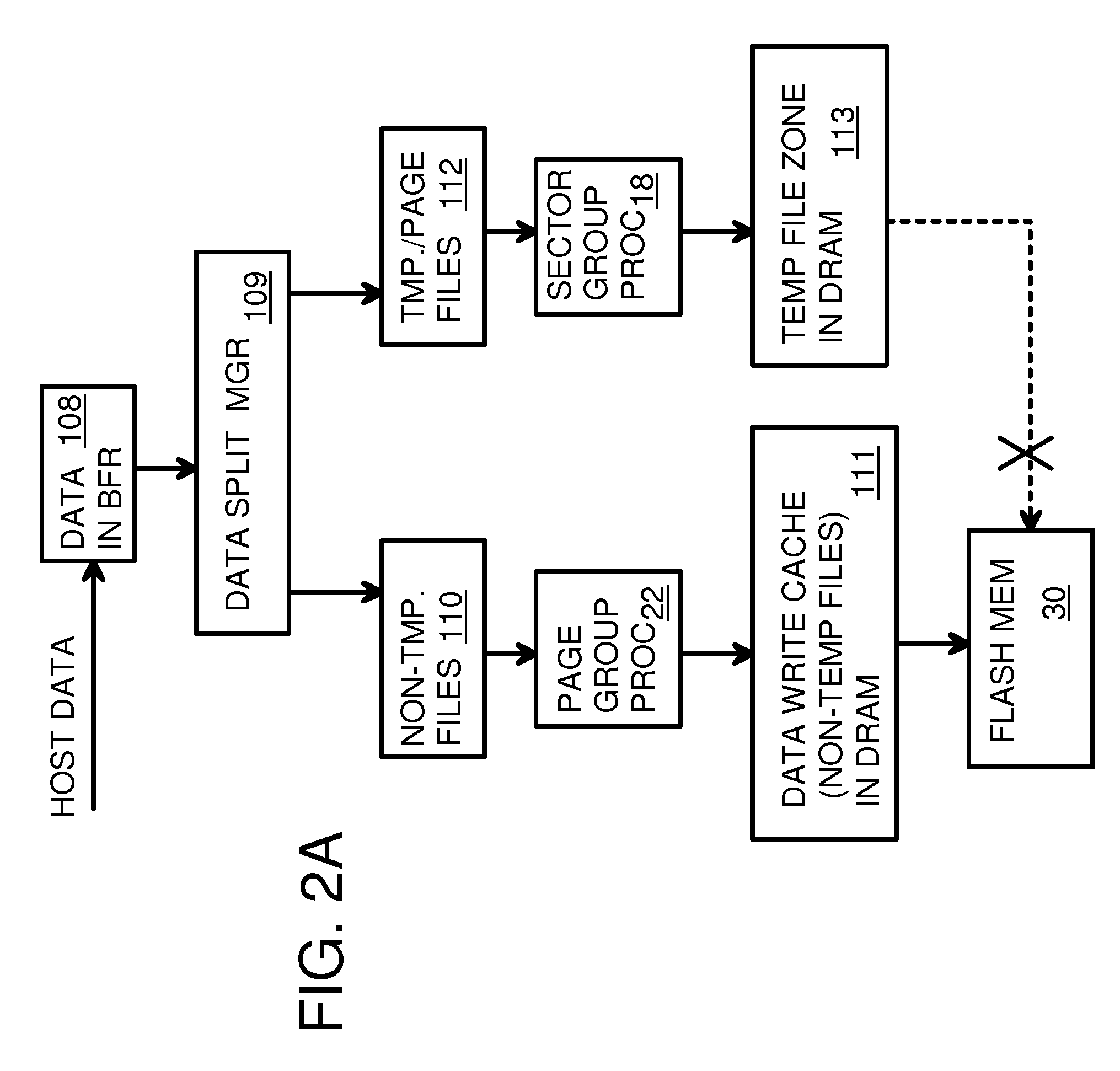
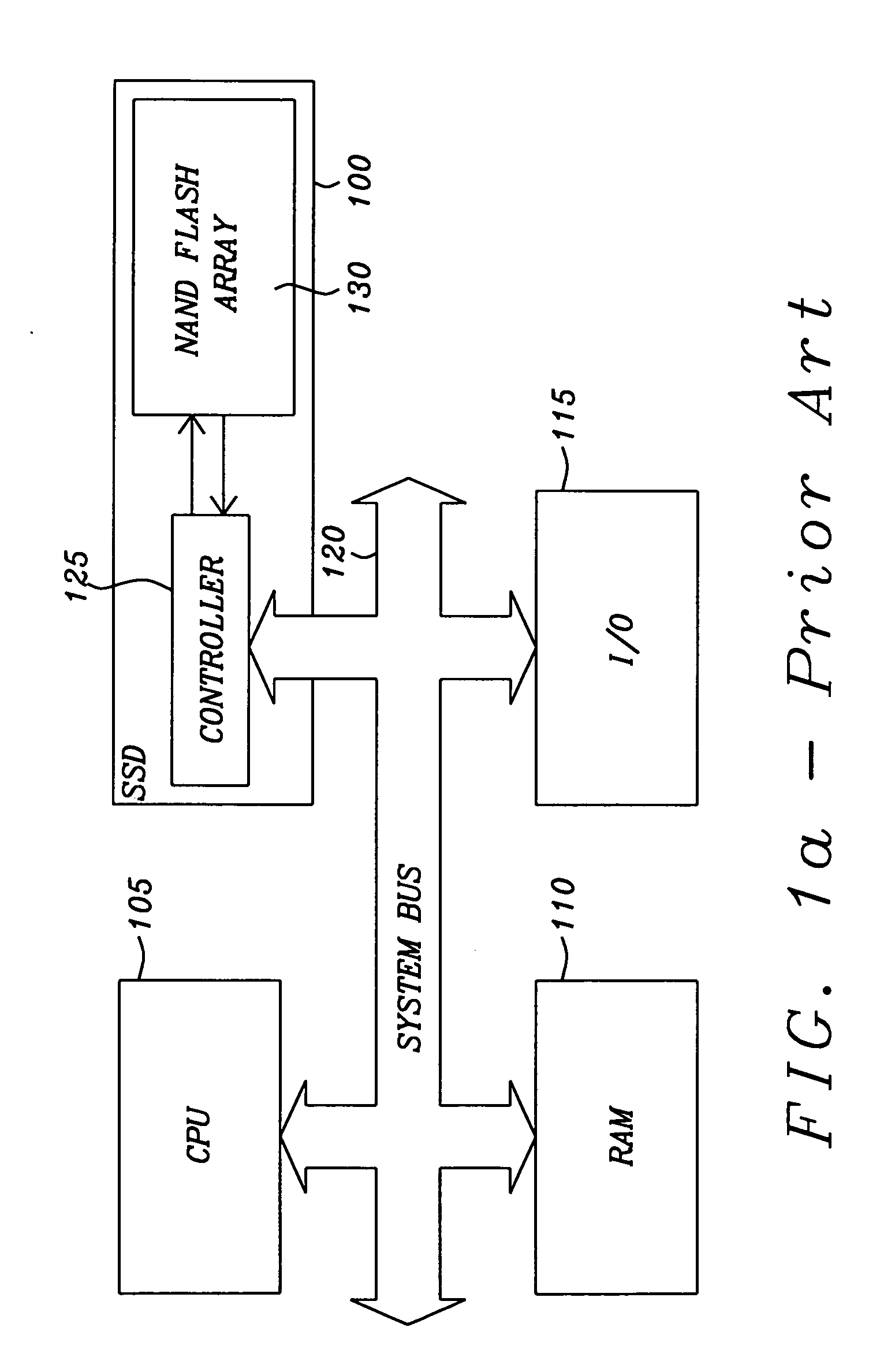
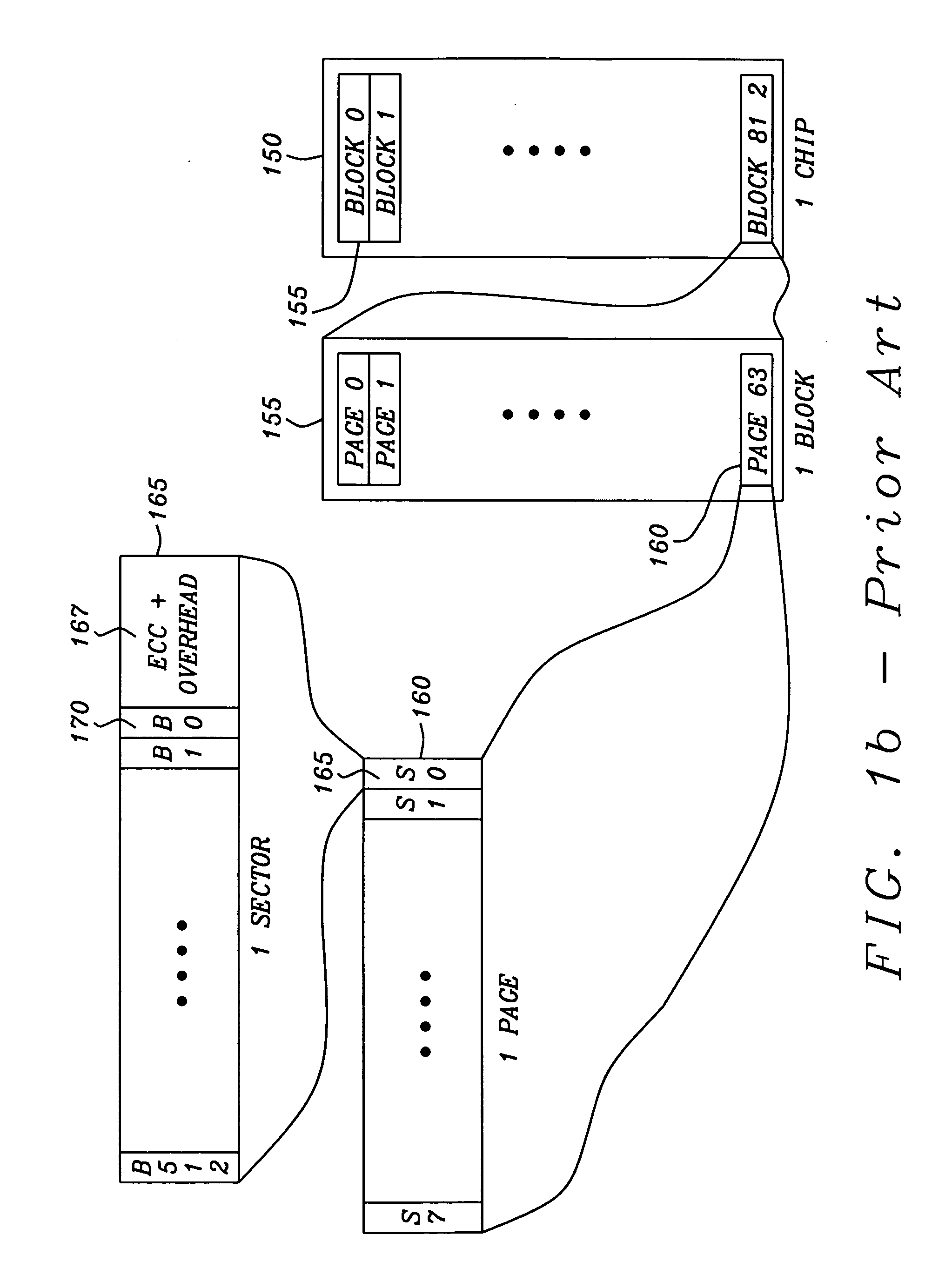
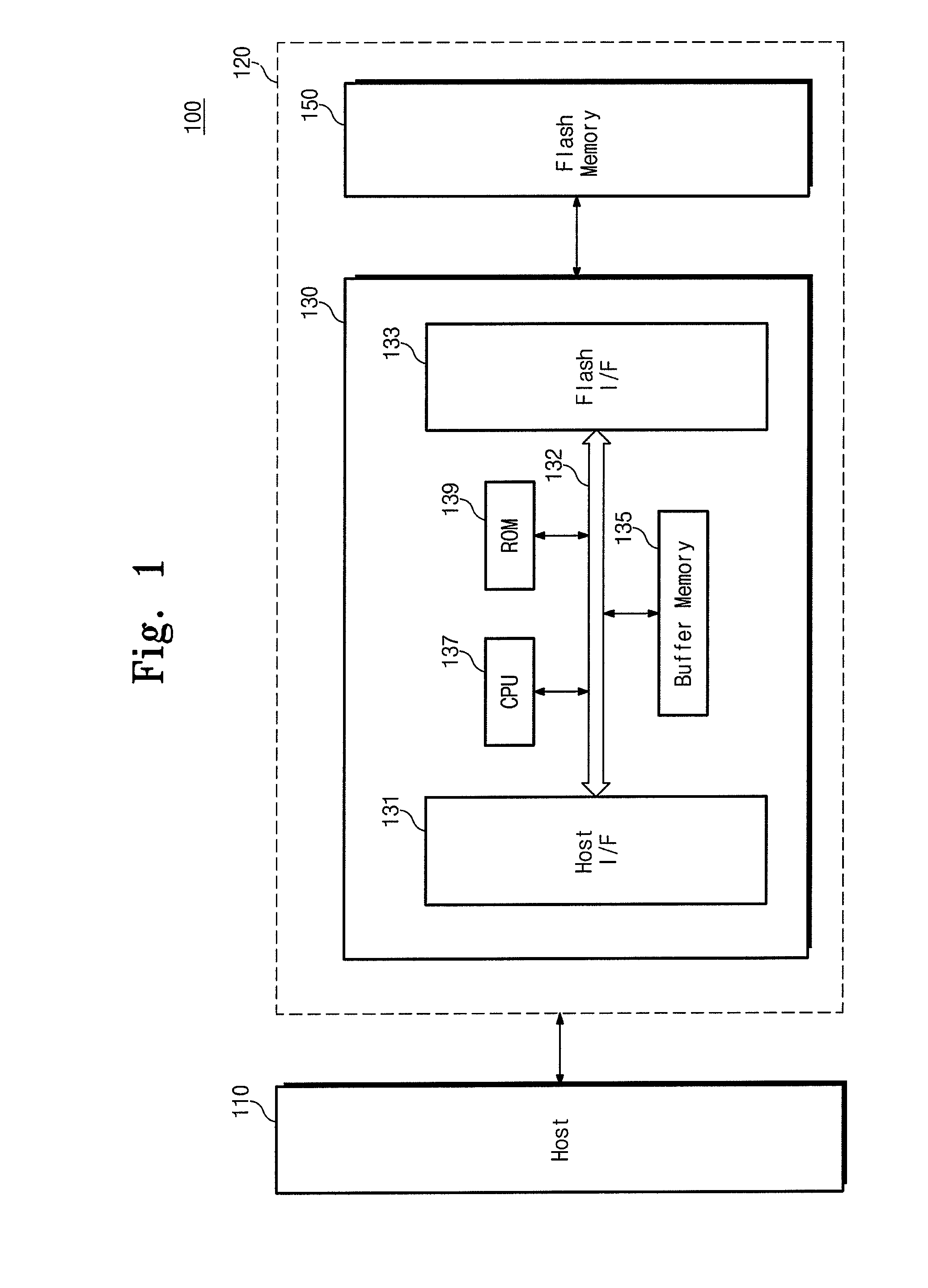
Super-Endurance Solid-State Drive with Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) and Diversion of Temp Files for Reduced Flash Wear
ActiveUS20120284587A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageFilename extensionData file
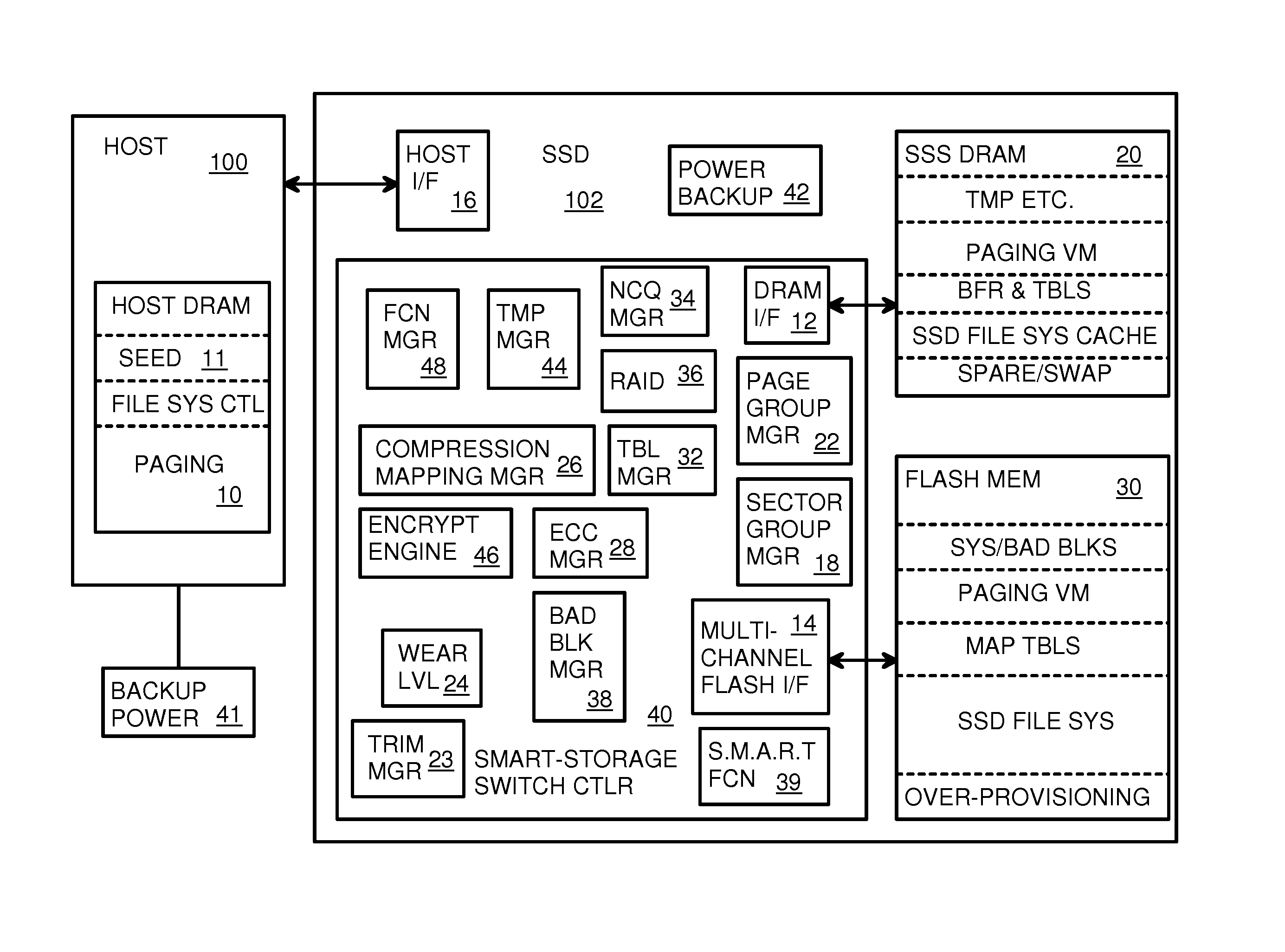
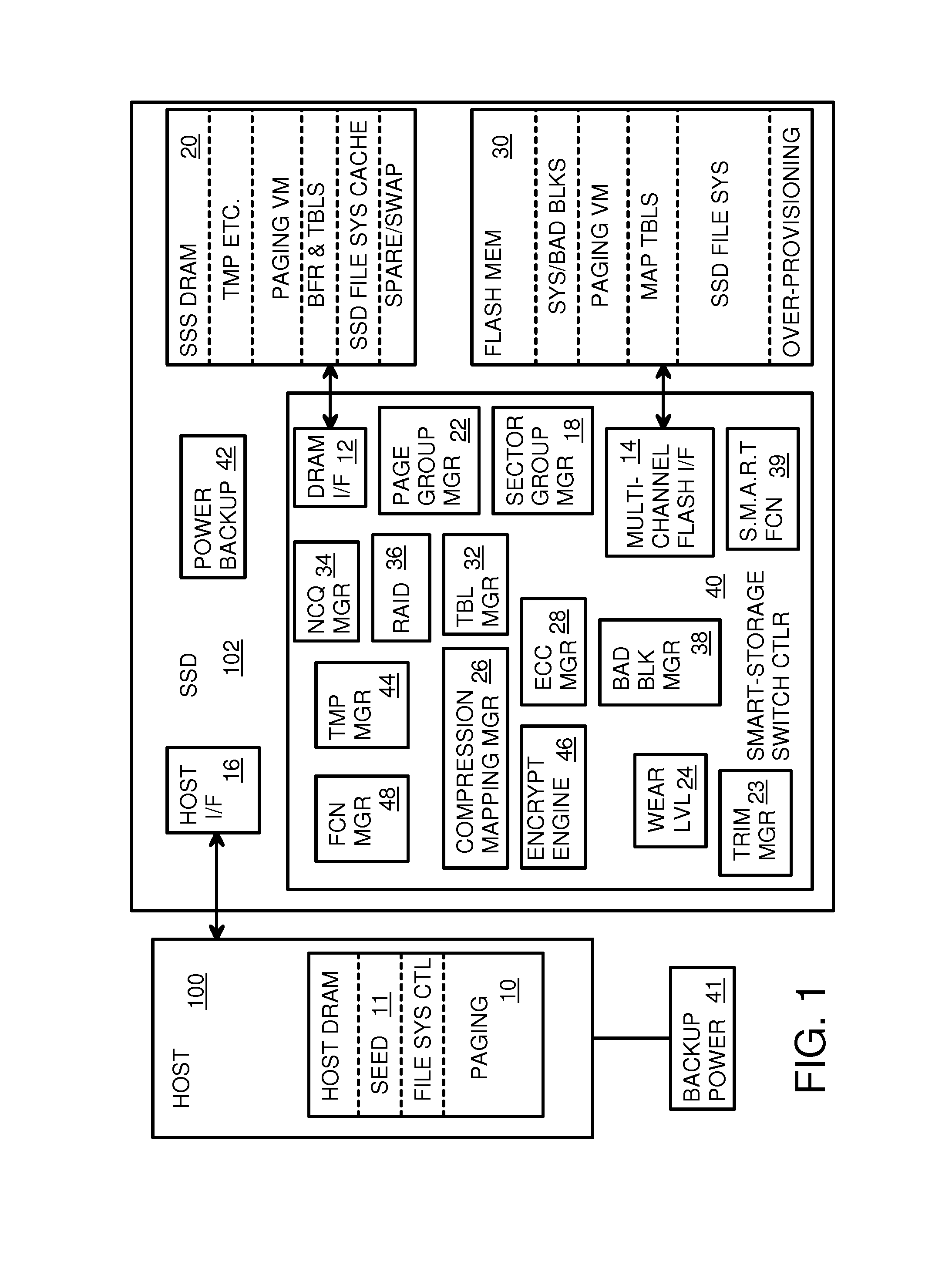
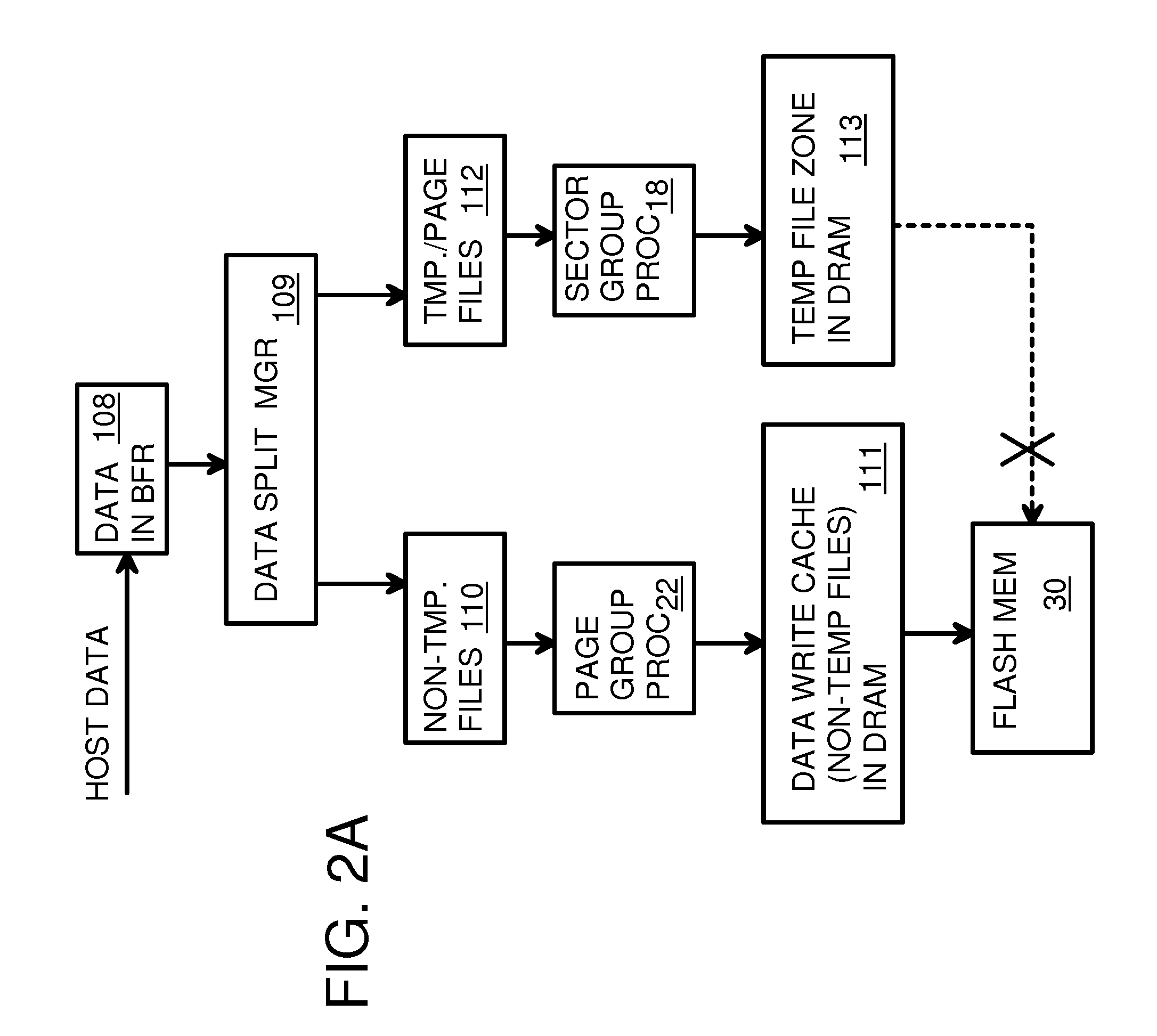
A flash drive has increased endurance and longevity by reducing writes to flash. An Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) is created in a DRAM buffer and provides temporary storage to reduce flash wear. A Smart Storage Switch (SSS) controller assigns data-type bits when categorizing host accesses as paging files used by memory management, temporary files, File Allocation Table (FAT) and File Descriptor Block (FDB) entries, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from FAT. Paging files and temporary files are never written to flash. Partial-page data is packed and sector mapped by sub-sector mapping tables that are pointed to by a unified mapping table that stores the data-type bits and pointers to data or tables in DRAM. Partial sectors are packed together to reduce DRAM usage and flash wear. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Multiple network protocol encoder/decoder and data processor
InactiveUS6034963AReduce system costLow costTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRaw socketByte
A multiple network protocol encoder / decoder comprising a network protocol layer, data handler, O.S. State machine, and memory manager state machines implemented at a hardware gate level. Network packets are received from a physical transport level mechanism by the network protocol layer state machine which decodes network protocols such as TCP, IP, User Datagram Protocol (UDP), PPP, and Raw Socket concurrently as each byte is received. Each protocol handler parses and strips header information immediately from the packet, requiring no intermediate memory. The resulting data are passed to the data handler which consists of data state machines that decode data formats such as email, graphics, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Java, and Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Each data state machine reacts accordingly to the pertinent data, and any data that are required by more than one data state machine is provided to each state machine concurrently, and any data required more than once by a specific data state machine, are placed in a specific memory location with a pointer designating such data (thereby ensuring minimal memory usage). Resulting display data are immediately passed to a display controller. Any outgoing network packets are created by the data state machines and passed through the network protocol state machine which adds header information and forwards the resulting network packet via a transport level mechanism.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Page based management of flash storage
InactiveUS20110055458A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl signalPaging
Methods and circuits for page based management of an array of Flash RAM nonvolatile memory devices provide paged base reading and writing and block erasure of a flash storage system. The memory management system includes a management processor, a page buffer, and a logical-to-physical translation table. The management processor is in communication with an array of nonvolatile memory devices within the flash storage system to provide control signals for the programming of selected pages, erasing selected blocks, and reading selected pages of the array of nonvolatile memory devices.
Owner:PIONEER CHIP TECH
Taint tracking mechanism for computer security
ActiveUS8510827B1Easy to trackAvoid modificationMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInformation dispersalOperation mode
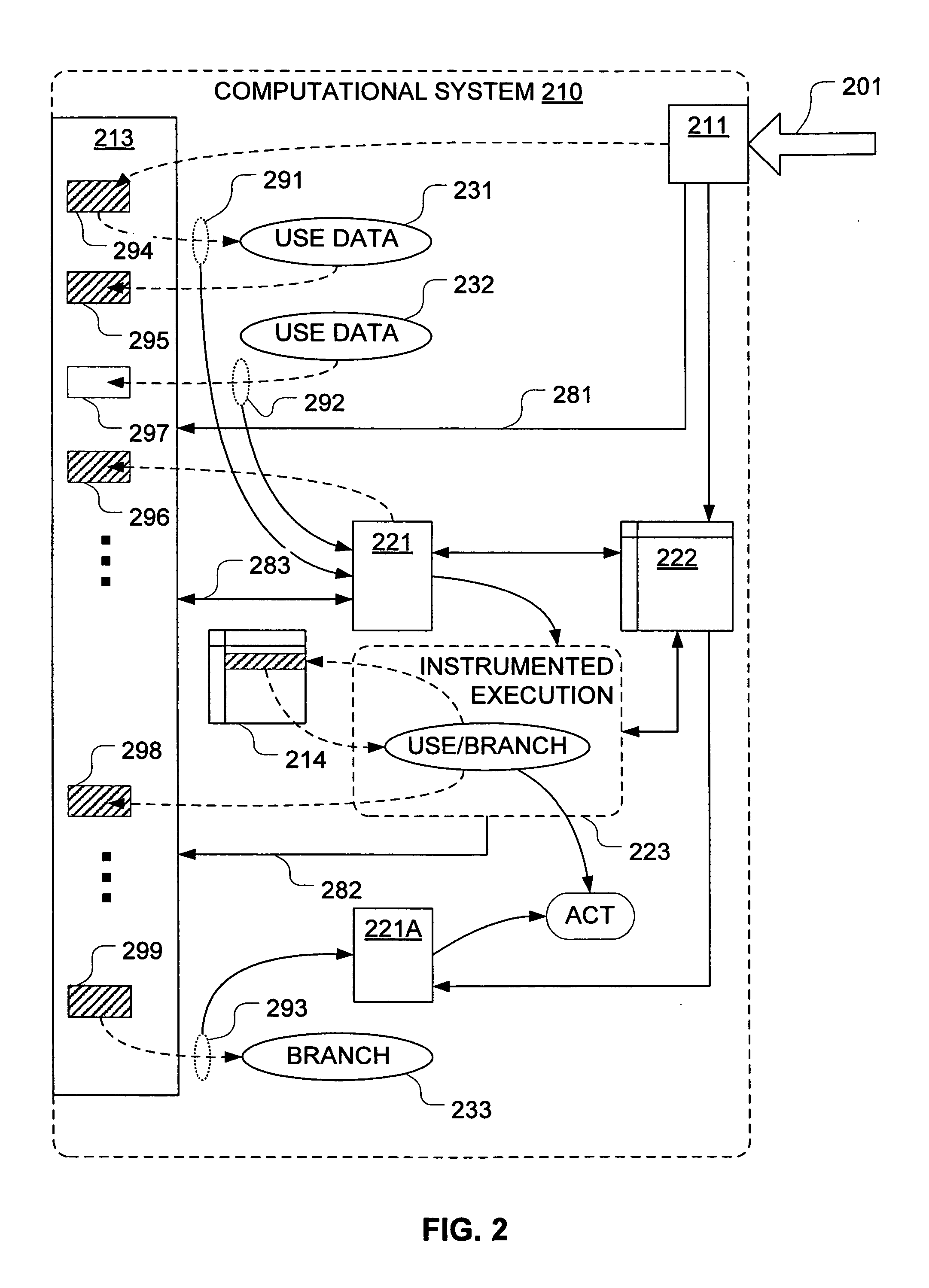
Mechanisms have been developed for securing computational systems against certain forms of attack. In particular, it has been discovered that, by maintaining and propagating taint status for memory locations in correspondence with information flows of instructions executed by a computing system, it is possible to provide a security response if and when a control transfer (or other restricted use) is attempted based on tainted data. In some embodiments, memory management facilities and related exception handlers can be exploited to facilitate taint status propagation and / or security responses. Taint tracking through registers of a processor (or through other storage for which access is not conveniently mediated using a memory management facility) may be provided using an instrumented execution mode of operation. For example, the instrumented mode may be triggered by an attempt to propagate tainted information to a register. In some embodiments, an instrumented mode of operation may be more generally employed. For example, data received from an untrusted source or via an untrusted path is often transferred into a memory buffer for processing by a particular service, routine, process, thread or other computational unit. Code that implements the computational unit may be selectively executed in an instrumented mode that facilitates taint tracking. In general, instrumented execution modes may be supported using a variety of techniques including a binary translation (or rewriting) mode, just-in-time (JIT) compilation / re-compilation, interpreted mode execution, etc. Using an instrumented execution mode and / or exception handler techniques, modifications to CPU hardware can be avoided if desirable.
Owner:VMWARE INC
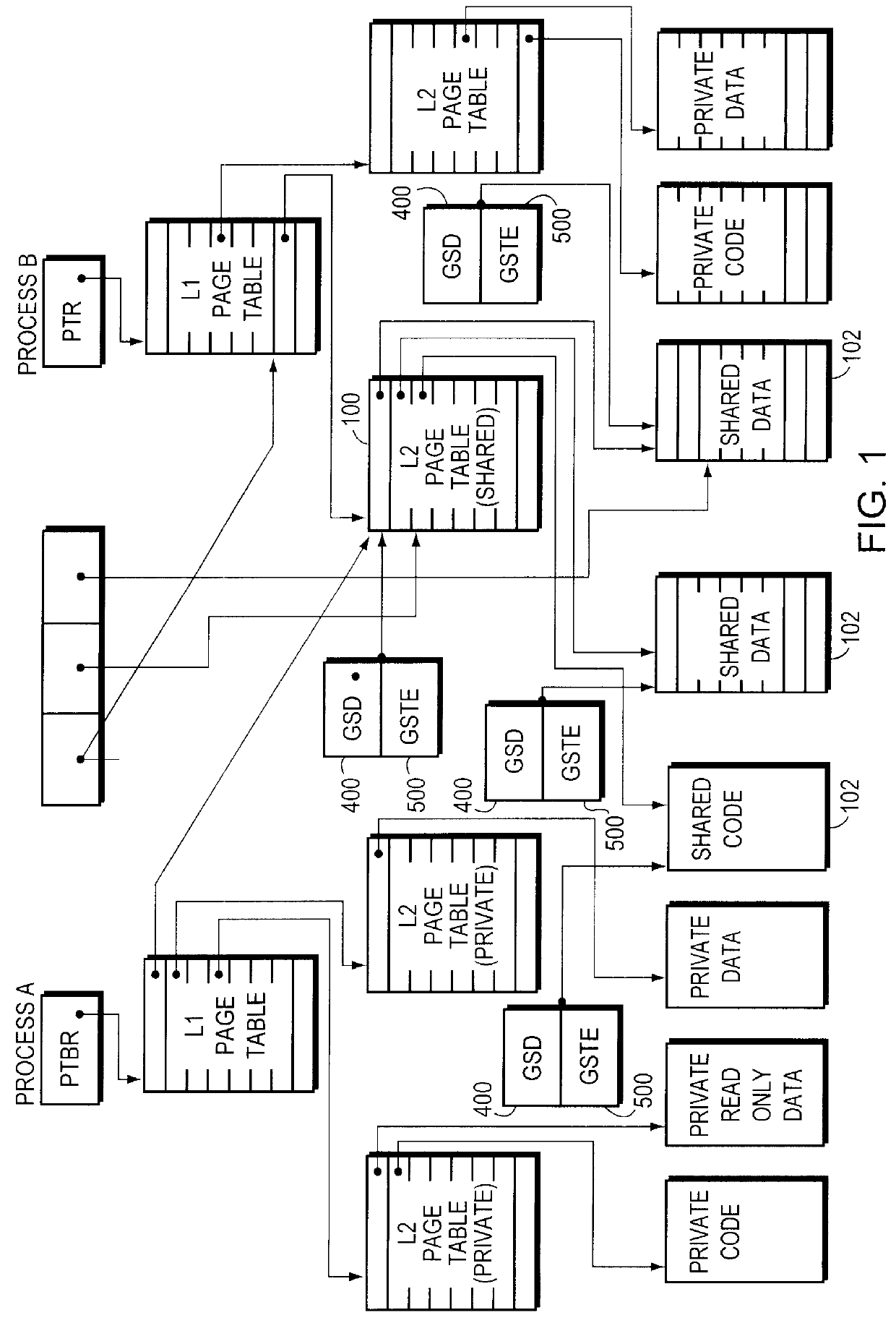
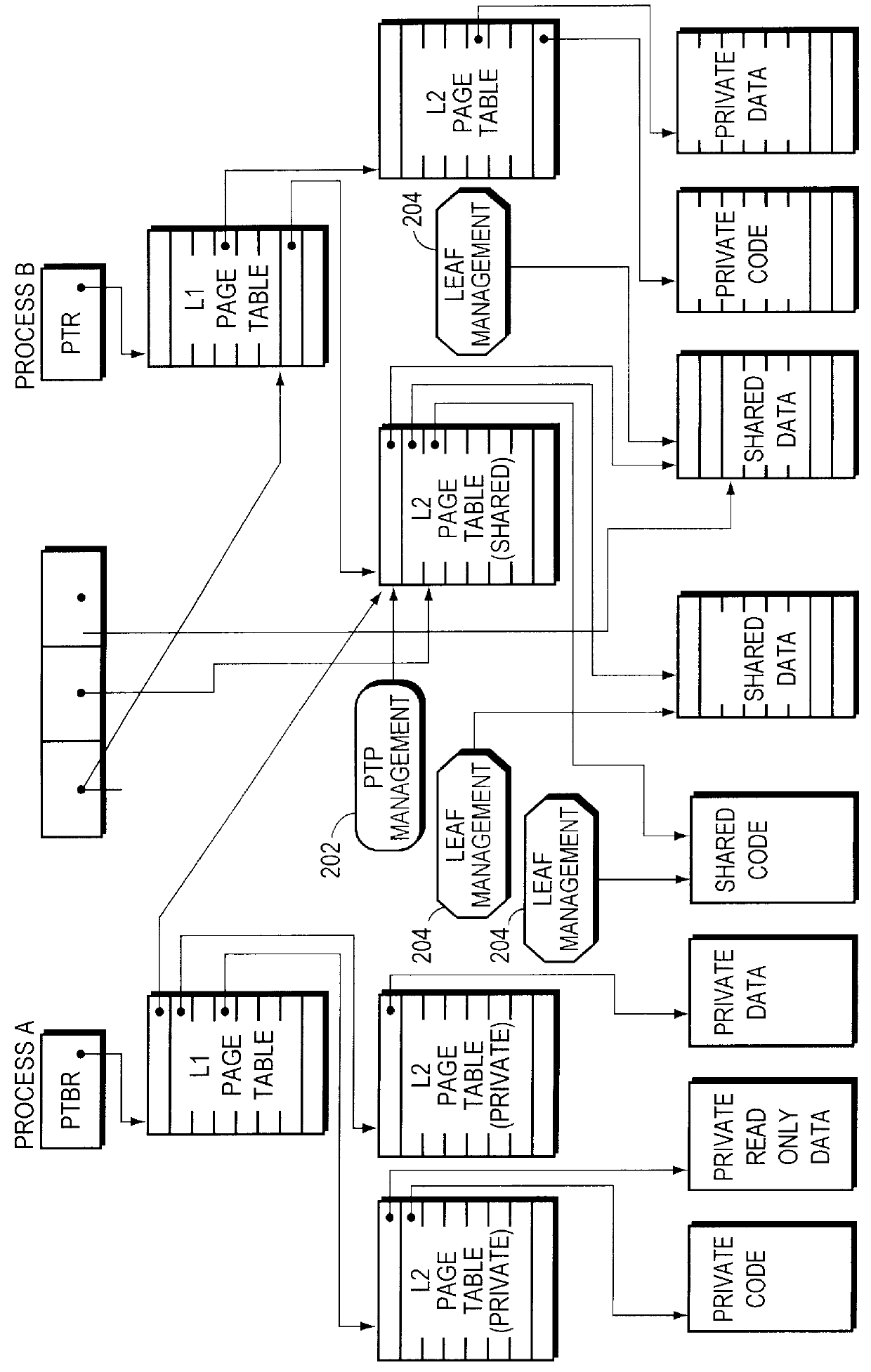
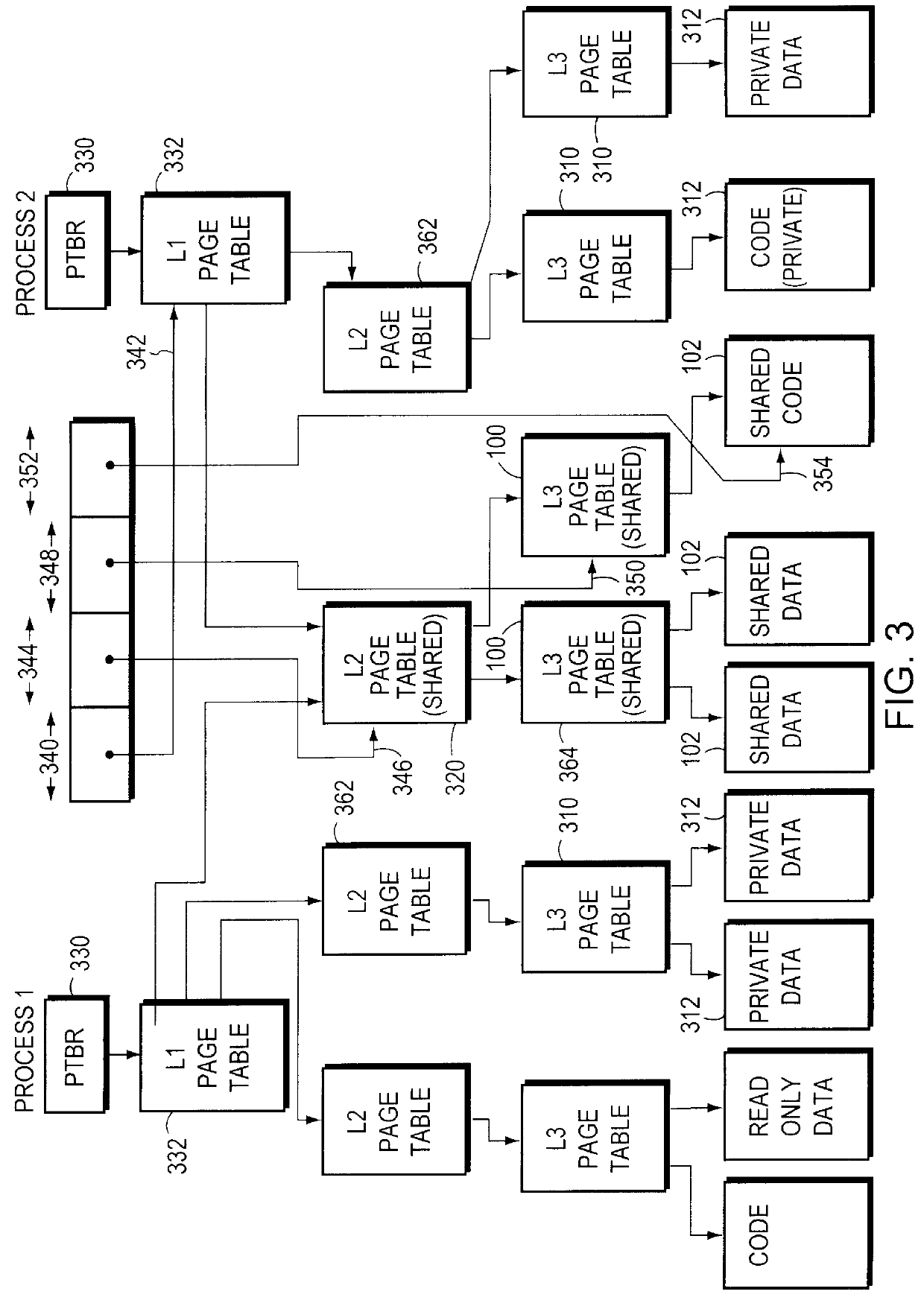
Sharing memory pages and page tables among computer processes
InactiveUS6085296AOptimizationReduce fragmentationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationPage tableComputer memory
A method of managing computer memory pages. The sharing of a program-accessible page between two processes is managed by a predefined mechanism of a memory manager. The sharing of a page table page between the processes is managed by the same predefined mechanism. The data structures used by the mechanism are equally applicable to sharing program-accessible pages or page table pages.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Systems and methods for providing nonvolatile memory management in wireless phones
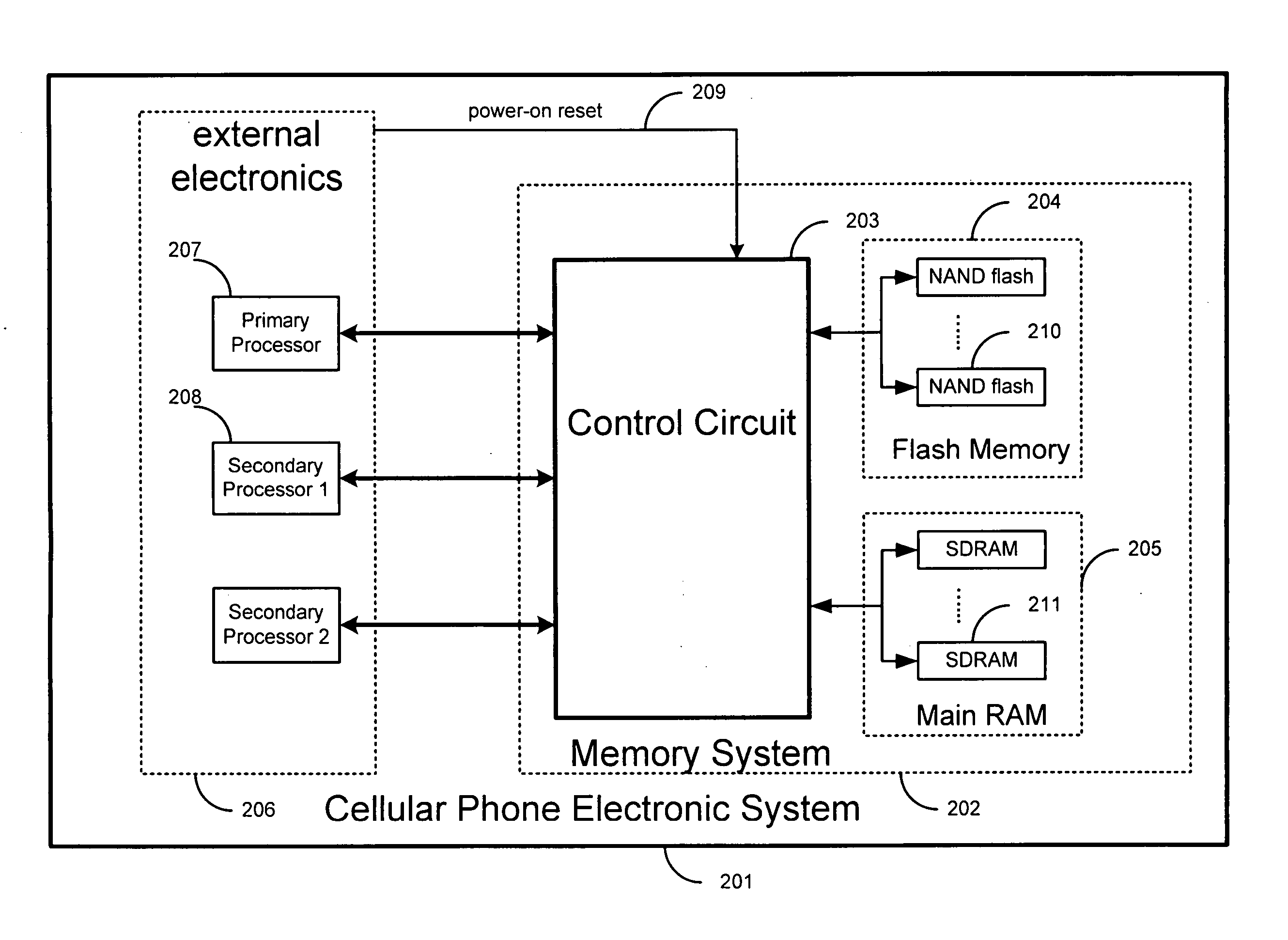
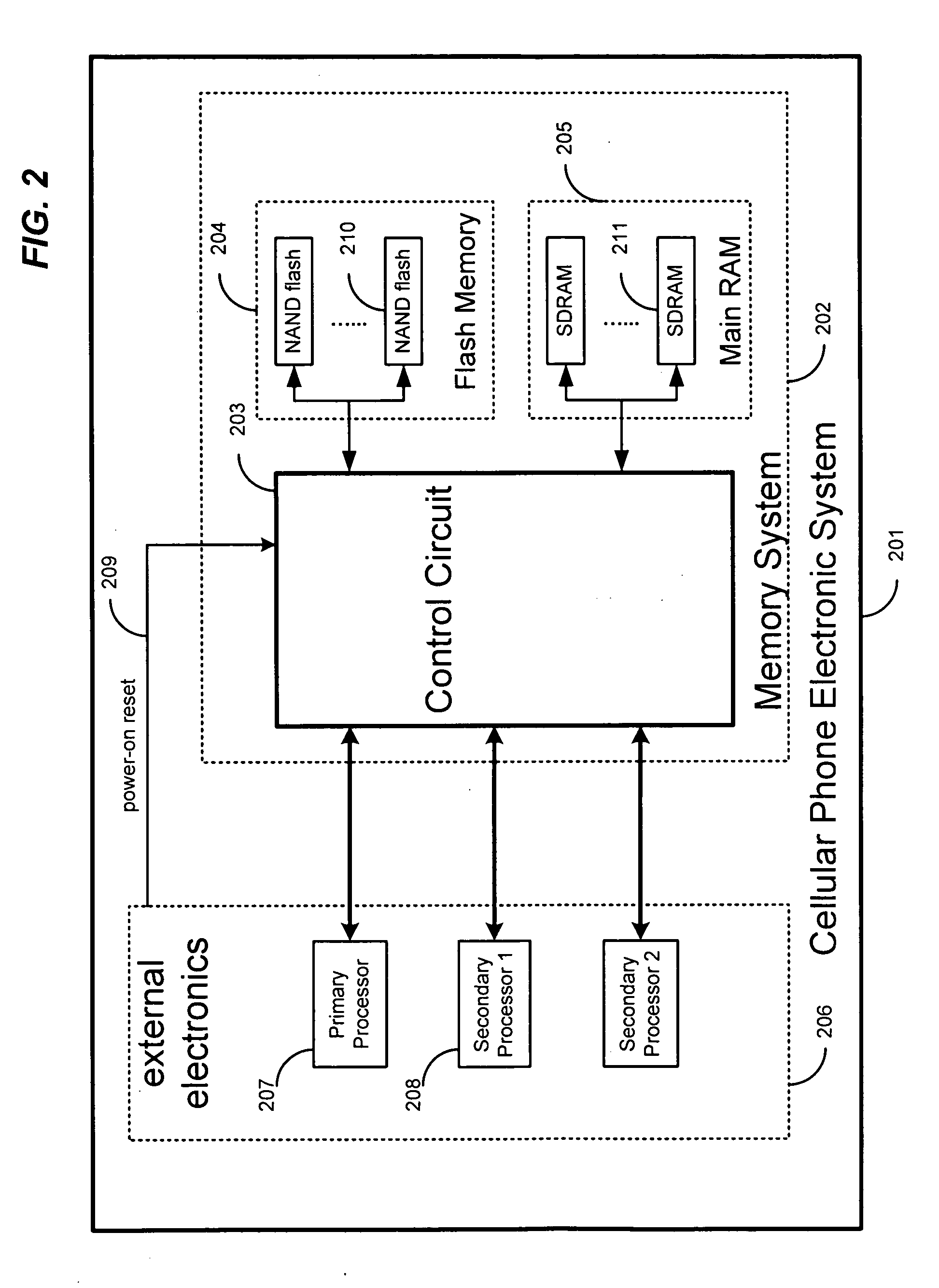
ActiveUS20060053246A1Low costSmall sizeUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital storageMemory controllerInterface circuits
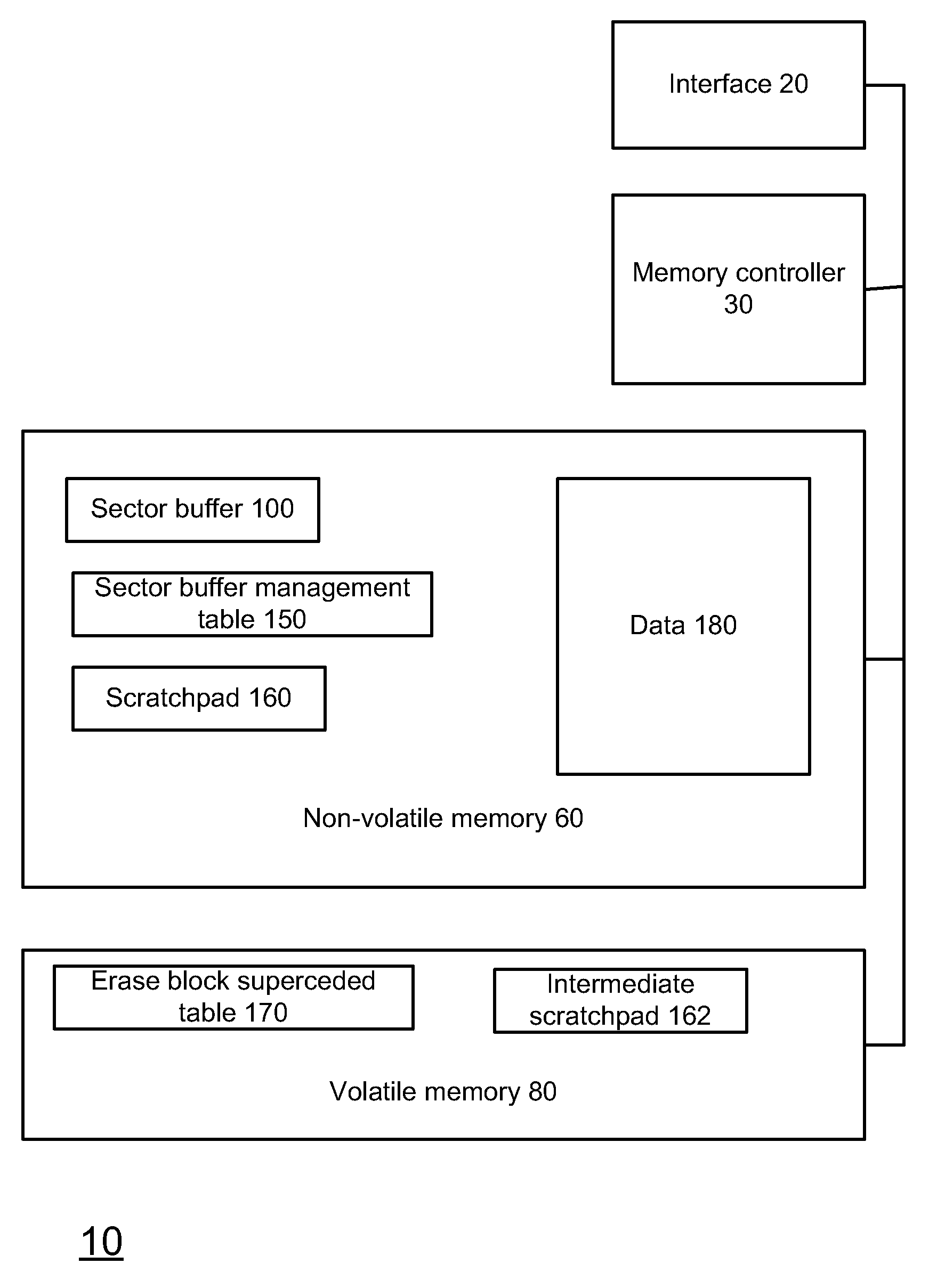
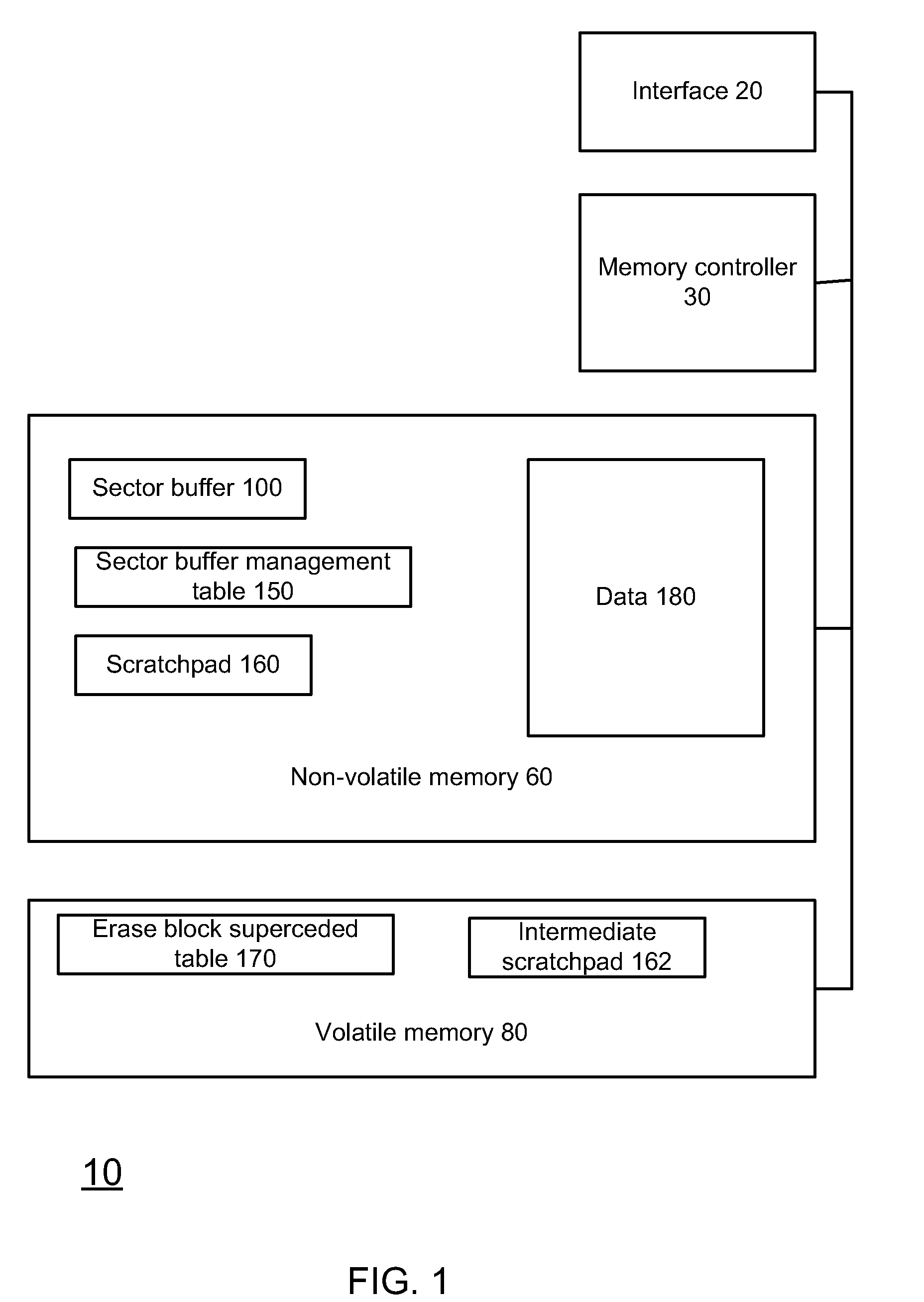
The present invention is related to memory management, and in particular, to methods and systems for accessing and managing nonvolatile, such as in a wireless phone. A wireless phone memory controller is disclosed that, comprises a first interface circuit configured to be coupled to wireless phone nonvolatile memory, a second interface circuit configured to be coupled to wireless phone volatile memory, a first processor interface configured to be coupled to a first wireless phone processor, wherein the first processor interface is configured to provide the first processor with access to the wireless phone volatile memory, a second processor interface configured to be coupled to a second wireless phone processor, and a controller circuit configured to copy at least a portion of wireless phone nonvolatile memory data to the wireless phone volatile memory.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
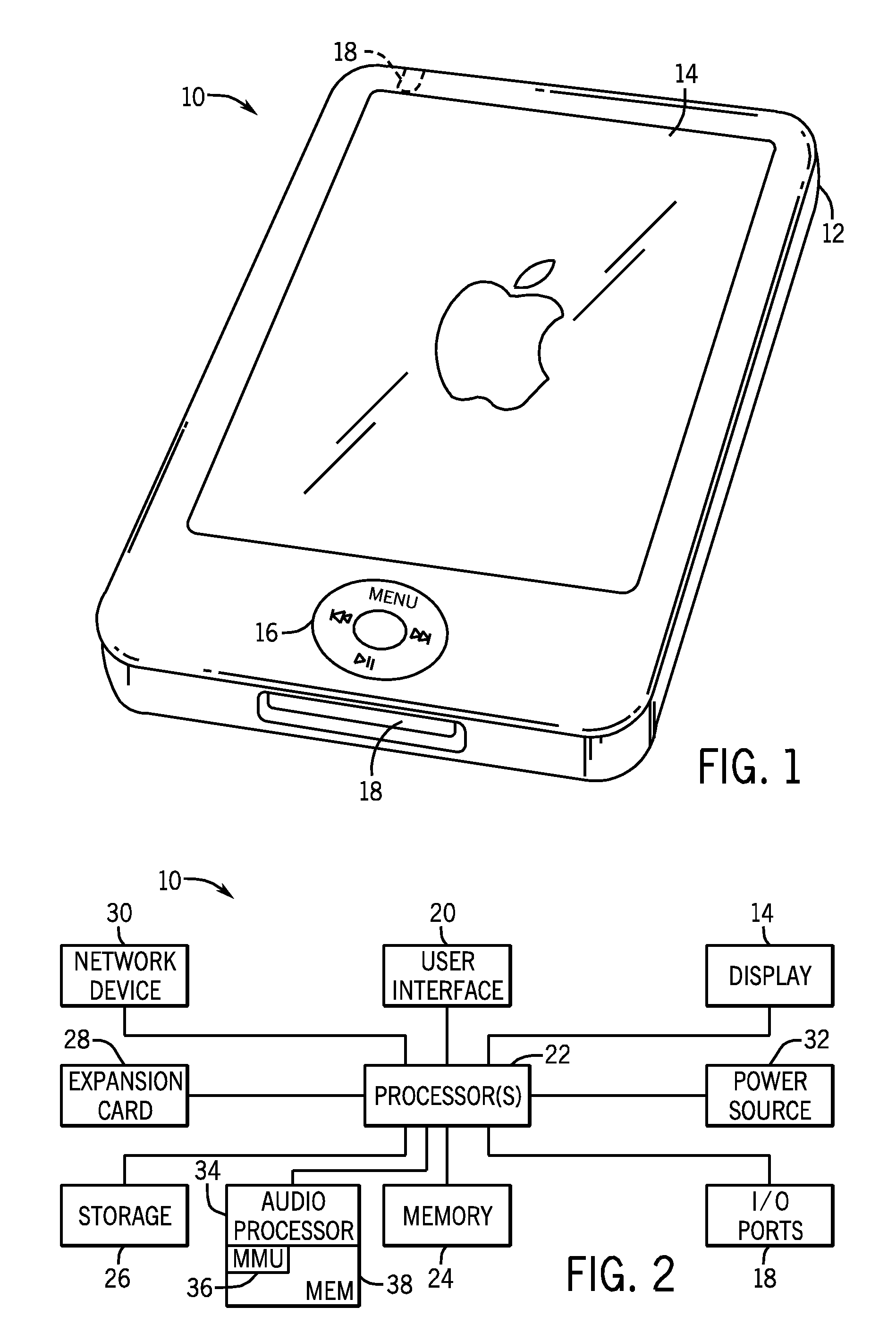
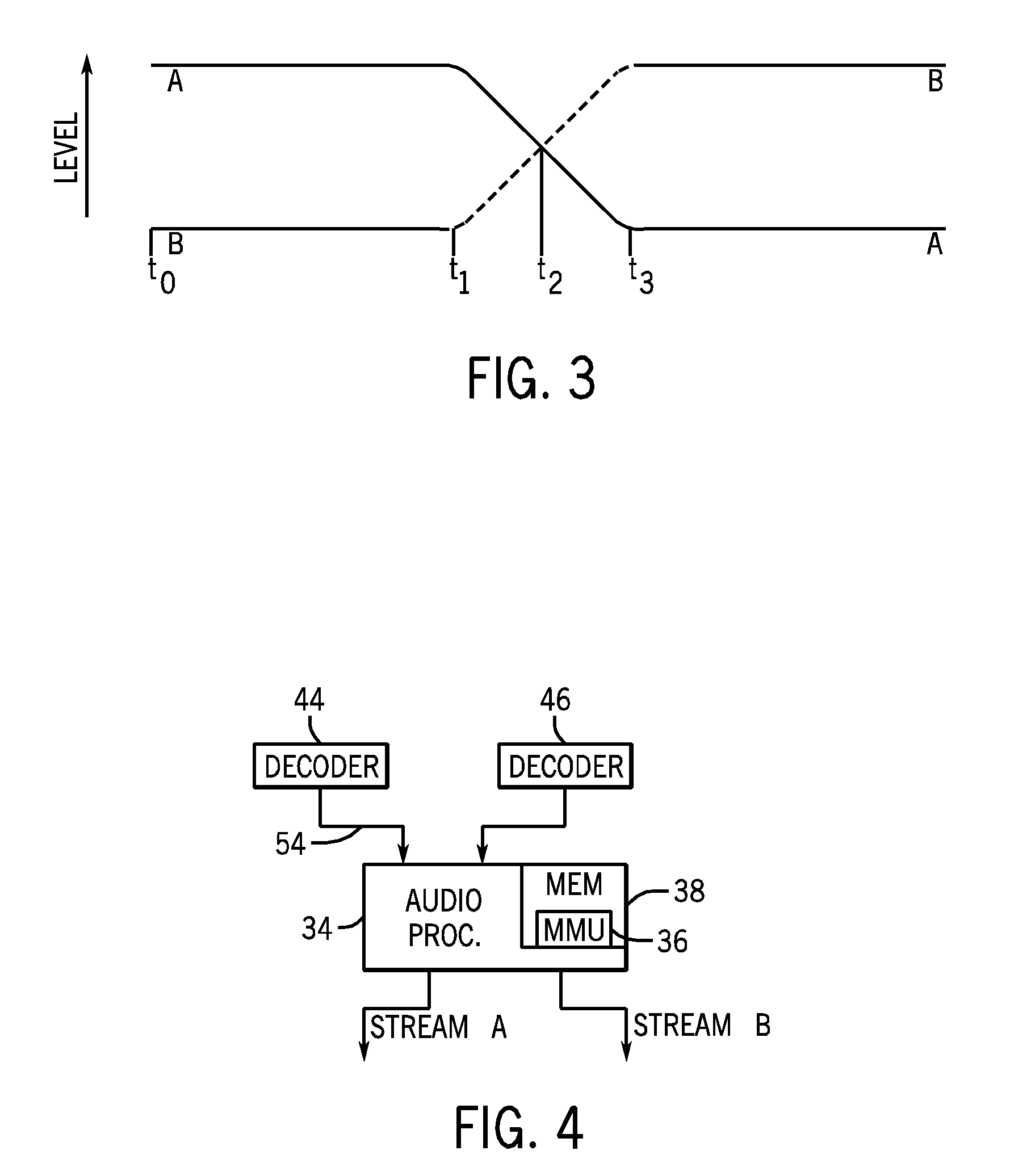
Systems and Methods for Memory Management and Crossfading in an Electronic Device
InactiveUS20100063825A1Sufficient dataLow costElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSpeech analysisCircular bufferAudio frequency
Systems and methods are disclosed for the management of memory used in a crossfading operation in an electronic device. In one embodiment, a processor is used to alternately decode two audio streams, one which is being faded out and one which is being faded in to implement a crossfade. The two audio streams may be encoded in the same or different formats and may be alternately decoded such that resource usage is reduced. The amount of decoded data of both audio streams and other parameters may determine which audio stream is to be actively decoded. In certain embodiments, the decoded data may be stored in a circular buffer, and a delta is determined between the decoded data and the empty space of the buffer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Media player and access system and method and media player operating system architecture
InactiveUS20050091107A1Reduce disadvantagesAdvertisementsMultimedia data browsing/visualisationOperational systemThe Internet
Owner:INSTANT MEDIA
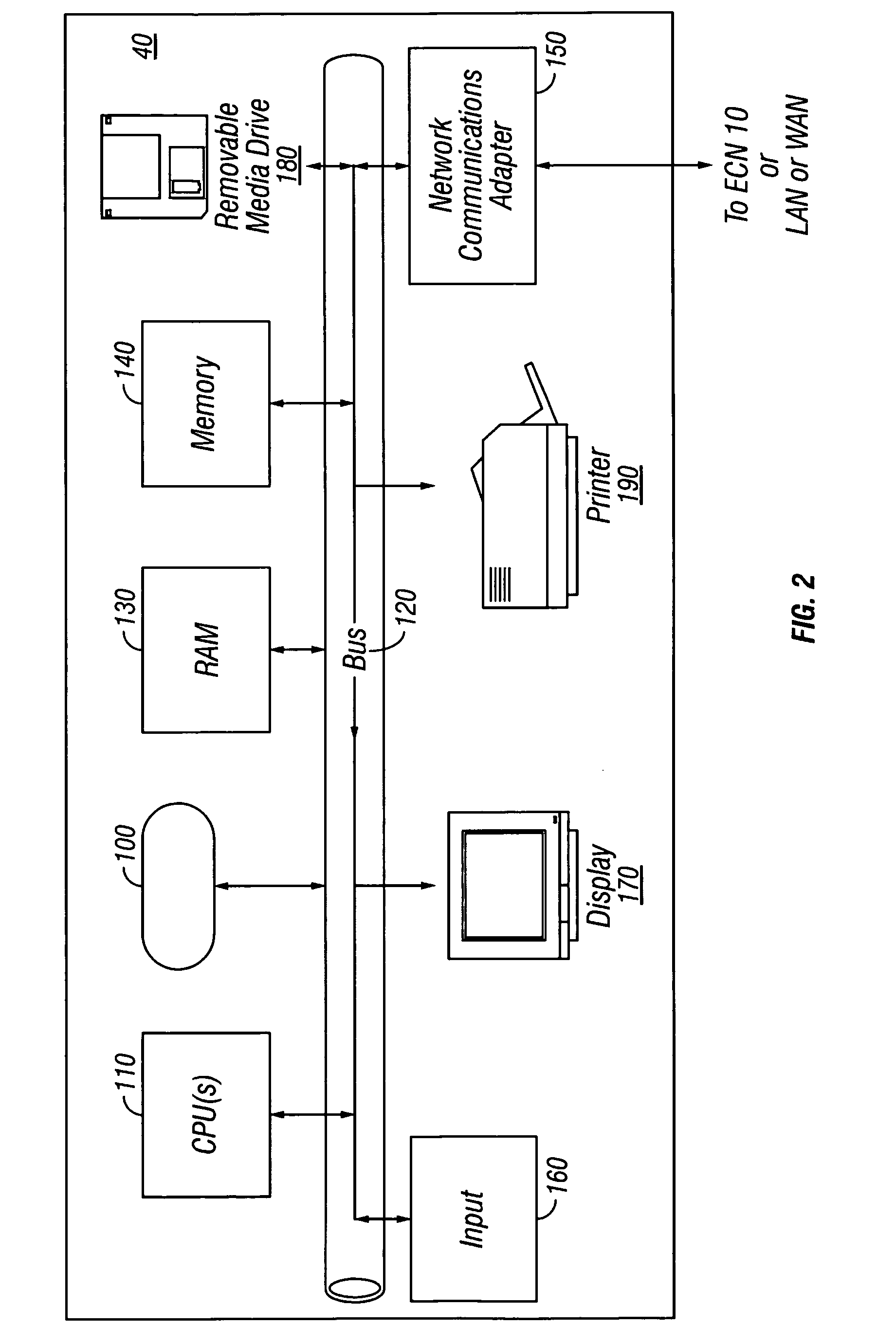
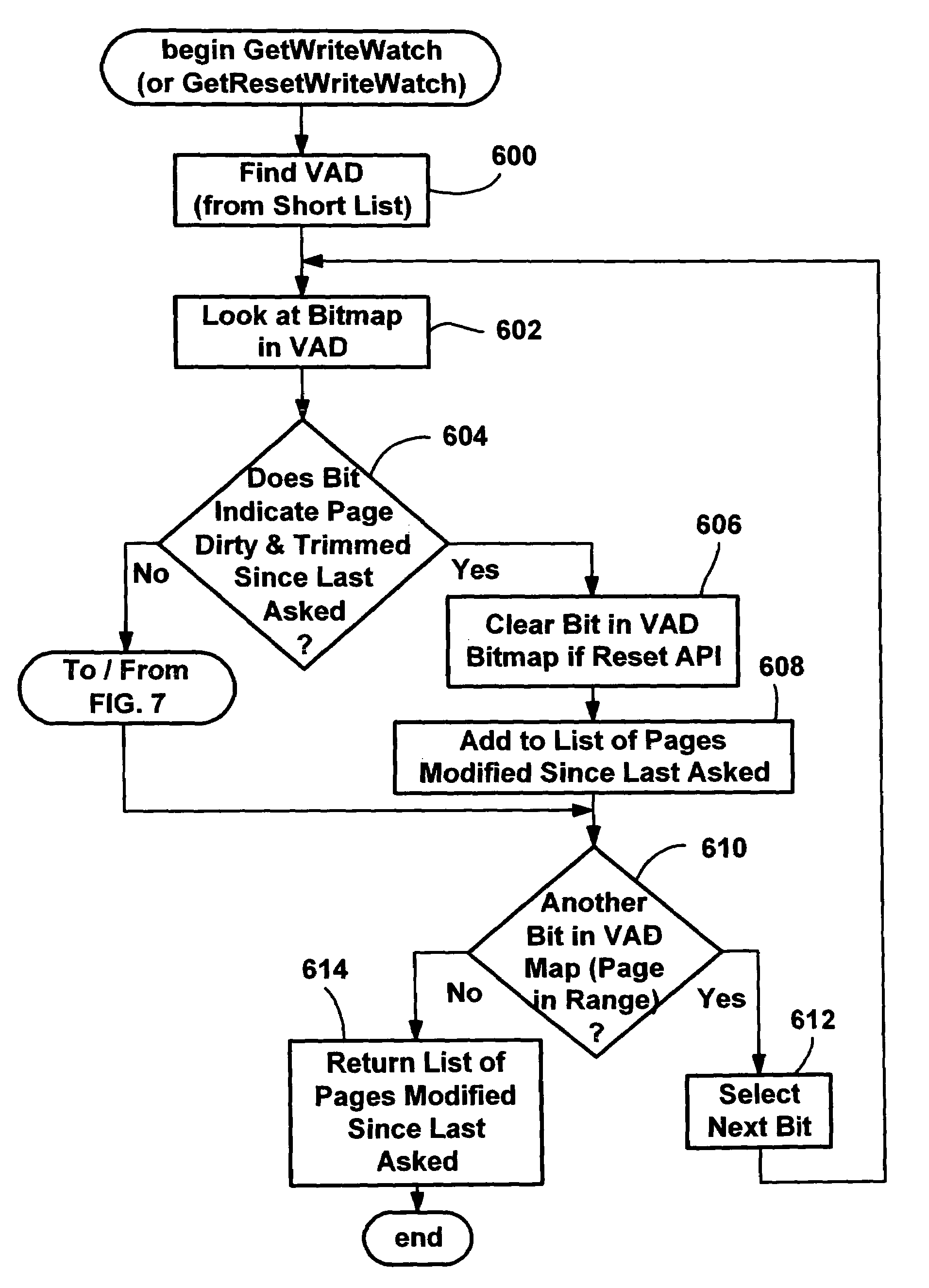
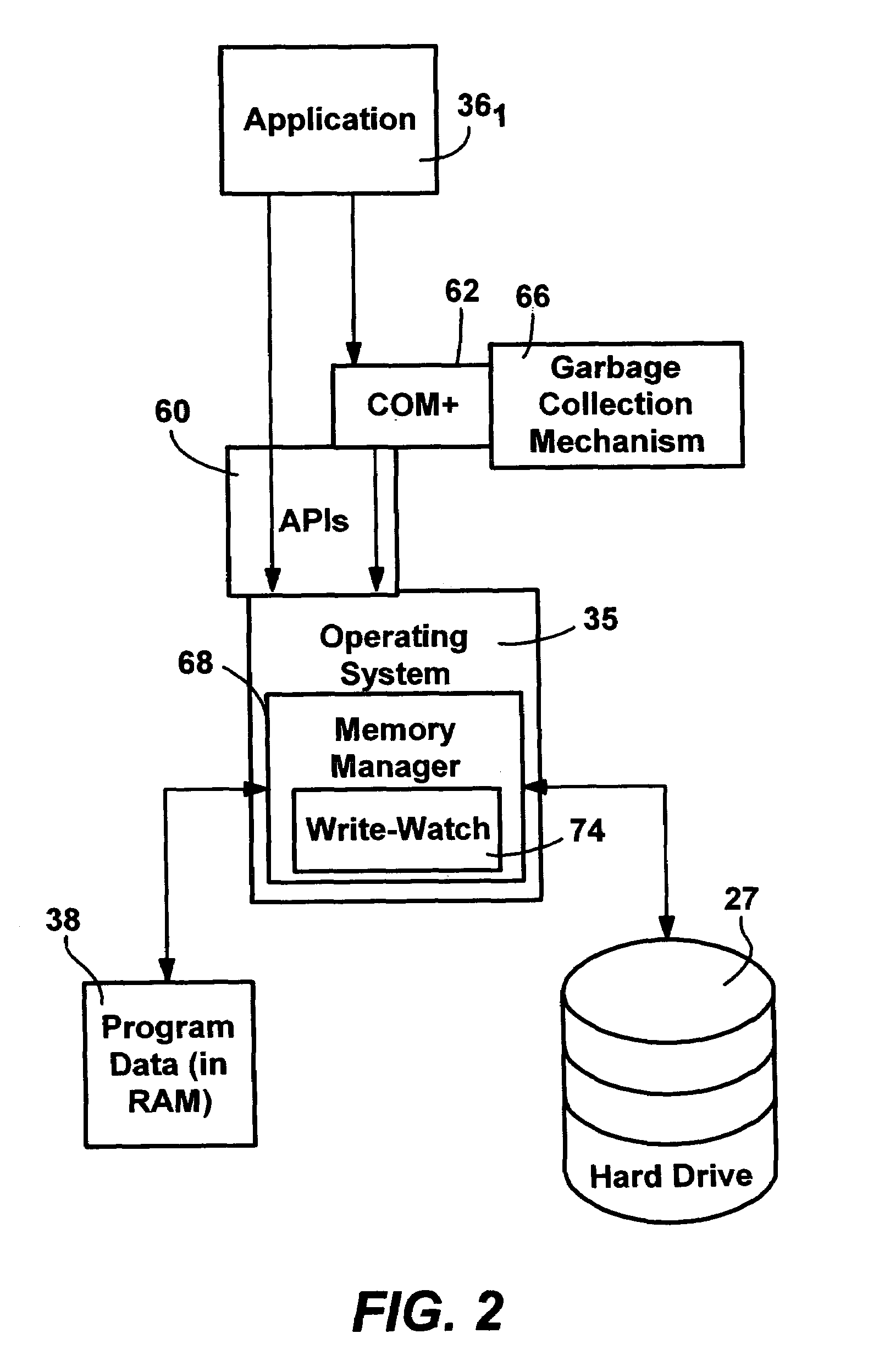
Efficient write-watch mechanism useful for garbage collection in a computer system
InactiveUS7065617B2Efficient write-watchReduce performanceData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemWaste collection
An efficient write-watch mechanism and process. A bitmap is associated with the virtual address descriptor (VAD) for a process, one bit for each virtual page address allocated to a process having write-watch enabled. As part of the write-watch mechanism, if a virtual address is trimmed to disk and that virtual address page is marked as modified, then the corresponding bit in the VAD is set for that virtual address page. In response to an API call (e.g., from a garbage collection mechanism) seeking to know which virtual addresses in a process have been modified since last checked, the memory manager walks the bitmap in the relevant VAD for the specified virtual address range for the requested process. If a bit is set, then the page corresponding to that bit is known to have been modified since last asked. If specified by the API, the bit is cleared in the VAD bitmap so that it will reflect the state since this time of asking. If the bit is not set, to determine if the page was modified, the page table entry (PTE) is checked for that page, and if the PTE indicates the page was modified, the page is known to be modified, otherwise that page is known to be unmodified since the last call. One enhancement uses page directory tables to locate a series of trimmed pages, sometimes avoiding the need to access the PTE.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
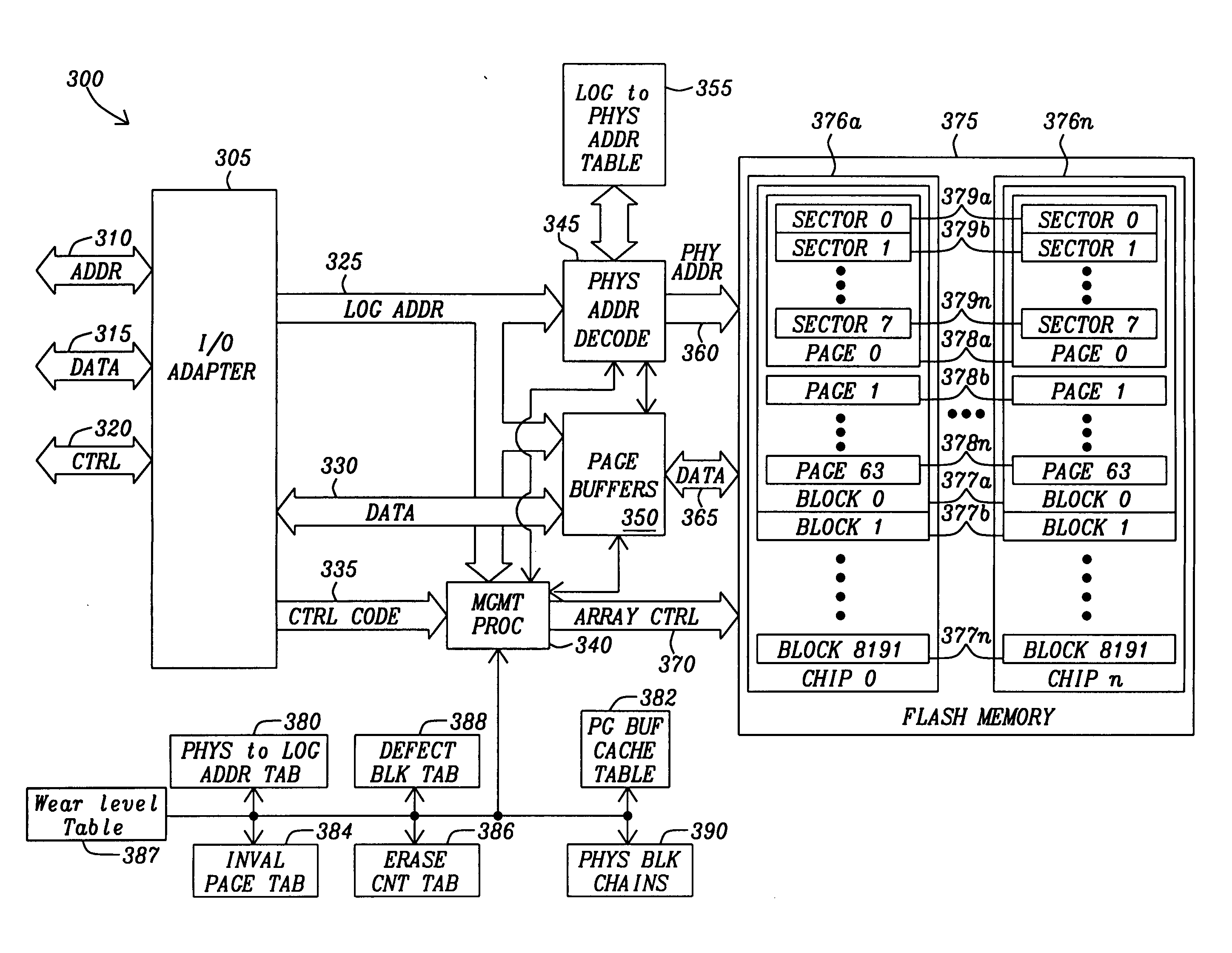
Flash memory management system and method utilizing multiple block list windows
InactiveUS6895464B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRapid accessBlock detection
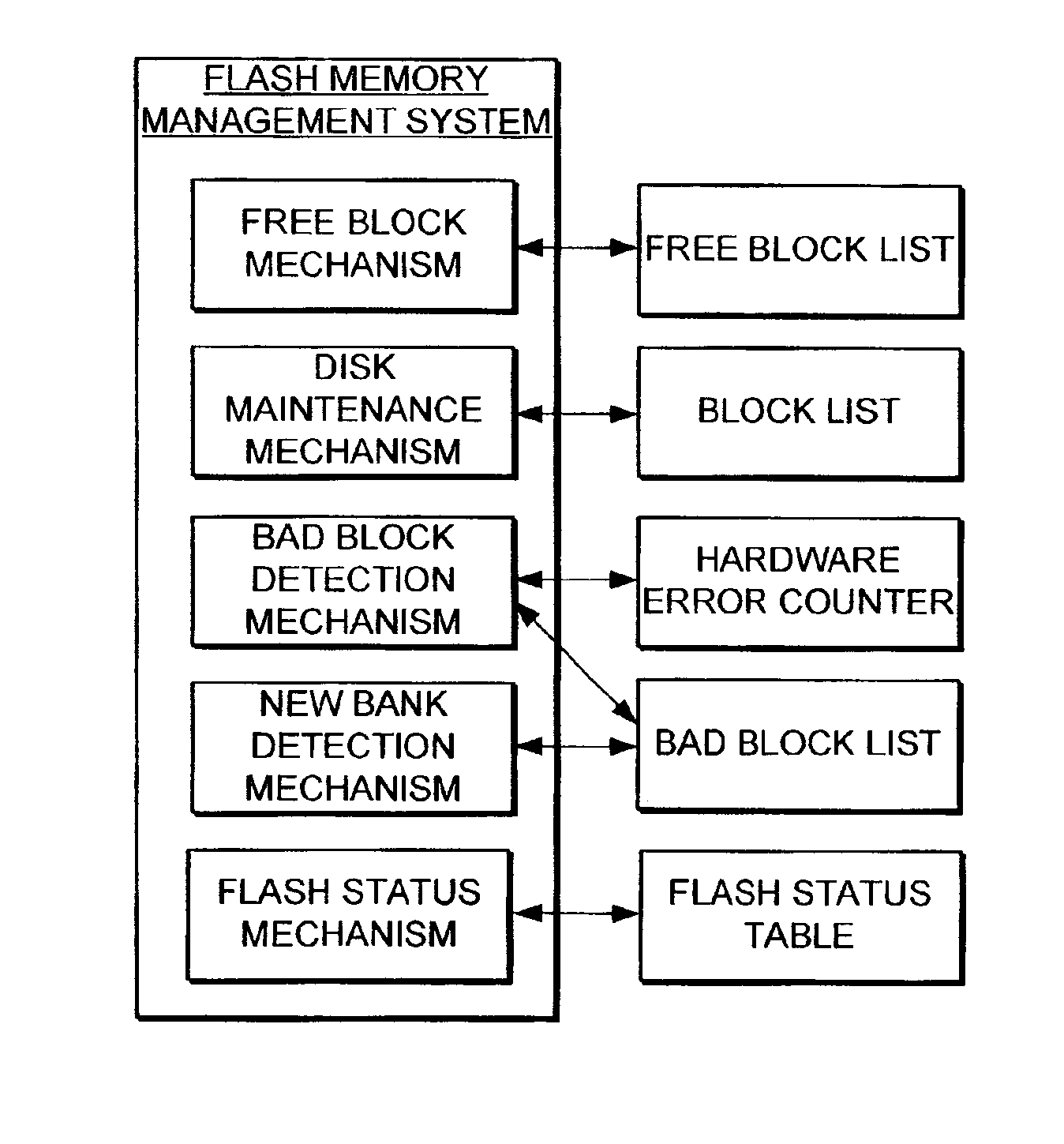
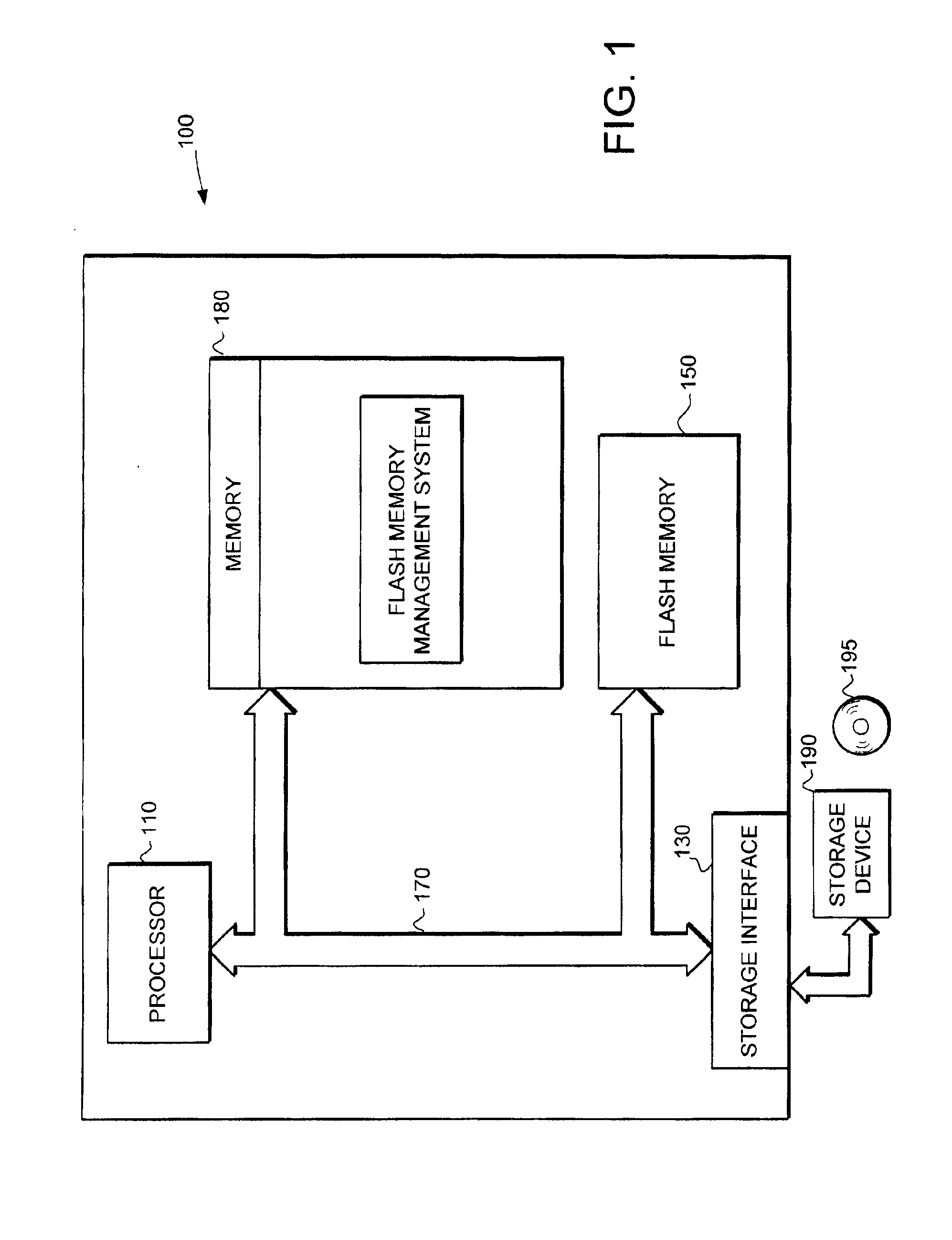
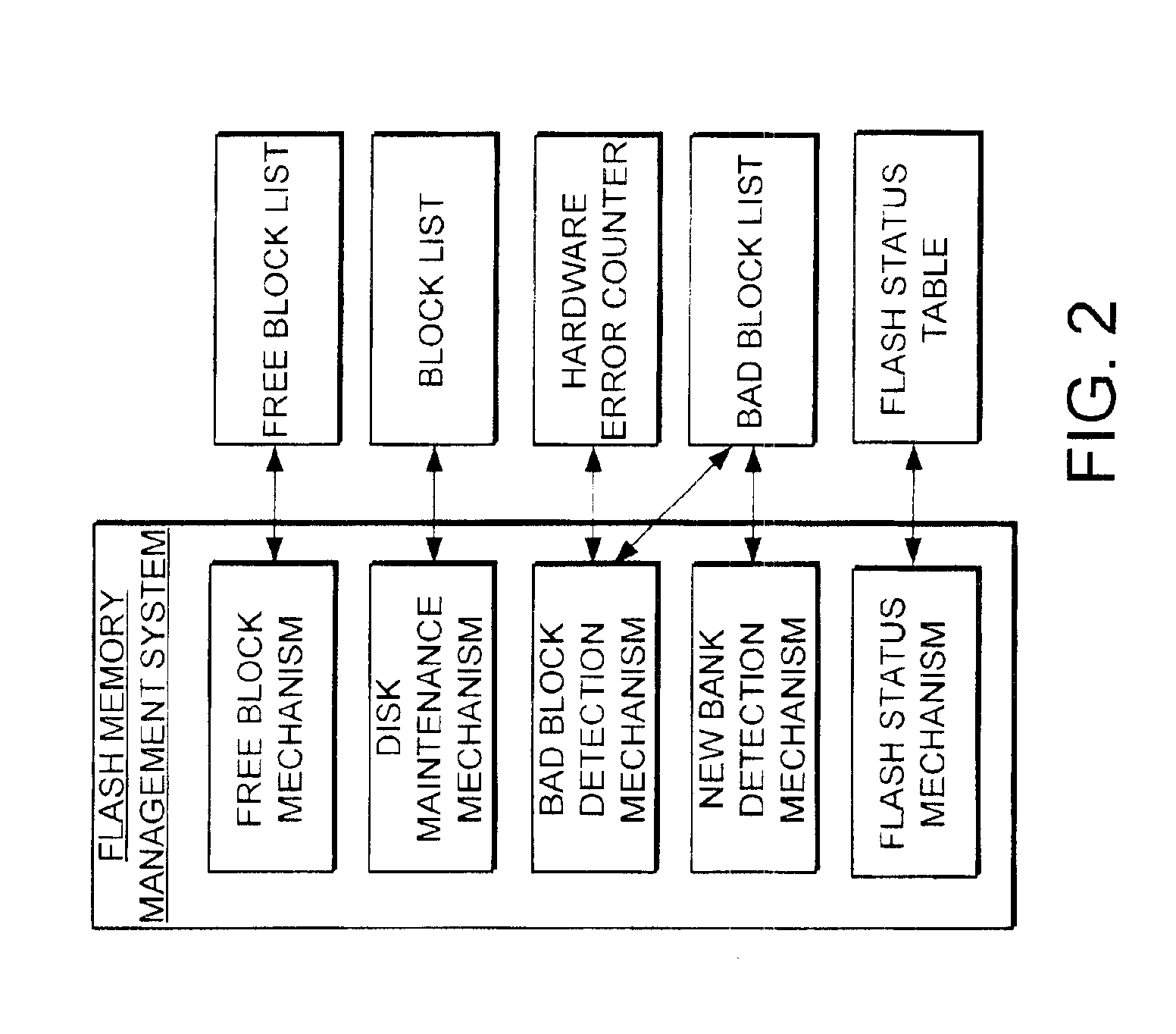
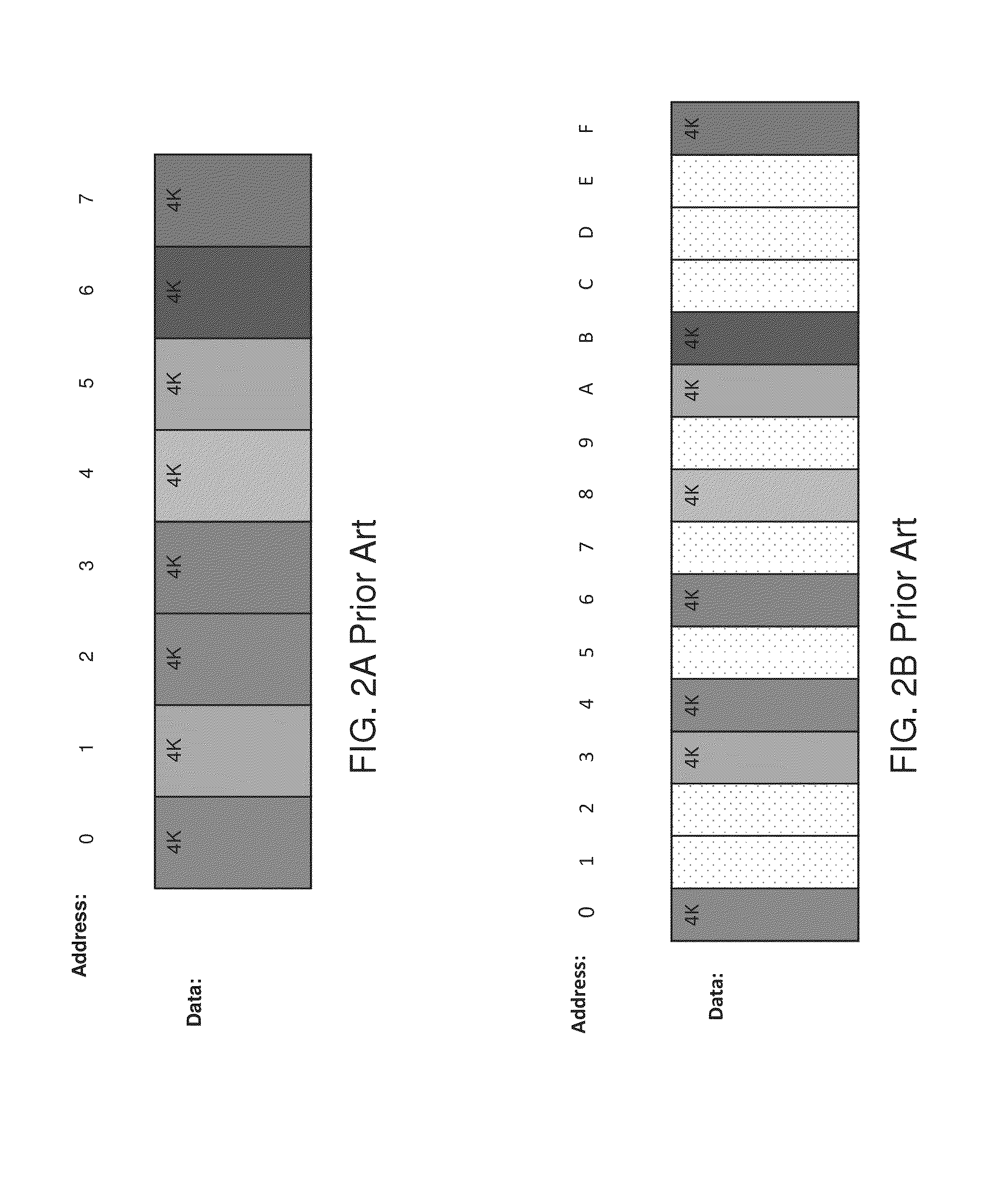
The present invention provides a flash memory management system and method with increased performance. The flash memory management system provides the ability to efficiently manage and allocate flash memory use in a way that improves reliability and longevity, while maintaining good performance levels. The flash memory management system includes a free block mechanism, a disk maintenance mechanism, and a bad block detection mechanism. The free block mechanism provides efficient sorting of free blocks to facilitate selecting low use blocks for writing. The disk maintenance mechanism provides for the ability to efficiently clean flash memory blocks during processor idle times. The bad block detection mechanism provides the ability to better detect when a block of flash memory is likely to go bad. The flash status mechanism stores information in fast access memory that describes the content and status of the data in the flash disk. The new bank detection mechanism provides the ability to automatically detect when new banks of flash memory are added to the system. Together, these mechanisms provide a flash memory management system that can improve the operational efficiency of systems that utilize flash memory.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
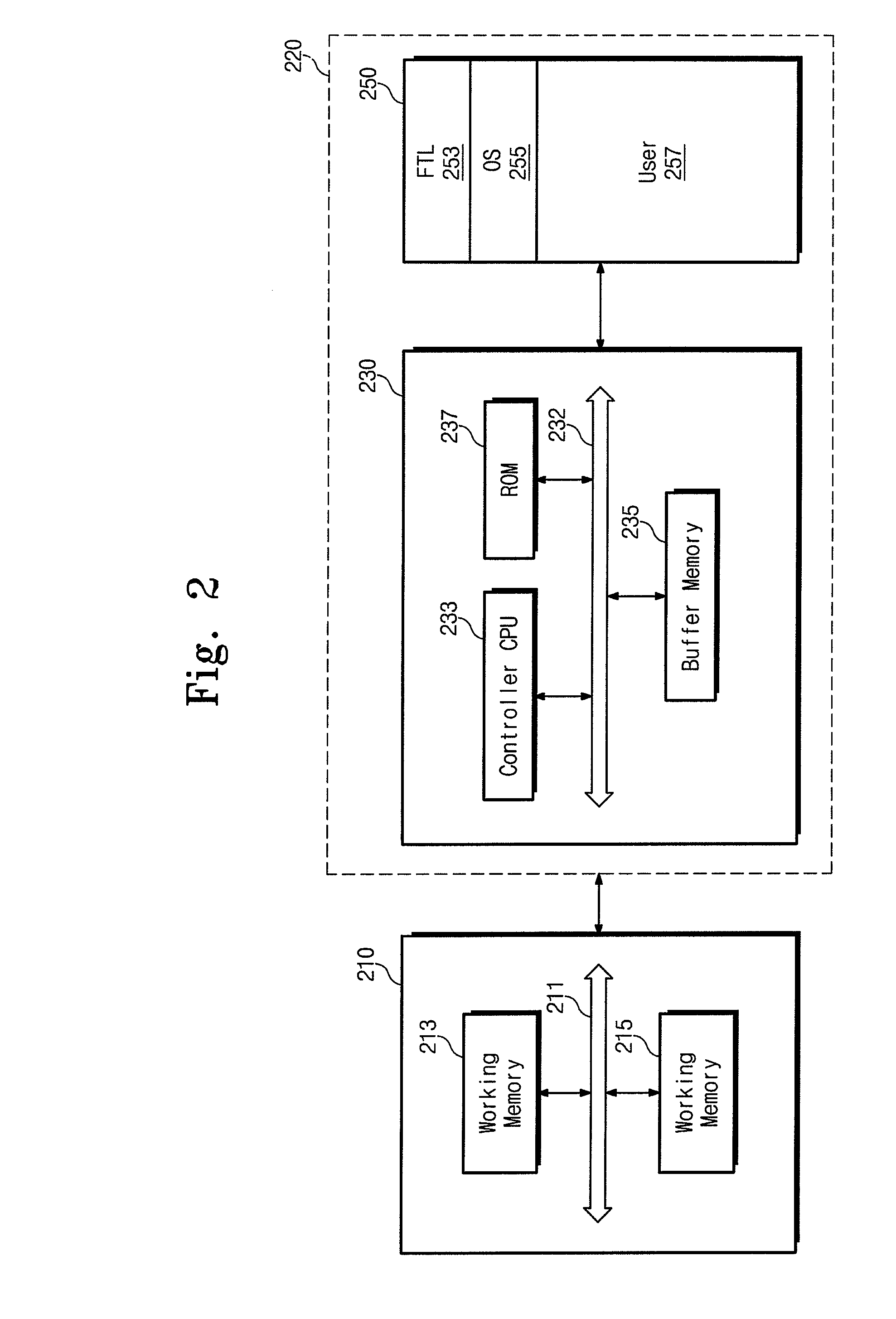
Integrated memory management and memory management method
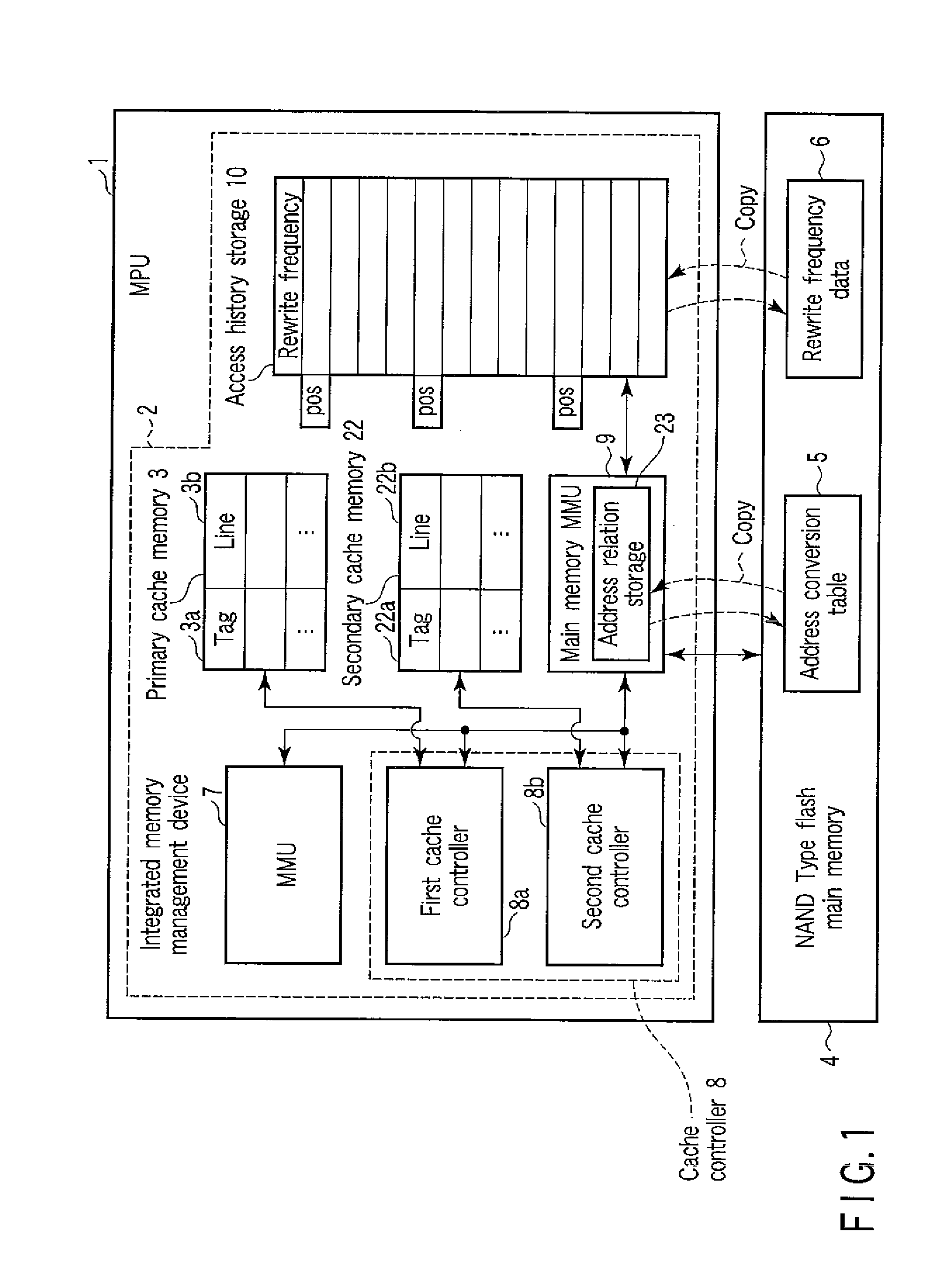
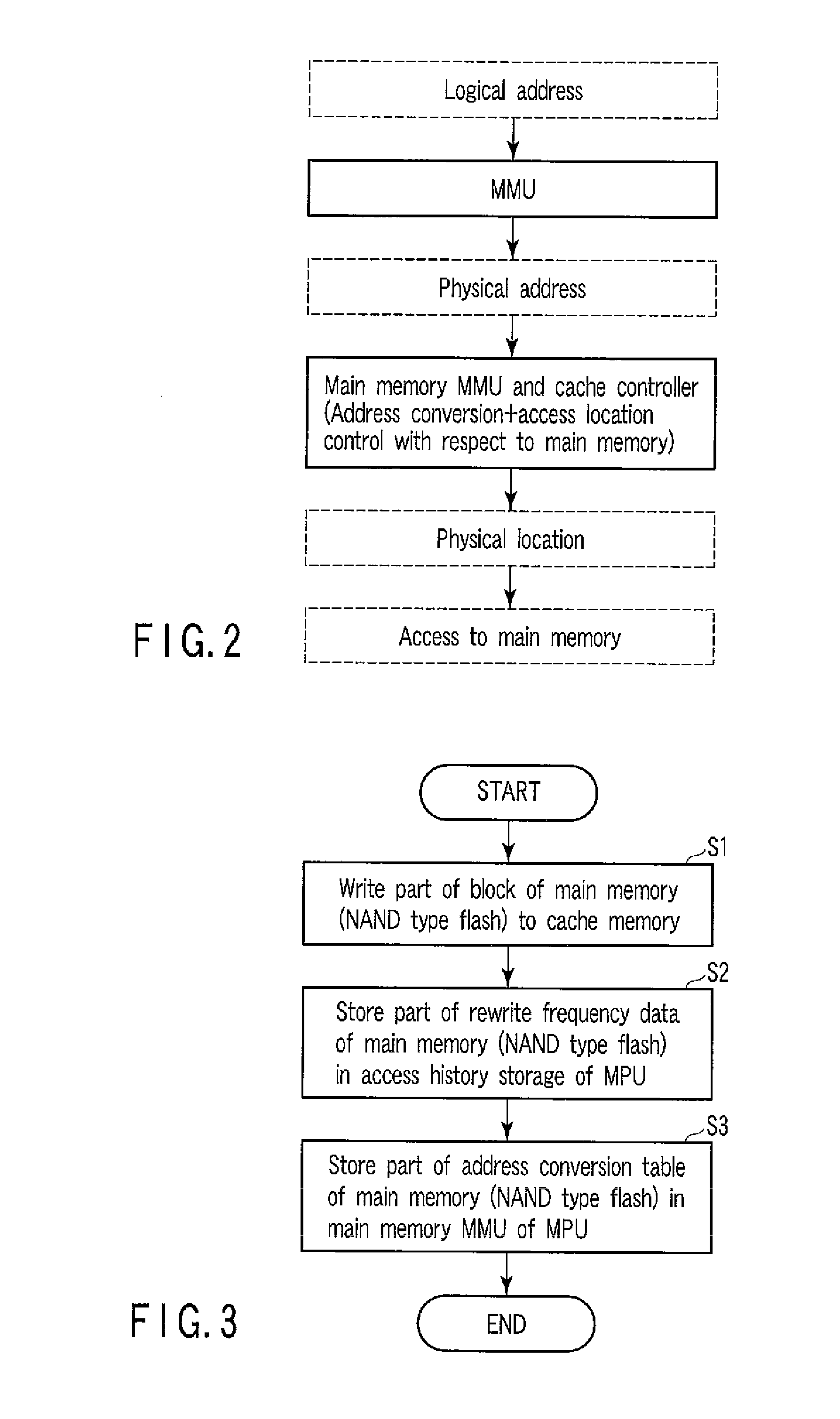
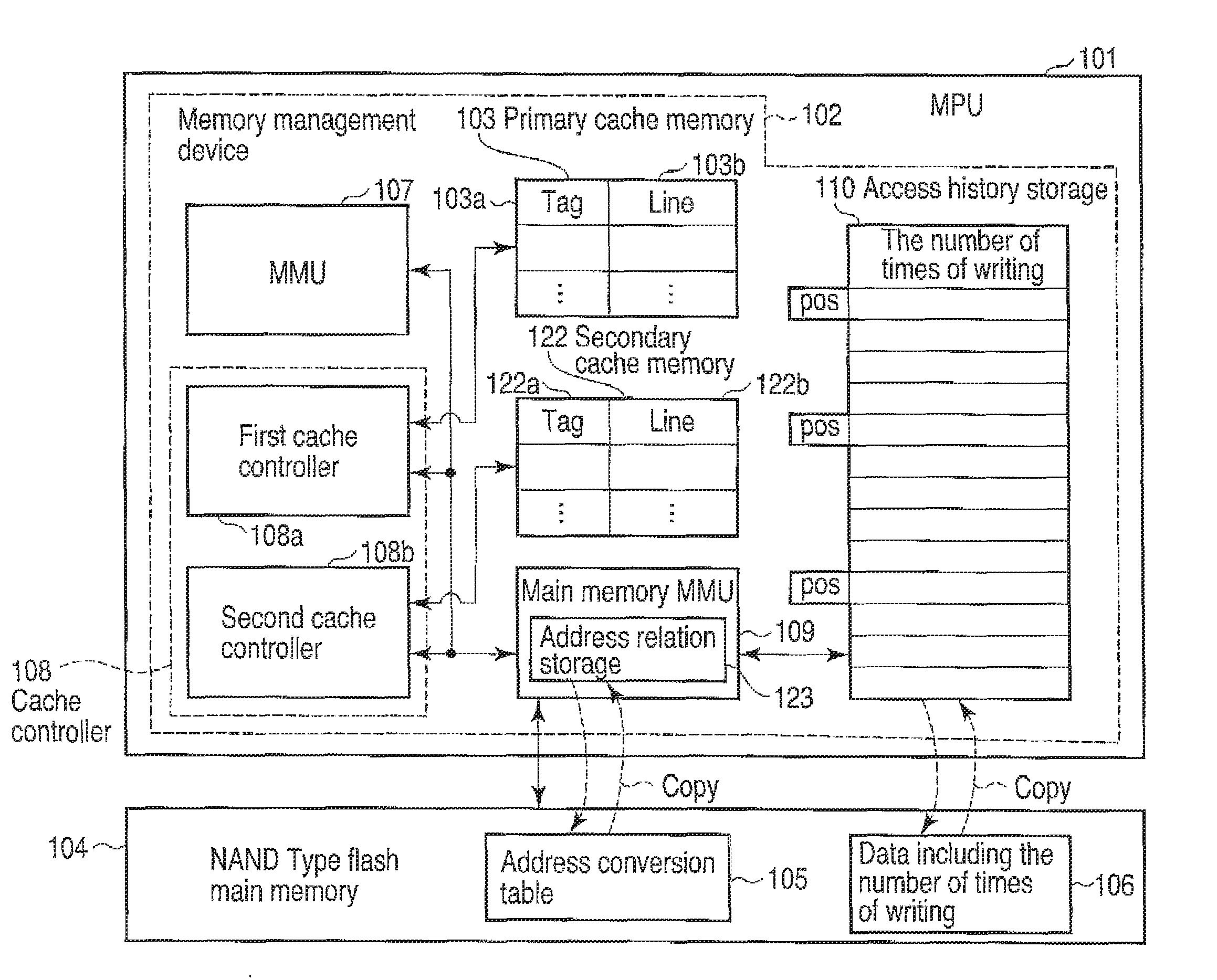
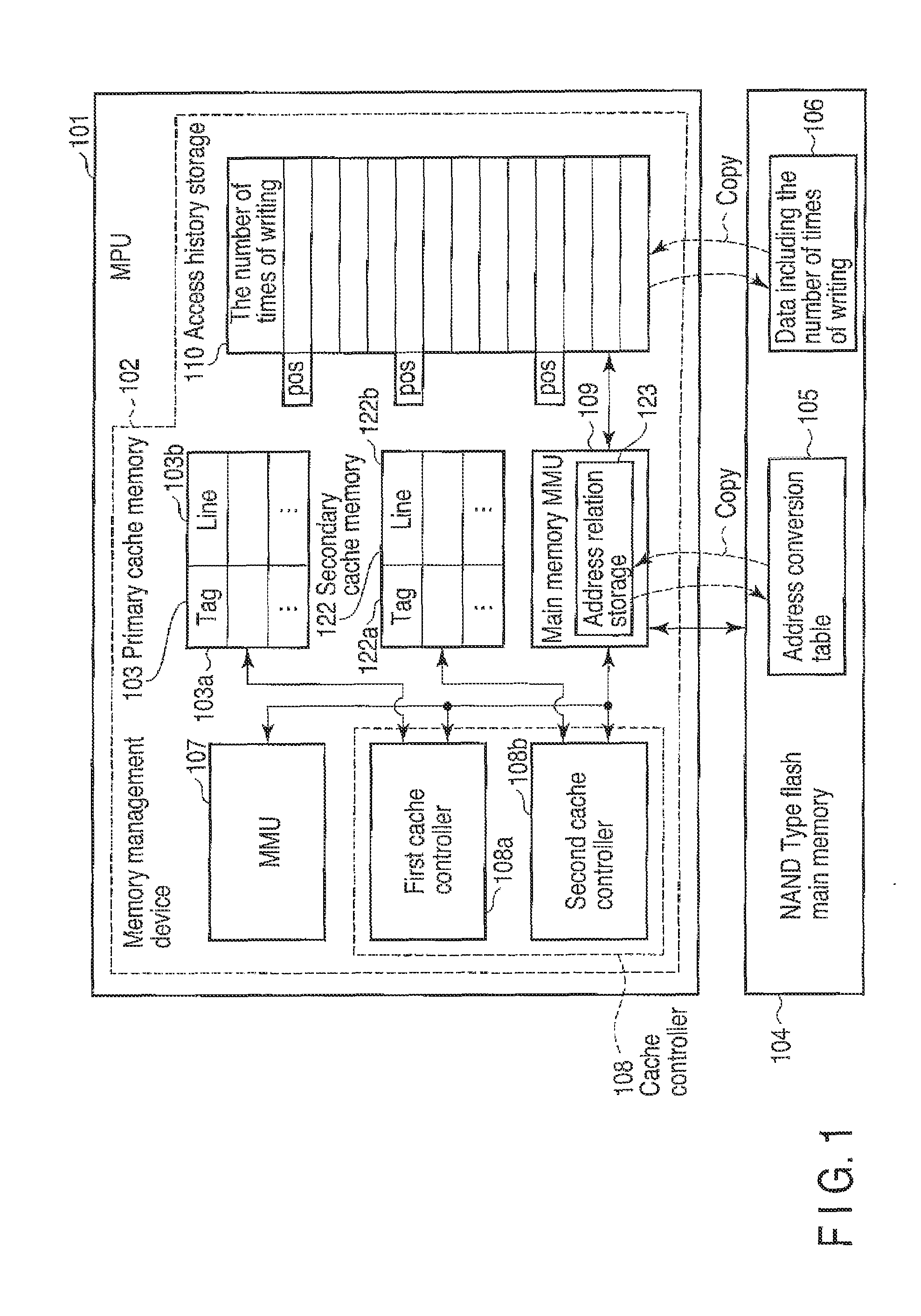
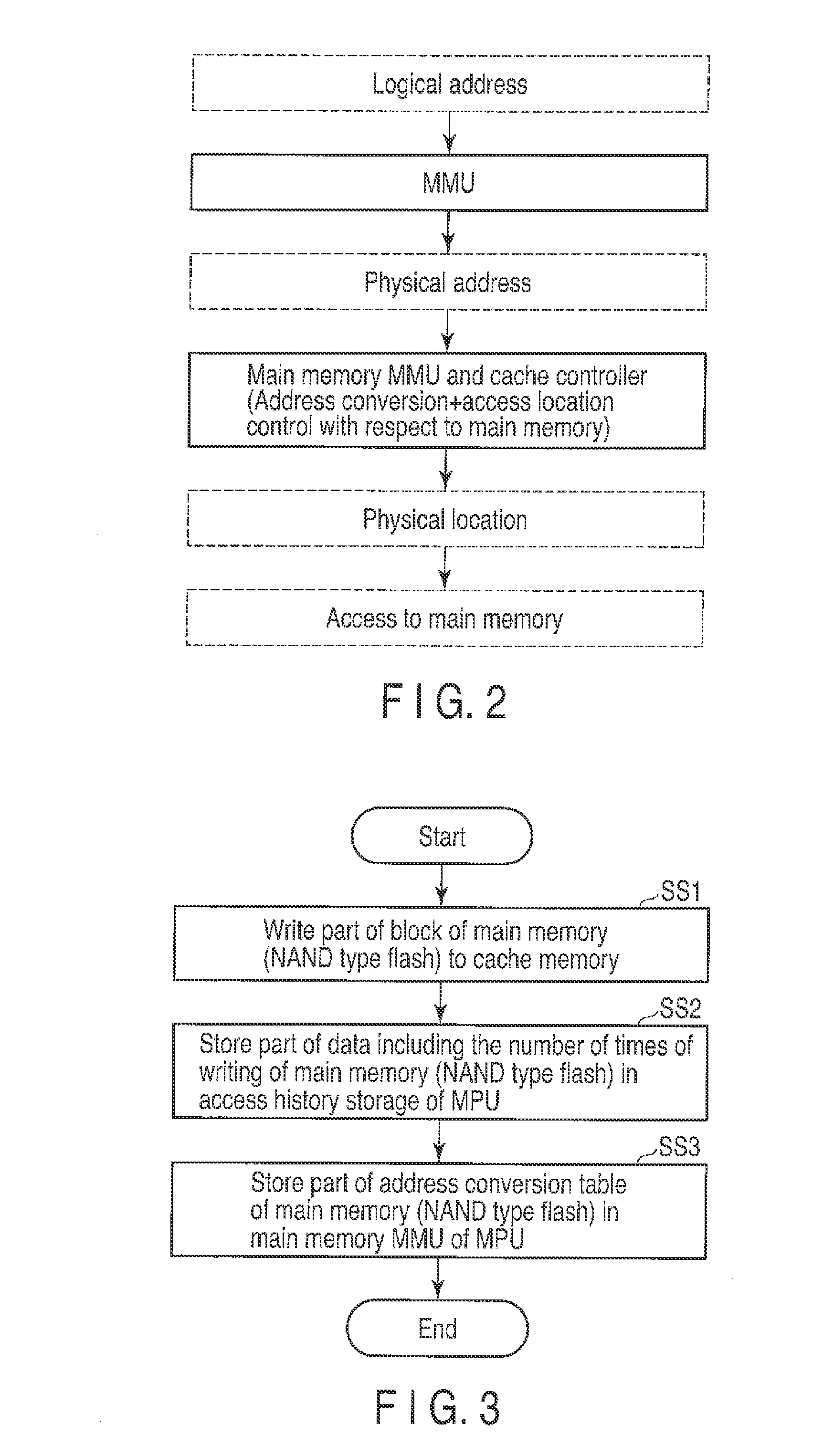
ActiveUS20090083478A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData transmissionMemory management unit
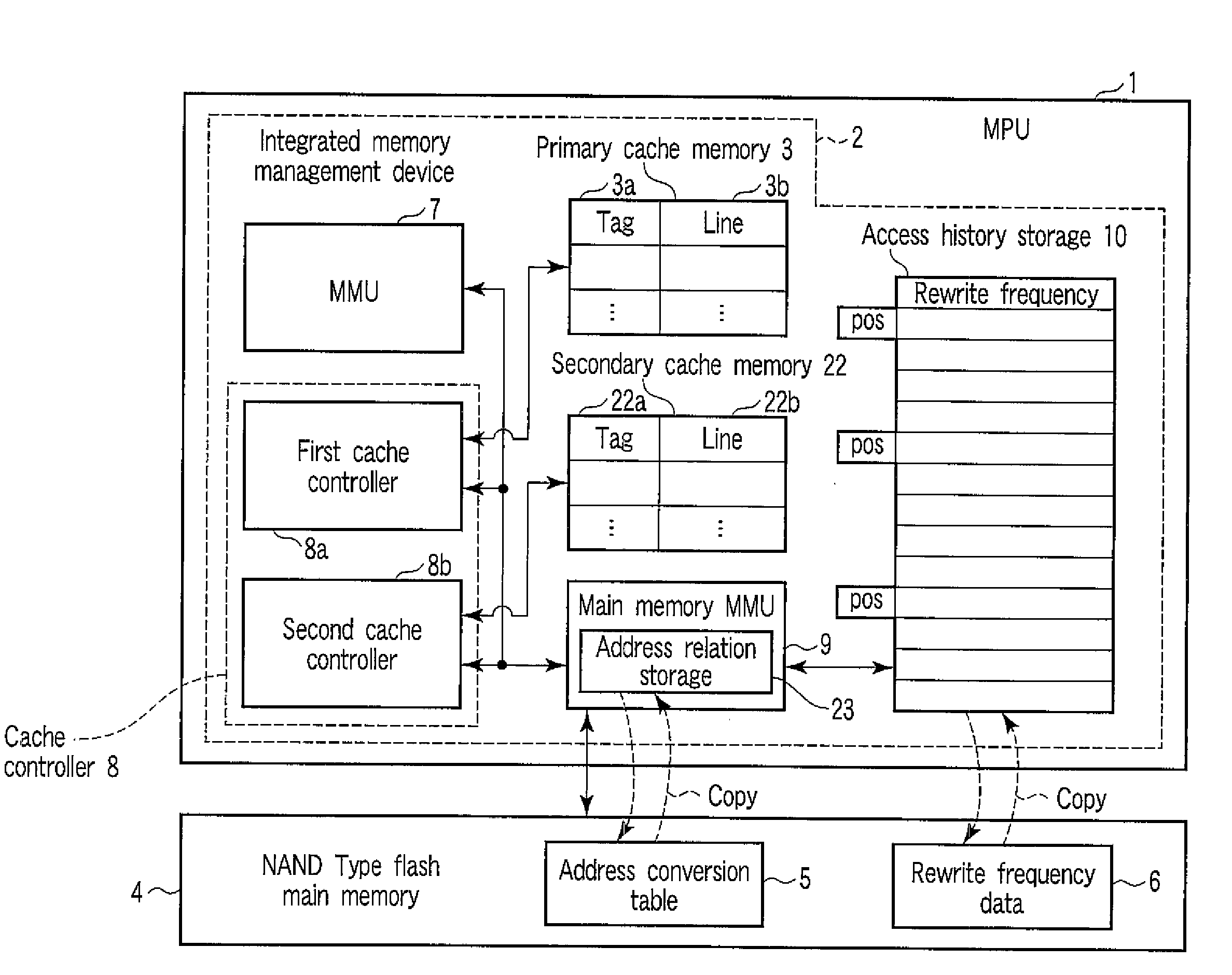
An integrated memory management device according to an example of the invention comprises an acquiring unit acquiring a read destination logical address from a processor, an address conversion unit converting the read destination logical address into a read destination physical address of a non-volatile main memory, an access unit reading, from the non-volatile main memory, data that corresponds to the read destination physical address and has a size that is equal to a block size or an integer multiple of the page size of the non-volatile main memory, and transmission unit transferring the read data to a cache memory of the processor having a cache size that depends on the block size or the integer multiple of the page size of the non-volatile main memory.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
RDMA enabled I/O adapter performing efficient memory management
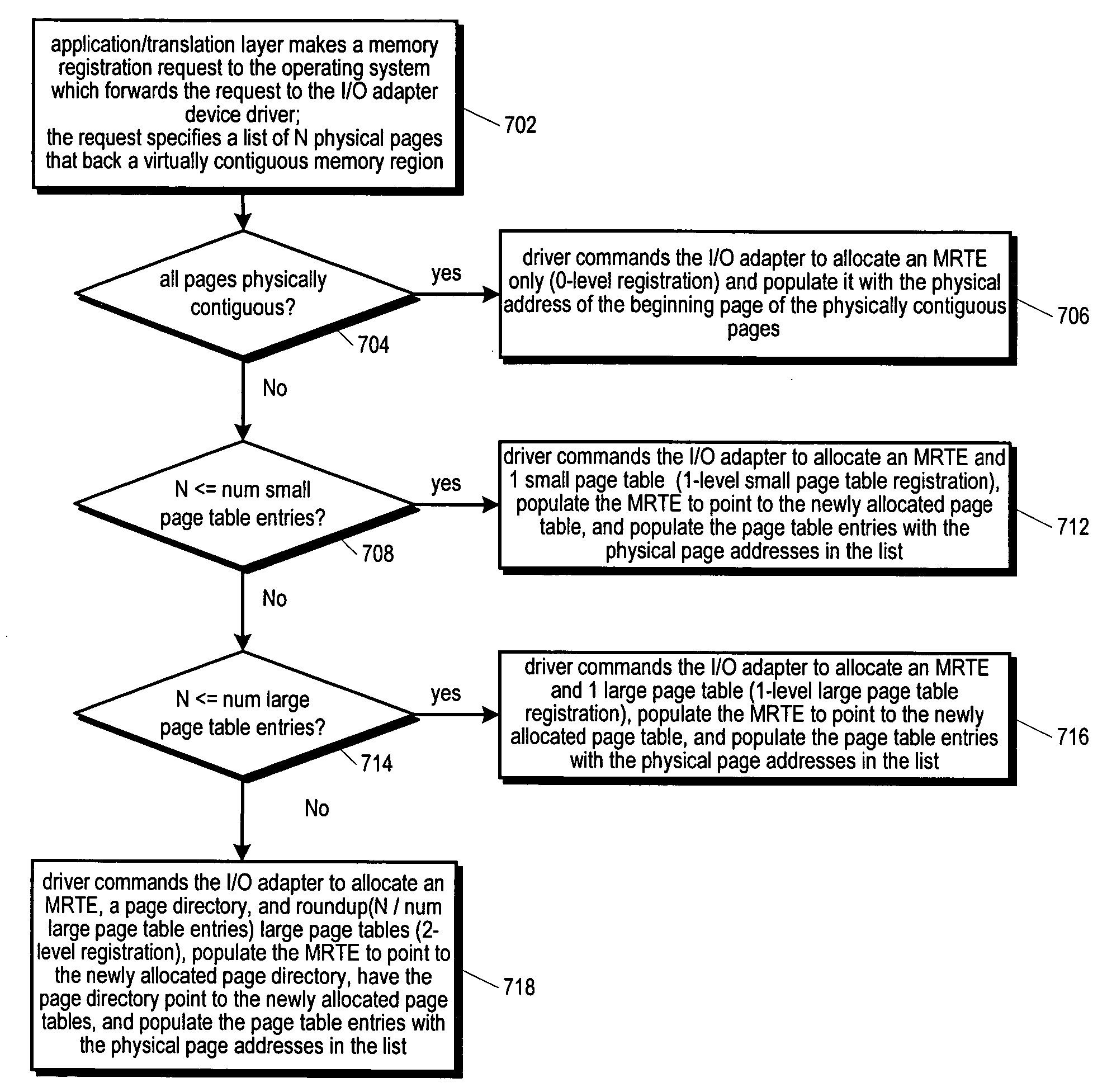
InactiveUS20060236063A1Reduce the numberReduce the amount requiredMemory systemsPhysical addressTerm memory
An RDMA enabled I / O adapter and device driver is disclosed. In response to a memory registration that includes a list of physical memory pages backing a virtually contiguous memory region, an entry in a table in the adapter memory is allocated. A variable size data structure to store the physical addresses of the pages is also allocated as follows: if the pages are physically contiguous, the physical page address of the beginning page is stored directly in the table entry and no other allocations are made; otherwise, one small page table is allocated if the addresses will fit in a small page table; otherwise, one large page table is allocated if the addresses will fit in a large page table; otherwise, a page directory is allocated and enough page tables to store the addresses are allocated. The size and number of the small and large page tables is programmable.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) and Diversion of Temp Files for Reduced Flash Wear of a Super-Endurance Solid-State Drive
ActiveUS20150106556A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFilename extensionData file
A flash drive has increased endurance and longevity by reducing writes to flash. An Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) is created in a DRAM buffer and provides temporary storage to reduce flash wear. A Smart Storage Switch (SSS) controller assigns data-type bits when categorizing host accesses as paging files used by memory management, temporary files, File Allocation Table (FAT) and File Descriptor Block (FDB) entries, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from FAT. Paging files and temporary files are never written to flash. Partial-page data is packed and sector mapped by sub-sector mapping tables that are pointed to by a unified mapping table that stores the data-type bits and pointers to data or tables in DRAM. Partial sectors are packed together to reduce DRAM usage and flash wear. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
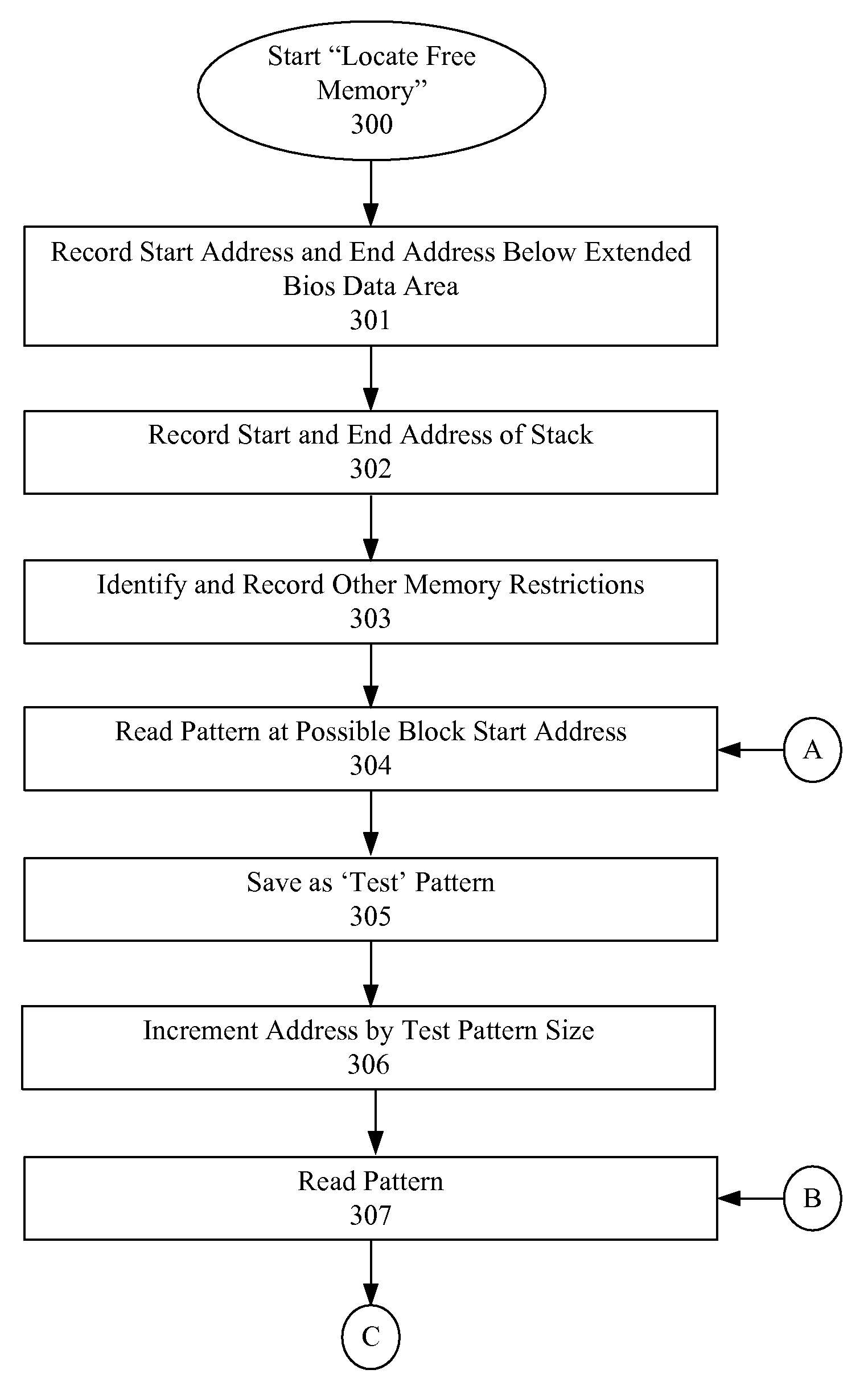
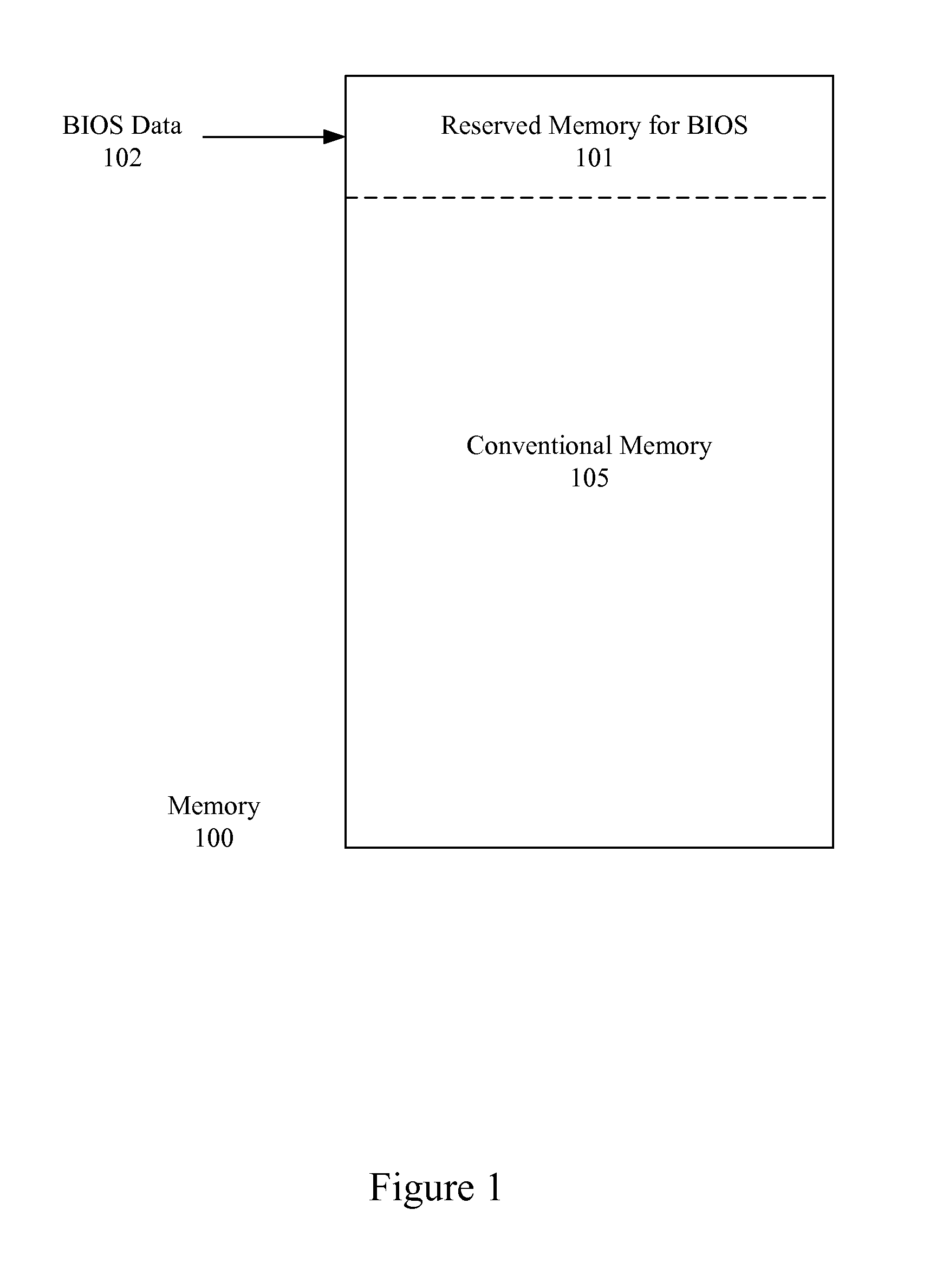
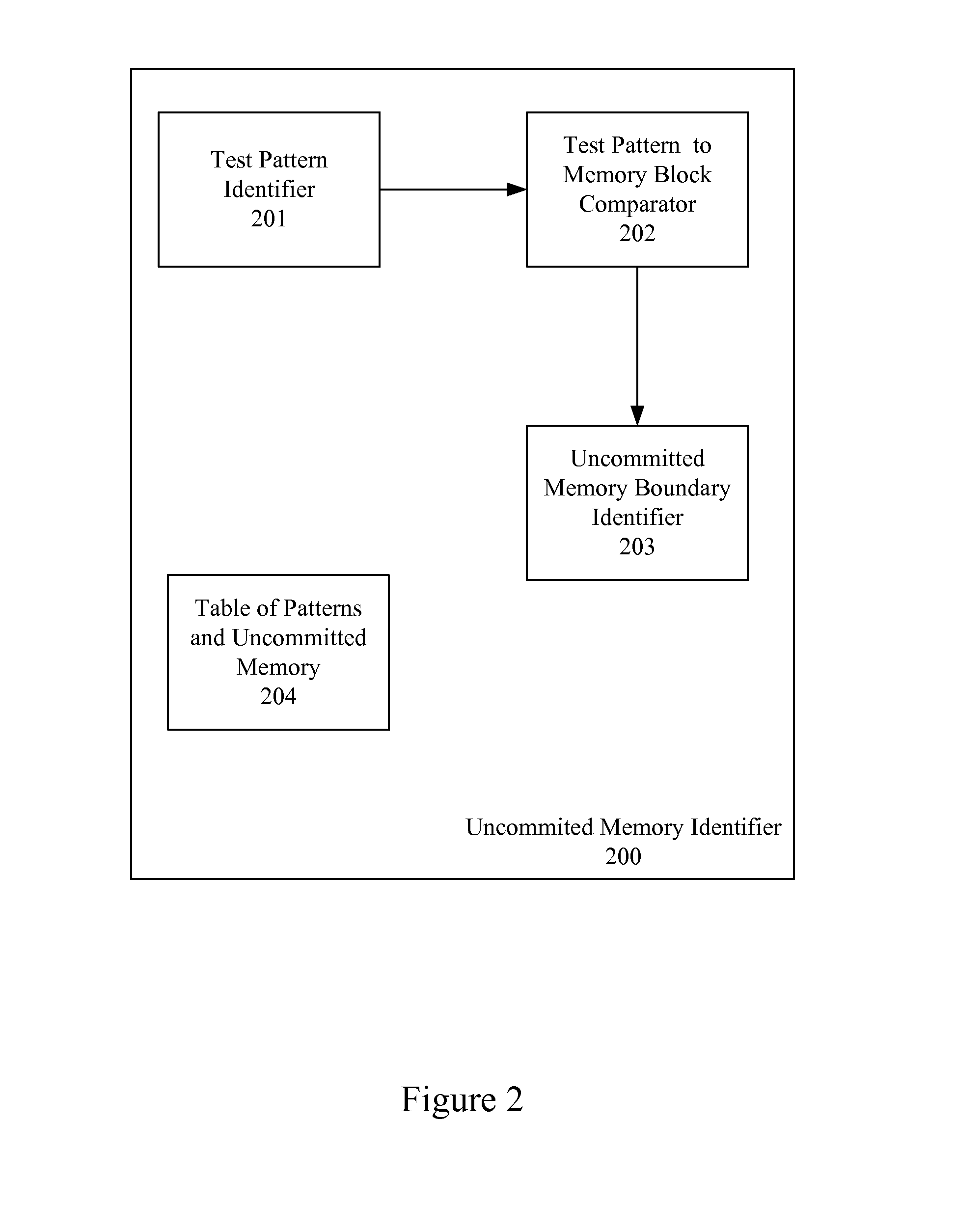
Identification of Uncommitted Memory Blocks During an Initialization Procedure
InactiveUS20080065852A1Easy to useDigital computer detailsProgram controlConventional memoryOption ROM
An apparatus and method are described for identifying uncommitted memory in a system RAM during an initialization process of a computer system, such as a boot procedure or power-on self test, during which memory management is uncontrolled. In various embodiments of the invention, repeating patterns that are indicative of uncommitted memory blocks are identified within a conventional memory area of the system RAM. At least some of the uncommitted memory blocks are allocated for use by an option ROM or other BIOS data and a table is created identifying these uncommitted memory blocks. After the BIOS code exits the system RAM, the table is used to restore the uncommitted memory blocks into their previous data states.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Cooperative memory management
ActiveUS20080189485A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTerm memoryMemory cards
A cooperative memory card system includes a memory card device, and a host in signal communication with the memory card device, where the host assumes at least one memory management function for the memory card device; and a corresponding method of cooperative memory management between a host and a memory card device includes selecting at least one of several memory management functions to be performed by the host for the device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
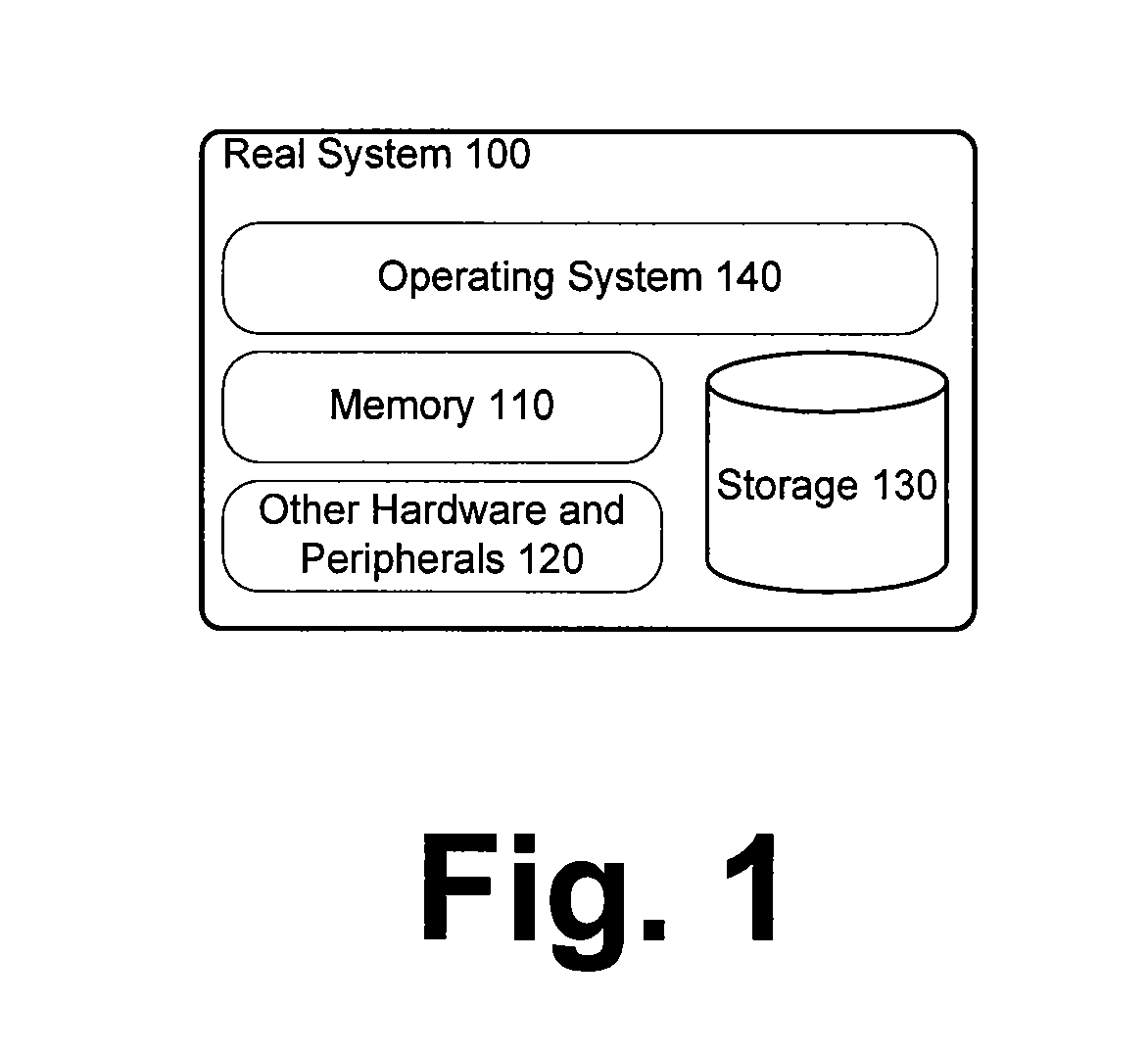
System and Method for Forensic Identification of Elements Within a Computer System
ActiveUS20100030996A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMemory forensicsComputer system design
A system and method for employing memory forensic techniques to determine operating system type, memory management configuration, and virtual machine status on a running computer system. The techniques apply advanced techniques in a fashion to make them usable and accessible by Information Technology professionals that may not necessarily be versed in the specifics of memory forensic methodologies and theory.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Recording and communication of handwritten information
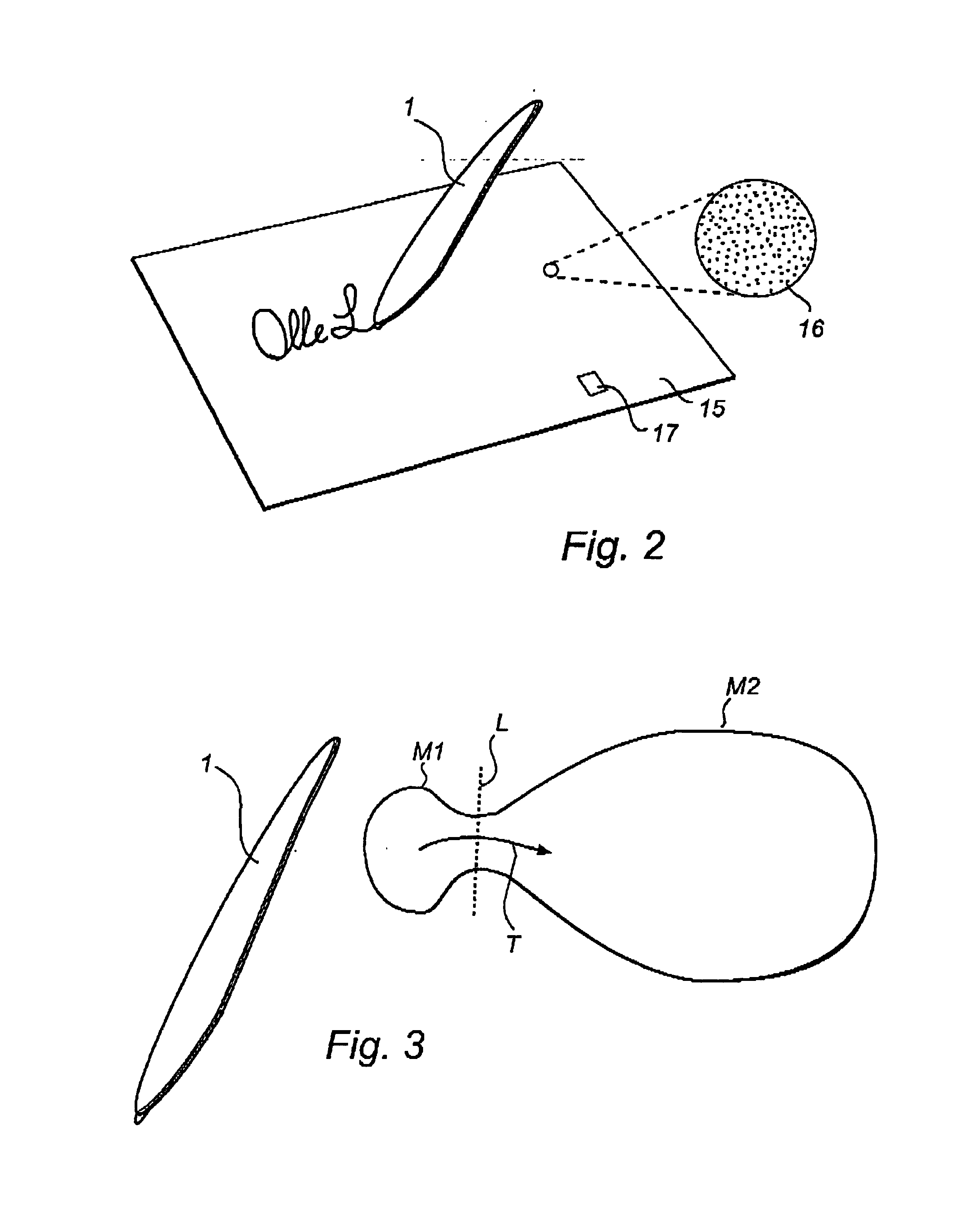
InactiveUS7167164B2Large capacityEasy searchTransmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionExternal dataHand held
A hand-held user unit (1), which can be part of a network-based information management system, allows for the writing down and recording of handwritten information. The user unit (1) has a memory for storing the recorded information. The memory comprises a first memory part (M1) located in the user unit and a second memory part (M2) located in an external data storage device, which memory parts are connected in such a way that, from the point of view of a user, they form a coherent memory unit.Methods for memory management in such a user unit are also described.
Owner:ANOTO AB
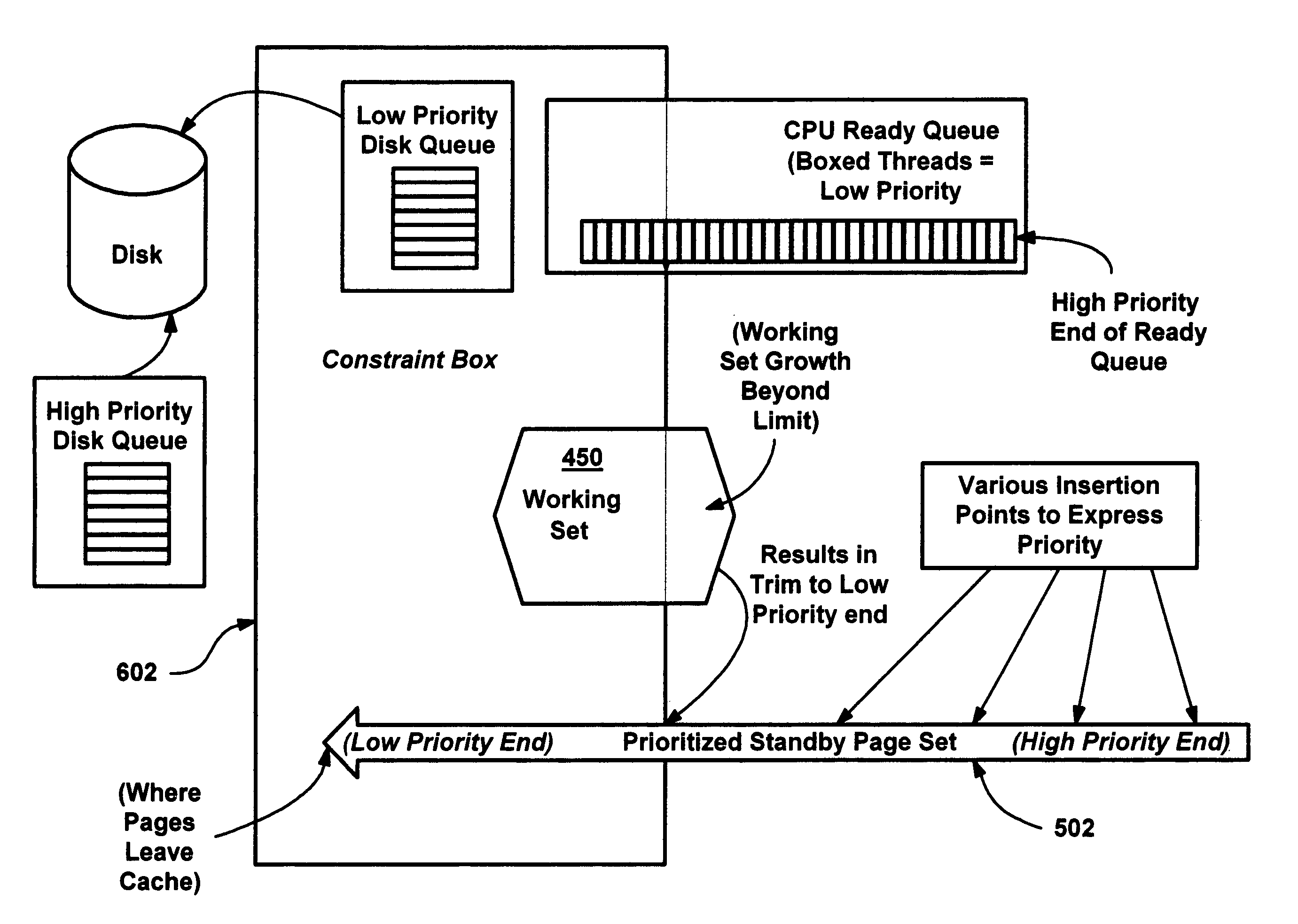
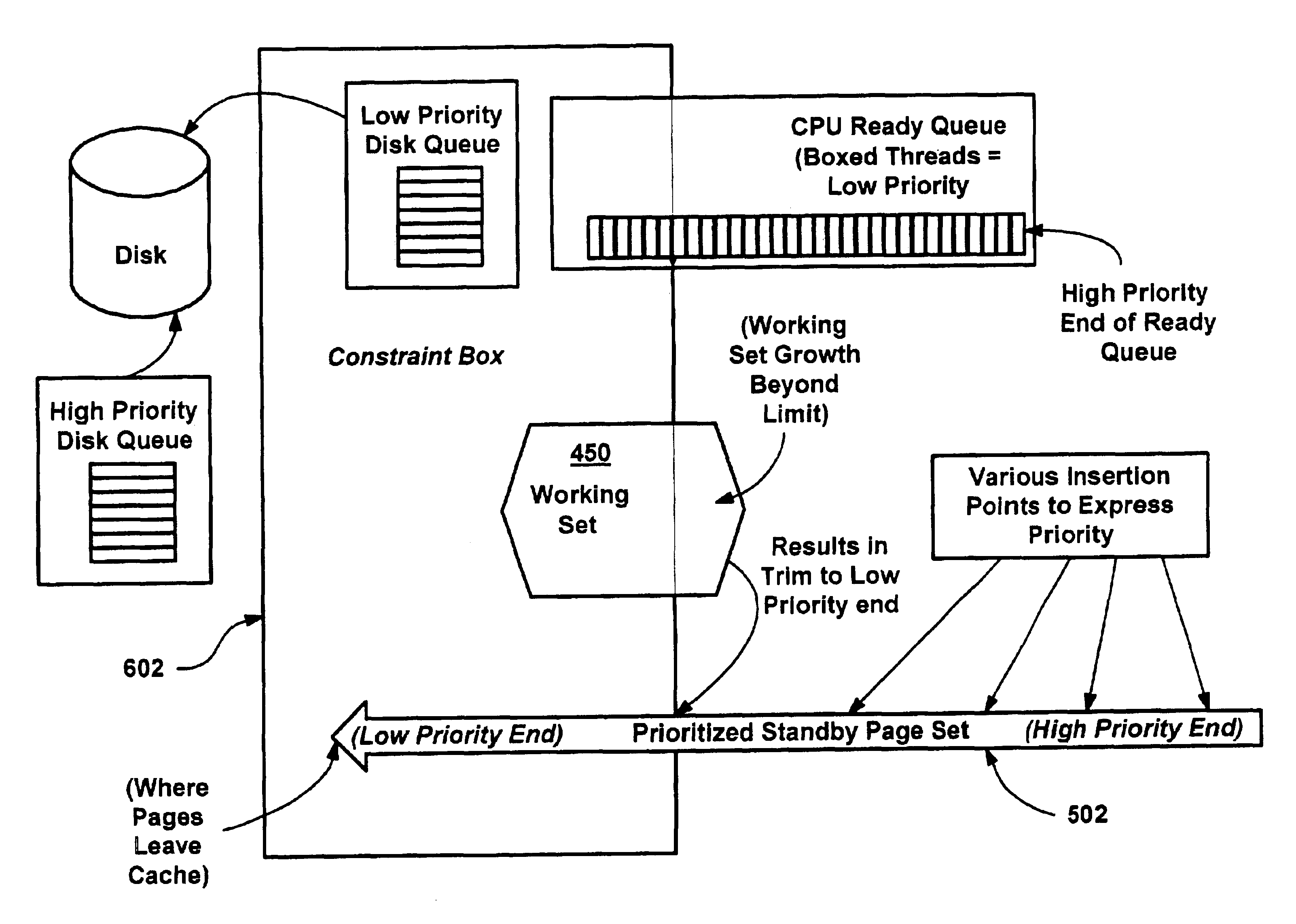
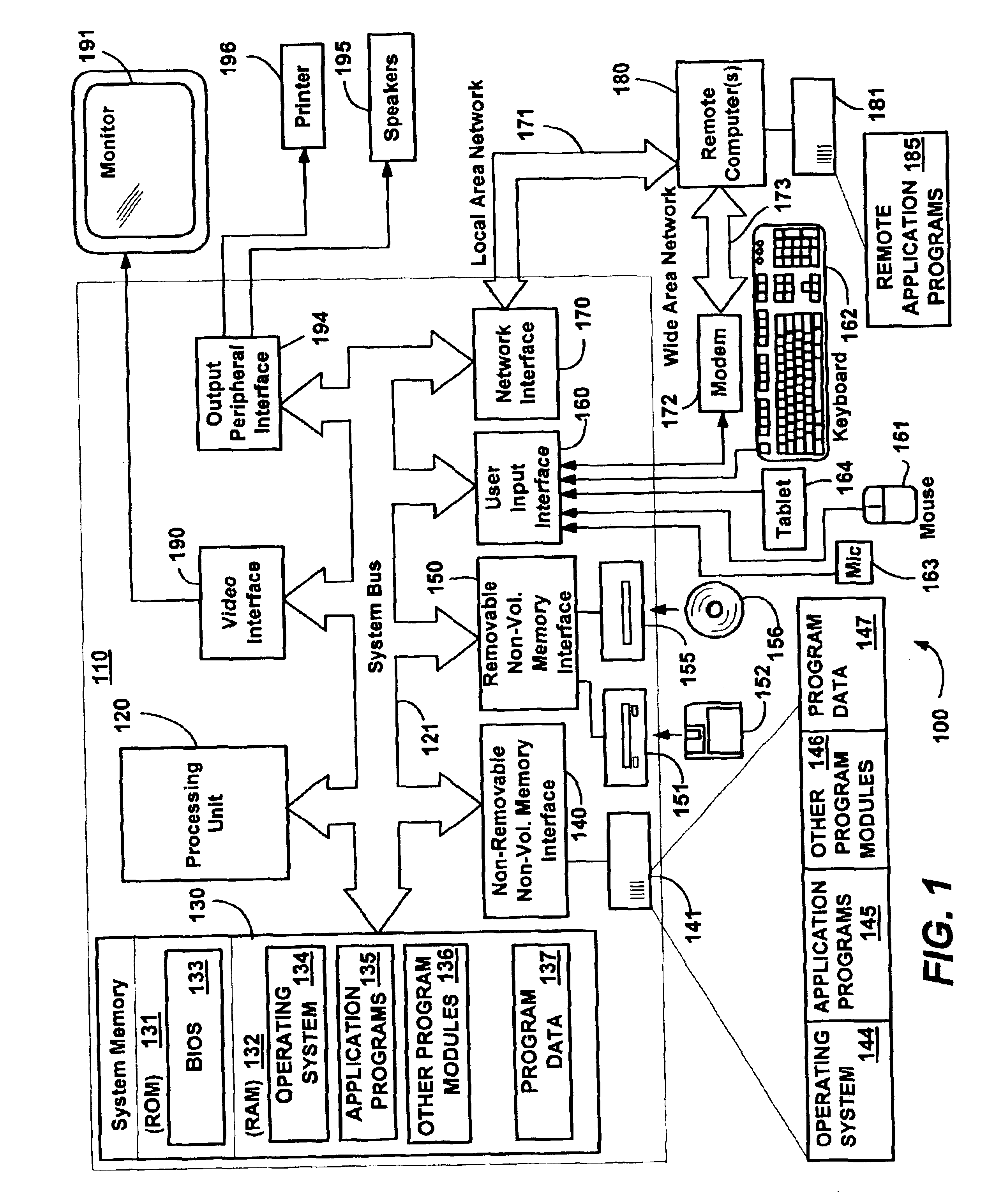
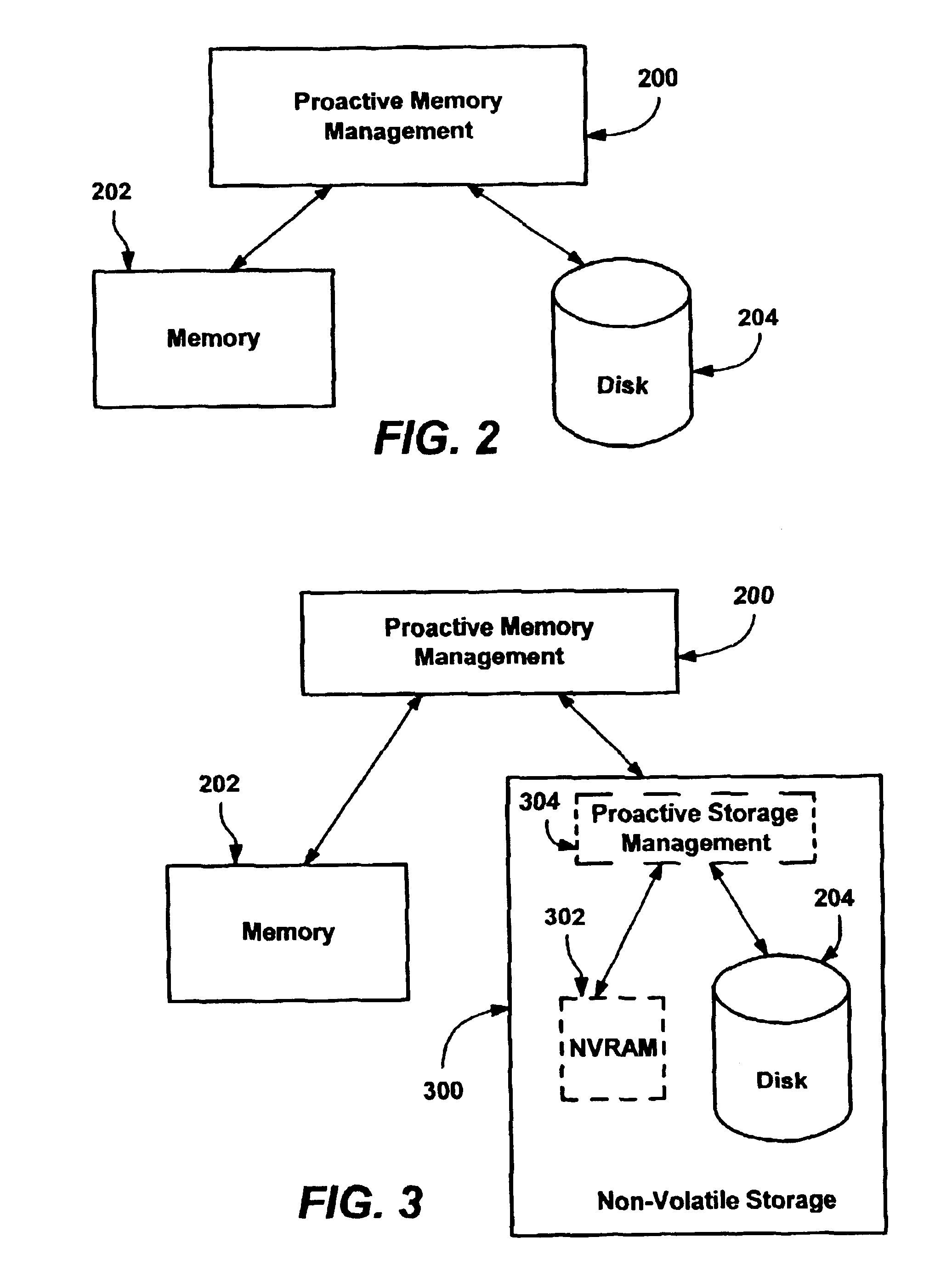
Methods and mechanisms for proactive memory management
InactiveUS20050228964A1Reduces or eliminates on-demand disk transfer operationsReduces or eliminates I/O bottlenecksInput/output to record carriersFault responseSelf-tuningTerm memory
A proactive, resilient and self-tuning memory management system and method that result in actual and perceived performance improvements in memory management, by loading and maintaining data that is likely to be needed into memory, before the data is actually needed. The system includes mechanisms directed towards historical memory usage monitoring, memory usage analysis, refreshing memory with highly-valued (e.g., highly utilized) pages, I / O pre-fetching efficiency, and aggressive disk management. Based on the memory usage information, pages are prioritized with relative values, and mechanisms work to pre-fetch and / or maintain the more valuable pages in memory. Pages are pre-fetched and maintained in a prioritized standby page set that includes a number of subsets, by which more valuable pages remain in memory over less valuable pages. Valuable data that is paged out may be automatically brought back, in a resilient manner. Benefits include significantly reducing or even eliminating disk I / O due to memory page faults.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and mechanisms for proactive memory management
InactiveUS6910106B2Raise priorityIncrease profitInput/output to record carriersFault responseSelf-tuningPaging
A proactive, resilient and self-tuning memory management system and method that result in actual and perceived performance improvements in memory management, by loading and maintaining data that is likely to be needed into memory, before the data is actually needed. The system includes mechanisms directed towards historical memory usage monitoring, memory usage analysis, refreshing memory with highly-valued (e.g., highly utilized) pages, I / O pre-fetching efficiency, and aggressive disk management. Based on the memory usage information, pages are prioritized with relative values, and mechanisms work to pre-fetch and / or maintain the more valuable pages in memory. Pages are pre-fetched and maintained in a prioritized standby page set that includes a number of subsets, by which more valuable pages remain in memory over less valuable pages. Valuable data that is paged out may be automatically brought back, in a resilient manner. Benefits include significantly reducing or even eliminating disk I / O due to memory page faults.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Storage management for fine grained tiered storage with thin provisioning
ActiveUS7949637B1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsStorage managementThin provisioning
A system for managing data includes providing at least one logical device having a table of information that maps sections of the logical device to sections of at least two storage areas. Characteristics of data associated with a one section of the logical device may be evaluated. The section of the data may moved between the at least two storage areas from a first location to a second location according to a policy and based on the characteristics of the data. A copy of the data may be retained in the first location and a list maintained that indentifies the copy of the data in the first location. The system provides for garbage collection processing for memory management.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Information processing device including memory management device managing access from processor to memory and memory management method
ActiveUS20100064111A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionInformation processingMemory management unit
A device according to an example of the invention comprises a section which accepts a write destination logical address and write target data from a processor, the write destination logical address indicating a write position to write the write target data into a composite memory which includes a first memory and a nonvolatile second memory, a section which determines a write destination physical address corresponding to the write destination logical address so that the number of times of access to the second memory is smaller than the number of times of access to the first memory, a section which stores, in a storage section, address conversion data associating the write destination logical address with the write destination physical address, and a section which writes the write target data into a position in the composite memory indicated by the write destination physical address.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
System and method for forensic identification of elements within a computer system
ActiveUS8881271B2Memory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationMemory forensicsOperational system
A system and method for employing memory forensic techniques to determine operating system type, memory management configuration, and virtual machine status on a running computer system. The techniques apply advanced techniques in a fashion to make them usable and accessible by Information Technology professionals that may not necessarily be versed in the specifics of memory forensic methodologies and theory.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
System and method for a multi-packet data link layer data transmission
ActiveUS7512128B2Fast network bandwidthWithout incurring the costly delayTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork packetData link layer
A kernel data transfer method and system for transmitting multiple packets of data in a single block of data presented by application programs to the kernel's network subsystem for processing in accordance with data transfer parameters set by the application program. The multi-packet transmit system includes logic that allows header information of the multiple packets of data to be generated in a single buffer and appended to a second buffer containing the data packets to be transmitted through the network stack. The multi-data transmit system allows a device driver to amortize the input / output memory management related overhead across a number of packets. With some assistance from the network stack, the device driver needs to only perform the necessary IOMMU operations on two contiguous memory blocks representing the header information and the data payload of multiple packets during each transmit call.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
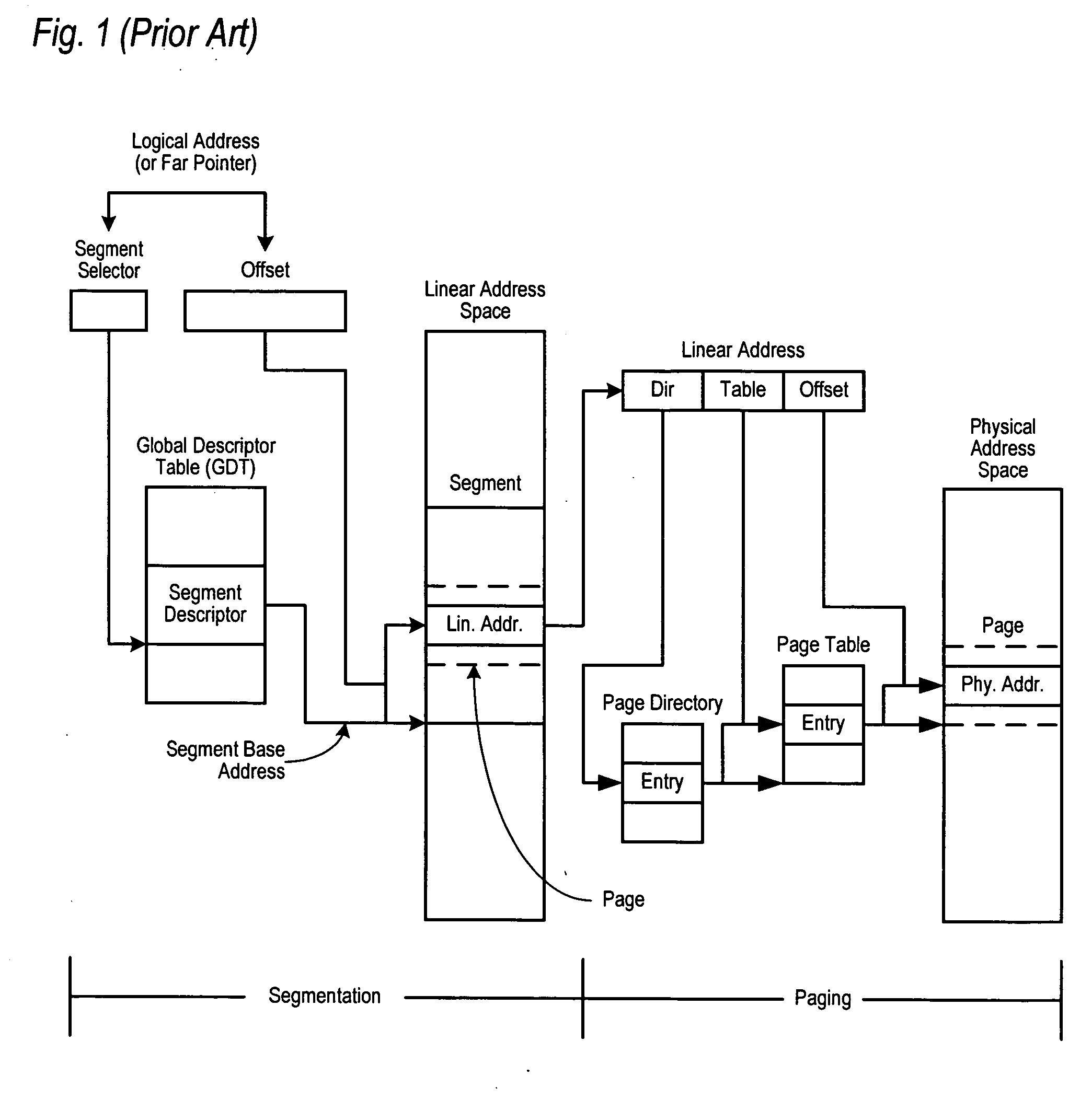
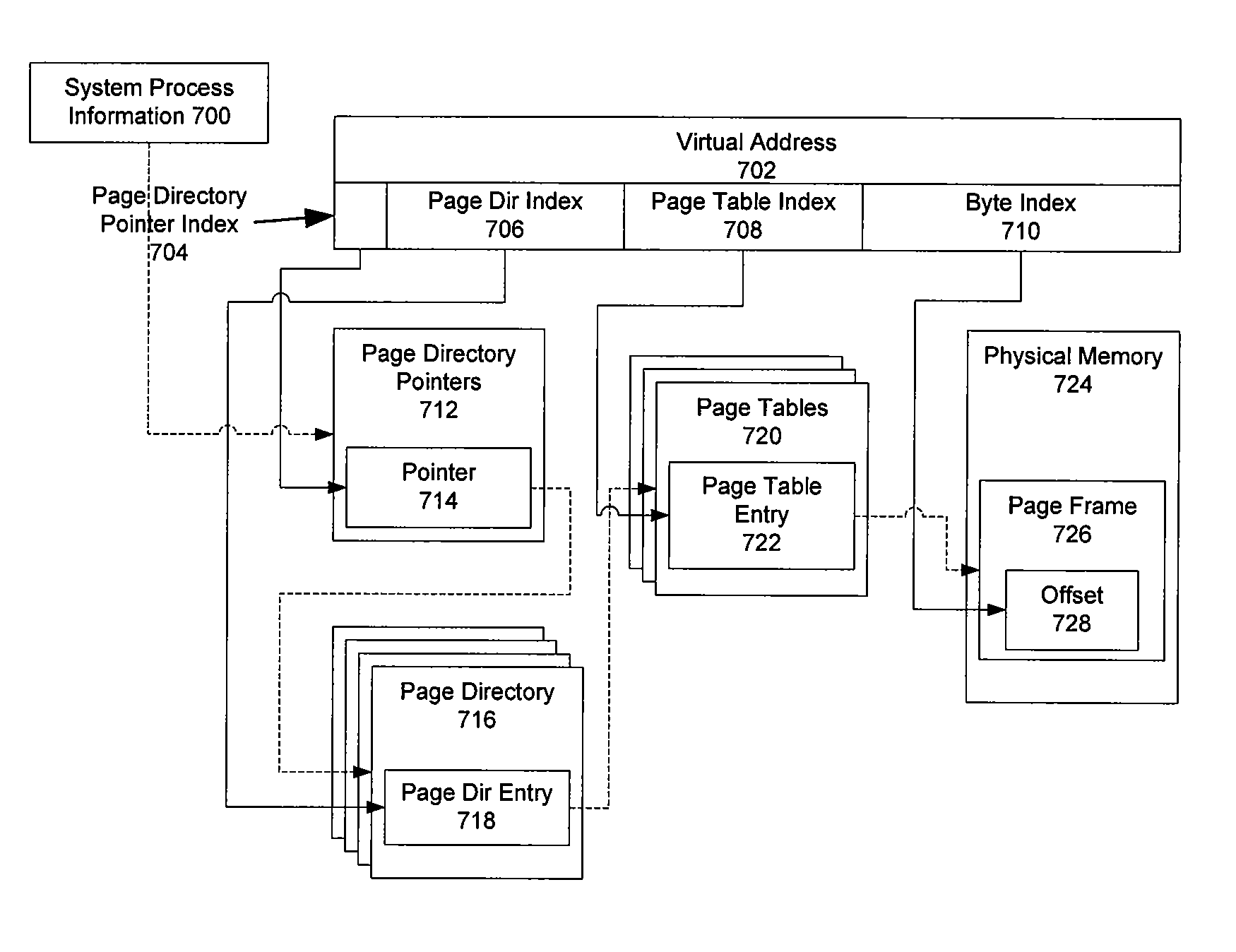
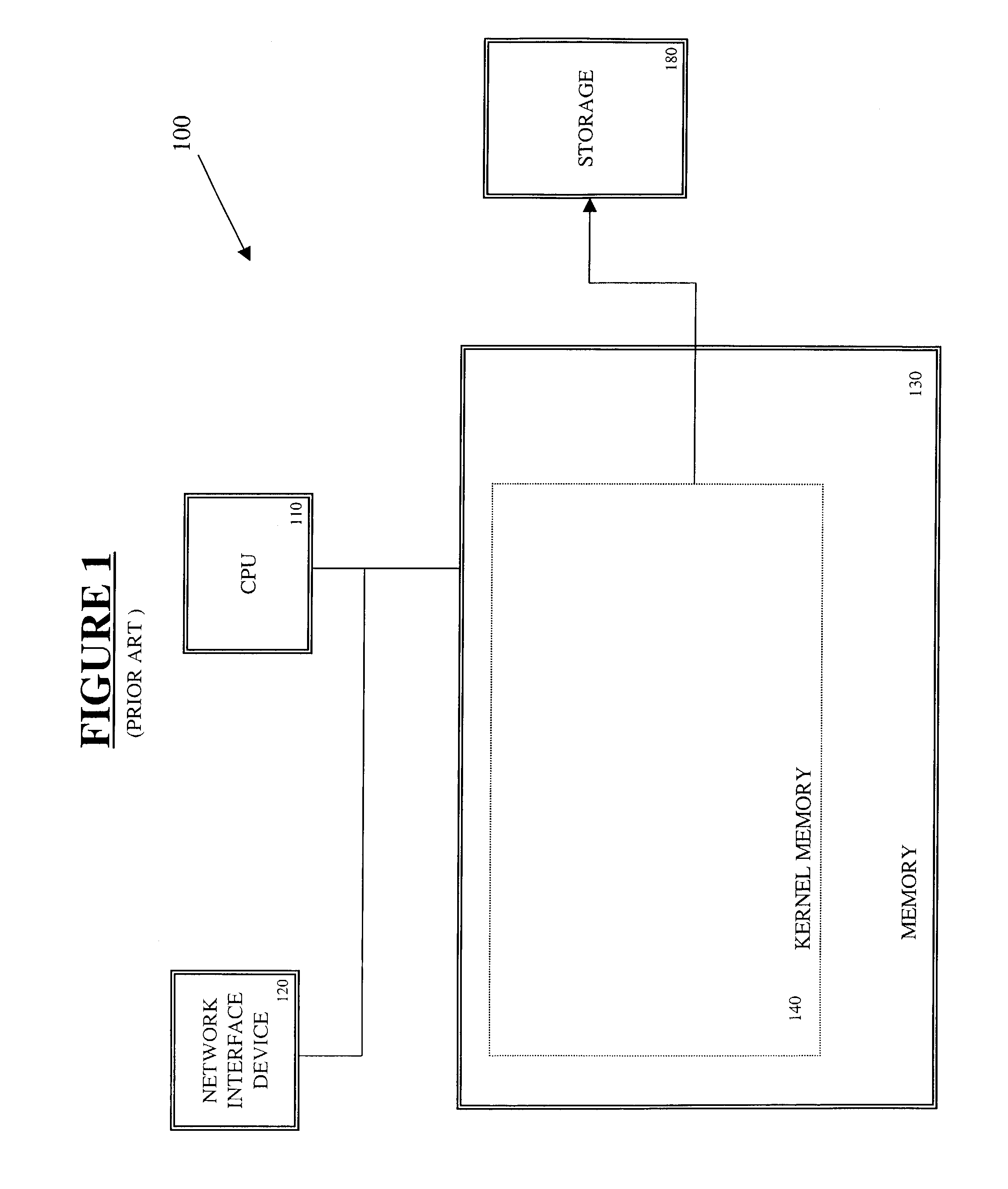
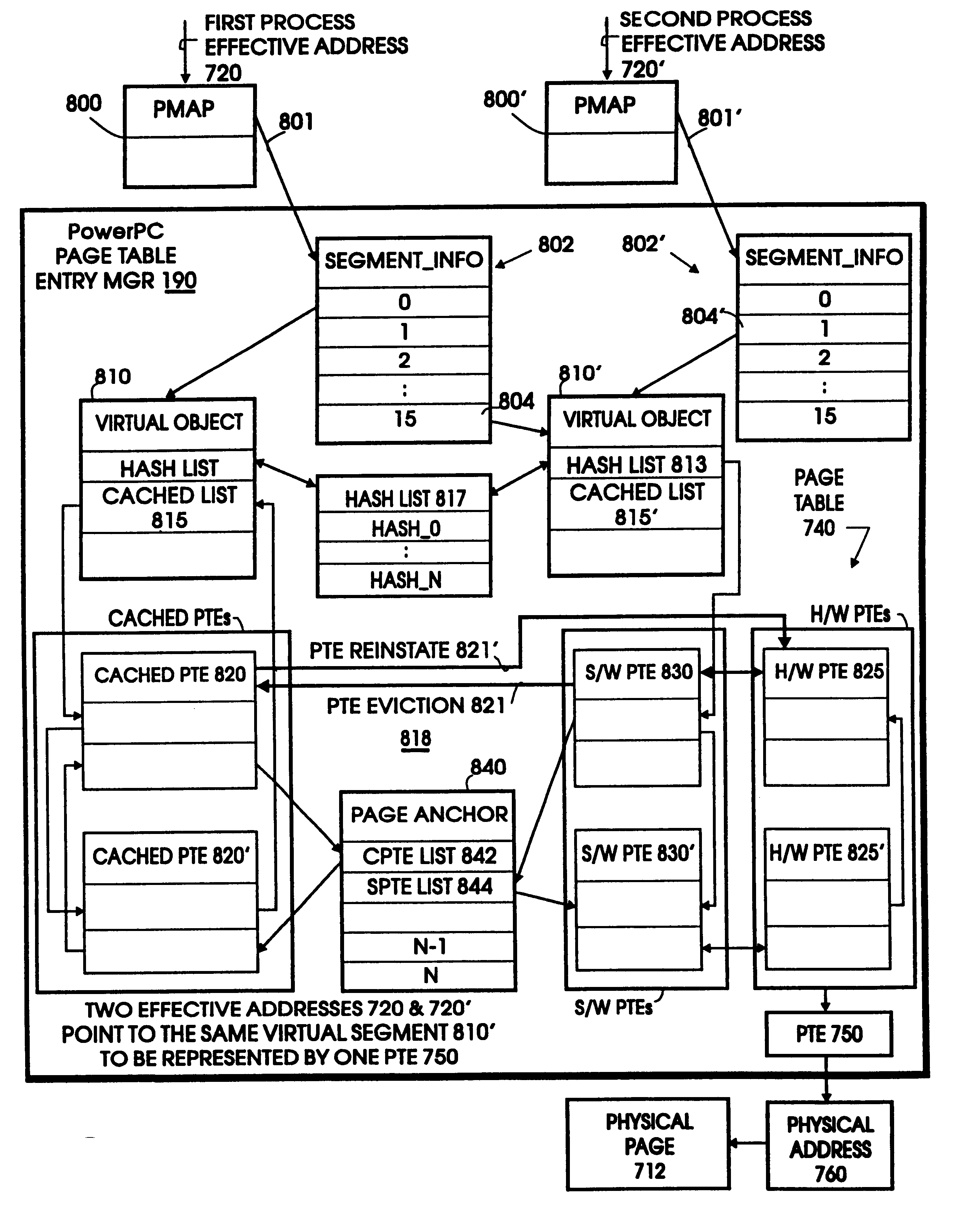
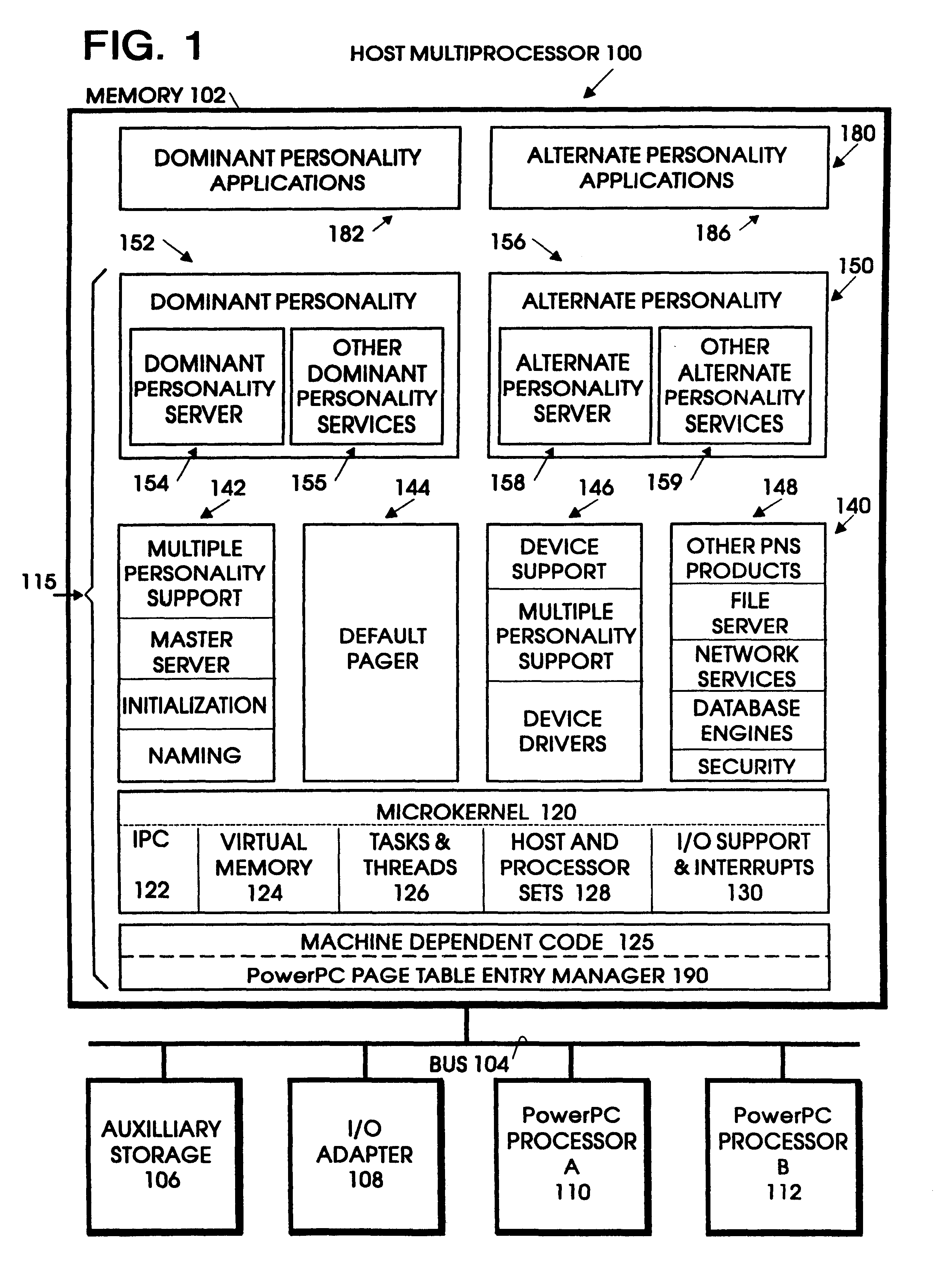
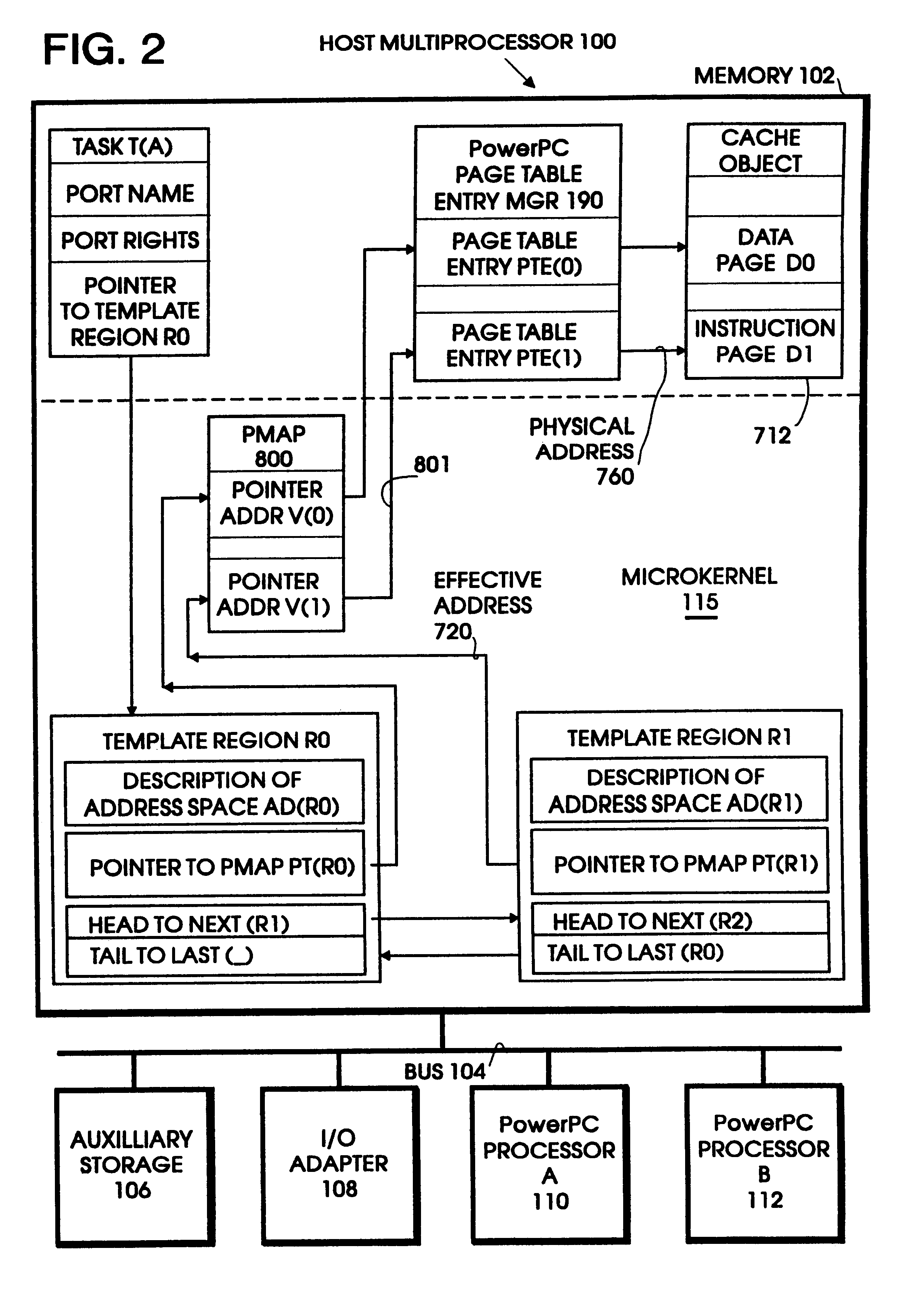
Page table entry management method and apparatus for a microkernel data processing system
InactiveUS6308247B1Maximize system performanceEasy to manageMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemManagement unit
A page table entry management method and apparatus provide the Microkernel System with the capability to program the memory management unit on the PowerPC family of processors. The PowerPC processors define a limited set of page table entries (PTEs) to maintain virtual to physical mappings. The page table entry management method and apparatus solves the problem of a limited number of PTEs by segment aliasing when two or more user processes share a segment of memory. The segments are aliased rather than duplicating the PTES. This significantly reduces the number of PTEs. In addition, the method provides for caching existing PTEs when the system actually runs out of PTEs. A cache of recently discarded PTEs provides a fast fault resolution when a recently used page is accessed again.
Owner:IBM CORP
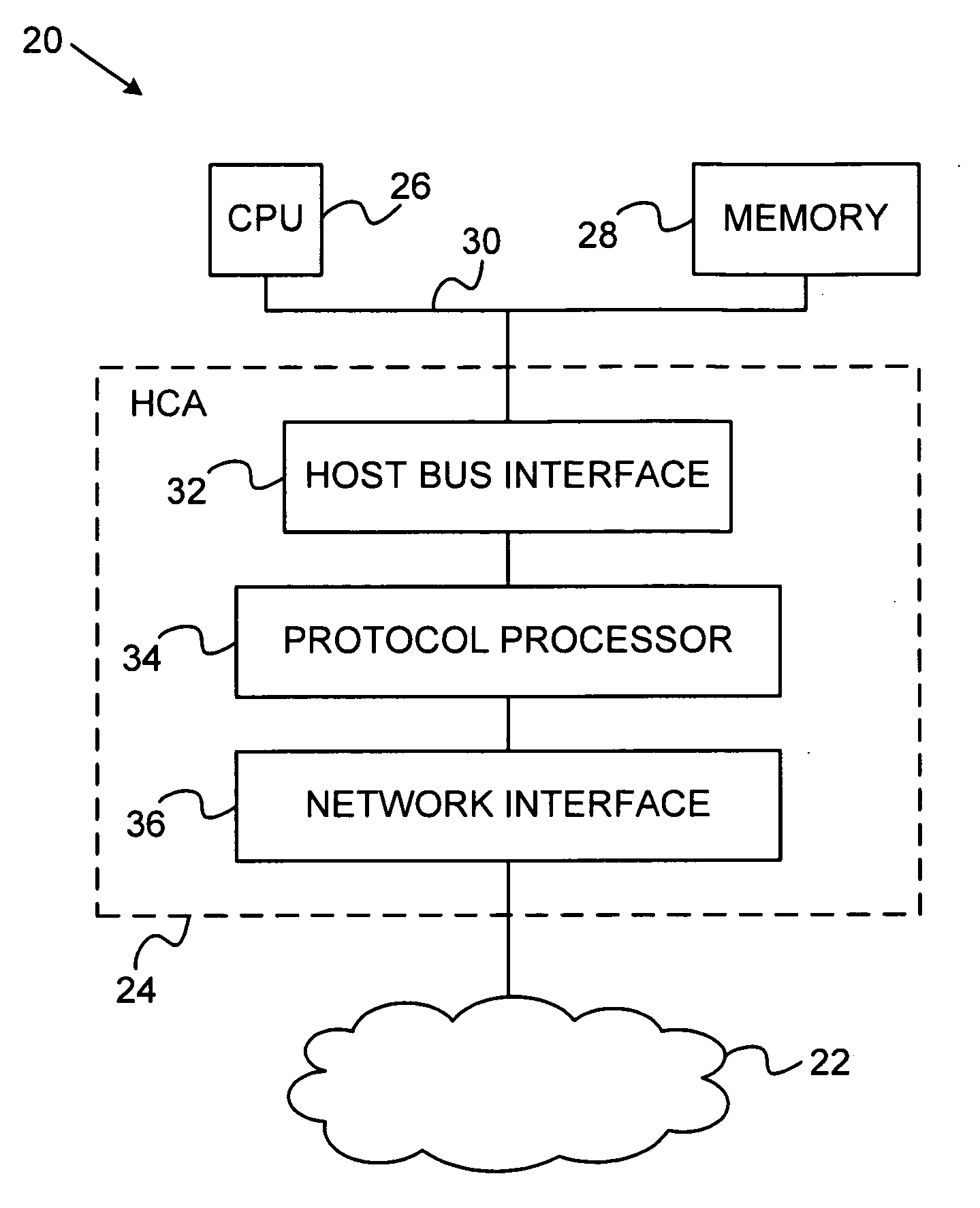
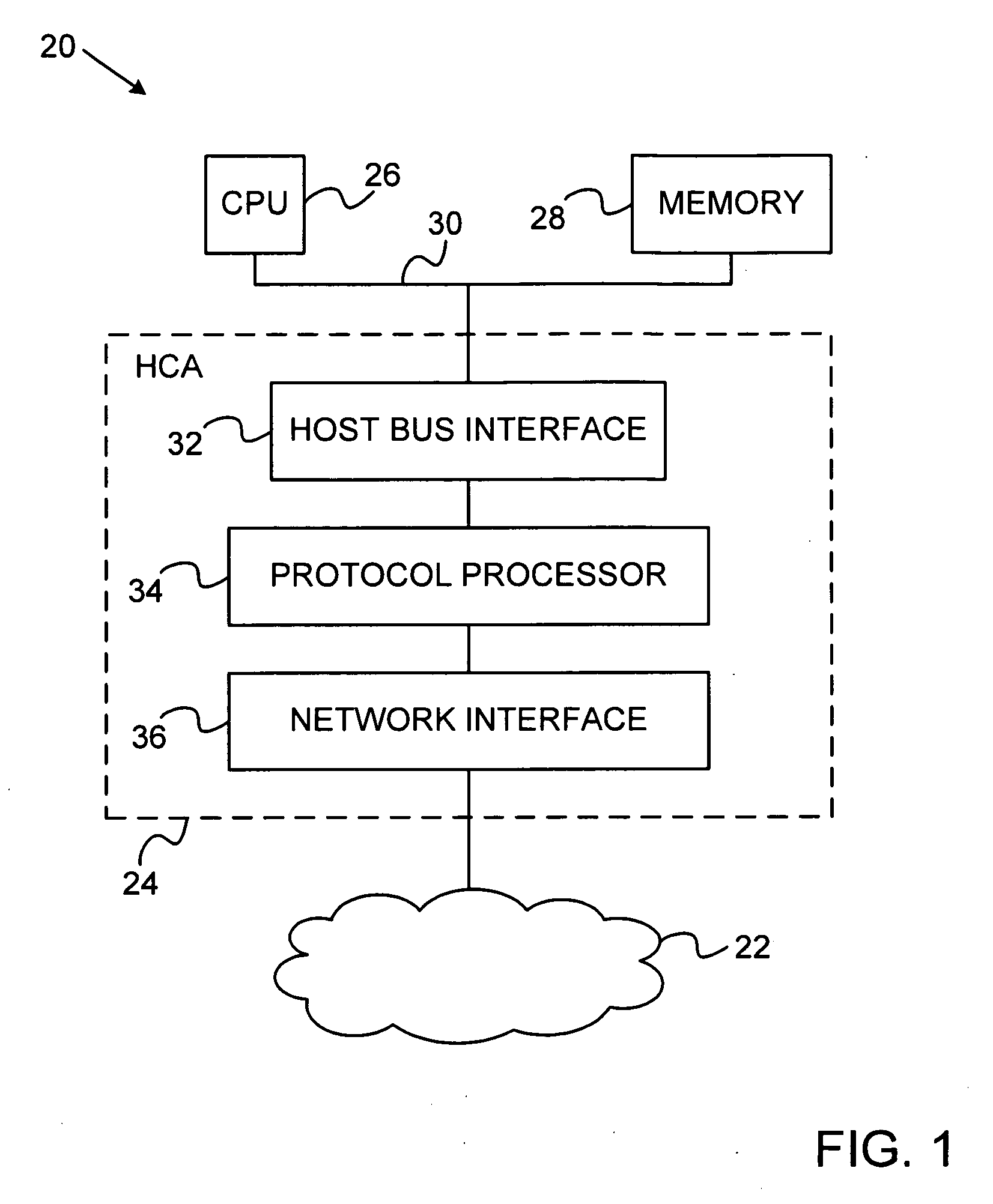
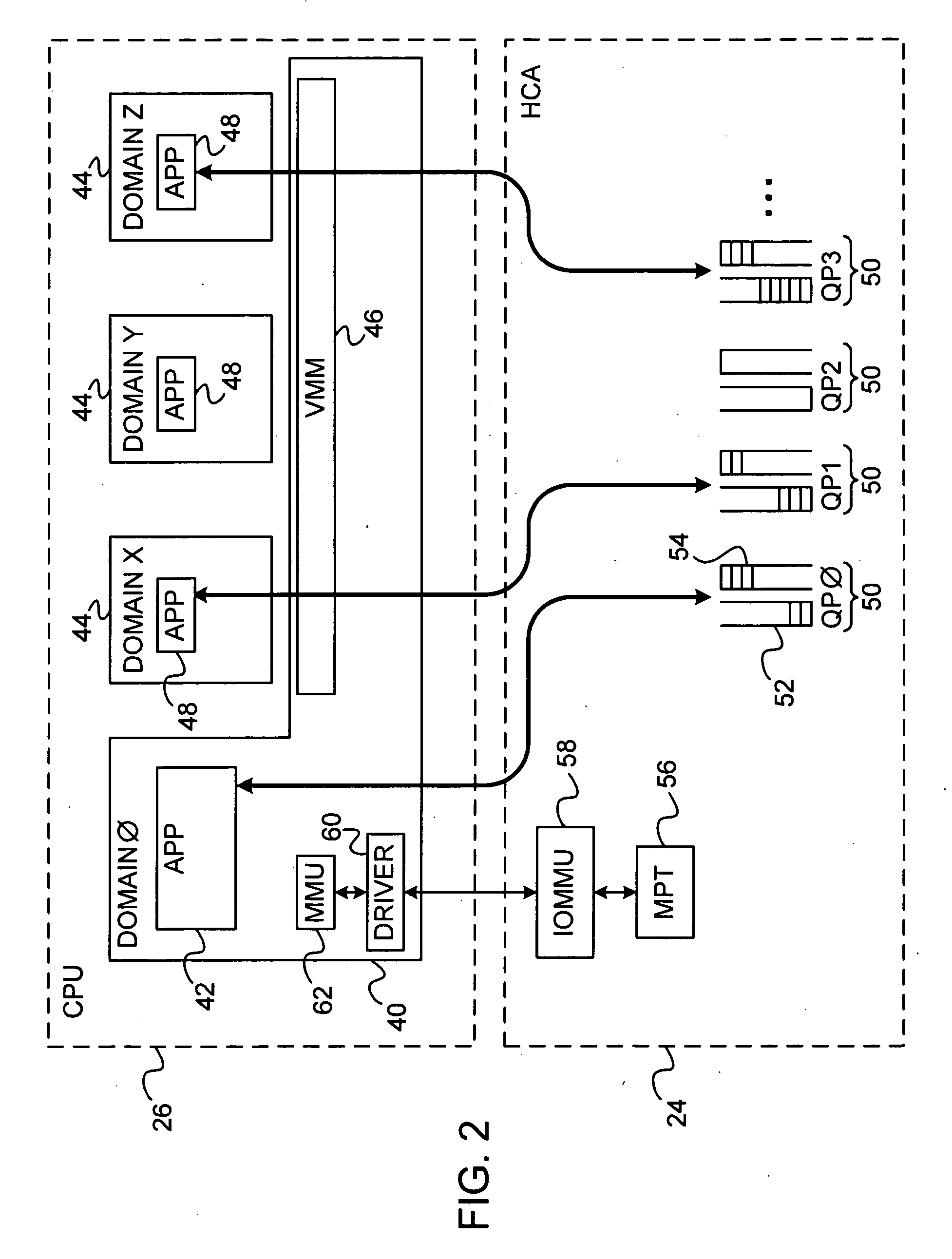
Network interface device with memory management capabilities
ActiveUS20100274876A1Multiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsNetwork interface devicePhysical address
An input / output (I / O) device includes a host interface for connection to a host device having a memory and a network interface, which is configured to receive, over a network, data packets associated with I / O operations directed to specified virtual addresses in the memory. Packet processing hardware is configured to translate the virtual addresses into physical addresses and to perform the I / O operations using the physical addresses, and upon an occurrence of a page fault in translating one of the virtual addresses, to transmit a response packet over the network to a source of the data packets so as to cause the source to refrain from transmitting further data packets while the page fault is serviced.
Owner:MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Method and system for run-time cache logging
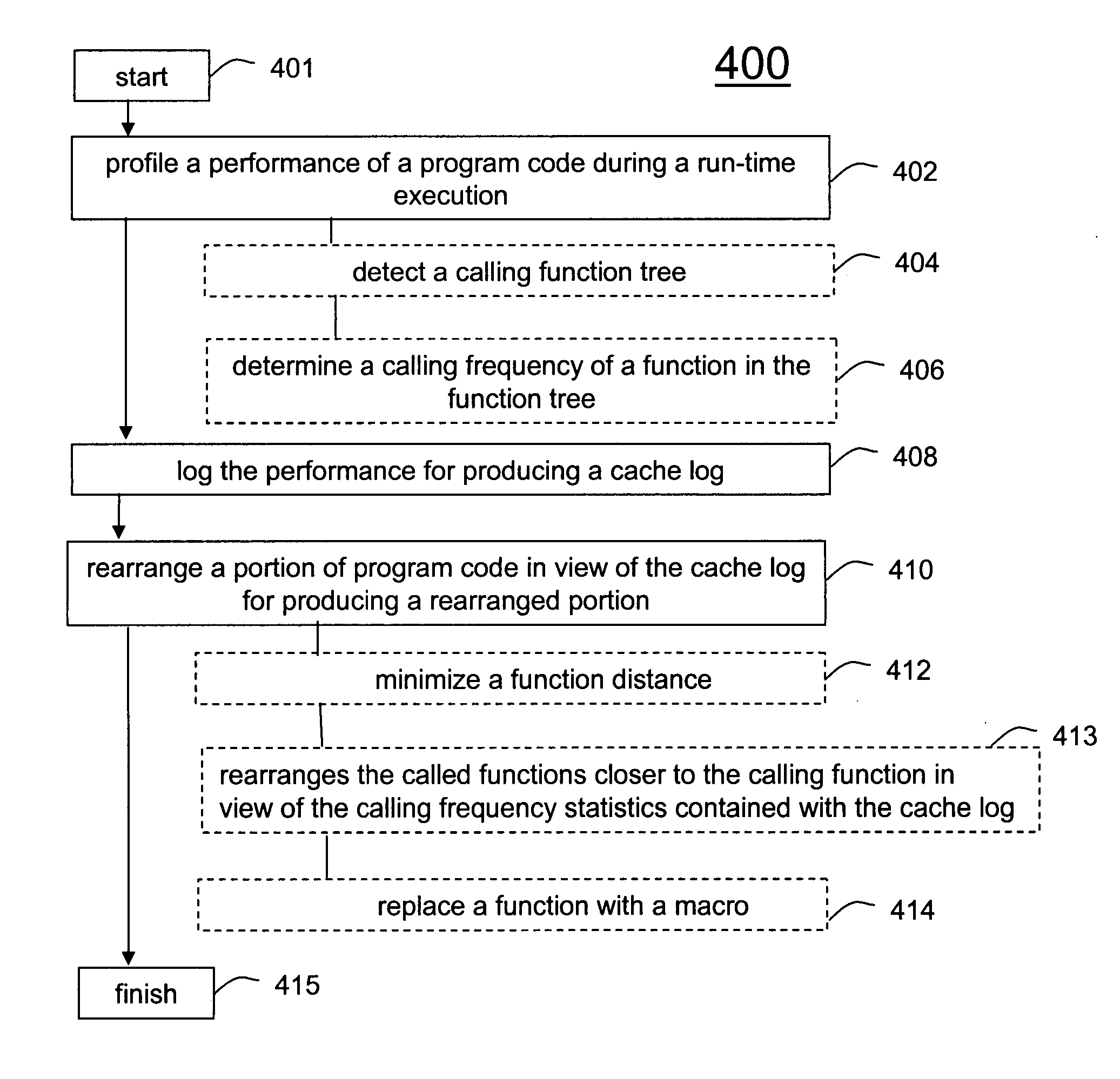
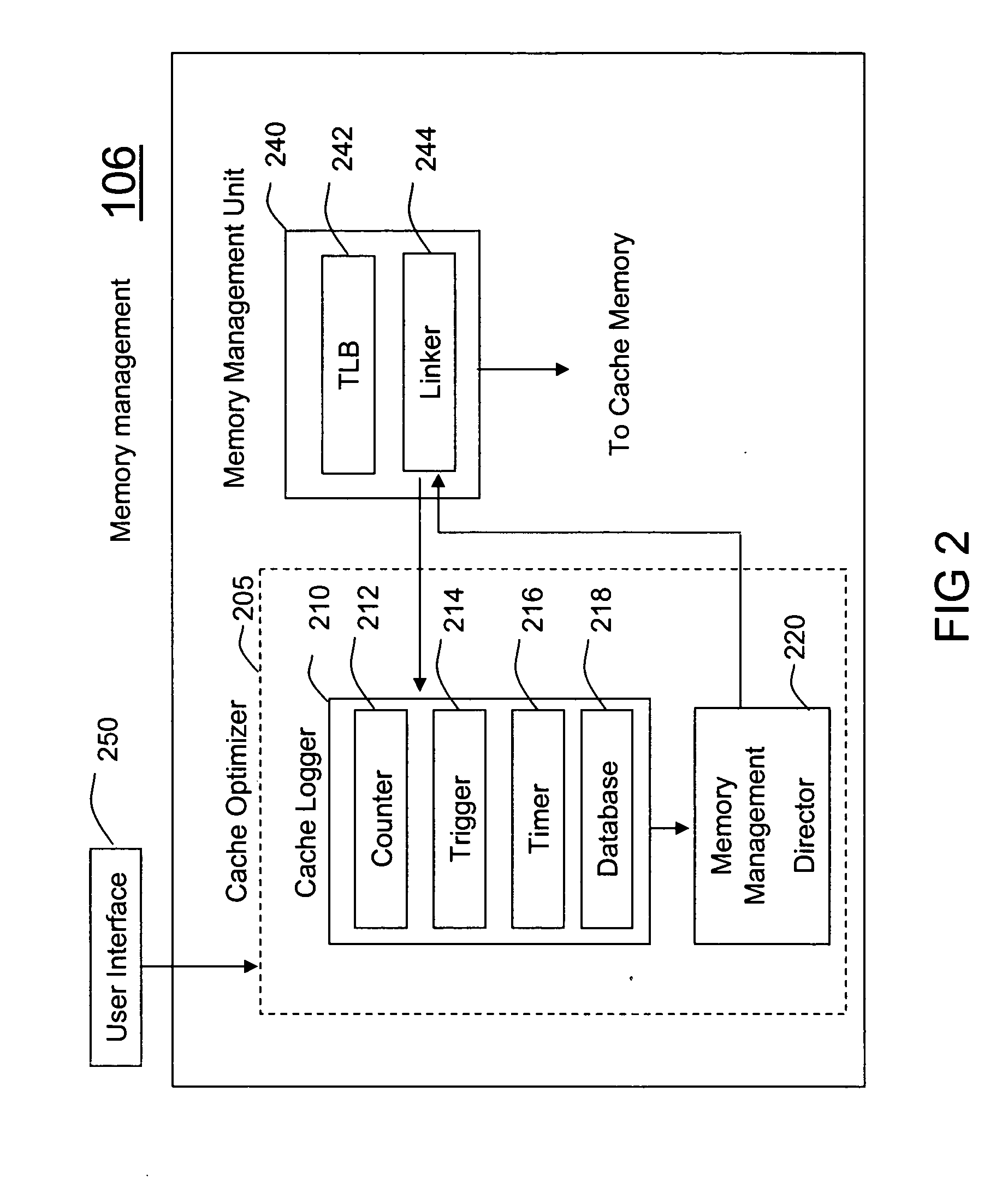
InactiveUS20070150881A1Increase heightMaximize cache locality compile timeError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsCache optimizationParallel computing
A method (400) and system (106) is provided for run-time cache optimization. The method includes profiling (402) a performance of a program code during a run-time execution, logging (408) the performance for producing a cache log, and rearranging (410) a portion of program code in view of the cache log for producing a rearranged portion. The rearranged portion is supplied to a memory management unit (240) for managing at least one cache memory (110-140). The cache log can be collected during a real-time operation of a communication device and is fed back to a linking process (244) to maximize a cache locality compile-time. The method further includes loading a saved profile corresponding with a run-time operating mode, and reprogramming a new code image associated with the saved profile.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
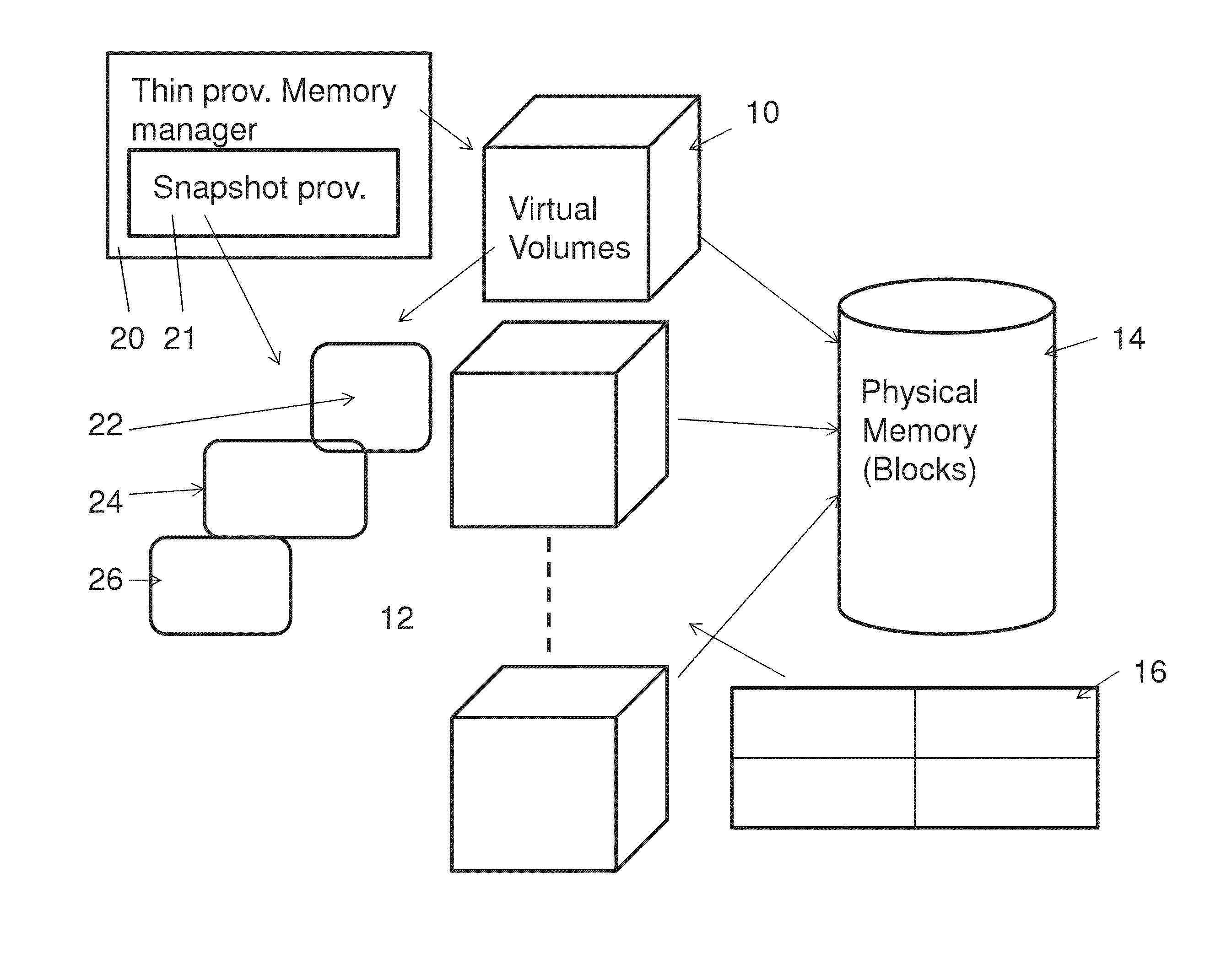
Snapshot mechanism
A memory management system for a thinly provisioned memory volume in which a relatively larger virtual address range of virtual address blocks is mapped to a relatively smaller physical memory comprising physical memory blocks via a mapping table containing entries only for addresses of the physical memory blocks containing data. The memory management system comprises a snapshot provision unit to take a given snapshot of the memory volume at a given time, the snapshot comprising a mapping table and memory values of the volume, the mapping table and memory values comprising entries only for addresses of the physical memory containing data. The snapshot is managed on the same thin provisioning basis as the volume itself, and the system is particularly suitable for RAM type memory disks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Systems and method for flash memory management
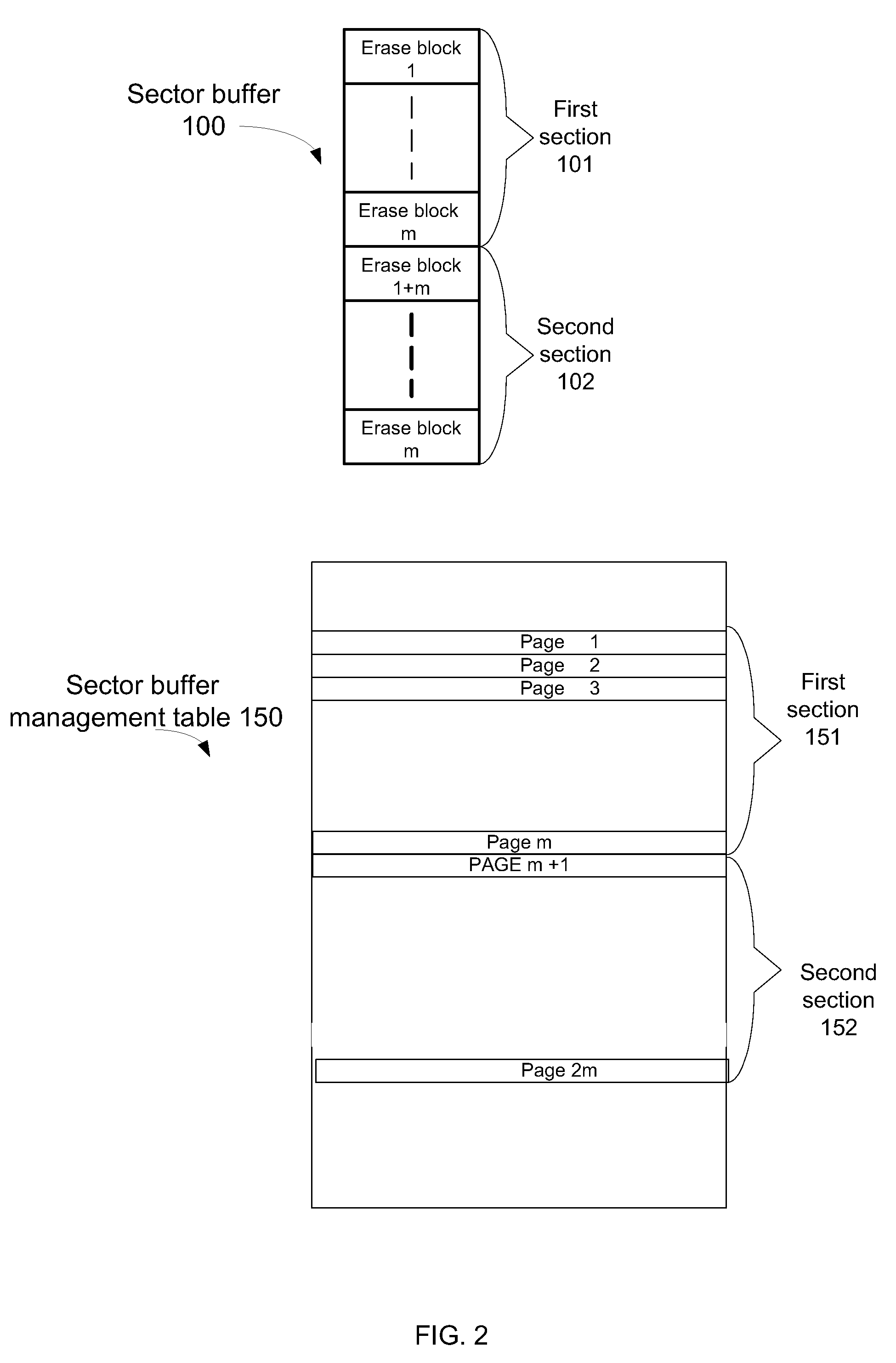
ActiveUS20100293321A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
A system and method for merging sectors of a flash memory module, the method includes: receiving multiple sectors, each received sector is associated with a current erase block out of multiple (L) erase blocks; accumulating the received sectors in a sector buffer, the sector buffer is stored in a non-volatile memory module; maintaining a merged sector map indicative of a sectors of the sector buffer that have been merged and sectors of the sector buffer waiting to be merged; finding a first sector waiting to be merged according to the merged sector map; merging the first sector and other sectors that belong to a same erase block as the first sector; and updating the merged sector map to indicate that that the first second and the other sectors that belonged to the same erase block were merged.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for virtualization in an integrated circuit
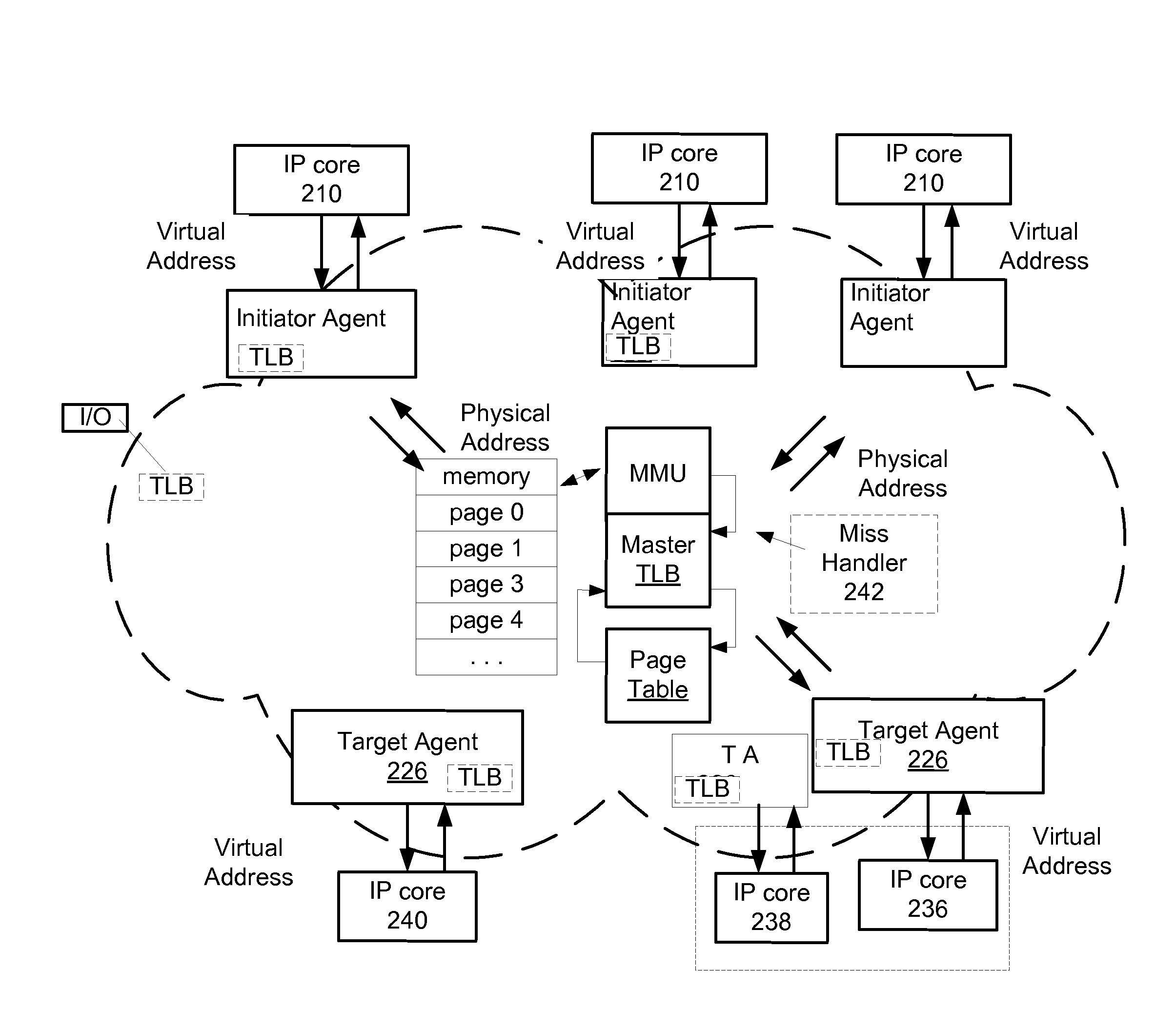
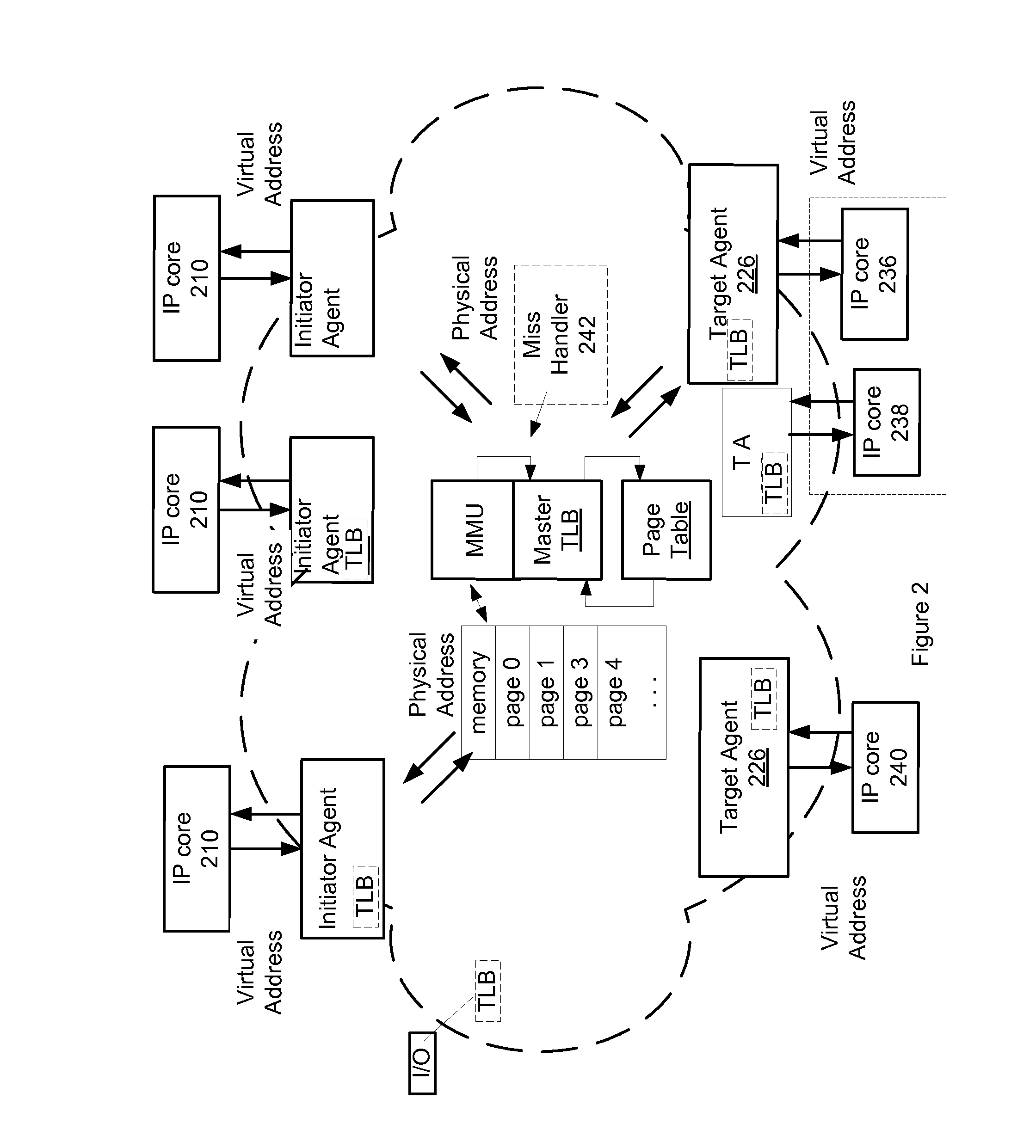
ActiveUS20120117301A1Reduced translation latencyIncreased total translation bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtualizationComputer architecture
Various methods and apparatus are described for communicating transactions between one or more initiator IP cores and one or more target IP cores coupled to an interconnect. A centralized Memory Management logic Unit (MMU) is located in the interconnect for virtualization and sharing of integrated circuit resources including target cores between the one or more initiator IP cores. A master translation look aside buffer (TLB) stores virtualization and sharing information in the entries of the master TLB. A set of two or more translation look aside buffers (TLBs) locally store virtualization and sharing information replicated from the master TLB. Logic in the MMU or other software updates the virtualization and sharing information replicated from the master TLB in the entries of one or more of the set of local TLBs.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
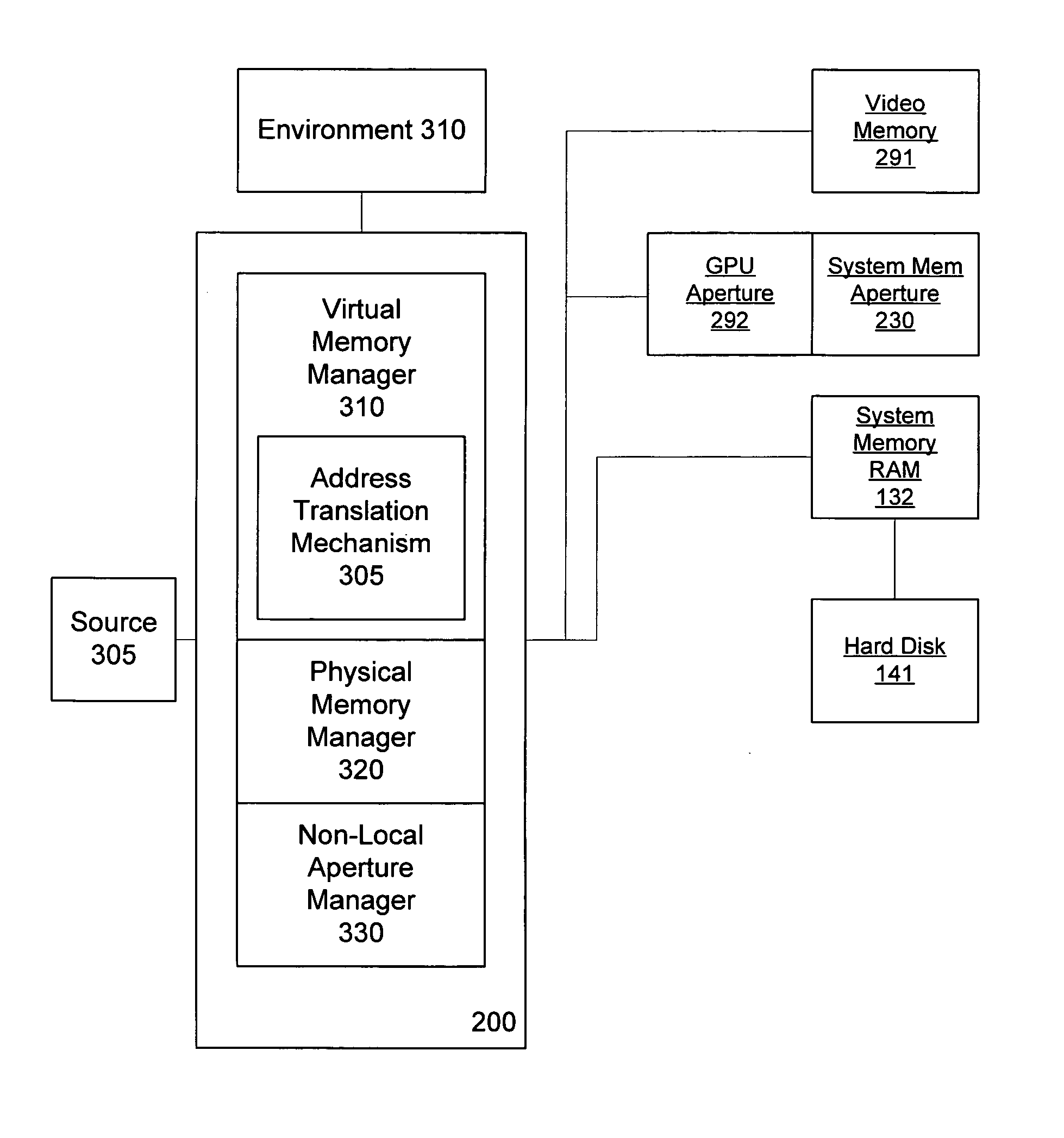
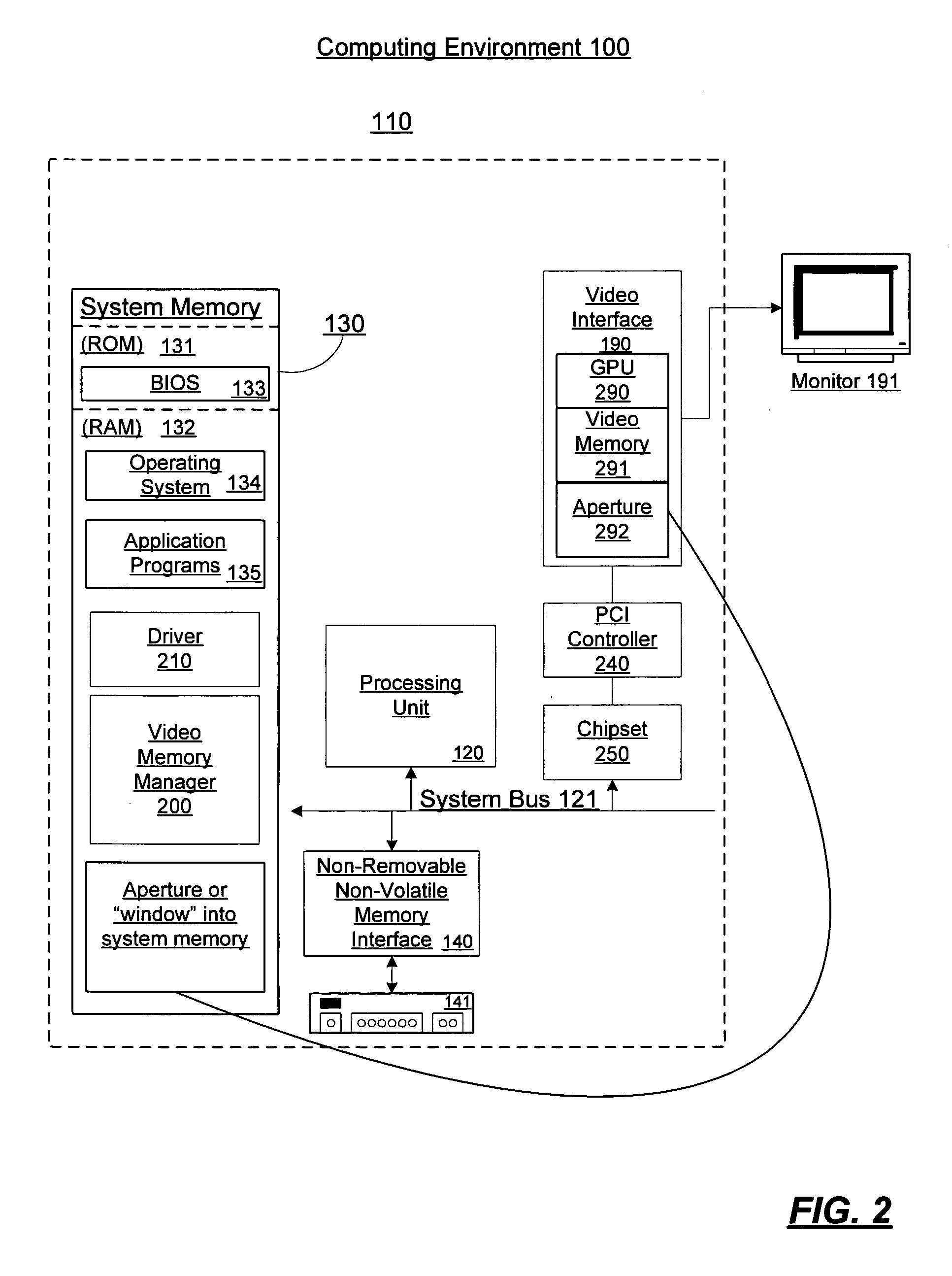
Video memory management
A video memory manager manages and virtualizes memory so that an application or multiple applications can utilize both system memory and local video memory in processing graphics. The video memory manager allocates memory in either the system memory or the local video memory as appropriate. The video memory manager may also manage the system memory accessible to the graphics processing unit via an aperture of the graphics processing unit. The video memory manager may evict memory from the local video memory as appropriate, thereby freeing a portion of local video memory use by other applications. In this manner, a graphics processing unit and its local video memory may be more readily shared by multiple applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com