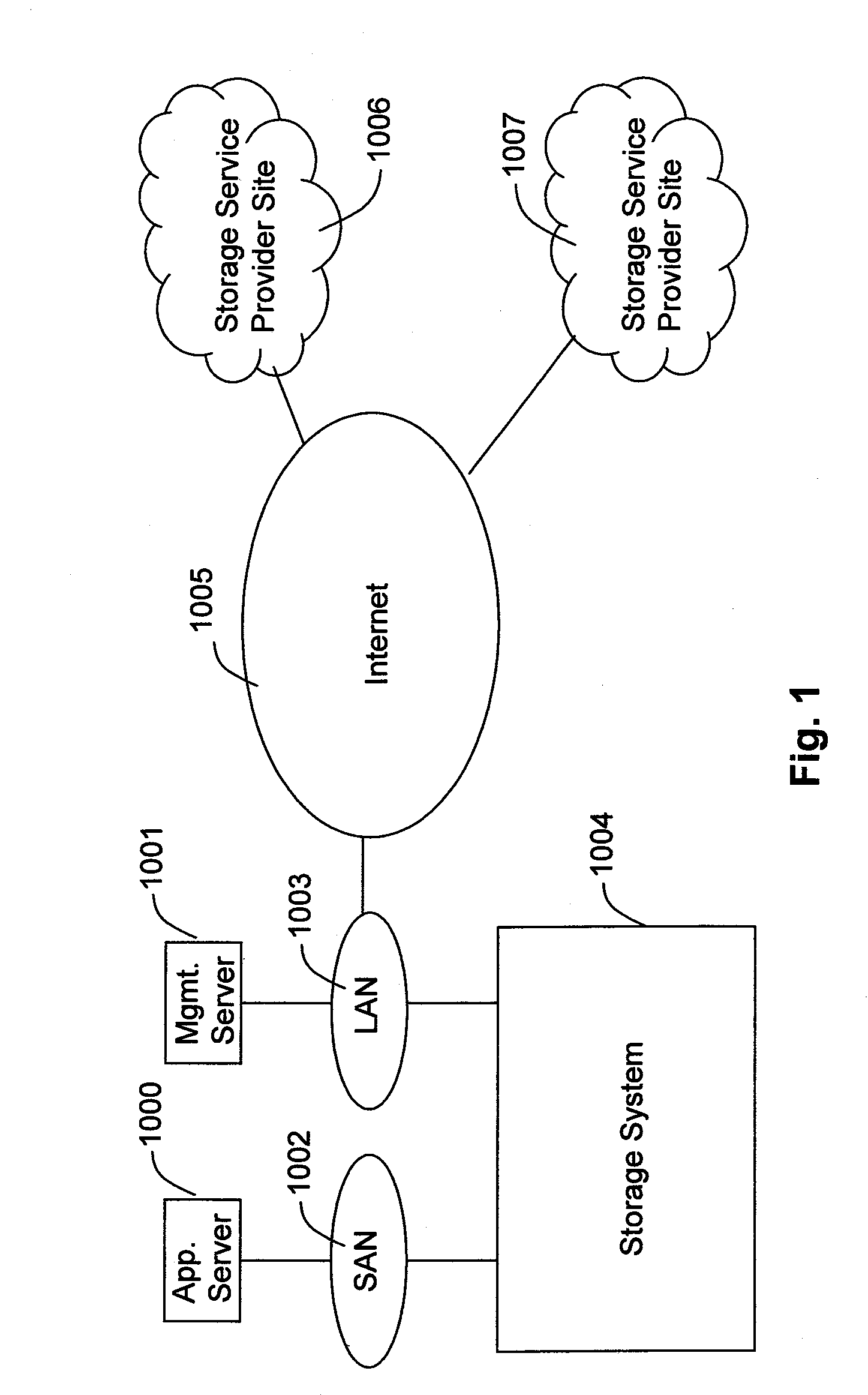
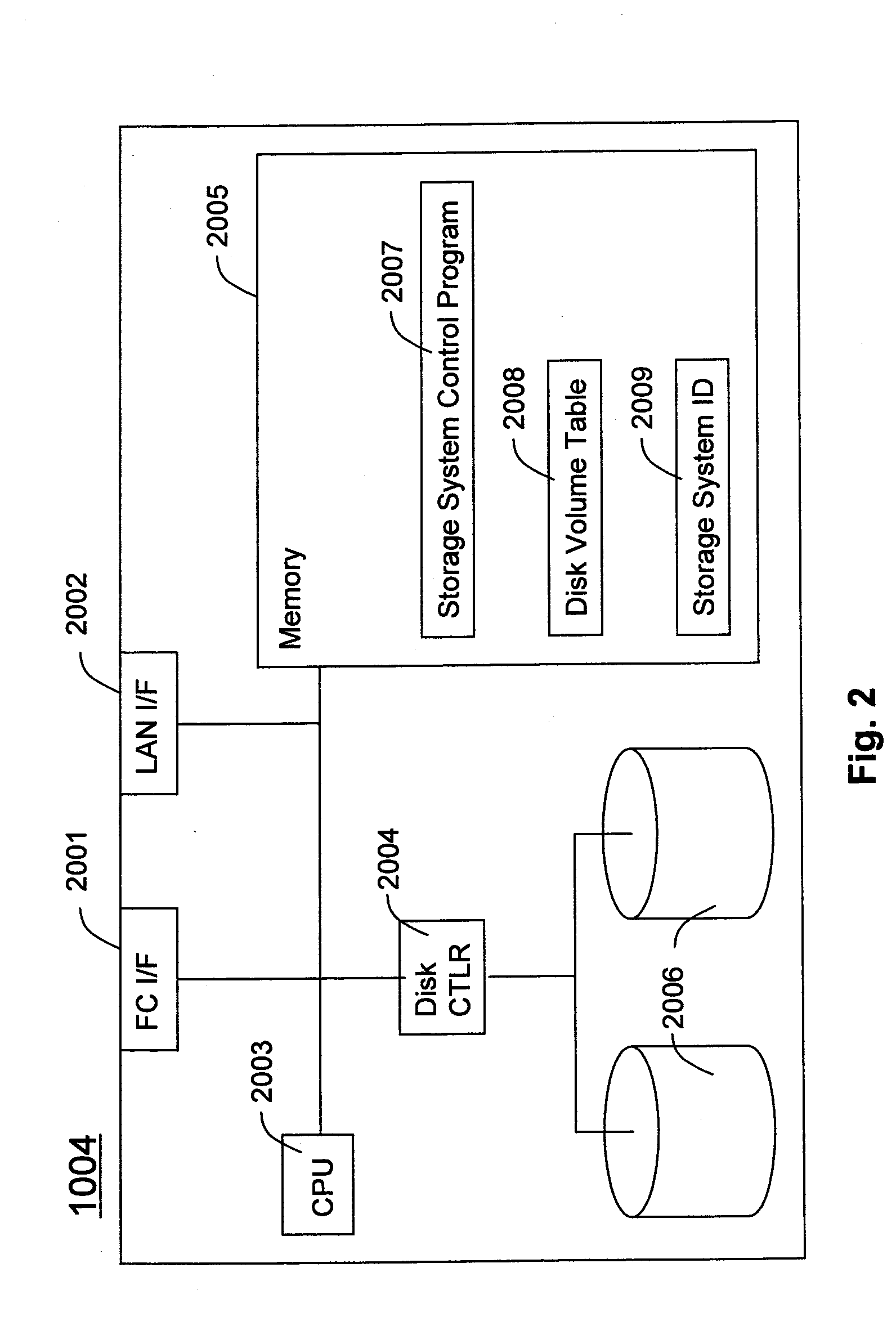
Patents
Literature
142 results about "Thin provisioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
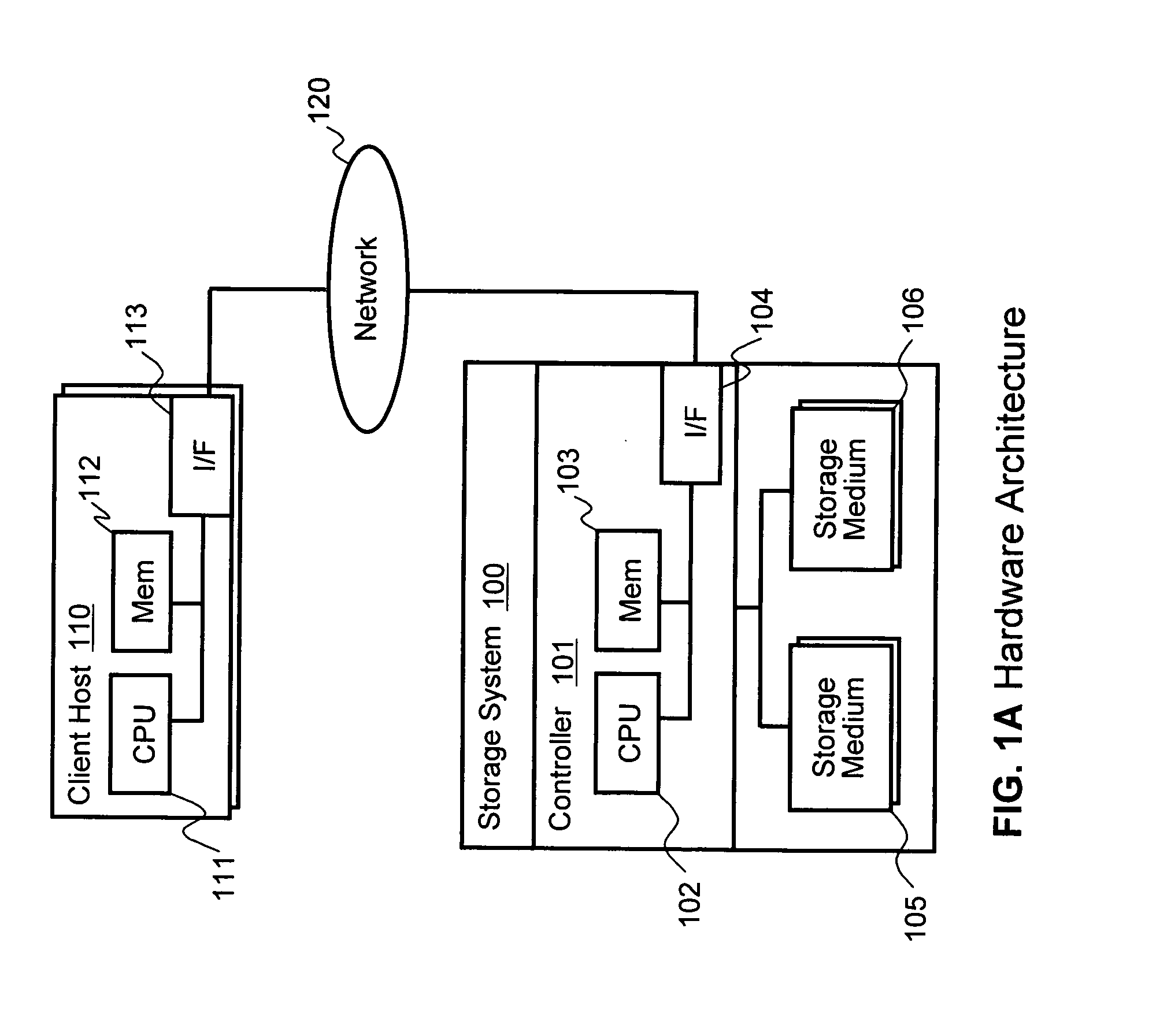
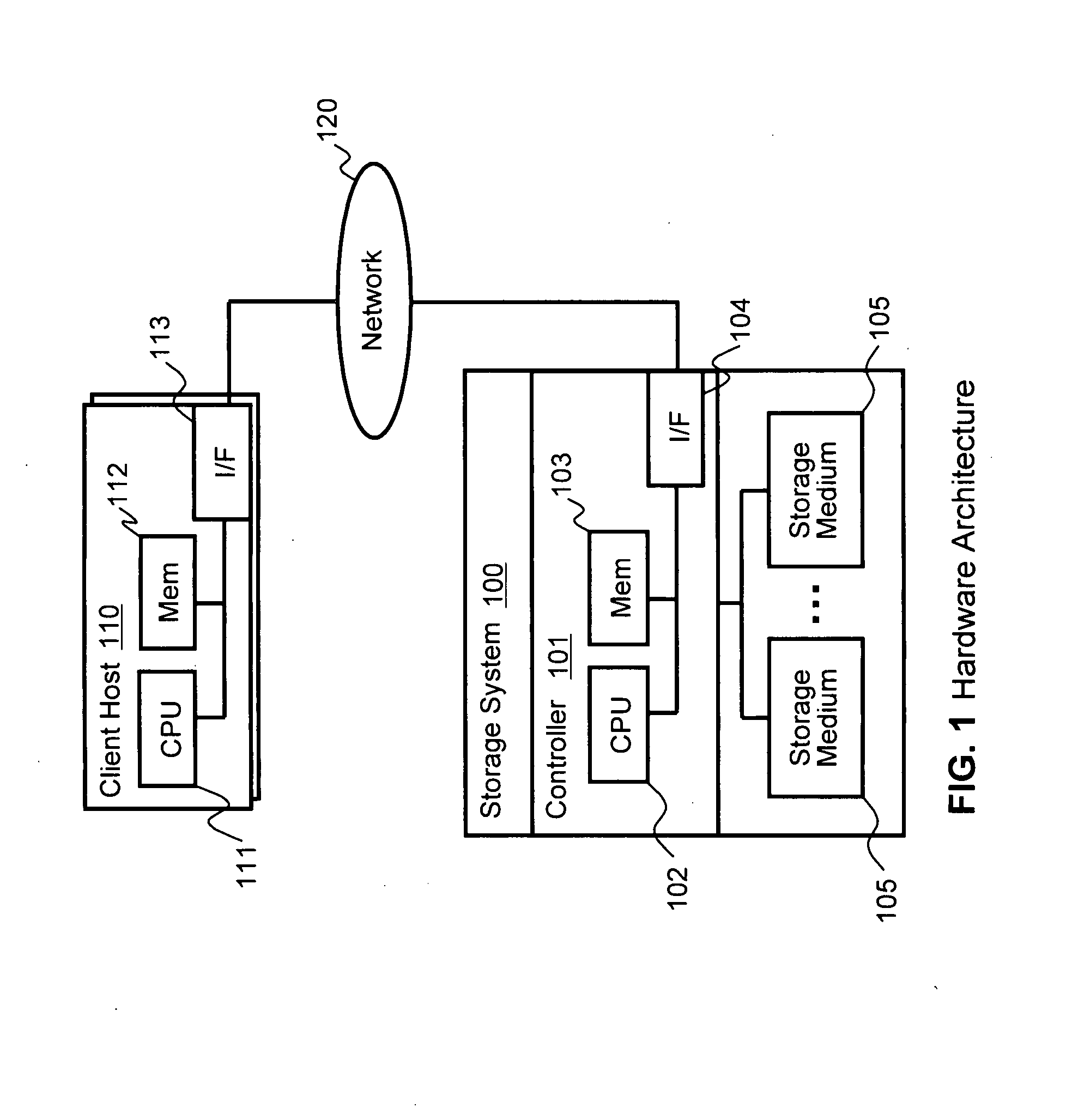
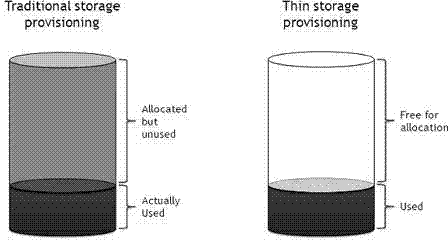
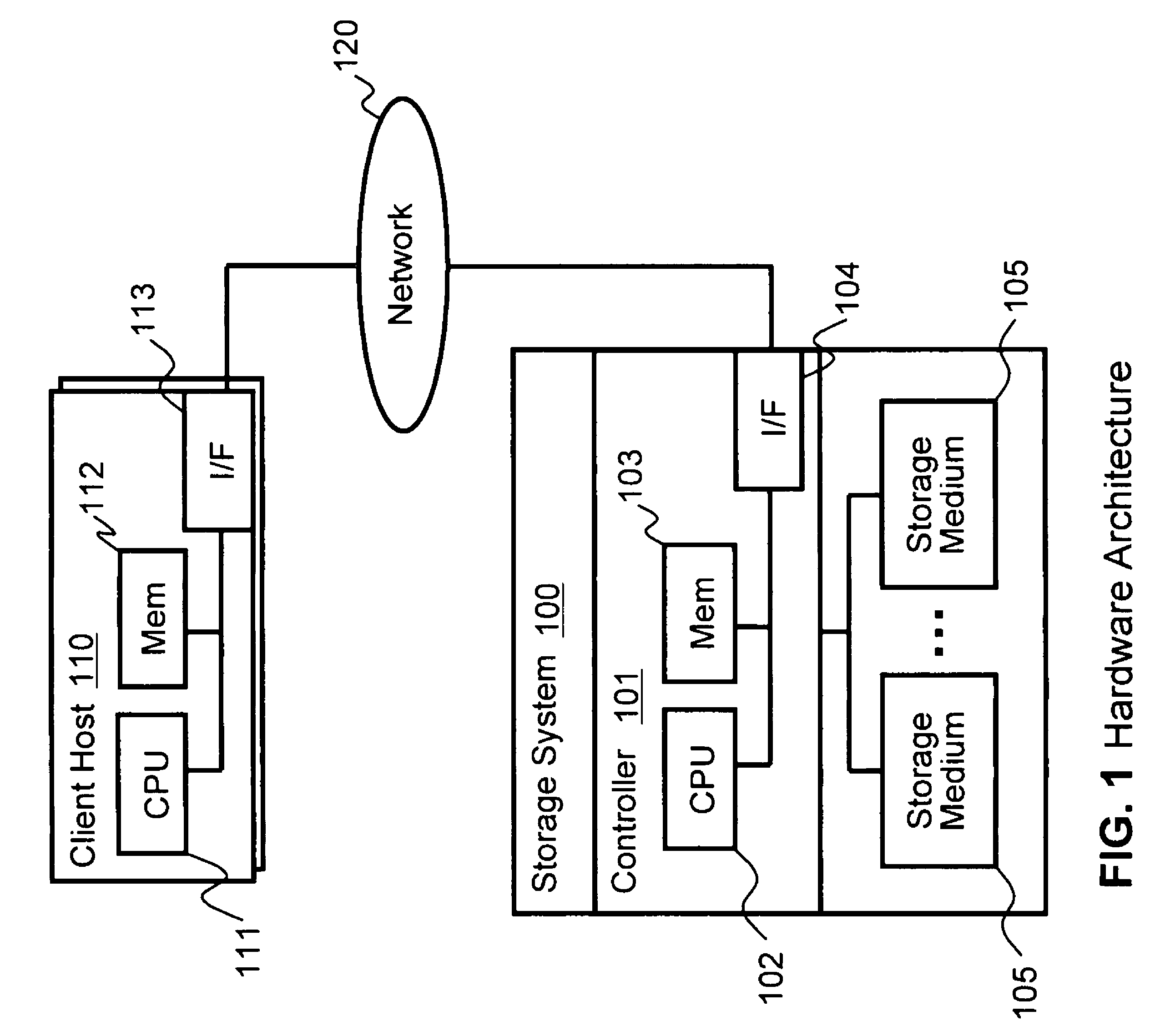
In computing, thin provisioning involves using virtualization technology to give the appearance of having more physical resources than are actually available. If a system always has enough resource to simultaneously support all of the virtualized resources, then it is not thin provisioned. The term thin provisioning is applied to disk layer in this article, but could refer to an allocation scheme for any resource. For example, real memory in a computer is typically thin-provisioned to running tasks with some form of address translation technology doing the virtualization. Each task acts as if it has real memory allocated. The sum of the allocated virtual memory assigned to tasks typically exceeds the total of real memory.
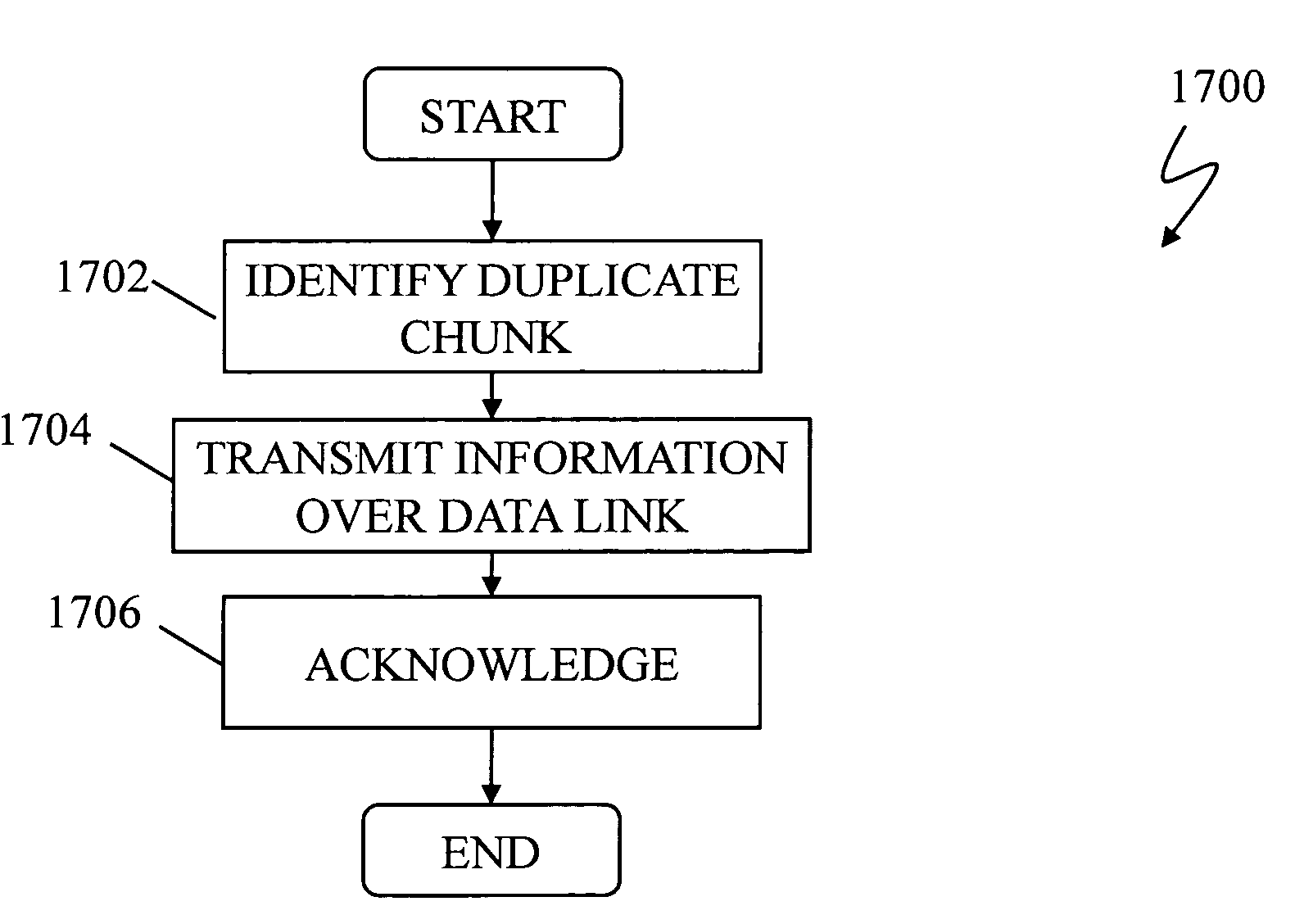
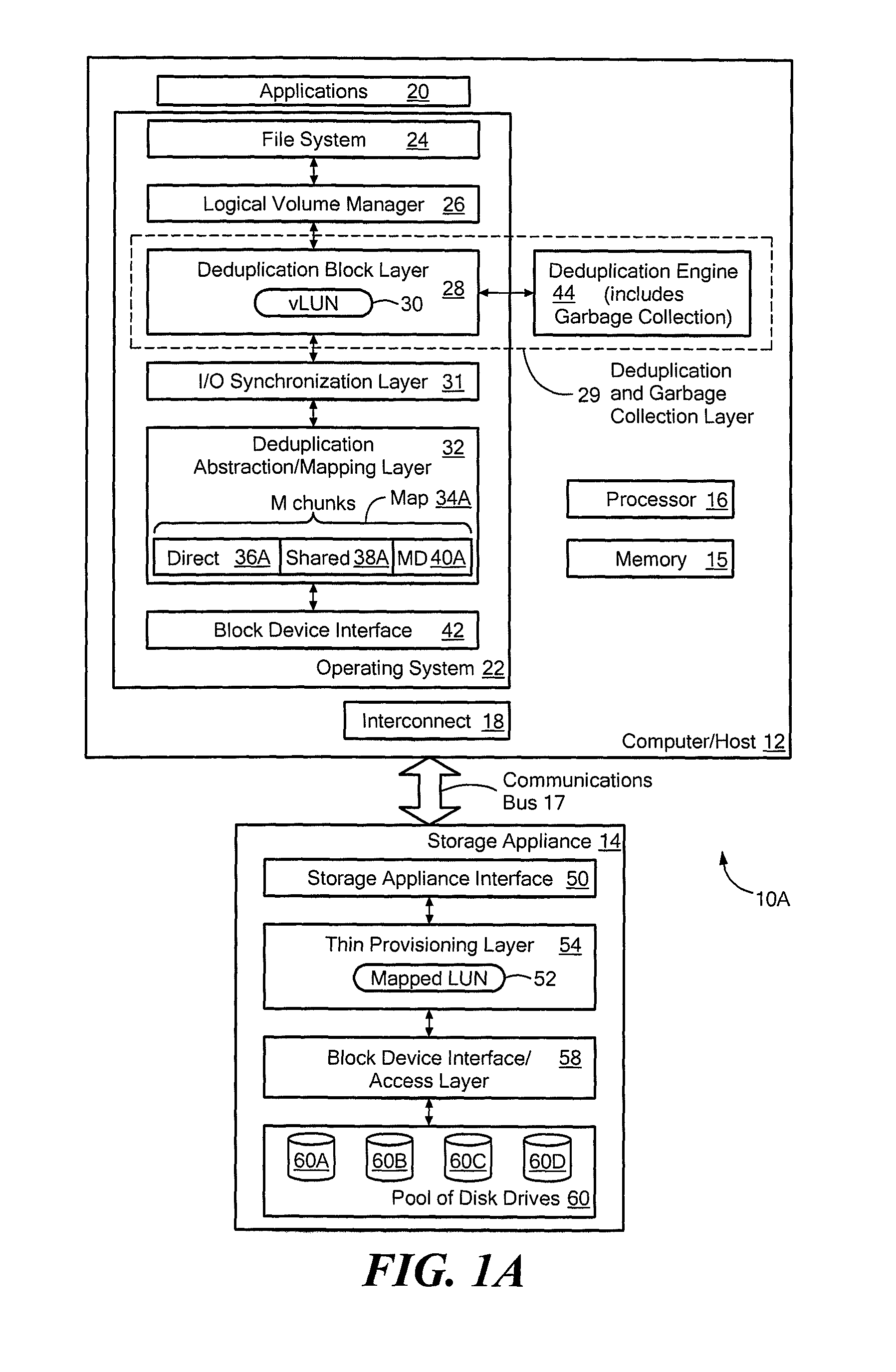
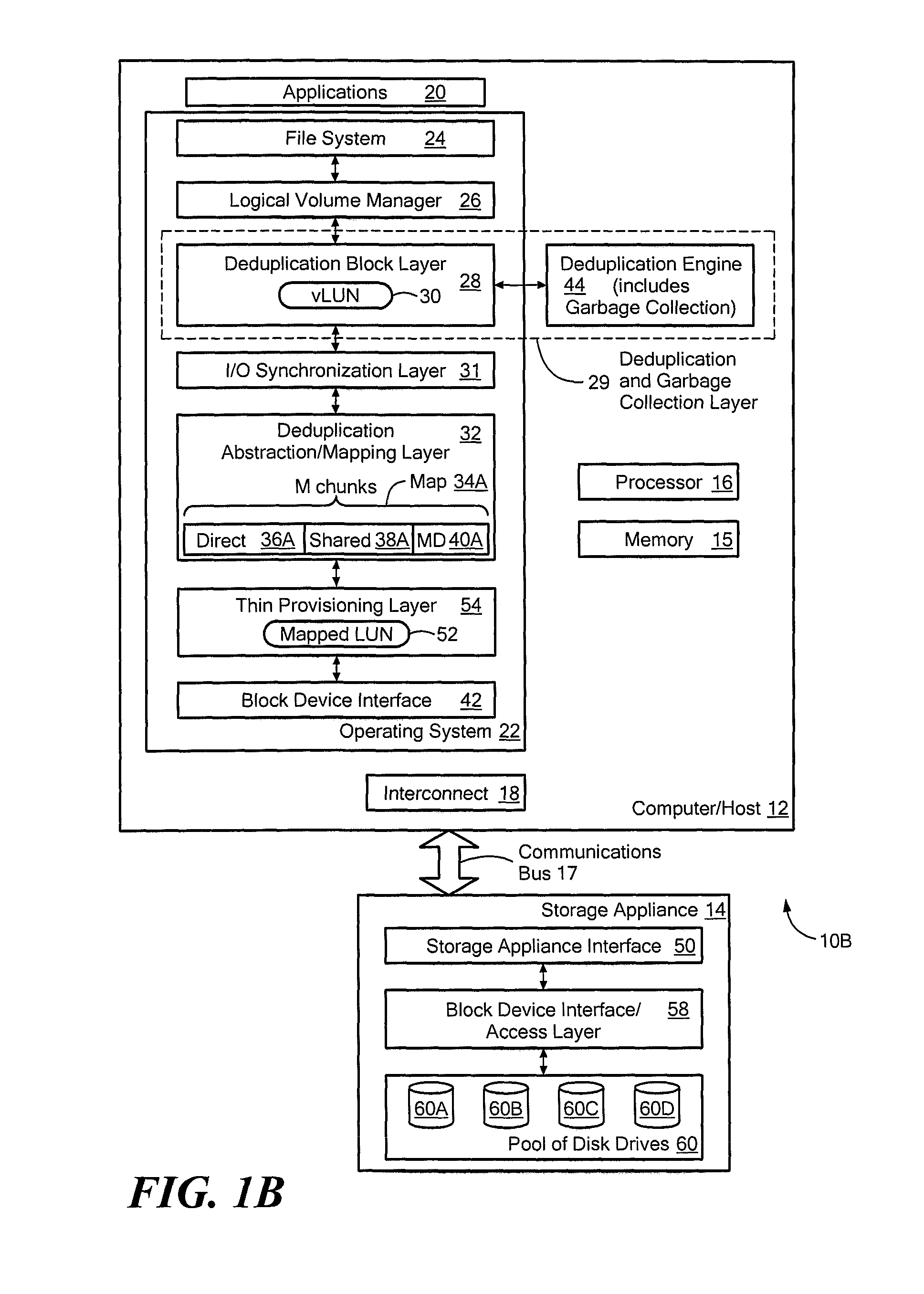
Data de-duplication using thin provisioning
ActiveUS7822939B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsThin provisioningData storing
A system for de-duplicating data includes providing a first volume including at least one pointer to a second volume that corresponds to physical storage space, wherein the first volume is a logical volume. A first set of data is detected as a duplicate of a second set of data stored on the second volume at a first data chunk. A pointer of the first volume associated with the first set of data is modified to point to the first data chunk. After modifying the pointer, no additional physical storage space is allocated for the first set of data.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
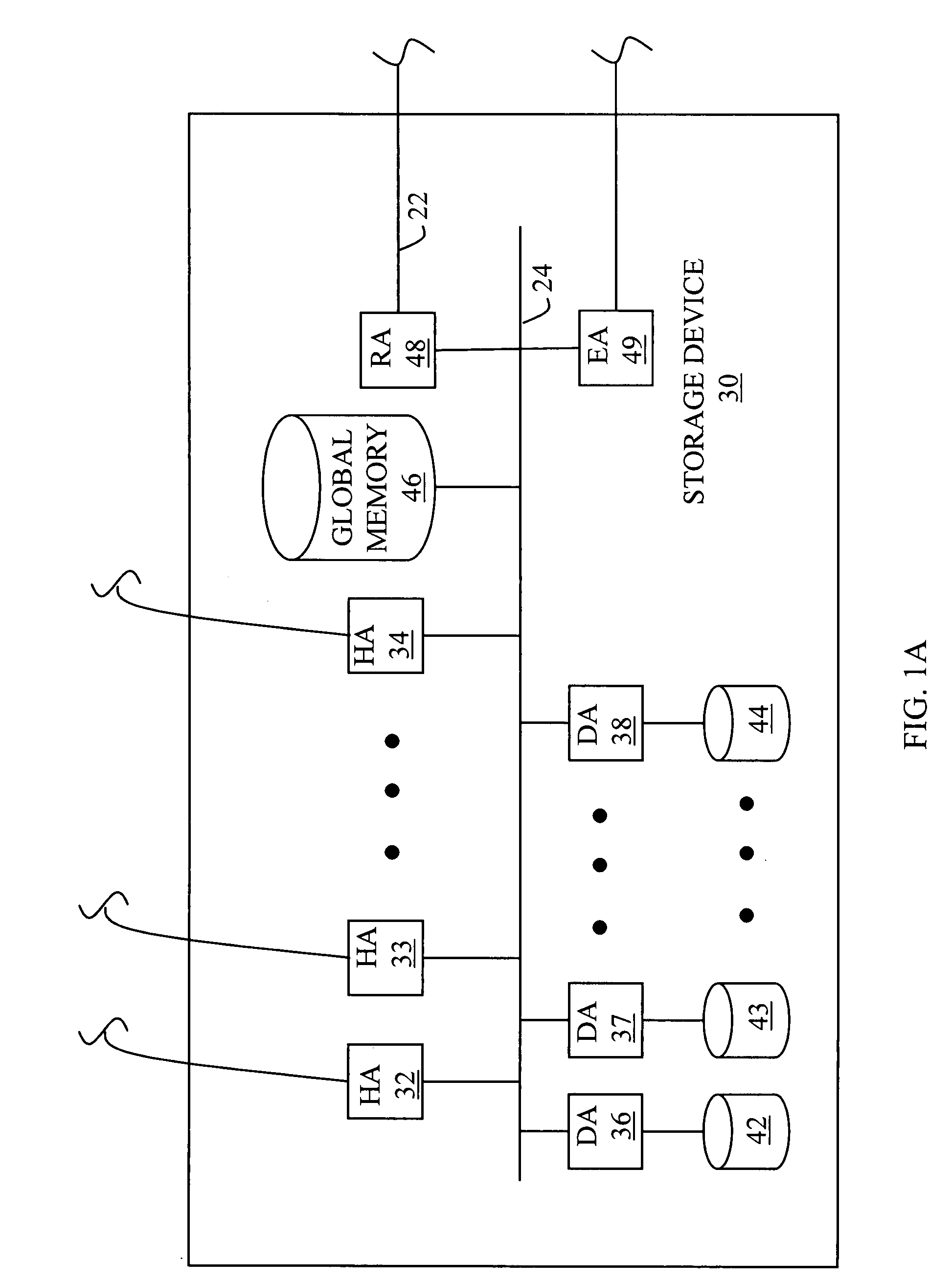
Free space utilization in tiered storage systems
ActiveUS20090276588A1Low costEliminate redundancyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingHybrid storage systemThin provisioning
Embodiments of the invention include first storage mediums having first storage characteristics for making up a first pool of capacity of a first tier of storage, and second storage mediums having second storage characteristics for making up a second pool of capacity of a second tier of storage. Free capacity of the first and second pools is shared between the first and second tiers of storage. When the first pool has an amount of free capacity available over a reserved amount of free capacity reserved for first tier data, a first quantity of second tier data is moved from the second tier to the first tier. In exemplary embodiments of the invention, the first and second storage mediums are contained within one or more thin provisioning storage systems, and data is moved between the first and second tiers by allocating thin provisioning chunks to the data being moved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
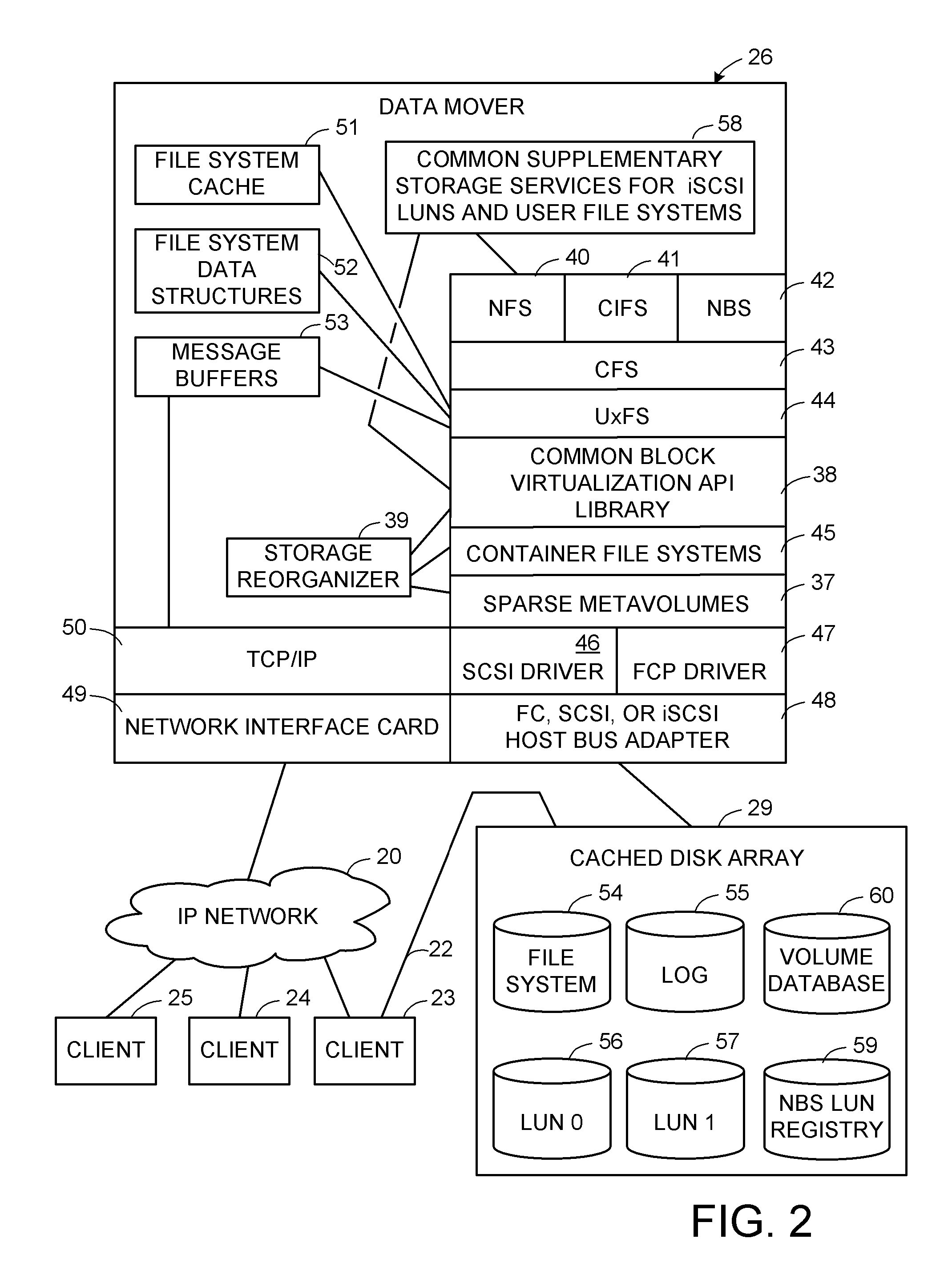
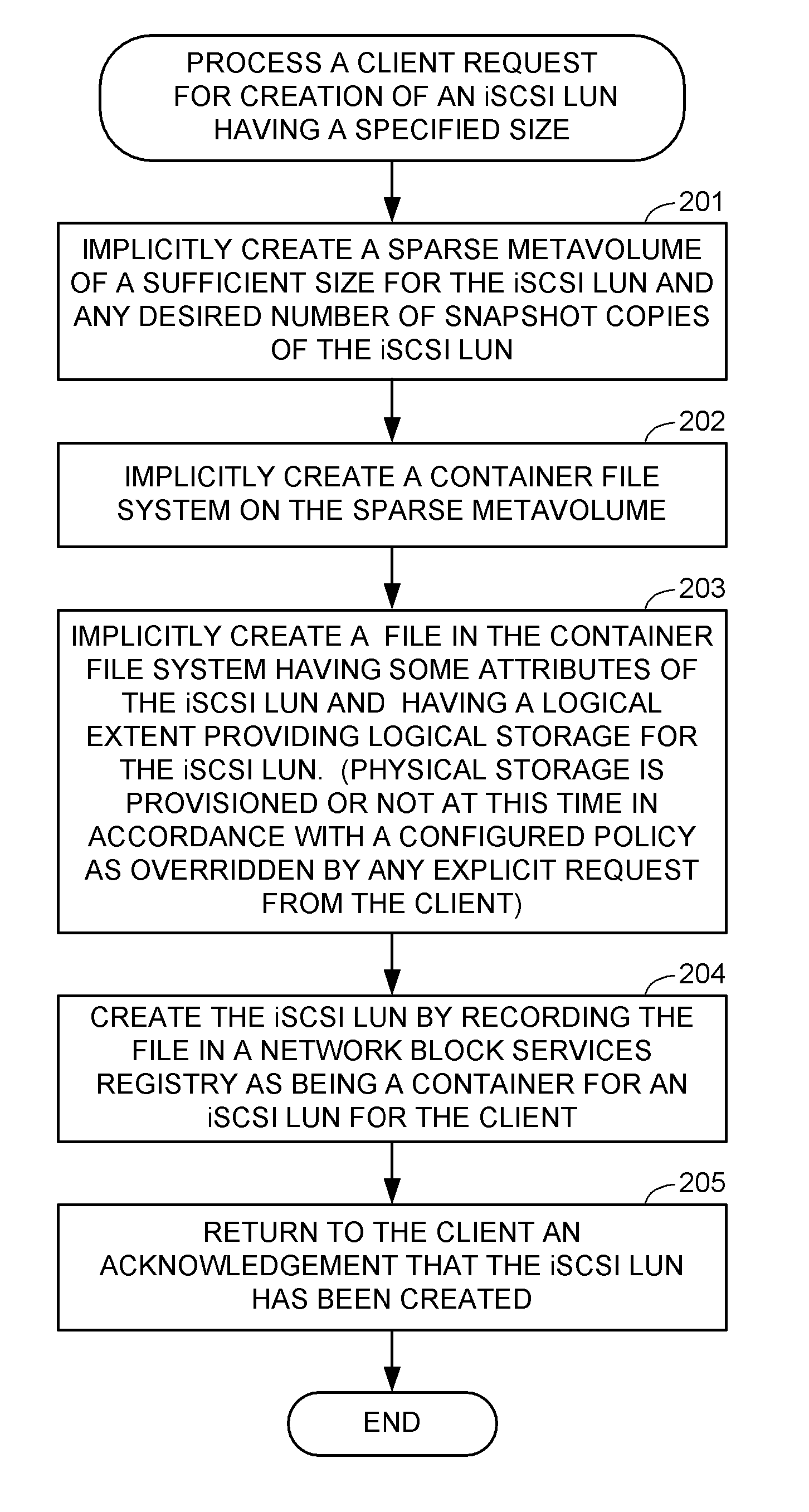
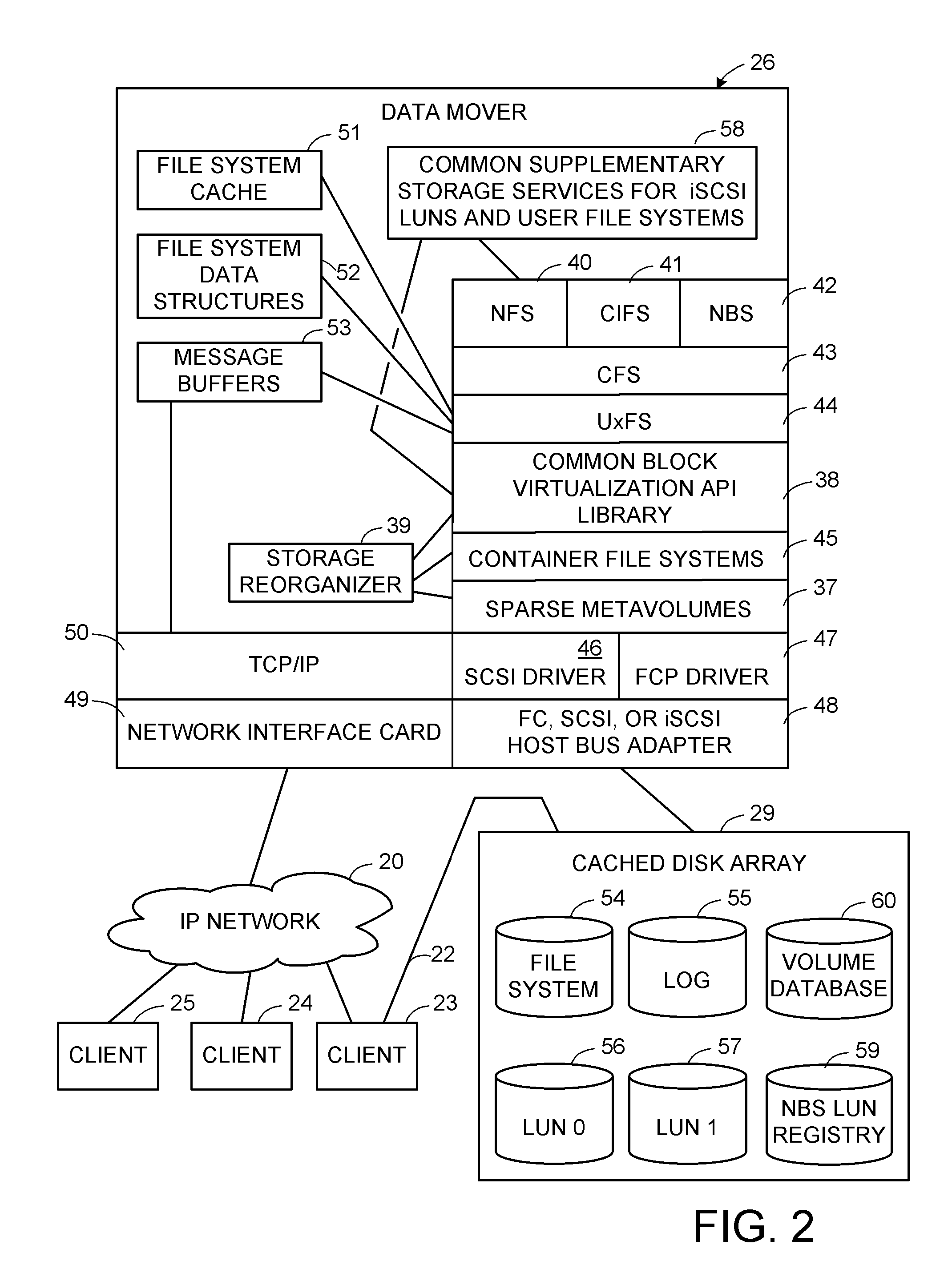
Thin provisioning of a file system and an iSCSI LUN through a common mechanism
ActiveUS7631155B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile systemThin provisioning
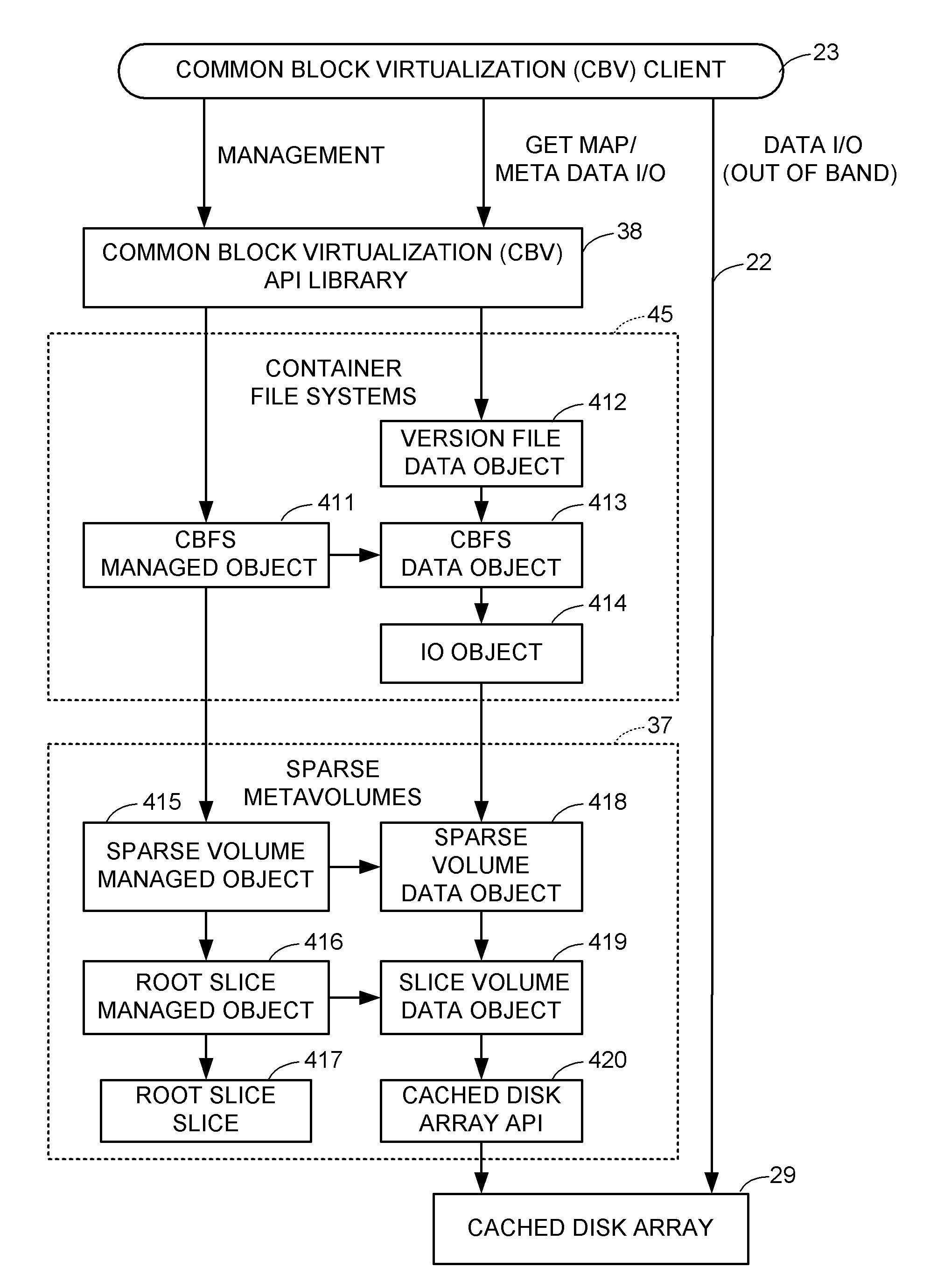
A container file system is built on a sparse metavolume for enhanced decoupling of logical storage from physical storage and for providing common supplementary storage services for iSCSI block access and for NFS or CIFS file system access. The container file system contains a production file system or iSCSI LUN and may also contain snapshot copies of the production file system or iSCSI LUN. The container file system manages storage space among the production file system or iSCSI LUN and its snapshot copies, and also improves fault containment. The sparse metavolume provides thin provisioning of the container file system. A slice map indicates whether or not each slice of logical storage in the sparse metavolume is provisioned with an associated configured slice of data storage.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
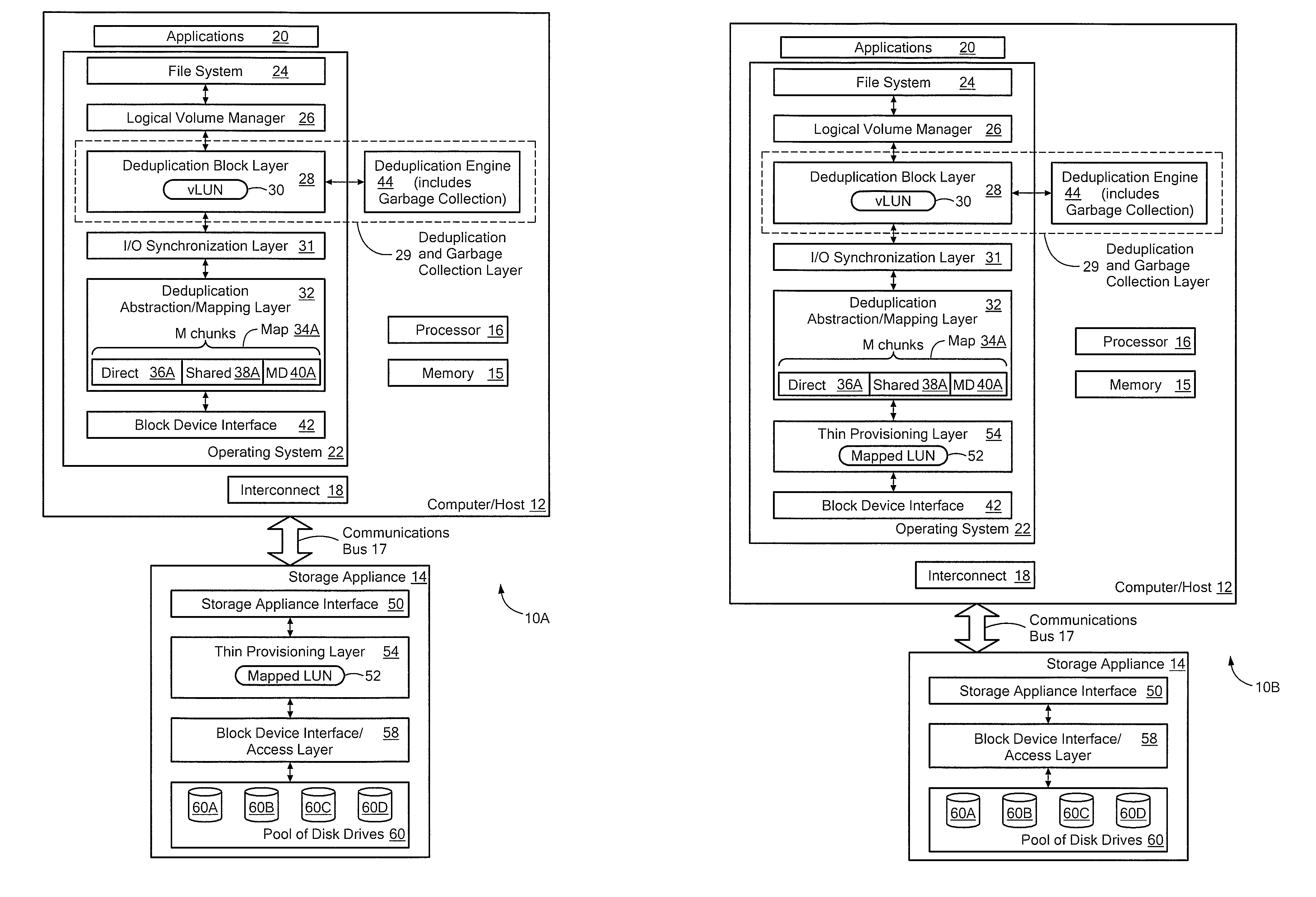
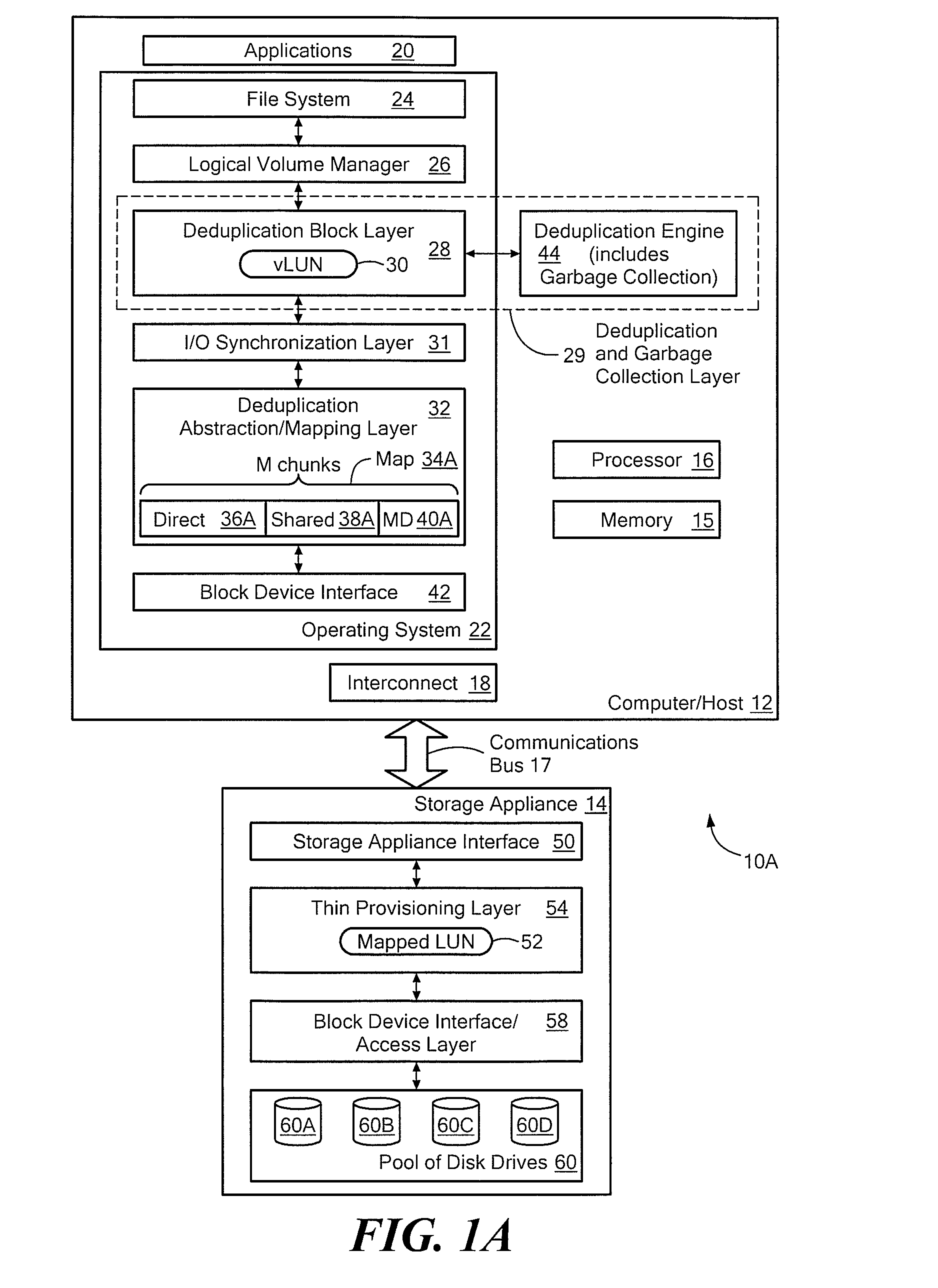
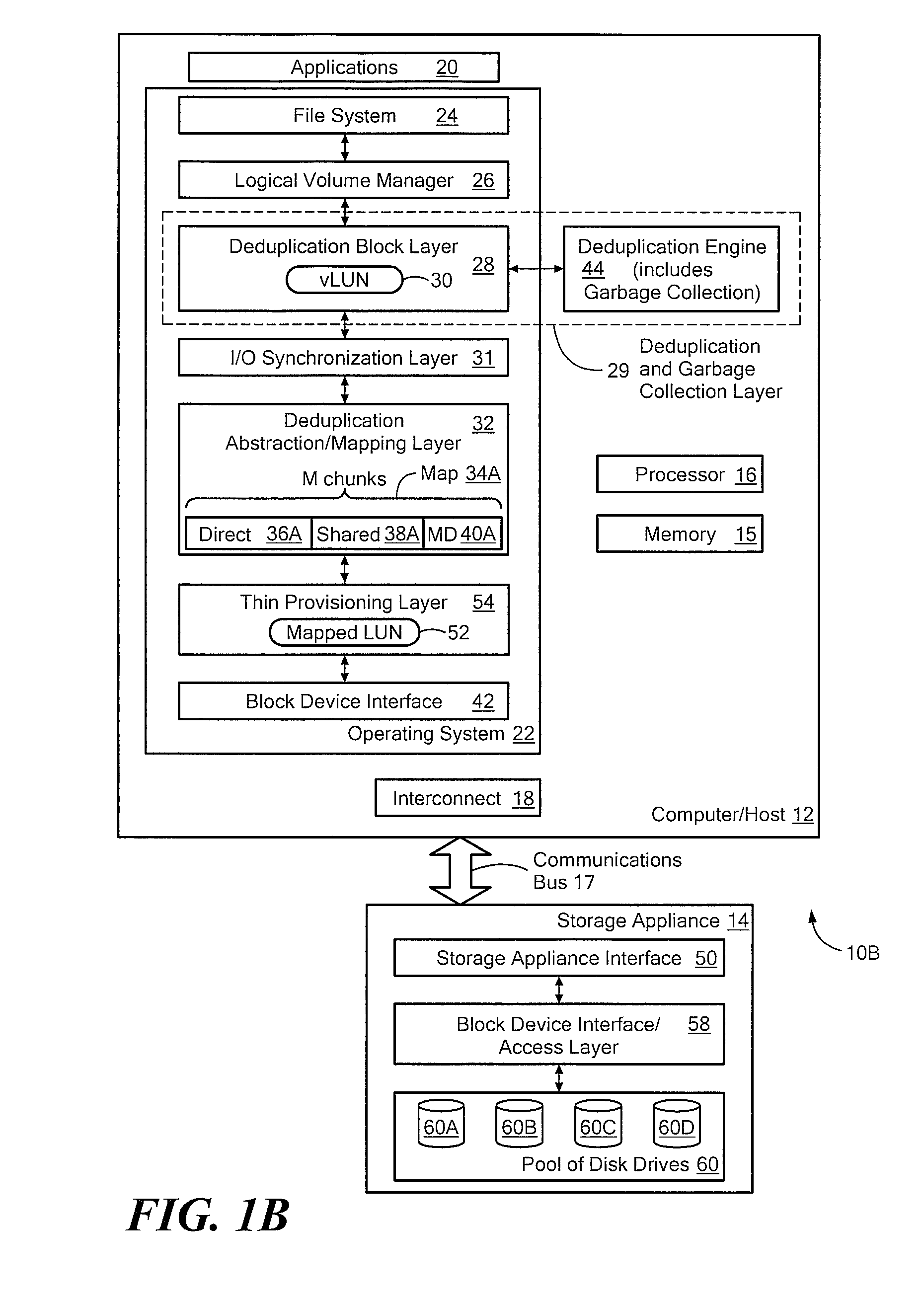
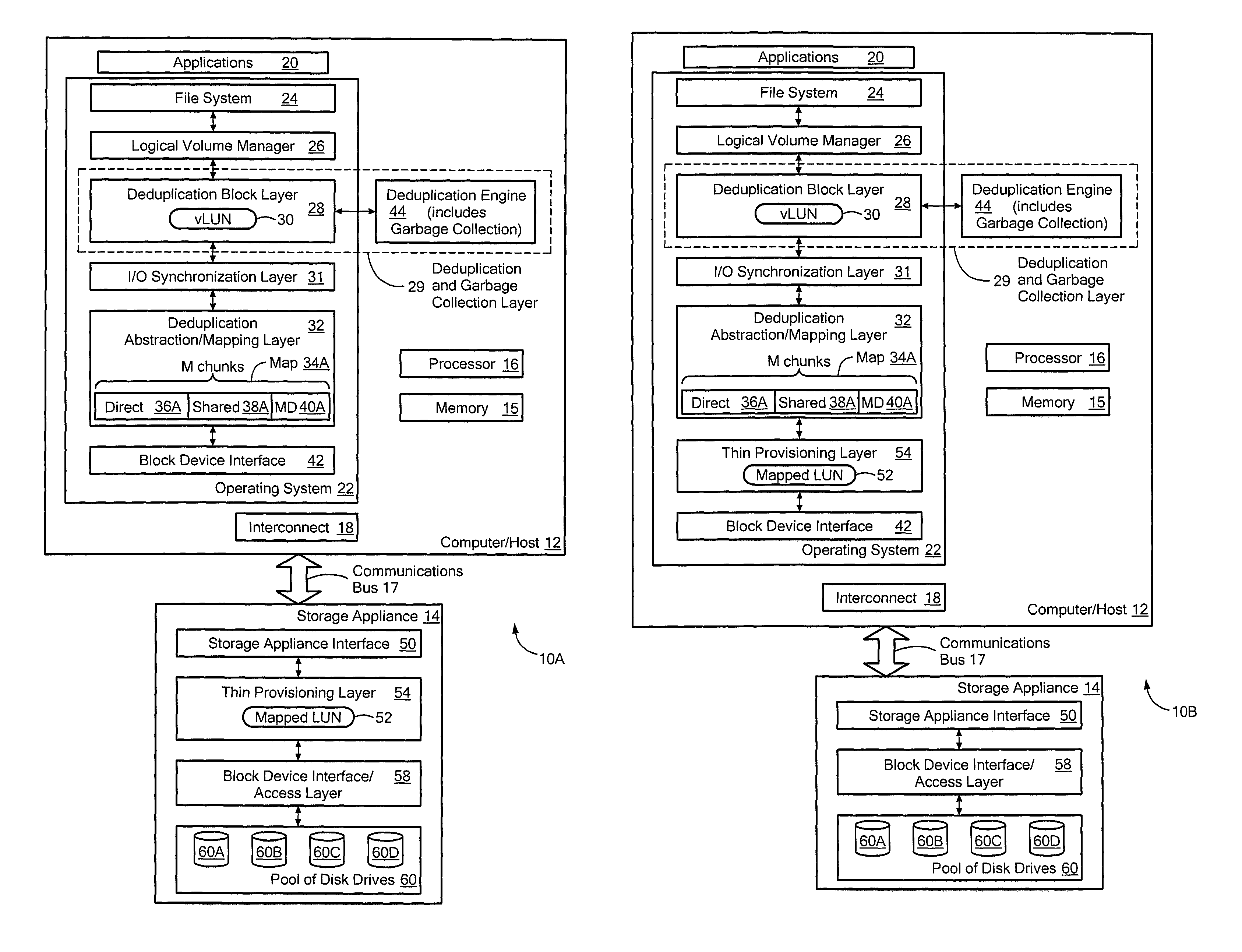
Systems and methods for using thin provisioning to reclaim space identified by data reduction processes
ActiveUS8156306B1Efficient accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceThin provisioning
The invention provides a system to reclaim space identified as no longer in use and comprises a vLUN, a thinly provisioned mapped LUN, a mapping layer, and a data reduction engine. Chunks of data are stored at logical chunk addresses (LCAs) in the vLUN and are mapped to corresponding physical chunk addresses (PCAs) in the thinly provisioned mapped LUN. The data reduction engine performs a data reduction process on a first logical chunk of data stored at a first LCA in the vLUN, where the first logical chunk has a size that is a nonzero integer multiple of the size of the storage extent of the thinly provisioned mapped LUN. After the data reduction process, the PCA associated with the first logical chunk is no longer needed, and the thinly provisioned mapped LUN is instructed to deallocate the PCA associated with the first logical chunk that is no longer needed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage management for fine grained tiered storage with thin provisioning
ActiveUS7949637B1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsStorage managementThin provisioning
A system for managing data includes providing at least one logical device having a table of information that maps sections of the logical device to sections of at least two storage areas. Characteristics of data associated with a one section of the logical device may be evaluated. The section of the data may moved between the at least two storage areas from a first location to a second location according to a policy and based on the characteristics of the data. A copy of the data may be retained in the first location and a list maintained that indentifies the copy of the data in the first location. The system provides for garbage collection processing for memory management.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Automated information life-cycle management with thin provisioning
ActiveUS20090070541A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationStructured data retrievalThin provisioningComputer science
A system for managing data includes providing at least one logical device having a table of information that maps sections of the logical device to sections of at least two storage areas. Characteristics of data associated with at least one section of the logical device may be evaluated. The at least one section of the data may moved between the at least two storage areas according to a policy and based on the characteristics of the data. The table of information is updated according to the movement of data between the at least two storage areas.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
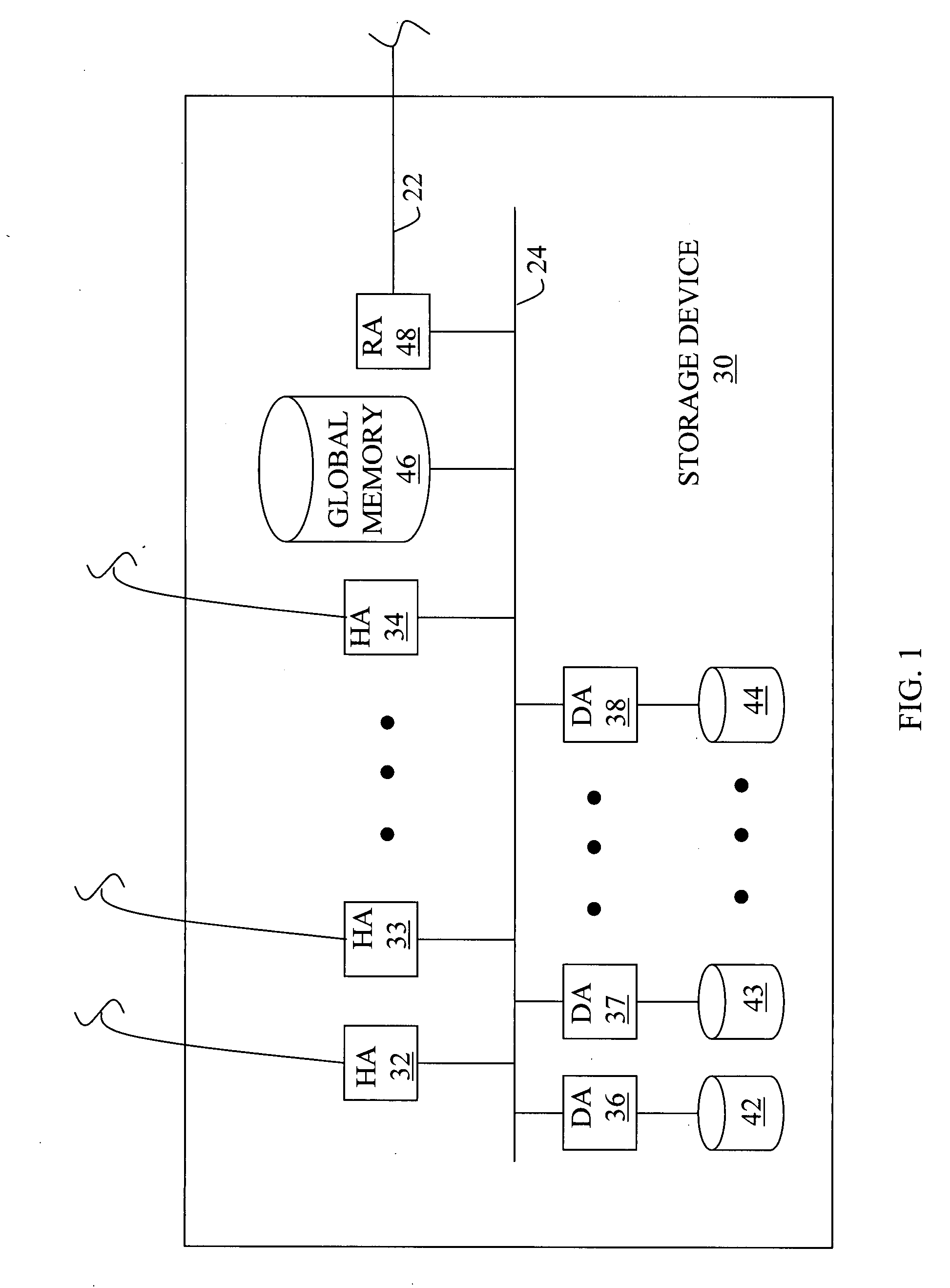
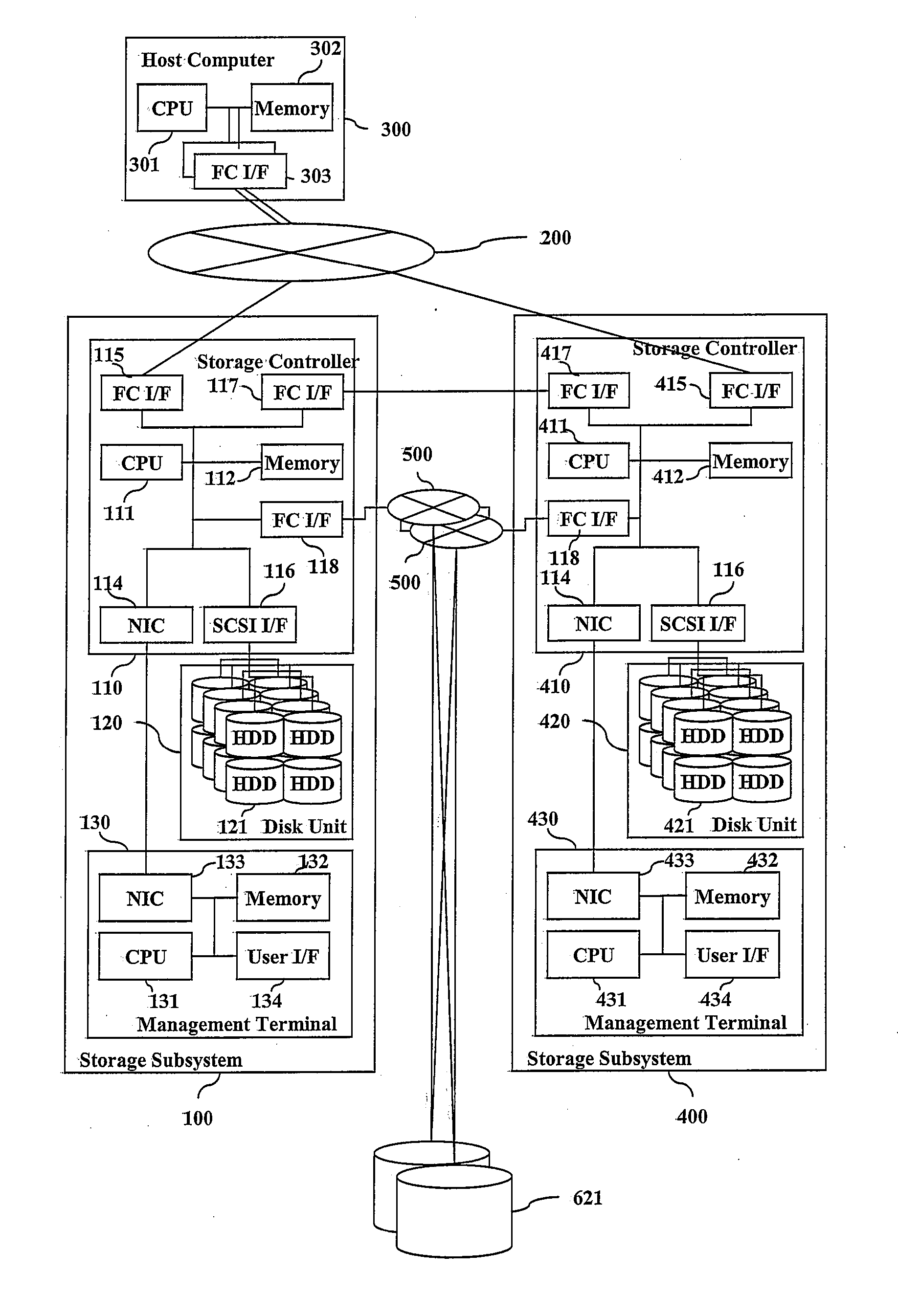
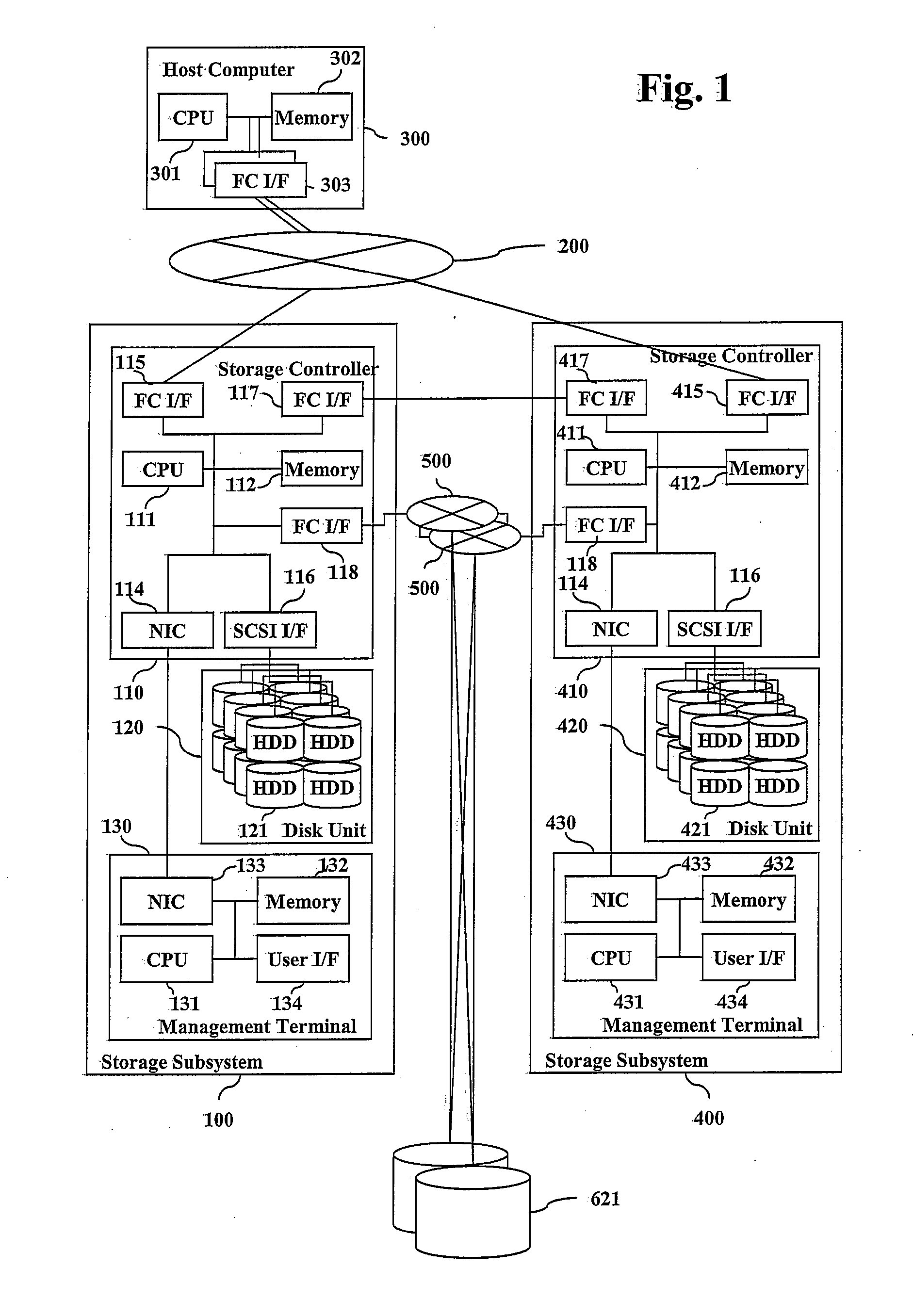
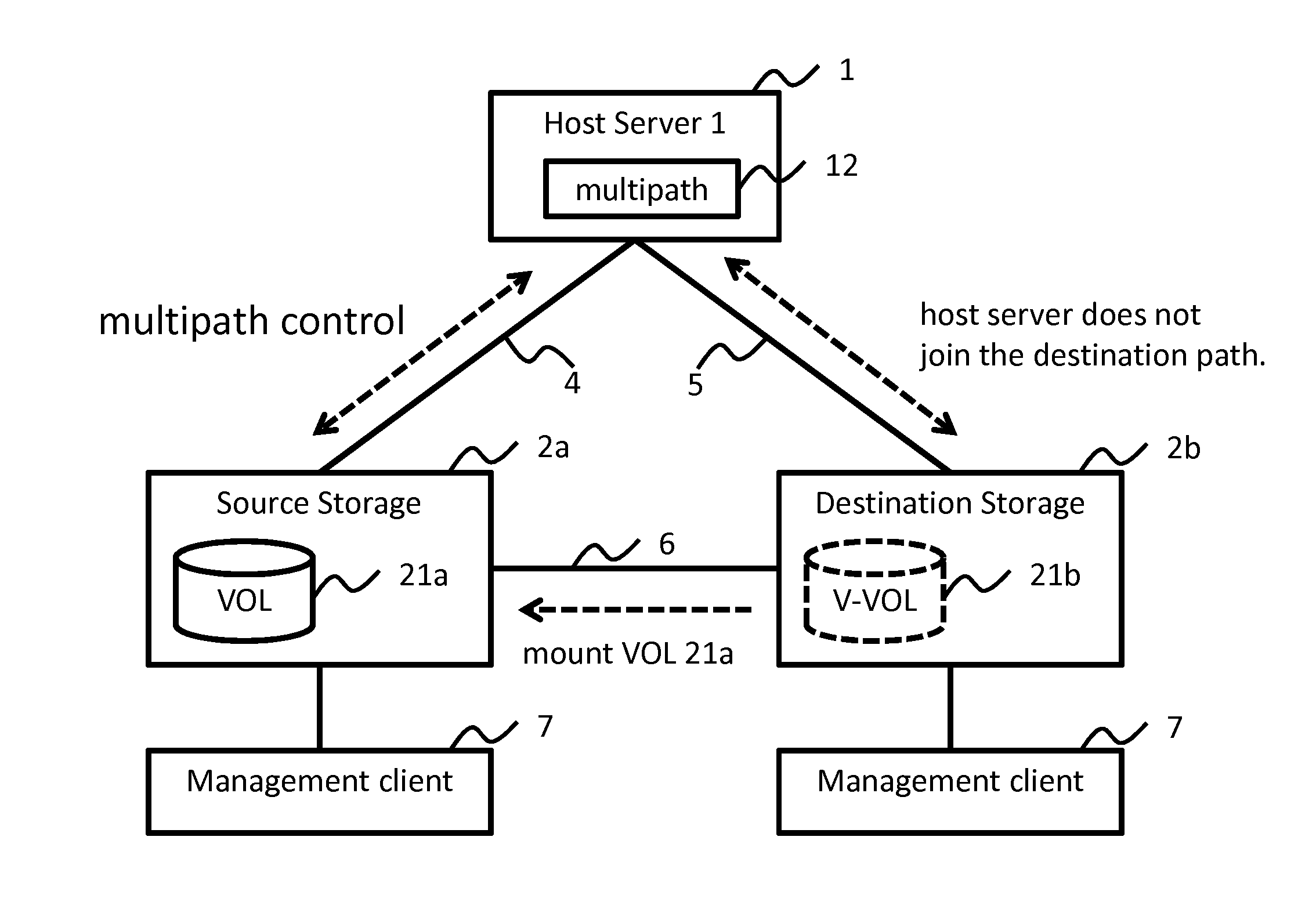
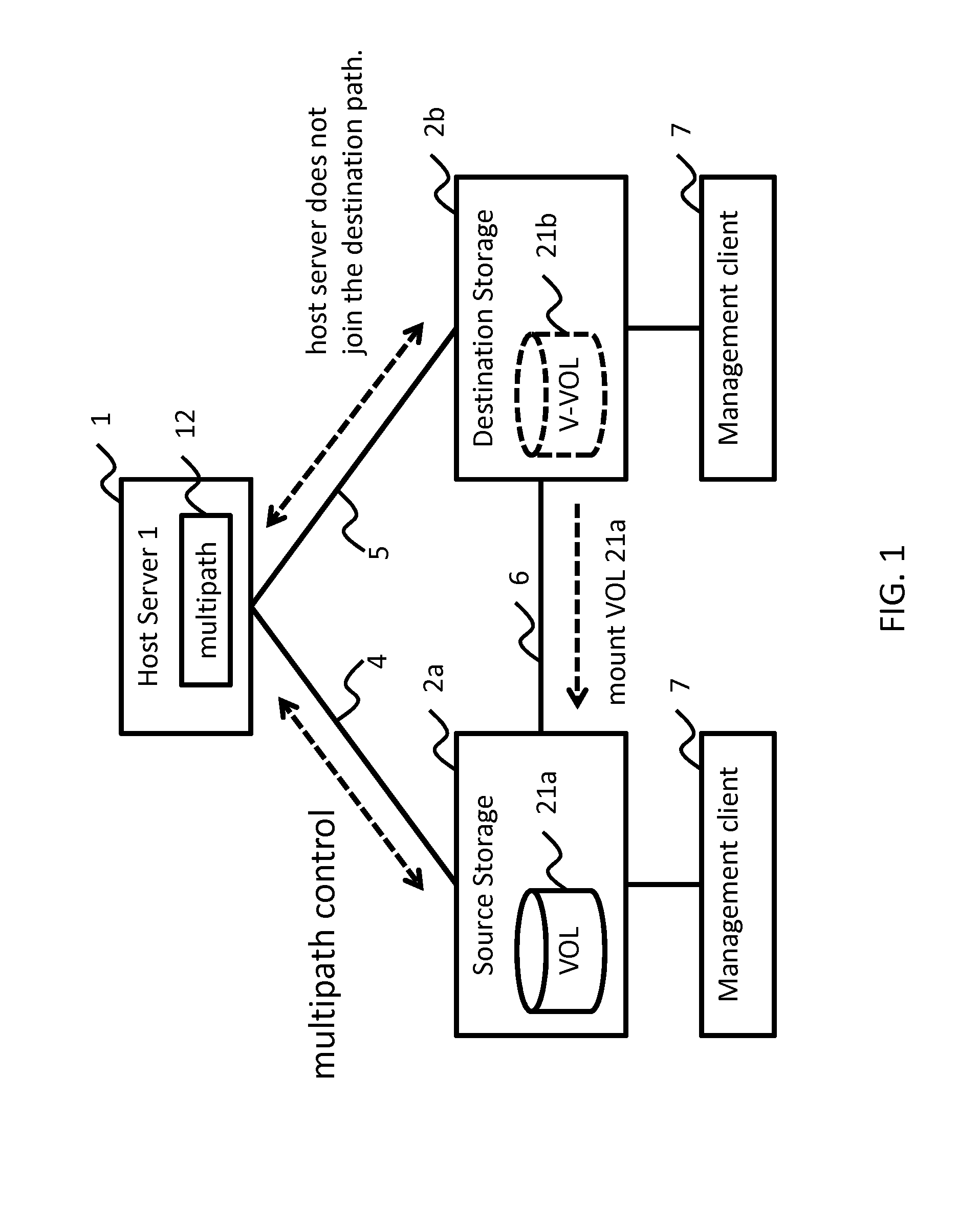
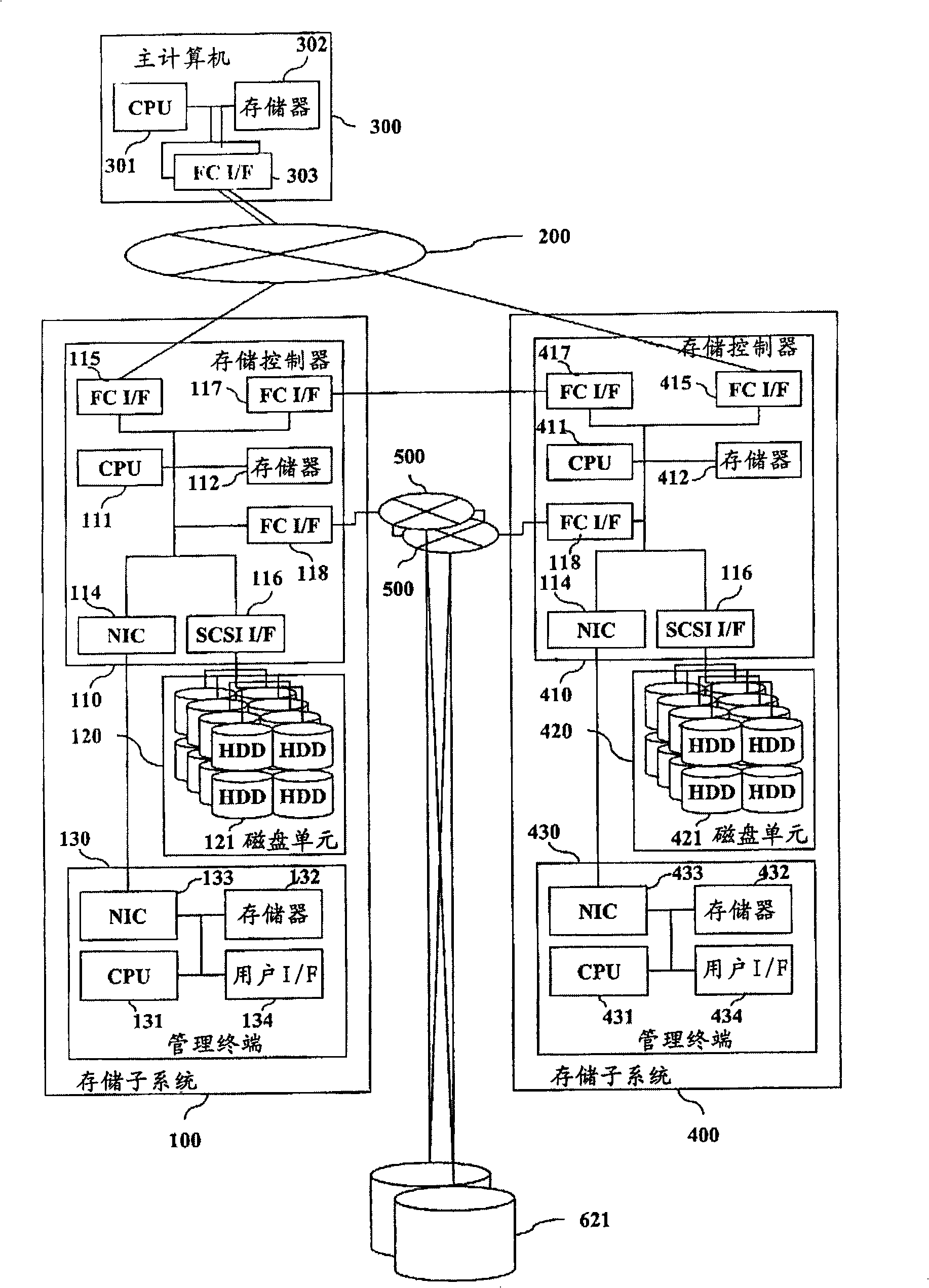
High availability and low capacity thin provisioning
InactiveUS20090240880A1Reduce capacity requirementsImprove usabilityMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsExternal storageHigh availability
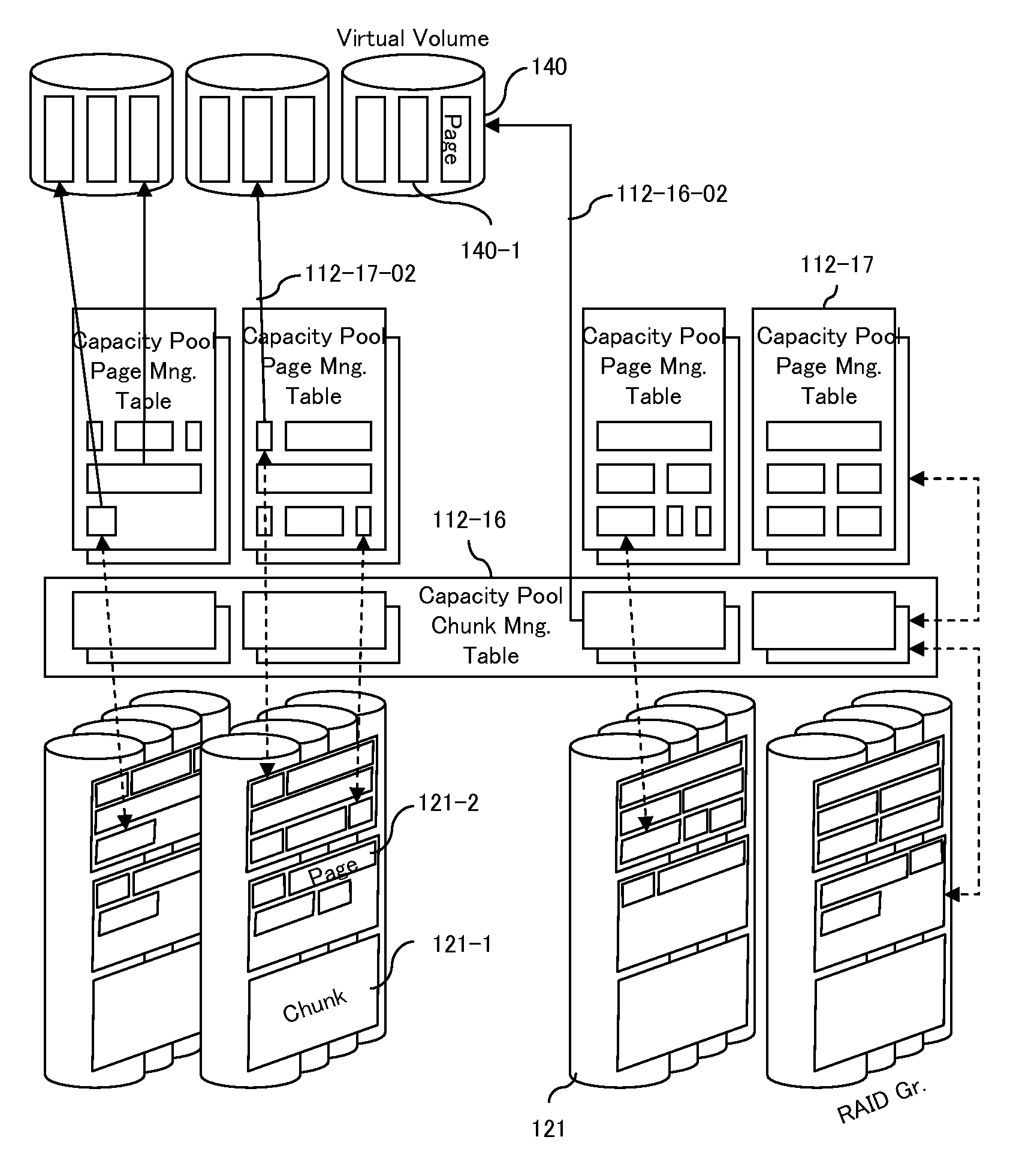
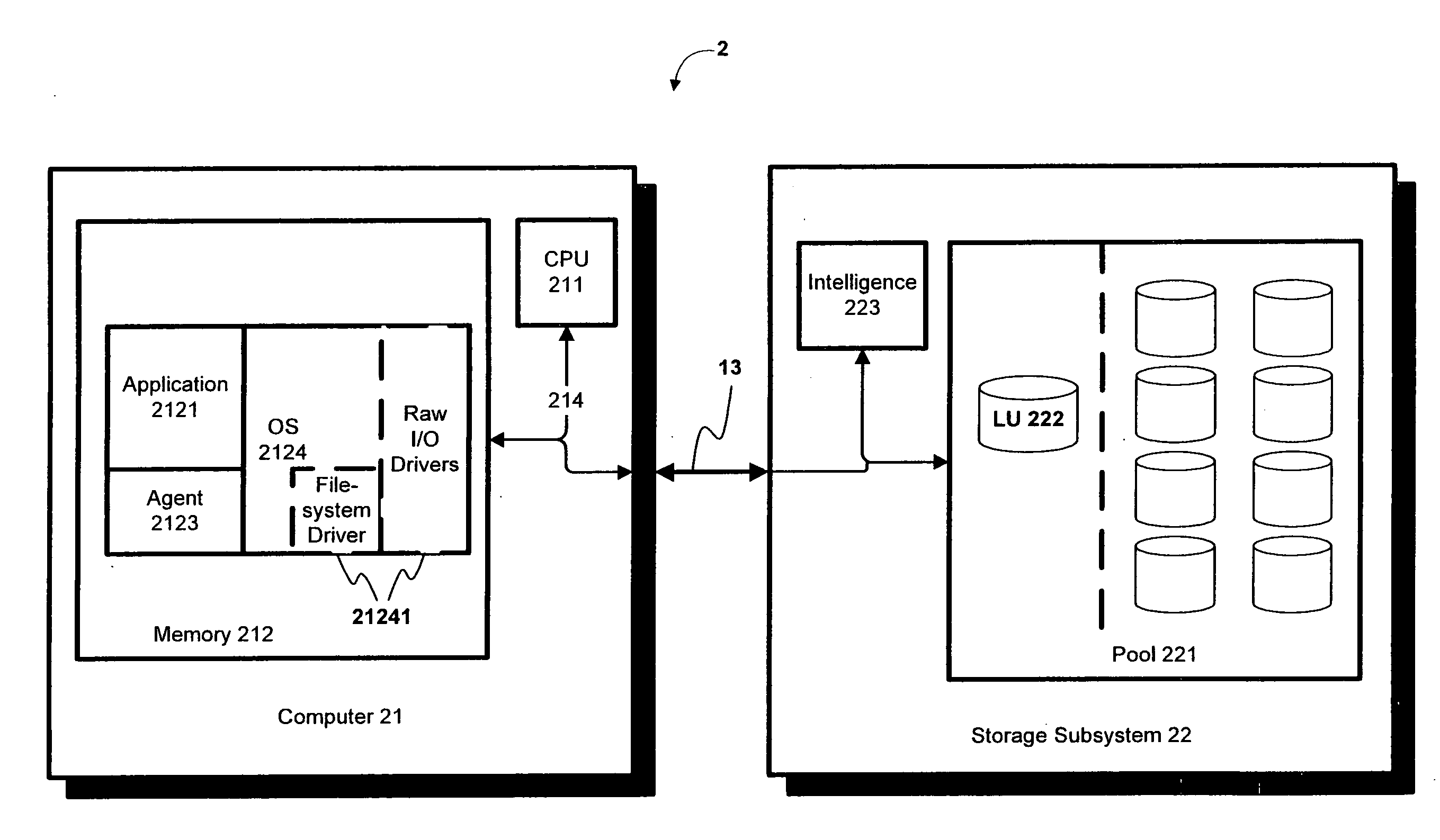
A data storage system and method for simultaneously providing thin provisioning and high availability. The system includes external storage volume and two storage subsystems coupled together and to external storage volume. Each of storage subsystems includes disk drives and a cache area, each of the storage subsystems includes at least one virtual volume and at least one capacity pool. The virtual volume is allocated from storage elements of the at least one capacity pool. The capacity pool includes the disk drives and at least a portion of external storage volume. The storage elements of the capacity pool are allocated to the virtual volume in response to a data access request. The system further includes a host computer coupled to the storage subsystems and configured to switch input / output path between the storage subsystems. Each of the storage subsystems is adapted to copy received write I / O request to other storage subsystems. Upon receipt of request from another storage subsystem, storage element of the capacity pool of storage subsystem is prevented from being allocated to the virtual volume of that storage subsystem.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
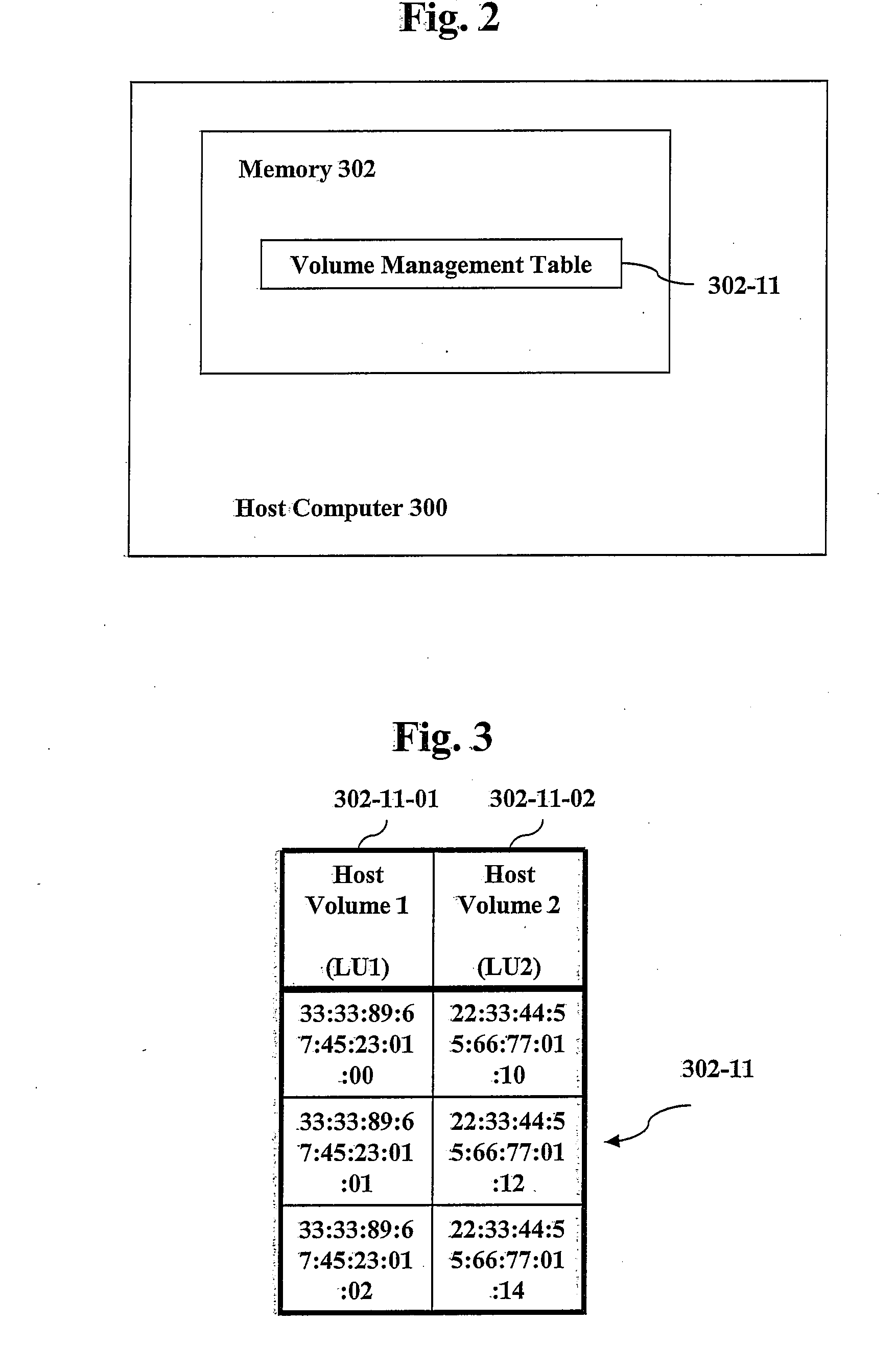
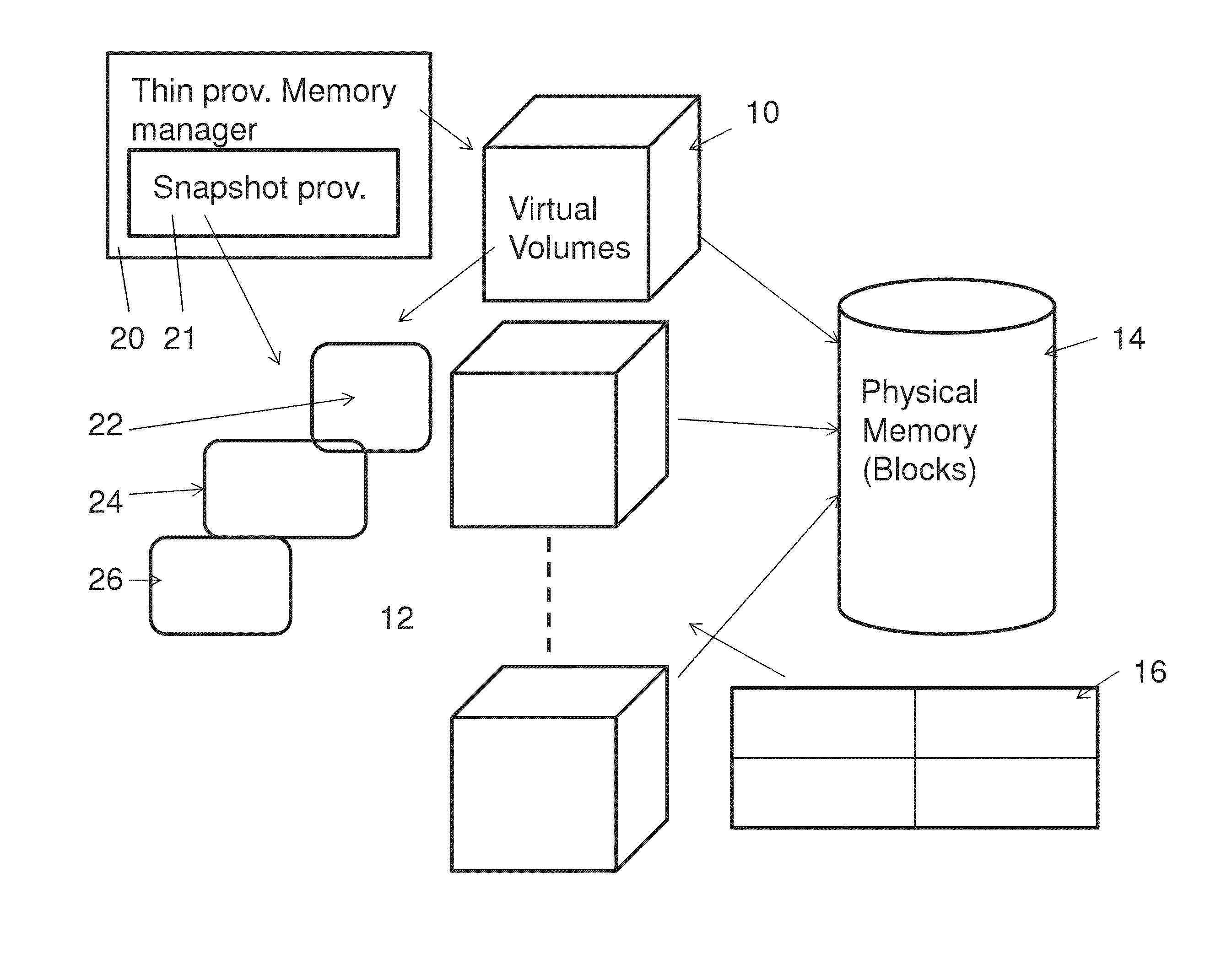
Snapshot mechanism
A memory management system for a thinly provisioned memory volume in which a relatively larger virtual address range of virtual address blocks is mapped to a relatively smaller physical memory comprising physical memory blocks via a mapping table containing entries only for addresses of the physical memory blocks containing data. The memory management system comprises a snapshot provision unit to take a given snapshot of the memory volume at a given time, the snapshot comprising a mapping table and memory values of the volume, the mapping table and memory values comprising entries only for addresses of the physical memory containing data. The snapshot is managed on the same thin provisioning basis as the volume itself, and the system is particularly suitable for RAM type memory disks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Fast accessible compressed thin provisioning volume
ActiveUS20090144496A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsData compressionData management
A computerized data storage system includes at least one storage device including a nonvolatile writable medium; a cache memory operatively coupled to the storage port and including a data storing area and a data management controller and a storage port. The storage port is operable to connect to a host computer, receive and send I / O information required by the host computer. The storage port is also operable to receive a request to read data, and, in response to the request to read data, the storage port is operable to send the data stored in the data storing area of the cache memory. The storage port is further operable to receive a request to write data, and, in response to the request to write data, the storage port is operable to send the write data to the data storing area of the cache memory. The storage system further includes a thin provisioning controller operable to provide a virtual volume having a virtual volume page, a capacity pool having a capacity pool page and manage a mapping between the virtual volume page and the capacity pool page. The storage system further includes a data compression controller operable to perform a compression operation, and a data decompression controller operable to perform a decompression operation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
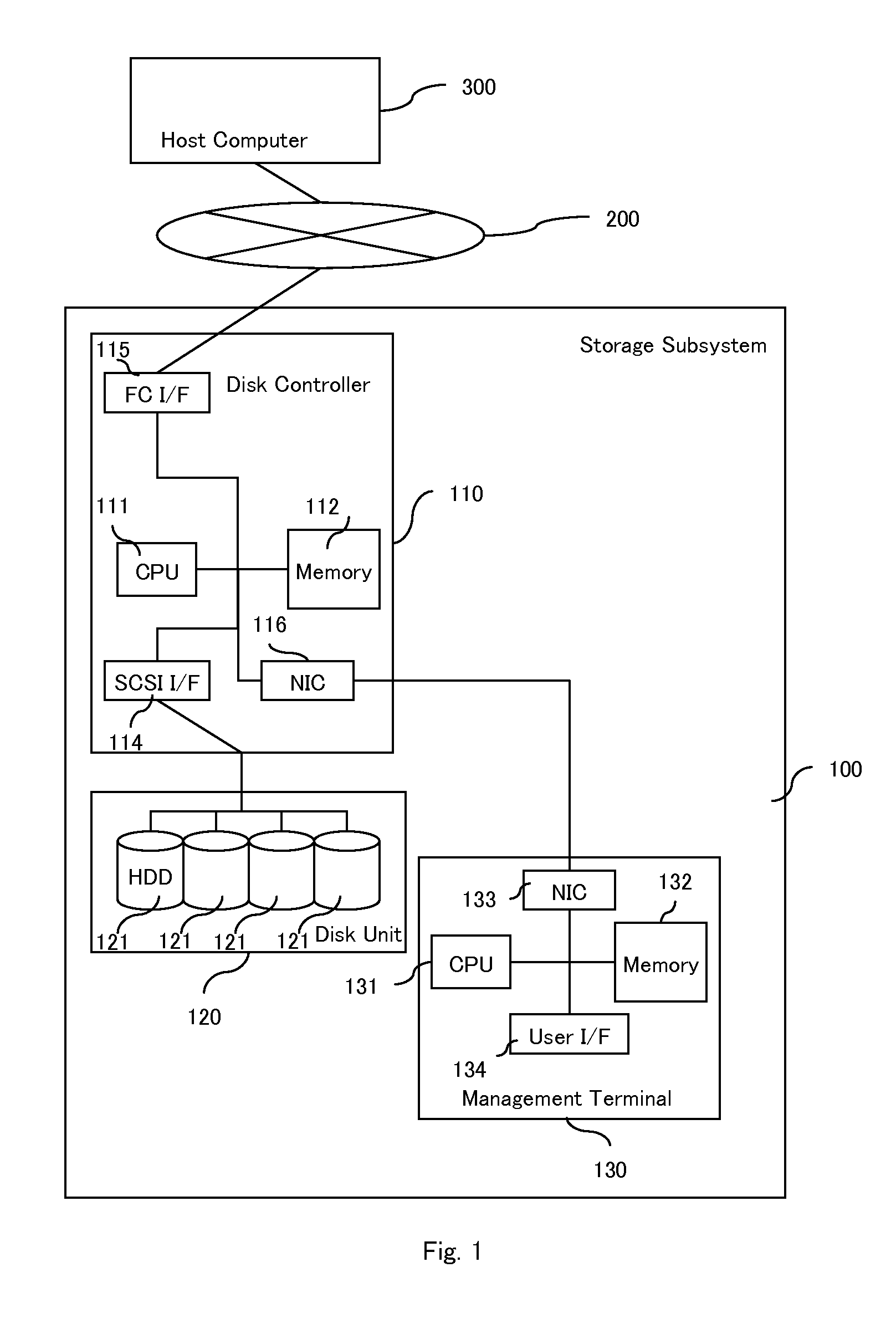
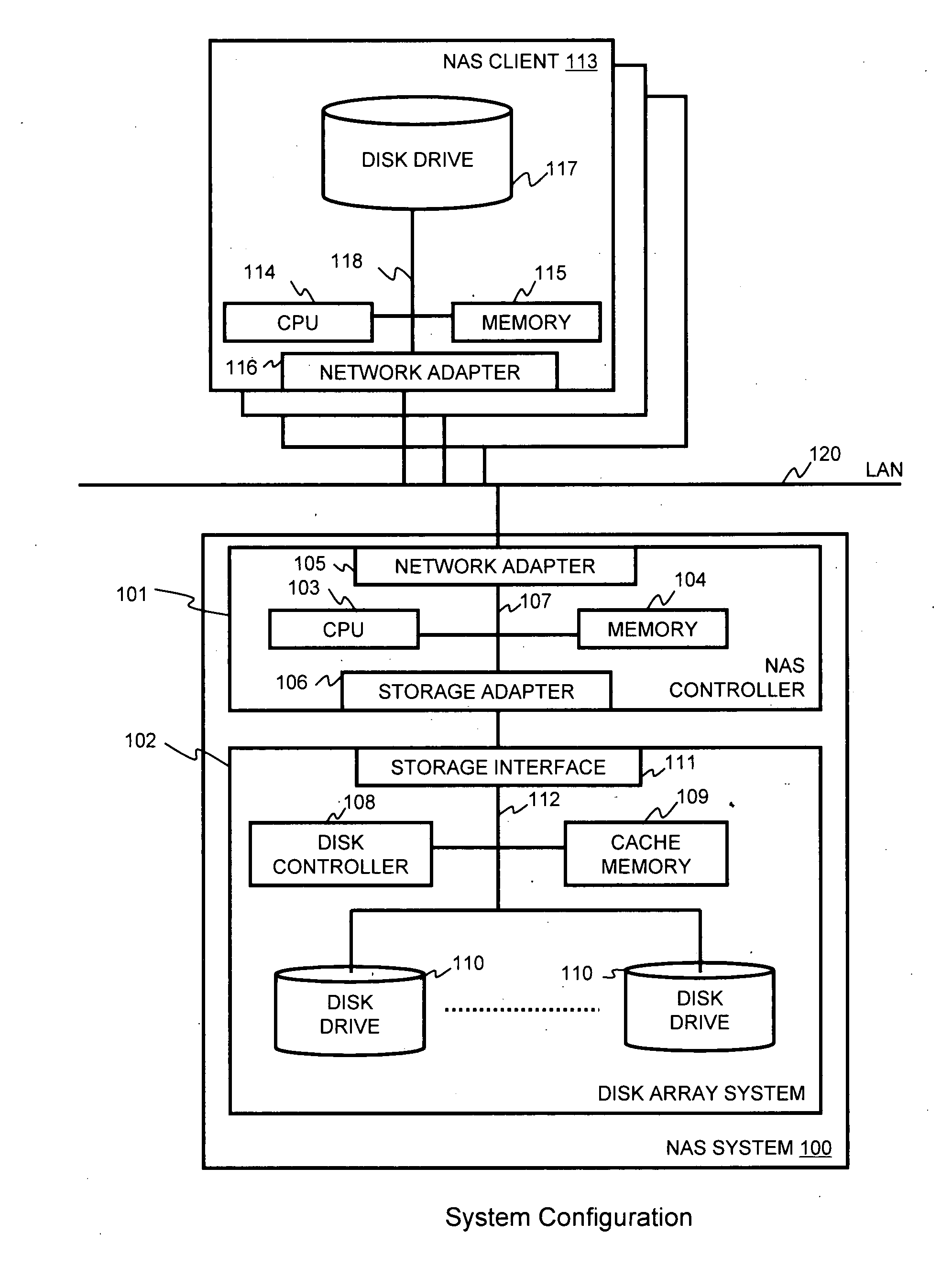
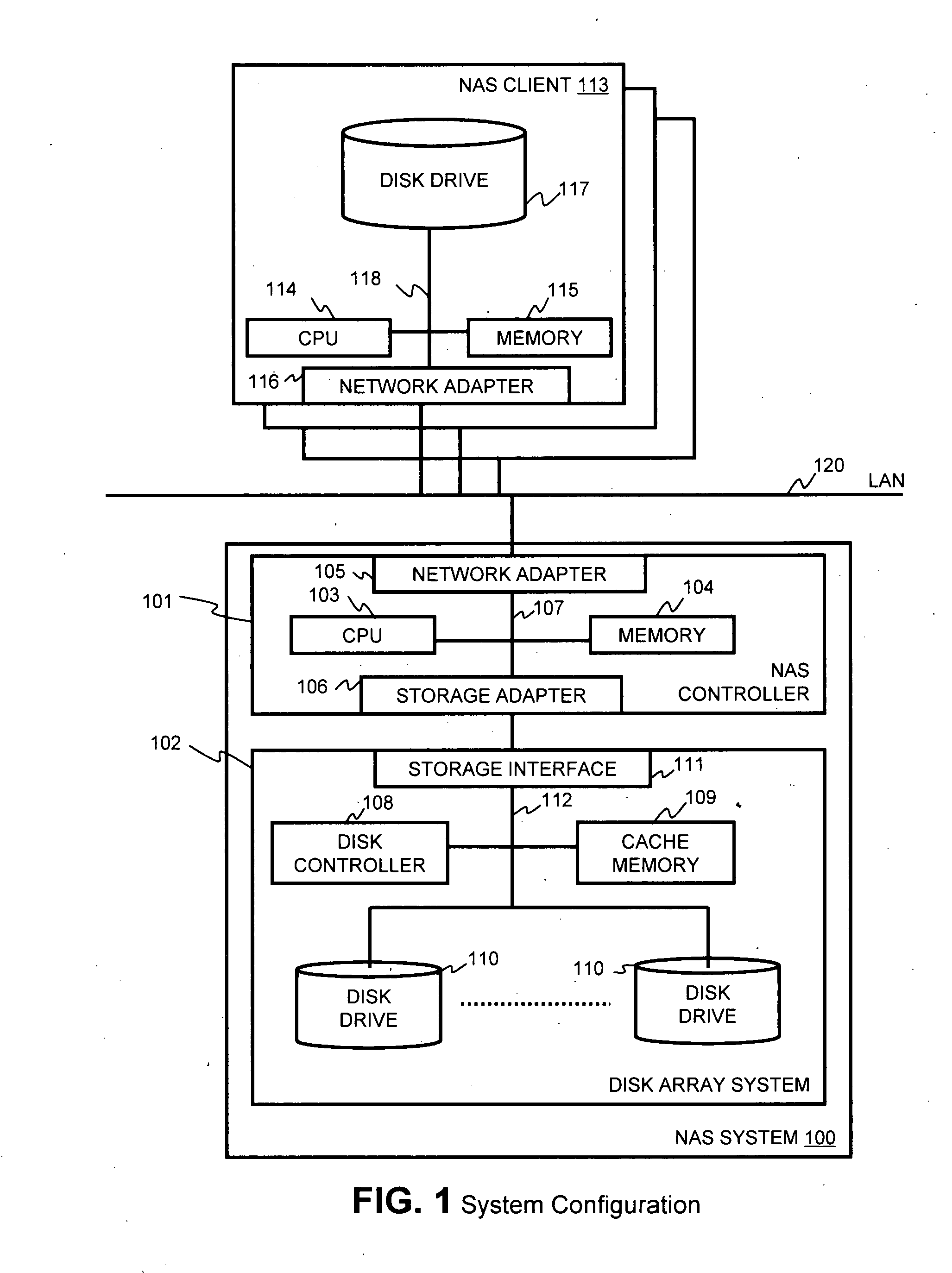
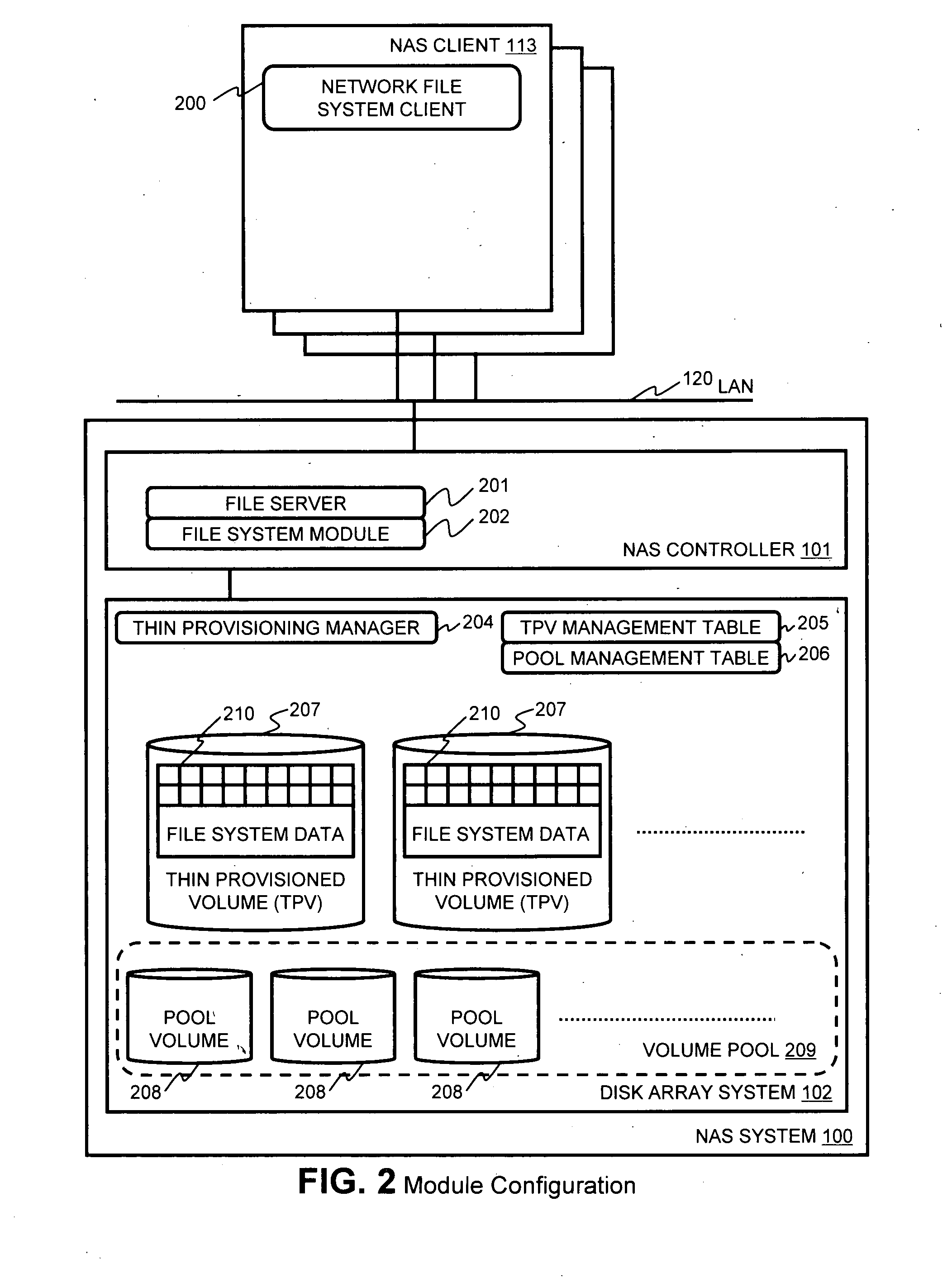
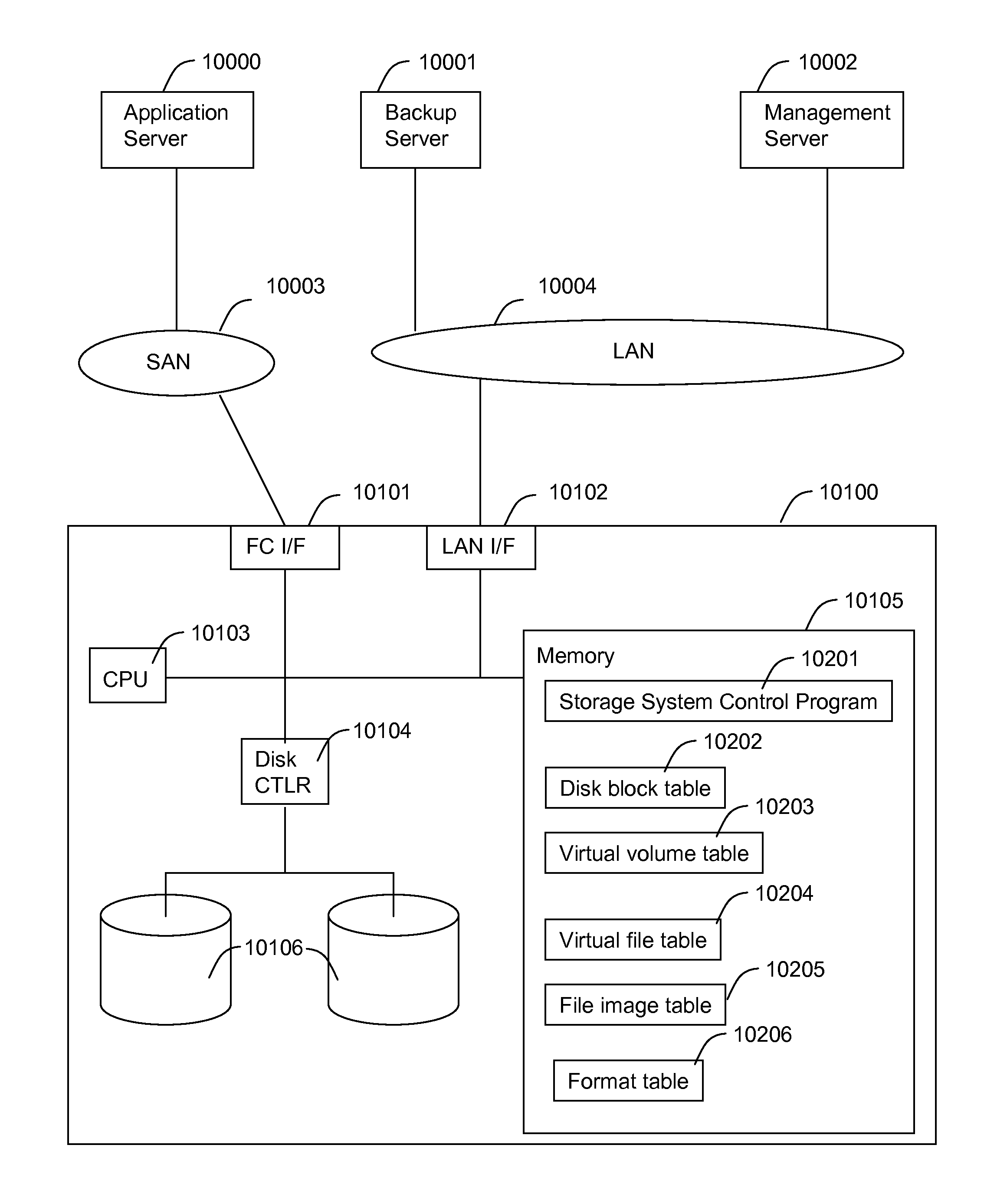
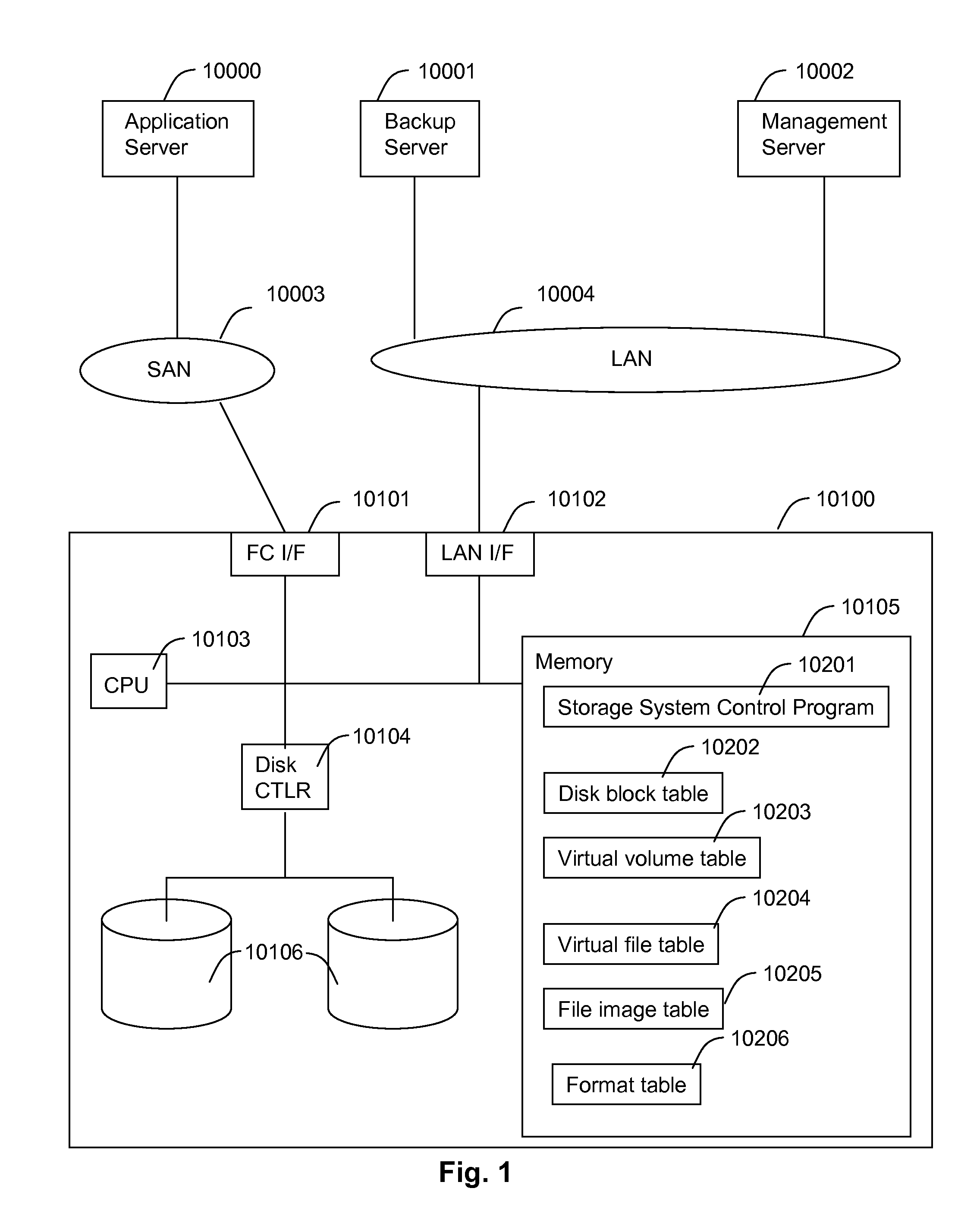
Method and apparatus for enabling a NAS system to utilize thin provisioning
InactiveUS20090077327A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingFile systemDisk array
A NAS (network attached storage) controller managing file system data is configured for use in a storage system having thin provisioning capability. Physical storage capacity is used efficiently by making it possible for the NAS controller to identify to a disk array system having thin provisioning capability which segments of a thin provisioned volume are no longer in use. File system blocks or block groups no longer in use by the NAS controller are identified by the NAS controller. The NAS controller sends a release request to the disk array system specifying thin provisioning segments that correspond to the identified FS blocks or block groups. The release request instructs the disk array system to release chunks of physical storage capacity assigned to the specified thin provisioning segments so that the physical storage capacity can be made available for reuse in the disk array storage system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Implicit container per version set
ActiveUS7818535B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemThin provisioning
When a client requests creation of a production file system or logical unit number (LUN) of storage, a sparse metavolume and a container file system built on the sparse metavolume are implicitly created for containing the production file system or LUN. By implicitly creating one container file system for each production file system or LUN, it is possible to hide the management of the container file system from the client or end user. The creation of snapshot copies in the container file system can also be hidden from the client or end user. Customer service level expectations and thin provisioning can be met automatically by storage policies implemented upon the container file system and the underlying sparse metavolume.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
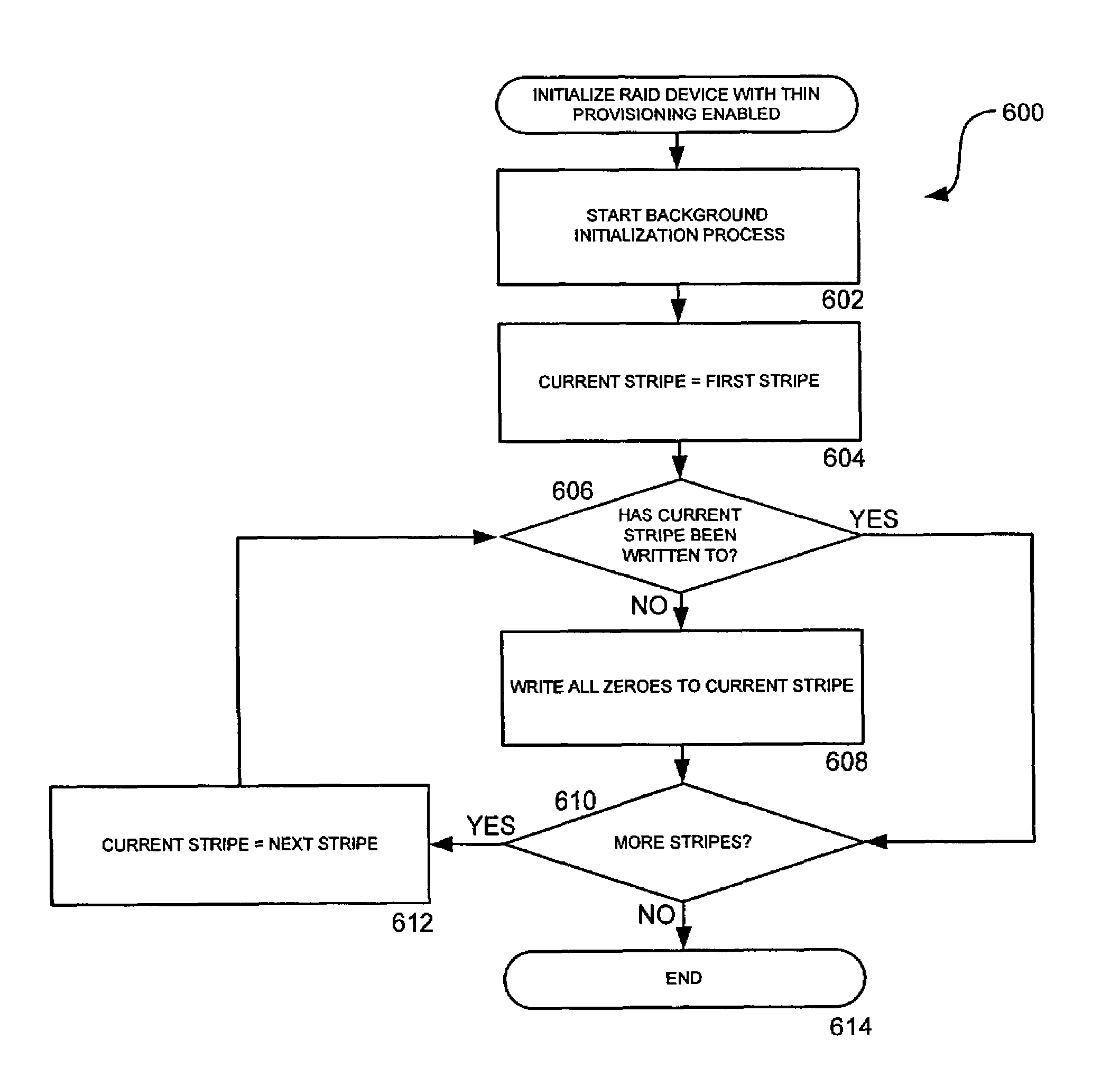
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for improving disk array performance
ActiveUS7711897B1Improve performanceEffective cachingMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDThin provisioning
A method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium are provided for improving storage in a disk array are provided. According to aspects of the invention, a redundant disk array is combined with a mechanism for thin provisioning of the array. Thin provisioning refers to a process of allocating physical capacity to logical volumes on an as-needed basis. Data structures containing a mapping between the logical location of stored data and its actual location on a physical device are maintained. Through the use of the thin provisioning mechanism, physical storage space can be allocated sequentially, regardless of the order of logical writes. In this manner, the data stored on the array grows in a linear manner. The data structures maintained by the thin provisioning mechanism can be used to identify the portions of a device or an array that have been previously written. This information allows redundant arrays, such as RAID arrays, to perform initialization, rebuild, and data migration operations only on portions that been written, and not on areas that have not been utilized by a higher layer.
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
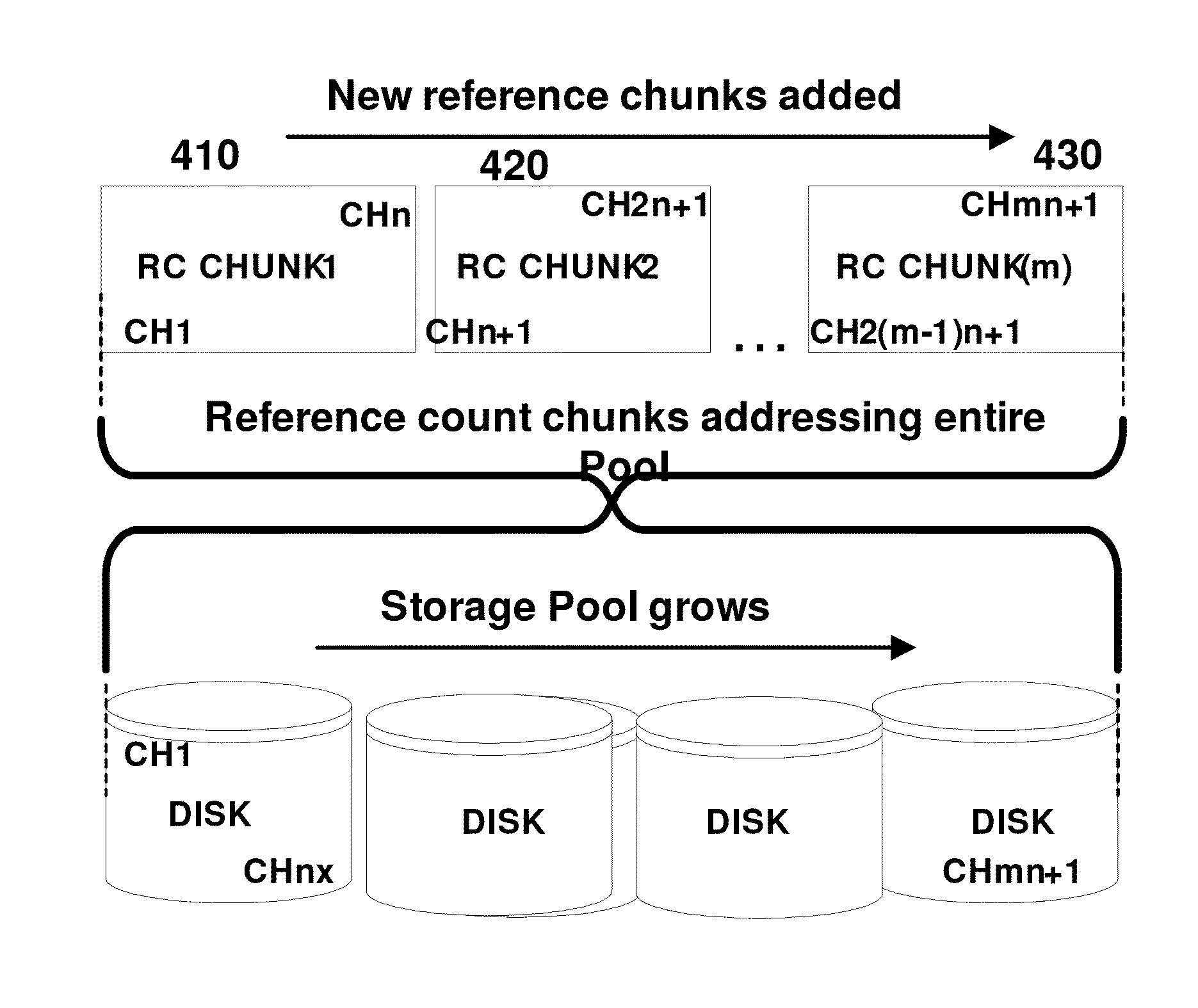
Thin provisioning row snapshot with reference count map
ActiveUS8806154B1Reduce redundant storageIncrease the number ofInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionThin provisioningStorage pool
Owner:CHELSIO COMMUNICATIONS
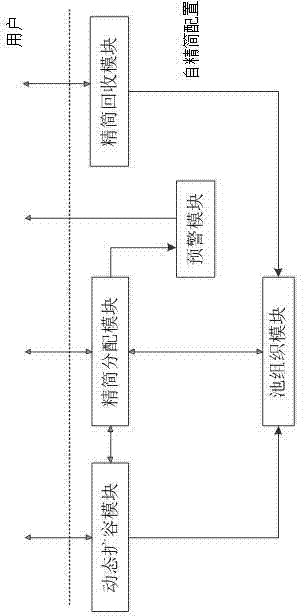
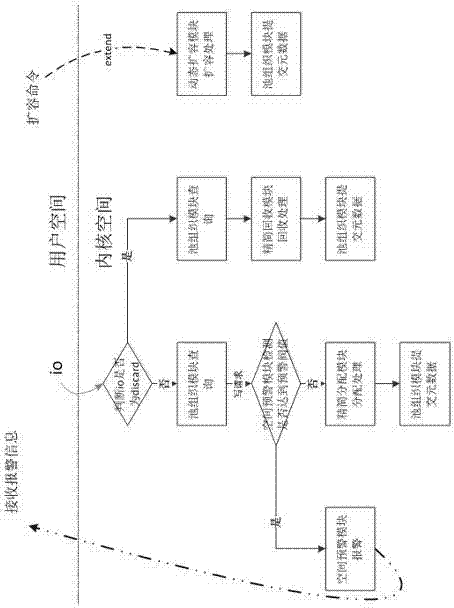
Method and apparatus for chunk allocation in a thin provisioning storage system
InactiveUS20080229048A1Maintain efficiencyReduce performanceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingThin provisioningData type
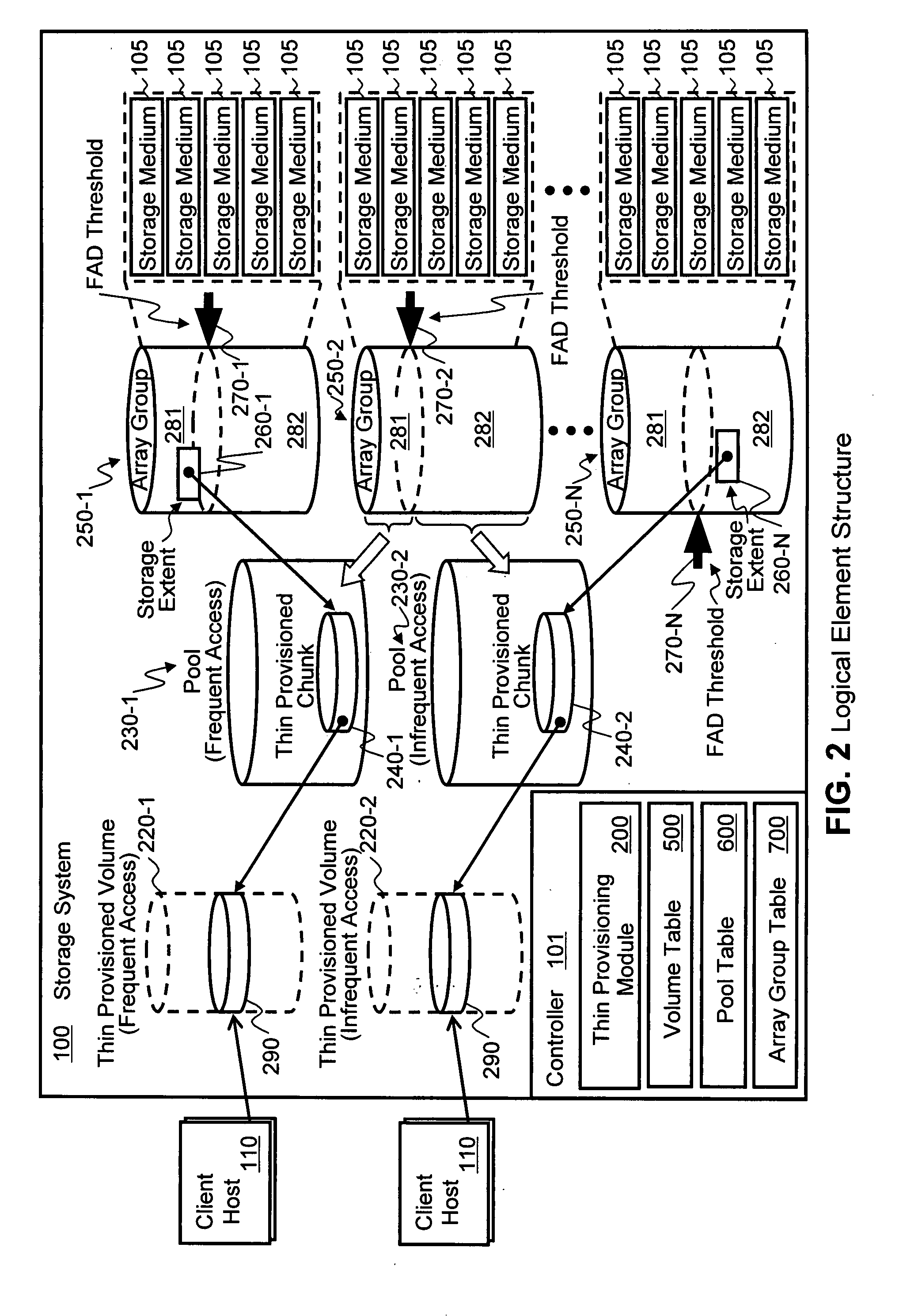
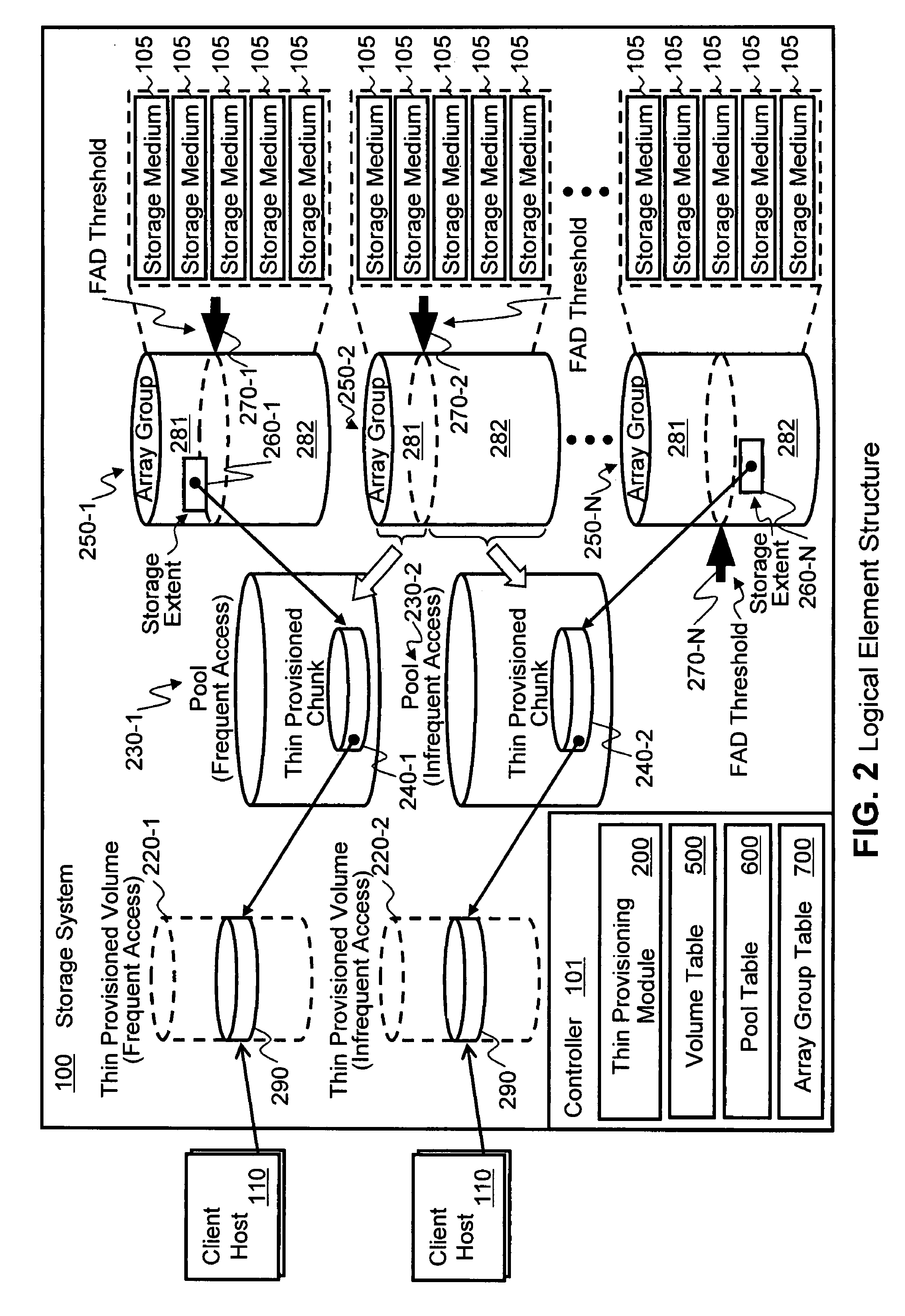
Physical storage space in a storage system is not allocated to a segment of a targeted volume until the segment of the volume is first targeted for storing write data. When write data is received, the storage system determines whether the targeted volume is designated for storing a first data type that is accessed frequently by I / O operations or designated for storing a second data type that is accessed less frequently than the first data type. Physical storage space for storing the write data is allocated from a first logical partition of the physical storage designated for storing the first data type when the targeted volume is of the first data type and from a second logical partition of the physical storage designated for storing the second data type when the targeted volume is of the second data type. Allocation of frequently accessed data is controlled and performance bottlenecking avoided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
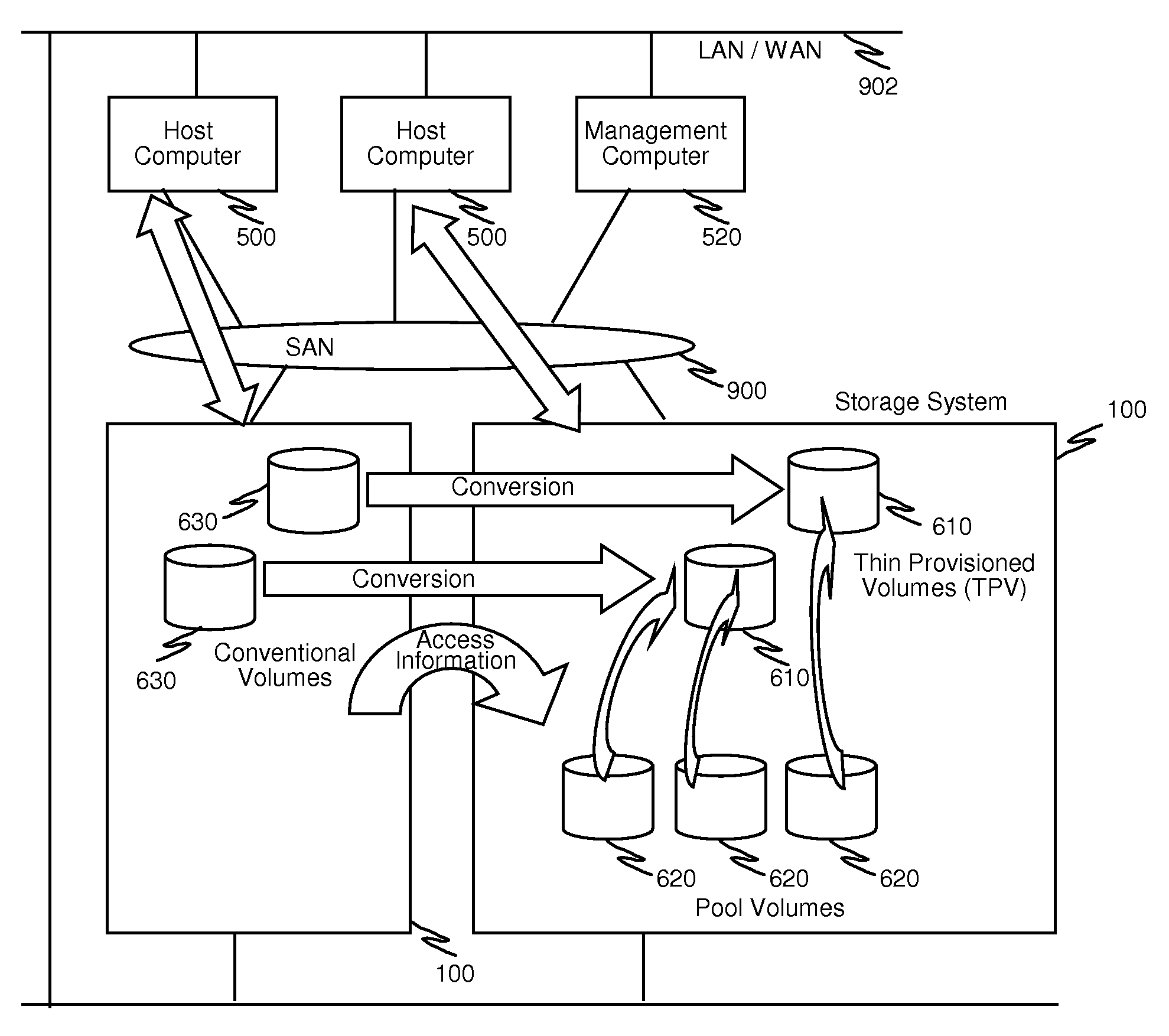
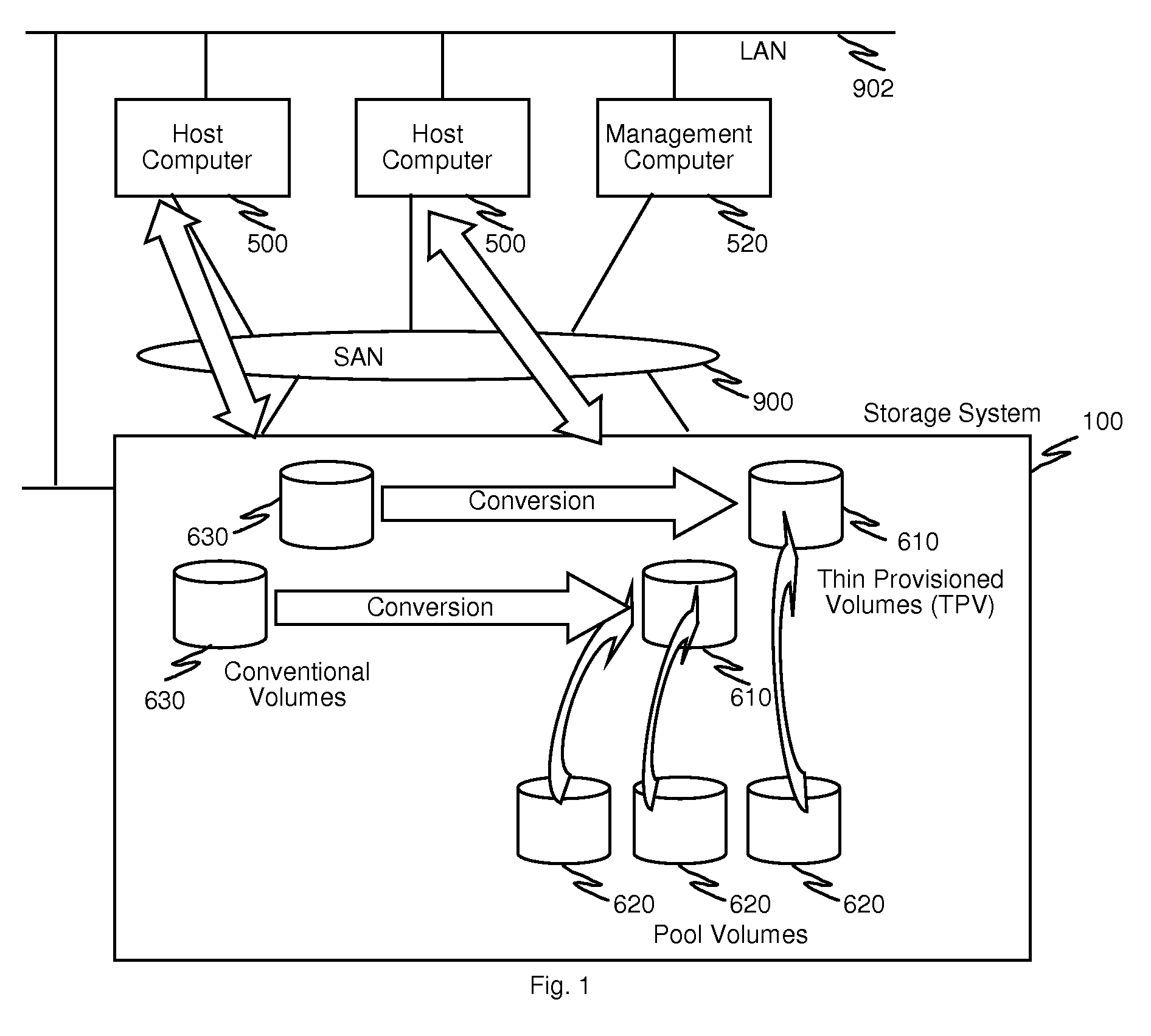
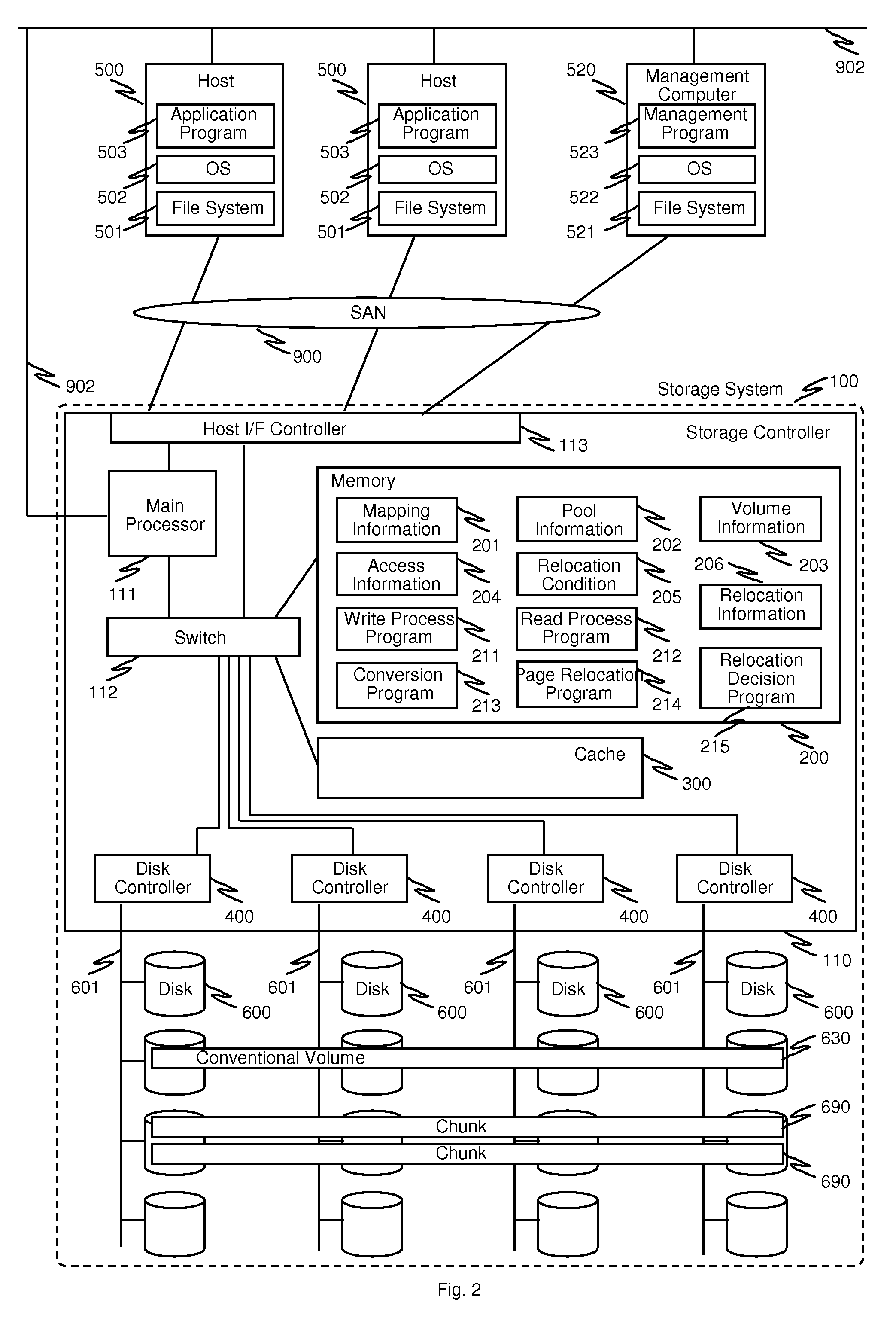
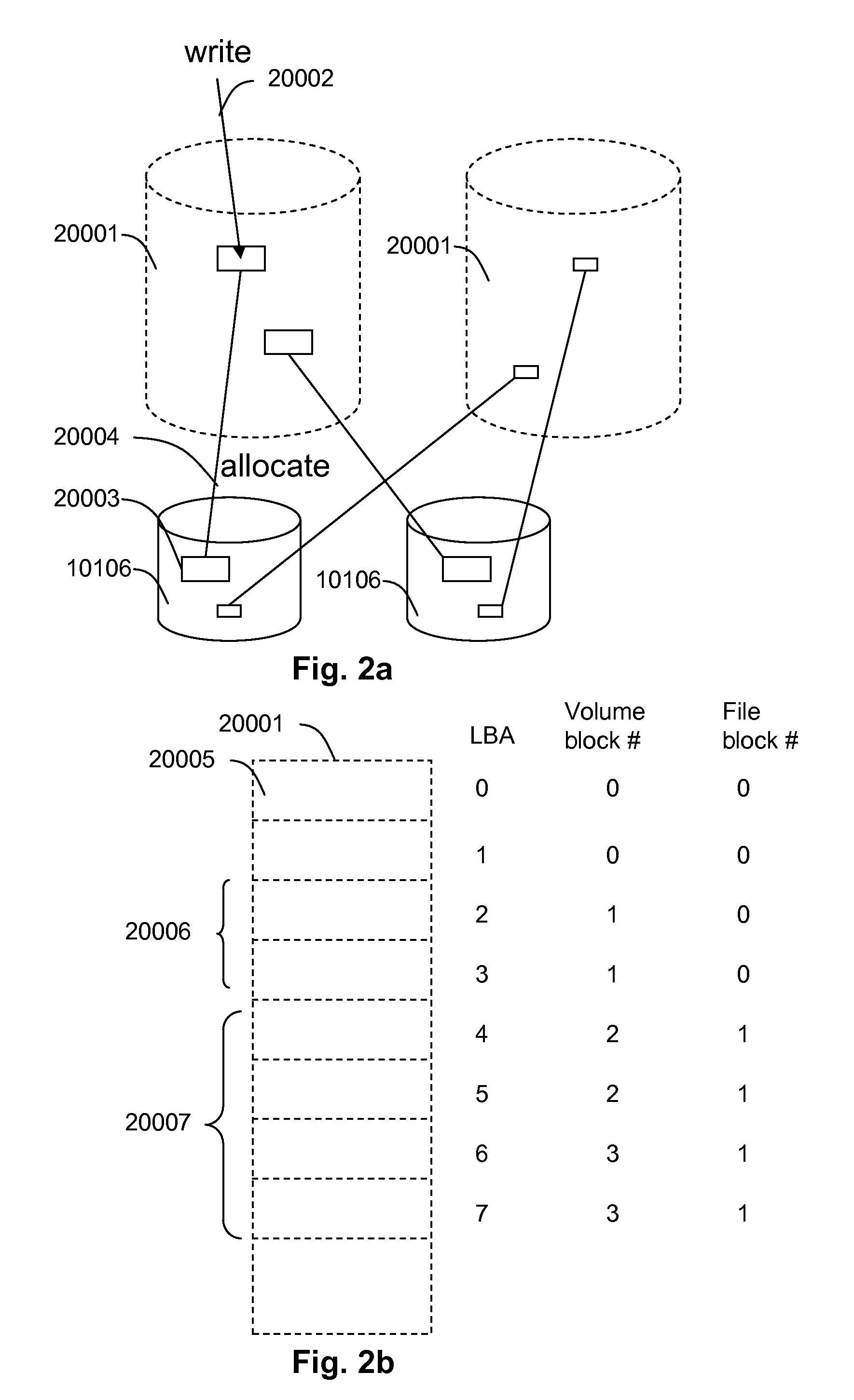
Method and apparatus for conversion between conventional volumes and thin provisioning with automated tier management
InactiveUS20100235597A1Improvement of of storage resourceGuaranteed continuous useMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingThin provisioningDatabase
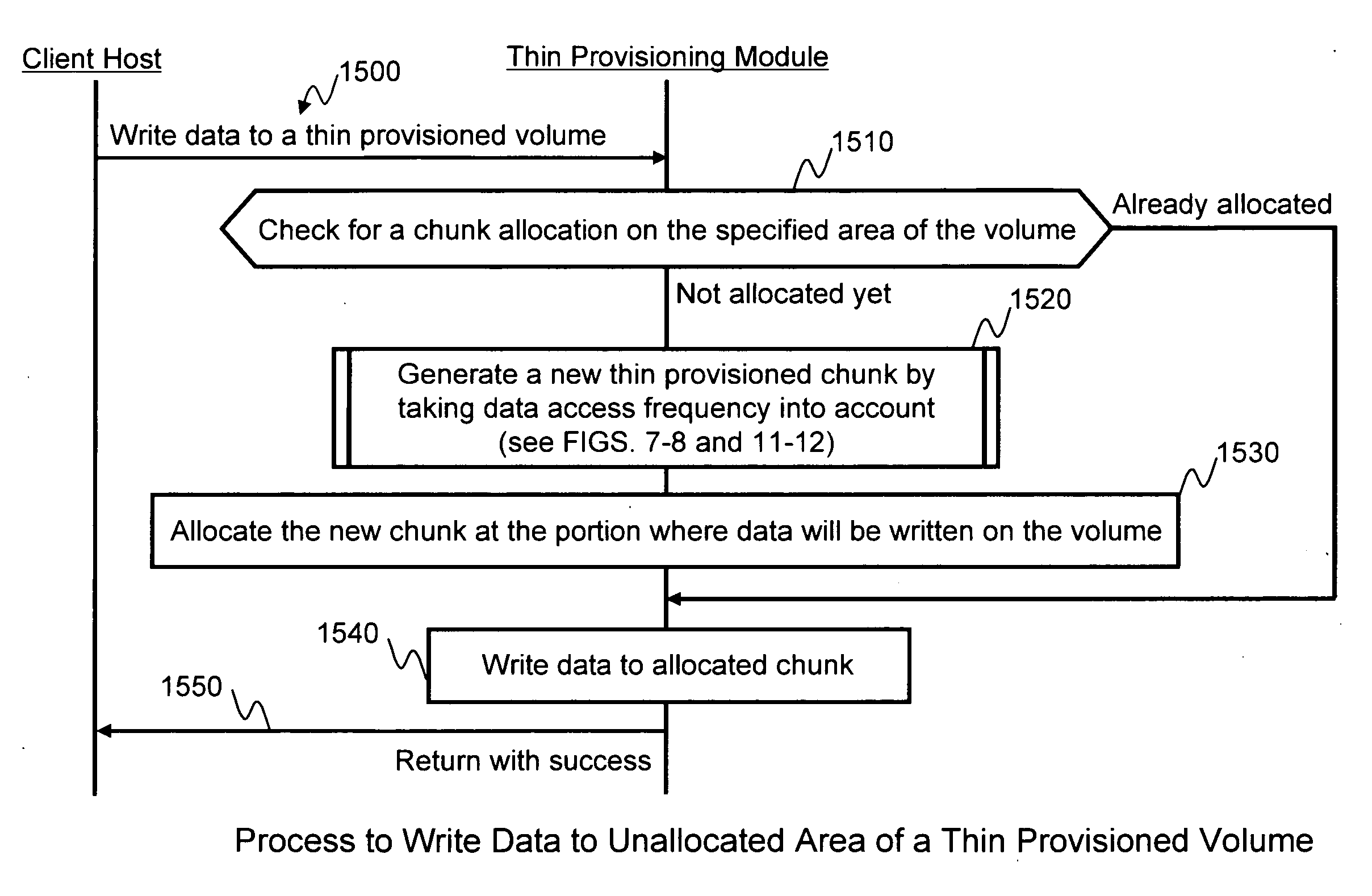
A method for providing storage volumes, which are to be converted to thin provisioned volumes, comprises receiving from a host computer a read / write request identifying a target storage volume among the storage volumes and a target area of access; processing the read / write request and updating an access information of the target storage volume; if the target storage volume does not have access information, generating access information for the converted thin provisioned volume from initial values; and if the target storage volume has access information, generating access information for the converted thin provisioned volume based on the access information of the target storage volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and apparatus for backup and restore of thin provisioning volume
InactiveUS20100250880A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirtual file systemData space
Methods and apparatuses for backing up virtual volumes effectively by eliminating transfer and preservation of parts of virtual volumes, which contain no data. By representing virtual volumes as virtual files in a virtual file system, it is thereby possible to avoid needlessly backing up empty data space in the virtual volume. In one implementation, a storage system includes multiple virtual volumes and a virtual file system as well as a storage system control module. Each virtual volume in the multiple virtual volumes is represented as a virtual file within the virtual file system with each virtual file representing data actually stored within the virtual volume; and the storage system control module facilitates backing up a selected virtual volume, the operations involving accessing the virtual file system on the storage system; and reading the virtual file corresponding to the selected virtual volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and apparatus for migrating thin provisioning volumes between storage systems
InactiveUS20100205390A1Memory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationResource poolExternal storage
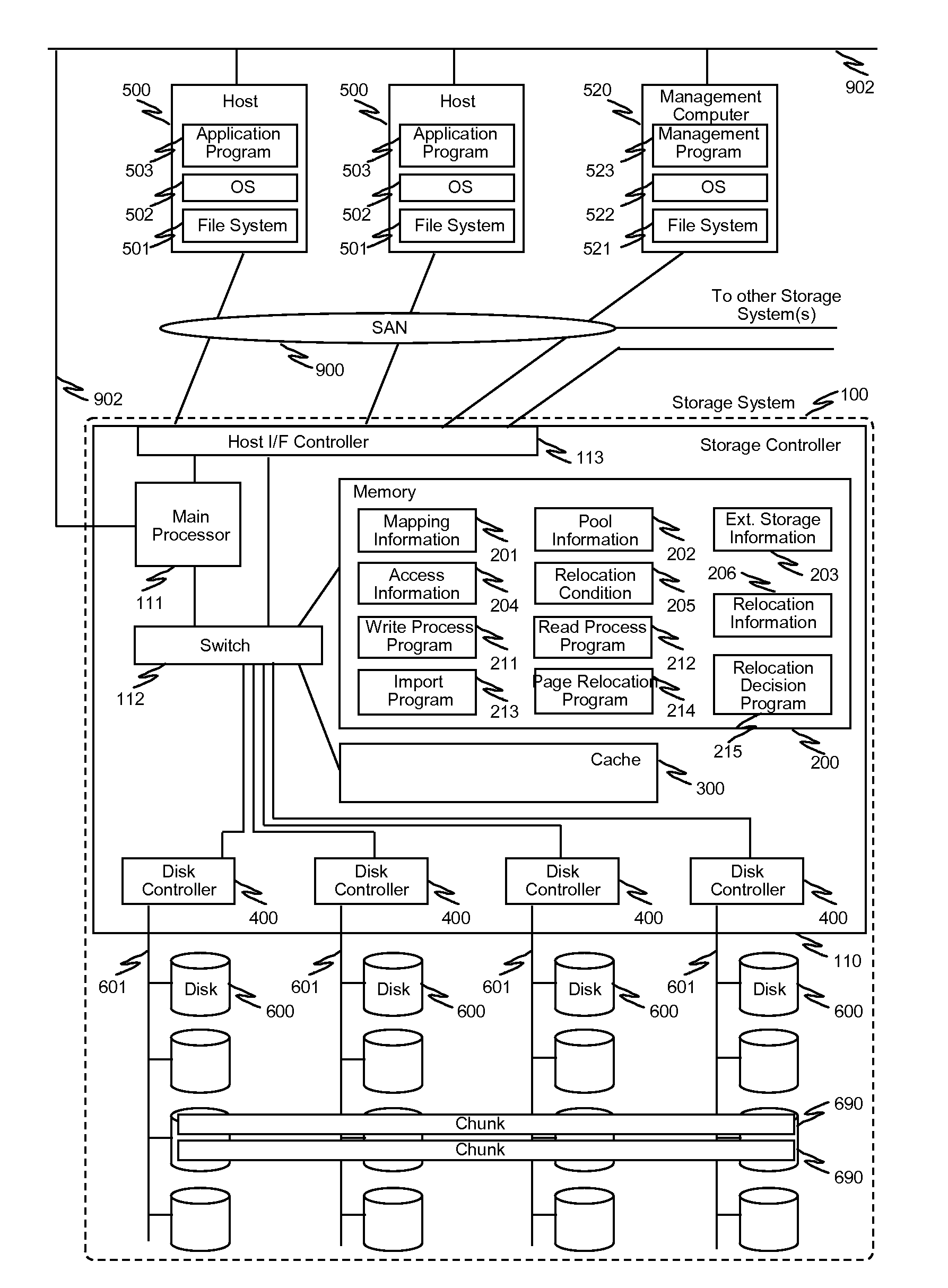
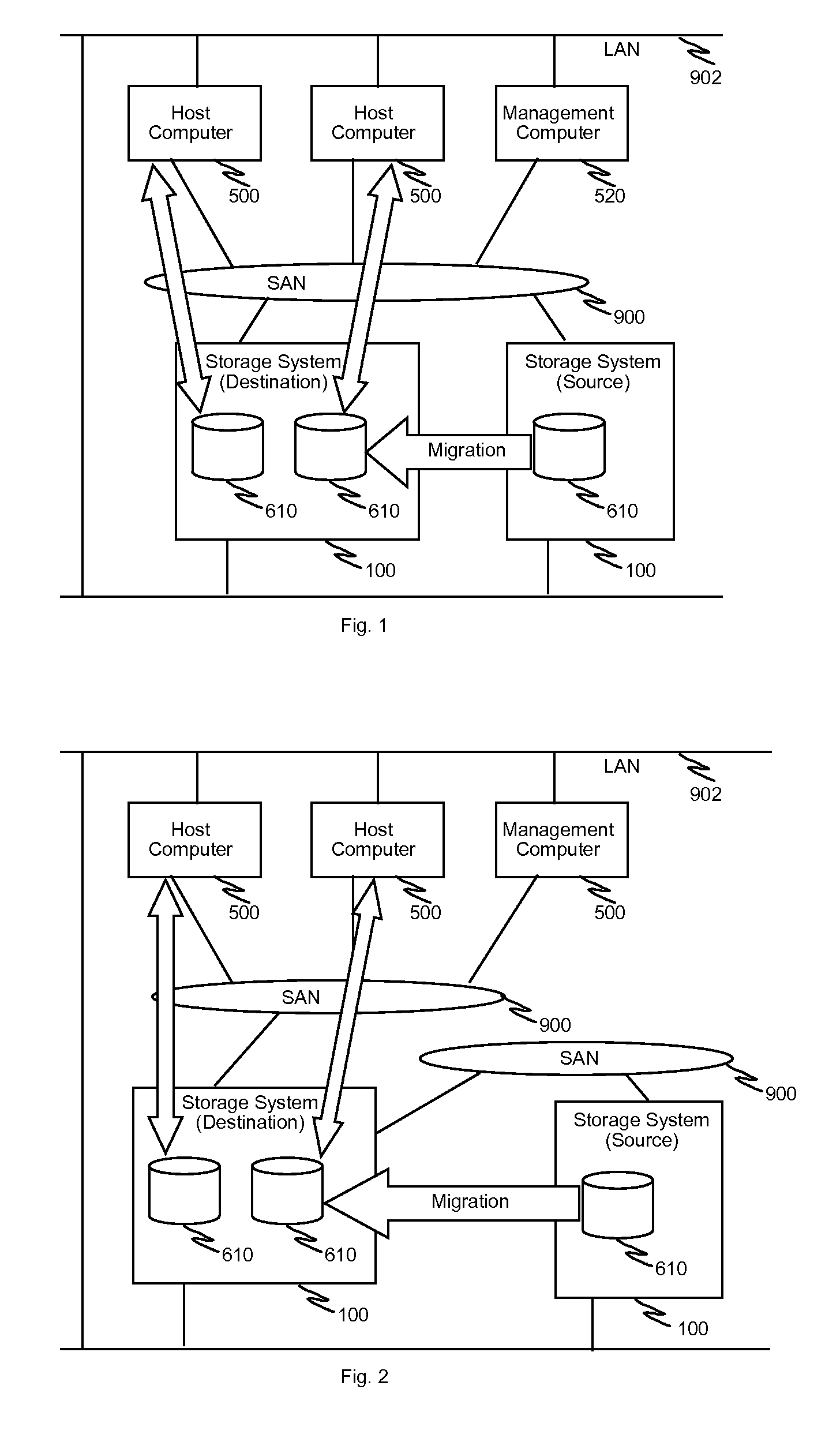
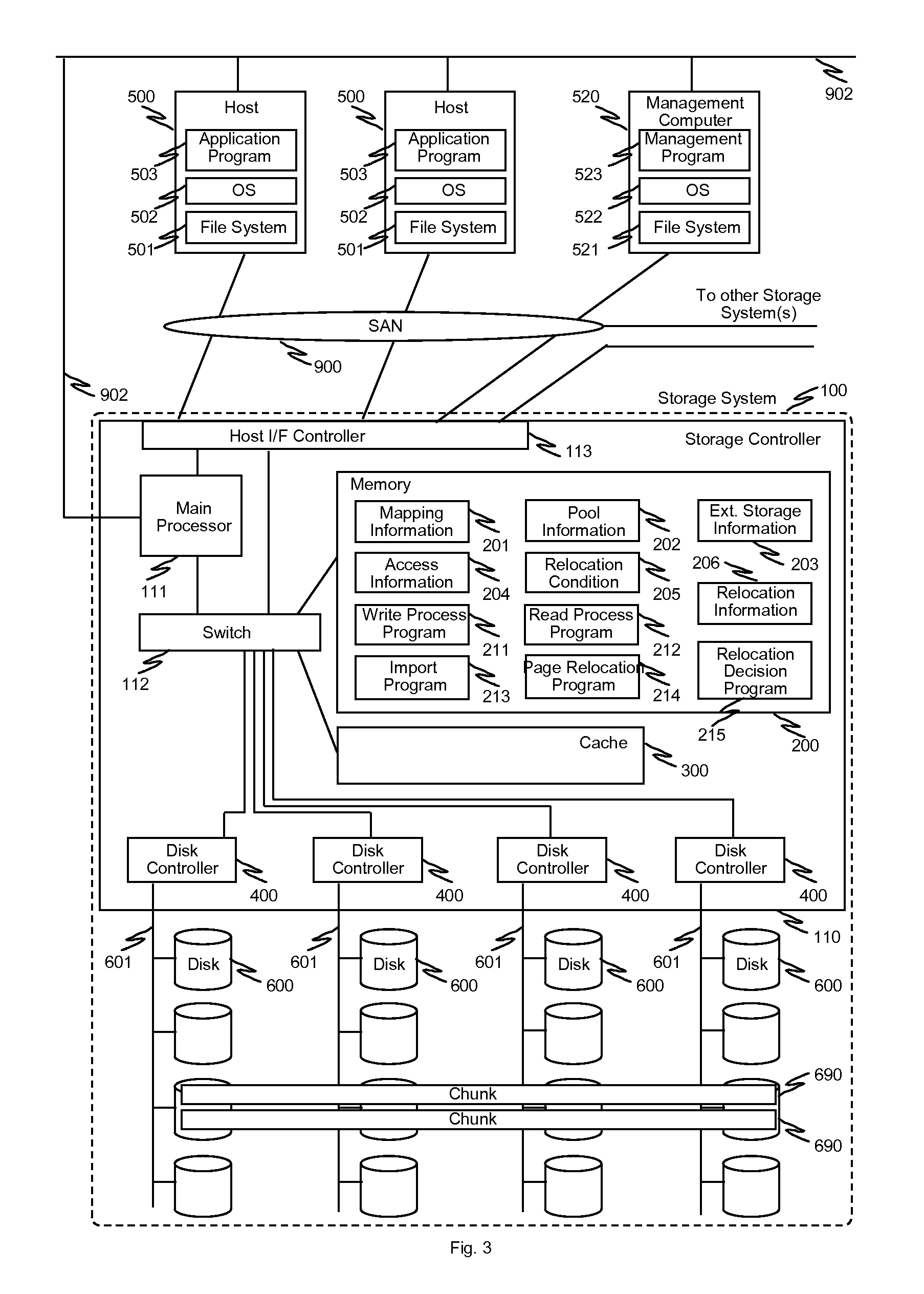
Multiple storage systems have capability to provide thin provisioning volumes to host computers and capability to transfer (import / export) management information regarding thin provisioning between storage systems. Moreover, at least one of the storage systems posses capability to provide storage area of other storage system as own storage area virtually via connection to the other storage system (i.e. external storage). Target storage system achieves efficient migration and unifying storage resource pool by importing or referring the management information obtained from source storage system and by utilizing the source storage system as external storage. One implementation involves method and process for migration of thin provisioning volumes using chunks having same length between source storage system and destination storage system. In this implementation, storage resource pool is unified by importing management information from the source storage system, and automated page-based relocation is performed to adjust actual location of data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Block device thin-provisioning method for log mapping
ActiveCN104035729AImprove bandwidth utilizationReduce overheadInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationResource managementResource based
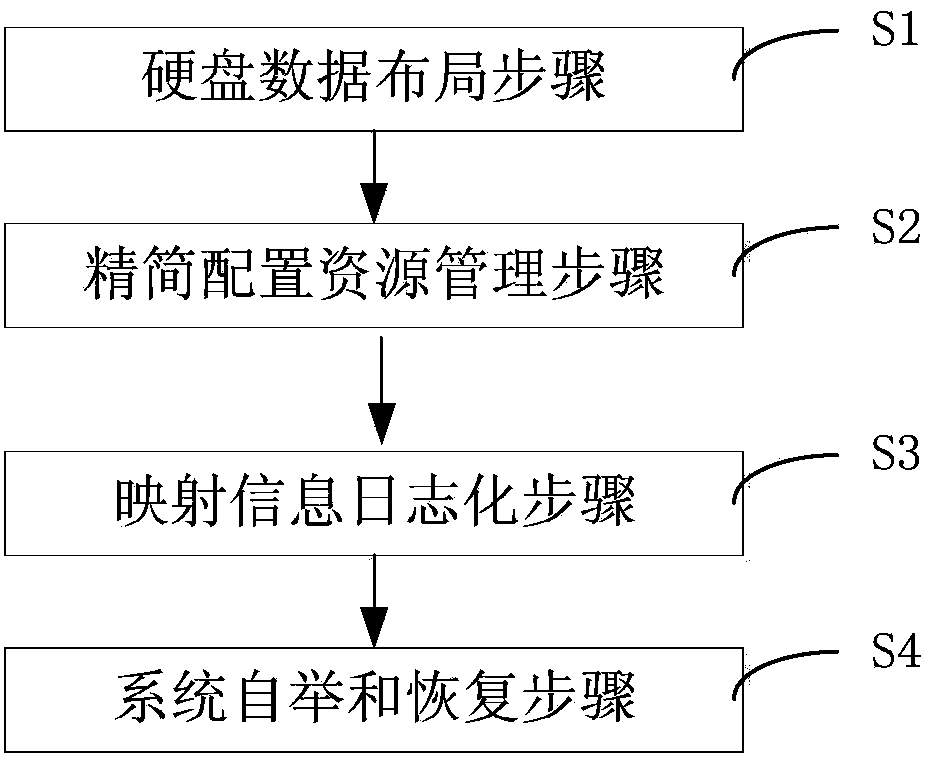
The invention discloses a block device thin-provisioning method for log mapping. The method comprises the step of hard disk data distribution, wherein storage resources are formatted, and resource pooling management is carried out on hard disk data distribution so as to support thin-provisioning resource allocation and storage and management of log mapping information, the step of thin-provisioning resource management, wherein on the basis of a hard disk with pooled resources, the data are sequentially written into a next free resource of the hard disk in a writing on-demand allocation mode of the storage resources, and mapping information corresponding to write operation is generated; the step of mapping information logging, wherein logging storage is carried out on the mapping information of the write operation according to an additional allocation mode, and on the basis of an asynchronous updating mode, the mapping information is amended so as to achieve data writing of the multi-user and multi-virtual-volume concurrence sequence.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Metrics and management for flash memory storage life
ActiveUS20100257306A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDThin provisioning
Embodiments of the invention provide a method and a system for the management of availability and reliability of flash memory media. In one embodiment, a method of evaluating reliability of flash memory media comprises measuring a flash memory remaining life for each disk of a plurality of flash memory media disks provided in one or more flash memory media groups each of which has a configuration, wherein each flash memory media group is one of a RAID group or a thin provisioning pool; obtaining a ratio of sequential to random write I / O types for each flash memory media group; and calculating a remaining life of each flash memory media group based on the measured flash memory remaining life for each disk in said each flash memory media group, the configuration of said each flash memory media group, and the ratio of sequential to random write I / O types for said each flash memory media group.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
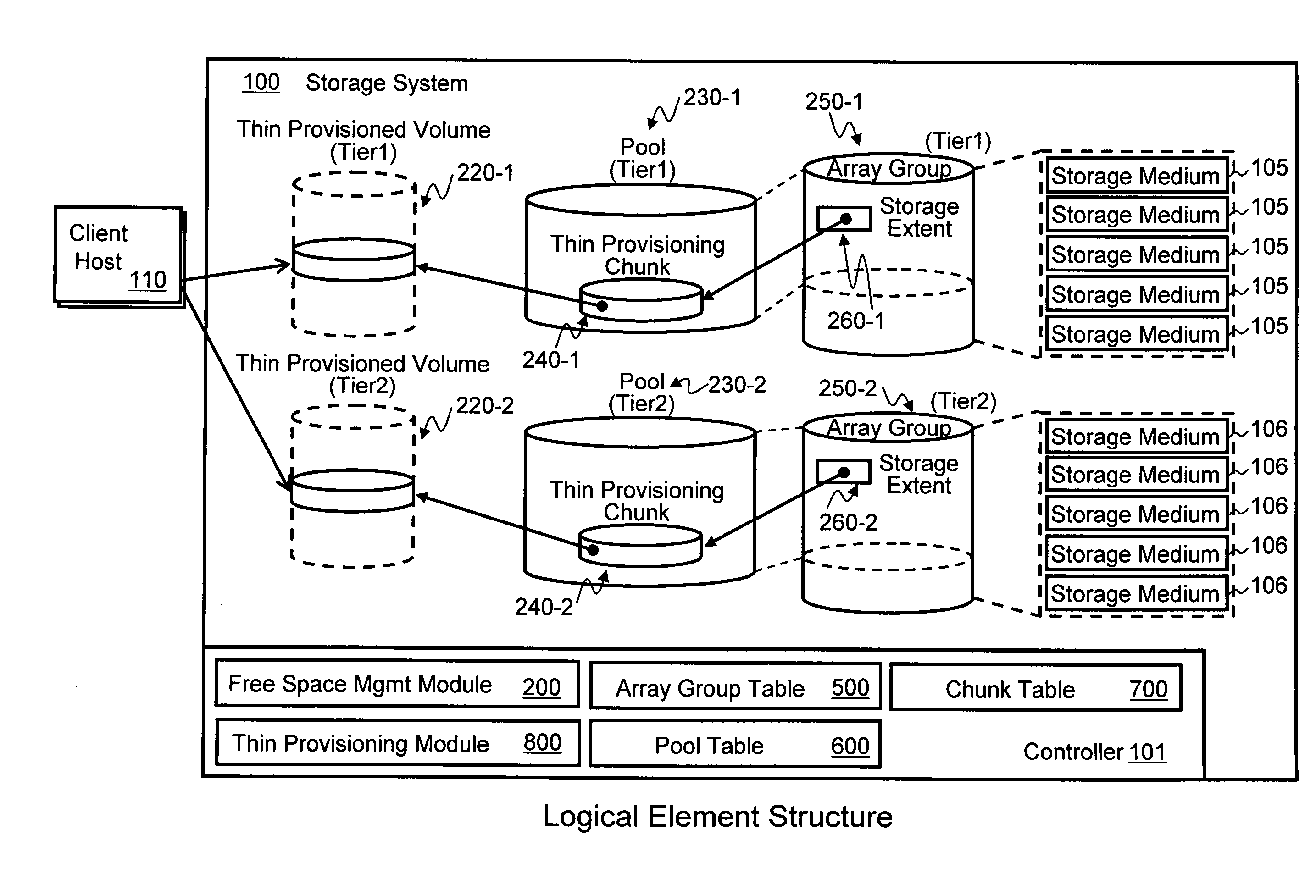
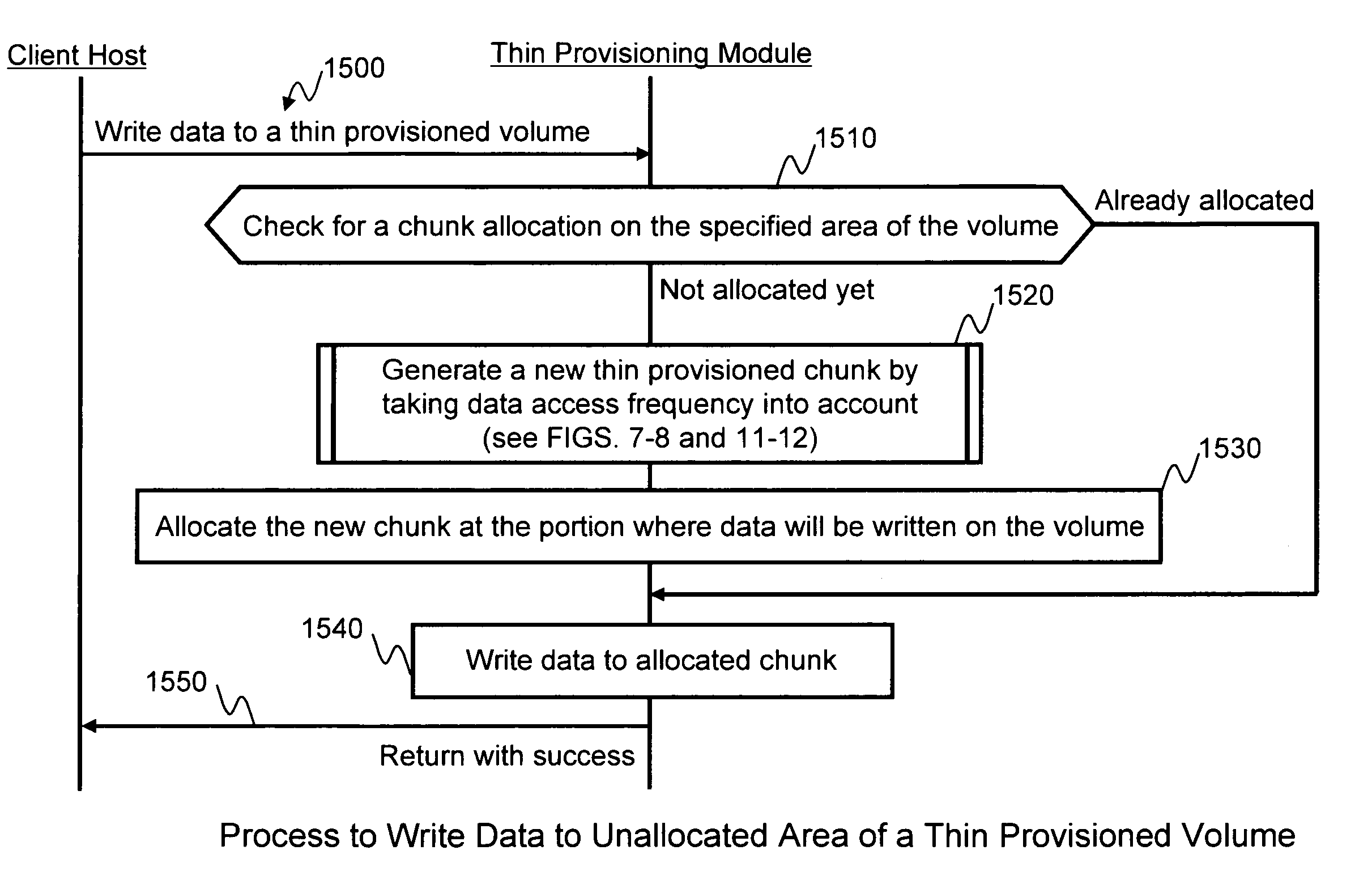
Storage extent allocation method for thin provisioning storage
InactiveUS7949847B2Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsThin provisioningOperating system
A thin provisioning storage system is able to present a thin provisioned volume to a computer, such that the computer stores data to the volume as if storage space on disk drives was already allocated for the volume. Upon receiving a write request from the computer, in which the write request is directed to an area of the volume for which storage space on the disk drives has not yet been allocated, the storage system allocates new space on the disk drives. When allocating the new space, the storage system obtains a designated performance level for the volume, and determines a number of storage extents to be allocated to the volume based upon the determined performance level. The storage system also is able to take into account performance metrics for the disk drives and / or array groups when selecting locations from which to allocate the storage extents.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dynamic storage pools with thin provisioning
InactiveUS20090019251A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDynamic storageThin provisioning
A method for data storage, including configuring in a data storage system a volume storage pool as data storage resources available for allocation of volumes in the data storage system. The method also includes defining a threshold value for the volume storage pool. When the allocation of the volumes causes the threshold value to be crossed, the method includes performing an action for managing the volume storage pool.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thin provisioning method for storage system
ActiveCN102968279AImplementing Automated Thin ProvisioningRealize the recycling functionInput/output to record carriersOperational systemThin provisioning
The invention provides a thin provisioning method for a storage system. Thin provisioning is generally applied to the storage system, and is used for providing a large-volume virtual driver for an operating system. According to a thin provisioning technology, a volume space which surpasses a practical space can be provided for an upper layer in a virtual way, i.e., the available volume of the operating system is assumed to be larger than the practically provided volume. Data in enterprises increase gradually instead of getting too many at the start, so that the utilization ratio of the storage volume can be increased by adopting thin provisioning. A large-volume virtual driver can be provided for the operating system by adopting a thin provisioning storage scheme. The operating system is provided with a large magnetic disk space during distribution of the magnetic disk space, so that enterprises can consider increasing storage equipment stepwise without adjusting the operating system along with the increase of the enterprise data volume. The hot plug function of the storage equipment is realized, and the storage efficiency and flexibility of magnetic disk equipment can be improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Method and apparatus for chunk allocation in a thin provisioning storage system
InactiveUS7971025B2Maintain efficiencyReduce performanceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingThin provisioningData type
Physical storage space in a storage system is not allocated to a segment of a targeted volume until the segment of the volume is first targeted for storing write data. When write data is received, the storage system determines whether the targeted volume is designated for storing a first data type that is accessed frequently by I / O operations or designated for storing a second data type that is accessed less frequently than the first data type. Physical storage space for storing the write data is allocated from a first logical partition of the physical storage designated for storing the first data type when the targeted volume is of the first data type and from a second logical partition of the physical storage designated for storing the second data type when the targeted volume is of the second data type. Allocation of frequently accessed data is controlled and performance bottlenecking avoided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for improving disk array performance
ActiveUS7802063B1Improve performanceEffective cachingMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsRAIDThin provisioning
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
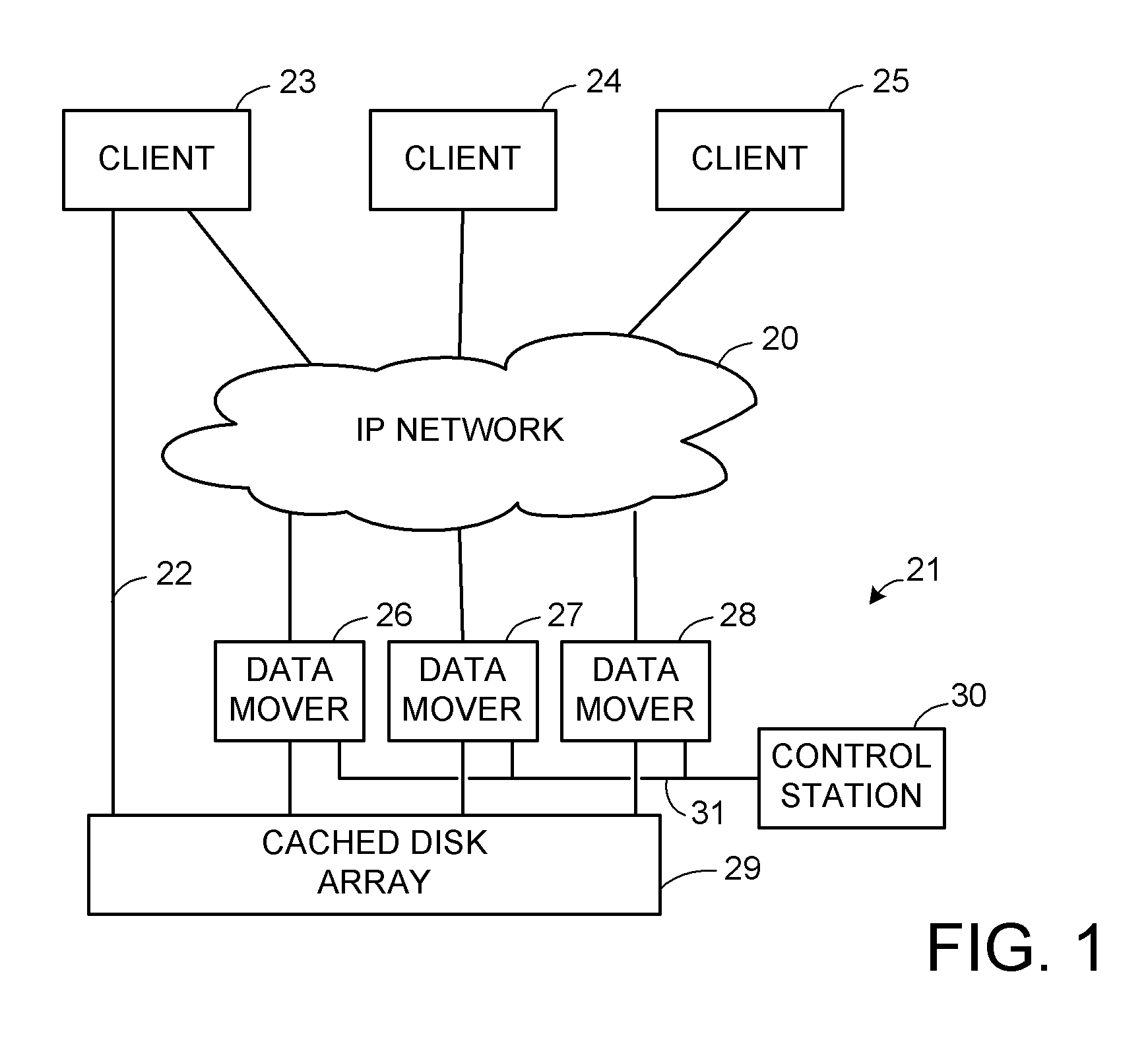
Method and apparatus of non-disruptive storage migration
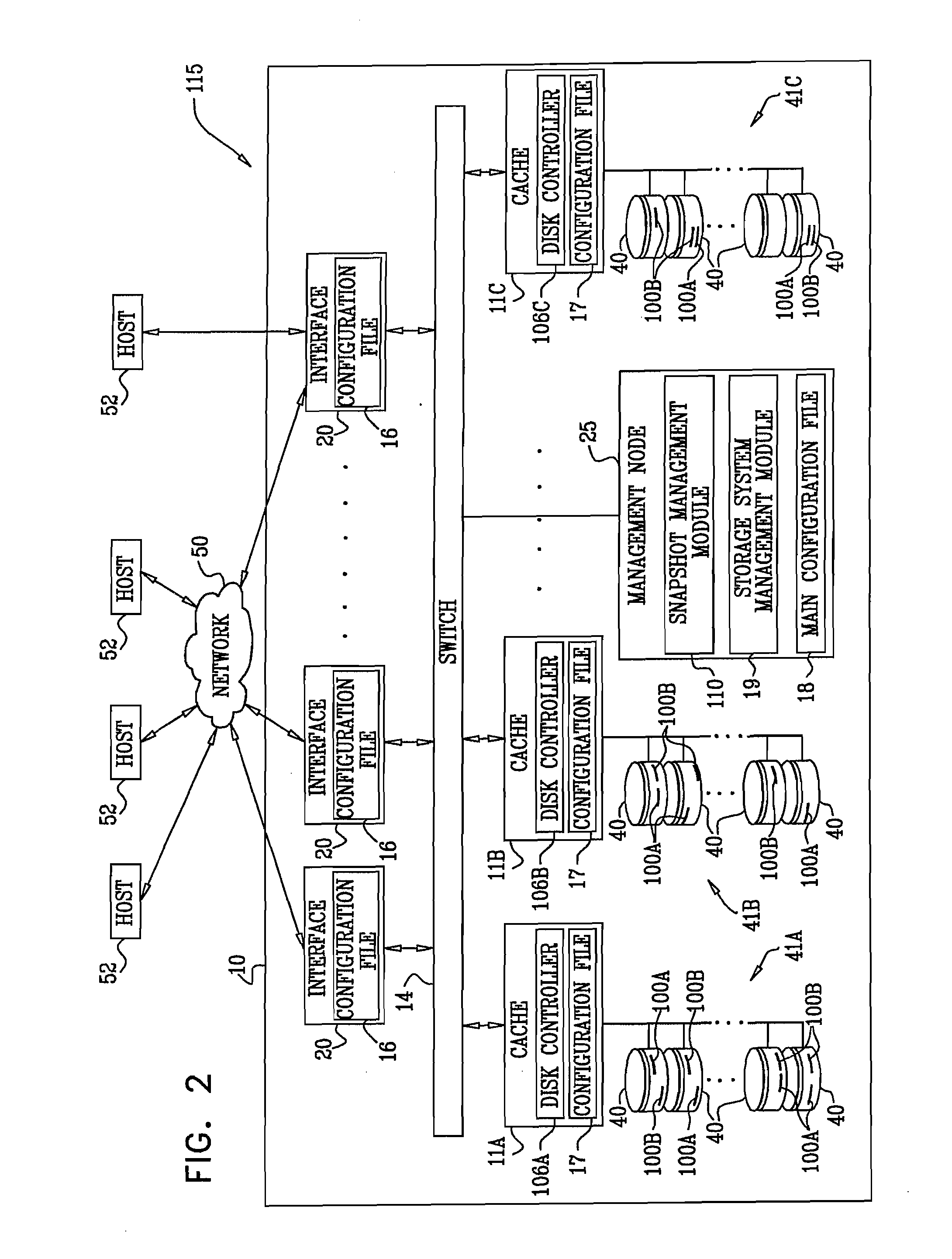
Example implementations described herein are directed to non-disruptive I / O storage migration between different storage types. In example implementations, virtual volume migration techniques such as snapshot, thin-provisioning, tier-provisioning, de-duplicated virtual volume, and so forth, are conducted between different storage types by using pool address re-mapping. In example implementations, asynchronous remote copy volume migration is performed without the initial secondary volume copy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for using thin provisioning to reclaim space identified by data reduction processes
ActiveUS8332612B1Efficient accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceThin provisioning
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
High availability and low capacity thin provisioning
ActiveCN101539841AInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationExternal storageData access
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optimizing thin provisioning in a data storage system through selective use of multiple grain sizes
ActiveUS20160188211A1Small granularityMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersParallel computingThin provisioning
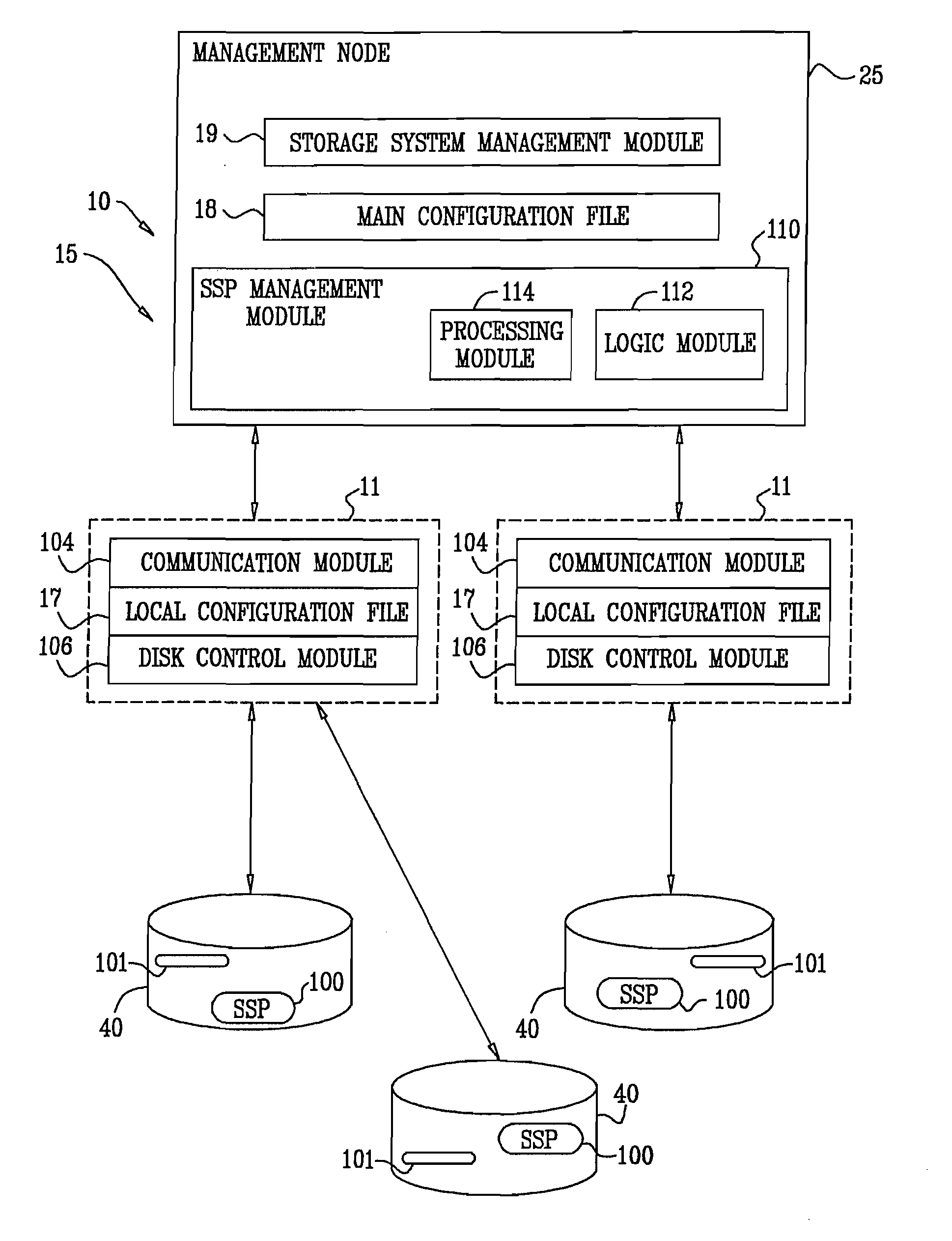
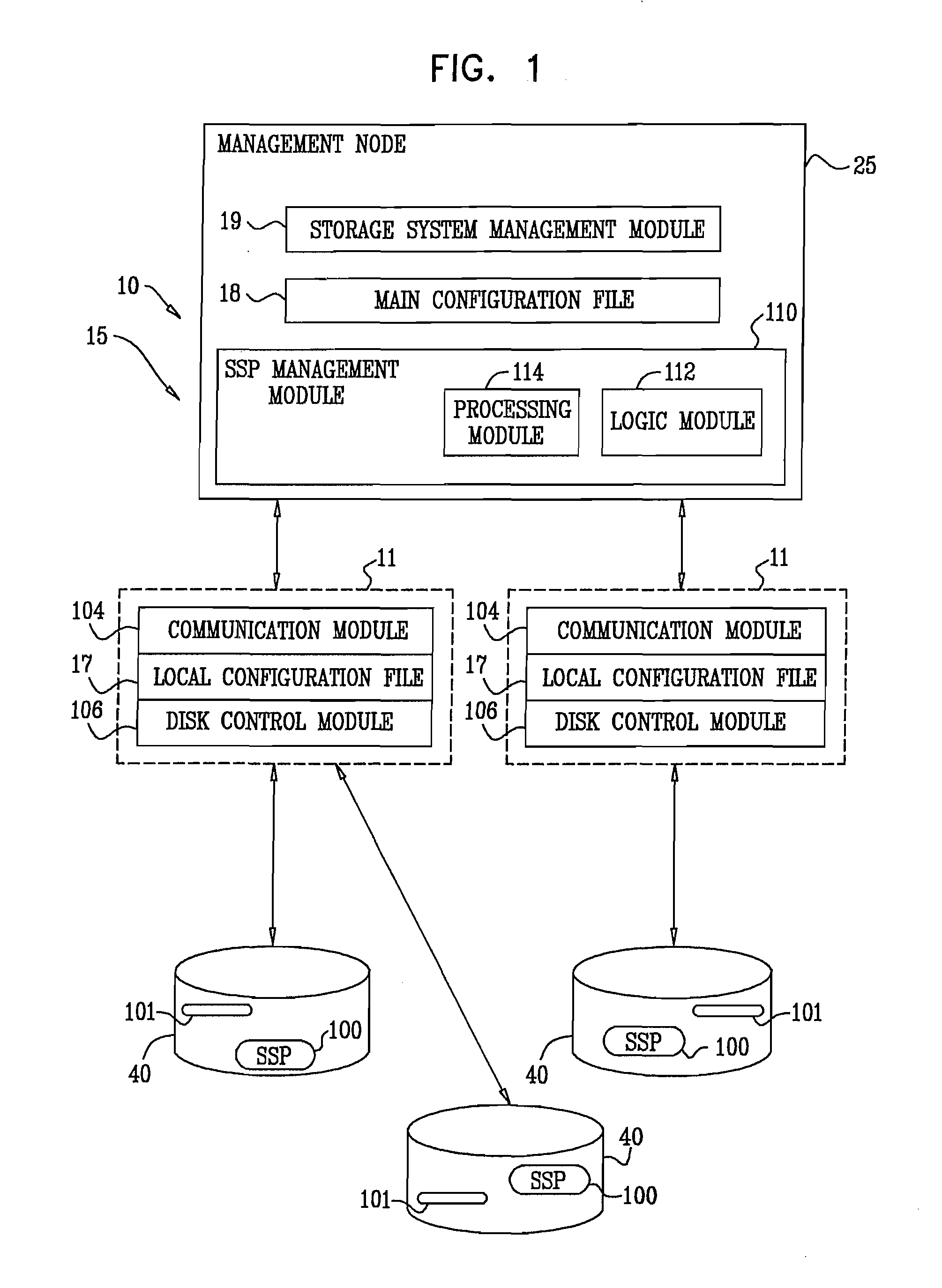
A data storage system includes a pre-cache and a plurality of storage devices across which a data storage array is distributed. In response to receipt of a write request specifying a logical address and write data, the data storage system buffers the write request among a plurality of write requests in the pre-cache without provisioning in the data storage array a physical extent corresponding to the logical address. A management node analyzes the plurality of write requests buffered in the pre-cache. In response to the analyzing identifying a first pattern of write requests, the management node provisions, in the data storage array, a first physical extent having a smaller grain size and destages the write data to the first physical extent. In response to the analyzing identifying a second pattern of write requests, the management node provisions a second physical extent having a larger grain size and destages the write data from the pre-cache to the second physical extent.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reclaiming storage on a thin-provisioning storage device
InactiveUS20090089516A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingThin provisioningComputer science
Owner:HITACHI DATA SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for managing thin provisioning volume by using file storage system
InactiveUS20100306500A1Thin provisioning capability with small amount of memoryMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareNetwork connection
In one embodiment, a method of operating block-based thin provisioning disk volumes in a system including a first storage system which is connected via a network to a second storage system comprises, in response to a volume creation request to create a thin provisioning disk volume in the first storage system, recording in the first storage system attribute information of the block-based thin provisioning disk volume; specifying a directory path for the block-based thin provisioning disk volume in a file system in the second storage system; and creating a directory for the block-based thin provisioning disk volume under the specified directory path.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com