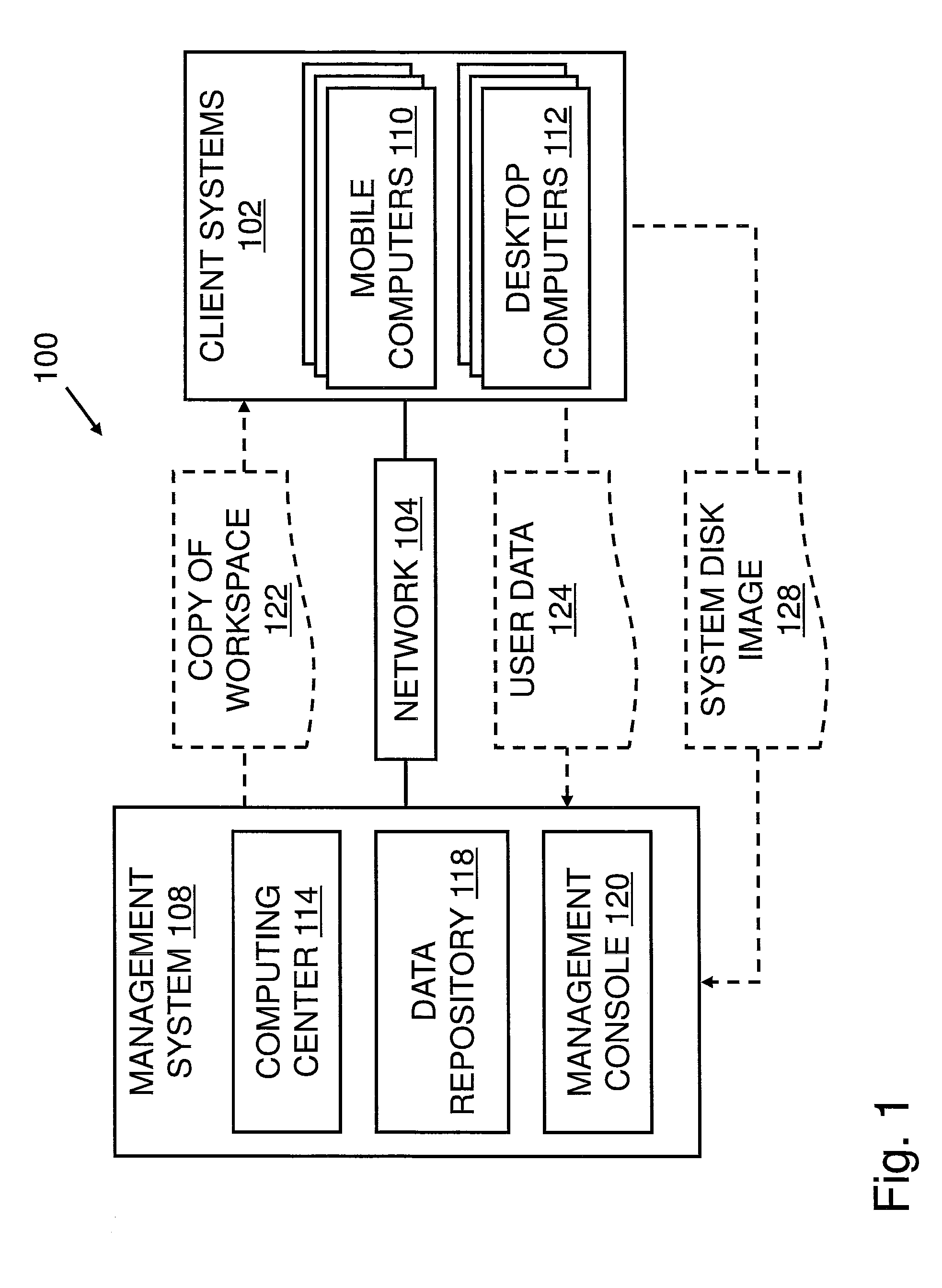
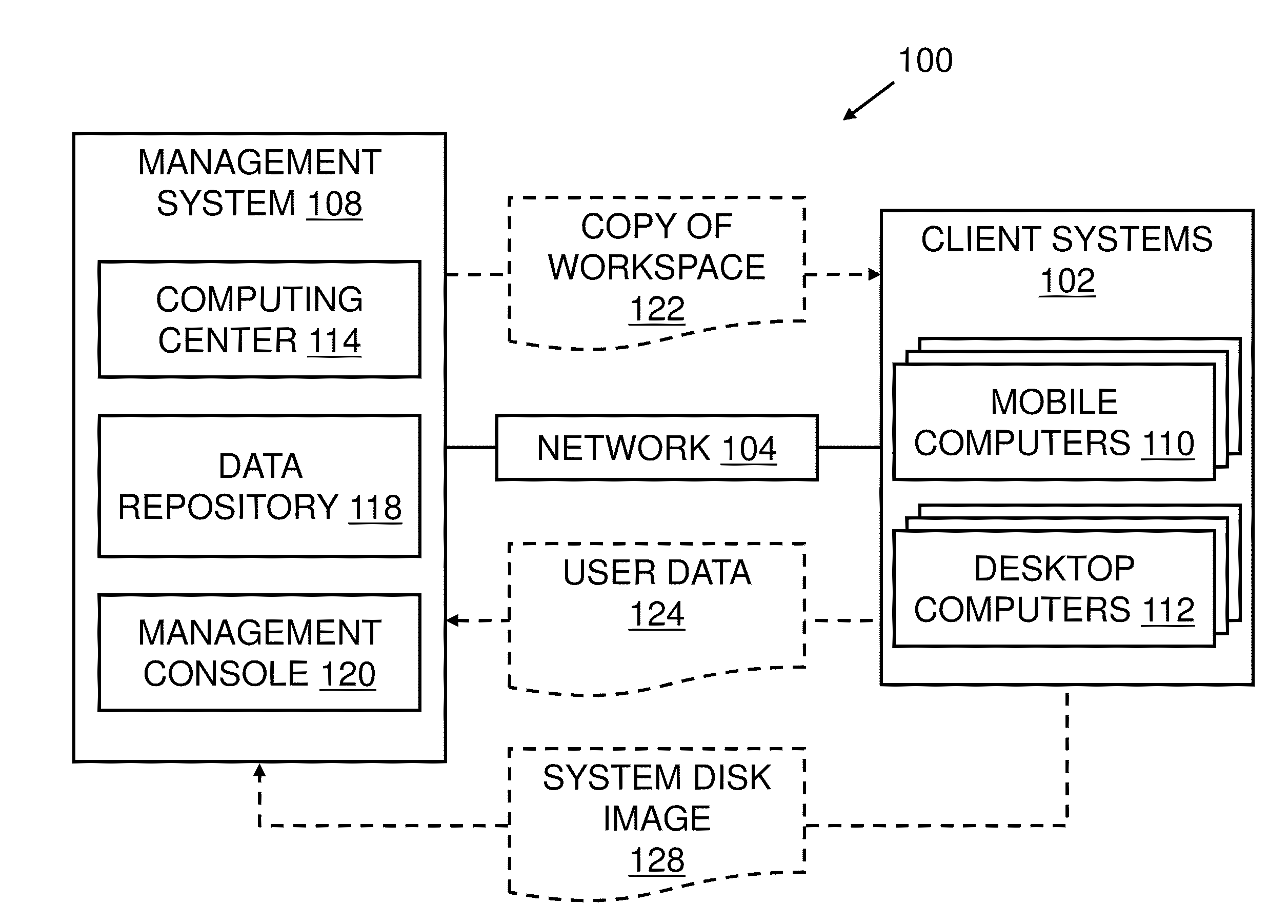
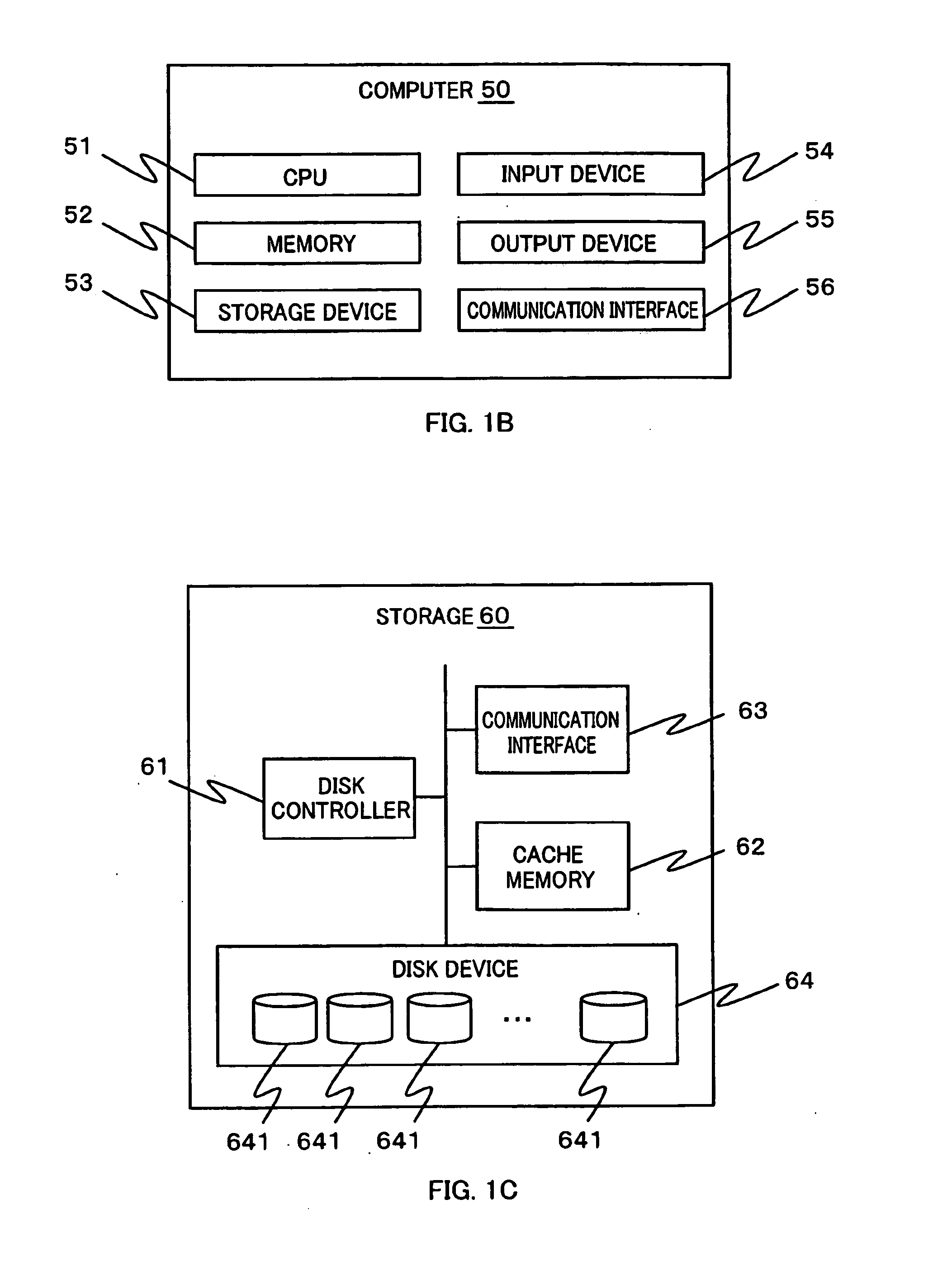
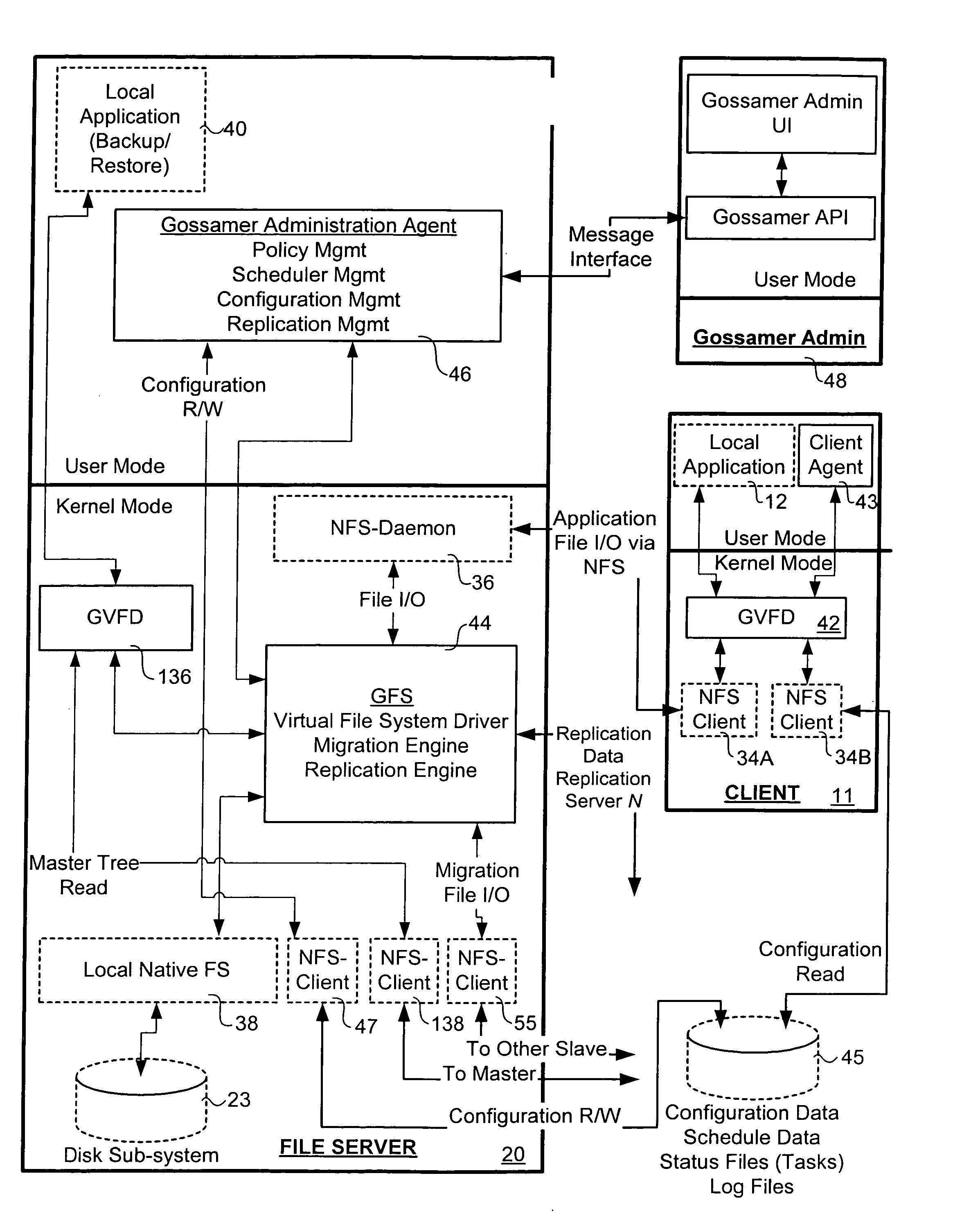
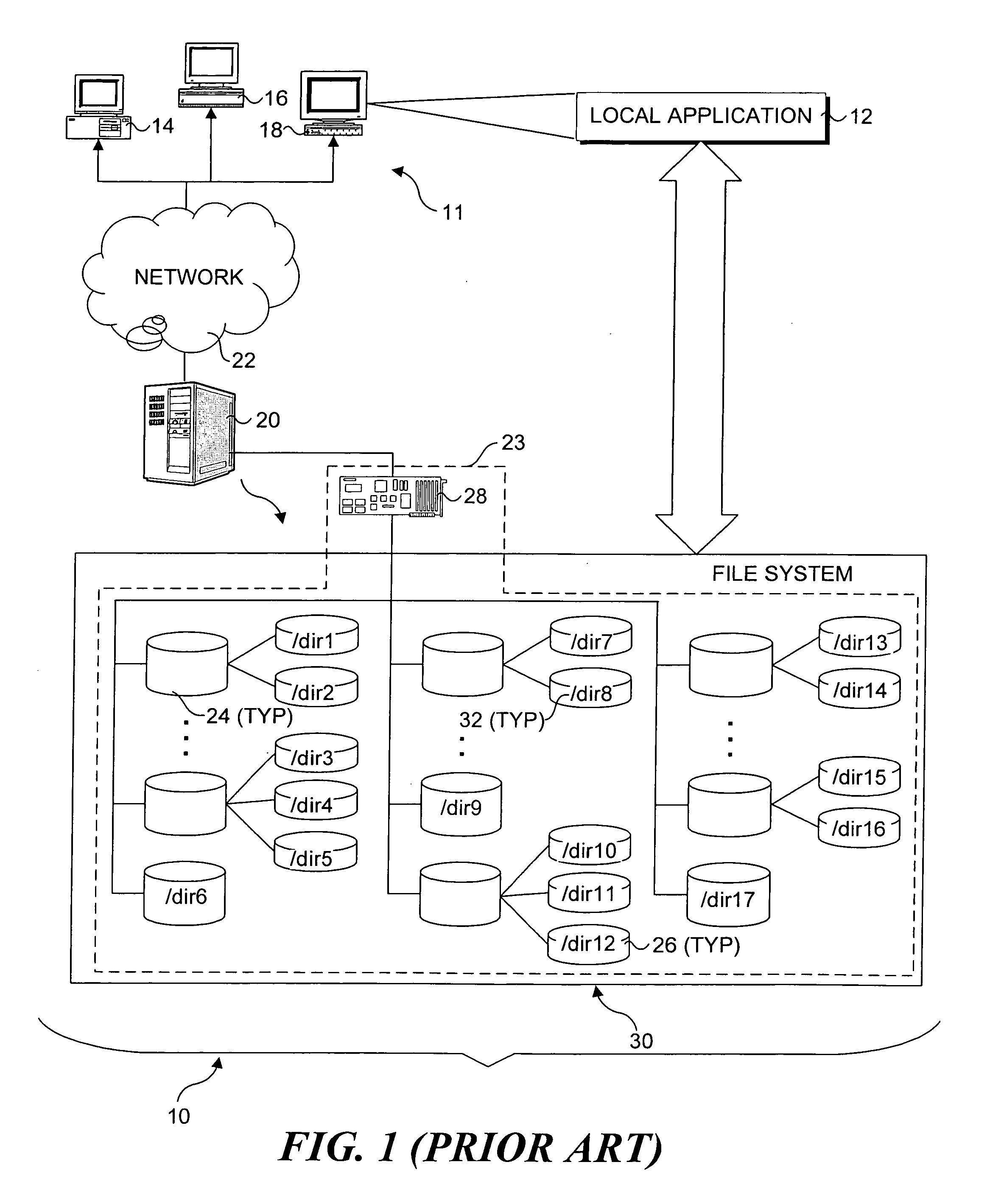
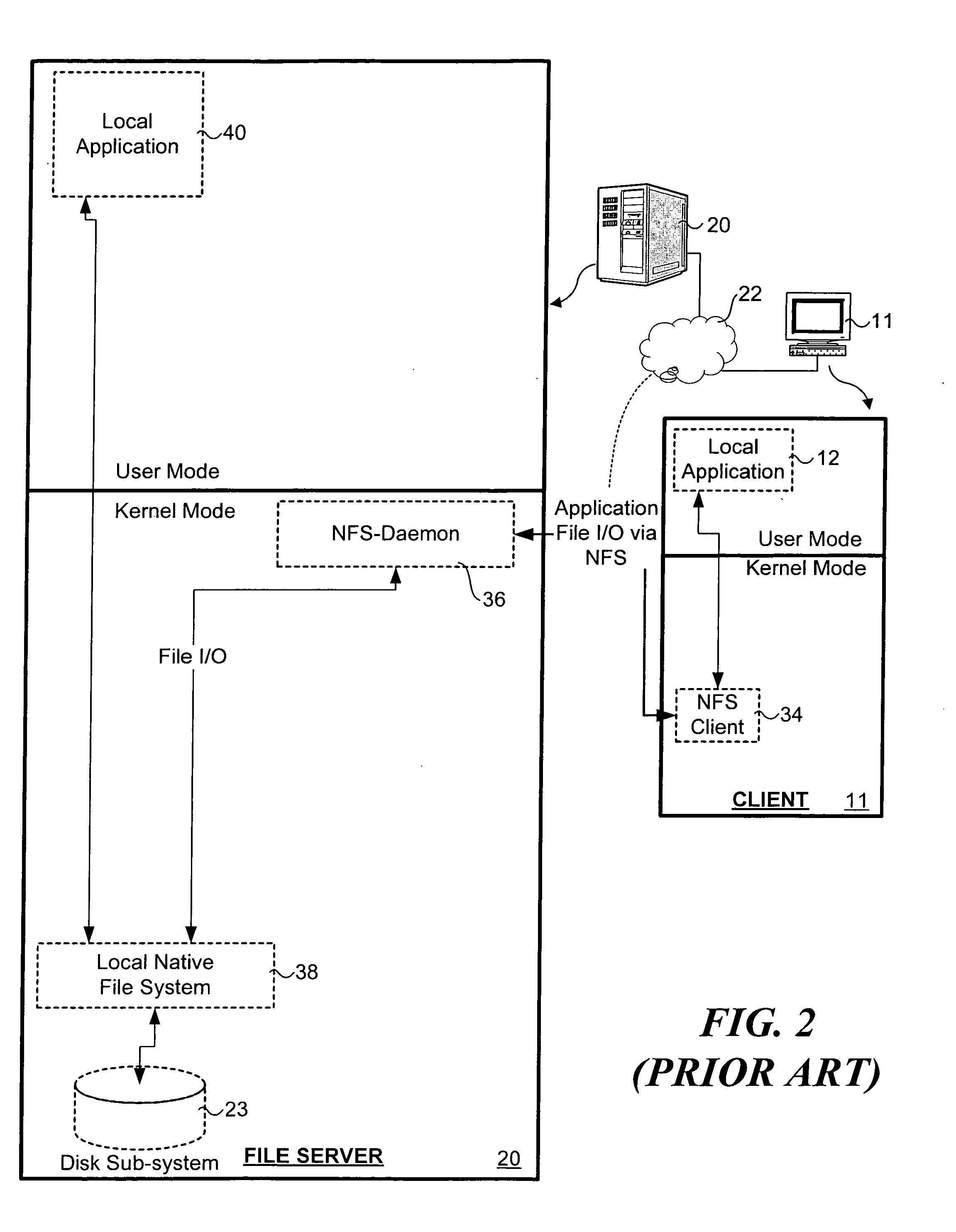
Patents
Literature
516 results about "Virtual file system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
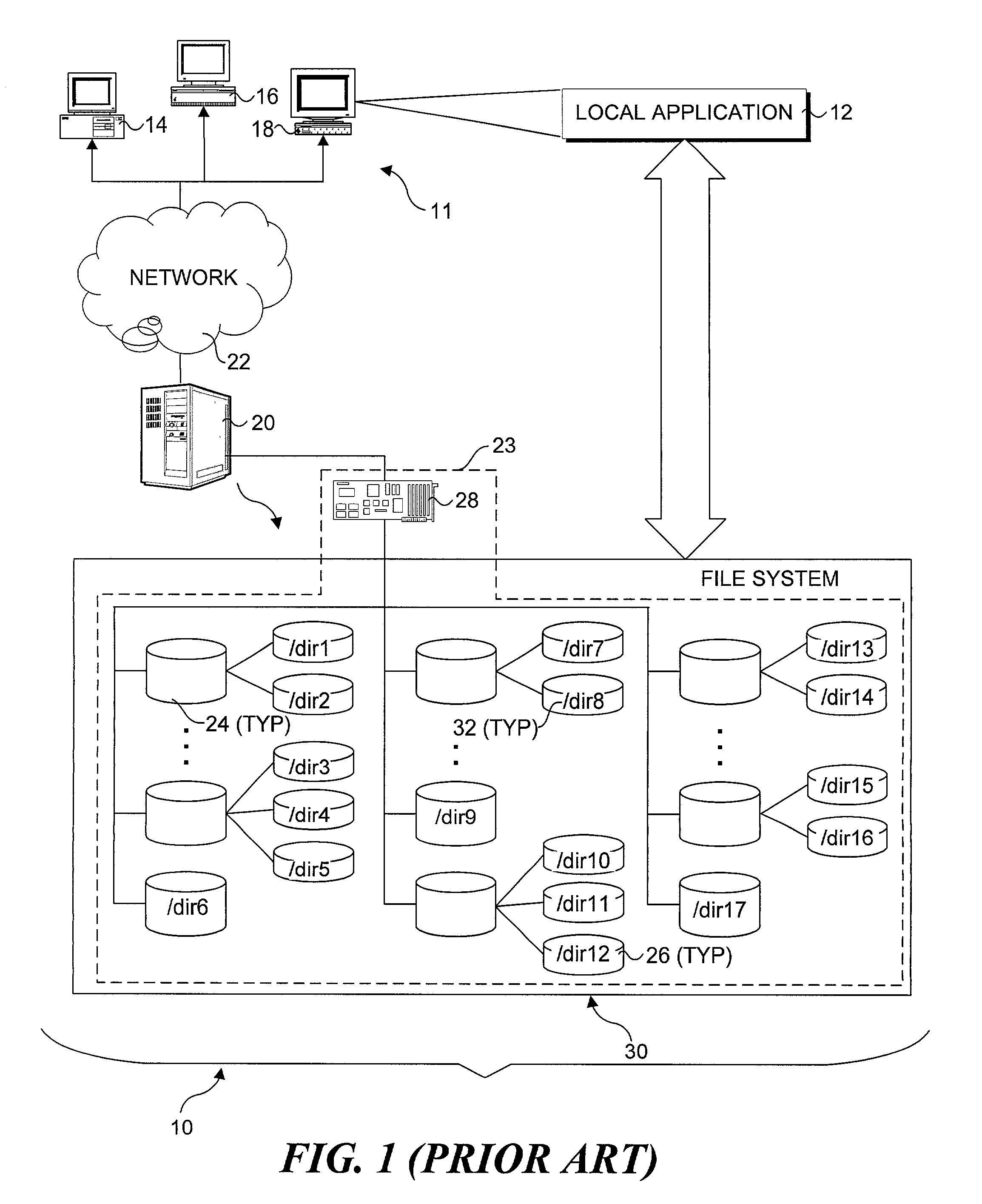
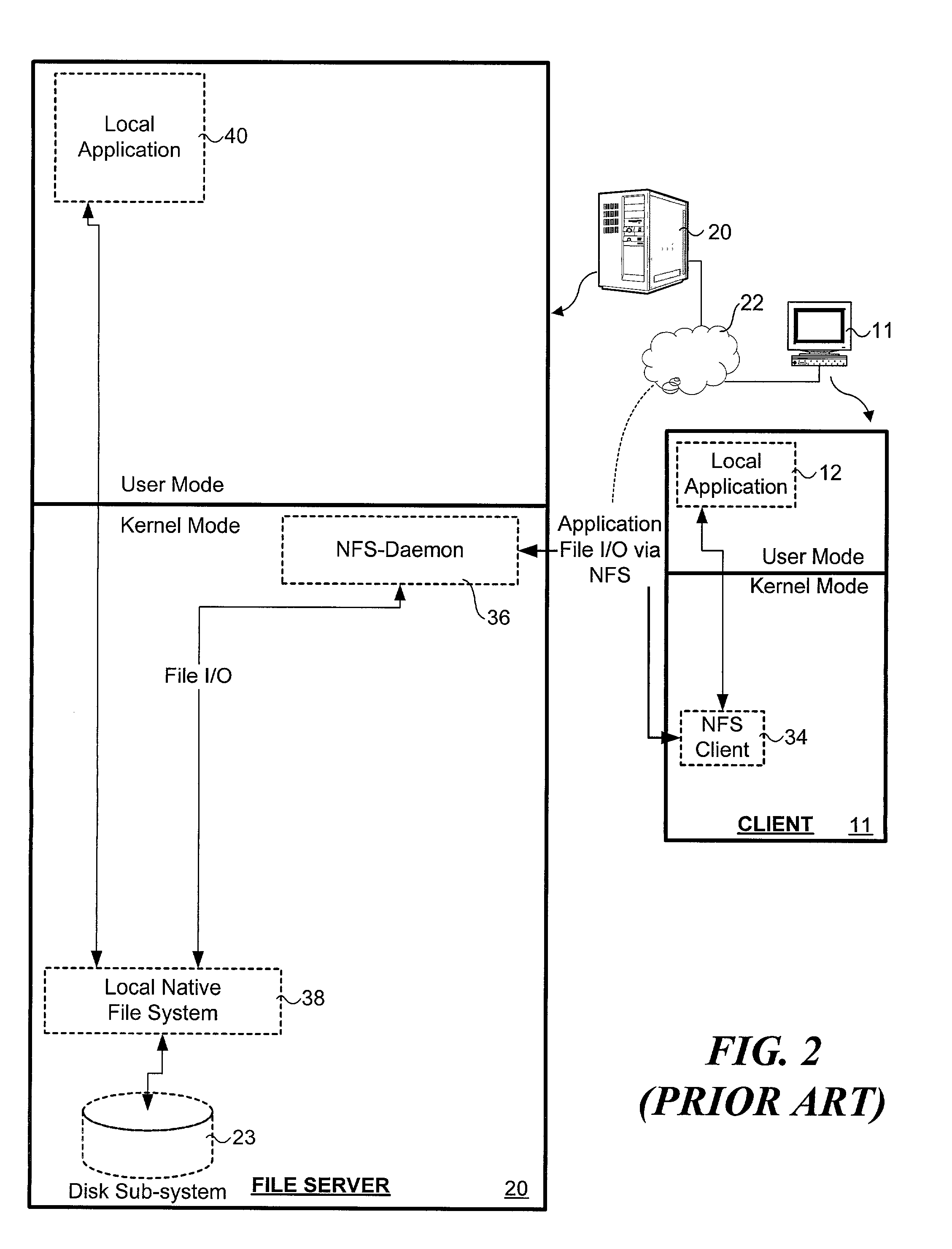
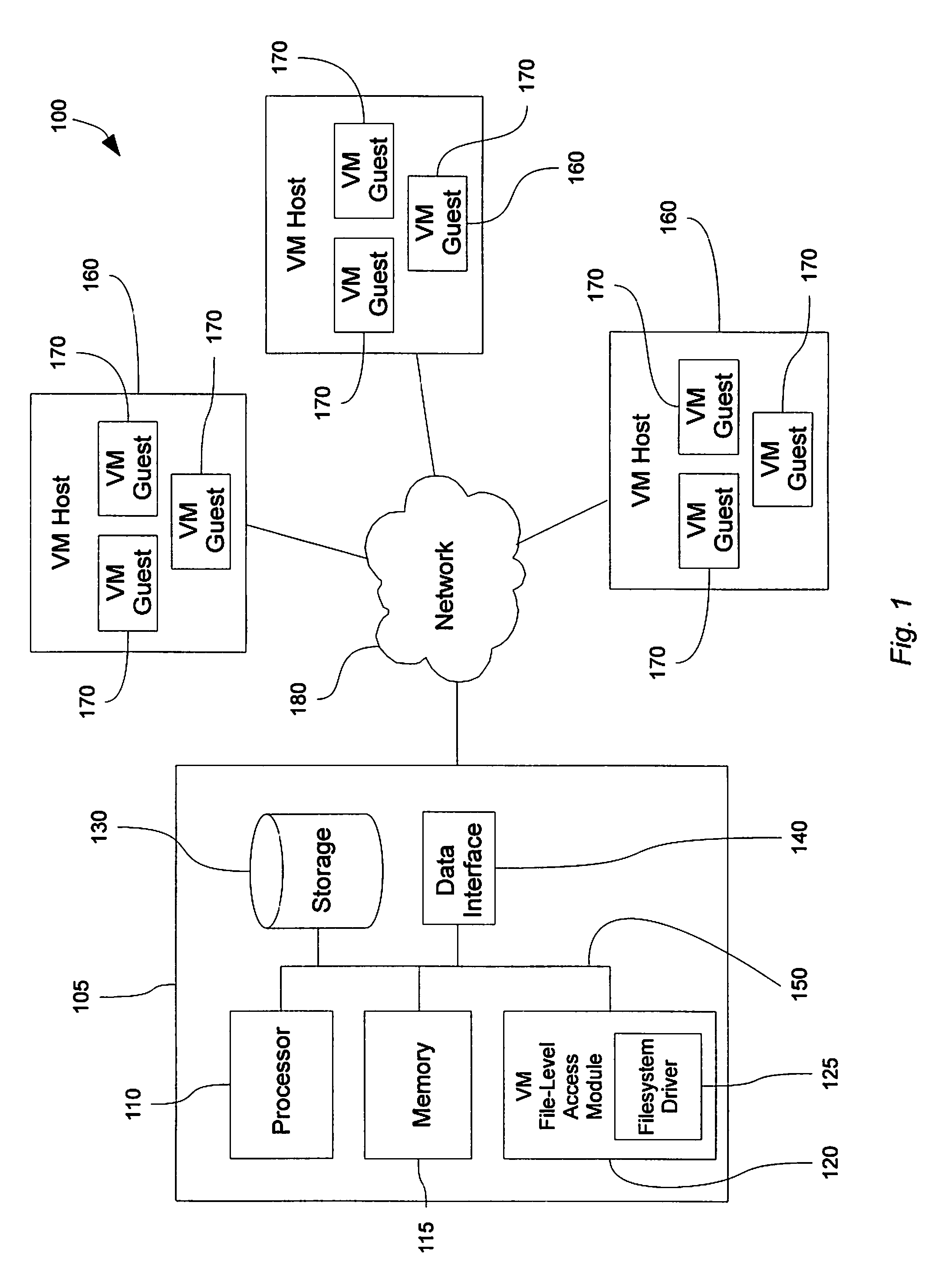
A virtual file system (VFS) or virtual filesystem switch is an abstract layer on top of a more concrete file system. The purpose of a VFS is to allow client applications to access different types of concrete file systems in a uniform way. A VFS can, for example, be used to access local and network storage devices transparently without the client application noticing the difference. It can be used to bridge the differences in Windows, classic Mac OS/macOS and Unix filesystems, so that applications can access files on local file systems of those types without having to know what type of file system they are accessing.
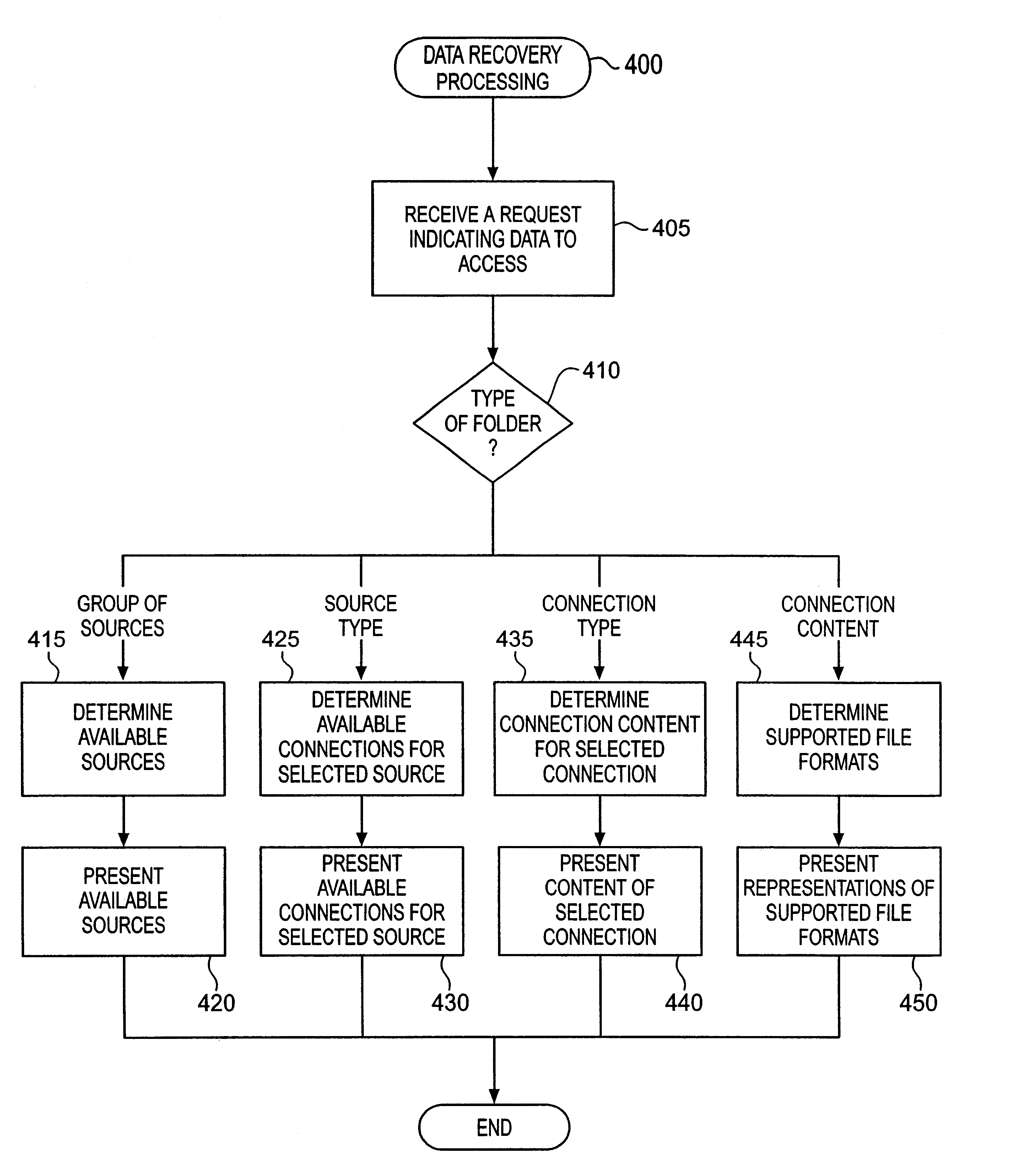
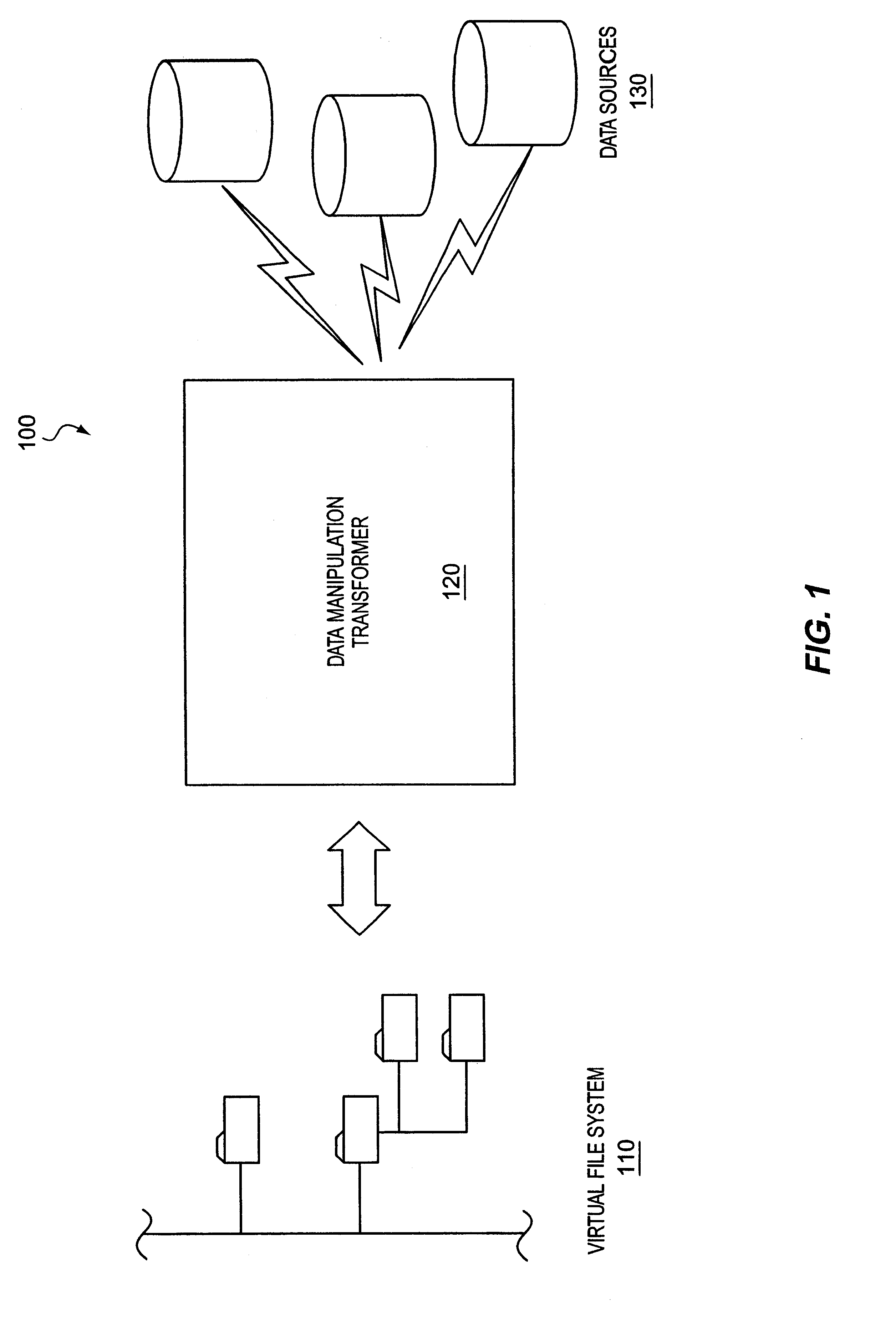
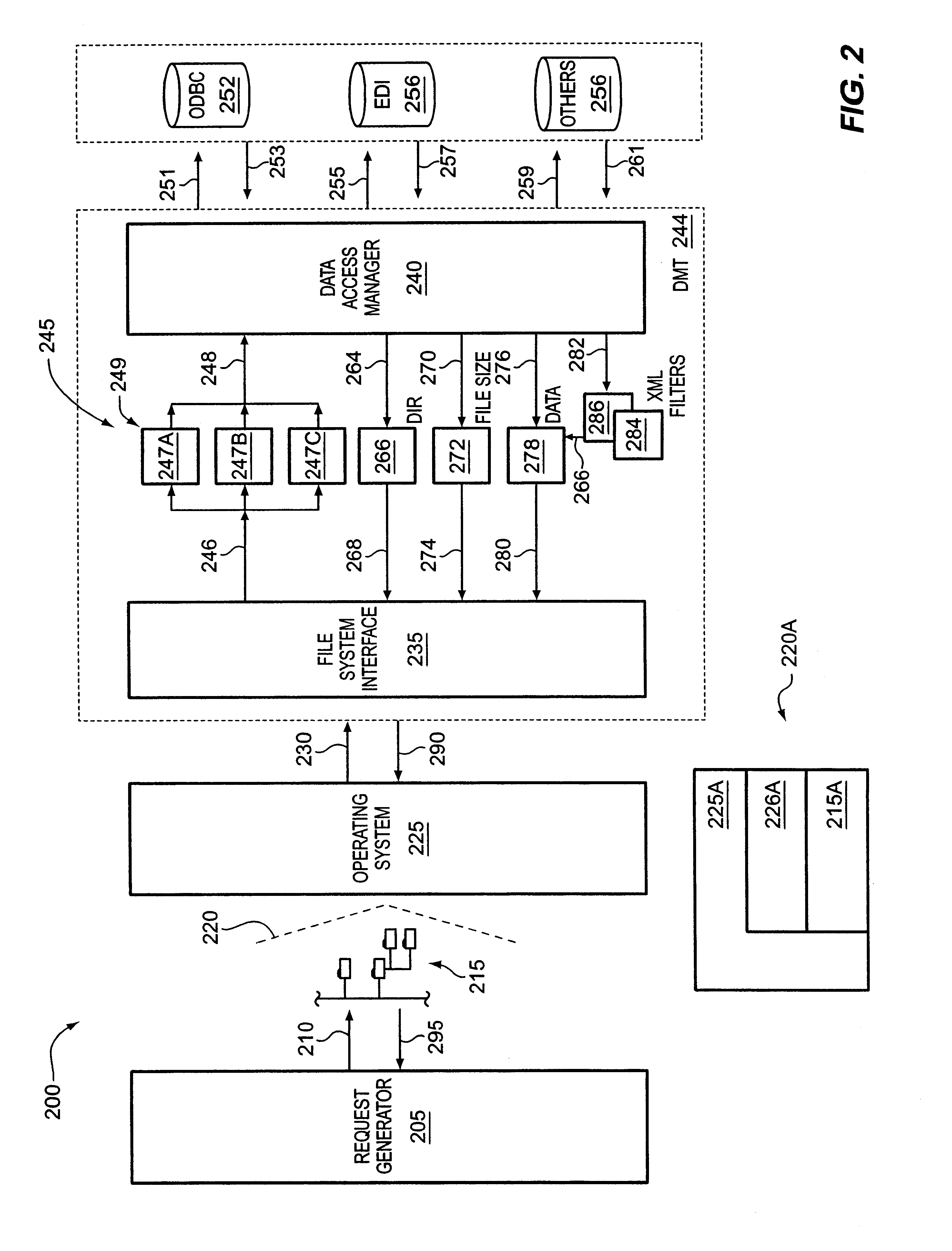
XML presentation of general-purpose data sources
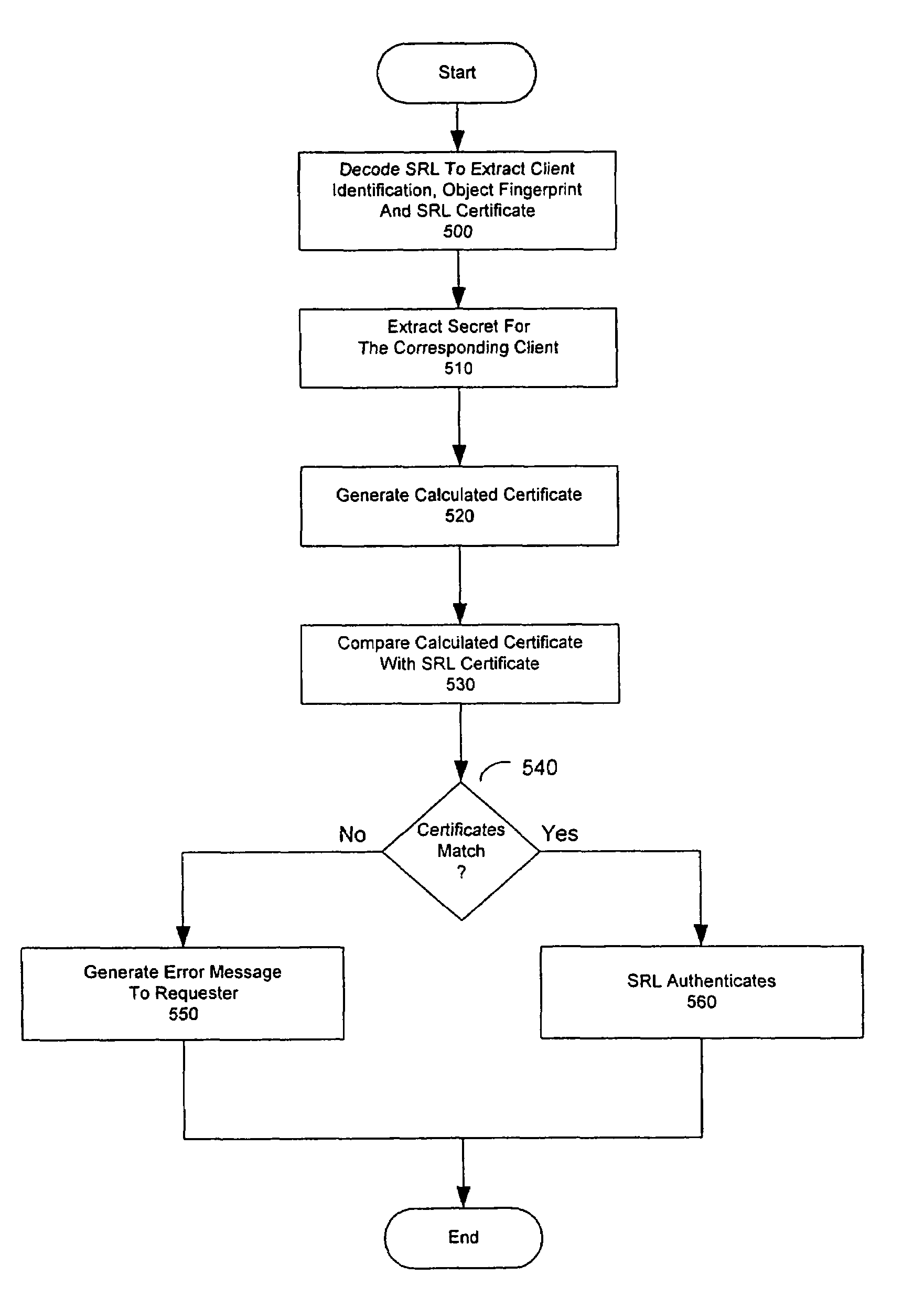
InactiveUS6901403B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGeneral purposeVirtual file system
A system and method for presenting one or more general-purpose application-accessible data sources as an XML representation is discussed. Information that describes the way data is structured or organized in the data source is accessed from the data source. A virtual file system representation comprising a plurality of hierarchical folders is provided to represent the structural information. Optionally, the virtual file system representation may be modified, either manually or according to rules sets. After any desired modification, the XML representation is generated based on the virtual file system representation.
Owner:ROGUE WAVE SOFTWARE
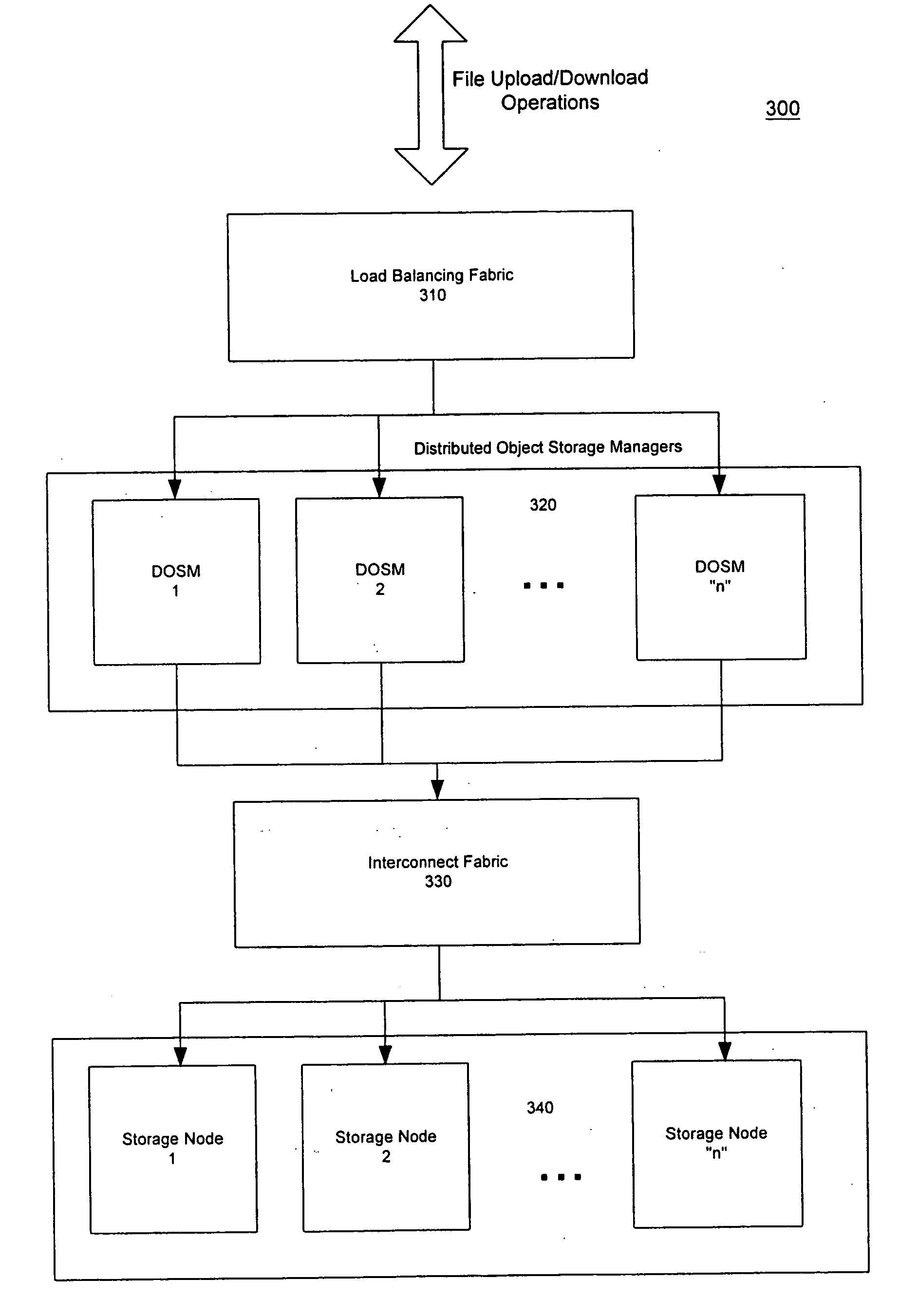
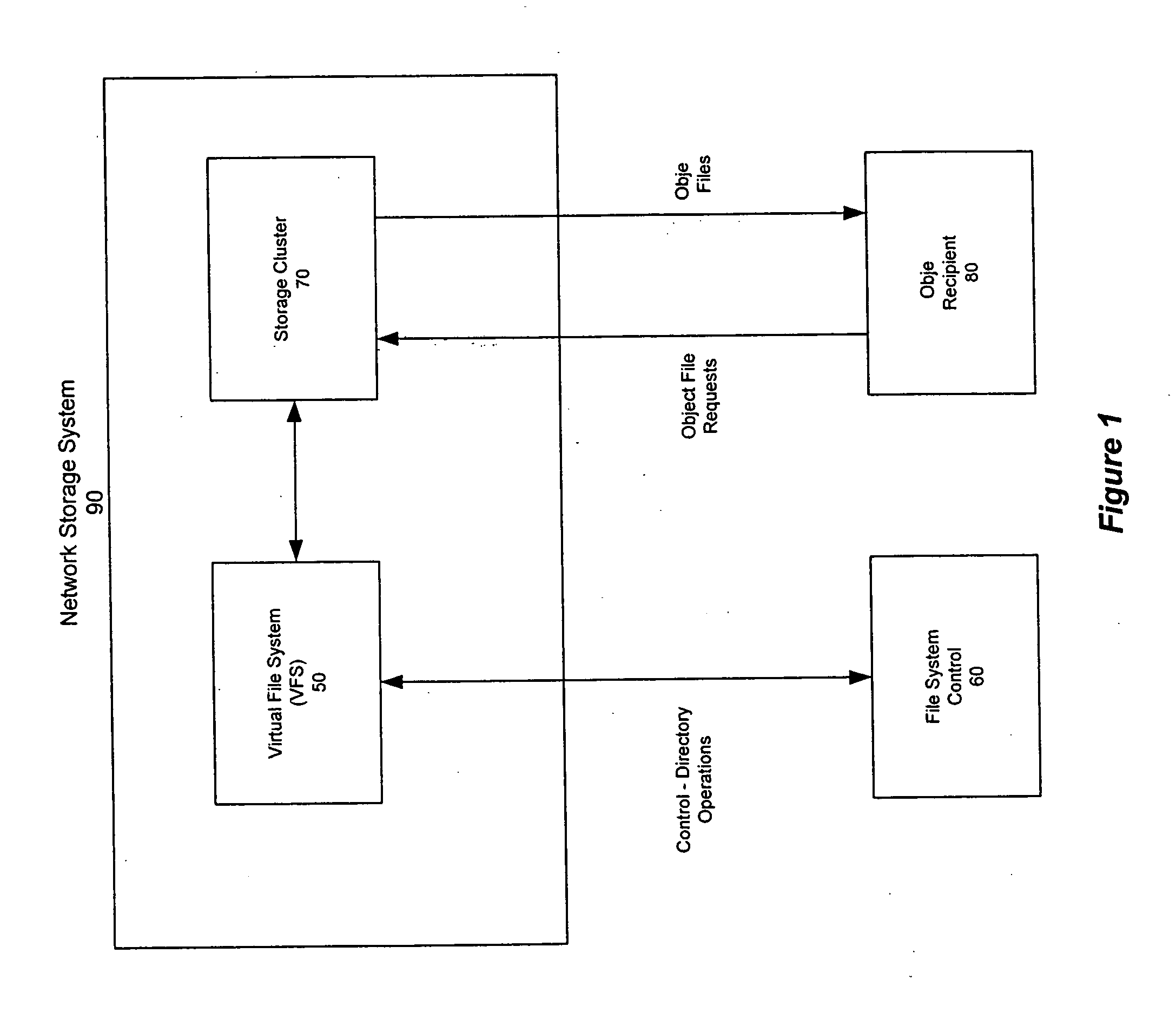
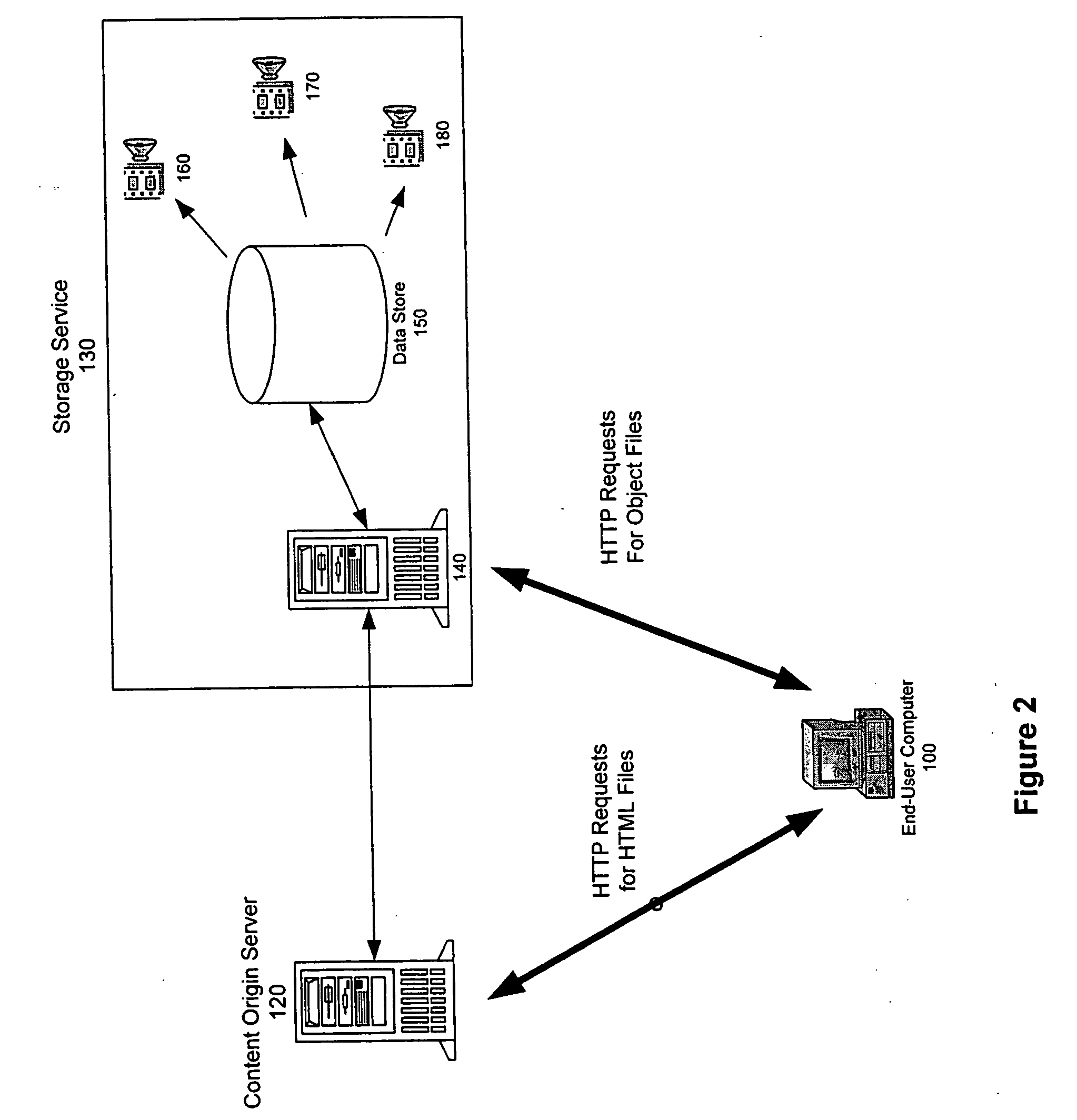
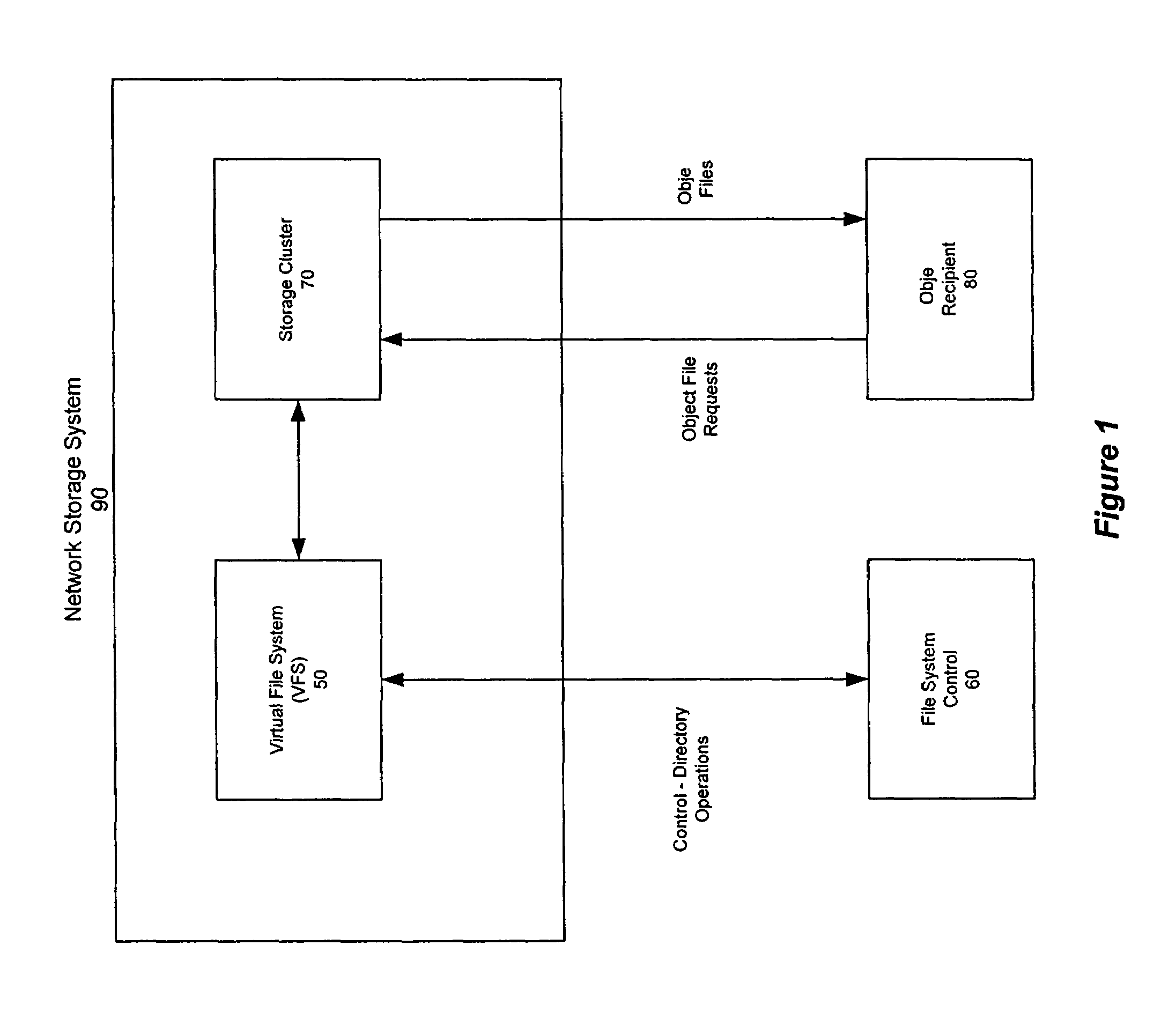
Distributed storage cluster architecture
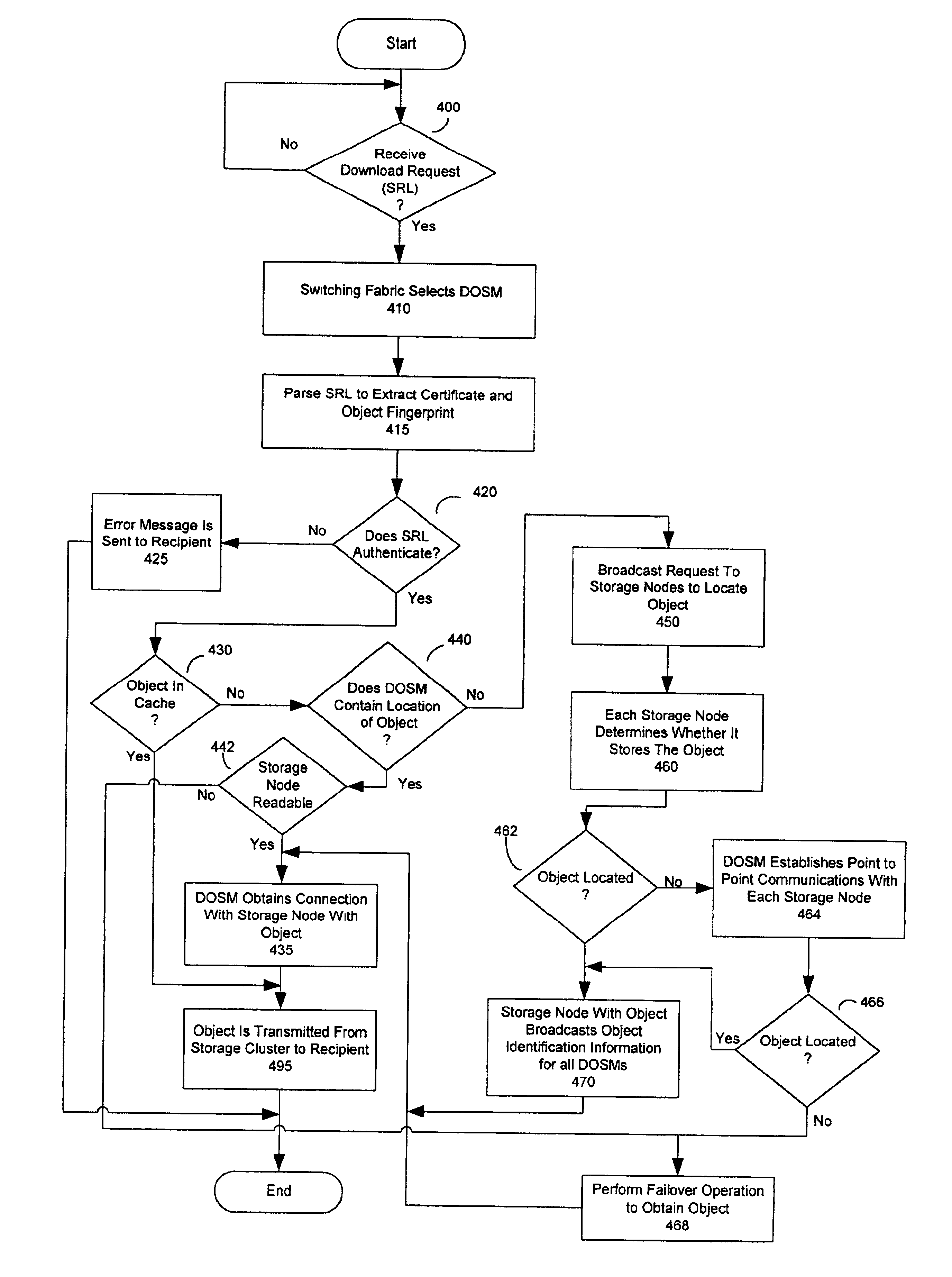
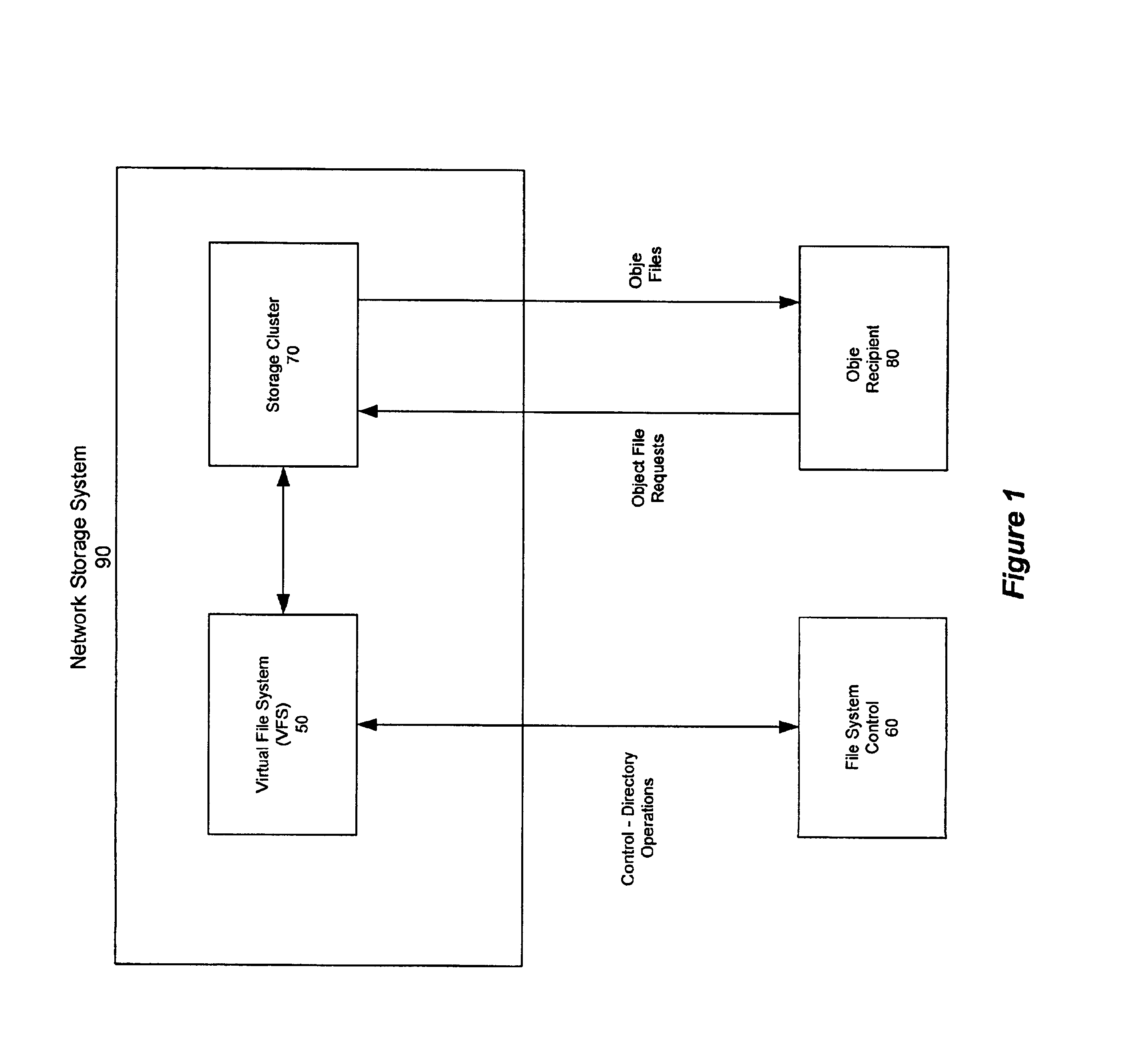
InactiveUS20050246393A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalVirtual file systemDistributed object
A network storage system includes a virtual file system (“VFS”) that manages the files of the network storage system, and a storage center that stores the files. The VFS and the storage center are separated, such that a client accesses the VFS to conduct file system operations and the client accesses the storage center to upload / download files. The client accesses the network storage system through one or more storage ports. The storage center includes a plurality of distributed object storage managers (DOSMs) and a storage cluster that includes a plurality of intelligent storage nodes. The network storage system includes additional storage centers at geographically disparate locations. The network storage system uses a multi-cast protocol to maintain file information at the DOSMs regarding files stored in the intelligent storage nodes, including files stored in disparate storage centers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
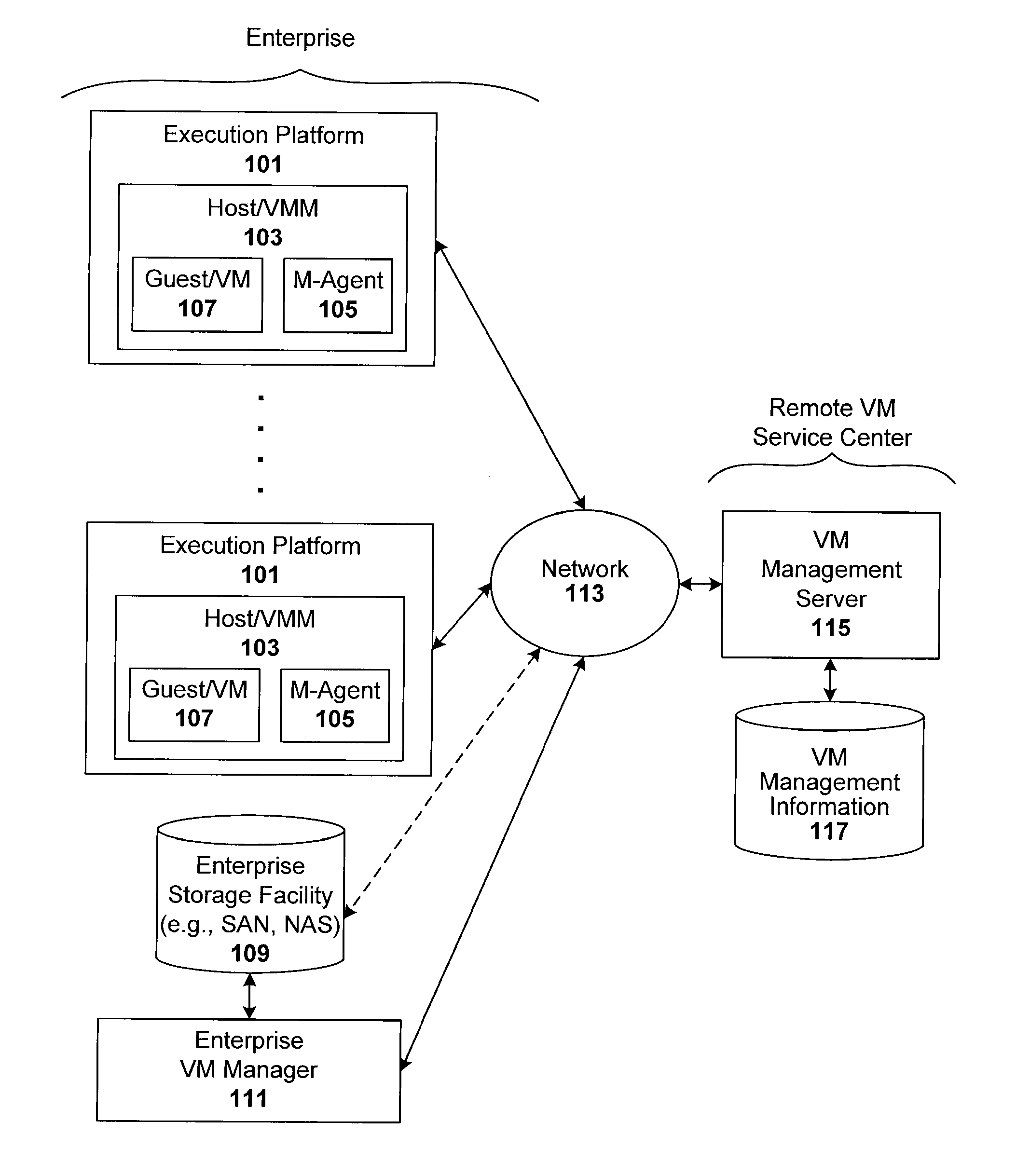
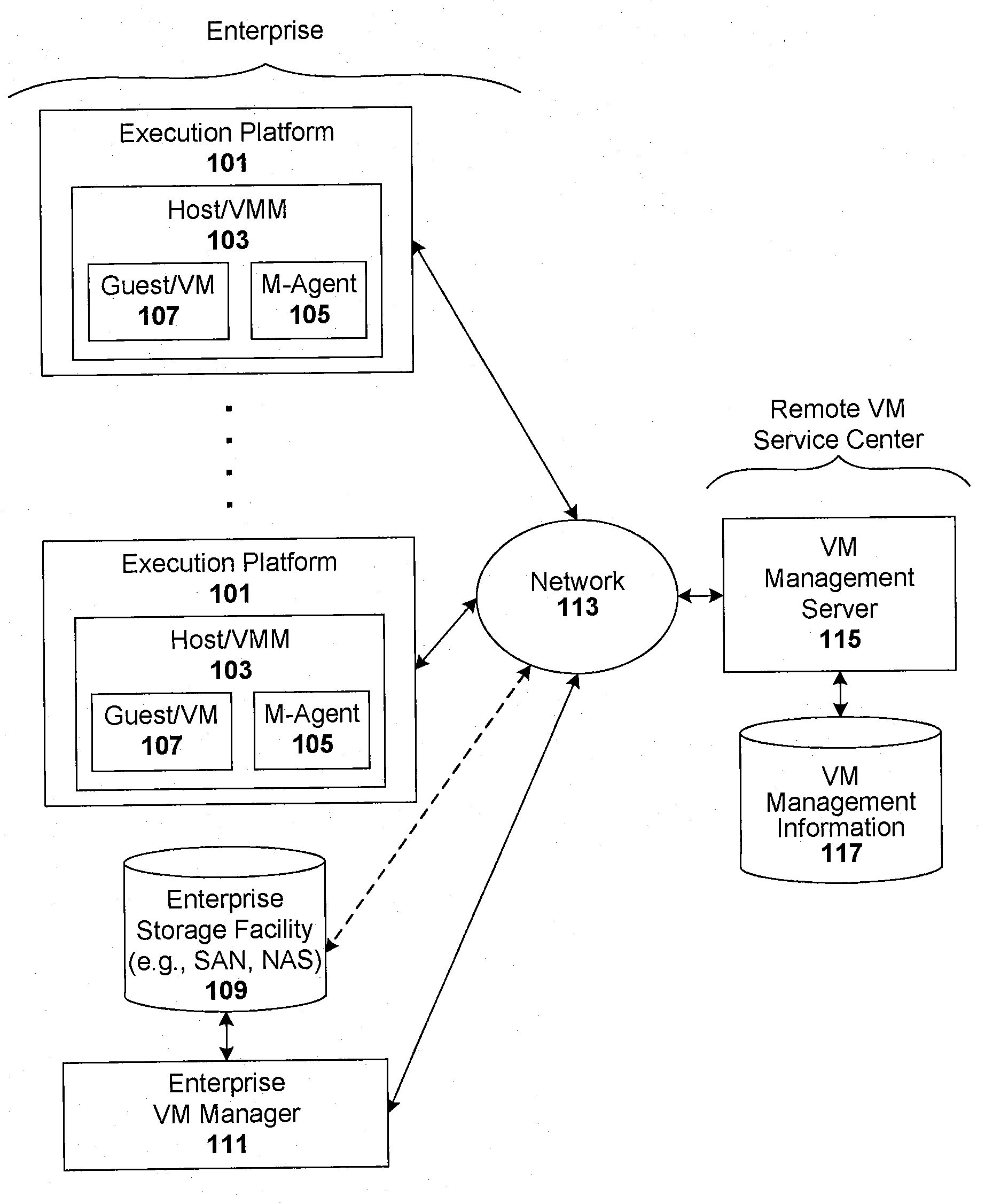
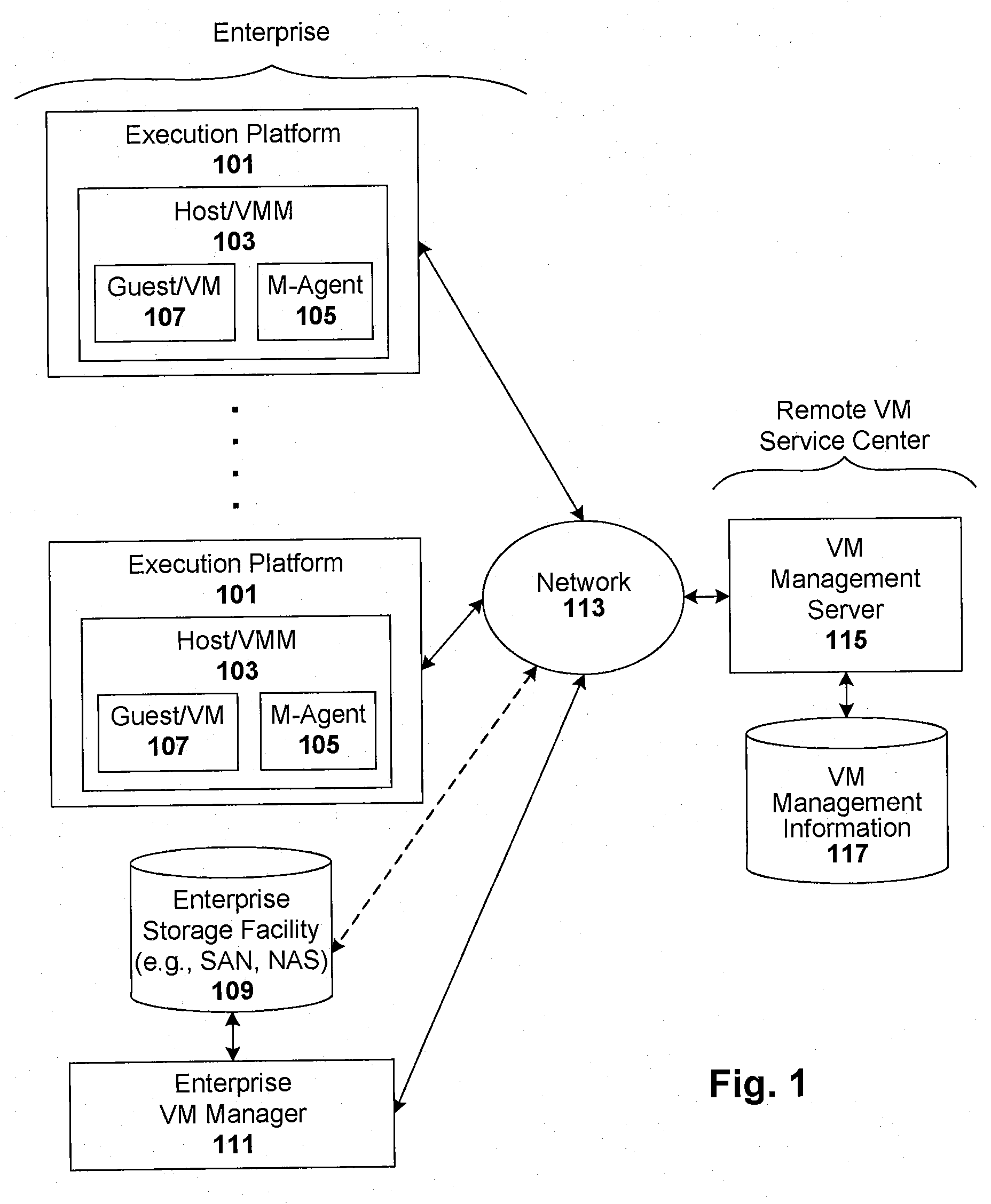
Compliance-based adaptations in managed virtual systems
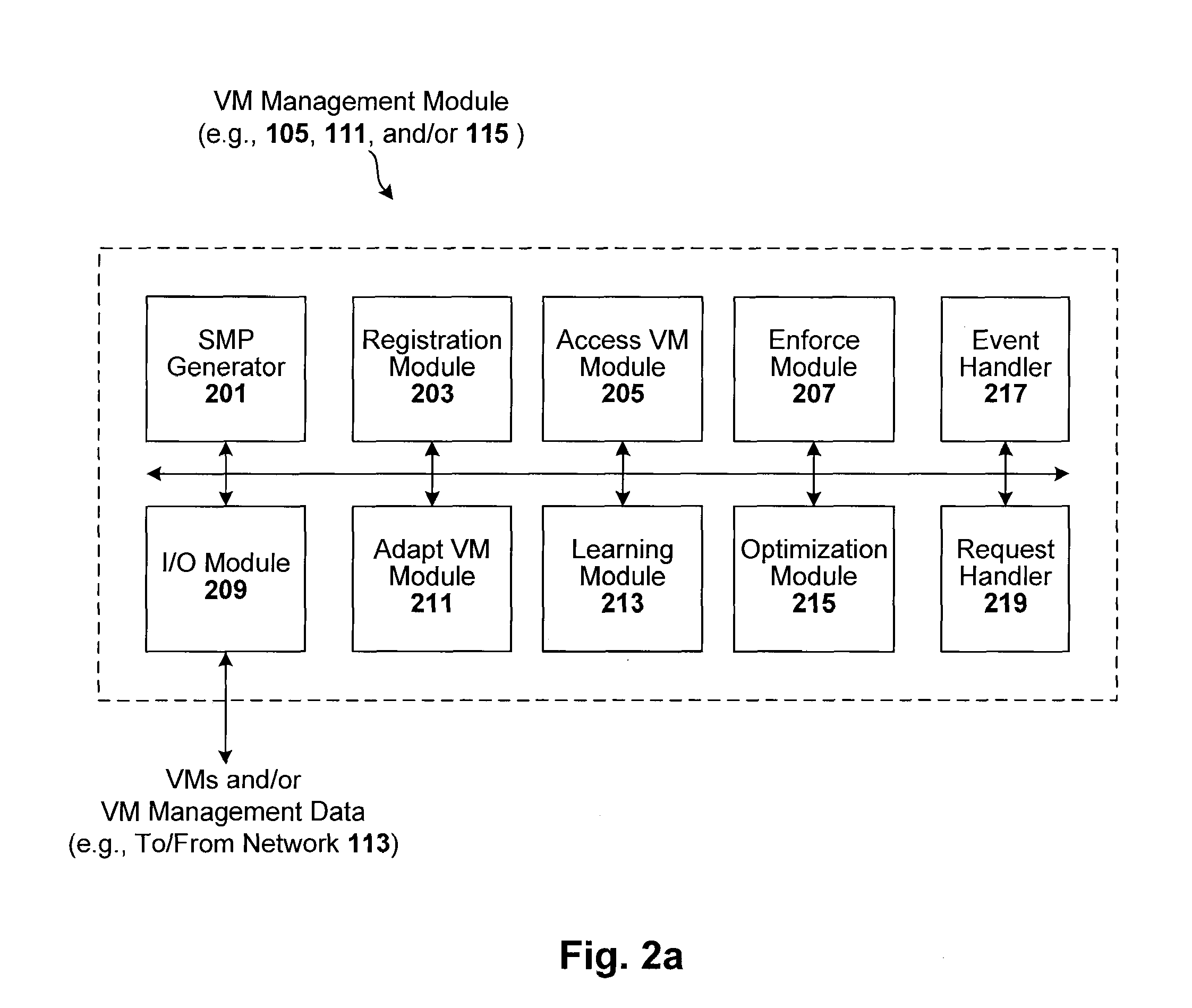
ActiveUS8234640B1Removing malwareDisabling malwareMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirtual file systemConsistency test
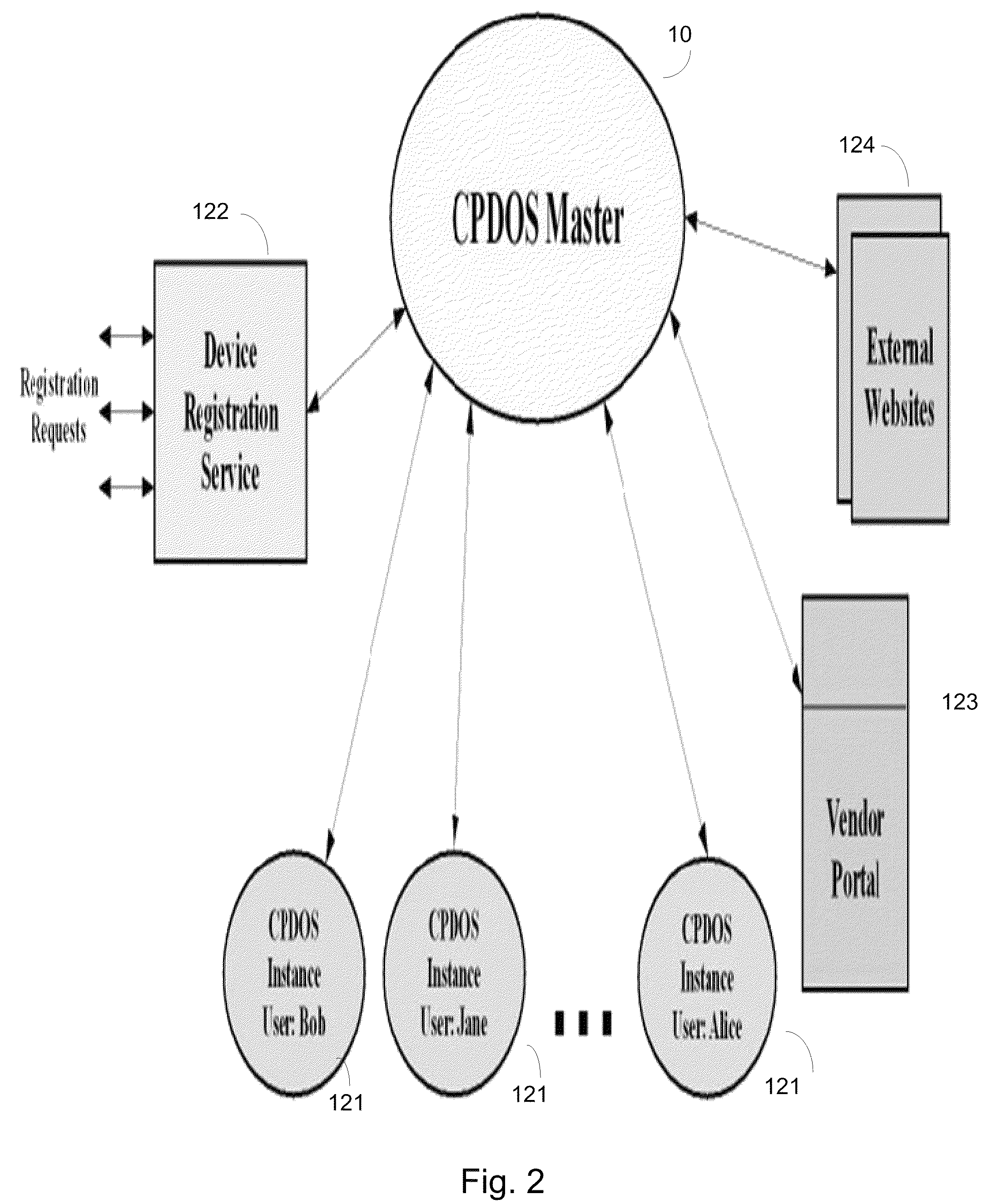
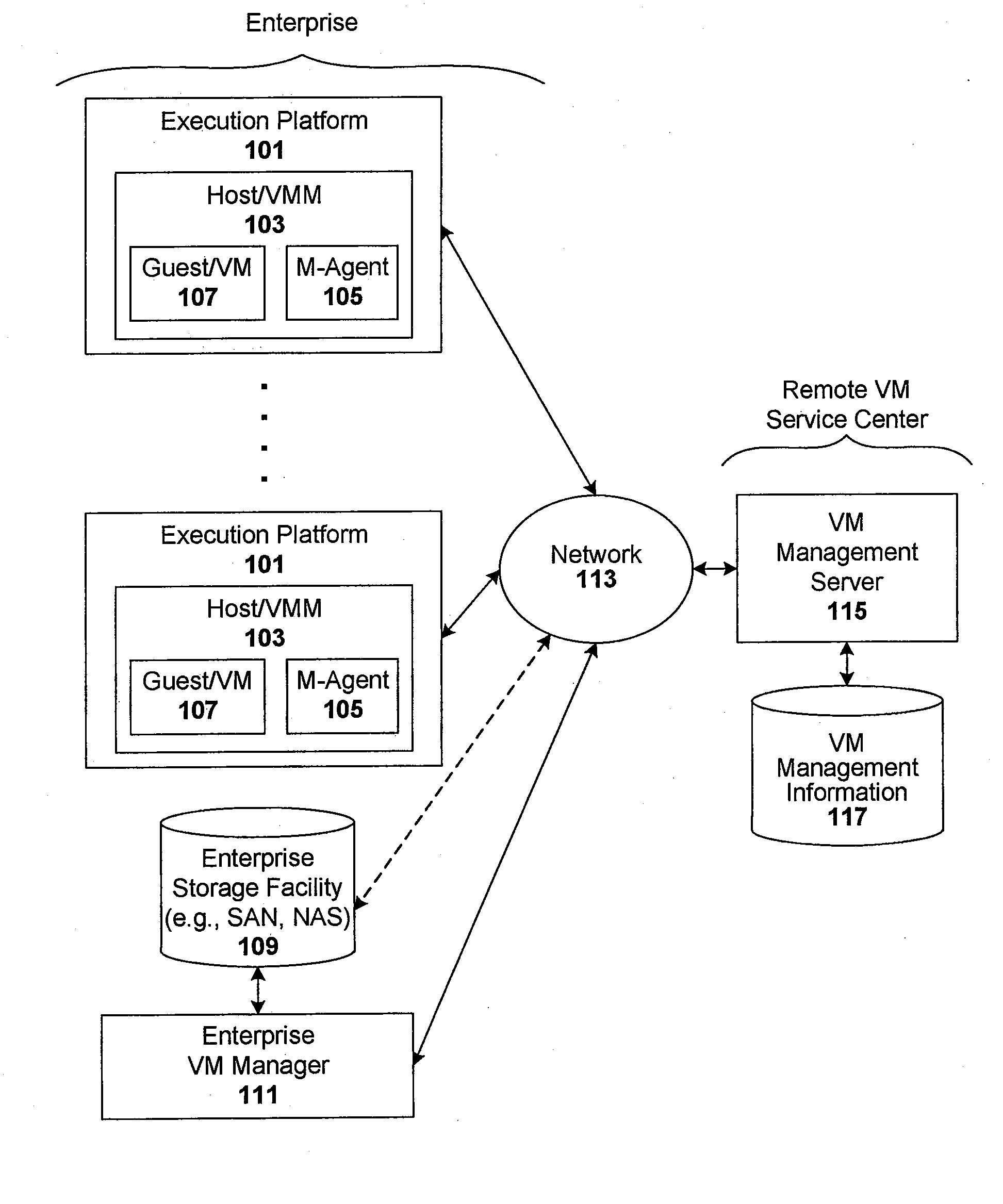
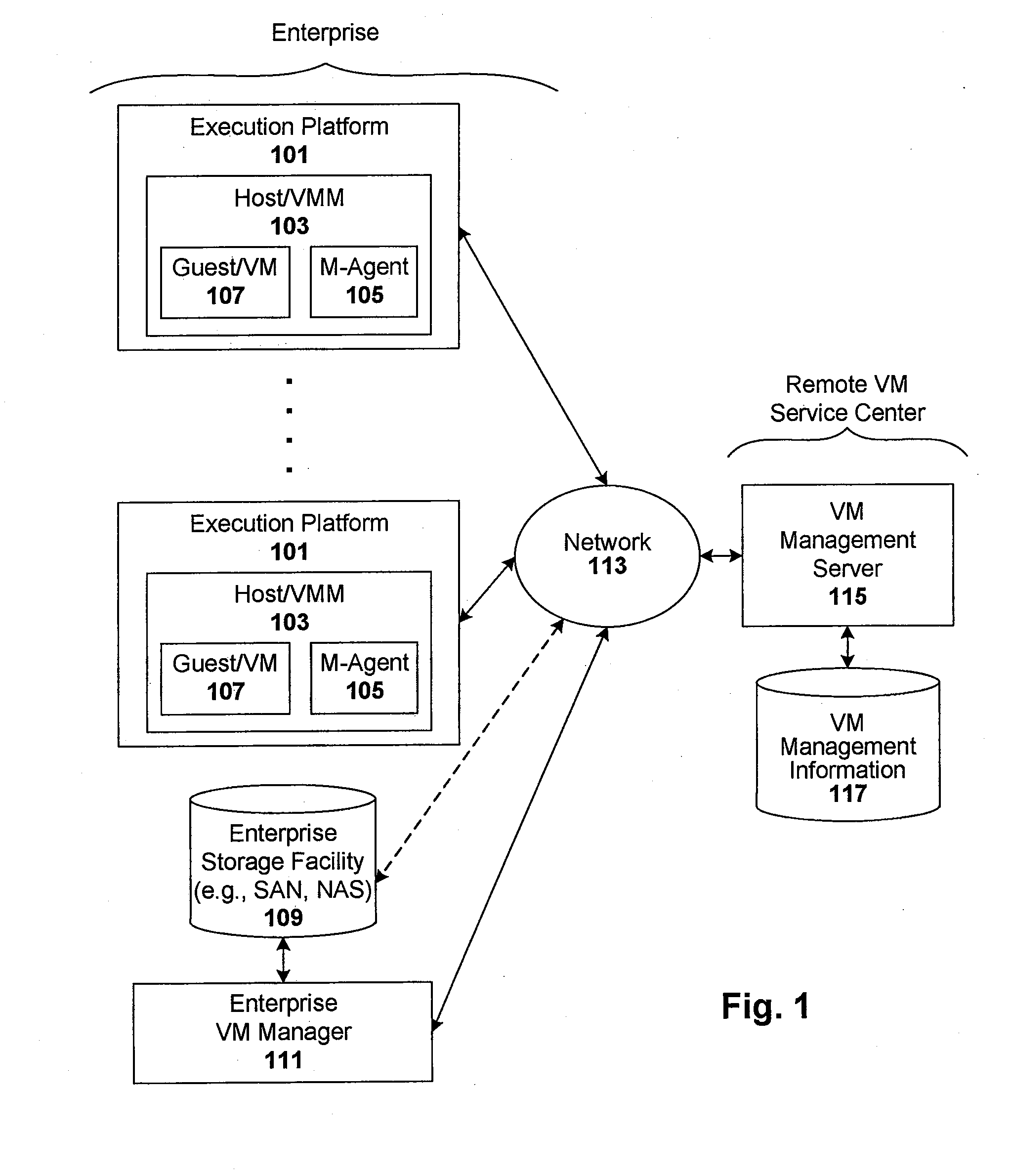
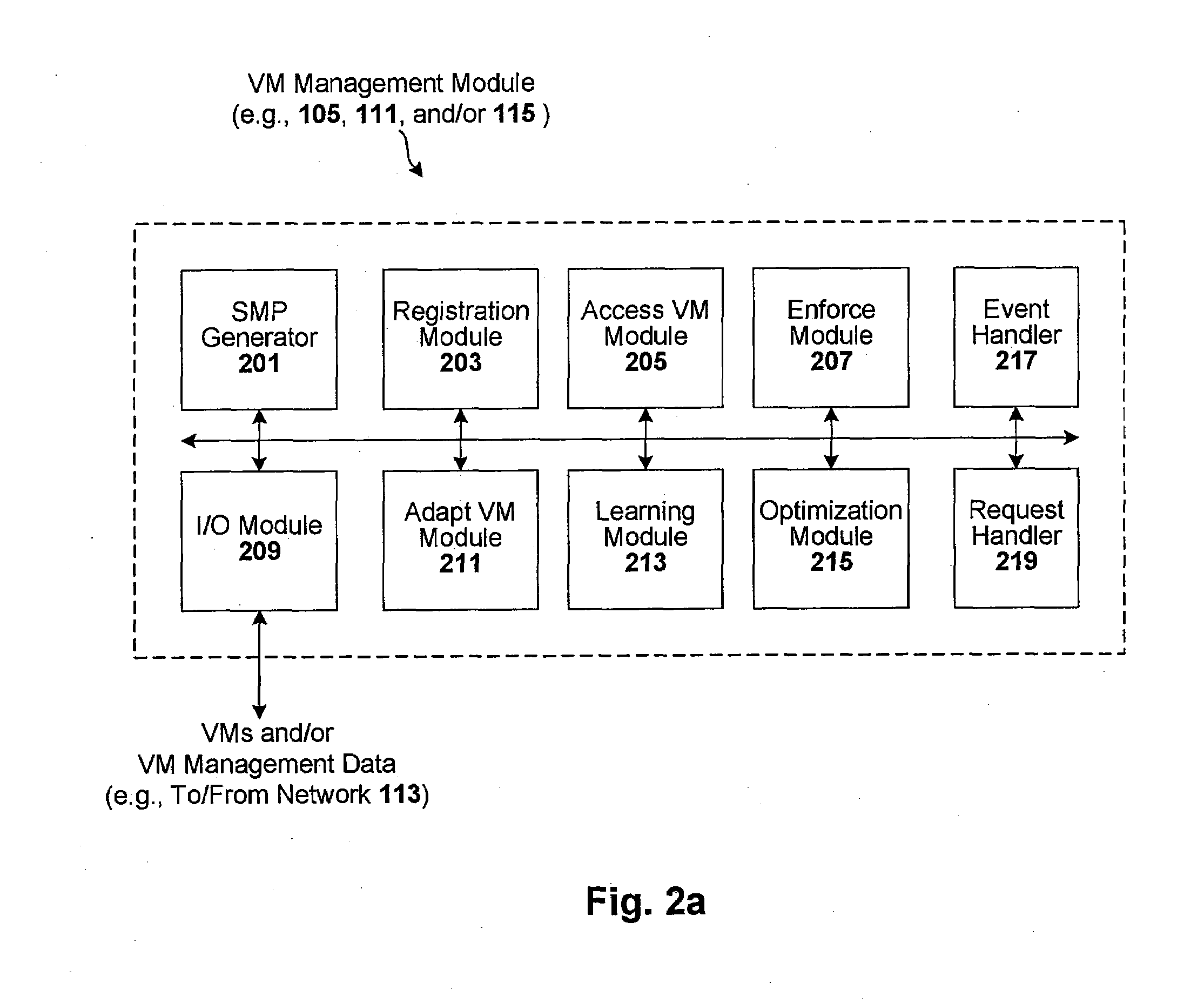
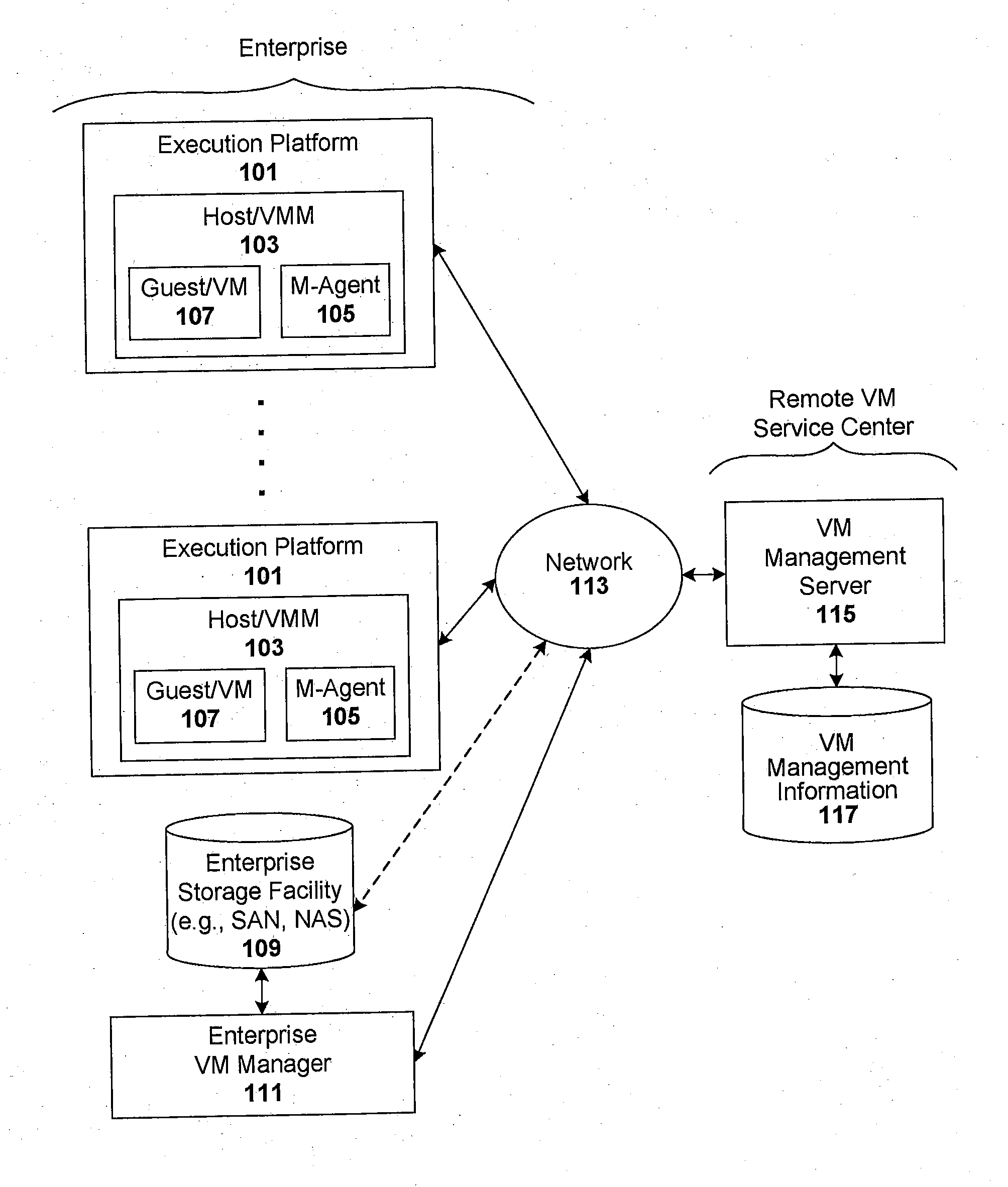
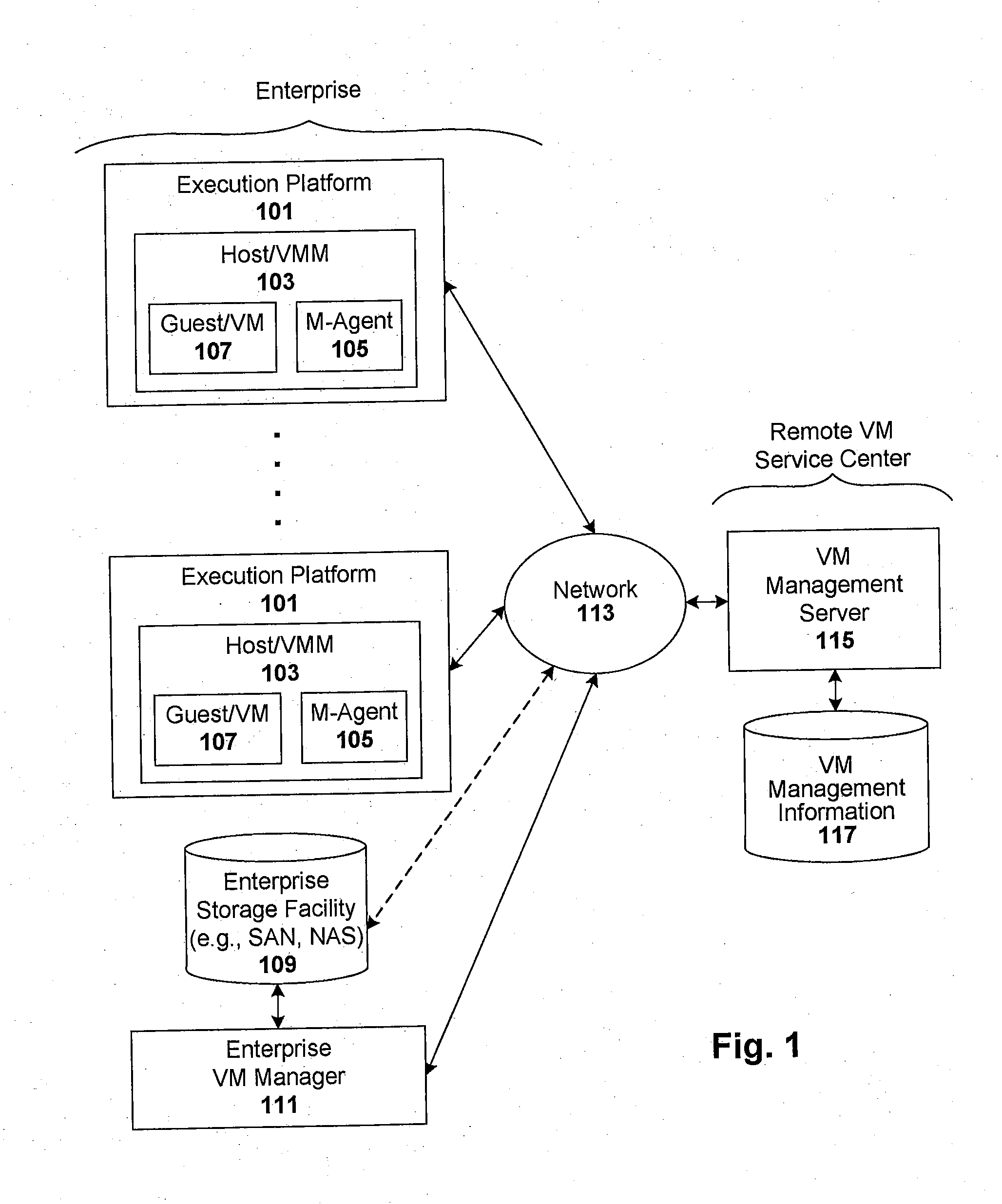
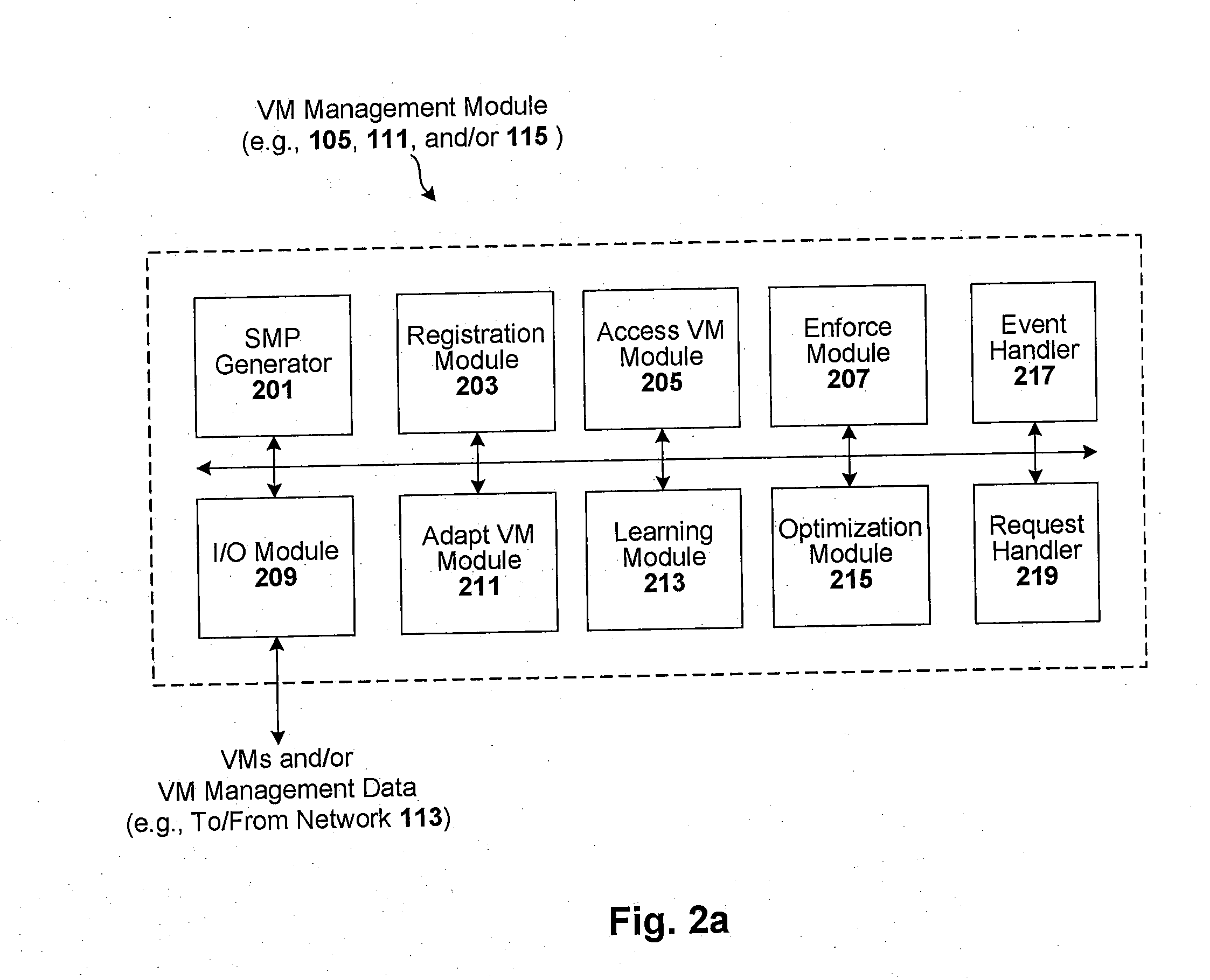
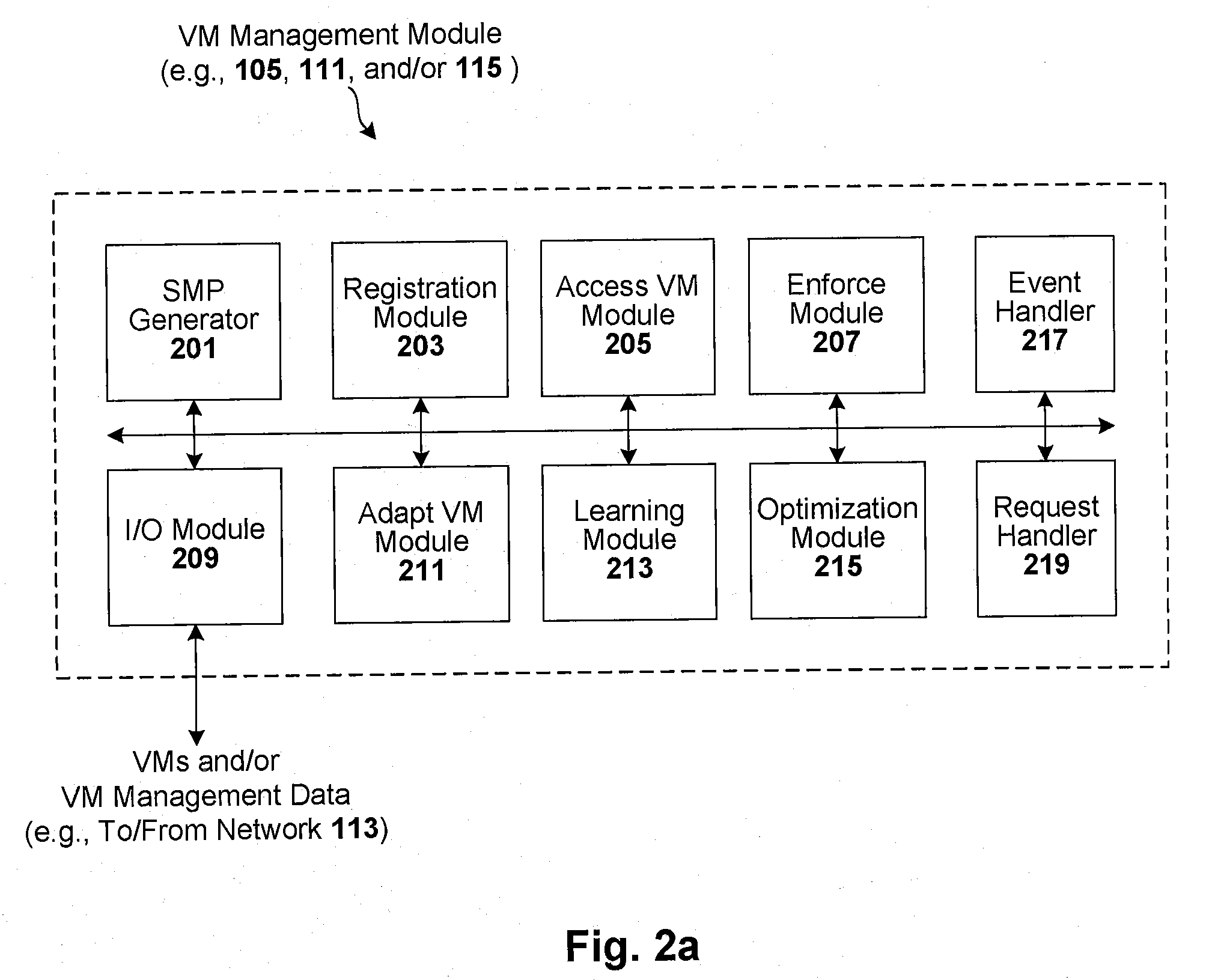
Techniques are disclosed for controlling and managing virtual machines and other such virtual systems. VM execution approval is based on compliance with policies controlling various aspects of VM. The techniques can be employed to benefit all virtual environments, such as virtual machines, virtual appliances, and virtual applications. For ease of discussion herein, assume that a virtual machine (VM) represents each of these environments. In one particular embodiment, a systems management partition (SMP) is created inside the VM to provide a persistent and resilient storage for management information (e.g., logical and physical VM metadata). The SMP can also be used as a staging area for installing additional content or agentry on the VM when the VM is executed. Remote storage of management information can also be used. The VM management information can then be made available for pre-execution processing, including policy-based compliance testing.
Owner:RED HAT
Method and apparatus for accessing remote storage in a distributed storage cluster architecture
InactiveUS6952737B1Digital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersVirtual file systemDistributed object
A network storage system includes a virtual file system (“VFS”) that manages the files of the network storage system, and a storage center that stores the files. The VFS and the storage center are separated, such that a client accesses the VFS to conduct file system operations and the client accesses the storage center to upload / download files. The client accesses the network storage system through one or more storage ports. The storage center includes a plurality of distributed object storage managers (DOSMS) and a storage cluster that includes a plurality of intelligent storage nodes. The network storage system includes additional storage centers at geographically disparate locations. The network storage system uses a multi-cast protocol to maintain file information at the DOSMs regarding files stored in the intelligent storage nodes, including files stored in disparate storage centers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
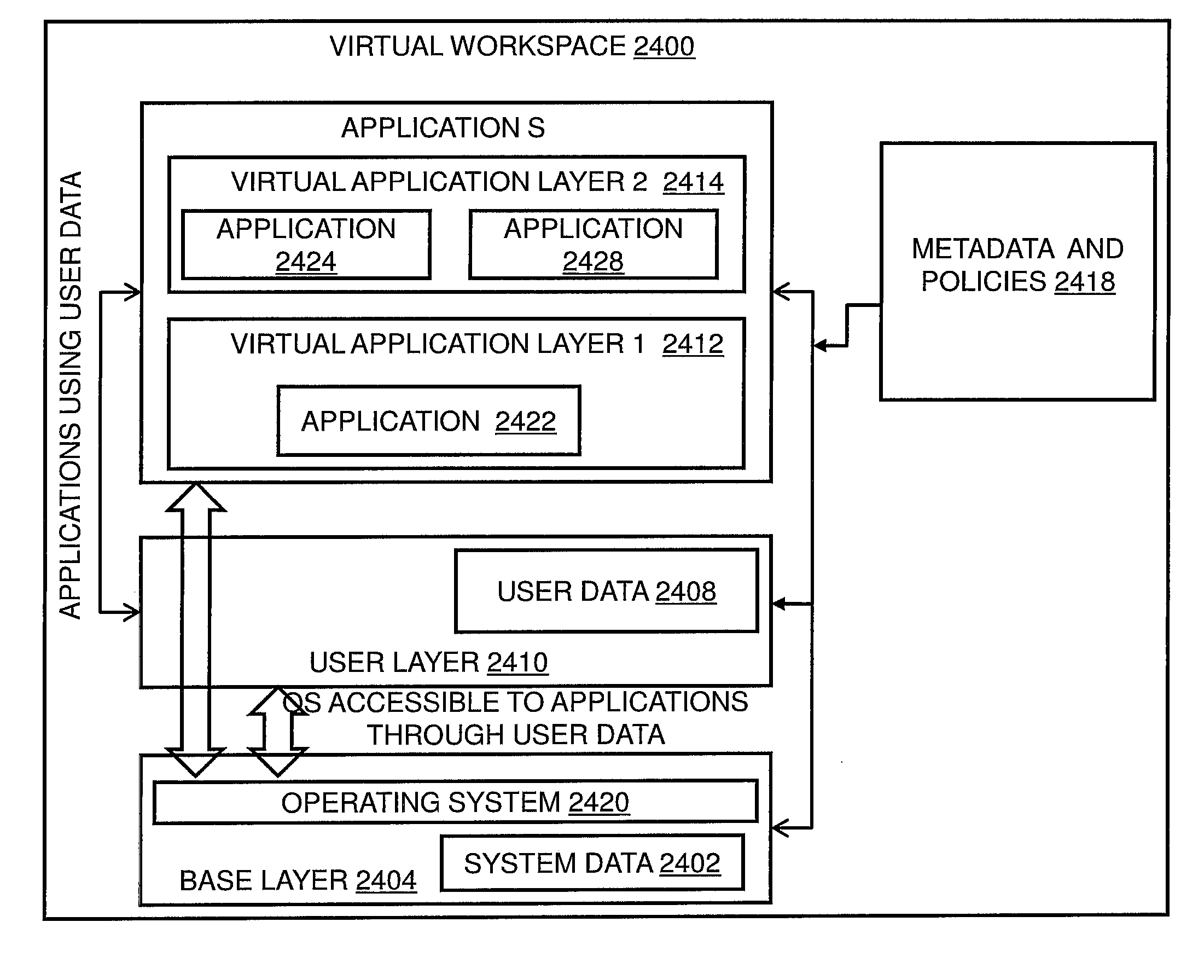
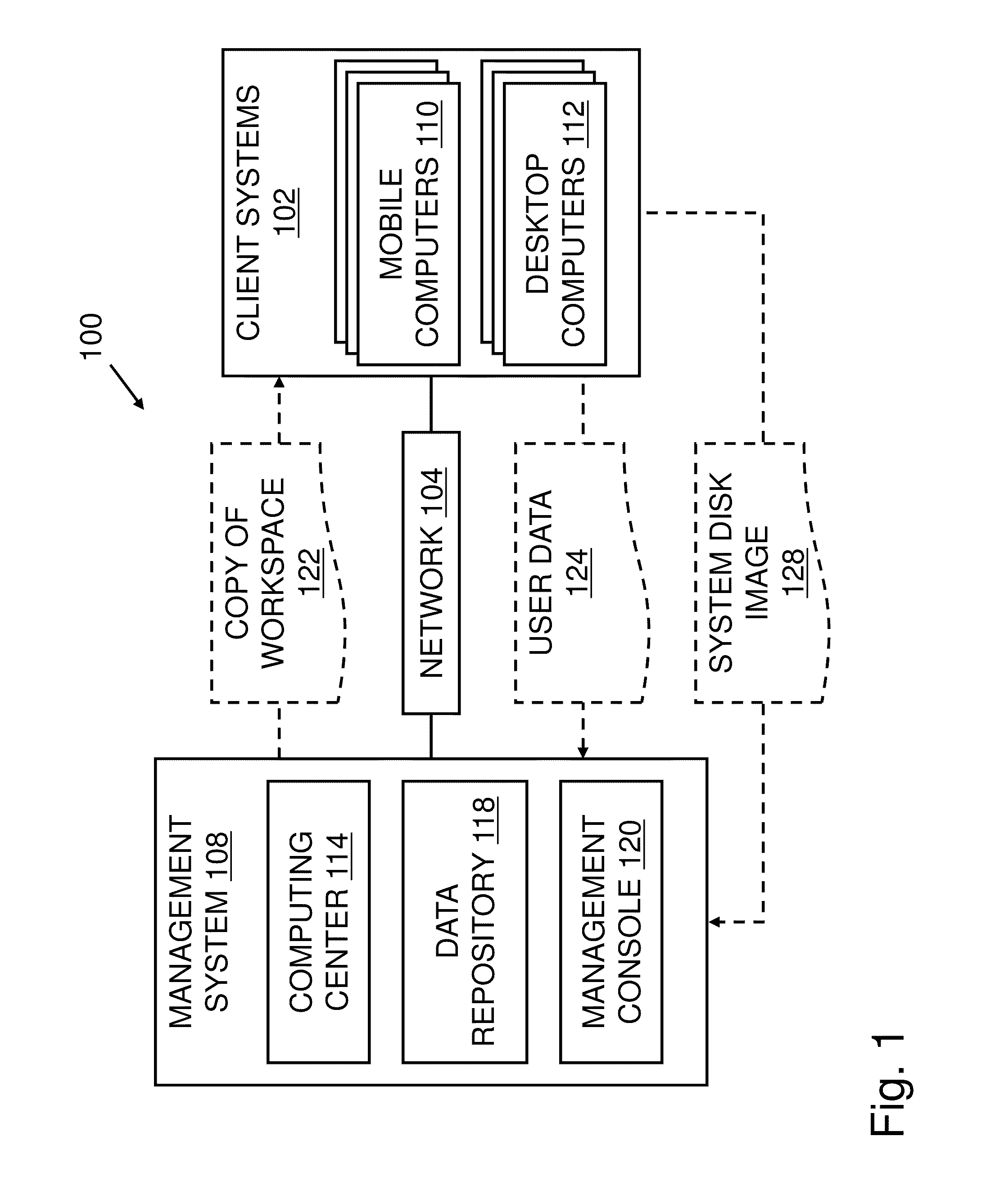
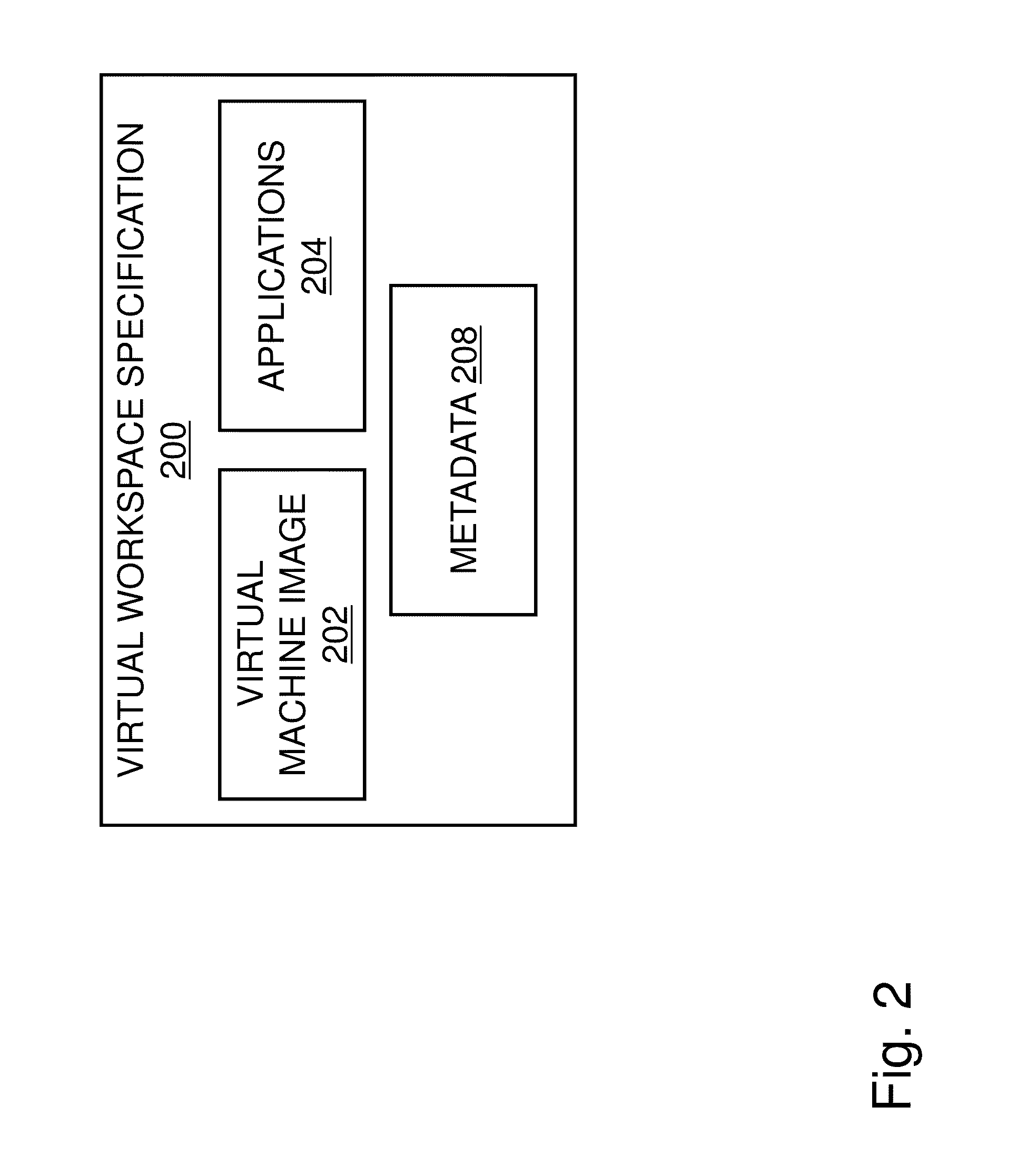
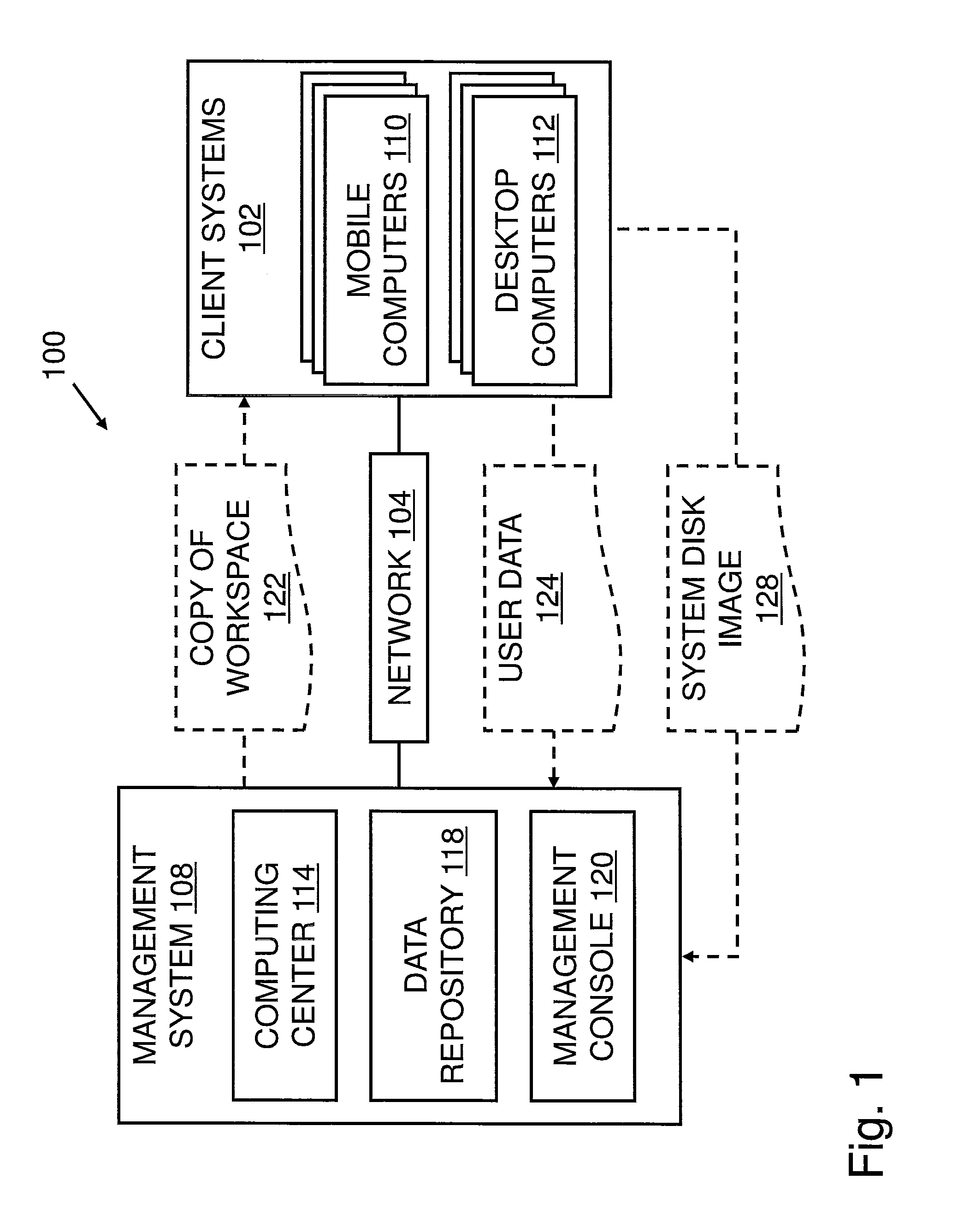
Operating Systems in a Layerd Virtual Workspace
InactiveUS20110061045A1Easy to manageImprove usabilitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtualizationVirtual file system
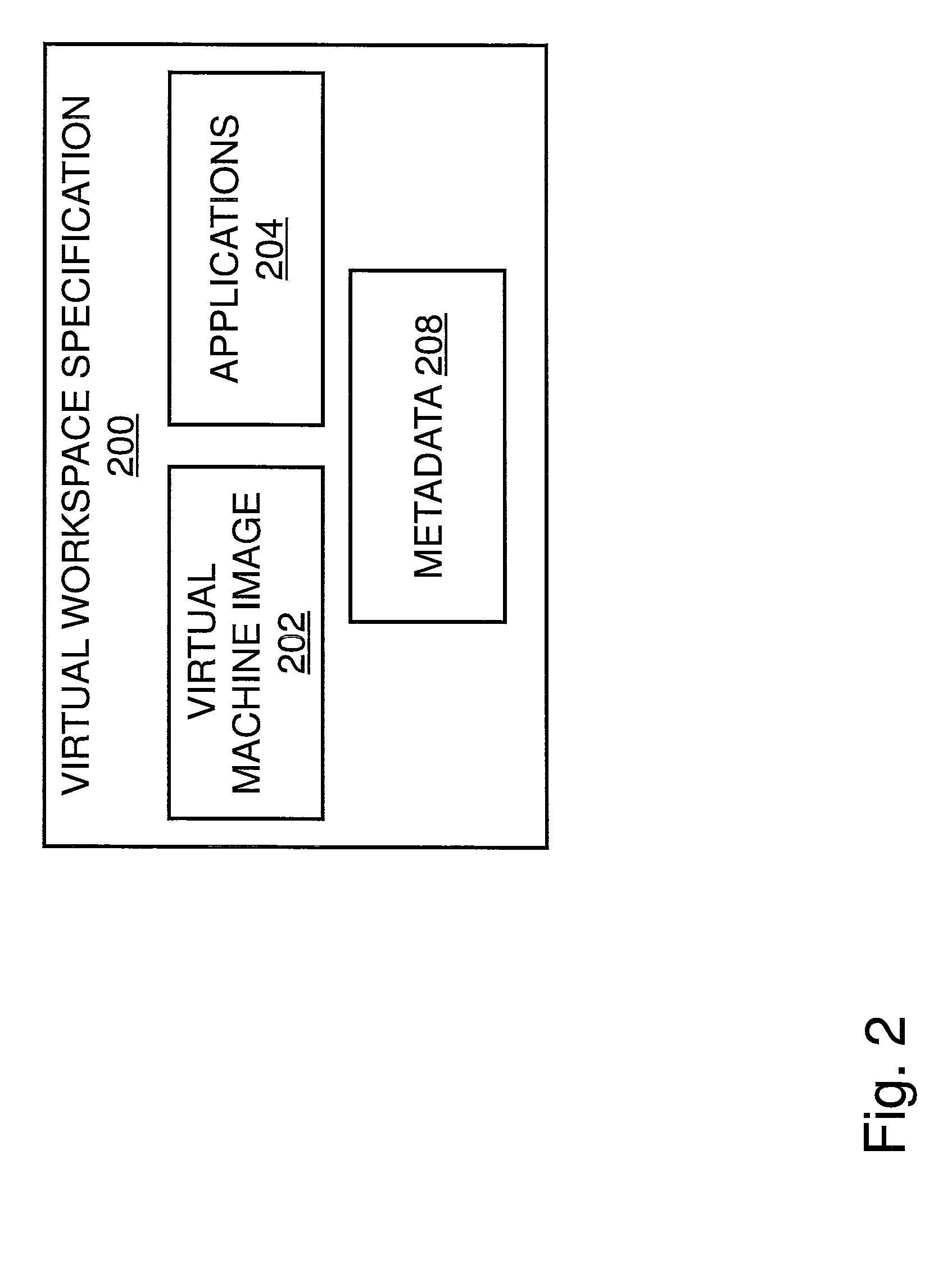
A virtual workspace can include an active instance of a layered virtual file system namespace. A layered virtual file system namespace is referred to by the virtual workspace and includes a collection of system data (e.g. layered virtual file system base layer), user data (e.g. layered virtual file system user layer), and virtualized applications (e.g. virtual app layer), metadata and policies (e.g. layered virtual file system layer scope). Because a virtual workspace can include software such as an operating system and one or more applications in addition to user data, a virtual workspace can be aligned with a namespace so that an operating system of the virtual workspace may be located at a “base layer”, one or more applications executing on the operating system may be located at an upper “virtual app” layer, and user data in a virtual workspace may be found at any layer at or above the user layer.
Owner:VIRTUAL COMP
Layered Virtual File System
InactiveUS20110040812A1Improves lifecycle managementEasy to manageProgram controlSpecial data processing applicationsVirtualizationVirtual file system
A virtual workspace can include an active instance of a layered virtual file system namespace. A layered virtual file system namespace is referred to by the virtual workspace and includes a collection of system data (e.g. layered virtual file system base layer), user data (e.g. layered virtual file system user layer), and virtualized applications (e.g. virtual app layer), metadata and policies (e.g. layered virtual file system layer scope). Because a virtual workspace can include software such as an operating system and one or more applications in addition to user data, a virtual workspace can be aligned with a namespace so that an operating system of the virtual workspace may be located at a “base layer”, one or more applications executing on the operating system may be located at an upper “virtual app” layer, and user data in a virtual workspace may be found at any layer at or above the user layer.
Owner:VIRTUAL COMP
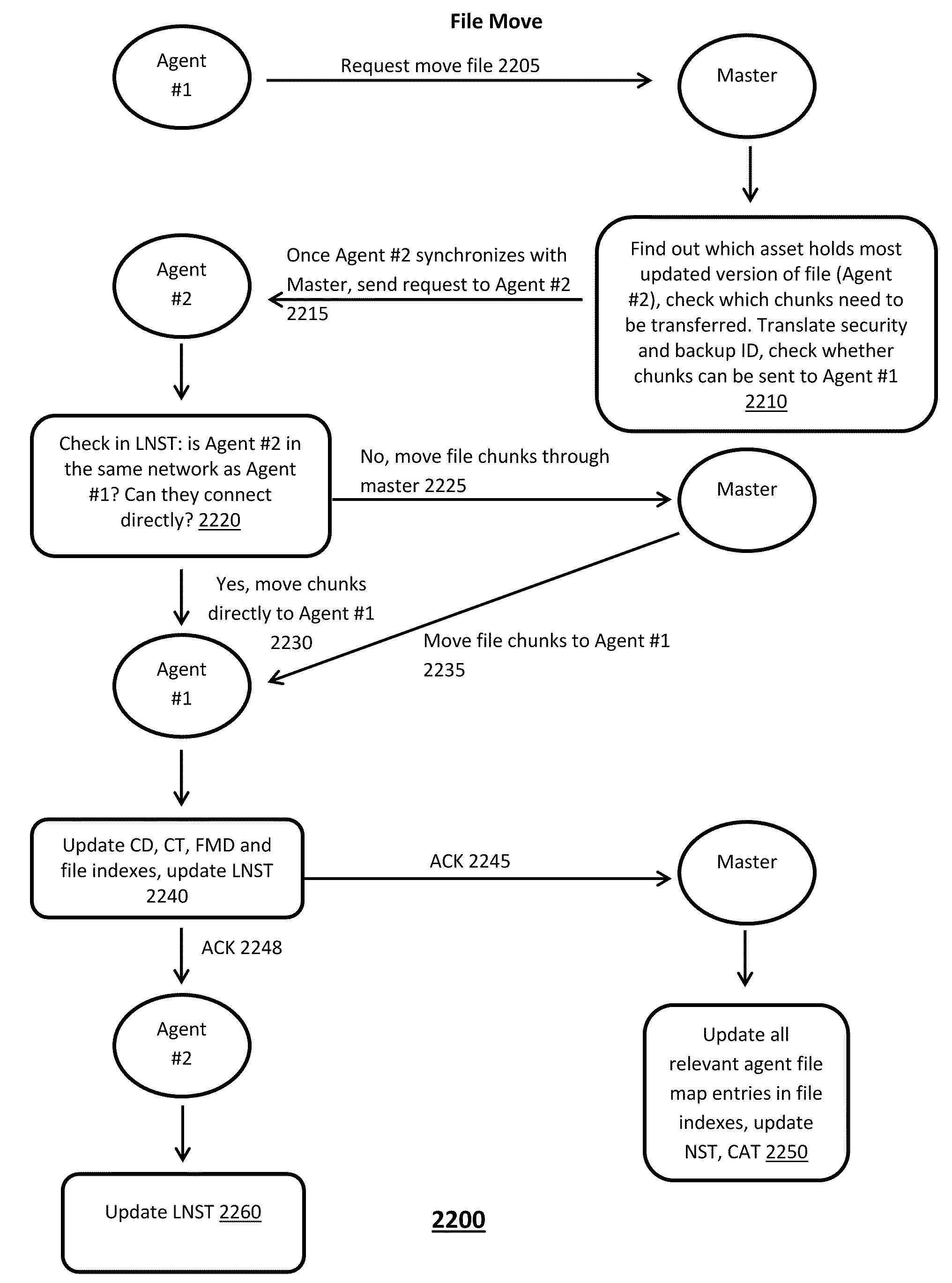
Cloud based operating and virtual file system
ActiveUS8527549B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemUser device
A method for managing a virtual distributed file system includes maintaining by a master device located in a cloud computing environment, a metadata data structure that stores metadata about locations of most updated versions of multiple file portions and security levels of the file portions, at least one file portion being stored at a user device coupled to the cloud computing environment, and maintaining by the master device, transaction of file portions to user entities, at least one user entity being hosted by the user device, based on at least metadata stored in the metadata data structure about the file portions.
Owner:BARRACUDA NETWORKS
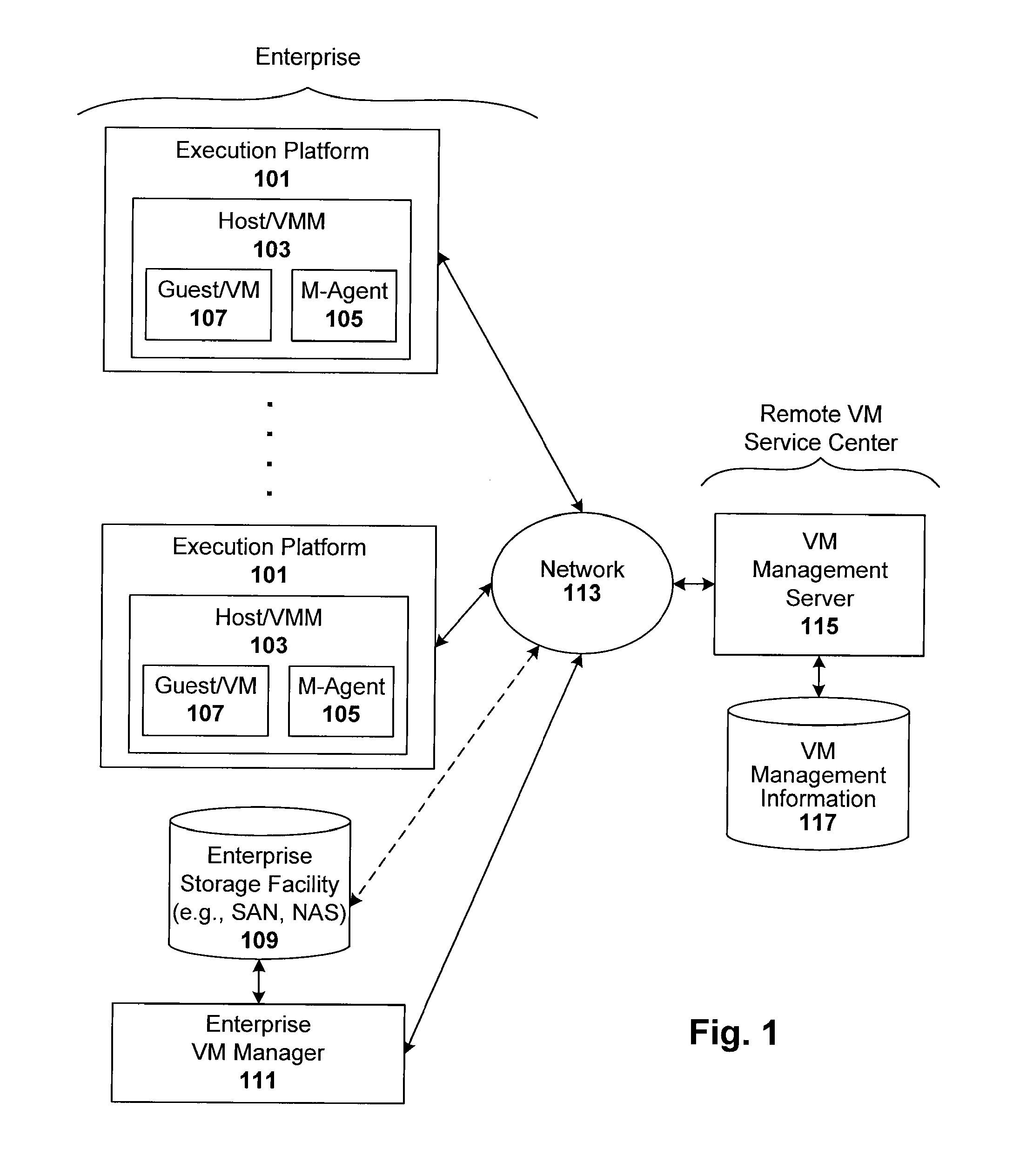
Registering and accessing virtual systems for use in a managed system
ActiveUS20080134175A1Platform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationConsistency testVirtual file system
Techniques are disclosed for controlling and managing virtual machines and other such virtual systems. VM execution approval is based on compliance with policies controlling various aspects of VM. The techniques can be employed to benefit all virtual environments, such as virtual machines, virtual appliances, and virtual applications. For ease of discussion herein, assume that a virtual machine (VM) represents each of these environments. In one particular embodiment, a systems management partition (SMP) is created inside the VM to provide a persistent and resilient storage for management information (e.g., logical and physical VM metadata). The SMP can also be used as a staging area for installing additional content or agentry on the VM when the VM is executed. Remote storage of management information can also be used. The VM management information can then be made available for pre-execution processing, including policy-based compliance testing.
Owner:RED HAT
System and Method For Secure Storage of Virtual Machines
ActiveUS20120110328A1Safe storageDigital data information retrievalInternal/peripheral component protectionVirtual file systemData center
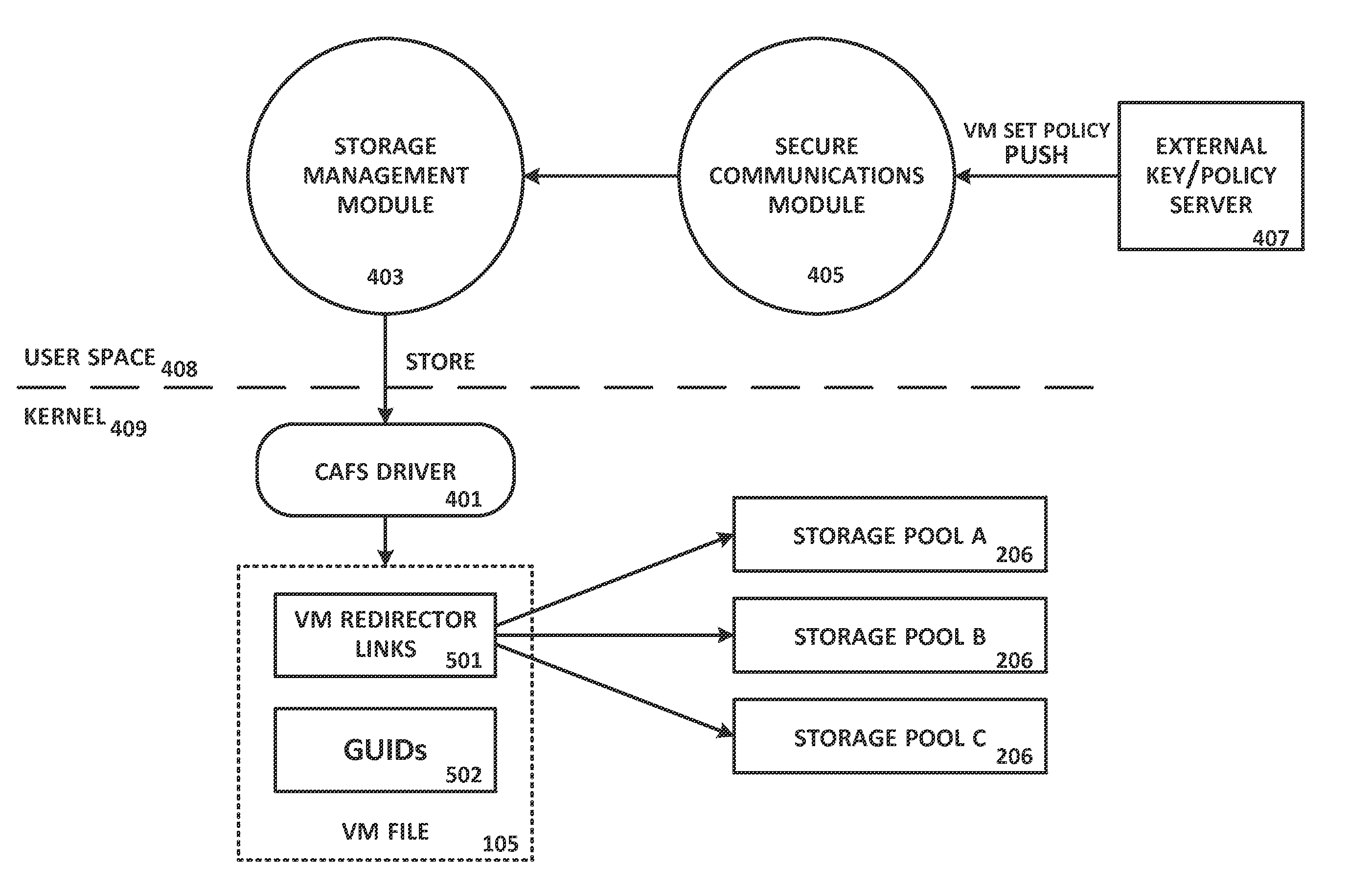
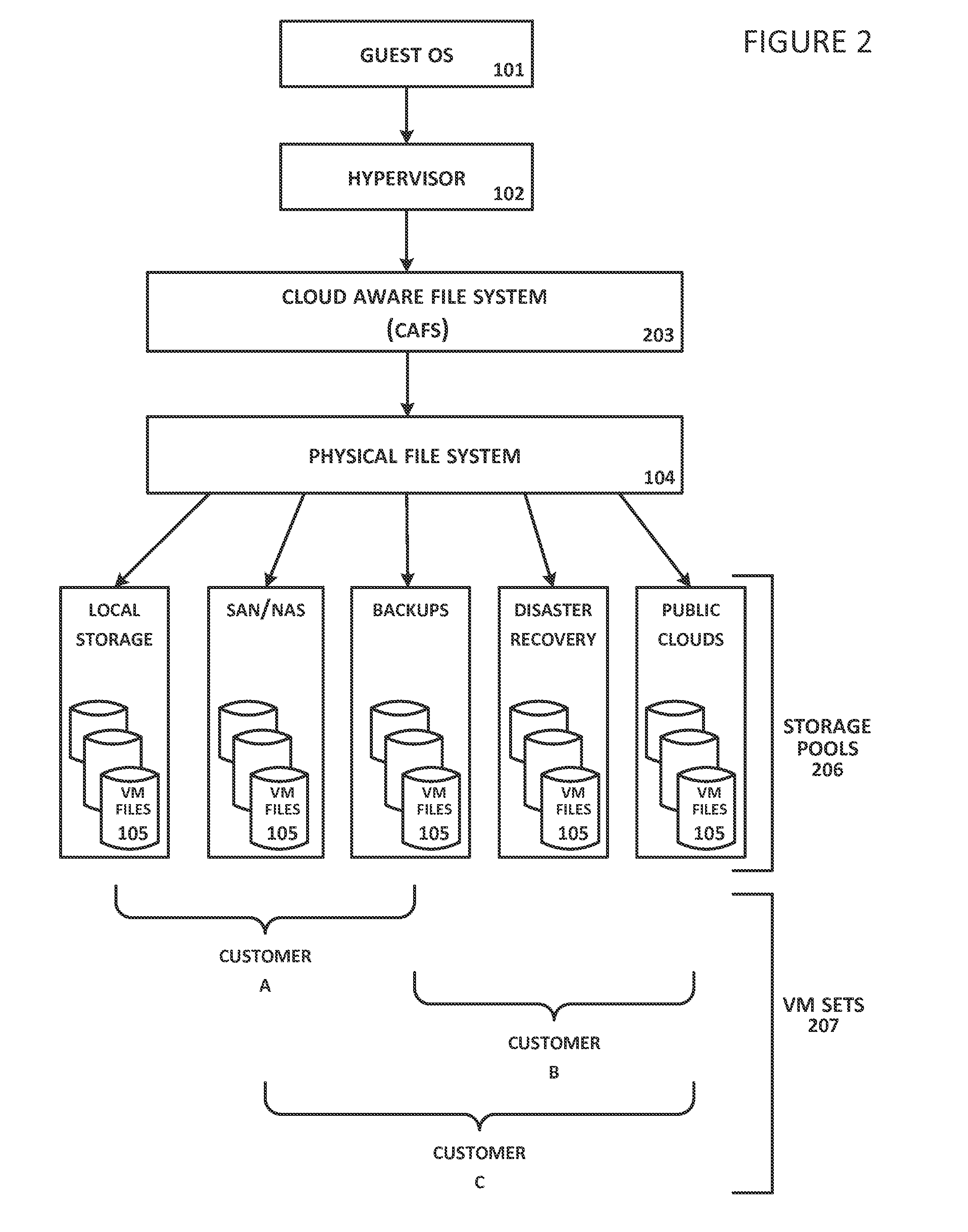
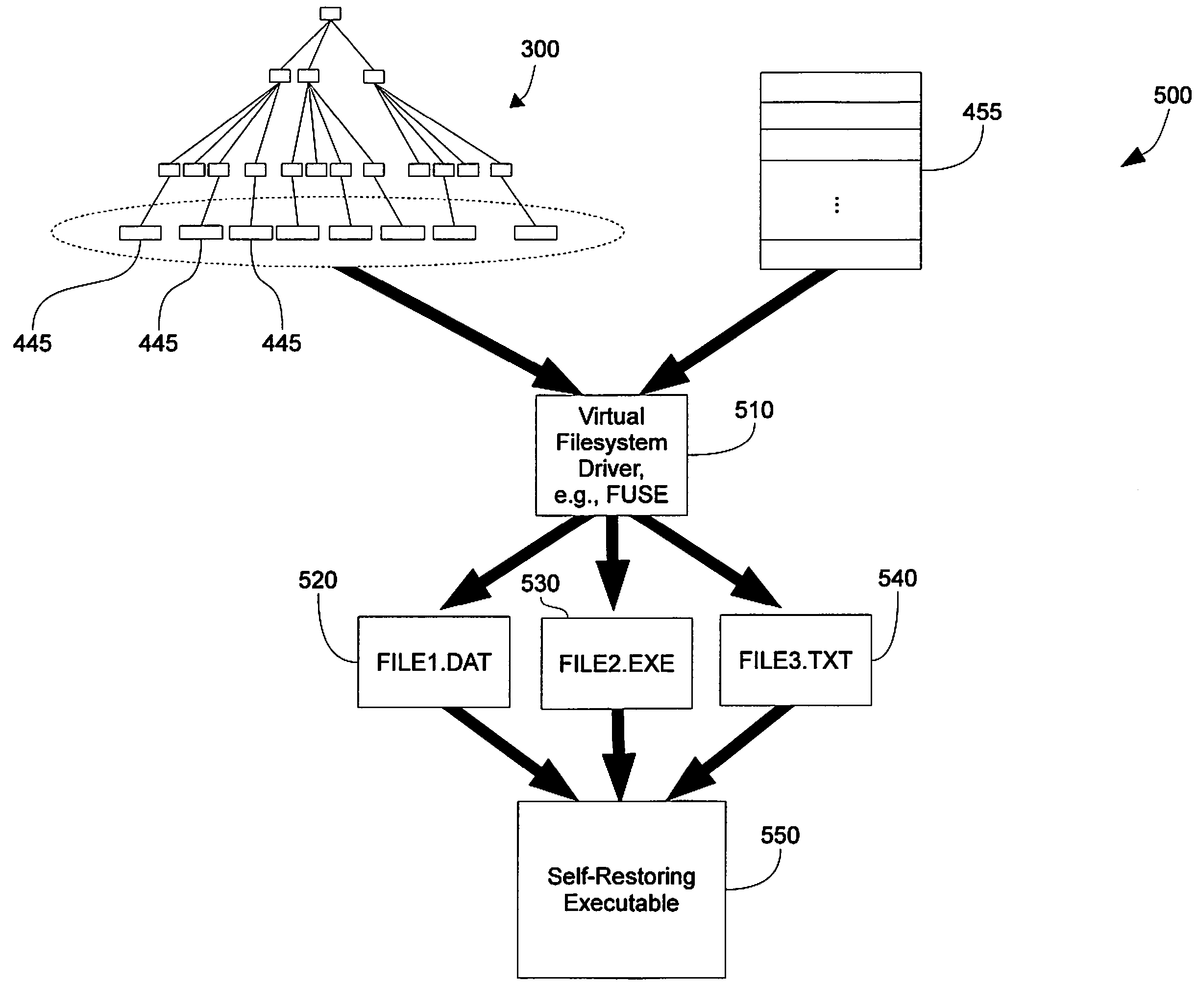
A virtual file system is described that is implemented in a virtualization platform as a stackable file system layer that intercepts file operations between a hypervisor and a physical file system. The virtual file system encrypts (at least in part) VM files to be stored, organizes the encrypted VM files into VM sets, and then maps and stores the encrypted VM sets into storage pools. Storage and access to files within the VM sets is controlled through the use of administrator-determined policies governing storage, security, access control, authentication, and auditing. The system and method described herein allow a seamless integration between a data center (e.g., a private cloud) and computing resources served across the internet and supported by cloud service providers (e.g., public clouds) while ensuring that the security needs of customers and cloud service providers are met.
Owner:HYTRUST
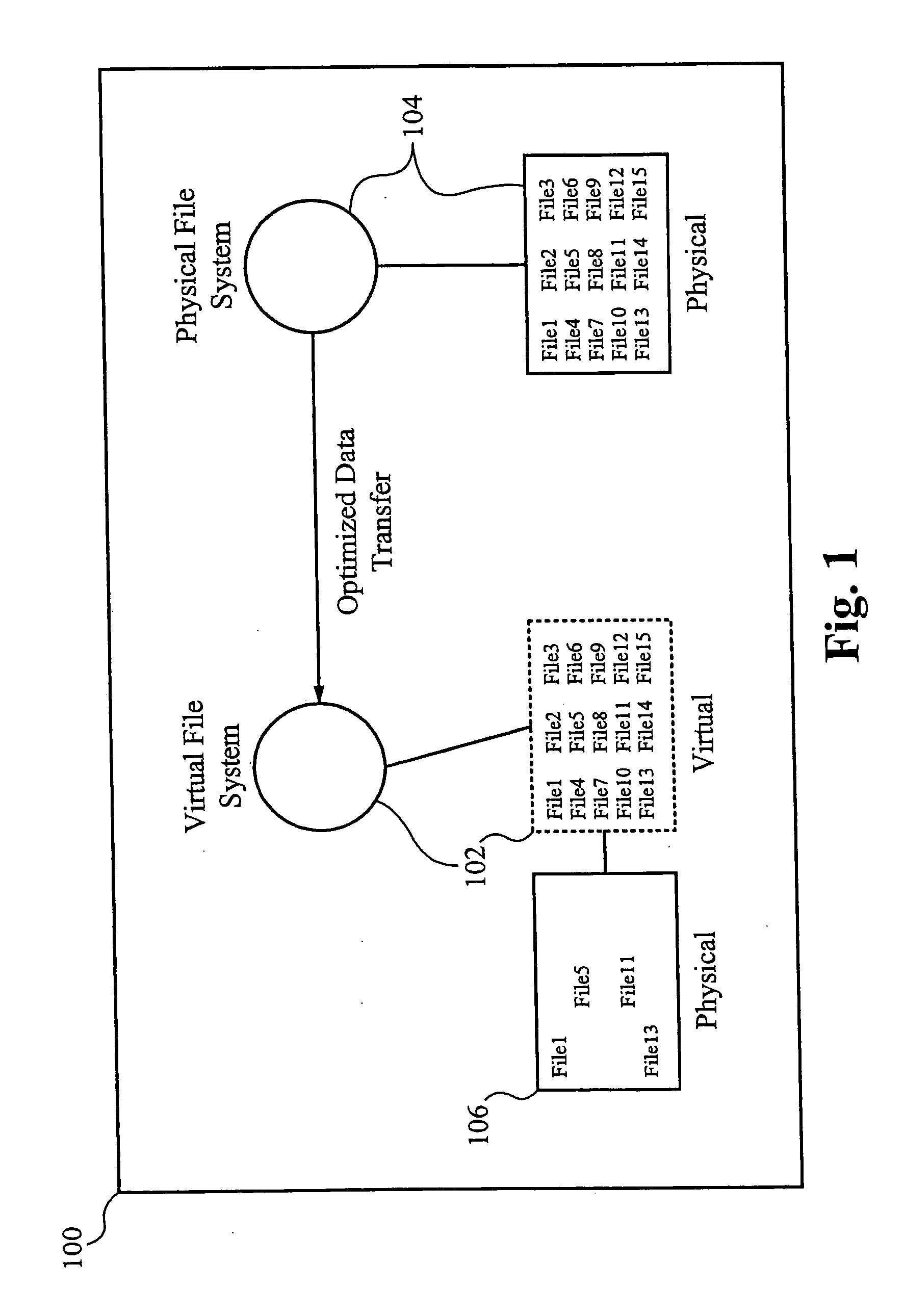
Virtual file system
InactiveUS7024427B2Function increaseDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersGlobal file systemData file
A virtual file system and method. The system architecture enables a plurality of underlying file systems running on various file servers to be “virtualized” into one or more “virtual volumes” that appear as a local file system to clients that access the virtual volumes. The system also enables the storage spaces of the underlying file systems to be aggregated into a single virtual storage space, which can be dynamically scaled by adding or removing file servers without taking any of the file systems offline and in a manner transparent to the clients. This functionality is enabled through a software “virtualization” filter on the client that intercepts file system requests and a virtual file system driver on each file server. The system also provides for load balancing file accesses by distributing files across the various file servers in the system, through migration of data files between servers.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Information processing system and method of acquiring backup in an information processing system
InactiveUS20110238625A1Backup fileCreate efficientlyError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsInformation processingVirtual file system
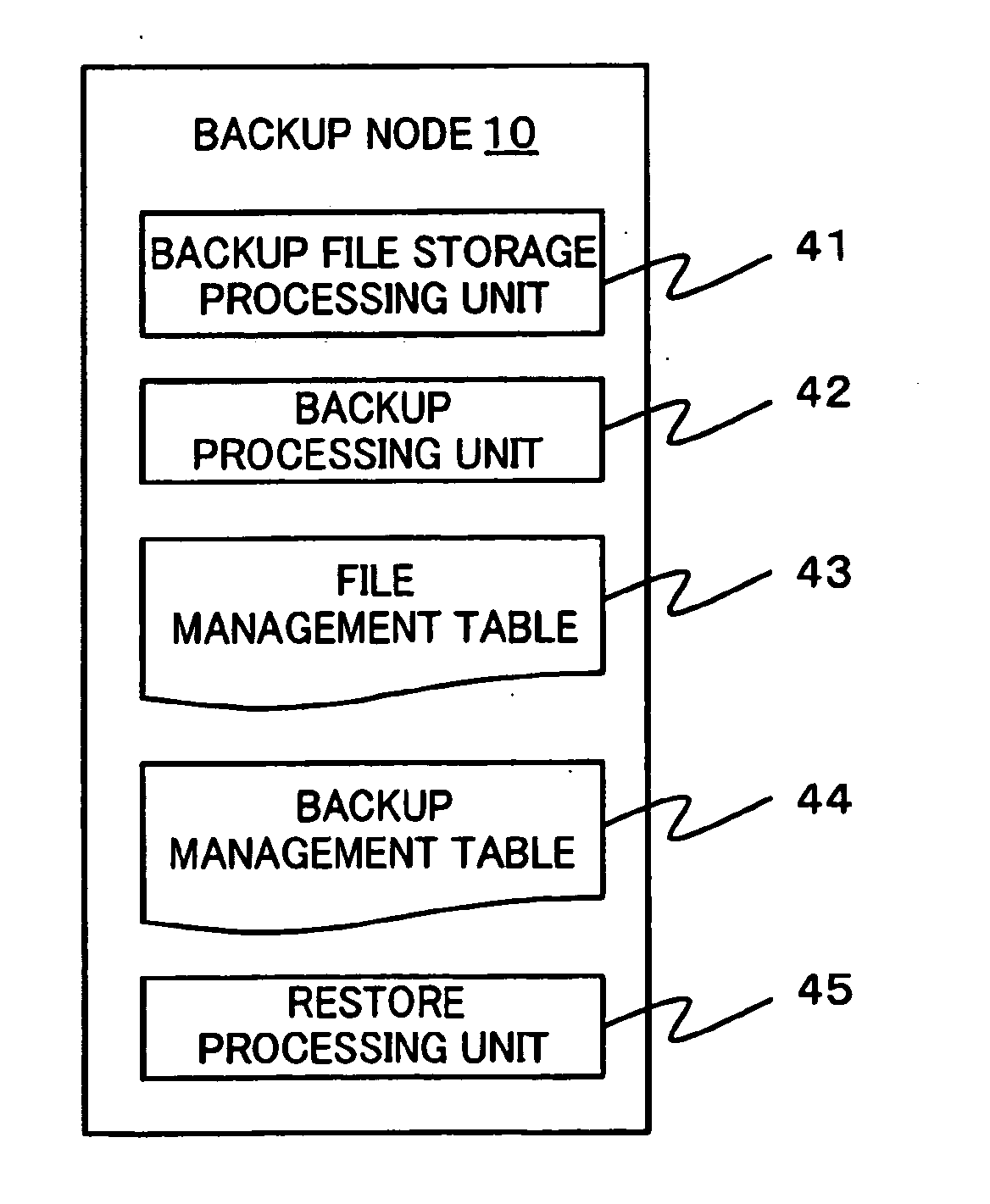
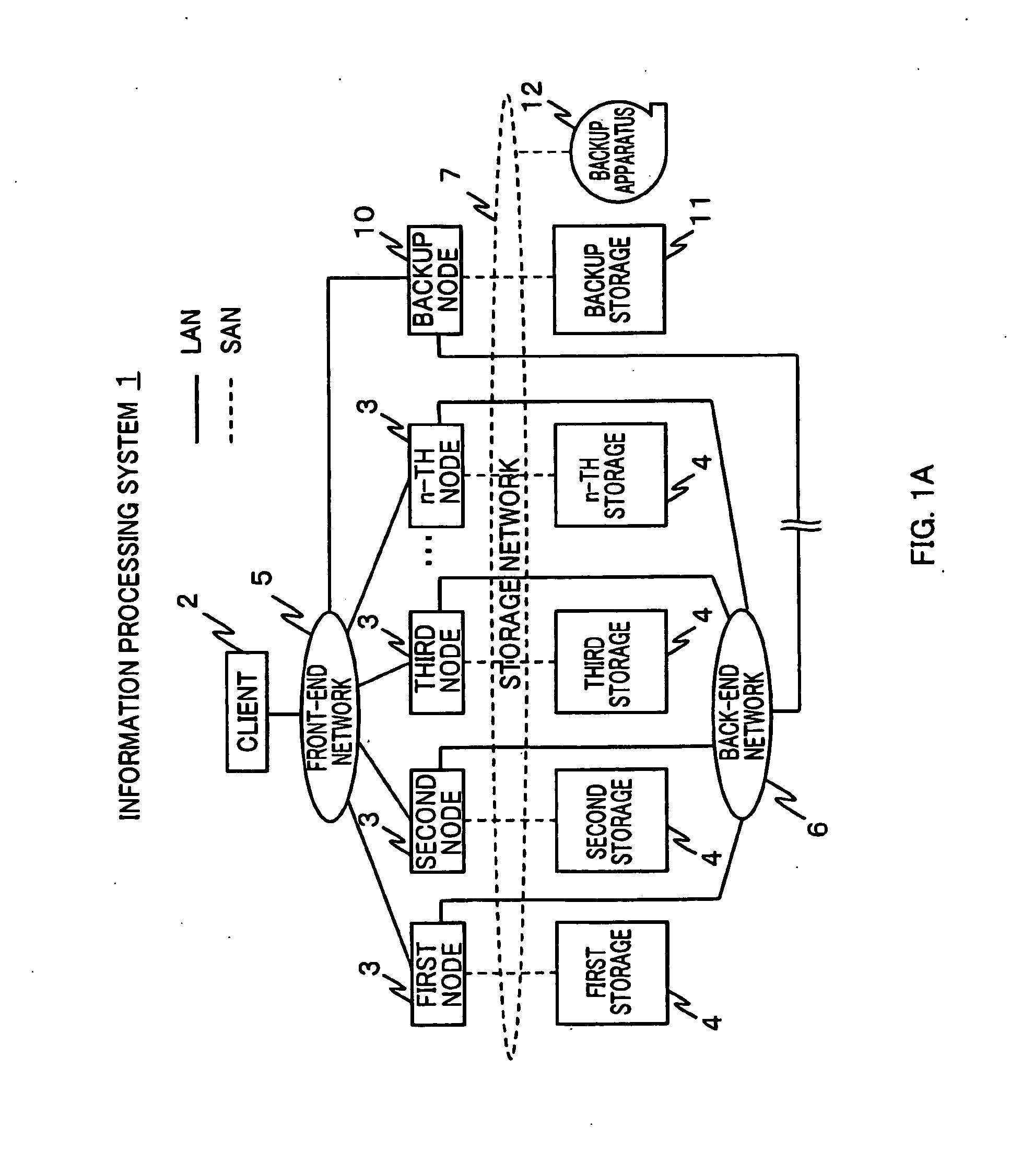
Provided is an information processing system including a plurality of nodes 3 and a plurality of storages 4 coupled subordinately to each of the nodes 3, each of the nodes 3 functioning as a virtual file system that provides a client 2 with storage regions of each of the storages 4 as a single namespace. This information processing system is further provided with a backup node 10 and a backup storage 11 coupled subordinately to the backup node 10. The backup node 10 synchronizes and holds location information (file management table 33) held by each of the nodes 3. Then, the backup node 10 creates a backup file, and stores the backup file in the backup storage 11 by accessing a location identified by the location information (file management table 43) synchronized and held by the backup node 10 itself to acquire a file.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Virtual file system
InactiveUS20060123062A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalVirtualizationVirtual file system
A virtual file system and method. The system architecture enables a plurality of underlying file systems running on various file servers to be “virtualized” into one or more “virtual volumes” that appear as a local file system to clients that access the virtual volumes. The system also enables the storage spaces of the underlying file systems to be aggregated into a single virtual storage space, which can be dynamically scaled by adding or removing file servers without taking any of the file systems offline and in a manner transparent to the clients. This functionality is enabled through a software “virtualization” filter on the client that intercepts file system requests and a virtual file system driver on each file server. The system also provides for load balancing file accesses by distributing files across the various file servers in the system, through migration of data files between servers.
Owner:EMC CORP
Automatic optimization for virtual systems
ActiveUS20080184225A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionConsistency testVirtual file system
Techniques are disclosed for controlling and managing virtual machines and other such virtual systems. VM execution approval is based on compliance with policies controlling various aspects of VM. The techniques can be employed to benefit all virtual environments, such as virtual machines, virtual appliances, and virtual applications. For ease of discussion herein, assume that a virtual machine (VM) represents each of these environments. In one particular embodiment, a systems management partition (SMP) is created inside the VM to provide a persistent and resilient storage for management information (e.g., logical and physical VM metadata). The SMP can also be used as a staging area for installing additional content or agentry on the VM when the VM is executed. Remote storage of management information can also be used. The VM management information can then be made available for pre-execution processing, including policy-based compliance testing.
Owner:RED HAT
Installing Software Applications in a Layered Virtual Workspace
InactiveUS20110061046A1Easy to manageImprove usabilityProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsVirtualizationVirtual file system
A virtual workspace can include an active instance of a layered virtual file system namespace. A layered virtual file system namespace is referred to by the virtual workspace and includes a collection of system data (e.g. layered virtual file system base layer), user data (e.g. layered virtual file system user layer), and virtualized applications (e.g. virtual app layer), metadata and policies (e.g. layered virtual file system layer scope). Because a virtual workspace can include software such as an operating system and one or more applications in addition to user data, a virtual workspace can be aligned with a namespace so that an operating system of the virtual workspace may be located at a “base layer”, one or more applications executing on the operating system may be located at an upper “virtual app” layer, and user data in a virtual workspace may be found at any layer at or above the user layer.
Owner:VIRTUAL COMP
Compliance-based adaptations in managed virtual systems
ActiveUS20080134177A1Removing malwareDisabling malwareMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirtual file systemSystems management
Techniques are disclosed for controlling and managing virtual machines and other such virtual systems. VM execution approval is based on compliance with policies controlling various aspects of VM. The techniques can be employed to benefit all virtual environments, such as virtual machines, virtual appliances, and virtual applications. For ease of discussion herein, assume that a virtual machine (VM) represents each of these environments. In one particular embodiment, a systems management partition (SMP) is created inside the VM to provide a persistent and resilient storage for management information (e.g., logical and physical VM metadata). The SMP can also be used as a staging area for installing additional content or agentry on the VM when the VM is executed. Remote storage of management information can also be used. The VM management information can then be made available for pre-execution processing, including policy-based compliance testing.
Owner:RED HAT
System and method for partitioning a file system for enhanced availability and scalability
ActiveUS7653699B1Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual file systemFile system
A method and system are provided for partitioning a file system. The system may include one or more server computer systems and a plurality of physical file systems. The physical file systems may be hosted by the one or more server computer systems. The physical file systems may be accessible to clients through a virtual file system having a single namespace. The virtual file system may include metadata which are partitioned across the plurality of physical file systems. The server computer systems may be configured to independently perform file system consistency checks on each of the physical file systems, in order to independently validate each partition of the metadata.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
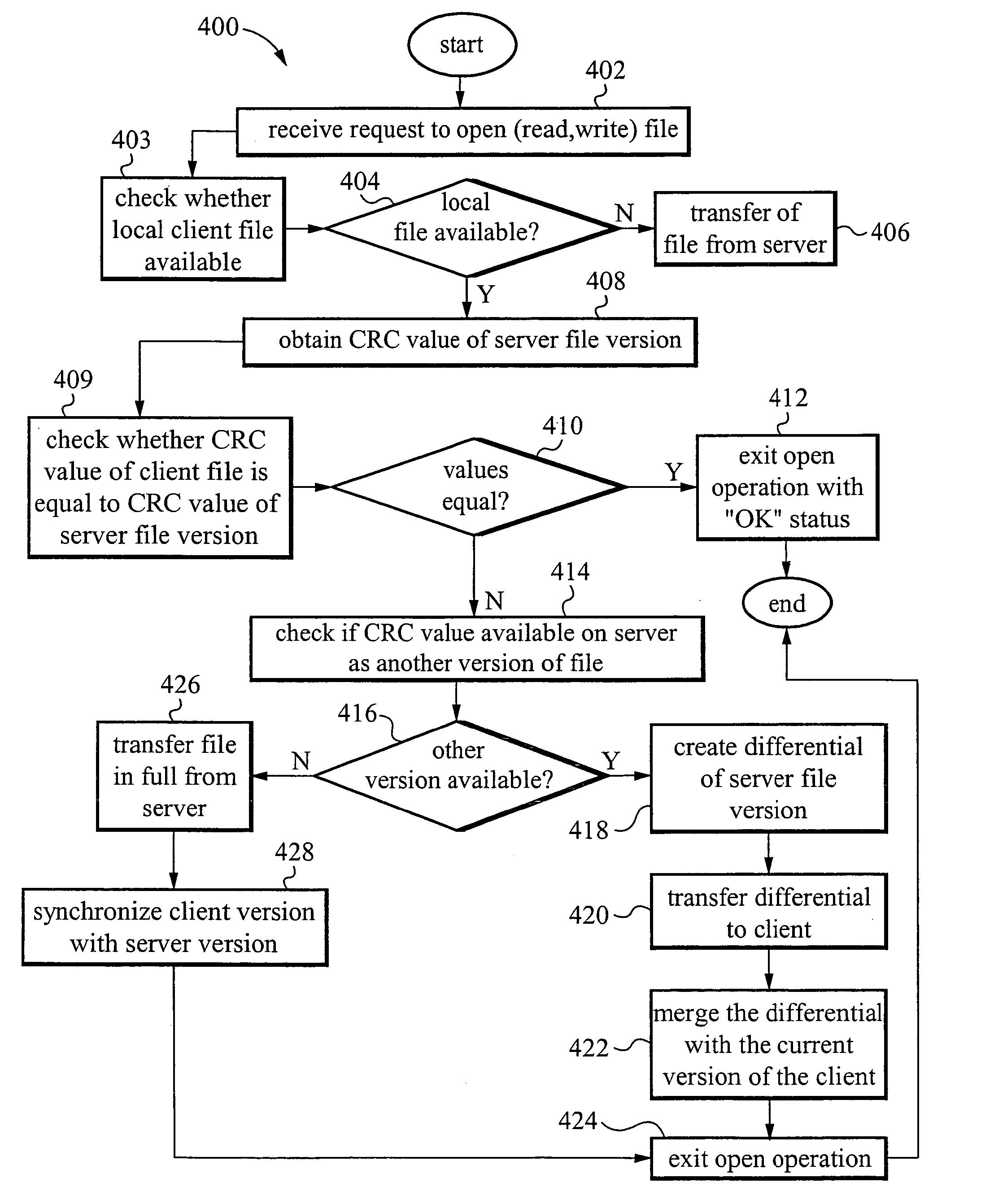
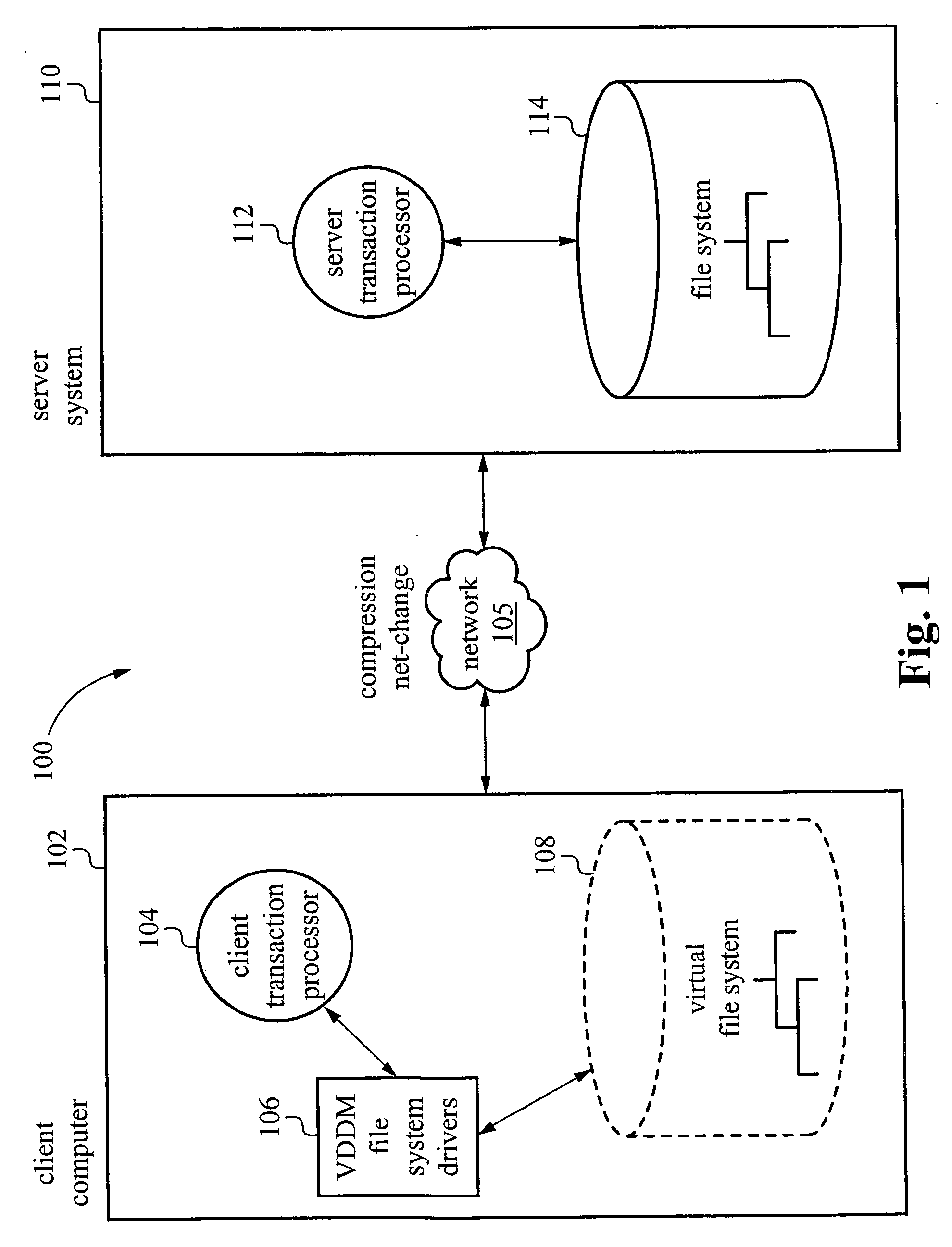
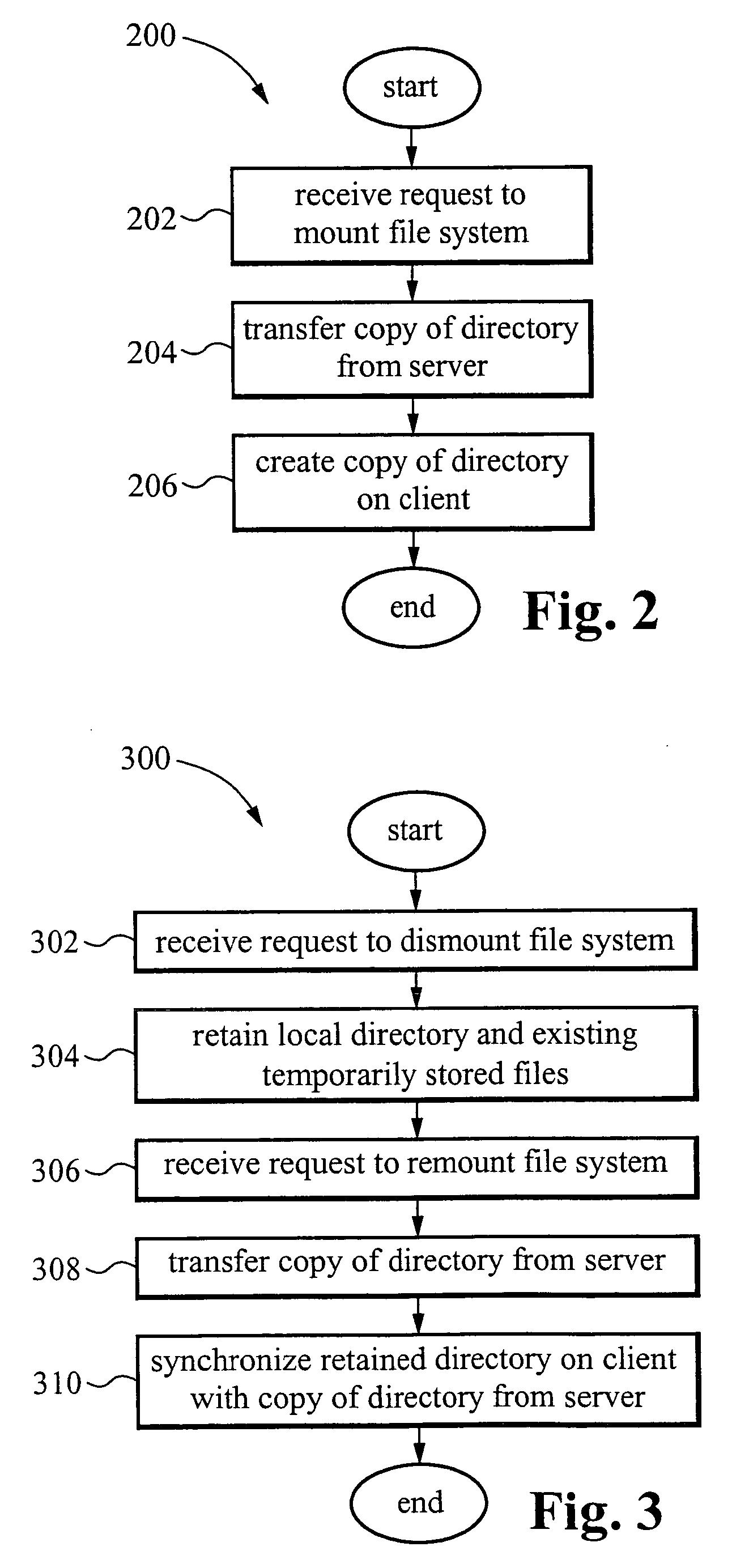
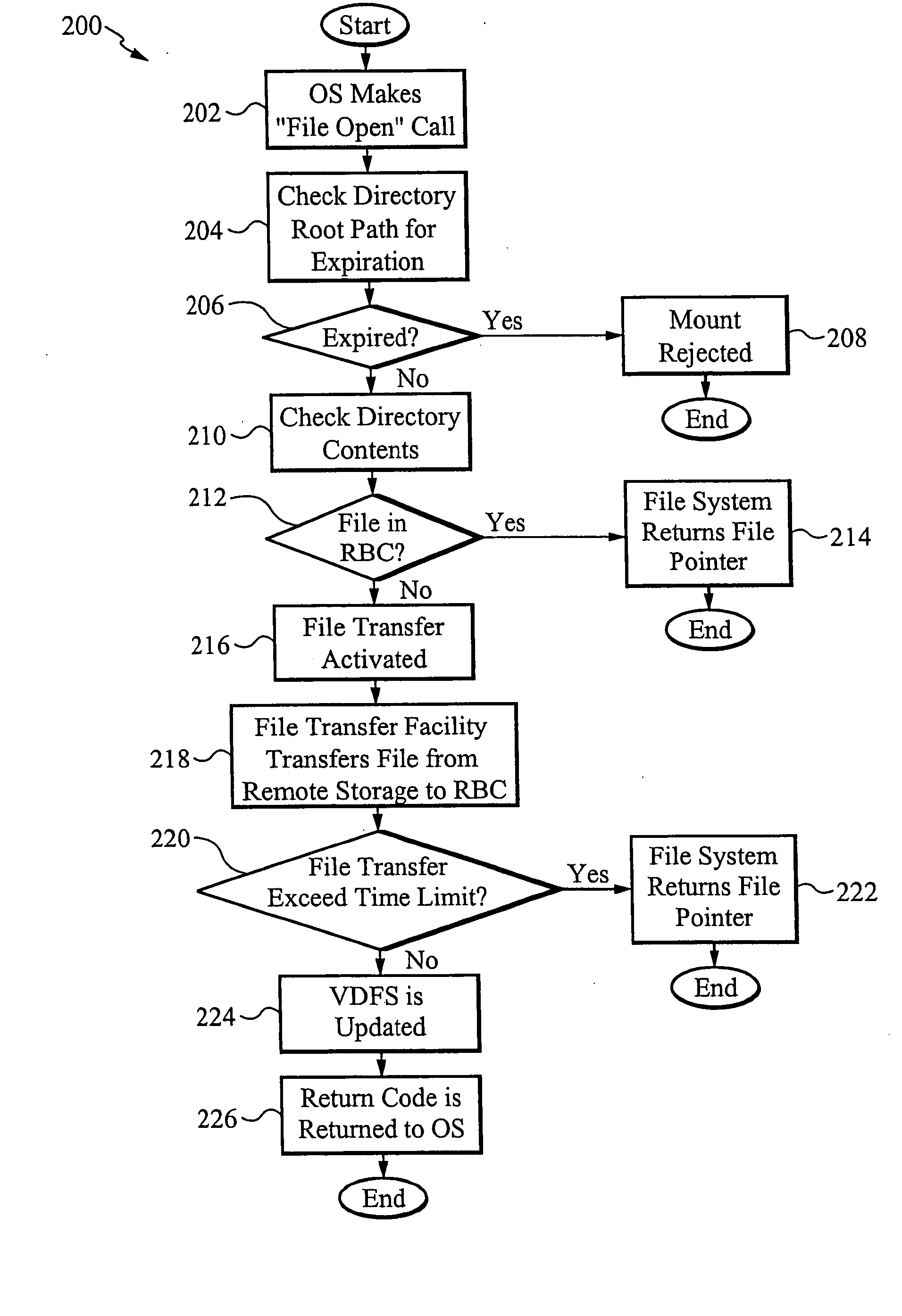
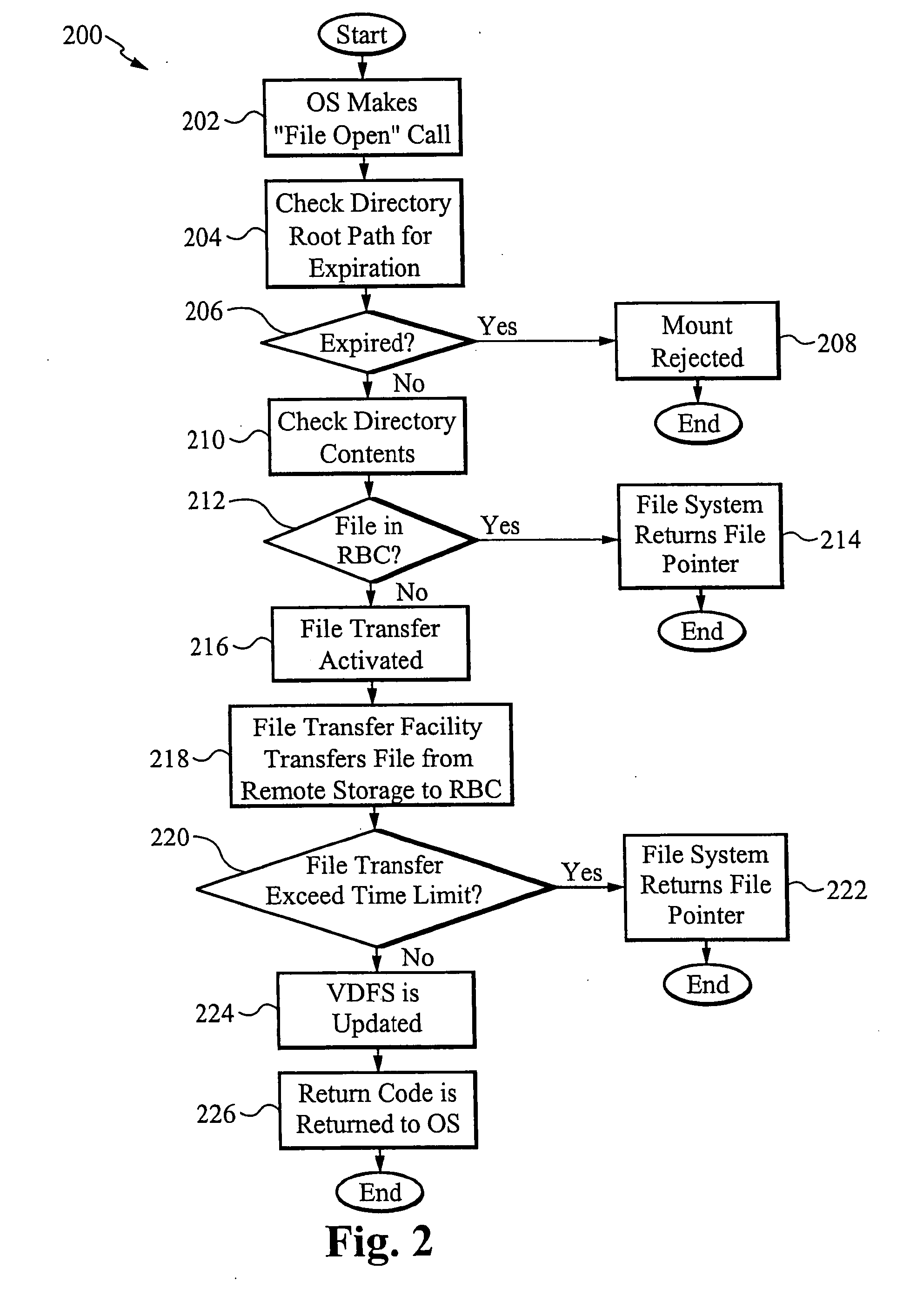
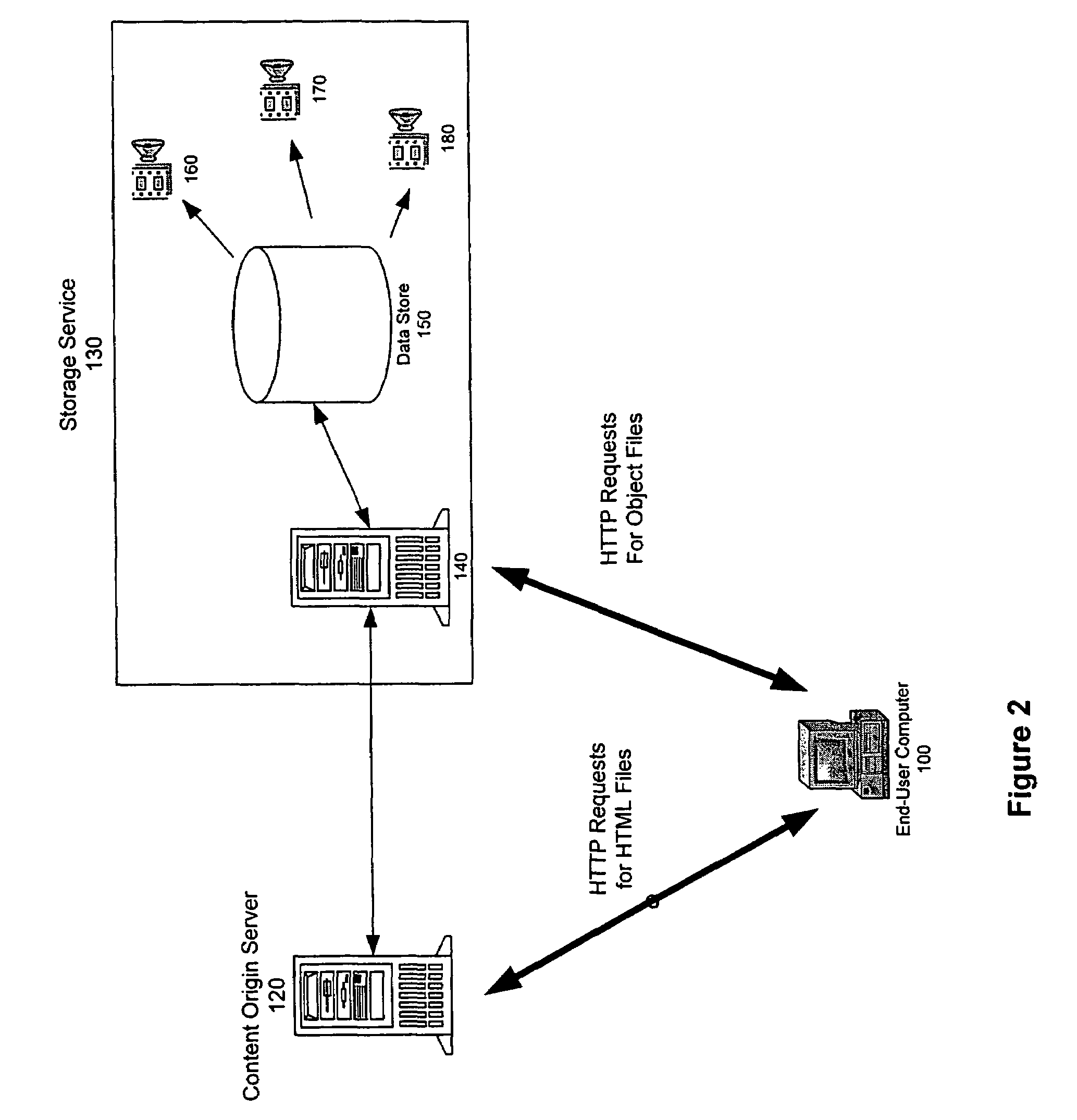
Transaction based virtual file system optimized for high-latency network connections
InactiveUS20060047716A1Problem can be addressedDigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual file systemFile system
A method and system are provided for a virtual distributed data manager. In one example of the method, the virtual data manager involves receiving a request to mount a file system onto the client computer, wherein the file system is stored on the server system and contains the one or more data files; transferring a copy of a directory structure of the file system stored on the server system to the client computer; and creating on the client computer a virtual file system including the copy of the directory structure. The method is preferably transaction based and provides high performance on high latency network connections.
Owner:GOODRICH JOHN B +1
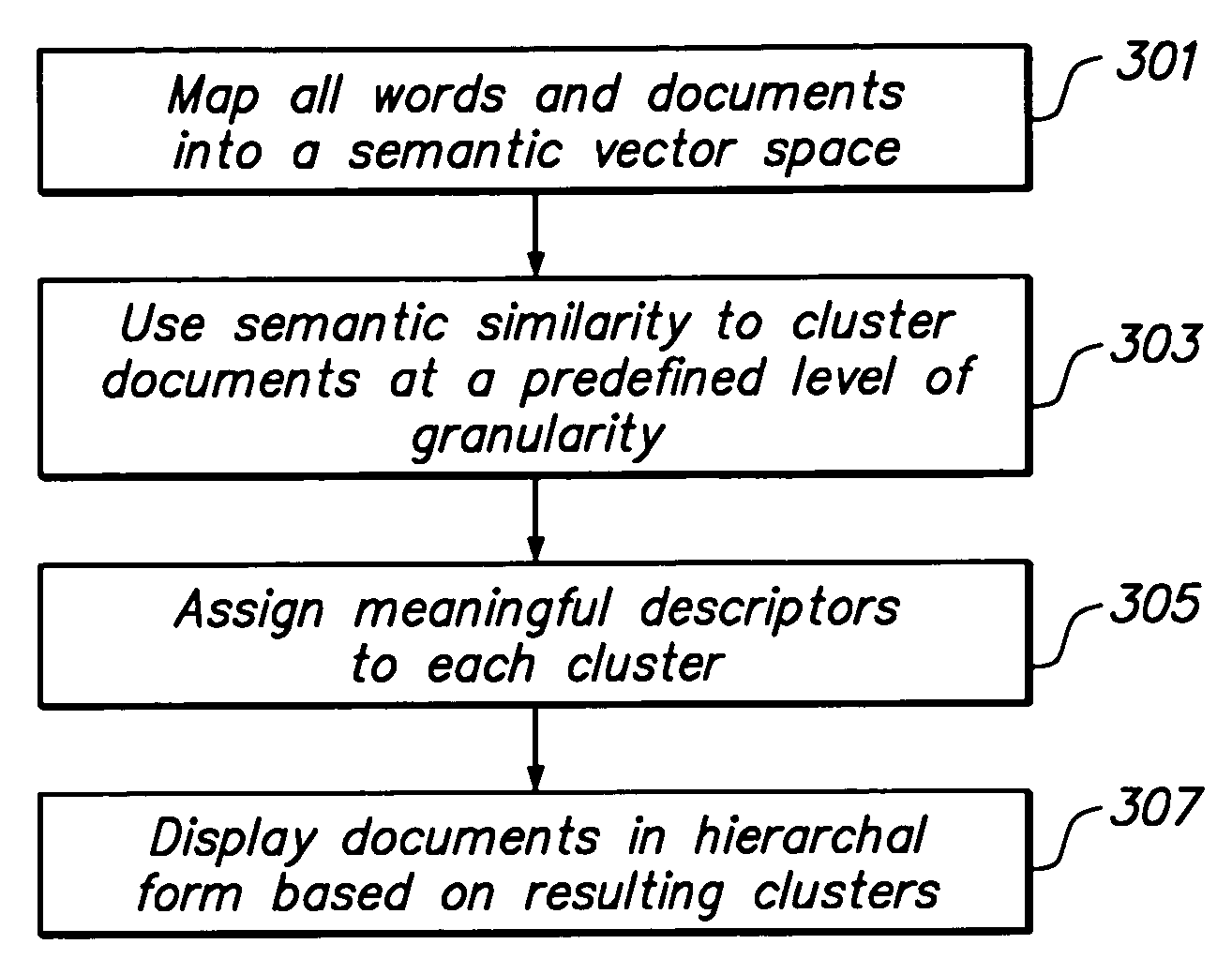
Method and apparatus for automatic file clustering into a data-driven, user-specific taxonomy
InactiveUS20050044487A1Digital computer detailsUnstructured textual data retrievalSemantic vectorCluster algorithm
An automatic file clustering algorithm enables documents within a file system to be displayed in a semantic view. The file clustering algorithm maps all words and documents into an appropriate semantic vector space, clusters the documents at a predetermined level of granularity, and assigns a meaningful descriptor to each resulting cluster. The documents are displayed to the user in a hierarchy in accordance with the resulting clusters. This results in a virtual file system with a semantic organization, that allows the user to navigate by content.
Owner:APPLE INC
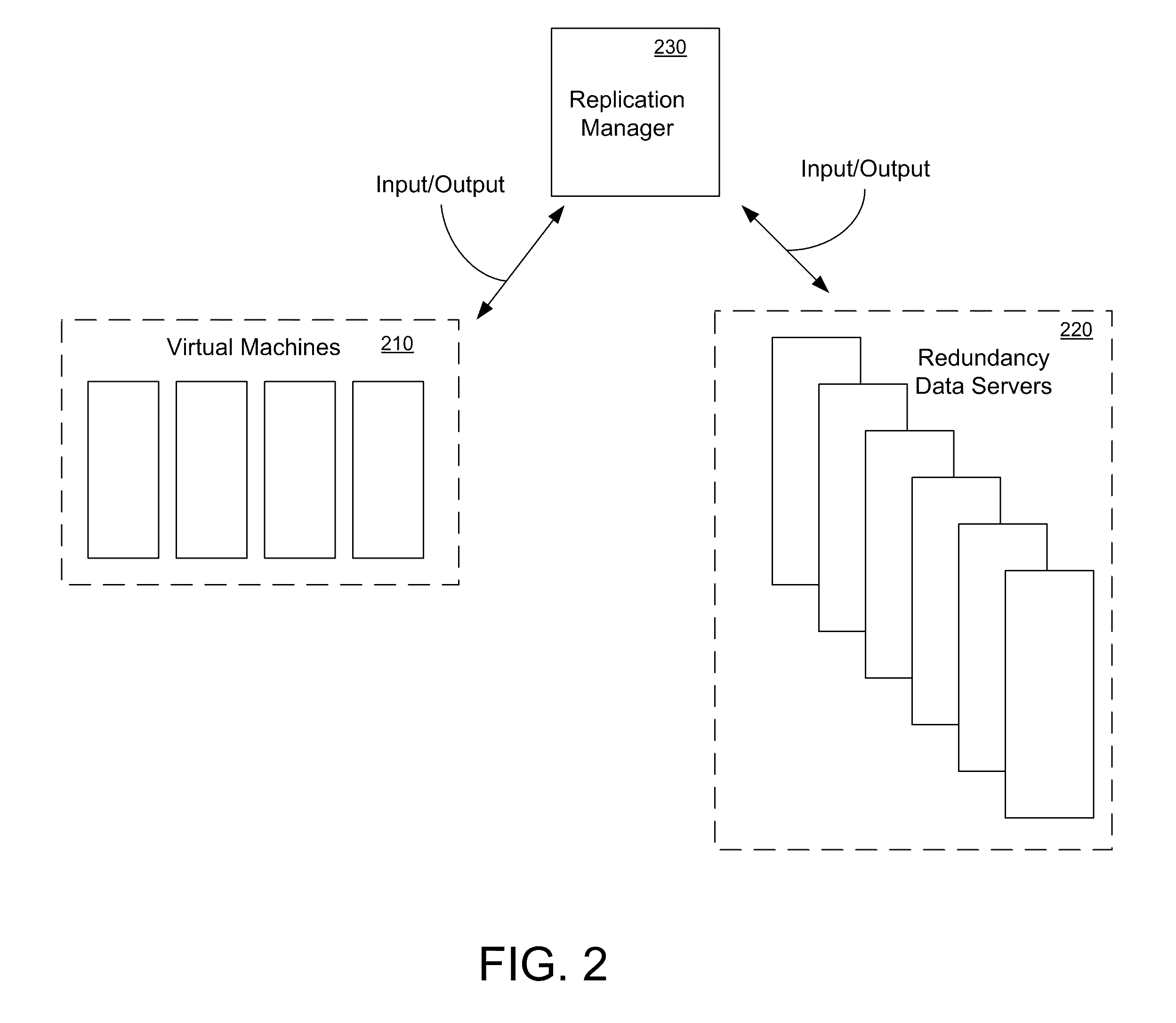
Virtual machine aware replication method and system
ActiveUS20120016840A1Efficient and highly available and highly scalable processEfficient, highly available, and highly scalableDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemReplication method
A method for replicating a virtual file system of a virtual machine. The method includes accessing a host file system usage map of a host machine that indicates active blocks out of a plurality of blocks of the host file system, and accessing a virtual file system usage map of a virtual machine that indicates active blocks out of a plurality of blocks of the virtual file system. A merged usage map is generated from information of the host file system usage map and the virtual file system usage map that identifies active blocks of the host file system associated with the virtual file system. The virtual file system is then replicated at a replication destination in accordance with the merged usage map.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
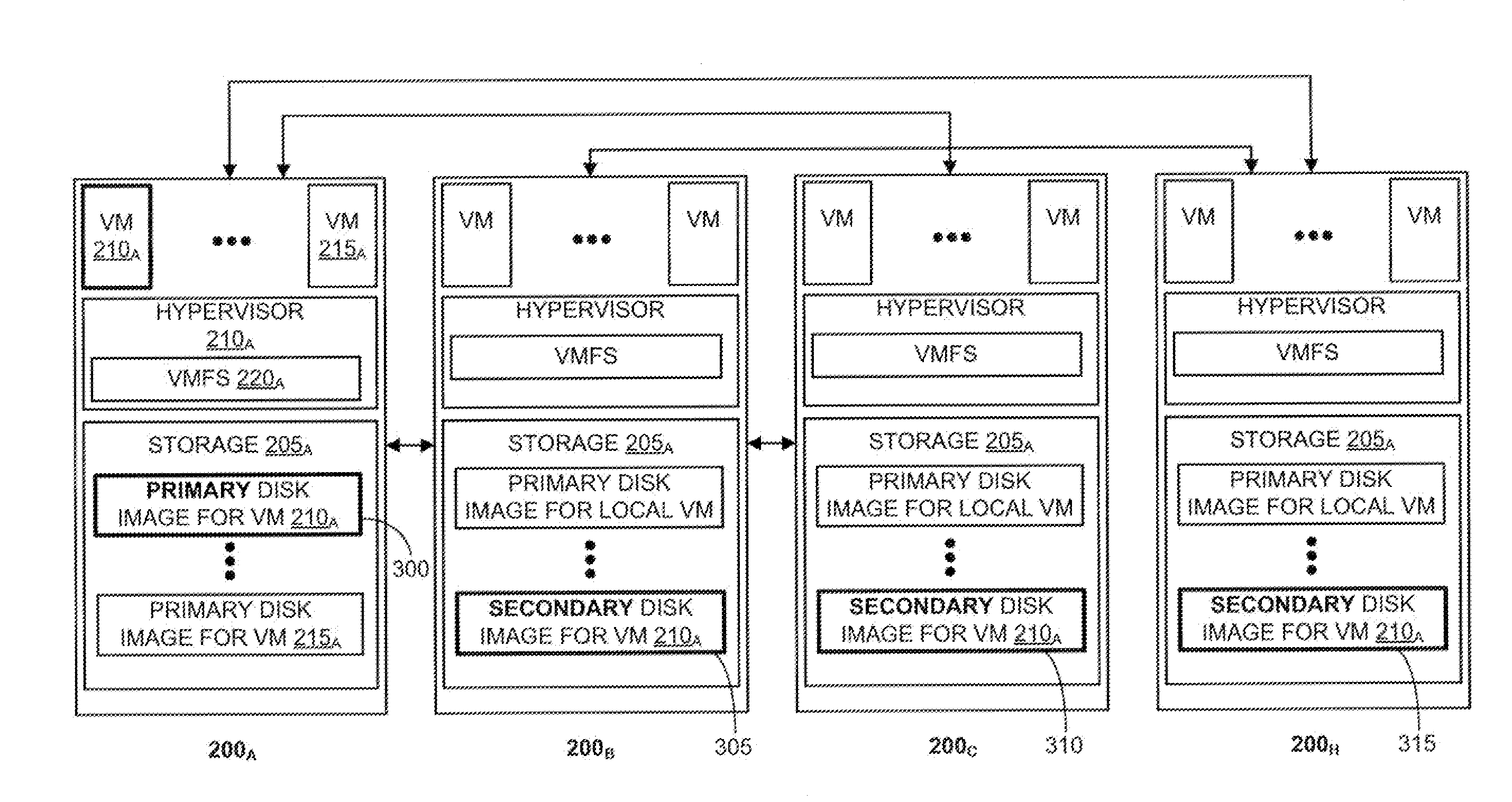
System and Method for Replicating Disk Images in a Cloud Computing Based Virtual Machine File System
ActiveUS20110022574A1Eliminate pointLess reliableKey distribution for secure communicationDatabase updatingFailoverVirtual file system
A replicated decentralized storage system comprises a plurality of servers that locally store disk images for locally running virtual machines as well as disk images, for failover purposes, for remotely running virtual machines. To ensure that disk images stored for failover purposes are properly replicated upon an update of the disk image on the server running the virtual machine, a hash of a unique value known only to the server running the virtual machine is used to verify the origin of update operations that have been transmitted by the server to the other servers storing replications of the disk image for failover purposes. If verified, the update operations are added to such failover disk images.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Virtual file system
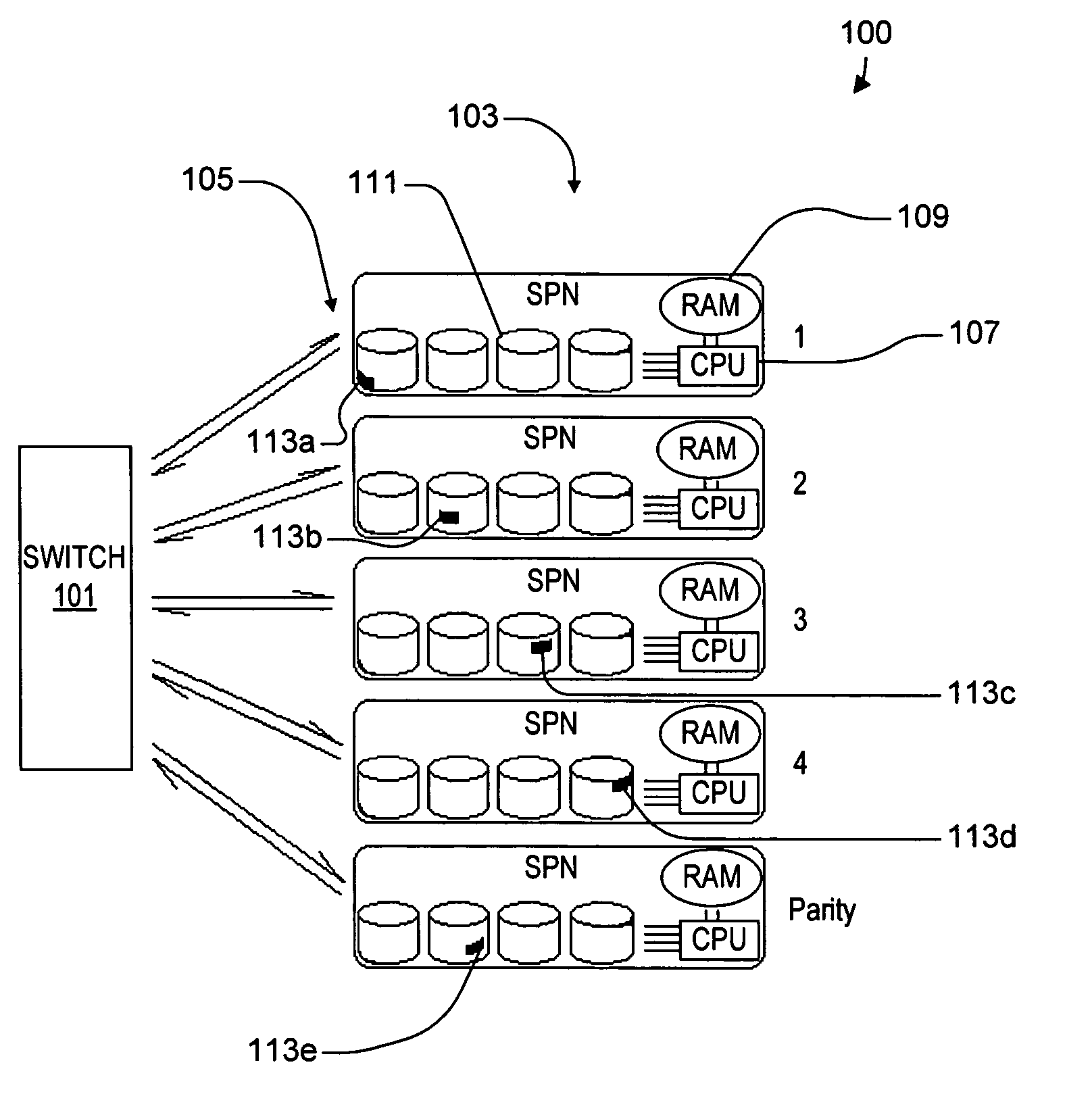
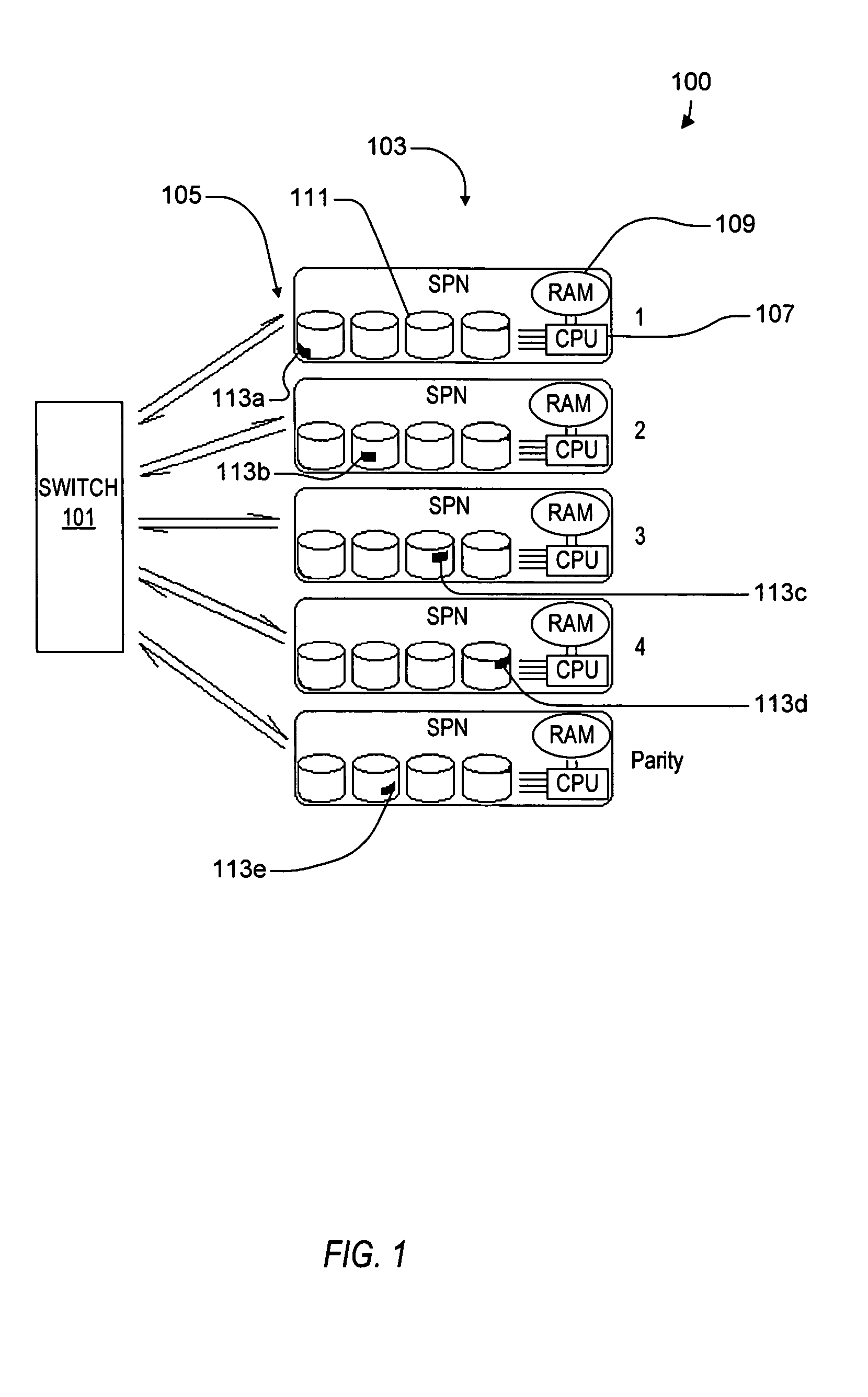
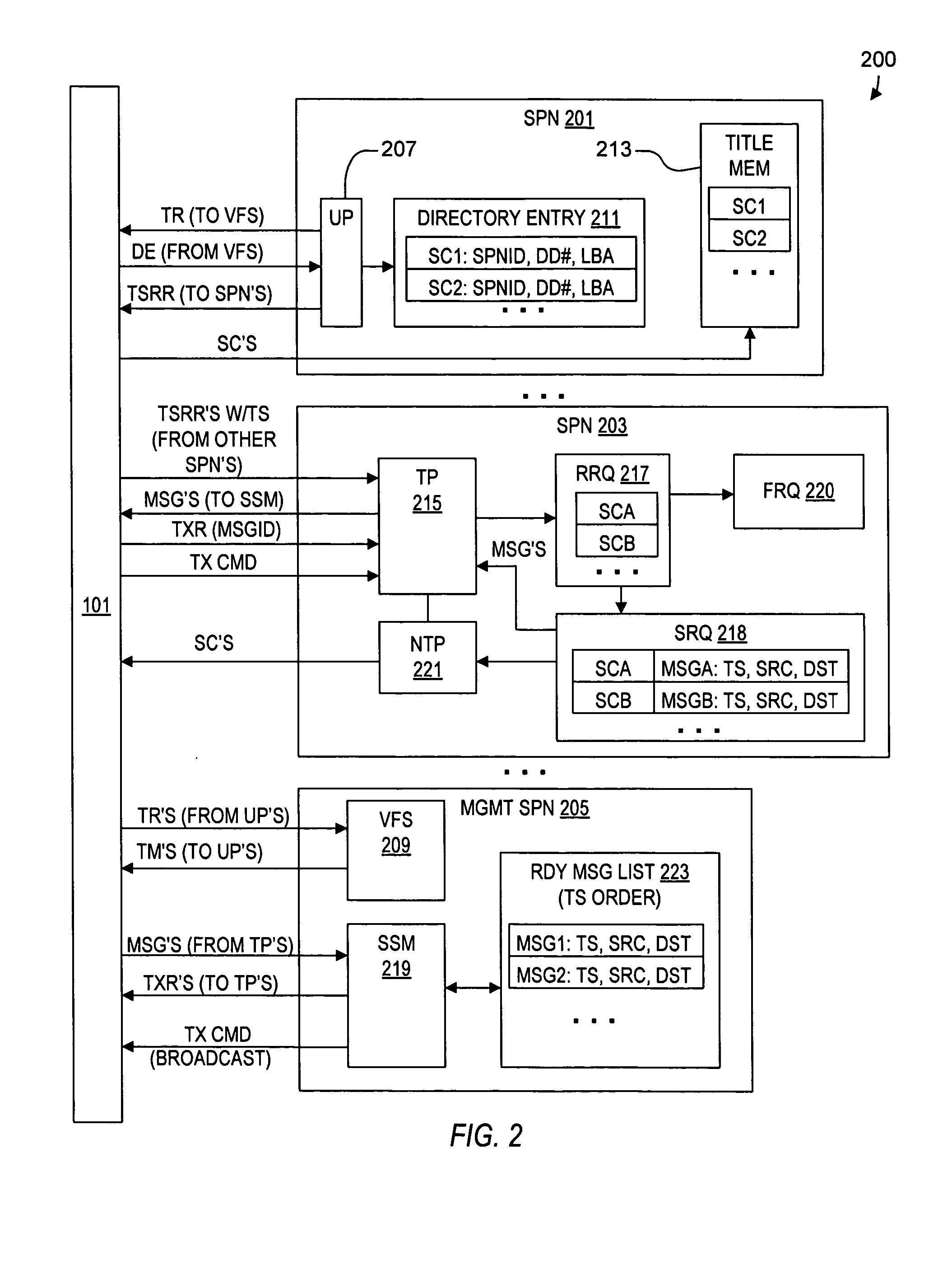
ActiveUS20050114350A1Input/output to record carriersRecording by optical meansVirtual file systemProcessor node
A virtual file system including multiple storage processor nodes including a management node, a backbone switch, a disk drive array, and a virtual file manager executing on the management node. The backbone switch enables communication between the storage processor nodes. The disk drive array is coupled to and distributed across the storage processor nodes and stores multiple titles. Each title is divided into data subchunks which are distributed across the disk drive array in which each subchunk is stored on a disk drive of the disk drive array. The virtual file manager manages storage and access of each subchunk, and manages multiple directory entries including a directory entry for each title. Each directory entry is a list of subchunk location entries in which each subchunk location entry includes a storage processor node identifier, a disk drive identifier, and a logical address for locating and accessing each subchunk of each title.
Owner:INTERACTIVE CONTENT ENGINES LLC
Data processing
ActiveUS20080005145A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemData stream
Data streams are stored in a non-structured arrangement in which related data is defined by a reference in a first data stream identifying a data element in a second data stream. Instructions are received from a user to establish a virtual file system that provides a structure for a plurality of application files, wherein the information in each of the application files is contained in a plurality of data streams. The structure is defined by at least one hierarchical index, the nodes of said index being data streams. Instructions are received to write data to or read data from the virtual file system, and relevant data streams are modified to reflect instructed manipulations to data presented to a user via the virtual file system.
Owner:DATA EQUATION
Virtual distributed file system
InactiveUS20050273486A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionCommunication interfaceOperational system
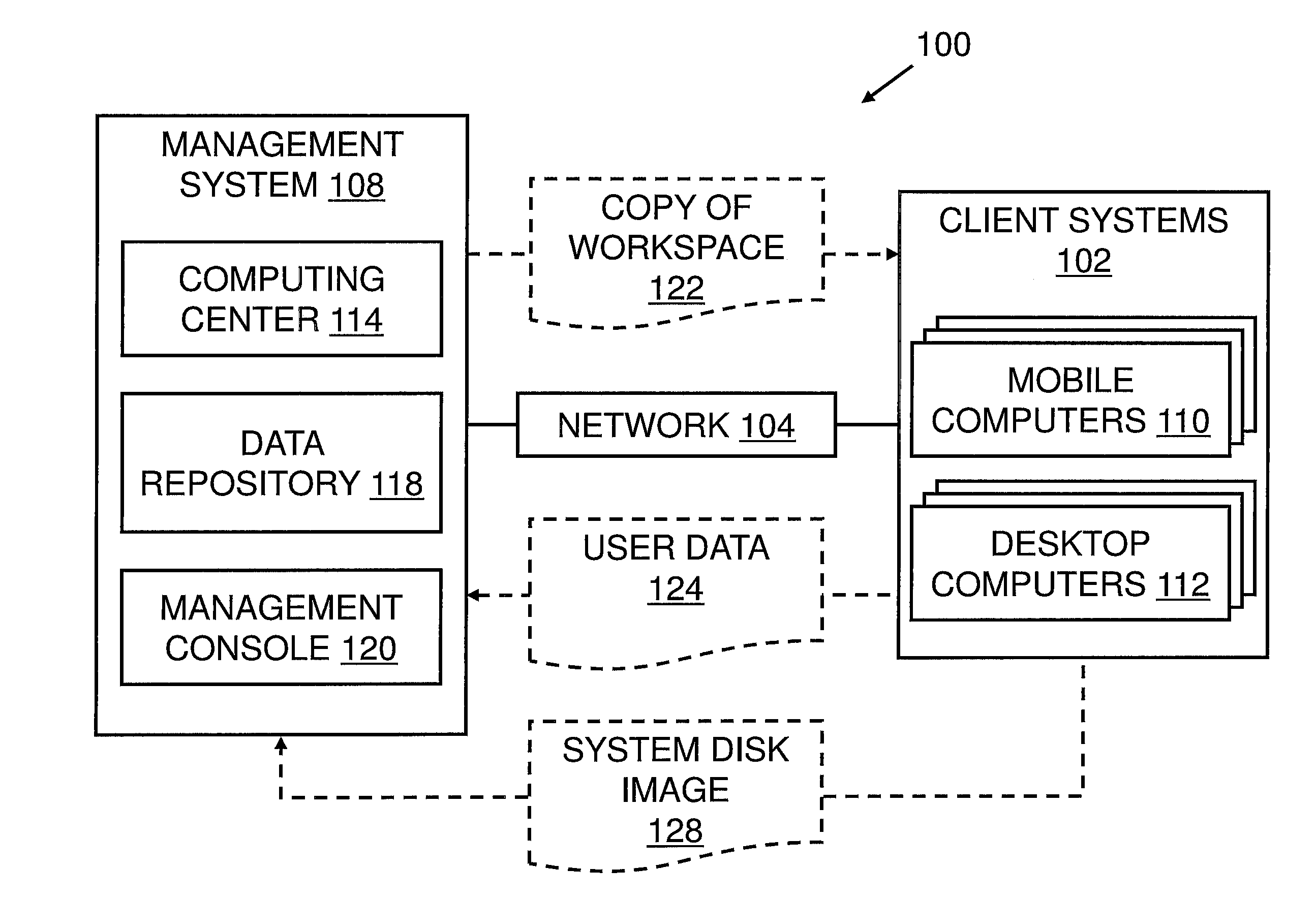
A virtual distributed file system for executing applications from a remote location comprises an application server for remotely storing an original copy of the applications, and a client computing device which contains an operating system for executing the applications, a communications interface configured for communicating with the application server, a virtual file system mapped to a remote file system located on the application server, and a ring buffer cache for storing the applications on the computing device. If the modules are not found locally, the modules are transferred from the application server. The computing device is from a group consisting of a thin client, personal computer, laptop or PDA. The applications are segmented into compressed modules when transferred. The ring buffer is pre-seeded with compressed modules. The computing device is usable online or offline a network. A movable profile is accessible by a user from a plurality of computing devices.
Owner:MAXSPEED CORP
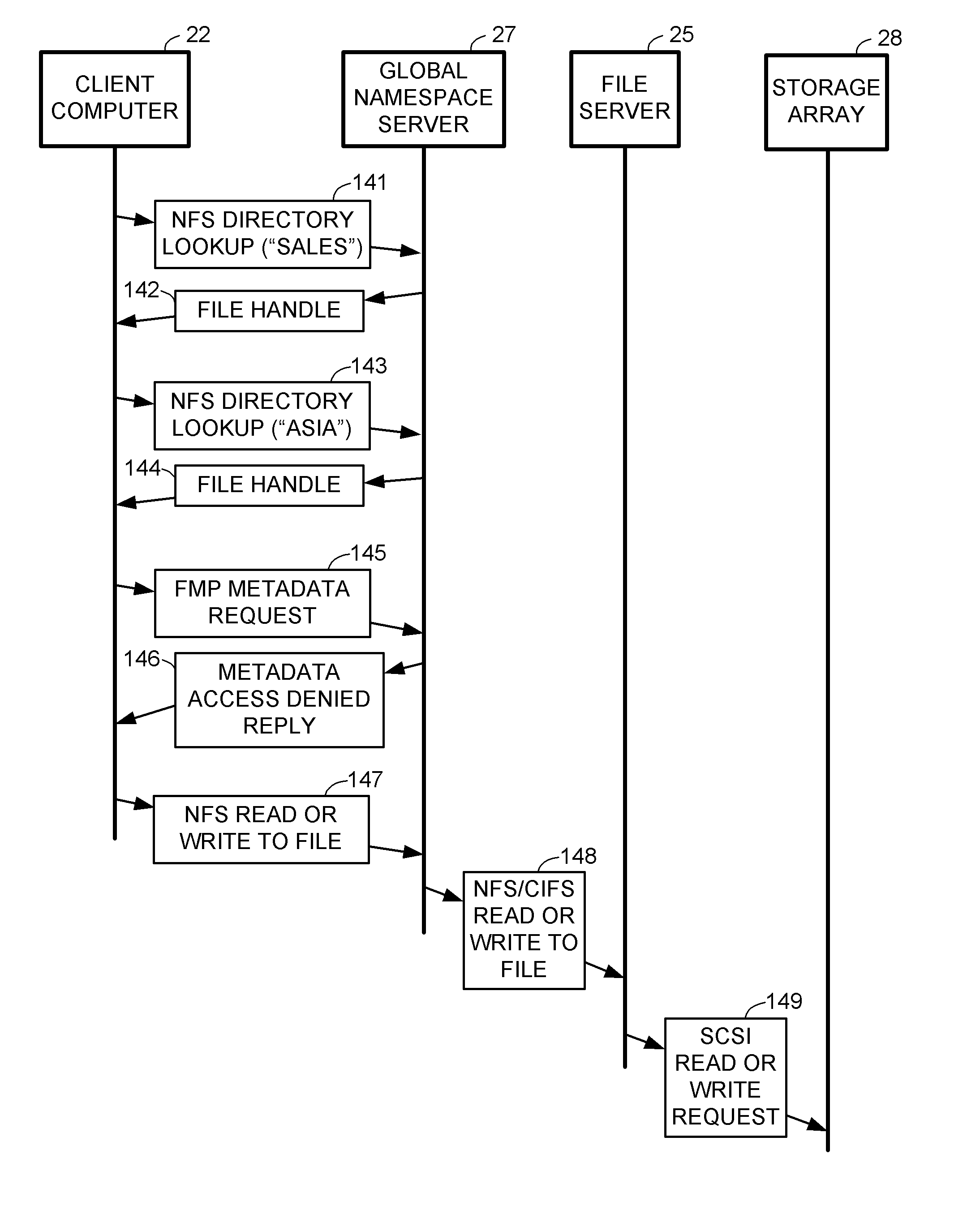
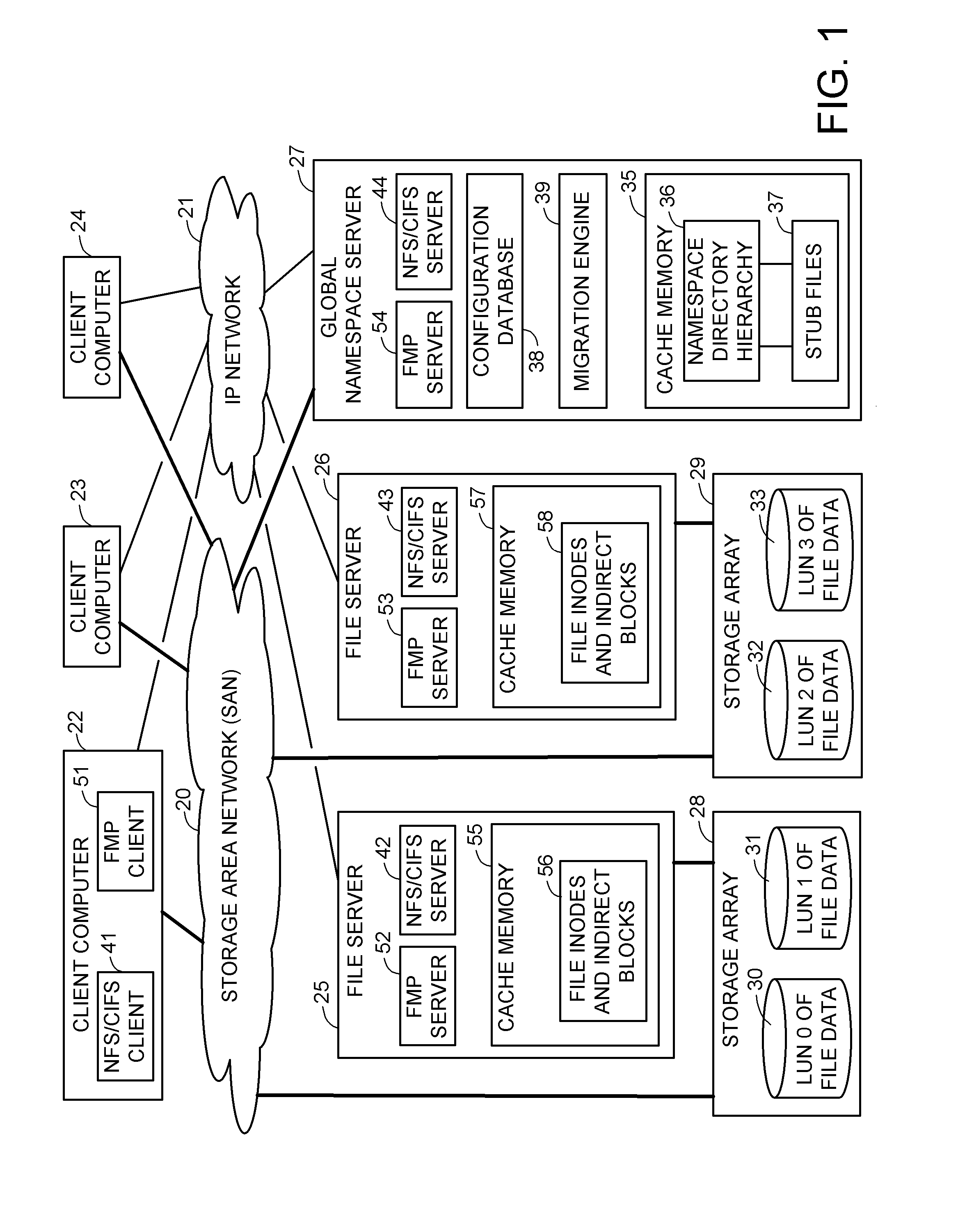
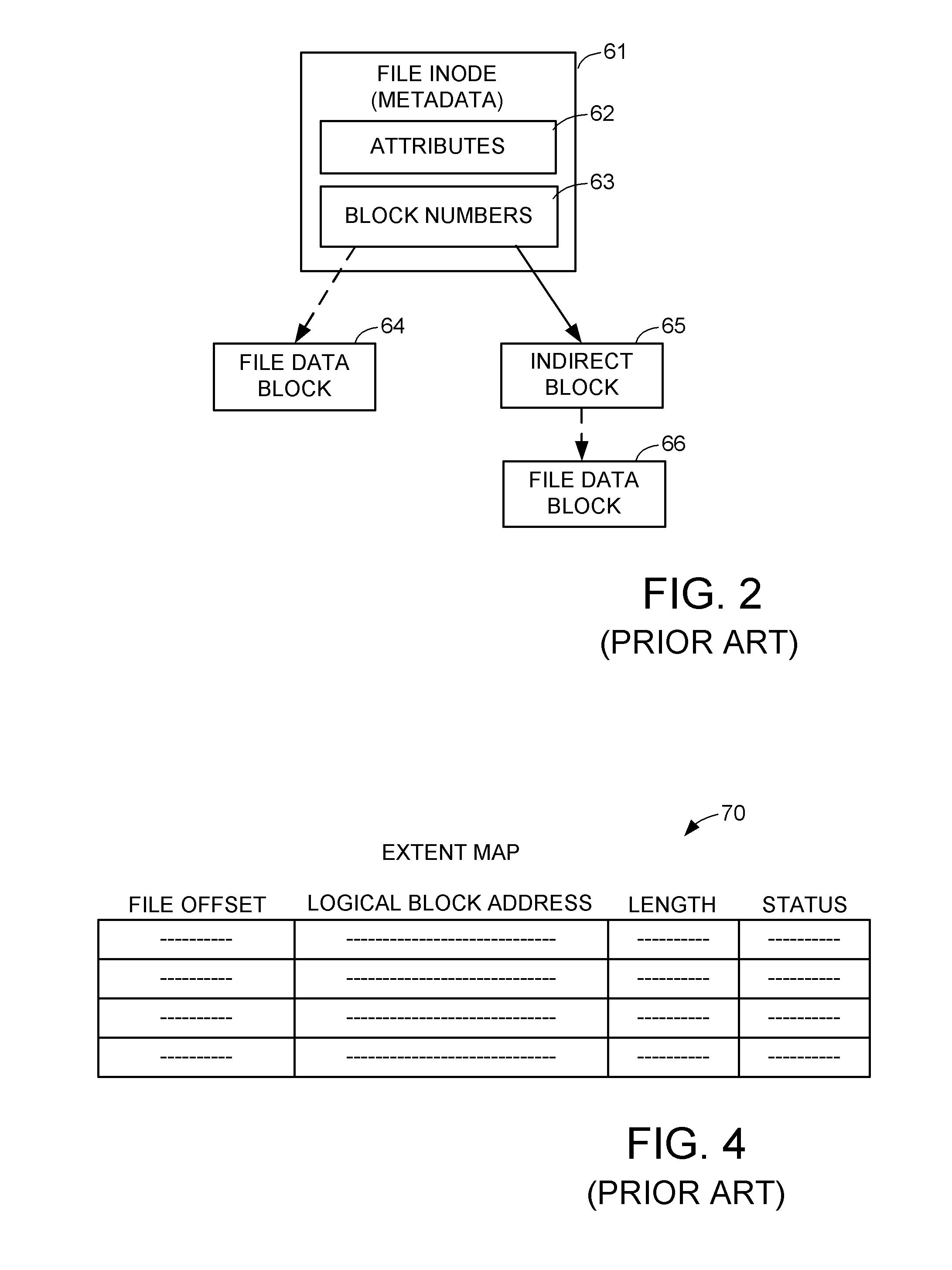
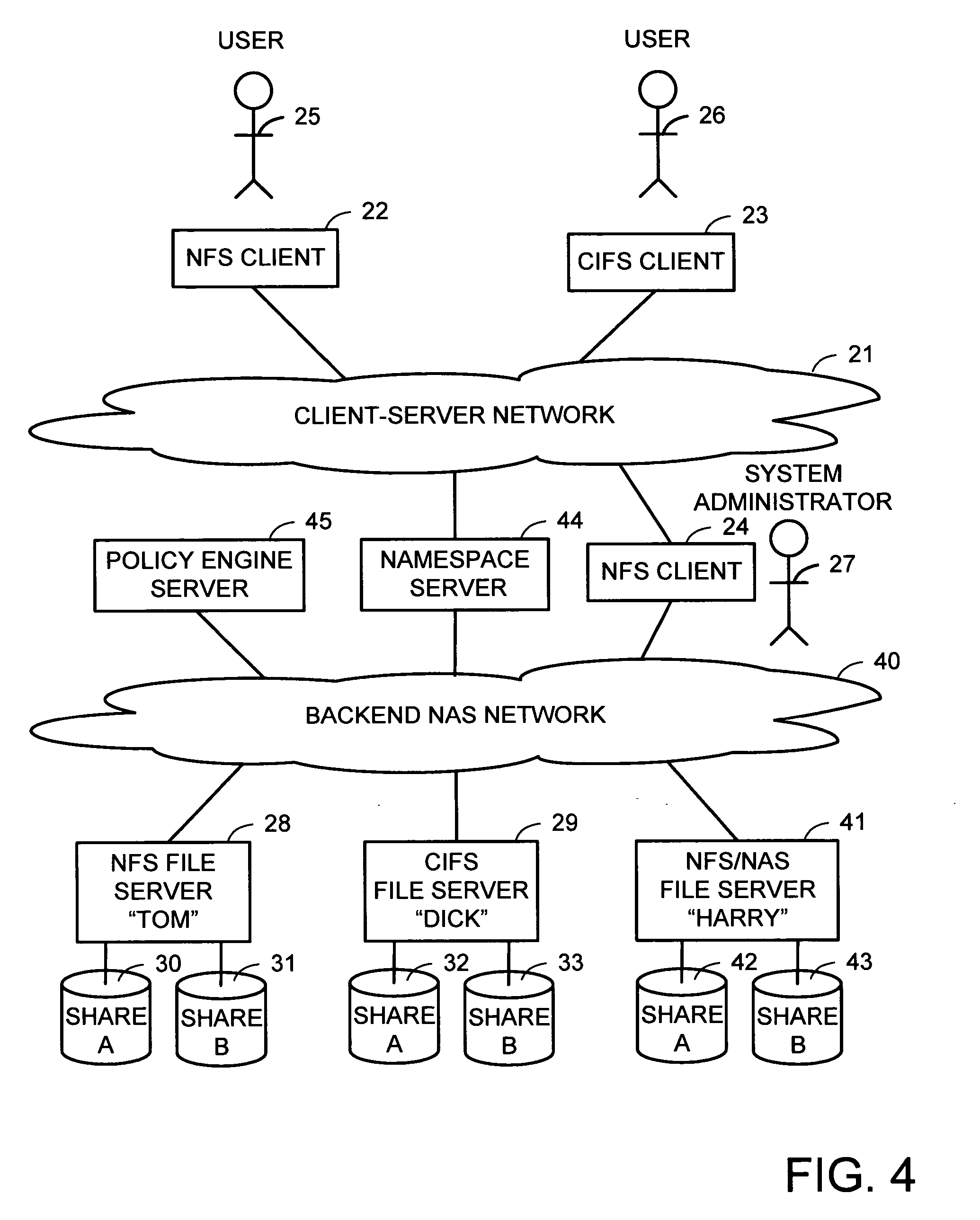
Scalable global namespace through referral redirection at the mapping layer
ActiveUS7937453B1Increase speedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemStorage area network
Client computers, a namespace server, and file servers are linked in a data network so that the namespace server provides the clients with NFS or CIFS access to a virtual file system including files stored in the file servers, and also provides migration of files between the file servers in a fashion transparent to the client access using NFS or CIFS. The client computers and storage arrays storing the file data are also linked in a storage area network so that the clients have high speed block access to the file data using a file mapping protocol. The namespace server redirects a metadata access request in the file mapping protocol from a client to the appropriate file server when the file is not being migrated, and otherwise denies the metadata access request when the file is being migrated so that the client reverts to NFS or CIFS access.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Distributed storage cluster architecture
InactiveUS7590747B2Input/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalVirtual file systemFile system
A network storage system includes a virtual file system (“VFS”) that manages the files of the network storage system, and a storage center that stores the files. The VFS and the storage center are separated, such that a client accesses the VFS to conduct file system operations and the client accesses the storage center to upload / download files. The client accesses the network storage system through one or more storage ports. The storage center includes a plurality of distributed object storage managers (DOSMs) and a storage cluster that includes a plurality of intelligent storage nodes. The network storage system includes additional storage centers at geographically disparate locations. The network storage system uses a multi-cast protocol to maintain file information at the DOSMs regarding files stored in the intelligent storage nodes, including files stored in disparate storage centers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
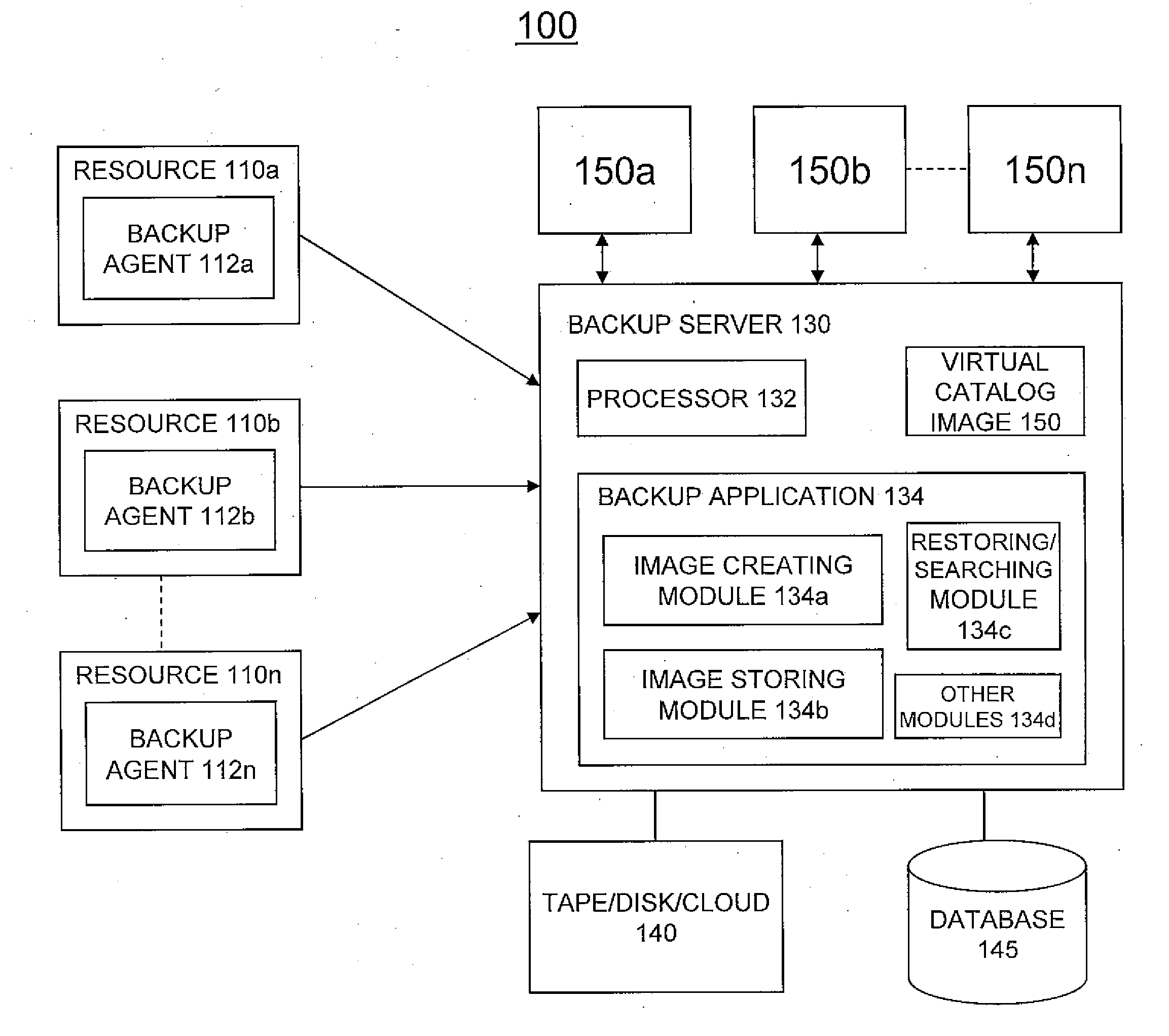
System and method of storing backup image catalog
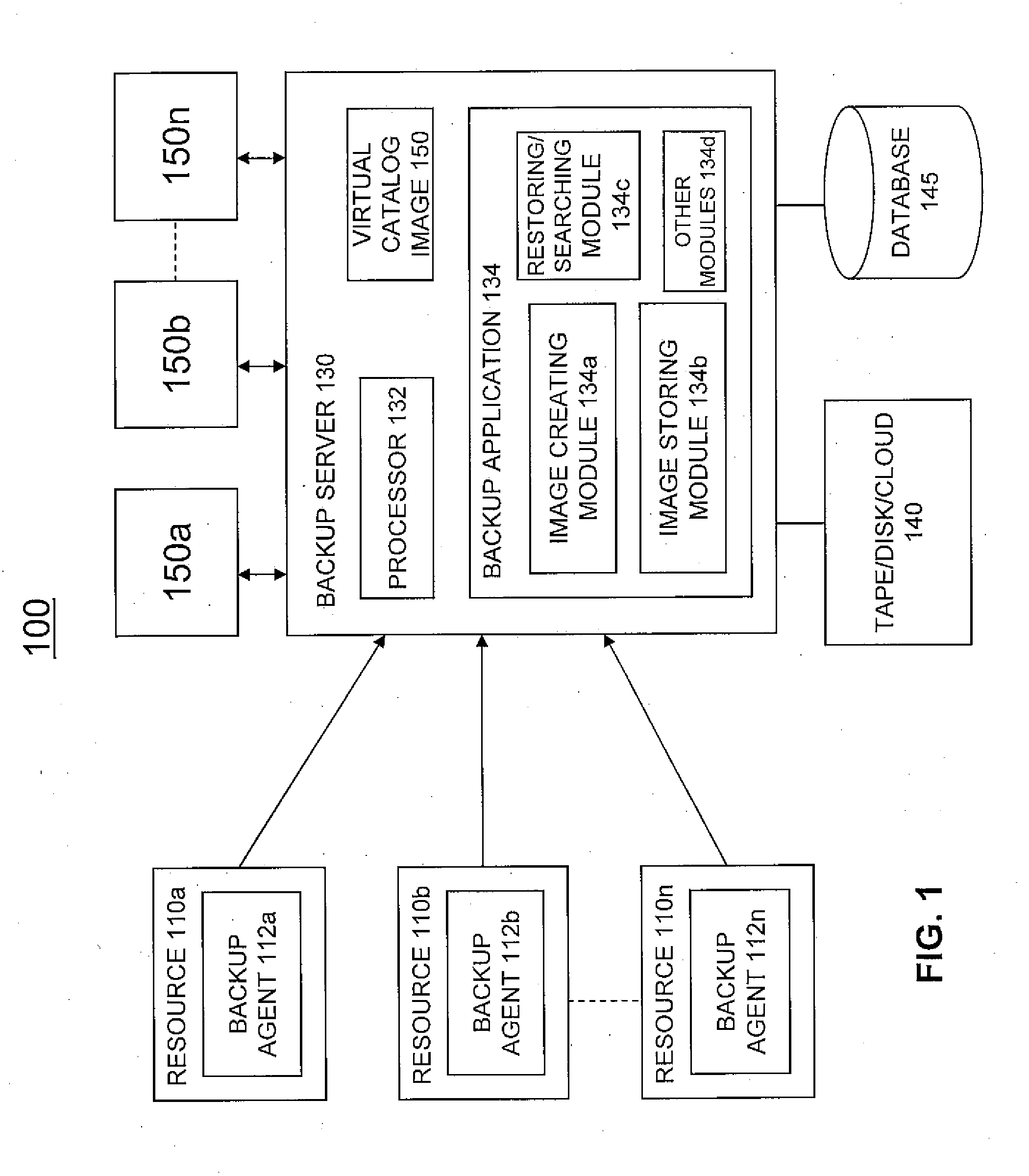
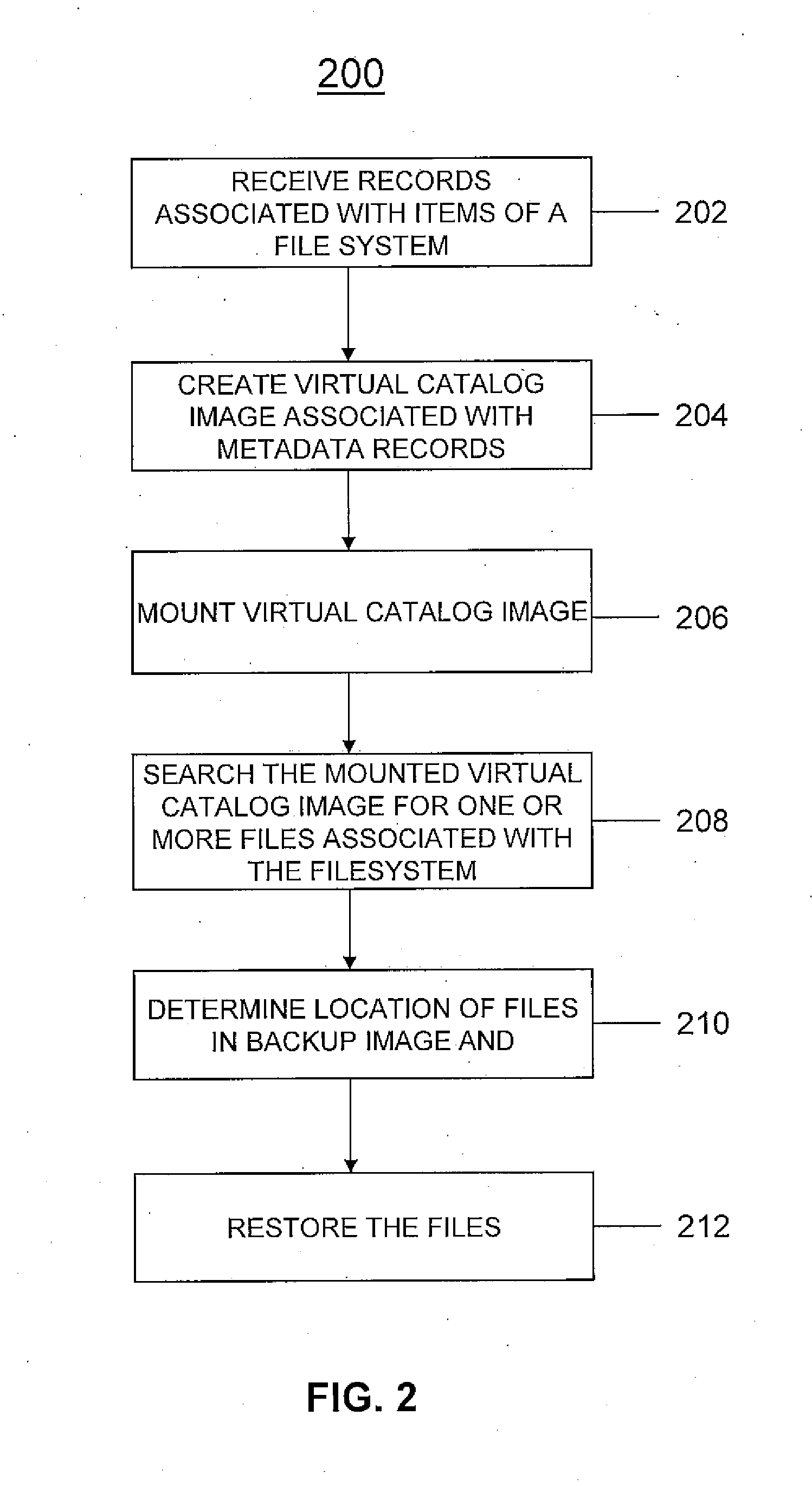
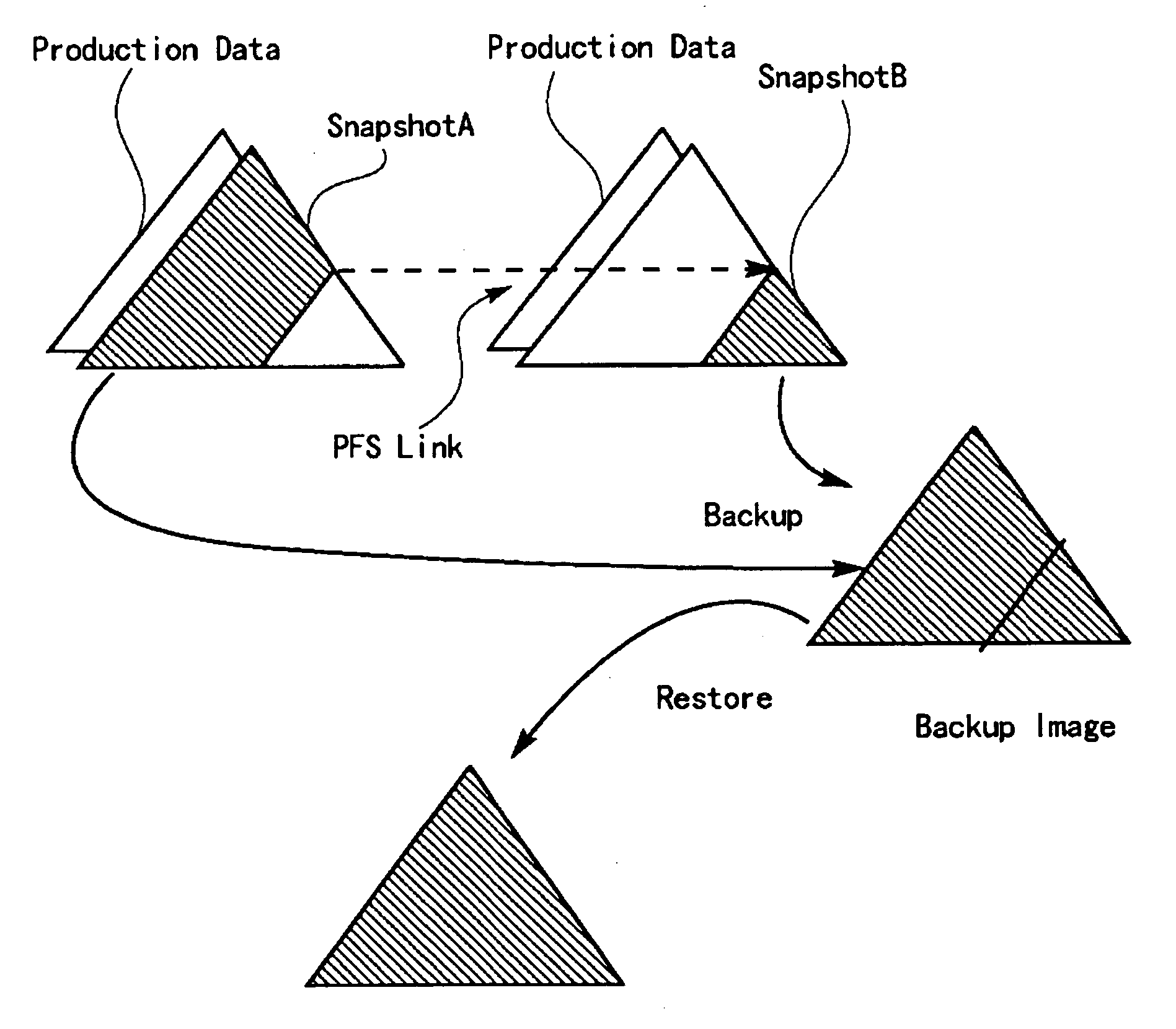
ActiveUS20110145199A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirtualizationVirtual file system
A system and method for managing backup and restore operations associated with a backup system. Metadata associated with files / directories of one or more file systems associated with one or more resources may be received. A virtual catalog image associated with the metadata may be created in a virtual file system image format. Once the virtual catalog image is created, virtualization vendor specific technology may be utilized to mount the image on the backup system and search and browse operations may be performed. The virtual catalog image may contain the file / directory hierarchy without containing actual file data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
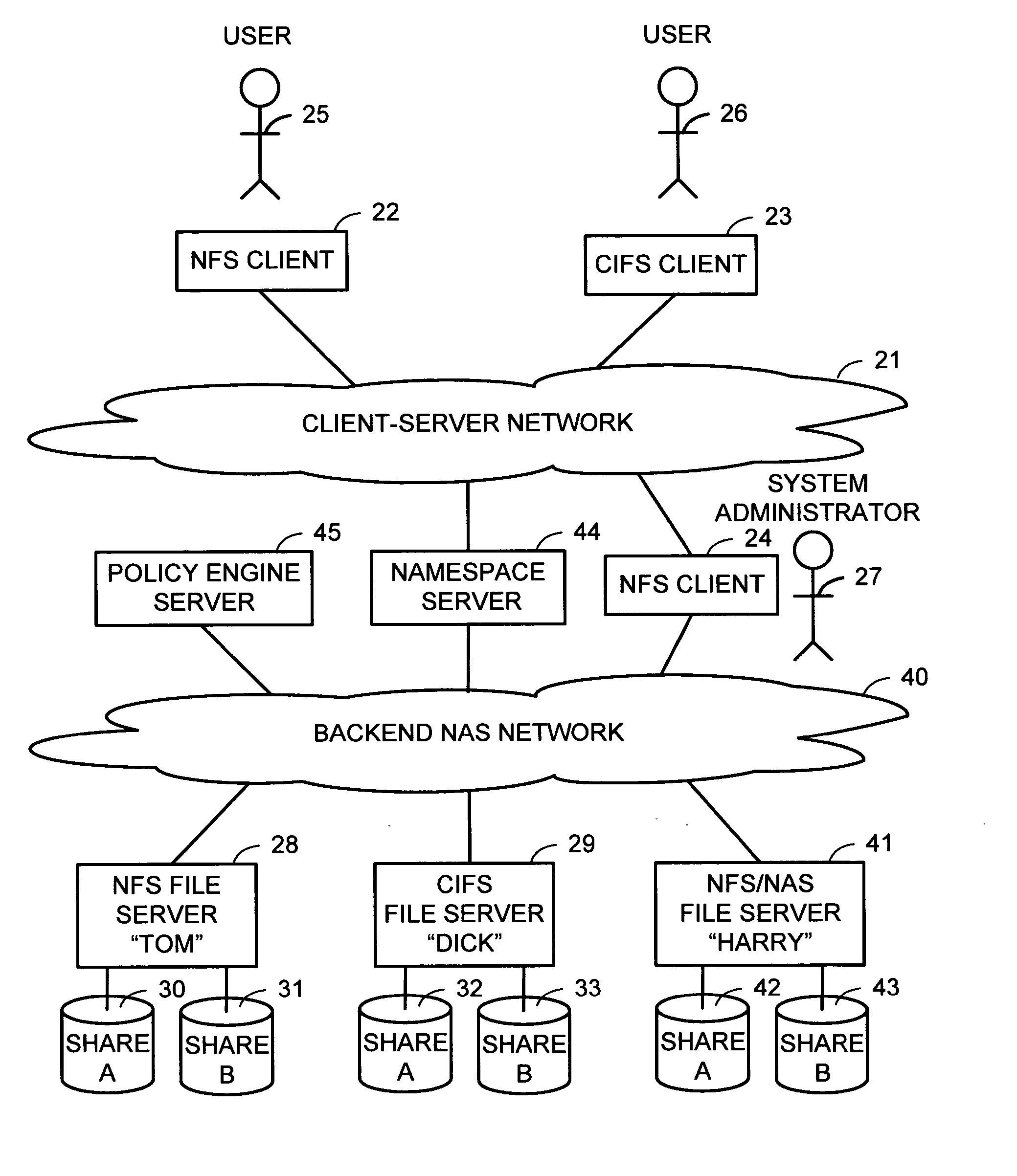
Multi-protocol namespace server
InactiveUS20070038697A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual file systemMulti protocol
A namespace server translates client requests for access to files referenced by pathnames in a client-server namespace into requests for access to files referenced by pathnames in a backend NAS network namespace. The namespace server also translates between different file access protocols. The namespace server may change the translation of a client-server network pathname from an old backend NAS network pathname to a new backend NAS network pathname for file migration without disruption to client access during file migration for load balancing or for a more appropriate service level. Client access can also be routed automatically and transparently to replicas in case of server or site failures. The namespace server may create the appearance of a virtual file system that contains multiple physical servers, a virtual share that contains physical shares from different servers, directories that contain files on different servers, and files that contain data from files on different servers.
Owner:EMC CORP
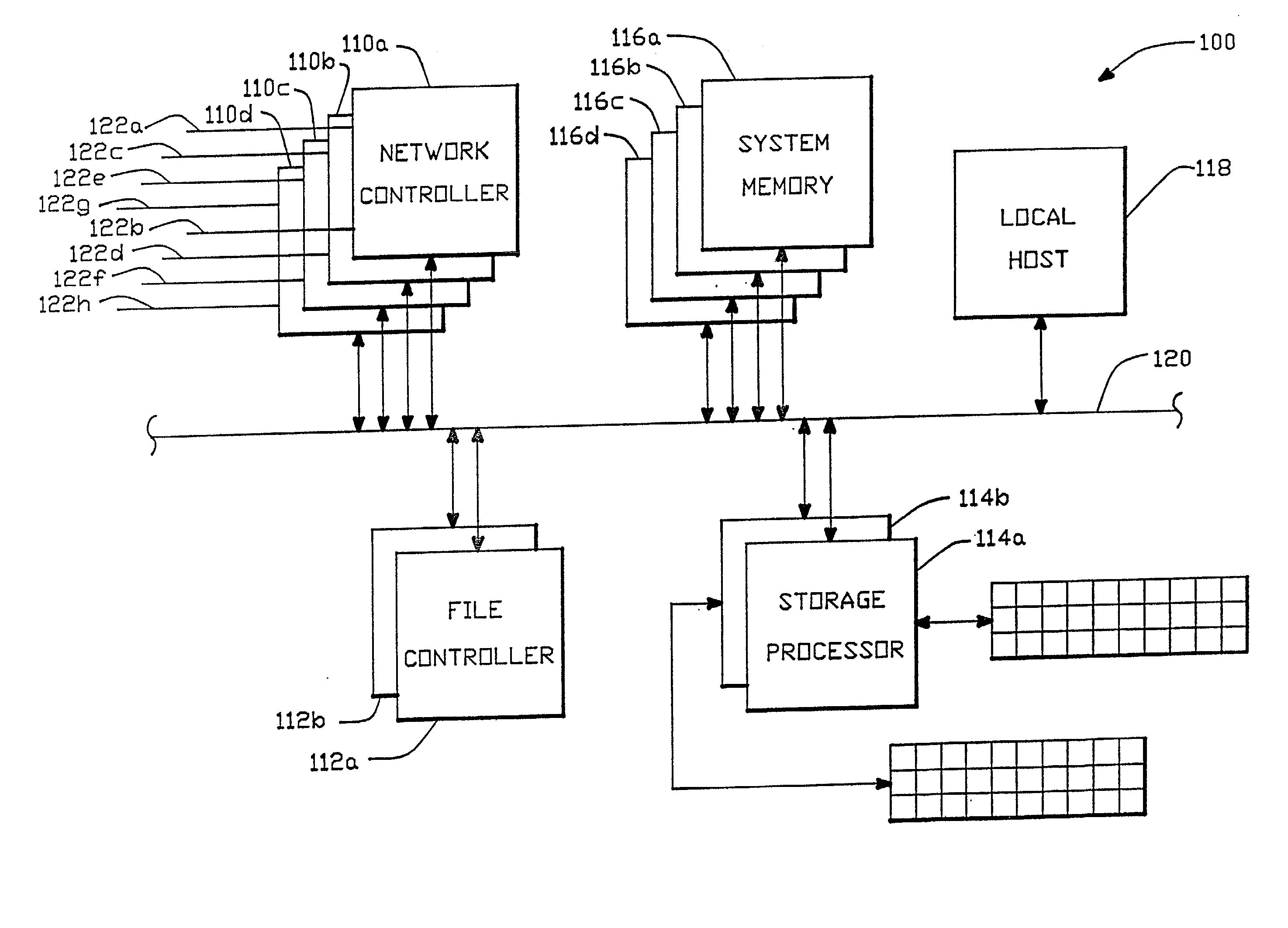
Parallel I/O network file server architecture
InactiveUS20020083111A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsMass storageVirtual file system
A file server architecture is disclosed, comprising as separate processors, a network controller unit, a file controller unit and a storage processor unit. These units incorporate their own processors, and operate in parallel with a local Unix host processor. All networks are connected to the network controller unit, which performs all protocol processing up through the NFS layer. The virtual file system is implemented in the file control unit, and the storage processor provides high-speed multiplexed access to an array of mass storage devices. The file controller unit control file information caching through its own local cache buffer, and controls disk data caching through a large system memory which is accessible on a bus by any of the processors.
Owner:AUSPEX SYST
Virtual machine file-level restoration
ActiveUS20100262585A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveVirtual file system
Disclosed is a method and system for selectively restoring file-level data from a disk image backup. In embodiments, a virtual machine backup may be performed by dividing a virtual machine virtual disk file into a plurality of discrete fixed-sized data blocks sharing a common index file that is stored on a backup medium, such as a hard drive, to form a backup set. The index file is referenced to determine which fixed-sized block contains volume information, such as a partition table, of the backed-up virtual machine file. The individual blocks are processed as a virtual filesystem which is presented to an access module, which traverses the filesystem and provide access to individual files in the image backup to a client process, the restore files may be delivered to the client in a container file, which may be compressed to increase transfer speed. The container file may include executable instructions for automatically restoring the files to a desired location.
Owner:UNITRENDS
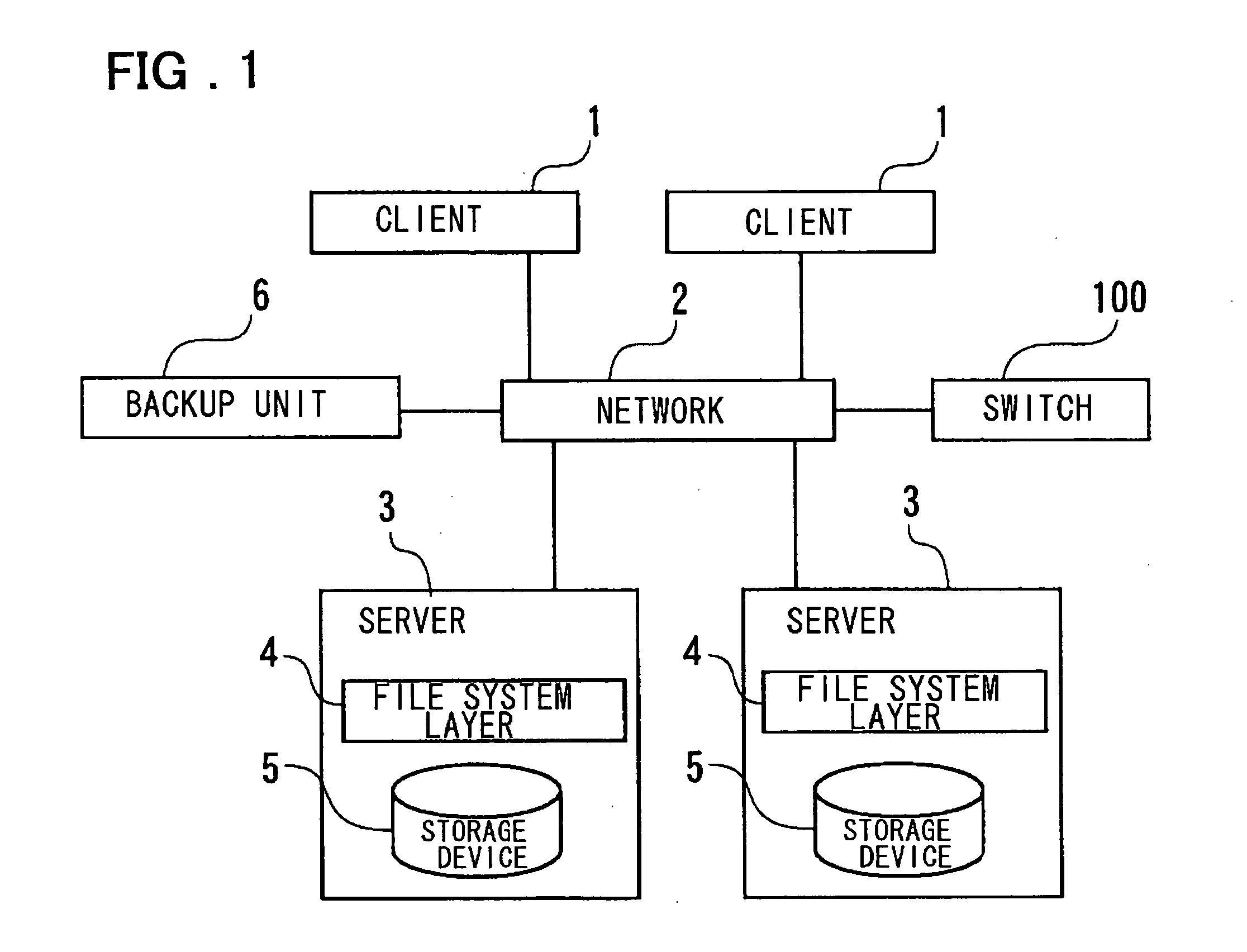
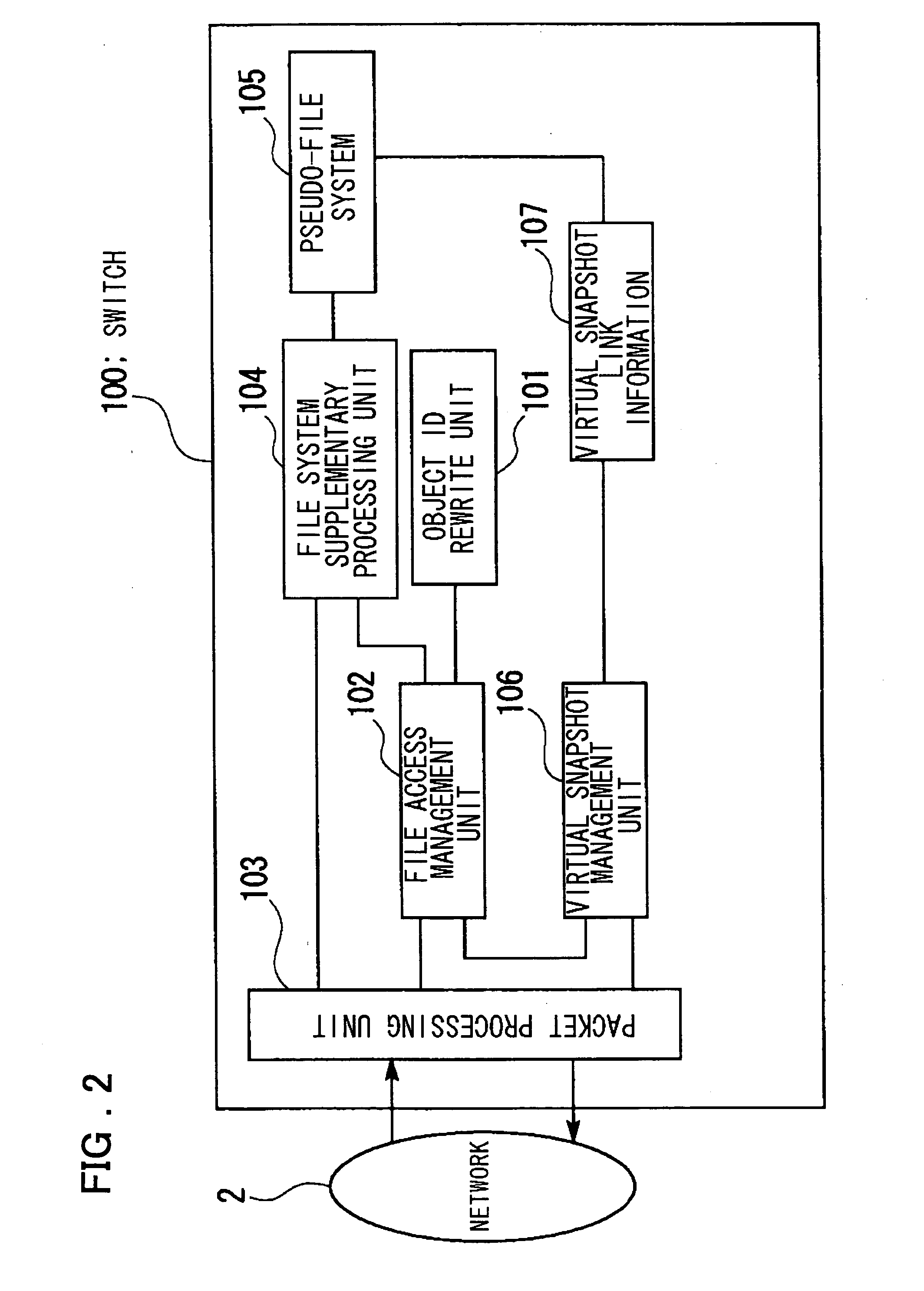
Switch device, system, backup method and computer program
ActiveUS20060080370A1Easy maintenanceImprove performanceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemFile system
Disclosed is a system which includes at least one client, a plural number of file servers, each having a file system, and a switch logically arranged between the client and the plural file servers to provide file access services which virtually render the plural file services accessible as a single file system, termed a ‘pseudo file system’, when viewed from the terminal. The switch distributes a command for start of generation of snapshots to the plural file servers, which file servers formulate respective snapshots responsive to the command for start of formation of the snapshots. The switch sets the plural snapshots, generated by the plural file servers, so as to be associated with the file system structure of the virtual file system at the time of formation of the snapshots.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com