Patents
Literature
194results about How to "Problem can be addressed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
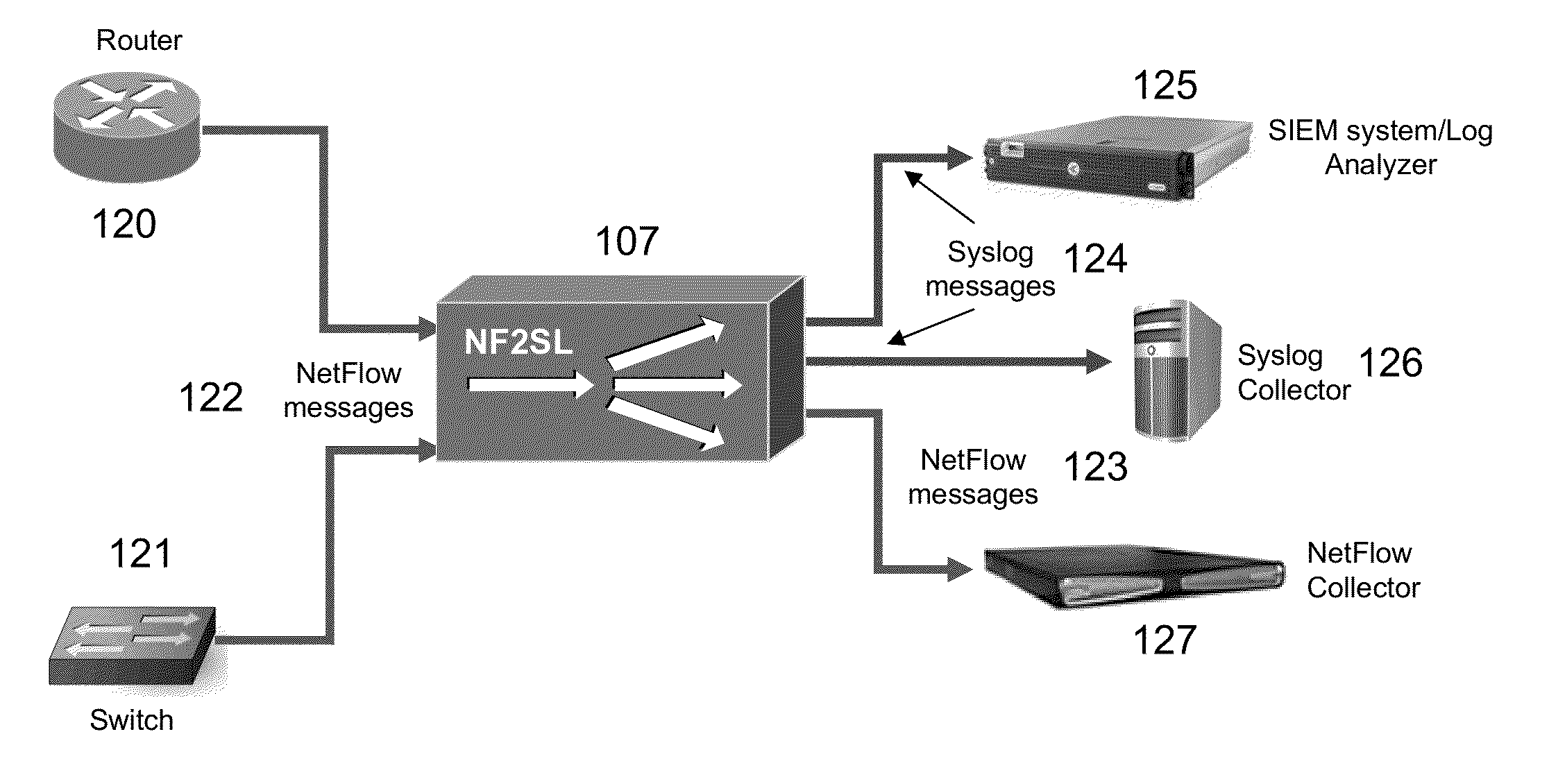
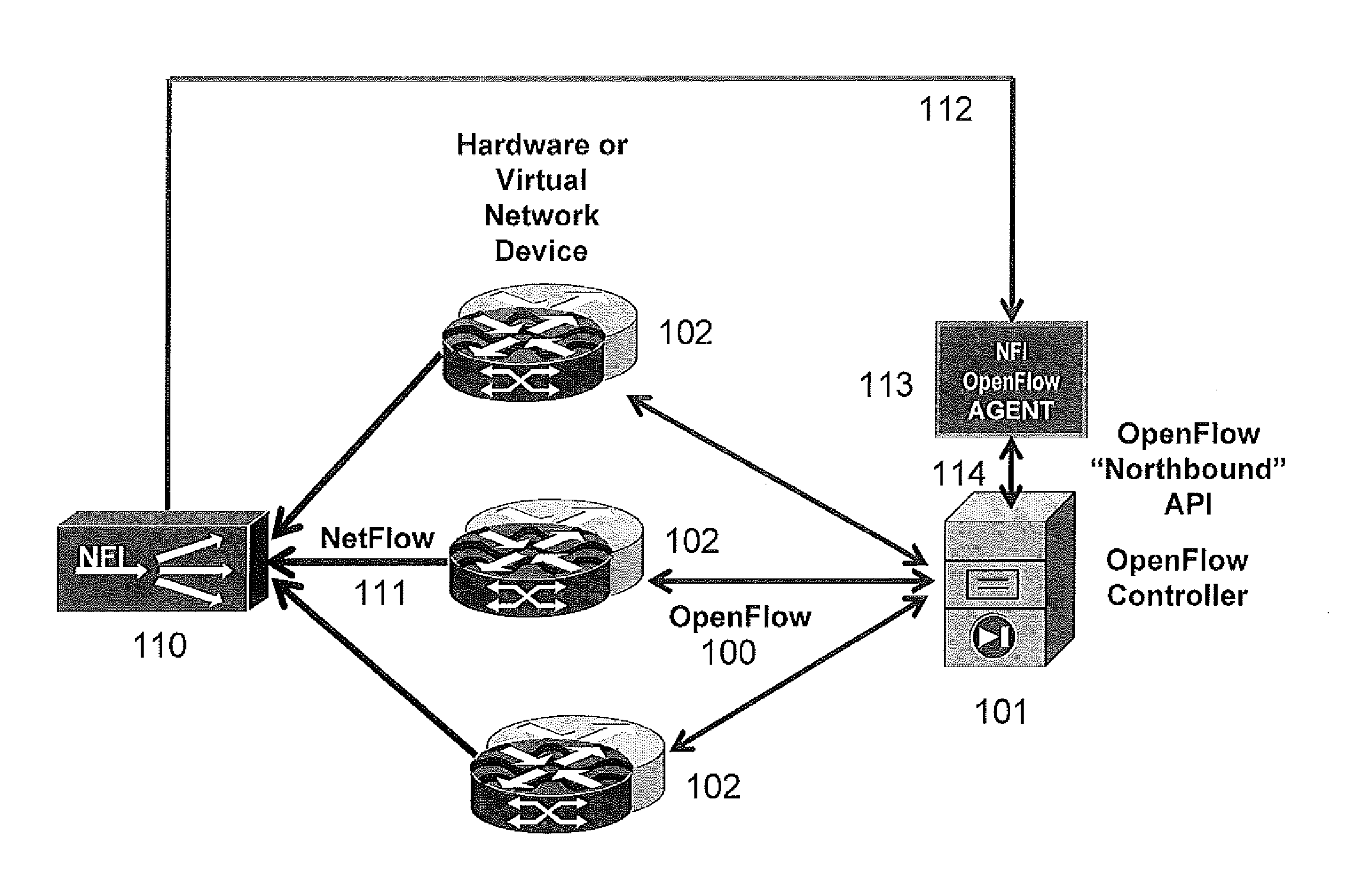
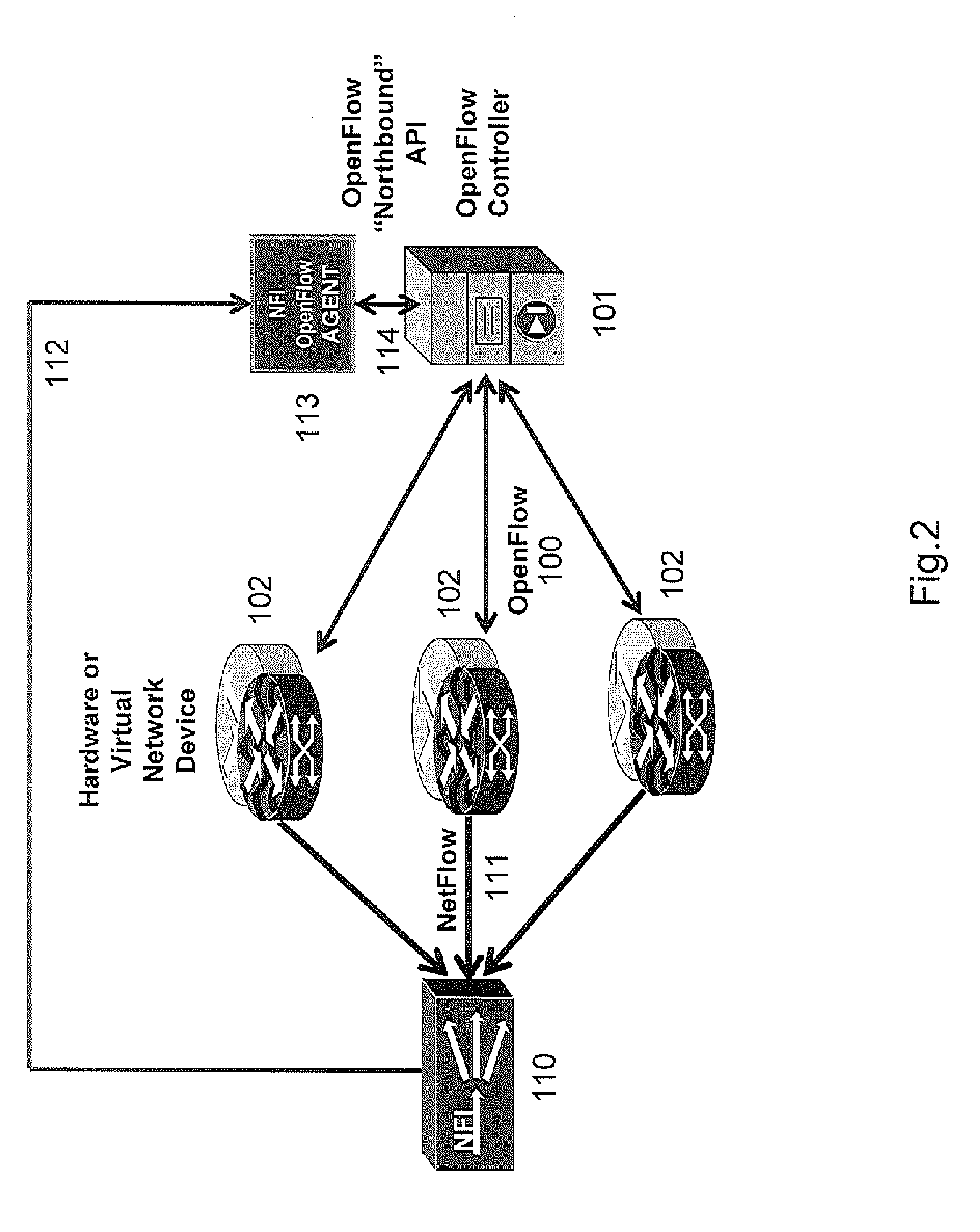
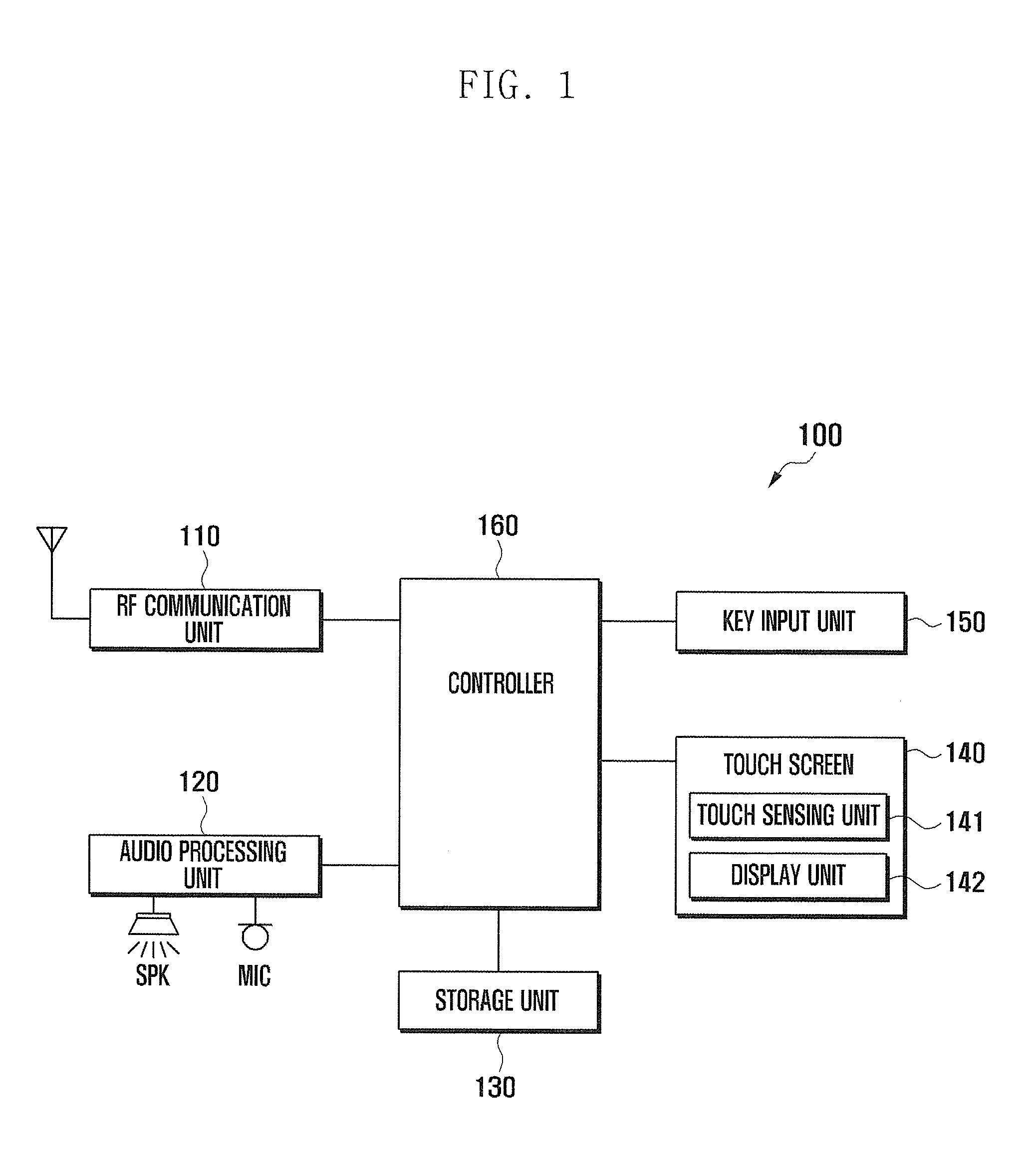
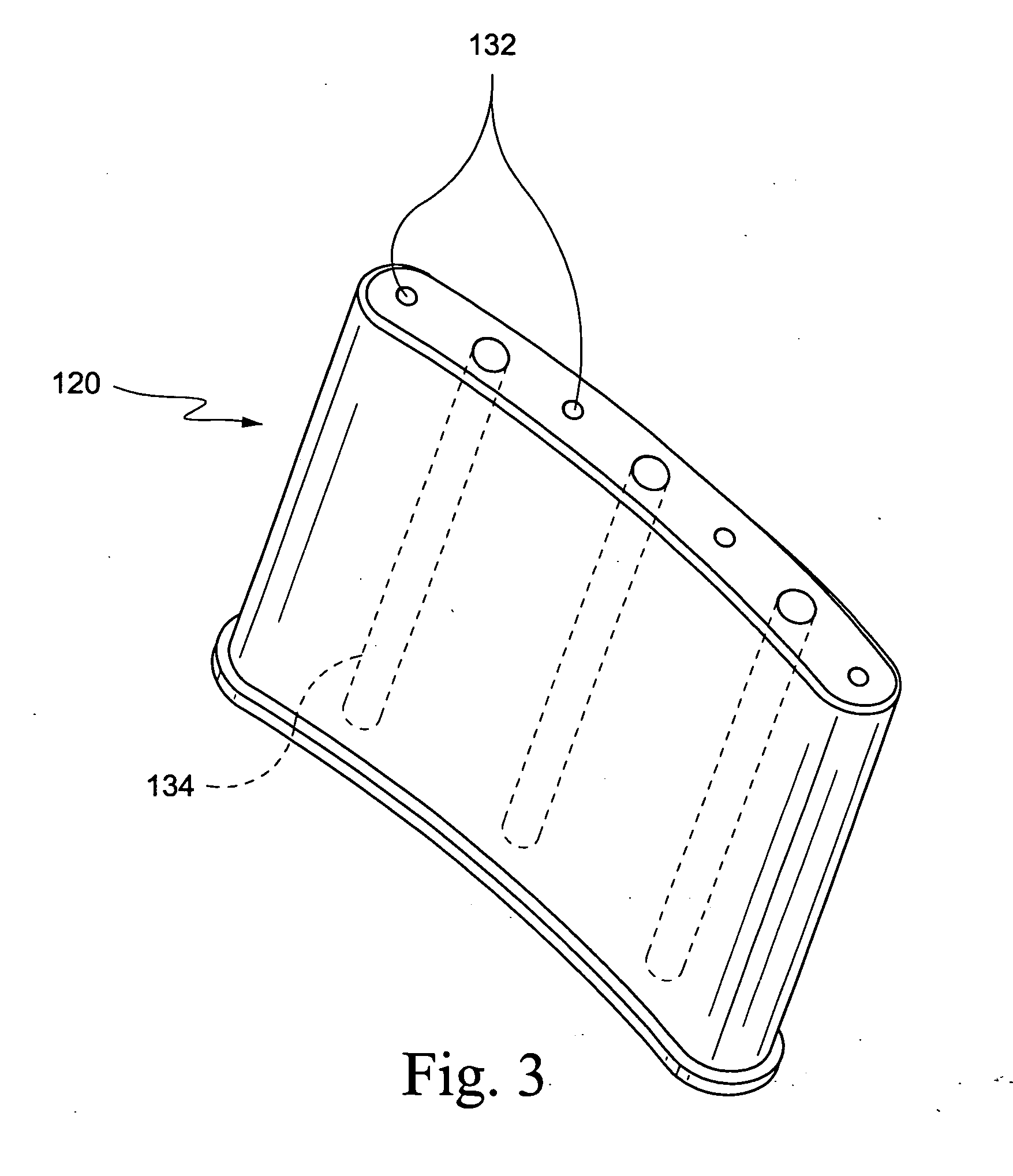
Streaming Method and System for Processing Network Metadata
ActiveUS20130117847A1Problem can be addressedEasily correlatedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTemplate basedSoftware modules
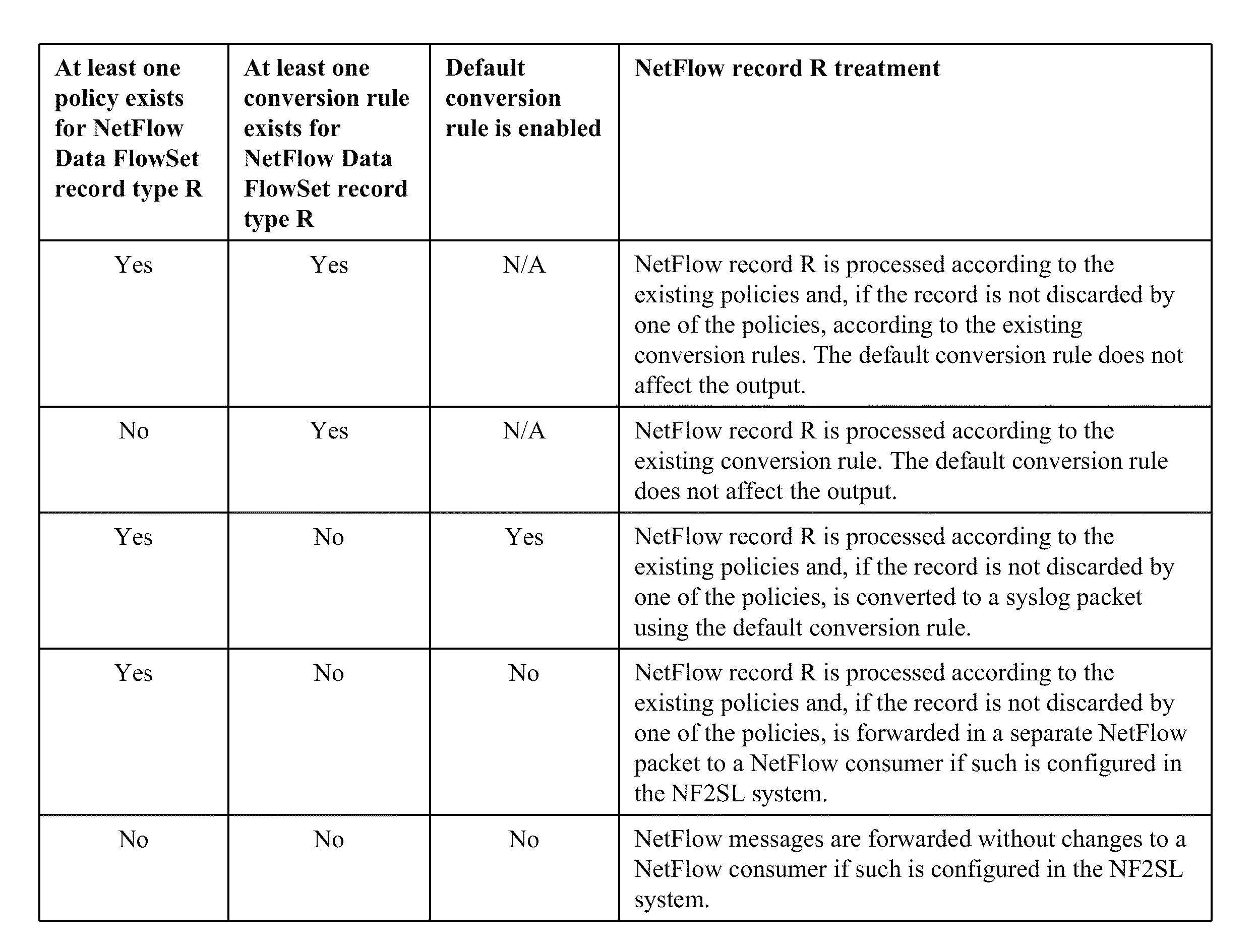
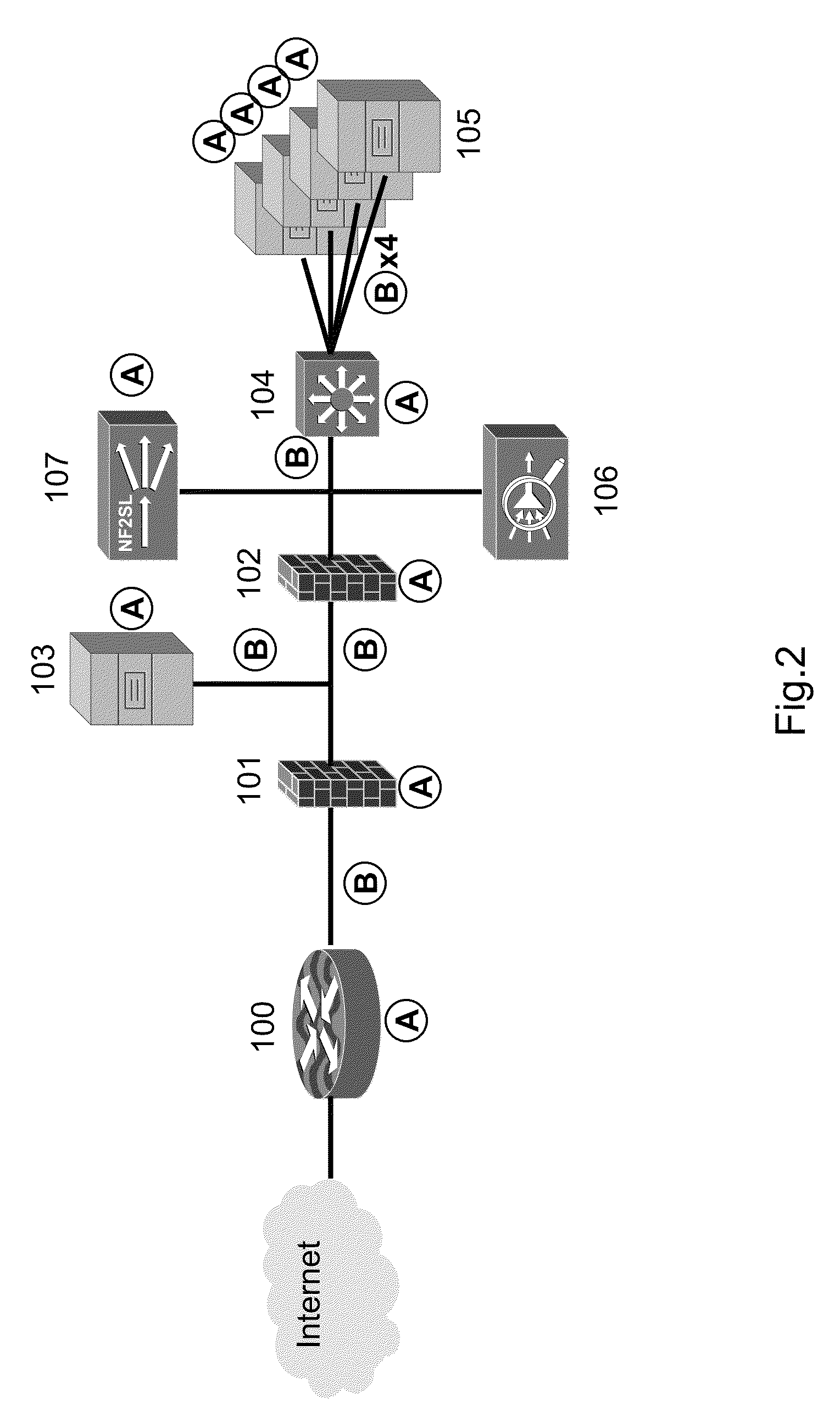
A method and system for processing network metadata is described. Network metadata may be processed by dynamically instantiated executable software modules which make policy-based decisions about the character of the network metadata and about presentation of the network metadata to consumers of the information carried by the network metadata. The network metadata may be type classified and each subclass within a type may be mapped to a definition by a unique fingerprint value. The fingerprint value may be used for matching the network metadata subclasses against relevant policies and transformation rules. For template-based network metadata such as NetFlow v9, an embodiment of the invention can constantly monitor network traffic for unknown templates, capture template definitions, and informs administrators about templates for which custom policies and conversion rules do not exist. Conversion modules can efficiently convert selected types and / or subclasses of network metadata into alternative metadata formats.
Owner:NETFLOW LOGIC
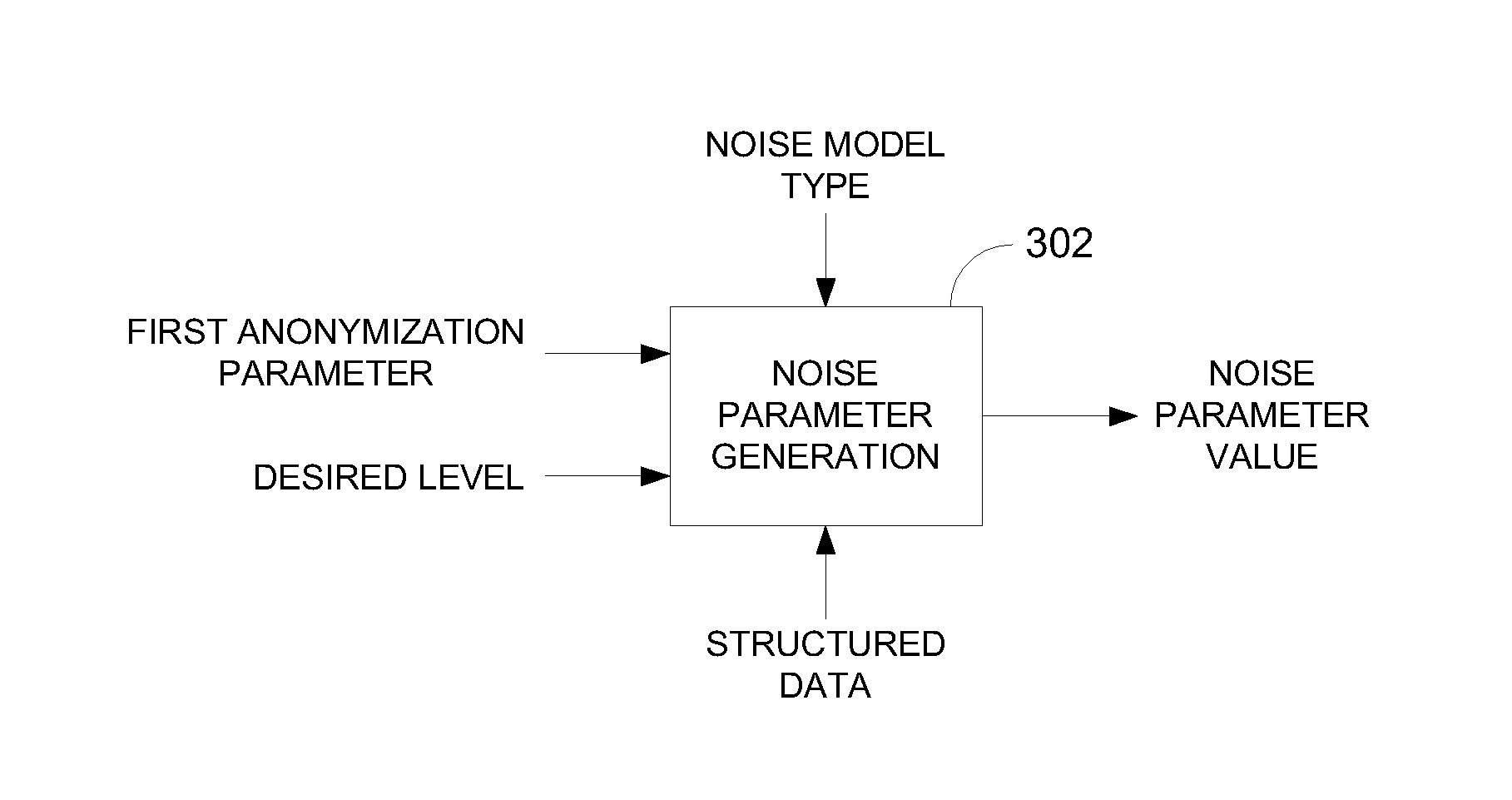
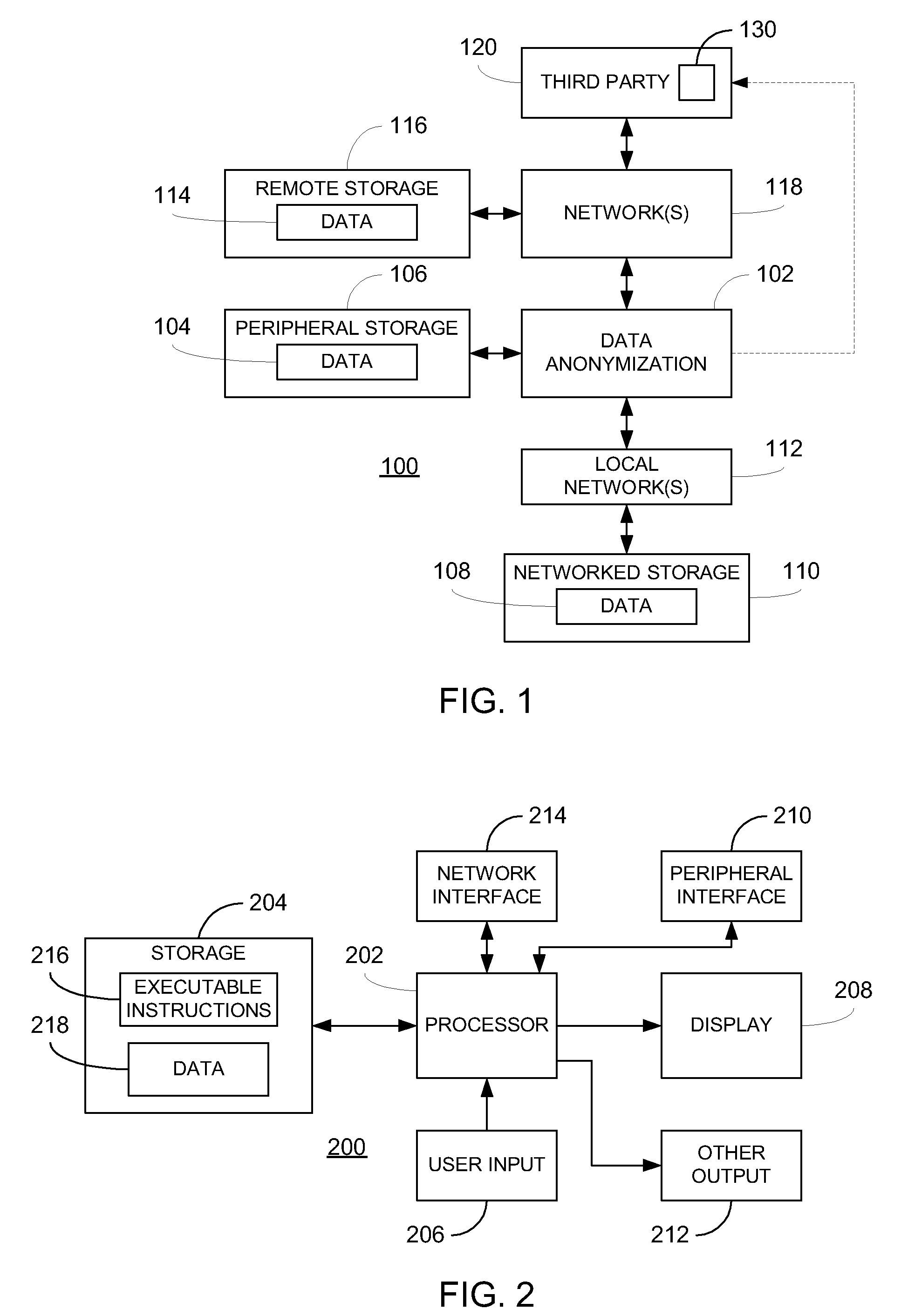
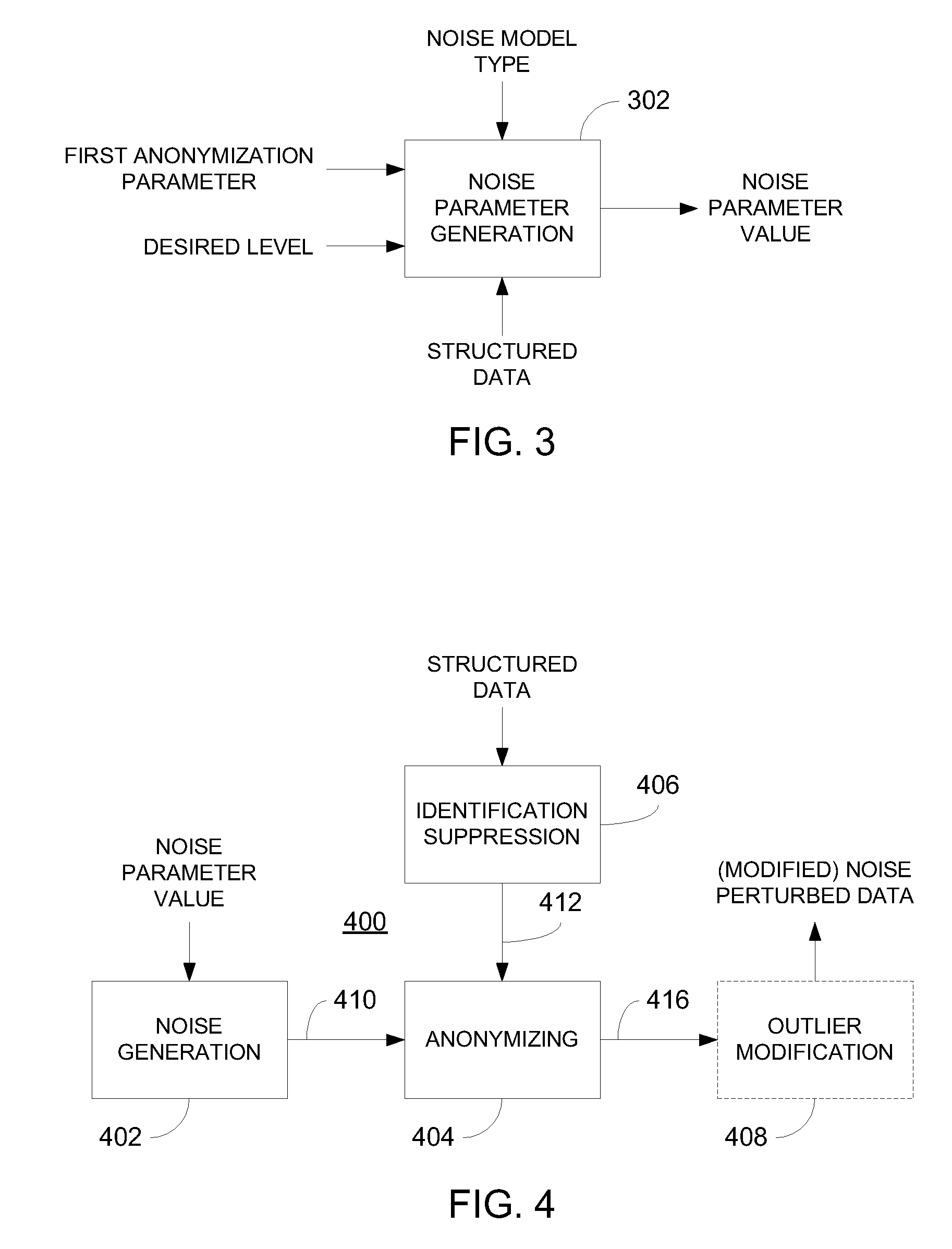
Data anonymization based on guessing anonymity
ActiveUS8627483B2Maximizes guessing anonymityMinimize distortionDigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationGame basedOptimization problem
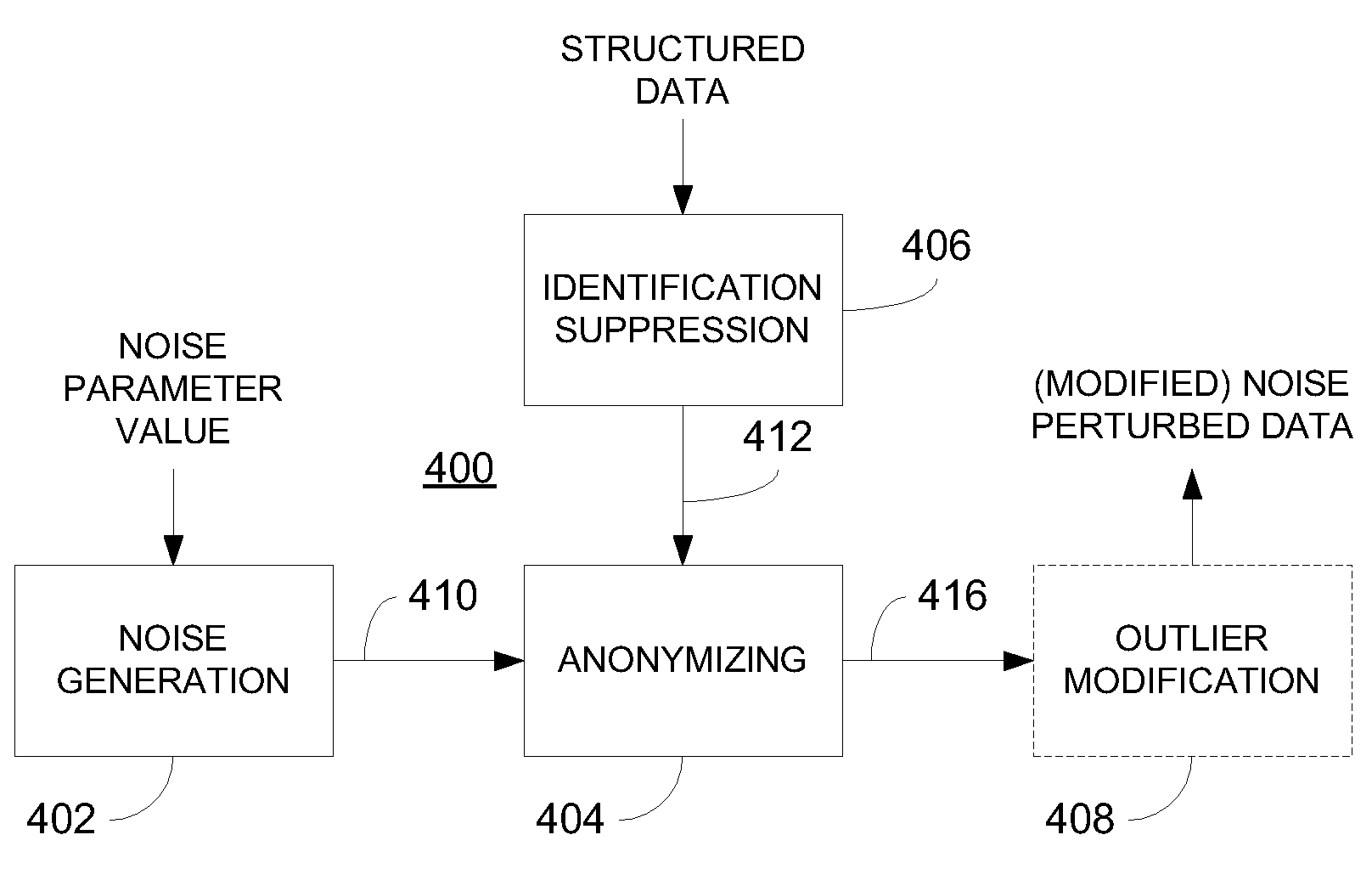
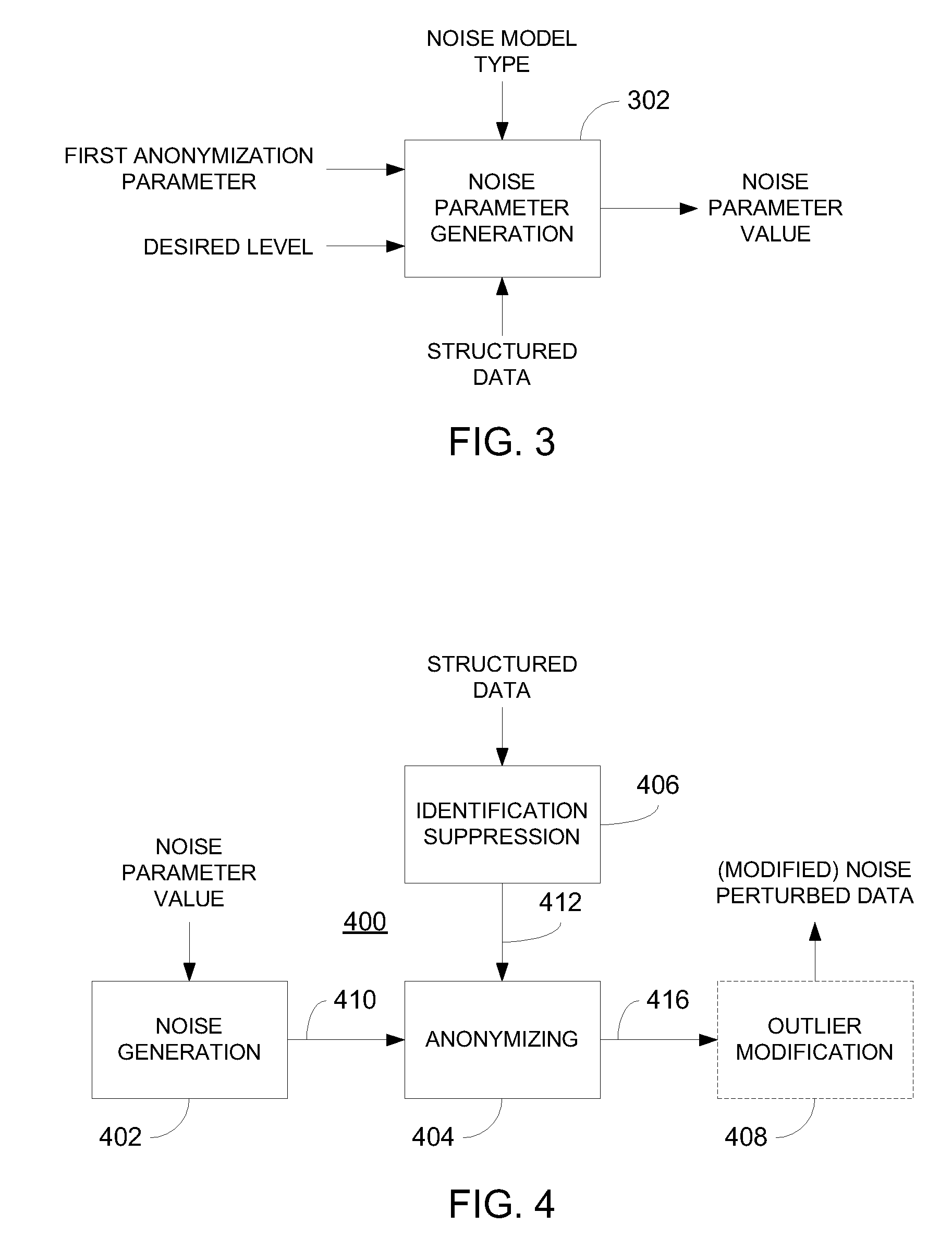
Privacy is defined in the context of a guessing game based on the so-called guessing inequality. The privacy of a sanitized record, i.e., guessing anonymity, is defined by the number of guesses an attacker needs to correctly guess an original record used to generate a sanitized record. Using this definition, optimization problems are formulated that optimize a second anonymization parameter (privacy or data distortion) given constraints on a first anonymization parameter (data distortion or privacy, respectively). Optimization is performed across a spectrum of possible values for at least one noise parameter within a noise model. Noise is then generated based on the noise parameter value(s) and applied to the data, which may comprise real and / or categorical data. Prior to anonymization, the data may have identifiers suppressed, whereas outlier data values in the noise perturbed data may be likewise modified to further ensure privacy.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
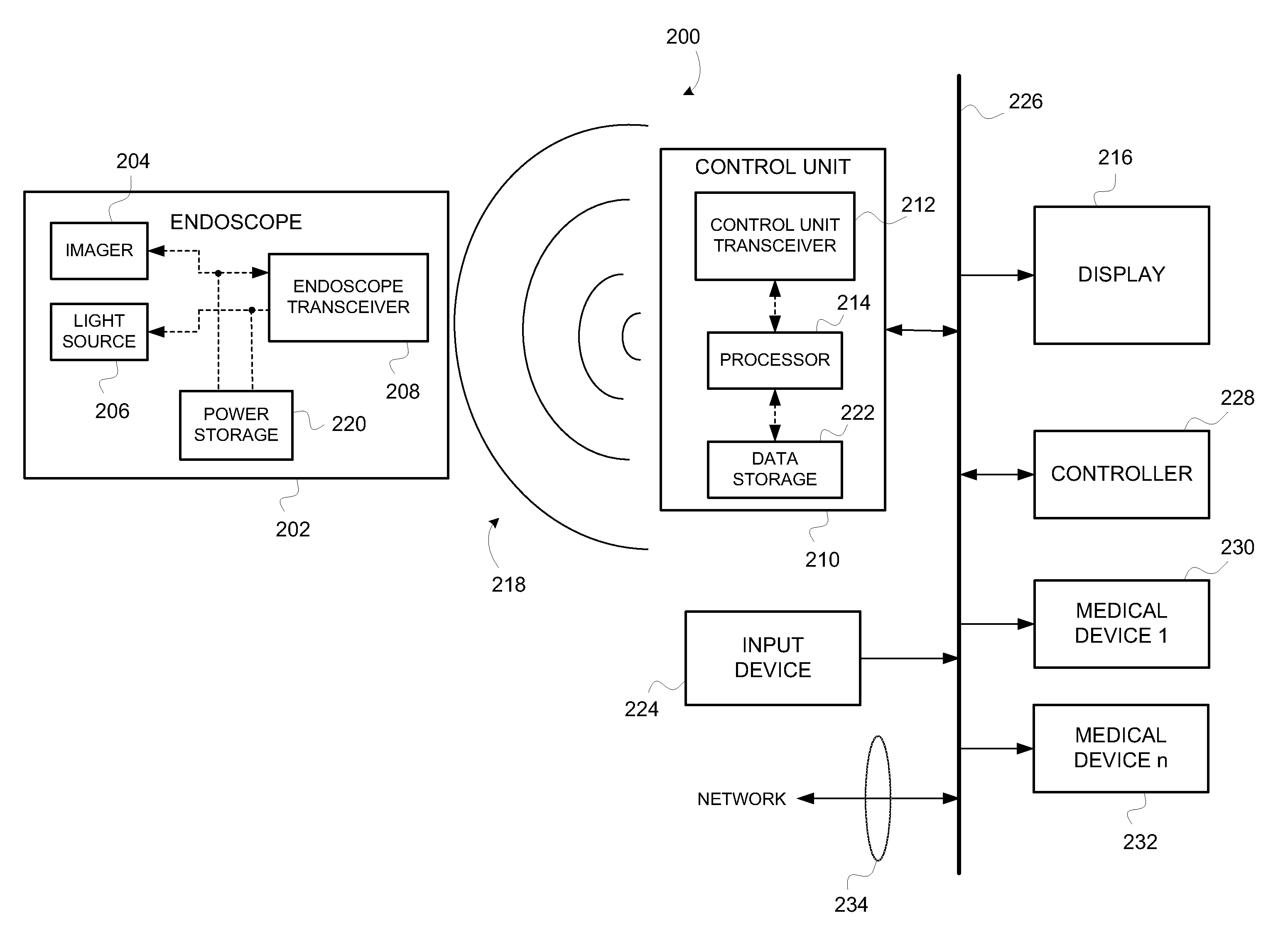
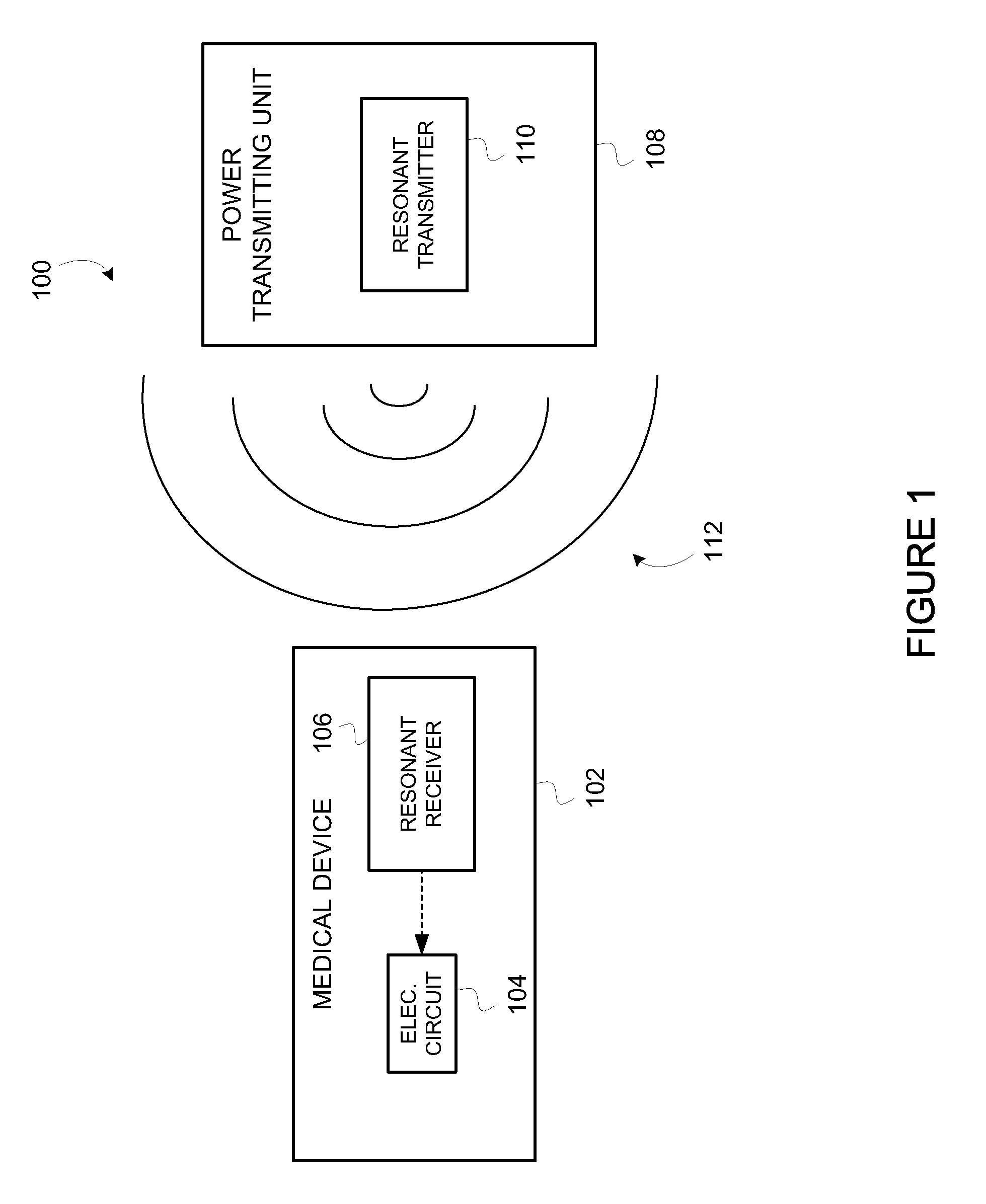
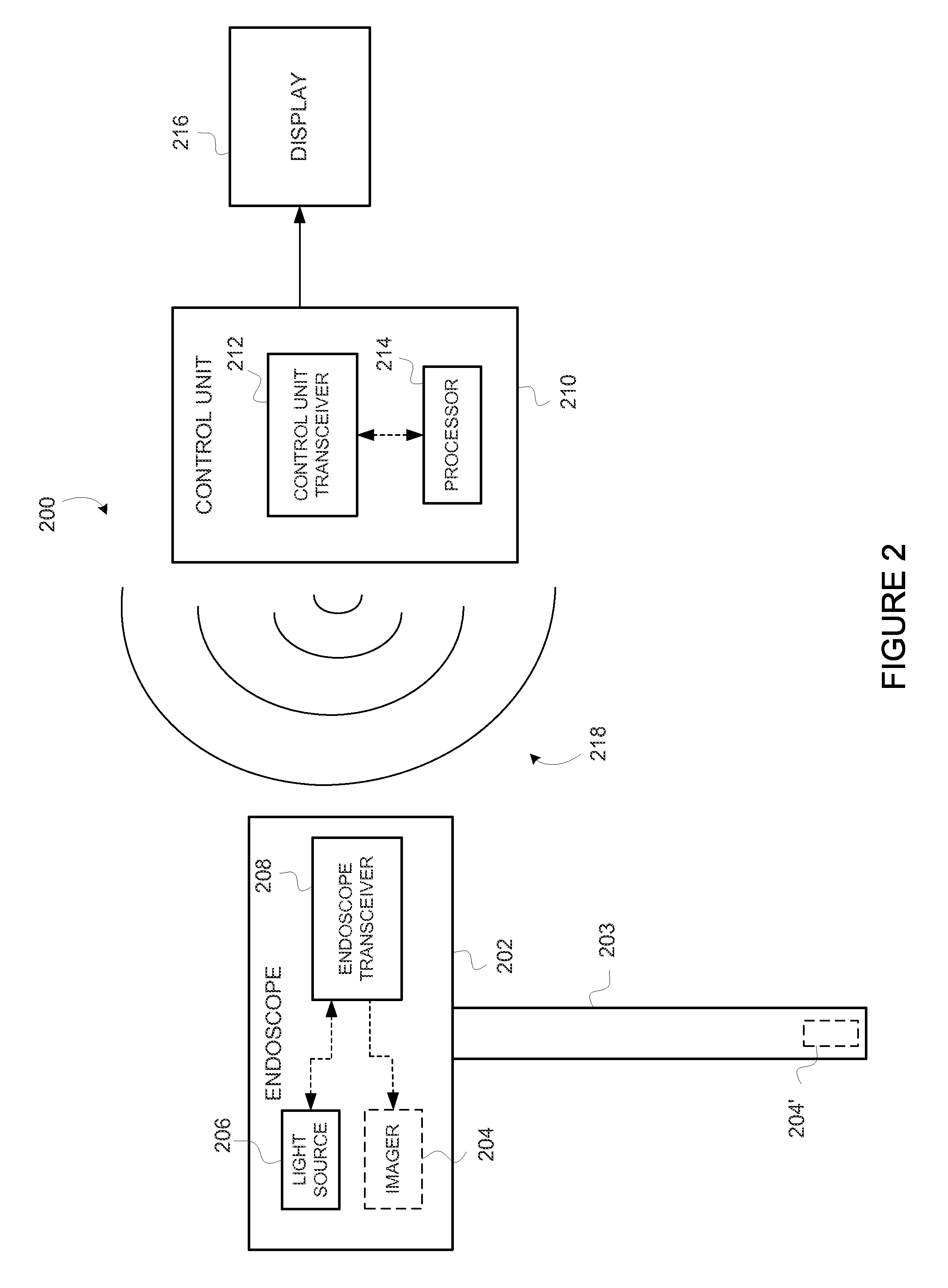
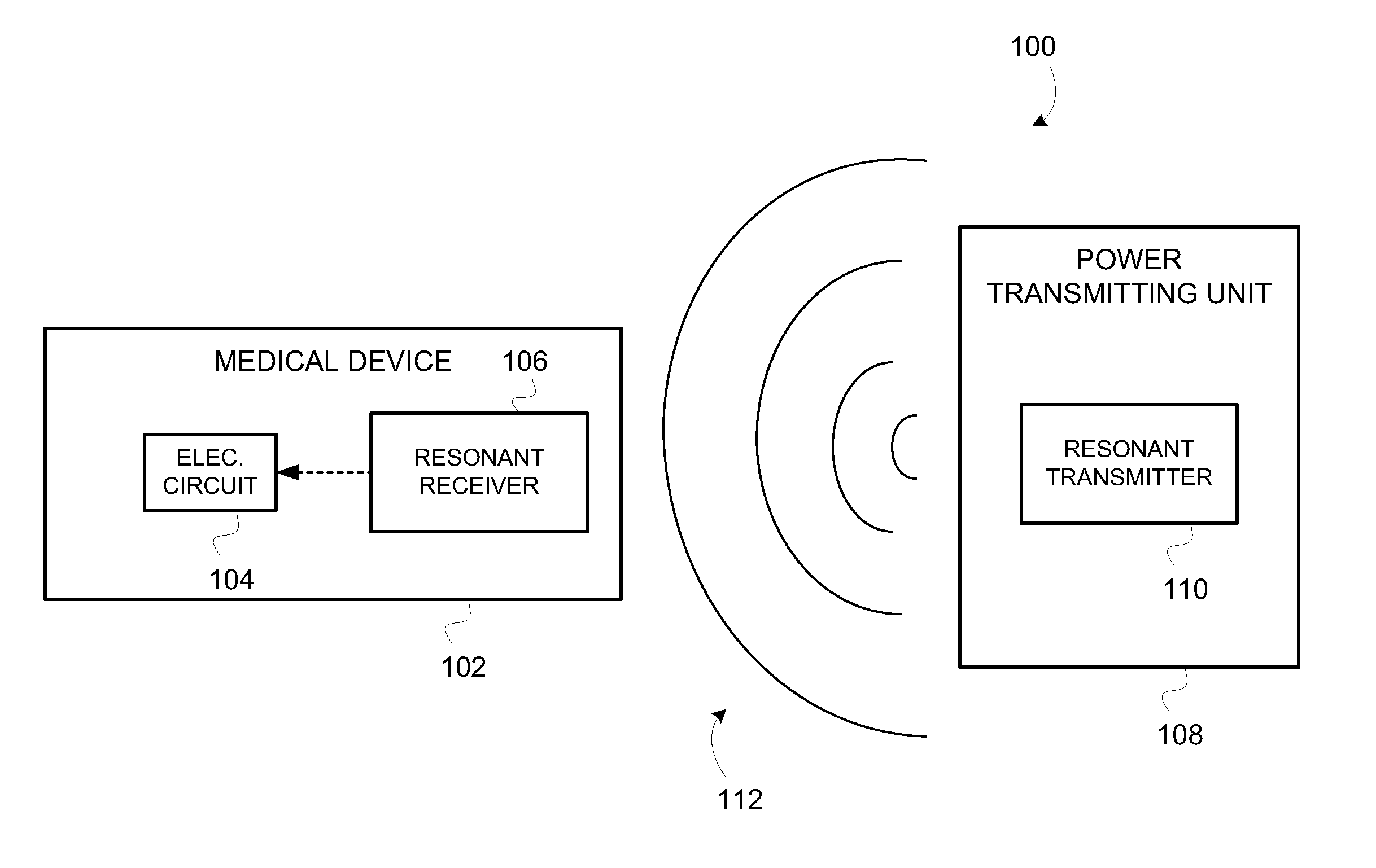
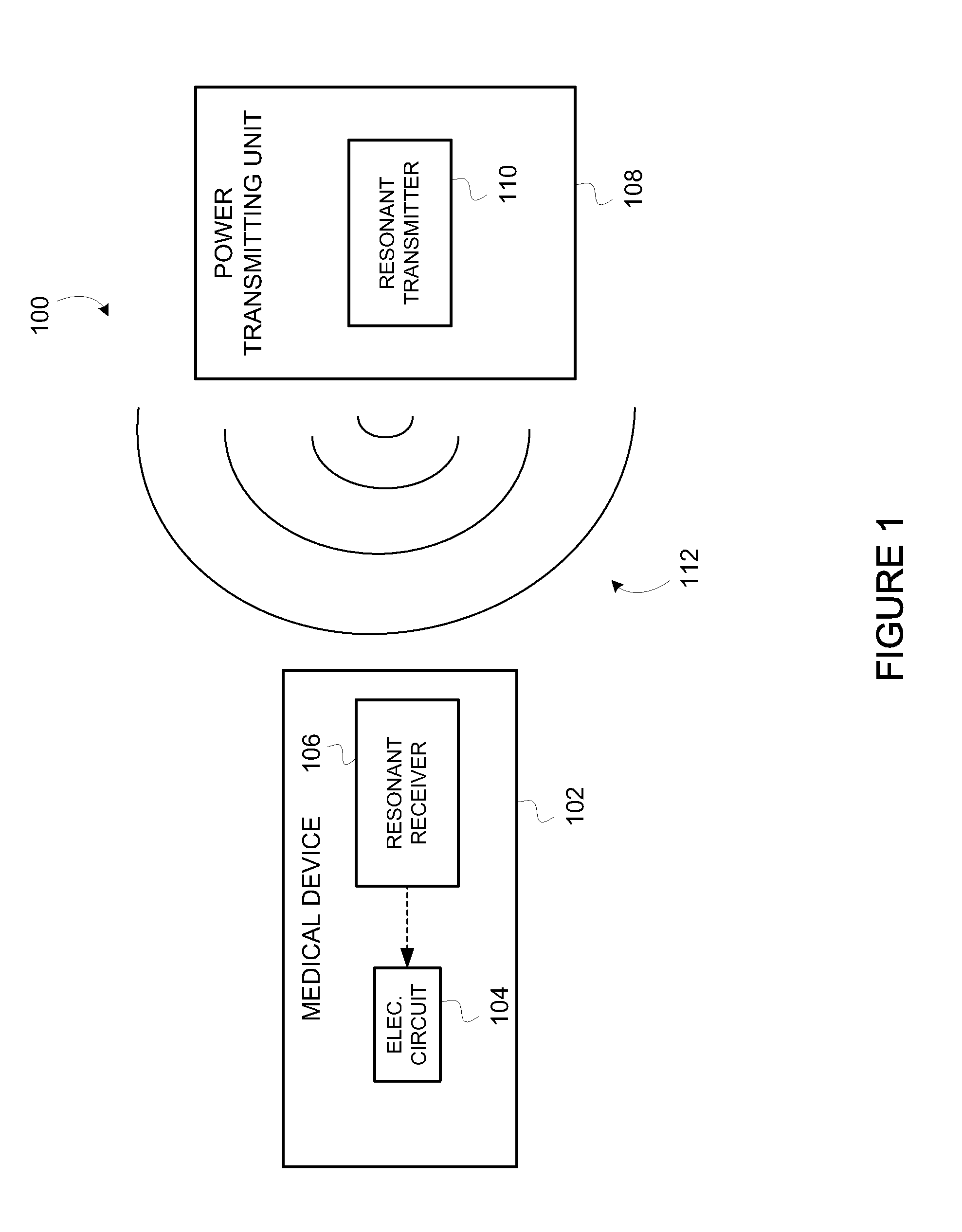
Wirelessly powered medical devices and instruments
ActiveUS9526407B2Eliminate the problemProblem can be addressedSurgeryEndoscopesMedical deviceMedical treatment
A medical device that is wirelessly powered by a resonant magnetic field, the device automatically coupling to a power transmitter in a control unit when brought within a threshold radius. In one embodiment, the control unit automatically identifies the medical device and automatically adjusts its settings to control the medical device.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
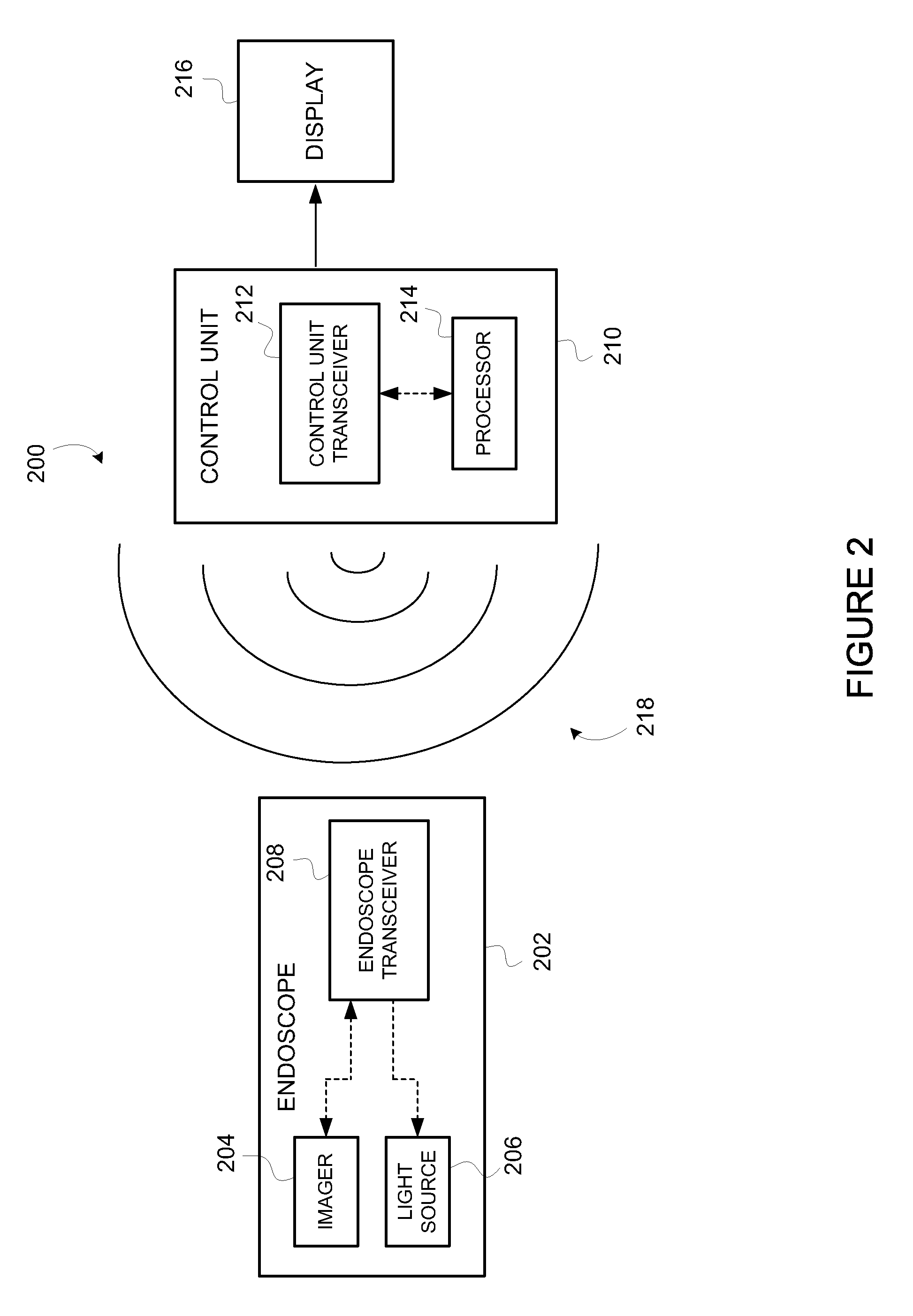
Wirelessly Powered Medical Devices And Instruments
ActiveUS20100179384A1Eliminate the problemProblem can be addressedSurgeryEndoscopesCamera controlTransceiver
A medical device that is wirelessly powered by a resonant magnetic field, the device automatically coupling to a power transmitter in a control unit when brought within a threshold radius. In one embodiment, the control unit automatically identifies the medical device and automatically adjusts its settings to control the medical device, where the device and power transceivers may be provided detachable from either or both the endoscope / camera and camera control unit or may be provide integral to either one or both.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Virtual application manager
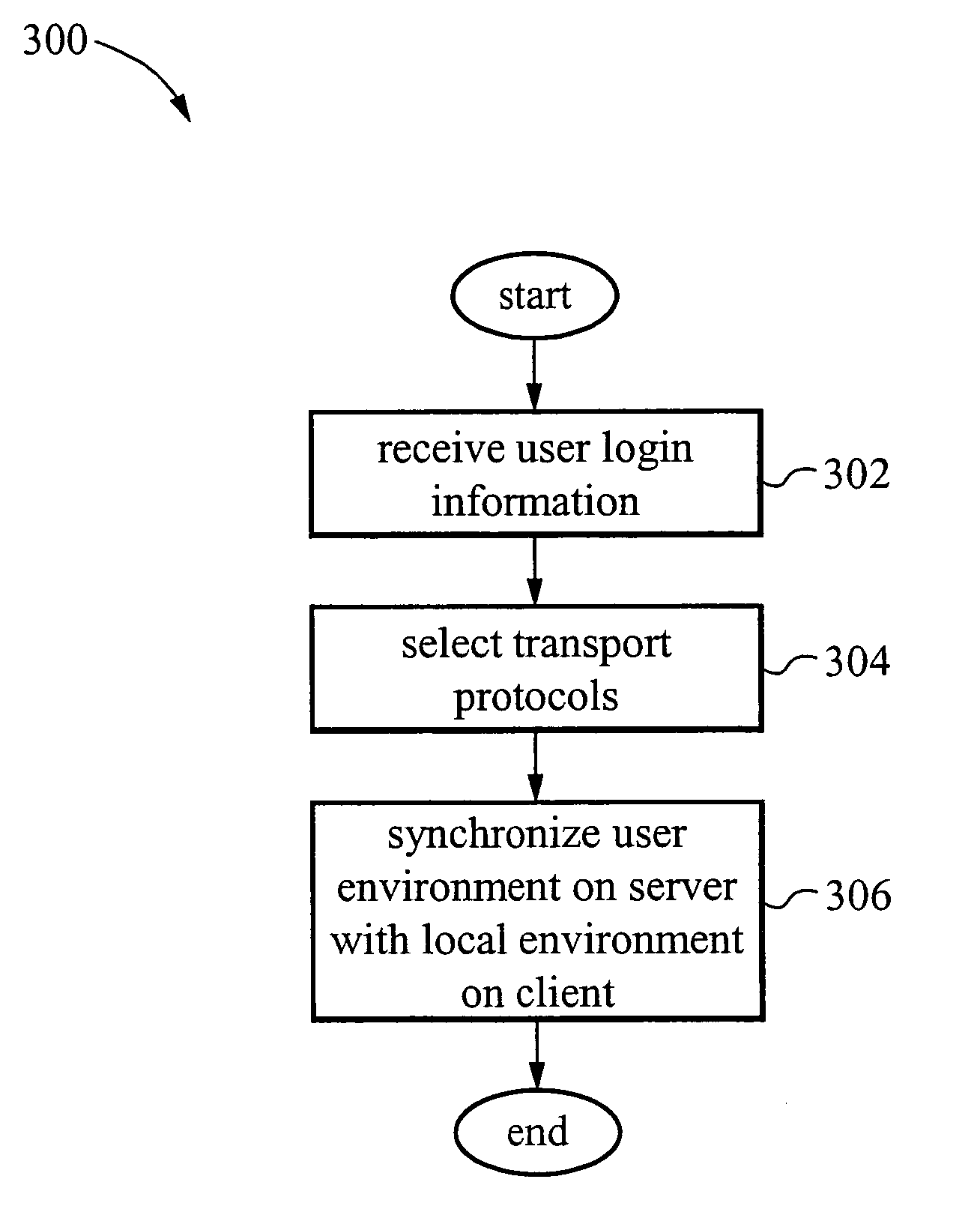
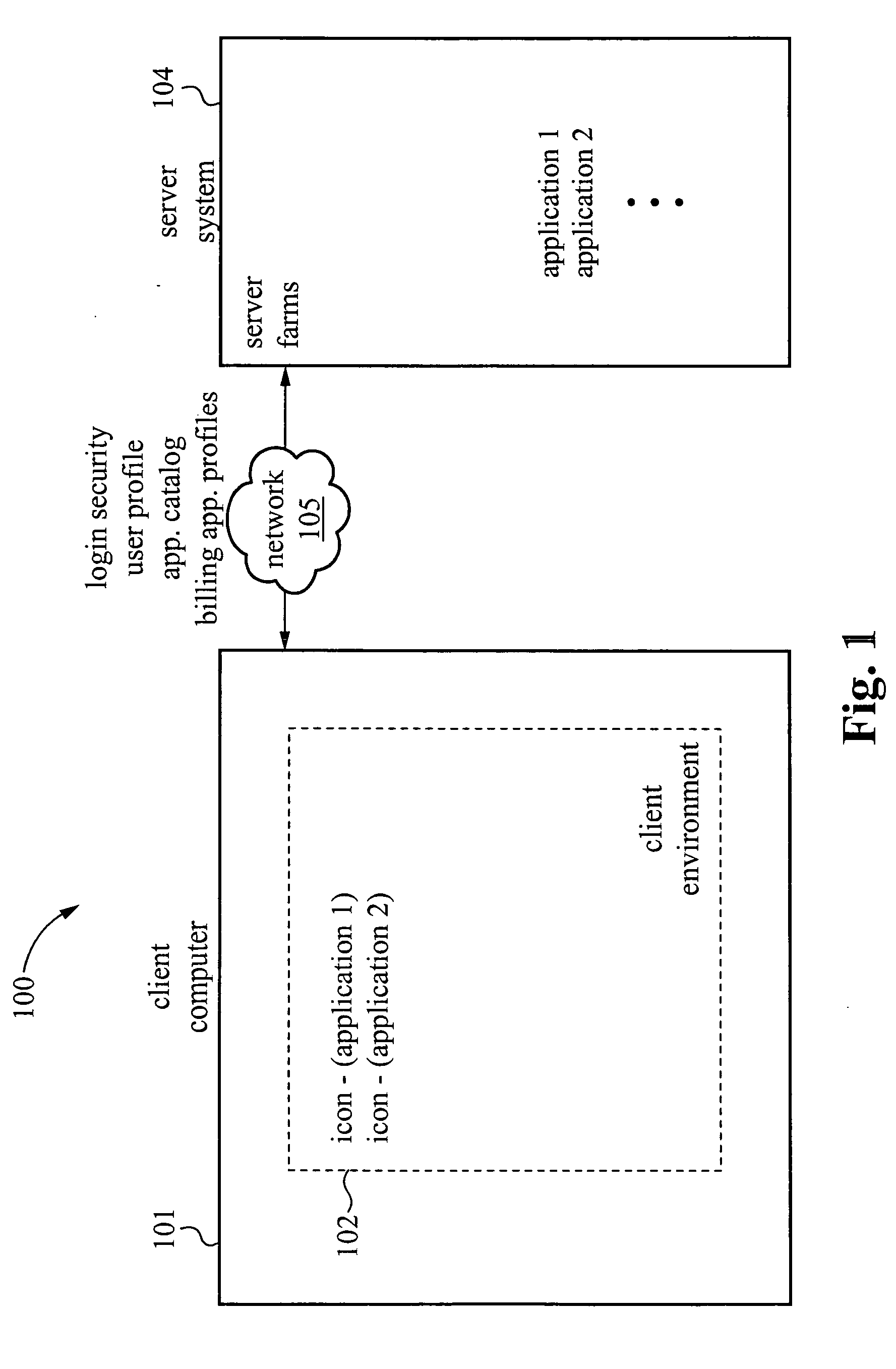
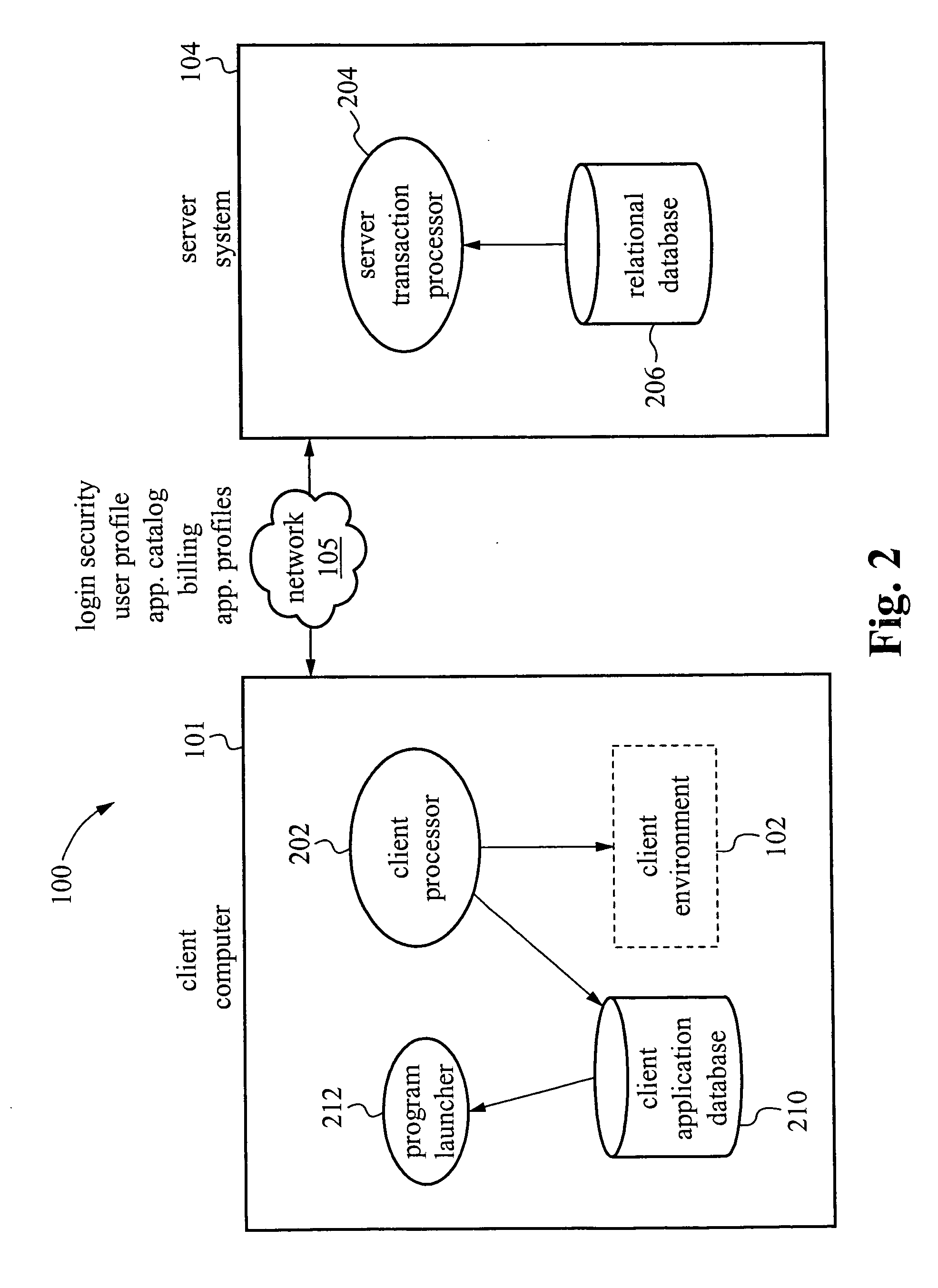
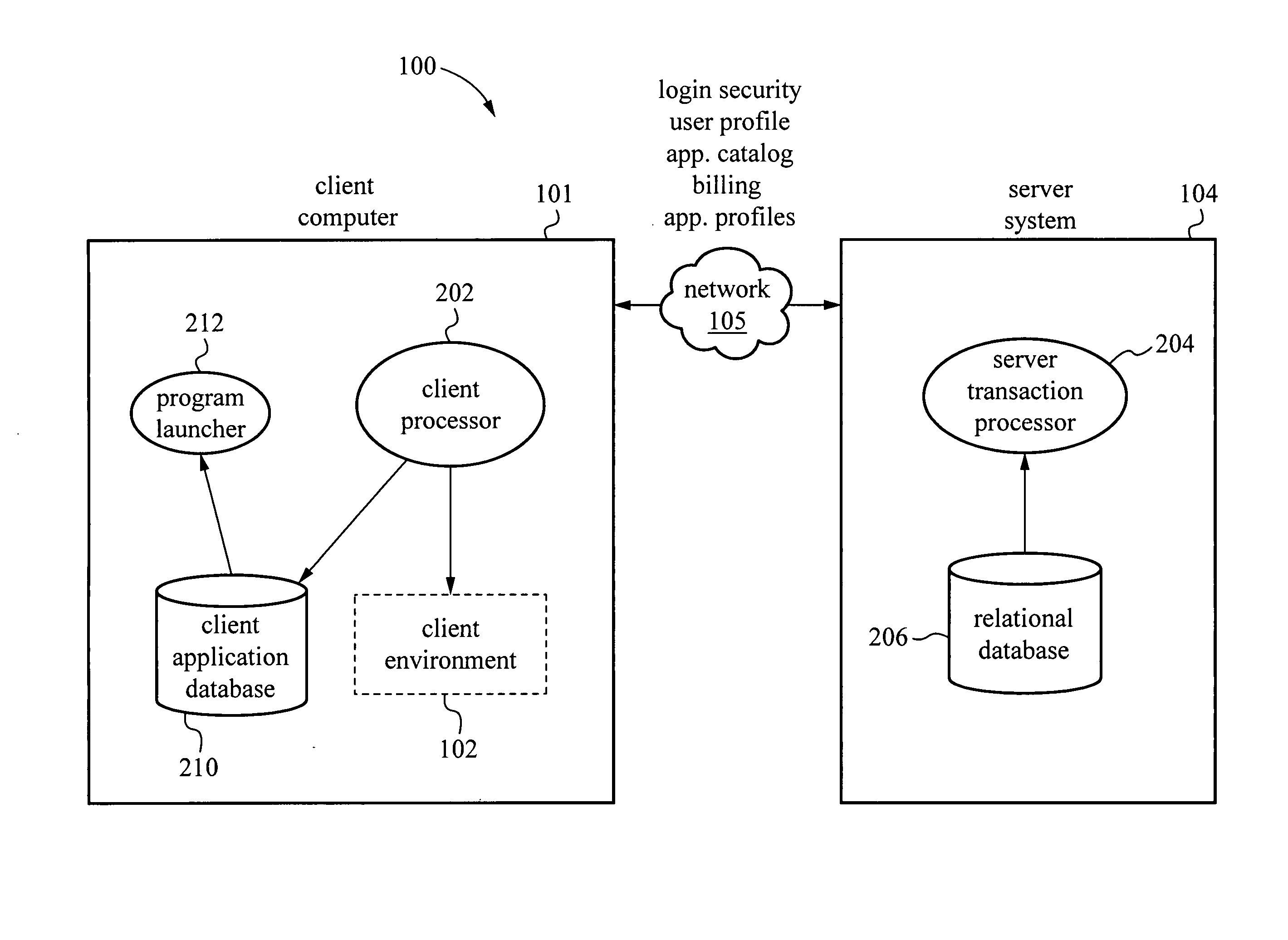
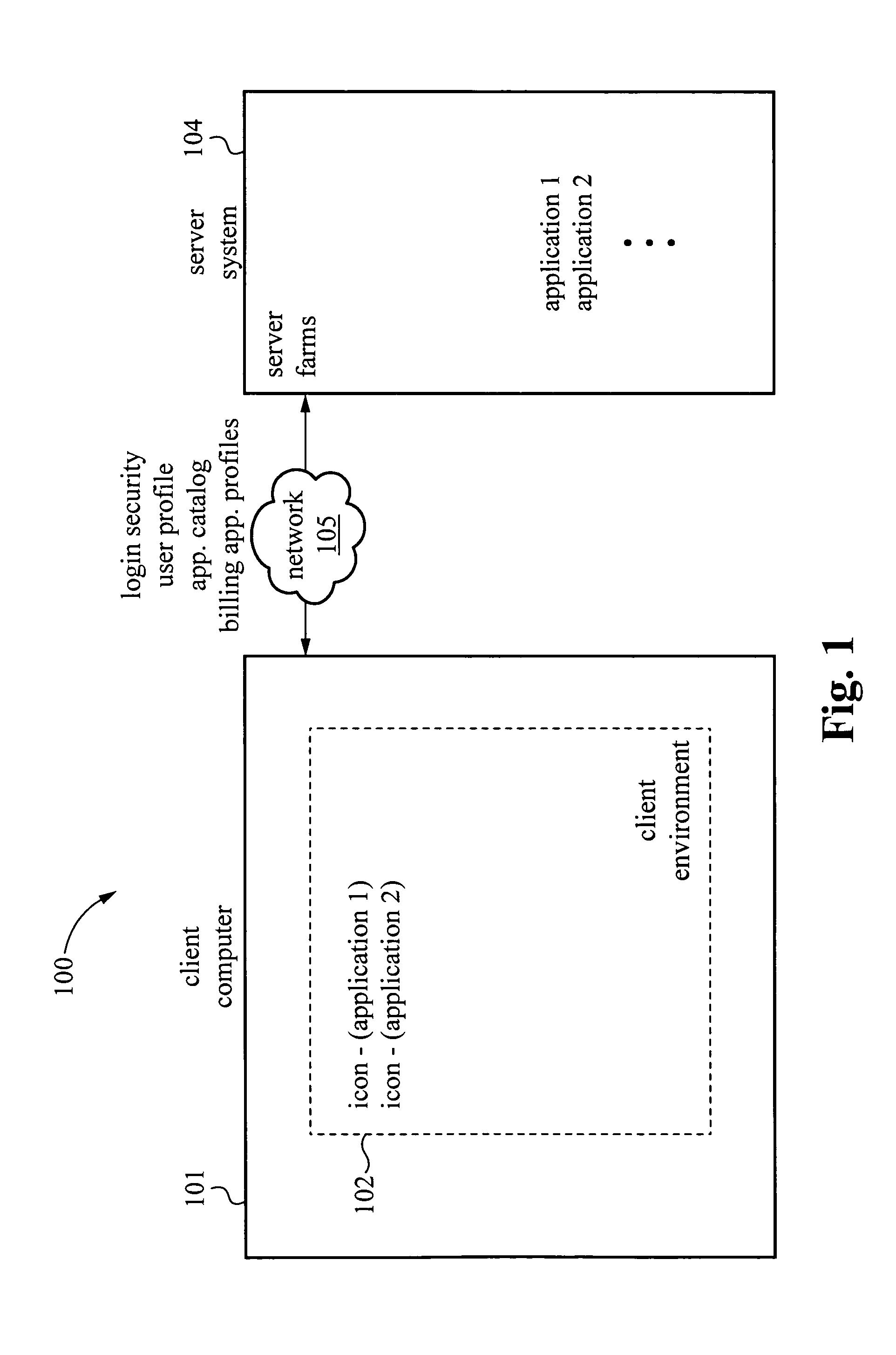
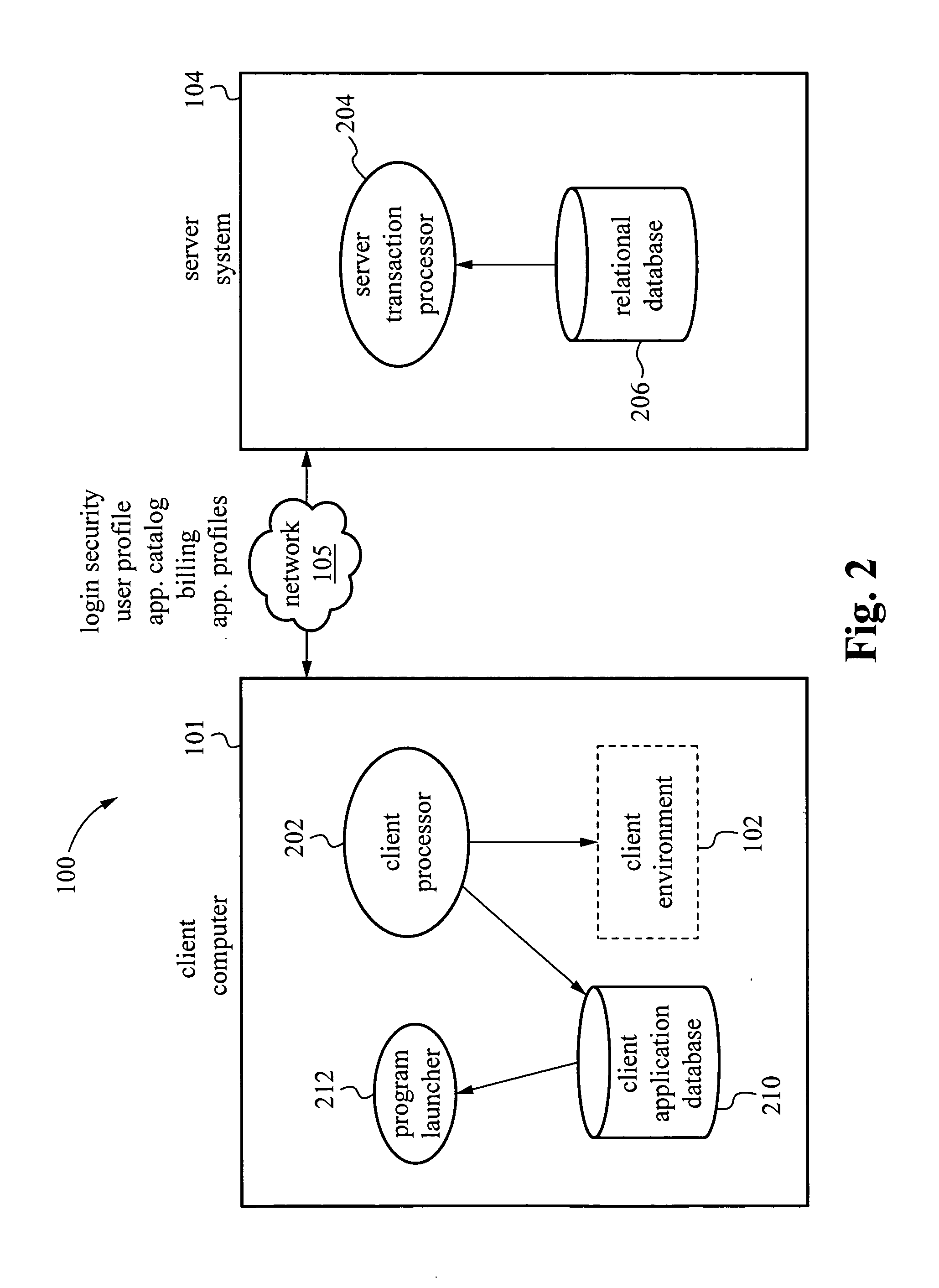
InactiveUS20060031529A1Problem can be addressedMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionClient-sideApplication software
A system and method are provided for managing applications over a network between a server system and client computers. In one example, the method involves receiving user login information from a client computer, then accessing on the server system a user profile associated with the login information. The user profile includes a user environment configuration for a client environment. Transport protocols are selected based on the user profile. The transport protocols are protocols for transporting information between the server system and the client computer. The user environment configuration stored on the server system is then synchronized with a client environment configuration on the client computer.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Alignment, Verification, and Optimization of High Power Wireless Charging Systems
ActiveUS20140217966A1Improve the level ofProblem can be addressedBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsParking spaceElectric vehicle
Provided are a method and apparatus and method for the alignment, verification and optimization of wireless charging systems manufactured for use and used with electric vehicles. With some minimal modifications the same apparatus may be used to align a charging coil mounted on a vehicle with a charging coil, mounted on or in an electric vehicle charging bay or parking space, or to verify and optimize manufactured wireless vehicle charging system elements before they are installed.
Owner:WIRELESS CHARGE
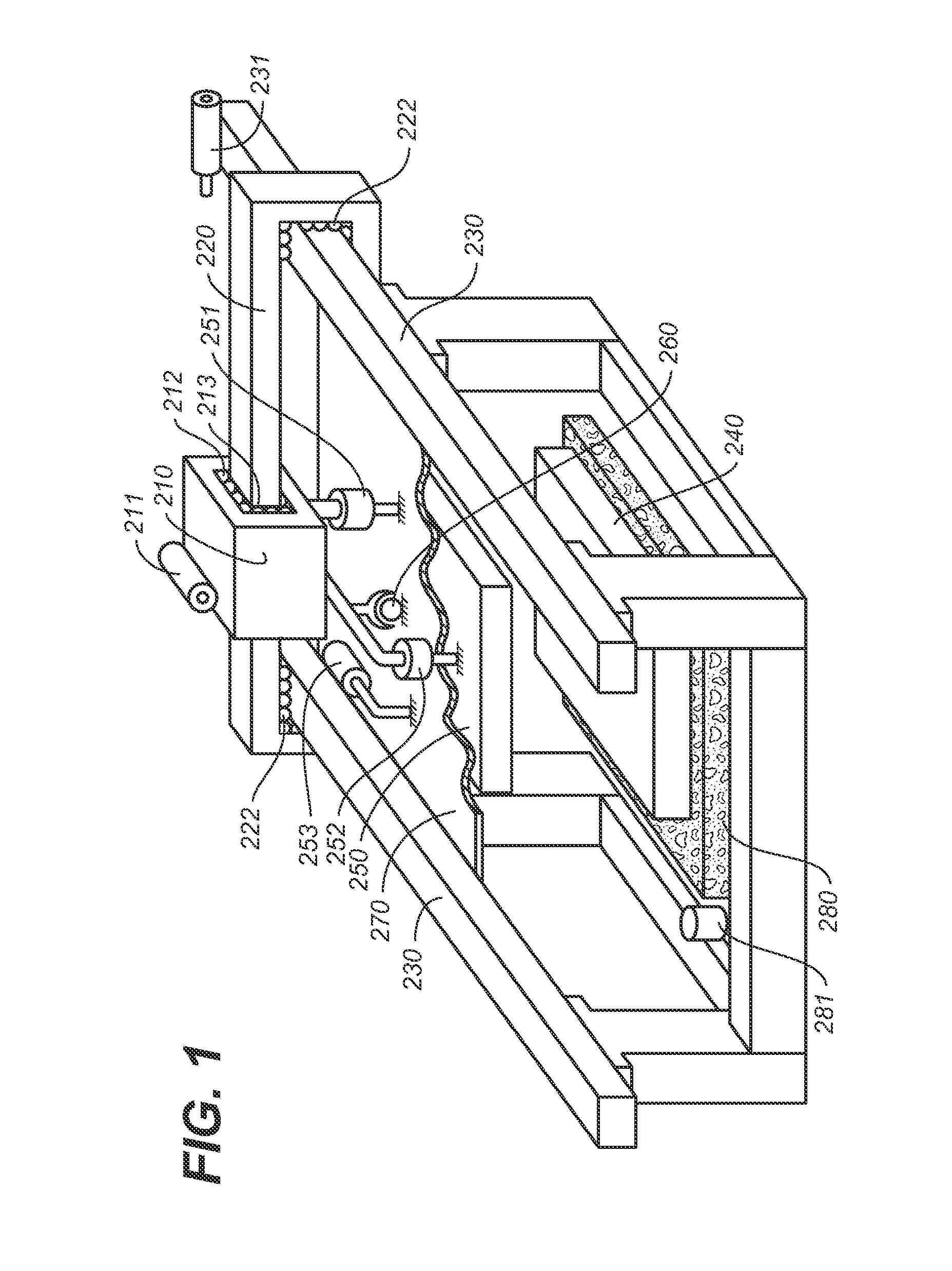
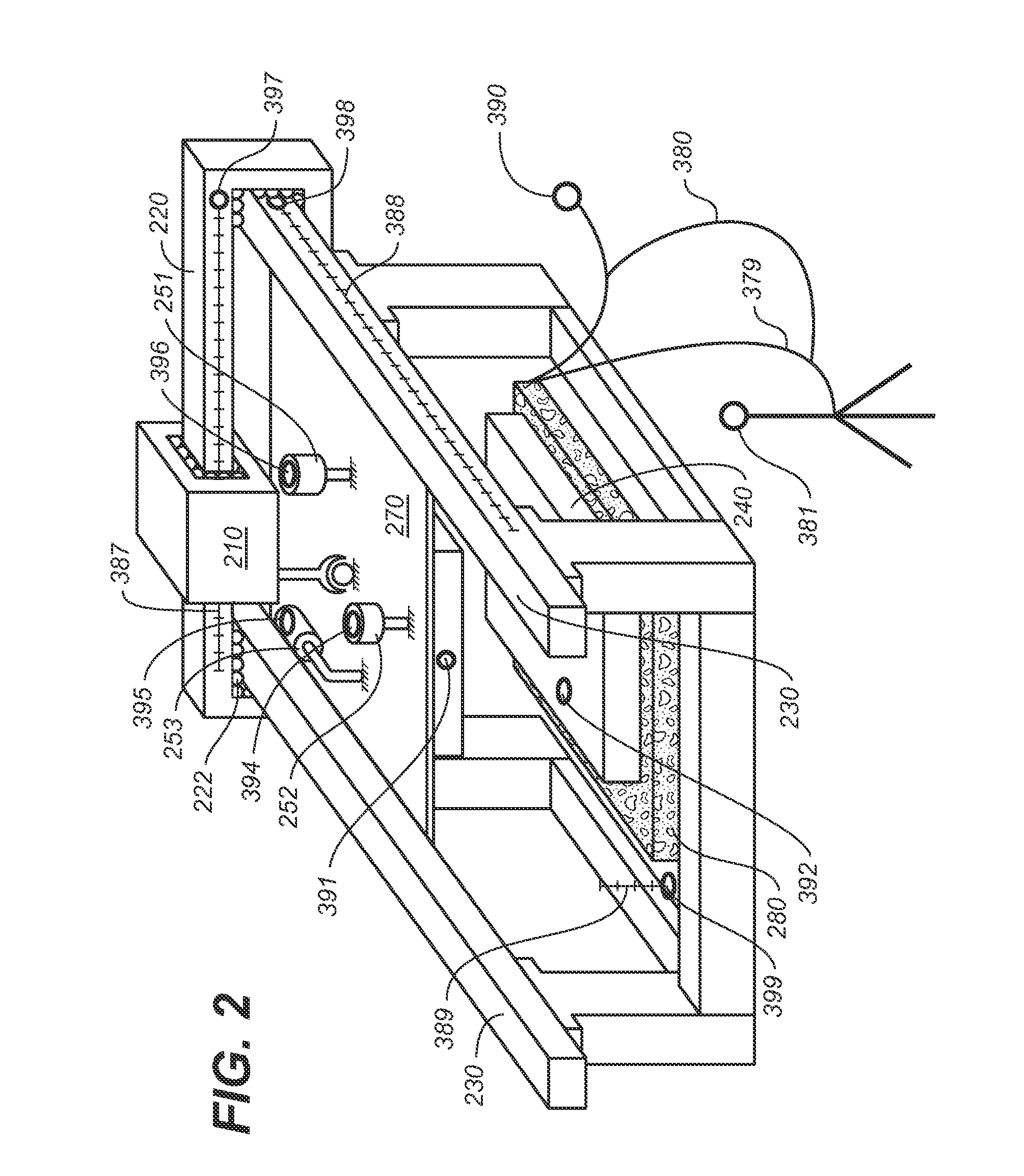
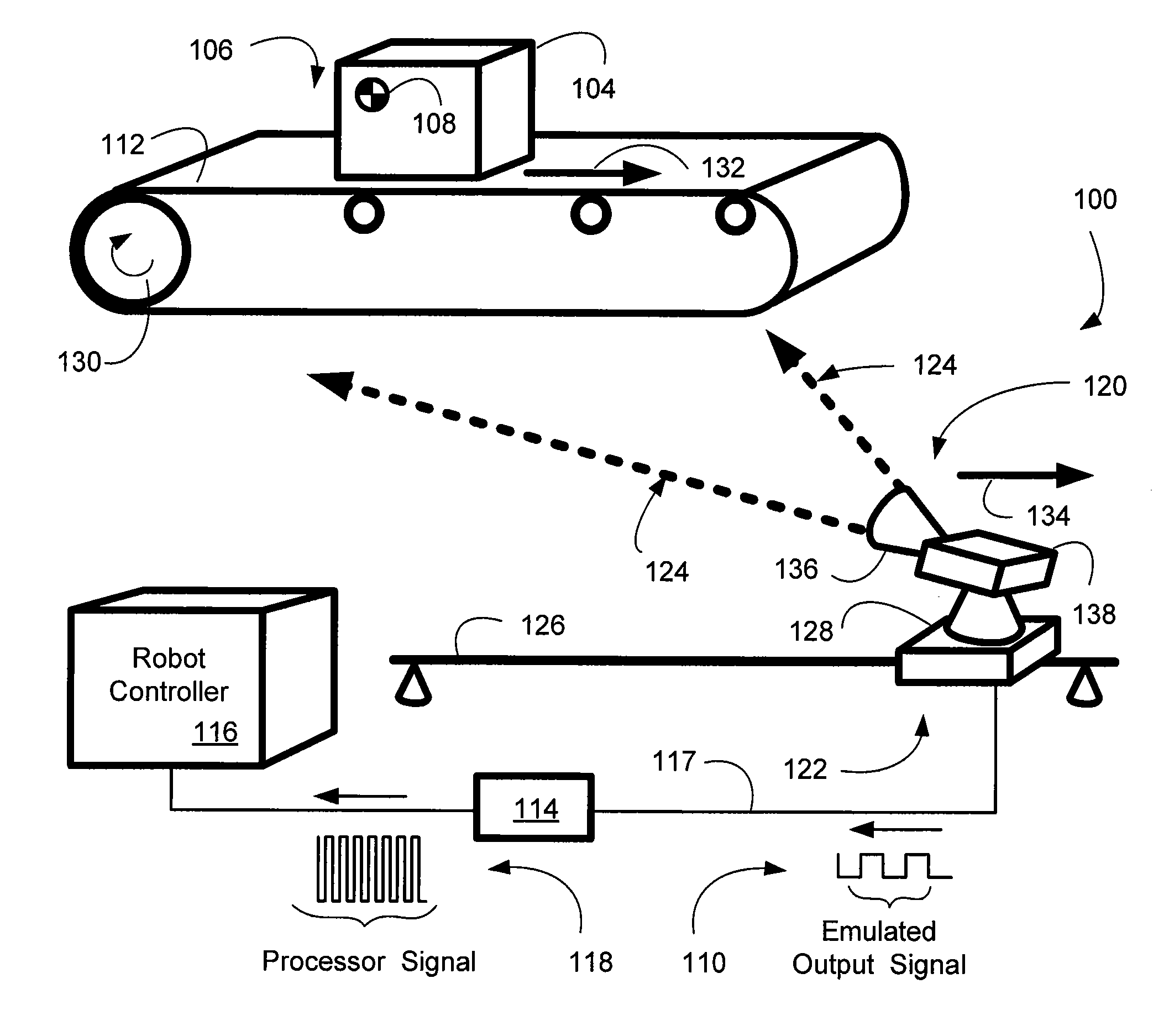
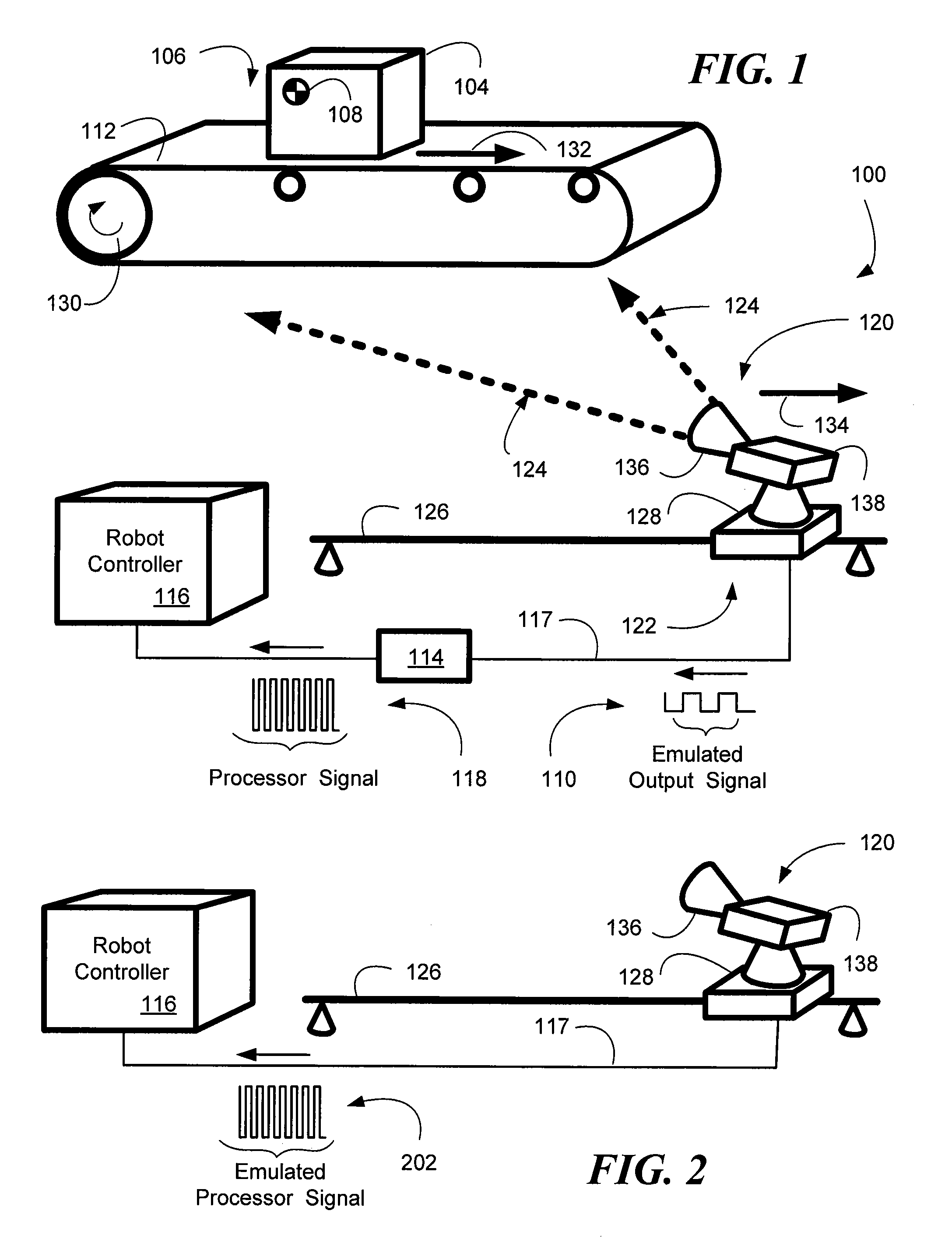
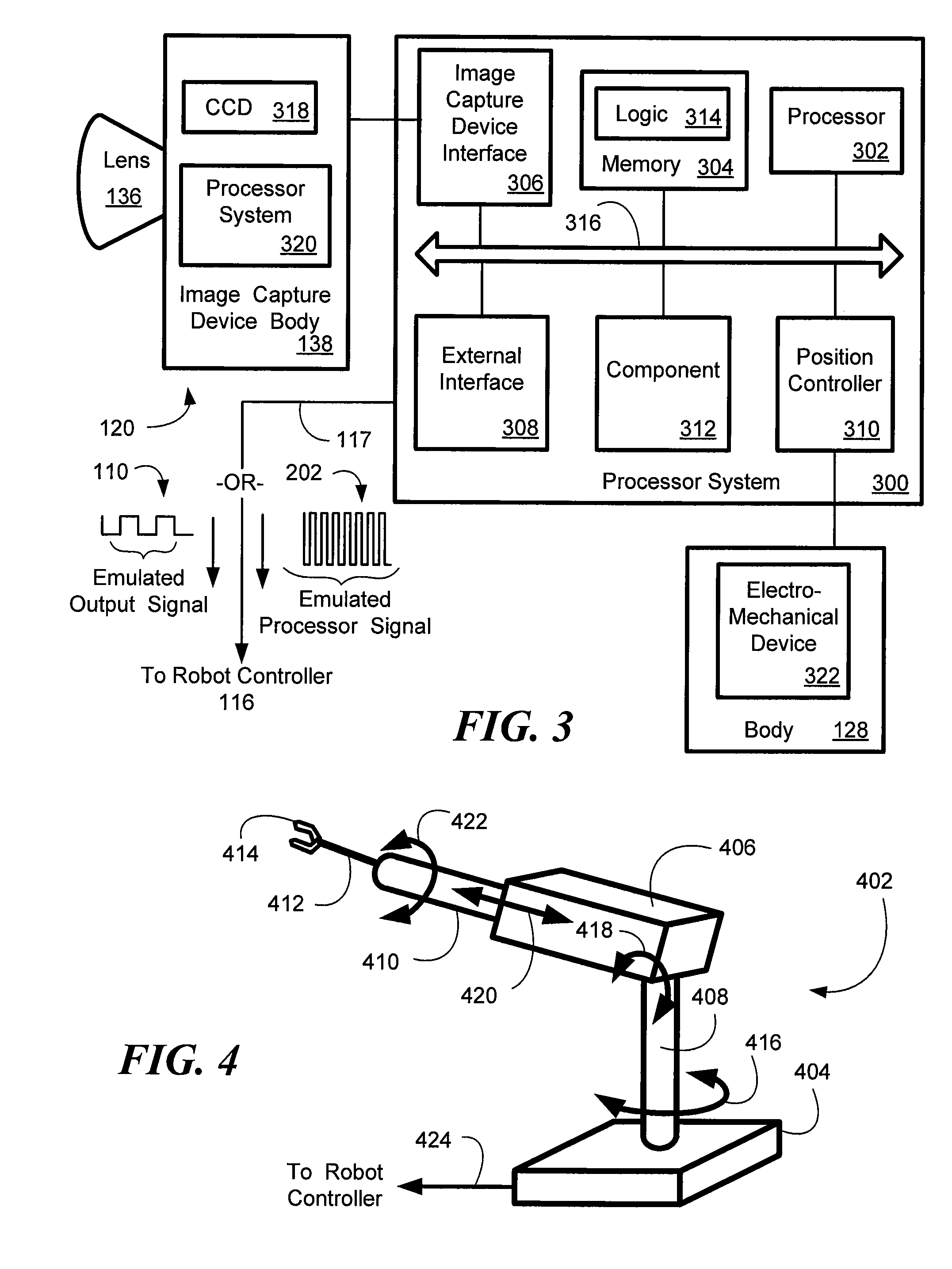
System and method of visual tracking
InactiveUS20070073439A1Eliminate dependenciesProblem can be addressedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital dataRobotics
A machine-vision system, method and article is useful in the field of robotics. One embodiment produces signals that emulate the output of an encoder, based on captured images of an object, which may be in motion. One embodiment provides digital data directly to a robot controller without the use of an intermediary transceiver such as an encoder interface card. One embodiment predicts or determines the occurrence of an occlusion and moves at least one of a camera and / or the object accordingly.
Owner:BRAINTECH
Streaming Method and System for Processing Network Metadata
InactiveUS20140075557A1Easy to deployImprove system throughputMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficTemplate based
An improved method and system for processing network metadata is described. Network metadata may be processed by dynamically instantiated executable software modules which make policy-based decisions about the character of the network metadata and about presentation of the network metadata to consumers of the information carried by the network metadata. The network metadata may be type classified and each subclass within a type may be mapped to a definition by a unique fingerprint value. The fingerprint value may be used for matching the network metadata subclasses against relevant policies and transformation rules. For template-based network metadata such as NetFlow v9, an embodiment of the invention can constantly monitor network traffic for unknown templates, capture template definitions, and informs administrators about templates for which custom policies and conversion rules do not exist. Conversion modules can efficiently convert selected types and / or subclasses of network metadata into alternative metadata formats.
Owner:NETFLOW LOGIC
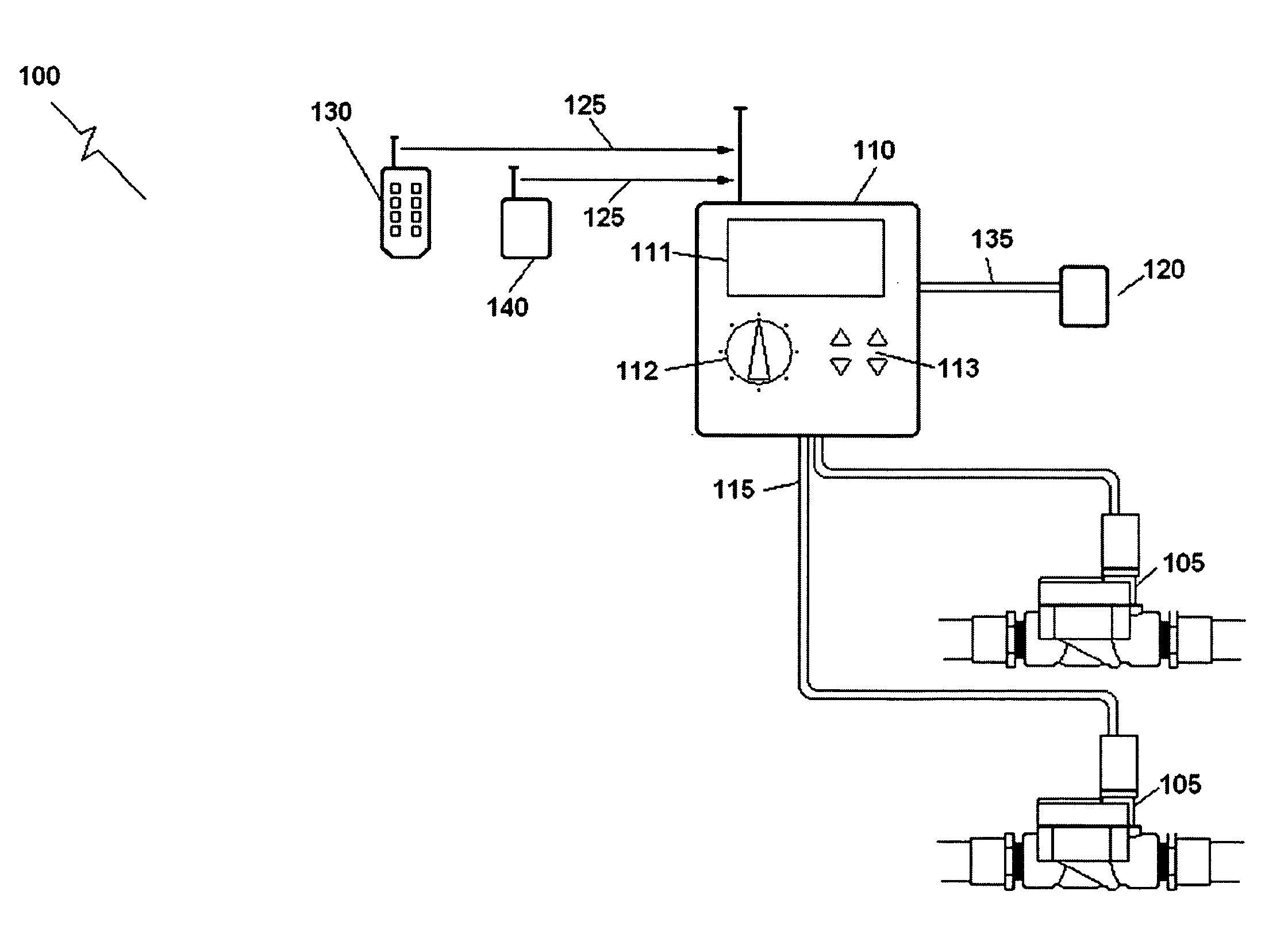
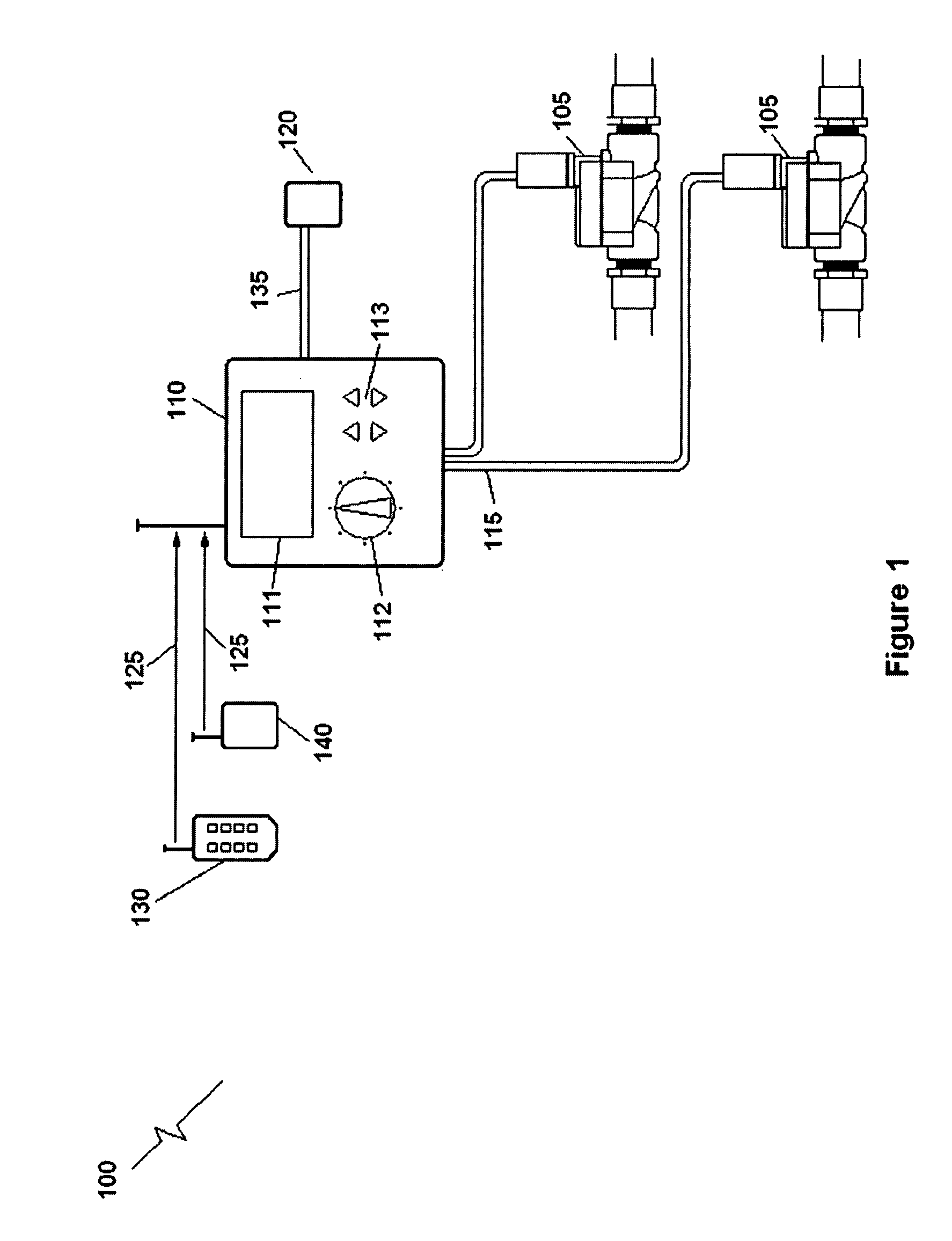
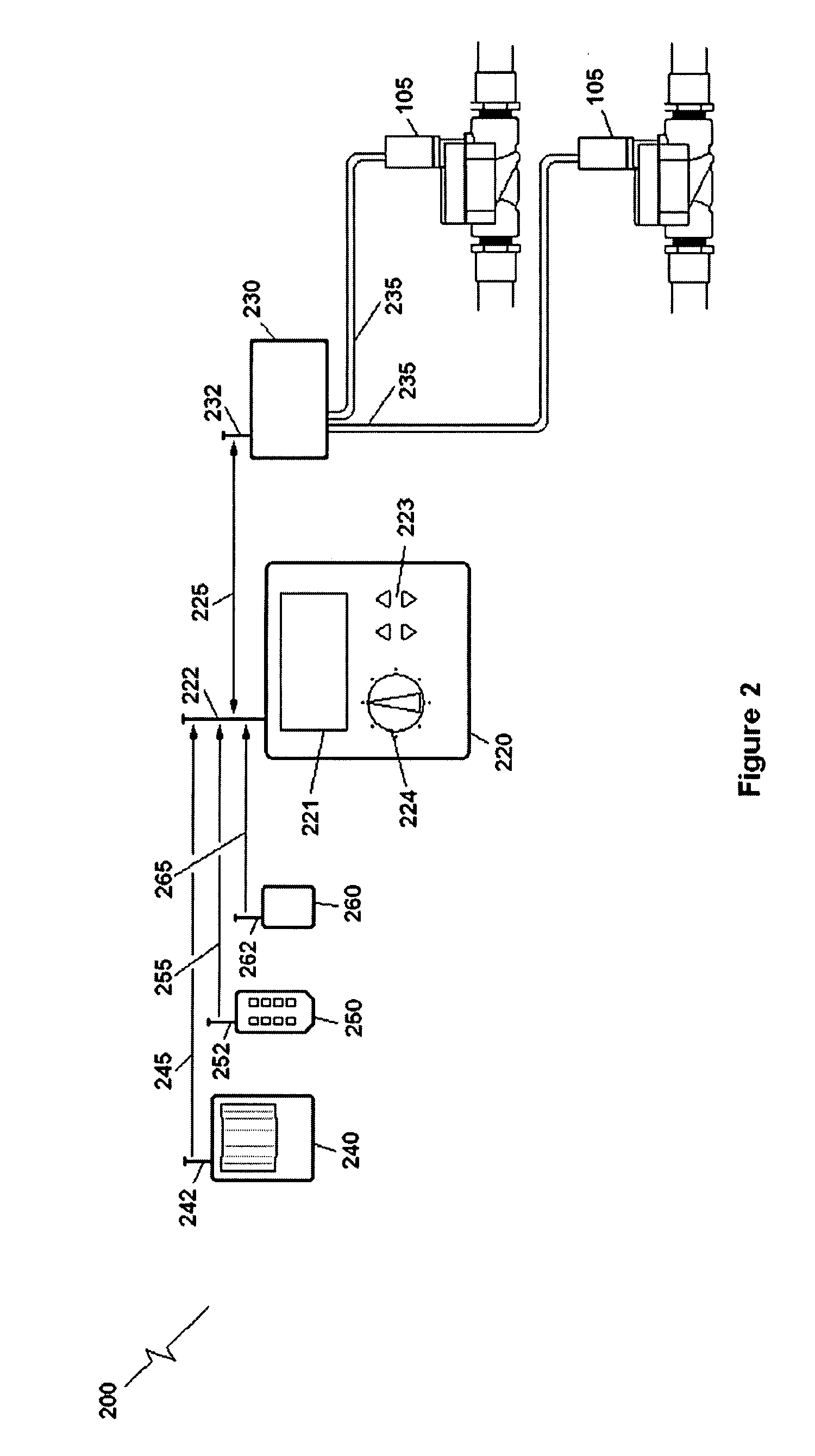
Wireless Irrigation and Trespasser Deterrent Control System (WITDCS)
InactiveUS20080251602A1Cost effectiveEliminate needSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationMotion detectorEngineering
A Wireless Irrigation and Trespasser Deterrent Control System used for controlling a remote irrigation system comprising a plurality of sprinklers connected by water pipes to one or more electric zone valves having wireless valve controllers. Included is a wireless system controller that communicates with the remote wireless valve controllers when a signal is received from a sensor such as a motion detector in order to turn the sprinklers on or off. Other sensors are possible such as soil moisture sensors and rain sensors. A handheld remote controller is also included.
Owner:LEGGETT CURTIS STEPHEN +1
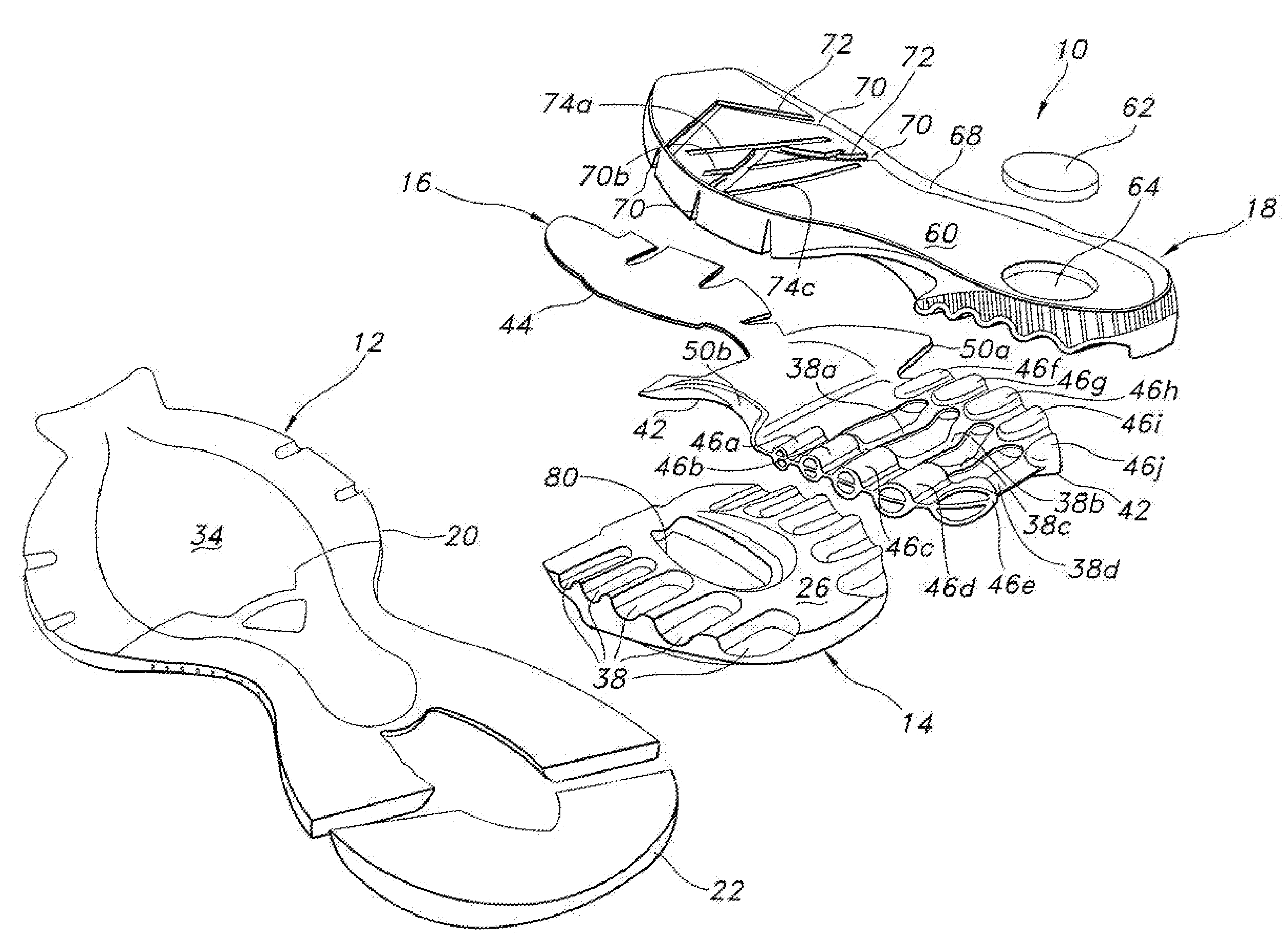
Footwear sole
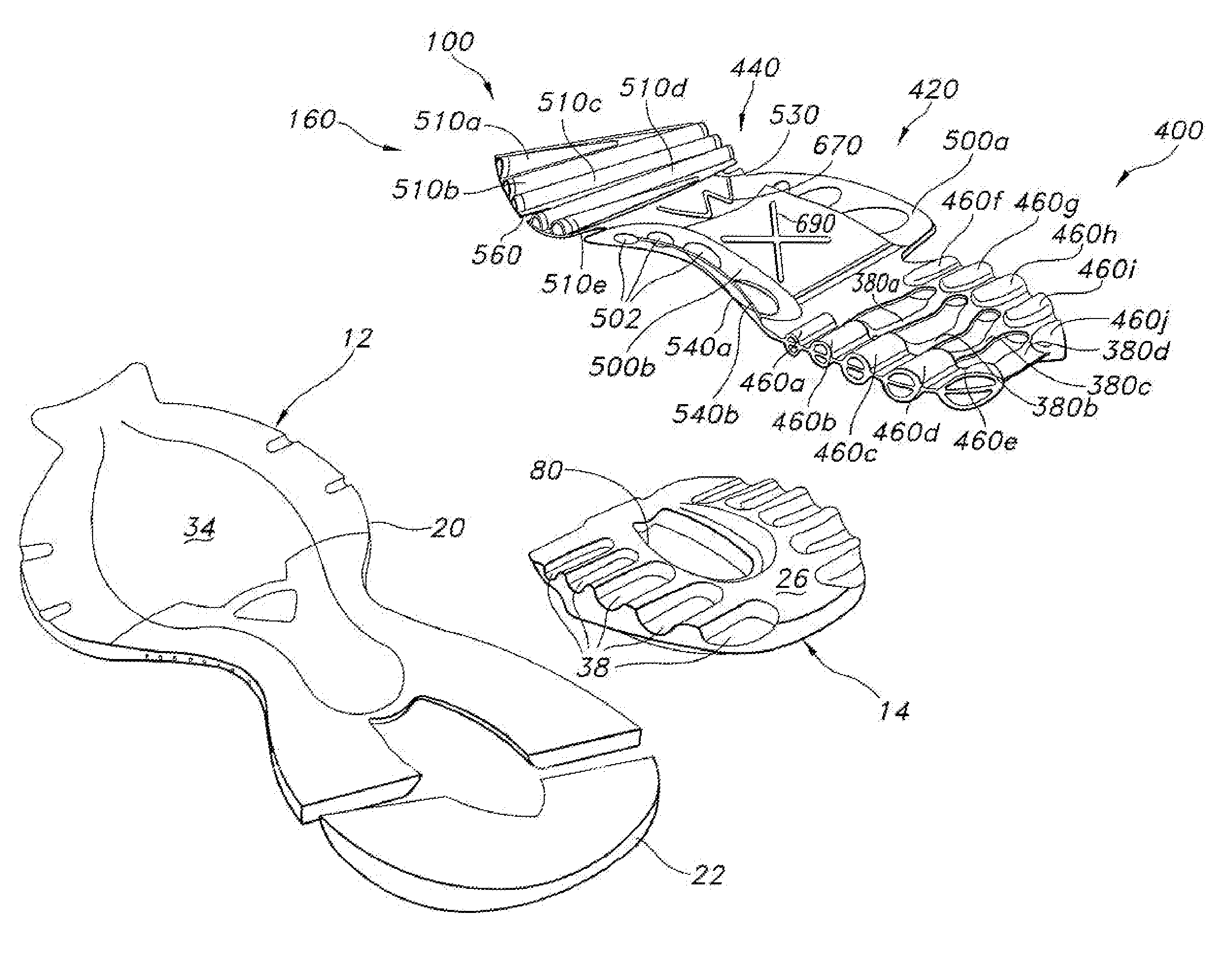
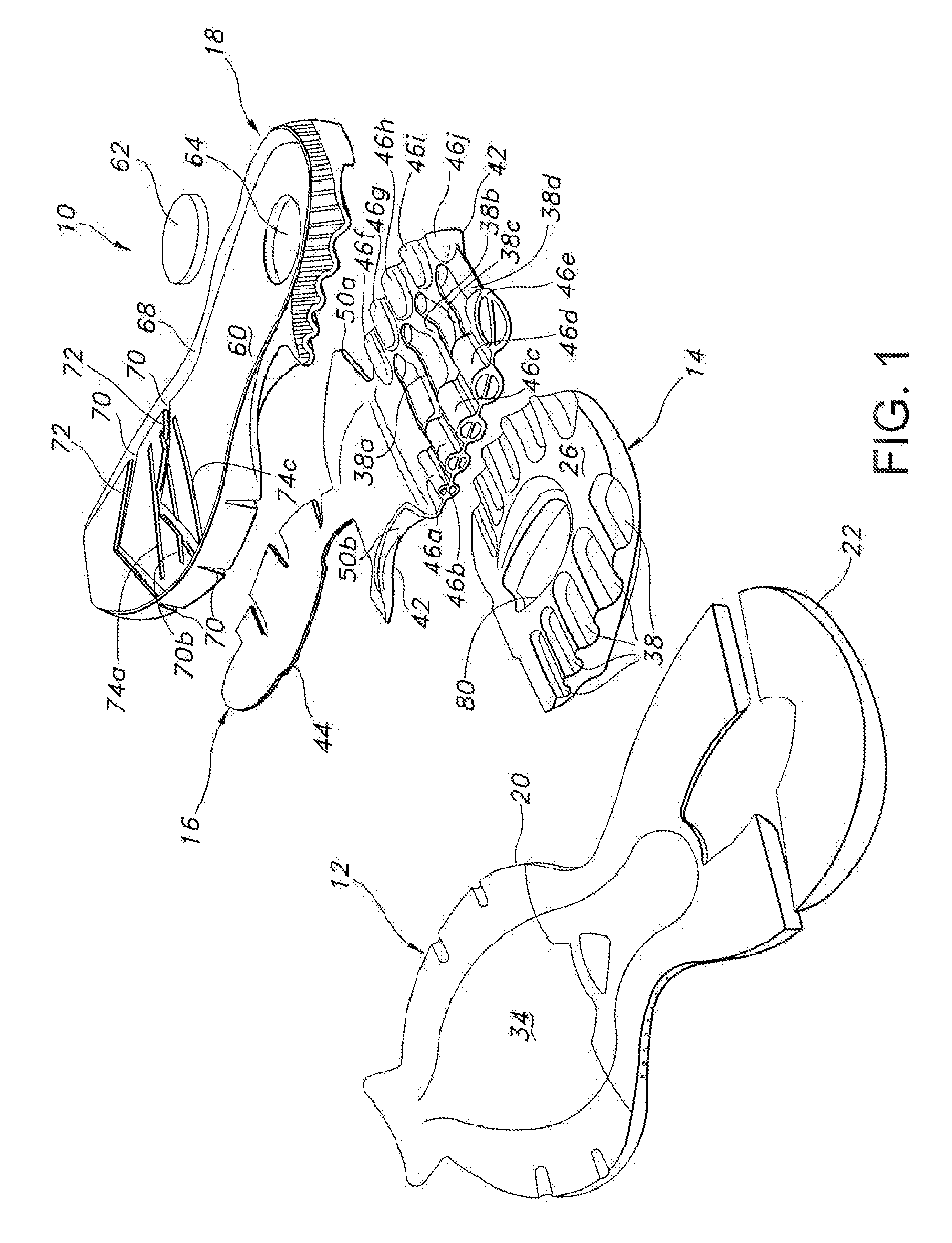
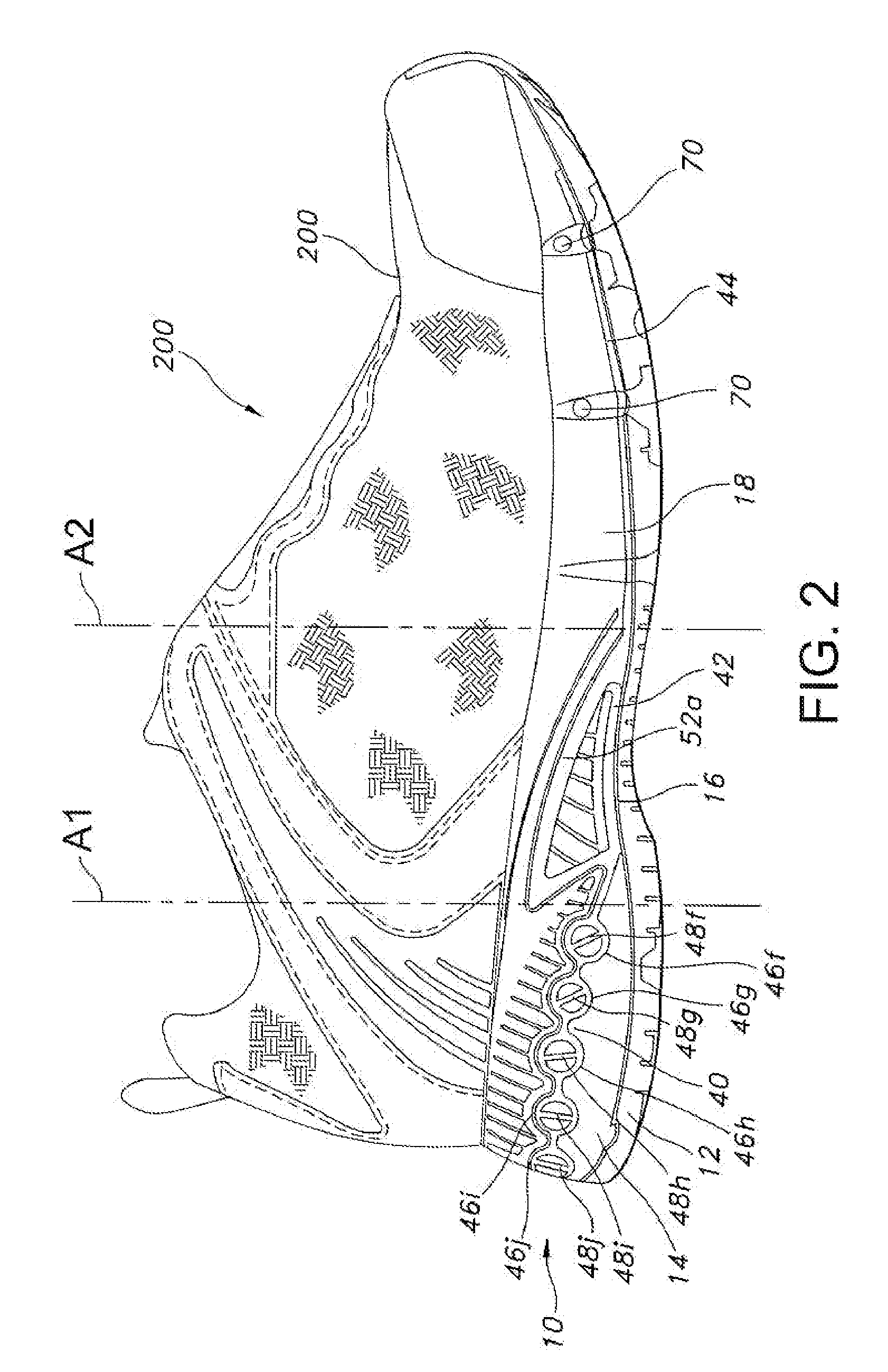
A sole for an article of footwear having an insert with a plurality of forefoot support tubes are configured to control the support characteristics of the sole in a forefoot region of the sole. In one embodiment, the forefoot support tubes each include a base, and a wall extending from the base. The wall is formed from a material that has a lower durometer value than the base. In another embodiment, the forefoot support tubes air arranged in a radiating pattern, such that at least two of the forefoot support tubes diverge as they extend toward the lateral side of the insert.
Owner:WOLVERINE WORLD WIDE INC
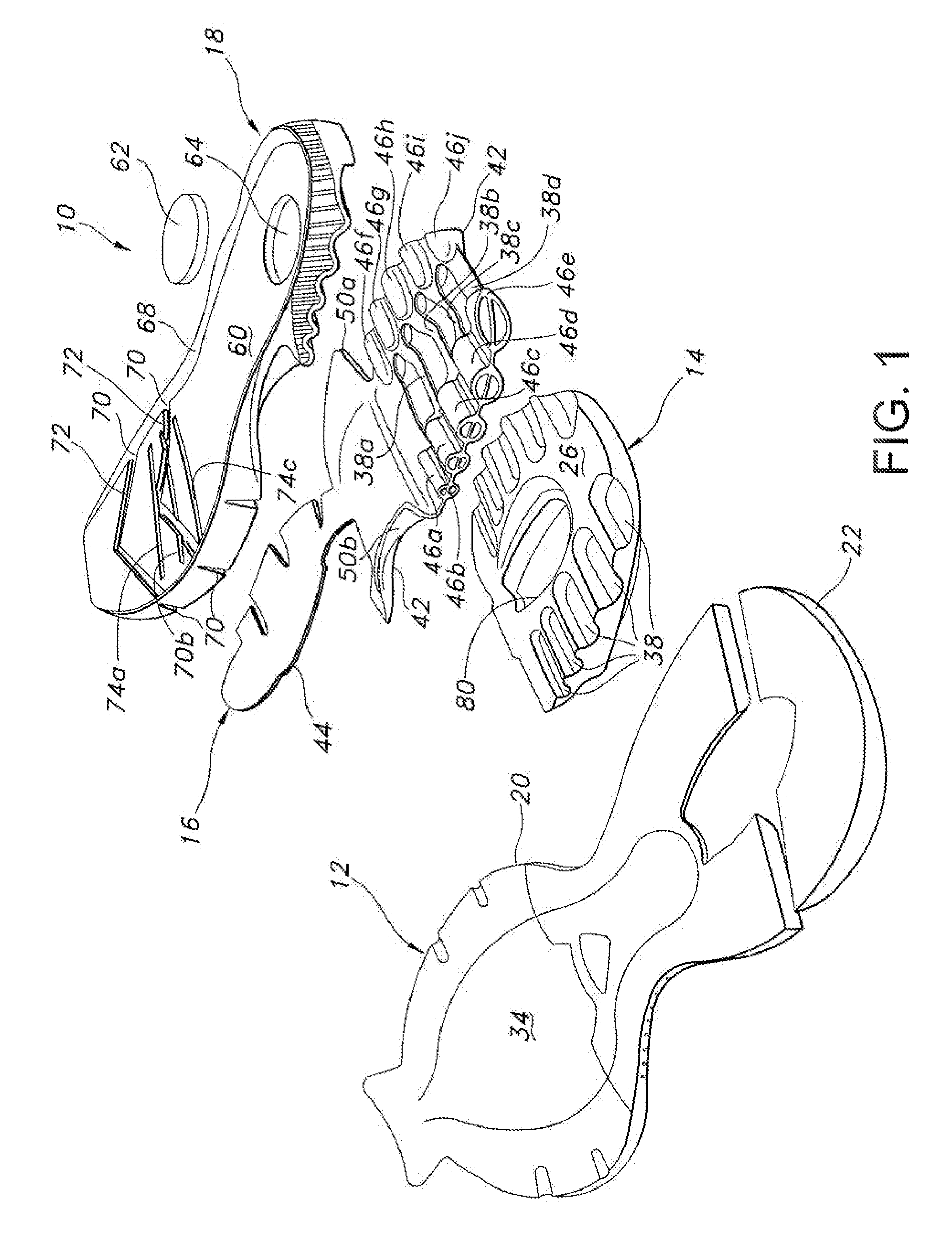
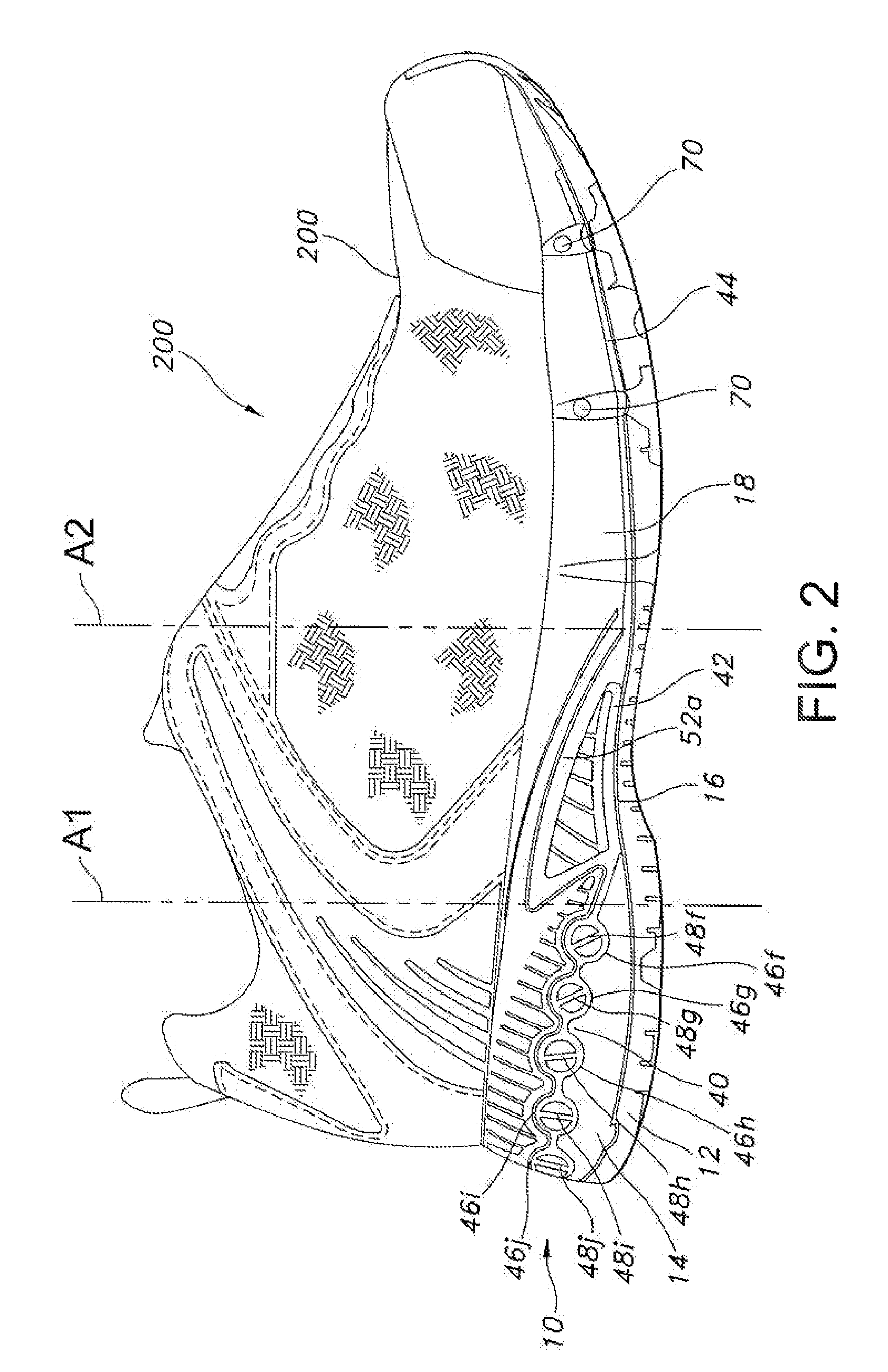
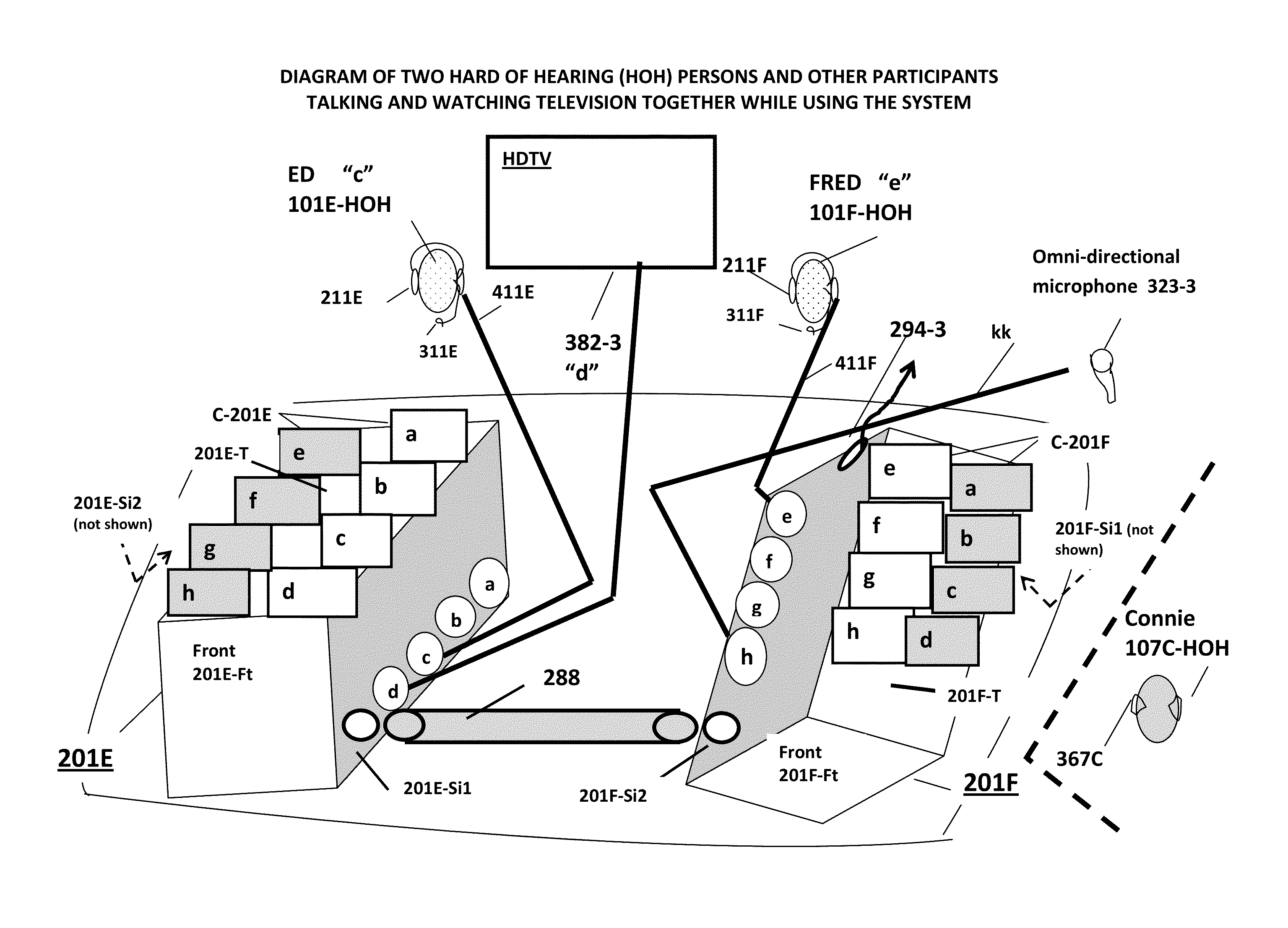
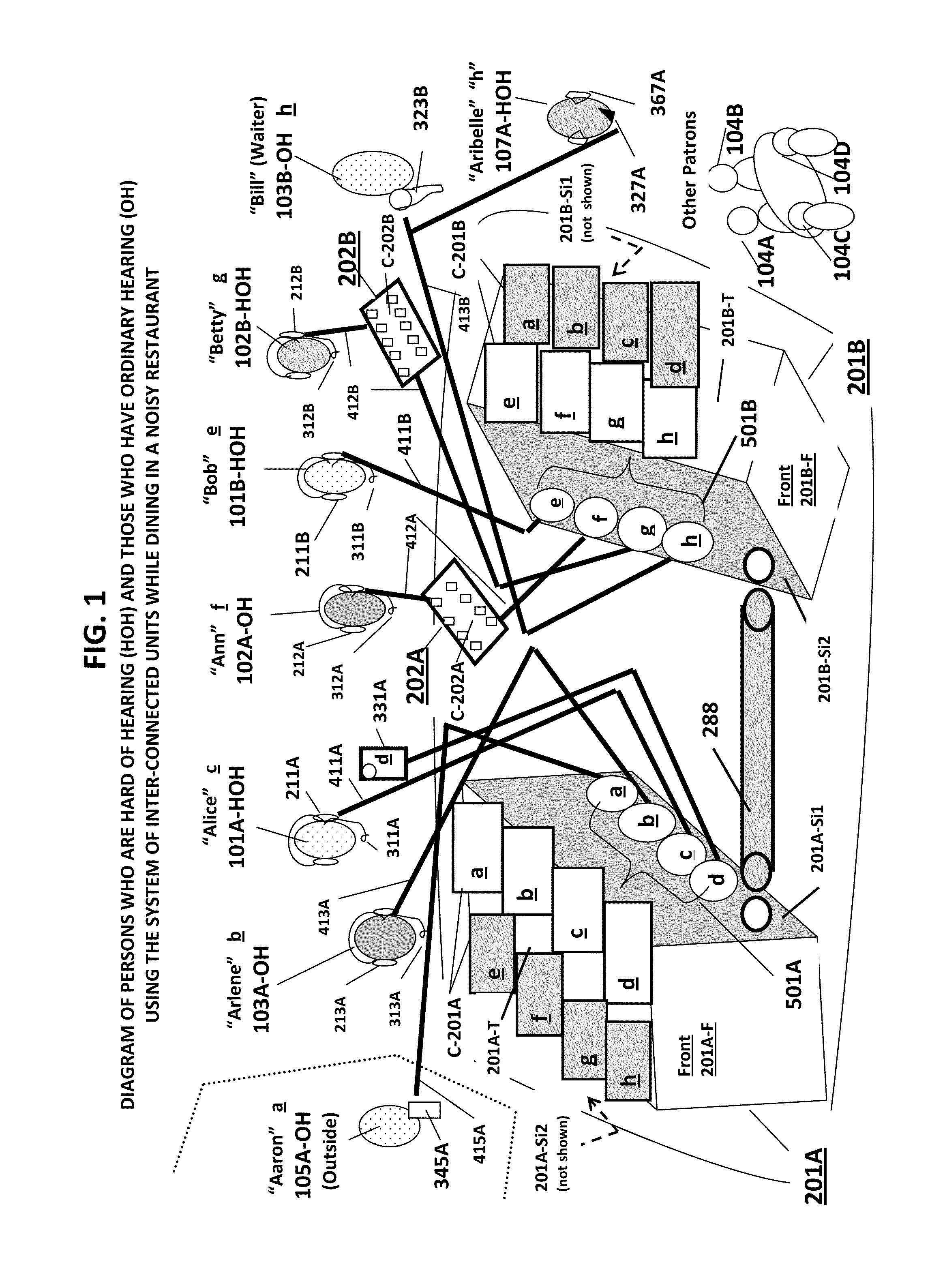
Portable hearing-assistive sound unit system
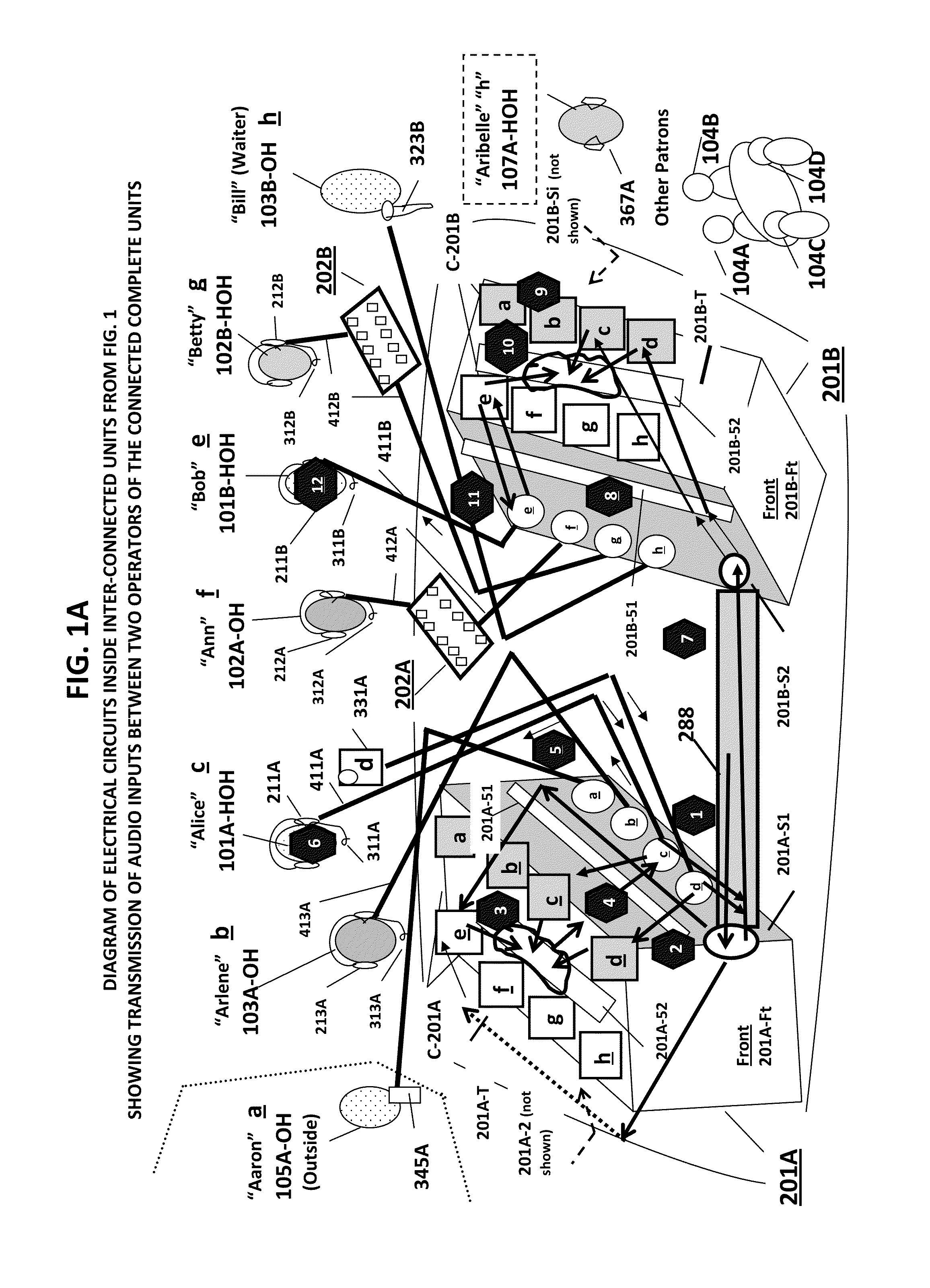
ActiveUS8995688B1Volume adjustableImprove claritySignal processingGain controlWord processingThe Internet
A system consisting of interconnectible, hearing-assistive, portable “units” which can address communication problems that persons who are hard of hearing experience in many social settings (such as while dining out with friends in a noisy restaurant). The system allows each unit operator to share multiple audio input signals coming into any of the connected units with the other participants using the system. The operator is also able to selectively amplify one or more of the incoming audio signals (such as from the voices of one or more of the participants) while blocking out or turning down another (such as from background music). The units are capable of integrating audio signals with video, word processing and internet data. An innovative method for improving communication for persons who are hard of hearing in public and private settings is also claimed.
Owner:CHEMTOB HELEN JEANNE +1
Footwear sole
A sole for an article of footwear having an insert with a plurality of forefoot support tubes are configured to control the support characteristics of the sole in a forefoot region of the sole. In one embodiment, the forefoot support tubes each include a base, and a wall extending from the base. The wall is formed from a material that has a lower durometer value than the base. In another embodiment, the forefoot support tubes air arranged in a radiating pattern, such that at least two of the forefoot support tubes diverge as they extend toward the lateral side of the insert.
Owner:WOLVERINE WORLD WIDE
Data anonymization based on guessing anonymity
ActiveUS20100162402A1Minimize distortionMaximizes guessing anonymityPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsGame basedData value
Privacy is defined in the context of a guessing game based on the so-called guessing inequality. The privacy of a sanitized record, i.e., guessing anonymity, is defined by the number of guesses an attacker needs to correctly guess an original record used to generate a sanitized record. Using this definition, optimization problems are formulated that optimize a second anonymization parameter (privacy or data distortion) given constraints on a first anonymization parameter (data distortion or privacy, respectively). Optimization is performed across a spectrum of possible values for at least one noise parameter within a noise model. Noise is then generated based on the noise parameter value(s) and applied to the data, which may comprise real and / or categorical data. Prior to anonymization, the data may have identifiers suppressed, whereas outlier data values in the noise perturbed data may be likewise modified to further ensure privacy.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
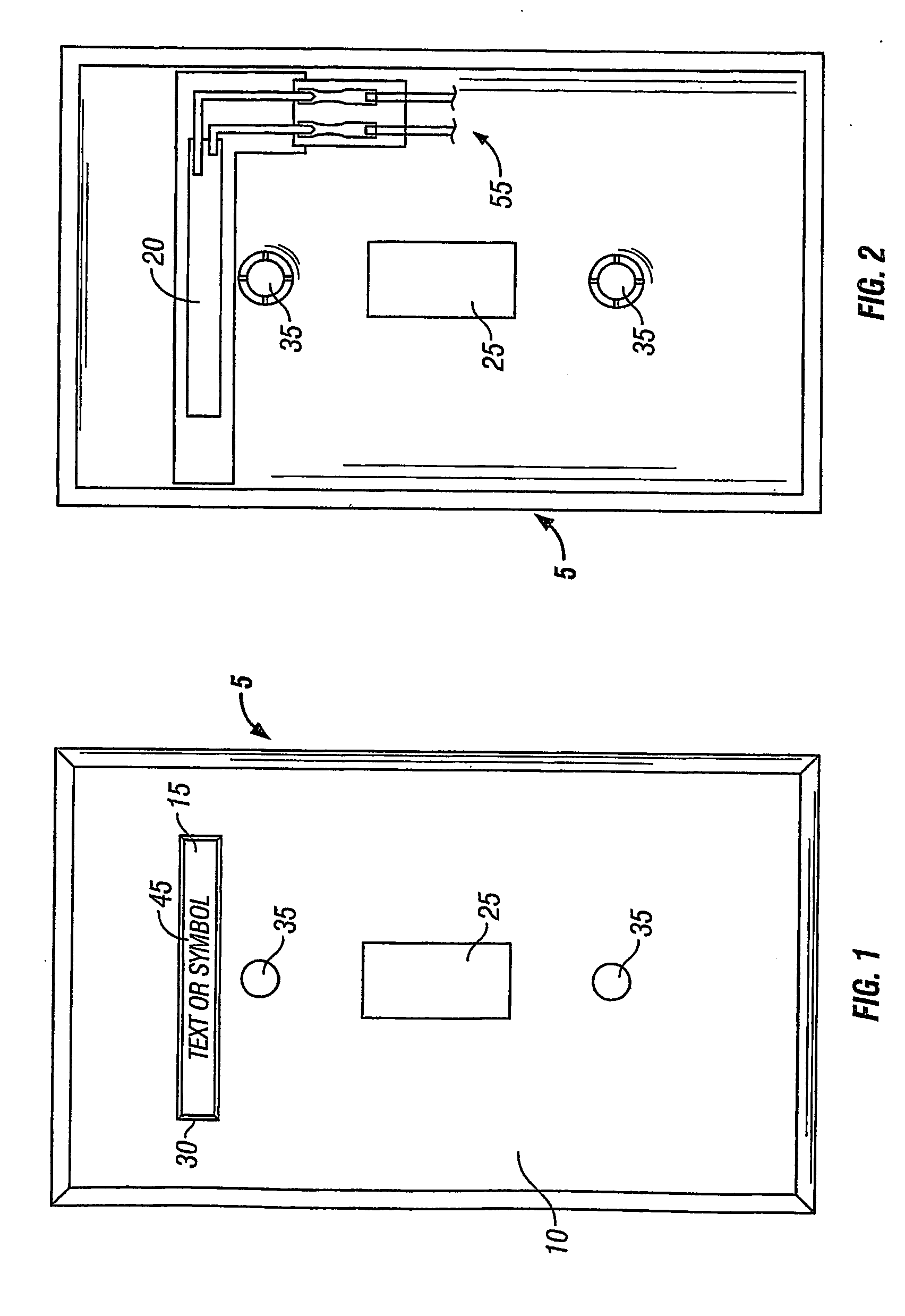
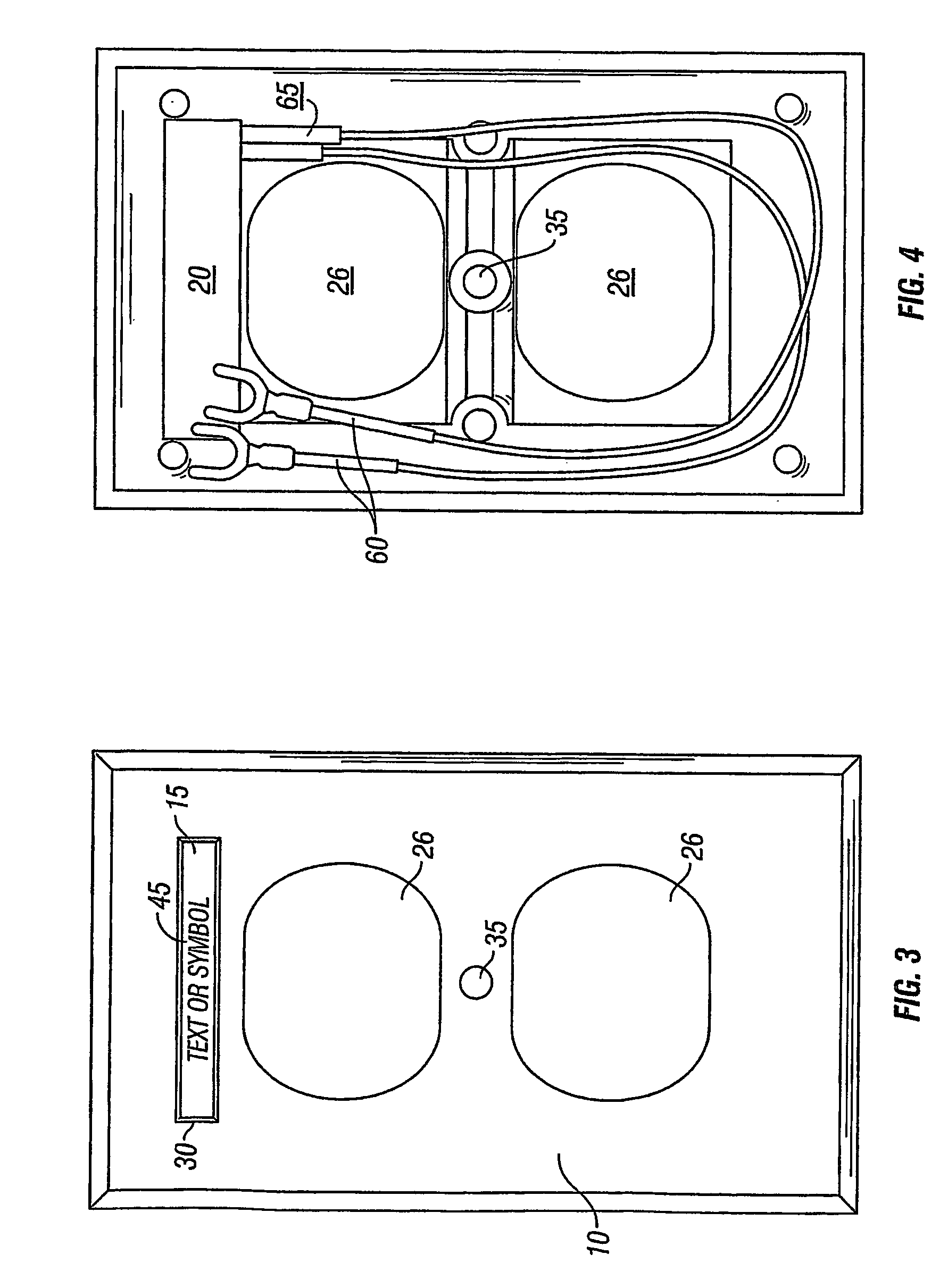
Backlighting for electrical cover plates
InactiveUS7270436B2Problem can be addressedImprove securityMeasurement apparatus componentsLegendsEffect lightEngineering
Owner:HEATHER LEIGH BRANTLEY TRUSTEE FOR THE BRANTLEY CHILDREN TRUST A TEXAS TRUST
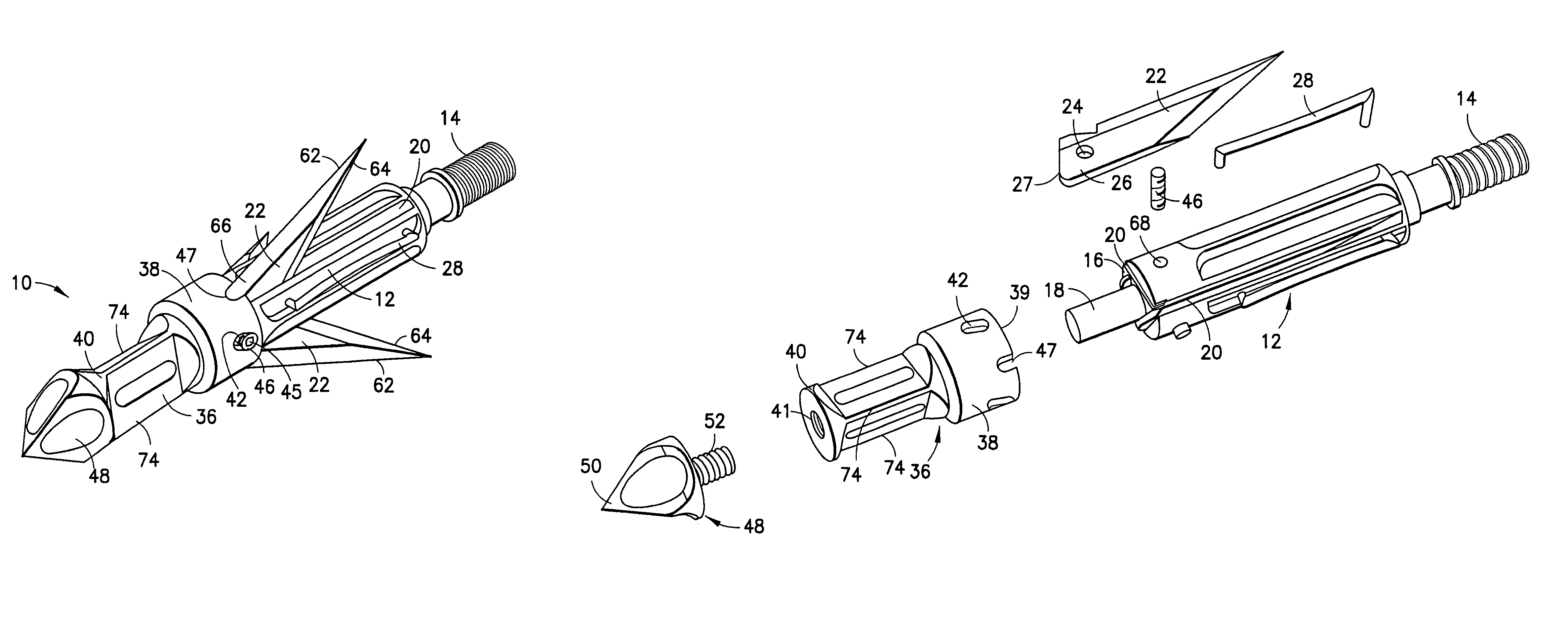
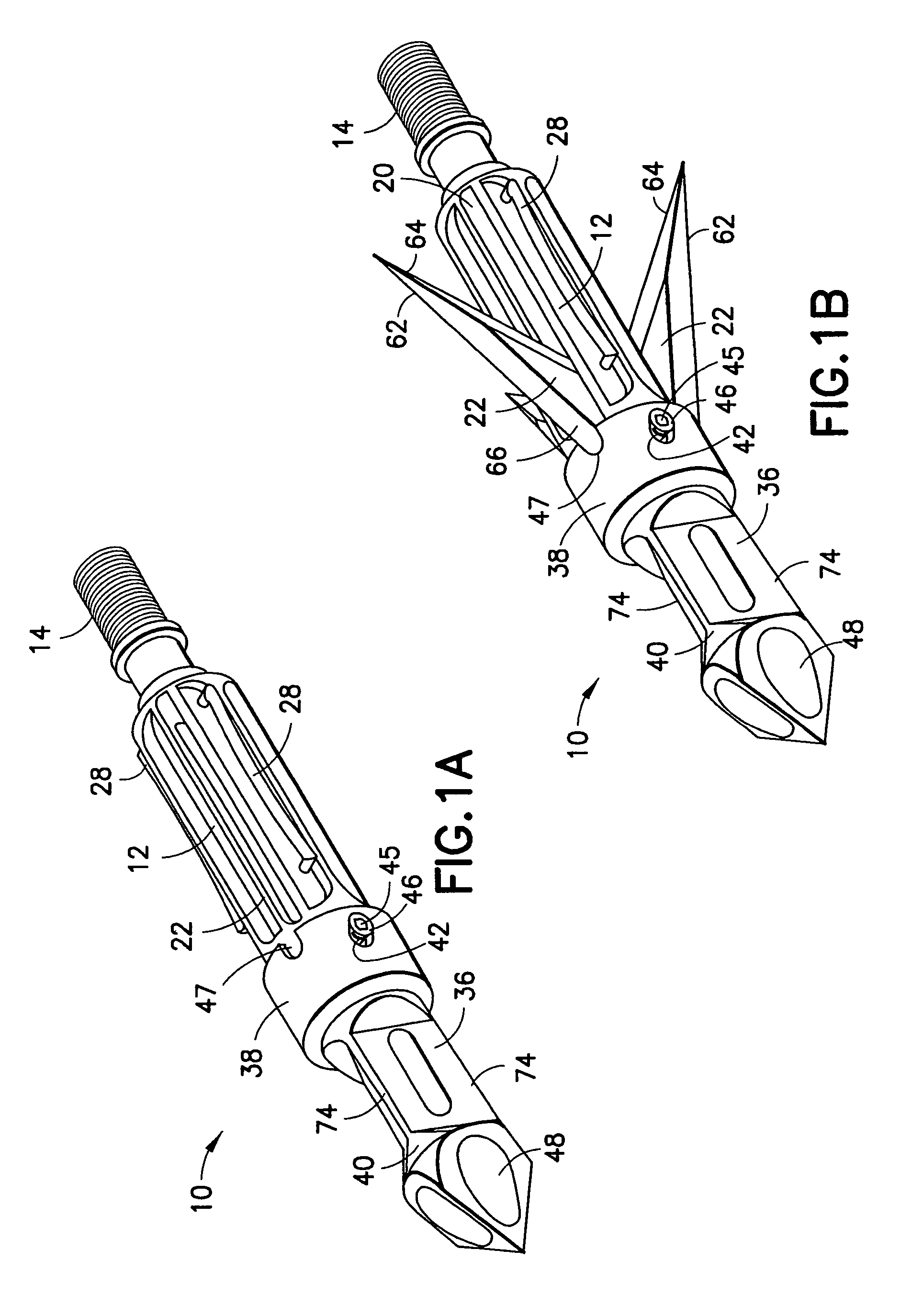
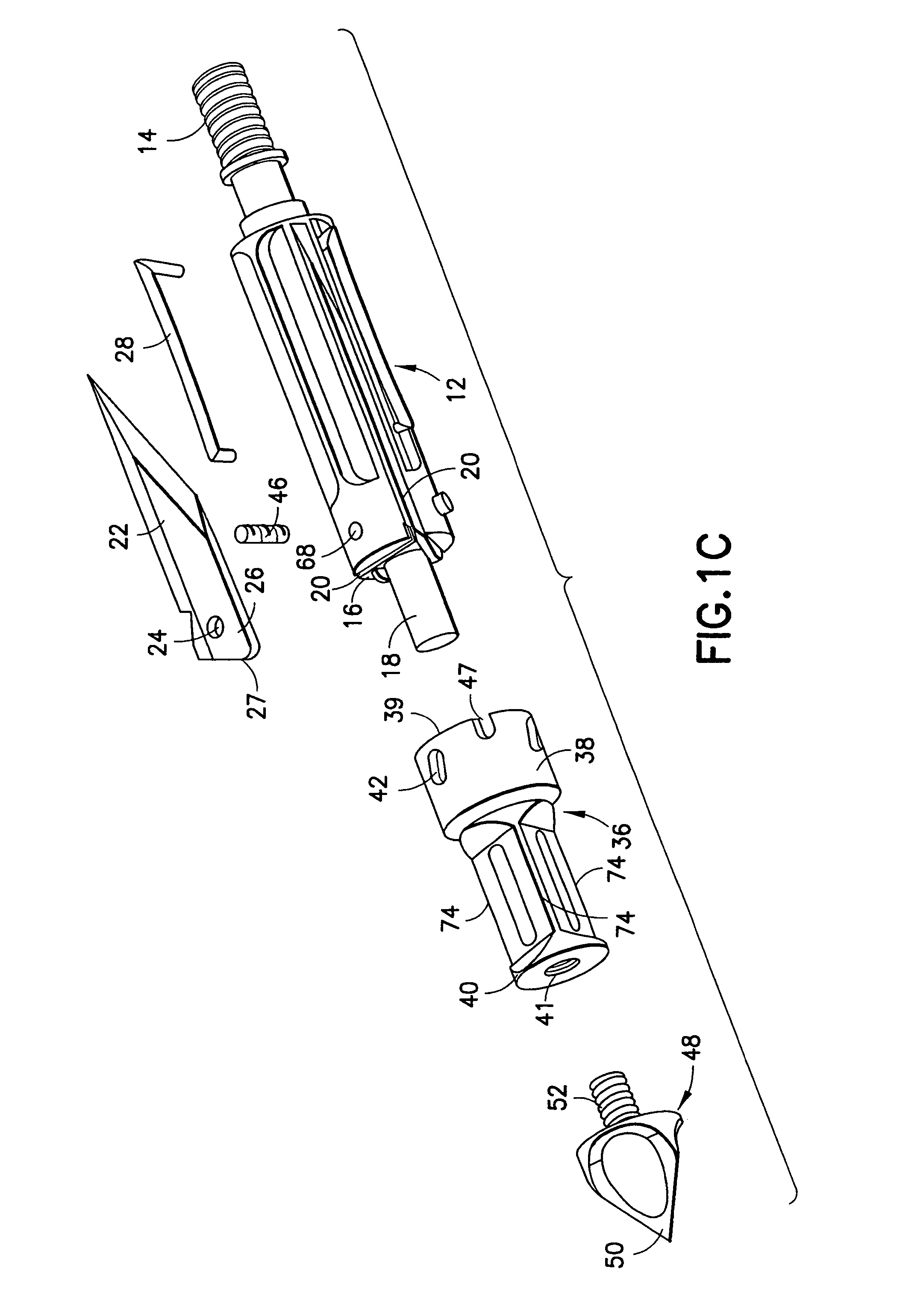
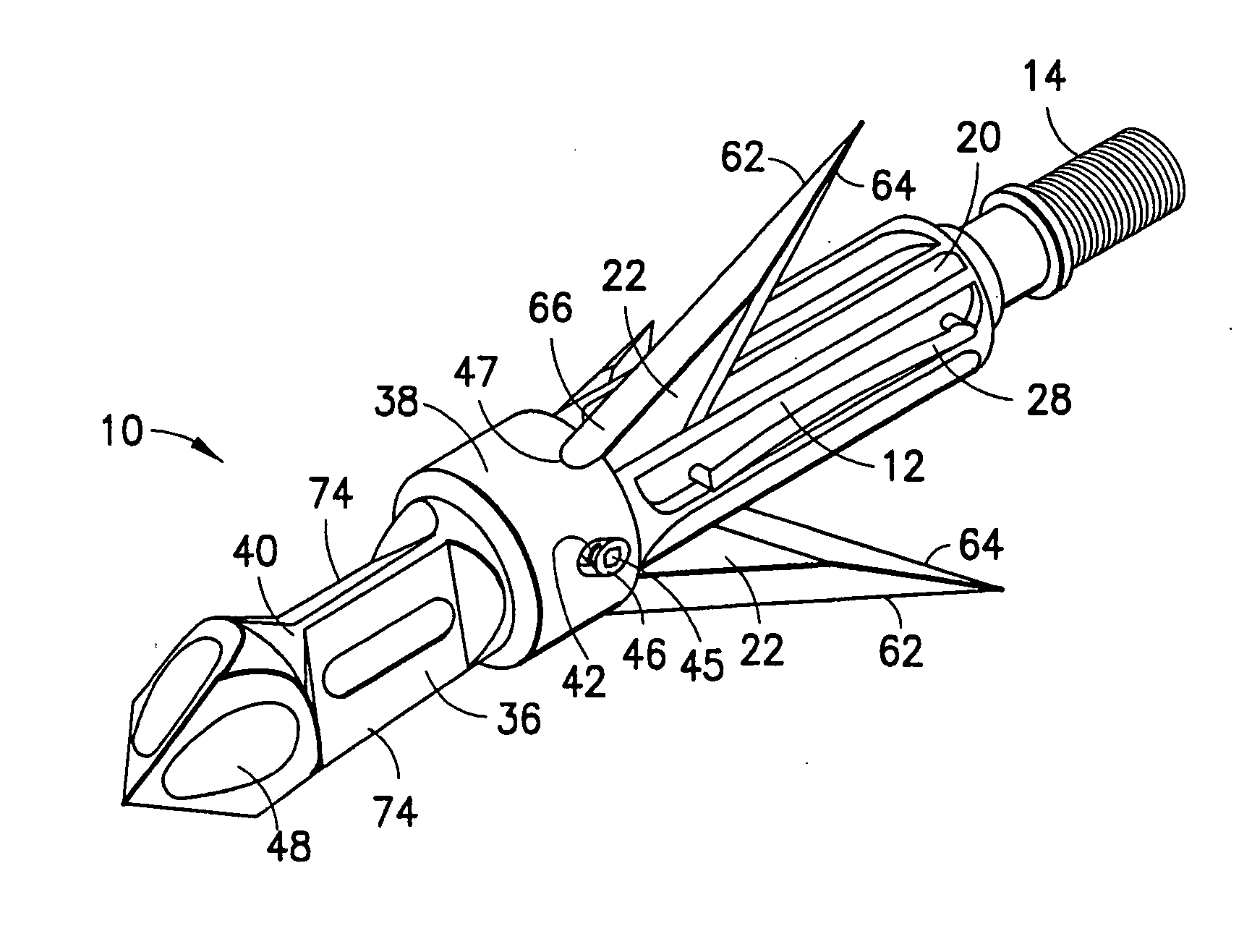
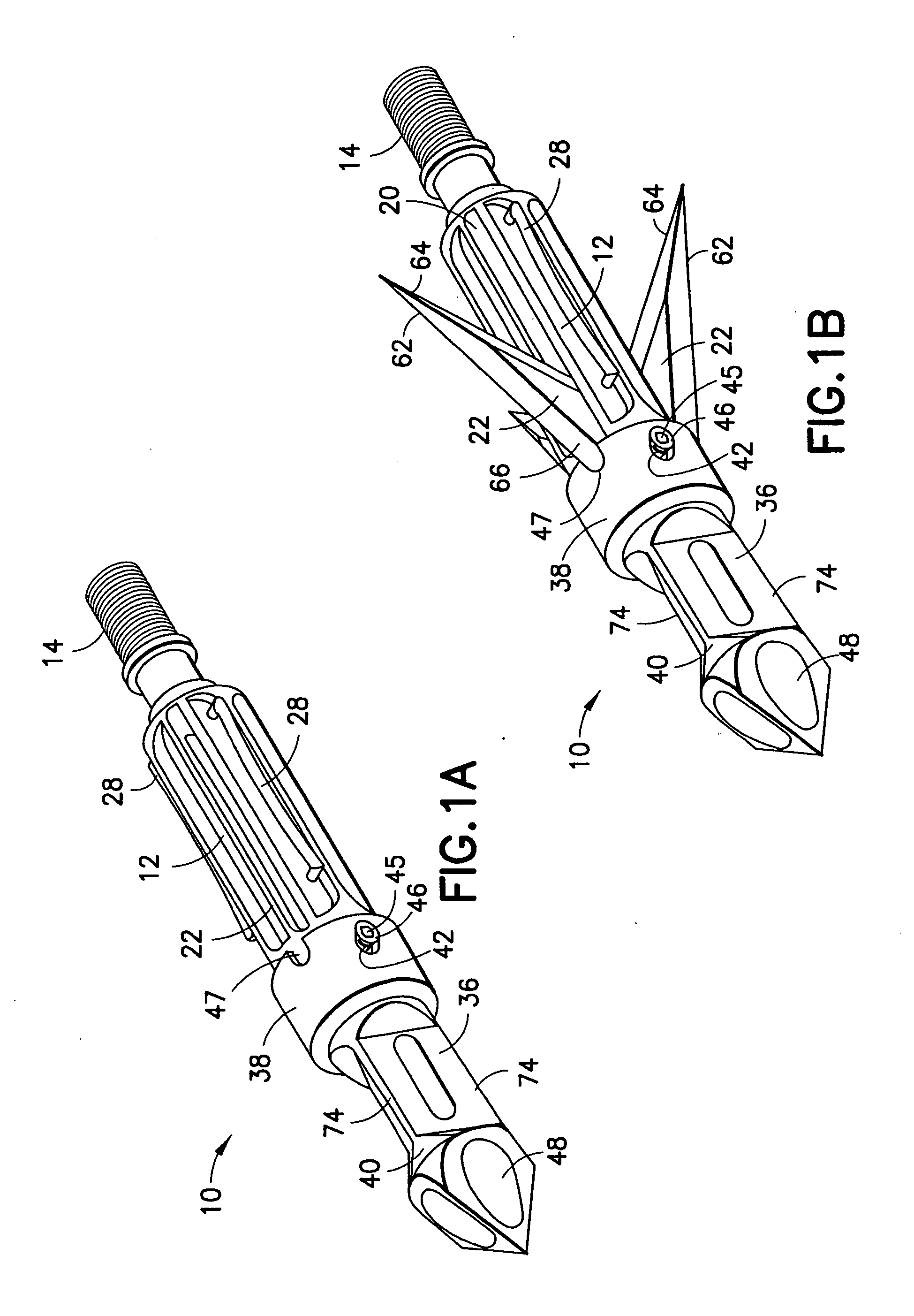
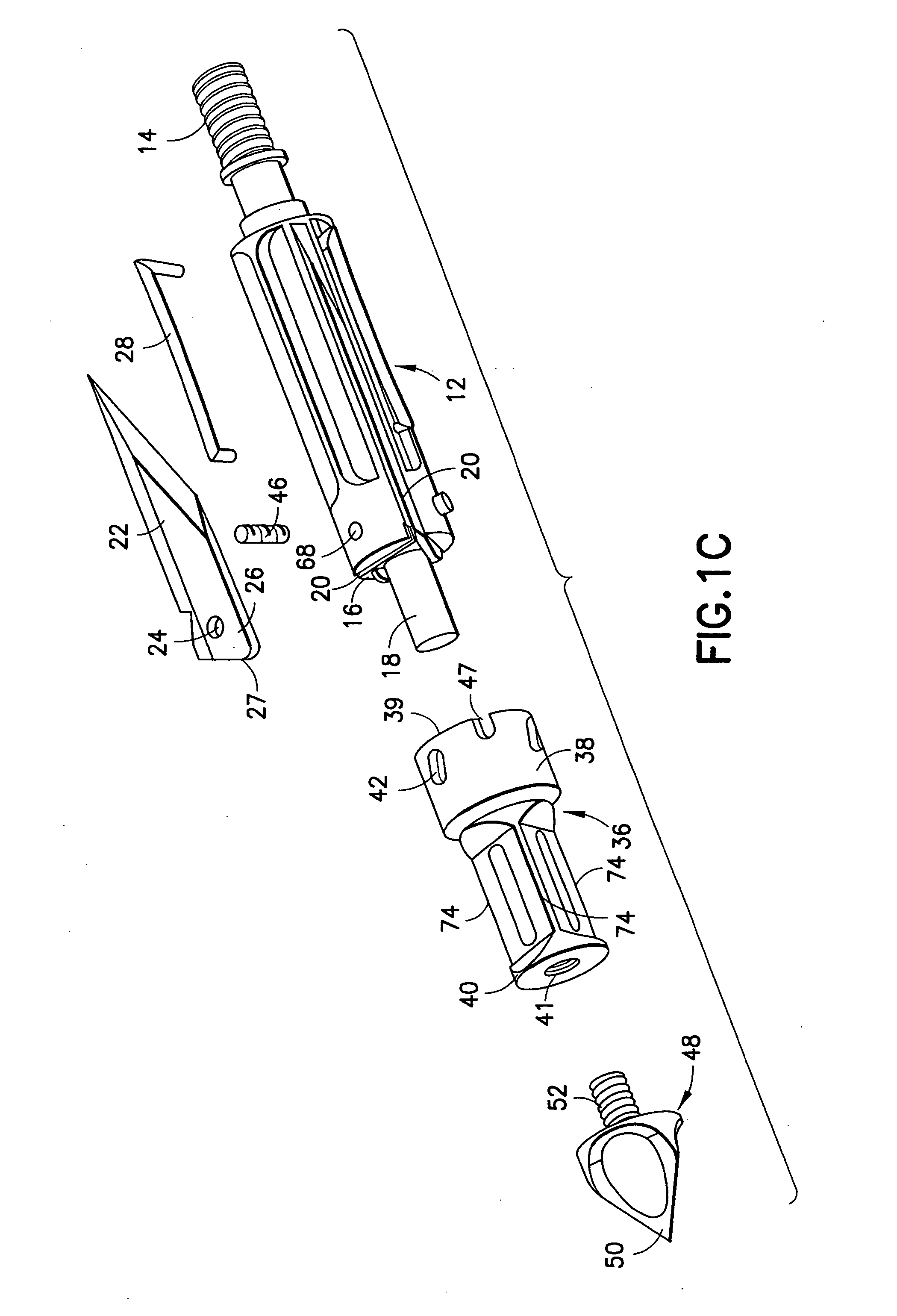
Mechanical broadhead with expandable blades
ActiveUS7713151B2Rule out the possibilityStrong materialThrow gamesArrowsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mechanical broadhead for attachment to an arrow having a broadhead body including a plurality of blade windows formed therein, a geometrically angled retractable blade attached within each of the blade windows, retaining springs for retaining the blades in a retracted position during flight, a front body slidably mounted onto the broadhead body, and a front tip secured to the front body. Upon contact with a target, the front tip and front body slide rearwardly into an end of the geometrically angled blades, thus pushing each of the blades through the blade windows into a deployed position. The blades of the broadhead are reset by inserting a sharp point underneath an end portion of the retaining springs and applying a slight twisting motion allowing the blades to retract back into the broadhead body into a loaded position.
Owner:RAMCAT LLC
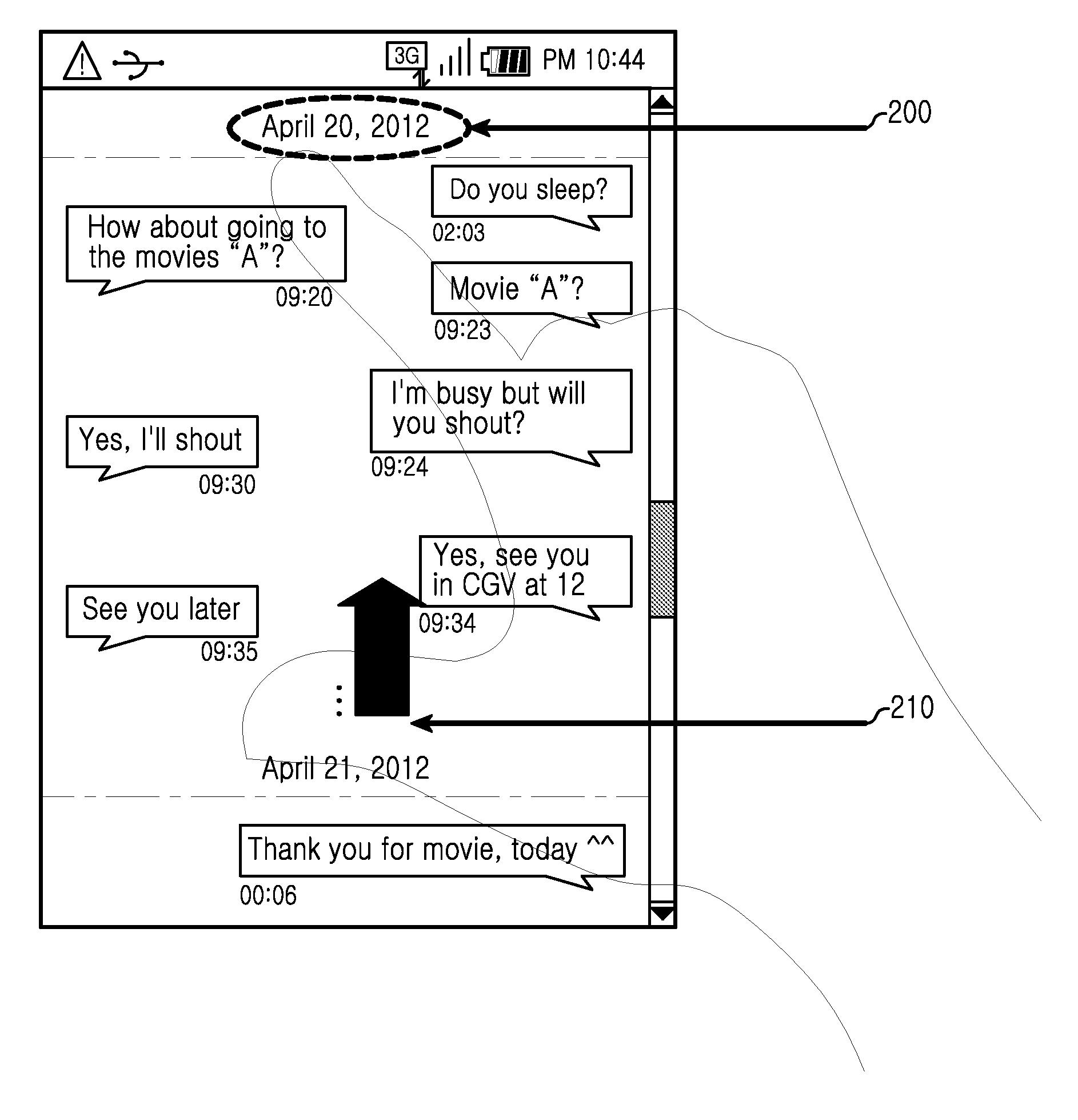
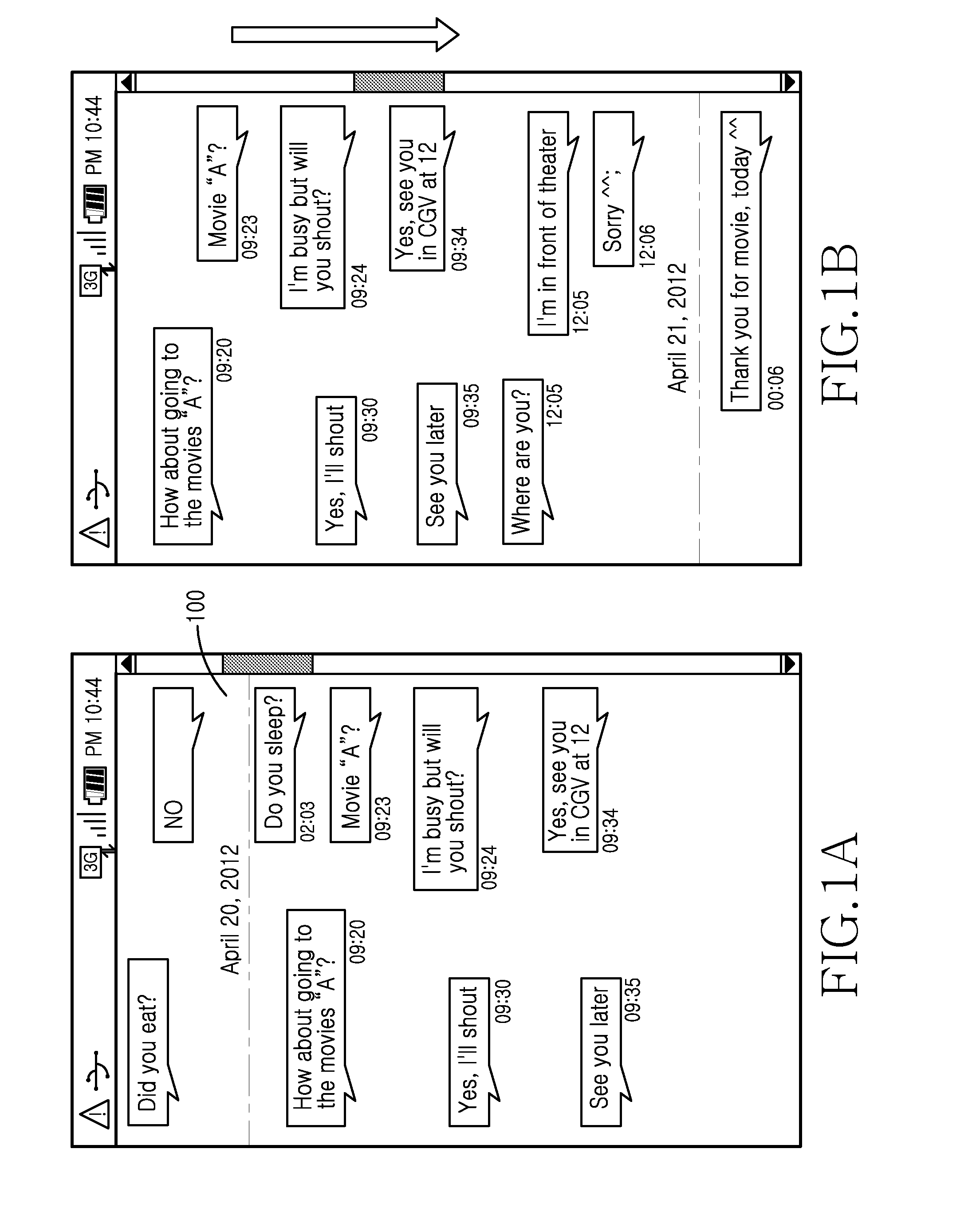
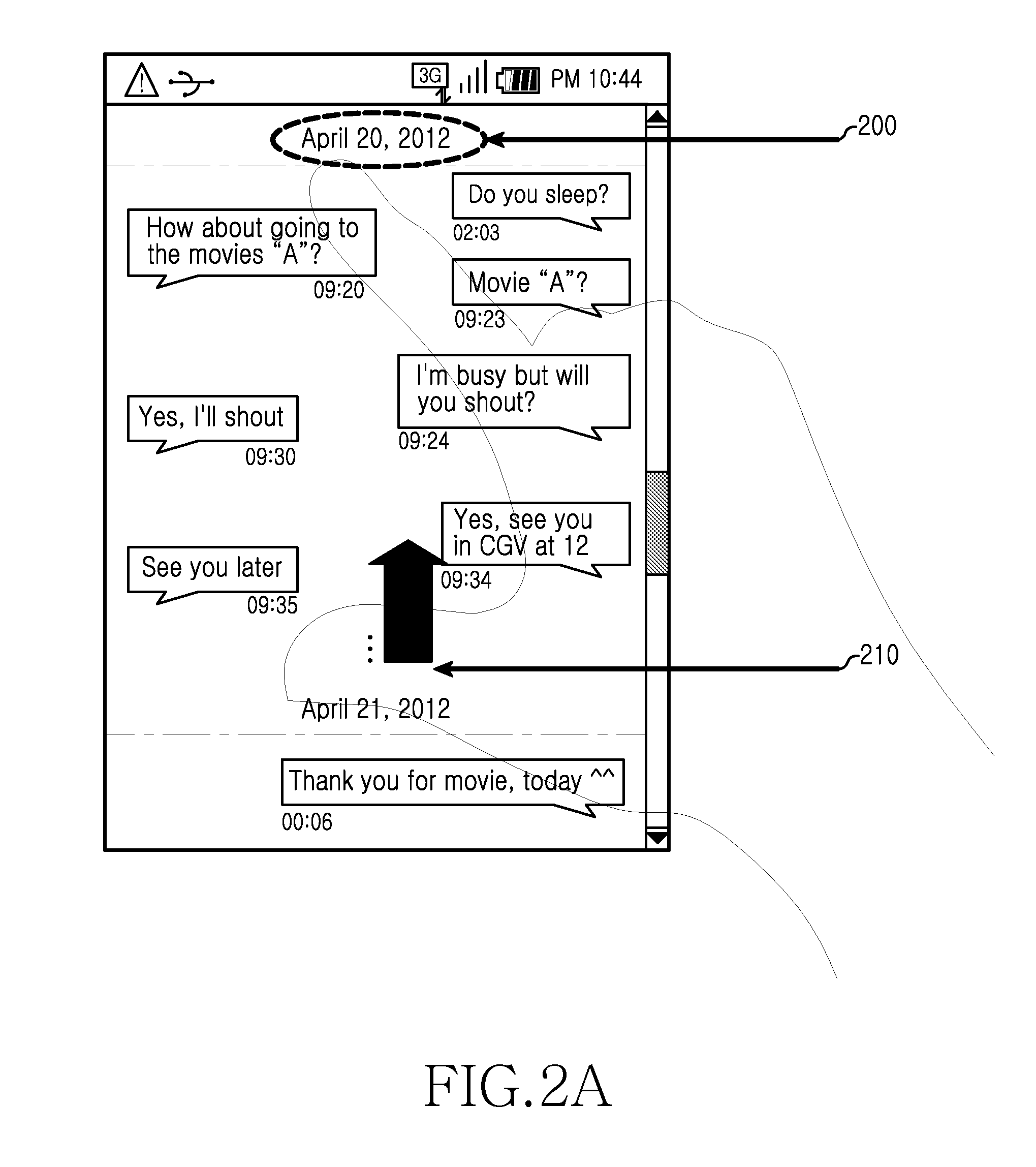
Method and apparatus for managing message, and method and apparatus for transmitting message in electronic device
ActiveUS20140136989A1Problem can be addressedSubstation equipmentMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsTouchscreenElectronic equipment
A method usable by an electronic device displays in display image, content of a plurality of transmitted and received conversation messages. In an aspect, the messages may be displayed for an individual date, sequentially collated by date and time. In response to at least one detected touch on a touch screen, the method may compress at least one of (a) the transmitted or (b) received, conversation messages and displays an image element representing at least one of the compressed conversation messages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Control apparatus for driving vehicle and control method for driving vehicle
InactiveUS20060037573A1Increased durabilitySmall amplitudeHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringControl equipment
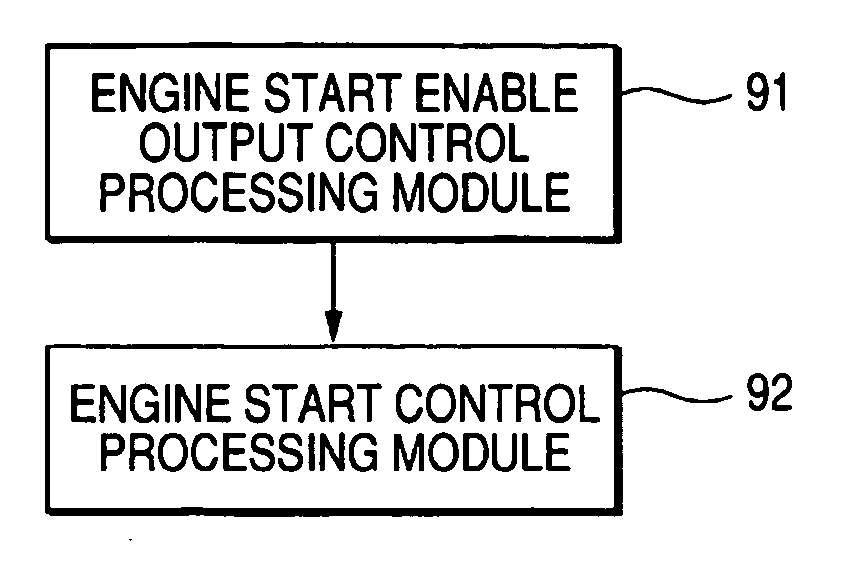
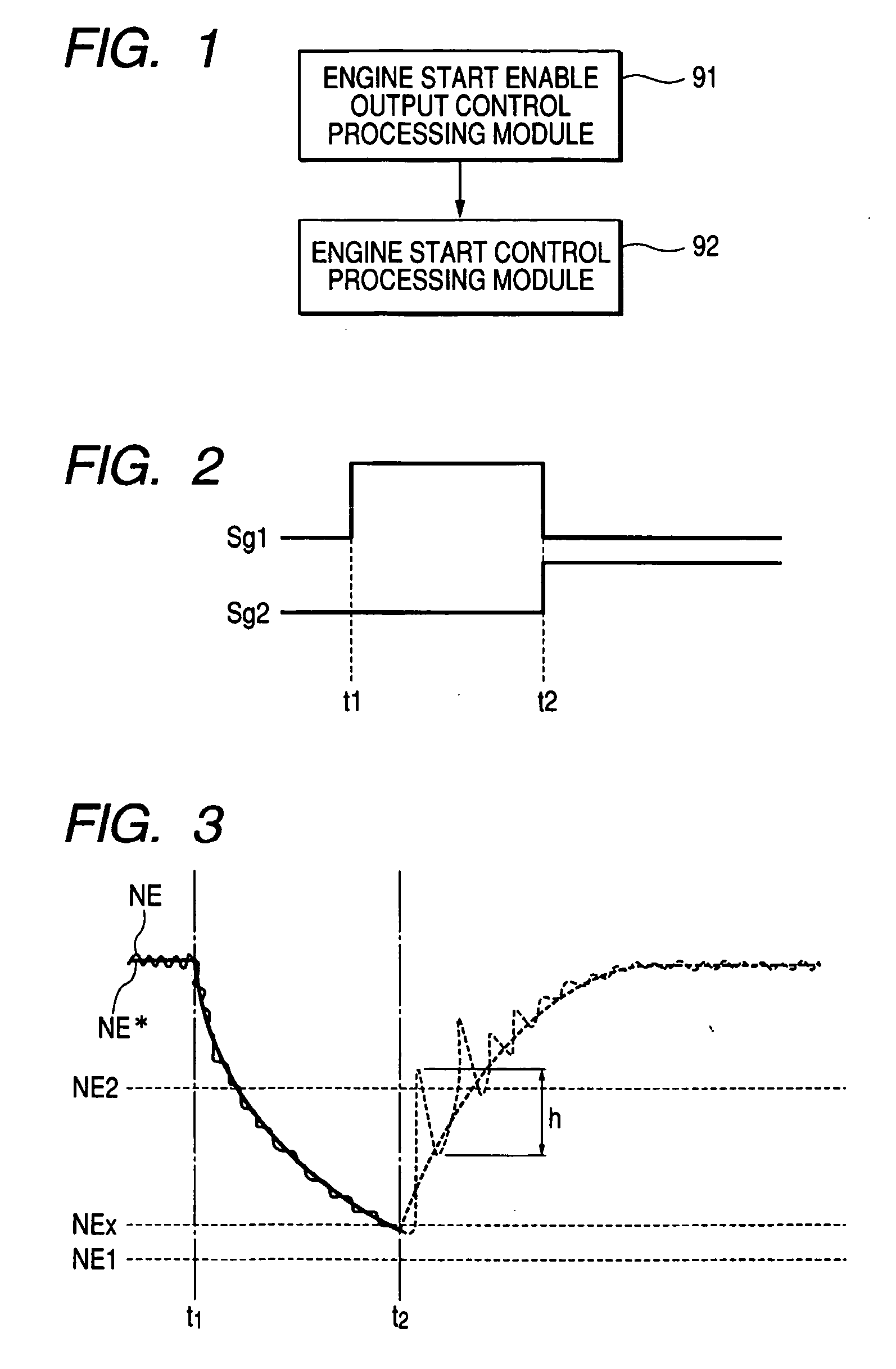
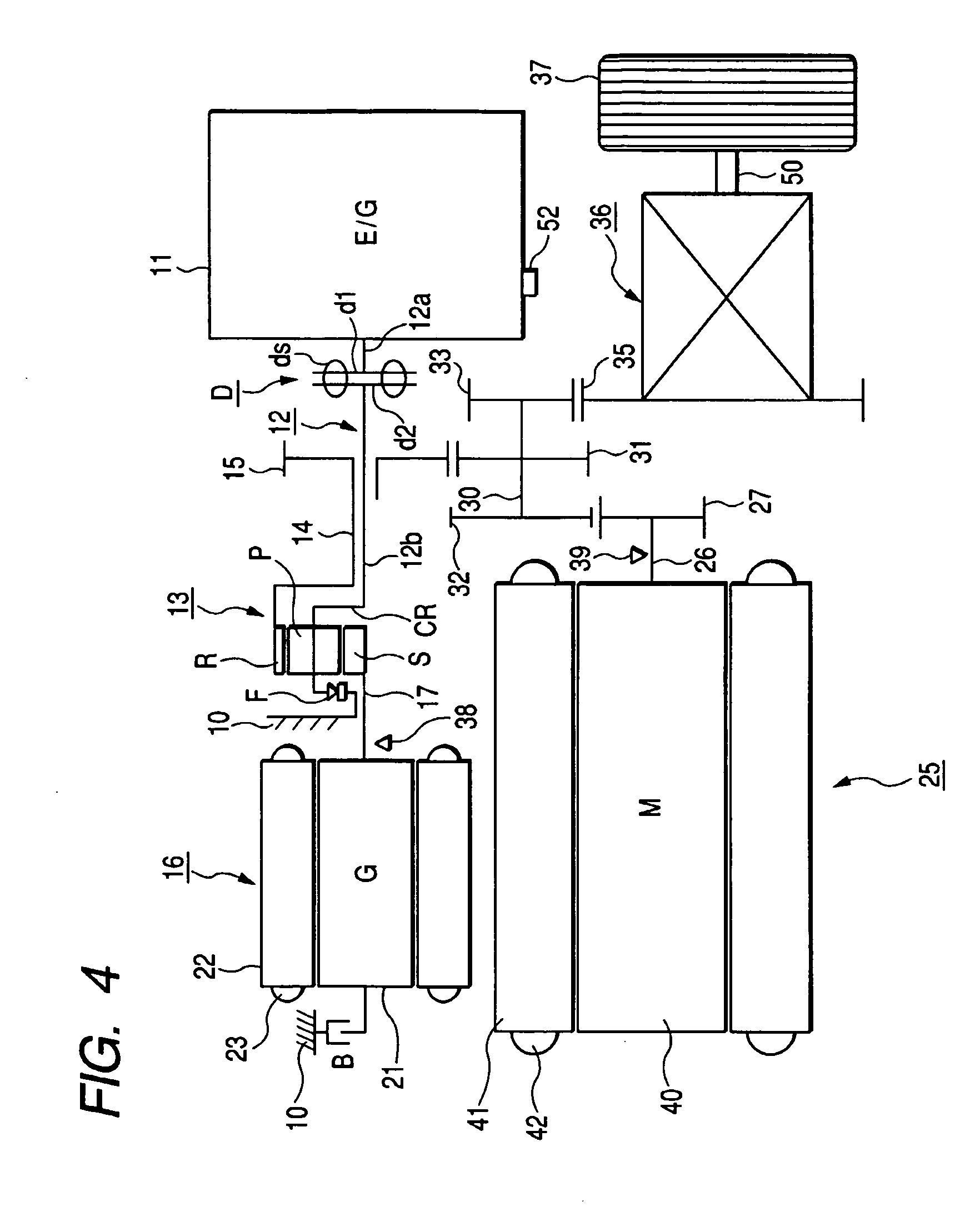
A control apparatus for driving a vehicle and a control method for driving a vehicle. A control apparatus for driving a vehicle has an engine start permission output control processing module which reads engine rotational speed; determines whether the engine rotational speed takes a value within a predetermined start disable range; does not output an engine start permission when the engine rotational speed takes a value within the start disable range; and outputs an engine start permission when the engine rotational speed takes a value except a value within the start disable range, and has an engine start control processing module which starts an engine when the engine start permission is outputted. An engine start permission is not outputted and the engine is not started when the engine rotational speed takes the value except the value within the start disable range.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Applications as a service
ActiveUS20130204975A1Problem can be addressedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTransmission protocolNetwork management application
A system and method are provided for managing applications over a network between a server system and client computers. In one example, the method involves receiving user login information from a client computer, then accessing on the server system a user profile associated with the login information. The user profile includes a user environment configuration for a client environment. Transport protocols are selected based on the user profile. The transport protocols are protocols for transporting information between the server system and the client computer. The user environment configuration stored on the server system is then synchronized with a client environment configuration on the client computer.
Owner:GOODRICH JOHN B +1
Apparatuses, systems, and methods to automate a procedural task
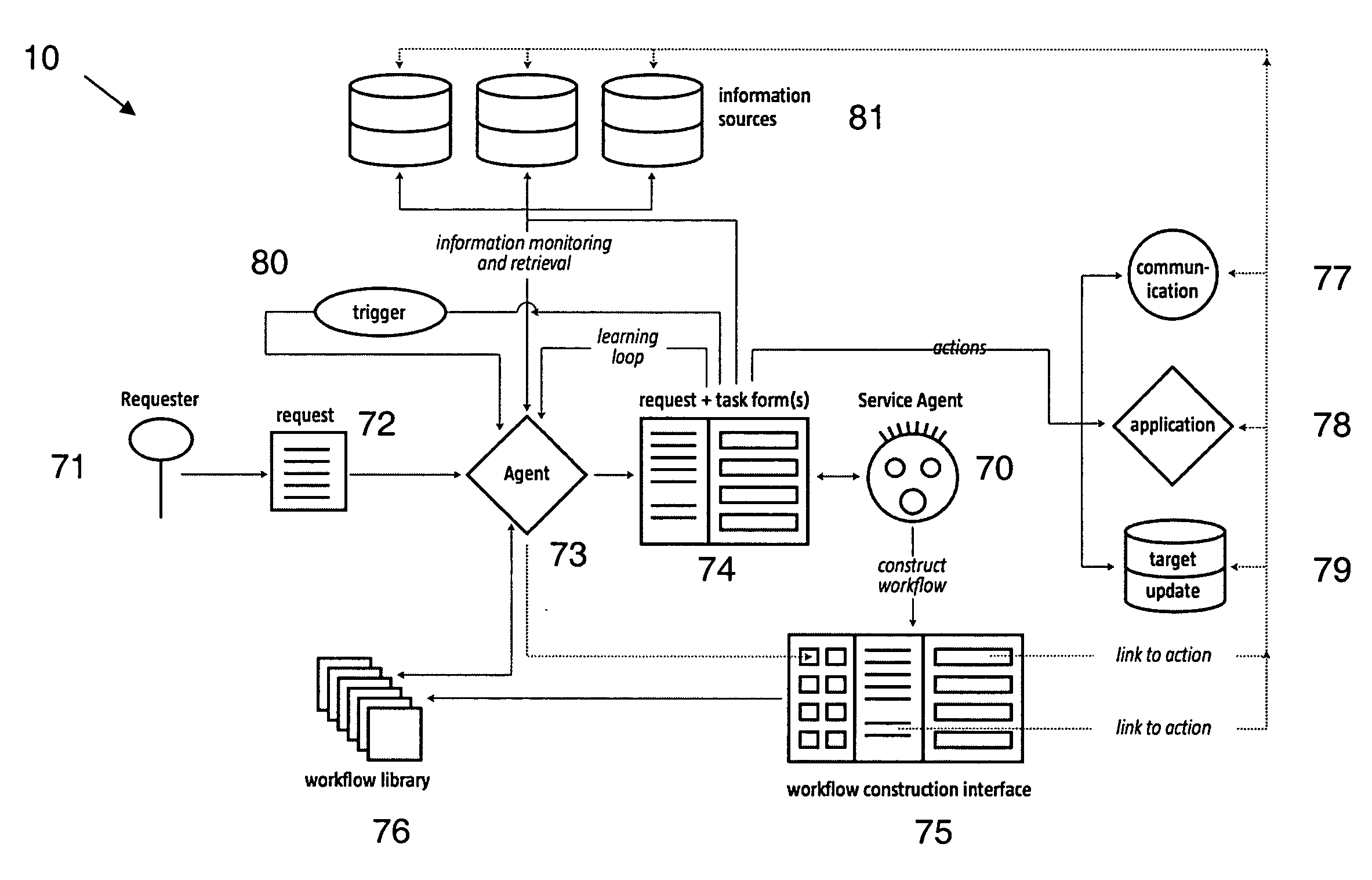
InactiveUS20100037127A1Improve performanceProblem can be addressedInput/output for user-computer interactionMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer scienceComputer generation
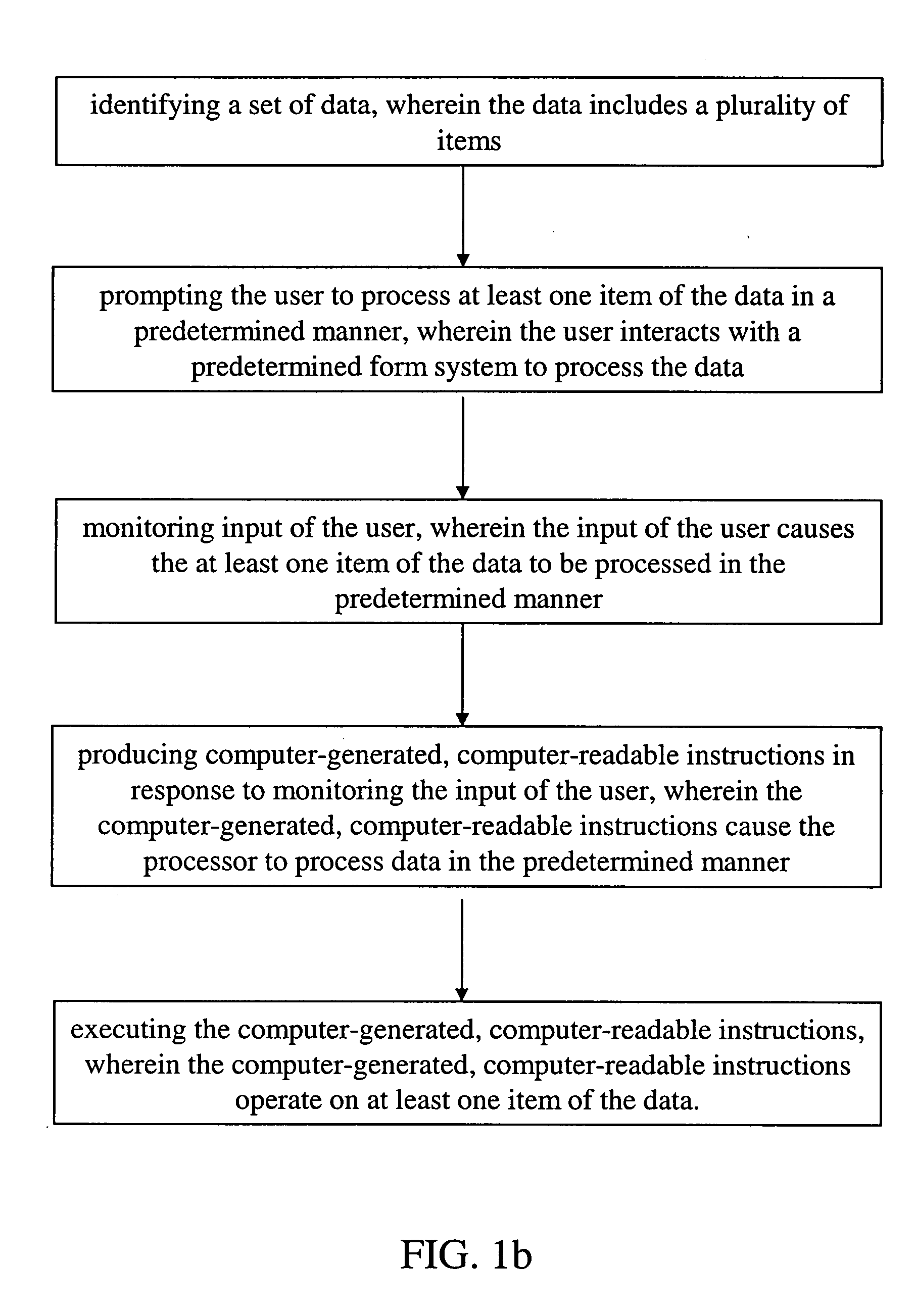
Methods, apparatuses, and systems to automate a procedural task. In one embodiment, computer-readable memory including computer readable instructions which, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to perform steps comprising: identifying a set of data, wherein the data includes a plurality of items; prompting the user to process at least one item of the data in a predetermined manner, wherein the user interacts with a predetermined form system to process the data; monitoring input of the user, wherein the input of the user causes the at least one item of the data to be processed in the predetermined manner; producing computer-generated, computer-readable instructions in response to monitoring the input of the user, wherein the computer-generated, computer-readable instructions cause the processor to process data in the predetermined manner; and executing the computer-generated, computer-readable instructions, wherein the computer-generated, computer-readable instructions operate on at least one item of the data.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Mechanical broadhead with expandable blades
ActiveUS20070161438A1Relieve pressureImproved cutting designThrow gamesArrowsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mechanical broadhead for attachment to an arrow having a broadhead body including a plurality of blade windows formed therein, a geometrically angled retractable blade attached within each of the blade windows, retaining springs for retaining the blades in a retracted position during flight, a front body slidably mounted onto the broadhead body, and a front tip secured to the front body. Upon contact with a target, the front tip and front body slide rearwardly into an end of the geometrically angled blades, thus pushing each of the blades through the blade windows into a deployed position. The blades of the broadhead are reset by inserting a sharp point underneath an end portion of the retaining springs and applying a slight twisting motion allowing the blades to retract back into the broadhead body into a loaded position.
Owner:RAMCAT LLC
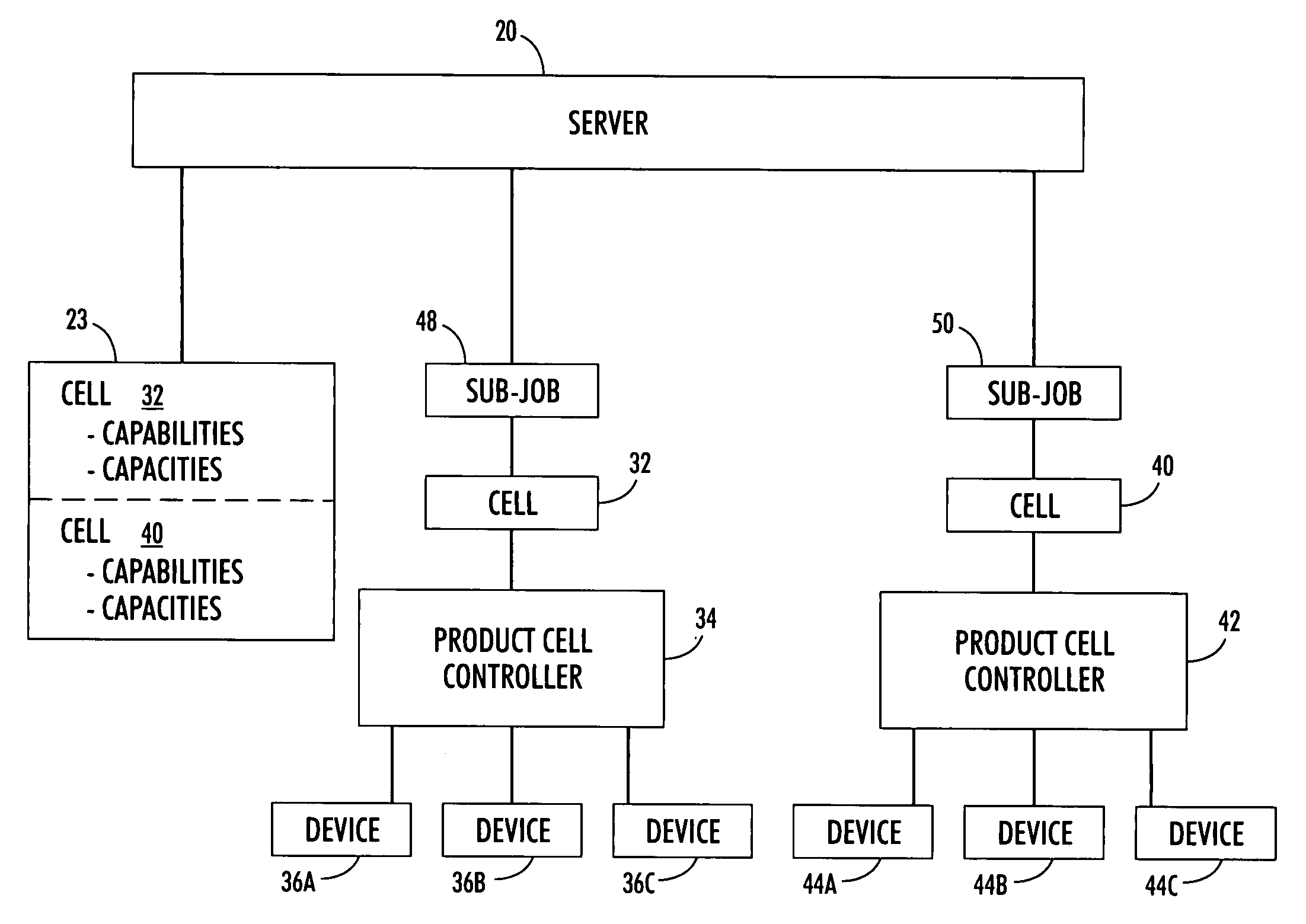
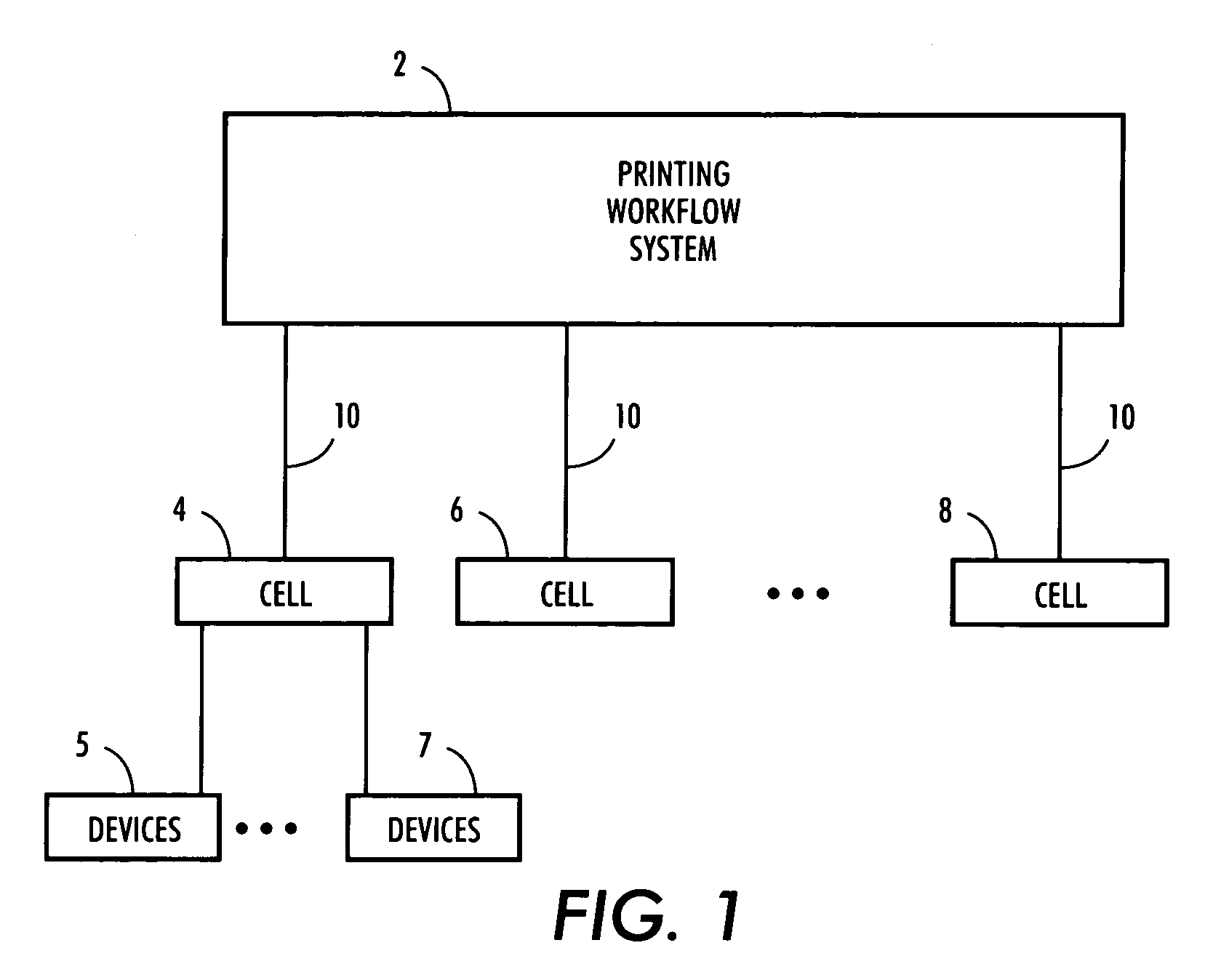
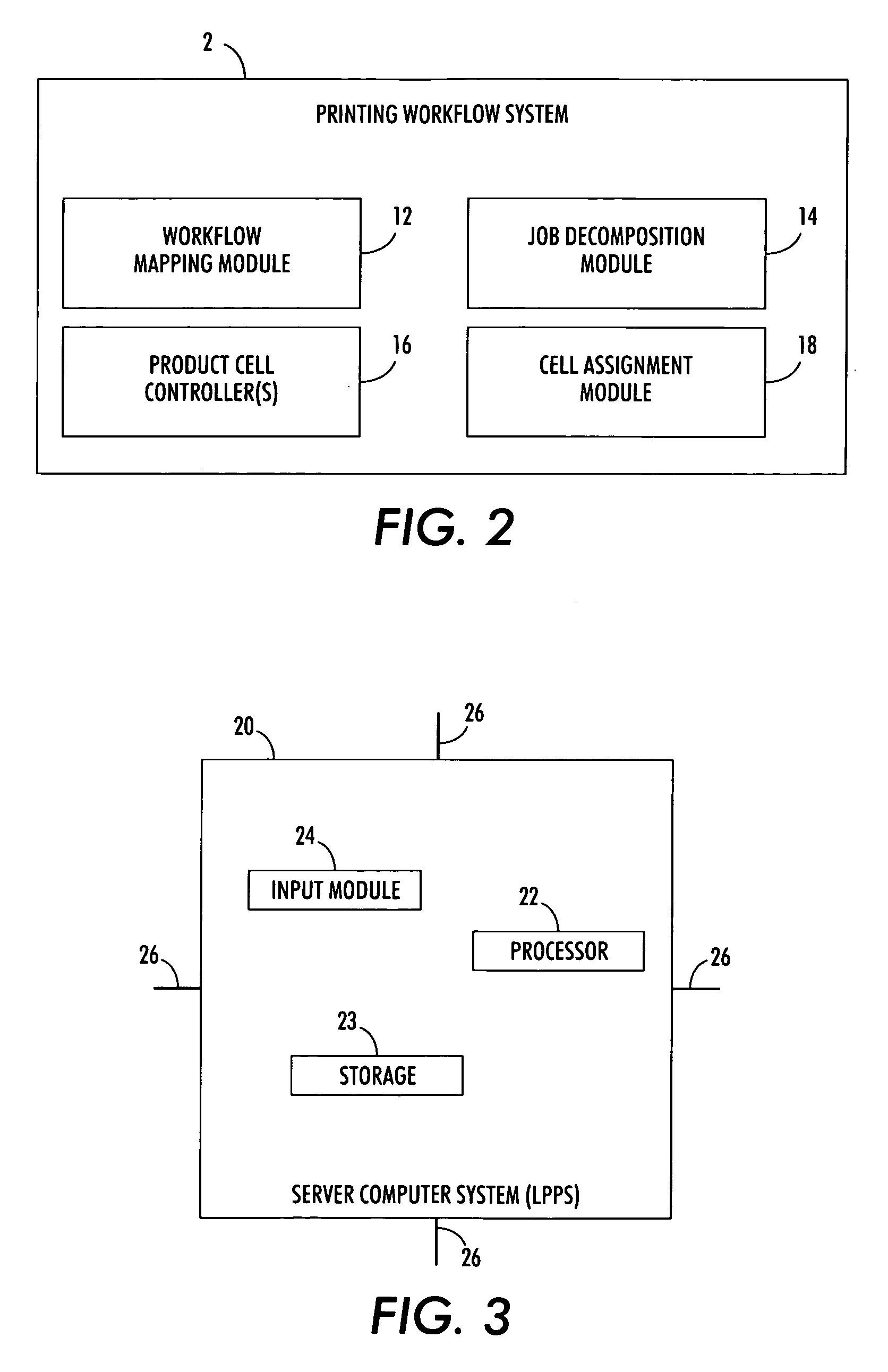
Print job management system
InactiveUS20070236724A1Significant time delayReduce turnaround timeDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsControl limitsComputer science
A system for managing the size of a print job to be processed in a print shop is provided. The print shop includes a plurality of autonomous cells and the job size management system includes a scheduling tool for generating a list including a plurality of jobs. A processor is used to (a) assign a job size related value to each one of the plurality of jobs so that the plurality of jobs are corresponded respectively with a set of job size related values, (b) use the set of job size related values to calculate a control limit, and (c) for each job size related value exceeding the control limit, splitting the job corresponding with the job size related value exceeding the control limit into n number of sub-jobs for processing at the plurality of autonomous cells.
Owner:XEROX CORP
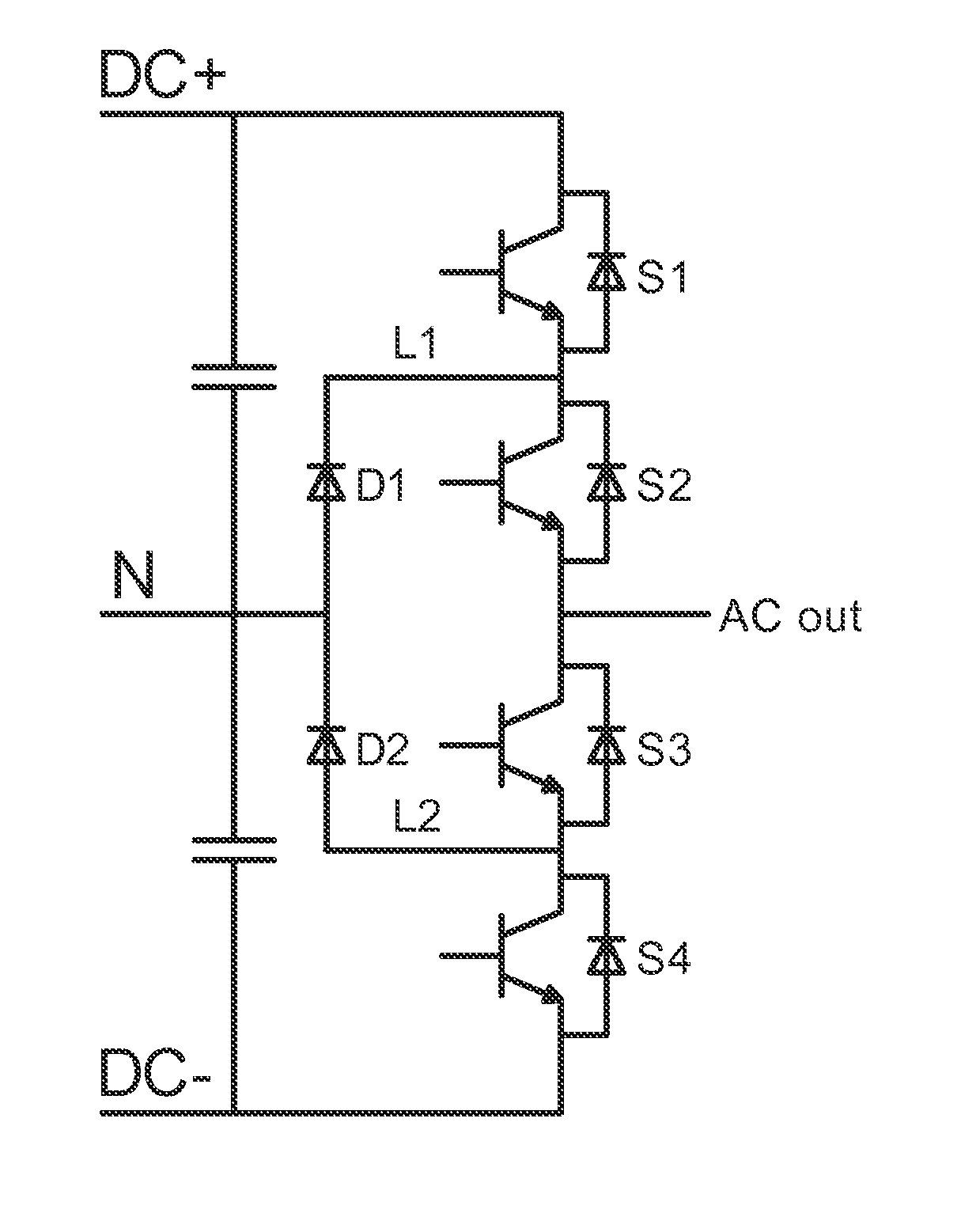
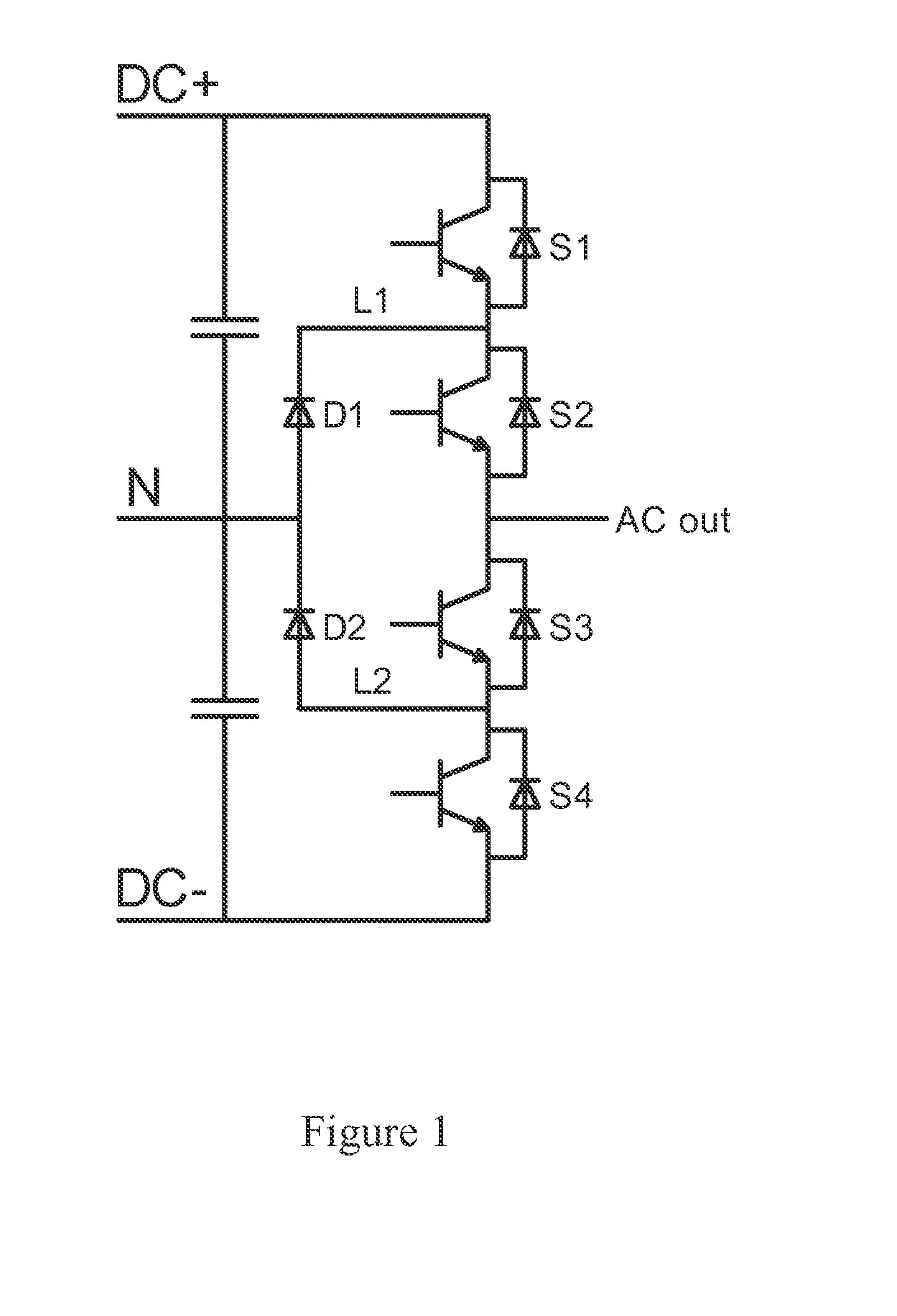
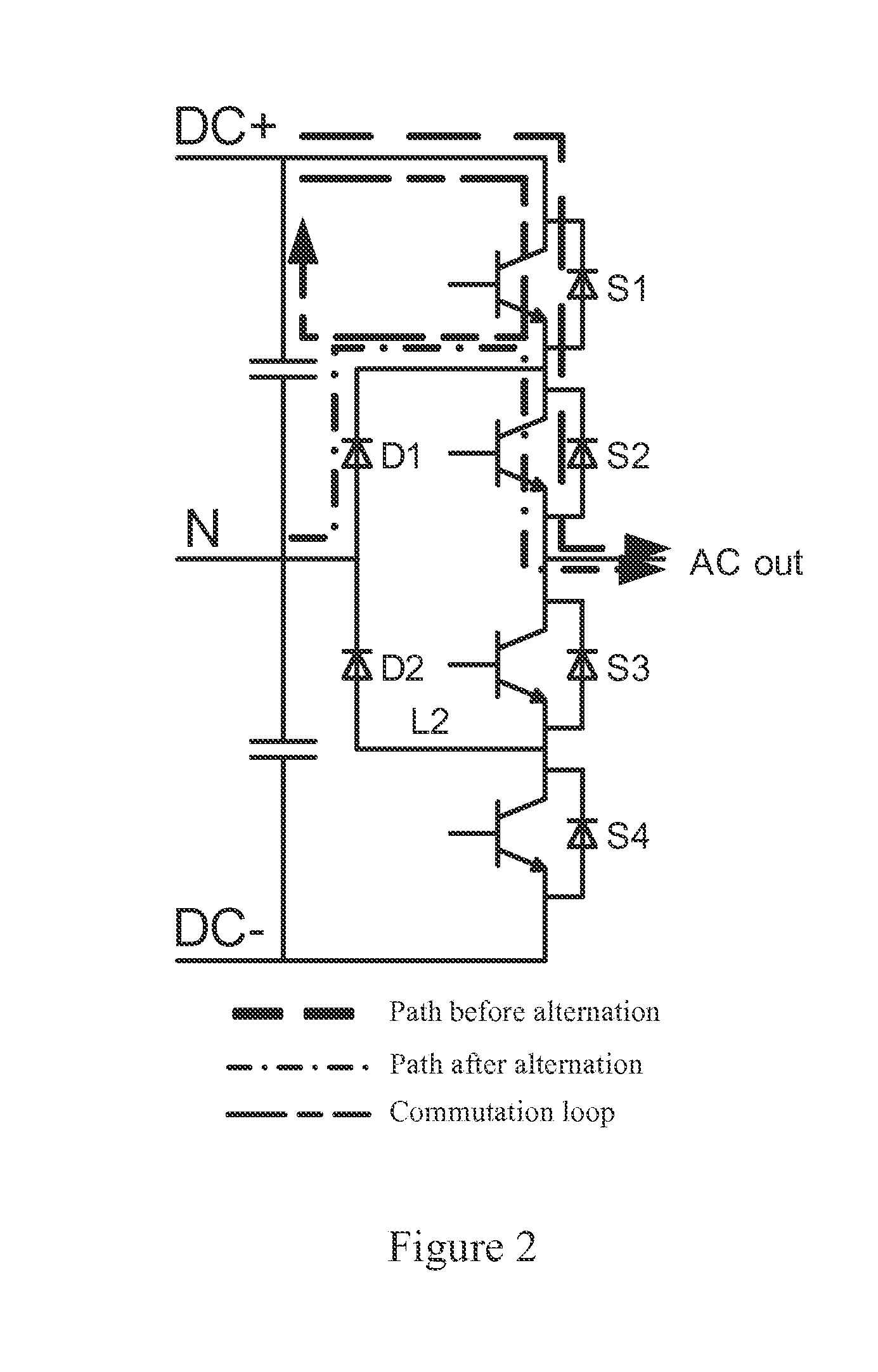
Three-level converter
ActiveUS20140254228A1Compact structureEasy to installConversion constructional detailsThree levelComputer module
A three-level converter includes at least one phase bridge arm, each including an upper-half and a lower-half bridge arm circuit modules. The upper-half bridge arm circuit module includes a first and a second switch units that are in series connection, and a first diode unit. The lower-half bridge arm circuit module includes a third and a fourth switch units that are in series connection, and a second diode unit. The first and second diode units are connected to the neutral point of the capacitor unit; the second and third switch units are connected to the alternating-current terminal; The first and the fourth switch unit is respectively connected to the positive terminal and negative terminal of the direct-current bus; the capacitor unit is connected to the direct-current bus between the positive and negative terminals. The two modules are disposed side by side and facing each other.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
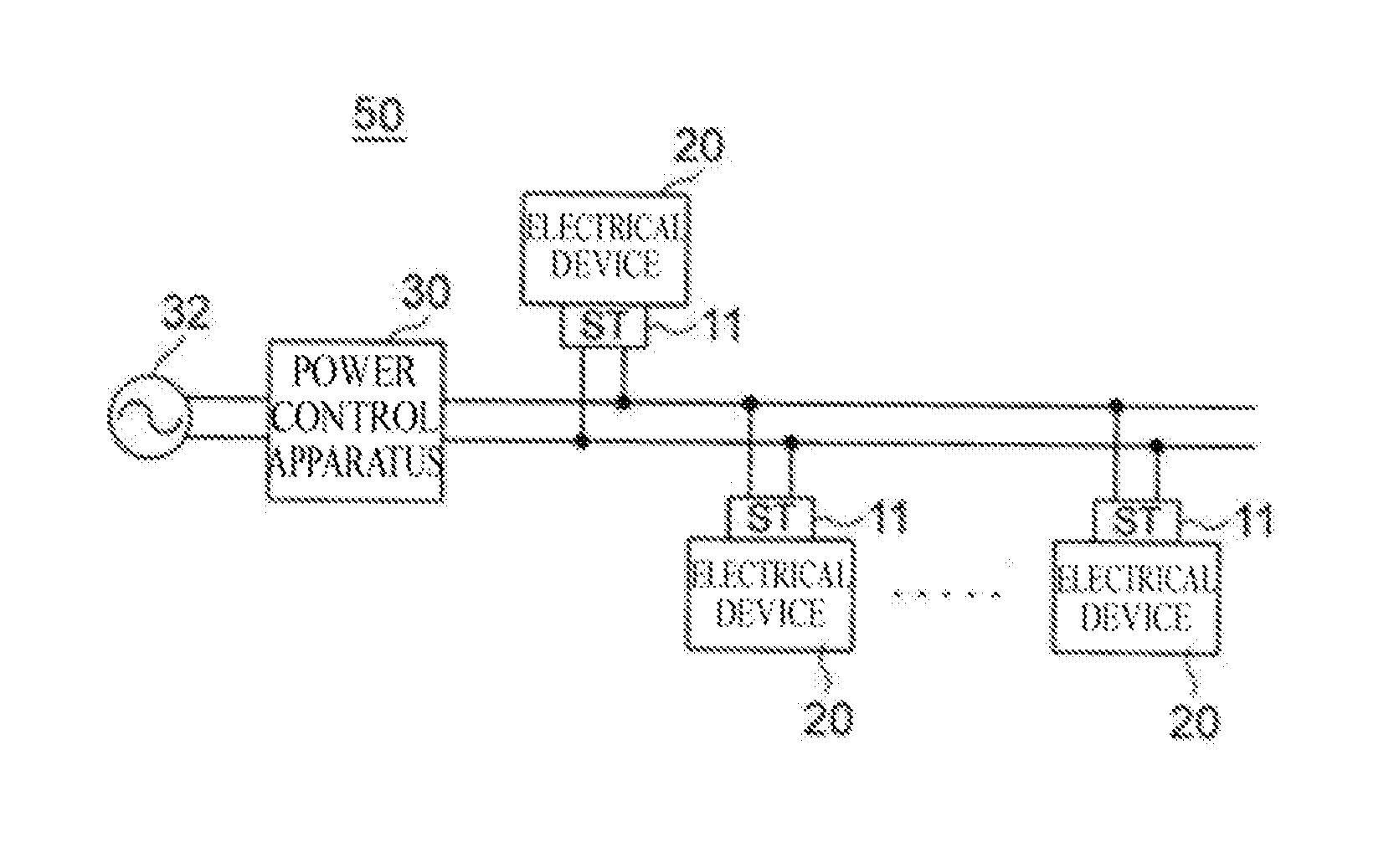
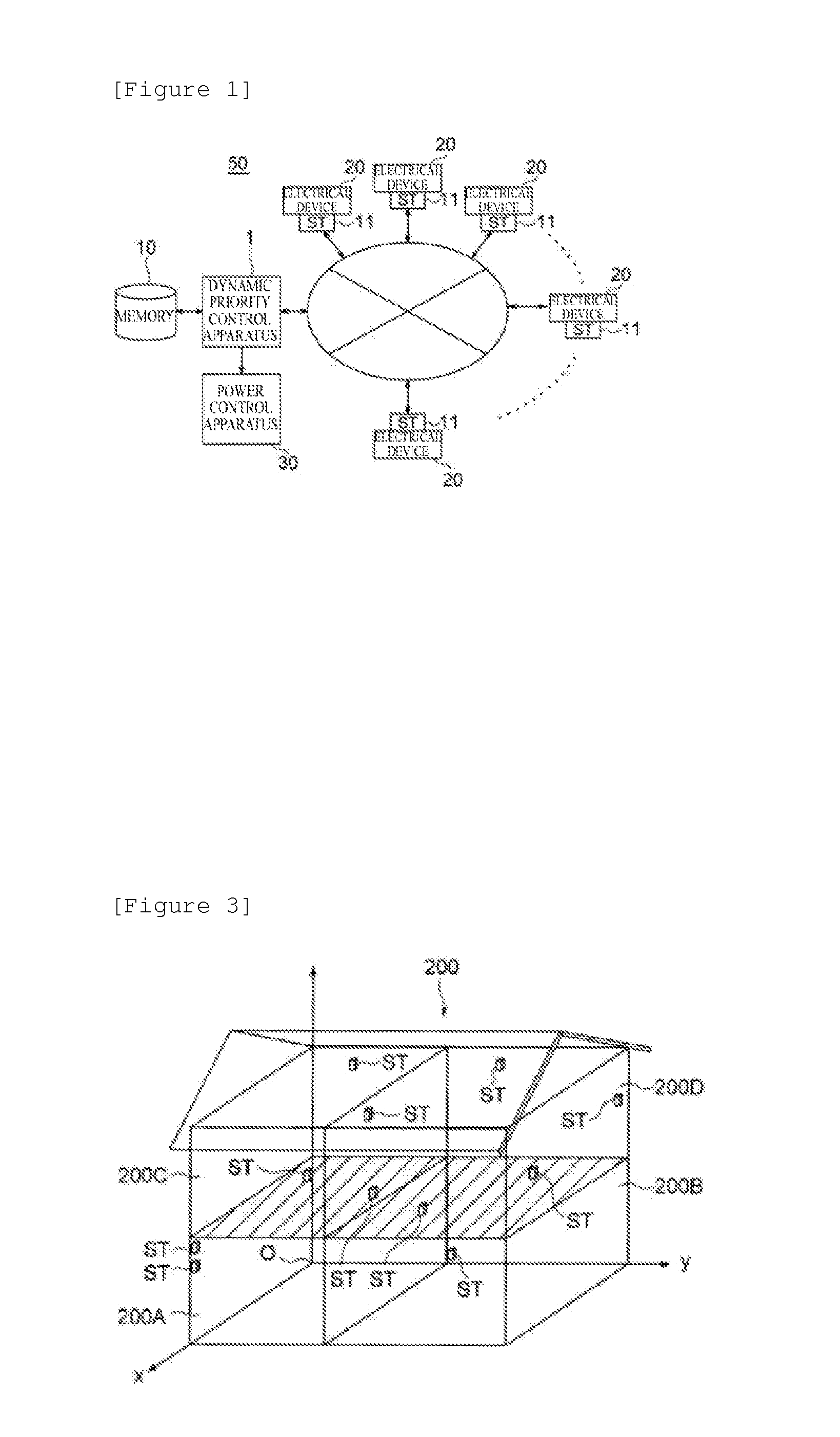
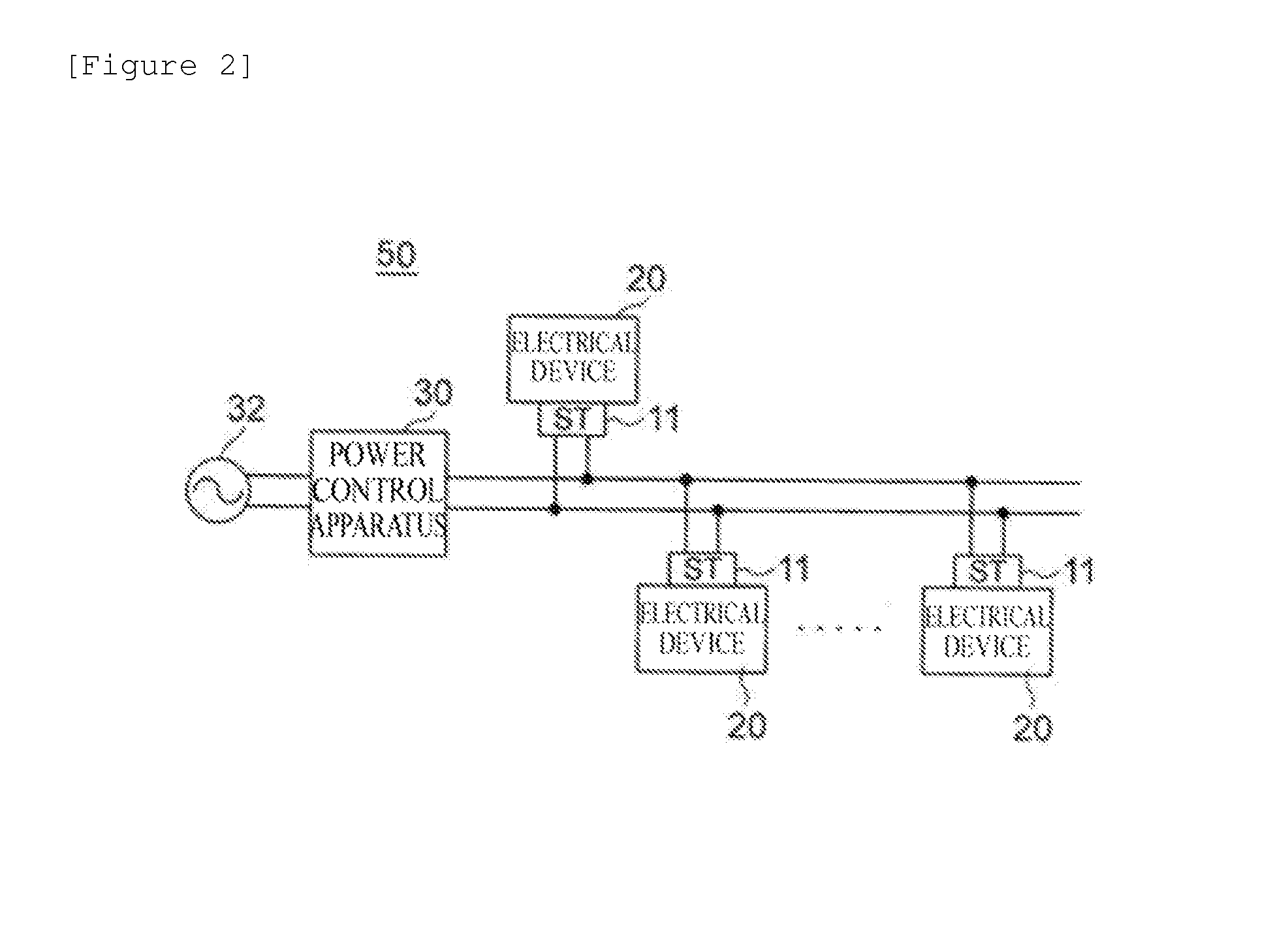
On-demand power control system, on-demand power control system program, and computer-readable recording medium recording the same program
InactiveUS20140074307A1Priority may changeWithout impair quality of lifeMechanical power/torque controlData processing applicationsDevice PropertiesElectrical installation
A dynamic priority control apparatus of the present invention is characterized by including means that calculate a difference between instantaneous power of an initial target value and actual instantaneous power, initial target value updating means that take into account the difference, calculating priorities of electrical devices means based on electrical device property class data, and power arbitration means that determines the electrical devices to be supplied power based on the total value of the consumed power and the priorities of the electrical devices.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Alignment, verification, and optimization of high power wireless charging systems
ActiveUS9637014B2Improve the level ofProblem can be addressedBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsParking spaceElectric cars
Provided are a method and apparatus and method for the alignment, verification and optimization of wireless charging systems manufactured for use and used with electric vehicles. With some minimal modifications the same apparatus may be used to align a charging coil mounted on a vehicle with a charging coil, mounted on or in an electric vehicle charging bay or parking space, or to verify and optimize manufactured wireless vehicle charging system elements before they are installed.
Owner:WIRELESS CHARGE
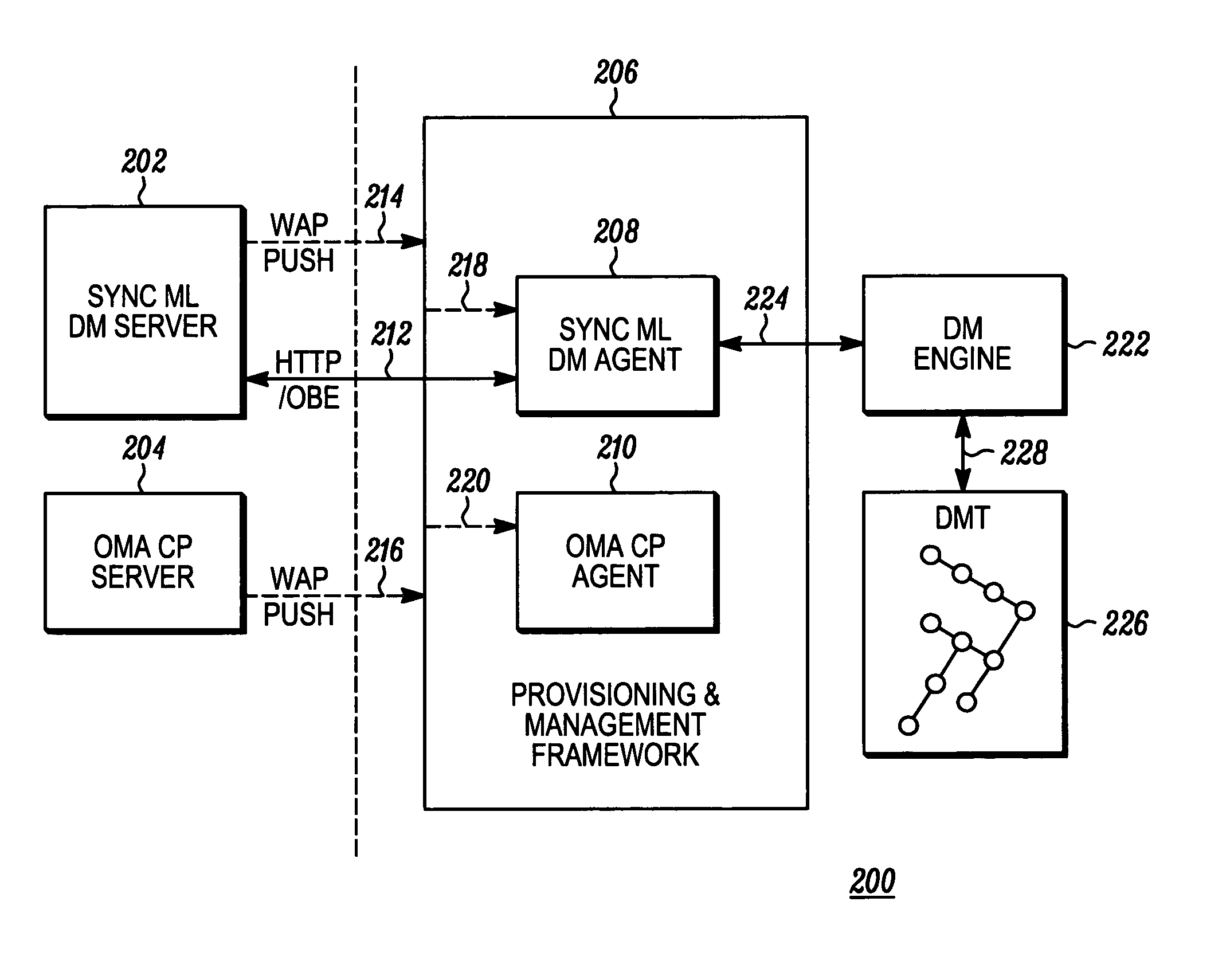
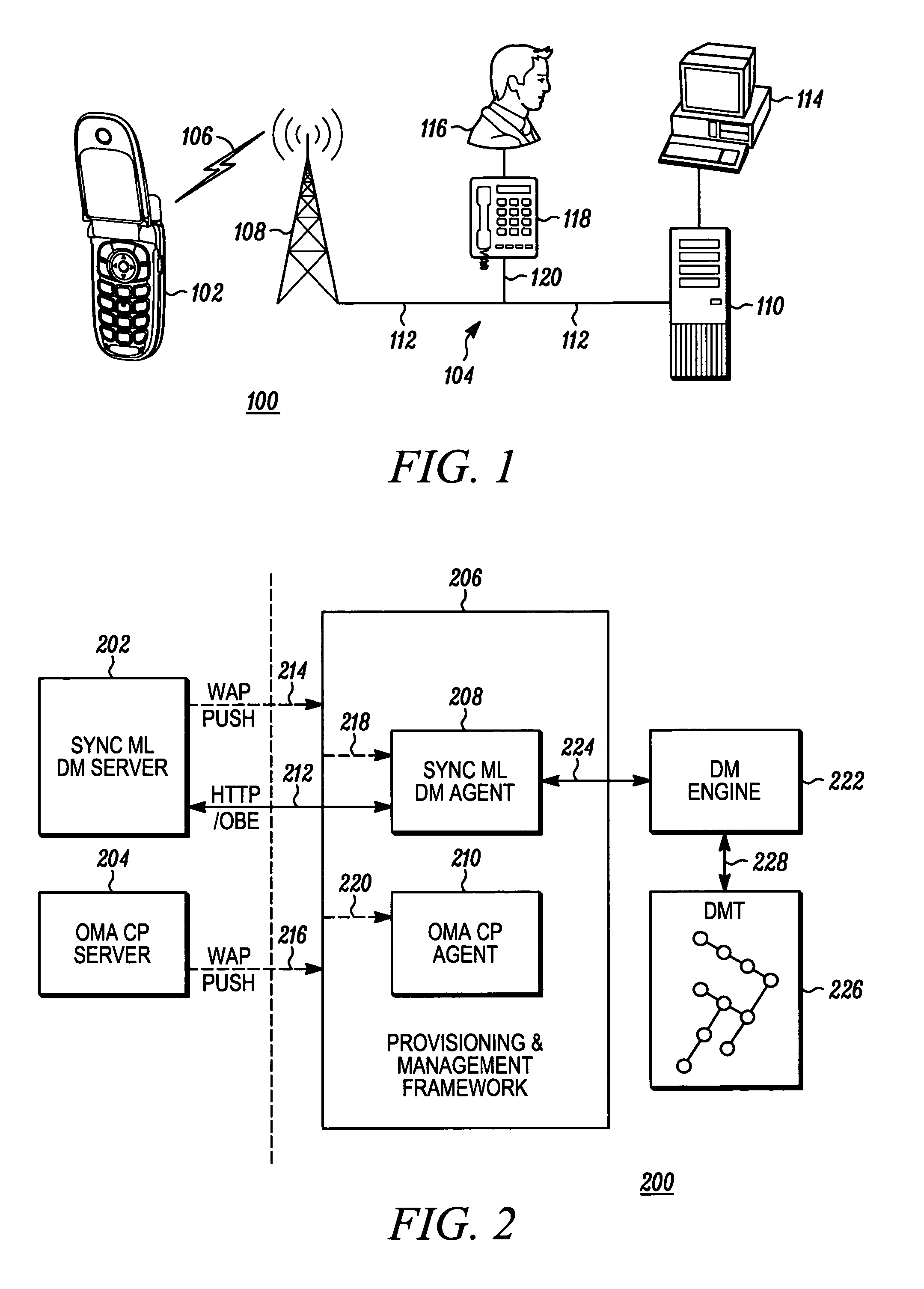
System and method for provisioning device management tree parameters over a client provisioning protocol
InactiveUS20050232175A1Maximum satisfaction of user experienceProblem can be addressedData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsCommunications systemPaper document
A client device (102) of a communication system (100) comprising a provisioning and management framework (206). The framework (206) receives (404) a client provisioning document from a source (110), and the client provisioning document includes a device management characteristic. The client device (102) then identifies (408) a device management characteristic from the client provisioning document. Thereafter, the client device (102) provides (424) data based on the device management characteristic of the client provisioning document to a device management tree (226, 426).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
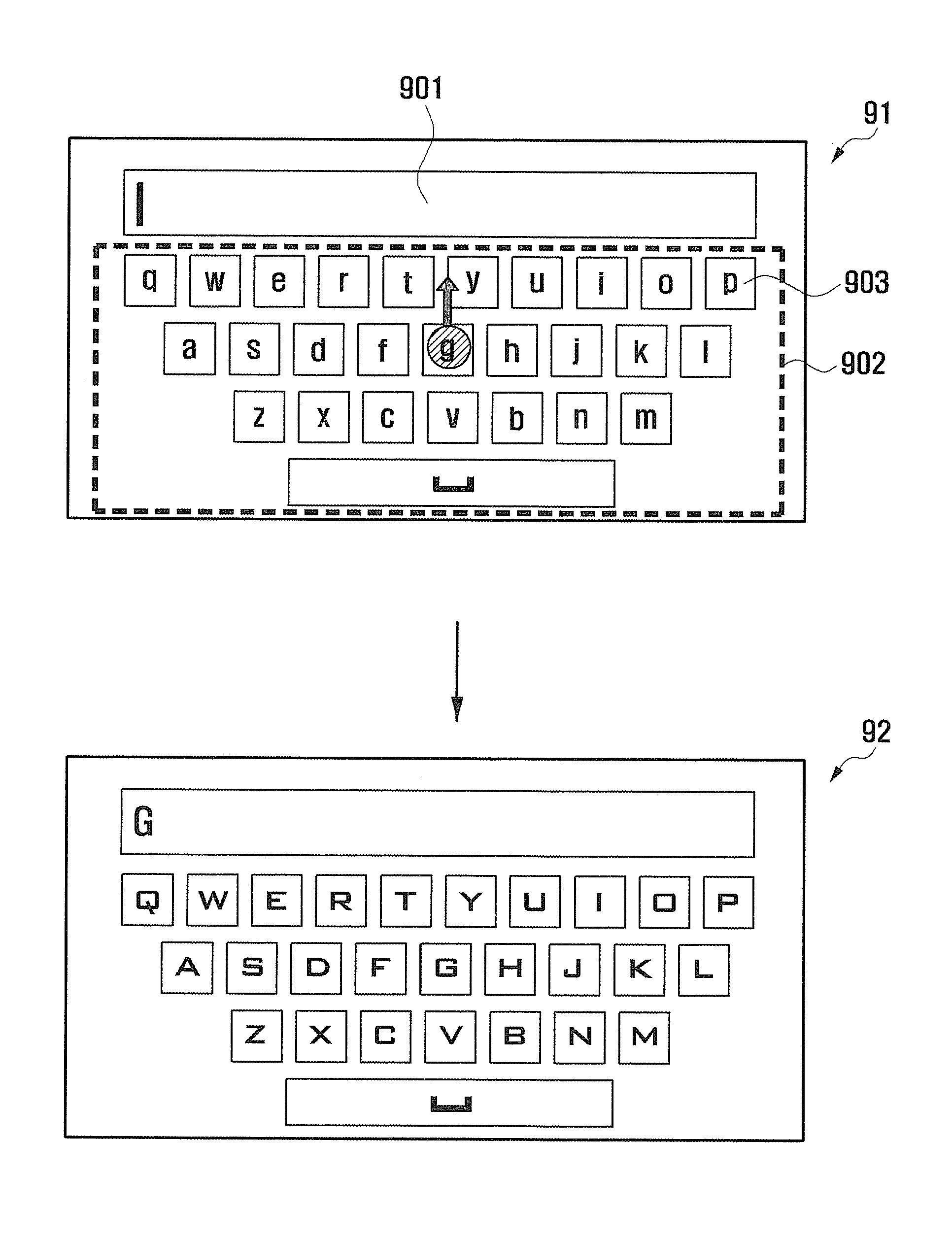
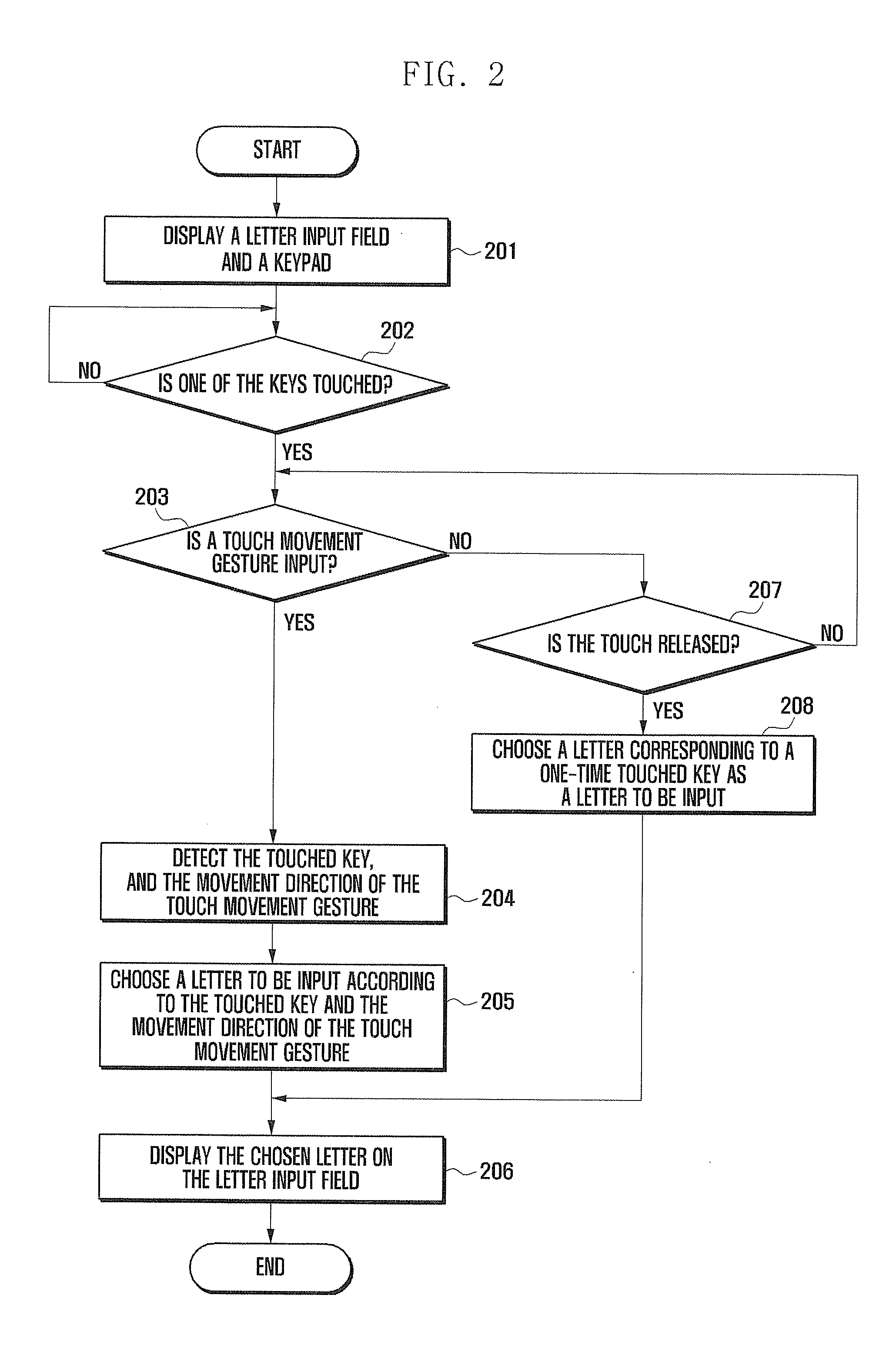
Letter input method and mobile device adapted thereto
InactiveUS20120044175A1Increase typing speedProblem can be addressedTransmissionTelephone set constructionsTouchscreenMobile device
A letter input method and a mobile device allow users to input letters via a virtual keypad on a touch screen. A letter input field and a virtual keypad with a number of keys are displayed. A touched key and a movement direction of a touch location movement gesture are detected. A letter to be input is chosen according to the touched key and the movement direction. And the chosen letter is displayed on the letter input field. The letter input method can allow users to rapidly and easily type letters to the touch screen of a mobile device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
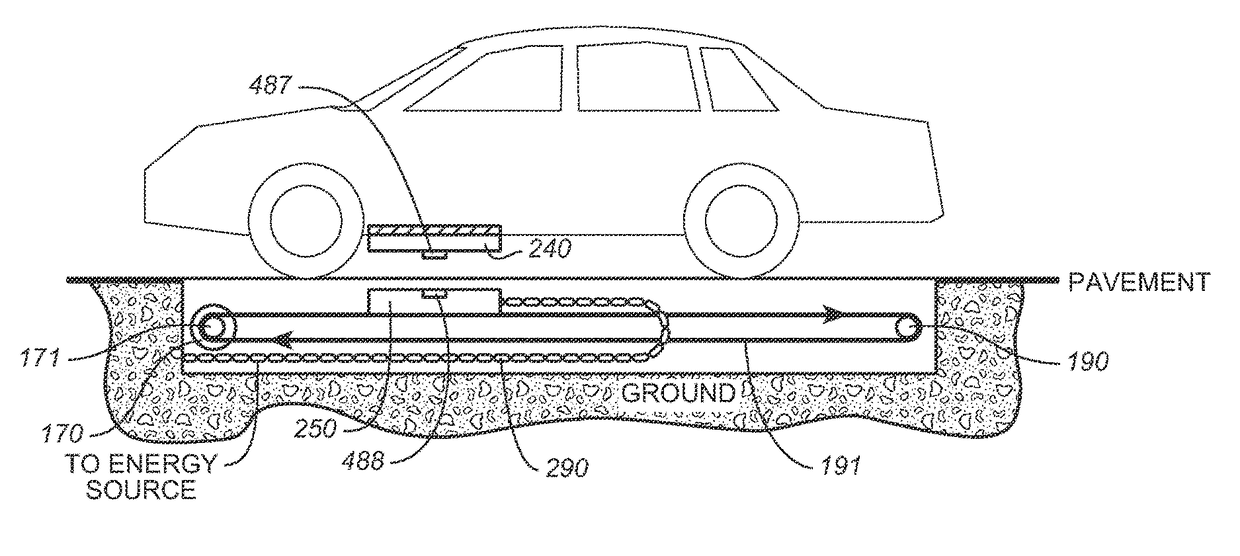
Hybrid device for cell therapies
InactiveUS20060024276A1Easy to addFavor engraftmentBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsInterior spaceBiological materials
A device for receiving implanted biological material includes a porous outer wall defining an inner space, a fluid manifold assembly for selectively infusing at least one of immunosuppressive and growth factor media to said space, and a pump structure operatively coupled to the manifold assembly. The device may comprise an additional plunger body for being disposed in said space and so as to define a peripheral gap between the plunger and the perforated wall of the device.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Streaming method and system for processing network metadata
ActiveUS9392010B2Problem can be addressedEasily correlatedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficTemplate based
A method and system for processing network metadata is described. Network metadata may be processed by dynamically instantiated executable software modules which make policy-based decisions about the character of the network metadata and about presentation of the network metadata to consumers of the information carried by the network metadata. The network metadata may be type classified and each subclass within a type may be mapped to a definition by a unique fingerprint value. The fingerprint value may be used for matching the network metadata subclasses against relevant policies and transformation rules. For template-based network metadata such as NetFlow v9, an embodiment of the invention can constantly monitor network traffic for unknown templates, capture template definitions, and informs administrators about templates for which custom policies and conversion rules do not exist. Conversion modules can efficiently convert selected types and / or subclasses of network metadata into alternative metadata formats.
Owner:NETFLOW LOGIC
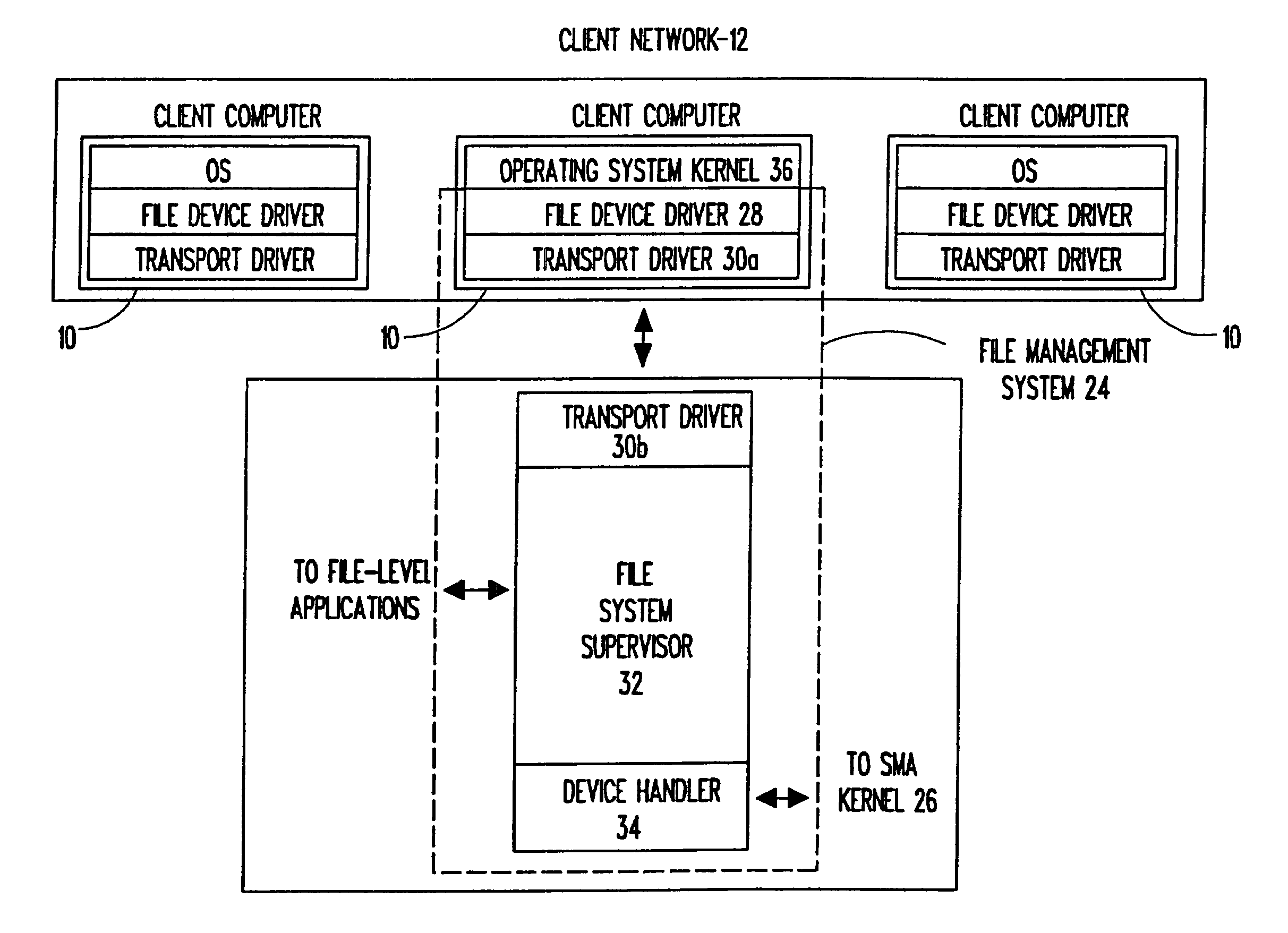
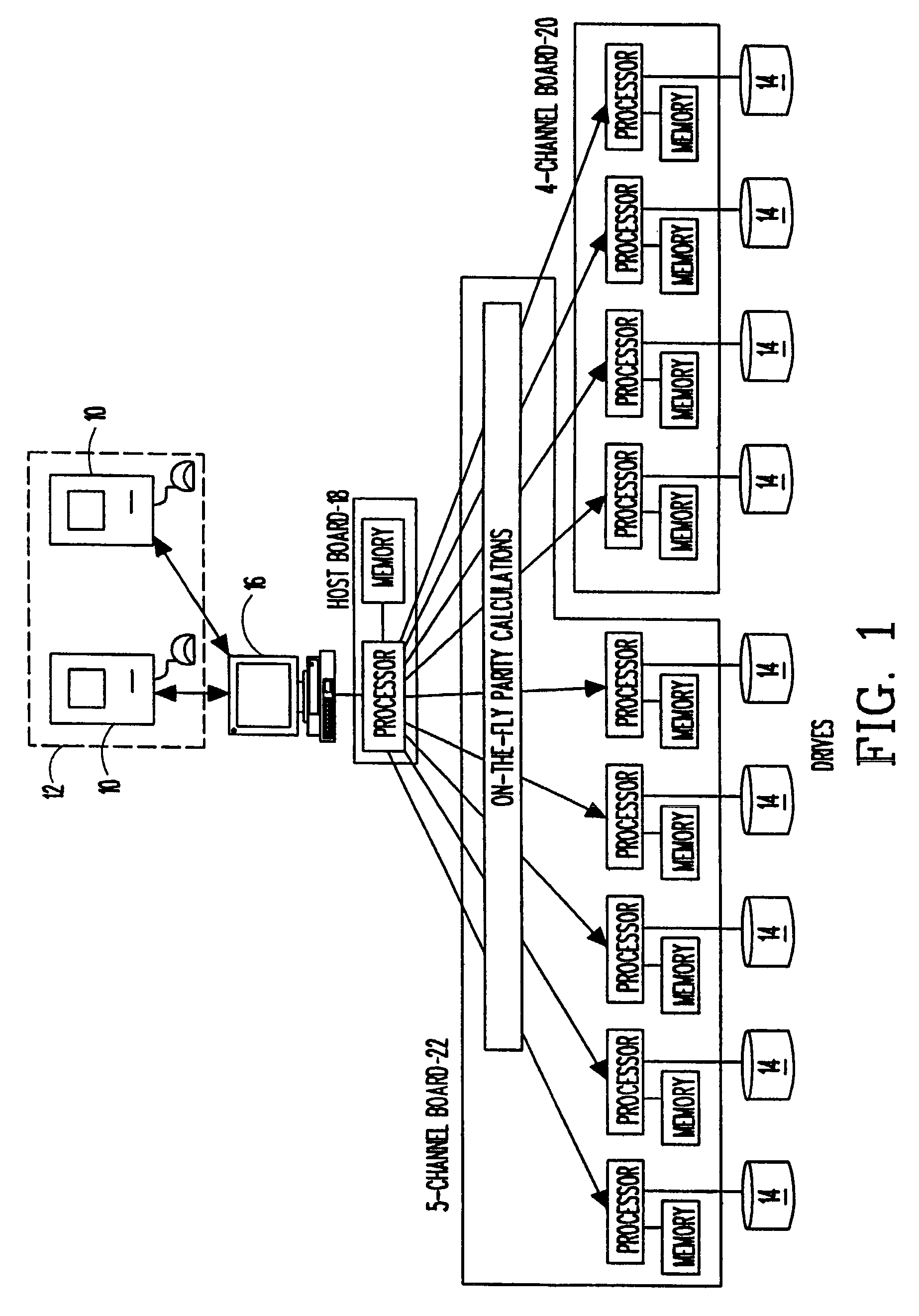
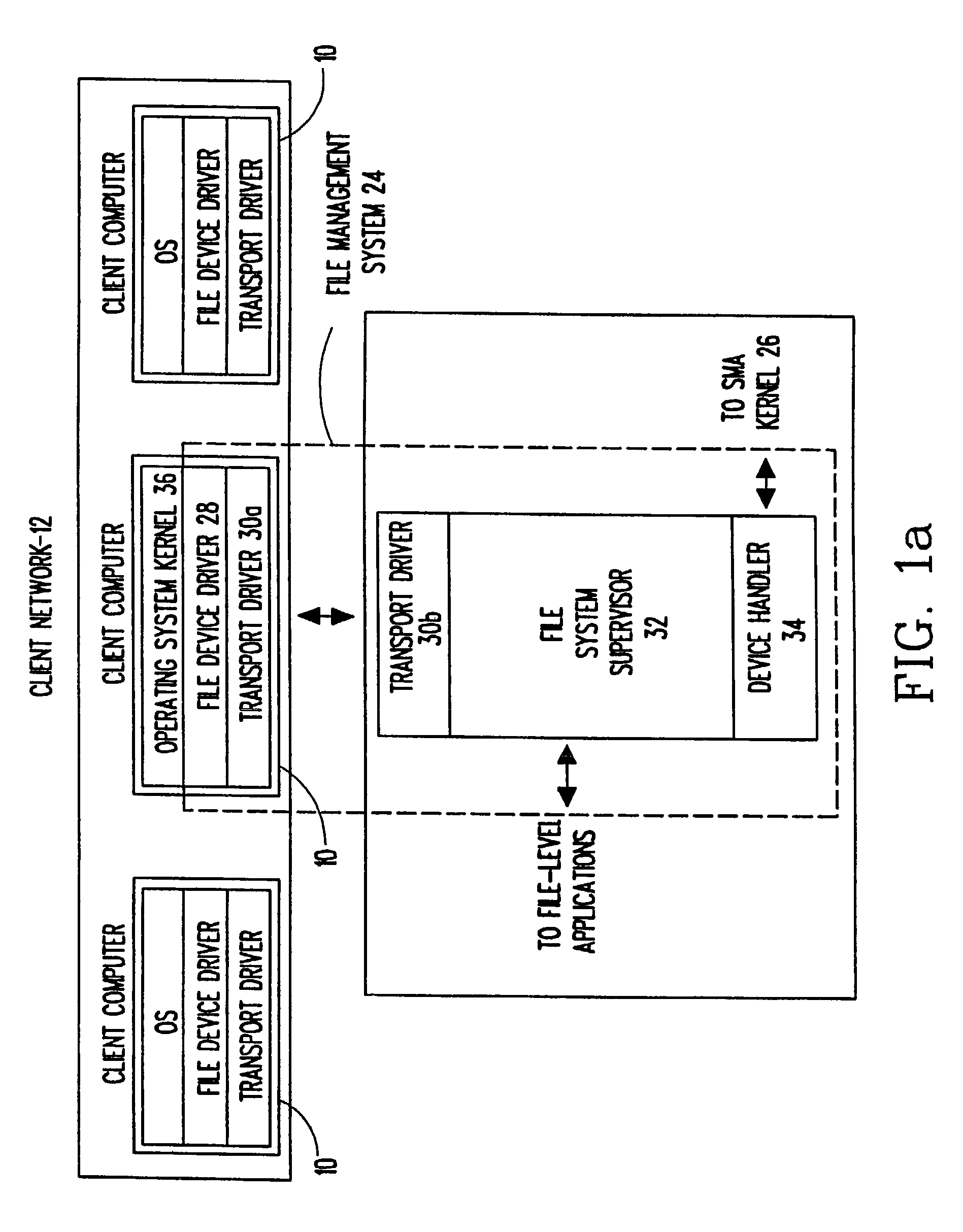
Universal storage management system
InactiveUSRE42860E1Save installation timeReduce overheadInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareInterconnection
A universal storage management system which facilitates storage of data from a client computer and computer network is disclosed. The universal storage management system functions as an interface between the client computer and at least one storage device, and facilitates reading and writing of data by handling I / O operations. I / O operation overhead in the client computer is reduced by translating I / O commands from the client computer into high level commands which are employed by the storage management system to carry out I / O operations. The storage management system also enables interconnection of a normally incompatible storage device and client computer by translating I / O requests into an intermediate common format which is employed to generate commands which are compatible with the storage device receiving the request. Files, error messages and other information from the storage device are similarly translated and provided to the client computer.
Owner:VELEZ MCCASKEY RICARDO E +1
Multi-leaf collimators
InactiveUS20090262901A1Drive great amountReduced shieldingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
A multi-leaf collimator for a radiotherapy apparatus comprises at least one array of laterally-spaced elongate leaves, each leaf being driven by an associated motor connected to the leaf via a drive means so as to extend or retract the leaf in its longitudinal direction, the drive means comprising a sub-frame on which at least a subset of the motors are mounted, the sub-frame being mounted at a location spaced from the leaf array in a direction transverse to the lateral and longitudinal directions, and including a plurality of leadscrews disposed longitudinally, each being driven by a motor and being operatively connected to a leaf thereby to drive that leaf.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com