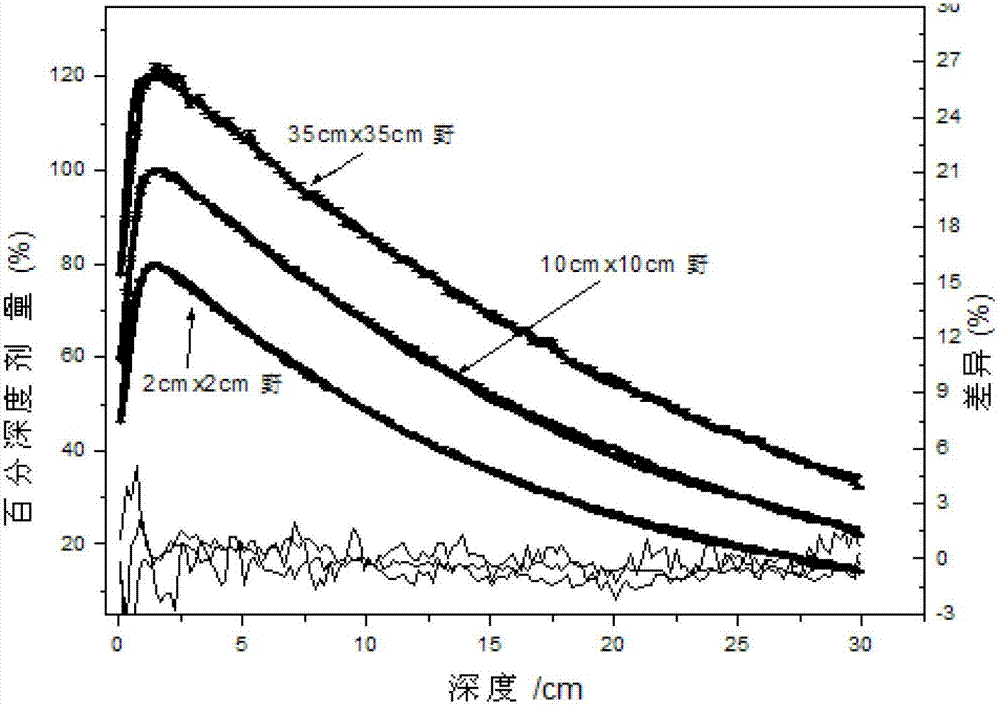
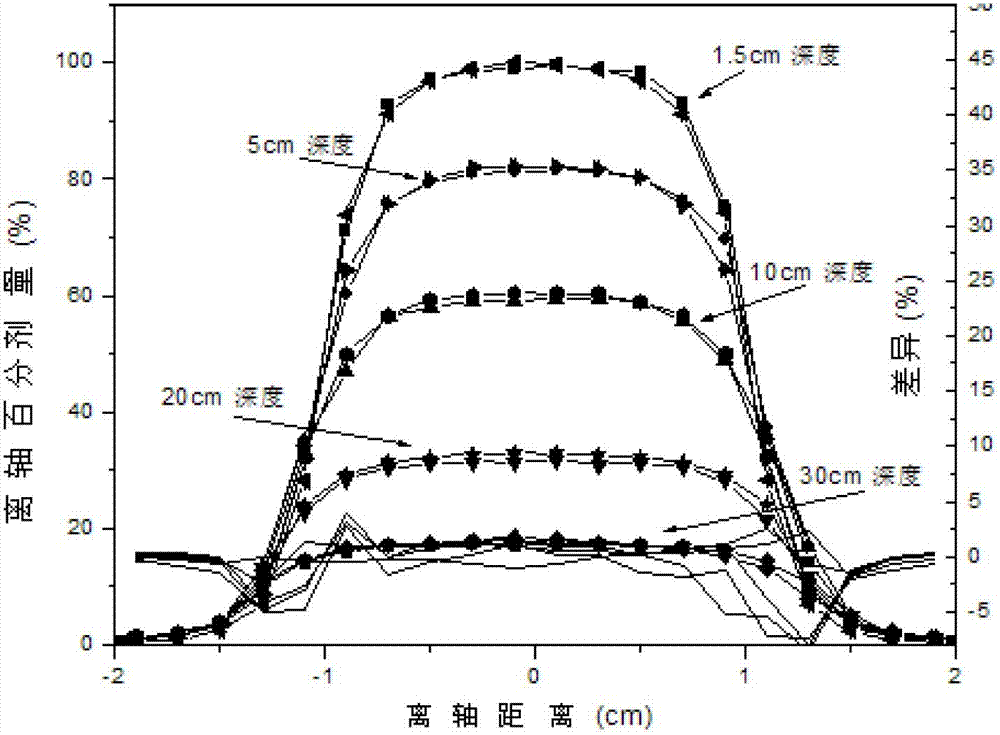
Patents
Literature
169 results about "Multi leaf collimator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
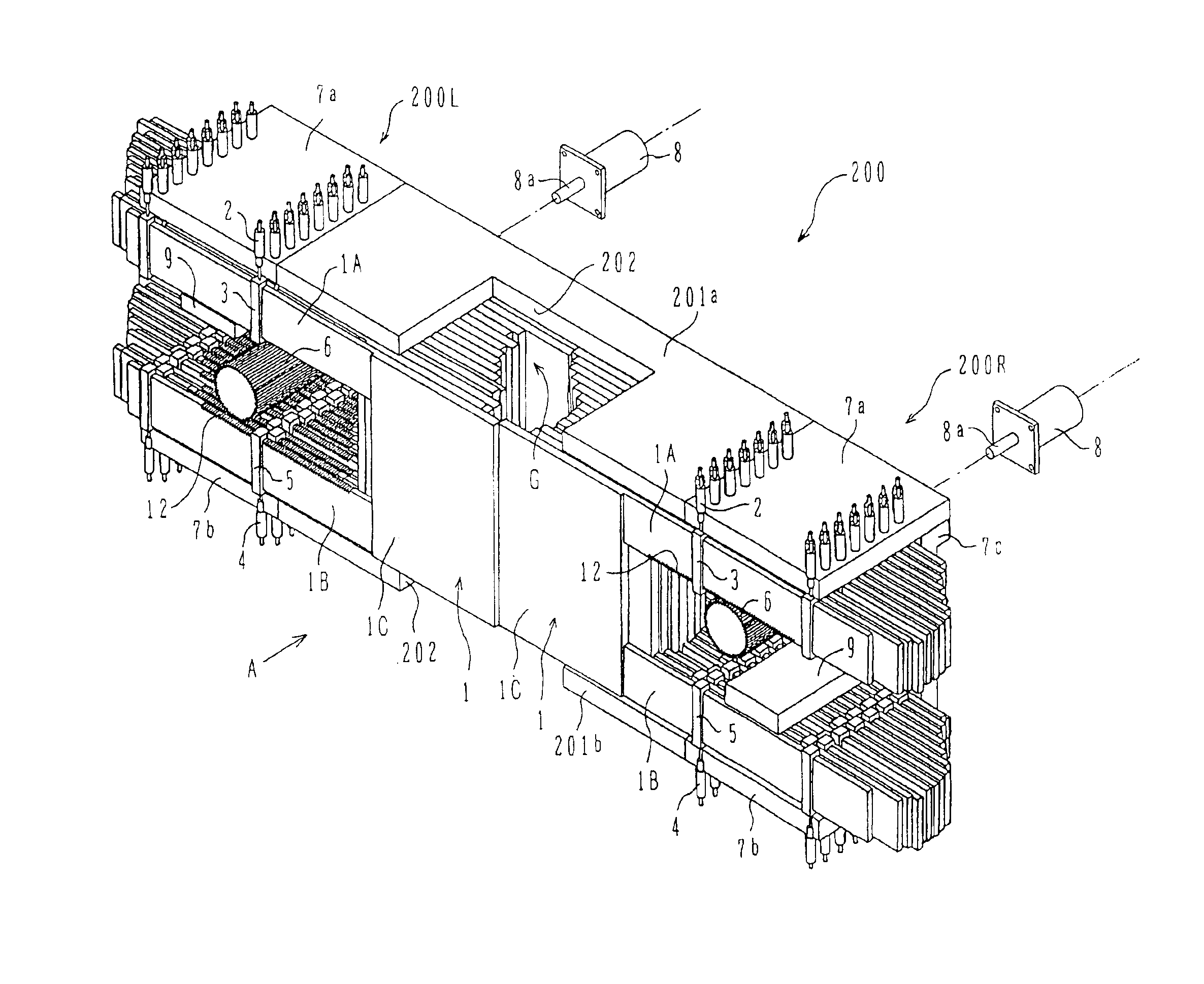
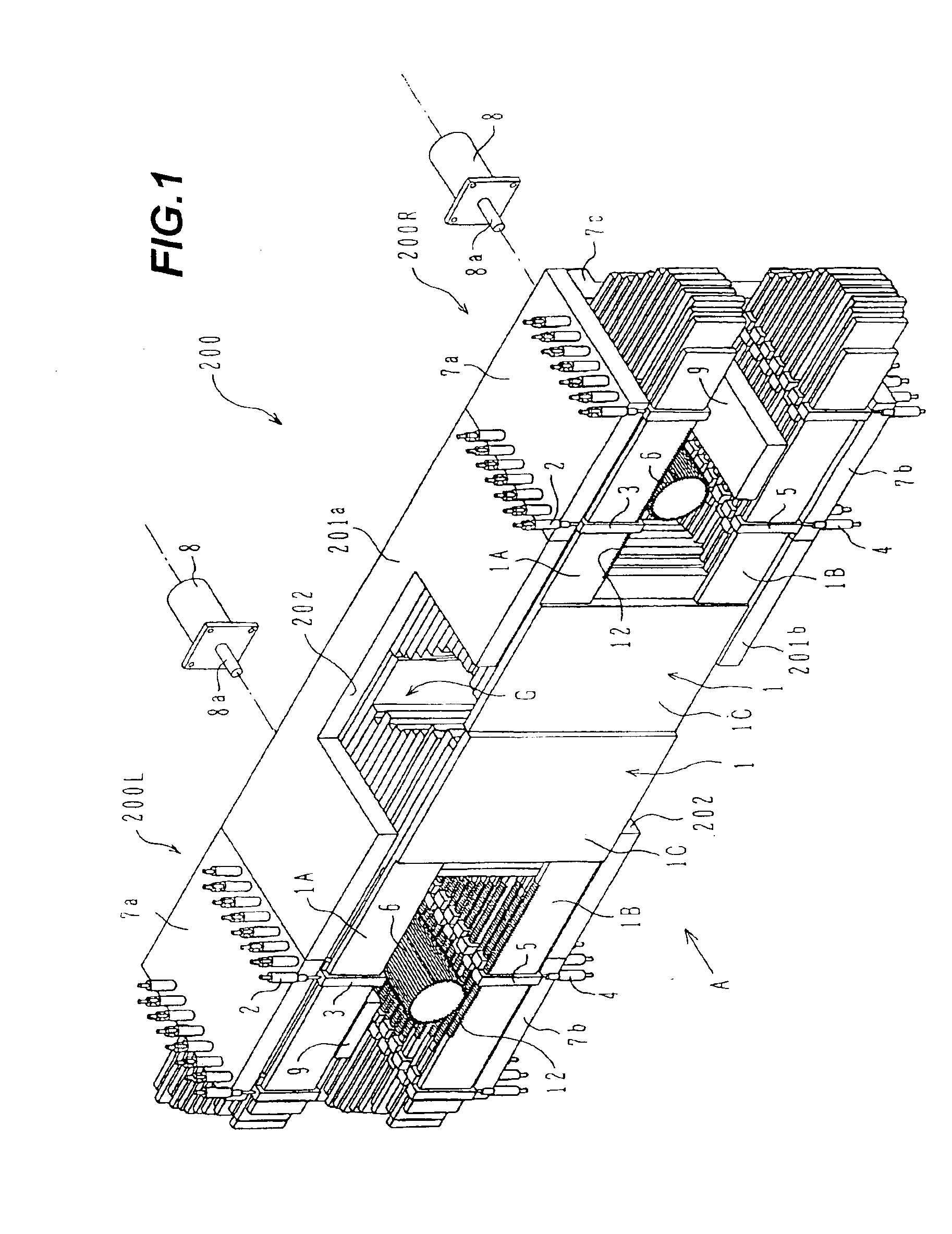
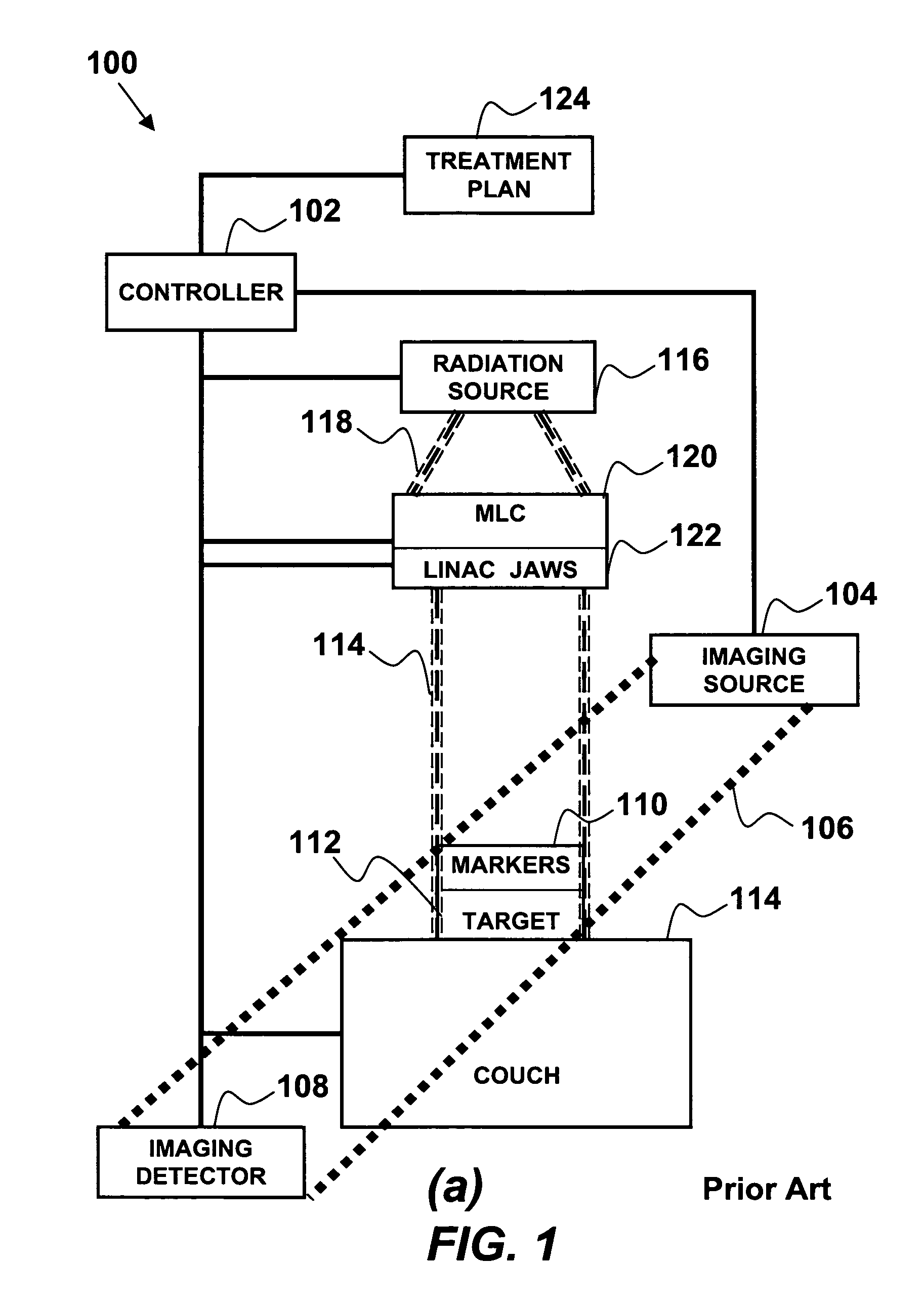
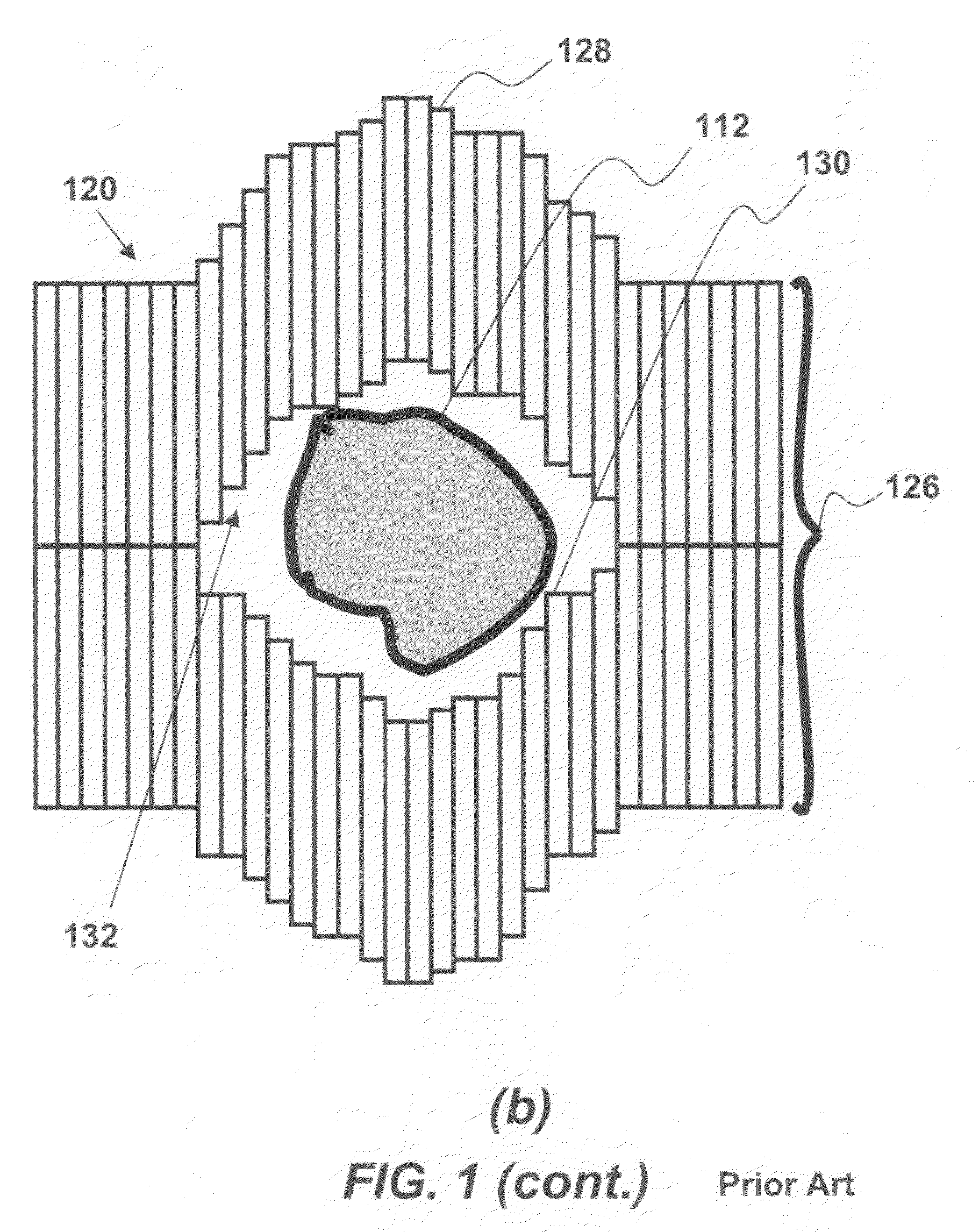
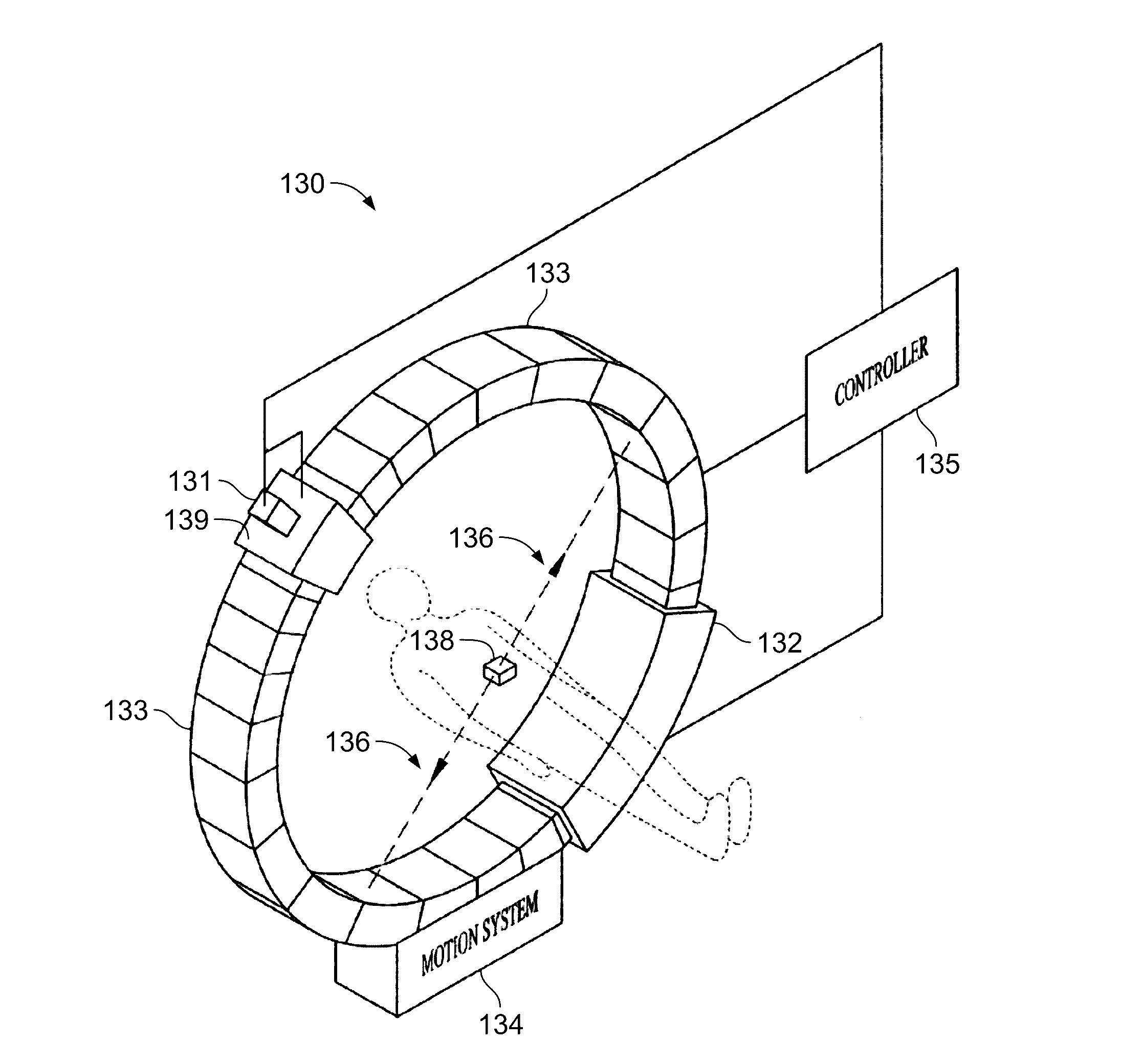
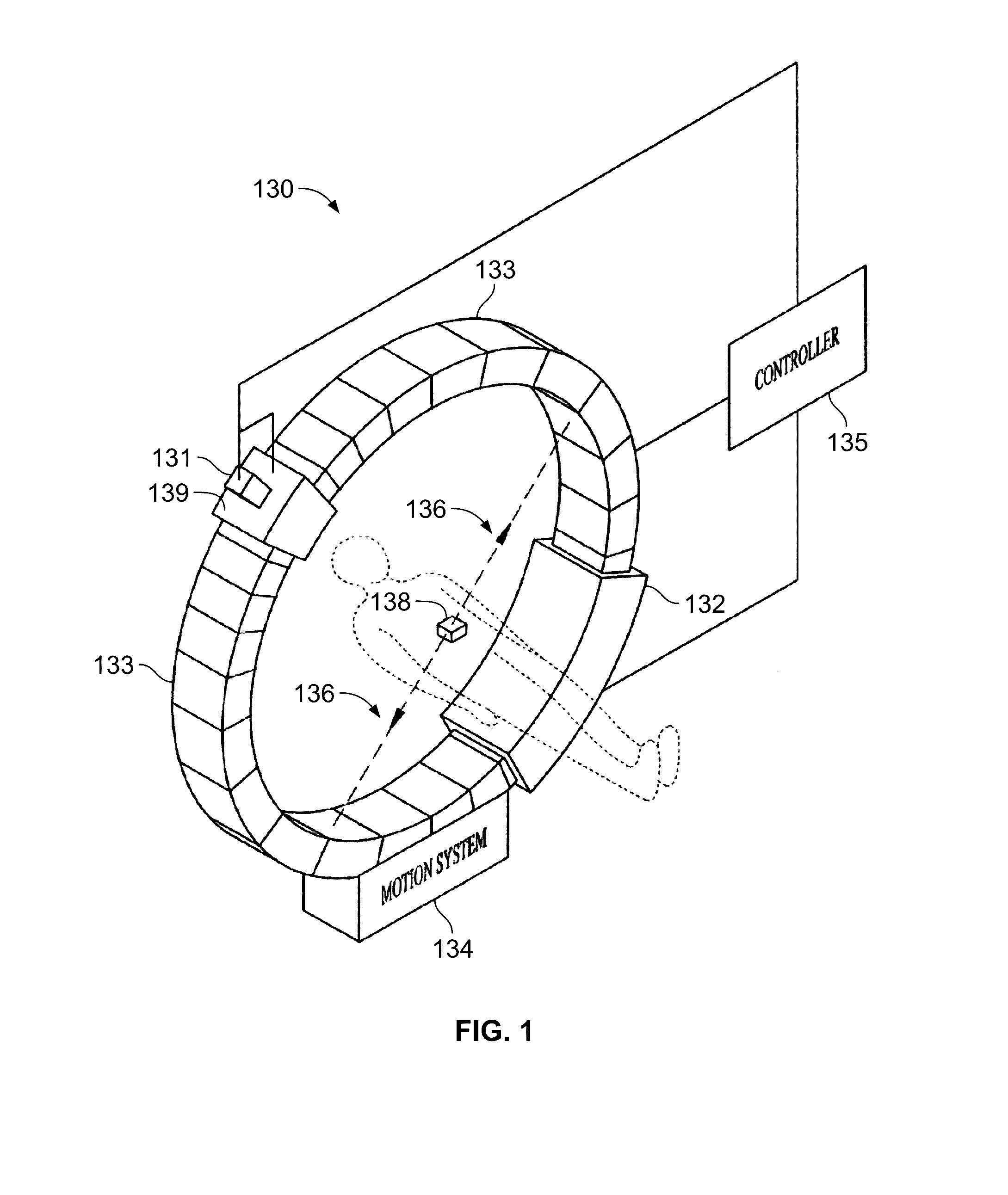
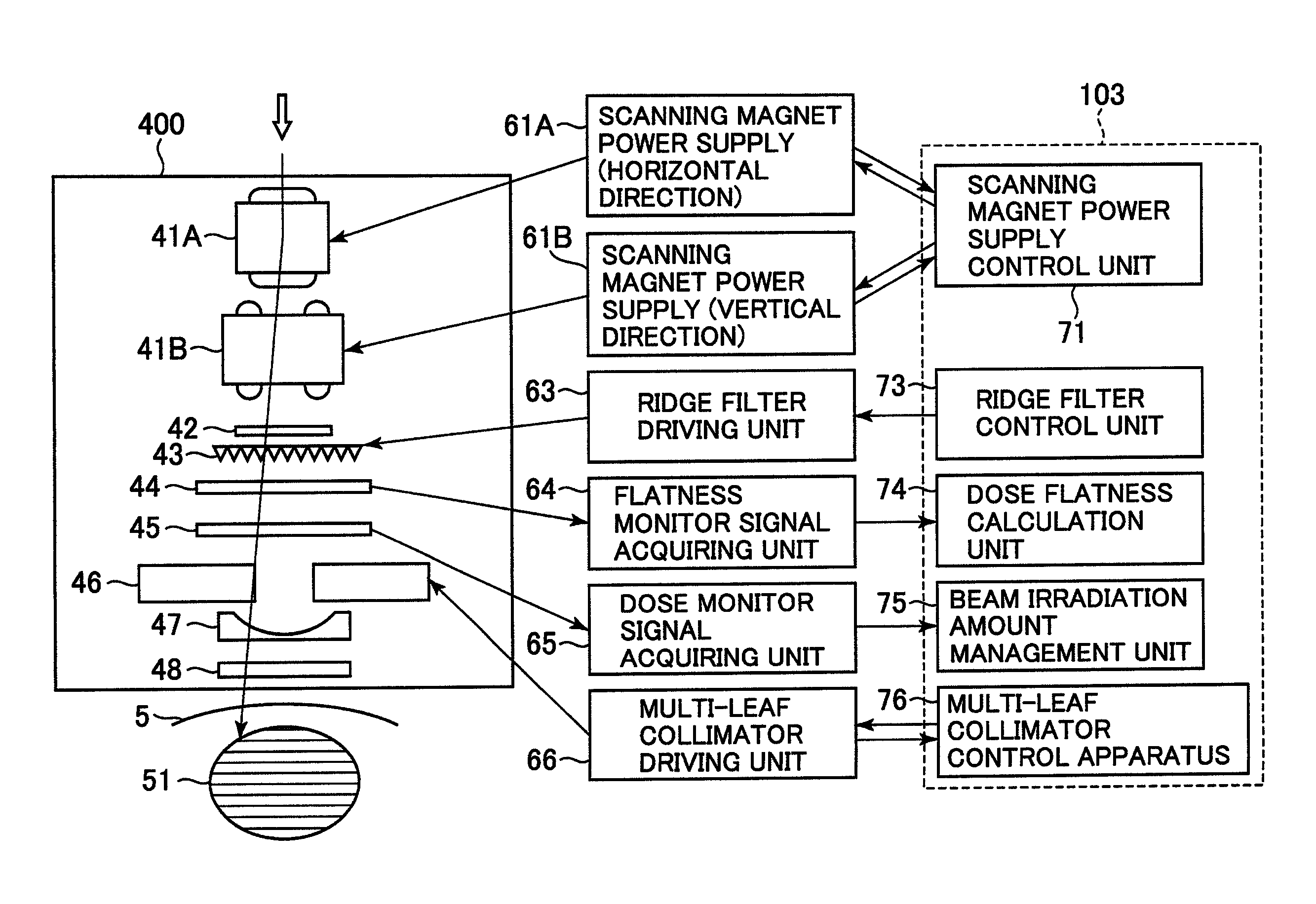
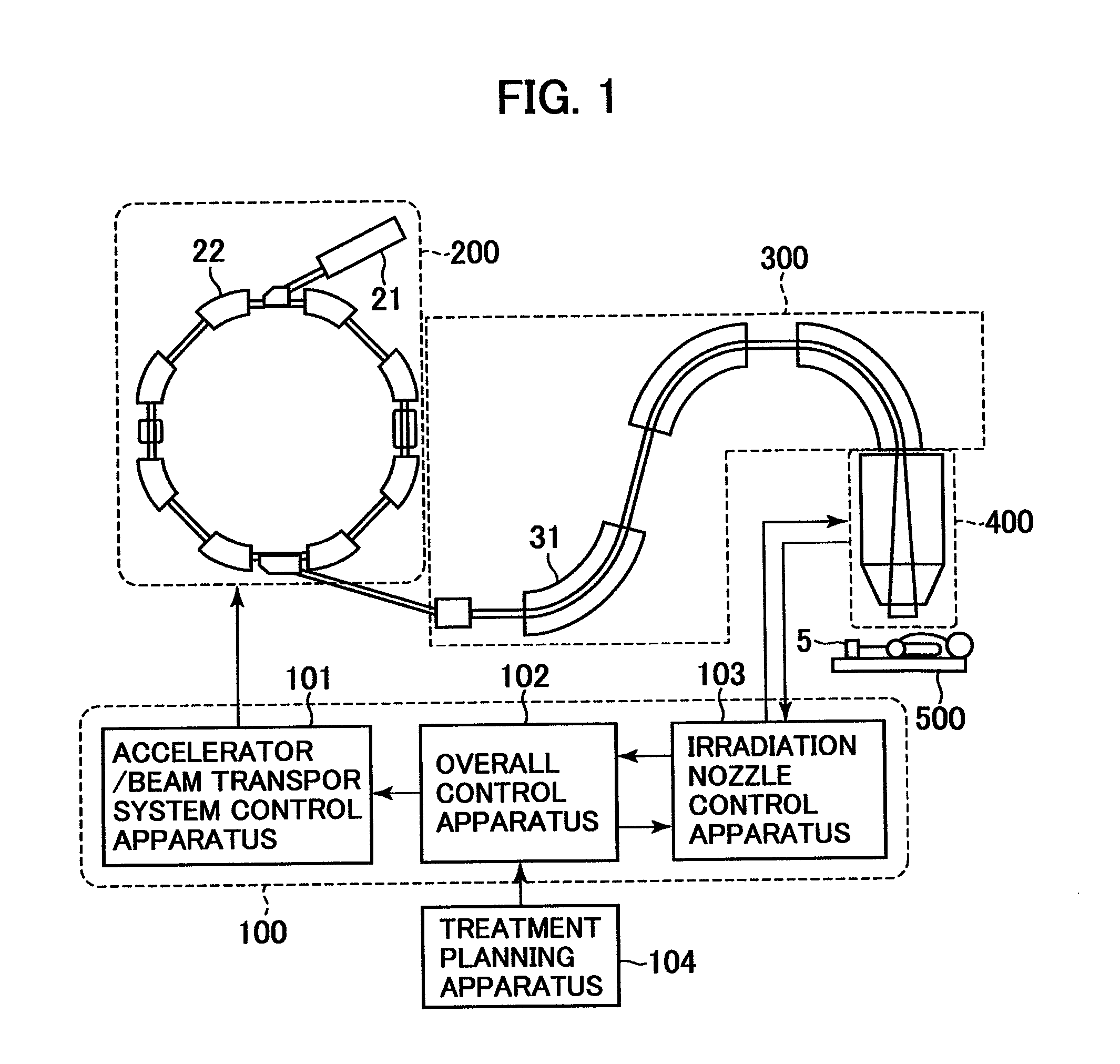
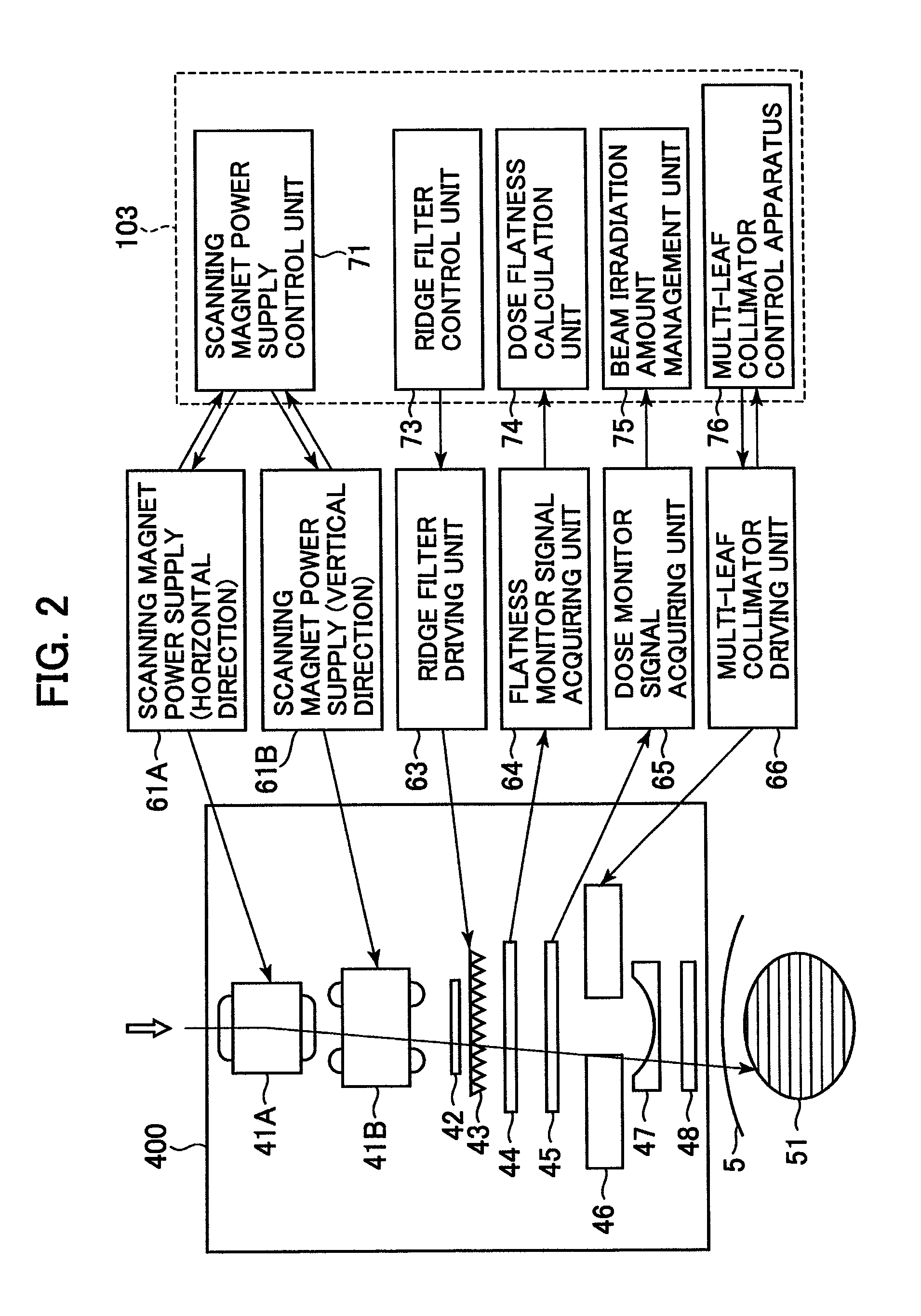
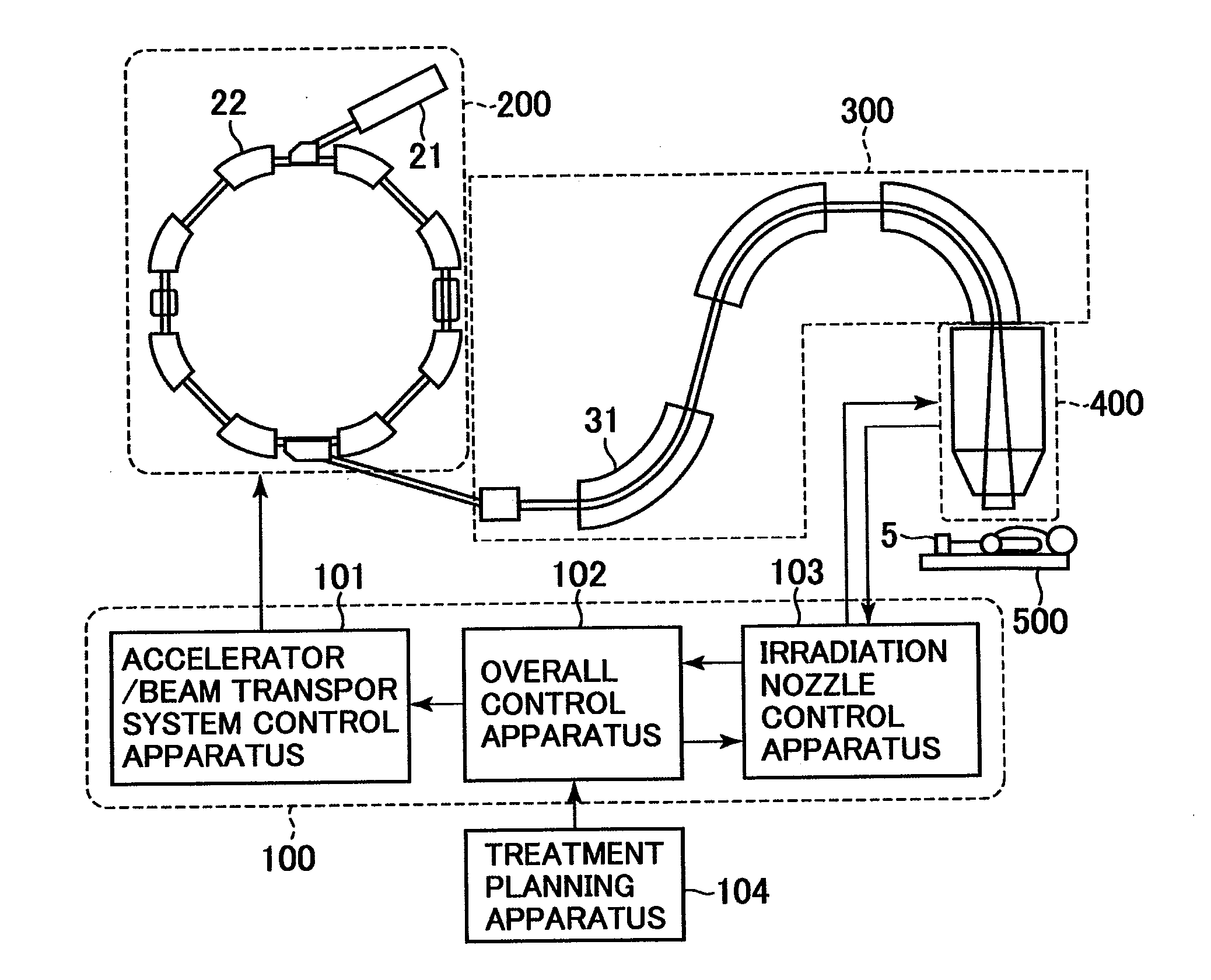
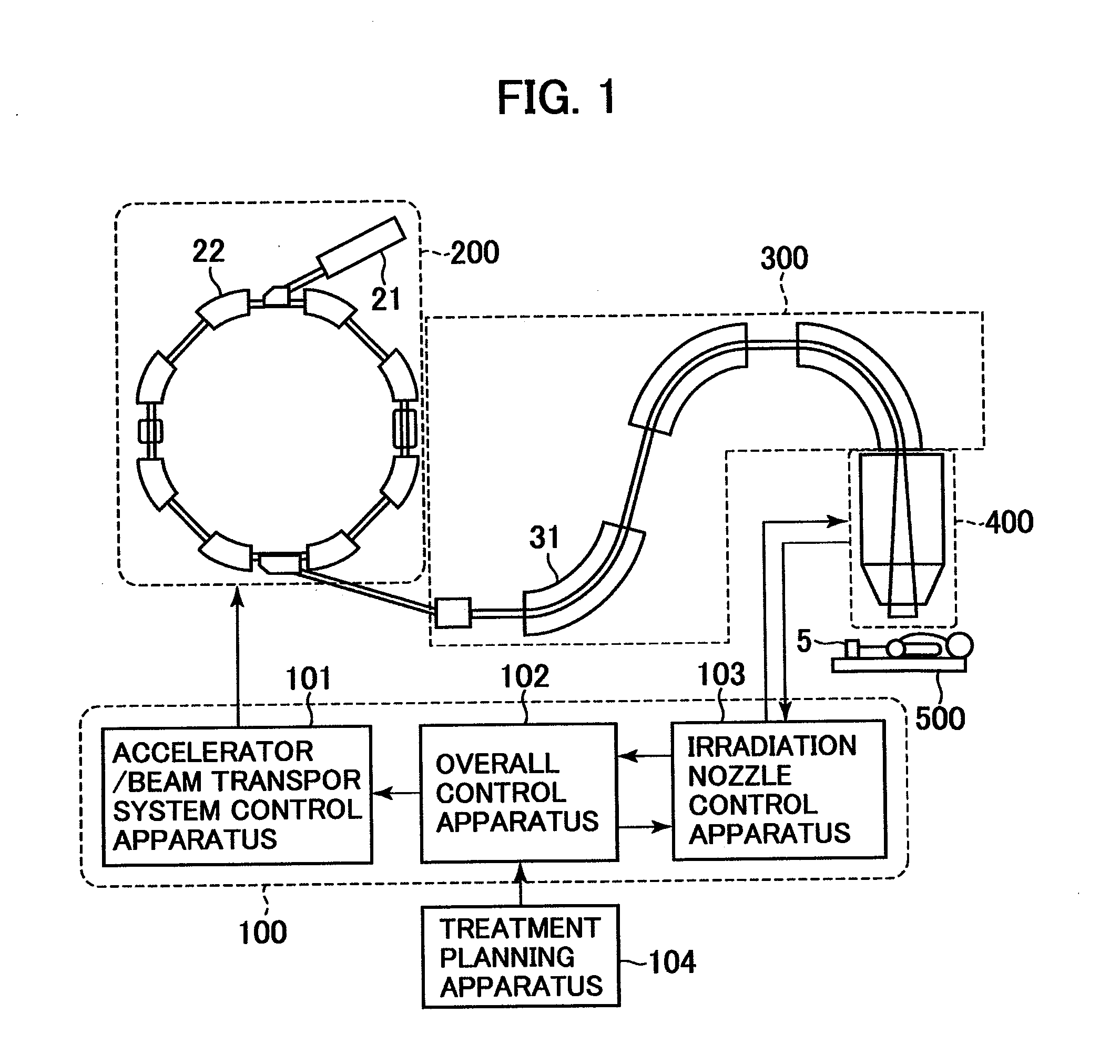
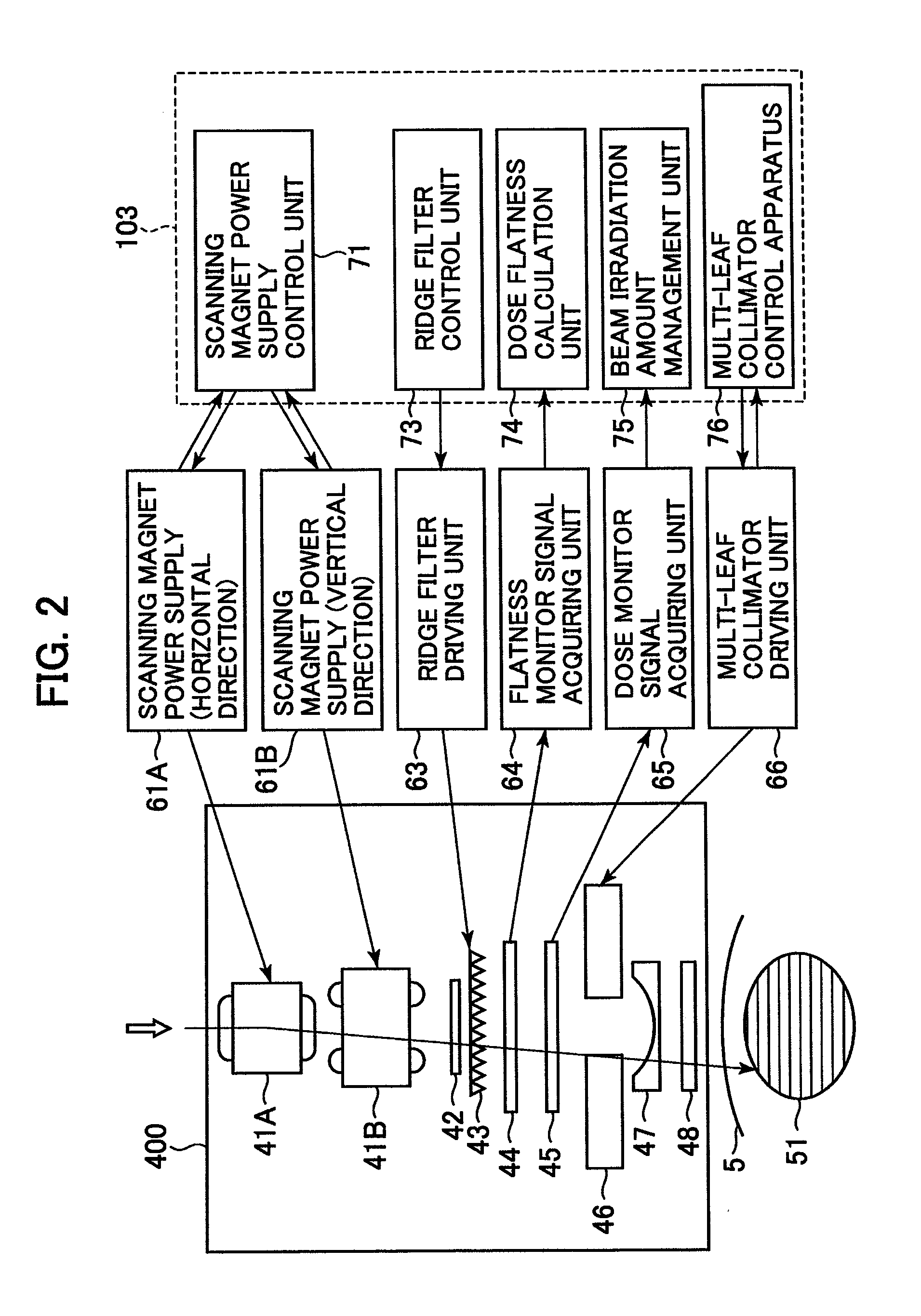
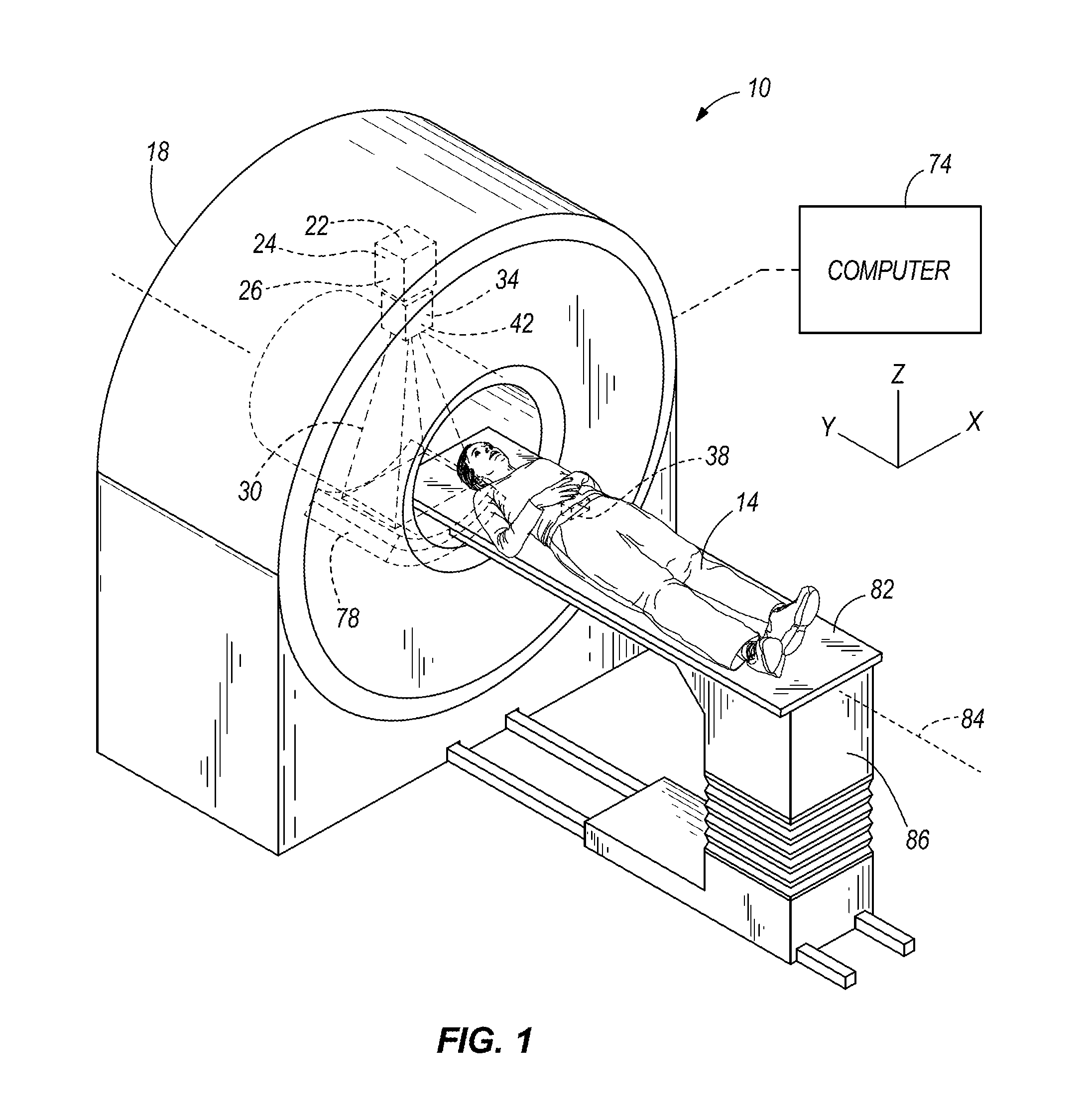
Multi-leaf collimator and medical system including accelerator
InactiveUS6931100B2Reduce physical and mental burdenShorten positioning timeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
Owner:HITACHI LTD
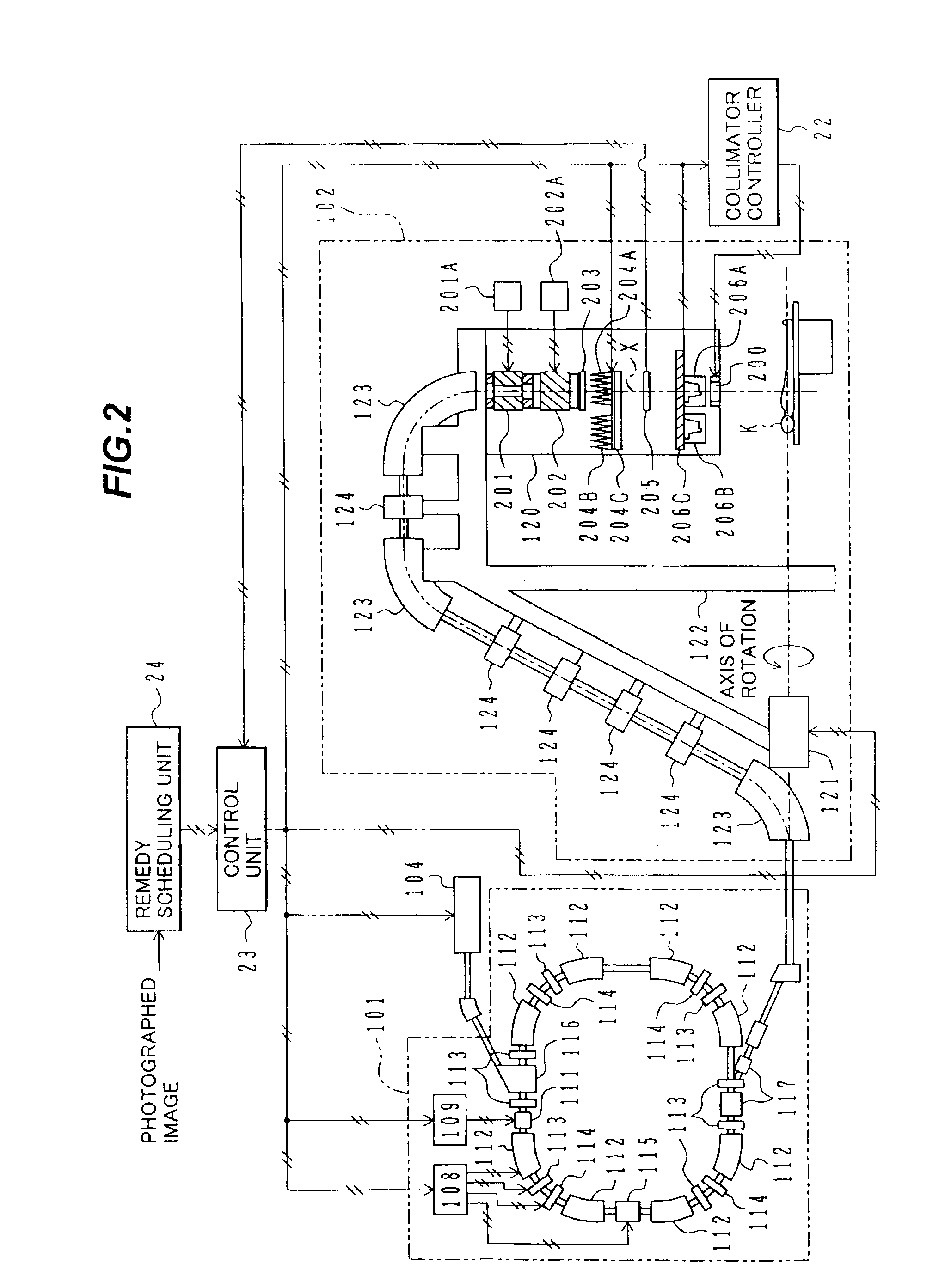
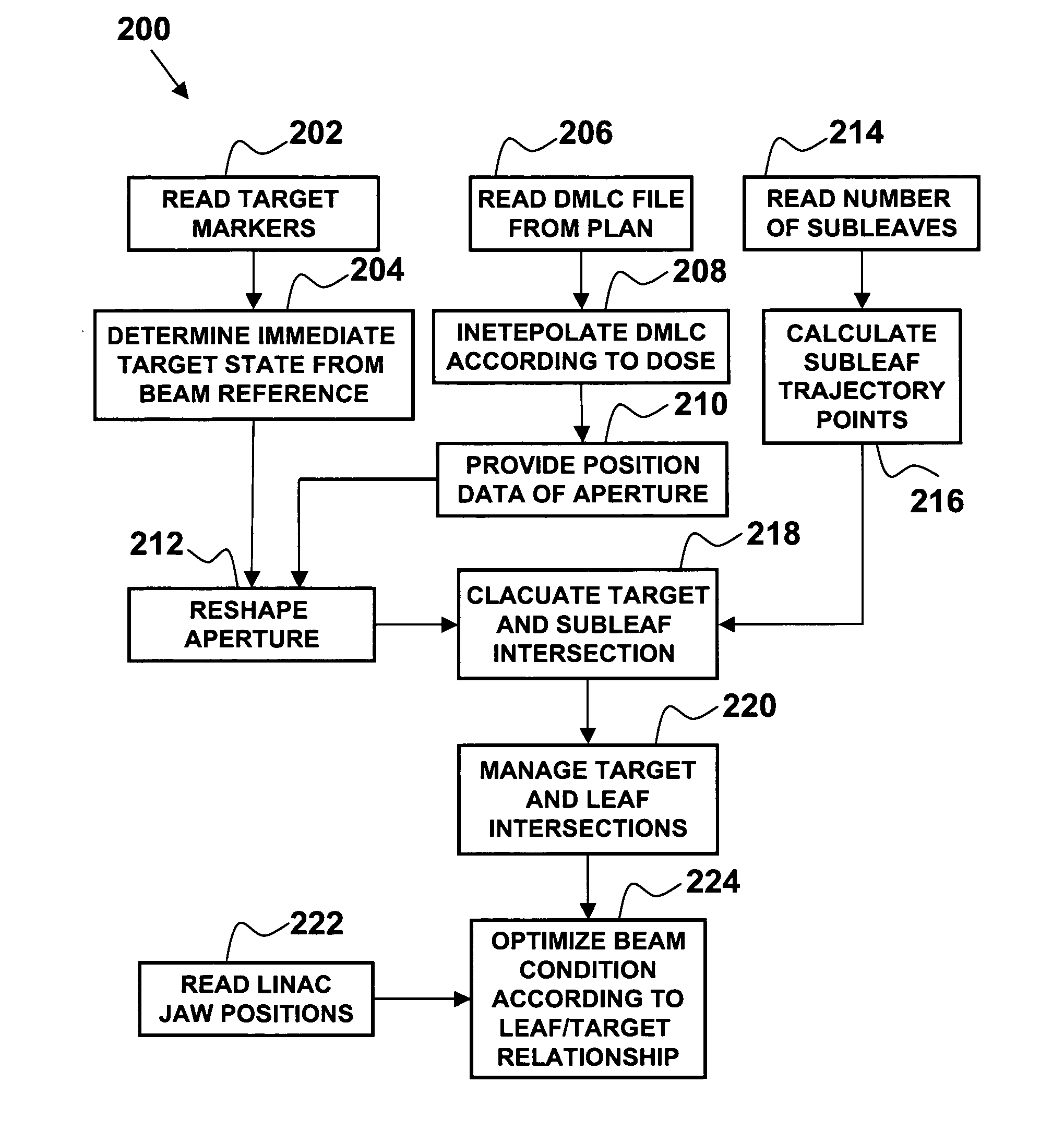
Method to track three-dimensional target motion with a dynamical multi-leaf collimator
InactiveUS20080159478A1Radiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsMulti leaf collimator
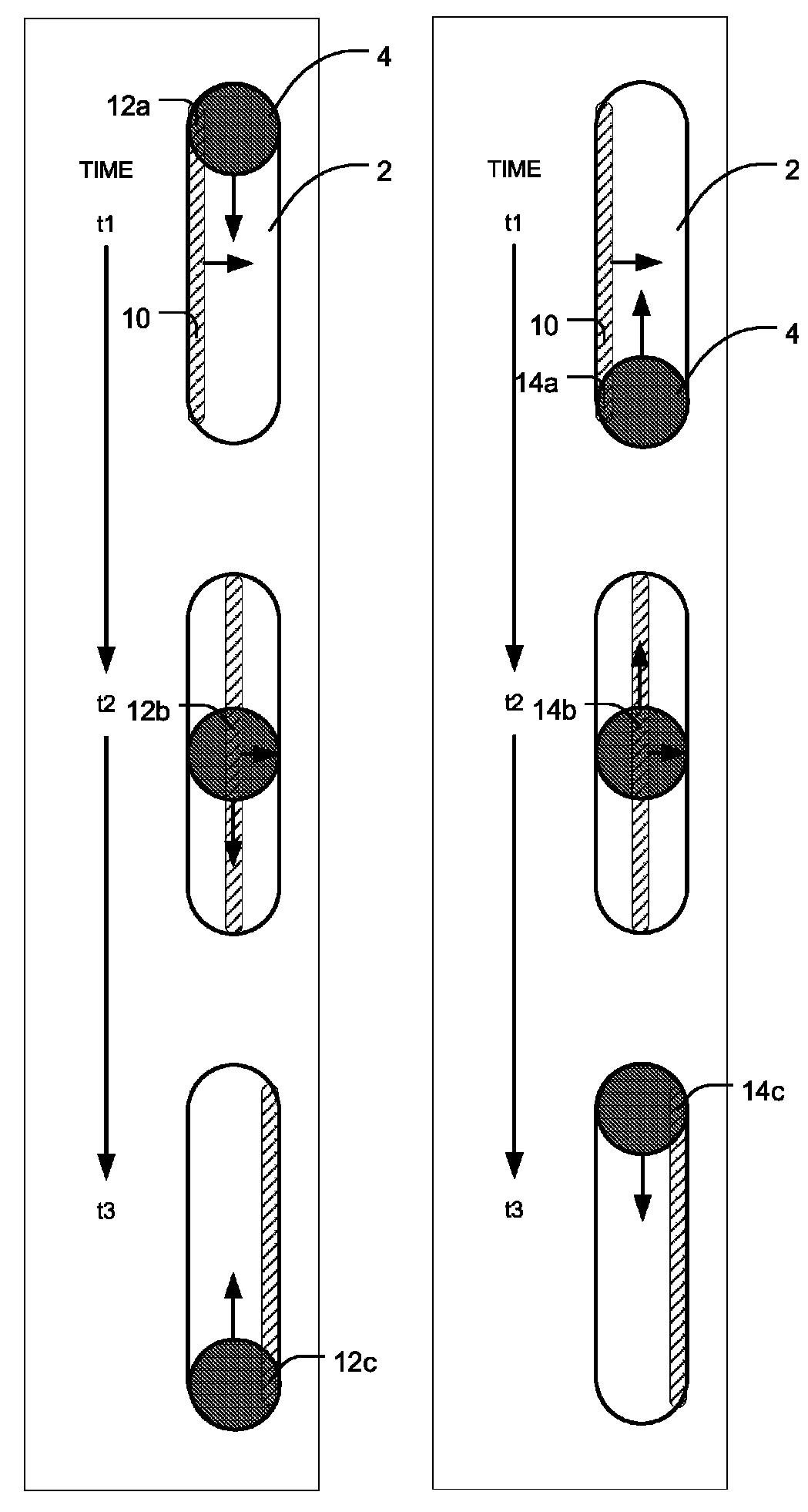
A method of continuous real-time monitoring and positioning of multi-leaf collimators during on and off radiation exposure conditions of radiation therapy to account for target motion relative to a radiation beam is provided. A prediction algorithm estimates future positions of a target relative to the radiation source. Target geometry and orientation are determined relative to the radiation source. Target, treatment plan, and leaf width data, and temporal interpolations of radiation doses are sent to the controller. Coordinates having an origin at an isocenter of the isocentric plane establish initial aperture end positions of the leaves that is provided to the controller, where motors to position the MLC midpoint aperture ends according to the position and target information. Each aperture end intersects a single point of a convolution of the target and the isocenter of the isocentric plane. Radiation source hold-conditions are provided according to predetermined undesirable operational and / or treatment states.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Implementation and experimental results of real-time 4d tumor tracking using multi-leaf collimator (MLC), and/or mlc-carriage (mlc-bank), and/or treatment table (COUCH)
InactiveUS20140107390A1Reduce radiationEasy to optimizeMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesVehicle frameControl system
Methods and systems of operating a support structure and beam shaping mechanism in a manner that compensates for motion patterns exhibited by a patient, promotes comfort of the patient, and optimizes accuracy of delivery of radiotherapy to a targeted location within the patient. The support structure can be a treatment table or couch and the beam shaping mechanism can be a multi-leaf collimator (MLC), and / or an MLC-bank / -carriage. The control system can utilize algorithms for predicting tumor motion and loading condition on the table / couch during radiation therapy.
Owner:ELEKTA AB +1
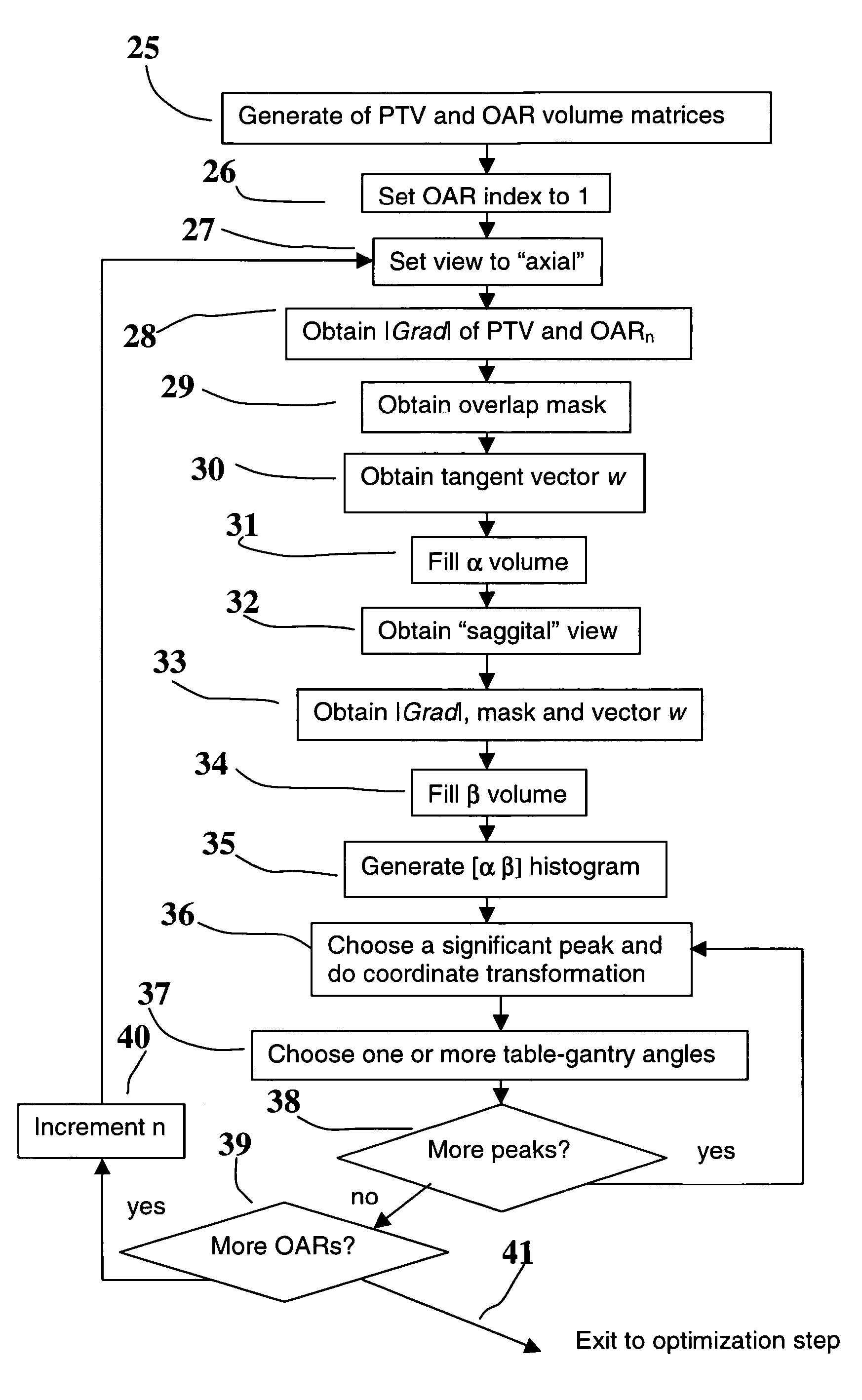
Method for assisted beam selection in radiation therapy planning
InactiveUS7027557B2Easy to mergeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlan treatmentMulti leaf collimator
A method to assist in the selection of optimum beam orientations for radiation therapy when a planning treatment volume (PTV) is adjacent to one or more organs-at-risk (OARs). A mathematical analysis of the boundaries between the PTV and OARs allows the definition of a continuum of pairs of gantry and table angles whose beam orientations have planes that are essentially parallel to those boundaries, and can, therefore, separate the PTV from the OARs when a multi-leaf collimator is used in the therapy. The Radiation Oncologist can then select one or more pairs of gantry and table angles from the continuum as input to a beam optimization step. The selected angles can deliver highly uniform dose to the PTV, while minimizing the radiation dose to the OARs.
Owner:LLACER JORGE
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
Method to track three-dimensional target motion with a dynamical multi-leaf collimator
InactiveUS7469035B2Radiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsMulti leaf collimator
A method of continuous real-time monitoring and positioning of multi-leaf collimators during on and off radiation exposure conditions of radiation therapy to account for target motion relative to a radiation beam is provided. A prediction algorithm estimates future positions of a target relative to the radiation source. Target geometry and orientation are determined relative to the radiation source. Target, treatment plan, and leaf width data, and temporal interpolations of radiation doses are sent to the controller. Coordinates having an origin at an isocenter of the isocentric plane establish initial aperture end positions of the leaves that is provided to the controller, where motors to position the MLC midpoint aperture ends according to the position and target information. Each aperture end intersects a single point of a convolution of the target and the isocenter of the isocentric plane. Radiation source hold-conditions are provided according to predetermined undesirable operational and / or treatment states.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
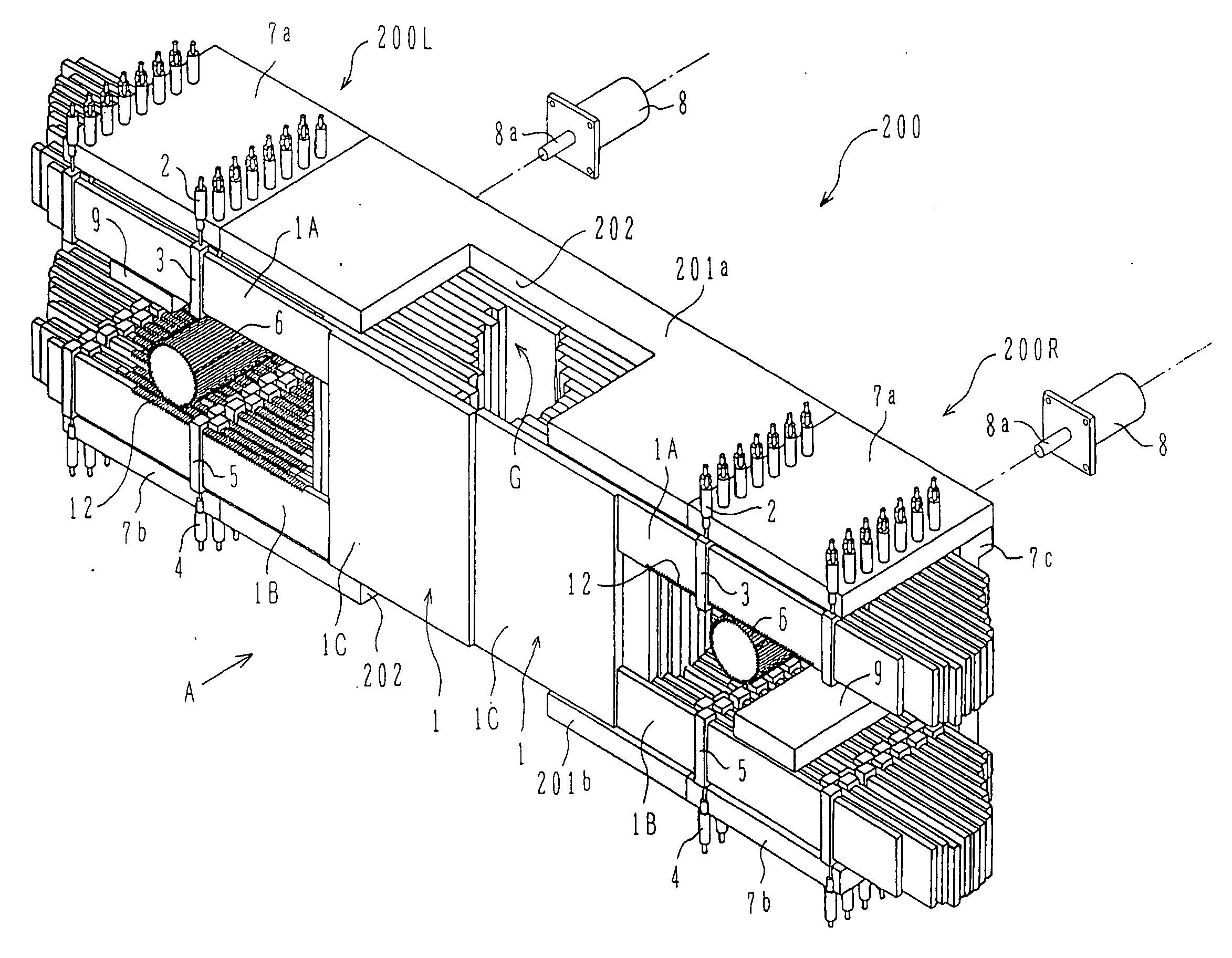
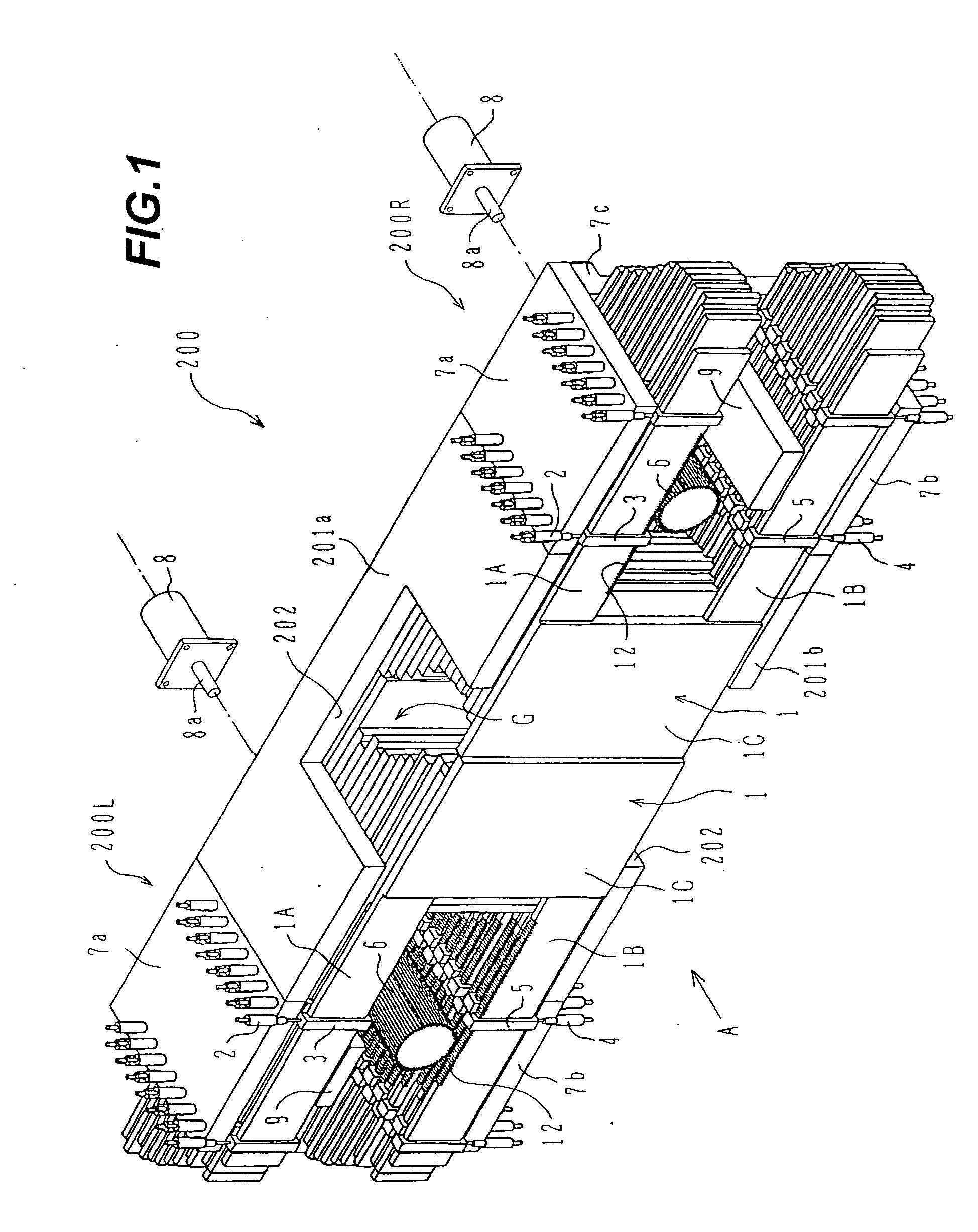
Multi-leaf collimator and medical system including accelerator
InactiveUS20050063516A1Reduce physical and mental burdenShorten positioning timeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
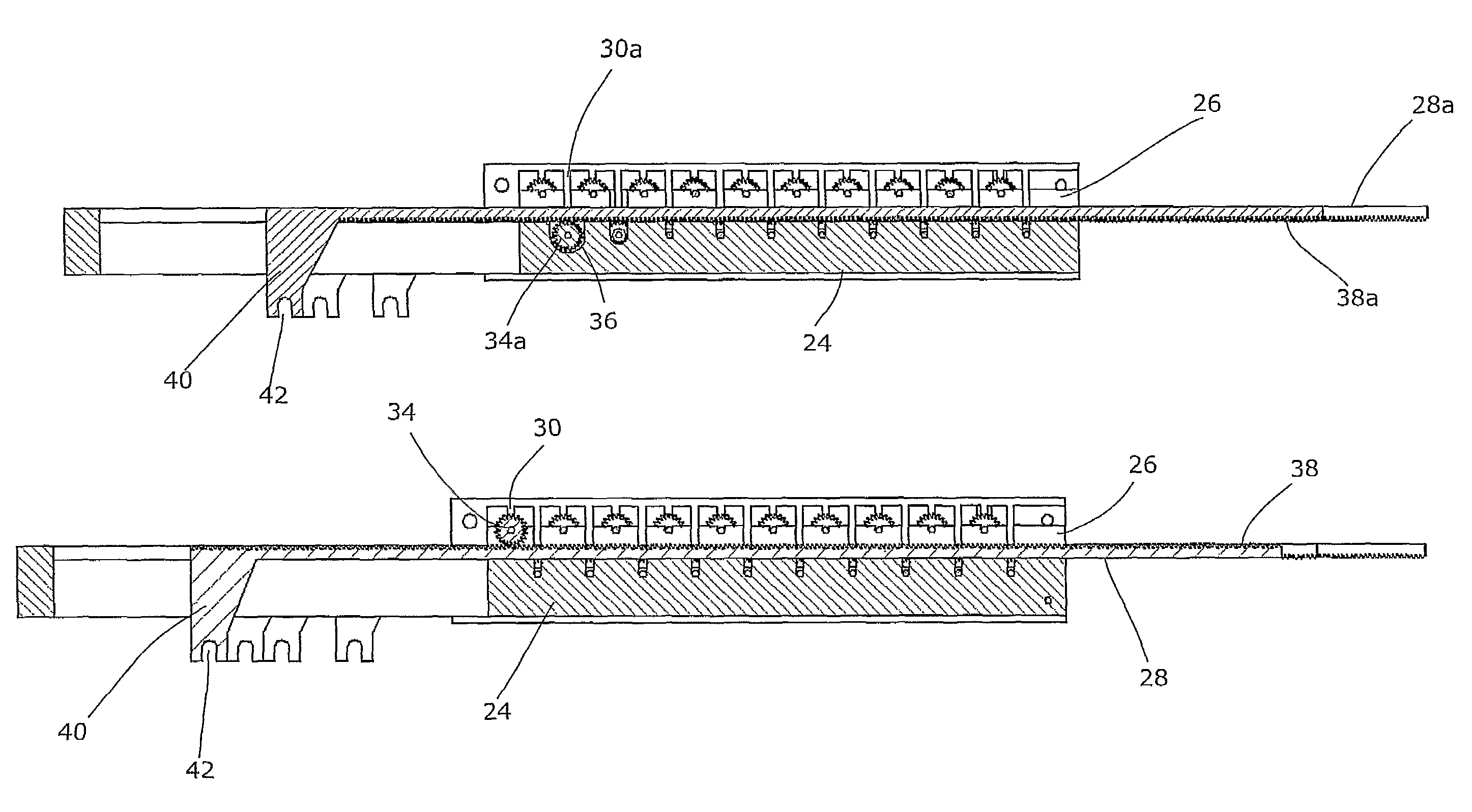
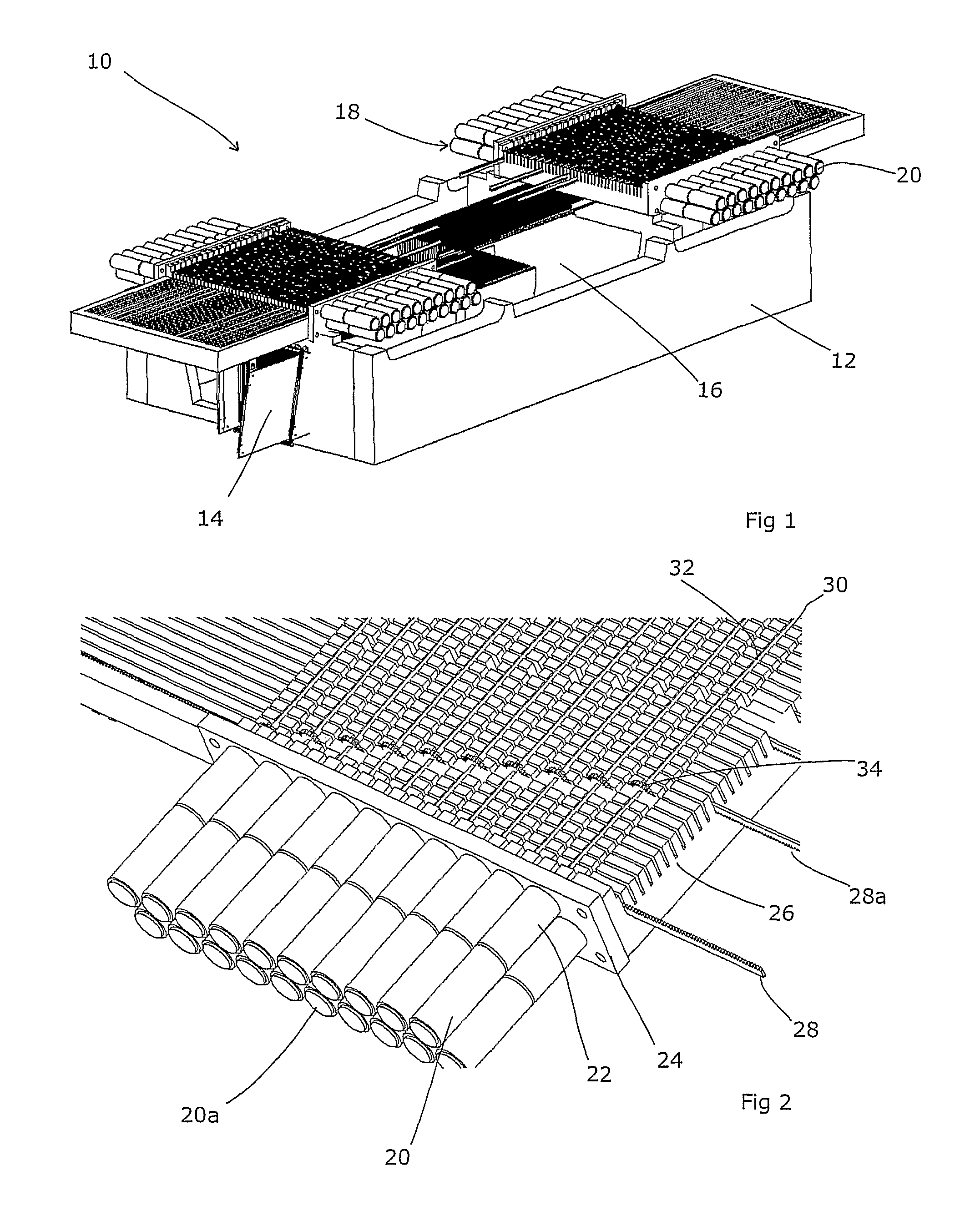
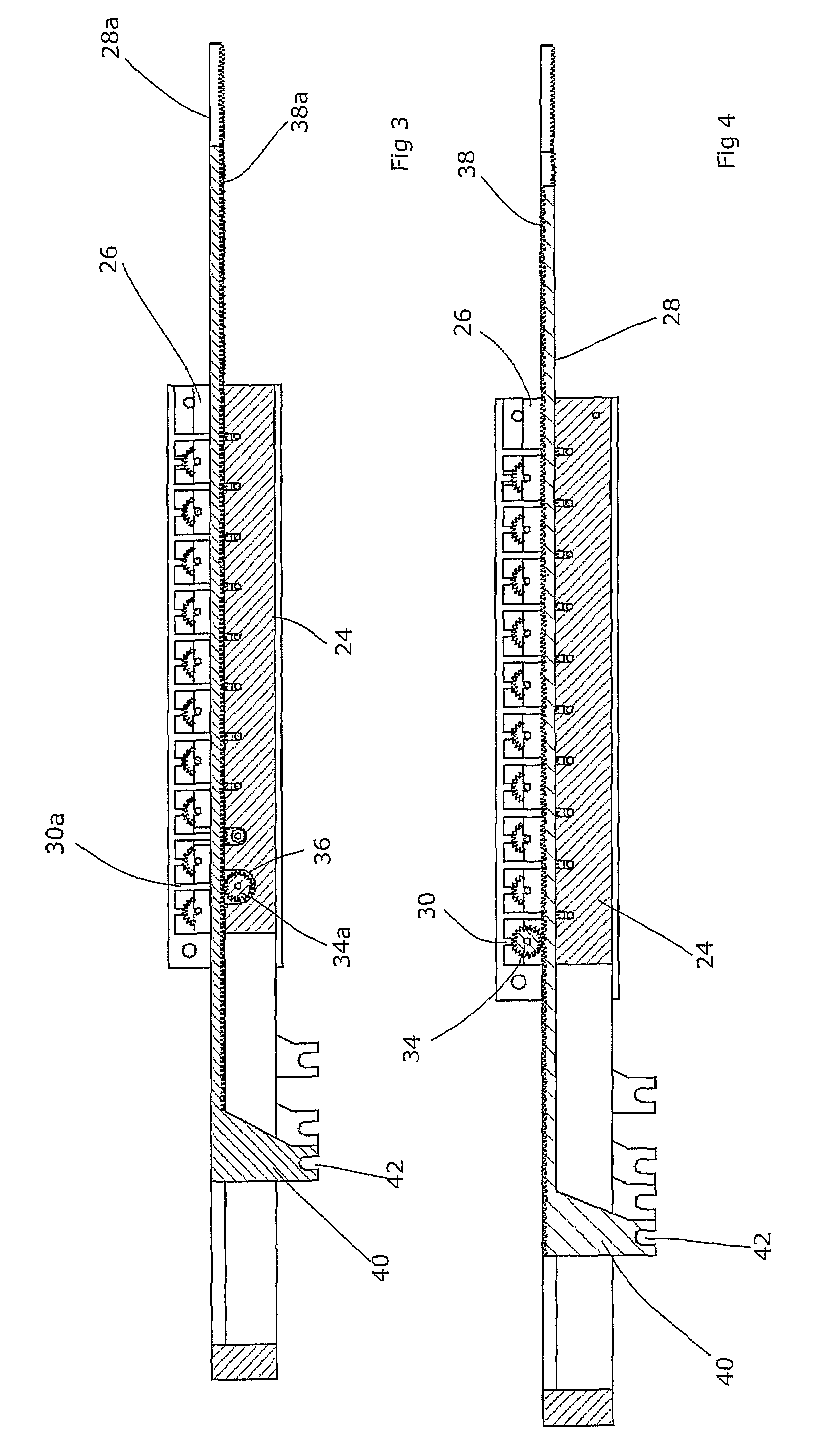
The invention is intended to shorten a positioning time required for forming an irradiation area with high accuracy using a number of leaf plates, and to reduce physical and mental burdens imposed on patients. A multi-leaf collimator comprises leaf plate driving body each including a plurality of movable leaf plates and provided respectively on one side and the other side, the plurality of leaf plates of the leaf plate driver on one side and the plurality of leaf plates of the leaf plate driver on the other side being disposed in an opposing relation to form an irradiation field of a radiation beam between the opposing leaf plates. Each of the leaf plate driving body includes a motor provided in common to the plurality of leaf plates. Driving force of the motor can be transmitted to the plurality of leaf plates at the same time through a pinion gear, upper and lower air cylinders, and upper and lower guides. Also, the driving force can be cut off selectively for each leaf plate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electromagnetically actuated multi-leaf collimator
ActiveUS20140239204A1Electrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMulti leaf collimatorElectrical current
A multi-leaf collimator with electromagnetically actuated leaves. The multi-leaf collimator includes a plurality of leaves, a leaf guide configured to support the plurality of leaves, and a plurality of magnets. Each leaf includes a blocking portion that is radio opaque, a drive portion connected to the blocking portion, and a coil embedded in the drive portion. The coil is operatively connected to an electrical current source to generate a first magnetic field. The first magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field generated by the magnet to thereby move the leave to a desired state. The leaves have the capability of moving at speeds of 50 cm / s up to and higher than 1 m / s.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC +1
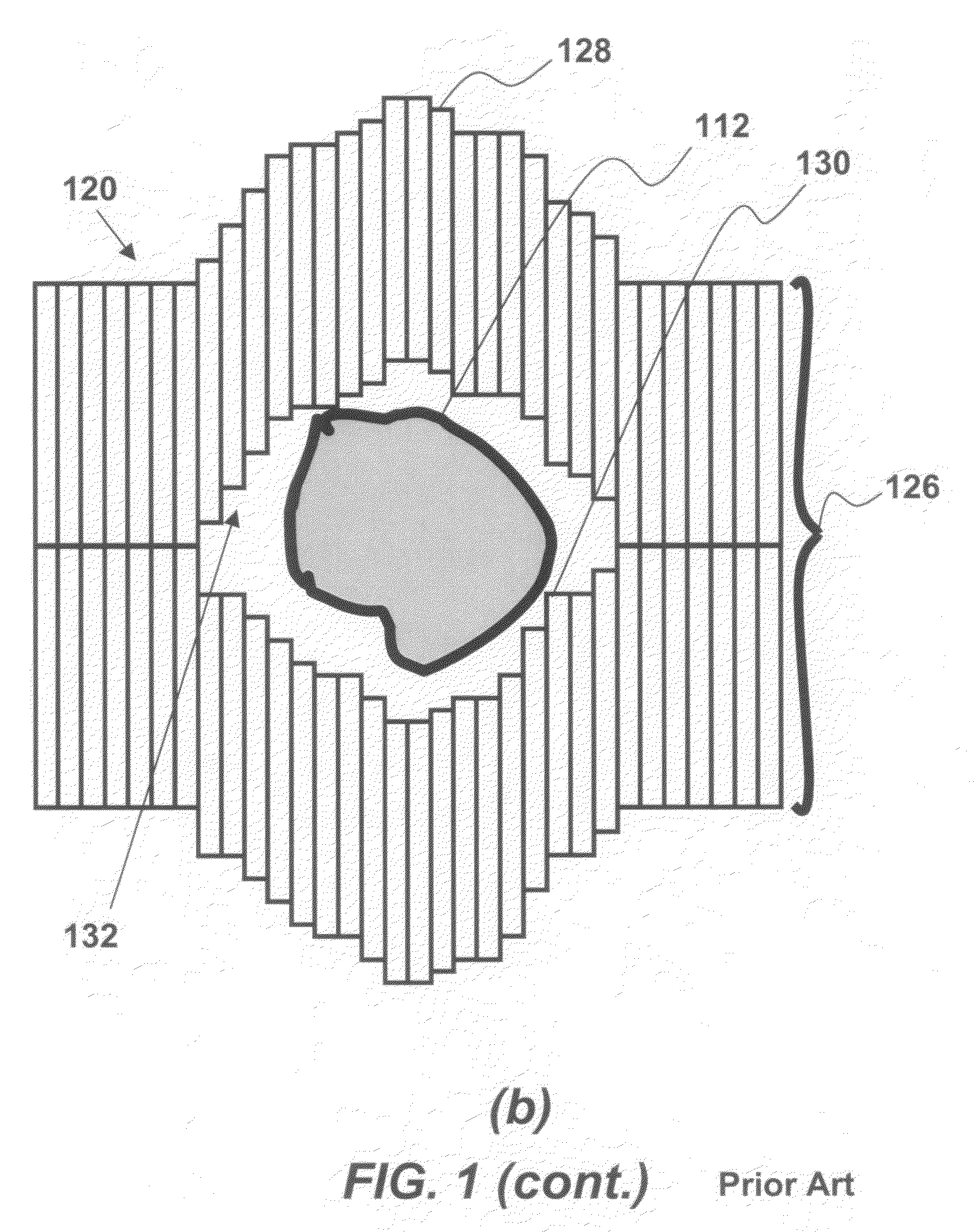
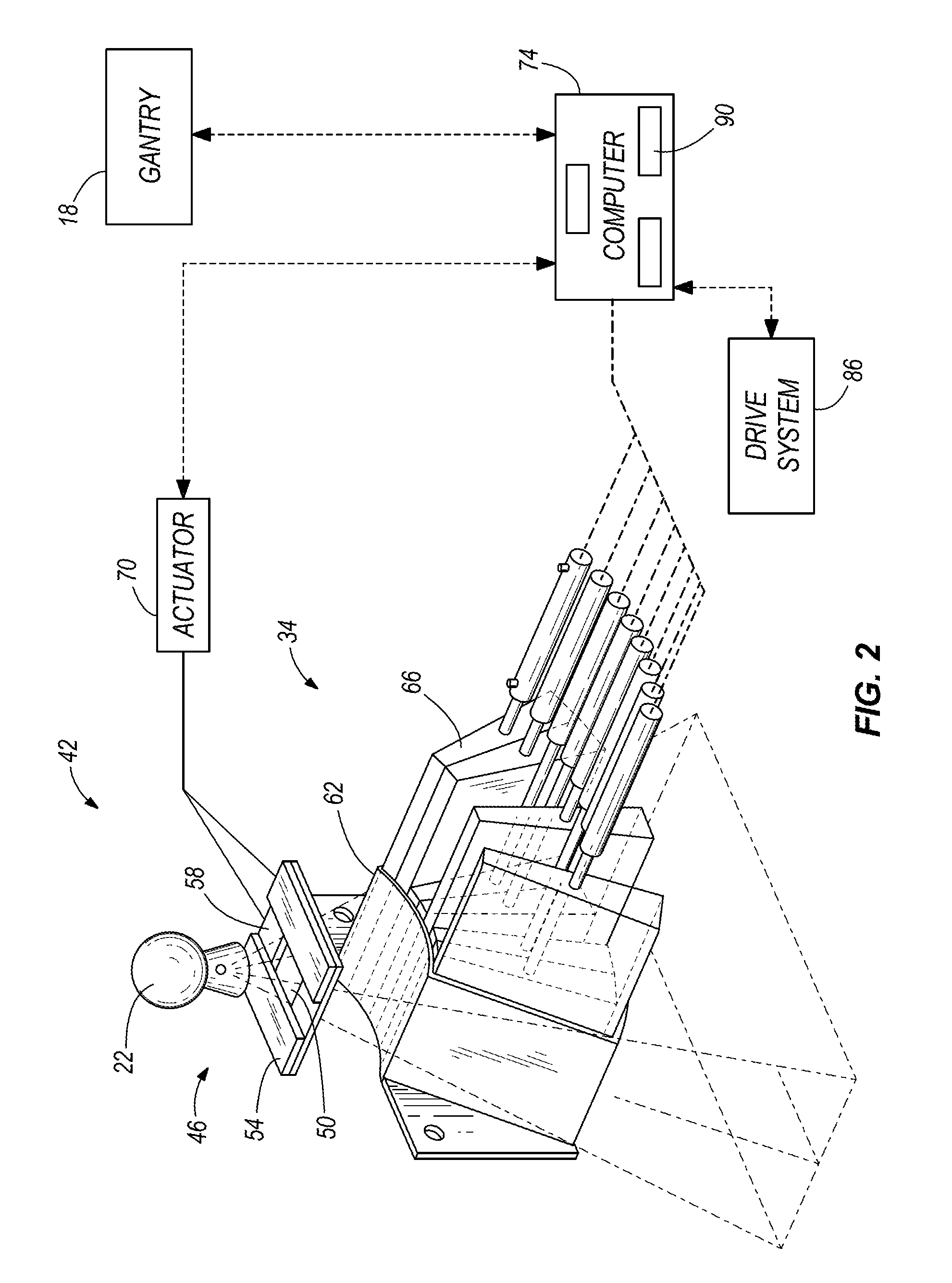
Multi-leaf collimator
ActiveUS7095823B2High resolutionIncrease the areaHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAcute angleMulti leaf collimator
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Method to control delivery of radiation therapy
InactiveUS7096055B1Rapid and accurate calculationReduce in quantitySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMulti leaf collimatorLight beam
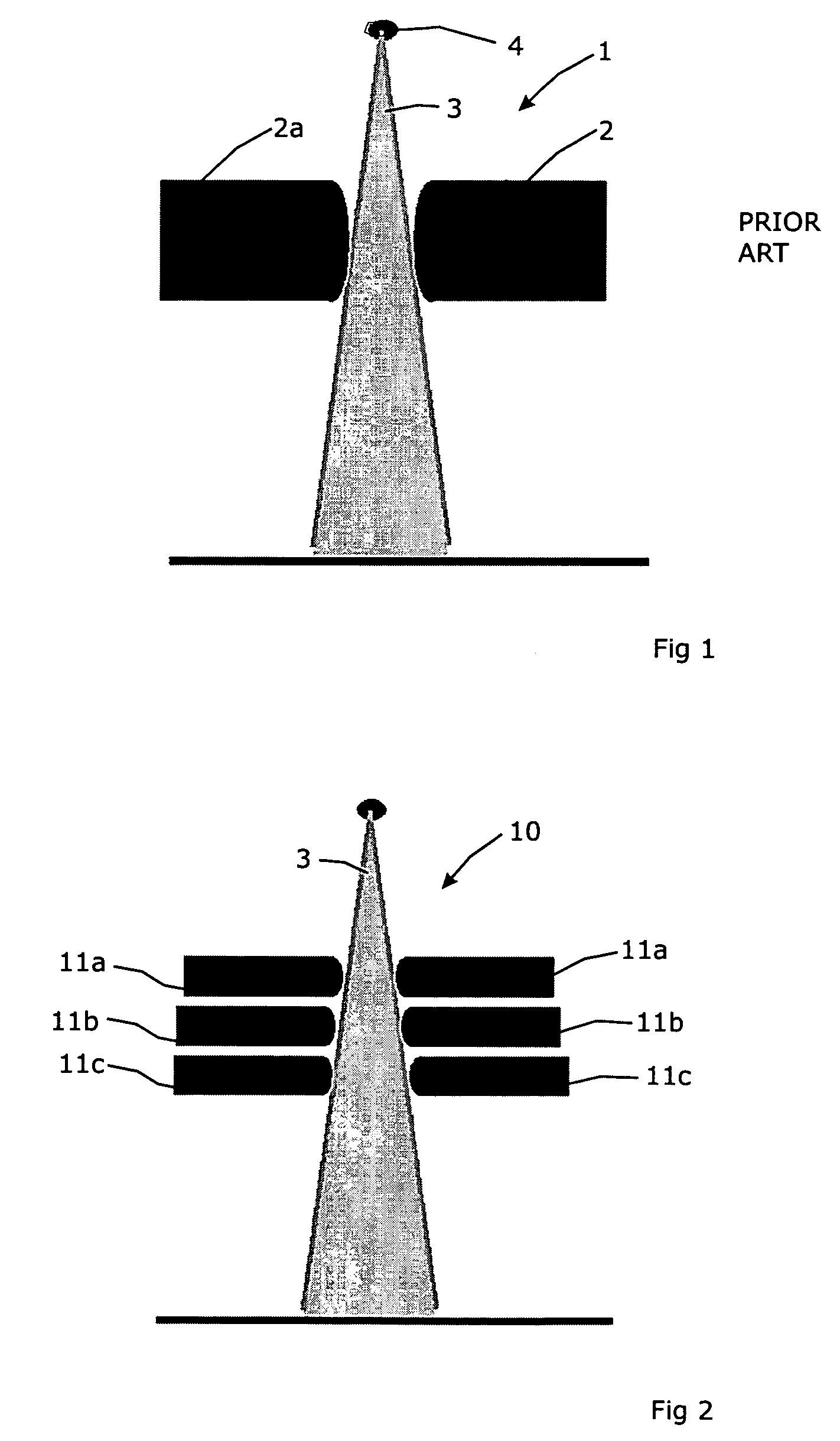
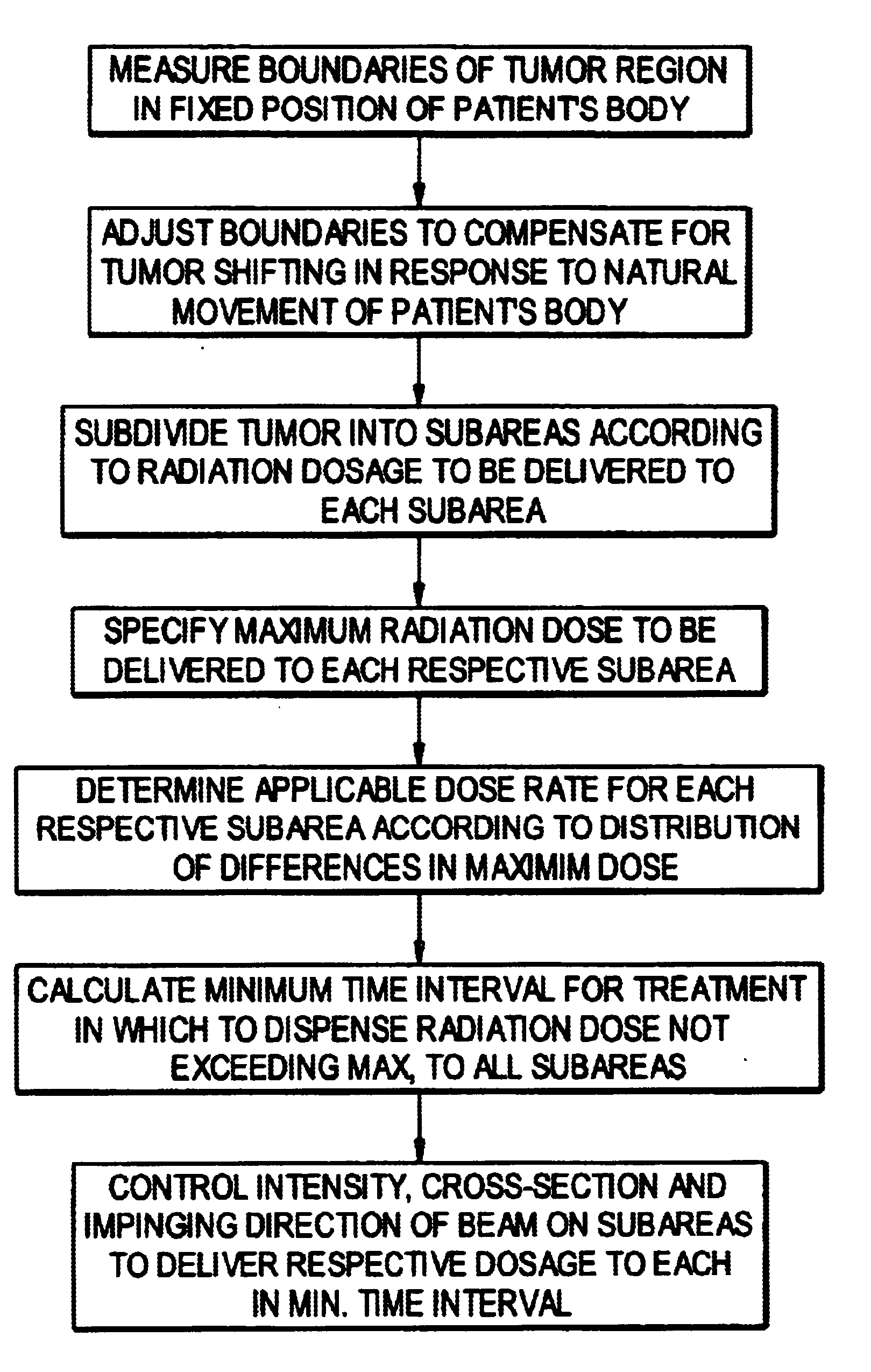
A method is disclosed for controlling the delivery of radiation therapy to a tumor of a patient from one or more beams of ionizing radiation, to conform to a prescribed dosage of radiation for each of predetermined plural respectively shaped portions of the tumor according to the shape and other characteristics of the tumor. A radiation beam is selectively generated from different directions with respect to travel of the beam along a plurality of spatial paths including oscillating and arcuate movements. Parameters of the beam are calculated from conditions of distribution of a target dose, and the cross-section of the beam is adjusted so as to deliver the prescribed dosage of radiation to each of the respectively shaped portions of the tumor on which the beam impinges. The cross-section of the beam is constantly adjusted according to a predetermined area of the tumor which is to receive radiation therapy, and adjusted cross-sections of the beam are moved along selected individual ones of the spatial paths at least one time. Also, movements of the beam along individual spatial paths are split according to the plural portions of the tumor which are to receive different radiation doses. Travel of the beam is controlled along the selected individual paths so as to deliver radiation therapy within the prescribed dosage to each of the plural portions of the tumor in a minimum amount of time. In one embodiment, a micro multi-leaf collimator is placed between the beam and the tumor, and the collimator leaves are adjusted to change the cross-section of the beam impinging on a specified portion of the tumor according to the shape of the specified portion.
Owner:SCHWEIKARD ACHIM
Method and System for Treating Moving Target
ActiveUS20110200170A1Easy transitionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray apparatusMedicineTreatment targets
A method and system for providing intensity modulated radiation therapy to a moving target is disclosed. According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, a treatment plan for providing radiotherapy using a multi-leaf collimator (“MLC”) comprises a plurality of sub-plans, each of which is optimized for a different phase of target movement. Movements of the treatment target are tracked in real time, and the choice of which sub-plan to implement is made in real time based on the tracked position of the target. Each of the sub-plans is preferably formulated to minimize interplay effects between target movements and MLC leaf movements, consistent with other planning goals. In addition, the sub-plans preferably include a predicted region corresponding to the next anticipated position of the target, in order to facilitate the transition to the next position.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
High bandwidth binary multi-leaf collimator design
ActiveUS20160361566A1Lower latencyMove quicklyRadiation/particle handlingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHigh bandwidthMulti leaf collimator
Described herein are multi-leaf collimators that comprise leaf drive mechanisms. The leaf drive mechanisms can be used in binary multi-leaf collimators used in emission-guided radiation therapy. One variation of a multi-leaf collimator comprises a pneumatics-based leaf drive mechanism. Another variation of a multi-leaf collimator comprises a spring-based leaf drive mechanism having a spring resonator.
Owner:REFLEXION MEDICAL INC
Residual map segmentation method for multi-leaf collimator-intensity modulated radiotherapy
InactiveUS6853705B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyMulti leaf collimator
In a method for sequentially generating segment fields for use in delivering intensity modulated radiotherapy an input continuous intensity map is generated. A segment field is generated directly from the input intensity map. A residual continuous intensity map is generated that is based on the respective photon fluence contributions from the input intensity map and a fractionally intensity map corresponding to the segment field. These steps are repeated for a number of iterations to generate a like number of additional segment fields and residual maps derived therefrom. In each iteration, the residual map generated in the previous iteration is used as the input intensity map.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method and system for evaluating quality assurance criteria in delivery of a treatment plan
ActiveUS8442287B2Affect qualityDetection errorCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringQuality assuranceMathematical model
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Treatment planning apparatus and particle therapy system
ActiveUS8847179B2Reduce lossesLow costComputer controlSimulator controlField sizeMulti leaf collimator
A charged particle beam reduces treatment time in the uniform scanning or in the conformal layer stacking irradiation. In the uniform scanning, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a collimator aperture area is calculated. In the conformal layer stacking irradiation, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer for each of the layers obtained by partitioning the target volume is calculated. Alternatively, a minimum irradiation field size that covers the multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer is calculated, and a scan path corresponding to the irradiation field size, prestored in a memory of a particle therapy control apparatus, is selected. The charged particle beam scan path is optimally changed in the lateral directions in conformity with the collimator aperture area in the uniform scanning or in each layer in the conformal layer stacking irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
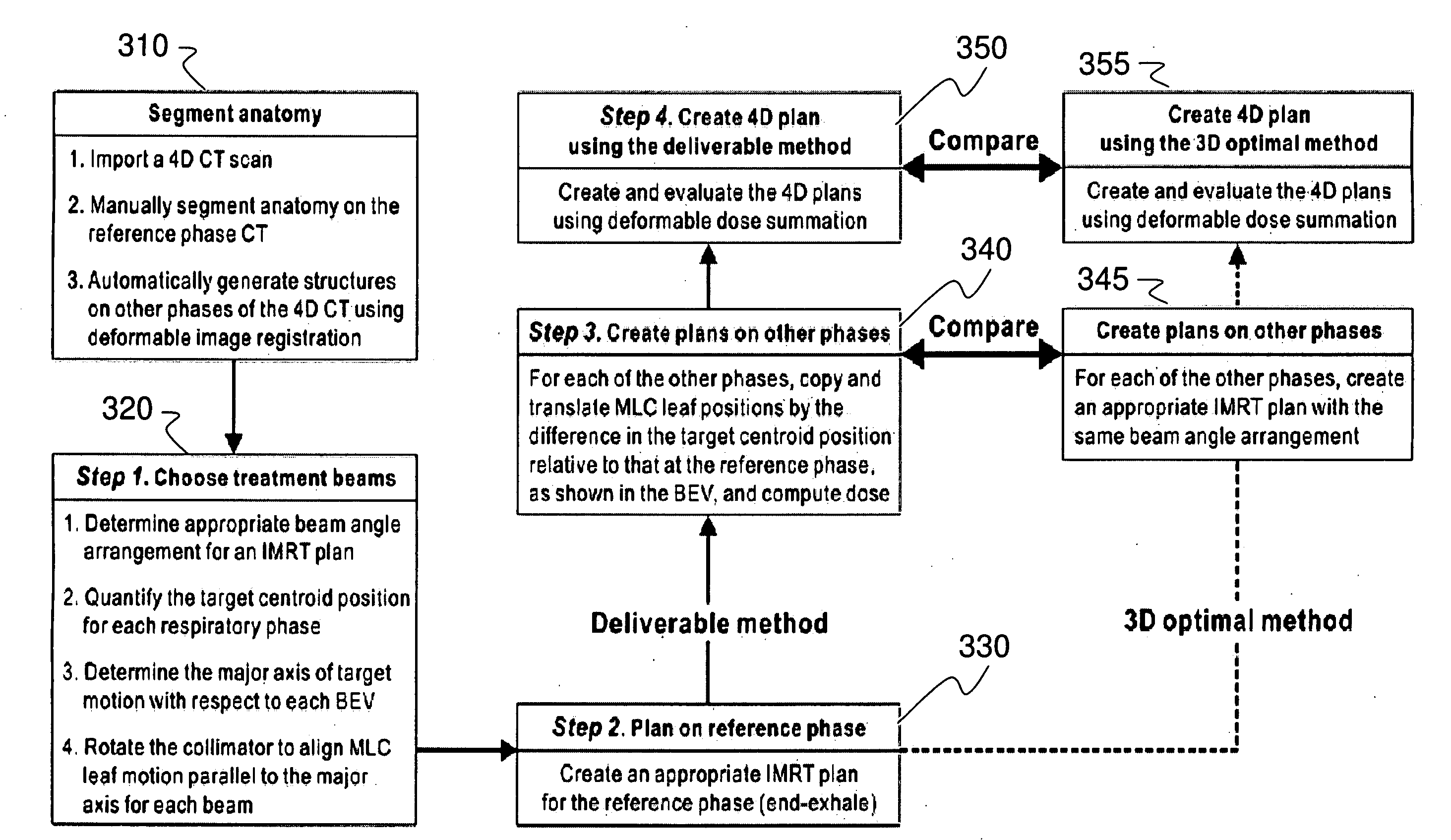
Method and system for four dimensional intensity modulated radiation therapy for motion compensated treatments
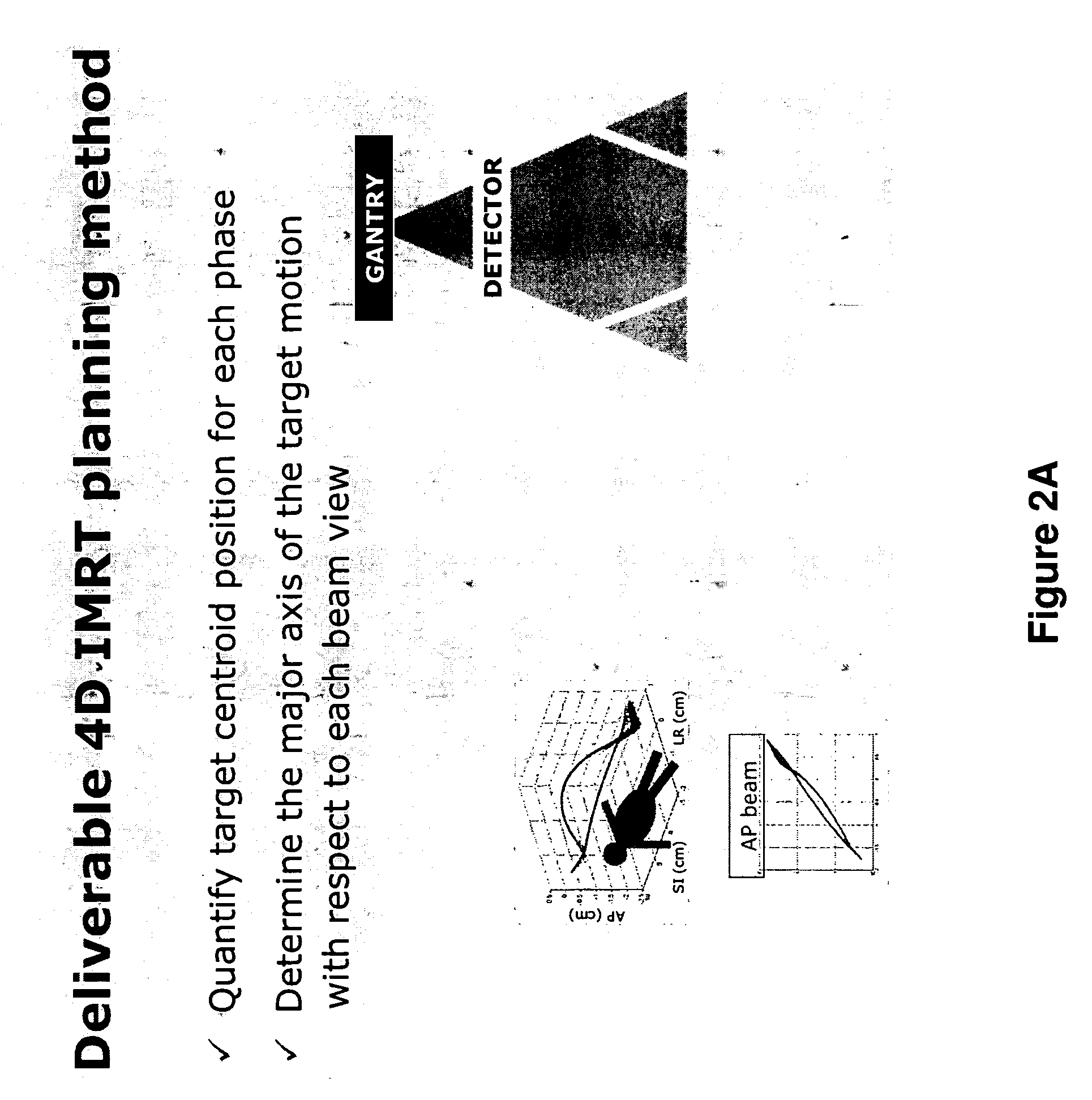
InactiveUS20090041188A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresTumour volume
A deliverable four dimensional (4D) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning method is disclosed, for delivery using a linear accelerator with a dynamic multi-leaf collimator (DMLC). A 4D computed tomography (CT) scan is used for segmenting tumor anatomy on a reference phase of periodic motion of the tumor. Deformable registration of the 4D CT data is used to generate corresponding anatomical structures on other phases. Preferably, the collimator for each beam position is aligned using the gross tumor volume (GTV) centroid motion corresponding to the periodic motion of the tumor, as determined from the two dimensional (2D) projection of a given beam position. A deliverable IMRT plan is created on the 4D CT image set in which the MLC leaf positions and beam on / off status can vary as a function of respiratory phase by solving a four dimensional optimization problem. The mechanical constraints of the MLC leaves are included in the optimization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Treatment planning apparatus and particle therapy system
ActiveUS20120264998A1Uniform dose distributionReduce radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyField sizeMulti leaf collimator
A charged particle beam reduces treatment time in the uniform scanning or in the conformal layer stacking irradiation. In the uniform scanning, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a collimator aperture area is calculated. In the conformal layer stacking irradiation, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer for each of the layers obtained by partitioning the target volume is calculated. Alternatively, a minimum irradiation field size that covers the multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer is calculated, and a scan path corresponding to the irradiation field size, prestored in a memory of a particle therapy control apparatus, is selected. The charged particle beam scan path is optimally changed in the lateral directions in conformity with the collimator aperture area in the uniform scanning or in each layer in the conformal layer stacking irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-leaf collimator
ActiveUS7596209B2Array is decreasedMany leavesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
A multi-leaf collimator comprises an elongate leaf moveable in a longitudinal direction, and having an associated toothed rack driven by a pinion, wherein the rack is carried on an elongate actuator section, having a transversely extending link section, the leaf being connected to the link section and thereby being spaced from the actuator section.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Radiation therapy apparatus
InactiveUS20080205599A1Increase flexibilityIncrease freedomHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
A radiation therapy apparatus has a multi-leaf collimator device, a driving gear, a torque wire and a driving unit. The multi-leaf collimator device has a pair of collimator components which respectively comprise a plurality of leaves arranged close to one another such that the leaves face one another across an irradiation axis, and configured to set a desired irradiation field by individually moving the leaves. The driving gear is engaged with a gear tooth of the each leaf, respectively. The torque wire is connected to a shaft center of the driving gear, respectively. The driving unit is configured to drive the driving gears through the torque wire.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Multi-leaf collimator position sensing
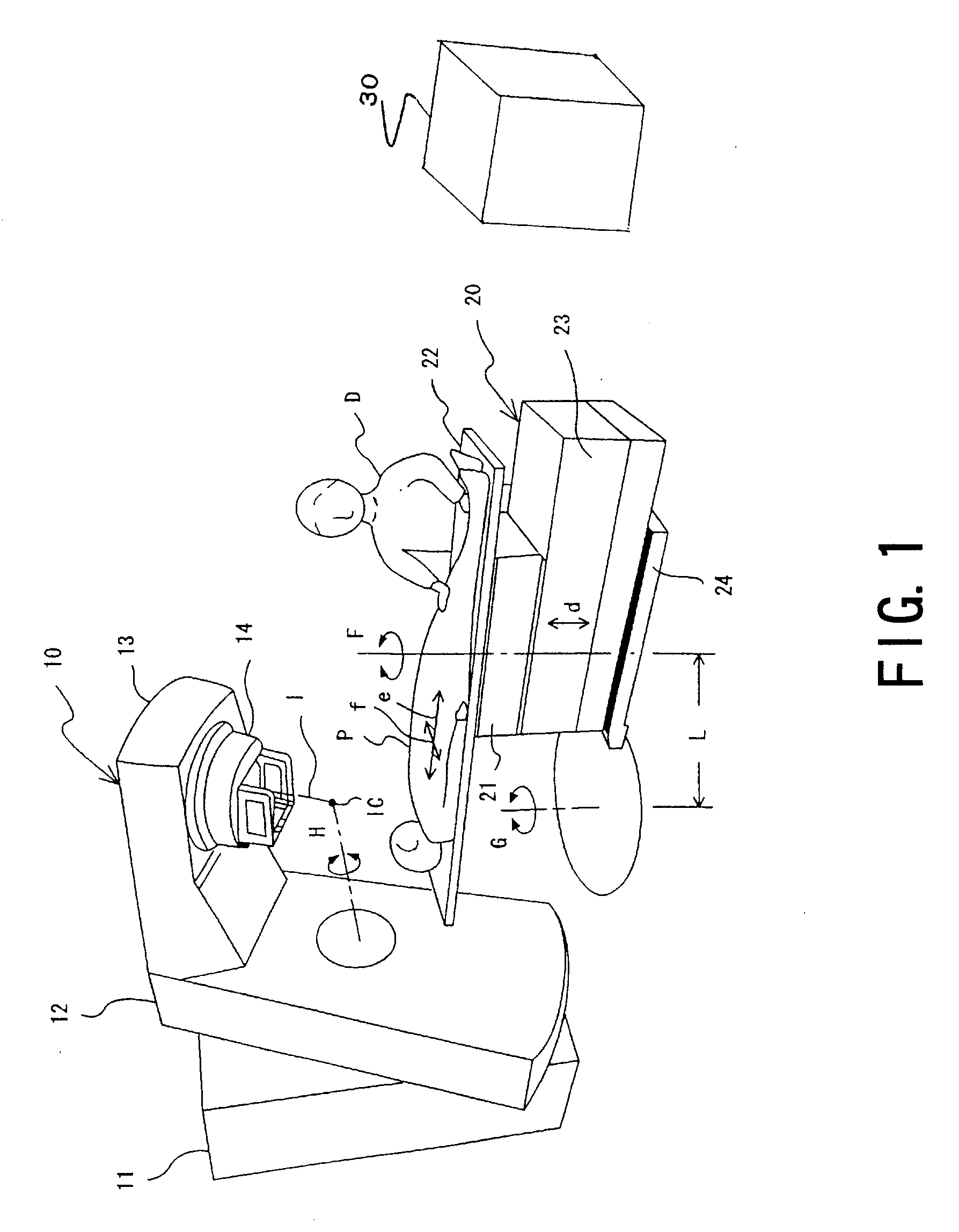
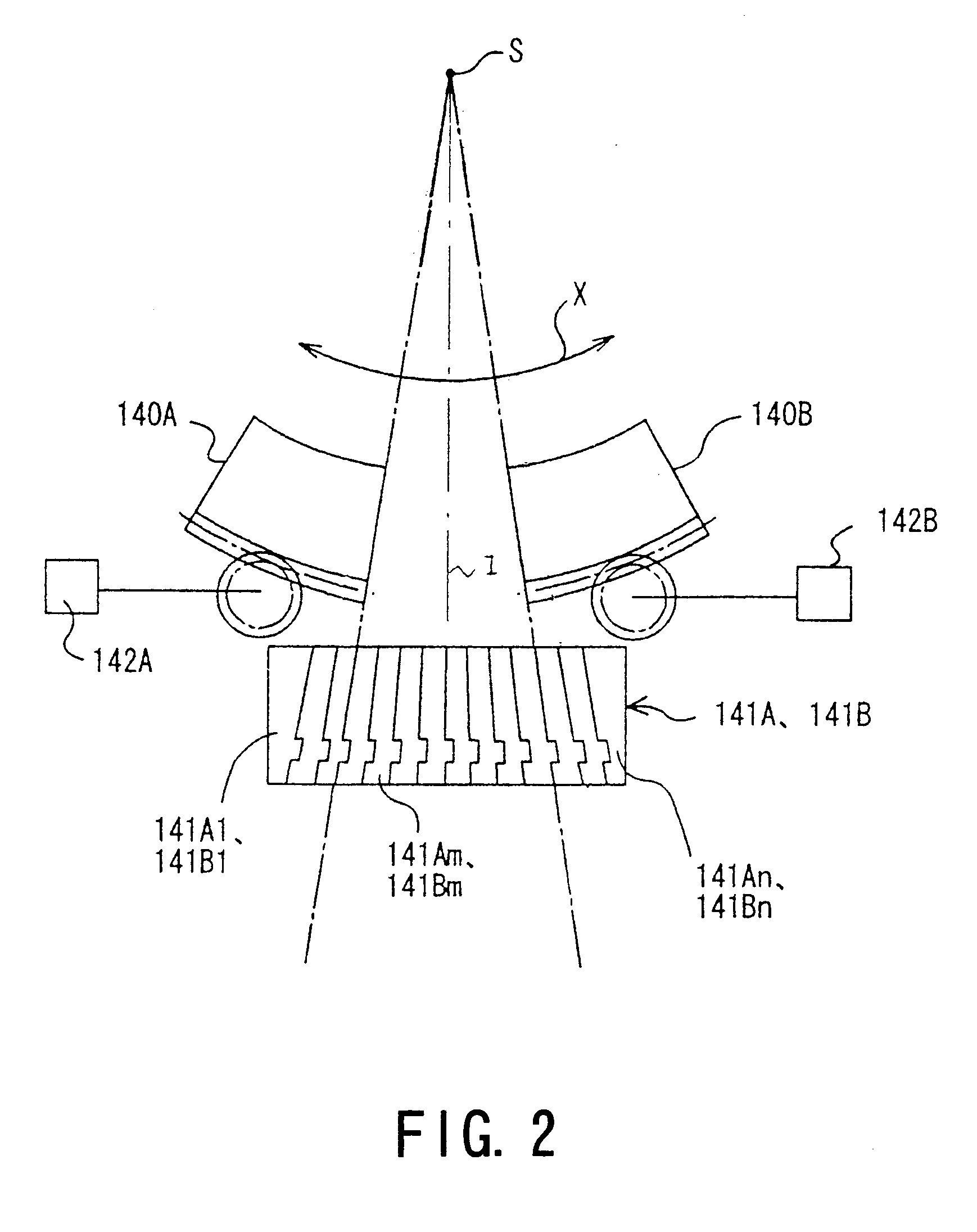
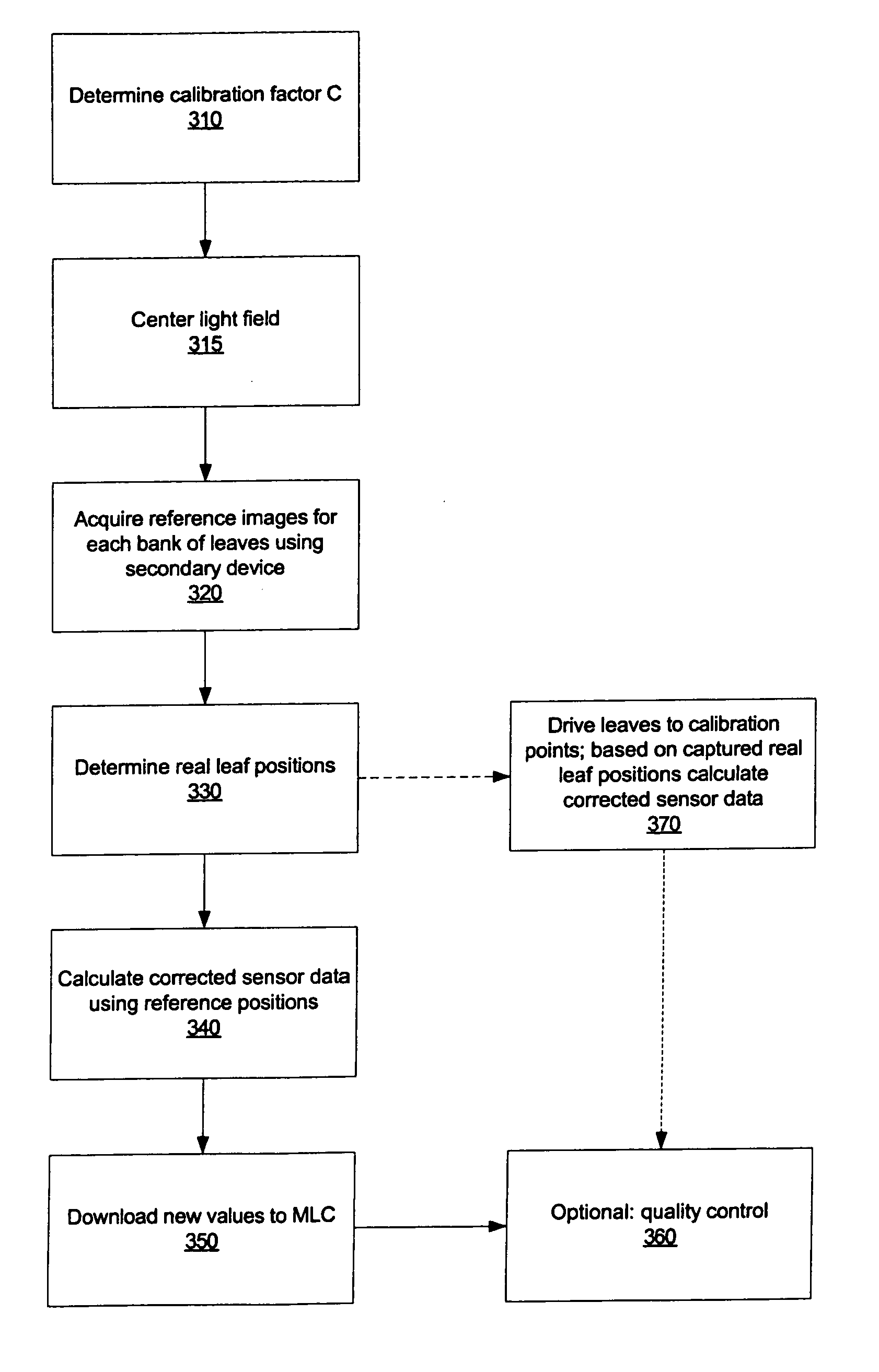
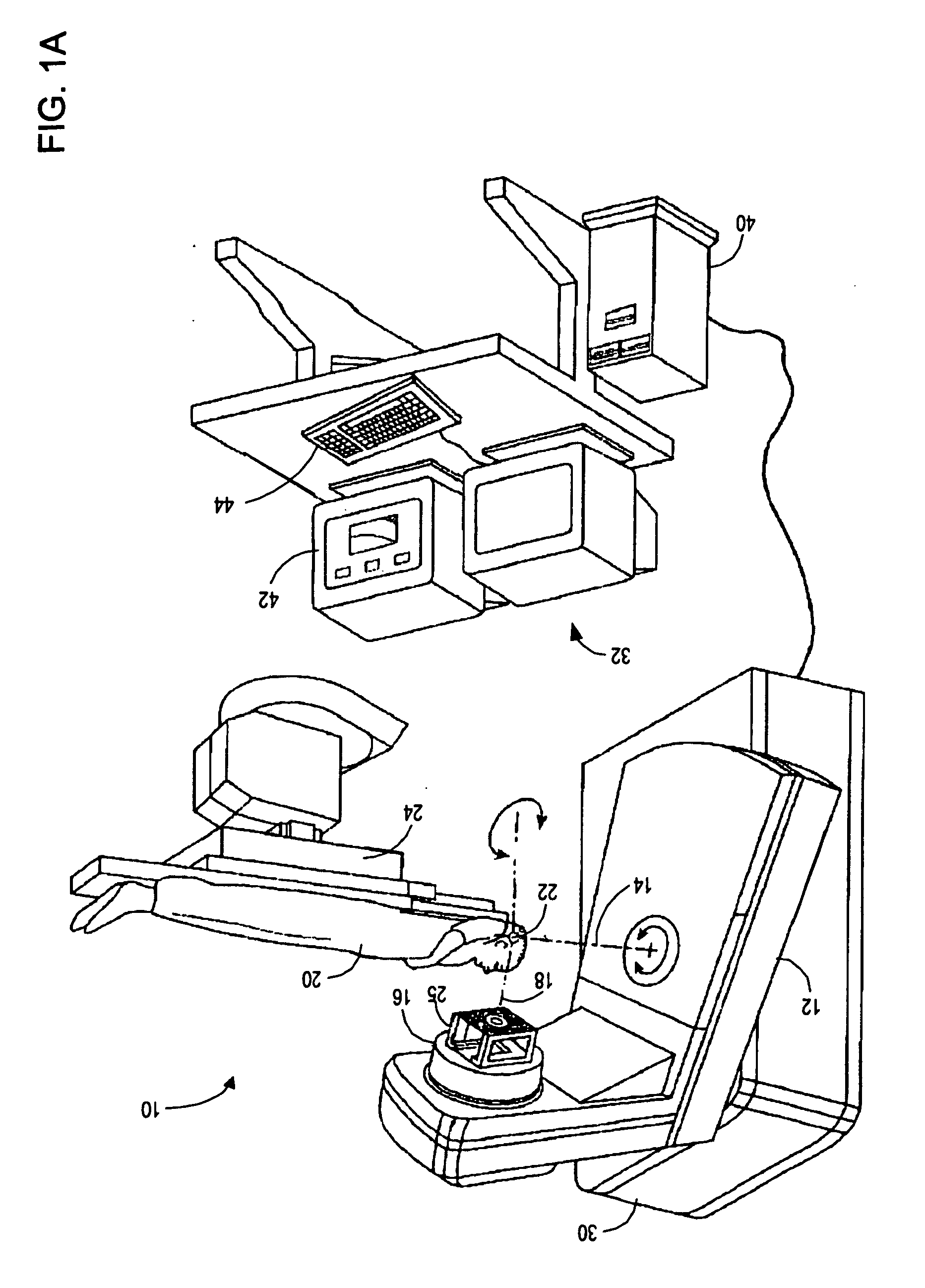
InactiveUS20060072849A1Character and pattern recognitionRadiation therapyReference imageMulti leaf collimator
A method for determining real positions in a multi-leaf collimator (MLC) is disclosed. A scanner or other secondary imaging device is used to acquire a series of reference images and to capture the light field when the MLC is in a particular position and has a particular geometry. The reference images are used together with the captured light field images in order to determine the real positions of the leaves in the MLC. The real positions are used to correct any calibration problems in the mechanism used to drive the leaves of the MLC.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multi-leaf collimator
ActiveUS7742575B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation beam directing meansMulti leaf collimatorBeam direction
A multi-leaf collimator for use in a radiotherapeutic apparatus comprises a plurality of elongate narrow leaves arranged side-by side and supported in a frame, the frame having upper and lower formations for guiding each leaf into which extend ridges on the upper and lower edges of the leaves, thereby to allow the leaves to move in a longitudinal direction, the upper and lower formations being aligned so that the sides of the leaves when fitted are at a non-zero angle to the beam direction, the upper and lower ridges being located on the upper and lower edges of the leaves so that a line joining their centres is at a non-zero angle to the sides of the leaf, tilted relative to the sides in a sense opposite to that of the beam. An outer face of the upper and / or lower ridges can be aligned with a side face of the leaf, for ease of manufacture. A radiotherapeutic apparatus is also disclosed, comprising a source of radiation and a multi-leaf collimator for shaping the radiation emitted by the source, the multi-leaf collimator being as set out above.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Radiotherapy apparatus and a multi-leaf collimator therefor
ActiveUS8384049B1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide a multi-leaf collimator with a plurality of leaves and at least one motor for each leaf. The motor for each leaf has a lateral width which is equal to or narrower than the corresponding leaf, and in this way the motors can be arranged within the lateral extent of the leaf. A cut-out section in the leaf allows the motor to lie at least partially within the depth of the leaf, and in this way the drive mechanism and the multi-leaf collimator as a whole are made extremely compact. This in turn allows the leaves to be deeper than would otherwise be the case, increasing their efficacy in blocking radiation.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Method and system for evaluating quality assurance criteria in delivery of a treatment plan
ActiveUS20110112351A1Affect qualityDetection errorCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringQuality assuranceMathematical model
System and method of determining whether a component of a radiation therapy system is operating within a dosimetric tolerance. The method can include the acts of generating a treatment plan for a patient, the treatment plan specifying a radiation amount to be delivered to the patient, delivering radiation to the patient according to the treatment plan, obtaining feedback during the delivery of radiation, the feedback related to one of a position, a velocity, and an acceleration for one of a multi-leaf collimator, a gantry, a couch, and a jaws, generating a mathematical model based on the feedback for one of the multi-leaf collimator, the gantry, the couch, and the jaws, calculating a delivered dose amount based on the mathematical model and treatment plan information, calculating a deviation in dose between the radiation amount specified in the treatment plan and the delivered dose amount, and determining whether the deviation in dose is within a dosimetric tolerance for the one of the multi-leaf collimator, the gantry, the couch, and the jaws.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
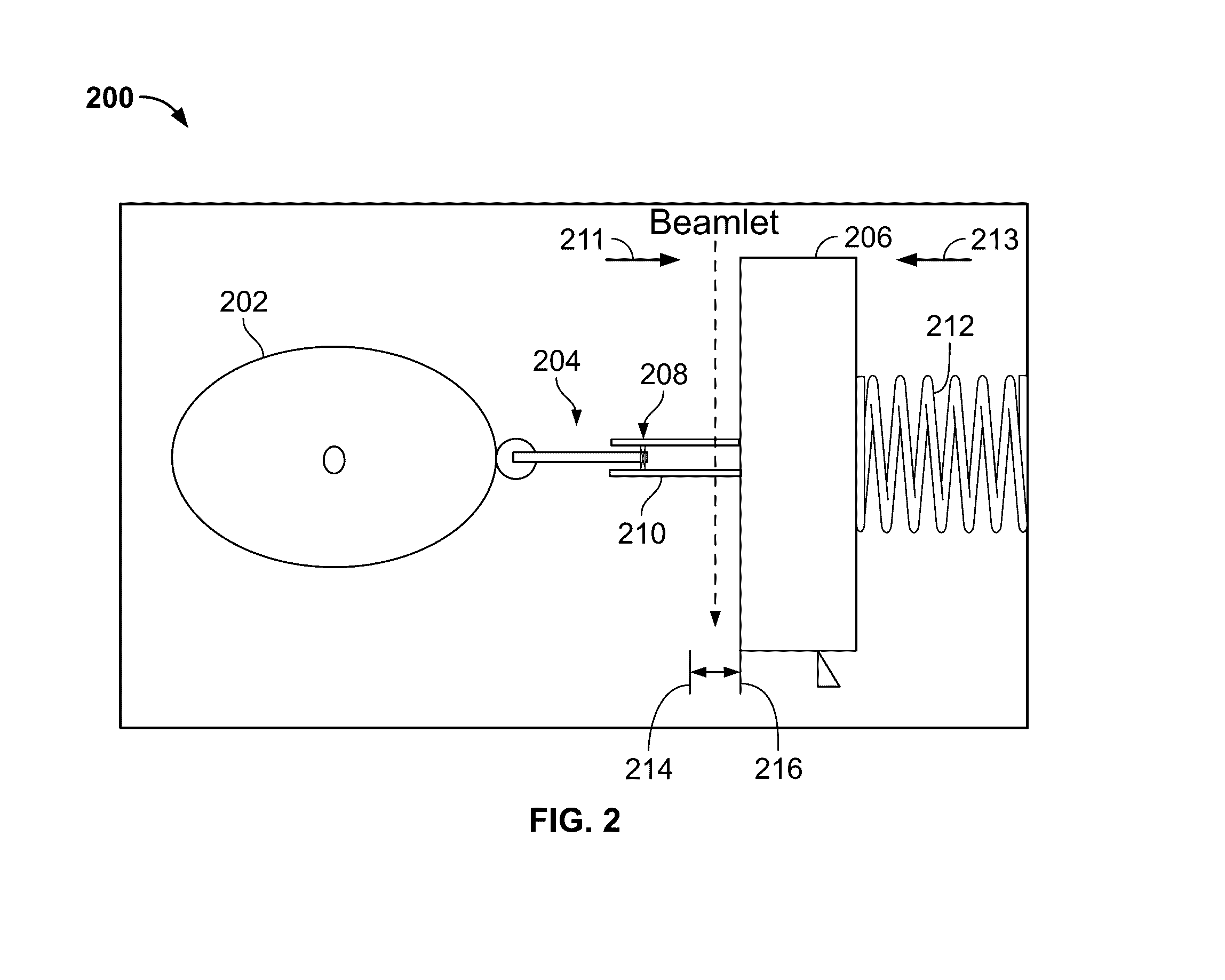
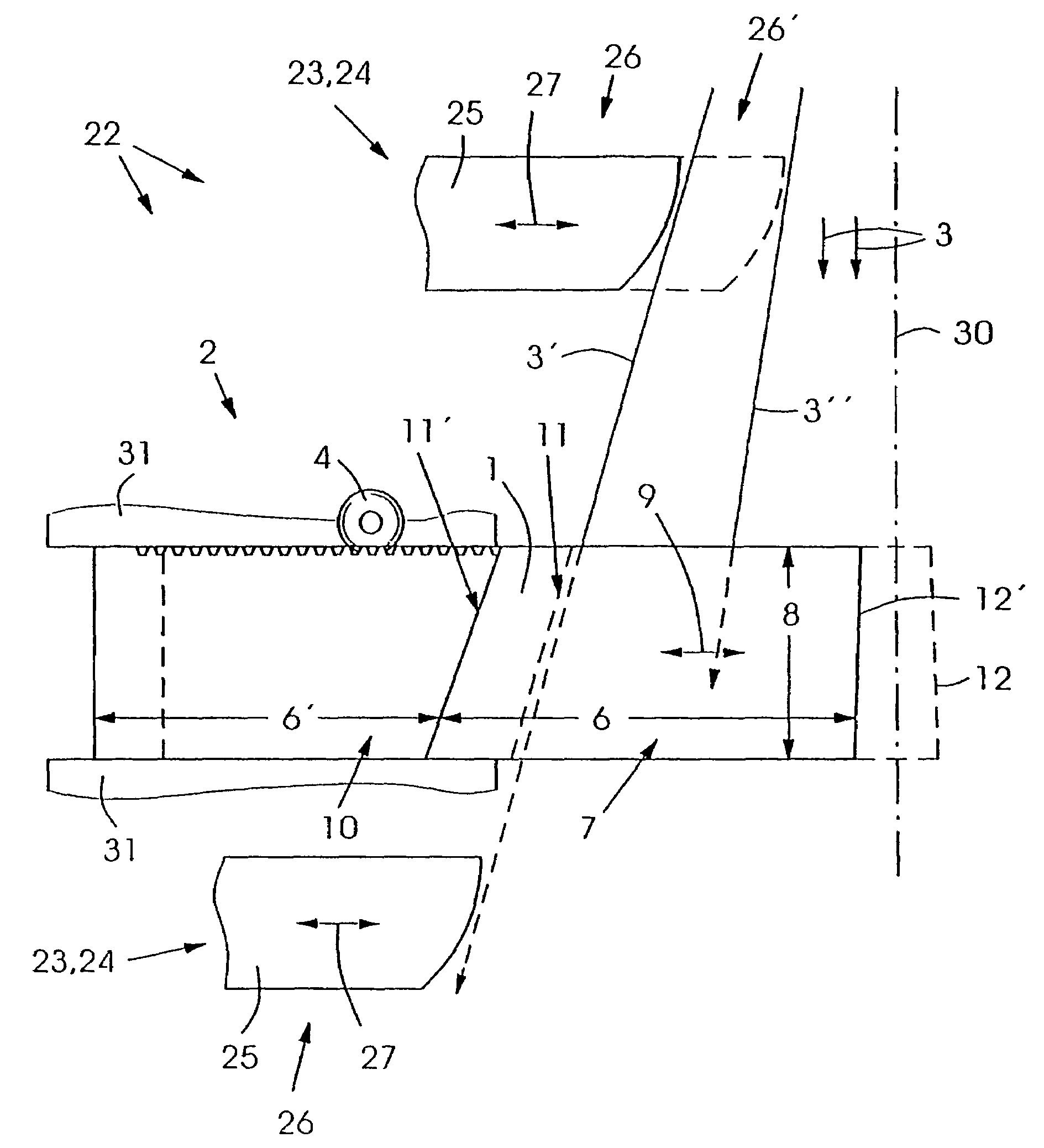
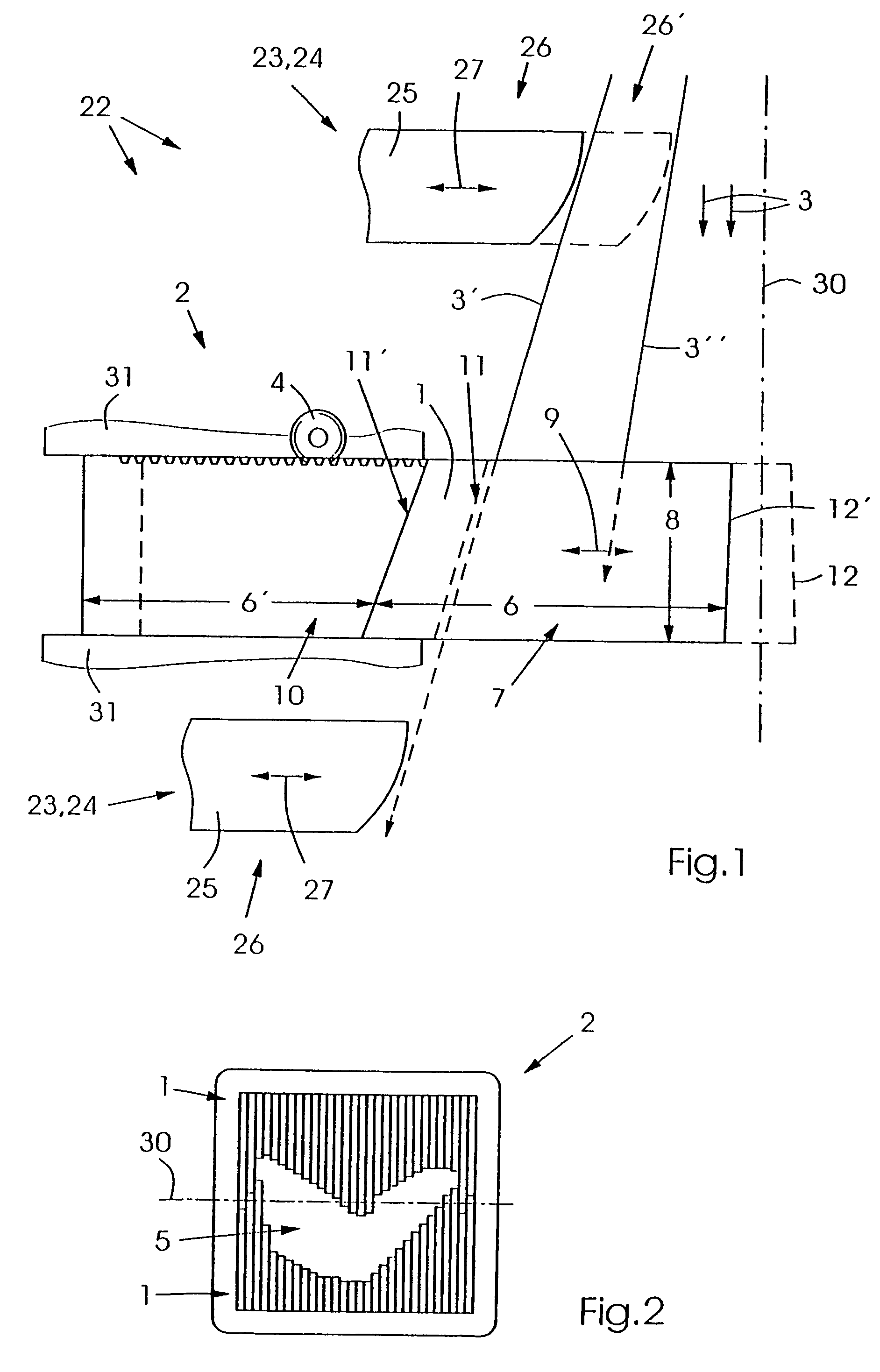
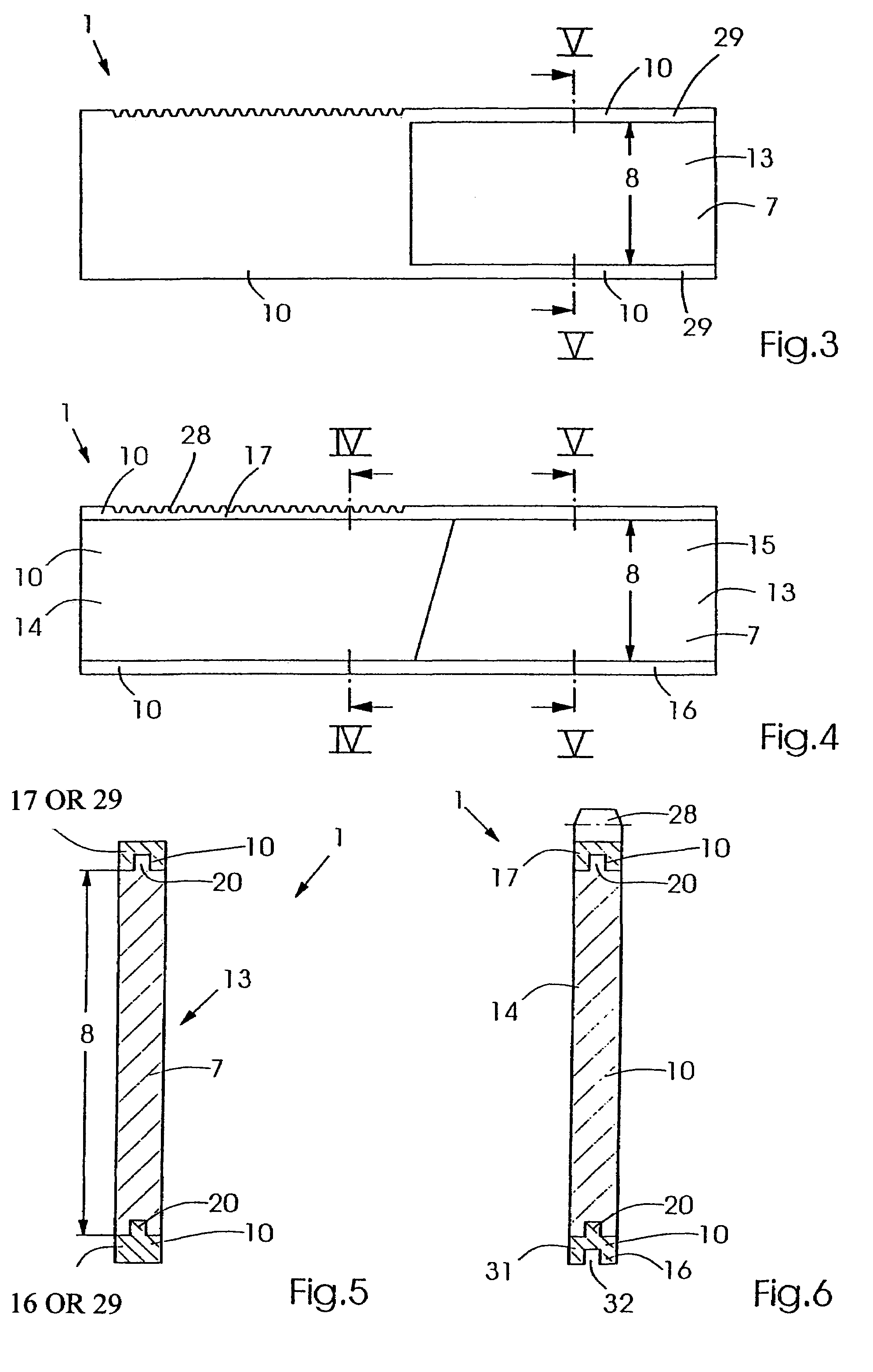
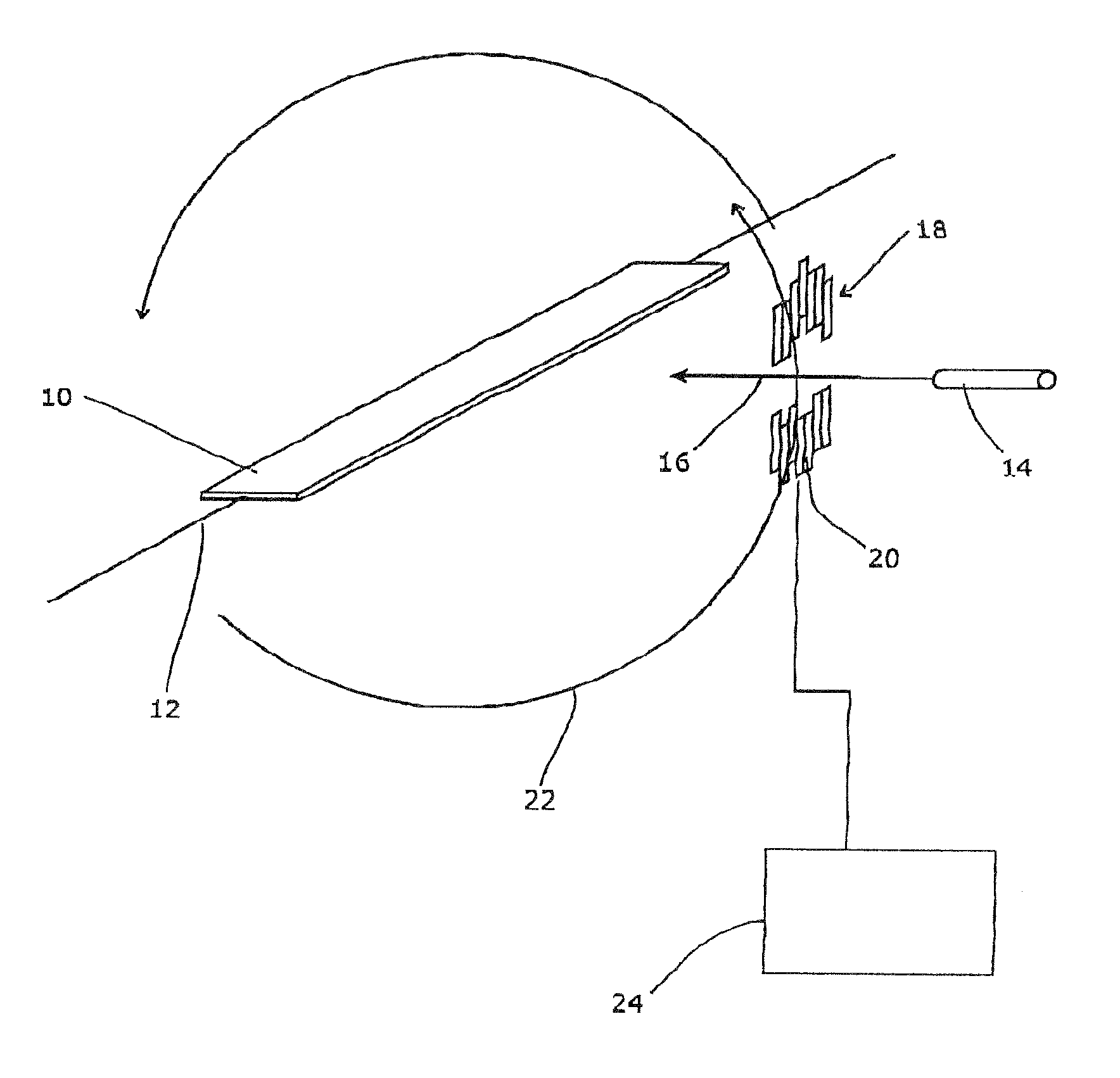
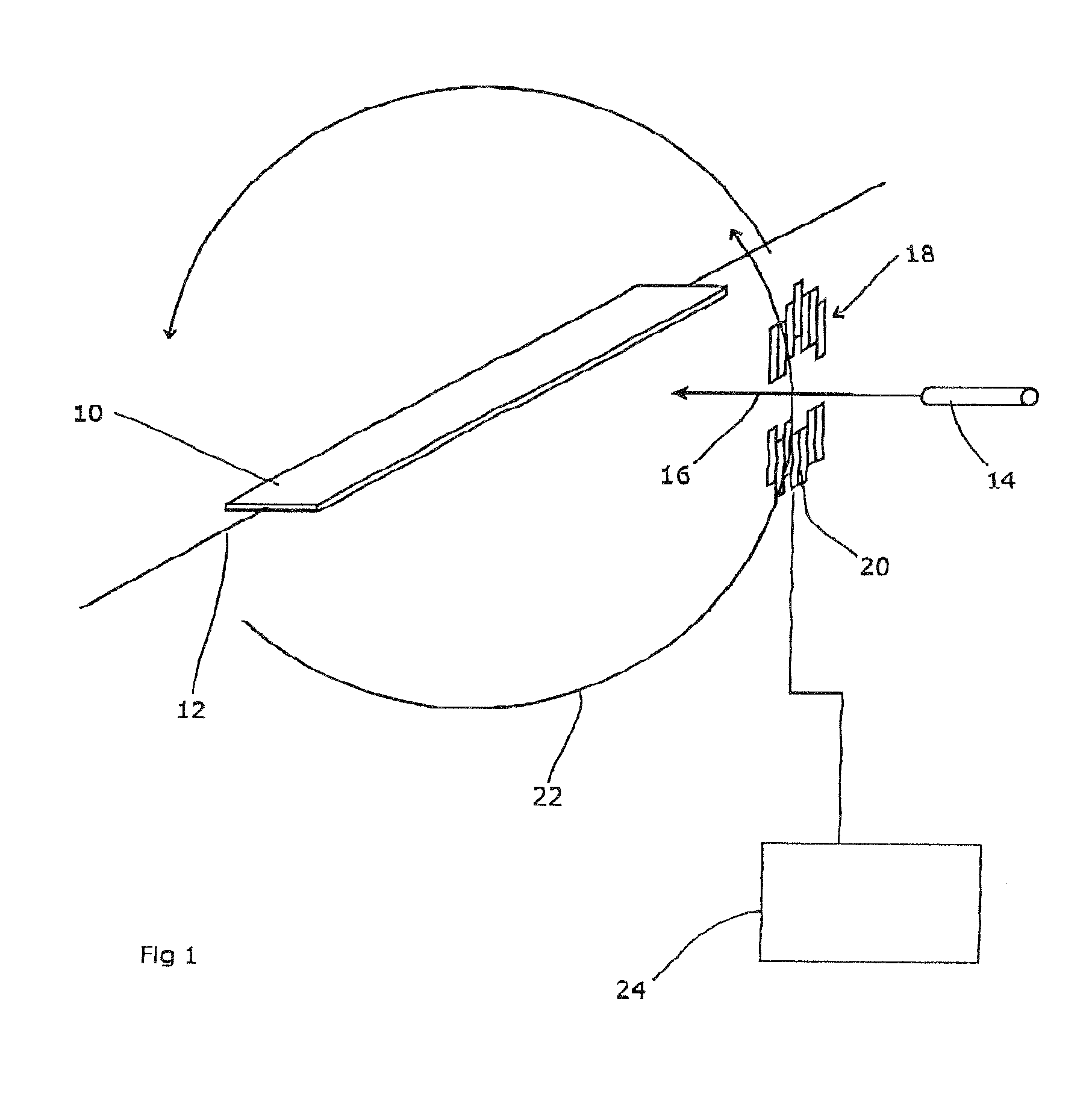
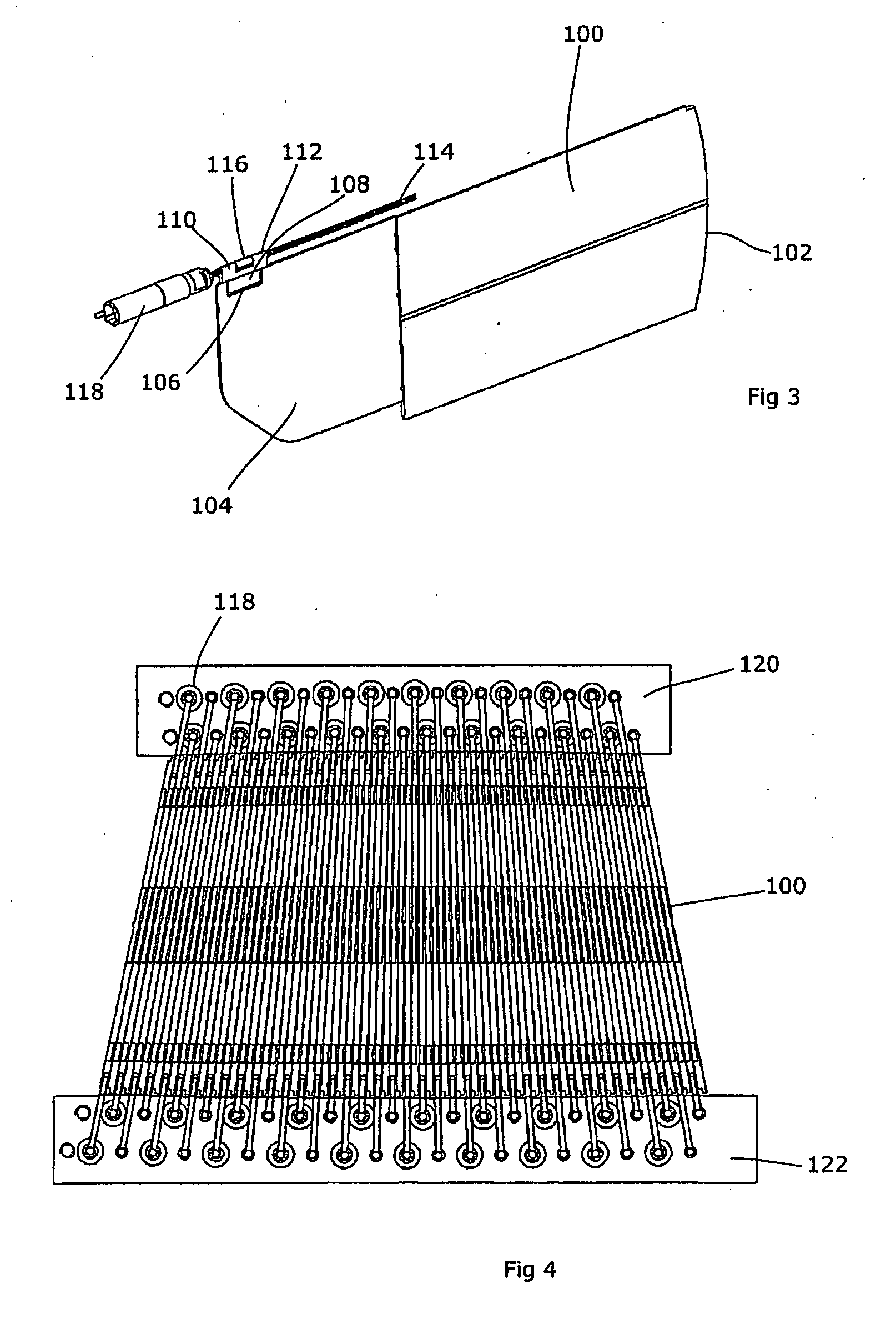
Leaf, multi-leaf collimator, device for delimiting beams and irradiation device
ActiveUS7397902B2Reduce weightReduce materialElectrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMulti leaf collimatorLight beam
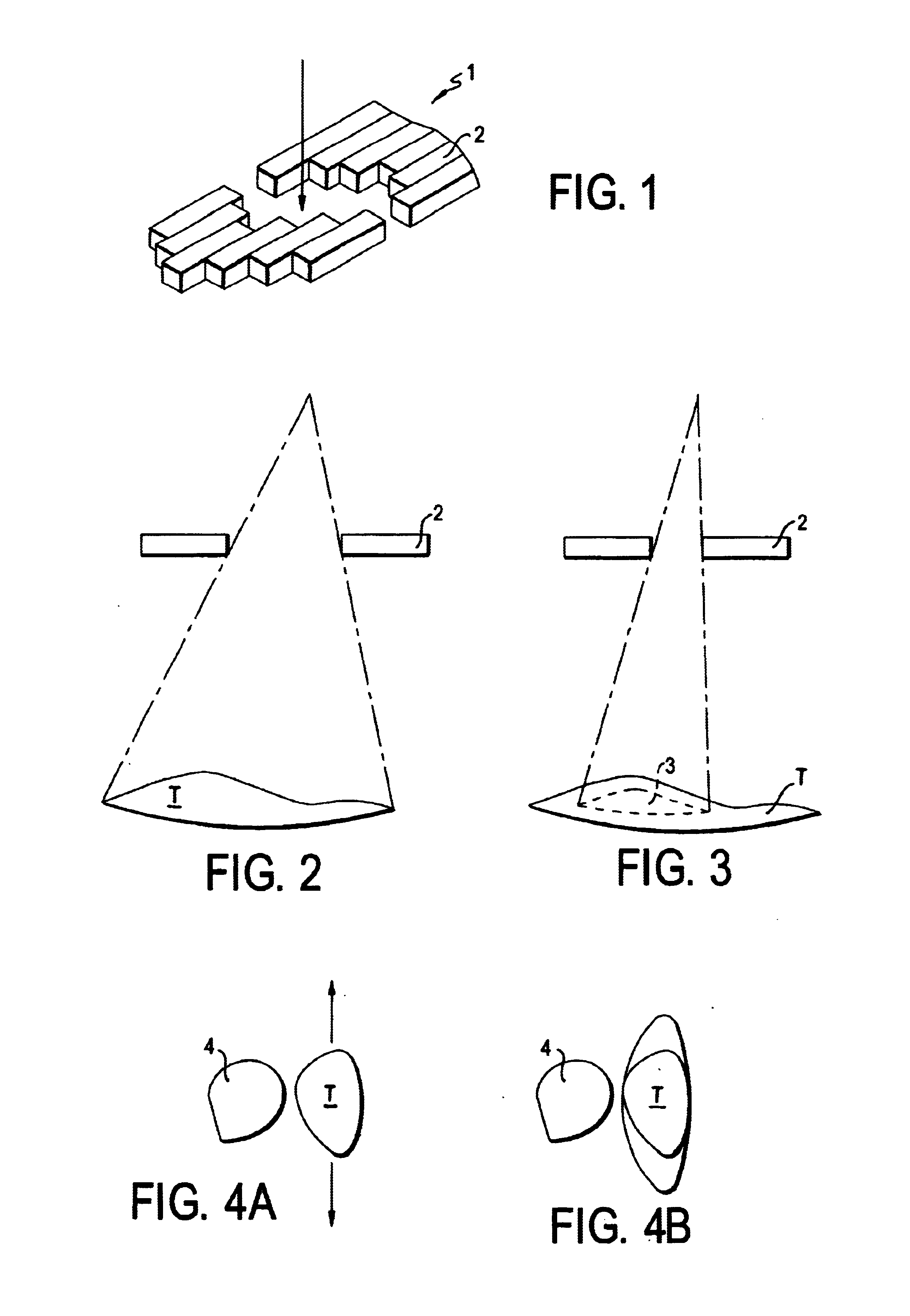
The invention relates to a leaf (1) for a multi-leaf collimator (2) for delimiting a high-energy beam (3, 3′, 3″) of an irradiation device, in particular for conformational radiation therapy. According to the invention, the multi-leaf collimator (2) comprises a plurality of opposing leaves (1), which can be brought into the beam path (3, 3′, 3″) by means of drives (4), in such a way that the contour (5) of said path can be shaped in accordance with the volume to be irradiated. The need for beam-absorbent material (7) is reduced, as the leaf (1) essentially only comprises a beam-absorbent material (7) of an appropriate thickness (8) in a region (6) that is brought into the path (3, 3′, 3″) of the high-energy beam (3) during the course of all possible positional displacements (9). The invention also relates to a corresponding multi-leaf collimator (2), a device (22) for delimiting beams, and an irradiation device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
ActiveUS8059782B2Limited lifetimeLow efficiencyHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryImage resolution
The present invention seeks to provide a radiotherapeutic apparatus that mitigates the various problems found in the techniques such as tomotherapy, IMAT, IMRT and the like. It provides a radiotherapeutic apparatus comprising a source of radiation whose output is collimated by a multi-leaf collimator, and a patient support, the source being rotatable around the support and the support being translatable along the axis of rotation, thereby to move the source helically relative to a patient on the support. The leaves of the MLC are preferably oriented orthogonal to the axis of rotation, to simplify computation of the dose distribution. The apparatus thus moves the patient on the patient support system along the axis of rotation, in the longitudinal direction. Thus, the device has an effectively unlimited treatable volume in the longitudinal direction and avoids the limitations of IMAT and IMRT techniques whilst enabling the use of thin MLC leaves to give a high longitudinal resolution. The apparatus is preferably combined with an optimization system providing a computational service similar to that provided for IMAT and IMRT devices. Essentially the same computational techniques could be used, with appropriate changes to the input conditions and characteristic equations. The long aperture length (compared to tomotherapy) makes the radiation delivery efficient and therefore the delivery of high doses a practicality; hypofractionation and radiosurgery therefore become possible over large treatable volumes.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
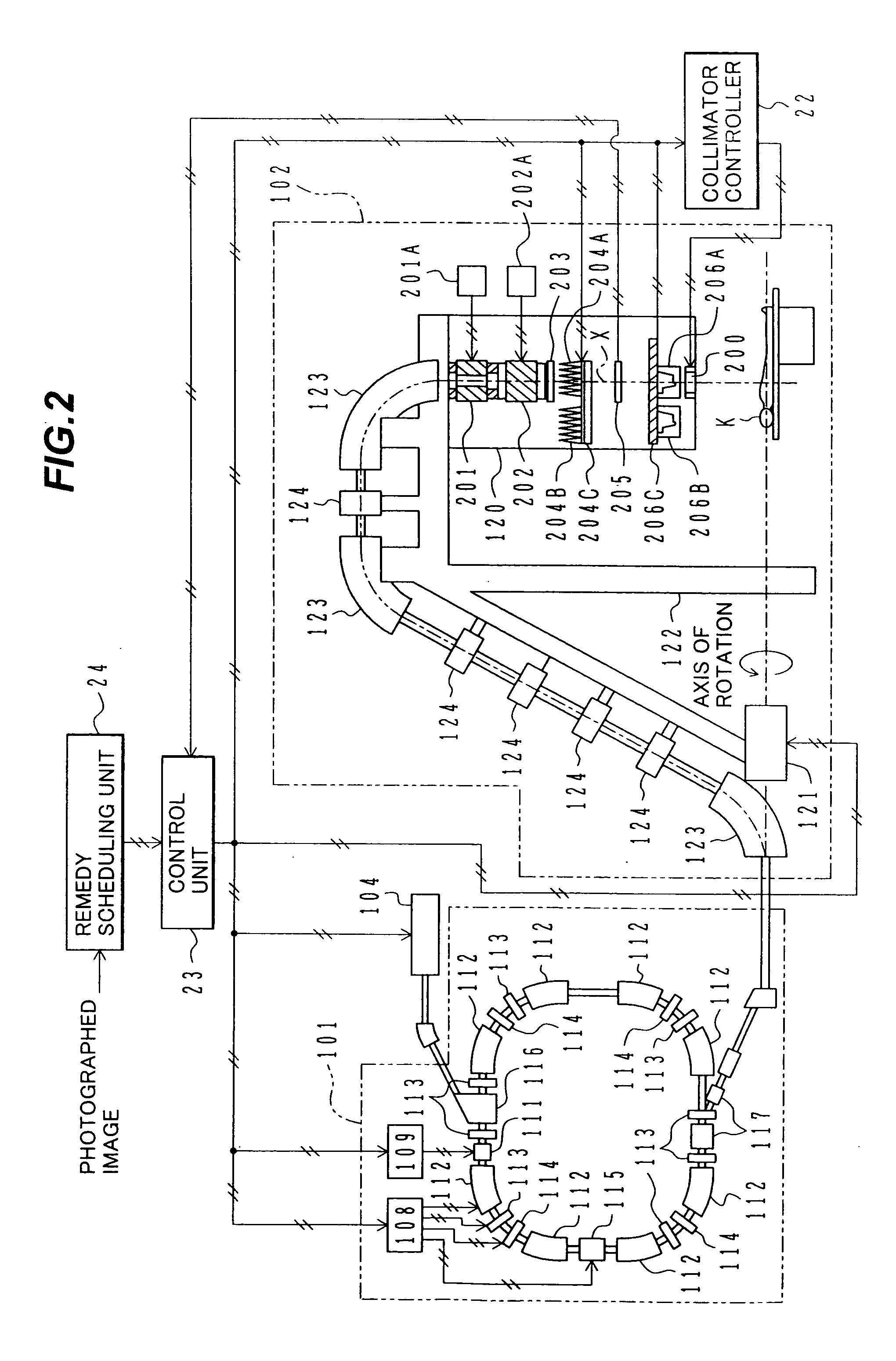
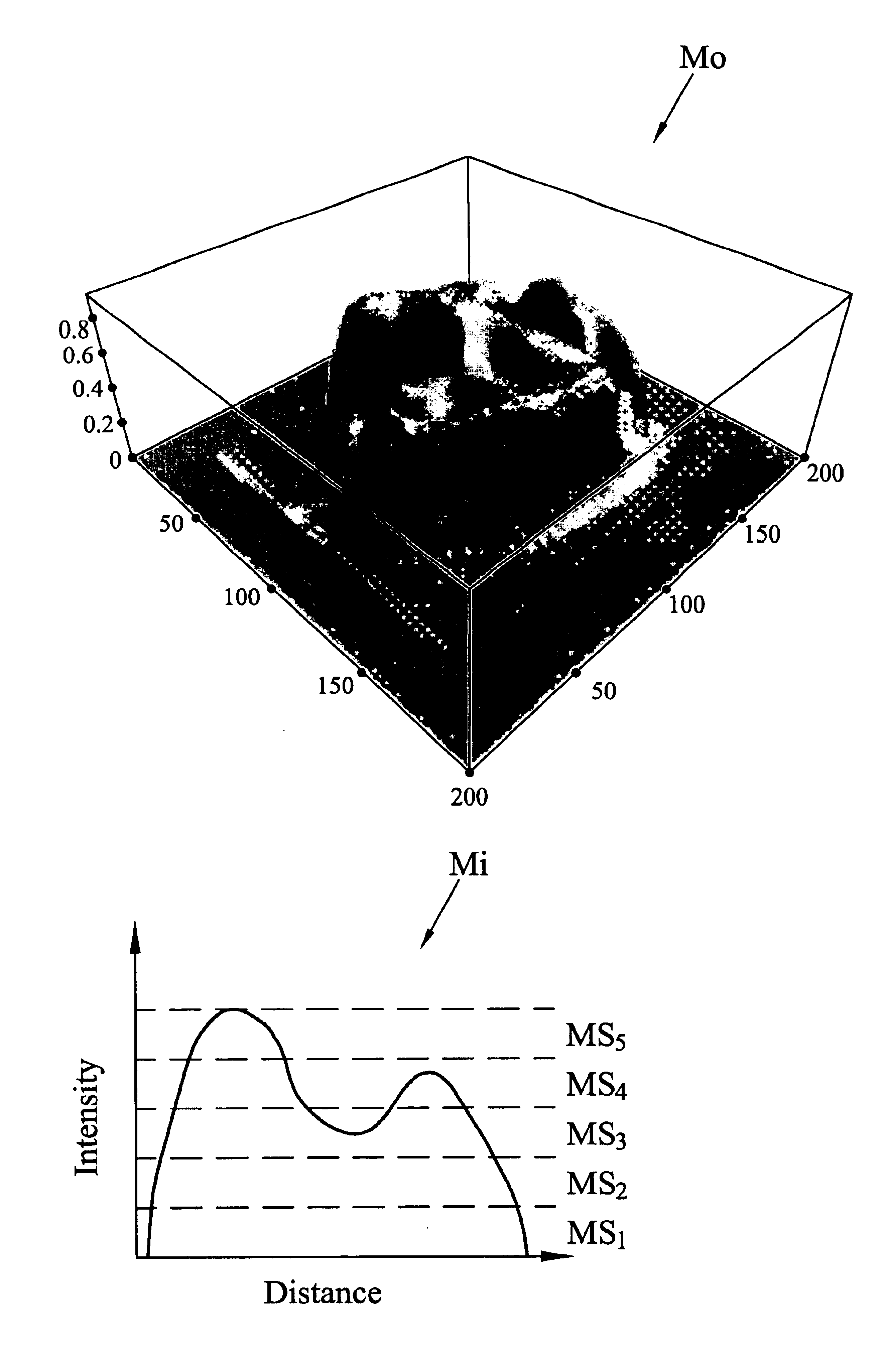
Method for establishing measurement data-based simple and convenient irradiation source model of medical linear accelerator
InactiveCN102921115AAvoid dependenceAvoid Heavy Computing TasksSpecial data processing applicationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorIrradiation
The invention discloses a method for establishing a measurement data-based simple and convenient irradiation source model of a medical linear accelerator. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: supposing that an irradiation source of the medical linear accelerator is on the part of the bottommost end of an MLC (Multi-leaf Collimator); measuring a flux pattern of data inversion from the accelerator through adjustment; and realizing simulation of the irradiation source of the medical linear accelerator by using a method of combining weight of outgoing particles and flux strength by combining the position of the outgaining particles with the flux distribution. Dose distribution in a template is obtained by using geometric description of a particle transport model of classic monte carlo program EGSnrc and a model of DOSXYZnrc. The method is established based on measurement data of the medical linear accelerator, so that the dependence of the conventional full accelerator simulation on the technical detail of the structure of the accelerator and heavy calculation task brought by need of sectional re-simulation in each modification process of the simulation parameter are avoided. The model can be used as an irradiation source model for an accurate monte carlo dosage calculation tool in a human body and can also be used for providing a source model for a dosage verification tool in a treatment planning system and an analytical dosage calculation tool of a treatment scheme optimization algorithm.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Multi-leaf collimators
InactiveUS20090262901A1Drive great amountReduced shieldingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
A multi-leaf collimator for a radiotherapy apparatus comprises at least one array of laterally-spaced elongate leaves, each leaf being driven by an associated motor connected to the leaf via a drive means so as to extend or retract the leaf in its longitudinal direction, the drive means comprising a sub-frame on which at least a subset of the motors are mounted, the sub-frame being mounted at a location spaced from the leaf array in a direction transverse to the lateral and longitudinal directions, and including a plurality of leadscrews disposed longitudinally, each being driven by a motor and being operatively connected to a leaf thereby to drive that leaf.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
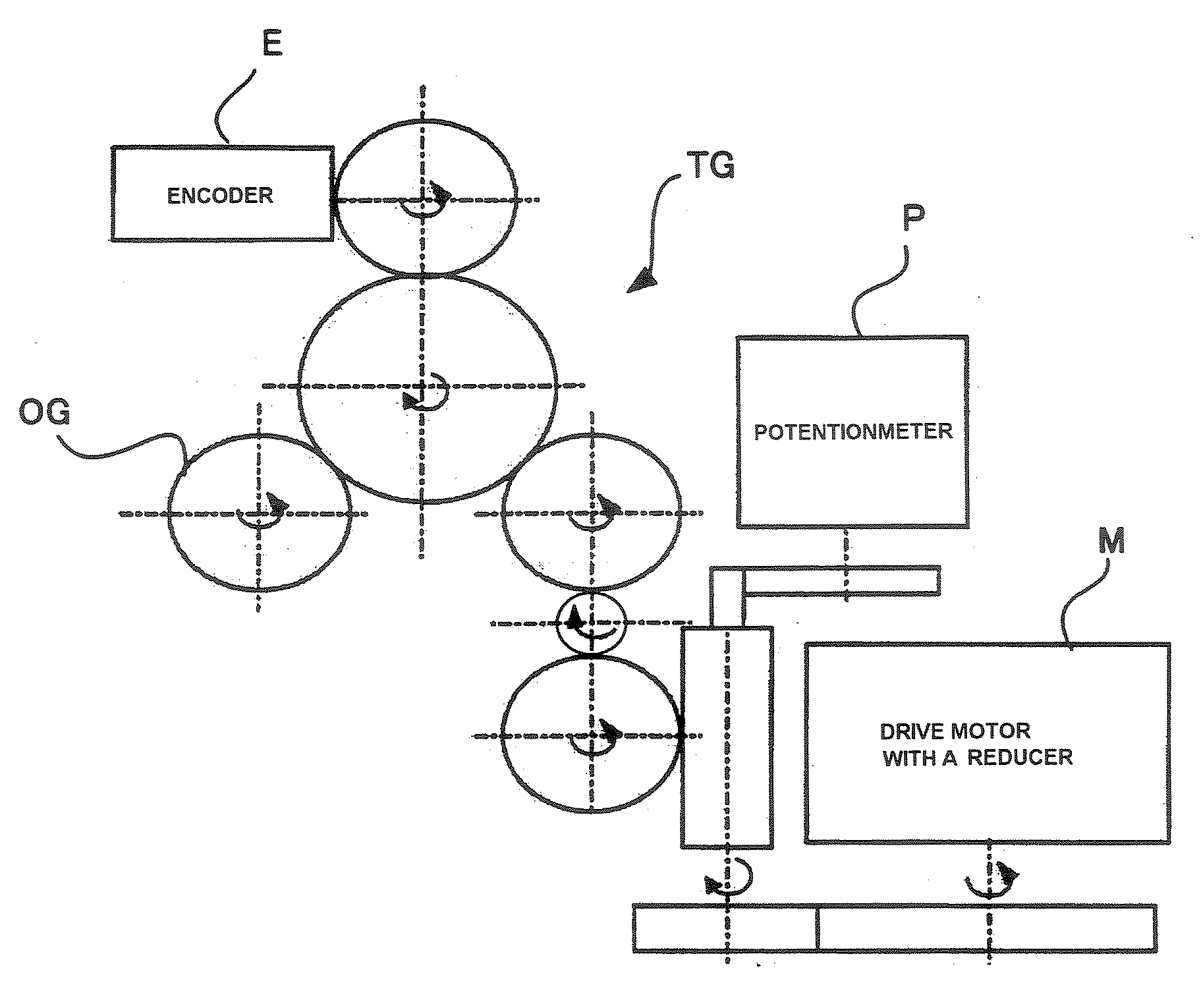
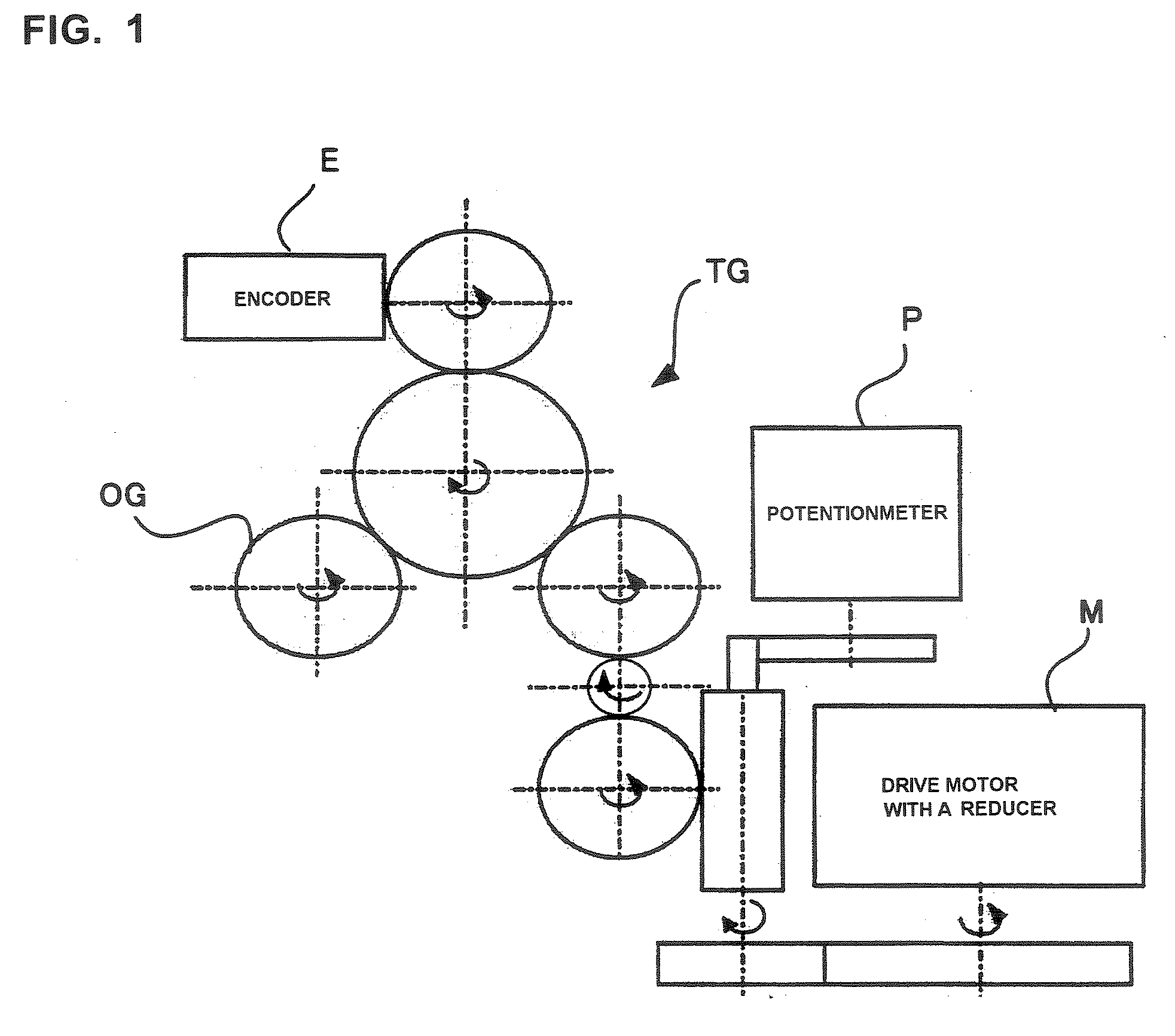
Multi-leaf collimator and a radiotherapy unit provided with the same
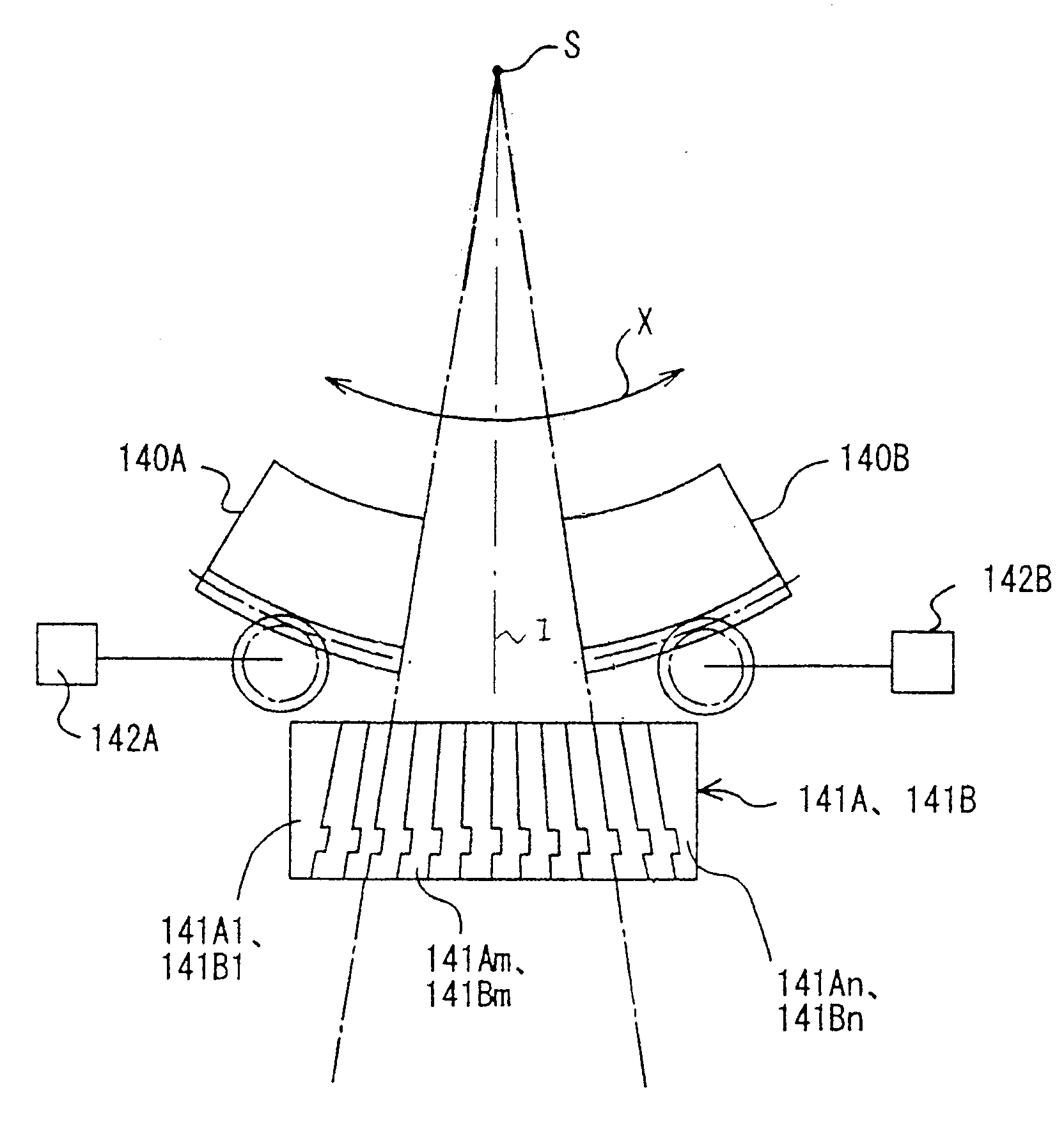
InactiveUS20070176126A1InhibitionImprove accuracyElectrode and associated part arrangementsPhotometryMulti leaf collimatorRadiotherapy unit
A multi-leaf collimator that narrows a radiation field to a predetermined shape is provided with leaf blocks movable in the direction of the radiation field and having pattern images drawn along the direction of movement on a predetermined surface, and detection part acquiring an image of fixed-point via fixed-point observation in the direction of that predetermined surface and for detecting displacement of said leaf blocks based on the arranged locations of the pattern images existing in this image of fixed-point. Moreover, it is provided with detection part acquiring an image of fixed-point via fixed-point observation in the direction of that predetermined surface and for detecting the locations of the leaf blocks based on the arranged locations of the pattern images existing in this image of fixed-point. According to the present invention, displacement and locations of leaf blocks can be detected without making contact, and displacement due to the effect of backlash and gear wear or errors in detecting locations can be prevented. Therefore, regardless of backlash, the locations of the leaf blocks can be detected with high precision, and the radiation field can be matched to the shape of an affected part with high precision.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and system for treating moving target
ActiveUS8331532B2Easy transitionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray apparatusMedicineTreatment targets
A method and system for providing intensity modulated radiation therapy to a moving target is disclosed. According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, a treatment plan for providing radiotherapy using a multi-leaf collimator (“MLC”) comprises a plurality of sub-plans, each of which is optimized for a different phase of target movement. Movements of the treatment target are tracked in real time, and the choice of which sub-plan to implement is made in real time based on the tracked position of the target. Each of the sub-plans is preferably formulated to minimize interplay effects between target movements and MLC leaf movements, consistent with other planning goals. In addition, the sub-plans preferably include a predicted region corresponding to the next anticipated position of the target, in order to facilitate the transition to the next position.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
System or method for calibrating a radiation detection medium
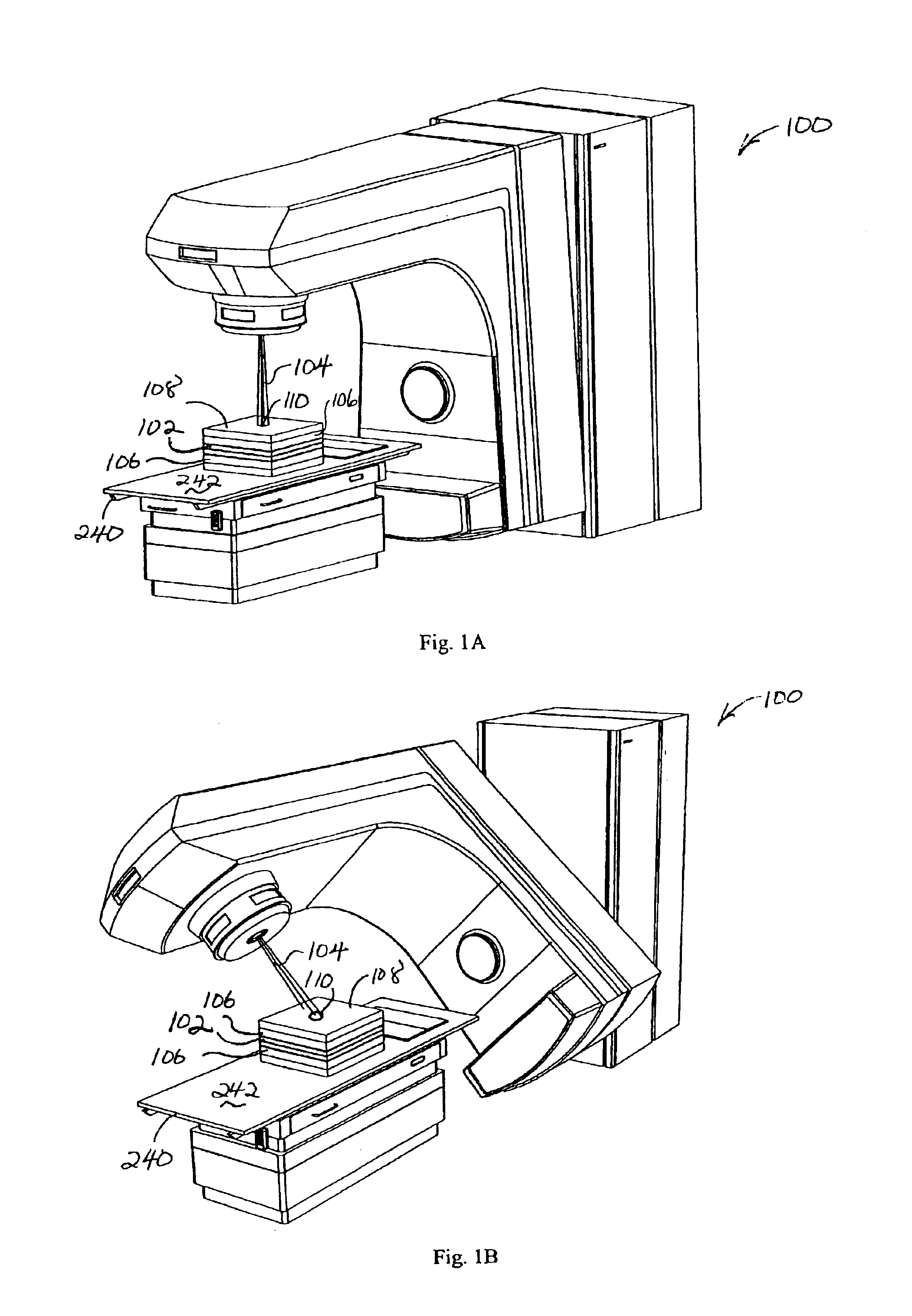
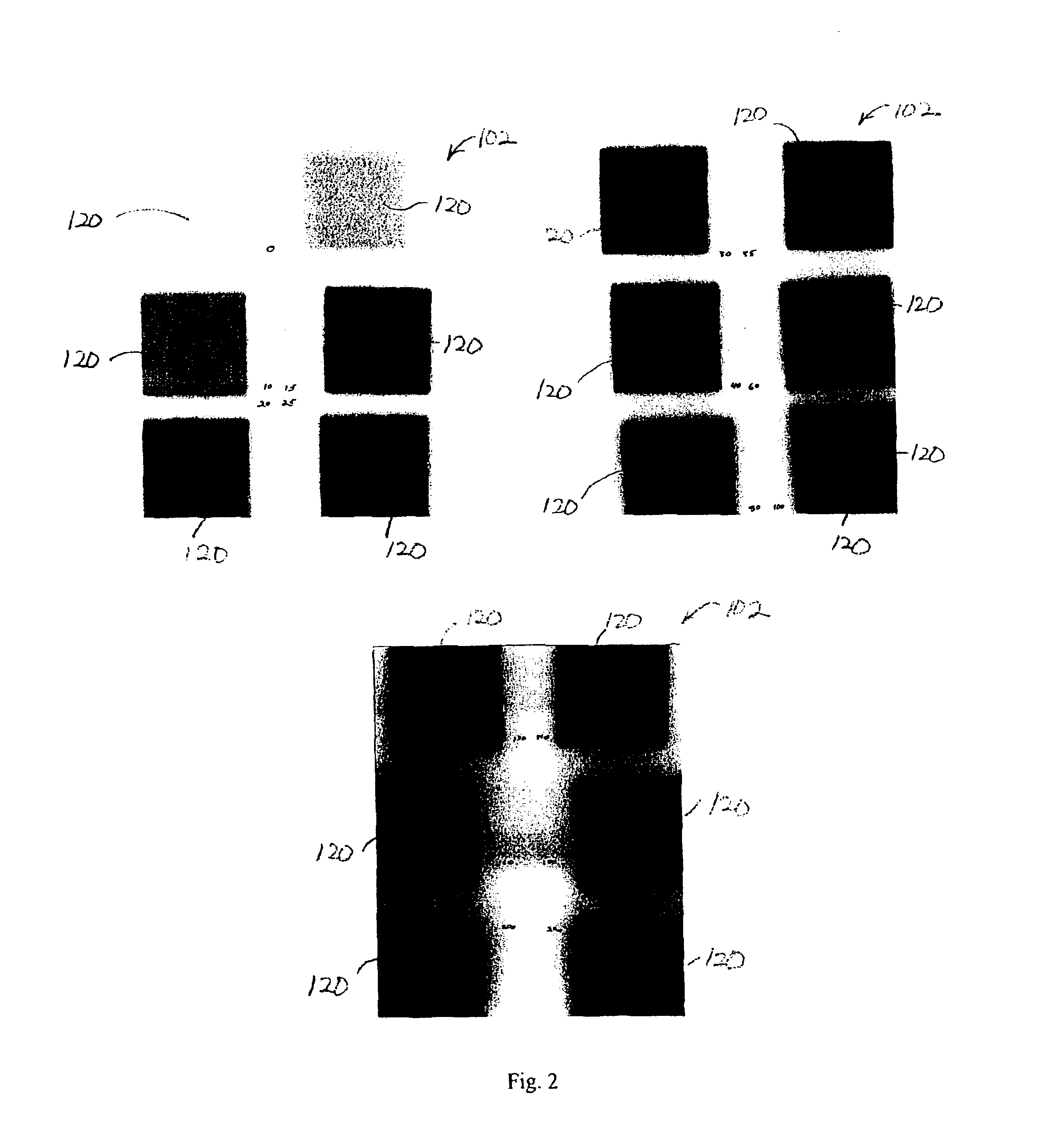
InactiveUS6934653B2Shorten the timeReduce in quantityTesting/calibration apparatusDosimetersUltrasound attenuationMulti leaf collimator
Methods and devices for calibrating a radiotherapy system are disclosed. The method includes providing a detection medium that responds to exposure to ionizing radiation, and preparing a calibration dose response pattern by exposing predefined regions of the detection medium to different ionizing radiation dose levels. The method also includes measuring responses of the detection medium in the predefined regions to generate a calibration that relates subsequent responses to ionizing radiation dose. Different dose levels are obtained by differentially shielding portions of the detection medium from the ionizing radiation using, for example, a multi-leaf collimator, a secondary collimator, or an attenuation block. Different dose levels can also be obtained by moving the detection medium between exposures. The disclosed device includes a software routine fixed on a computer-readable medium that is configured to generate a calibration that relates a response of a detection medium to ionizing radiation dose.
Owner:RADIOLOGICAL IMAGING TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com