Patents
Literature
2936 results about "Centroid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and physics, the centroid or geometric center of a plane figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the figure. Informally, it is the point at which a cutout of the shape could be perfectly balanced on the tip of a pin.
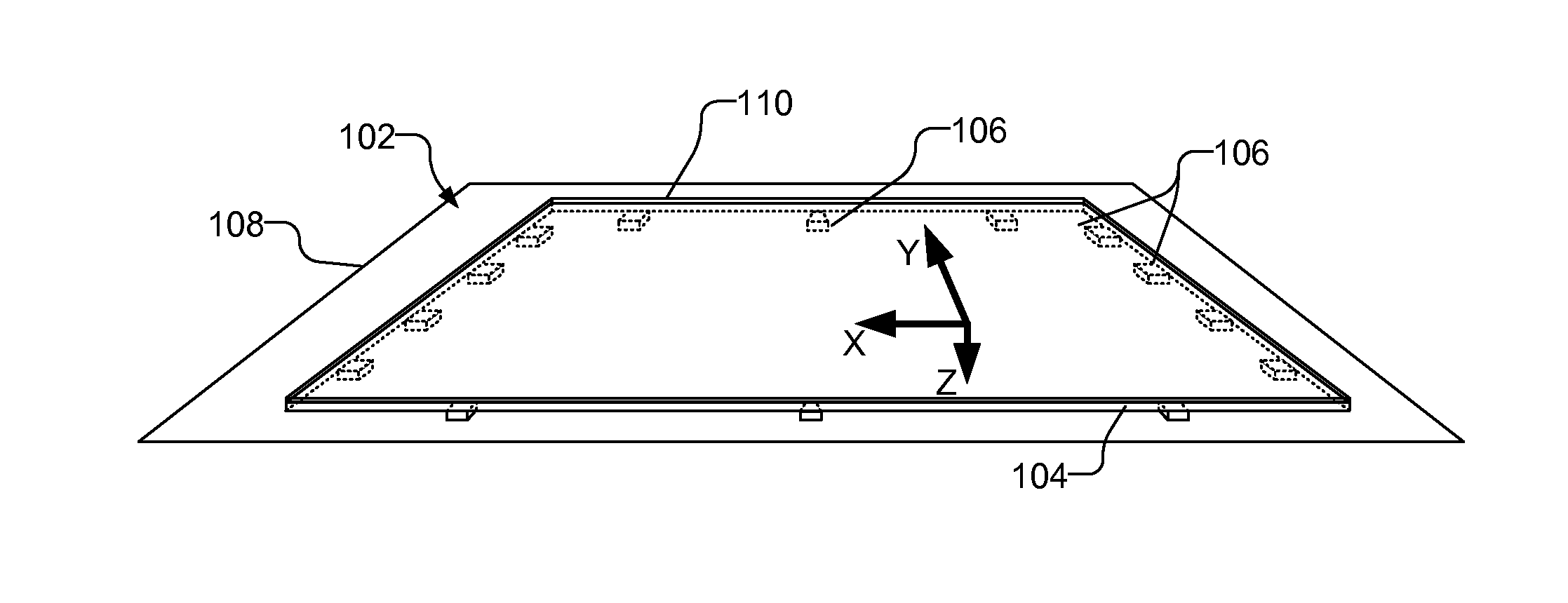
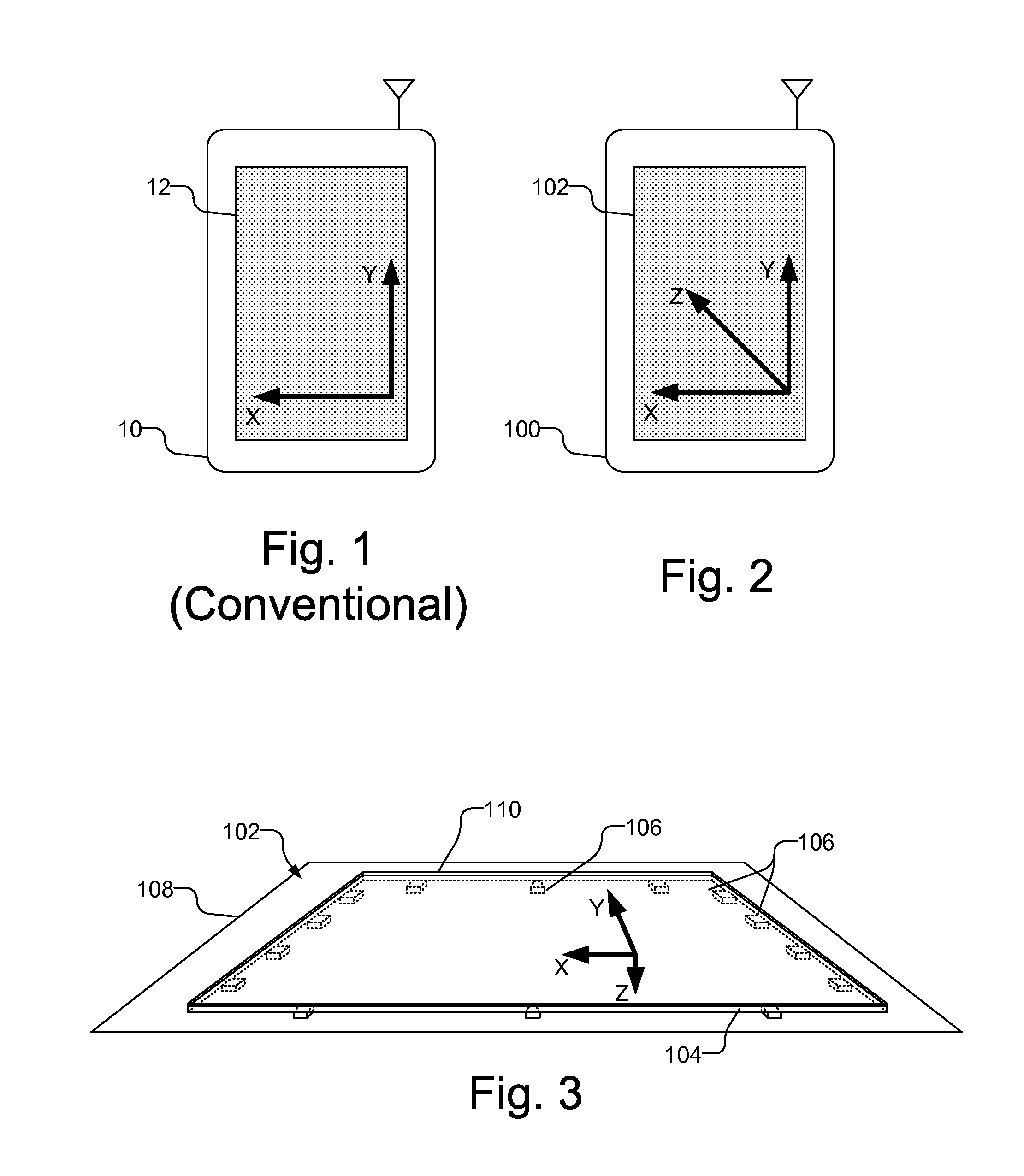
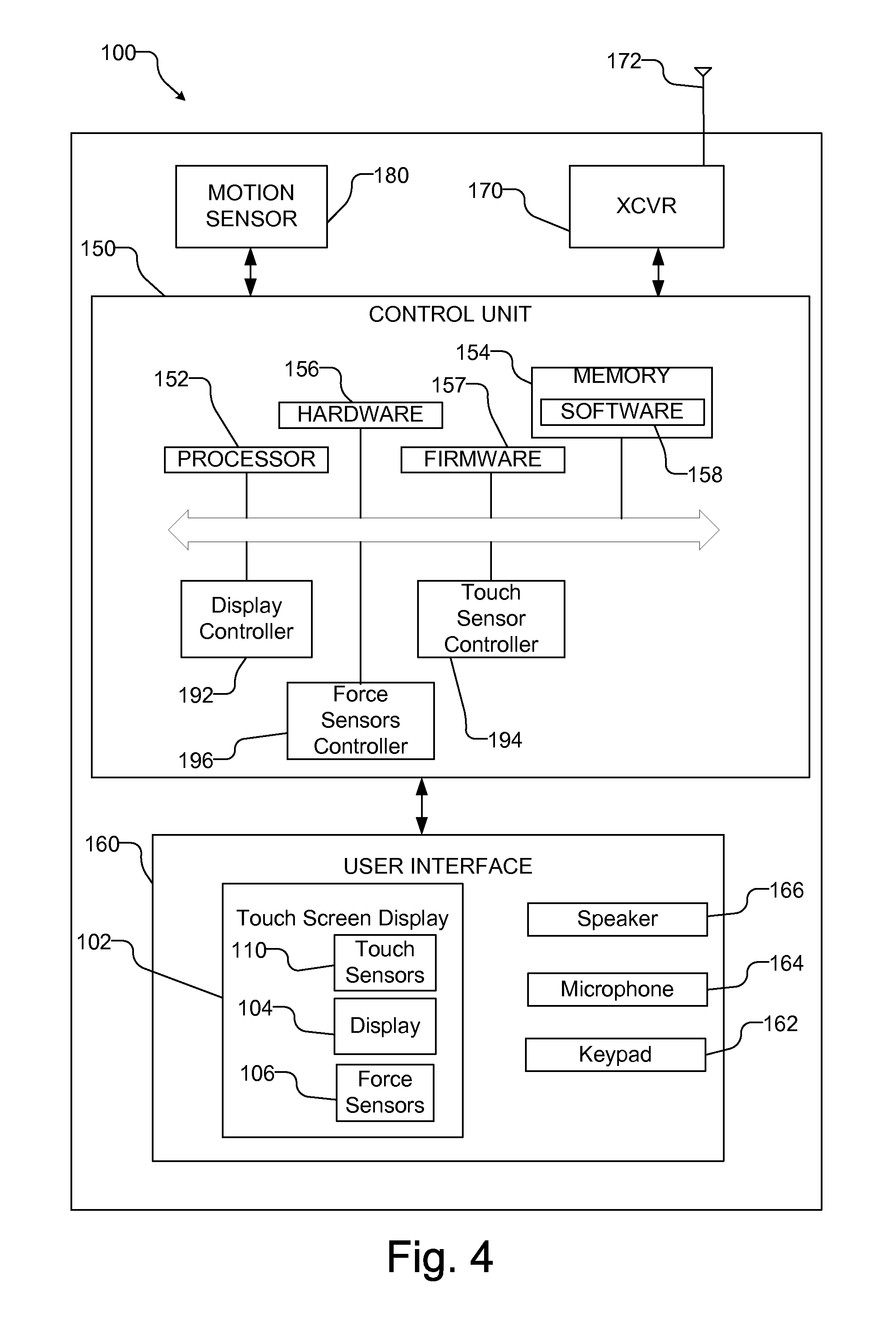
Force sensing touch screen
A computing device includes a touch screen display with a plurality of force sensors, each of which provides a signal in response to contact with the touch screen display. Using force signals from the plurality of force sensors, a characteristic of the contact is determined, such as the magnitude of the force, the centroid of force and the shear force. The characteristic of the contact is used to select a command which is processed to control the computing device. For example, the command may be related to manipulating data displayed on the touch screen display, e.g., by adjusting the scroll speed or the quantity of data selected in response to the magnitude of force, or related to an operation of an application on the computing device, such as selecting different focal ranges, producing an alarm, or adjusting the volume of a speaker in response to the magnitude of force.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Business directory search engine
A system and method for efficiently searching directory listing information to obtain more relevant results is provided. In a computer system running a computing application, it is advantageous to provide search capabilities, in the form of a search engine, to operators to assist them in their effort of retrieving desired data. The search engine may cooperate with a data store having directory listing information to provide listings data to an operator. In an illustrative implementation, this search engine may be deployed on an Internet Web site that offers business listing information. The search system may comprise a user interface to enter search query information, a data store that houses a variety of directory listing information according to a predefined data taxonomy, and a means for displaying the search results. In operation, the search engine offers a variety of search options, such as, search by business name, by business categories levels, by geographic position of the user or the business, or a combination thereof. Depending on the search query entered, the search engine will perform either a bounded search (i.e. a search bounded to a specific geographic area), a proximity search (i.e. a search proximate to a computed centroid), or a combination of the two to find the most relevant directory listings. Using the inputted search qualifiers, the search engine polls the data store according to a predefined set of rules and instructions for the relevant directory listing information. These rules are directly related to the taxonomy of the data store.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Object position detection system and method
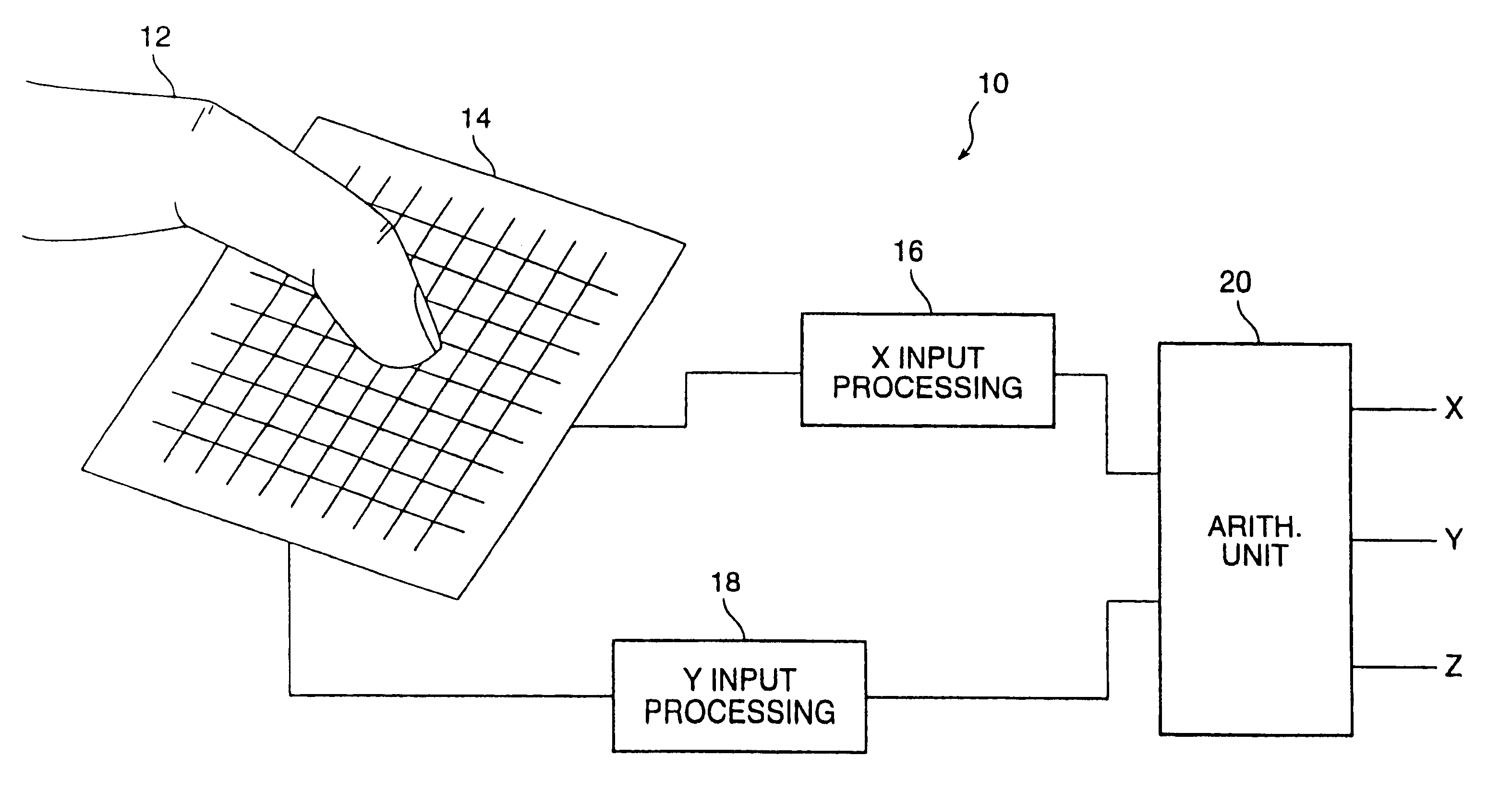
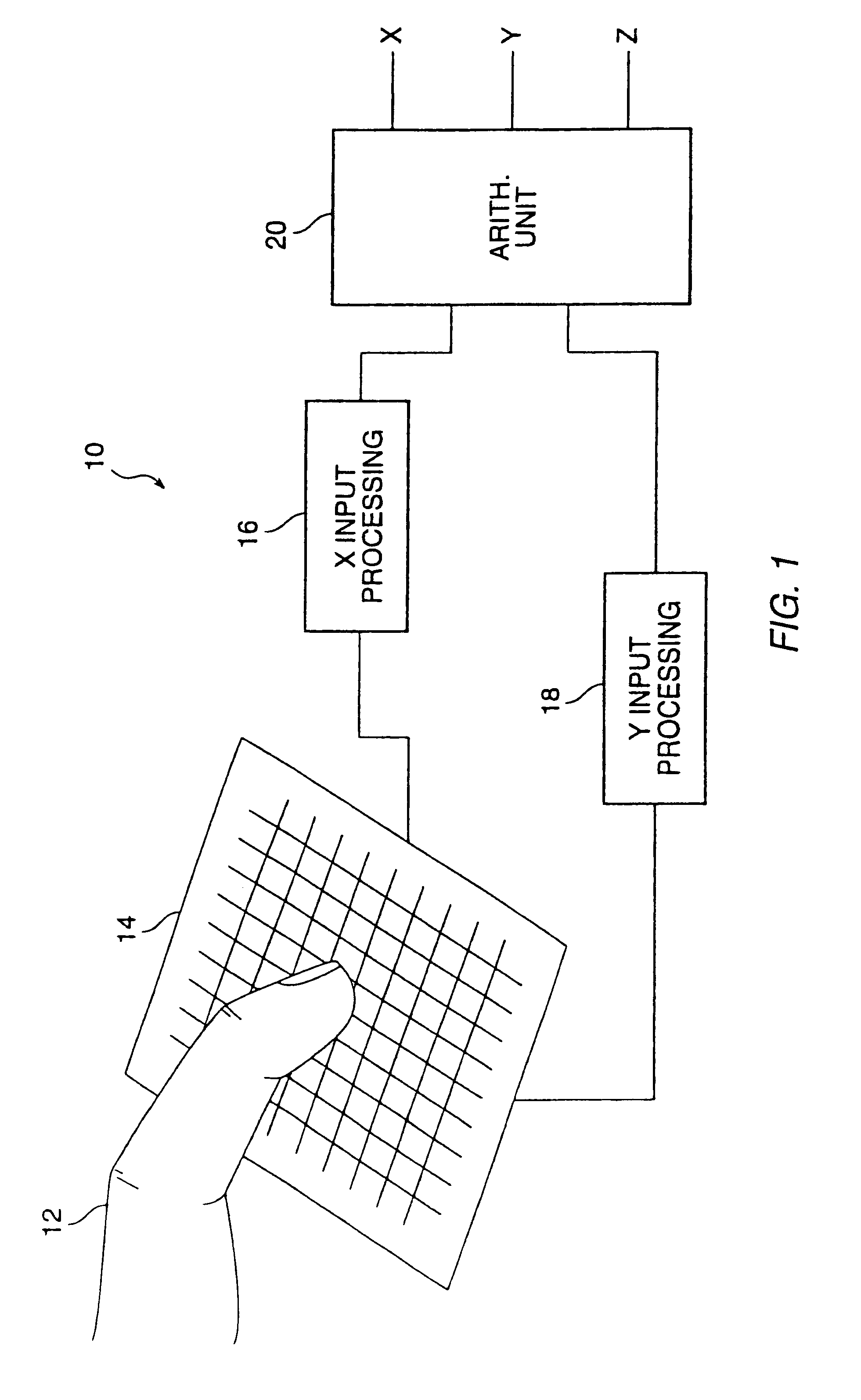
InactiveUS6239389B1Effective positioningEasy CalibrationTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A proximity sensor system includes a sensor matrix array having a characteristic capacitance on horizontal and vertical conductors connected to sensor pads. The capacitance changes as a function of the proximity of an object or objects to the sensor matrix. The change in capacitance of each node in both the X and Y directions of the matrix due to the approach of an object is converted to a set of voltages in the X and Y directions. These voltages are processed by digital circuitry to develop electrical signals representative of the centroid of the profile of the object, i.e, its position in the X and Y dimensions. Noise reduction and background level setting techniques inherently available in the architecture are employed.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Methods, systems, and devices for deep brain stimulation using helical movement of the centroid of stimulation
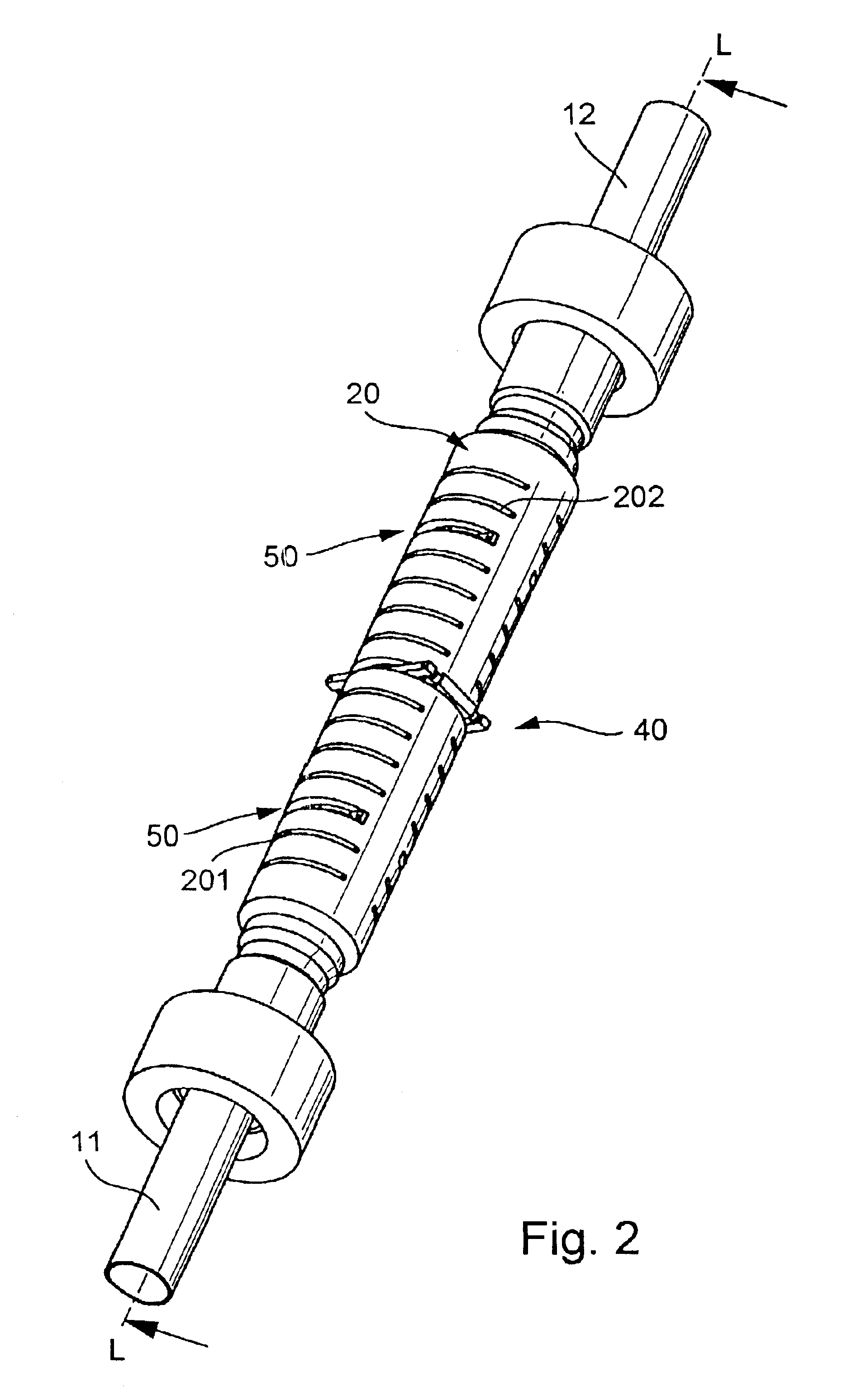
A method of treating a target region in the brain includes a) contacting tissue to be stimulated with a lead of a stimulation device, the stimulation device comprising a pulse generator coupled to the lead, the lead having a plurality of segmented electrodes disposed at a distal end of the lead, the stimulation device being configured and arranged to stimulate a target region using a positionable centroid of stimulation; b) providing stimulation current to at least one of the segmented electrodes of the lead to generate a centroid of stimulation at a location and stimulate tissue around the location of the centroid of stimulation; c) repositioning the centroid of stimulation to a next location along a helical path by altering the provision of stimulation current to the plurality of electrodes and stimulating tissue around the location of the repositioned centroid of stimulation; and d) repeating c) for each location along the helical path. The method may optionally include collecting data associated with each of the locations of the centroid of stimulation; and displaying at least a portion of the collected data.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
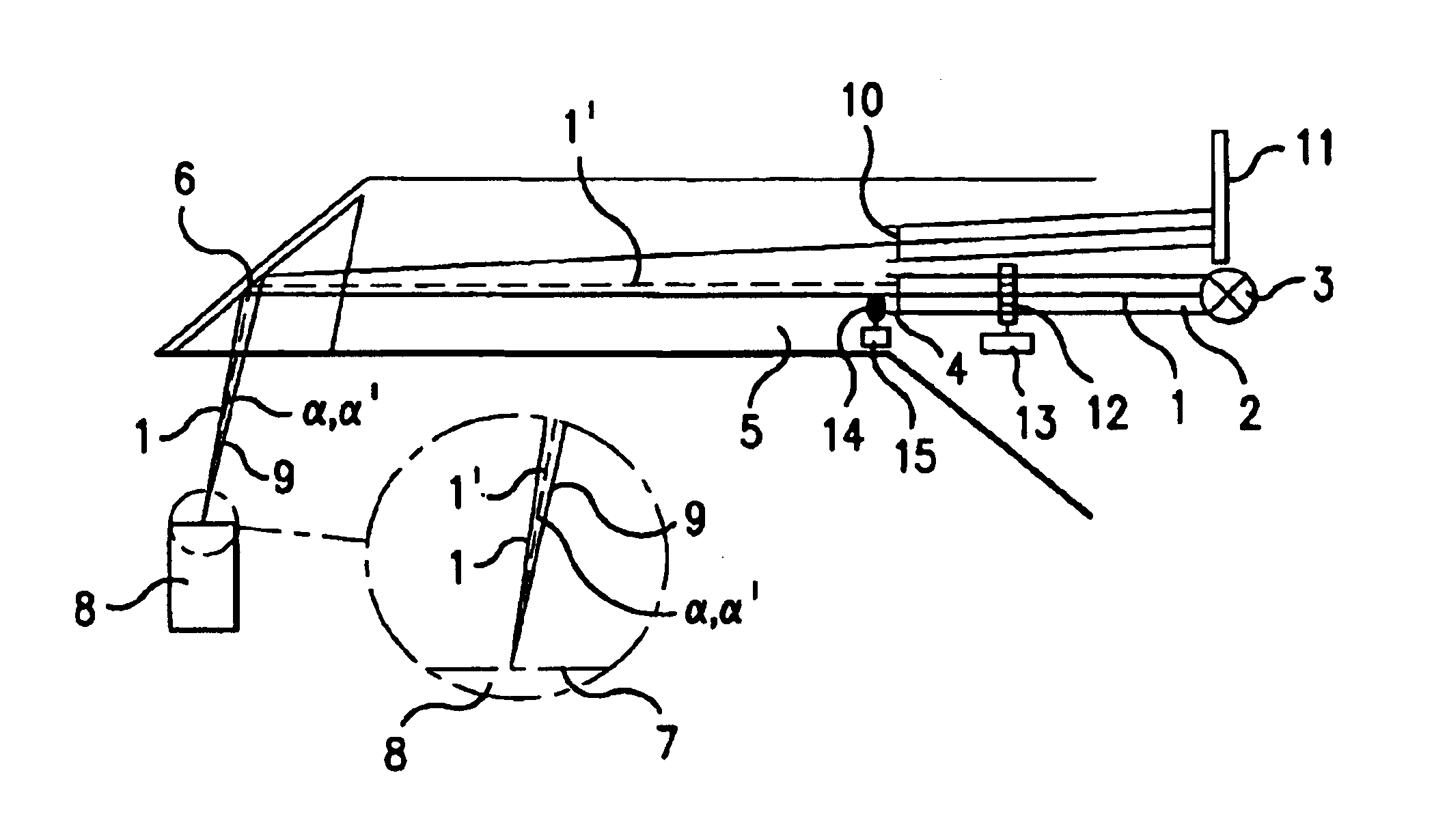
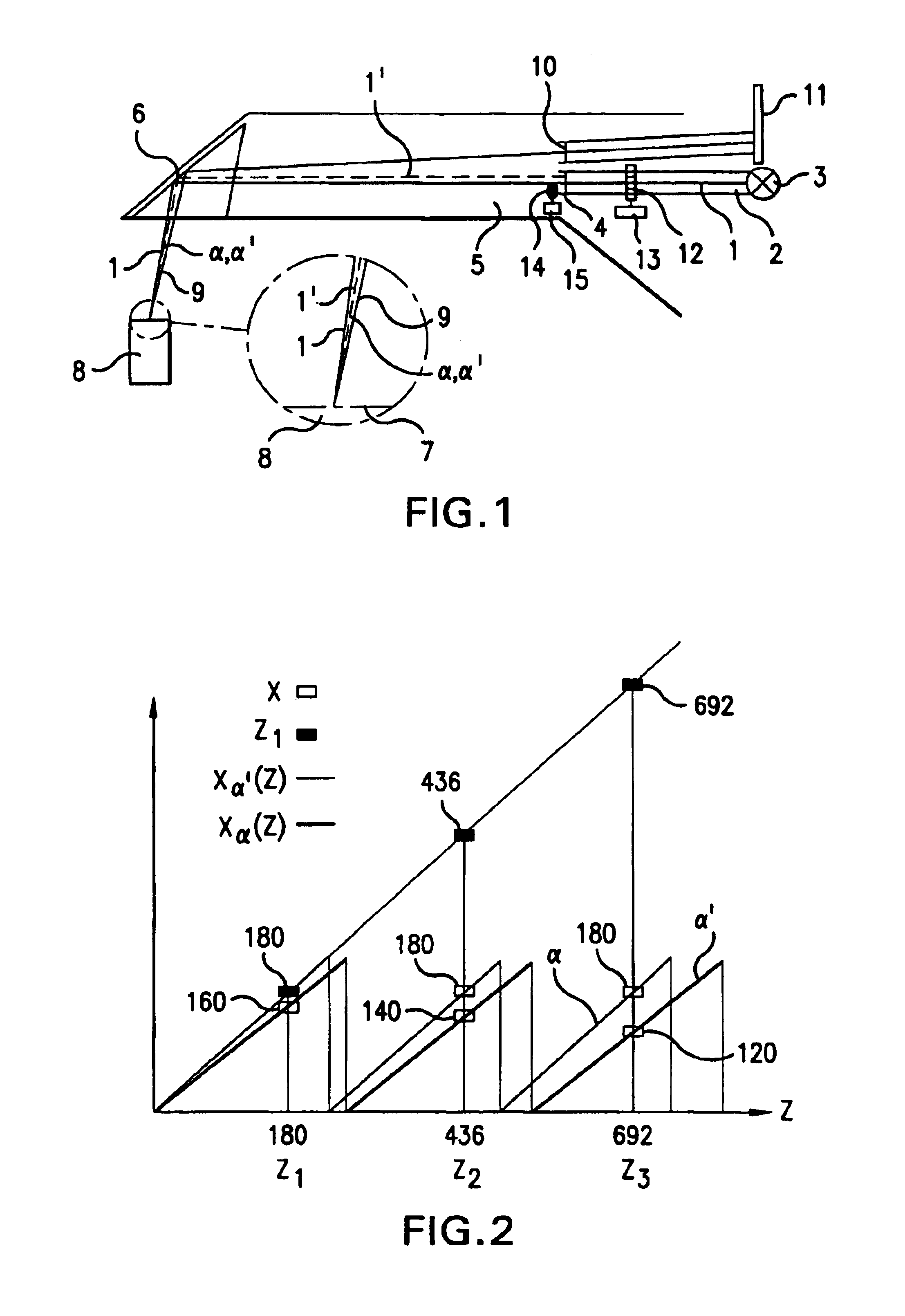
3-D camera for recording surface structures, in particular for dental purposes
InactiveUS6885464B1Reduced measurement accuracyRequires low equipmentImpression capsOptical rangefindersTriangulationLight beam
A 3-D camera and a method for recording surface structures on an object of interest by triangulation, in particular for dental purposes. The camera provides for producing a group of light beams in order to illuminate the object of interest via a projection optical path, an image sensor for receiving light back-scattered by the object of interest via an observation optical path, and provides, in the projection optical path, for producing a pattern projected onto the object of interest. To avoid ambiguities in the event of large height differences, the camera provides for the projection optical path and / or the observation optical path for altering the triangulation angle, which is defined by the angle between the centroid beam of the projection optical path and the centroid beam of the observation optical path. The proposed process involves the taking of at least two 3-D measurements of the same object of interest with different triangulation angles.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
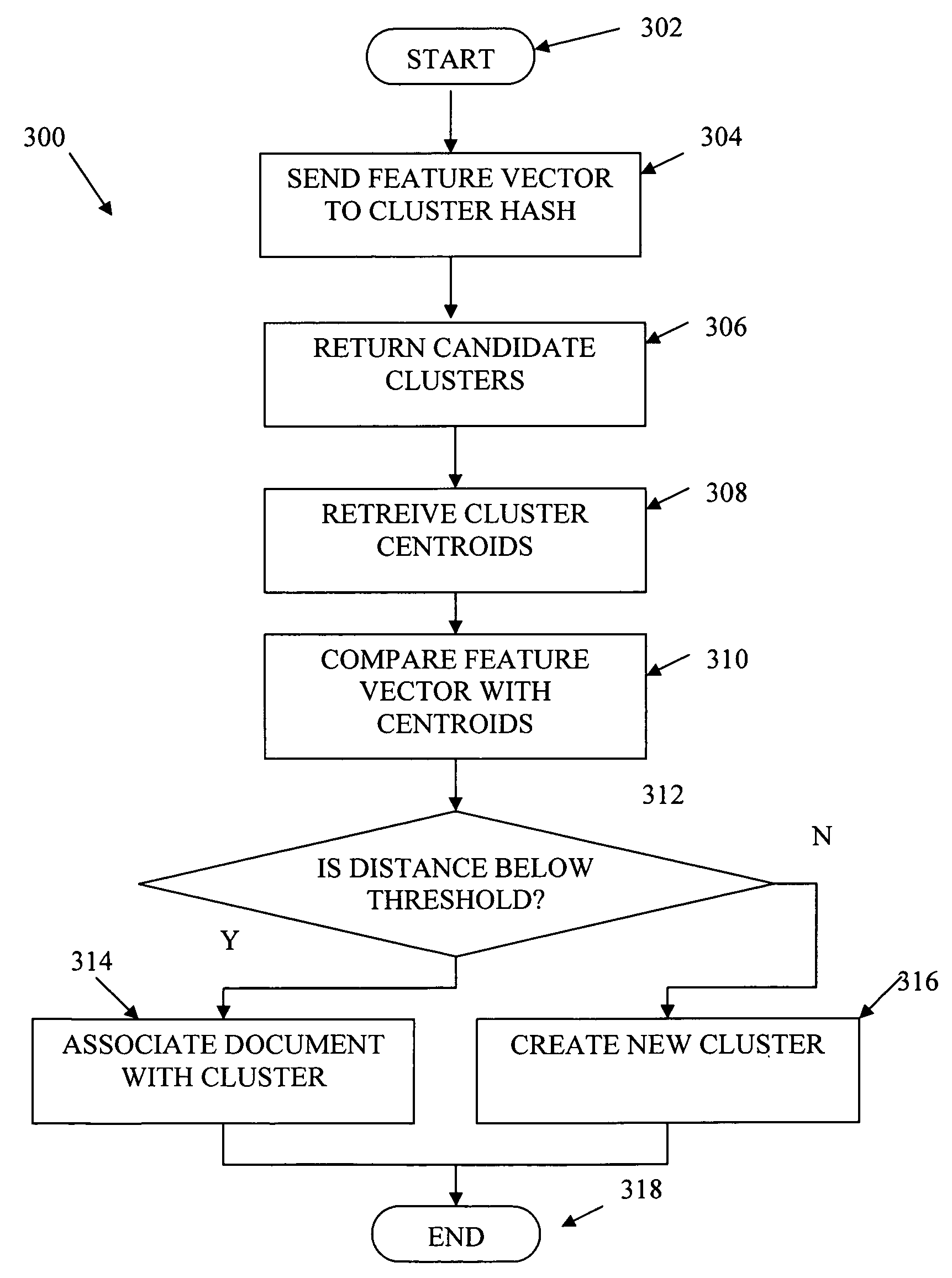
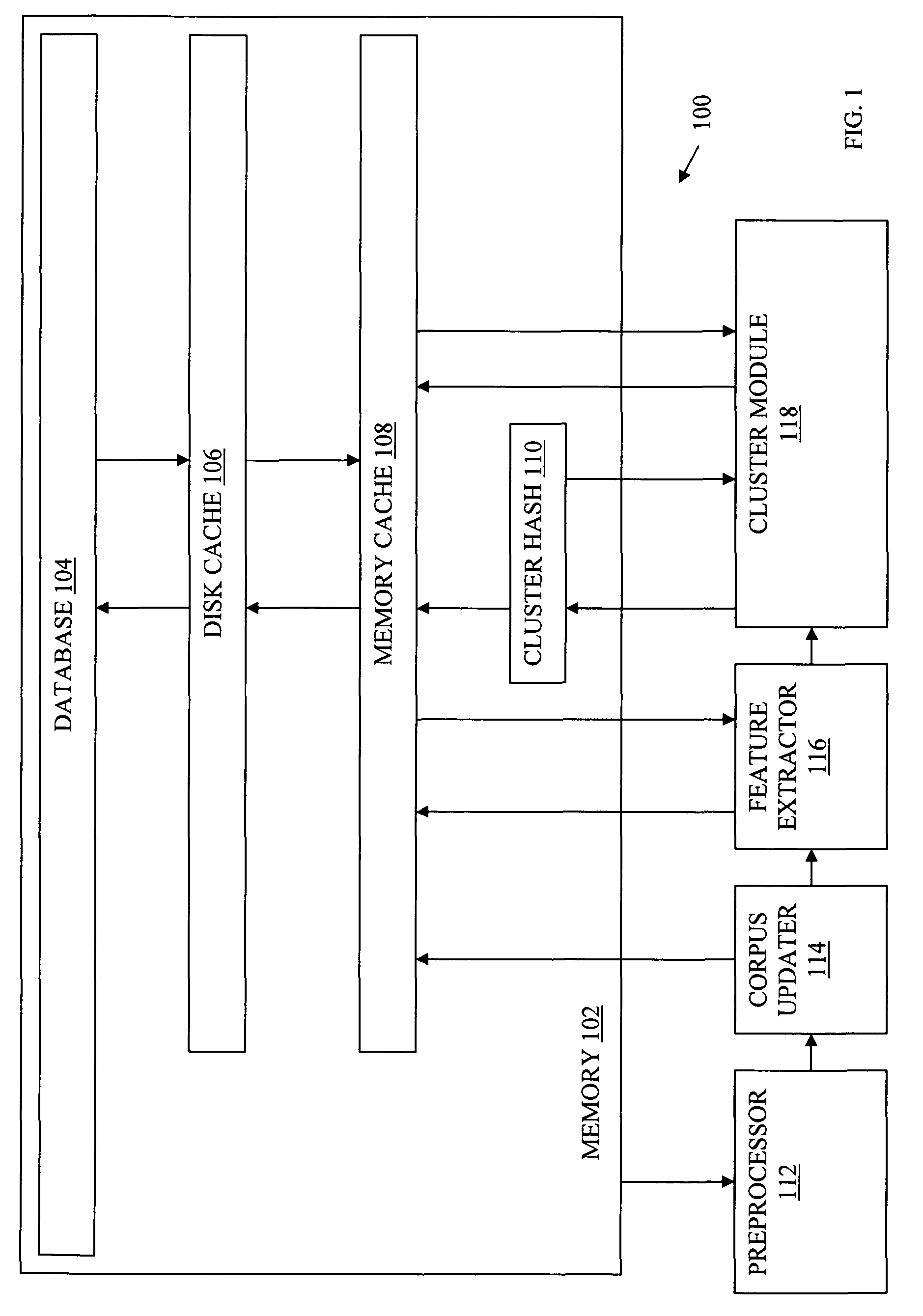
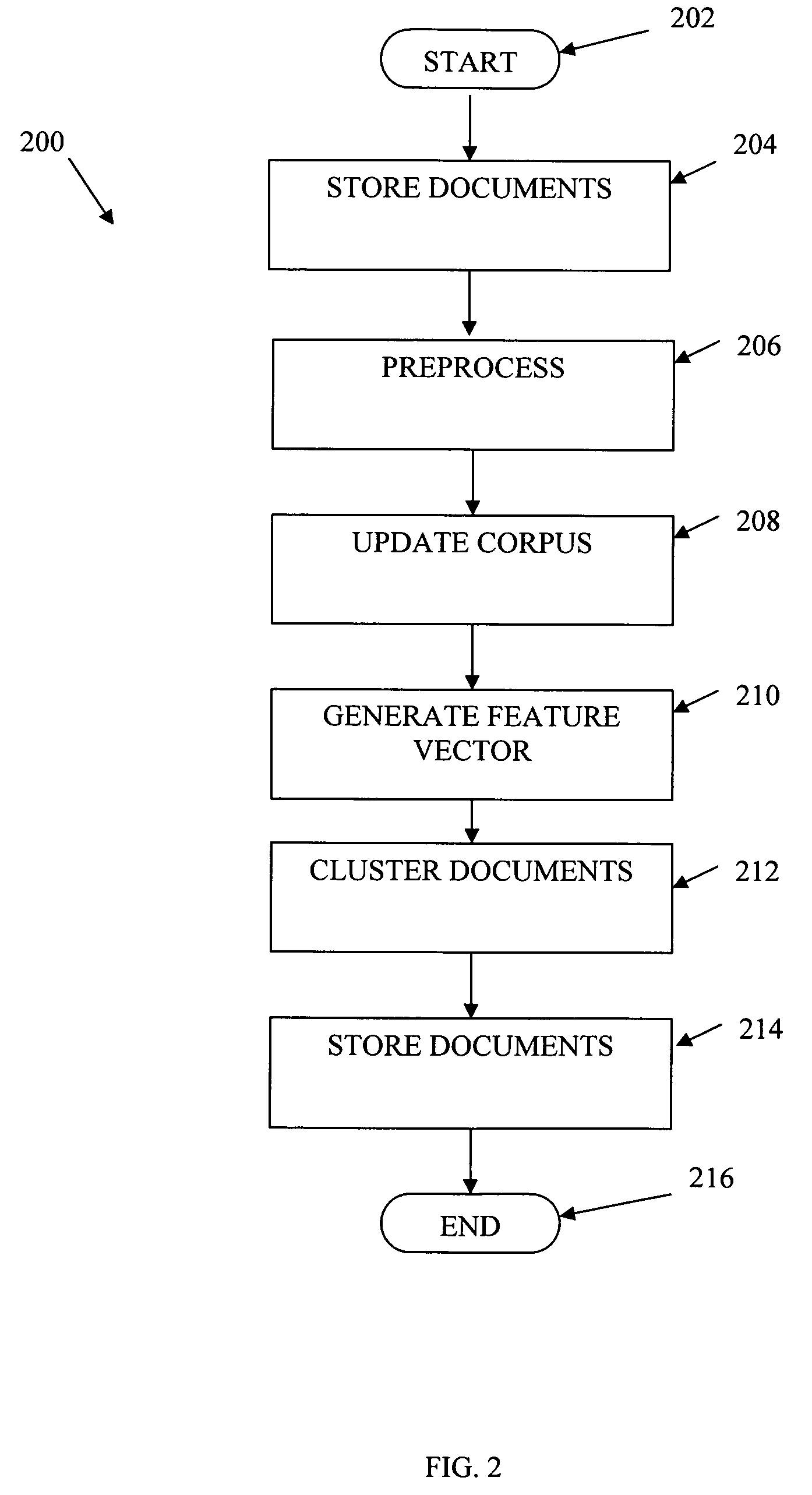
Document clustering that applies a locality sensitive hashing function to a feature vector to obtain a limited set of candidate clusters
InactiveUS7797265B2Increase speedReduce in quantityDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsFeature vectorData stream
Documents from a data stream are clustered by first generating a feature vector for each document. A set of cluster centroids (e.g., feature vectors of their corresponding clusters) are retrieved from a memory based on the feature vector of the document using a locality sensitive hashing function. The centroids may be retrieved by retrieving a set of cluster identifiers from a cluster table, the cluster identifiers each indicative of a respective cluster centroid, and retrieving the cluster centroids corresponding to the retrieved cluster identifiers from a memory. Documents may then be clustered into one or more of the candidate clusters using distance measures from the feature vector of the document to the cluster centroids.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
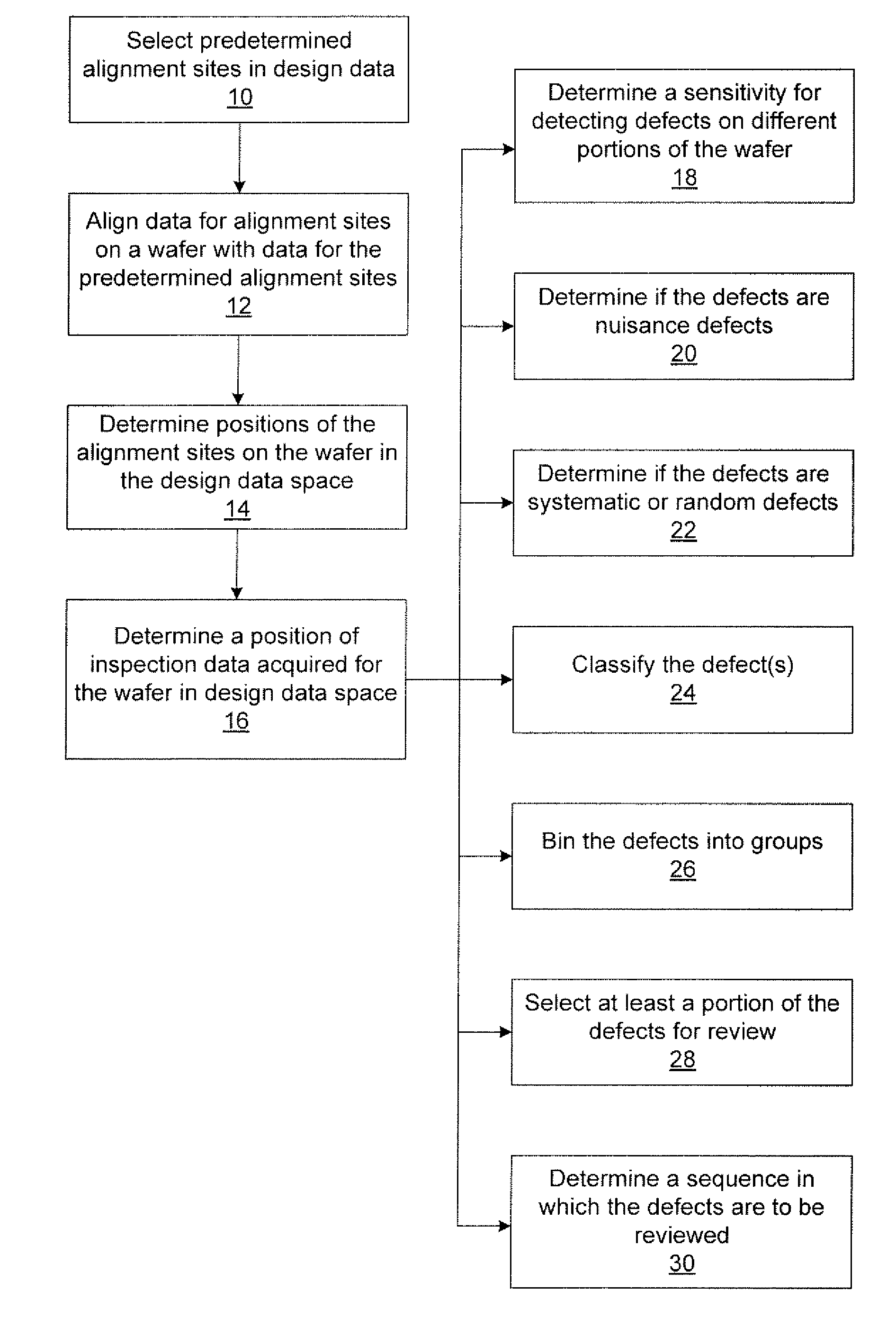
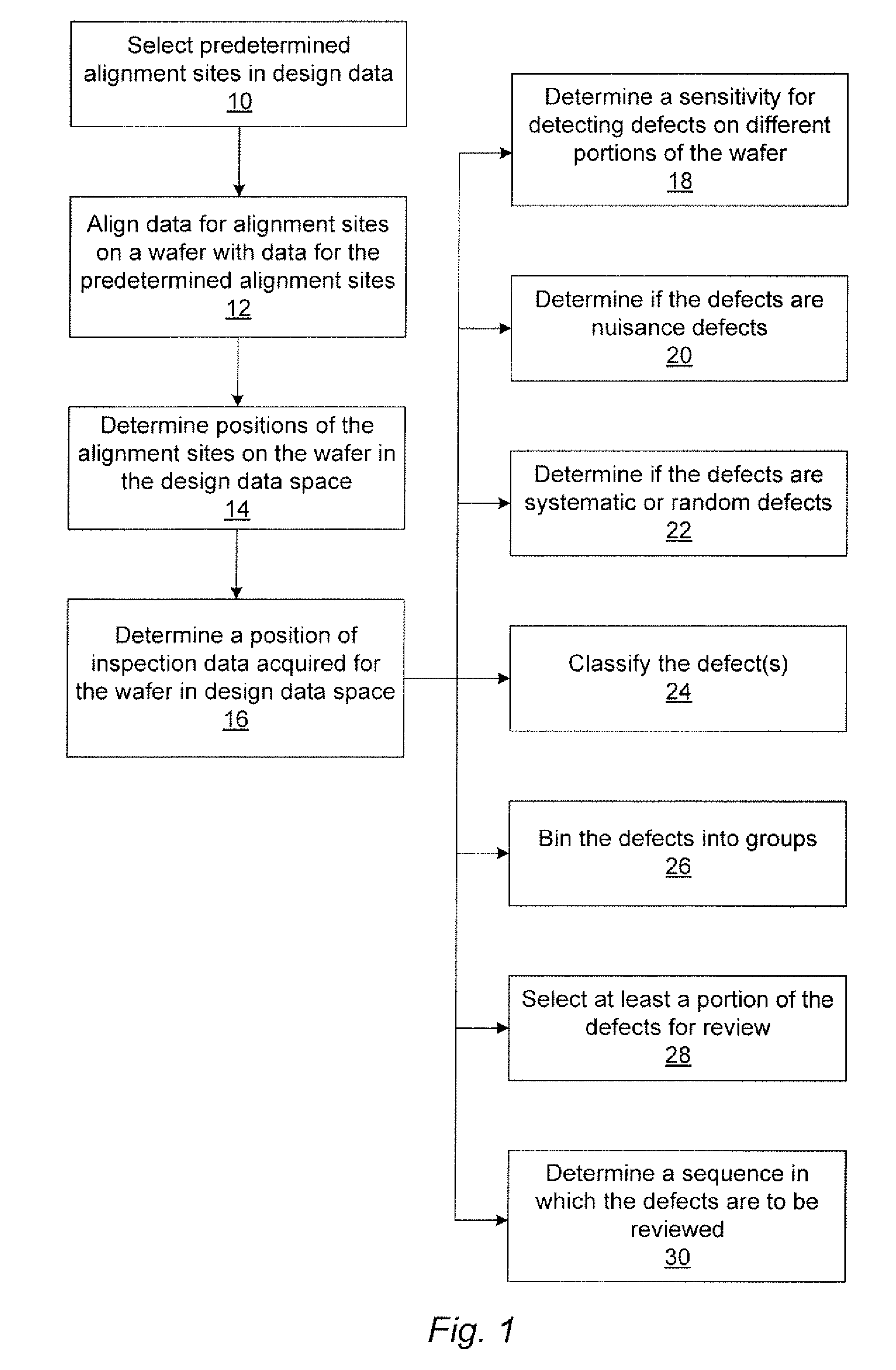
Methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space
Various methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space are provided. One computer-implemented method includes determining a centroid of an alignment target formed on a wafer using an image of the alignment target acquired by imaging the wafer. The method also includes aligning the centroid to a centroid of a geometrical shape describing the alignment target. In addition, the method includes assigning a design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target as a position of the centroid of the geometrical shape in the design data space. The method further includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer in the design data space based on the design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Arrangements of color pixels for full color OLED
InactiveUS20080001525A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesGreen-lightLight emission
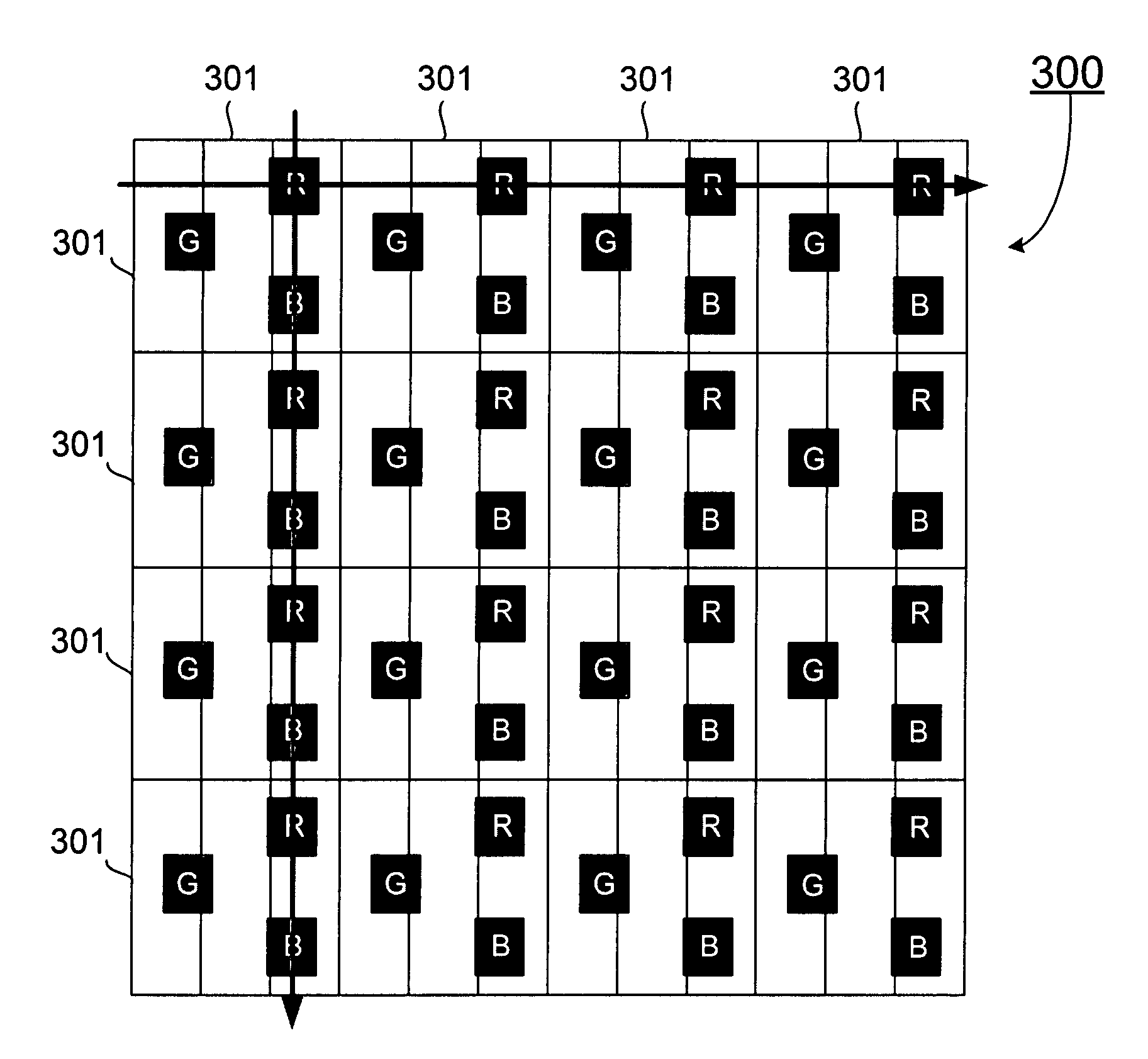
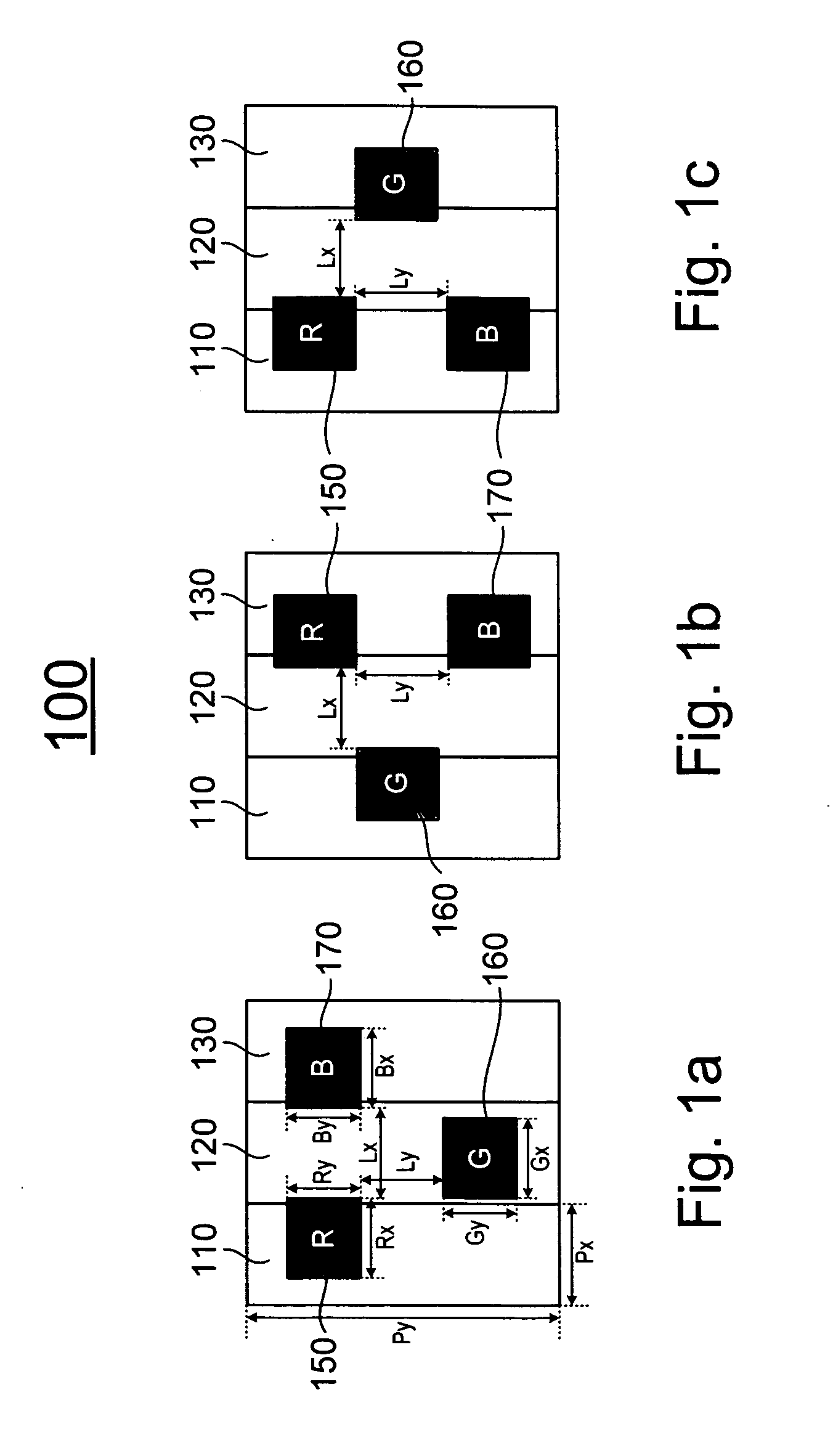
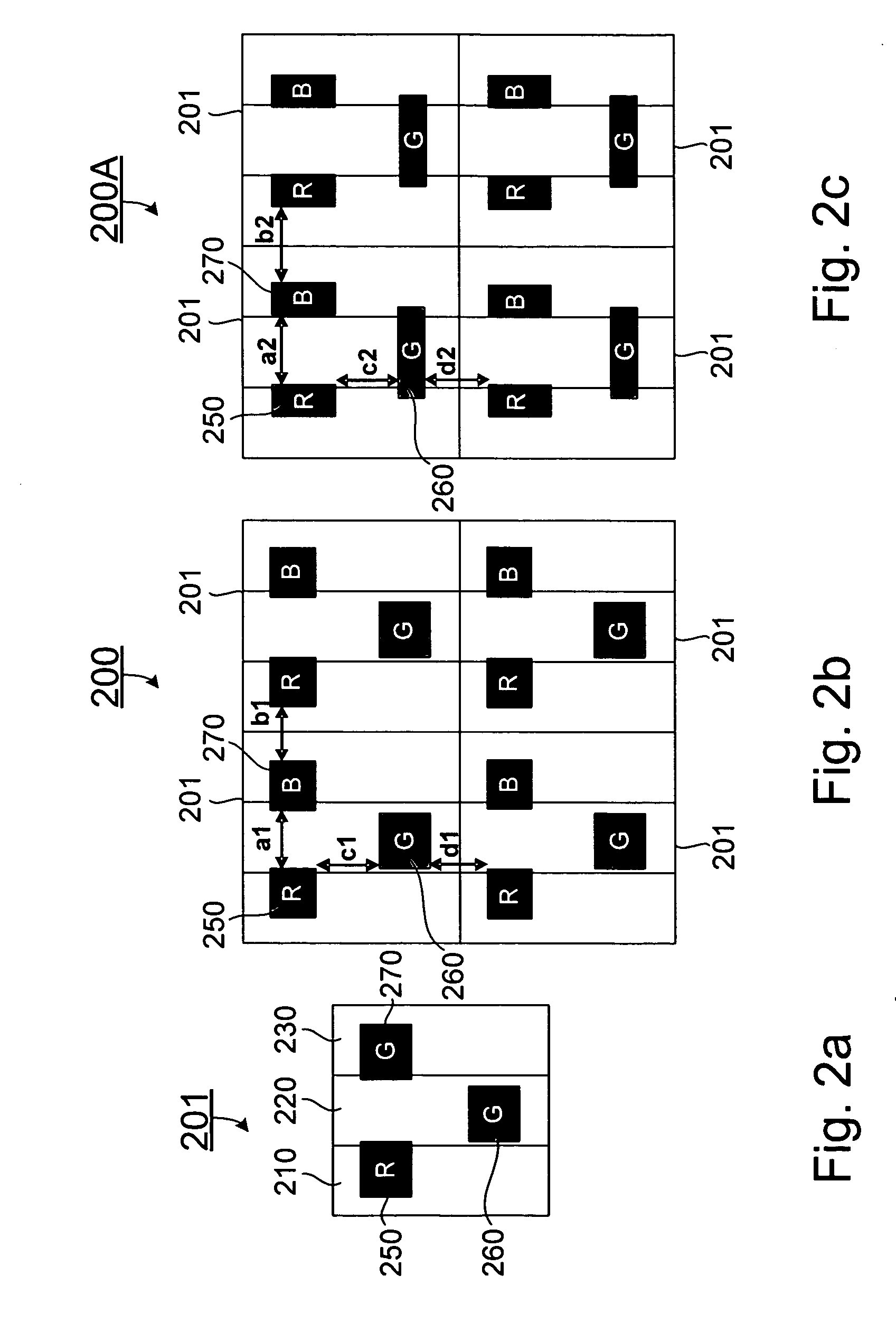
A color display panel formed with a plurality of pixels in a matrix with a row direction and a column direction, wherein each pixel comprises a first sub-pixel, a second sub-pixel and a third sub-pixel adjacently aligned along the row direction of the pixel matrix, and a red light emission zone, a green light emission zone and a blue light emission zone. In one embodiment, the color display panel comprises an arrangement of the red, green and blue light emission zones of a pixel in a triangle with the geometrical center of each emission zone located at a respective vertex of the triangle such that one side of the triangle is substantially parallel to one of the row direction and the column direction, thereby in the plurality of pixels, any two adjacent light emission zones of different colors in the row direction define a gap having a distance, and any two adjacent light emission zones of different colors in the column direction define a gap having a distance that is substantially or nearly the same as the distance of the gap defined between two adjacent light emission zones of different colors in the row direction.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
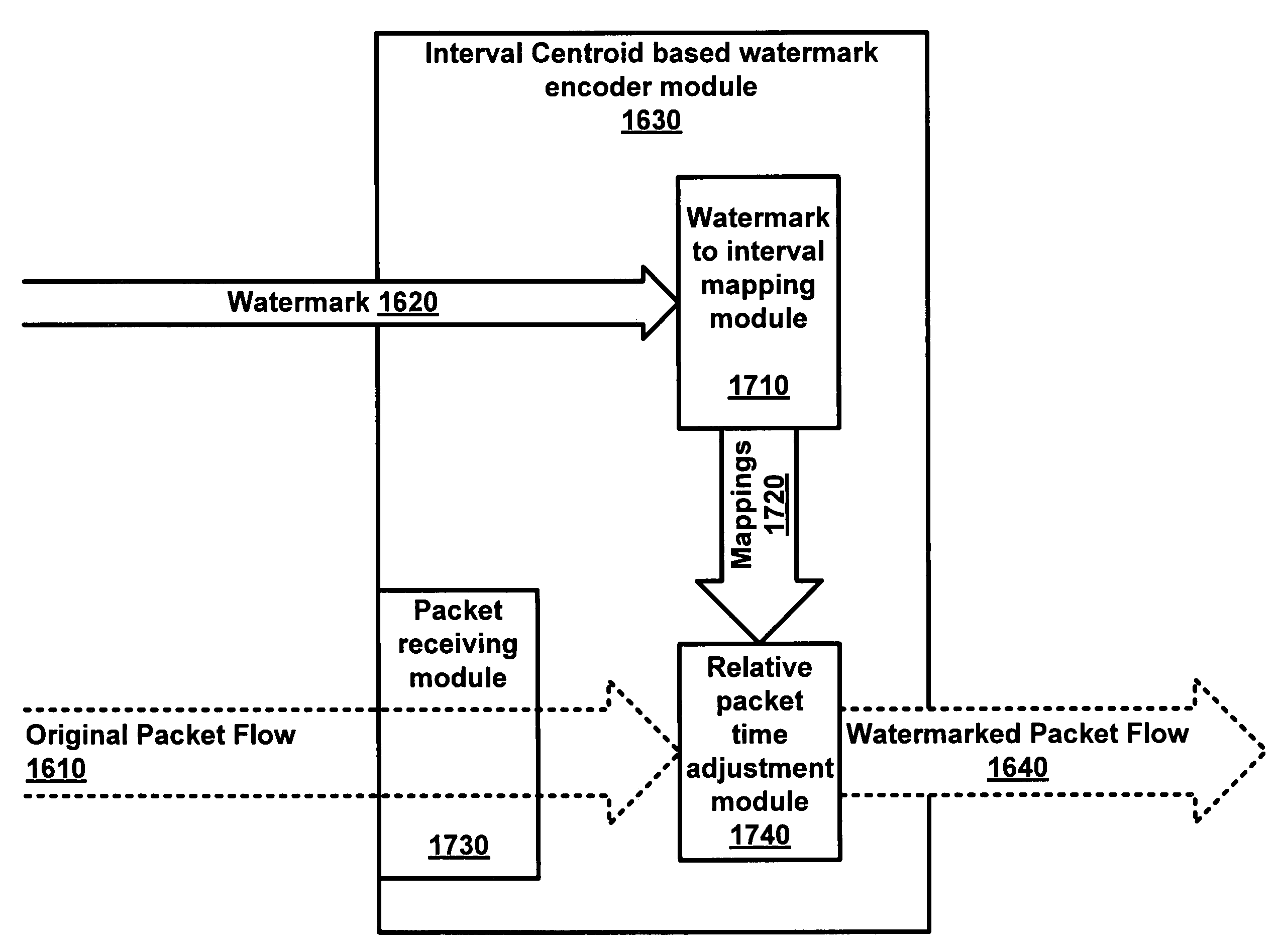
Interval centroid based watermark
An interval centroid-based watermark encoder encodes a watermark into a packet flow. Intervals are defined for the packet flow. Some of the intervals are selected as group A intervals while other intervals are selected as group B intervals. Group A and group B intervals are paired and assigned to watermark bits. A first or second value may be encoded by increasing the relative packet time between packets in either the group A (for the first bit value) or group B (for the second bit value) interval(s) of the interval pair(s) assigned to the watermark bits that are to represent the first or second bit value and the beginning of the same group interval(s). The relative packet times may be measured by a decoder and used to calculate a centroid difference for each interval pair. The centroid differences may be used to reconstruct the watermark.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
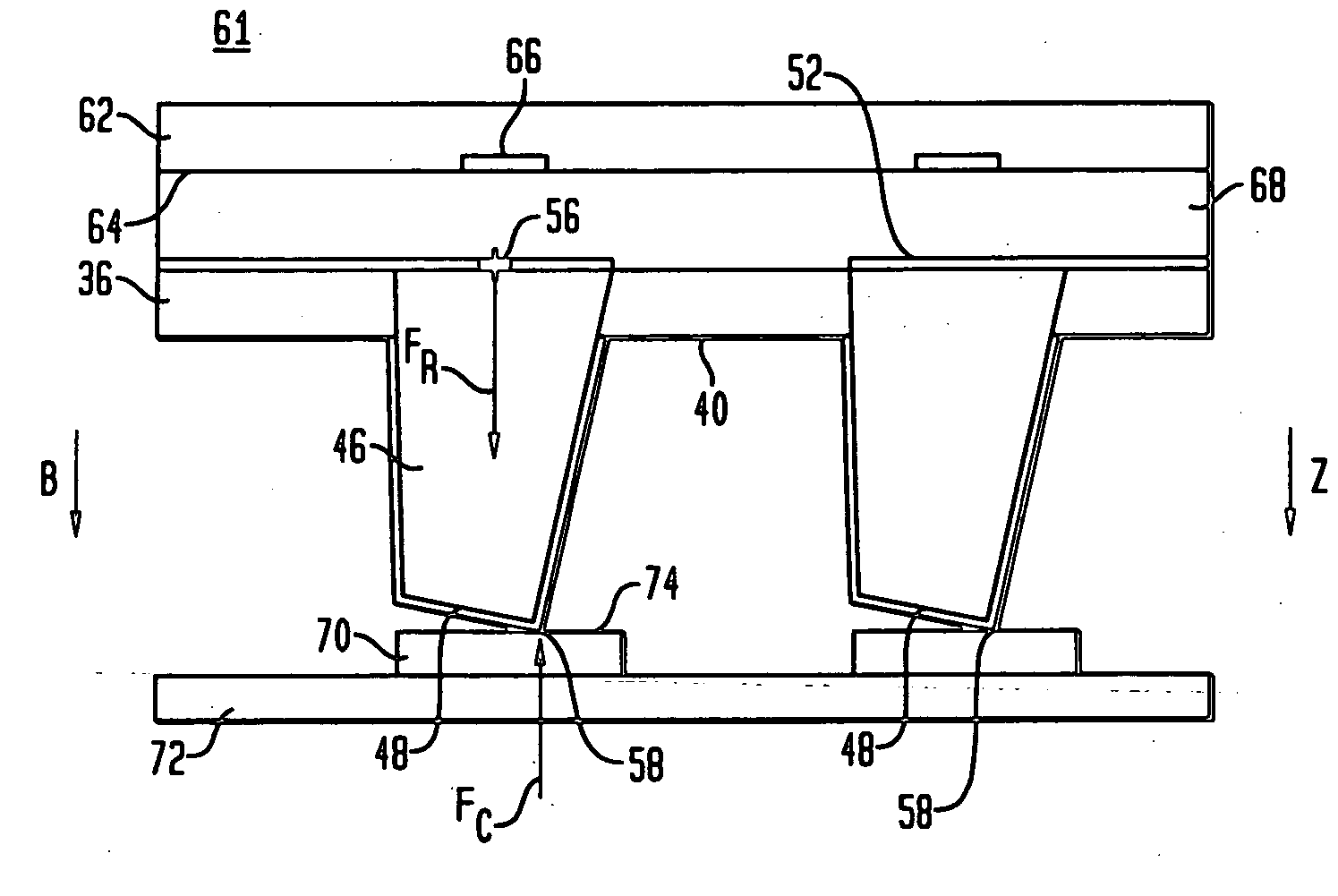
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6840109B2Simple and robust mannerSimplifies isolationVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerEngineering
To conduct a fluid, the transducer has a flow tube which in operation vibrated by an excitation assembly. Inlet-side and outlet-side vibrations of the flow tube are sensed by means of a sensor arrangement. To produce shear forces in the fluid, the flow tube is at least intermittently excited into torsional vibrations about a longitudinal flow-tube axis. An internal portion of the transducer, formed at least by the flow tube, an antivibrator, the sensor arrangement, and the excitation assembly and mounted at least on the inlet and outlet tube sections, has a centroid which is located inside the flow tube. The transducer is suitable for use in viscometers or Coriolis mass flowmeter-viscometers. In spite of using only a single straight flow tube, it is dynamically well balanced in operation, and the development of bending moments by the torsionally vibrating flow tube is largely prevented. This also effectively prevents the transducer case or the connected pipe from being excited into sympathetic vibration. Measurement signals representative of mass flow rate are readily distinguishable from measurement signals representative of viscosity, particularly if the sensors used for the viscosity measurement are also used for the mass flow measurement.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Device, image processing device and method for optical imaging
ActiveUS20110228142A1Short focal lengthShorten build lengthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging processingGrating
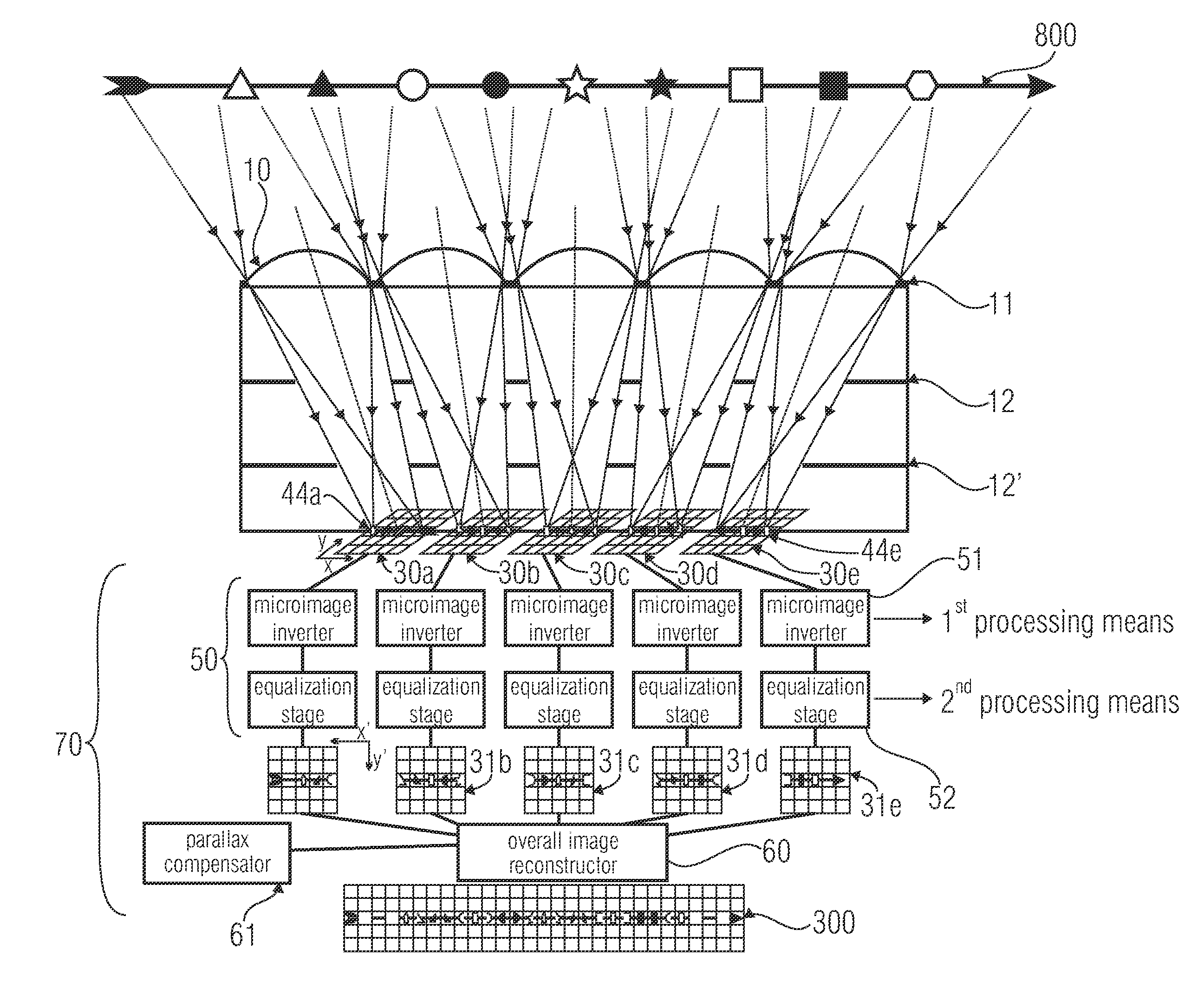
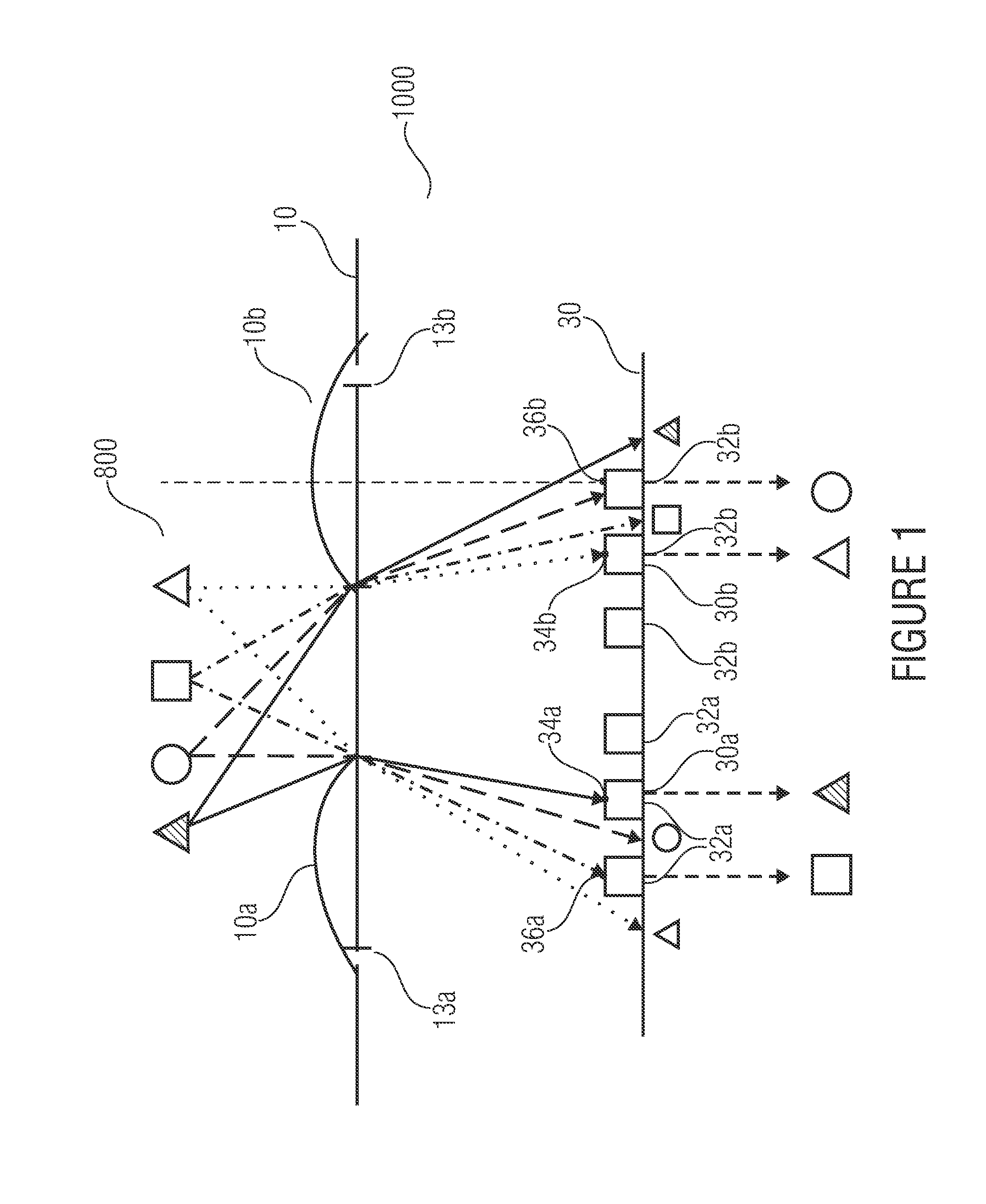
An optical device for imaging is disclosed having at least one micro lens field with at least two micro lenses and one image sensor with at least two image detector matrices. The at least two image detector matrices each include a plurality of image detectors and there is an allocation between the image detector matrices and the micro lenses, so that each micro lens together with an image detector matrix forms an optical channel. The center points of the image detector matrices are shifted laterally by different distances, with respect to centroids, projected onto the image detector matrices, of the micro lens apertures of the associated optical channels, so that the optical channels have different partially overlapping detection areas and so that an overlapping area of the detection areas of two channels is imaged onto the image detector matrices offset with respect to an image detector raster of the image detector matrices. Further, an image processing device and a method for optical imaging are described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
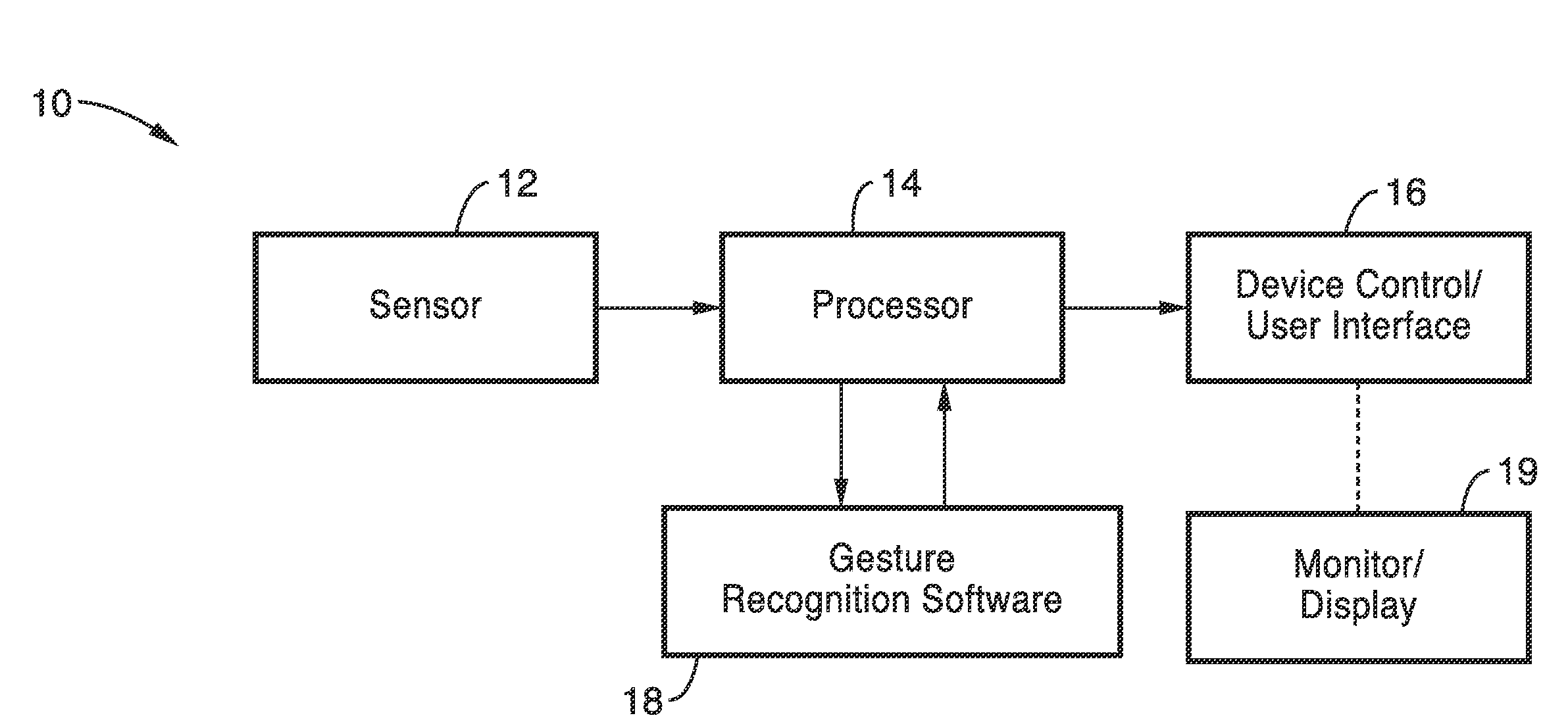
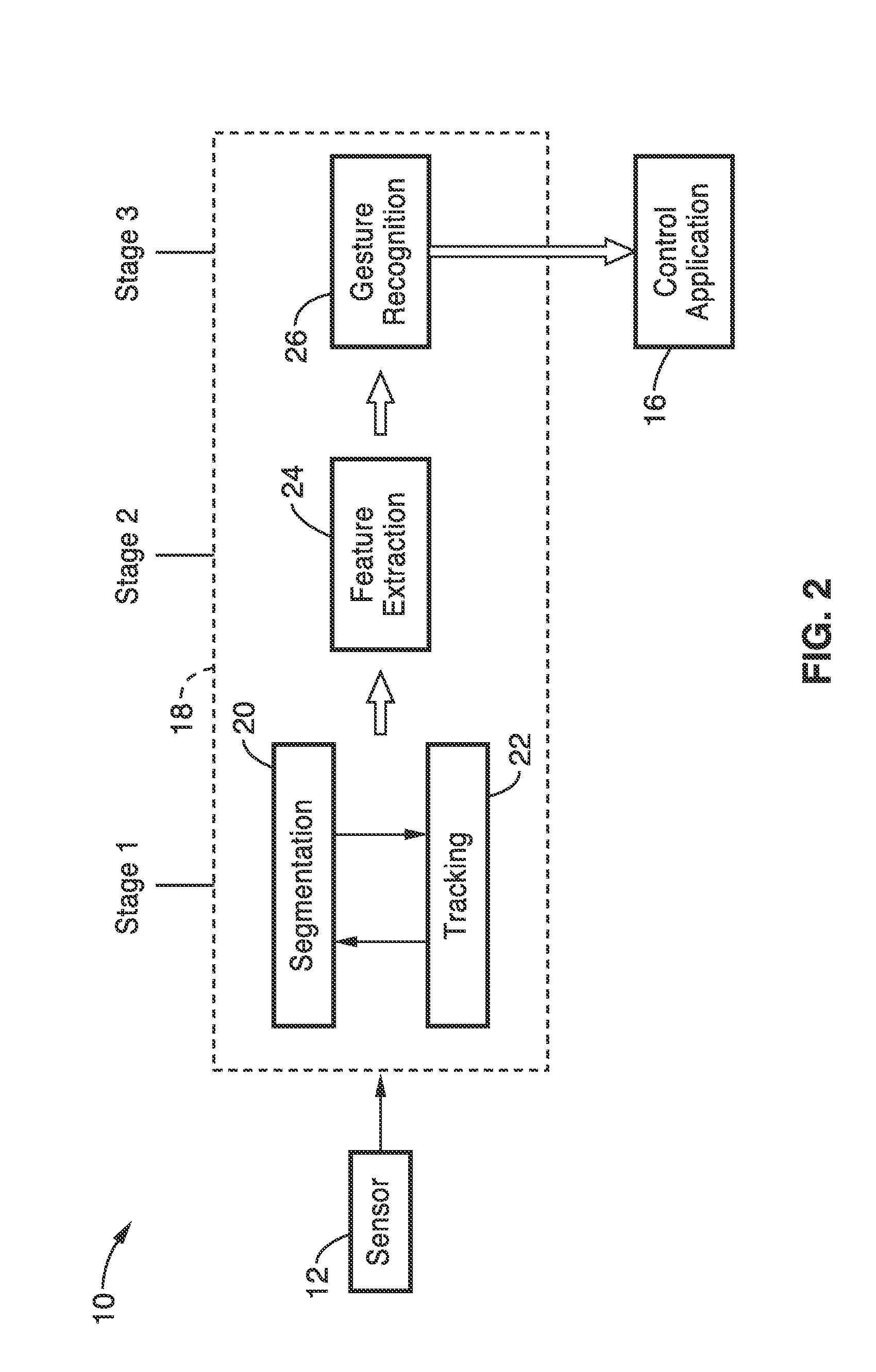
Gesture recognition system for TV control
ActiveUS20120069168A1Reduce computational complexityEasy to useImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionKaiman filter
A gesture recognition system using a skin-color based method combined with motion information to achieve real-time segmentation. A Kalman filter is used to track the centroid of the hand. The palm center, palm bottom, as well as the largest distance from the palm center to the contour from extracted hand mask are computed. The computed distance to a threshold is then compared to decide if the current posture is “open” or “closed.” In a preferred embodiment, the transition between the “open” and “closed” posture to decide if the current gesture is in “select” or “grab” state.
Owner:SONY CORP
Micro pin grid array with wiping action
ActiveUS20050181655A1Promote formationIncrease in sizeEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact padPin grid array
A microelectronic package includes a mounting structure, a microelectronic element associated with the mounting structure, and a plurality of conductive posts physically connected to the mounting structure and electrically connected to the microelectronic element. The conductive posts project from the mounting structure in an upward direction, at least one of the conductive posts being an offset post. Each offset post has a base connected to the mounting structure, the base of each offset post defining a centroid. Each offset post also defines an upper extremity having a centroid, the centroid of the upper extremity being offset from the centroid of the base in a horizontal offset direction transverse to the upward direction. The mounting structure is adapted to permit tilting of each offset post about a horizontal axis so that the upper extremities may wipe across a contact pad of an opposing circuit board.
Owner:TESSERA INC
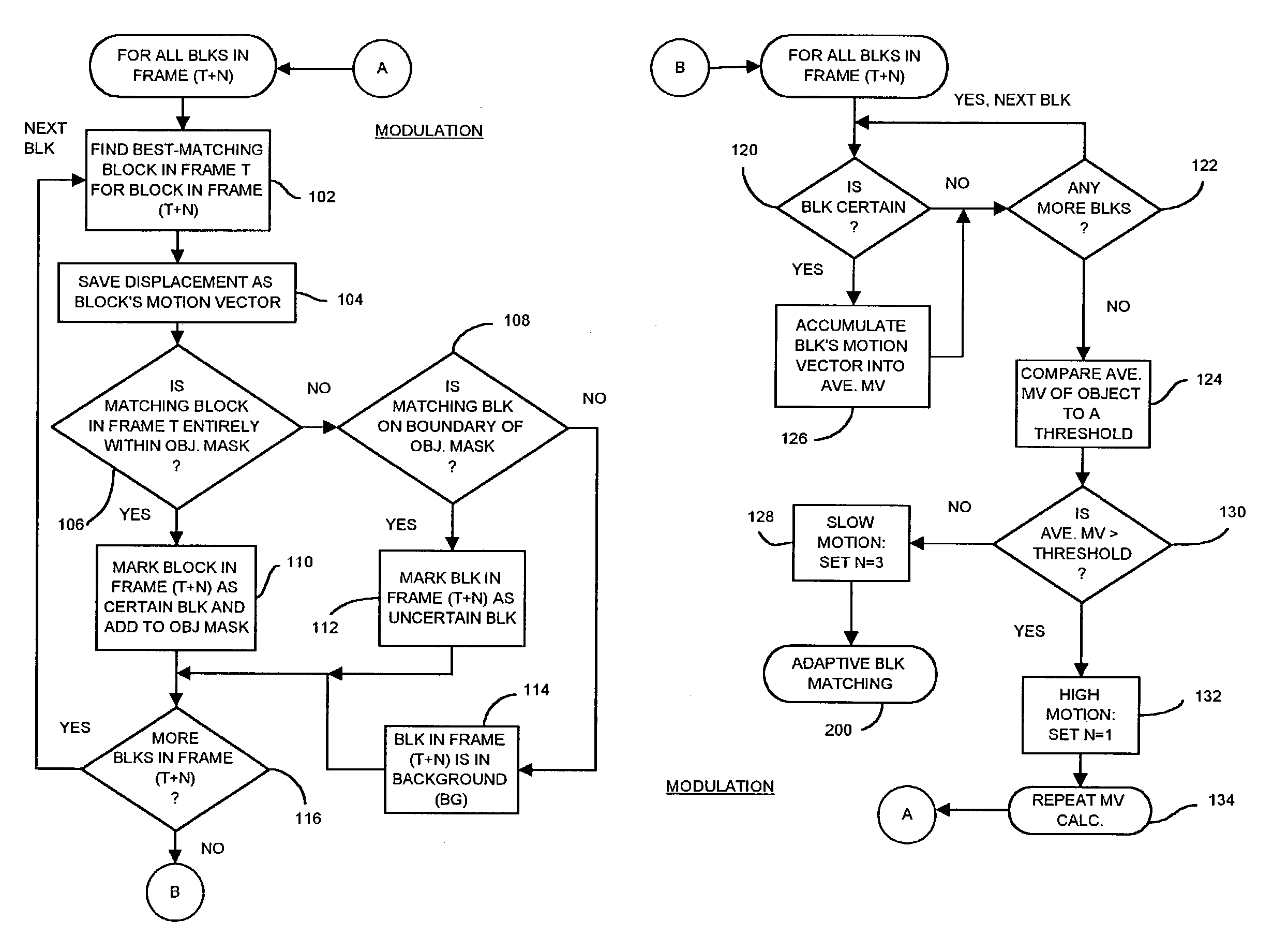
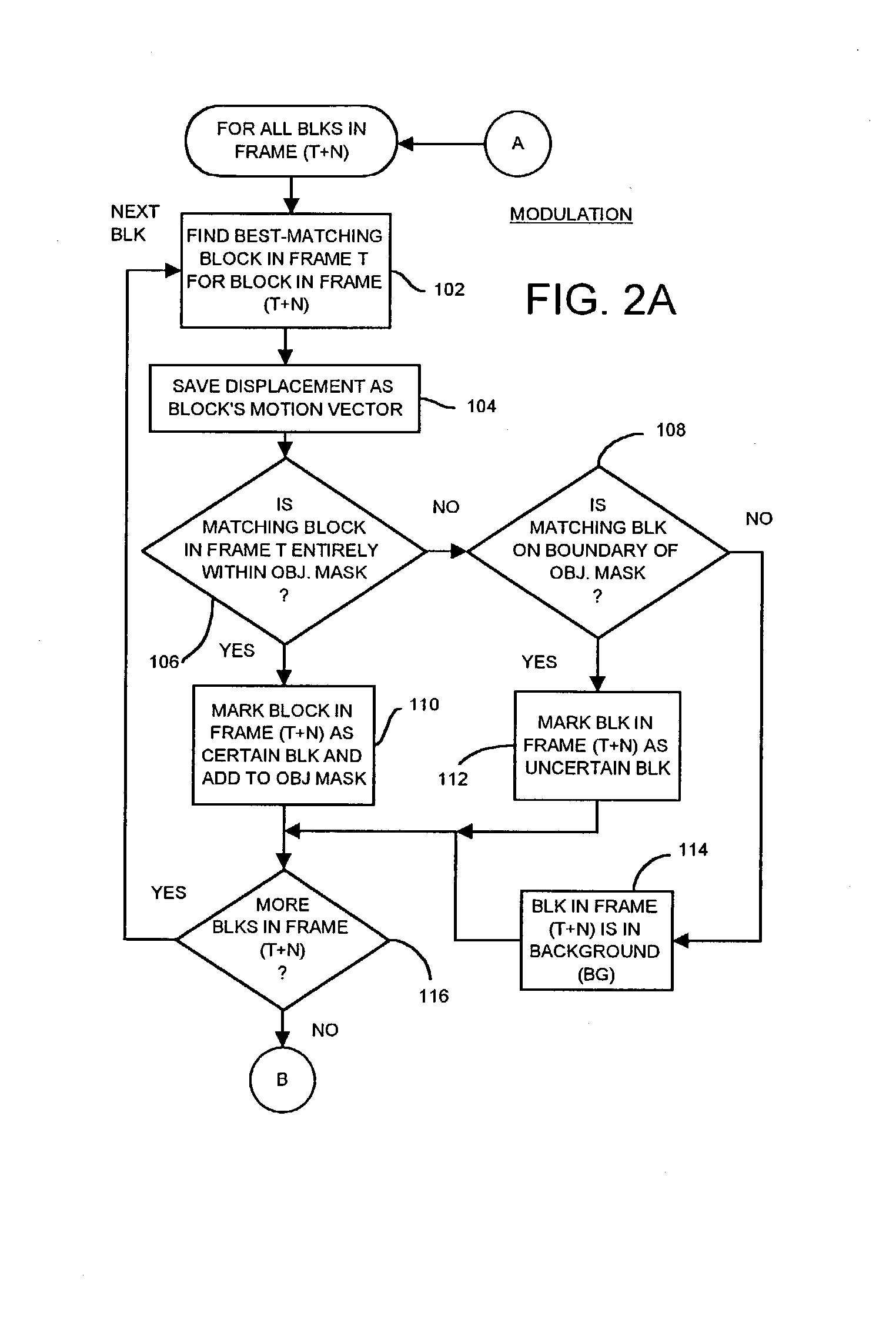
Occlusion/disocclusion detection using K-means clustering near object boundary with comparison of average motion of clusters to object and background motions
ActiveUS7142600B1Reduce varianceAccurate representationColor television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorVideo sequence
An object in a video sequence is tracked by object masks generated for frames in the sequence. Macroblocks are motion compensated to predict the new object mask. Large differences between the next frame and the current frame detect suspect regions that may be obscured in the next frame. The motion vectors in the object are clustered using a K-means algorithm. The cluster centroid motion vectors are compared to an average motion vector of each suspect region. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is considered part of the object and removed from the object mask as an occlusion. Large differences between the prior frame and the current frame detect suspected newly-uncovered regions. The average motion vector of each suspect region is compared to cluster centroid motion vectors. When the motion differences are small, the suspect region is added to the object mask as a disocclusion.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
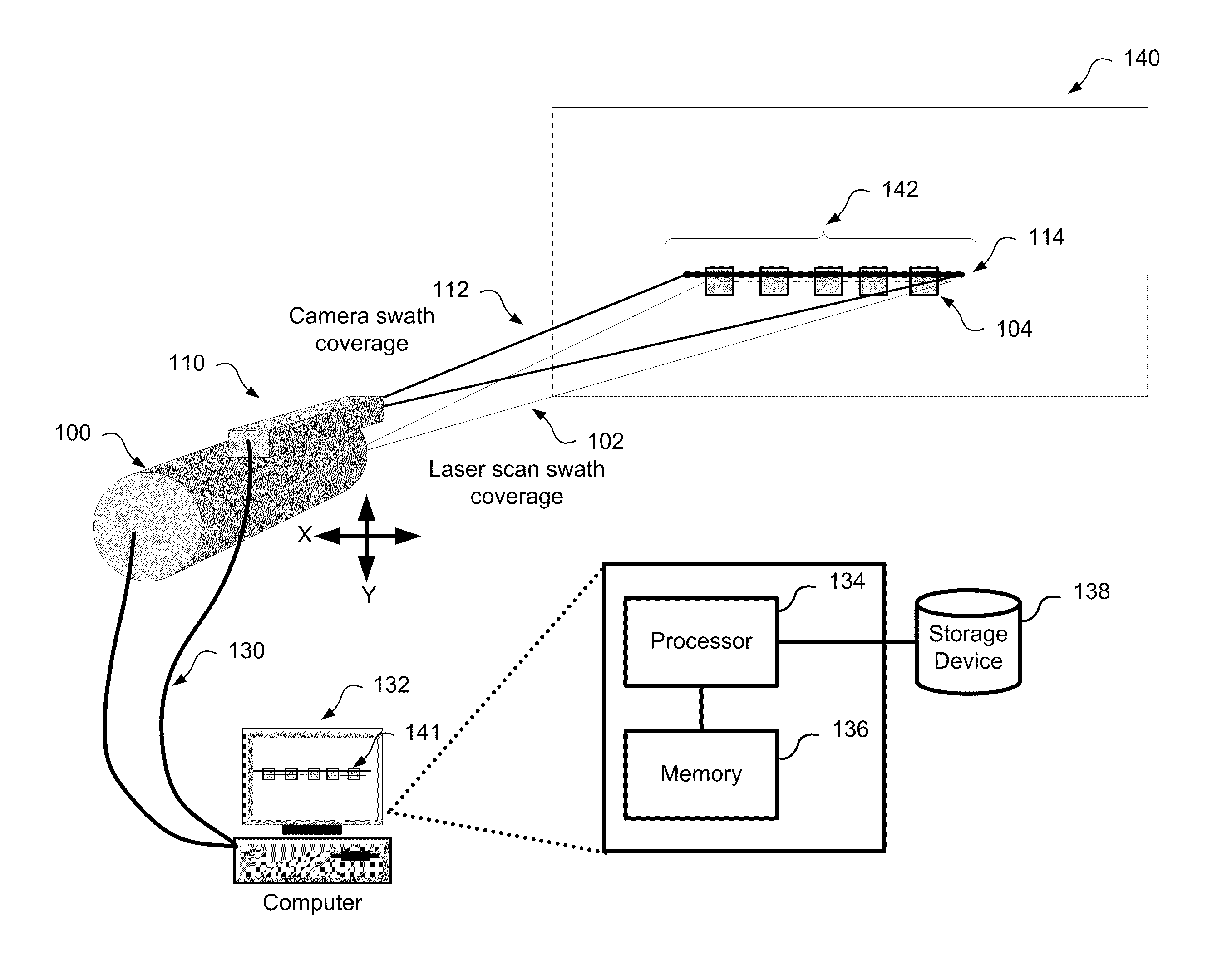
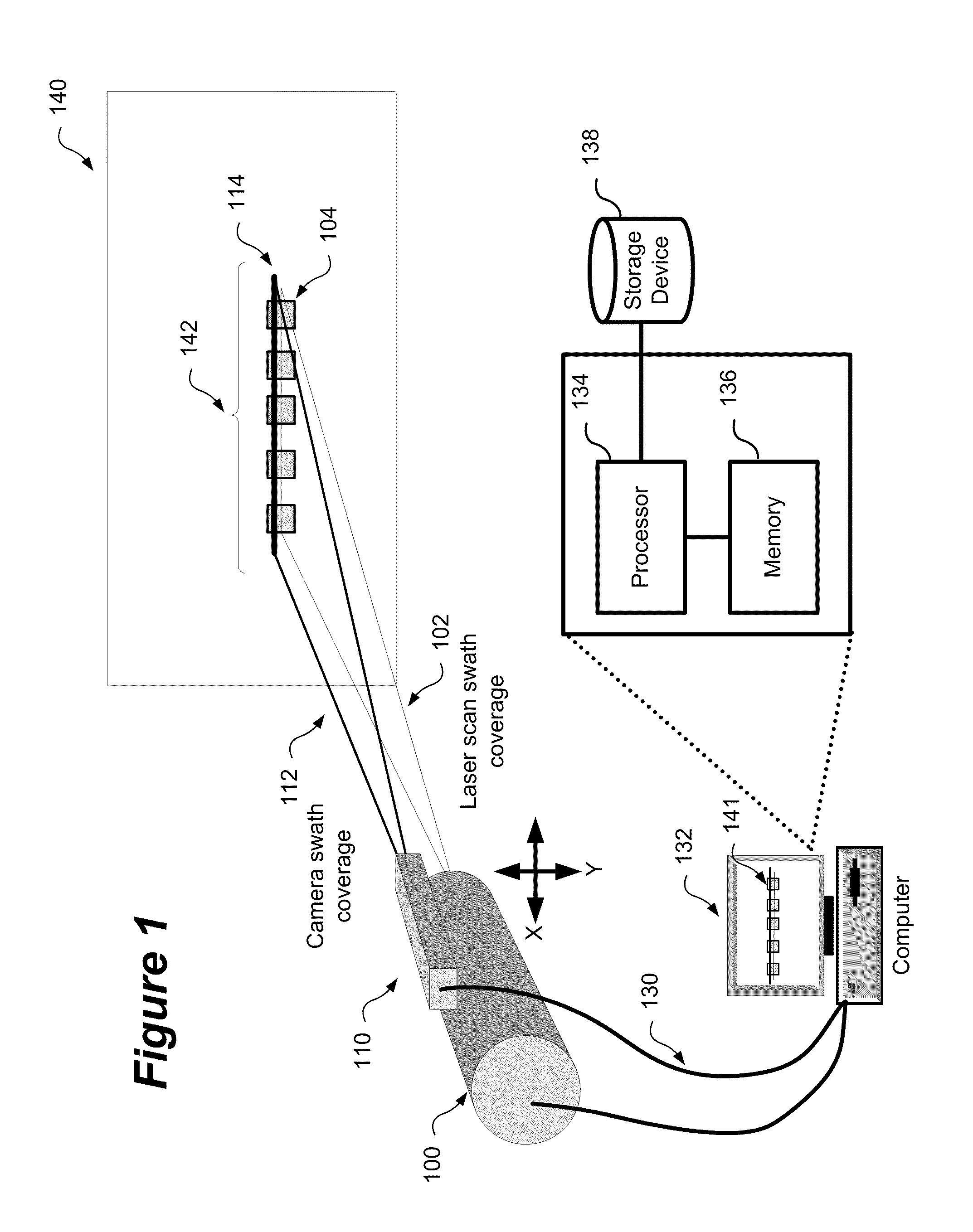
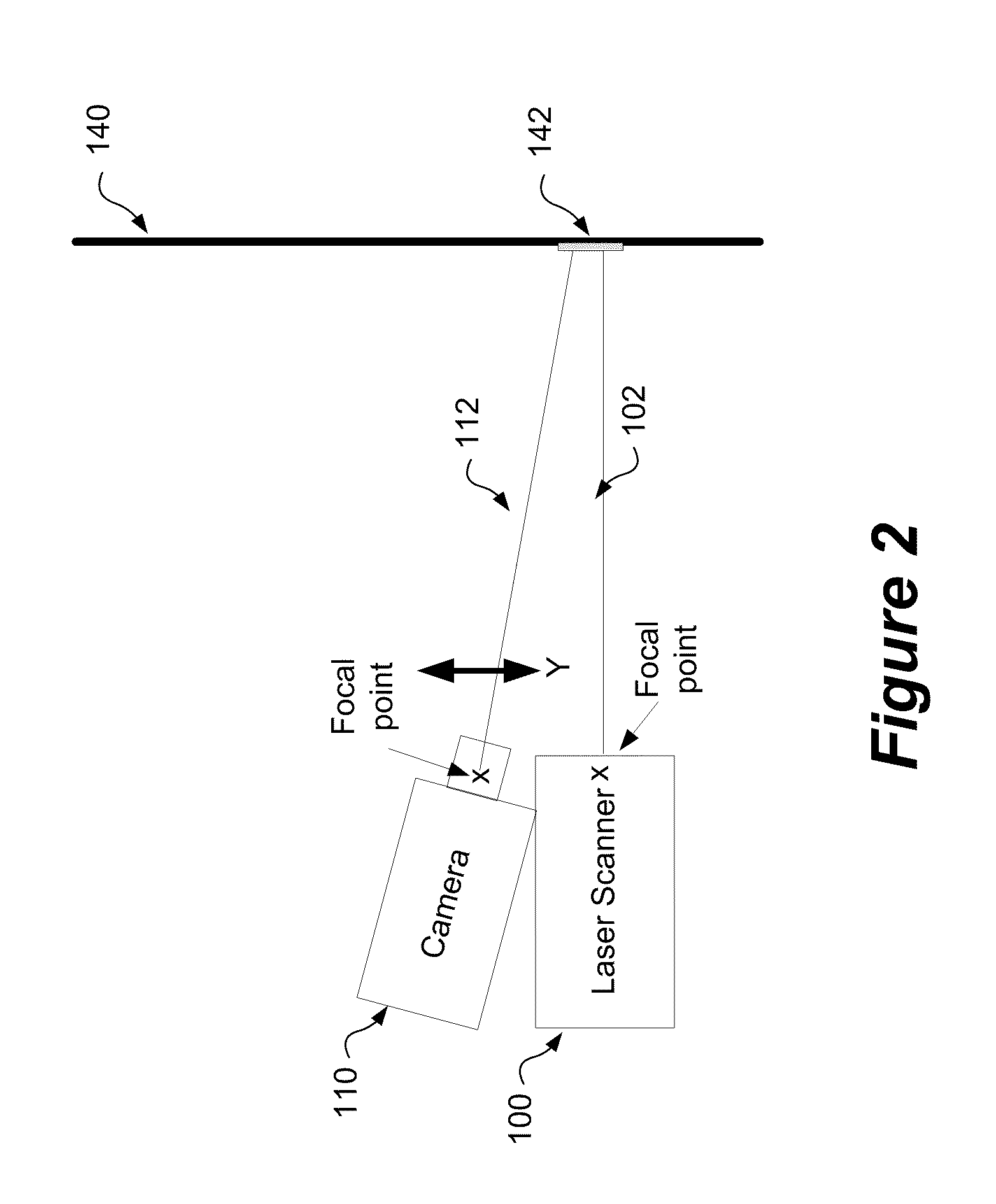
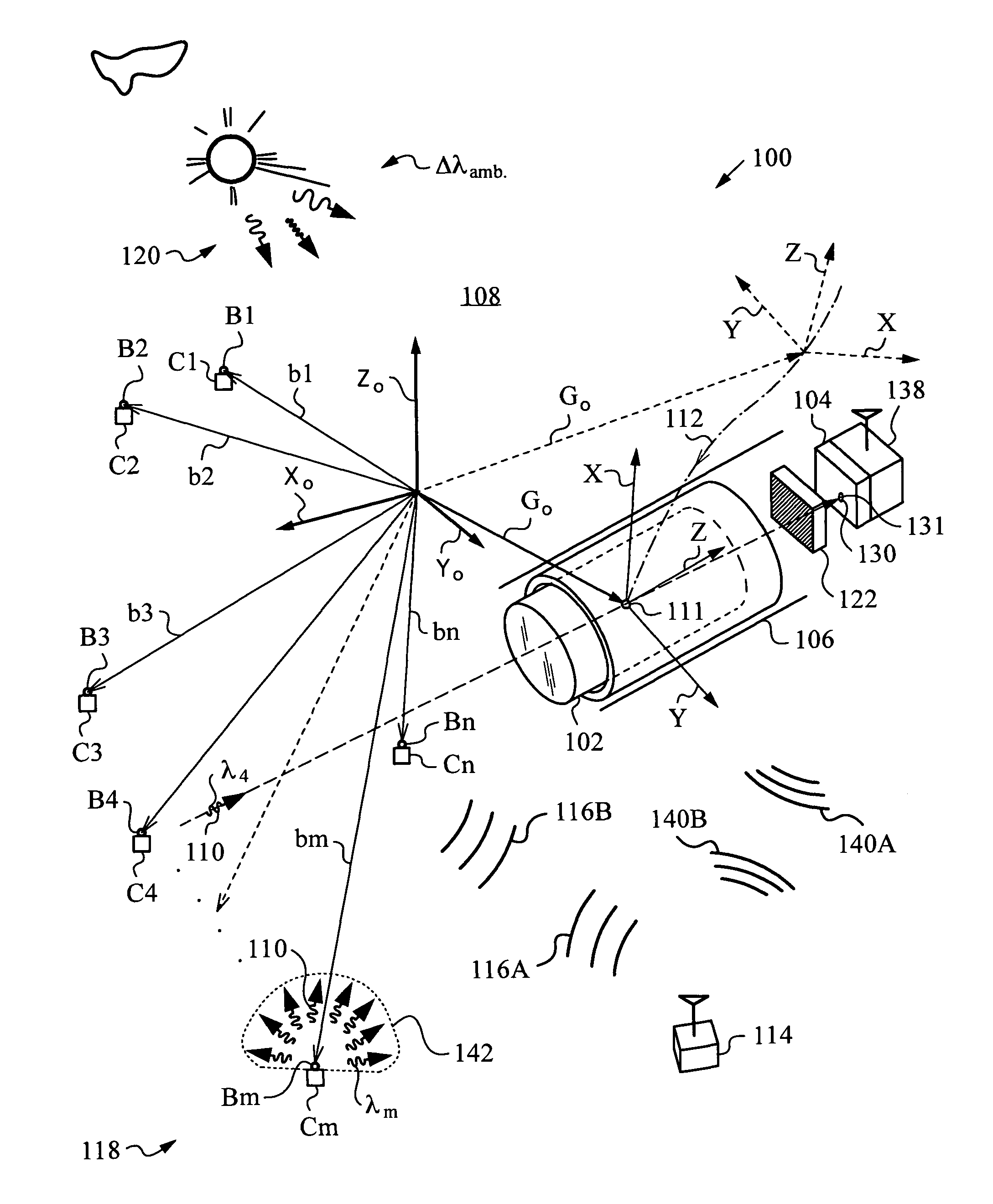
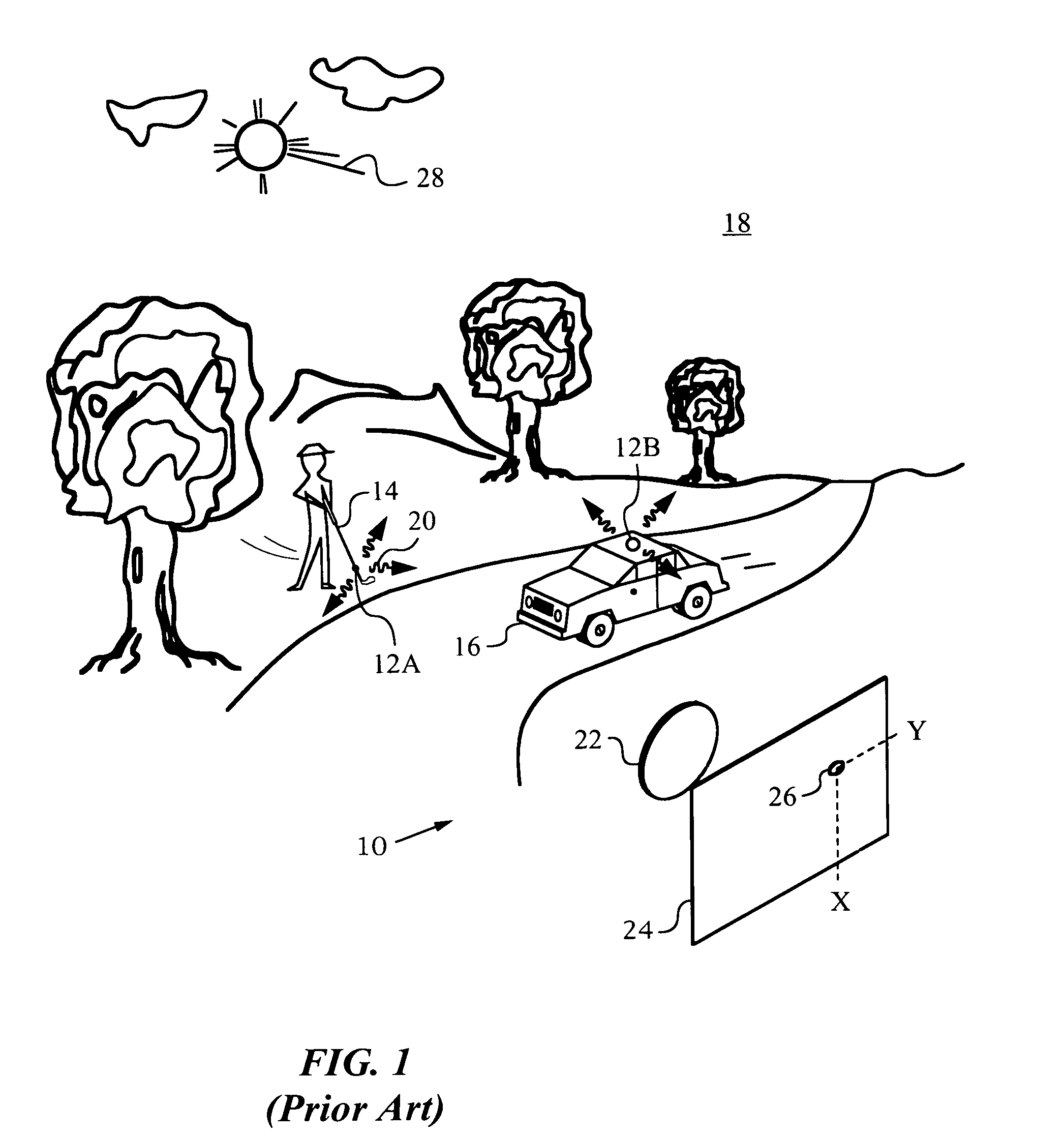
Method and system for aligning a line scan camera with a lidar scanner for real time data fusion in three dimensions
An apparatus and method for aligning a line scan camera with a Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) scanner for real-time data fusion in three dimensions is provided. Imaging data is captured at a computer processor simultaneously from the line scan camera and the laser scanner from target object providing scanning targets defined in an imaging plane perpendicular to focal axes of the line scan camera and the LiDAR scanner. X-axis and Y-axis pixel locations of a centroid of each of the targets from captured imaging data is extracted. LiDAR return intensity versus scan angle is determined and scan angle locations of intensity peaks which correspond to individual targets is determined. Two axis parallax correction parameters are determined by applying a least squares. The correction parameters are provided to post processing software to correct for alignment differences between the imaging camera and LiDAR scanner for real-time colorization for acquired LiDAR data.
Owner:AMBERCORE SOFTWARE
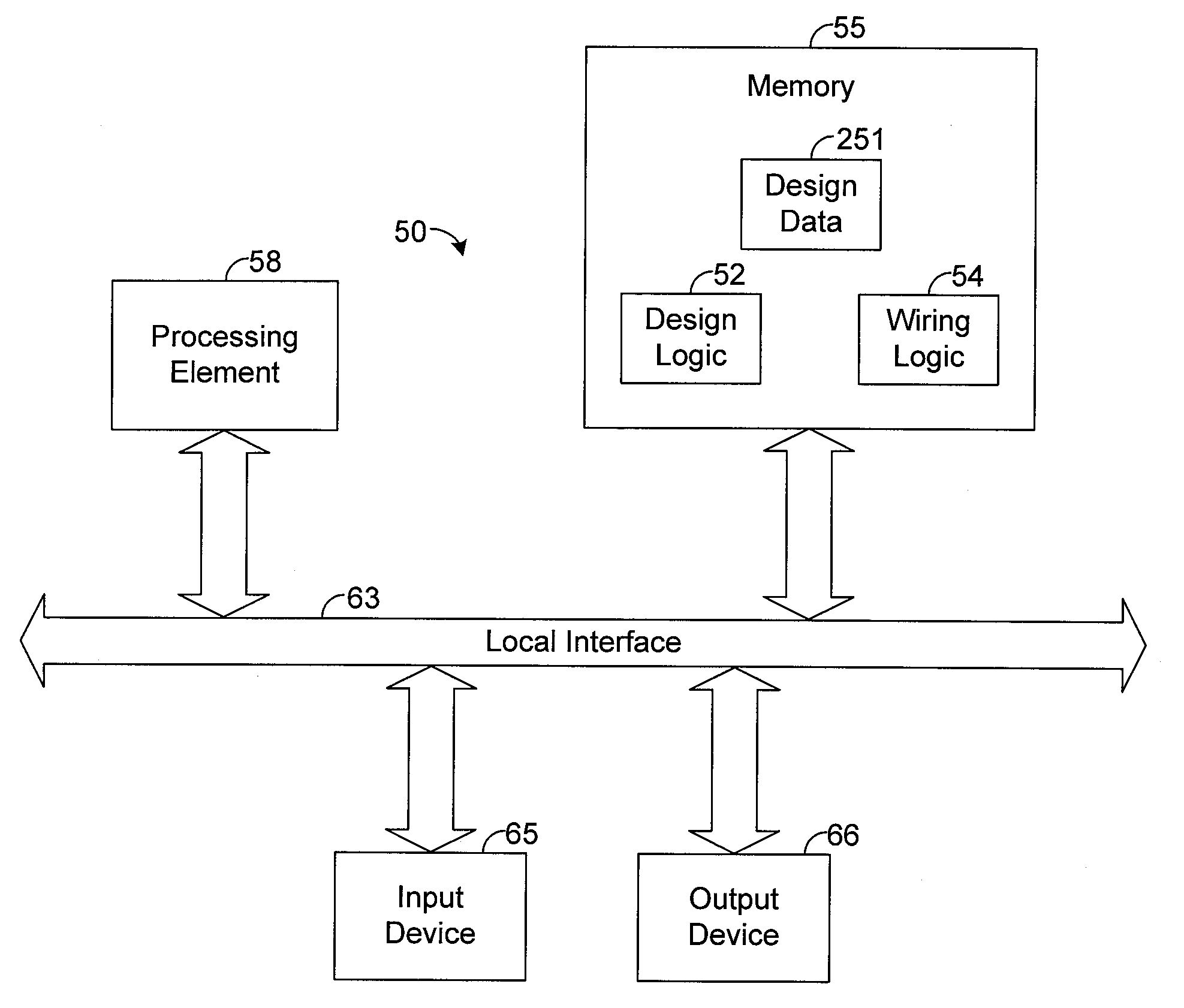
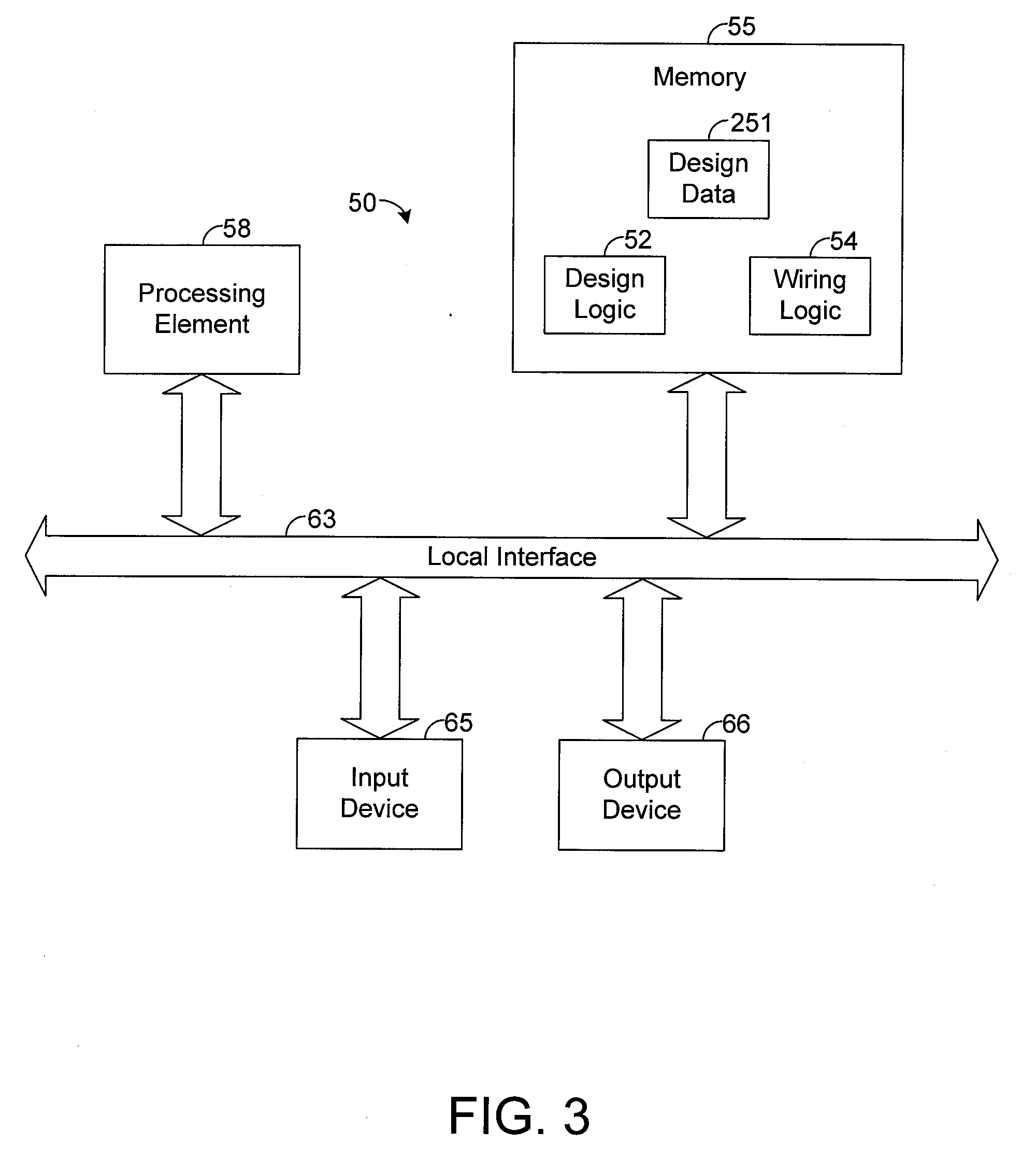
System and method for designing a common centroid layout for an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20070294652A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designEngineeringLinearity
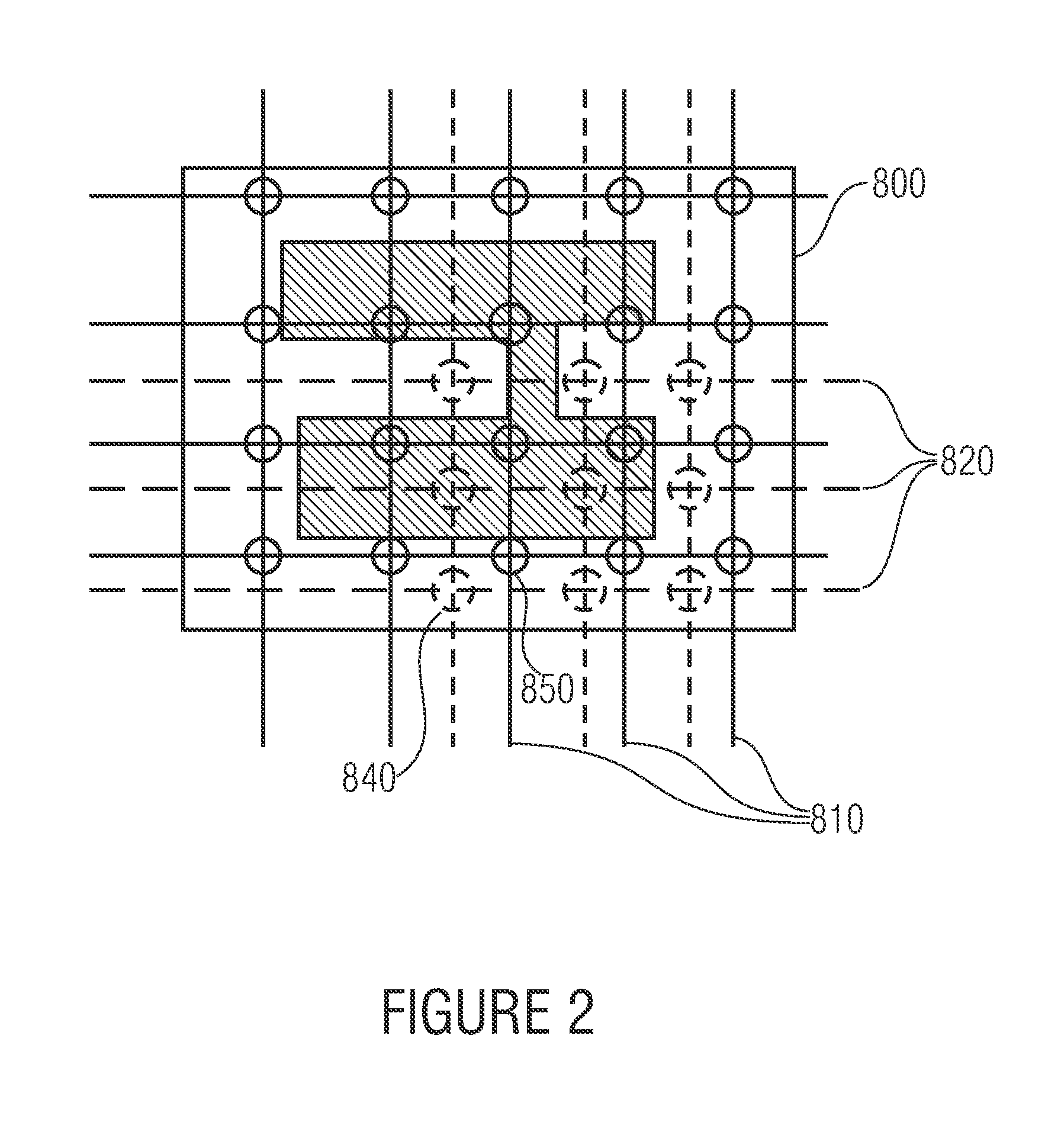
An exemplary common centroid layout design system receives various inputs about an integrated circuit (IC) design. Based on such inputs, the system calculates a common centroid unit, which represents an array of segments of each device in the IC design. The number of segments for each device within the common centroid unit is selected based on the respective sizes of the devices. The common centroid unit is then tiled to automatically define the complete layout for the IC object. The system selects an algorithm for tiling the common centroid unit based on the size of such unit such that, upon completion of the tiling process, all of the devices have a common centroid. In other words, the system selects an algorithm for tiling such that a common centroid layout design is generated. Using the common centroid layout design, the IC object can be manufactured so that it is immune to linear process gradients and more resistant to non-linear gradients relative to ICs that do not have a common centroid layout design.
Owner:ADTRAN
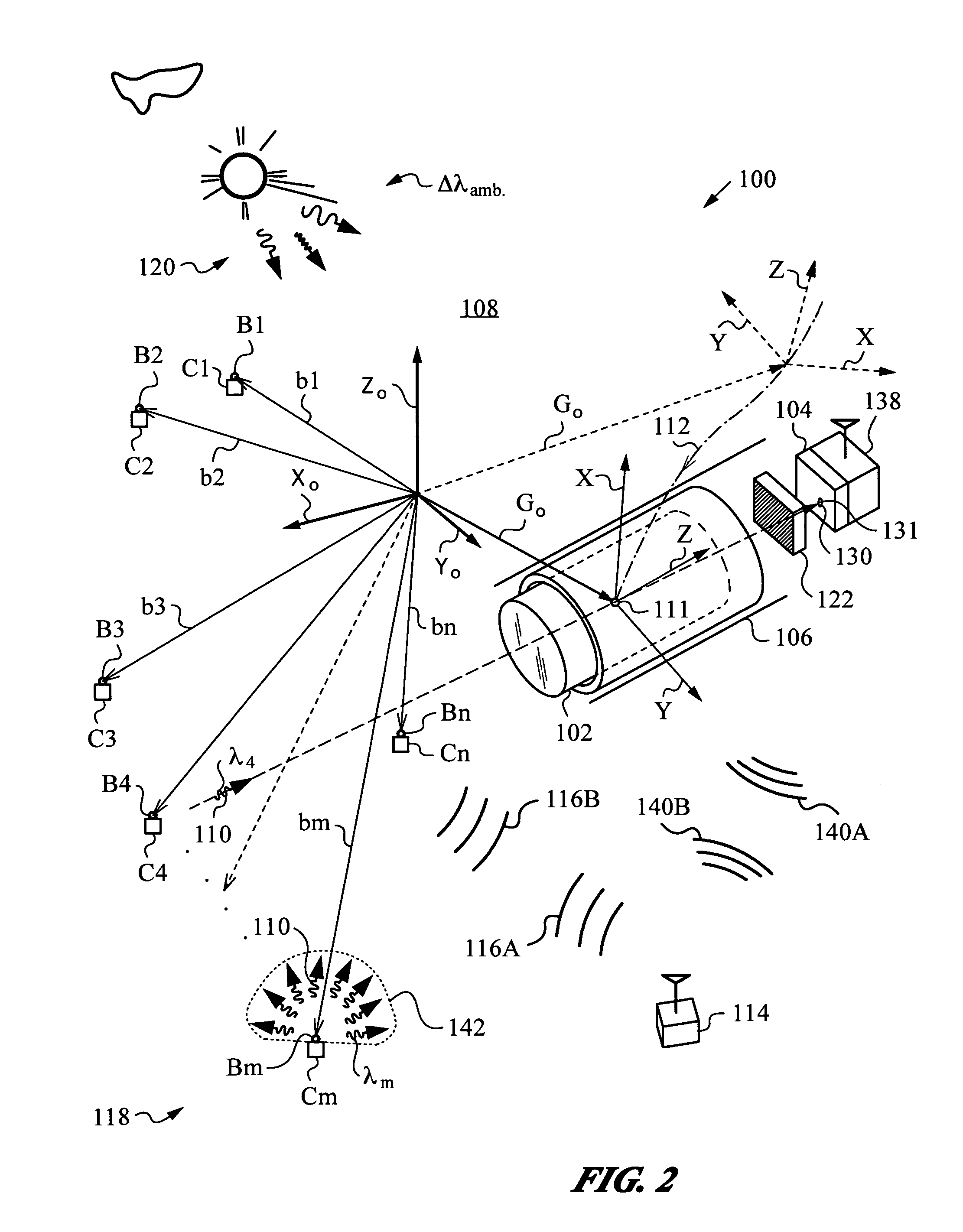
Optical navigation apparatus using fixed beacons and a centroid sensing device
The present invention relates to an optical navigation system for determining a pose, which includes the position and orientation of an object in an environment. The optical navigation system uses a number of beacons affixed at known locations in the environment to provide electromagnetic radiation in a sequenced pattern. An on-board optic images the radiation from the beacons onto an on-board centroid sensing device to obtain an imaged distribution of the radiation on the on-board centroid sensing device. The centroid sensing device determines the centroid of the imaged distribution and provides centroid information to a navigation unit for determining the pose of the object from the centroid. The navigation system is particularly well-suited for navigating hand-held objects.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
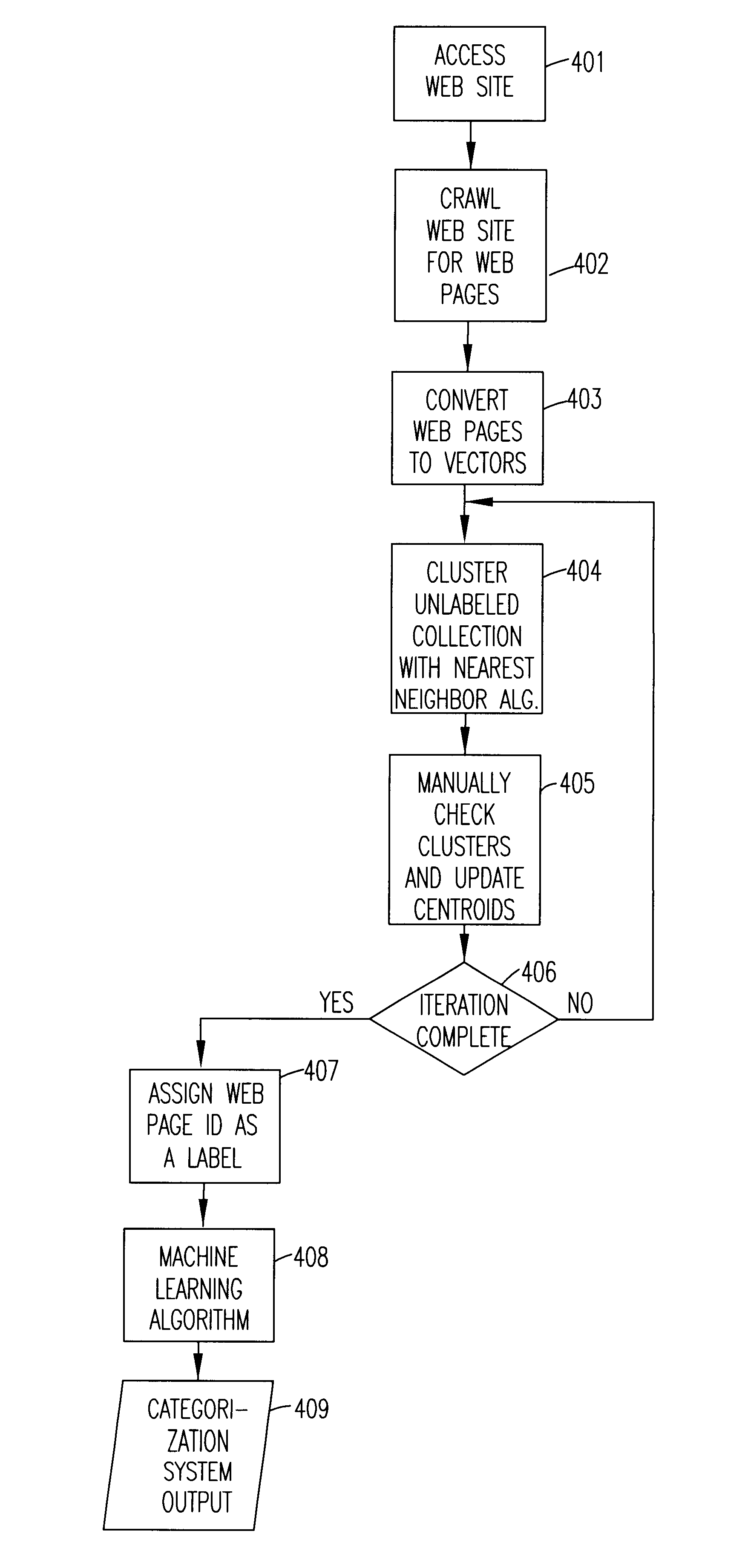
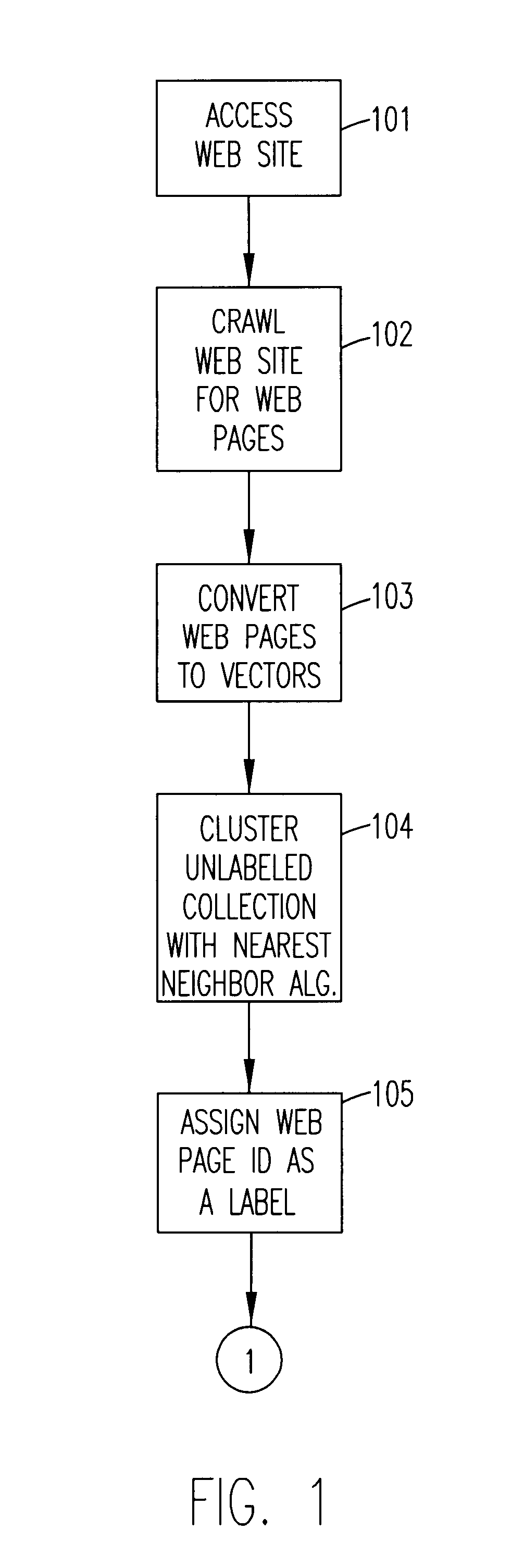
Automatic labeling of unlabeled text data
InactiveUS6697998B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsNearest neighbour algorithmNear neighbor
A method of automatically labeling of unlabeled text data can be practiced independent of human intervention, but that does not preclude manual intervention. The method can be used to extract relevant features of unlabeled text data for a keyword search. The method of automated labeling of unlabeled text data uses a document collection as a reference answer set. Members of the answer set are converted to vectors representing centroids of unknown groups of unlabeled text data. Unlabeled text data are clustered relative to the centroids by a nearest neighbor algorithm and the ID of the relevant answer is assigned to all documents in the cluster. At this point in the process, a supervised machine learning algorithm is trained on labeled data, and a classifier for assigning labels to new text data is output. Alternatively, a feature extraction algorithm may be run on classes generated by the step of clustering, and search features output which index the unlabeled text data.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Miniature resonating marker assembly
InactiveUS7135978B2Loop antennas with ferromagnetic corePulse automatic controlEngineeringSignal element
A miniature resonating marker assembly that includes, in one embodiment, a ferromagnetic core, a wire coil disposed around the core, and a capacitor connected to the wire coil adjacent to the magnetic core. The core, coil, and capacitor form a signal element that, when energized, generates a magnetic field at a selected resonant frequency. The magnetic field has a magnetic center point positioned along at least one axis of the signal element. An inert encapsulation member encapsulates the signal element therein and defines a geometric shape of the resonating marker assembly. The geometric shape has a geometric center point substantially coincident with the magnetic center point along at least a first axis of the signal element. The shape and configuration of the assembly also provides for a miniature signal element specifically tuned to resonate at a selected frequency with a high quality factor.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for classifying known specimens and media using spectral properties and identifying unknown specimens and media
ActiveUS8429153B2Quick searchRapid isolationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsElectrical devicesDevice specimen
Method and apparatus for determining a metric for use in predicting properties of an unknown specimen belonging to a group of reference specimen electrical devices comprises application of a network analyzer for collecting impedance spectra for the reference specimens and determining centroids and thresholds for the group of reference specimens so that an unknown specimen may be confidently classified as a member of the reference group using the metric. If a trait is stored with the reference group of electrical device specimens, then, the trait may be predictably associated with the unknown specimen along with any traits identified with the unknown specimen associated with the reference group.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Arbitrary object tracking augmented reality applications
ActiveUS7050078B2Accurate trackingInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsVideo image
Video images of objects in a real-world environment are taken from the perspective of a viewer. The user's field of view may be captured in the video images that are processed to select a segment of the video image or an object depicted in the video image. An image such as a computer-generated annotation or graphic overlay way be registered to the segment, and therefore track the segment from the user's field of view of the segment, without prior knowledge of the spatial relationship of the segment to the real-world environment according to a centroid for an interframe difference of the video image associated with the selected object. The image may be displayed in the user's field of view or in the video image. The computer-generated image tracks the movement of the segment with respect to the video image.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Method and apparatus for classifying known specimens and media using spectral properties and identifying unknown specimens and media
ActiveUS20130054603A1Quick searchRapid isolationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsElectrical devicesDevice specimen
Method and apparatus for determining a metric for use in predicting properties of an unknown specimen belonging to a group of reference specimen electrical devices comprises application of a network analyzer for collecting impedance spectra for the reference specimens and determining centroids and thresholds for the group of reference specimens so that an unknown specimen may be confidently classified as a member of the reference group using the metric. If a trait is stored with the reference group of electrical device specimens, then, the trait may be predictably associated with the unknown specimen along with any traits identified with the unknown specimen associated with the reference group.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
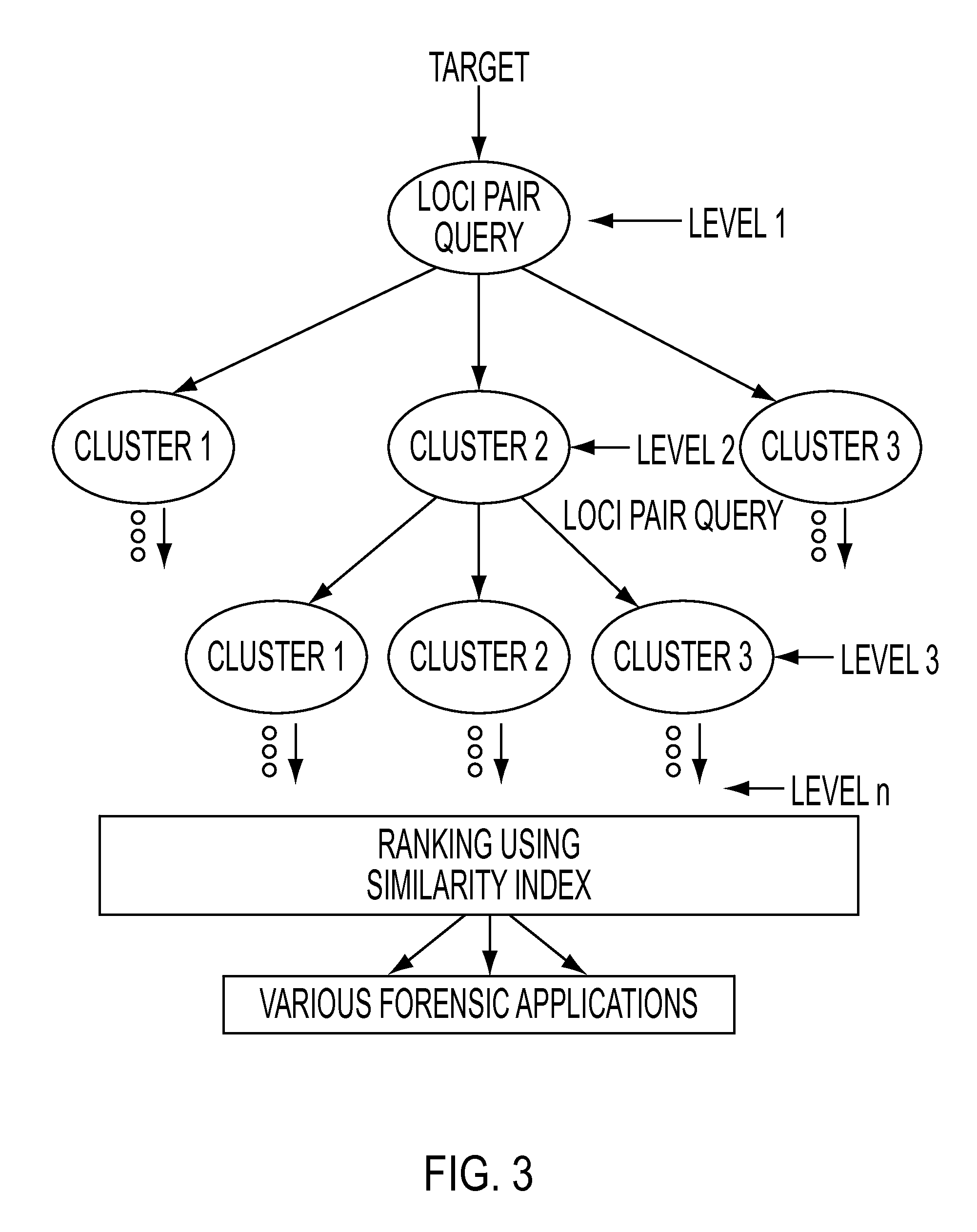
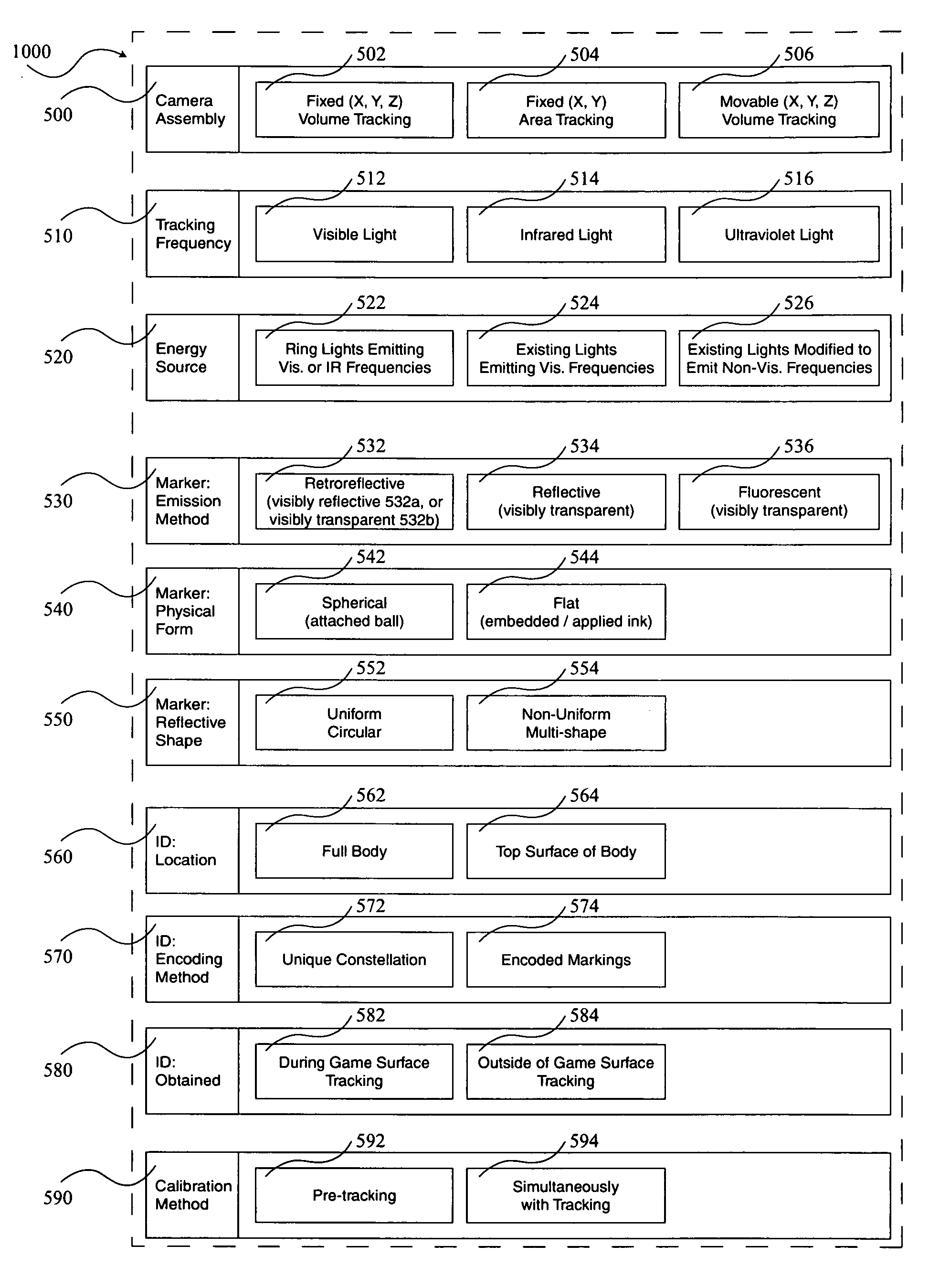
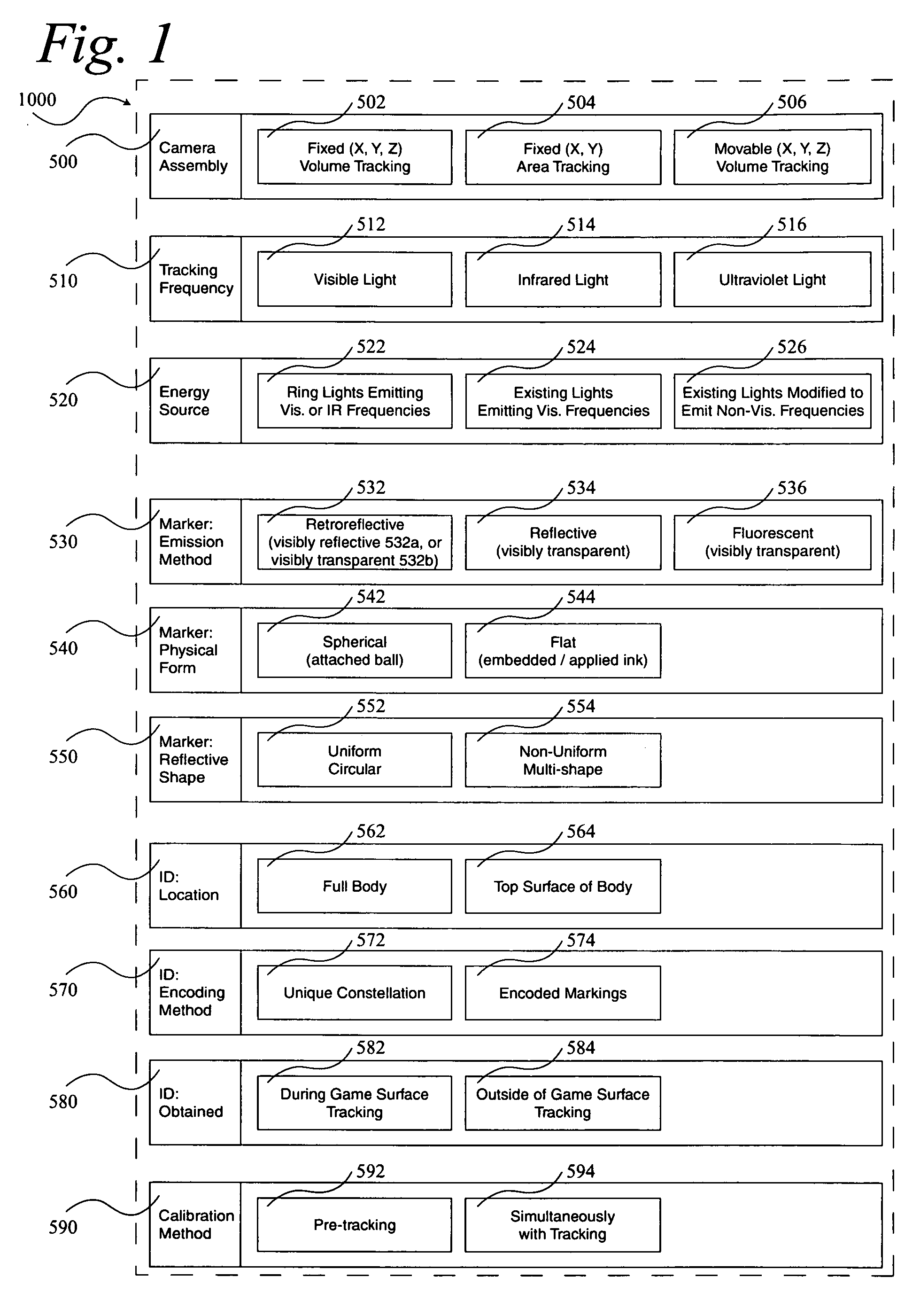
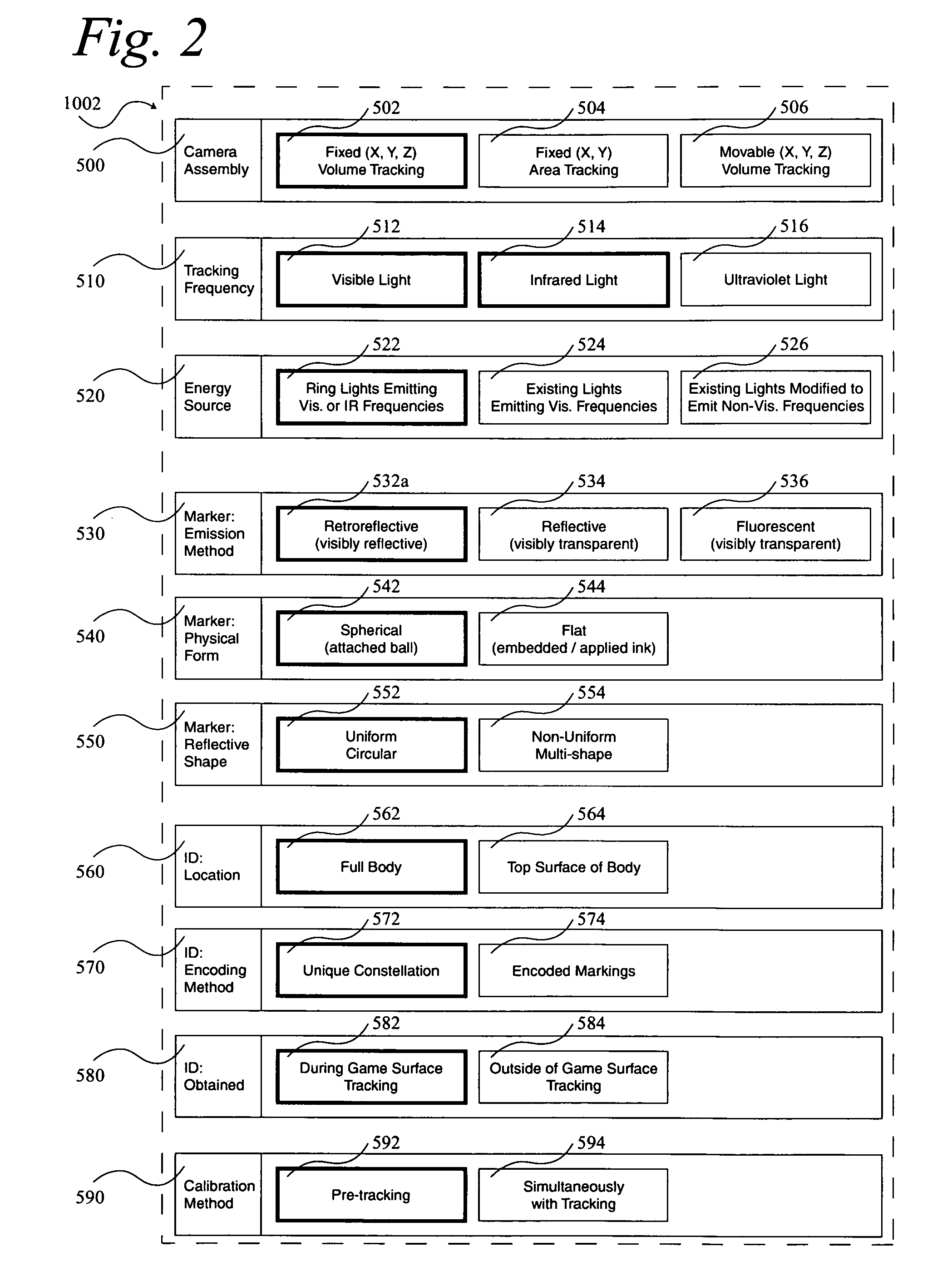
Optimizations for live event, real-time, 3D object tracking
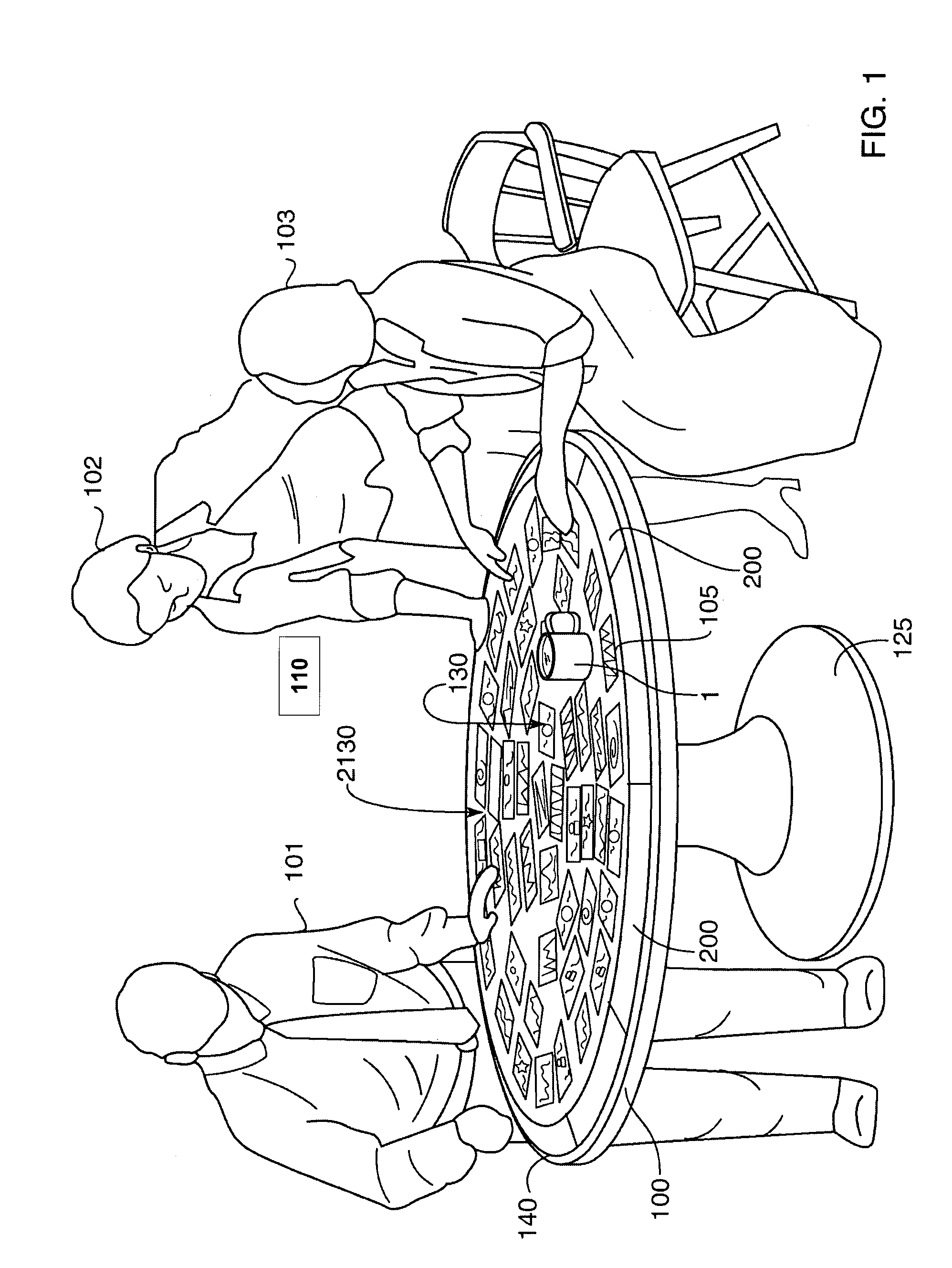
InactiveUS20090046152A1Maximized manufacturingMaximized installation costTelevision system detailsImage analysisView cameraIce hockey
A system 1000, and its alternates 1002 through 1022, for automatically tracking and videoing the movements of multiple participants and objects during an event. System 1000 and its alternates comprise a scalable area tracking matrix of overhead tracking cameras 120c, whose individual field-of-views 120v combine to form a contiguous view 504m of the performance area where the event is being held. As participants 110, and all other necessary objects such as 103 (e.g. a puck in ice-hockey) and 104 (e.g. a stick in ice-hockey) move about during the event, computer 160 analyzes the images from contiguous view 504m to create a real-time tracking database at least including participant and object centroid locations respective to the performance area, and preferably including their identities matched to these ongoing locations. System 1000 and its alternates then employ the real-time database to automatically direct, without operator intervention, one or more side-view cameras such as 140-a, 140-b, 140-c and 140-d, to maintain optimal viewing of the event. The participants and objects may additionally be marked with encoded or non-encoded, visible or non-visible markers, either denoting centroid locations visible from their upper surfaces, and / or non-centroid locations visible from perspective views. The encoded markers are preferably placed on upper surfaces and detectable by computer 160 as it analyzes the images from contiguous overhead field-of-view 504m, thus providing participant and object identities to correspond with ongoing locations, further enhancing algorithms for subsequently controlling side-view cameras 140-a through 140-d. The non-encoded markers are preferably placed on multiple non-centroid locations at least on the participants that are then adjustably viewable by system 1000 and its alternates as the system uses the determined locations of each participant from the overhead view to automatically adjust one or more side-view cameras to tightly follow the participant. The resulting images from side-view cameras 140-a through 140-d may then be subsequently processed to determine the non-encoded marker locations, thus forming a three dimensional model of each participant and objects movements.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
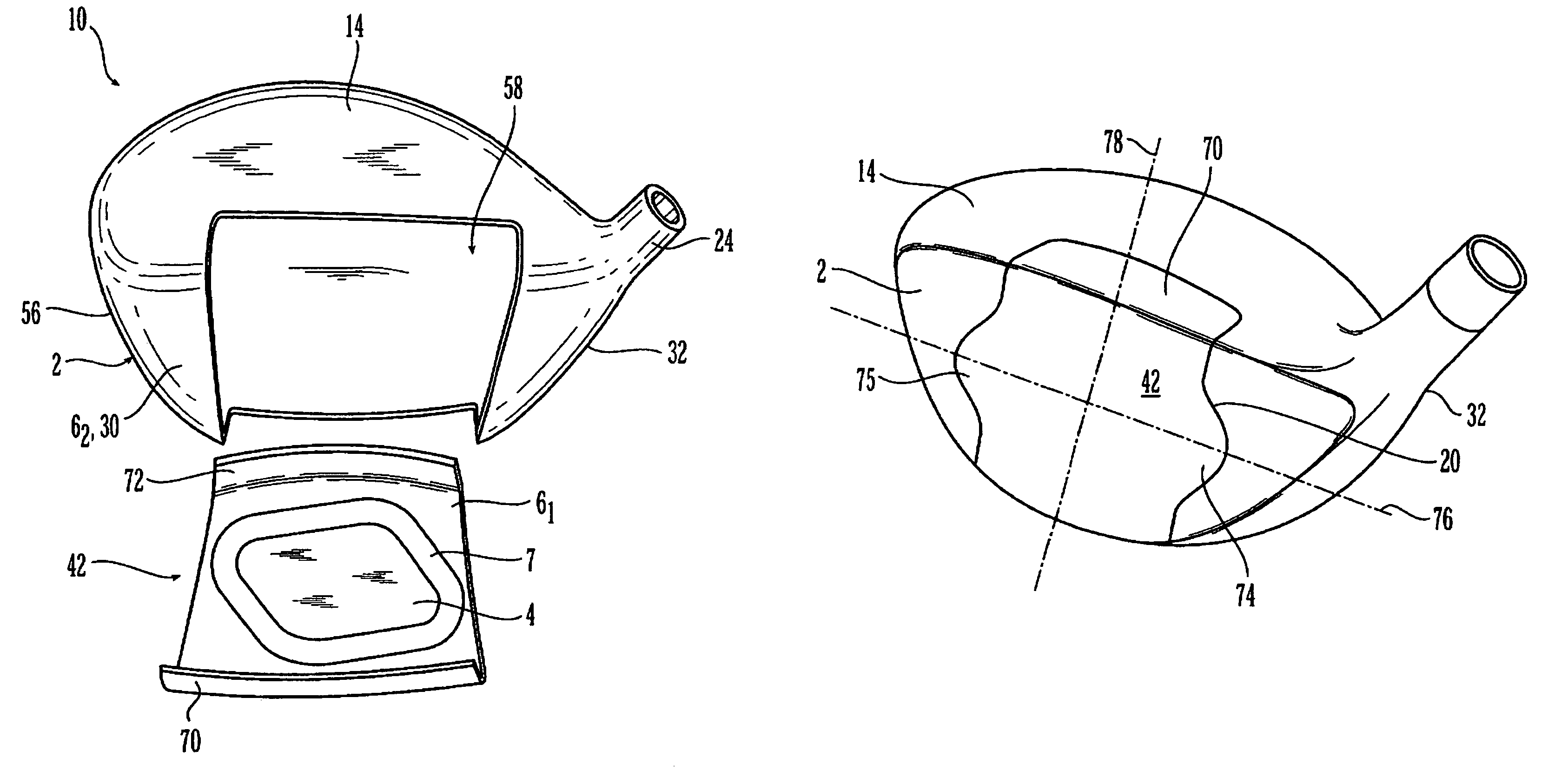
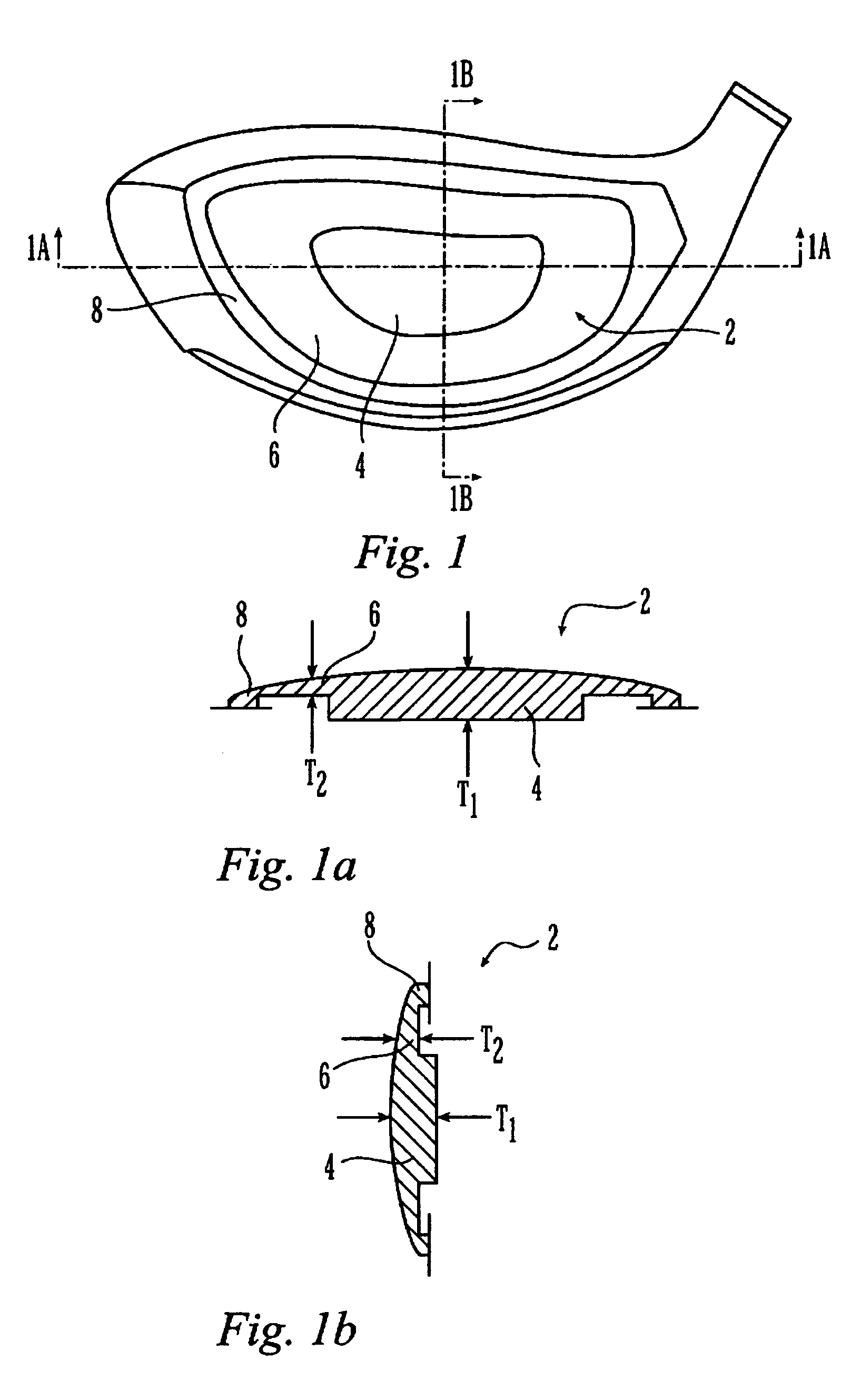
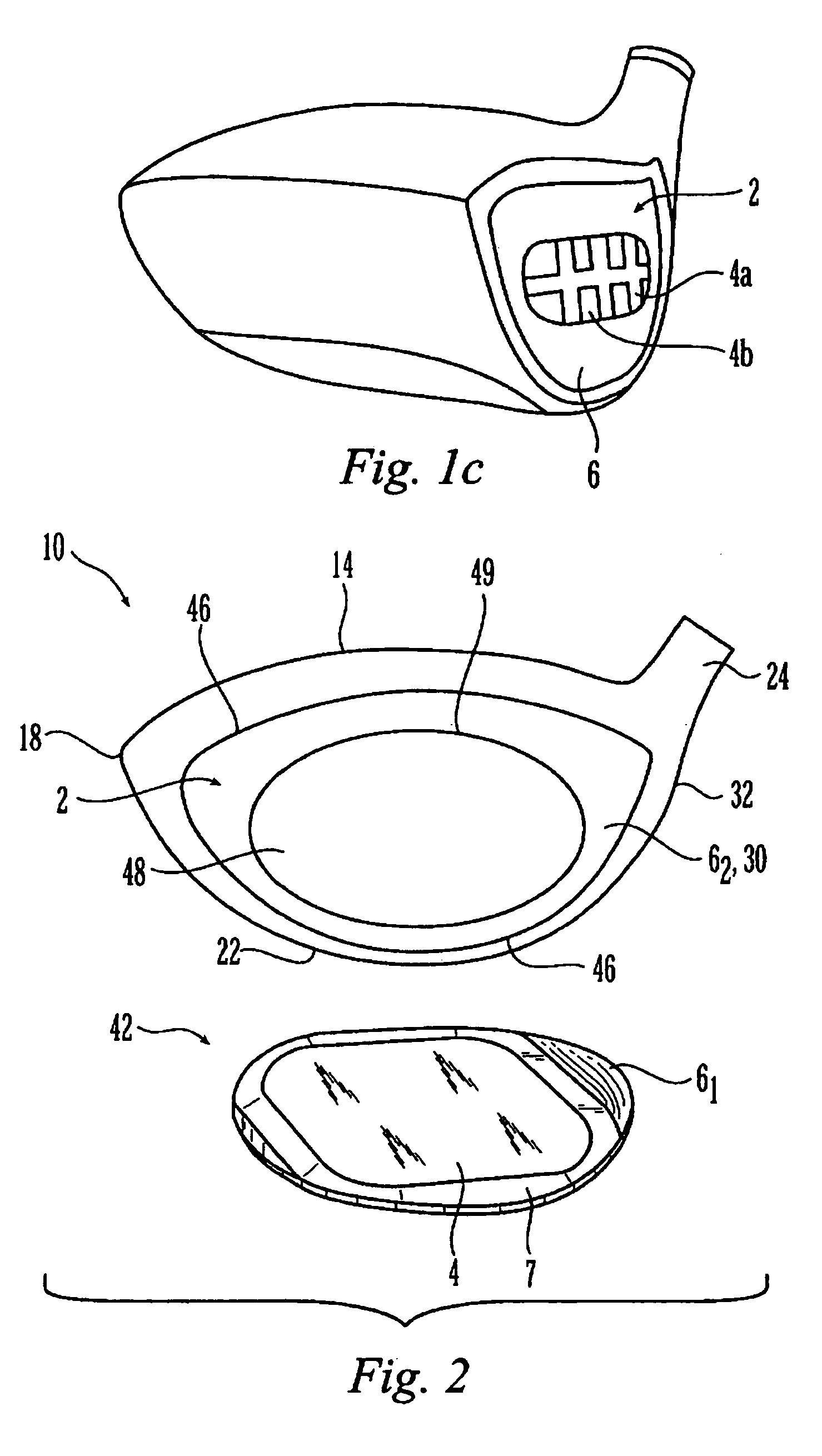
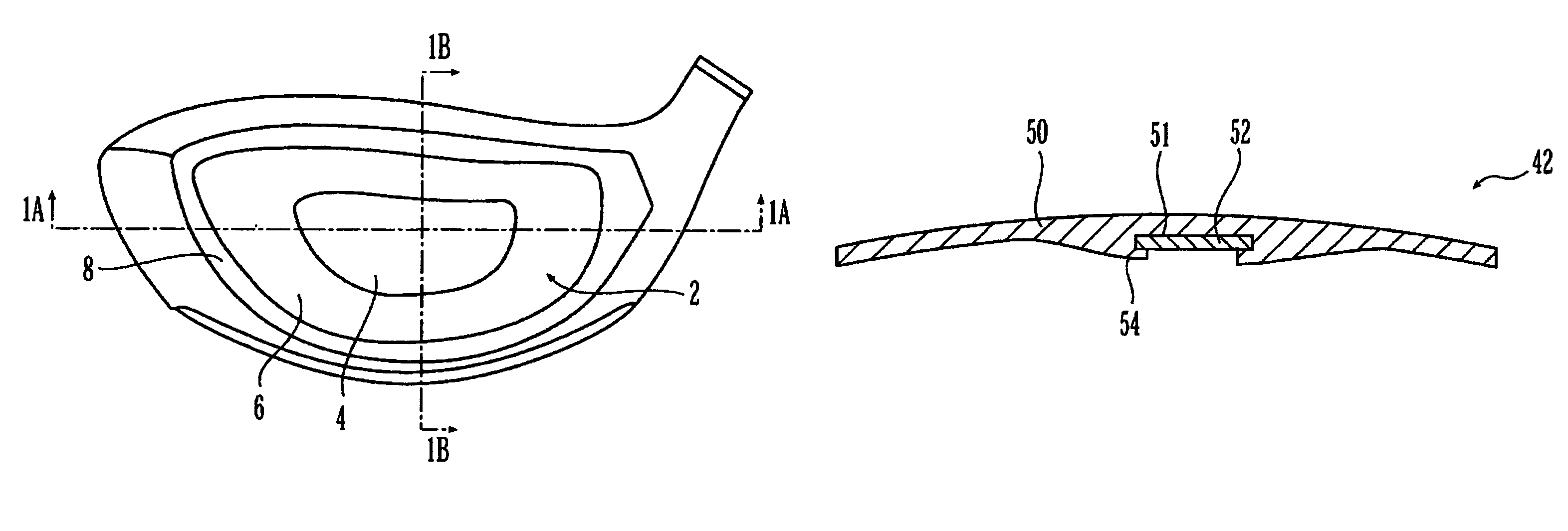
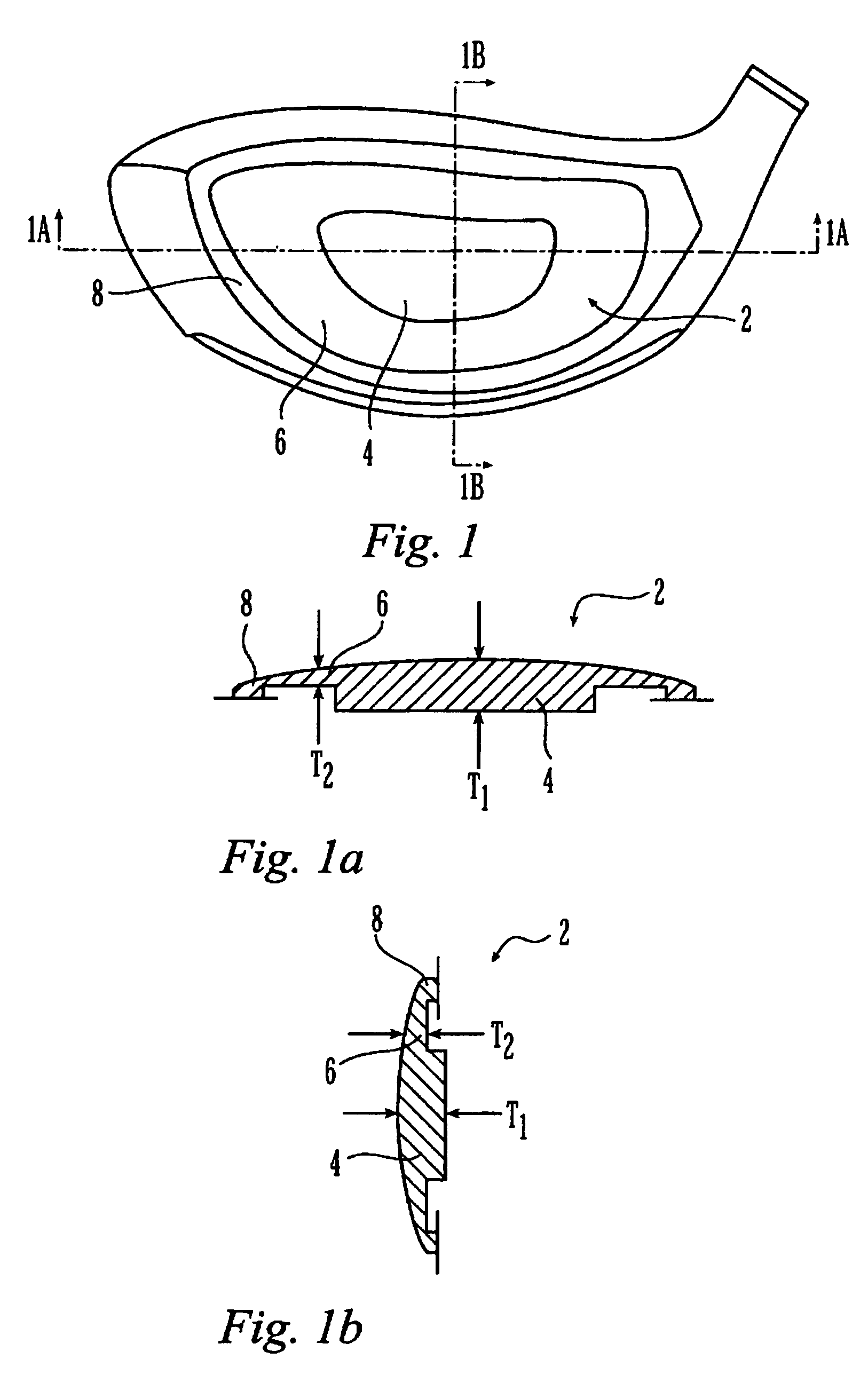
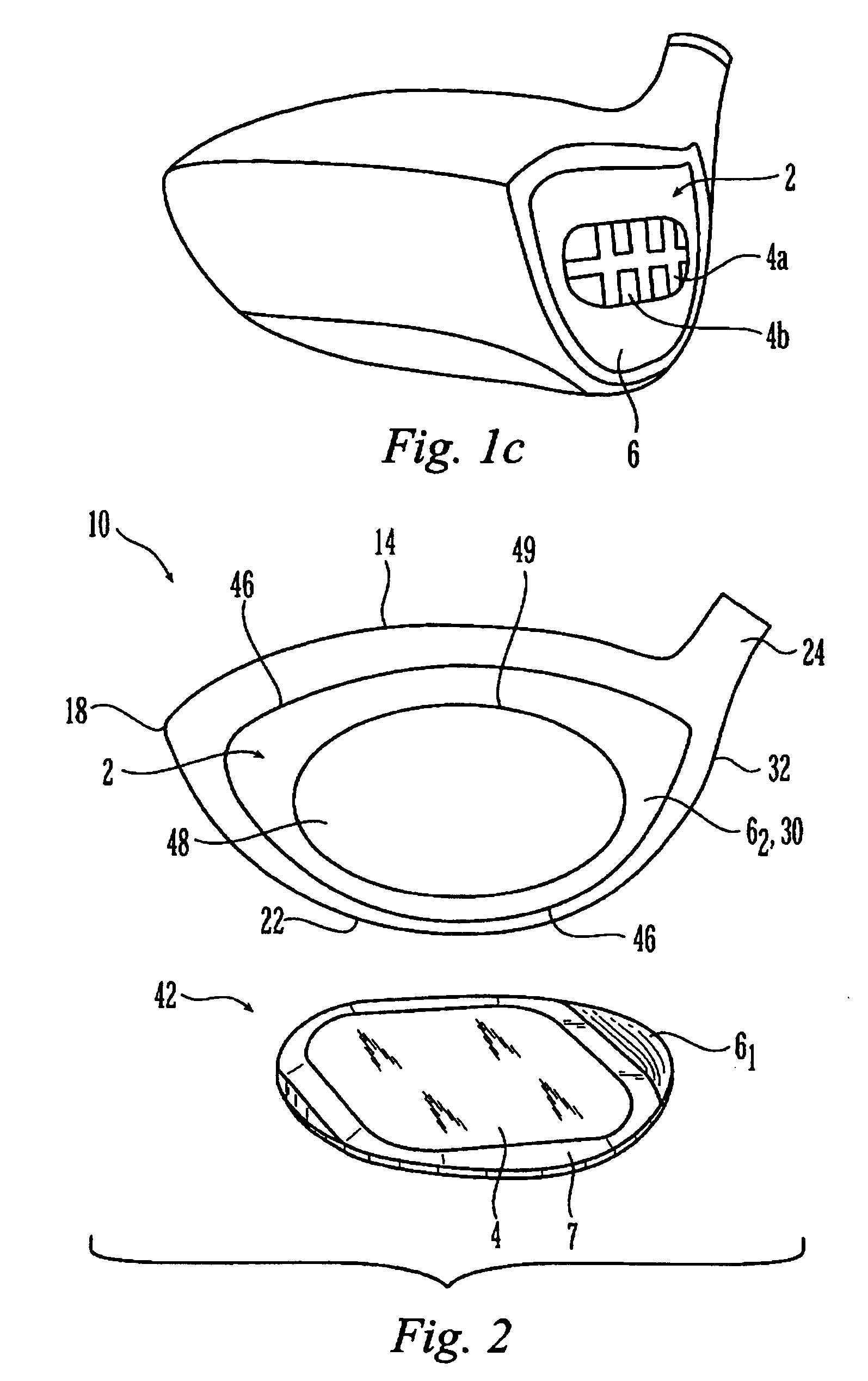
Metal wood club with improved hitting face
InactiveUS7207898B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGolf clubsMulti materialGolf Ball
A hitting face of a golf club head having improved flexural stiffness properties. In one embodiment, the hitting face is made from multiple materials. The main portion of the hitting face is a plate-like face made from a first material having a first density. A dense insert made from a second material having a second density that is greater than the first density is attached directly or indirectly to the plate-like face at or near the geometric center thereof. The dense insert increases the flexural stiffness of in a central zone of the hitting face so that a golf club head that has a larger zone of substantially uniform high initial ball speed. In another embodiment, the hitting face includes an insert that includes main plate and at least one wing extending therefrom. The insert is welded to the golf club head so that the main plate does not deflect separately from the remainder of the hitting face. The geometry of the insert controls the stiffness in the axial directions.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Metal wood club with improved hitting face
InactiveUS7261643B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGolf clubsMulti materialEngineering
A hitting face of a golf club head having improved flexural stiffness properties. In one embodiment, the hitting face is made from multiple materials. The main portion of the hitting face is a plate-like face made from a first material having a first density. A dense insert made from a second material having a second density that is greater than the first density is attached directly or indirectly to the plate-like face at or near the geometric center thereof. The dense insert increases the flexural stiffness of in a central zone of the hitting face so that a golf club head that has a larger zone of substantially uniform high initial ball speed. In another embodiment, the hitting face includes an insert that includes main plate and at least one wing extending therefrom. The insert is welded to the golf club head so that the main plate does not deflect separately from the remainder of the hitting face. The geometry of the insert controls the stiffness in the axial directions.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
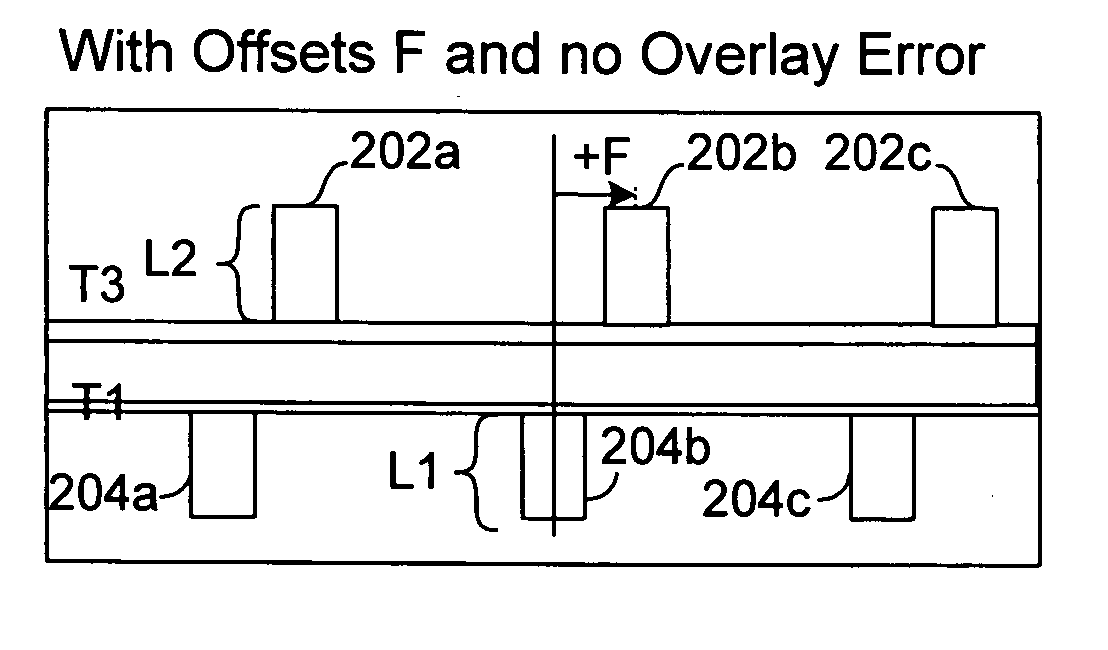
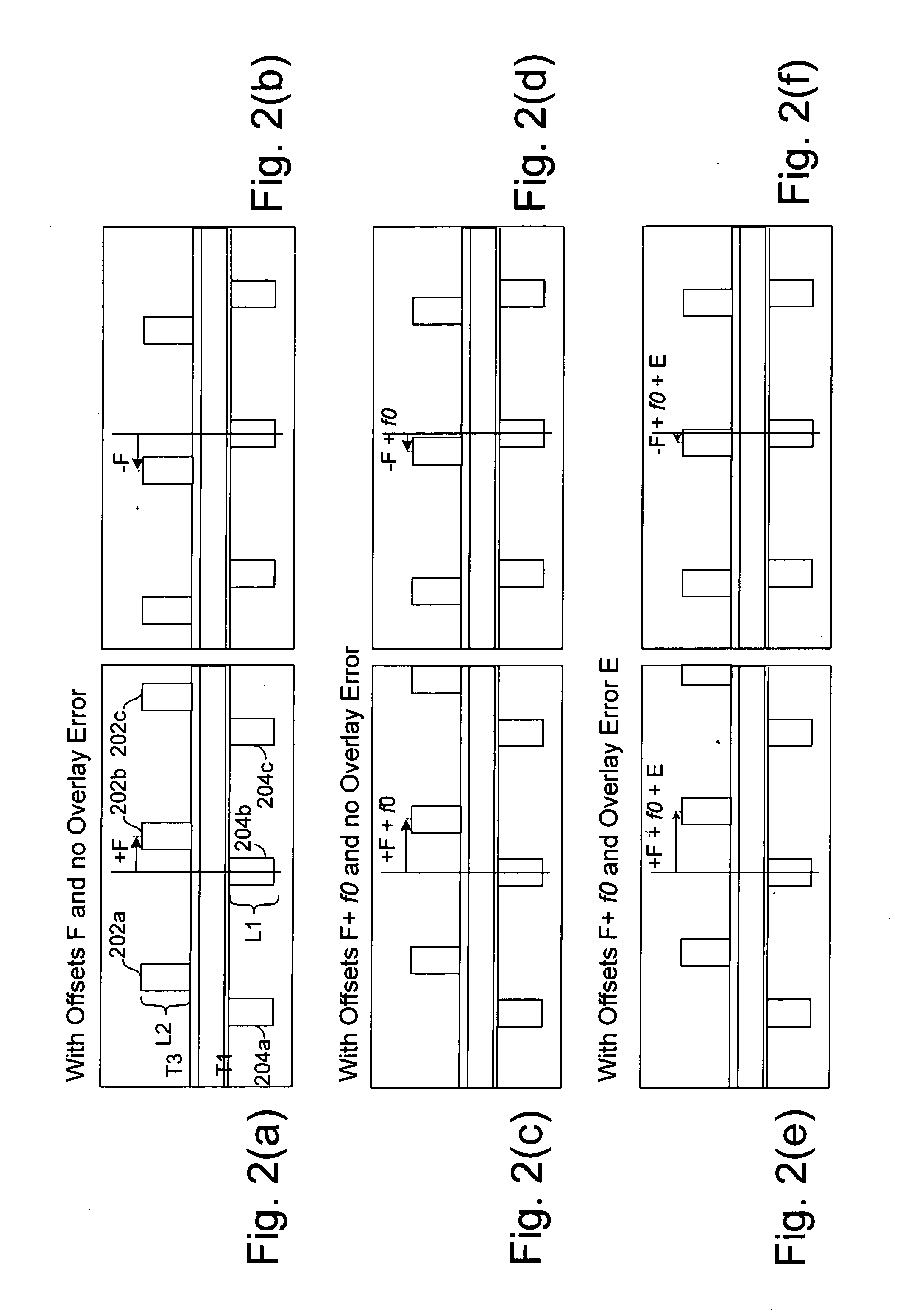
Continuously varying offset mark and methods of determining overlay
ActiveUS20050195398A1Small differenceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGratingComputer science
The present invention relates to overlay marks and methods for determining overlay error. One aspect of the present invention relates to a continuously varying offset mark. The continuously varying offset mark is a single mark that includes over laid periodic structures, which have offsets that vary as a function of position. By way of example, the periodic structures may correspond to gratings with different values of a grating characteristic such as pitch. Another aspect of the present invention relates to methods for determining overlay error from the continuously varying offset mark. The method generally includes determining the center of symmetry of the continuously varying offset mark and comparing it to the geometric center of the mark. If there is zero overlay, the center of symmetry tends to coincide with the geometric center of the mark. If overlay is non zero (e.g., misalignment between two layers), the center of symmetry is displaced from the geometric center of the mark. The displacement in conjunction with the preset gain of the continuously varying offset mark is used to calculate the overlay error.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
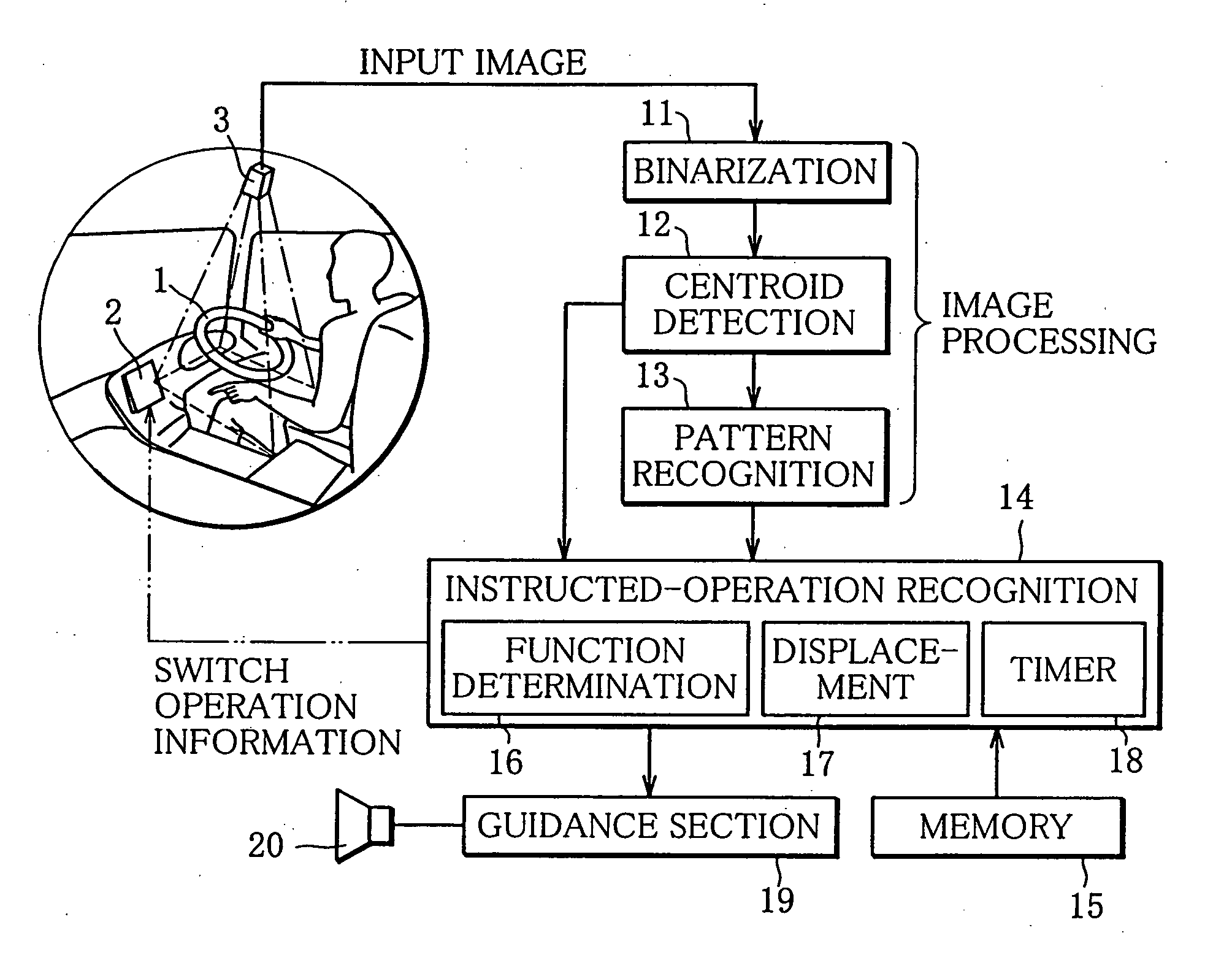
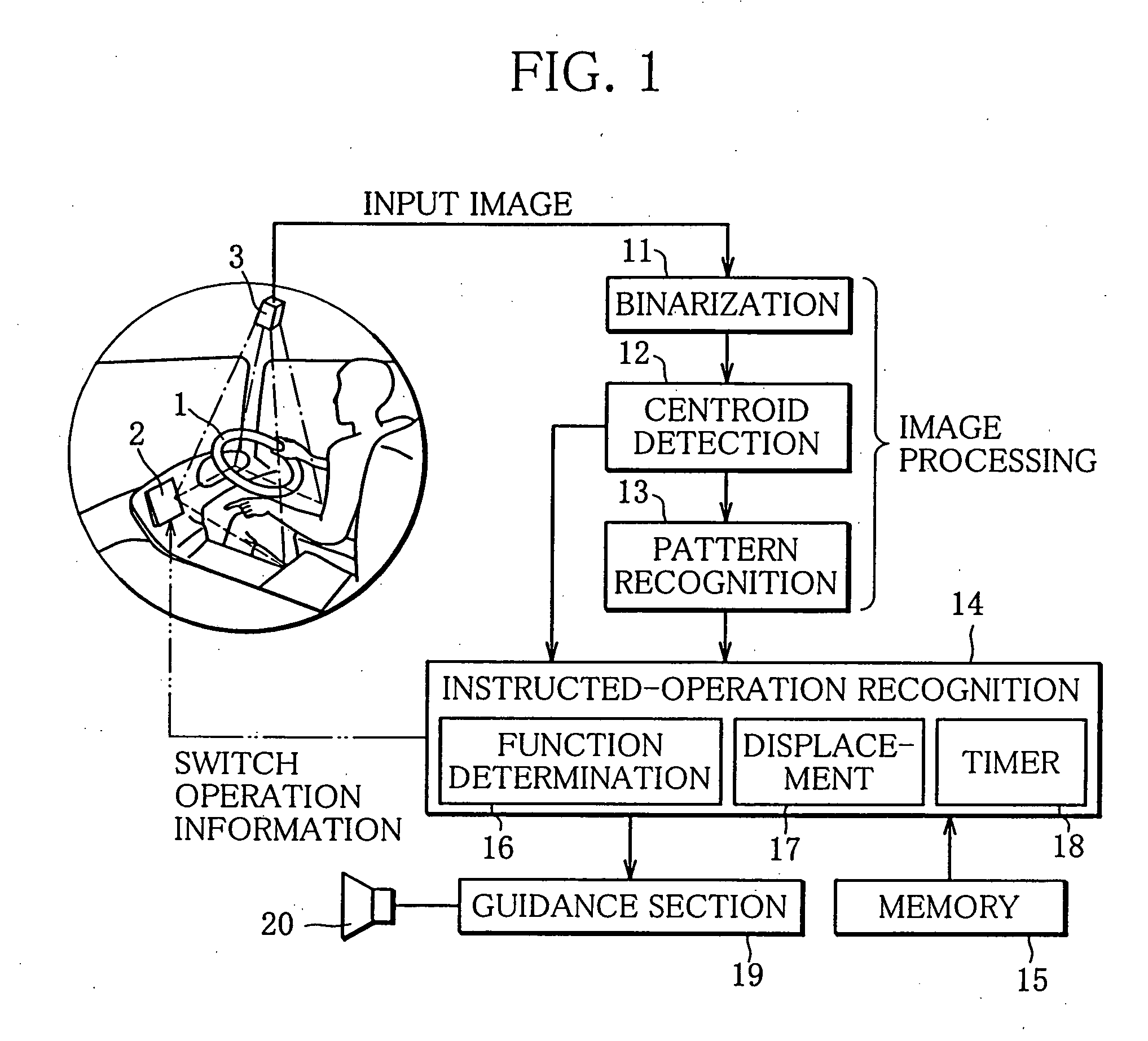
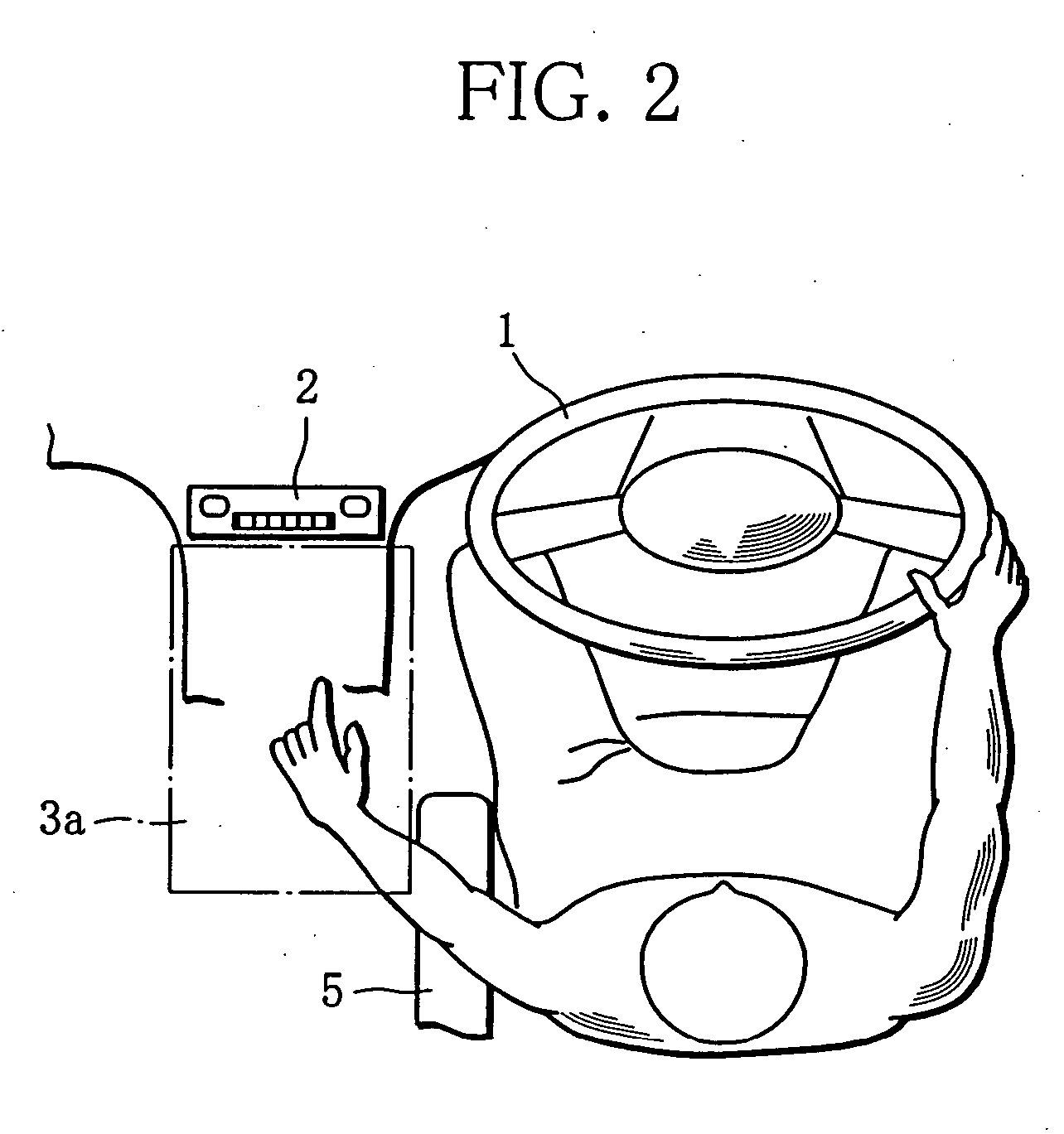
Hand pattern switch device
InactiveUS20050063564A1Easily and reliably detecting hand patternEnter exactlyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisParalemminEngineering
A hand pattern switch device capable of easily and reliably detecting a hand pattern or a palm motion of an operator. From a picked-up image of a distal arm, an axis passing through the centroid of a hand is determined as a central axis passing through the center of arm. At least either first scanning lines perpendicular to the central axis or second scanning lines extending along the central axis are set between a fingertip and a palm center. While changing the scanning line to be examined from the fingertip side toward the palm center, a determination is made to determine how many number of scanning lines for each of which a finger width equal to or larger than a predetermined width is detected are present, thereby making a detection of whether or not the finger is extended from the palm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION +1
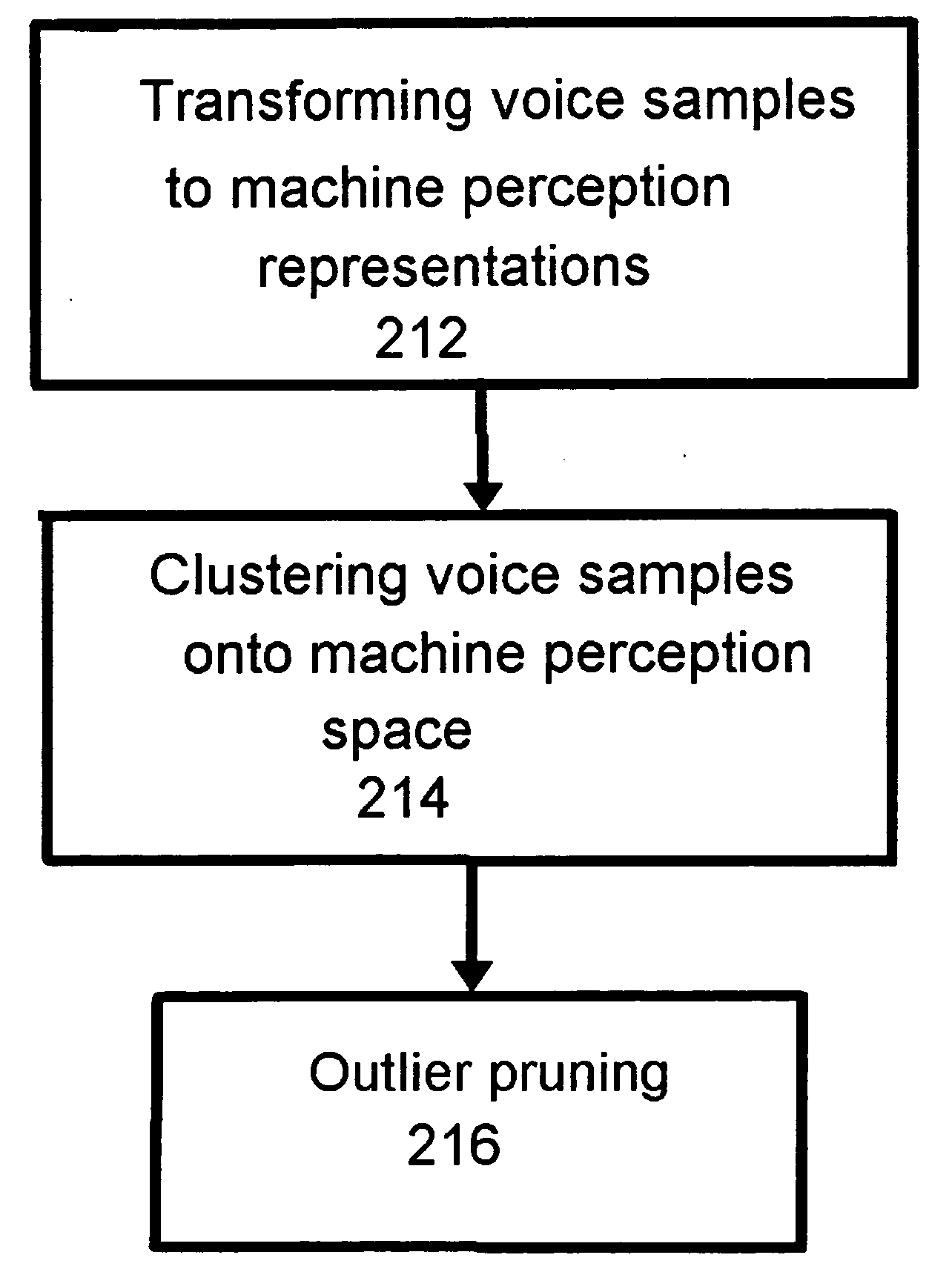
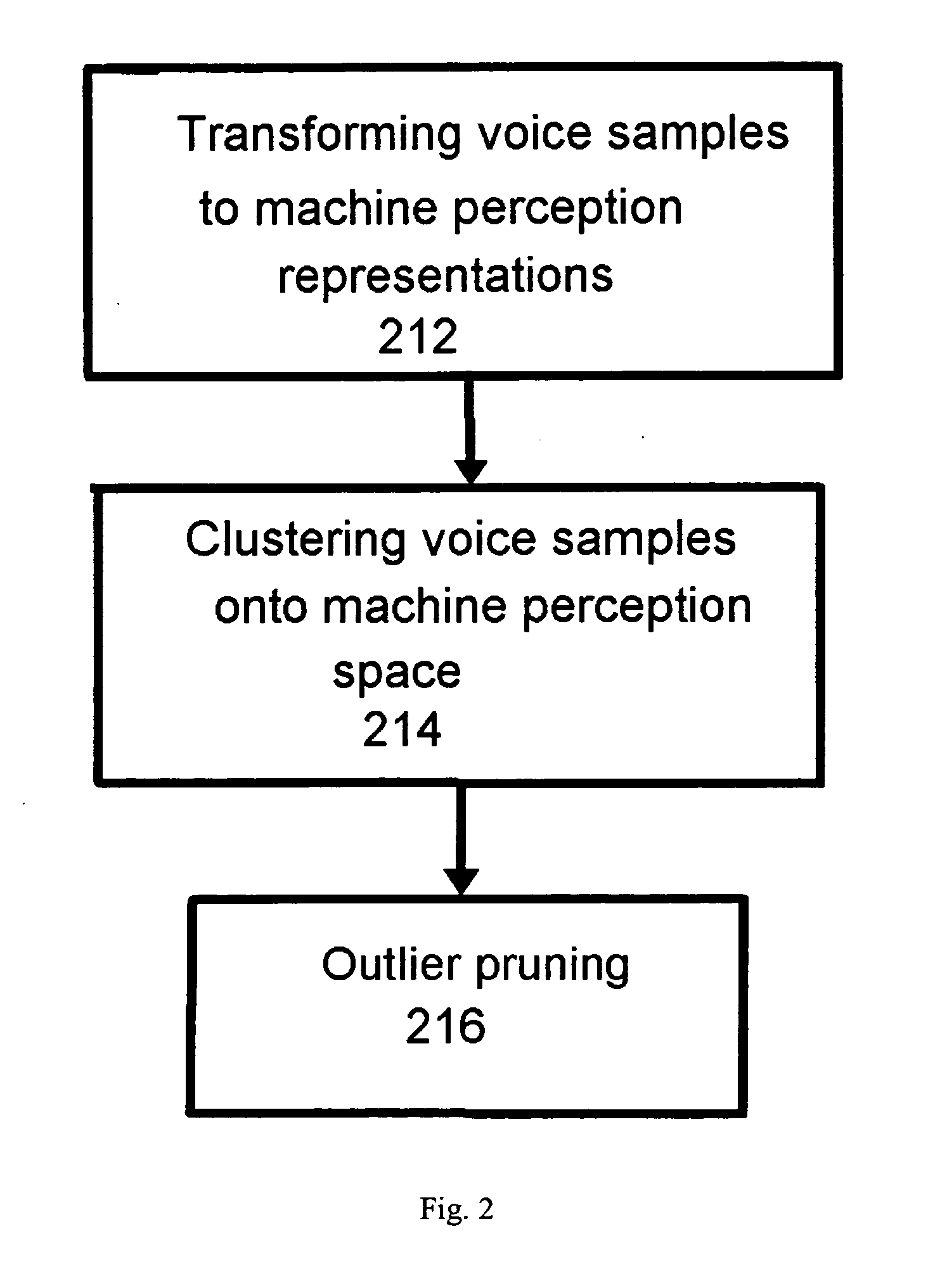
Methods and apparatus related to pruning for concatenative text-to-speech synthesis
InactiveUS20080091428A1Speech recognitionSpeech synthesisSingular value decompositionCharacteristic space
The present invention provides, among other things, automatic identification of near-redundant units in a large TTS voice table, identifying which units are distinctive enough to keep and which units are sufficiently redundant to discard. According to an aspect of the invention, pruning is treated as a clustering problem in a suitable feature space. All instances of a given unit (e.g. word or characters expressed as Unicode strings) are mapped onto the feature space, and cluster units in that space using a suitable similarity measure. Since all units in a given cluster are, by construction, closely related from the point of view of the measure used, they are suitably redundant and can be replaced by a single instance. The disclosed method can detect near-redundancy in TTS units in a completely unsupervised manner, based on an original feature extraction and clustering strategy. Each unit can be processed in parallel, and the algorithm is totally scalable, with a pruning factor determinable by a user through the near-redundancy criterion. In an exemplary implementation, a matrix-style modal analysis via Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) is performed on the matrix of the observed instances for the given word unit, resulting in each row of the matrix associated with a feature vector, which can then be clustered using an appropriate closeness measure. Pruning results by mapping each instance to the centroid of its cluster.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-user collaborative graphical user interfaces
InactiveUS7327376B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A multi-user collaborative graphical user interface has a display area with a horizontal orientation, the display surface is positioned between the multiple users. The display area also has a centroid and a circumference. The display area is partitioned into work areas so that there is one working area for each user of the multiple users. An item is displayed in a particular working area using a global polar coordinate system centered on the centroid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
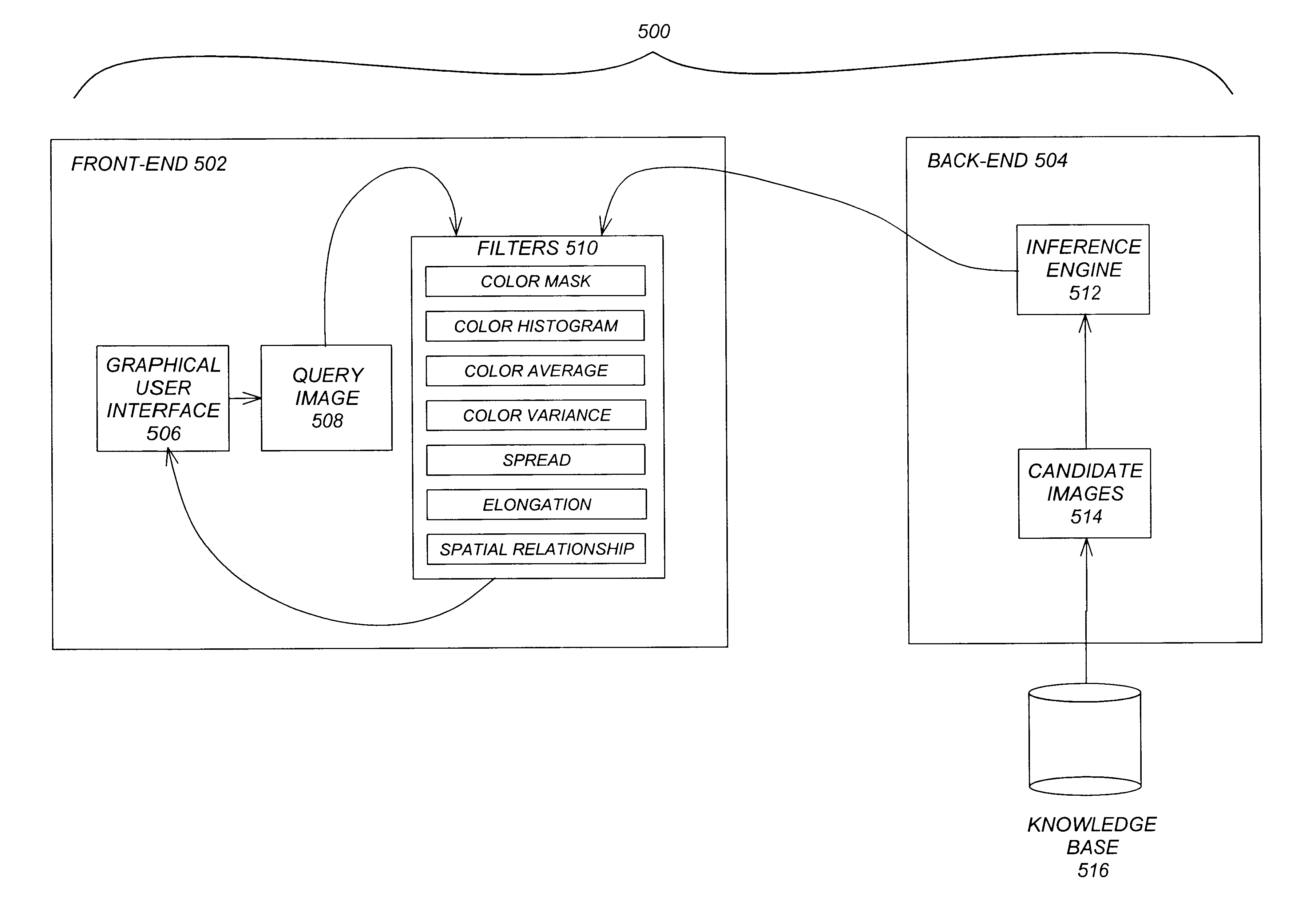
Perception-based image retrieval
InactiveUS6865302B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAverage filterPattern perception
A content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has a front-end that includes a pipeline of one or more dynamically-constructed filters for measuring perceptual similarities between a query image and one or more candidate images retrieved from a back-end comprised of a knowledge base accessed by an inference engine. The images include at least one color set having a set of properties including a number of pixels each having at least one color, a culture color associated with the color set, a mean and variance of the color set, a moment invariant, and a centroid. The filters analyze and compare the set of properties of the query image to the set of properties of the candidate images. Various filters are used, including: a Color Mask filter that identifies identical culture colors in the images, a Color Histogram filter that identifies a distribution of colors in the images, a Color Average filter that performs a similarity comparison on the average of the color sets of the images, a Color Variance filter that performs a similarity comparison on the variances of the color sets of the images, a Spread filter that identifies a spatial concentration of a color in the images, an Elongation filter that identifies a shape of a color in the images, and a Spatial Relationship filter that identifies a spatial relationship between the color sets in the images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com