Patents
Literature
5170 results about "Light detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is a light-based method used the inspection of the interior of pipes. The technology is also used in a wide variety of applications across industries.
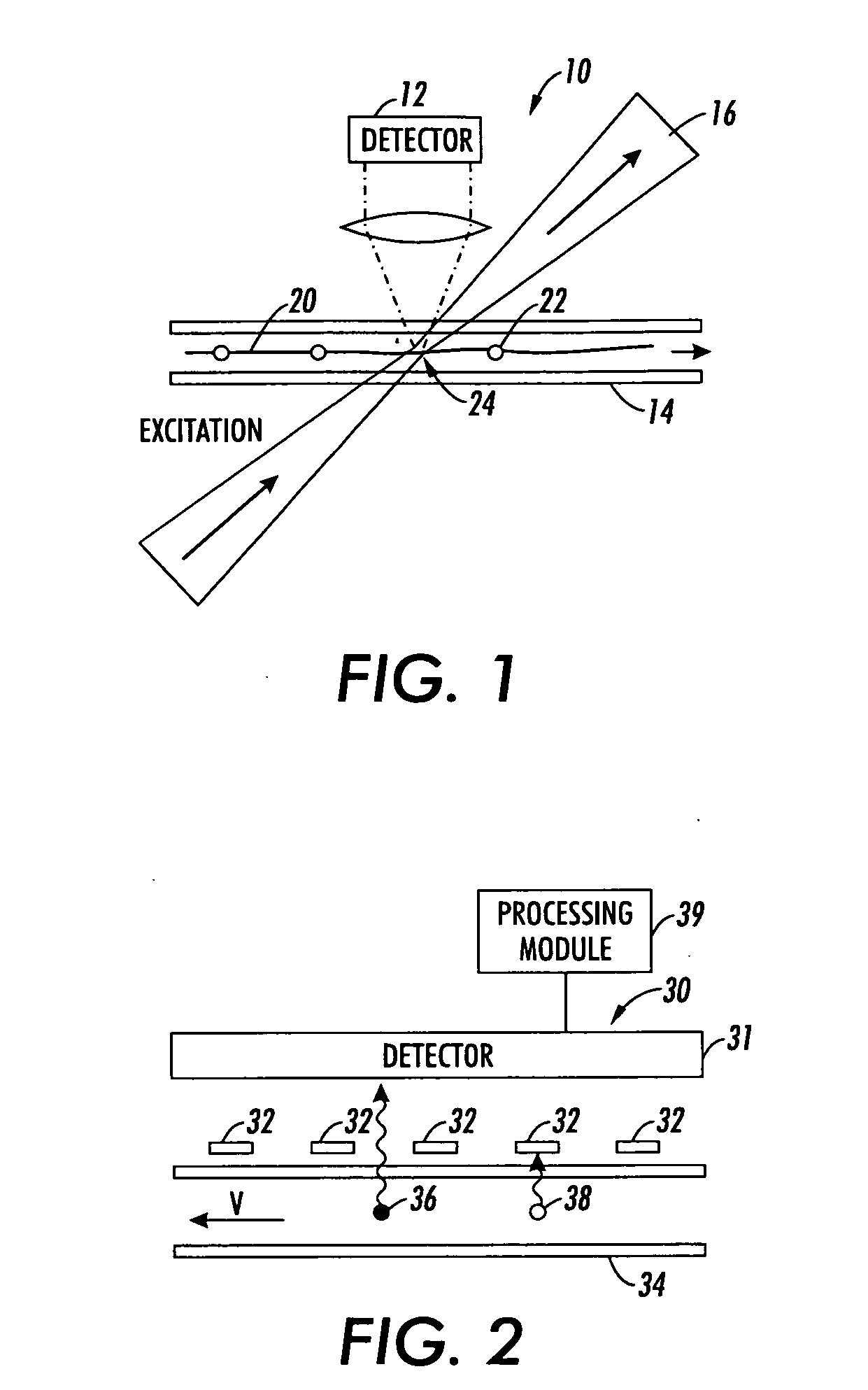
Method and system for monitoring smart structures utilizing distributed optical sensors
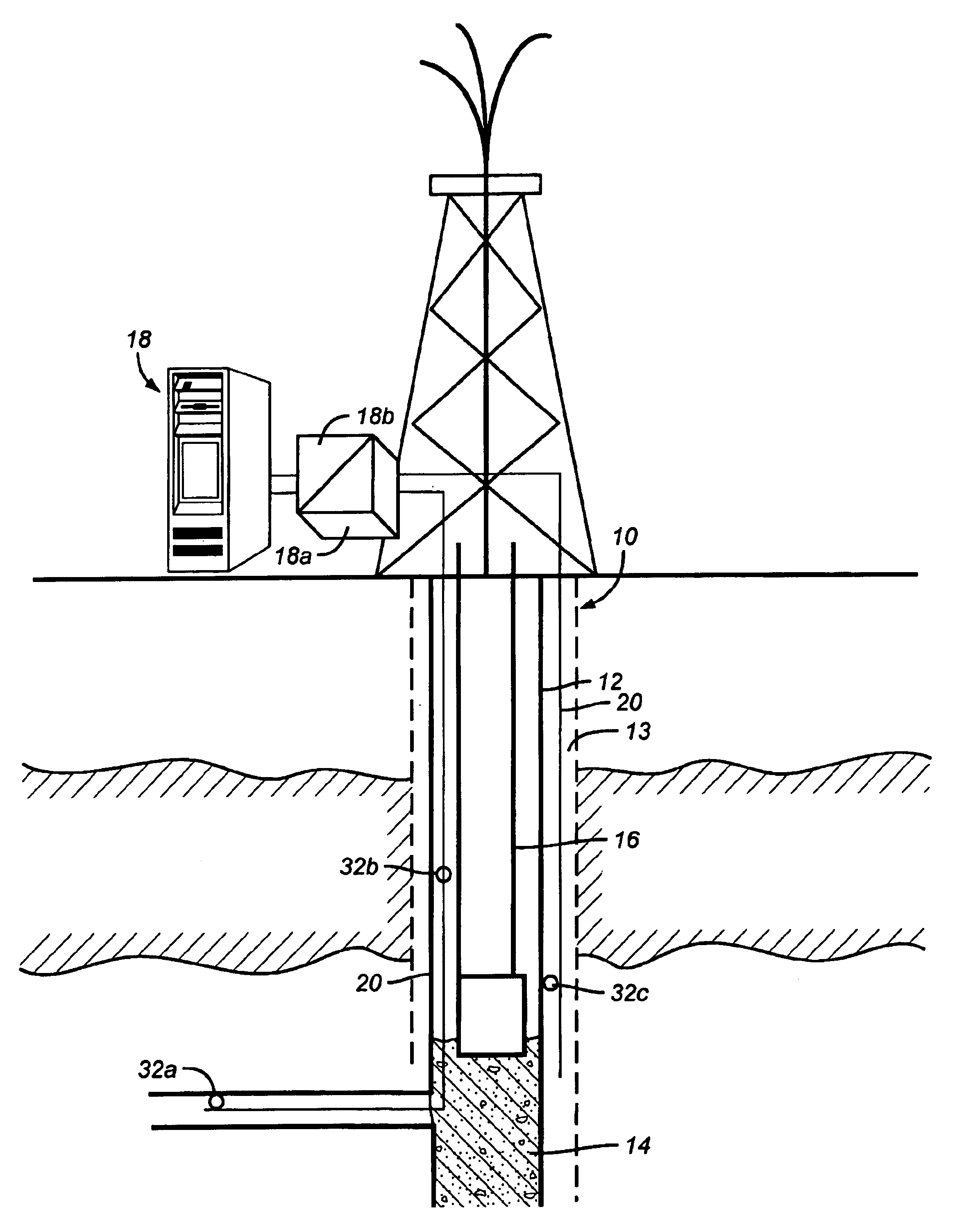
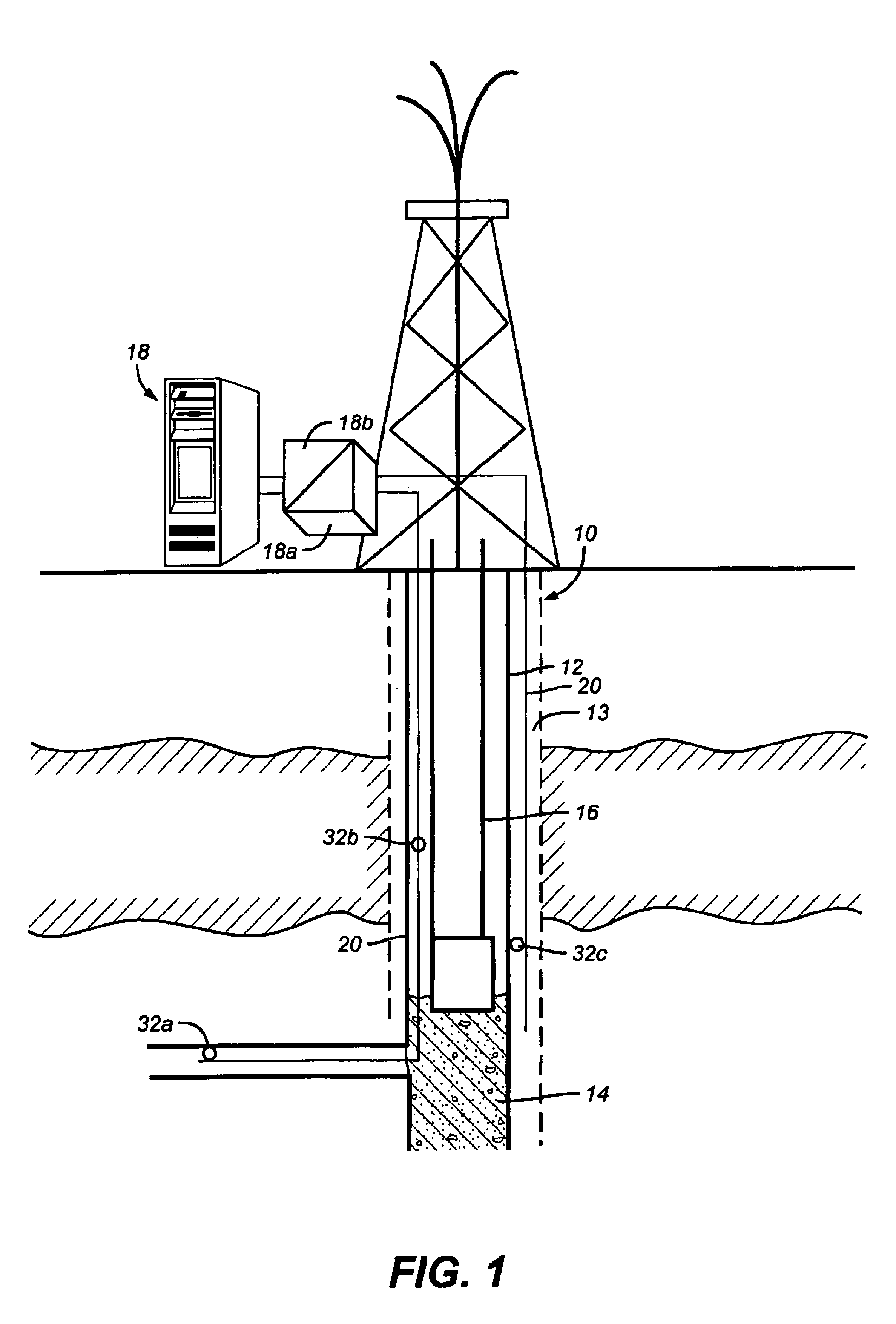
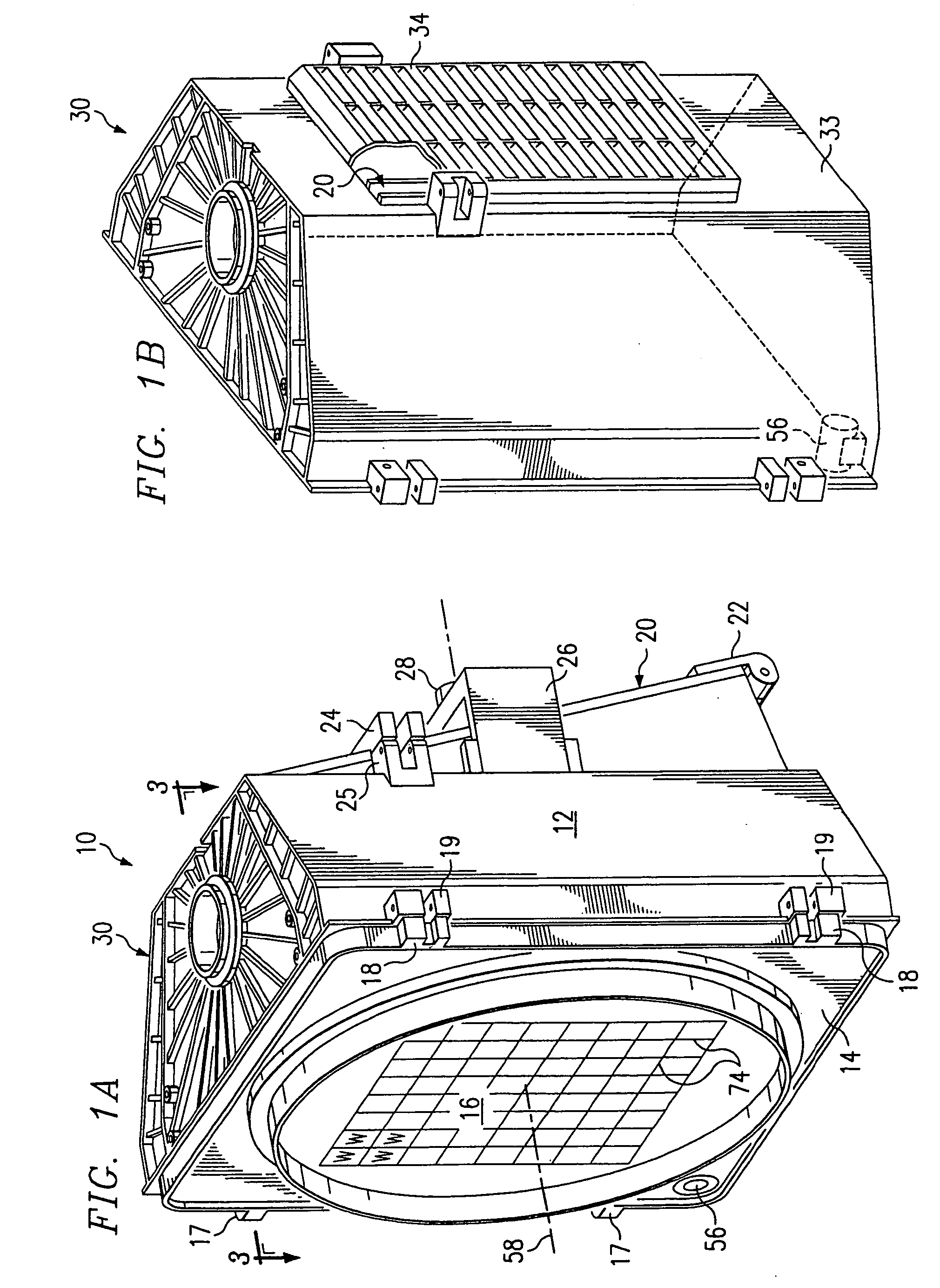
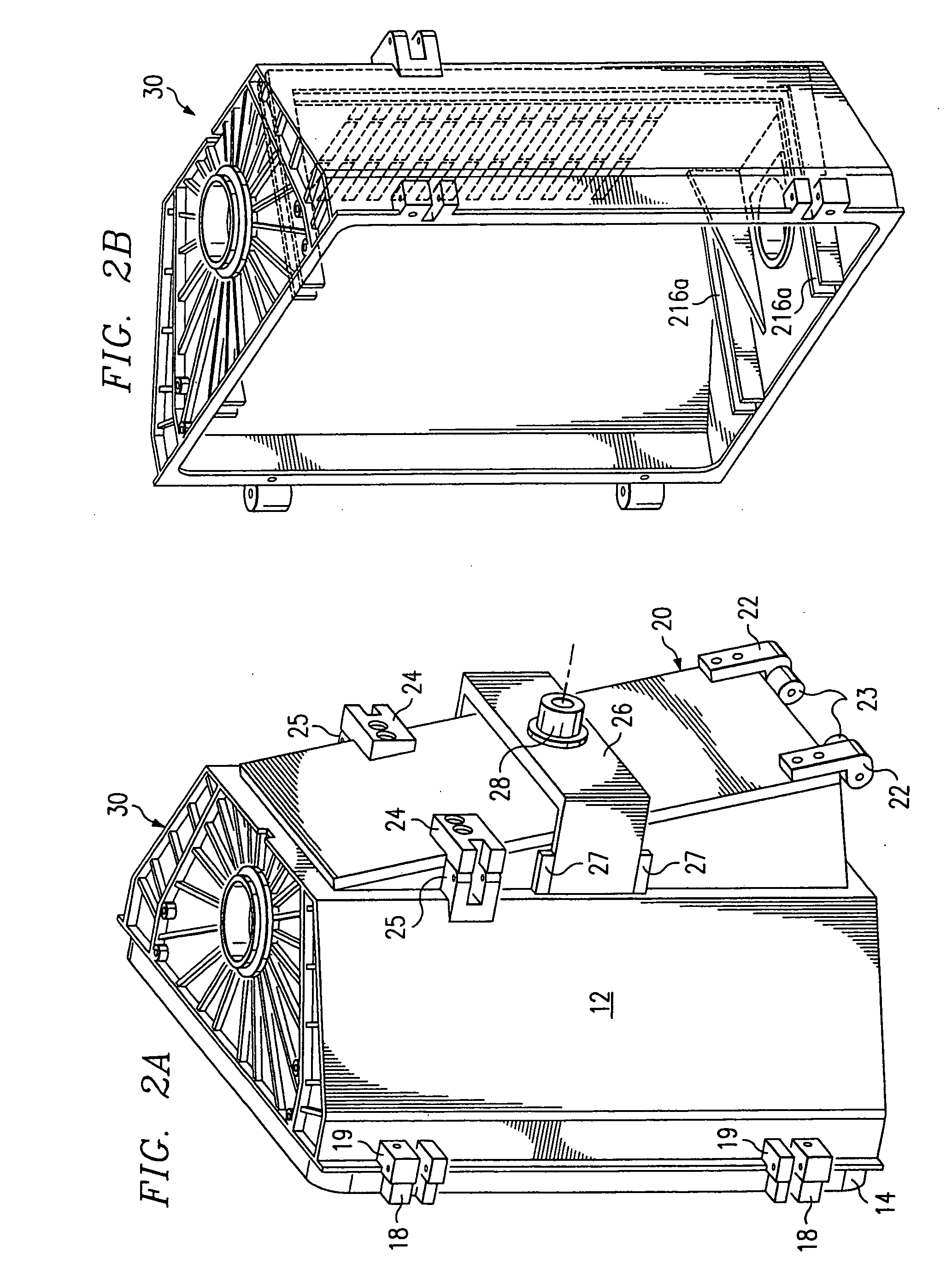
A monitoring system and method for monitoring a predetermined set of physical characteristics associated with a structure using the monitoring system. The system is distributed in the structure and comprises a distributed optical sensing device (30), further comprising a fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light source (18a) operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light detection device (18b), operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22), for measuring the light received at the light detection device (18b) from the fiber optic cable (20, 22); and a data processor (18) capable of using the light measured to calculate a predetermined set of physical parameters describing the predetermined set of physical characteristics.
Owner:ZIEBEL AS
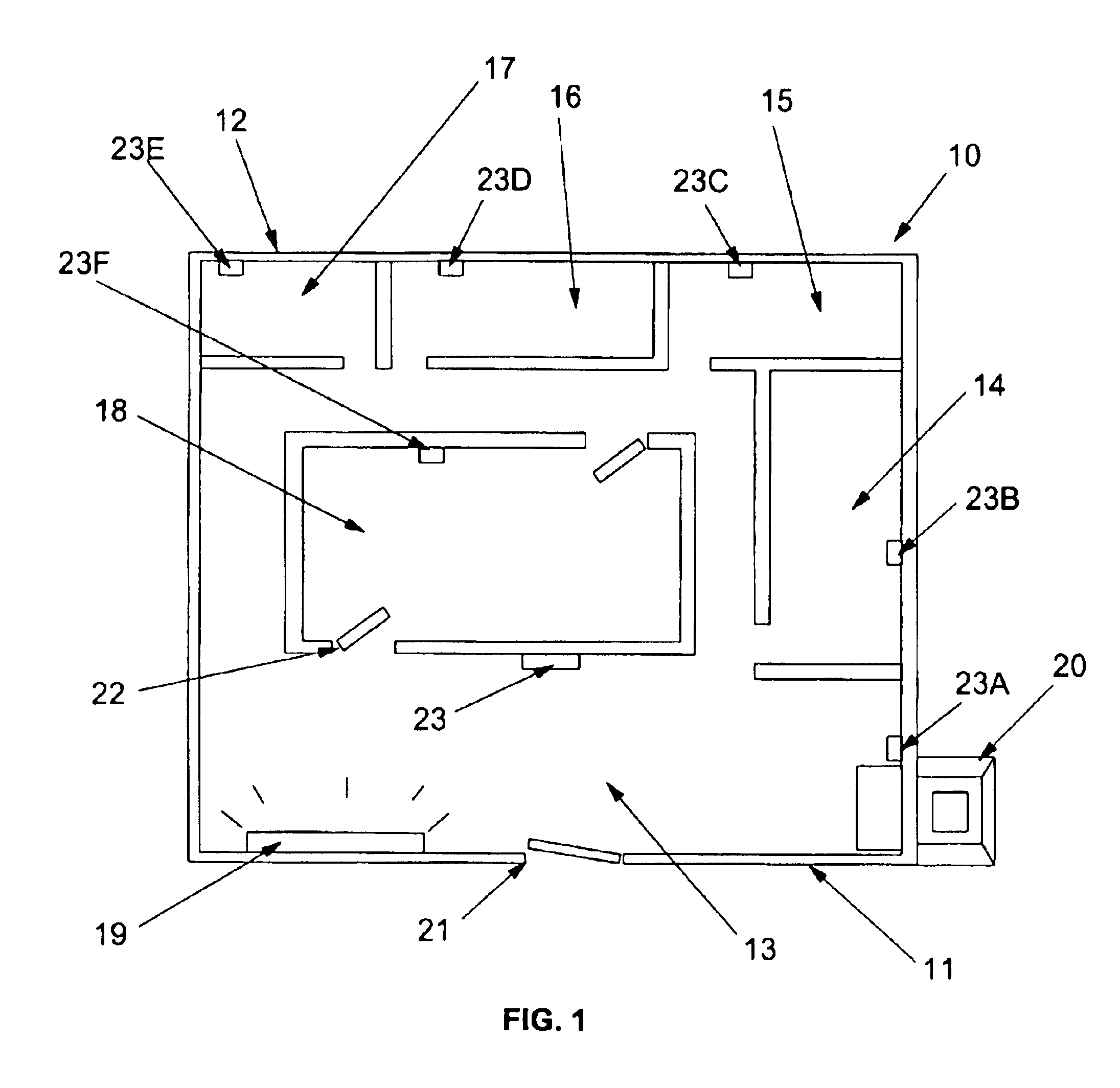
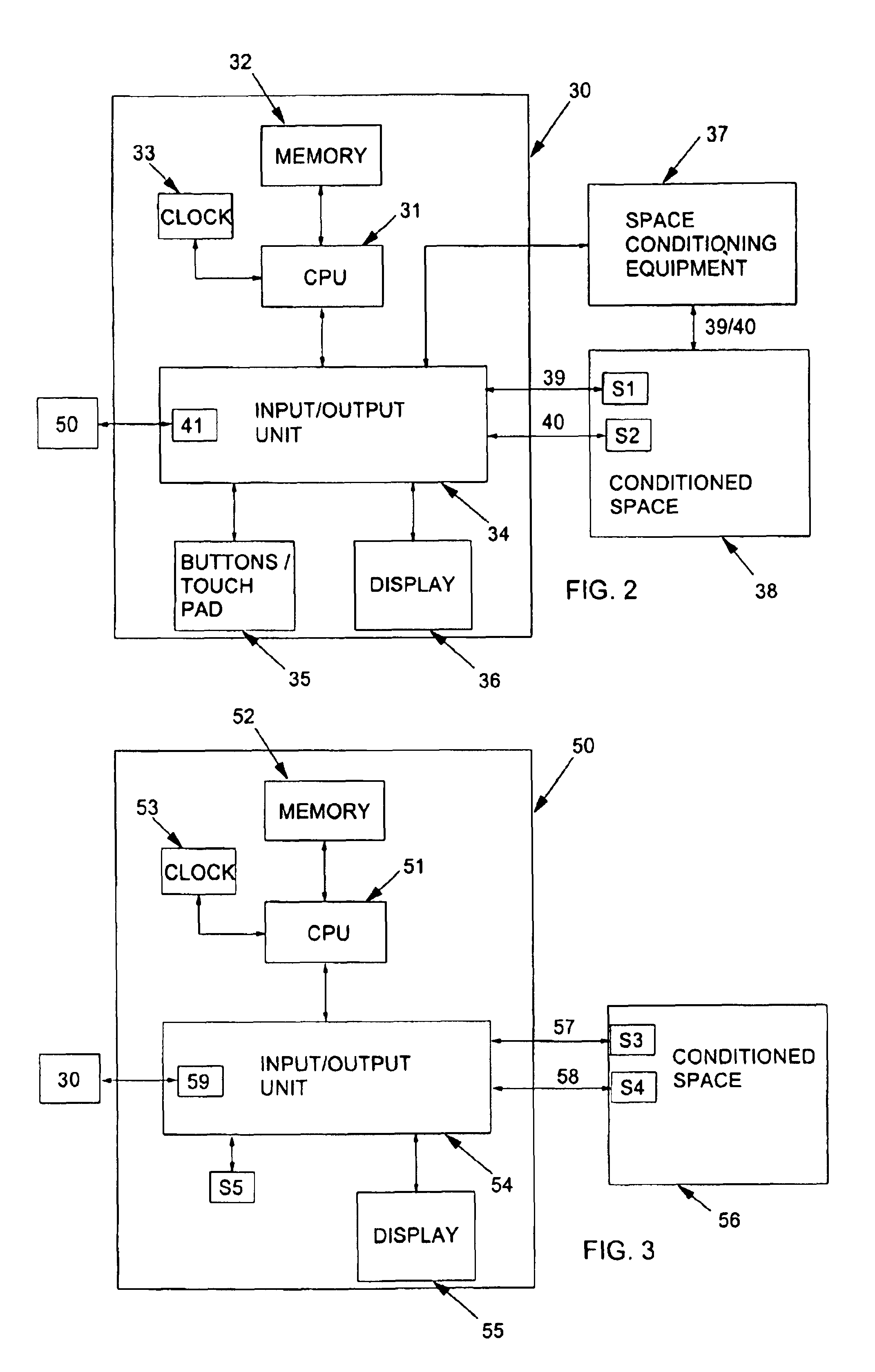
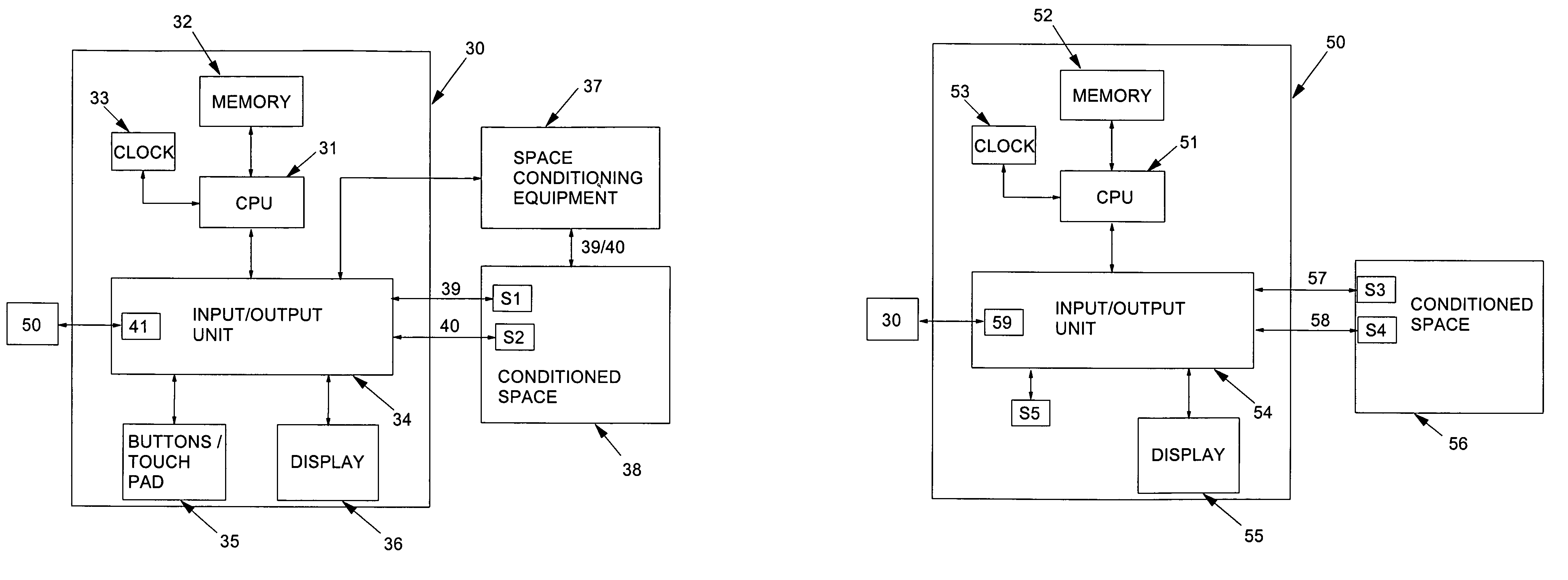
Thermostat system with remote data averaging
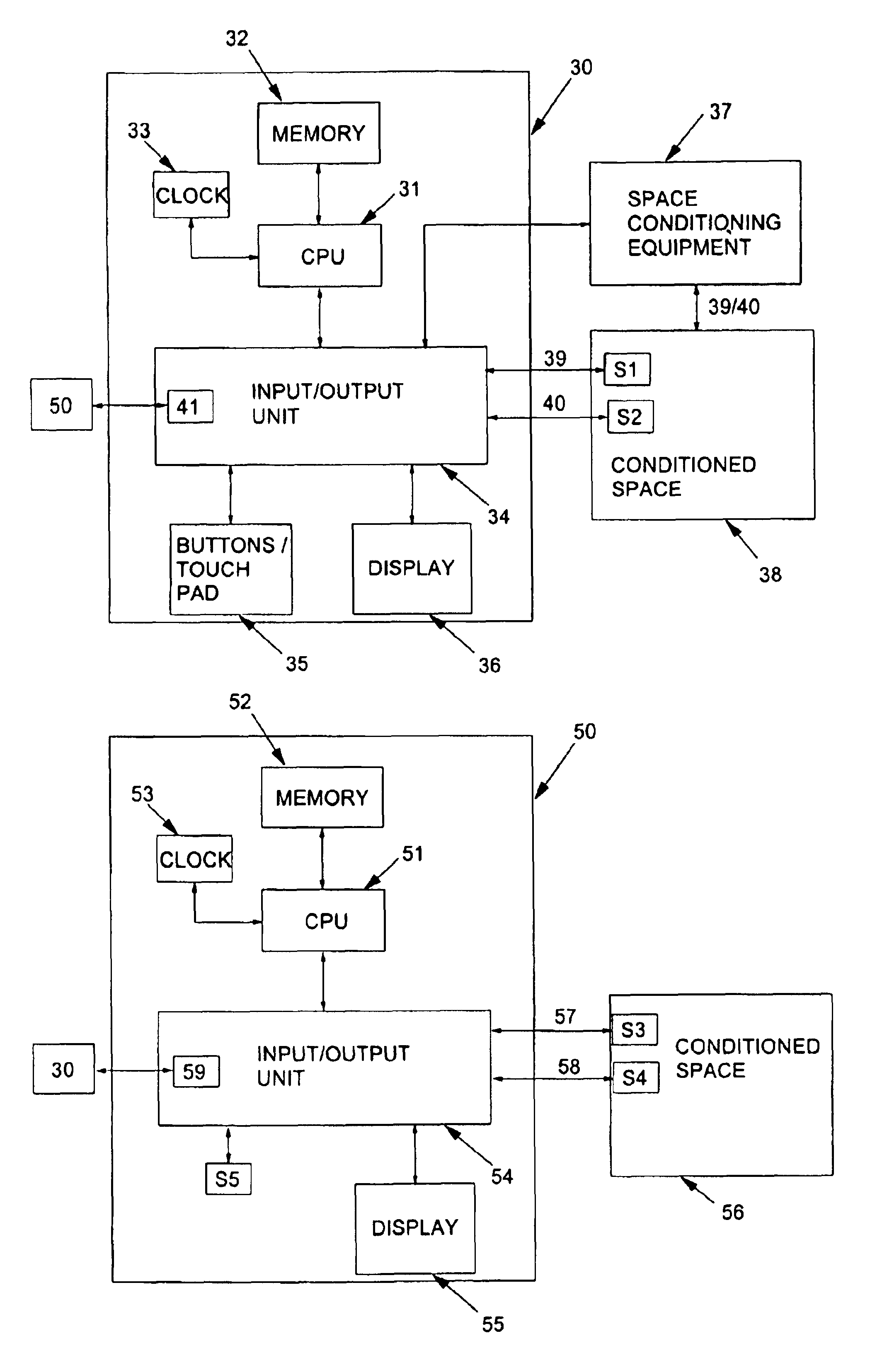
ActiveUSRE40437E1Sampled-variable control systemsTemperature control without auxillary powerData averagingData information
A thermostat system according to the invention includes: a central control device (typically a programmable thermostat with a processor having: a CPU, real time clock and a memory for storing a control program and data information), multiple rooms comprising a conditioned space, environmental control equipment, and multiple environmental sensors capable of sensing an environmental condition (such as temperature, humidity, or other condition). The sensors are associated with transmission means, which control transmission of sensor signals, and occupancy sensors. Each sensor measures a local environmental condition. Occupancy sensors comprise infrared or other motion sensors, light detection sensors, door opening sensors, and other such sensors that detect the presence of humans in a room of the conditioned space where its associated sensor is located. Space conditioning equipment is activated by comparison of a setpoint to a control value averaged from values of environmental conditions in occupied rooms.
Owner:ROSEN TECH LLC
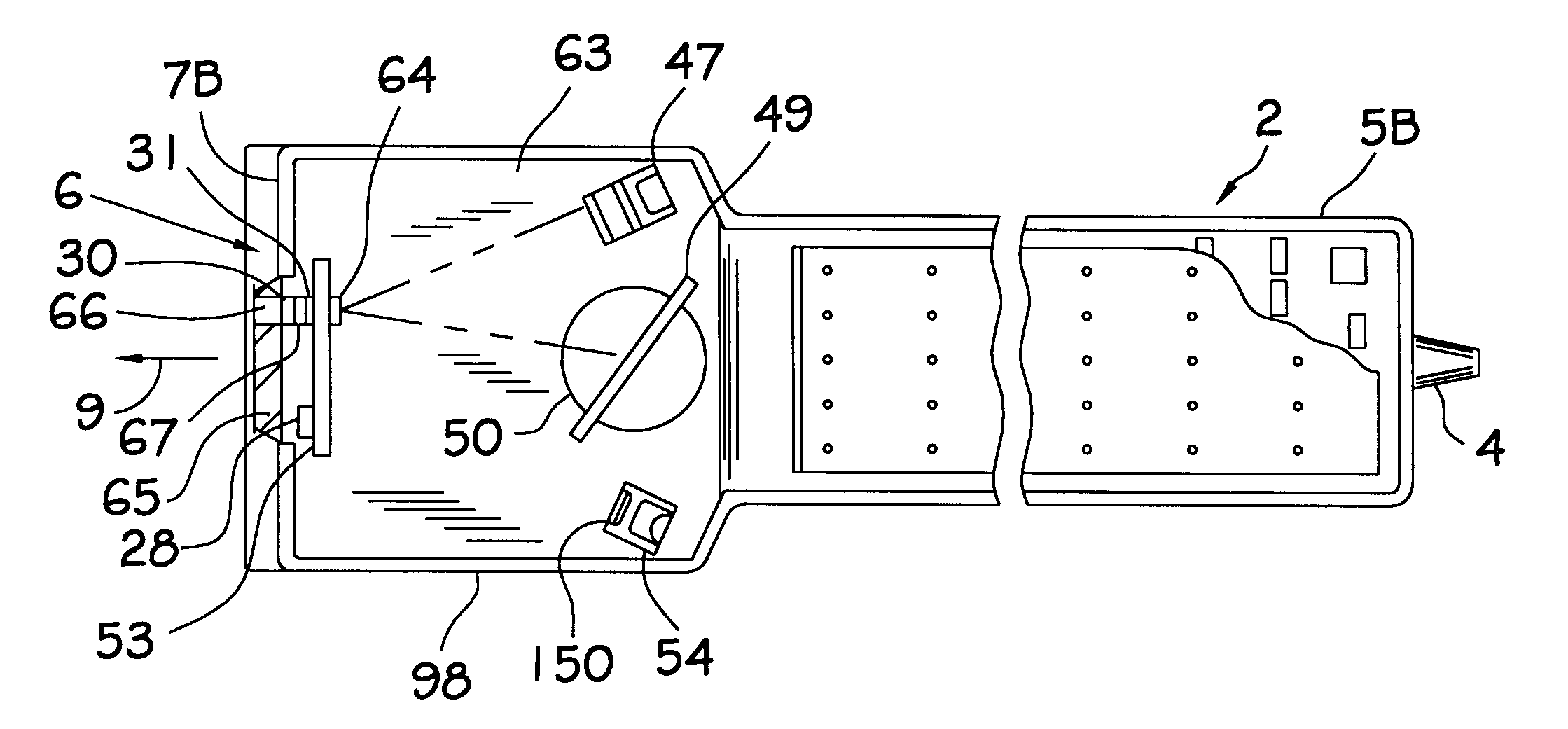
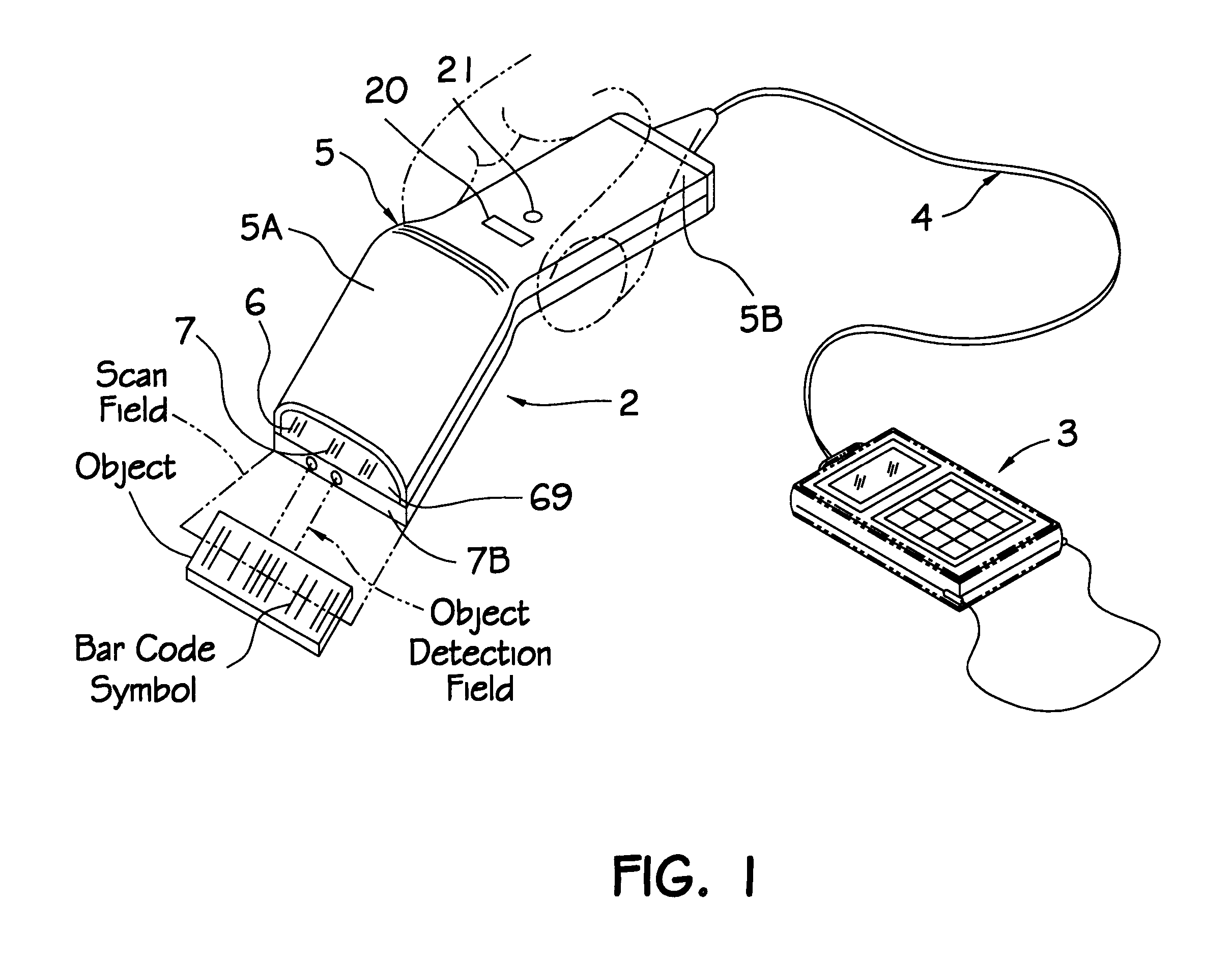
Optical filtering system for a laser bar code scanner having narrow band-pass characteristics employing spatially separated filtering elements including a scanner window
InactiveUS6209789B1Good lookingImprove manufacturabilityMirrorsCo-operative working arrangementsBand-pass filterBarcode
A novel optical filtering system for a laser bar code scanner having narrow band-pass characteristics is disclosed. The optical filtering system has two different optical filtering elements which are disposed in a scanner housing in a spatially separate relationship. One of the optical filtering elements is positioned inside of the scanner housing in front of and close to the light detection element. The other optical filtering element is positioned in the light transmission aperture of the scanner housing and forms the scanning window. The optical filtering characteristics of the scanning window obscure the internal components of the scanner from plain view making the scanner appear more aesthetically pleasing. Together the optical filtering element cooperate to form a narrow-band pass filter to provide for better light collection and scanning.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
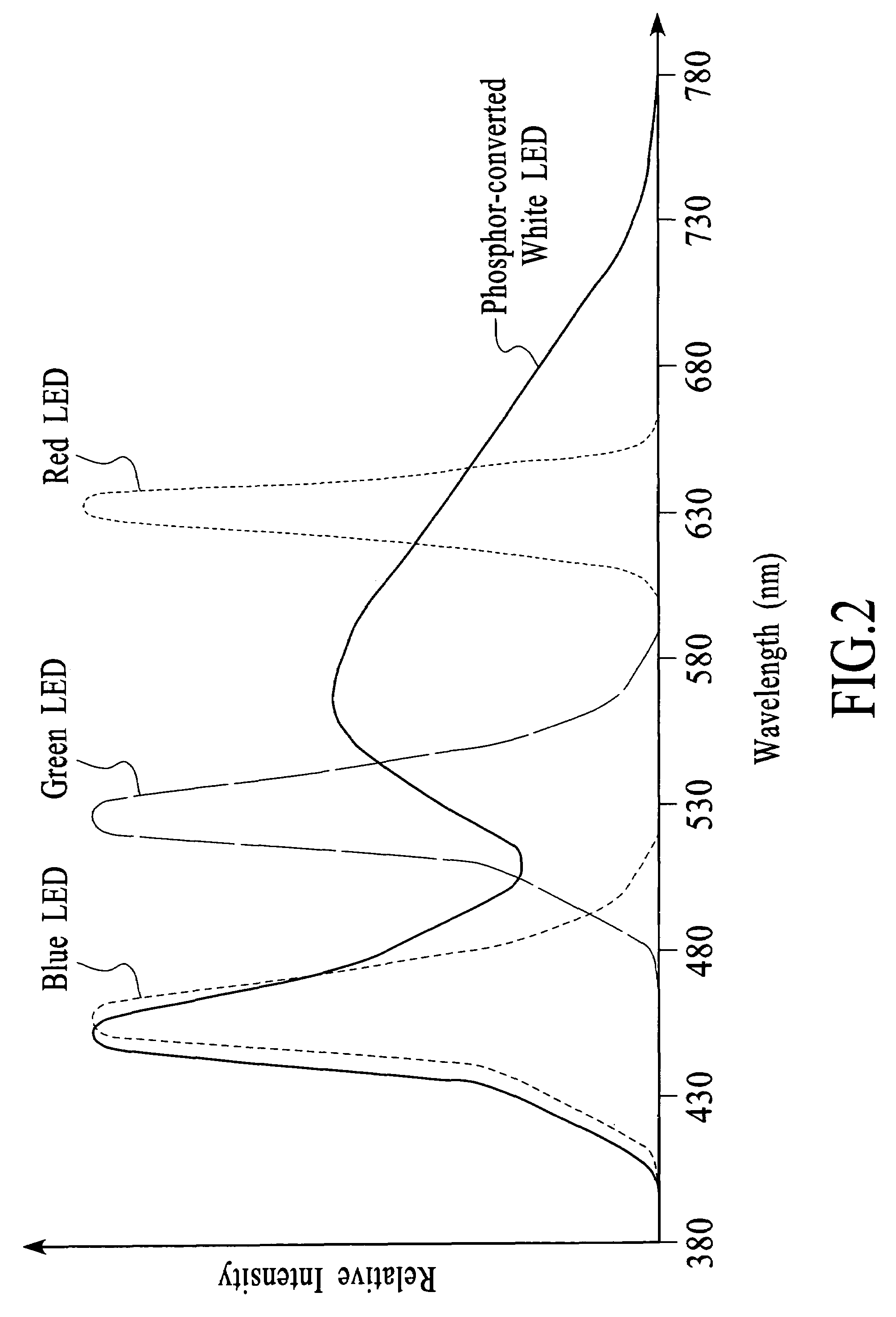
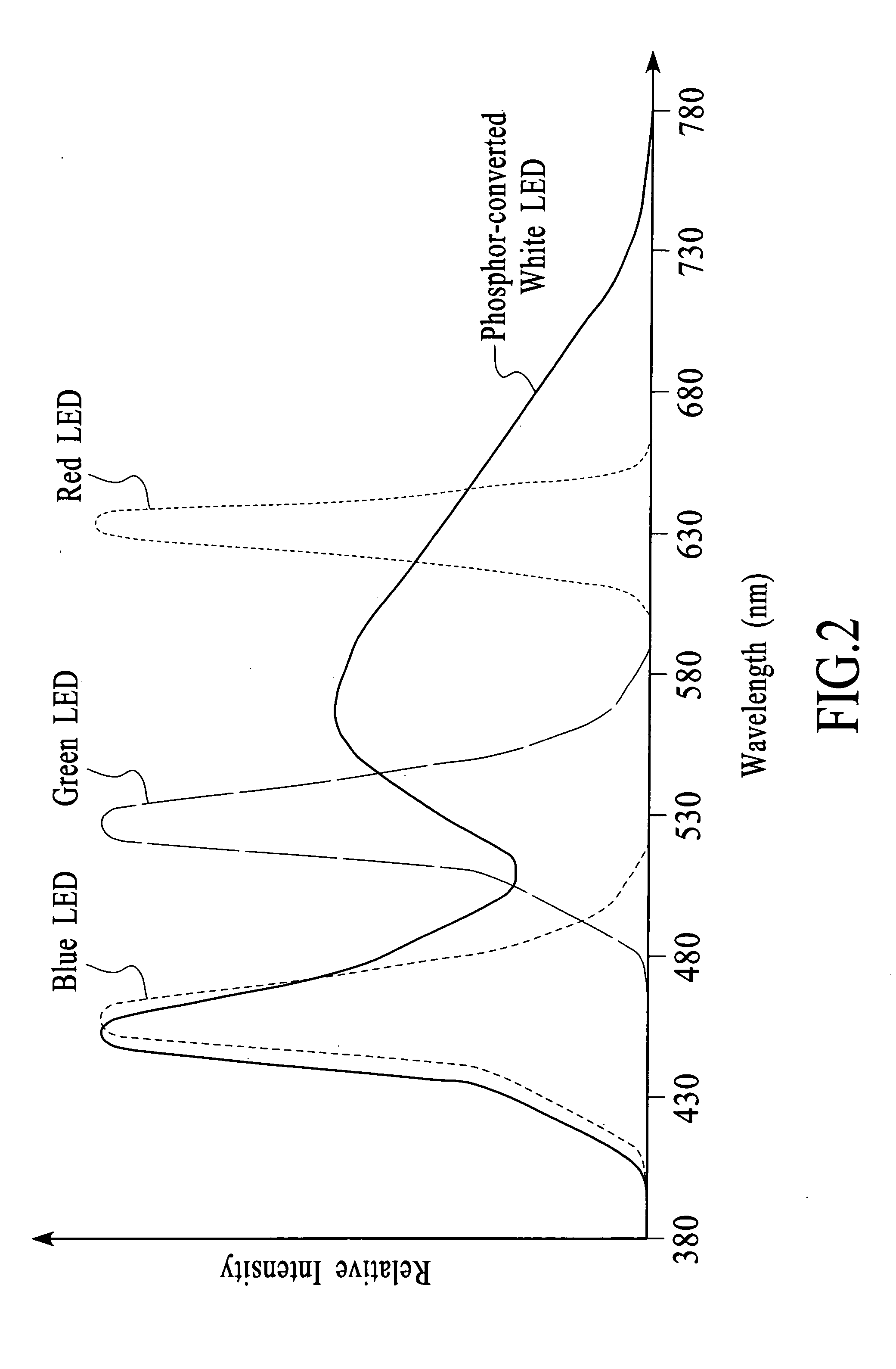
System and method for producing white light using LEDs
ActiveUS7009343B2High color rendering indexWide SPDStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesControl systemControl signal
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Input device based on frustrated total internal reflection
ActiveUS7432893B2Reduce decreaseInternal reflectionStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingLight beamTotal external reflection
A touch panel in which two or more light sensors emit light into a transparent panel at an angle to sustain transmission through the panel by total internal reflection. The transmitted light is detected at an array of light detection positions around the periphery of the panel opposite to each light source. When an object contact the surface of the panel, light transmitted along the pathway from a given source past the contact point to one of the detection points is attenuated by the frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR) effect. Each contact causes two or more intersecting light beams having known end points to be attenuated, enabling a connected processor to determine the position and size of the contact area.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Full-Field Light Detection and Ranging Imaging System
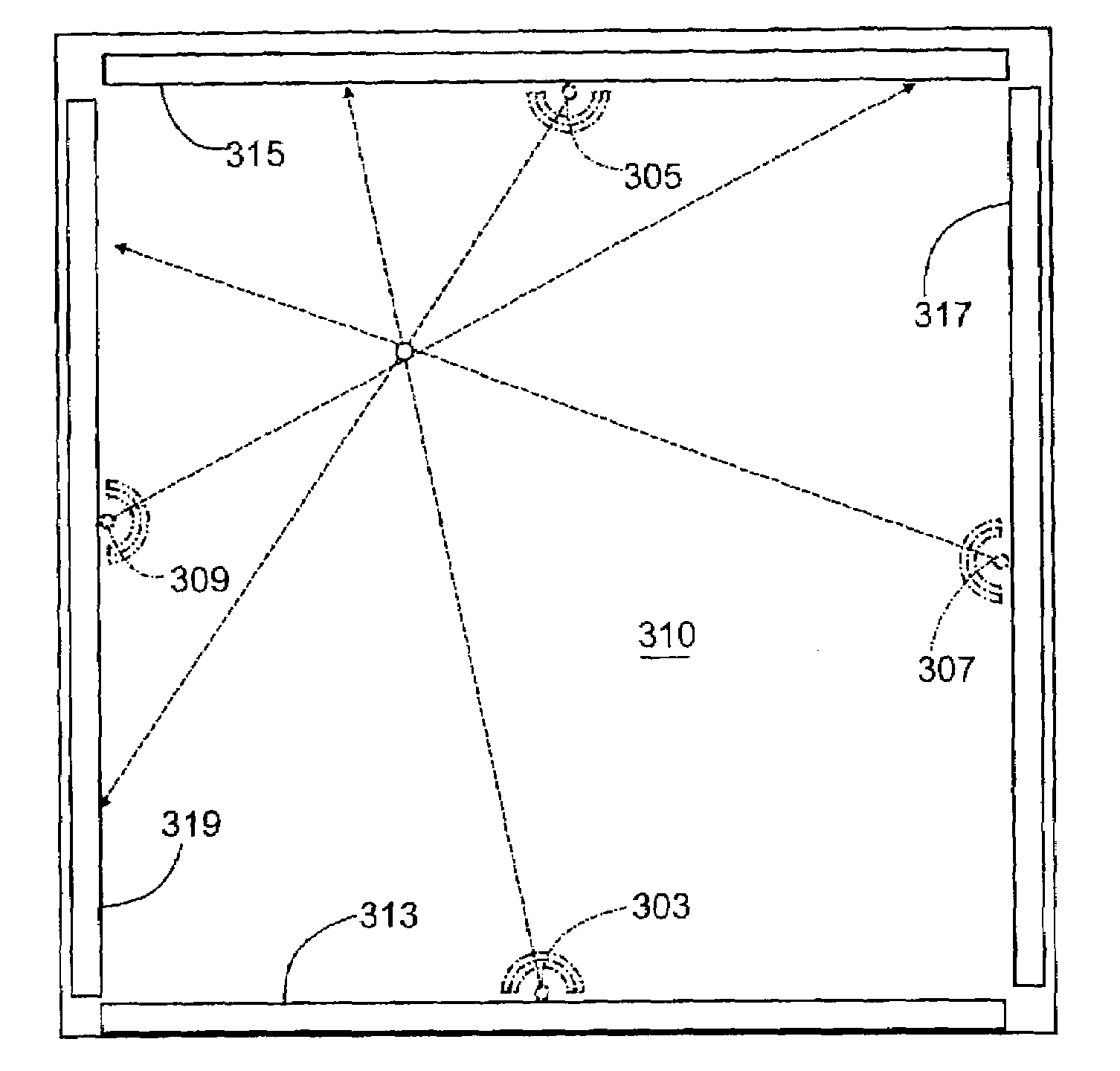
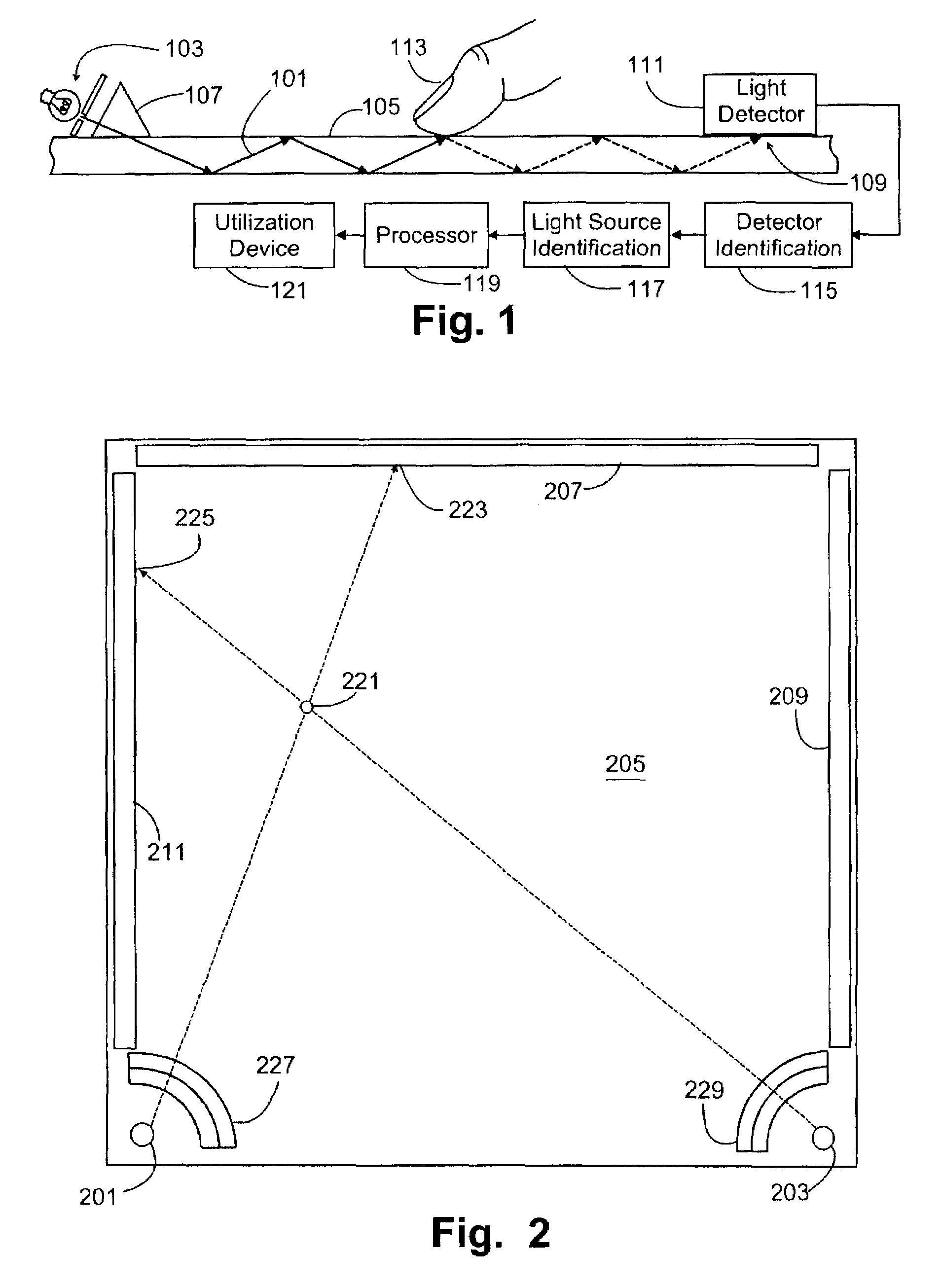
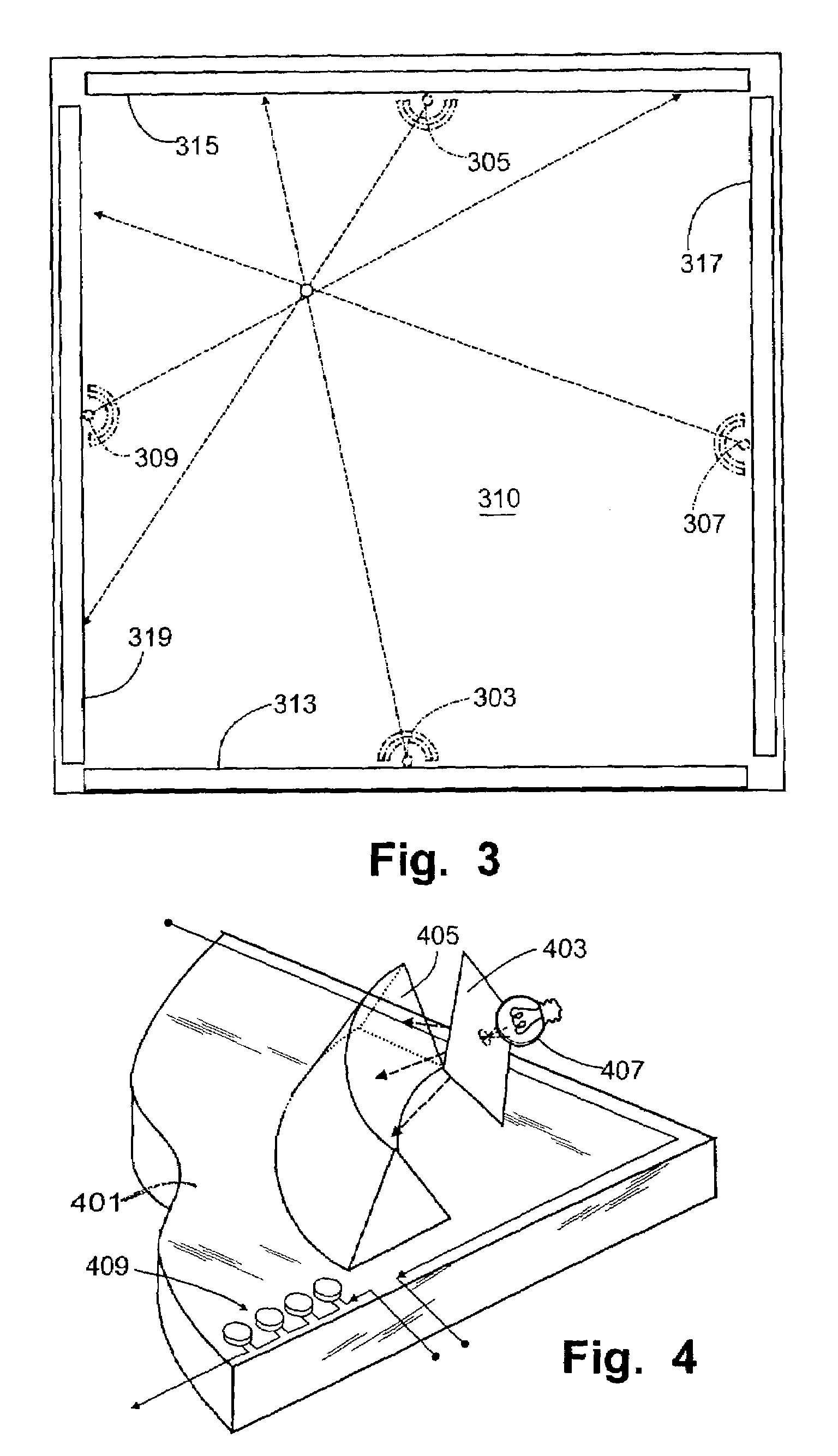
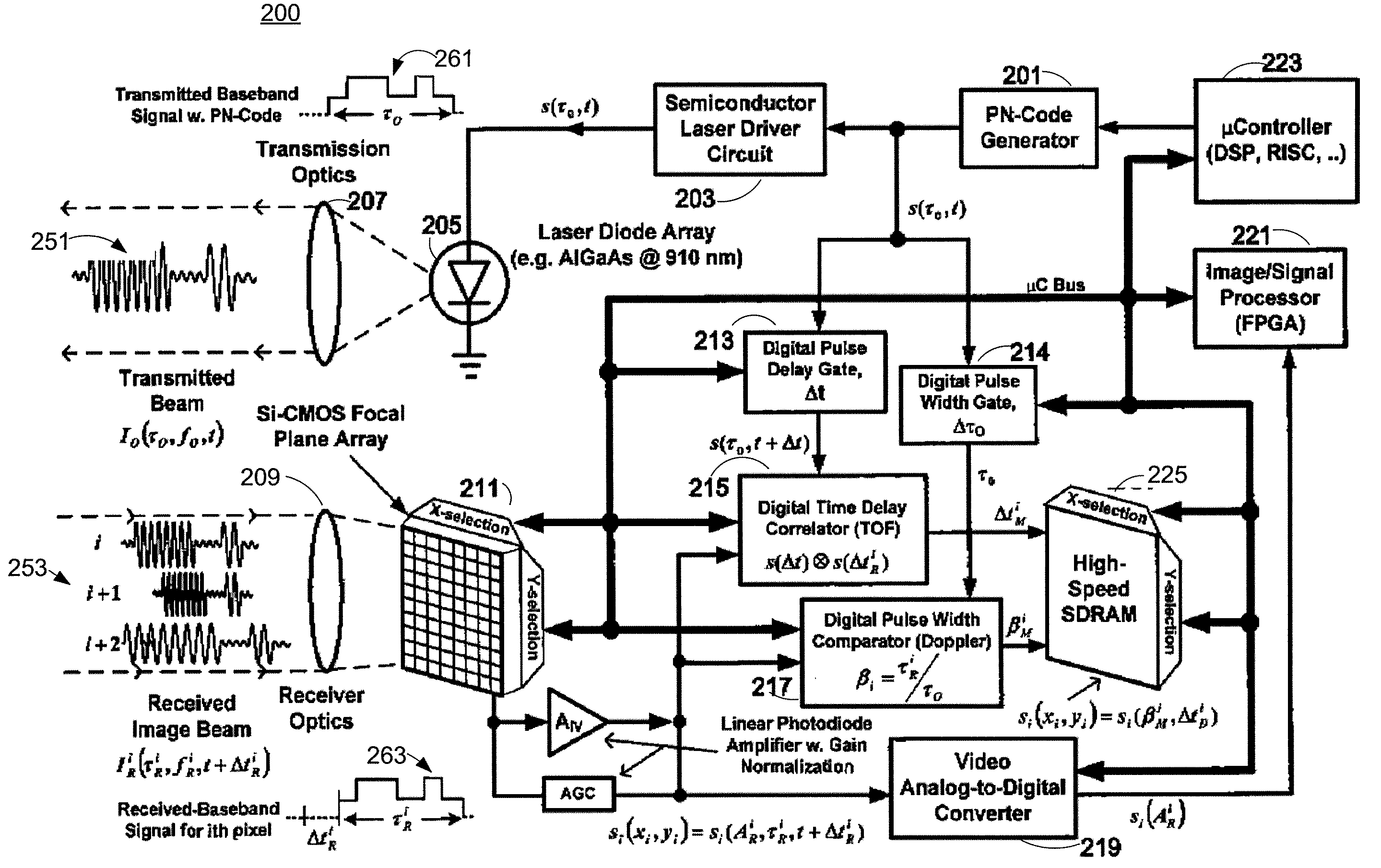
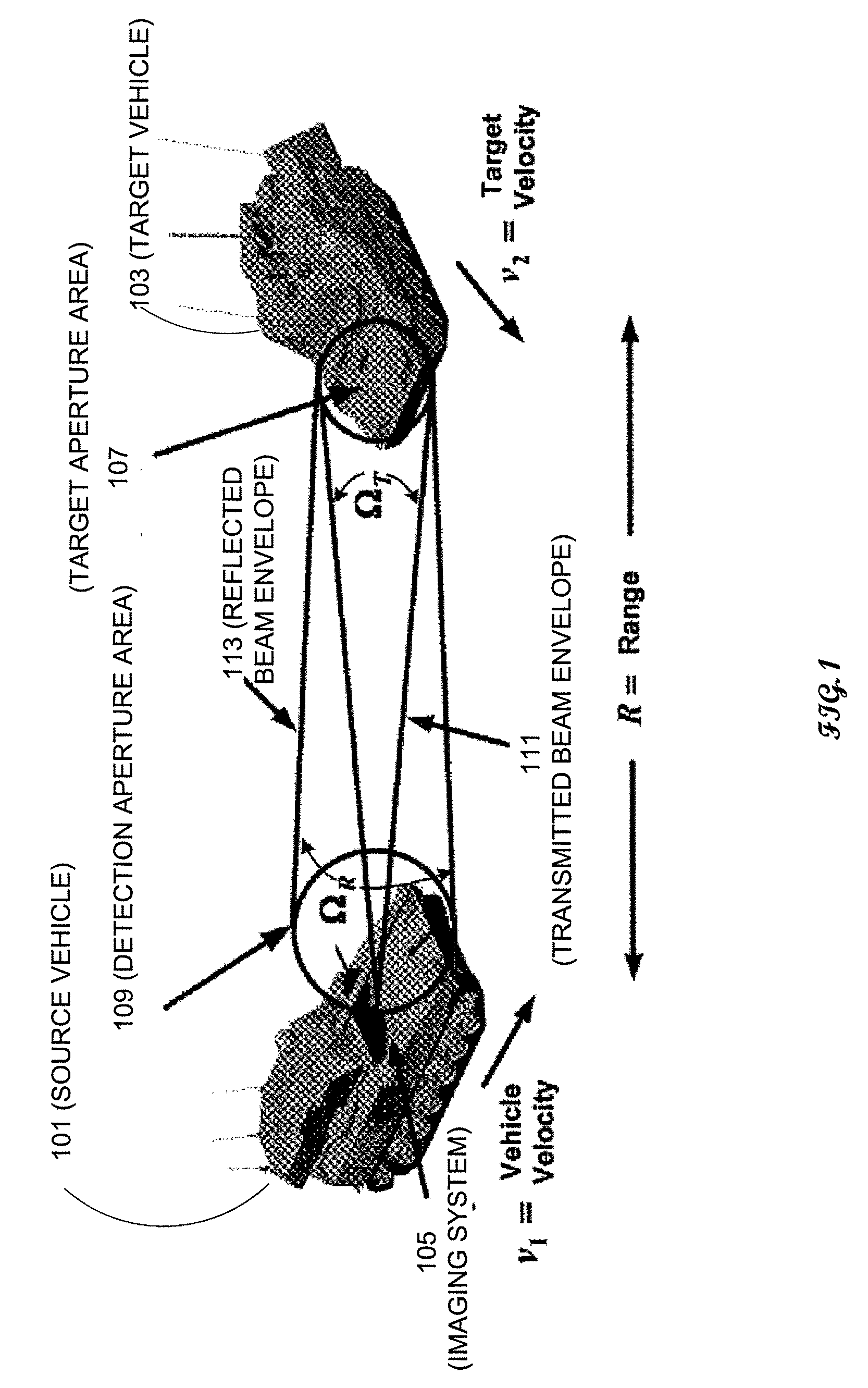
Apparatuses and methods determine positional information from a reflected optical signal for an object on a per pixel basis. A spread spectrum imaging system includes a transmitting module transmitting a transmitted optical signal that illuminates a target space and contains a transmitted pulse that is modulated with a first pseudo-noise (PN) code. The imaging system includes a receiving module that receives a reflected optical signal from an object. The reflected signal is processed by an optical array that detects a detected signal from the reflected optical signal, where the detected signal contains a plurality of pixels spanning a target space. When the determined PN code corresponds to the selected PN code, image information and the positional information is presented for the object. When different positional information is obtained for different pixels in the image, the imaging system may determine that different objects appear in the received image.
Owner:SCI APPL INT CORP
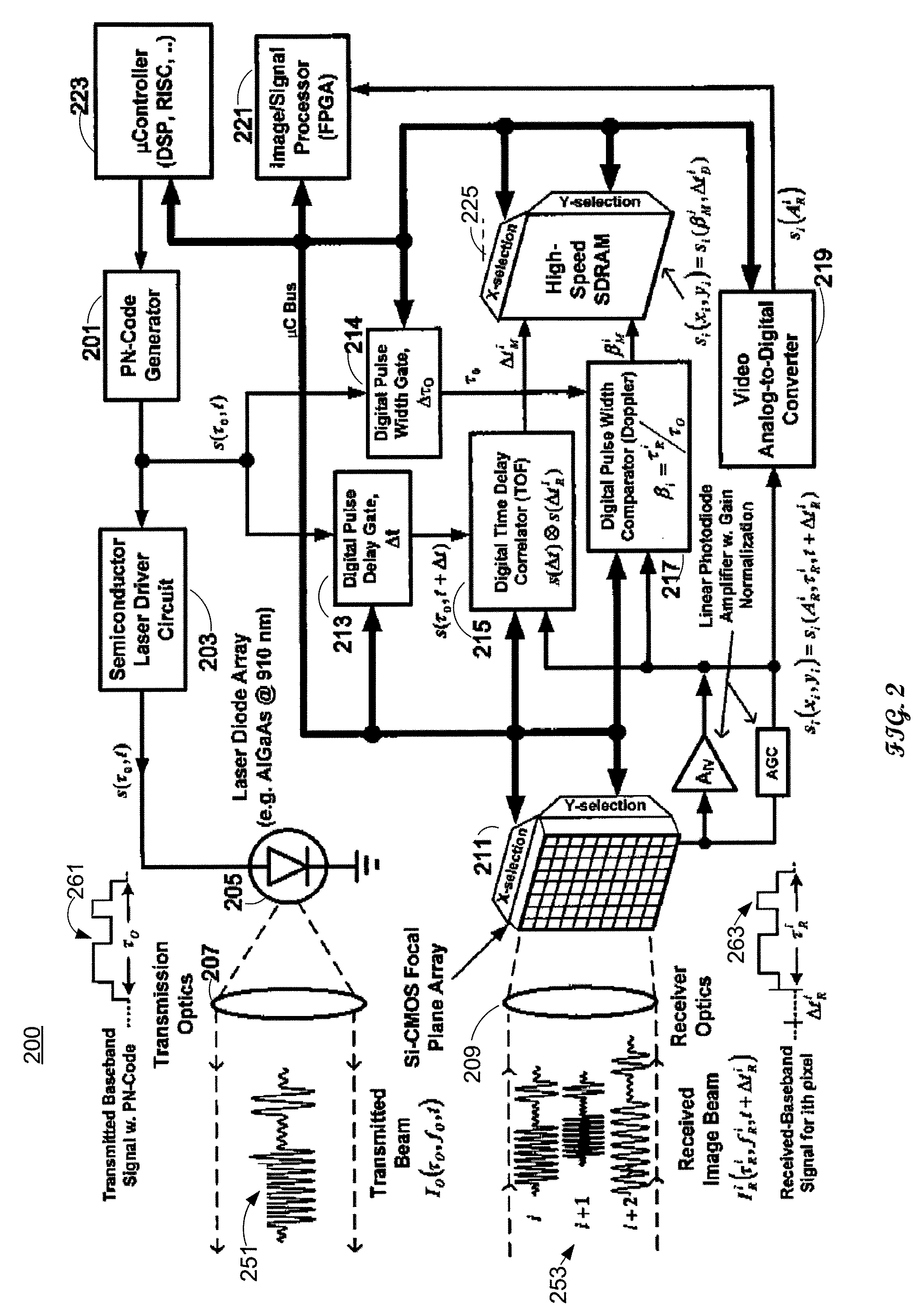
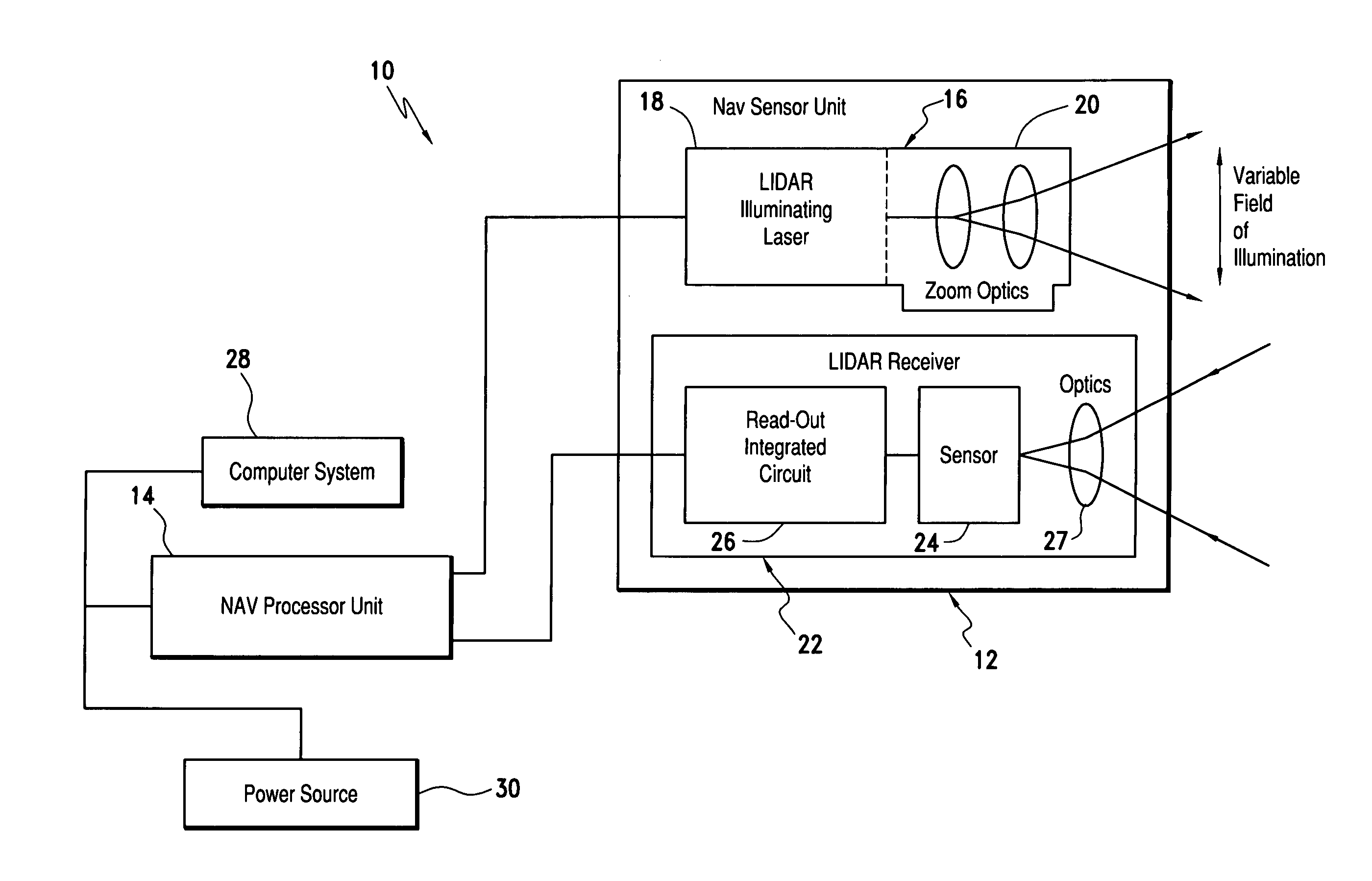
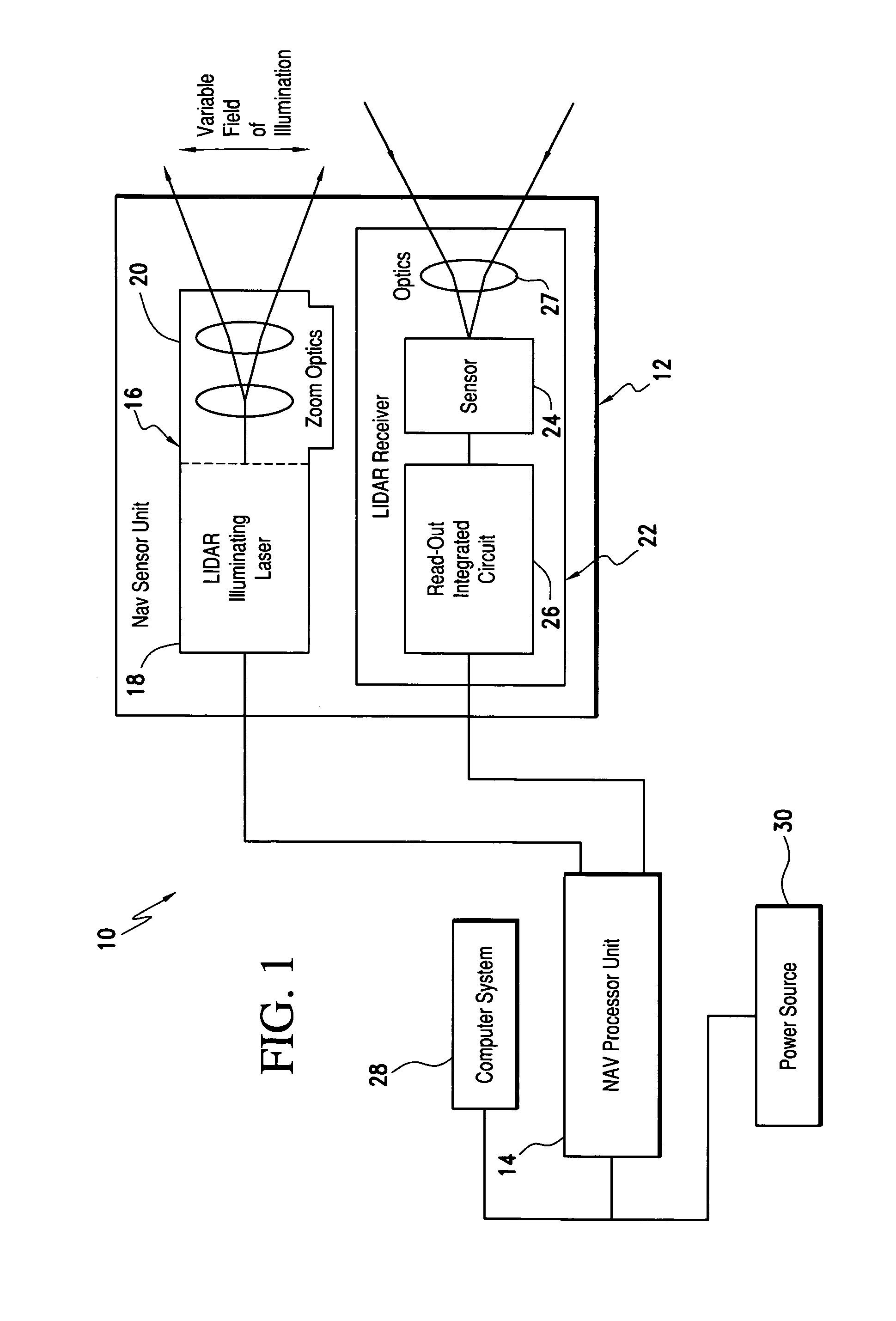
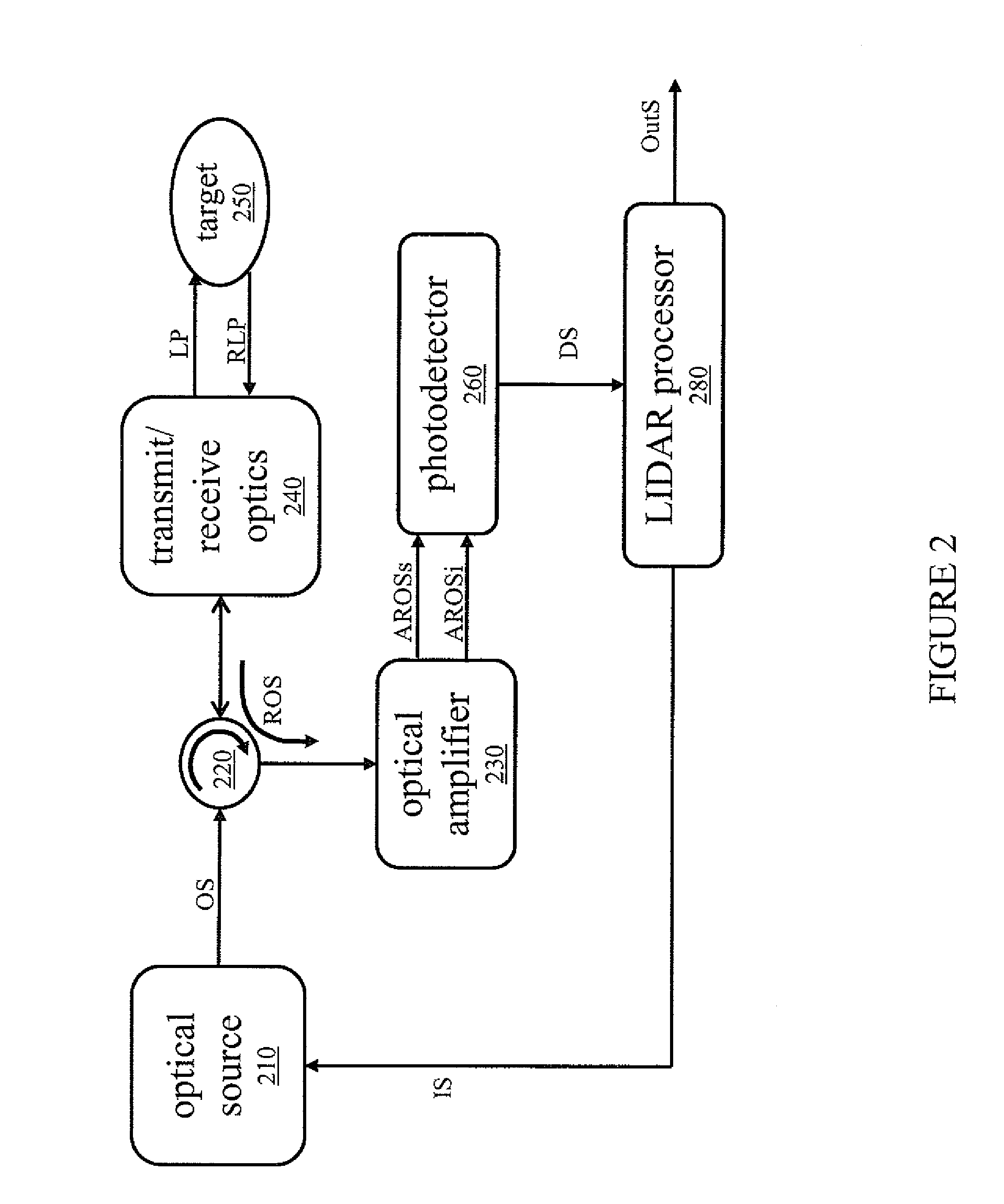
Laser range finding system using variable field of illumination flash lidar
ActiveUS8072581B1Reduce areaReduce resolutionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingImage resolution
The laser range finding system includes a light detection and ranging (LIDAR) sensor unit (SU) and a LIDAR processor unit (PU). The LIDAR SU is for transmitting light pulses and receiving resulting input light signals reflected from objects within the field of view of the SU. The LIDAR SU includes a flash LIDAR illuminating laser source for transmitting light pulses. The LIDAR illuminating laser source includes an illuminating laser and zoom optics operatively associated with the laser. A LIDAR receiver receives resulting input light signals reflected from the objects. The LIDAR receiver includes a sensor; and, a flash readout integrated circuit (IC). The flash readout IC measures the transit time of the light pulses. The LIDAR processor unit (PU) is operatively associated with the LIDAR SU and it utilizes flash LIDAR ranging. A power source is operatively coupled to the LIDAR PU. Zooming of the transmitted light pulses results in the received resulting input light signals illuminating a relatively reduced area of the frame. Thus, a flash LIDAR image of relatively reduced resolution but enhanced range is provided by utilization of the transit time measurements.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
GNSS and optical guidance and machine control
ActiveUS20140324291A1Accurate and economical preplannedEasy to correctDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalSteering control
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and gyroscope control system for vehicle steering control comprising a GNSS receiver and antennas at a fixed spacing to determine a vehicle position, velocity and at least one of a heading angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle based on carrier phase position differences. The system also includes a control system configured to receive the vehicle position, heading, and at least one of roll and pitch, and configured to generate a steering command to a vehicle steering system. A vehicle control method includes the steps of computing a position and a heading for the vehicle using GNSS positioning and a rate gyro for determining vehicle attitude, which is used for generating a steering command. Relative orientations and attitudes between tractors and implements can be determined using optical sensors and cameras. Laser detectors and rangefinders can also be used.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
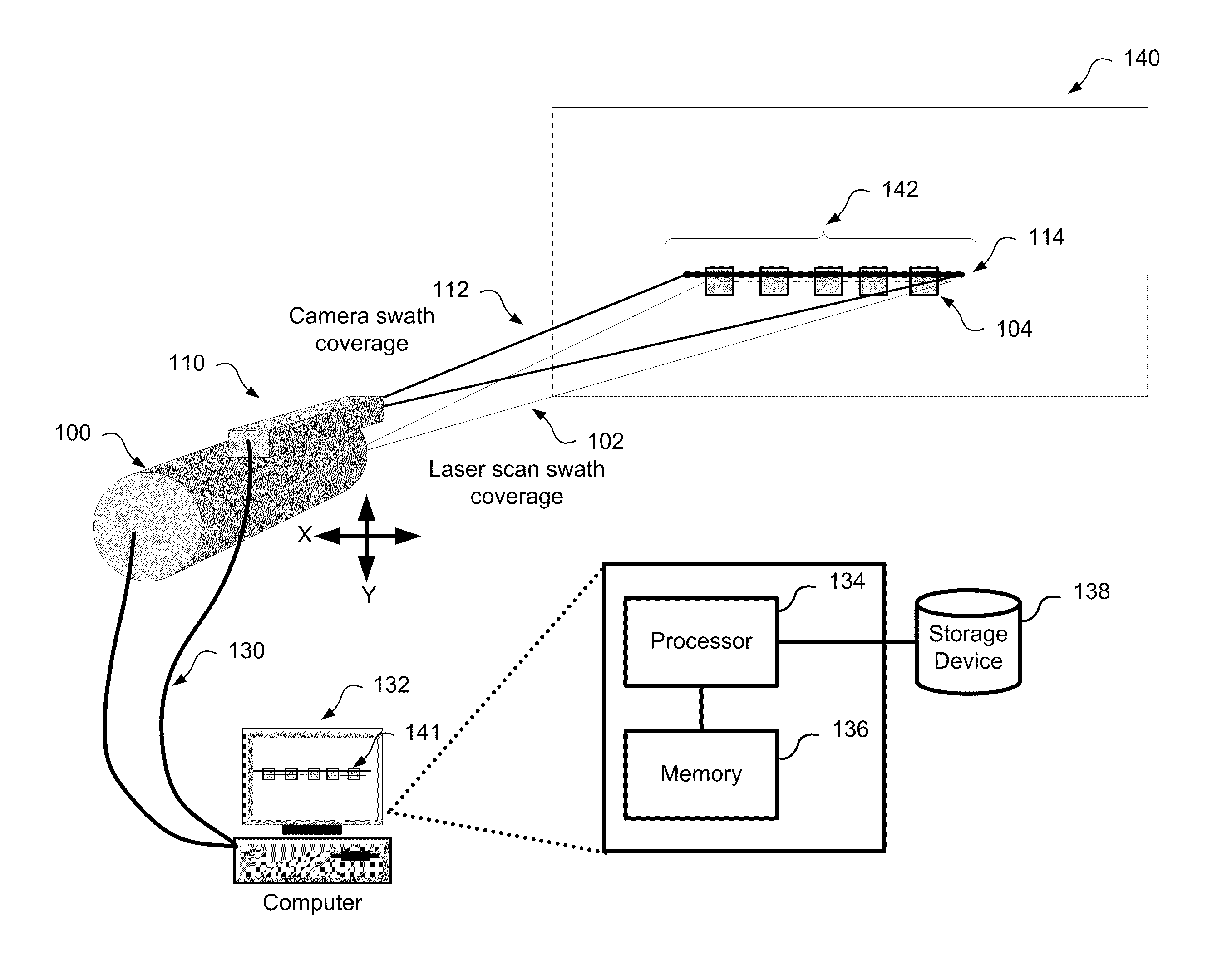
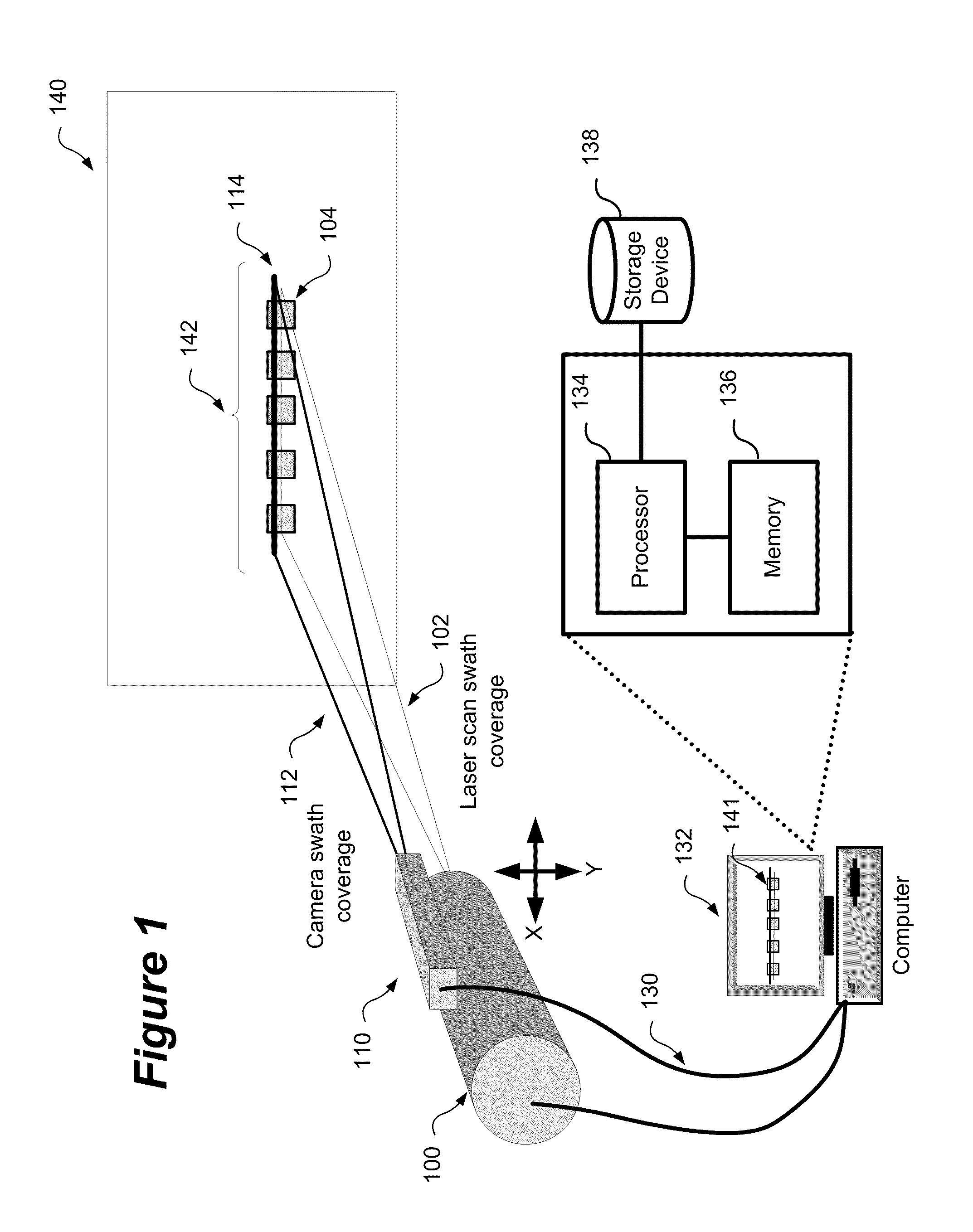
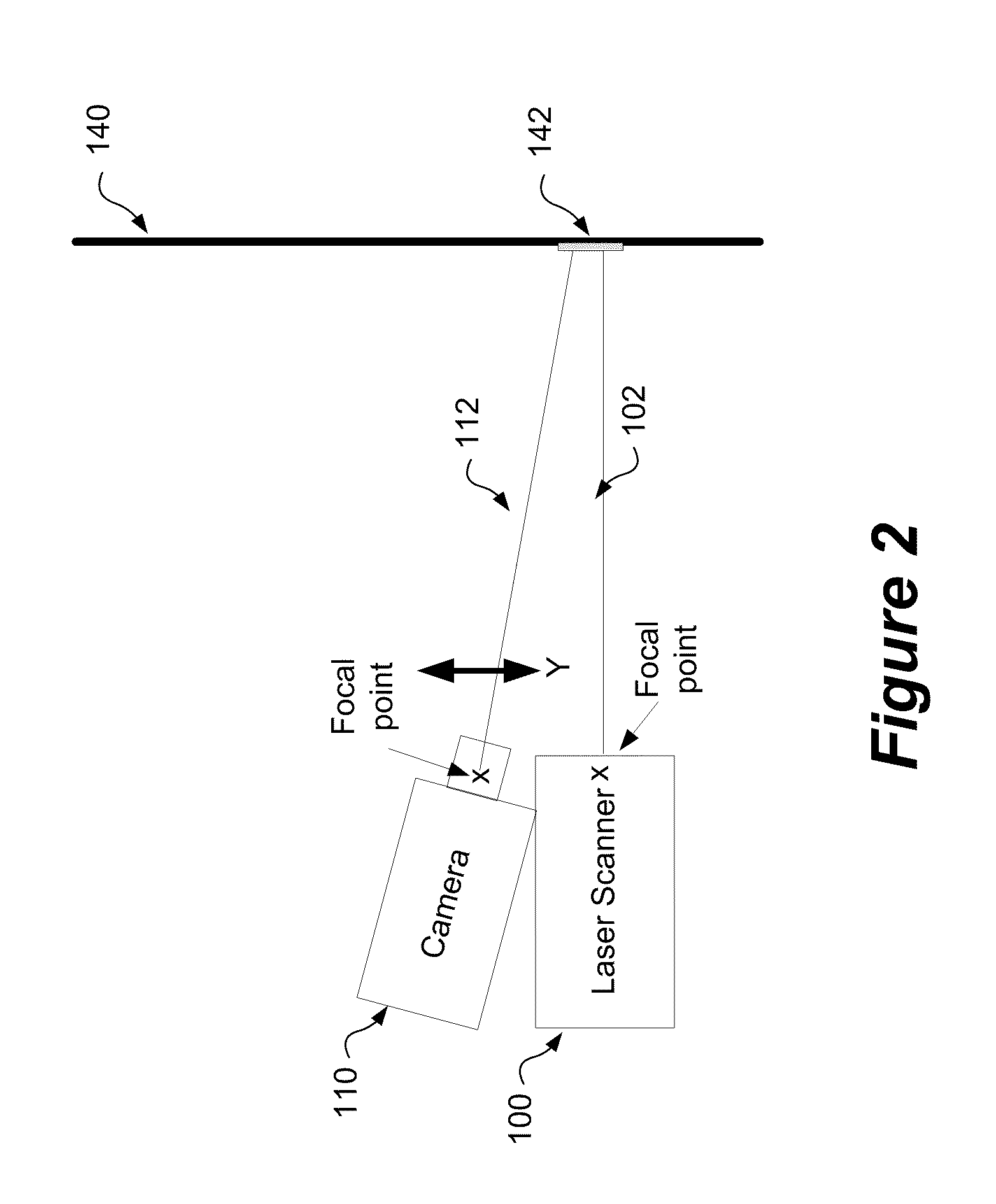
Method and system for aligning a line scan camera with a lidar scanner for real time data fusion in three dimensions
An apparatus and method for aligning a line scan camera with a Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) scanner for real-time data fusion in three dimensions is provided. Imaging data is captured at a computer processor simultaneously from the line scan camera and the laser scanner from target object providing scanning targets defined in an imaging plane perpendicular to focal axes of the line scan camera and the LiDAR scanner. X-axis and Y-axis pixel locations of a centroid of each of the targets from captured imaging data is extracted. LiDAR return intensity versus scan angle is determined and scan angle locations of intensity peaks which correspond to individual targets is determined. Two axis parallax correction parameters are determined by applying a least squares. The correction parameters are provided to post processing software to correct for alignment differences between the imaging camera and LiDAR scanner for real-time colorization for acquired LiDAR data.
Owner:AMBERCORE SOFTWARE
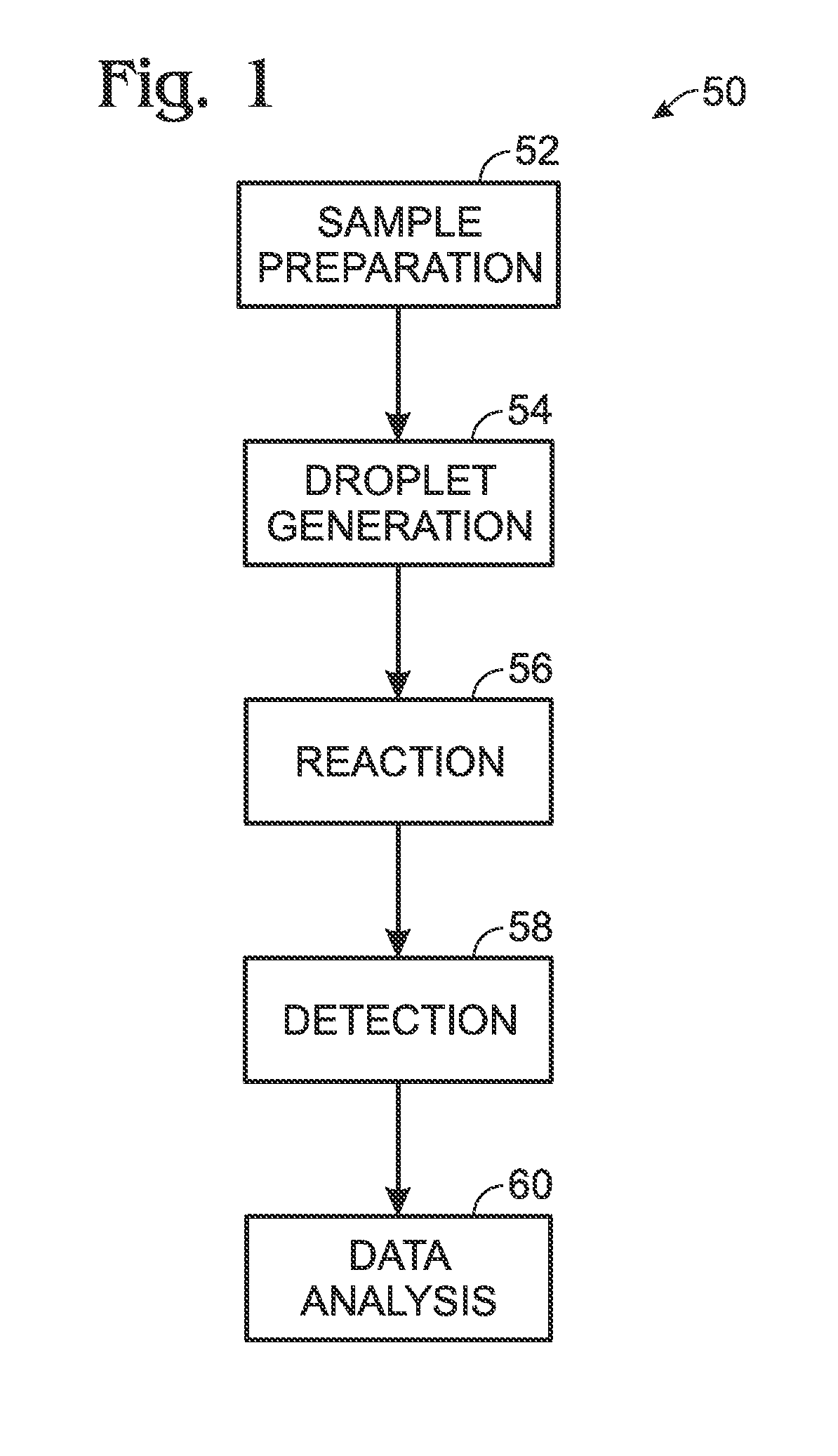
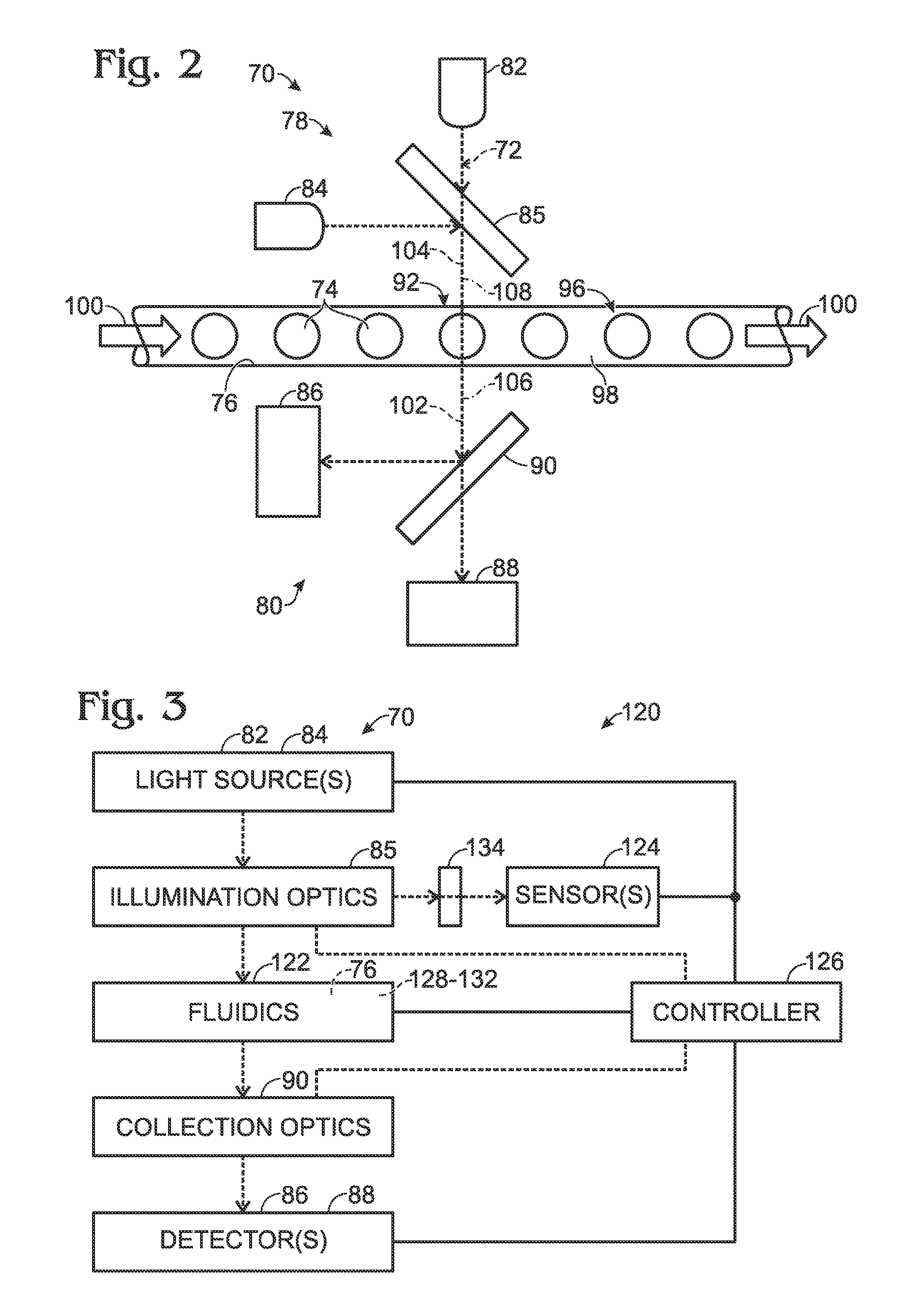
Detection system for droplet-based assays
ActiveUS20120194805A1High-confidence resultLow costPhotometryLaboratory glasswaresAssaySignal processing
System, including methods and apparatus, for light detection and signal processing for droplet-based assays.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Thermostat system with remote data averaging
ActiveUS7058477B1Temperature control without auxillary powerSampled-variable control systemsData averagingData information
A thermostat system according to the invention includes: a central control device (typically a programmable thermostat with a processor having: a CPU, real time clock and a memory for storing a control program and data information), multiple rooms comprising a conditioned space, environmental control equipment, and multiple environmental sensors capable of sensing an environmental condition (such as temperature, humidity, or other condition). The sensors are associated with transmission means, which control transmission of sensor signals, and occupancy sensors. Each sensor measures a local environmental condition. Occupancy sensors comprise infrared or other motion sensors, light detection sensors, door opening sensors, and other such sensors that detect the presence of humans in a room of the conditioned space where its associated sensor is located. Space conditioning equipment is activated by comparison of a setpoint to a control value averaged from values of environmental conditions in occupied rooms.
Owner:ROSEN TECH LLC
System and Method for In Vivo Measurement of Biological Parameters
ActiveUS20090209834A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce decreaseCatheterSensorsControl systemDynamic light scattering
A system, method and medical tool are presented for use in non-invasive in vivo determination of at least one desired parameter or condition of a subject having a scattering medium in a target region. The measurement system comprises an illuminating system, a detection system, and a control system. The illumination system comprises at least one light source configured for generating partially or entirely coherent light to be applied to the target region to cause a light response signal from the illuminated region. The detection system comprises at least one light detection unit configured for detecting time-dependent fluctuations of the intensity of the light response and generating data indicative of a dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement. The control system is configured and operable to receive and analyze the data indicative of the DLS measurement to determine the at least one desired parameter or condition, and generate output data indicative thereof.
Owner:ELFI TECH
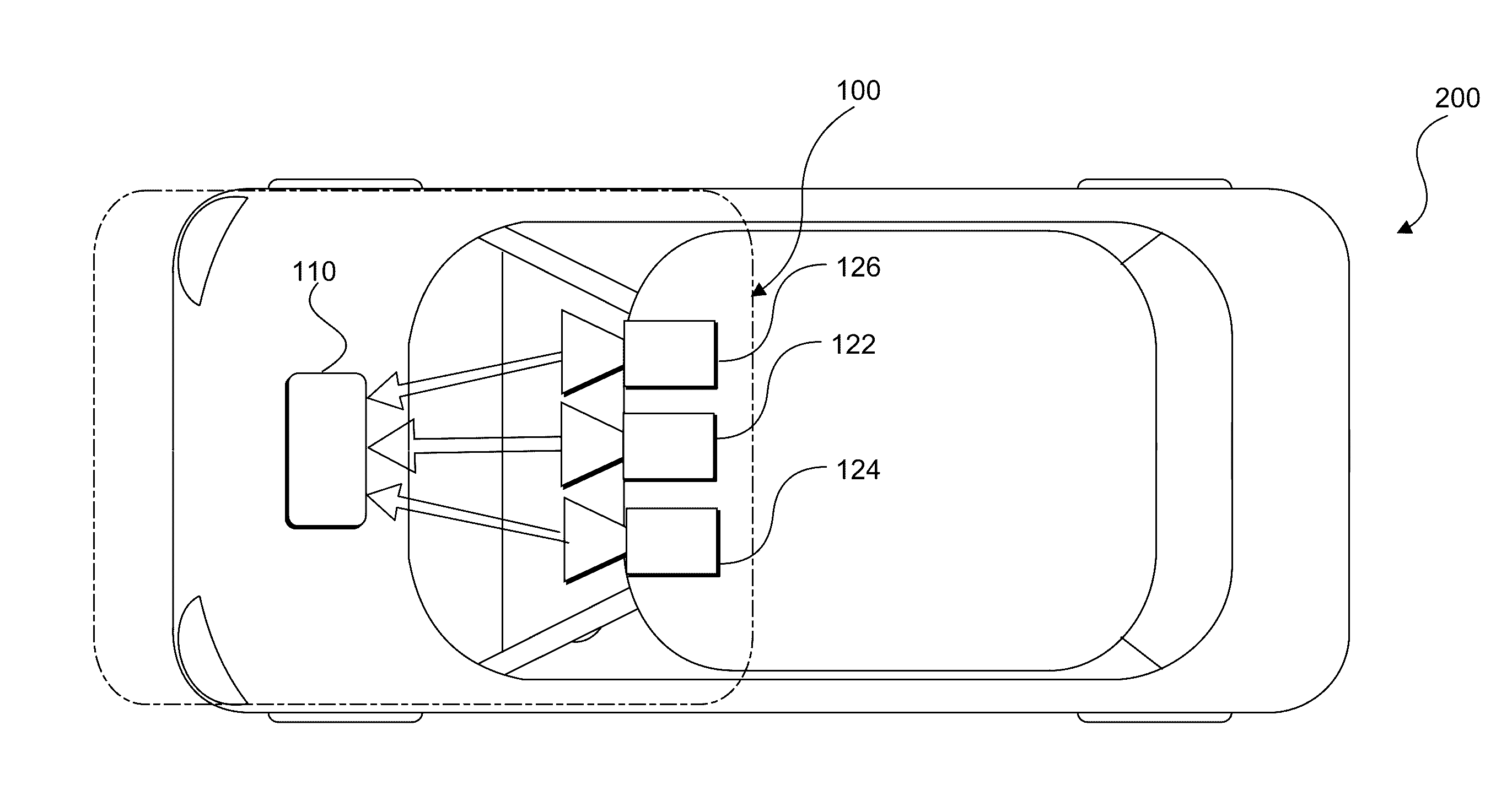
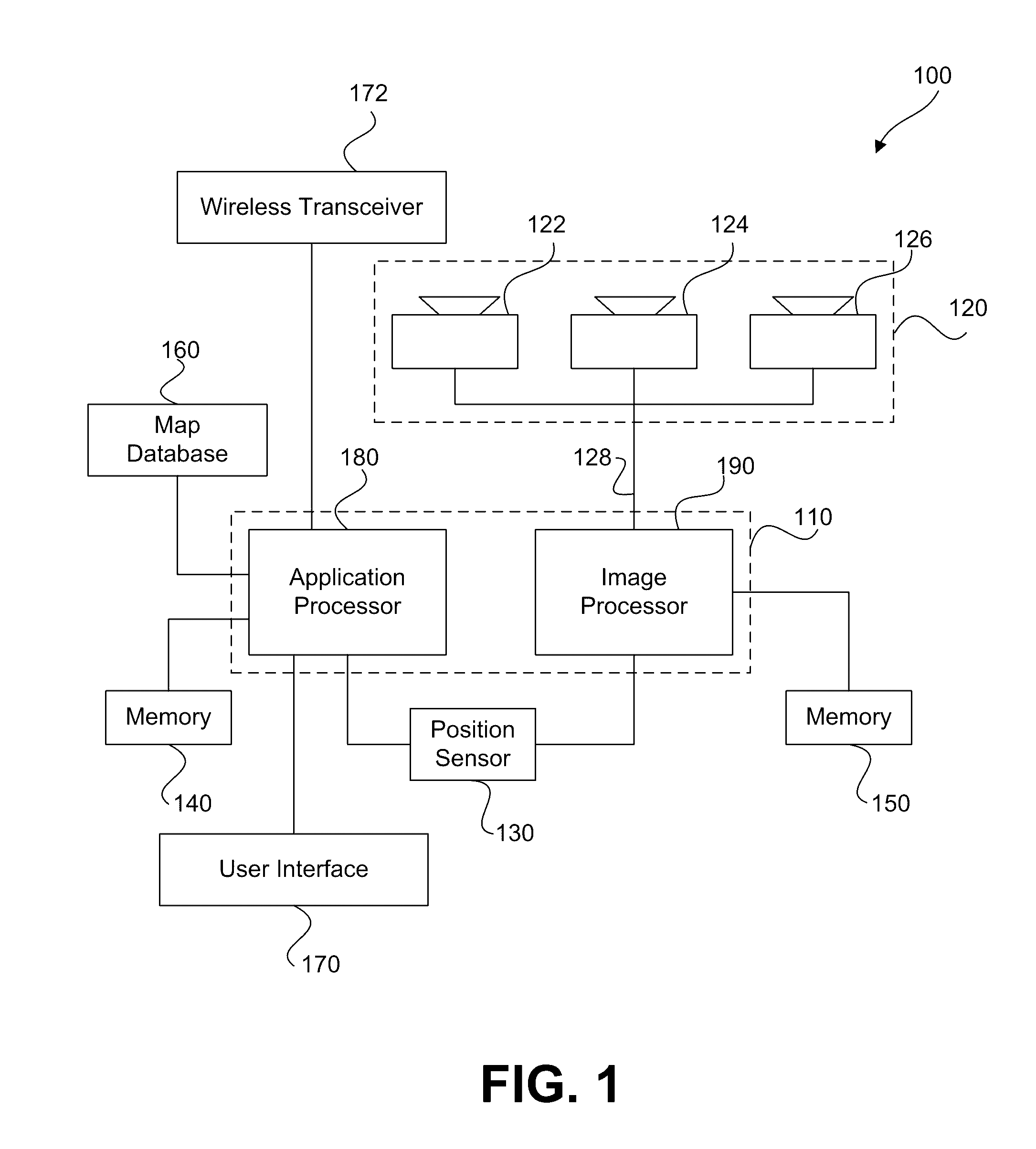
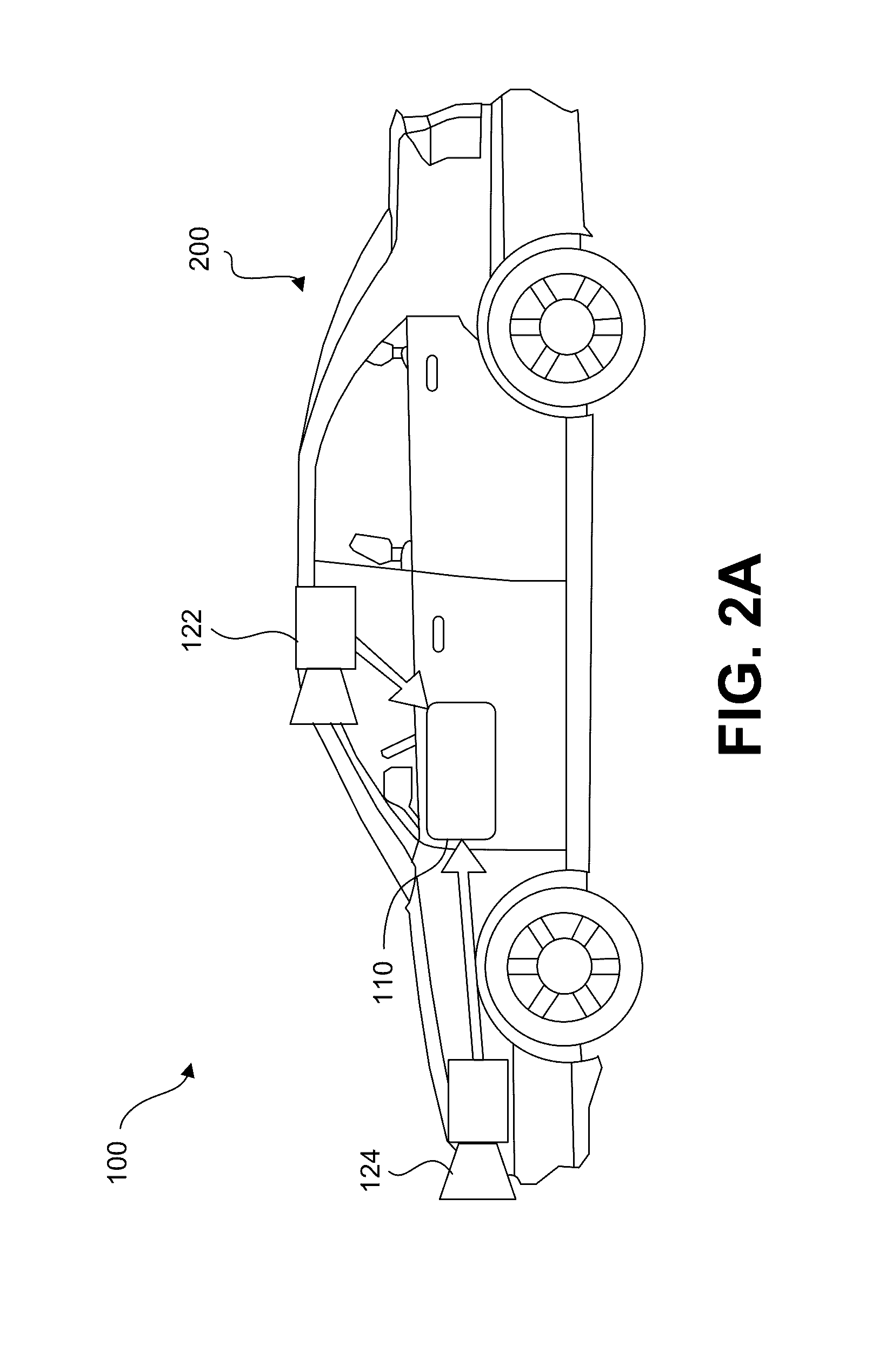
Systems and methods for causing a vehicle response based on traffic light detection
ActiveUS20160318490A1Autonomous decision making processVehicle fittingsImage captureReal-time computing
A traffic light detection system for a vehicle is provided. The system may include at least one processing device programmed to receive, from at least one image capture device, a plurality of images representative of an area forward of the vehicle, the area including a traffic light fixture having at least one traffic light. The at least one processing device may also be programmed to analyze at least one of the plurality of images to determine a status of the at least one traffic light, and determine an estimated amount of time until the vehicle will reach an intersection associated with the traffic light fixture. The at least one processing device may further be programmed to cause a system response based on the status of at least one traffic light and the estimated amount of time until the vehicle will reach the intersection.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080158137A1Reduce power consumptionHighly convenientStatic indicating devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansIlluminanceAudio power amplifier
A photoelectric conversion device includes a light detection circuit which includes an optical sensor to output a current signal corresponding to illuminance and a current-voltage conversion circuit to convert the current signal output from the optical sensor into a voltage signal; an amplifier to amplify the voltage signal output from the light detection circuit; a comparison circuit to compare voltage output from the amplifier and reference voltage and output the result to a control circuit; and the control circuit to determine an illuminance range to be detected depending on the output from the comparison circuit and output a control signal to the light detection circuit. The current-voltage conversion circuit has a function of changing a resistance value in accordance with the control signal.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
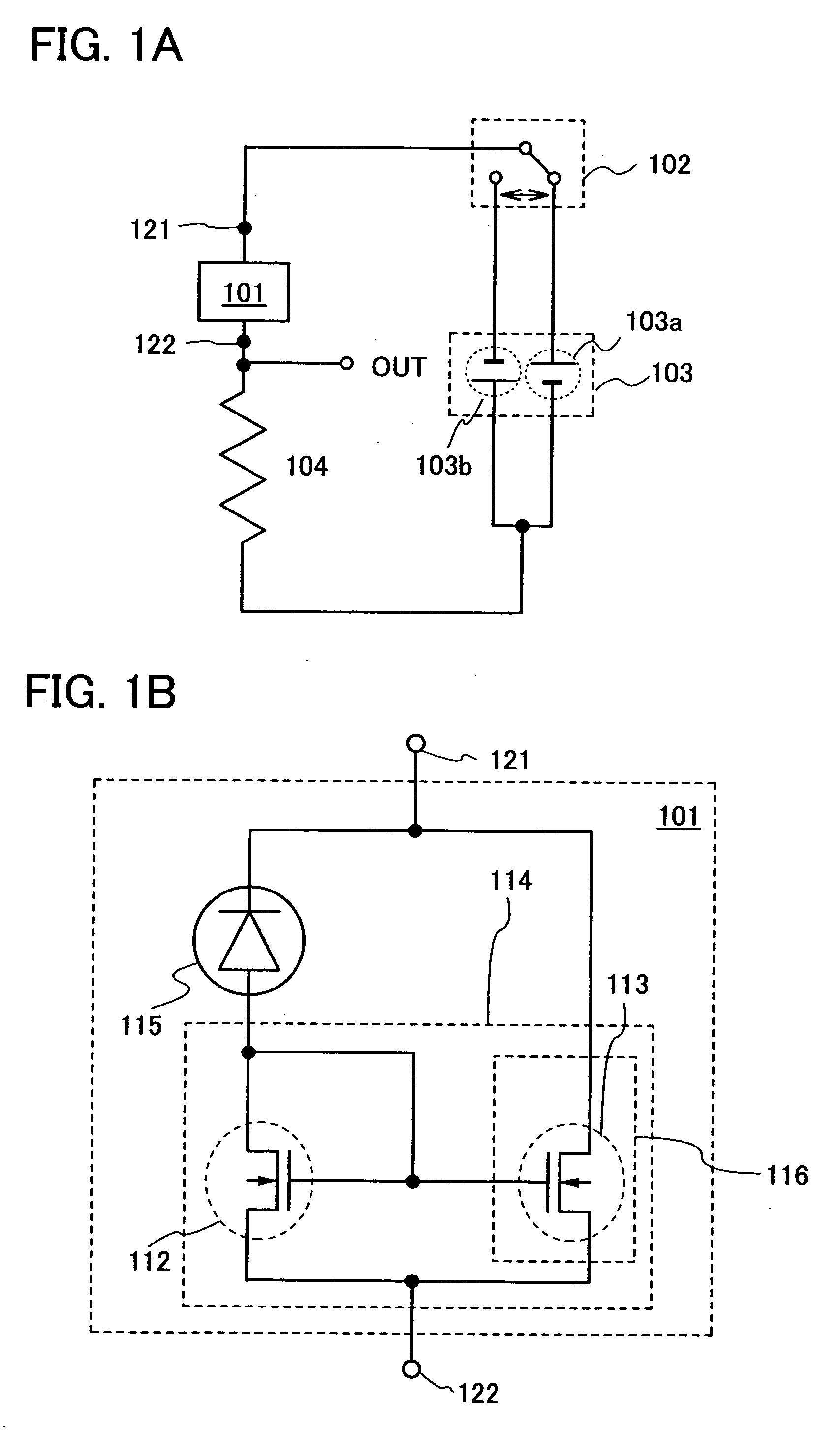
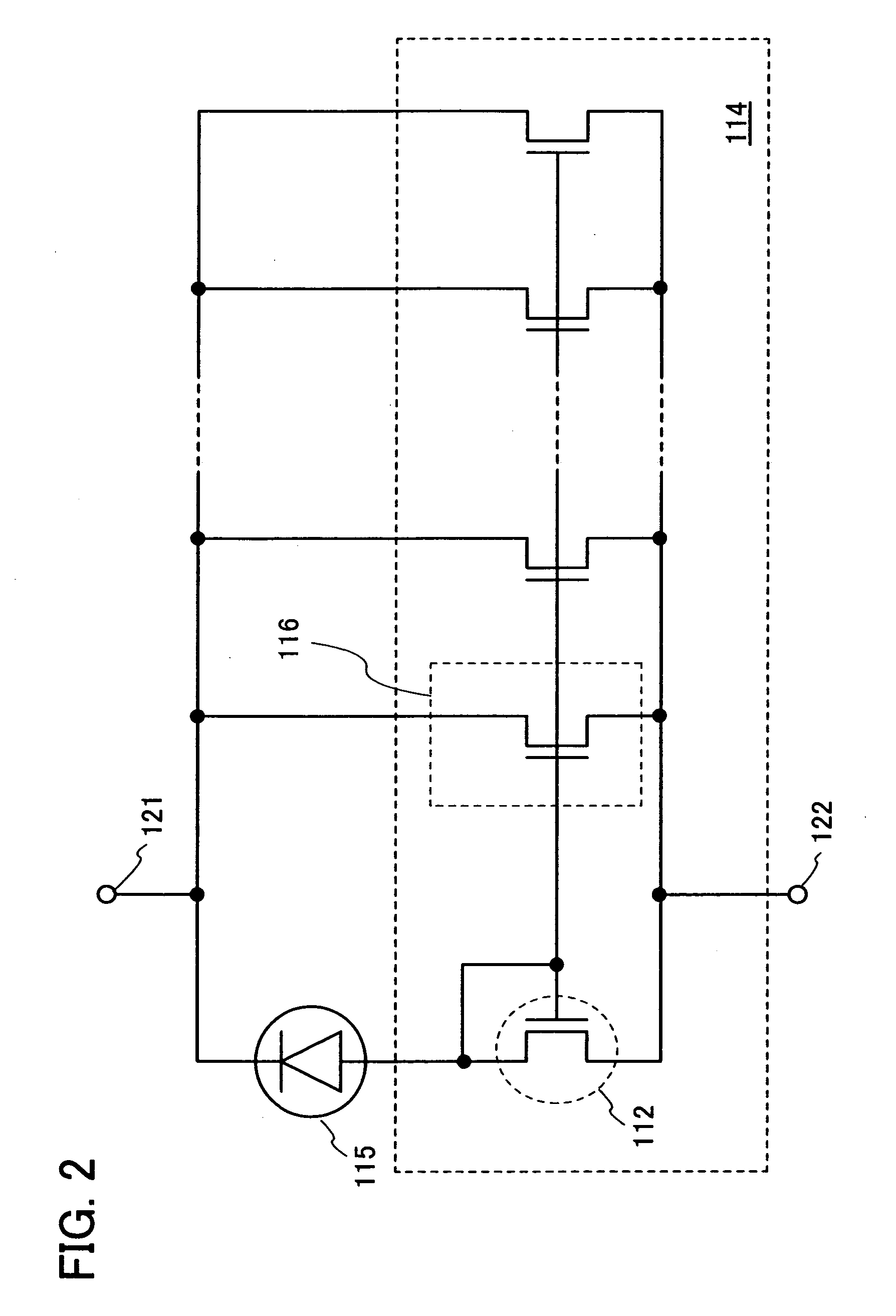
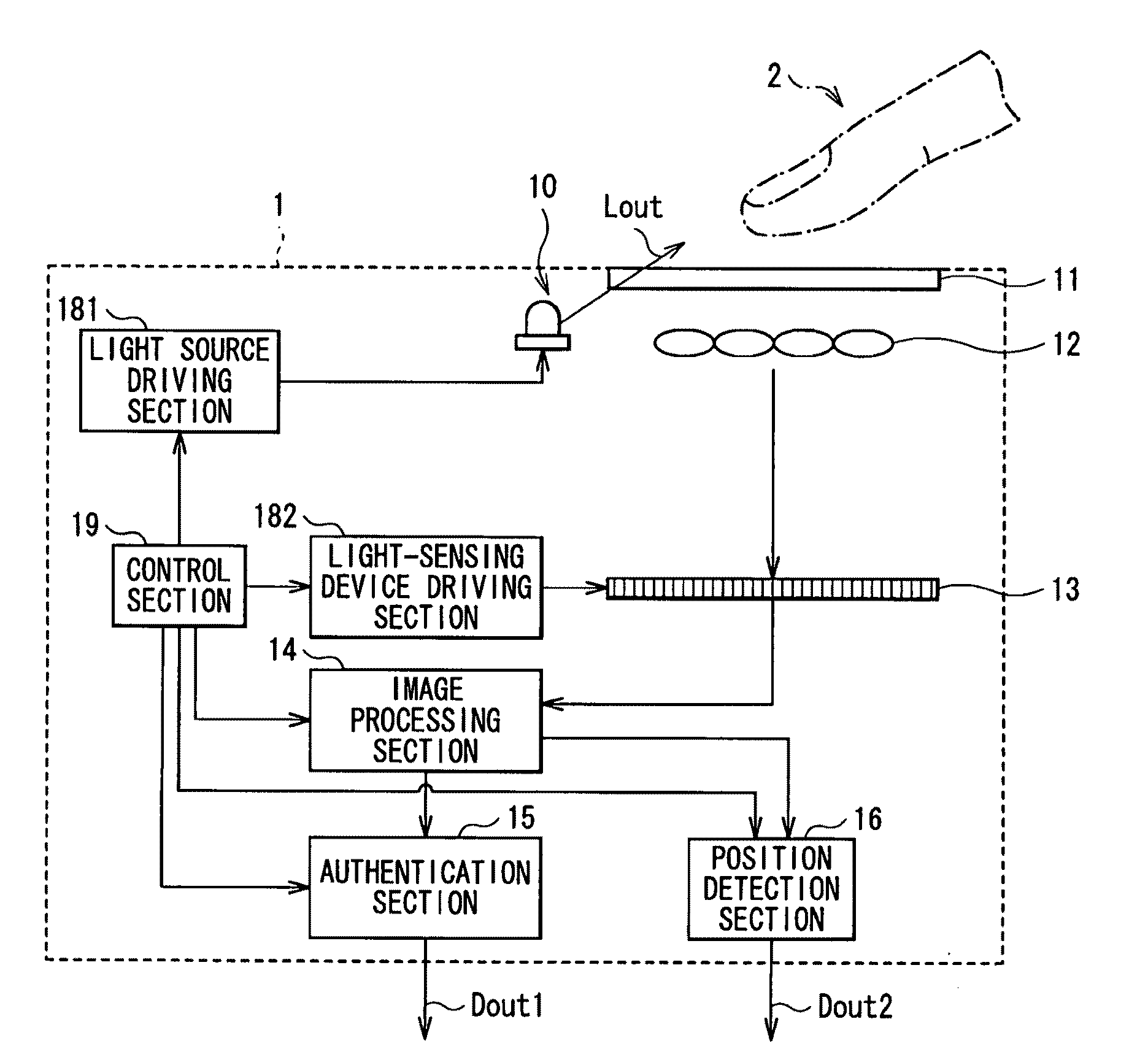
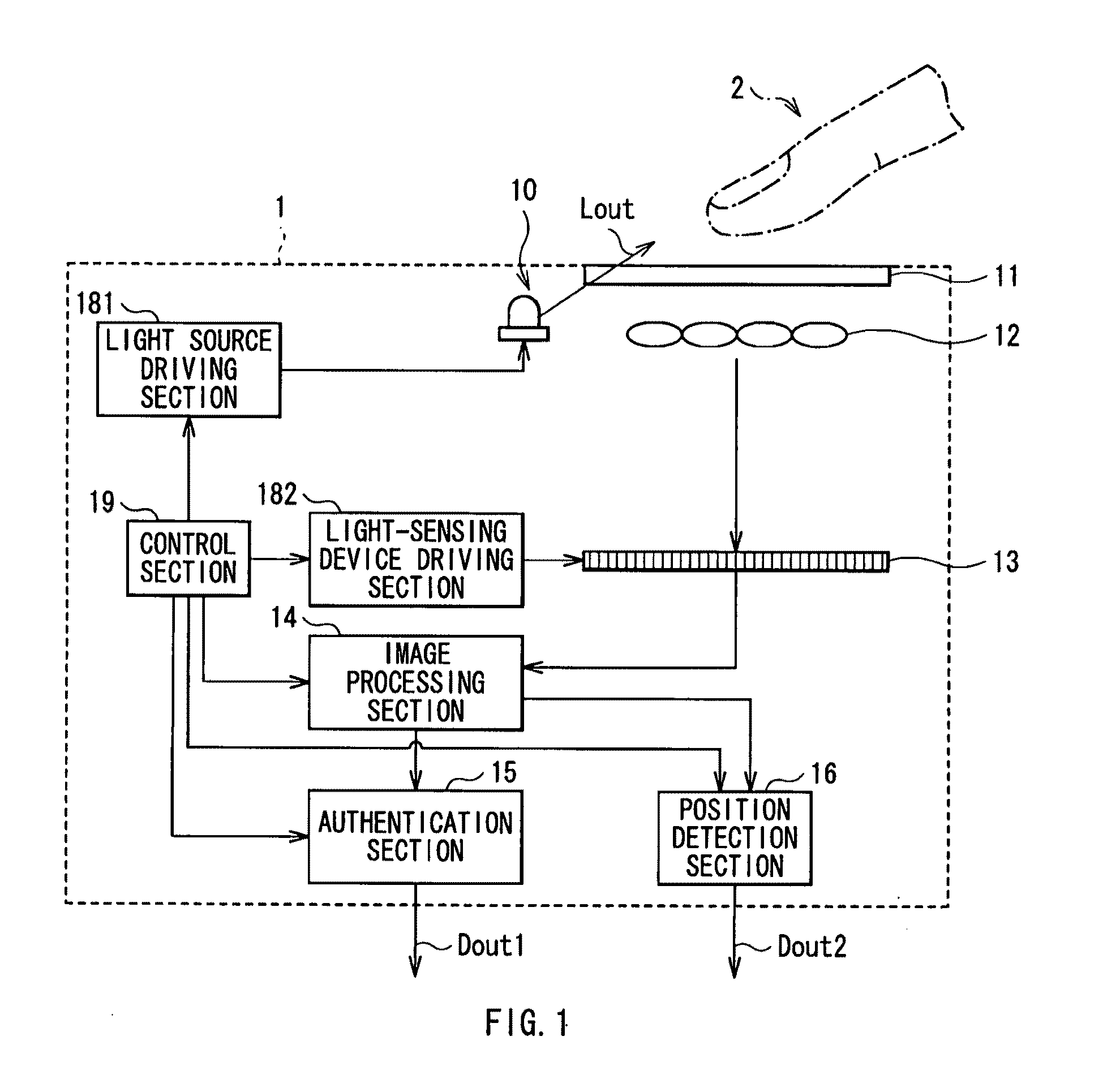
Biometrics authentication system
InactiveUS20100026453A1Small and simple configurationSimple configurationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisLight sensingLiving body
A biometrics authentication system having a small and simple configuration and being capable of implementing both of biometrics authentication and position detection is provided. A biometrics authentication system includes: a light source emitting light to an object; a microlens array section condensing light from the object; a light-sensing device obtaining light detection data of the object on the basis of the light condensed by the microlens array section; a position detection section detecting the position of the object on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device; and an authentication section, in the case where the object is a living body, performing authentication of the living body on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
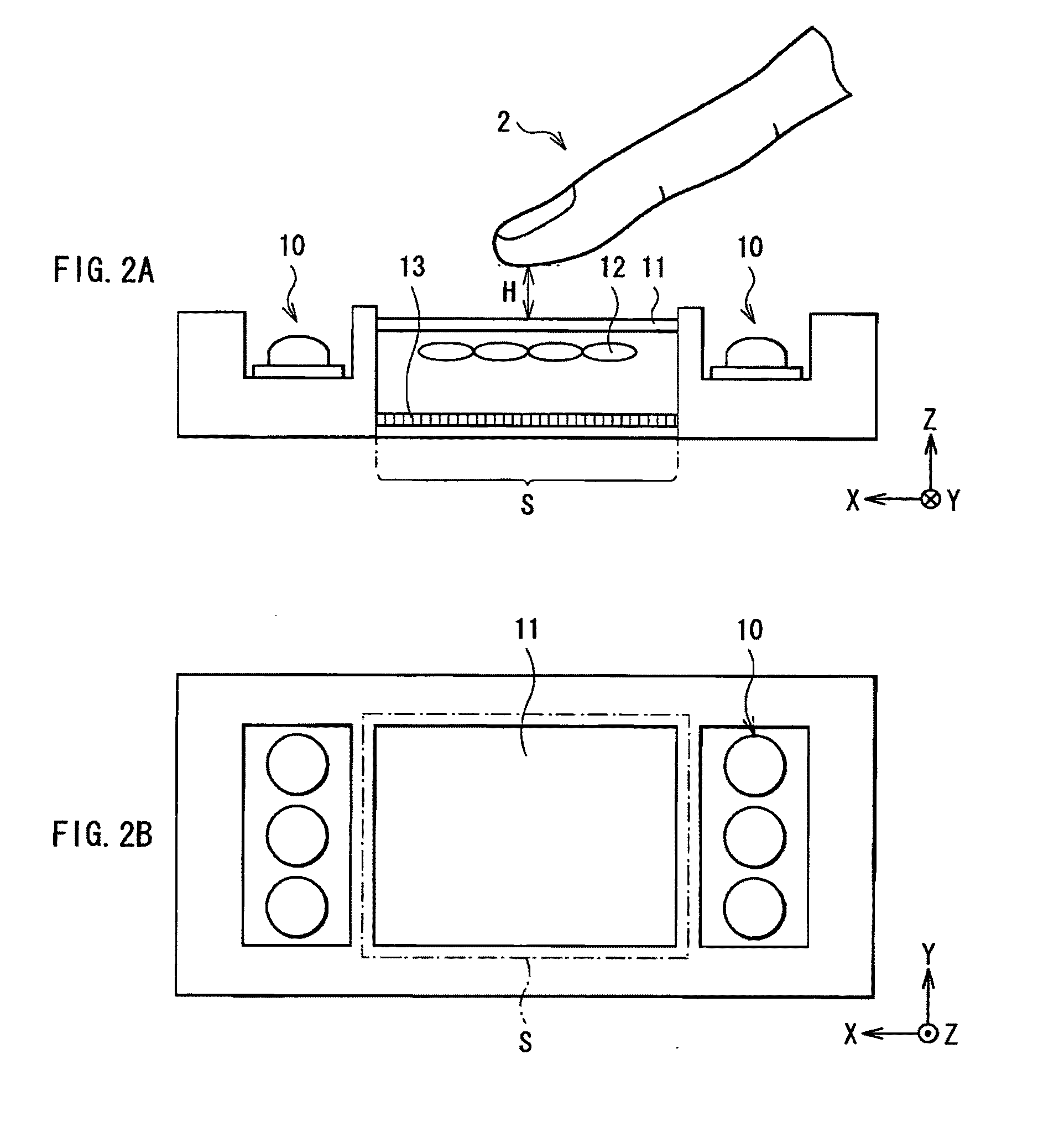
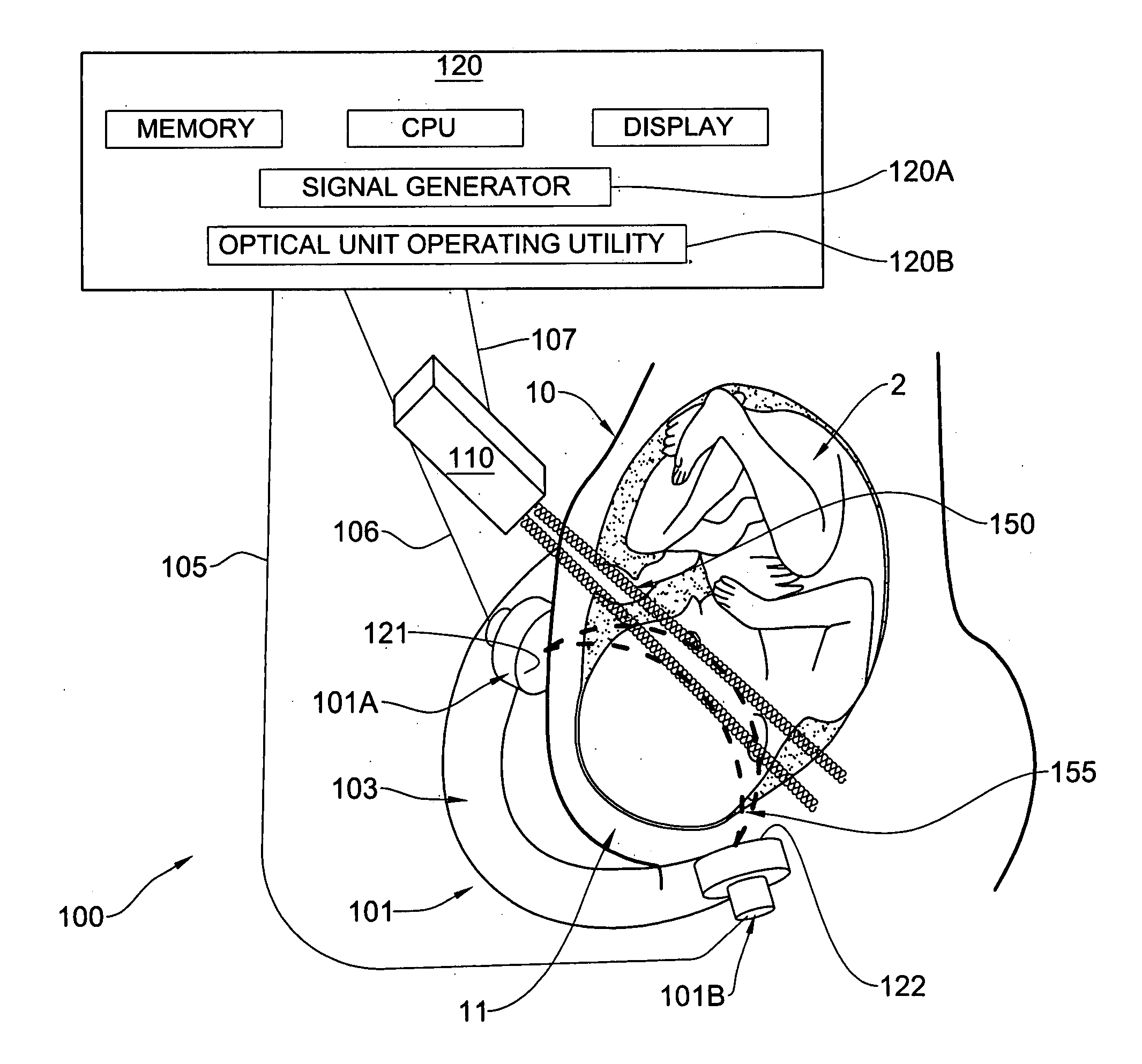
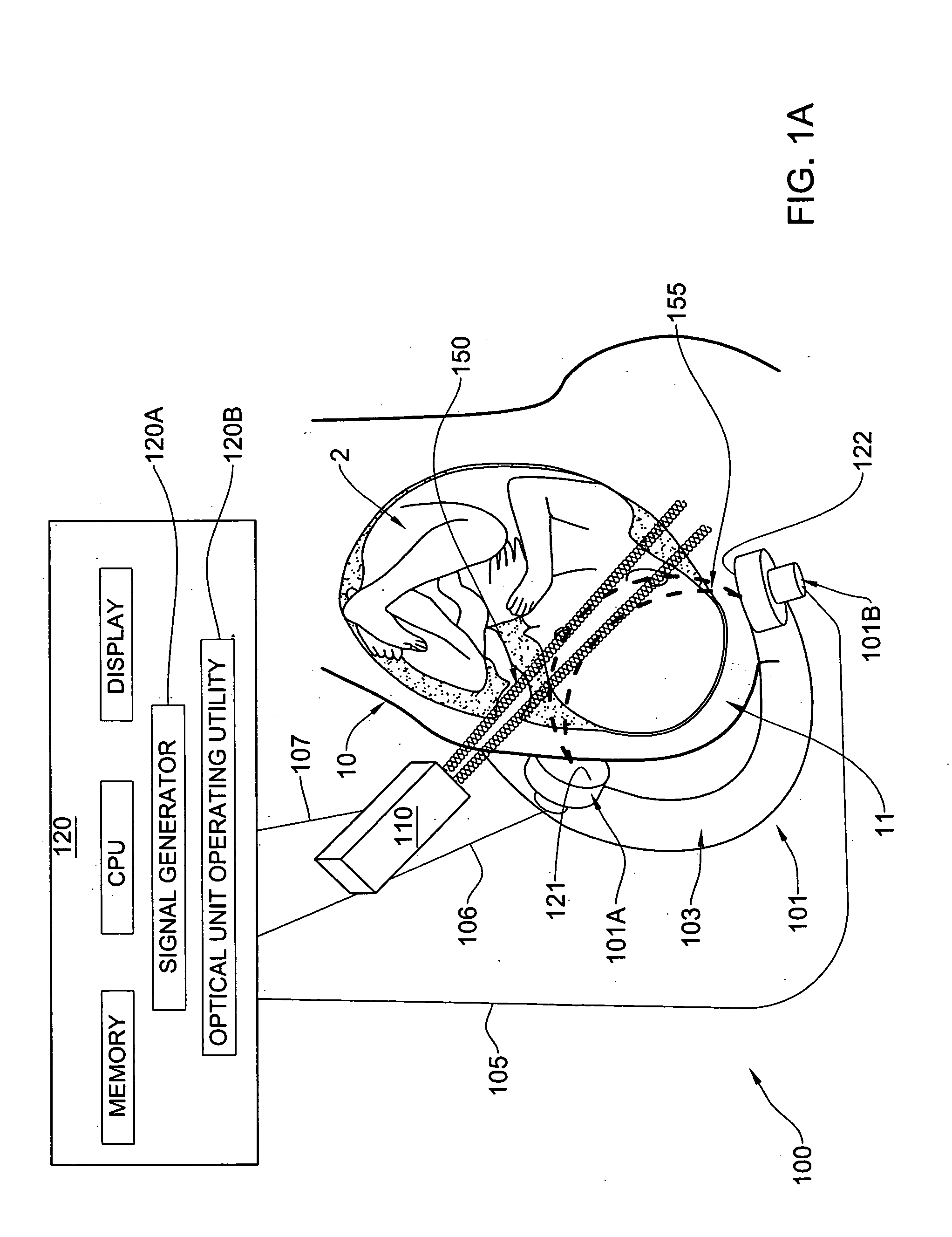
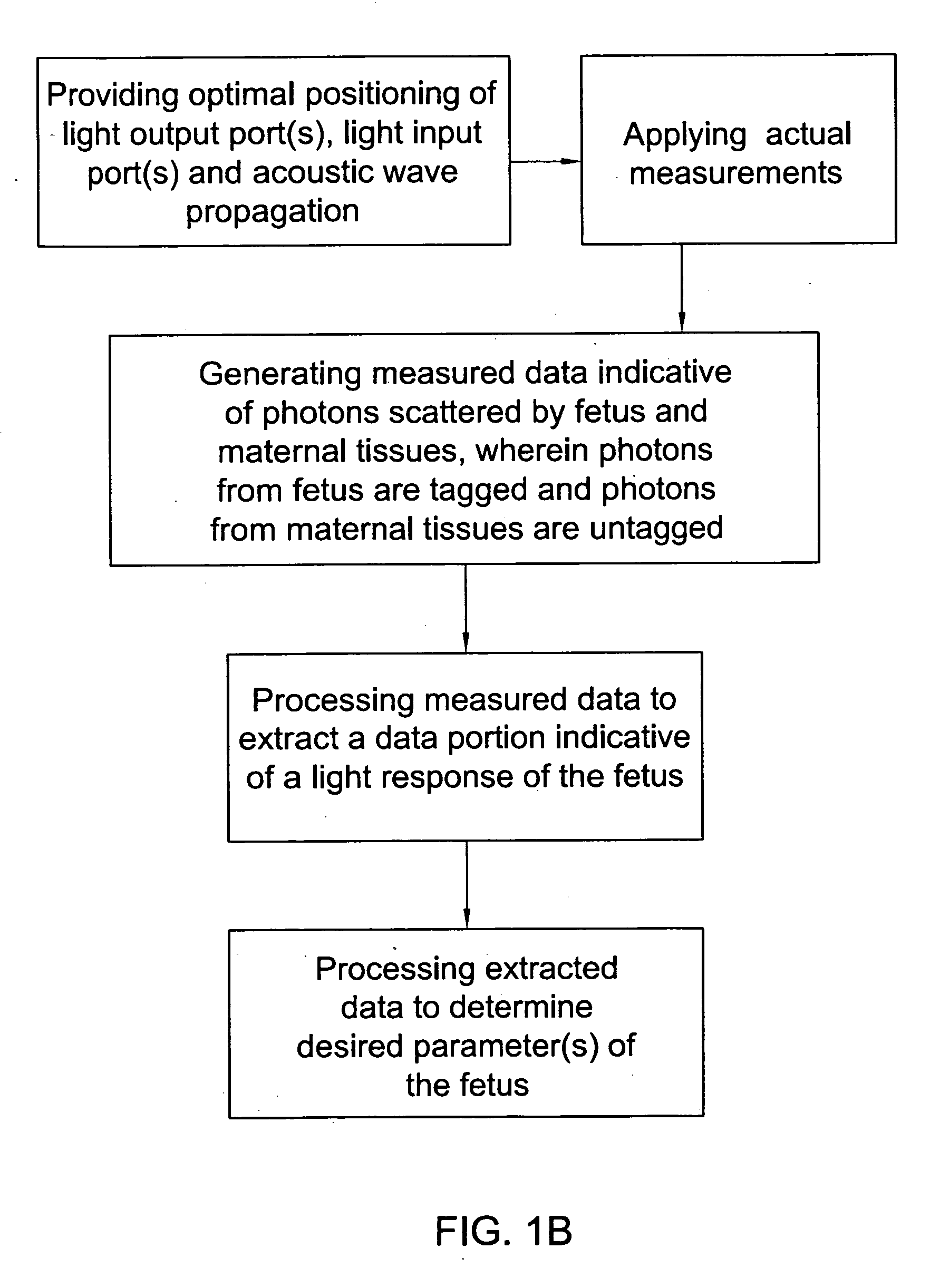
Method and apparatus for noninvasively monitoring parameters of a region of interest in a human body
ActiveUS20060122475A1Precise positioningEasy to measureRespiratory organ evaluationOptical sensorsHuman bodyEngineering
A method and system are presented for use in noninvasive monitoring at least one parameter of a region of interest in a human body. The system comprises a measurement unit and a control unit. The measurement unit comprises an optical unit having an illumination assembly configured to define at least one output port for illuminating light, and a light detection assembly configured to define at least one light input port for collecting light and to generate measured data indicative of the collected light; and an acoustic unit configured to generate acoustic waves of a predetermined ultrasound frequency range. The measurement unit is configured and operable to provide an operating condition such that the acoustic waves of the predetermined frequency range overlap with an illuminating region within the region of interest and substantially do not overlap with a region outside the region of interest, and that the detection assembly collects light scattered from the region of interest and light scattered from the region outside the region of interest. The measured data is thus indicative of scattered light having both ultrasound tagged and untagged light portions, thereby enabling to distinguish between light responses of the region of interest and the region outside the region of interest. The control unit is connectable to the optical unit and to the acoustic unit to operate these units, and is responsive to the measured data and preprogrammed to process and analyze the measured data to extract therefrom data indicative of a light response of the region of interest and determine the at least one desired parameter.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
Dynamic display control of a portable electronic device display
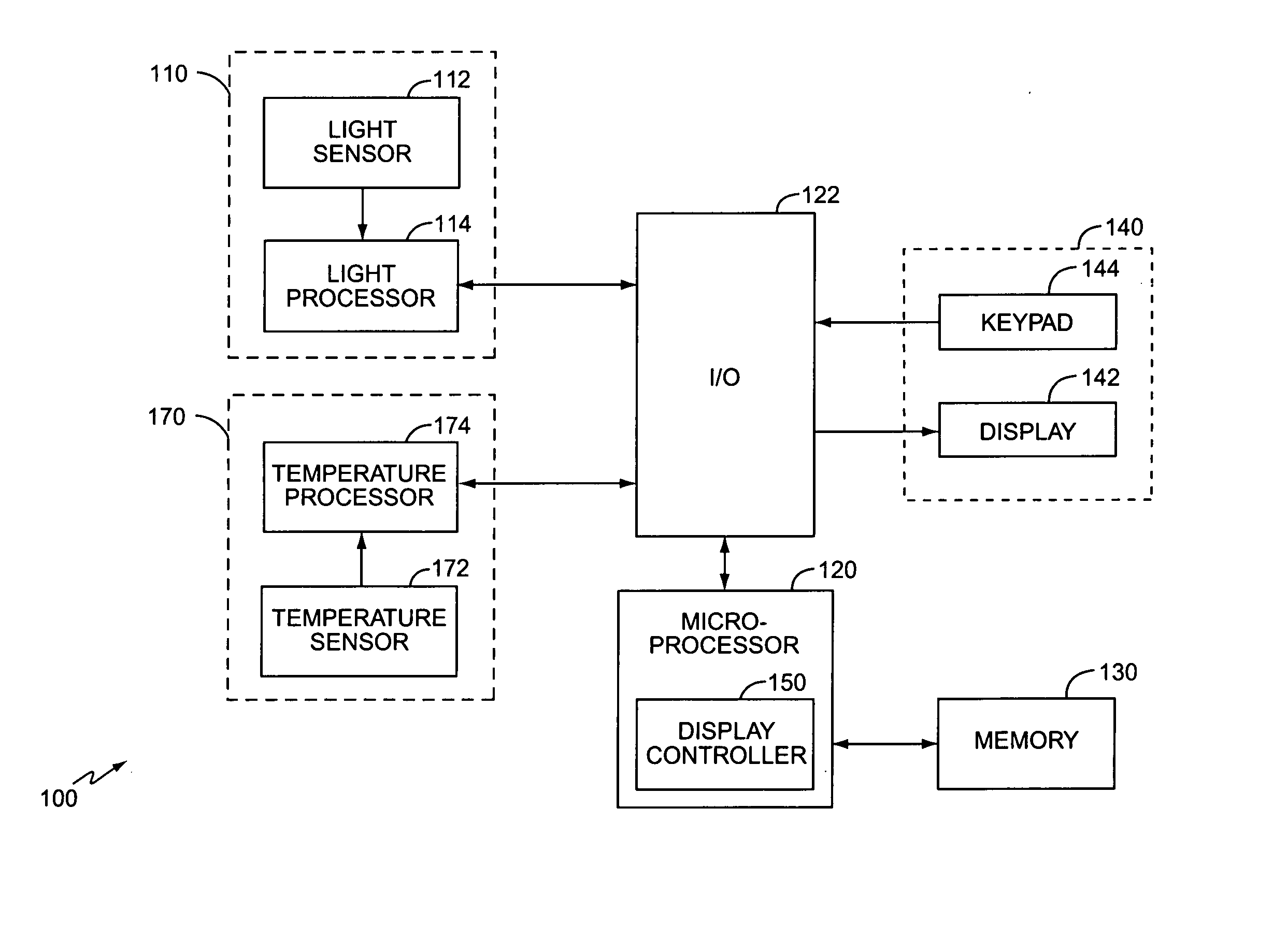
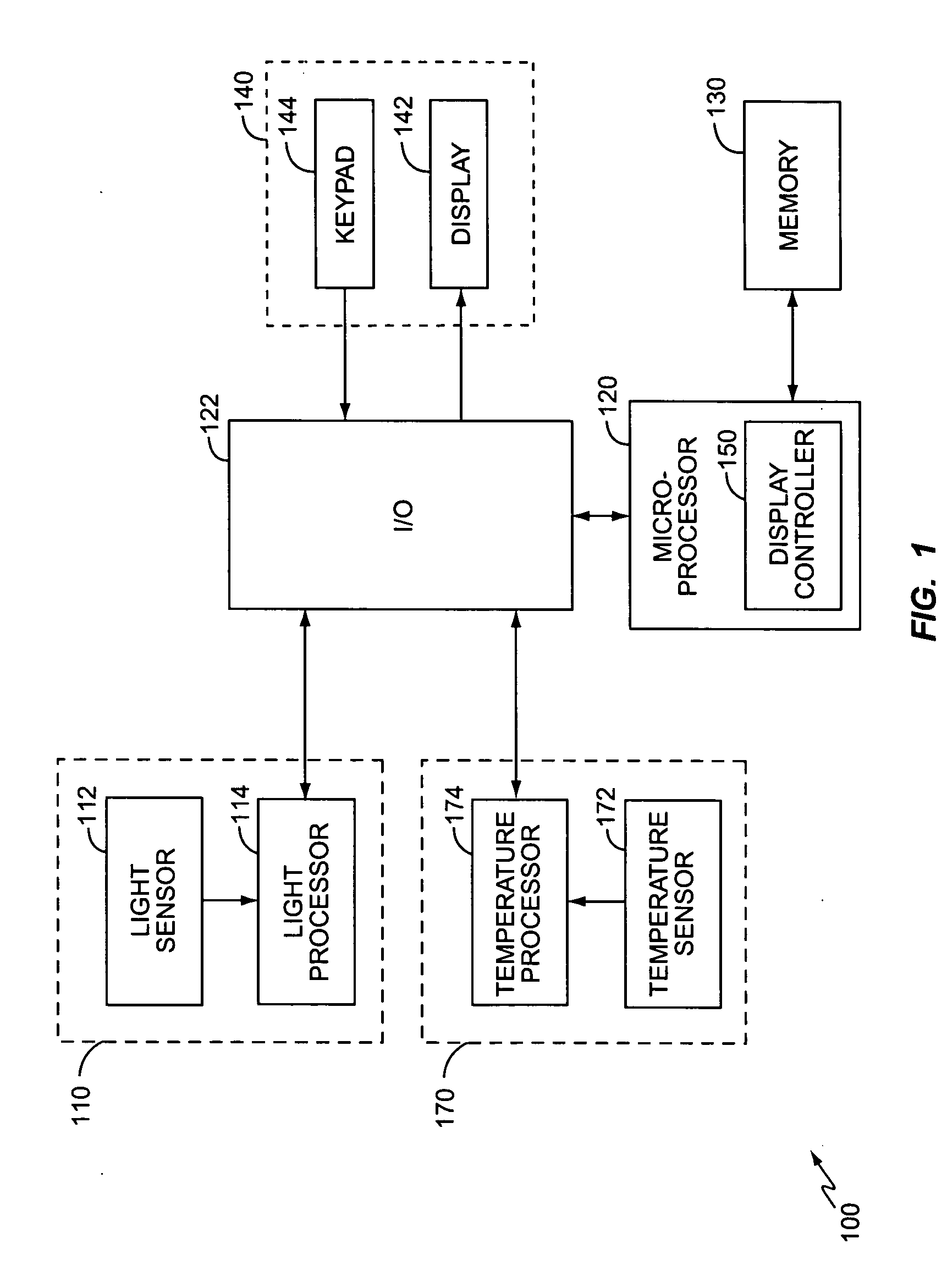
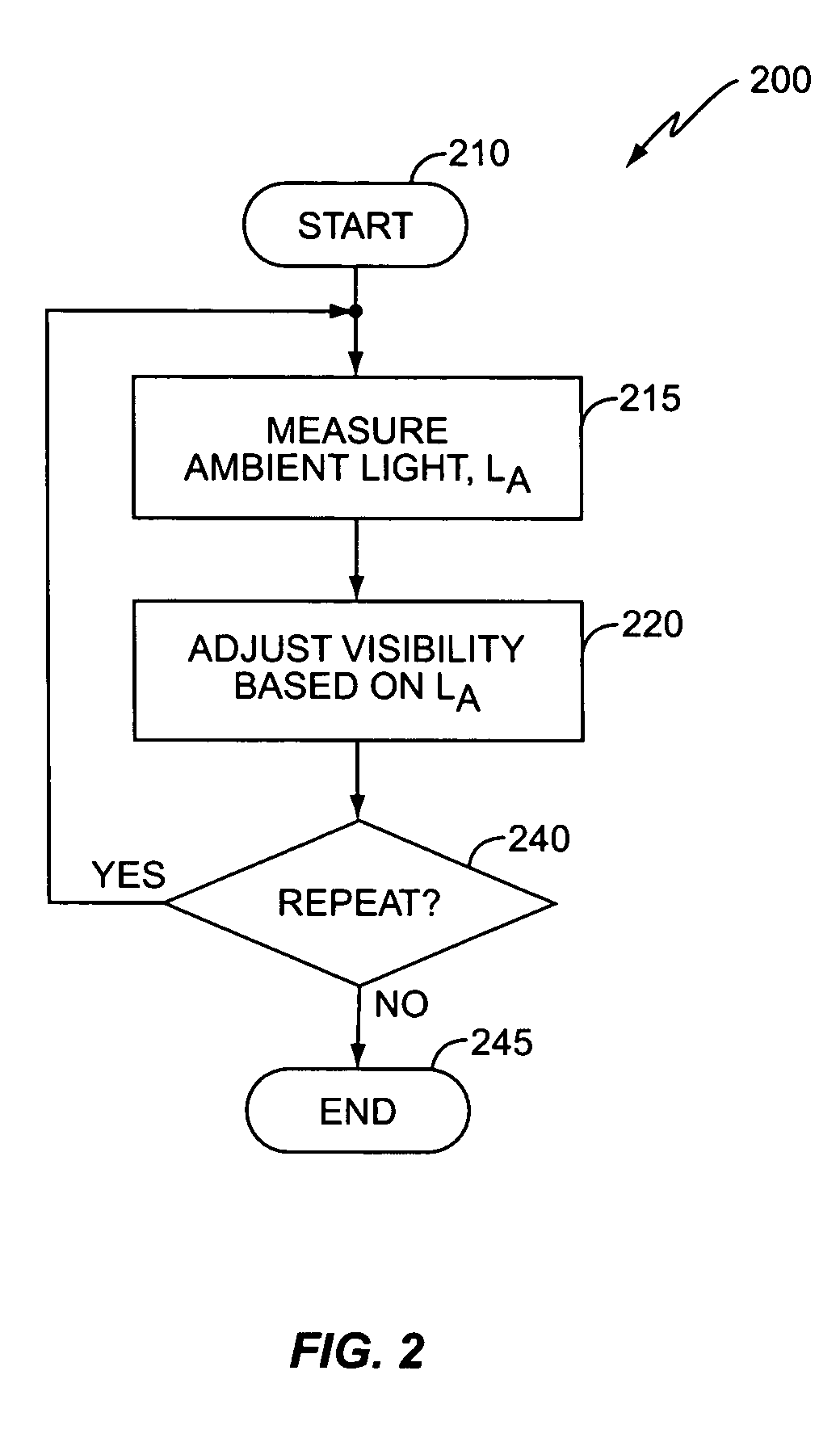
InactiveUS20050212824A1Increase awarenessImproving visibility of displayCathode-ray tube indicatorsWireless communicationDisplay contrastVisibility
A method and apparatus improves the visibility of information displayed on a portable electronic device display in various ambient lighting conditions. The portable electronic device measures the ambient light associated with the display and adjusts the display based on the measured ambient light to improve the visibility of the displayed information. In an exemplary embodiment, light detection electronics detect the ambient light associated with the display. A light processor processes the raw data to determine the measured ambient light based on the detected ambient light. A display controller of the portable electronic device adjusts the display based on the measured ambient light. An exemplary display controller may adjust the size of the displayed information, a backlight intensity of the display, or a display contrast based on the measured ambient light.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS8301027B2Turn fasterWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayBeam steering
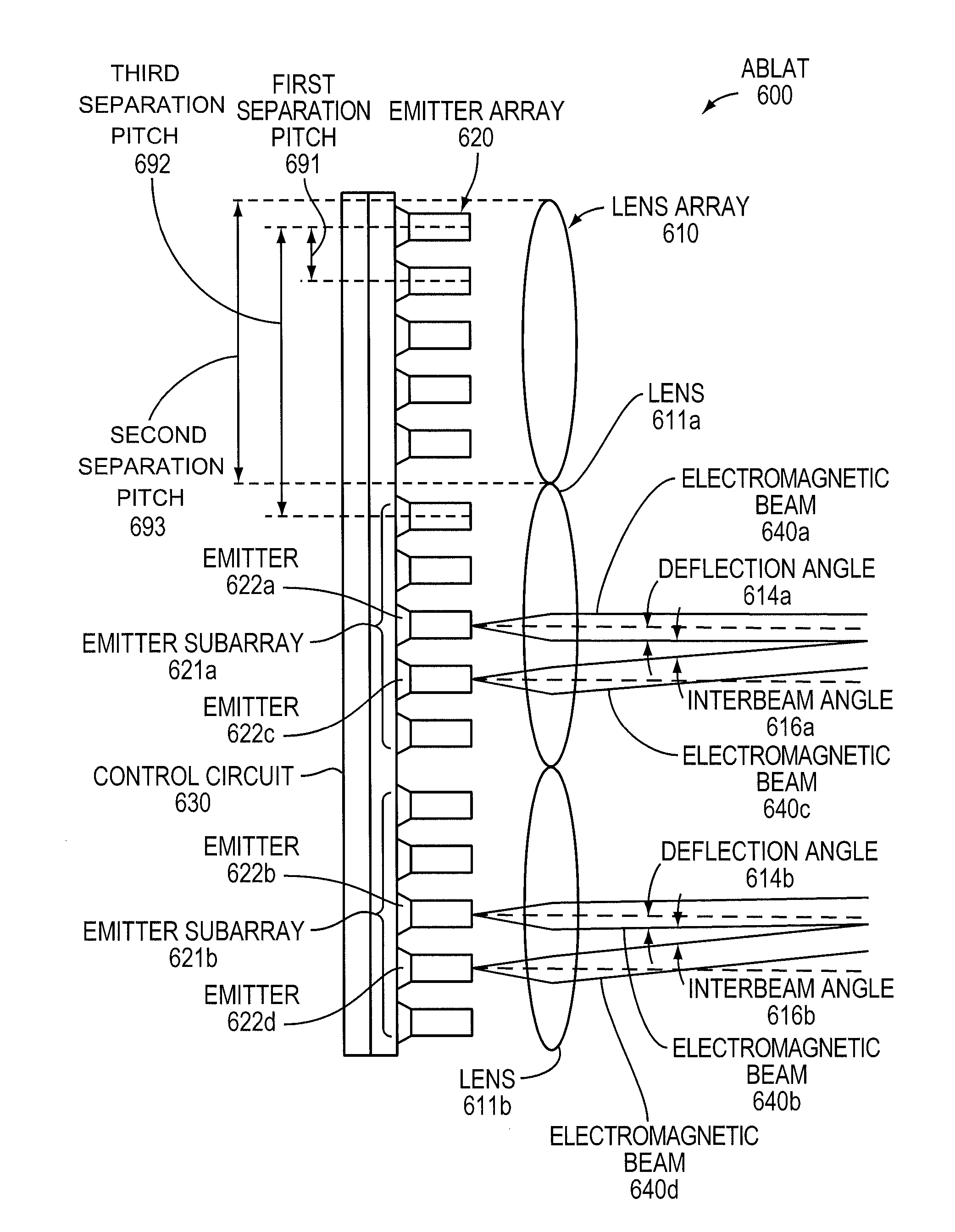
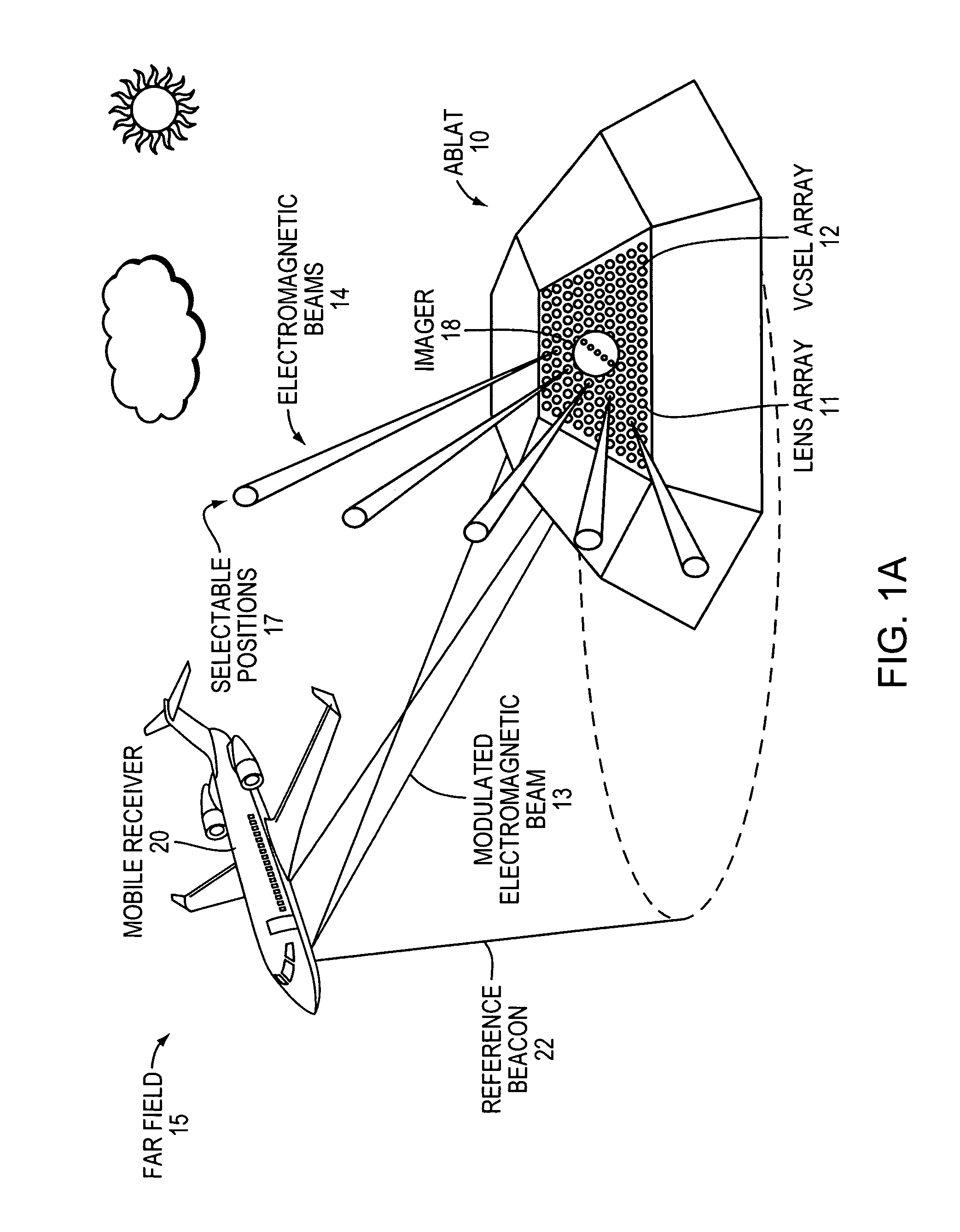
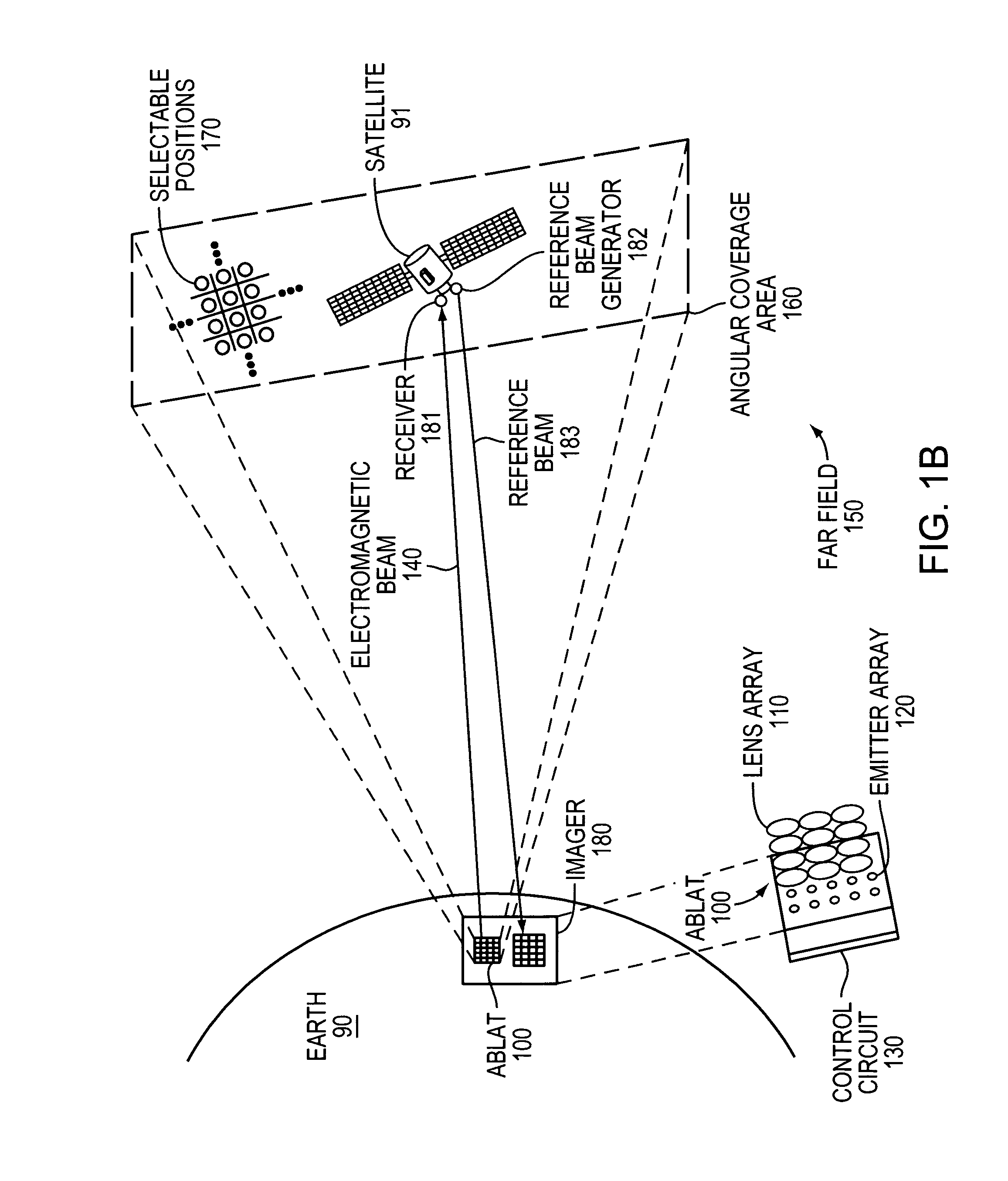
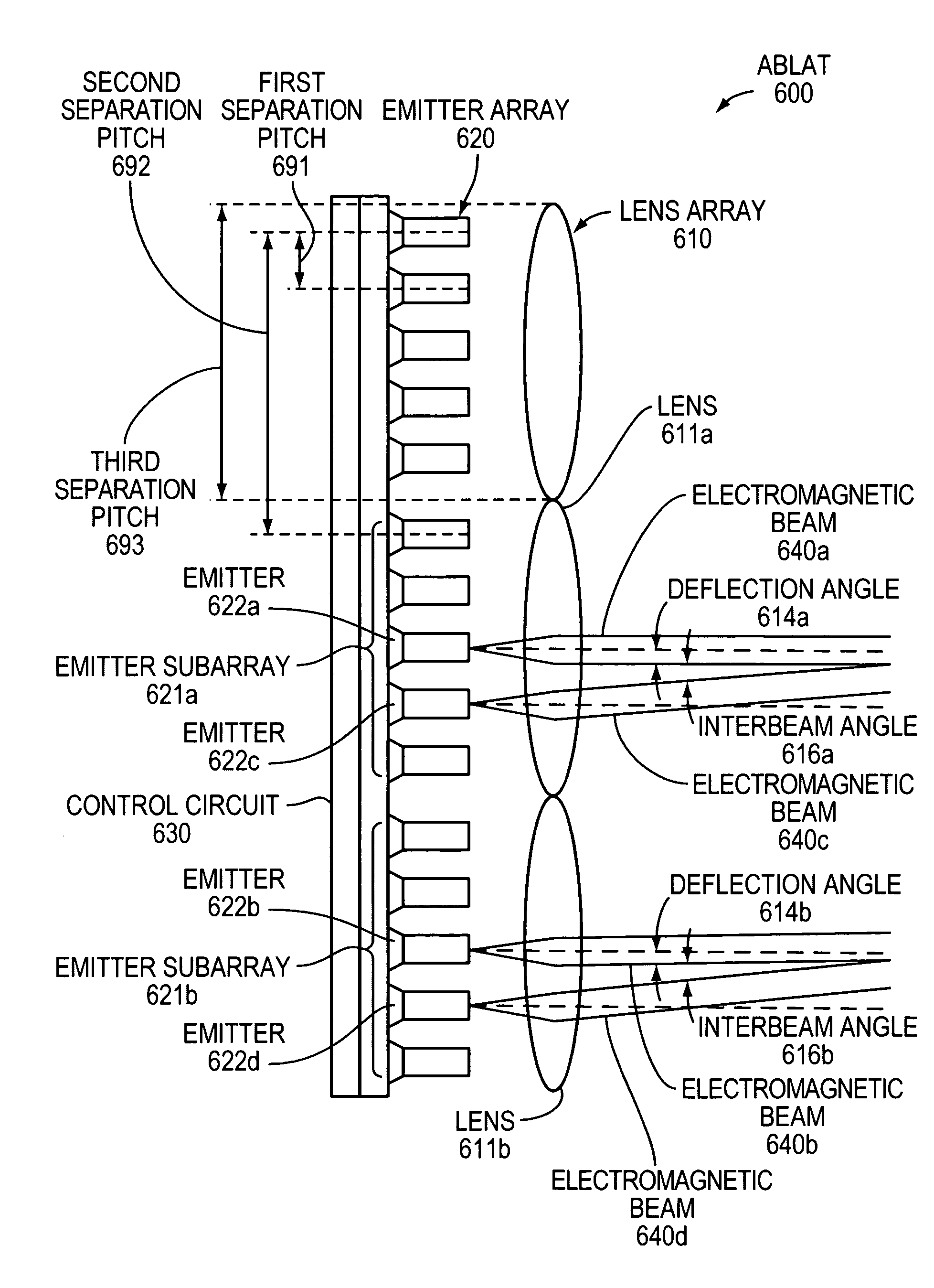
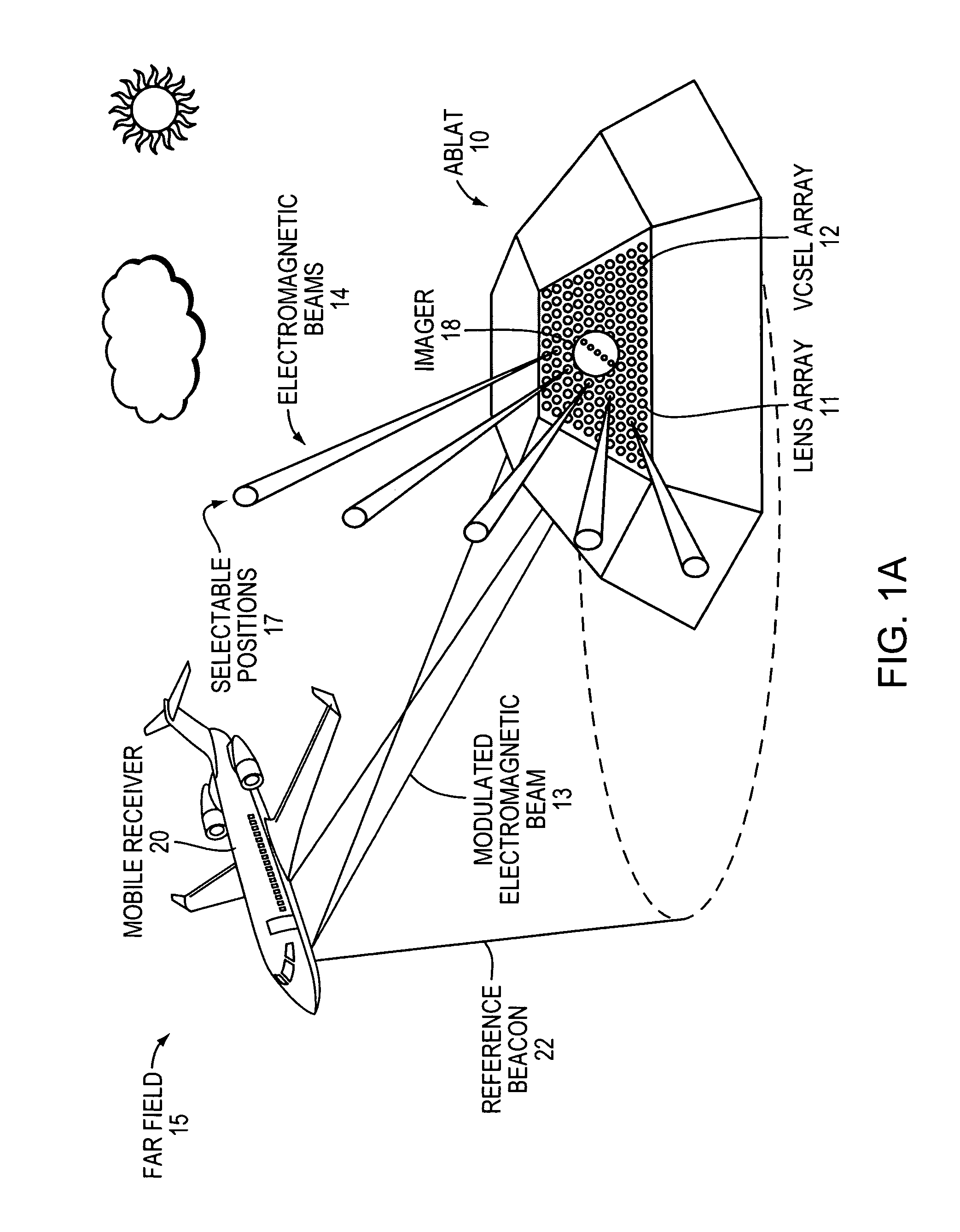
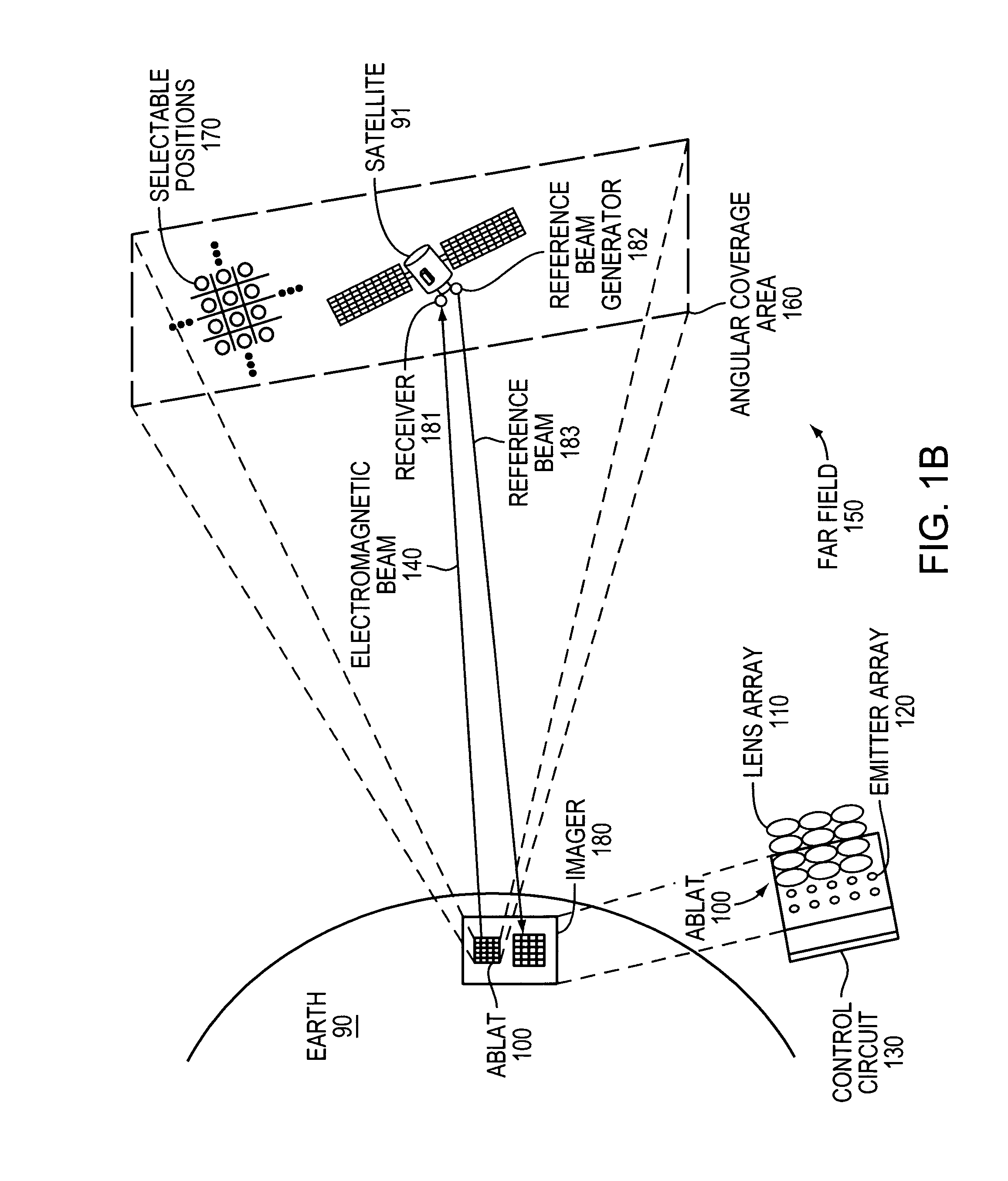
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Programmable power controller
InactiveUS20060250745A1Electric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesMicrocontrollerPower controller
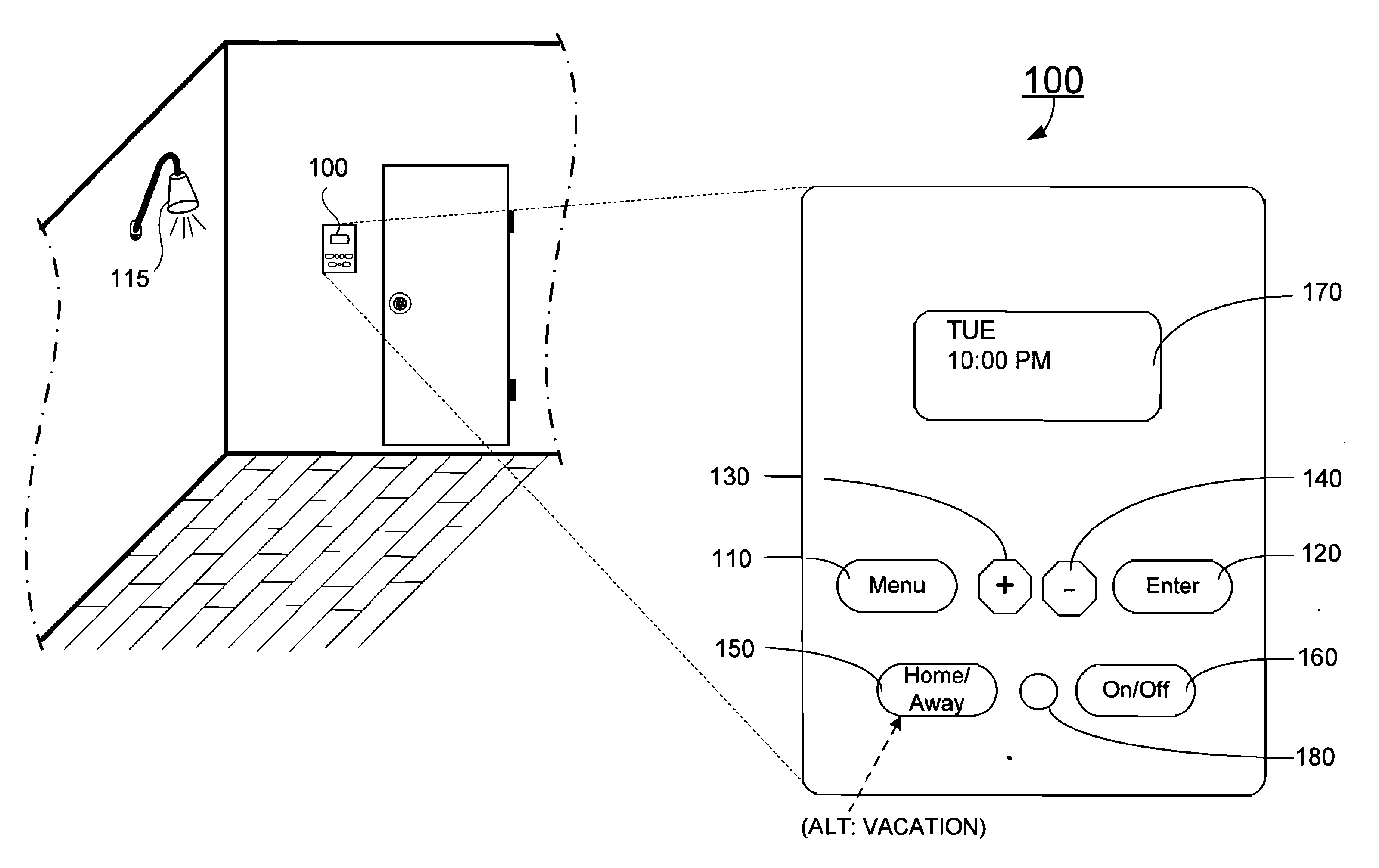
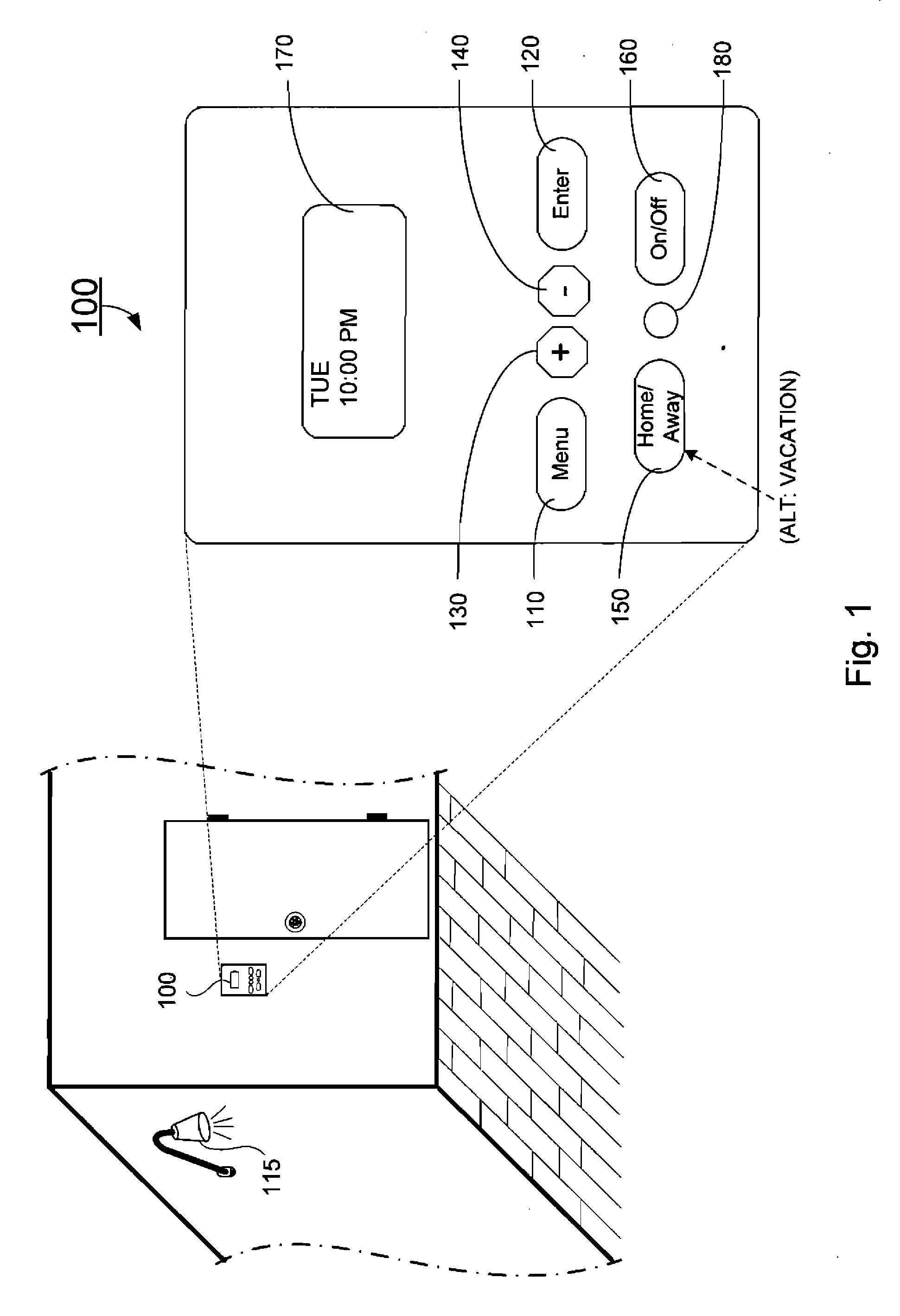
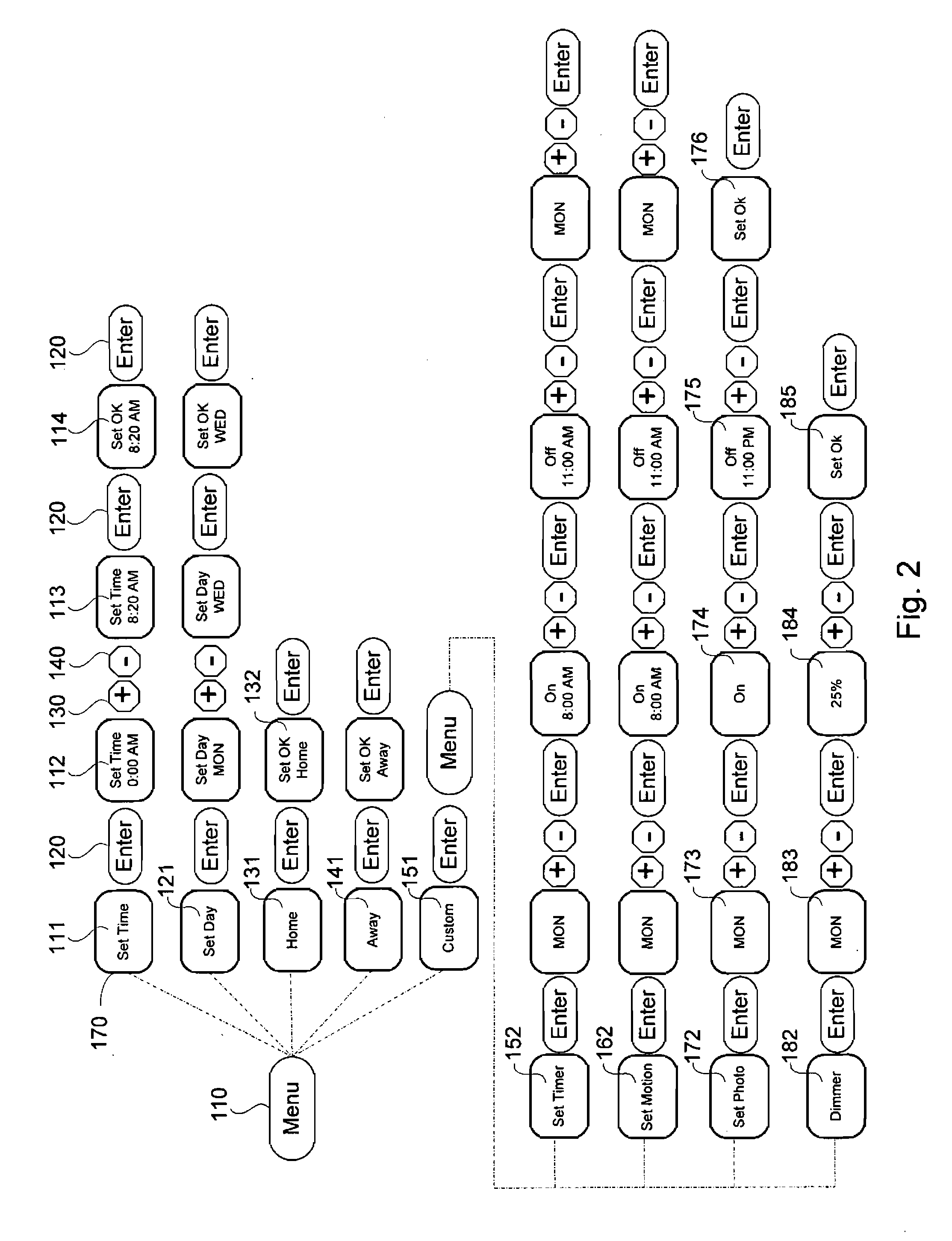
A device connected between a source of power and at least one load for selectively providing power from the source of power to the at least one load to operate in an area responsive to an environmental condition in the area. In one embodiment, the device includes a home mode, an away mode, and a custom mode, and a user interface for selecting one of the home mode and the custom mode to be operated. The device further includes at least one timer for timing a plurality of predefined operations, a first detector for generating a low light detection signal responsive to an ambient light level being below a predetermined threshold value, a second detector for generating a motion signal responsive to detection of a movement in the area, a dimmer for adjusting power supplying to the at least one load at a predetermined level, and a microcontroller coupled to the first detector and the second detector and coupled with the user interface for operatively controlling transmission of the source of power to the at least one load.
Owner:GARDNER GROFF GREENWALD & VILLANUEVA P C
Ladar System with Dichroic Photodetector for Tracking the Targeting of a Scanning Ladar Transmitter
InactiveUS20170242102A1Clearer understandingLow costElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
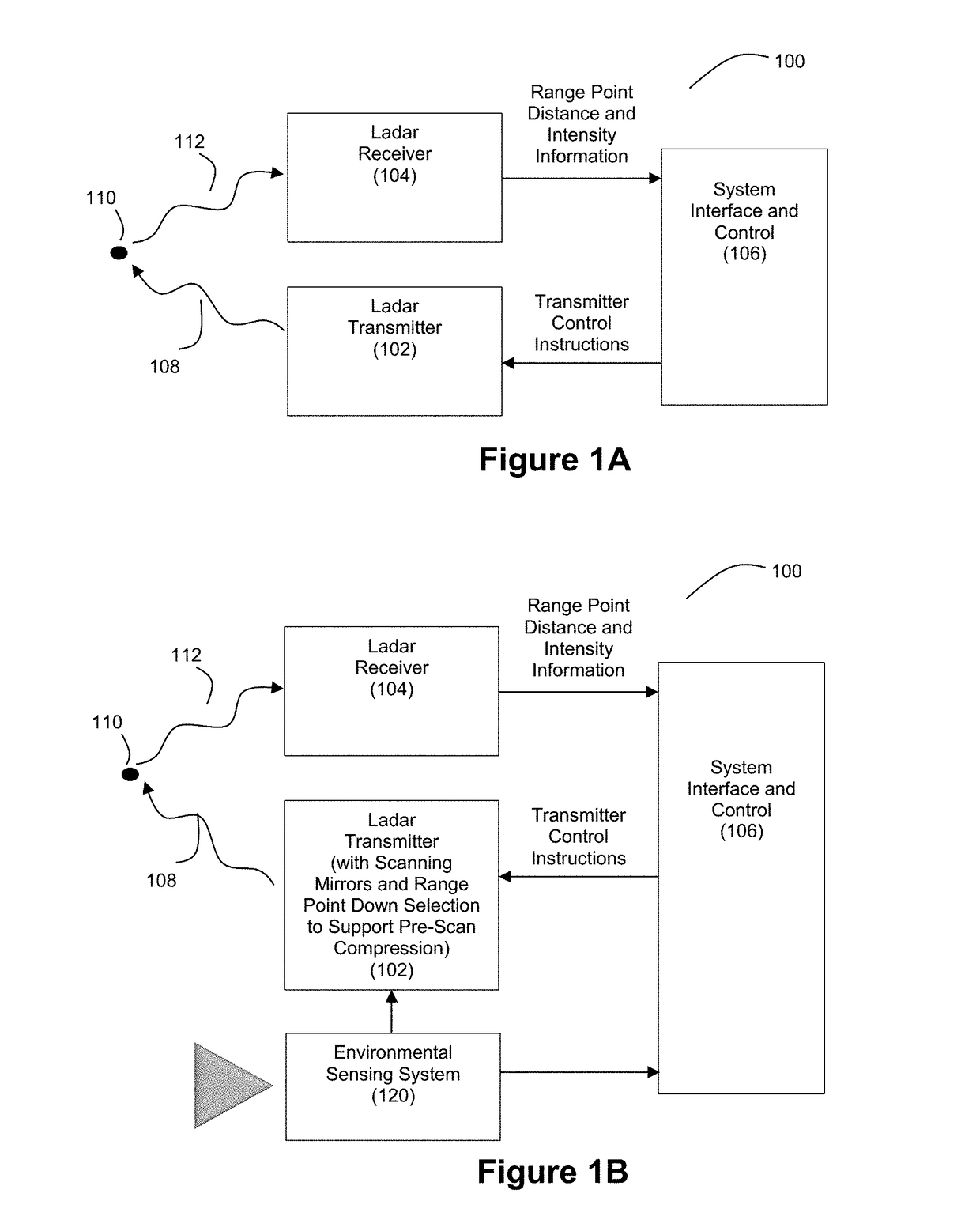
Disclosed herein are various embodiment of an adaptive ladar receiver and associated method whereby the active pixels in a photodetector array used for reception of ladar pulse returns can be adaptively controlled based at least in part on where the ladar pulses were targeted. Additional embodiments disclose improved imaging optics for use by the receiver and further adaptive control techniques for selecting which pixels of the photodetector array are used for sensing incident light.
Owner:AEYE INC
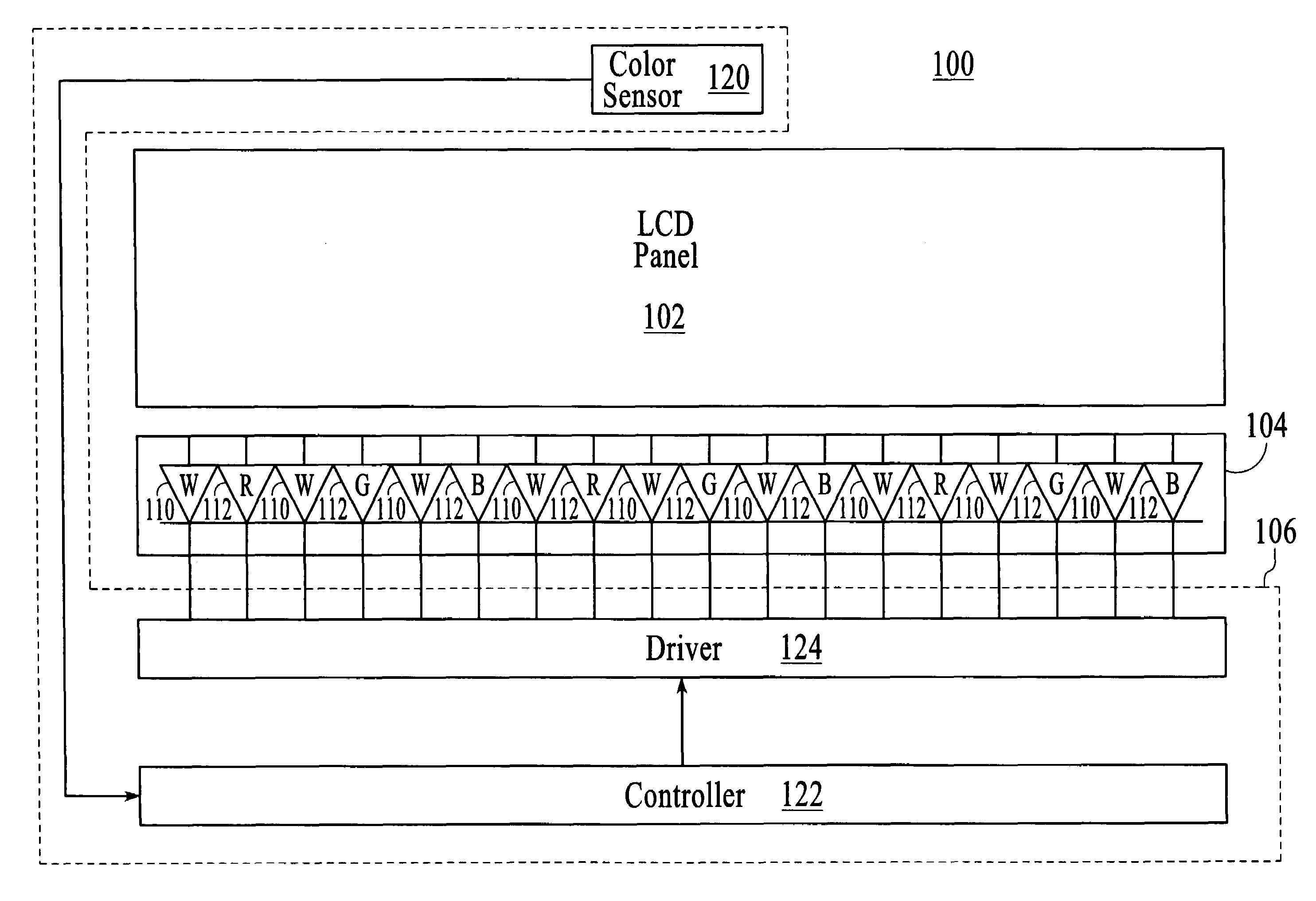
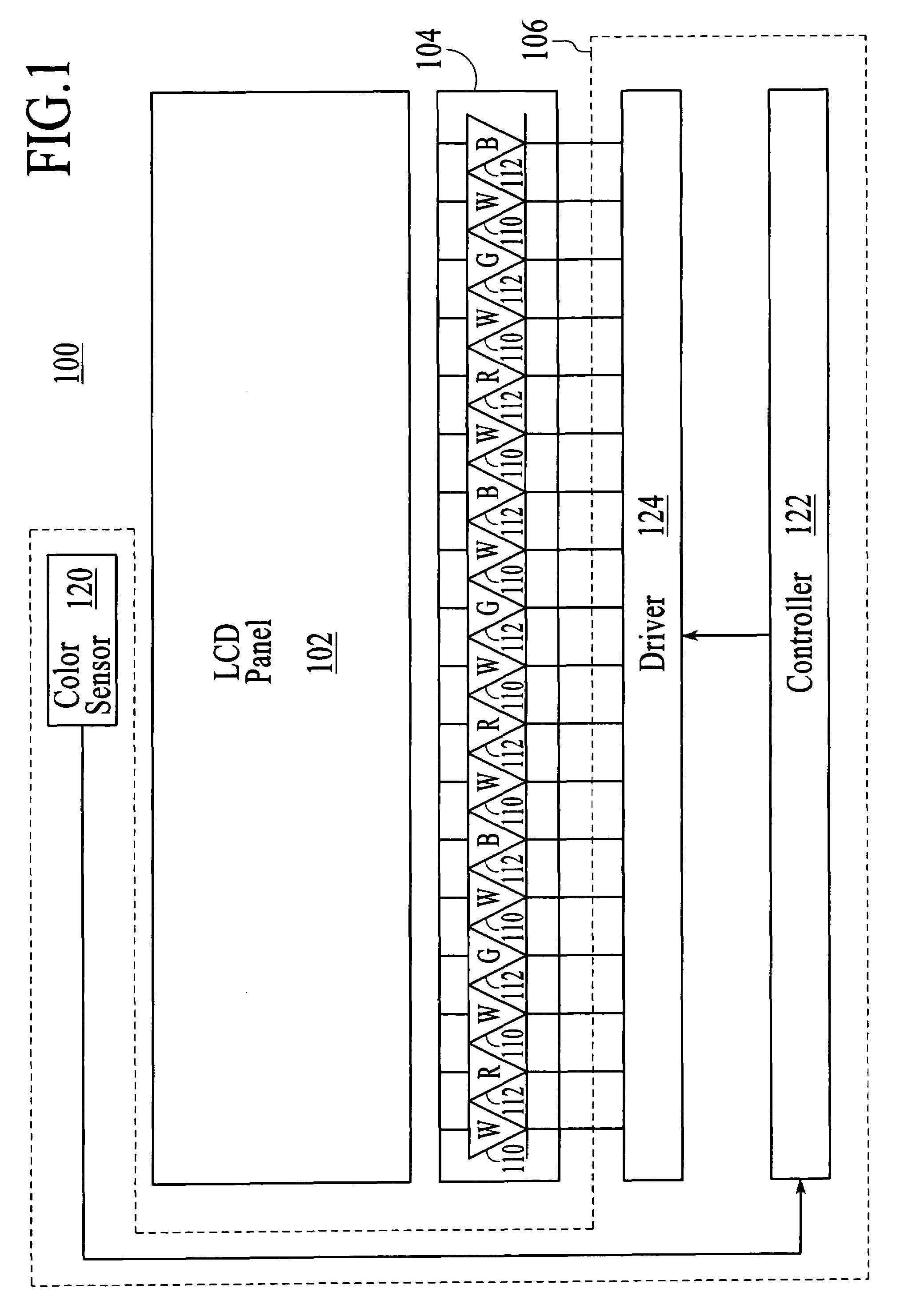
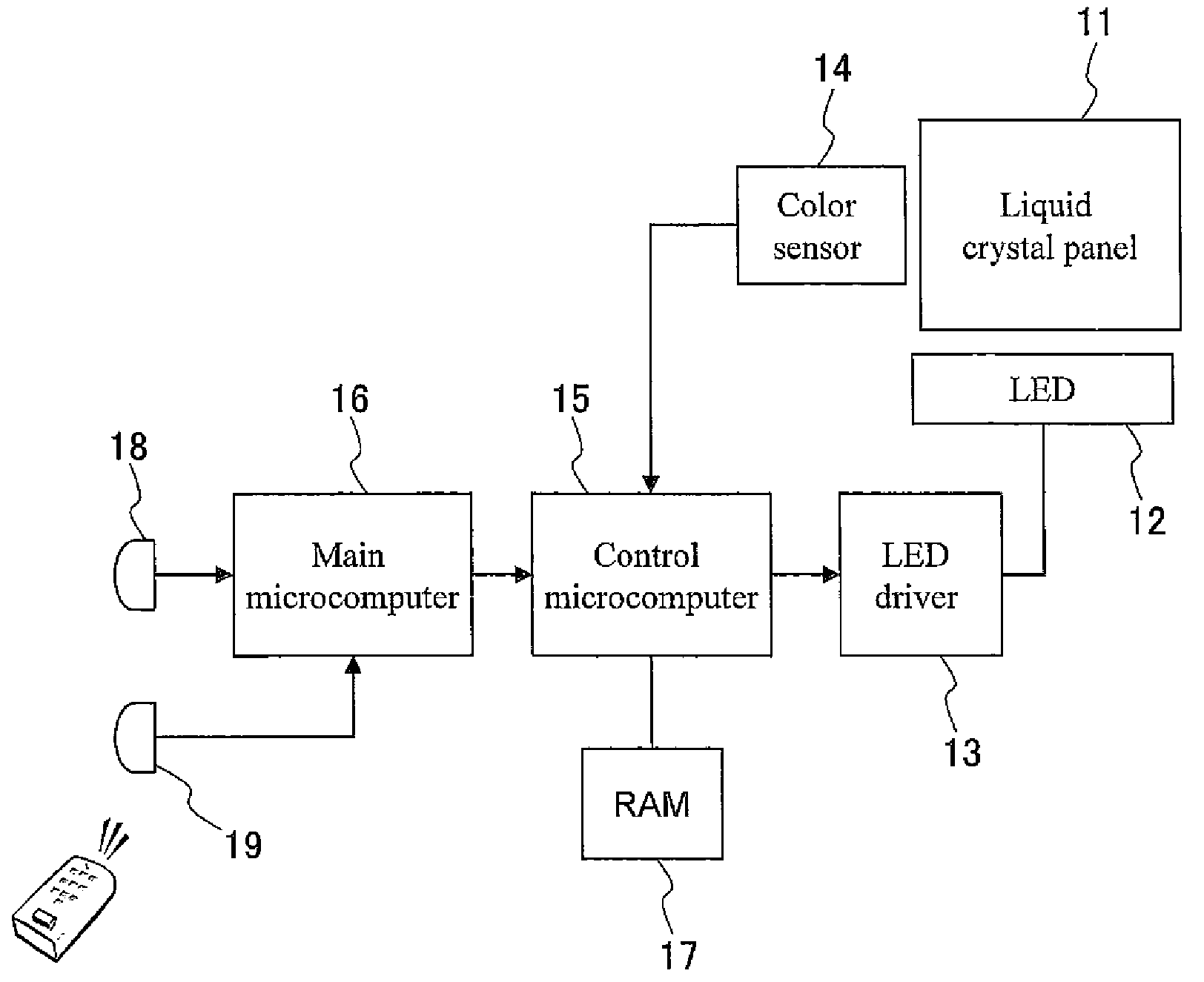
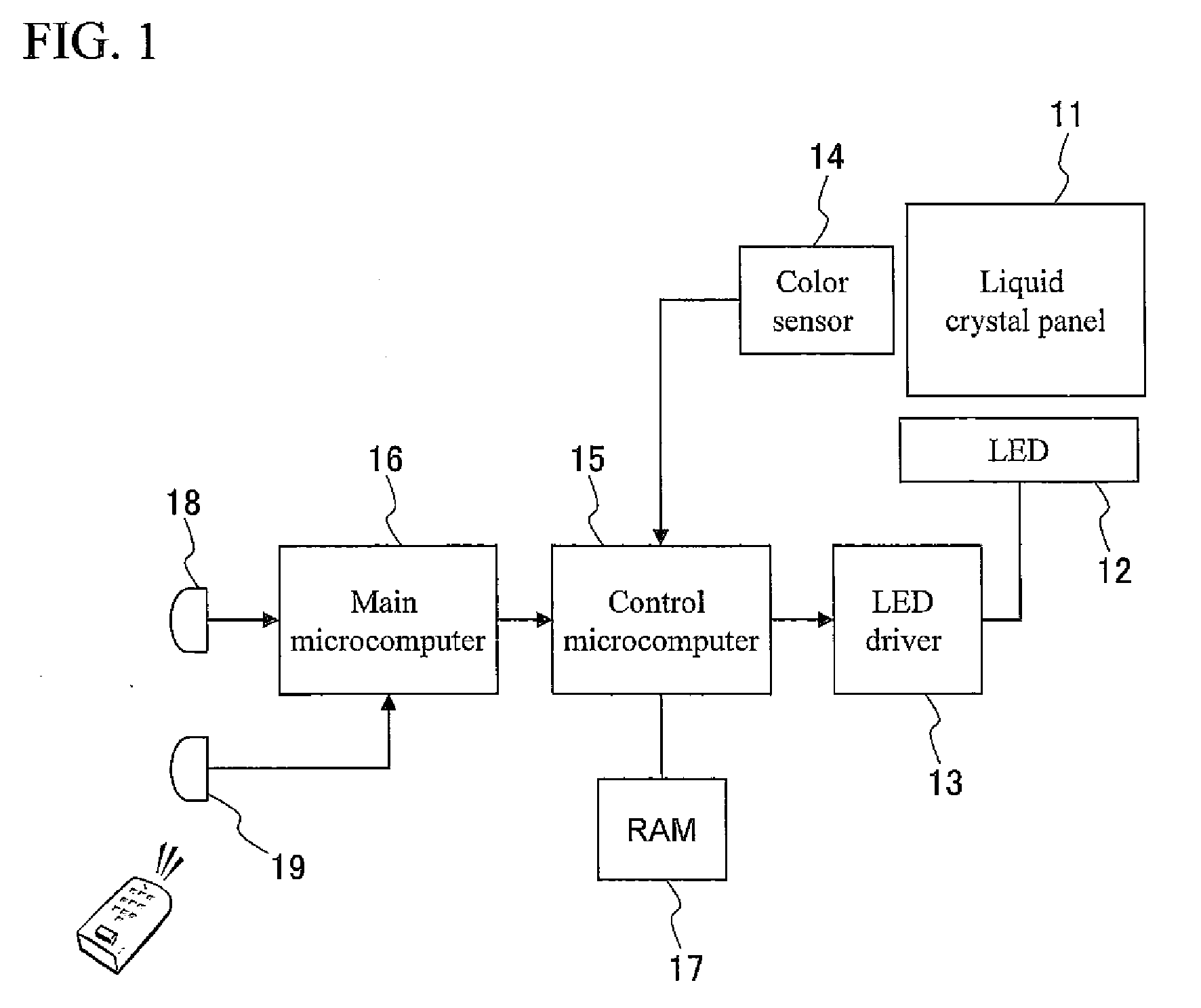
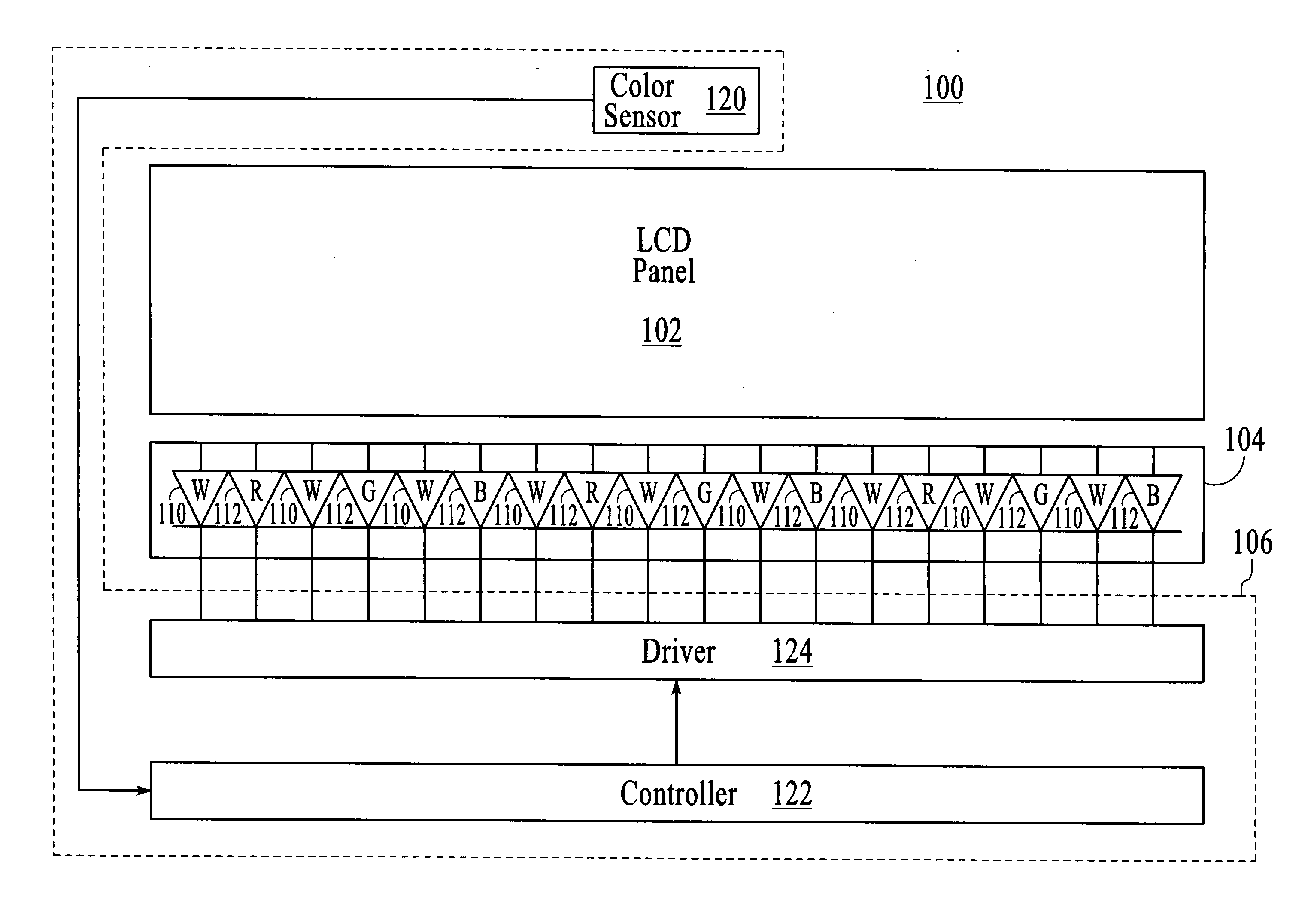
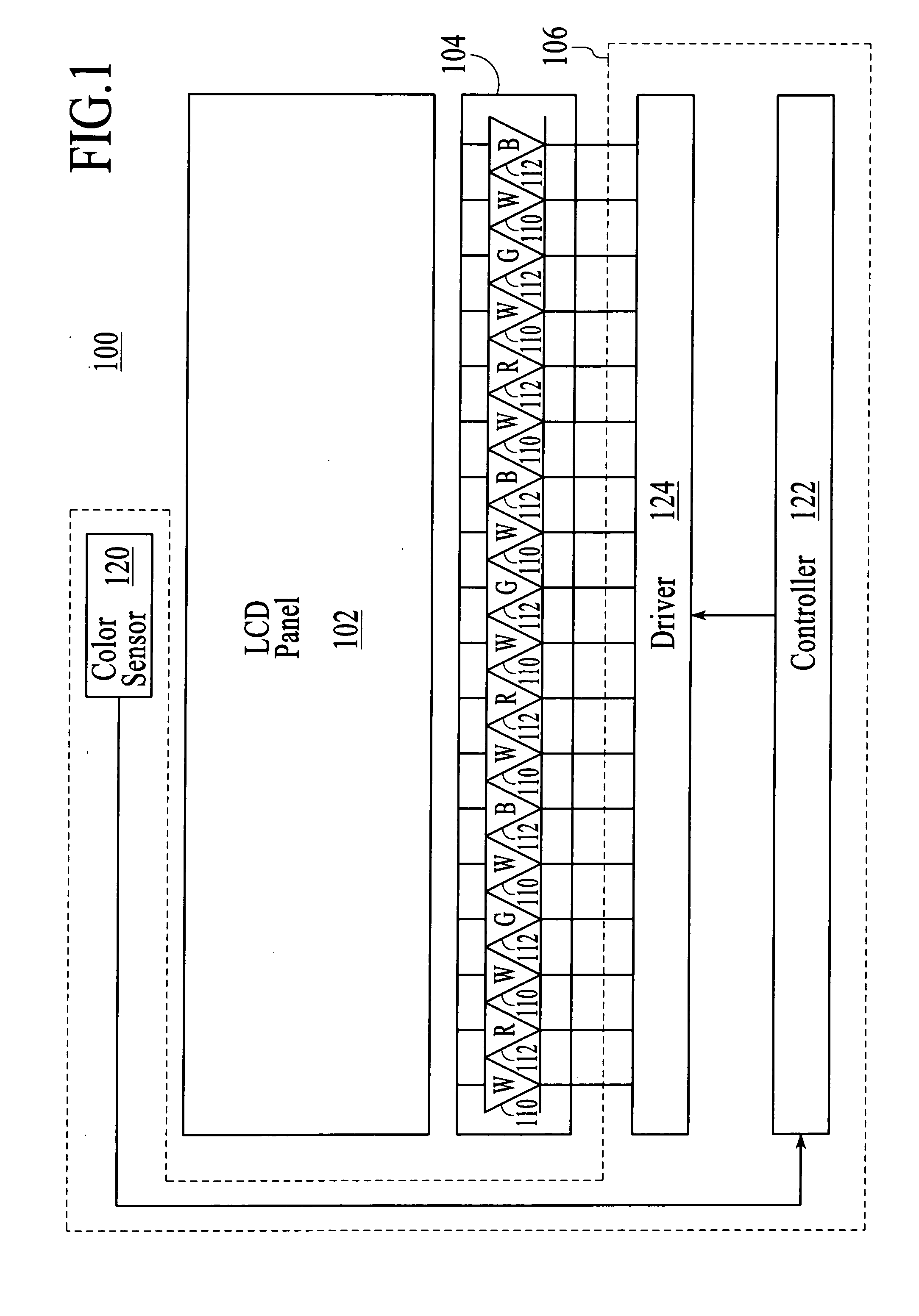
Light source control device, illuminaton device, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090140656A1Uniform colorPhotometry using reference valueElectrical apparatusLiquid-crystal displayLight emission
A light emission device capable of holding a uniform color in various environments. A light source control device has a light detection device for detecting emission brightness of light sources that emit different colors and controlling emission brightness of at least one light source of the light sources based on the detection result of the light detection device. A through-hole is formed in a reflection member for reflecting light emitted from the light source, and the reflection is in a predetermined direction. The light detection device is provided across the reflection member from the light source, and the light propagation member is provided at the through-hole.
Owner:SHARP KK
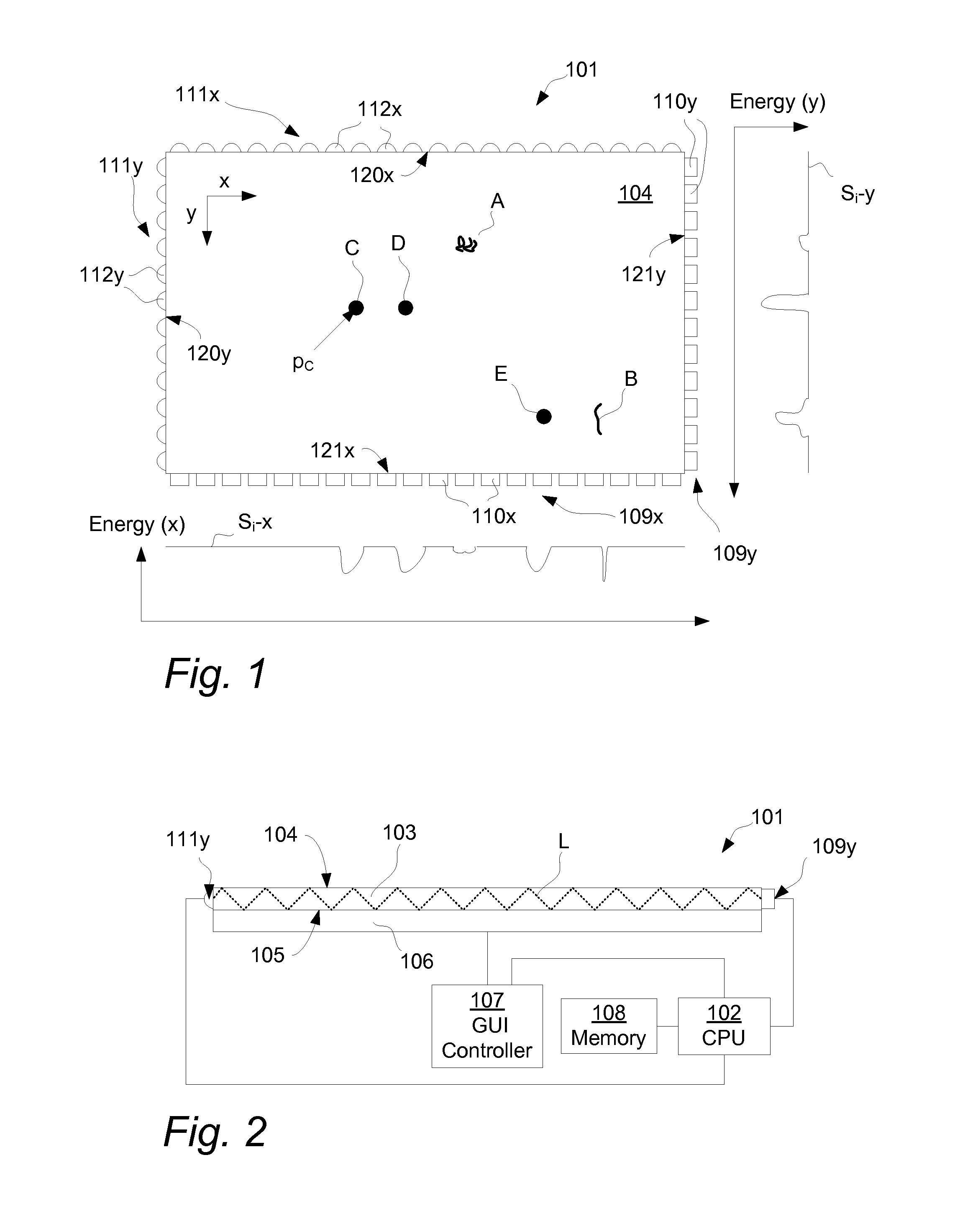
Touch Surface With A Compensated Signal Profile
InactiveUS20120162144A1Reduce impactAccurate measurementInput/output processes for data processingComputational physicsLight detection
An apparatus, method and computer-readable medium for determining a location of at least one object on a touch surface of a light transmissive panel. The method comprises the steps of: introducing light into the panel for propagation by internal reflection between the touch surface and an opposite surface; receiving the light propagating in the panel; and iteratively i) determining a current signal profile of light received by the light detection arrangement, ii) updating, when a condition is met, a background signal profile of light received by the light detection arrangement, iii) calculating a current compensated signal profile as a function of the background signal profile and the current signal profile and iv) determining, when the object touches the touch surface and thereby attenuates the light propagating in the panel, the location as a function of the compensated signal profile.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
System and method for producing white light using LEDs
ActiveUS20050200295A1High color rendering indexWide SPDStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalFeedback control
A system and method for generating white light involves using a combination of white, red, green, and blue LEDs to produce white light and adjusting the emitted light in response to feedback signals. A light system has a light source that includes at least one white LED and multiple color LEDs and a spectral feedback control system configured to detect light that is output from the light source and to adjust the light that is output from the light source in response to the light detection. The spectral feedback control system may include a color sensor configured to provide color-specific feedback signals, a controller configured to generate color-specific control signals in response to the color-specific feedback signals, and a driver configured to generate color-specific drive signals in response to the color-specific control signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
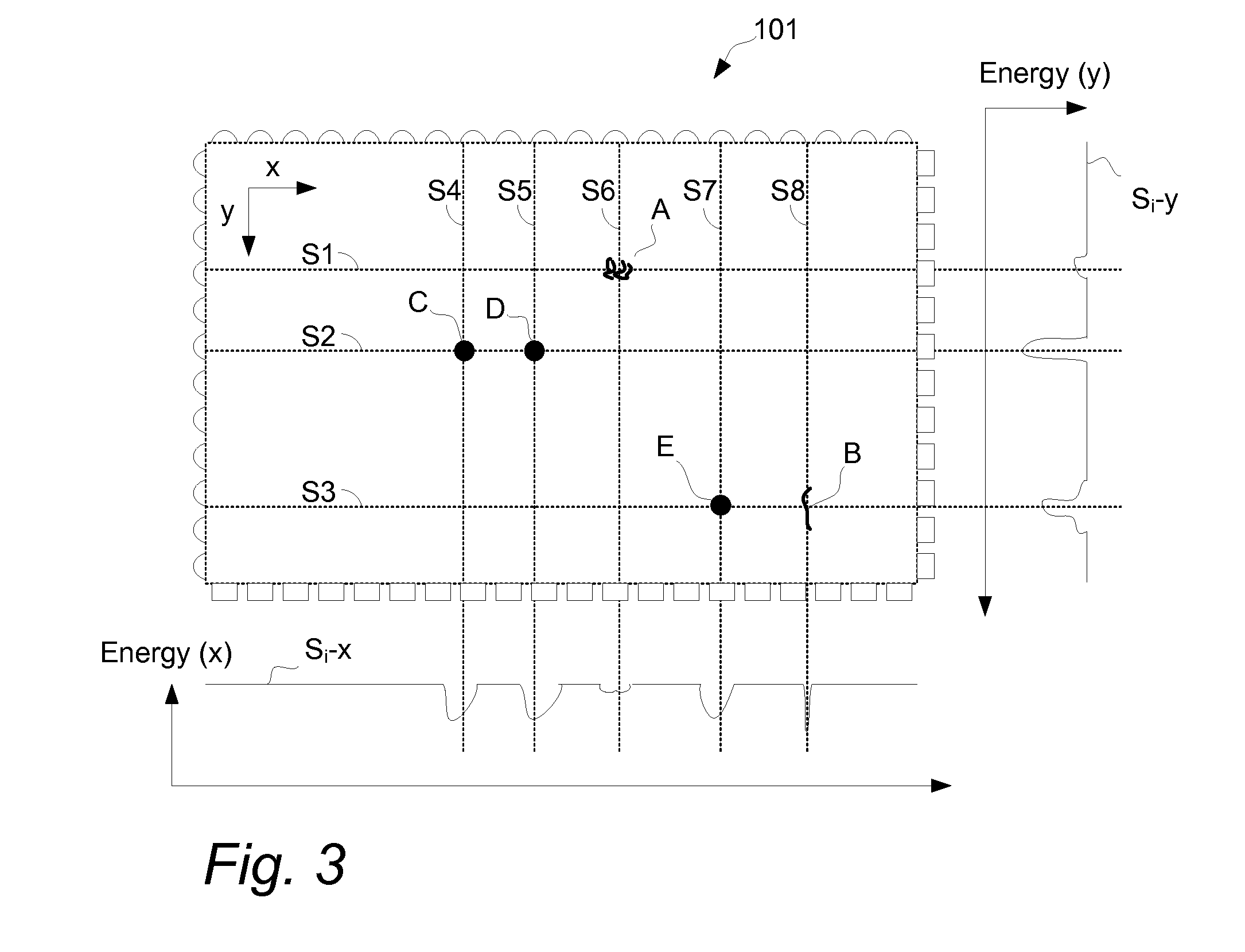
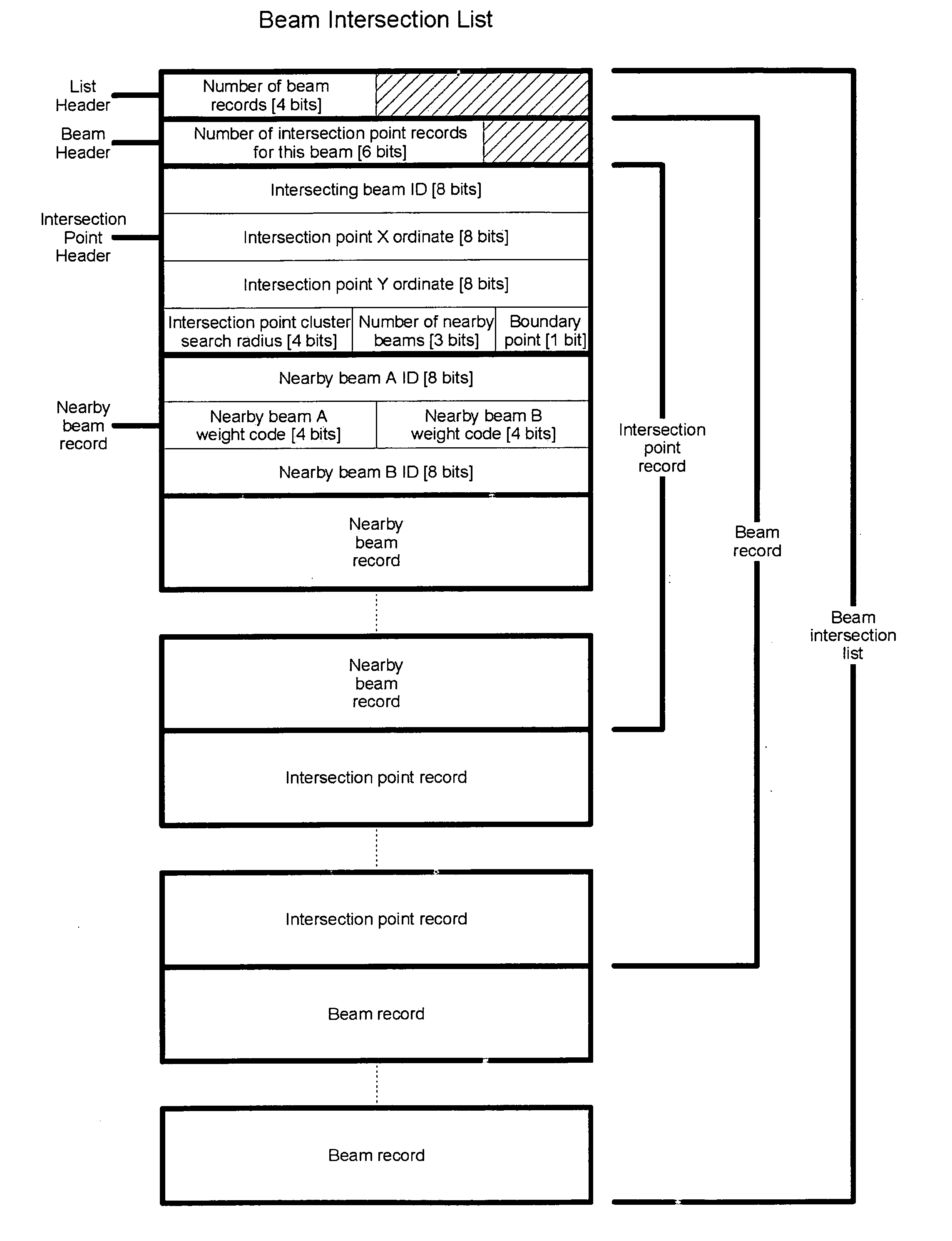
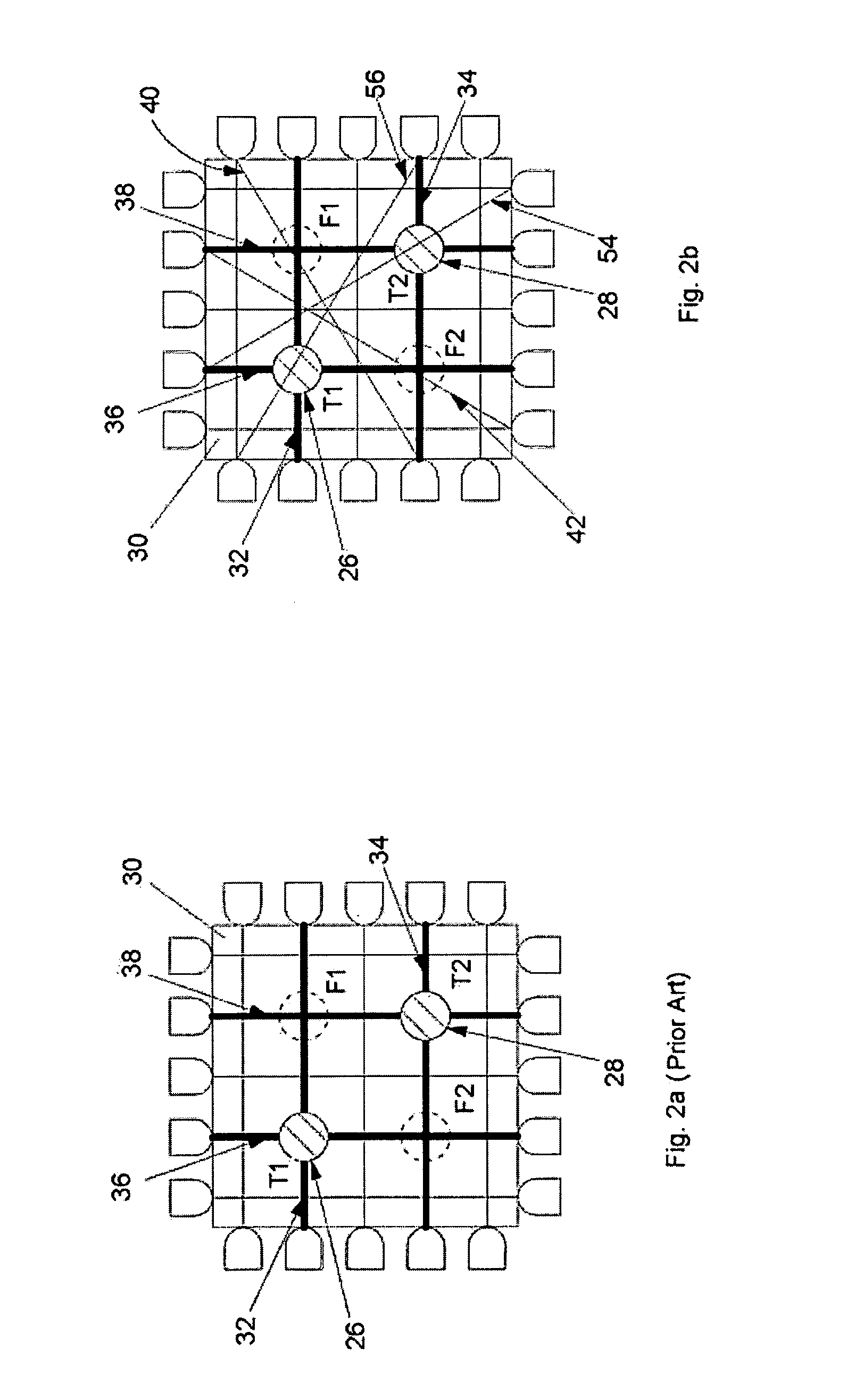
Method and Apparatus For Detecting A Multitouch Event In An Optical Touch-Sensitive Device
ActiveUS20110157096A1Low costHigh resolutionInput/output processes for data processingOptical controlTest beam
A touch sensitive optical control device comprising a set of light emitters 14, 22 and light detectors 18, 24 arranged relative to a touchable surface 30 such that light transmitted by the emitters is received by the detectors along multiple intersecting beams which pass transversely of the surface and touching the surface at a beam interrupts the light transmitted along the beam. Candidate touch points T1, T2, F1, F2 are defined at the intersections of interrupted beams and are confirmed or not as actual touch points by examining test beams 40, 42, 54, 56 near to or coincident with the candidate touch point.
Owner:BEECHROCK LTD
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS20100046953A1Turn fasterWide field of viewWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayColor printing
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
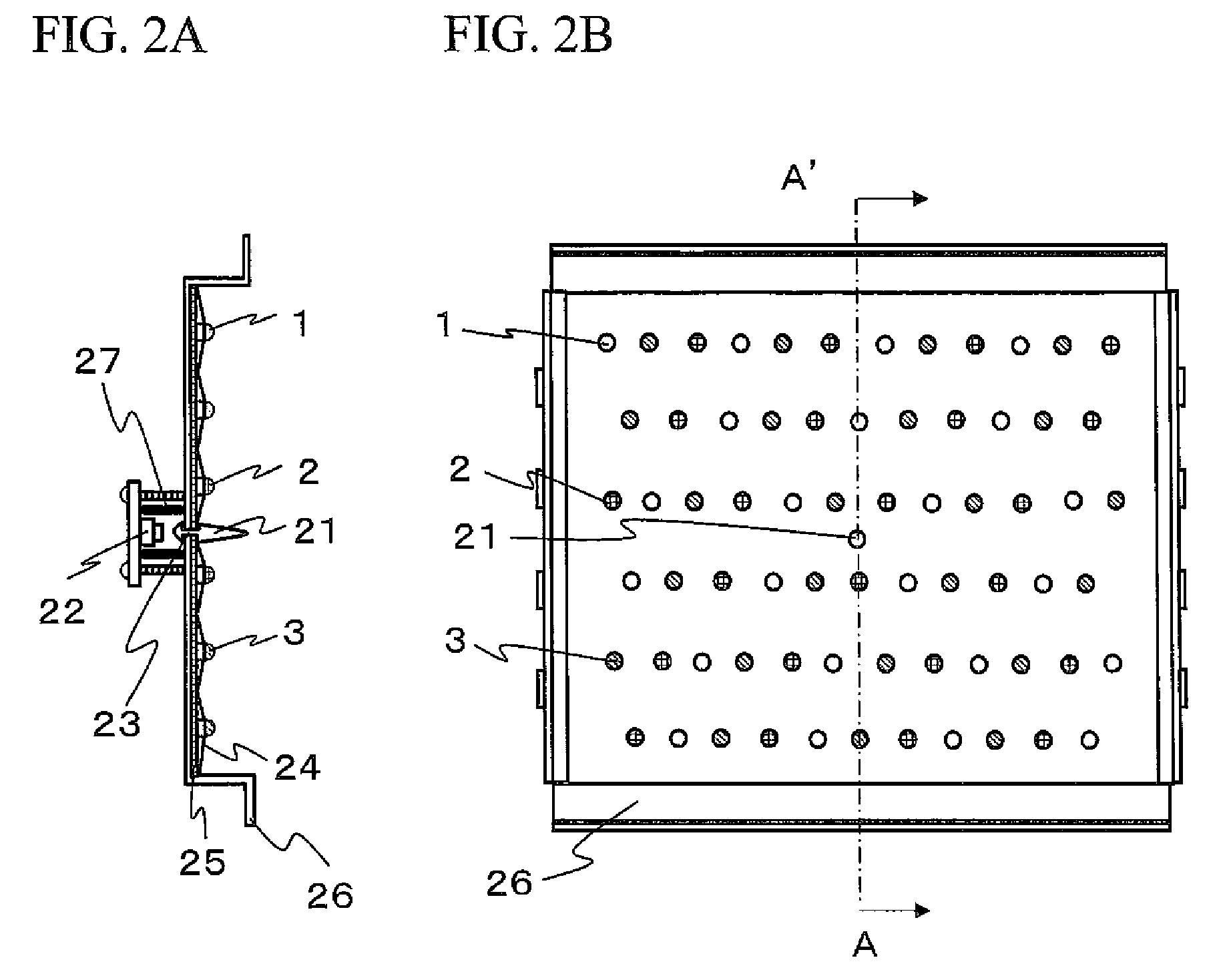
Traffic signal light having ambient light detection
InactiveUS20050030203A1Facilitate easeInhibitionElectrical apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlPhotovoltaic detectorsTraffic signal
A traffic signal (310) having a reflector (322, 400) having a plurality of reflective surfaces (330, 402) directing incident ambient light received from the signal lens (318) to a photodetector (322). The reflector is disposed proximate and about a plurality of LEDs (324, 406) which are pulse width modulated by an integrated controller (360) to generate light which is also transmitted through the lens. The photodetector senses the incoming ambient light when the LEDs are in the “off” mode. Incident ambient light is focused by a lens to overfill the reflector and LEDs, and the photodetector is positioned within the redirected incident ambient light from the lens.
Owner:OPTISOFT +1
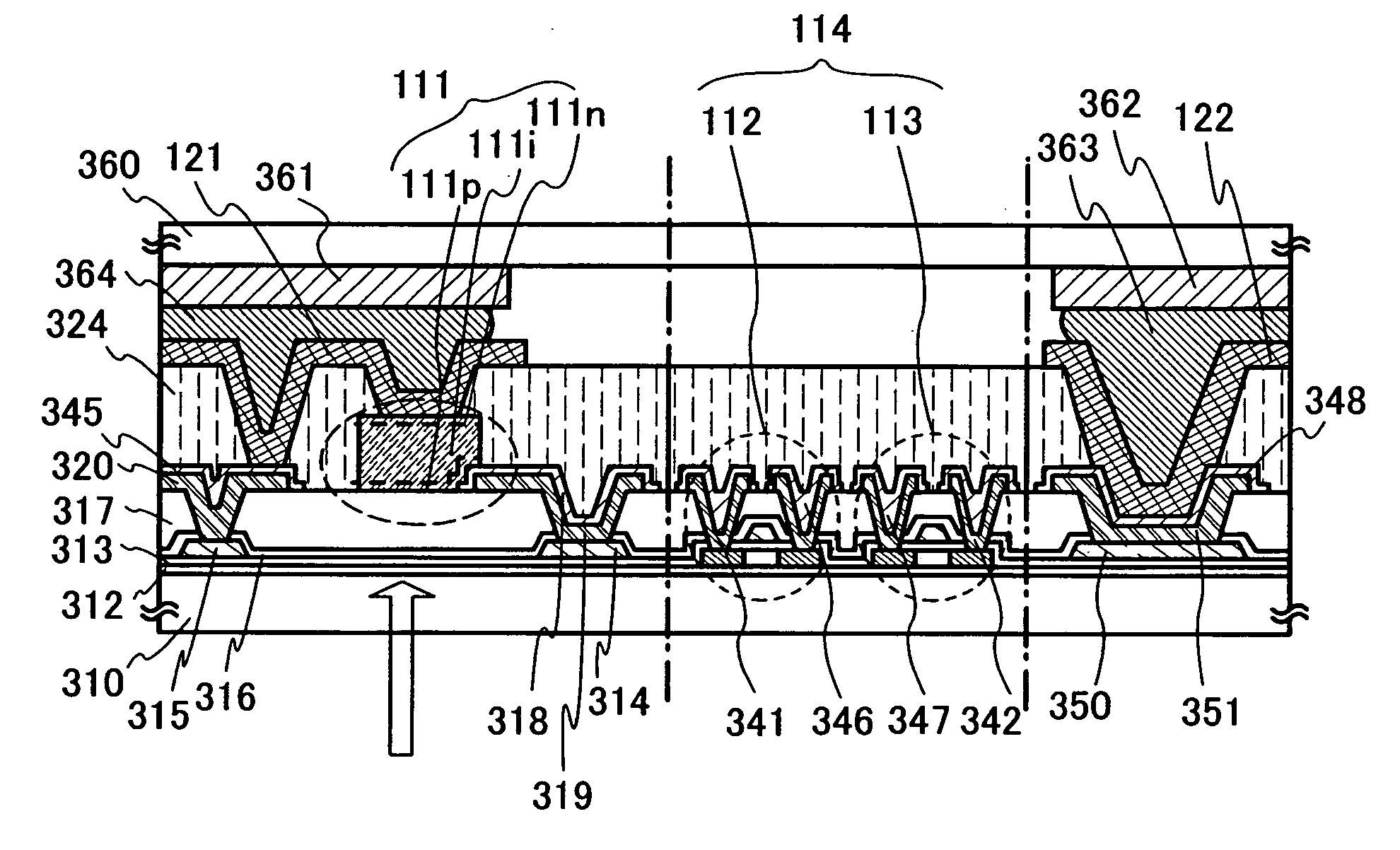
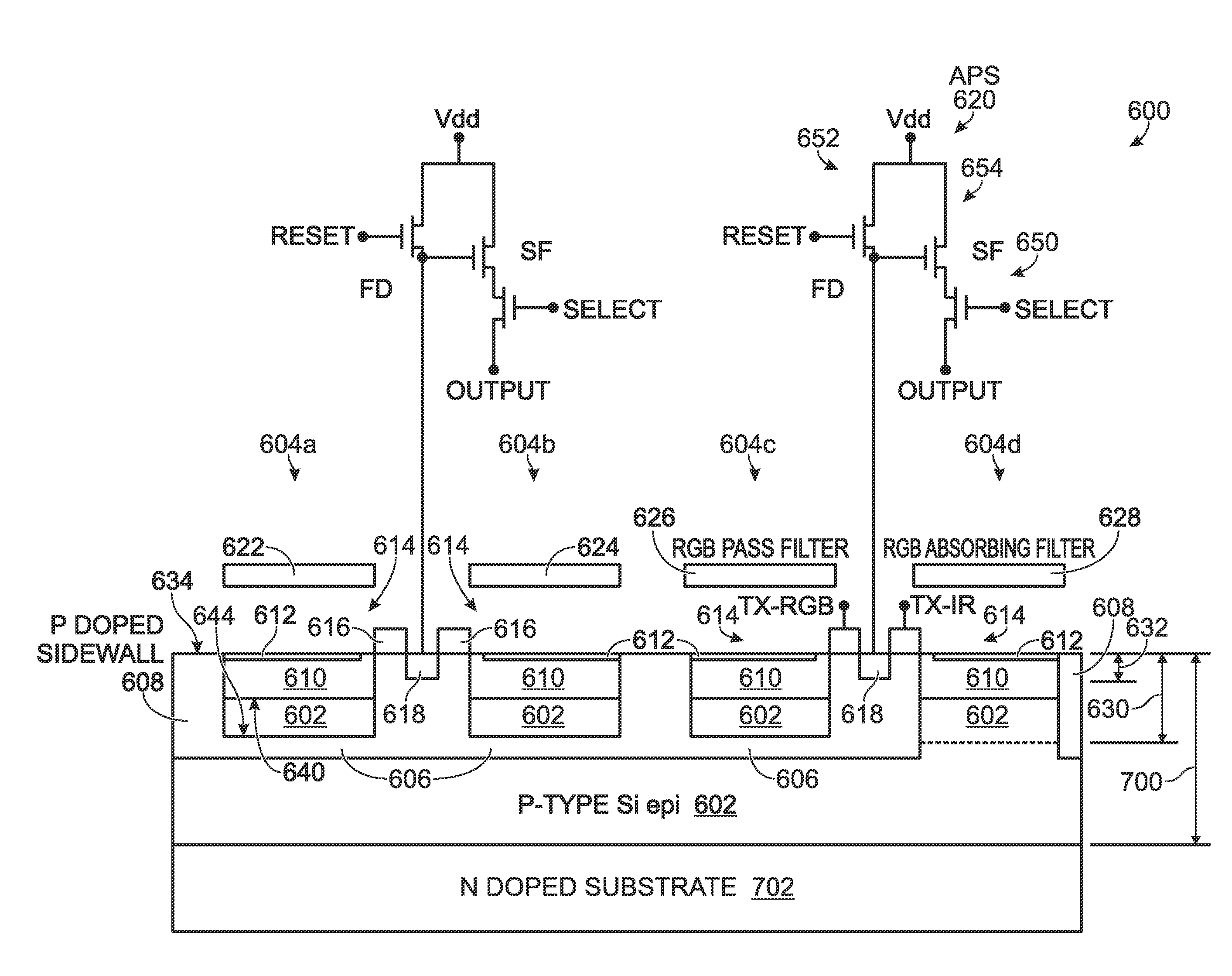
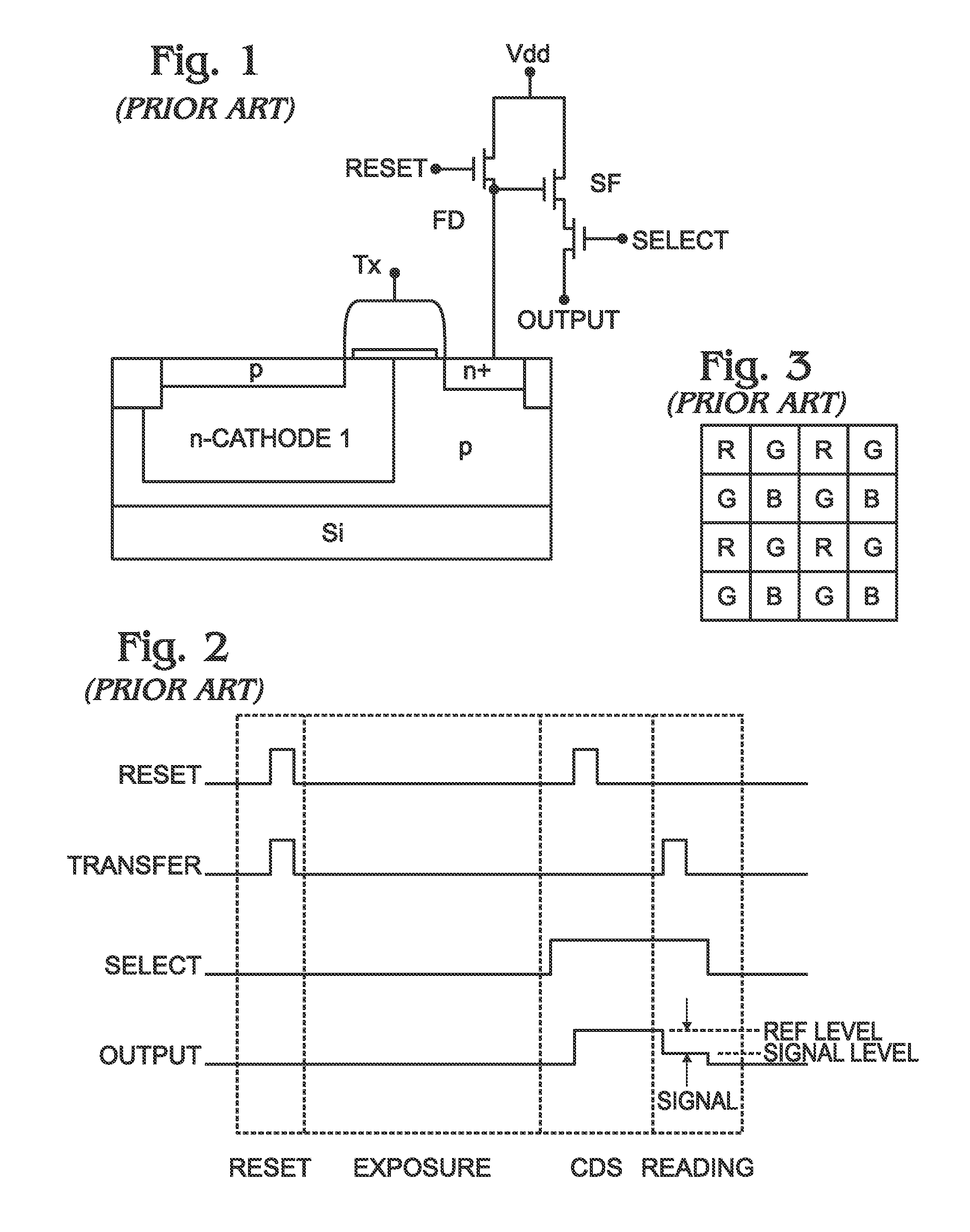
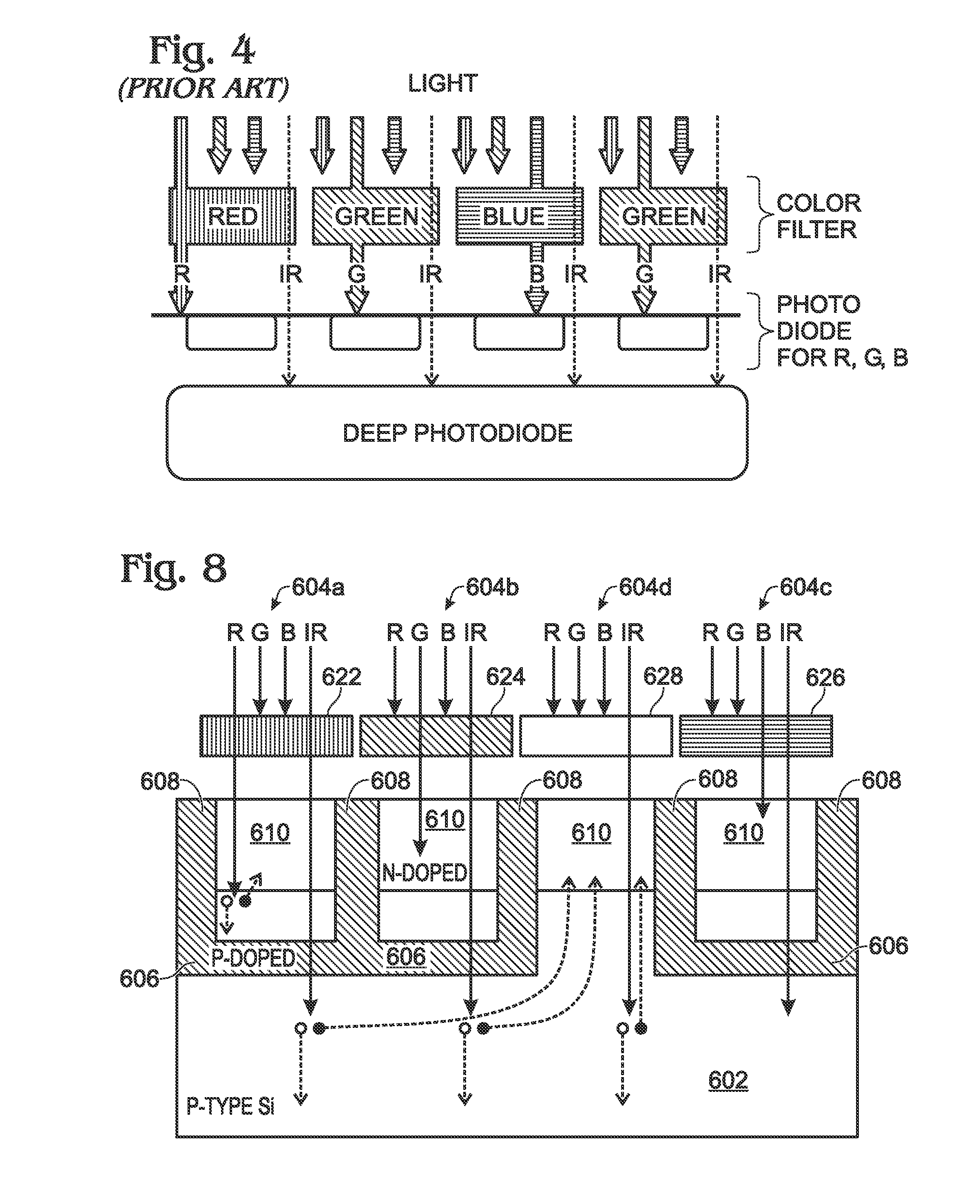
Integrated Infrared and Color CMOS Imager Sensor
ActiveUS20100102366A1Low reset noiseReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInfraredFloating diffusion
An integrated infrared (IR) and full color complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) imager array is provided. The array is built upon a lightly doped p doped silicon (Si) substrate. Each pixel cell includes at least one visible light detection pixel and an IR pixel. Each visible light pixel includes a moderately p doped bowl with a bottom p doped layer and p doped sidewalls. An n doped layer is enclosed by the p doped bowl, and a moderately p doped surface region overlies the n doped layer. A transfer transistor has a gate electrode overlying the p doped sidewalls, a source formed from the n doped layer, and an n+ doped drain connected to a floating diffusion region. The IR pixel is the same, except that there is no bottom p doped layer. An optical wavelength filter overlies the visible light and IR pixels.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
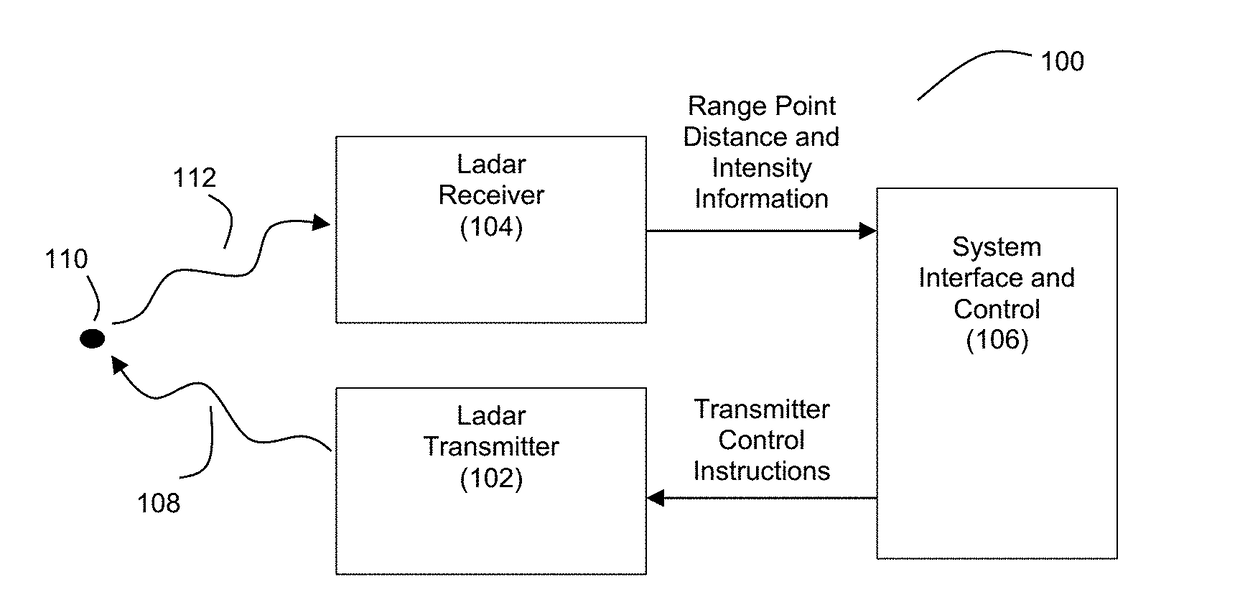
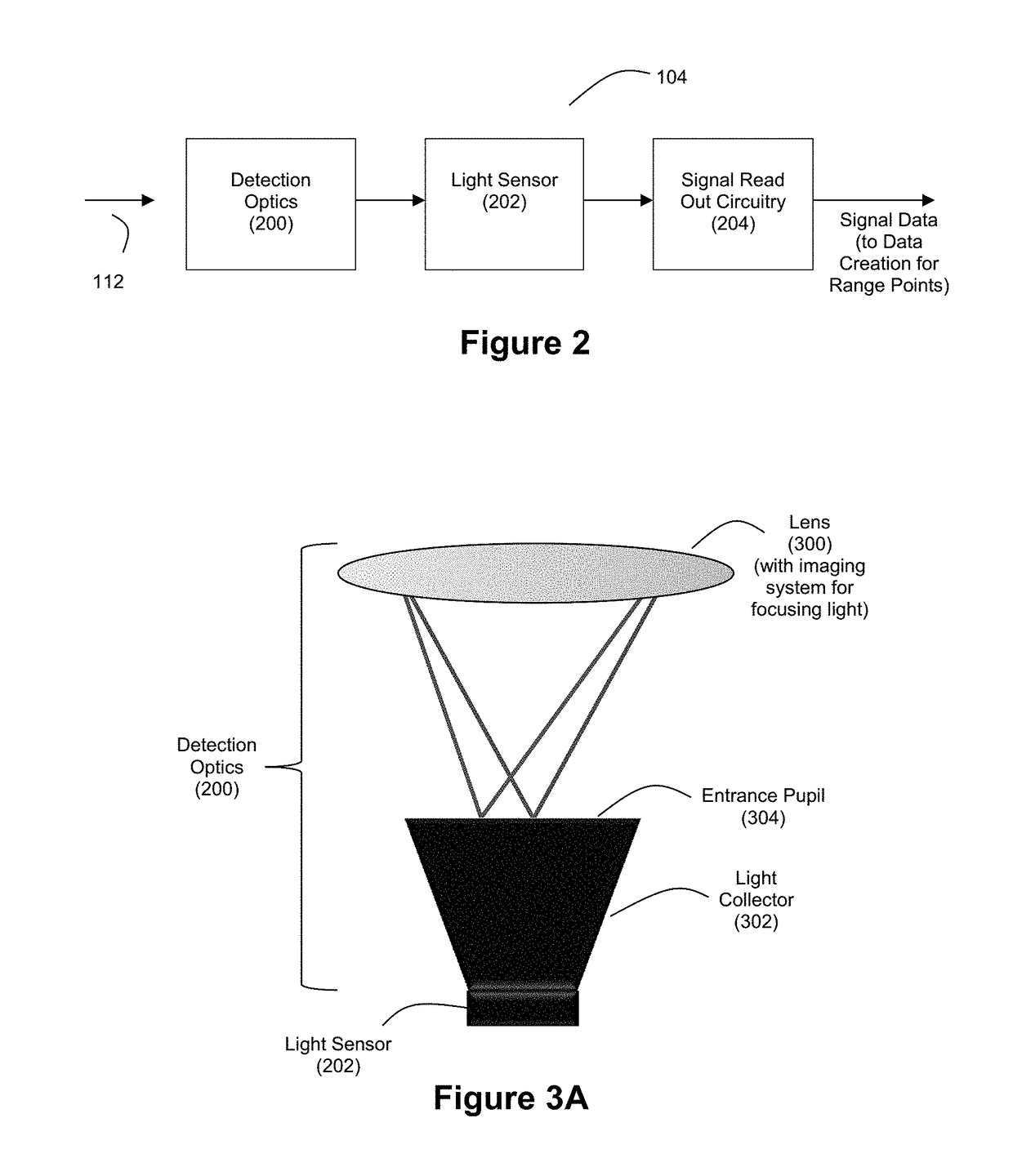
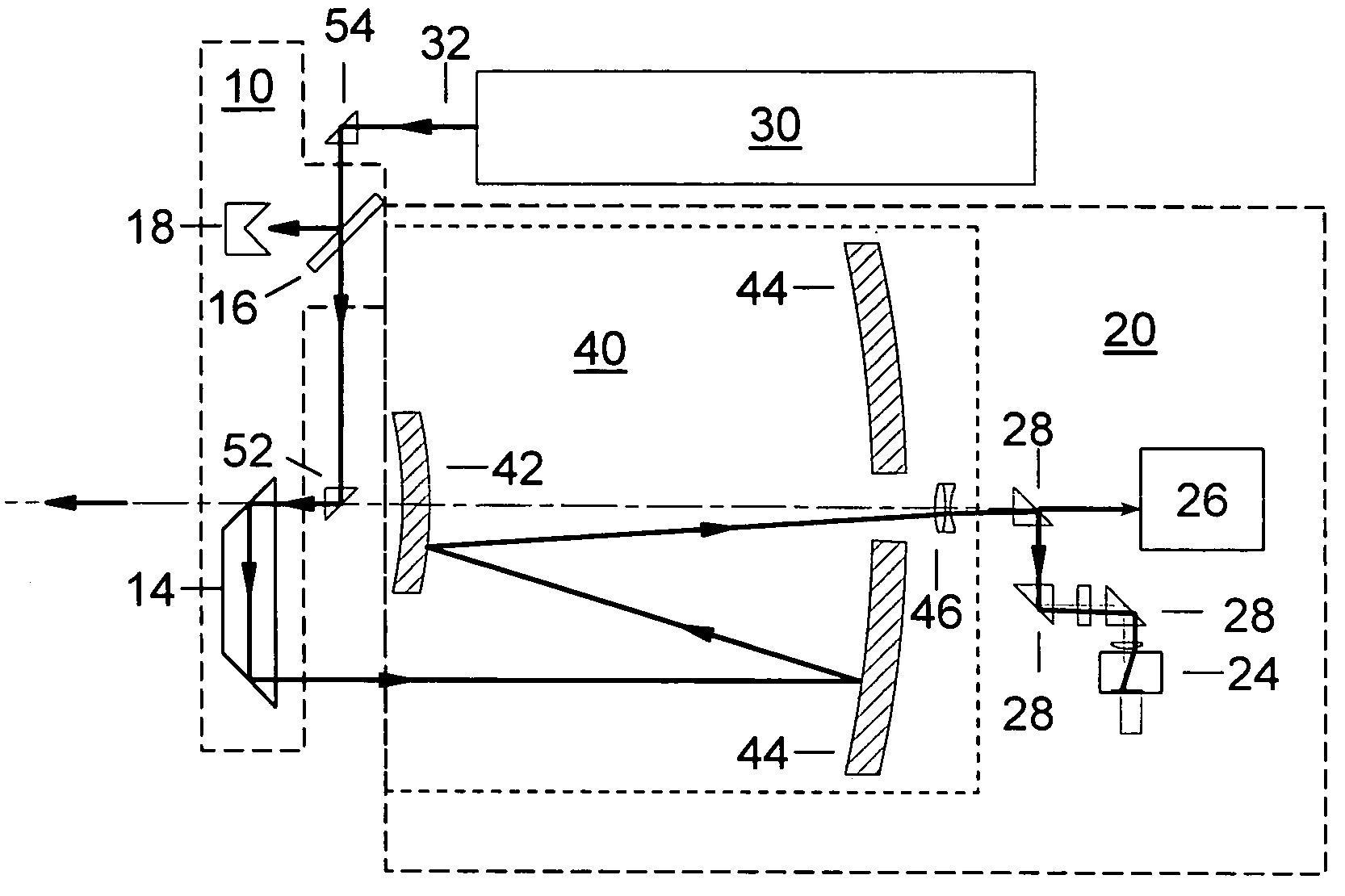
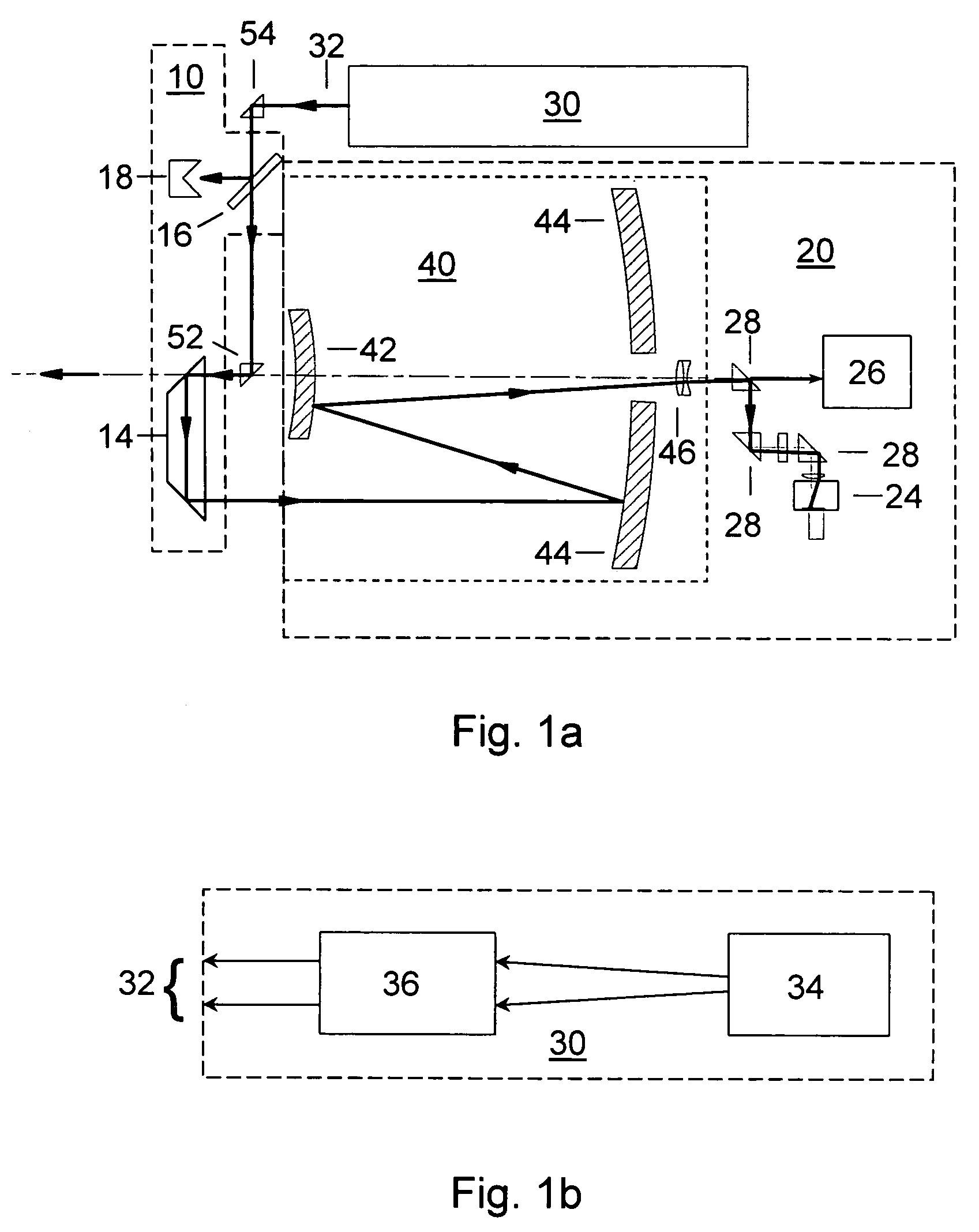
Method to determine and adjust the alignment of the transmitter and receiver fields of view of a LIDAR system
A method to determine the alignment of the transmitter and receiver fields of view of a light detection and ranging (LIDAR) system. This method can be employed to determine the far-field intensity distribution of the transmitter beam, as well as the variations in transmitted laser beam pointing as a function of time, temperature, or other environmental variables that may affect the co-alignment of the LIDAR system components. In order to achieve proper alignment of the transmitter and receiver optical systems when a LIDAR system is being used in the field, this method employs a laser-beam-position-sensing detector as an integral part of the receiver optics of the LIDAR system.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
System and method for nonlinear optical devices
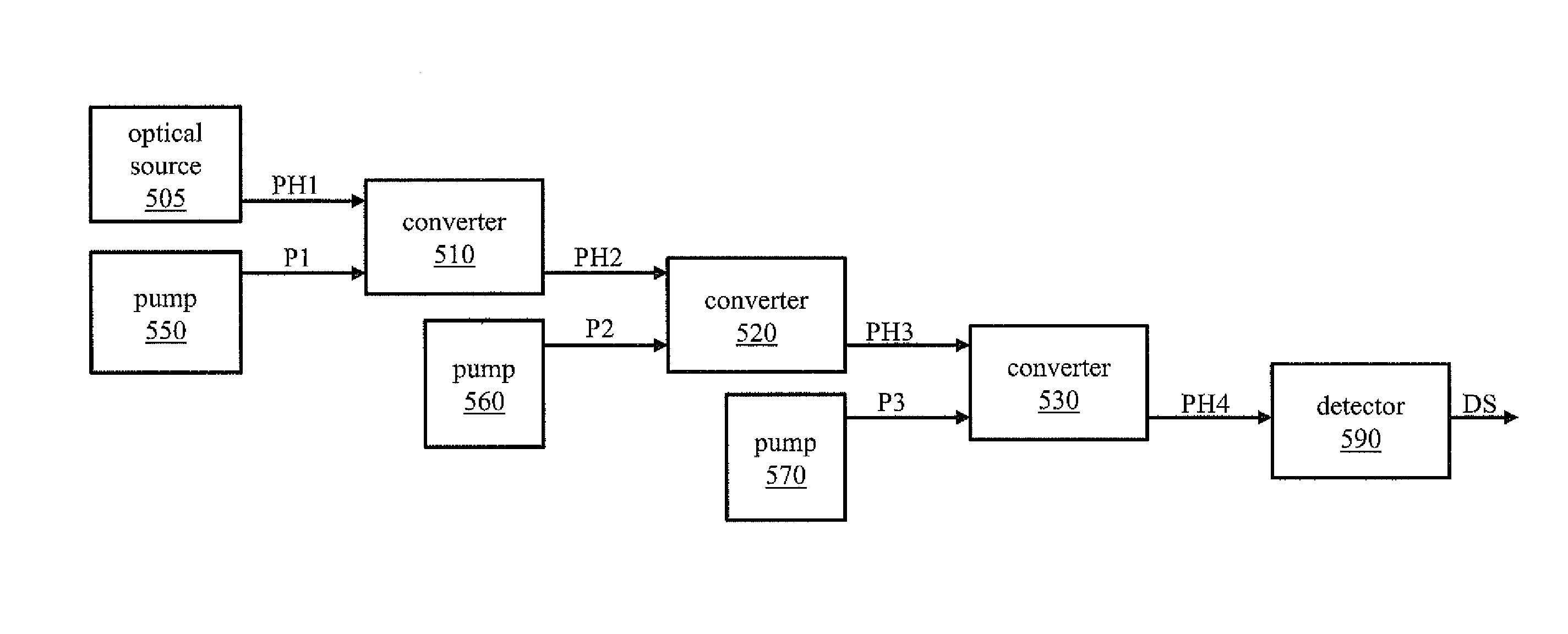
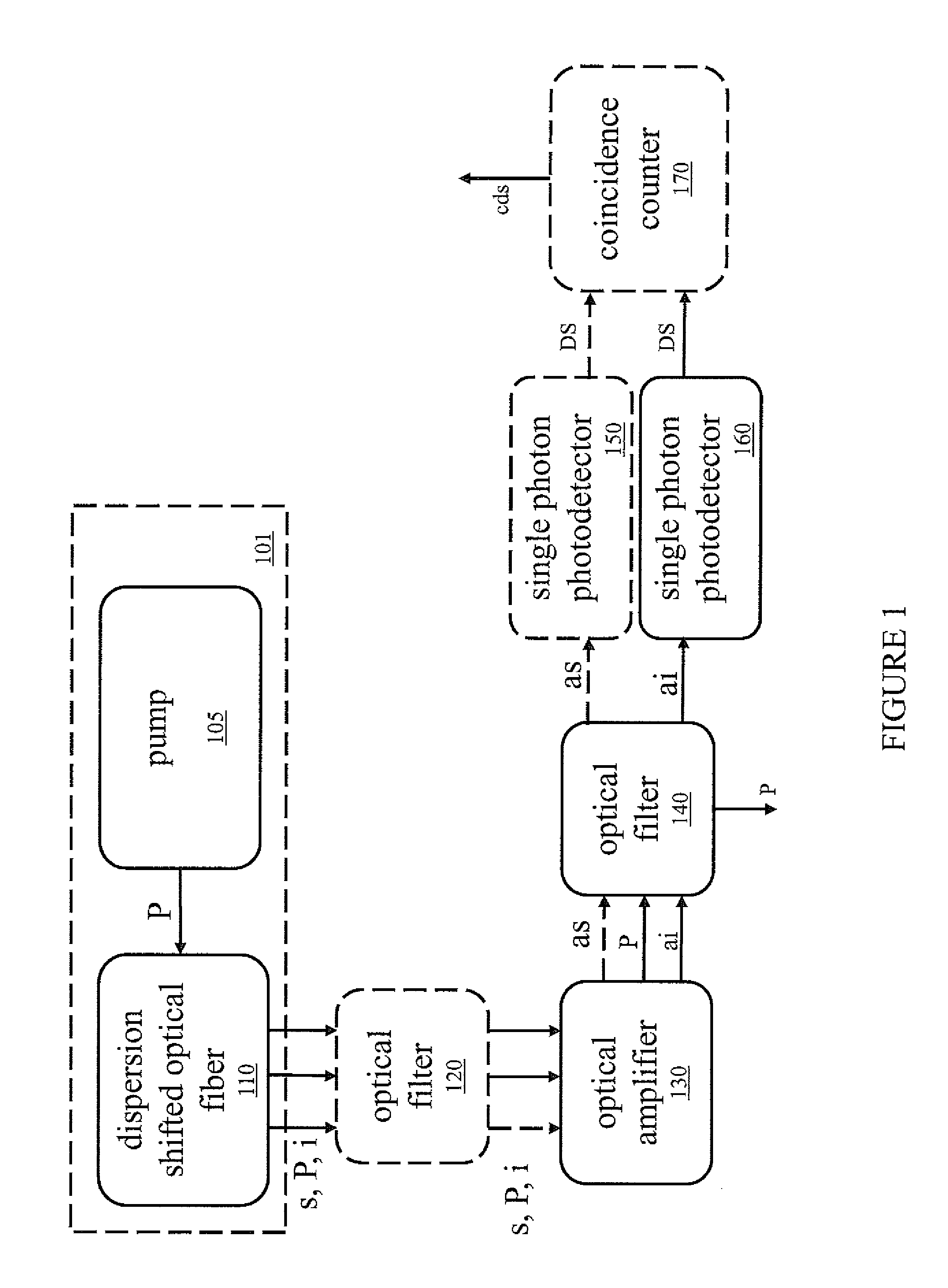
InactiveUS9000347B2High sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
Systems for enhancing the sensitivity of detecting an optical signal using nonlinear optics and method of performing the same. In one embodiment, a single-photon detection system includes an optical amplifier realized in a waveguide, and a photodetector coupled to an output of the optical amplifier. A light detection and ranging system includes the optical amplifier coupled to an optical source and one photodetector. In another embodiment, a photodetection system includes a plurality of optical frequency converters, coupled to an optical source, that sequentially convert a wavelength of photons of the optical source to a final wavelength, and a single-photon photodetector coupled to the optical frequency converters to detect single photons produced by the optical source. In another embodiment, an optical sensor includes an optical pump, and a transducer including an optical ring cavity coupled to the optical pump and configured to utilize optical four-wave mixing to detect an external stimulus.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
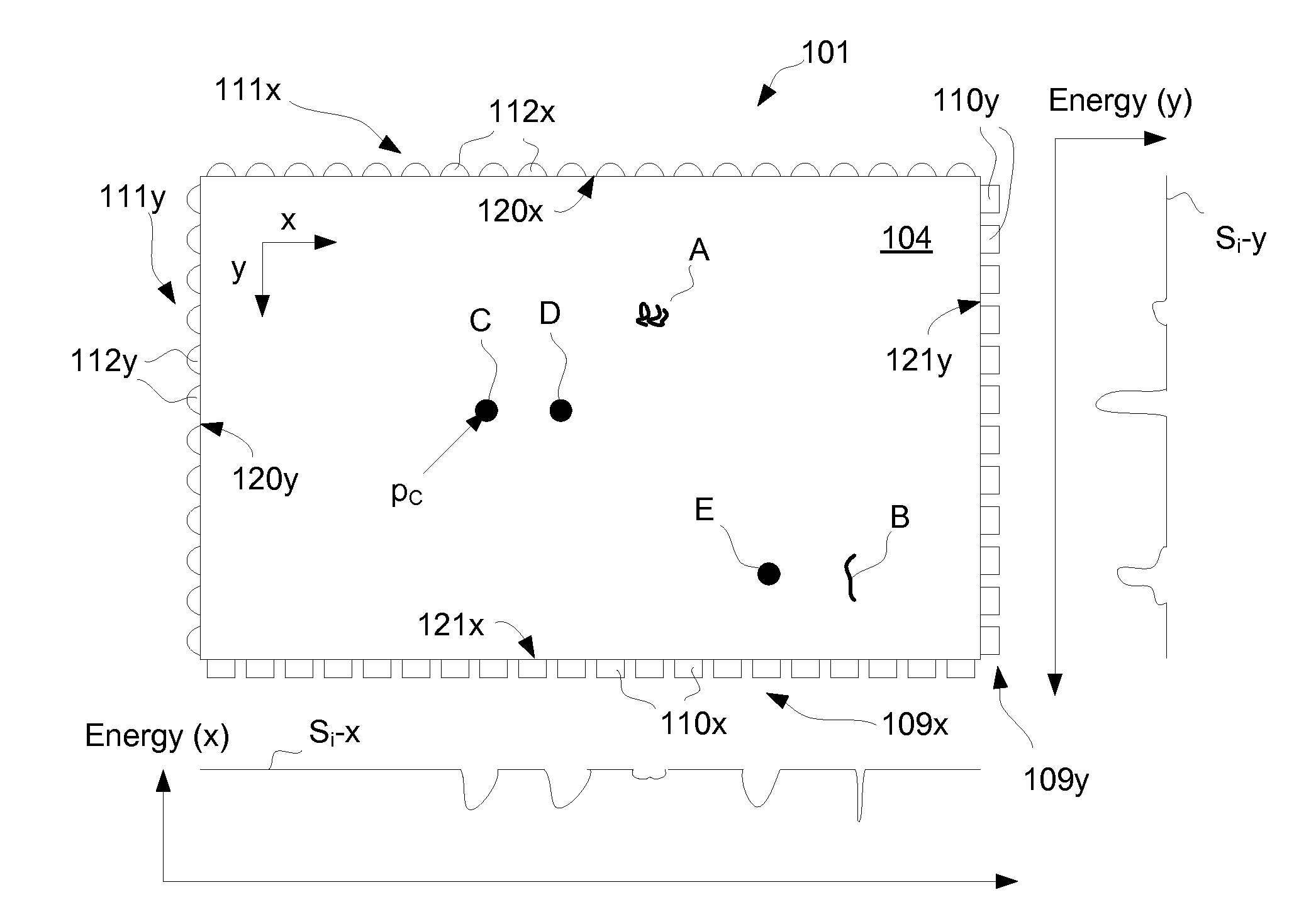
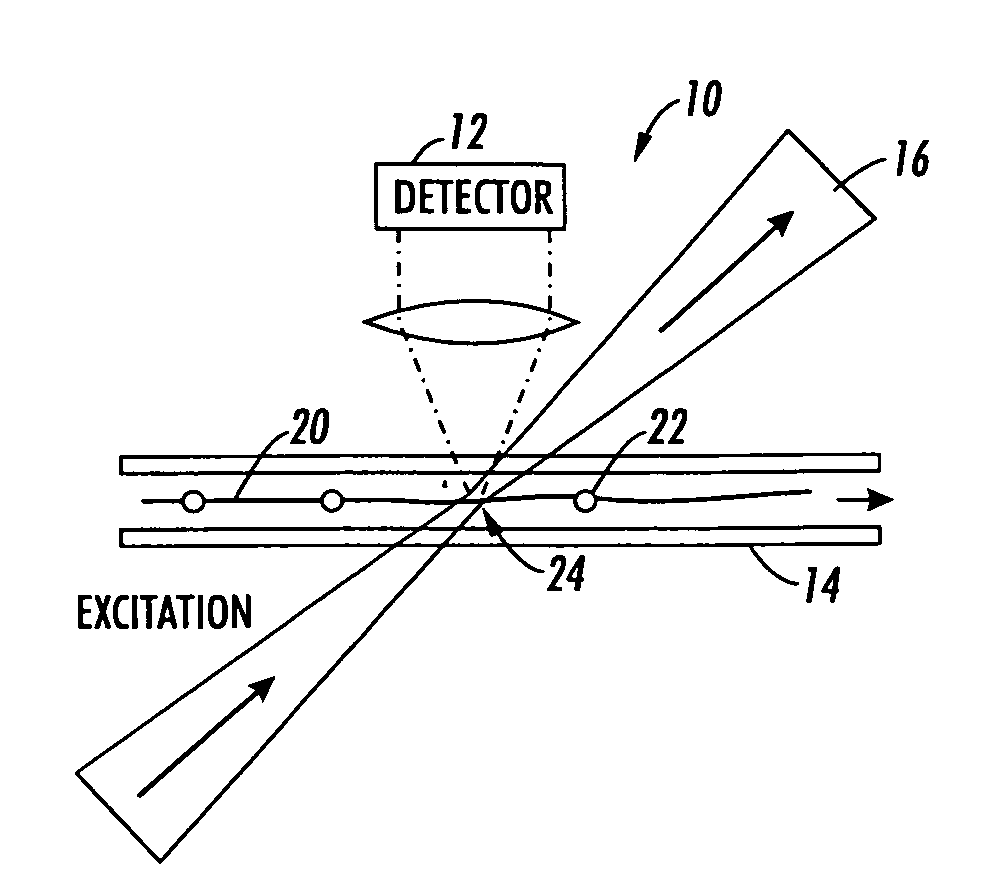
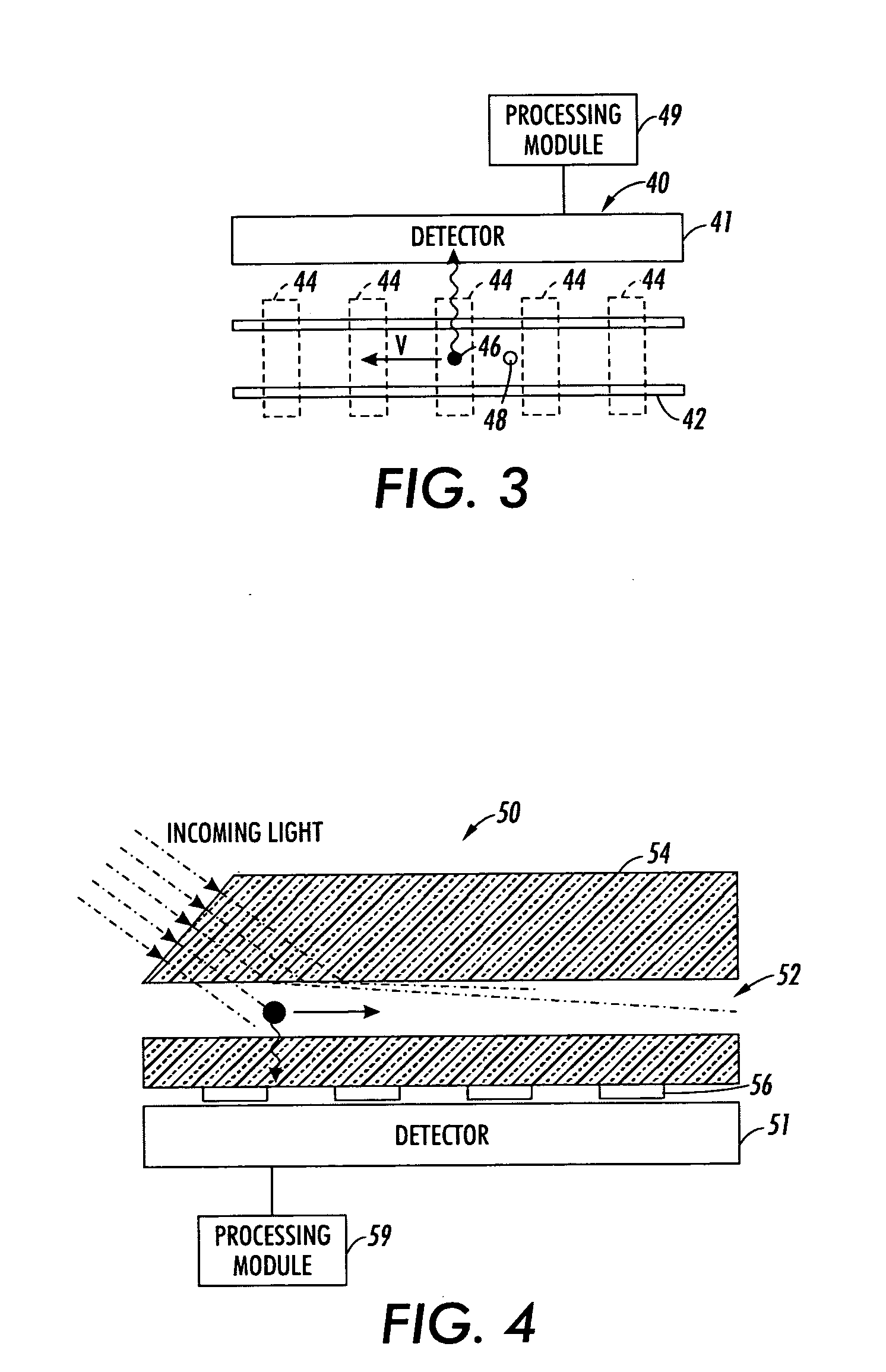
Method and system implementing spatially modulated excitation or emission for particle characterization with enhanced sensitivity
ActiveUS20080181827A1SamplingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRelative motionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and system for using spatially modulated excitation / emission and relative movement between a particle (cell, molecule, aerosol, . . . ) and an excitation / emission pattern are provided. In at least one form, an interference pattern of the excitation light with submicron periodicity perpendicular to the particle flow is used. As the particle moves along the pattern, emission is modulated according to the speed of the particle and the periodicity of the stripe pattern. A single detector, which records the emission over a couple of stripes, can be used. The signal is recorded with a fast detector read-out in order to capture the “blinking” of the particles while they are moving through the excitation pattern. This concept enables light detection with high signal-to-noise ratio and high spatial resolution without the need of expensive and bulky optics.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com