Patents
Literature
198 results about "Readout integrated circuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
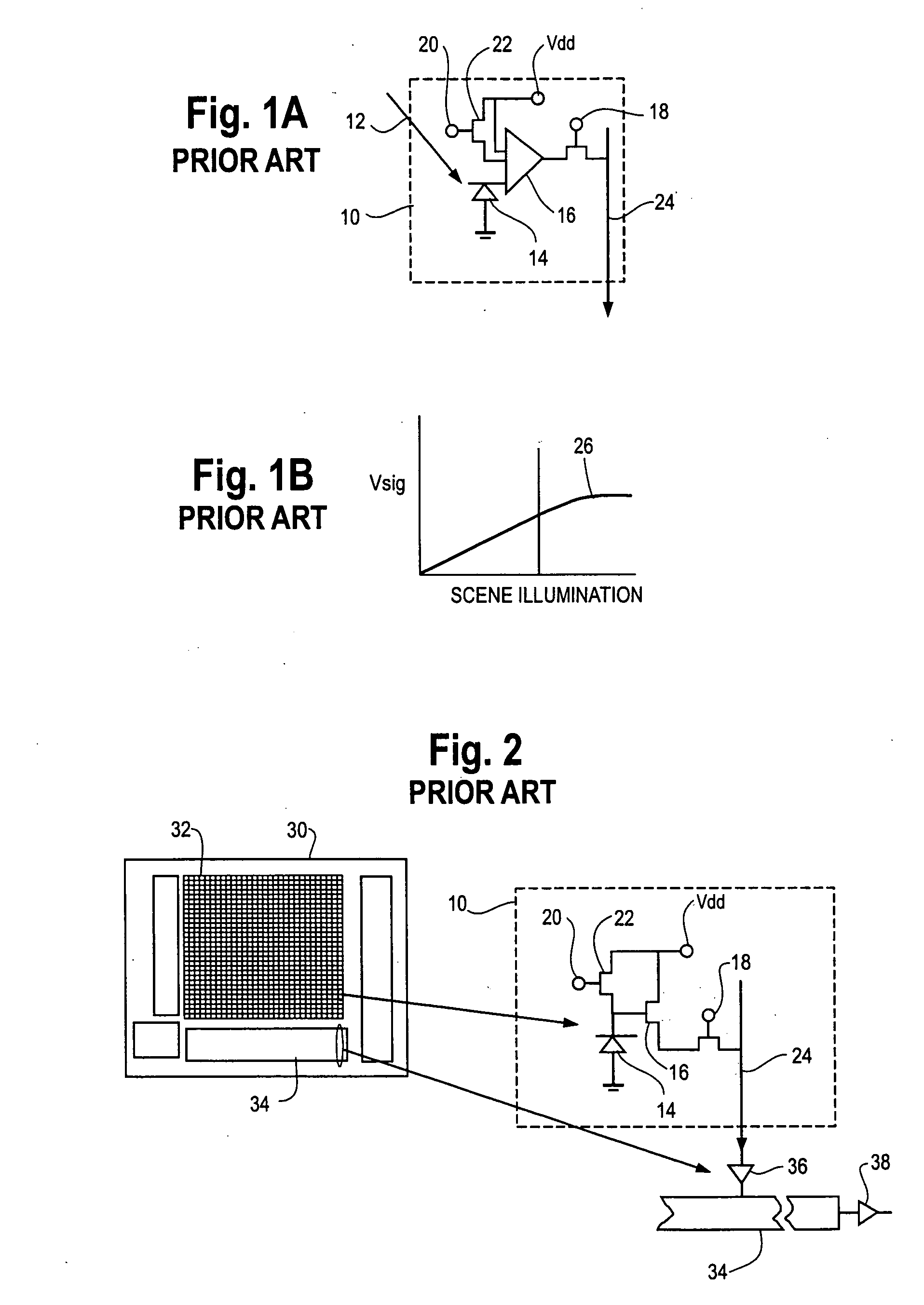
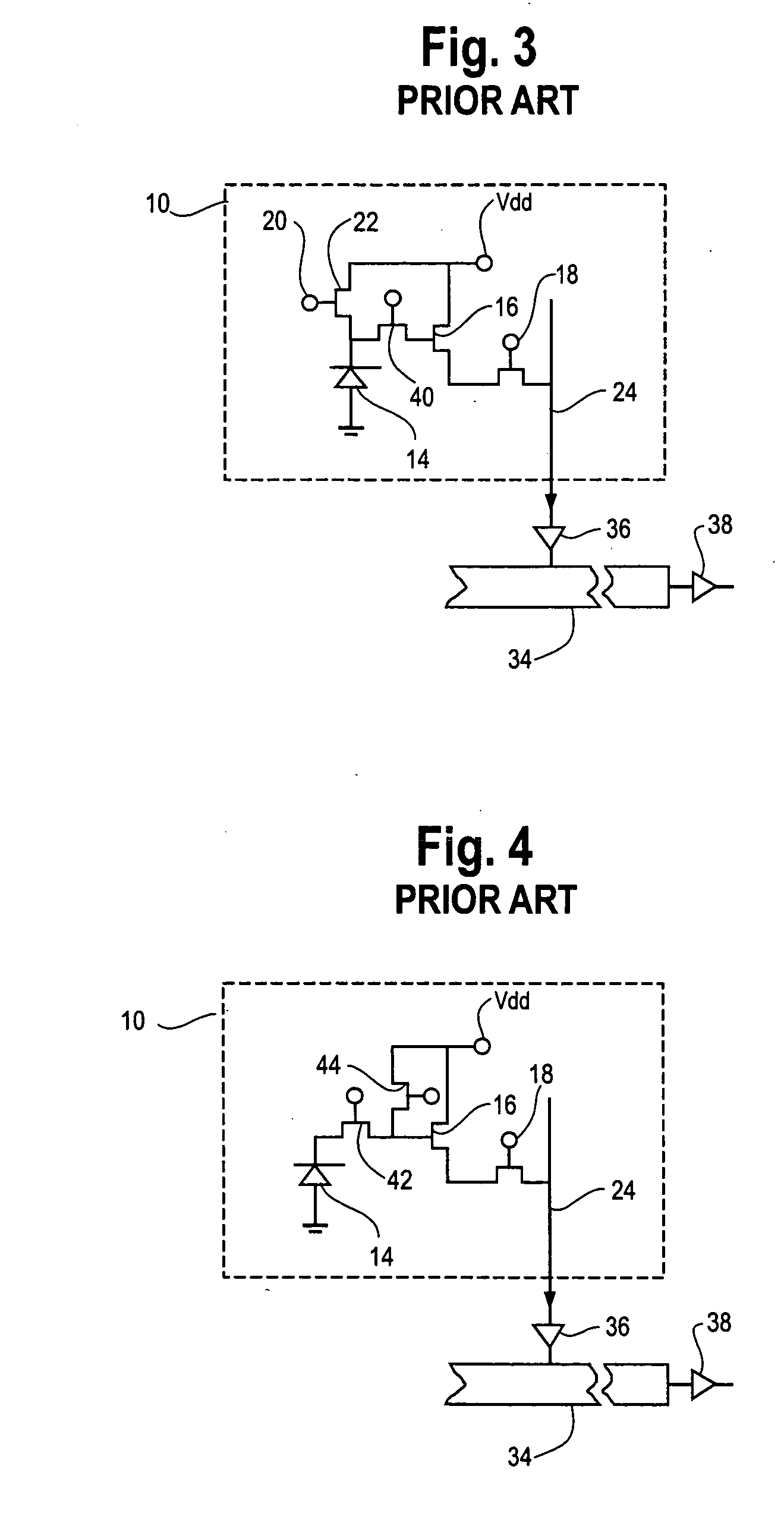
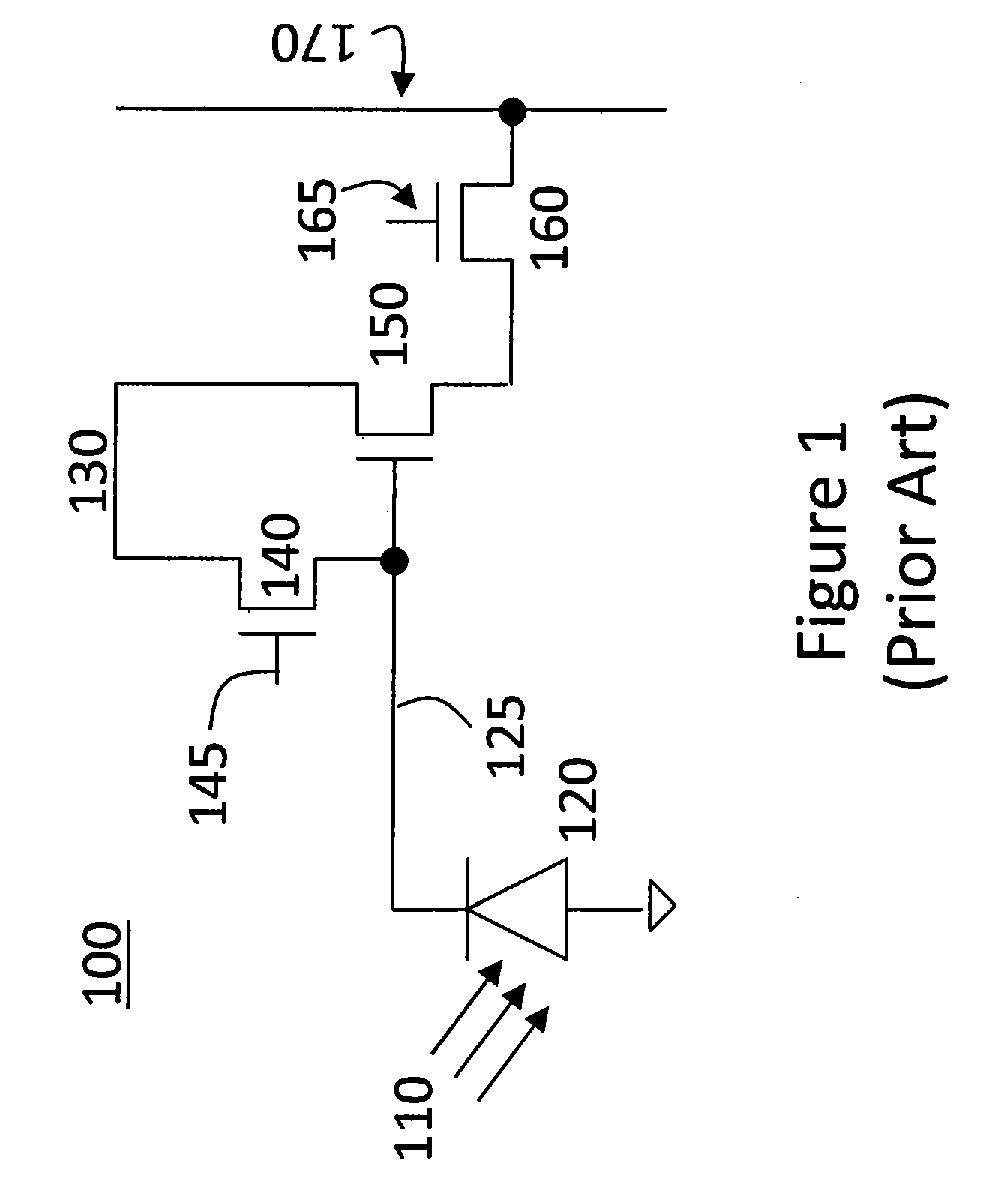
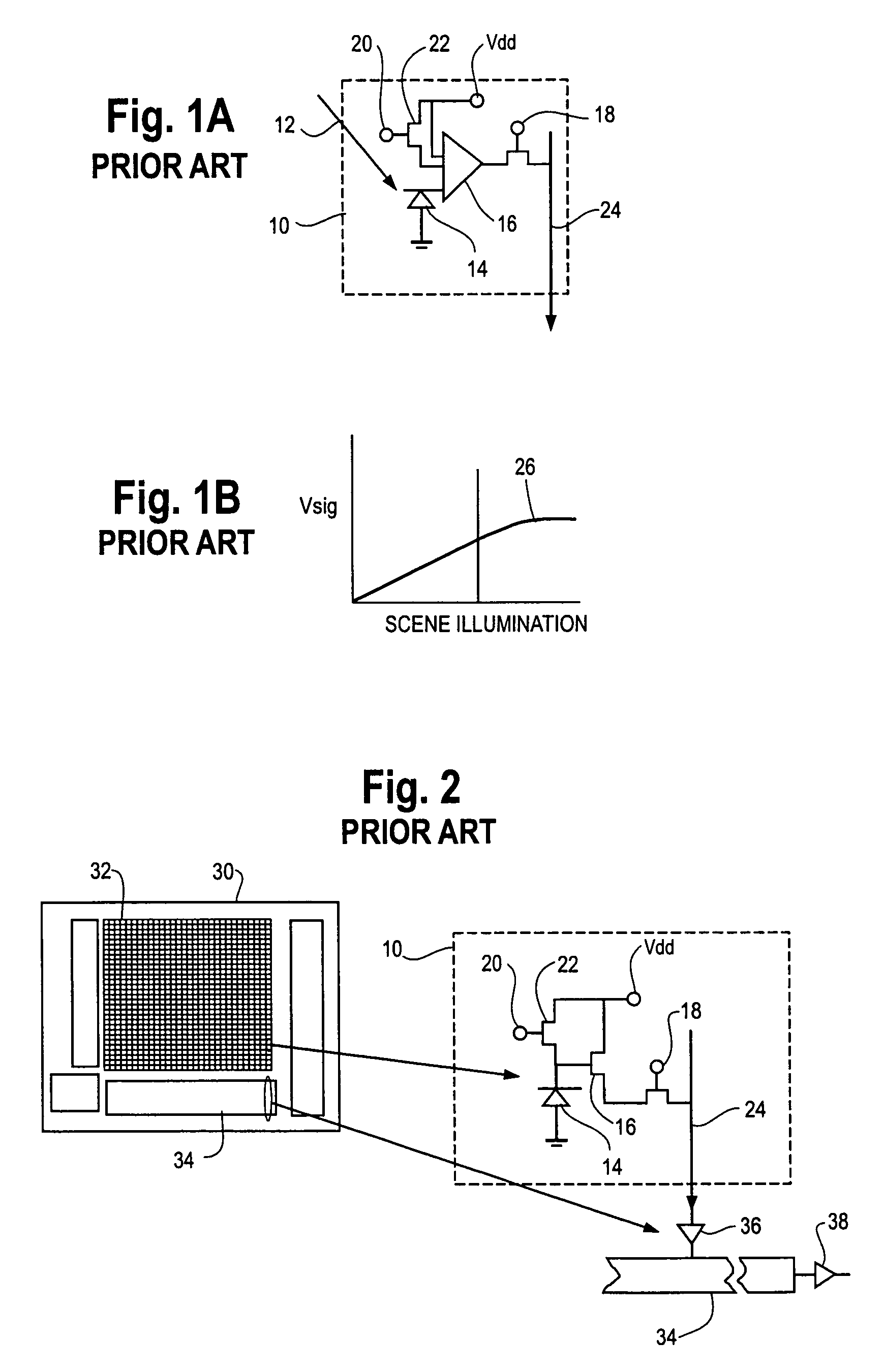
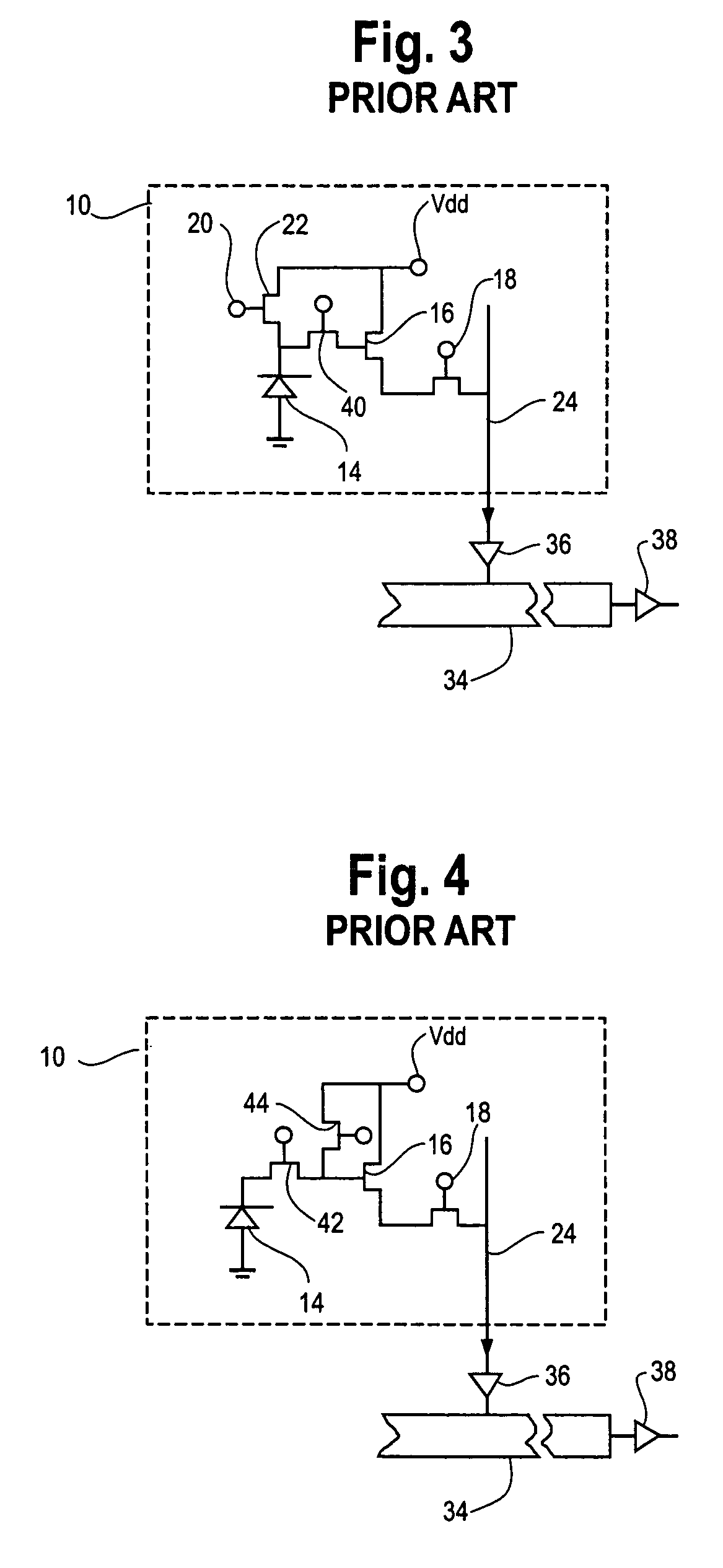
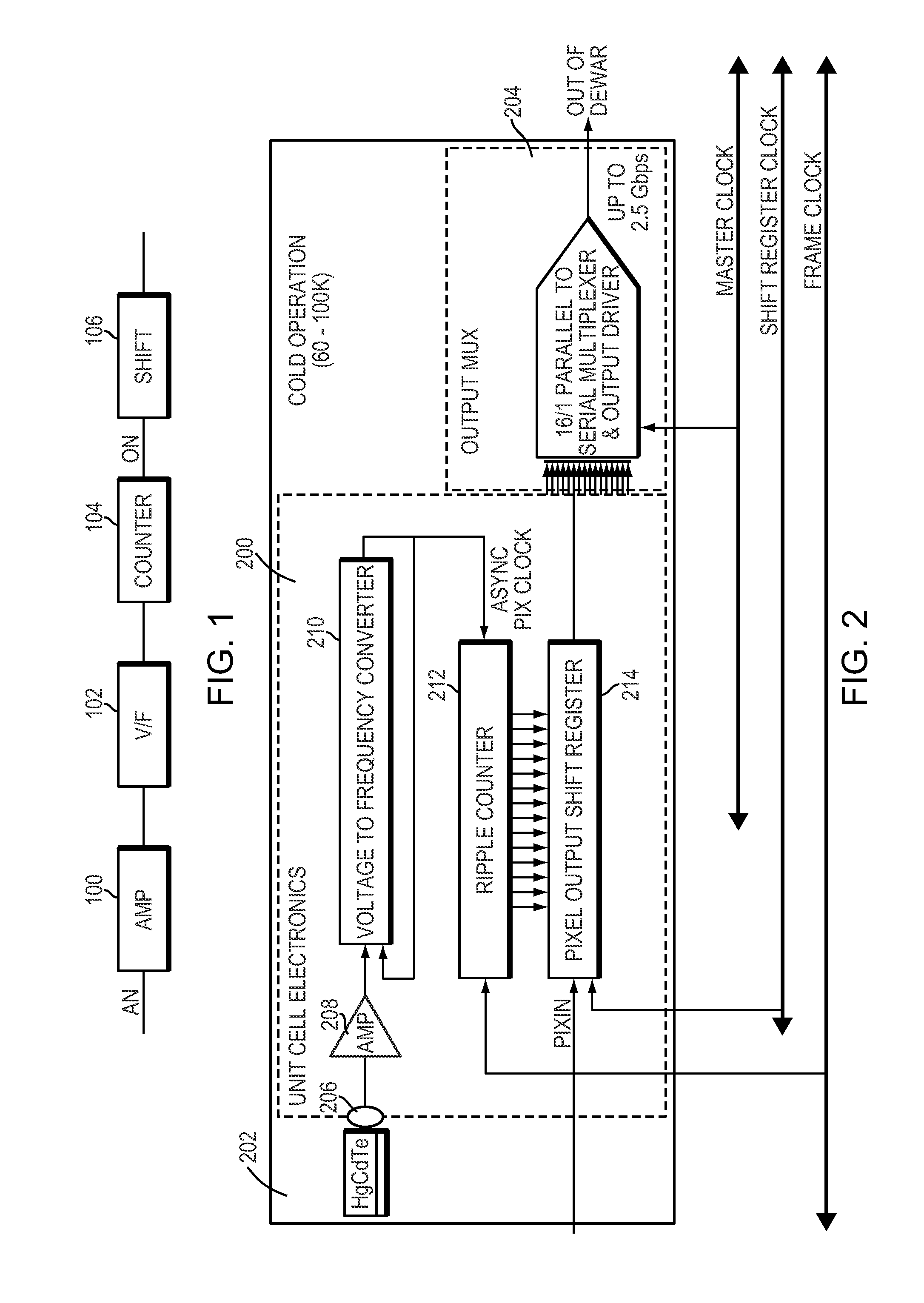
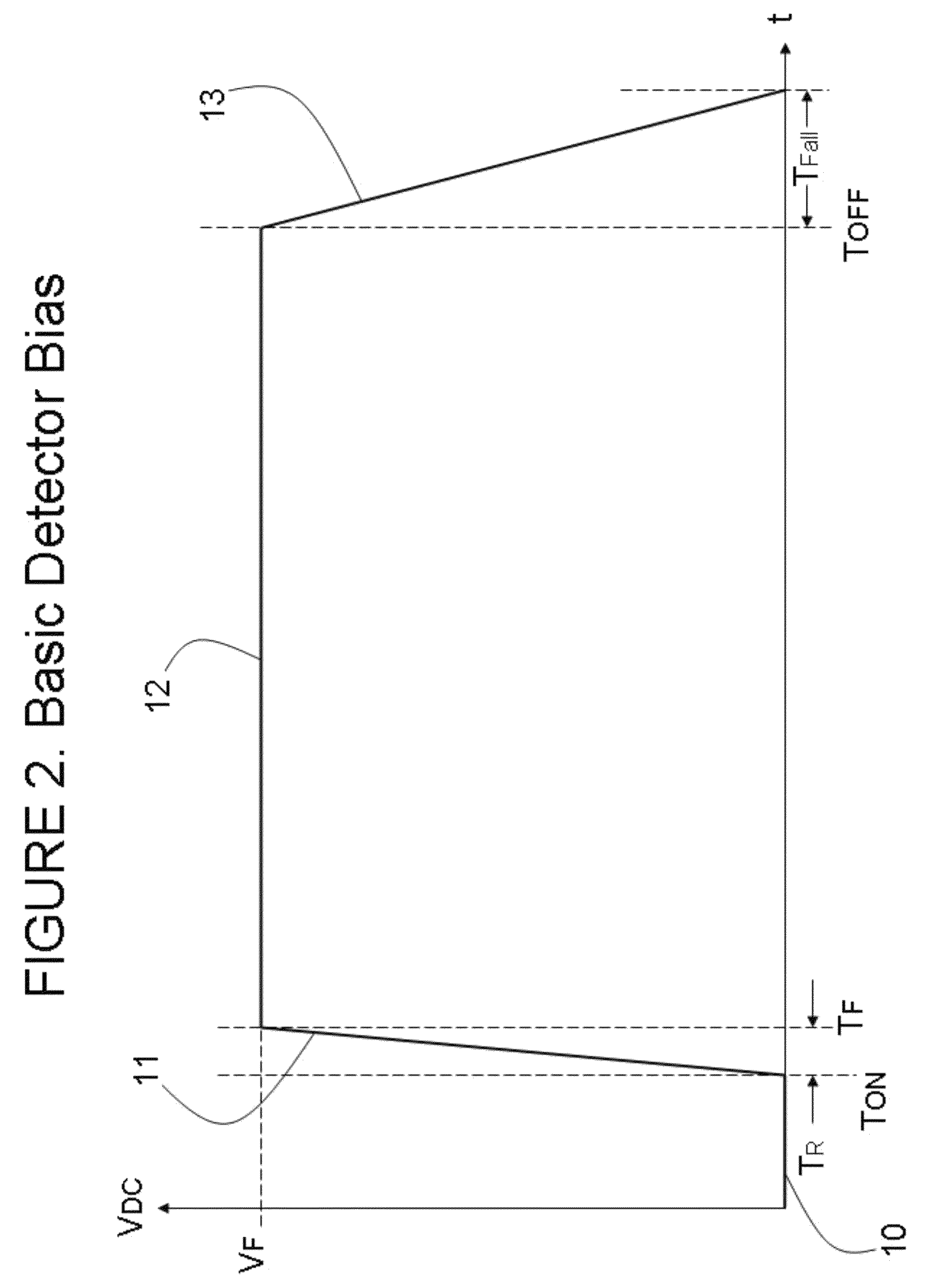
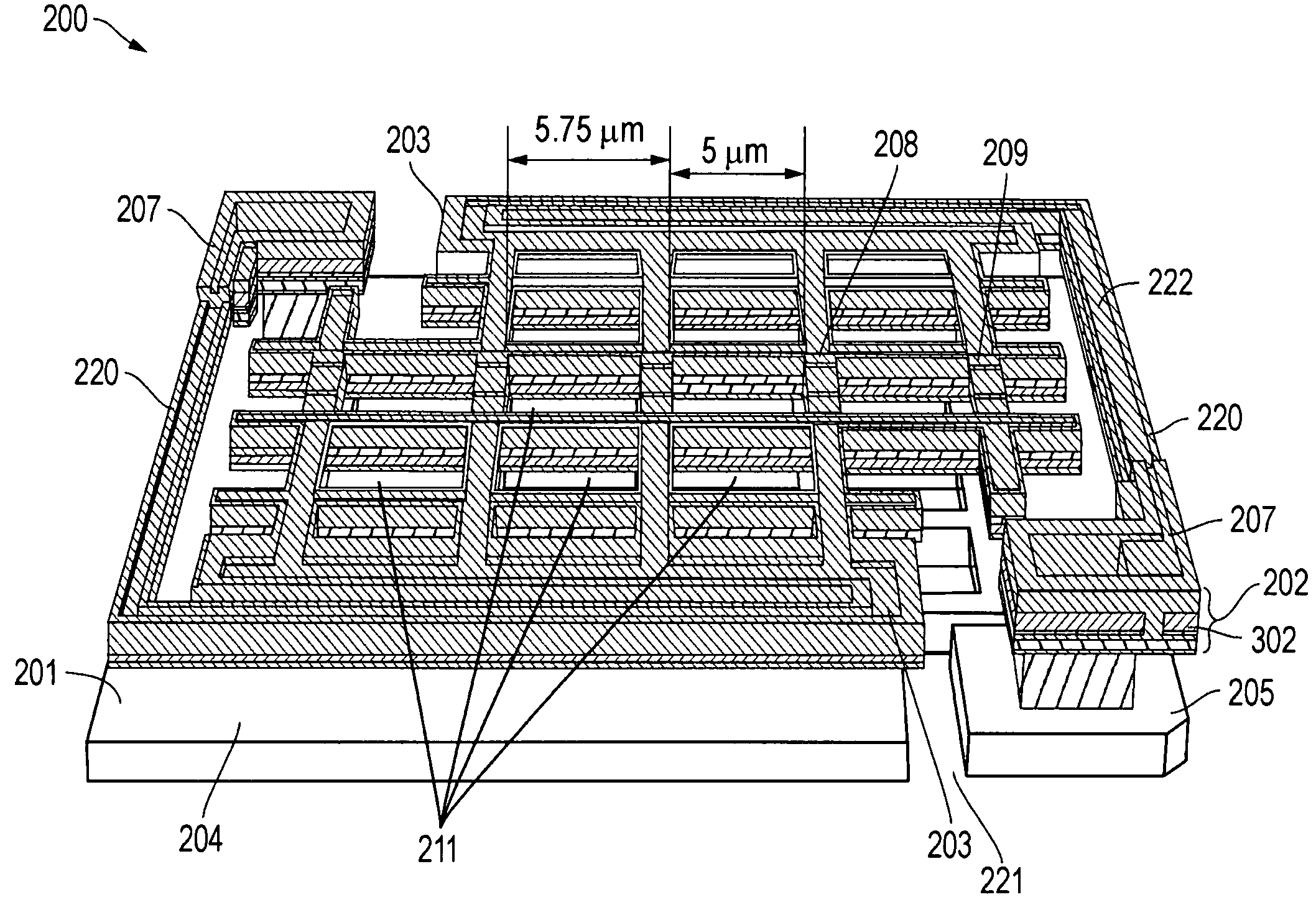
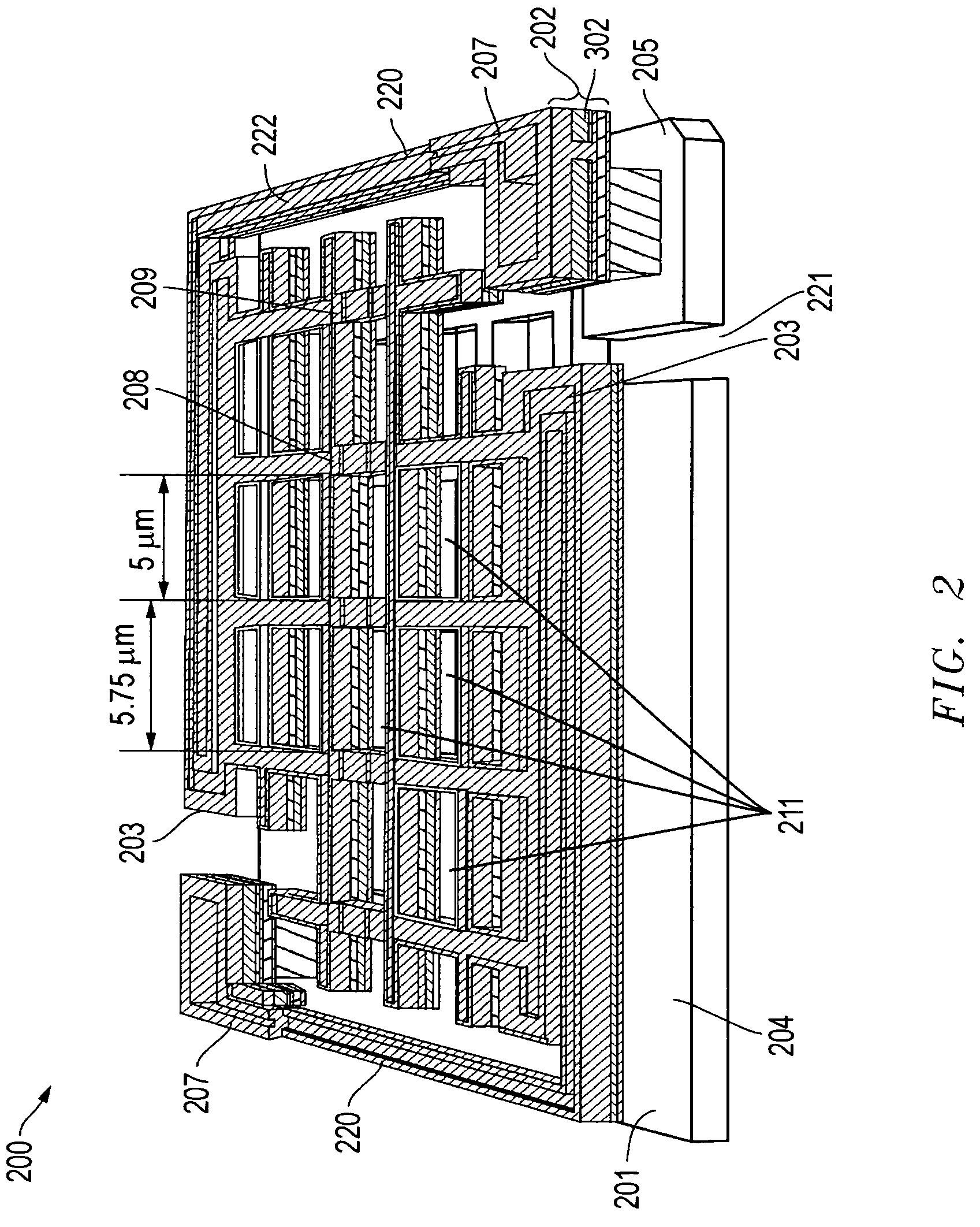
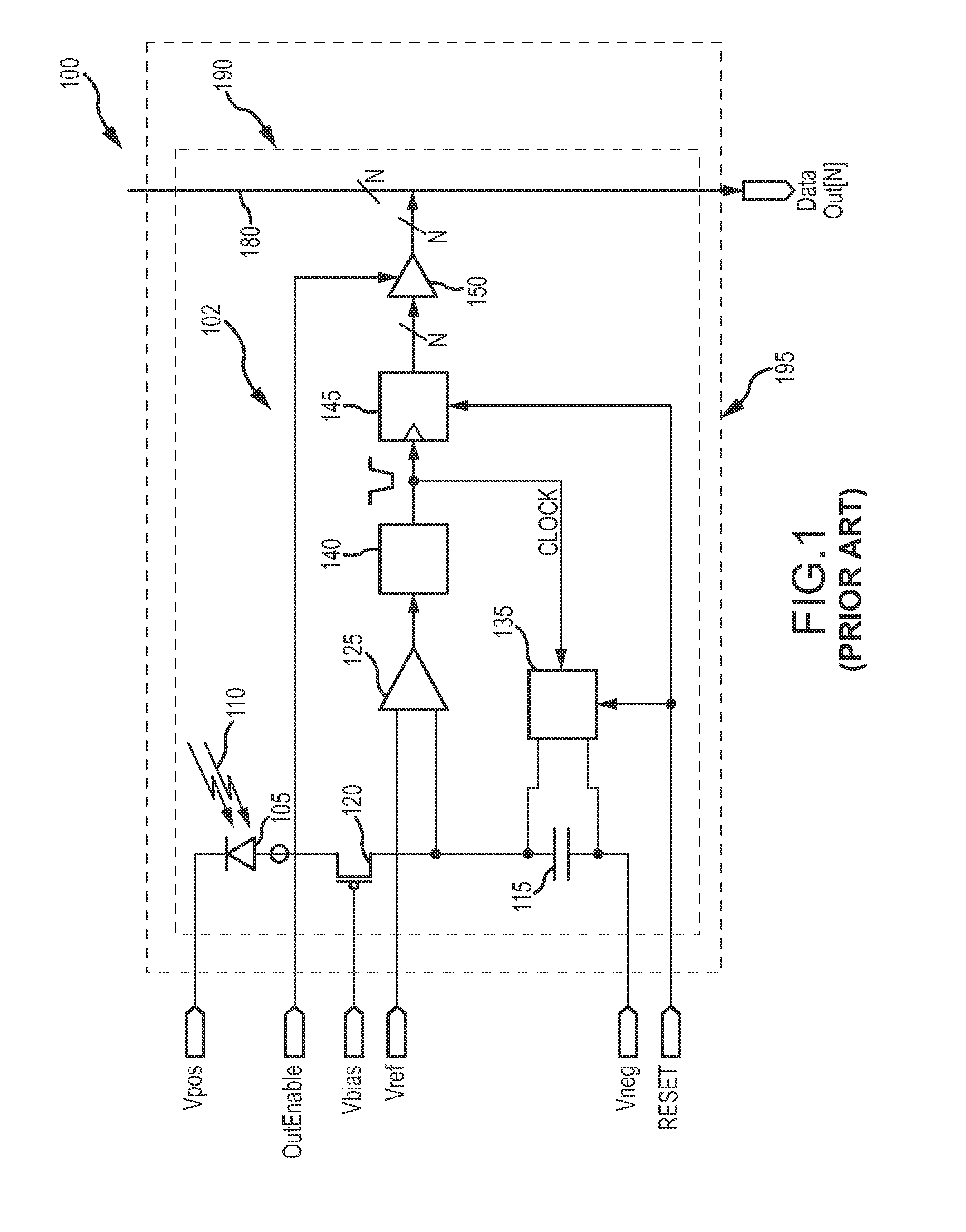
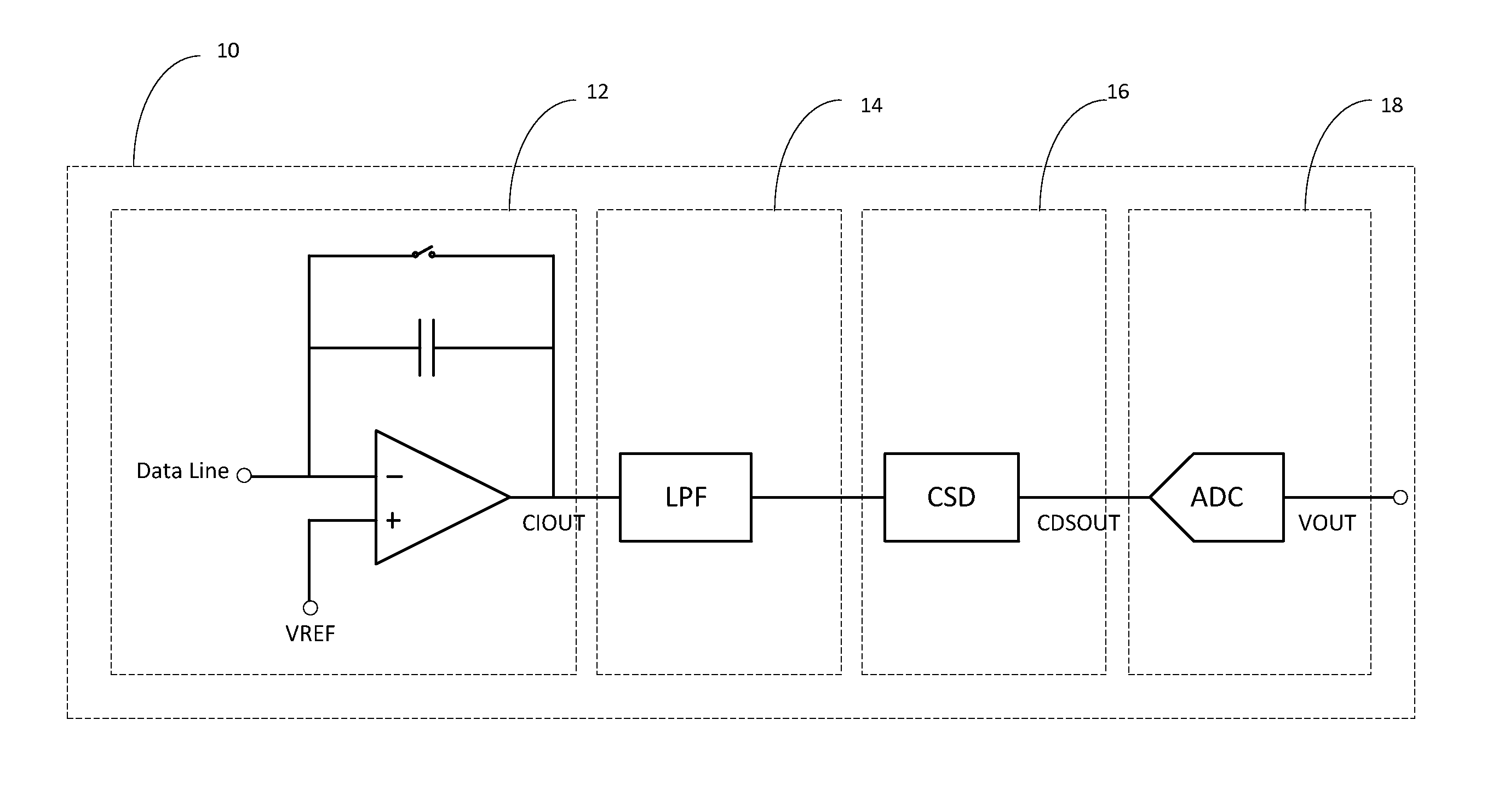
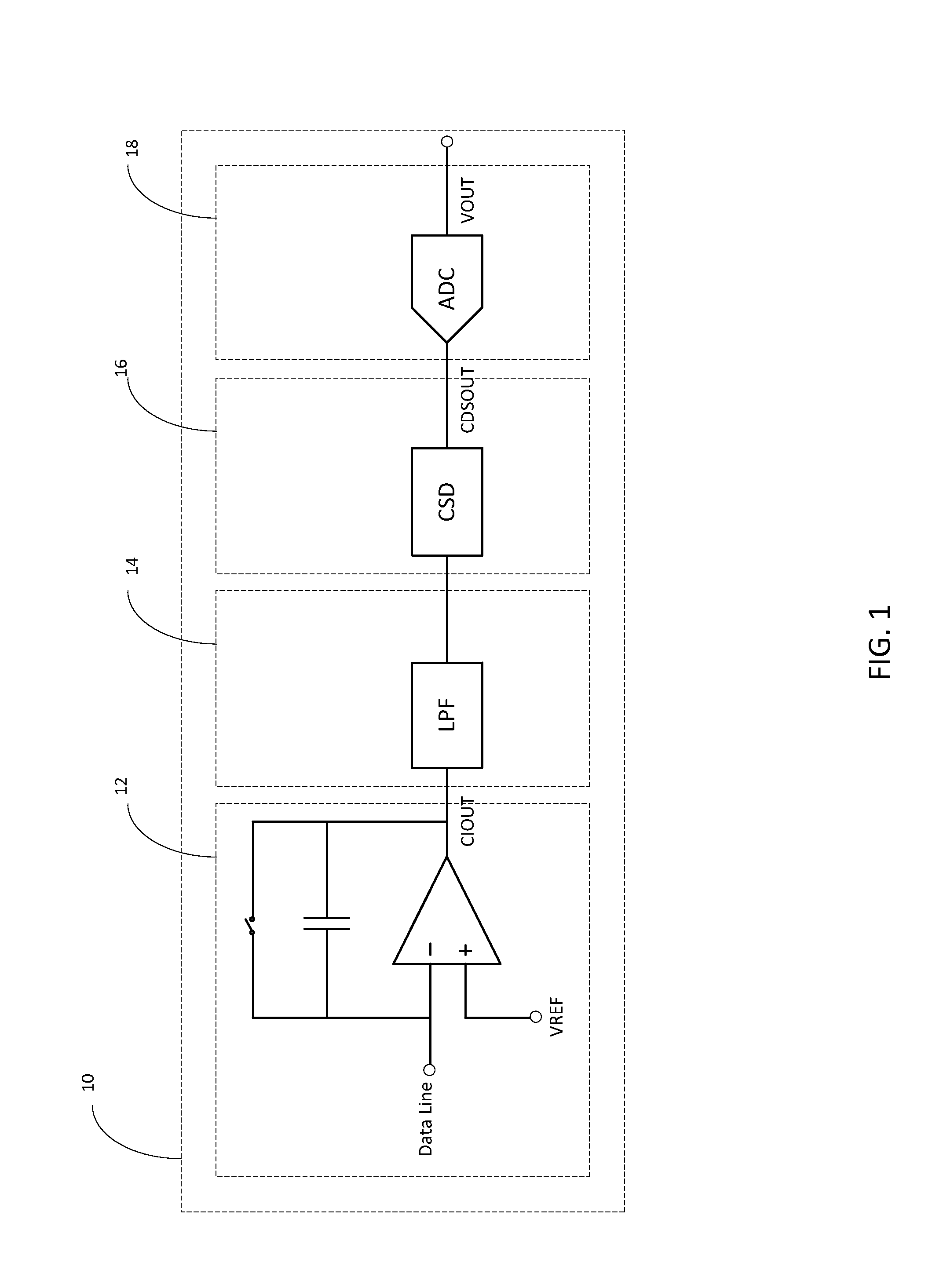
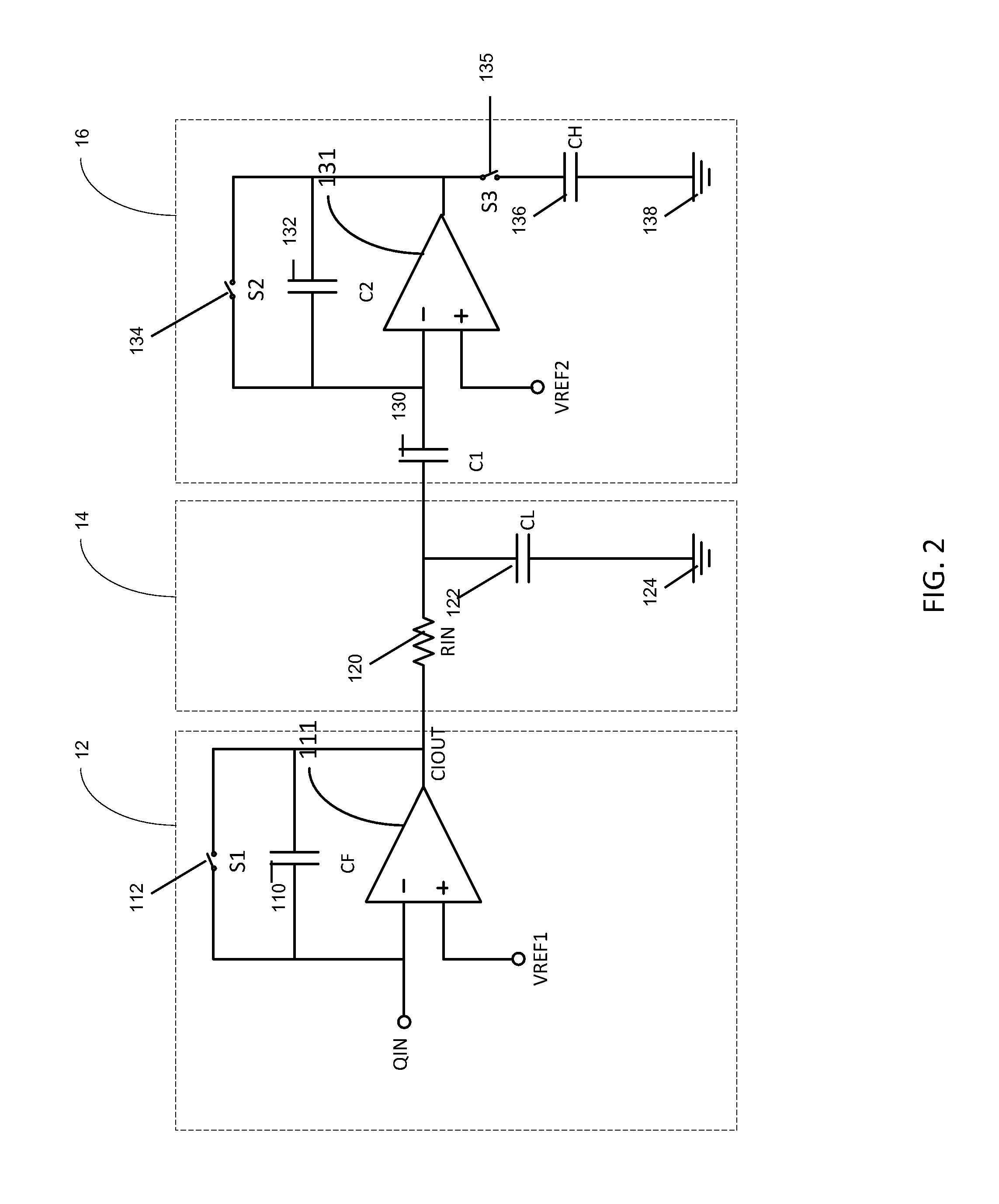
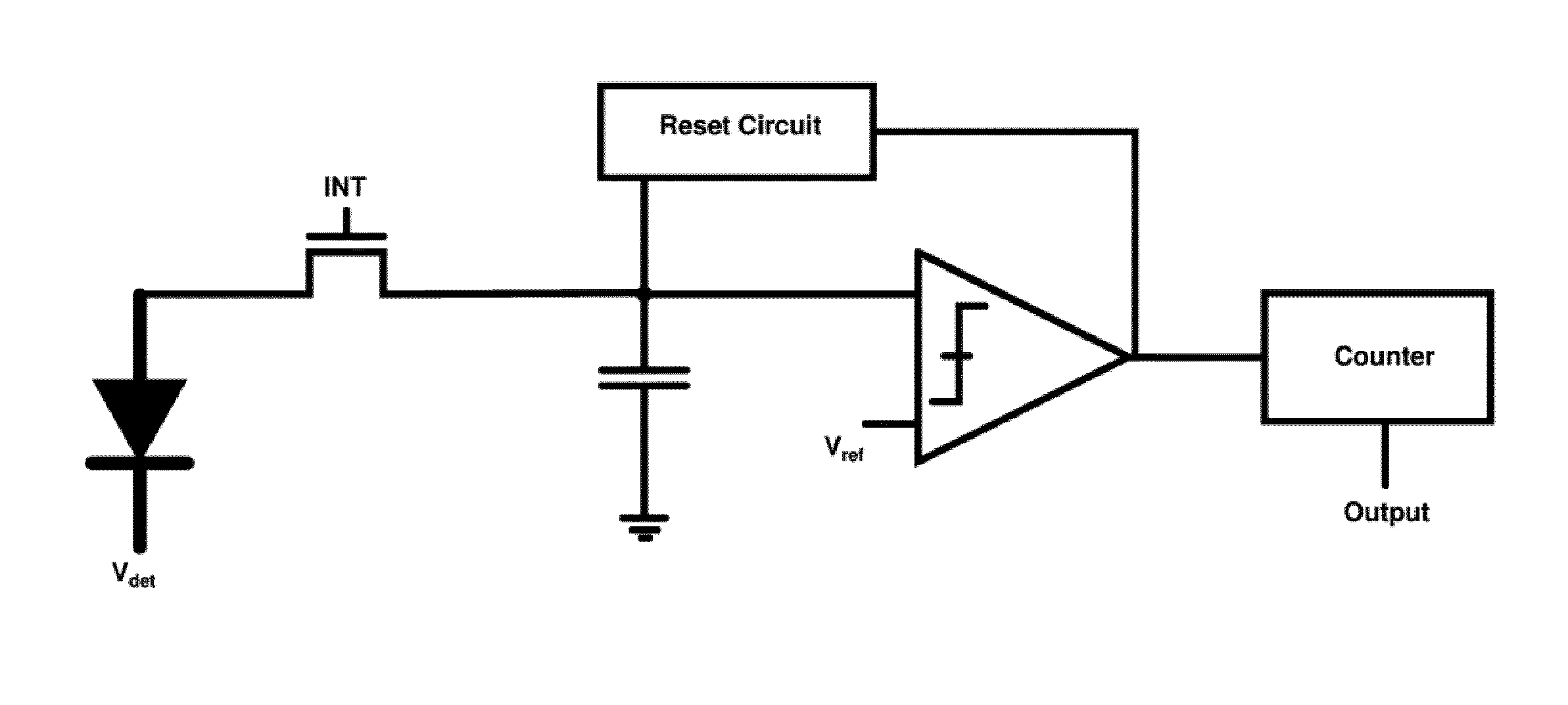
Readout Integrated Circuit (ROIC) is an integrated circuit specifically used for reading detectors of a particular type. They are compatible with different types of detectors such as infrared and ultraviolet. The primary purpose for ROICs is to accumulate the photocurrent from each pixel and then transfer the resultant signal onto output taps for readout. Conventional ROIC technology stores the signal charge at each pixel and then routes the signal onto output taps for readout. This requires storing large signal charge at each pixel site and maintaining signal-to-noise ratio (or dynamic range) as the signal is read out and digitized.
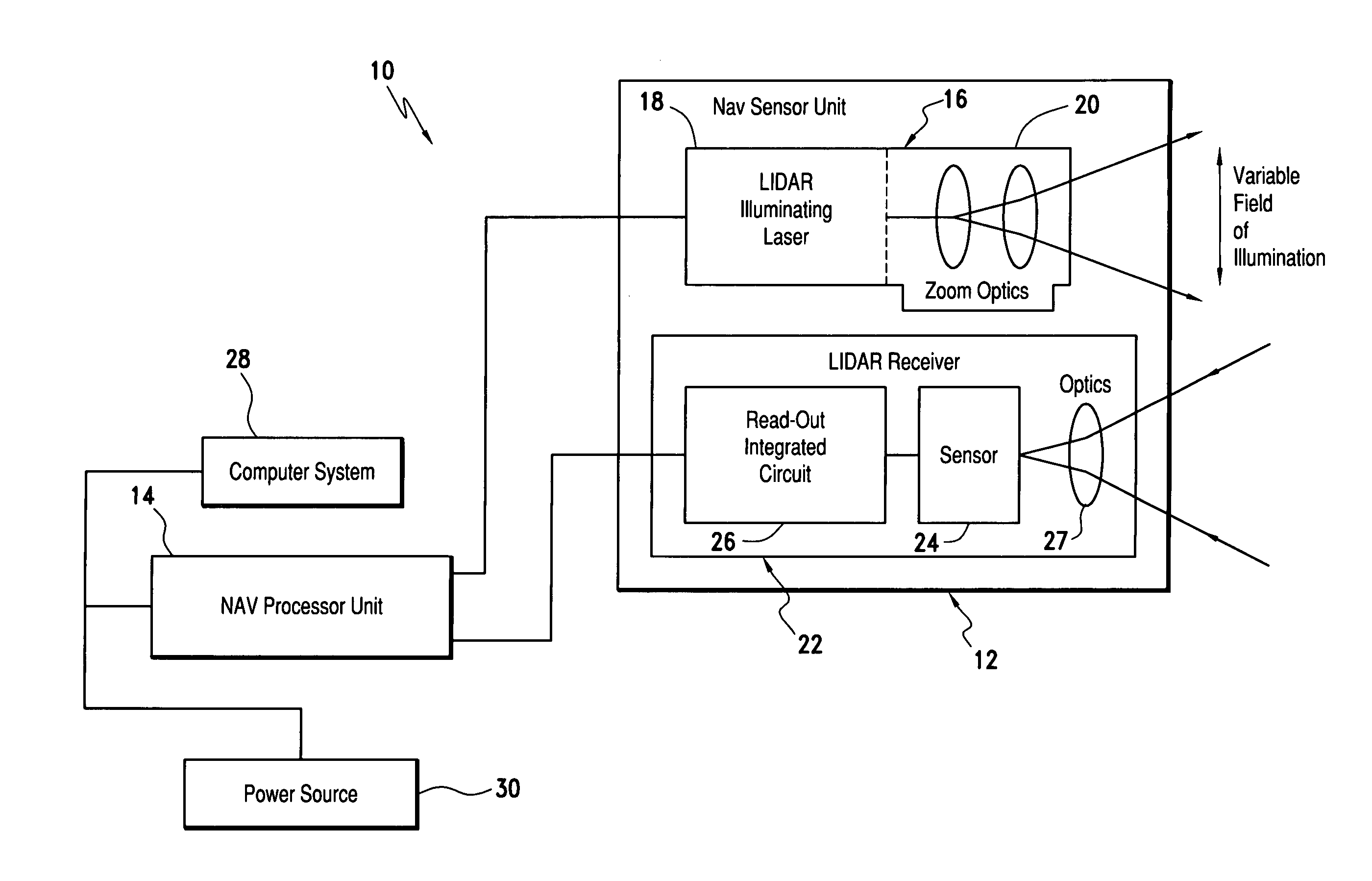
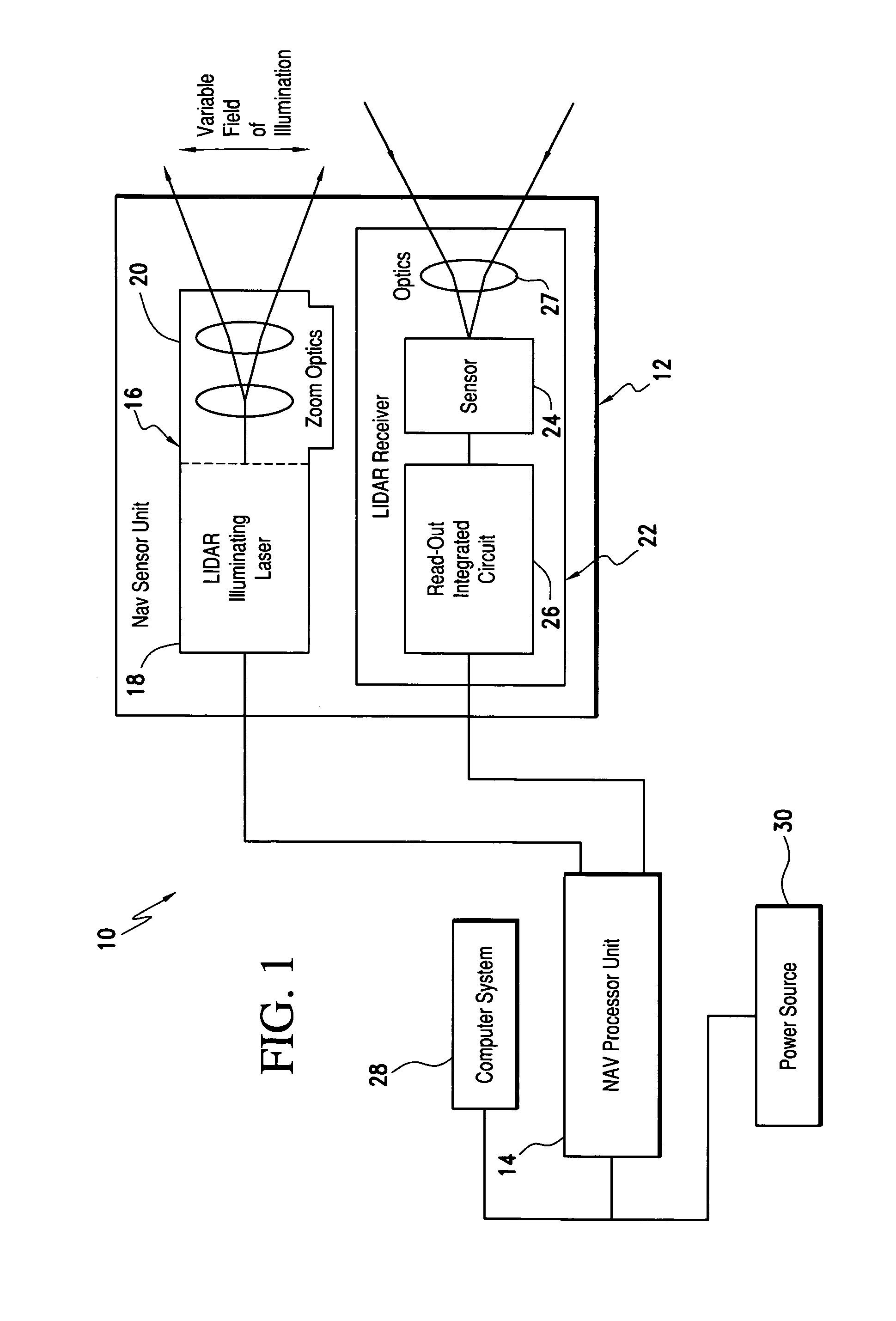
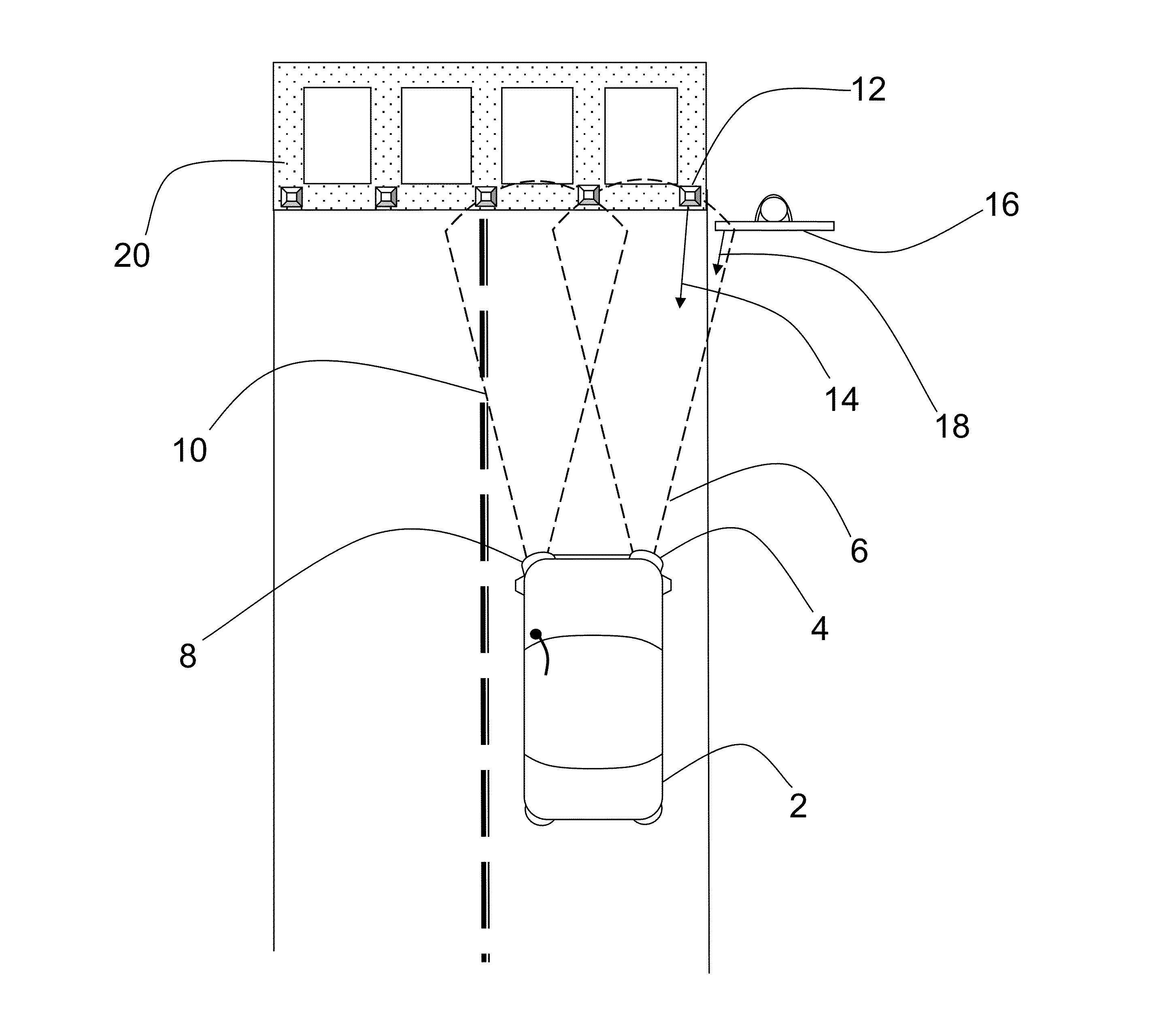
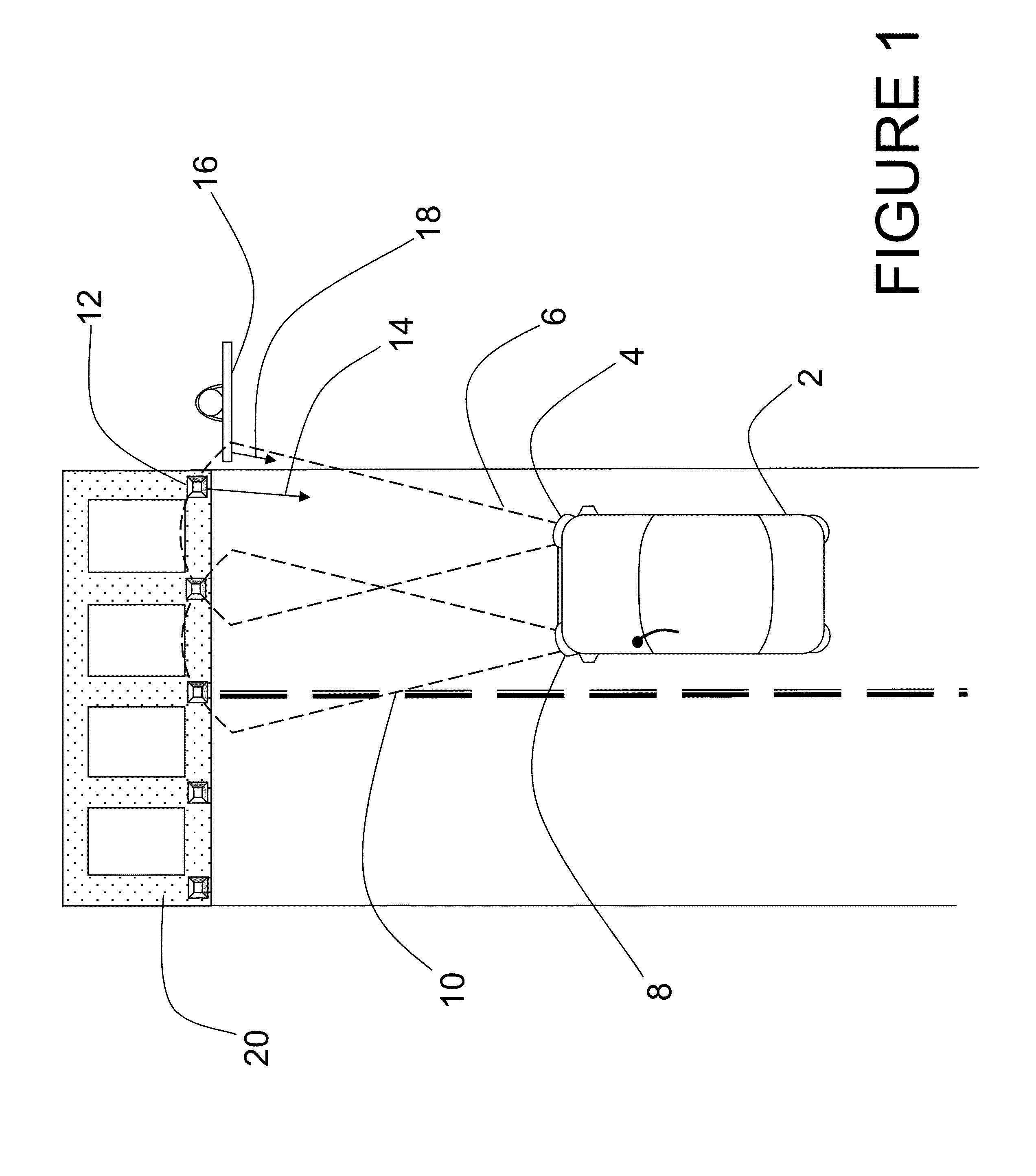
Laser range finding system using variable field of illumination flash lidar
ActiveUS8072581B1Reduce areaReduce resolutionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingImage resolution
The laser range finding system includes a light detection and ranging (LIDAR) sensor unit (SU) and a LIDAR processor unit (PU). The LIDAR SU is for transmitting light pulses and receiving resulting input light signals reflected from objects within the field of view of the SU. The LIDAR SU includes a flash LIDAR illuminating laser source for transmitting light pulses. The LIDAR illuminating laser source includes an illuminating laser and zoom optics operatively associated with the laser. A LIDAR receiver receives resulting input light signals reflected from the objects. The LIDAR receiver includes a sensor; and, a flash readout integrated circuit (IC). The flash readout IC measures the transit time of the light pulses. The LIDAR processor unit (PU) is operatively associated with the LIDAR SU and it utilizes flash LIDAR ranging. A power source is operatively coupled to the LIDAR PU. Zooming of the transmitted light pulses results in the received resulting input light signals illuminating a relatively reduced area of the frame. Thus, a flash LIDAR image of relatively reduced resolution but enhanced range is provided by utilization of the transit time measurements.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
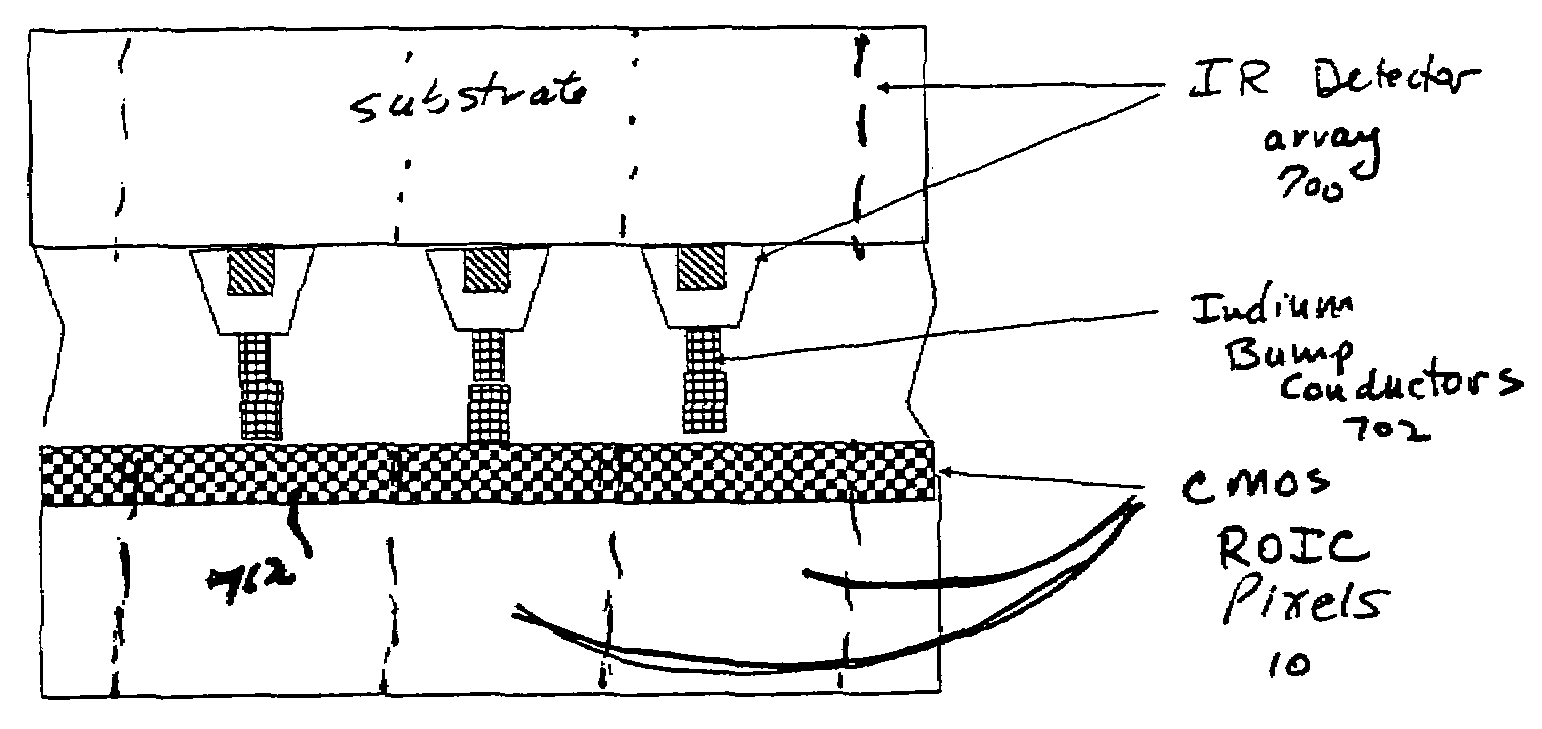
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS20060181627A1High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
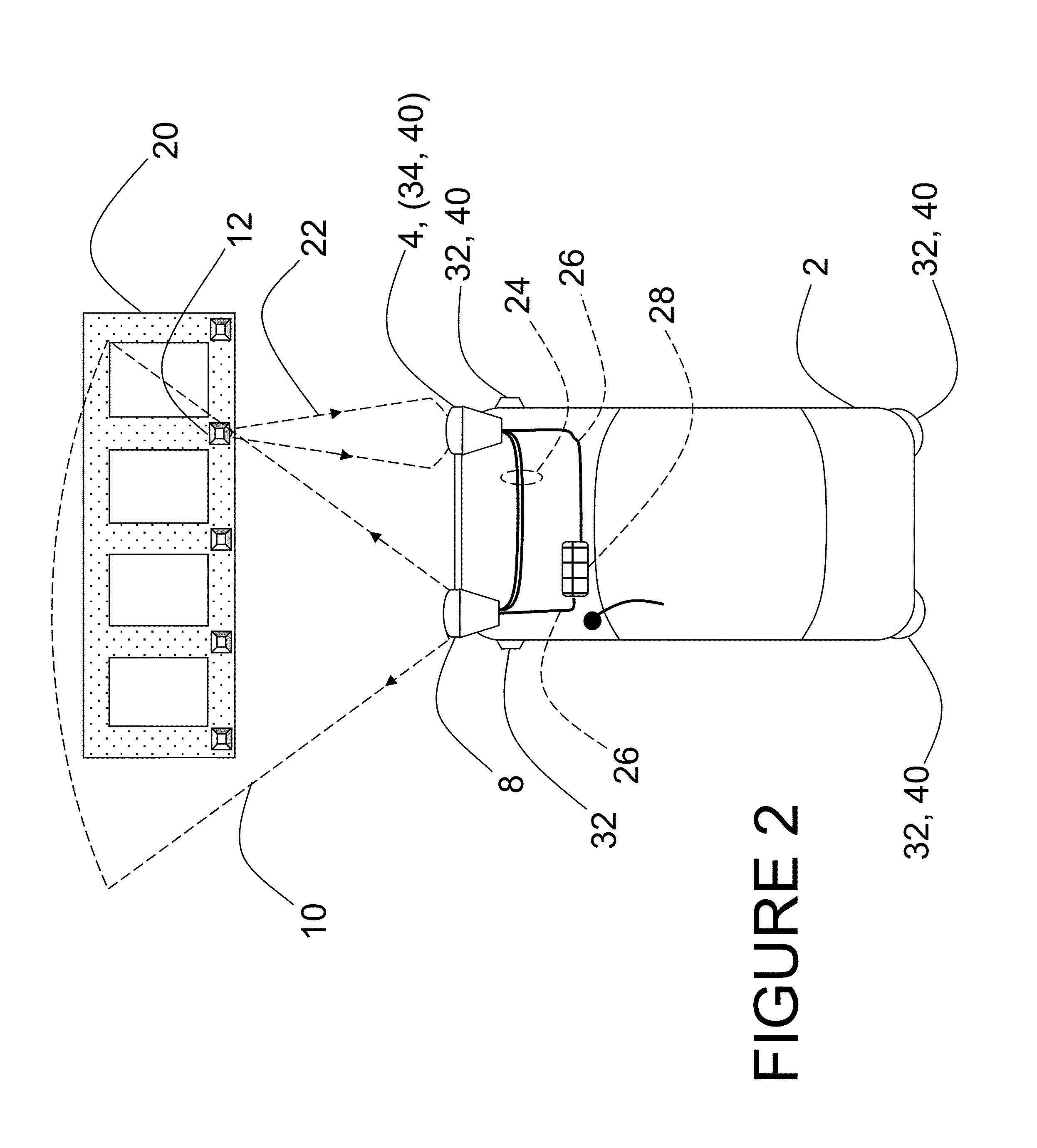
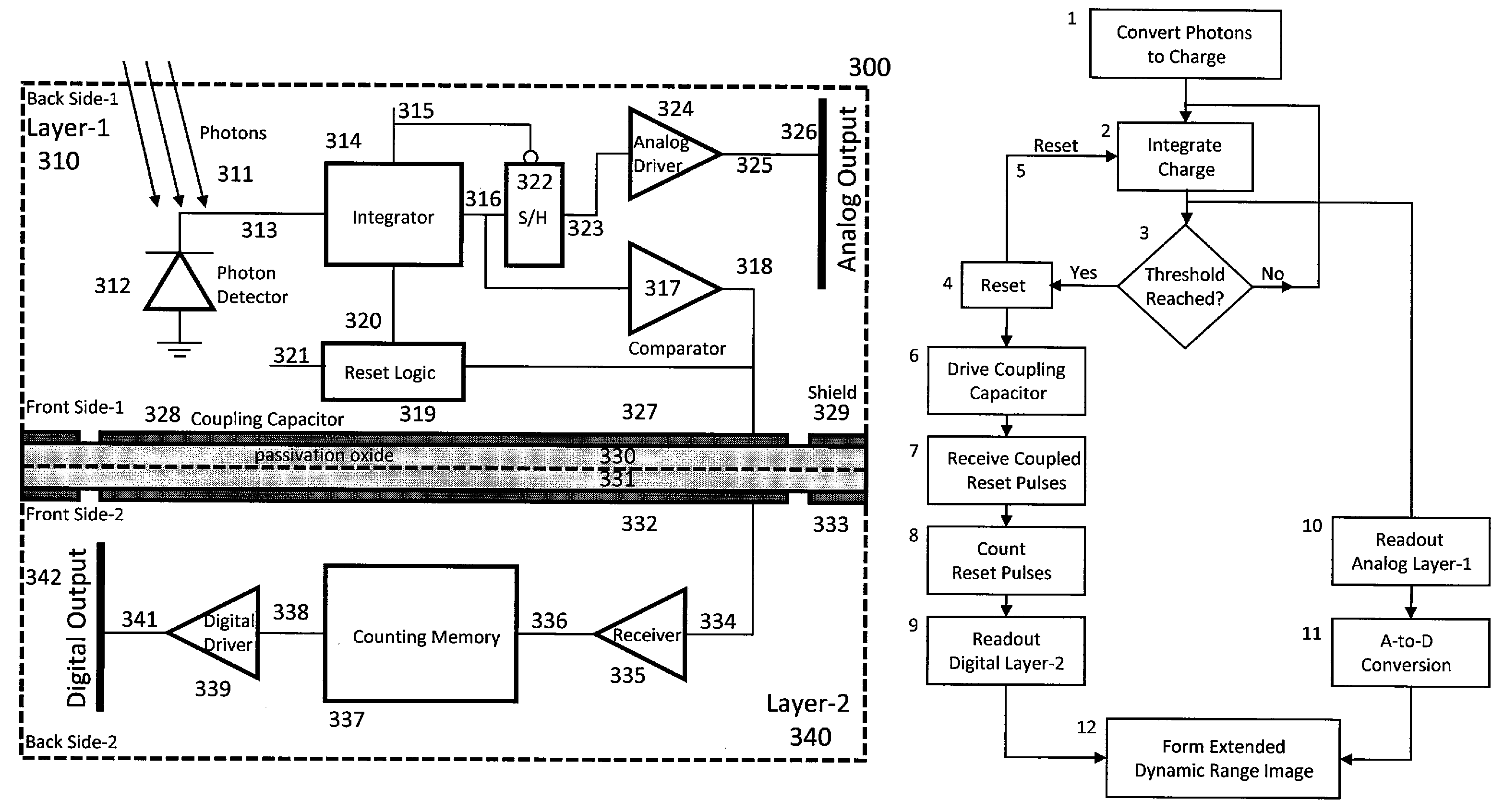
Method and apparatus for backside illuminated image sensors using capacitively coupled readout integrated circuits
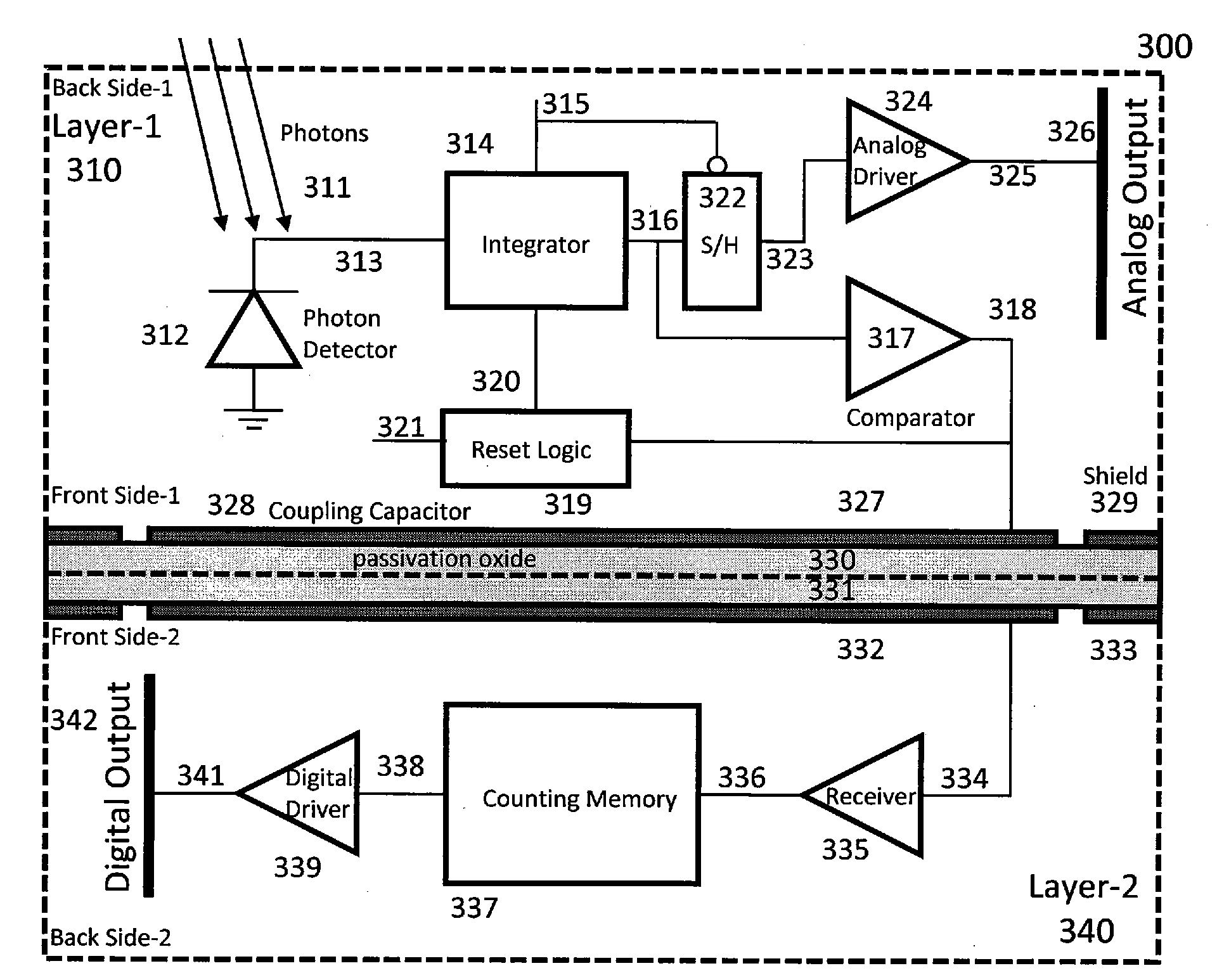
InactiveUS20100140732A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove scanning rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
The images sensor includes a readout circuit capacitatively coupled to a memory circuit. The readout circuit includes: (i) a photon detector to receive a plurality of photons and to provide a charge signal corresponding to the received photons, (ii) a resettable integrator that is reset multiple times over a single exposure time and provides an analog representation of the incident photons during the last integration cycle, and (iii) a comparator that monitors the integrator output and generates a reset pulse when the integrator reaches a built-in threshold value. The memory circuit includes: (i) a receiver circuit that detects the output of the digital driver in the front-end readout circuit via capacitive coupling and generates a digital voltage pulse for each received signal, and (ii) a digital counting memory to count the received pulses to provide a coarse digital representation of how many times the integrator is reset.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
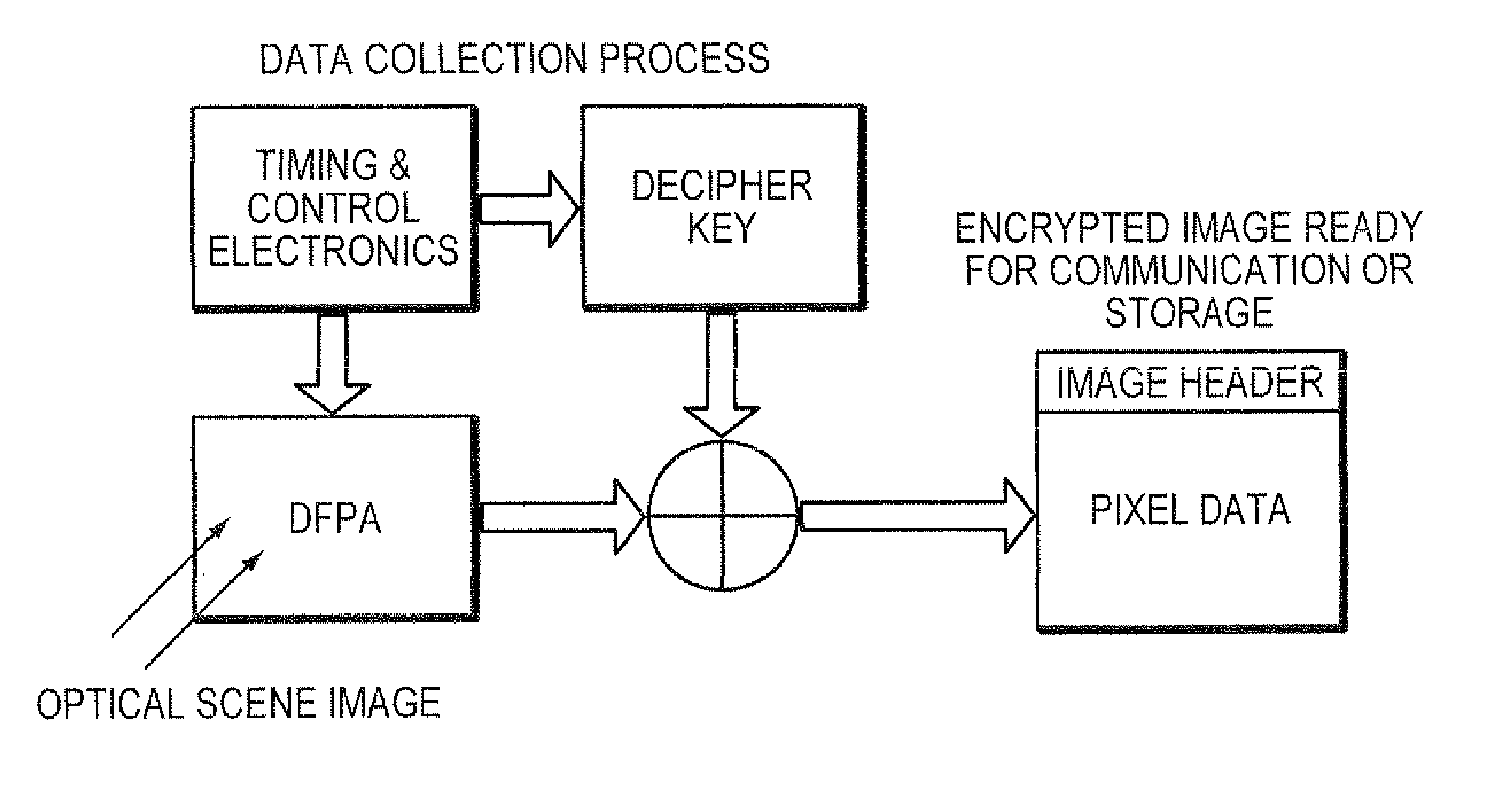
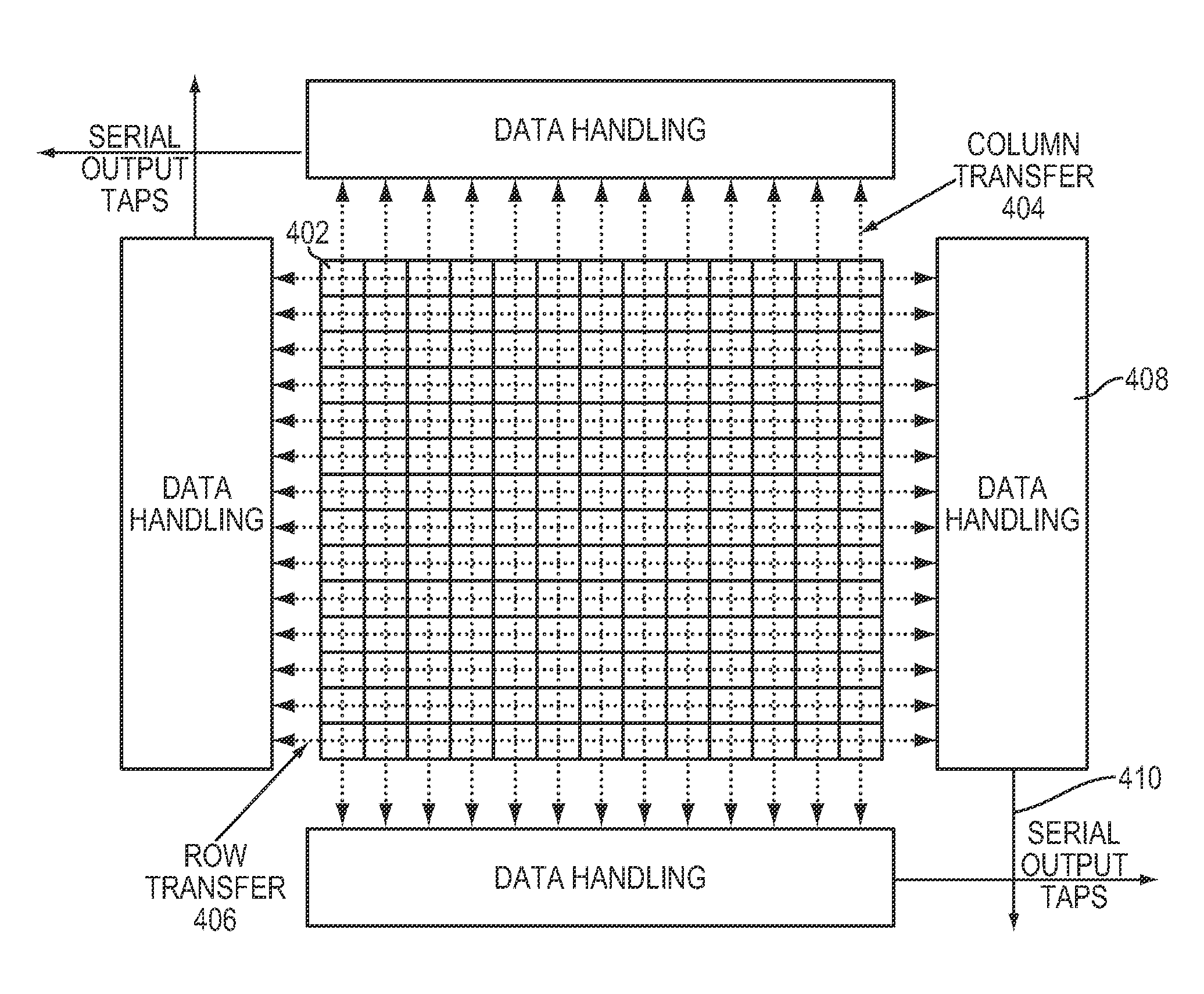
Digital readout method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100226495A1Television system detailsSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesDetector arrayReadout integrated circuit
A digital focal plane array includes an all-digital readout integrated circuit in combination with a detector array. The readout circuit includes unit cell electronics, orthogonal transfer structures, and data handling structures. The unit cell electronics include an analog to digital converter. Orthogonal transfer structures enable the orthogonal transfer of data among the unit cells. Data handling structures may be configured to operate the digital focal plane array as a data encryptor / decipherer. Data encrypted and deciphered by the digital focal plane array need not be image data.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
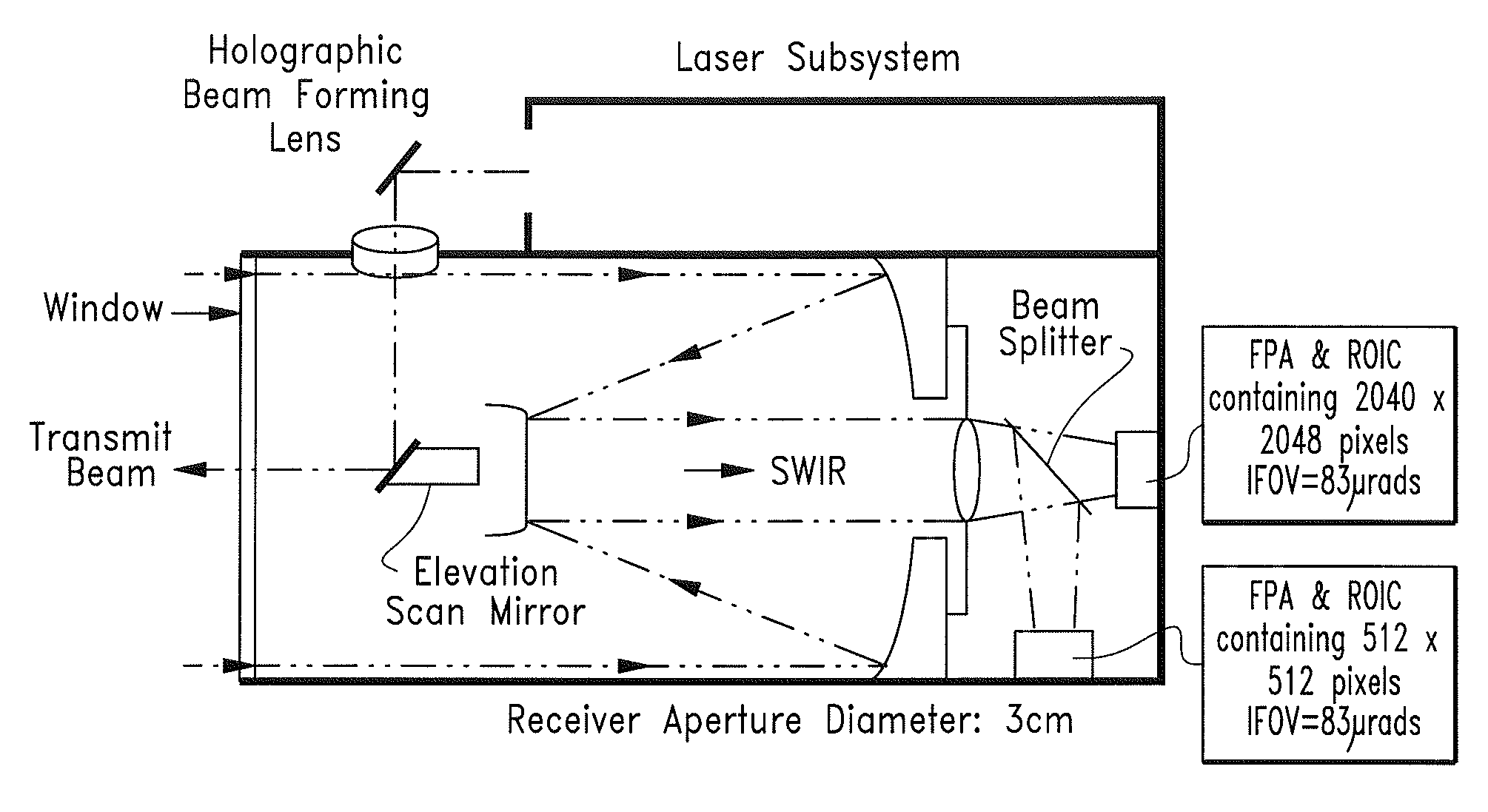
Sensor Element and System Comprising Wide Field-of-View 3-D Imaging LIDAR
InactiveUS20110285981A1Optical rangefindersVehicle position/course/altitude controlPhotodetectorBeam steering
A LIDAR sensor element and system for wide field-of-view applications such as autonomous UAS landing site selection is disclosed. The sensor element and system have an imaging source such as a SWIR laser for imaging a field of regard or target with a beam having a predefined wavelength. The beam is scanned over the field of regard or target with a beam steering device such as Risley prism. The reflected beam is captured by the system by receiving optics which may comprise a Risley prism for receiving and imaging the reflected beam upon a photodetector array such as a focal plane array. The focal plane array may be bonded to and a part of a three-dimensional stack of integrated circuits, a plurality of which may comprise one or more read out integrated circuits.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7551059B2High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
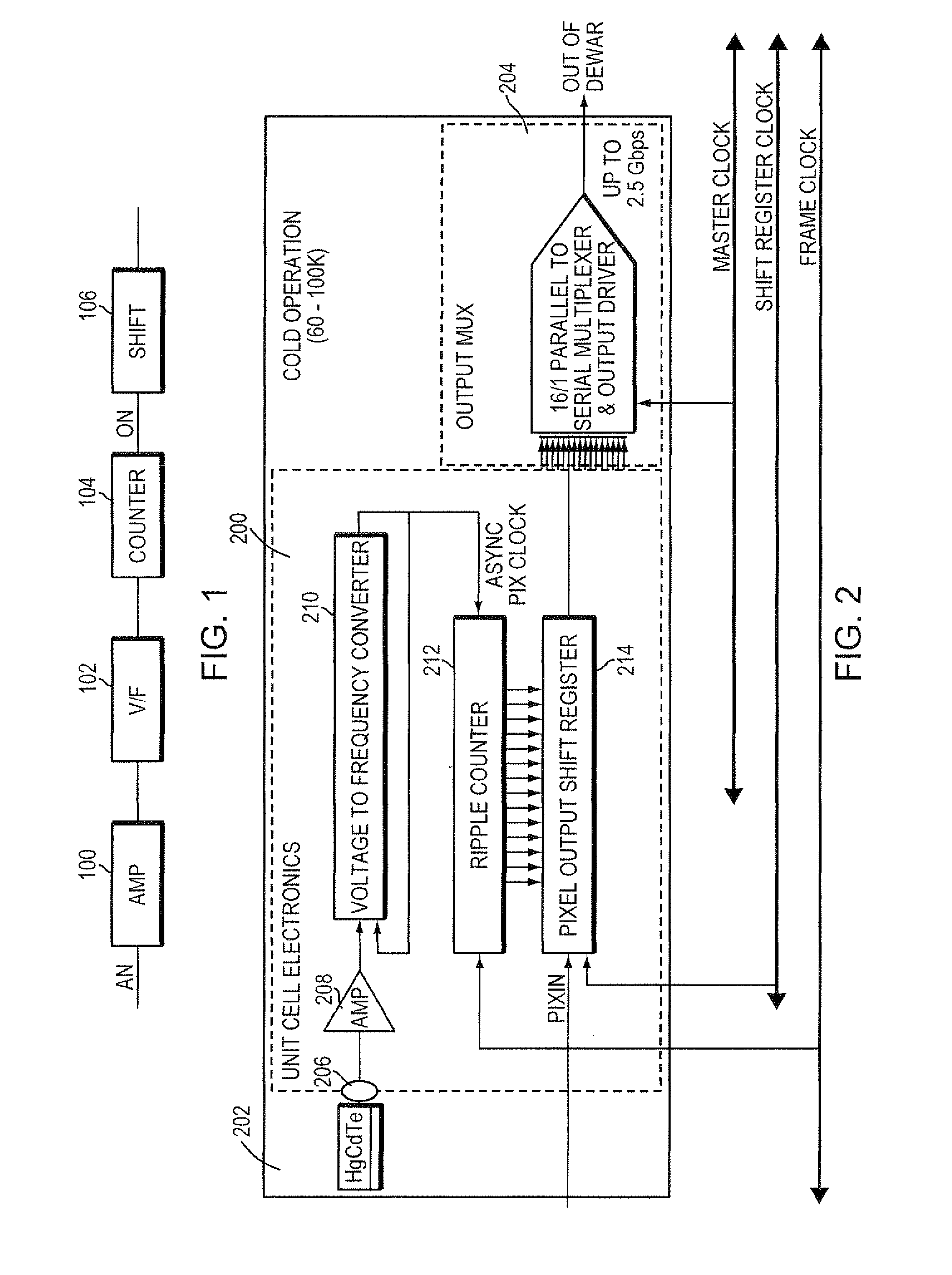
Digital readout method and apparatus
ActiveUS8179296B2Large chargeHighly linear analog electronics can be eliminatedTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSensor arrayDigital signal processing
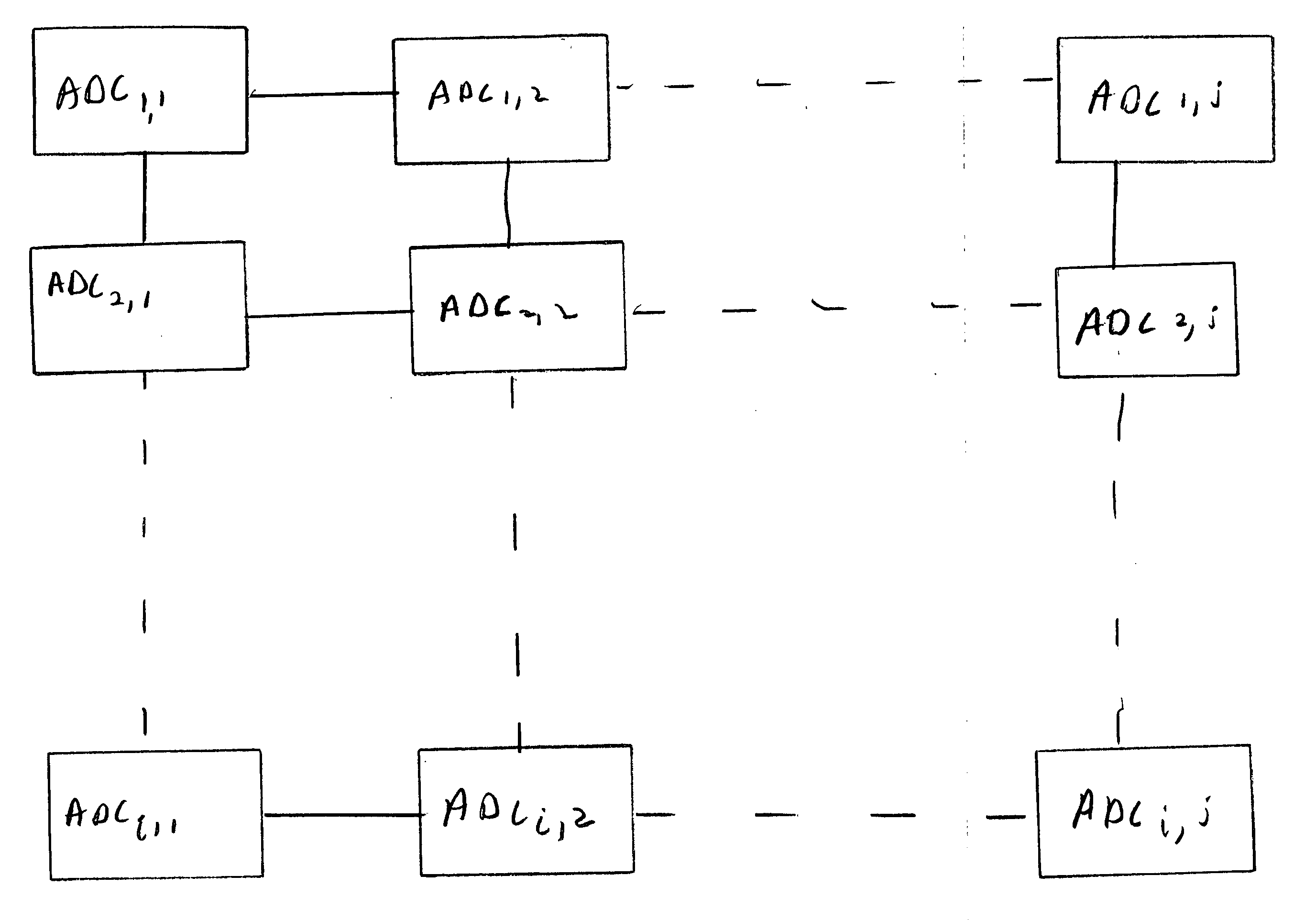
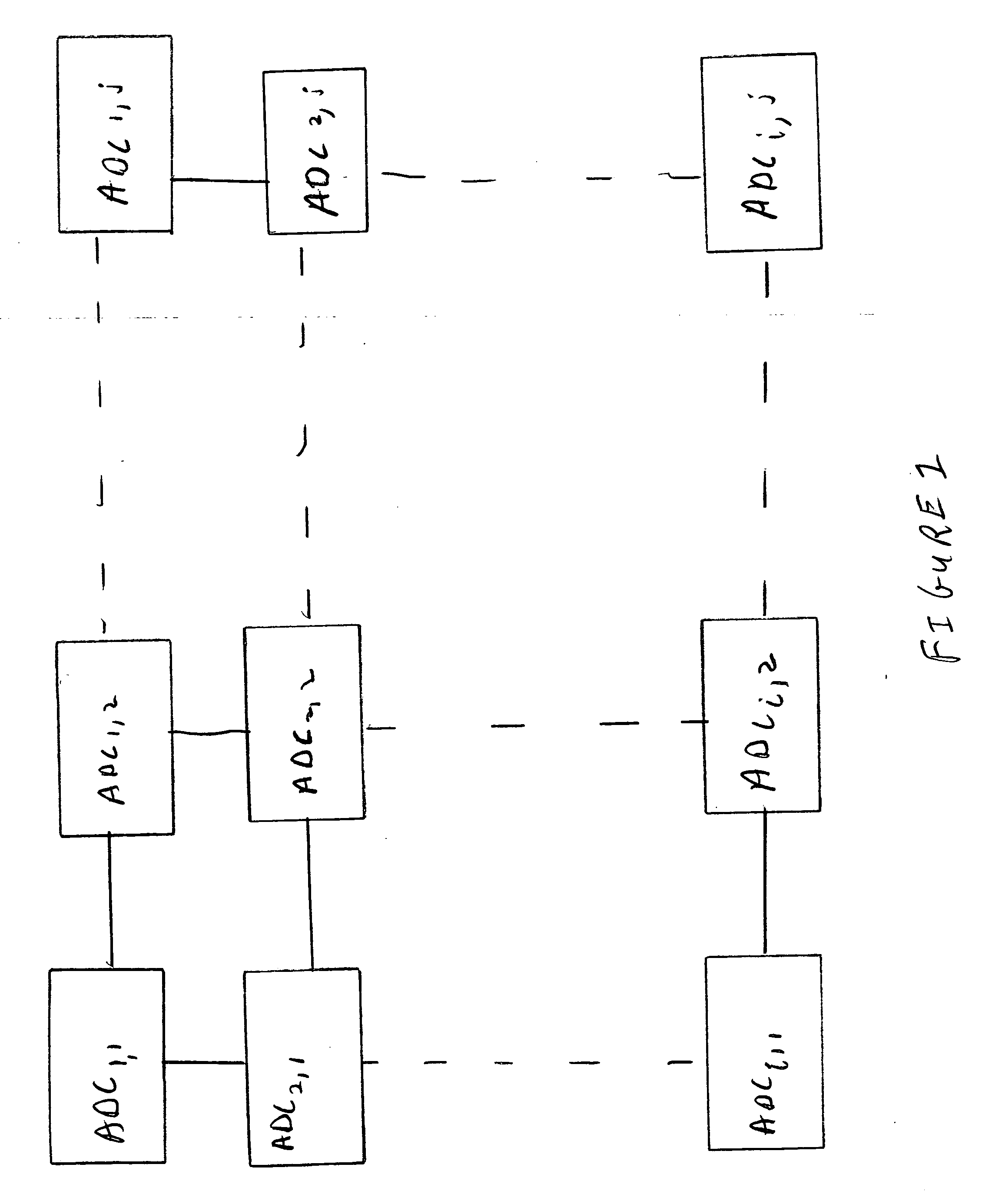
Autonomously operating analog to digital converters are formed into a two dimensional array. The array may incorporate digital signal processing functionality. Such an array is particularly well-suited for operation as a readout integrated circuit and, in combination with a sensor array, forms a digital focal plane array.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Digital readout method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070075888A1Large charge storageConsiderable power savingTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsA d converterReadout integrated circuit
Autonomously operating analog to digital converters are formed into a two dimensional array. The array may incorporate digital signal processing functionality. Such an array is particularly well-suited for operation as a readout integrated circuit and, in combination with a sensor array, forms a digital focal plane array.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Beam steering ladar sensor
ActiveUS20160266242A1Low costLow parasitic packagingElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Audio power amplifier
A beam steering capability is proposed for a ladar sensor operating with limited laser transmit power, as may be typical of an airborne or automotive application. The ladar system also makes use of optical gain elements in the receiver which act to increase the signal to noise ratio at the receiver when the laser transmit power available is restricted by power, size, and / or cost limitations. In one embodiment, the calibration of each pixel in the ladar sensor is provided for by an electrical amplifier array with a number of pixel amplifiers. Each pixel amplifier may be individually calibrated to a mating detector element so as to eliminate the variations in dark current and gain between all pixels in the detector array. A number of new detector array designs are described which may lower cost and improve performance, and new low cost and high performance packaging for the detector array, amplifier array, and readout integrated circuit is introduced.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Method and apparatus for backside illuminated image sensors using capacitively coupled readout integrated circuits
InactiveUS7795650B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove scanning rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
The images sensor includes a readout circuit capacitatively coupled to a memory circuit. The readout circuit includes: (i) a photon detector to receive a plurality of photons and to provide a charge signal corresponding to the received photons, (ii) a resettable integrator that is reset multiple times over a single exposure time and provides an analog representation of the incident photons during the last integration cycle, and (iii) a comparator that monitors the integrator output and generates a reset pulse when the integrator reaches a built-in threshold value. The memory circuit includes: (i) a receiver circuit that detects the output of the digital driver in the front-end readout circuit via capacitive coupling and generates a digital voltage pulse for each received signal, and (ii) a digital counting memory to count the received pulses to provide a coarse digital representation of how many times the integrator is reset.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Method and apparatus for multi-spectral photodetection
InactiveUS20050205758A1Increase luminous fluxEliminate needRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral responseElectrical conductor
A multispectral photodetector array includes a two-dimensional array of photodetectors, either photodiodes or photoconductors, are coupled to a read out integrated circuit. The integrated circuit collects electrical signals from individual pixels of the array. Such an array differs from a conventional array in that each row or group of rows in the array has a distinct spectral response.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTATED BY THE DEPT OF THE ARMY
Microthermistor based fingerprint sensor
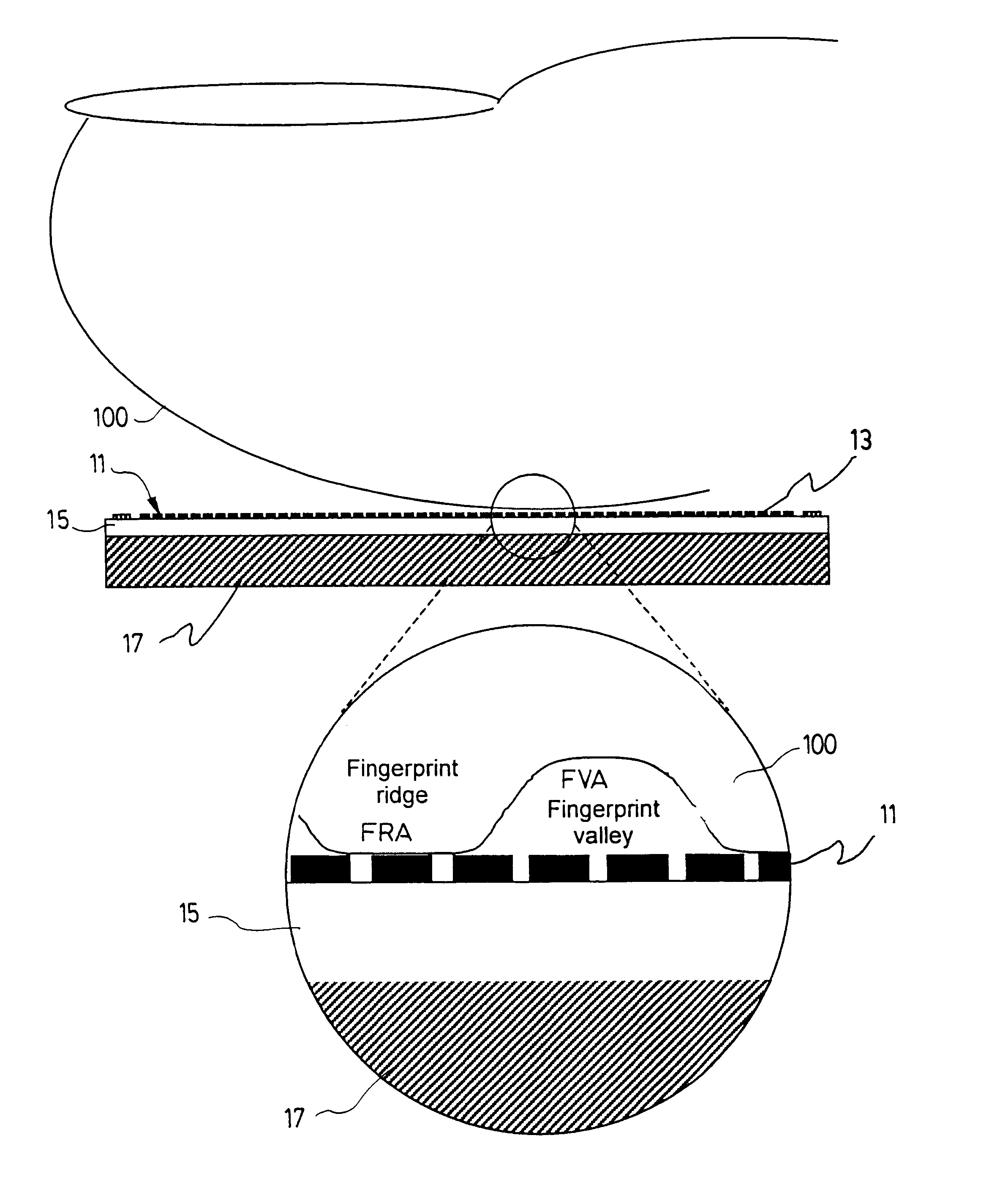
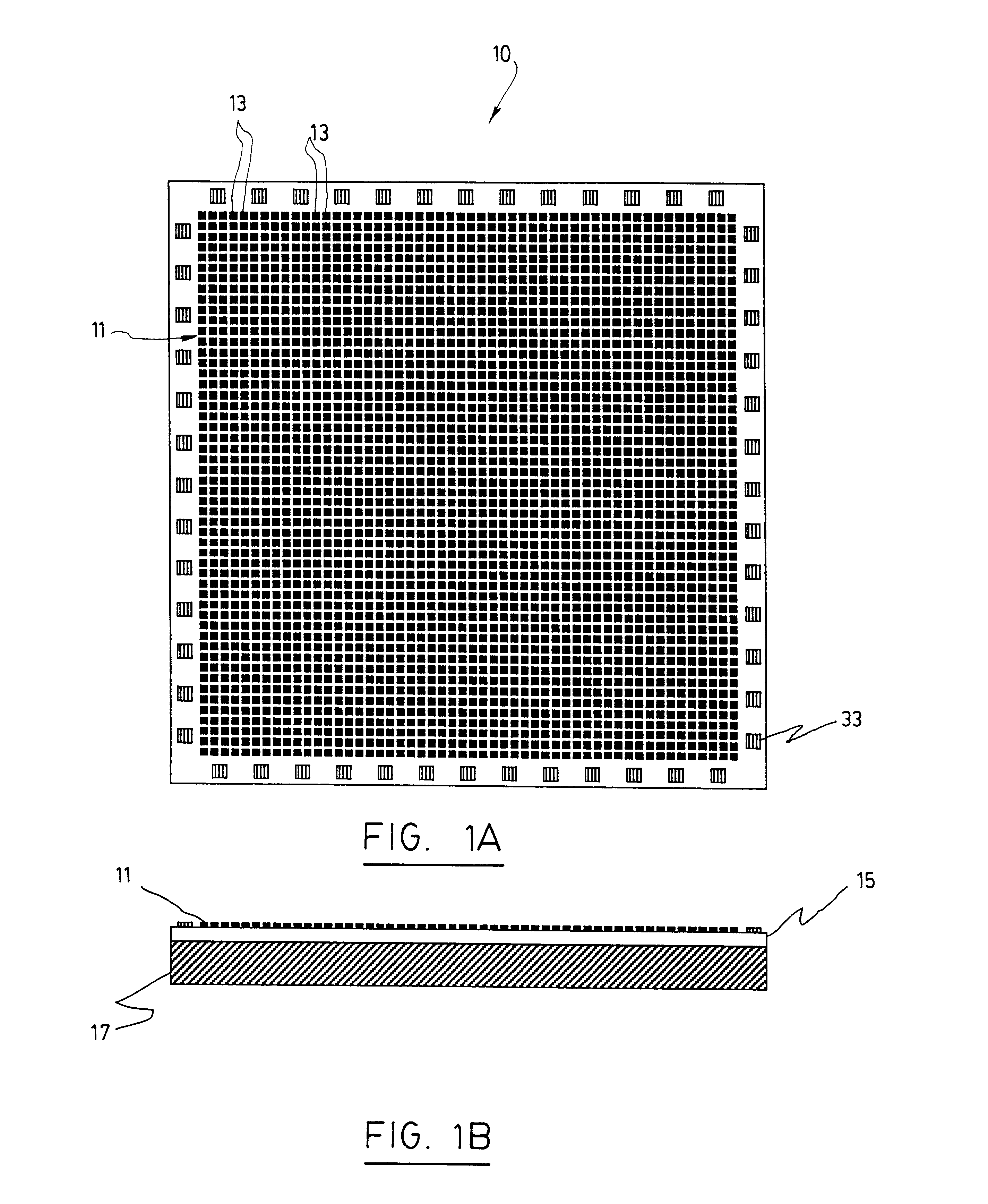
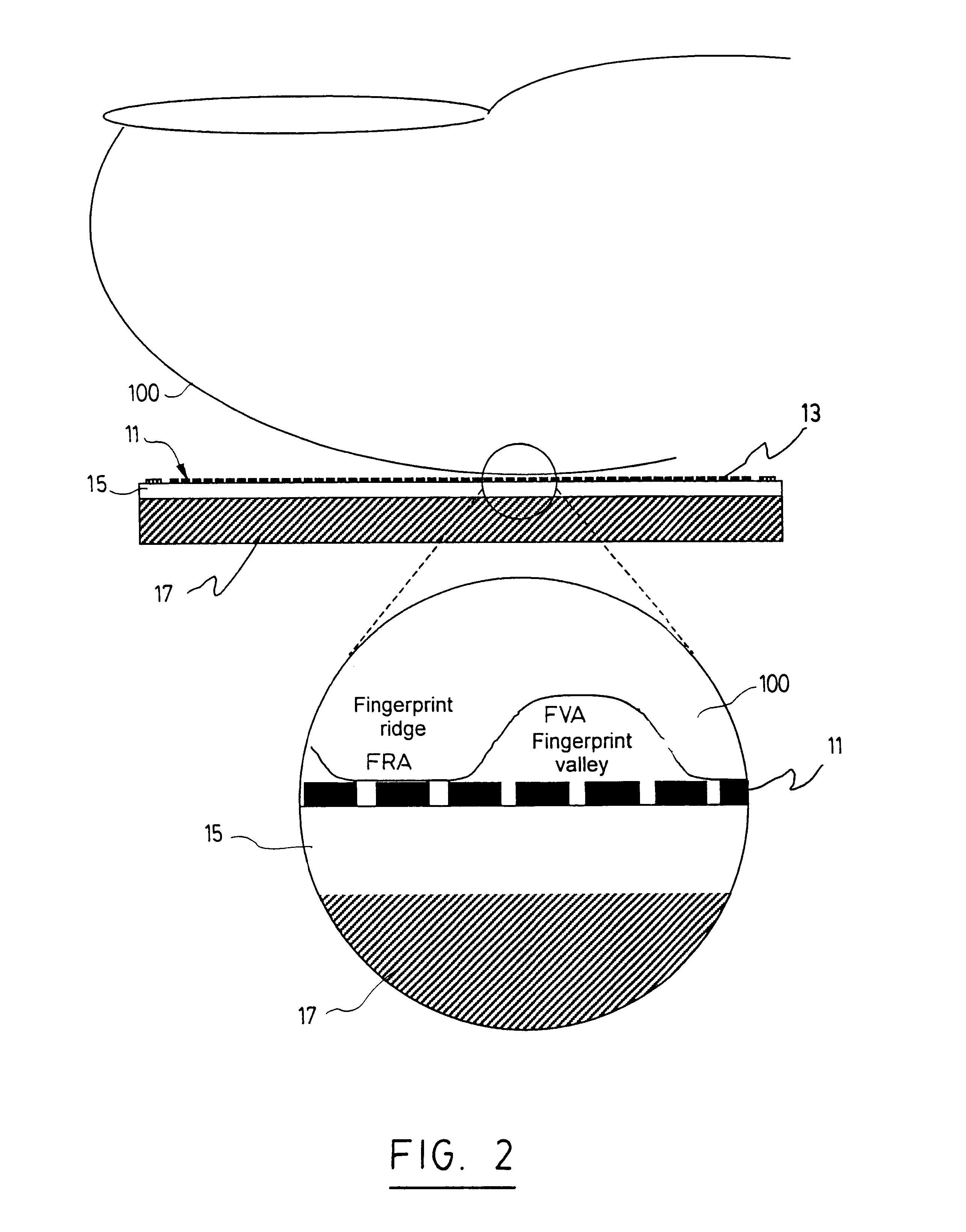
The present invention concerns a fingerprint sensor which is small; demonstrates high sensitivity, low power consumption, high data acquisition rate and is insensitive to vibration and pressure. The sensor produces a high contrast fingerprint representation and is not subject to repeated deformation which could potentially reduces its lifetime. The fingerprint sensor has a microthermistor array for converting temperature variation into an electrical signal, the array being composed of a plurality of microthermistors, each of the thermistors being adapted to output an electrical signal proportional to a temperature variation; a read-out integrated circuit operatively connected to the microthermistor array for receiving the electrical signal and converting it into an electronic output signal representative of the ridge and valley structure of a finger; and a substrate for supporting the read-out integrated circuit and the microthermistor array. The invention is based on microthermistor array. The ohmic resistance of these sensors varies strongly with temperature. The parameter directly measured in this case is the temperature-induced resistance variation of each individual microthermistor. Signals from each of the microthermistor part of the array represent the fingerprint pattern.< / PTEXT>
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
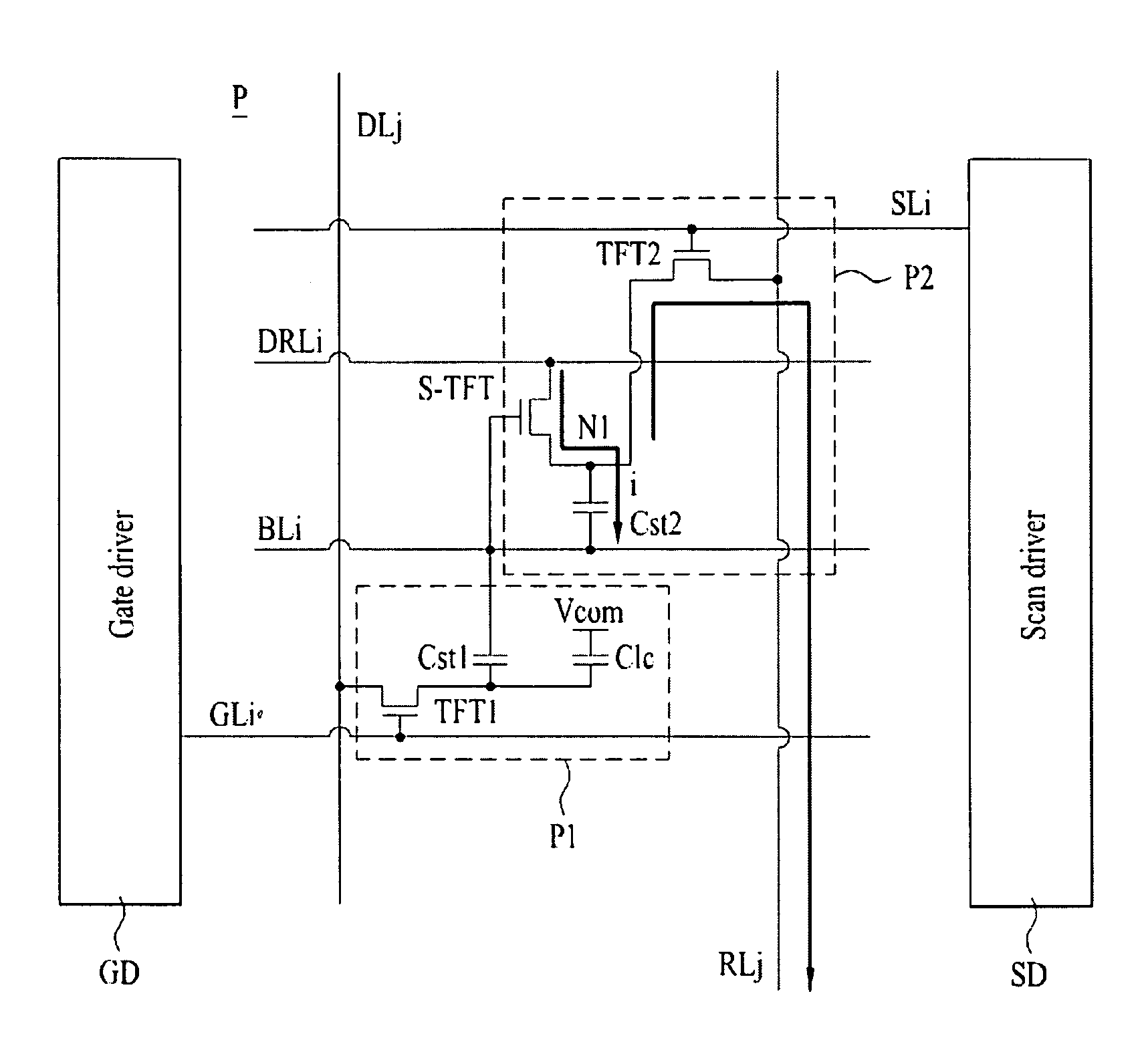
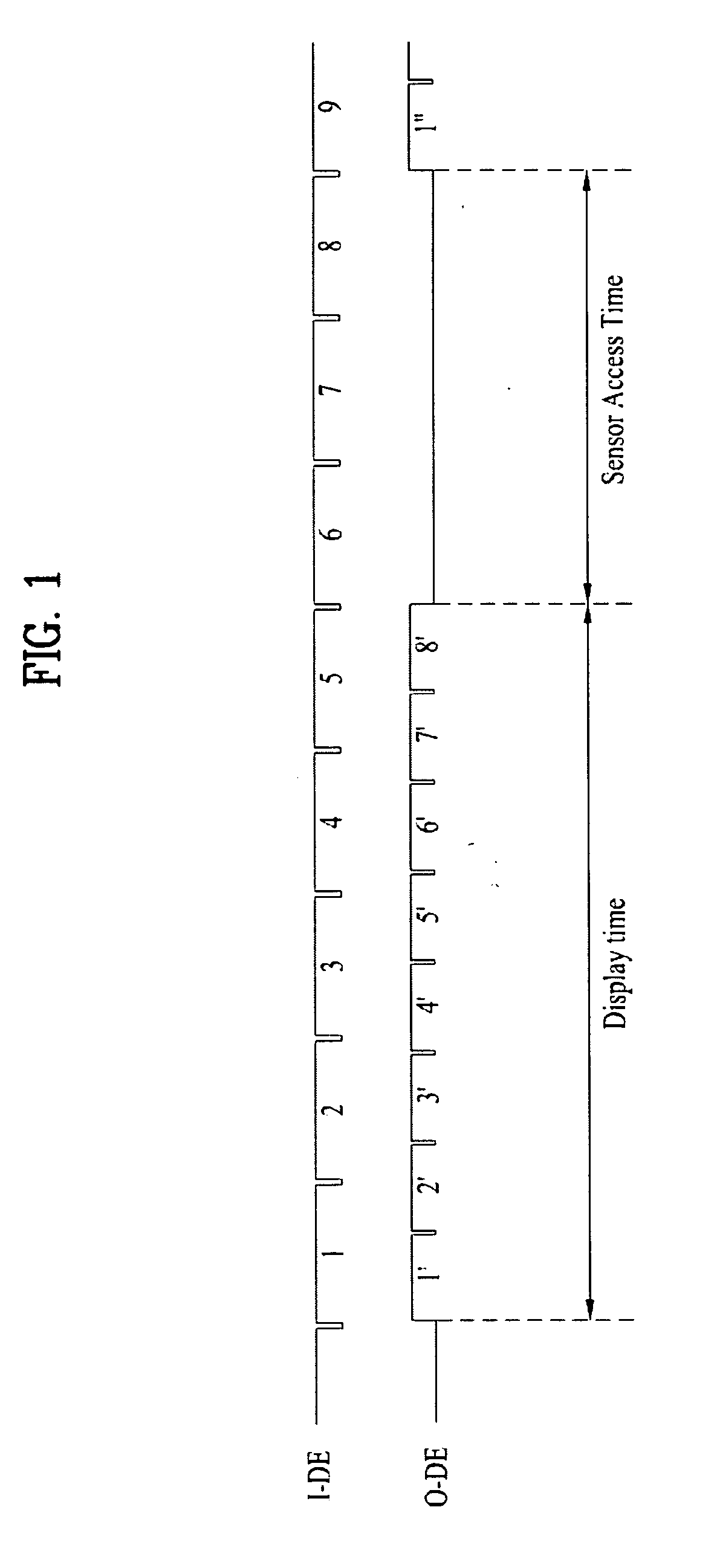
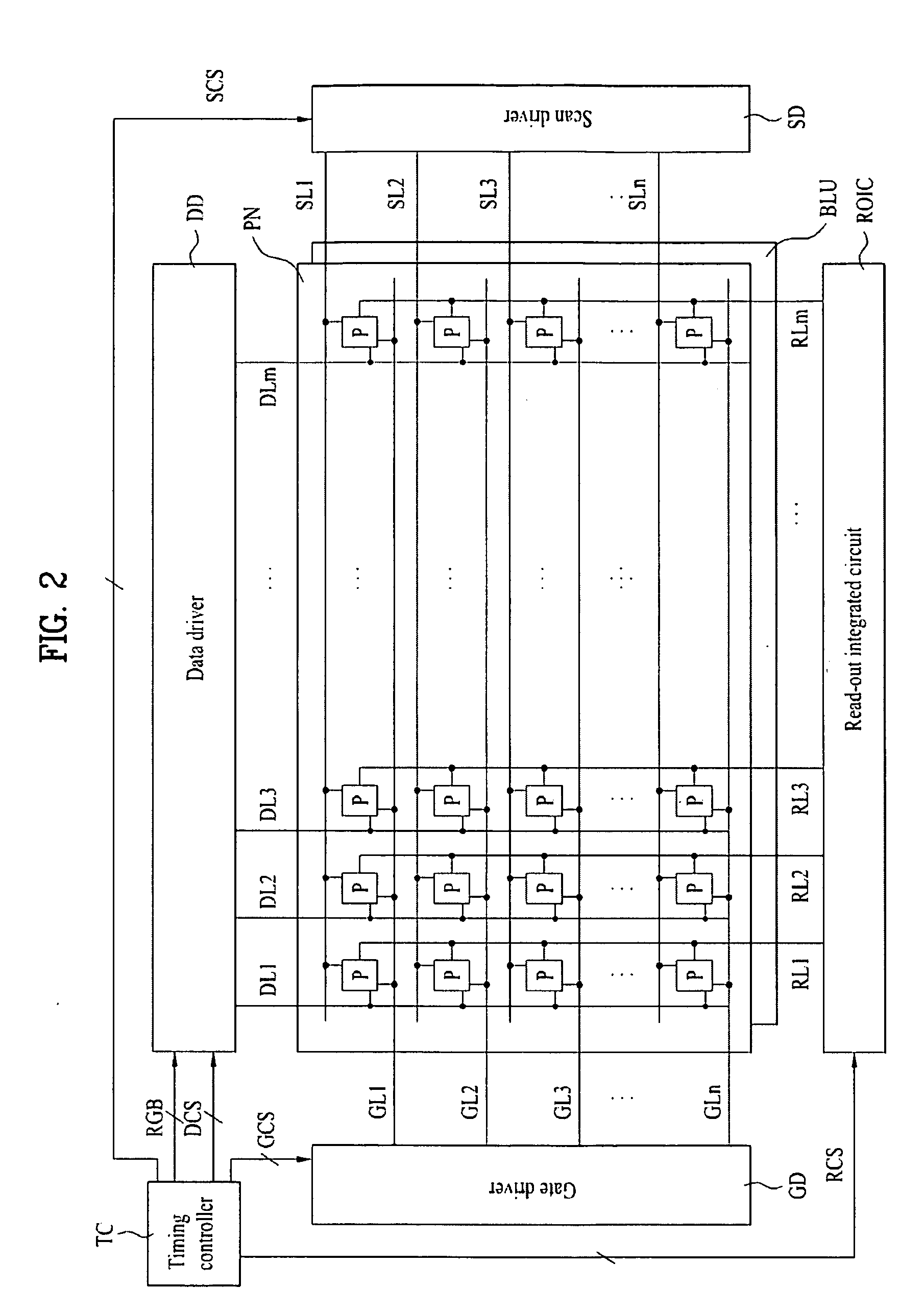
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20100026636A1Solve the insufficient charging timeSufficient access timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLight sensingLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display device having a plurality of pixel cells for displaying an image and sensing light incident on the pixel cells, each of the pixel cells includes a pixel circuit that displays an image based on a data voltage supplied from a data line in accordance with a gate signal from a gate line; and a touch sensor that senses light incident on the pixel cell, storing a light sensing signal based on the sensed light, and supplying the stored light sensing signal to a read-out integrated circuit via a read-out line in accordance with a scan signal from a scan line.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Focal plane array processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20120138774A1Television system detailsSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesDetector arrayReadout integrated circuit
A digital focal plane array includes an all-digital readout integrated circuit in combination with a detector array. The readout circuit includes unit cell electronics, orthogonal transfer structures, and data handling structures. The unit cell electronics include an analog to digital converter. Orthogonal transfer structures enable the orthogonal transfer of data among the unit cells. Data handling structures may be configured to operate the digital focal plane array as a data encryptor / decipherer. Data encrypted and deciphered by the digital focal plane array need not be image data.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
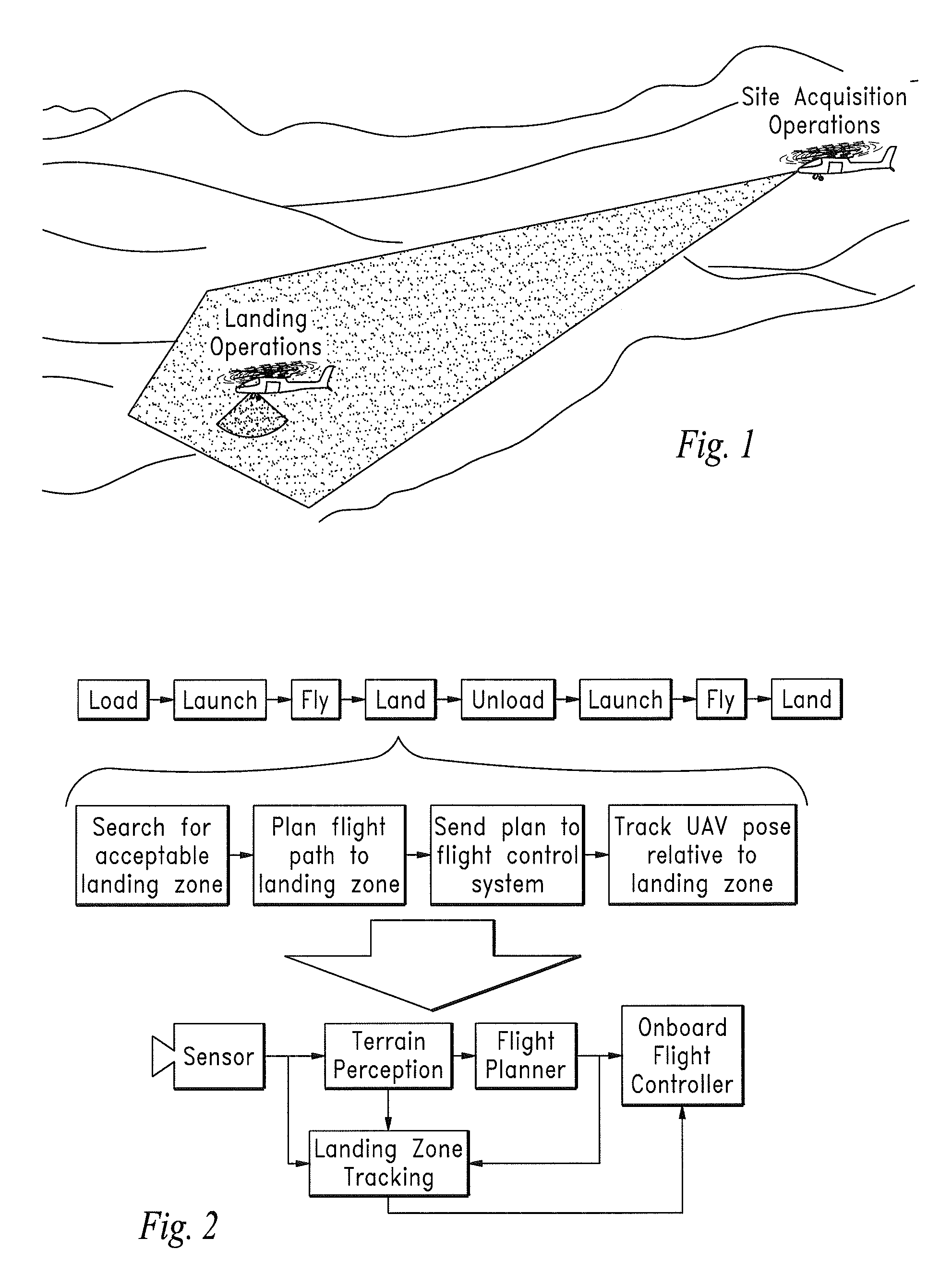
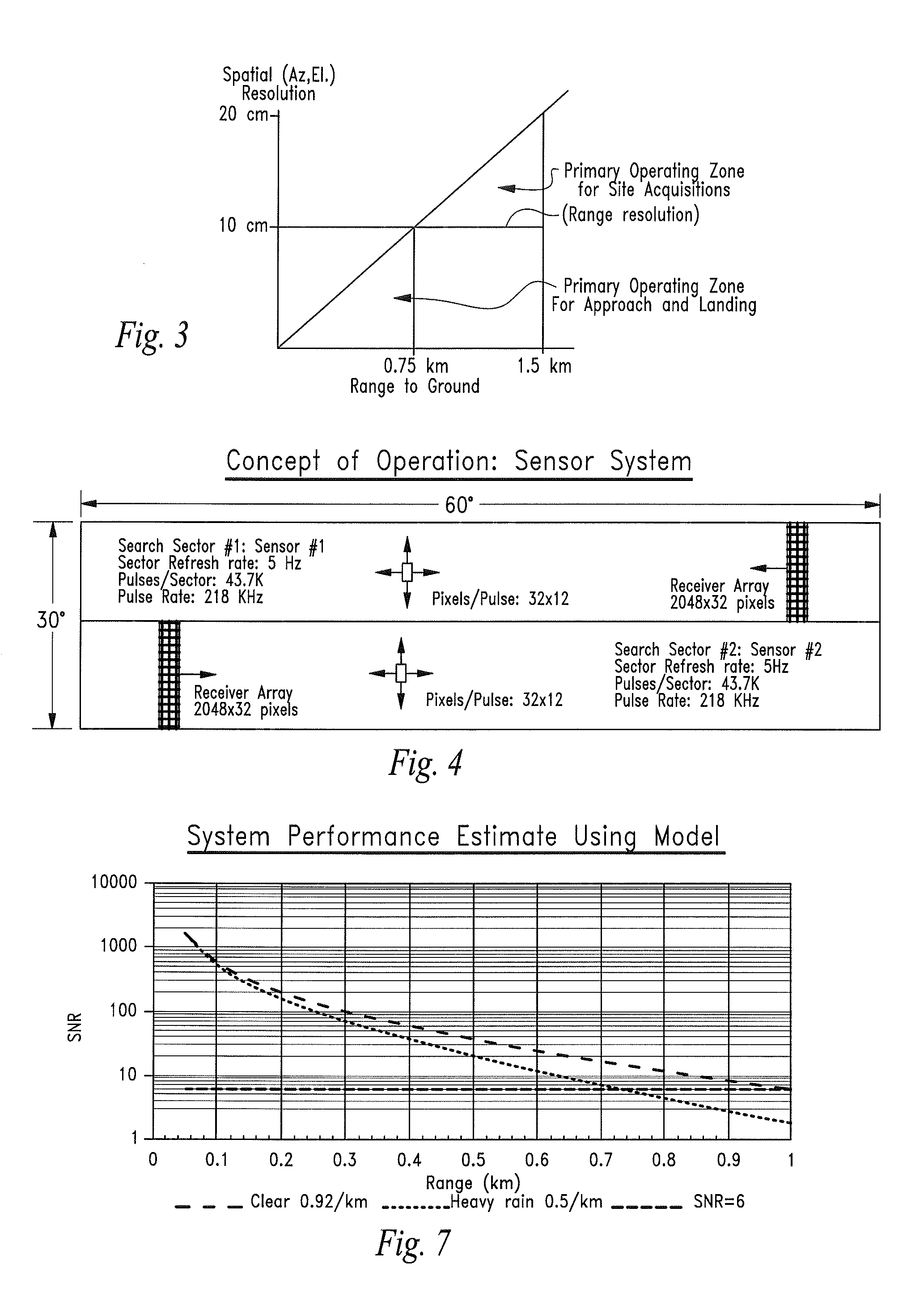
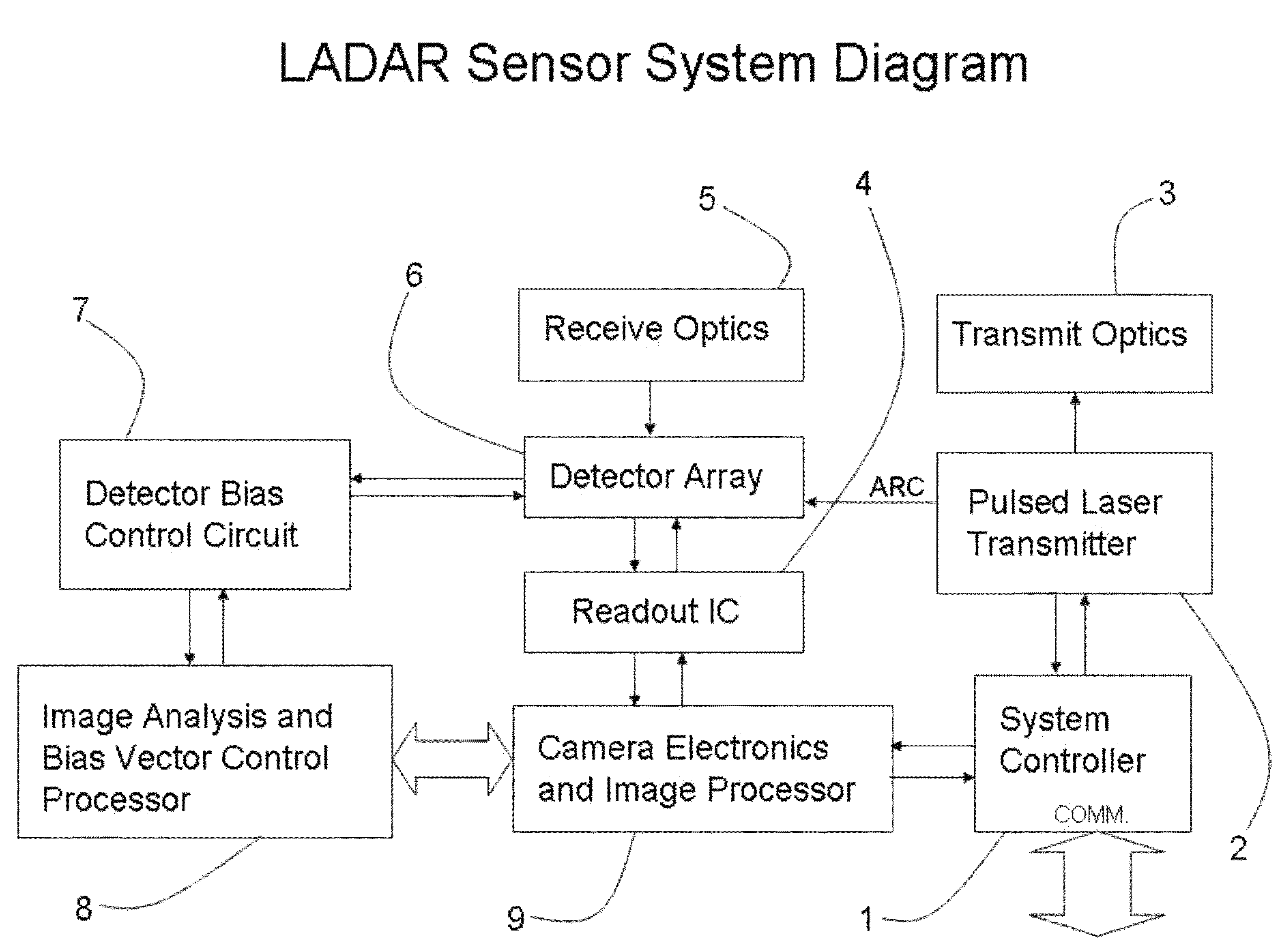
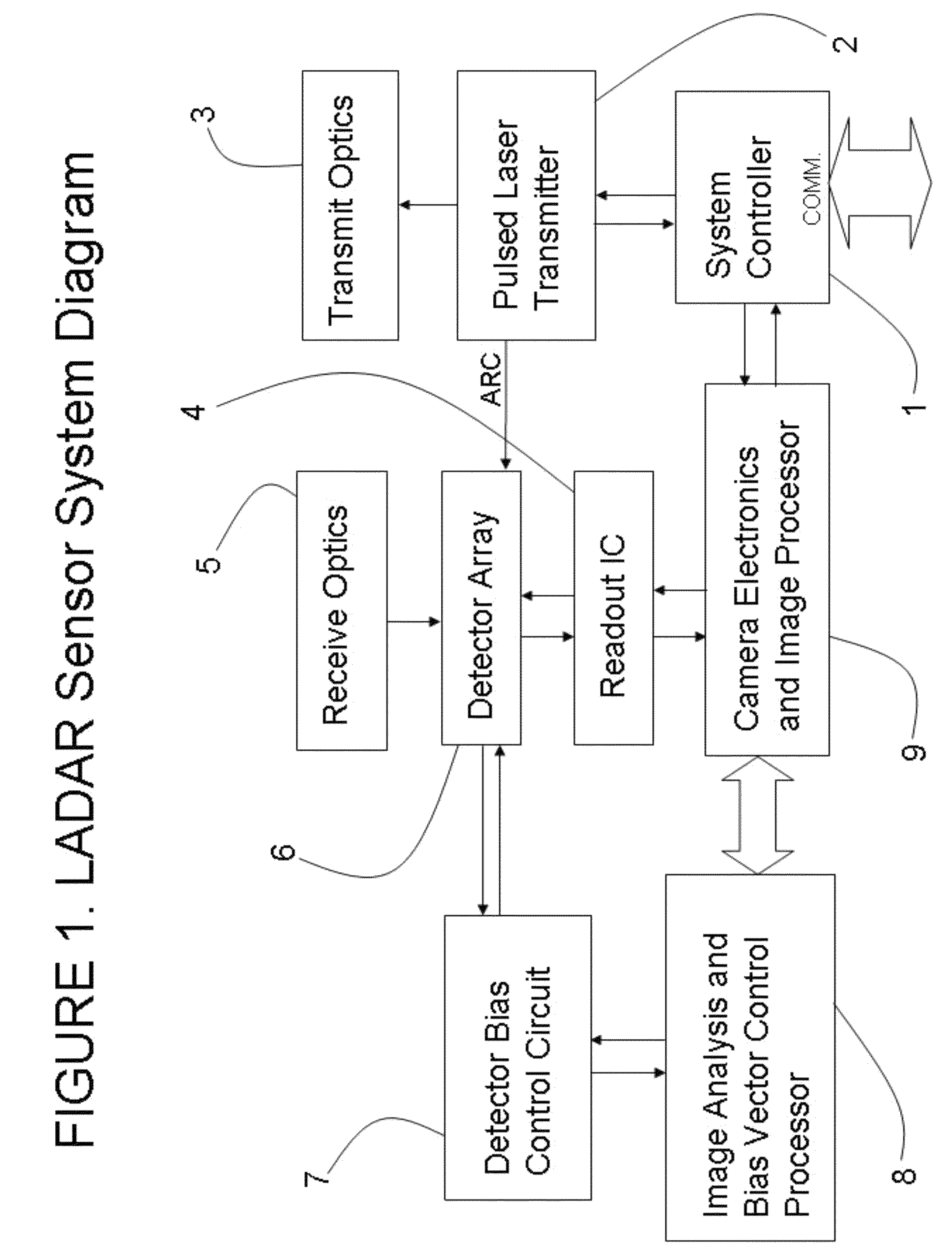
Ladar sensor for landing, docking and approach
ActiveUS8976340B2Improve performanceImprove ranging accuracyAircraft componentsOptical rangefindersLaser transmitterDetector array
A system for landing or docking a mobile platform is enabled by a flash LADAR sensor having an adaptive controller with Automatic Gain Control (AGC). Range gating in the LADAR sensor penetrates through diffuse reflectors. The LADAR sensor adapted for landing / approach comprises a system controller, pulsed laser transmitter, transmit optics, receive optics, a focal plane array of detectors, a readout integrated circuit, camera support electronics and image processor, an image analysis and bias calculation processor, and a detector array bias control circuit. The system is capable of developing a complete 3-D scene from a single point of view.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Systems and methods for integrating focal plane arrays
ActiveUS7459686B2Shorten the timeHigh frame rate operationTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationMulti bandMultispectral image
Systems and methods for providing multi-spectral image capability using an integrated multi-band focal plane array that, in one example, may be employed to simultaneously image in the visible spectrum and infrared spectrum using an integrated dual-band focal plane array, e.g., by including visible imaging circuitry within read out integrated circuitry (ROIC) used to readout infrared detector elements within the same pixel element / s.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Background Limited Focal Plane Array Assembly
InactiveUS20130206990A1Improve the detection rateSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermoelectric materialsLow noise
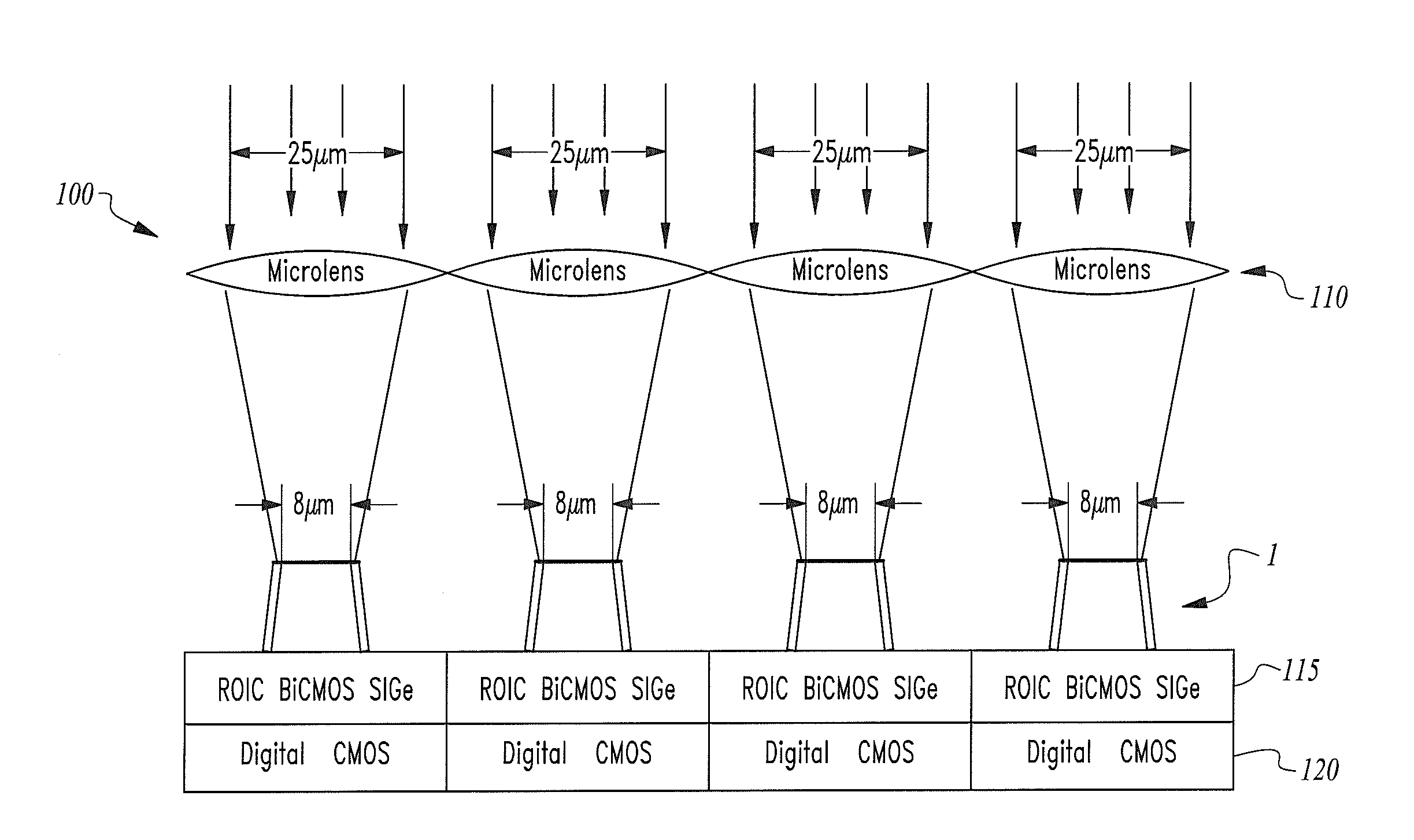
The thermoelectric detector comprises an infrared absorber pixel structure supported by two electrically connected beams made of a thermoelectric material. One end of the thermoelectric beam connects to the infrared absorber pixel structure; the other end connects to the substrate. The detector comprises a microlens for collecting and focusing infrared radiation on the detector. Infrared radiation is incident on the infrared absorber pixel structure results in a temperature gradient along the length of the thermoelectric legs, and generating an electrical voltage proportional to the gradient. A low noise SIGe BiCMOS readout integrated circuit is coupled to the detector to provide a background limited detector having improved detectivity.
Owner:PFG IP
Address mapped repartitioned digital pixel
ActiveUS20150116564A1Avoiding extrapolation errorHigh stability and precisionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
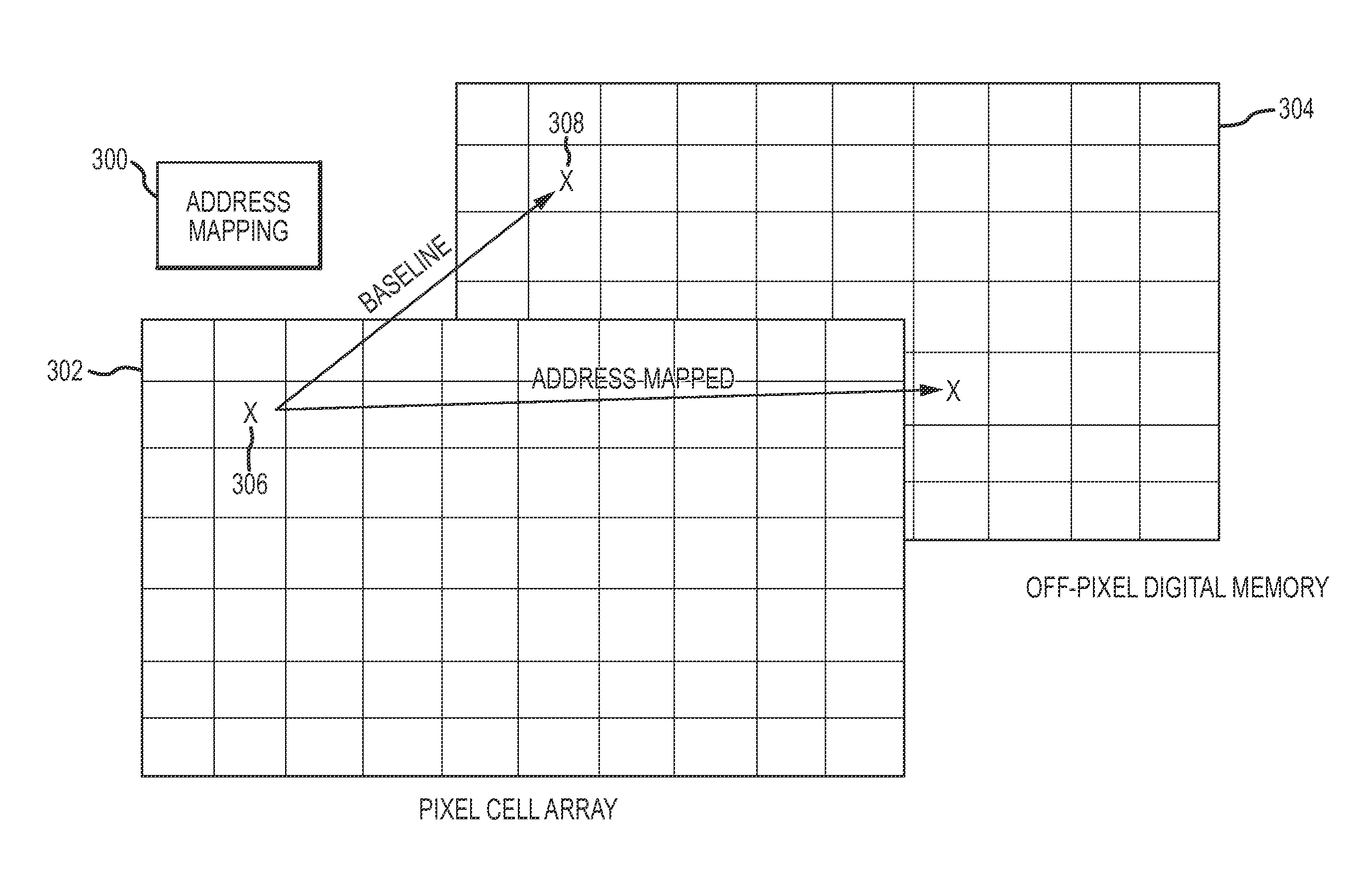
By adding stabilization and super-sampling to a digital pixel readout integrated circuit (ROIC), line of sight motion, that is usually costly and difficult to control, instead becomes an ally, doubling the effective FPA resolution in some systems. The base repartitioned digital pixel architecture supplements analog signal accumulation with off-pixel digital accumulation, greatly increasing dynamic range. Adding address mapping and increasing the ratio of memory locations to pixels, enables stabilization and resolution enhancement. Additional stabilization at sub-frame intervals limits the effect of latency and simplifies complex address mapping. Pixels gains are compensated in-ROIC, without requiring multipliers. A unique partitioning of functions between the ROIC and subsequent logic allows pixel biases and non-isomorphic sampling effects to be compensated off-ROIC, reducing overall system complexity and power.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
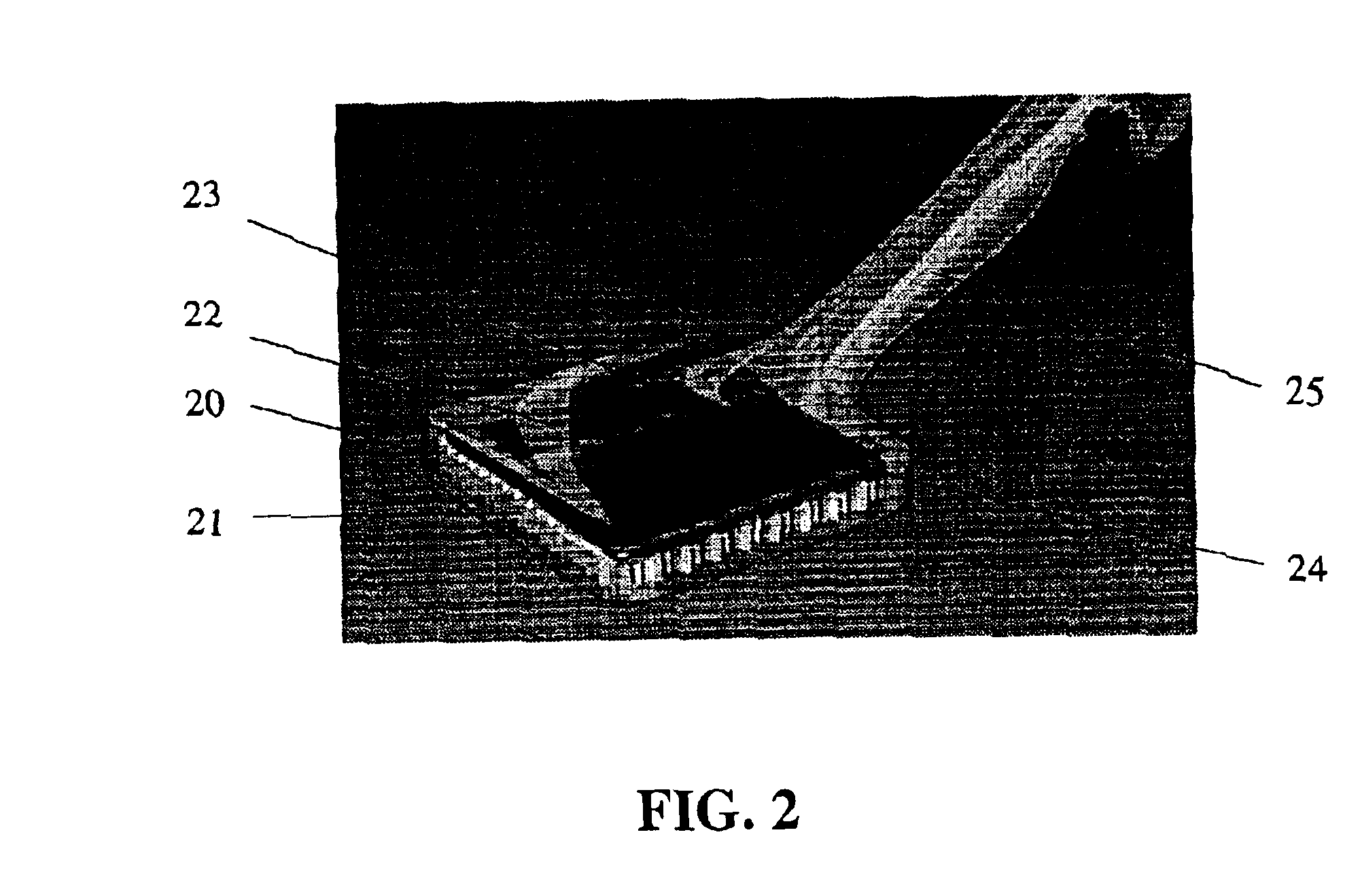
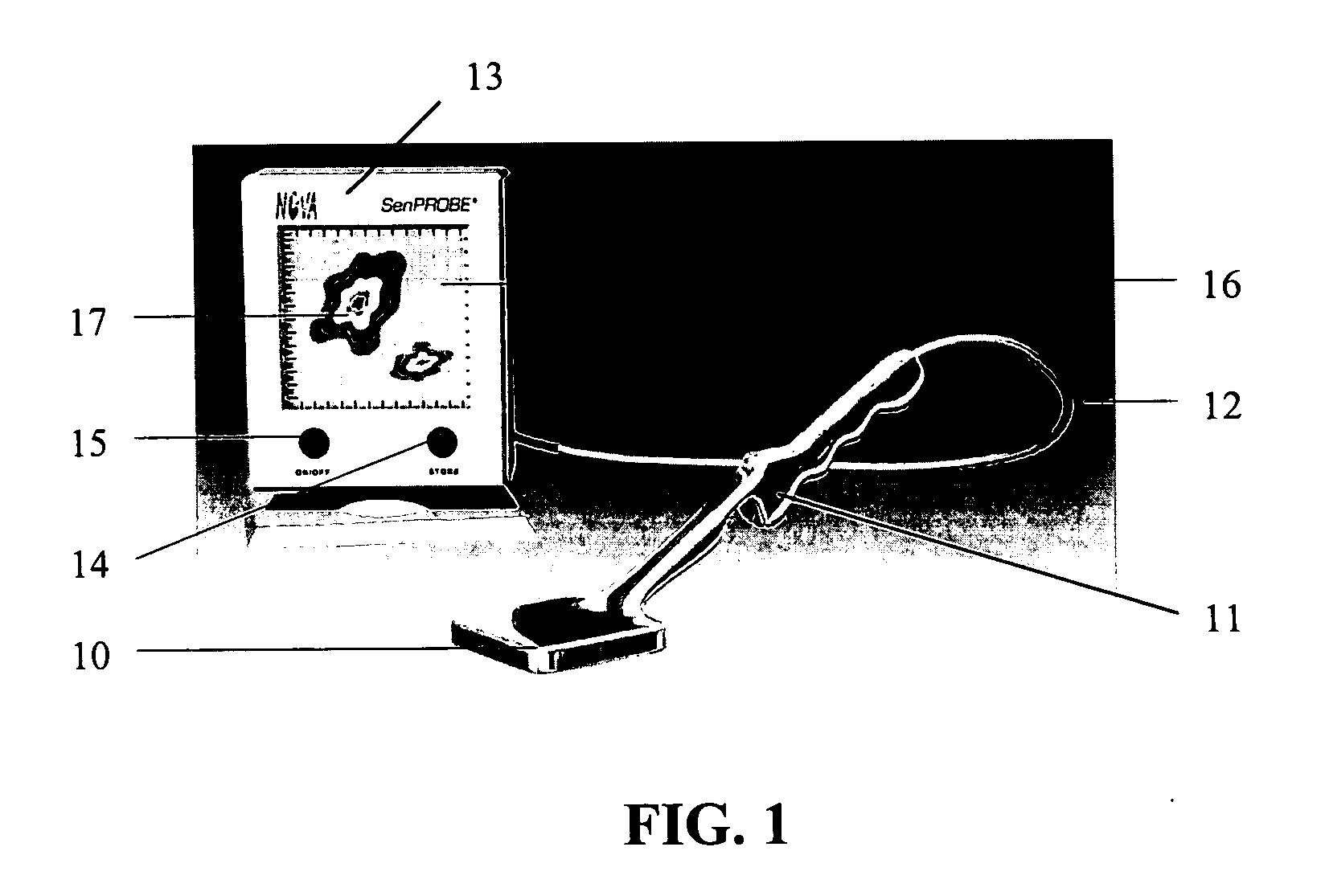
Imaging probe
InactiveUS6940070B2High sensitivityImprove quantum efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLow noiseRadioactive agent
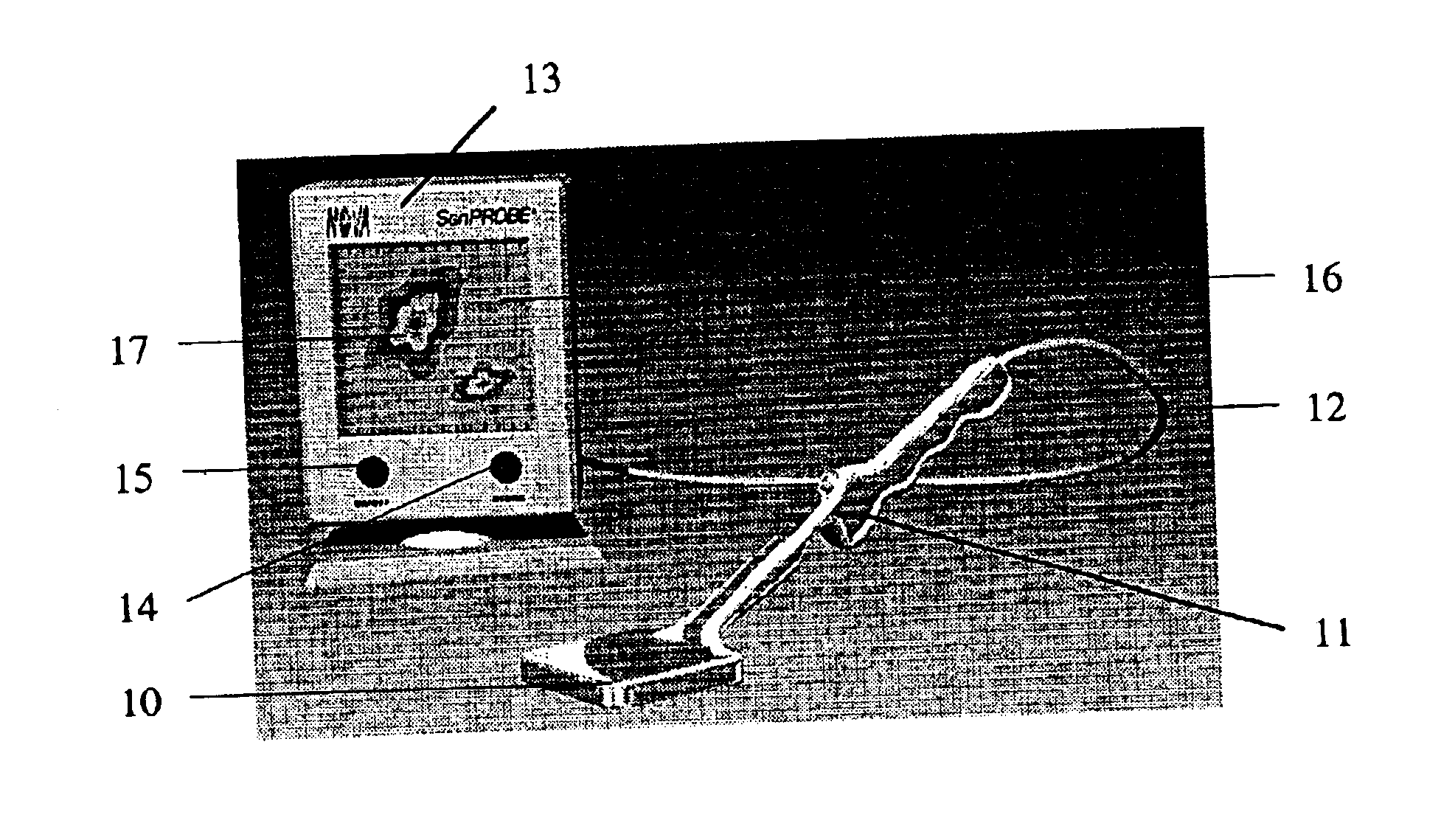
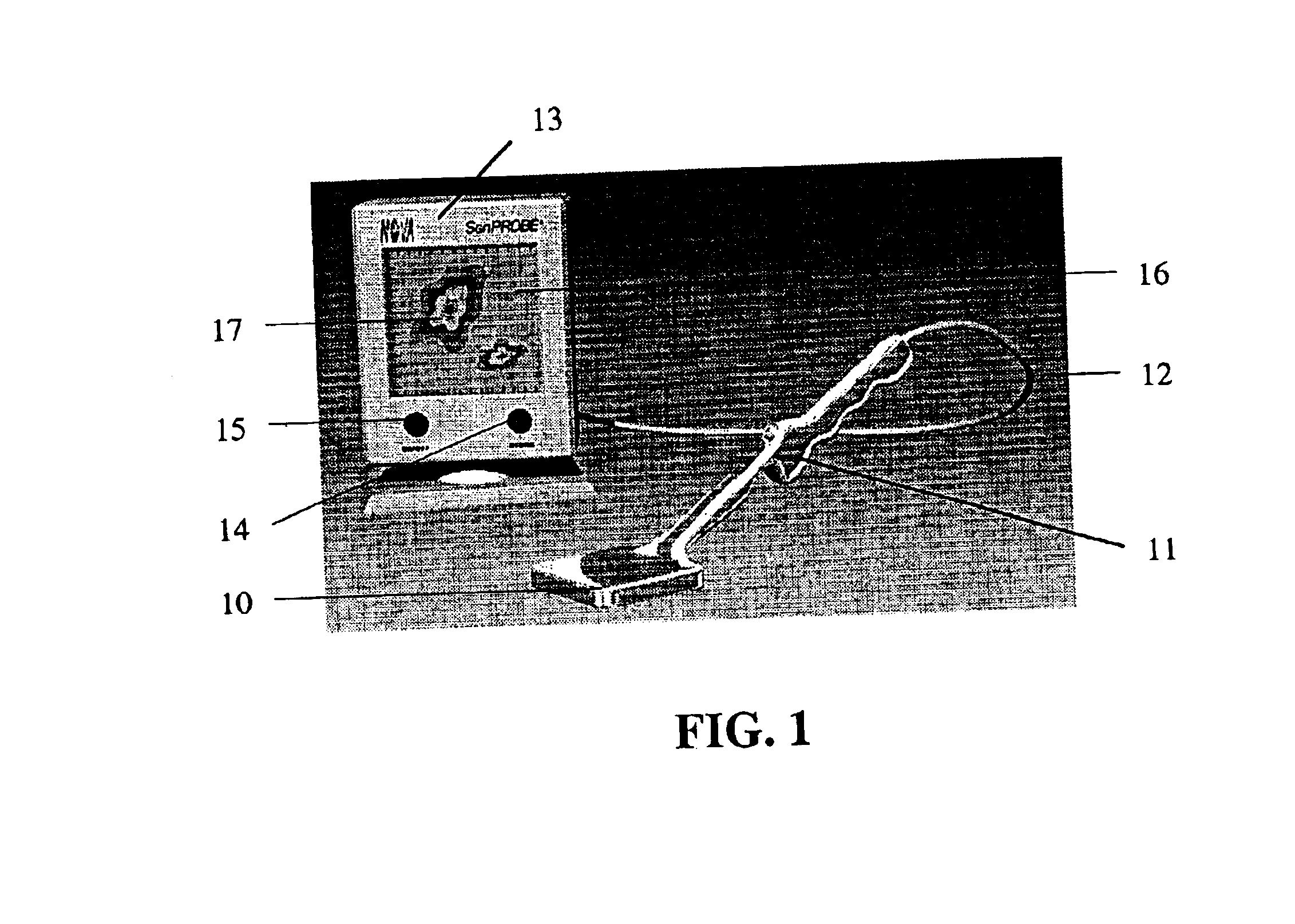
The design of a compact, handheld, solid-state and high-sensitivity imaging probe and a micro imager system is reported. These instruments can be used as a dedicated tool for detecting and locating sentinel lymph nodes and also for detecting and imaging radioactive material. The reported device will use solid state pixel detectors and custom low-noise frontend / readout integrated circuits. The detector will be designed to have excellent image quality and high spatial resolution. The imaging probes have two different embodiments, which are comprised of a pixelated detector array and a highly integrated readout system, which uses a custom multi-channel mixed signal integrated circuit. The instrument usually includes a collimator in front of the detector array so that the incident photons can be imaged. The data is transferred to an intelligent display system. A hyperspectral image can also be produced and displayed. These devices are designed to be portable for easy use.
Owner:NOVA R&D
Imaging probe
ActiveUS20060036157A1High sensitivityImprove quantum efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadioactive agentImaging quality
The design of a compact, handheld, solid-state and high-sensitivity imaging probe and a micro imager system is reported. These instruments can be used as a dedicated tool for detecting and locating sentinel lymph nodes and also for detecting and imaging radioactive material. The reported device will use solid state pixel detectors and custom low-noise frontend / readout integrated circuits. The detector will be designed to have excellent image quality and high spatial resolution. The imaging probes have two different embodiments, which are comprised of a pixelated detector array and a highly integrated readout system, which uses a custom multi-channel mixed signal integrated circuit. The instrument usually includes a collimator in front of the detector array so that the incident photons can be imaged. The data is transferred to an intelligent display system. A hyperspectral image can also be produced and displayed. These devices are designed to be portable for easy use.
Owner:NOVA R&D
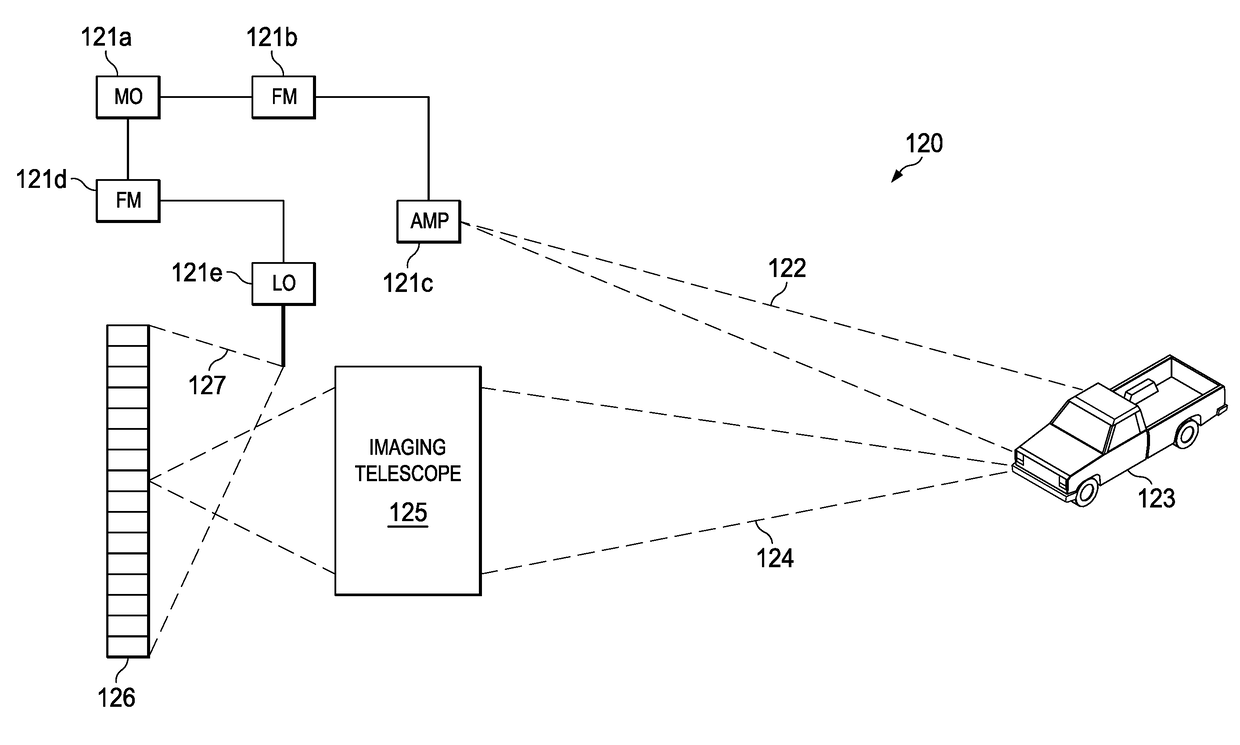
Coherent LADAR using intra-pixel quadrature detection
ActiveUS10000000B2Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLocal oscillatorReadout integrated circuit
A frequency modulated (coherent) laser detection and ranging system includes a read-out integrated circuit formed with a two-dimensional array of detector elements each including a photosensitive region receiving both return light reflected from a target and light from a local oscillator, and local processing circuitry sampling the output of the photosensitive region four times during each sample period clock cycle to obtain quadrature components. A data bus coupled to one or more outputs of each of the detector elements receives the quadrature components from each of the detector elements for each sample period and serializes the received quadrature components. A processor coupled to the data bus receives the serialized quadrature components and determines an amplitude and a phase for at least one interfering frequency corresponding to interference between the return light and the local oscillator light using the quadrature components.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Phase-coupled arrays of nanowire laser devices and method of controlling an array of such devices
ActiveUS9106056B1High densitySemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureNanowireQuantum well
According to various embodiments, the present teachings include an array of nanowire devices. The array of nanowire devices comprises a readout integrated circuit (ROIC). An LED array is disposed on the ROIC. The LED array comprises a plurality of LED core-shell structures, with each LED core-shell structure comprising a layered shell enveloping a nanowire core, wherein the layered shell comprises a multi-quantum-well (MQW) active region. The LED array further comprises a p-side electrode enveloping the layered core-shell structure and electrically connecting the ROIC, wherein each p-side electrode has an average thickness ranging from about 100 nm to about 500 nm. A dielectric layer is disposed on the plurality of LED core-shell structures, with each nanowire core disposed through the dielectric to connect with an n-side semiconductor that is situated on the dielectric.
Owner:STC UNM
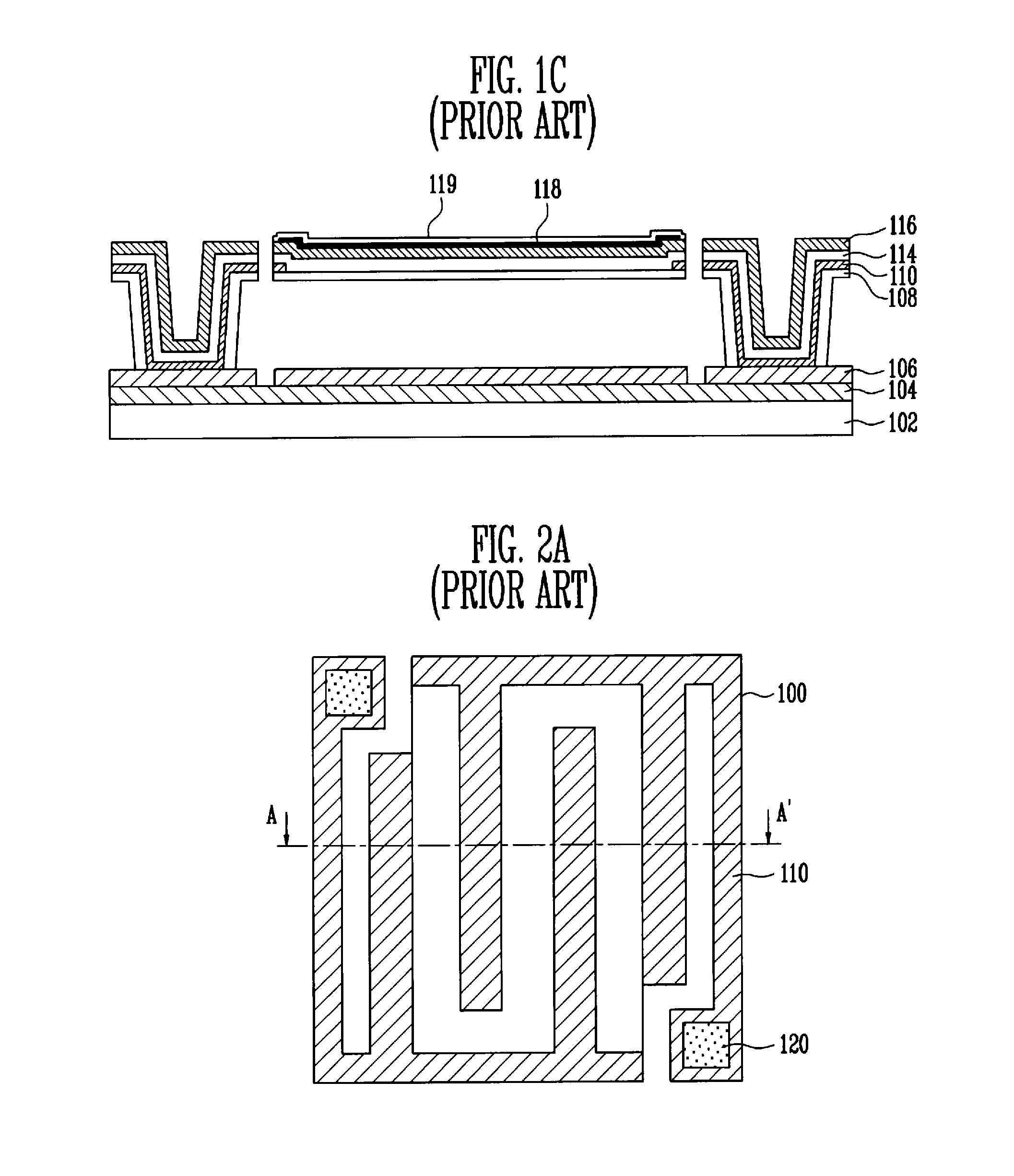
Bolometer structure, infrared detection pixel employing bolometer structure, and method of fabricating infrared detection pixel
InactiveUS20100148067A1Improve processing yieldImprove responsivityMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsResponsivityReadout integrated circuit
Provided are a bolometer structure, an infrared detection pixel employing the bolometer structure, and a method of fabricating the infrared detection pixel.The infrared detection pixel includes a substrate including a read-out integrated circuit (ROIC) and on which a reflection layer for reflecting infrared light is stacked, a bolometer structure formed to be spaced apart from the substrate and including a temperature-sensitive resistive layer, a first metal layer formed in a pattern on one surface of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer, a second metal layer formed in a pattern complementary to the pattern of the first metal layer on the other surface of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer in order to complementarily absorb infrared light, and an insulating layer formed between the temperature-sensitive resistive layer and the first metal layer, and a metal pad receiving a change in resistance of the temperature-sensitive resistive layer according to infrared light absorbed by the first metal layer and the second metal layer from the second metal layer, and transferring the change in resistance to the ROIC.Thus, it is possible to improve responsivity, and implement a simple bolometer structure robust against stress. Consequently, process yield can be improved, and the volume, weight, price, etc., of application products can be reduced by reducing the volume of a bolometer structure.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Non-refrigeration infrared focal plane array detector of double-layer structure
InactiveCN103776546AExpand the effective absorption areaImprove space utilizationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsReadout integrated circuitIntegrated circuit
The invention relates to a non-refrigeration infrared focal plane array detector of a double-layer structure. The non-refrigeration infrared focal plane array detector of the double-layer structure is composed of a substrate, a bridge floor layer and at least one bridge leg layer and is of the double-layer structure comprises an upper-layer bridge floor layer and a lower-layer bridge floor layer. The bridge floor layer is composed of an infrared thermal radiation absorption layer and a heat reactive layer. The bridge leg layer is composed of a supporting layer and a metal conductive layer. The bridge floor layer and the bridge leg layer are located on the upper plane and the lower plane which are mutually parallel and are fixedly connected through an electrical conduction anchor post. The bridge leg layer is suspended above the substrate and is connected to the substrate through the other electrical conduction anchor post. The substrate is a reading integrated circuit substrate, and the infrared radiation absorption layer is arranged on the surface of the substrate. The non-refrigeration infrared focal plane array detector is obtained through the double-layer structure, the stuffing efficiency of a detector unit can be effectively improved, absorption of infrared thermal radiation is enhanced, the heat insulation capacity of the detector can be effectively improved through a broken line bridge leg structure, the heat loss is reduced, and the overall detection performance is improved.
Owner:WUHAN GAOXIN TECH
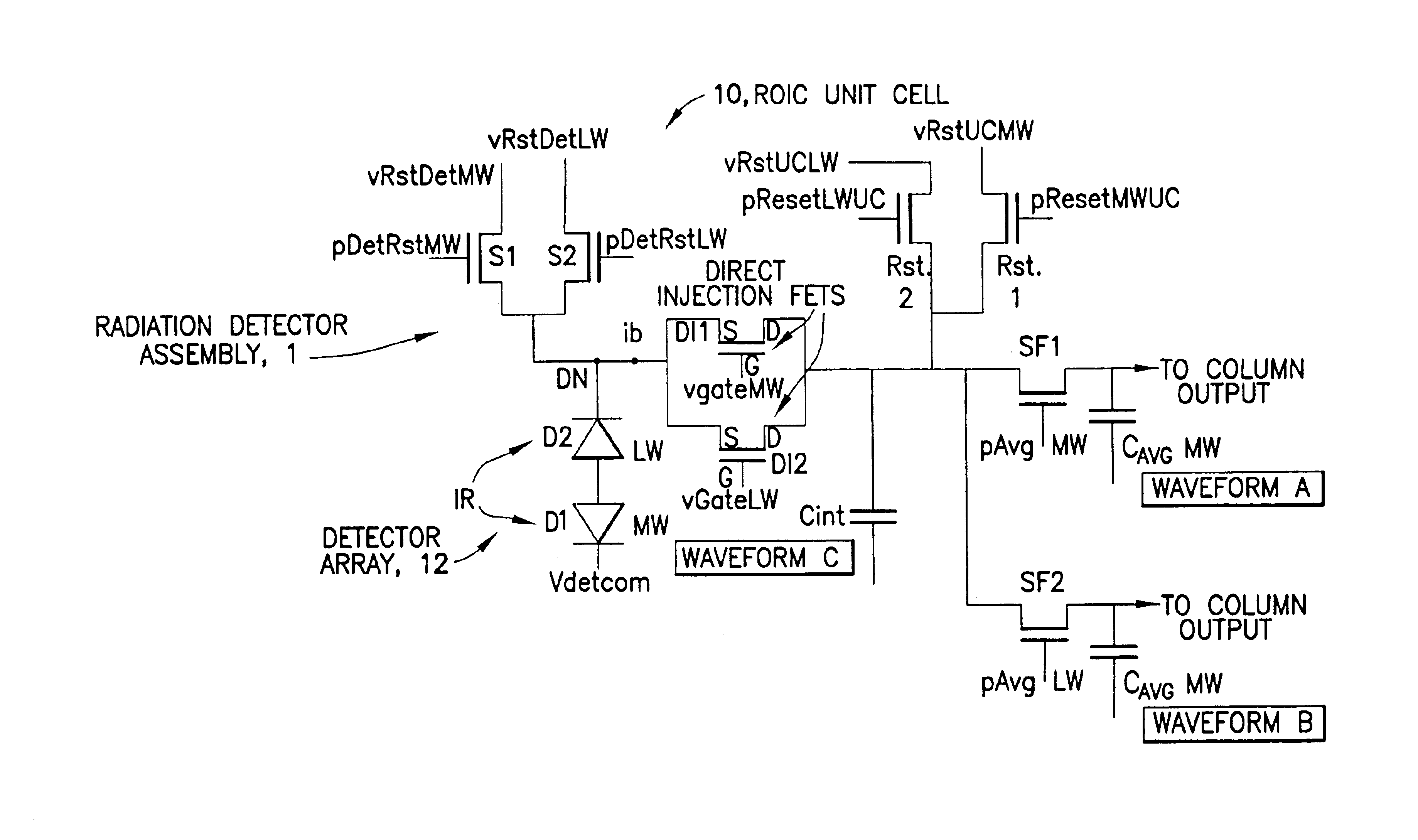
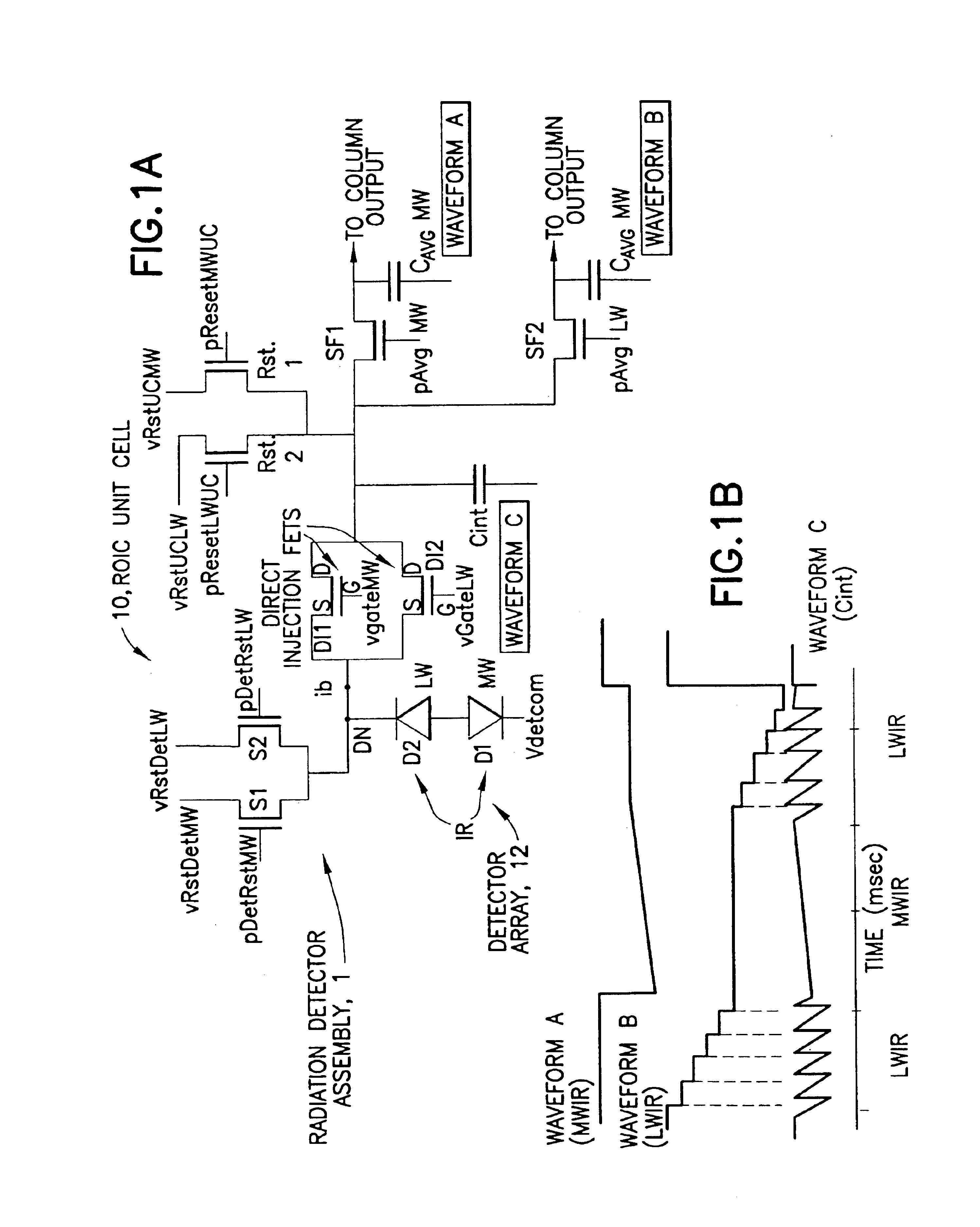
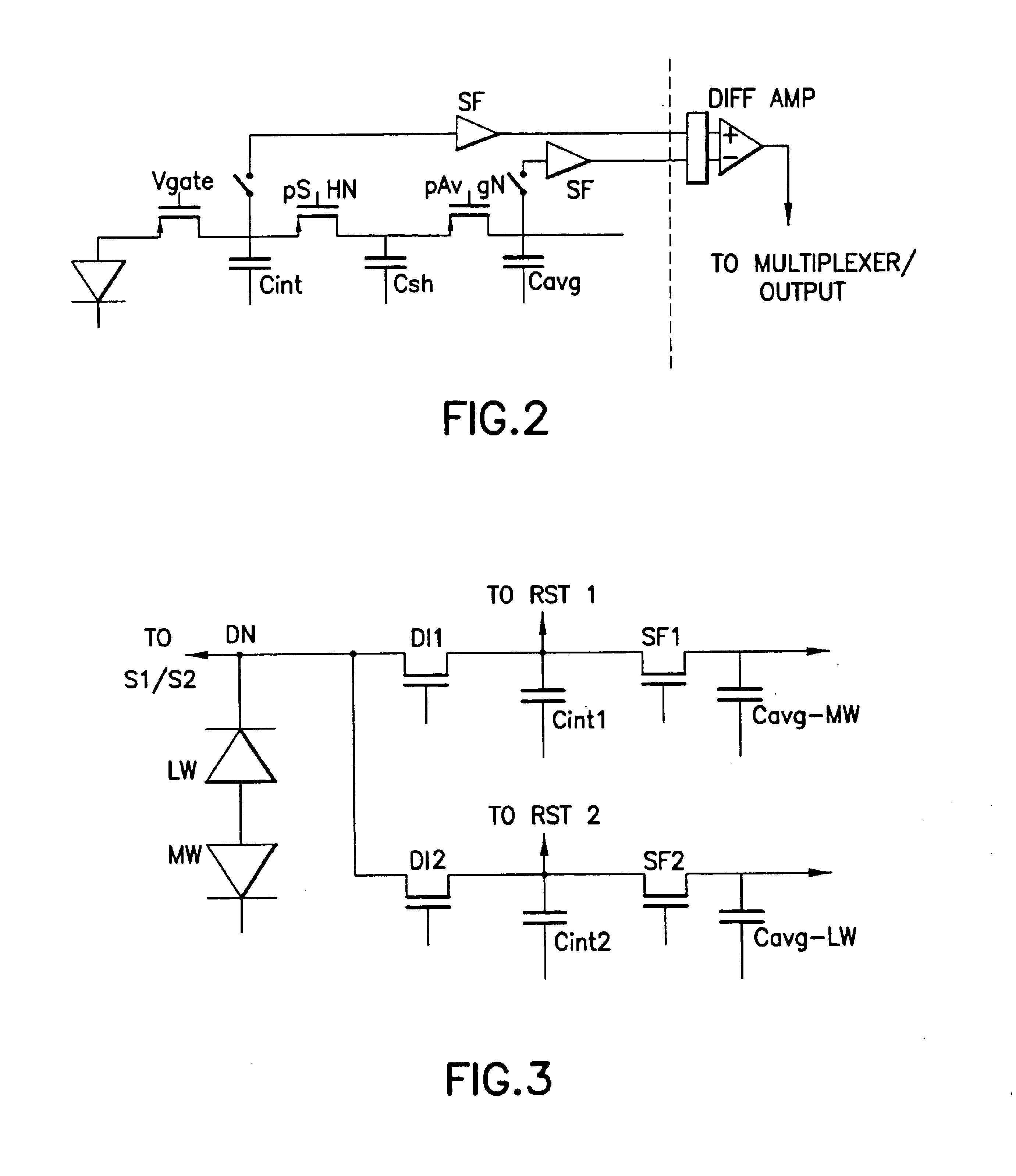
IRFPA ROIC with dual TDM reset integrators and sub-frame averaging functions per unit cell
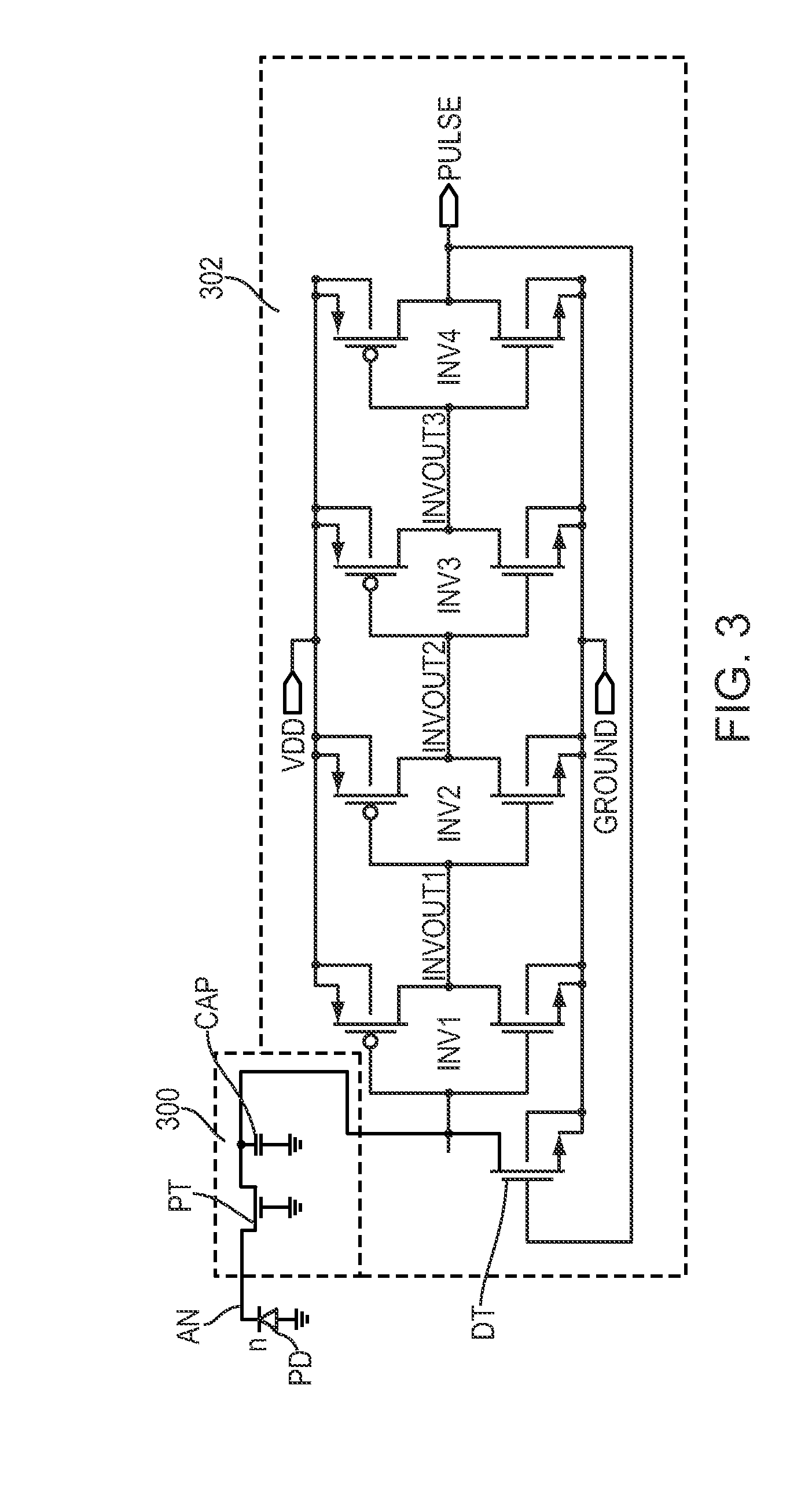
InactiveUS6885002B1Improved temporal registrationFast integrationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
A unit cell (10) of a readout integrated circuit is constructed and operated so as to temporally align an image obtained in a first spectral band with a an image obtained in a second spectral band. A method operates, during a frame period, to sub-frame average a first signal detected in the first spectral band by a multi-spectral detector (12), to sub-frame average a first signal detected in the second spectral band by the multi-spectral detector, and to sub-frame average a second signal detected in the first spectral band by the multi-spectral detector. The method then reads out the sub-frame averaged signals for each spectral band. The sub-frame averaged may be read out simultaneously from the unit cell. When sub-frame averaging the first and second signals in the first spectral band the method performs a plurality of consecutive sub-integrations and stores the result of each sub-integration on a first sub-frame averaging capacitance, and when sub-frame averaging the first signal of the second spectral band the method performs a single integration of the second signal, and stores the result of the integration on a second sub-frame averaging capacitance. The first spectral band may correspond to long wavelength infrared radiation (LWIR), and the second spectral band may correspond to medium wavelength infrared radiation (MWIR).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Detection device, light-receiving element array, semiconductor chip, method for manufacturing the same, and optical sensor apparatus
InactiveUS20120032145A1Preventing bump bonding failureAvoid insulation failureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipThermal expansion
A detection device includes a light-receiving element array and a read-out integrated circuit (CMOS), bumps of the light-receiving element array being bonded to bumps of the read-out integrated circuit, and at least one of the light-receiving element array and the read-out integrated circuit having a concaved surface which faces the other. The bonded bumps positioned in a region near the periphery of the arrangement region of the bonded bumps have a larger diameter and a lower height than those of the bumps positioned in a central region. Therefore, it is possible to prevent bonding failure and insulation failure in the bumps from occurring due to a difference in coefficient of thermal expansion, while securing a small size and low cost.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
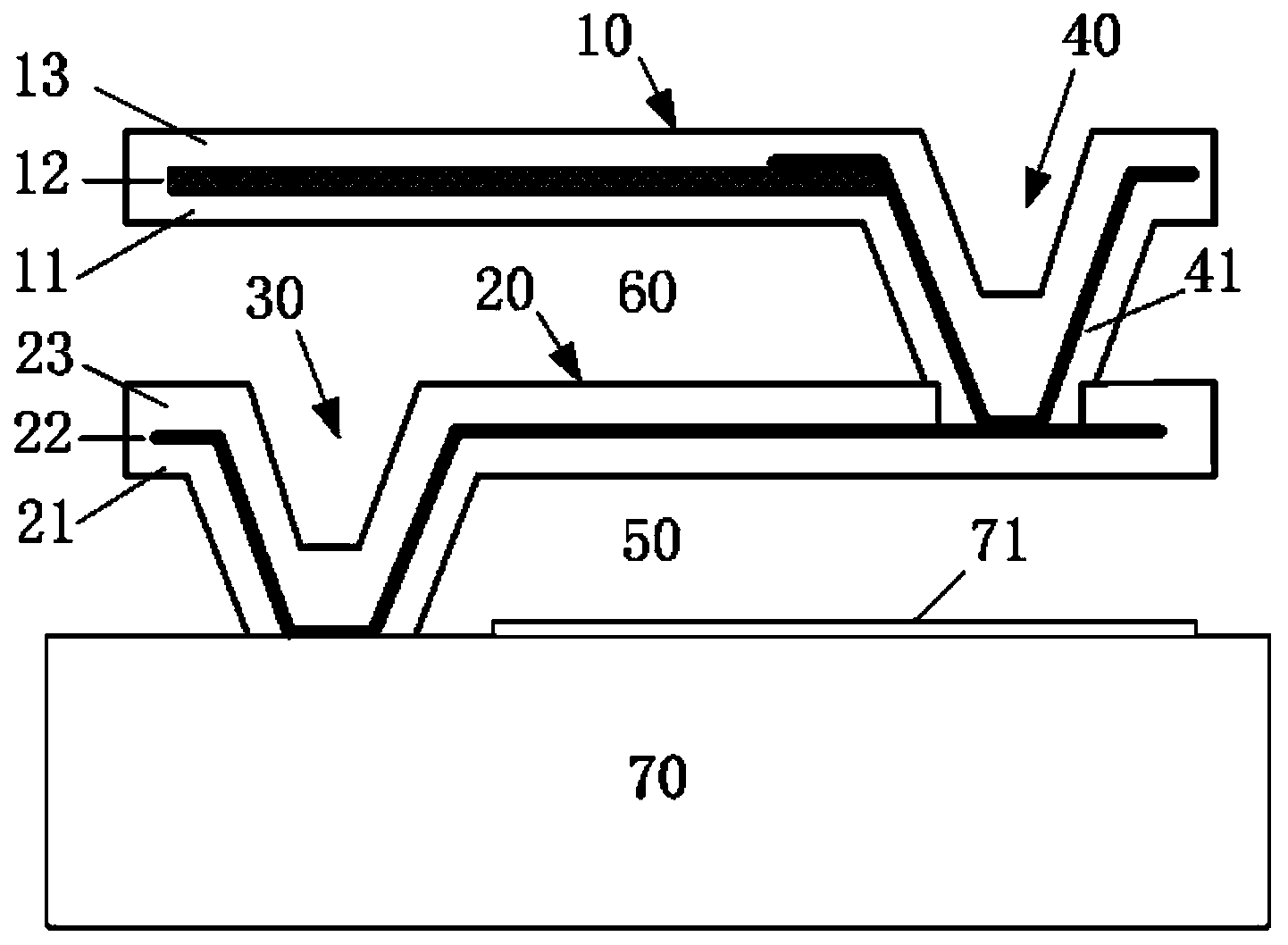
An uncooled infrared focal plane array detector
ActiveCN102280455AReduce the occupied areaReduce processing difficultyRadiation controlled devicesPyrometry using electric radation detectorsInsulation layerSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a non-refrigeration infrared focal plane array seeker. The structure is characterized in that one end part of a bridge leg is connected with a bridge surface, and the other end part of the bridge leg is connected to a base through an anchor post; the base is a read-out integrated circuit substrate, and the surface of the base is provided with a reflection film layer; the bridge surface is hanged deadly above the reflection film layer, and forms a vacuum clearance layer with the base; the bridge leg is arranged at two sides corresponding to the bridge surface, and the respective lower surface of the bridge leg and the bridge surface are distributed on the same plane; the bridge surface is sequentially provided with a support layer, an absorption layer, an insulation layer, a heat sensitive layer and a protection layer from bottom to up; the bridge leg is sequentially provided with a heat resistance layer, an electric conduction layer and a passivation layer from bottom to up; and the anchor post consists of a metal tungsten post and an oxide silicon post, and is sequentially provided with metal tungsten and silicon oxide materials from the inside to outside. The anchor post provided by the invention is a novel anchor post, compared with the traditional anchor post formed by the traditional filling technology, the area occupied by the anchor post is shortened, and the technology difficulty is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN GUIDE INFRARED CO LTD
Perforated blocking layer for enhanced broad band response in a focal plane array
ActiveUS9111830B1Enhanced visible responseImprove responseSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Provided is a focal plane array that includes an array of photodetectors, with each photodetector being in electrical communication with a corresponding one of an electrode of a read out integrated circuit. The array of photodetectors include an insulating layer, a blocking layer comprising at least one blind via, and an active layer formed between the insulating layer and the blocking layer. A first portion of the blocking layer transmits radiation having a first wavelength and reflects radiation having second wavelength that is lower than that of the first wavelength. A diameter of the at least one blind via is selected to allow radiation of the second wavelength to pass through the at least one blind via.
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD
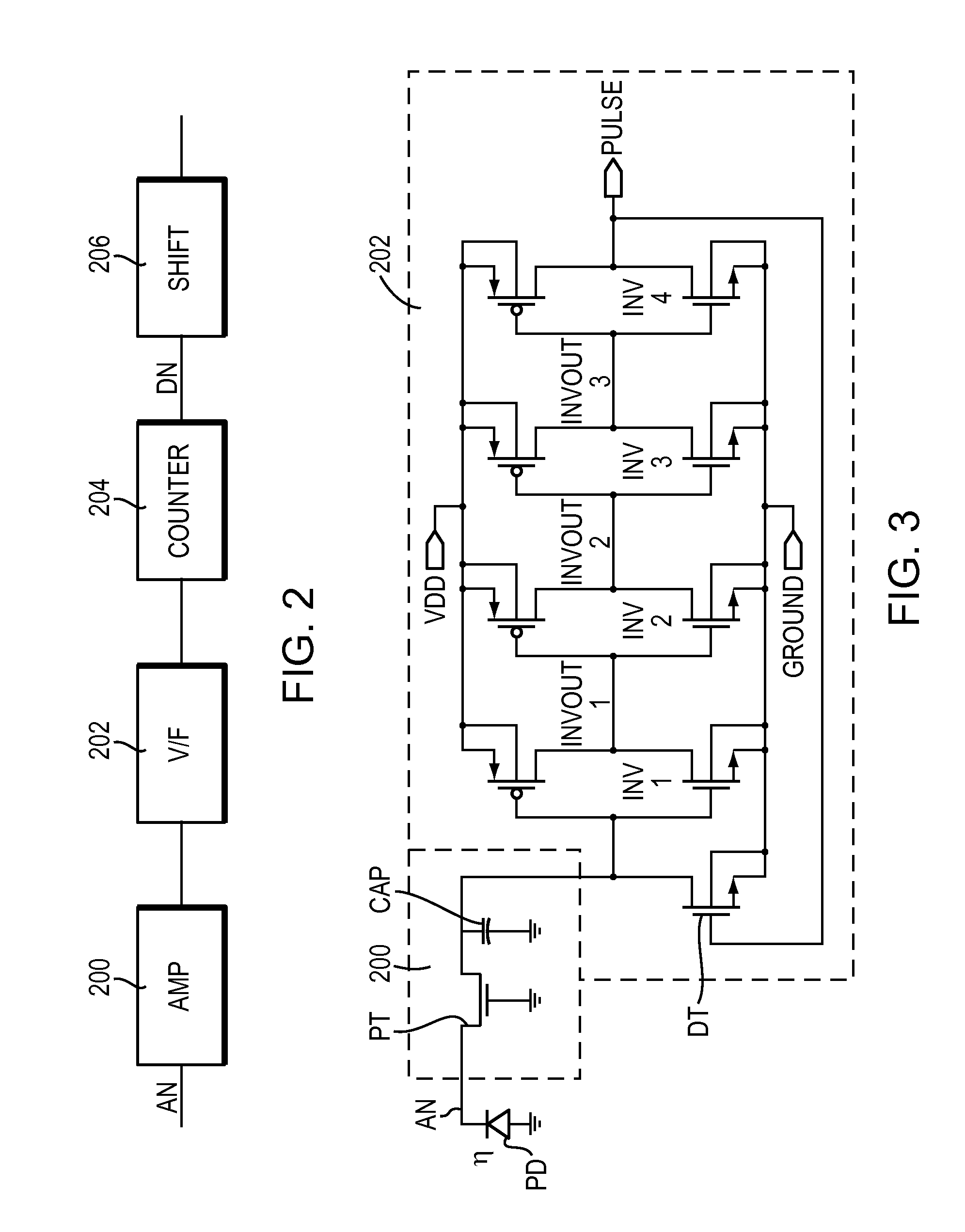
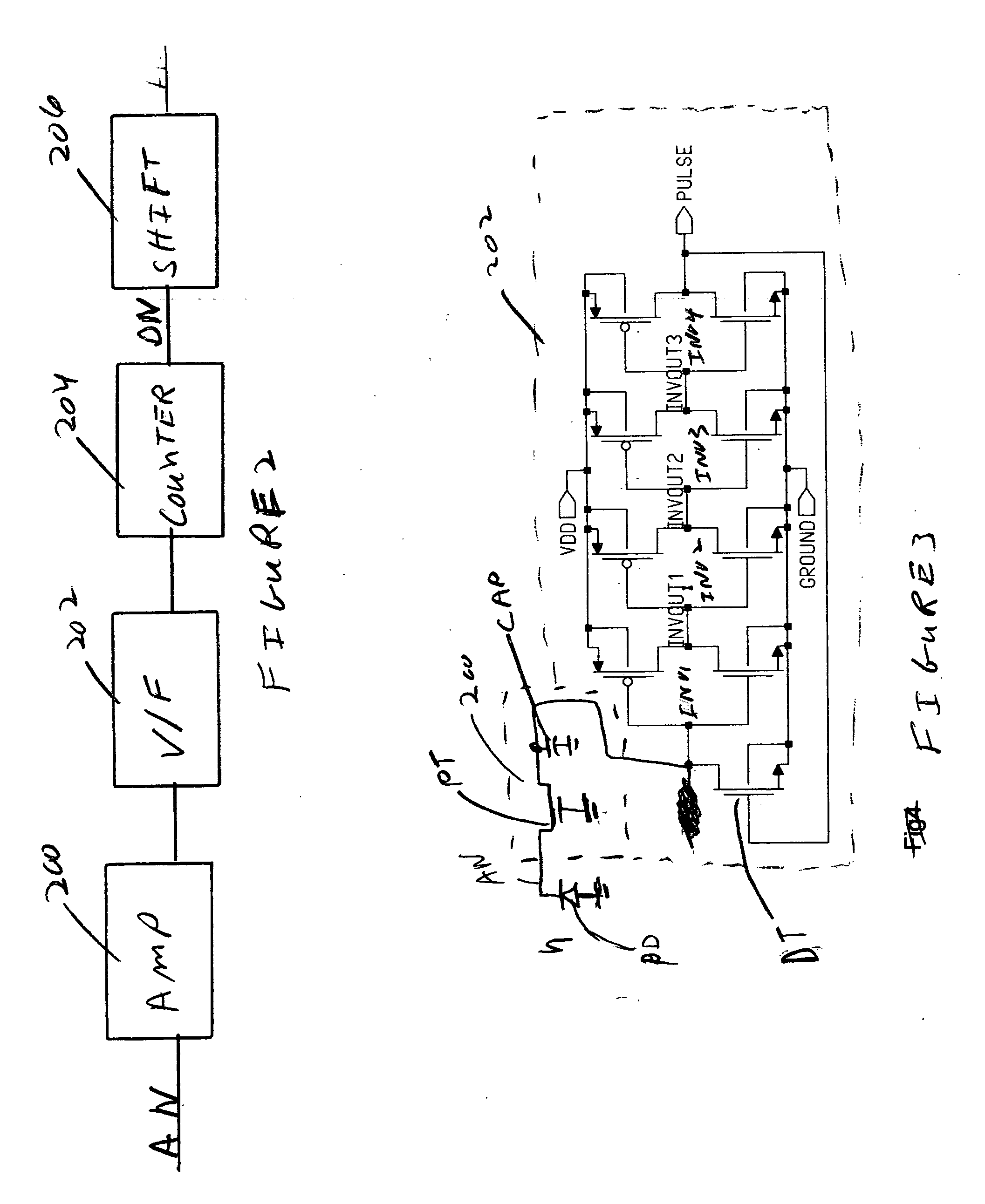
Readout integrated circuit for dynamic imaging
InactiveUS20140048683A1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalSoftware engineering
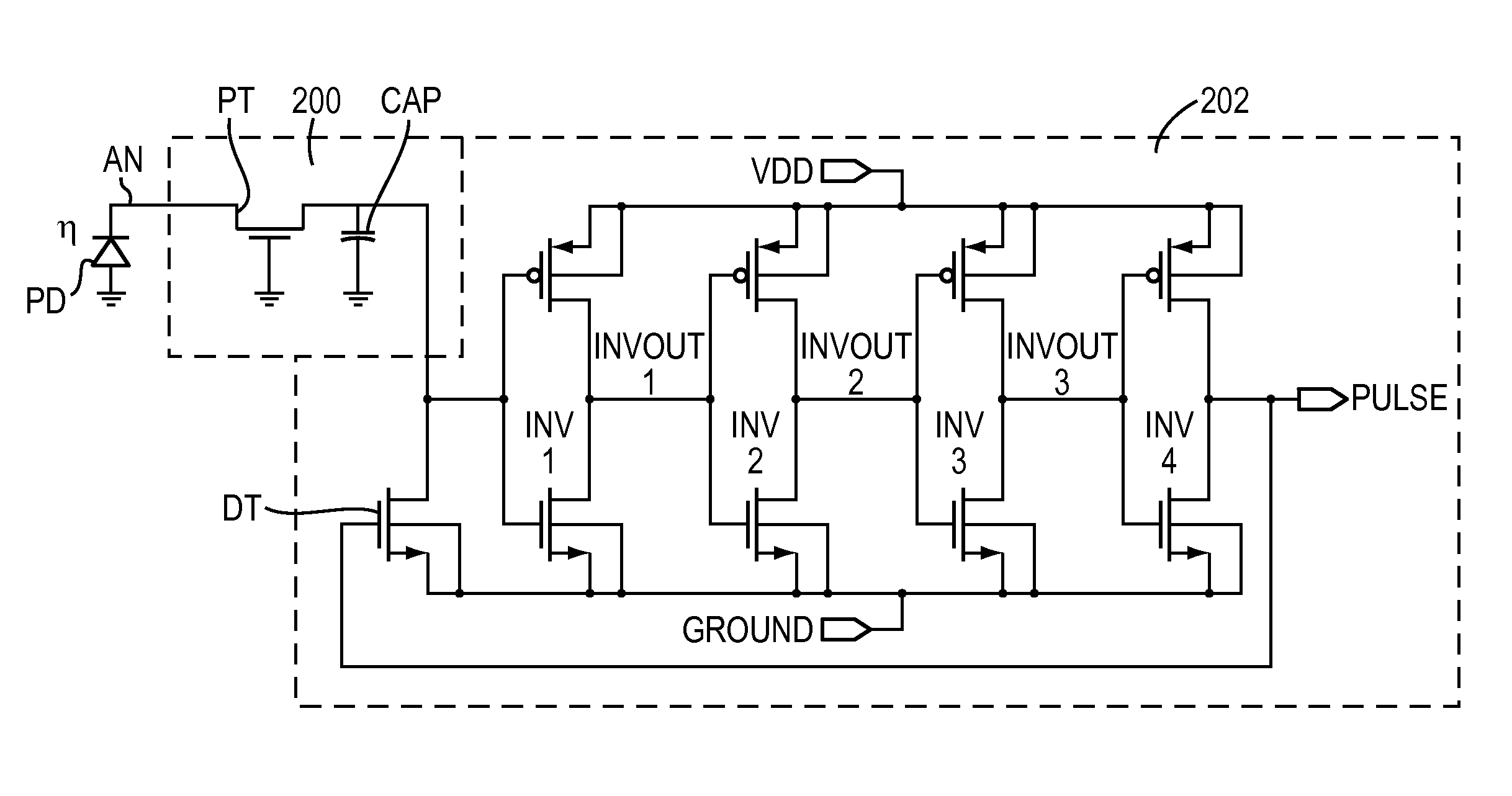
A sampling circuit for dynamic imaging is provided. Specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to a readout integrated circuit (ROIC) for dynamic imaging and a related image sensor. In one embodiment of the present invention, a sampling circuit is provided that comprises: an amplifier circuit, which amplifies charge signals generated at photo diodes and converts them to voltage signals; a filter circuit (optional) that receives and filters the voltage signals to yield a filtered signal; a sampling circuit, which samples the voltage signals and outputs a sampled signal in accordance with a sampling control signal; and a digital converter, which converts the sampled signal into a digital format and outputs a digital signal.
Owner:LUXEN TECH +1
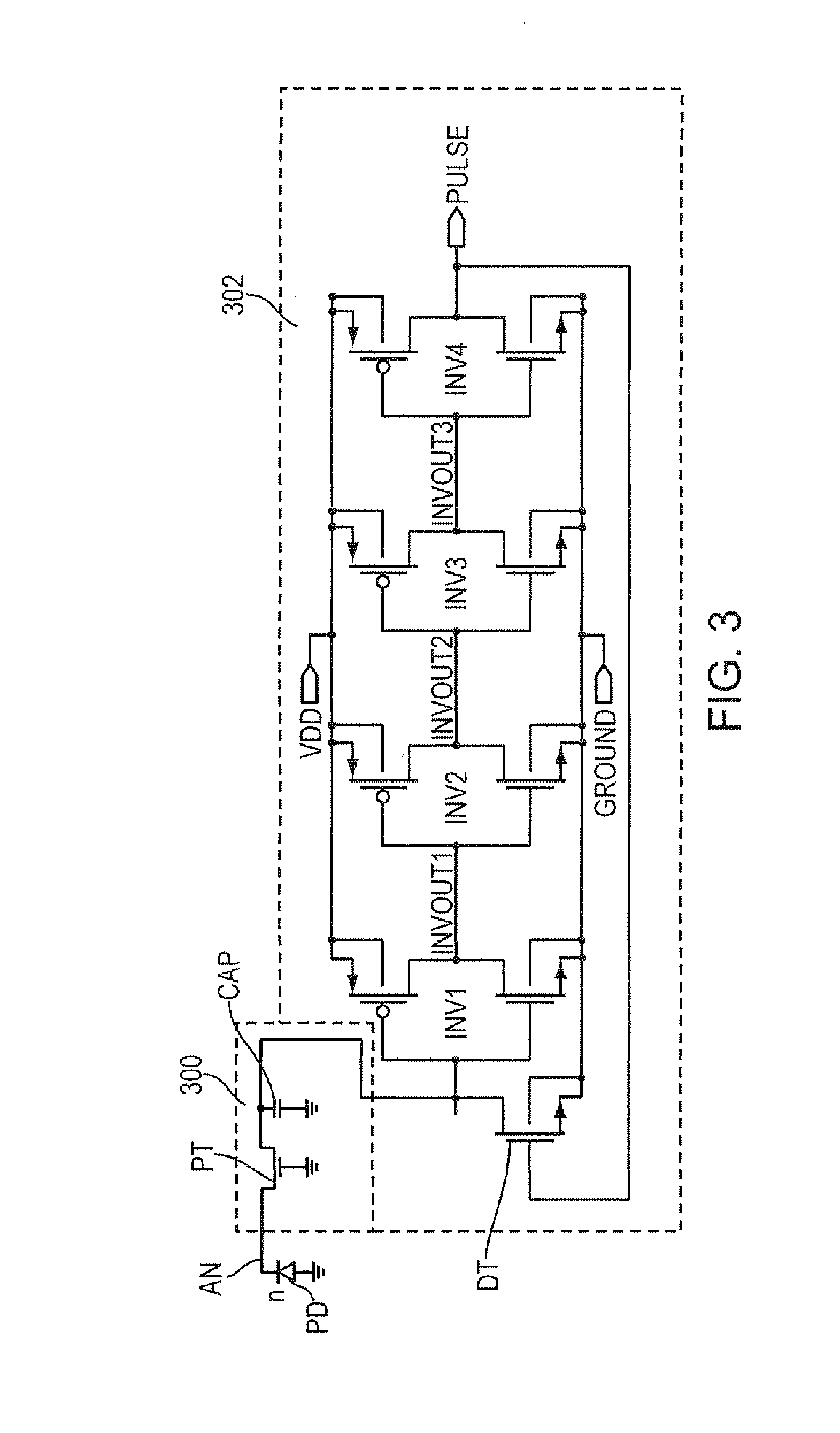
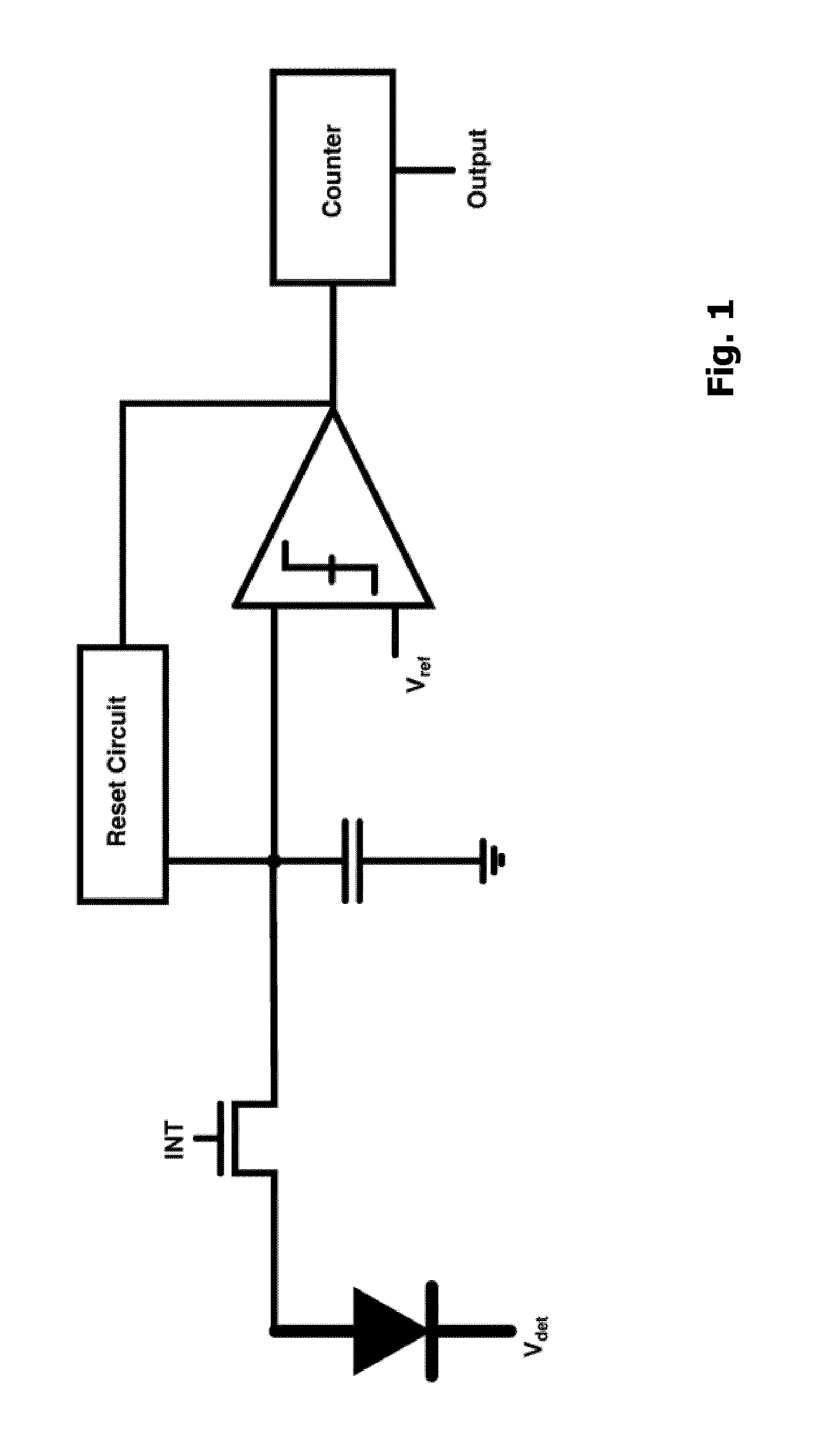
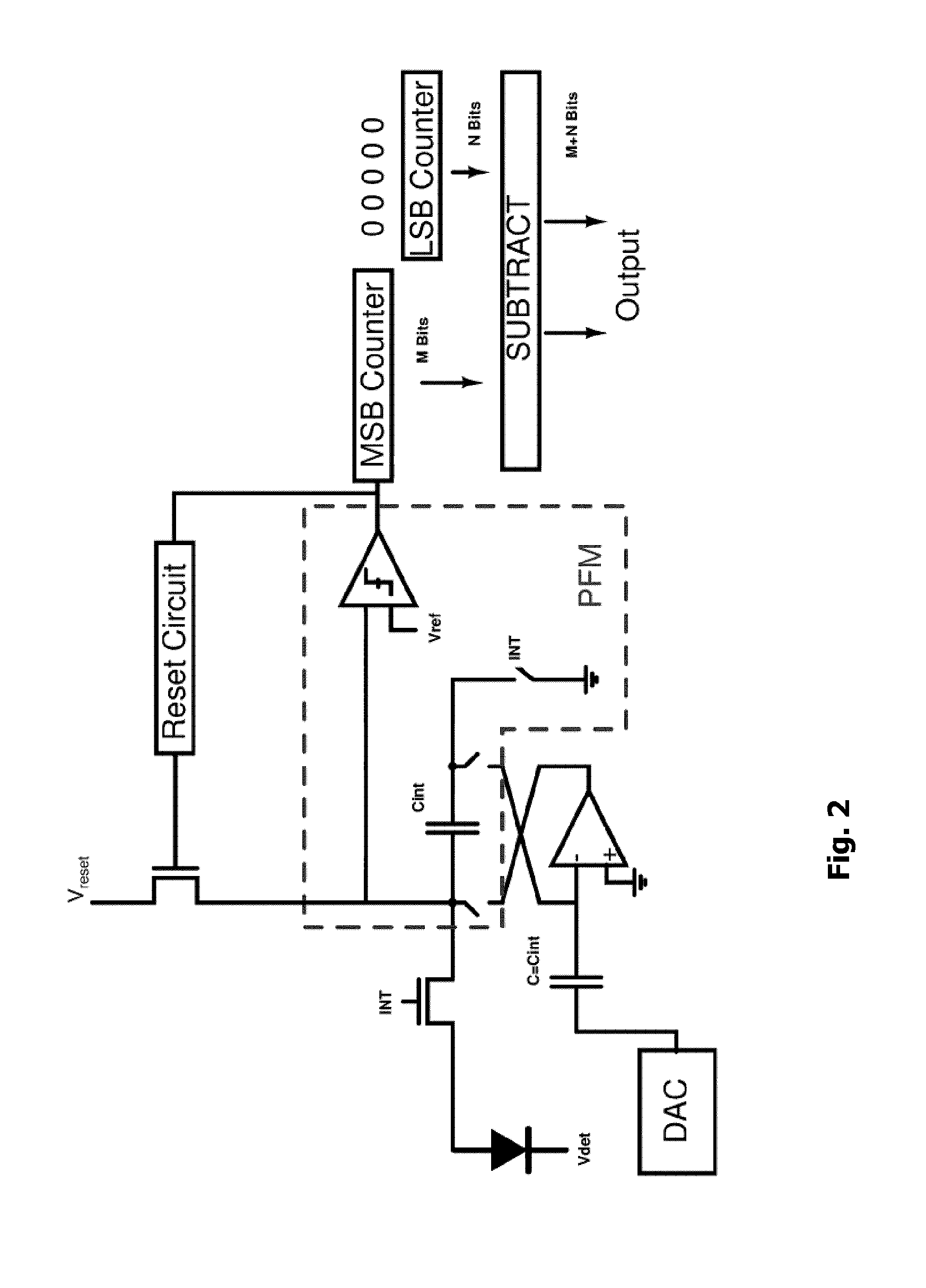
Self-reset asynchronous pulse frequency modulated droic with extended counting and having reduced quantization noise
InactiveUS20150015759A1Quantization noise is very lowLower frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorIntegrator
The present invention proposes a CMOS sensor pixel with a pulse frequency modulated digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) comprising a photon sensitive element for receiving a plurality of photons and providing a charge signal indicative of the received photons, an integration capacitor connected to said photon sensitive element for determining a cumulative signal based on the charge signal for a certain integration time and producing an integrator output signal based on the cumulative signal and a comparator connected to the integrator for producing a comparator output signal. Each of said pixels further comprises a DAC that switches at each clock cycle following the end of an integration time and two counters respectively counting nunber of resets of said integration capacitor and voltage difference between an integrator output residue signal and a reference voltage of said comparator.
Owner:SABANCI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com