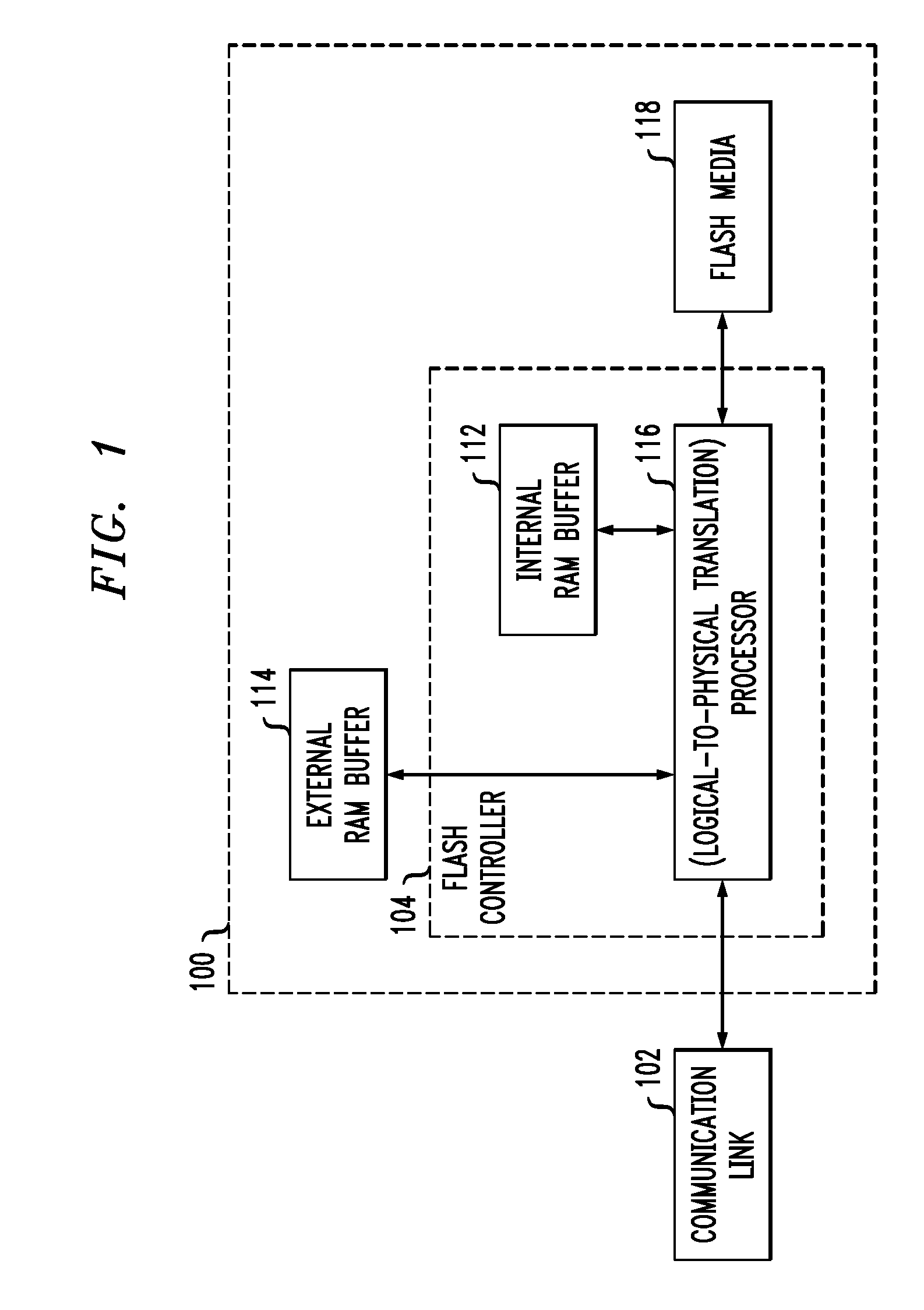
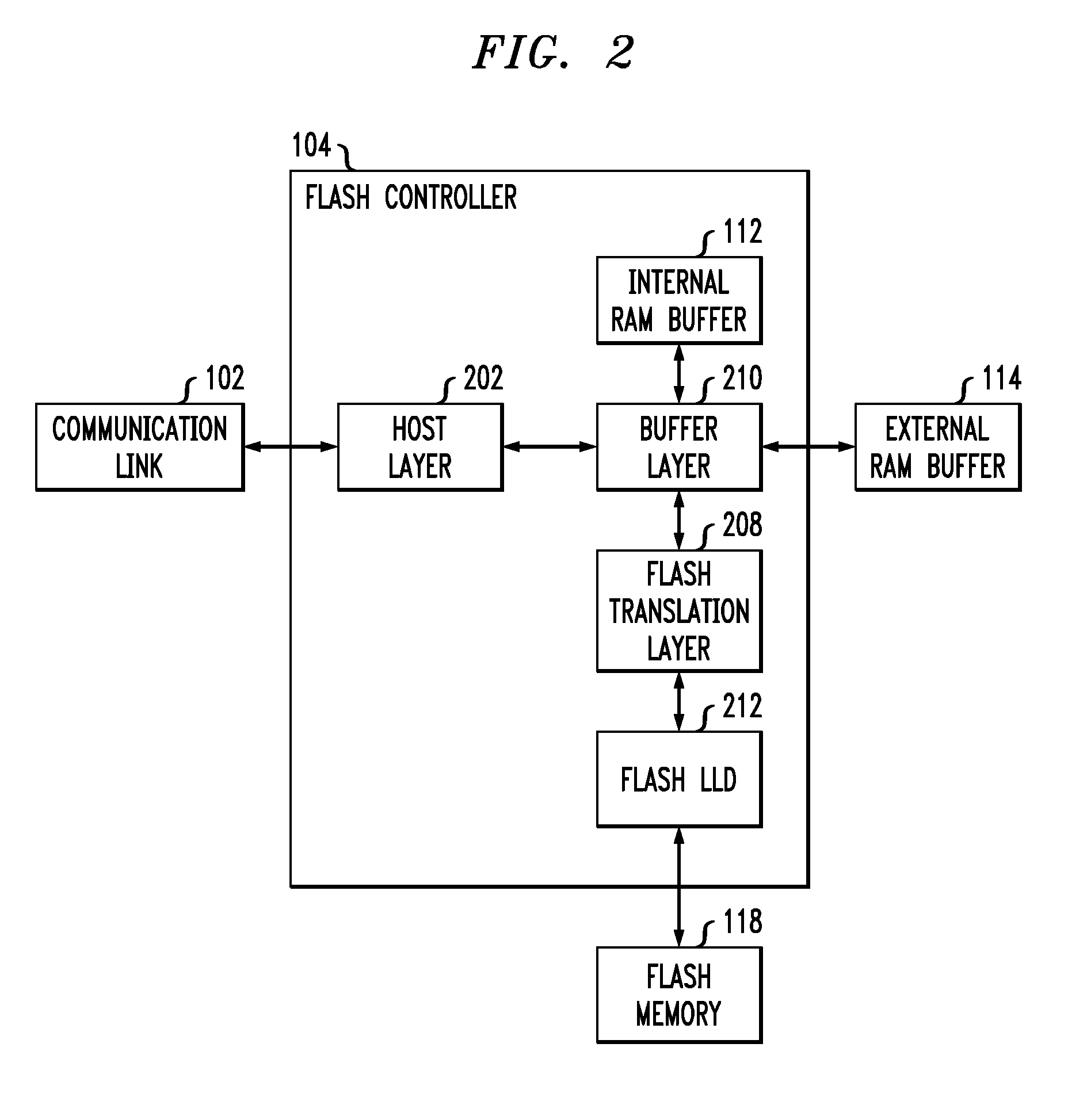
Patents
Literature
2080 results about "Address mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
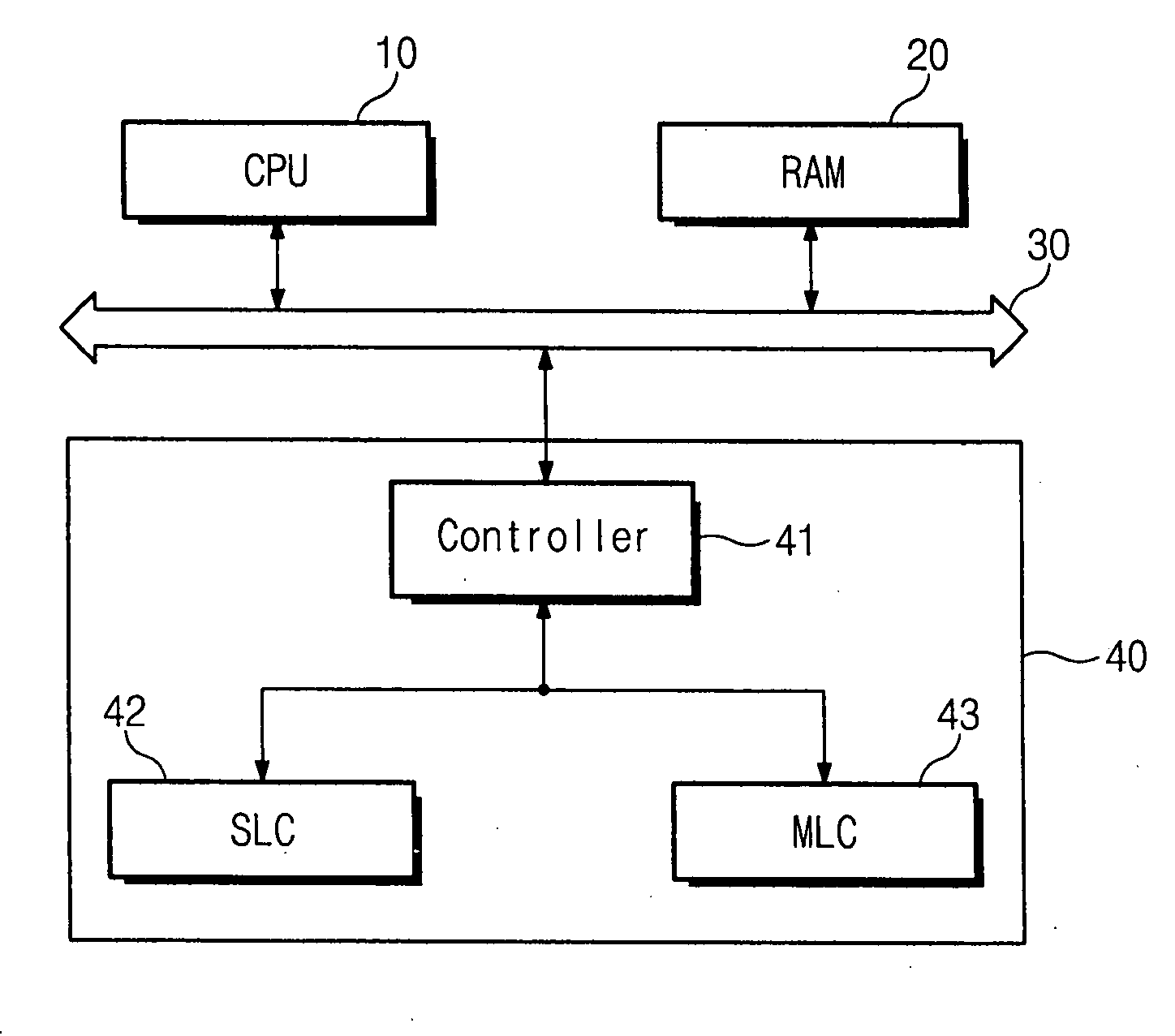
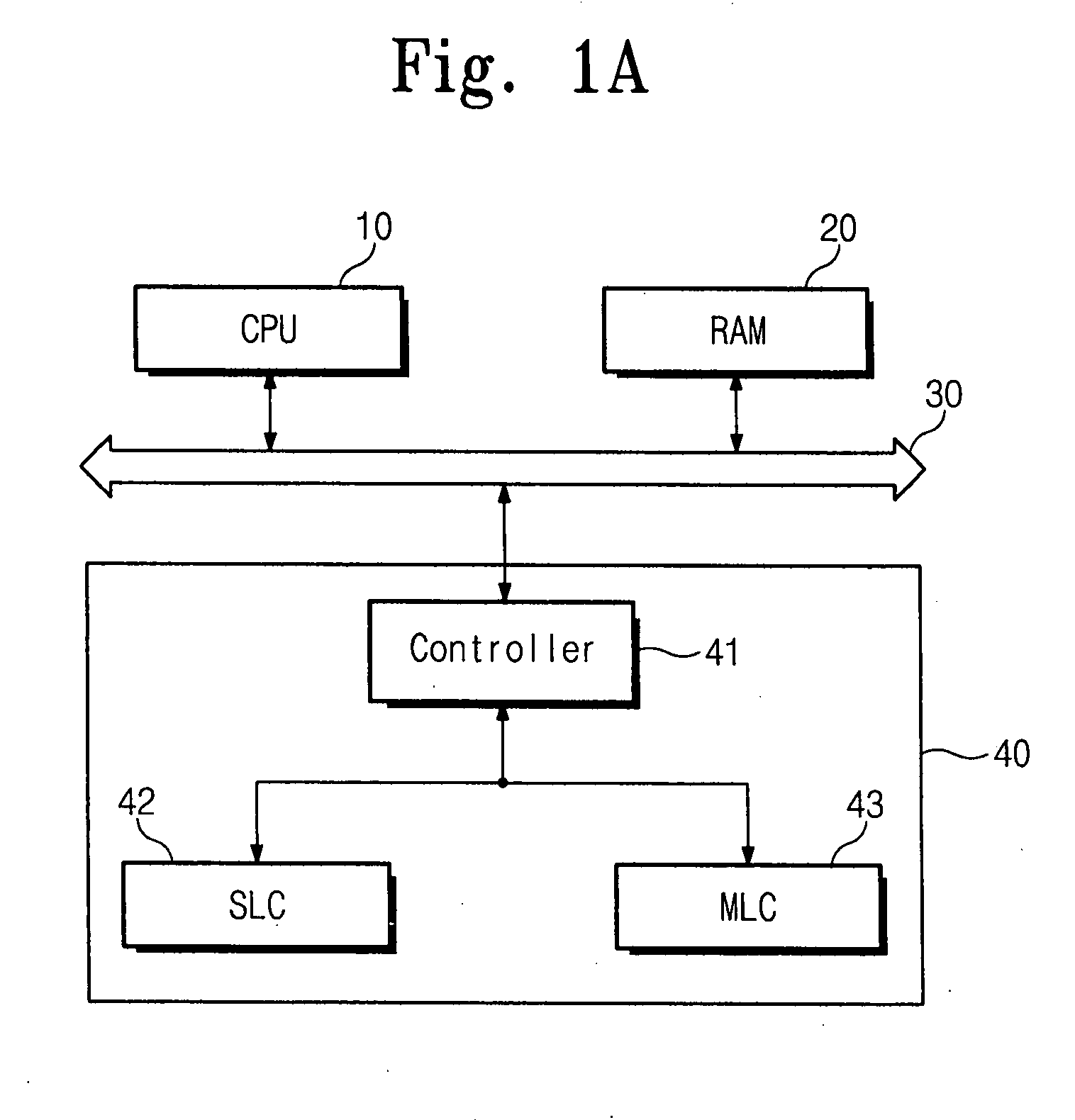
Flash memory device with multi-level cells and method of writing data therein
ActiveUS20080104309A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti-level cellAddress mapping
In one aspect, a method of writing data in a flash memory system is provided. The flash memory system forms an address mapping pattern according to a log block mapping scheme. The method includes determining a writing pattern of data to be written in a log block, and allocating one of SLC and MLC blocks to the log block in accordance with the writing pattern of the data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Locking technique for control and synchronization
InactiveUS6973549B1Digital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsFast pathLocking mechanism
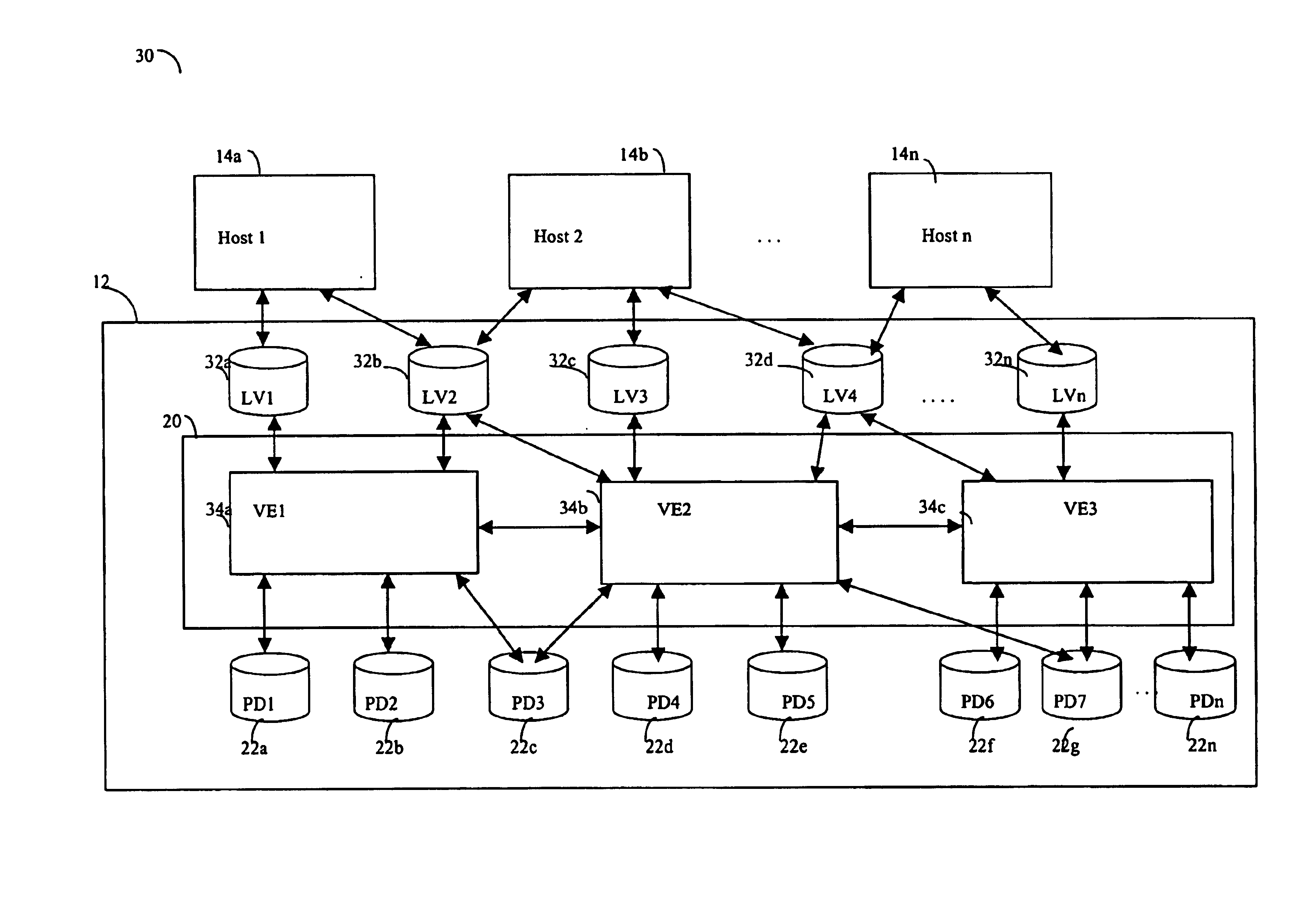
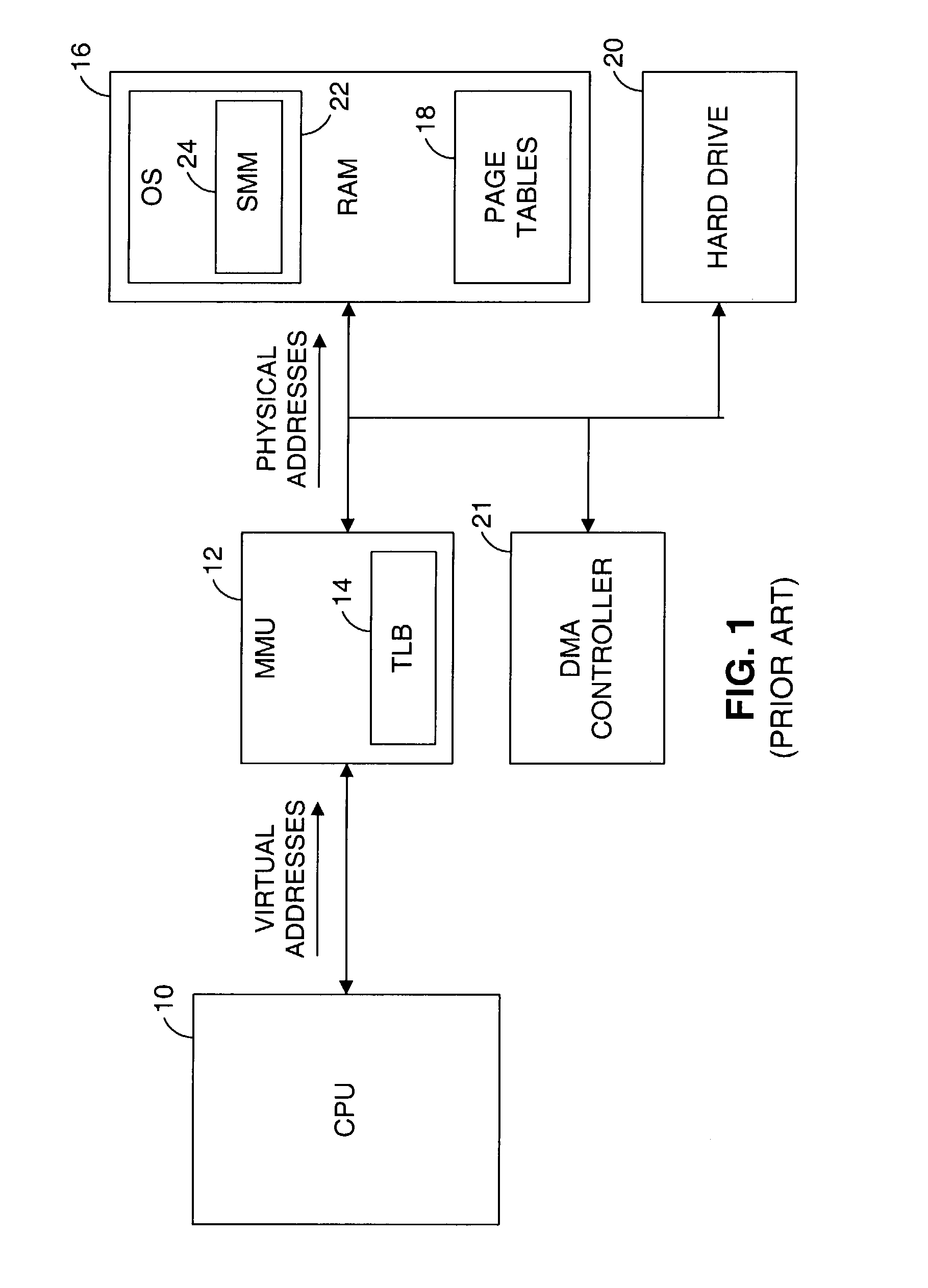
Described are techniques used in a computer system for handling data operations to storage devices. A switching fabric includes one or more fast paths for handling lightweight, common data operations and at least one control path for handling other data operations. A control path manages one or more fast paths. The fast path and the control path are utilized in mapping virtual to physical addresses using mapping tables. The mapping tables include an extent table of one or more entries corresponding to varying address ranges. The size of an extent may be changed dynamically in accordance with a corresponding state change of physical storage. The fast path may cache only portions of the extent table as needed in accordance with a caching technique. The fast path may cache a subset of the extent table stored within the control path. A set of primitives may be used in performing data operations. A locking mechanism is described for controlling access to data shared by the control paths.
Owner:IBM CORP
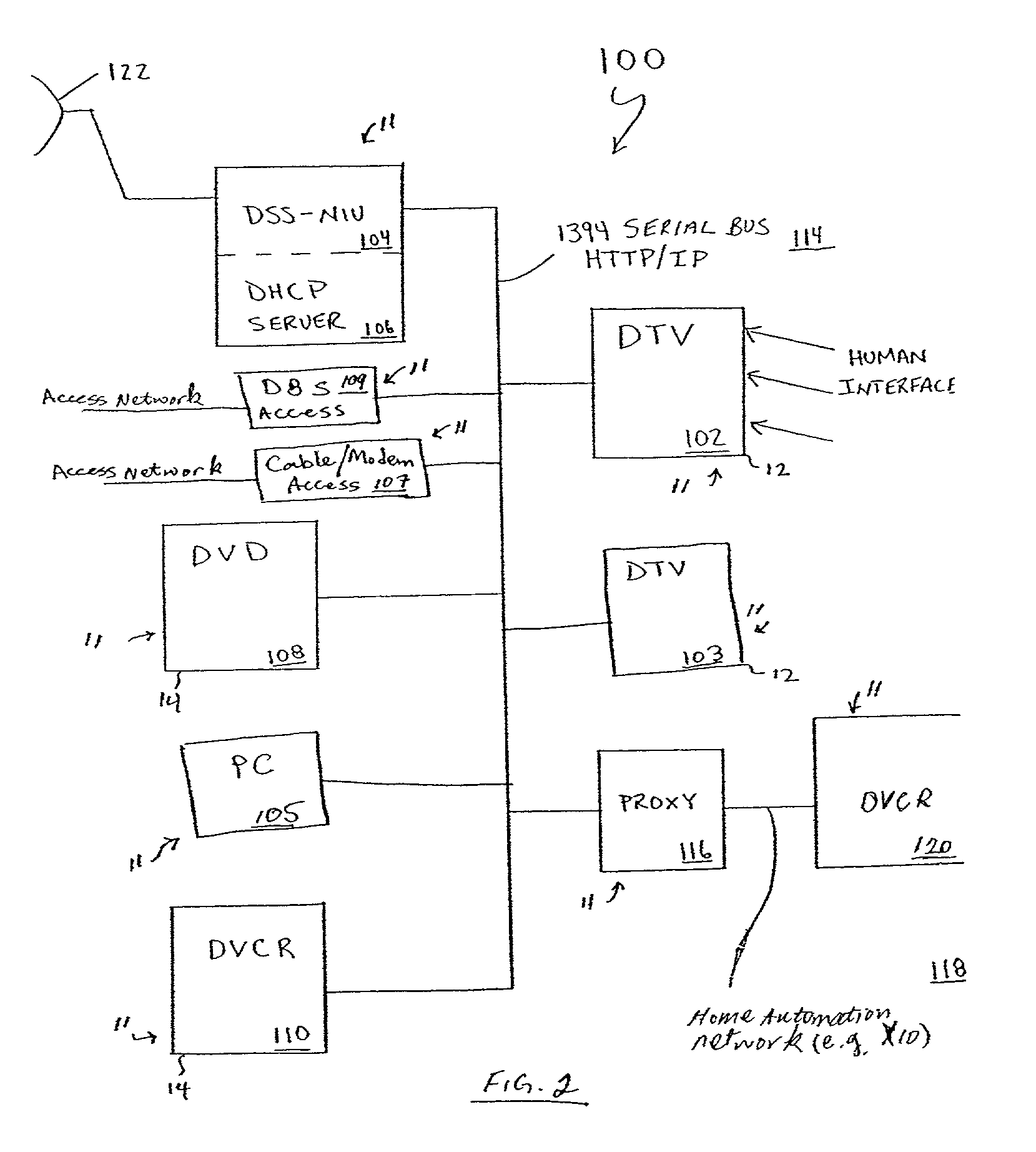
Architecture for home network on world wide web with private-public IP address/URL mapping
InactiveUS7349967B2Special service provision for substationTelevision system detailsIp addressNetwork on
A method for providing user interfaces in a first network to a remote access device, the first network including interconnected first devices and at least one interface device for connecting the first network to a second network. The remote access device establishes communication with the second network and sends a request to the interface device for accessing the first network; at least one of the first devices obtains information from one or more of the first devices, and generates a user interface description including at least one reference associated with the device information, the reference including an external address such that the device is accessible from the remote access device; the interface device sends the user interface description to the remote access device; and the remote access device displays a user interface based on the user interface description.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
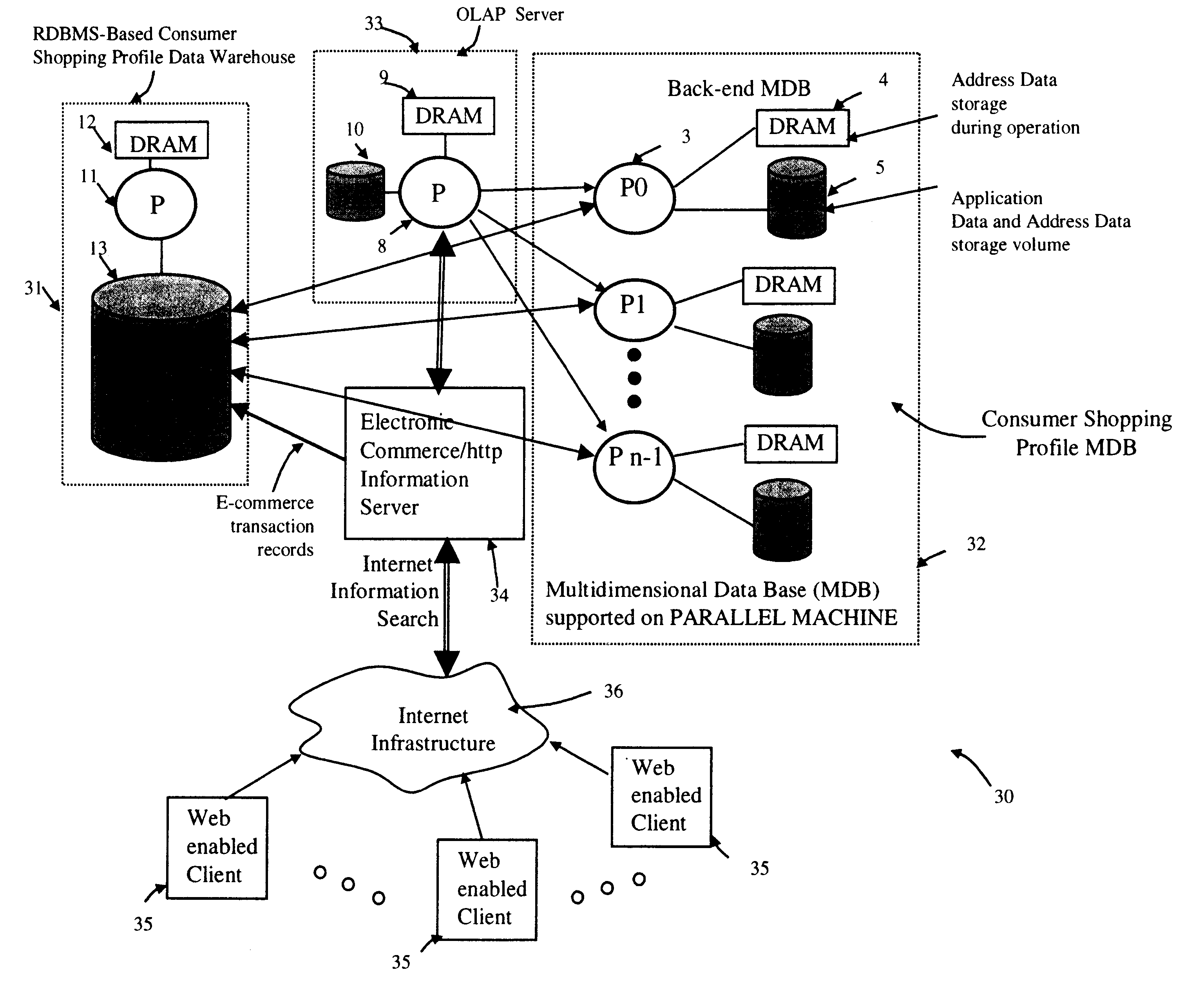
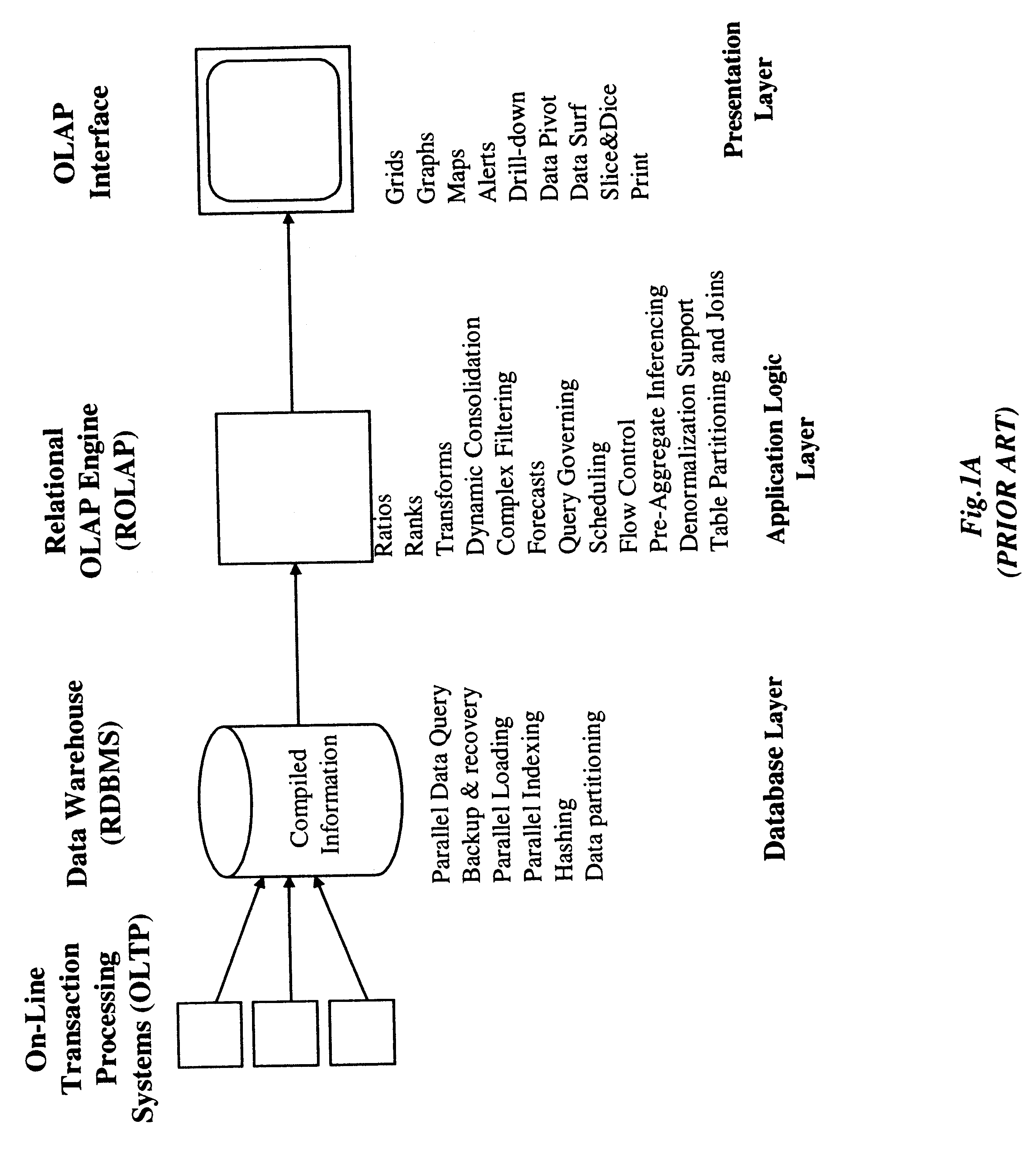
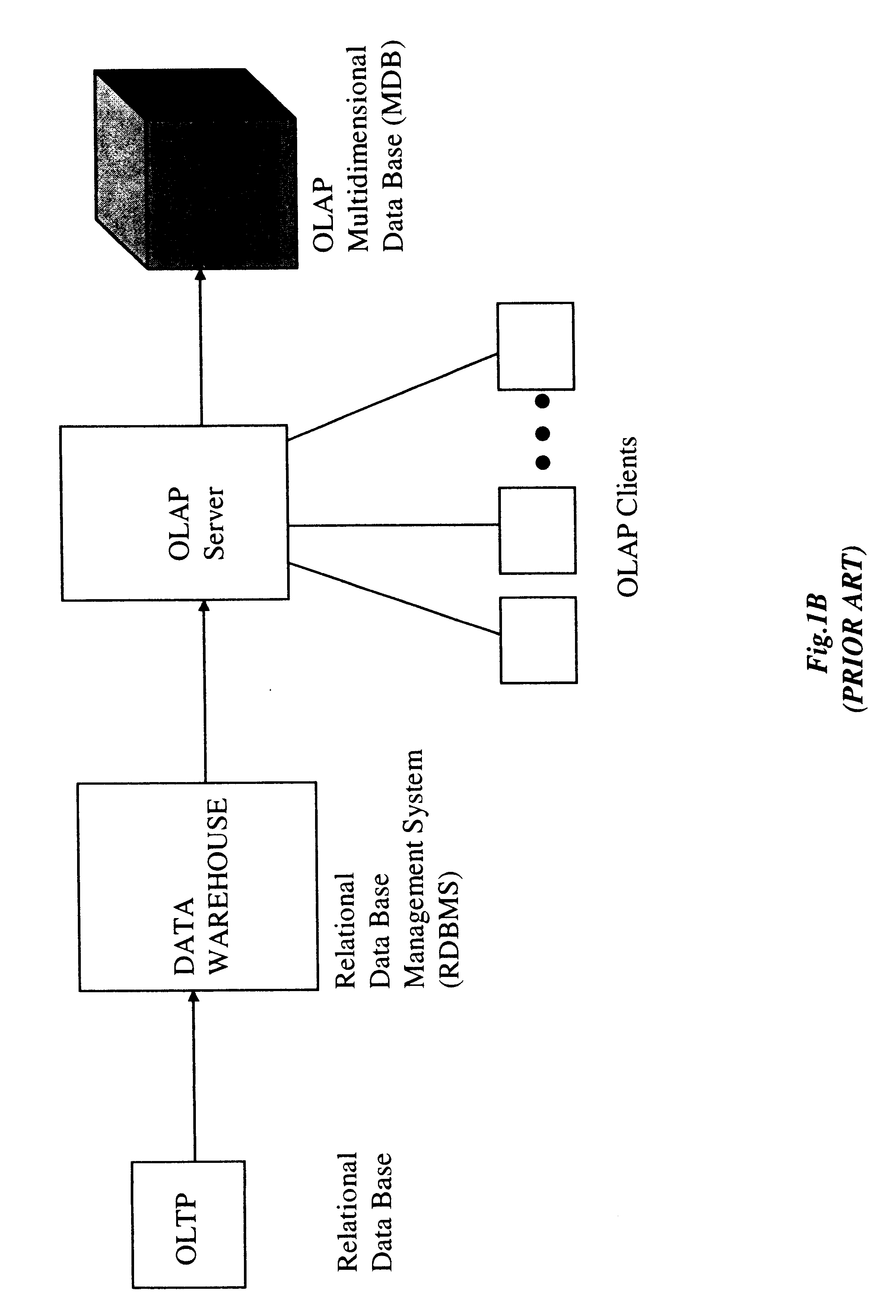
Method of and system for managing multi-dimensional databases using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping processes on integer-encoded business dimensions
InactiveUS6408292B1Improve performanceFast knowledge discoveryData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesData warehouseThe Internet
An improved method of and a system for managing data elements in a multidimensional database (MDB) supported upon a parallel computing platform using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping (i.e. translation) processes on integer-encoded business dimensions. The parallel computing platform has a plurality of processors and one or more storage volumes for physically storing data elements therein at integer-encoded physical addresses in Processor Storage Space (i.e. physical address space in the one or more storage volumes associated with a given processor). The location of each data element in the MDB is specified in MDB Space by integer-encoded business dimensions associated with the data element. A data loading mechanism loads the integer-encoded business dimensions and associated data elements from a data warehouse. The address data mapping mechanism performs a two part address mapping processing. The first step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element to a given processor identifier (which uniquely identifies the processor amongst the plurality of processors of the parallel computing platform). The second step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element into an integer-encoded physical data storage address in Processor Storage Space associated with the processor identified by the processor identifier generated in the first mapping step. The mapping performed in this second step is based upon size of the integer encoded business dimensions. The data management mechanism manages the data elements stored in the storage volumes using the integer-encoded data storage addresses generated during the two-part address data mapping process. The use of modular-arithmetic functions in the two-part address data mapping mechanism ensures that the data elements in the MDB are uniformly distributed among the plurality of processors for balanced loading and processing. The present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDB.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
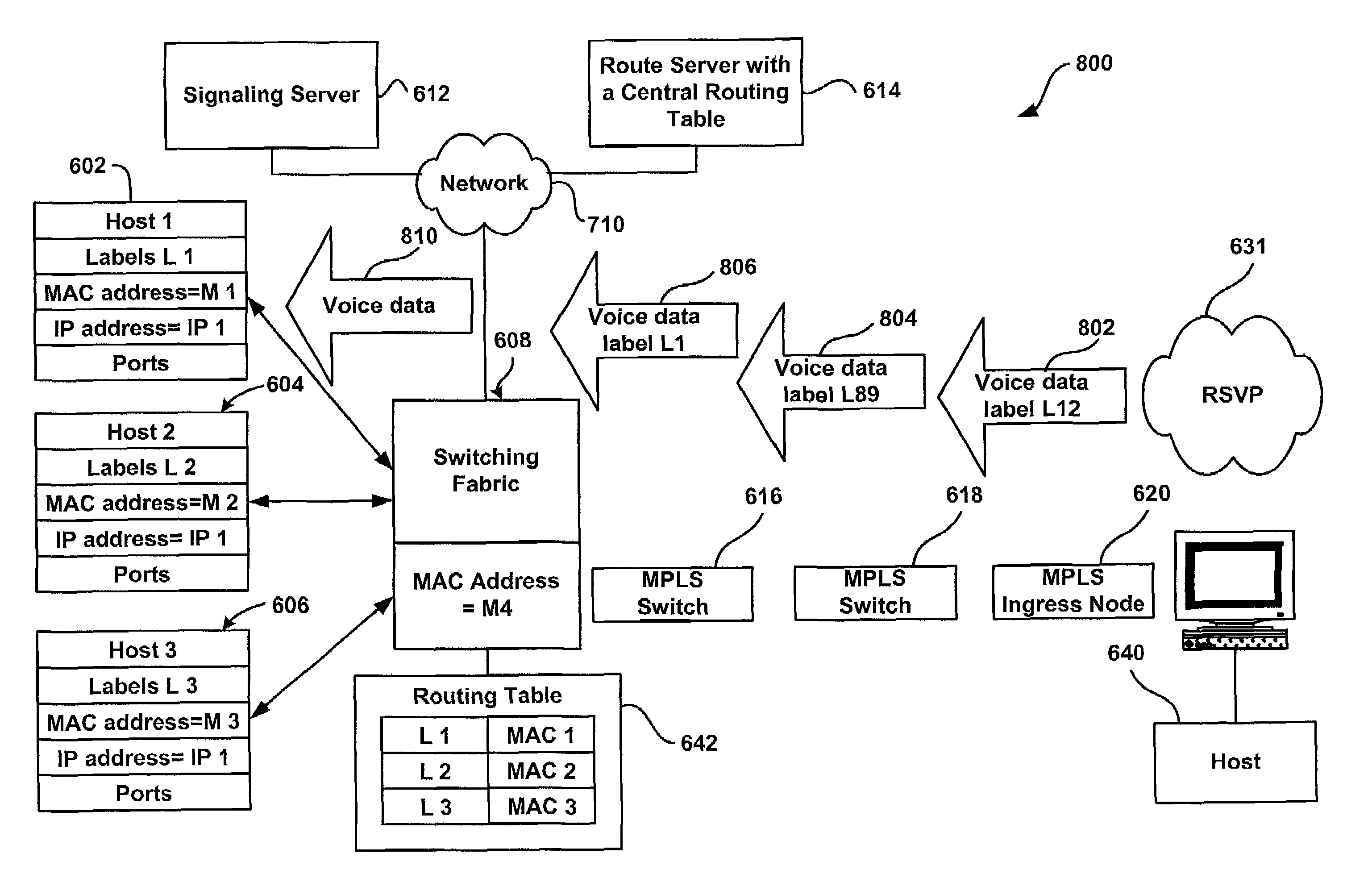
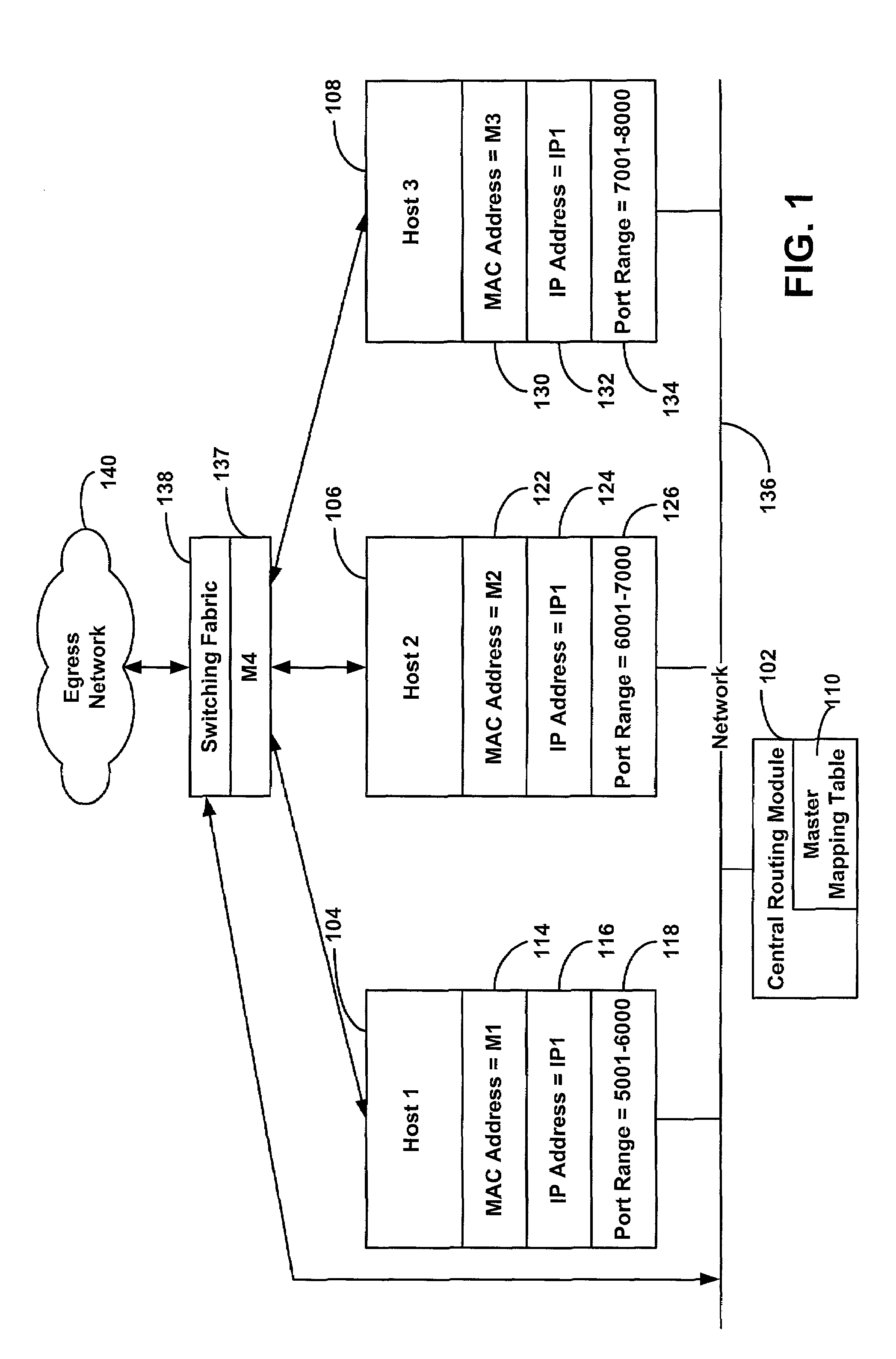
System and method for providing masquerading using a multiprotocol label switching
A system and method for transmitting information between a source host and a destination host. A source host generates a message and forwards the message via a label switched path to the destination host so that when a central routing module receives the message, the message includes a label. A central routing module establishes a local master mapping table including a plurality of physical addresses, and each of the plurality of physical addresses is associated with a unique identifier such as a label. When a switch egress module receives the message with the label, the switch egress module determines a physical address associated with the label, maps the physical address to the message, and forwards the message to the destination host associated with the label.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
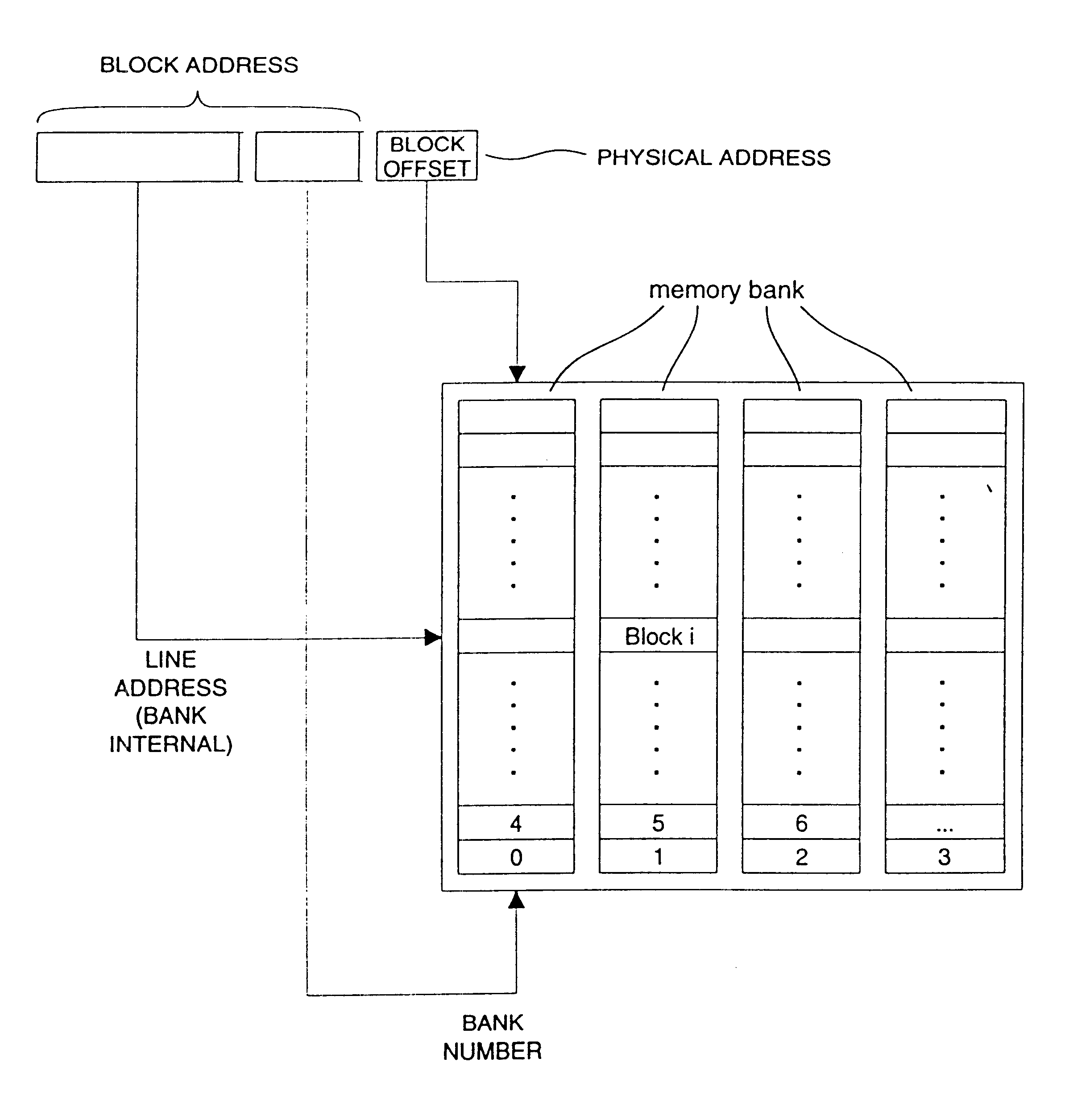
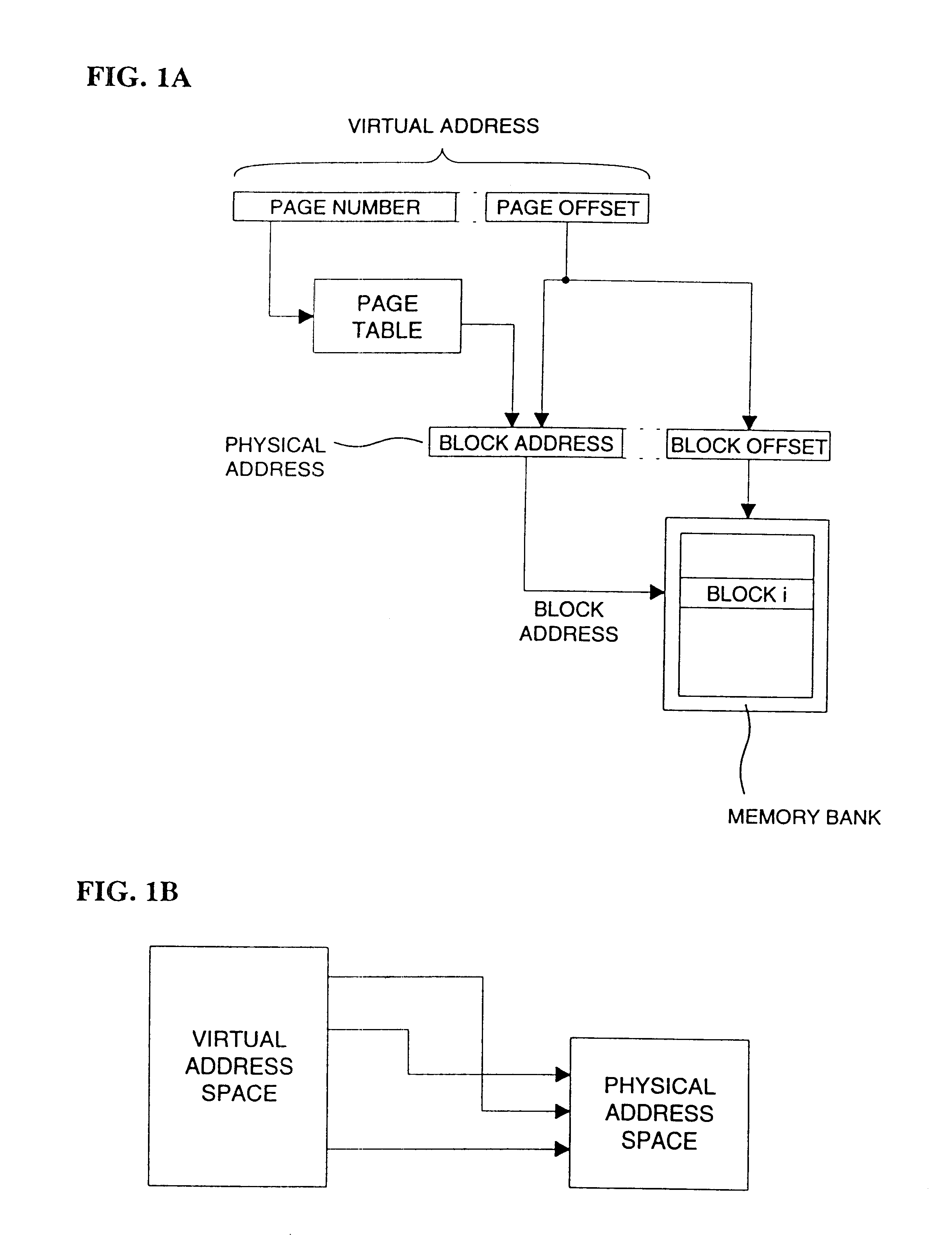
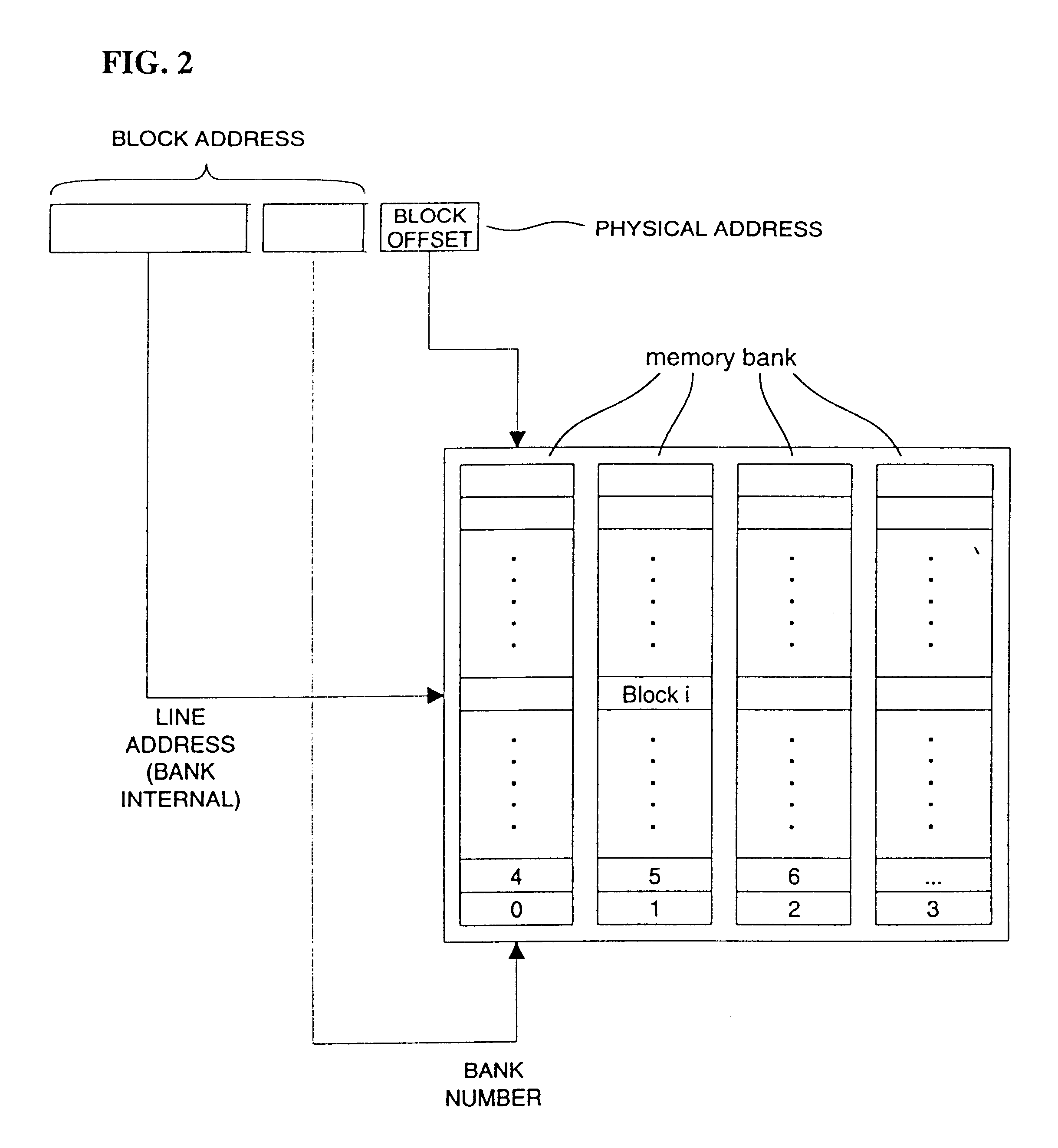
Address mapping for system memory
InactiveUS6381668B1Flexible choiceEasy to changeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationMemory bankParallel computing
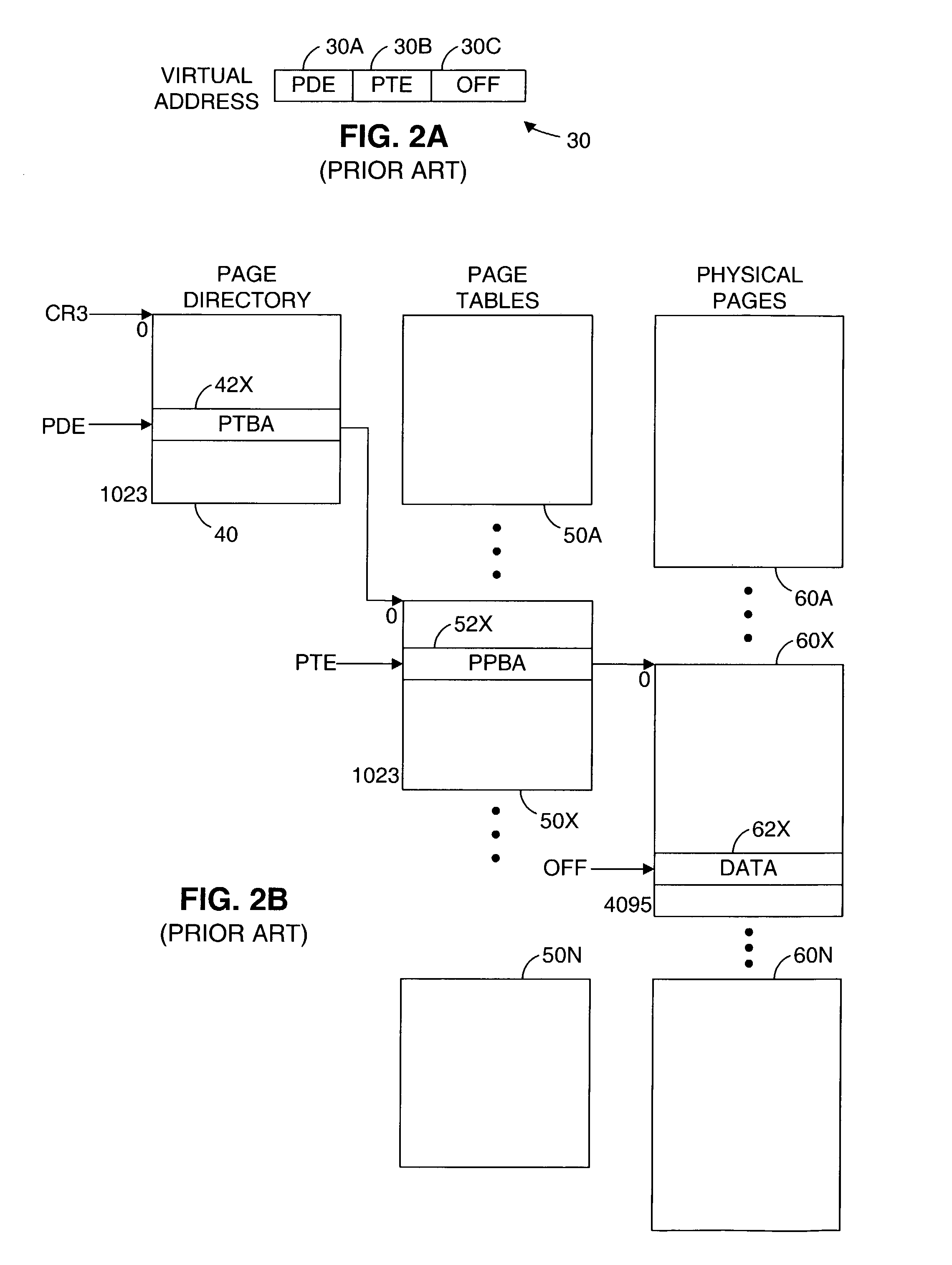
For optimizing access to system memory having a plurality of memory banks, interleaving can be used when storing data so that data sequences are distributed over memory banks. The invention introduces an address-mapping method applying a table lookup procedure so that arbitrary, non-power-of-two interleave factors and numbers of memory banks are possible for various strides.
Owner:TWITTER INC
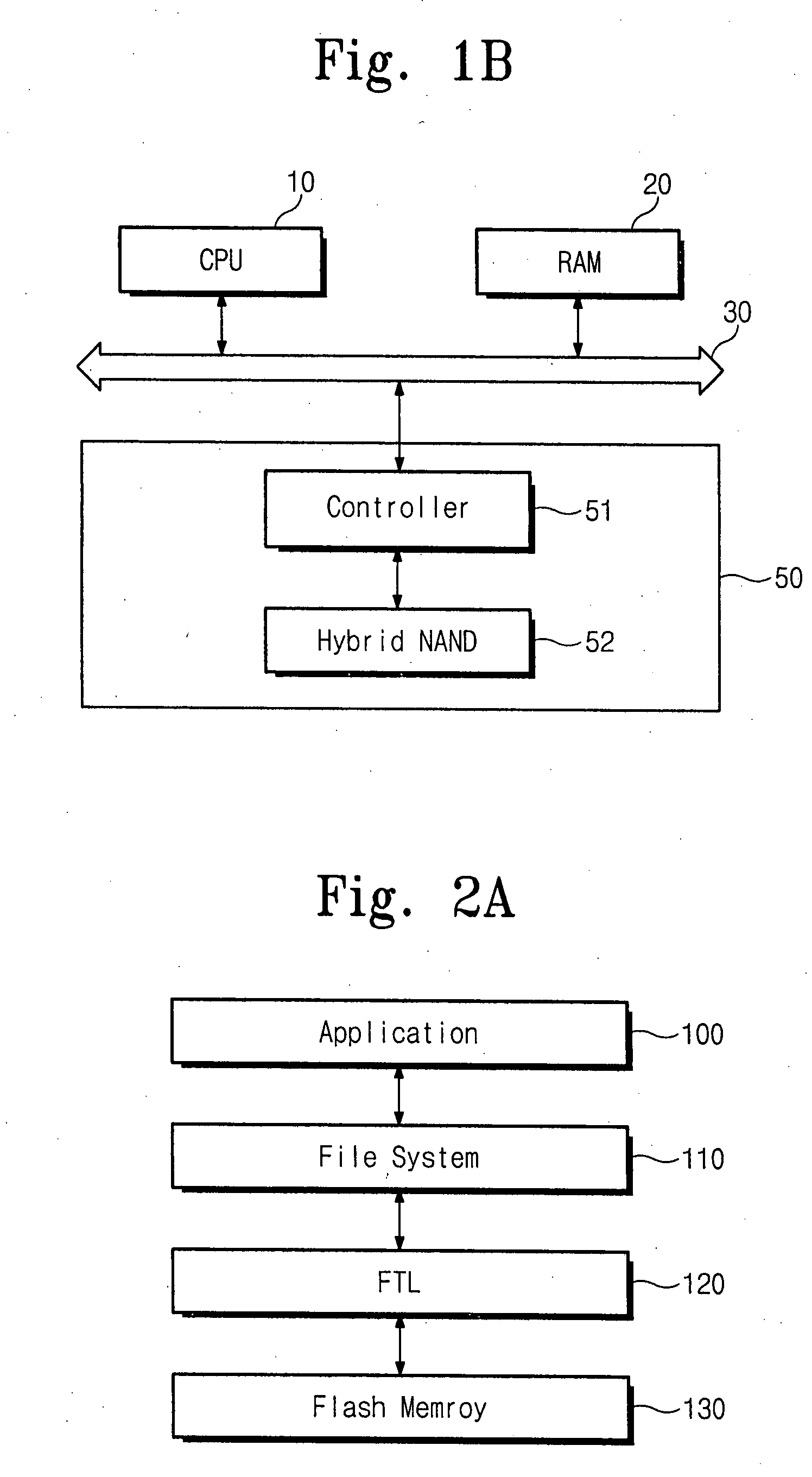
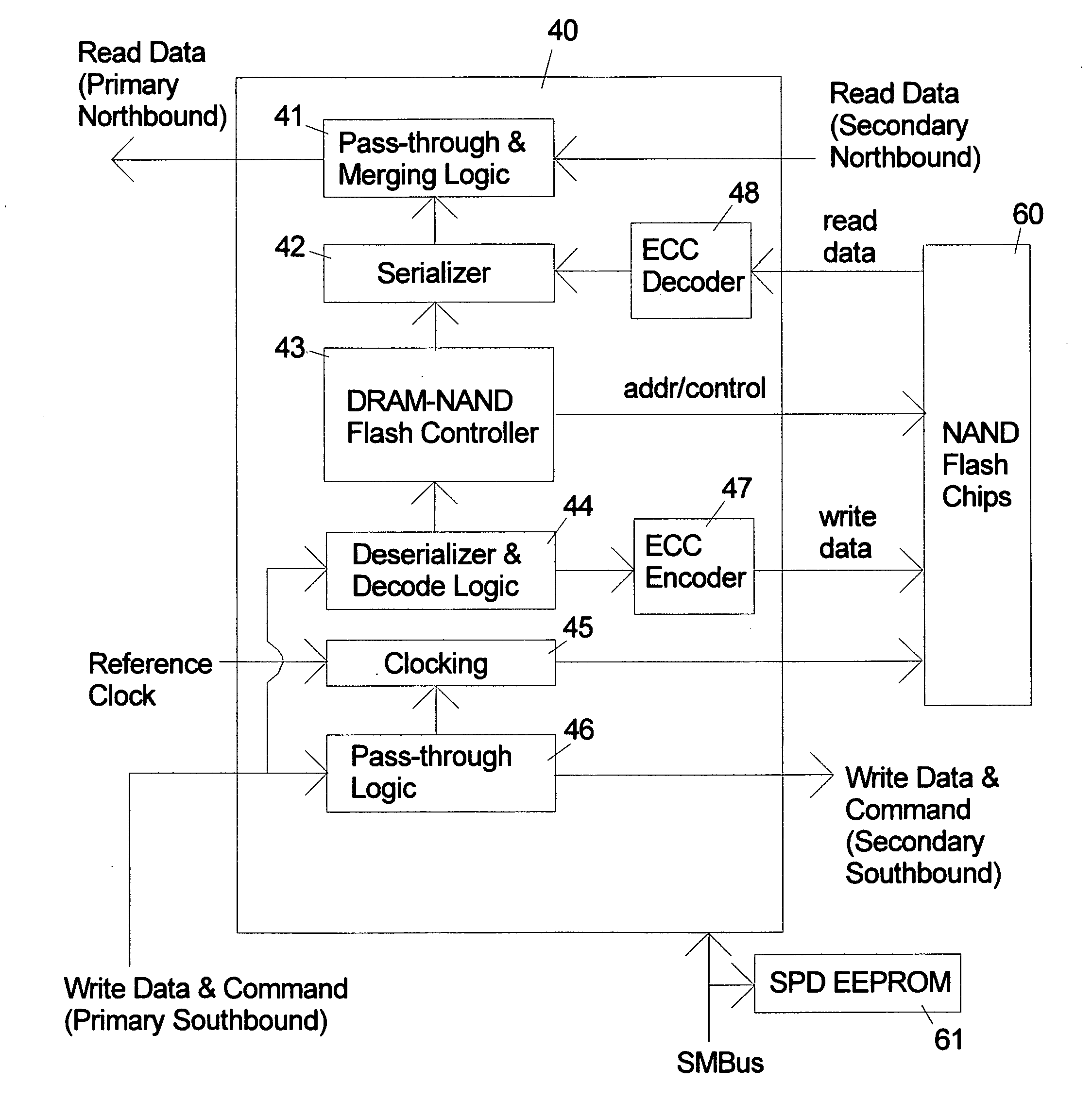
NAND flash module replacement for DRAM module
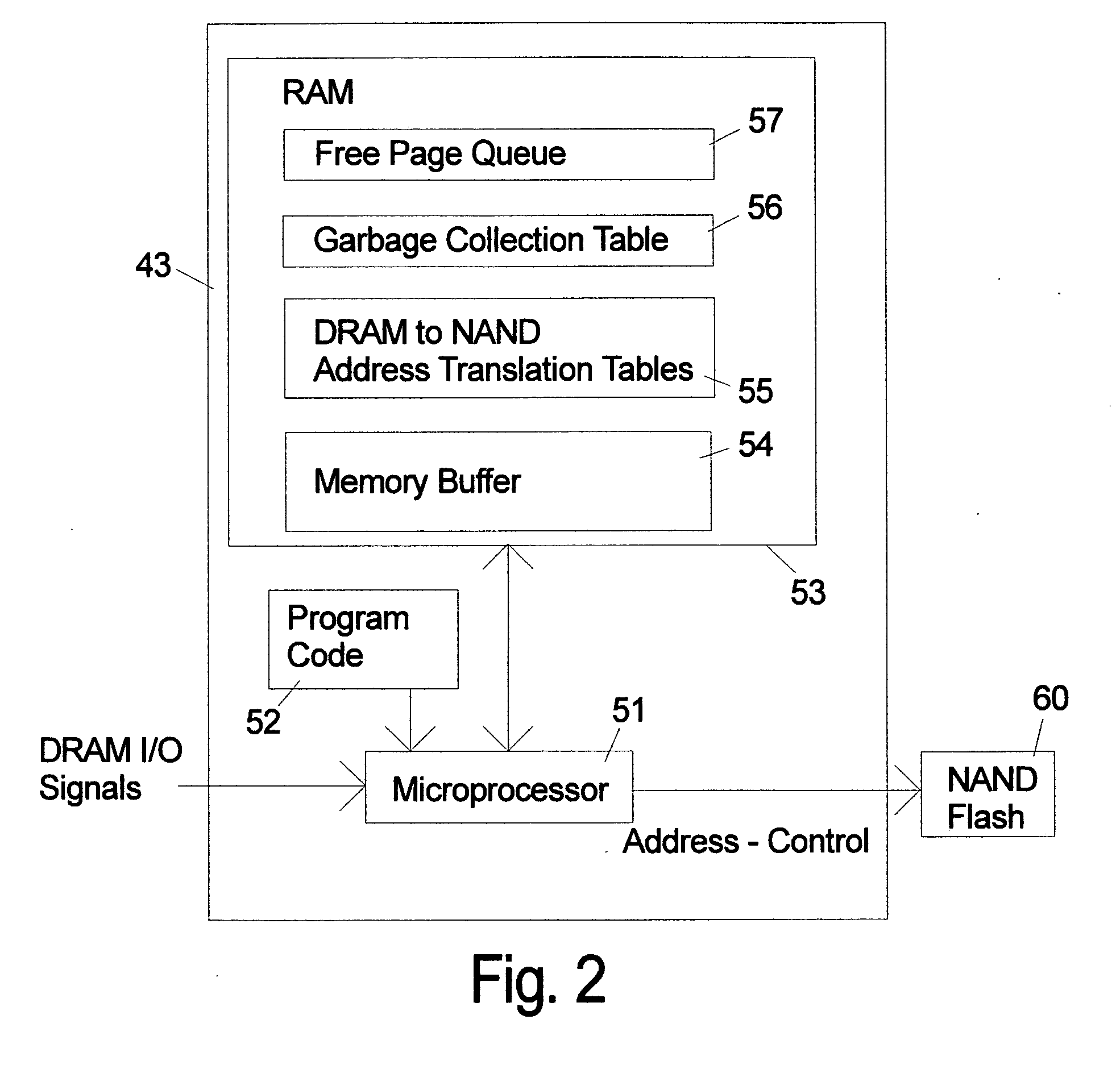
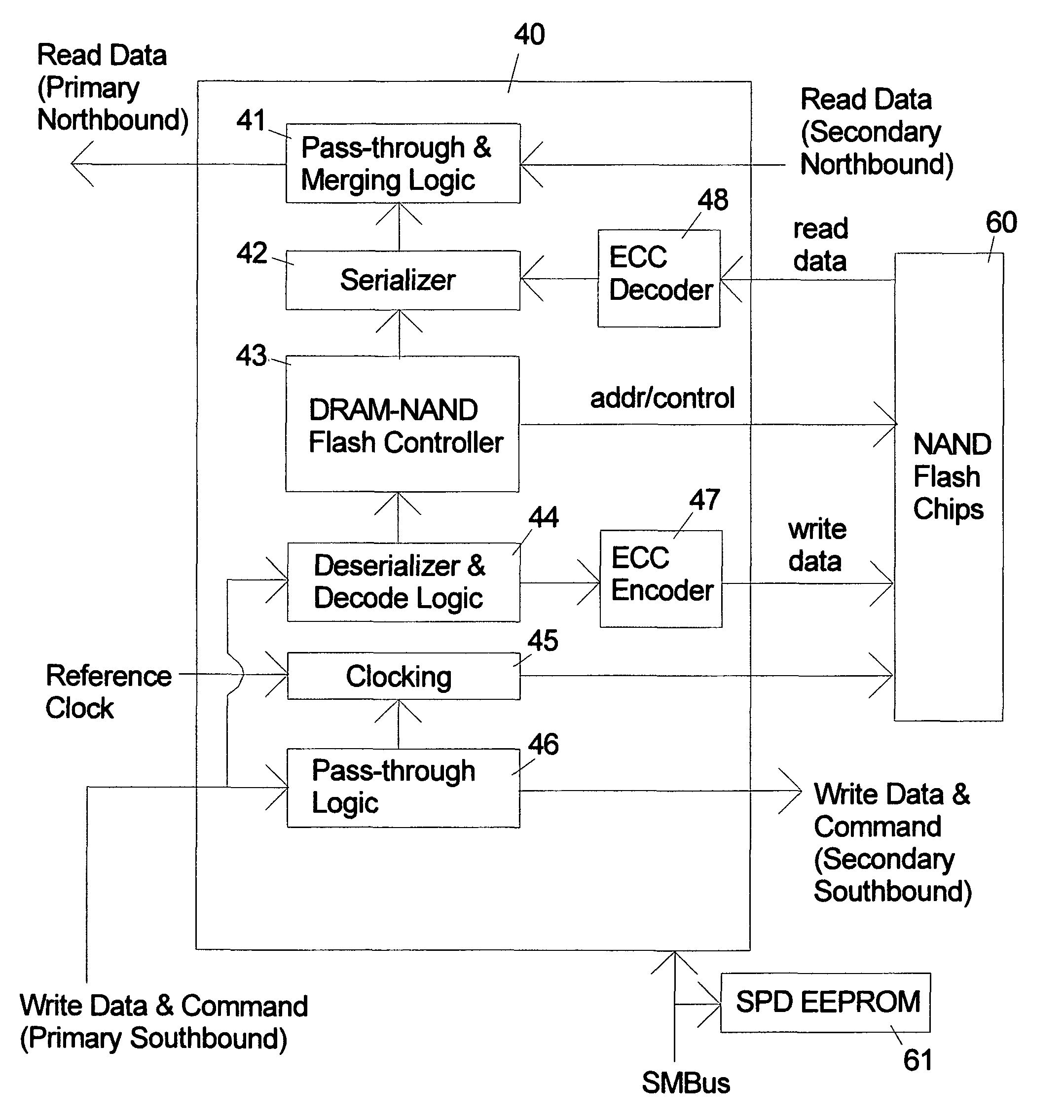
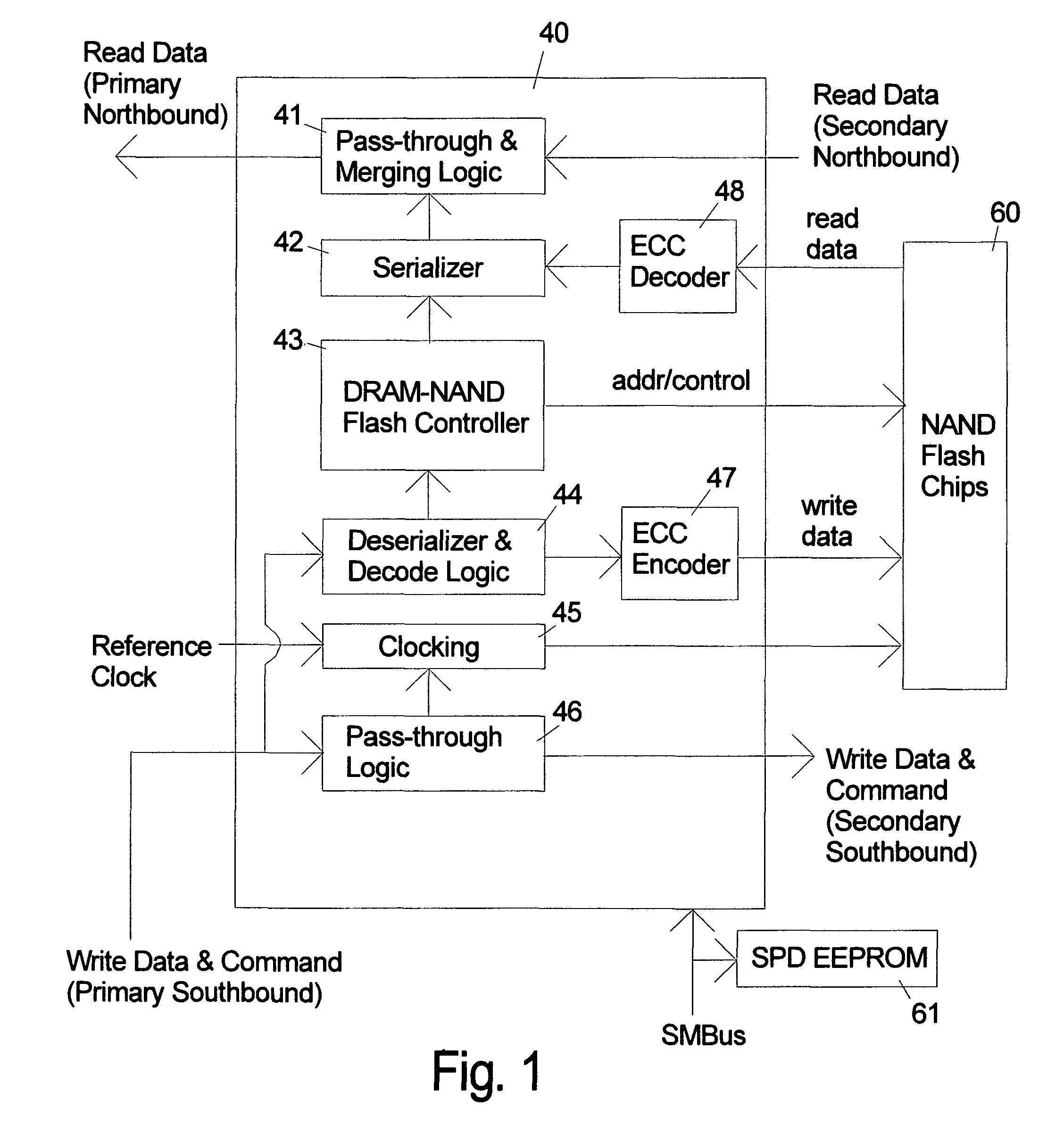
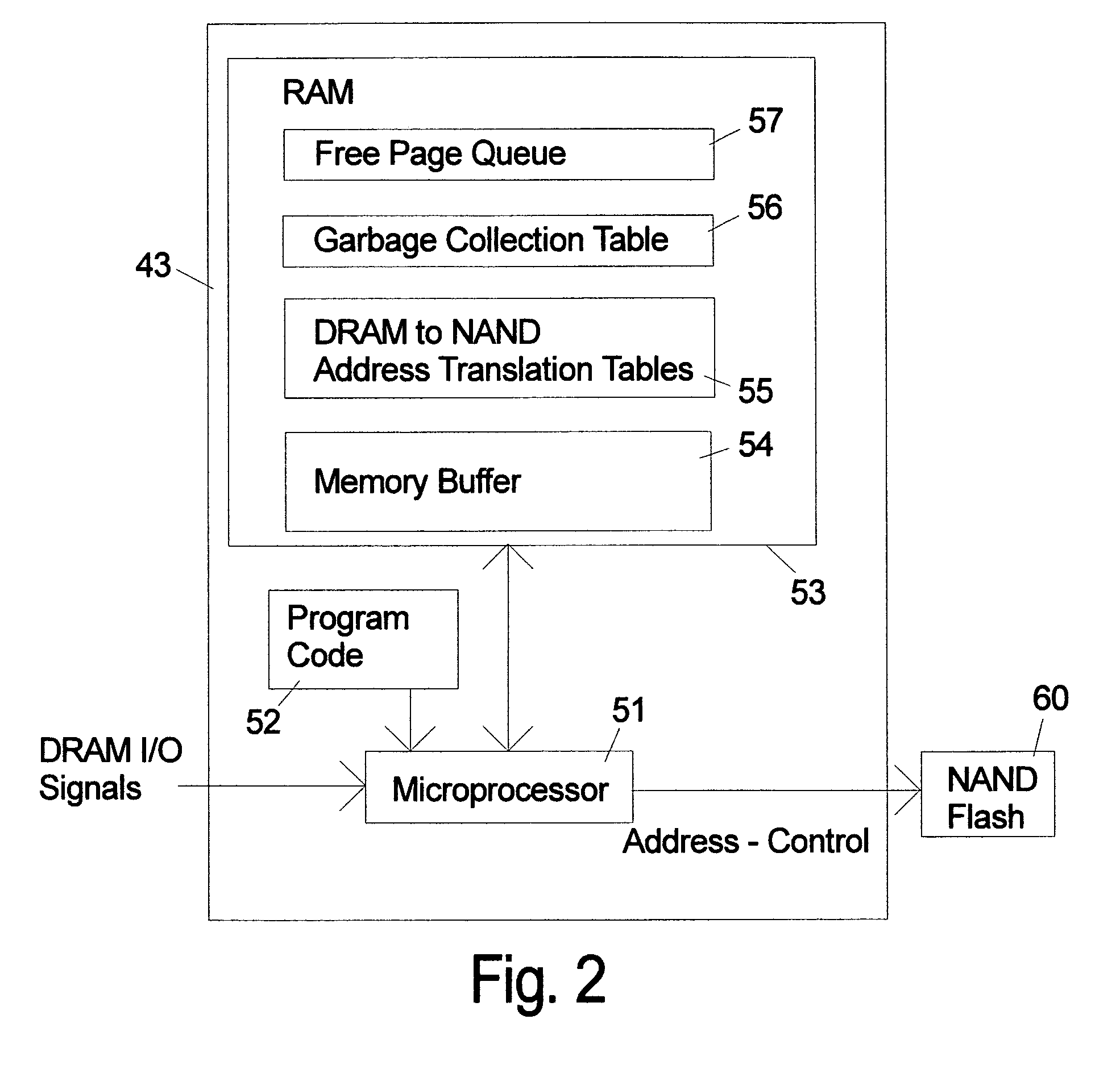
ActiveUS20090157950A1Most efficientAddressing slow performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl signalFlash memory controller
An electronic memory module according to the invention provides non-volatile memory that can be used in place of a DRAM module without battery backup. An embodiment of the invention includes an embedded microprocessor with microcode that translates the FB-DIMM address and control signals from the system into appropriate address and control signals for NAND flash memory. Wear-leveling, bad block management, garbage collection are preferably implemented by microcode executed by the microprocessor. The microprocessor, additional logic, and embedded memory provides the functions of a flash memory controller. The microprocessor memory preferably contains address mapping tables, free page queue, and garbage collection information.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Managing Bad Blocks In Flash Memory For Electronic Data Flash Card
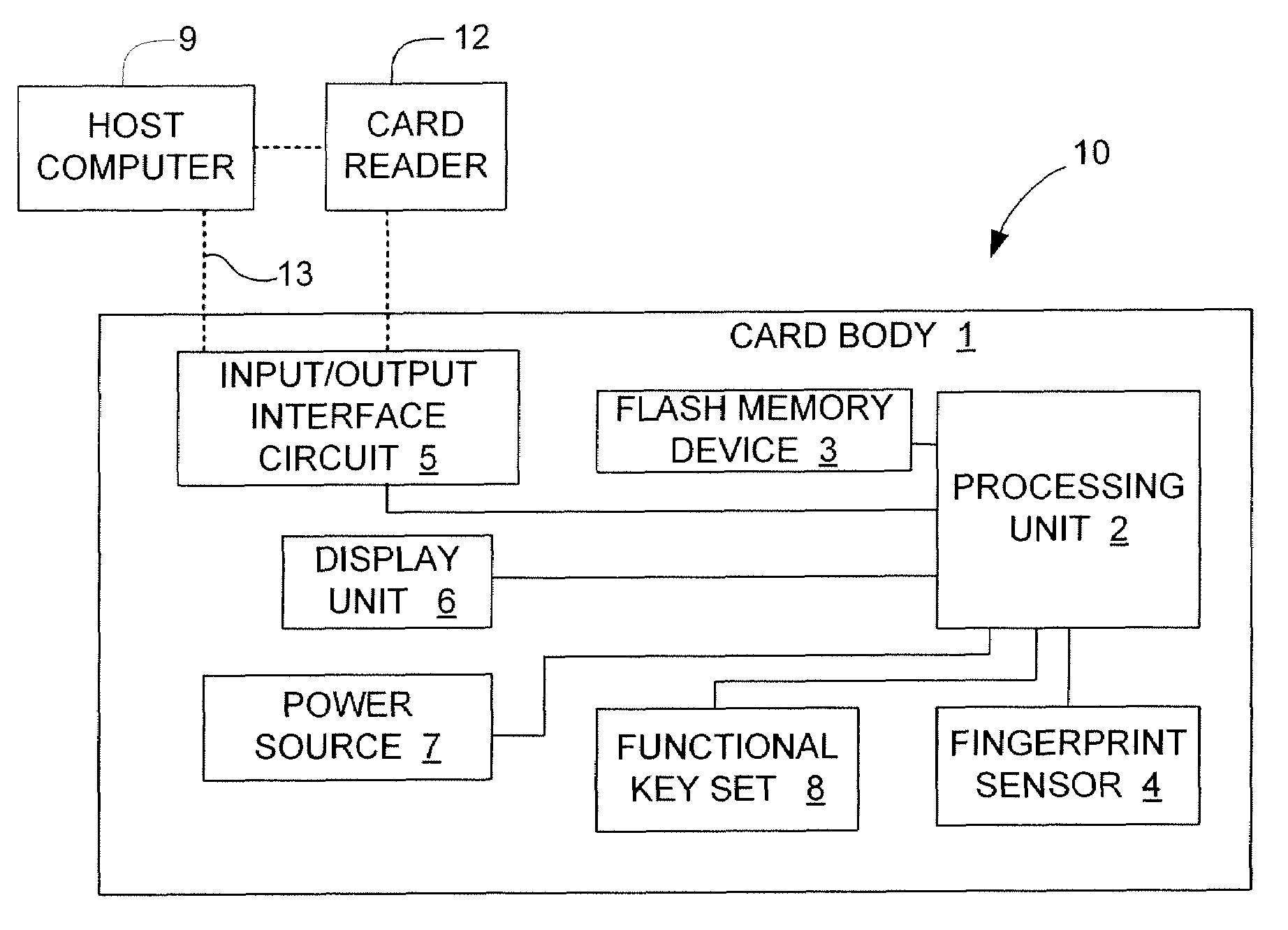
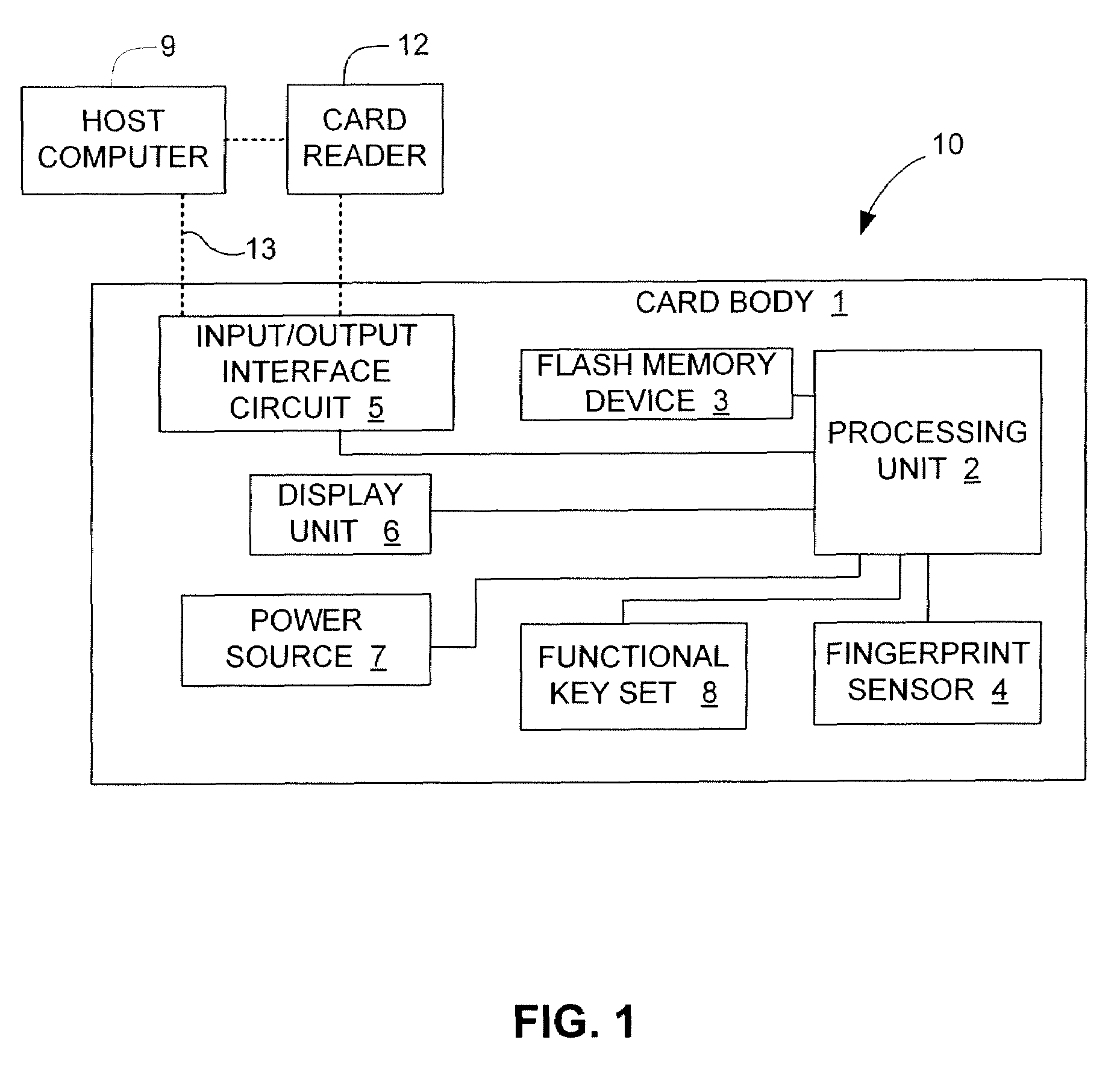
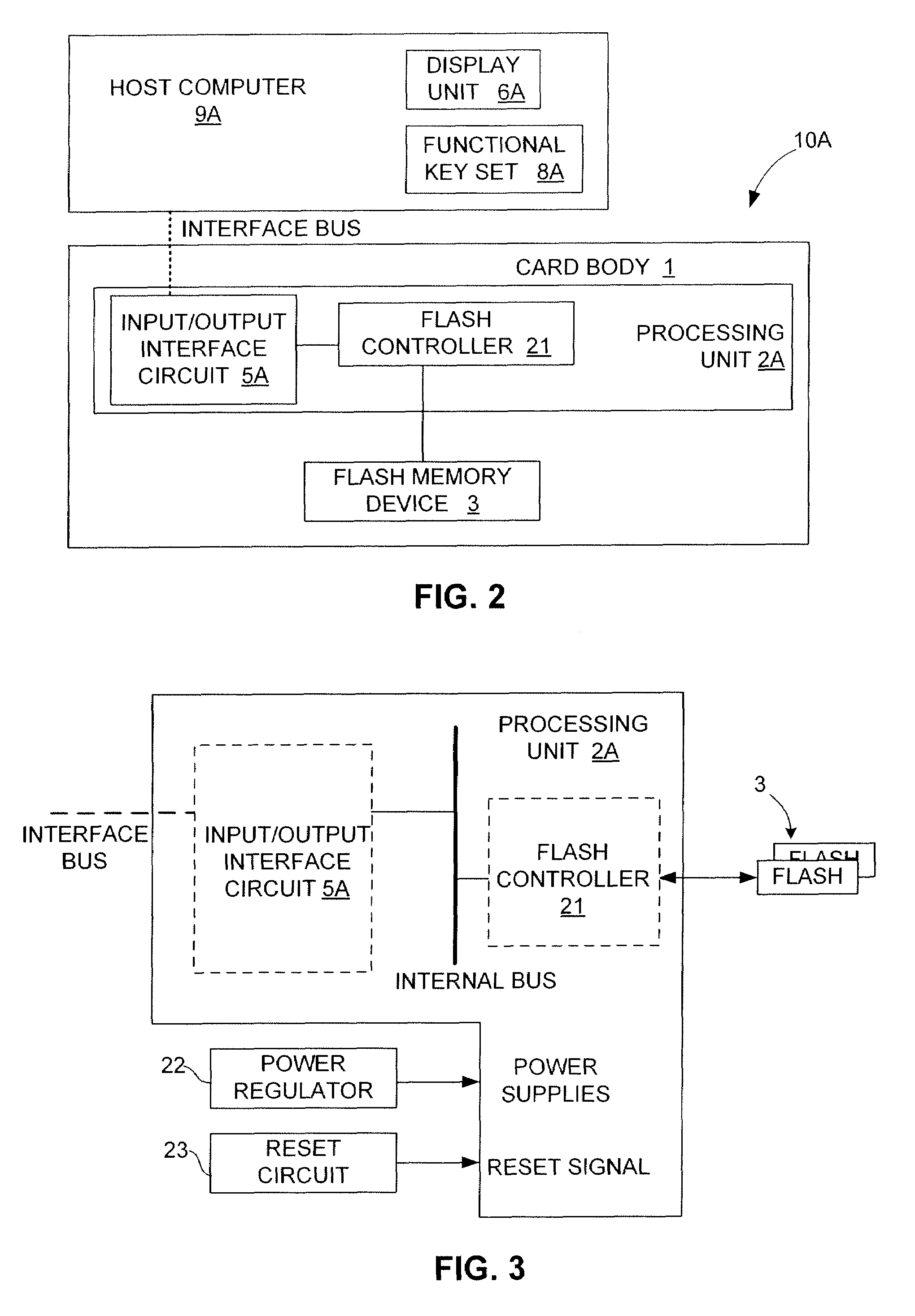
InactiveUS20070283428A1Reduce search timeAvoid congestionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationLogical block addressingComputer access
An electronic data flash card accessible by a host computer, includes a flash memory controller connected to a flash memory device, and an input-output interface circuit activated to establish a communication with the host. In an embodiment, the flash card uses a USB interface circuit for communication with the host. A flash memory controller includes an arbitrator for mapping logical addresses with physical block addresses, and for performing block management operations including: storing reassigned data to available blocks, relocating valid data in obsolete blocks to said available blocks and reassigning logical block addresses to physical block addresses of said available blocks, finding bad blocks of the flash memory device and replacing with reserve blocks, erasing obsolete blocks for recycling after relocating valid data to available blocks, and erase count wear leveling of blocks, etc. Furthermore, each flash memory device includes an internal buffer for accelerating the block management operations.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
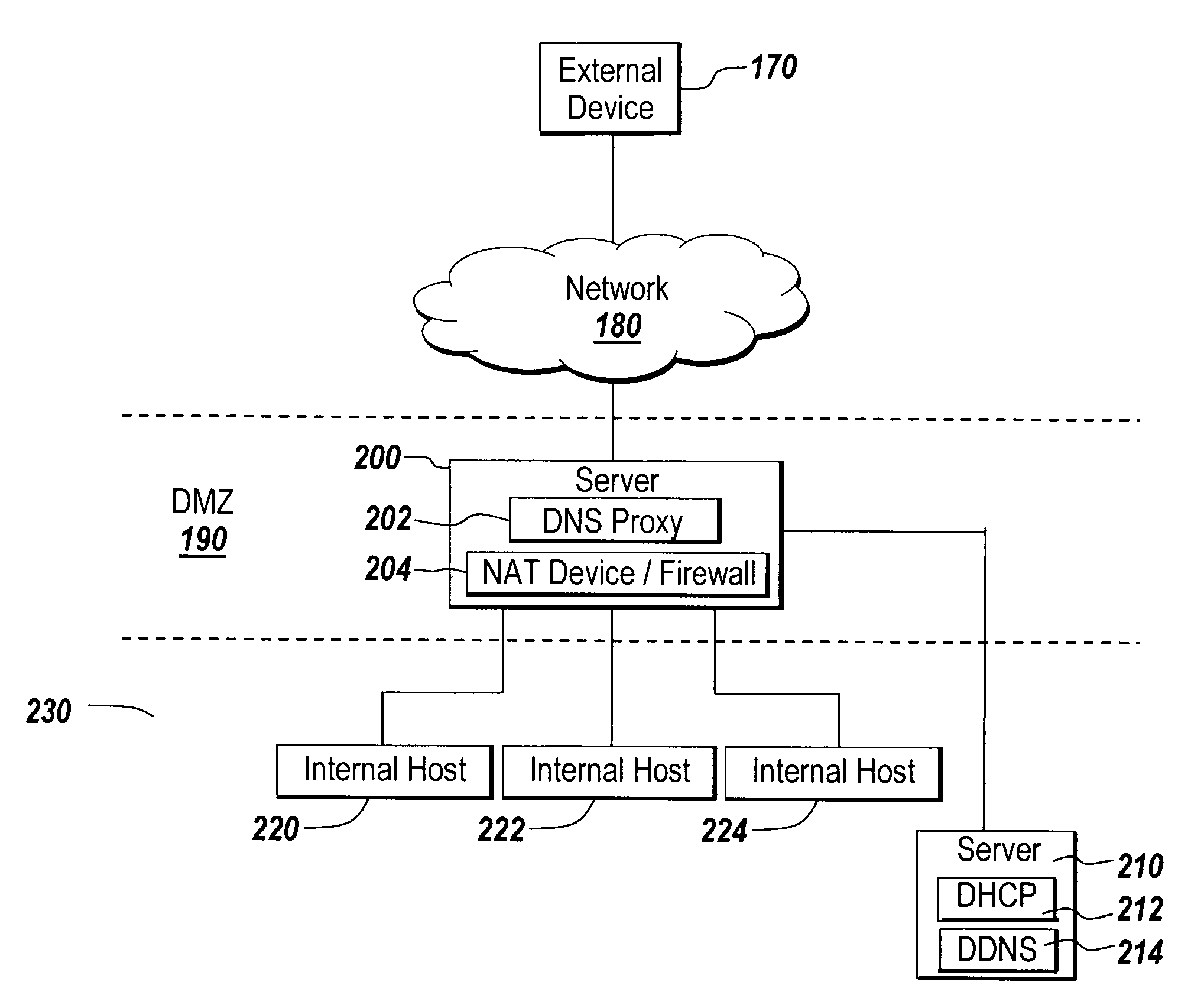
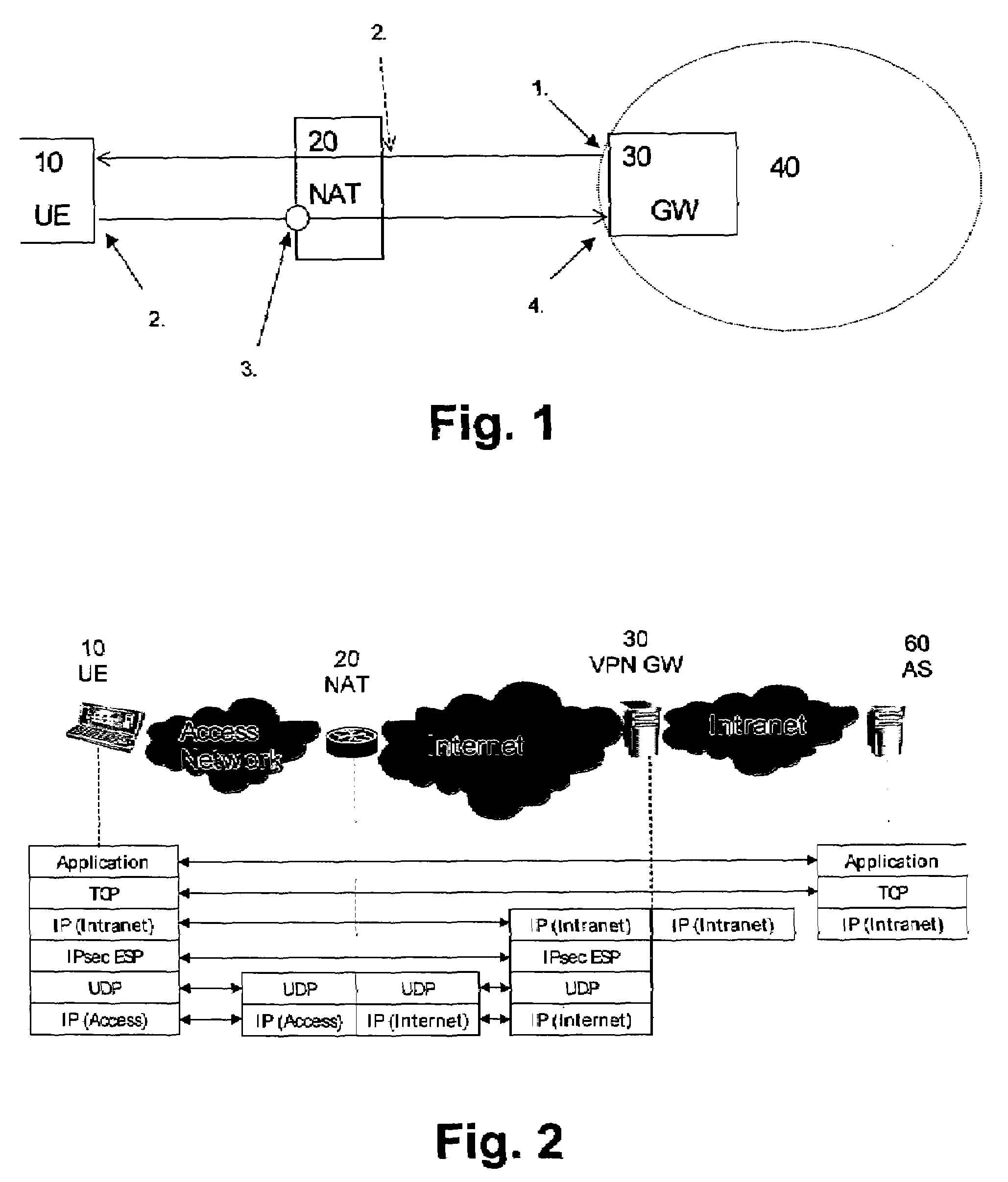
System and method for increasing host visibility in network address translation environments
ActiveUS7684394B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsVisibilityDomain name
A mechanism for dynamically performing Network Address Translation that allows external devices to contact internal host systems that would otherwise be hidden behind a NAT device is discussed. The dynamic NAT mechanism of the present invention maps internal host system addresses to external network addresses and reconfigures the NAT configuration of the network firewall to account for the new mapping on demand. Domain Name Service (DNS) lookup requests for an authorized internal system serve as a trigger to create a new mapping between the internal host system and the external network address. The new mappings may have a lifecycle controlled by dynamic leases that are created for each new mapping.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
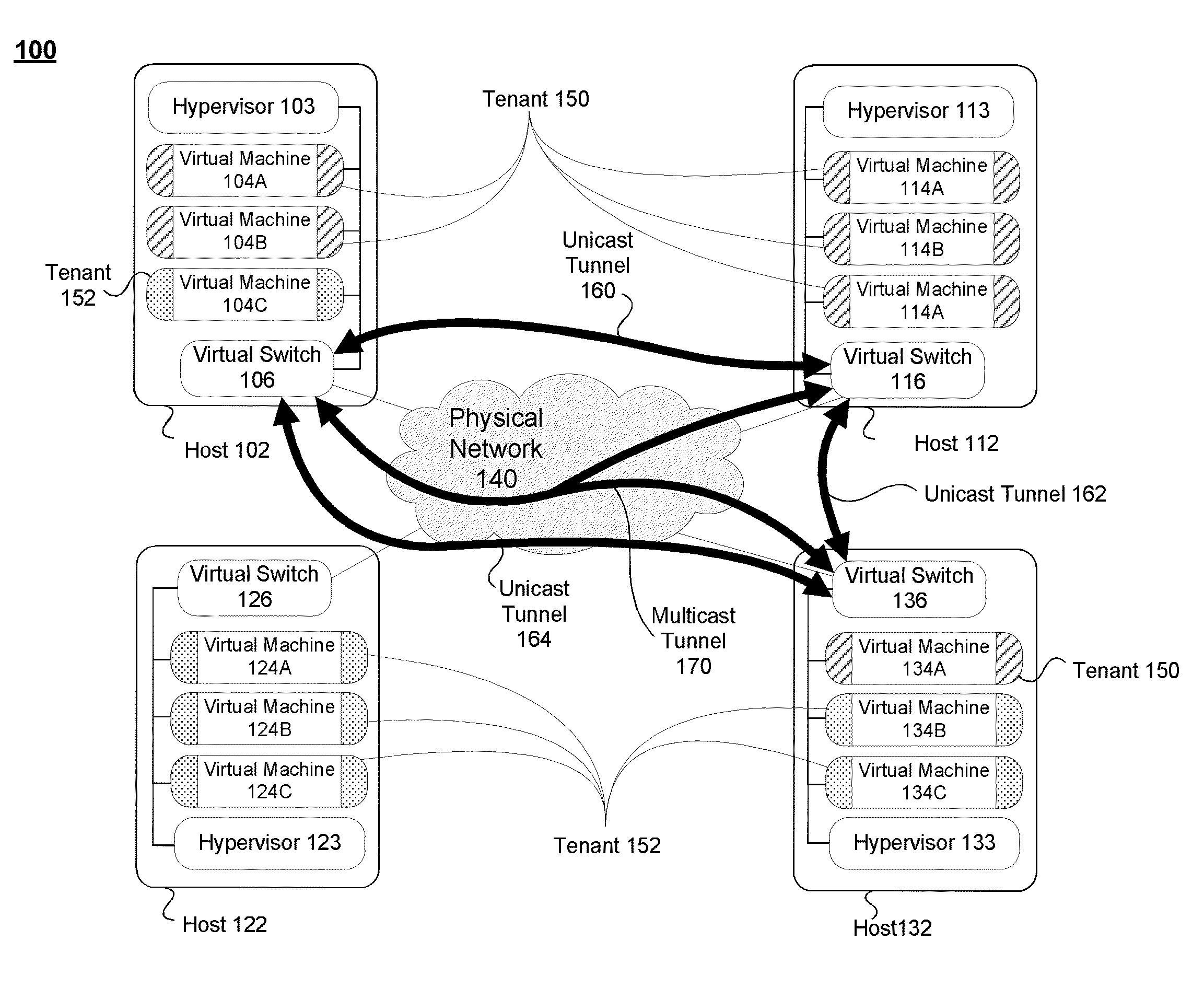
Systems and methods for providing multicast routing in an overlay network
ActiveUS20140192804A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationIp addressMulticast address
An information handling system is provided. The information handling system includes a first hypervisor running on a first host and a second hypervisor running on a second host. The first hypervisor managing a first virtual switch, and the second hypervisor managing a second virtual switch. The information handling system also includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs), including a first VM, which is part of a first tenant, running on the first host, and a second VM, part of a second tenant, running on the second host. The first virtual switch has a mapping in memory that maps a customer-specific multicast IP address, used by the plurality of VMs to indicate a multicast group that includes VMs on the first and second tenants, to a global multicast IP address used by the first and second hosts.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
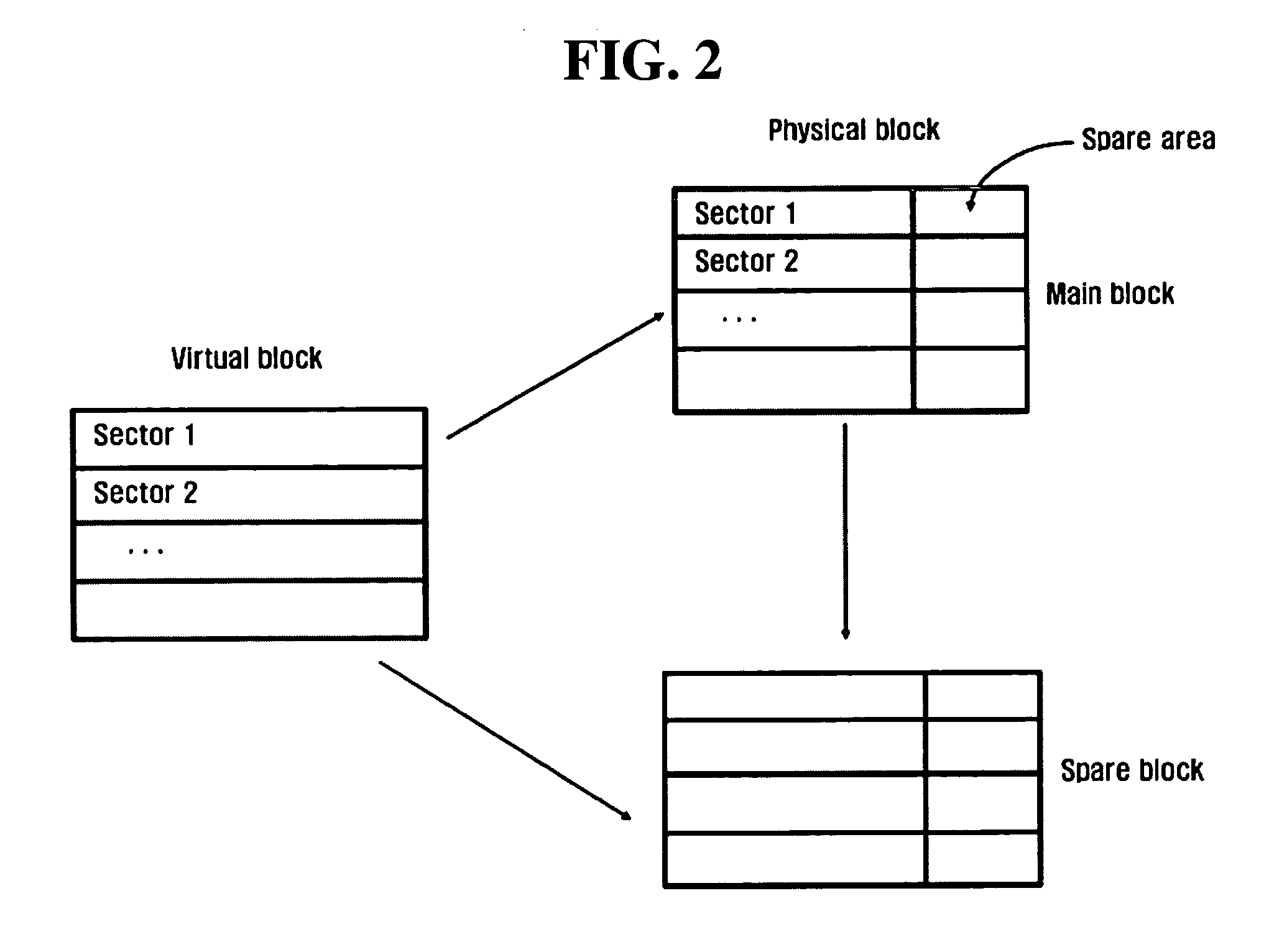
Address mapping method and mapping information managing method for flash memory, and flash memory using the same
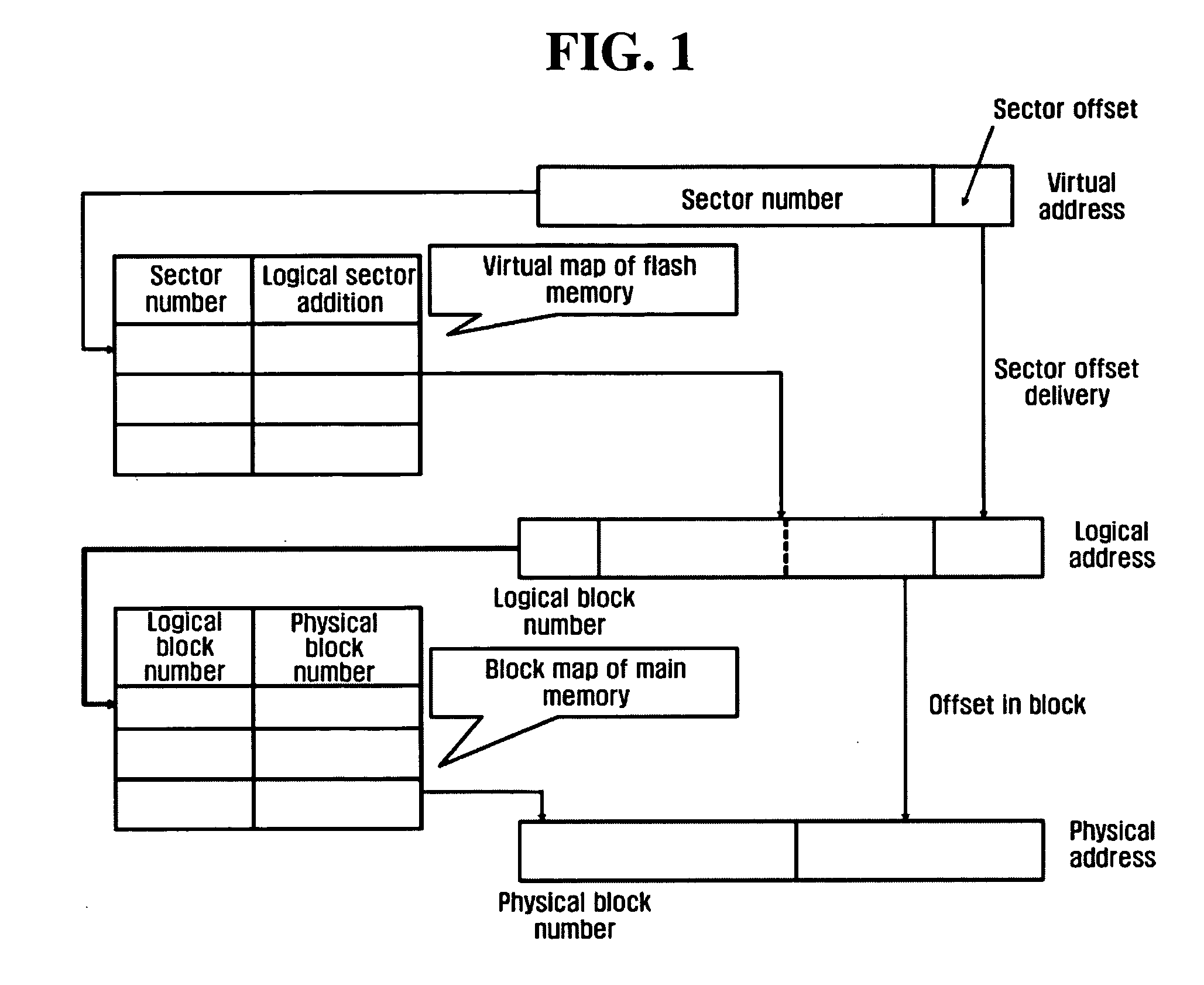
ActiveUS20050144368A1Performance maximizationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceAddress mapping
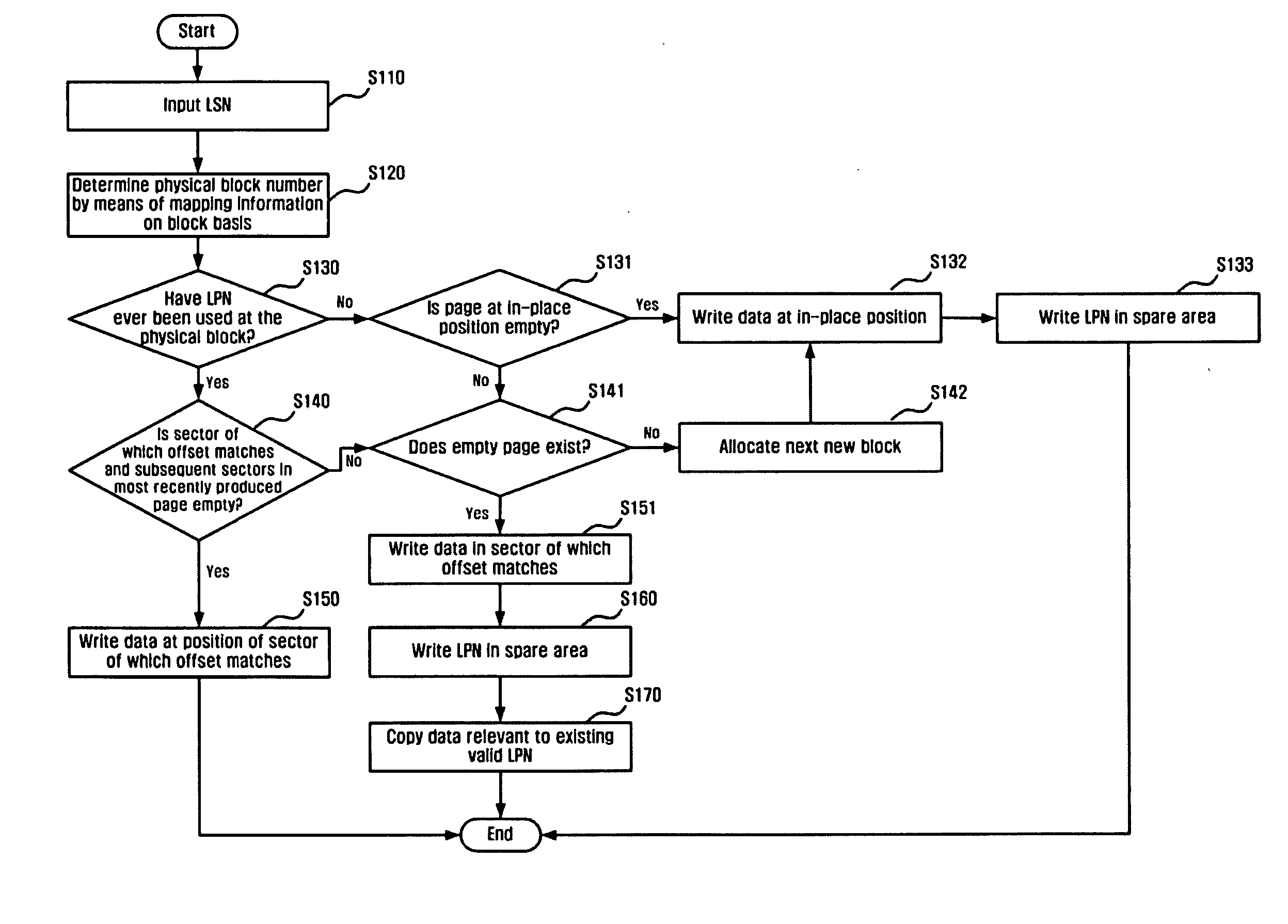
A method for minimizing the degradation of performance upon accessing a flash memory using a logical-physical mapping scheme, and a method for efficiently storing and managing information on logical-physical mapping in a flash memory. A method for writing data in a flash memory includes determining whether a sector is empty in a physical page having a most recently written logical page number of data to be written, the offset of the sector matching that of the data to be written; if the sector is empty, writing the data in the sector to the physical page; and if the sector is not empty, selecting an empty physical page to write the data to a sector in the selected empty physical page of which the offset matches that of the data to be written and writing a logical page number for the data to the selected empty physical page.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reliability High Endurance Non-Volatile Memory Device with Zone-Based Non-Volatile Memory File System
InactiveUS20080209114A1Extend the life cycleMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemComputerized system
Improved reliability high endurance non-volatile memory device with zone-based non-volatile memory file system is described. According to one aspect of the present invention, a zone-based non-volatile memory file system comprises a two-level address mapping scheme: a first level address mapping scheme maps linear or logic address received from a host computer system to a virtual zone address; and a second level address mapping scheme maps the virtual zone address to a physical zone address of a non-volatile memory module. The virtual zone address represents a number of zones each including a plurality of data sectors. Zone is configured as a unit smaller than data blocks and larger than data pages. Each of the data sector consists of 512-byte of data. The ratio between zone and the sectors is predefined by physical characteristics of the non-volatile memory module. A tracking table is used for correlating the virtual zone address with the physical zone address. Data programming and erasing are performed in a zone basis.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
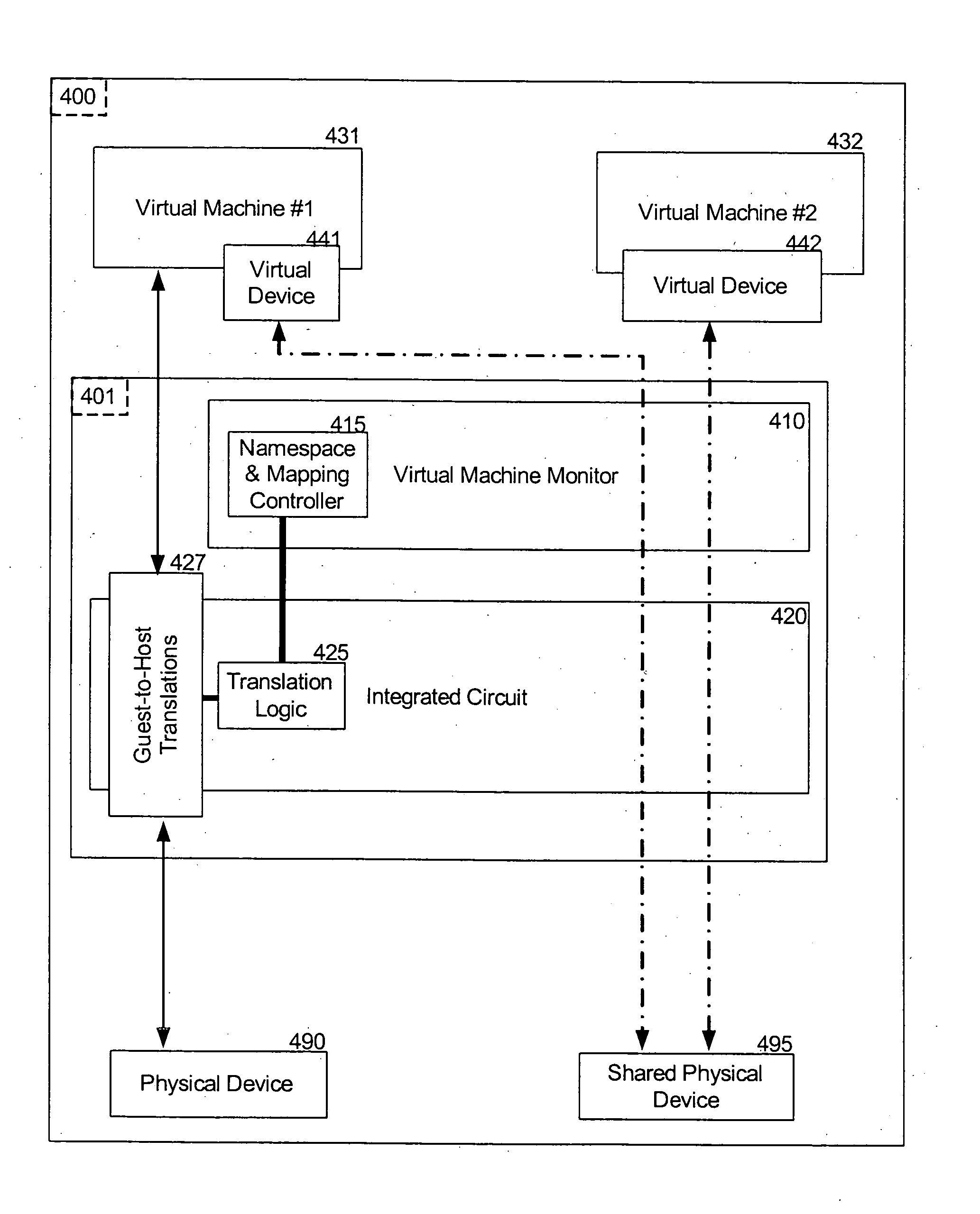
Resource partitioning and direct access utilizing hardware support for virtualization
ActiveUS20050132365A1Resource allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtualizationResource management
The present disclosure relates to the resource management of virtual machine(s) using hardware address mapping, and, more specifically, to facilitate direct access to devices from virtual machines, utilizing control of hardware address translation facilities.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Method and system for performing virtual to physical address translations in a virtual machine monitor
InactiveUS7069413B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationComputer security arrangementsPhysical addressEngineering
The invention is used in a virtual machine monitor for a multiprocessing system that includes a virtual memory system. During a software-based processing of a guest instruction, including translating or interpreting a guest instruction, mappings between virtual addresses and physical addresses are retained in memory until processing of the guest instruction is completed. The retained mappings may be cleared after each guest instruction has been processed, or after multiple guest instructions have been processed. Information may also be stored to indicate that an attempt to map a virtual address to a physical address was not successful. The invention may be extended beyond virtual machine monitors to other systems involving the software-based processing of instructions, and beyond multiprocessing systems to other systems involving concurrent access to virtual memory management data.
Owner:VMWARE INC
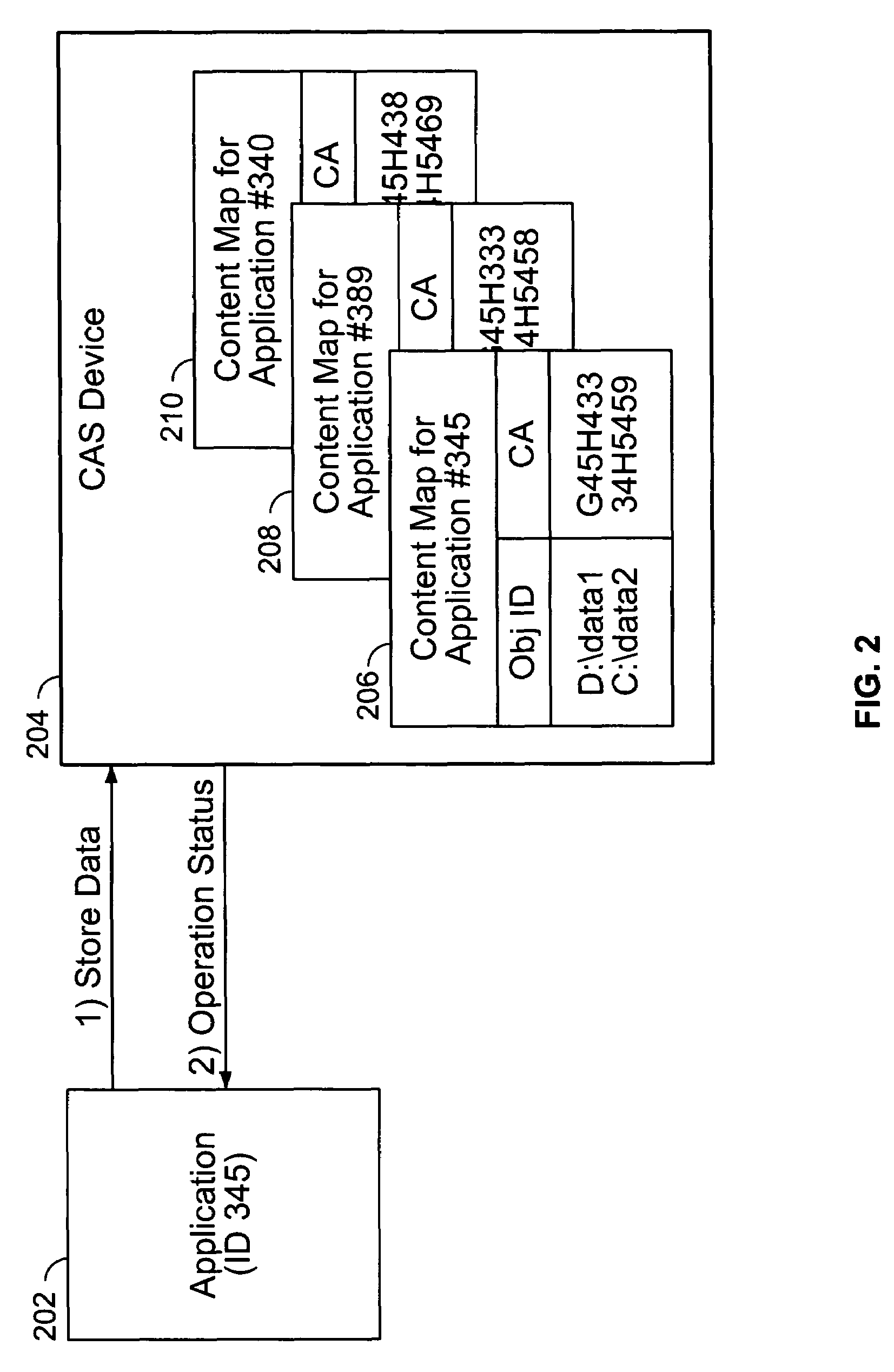
Content addressed storage device configured to maintain content address mapping
ActiveUS7444464B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDigital objectObject identifier
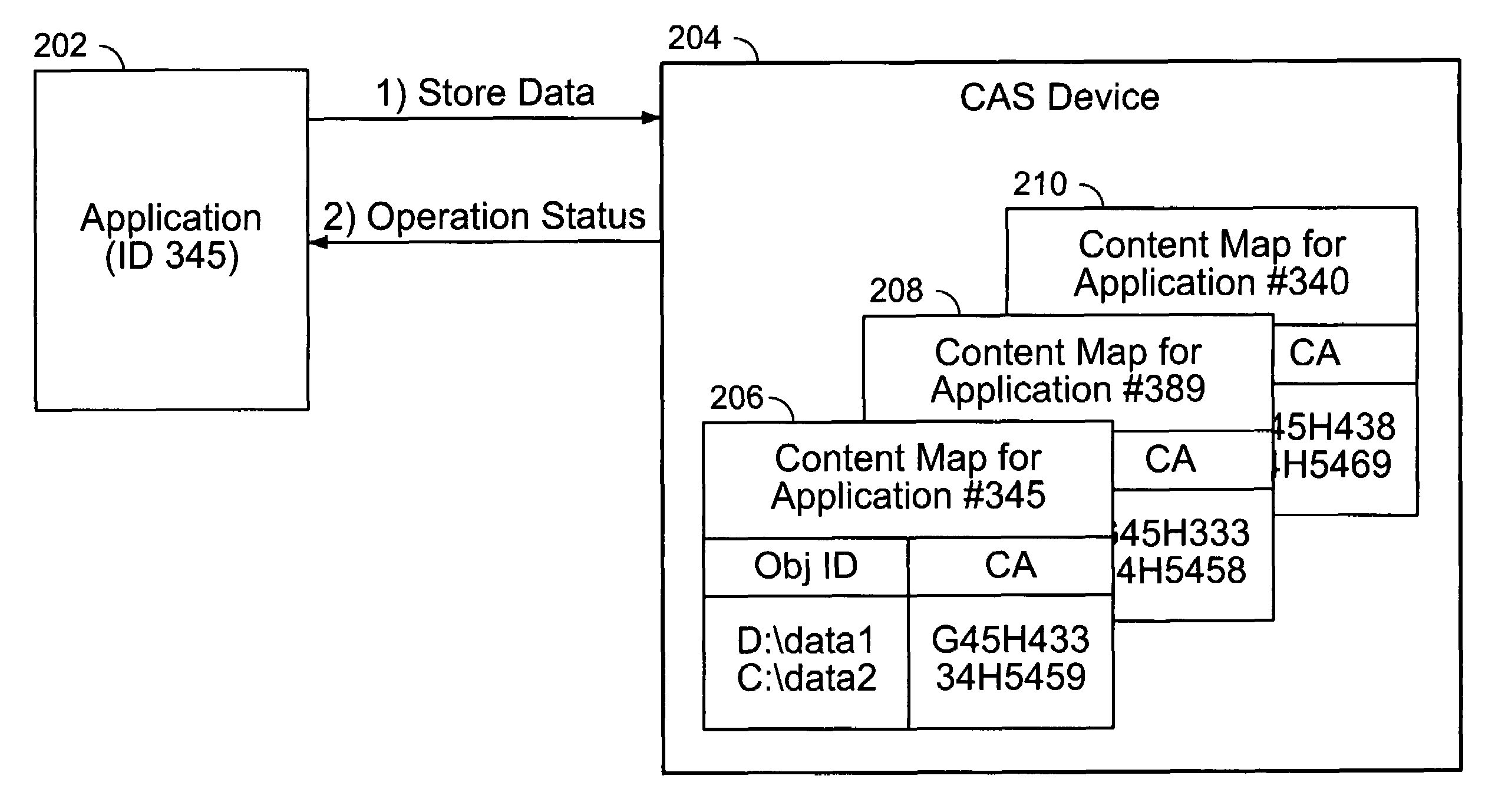
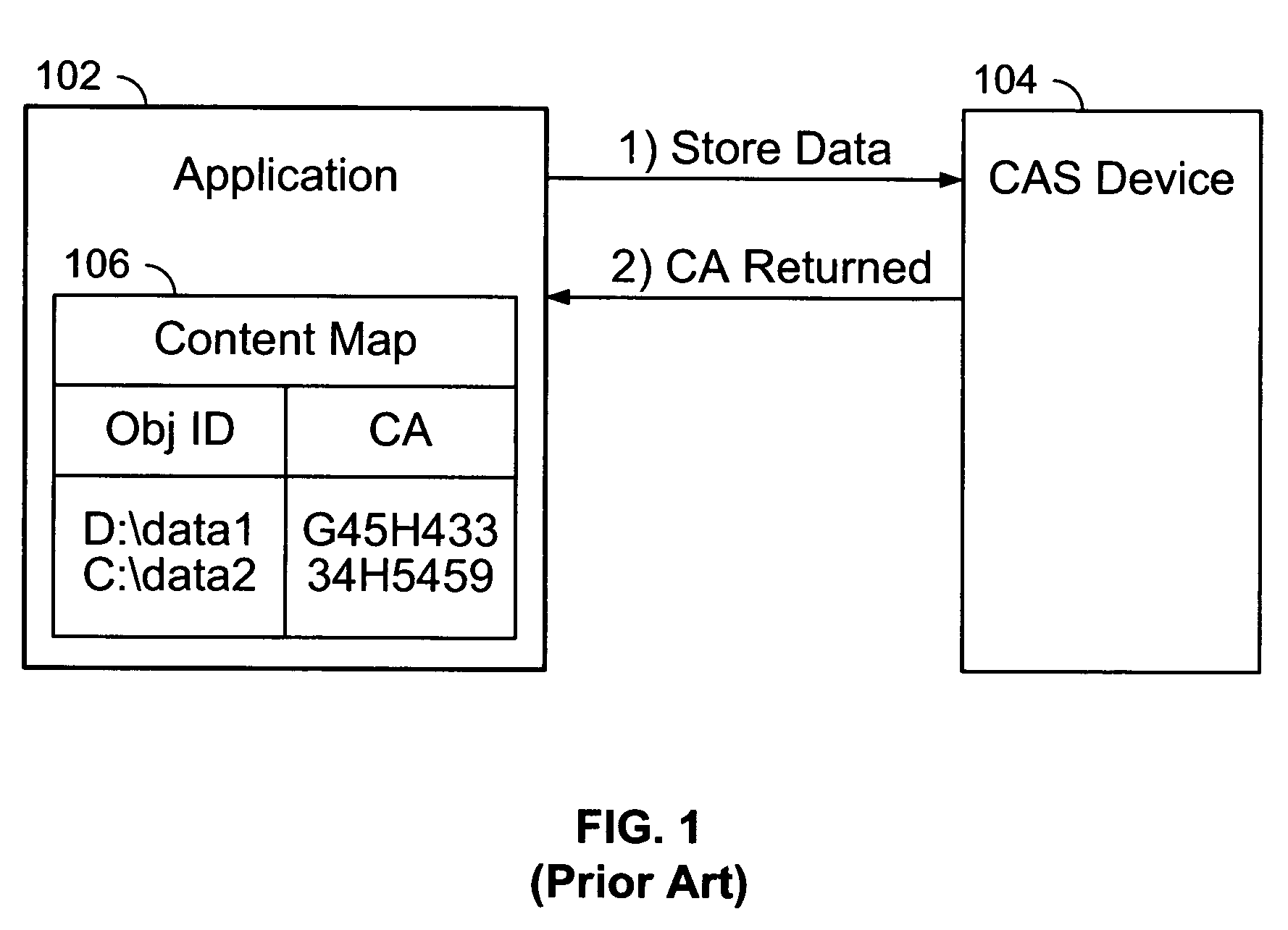
A content addressed storage device configured to maintain content address mapping is disclosed. A data object to be stored on the content addressed storage device and a local data object identifier by which the data object is known to the sending source are received from a sending source. A content address to be associated with the data object on the content addressed storage device is determined based at least in part on the contents of the data object. The data object is stored on the content addressed storage device in a storage location associated with the content address. A mapping that associates the local data object identifier with the content address is maintained on the content addressed storage device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
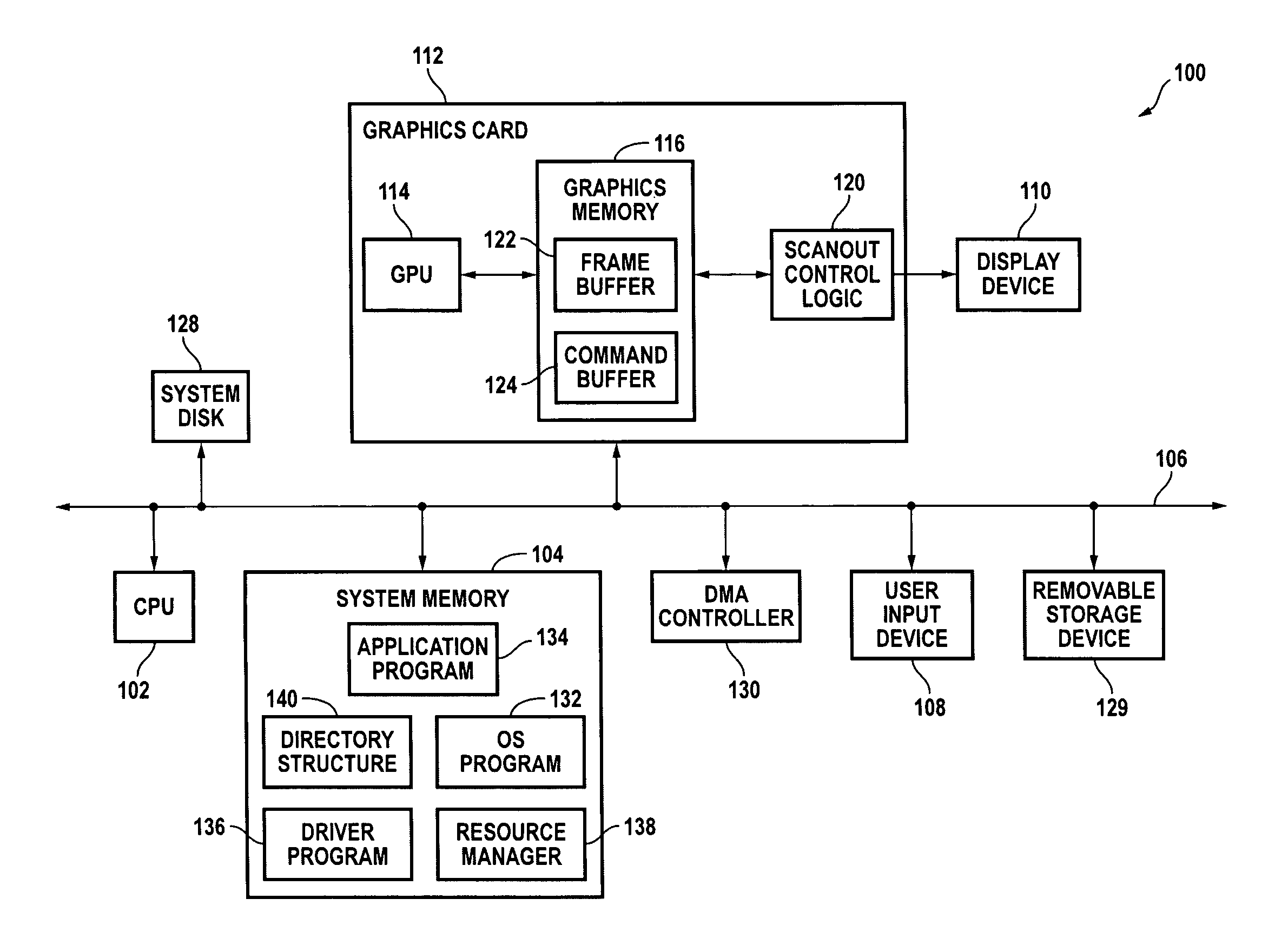
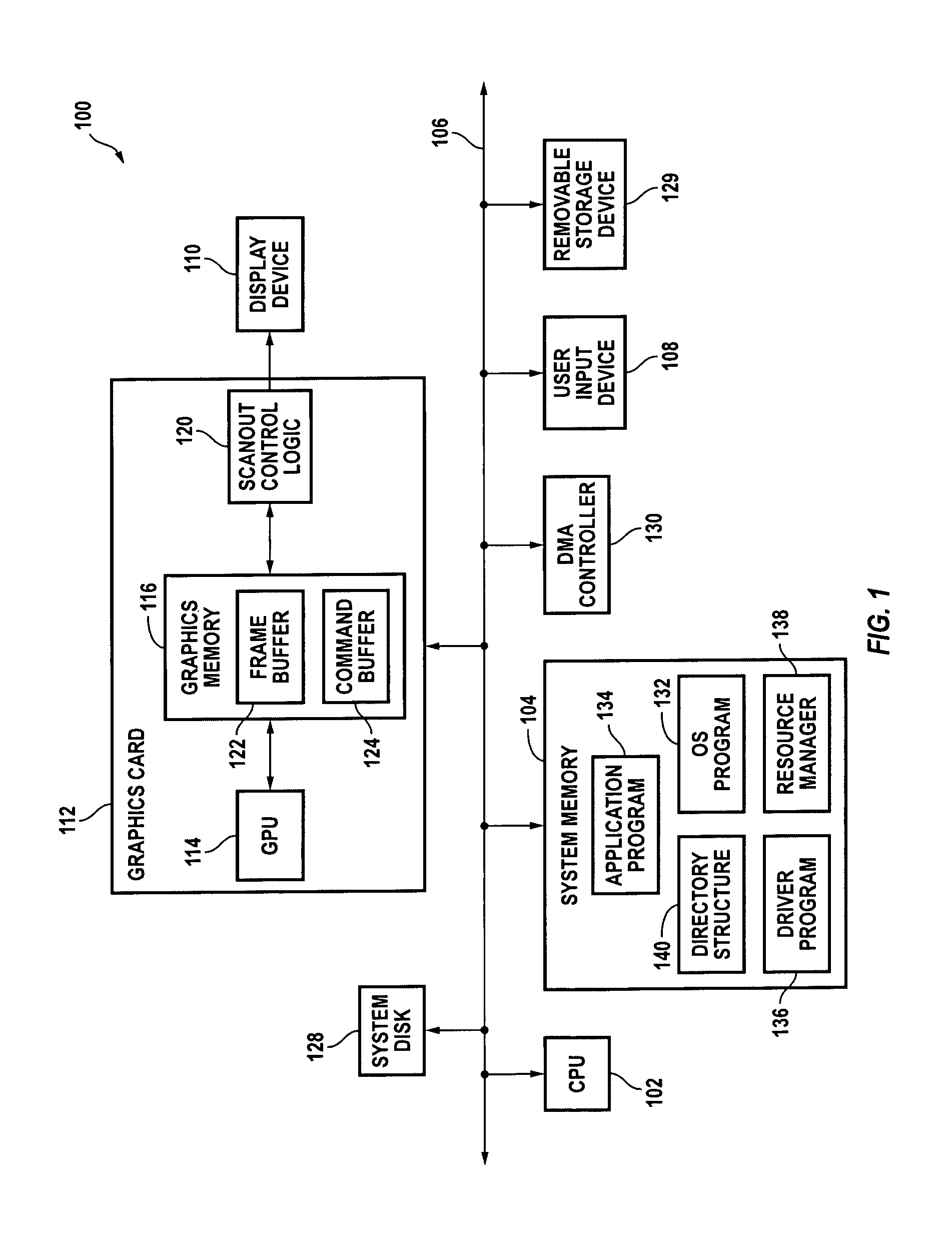
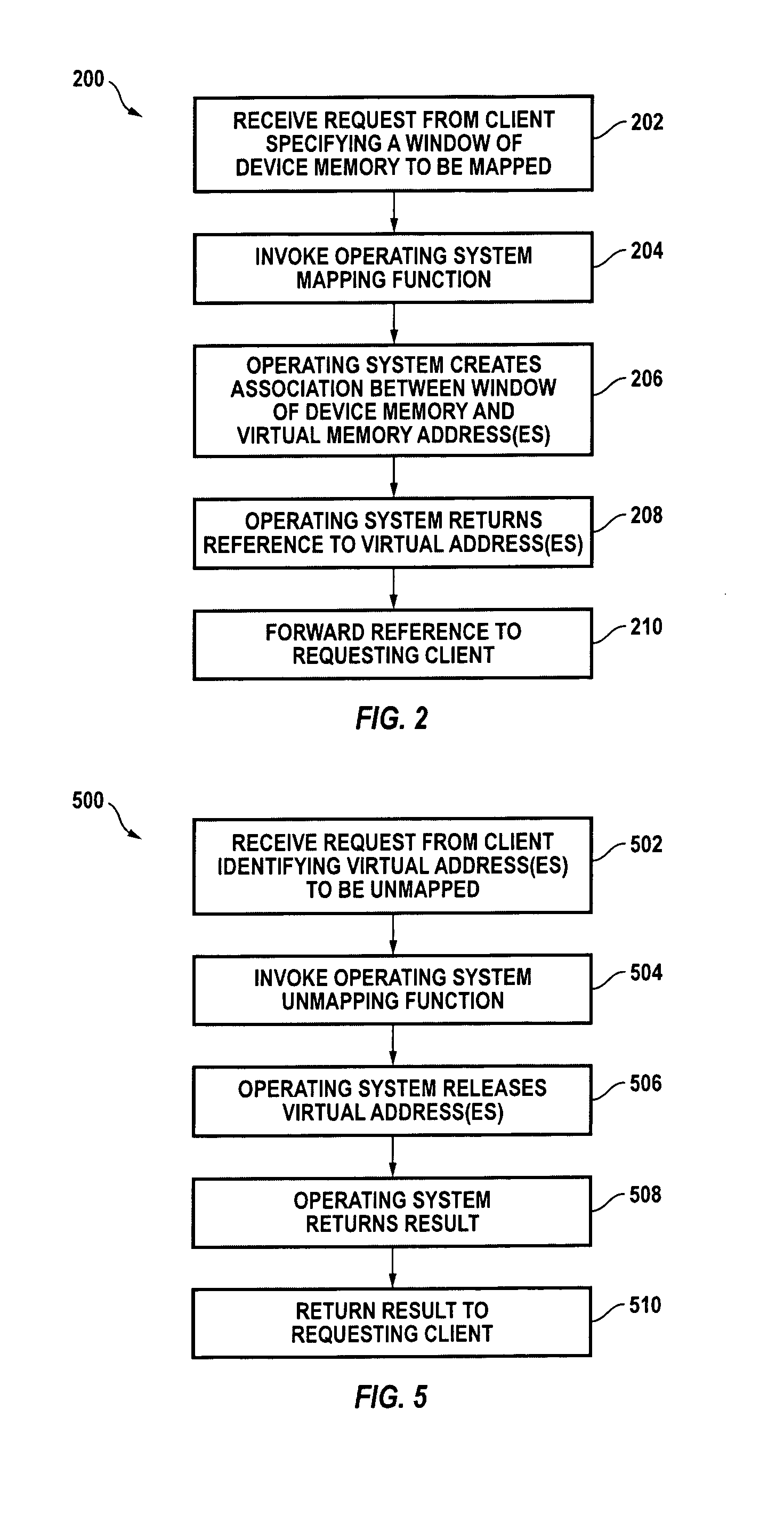
Dynamically creating or removing a physical-to-virtual address mapping in a memory of a peripheral device
ActiveUS7065630B1Easy to useMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingVirtual memoryParallel computing
Systems and methods for providing on-demand memory management. In response to a mapping request from a device driver or other program, a first portion of the memory is mapped to one or more virtual addresses in a first region of a virtual memory space so that it can be directly accessed by the CPU. In response to an unmapping request the first portion of the memory is unmapped. Mapping and unmapping requests may be made at any time.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
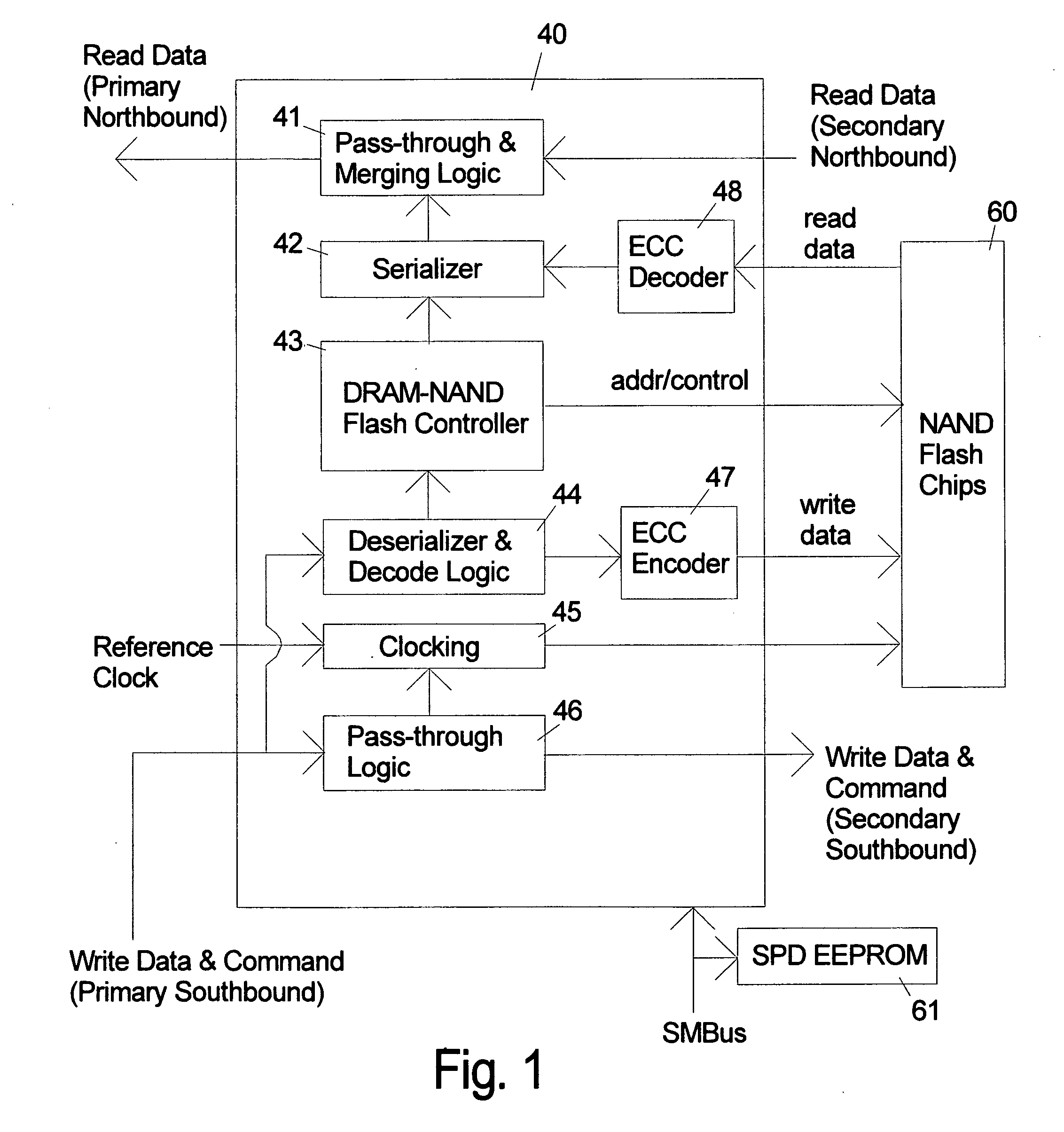
NAND flash module replacement for DRAM module
ActiveUS8185685B2Reduce speedMost efficientMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcess memoryControl signal
An electronic memory module according to the invention provides non-volatile memory that can be used in place of a DRAM module without battery backup. An embodiment of the invention includes an embedded microprocessor with microcode that translates the FB-DIMM address and control signals from the system into appropriate address and control signals for NAND flash memory. Wear-leveling, bad block management, garbage collection are preferably implemented by microcode executed by the microprocessor. The microprocessor, additional logic, and embedded memory provides the functions of a flash memory controller. The microprocessor memory preferably contains address mapping tables, free page queue, and garbage collection information.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Fast path for performing data operations
InactiveUS7280536B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationFast pathPathPing
Described are techniques used in a computer system for handling data operations to storage devices. A switching fabric includes one or more fast paths for handling lightweight, common data operations and at least one control path for handling other data operations. A control path manages one or more fast paths. The fast path and the control path are utilized in mapping virtual to physical addresses using mapping tables. The mapping tables include an extent table of one or more entries corresponding to varying address ranges. The size of an extent may be changed dynamically in accordance with a corresponding state change of physical storage. The fast path may cache only portions of the extent table as needed in accordance with a caching technique. The fast path may cache a subset of the extent table stored within the control path. A set of primitives may be used in performing data operations. A locking mechanism is described for controlling access to data shared by the control paths.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
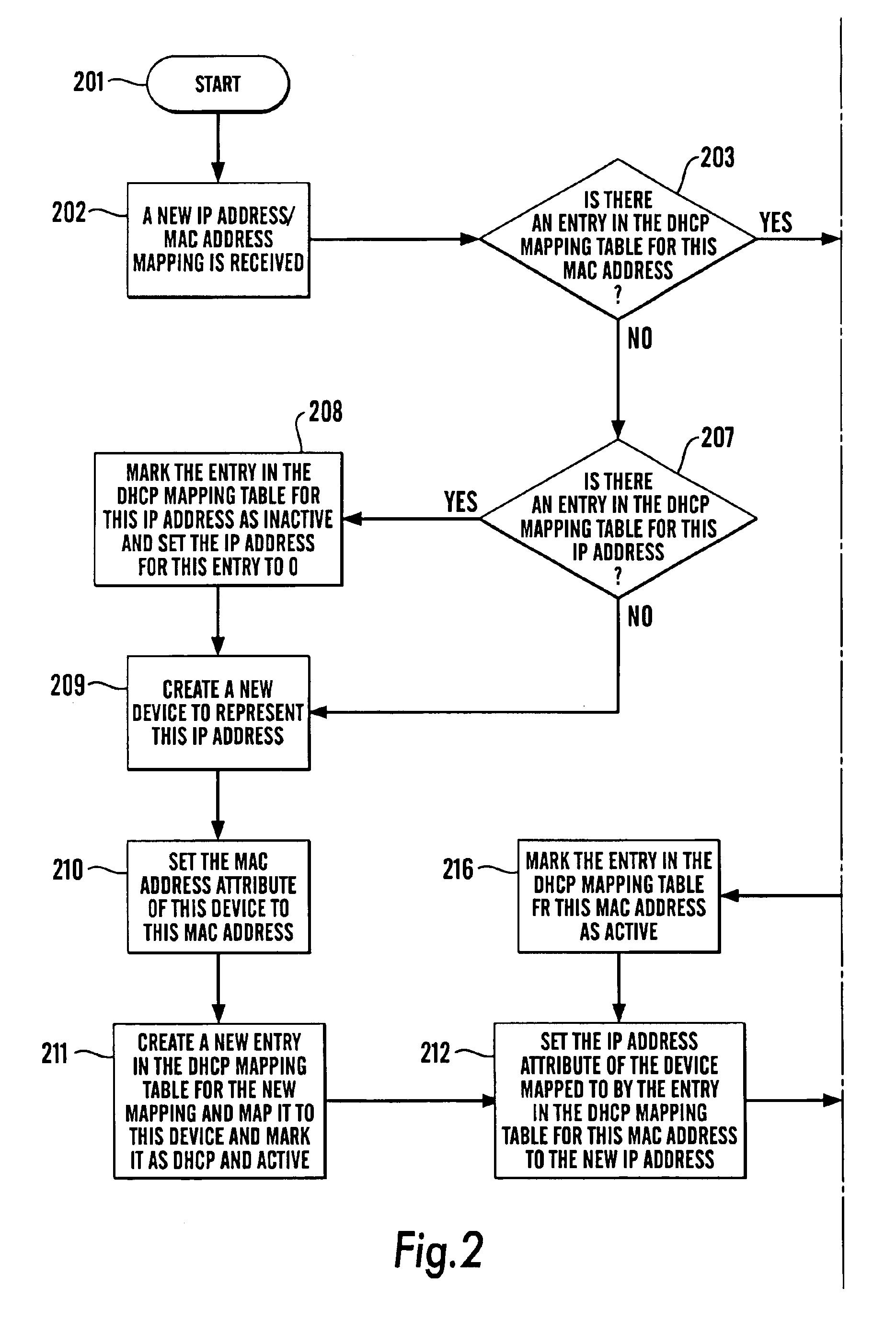
Tracking dynamic addresses on a network
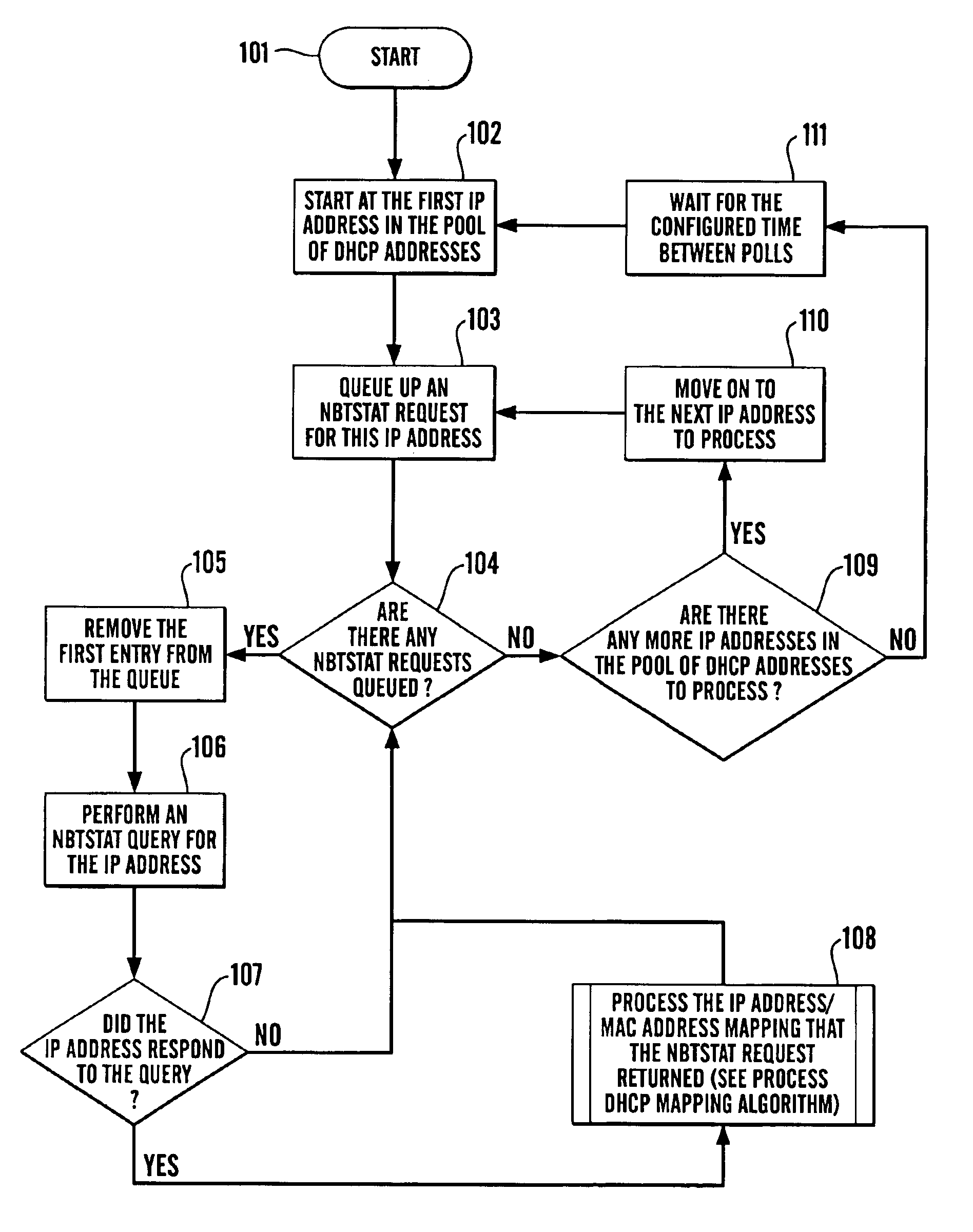
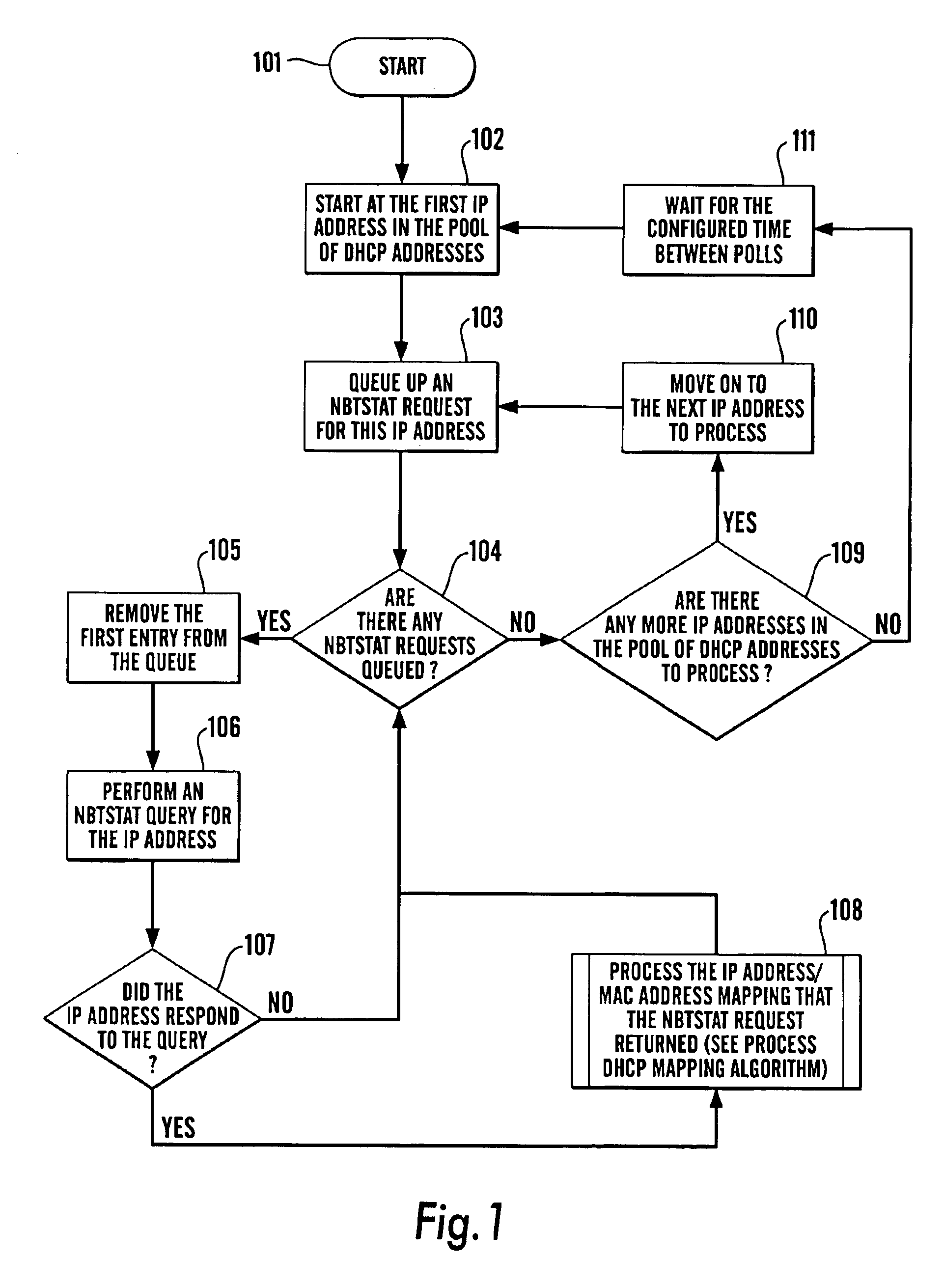
InactiveUS6862286B1Problem still existData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityIp address
In a computer network of devices, at least some of the devices (i.e. the DCHP devices) have a static (e.g. MAC) address which does not change over time and a dynamic (e.g. IP) address which may change over time. There is disclosed a method and computer program for mapping the static address and dynamic address for the devices comprising polling said devices using said IP addresses and during said polling determining the MAC addresses of the devices, and providing a set of mapped static and dynamic addresses, said method including repeating the steps of the method at intervals.Using the method of the invention, it is possible, when entering a particular conversation in a database, to access the IP addresses, to determine which is the current DHCP device that address maps to, and assign the conversation to that device and store it in the database assigned to that device. Therefore, for each DHCP device, one can store a history of the conversations or traffic involved in that device.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
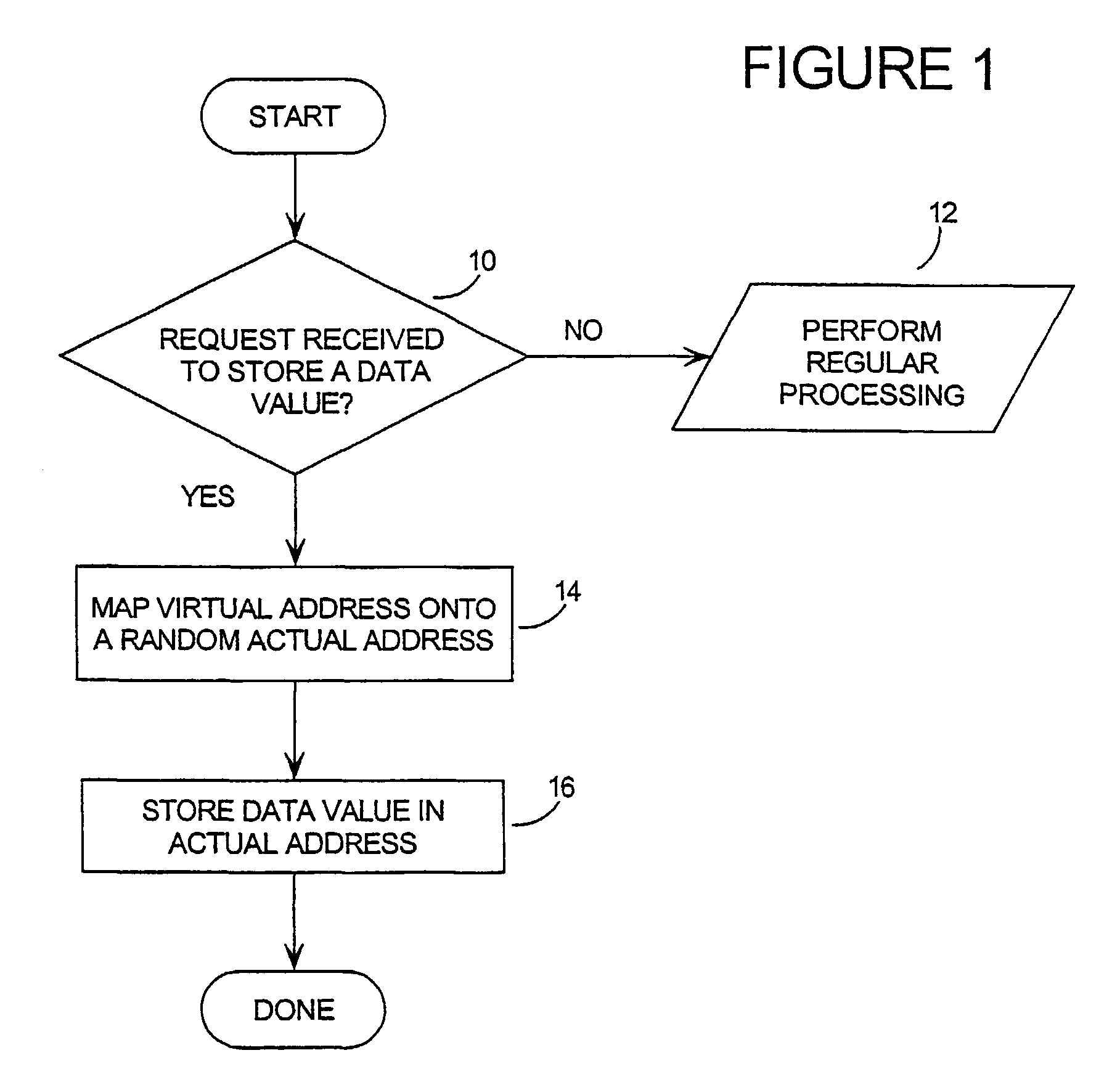
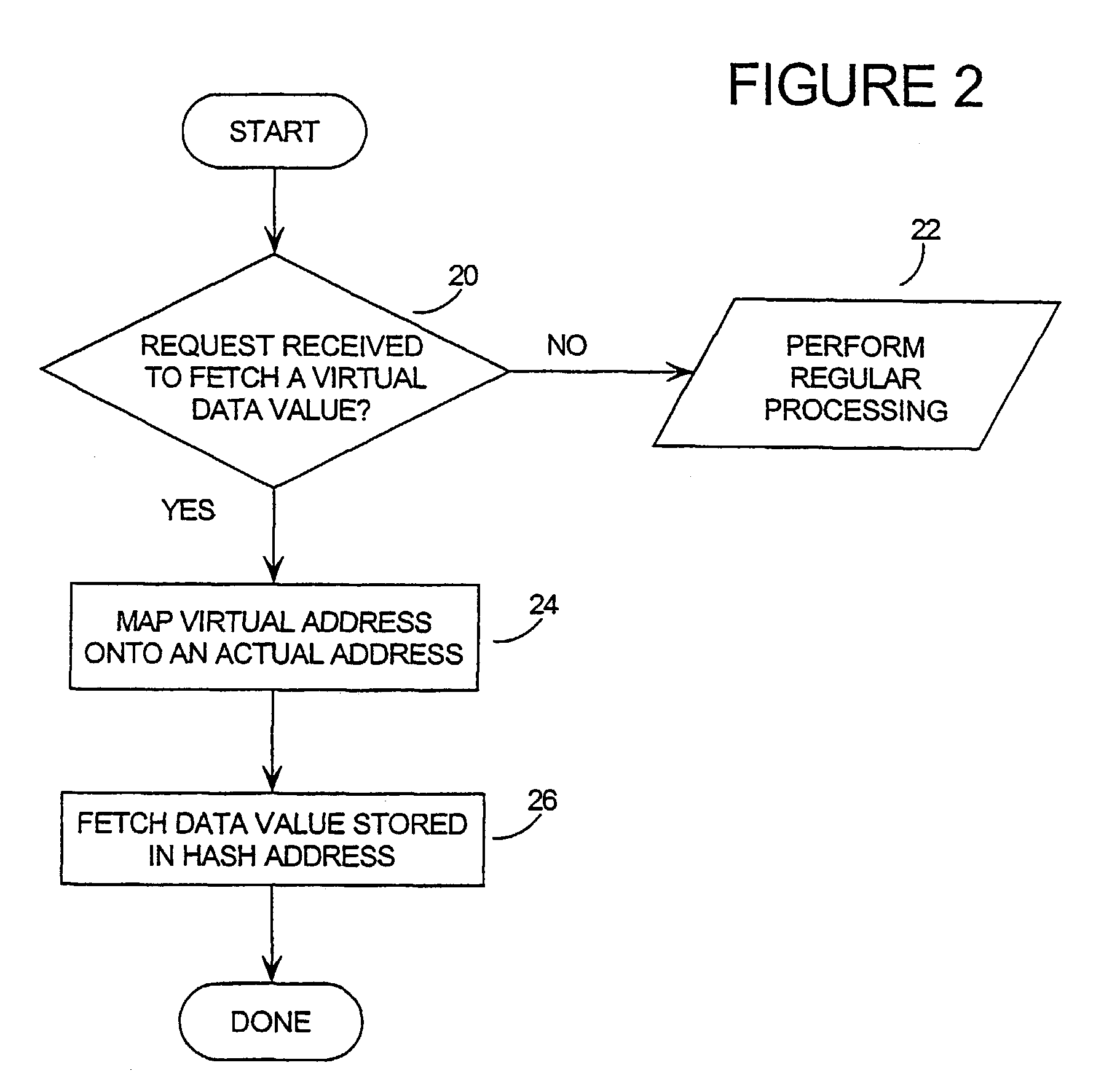
Tamper resistant software-mass data encoding
InactiveUS7350085B2Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringArray data structureBiometric data
Mass data (the contents of arrays, large data structures, linked data structures and similar data structures stored in memory) are common targets for attack. The invention presents a method and system of protecting mass data by mapping virtual addresses onto randomly or pseudo-randomly selected actual addresses. This mapping distributes data values throughout the memory so an attacker cannot locate the data he is seeking, or identify patterns which might allow him to obtain information about his target (such as how the software operates, encryption keys, biometric data or passwords stored therein, or algorithms it uses). Additional layers of protection are described, as well as efficient techniques for generating the necessary transforms to perform the invention.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
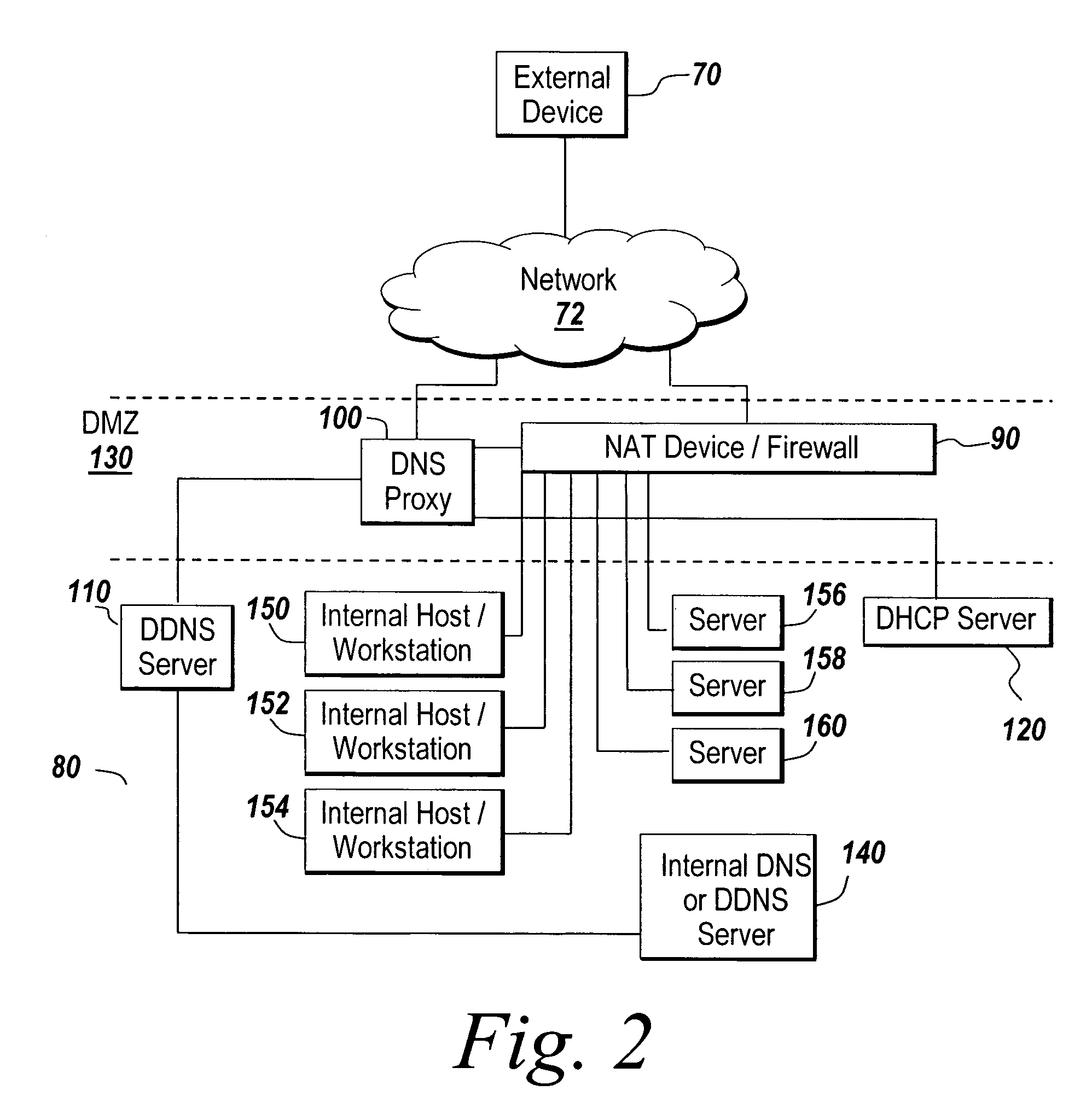
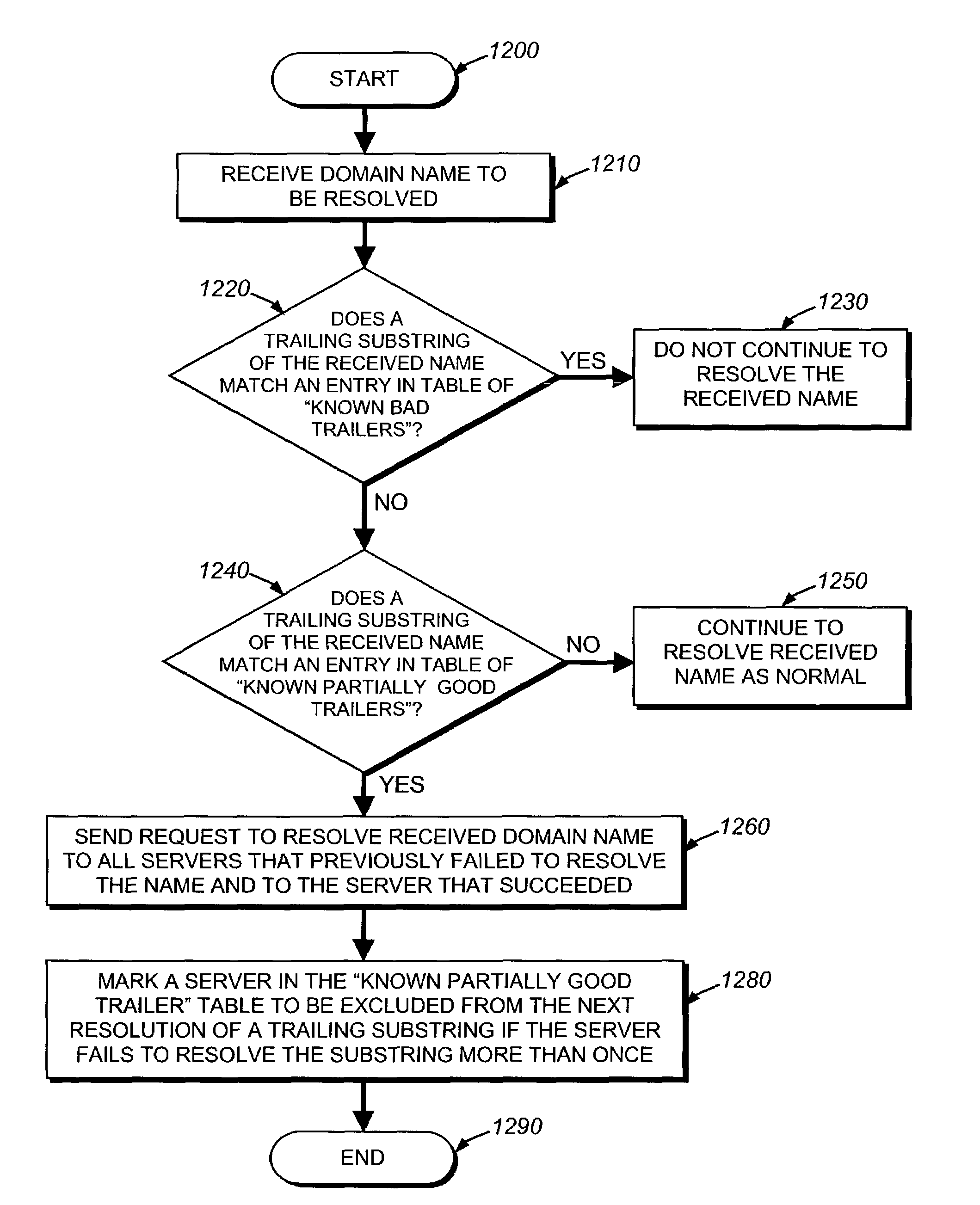
Highly available DNS resolver and method for use of the same
ActiveUS7426576B1Network degradationReliance has been minimizedMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDomain nameOperational system
The present invention relates to an enhanced DNS resolver architecture configured to operate in high availability environments, such as the Internet. Specifically, the DNS resolver code of the present invention may be implemented by a storage operating system in a filer. The resolver code modifies a conventional resolver algorithm so as to reduce the time necessary to map IP addresses to alphanumeric domain names and vice versa. Advantageously, the enhanced resolver code keeps track of non-responsive or “dead” DNS servers as well as non-resolvable or “bad” domain names and IP addresses.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
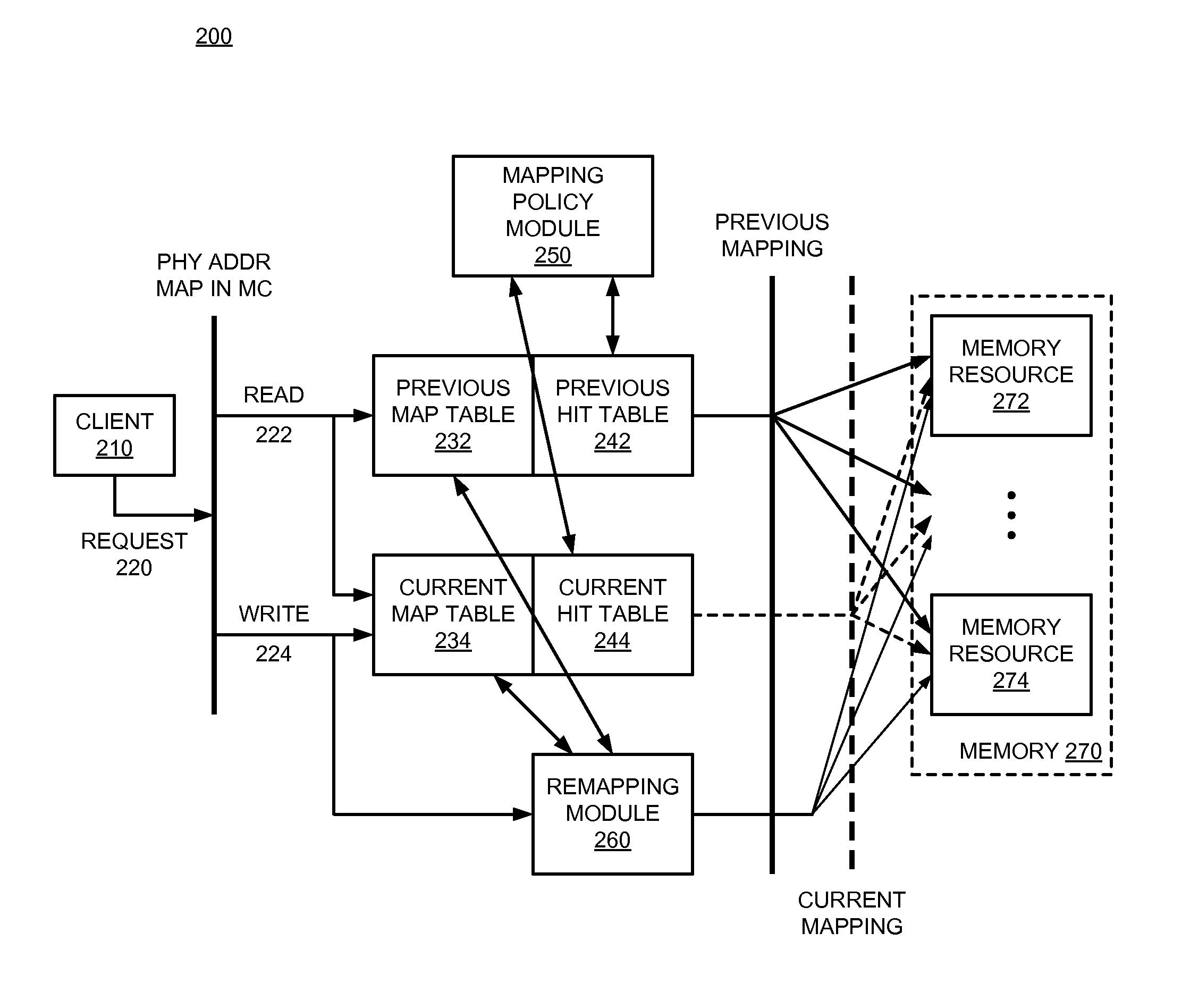
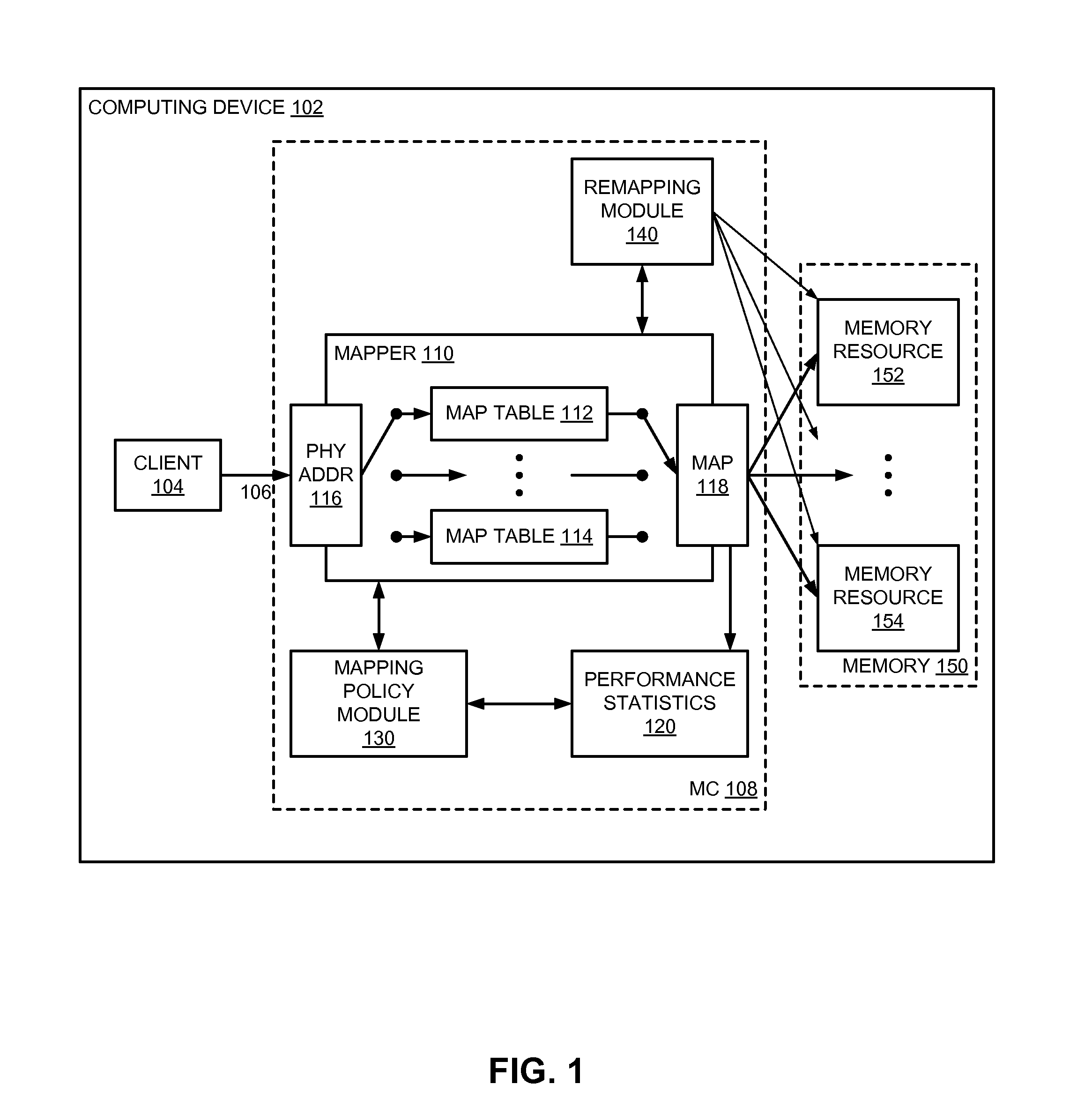
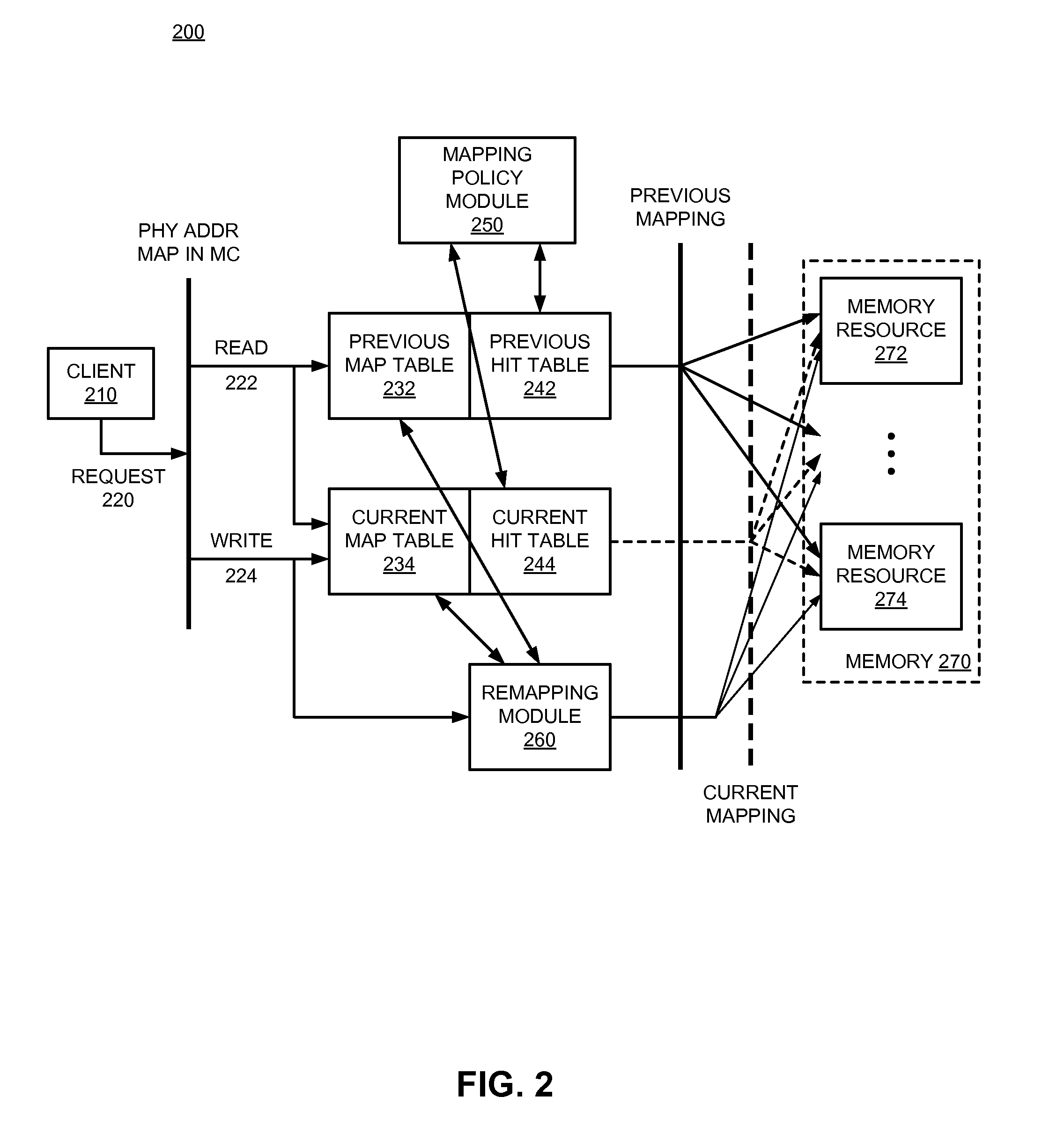
Adaptive address mapping with dynamic runtime memory mapping selection
InactiveUS20110153908A1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGranularityParallel computing
A system monitors and dynamically changes memory mapping in a runtime of a computing system. The computing system has various memory resources, and multiple possible mappings that indicate how data is to be stored in and subsequently accessed from the memory resources. The performance of each memory mapping may be different under different runtime or load conditions of the computing device. A memory controller can monitor runtime performance of the current memory mapping and dynamically change memory mappings at runtime based on monitored or observed performance of the memory mappings. The performance monitoring can be modified for any of a number of different granularities possible within the system, from the byte level to memory channel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
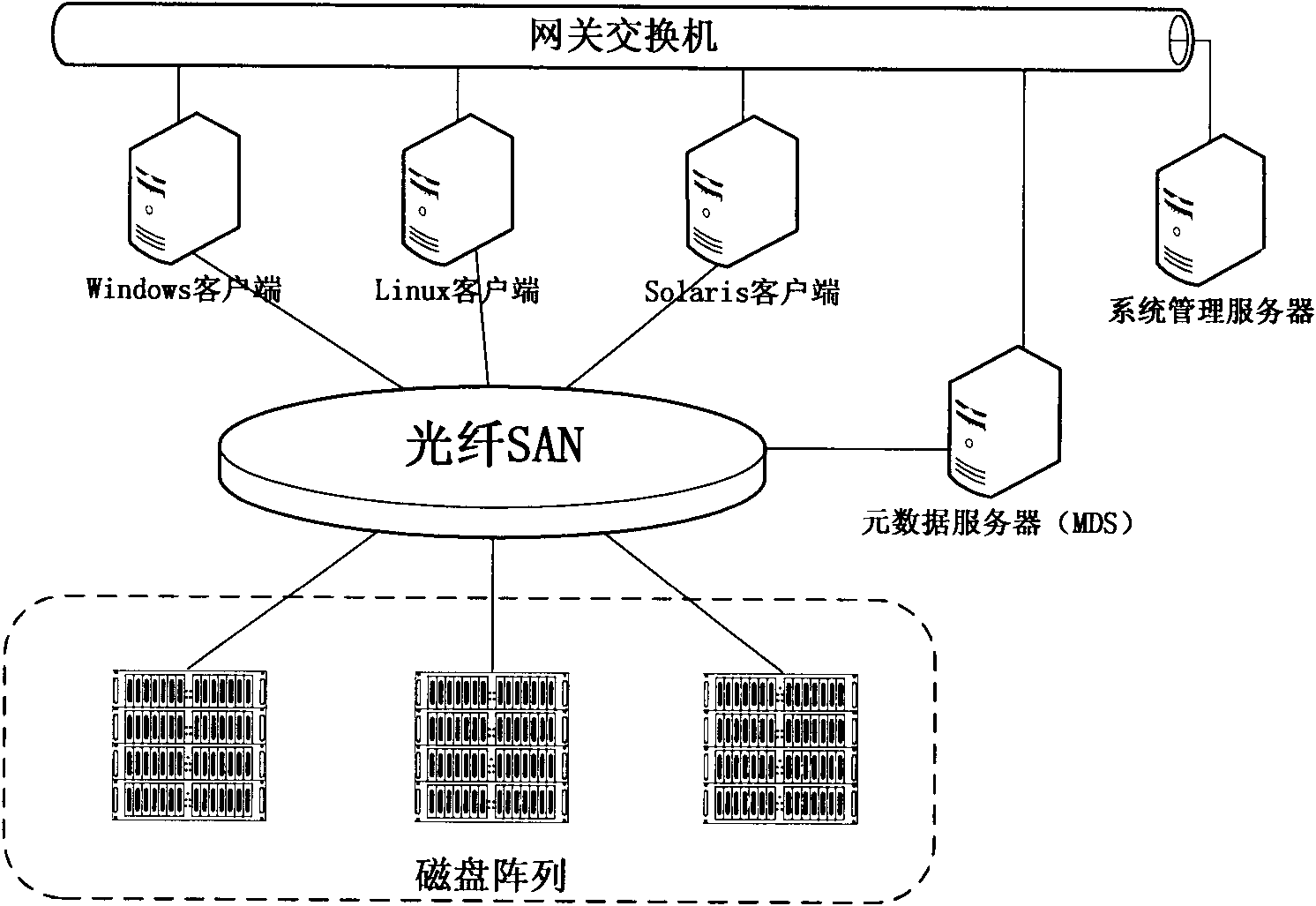
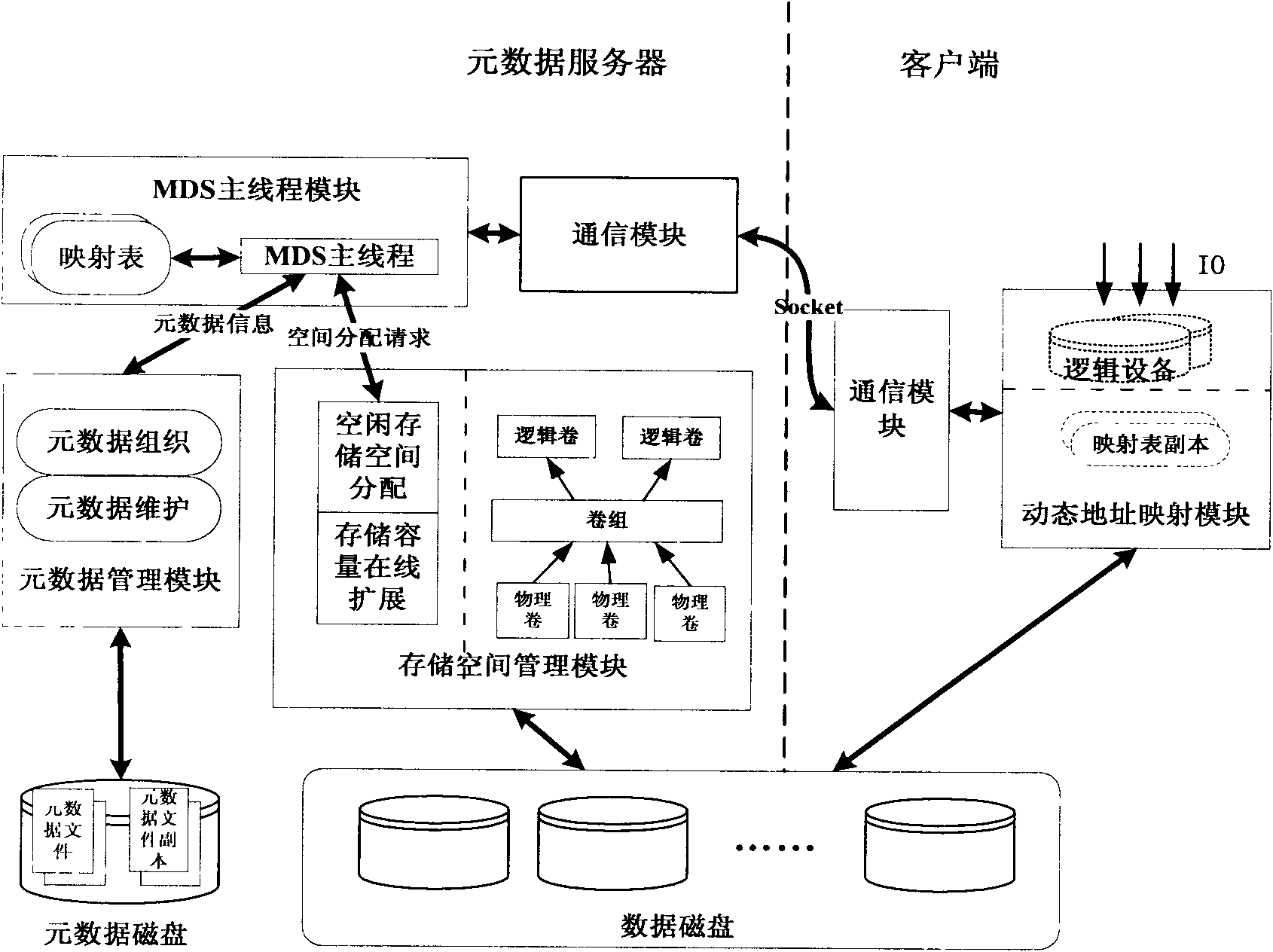
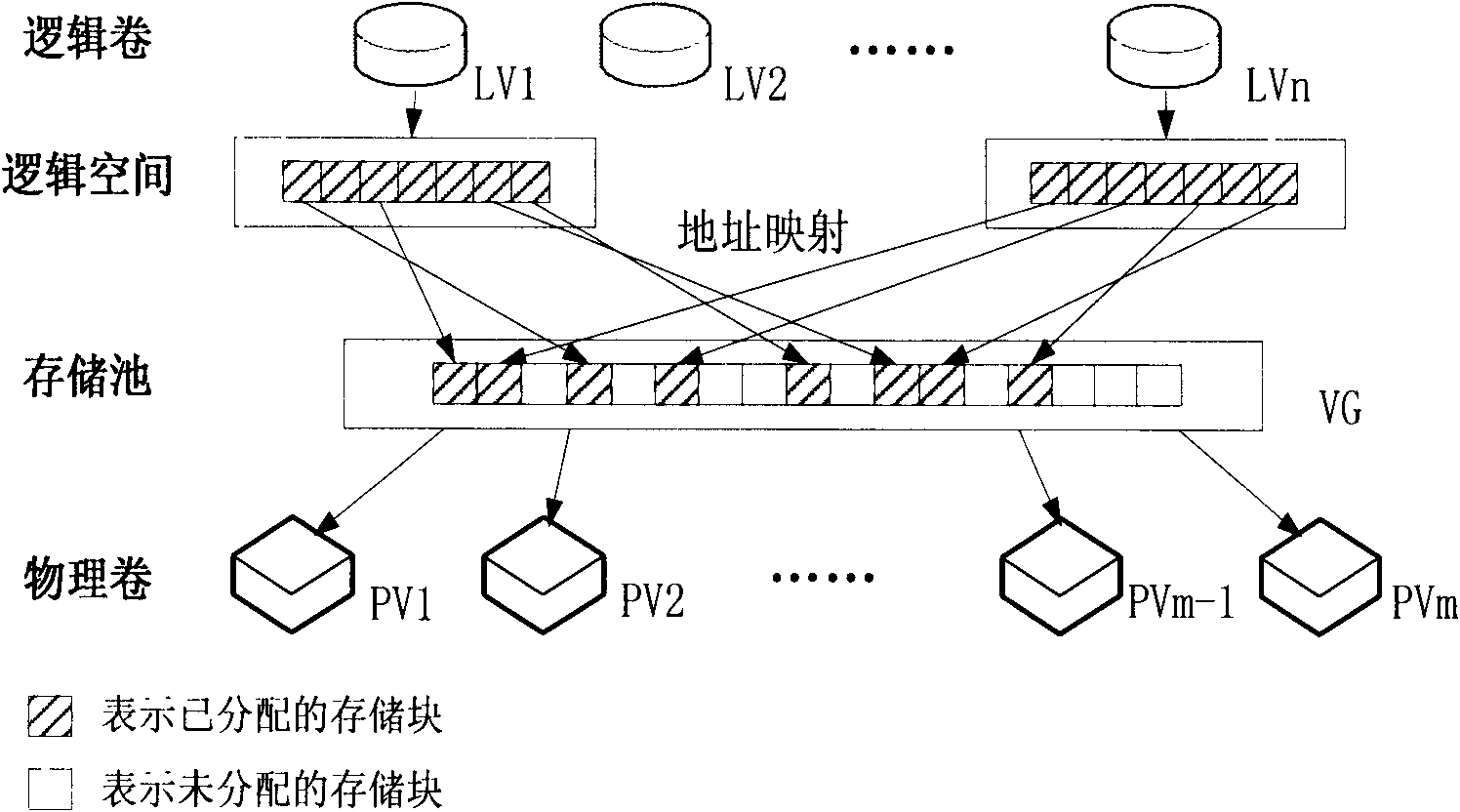
Method for allocating mass storage resources according to needs in heterogeneous SAN (Storage Area Network) environment
InactiveCN101997918AIncrease profitReduce procurement costsTransmissionMass storageApplication server
The invention relates to a method for allocating mass storage resources according to needs in a heterogeneous SAN (Storage Area Network) environment, belonging to the field of storage area networks, in particular to the technical field of storage virtualization therein. The invention is characterized by designing and realizing an out-of-band storage virtualization system aiming at a heterogeneousstorage application server and various storage devices in the SAN environment and providing a method for allocating the mass storage resources according to needs based on allocation while writing anddynamic address mapping mechanism on the basis of the system. The method can be used for allocating the storage resources according to the actual needs of applications, dynamically expanding the mapping relation between the logic storage space and the physical storage space, effectively increasing the utilization rate of the storage resources and the expandability of storage capacity, reducing the maintenance cost of the storage devices and realizing instant storage purchase.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
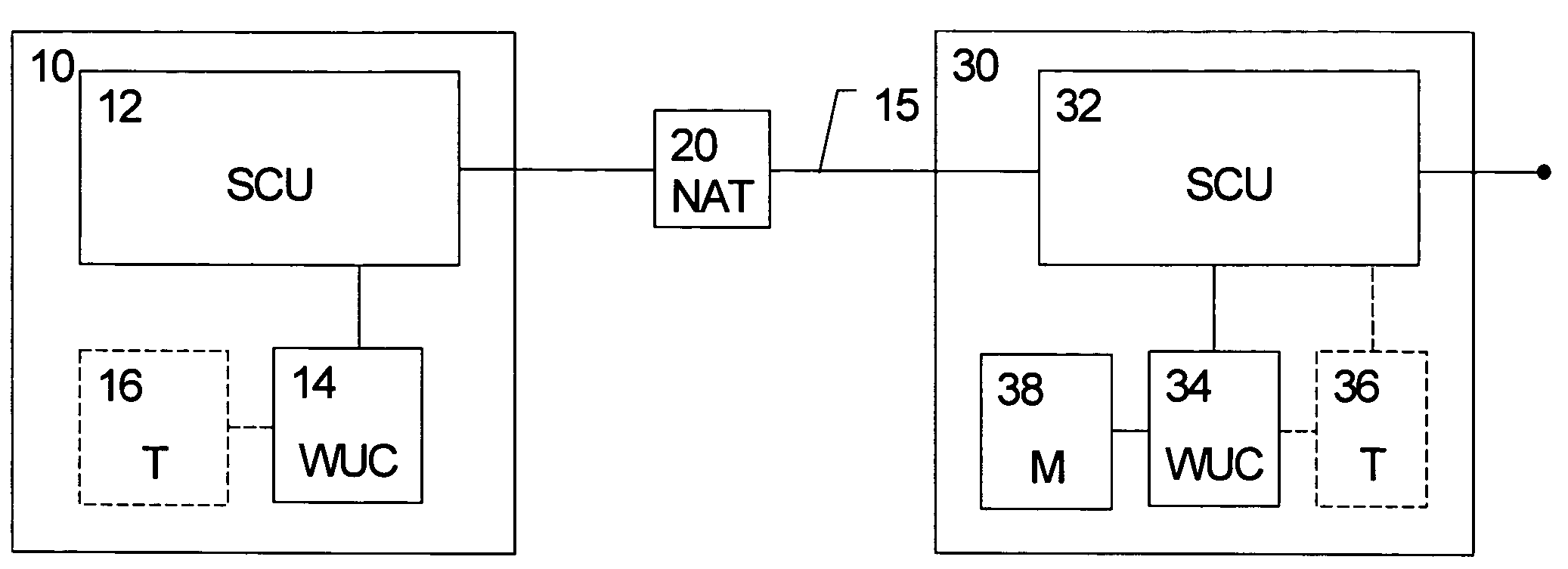
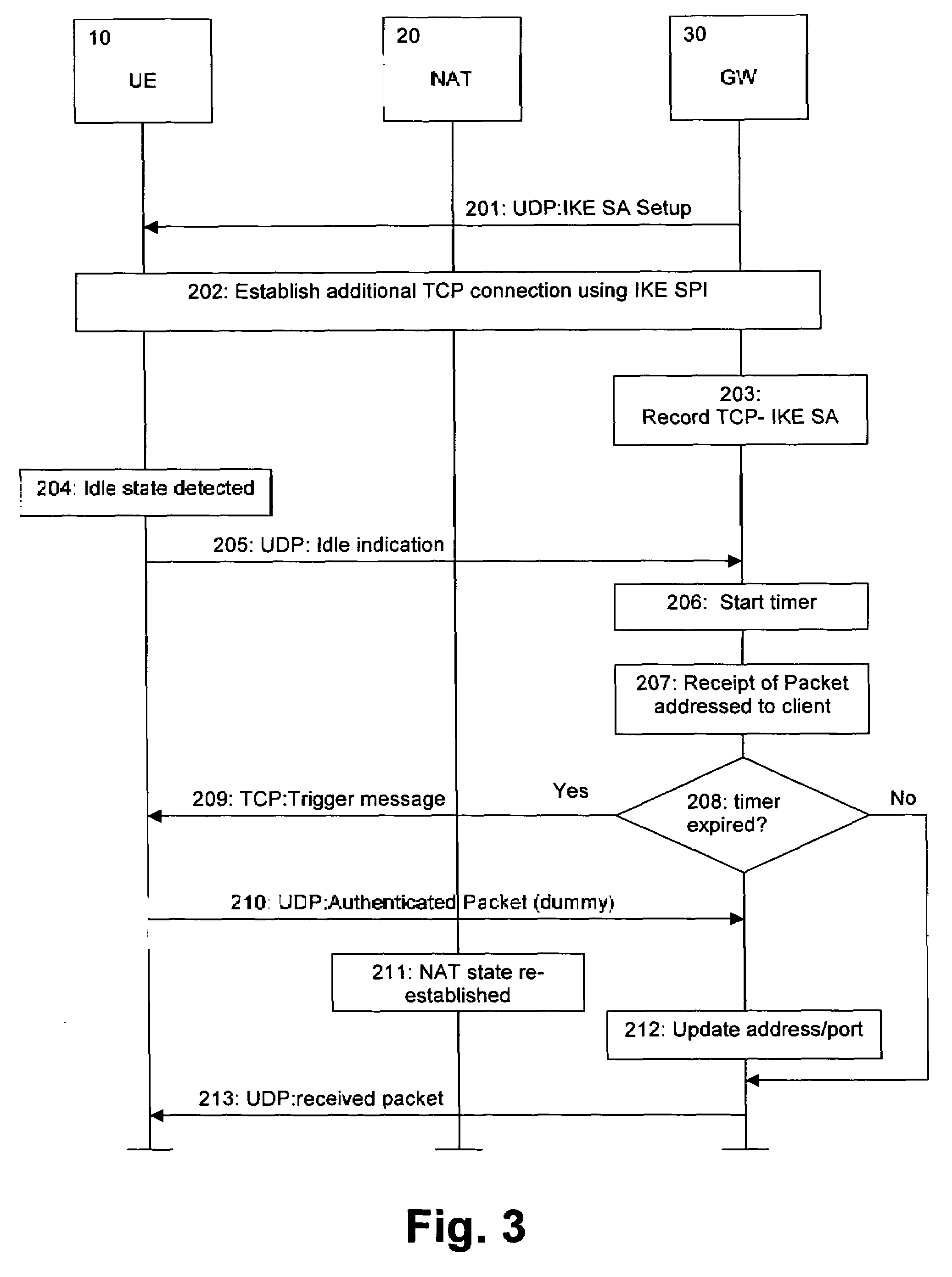
Power-efficient address mapping scheme
InactiveUS20070140159A1Reduce power consumptionMaintained for very long times without compromising battery lifeEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexPower efficientEncapsulated data
The present invention relates to a method, system, client device, gateway device and computer program product for maintaining a state information in an intermediate network function, wherein the state information expires after a predetermined idle period. Detecting means are provided for detecting an idle state of a connection. In response to the detecting means, a transport protocol used for encapsulating data is changed from a first protocol with a first predetermined idle period to a second protocol with a second predetermined idle period, said second predetermined idle period being longer than said first predetermined idle period. Alternatively, a connection parameter is provided to a device for a parallel second connection in a set-up negotiation via said first connection. This connection parameter is then used for setting up a parallel second connection to the device based on the second transport protocol used for encapsulating data with the second predetermined idle period. Then, an information linking the first and second connections is transmitted from the device to the data network, wherein the second connection is used for transmitting a wake-up notification to the device in response a detected idle state. Both alternatives provide the advantage of reduced keep-alive signaling and thus enhanced battery efficiency.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Systems and methods for program directed memory access patterns
InactiveUS20080046666A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationDirect memory accessVirtual memory management
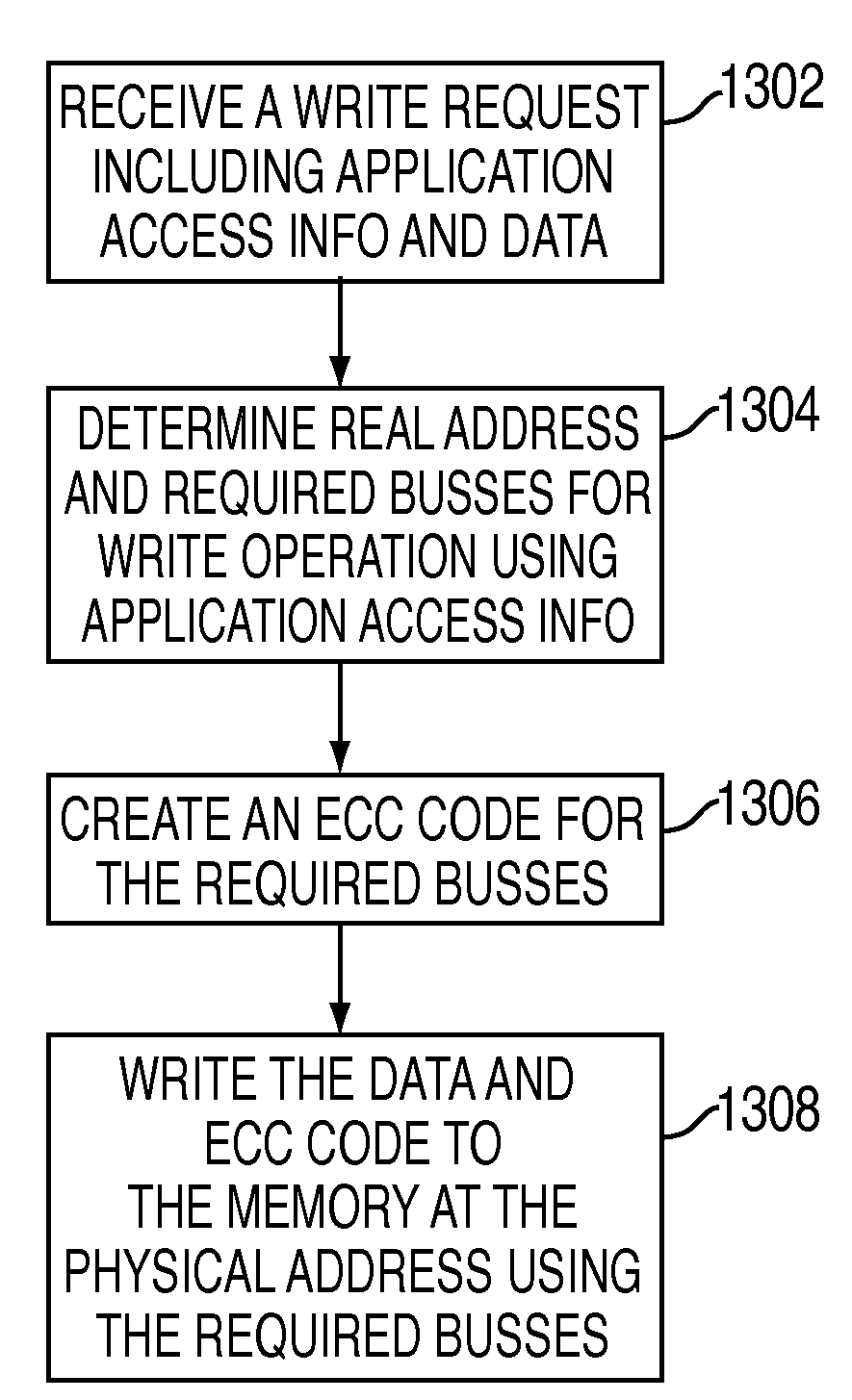
Systems and methods for program directed memory access patterns including a memory system with a memory, a memory controller and a virtual memory management system. The memory includes a plurality of memory devices organized into one or more physical groups accessible via associated busses for transferring data and control information. The memory controller receives and responds to memory access requests that contain application access information to control access pattern and data organization within the memory. Responding to memory access request includes accessing one or more memory devices. The virtual memory management system includes: a plurality of page table entries for mapping virtual memory addresses to real addresses in the memory; a hint state responsive to application access information for indicating how real memory for associated pages is to be physically organized within the memory; and a means for conveying the hint state to the memory controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for managing a NAND flash memory
ActiveUS20100332730A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPagingDatabase
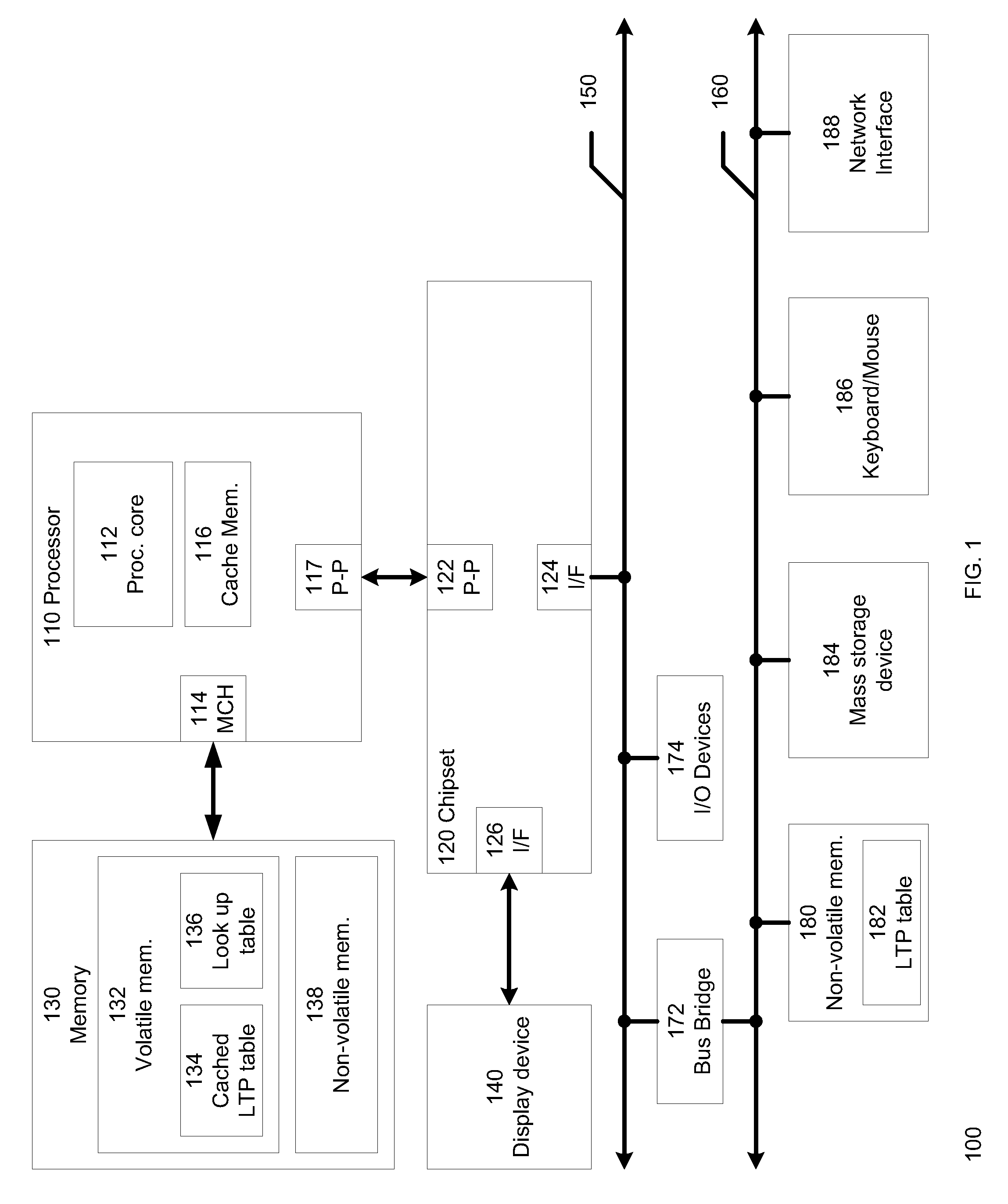
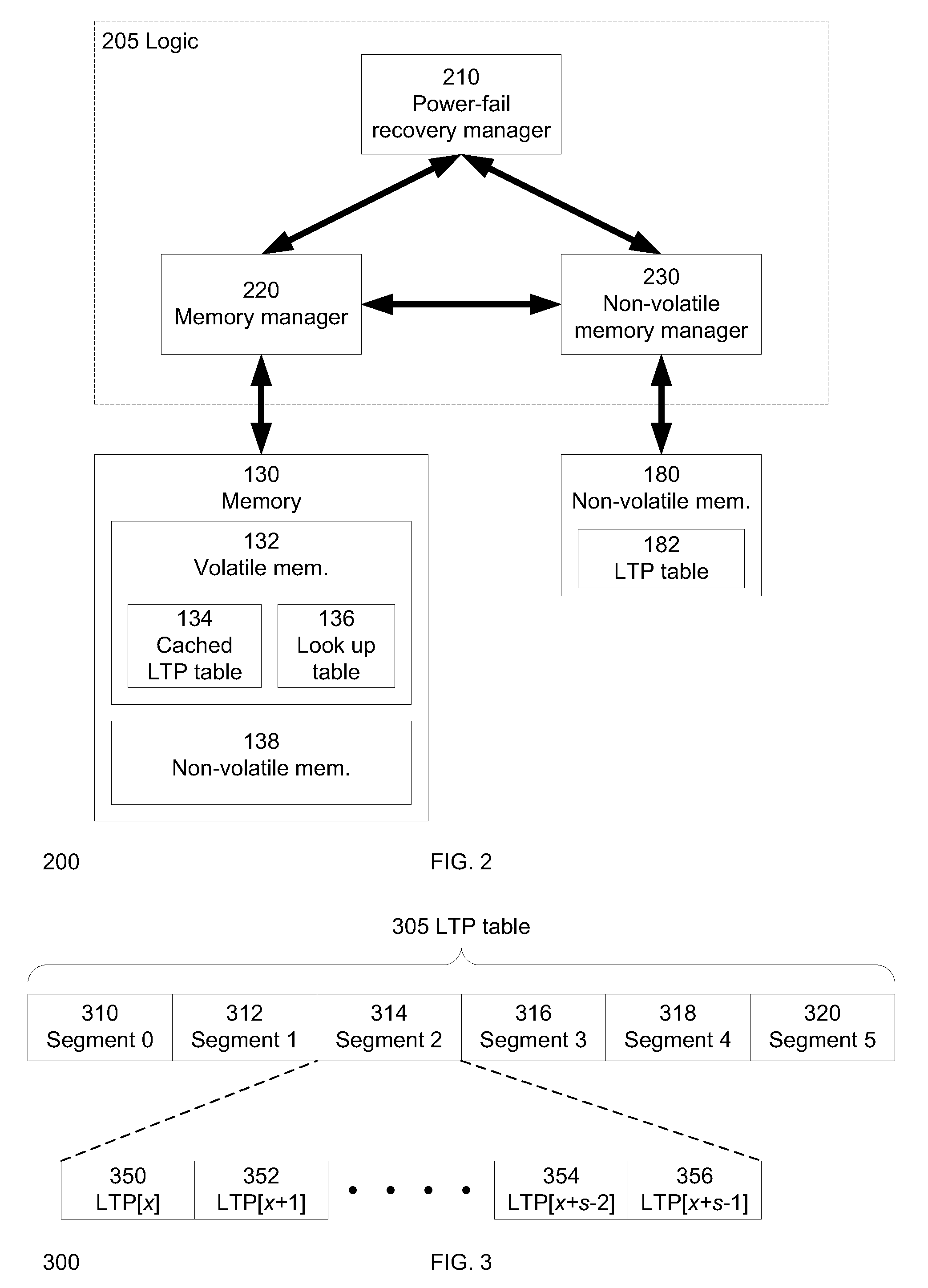
A method and system to facilitate paging of one or more segments of a logical-to-physical (LTP) address mapping structure to a non-volatile memory. The LTP address mapping structure is part of an indirection system map associated with the non-volatile memory in one embodiment of the invention. By allowing one or more segments of the LTP address mapping structure to be paged to the non-volatile memory, the amount of volatile memory required to store the LTP address mapping structure is reduced while maintaining the benefits of the LTP address mapping structure in one embodiment of the invention.
Owner:SK HYNIX NAND PROD SOLUTIONS CORP
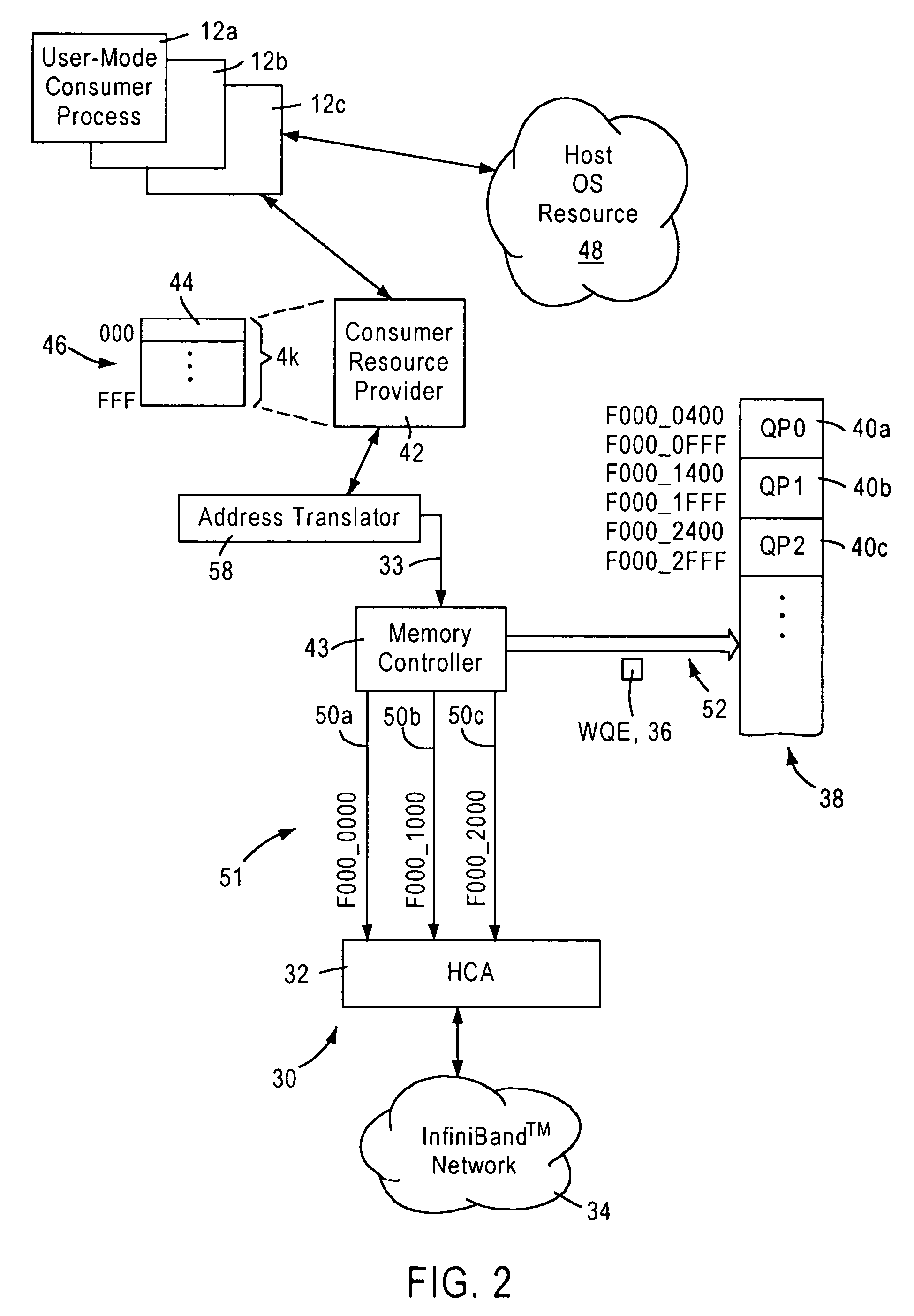
Arrangement for implementing kernel bypass for access by user mode consumer processes to a channel adapter based on virtual address mapping
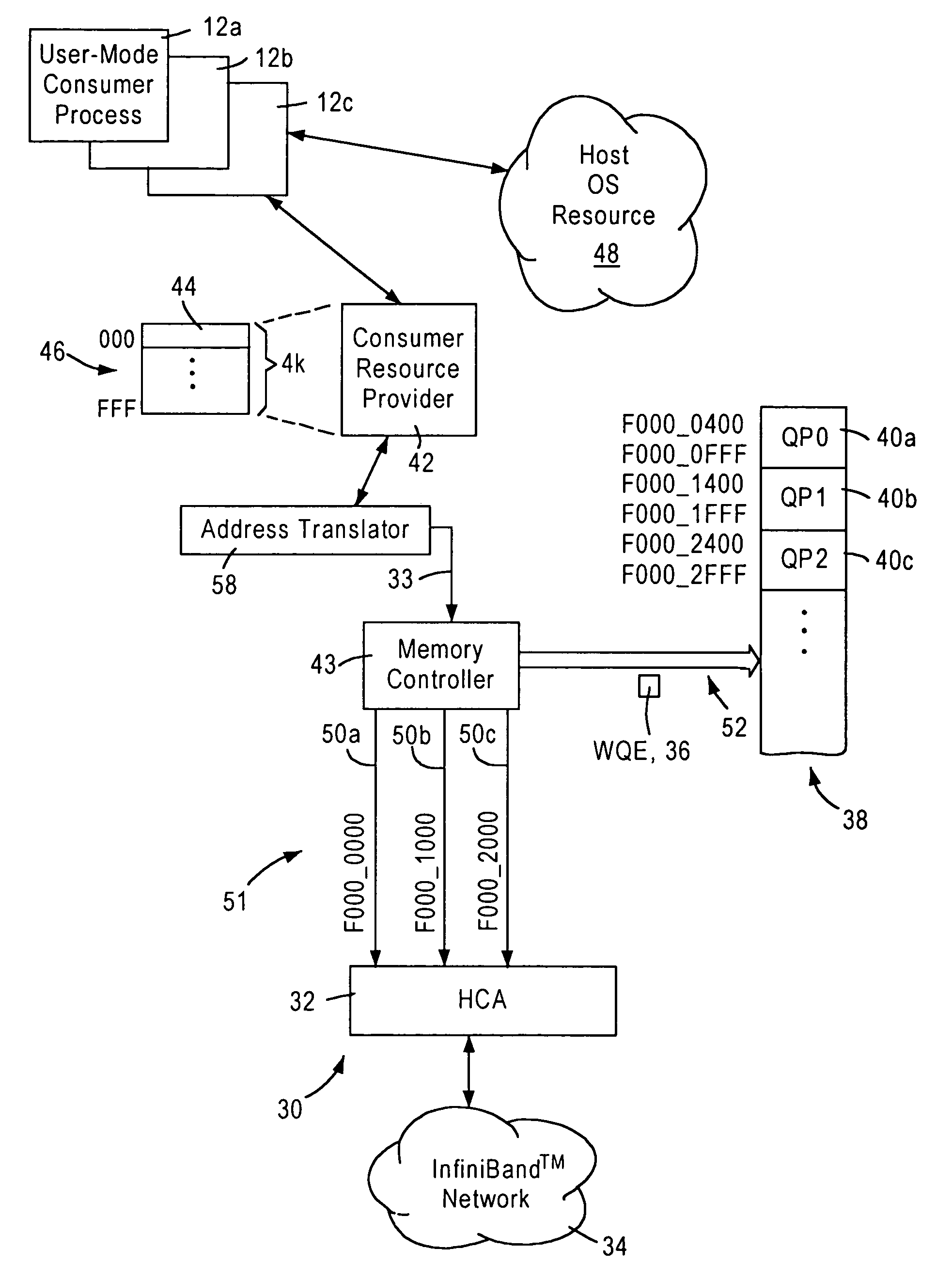
InactiveUS7003586B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual destinationOperational system
A consumer resource provider is configured for generating a work request to a prescribed virtual destination address on behalf of a user-mode consumer process requiring a memory access. An operating system resource, configured for establishing communications between the consumer resource provider and a host channel adapter configured for servicing the work notifications, assigns virtual address space for use by the consumer resource provider, and respective unique mapping values specified as user mode access for use by the consumer resource provider in executing the memory accesses on behalf of the respective user-mode consumer processes. An address translator includes a translation map for uniquely mapping the virtual address space used by the consumer resource provider to a prescribed physical address space accessible by the host channel adapter. The address translator, in response to receiving the work notification at a virtual address from the consumer resource provider on behalf of an identified user-mode consumer process, maps the work notification to a corresponding prescribed physical address based on the corresponding mapping value assigned for the identified user-mode consumer process, enabling the host channel adapter to detect the work notification at the mapped physical address.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
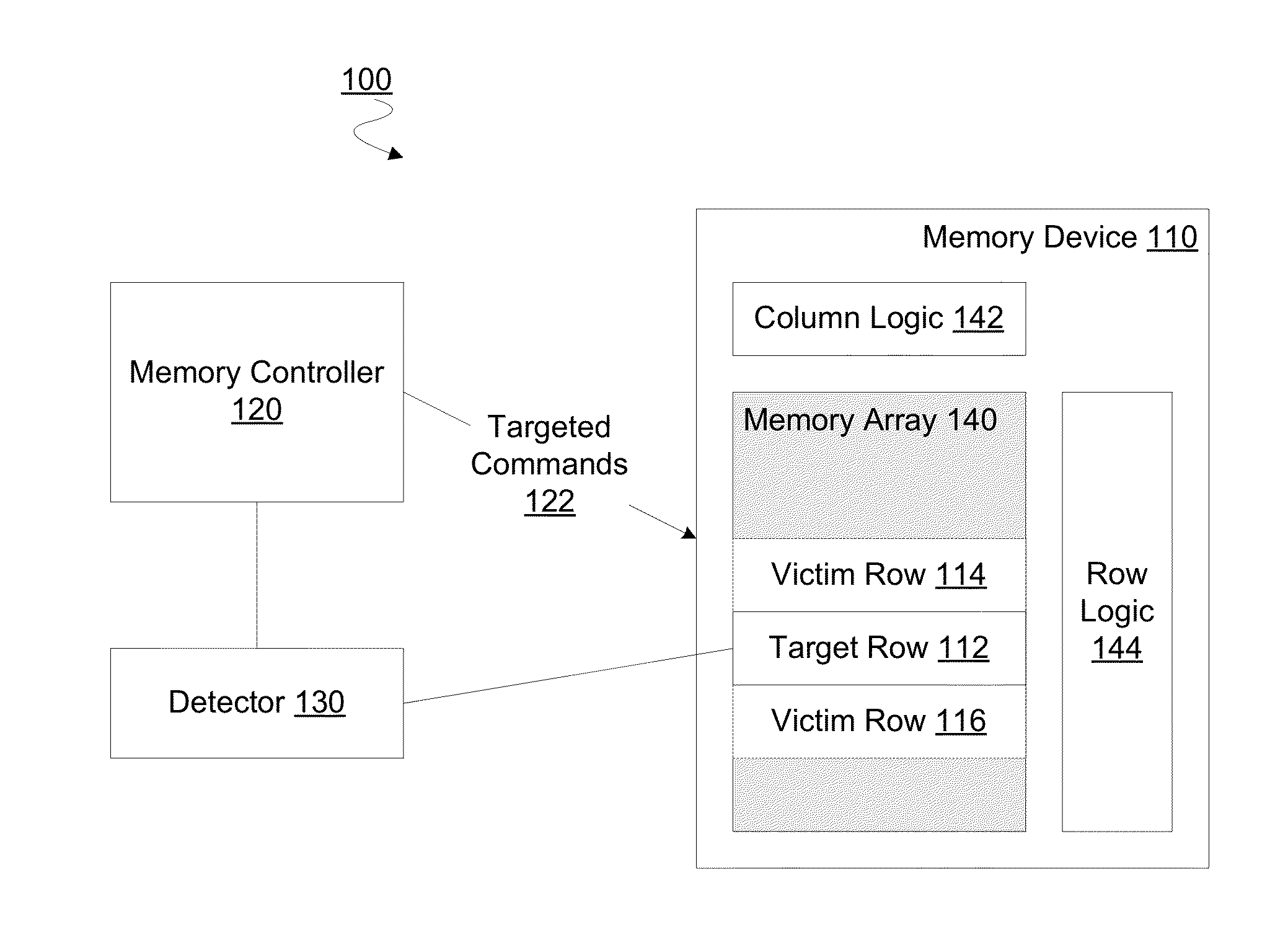
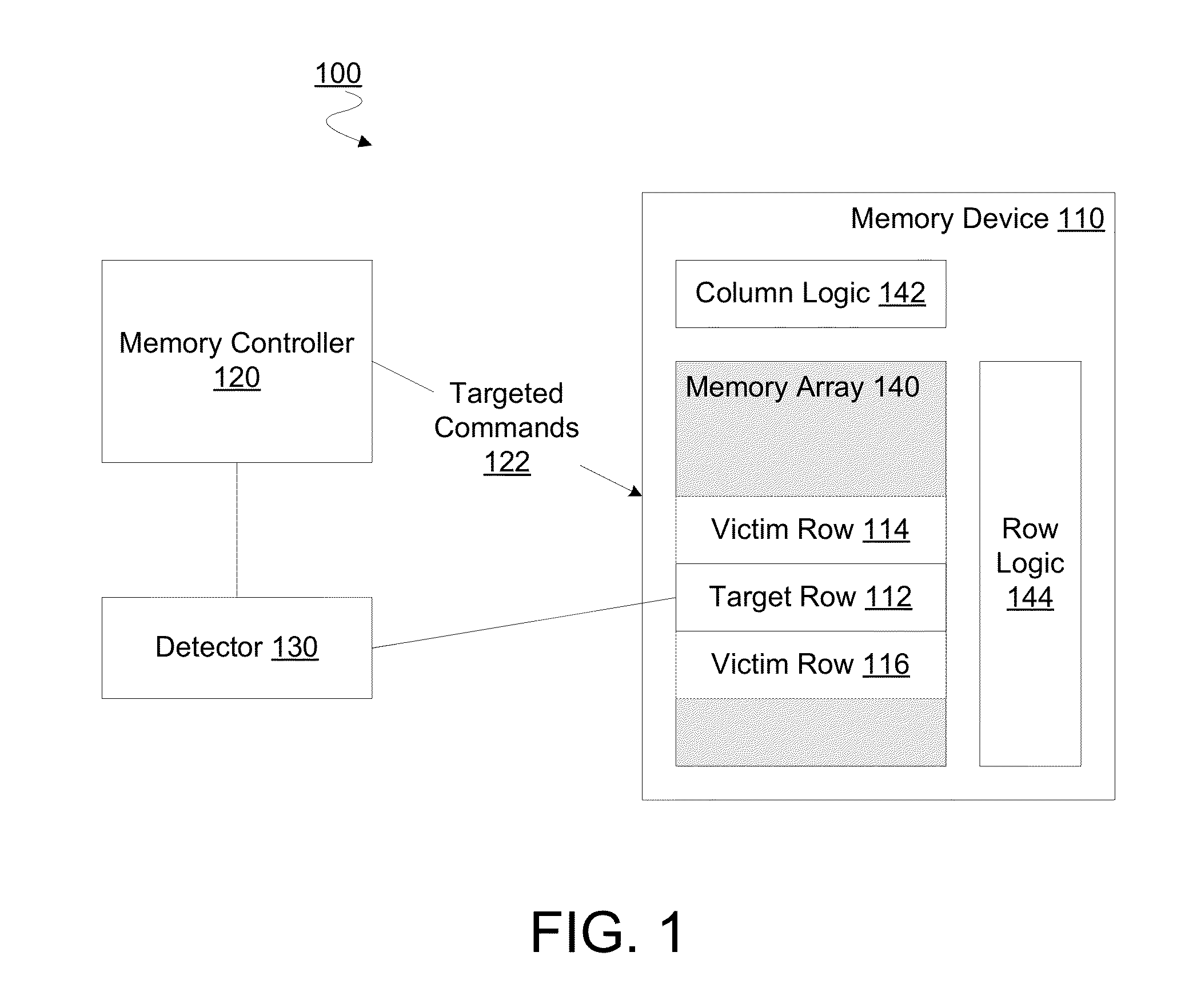
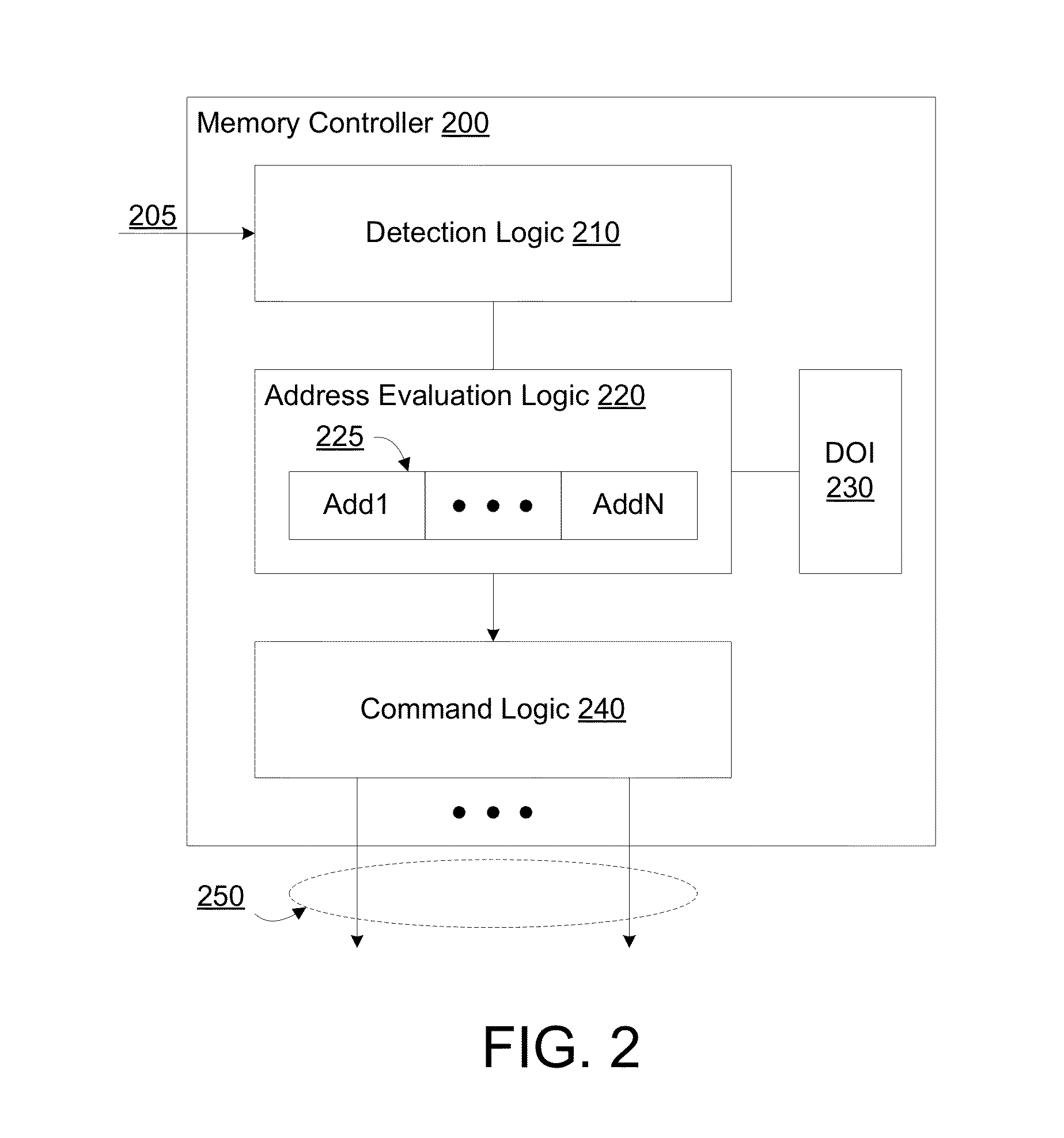
Method, apparatus and system for providing a memory refresh
A memory controller to implement targeted refreshes of potential victim rows of a row hammer event. In an embodiment, the memory controller receives an indication that a specific row of a memory device is experiencing repeated accesses which threaten the integrity of data in one or more victim rows physically adjacent to the specific row. The memory controller accesses default offset information in the absence of address map information which specifies an offset between physically adjacent rows of the memory device. In another embodiment, the memory controller determines addresses for potential victim rows based on the default offset information. In response to the received indication of the row hammer event, the memory controller sends for each of the determined plurality of addresses a respective command to the memory device, where the commands are for the memory device to perform targeted refreshes of potential victim rows.
Owner:INTEL CORP
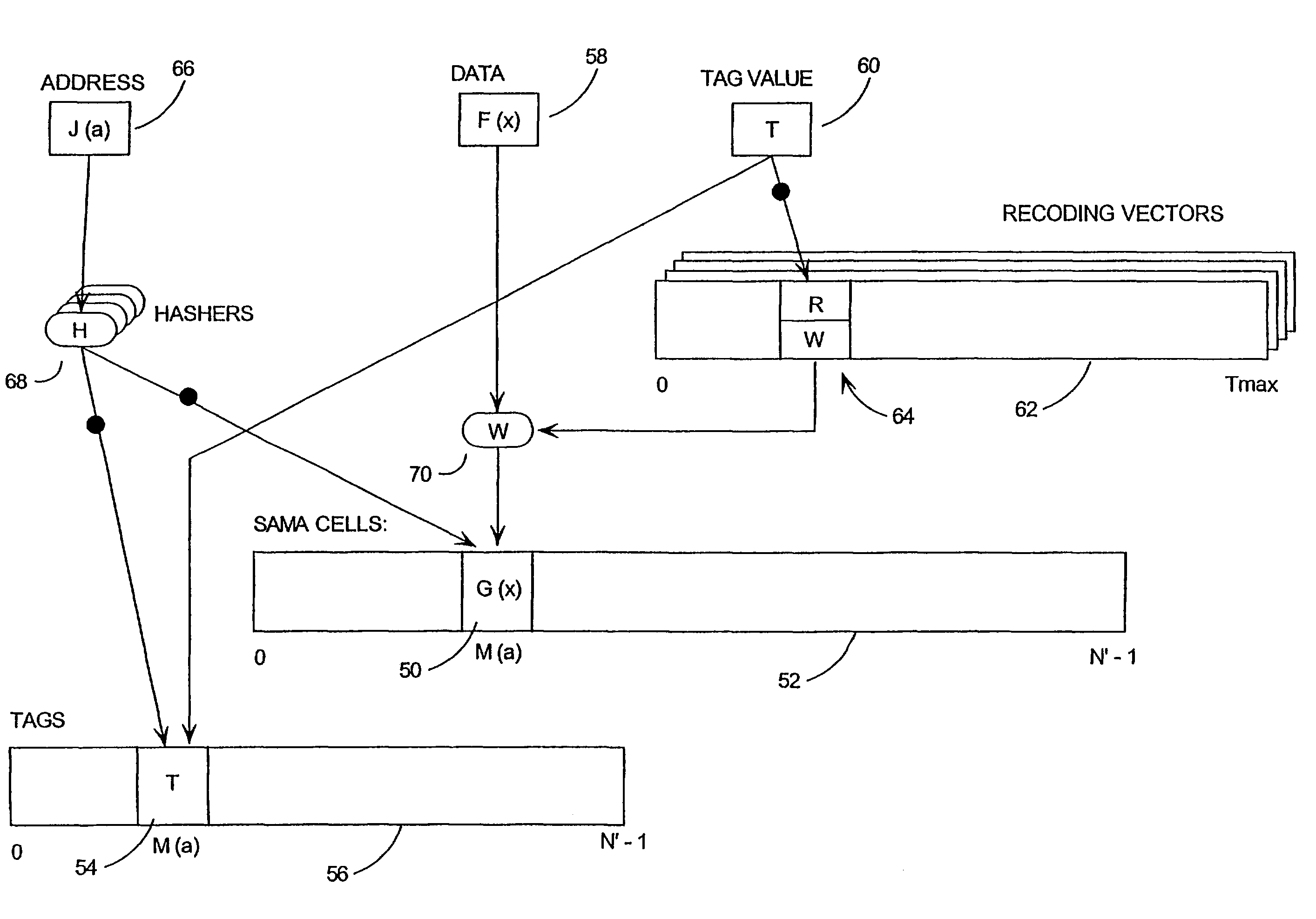
Perfect hashing of variably-sized data
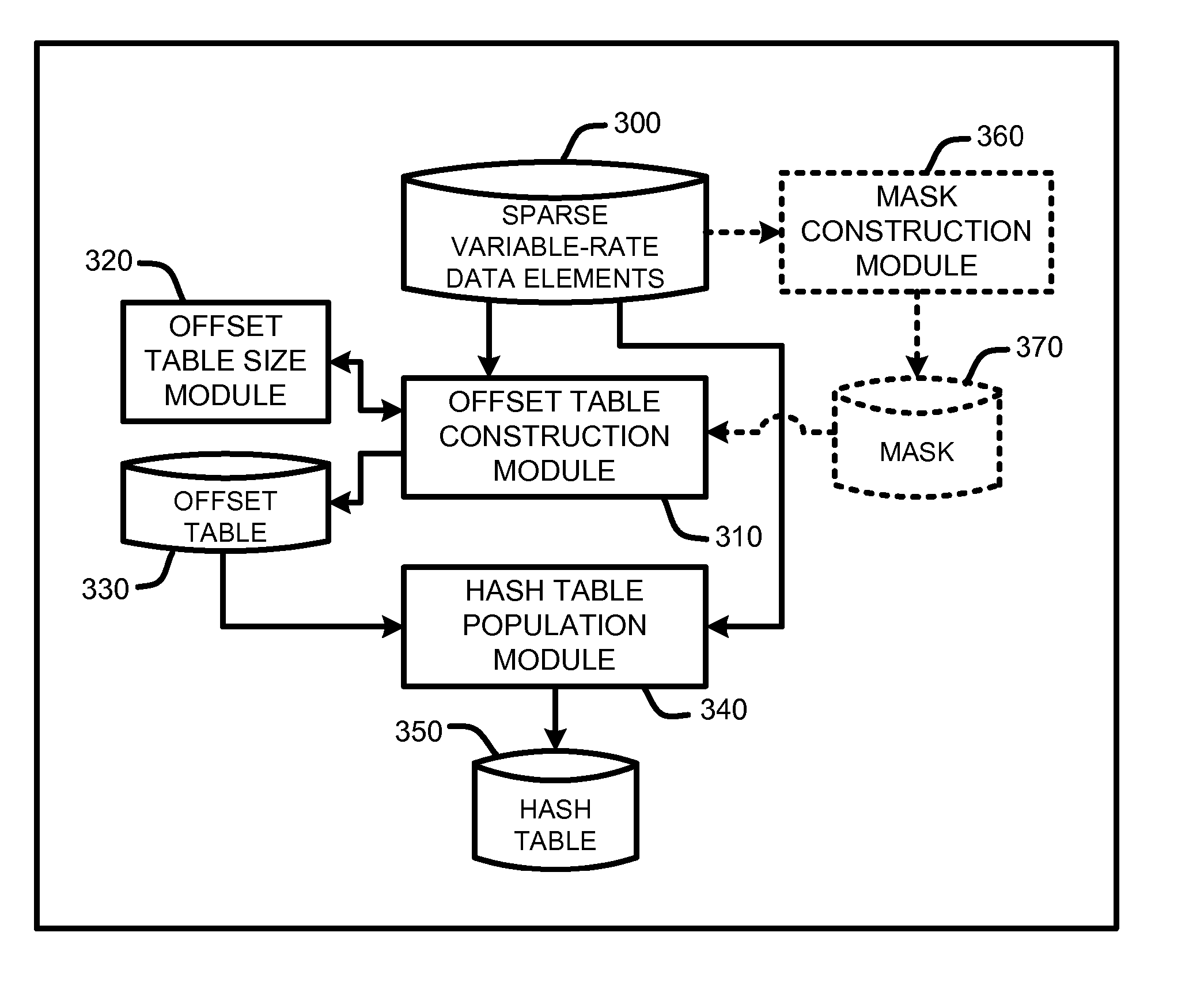
InactiveUS20070245119A1Efficient random accessEliminate needDigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTheoretical computer sciencePerfect hash function
A “Variable-Rate Perfect Hasher” maps sparse variable-rate data of one or more dimensions into a hash table using a perfect hash function. In various embodiments, perfect hash tables are populated by first computing offset table address for each data point of a domain of sparse variable-rate data elements. Offset vectors are then computed for each offset table address based in part on the size of each data element by evaluating offset vectors in order of a sum of the data point addresses mapping to each offset vector. These offset vectors are then stored in the offset table. For each data point, the corresponding offset vector is then used to compute a hash table address. Data elements are then perfectly hashed into the hash table using the computed hash table addresses. The resulting hash tables support efficient random access of the variable-sized data elements stored therein.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Startup reconstruction of logical-to-physical address translation data for solid state disks
InactiveUS20110072199A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPhysical addressMedia layer
Described embodiments provide reconstruction of logical-to-physical address mapping data for one or more sectors of a storage device at startup of a media controller. The sectors of the storage device are organized into blocks and superblocks and the address mapping data is stored in a volatile memory. At a startup condition of the media controller, a buffer layer module of the media controller allocates space in the volatile memory for one or more logical-to-physical address mapping data structures. A media layer module of the media controller determines a block type of each block of the storage device and places each block of the storage device into corresponding groups based on the determined block type of each block. The one or more blocks of each group are processed, and one or more address mapping data structures for the storage device are constructed in the allocated space in the volatile memory.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com