Patents
Literature
817 results about "Flash memory controller" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
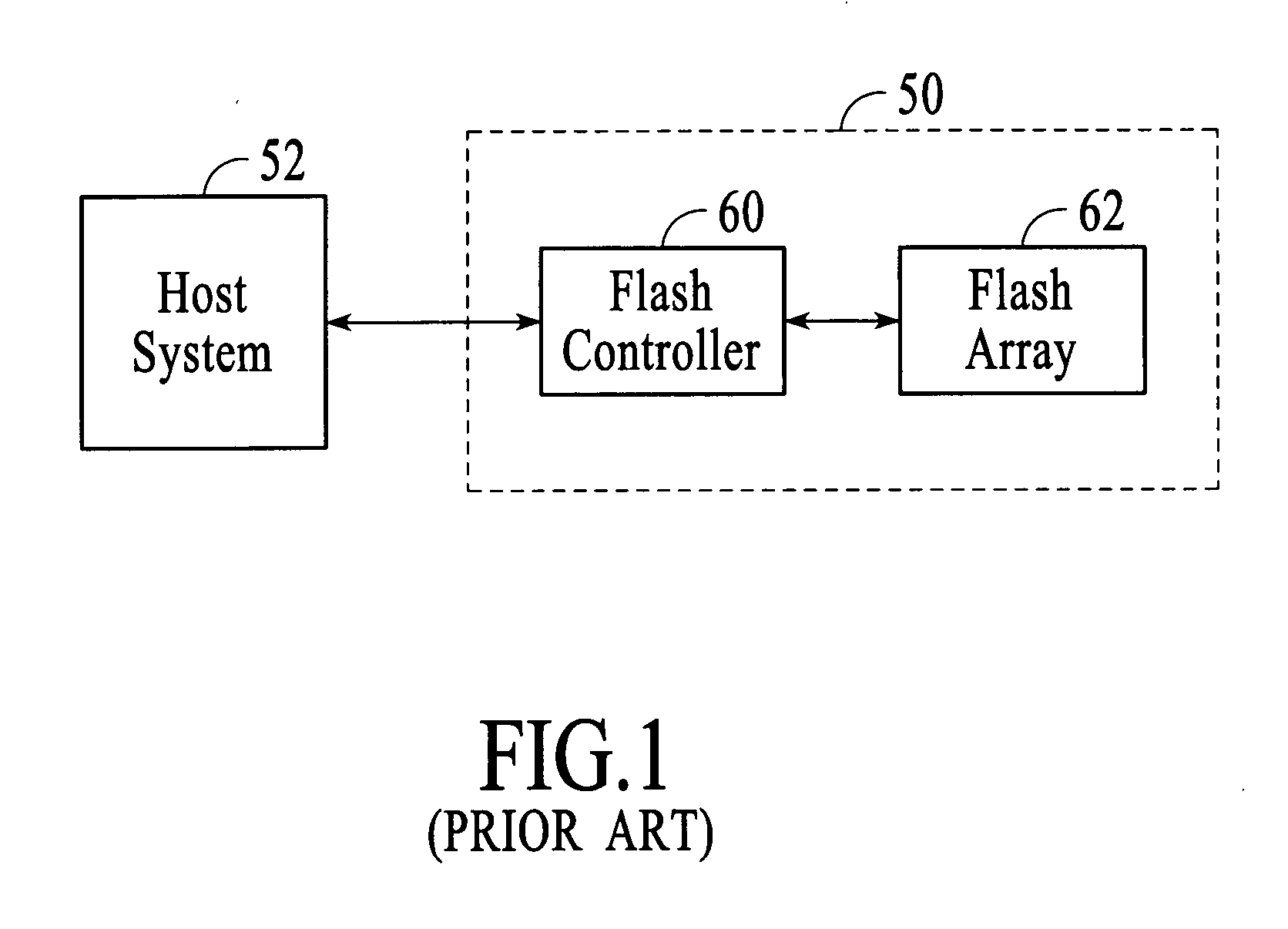
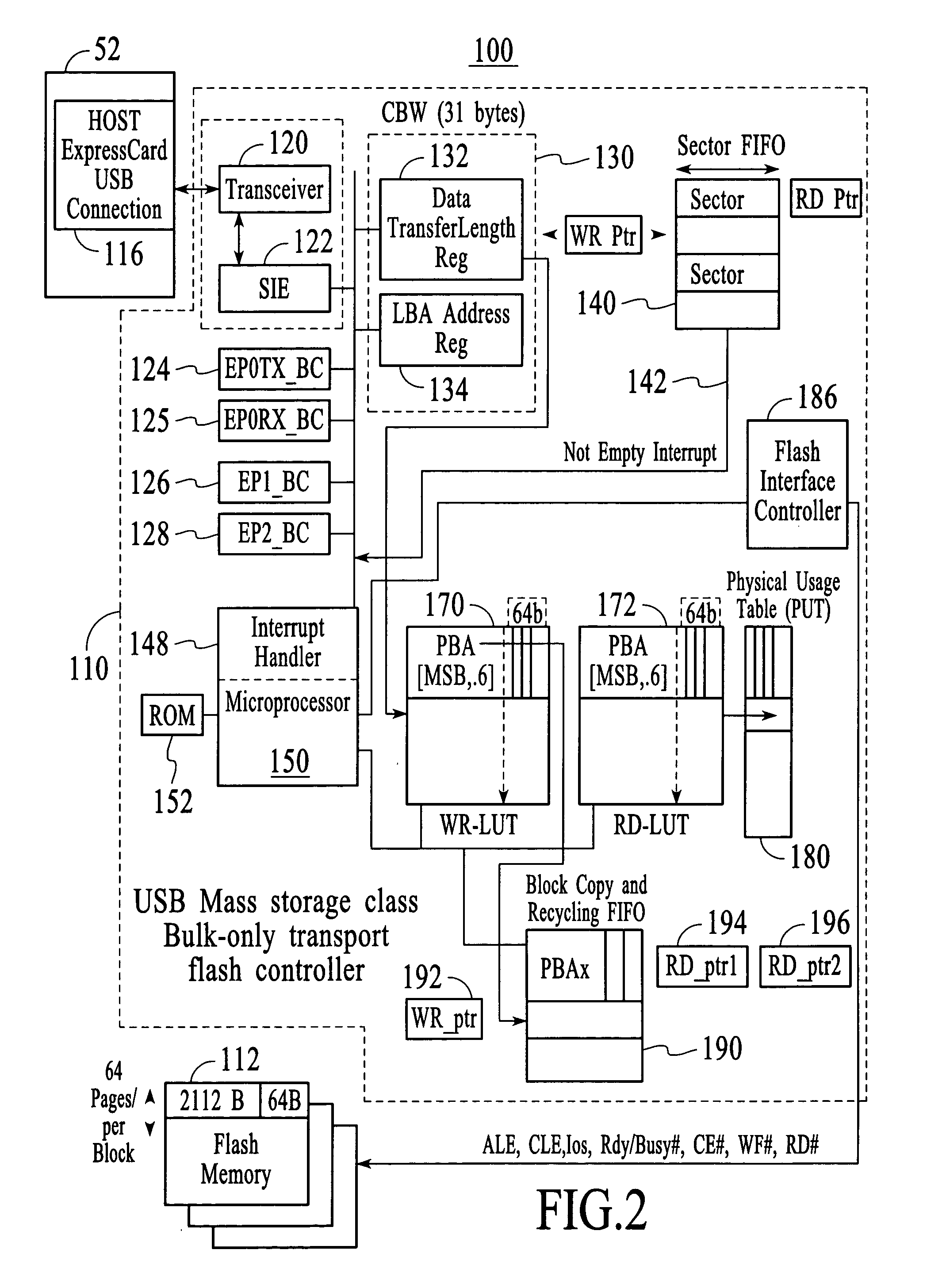
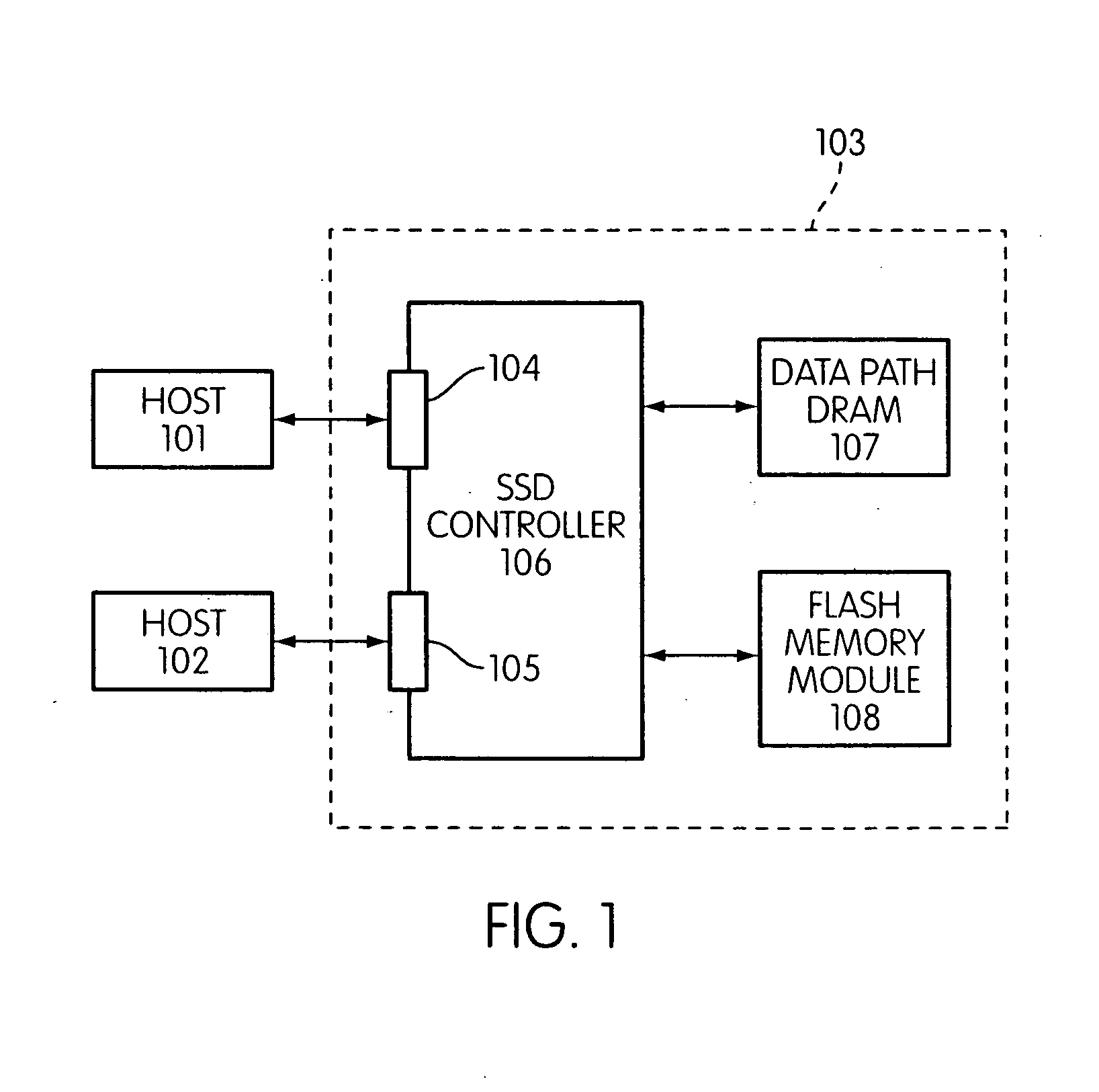
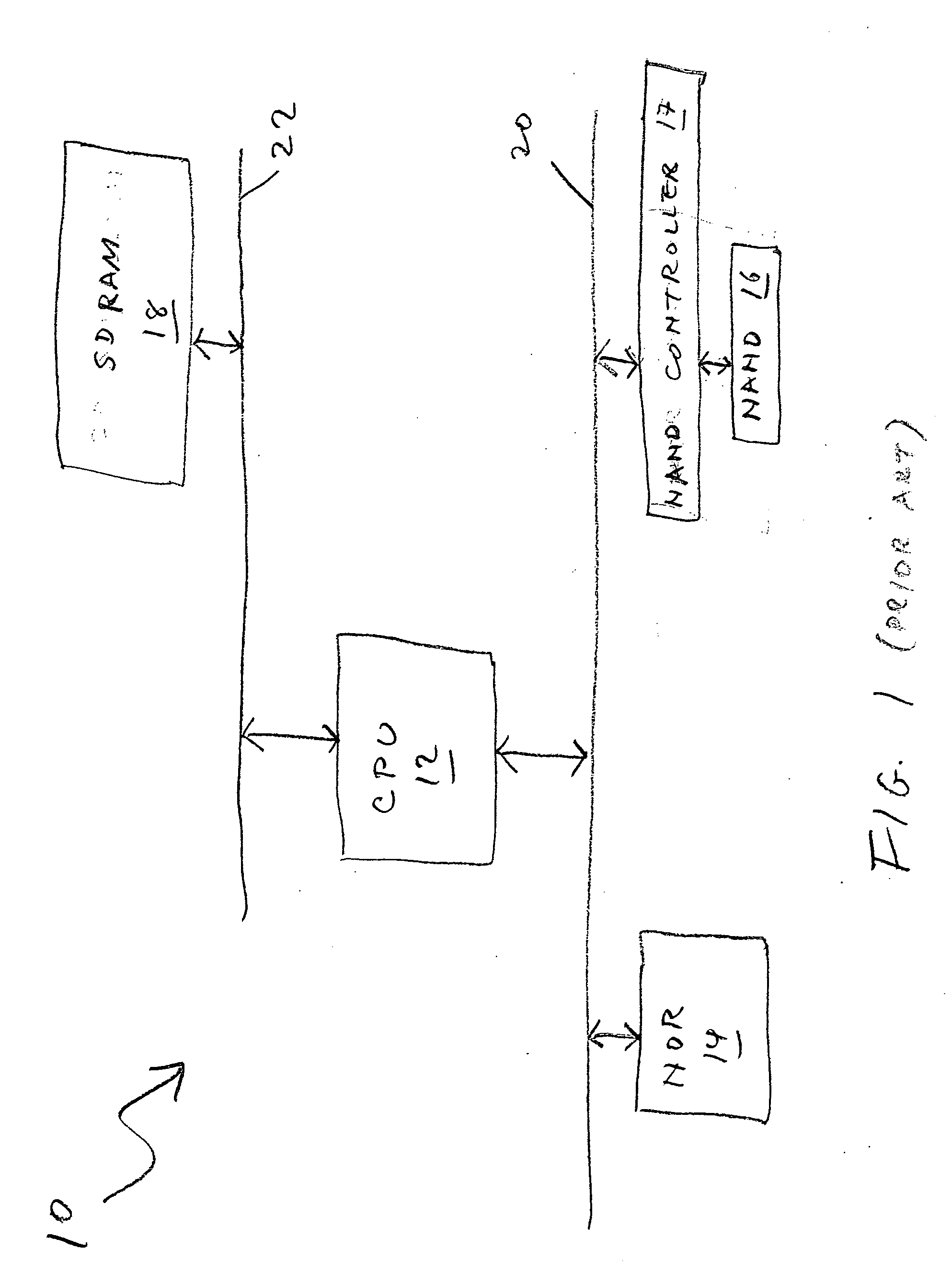
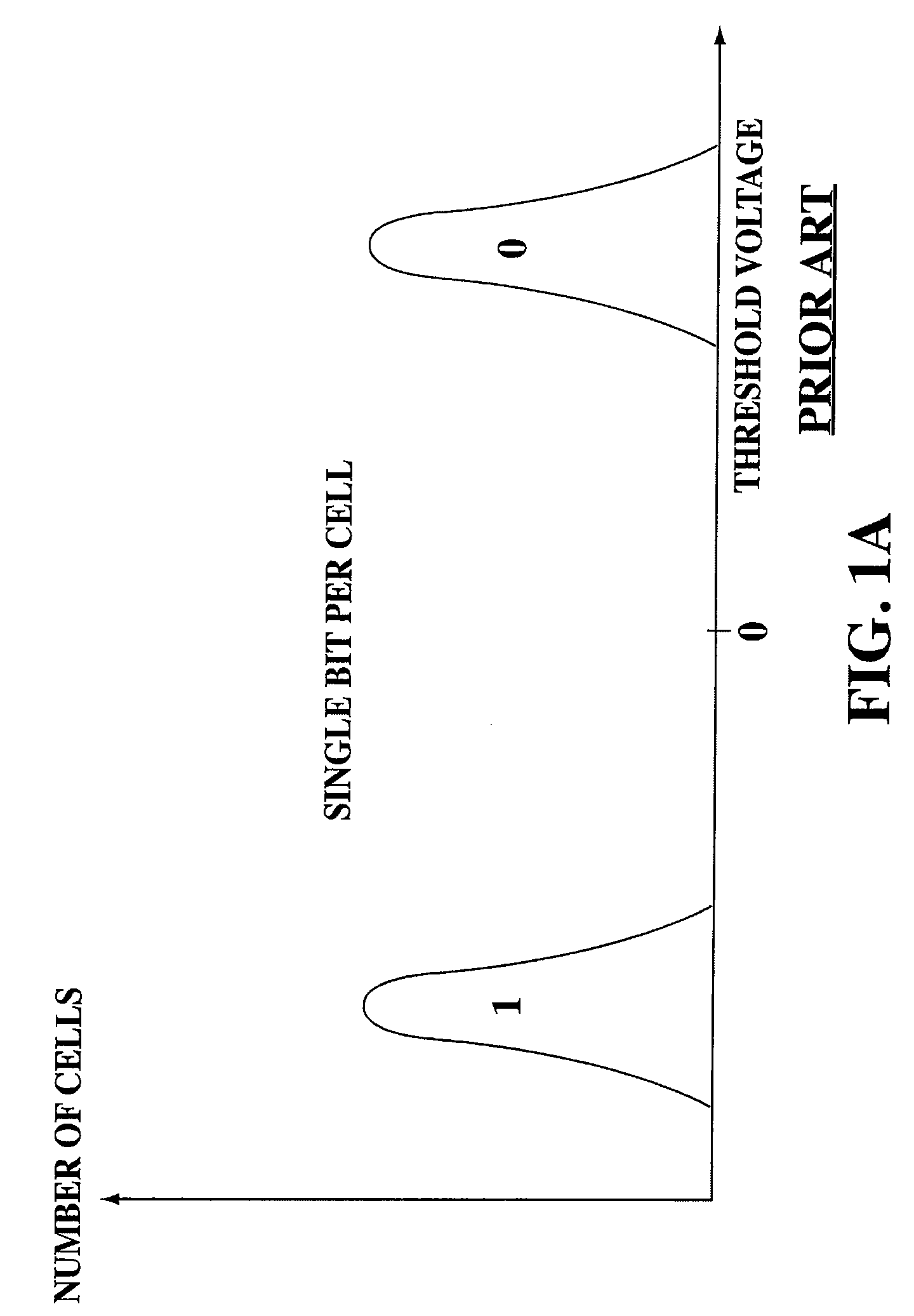
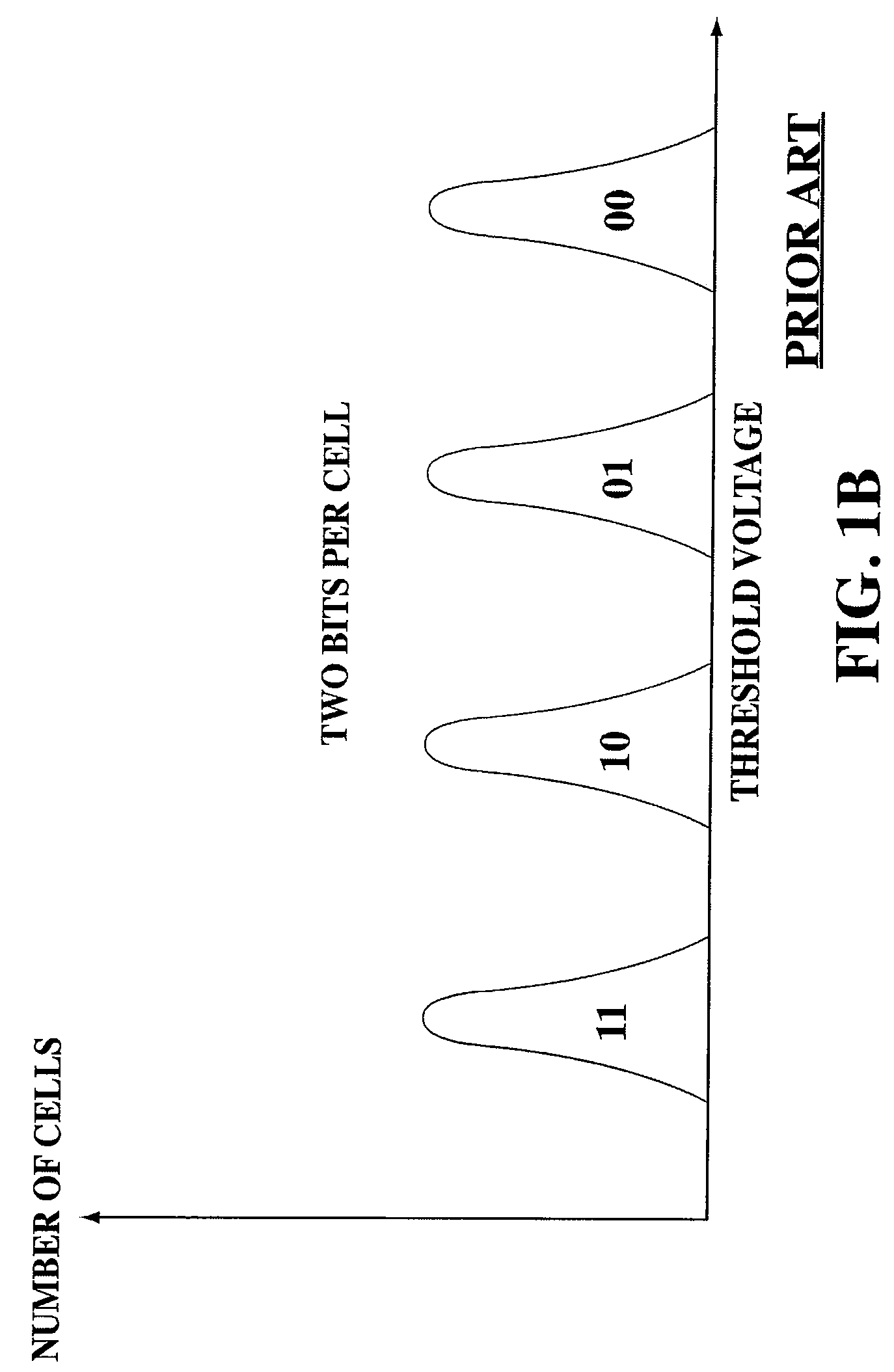
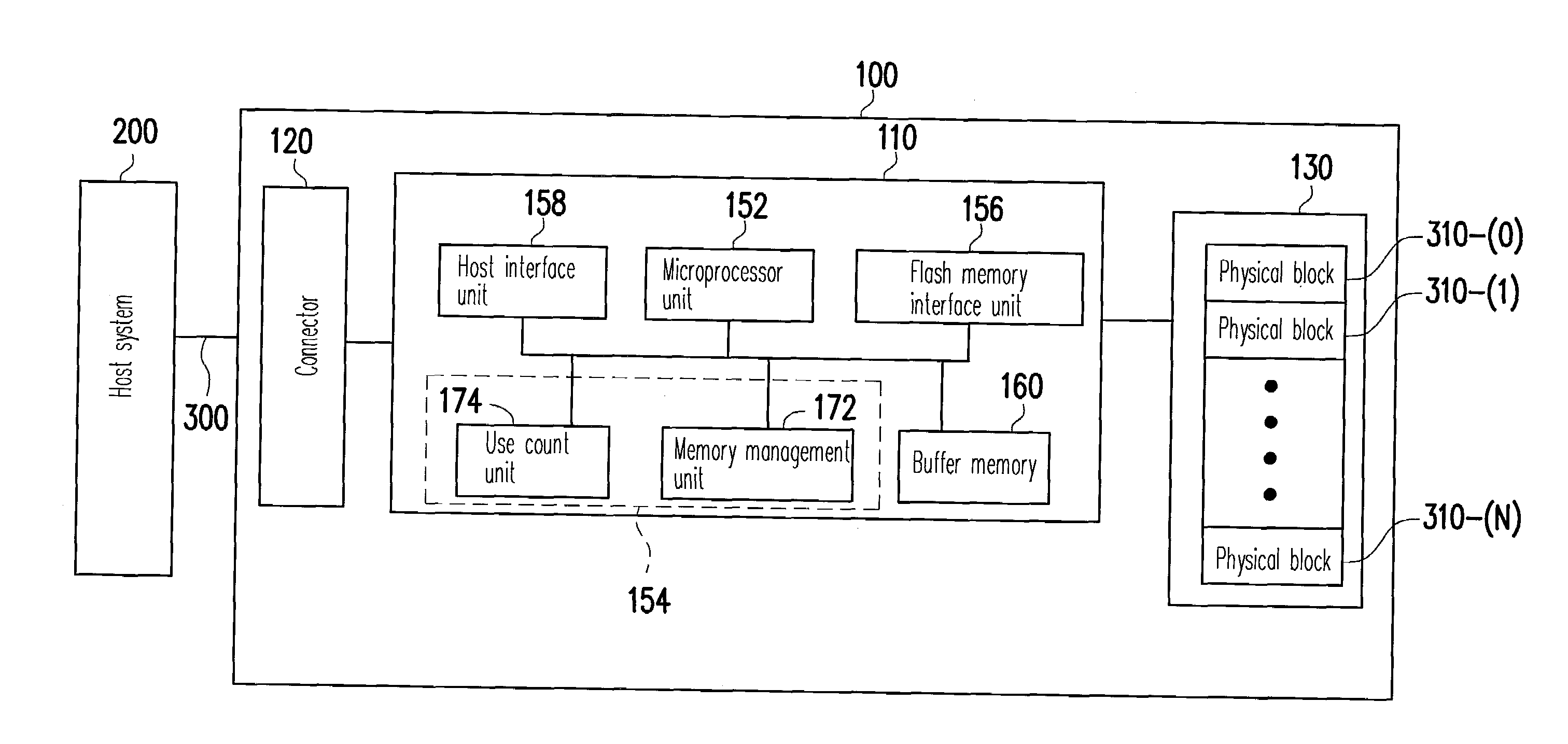
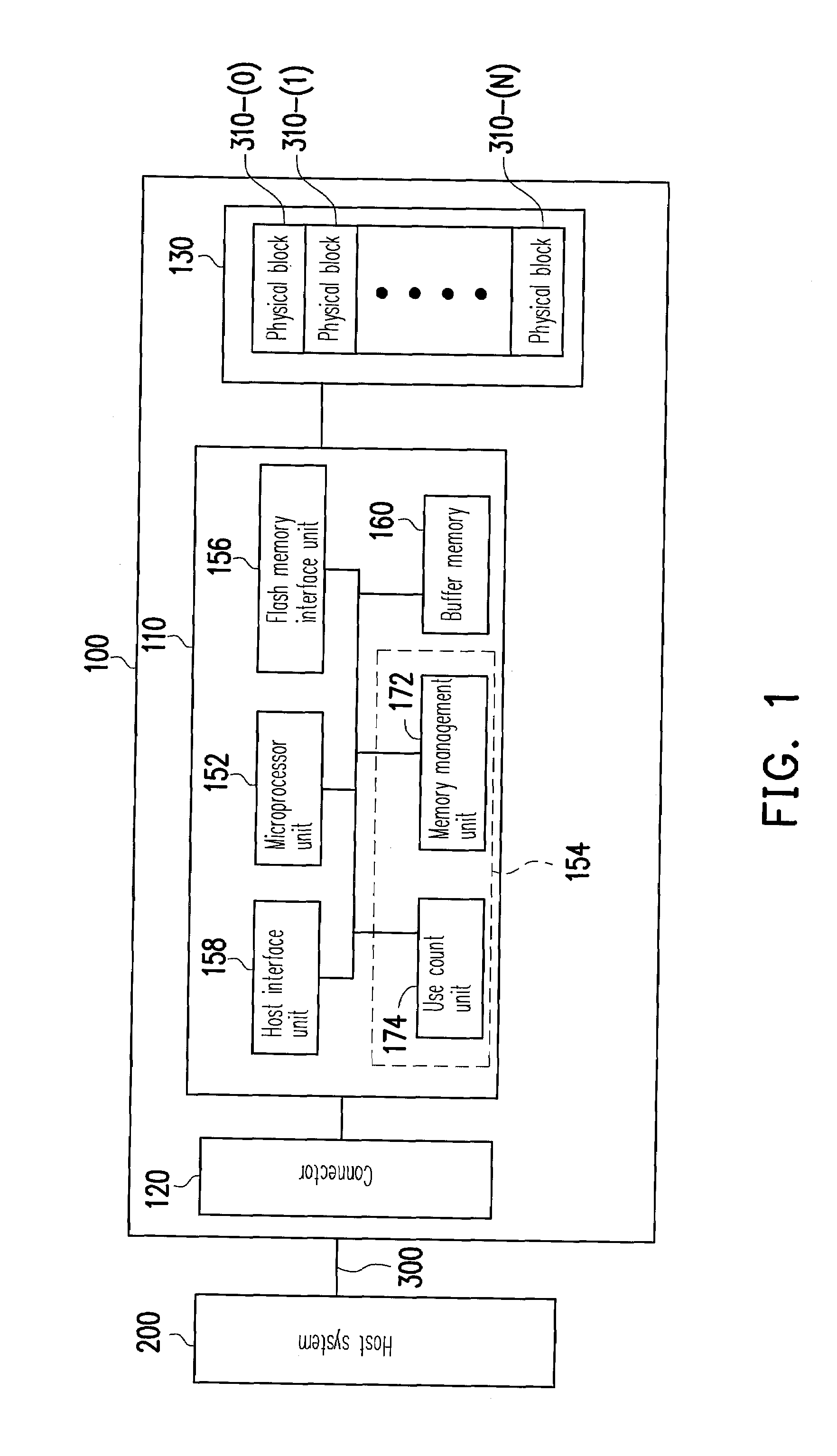
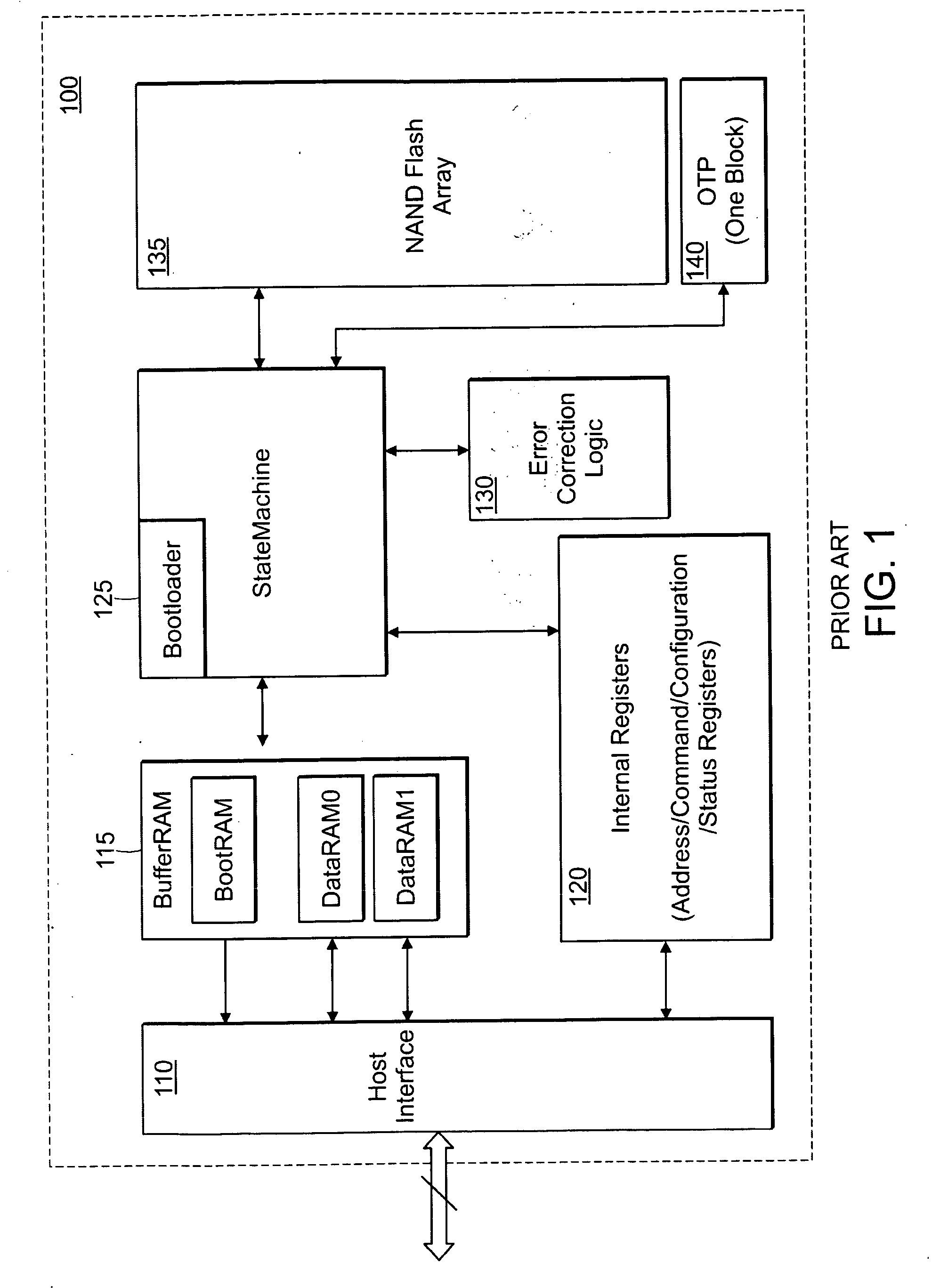
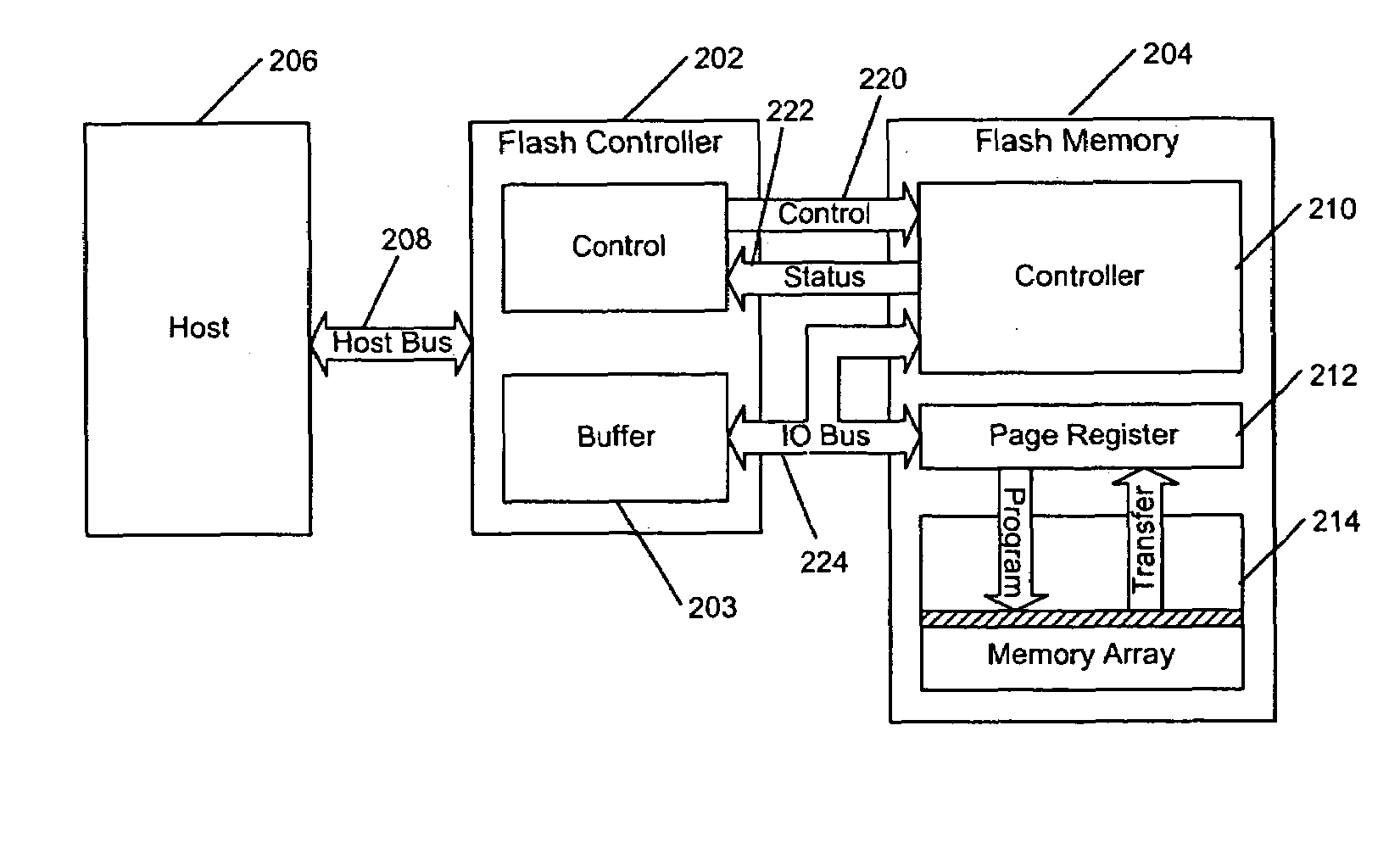
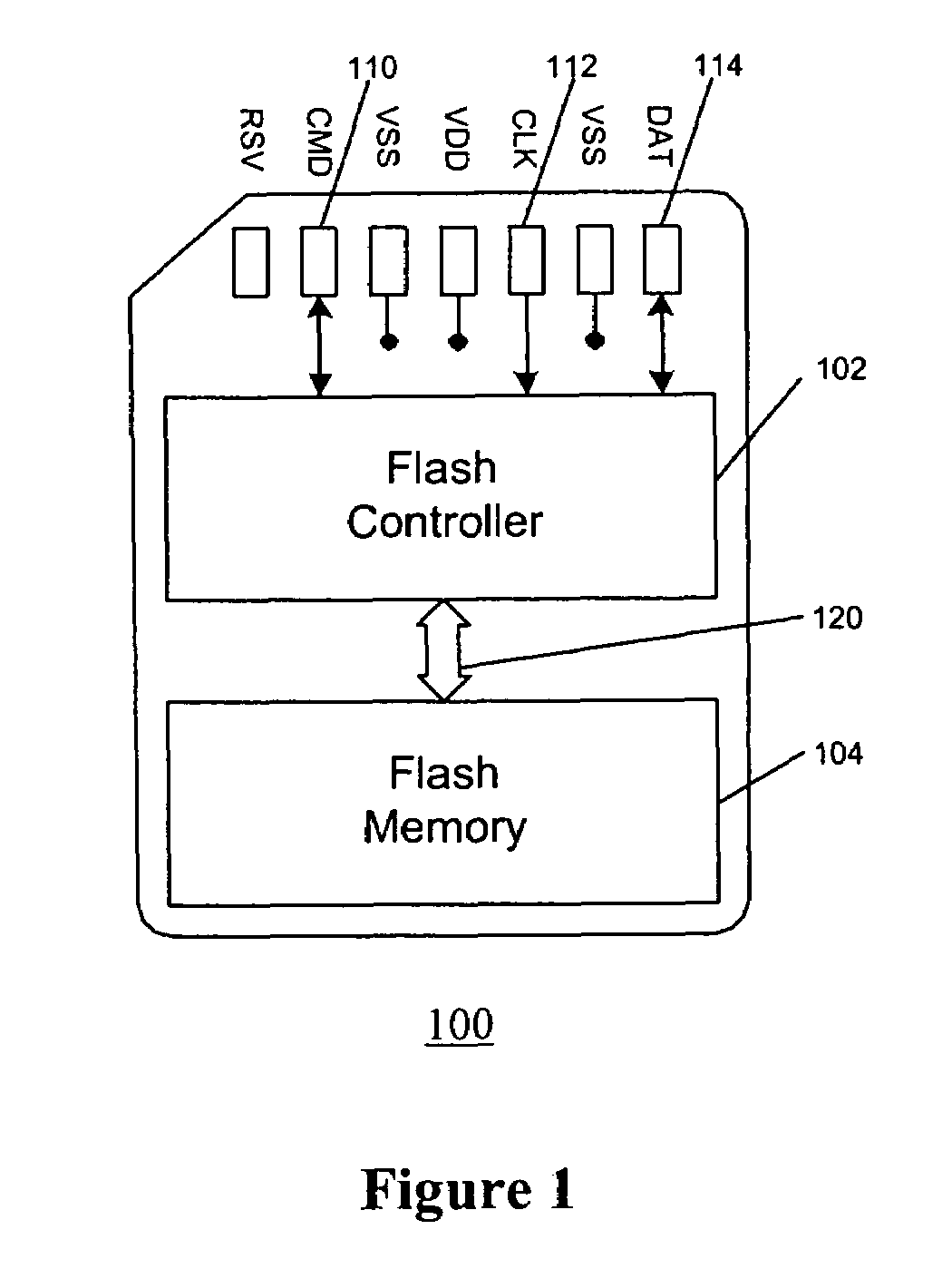
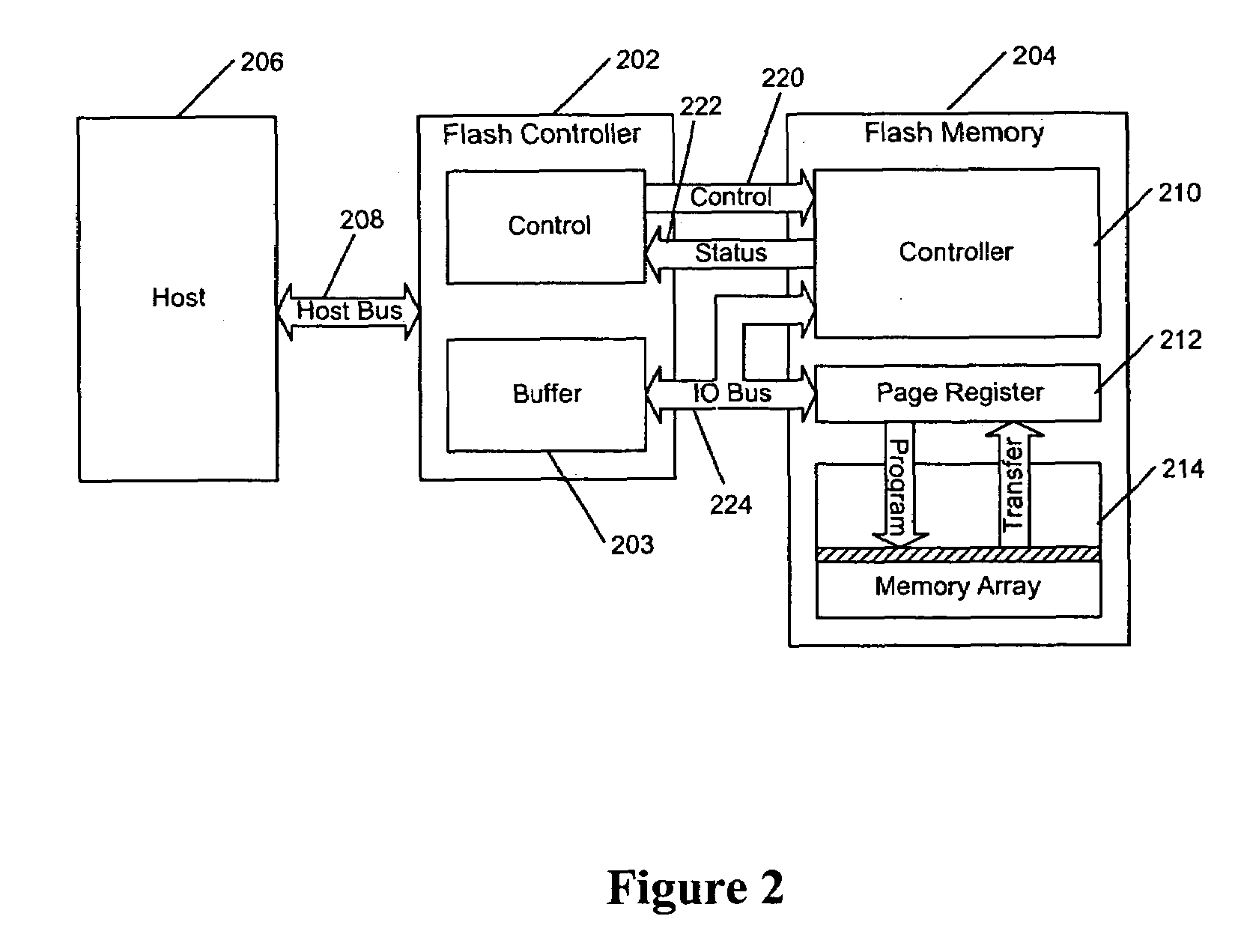
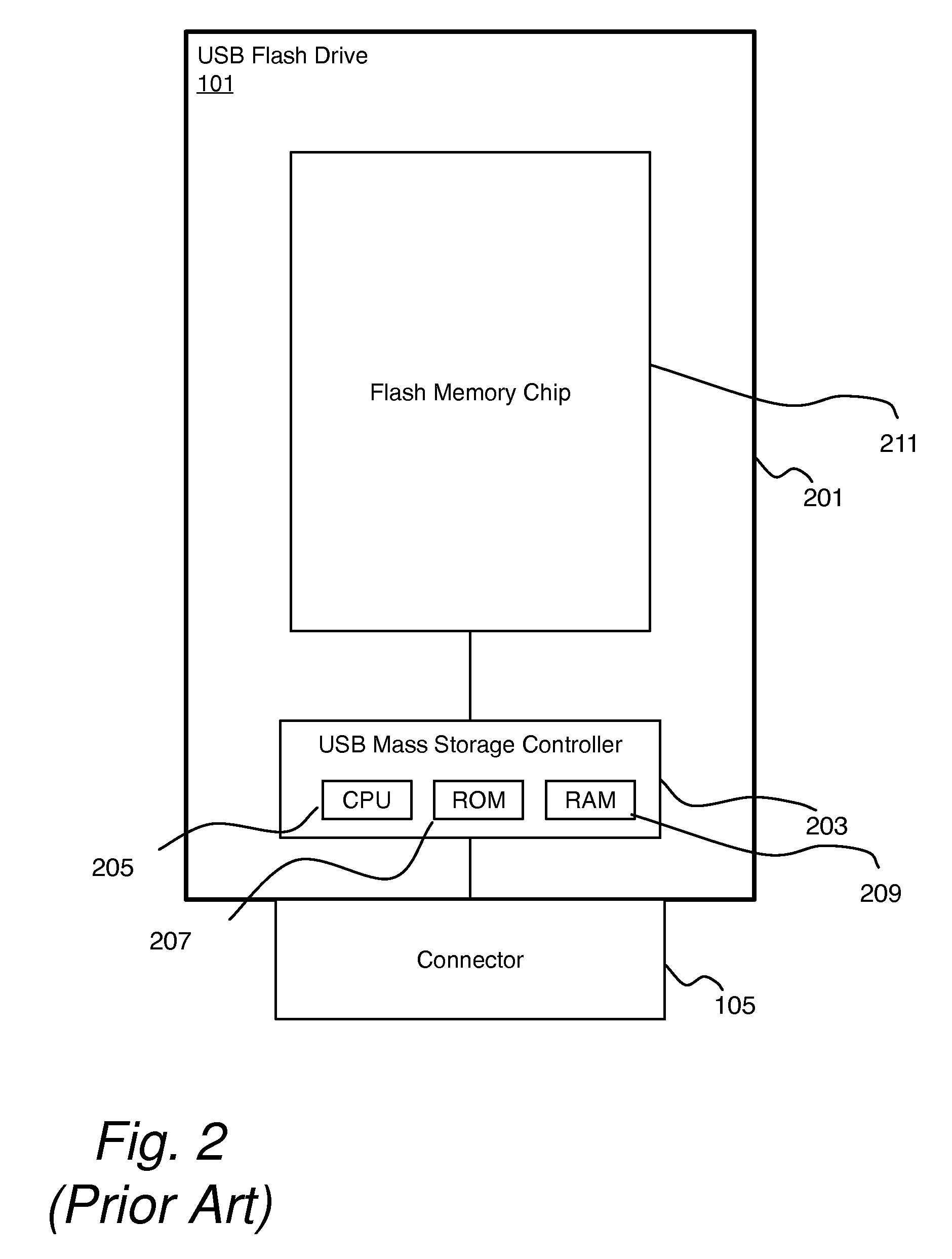
A flash memory controller (or flash controller) manages data stored on flash memory and communicates with a computer or electronic device. Flash memory controllers can be designed for operating in low duty-cycle environments like SD cards, CompactFlash cards, or other similar media for use in digital cameras, PDAs, mobile phones, etc. USB flash drives use flash memory controllers designed to communicate with personal computers through the USB port at a low duty-cycle. Flash controllers can also be designed for higher duty-cycle environments like solid-state drives (SSD) used as data storage for laptop computer systems clear up to mission-critical enterprise storage arrays.
Managing bad blocks in various flash memory cells for electronic data flash card
InactiveUS20080082736A1Small sizeLow costMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsComputer accessFlash memory controller
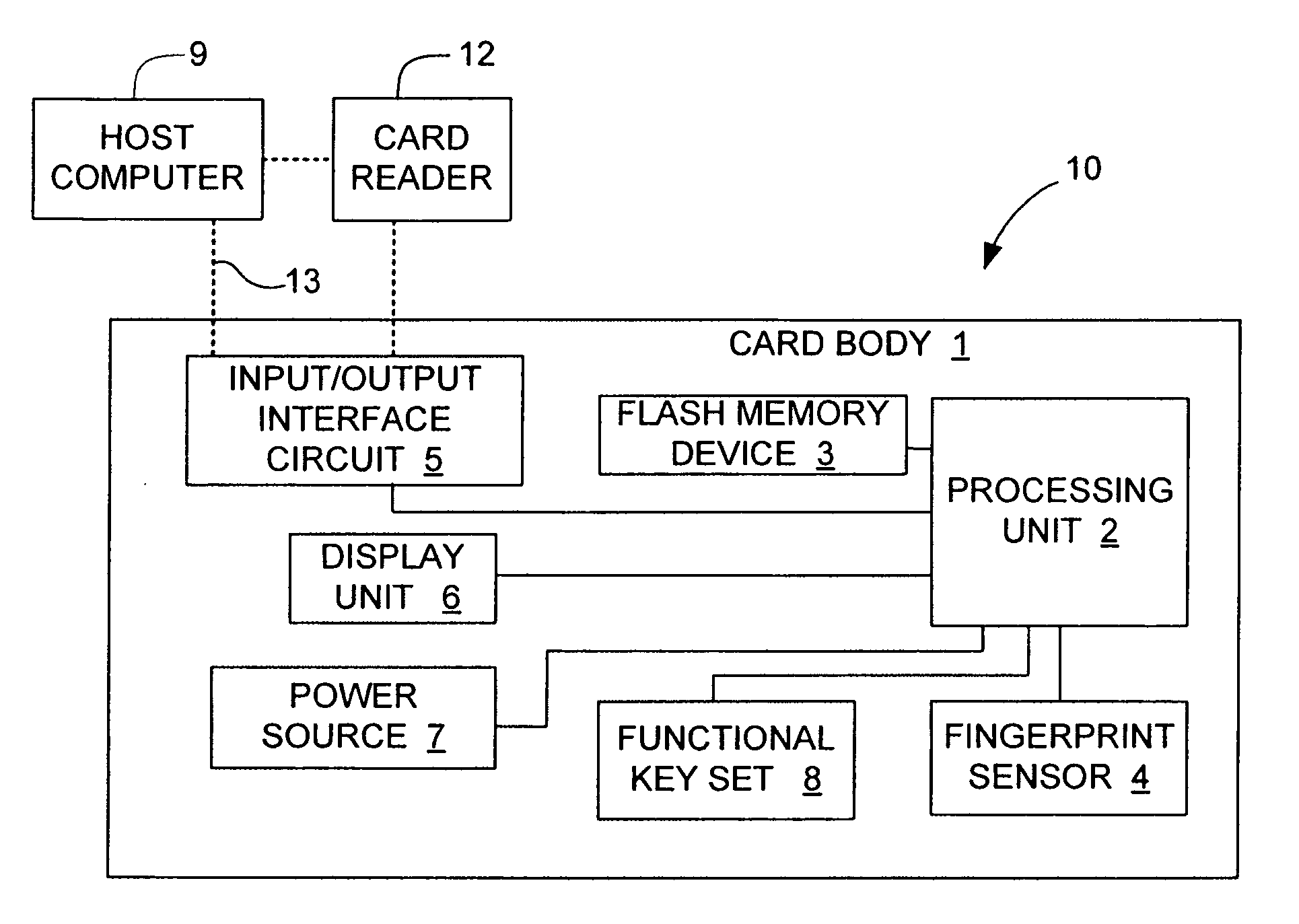
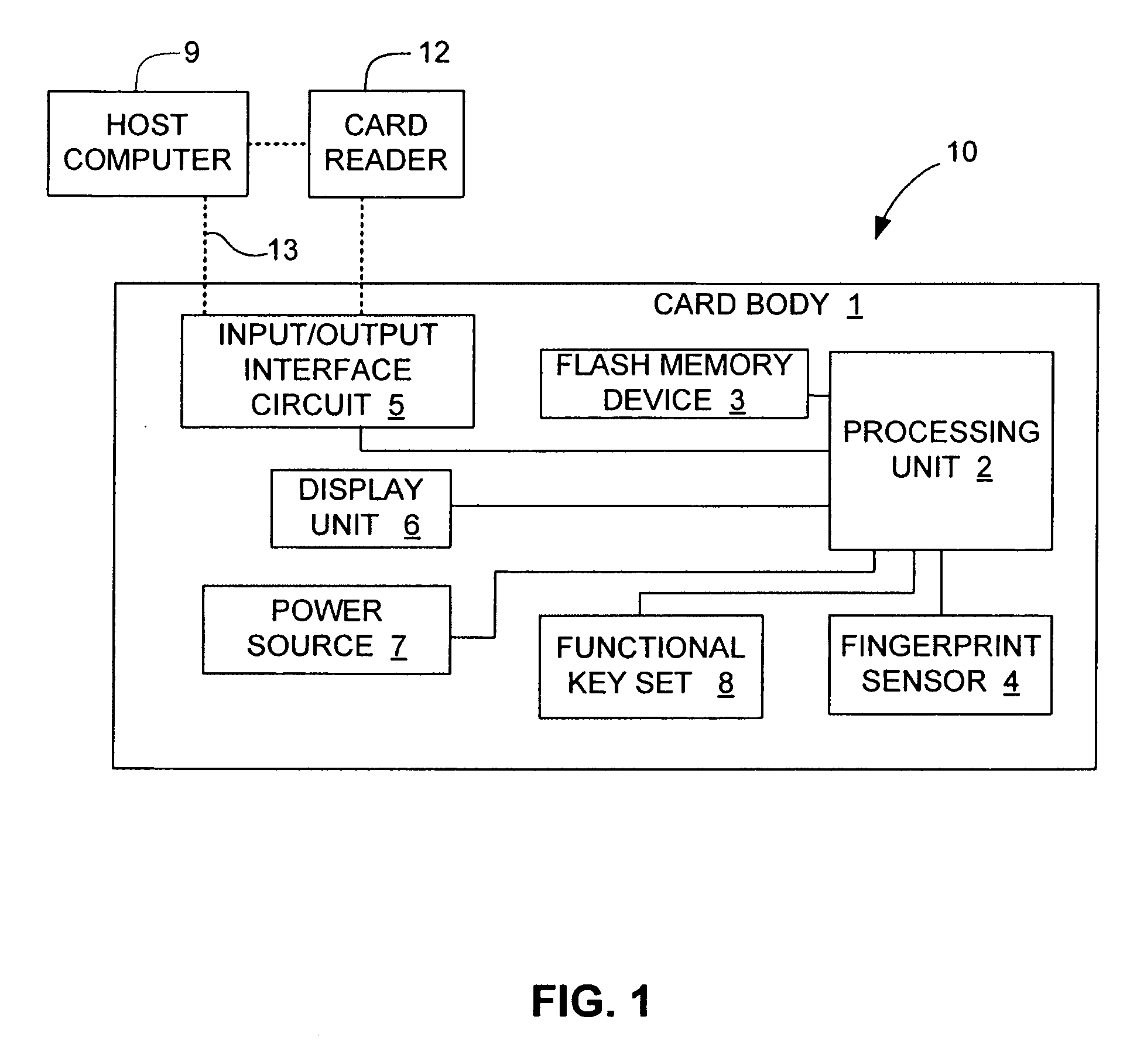
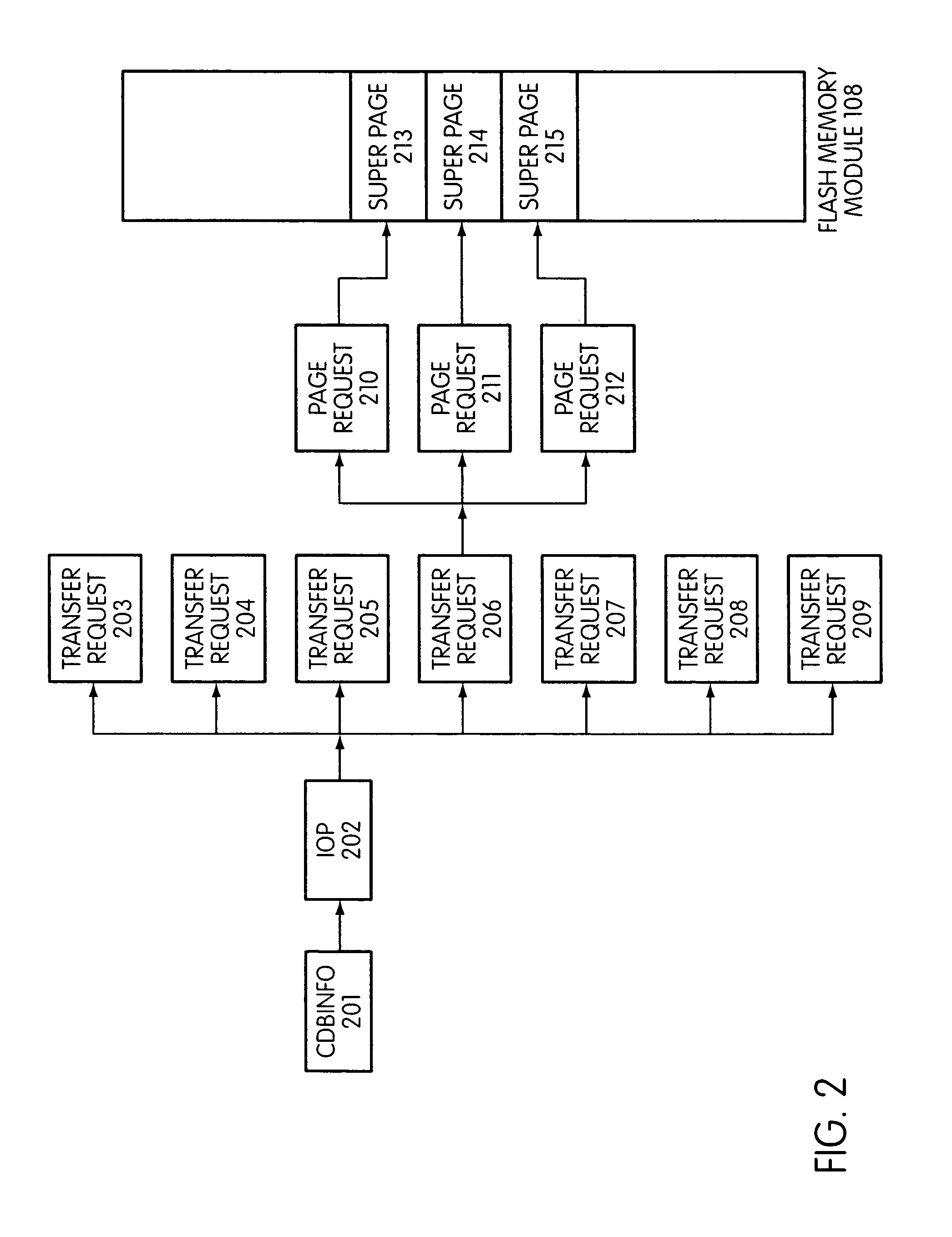
An electronic data flash card accessible by a host computer, includes a flash memory controller connected to a flash memory device, and an input-output interface circuit activated to establish a communication with the host. In an embodiment, the flash card uses a USB interface circuit for communication with the host. A flash memory controller includes an arbitrator for mapping logical addresses with physical block addresses, and for performing block management operations including: storing reassigned data to available blocks, relocating valid data in obsolete blocks to said available blocks and reassigning logical block addresses to physical block addresses of said available blocks, finding bad blocks of the flash memory device and replacing with reserve blocks, erasing obsolete blocks for recycling after relocating valid data to available blocks, and erase count wear leveling of blocks, etc. Furthermore, each flash memory device includes an internal buffer for accelerating the block management operations.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
ExpressCard with On-Card Flash Memory with Shared Flash-Control Bus but Separate Ready Lines
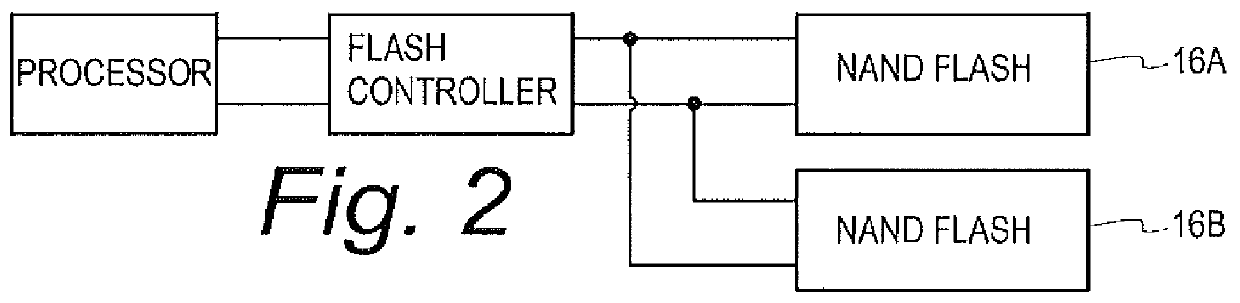
An ExpressCard contains flash memory. The ExpressCard has an ExpressCard connector that plugs into a host, such as a personal computer, digital camera, or personal digital assistant (PDA). A controller chip on the ExpressCard uses a pair of differential Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) data lines in the connector to communicate with the USB host, or can use PCI Express, Firewire, or other protocols. One or more flash-memory chips on the ExpressCard are controlled by a flash-memory controller in the controller chip. Two or more channels of a flash bus have a shared control bus but separate ready lines. The separate ready lines allow flash-memory chips in the two channels to finish operations at different times.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
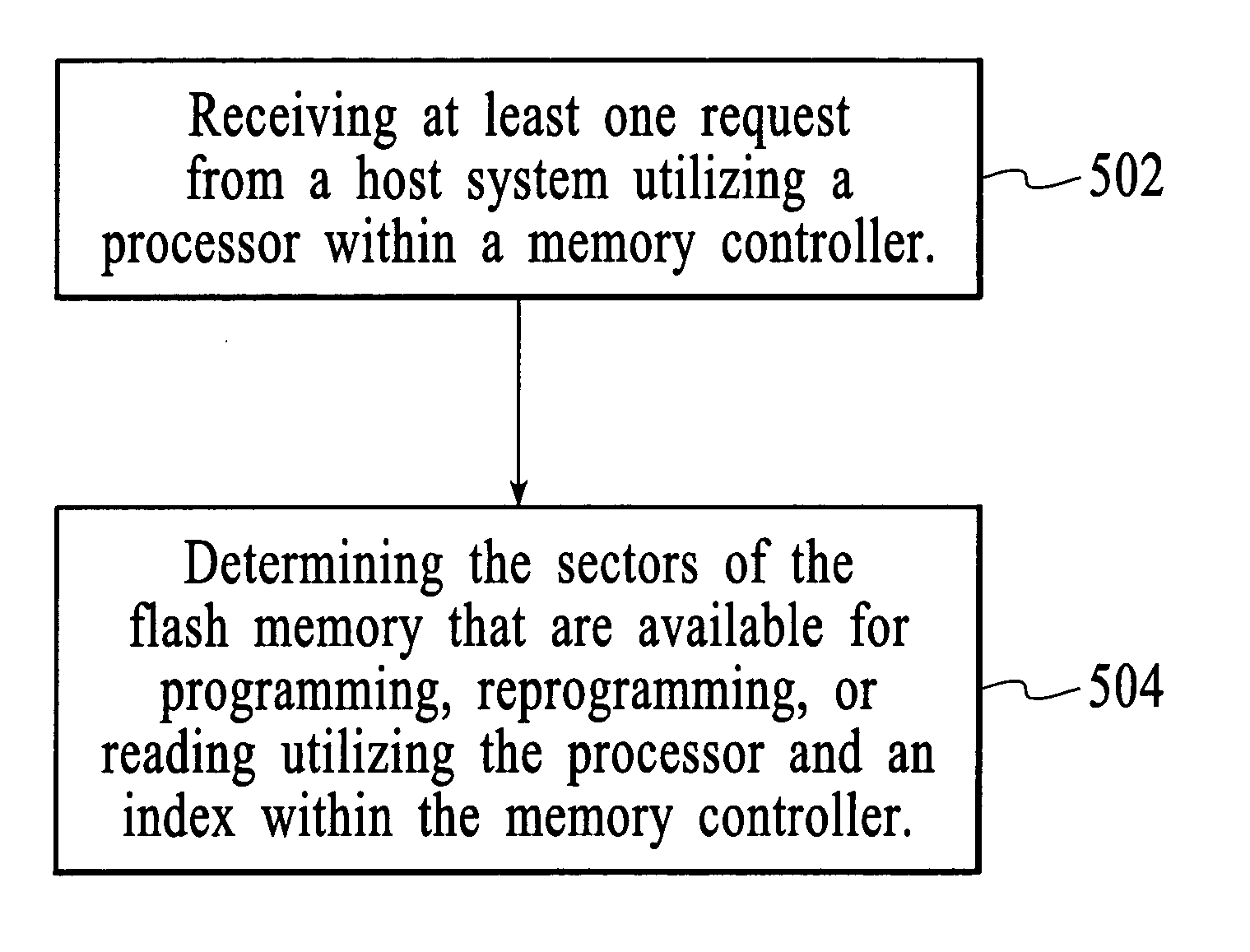
System and method for controlling flash memory
InactiveUS20050193161A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerInformation processor
A flash memory controller is disclosed. The flash memory controller includes a processor for receiving at least one request from a host system. The flash memory controller further includes an index comprising information regarding sectors of a flash memory. The processor can utilize the index to determine the sectors of the flash memory that are available for programming, reprogramming, or reading. In another aspect of the present invention, the flash memory controller further includes a first-in-first-out unit (FIFO) for recycling obsolete sectors so that they are available for reprogramming.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
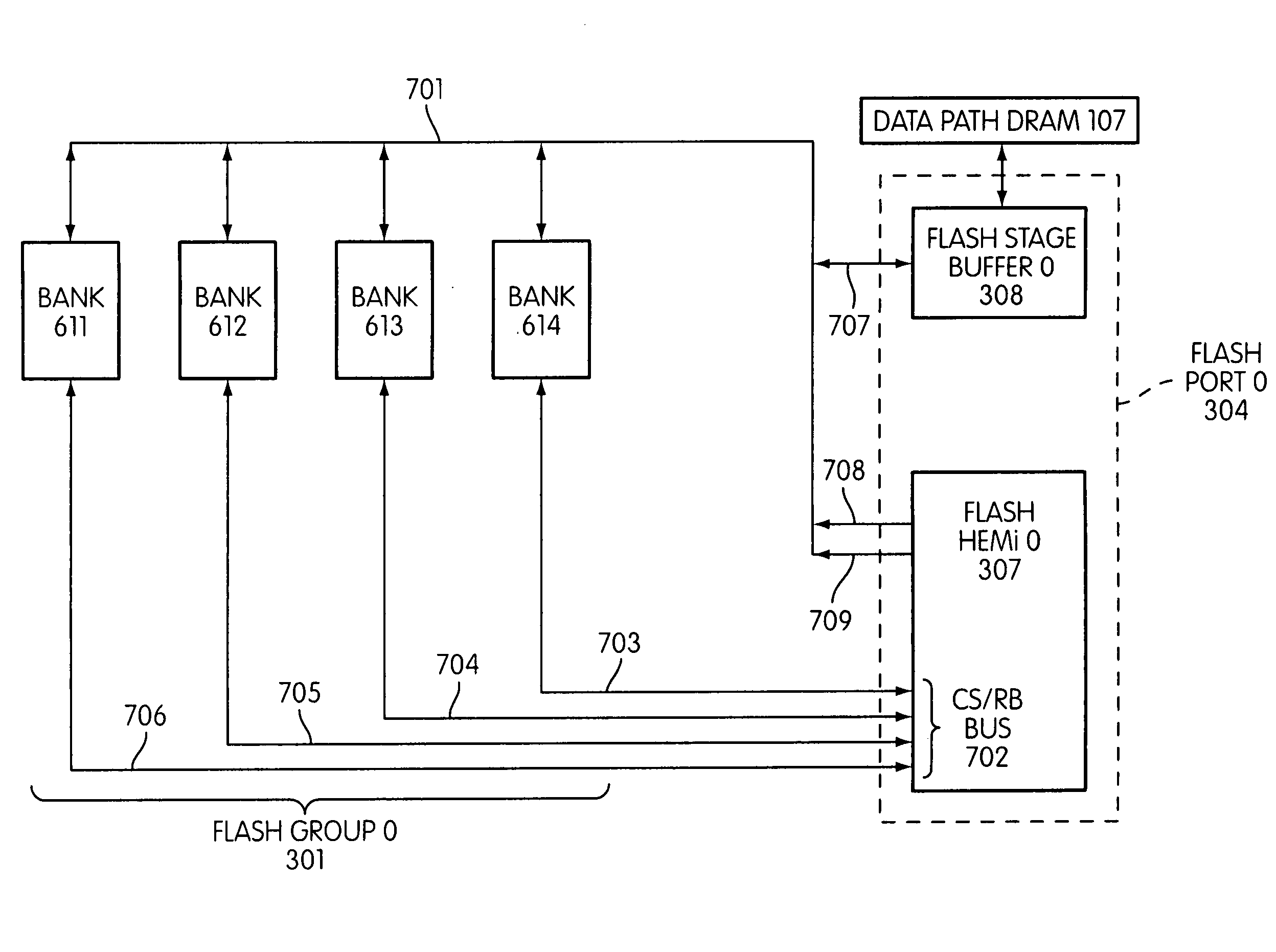
Flash memory controller having reduced pinout
InactiveUS20090168525A1Affect performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationChip selectFlash memory controller
Disclosed is a flash memory controller connected to a flash memory module. The pin-out of the flash memory controller combines ready-busy and chip-select signals. In one embodiment, the flash memory module is made up of a set of banks, each consisting of a plurality of devices, with each bank sharing a single chip-select / ready-busy connection to the controller.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
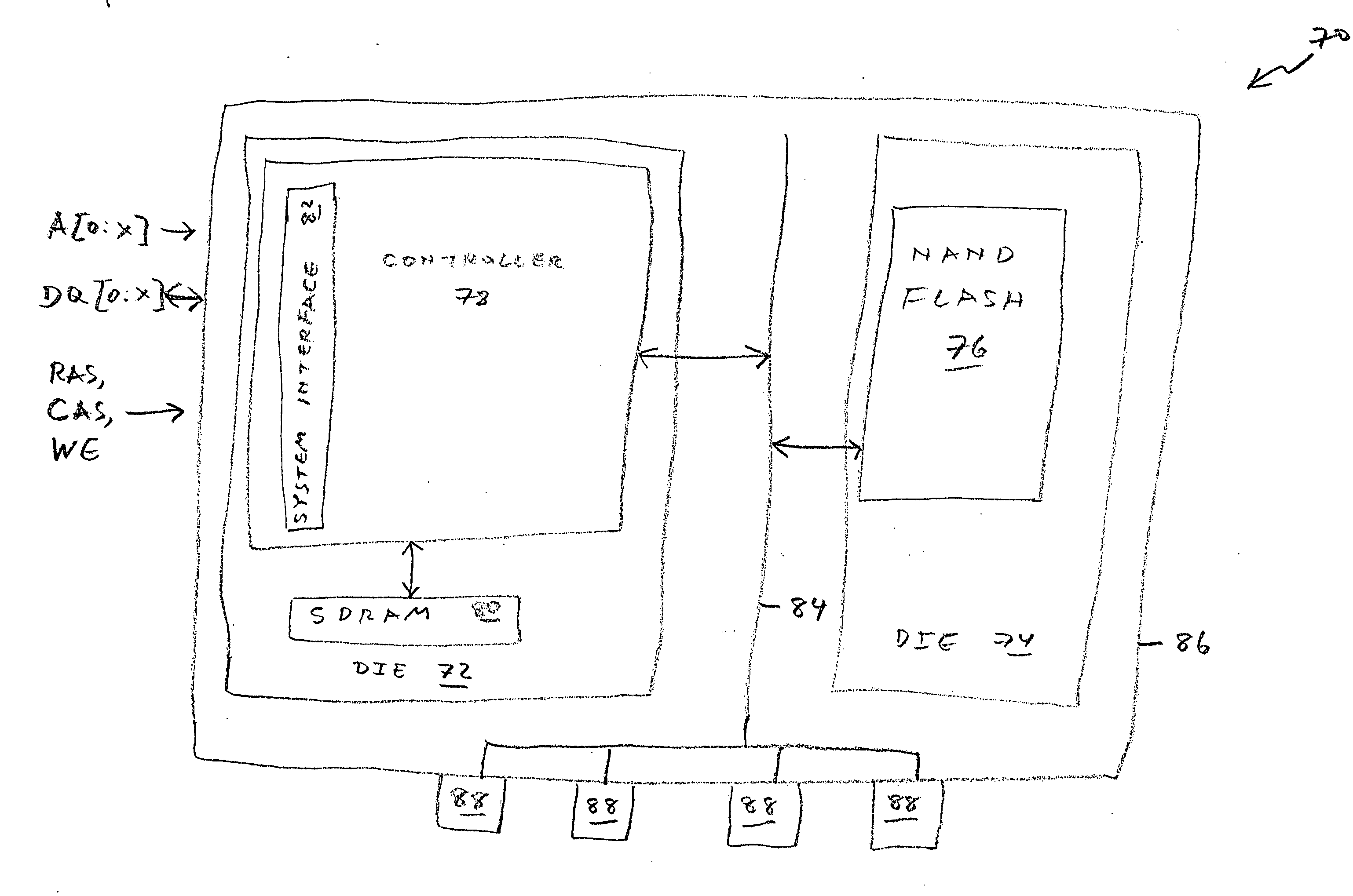
SDRAM memory device with an embedded NAND flash controller
A memory device includes two dies. A first memory is fabricated on one die. A controller of the first memory is fabricated on the other die. Also fabricated on the other die is another component, such as a second memory, that communicates with a host system using a plurality of signals different from the signals used by the first memory. The device includes a single interface for communicating with the host system using only the respective signals of the second component. In a most preferred embodiment, the first memory is a NAND flash memory and the second memory is a SDRAM.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
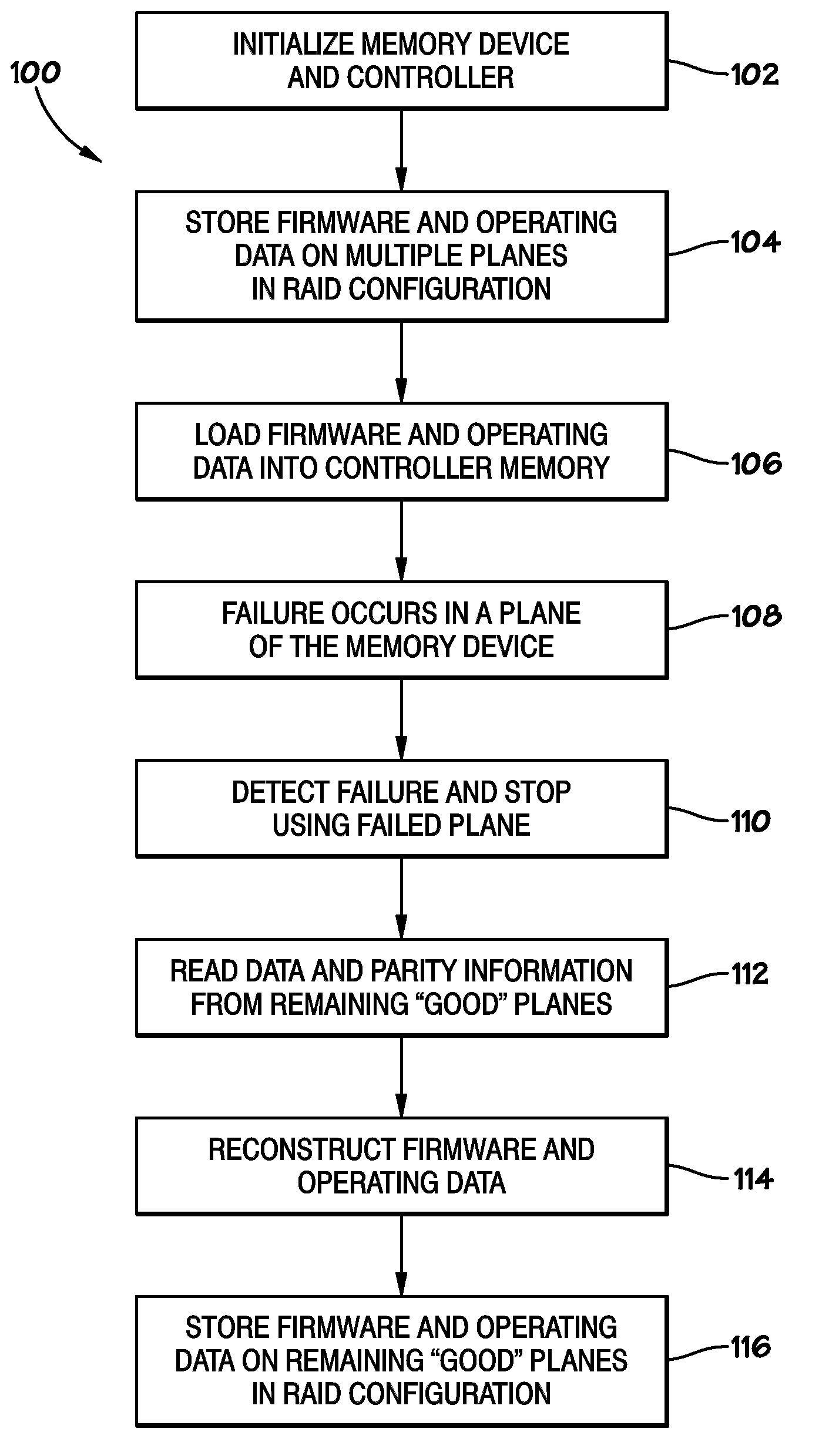
Systems and Methods for Storing and Recovering Controller Data in Non-Volatile Memory Devices
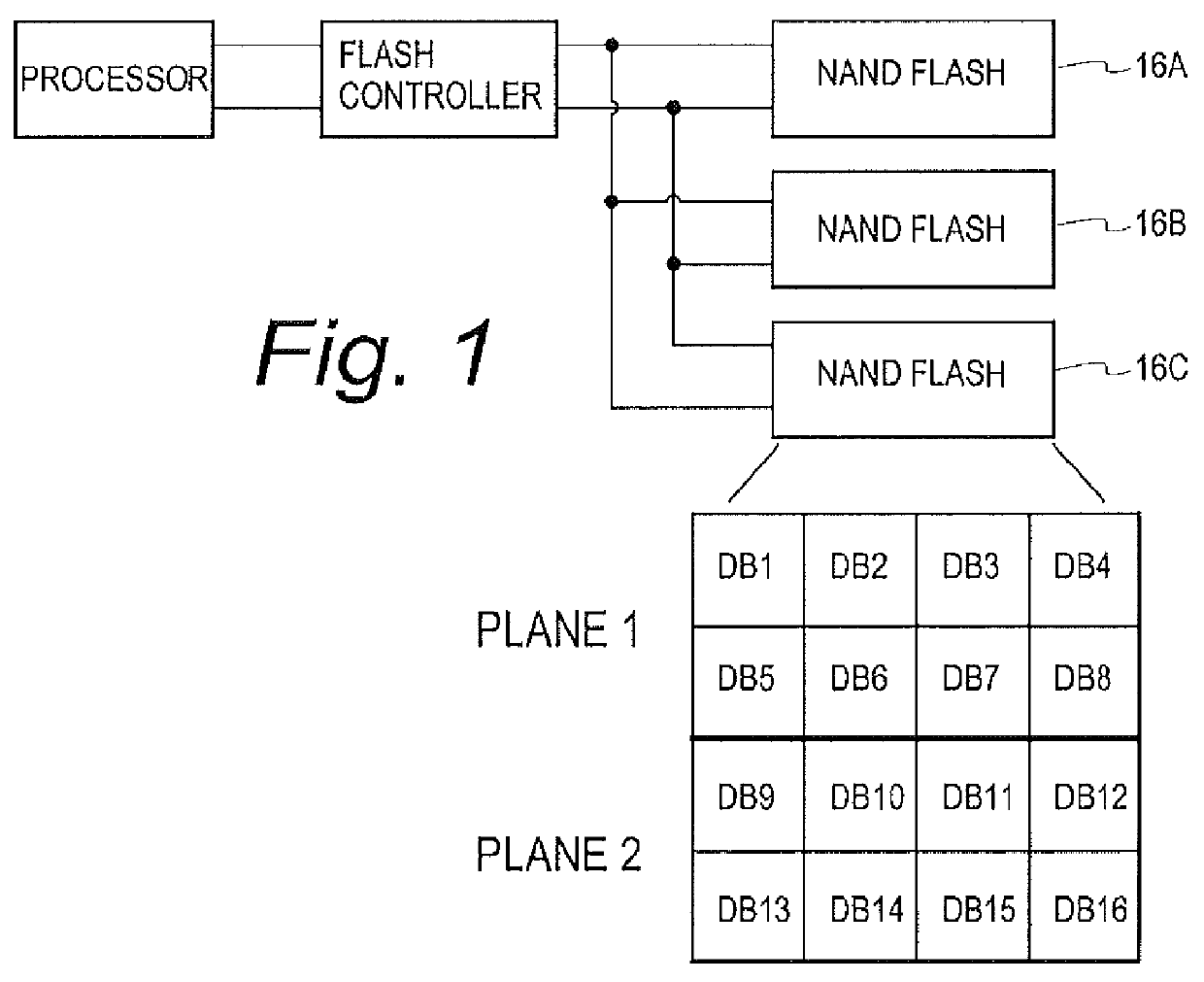
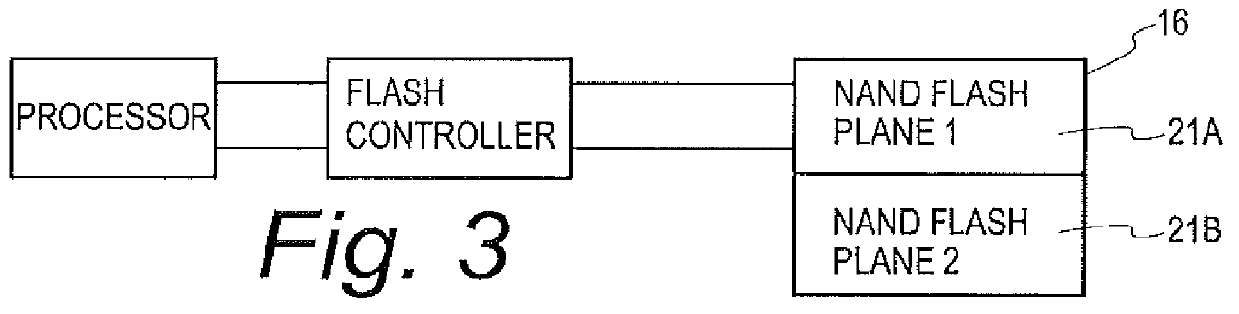
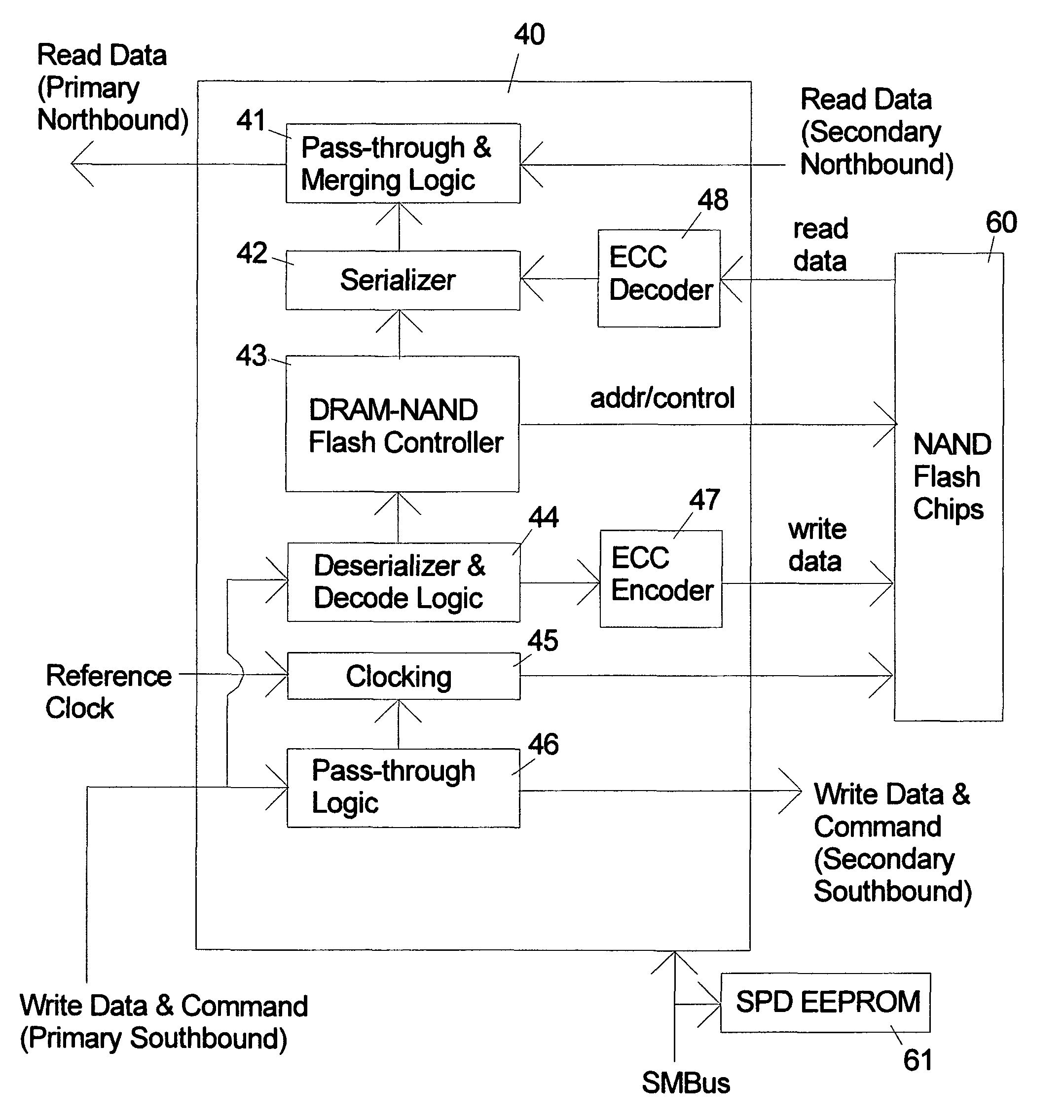
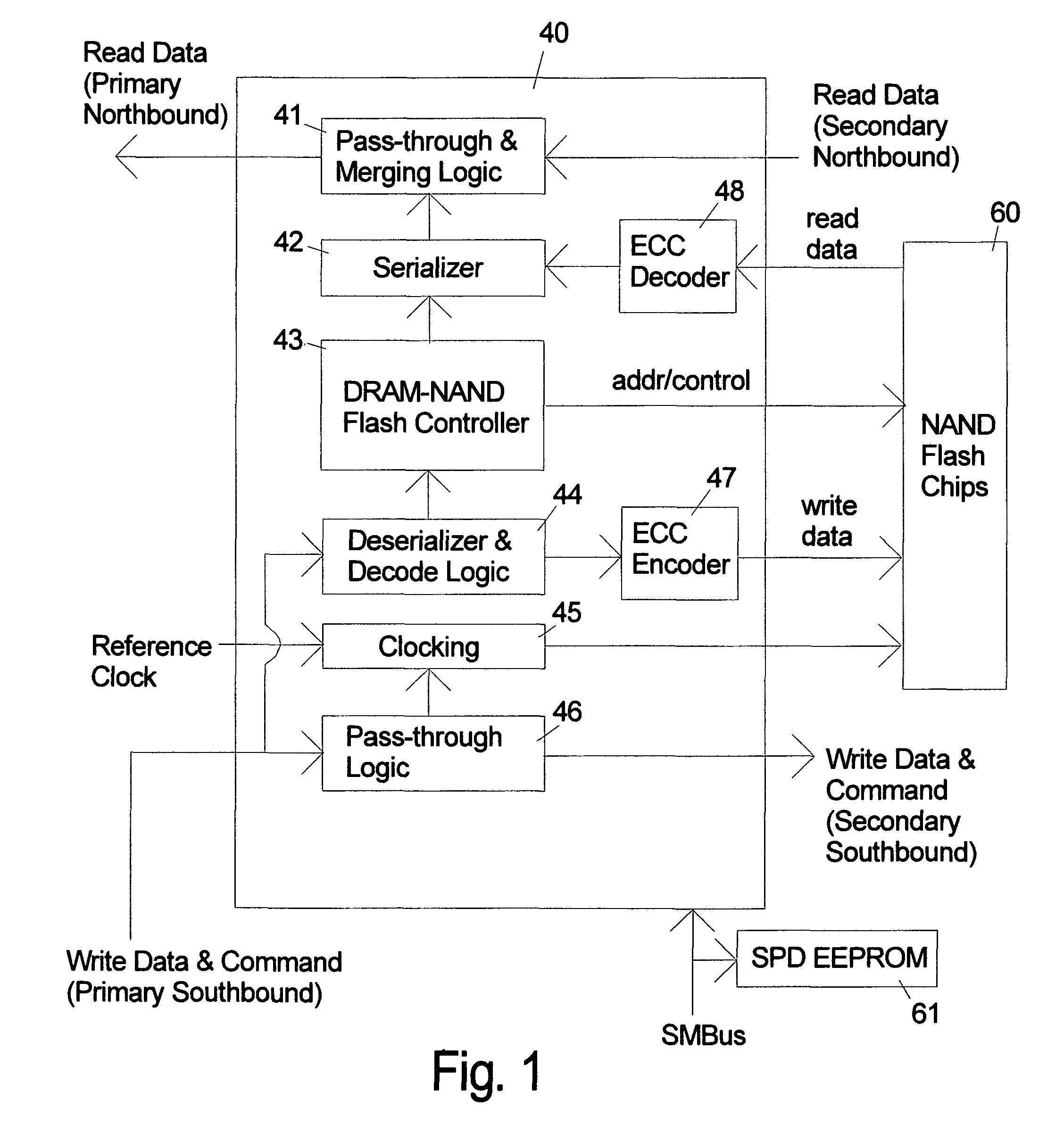
Systems and methods are disclosed for storing the firmware and other data of a flash memory controller, such as using a RAID configuration across multiple flash memory devices or portions of a single memory device. In various embodiments, the firmware and other data used by a controller, and error correction information, such as parity information for RAID configuration, may be stored across multiple flash memory devices, multiple planes of a multi-plane flash memory device, or across multiple blocks or pages of a single flash memory device. The controller may detect the failure of a memory device or a portion thereof, and reconstruct the firmware and / or other data from the other memory devices or portions thereof.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Flash Module with Plane-Interleaved Sequential Writes to Restricted-Write Flash Chips
InactiveUS20080034153A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesFlash memory controllerBlock number
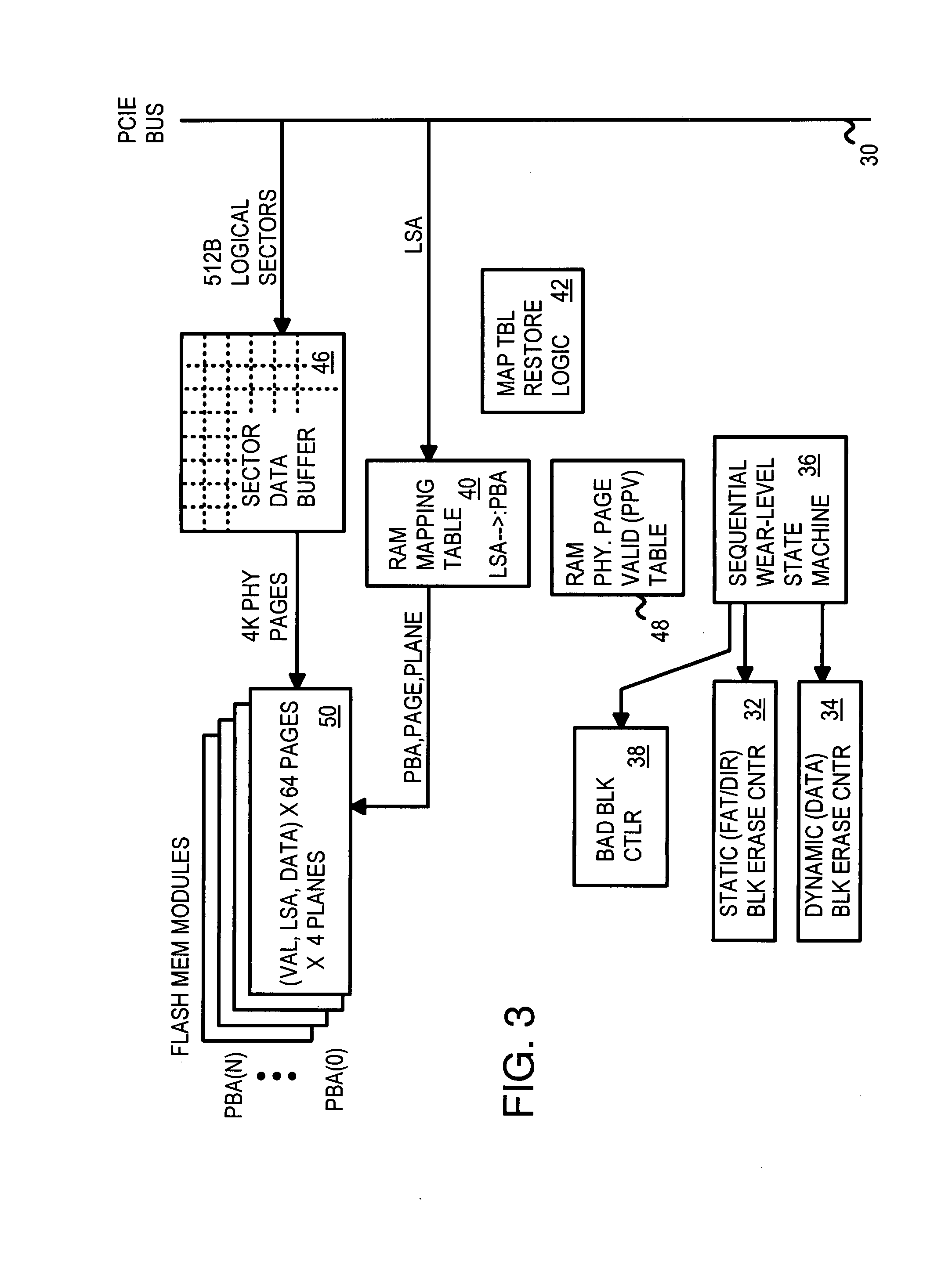
A flash memory controller on a PCIE bus controls flash-memory modules on a flash bus. The flash-memory modules are plane-interleaved using interleaved bits extracted from the lowest bits of the logical block index. These plane-interleave bits are split into a LSB and a MSB, with middle physical block bits between the LSB and MSB. A physical sequential address counter generates a physical block number by incrementing the plane-interleave bits before the middle physical block bits, and then relocating the MSB to above the middle physical block bits. This causes blocks to be accessed in a low-high sequence of 0, 1, 4096, 4097, 2, 3, 4098, 4099, etc. in the four planes of flash memory. A RAM physical page valid table tracks valid pages in the four planes, while a RAM mapping table stores the plane, block, and page addresses for logical sectors generated by the physical sequential address counter.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Highly integrated mass storage device with an intelligent flash controller
InactiveUS20050160218A1Increases serial throughputImprove throughputInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsMass storageFlash memory controller
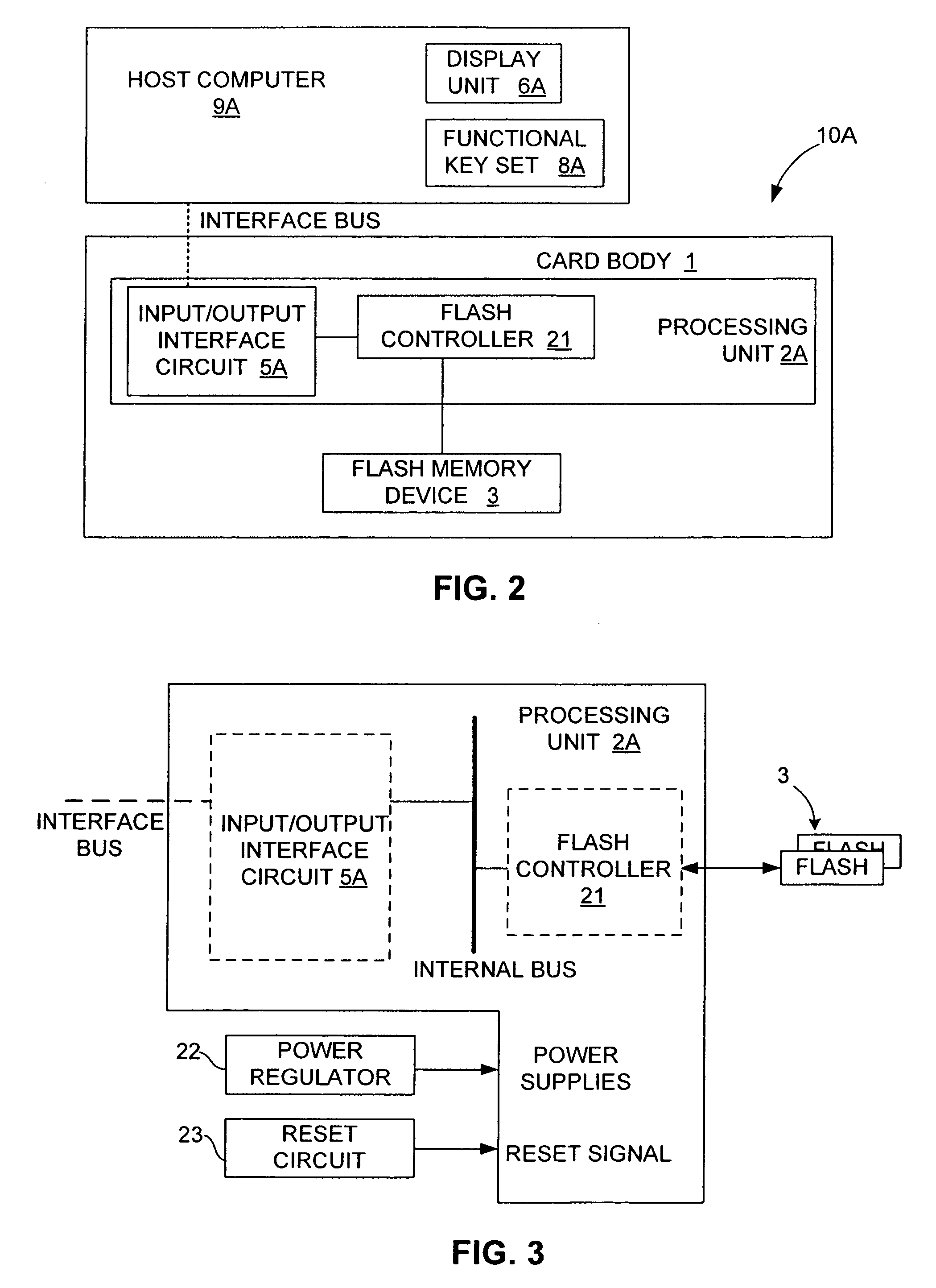
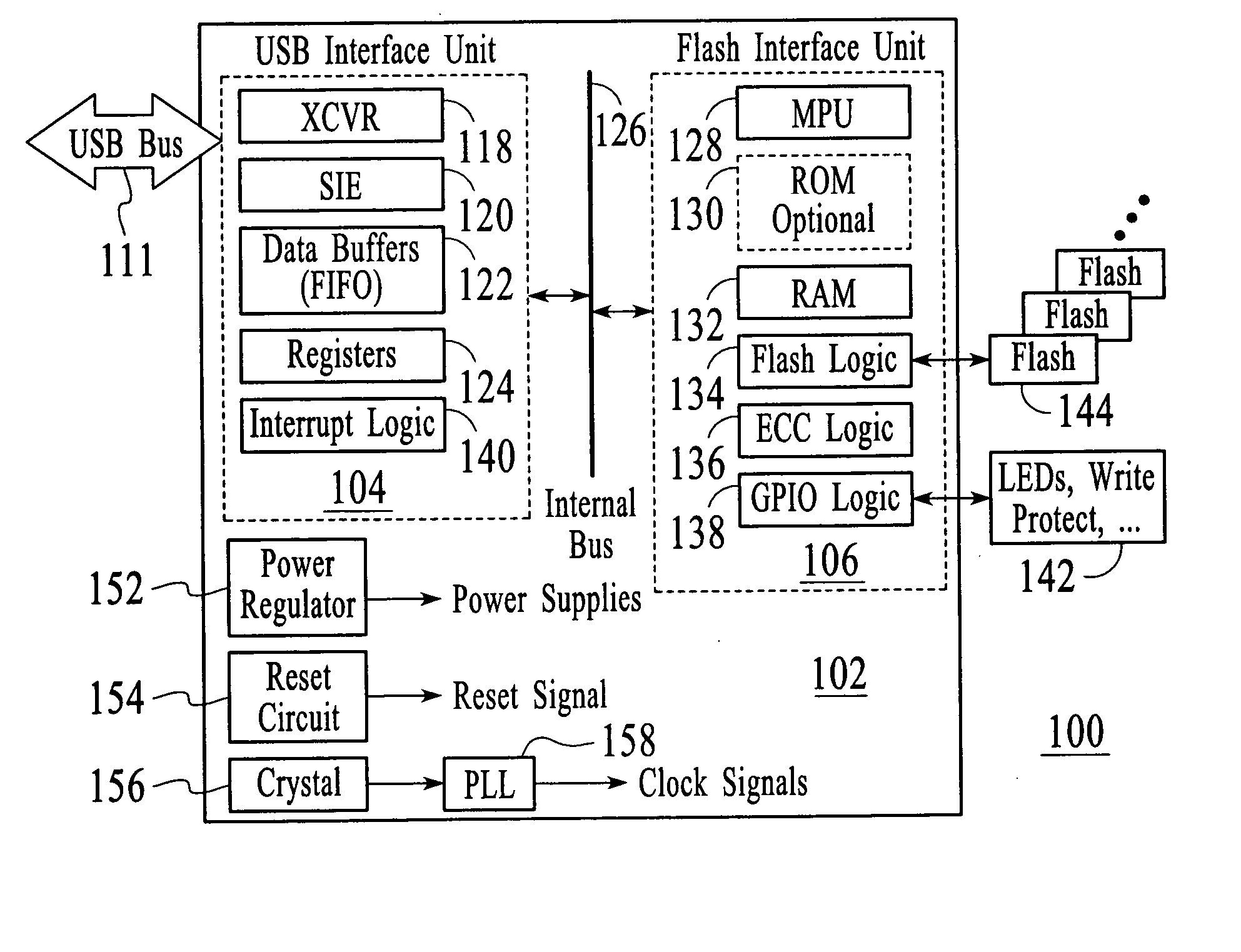
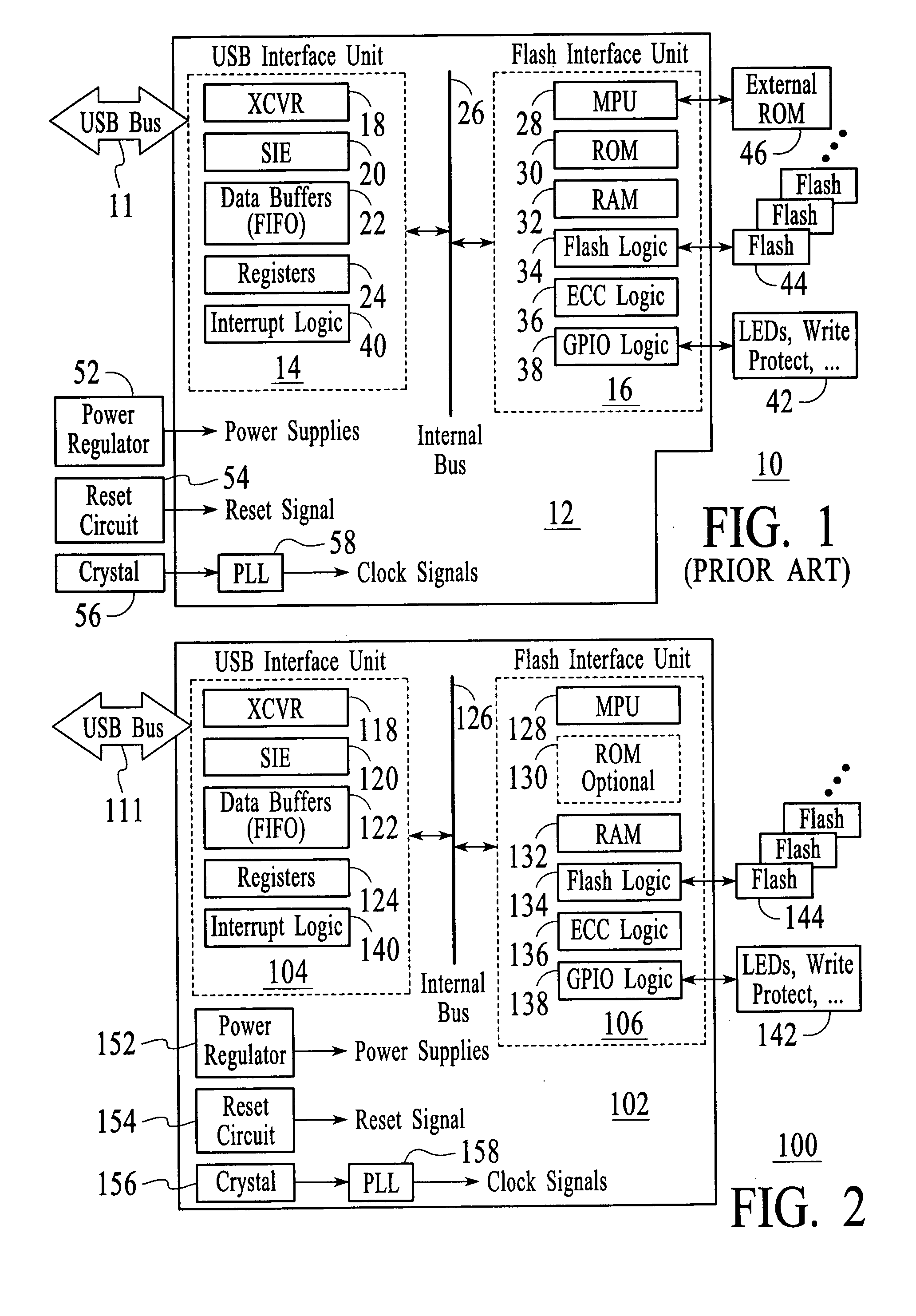
A FLASH controller is disclosed. The controller comprises a USB interface unit. The USB interface unit implements a USB standard that has a bus speed equal or greater than 12 Mb / s. The controller includes an internal bus coupled to the USB interface unit; and a FLASH interface unit coupled to the internal bus. The FLASH interface unit includes FLASH controller logic that allows the throughput for access to the FLASH memory to match the speed of the USB standard. Advantages of the FLASH controller in accordance with the present invention include (1) utilizing the higher speed USB interface such as the USB 2.0 standard, which substantially increases the serial throughput between USB host and FLASH controller; (2) utilizing more advanced FLASH control logic which is implemented to raise the throughput for the FLASH memory access; (3) utilizing an intelligent algorithm to detect and access the different FLASH types, which broadens the sourcing and the supply of FLASH memory; (4) by storing the software program along with data in FLASH memory which results in the cost of the controller being reduced, and also makes the software program field changeable and upgradeable; and (5) providing high integration, which substantially reduces the overall space needed and reduces the complexity and the cost of manufacturing.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
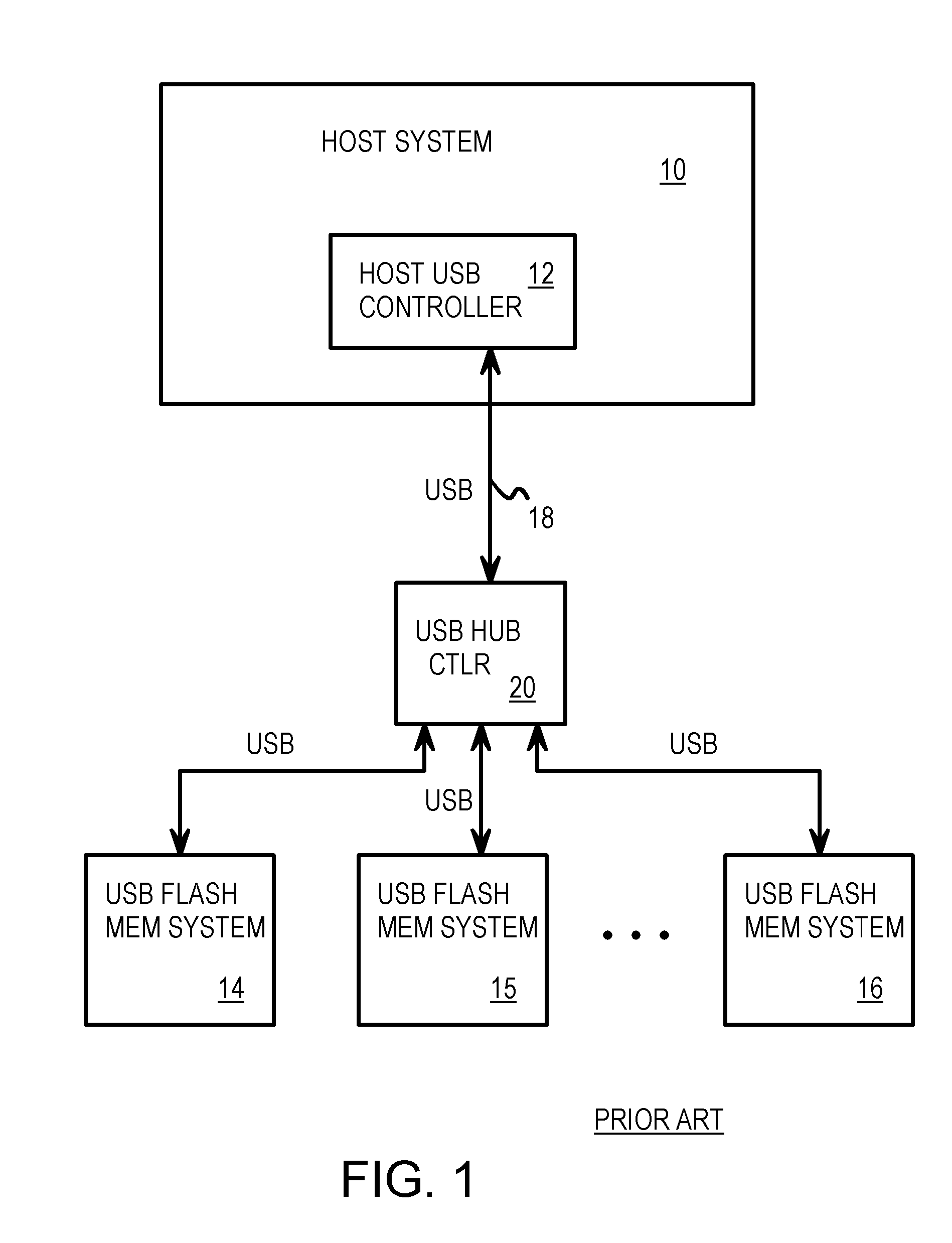
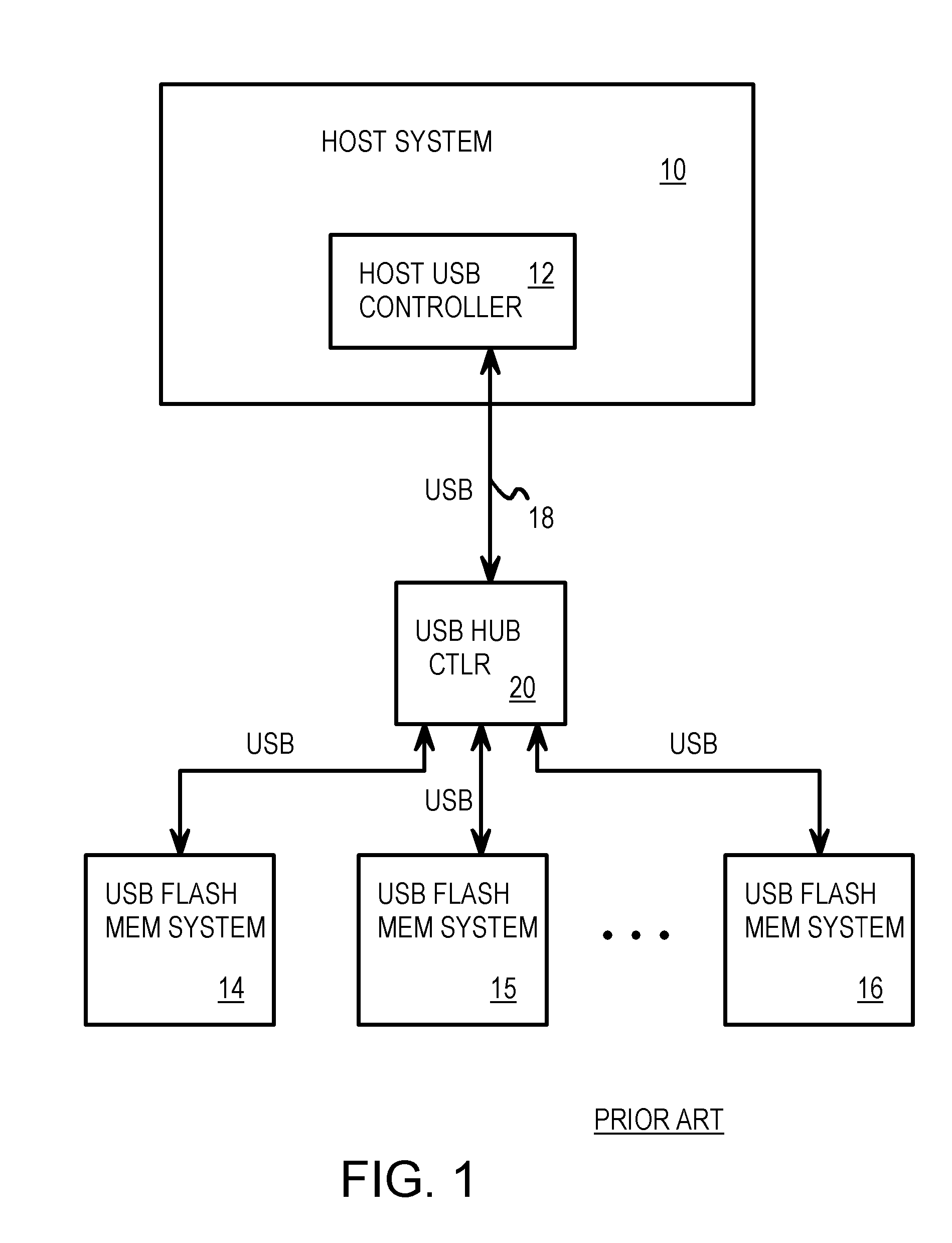
Capacity Expansion of Flash Memory Device with a Daisy-Chainable Structure and an Integrated Hub
InactiveUS20050086413A1Record carriers used with machinesElectric digital data processingUSB hubEngineering
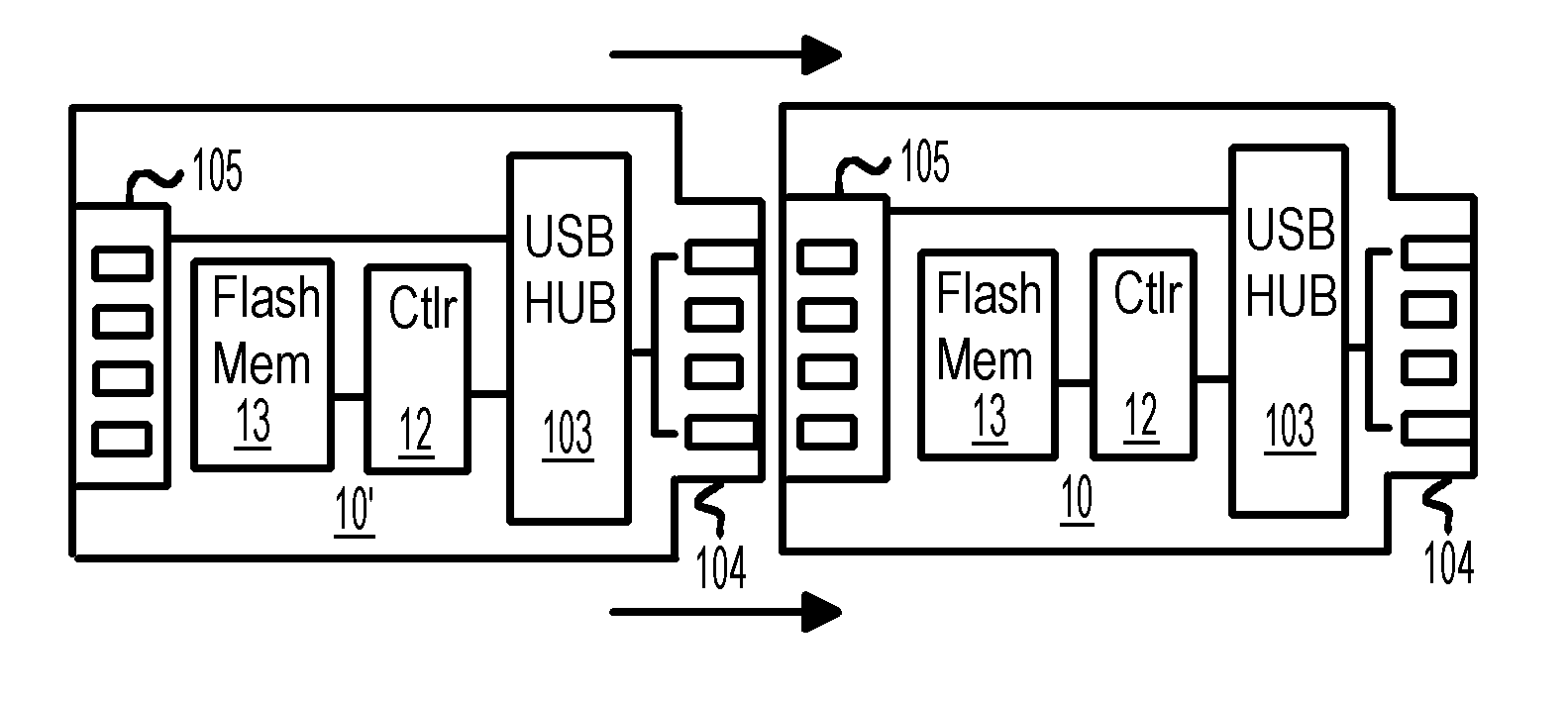
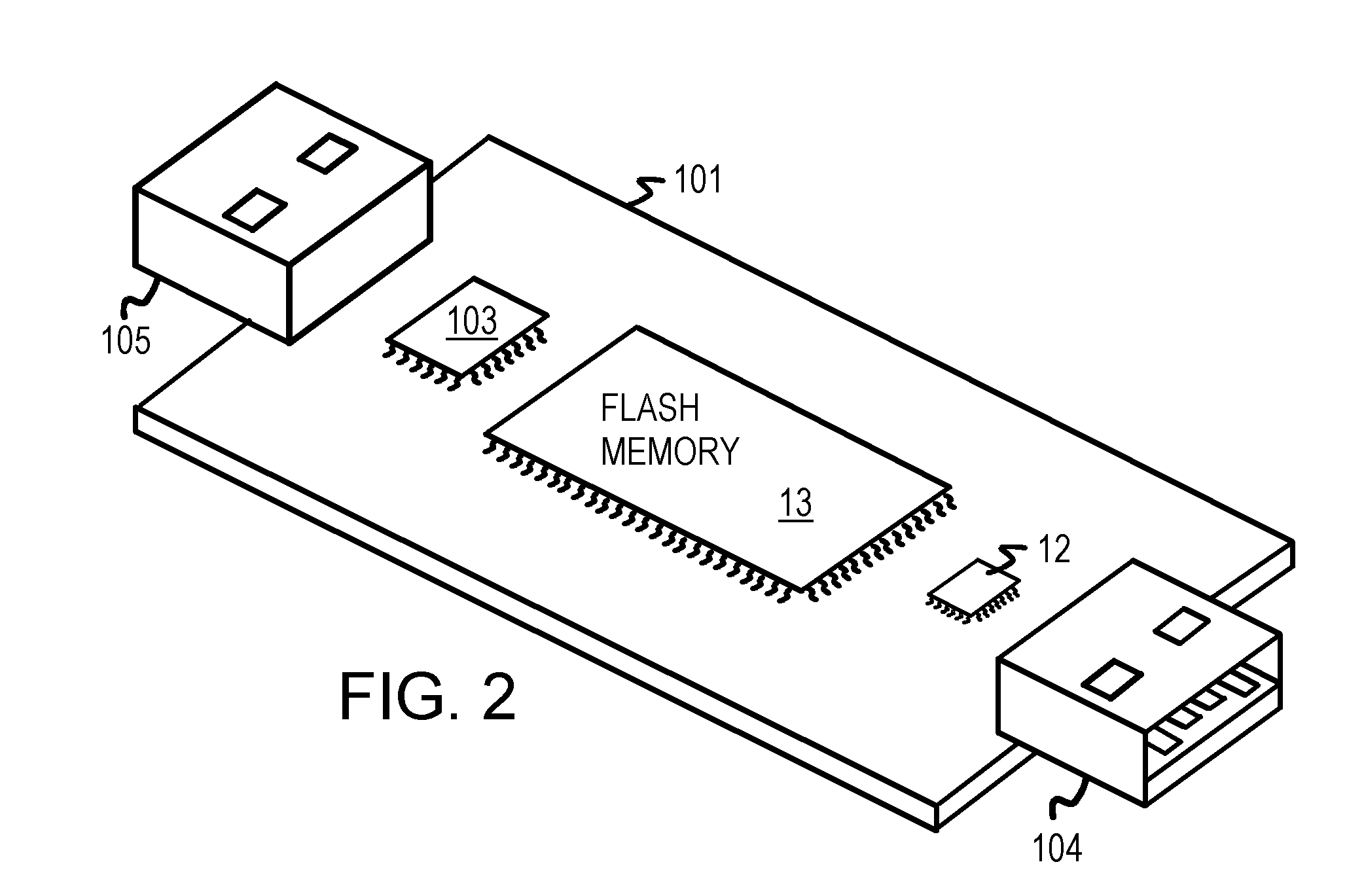
A chainable Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) flash-memory drive has both a female USB connector and a male USB connector mounted on a printed-circuit board (PCB) substrate. A USB hub mounted on the substrate connects to a host through the male USB connector. One of the ports of the USB hub is connected to the female USB connector to allow the host to connect to downstream USB devices connected to the chainable USB flash-memory drive. Other ports of the USB hub connect to one or more flash controller chips that drive flash memory chips. The flash memory chips may be mounted on the substrate, or may be on daughter-cards that plug into sockets on the chainable USB flash-memory drive's substrate. The flash controller chip may be mounted on the drive substrate or on the daughter-cards. Several chainable USB flash-memory drives may be connected together in a daisy chain.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
Mission critical NAND flash
InactiveUS20120226934A1Data storage is reliableAccurate contentMemory systemsRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareComputer architecture
A flash controller reliably stores data in NAND FLASH by encoding data using an encoding algorithm, and storing that data across multiple pages of the memory. In one embodiment, true data is accepted by the controller, and the controller in turn creates coded data that is the bit-for-bit complement of the true data. The true data and the coded data are then written to the NAND FLASH on a page by page basis. A property of the coding techniques used is that, in at least some cases, detected errors can be corrected.
Owner:GREENTHREAD
Metadata rebuild in a flash memory controller following a loss of power
ActiveUS20090172262A1Maximize useImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerMemory controller
A method of rebuilding metadata in a flash memory controller following a loss of power. The method includes reading logical address information associated with an area of flash memory, and using time stamp information to determine if data stored in the flash memory area is valid.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
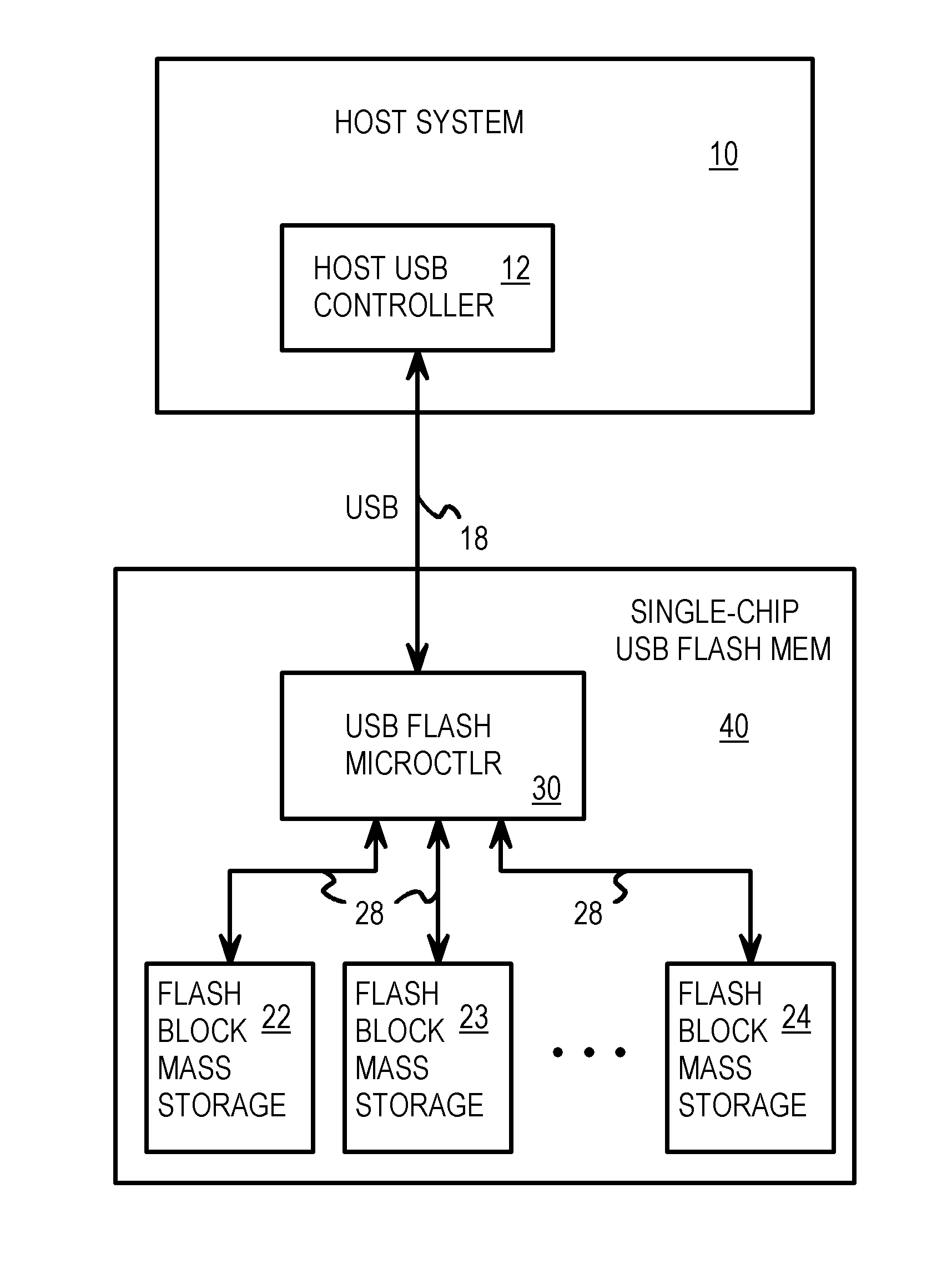
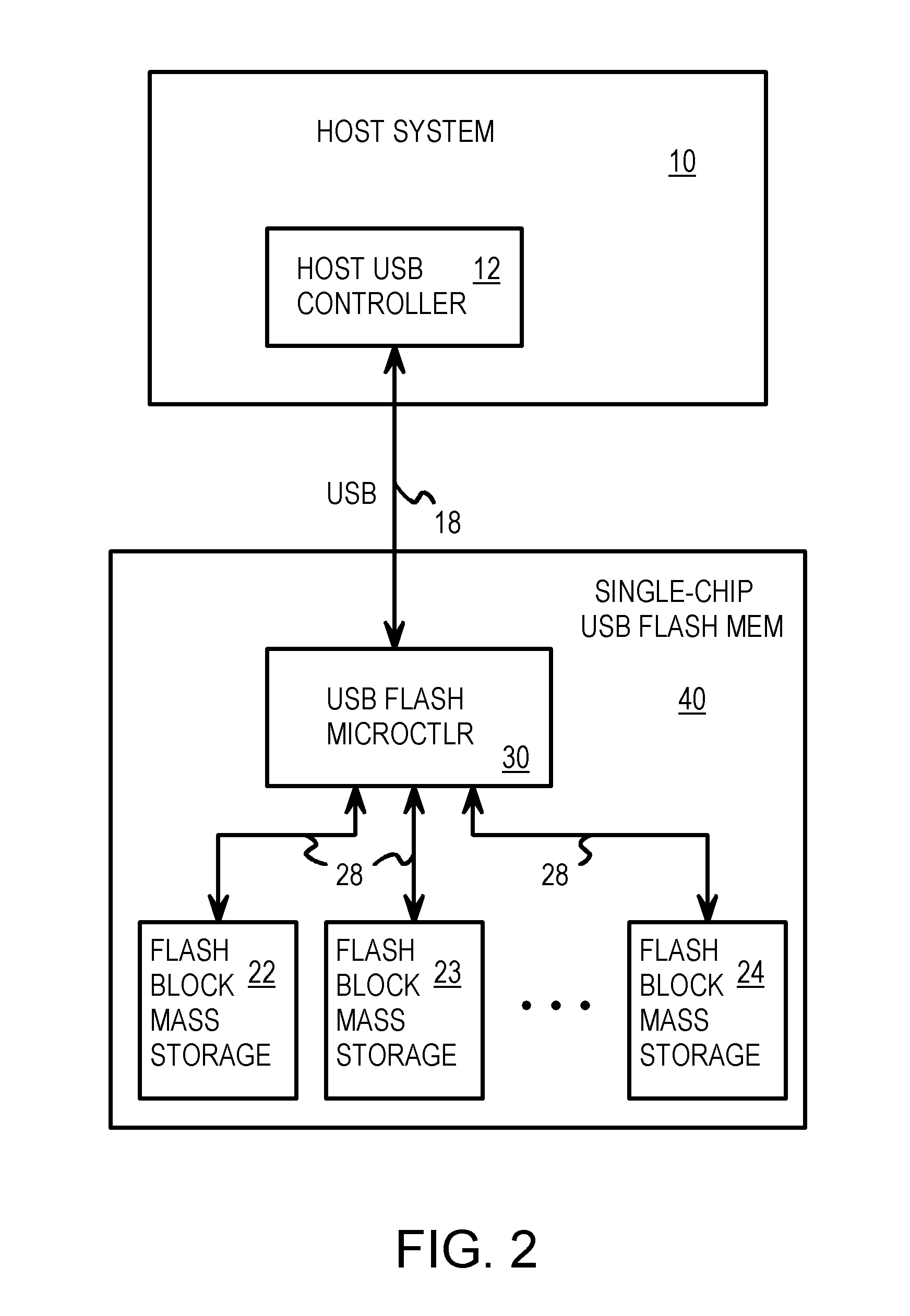
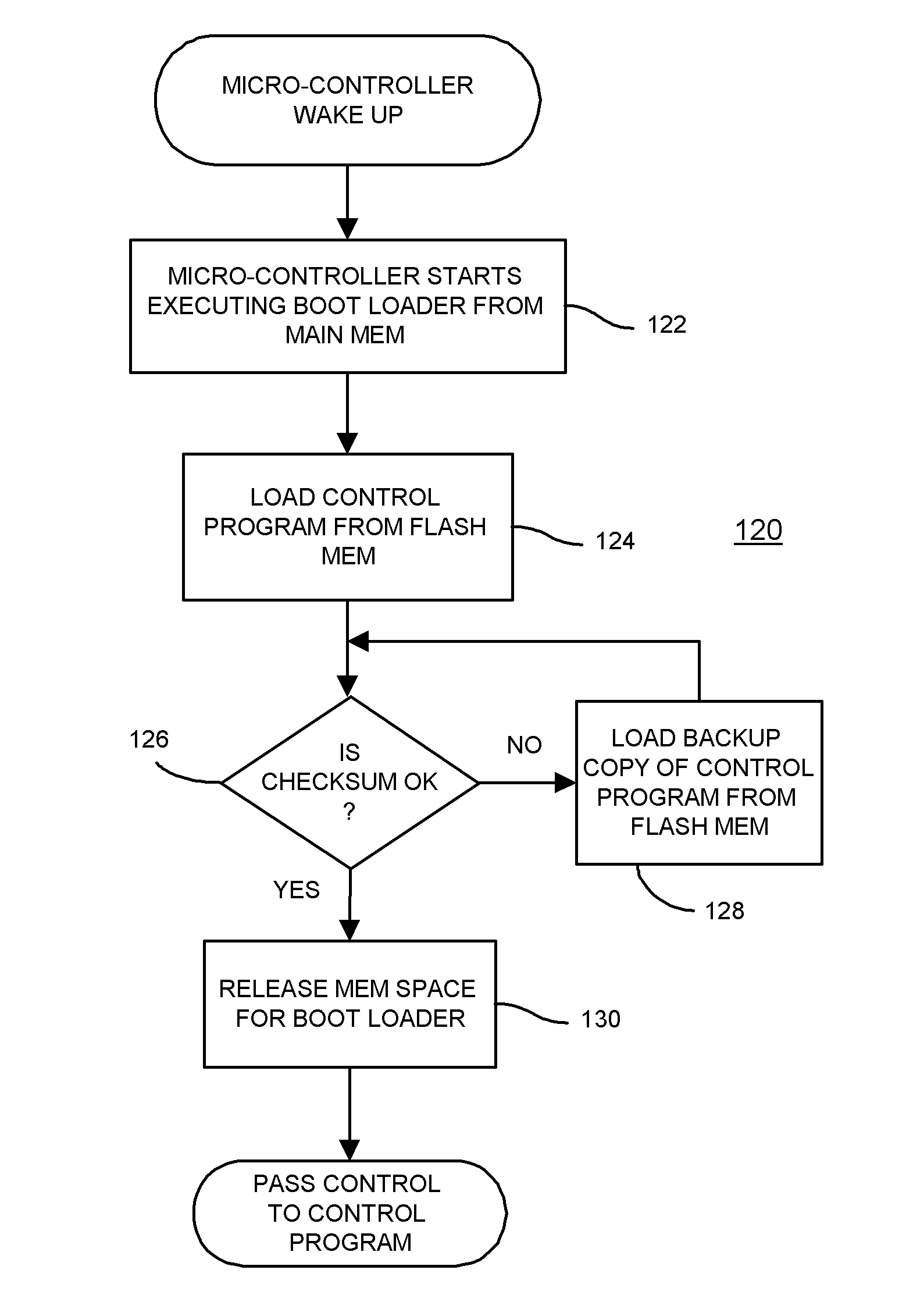
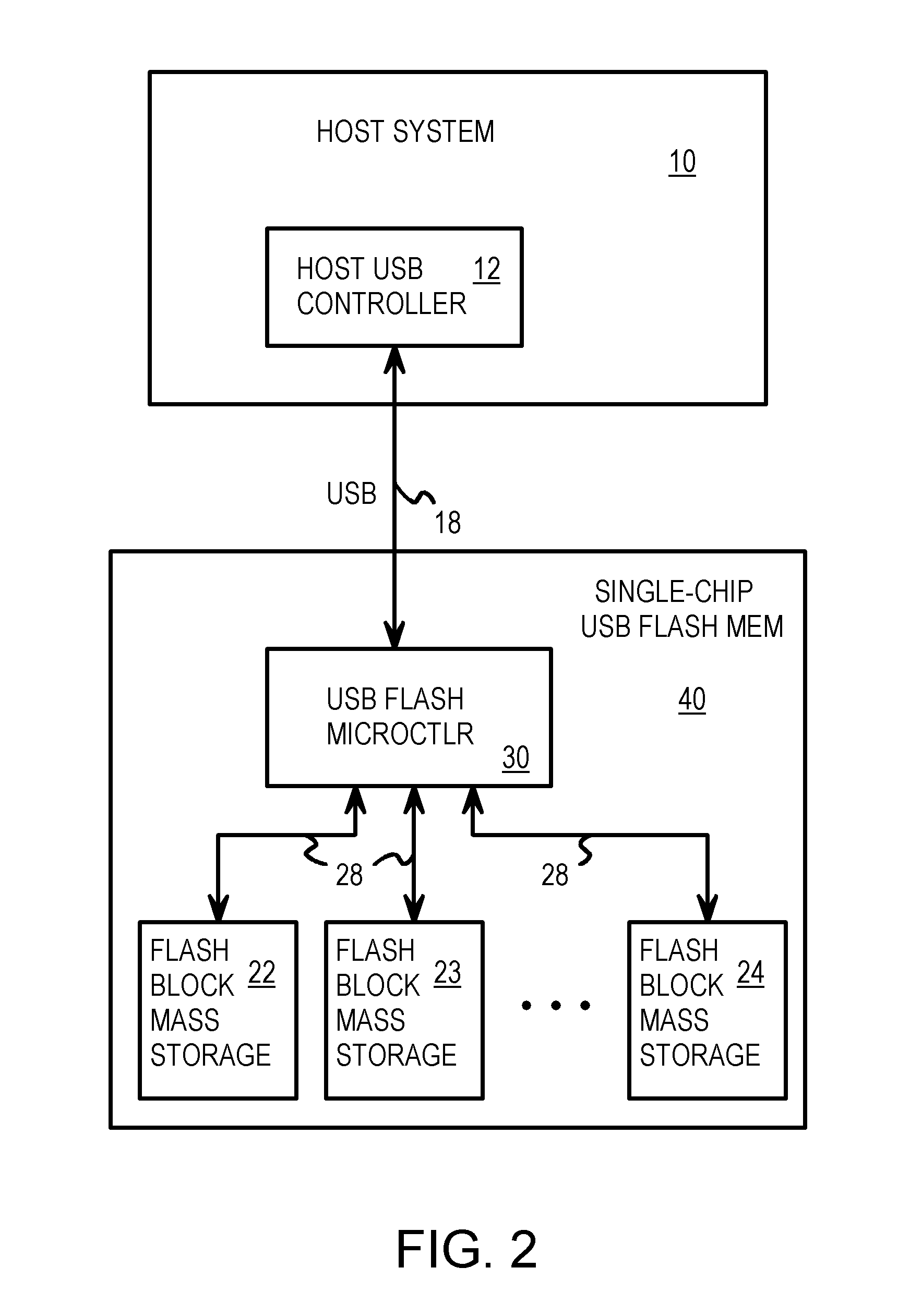
Single-Chip USB Controller Reading Power-On Boot Code from Integrated Flash Memory for User Storage
A Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) single-chip flash device contains a USB flash microcontroller and flash mass storage blocks containing flash memory arrays that are block-addressable rather than randomly-addressable. USB packets from a host USB bus are read by a serial engine on the USB flash microcontroller. Various routines that execute on a CPU in the USB flash microcontroller are activated in response to commands in the USB packets. A flash-memory controller in the USB flash microcontroller transfers data from the serial engine to the flash mass storage blocks for storage. Rather than boot from an internal ROM coupled to the CPU, a boot loader is transferred by DMA from the first page of the flash mass storage block to an internal RAM. The flash memory is automatically read from the first page at power-on. The CPU then executes the boot loader from the internal RAM to load the control program.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Flash memory controller garbage collection operations performed independently in multiple flash memory groups
ActiveUS20090172258A1Affect performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesWaste collectionFlash memory controller
A flash memory controller connected to multiple flash memory groups performs independent garbage collection operations in each group. For each group, the controller independently determines the amount of free space and performs garbage collection operations if the amount falls below a threshold.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
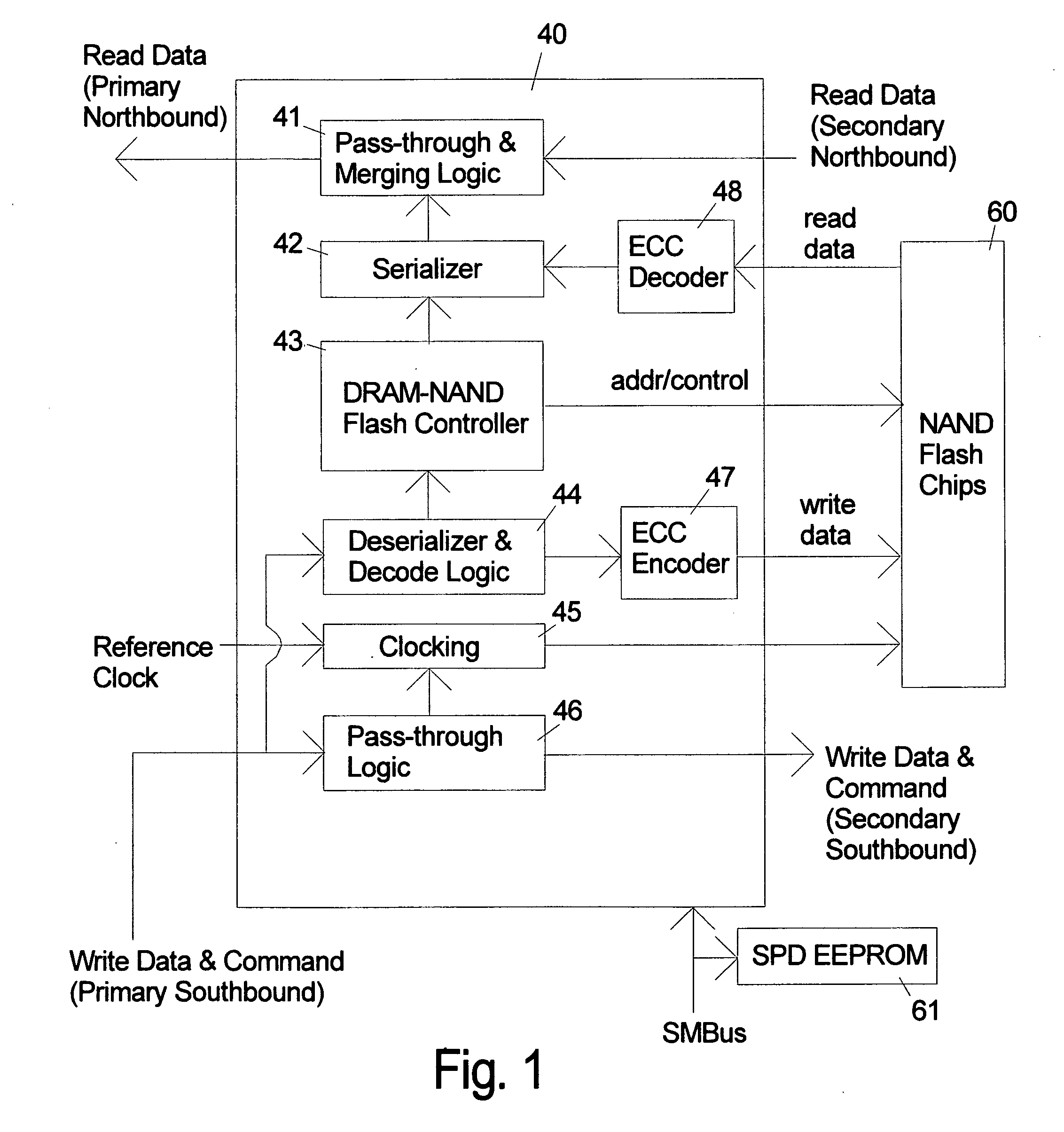
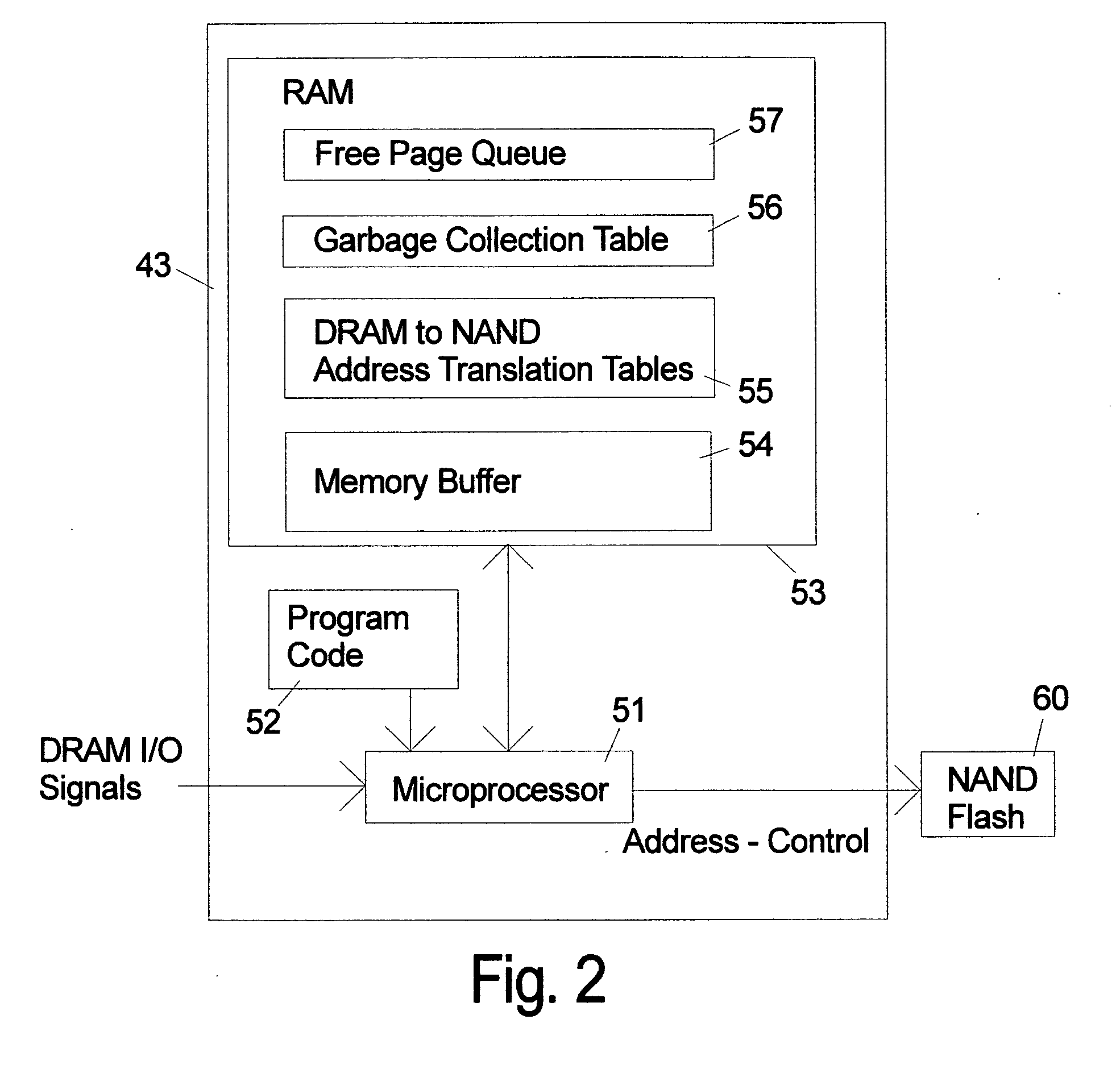
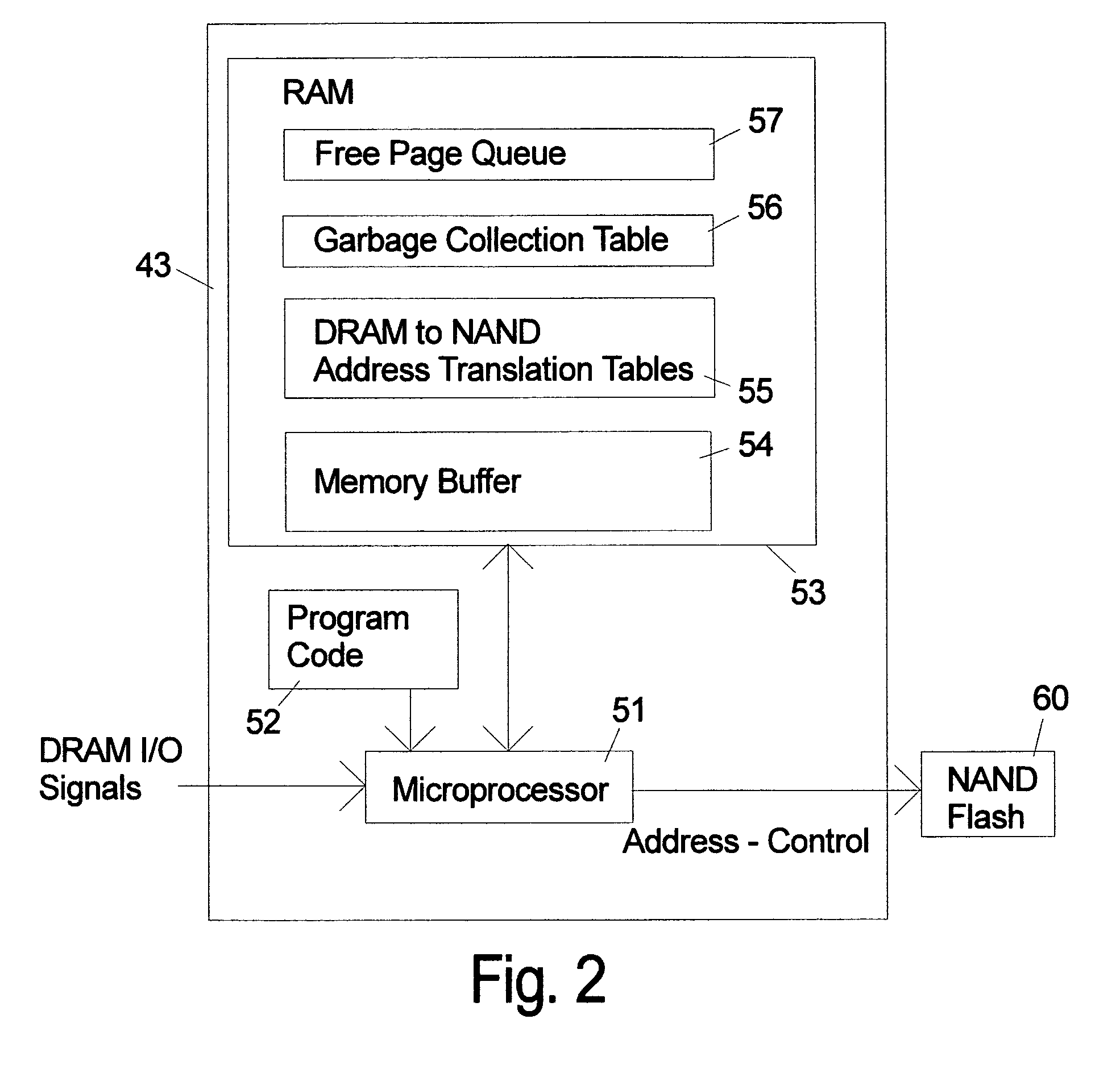
NAND flash module replacement for DRAM module
ActiveUS20090157950A1Most efficientAddressing slow performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl signalFlash memory controller
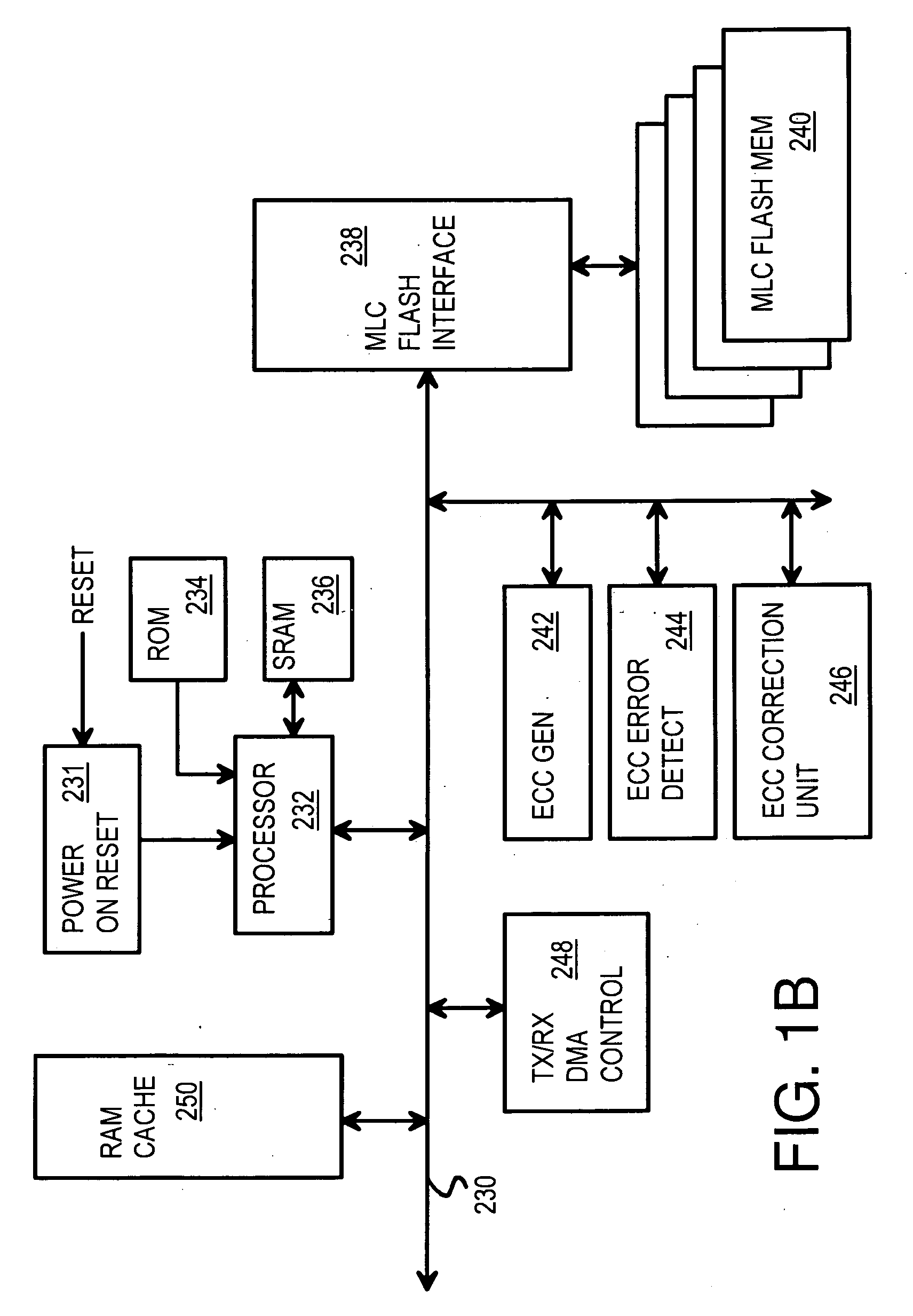
An electronic memory module according to the invention provides non-volatile memory that can be used in place of a DRAM module without battery backup. An embodiment of the invention includes an embedded microprocessor with microcode that translates the FB-DIMM address and control signals from the system into appropriate address and control signals for NAND flash memory. Wear-leveling, bad block management, garbage collection are preferably implemented by microcode executed by the microprocessor. The microprocessor, additional logic, and embedded memory provides the functions of a flash memory controller. The microprocessor memory preferably contains address mapping tables, free page queue, and garbage collection information.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
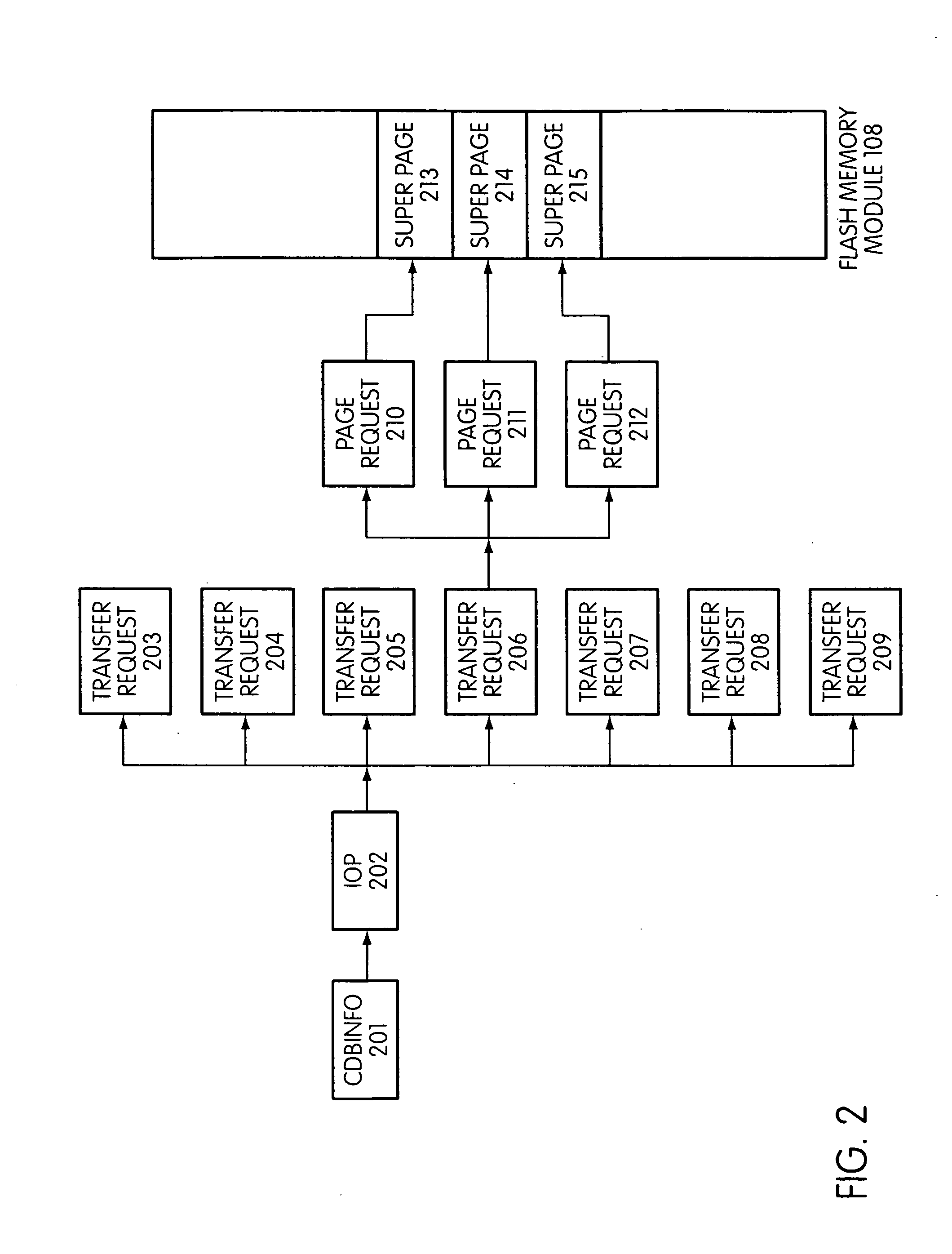
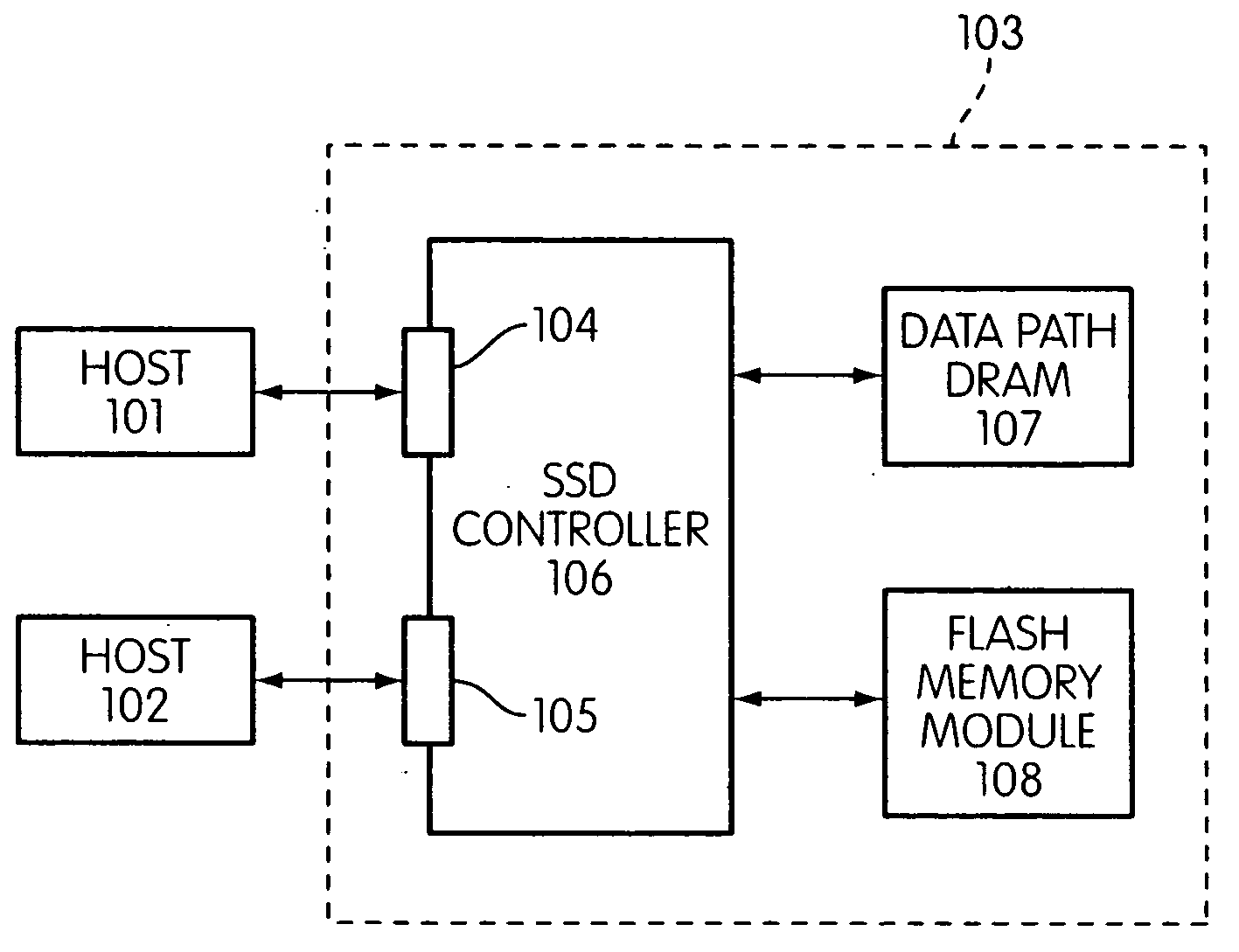
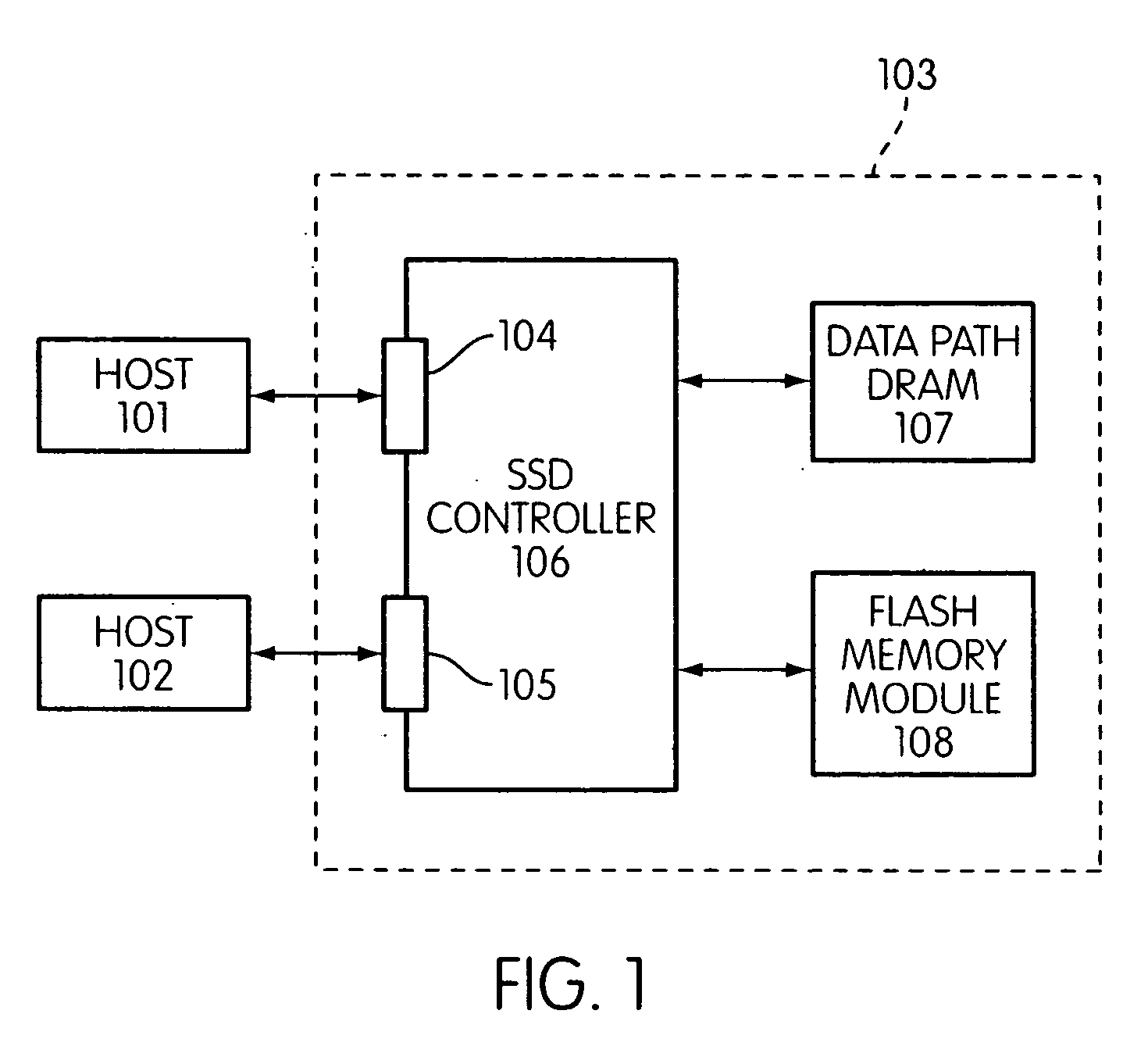
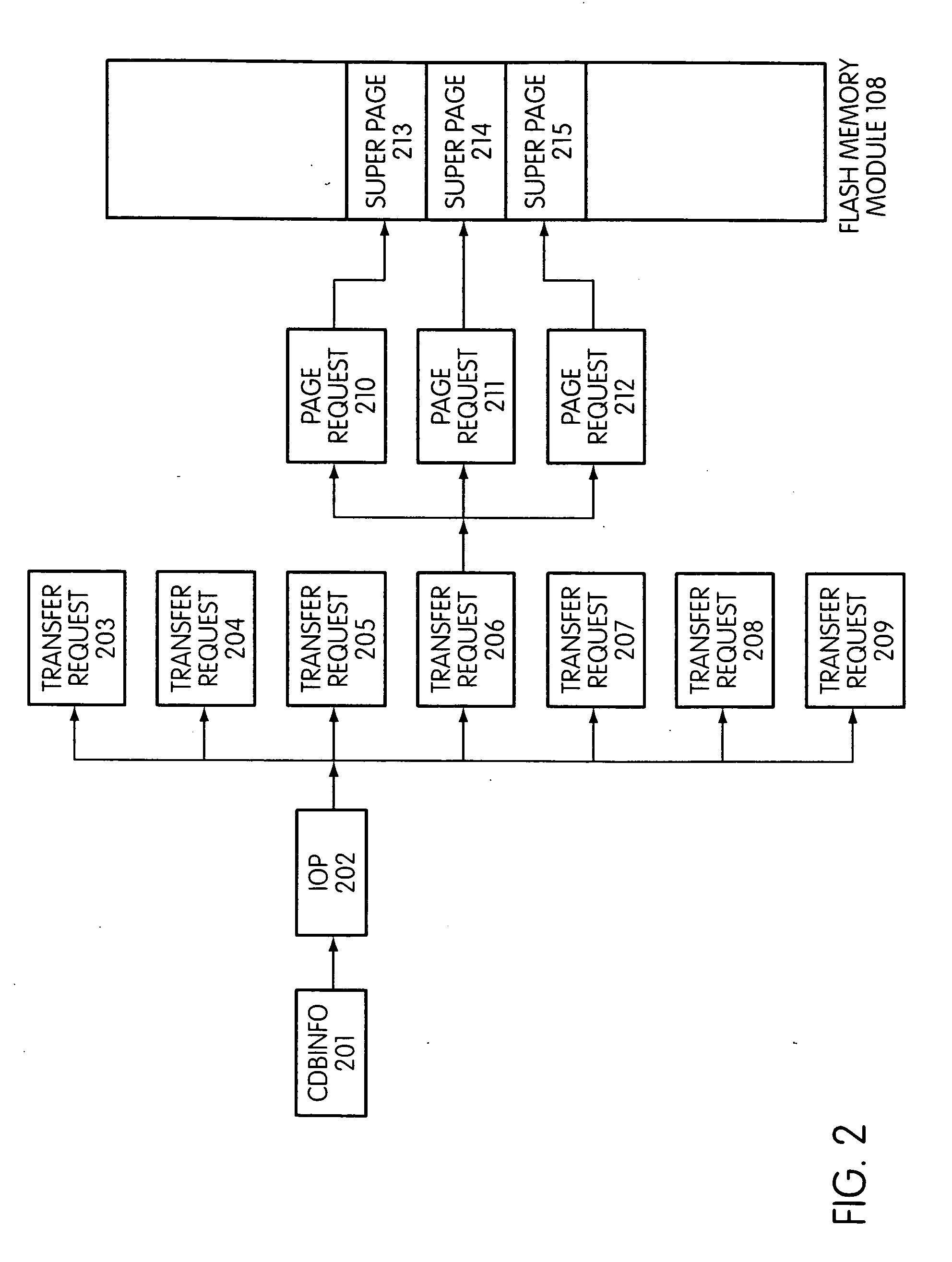
System and method for performing host initiated mass storage commands using a hierarchy of data structures
ActiveUS7934052B2Maximize useImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerParallel processing
Disclosed is a mass storage system and method for breaking a host command into a hierarchy of data structures. Different types of data structures are designed to handle different phases of tasks required by the host command, and multiple data structures may be used to handle portions of the host command in parallel, thereby allowing increased performance. The disclosed embodiments include a flash memory controller designed to allow a high degree of pipelining and parallelism.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Managing Bad Blocks In Flash Memory For Electronic Data Flash Card
InactiveUS20070283428A1Reduce search timeAvoid congestionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationLogical block addressingComputer access
An electronic data flash card accessible by a host computer, includes a flash memory controller connected to a flash memory device, and an input-output interface circuit activated to establish a communication with the host. In an embodiment, the flash card uses a USB interface circuit for communication with the host. A flash memory controller includes an arbitrator for mapping logical addresses with physical block addresses, and for performing block management operations including: storing reassigned data to available blocks, relocating valid data in obsolete blocks to said available blocks and reassigning logical block addresses to physical block addresses of said available blocks, finding bad blocks of the flash memory device and replacing with reserve blocks, erasing obsolete blocks for recycling after relocating valid data to available blocks, and erase count wear leveling of blocks, etc. Furthermore, each flash memory device includes an internal buffer for accelerating the block management operations.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
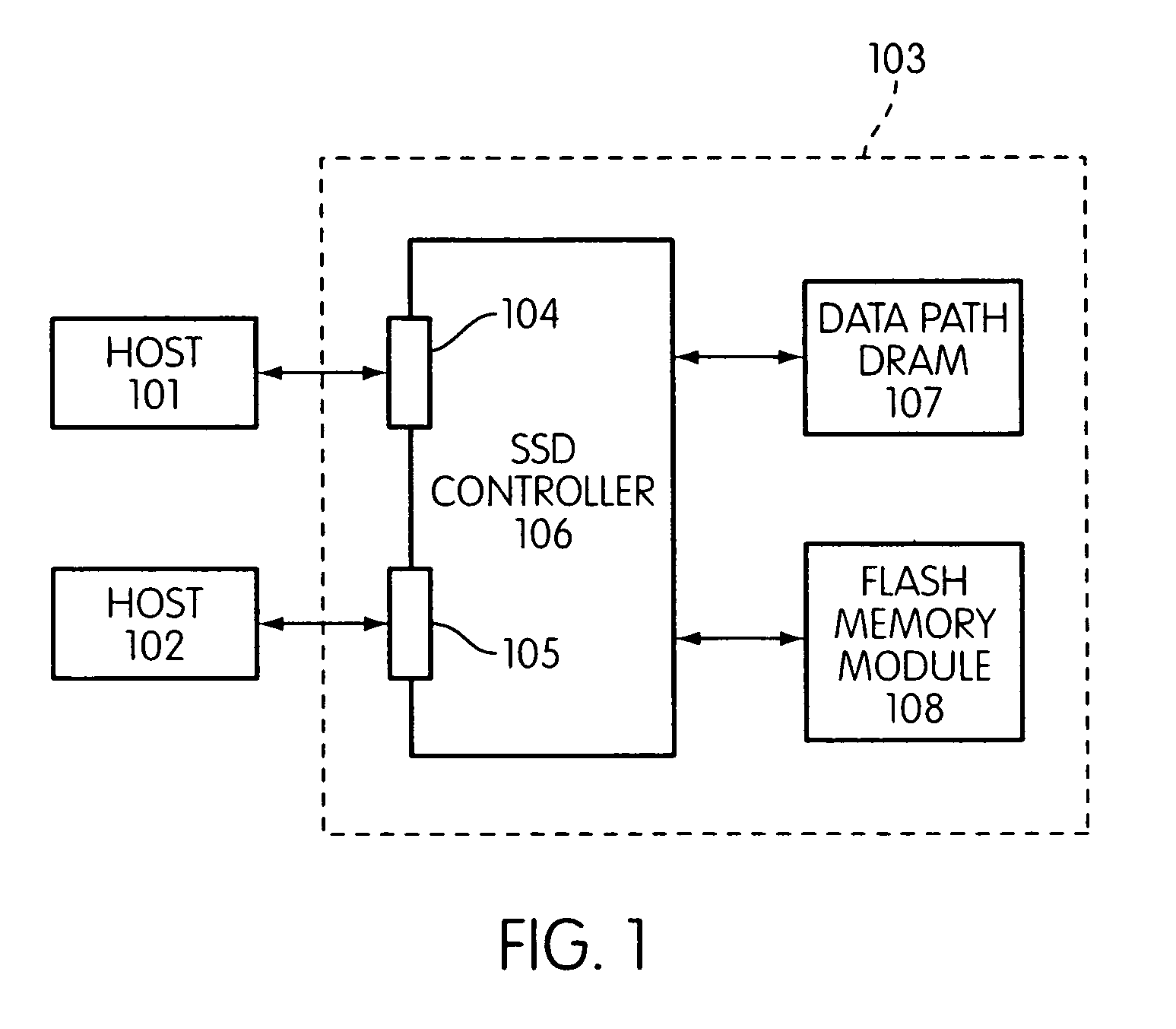
Solid state memory device with PCI controller
ActiveUS8086791B2Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingSolid-state storageProcessor register
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
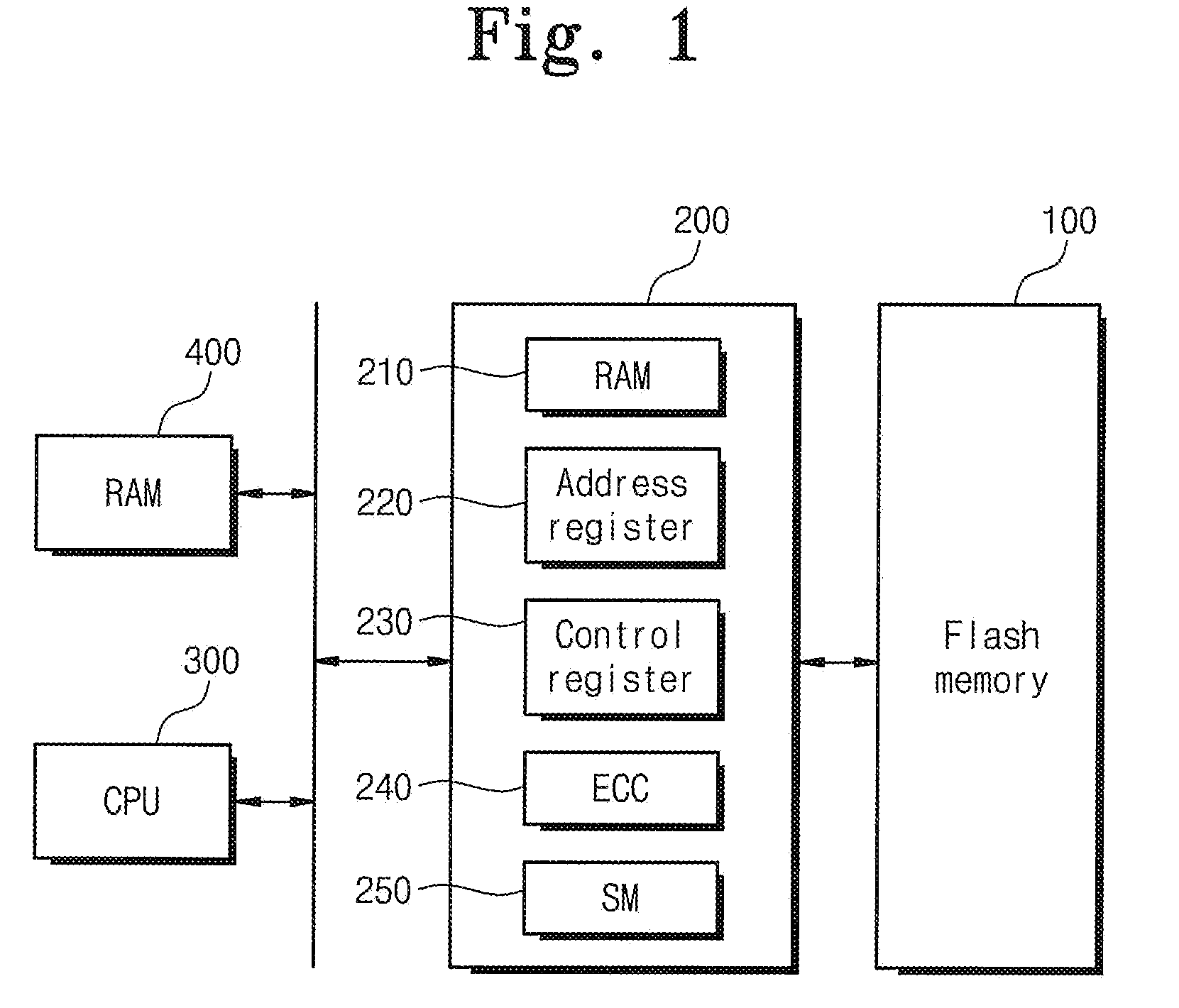
Flash memory device and memory system
ActiveUS20080229000A1Program control using stored programsMemory loss protectionControl registerProcessing element
A memory system comprises a flash memory, a processing unit, and a flash controller including address and control registers, the address and control registers being configured to receive information from the processing unit, wherein the flash controller is configured to control a copy-back program operation of the flash memory in hardware based on information stored in the address and control registers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Single-chip USB controller reading power-on boot code from integrated flash memory for user storage
A Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) single-chip flash device contains a USB flash microcontroller and flash mass storage blocks containing flash memory arrays that are block-addressable rather than randomly-addressable. USB packets from a host USB bus are read by a serial engine on the USB flash microcontroller. Various routines that execute on a CPU in the USB flash microcontroller are activated in response to commands in the USB packets. A flash-memory controller in the USB flash microcontroller transfers data from the serial engine to the flash mass storage blocks for storage. Rather than boot from an internal ROM coupled to the CPU, a boot loader is transferred by DMA from the first page of the flash mass storage block to an internal RAM. The flash memory is automatically read from the first page at power-on. The CPU then executes the boot loader from the internal RAM to load the control program.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
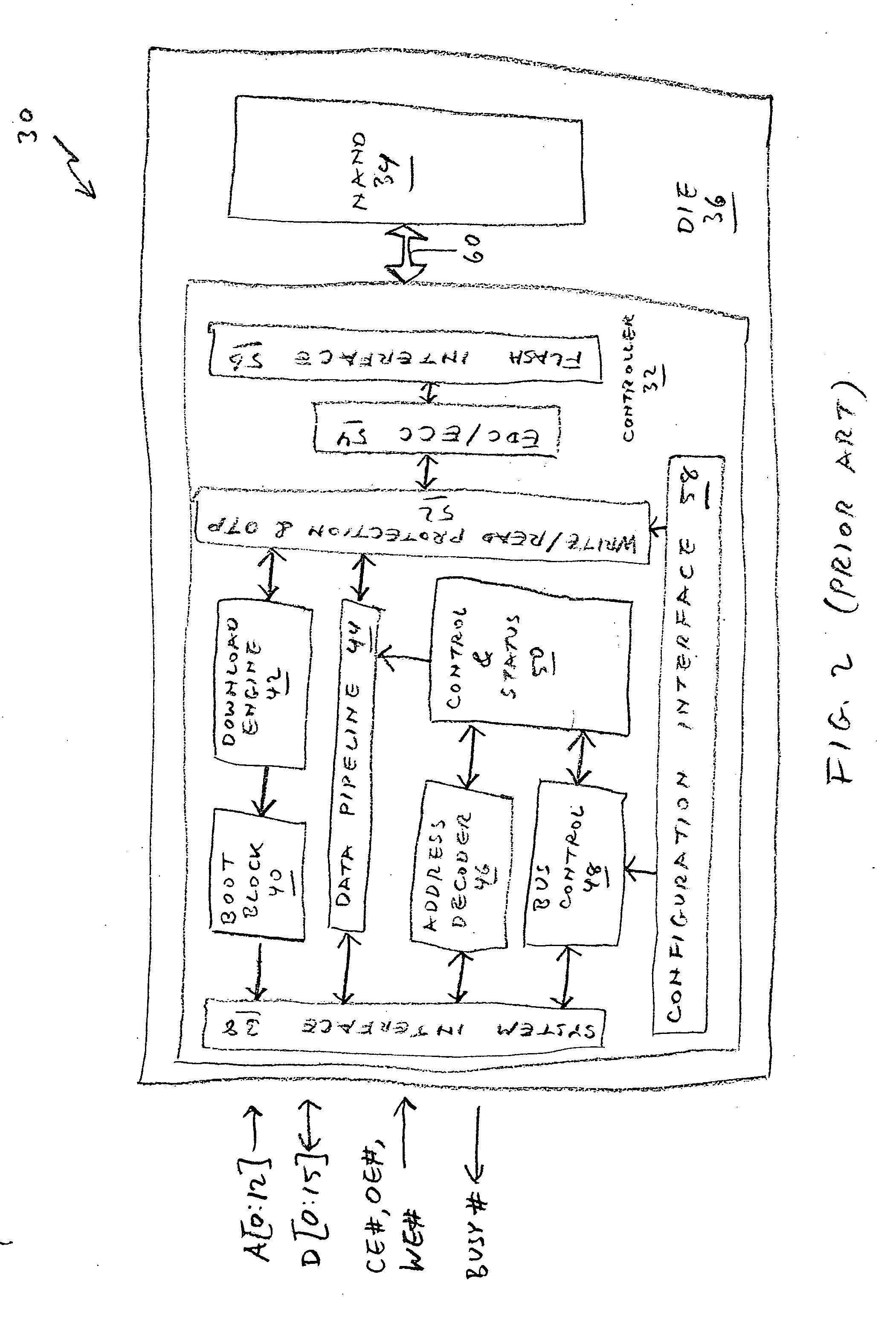
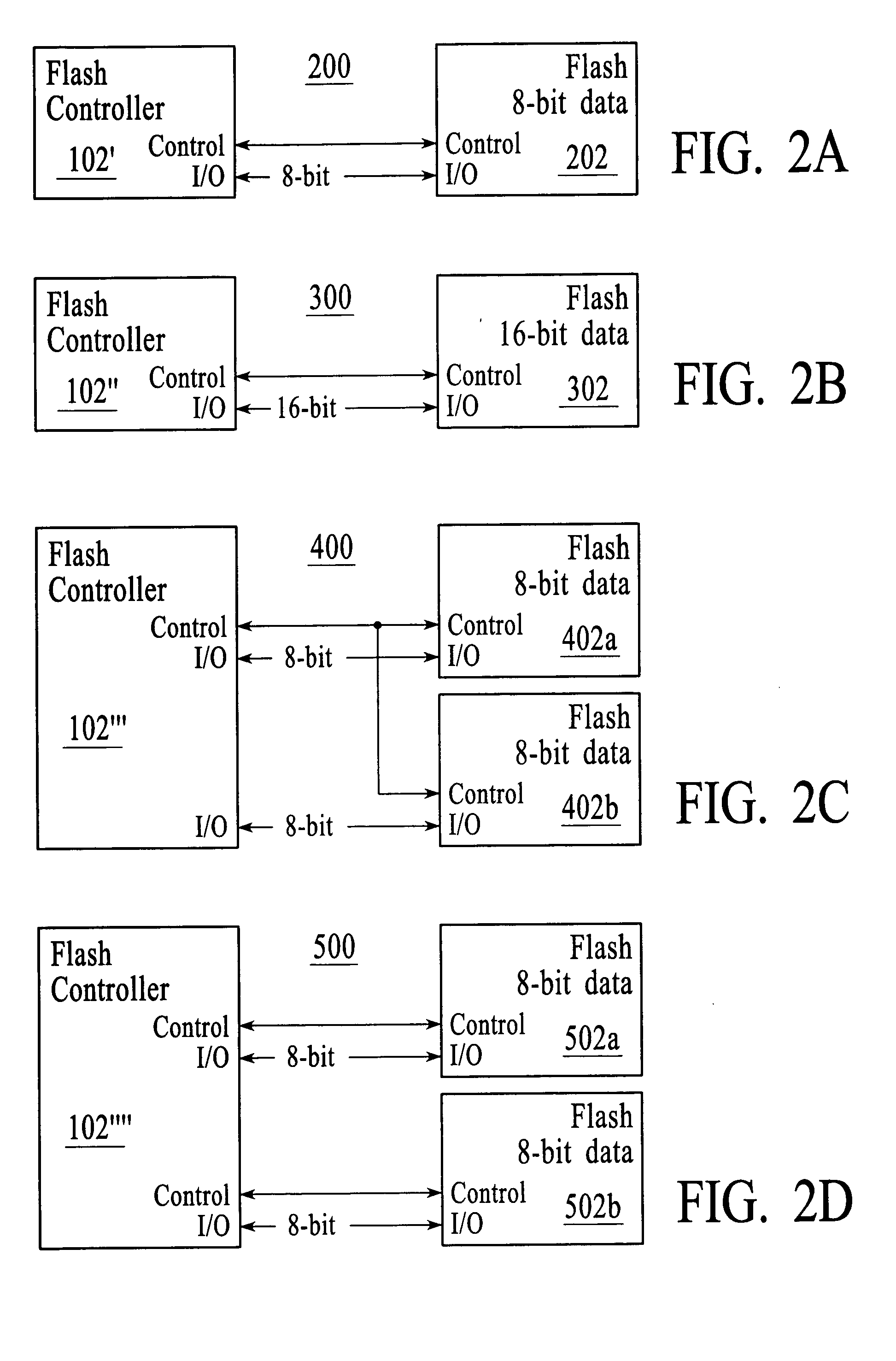
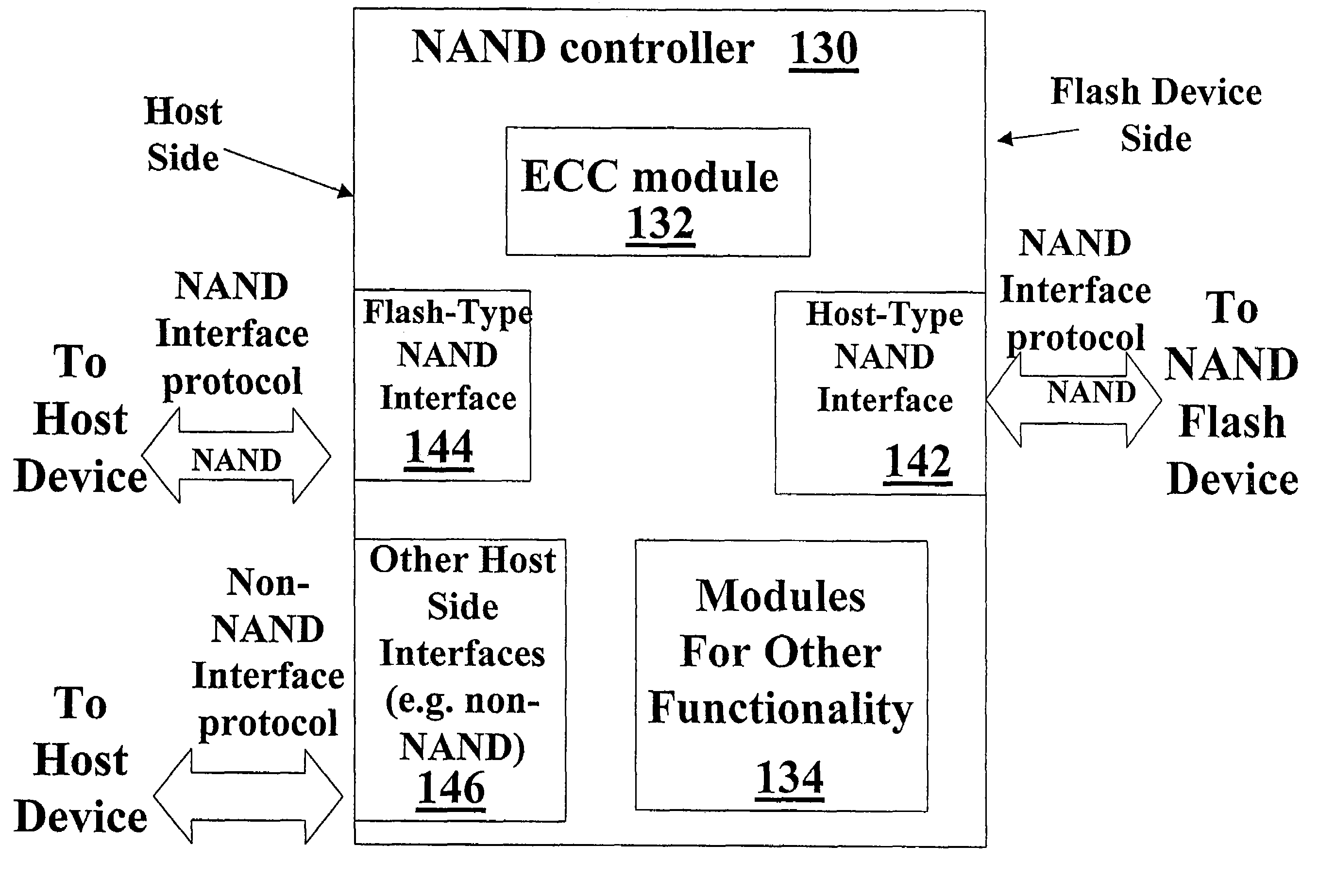
NAND flash memory controller exporting a NAND interface
A NAND controller for interfacing between a host device and a flash memory device (e.g. a NAND flash memory device) fabricated on a flash die is disclosed. In some embodiments, the presently disclosed NAND controller includes electronic circuitry fabricated on a controller die, the controller die being distinct from the flash die, a first interface (e.g. a host-type interface, for example, a NAND interface) for interfacing between the electronic circuitry and the flash memory device, and a second interface (e.g. a flash-type interface) for interfacing between the controller and the host device, wherein the second interface is a NAND interface. According to some embodiments, the first interface is an inter-die interface. According to some embodiments, the first interface is a NAND interface. Systems including the presently disclosed NAND controller are also disclosed. Methods for assembling the aforementioned systems, and for reading and writing data using NAND controllers are also disclosed.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
Swappable Sets of Partial-Mapping Tables in a Flash-Memory System With A Command Queue for Combining Flash Writes
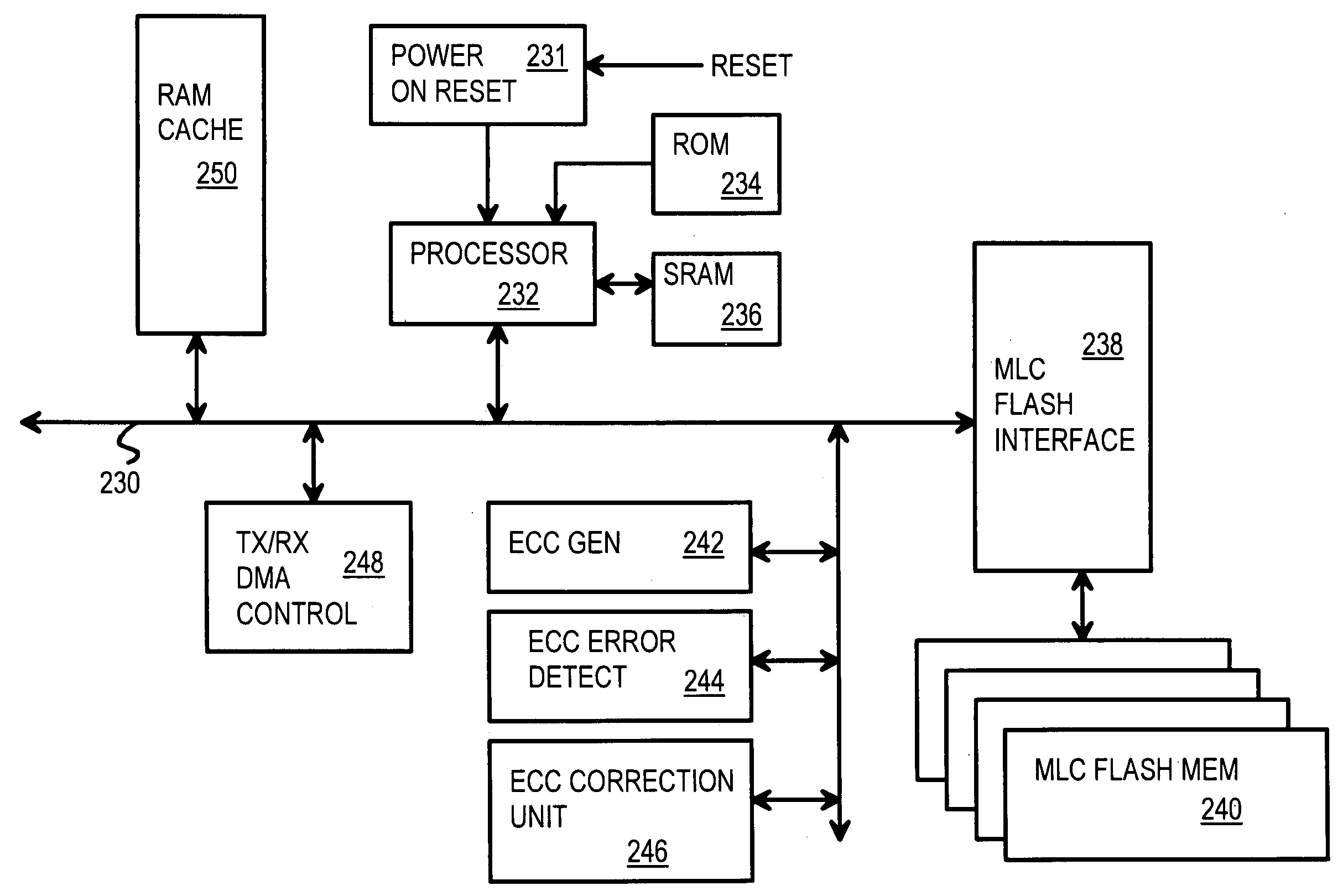
InactiveUS20090113121A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDistillation regulation/controlFlash memory controllerMulti-level cell
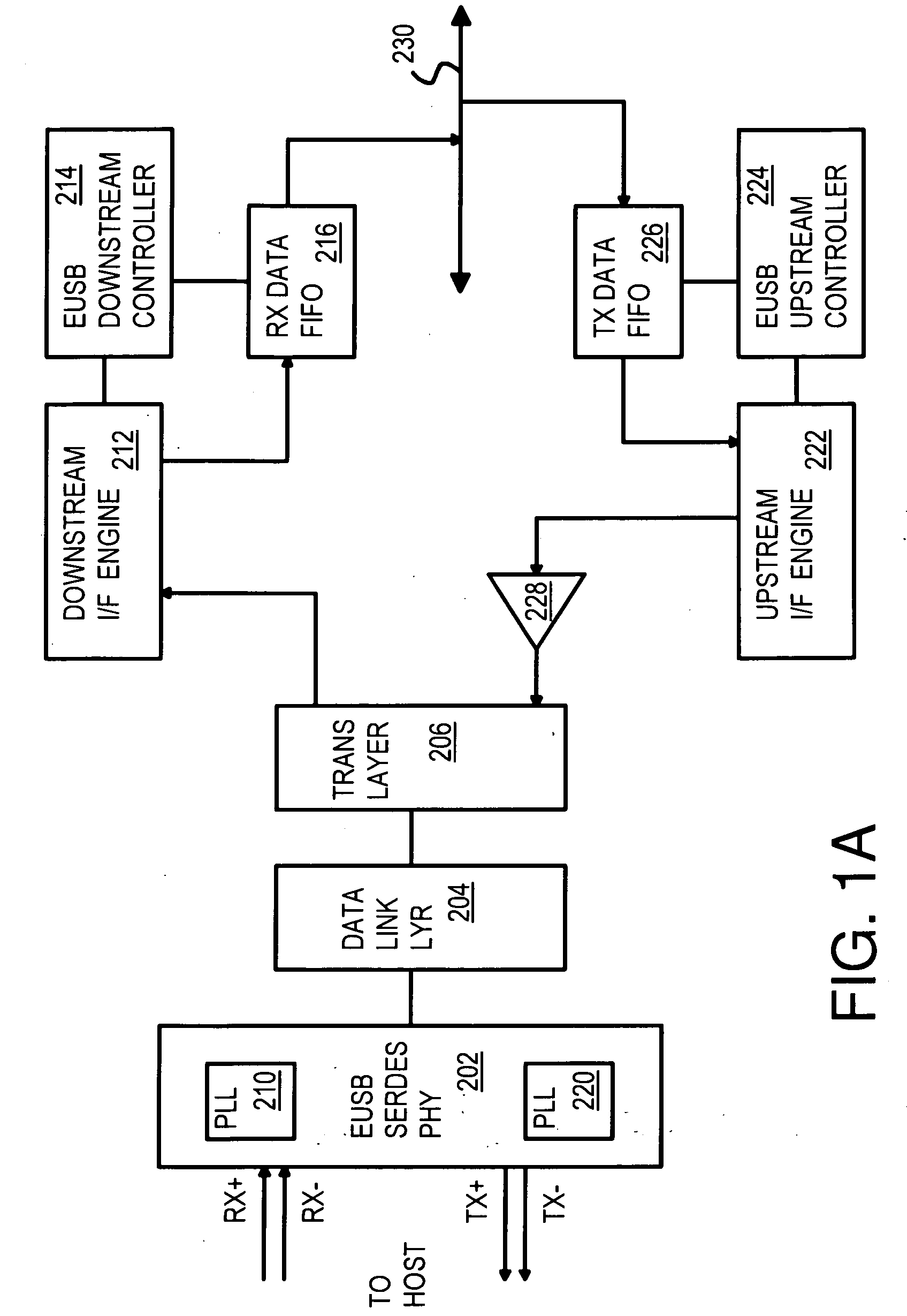
A flash controller has a flash interface accessing physical blocks of multi-level-cell (MLC) flash memory. An Extended Universal-Serial-Bus (EUSB) interface loads host commands into a command queue where writes are re-ordered and combined to reduce flash writes. A partial logical-to-physical L2P mapping table in a RAM has entries for only 1 of N sets of L2P mapping tables. The other N−1 sets are stored in flash memory and fetched into the RAM when a L2P table miss occurs. The RAM required for mapping is greatly reduced. A data buffer stores one page of host write data. Sector writes are merged using the data buffer. The data buffer is flushed to flash when a different page is written, while the partial logical-to-physical mapping table is flushed to flash when a L2P table miss occurs, when the host address is to a different one of the N sets of L2P mapping tables.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
NAND flash module replacement for DRAM module
ActiveUS8185685B2Reduce speedMost efficientMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcess memoryControl signal
An electronic memory module according to the invention provides non-volatile memory that can be used in place of a DRAM module without battery backup. An embodiment of the invention includes an embedded microprocessor with microcode that translates the FB-DIMM address and control signals from the system into appropriate address and control signals for NAND flash memory. Wear-leveling, bad block management, garbage collection are preferably implemented by microcode executed by the microprocessor. The microprocessor, additional logic, and embedded memory provides the functions of a flash memory controller. The microprocessor memory preferably contains address mapping tables, free page queue, and garbage collection information.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Cache coherent support for flash in a memory hierarchy
ActiveUS20100293420A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory hierarchyRandom access memory
System and method for using flash memory in a memory hierarchy. A computer system includes a processor coupled to a memory hierarchy via a memory controller. The memory hierarchy includes a cache memory, a first memory region of random access memory coupled to the memory controller via a first buffer, and an auxiliary memory region of flash memory coupled to the memory controller via a flash controller. The first buffer and the flash controller are coupled to the memory controller via a single interface. The memory controller receives a request to access a particular page in the first memory region. The processor detects a page fault corresponding to the request and in response, invalidates cache lines in the cache memory that correspond to the particular page, flushes the invalid cache lines, and swaps a page from the auxiliary memory region to the first memory region.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
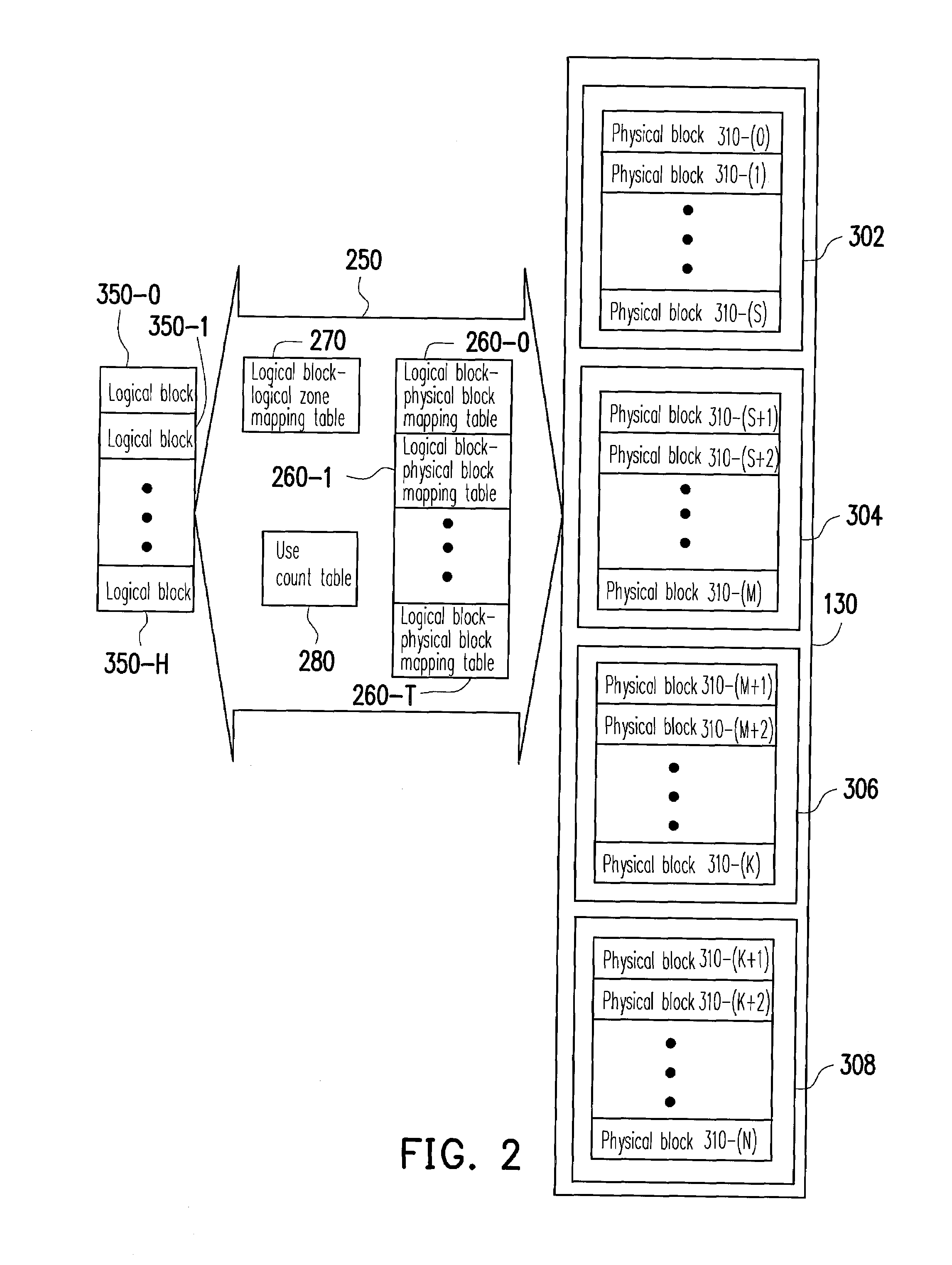
Logical block management method for a flash memory and control circuit storage system using the same
ActiveUS20110010489A1Extended writing timeShorten write timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerControl circuit
A logical block management method for managing a plurality of logical blocks of a flash memory device is provided. The logical block management method includes providing a flash memory controller, grouping the logical blocks into a plurality of logical zones, wherein each logical block maps to one of the logical zones. The logical block management method also includes counting a use count value for each logical block, and dynamically adjusting mapping relations between the logical blocks and the logical zones according to the use count values. Accordingly, the logical block management method can effectively utilizing the logical zones to determine usage patterns of the logical blocks and use different mechanisms to write data, so as to increase the performance of the flash memory storage device.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
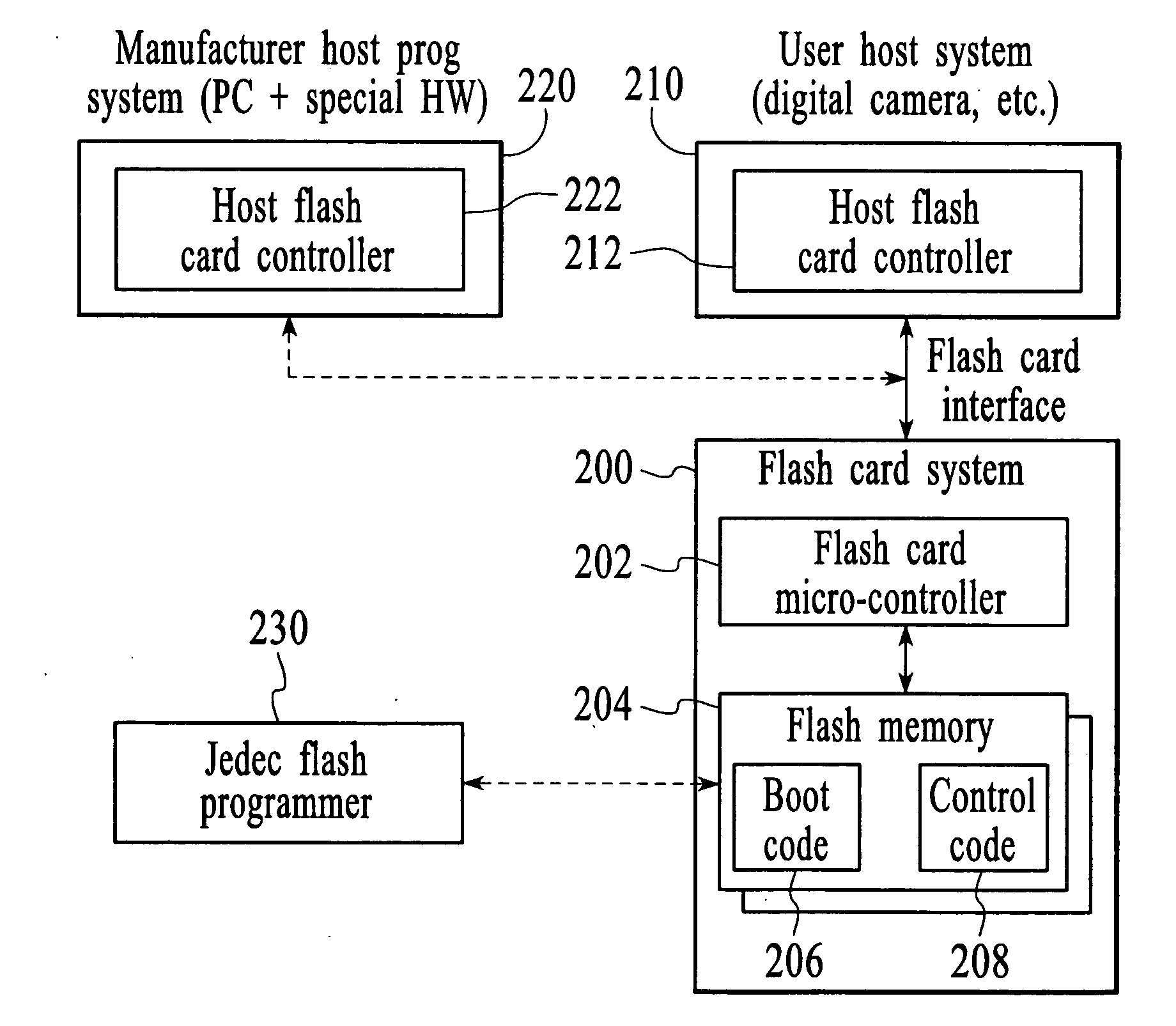
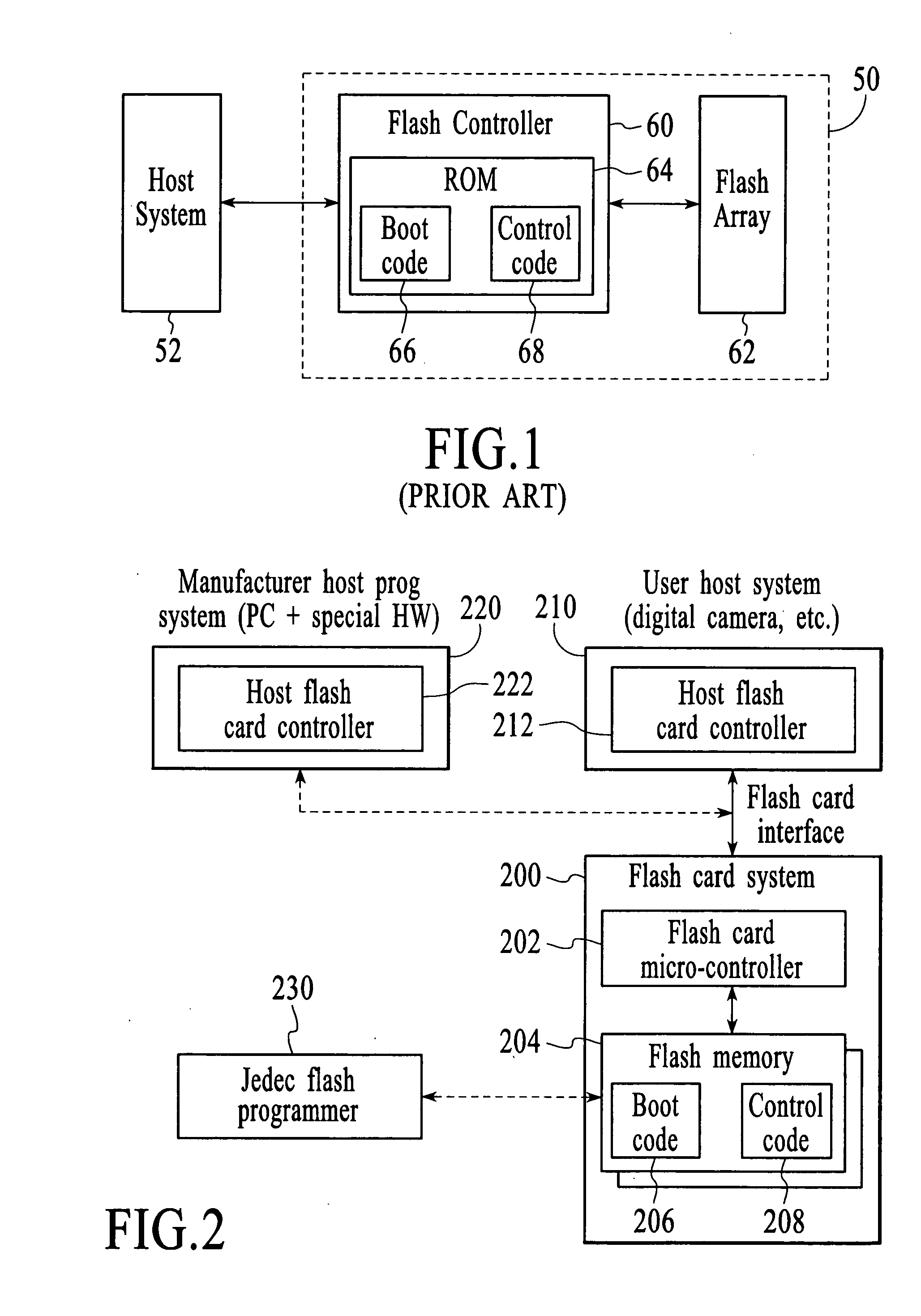
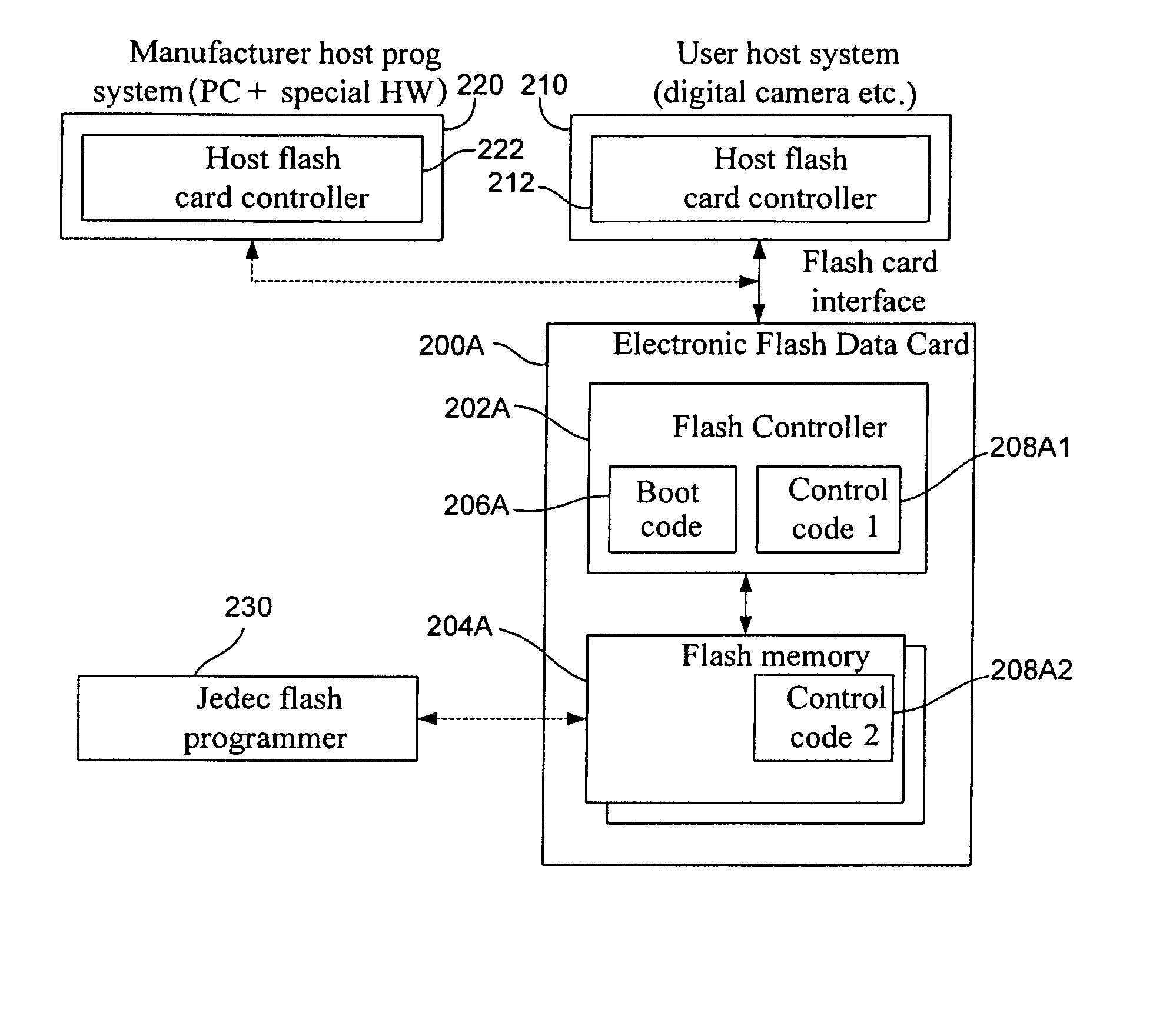
Flash card system
InactiveUS20060075395A1Software engineeringRead-only memoriesFlash memory controllerComputer science
A flash memory system is disclosed. The flash memory system includes a flash controller and at least one flash memory device coupled to the flash controller. The boot code and control code for the flash memory system are stored in the flash memory device. Because the boot code and the control code are stored in the flash memory device instead of in a ROM, the boot code and control code can be updated in the field. Also, the flash controller can support multiple brands and types of flash memory in the flash memory system to eliminate stocking issues.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
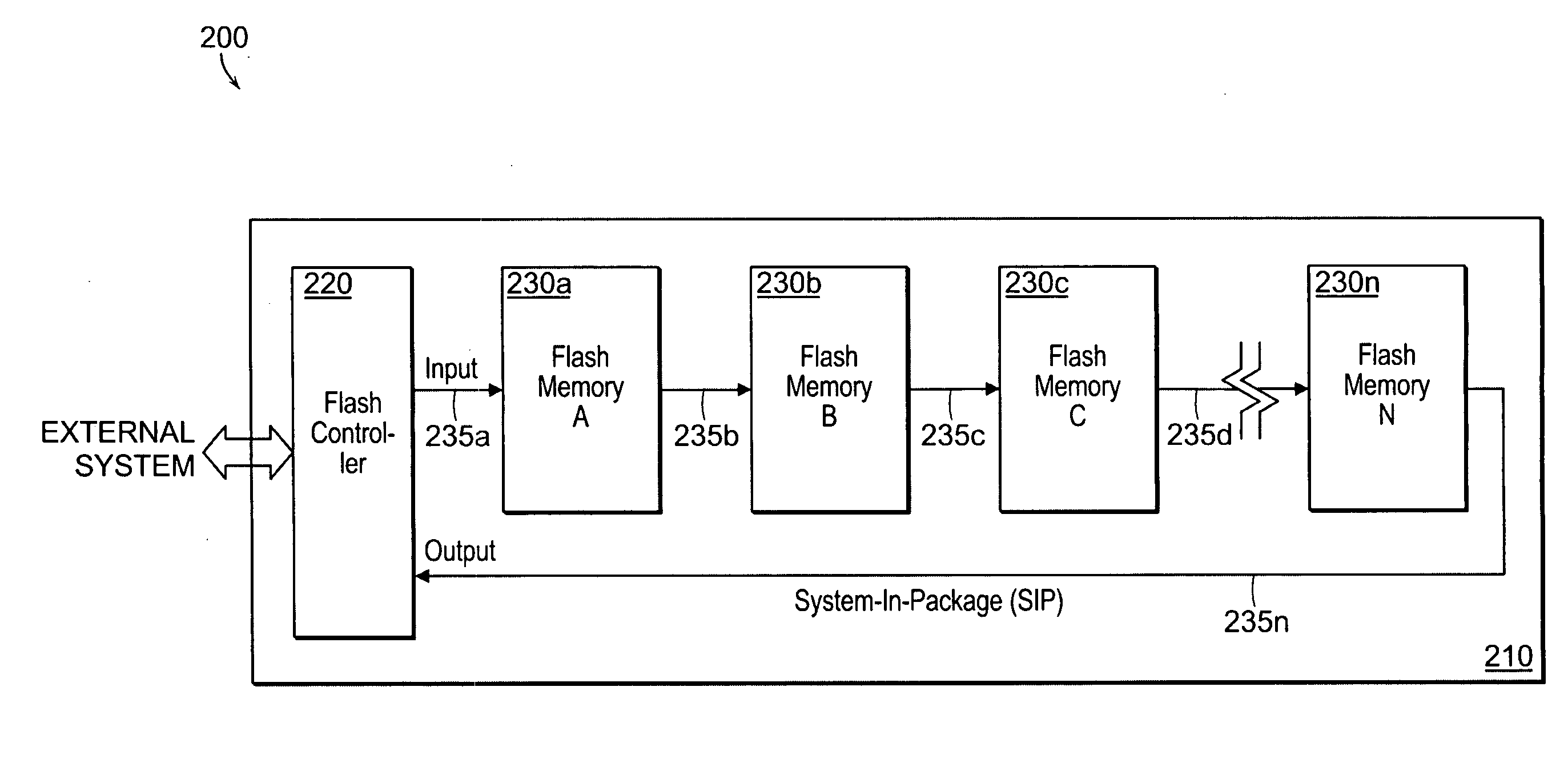
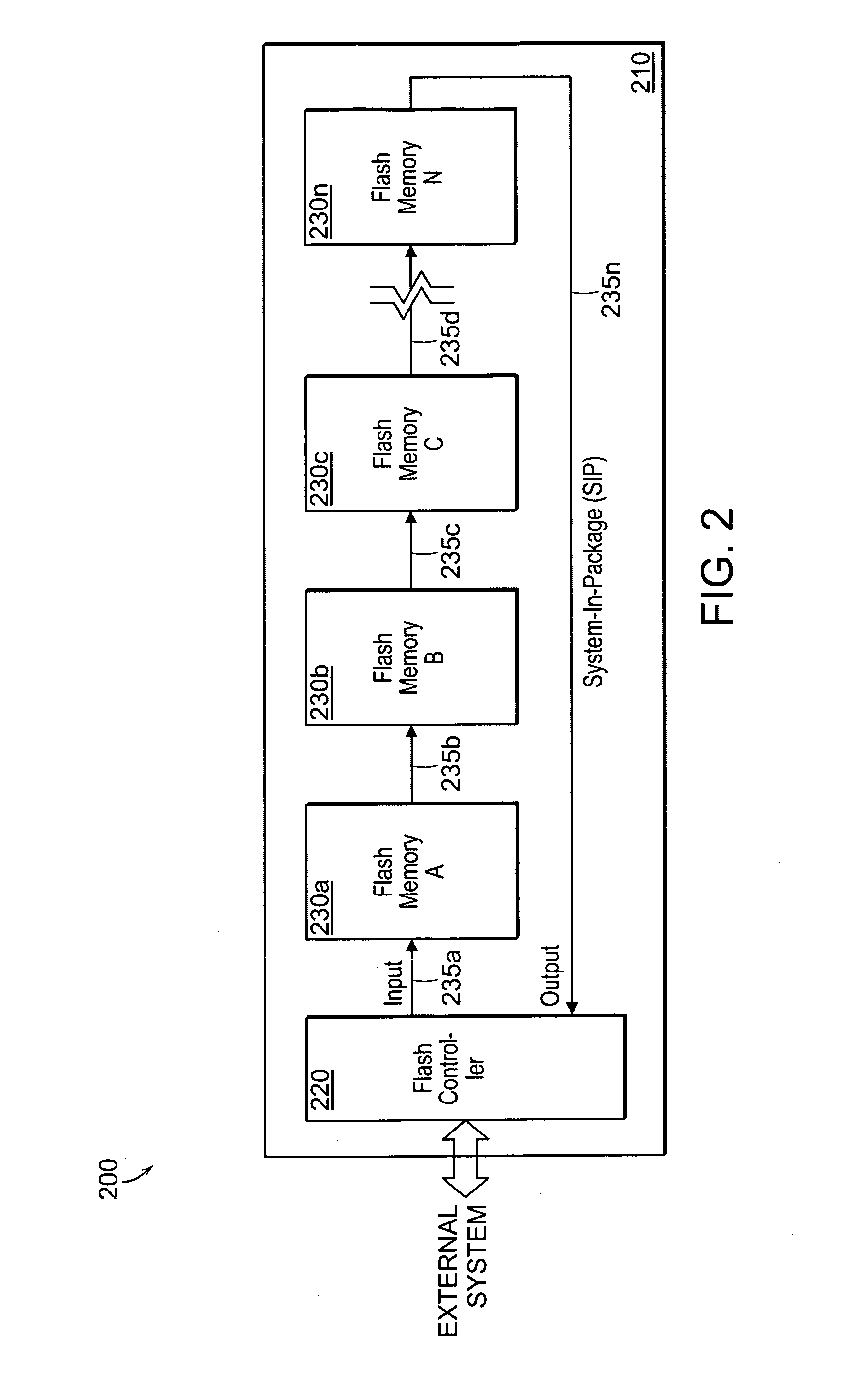
Nonvolatile memory system
InactiveUS20070165457A1Increase memory capacitySignificant overheadSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDaisy chainFlash memory controller
A Flash memory system is implemented in a system-in-package (SIP) enclosure, the system comprising a Flash memory controller and a plurality Flash memory devices. An SIP relates to a single package or module comprising a number of integrated circuits (chips). The Flash memory controller is configured to interface with an external system and a plurality of memory devices within the SIP. The memory devices are configured in a daisy chain cascade arrangement, controlled by the Flash memory controller through commands transmitted through the daisy chain cascade.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
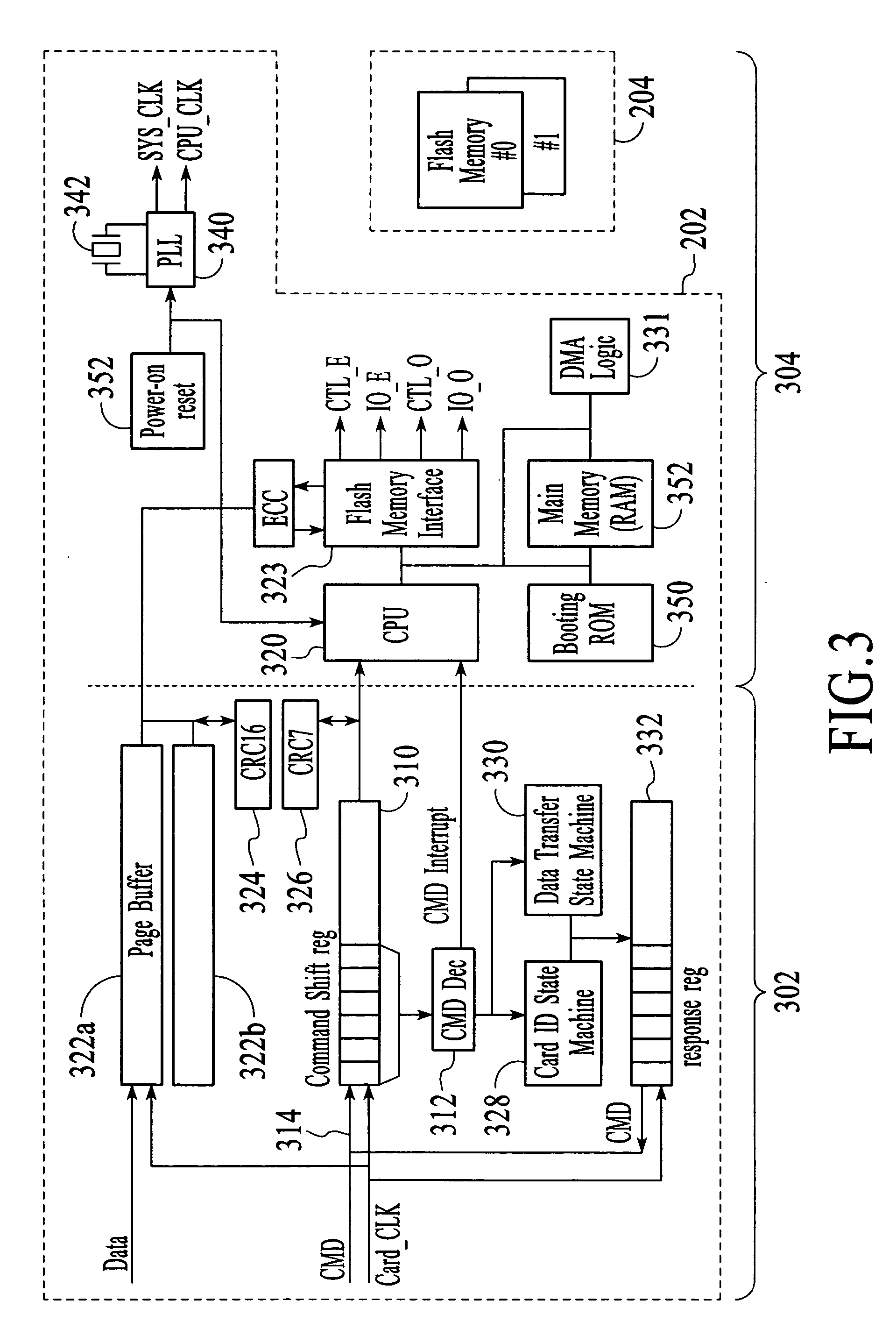
Flash memory system with a high-speed flash controller
InactiveUS7243185B2Improve throughputIncrease in sizeMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesFlash memory controllerMulti media card
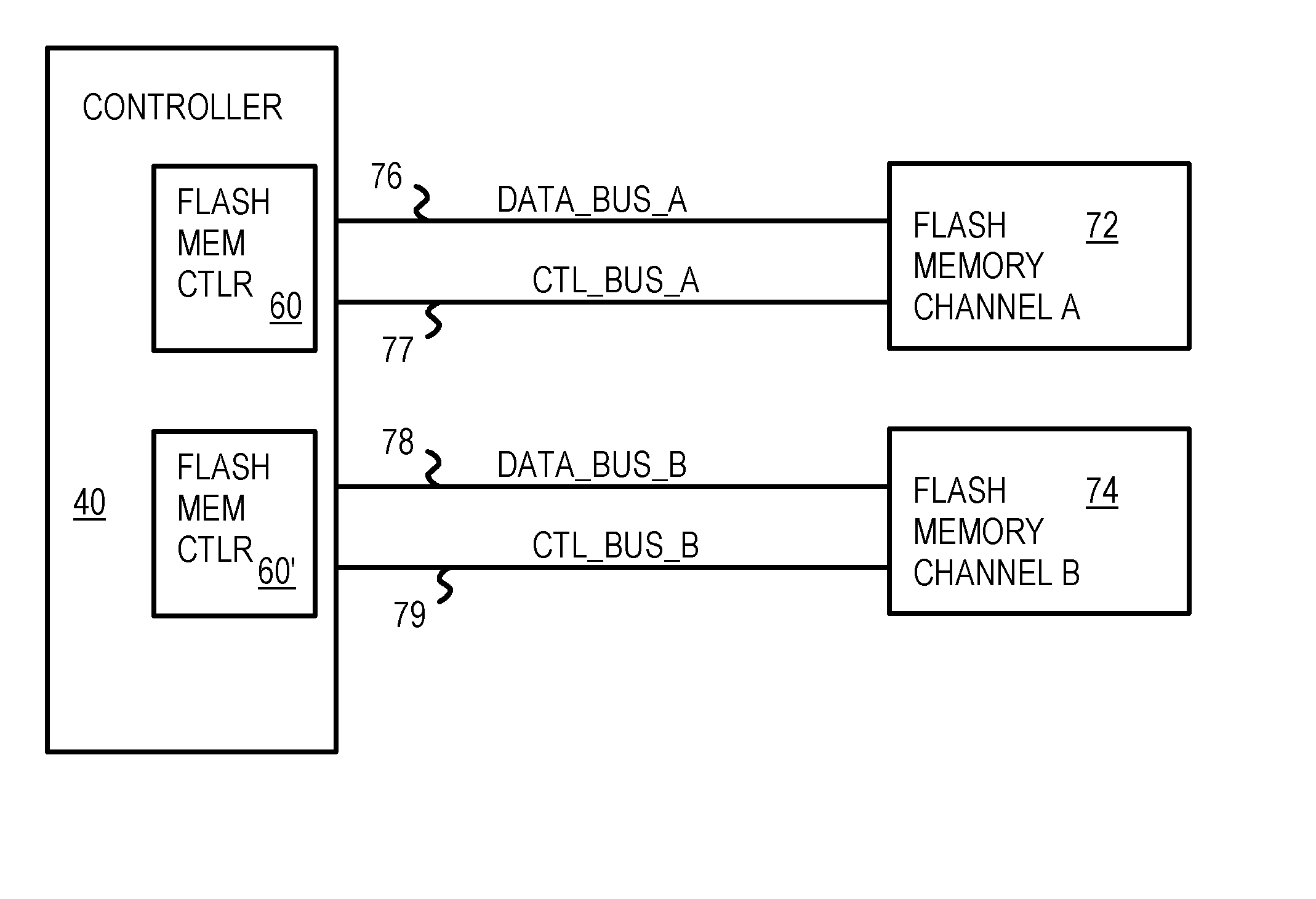
A multi media card (MMC) is disclosed. The MMC includes a flash controller and at least one flash memory device. The flash controller increases the throughput of the at least one flash memory device to match the speed of a host bus coupled to the MMC. The flash controller increases the throughput by performing one or more of performing a read-ahead memory read operation, performing a write-ahead memory write operation, increasing the size of a page register of the at least one flash memory device, increasing the width of a memory data bus, performing a dual-channel concurrent memory read operation, performing a dual-channel concurrent memory write operation, performing a write-cache memory write operation, and any combination thereof.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
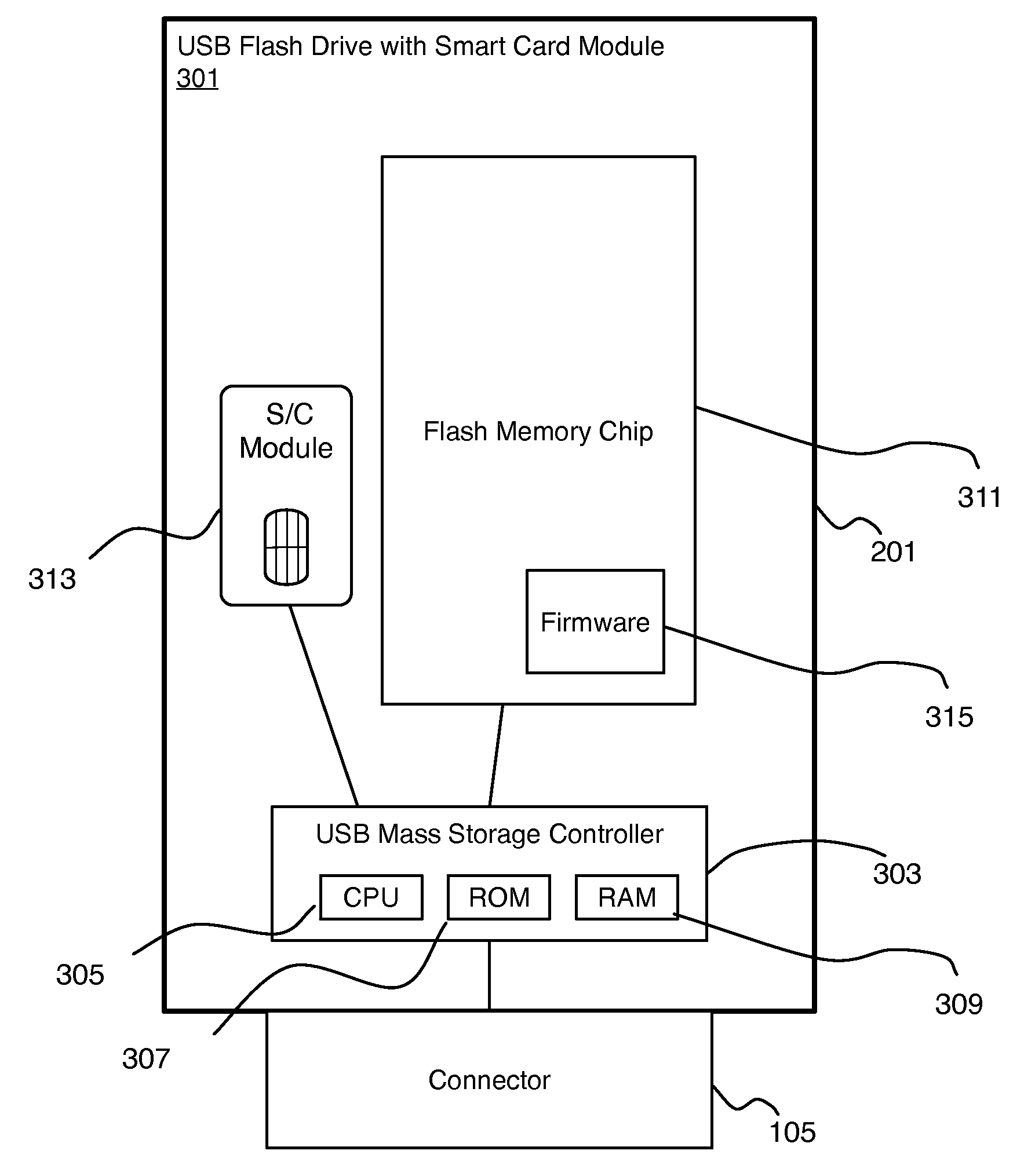
System and method for secure firmware update of a secure token having a flash memory controller and a smart card
ActiveUS20100023777A1User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionMicrocontrollerSmart card
A system and method of operating a device to securely update the control firmware controlling the device. Downloading a firmware update package to a first microcontroller of the device. Determining a firmware update portion and an encrypted hash portion of the firmware update package wherein the encrypted hash portion is cryptographically signed by a signatory. Confirm that the encrypted hash portion conforms to the firmware update by independently computing the hash of the encrypted firmware update portion on the first microcontroller and comparing that value to the signed hash. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:GEMPLU
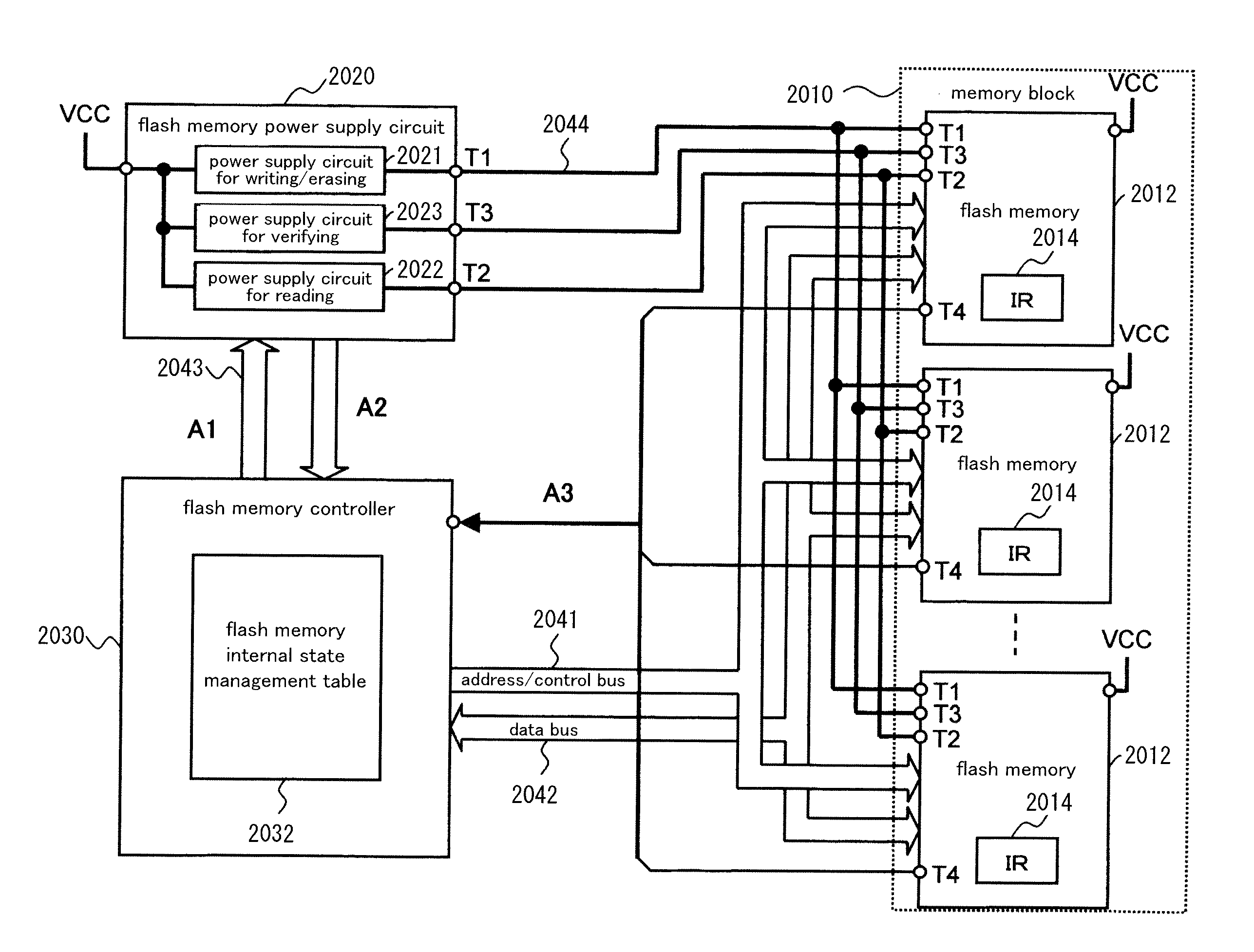
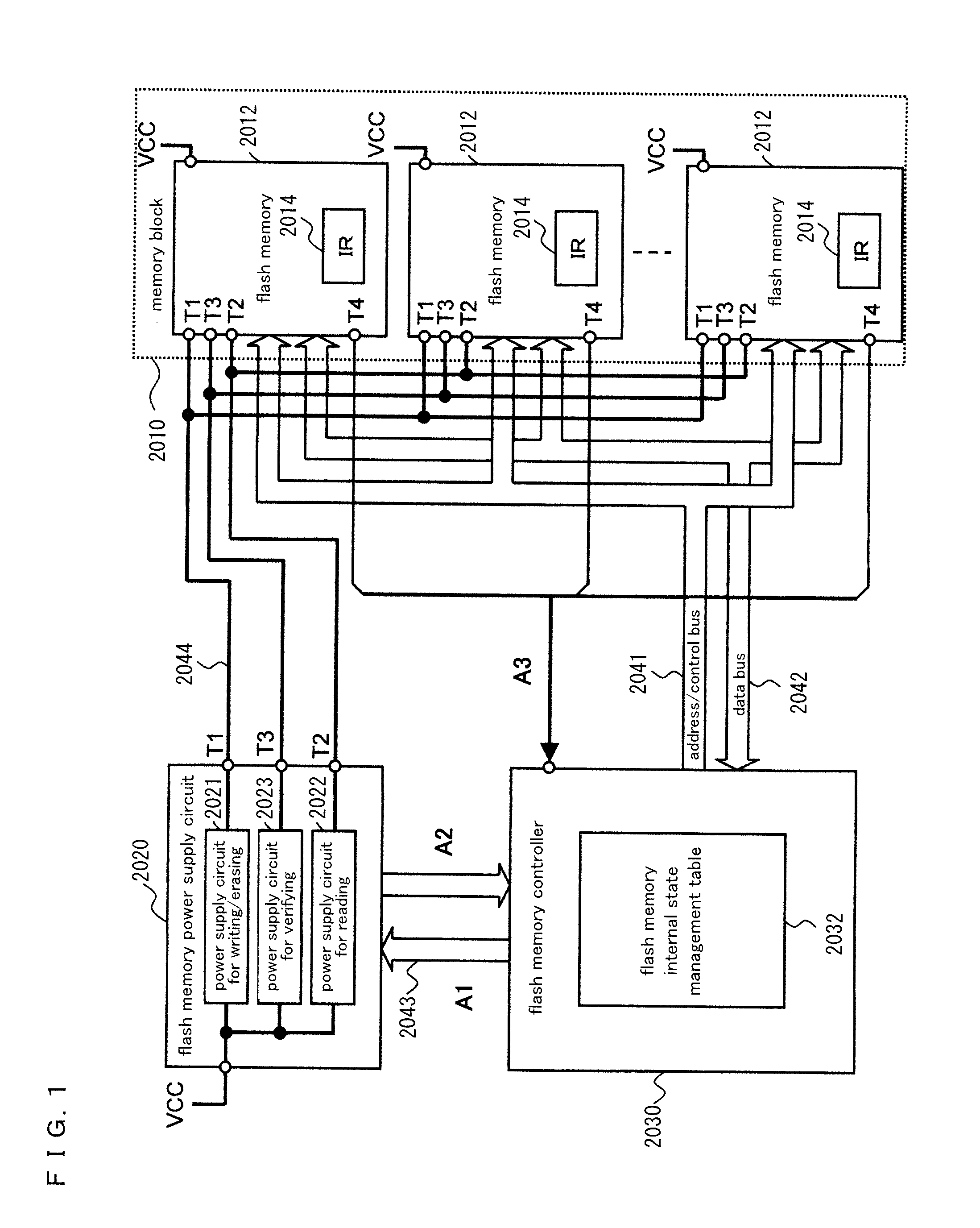
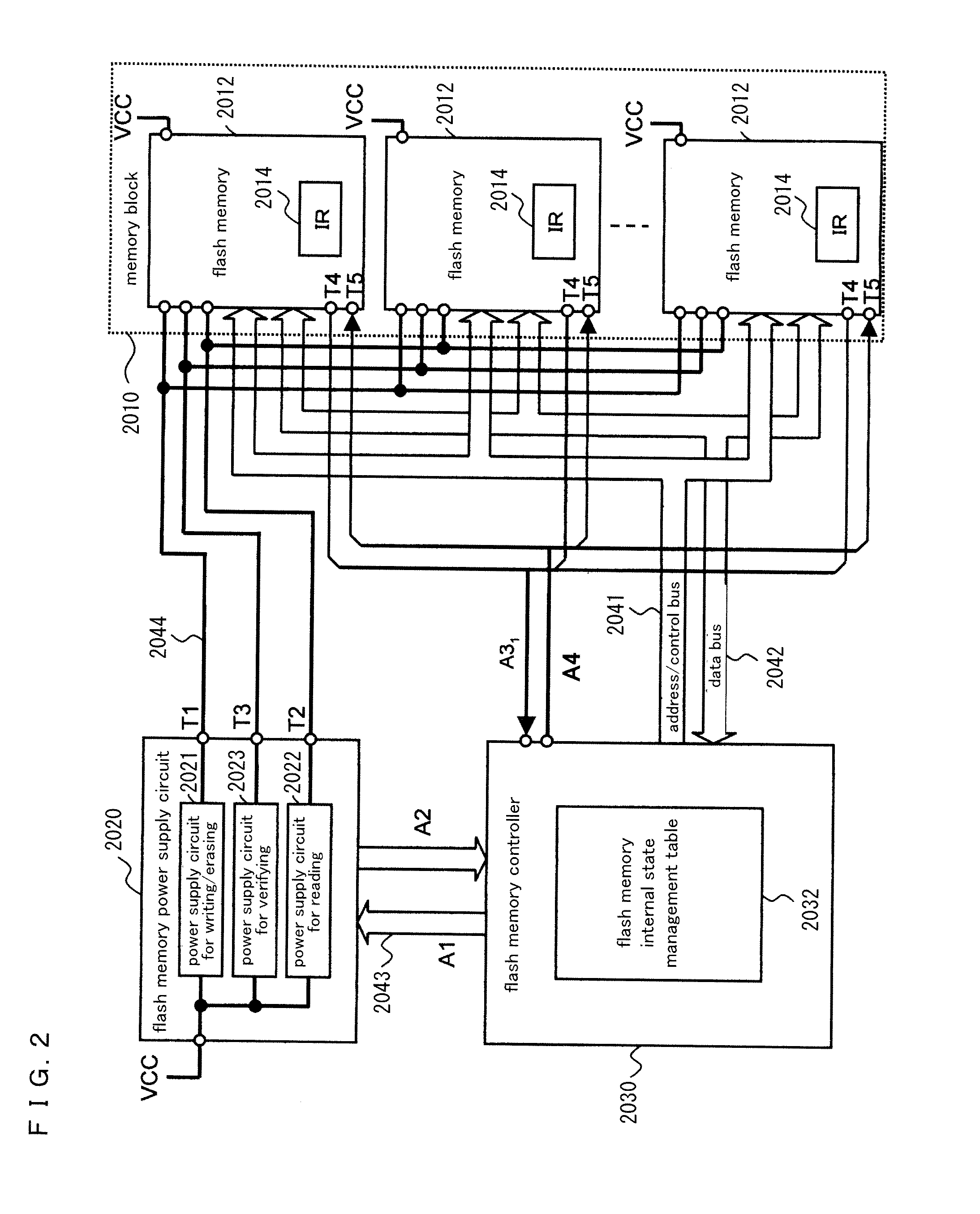
Nonvolatile storage system, power supply circuit for memory system, flash memory, flash memory controller, and nonvolatile semiconductor storage device
ActiveUS20130124888A1Stably execute processReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSemiconductor storage devicesFlash memory controller
Disclosed is a nonvolatile storage system including: a memory block having a plurality of flash memories; a flash memory power supply circuit outside of the memory block; and a flash memory controller. The flash memory power supply circuit has a plurality of types of power supply circuits for process execution, the power supply circuits for process execution generating and supplying power at a plurality of voltage levels needed to execute processes in the flash memories. The flash memory controller monitors changes of the internal states of the flash memories by communicating with the flash memories, thereby controlling the power supply circuits for process execution and the flash memories.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Flash memory controller controlling various flash memory cells
InactiveUS20080086631A1Easy to updateSoftware engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSingle flashRandom access memory
An electronic data flash card is accessible by a host system, and includes a flash memory controller and at least one flash memory device coupled to the flash controller. The boot code and control code for the flash memory system (flash card) are stored in the flash memory device during a programming procedure. The flash controller transfers the boot code and control code to a volatile main memory (e.g., random access memory or RAM) at start up or reset making a RAM-based memory system. Boot code and control code are selectively overwritten during a code updating operation. A single flash controller thus supports multiple brands and types of flash memory to eliminate stocking issues.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com