Patents
Literature
320results about How to "Increase memory capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
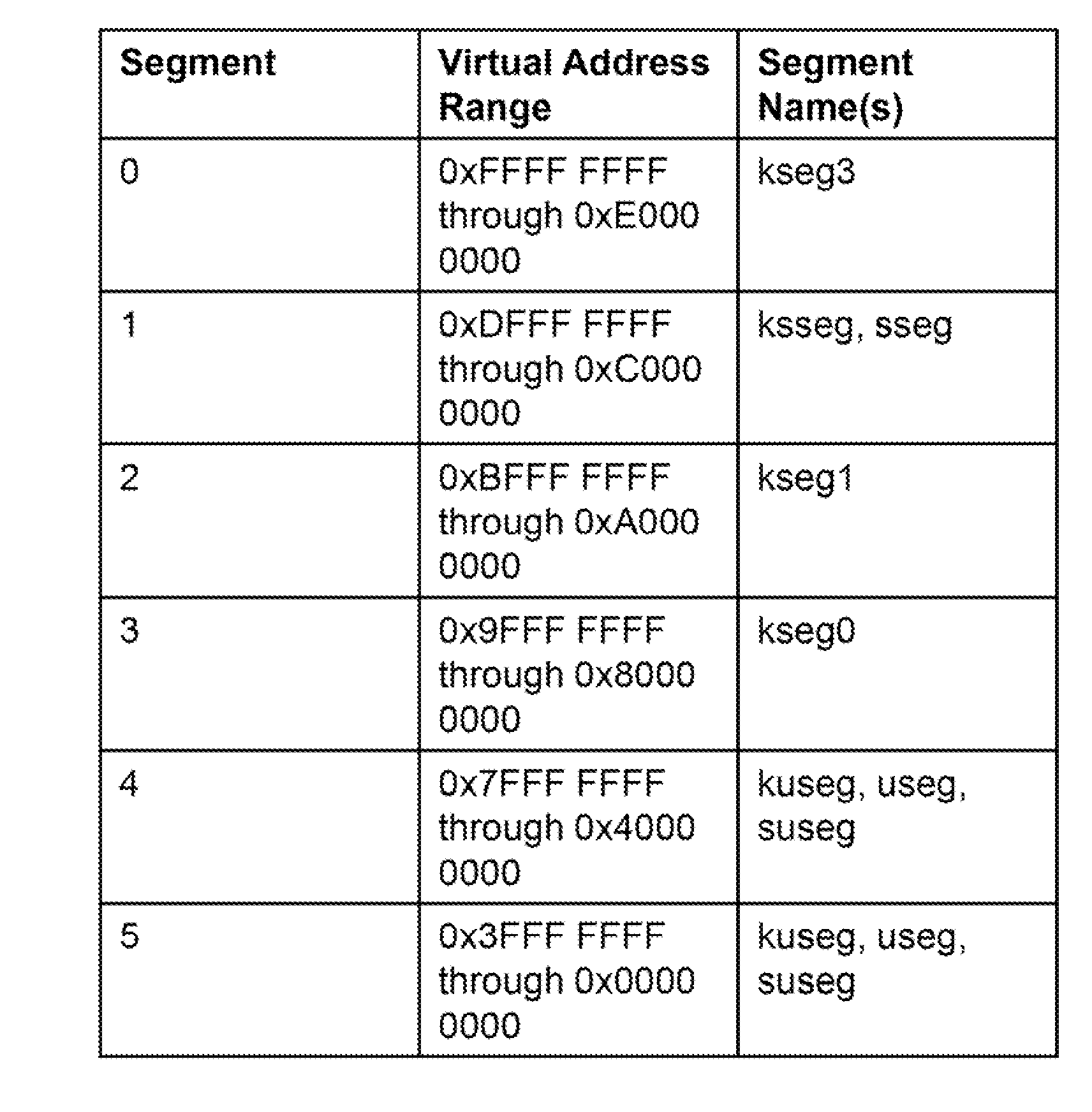
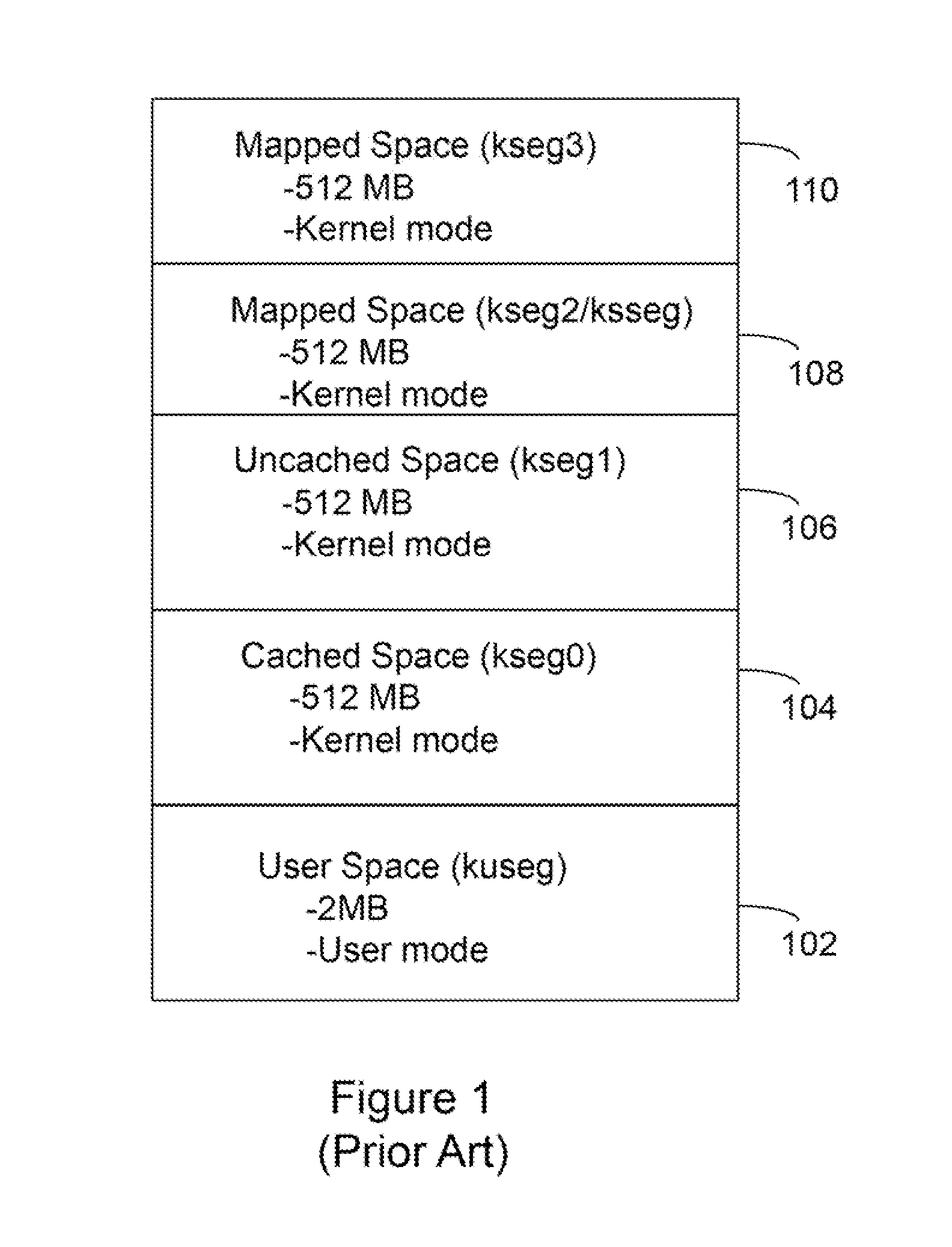
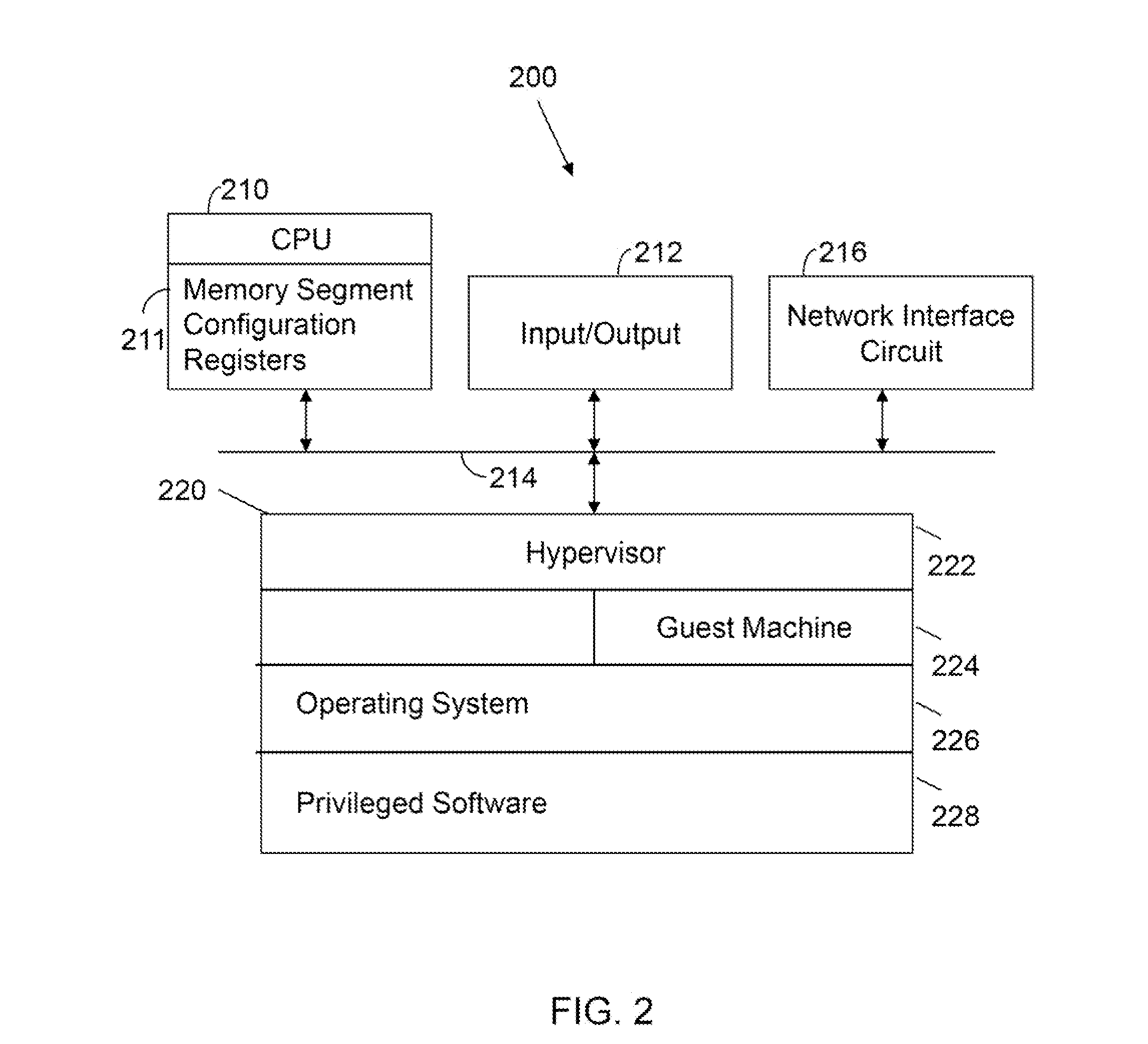
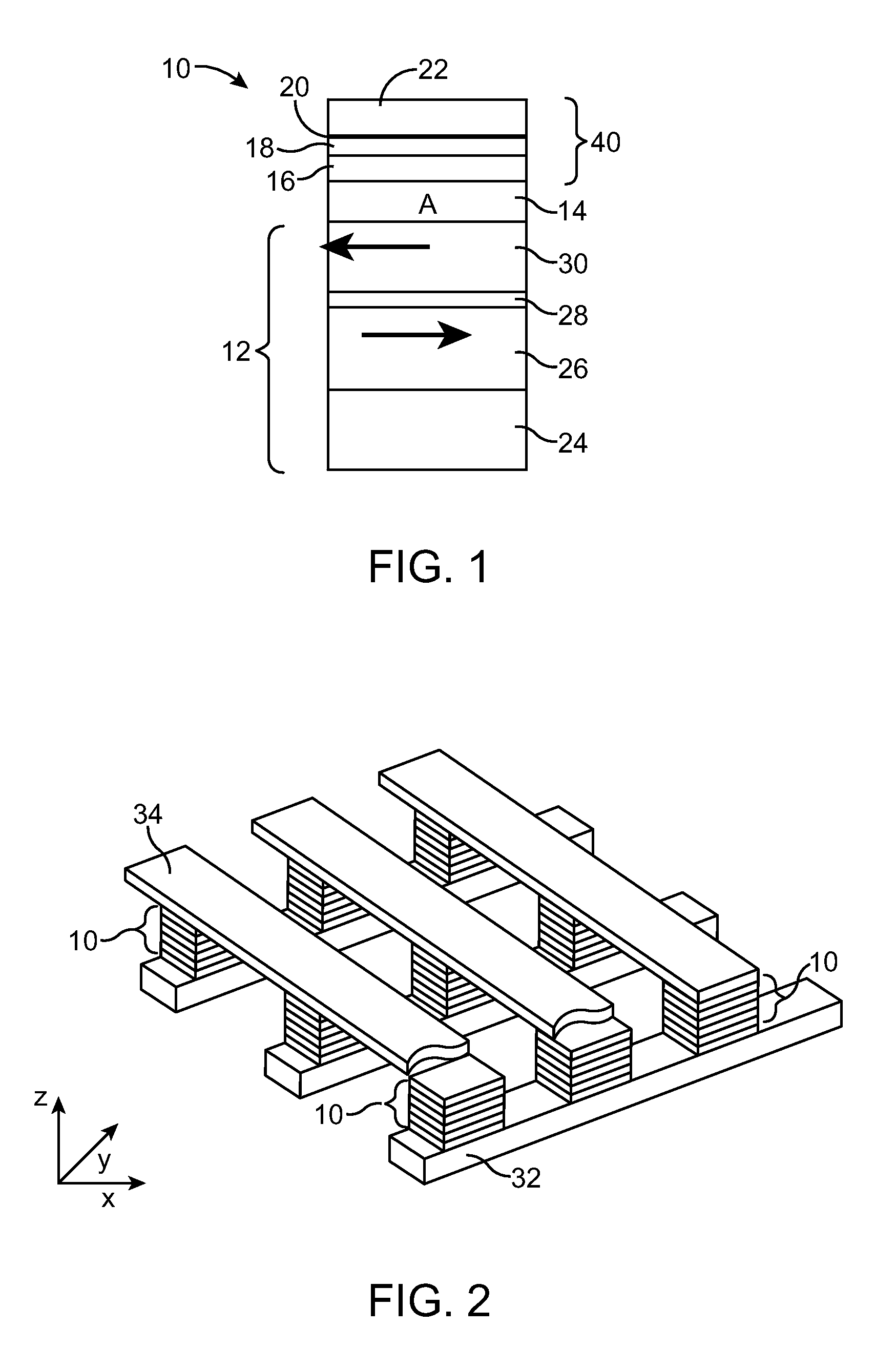
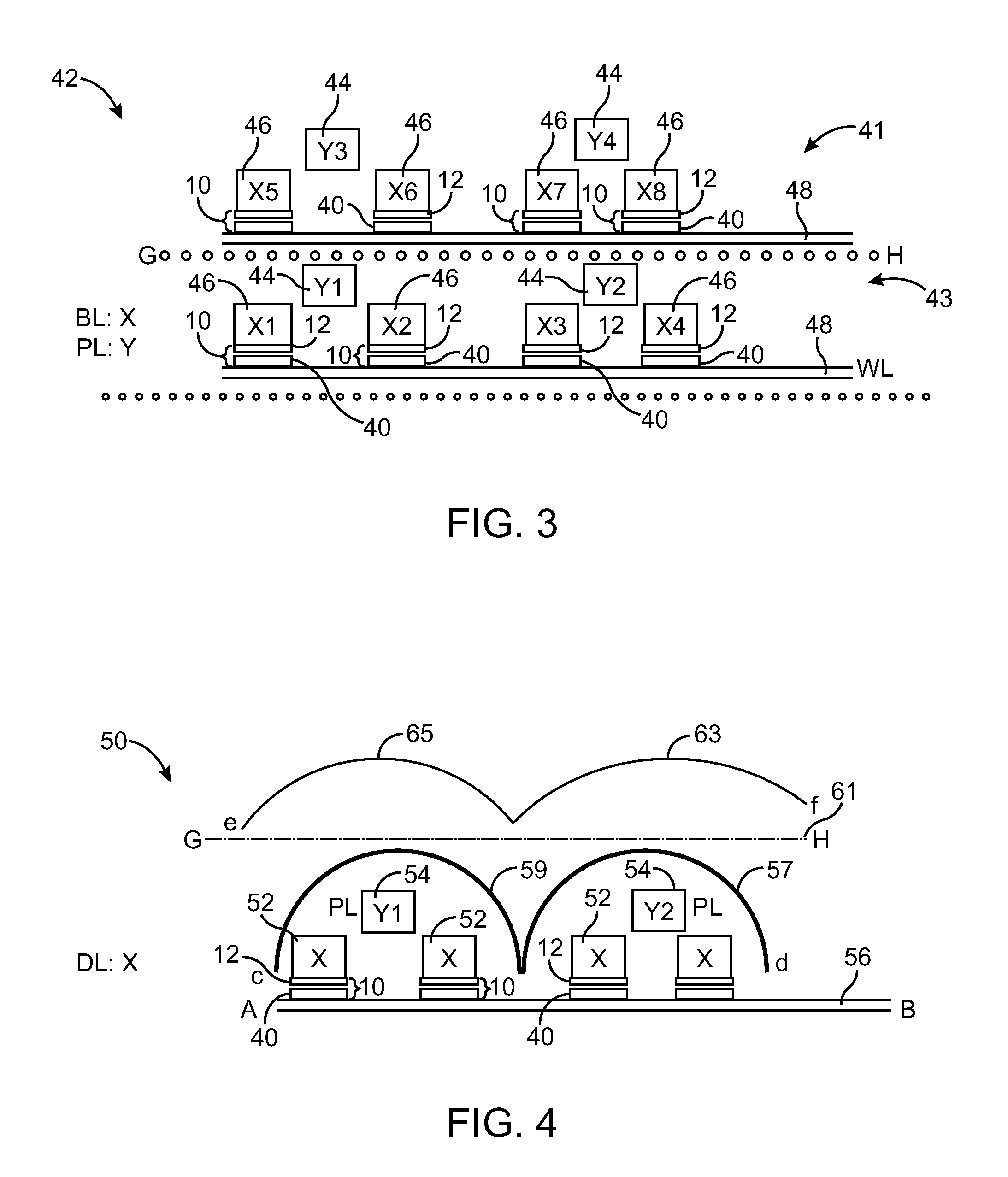
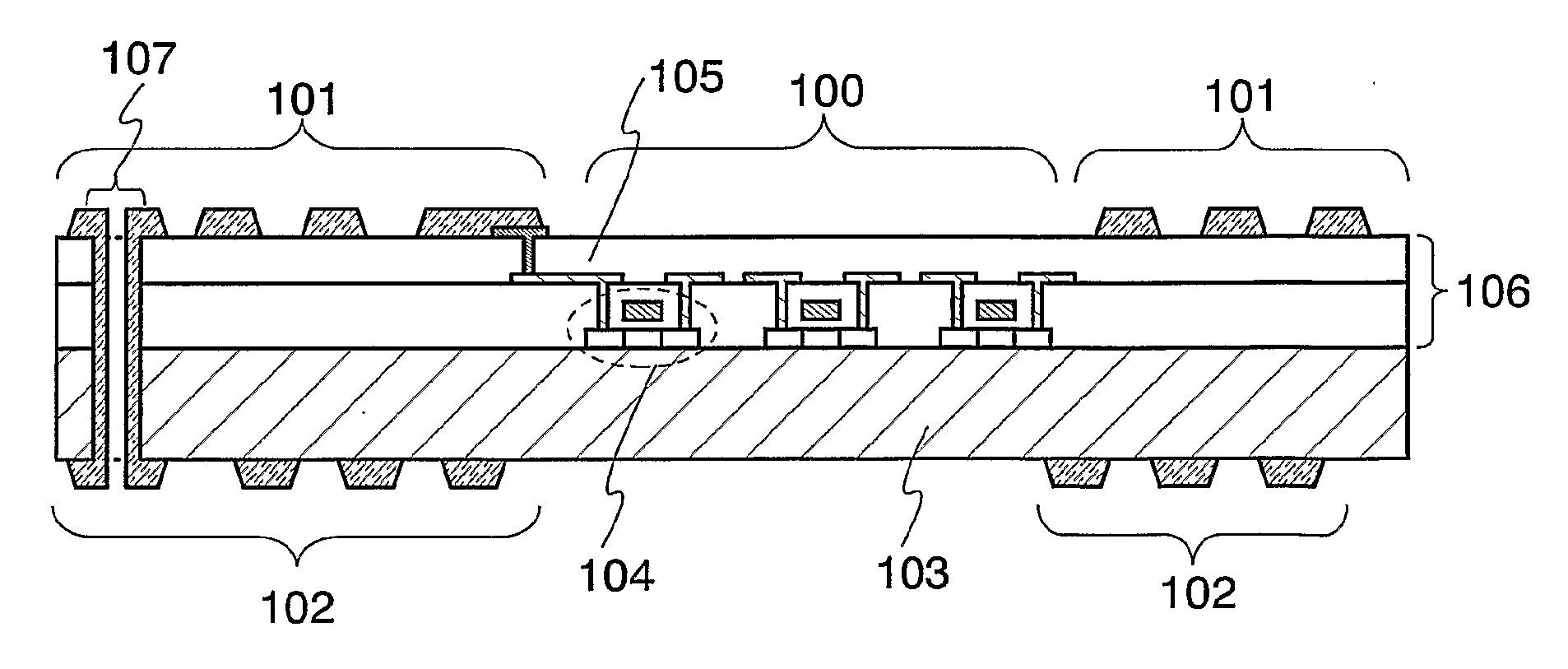
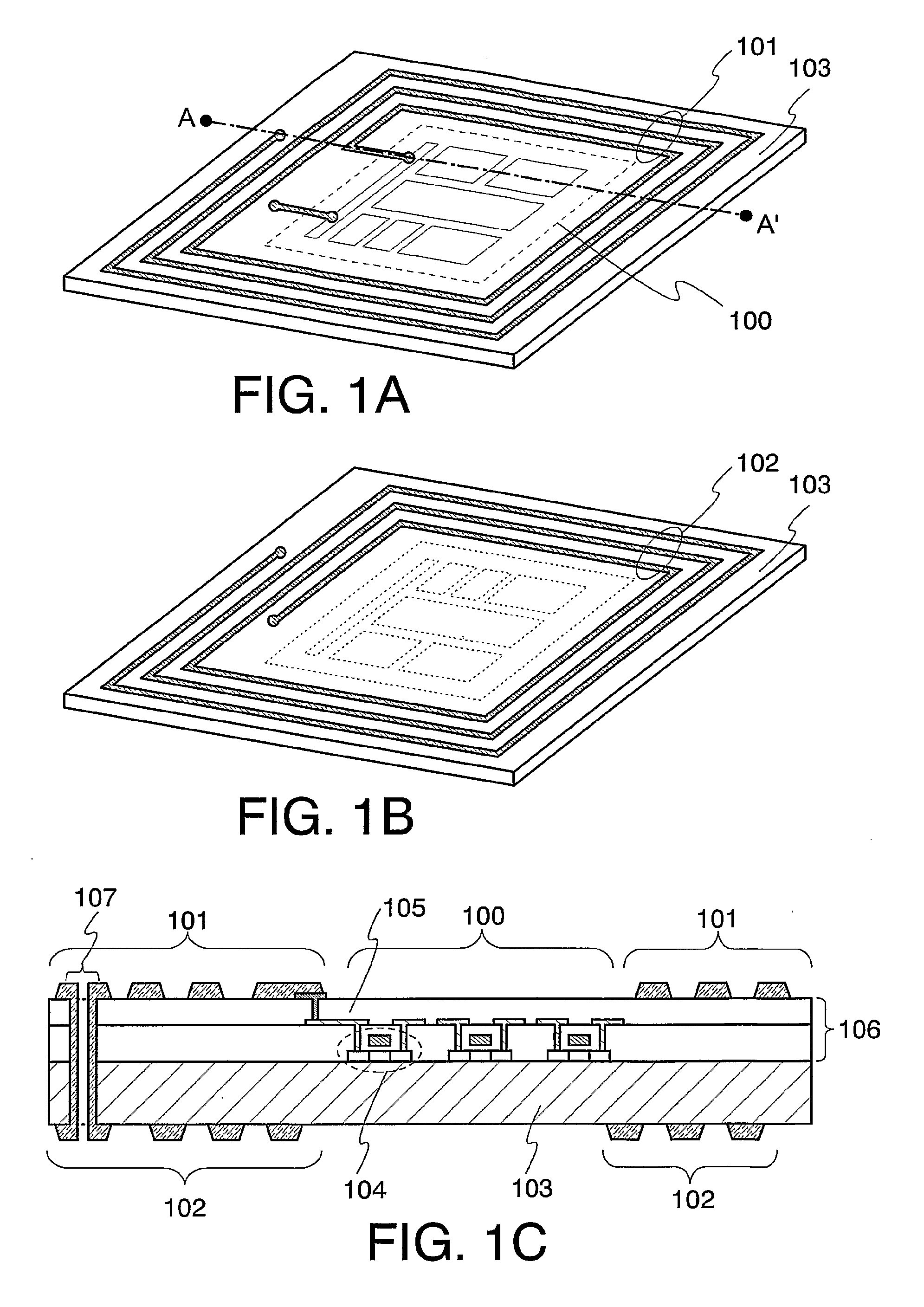
Processor with Kernel Mode Access to User Space Virtual Addresses
ActiveUS20130132702A1Enhanced kernel mode memory capacityIncrease memory capacityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory addressParallel computing
A computer includes a memory and a processor connected to the memory. The processor includes memory segment configuration registers to store defined memory address segments and defined memory address segment attributes such that the processor operates in accordance with the defined memory address segments and defined memory address segment attributes to allow kernel mode access to user space virtual addresses for enhanced kernel mode memory capacity.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
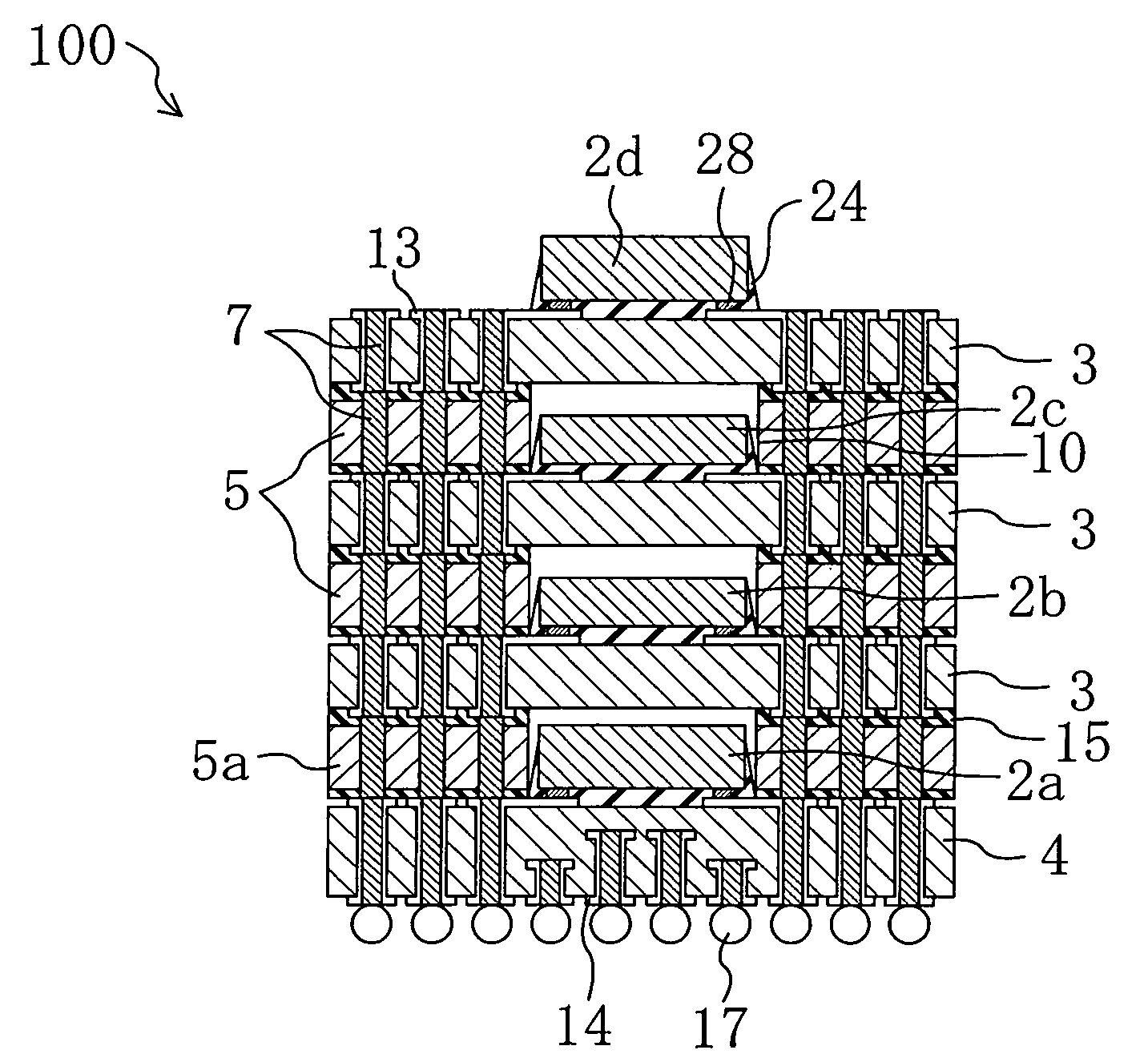
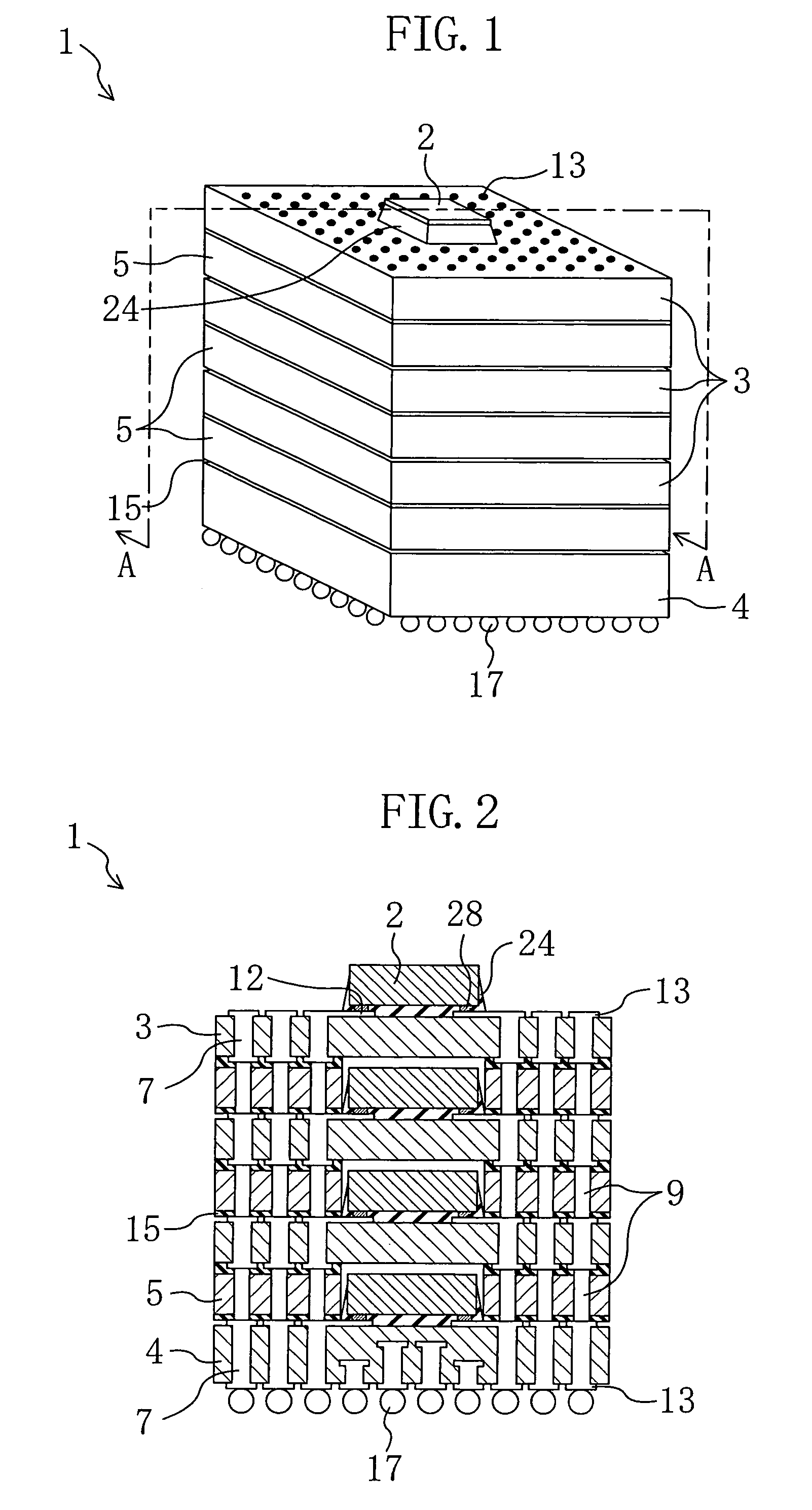
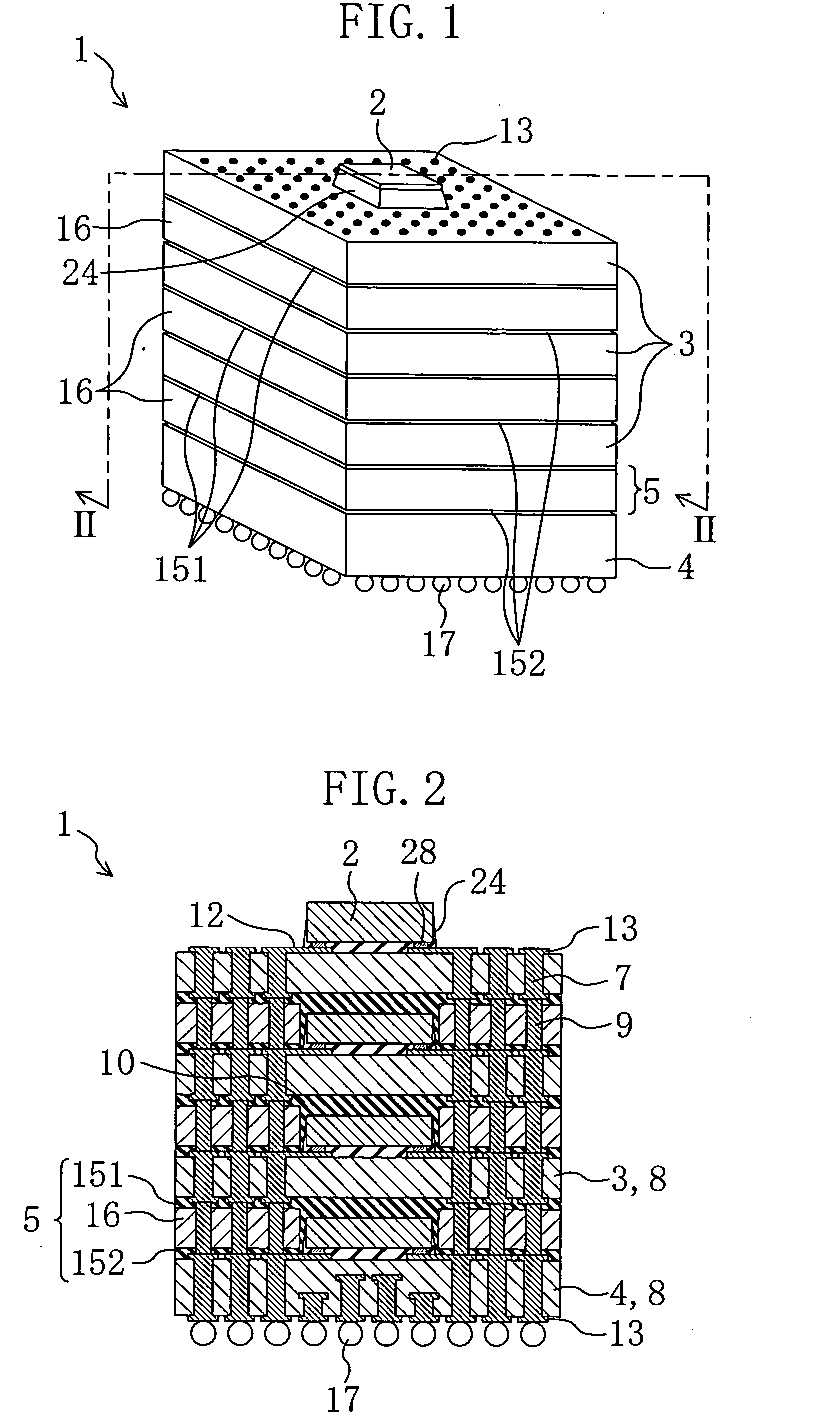
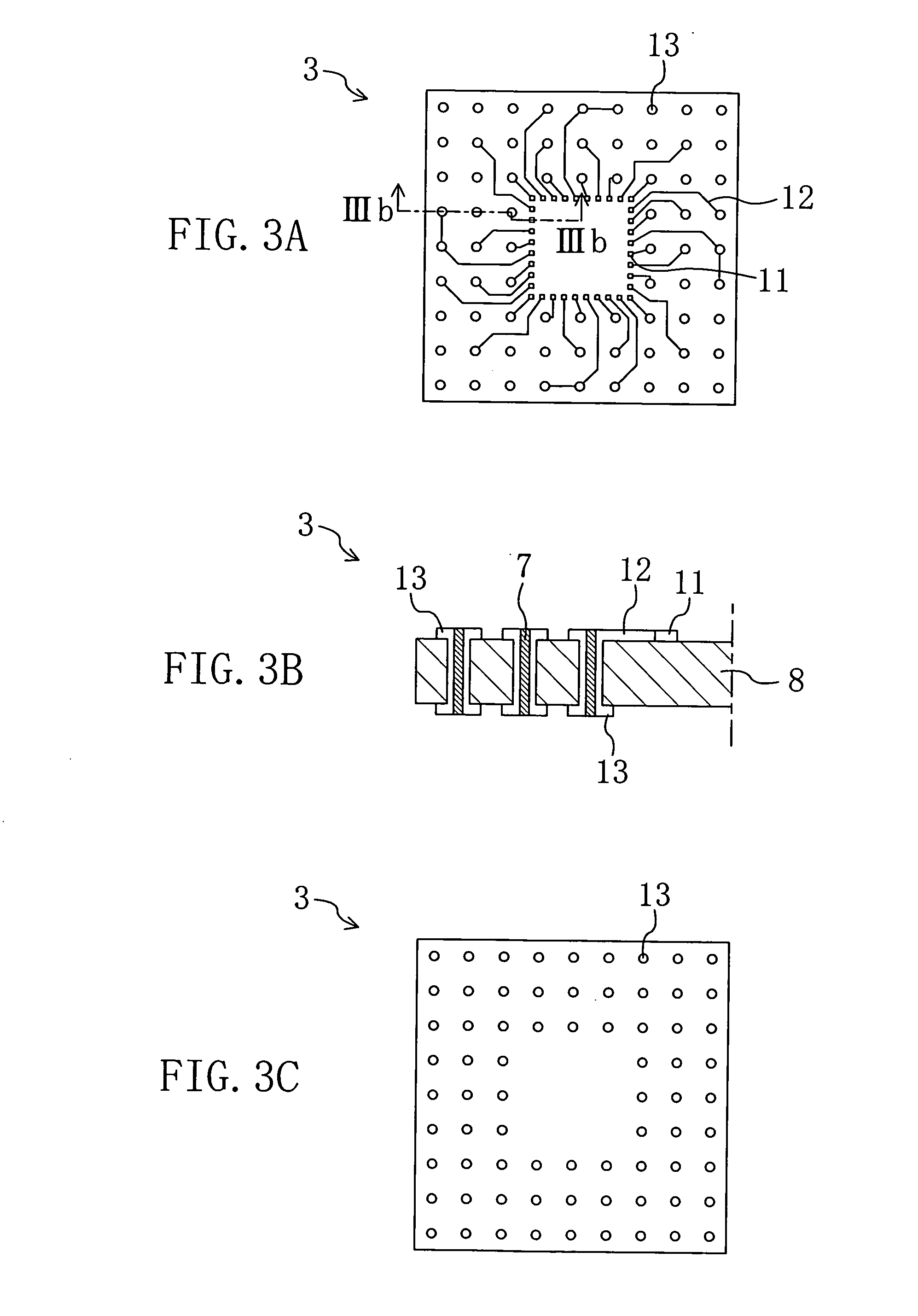
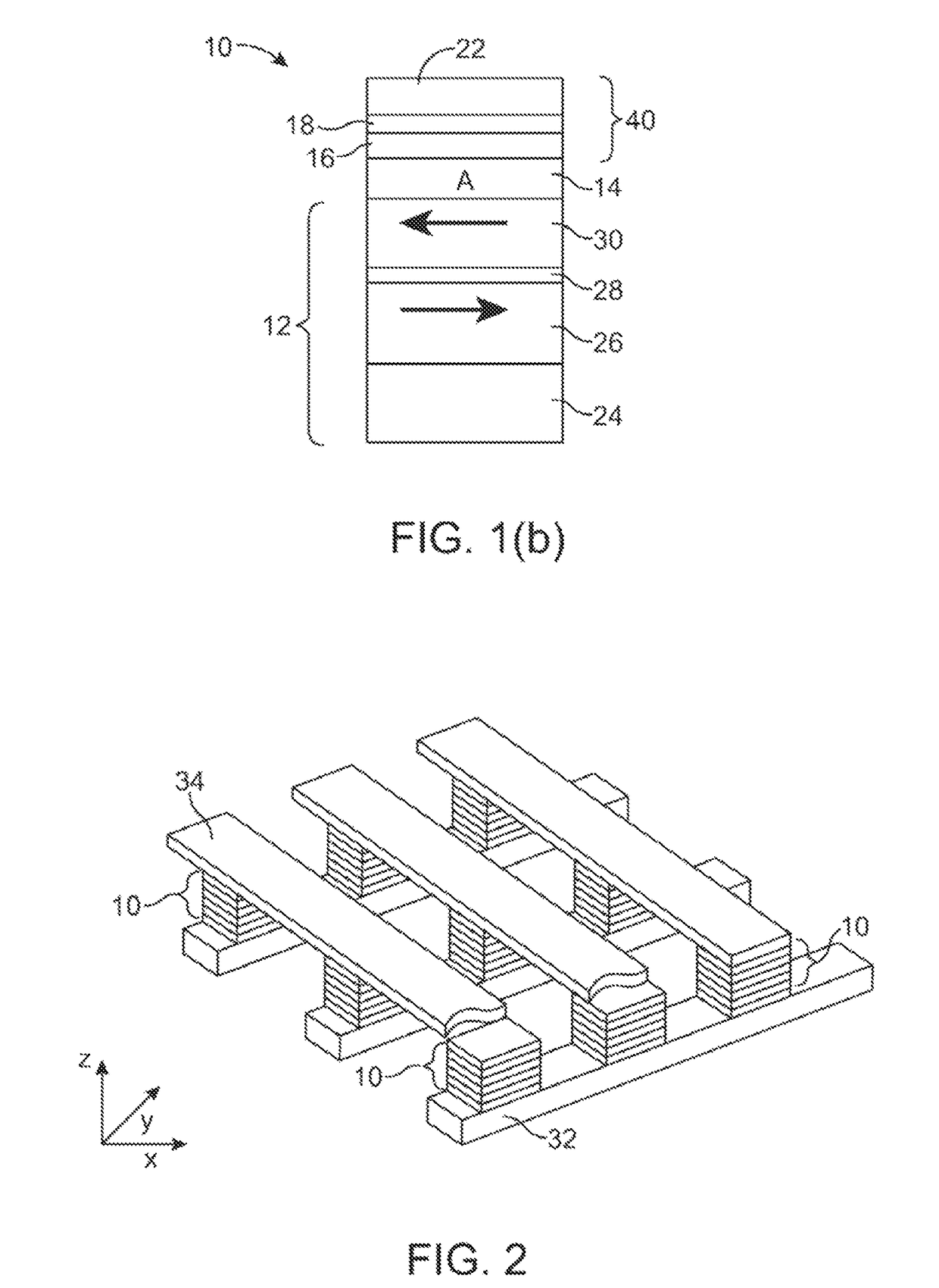
Multi-chip device and method for producing a multi-chip device
InactiveUS7297574B2Increase productionIncrease memory capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringContact element
The present invention relates to a multi-chip device comprising a plurality of chip stacks each including a plurality of single chips stacked on each other, wherein the stacked single chips are electrically interconnected by one or more through-chip-connection extending through at least one of the single chips and a substrate providing one or more first contact elements each of which is in contact with one of the through-chip-connections and providing one or more second contact elements being in electrical contact with the first contact elements, wherein the plurality of chip stacks are stacked onto each other and wherein the second contact elements of one of the chip stacks each being arranged to be in contact to one or more third contact elements of an adjacent one of the chip stacks.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
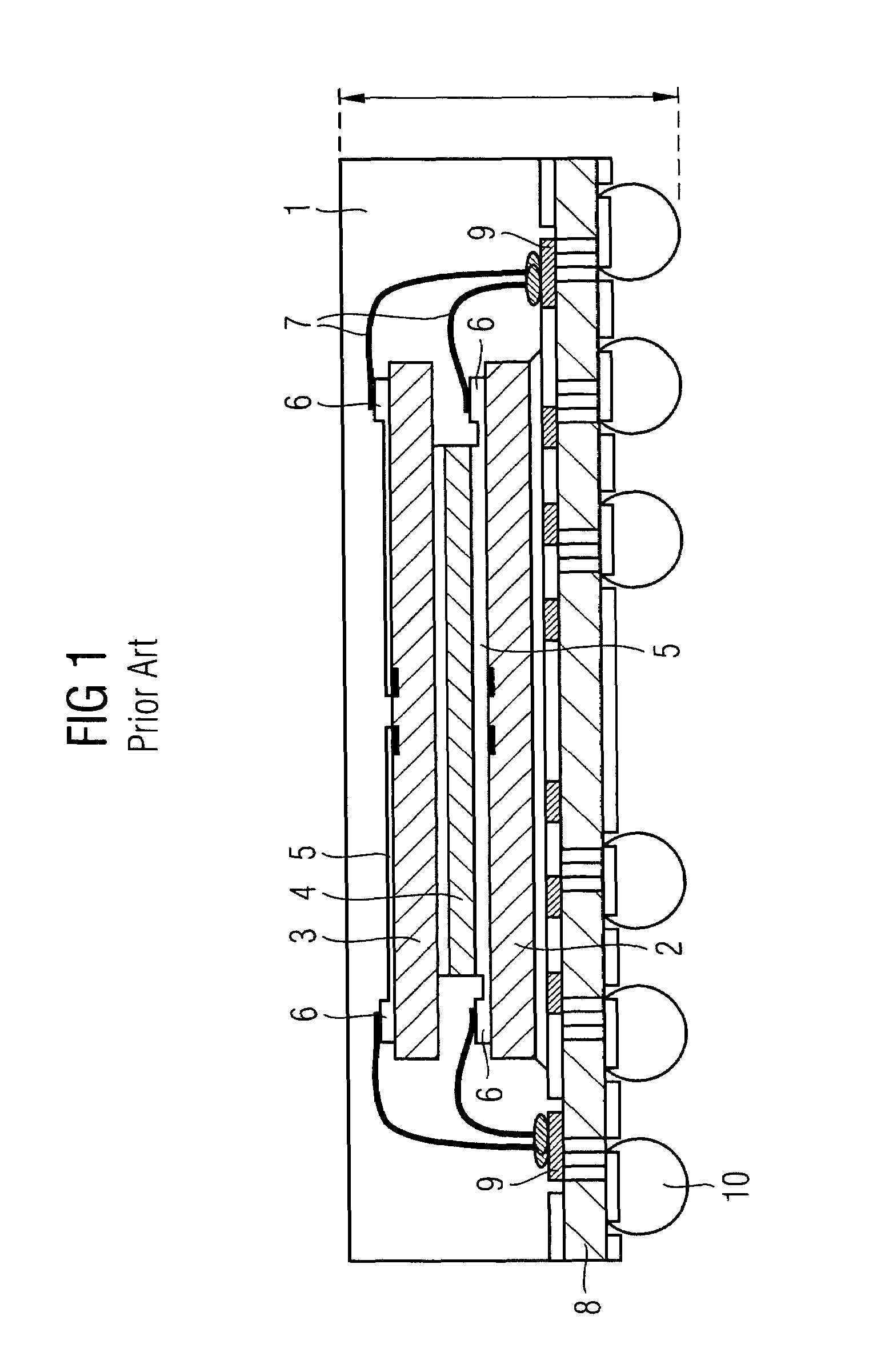
Multi-level semiconductor module and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7365416B2InhibitionReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor module is formed by alternately stacking resin boards 3 on which semiconductor chips 2 are mounted and sheet members having openings larger than the semiconductor chips 2 and bonded to the resin boards 3. The resin board 4 located at the bottom out of the resin boards 3 is thicker than the other resin boards 3.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
System and method for writing to a magnetic shift register
InactiveUS6898132B2Variable capacityHigh cost of readingLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerMolecular physics
A writing device can change the direction of the magnetic moment in a magnetic shift register, thus writing information to the domains or bits in the magnetic shift register. Associated with each domain wall are large magnetic fringing fields. The domain wall concentrates the change in magnetism from one direction to another in a very small space. Depending on the nature of the domain wall, very large dipolar fringing fields can emanate from the domain wall. This characteristic of magnetic domains is used to write to the magnetic shift register. When the domain wall is moved close to another magnetic material, the large fields of the domain wall change the direction of the magnetic moment in the magnetic material, effectively “writing” to the magnetic material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Magnetic shift register with shiftable magnetic domains between two regions, and method of using the same
InactiveUS7031178B2Highly localized and large magnetic fieldsComparable in costLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerProcessor register
A magnetic shift register uses the inherent, natural properties of domain walls in magnetic materials to store data. The shift register uses spin electronics without changing the physical nature of its constituent materials. The shift register comprises a fine track or strip of magnetic materials. Information is stored as domain walls in the track. An electric current is applied to the track to move the magnetic moments along the track past a reading or writing device. In a magnetic material with domain walls, a current passed across the domain wall moves the domain wall in the direction of the current flow. As the current passes through a domain, it becomes “spin polarized”. When this spin polarized current passes through the next domain and across a domain wall, it develops a circle of spin torque. This spin torque moves the domain wall.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Multilevel semiconductor module and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060231939A1InhibitionReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor module is formed by alternately stacking resin boards and sheet members. Each of the resin boards includes first buried conductors. A semiconductor chip is mounted on the upper face of each of the resin boards. Each of the sheet members having an opening for accommodating the semiconductor chip and including second buried conductors electrically connected to the first buried conductors. A first resin board located at the bottom is thicker than second resin boards. Each of the sheet members includes an adhesive member covering the upper and side faces of the semiconductor chip.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
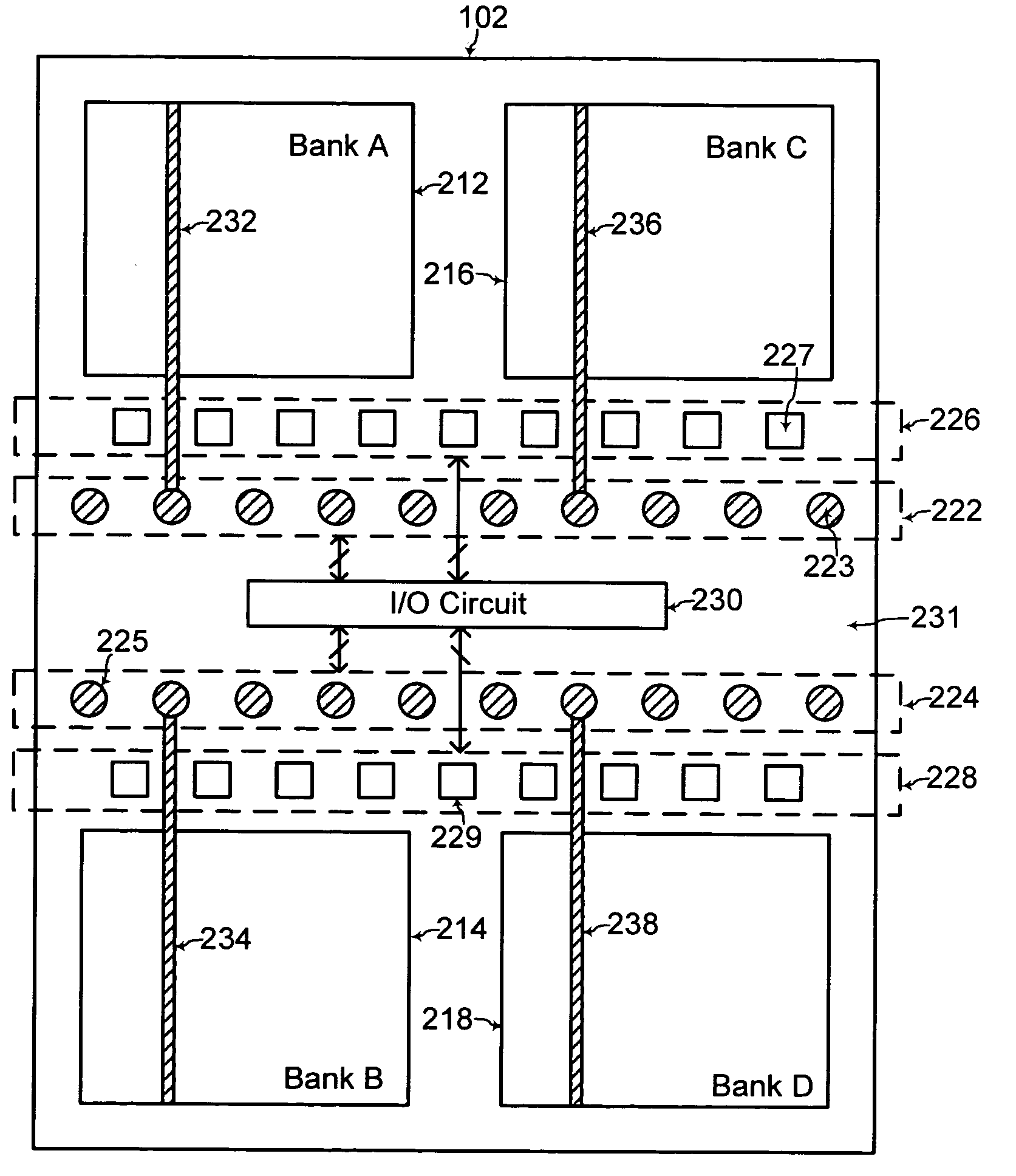
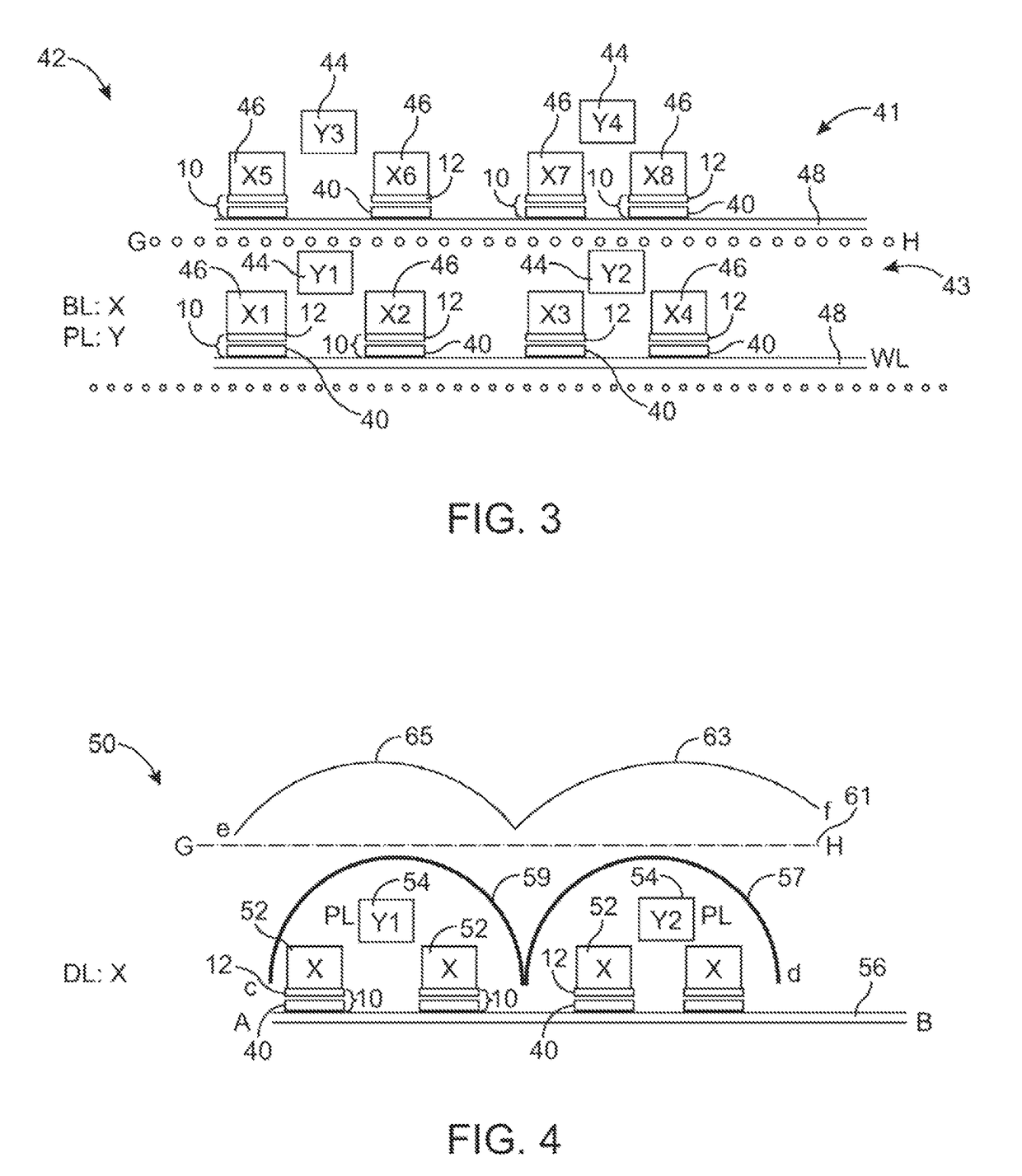
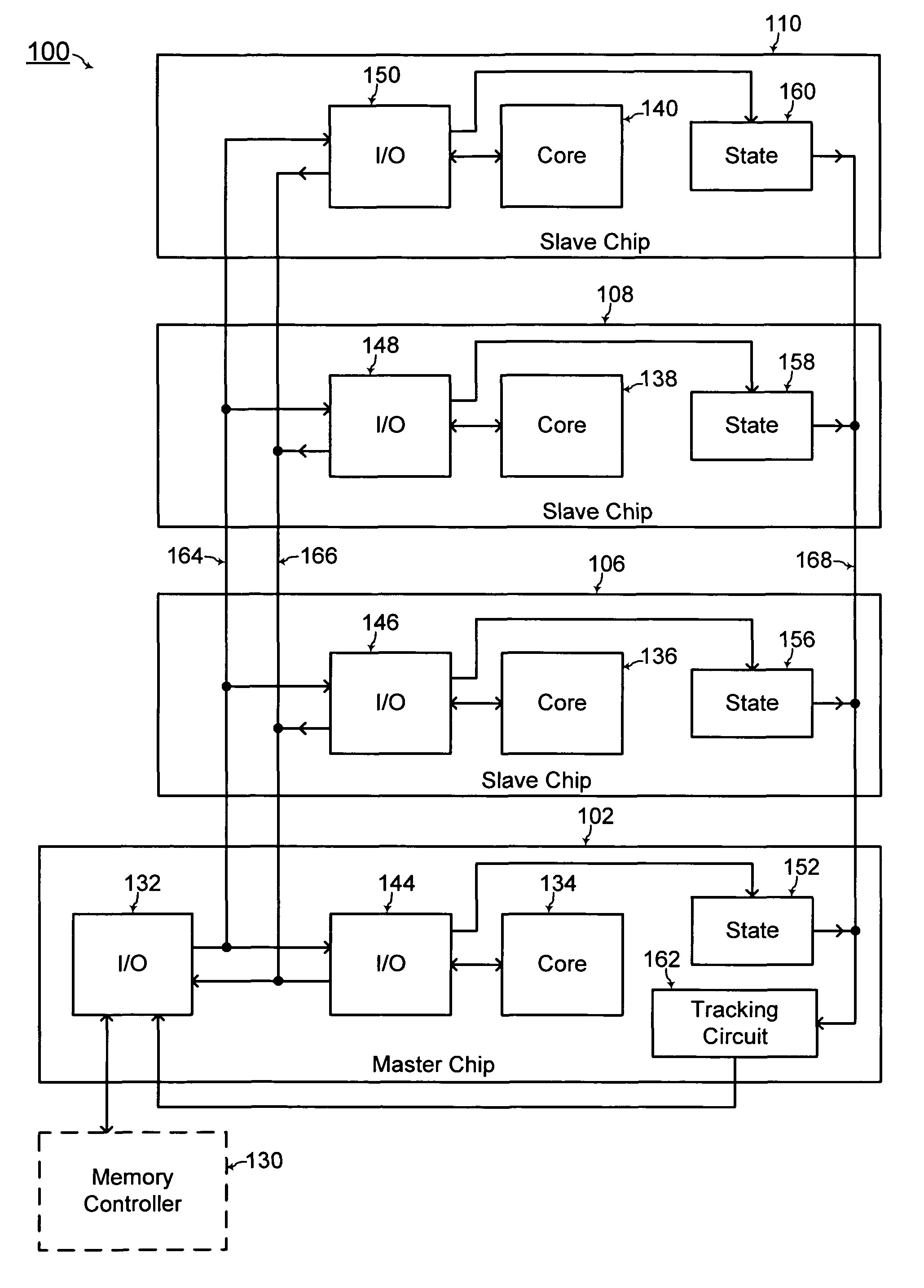
Stacked memory module and system
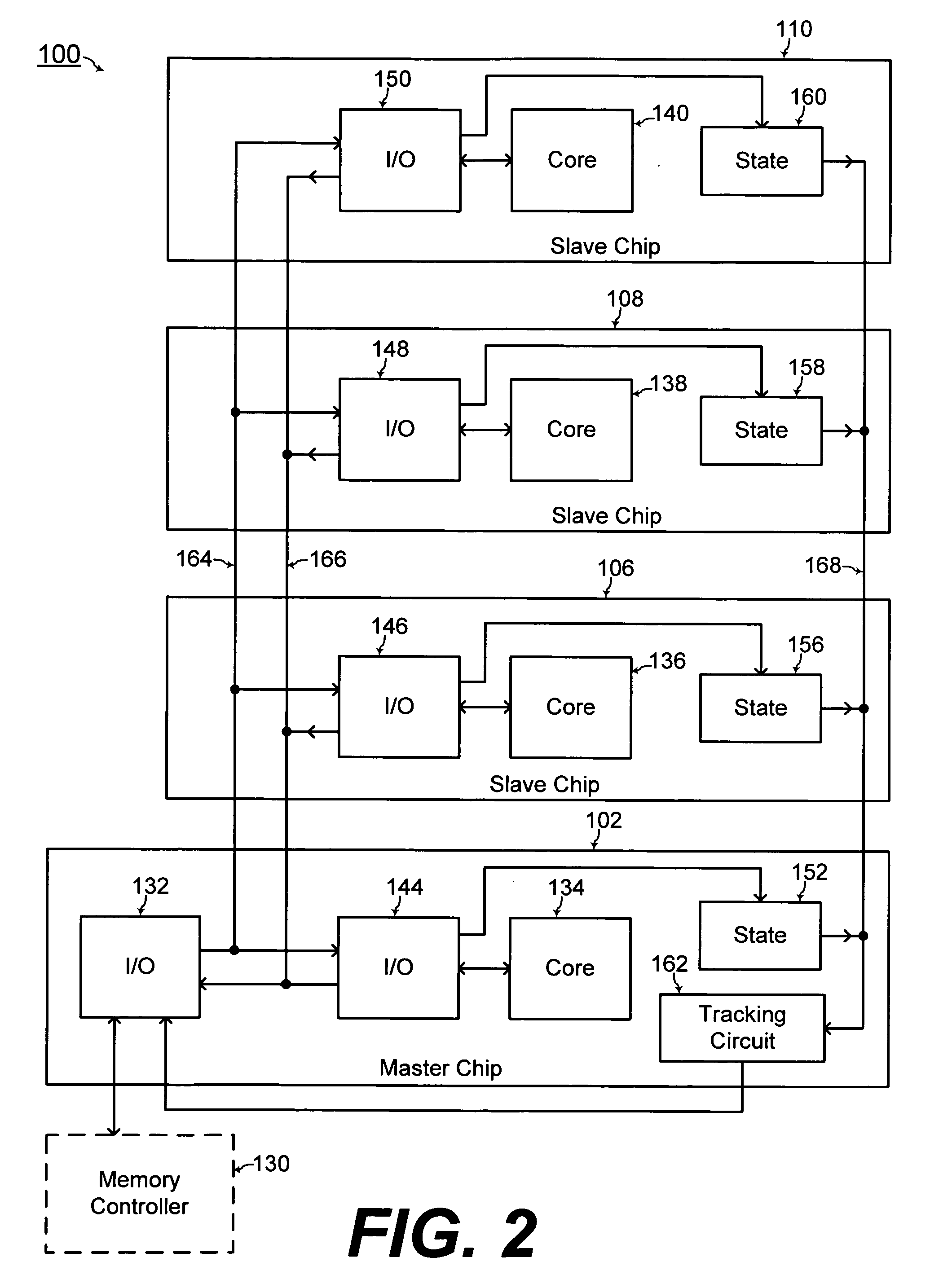
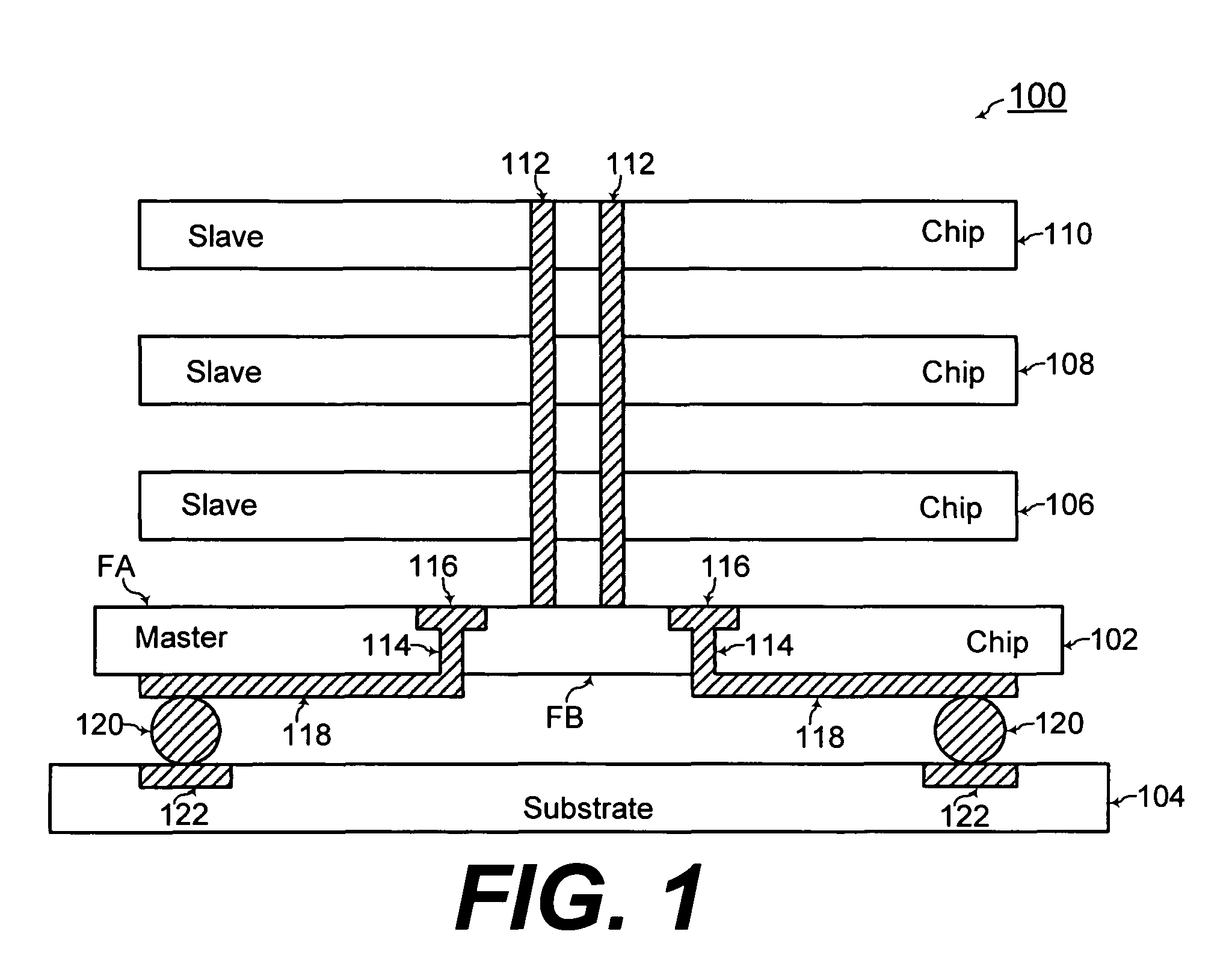
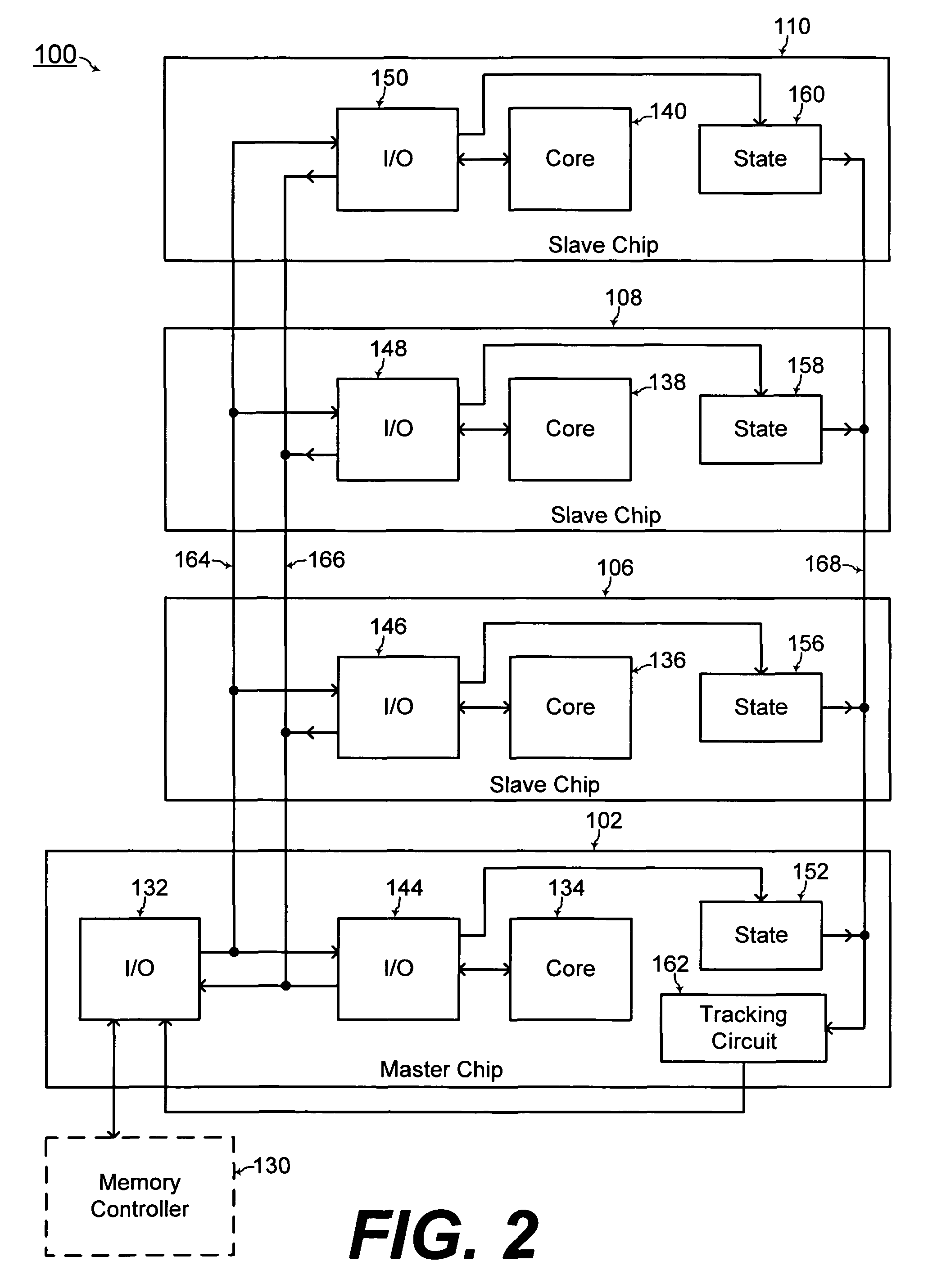
ActiveUS20100020583A1Increase memory capacityEfficient wiring and capacity organizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory bankComputer module
A three dimensional memory module and system are formed with at least one slave chip stacked over a master chip. Through semiconductor vias (TSVs) are formed through at least one of the master and slave chips. The master chip includes a memory core for increased capacity of the memory module / system. In addition, capacity organizations of the three dimensional memory module / system resulting in efficient wiring is disclosed for forming multiple memory banks, multiple bank groups, and / or multiple ranks of the three dimensional memory module / system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for reading data stored on a magnetic shift register
A reading device reads the direction of the magnetic moment of domains in a magnetic shift register, thus reading information stored in the domains or bits in the magnetic shift register. Associated with each domain wall are large magnetic fringing fields. The domain wall concentrates the change in magnetism from one direction to another in a very small space. Depending on the nature of the domain wall, very large dipolar fringing fields can emanate from the domain wall. This characteristic of magnetic domains is used to read data stored on to the magnetic shift register. The reading device reads the direction of the magnetic moment in a magnetic shift register, thus reading information stored in the domains.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
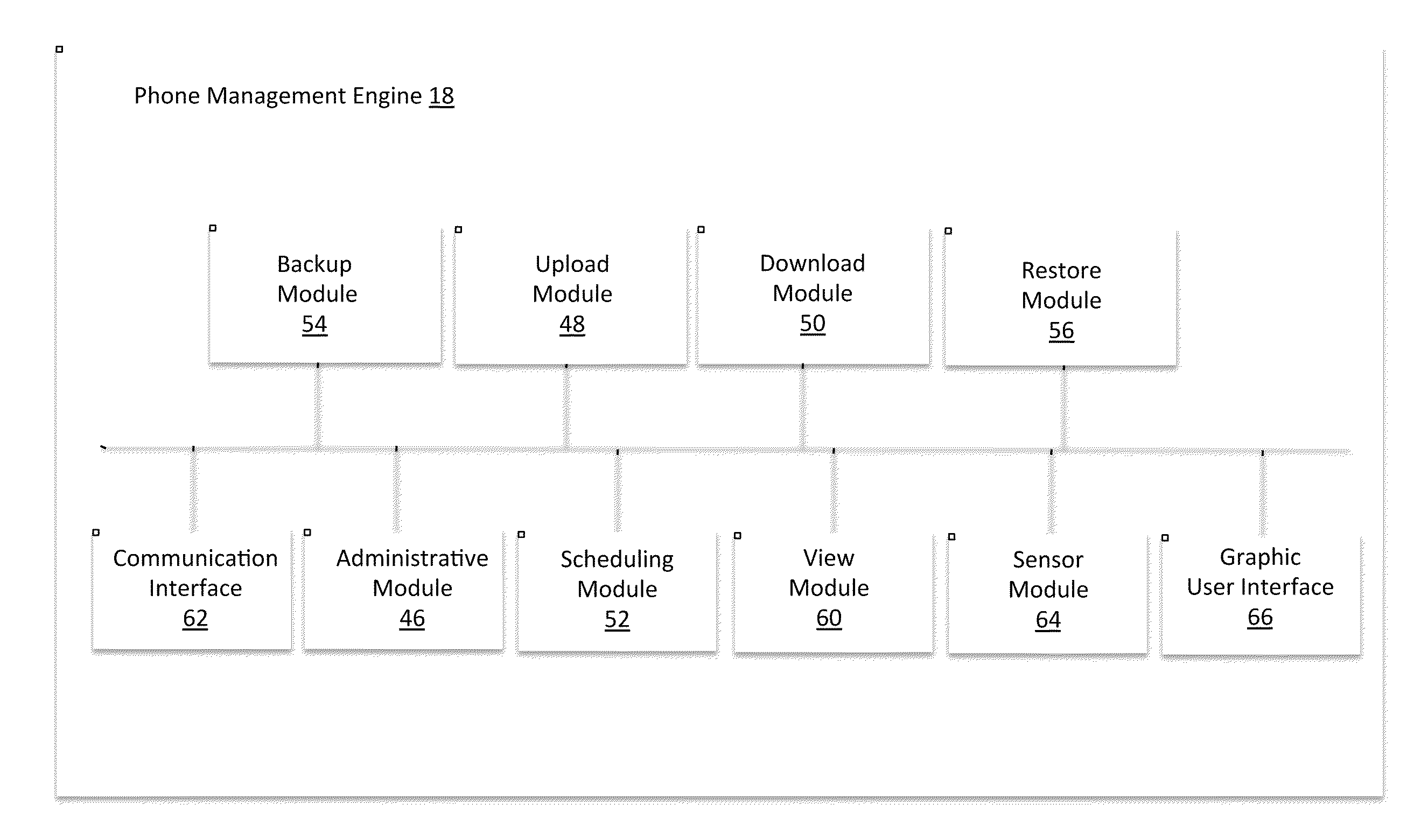
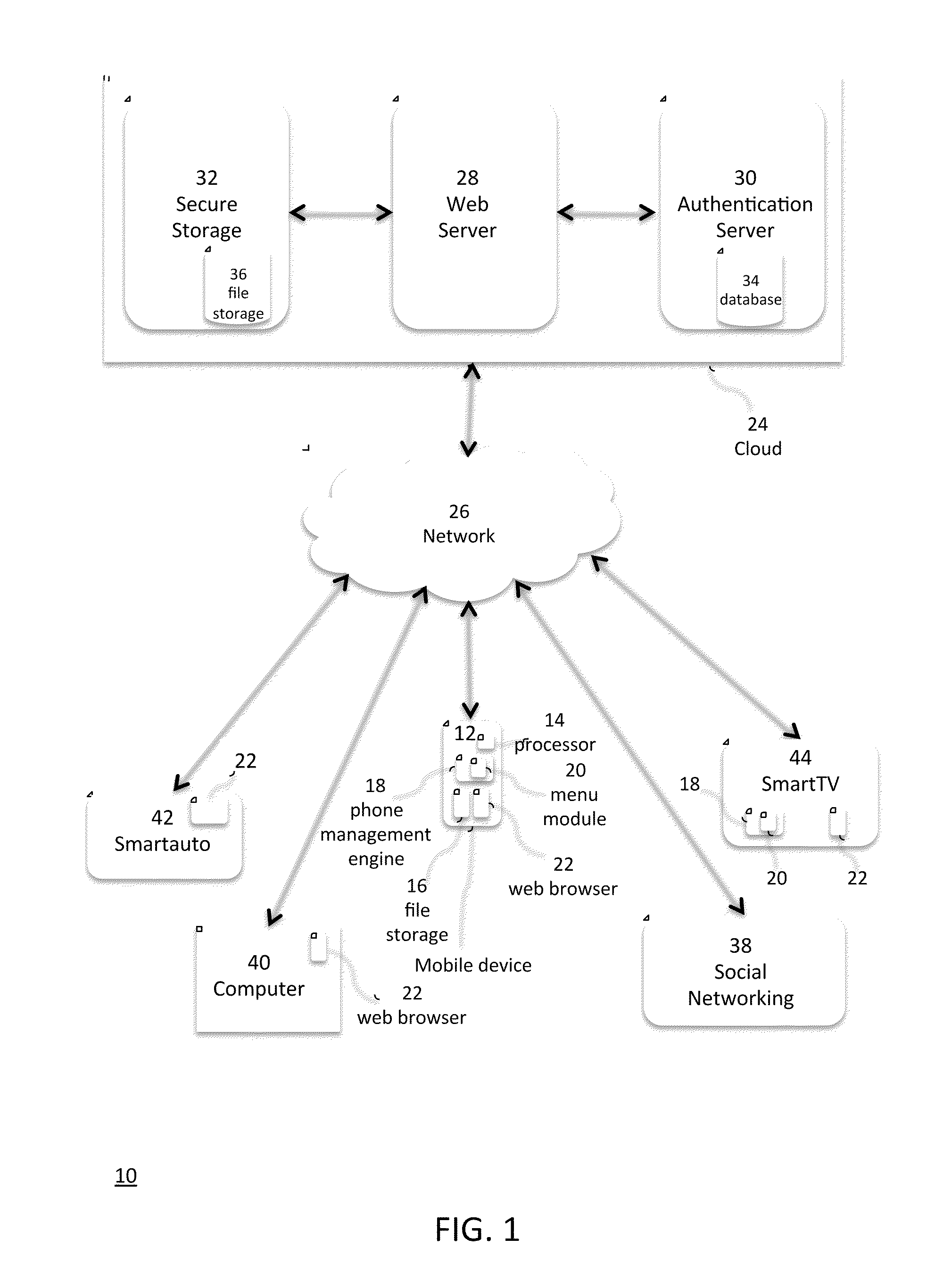
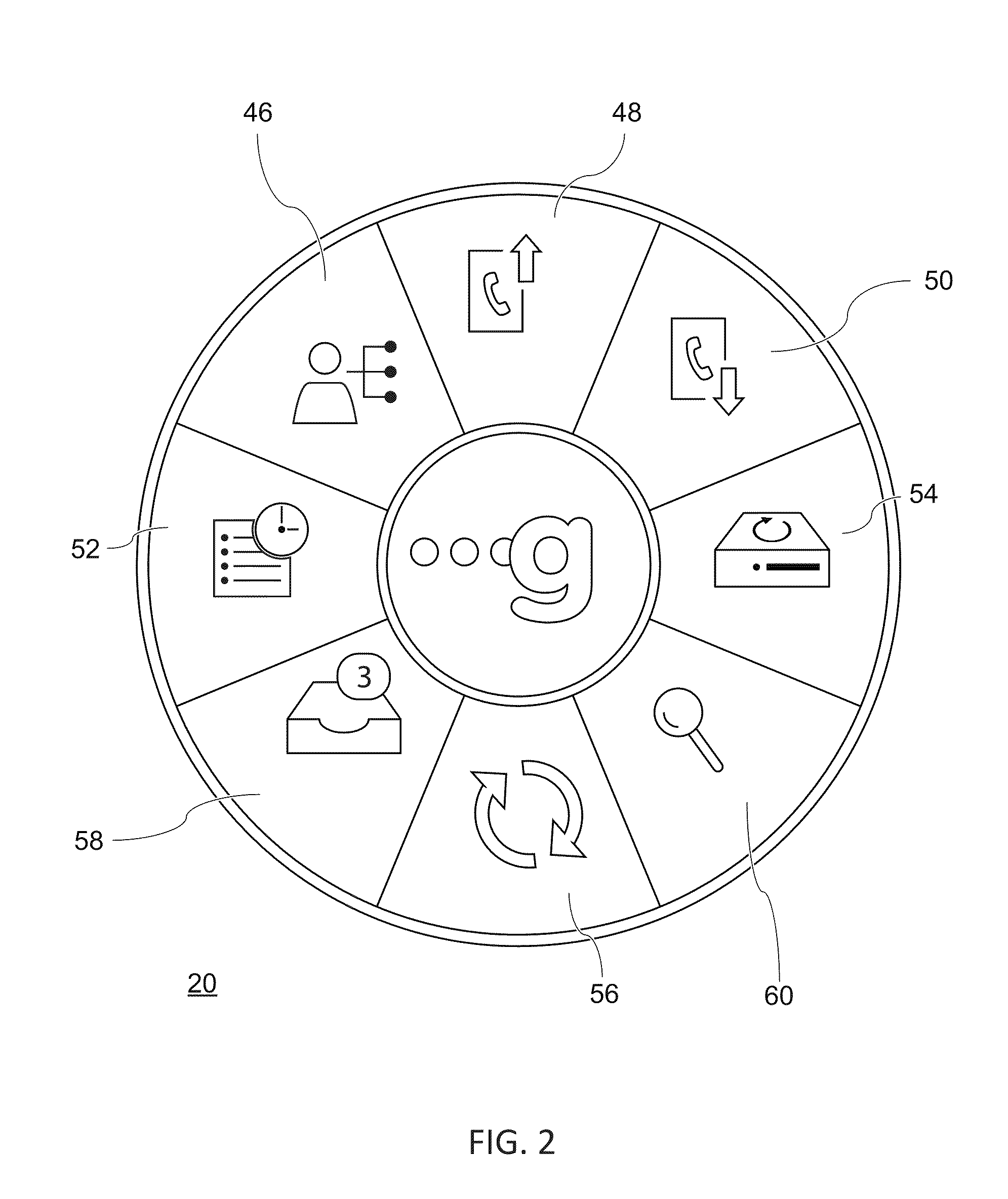
Smartphone Management System and Method
ActiveUS20110306326A1Reduce the burden onIncrease memory capacityError detection/correctionSpecial service for subscribersWeb browserAuthentication server
A mobile device management system is described for managing files that are locally generated or stored on the mobile device in a cloud environment. The mobile device is configured with a phone application module, a menu module, and a web browser module to conduct a backup operation of the files on the mobile device to a cloud through a network. The cloud comprises a web server, an authentication server, and a secure storage for authenticating the mobile user's access to the cloud, and provide a secure connection to backup the files from the mobile device to the secure storage of the cloud. The mobile device can also upload the files from the mobile device to secure storage of the cloud, which alleviates the burden of carrying a large amount of files on the file storage of the mobile device. In the upload operation, the mobile device deletes the files that have been uploaded to the cloud.
Owner:FIDELITHON SYST
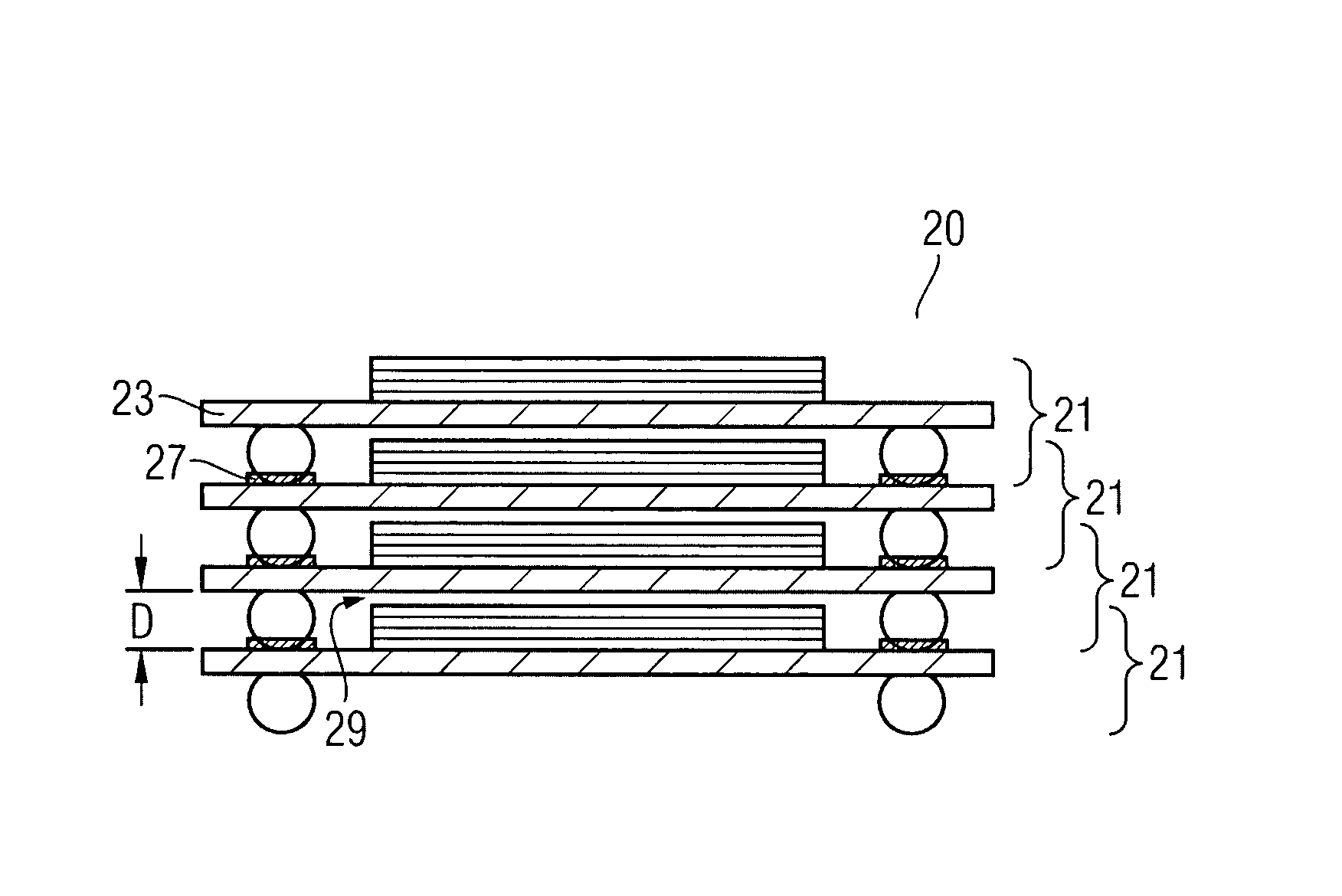
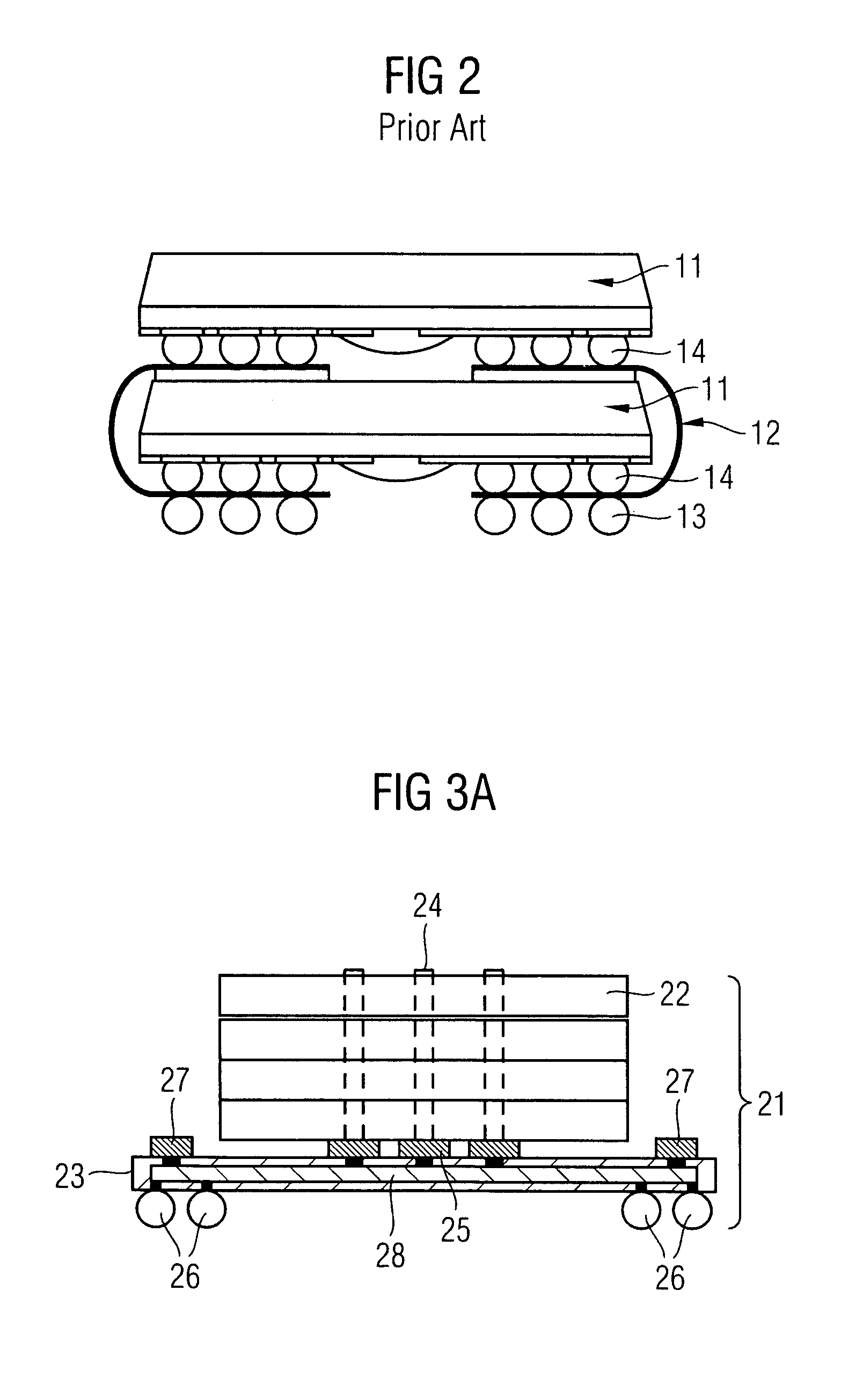
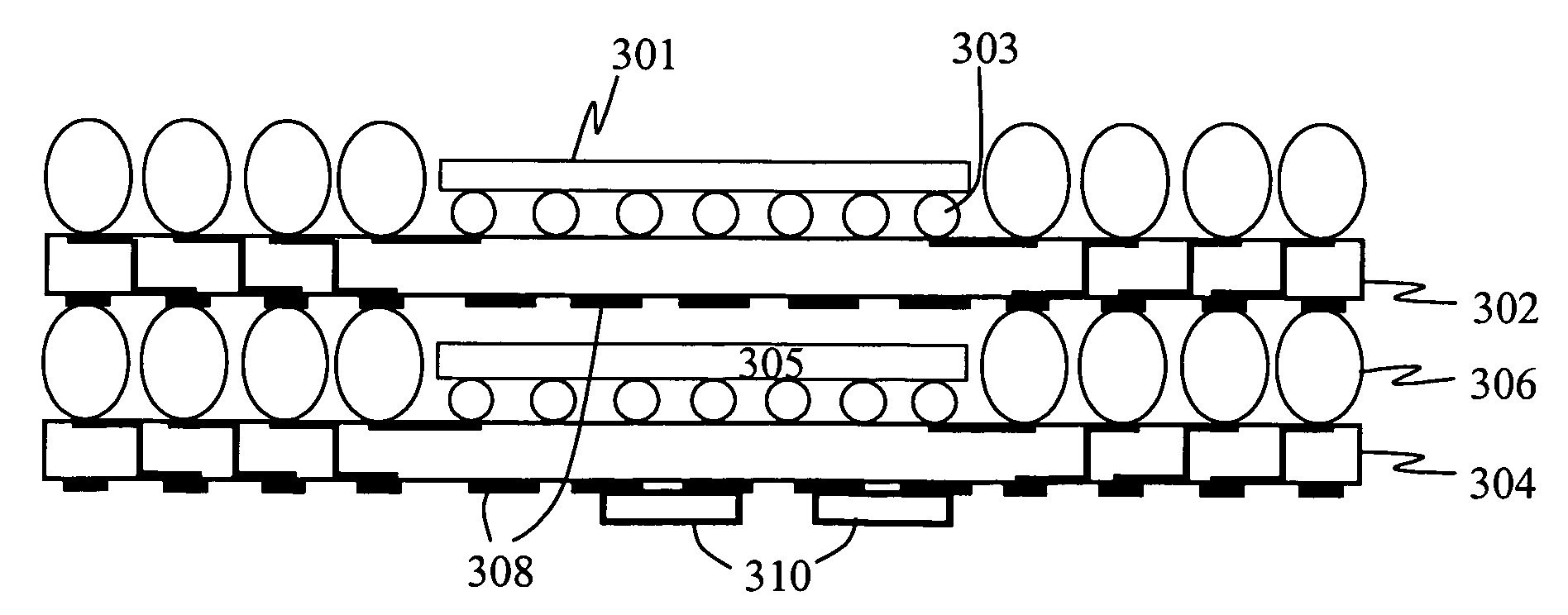
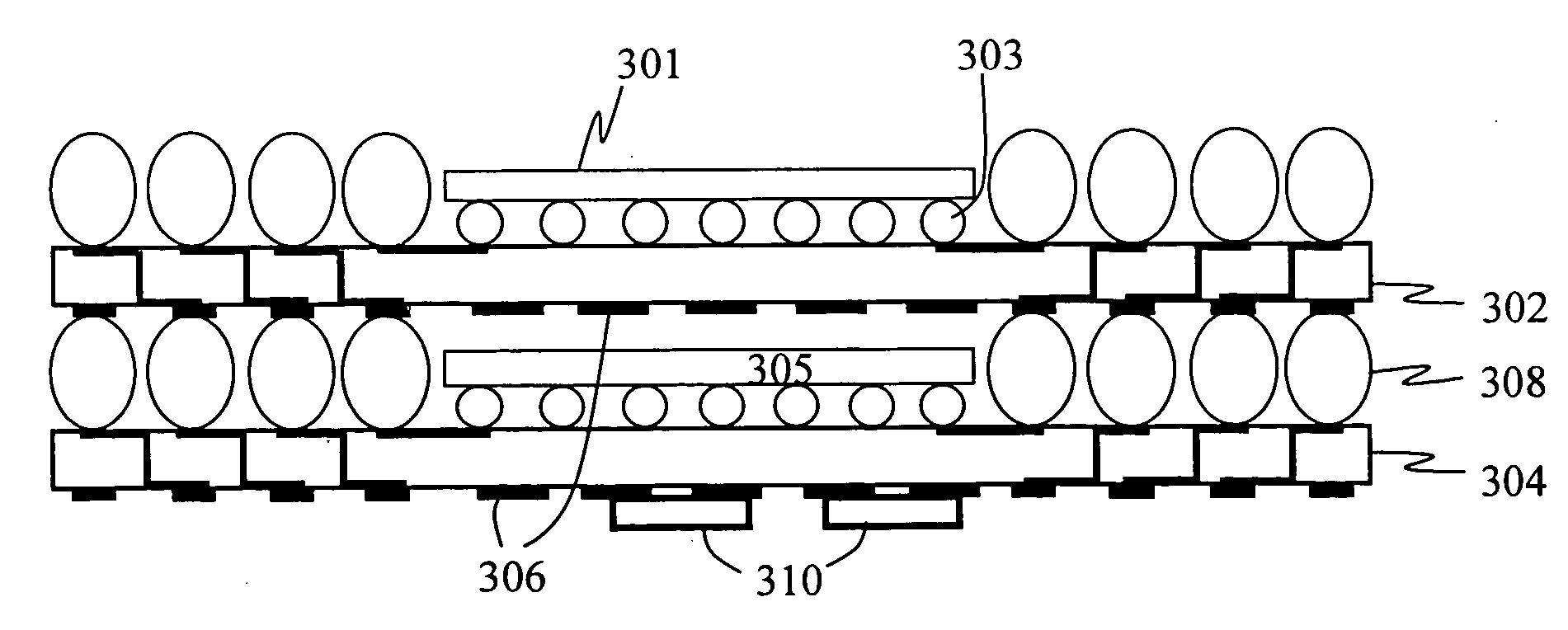
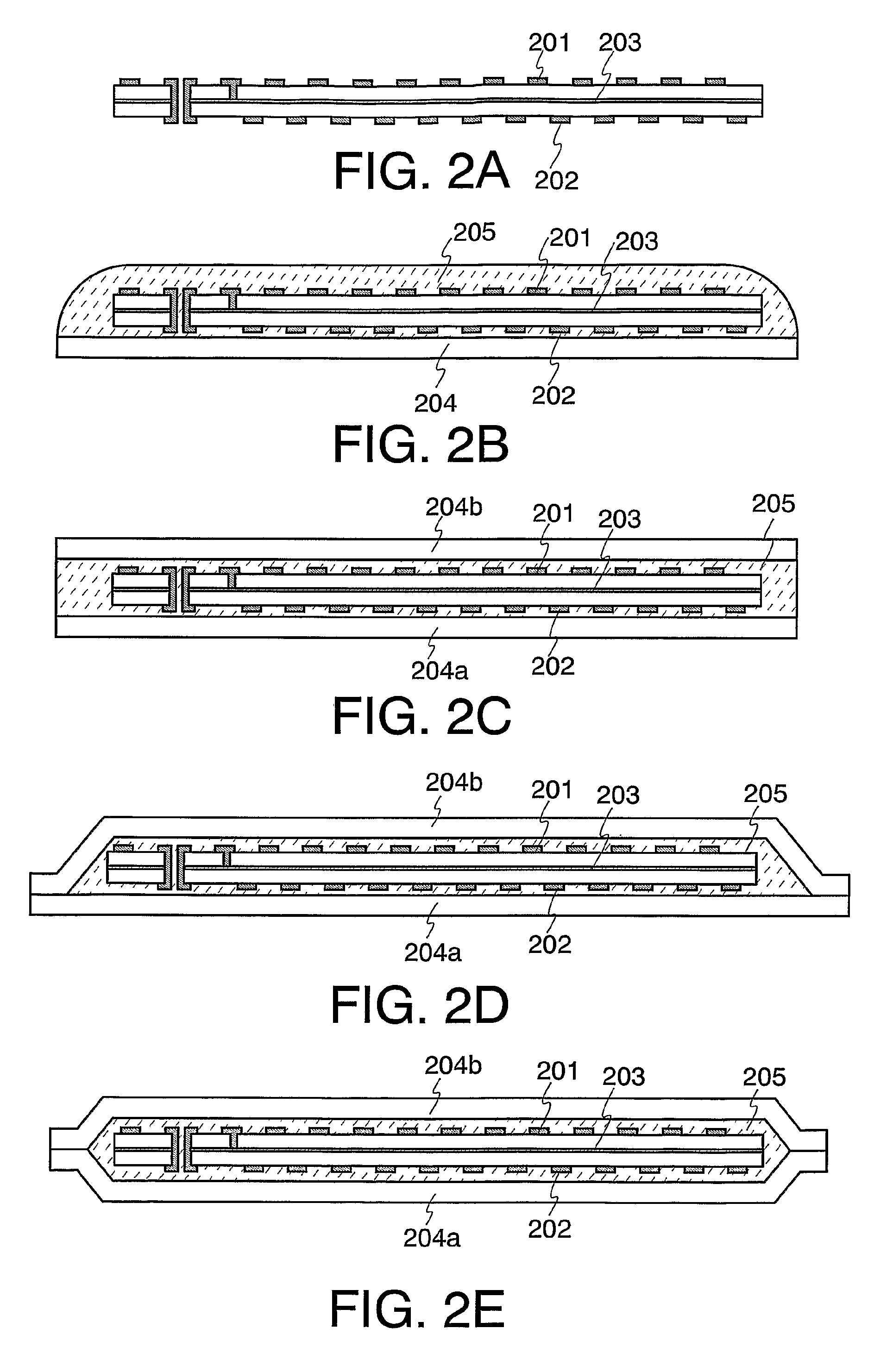
Stackable electronic assembly
InactiveUS7180165B2Reduce crackingImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCombined useEngineering
On implementation of the invention provides a stackable chip-scale package for improving memory density that may be mounted within a limited area or module. A novel staggered routing scheme enables the use of the same trace routing at every level of the stacked architecture for efficiently accessing individual memory devices in a chip-scale package stack. The use of a ball grid array chip-scale package architecture in combination with thermally compatible materials decreases the risk of thermal cracking while improving heat dissipation. Moreover, this architecture permits mounting support components, such as capacitors and resistors, on the chip-scale package.
Owner:SANMINA-SCI CORPORATION
System and method for reading data stored on a magnetic shift register
InactiveUS6920062B2Highly localized and large magnetic fieldsComparable in costDigital storageShift registerData storing
A reading device reads the direction of the magnetic moment of domains in a magnetic shift register, thus reading information stored in the domains or bits in the magnetic shift register. Associated with each domain wall are large magnetic fringing fields. The domain wall concentrates the change in magnetism from one direction to another in a very small space. Depending on the nature of the domain wall, very large dipolar fringing fields can emanate from the domain wall. This characteristic of magnetic domains is used to read data stored on to the magnetic shift register. The reading device reads the direction of the magnetic moment in a magnetic shift register, thus reading information stored in the domains.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
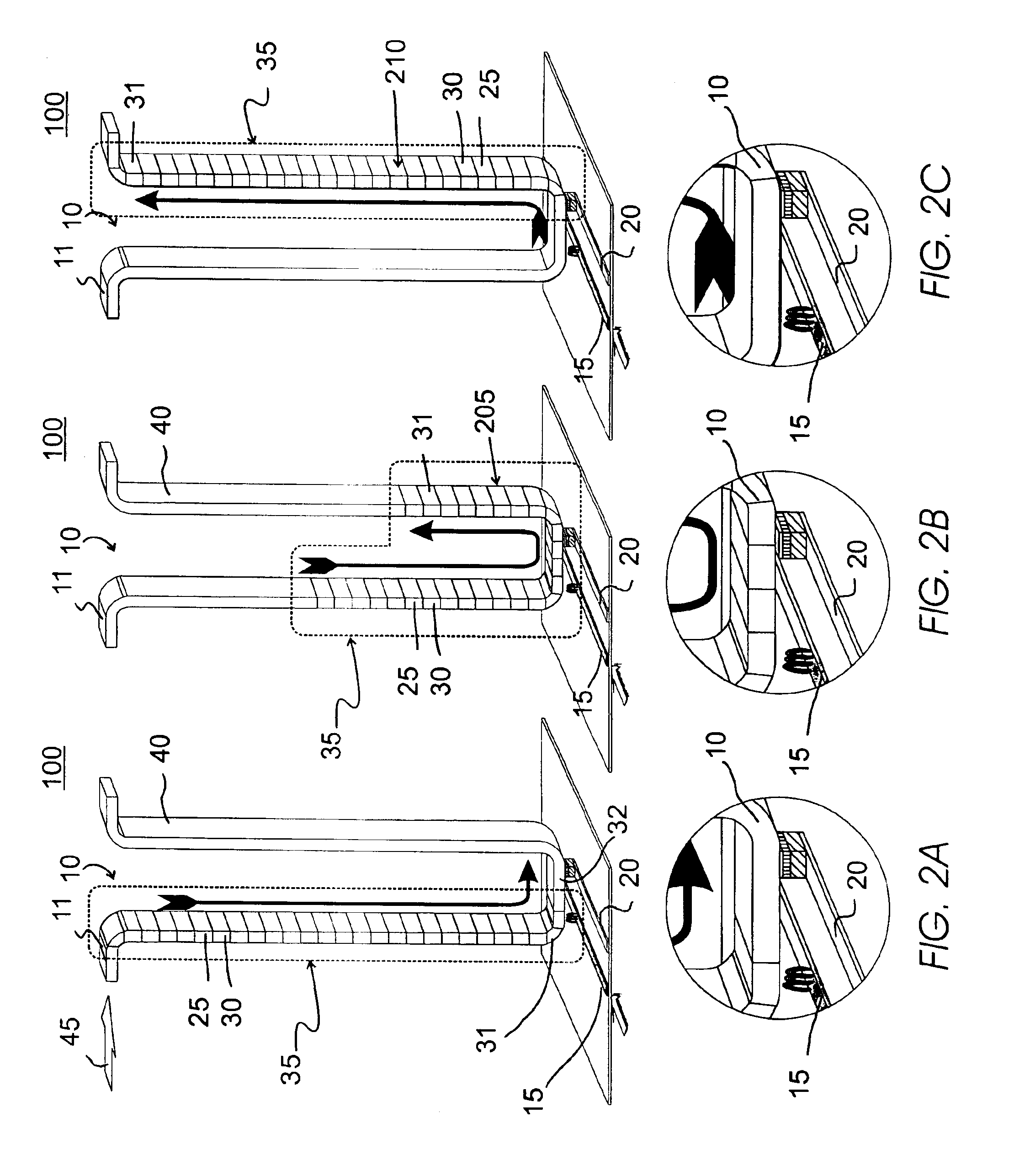
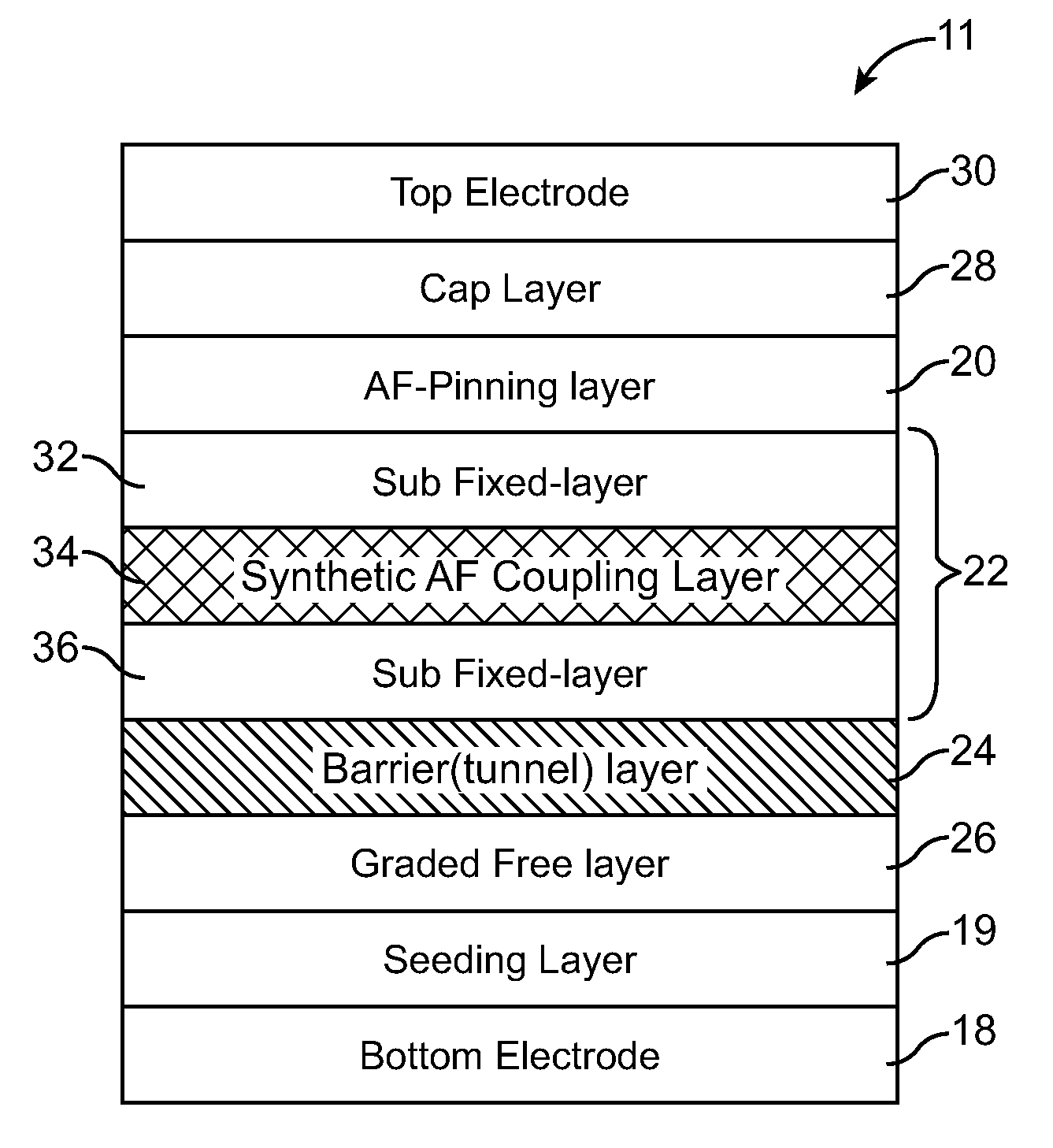
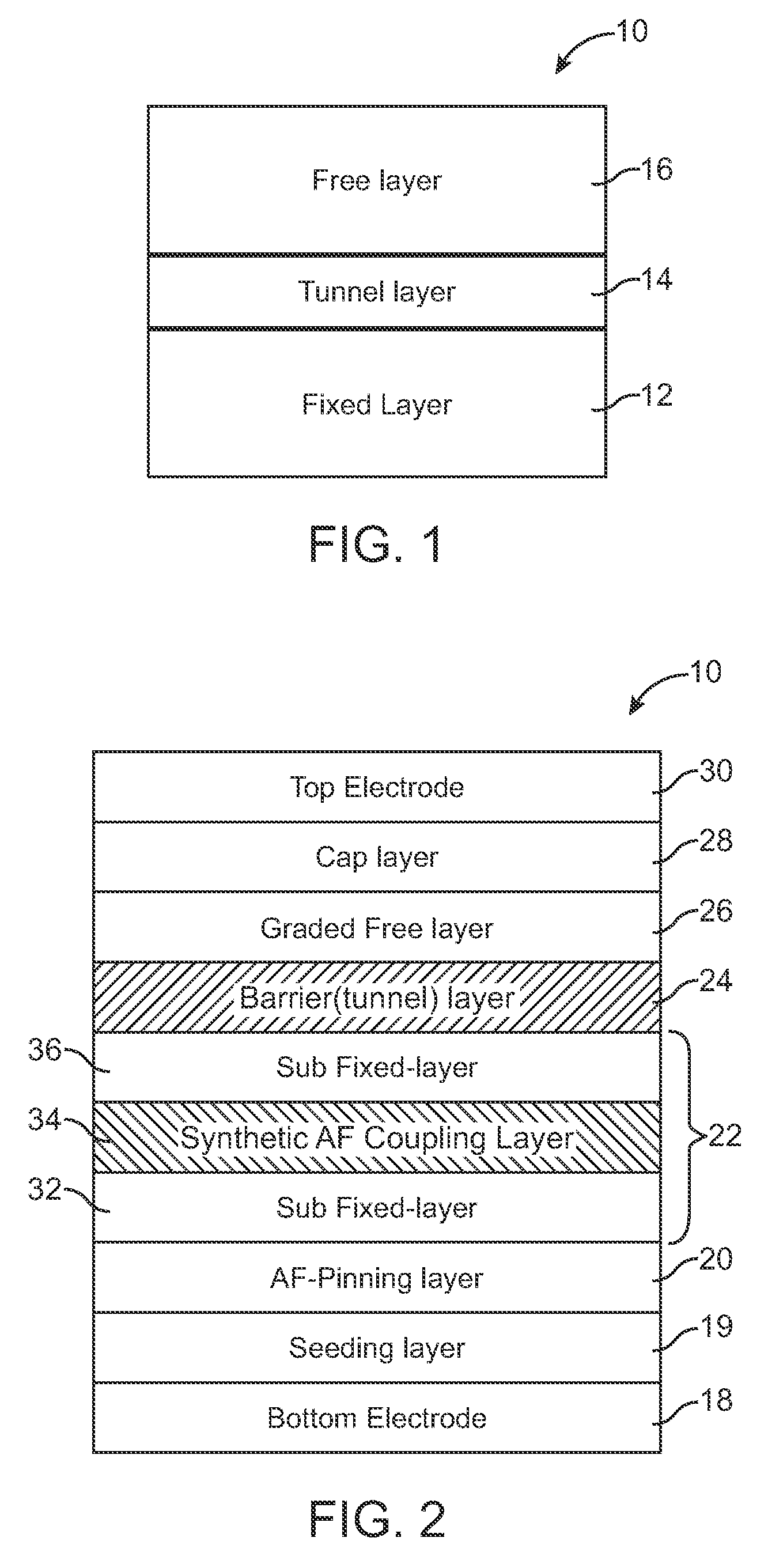
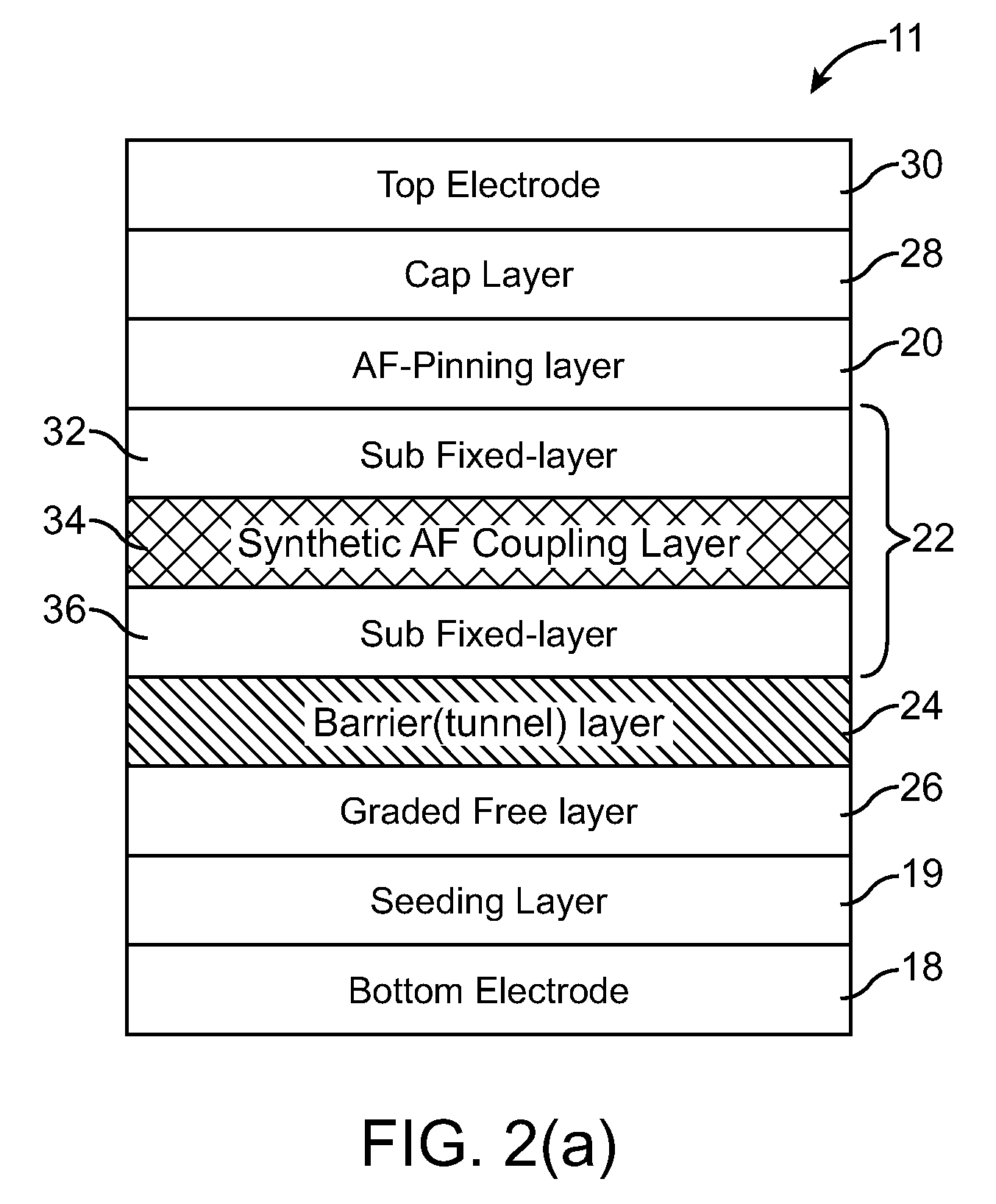
Non-Volatile Magnetic Memory Element with Graded Layer
ActiveUS20080191295A1Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacityNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic memoryNuclear magnetic resonance
One embodiment of the present invention includes a non-volatile magnetic memory element including layers any of which are graded.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Stackable ball grid array
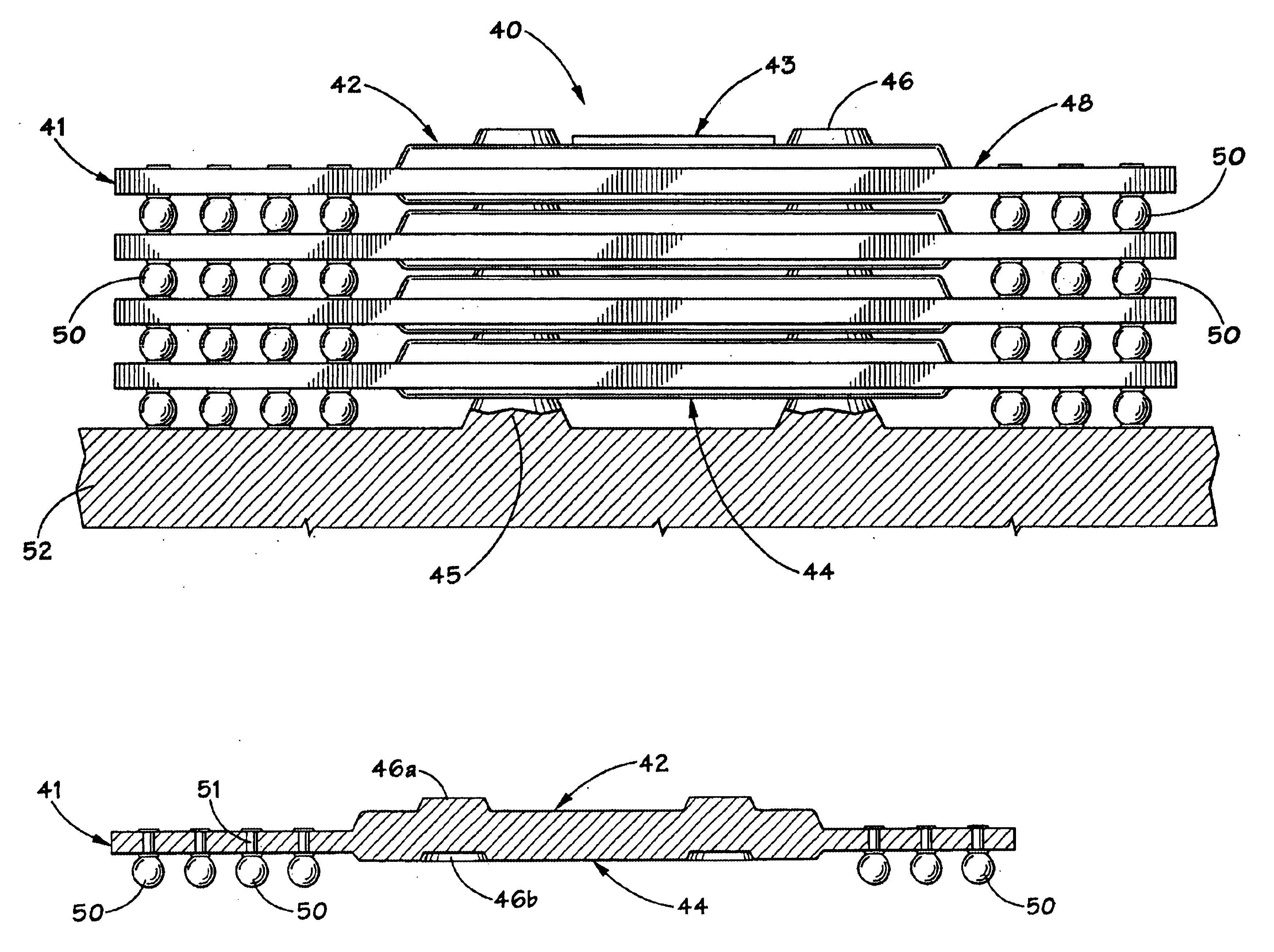
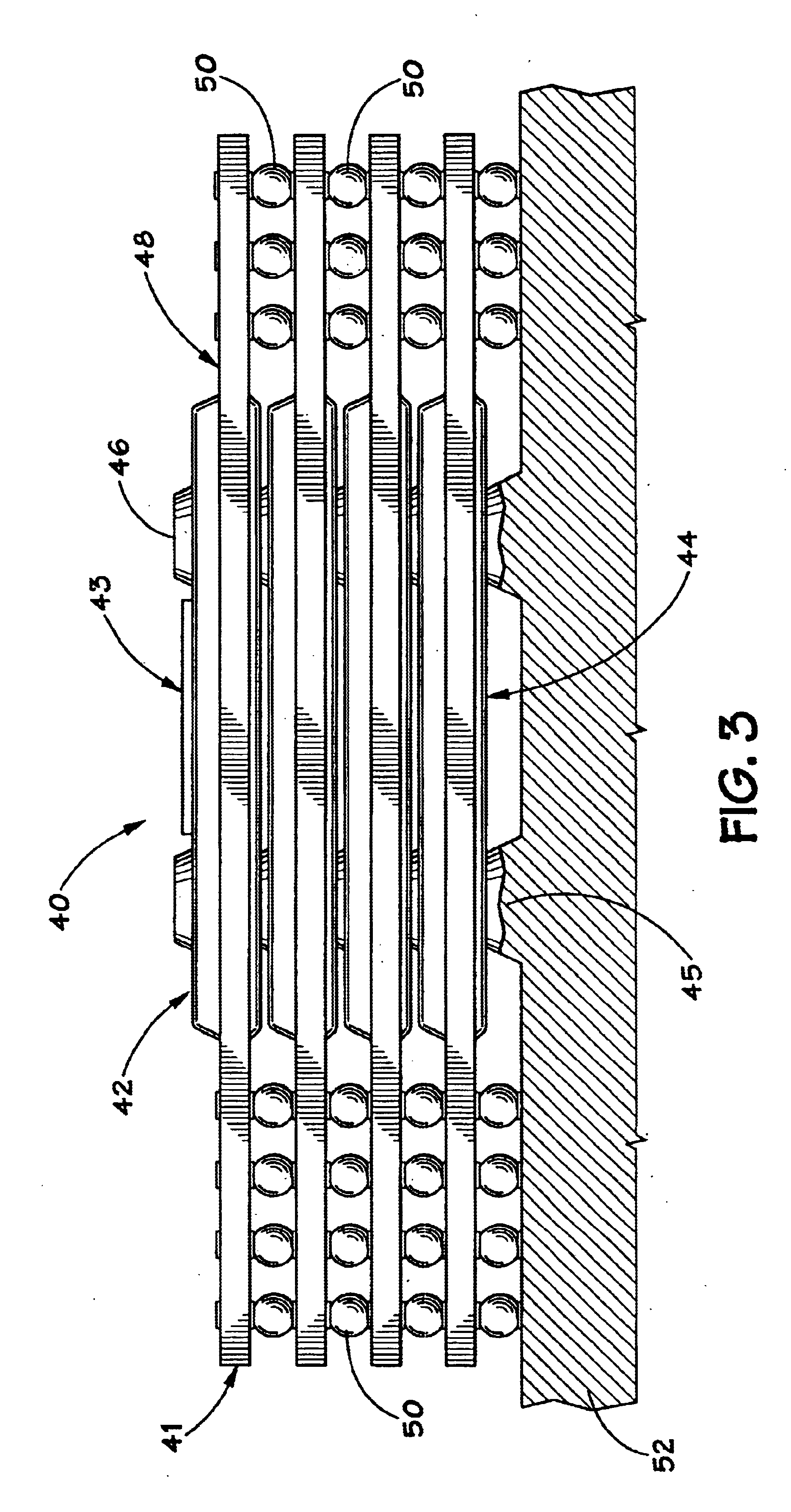
InactiveUS6778404B1Increase memory capacityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit boardSolder ball
A stackable package to create a 3-dimensional memory array using ball grid array technology. Specifically, memory chips are coupled to a pre-formed packages which have alignment features to allow for the stacking of the ball grid arrays. The alignment features are used to align and orient each package with respect to an adjacent package, substrate or printed circuit board. The alignment features also support the weight of the adjacent package during solder ball reflow to maintain stack height and parallelism between packages. Each memory device is serially connected to the adjacent memory device through the vias and solder balls on each package.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Low-cost non-volatile flash-RAM memory
ActiveUS8120949B2Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer hardwareNon-volatile random-access memory
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
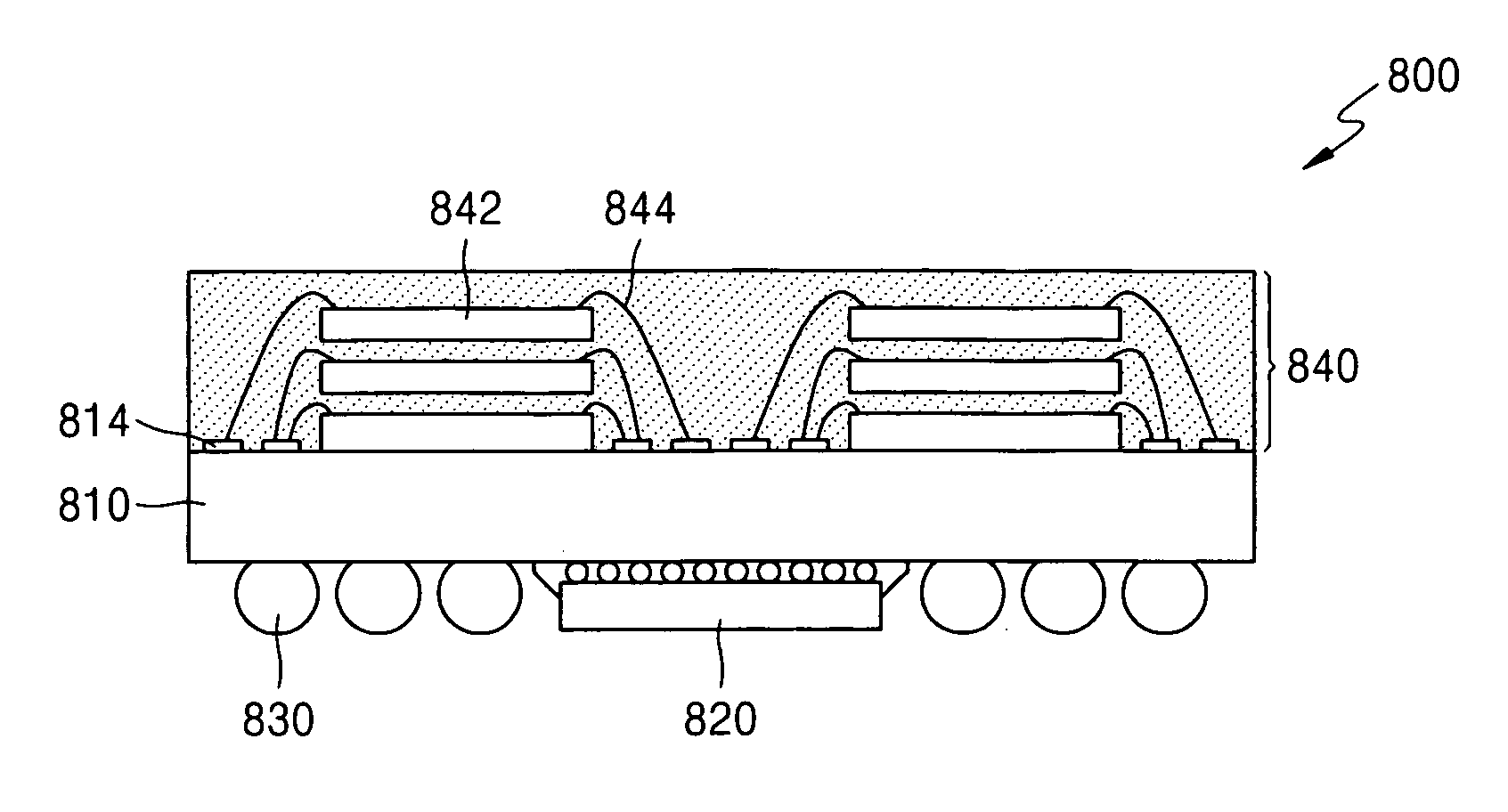
Semiconductor device package having buffered memory module and method thereof
ActiveUS20050224948A1Excellent electrical propertiesReduce distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsMemory chipDevice material
A method and apparatus of fabricating a semiconductor device are disclosed. The semiconductor device may include a buffer chip package having a buffer chip mounted on a buffer chip substrate and at least one memory package mounted on the buffer chip substrate, wherein the at least one memory package may include a plurality of memory chips. Further, the buffer chip package may have a plurality of external connection terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device for use as multimedia memory card, has encapsulant with chamfer such that portion of substrate and chamfer are exposed from encapsulant and remaining portion of surface of substrate is covered by encapsulant
InactiveUS7443016B2Cost-effective fabricationIncrease memory capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsMultimedia storageSealant
A semiconductor device and a fabrication method thereof are provided. An opening having at least one slanted side is formed on a substrate. At least one chip and at least one passive component are mounted on the substrate. An encapsulant having a cutaway corner is formed on the substrate to encapsulate the chip and the passive component, wherein the cutaway corner of the encapsulant is spaced apart from the slanted side of the opening by a predetermined distance. A singulation process is performed to cut the encapsulant to form a package with a chamfer. The package is embedded in a lid to form the semiconductor device, wherein a portion of the substrate located between the slanted side of the opening and the cutaway corner of the encapsulant is exposed from the encapsulant to form an exposed portion. The present invention also provides a carrier for the semiconductor device.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
Memory element and memory device
ActiveUS20100195371A1Improve retentionMaintain performanceSolid-state devicesDigital storageHigh resistanceSulfur
The capability of retaining a resistance value of a stored state and an erased state is improved in a resistance variation-type memory device. A memory layer 5 including a high-resistance layer 2 and an ion source layer 3 is provided between a lower electrode 1 and an upper electrode 4. The ion source layer 3 contains Al (aluminum) as an additive element together with an ion conductive material such as S (sulfur), Se (selenium), and Te (tellurium) (chalcogenide element) and a metal element to be ionized such as Zr (zirconium). Since Al is included in the ion source layer 3, the high-resistance layer which includes Al (Al oxide) is formed on an anode in erasing operation. Thus, a retaining property in a high-resistance state improves, and at the same time, an operating speed is improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
High Capacity Low Cost Multi-Stacked Cross-Line Magnetic Memory
InactiveUS20070253245A1Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacityNanotechSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryMagnetization
One embodiment of the present invention includes a diode-addressable current-induced magnetization switching (CIMS) memory element including a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) and a diode formed on top of the MTJ for addressing the MTJ.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
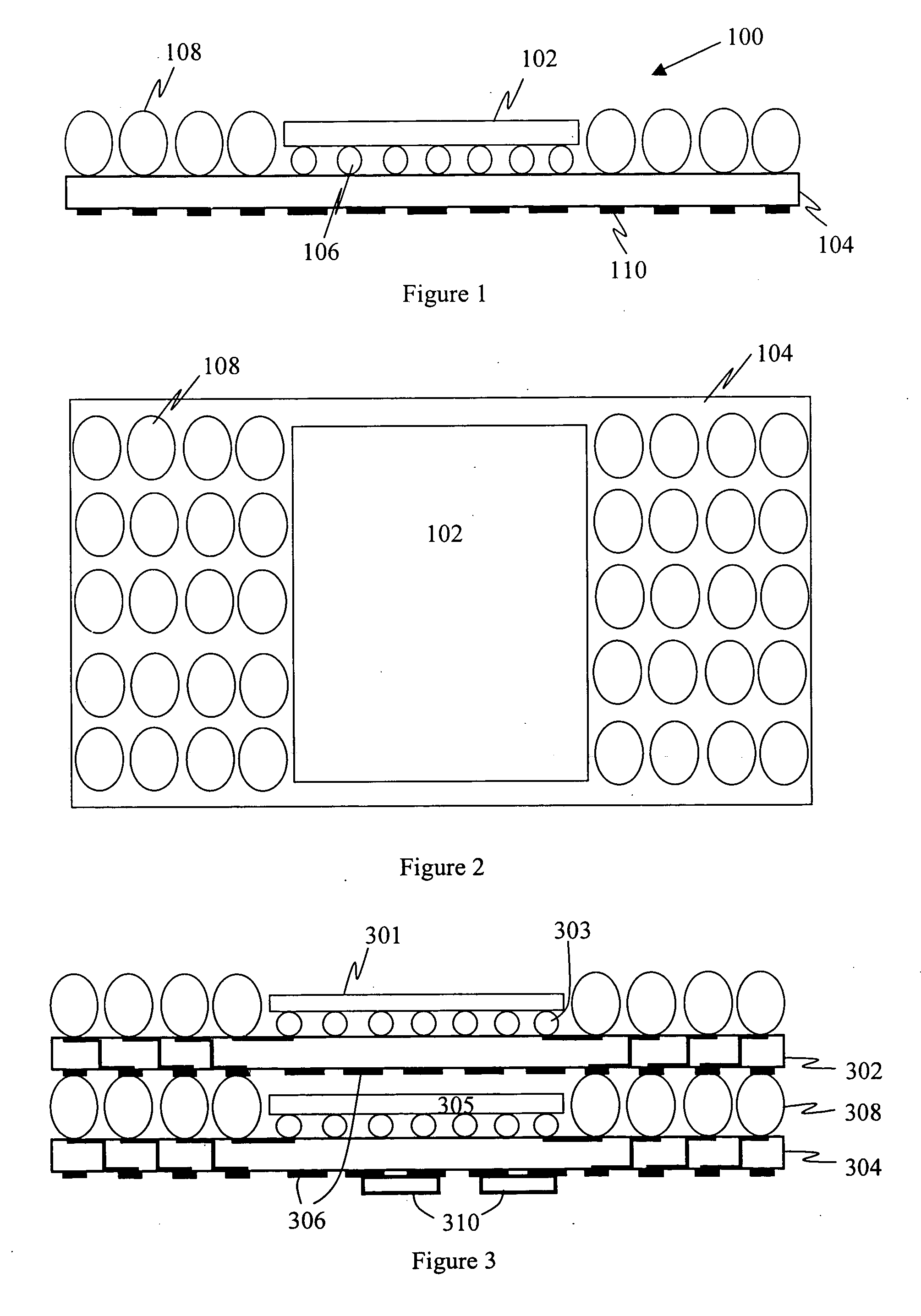
Stackable electronic assembly
ActiveUS20050051903A1Improve heat dissipationIncreased memory capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic assemblies
On implementation of the invention provides a stackable chip-scale package for improving memory density that may be mounted within a limited area or module. A novel staggered routing scheme enables the use of the same trace routing at every level of the stacked architecture for efficiently accessing individual memory devices in a chip-scale package stack. The use of a ball grid array chip-scale package architecture in combination with thermally compatible materials decreases the risk of thermal cracking while improving heat dissipation. Moreover, this architecture permits mounting support components, such as capacitors and resistors, on the chip-scale package.
Owner:SANMINA-SCI CORPORATION
Magnetic shift register with shiftable magnetic domains between two regions, and method of using the same
InactiveUS20050094427A1Comparable in costIncrease memory capacityLiquid applicationDigital storageShift registerSpins
A magnetic shift register uses the inherent, natural properties of domain walls in magnetic materials to store data. The shift register uses spin electronics without changing the physical nature of its constituent materials. The shift register comprises a fine track or strip of magnetic materials. Information is stored as domain walls in the track. An electric current is applied to the track to move the magnetic moments along the track past a reading or writing device. In a magnetic material with domain walls, a current passed across the domain wall moves the domain wall in the direction of the current flow. As the current passes through a domain, it becomes “spin polarized”. When this spin polarized current passes through the next domain and across a domain wall, it develops a circle of spin torque. This spin torque moves the domain wall.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070176845A1High gainSmall size limitOther printing matterAntenna supports/mountingsDevice materialEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide an ID chip in which gain of an antenna is increased and the mechanical strength of an integrated circuit can be enhanced without suppressing a circuit scale. A semiconductor device typified by an ID chip of the present invention includes an integrated circuit using a semiconductor element formed from a thin semiconductor film and an antenna connected to the integrated circuit. The antenna and the integrated circuit are formed on a substrate, and a conducting wire or a conductive film included in the antenna is divided into two layers and formed so as to sandwich the substrate provided with the integrated circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Stacked memory module and system
ActiveUS8031505B2Increase memory capacityEfficient wiring and capacity organizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory bankEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
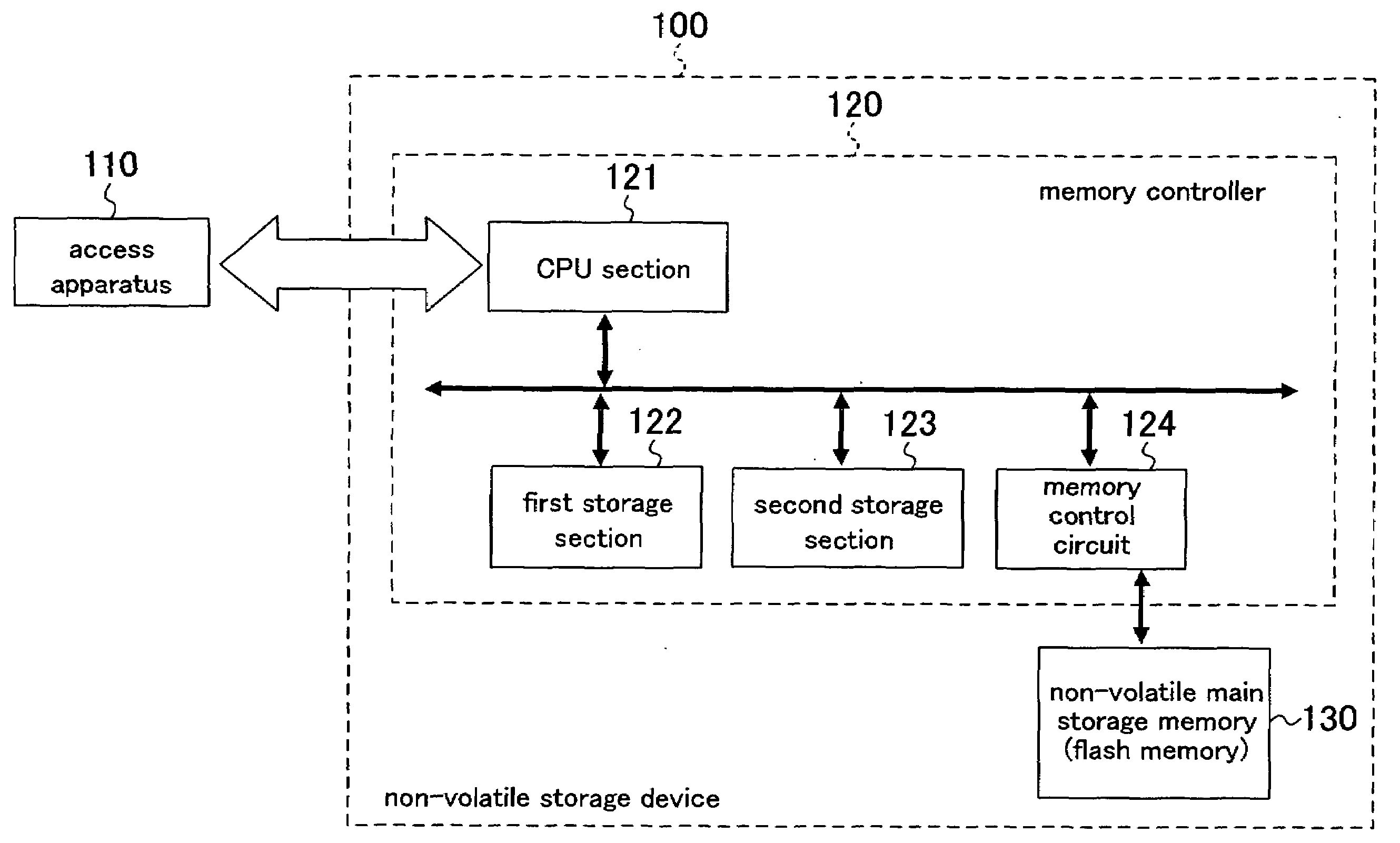
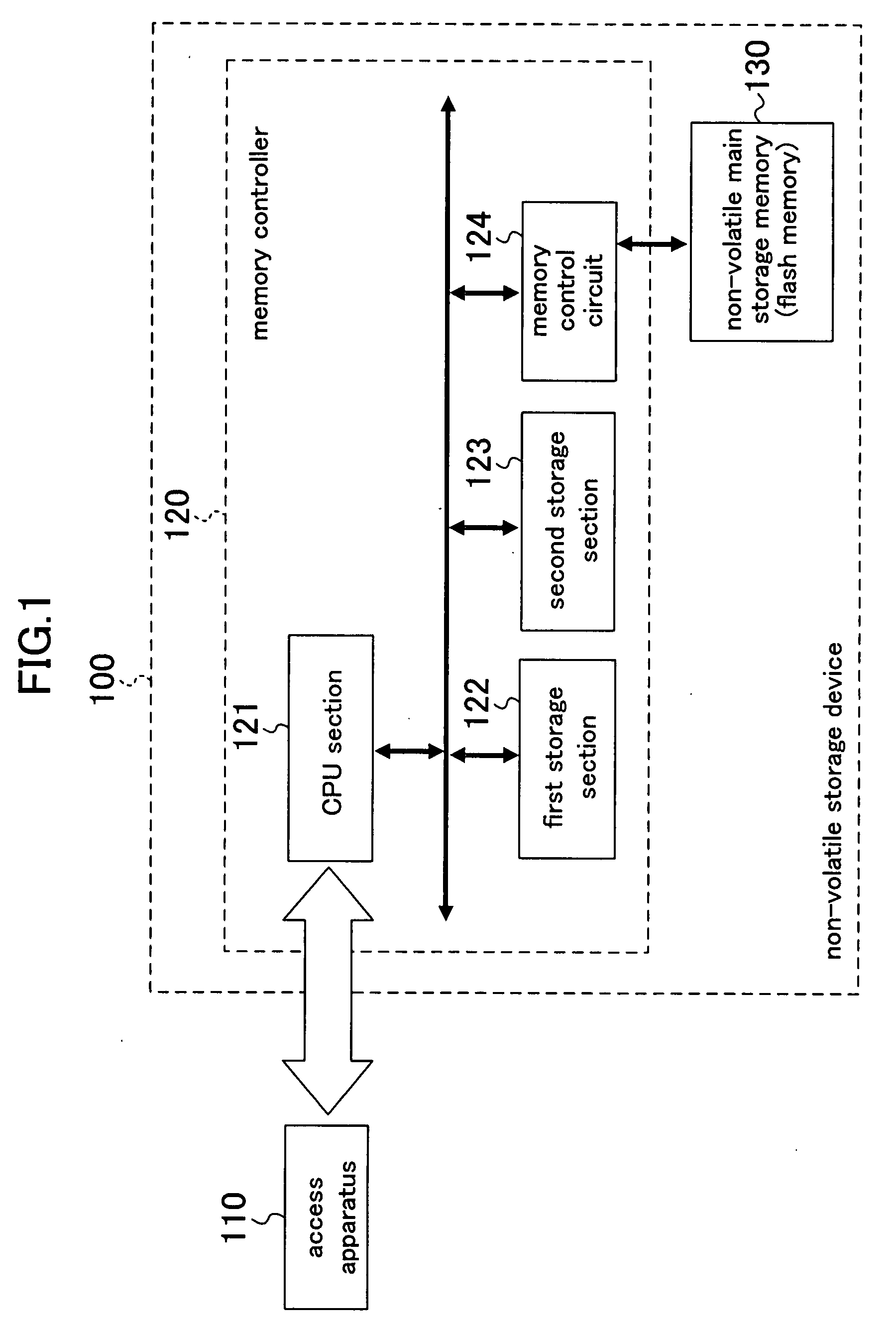
Non-volatile storage device, data storage system, and data storage method
InactiveUS20080028132A1Quickly and efficiently writtenLarge capacityMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMemory controllerOperating system
A non-volatile storage device comprises a non-volatile memory into which data is written per unit area, and a memory controller for controlling writing of data into the non-volatile memory. The memory controller comprises a first storage section for holding data input from the outside of the device, a first control section for writing data which is held by the first storage section and whose amount corresponds to the unit area, into the non-volatile memory in a unit area-by-unit area basis, and writing data which is held by the first storage section and whose amount is less than the unit area, into a second storage section, and a second control section for writing data held by the second storage section into the non-volatile memory.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Integrated circuit, semiconductor device comprising the same, electronic device having the same, and driving method of the same
InactiveUS20040246765A1Increase memory capacityReduced footprintTransistorSolid-state devicesActive layerElectron
An integrated circuit mounting a DRAM which can realize high integration without complicated manufacturing steps. The integrated circuit according to the invention comprises a DRAM in which a plurality of memory cells each having a thin film transistor are disposed. The thin film transistor comprises an active layer including a channel forming region, and first and second electrodes overlapping with each other with the channel forming region interposed therebetween. By controlling a drain voltage of the thin film transistor according to data, it is determined whether to accumulate holes in the channel forming region or not, and data is read out by confirming whether or not holes are accumulated,.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110297911A1Improve reliabilityIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryDevice material
A technique used for a semiconductor device formed by stacking multiple structural bodies each having a semiconductor device, for preventing generation of thermal load on a structural body at a lower layer which is caused by a laser used in a step of forming a structural body at an upper layer. In a phase-change memory including multiple stacked memory matrices, a metal film is disposed between a memory matrix at a lower layer and a memory matrix at an upper layer formed over the memory matrix at the lower layer, in which the laser used for forming the memory matrix is reflected at the metal film and prevented from transmitting the metal film, thereby preventing the phase-change material layer, etc. in the memory matrix at the lower layer from being directly heated excessively by the laser.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Transparent Memory for Transparent Electronic Device
InactiveUS20120132882A1High transparencyImprove switching characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransparent electronicsData store
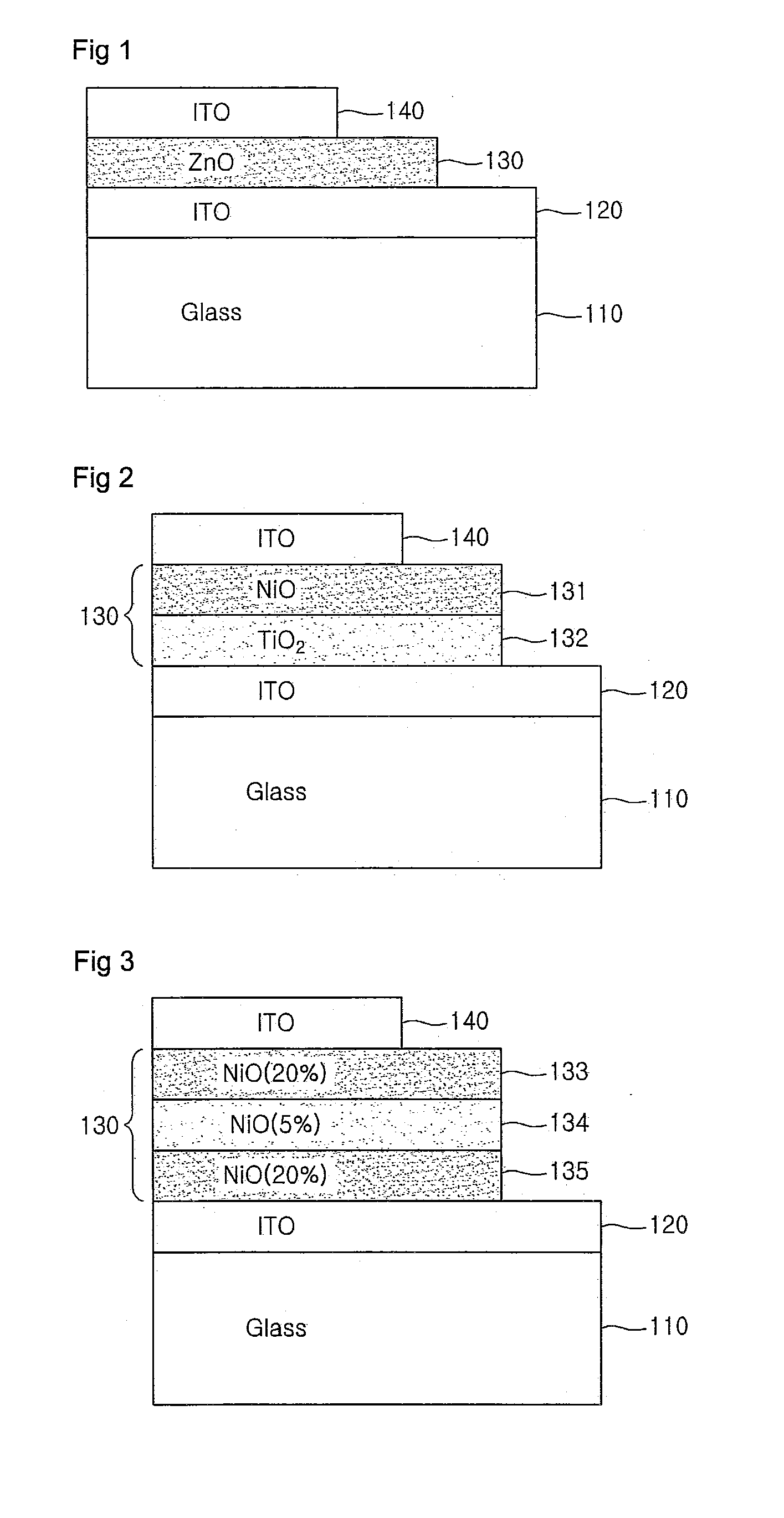
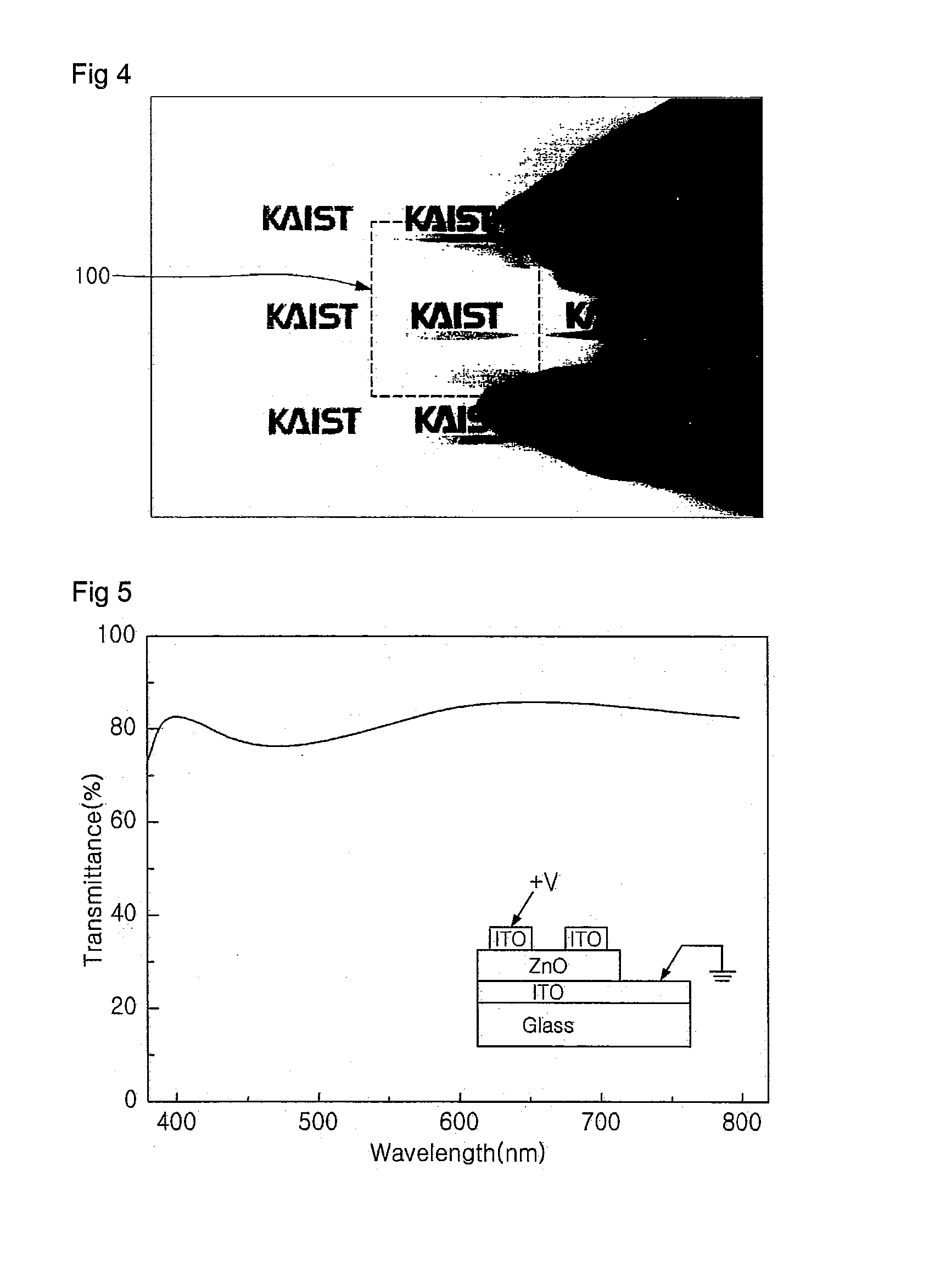
The present invention relates to a transparent memory for a transparent electronic device. The transparent memory includes: a lower transparent electrode layer that is sequentially formed on a transparent substrate, and a data storage region and an upper transparent layer which are made of at least one transparent resistance-variable material layer. The transparent resistance-variable material layer has switching characteristics as a result of the resistance variance caused by the application of a certain voltage between the lower and upper transparent electrode layers. An optical band gap of the transparent resistance-variable material layer is 3 eV or more, and transmittivity of the material layer for visible rays is 80% or more. The invention provides transparent and resistance-variable memory that: has very high transparency and switching characteristics depending on resistance variation at a low switching voltage, and can maintain the switching characteristics thereof after a long time elapses.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Multi-chip device and method for producing a multi-chip device
InactiveUS20060286822A1Increased memory capacityIncreased yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringContact element
The present invention relates to a multi-chip device comprising a plurality of chip stacks each including a plurality of single chips stacked on each other, wherein the stacked single chips are electrically interconnected by one or more through-chip-connection extending through at least one of the single chips and a substrate providing one or more first contact elements each of which is in contact with one of the through-chip-connections and providing one or more second contact elements being in electrical contact with the first contact elements, wherein the plurality of chip stacks are stacked onto each other and wherein the second contact elements of one of the chip stacks each being arranged to be in contact to one or more third contact elements of an adjacent one of the chip stacks.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Memory cell
Owner:QS SEMICON AUSTRALIA
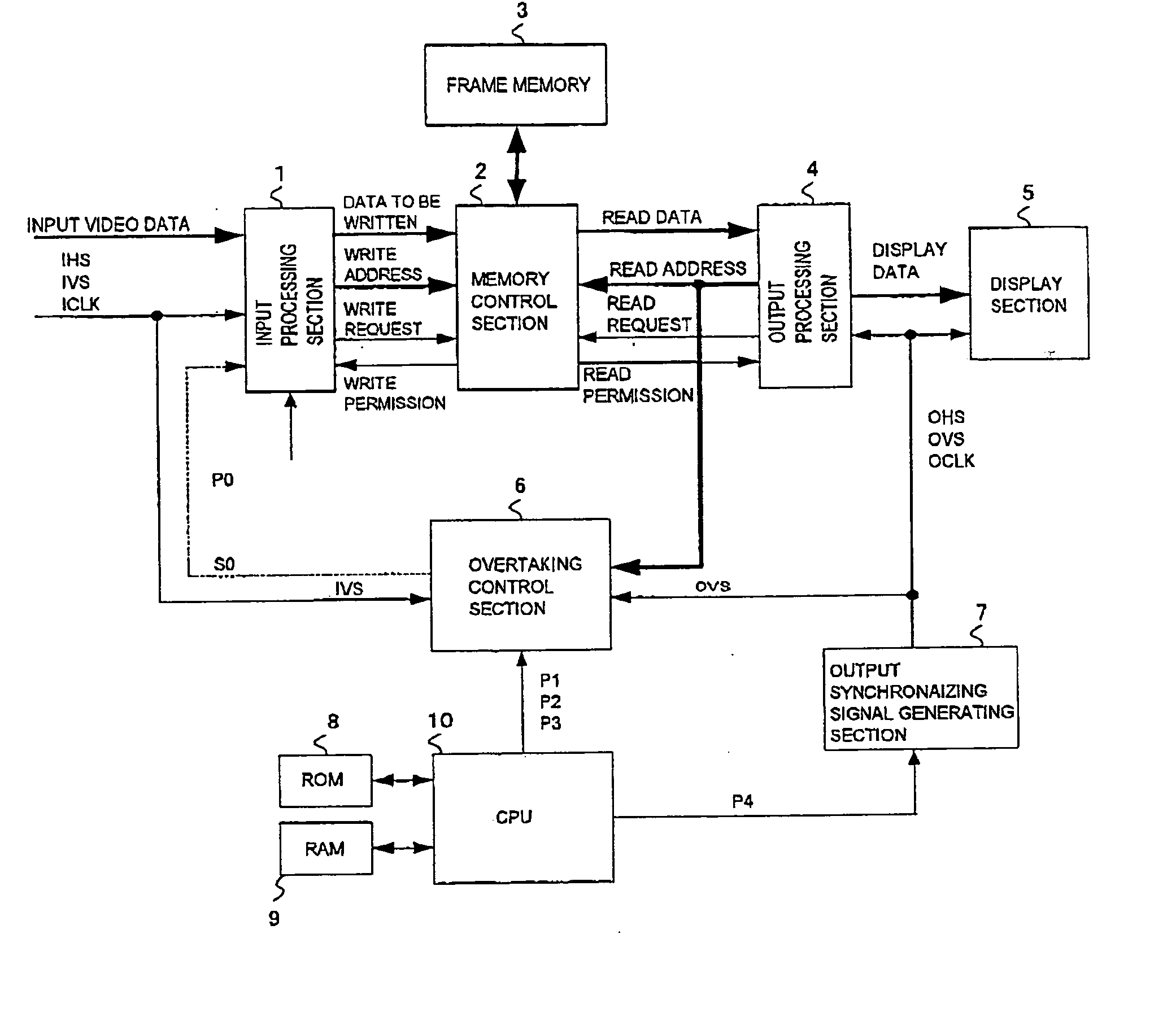
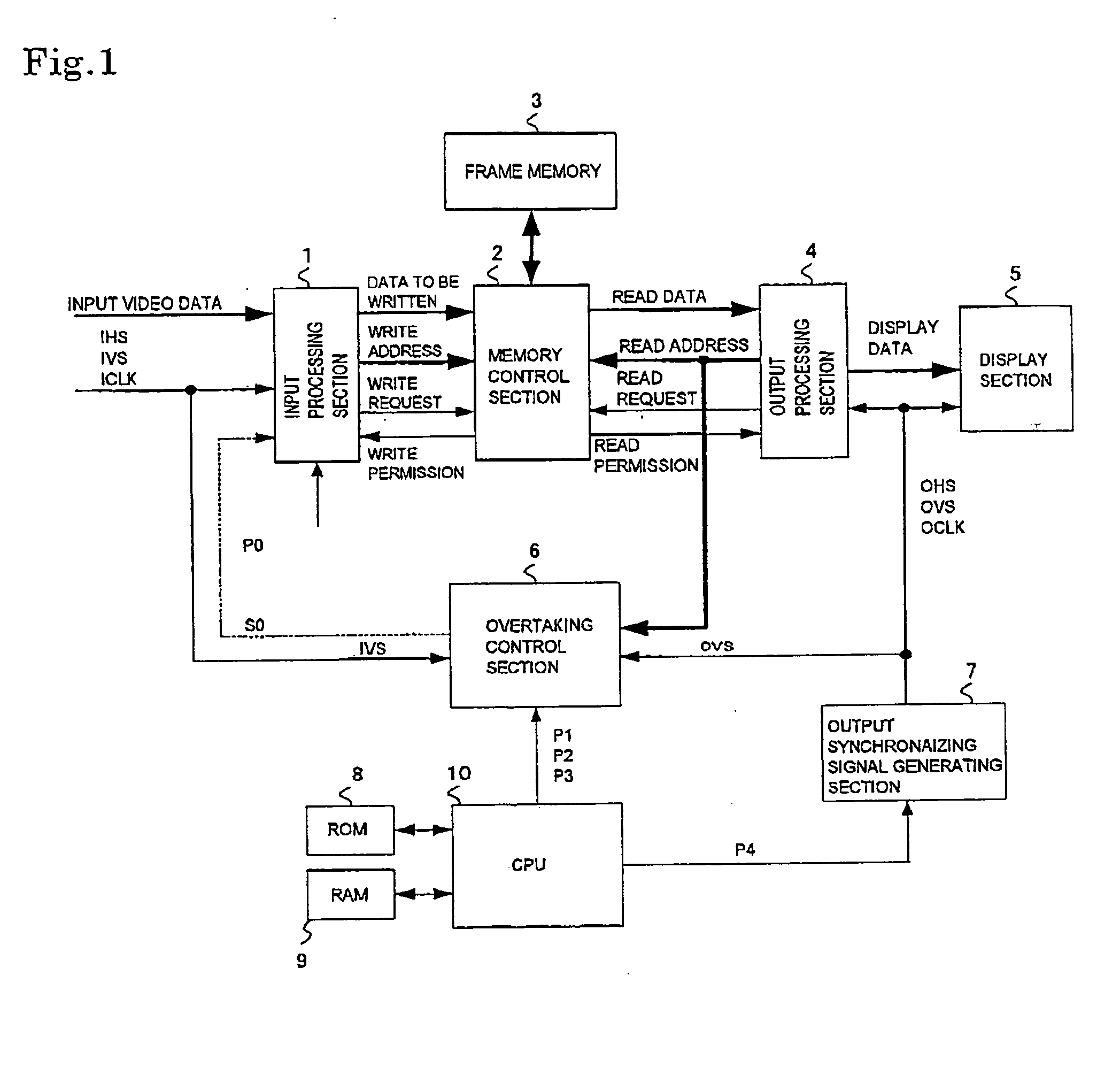
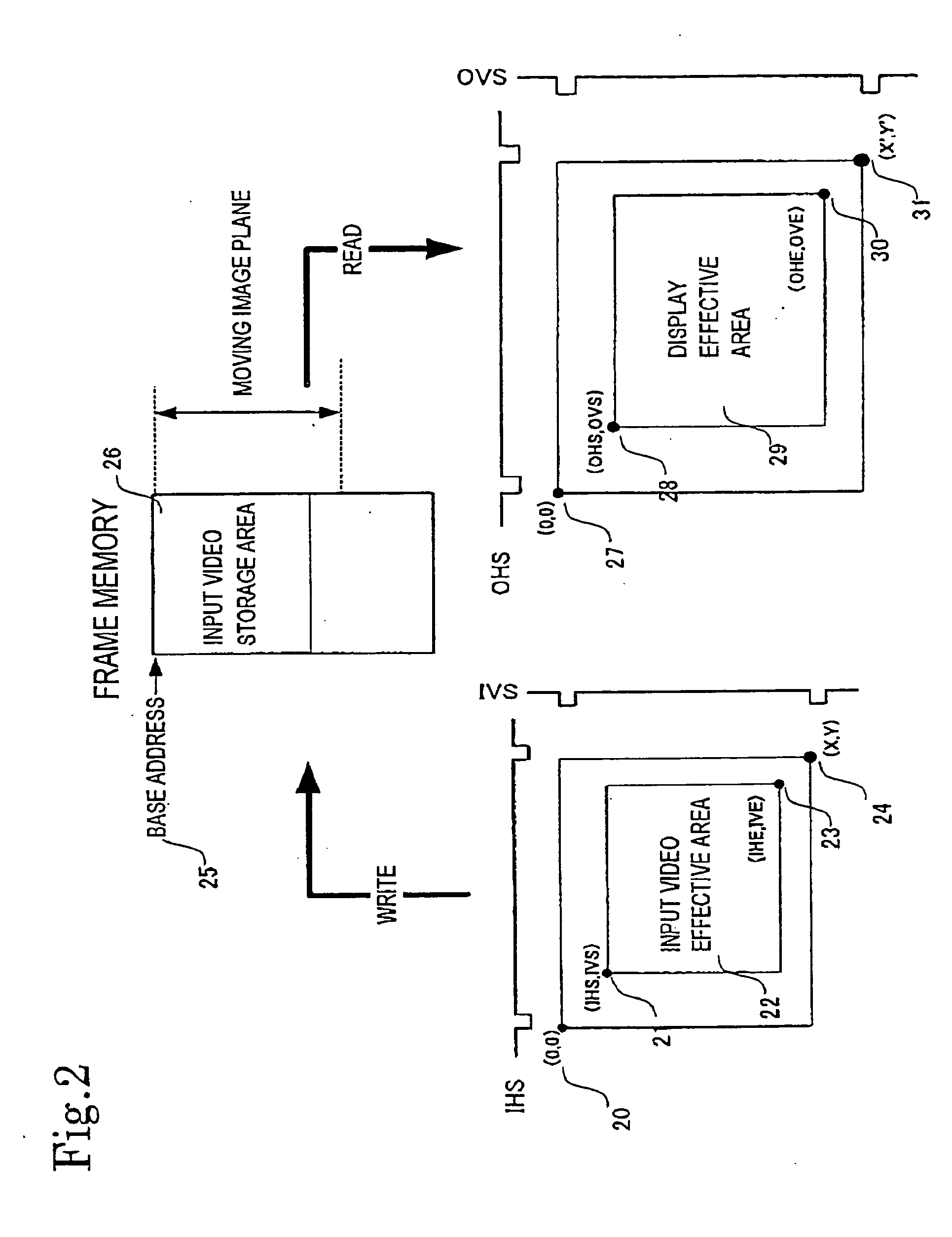
Frame rate conversion device, overtaking prediction method for use in the same, display control device and video receiving display device
InactiveUS20050105001A1Improve accuracyAvoid interferenceTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareOvertaking
An overtaking prediction method of, when input and output of data to and from a common memory are being performed with an input frame frequency and an output frame frequency made different from each other, predicting a frame in which overtaking occurs between the input and the output of the data to and from the memory. The overtaking prediction method includes a step of predicting the frame in which the overtaking occurs between the input and the output of the data, on the basis of a first parameter corresponding to a difference amount between a progress speed of a write address and a progress speed of a read address and a second parameter corresponding to a difference between a write address and a read address at an overtaking prediction point and to an offset address difference amount between an input offset address and an output offset address.
Owner:CANON KK
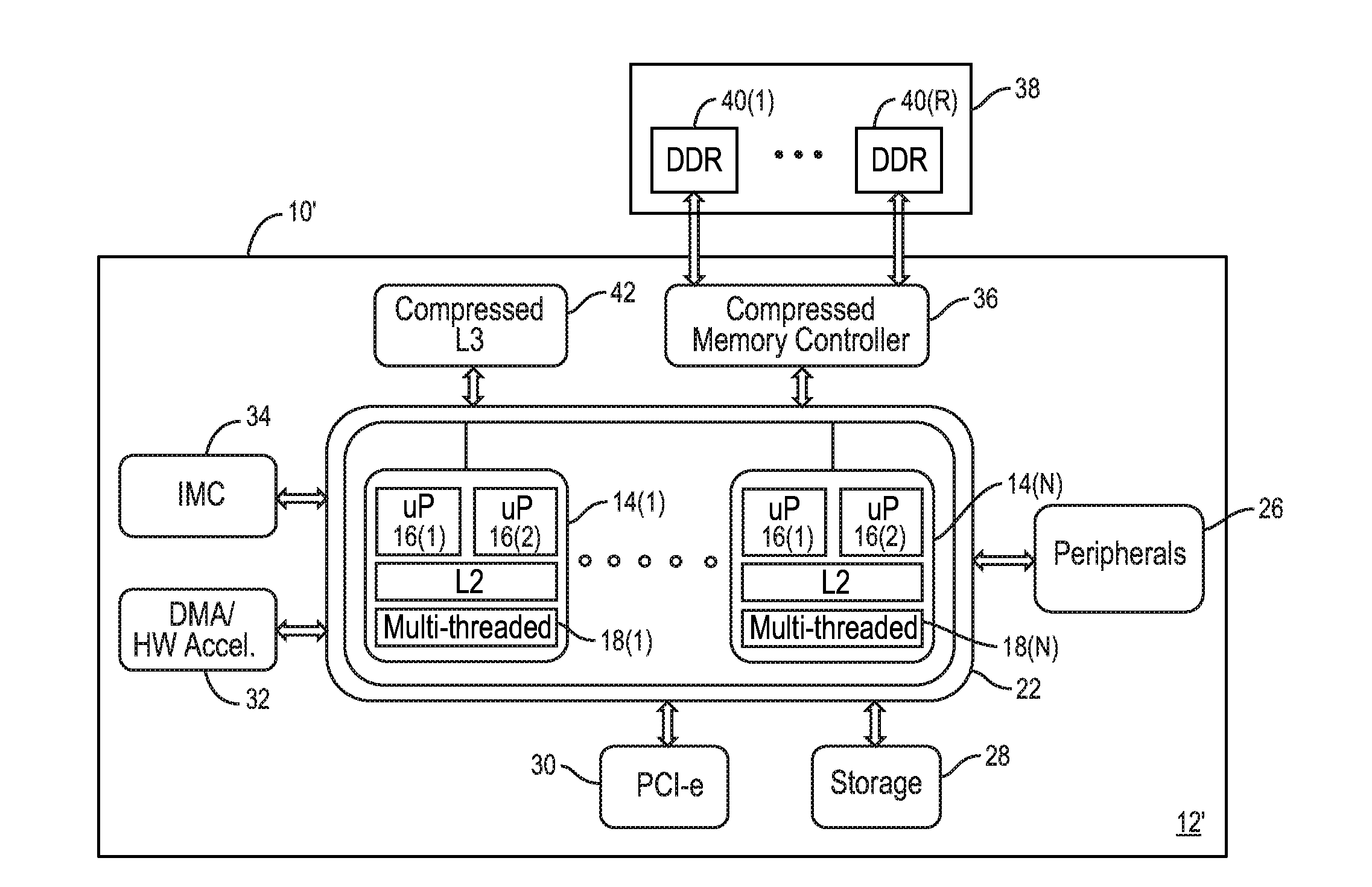
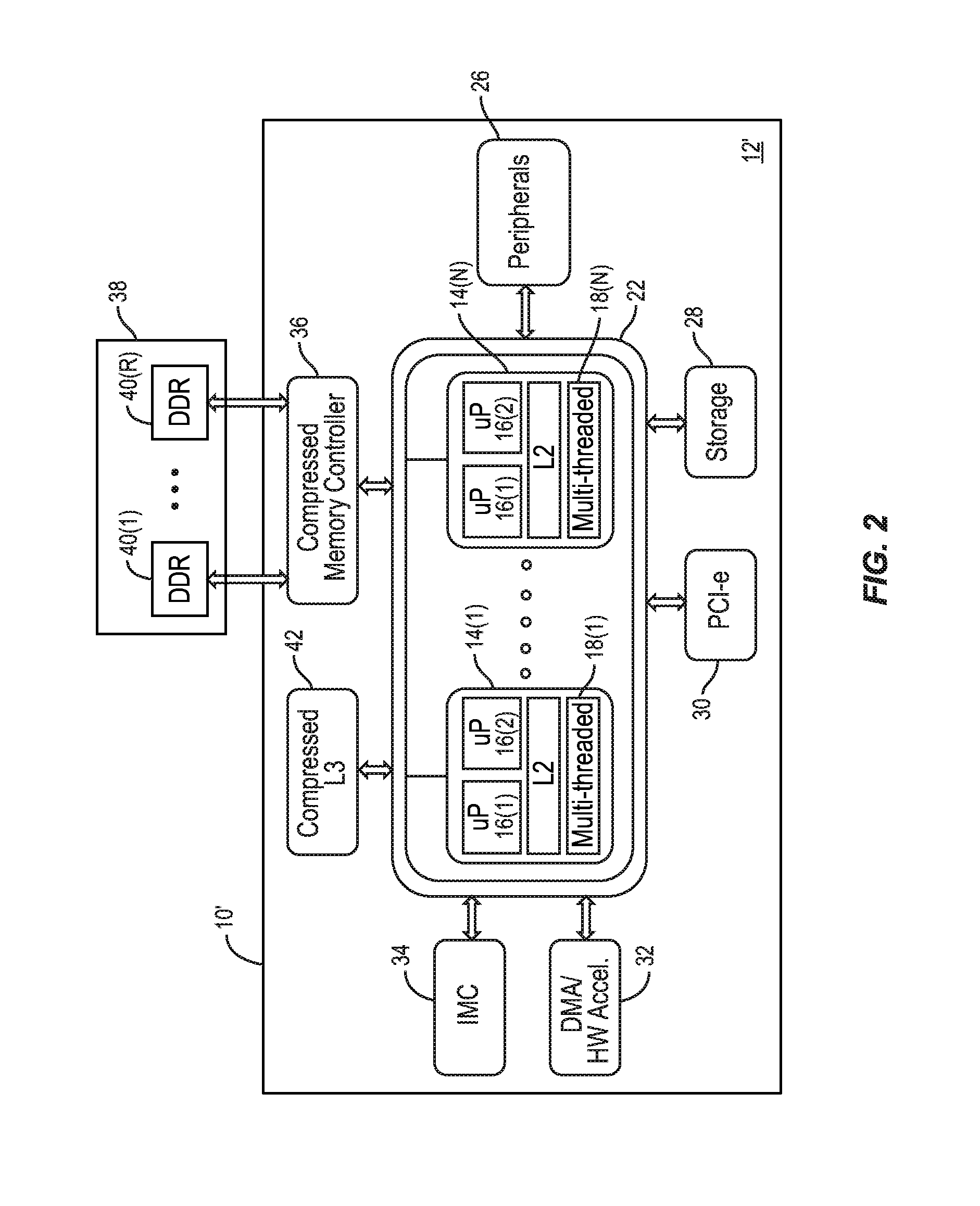
Memory controllers employing memory capacity compression, and related processor-based systems and methods
ActiveUS20150339228A1Efficient executionOptimize data compressionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerTranslation lookaside buffer
Aspects disclosed herein include memory controllers employing memory capacity compression, and related processor-based systems and methods. In certain aspects, compressed memory controllers are employed that can provide memory capacity compression. In some aspects, a line-based memory capacity compression scheme can be employed where additional translation of a physical address (PA) to a physical buffer address is performed to allow compressed data in a system memory at the physical buffer address for efficient compressed data storage. A translation lookaside buffer (TLB) may also be employed to store TLB entries comprising PA tags corresponding to a physical buffer address in the system memory to more efficiently perform the translation of the PA to the physical buffer address in the system memory. In certain aspects, a line-based memory capacity compression scheme, a page-based memory capacity compression scheme, or a hybrid line-page-based memory capacity compression scheme can be employed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com