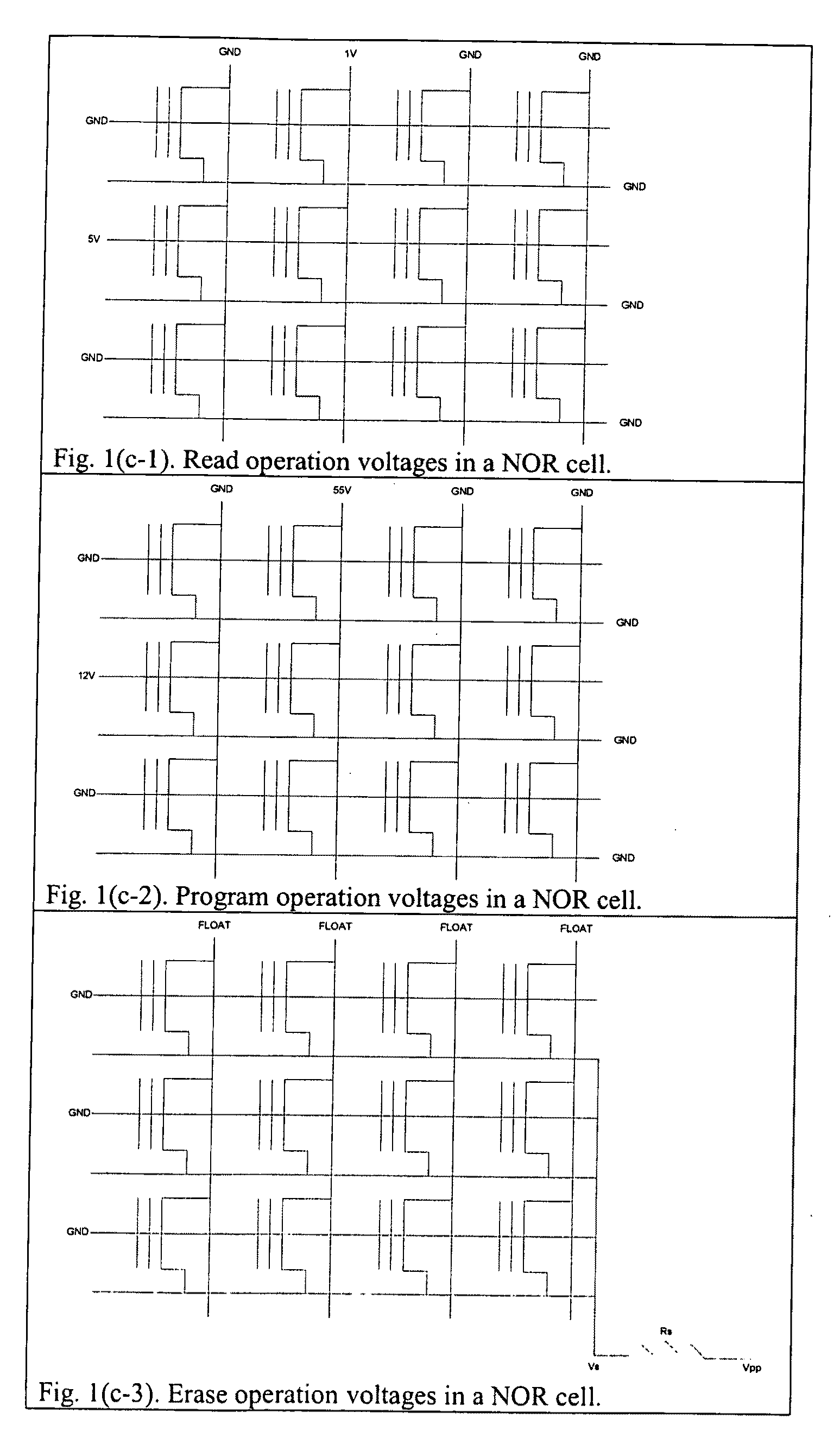
Patents
Literature
317 results about "Non-volatile random-access memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
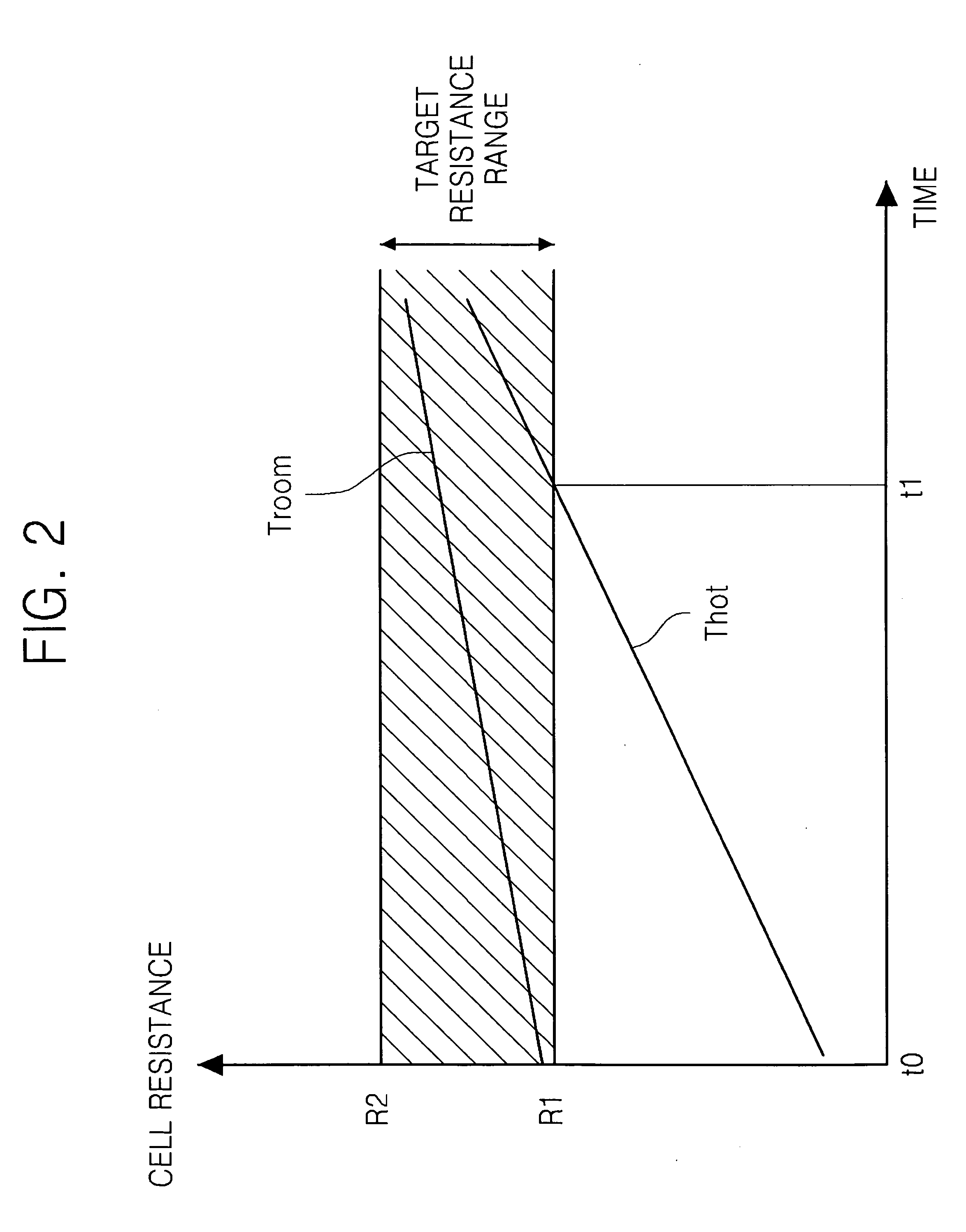
Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) is random-access memory that is non-volatile. This is in contrast to dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and static random-access memory (SRAM), which both maintain data only for as long as power is applied.
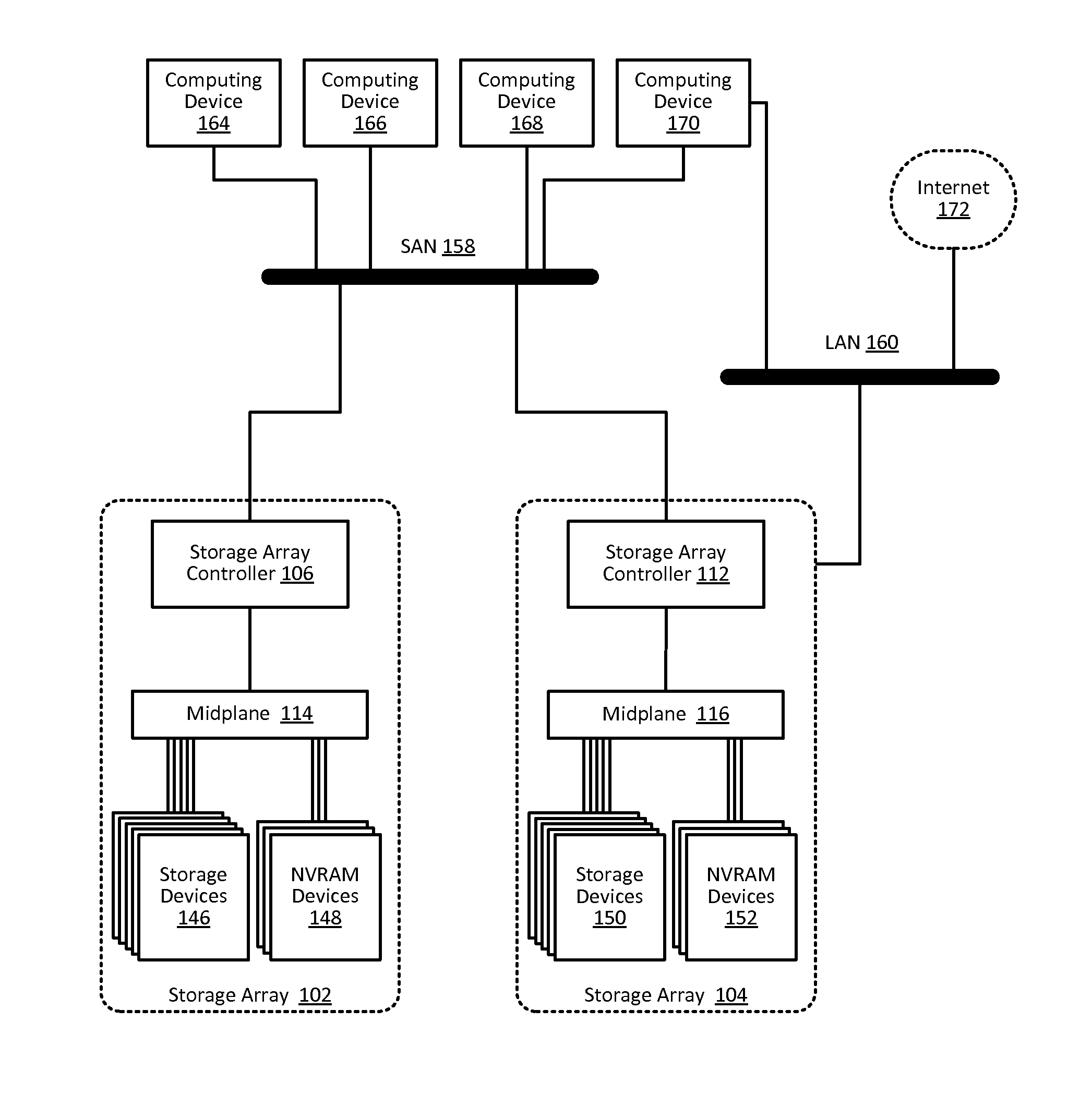
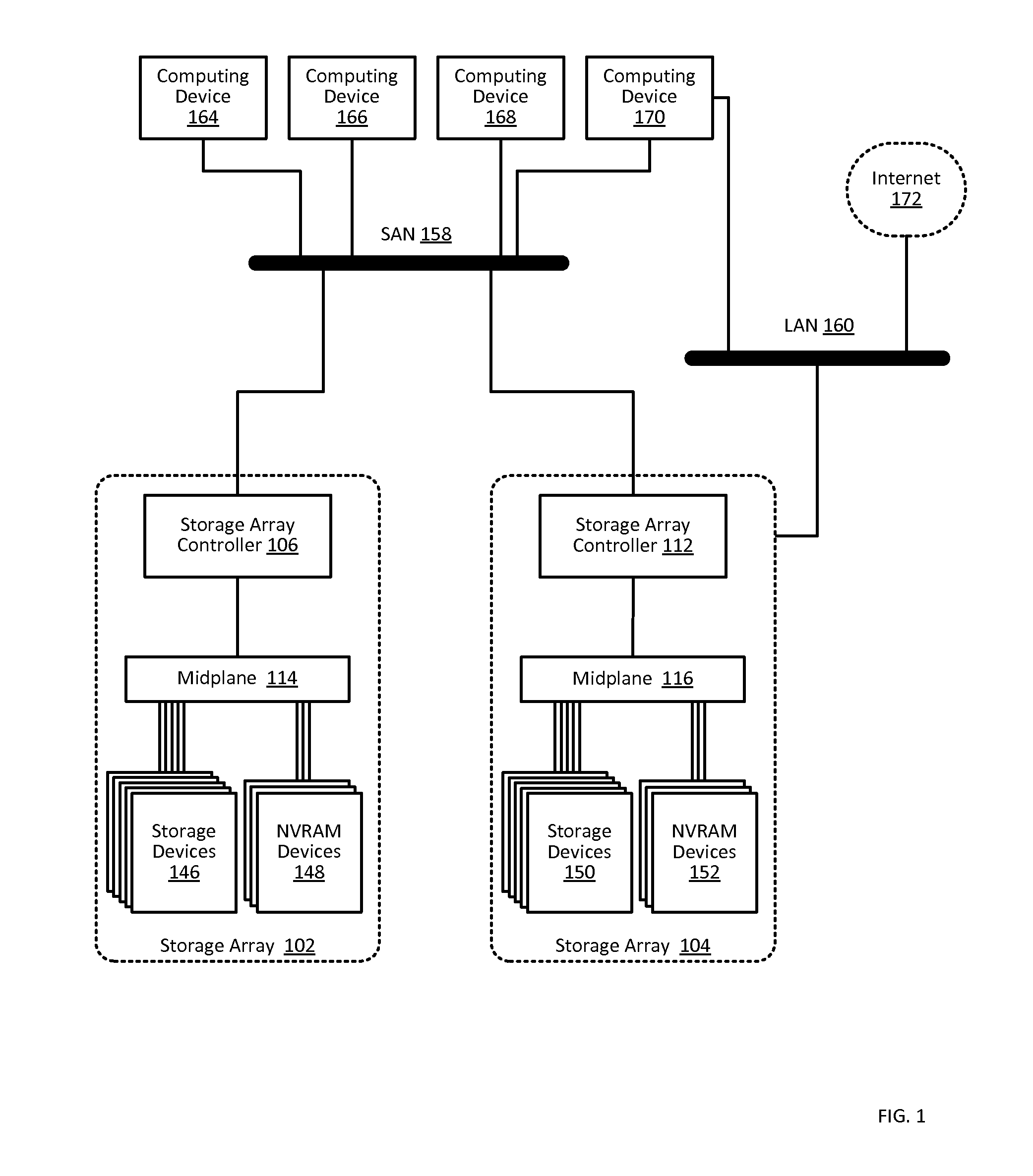
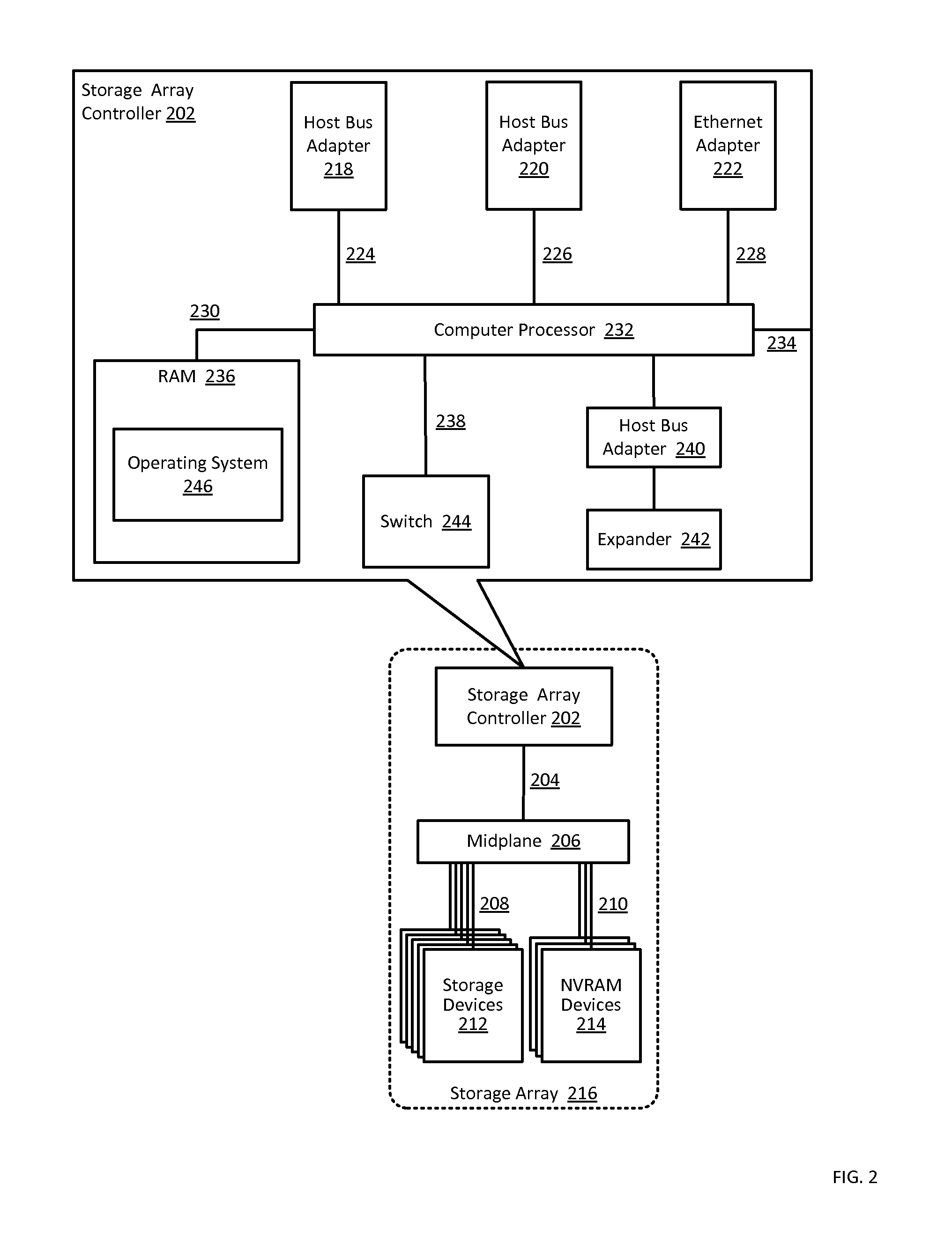
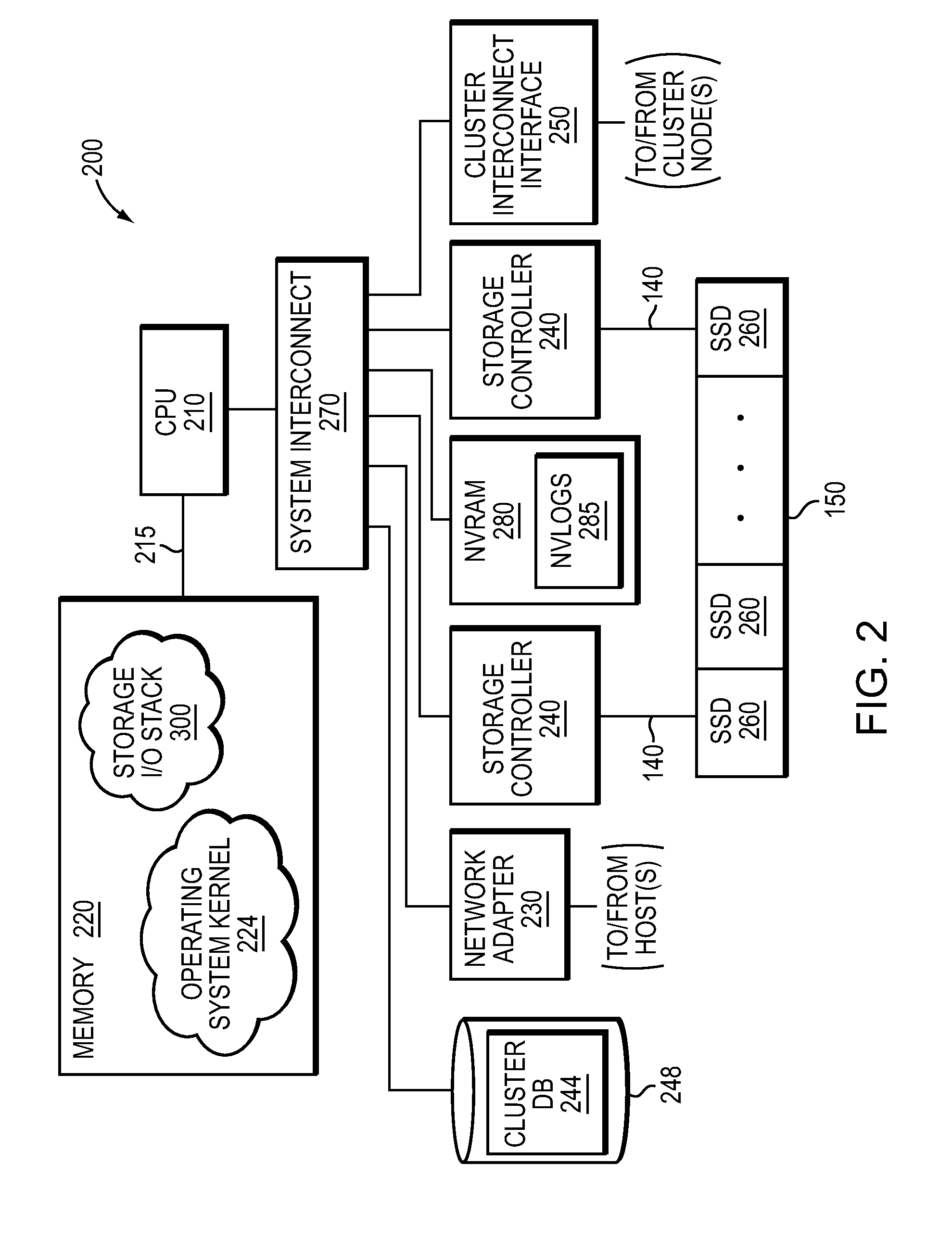
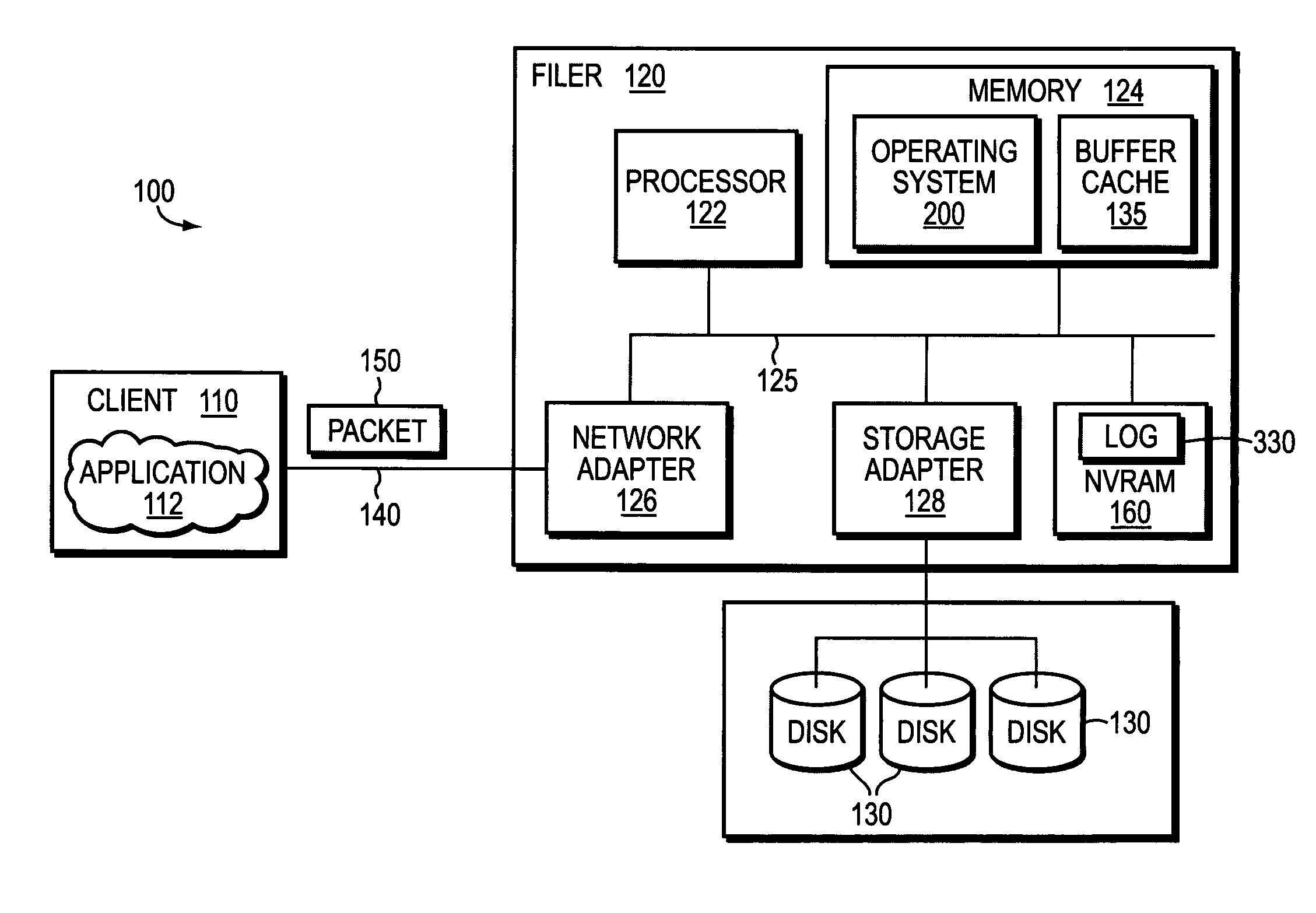
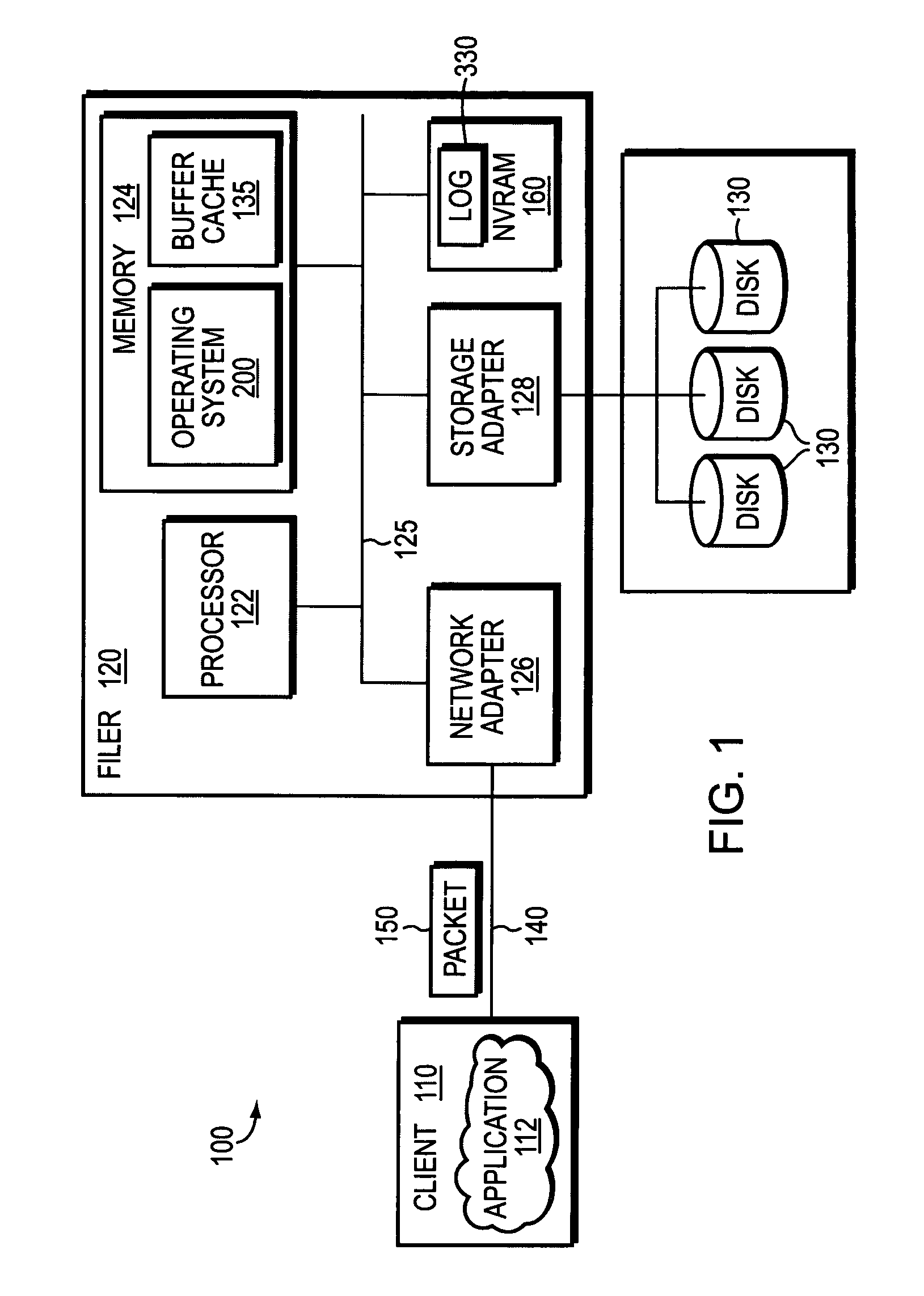
Buffering data to be written to an array of non-volatile storage devices
InactiveUS20160350009A1Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionComputer hardwareStandby power
Buffering data to be written to an array of non-volatile storage devices, including: receiving a request to write data to the array of non-volatile storage devices; sending, to a non-volatile random access memory (‘NVRAM’) device, an instruction to write the data to dynamic random access memory (‘DRAM’) in the NVRAM device, the DRAM configured to receive power from a primary power source, the DRAM further configured to receive power from a backup power source in response to the primary power source failing; and writing the data to the DRAM in the NVRAM device.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
Data boundary management
InactiveUS20050144363A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
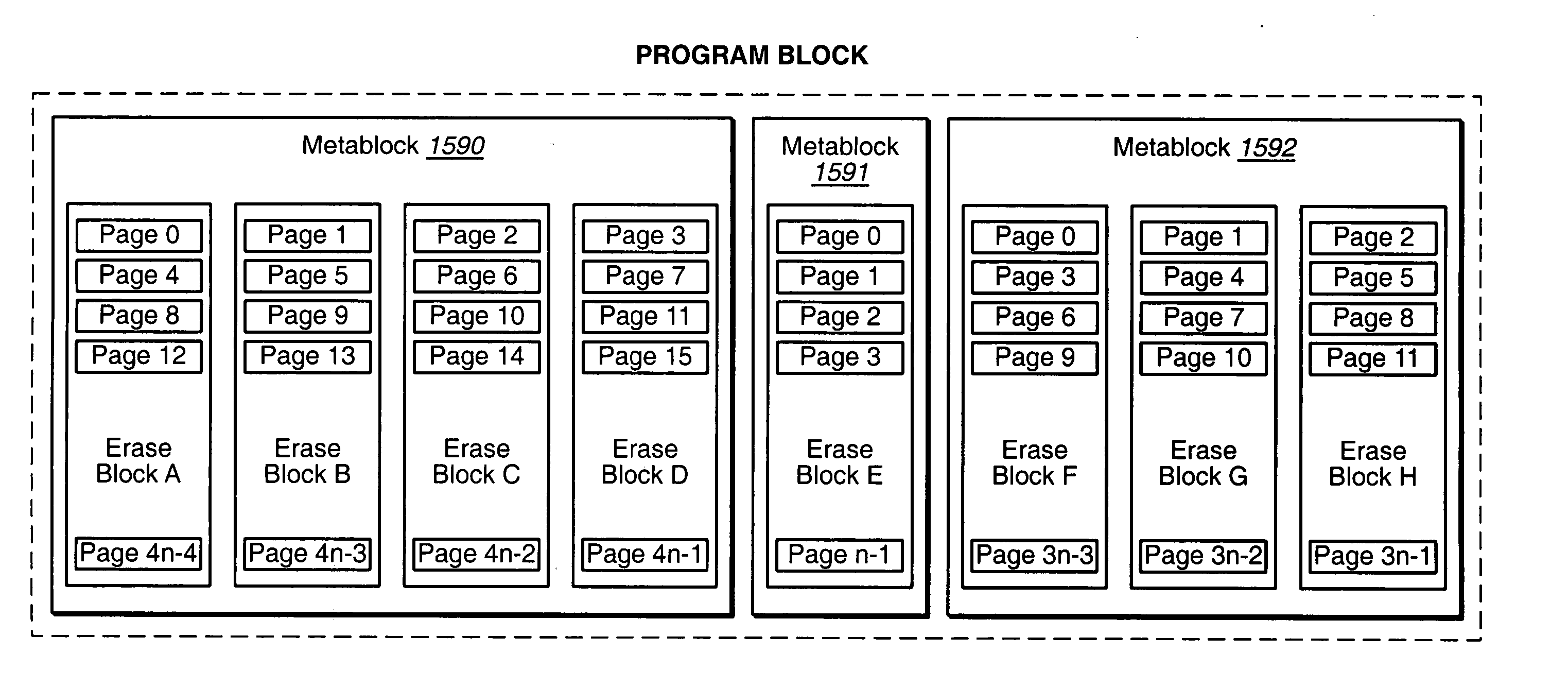
Data may be stored in a non-volatile memory array in adaptive metablocks that are configured according to the locations of data boundaries in the data. Data may be stored in an intermediate format and later copied to adaptive metablocks configured for the data. Data in intermediate format may be stored in non-volatile random access memory or in a portion of the non-volatile memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
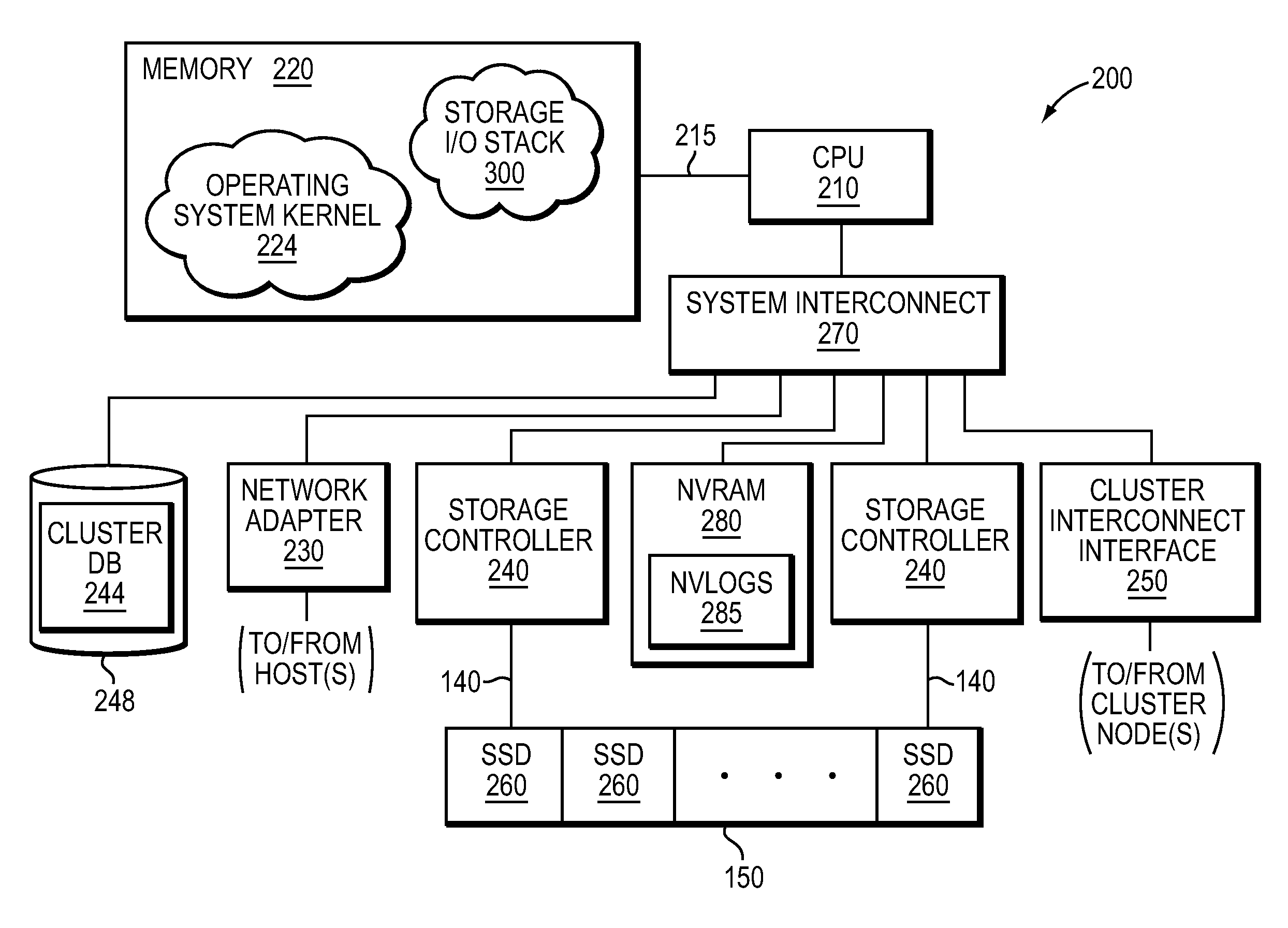
NVRAM caching and logging in a storage system
ActiveUS8898388B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersLatency (engineering)Solid-state drive
In one embodiment, non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) caching and logging delivers low latency acknowledgements of input / output (I / O) requests, such as write requests, while avoiding loss of data. Write data may be stored in a portion of an NVRAM configured as, e.g., a persistent write-back cache, while parameters of the request may be stored in another portion of the NVRAM configured as one or more logs, e.g., NVLogs. The write data may be organized into separate variable length blocks or extents and “written back” out-of-order from the write back cache to storage devices, such as solid state drives (SSDs). The write data may be preserved in the write-back cache until each extent is safely and successfully stored on SSD (i.e., in the event of power loss), or operations associated with the write request are sufficiently logged on NVLog.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
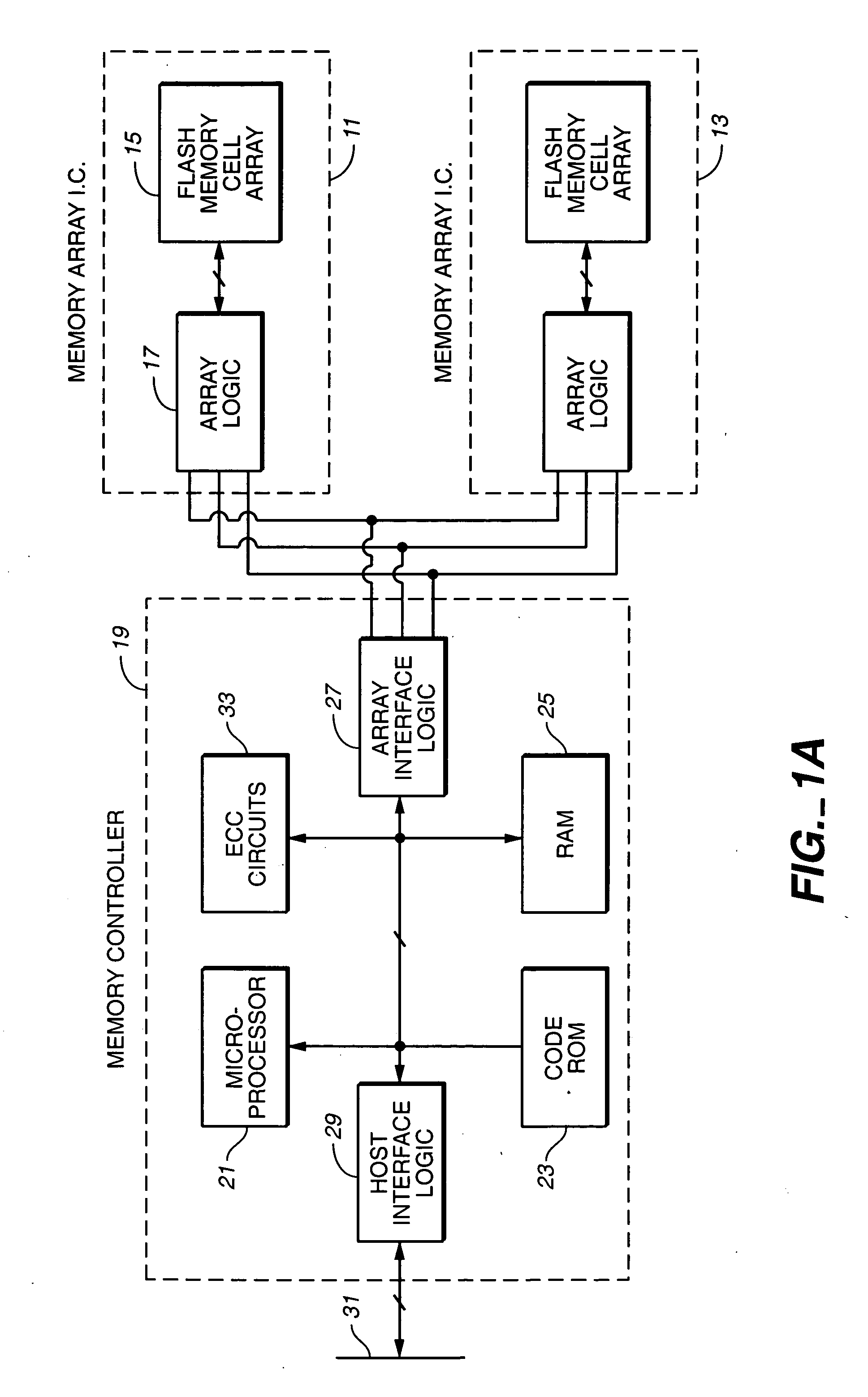
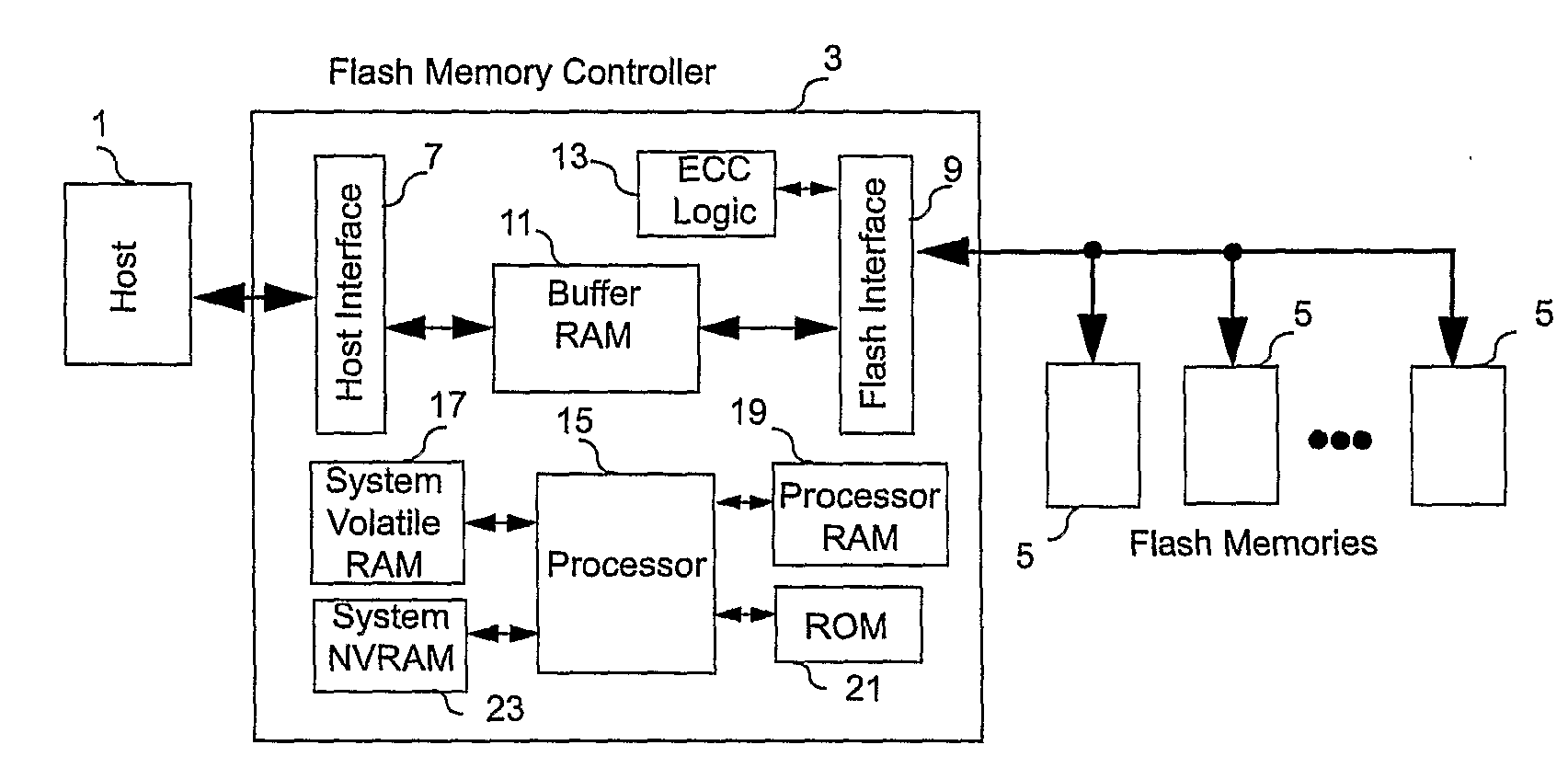
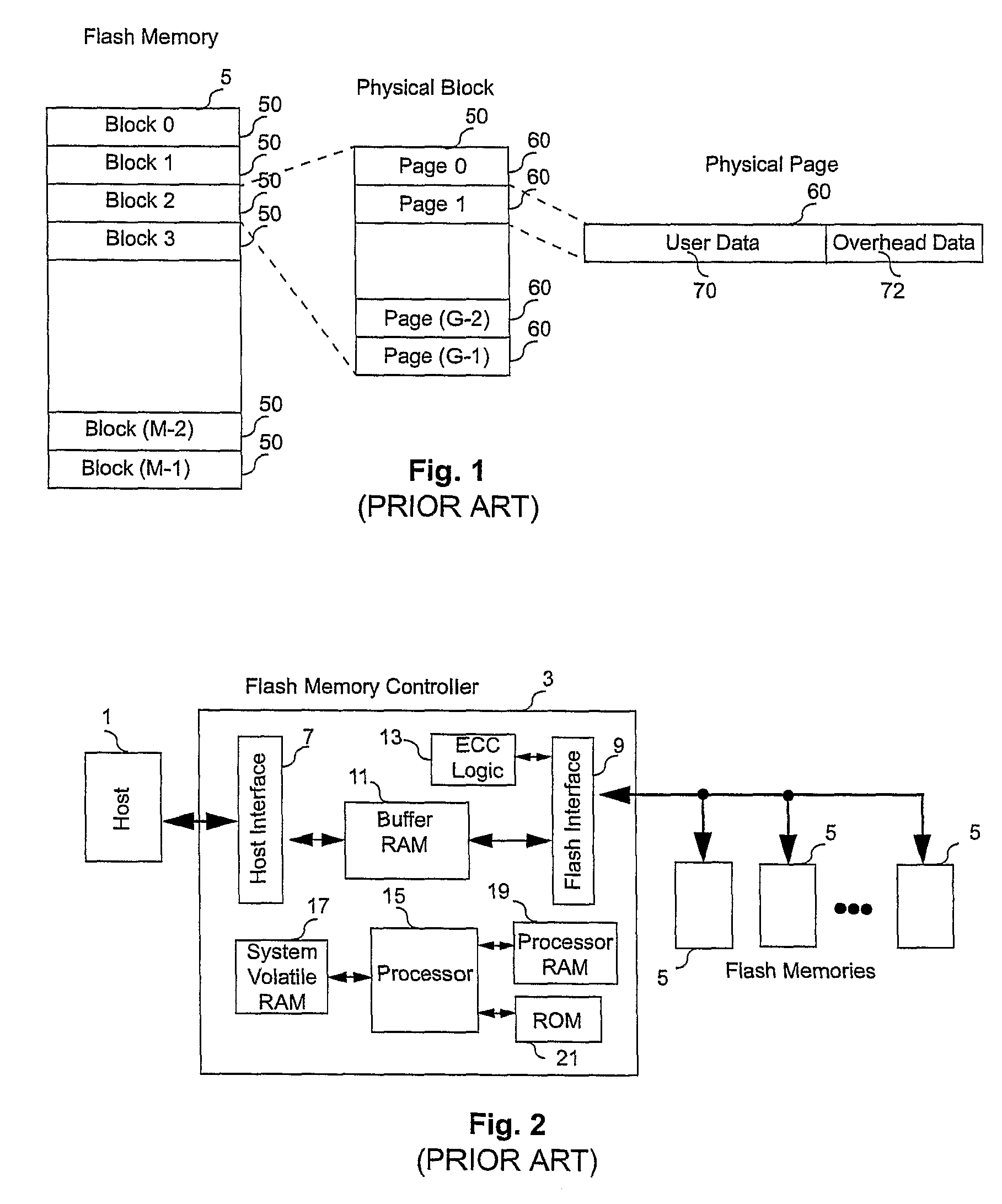
Controller for Non-Volatile Memories and Methods of Operating the Memory Controller
ActiveUS20080270680A1Improve system performanceReduce stepsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesMemory controllerByte
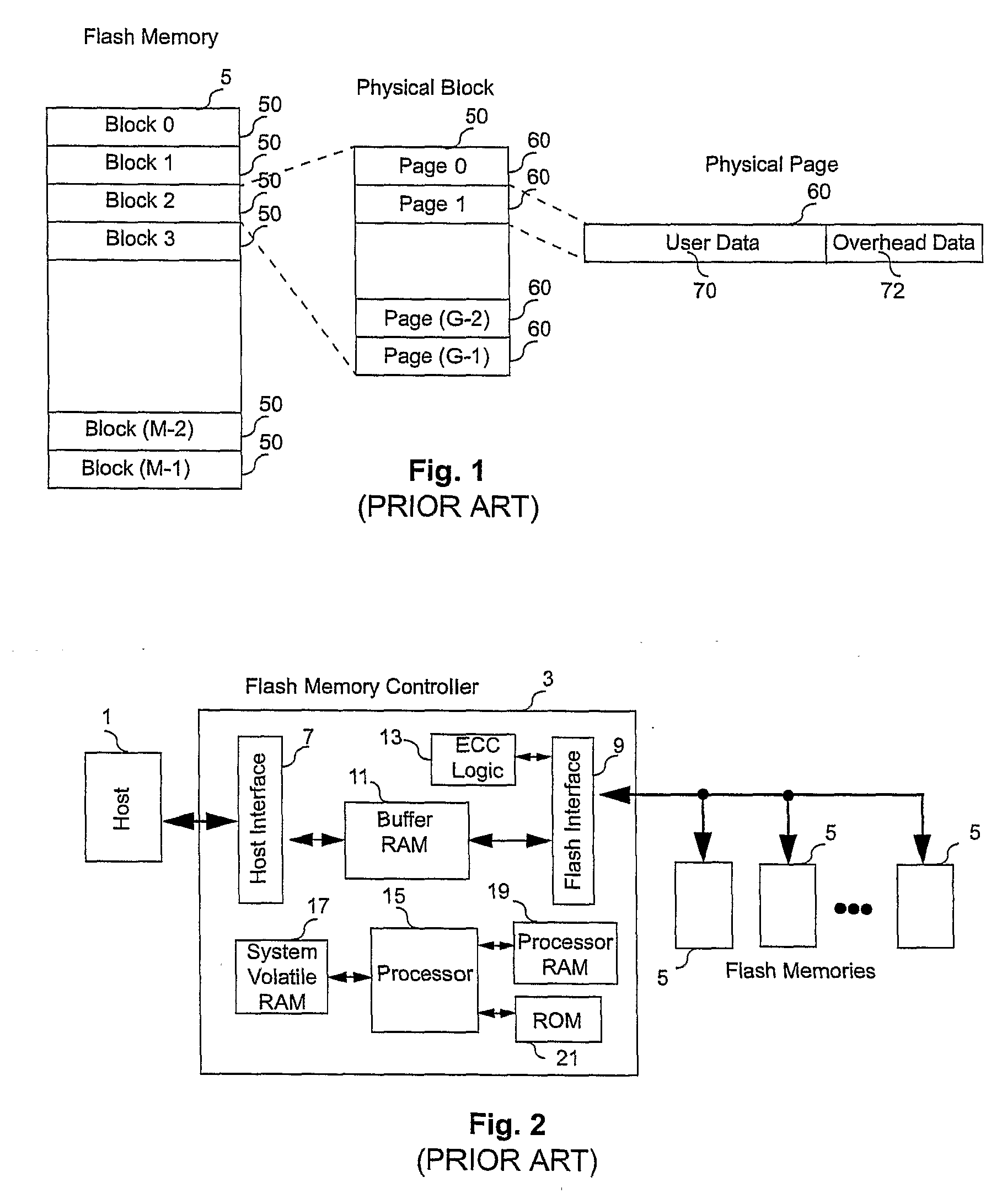
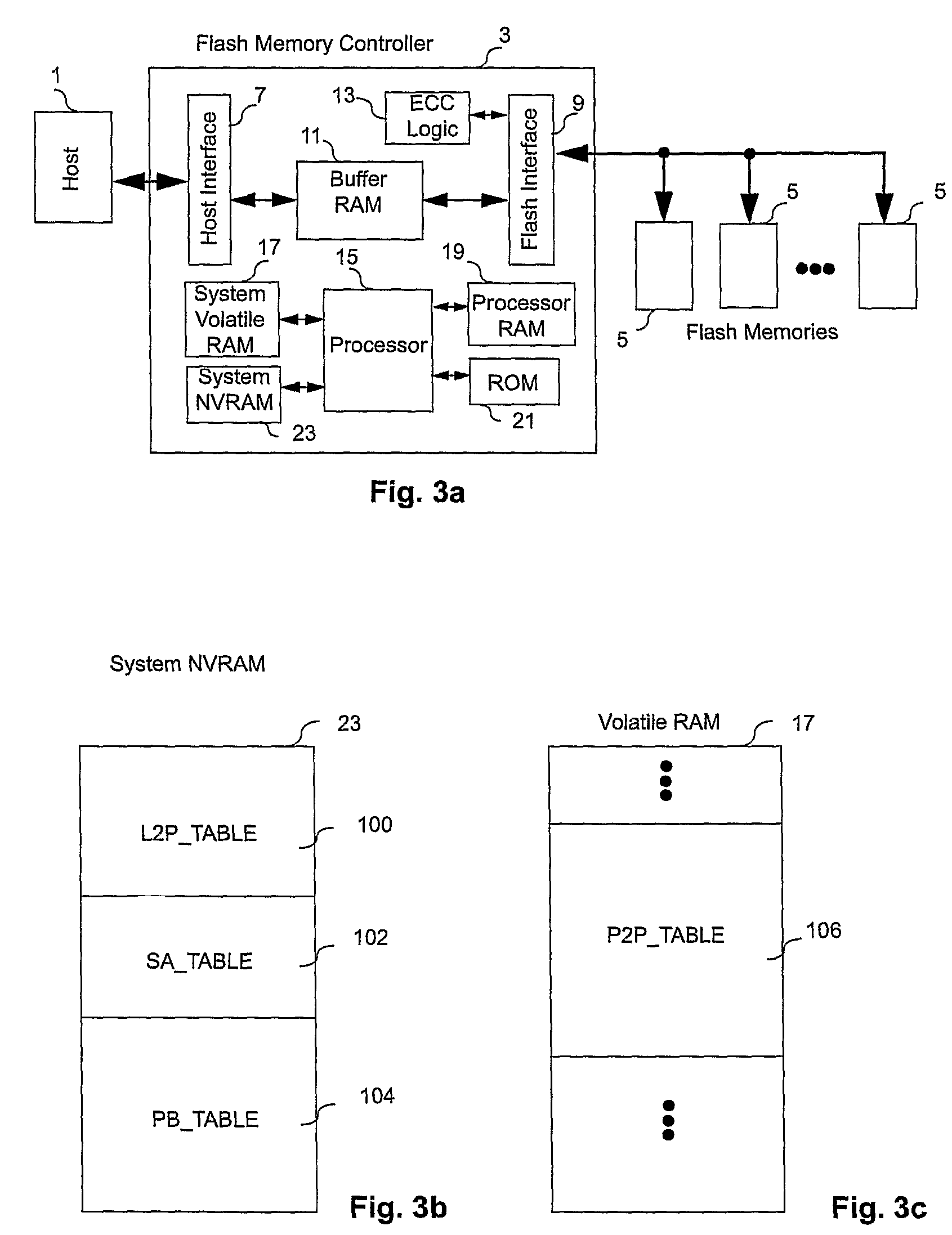
A non-volatile memory system (3) is proposed consisting of a first non-volatile flash memory (5) having a plurality of blocks, each block having a plurality of pages, each block being erasable and each page being programmable, and a second non-volatile random access memory (23) having a plurality of randomly accessible bytes. The second non-volatile memory (23) stores data for mapping logical blocks to physical blocks and status information of logical blocks. Each logical block has an associated physical page pointer stored in the second non-volatile memory (23) that identifies the next free physical page of the mapped physical block to be written. The page pointer is incremented after every page write to the physical block, allowing all physical pages to be fully utilized for page writes. Furthermore, a method of writing and reading data is disclosed whereby the most recently written physical page associated with a logical address is identifiable by the memory system without programming flags into superseded pages, or recording time stamp values in any physical page or block of the first non-volatile memory (5). Furthermore, a method is provided for a logical block to be mapped to two physical blocks instead of one to provide additional space for page writes, resulting in reduction in page copy operations, thereby increasing the performance of the system.
Owner:CHANG CHEE KENG
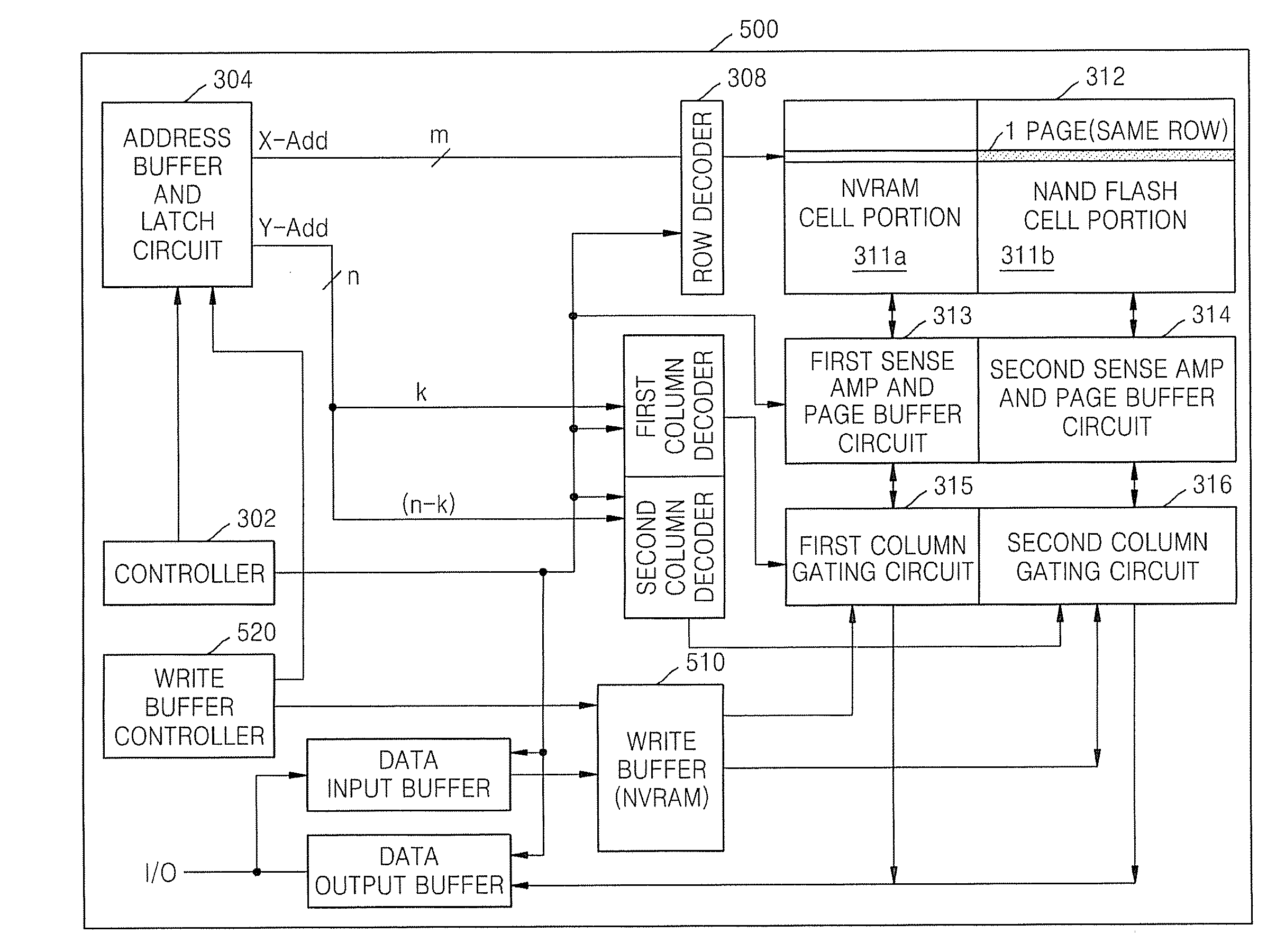
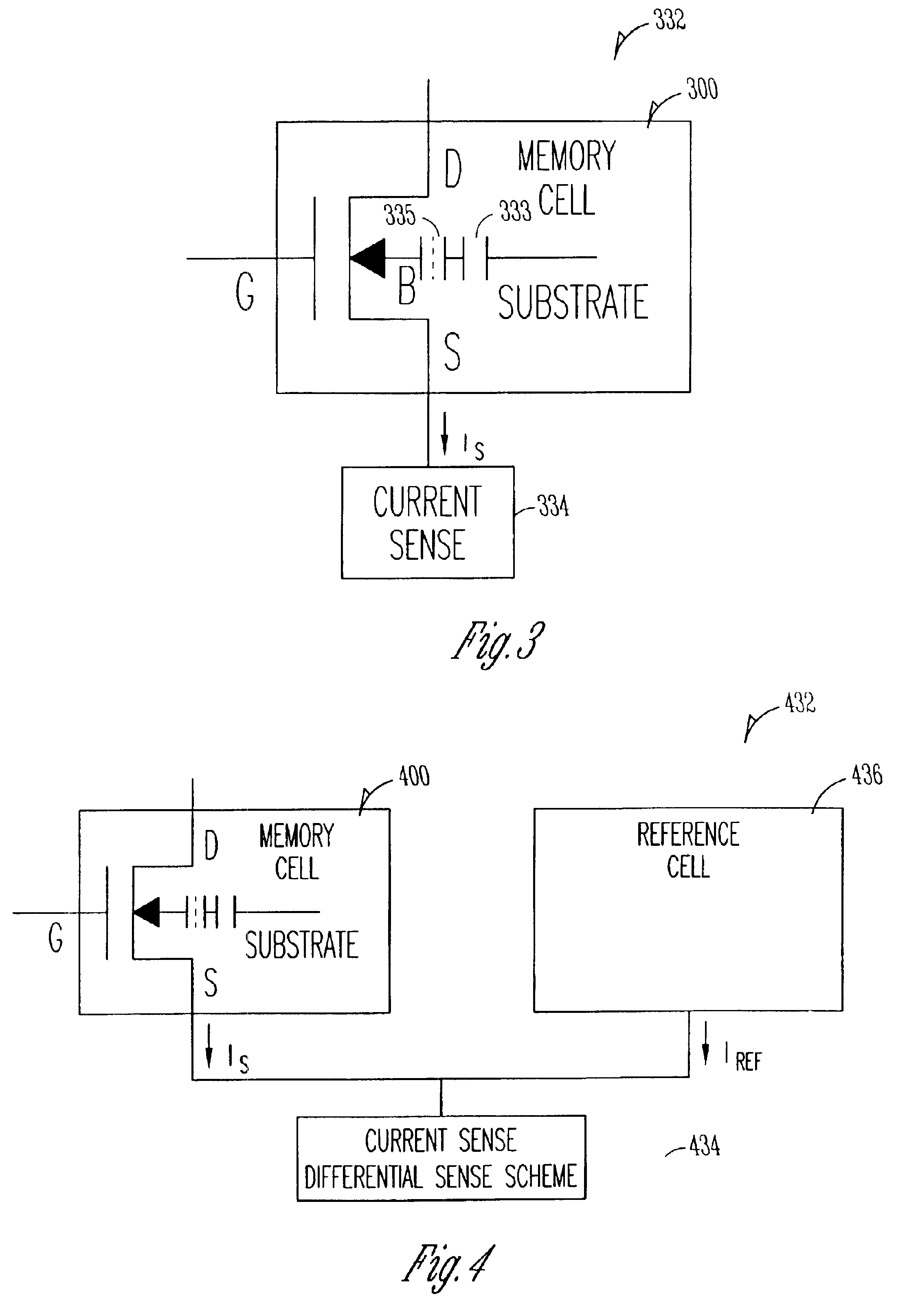
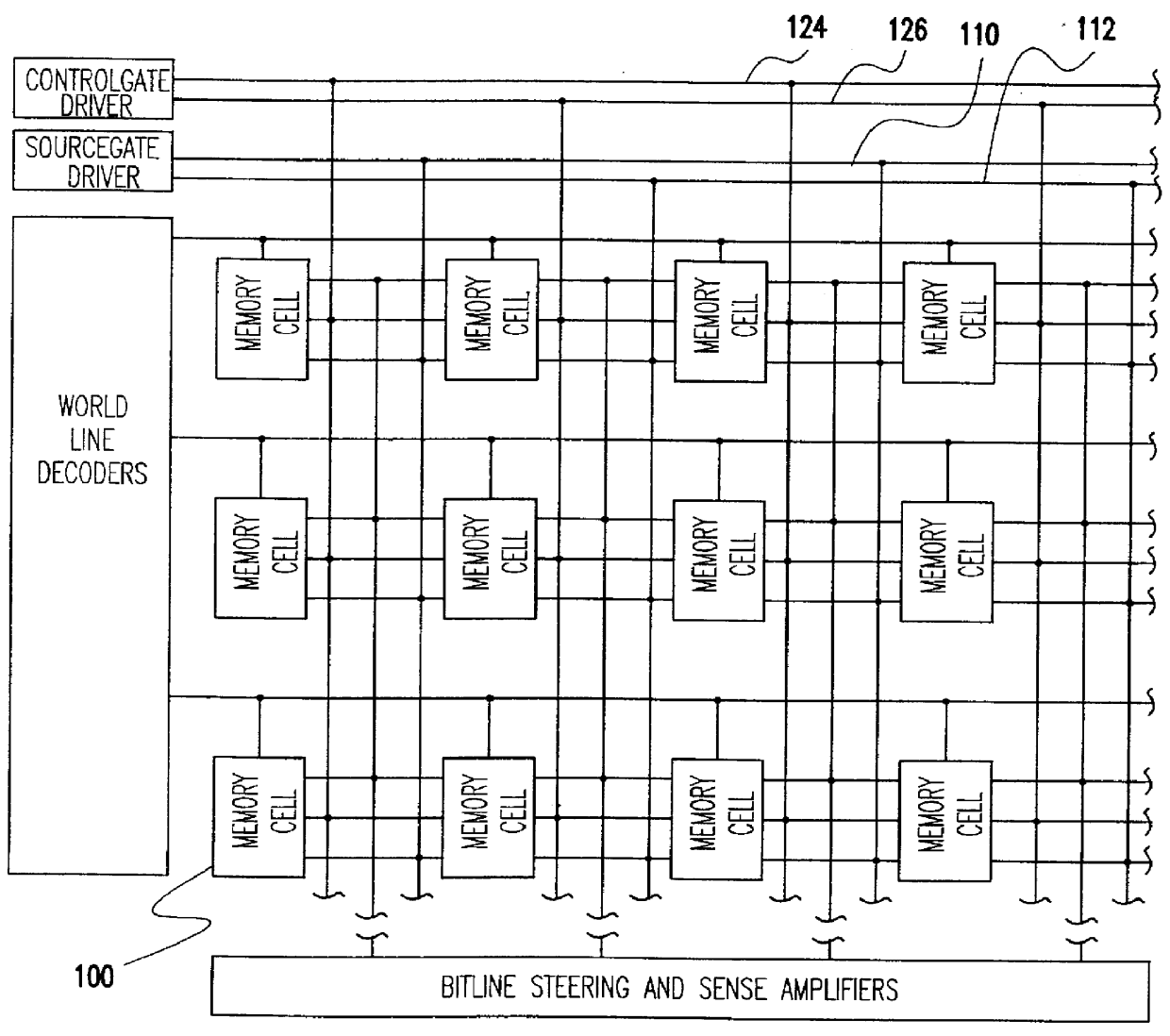
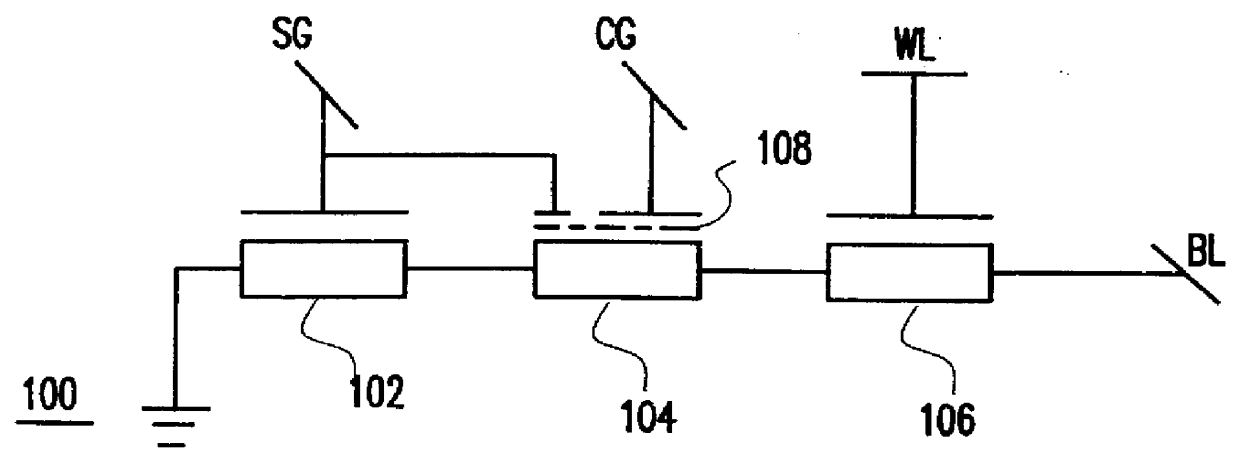
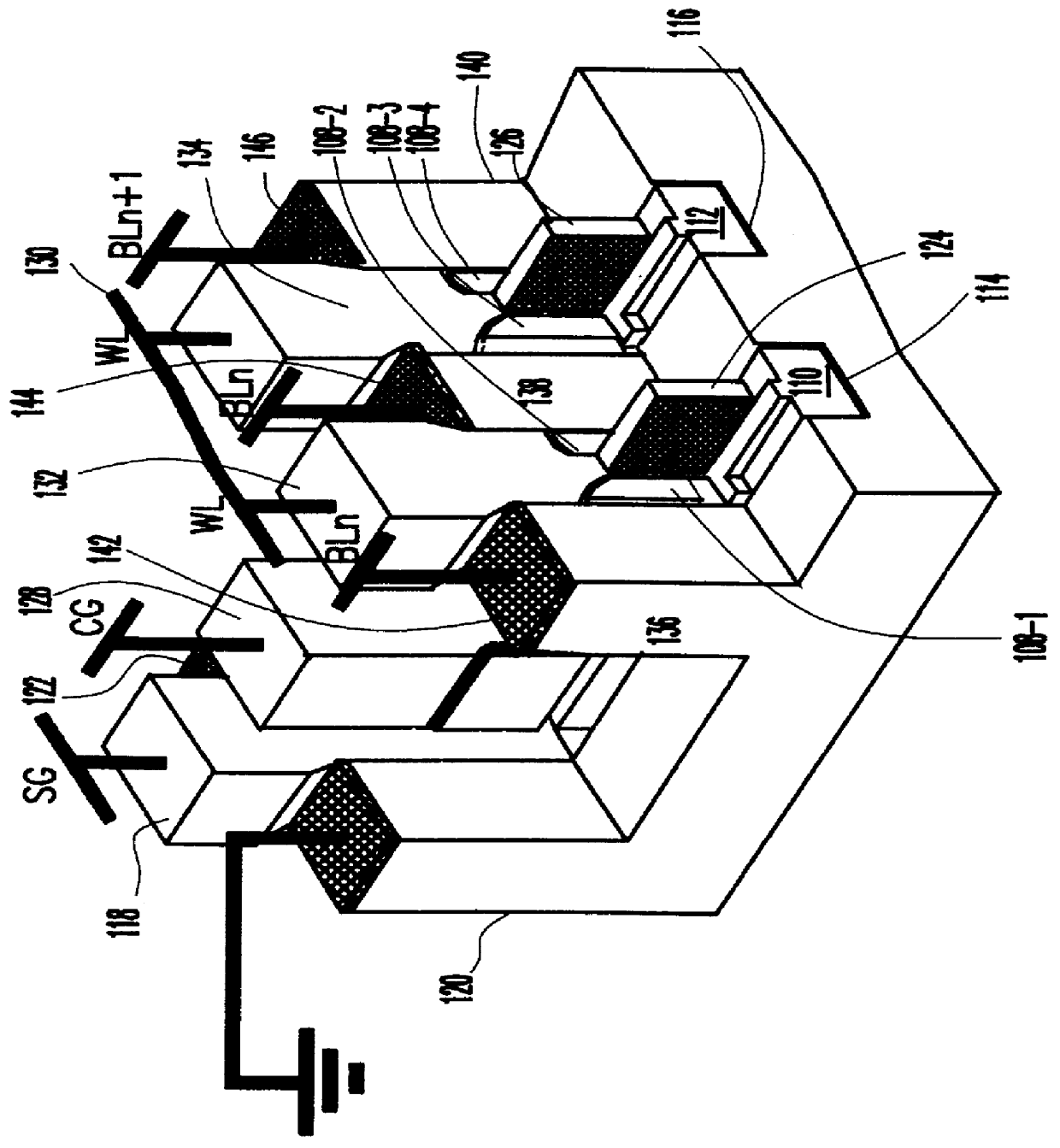
Memory device employing NVRAM and flash memory cells
A memory device includes a memory cell array including a NAND flash cell portion including a plurality of first columns of serially-connected flash memory cells and a non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) cell portion including a plurality of second columns of NVRAM cells. The flash memory cells and the NVRAM cells are arranged such that respective word lines are connected to flash memory cells and NVRAM cells in each of respective rows, which may correspond to page units including flash memory cells and NVRAM cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
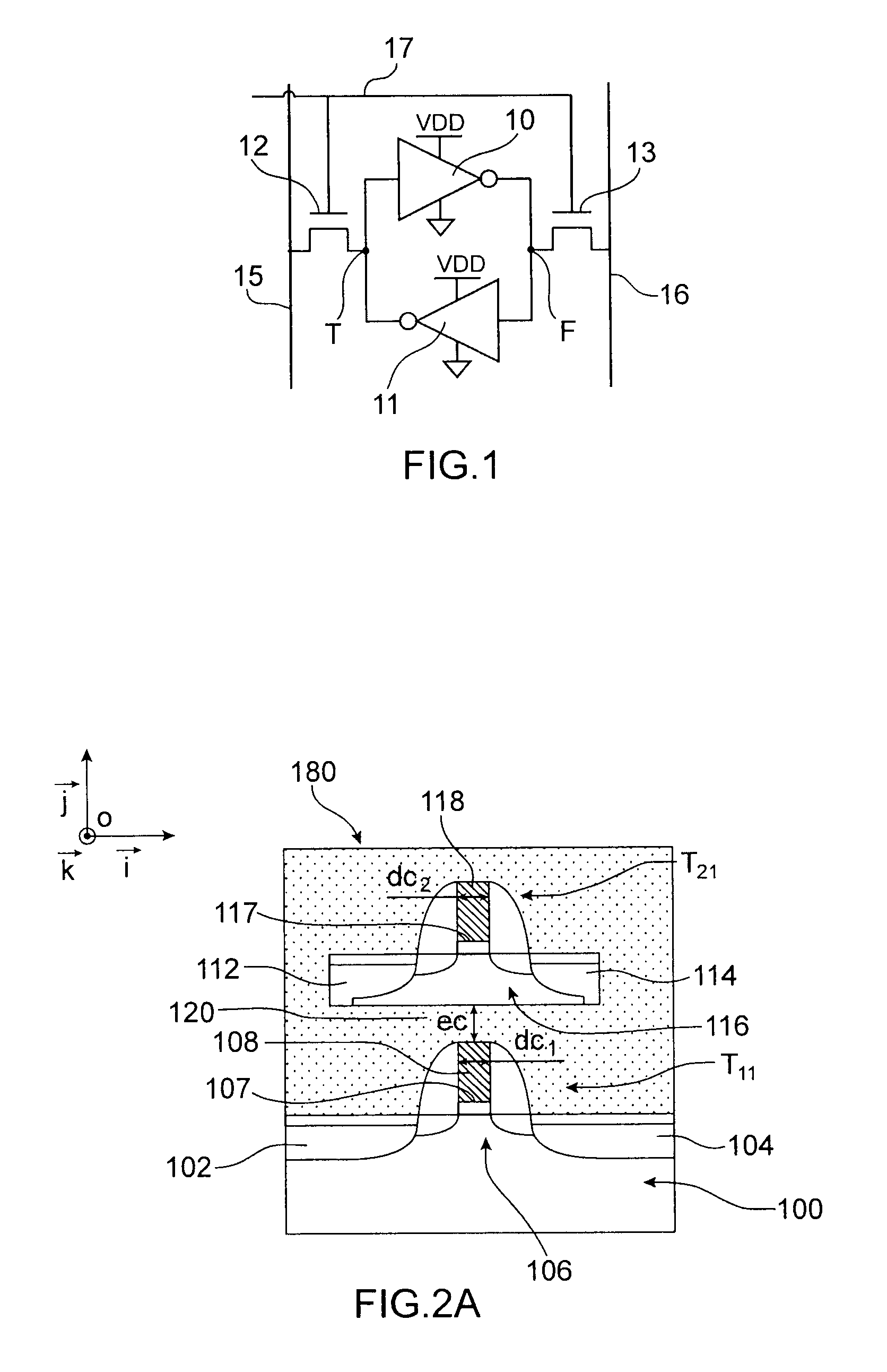
SRAM memory cell having transistors integrated at several levels and the threshold voltage vt of which is dynamically adjustable
ActiveUS20090294861A1Improve integration densityImprove electrical performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineCoupling
A non-volatile random access memory cell which, on a substrate surmounted by a stack of layers, comprises:a first plurality of transistors situated at a given level of the stack of which at least one first access transistor and at least one second access transistor, which are arranged between a first bit line and a first storage node, and between a second bit line and a second storage node, respectively, the first access transistor and the second access transistor having a gate connected to a word line,a second plurality of transistors forming a flip-flop and situated at, at least one other level of the stack, beneath said given level,the transistors of the second plurality of transistors each comprising a gate electrode situated opposite a channel region of a transistor of the first plurality of transistors and separated from this channel region by means of an insulating region provided to enable coupling of said gate electrode and said channel region.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
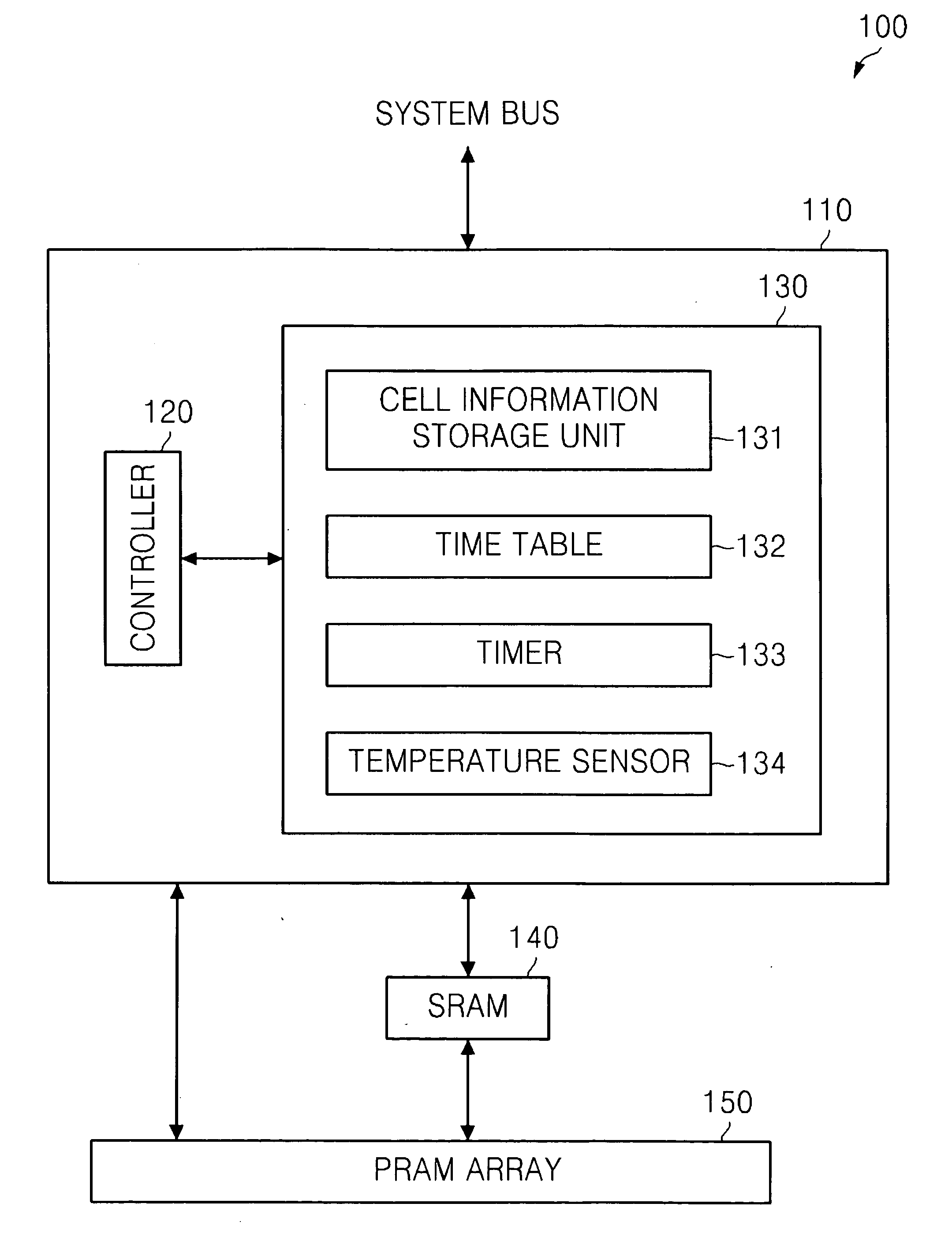
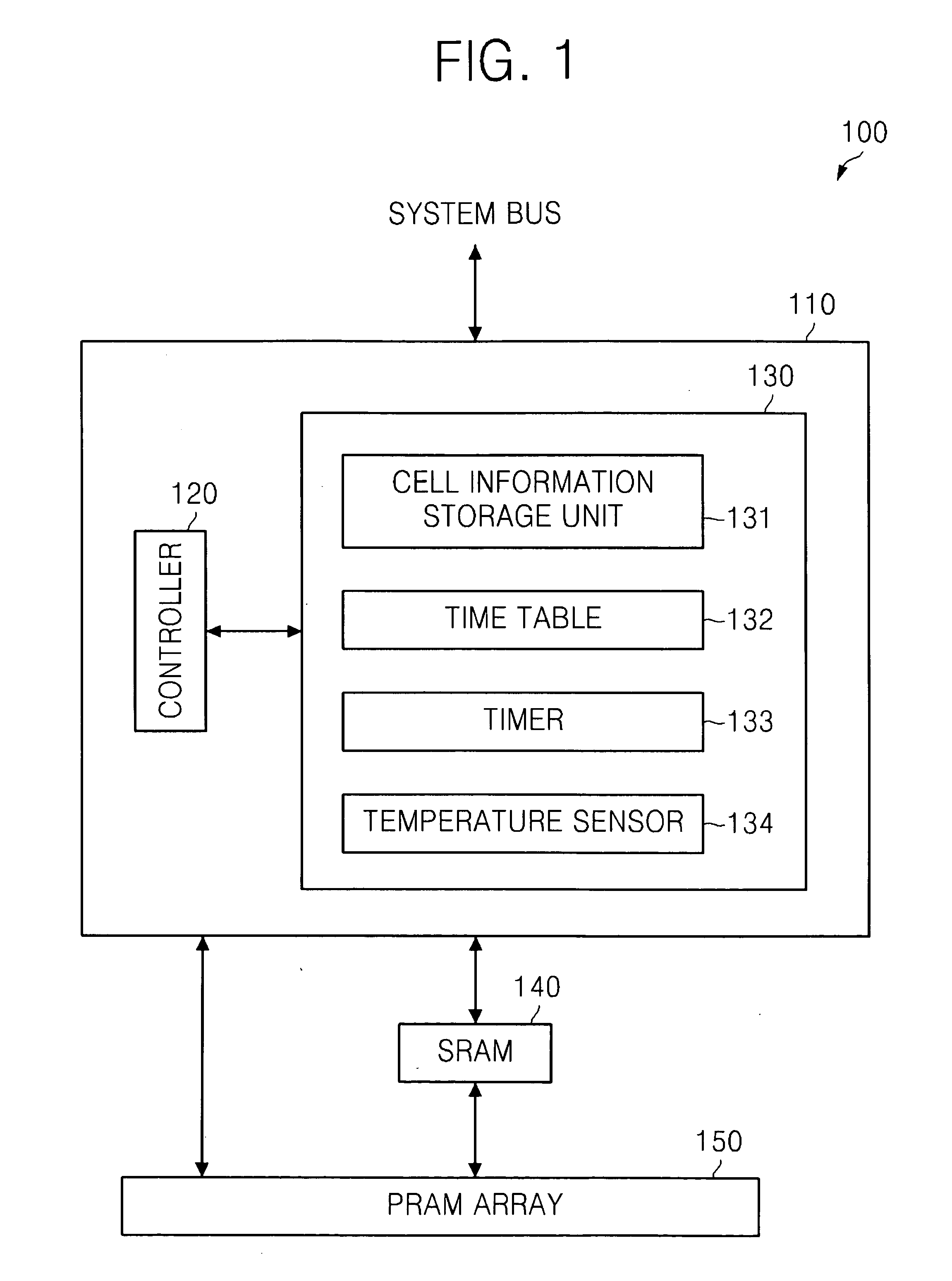
Non-volatile RAM, and solid state drive and computer system including the same
ActiveUS20100259998A1Reduce the likelihood of failureReduce and prevent likelihoodRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputerized systemSolid-state drive
The non-volatile random access memory (RAM) includes a non-volatile RAM array, a buffer configured to buffer data to be programmed in the non-volatile RAM array and configured to buffer data read from the non-volatile RAM array, and a control block configured to read data from at least one of the non-volatile RAM array and the buffer based on whether the data to be read has been stored in the buffer, a temperature when the data was programmed, and a time lapse since the programming of the data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
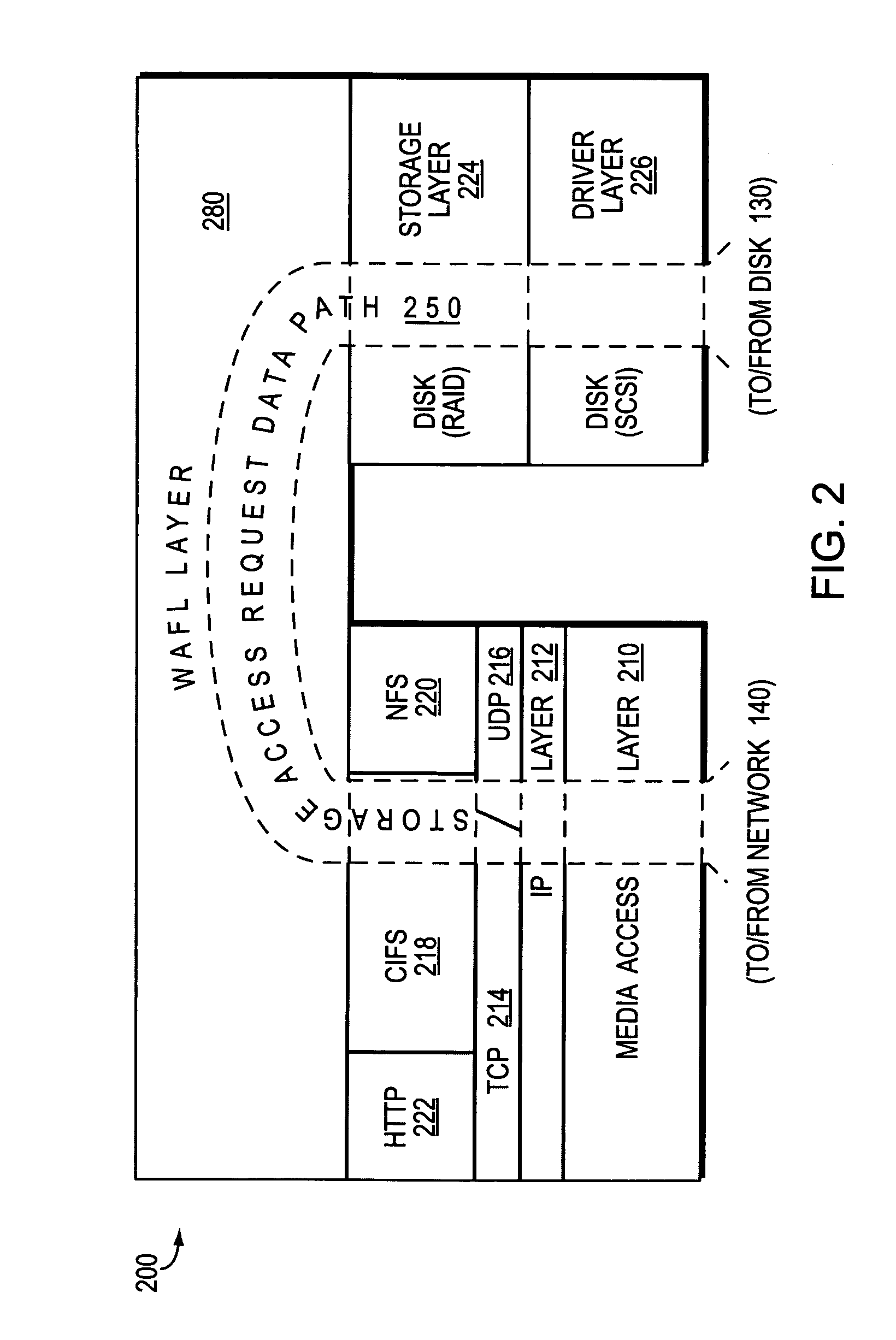
System and method for parallelized replay of an NVRAM log in a storage appliance
InactiveUS7249150B1Avoid mistakesError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemClient-side
A system and method for enabling parallel replay of a backup memory log of client transaction request entries to a network storage appliance file system is provided. The backup memory is typically implemented as a non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM). An initiator establishes a swarm of messages with a plurality of transaction blocks pointing to logged request entries and related states associated therewith. The states represent the various phases of file system recovery and disk storage including a retrieval of disk information (data and meta-data), typically in the form of a LOAD, and a subsequent modify phase. The swarm is transferred to the file system for parallel disk information-retrieval in an interleaved process. Any transactions that cannot be performed due to a required prerequisite action (e.g. a prior file-create) are returned to the initiator for reloading once the prerequisite action has occurred.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Low-cost non-volatile flash-ram memory
ActiveUS20090046501A1Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer hardwareNon-volatile random-access memory
A flash-RAM memory includes non-volatile random access memory (RAM) formed on a monolithic die and non-volatile page-mode memory formed on top of the non-volatile RAM, the non-volatile page-mode memory and the non-volatile RAM reside on the monolithic die.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
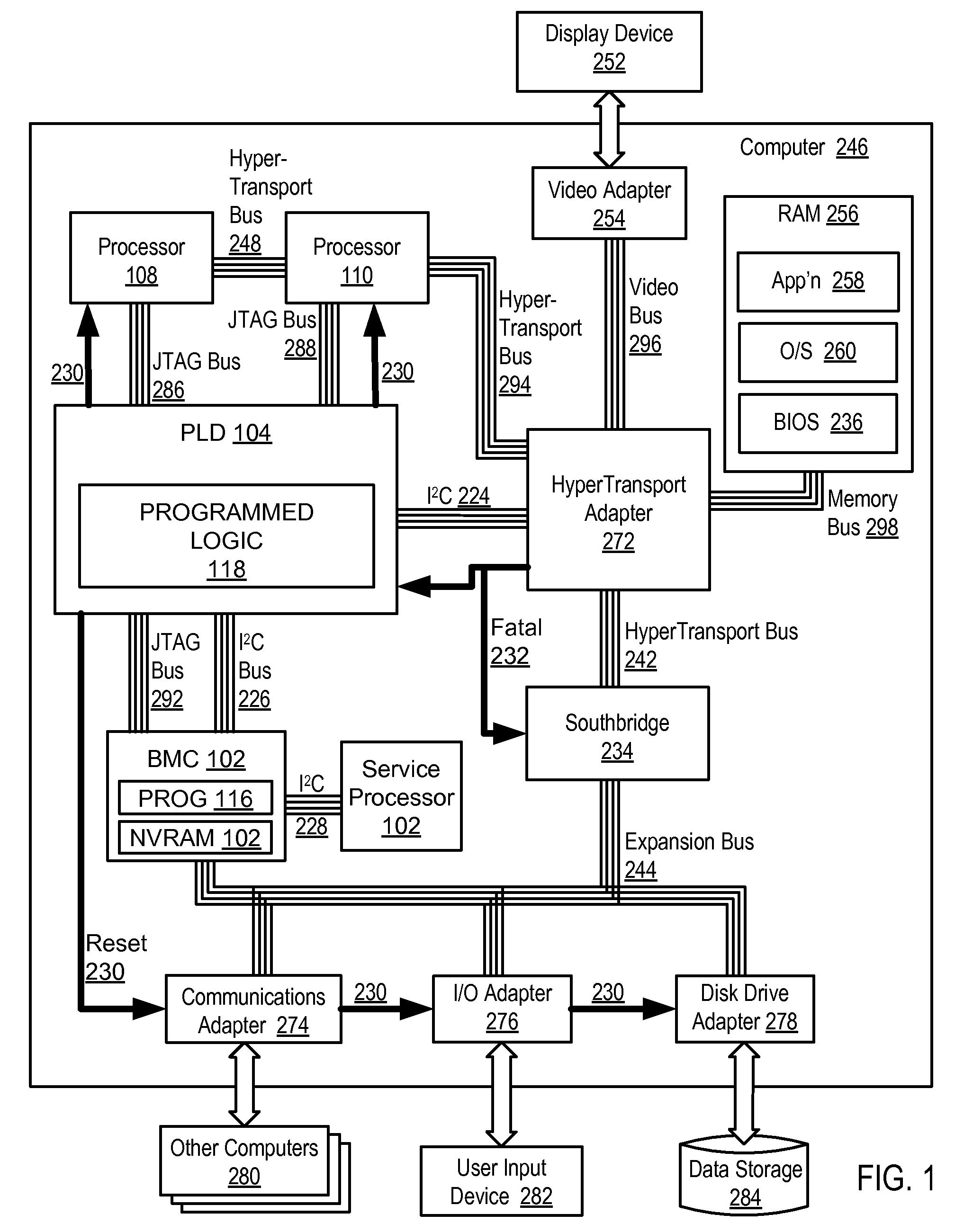
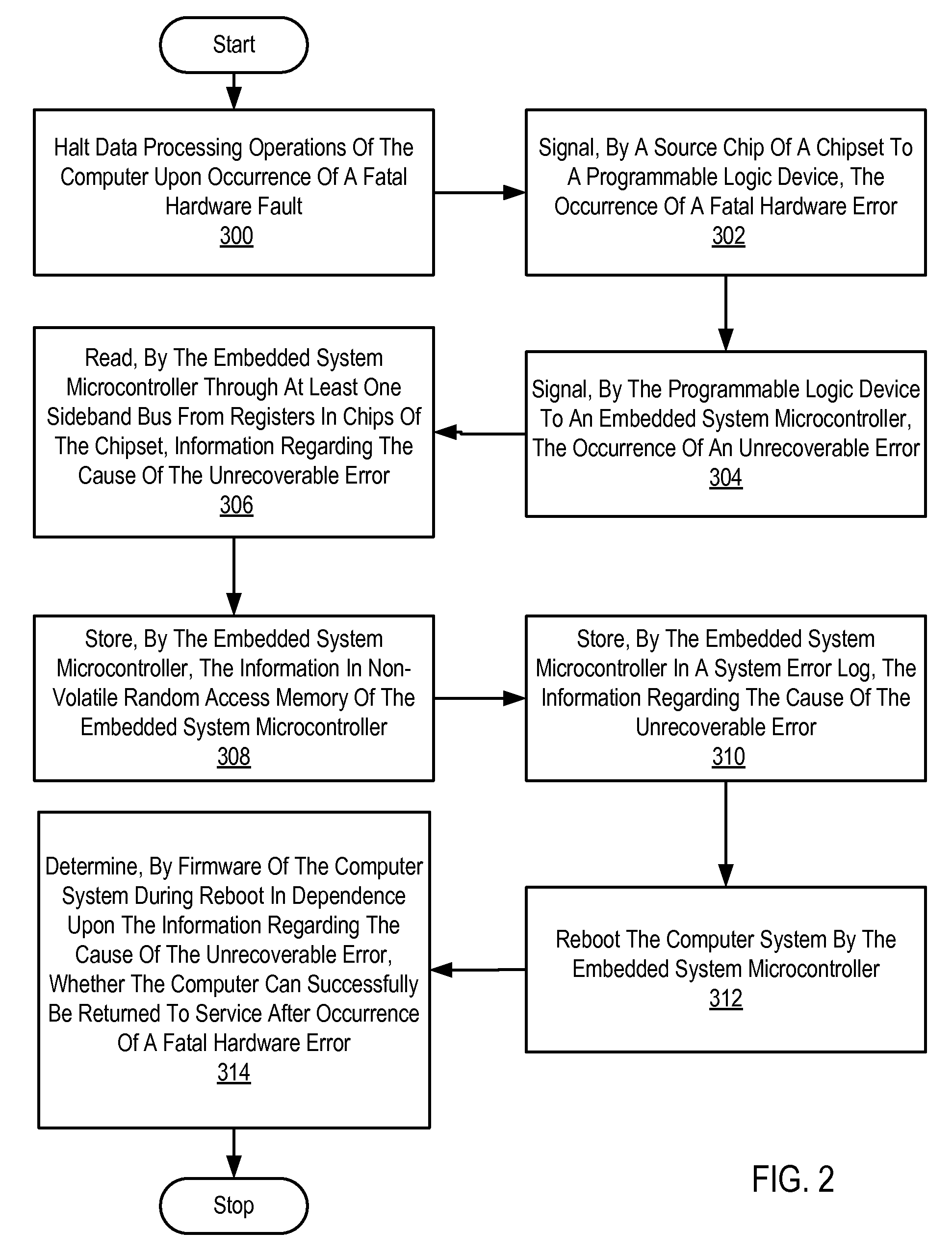
Handling Fatal Computer Hardware Errors
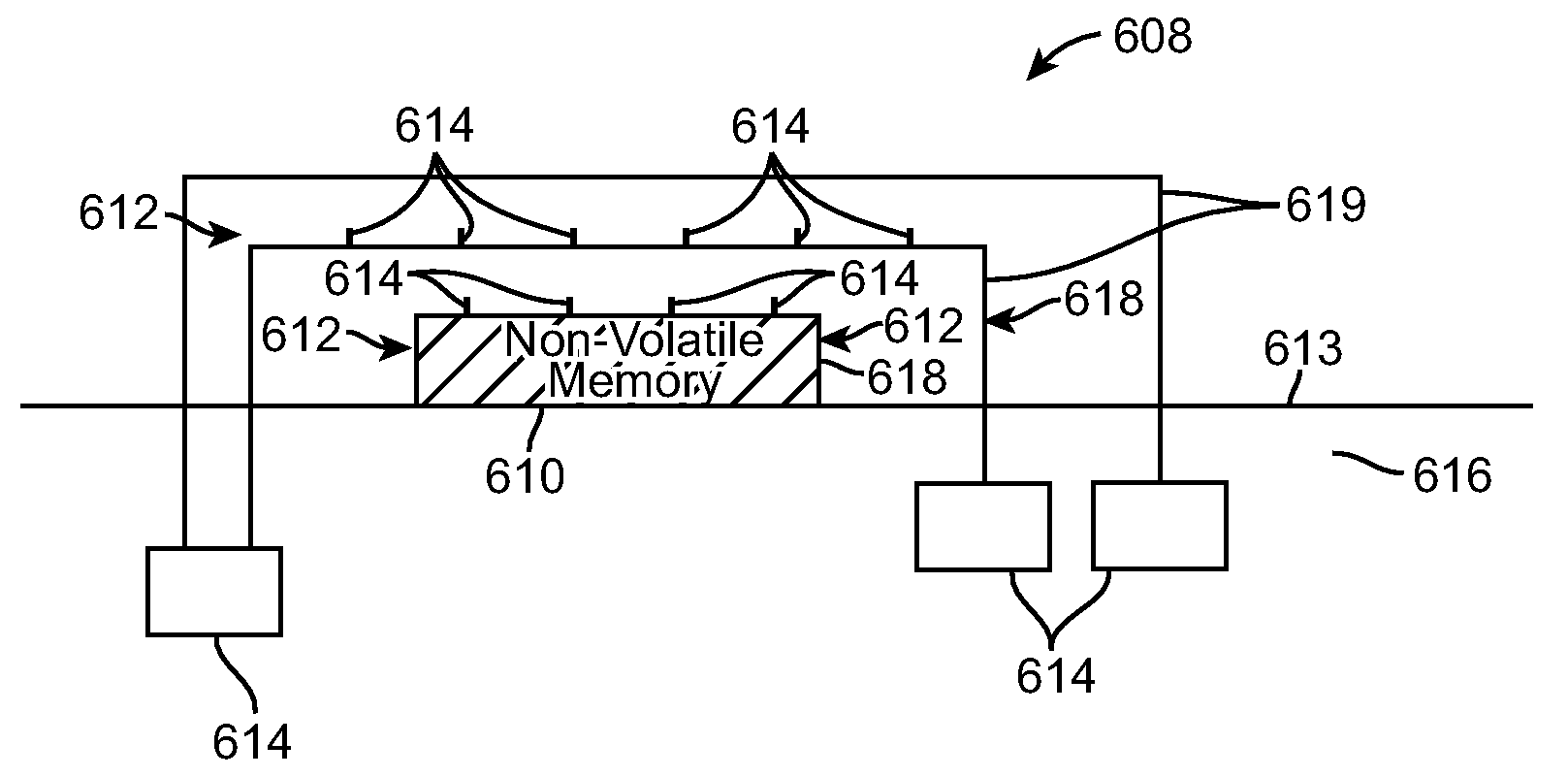
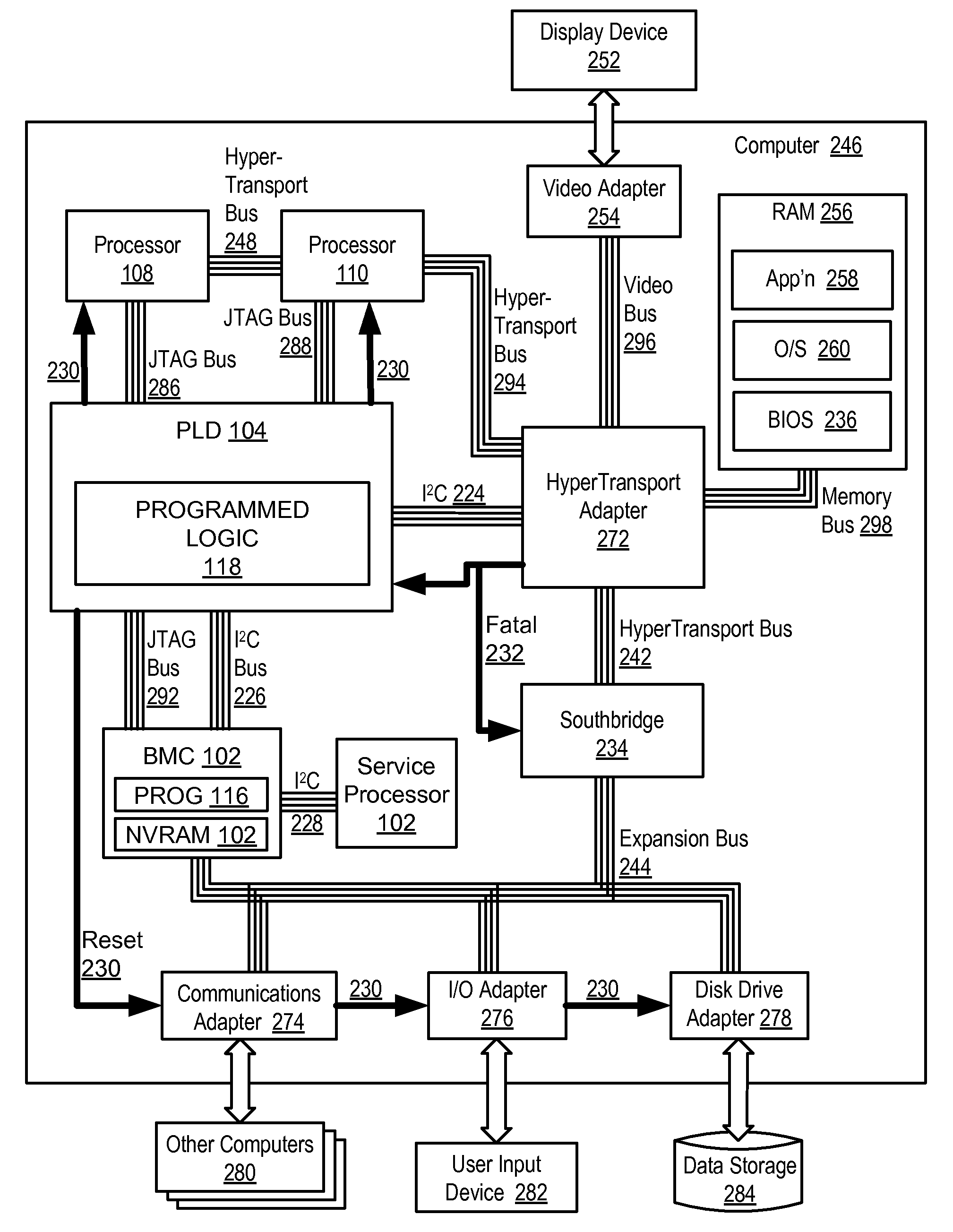
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for handling fatal computer hardware errors on a computer that include halting data processing operations of the computer upon occurrence of a fatal hardware error; signaling by a source chip of a chipset to the programmable logic device the occurrence of a fatal hardware error; signaling by the programmable logic device to an embedded system microcontroller the occurrence of a fatal hardware error; reading by the embedded system microcontroller through at least one sideband bus from registers in chips of the chipset information regarding the cause of the fatal hardware error; and storing by the embedded system microcontroller the information in non-volatile random access memory of the embedded system microcontroller.
Owner:IBM CORP
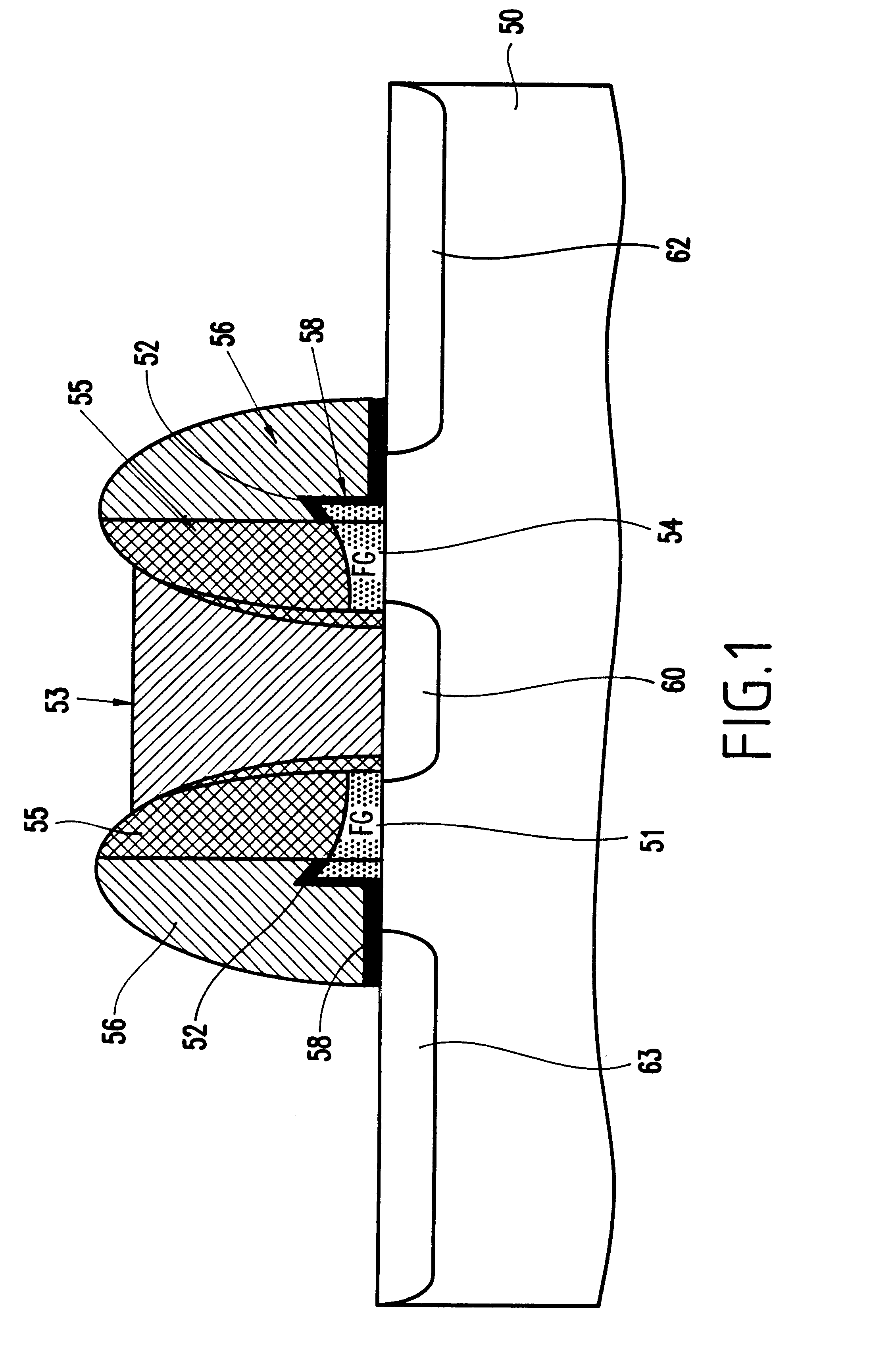
One transistor SOI non-volatile random access memory cell
InactiveUS6888200B2Long charge retention and non-volatilityHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesTrappingRandom access memory
One aspect of the present subject matter relates to a memory cell, or more specifically, to a one-transistor SOI non-volatile memory cell. In various embodiments, the memory cell includes a substrate, a buried insulator layer formed on the substrate, and a transistor formed on the buried insulator layer. The transistor includes a floating body region that includes a charge trapping material. A memory state of the memory cell is determined by trapped charges or neutralized charges in the charge trapping material. The transistor further includes a first diffusion region and a second diffusion region to provide a channel region in the body region between the first diffusion region and the second diffusion region. The transistor further includes a gate insulator layer formed over the channel region, and a gate formed over the gate insulator layer. Other aspects are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
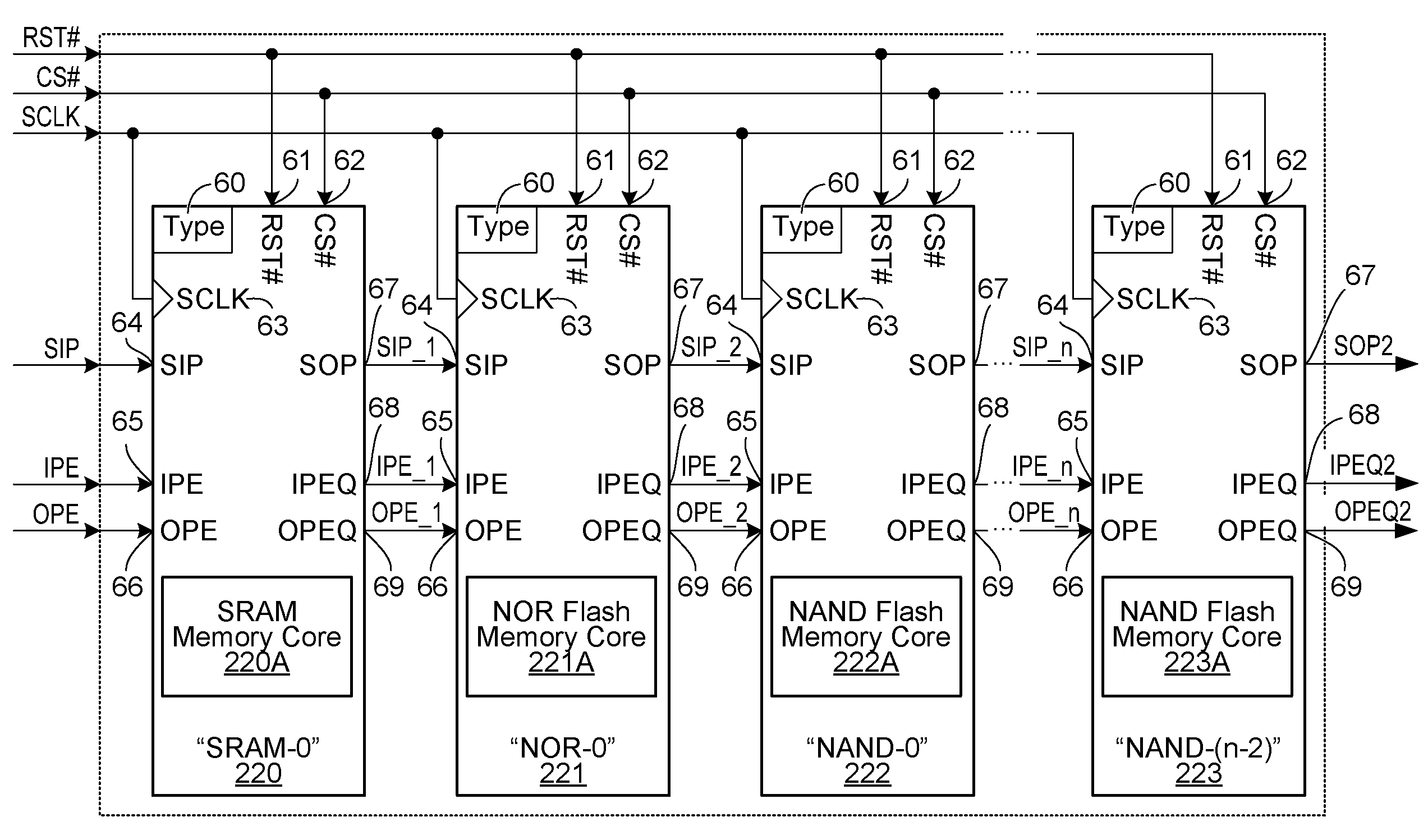
System and method of operating memory devices of mixed type
InactiveUS20080140916A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesHybrid typeStatic random-access memory
A memory system architecture is provided in which a memory controller controls memory devices in a serial interconnection configuration. The memory controller has an output port for sending memory commands and an input port for receiving memory responses for those memory commands requisitioning such responses. Each memory device includes a memory, such as, for example, NAND-type flash memory, NOR-type flash memory, random access memory and static random access memory. Each memory command is specific to the memory type of a target memory device. A data path for the memory commands and the memory responses is provided by the interconnection. A given memory command traverses memory devices in order to reach its intended memory device of the serial interconnection configuration. Upon its receipt, the intended memory device executes the given memory command and, if appropriate, sends a memory response to a next memory device. The memory response is transferred to the memory controller.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
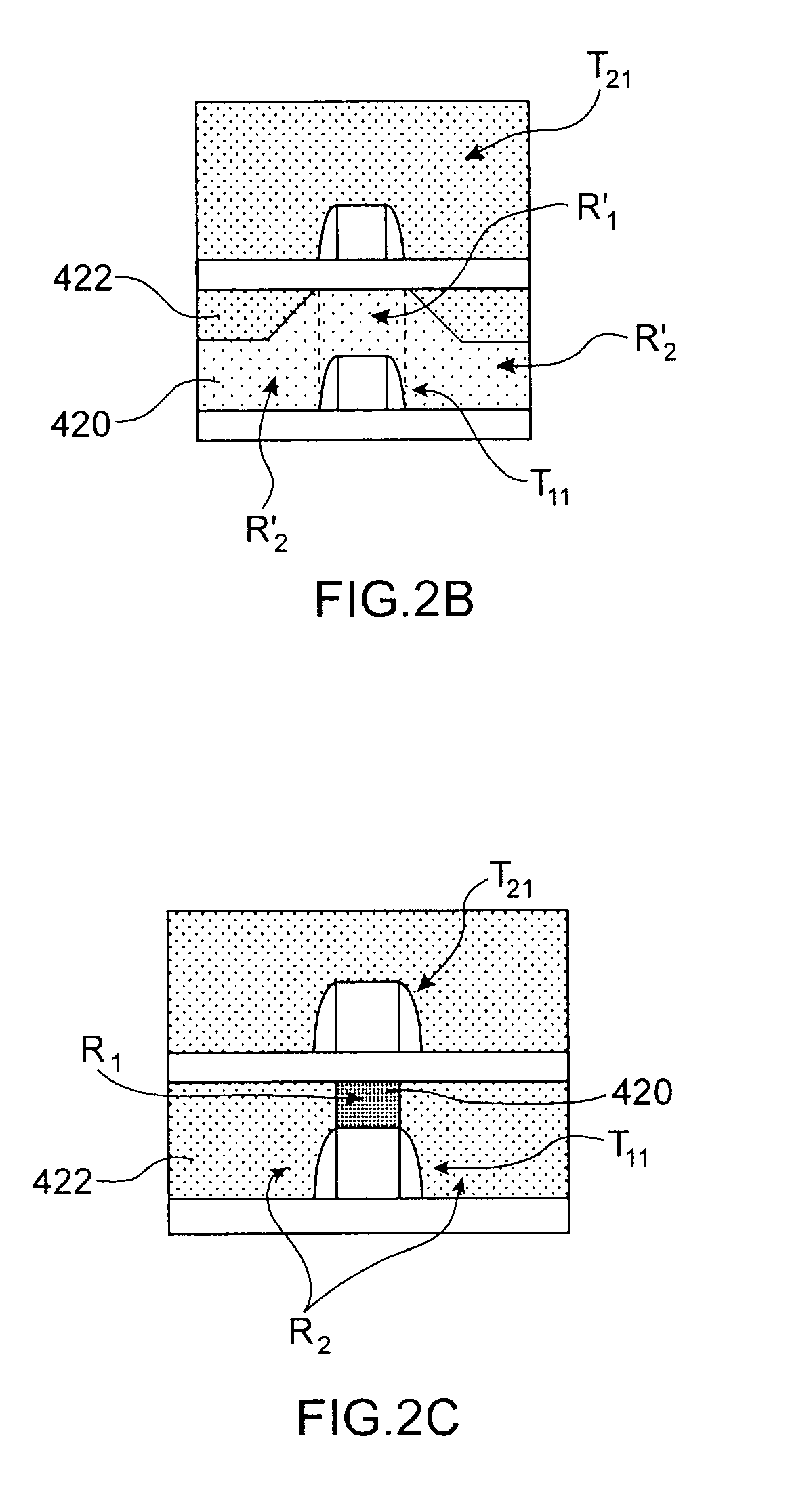
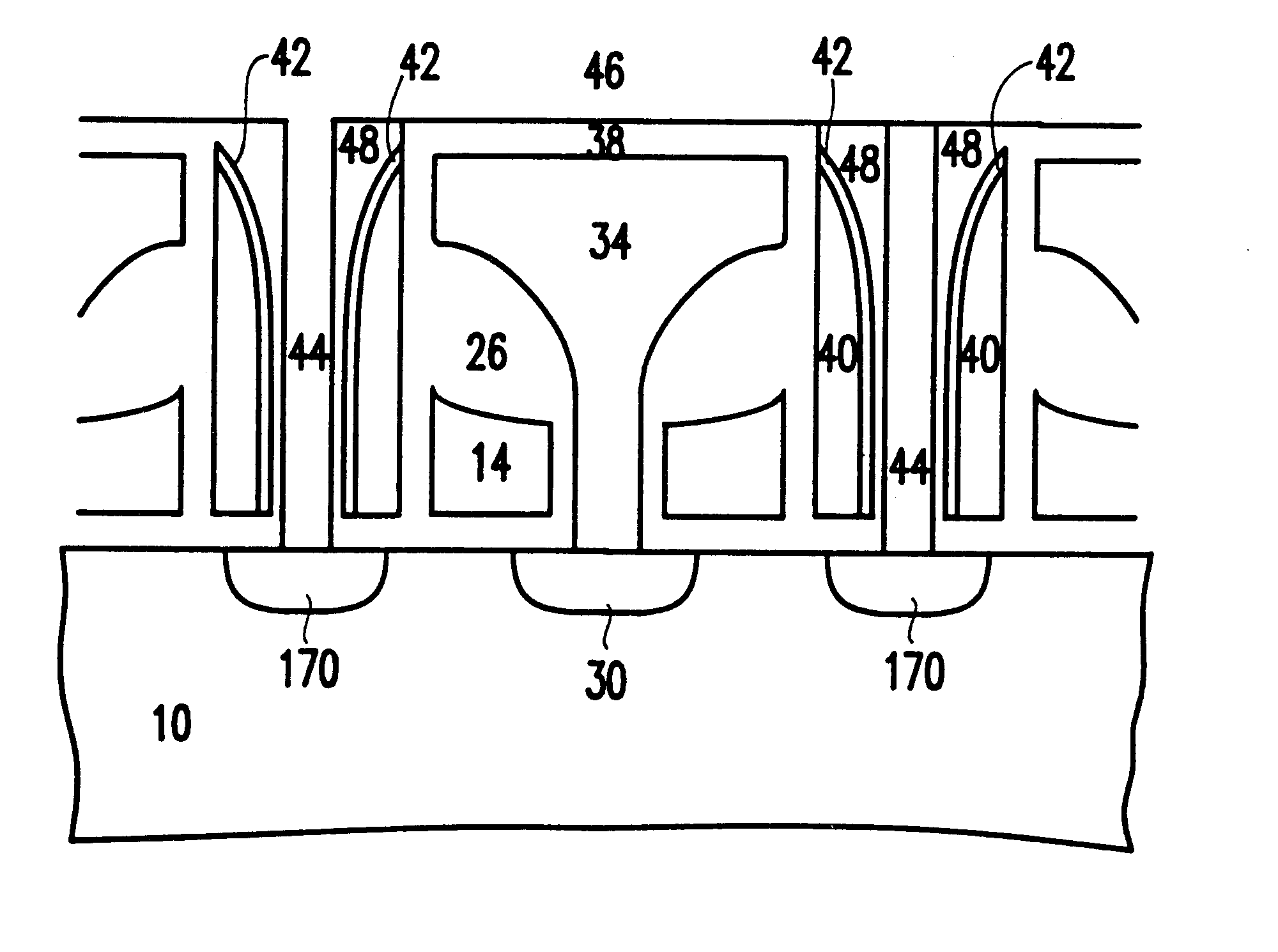
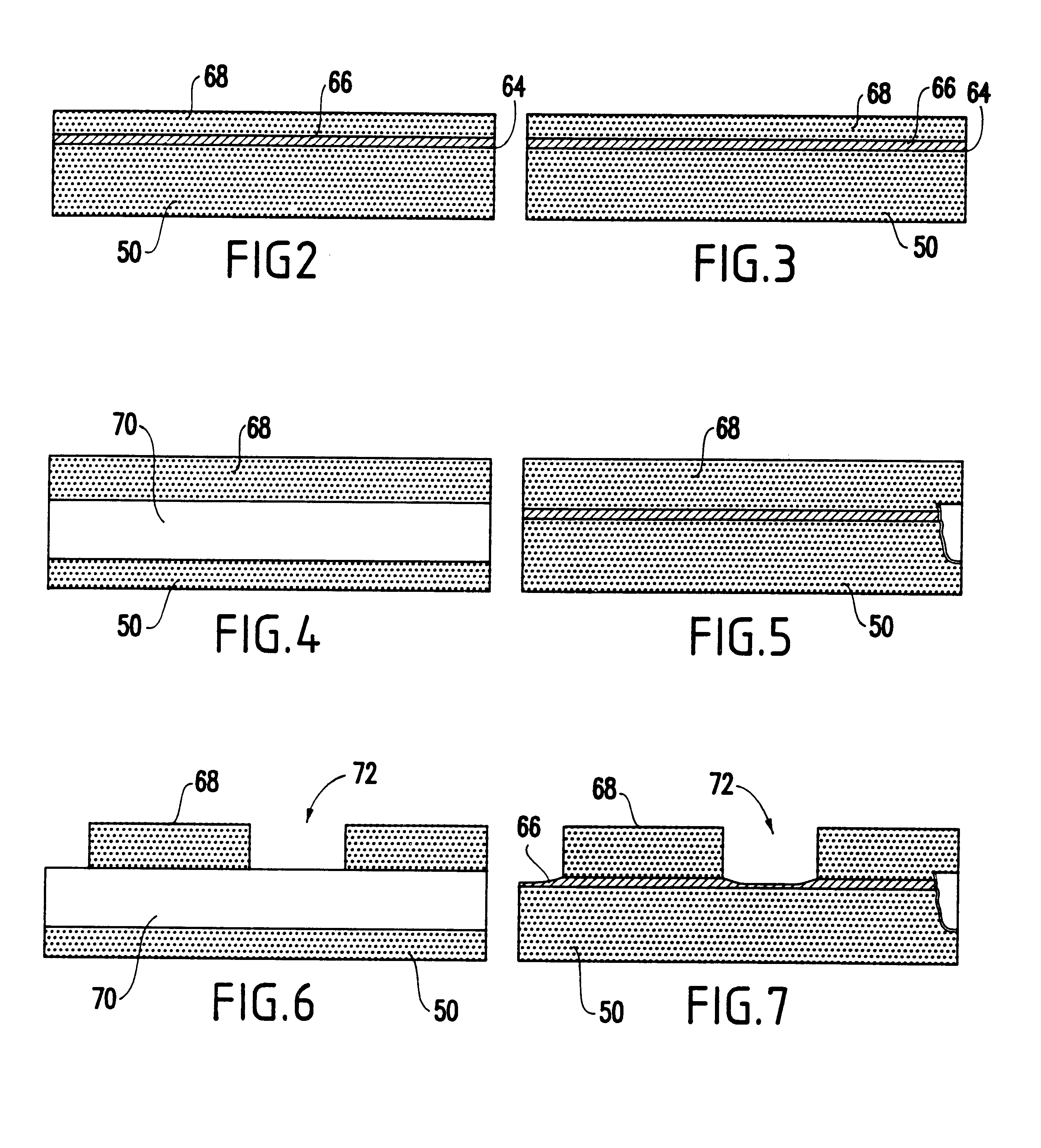
Self-aligned non-volatile random access memory cell and process to make the same
A self aligned method of forming a semiconductor memory array of floating gate memory cells in a semiconductor substrate has a plurality of spaced apart isolation regions on the substrate substantially parallel to one another. An active region is between each pair of adjacent isolation regions. The active and isolation regions are formed in parallel and in the column direction. In the row direction, strips of spaced apart silicon nitride are formed. A source line plug is formed between adjacent pairs of silicon nitride and is in contact with a first region in the active regions, and the isolation regions. The strips of silicon nitride are removed and isotropically etched. In addition, the materials beneath the silicon nitride are also isotropically etched. Polysilicon spacers are then formed in the row direction parallel to the source line plug and adjacent to the floating gates to form connected control gates. A second region is formed between adjacent, spaced apart, control gates. A bit line is formed in the bit line direction contacting the second region in the space between the control gates.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY +1
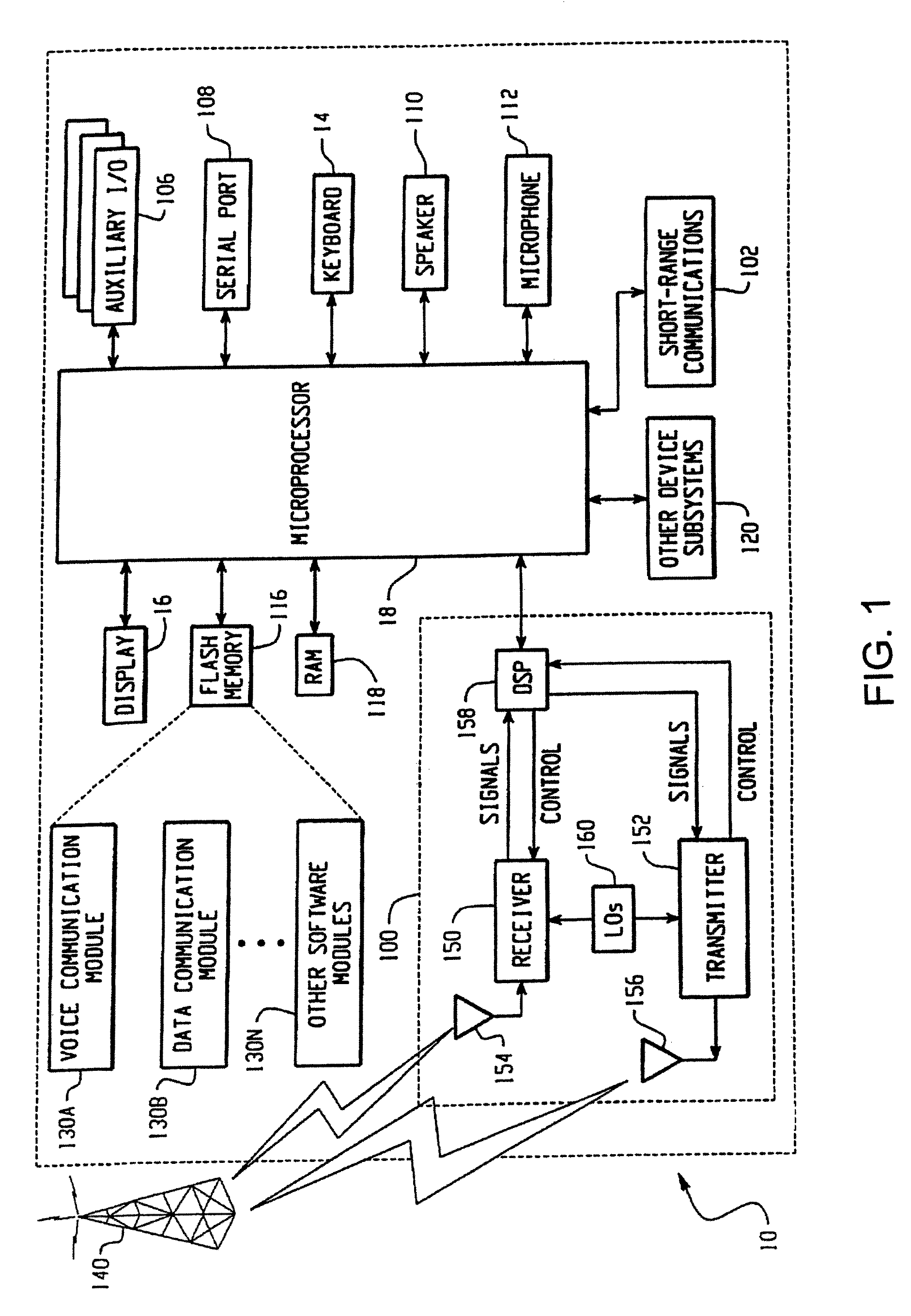
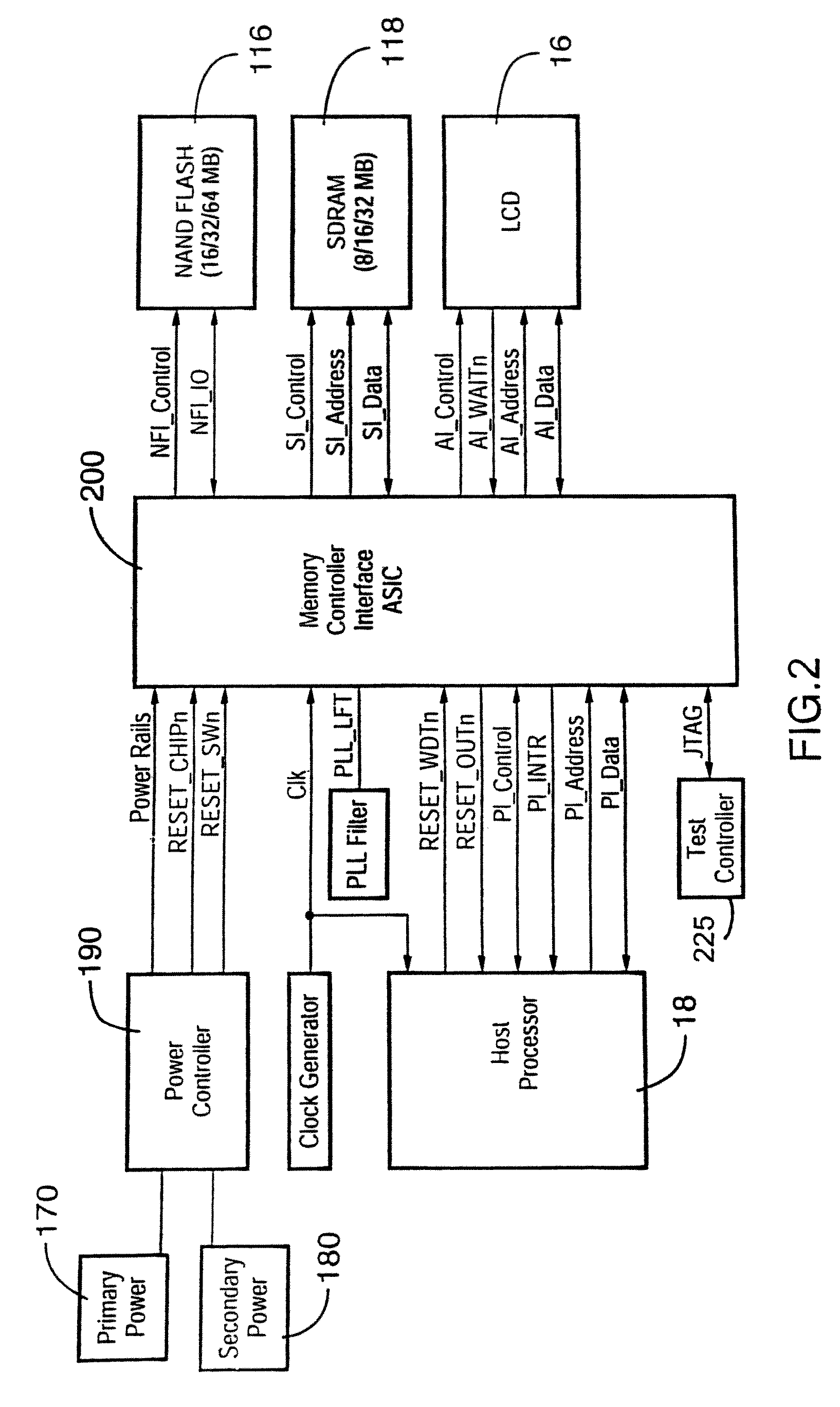
Memory controller interface
ActiveUS7610433B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionStatic random-access memoryMemory interface
A memory interface controller and method to allow a processor designed and configured to operate with NOR flash and static random access memory (SRAM) memory devices to instead operate using NAND flash and synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). The system accomplishes this by caching sectors out of NAND flash into SDRAM, where the data can be randomly accessed by the processor as though it were accessing data from NOR flash / SRAM. Sectors containing data required by the processor are read out of NAND flash and written into SDRAM, where the data can be randomly accessed by the processor.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
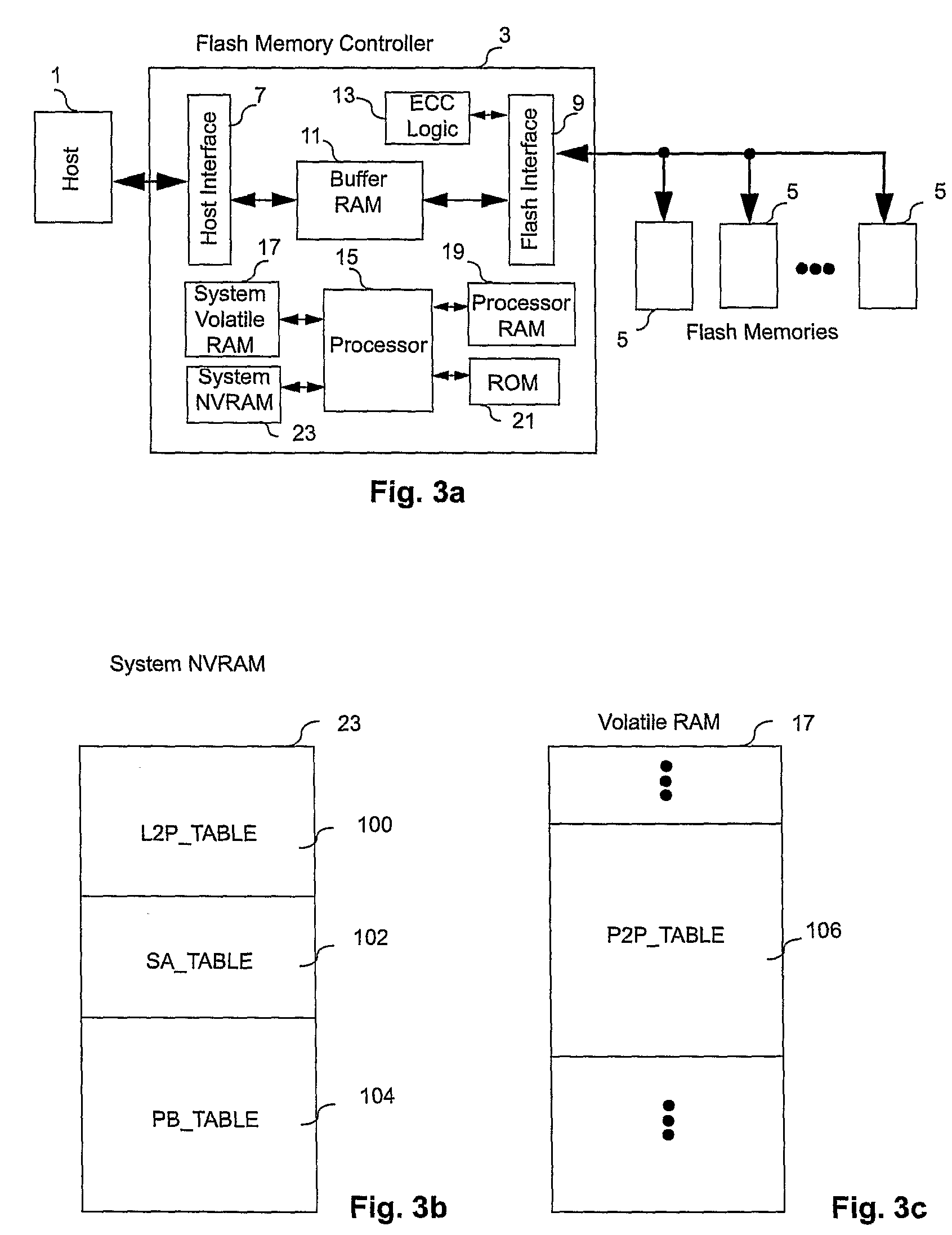
Controller for non-volatile memories and methods of operating the memory controller
ActiveUS8041884B2Efficient use ofHigh speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageMemory controllerSystem identification
A non-volatile memory system (3) is proposed consisting of a first non-volatile flash memory (5) having a plurality of blocks, each block having a plurality of pages, each block being erasable and each page being programmable, and a second non-volatile random access memory (23) having a plurality of randomly accessible bytes. The second non-volatile memory (23) stores data for mapping logical blocks to physical blocks and status information of logical blocks. Each logical block has an associated physical page pointer stored in the second non-volatile memory (23) that identifies the next free physical page of the mapped physical block to be written. The page pointer is incremented after every page write to the physical block, allowing all physical pages to be fully utilized for page writes. Furthermore, a method of writing and reading data is disclosed whereby the most recently written physical page associated with a logical address is identifiable by the memory system without programming flags into superseded pages, or recording time stamp values in any physical page or block of the first non-volatile memory (5). Furthermore, a method is provided for a logical block to be mapped to two physical blocks instead of one to provide additional space for page writes, resulting in reduction in page copy operations, thereby increasing the performance of the system.
Owner:CHANG CHEE KENG
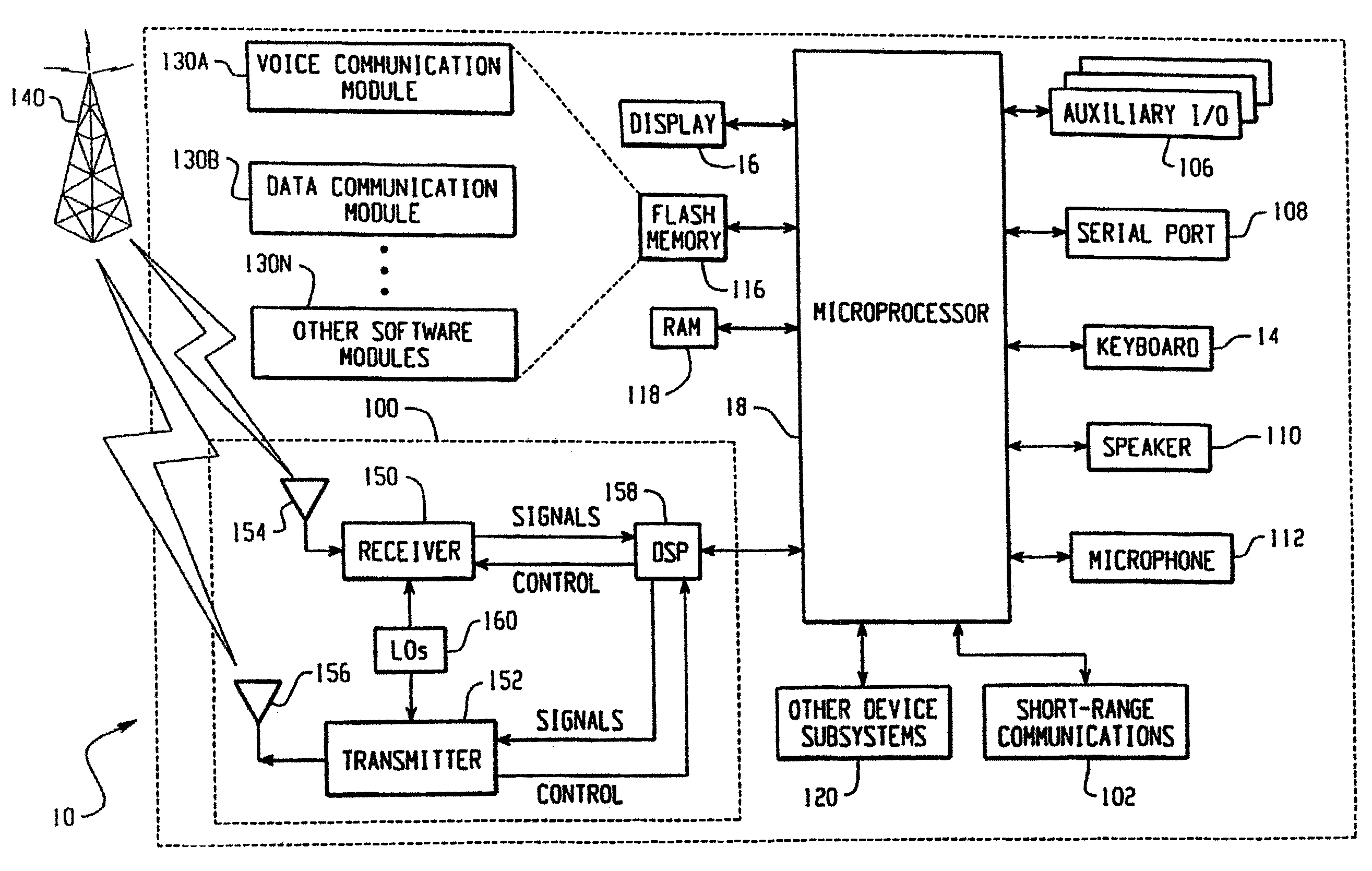
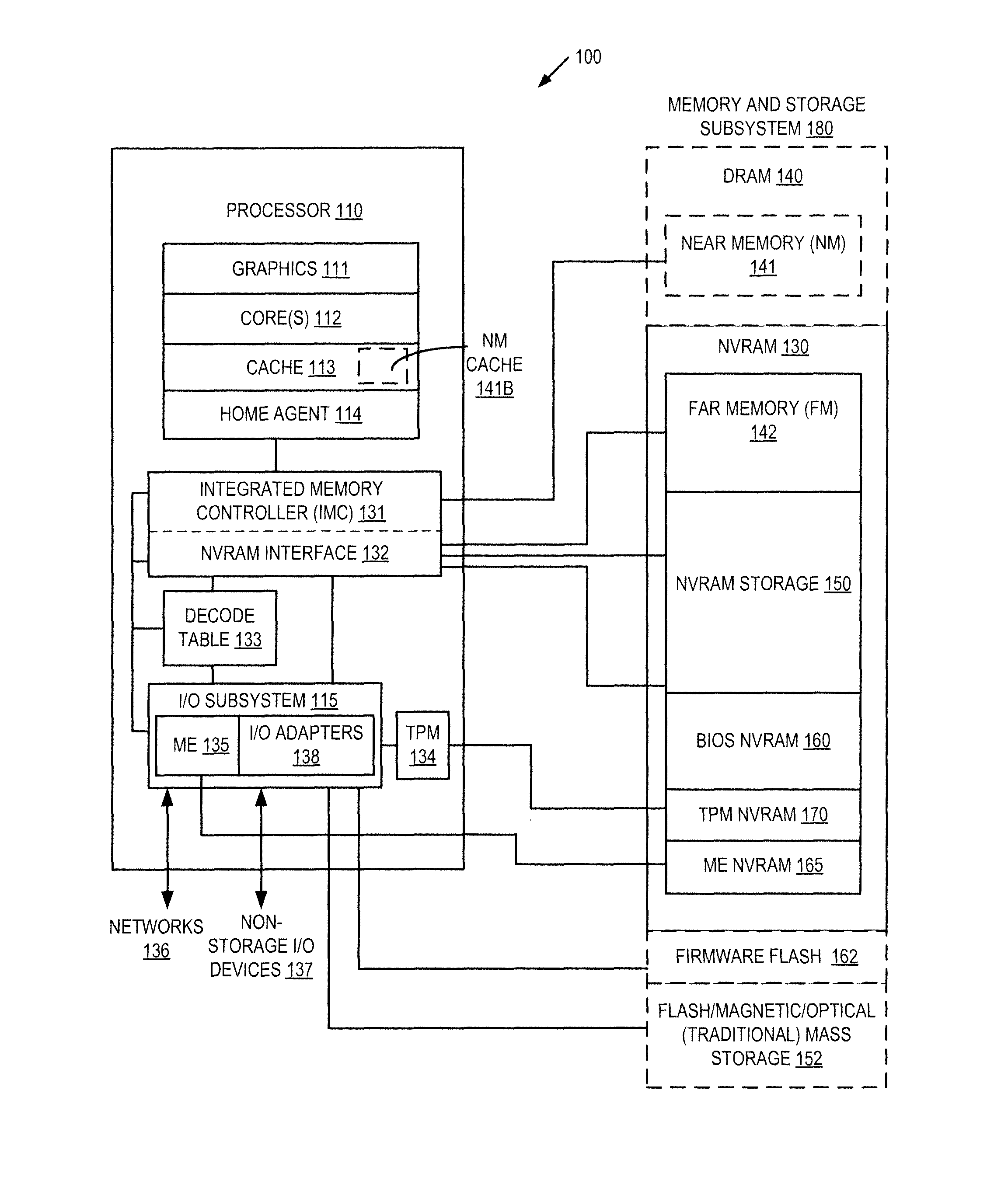
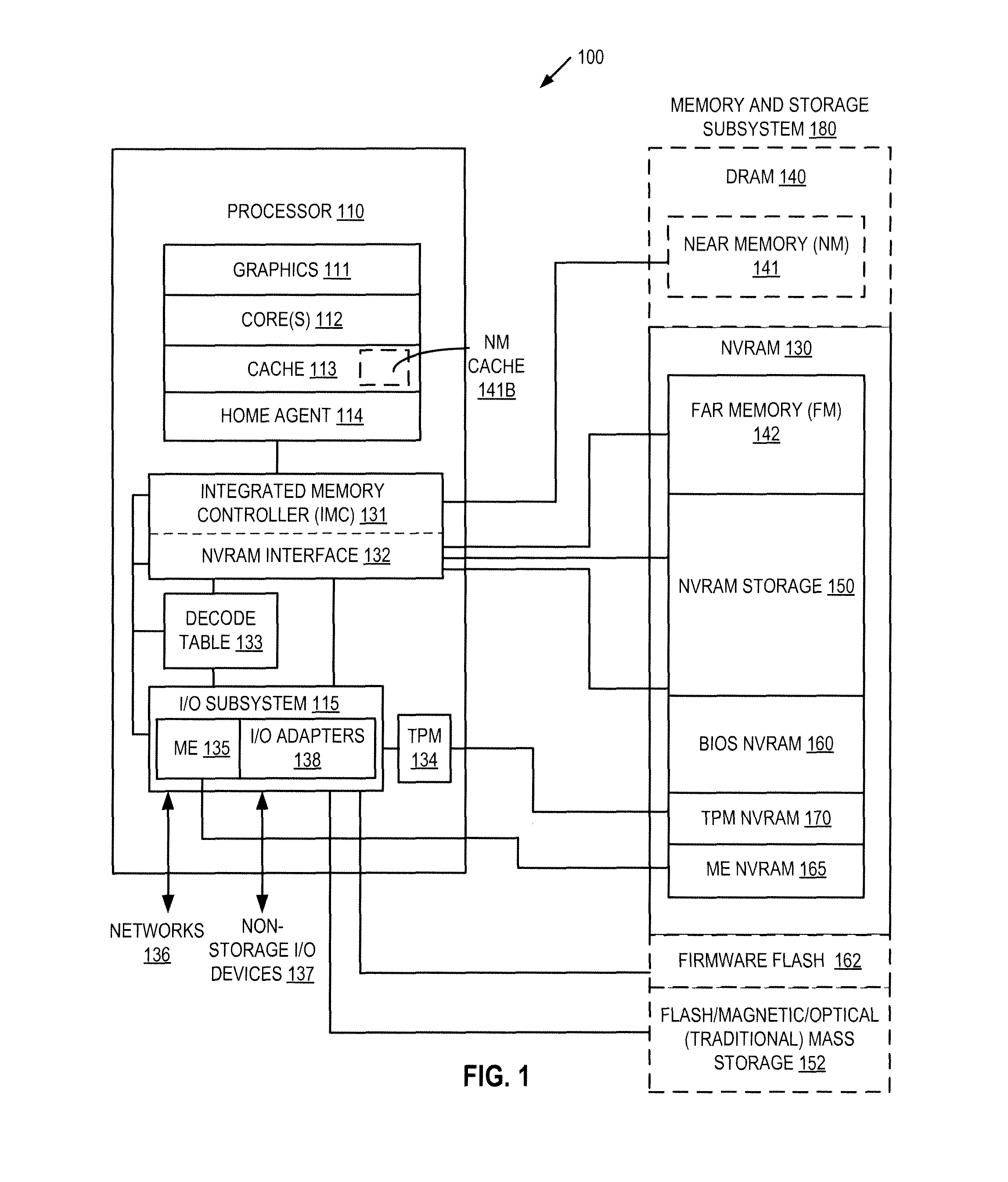
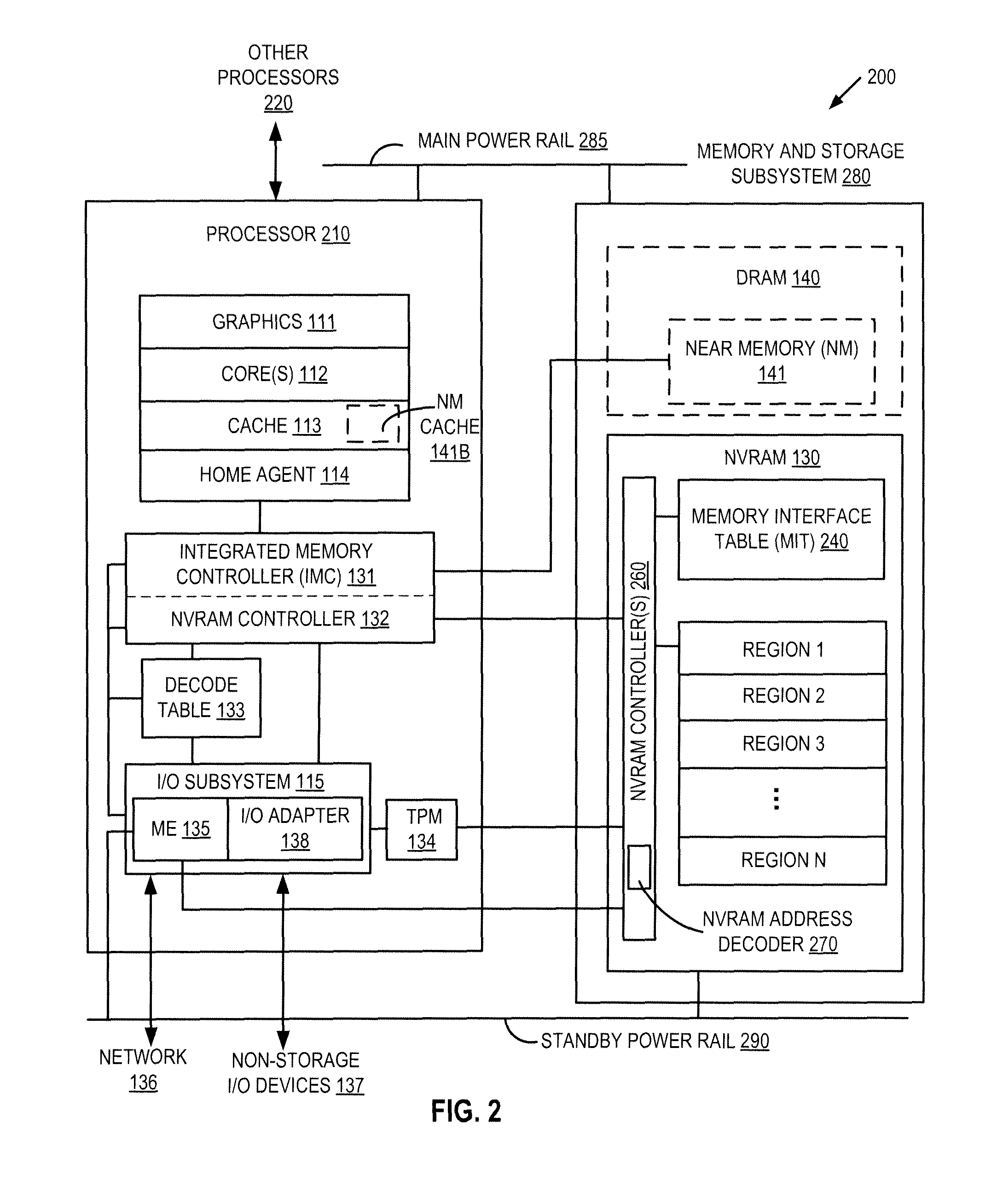
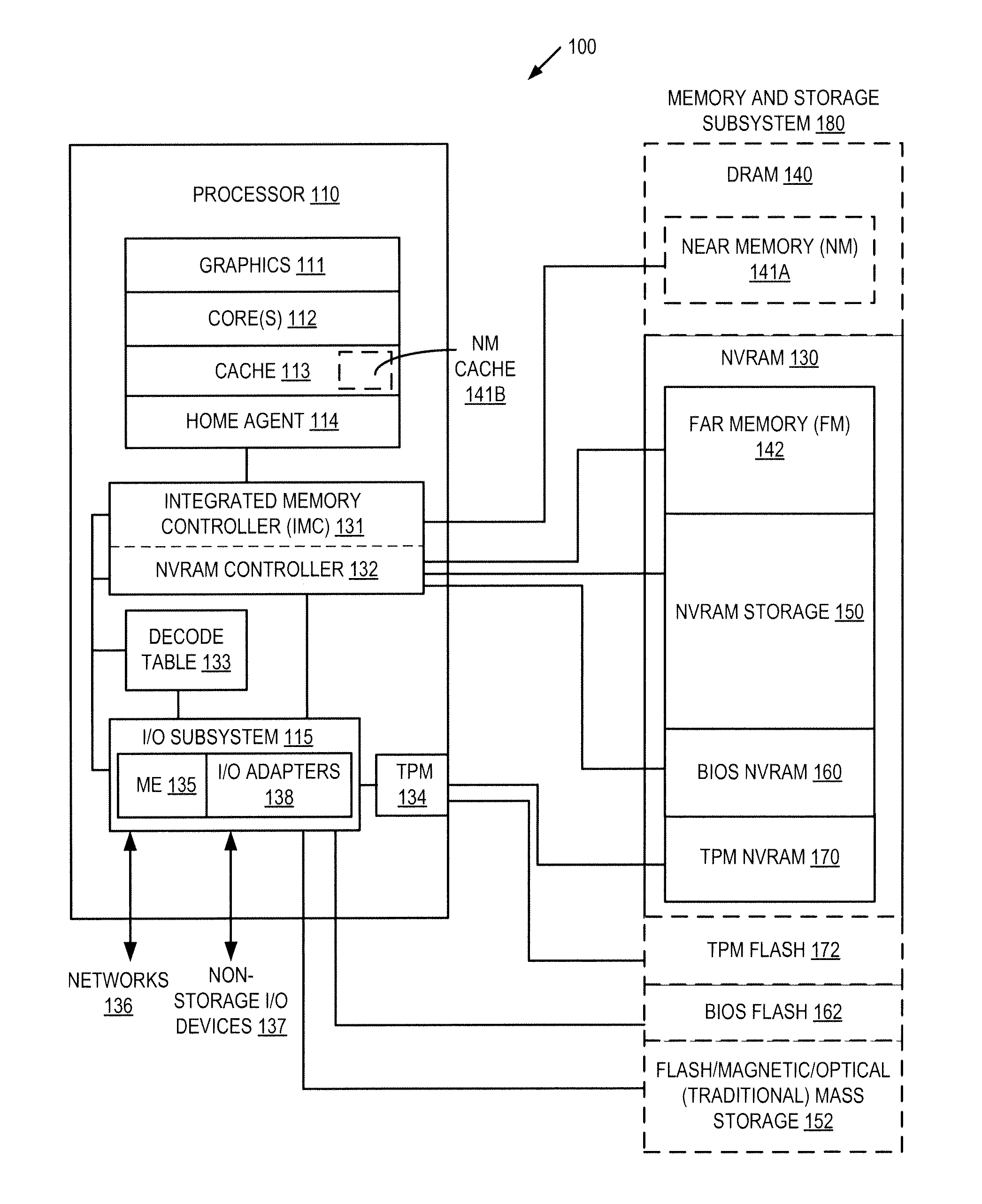
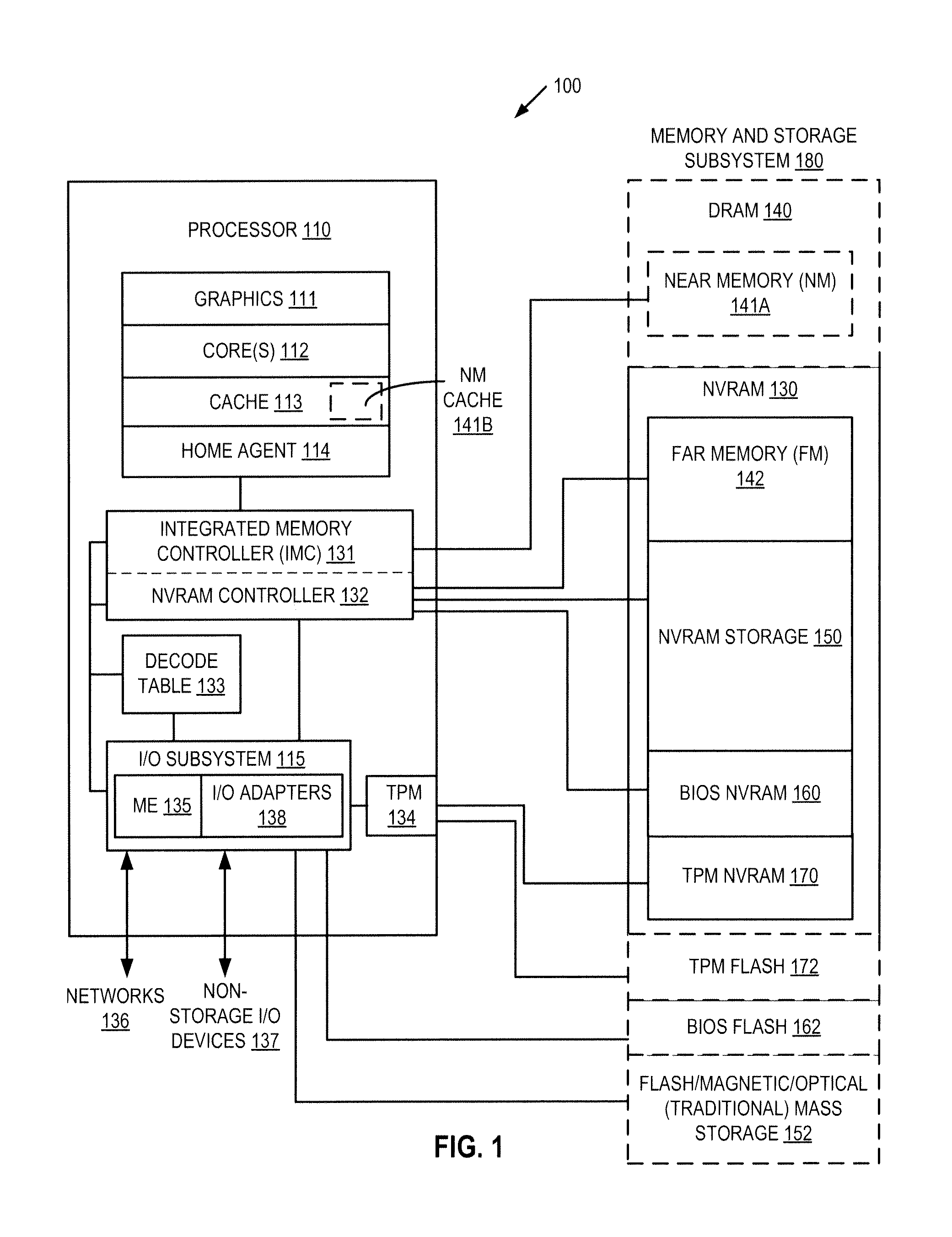
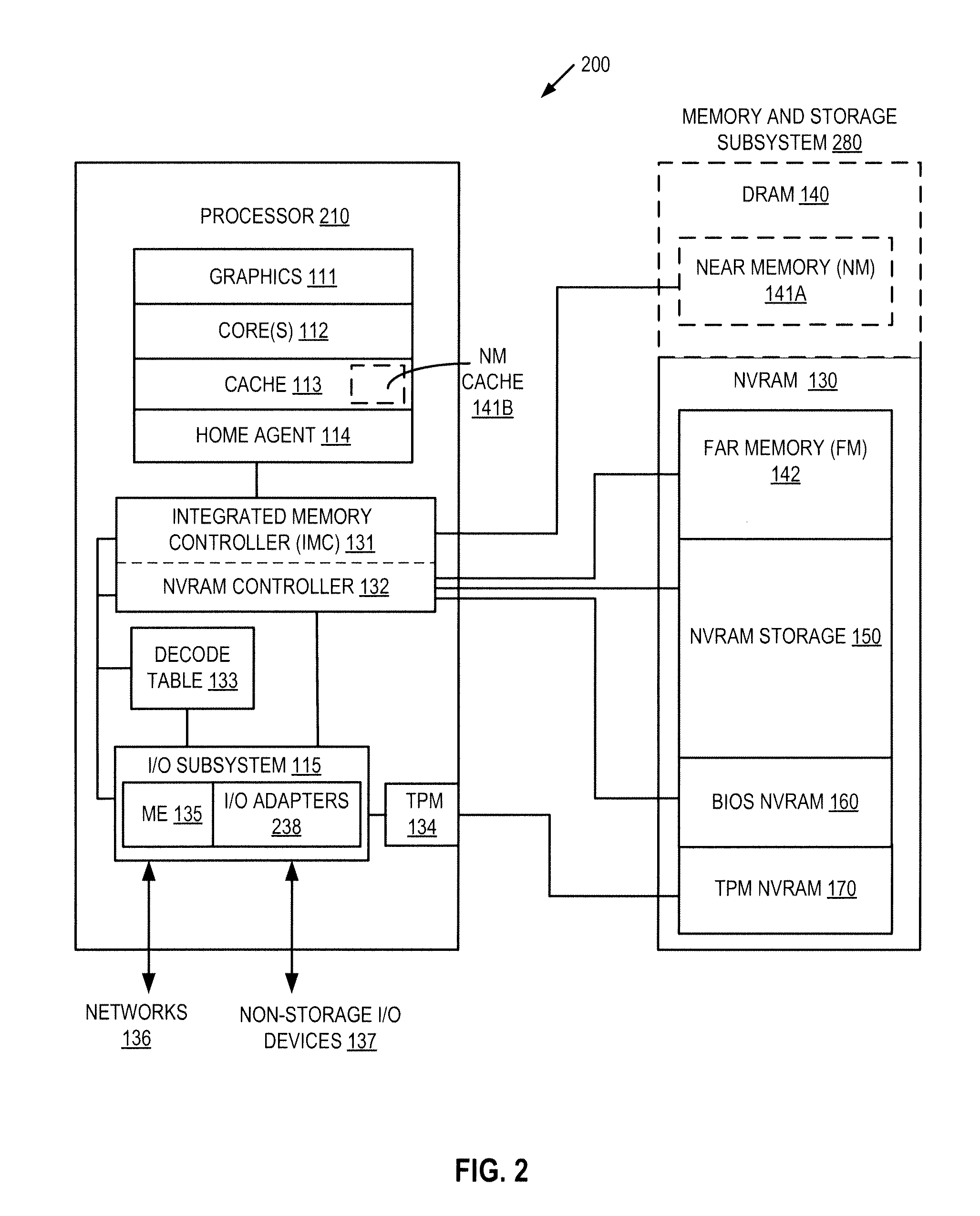
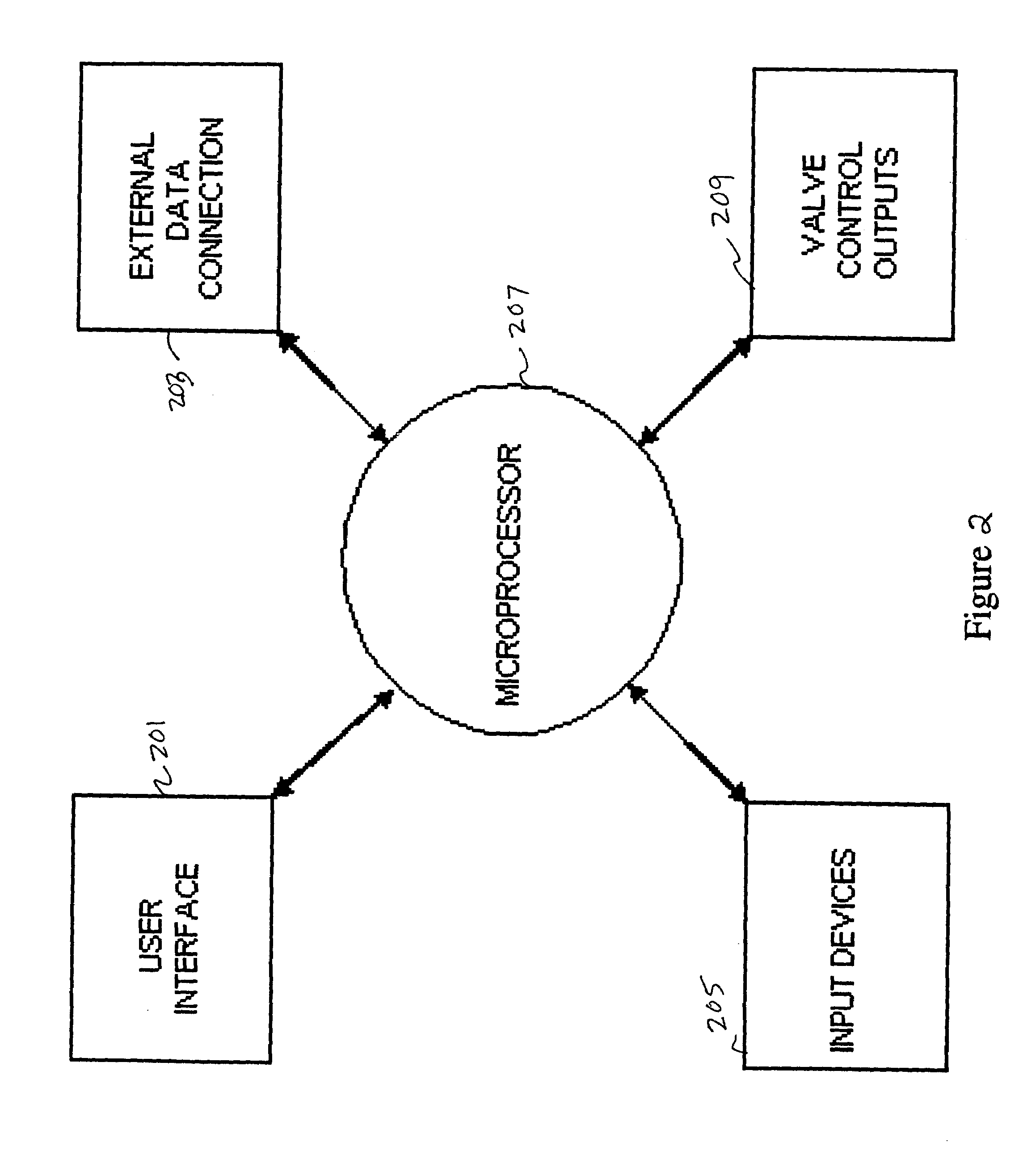
Autonomous initialization of non-volatile random access memory in a computer system
A non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) is used in a computer system to store information that allows the NVRAM to autonomously initialize itself at power-on. The computer system includes a processor, an NVRAM controller coupled to the processor, and an NVRAM that comprises the NVRAM controller. The NVRAM is byte-rewritable and byte-erasable by the processor. The NVRAM stores a memory interface table containing information for the NVRAM controller to autonomously initialize the NVRAM upon power-on of the computer system without interacting with the processor and firmware outside of the NVRAM. The information is provided by the NVRAM controller to the processor to allow the processor to access the NVRAM.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low-cost non-volatile flash-RAM memory
ActiveUS8120949B2Reduced switching currentIncrease memory capacitySolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer hardwareNon-volatile random-access memory
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
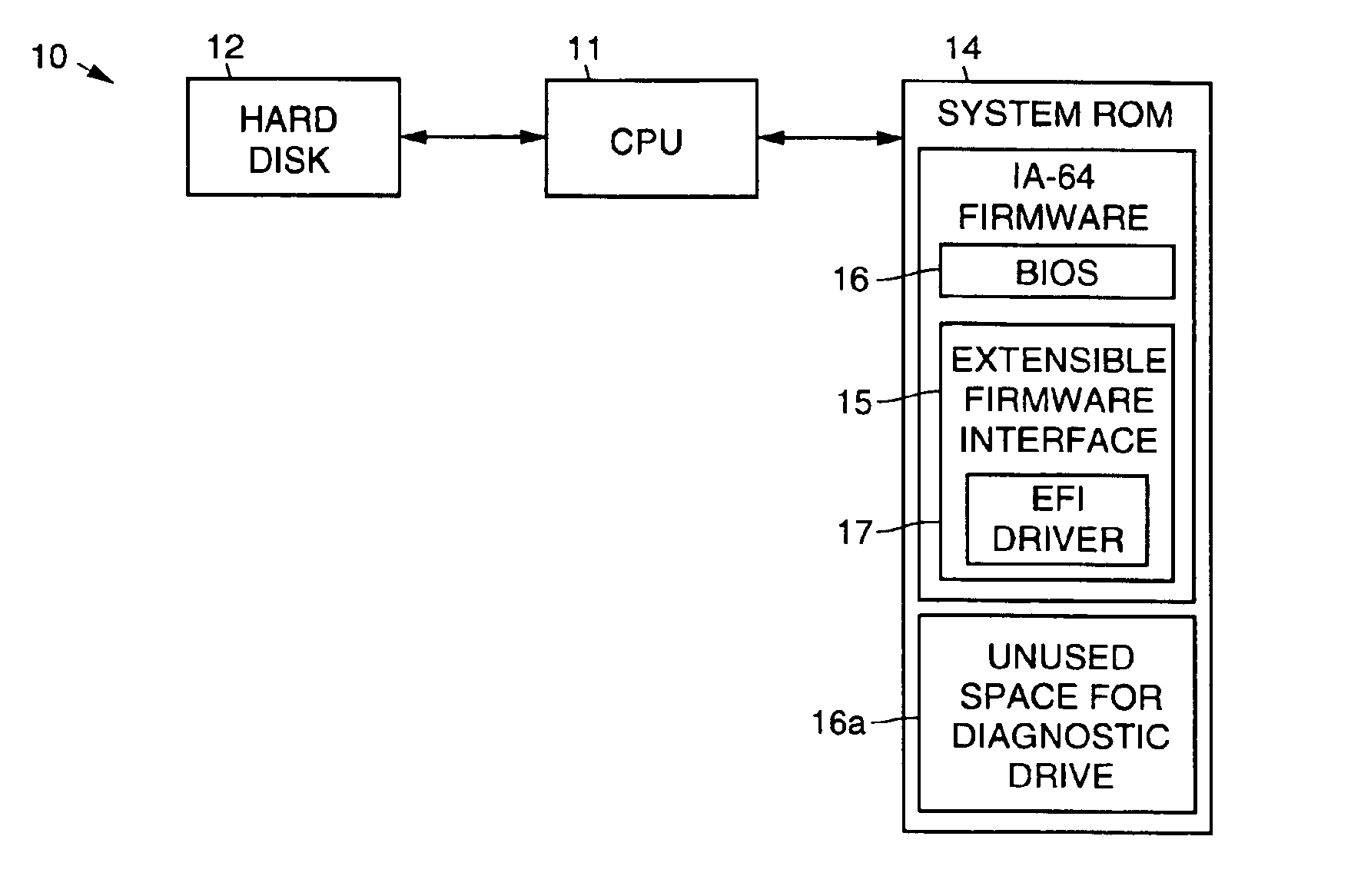
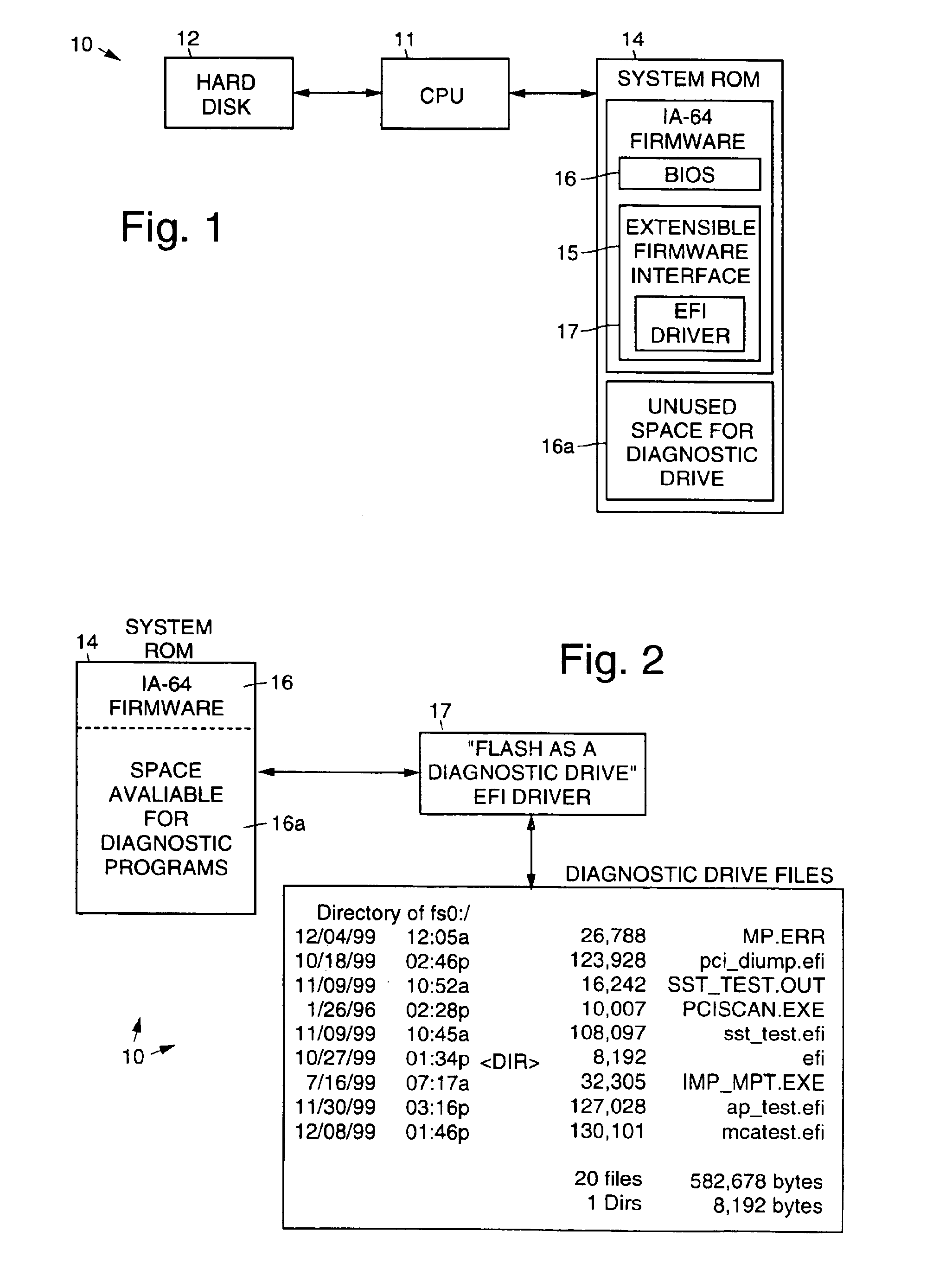
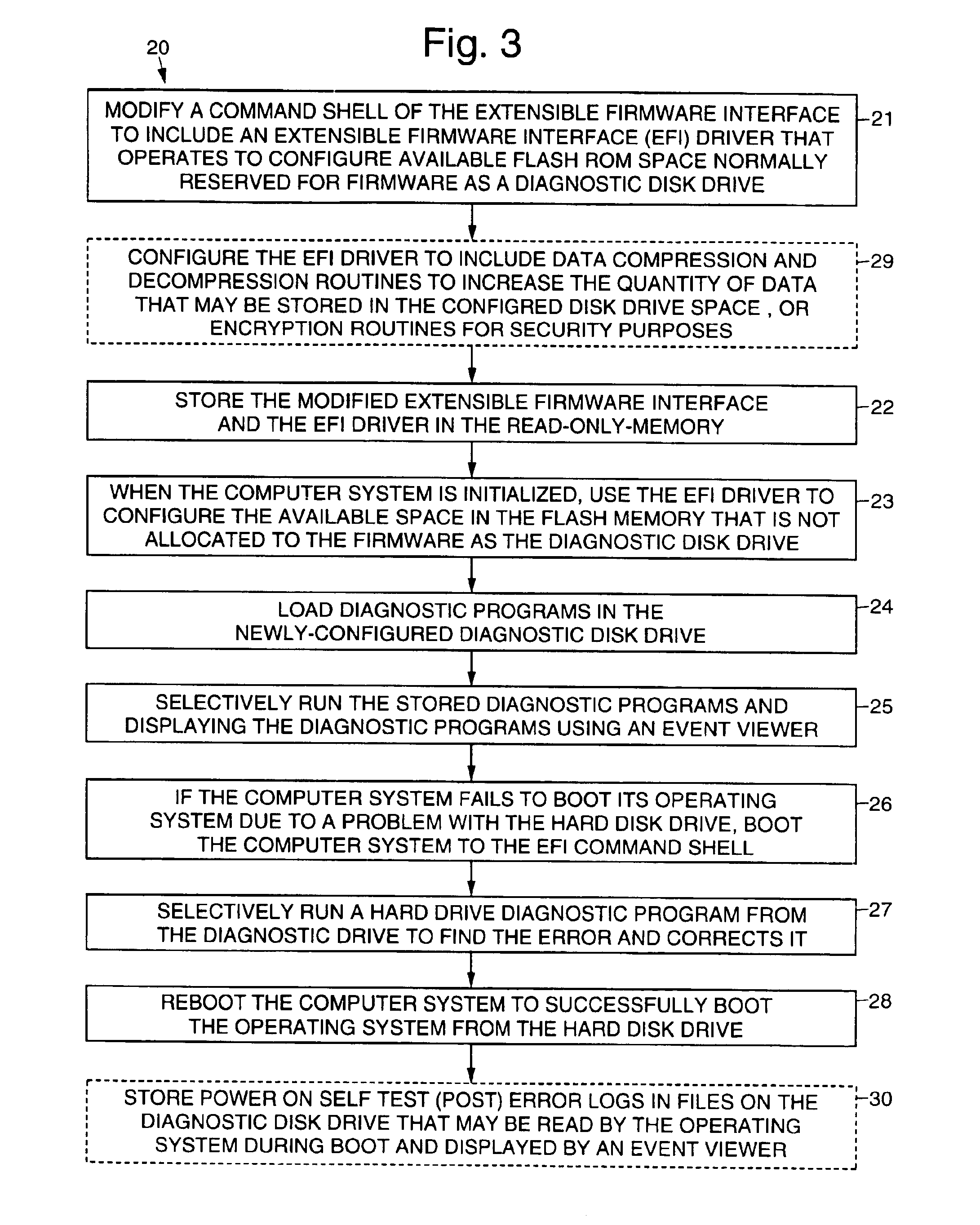
Use of extra firmware flash ROM space as a diagnostic drive
InactiveUS6889340B1Increase the number ofEasy to updateDetecting faulty hardware by power-on testData compressionDiagnostic program
A method 20 and computer apparatus for using available firmware flash ROM space as a diagnostic drive. The computer apparatus has a nonvolatile random access memory, an Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) and a basic input and output system (BIOS). To implement the functionality provided by the present invention, a command shell of the EFI is modified to include the EFI driver and operates to configure available flash space normally reserved for firmware (BIOS) as a diagnostic disk drive. The modified EFI and the EFI driver are stored in the flash memory. When the computer system 10 is initialized (booted), the EFI driver configures the available space in the flash memory that is not allocated to the firmware as the diagnostic disk drive. Diagnostic programs are loaded into the diagnostic disk drive, which are selectively run by a user, such as by using the command shell. The method may also be configured to include data compression and decompression routines to increase the quantity of data that may be stored in the configured disk drive space, or encryption routines for security purposes. The diagnostic disk drive space may be used to store power on self test (POST) error logs in files that may be read by the operating system during its boot process and displayed by an event viewer.
Owner:PHOENIX TECH EMEA LTD
Platform storage hierarchy with non-volatile random access memory with configurable partitions
InactiveUS20130275661A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageStatic random-access memory
A non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) is used in a computer system to perform multiple roles in a platform storage hierarchy. The NVRAM is byte-addressable by the processor and can be configured into one or more partitions, with each partition implementing a different tier of the platform storage hierarchy. The NVRAM can be used as mass storage that can be accessed without a storage driver.
Owner:INTEL CORP
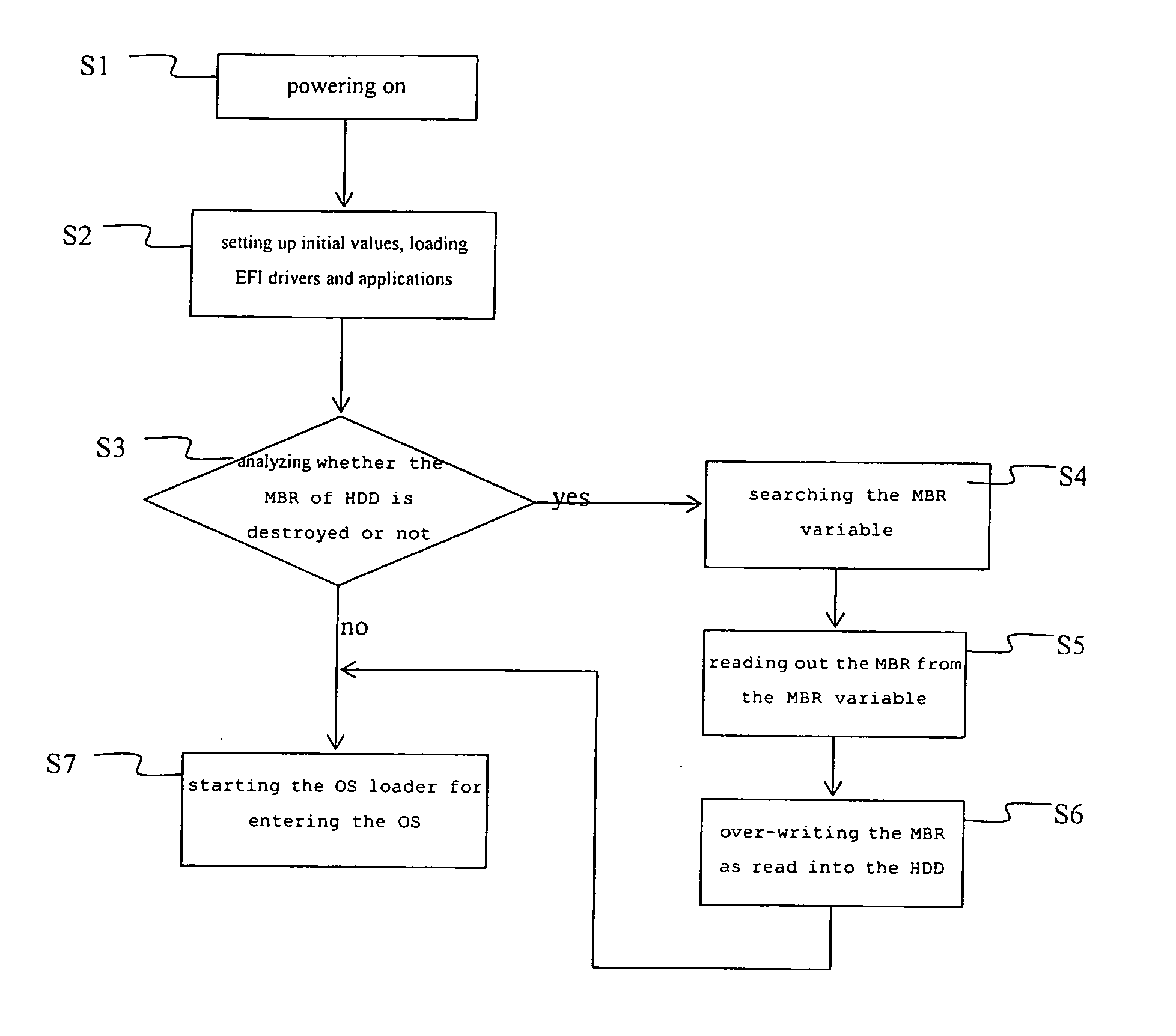
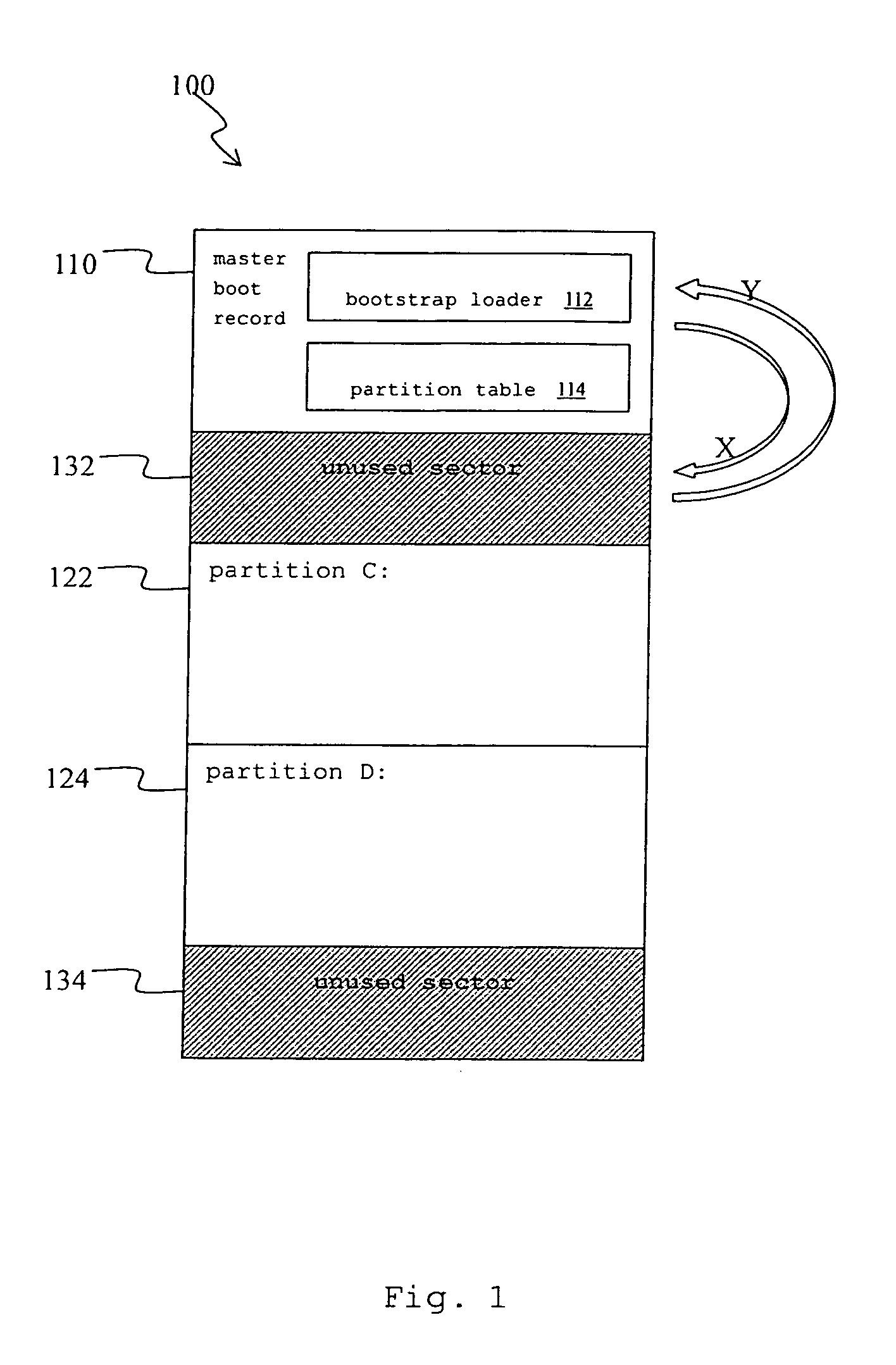
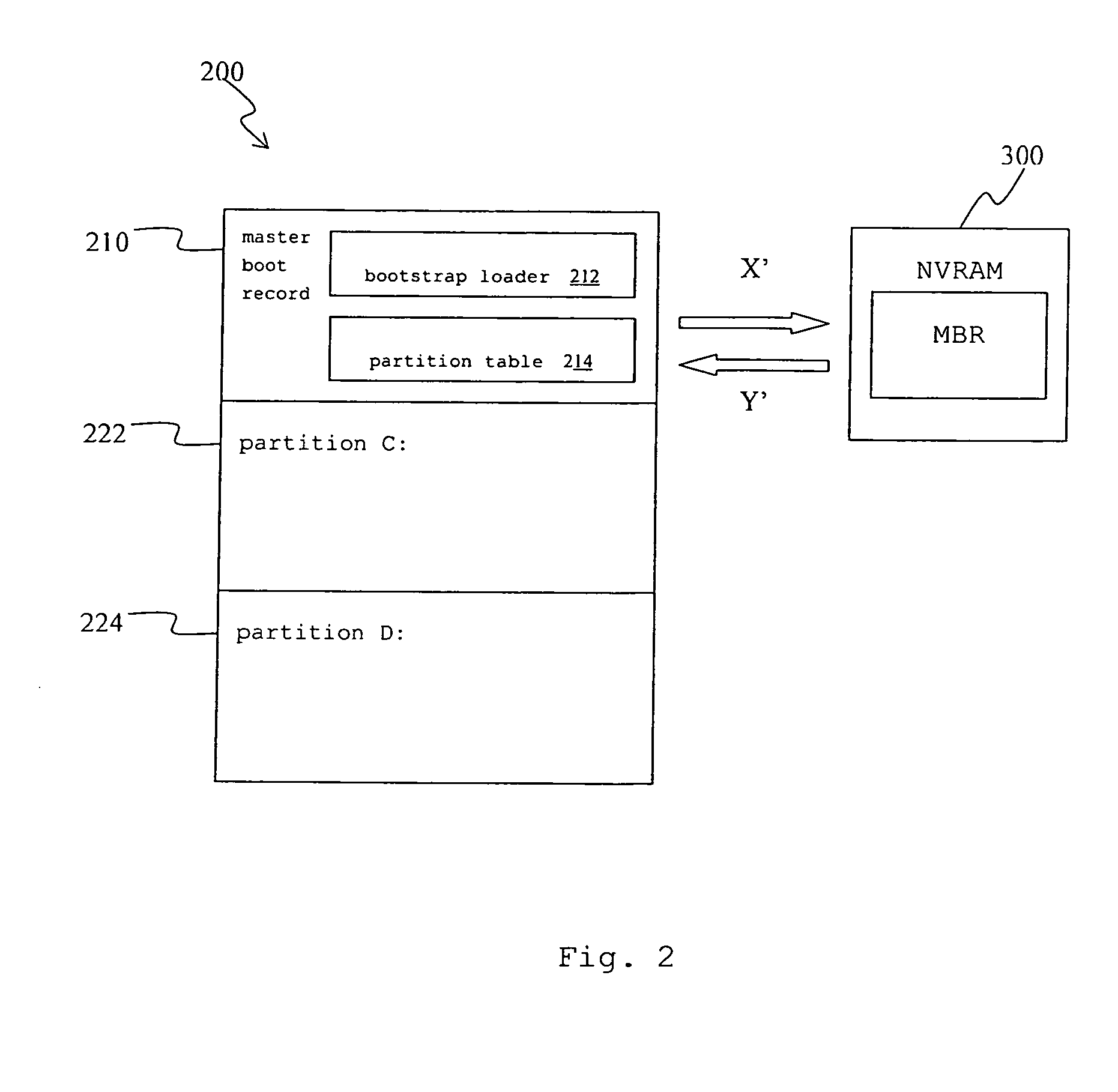
Recovery method for master boot record of hard disk drive
InactiveUS20060041738A1Avoid backupAvoid damageError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsRecovery methodHard disc drive
A recovery method for a master boot record of a hard disk drive is adapted to a computer system incorporating extensible firmware interface (EFI). When modification occurs in the master boot record, the extensible firmware interface stores the master boot record in an NVRAM (Non-volatile Random Access Memory) as a backup. The backup is read out for recovery of the hard disk driver if the master boot record is destroyed. The NVRAM is write-protected during runtime and the backup data stored therein is therefore free from destruction.
Owner:INSYDE SOFTWARE CORP
Two square NVRAM cell
A non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) cell and method of fabrication thereof. Pairs of NVRAM cells, each including three FETs stacked in a NAND-like structure are formed vertically in silicon pillars. Source devices at the bottom of the pillar selectively provide ground to one of the cells. A floating gate extends upward from the source device's gate line. A control gate plate extending between adjacent pillars selectively provides a programming voltage to the control gate. Both the source gate and the control gate are capacitively coupled through silicon rich oxide to the floating gate. Polysilicon plugs between silicon pillars are word line gates for cells in adjacent pillars. A diffusion at the top of each pillar is a bit line contact for both cells at the pillar. Each pair of cells on a pillar are on a common bit line and a common word line. The word line, control gate and source gate line select individual cells in the pair.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
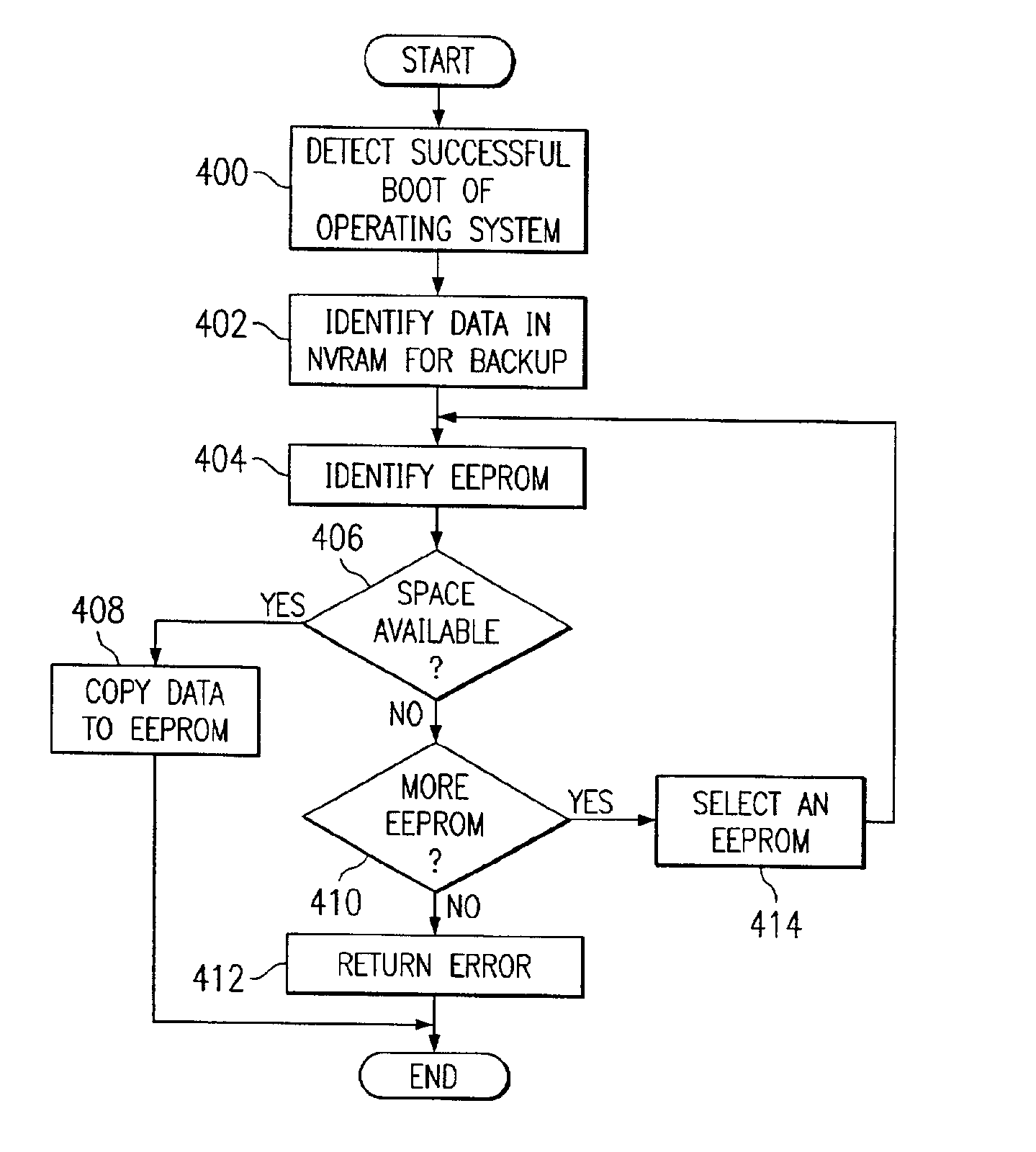
Method and apparatus for backing up and restoring data from nonvolatile memory
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for backing up data in a nonvolatile random access memory. Selected data is stored in the nonvolatile random access memory in available space in at least one electrically erasable programmable read only memory in the data processing system to form stored data. The stored data is used to restore the nonvolatile random access memory if nonvolatile random access memory becomes corrupted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Nonvolatile memory and three-state FETs using cladded quantum dot gate structure
ActiveUS20090173934A1TransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryField-effect transistor
The present invention discloses use of quantum dot gate FETs as a nonvolatile memory element that can be used in flash memory architecture as well as in a nonvolatile random access memory (NVRAM) configuration that does not require refreshing of data as in dynamic random access memories. Another innovation is the design of quantum dot gate nonvolatile memory and 3-state devices using modulation doped field-effect transistors (MODFETs), particularly MOS-gate field effect transistors. The cladded quantum dot gate MODFETs can be designed in Si—SiGe, InGaAs—InP and other material systems. The incorporation of 3-state FET devices in static random access memory (SRAM) cell is described to result in advanced multi-state memory operation. Unlike conventional SRAMs, the 3-state QD-FET based of SRAMs provides 3 and 4-state memory operation due to the utilization of the intermediate states particularly in CMOS configuration. QD-gate FETs, potentially suitable for 8 nm channel lengths, in vertical configuration (VFET) are also described.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR C
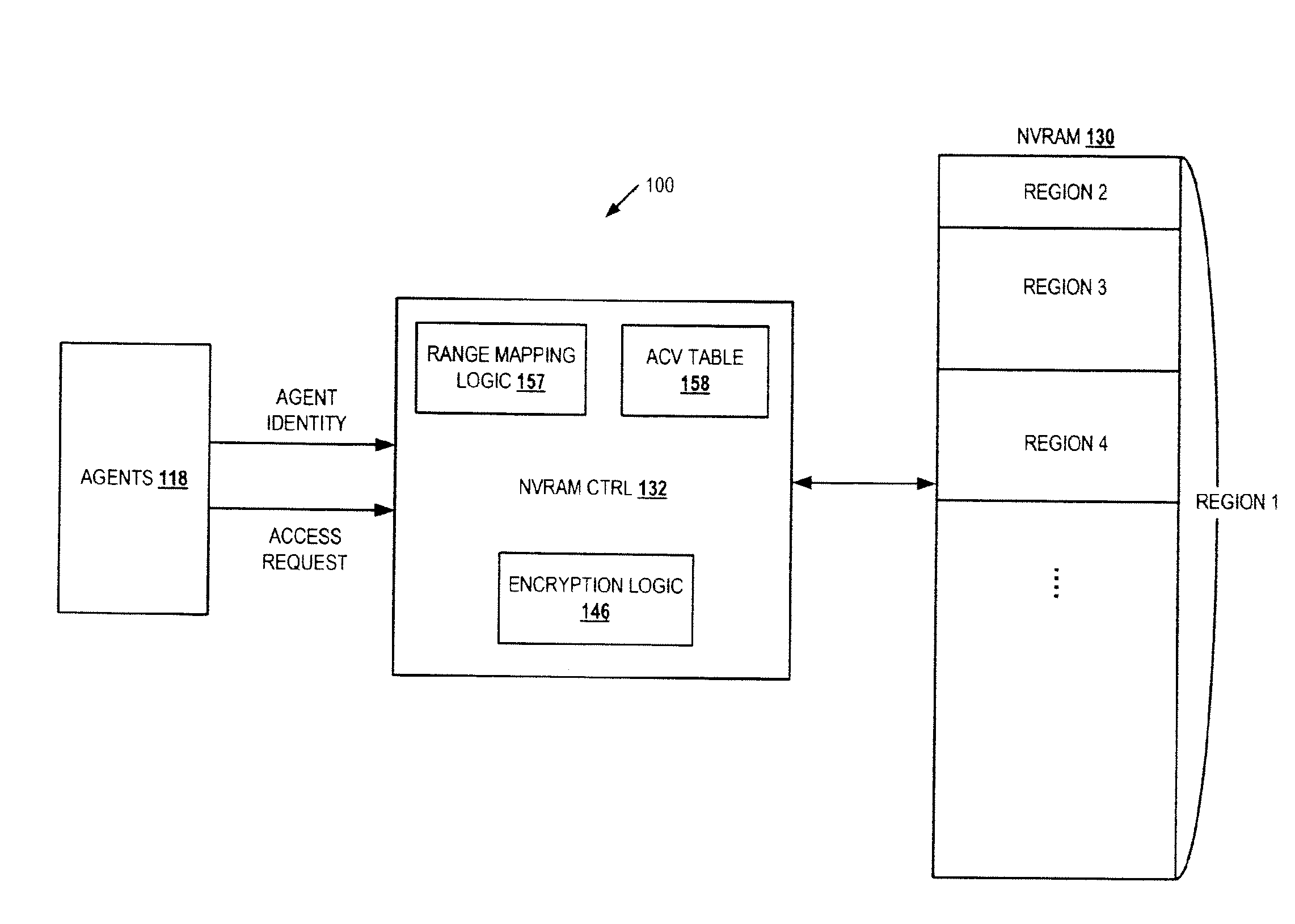
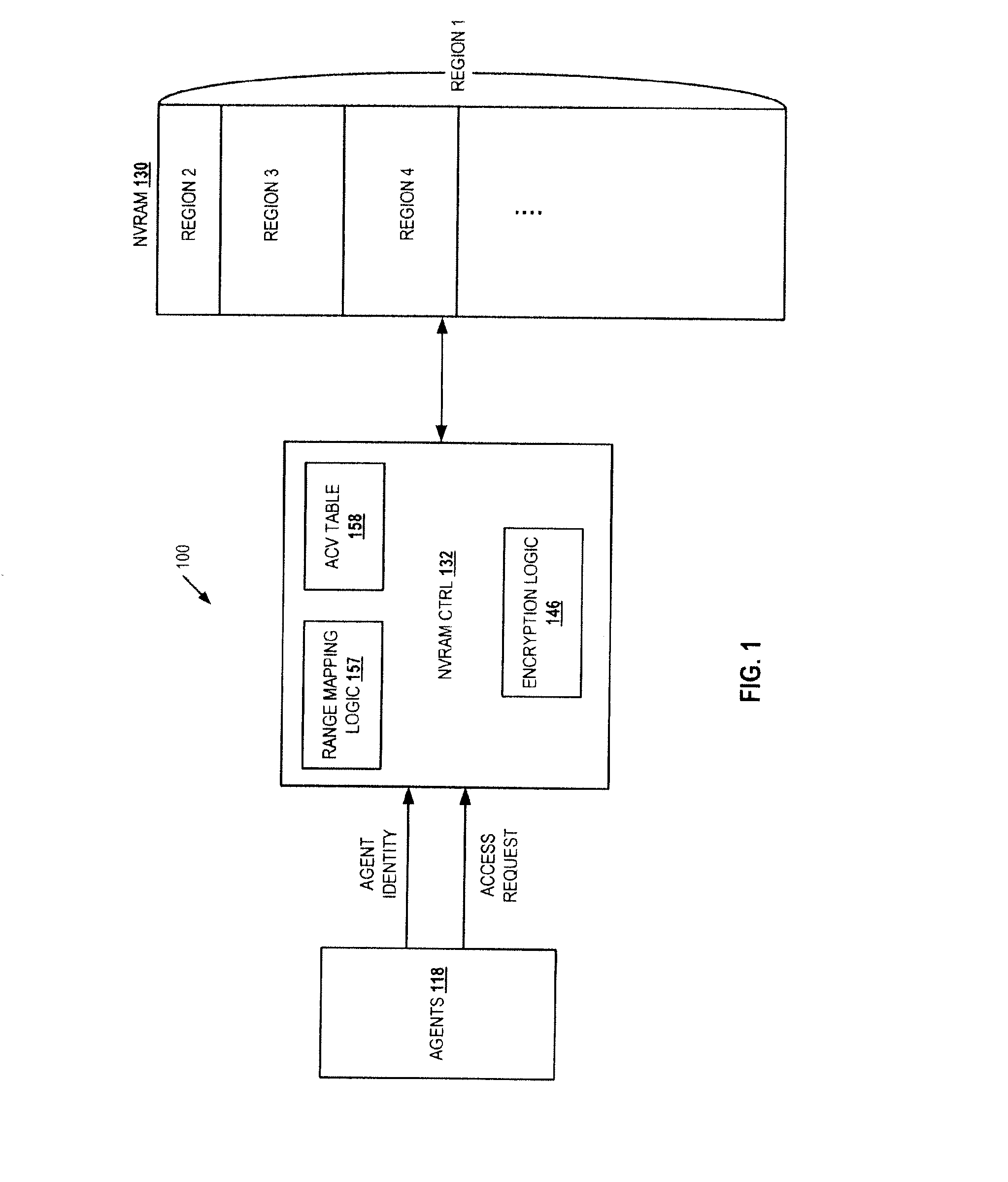
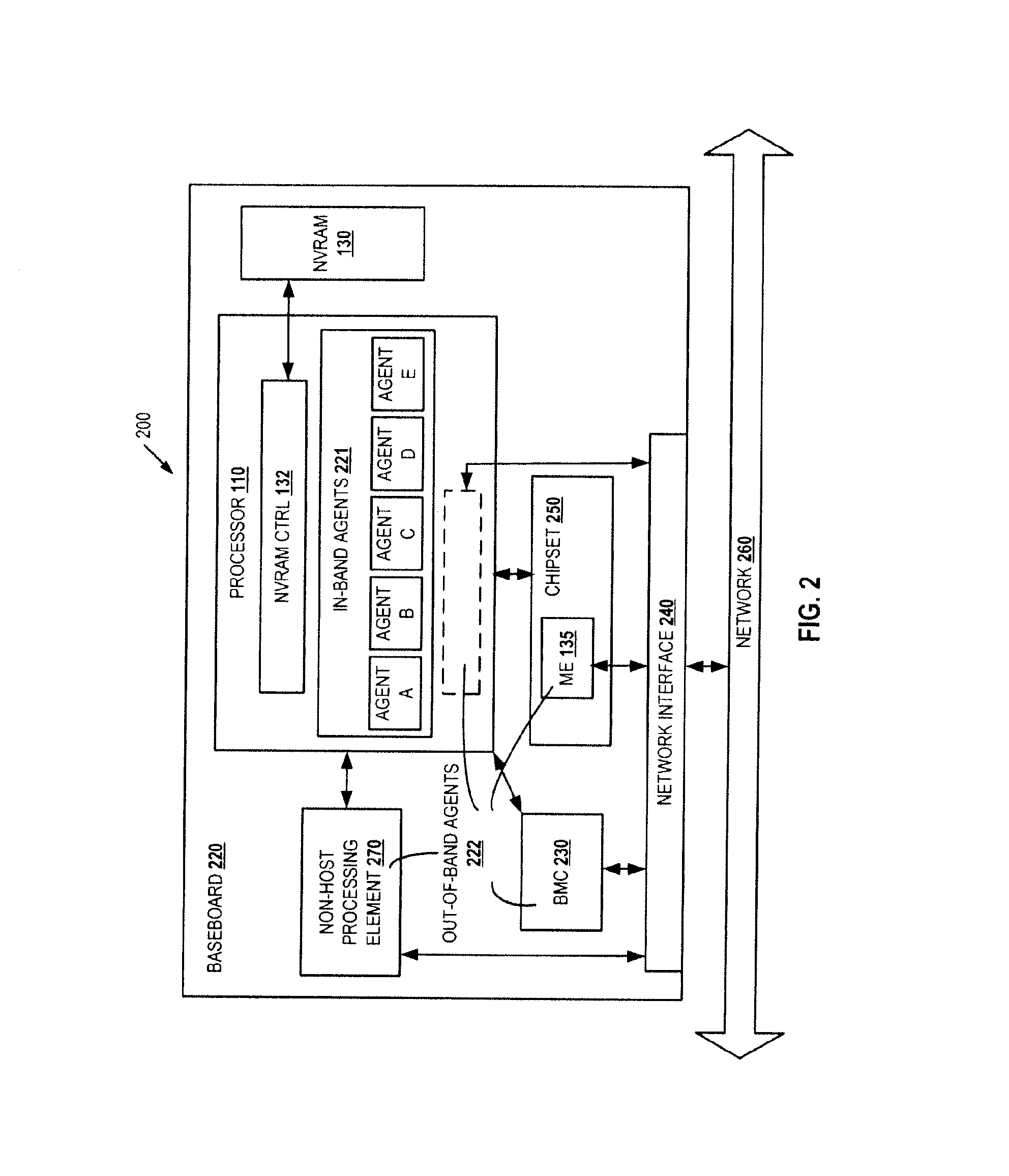
Access control for non-volatile random access memory across platform agents
A controller is used in a computer system to control access to an NVRAM. The computer system includes a processor coupled to a non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM). The NVRAM is byte-rewritable and byte-erasable. The NVRAM stores data to be used by a set of agents including in-band agents and an out-of-band agent. The in-band agents run on a processor having one or more cores, and the out-of-band agent that runs on a non-host processing element. When the controller receives an access request from the out-of-band agent, the controller determines, based on attributes associated with the out-of-band agent, whether a region in the NVRAM is shareable by the out-of-band agent and at least one of the in-band agents.
Owner:INTEL CORP
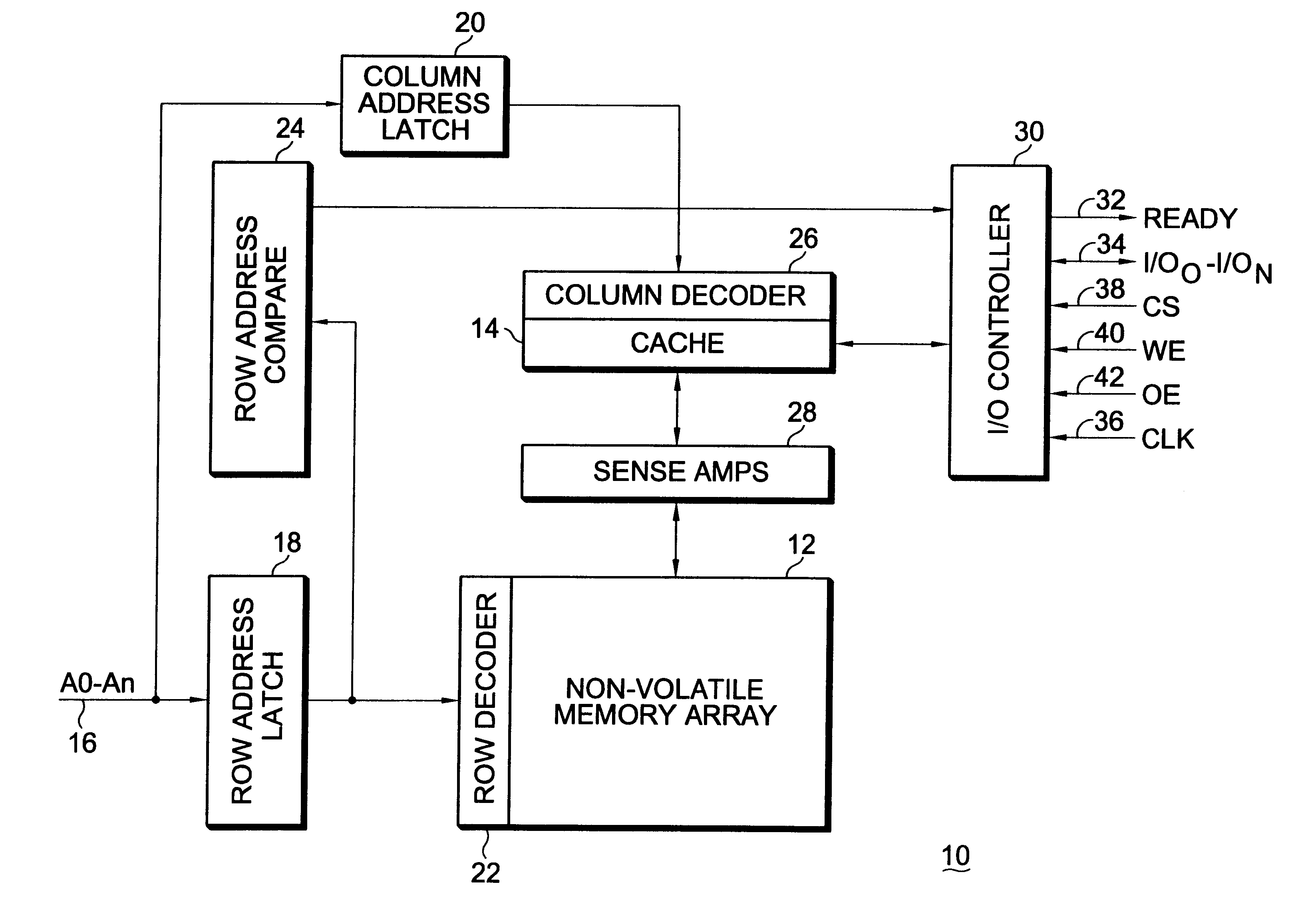
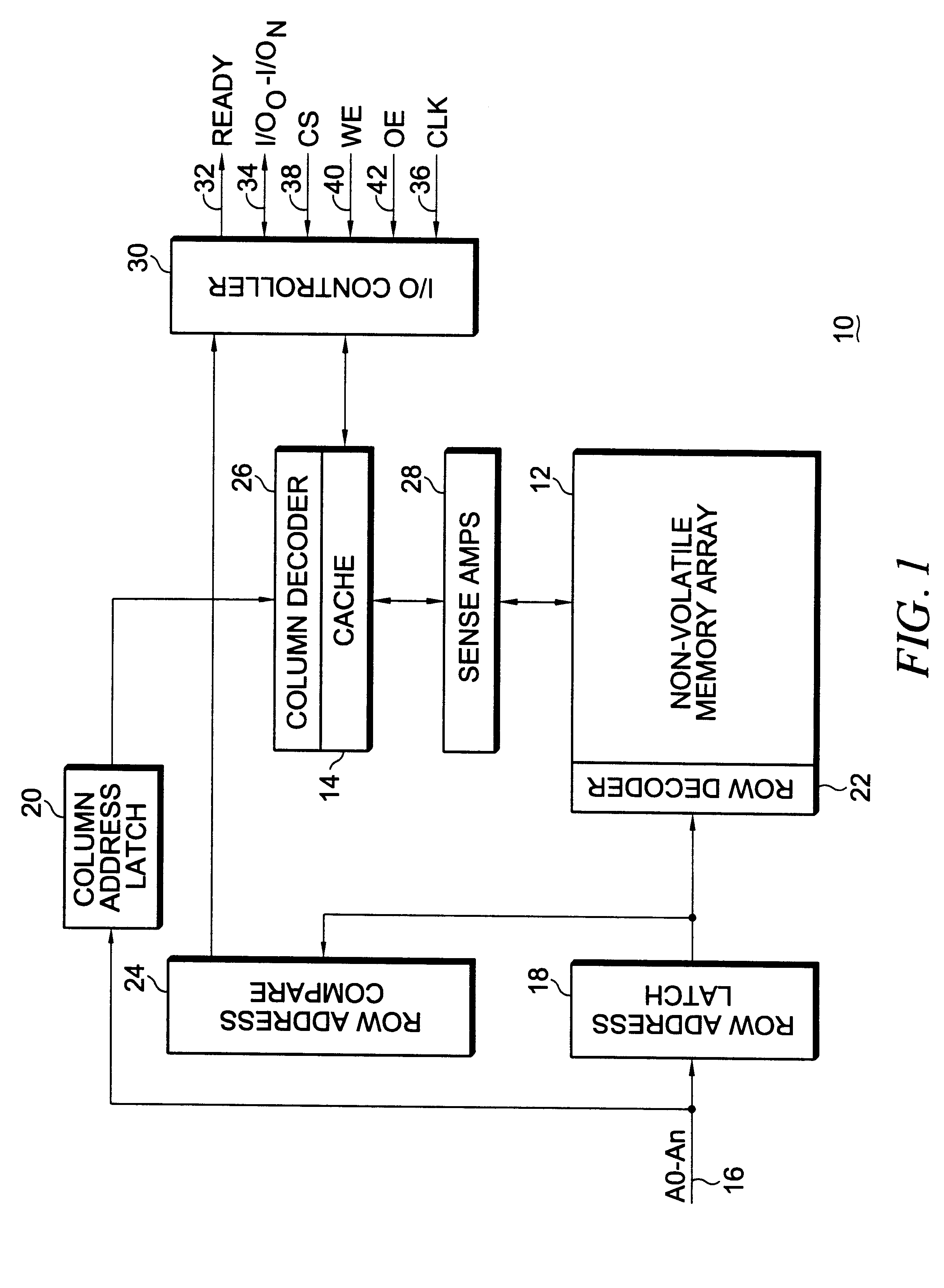
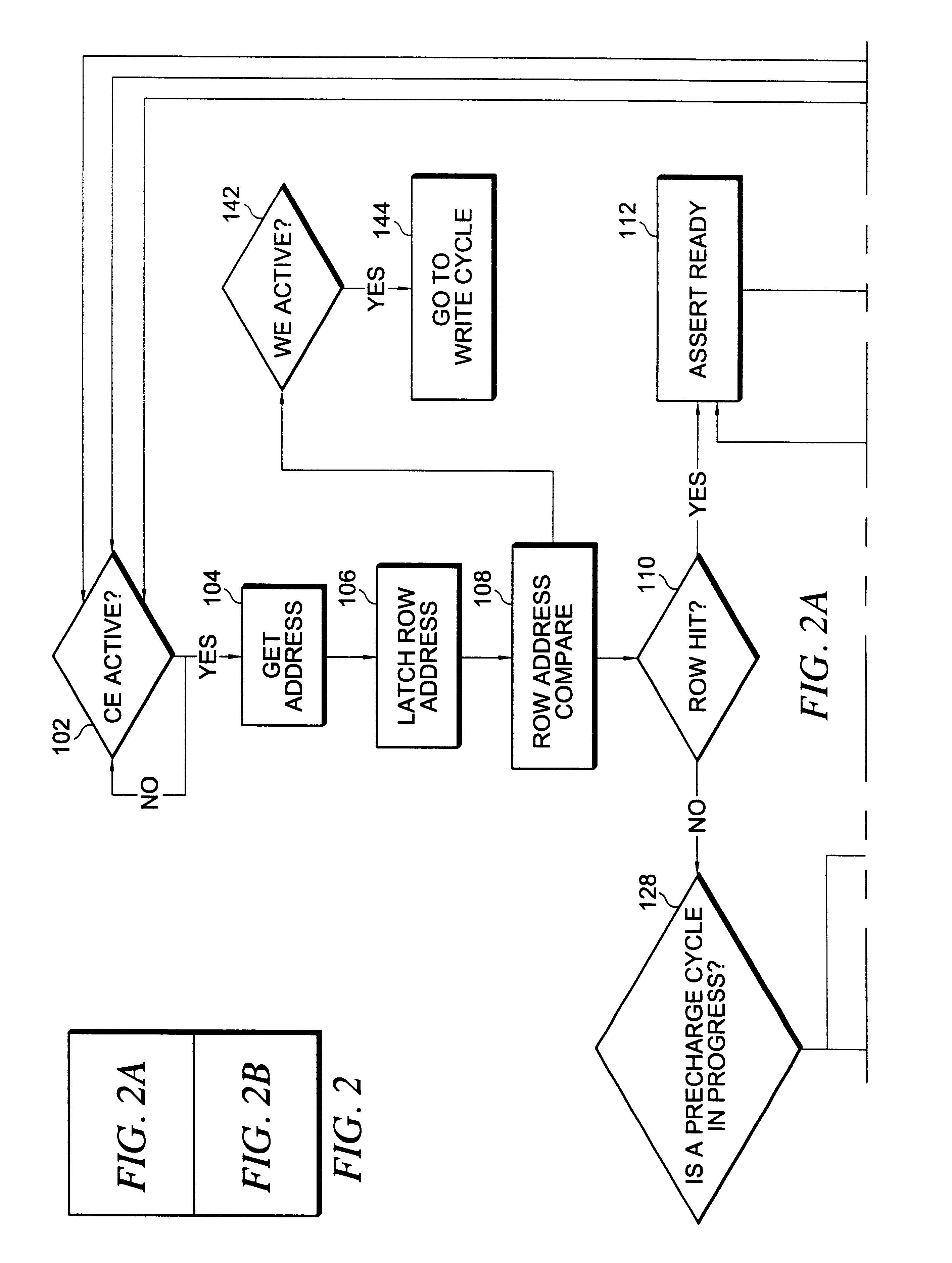
Integrated circuit memory device incorporating a non-volatile memory array and a relatively faster access time memory cache
InactiveUS6263398B1Increases access timeFaster access timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memoryAccess time
An integrated circuit memory device incorporating a non-volatile memory array and a relatively faster access time memory cache integrated monolithically therewith improves the overall access time in page and provides faster cycle time for read operations. In a particular embodiment, the cache may be provided as static random access memory ("SRAM") and the non-volatile memory array provided as ferroelectric random access memory wherein on a read, the row is cached and the write back cycle is started allowing subsequent in page reads to occur very quickly. If in page accesses are sufficient the memory array precharge may be hidden and writes can occur utilizing write back or write through caching. In alternative embodiments, the non-volatile memory array may comprise electrically erasable read only memory ("EEPROM") or Flash memory in conjunction with an SRAM cache or a ferroelectric random access memory based cache which has symmetric read / write times and faster write times than either EEPROM or Flash memory.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
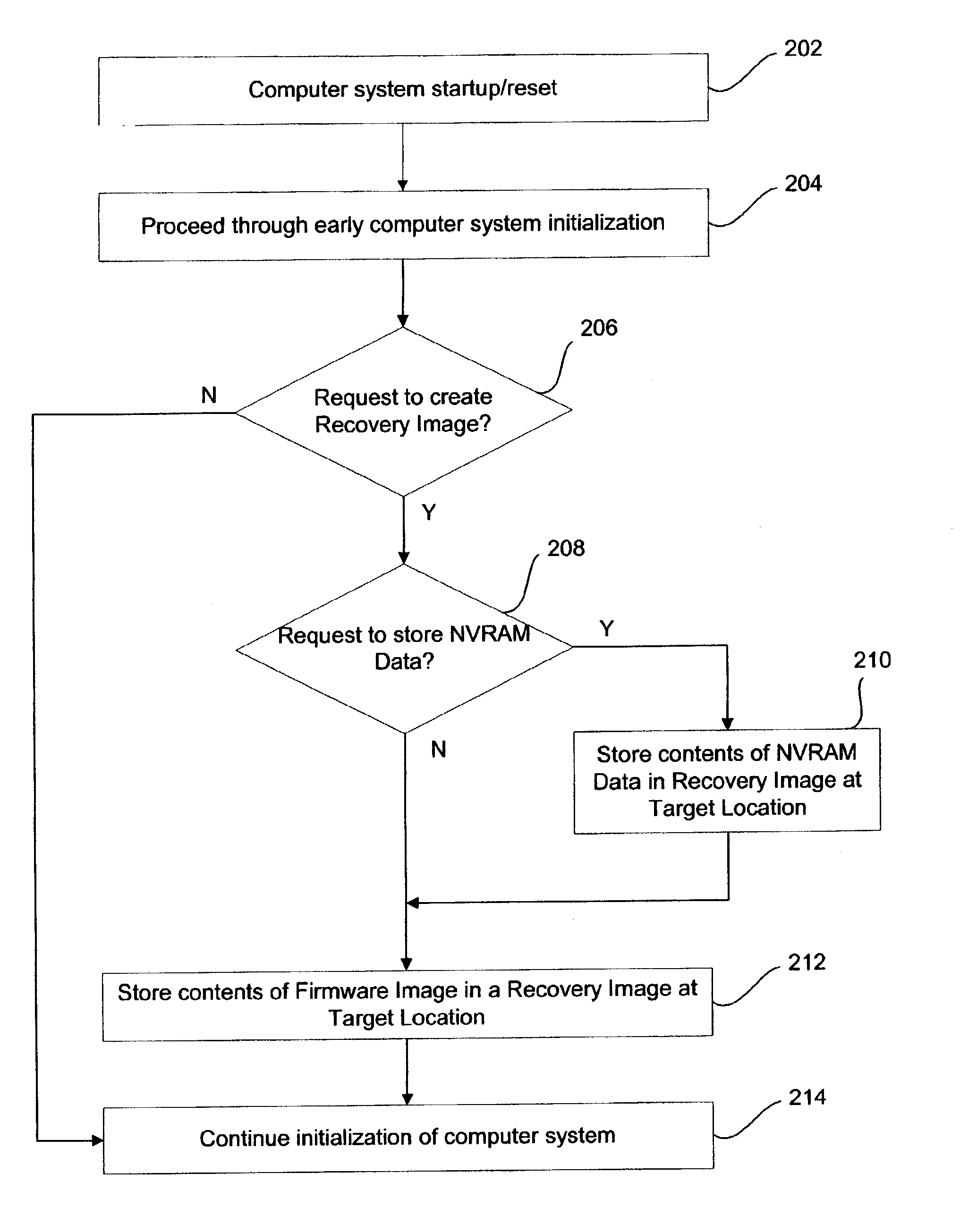
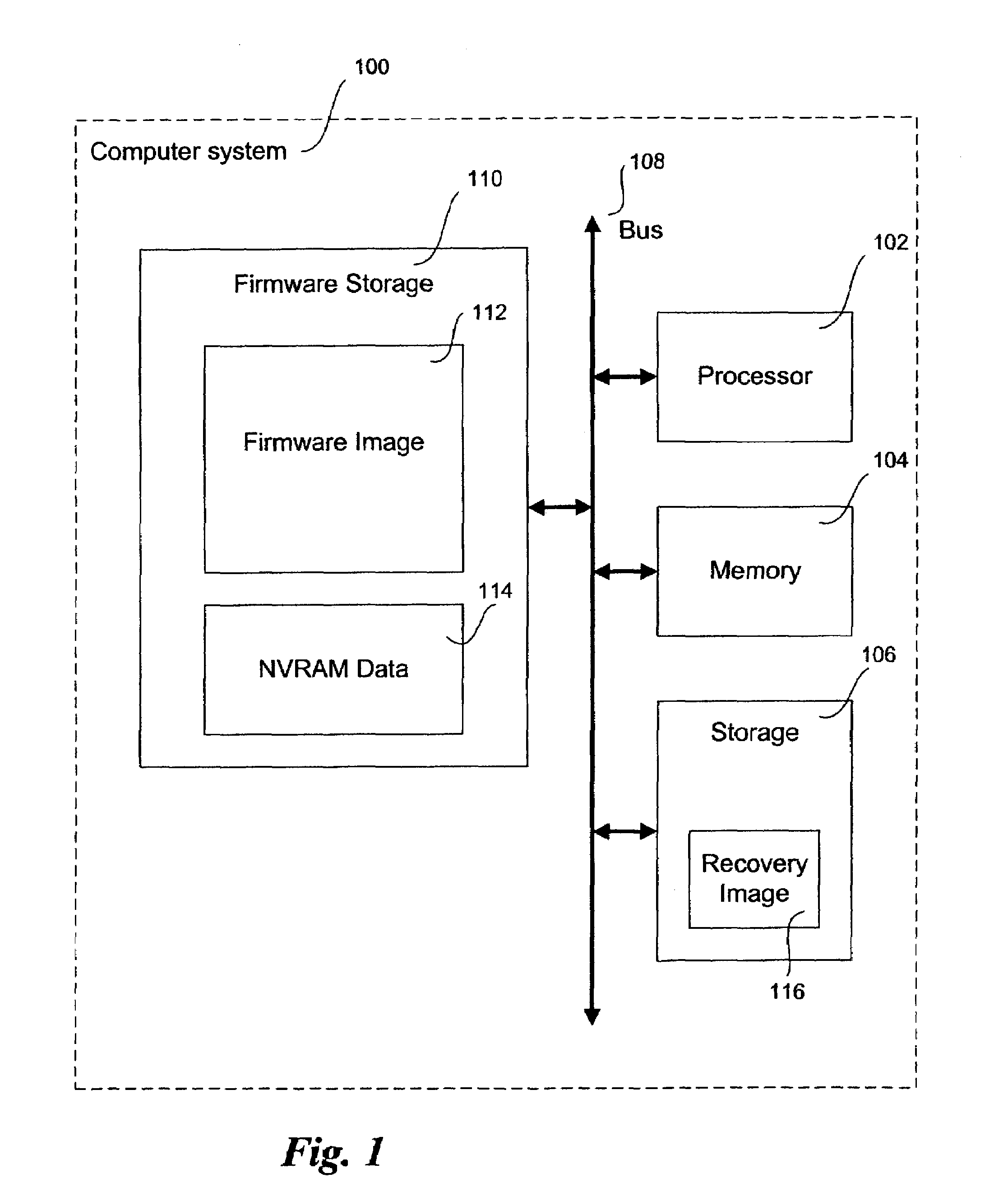
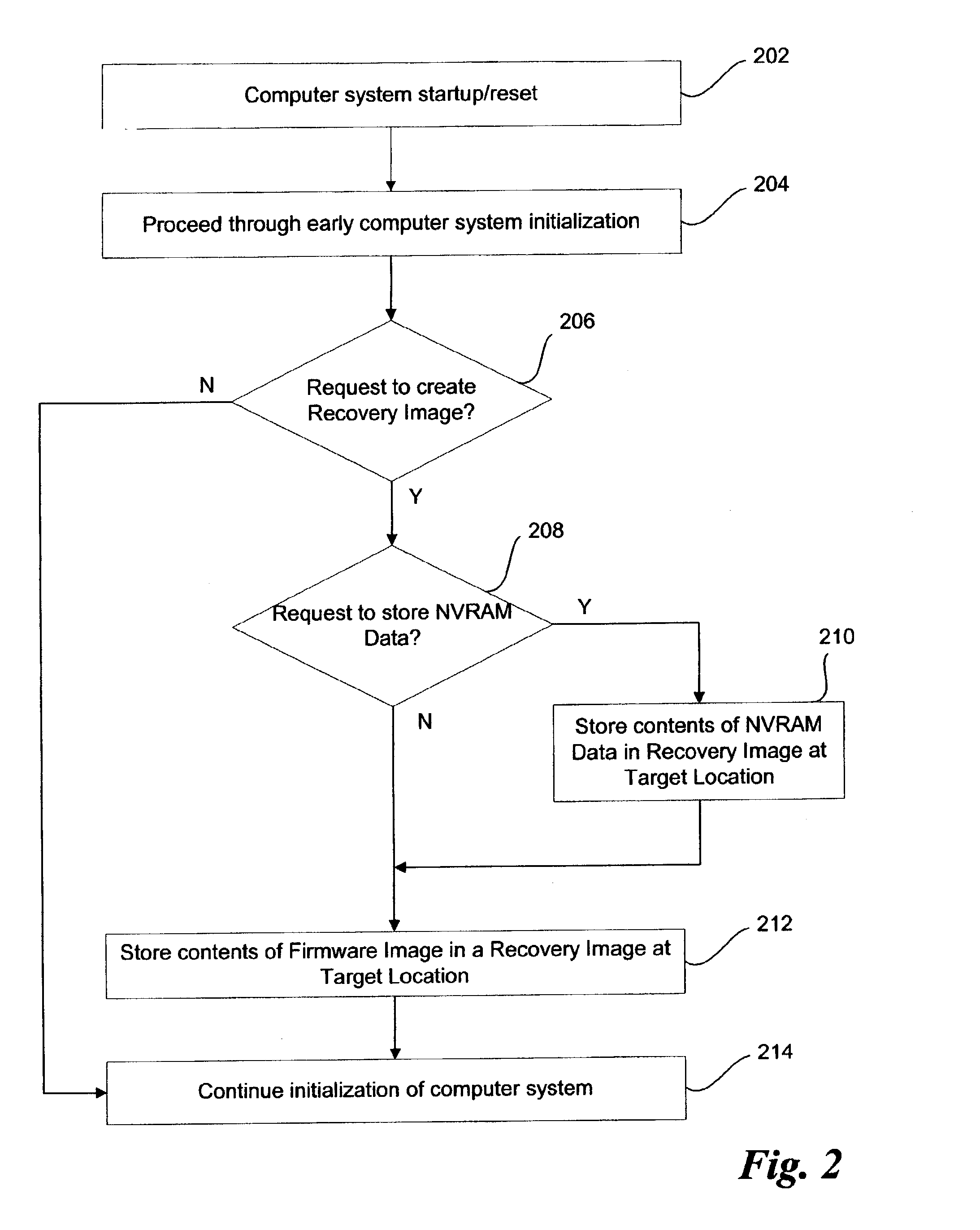
Recovery images in an operational firmware environment
A method and system to create a recovery image of firmware stored in a firmware storage device of a computer system. A recovery image of firmware is created and stored at a target location, wherein the target location includes a magnetic disk. The firmware storage device to store Basic Input / Output System (BIOS) firmware and / or Non-Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM) Data of an Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) compliant computer system. In one embodiment, the firmware of the computer system is recovered from the recovery image.
Owner:INTEL CORP
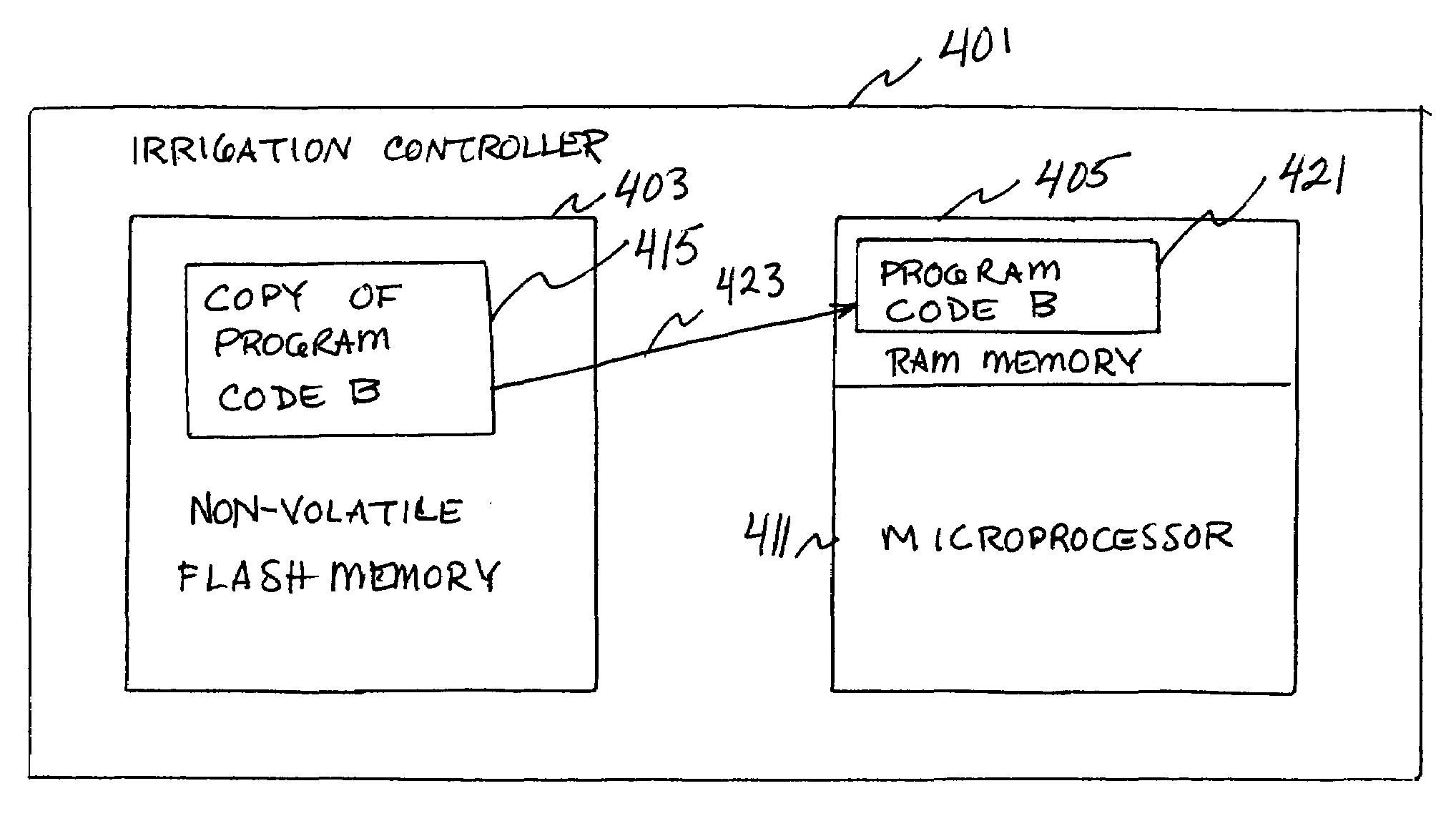
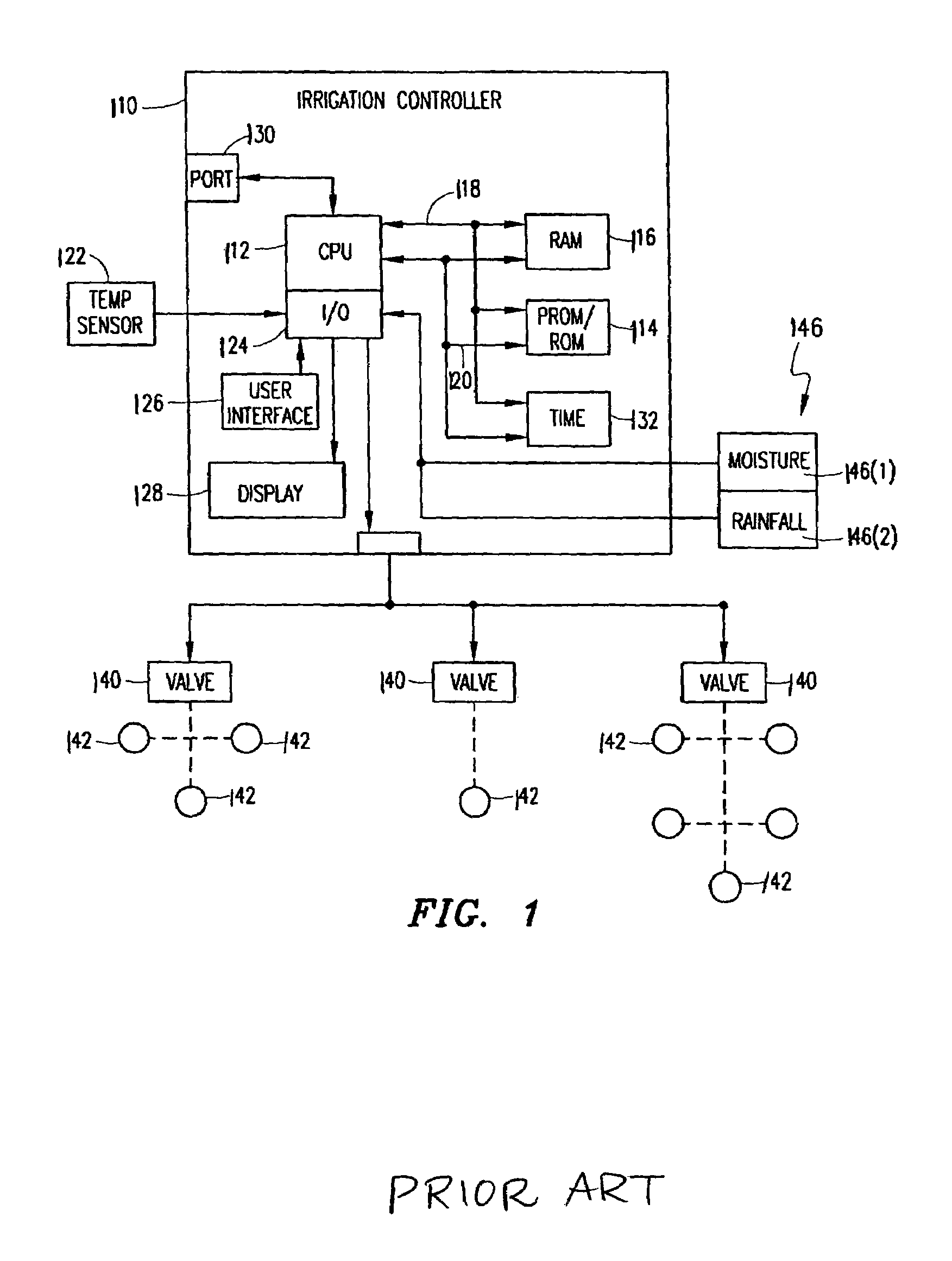
Method and system for remote update of microprocessor code for irrigation controllers
ActiveUS7269829B2Reduce deficiencySimple meansComputer controlSimulator controlRandom access memoryNon-volatile random-access memory
A remote download of microprocessor code for an irrigation controller is provided. A microprocessor, on an irrigation controller, is executing program code (in volatile memory) and receives a remote download of updated program code, which it stores into non-volatile random access memory, e.g., flash memory. The microprocessor is configured to receive the updated program code, via a communication port, and to store the updated program code into the non-volatile flash memory. Optionally, the updated program code is received at multiple controllers via a global transmission on a communication bus. The microprocessor receives a communication causing it to re-start. In response to the re-start communication, the microprocessor fetches the updated program code stored in the non-volatile flash memory into the program memory RAM to replace the original program code, and begins execution of the updated program code in the program memory RAM. A device is also provided for directing the download of program code to irrigation controllers. Options provide for global download of entirely new program code, global and / or individual download of particular pages of updated program code, and global downloads to controllers grouped by communication speed.
Owner:SIGNATURE CONTROL SYST
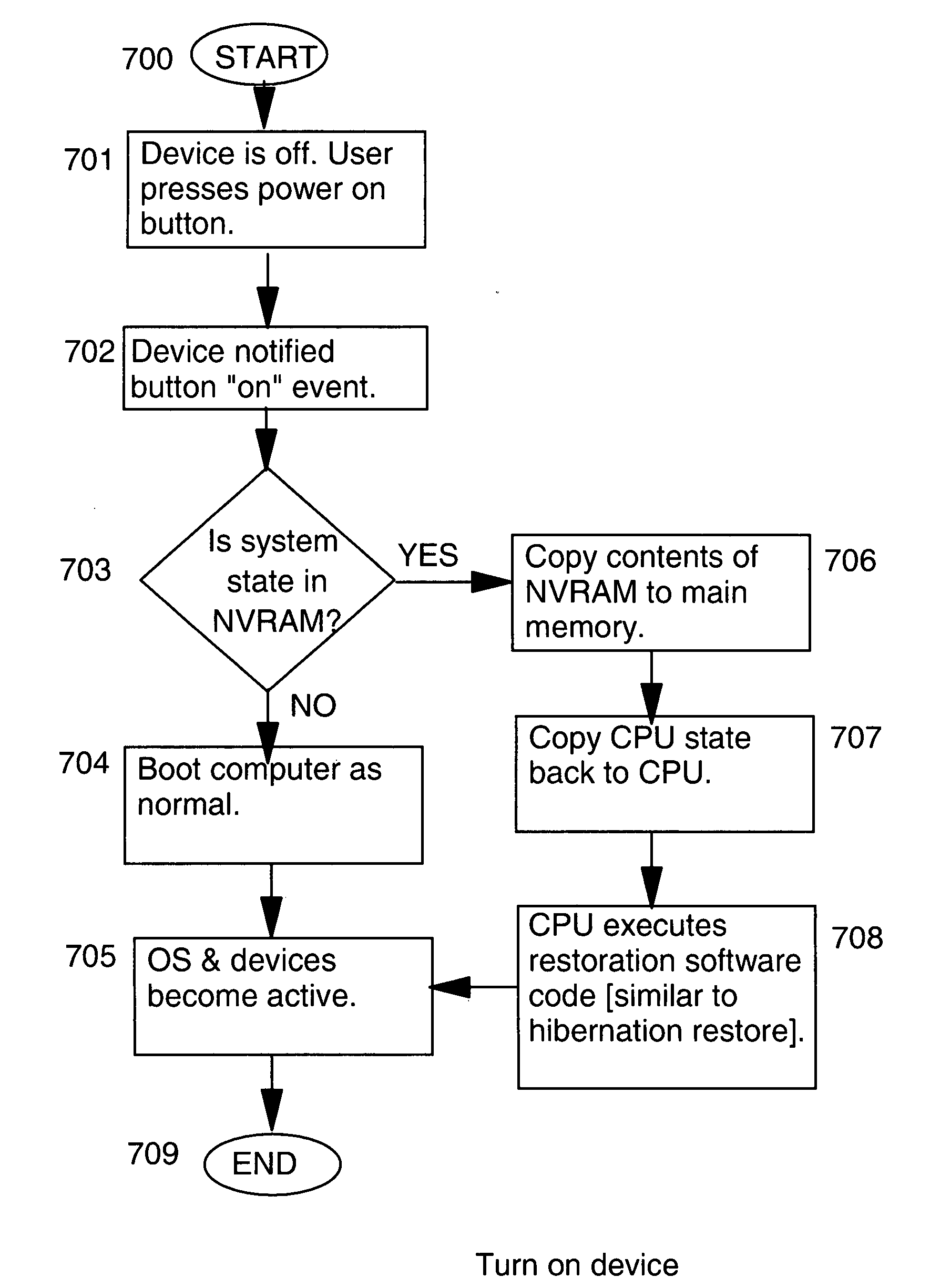
Mirroring system memory in non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) for fast power on/off cycling
InactiveUS20070101077A1Power is consumedSignificant delayMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A computer comprising a processor, a volatile main store, a non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) mirror store, and optionally a cache for the non-volatile mirror store. While programs of the computer are operational, the contents of the volatile main store are mirrored in the non-volatile mirror store such that when a startup signal is received, the contents of the volatile main store are quickly restored from the contents of the non-volatile mirror store.
Owner:IBM CORP
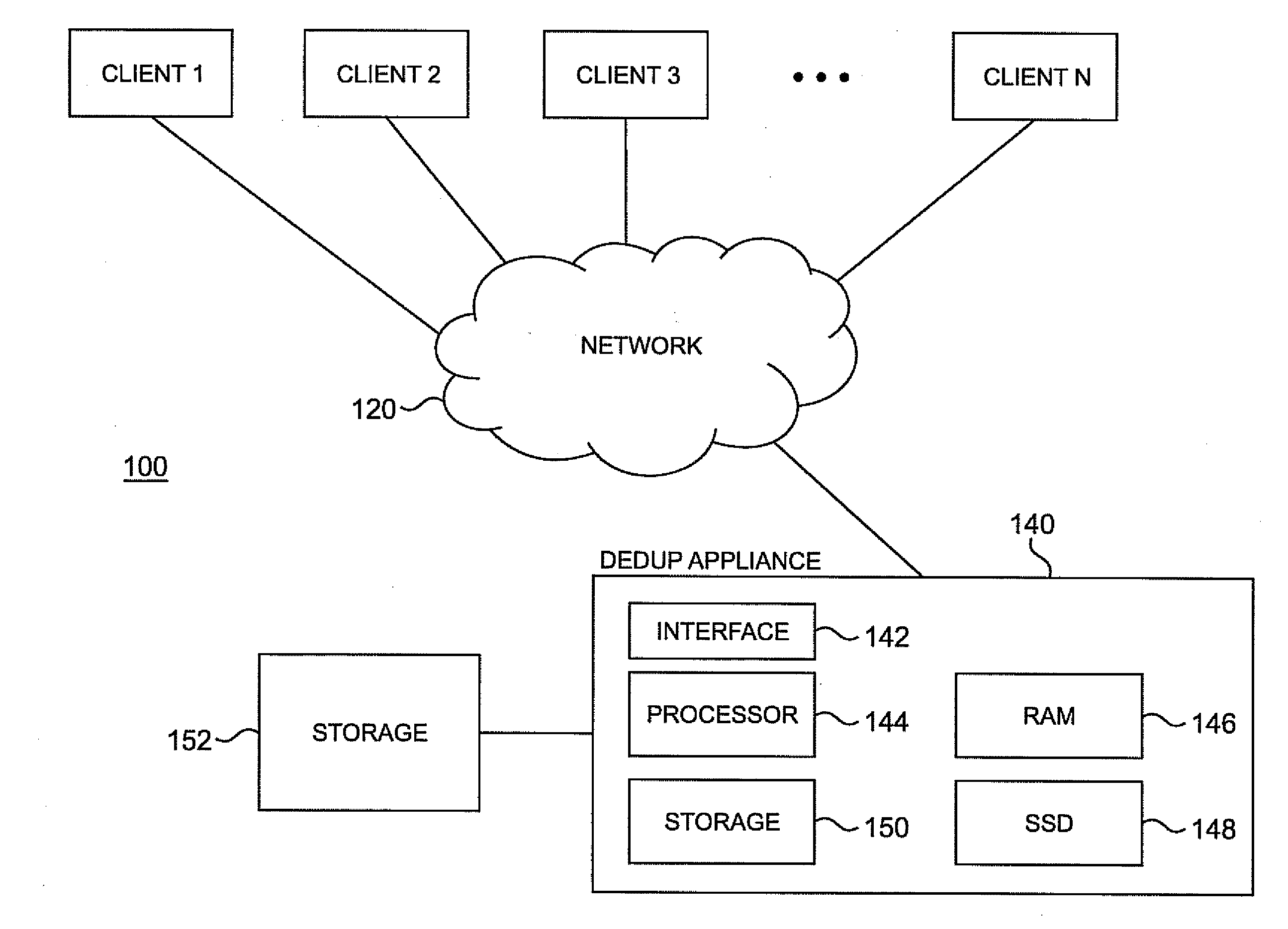
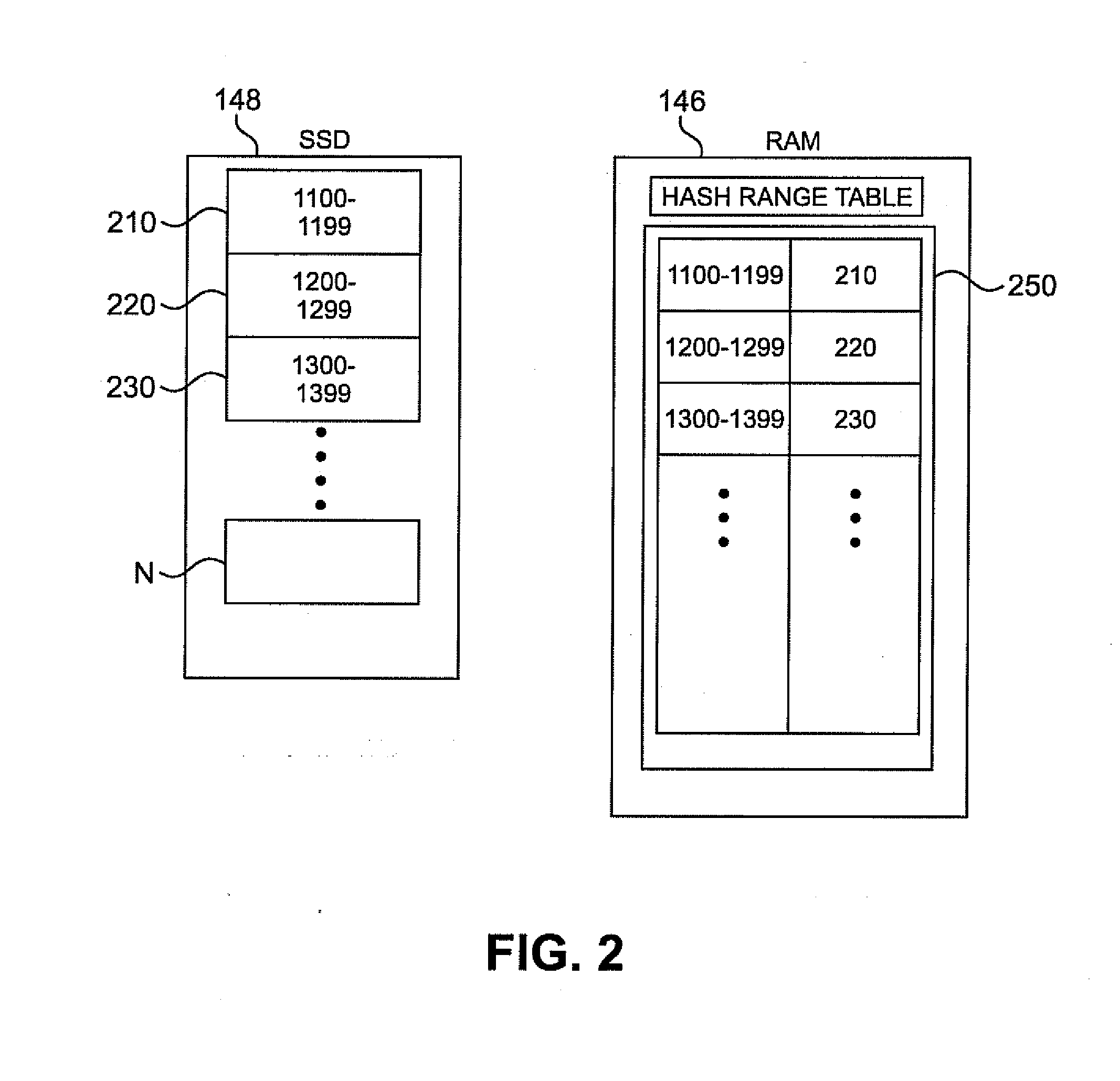
Use of solid state storage devices and the like in data deduplication
ActiveUS20150127621A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesSolid-state storageNon-volatile random-access memory
Systems and methods of data deduplication are disclosed comprising generating a hash value of a data block and comparing the hash value to a table in a first memory that correlates ranges of hash values with buckets of hash values in a second memory different from the first memory. A bucket is identified based on the comparison and the bucket is searched to locate the hash value. If the hash value is not found in the bucket, the hash value is stored in the bucket and the data block is stored in a third memory. The first memory may be volatile memory and the second memory may be non-volatile random access memory, such as an SSD. Rebalancing of buckets and the table, and use of additional metadata to determine where data blocks should be stored, are also disclosed.
Owner:FALCONSTOR
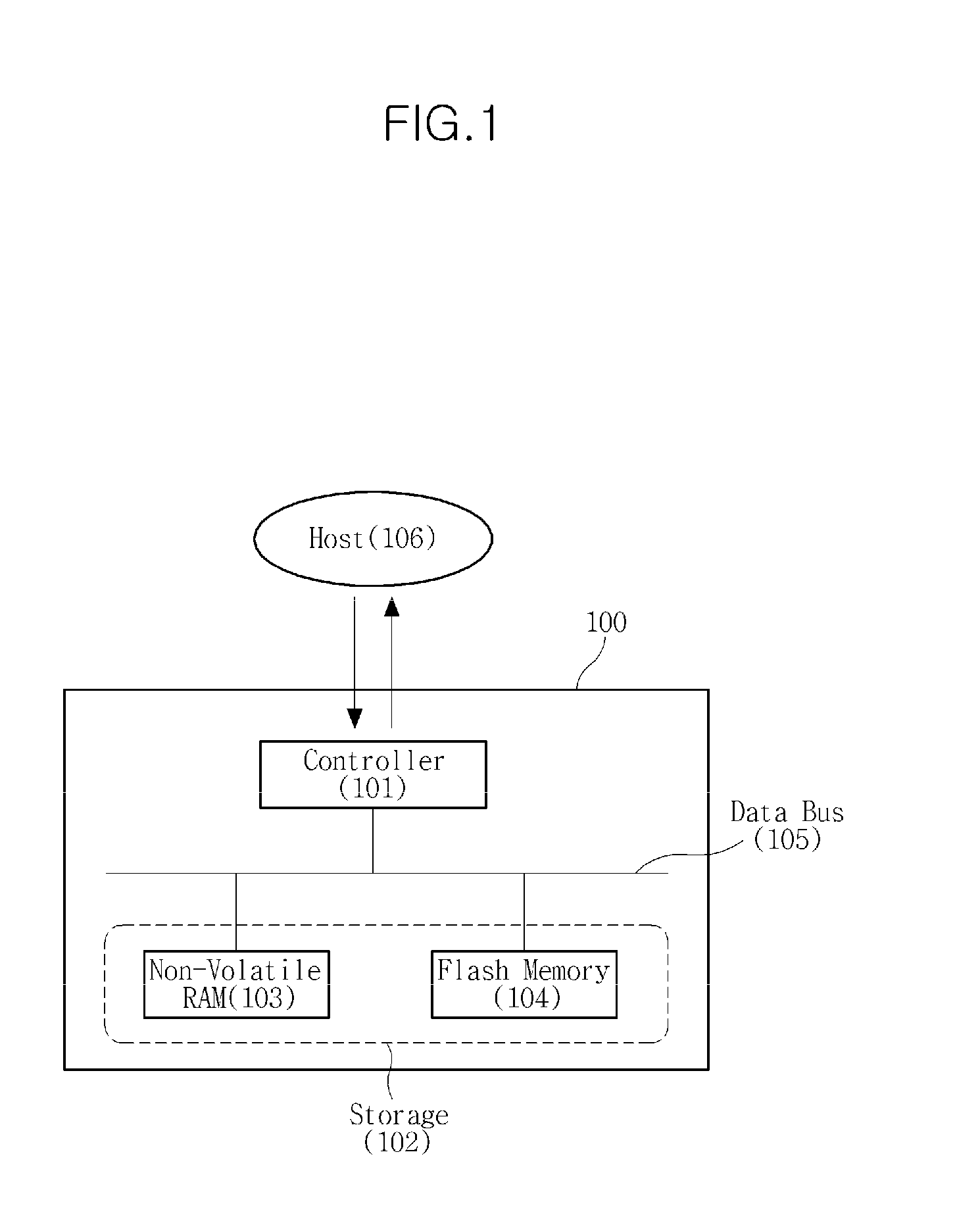
Complex memory device and I/O processing method using the same
InactiveUS20100191898A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageControl memory
A non-volatile mass storage memory and an input / output processing method using the memory are provided. The memory device includes a storage unit including a non-volatile random access memory and a flash memory and a controller to control the storage to process an input / output request. Accordingly, system memories having different purposes and functionalities, such as a flash memory and a dynamic random access memory (DRAM), may be integrated with each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com