Patents
Literature
3601 results about "Programmable logic device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike integrated circuits (IC) which consist of logic gates and have a fixed function, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed (reconfigured) by using a specialized program.
Programmable multimedia controller with programmable services
ActiveUS20070142022A1Easy to useEfficient modificationLink editingTransmission systemsControl systemProgrammable logic device
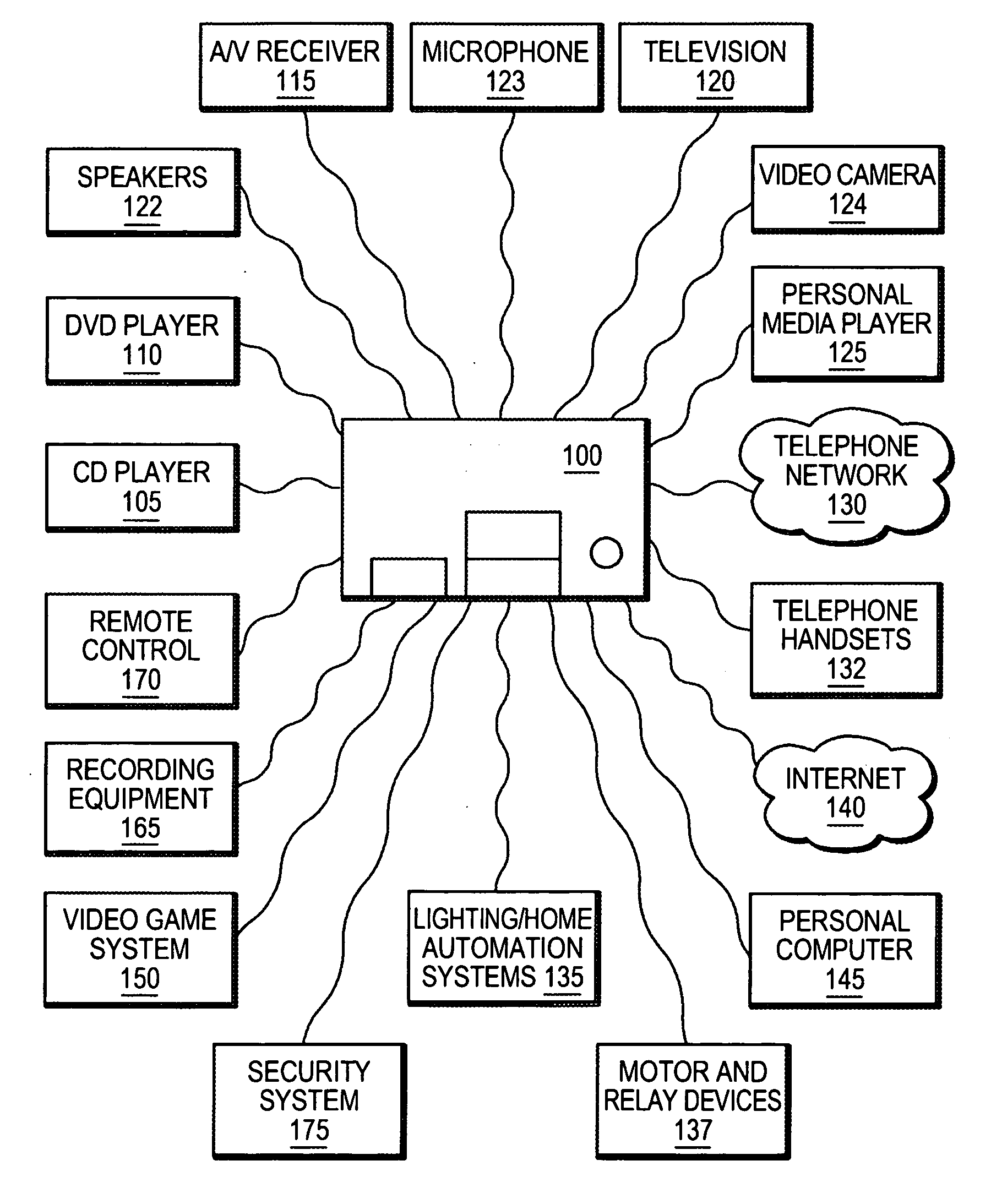
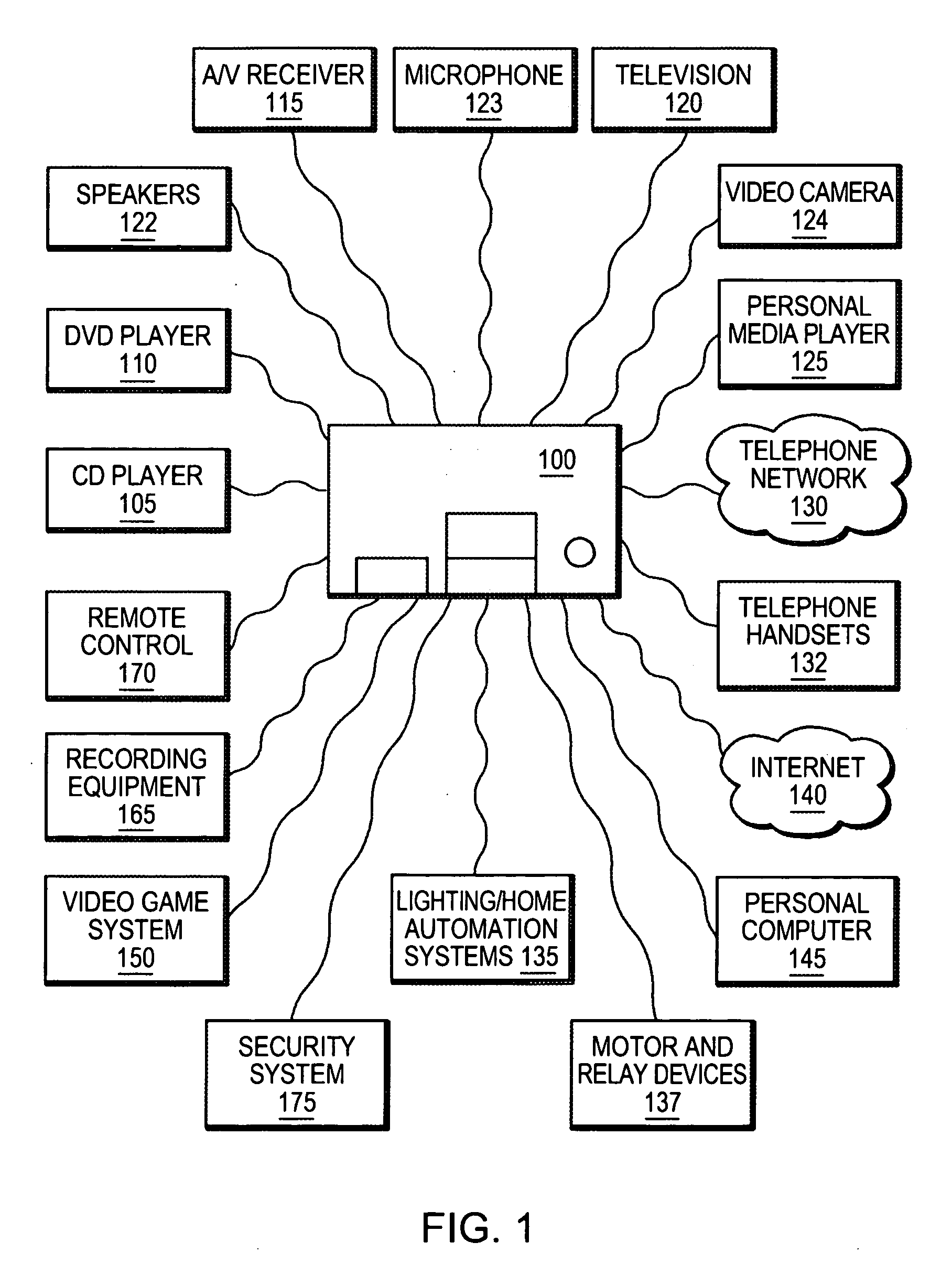
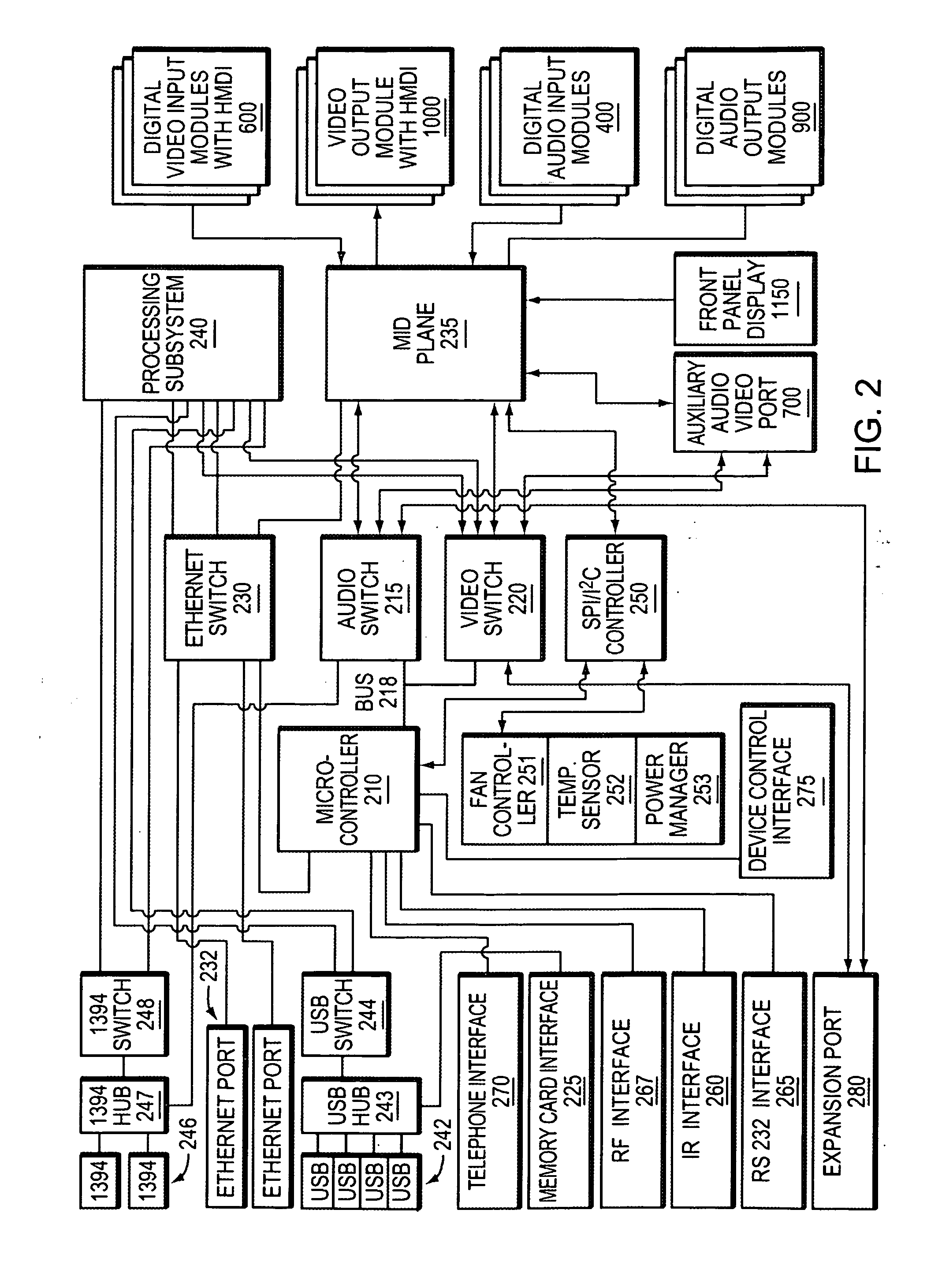
An integrated multimedia, entertainment, communications and control system. The system is based on a general purpose computer and is capable of interfacing with, controlling or managing a wide variety of audio, video, telecommunications, data communications or other devices. The system includes a programming environment for creating services or user experiences that may incorporate features or functionalities of several devices that are conventionally operated as separate, standalone devices.
Owner:SAVANT SYST INC
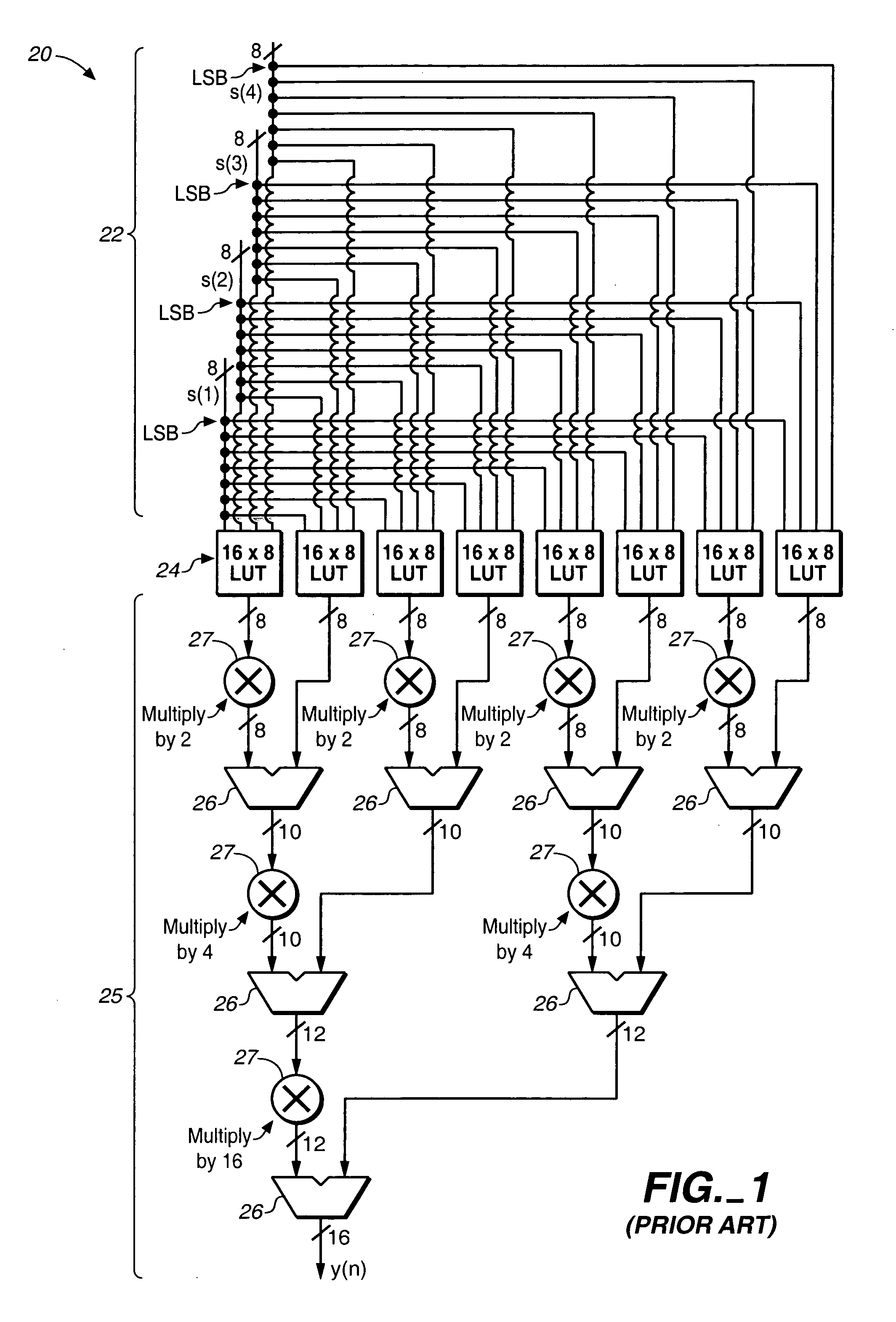
Variable fixed multipliers using memory blocks
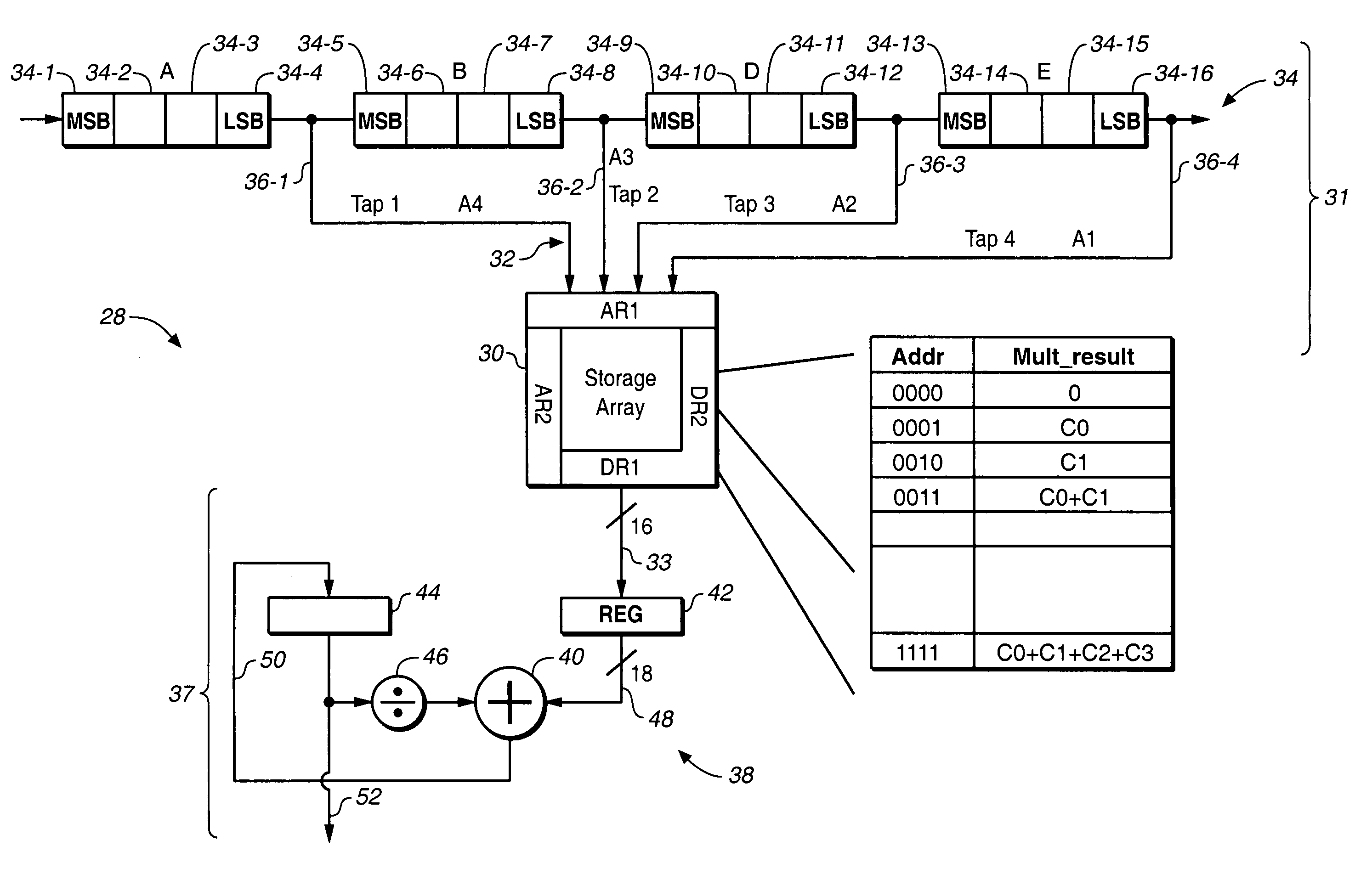
InactiveUS6943579B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProgrammable logic deviceOperand
A programmable logic device includes at least one RAM block generating a first multi-bit calculation result which may, but does not necessarily, involve a multiplication of two operands. A shift operation is driven by a second multi-bit calculation result shifts the second multi-bit calculation result by at least one bit to generate a shifted second multi-bit calculation result. A multi-bit adder coupled to the at least one RAM block adds the shifted second multi-bit calculation result to the first multi-bit calculation result.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Signal loss detector for high-speed serial interface of a programmable logic device
InactiveUS7996749B2Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPattern matchingProgrammable logic device
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Multi-chip programmable logic device having configurable logic circuitry and configuration data storage on different dice
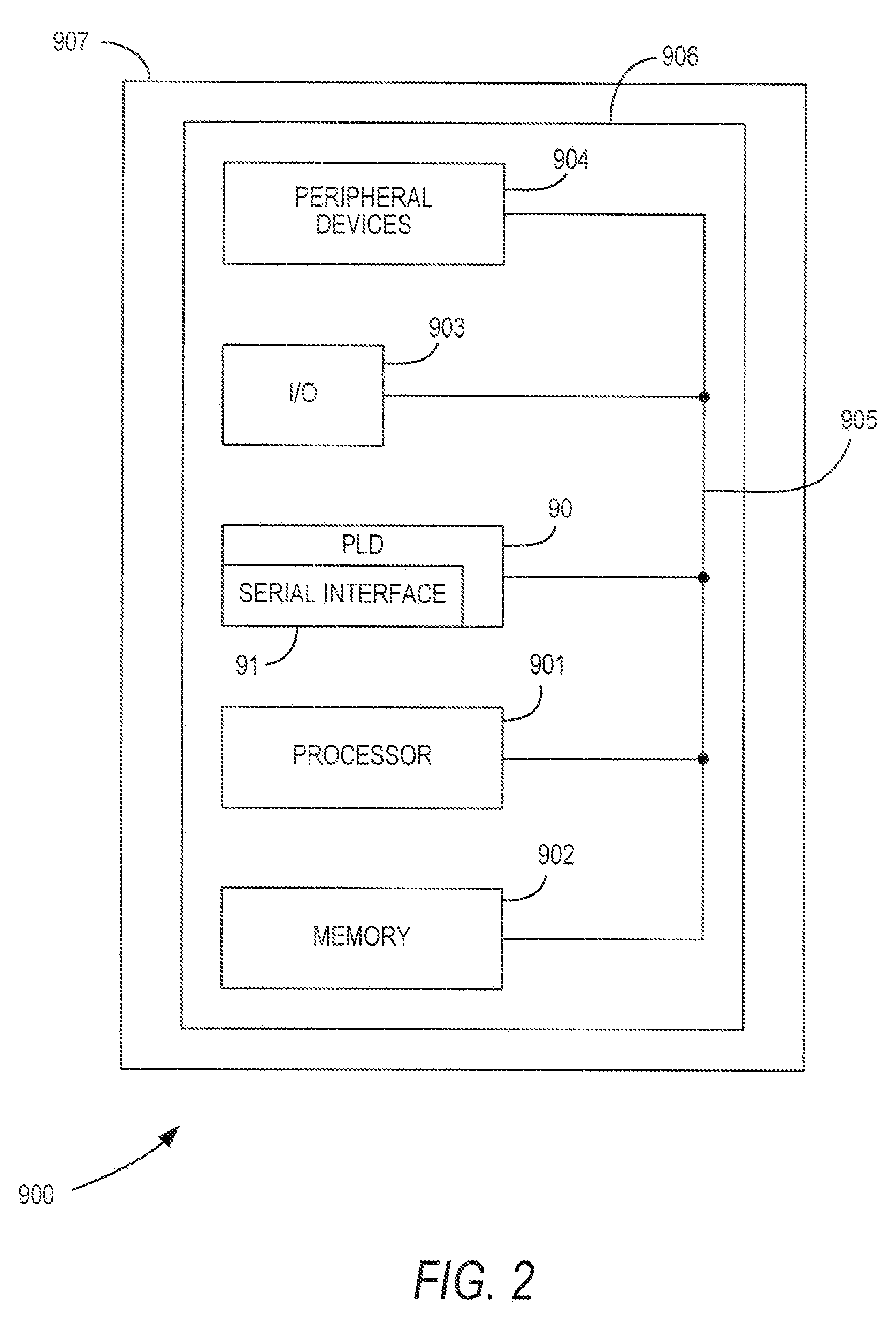
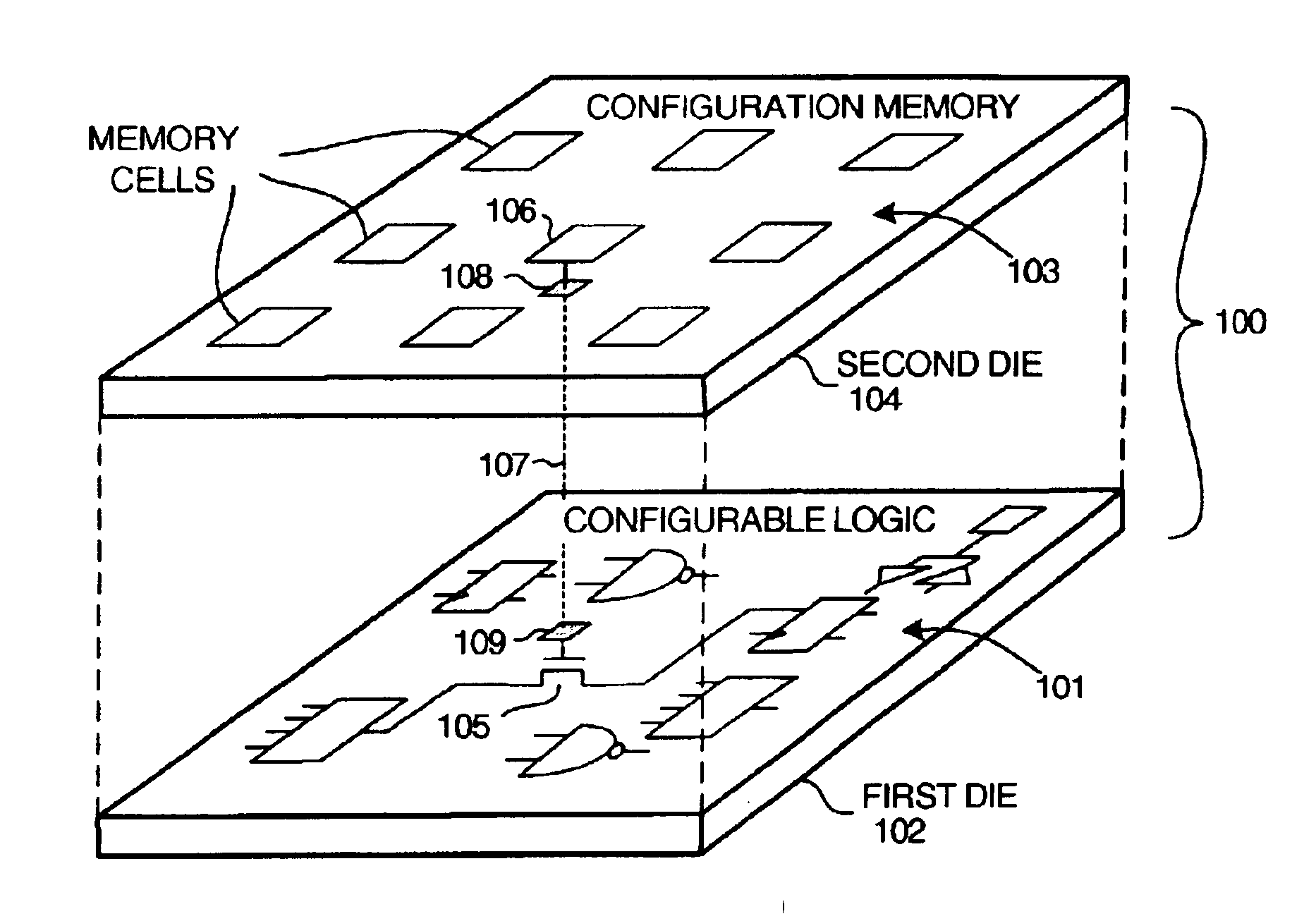
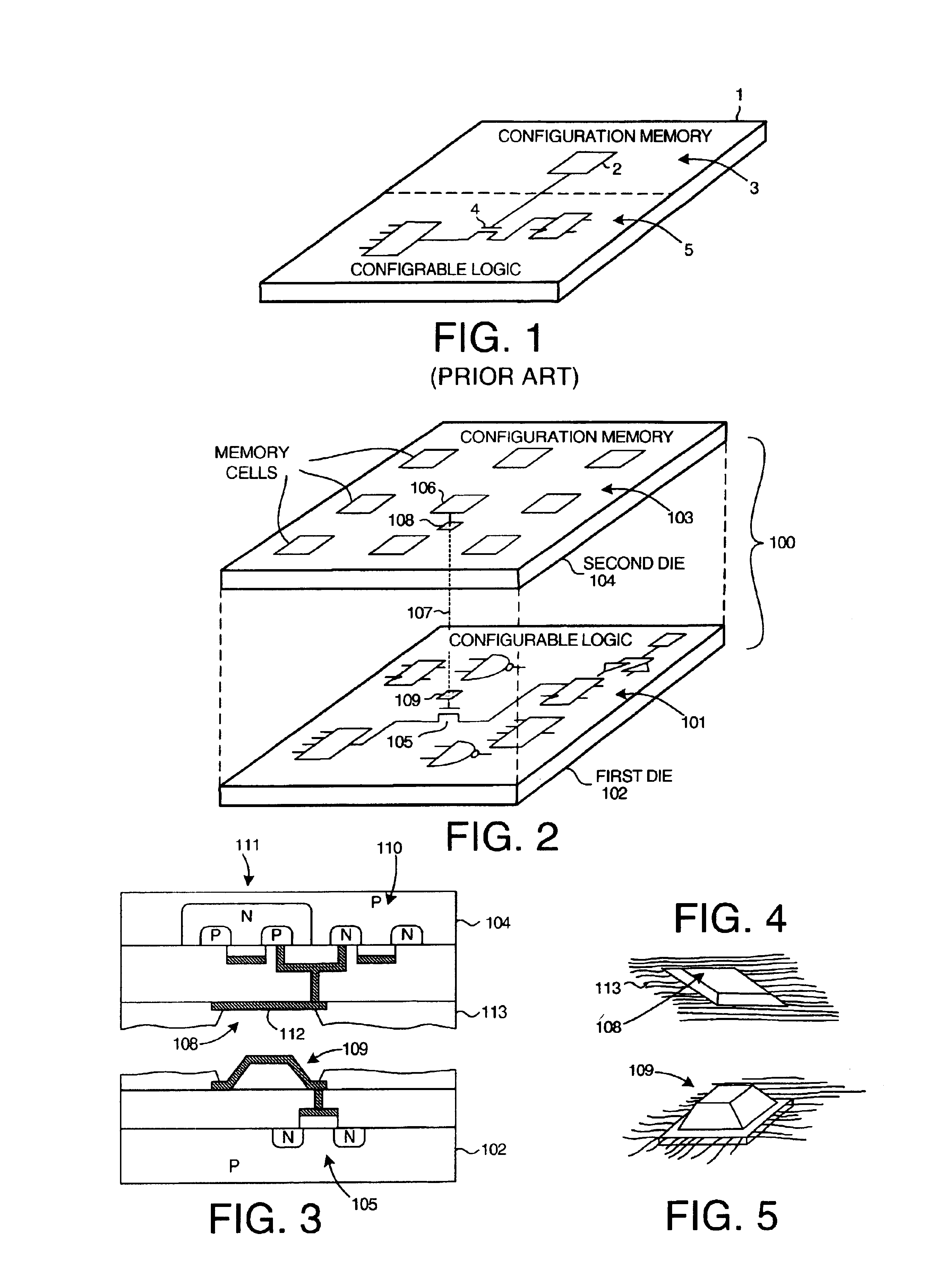
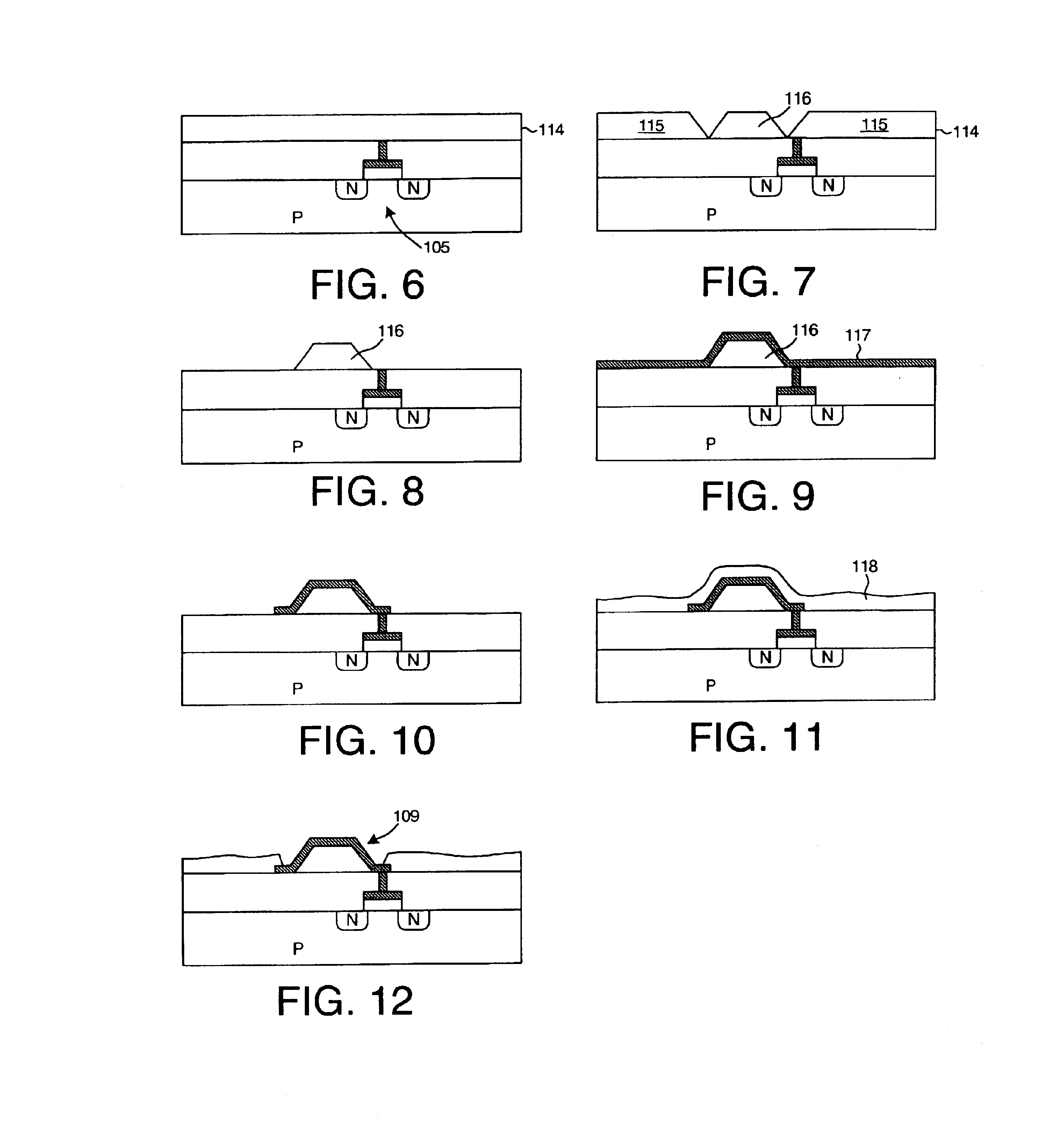
InactiveUS6917219B2Increase volumeIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceLogical part
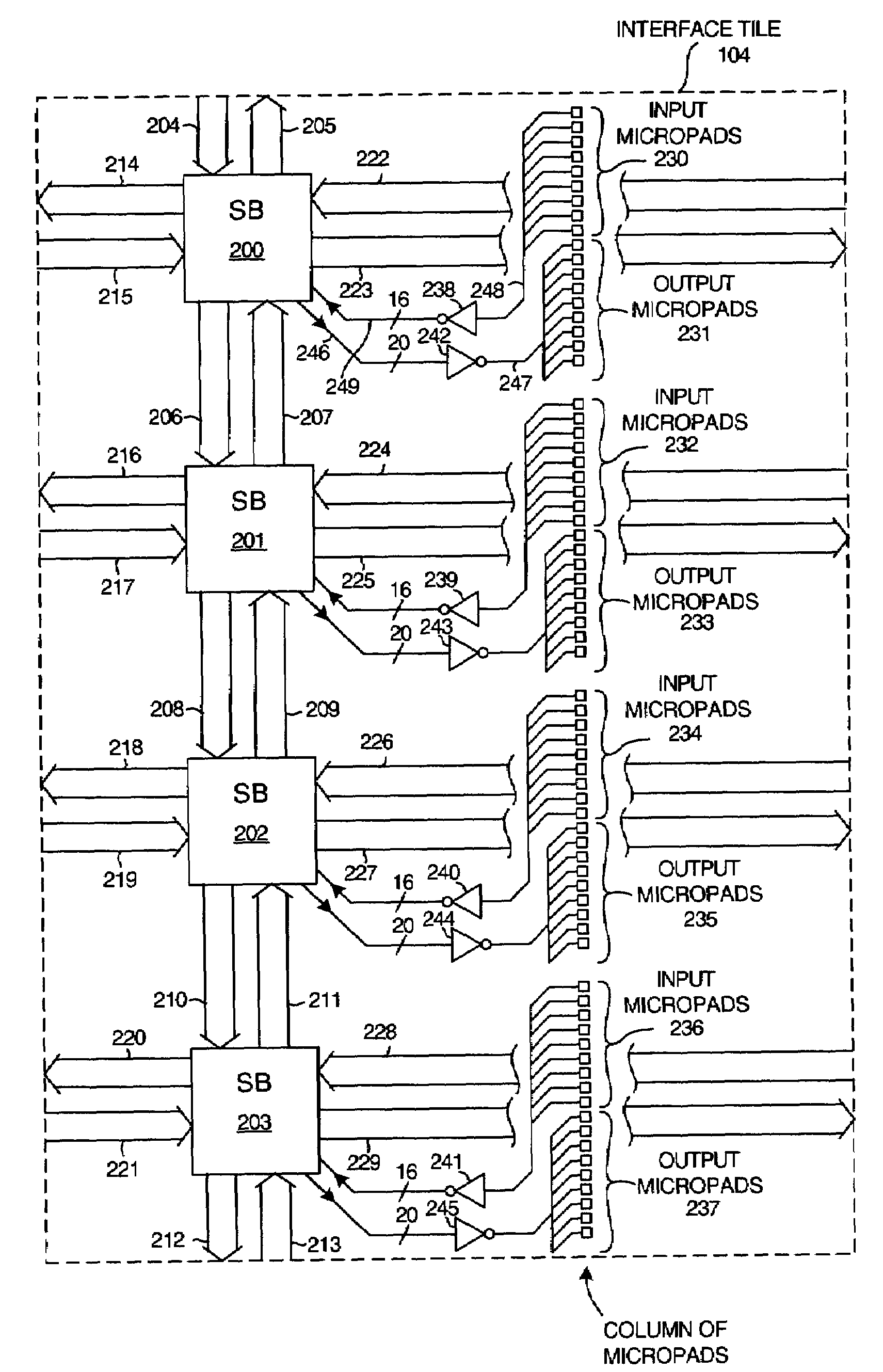
The circuitry of a programmable logic device (for example, an FPGA) includes a configurable logic portion and a configuration memory. The configuration memory stores configuration data that configures the configurable logic portion to realize a user-defined circuit. The configurable logic portion is disposed on a first die whereas the configuration memory is disposed on a second die. The second die is bonded to the first die in stacked relation. Each bit of configuration data passes from the second die to the first die through a pair of micropads. One micropad of the pair is disposed on the first die and the other micropad of the pair is disposed on the second die. When the first die and second die are brought together in face-to-face relation, the two micropads form an electrical connection through which the configuration data bit passes from the second die to the first die.
Owner:XILINX INC
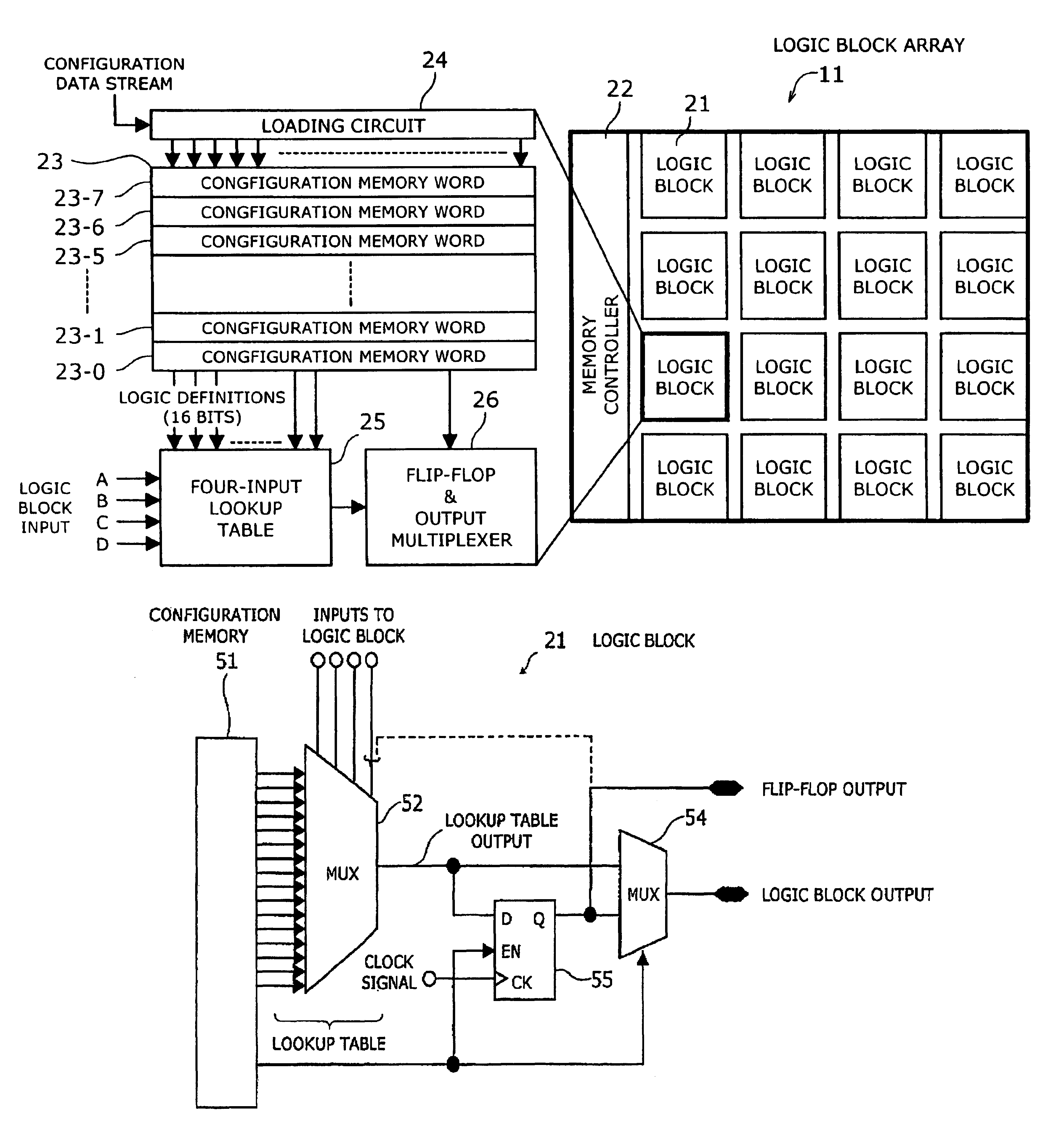
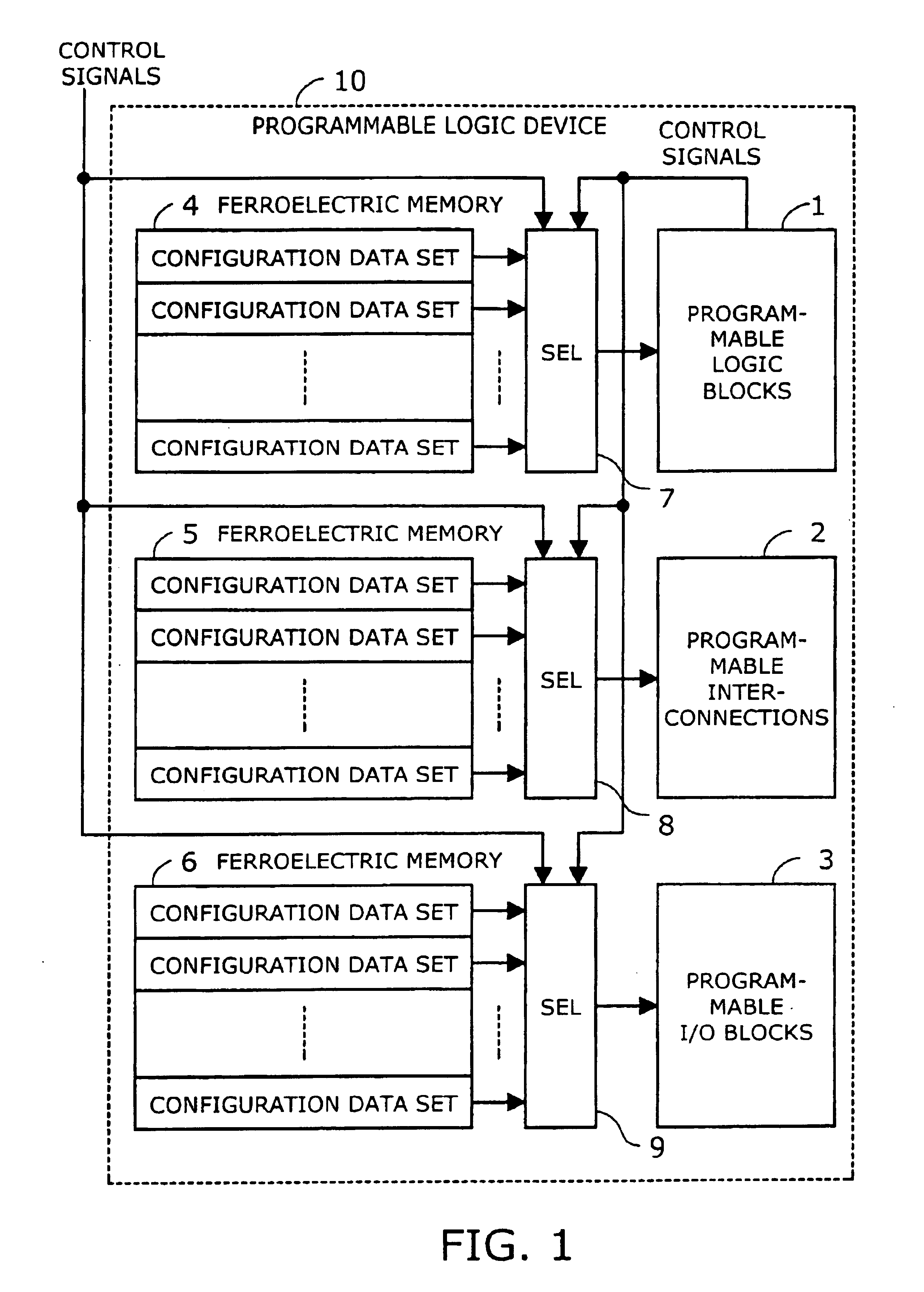
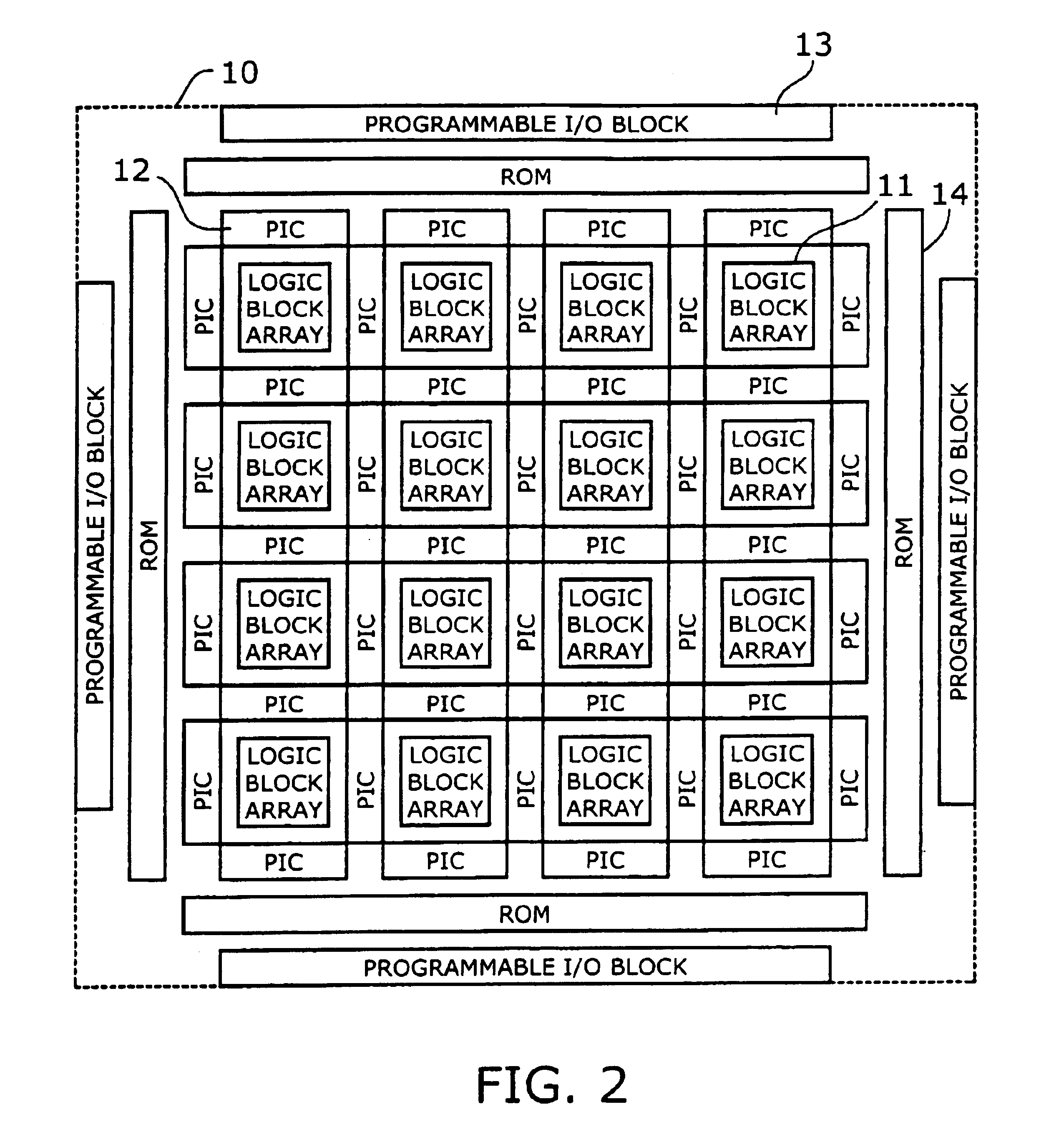
Programmable logic device with ferroelectric configuration memories
InactiveUS6924663B2Increase the effective amountEfficient architectureDigital storageInternal/peripheral component protectionElectricityData stream
A programmable logic device with ferroelectric configuration memories storing multiple configuration data sets. The device has programmable logic blocks, interconnections, and I / O blocks to provide desired logic functions. Those building blocks can be dynamically reconfigured by changing the selection of configuration data stored in the device's integral configuration memories. The configuration memories are divided into groups, so that they can be loaded concurrently with multiple configuration data streams. To protect the content of configuration memories from unauthorized access, the device employs an authentication mechanism that uses security IDs stored in the configuration memories. The device has a memory controller to provide an appropriate power supply sequence for ferroelectric memory cells to ensure the reliable data retention when the device is powered up or shut down.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Packet capture for error tracking
A method of tracking network traffic anomalies in a computing system, comprises receiving an ingress network packet at a configurable logic device (CLD), associating a timestamp with the packet, identifying at least one anomaly based on the contents of the packet, and storing the anomalous packet and the timestamp in a persistent memory.
Owner:BREAKINGPOINT SYST
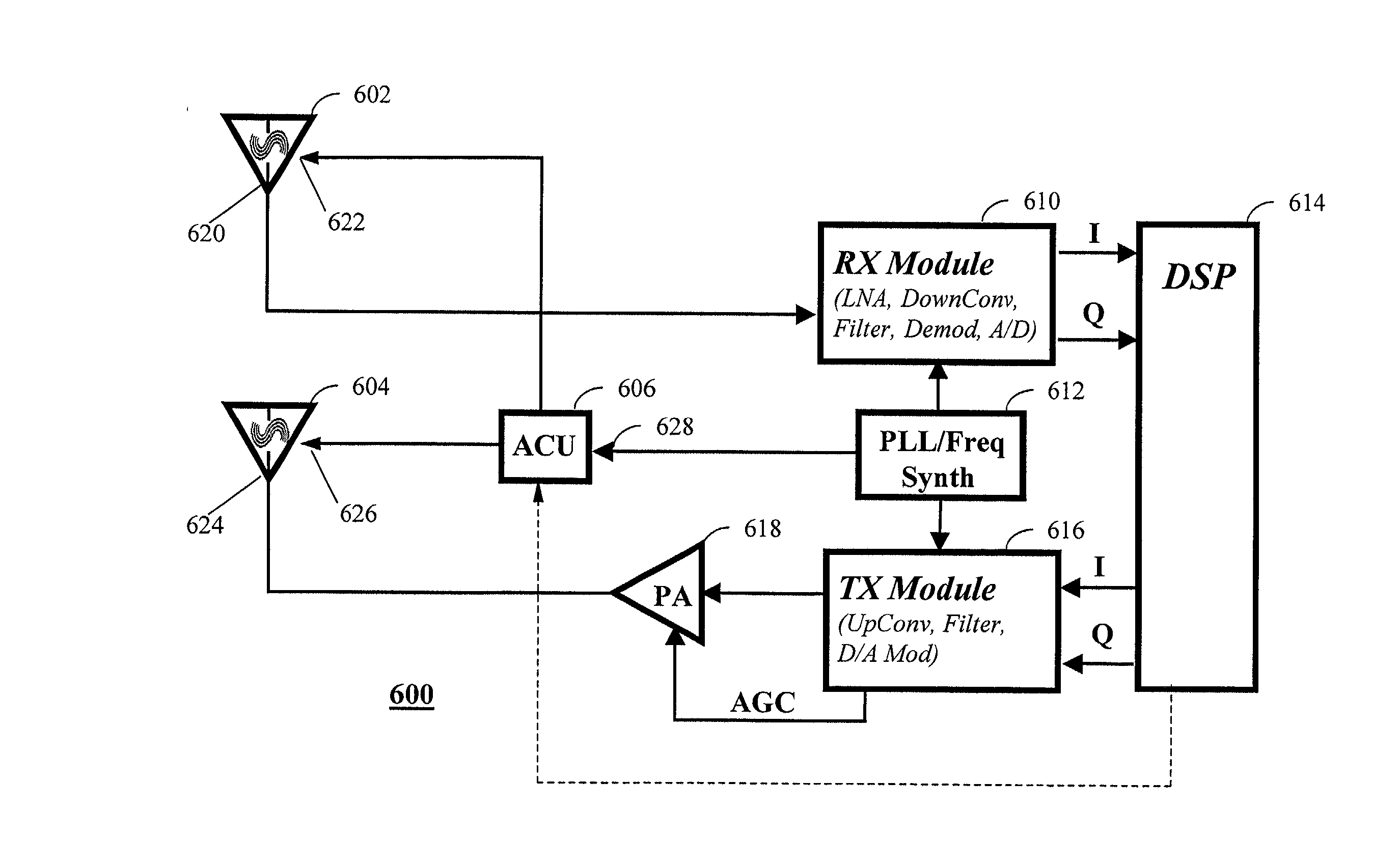
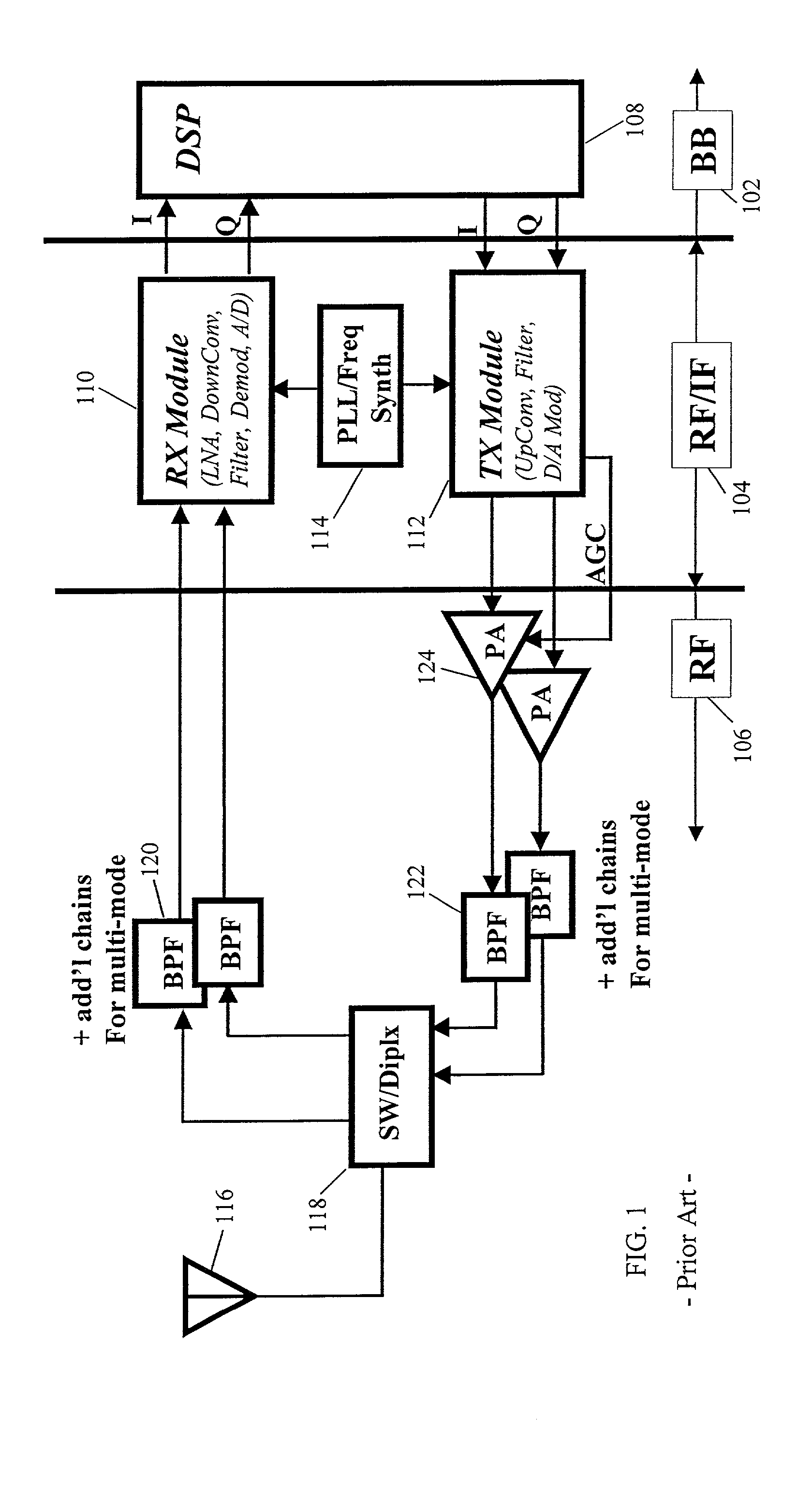
Programmable radio frequency sub-system with integrated antennas and filters and wireless communication device using same
InactiveUS20020183013A1Maximum flexibilityImprove user convenienceAntenna supports/mountingsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCapacitanceRF front end
The present invention relates generally to radio communication devices. More particularly, the present invention relates to a programmable radio frequency (RF) sub-system and wireless communications devices using such an integrated antenna / filter sub-system. In one embodiment, the programmable RF front end subassembly includes two antennas, RF filter sections that are integral to each antenna, and a programmable logic device as an antenna control unit. Each antenna consists of a planar inverted "F" antenna (PIFA) that is tuned to operate over a range of frequencies using voltage variable capacitors or RF switches that connect various capacitive loads in order to achieve the desired resonant frequencies. The wireless communication device further includes a control circuit coupled to the antenna to provide the control signals.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
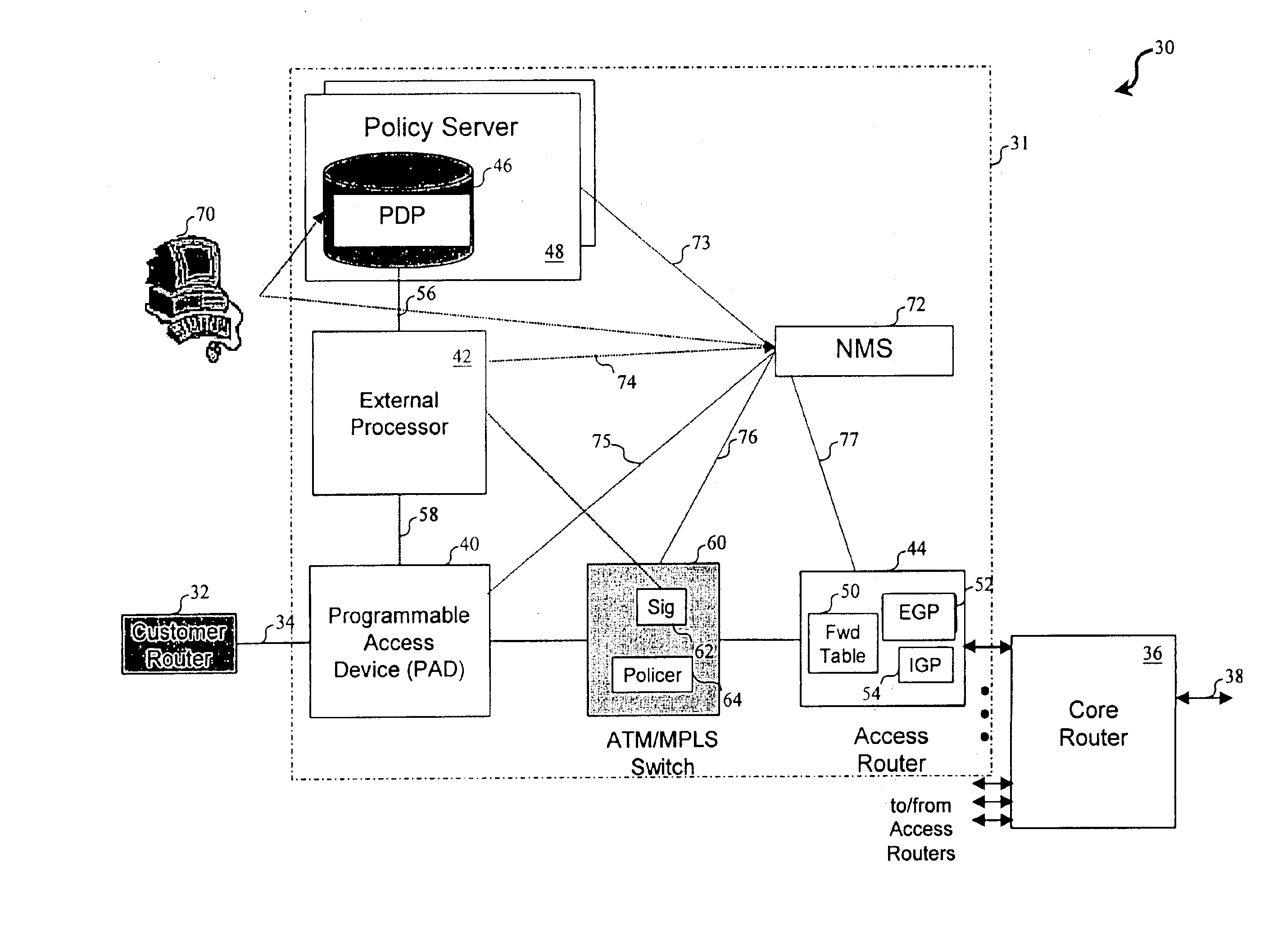
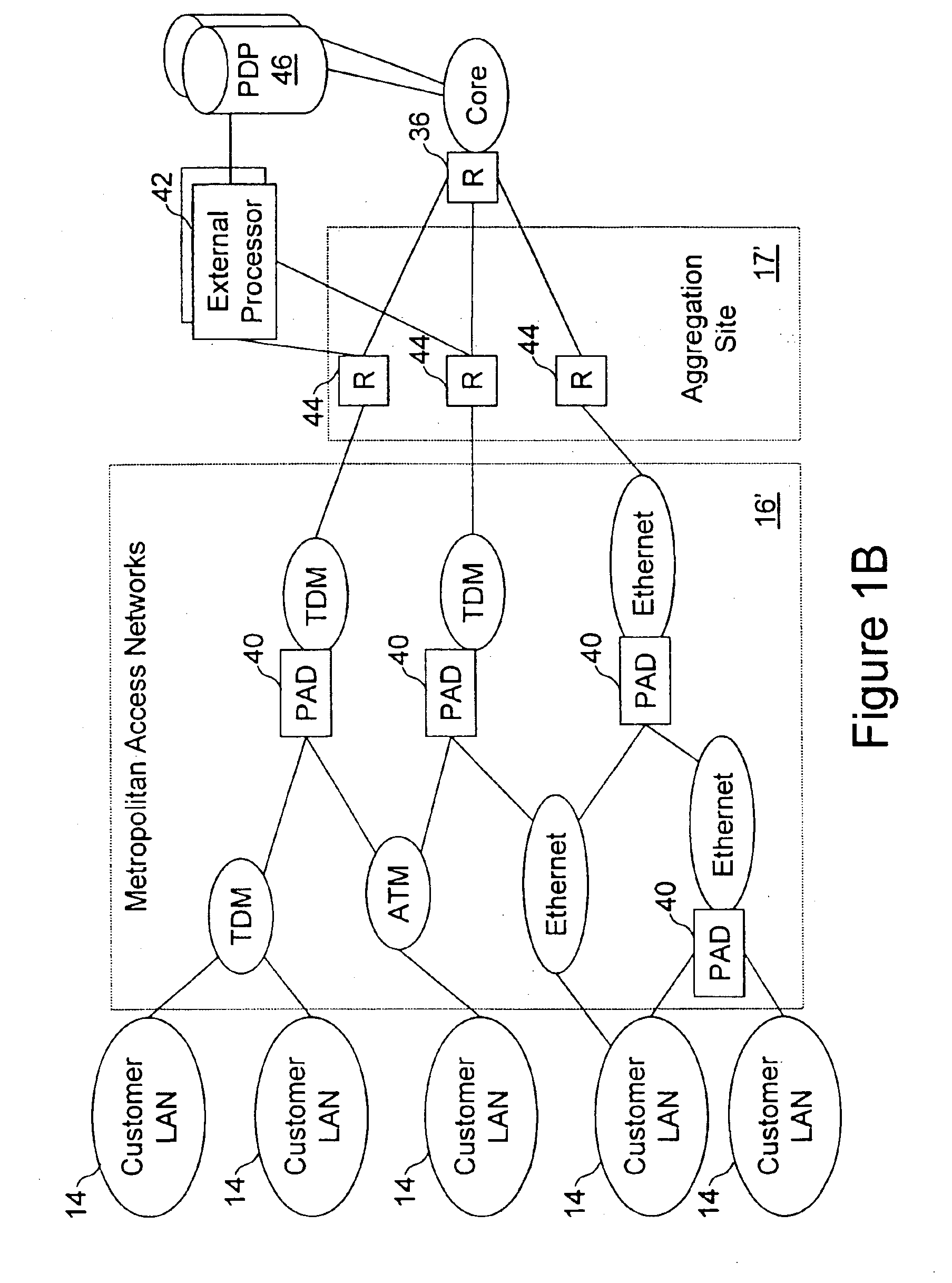
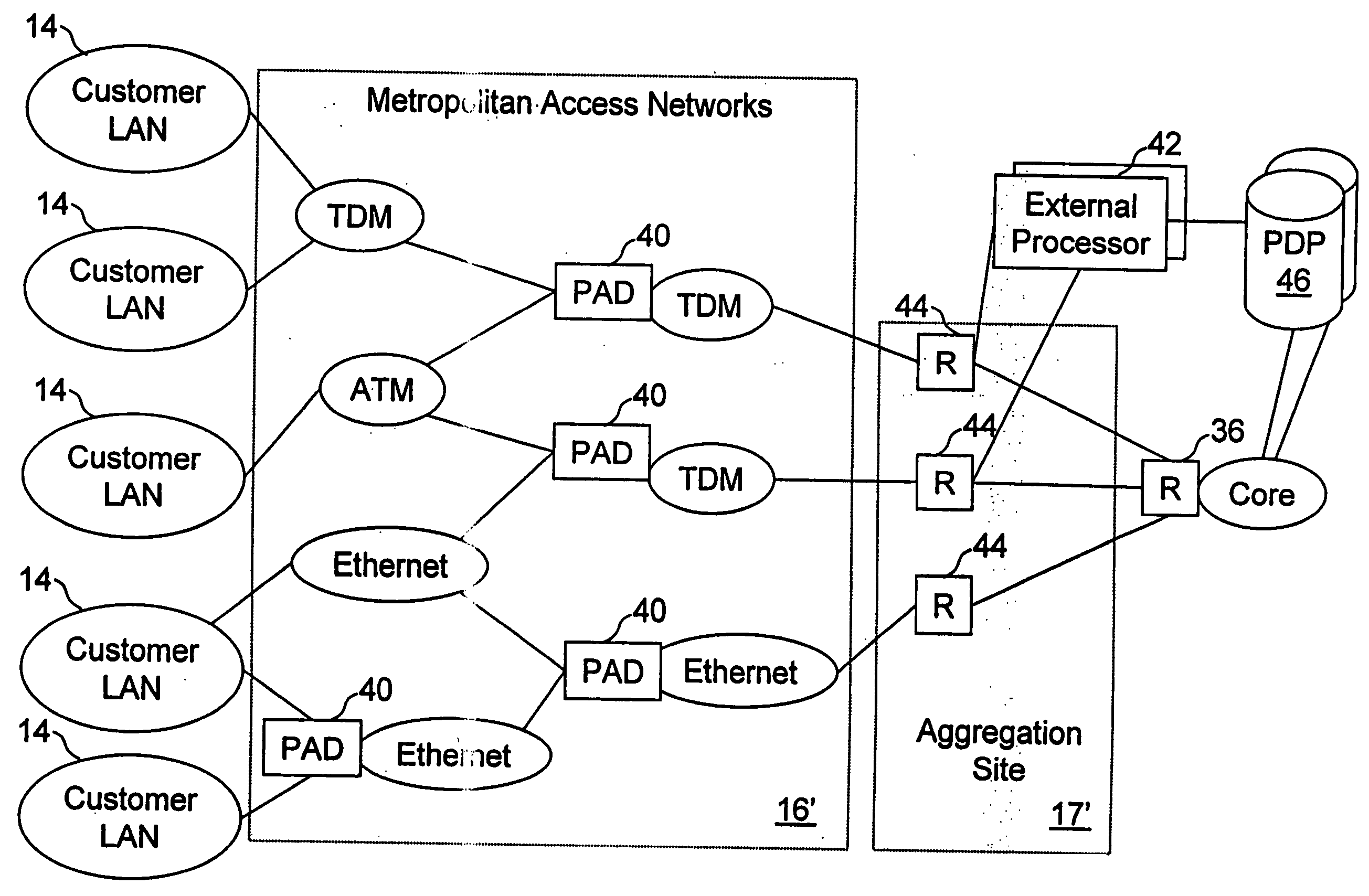
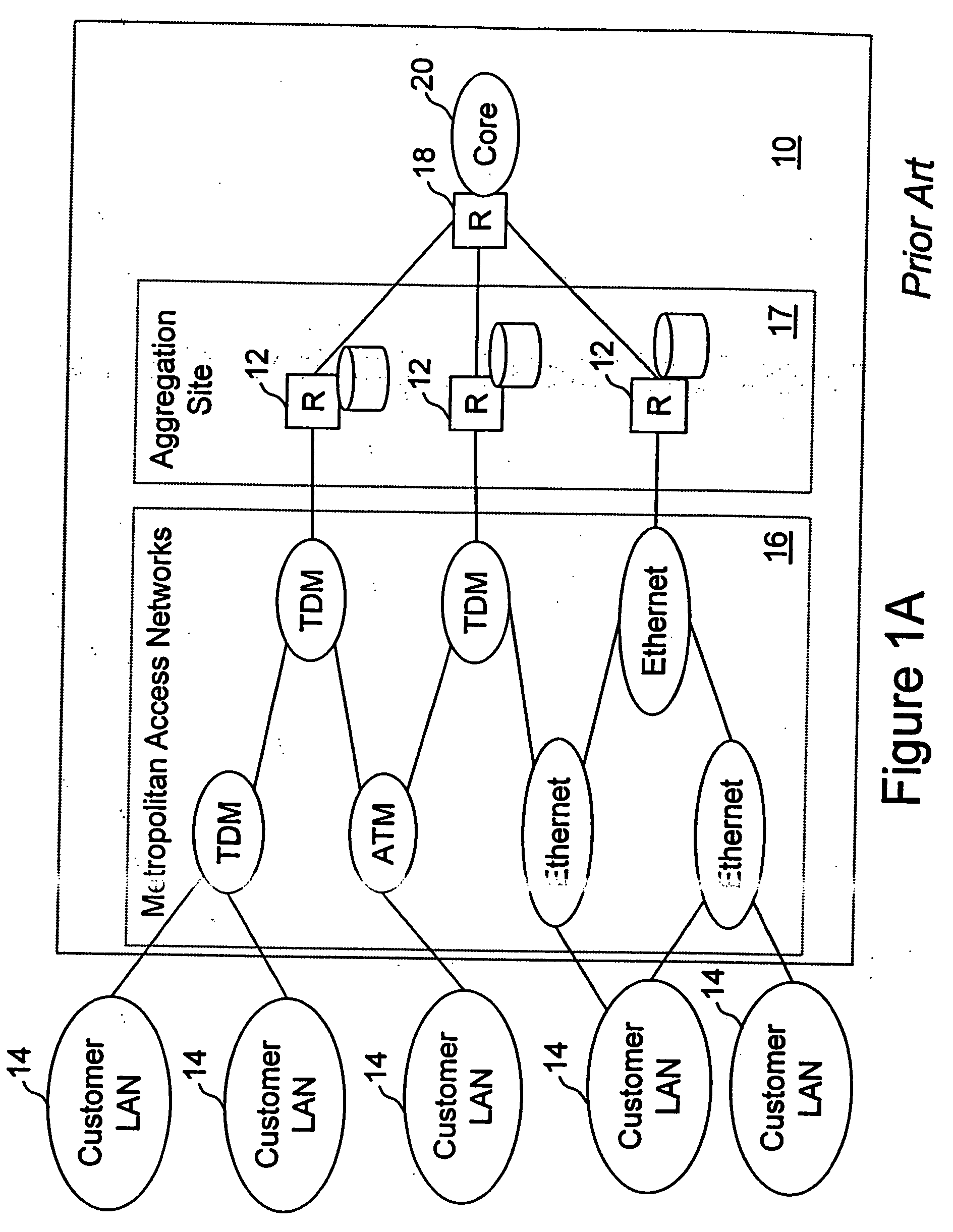
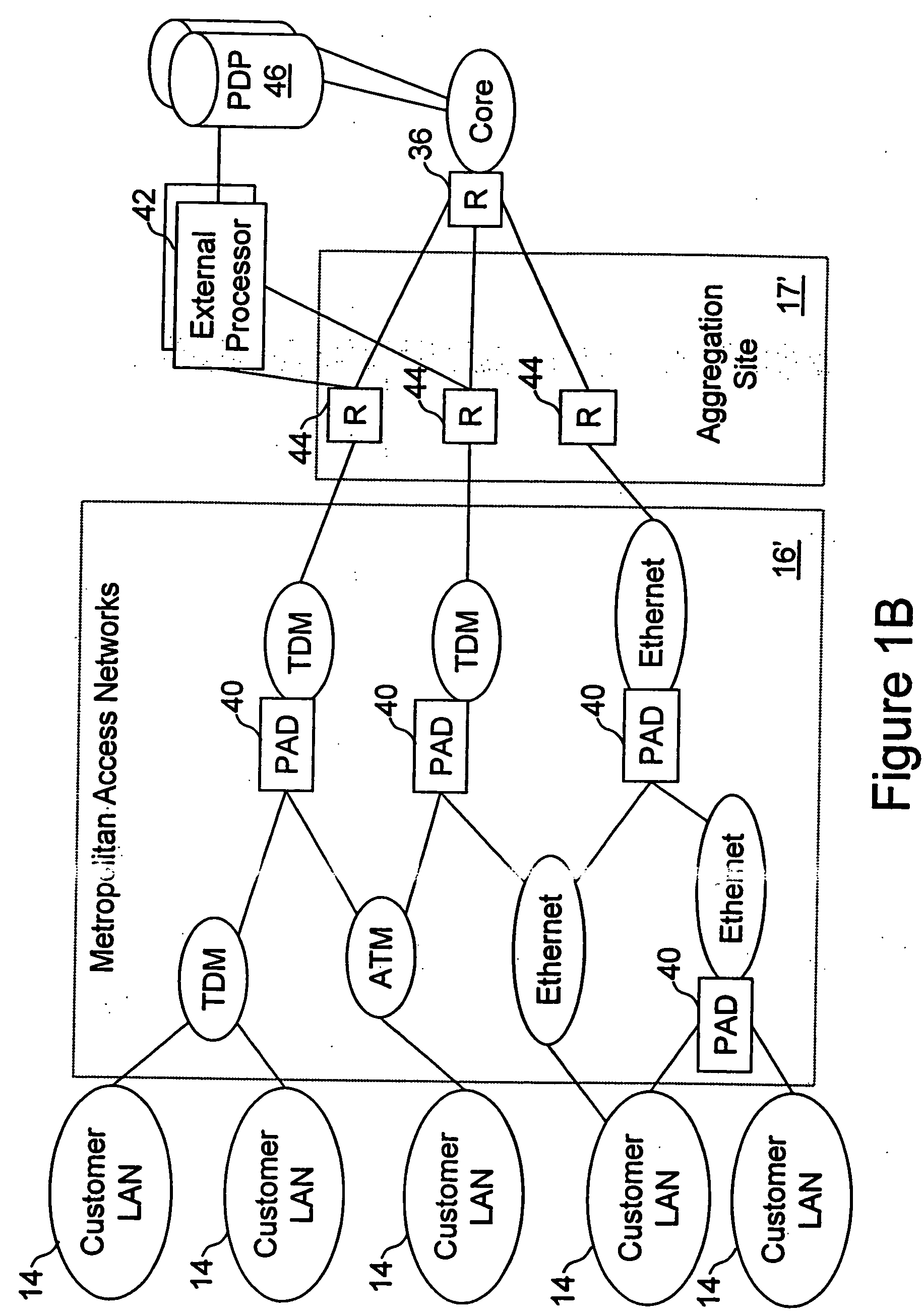
Network access system including a programmable access device having distributed service control
InactiveUS7046680B1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgrammable logic deviceMessage Passing Interface
A distributed network access system in accordance with the present invention includes at least an external processor and a programmable access device. The programmable access device has a message interface coupled to the external processor and first and second network interfaces through which packets are communicated with a network. The programmable access device includes a packet header filter and a forwarding table that is utilized to route packets communicated between the first and second network interfaces. In response to receipt of a series of packets, the packet header filter in the programmable access device identifies messages in the series of messages upon which policy-based services are to be implemented and passes identified messages via the message interface to the external processor for processing. In response to receipt of a message, the external processor invokes service control on the message and may also invoke policy control on the message.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
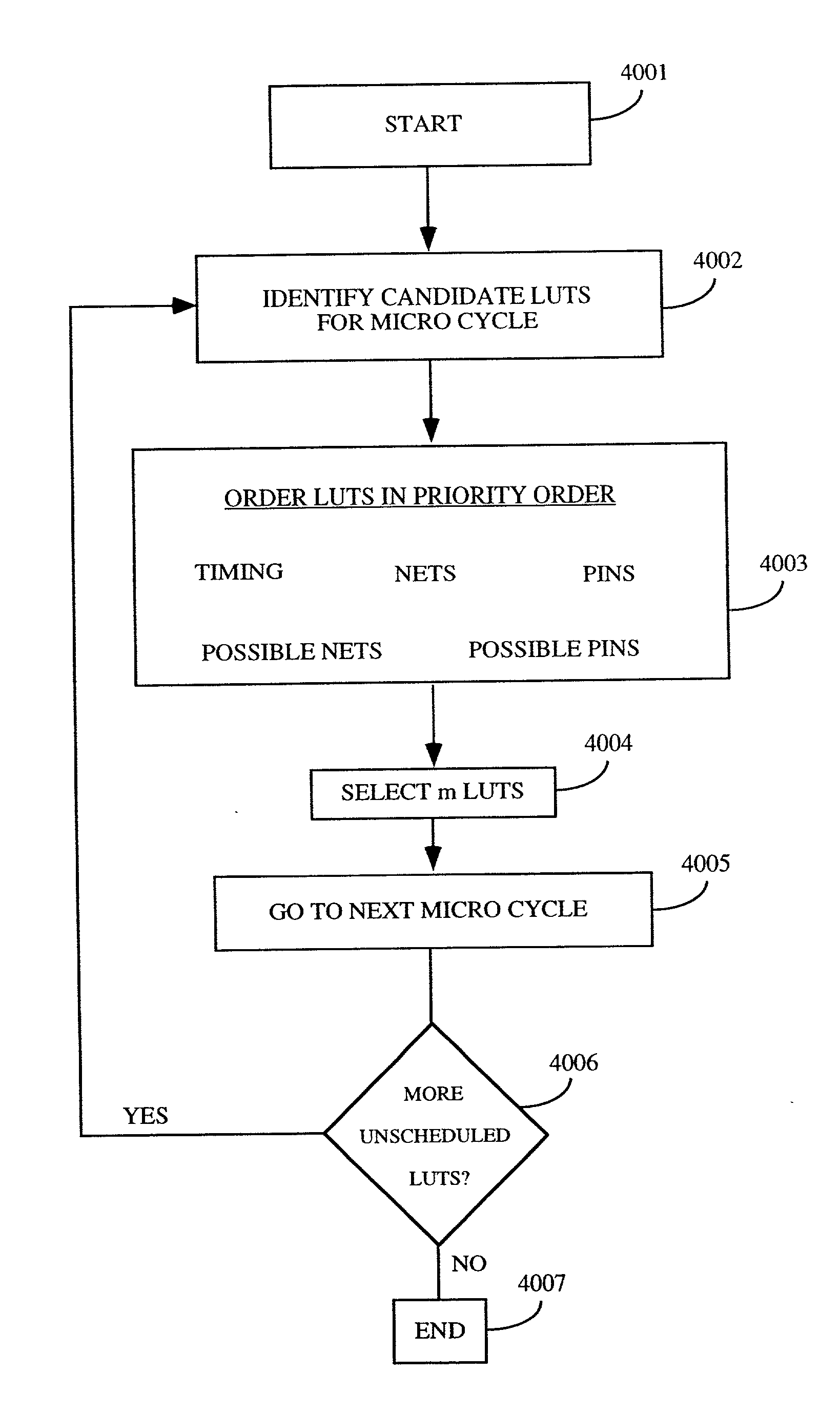
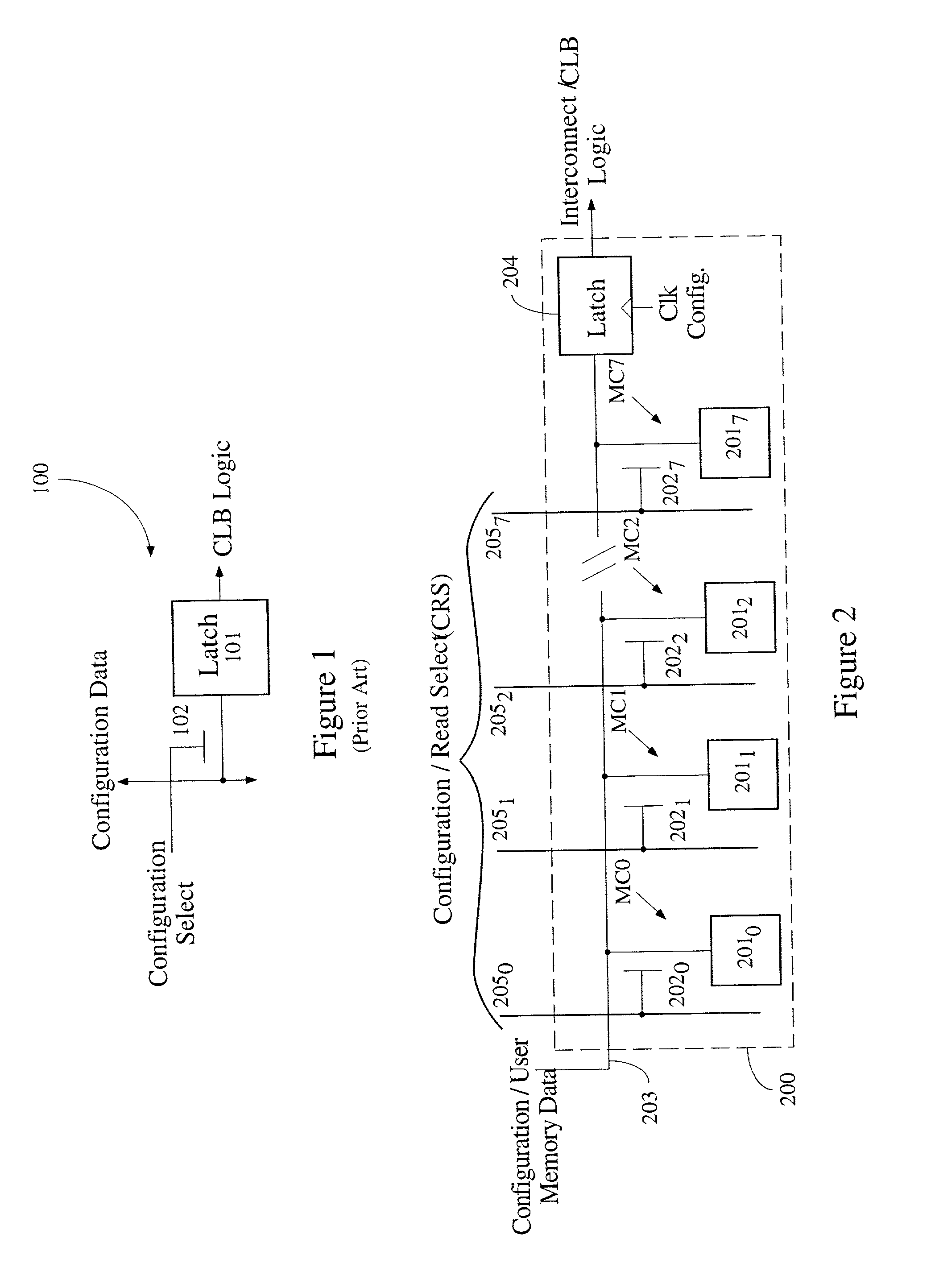
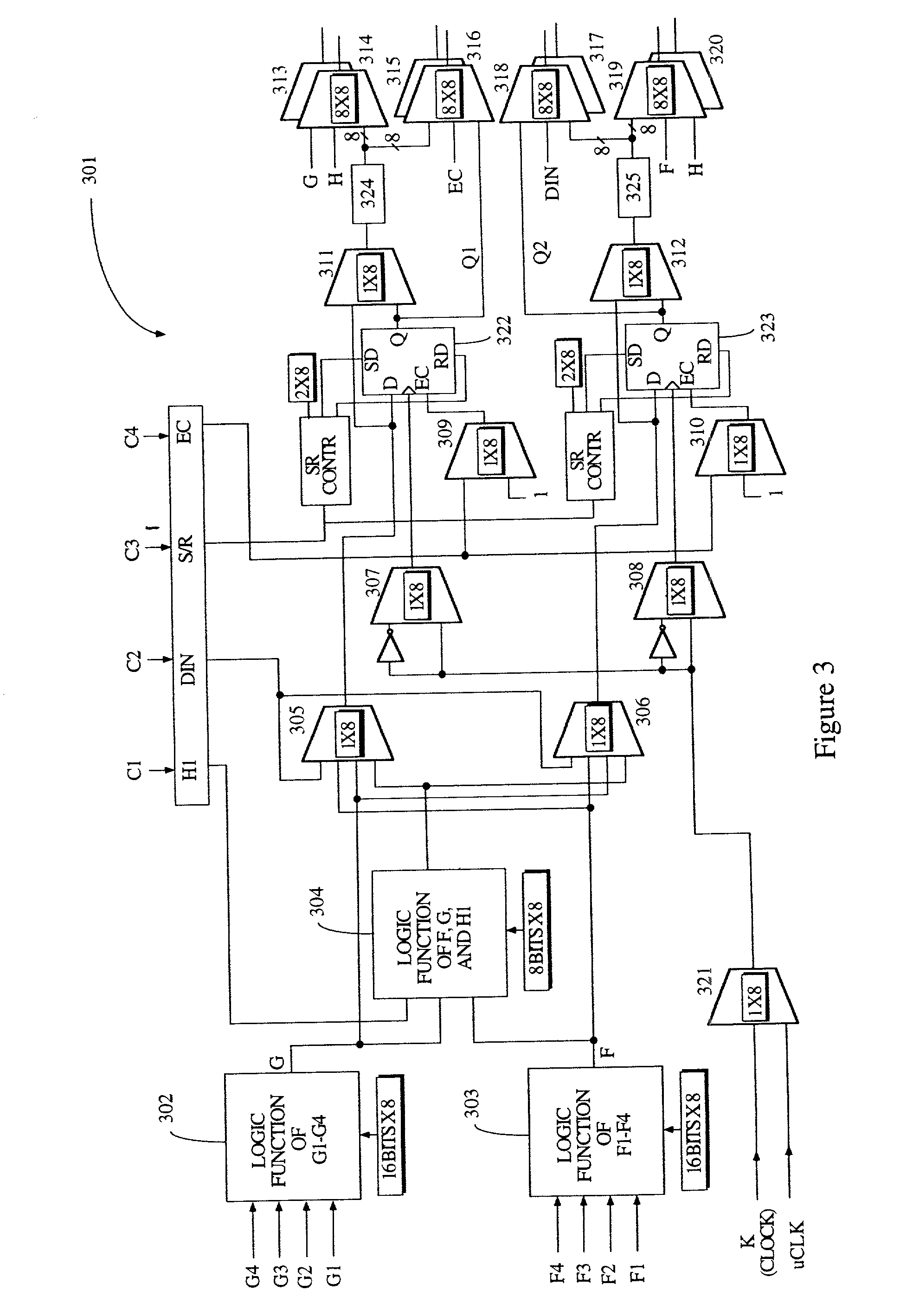
Method of time multiplexing a programmable logic device
InactiveUS20020010853A1Reduce in quantityEasy to reuseDigital computer detailsData resettingProgrammable logic deviceLogic element
A programmable logic device (PLD) comprises at least one configurable element, and a plurality of programmable logic elements for configuring the configurable element(s). Alternatively, a PLD comprises an interconnect structure and a plurality of programmable logic elements for configuring the interconnect structure. In either embodiment, at least one of the programmable logic elements includes N memory cells. A predetermined one of the N memory cells forms part of a memory slice, wherein at least a portion of each slice of the programmable logic device is allocated to either configuration data or user data memory. Typically, one memory slice provides one configuration of the programmable logic device. In accordance with one embodiment, a memory access port is coupled between at least one of the N memory cells and either one configurable element or the interconnect, thereby facilitating loading of new configuration data into other memory slices during the one configuration. The new configuration data may include off-chip or on-chip data. The present invention typically allocates at least one slice to user data memory and includes means for disabling access to at least one of the N memory cells.
Owner:XILINX INC
Network access system including a programmable access device having distributed service control
InactiveUS20050117576A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityData switching by path configurationPacket communicationService control
A distributed network access system in accordance with the present invention includes at least an external processor and a programmable access device. The programmable access device has a message interface coupled to the external processor and first and second network interfaces through which packets are communicated with a network The programmable access device includes a packet header filter and a forwarding table that is utilized to route packets communication between the first and second network interfaces. In response to receipt of a series of packets, the packet header filter in the programmable access device identifies messages in the series of messages upon which policy-based services are to be implemented and passes identified messages via the message interface to the external processor for processing. In response to receipt of a message, the external processor invokes service control on the message and may also invoke policy control on the message.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
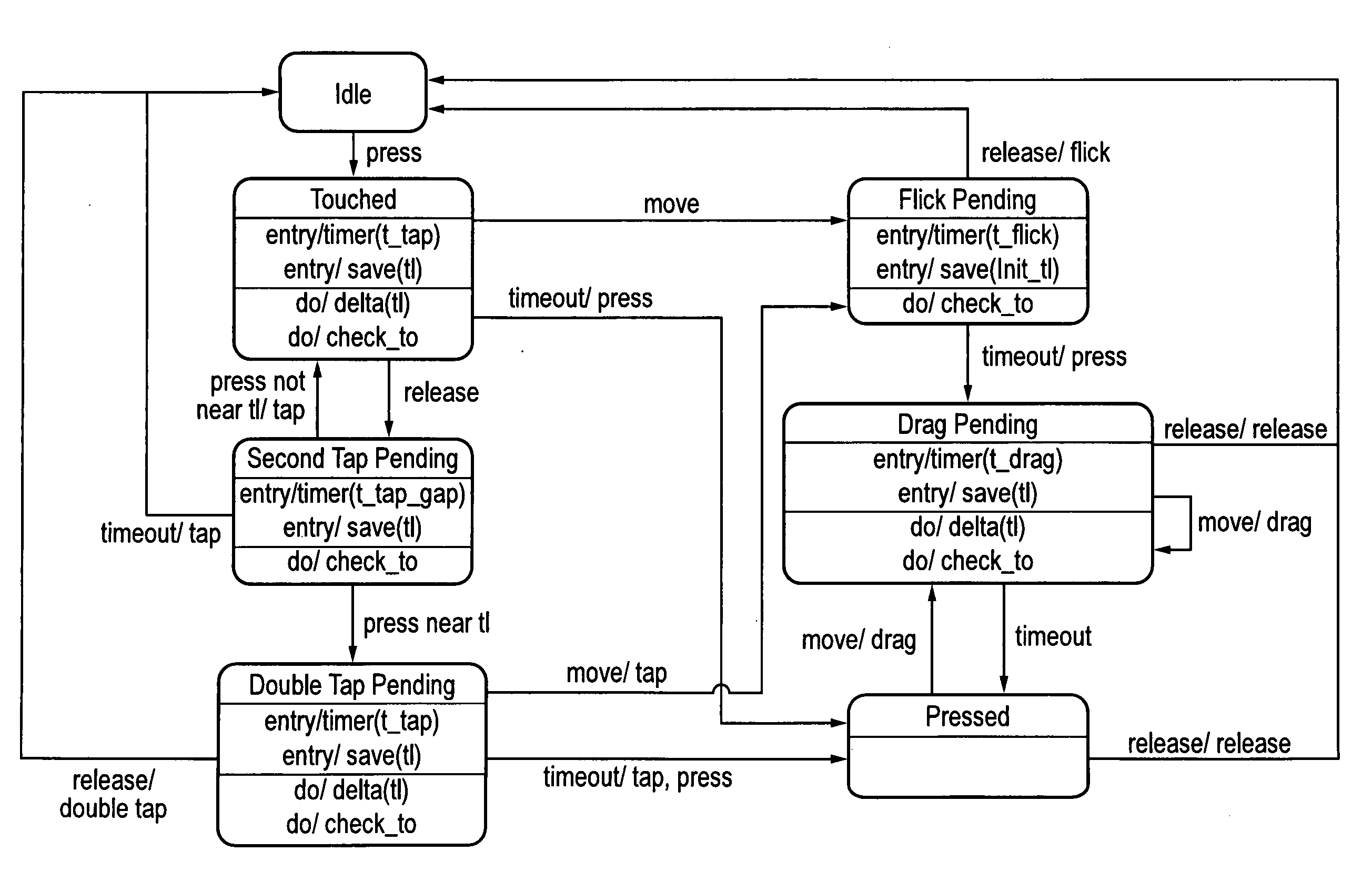
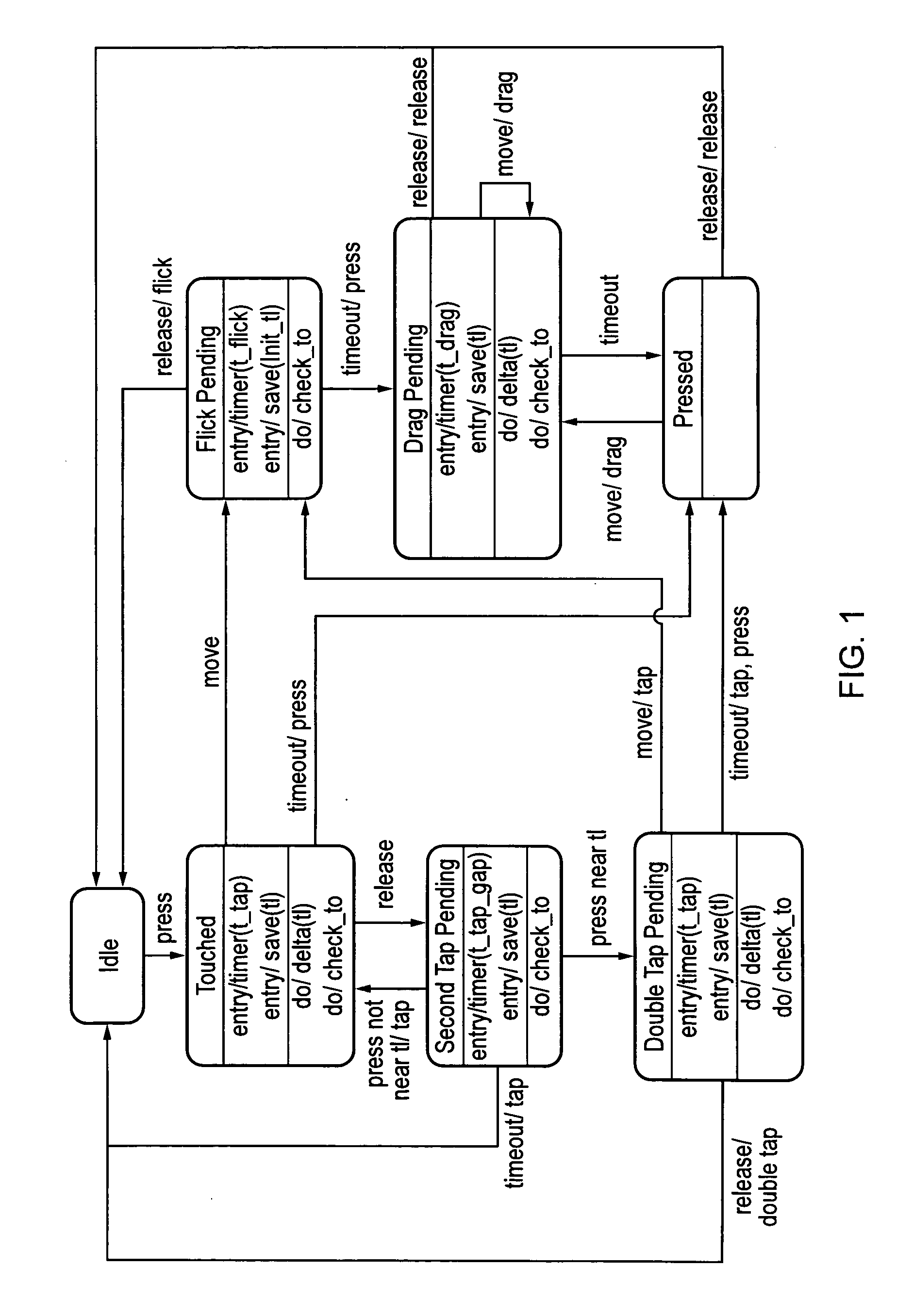
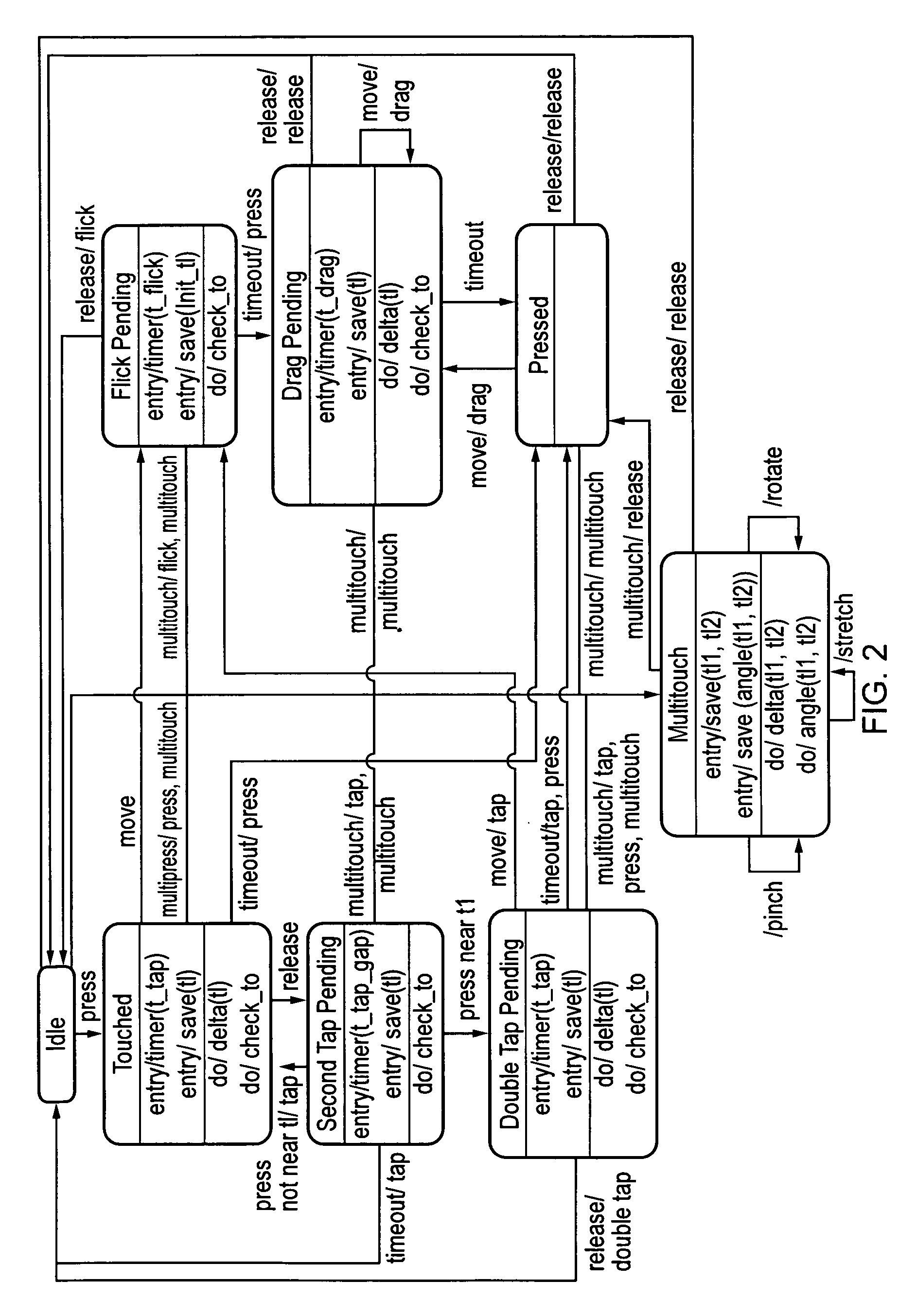
Gesture Recognition
ActiveUS20090273571A1Transmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicrocontrollerProgrammable logic device
A state machine gesture recognition algorithm for interpreting streams of coordinates received from a touch sensor. The gesture recognition code can be written in a high level language such as C and then compiled and embedded in a microcontroller chip, or CPU chip as desired. The gesture recognition code can be loaded into the same chip that interprets the touch signals from the touch sensor and generates the time series data, e.g. a microcontroller, or other programmable logic device such as a field programmable gate array.
Owner:SOLAS OLED LTD
Integrated circuit with interface tile for coupling to a stacked-die second integrated circuit
ActiveUS7068072B2Designing can be facilitatedPromote formationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGeneral purposeProgrammable logic device
A general purpose interface tile of a first integrated circuit includes a plurality of micropads. A second integrated circuit may be stacked on the first integrated circuit such that signals from the second integrated circuit are communicated through the micropads and the interface tile to other circuitry on the first integrated circuit. Similarly, signals from the first integrated circuit are communicated through the interface tile and the micropads to the second integrated circuit. In the event that the first integrated circuit is a programmable logic device having a programmable interconnect structure, the interface tile is part of and hooks into the programmable interconnect structure and provides a general purpose mechanism for coupling signals from the second integrated circuit to the programmable interconnect structure and / or for coupling signals from the programmable interconnect structure to the second integrated circuit.
Owner:XILINX INC
Medical apparatus using selective graphical interface
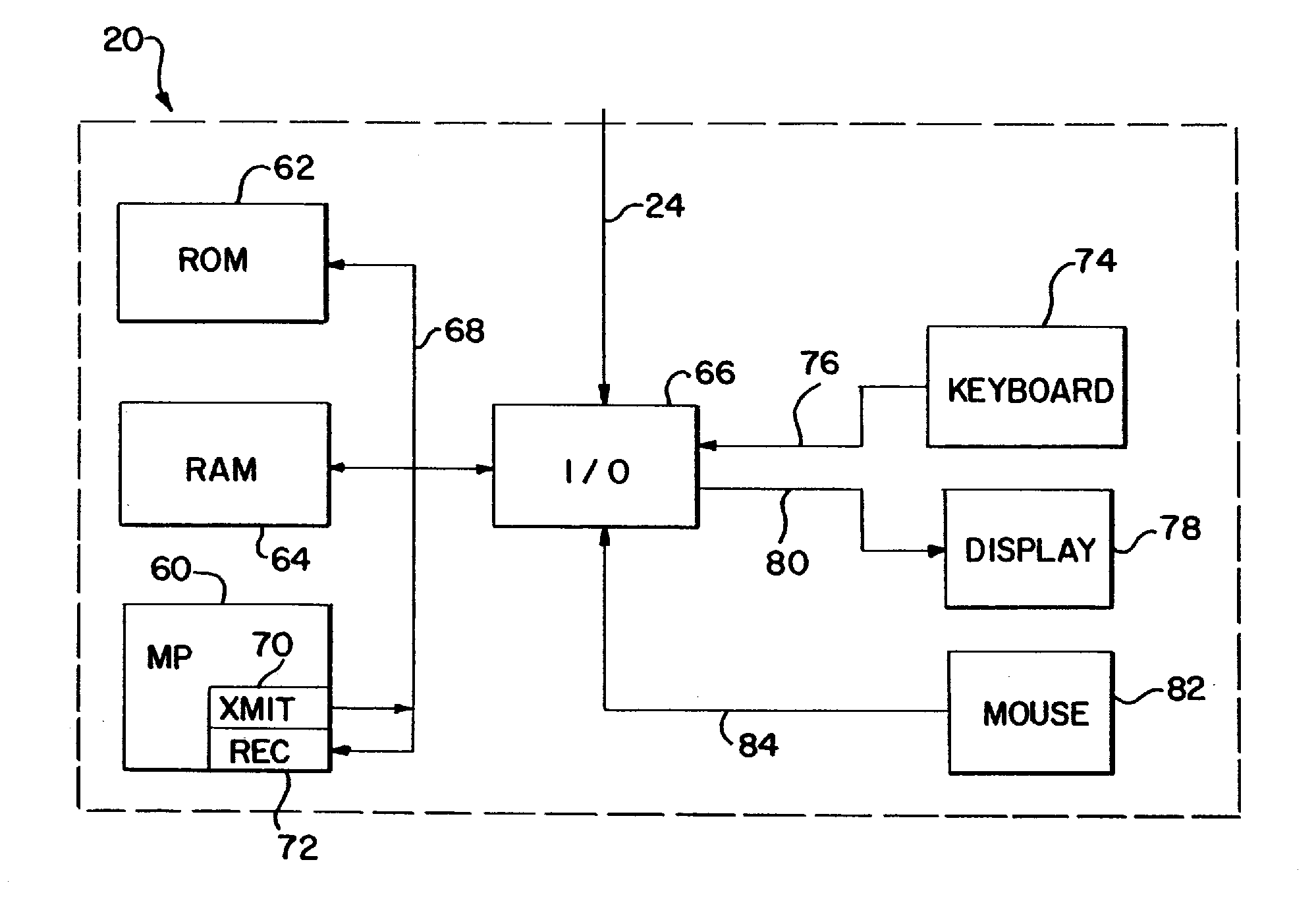
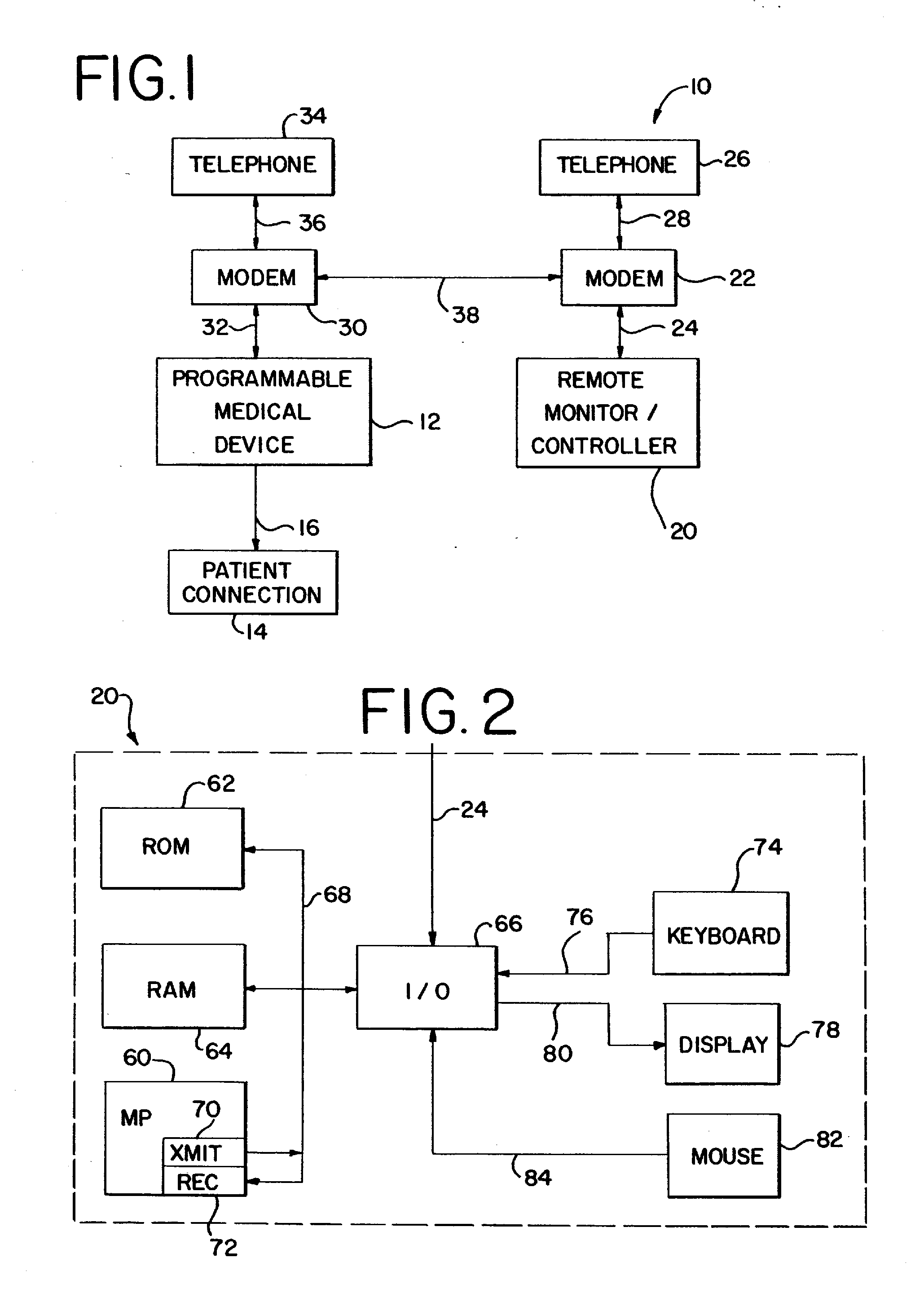
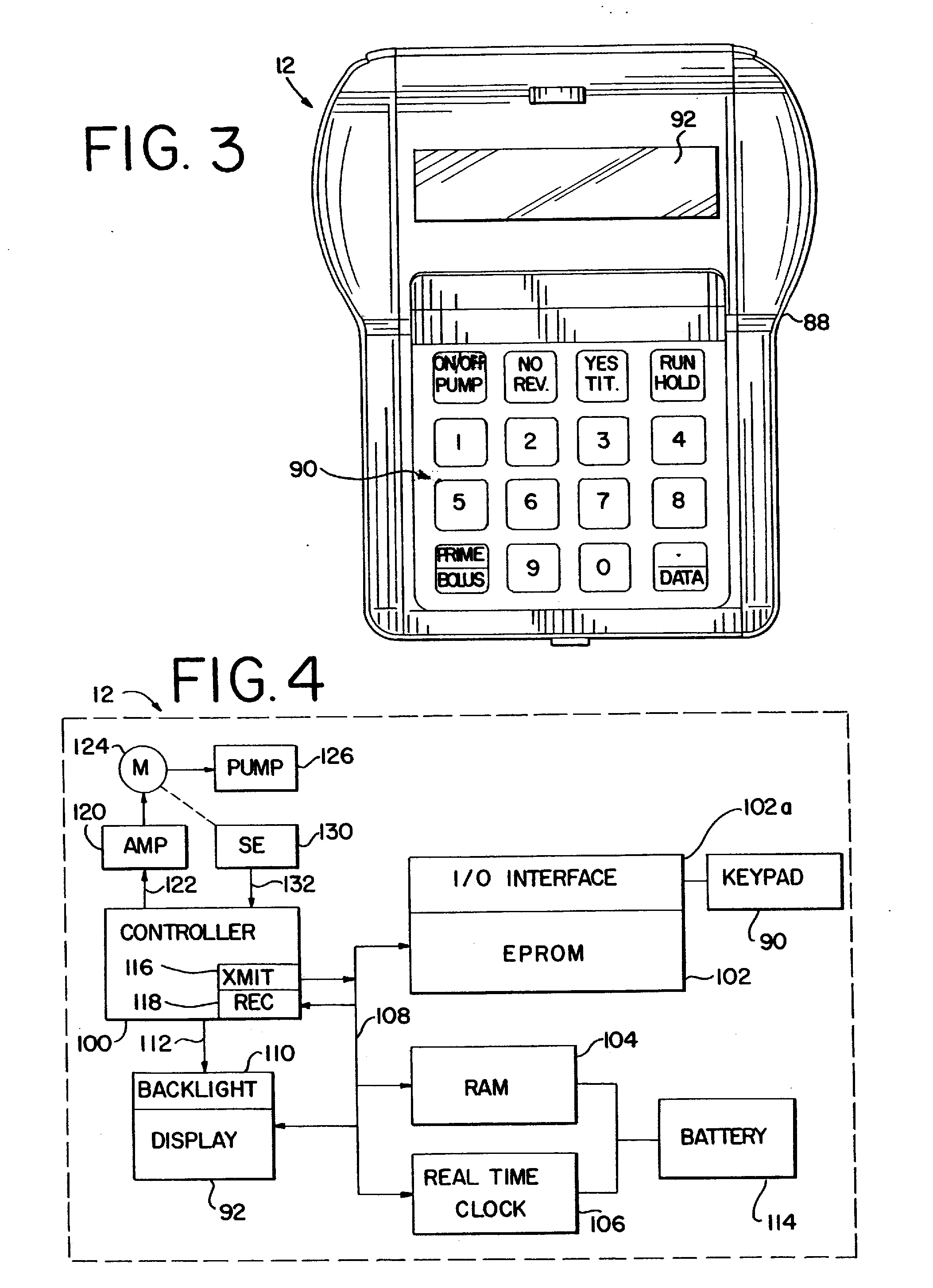
InactiveUS20040158193A1Easy to useLikelihoodRespiratorsInput/output for user-computer interactionProgrammable logic deviceMedical device
Abstract of the Disclosure A programmable medical device, such as an infusion pump, is programmed or configured to display, or make, as active, only those keys which can provide valid input during each particular programming or operational step. Similarly, a remote controller for controlling a programmable medical device is programmed or configured to display, or make, as active, only those keys which can provide valid input during each particular programming or operational step.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
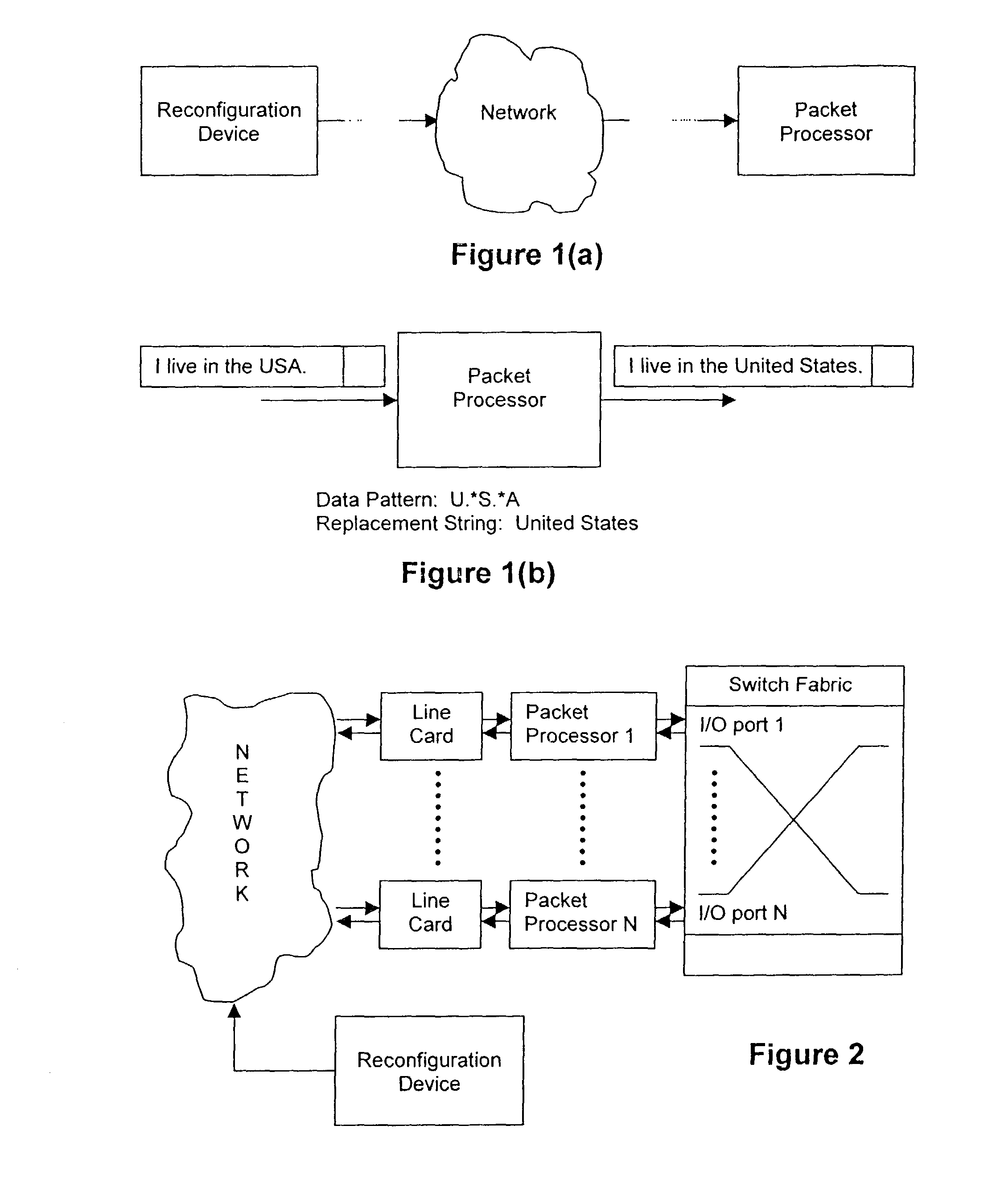
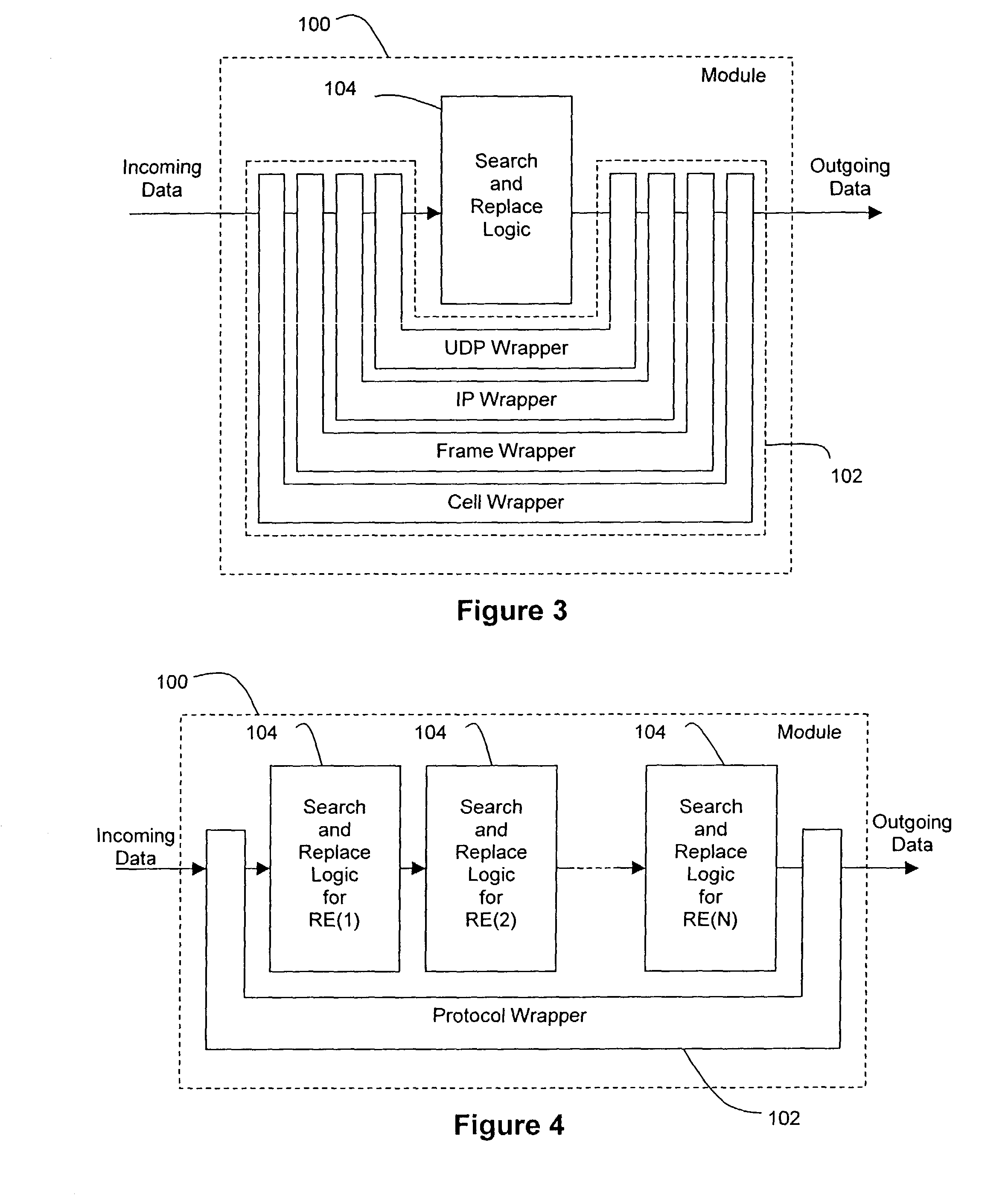
Methods, systems, and devices using reprogrammable hardware for high-speed processing of streaming data to find a redefinable pattern and respond thereto
InactiveUS7093023B2Prevent materialPrevented from reachingError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsProgrammable logic devicePacket processing
A reprogrammable packet processing system for processing a stream of data is disclosed herein. A reprogrammable data processor is implemented with a programmable logic device (PLD), such as a field programmable gate array (FPGA), that is programmed to determine whether a stream of data applied thereto includes a string that matches a redefinable data pattern. If a matching string is found, the data processor performs a specified action in response thereto. The data processor is reprogrammable to search packets for the presence of different data patterns and / or perform different actions when a matching string is detected. A reconfiguration device receives input from a user specifying the data pattern and action, processes the input to generate the configuration information necessary to reprogram the PLD, and transmits the configuration information to the packet processor for reprogramming thereof.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Reconfigurable computer architecture using programmable logic devices
A method and system for computing using reconfigurable computer architecture utilizing logic devices is disclosed. The computing may be accomplished by configuring a first programmable logic unit as a system controller. The system controller directs the implementation of an algorithm in a second one of the programmable logic units concurrently with reconfirguring a third one of the programmable logic units. In another aspect, the computing system may include a pair of independent, bi-directional busses each of which is arranged to electrically interconnect the system controller and the plurality of programmable logic devices. With this arrangement, a first bus may be used to reconfigure a selected one of the programmable logic devices as directed by the system controller while the second bus is used by an operational one of the programmable logic devices.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
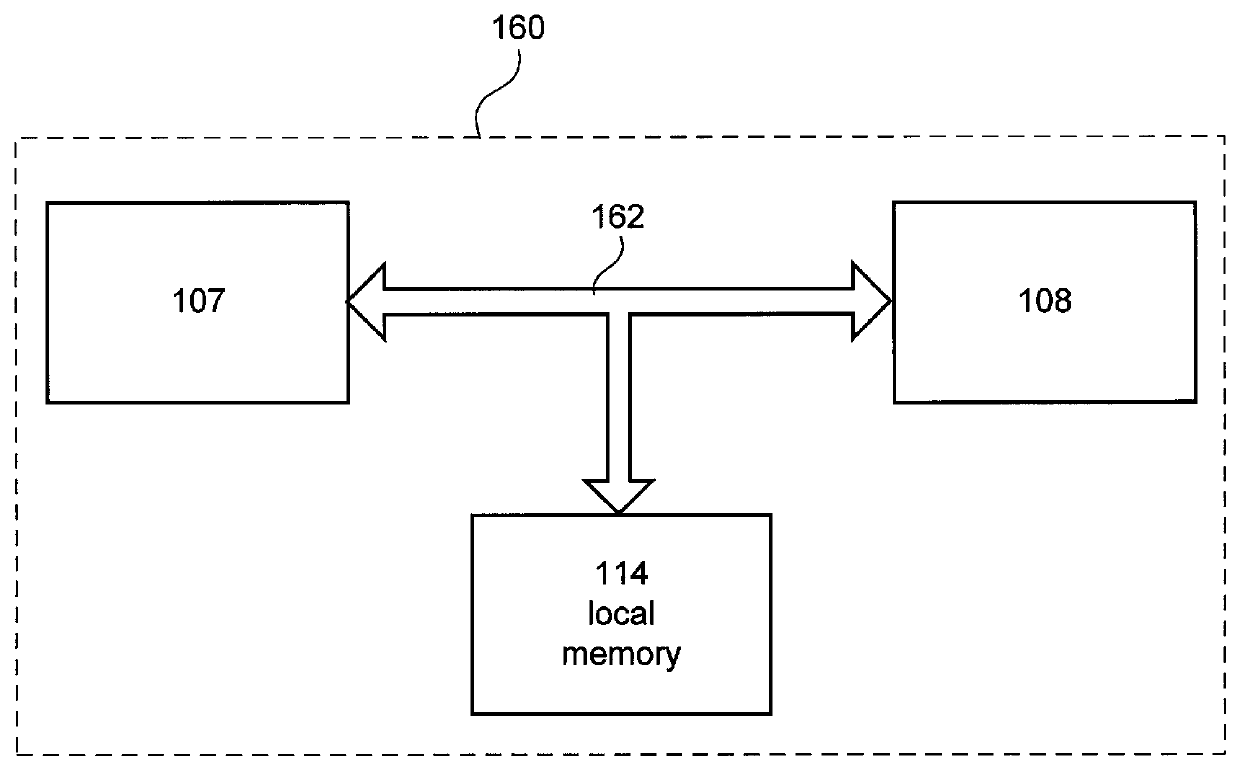
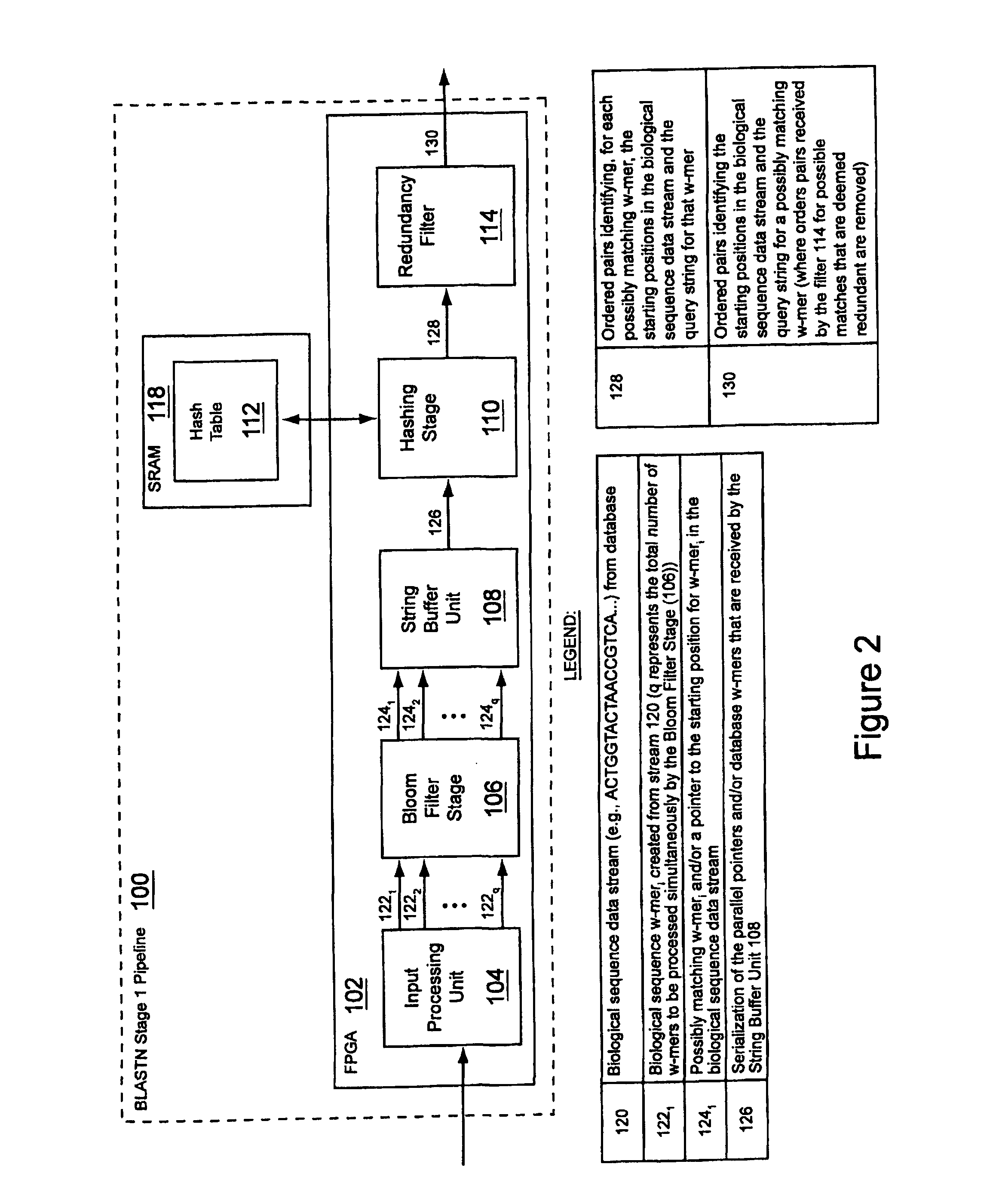
Method and apparatus for performing similarity searching on a data stream with respect to a query string
ActiveUS7917299B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData streamQuery string
An apparatus and method for performing similarity searching on a data stream with respect to a query string are disclosed, where the data stream comprises a plurality of data substrings, and where the query string comprises a plurality of query substrings. A programmable logic device is used to filter the data stream to find a plurality of possible matches between the data substrings and a plurality of the query substrings, wherein the data substrings and the query substrings comprise a plurality of characters. From these possible matches, a determination can be made as to a similarity between the query string and at least a portion of the data stream.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
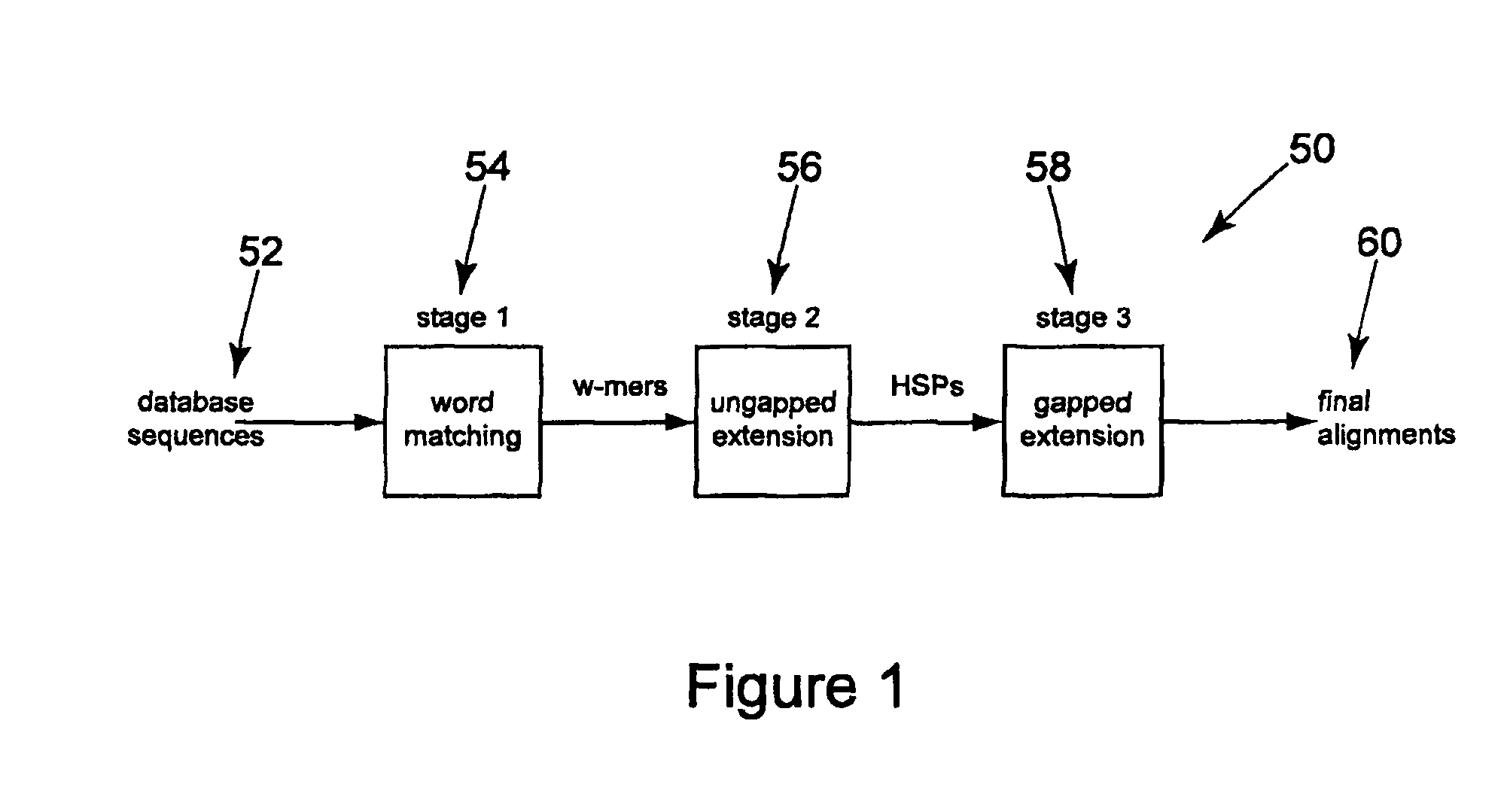
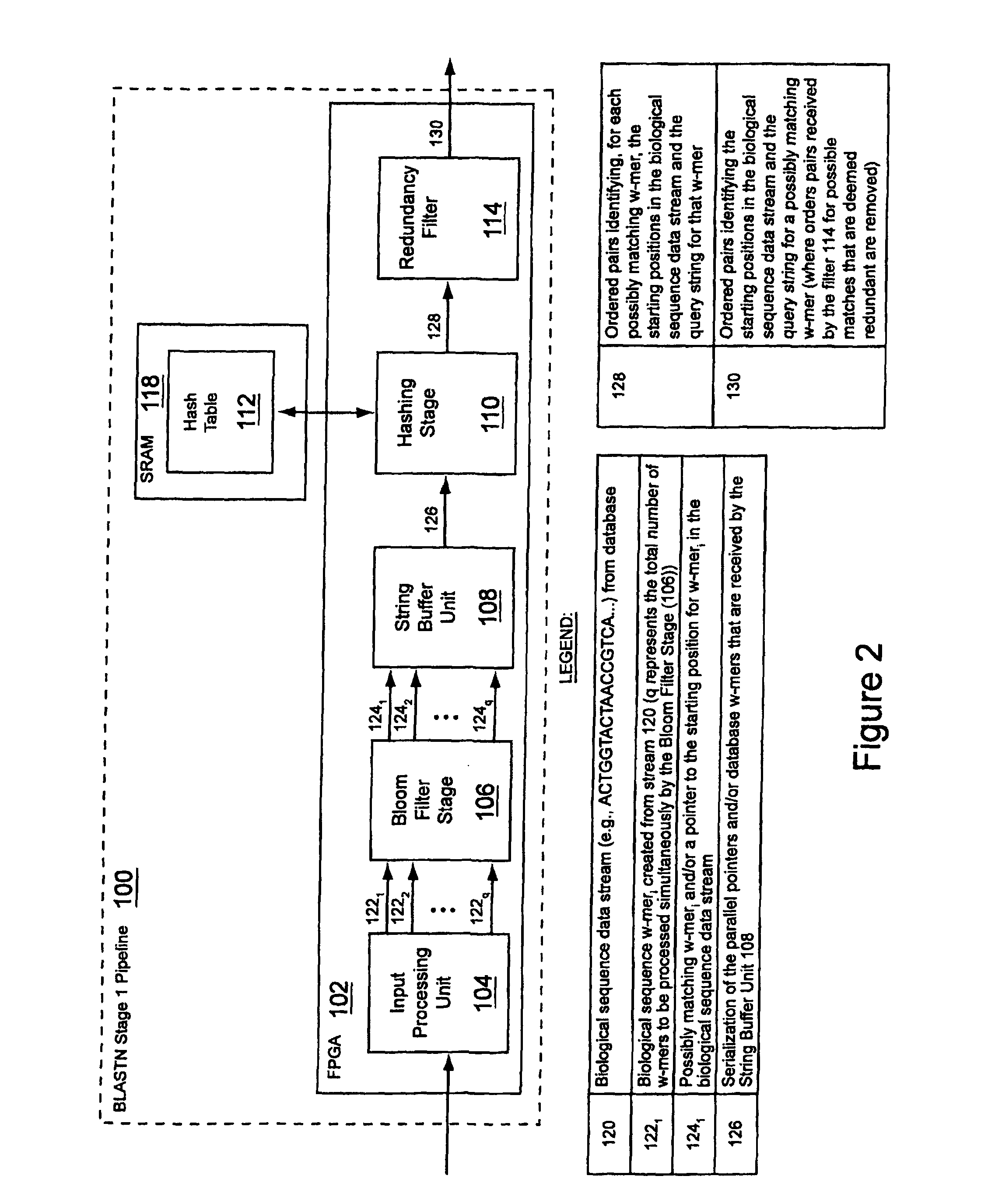
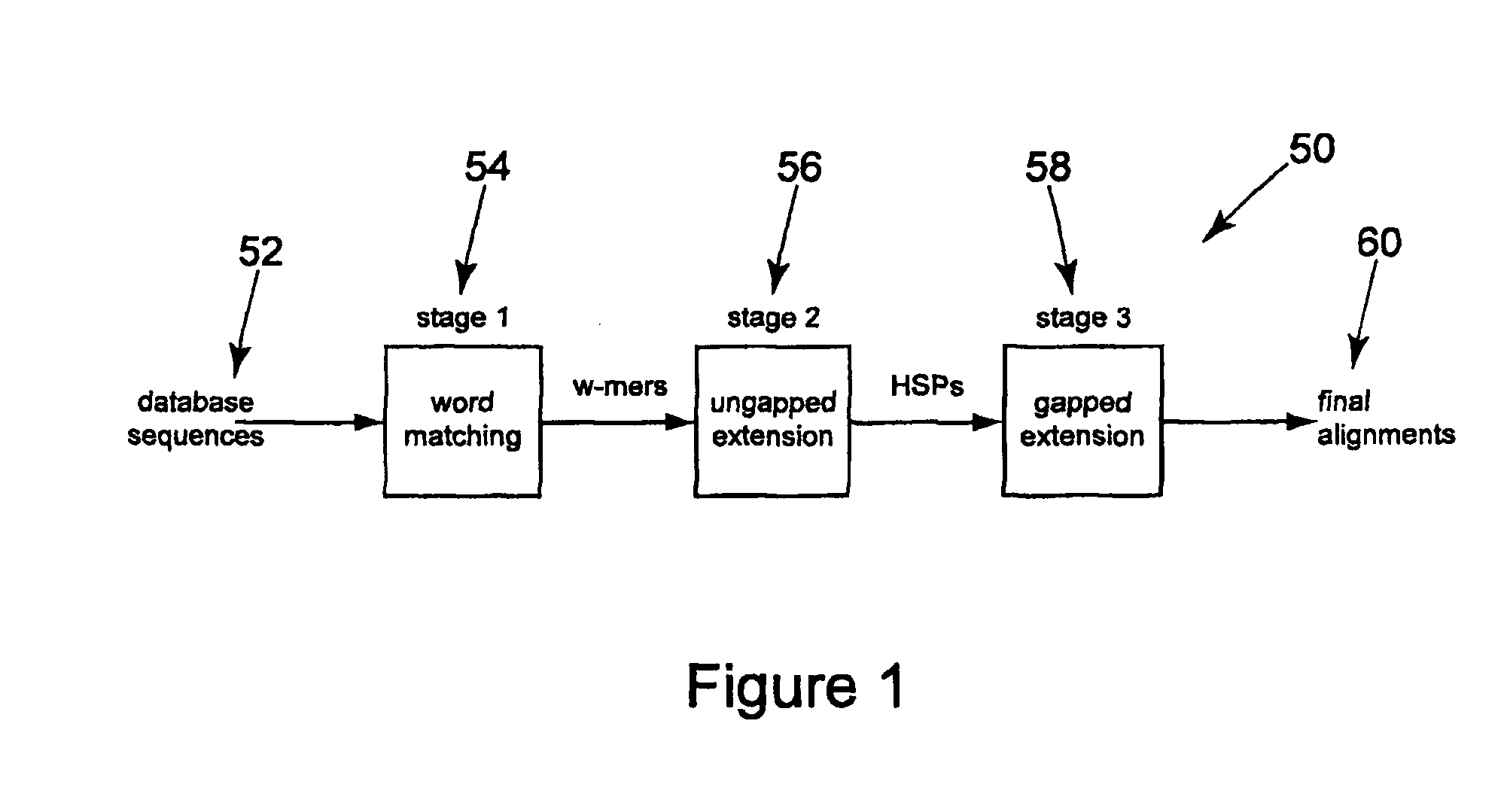
Method and apparatus for performing biosequence similarity searching
A system and method for performing biological sequence similarity searching is disclosed. This includes a programmable logic device configured to include a pipeline that comprises a matching stage, the matching stage being configured to receive a data stream comprising a plurality of possible matches between a plurality of biological sequence data strings and a plurality of substrings of a query string. The pipeline may further include a ungapped extension prefilter stage located downstream from the matching stage, the prefilter stage being configured to shift through pattern matches between the biological sequence data strings and the plurality of substrings of a query string and provide a score so that only pattern matches that exceed a user defined score will pass downstream from the prefilter stage. The matching stage may include at least one Bloom filter.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
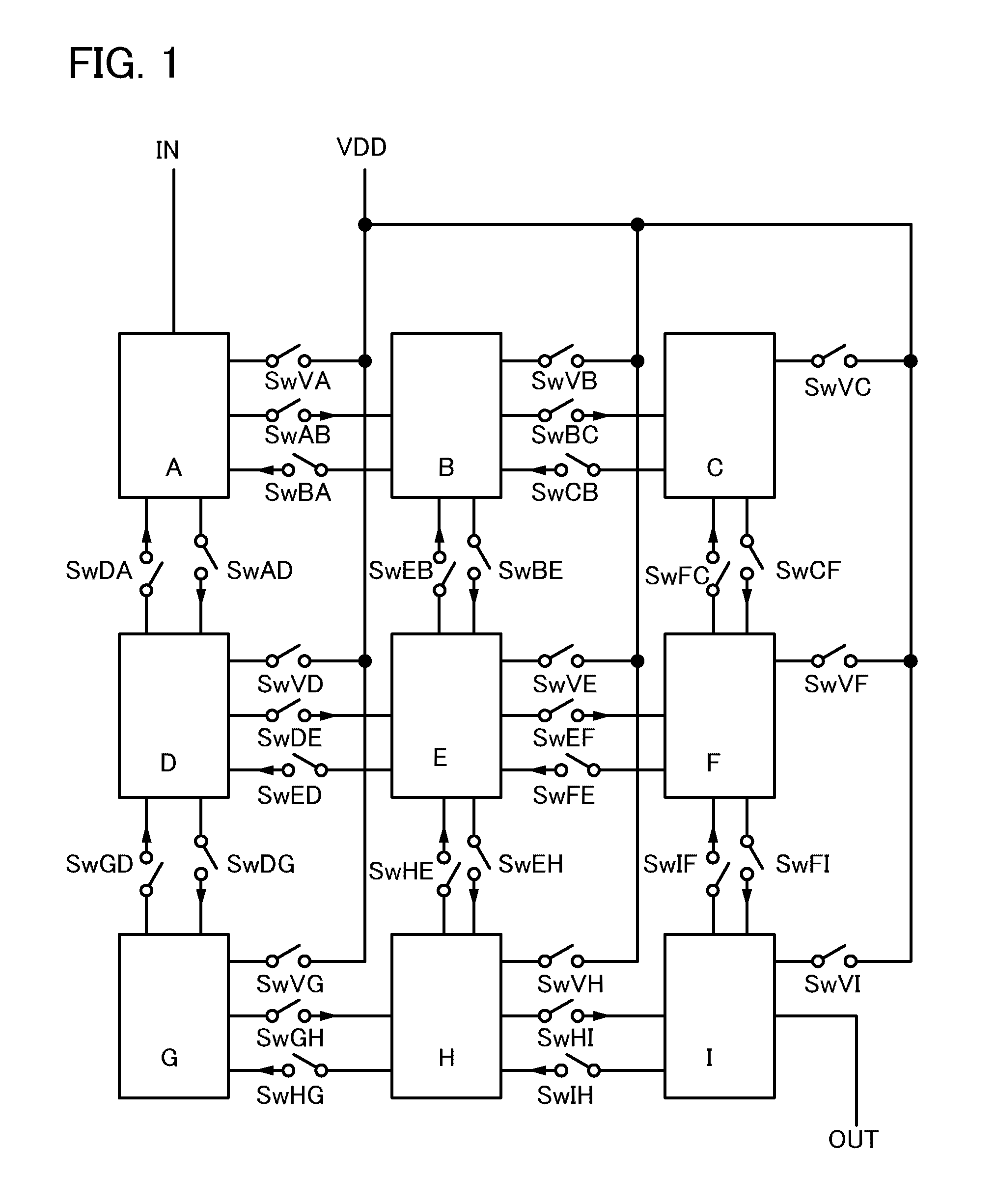
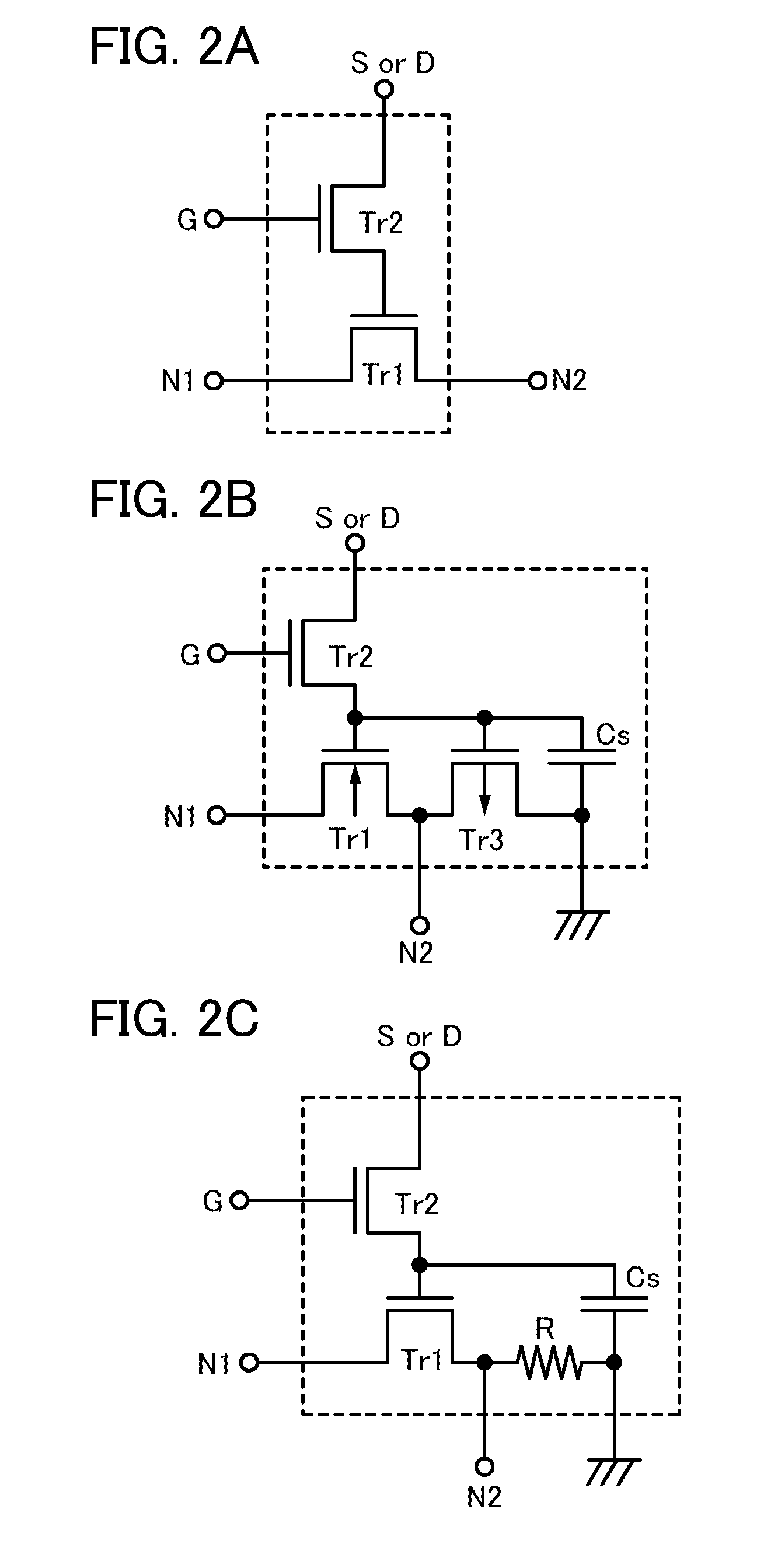
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110175646A1Suppress power consumptionPrevent degradationTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsProgrammable logic deviceLow leakage
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device in which power consumption can be reduced. It is another object to provide a highly reliable semiconductor device using a programming cell, such as a programmable logic device (PLD). In accordance with a change in a configuration of connections between basic blocks, power supply voltage furnishing to the basic blocks is changed. That is, when the structure of connections between the basic blocks is such that a basic block does not contribute to a circuit, the supply of the power supply voltage to this basic block is stopped. Further, the supply of the power supply voltage to the basic blocks is controlled using a programming cell formed using a field effect transistor whose channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor, the field effect transistor having extremely low off-state current or extremely low leakage current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
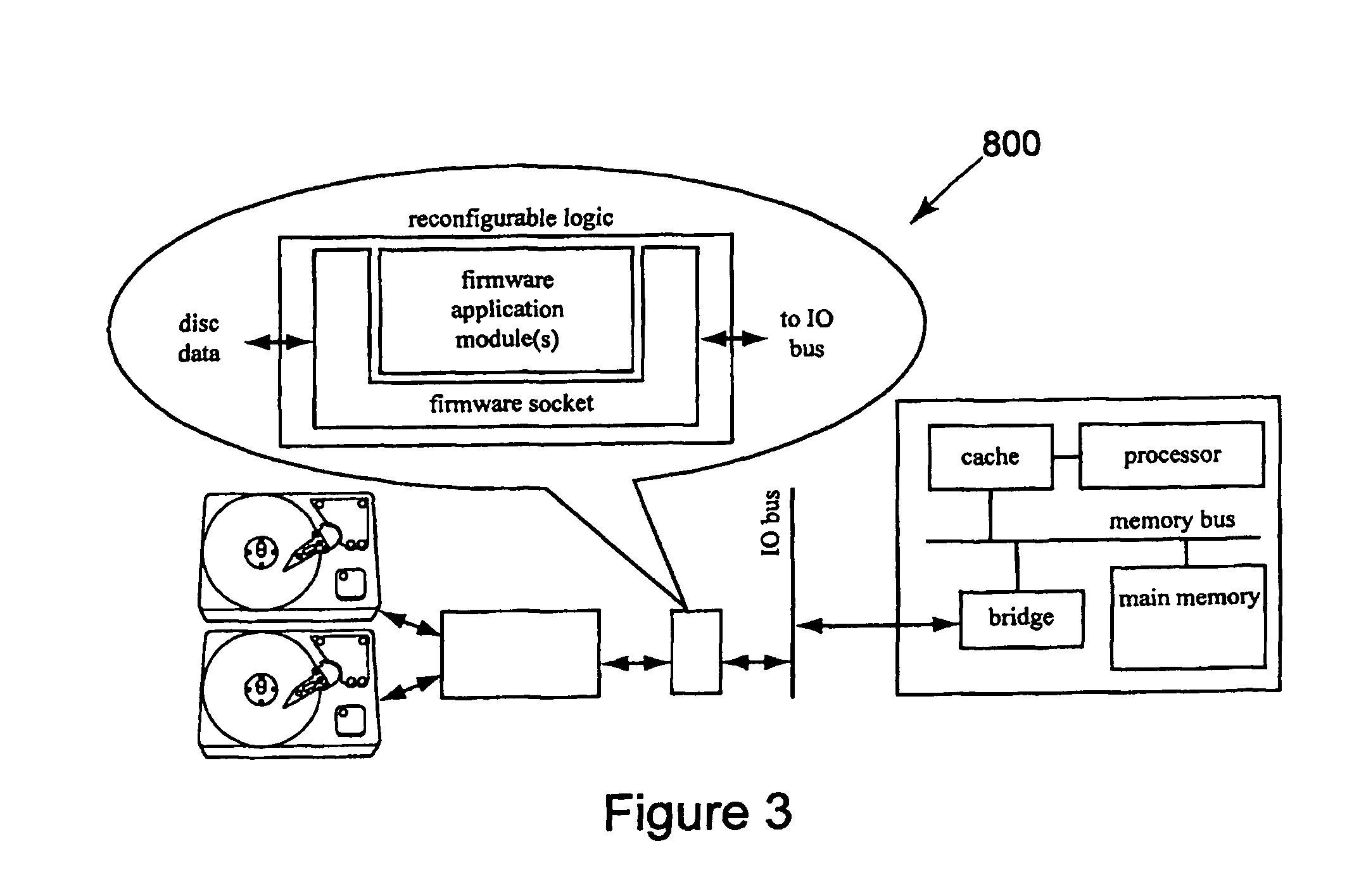
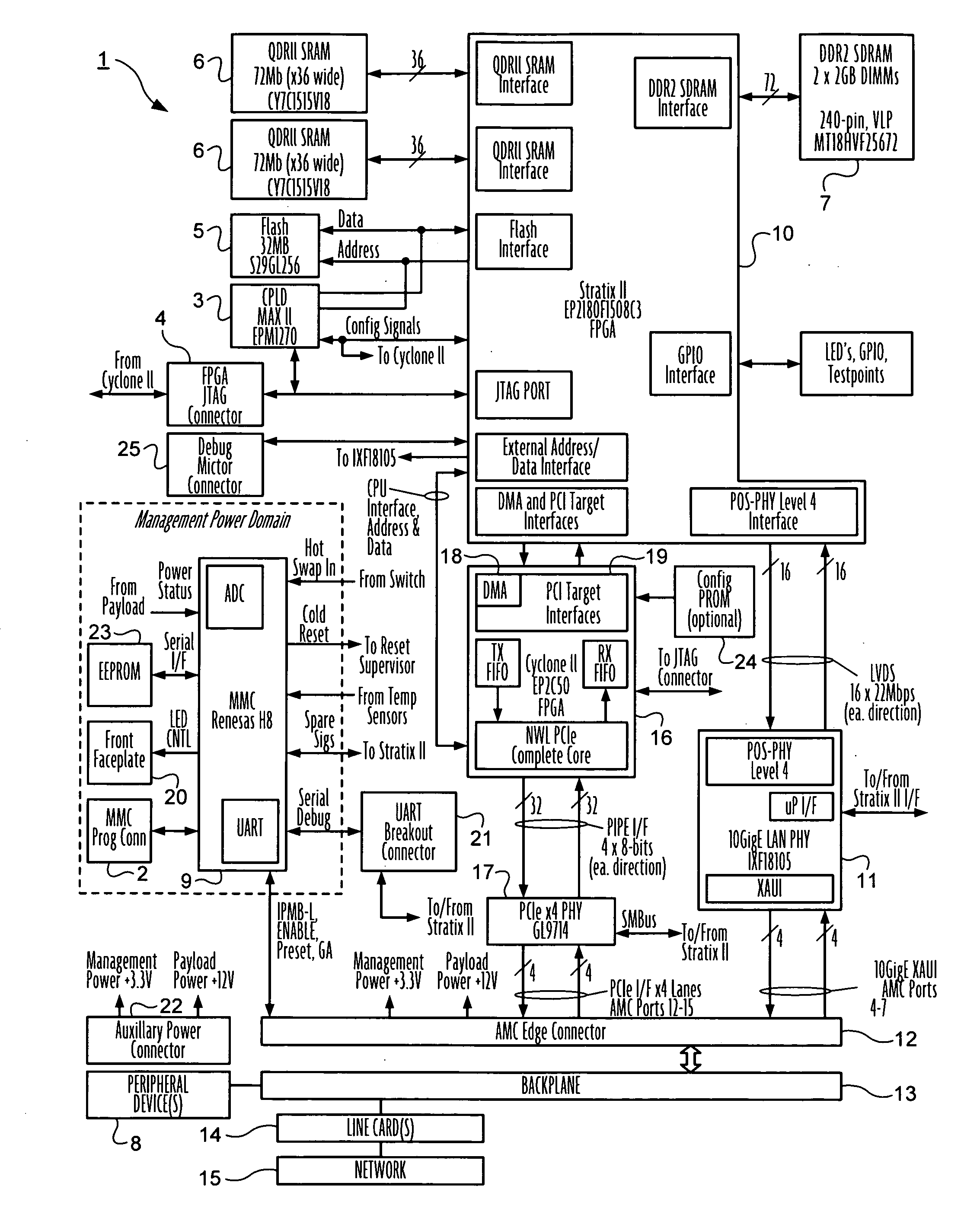
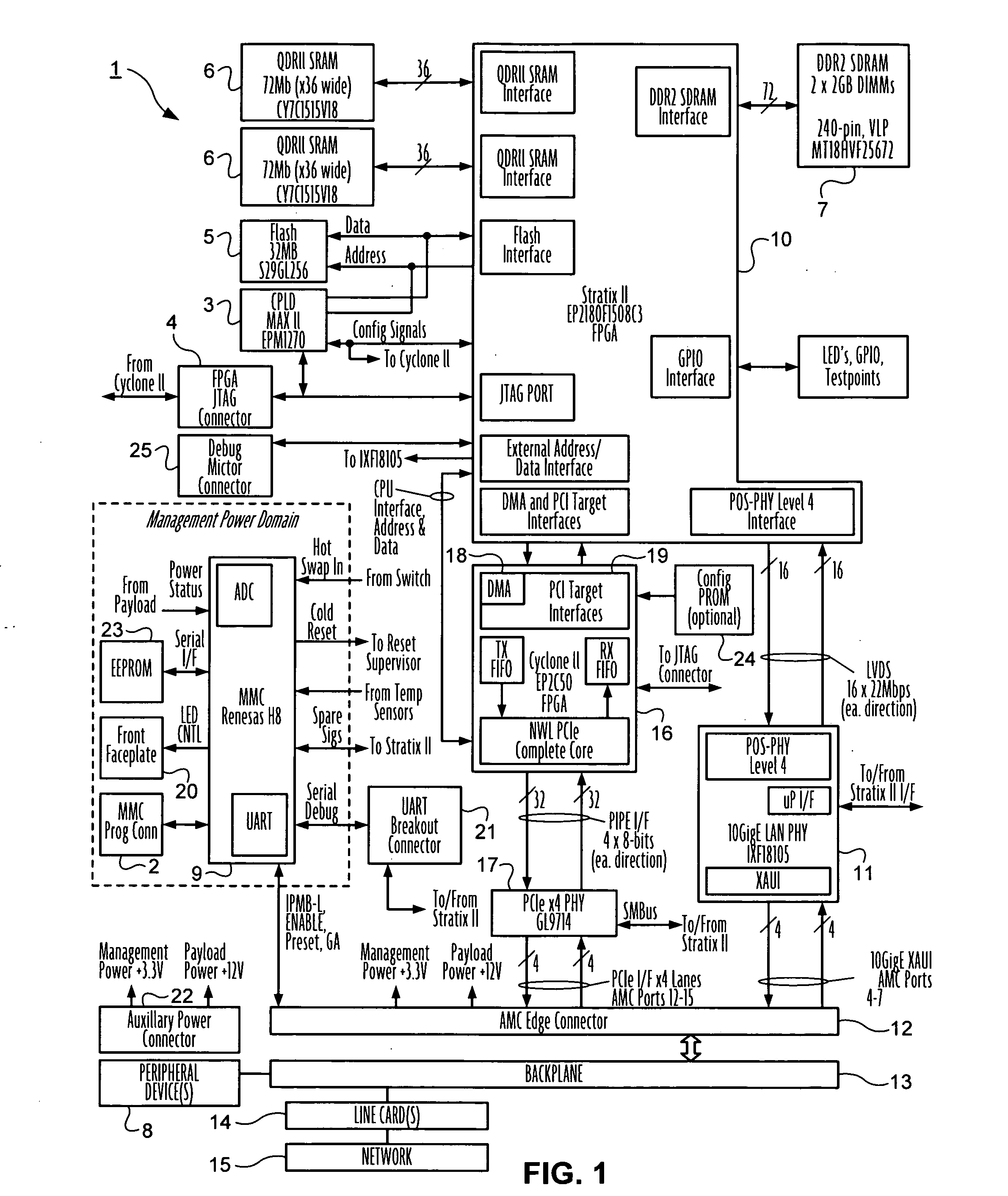
Advanced mezzanine card for digital network data inspection
Telecommunications computing apparatus and methods for performing deep packet inspection and other processing of data packets traversing high speed digital networks (15) such as the Internet. An apparatus embodiment of the present invention comprises a reconfigurable logic device (10); coupled to the reconfigurable logic device (10), means (11) for coupling the reconfigurable logic device (10) to an external digital network (15); and coupled to the reconfigurable logic device (10), an interface (16-19) for coupling the reconfigurable logic device (10) to at least one peripheral device (8) that is not part of said external digital network (15).
Owner:GLOBAL VELOCITY
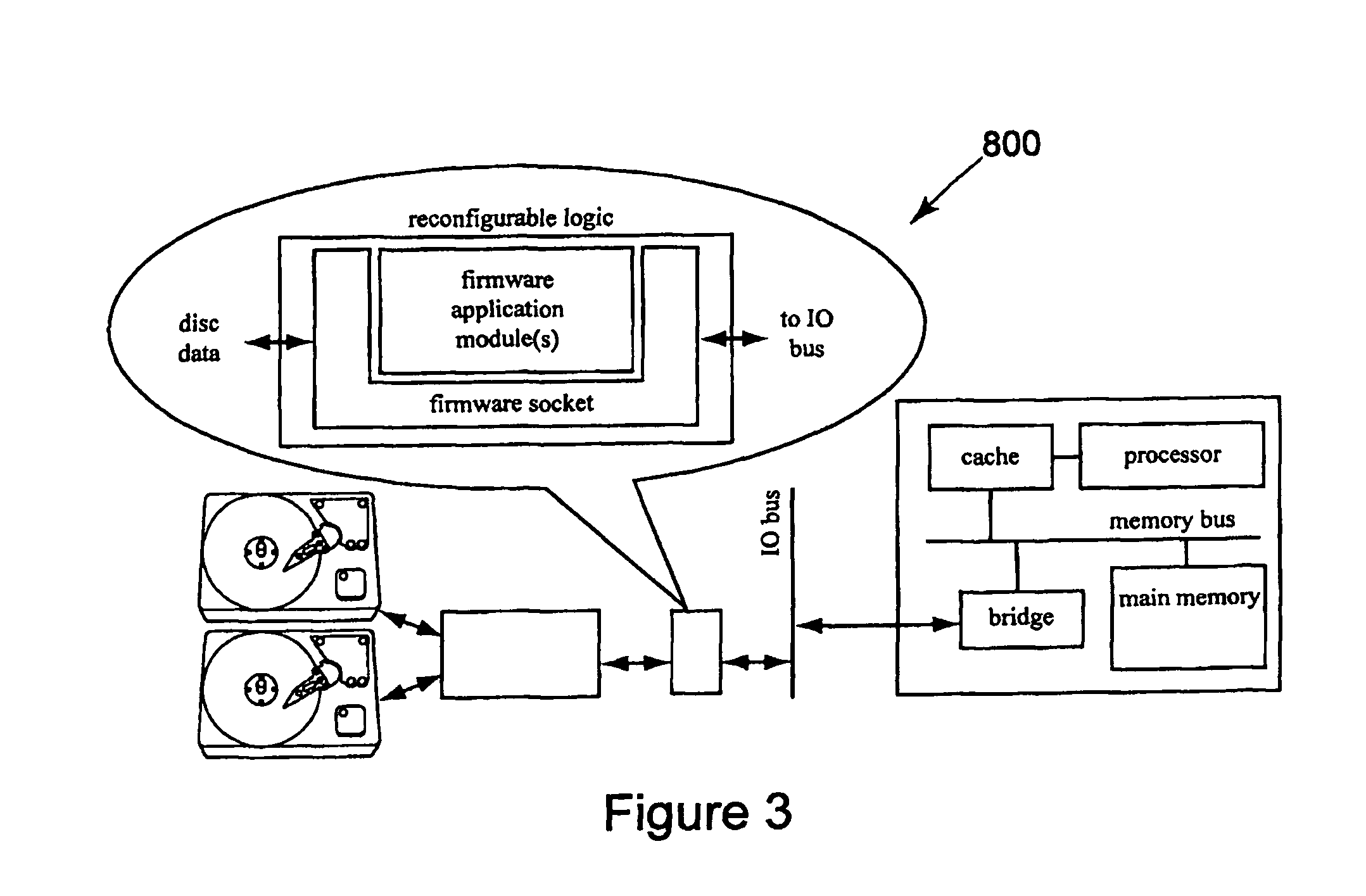
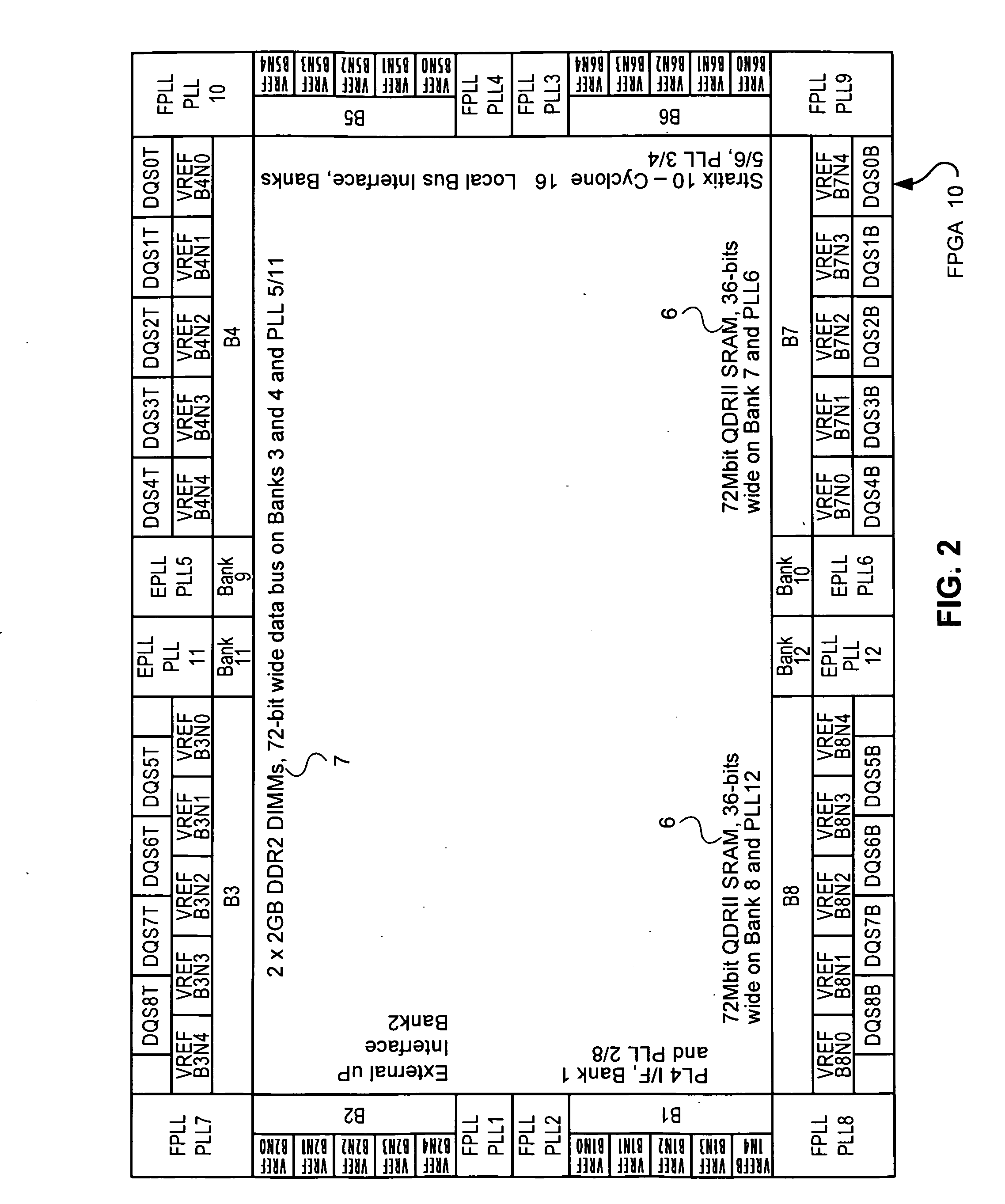
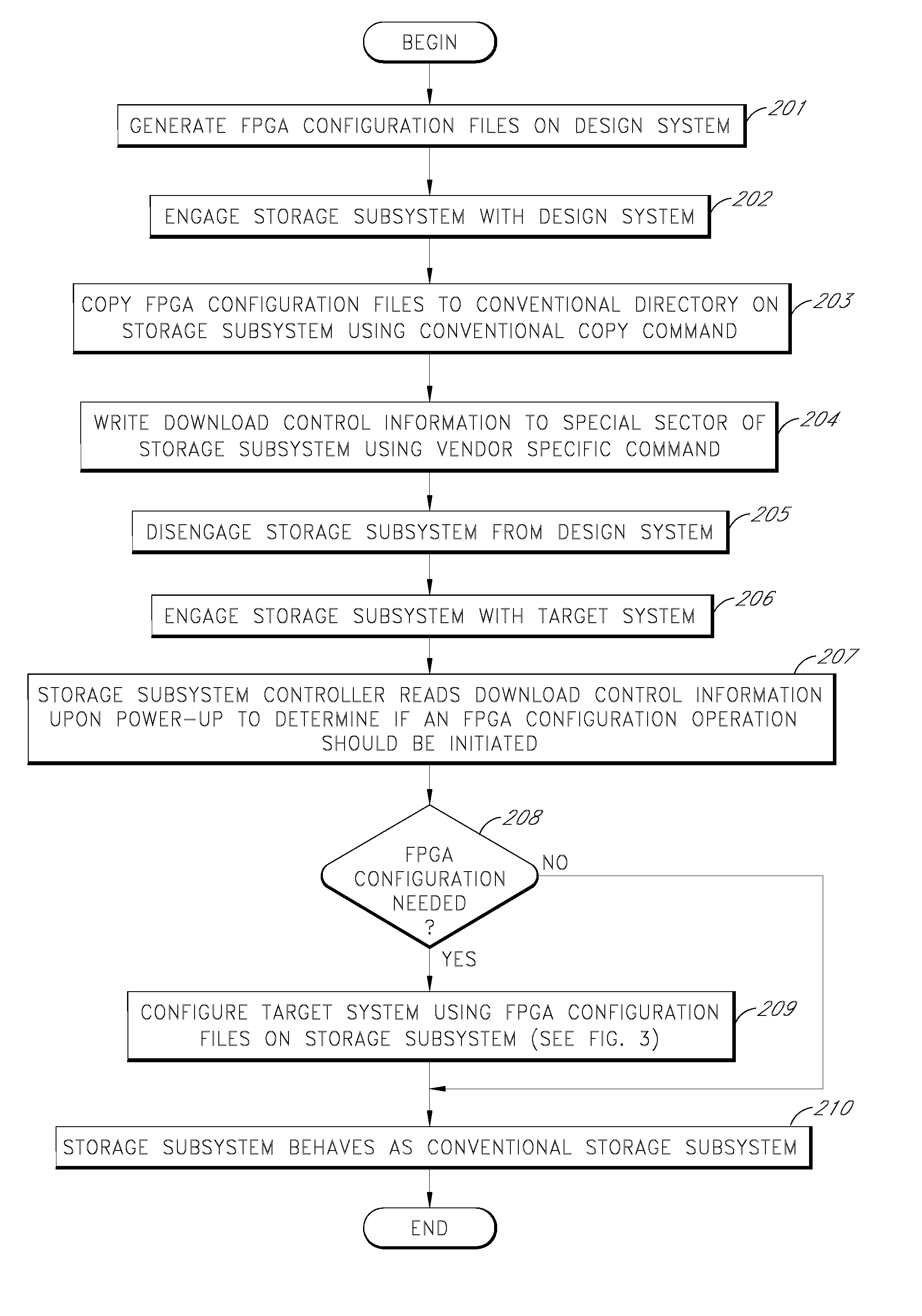
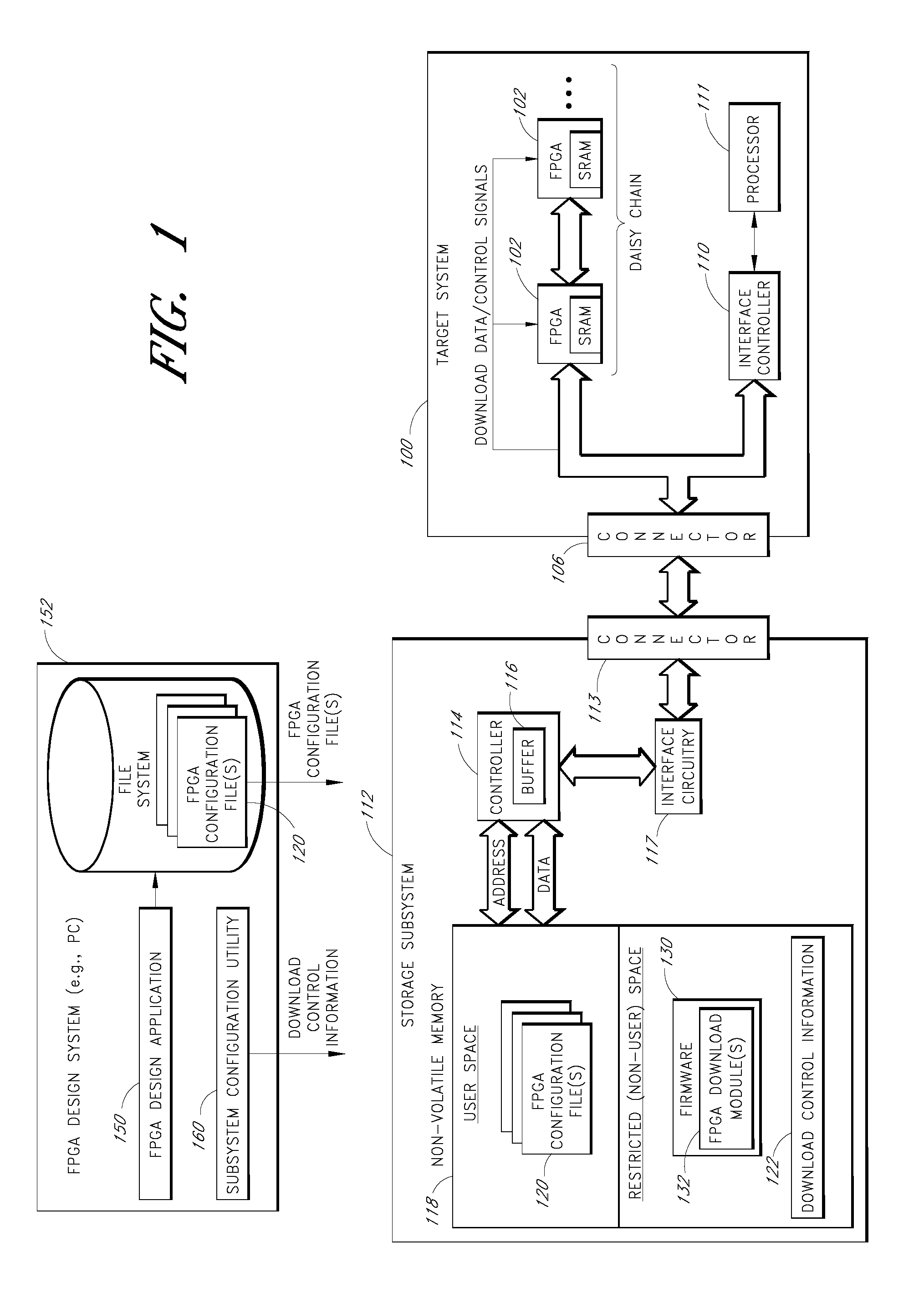
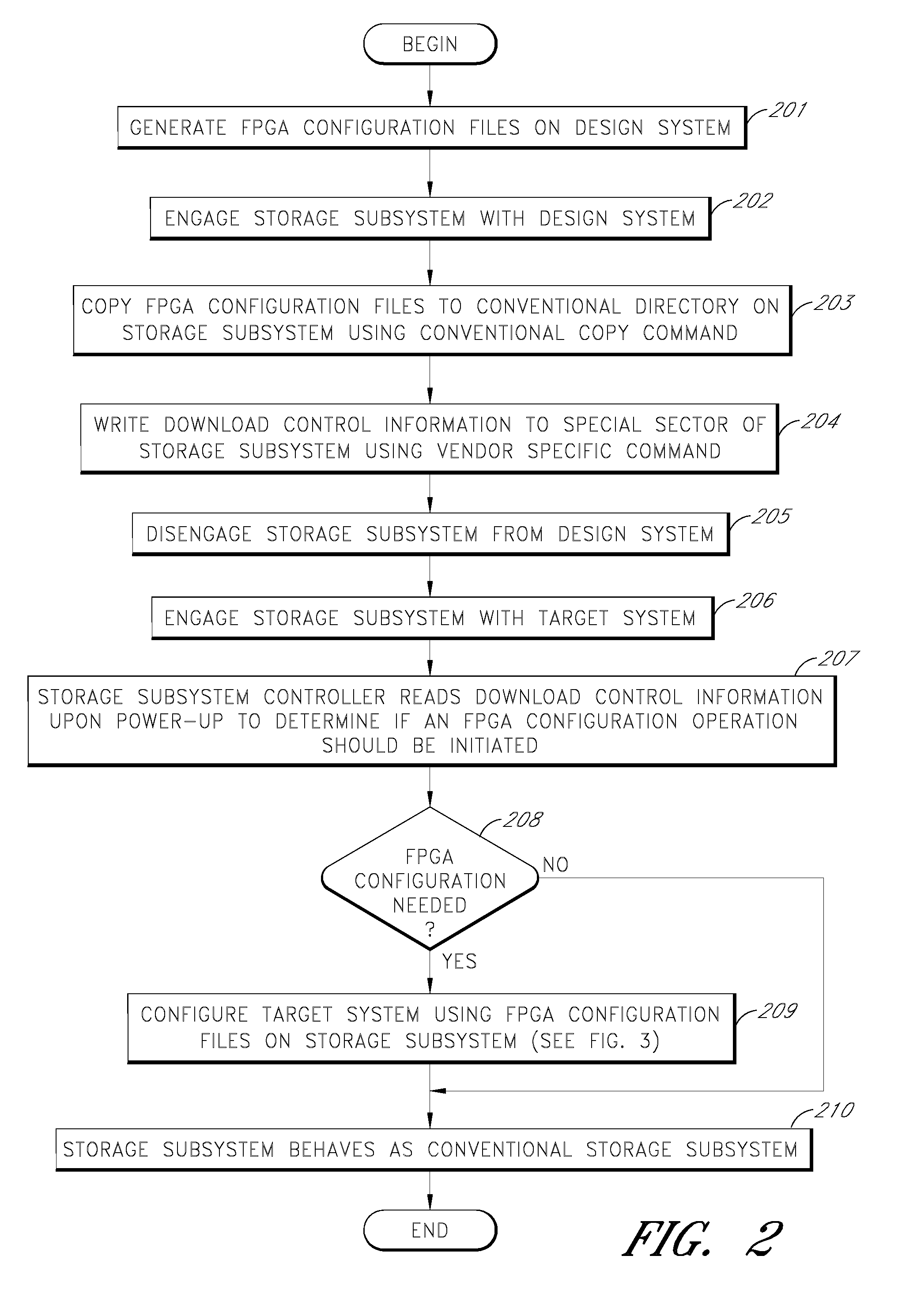
Storage subsystem capable of programming field-programmable devices of a target computer system
InactiveUS8161227B1Avoid the needInput/output to record carriersError preventionProgrammable logic deviceGoal system
A non-volatile storage subsystem is capable of serving as a configuration controller for configuring / programming one or more field-programmable devices, such as FPGAs, of a target computer system. The storage subsystem may be in the form of a memory card or drive that plugs into a standard slot or external port of the target system. When connected to the target system, the storage subsystem uses the appropriate download interface / protocol to stream or otherwise send configuration data stored in its non-volatile storage to the target system's field-programmable device(s). Thus, the need for a configuration controller in the target system is avoided. Once the configuration process is complete, the storage subsystem preferably acts as a standard storage subsystem, such as an ATA storage drive, that may be used by the target system to store data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
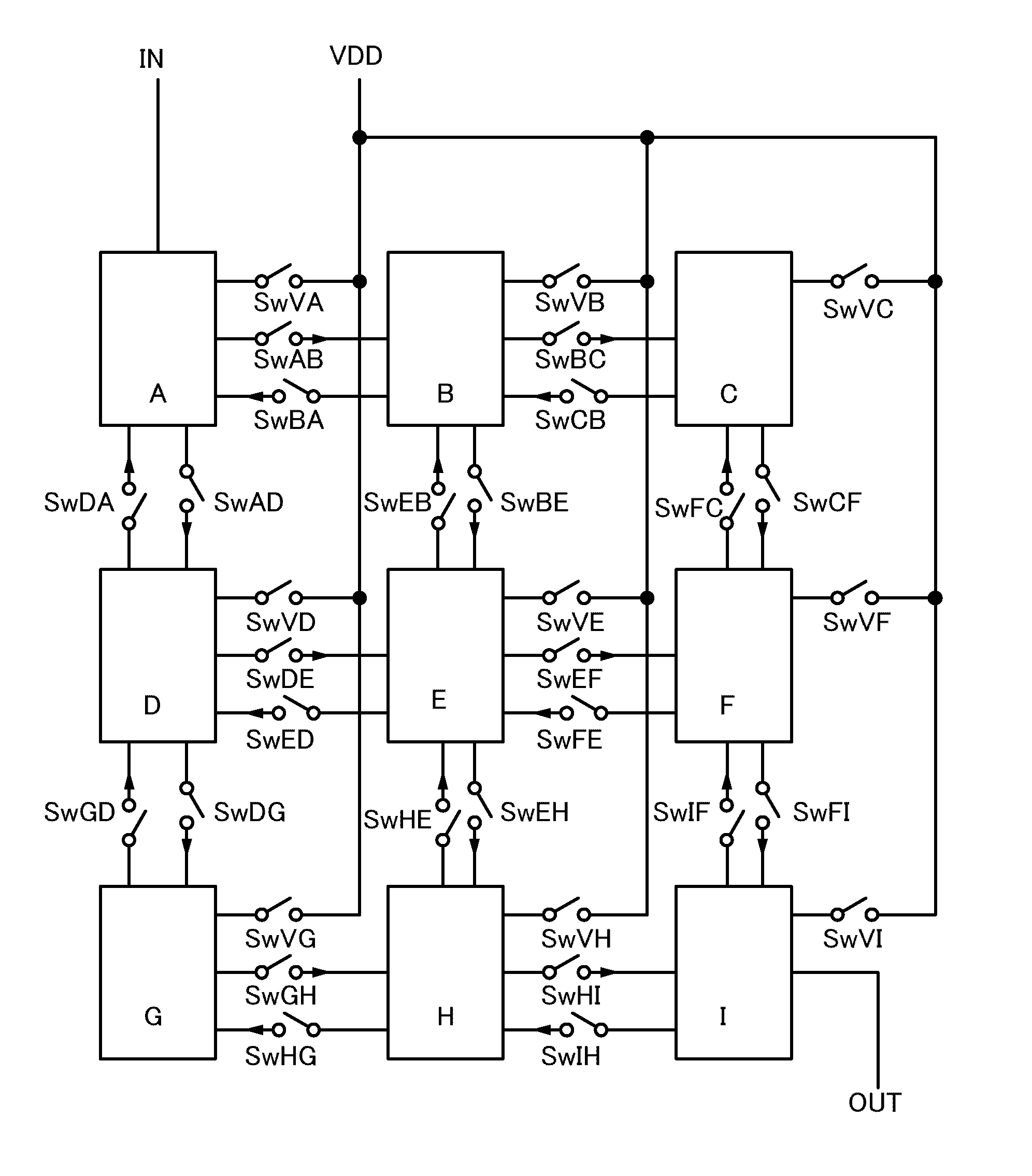
Programmable logic device with embedded switch fabric
InactiveUS20080278197A1Telephonic communicationBootstrappingCrossbar switchProgrammable logic device
The invention in the simplest form is a programmable logic device consisting of gate arrays, external I / O endpoints, and an embedded switch fabric configurable for connecting gates to gates, endpoints to endpoints and gates to endpoints. The architecture may employ a fabric interface of non-blocking crossbar switches for making complex bus connections of multiple devices to facilitate high speed processing.
Owner:TECNICA
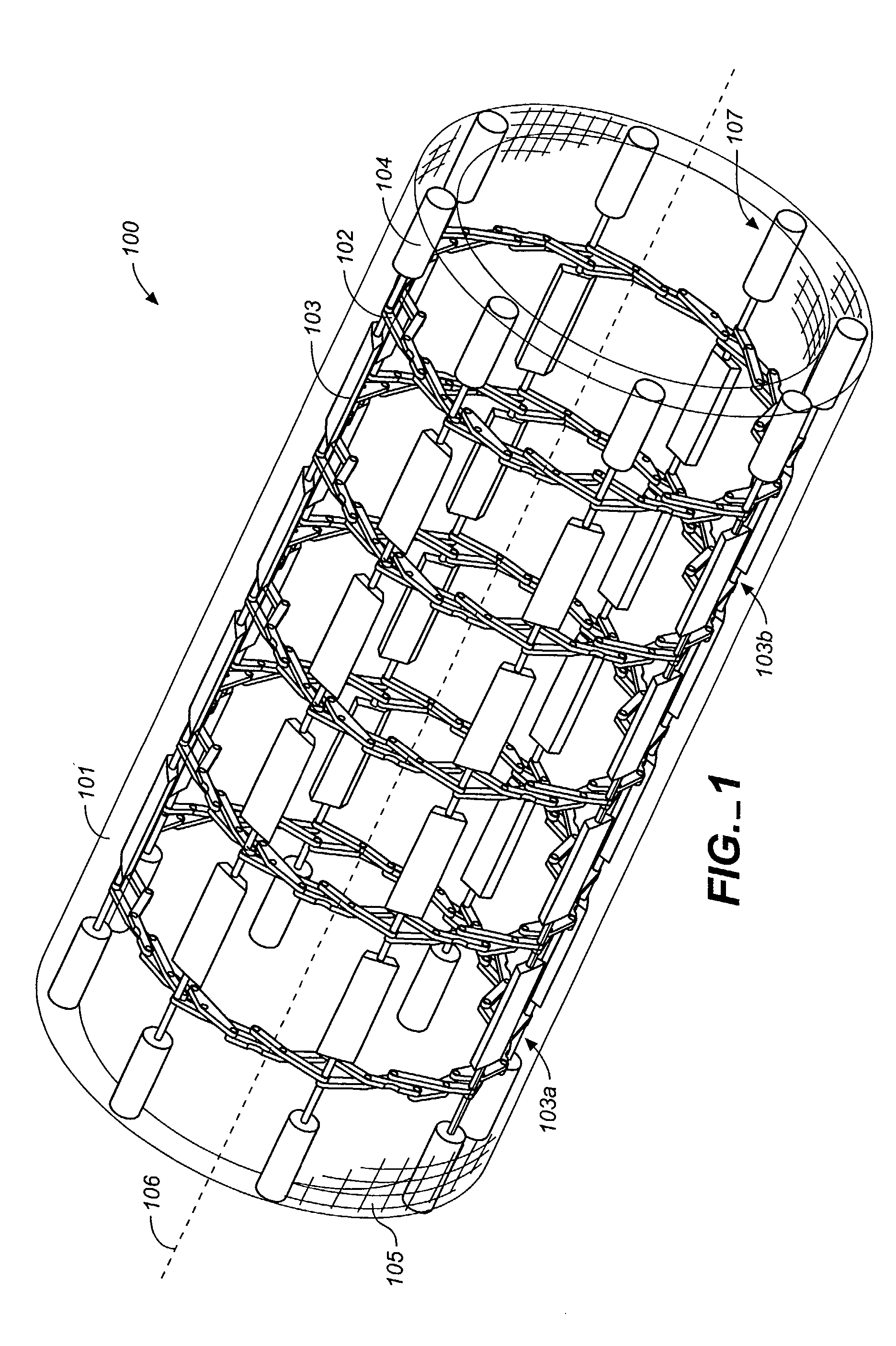
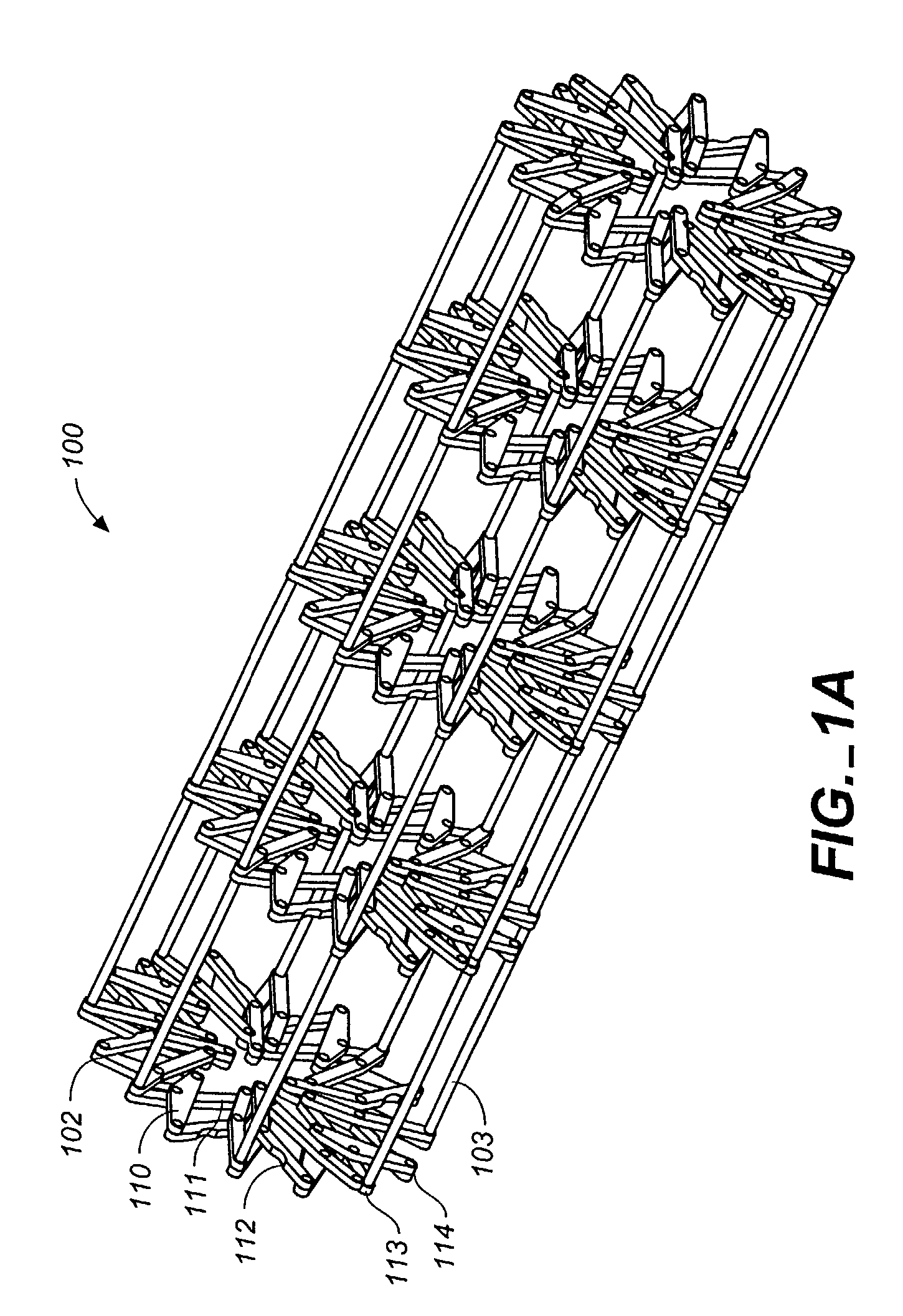
Flexible MEMS actuated controlled expansion stent
InactiveUS7097658B2Minimize damageMaintains overall tubular structureStentsBlood vesselsAutomatic controlProgrammable logic device
An automatically controlled expansion stent having an expansible stent body, actuation means for expanding the stent body, and control means for actively controlling the actuation means. The stent body is substantially tubular and includes material layers covering a plurality of radial expansion trusses. The stent employs MEMS motors under the control of a programmable logic device to expand the trusses and the stent body. Force from the motor is communicated to the expansion trusses through interconnects, which pivotally connect the trusses and provide channels for pull wires extending from the motors to the trusses. The trusses comprise a plurality of hinged links which produce symmetrical expansion of the stent body when actuated by the MEMS motor.
Owner:OKTAY HASAN SEMIH
Programmable vaporizer device and method
The invention relates to a programmable vaporizer device and method that allows a user to controllably atomize a plurality of aerosol-forming substrates having different flavors in order to generate an aerosol mixture with a specific flavor profile and share that flavor profile with other users over a computer network. Preferably, the vaporizer device includes a user interface adapted to create a flavor profile by allowing a user to determine the intensity of specific flavors over the duration of inhalation.
Owner:KERDEMELIDIS ANDREW
Circuits and methods of implementing time-average-frequency direct period synthesizer on programmable logic chip and driving applications using the same
ActiveUS9621173B1Innovative designPowerful frequency generation capabilityPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsUnit generatorProgrammable logic device
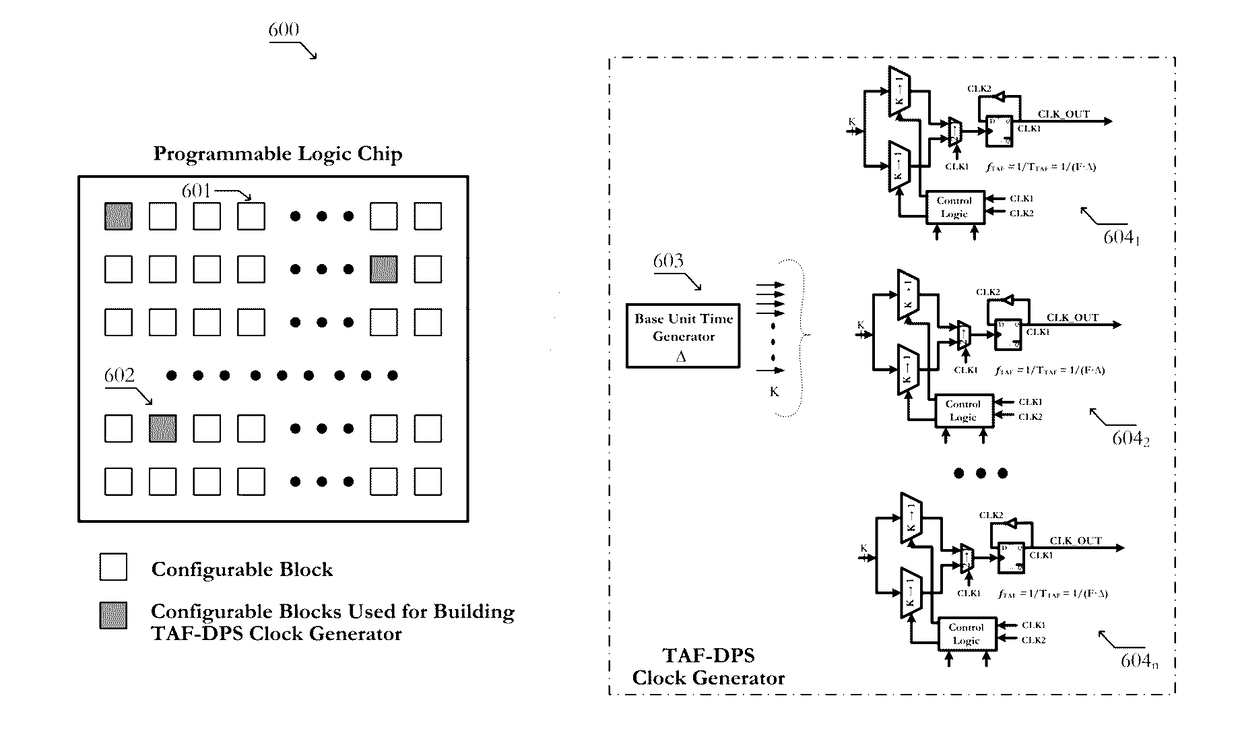
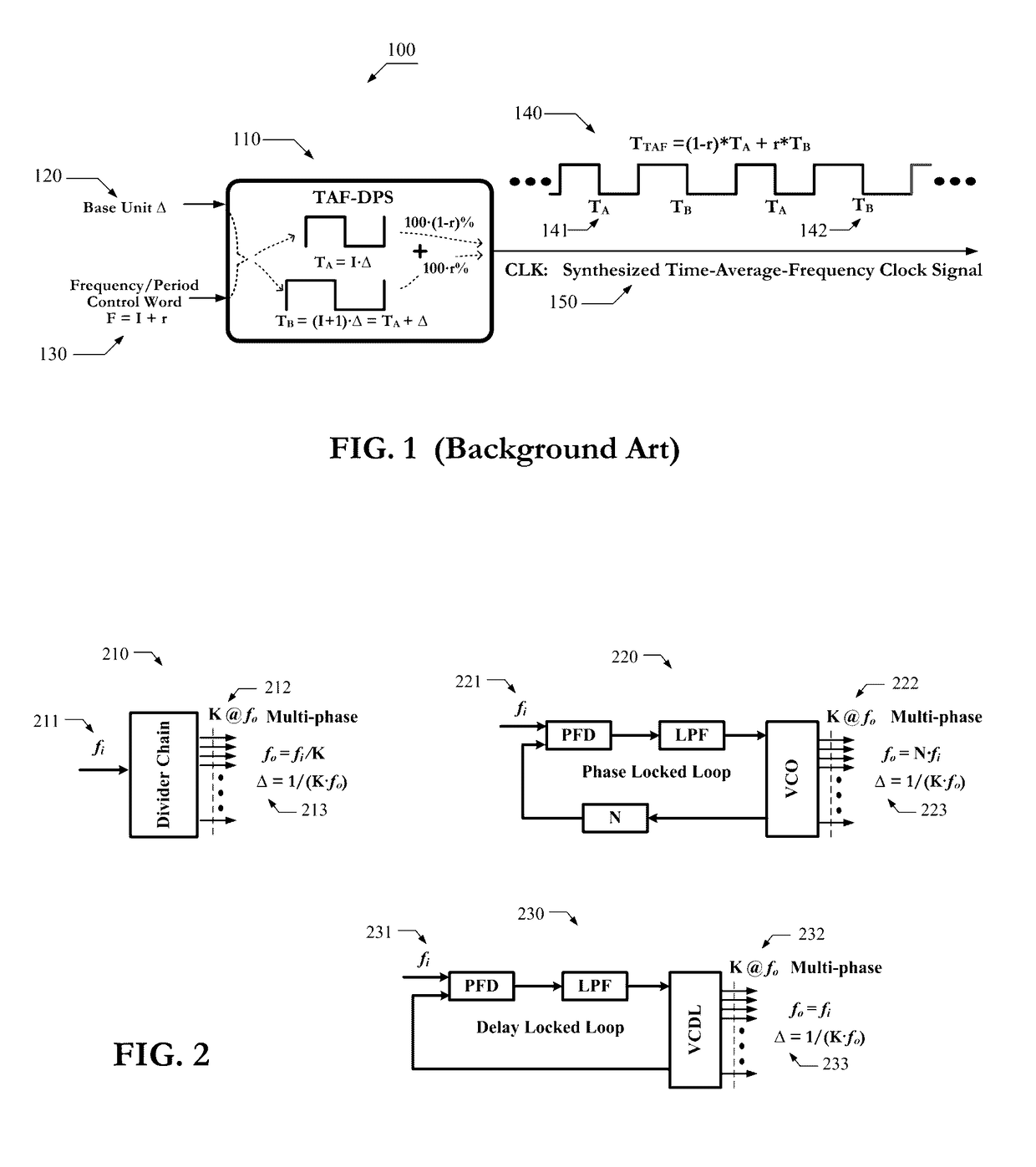
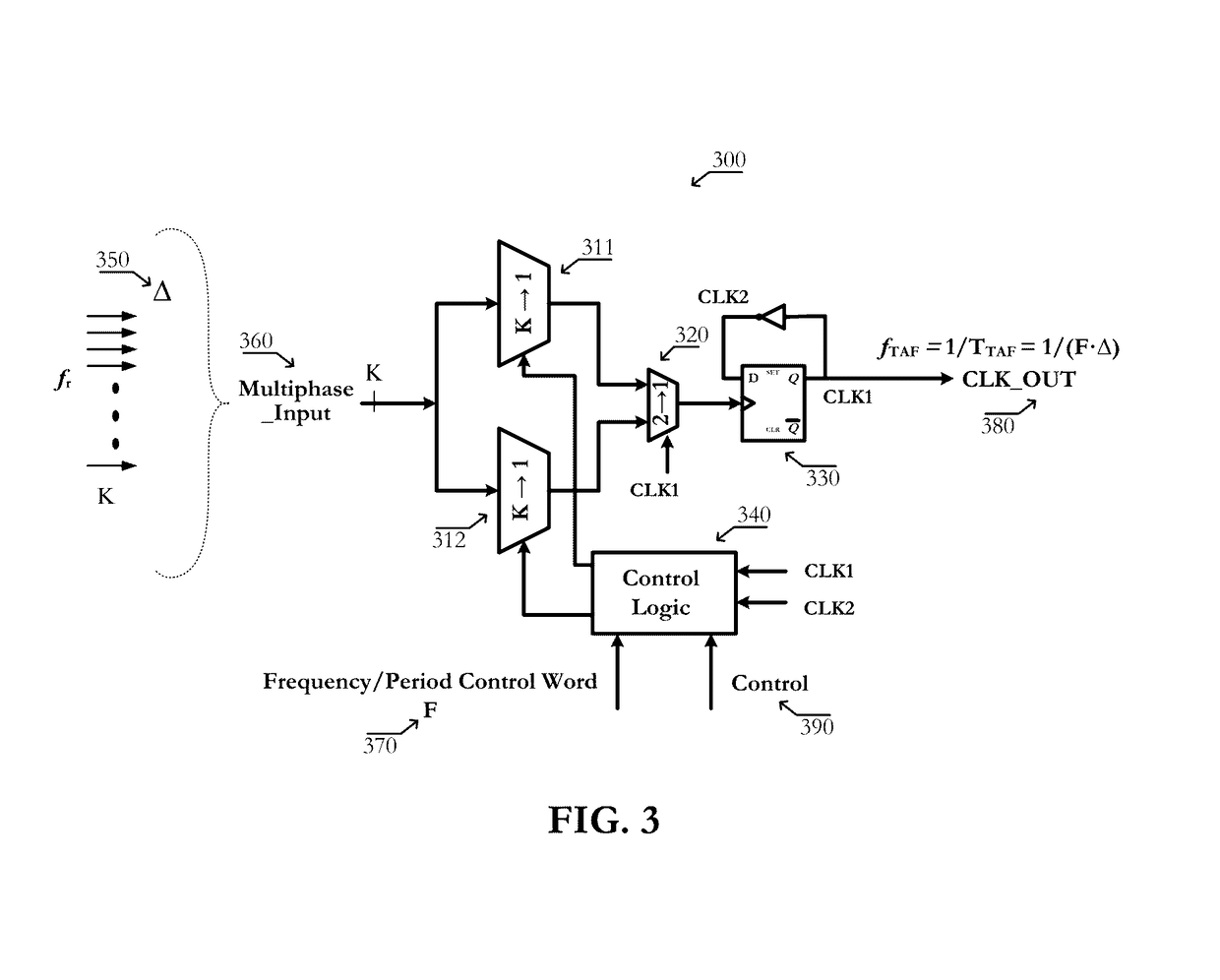
Circuits of a TAF-DPS clock generator implemented on programmable logic chip comprise: 1) a base time unit generator created from configurable blocks, or on-chip PLL, or on-chip DLL, said base time unit generator produces a plurality of phase-evenly-spaced-signals; 2) a TAF-DPS frequency synthesizer created by configuring configurable blocks of said programmable logic chip, said TAF-DPS frequency synthesizer takes said plurality of phase-evenly-spaced-signals as its input. Methods of creating flexible clock signal to drive application comprise: 1) selecting one or more strategic areas in said programmable logic chip; 2) creating one or more TAF-DPS clock generator for each said area by using the configurable resource in said area; 3) creating control function to control the frequency and duty-cycle of the TAF-DPS clock generator output, said control function can be circuit created from configuring configurable blocks, said control function can also be achieved by software; 4) driving the circuits in application by the flexible clock generated from said TAF-DPS clock generator.
Owner:XIU LIMING
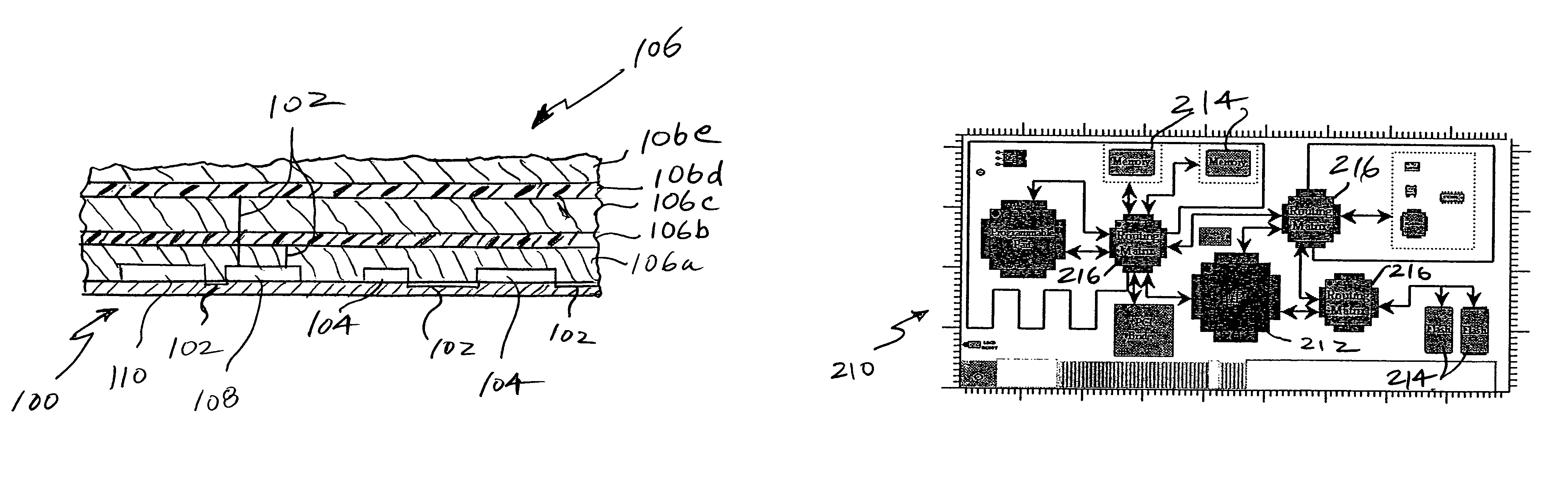
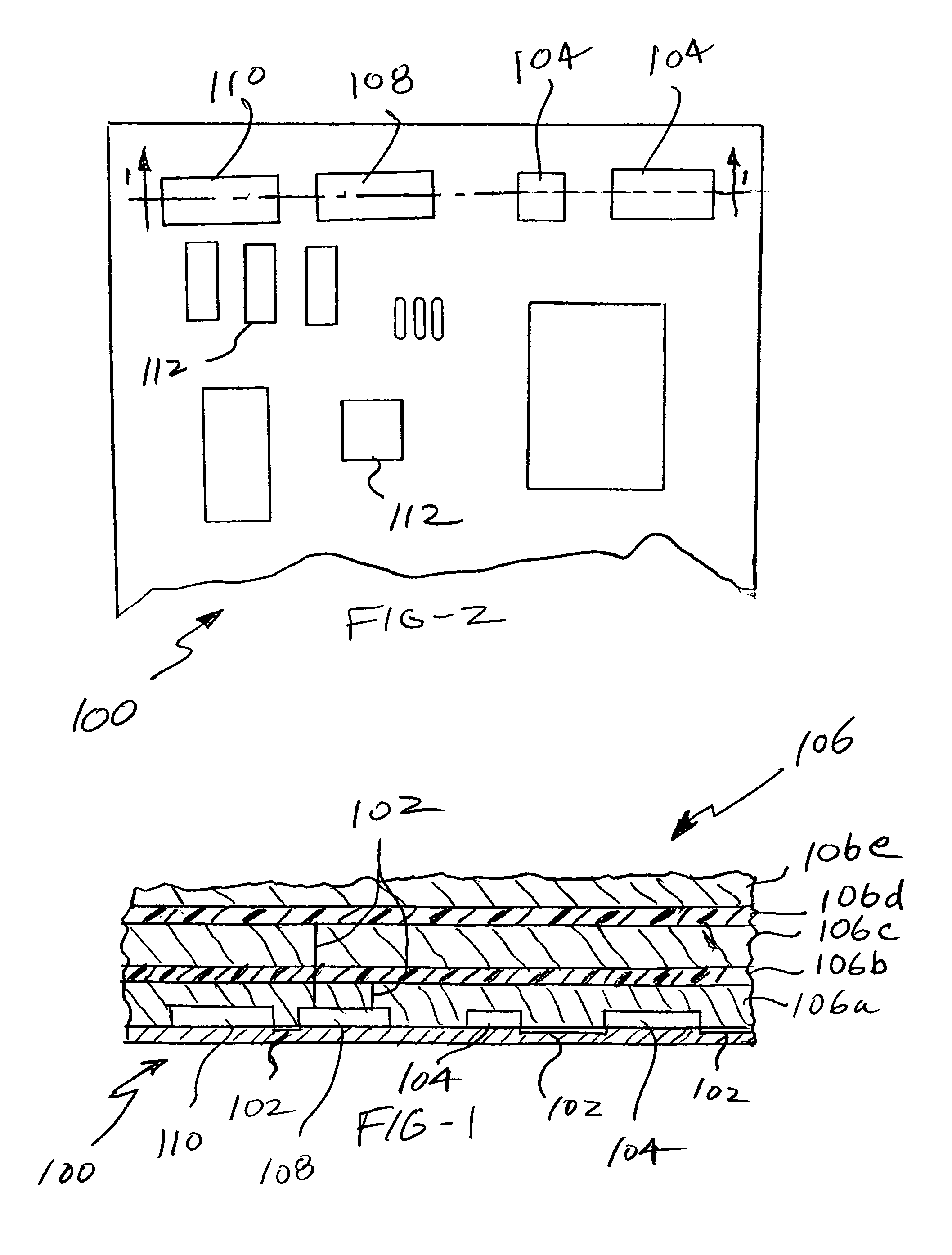
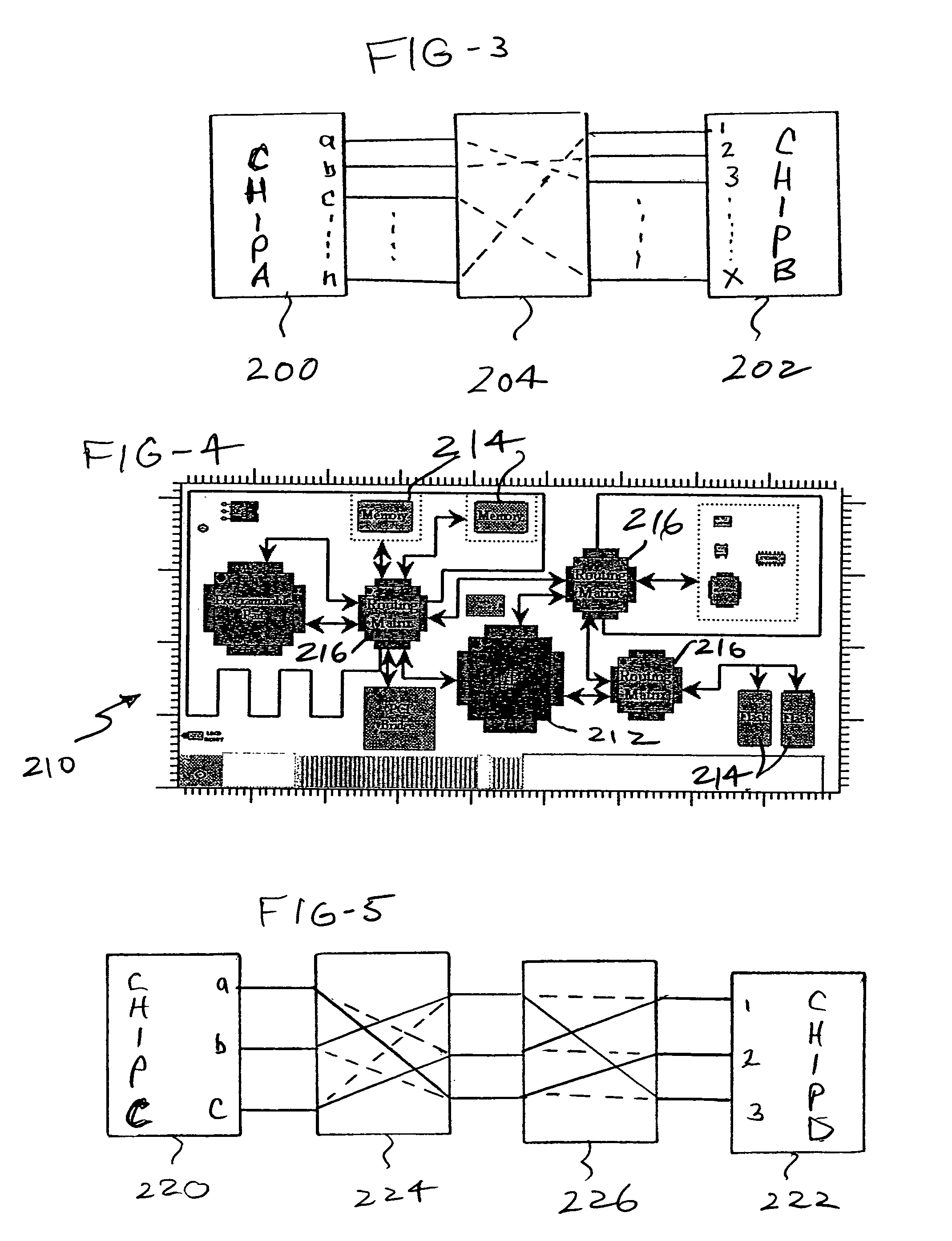
Tamper resistant circuit boards
InactiveUS7015823B1Circuit security detailsPrinted circuit aspectsProgrammable logic devicePhysical Barrier
A physical barrier for a circuit board also functions as a tampering sensor or sensors monitored by electrical circuitry that generates a tamper signal for erasing information critical for the operation of the circuit board in the event of sensed tampering. One or more routing matrices configured in at least one programmable device is programmed to interconnect operating as well as optional dummy components on the board so that routing information is erased in the event of sensed tampering.
Owner:INFOSCITEX
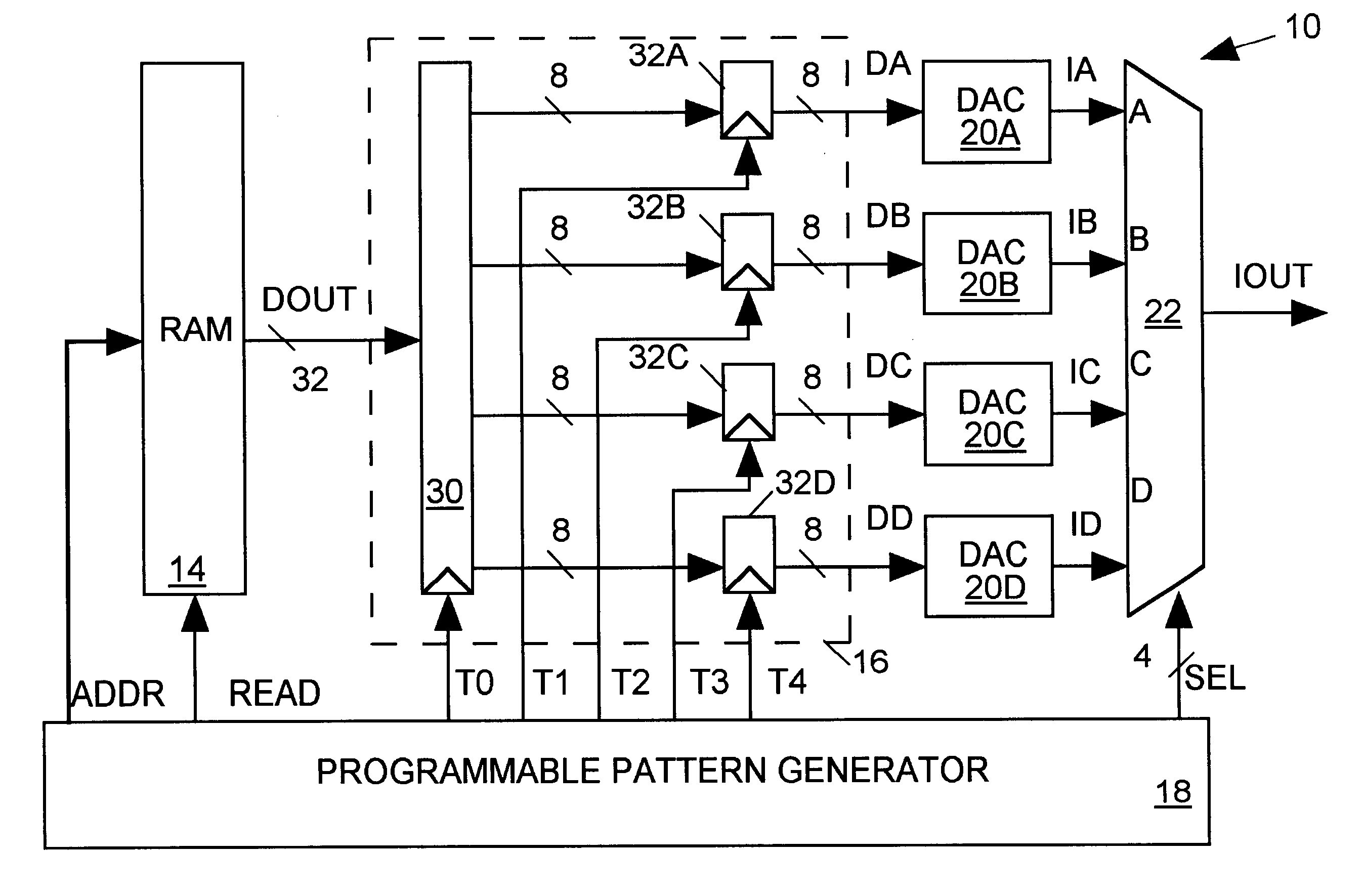
Arbitrary waveform generator having programmably configurable architecture
InactiveUS6356224B1Electric signal transmission systemsOscillations generatorsDigital analog converterMultiplexer
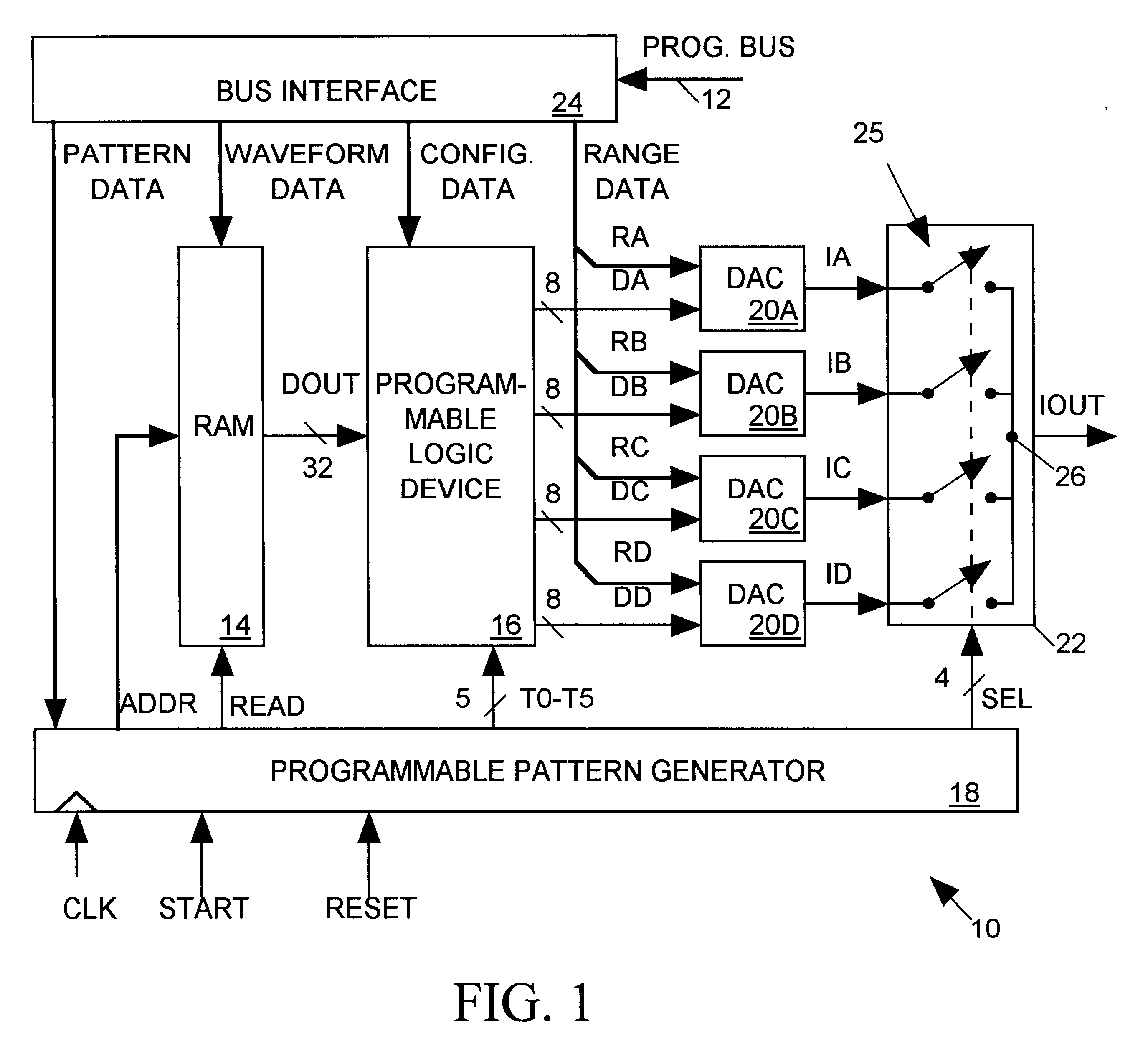
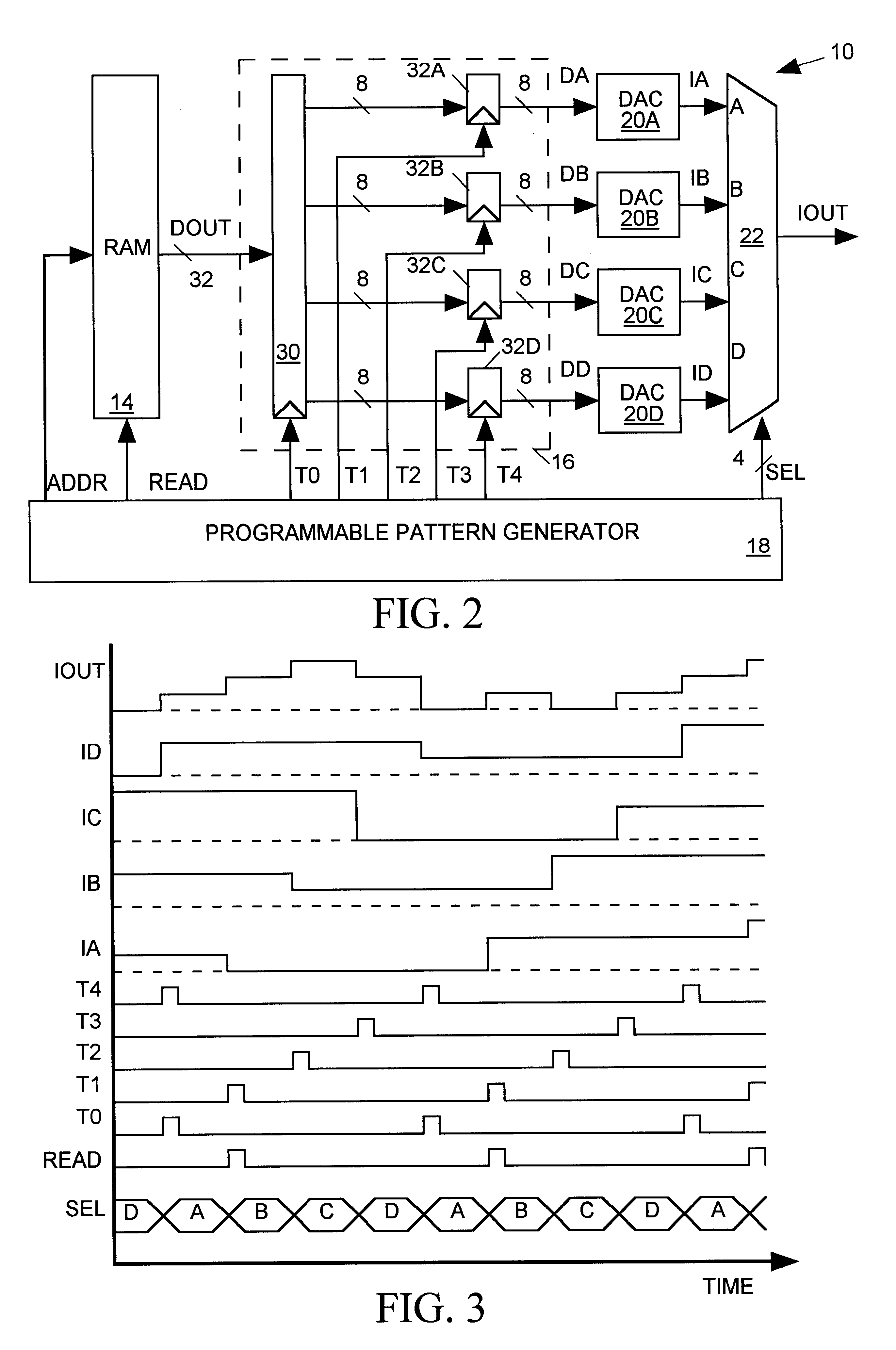
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) for producing an analog output current signal includes a random access memory (RAM), a programmable logic device (PLD), a programmable pattern generator, several digital-to analog converters (DACS) and a current multiplexer. The RAM store data sequences representing the analog waveform to be generated. The pattern generator read addresses the RAM causing it to sequentially read out its stored data sequence to the PLD. The PLD routes selected fields of each data sequence word to one or more of the DACs in response to timing signals provided by the pattern generator. Each DAC produces an output current of magnitude determined by its input waveform and range data. The pattern generator also signals the analog multiplexer to sum currents produced by one or more selected DACs to produce the AWG output waveform. The nature of the AWG output waveform is flexibly determined by the nature of the data sequence and the frequency at which it is read out of the RAM, the manner in which the PLD routes the data sequence to the DACs, the value of the range data supplied to each DAC, and the output pattern generated by the pattern generator. The flexible AWG architecture permits the AWG to be appropriately configured for various combinations of output waveform frequency, bandwidth and resolution requirements.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Programmable microelectronic device, structure, and system and method of forming the same
InactiveUS6985378B2Easy and inexpensive to manufactureVariably programmedTransistorNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorProgrammable logic device
A microelectronic programmable structure suitable for storing information and a method of forming and programming the structure are disclosed. The programmable structure generally includes an ion conductor and a plurality of electrodes. Electrical properties of the structure may be altered by applying energy to the structure, and thus information may be stored using the structure.
Owner:AXON TECH
Programmable AC power switch
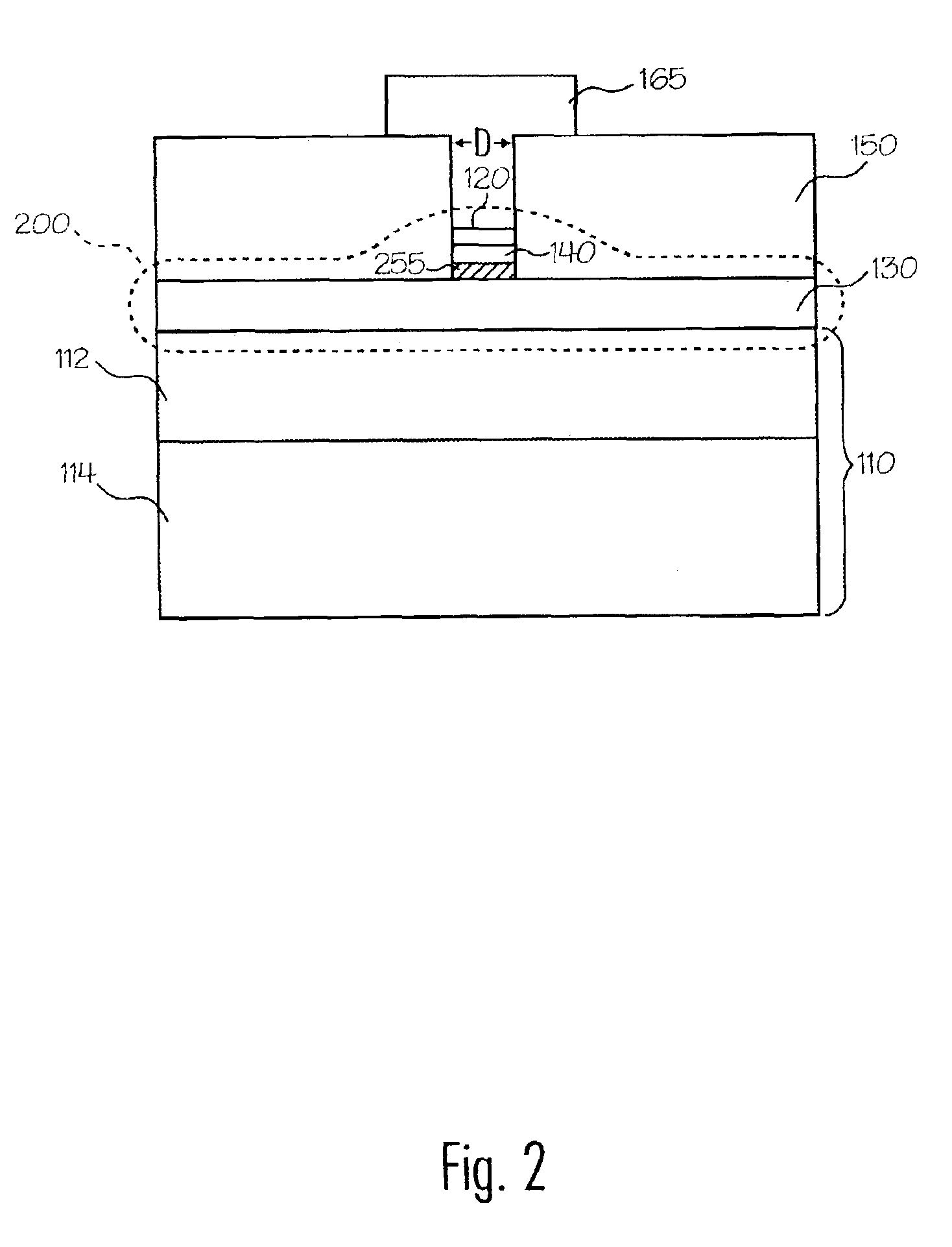
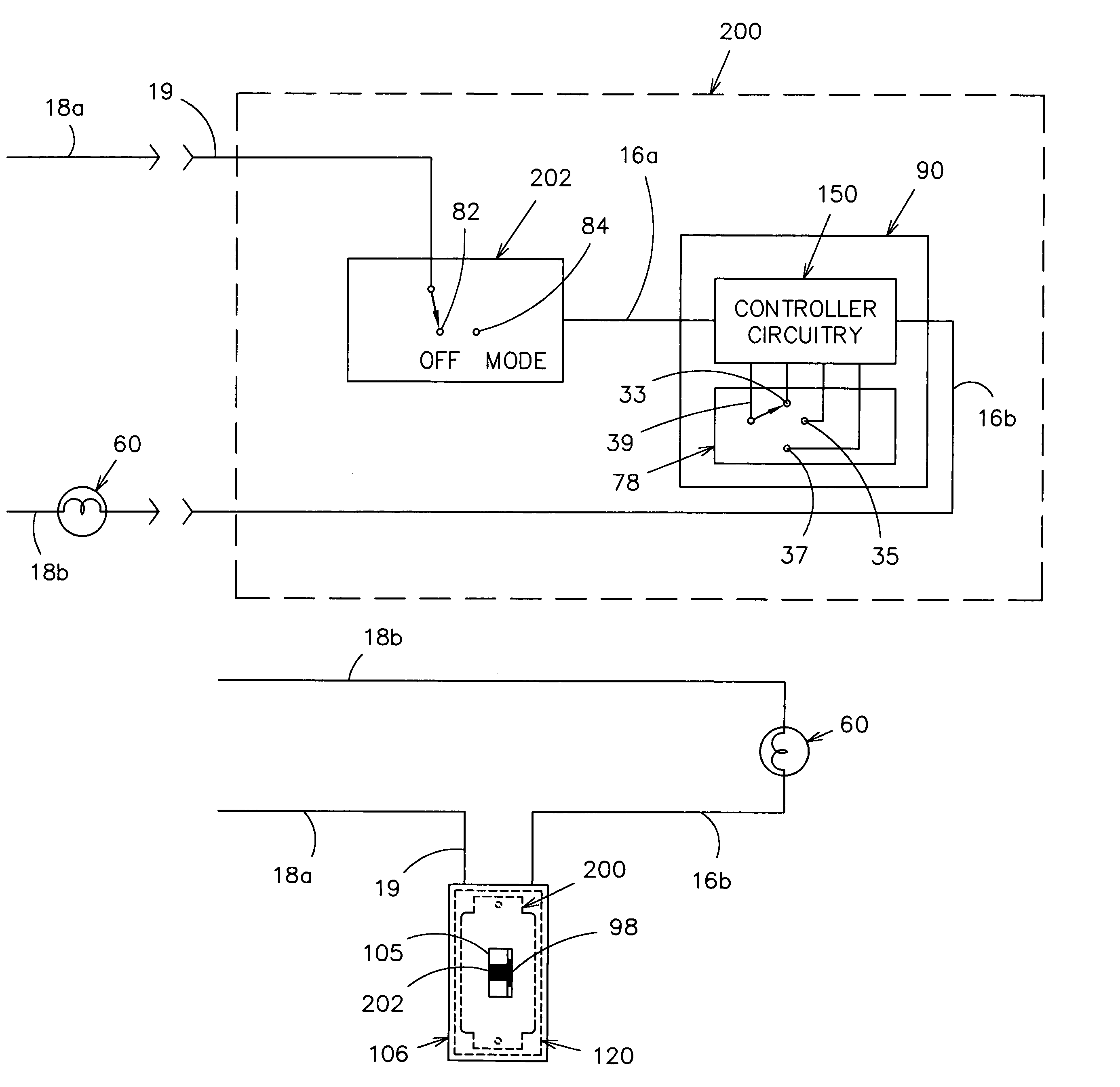
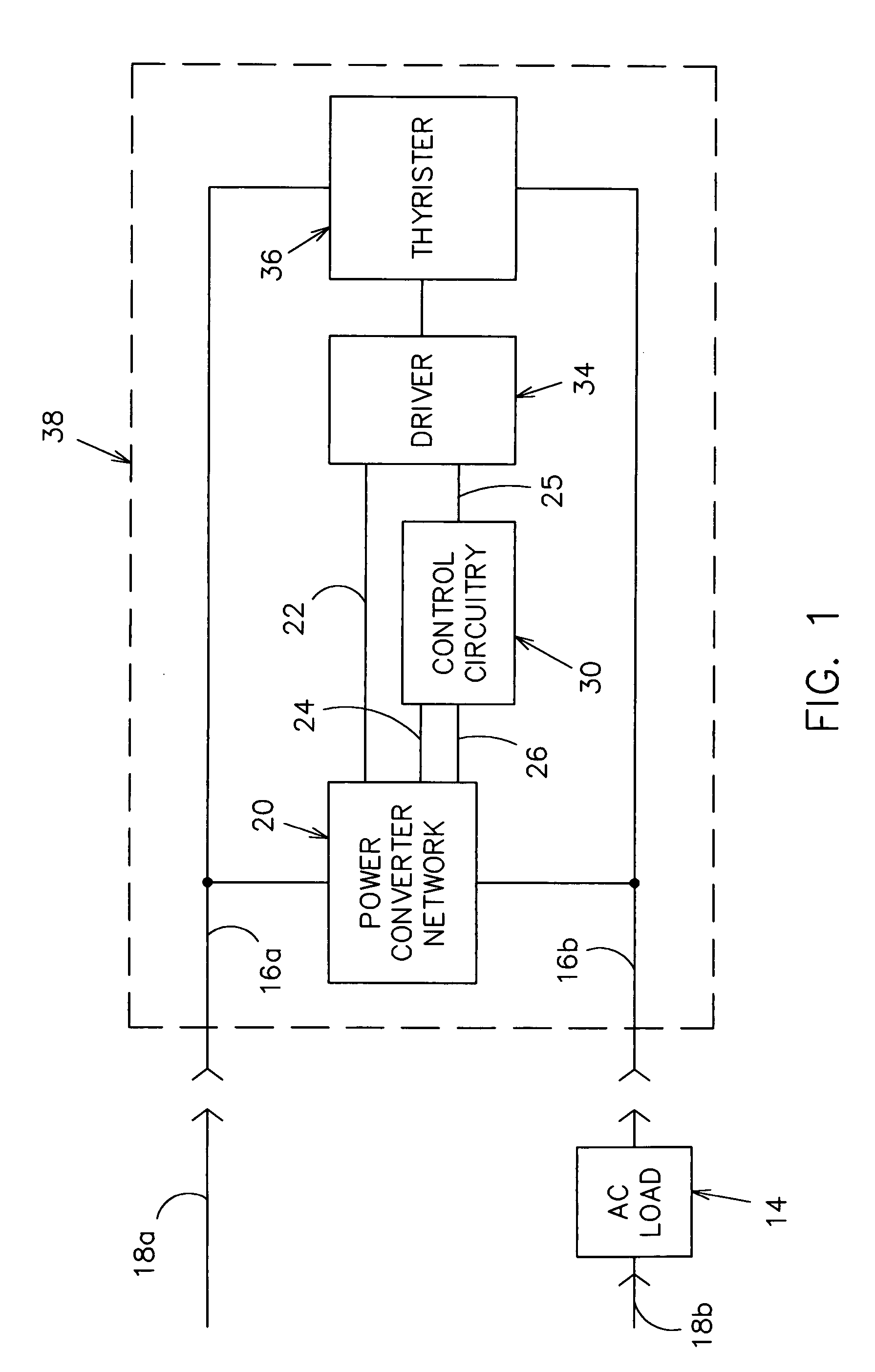
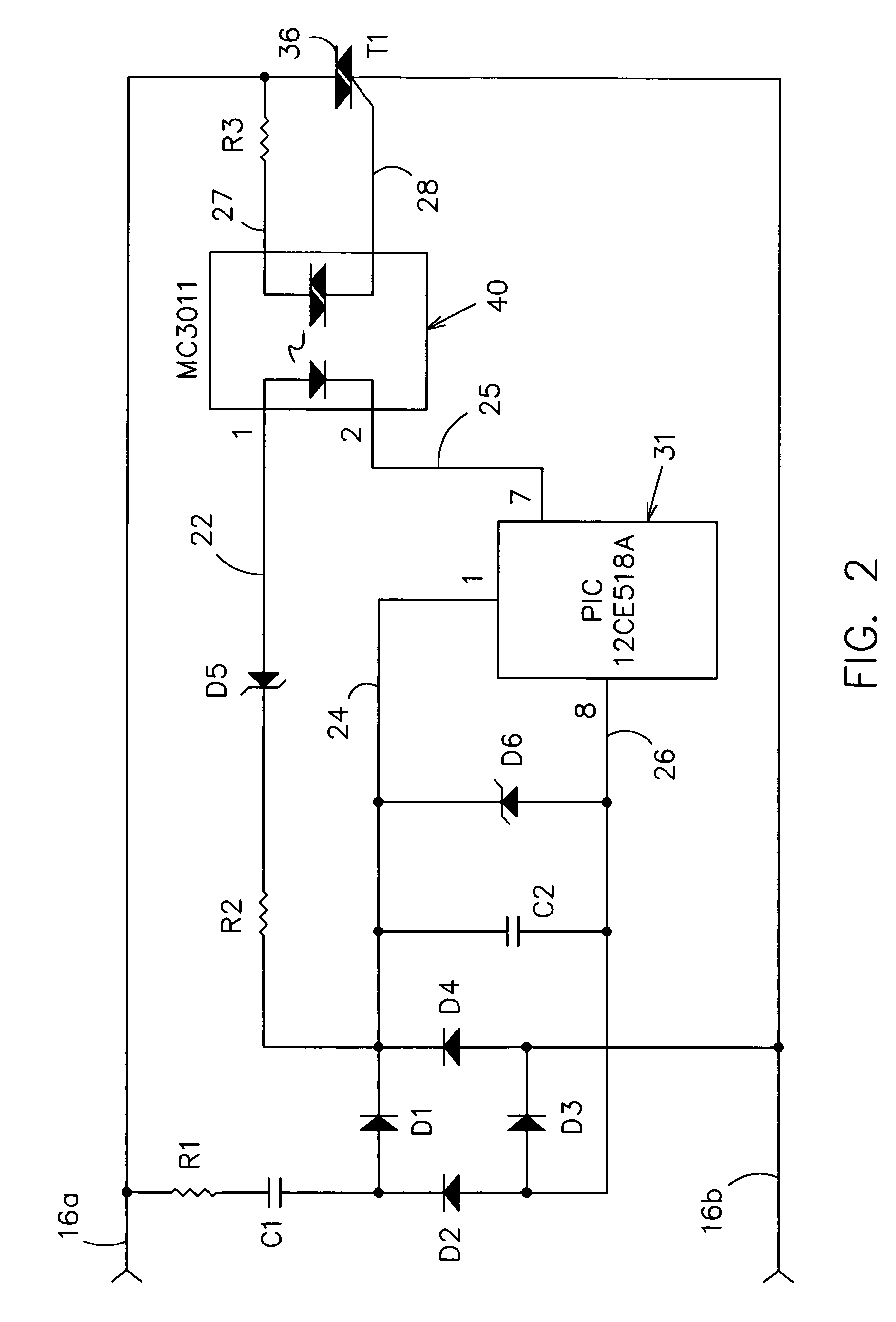
InactiveUS6933686B1Low costInexpensive and effectiveTime indicationBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsMicrocontrollerTime delays
An AC controller provides programmable switching of AC power flow, together with producing a source of DC power for the AC controller. The AC controller is connected in series with only one side of the AC power source and the AC load, and uses a microcontroller or a Programmable Logic Device (PLD) for the programmable capability. The AC controller can be programmed to provide a light flasher function, a time delay off function, an automatic fade function, a dimming function, a burglar deterrent function, and a time delay dim function. With a multiple-position switch replacing a current wall switch, the operator can easily select many pre-programmed functions.
Owner:BISHEL RICHARD A
Physical resynthesis of a logic design
InactiveUS7337100B1Simple designMinimize time delayElectronic circuit testingAnalogue computers for electric apparatusThird partyVisibility
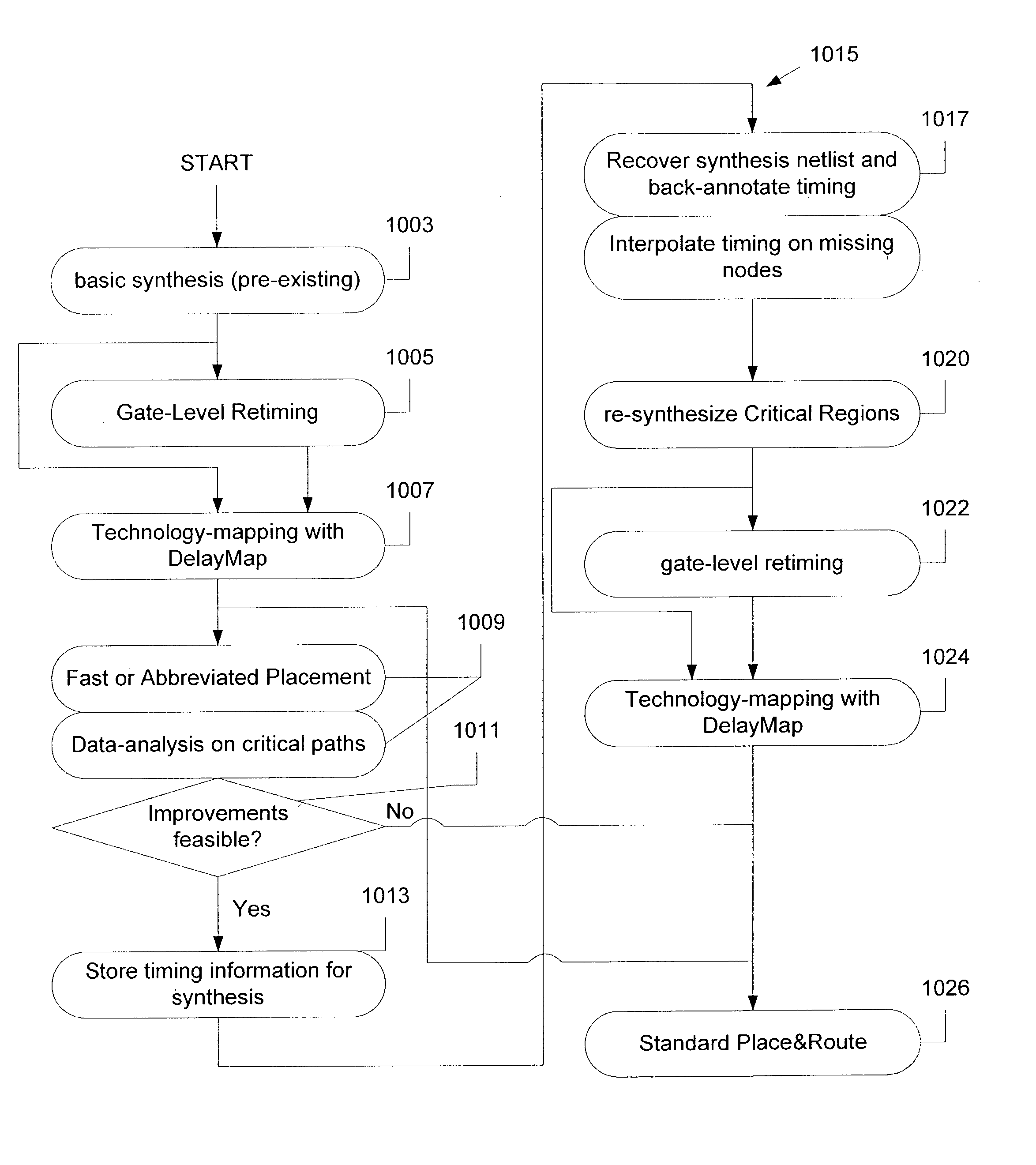
A multiple-pass synthesis technique improves the performance of a design. In a specific embodiment, synthesis is performed in two or more passes. In a first pass, a first synthesis is performed, and in a second or subsequent pass, a second synthesis or resynthesis is performed. During the first synthesis, the logic will be mapped to for example, the logic structures (e.g., logic elements, LUTs, synthesis gates) of the target technology such as a programmable logic device. Alternatively a netlist may be provided from a third party. Before the second synthesis, a fast or abbreviated fit may be performed of the netlist to a specific device (e.g., specific programmable logic device product). Before the second synthesis, the netlist obtained from the first synthesis (or provided by a third party) is unmapped and then the second synthesis is performed. Since a partial fit is performed, the second synthesis has more visibility and optimize the logic better than by using a single synthesis pass. After the second synthesis pass, a more detailed fit is performed.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
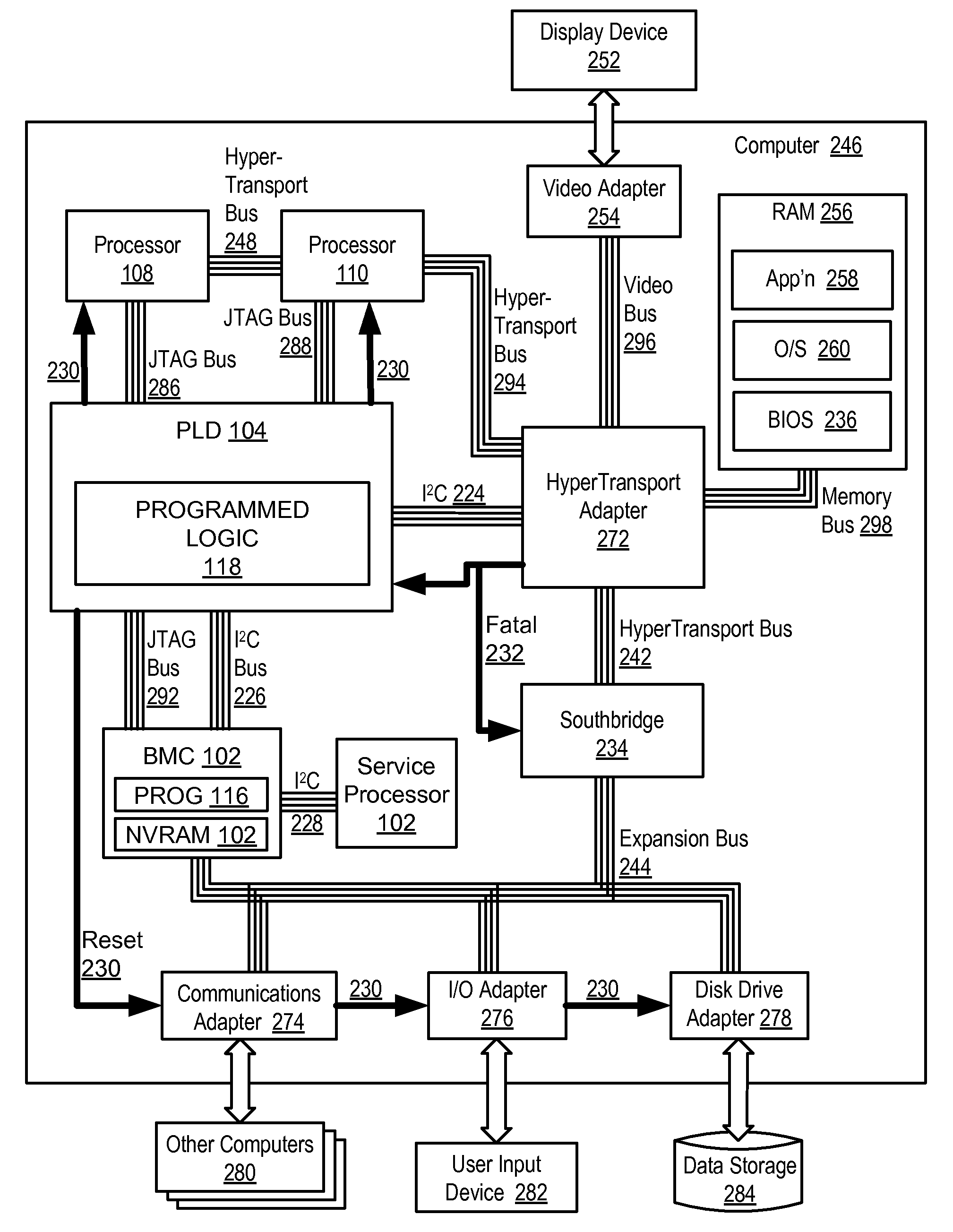
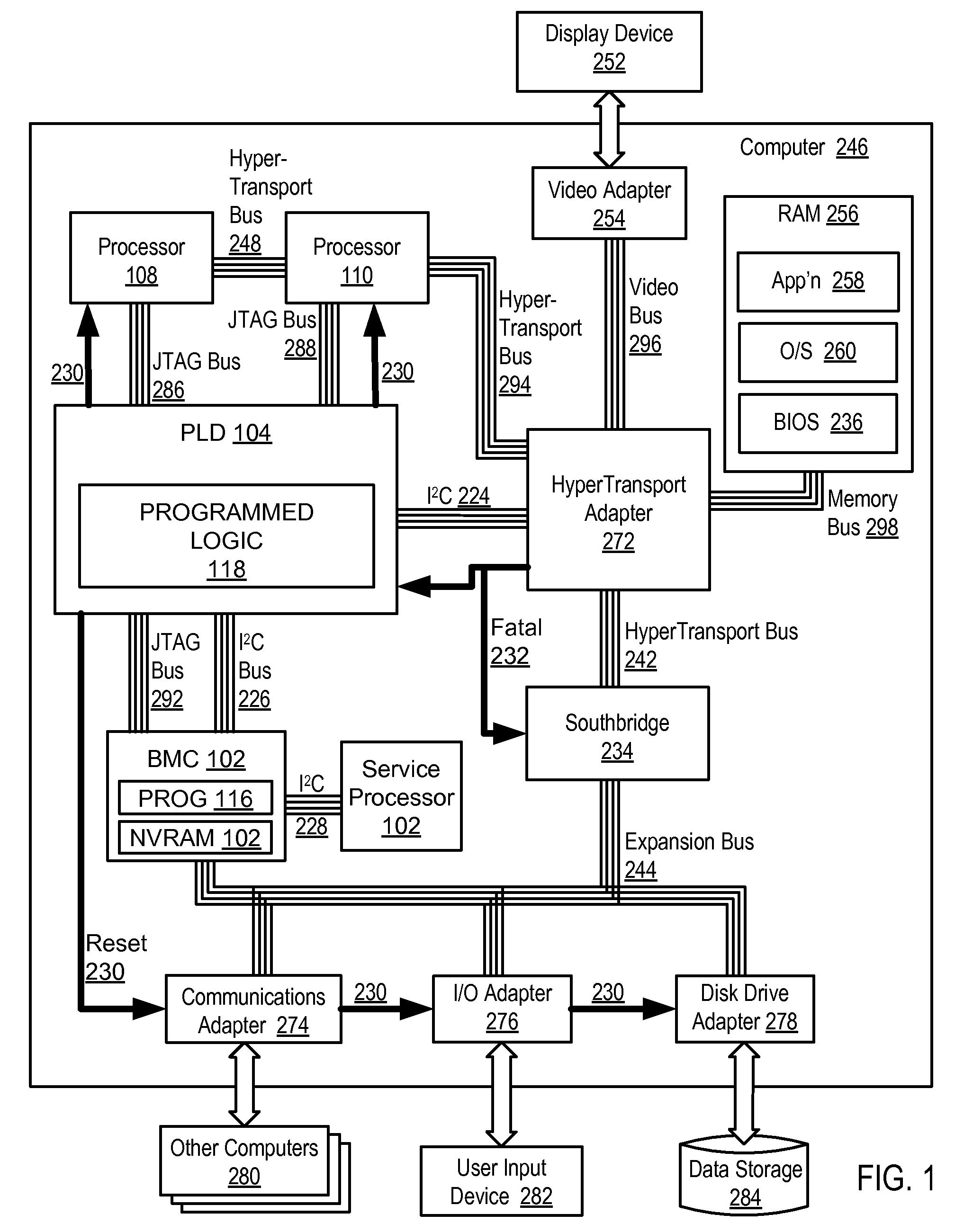
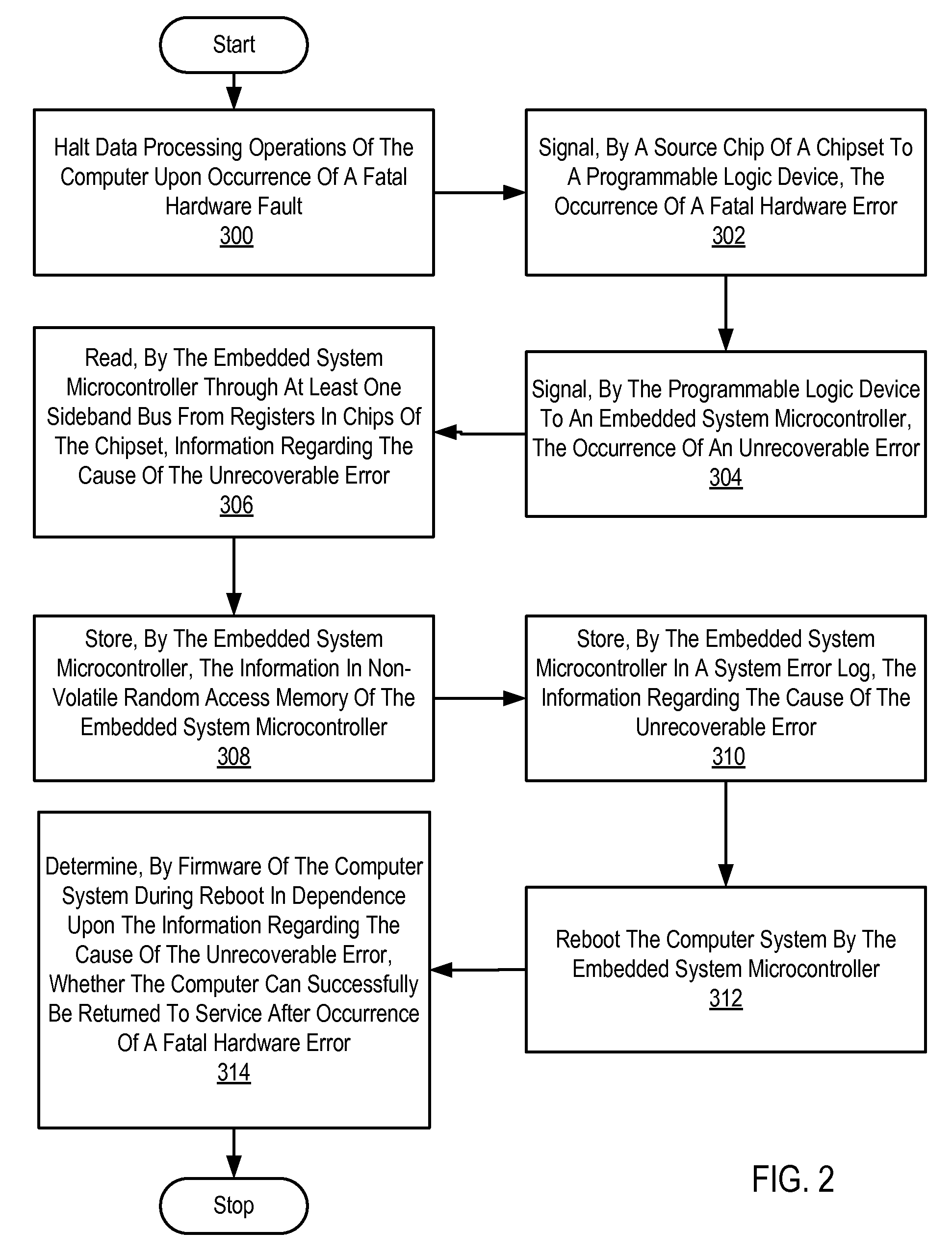
Handling Fatal Computer Hardware Errors
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for handling fatal computer hardware errors on a computer that include halting data processing operations of the computer upon occurrence of a fatal hardware error; signaling by a source chip of a chipset to the programmable logic device the occurrence of a fatal hardware error; signaling by the programmable logic device to an embedded system microcontroller the occurrence of a fatal hardware error; reading by the embedded system microcontroller through at least one sideband bus from registers in chips of the chipset information regarding the cause of the fatal hardware error; and storing by the embedded system microcontroller the information in non-volatile random access memory of the embedded system microcontroller.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com