Patents
Literature
2954 results about "Digital analog converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Speakerphone
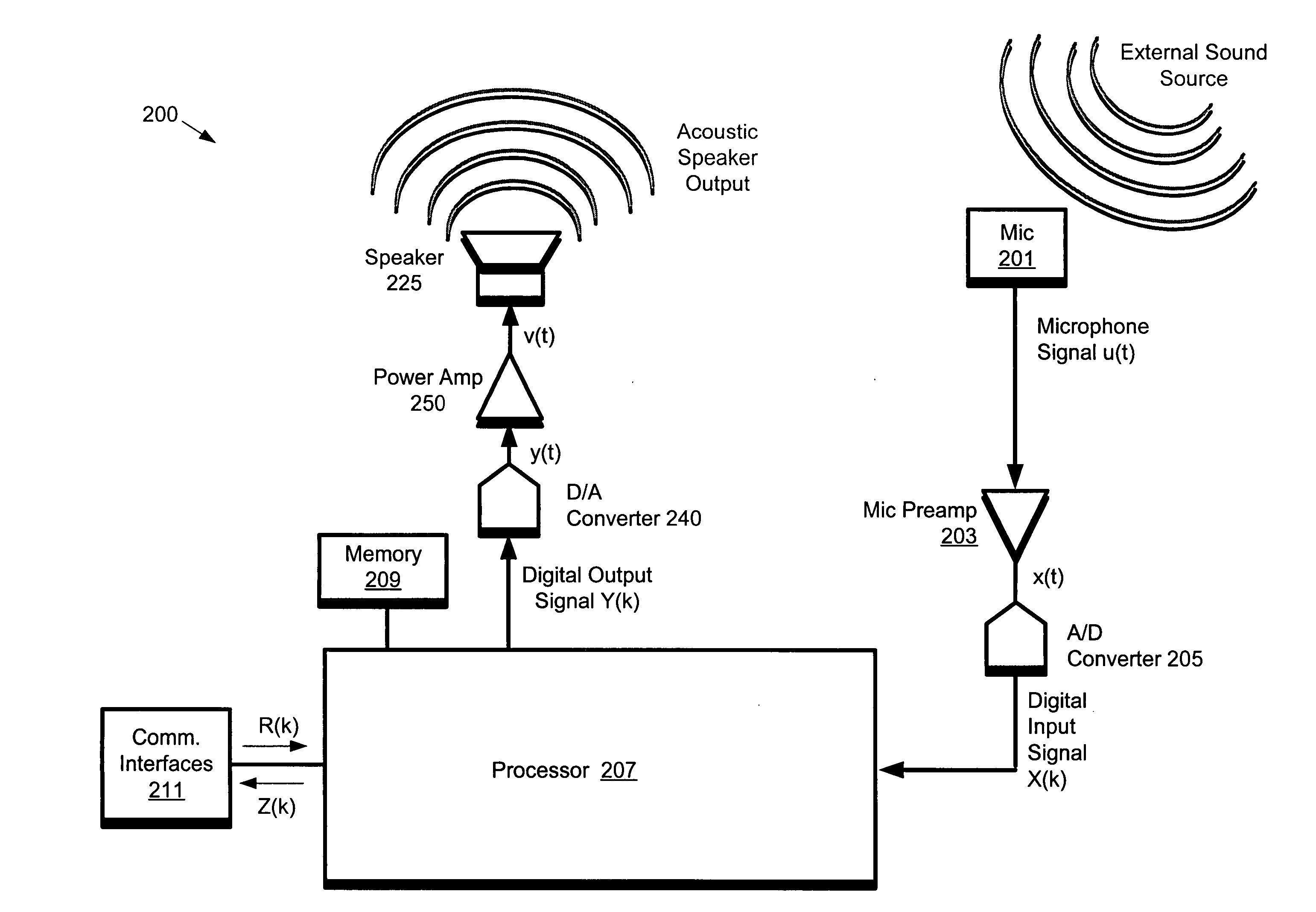
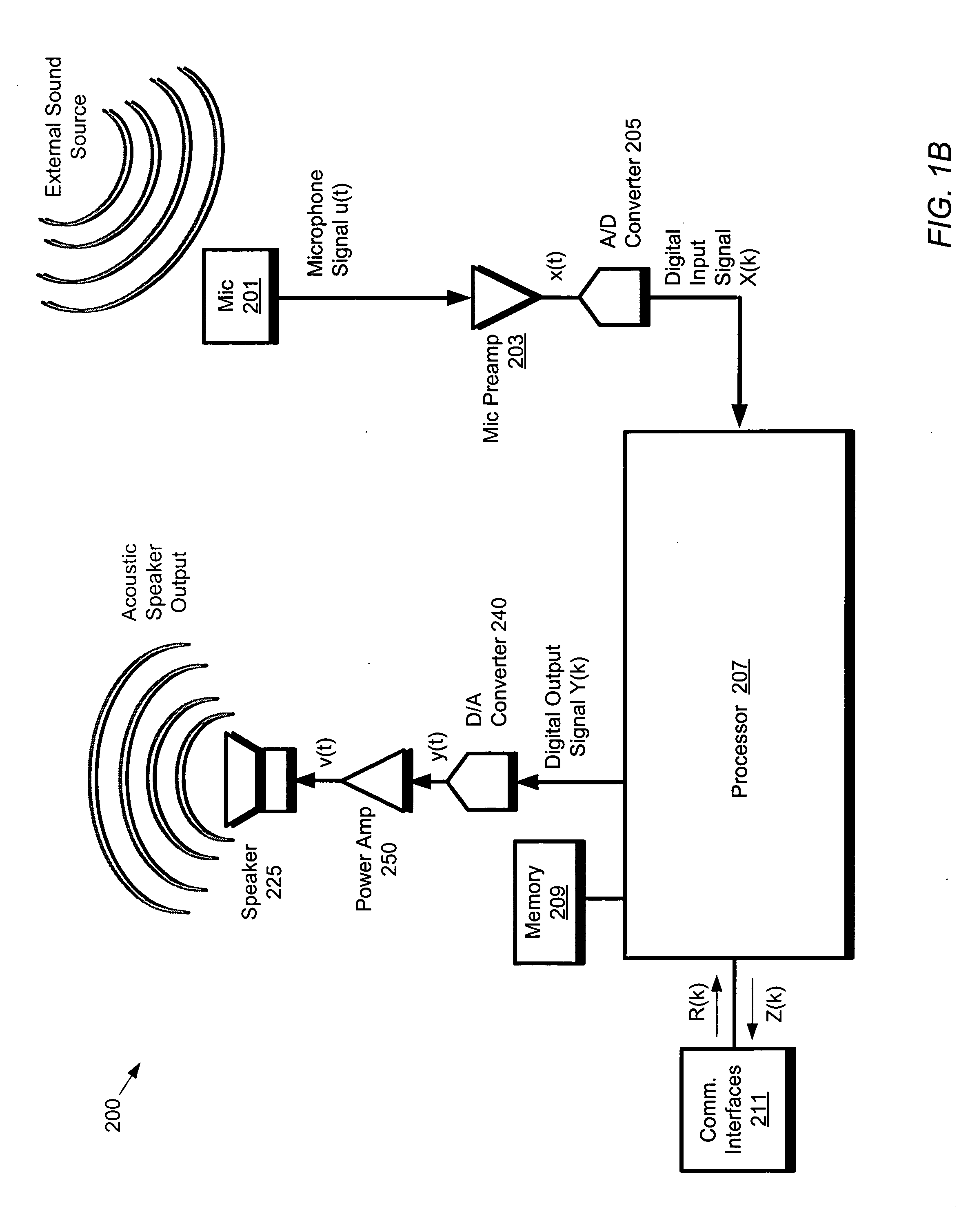
ActiveUS20060093128A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsPublic address systemsDigital analog converterDirect path
A processor operates on samples of a digital output signal to determine samples of a digital correction signal. The output signal samples are directed to an output channel for transmission from a speaker. The digital correction signal samples are supplied to a first digital-to-analog converter for conversion into an analog correction signal. The subtraction circuit generates a difference between a first analog signal provided by a microphone and the analog correction signal. The analog correction signal is an estimate of a contribution to the first analog signal due to a direct path transmission between the speaker and the microphone. The processor also receives a digital input signal derived from the difference signal, and, performs acoustic echo cancellation on the digital input signal to obtain a resultant signal. The acoustic echo cancellation is configured to remove contributions to the digital input signal due to reflected path transmissions.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
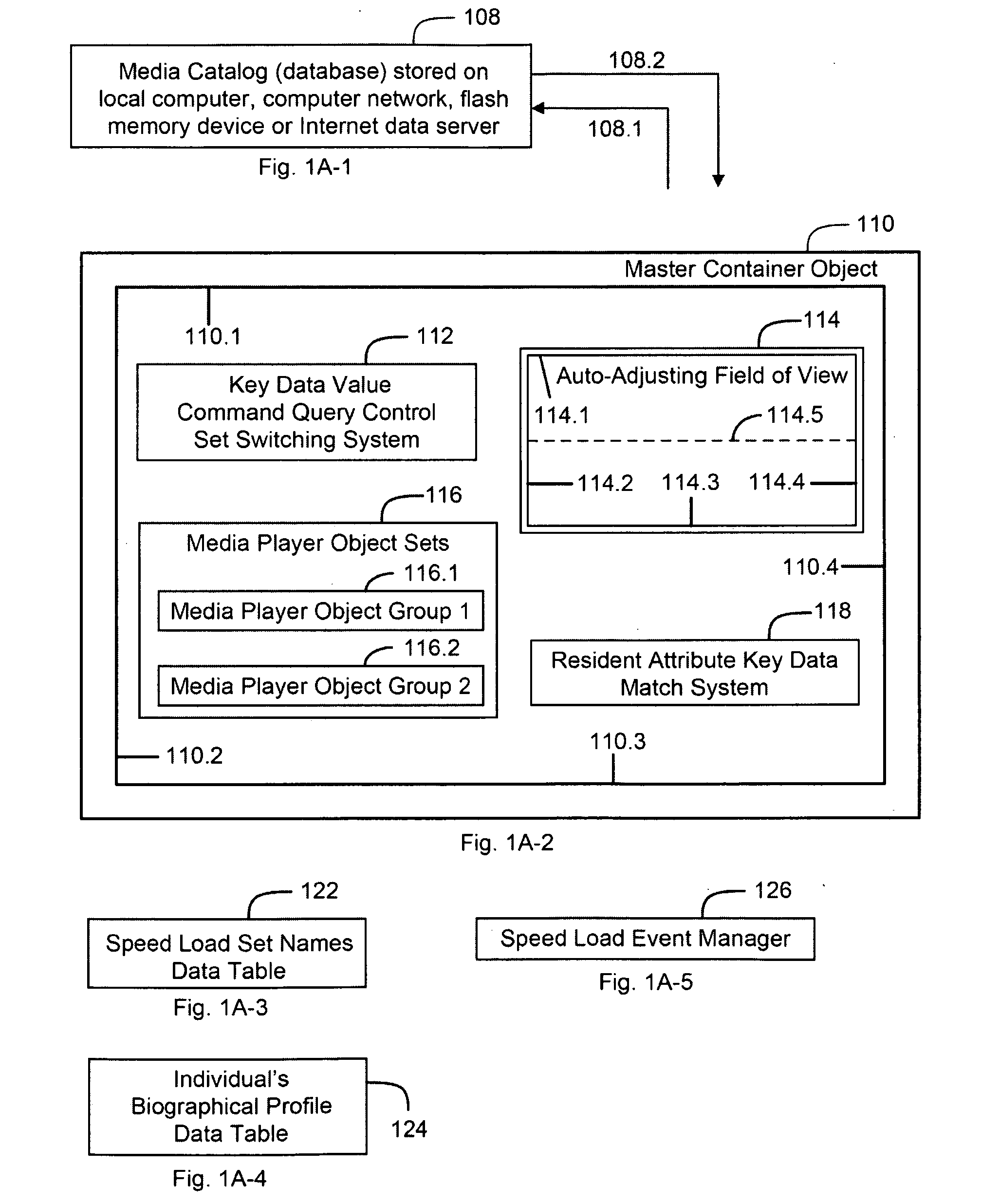
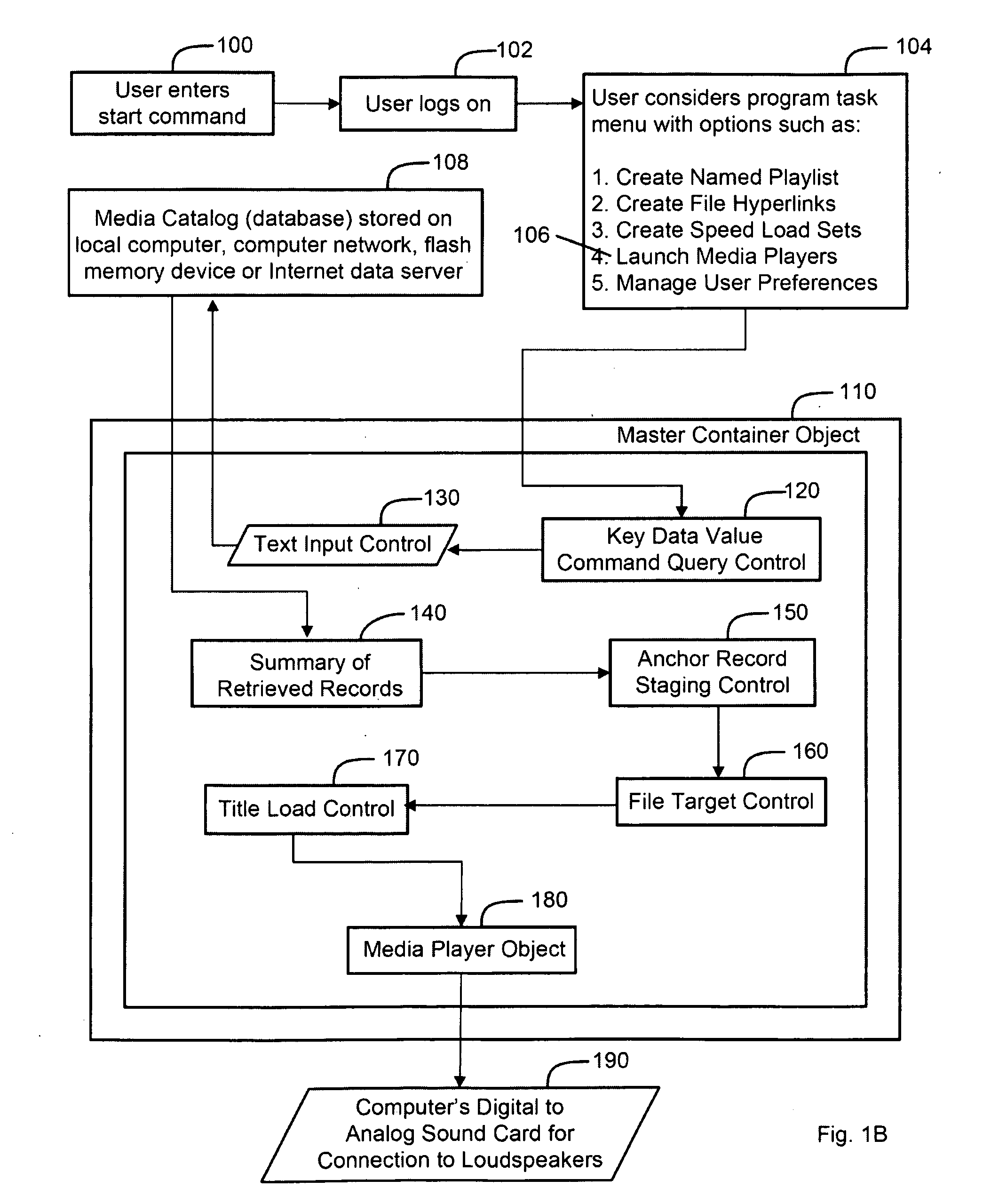
Scalable system and method for an integrated digital media catalog, management and reproduction system
InactiveUS20090177301A1Reduce stepsEfficient managementRecord information storageSpecial data processing applicationsScalable systemVisually guided
A system and method for creating an integrated digital media management and reproduction device comprised of a database with key data values for a plurality of records, and a module with search controls that include sets of compound parallel attribute queries that can execute instructions for a data category, and concurrently retrieve and display records across a plurality of related categories—thereby revealing the associations between discrete records. The invention also has a plurality of software instantiated media players which, through instructions managed by a “master container” design, function as if they were dynamically aware of user actions and the quantifiable states of each other player object—and respond according to logic rules, visually guiding event workflow. The system has a memory module for storing query information, a processor configured to retrieve data, a display unit for retrieved data and a digital-to-analog converter for providing capability for connection to loudspeakers.
Owner:CODENTITY
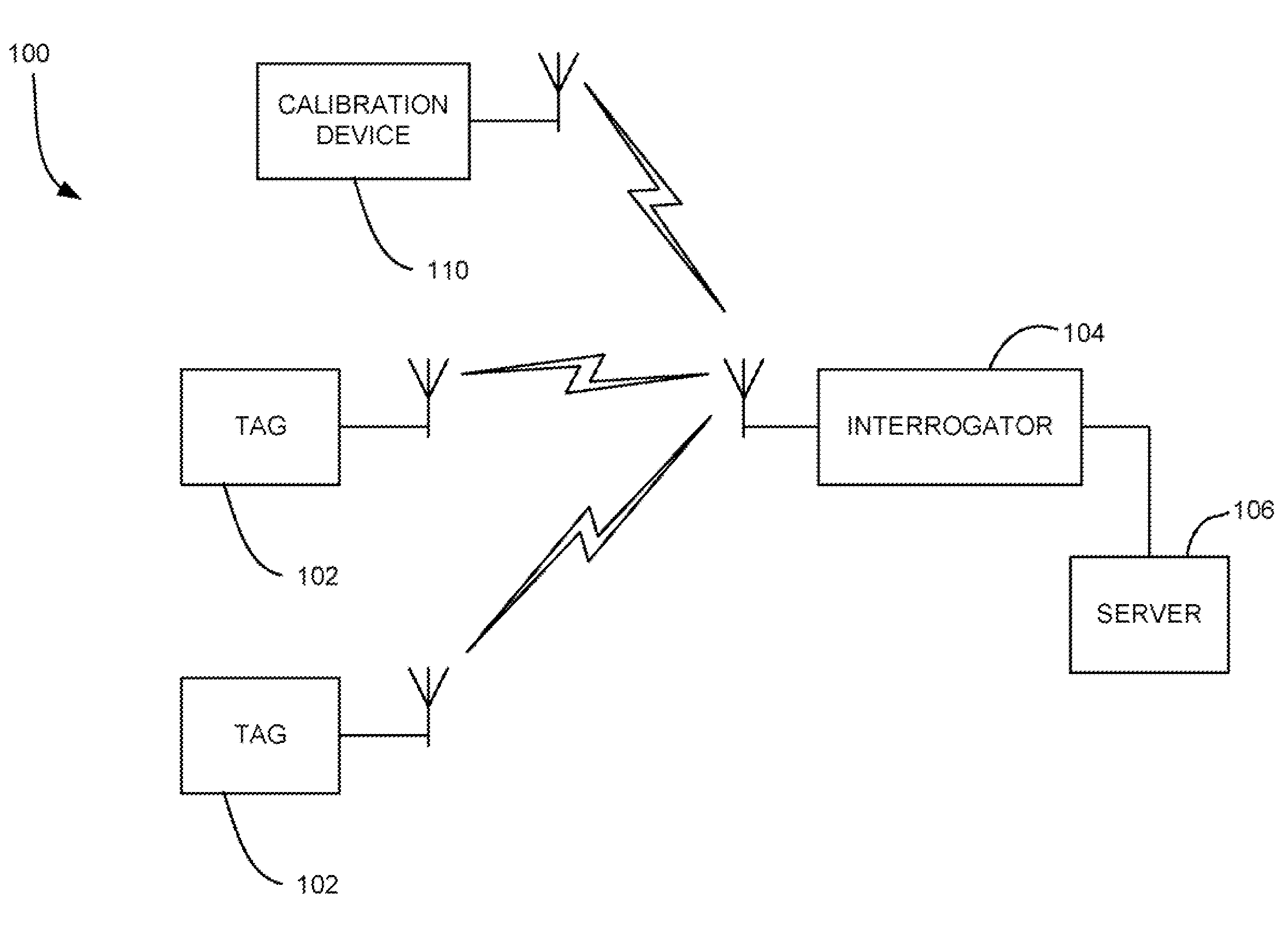
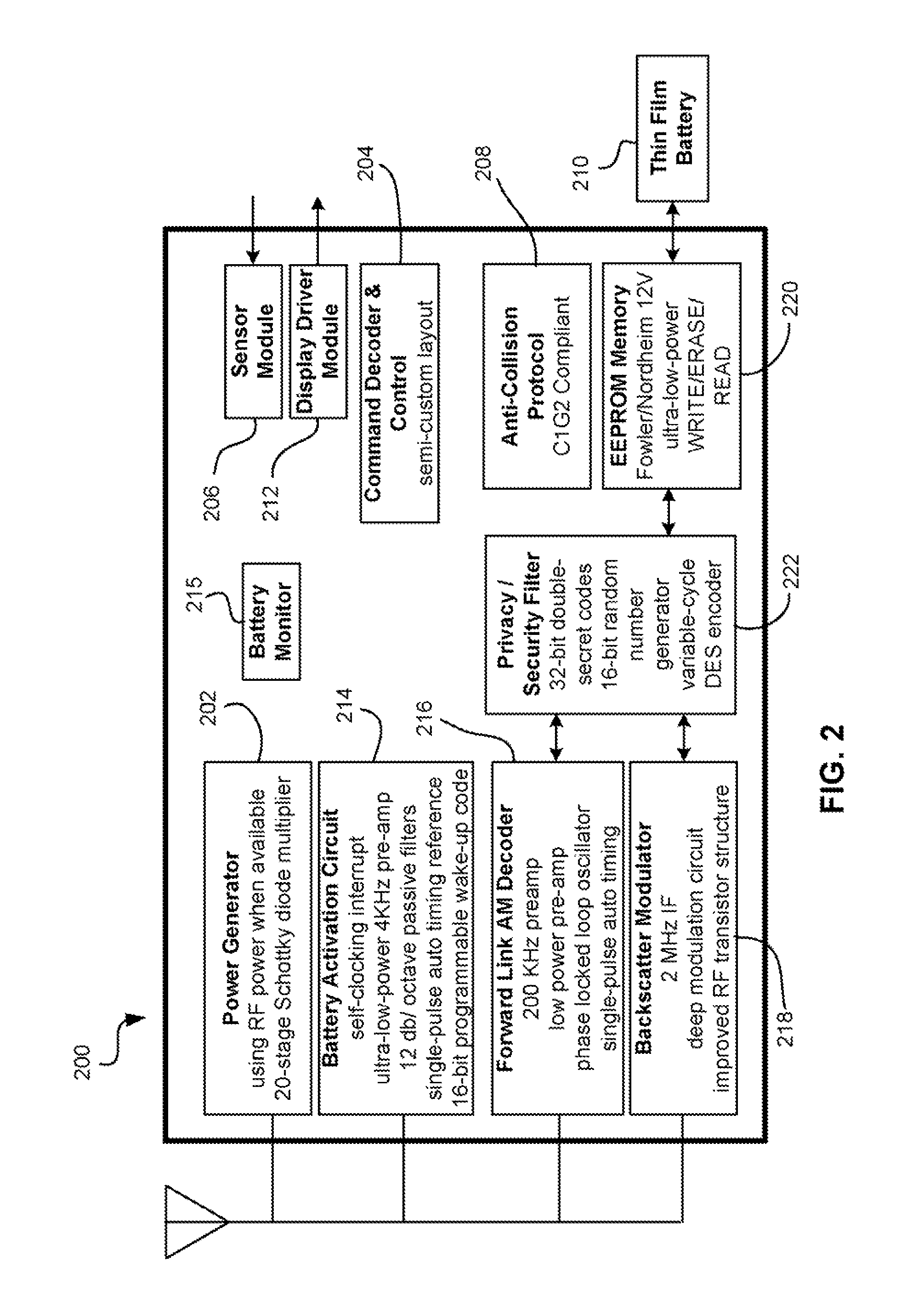
RF device comparing DAC output to incoming signal for selectively performing an action
ActiveUS8098159B2Subscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesDigital analog converterEngineering
Owner:ZEST LABS INC
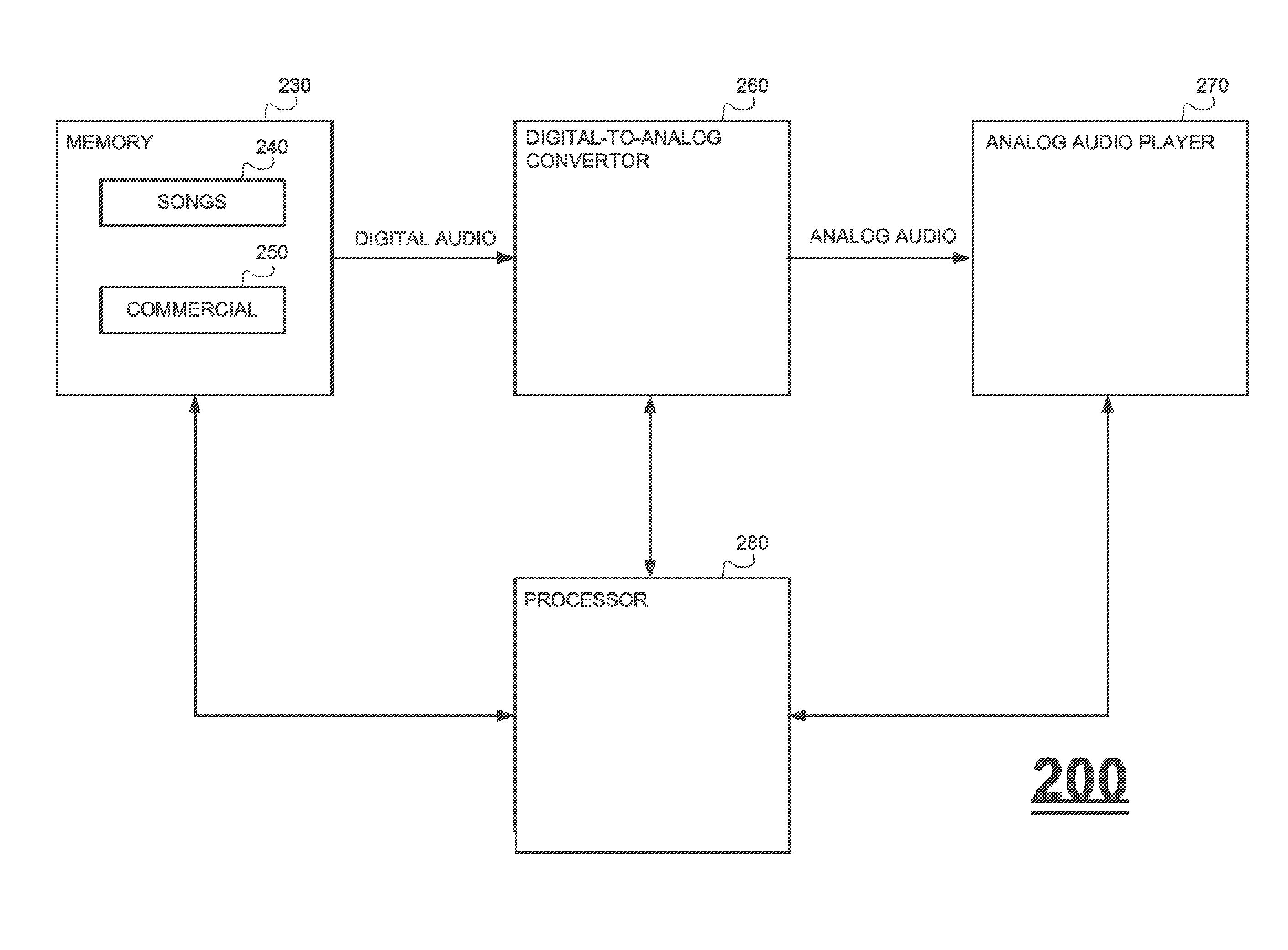
Promotional portable music players
A digital audio player, including a casing, a memory within said casing for storing digital audio including songs and a commercial, a digital-to-analog converter within said casing and operatively connected to said memory for converting digital audio to analog audio, an analog audio player within said casing and operatively coupled to said digital-to-analog converter, for playing the songs in response to manual user commands, and for automatically playing the commercial, and a processor for stopping the automatic playing of the commercial after a specific event has occurred. A method and a computer-readable storage medium are also described.
Owner:CATCH MEDIA
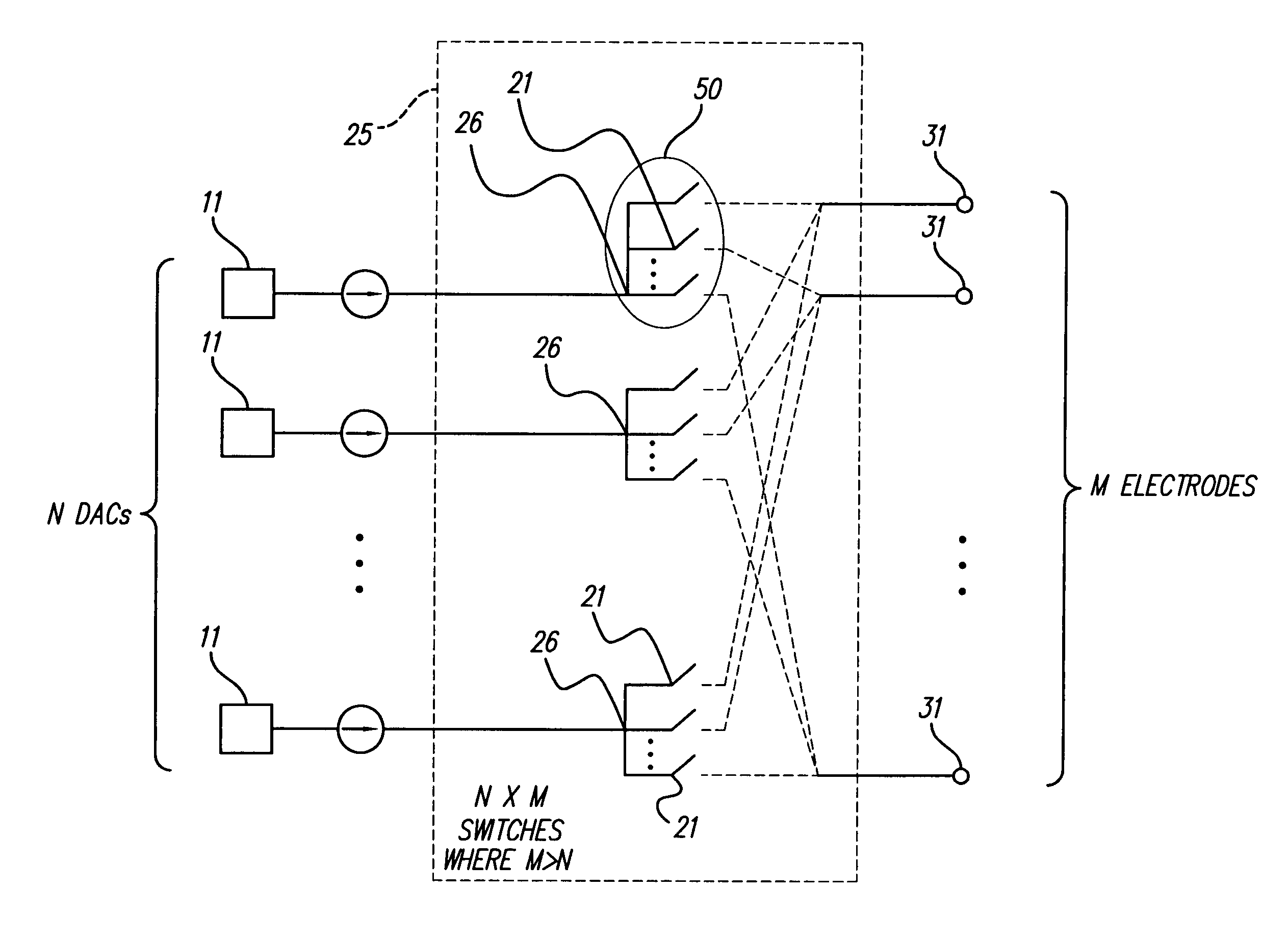
Switched-matrix output for multi-channel implantable stimulator
ActiveUS7127298B1Saving limited device spaceLimited spaceElectrotherapyDigital analog converterElectrode Contact
The invention is a switched-matrix output for a multi-channel stimulator. The switch-matrix output system uses groups of switches connectively placed between N number of digital-to-analog convertors (DACs) and M electrode contacts to permit fewer, space-consuming DACs to be used in an implantable stimulator, thereby saving internal stimulator space. One embodiment of the switched matrix output uses switches to activate only one active-electrode subset of M electrode contacts at any one time, so that the total number of DACs contained in the stimulator can be less than the M total number of electrode contacts.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
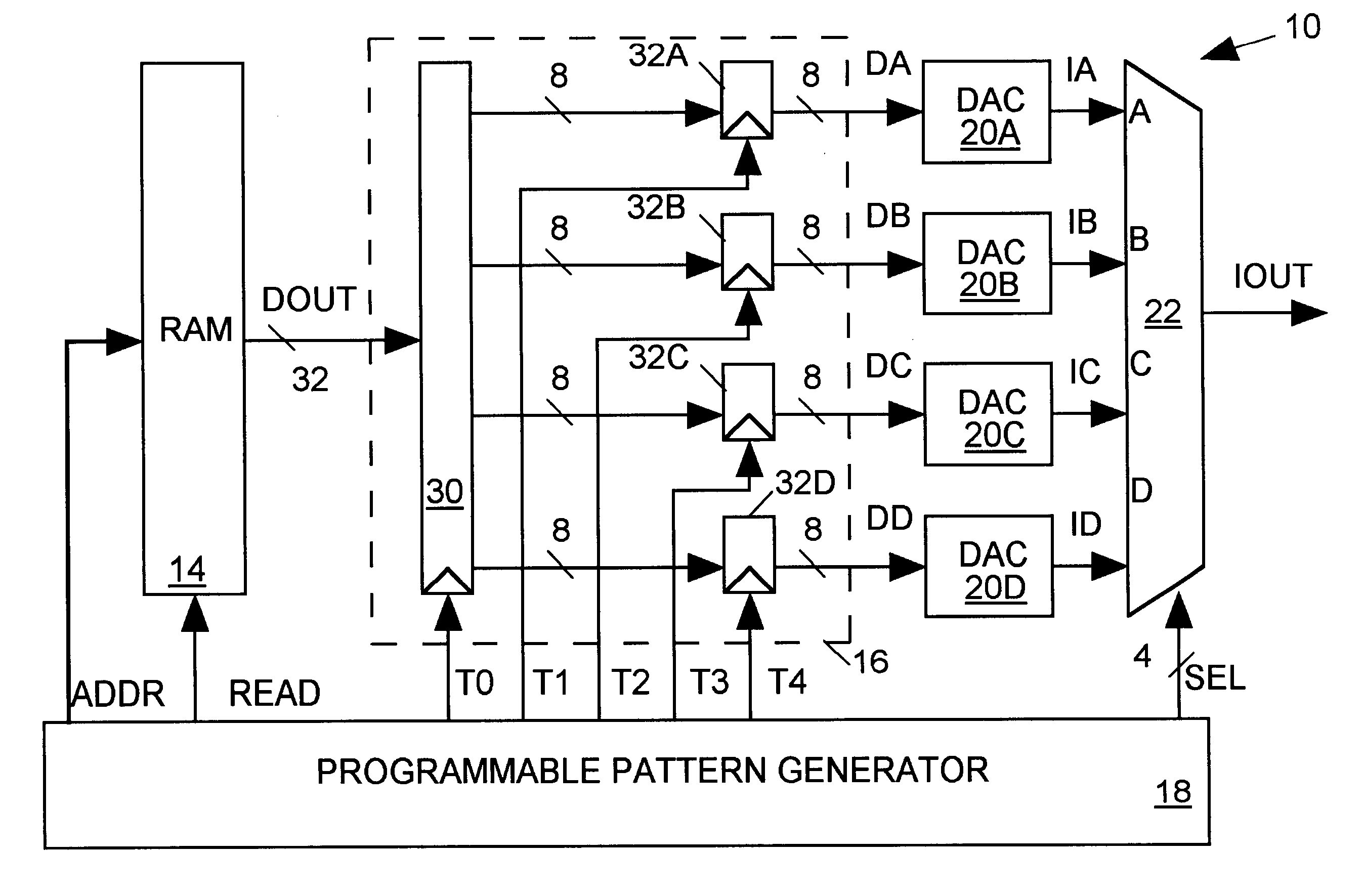
Arbitrary waveform generator having programmably configurable architecture
InactiveUS6356224B1Electric signal transmission systemsOscillations generatorsDigital analog converterMultiplexer
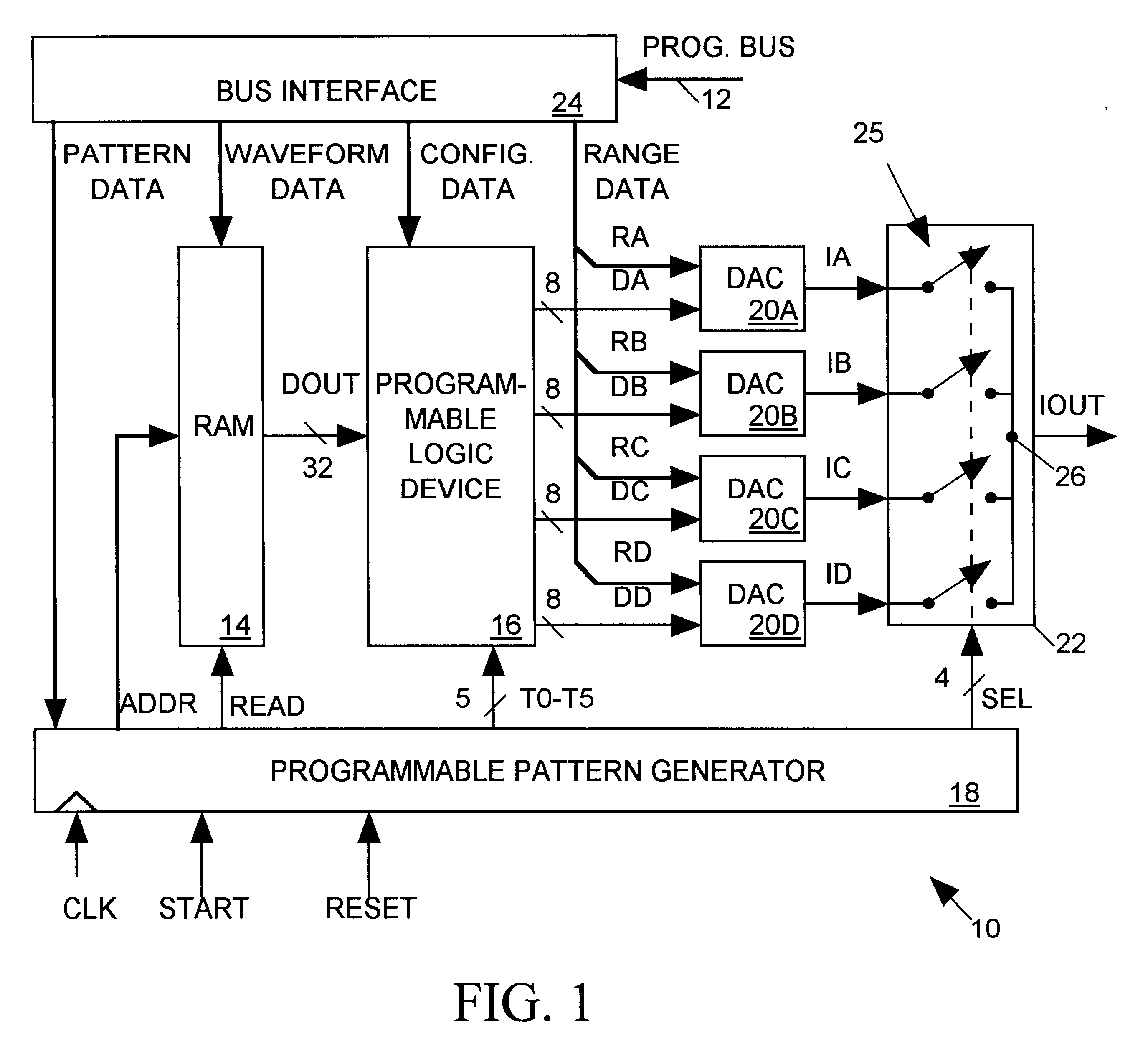
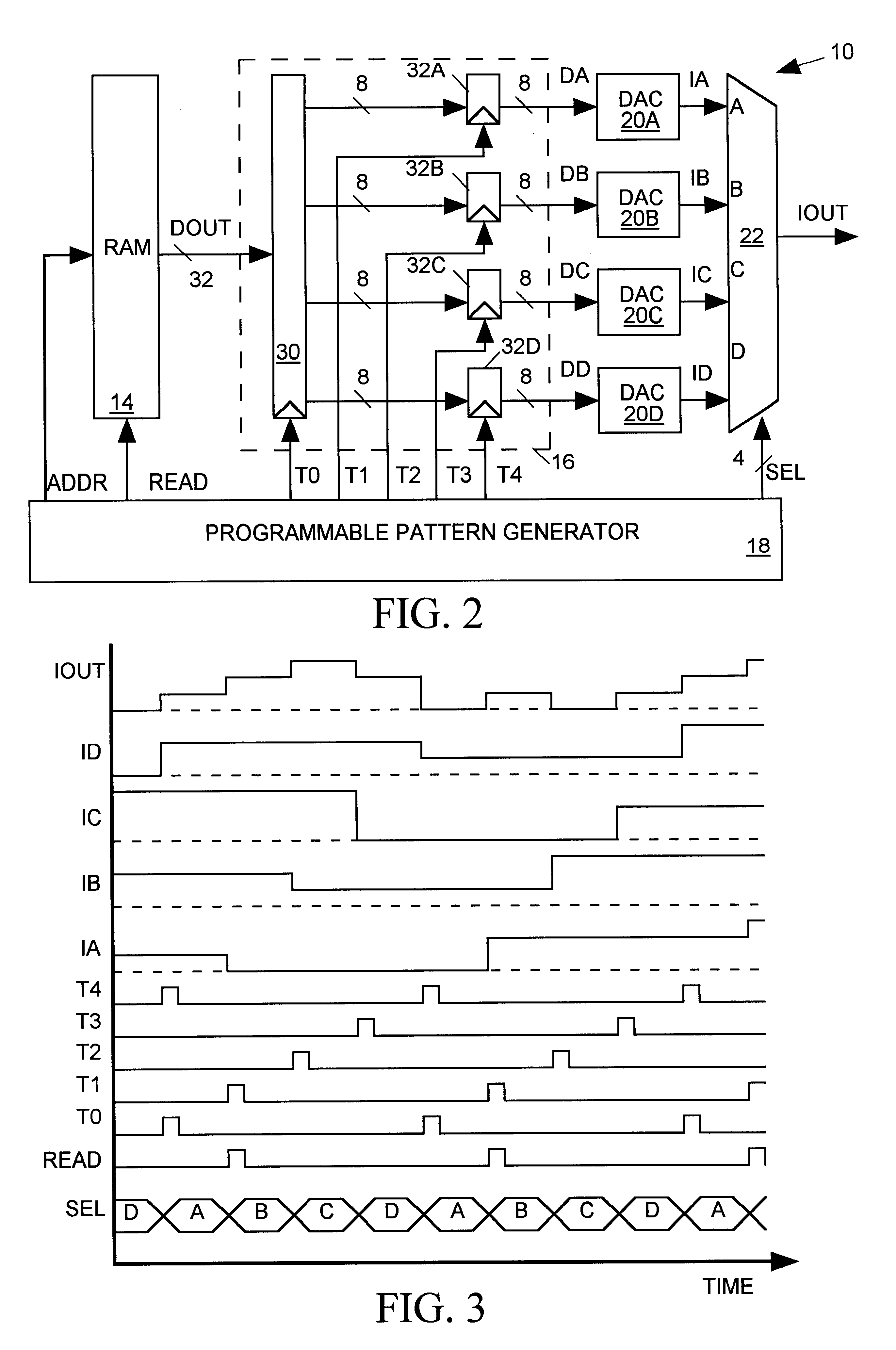
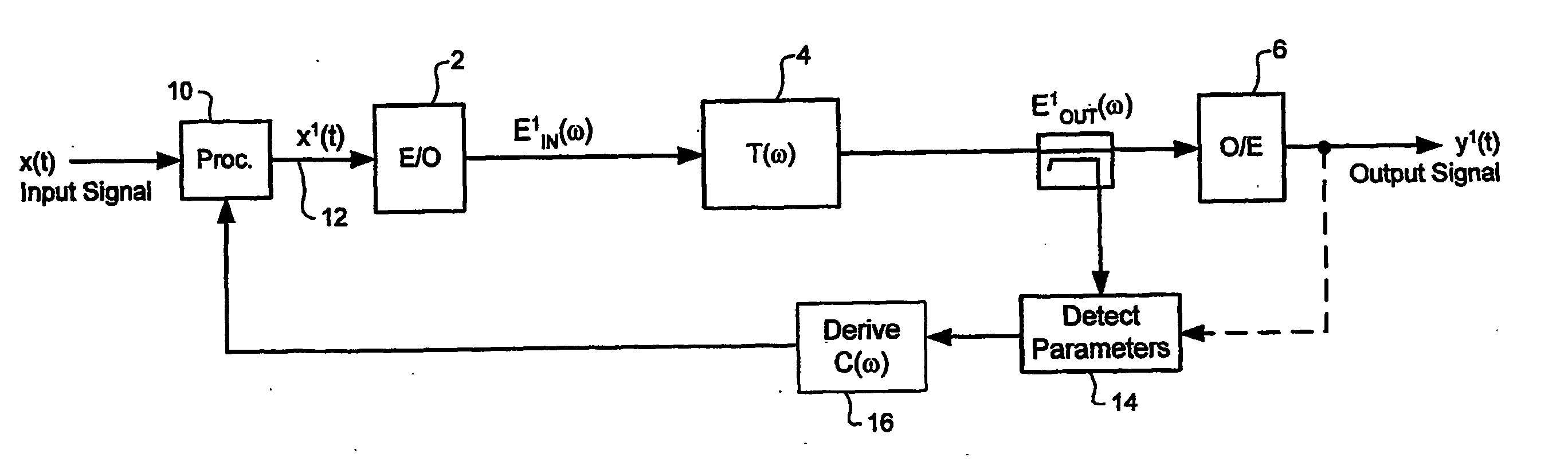
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) for producing an analog output current signal includes a random access memory (RAM), a programmable logic device (PLD), a programmable pattern generator, several digital-to analog converters (DACS) and a current multiplexer. The RAM store data sequences representing the analog waveform to be generated. The pattern generator read addresses the RAM causing it to sequentially read out its stored data sequence to the PLD. The PLD routes selected fields of each data sequence word to one or more of the DACs in response to timing signals provided by the pattern generator. Each DAC produces an output current of magnitude determined by its input waveform and range data. The pattern generator also signals the analog multiplexer to sum currents produced by one or more selected DACs to produce the AWG output waveform. The nature of the AWG output waveform is flexibly determined by the nature of the data sequence and the frequency at which it is read out of the RAM, the manner in which the PLD routes the data sequence to the DACs, the value of the range data supplied to each DAC, and the output pattern generated by the pattern generator. The flexible AWG architecture permits the AWG to be appropriately configured for various combinations of output waveform frequency, bandwidth and resolution requirements.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
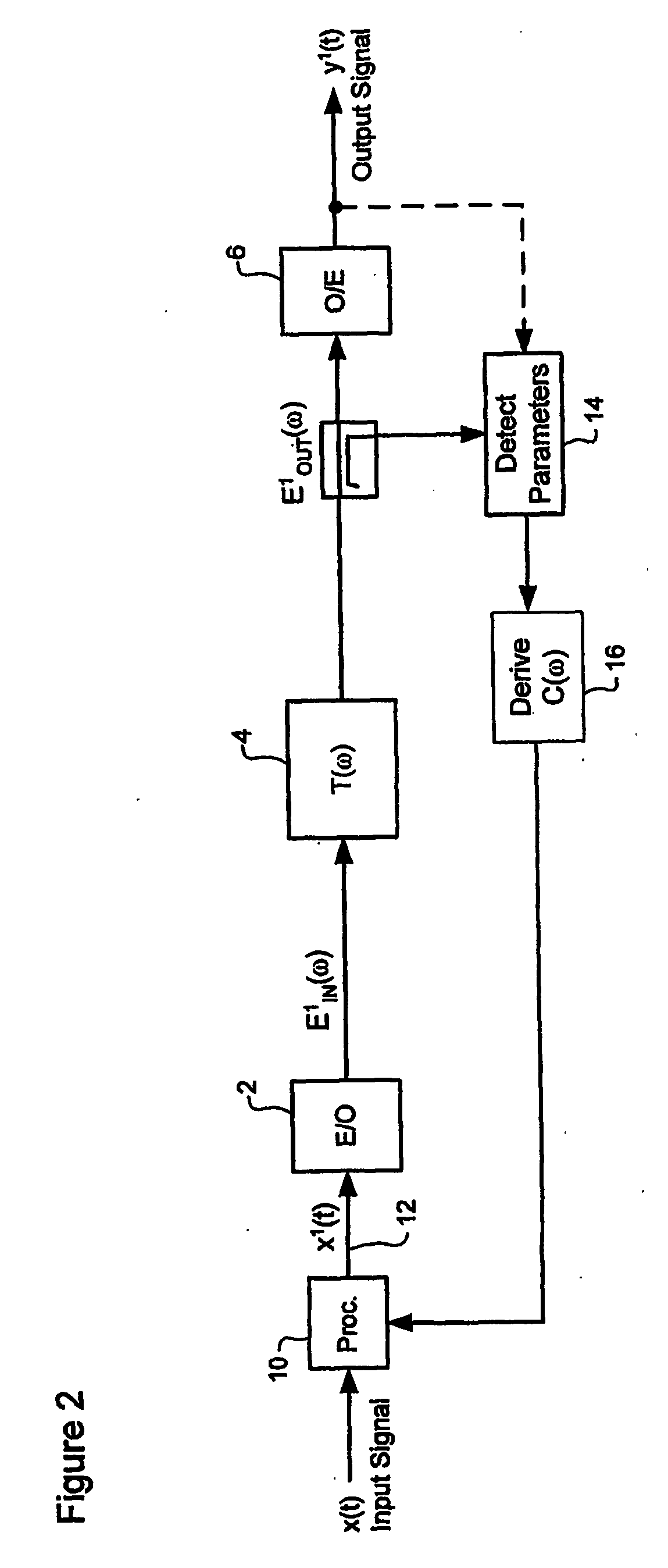
Optical dispersion compesnation in the electrical domain in an optical communications system
ActiveUS20060078336A1Reduce impactOptical signal enhancementElectromagnetic transmissionDigital analog converterCommunications system
Optical dispersion imposed on a communications signal conveyed through an optical communications system is compensated by modulating the communications signal in the electrical domain. A compensation function is determined that substantially mitigates the chromatic dispersion. The communications signal is then modulated in the electrical domain using the compensation function. In preferred embodiments, compensation is implemented in the transmitter, using a look-up-table and digital-to-analog converter to generate an electrical predistorted signal. The electrical predistorted signal is then used to modulate an optical source to generate a corresponding predistorted optical signal for transmission through the optical communications system.
Owner:CIENA
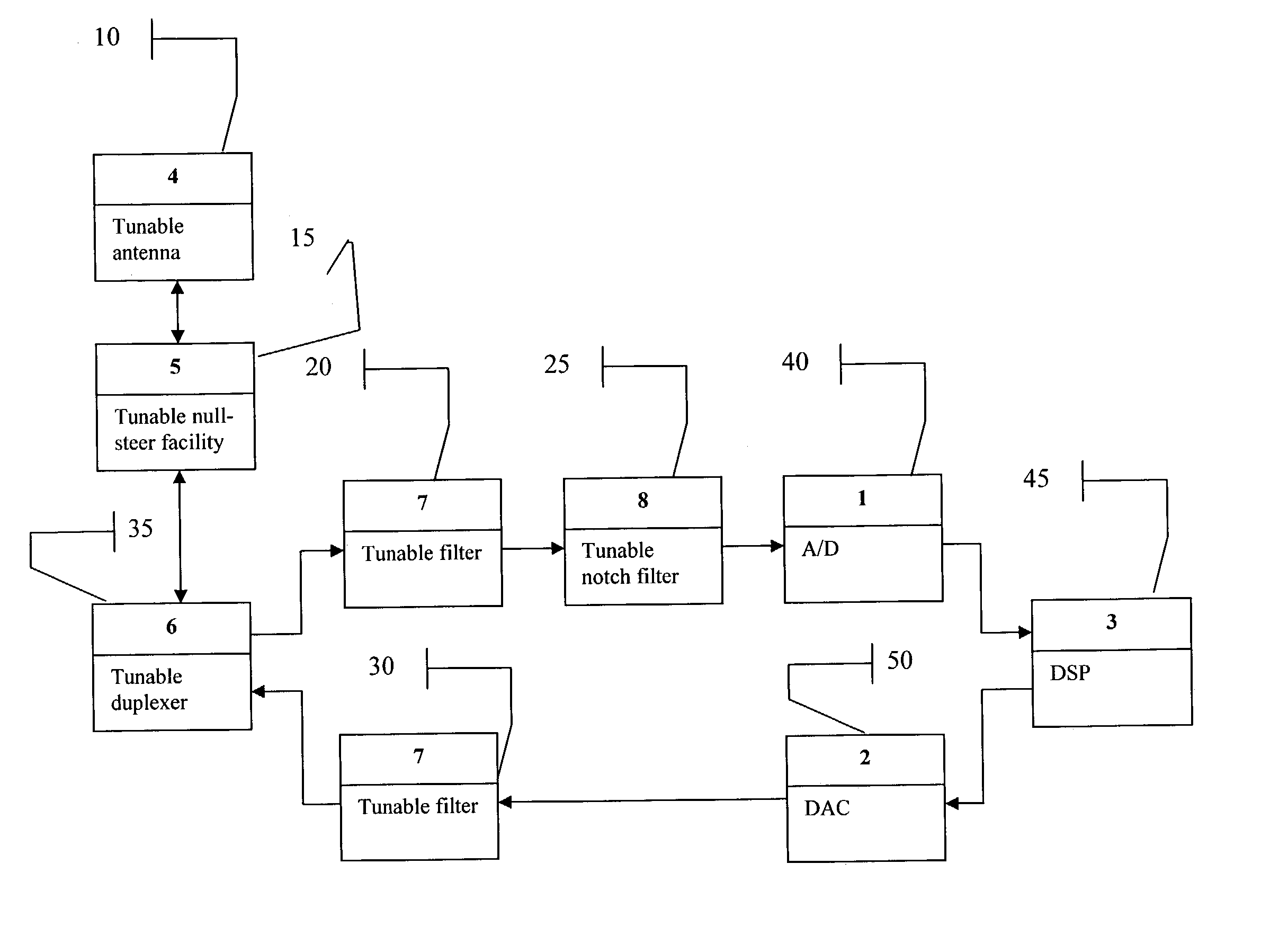
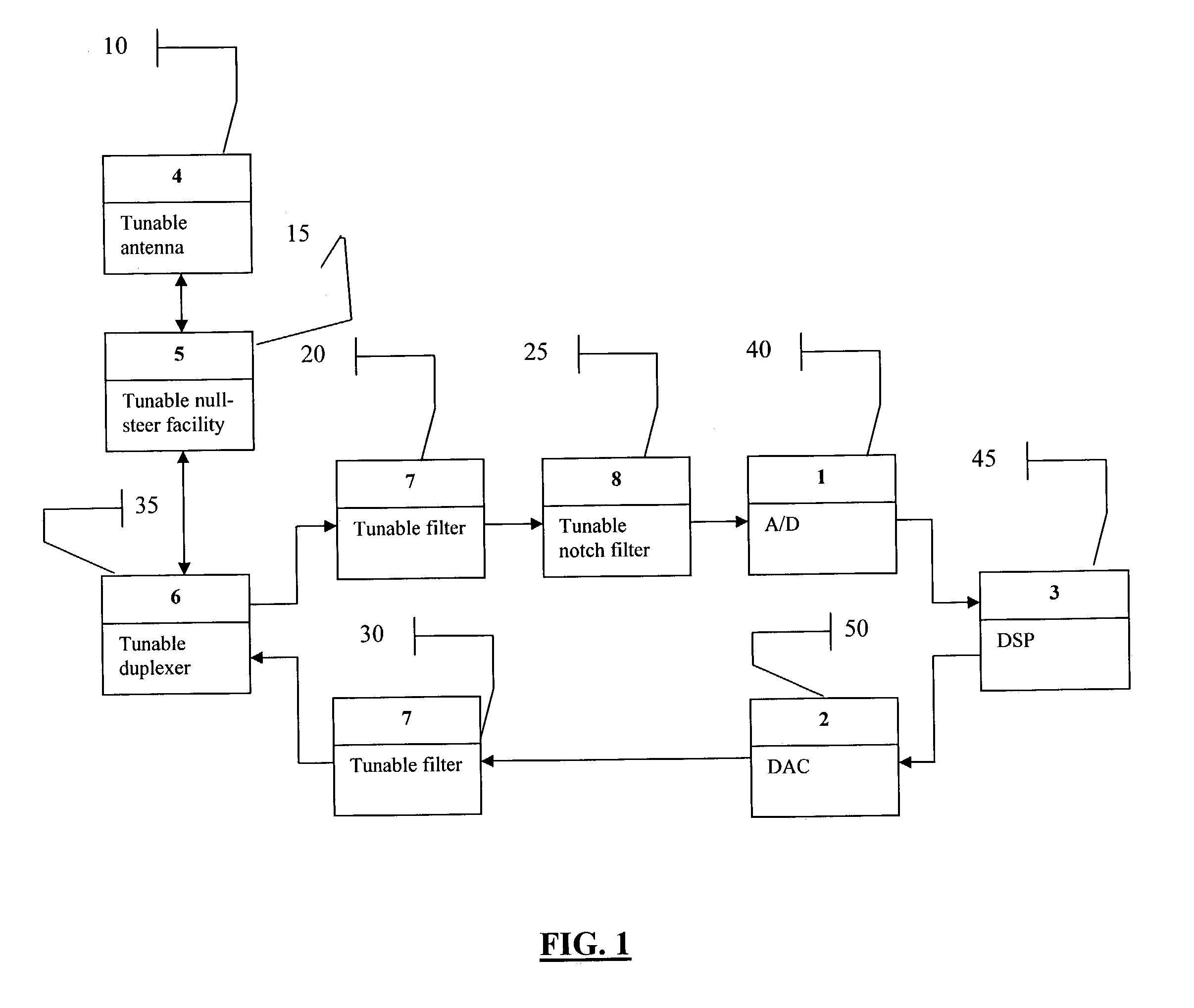
Smart radio incorporating Parascan(R) varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end
ActiveUS7107033B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterRF front end
A smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end. More specifically, this is provided for by a smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end that comprises at least one tunable antenna; at least one antenna null steering facility associated with said at least on tunable antenna; at least one tunable duplexer receiving the output from and providing input to said at least one antenna null steering facility; a first tunable RF filter receiving the output from said at least one tunable duplexer and providing the input to an analog to digital converter, said analog to digital converter providing the input to a digital signal processor, the output of which is input for a digital to analog converter; a second tunable RF filter receiving the analog output of said digital to analog converter and providing an input to said at least one tunable duplexer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
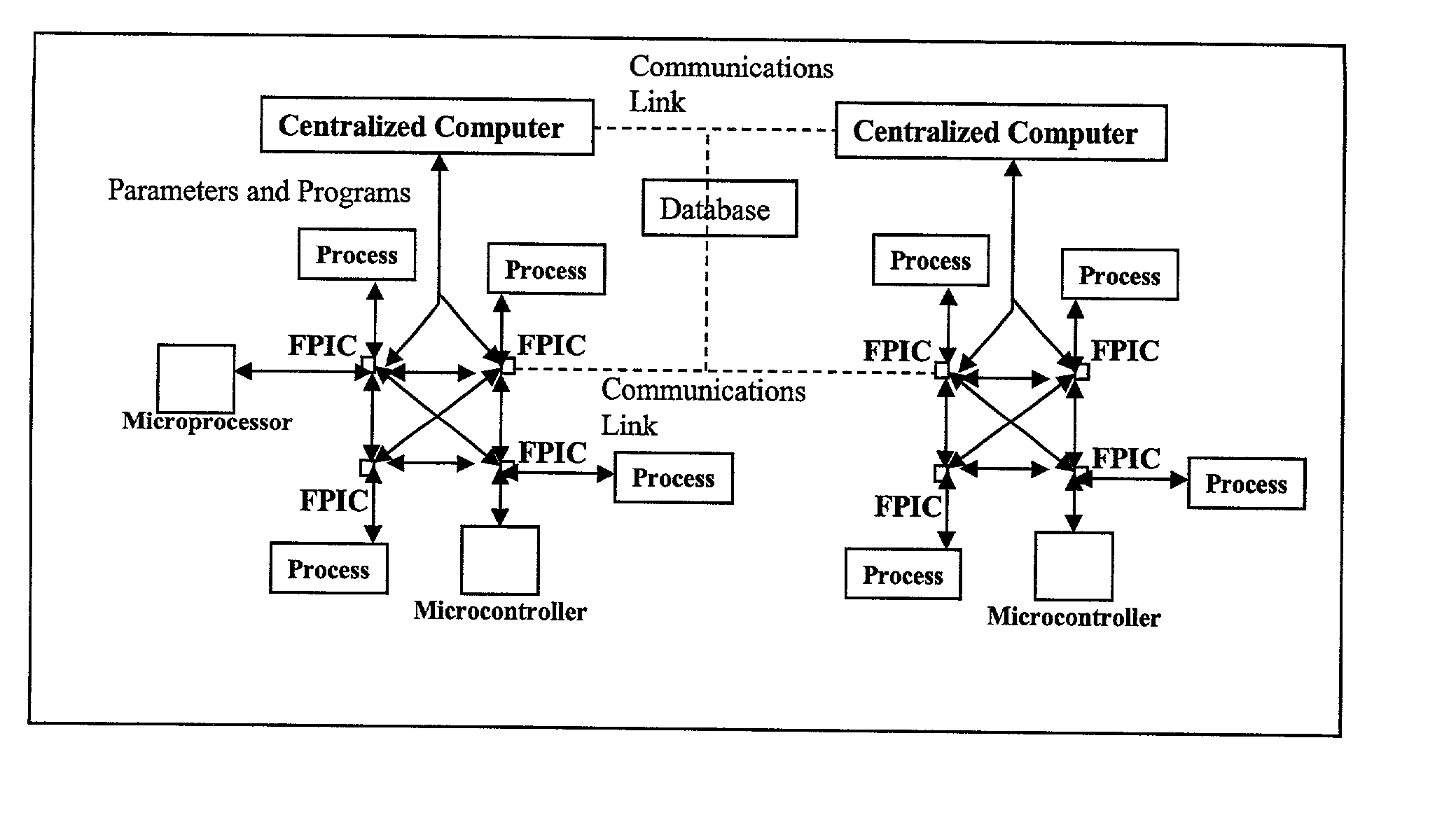
High performance hybrid micro-computer
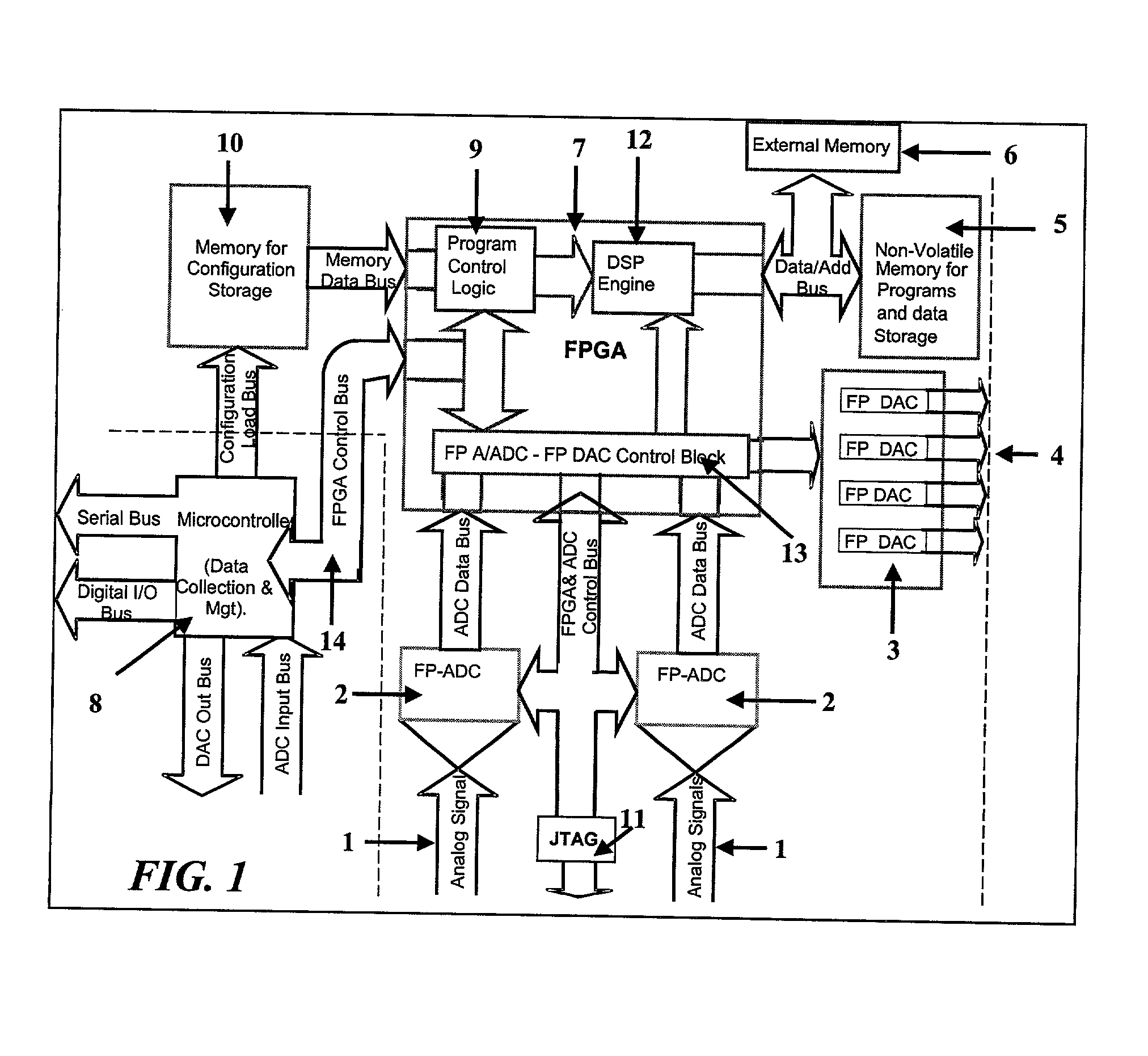
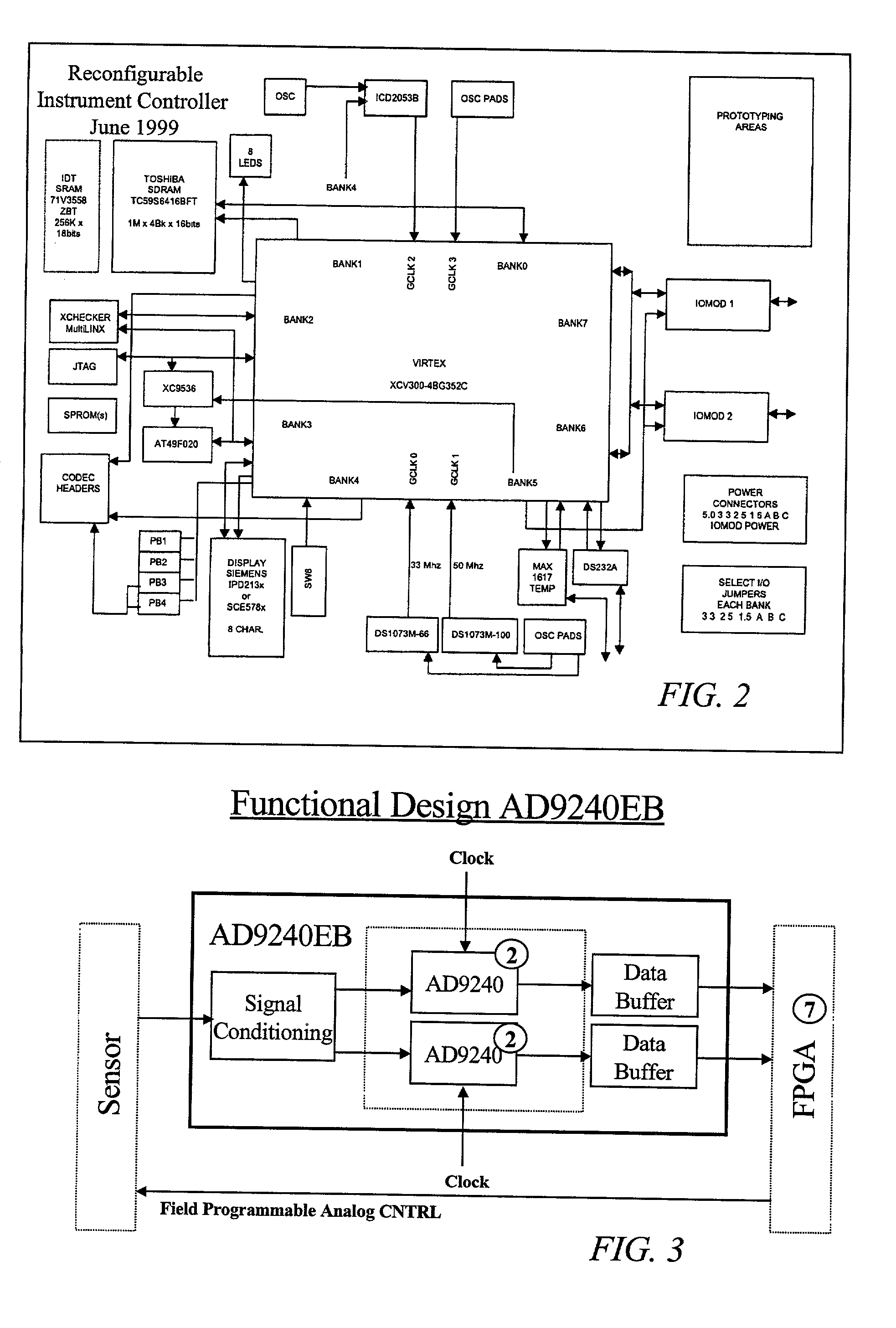
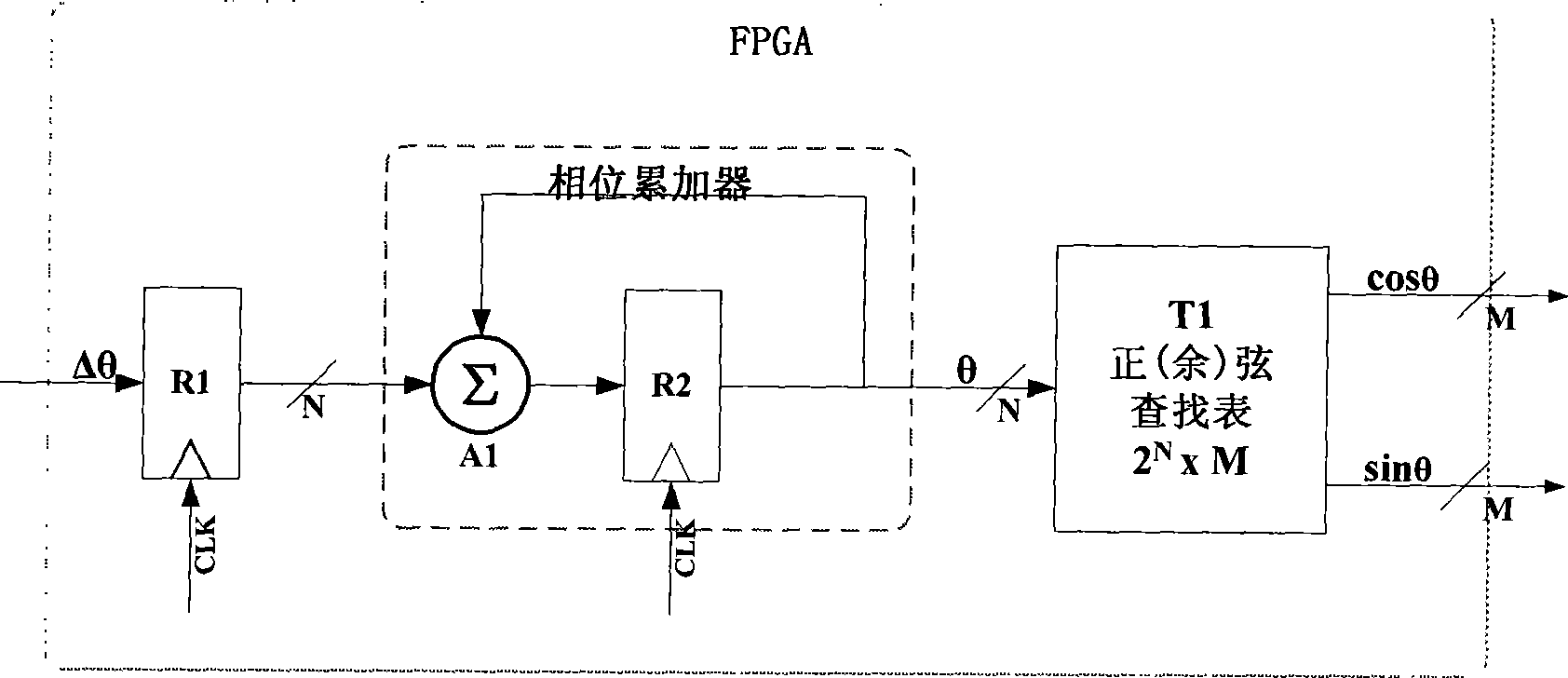
The Field Programmable Instrument Controller (FPIC) is a stand-alone low to high performance, clocked or unclocked multi-processor that operates as a microcontroller with versatile interface and operating options. The FPIC can also be used as a concurrent processor for a microcontroller or other processor. A tightly coupled Multiple Chip Module design incorporates non-volatile memories, a large field programmable gate array (FPGA), field programmable high precision analog to digital converters, field programmable digital to analog signal generators, and multiple ports of external mass data storage and control processors. The FPIC has an inherently open architecture with in-situ reprogrammability and state preservation capability for discontinuous operations. It is designed to operate in multiple roles, including but not limited to, a high speed parallel digital signal processing; co-processor for precision control feedback during analog or hybrid computing; high speed monitoring for condition based maintenance; and distributed real time process control. The FPIC is characterized by low power with small size and weight.
Owner:BLEMEL KENNETH G
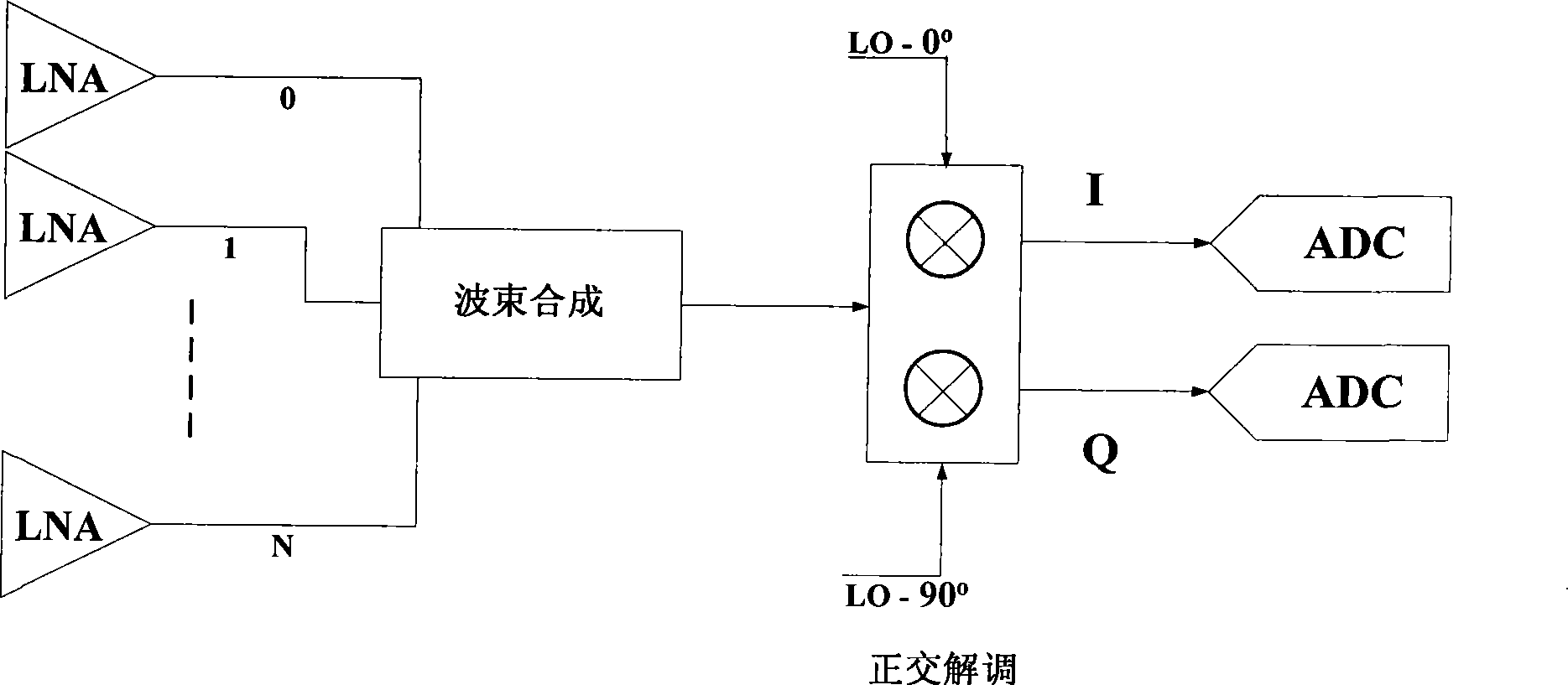
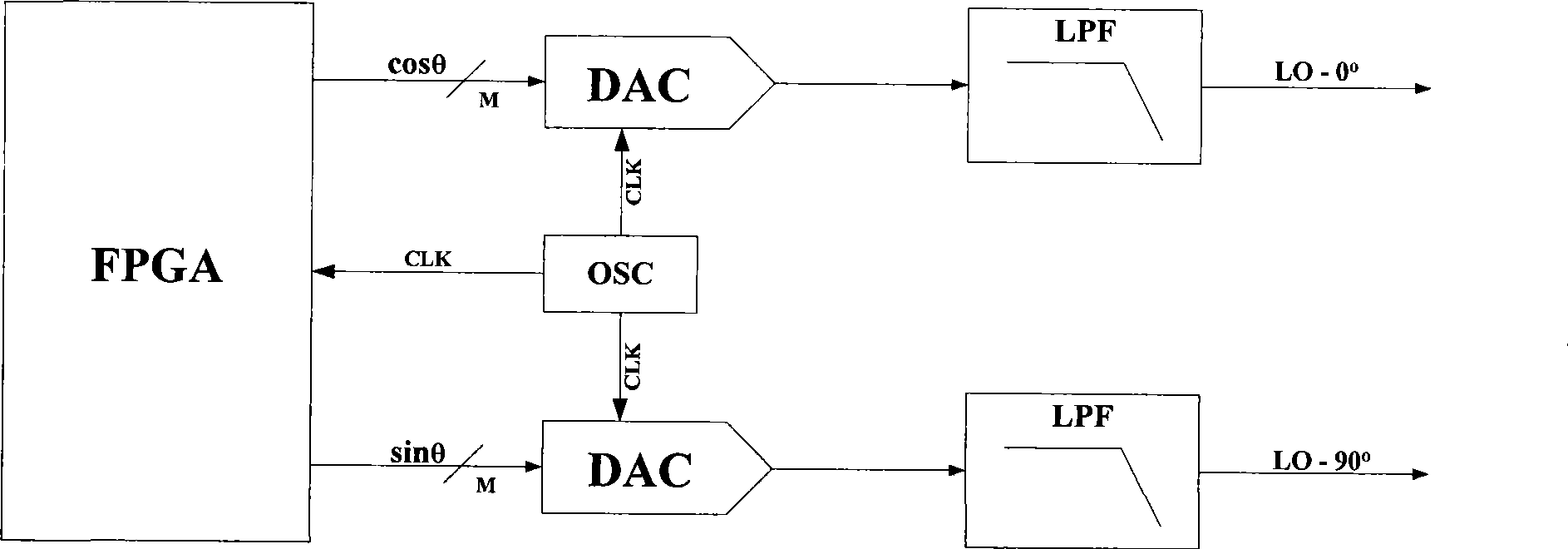
Device for producing orthogonal local oscillation signal in continuous Doppler ultrasound imaging system
InactiveCN101474081AReduce Design ComplexityReduce manufacturing costBlood flow measurement devicesDoppler Ultrasound ImagingSonification
The invention discloses a continuous Doppler US imaging system orthogonal intrinsic signal generation device, which comprise a field programmable gate array (FPGA), a crystal oscillator, a first digital-analog converter and a second digital-analog converter. The output end of the field programmable gate array (FPGA) is connected with the input ends of the first digital-analog converter and the second digital-analog converter; the crystal oscillator is respectively connected with the field programmable gate array (FPGA), the first digital-analog converter and the second digital-analog converter; the crystal oscillator is used for supplying synchronizing clock signals to the field programmable gate array (FPGA), the first digital-analog converter and the second digital-analog converter; the field programmable gate array (FPGA) is used for outputting the sine value corresponding to the phase value to the first digital-analog converter according to the input phase value and outputting the cosine value corresponding to the phase value to the second digital-analog converter; the first digital-analog converter is used for converting the sine value into the corresponding analog signals; the second digital-analog converter is used for converting the cosine value into the corresponding analog signals.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDWIND IND
Radio frequency control for communication systems
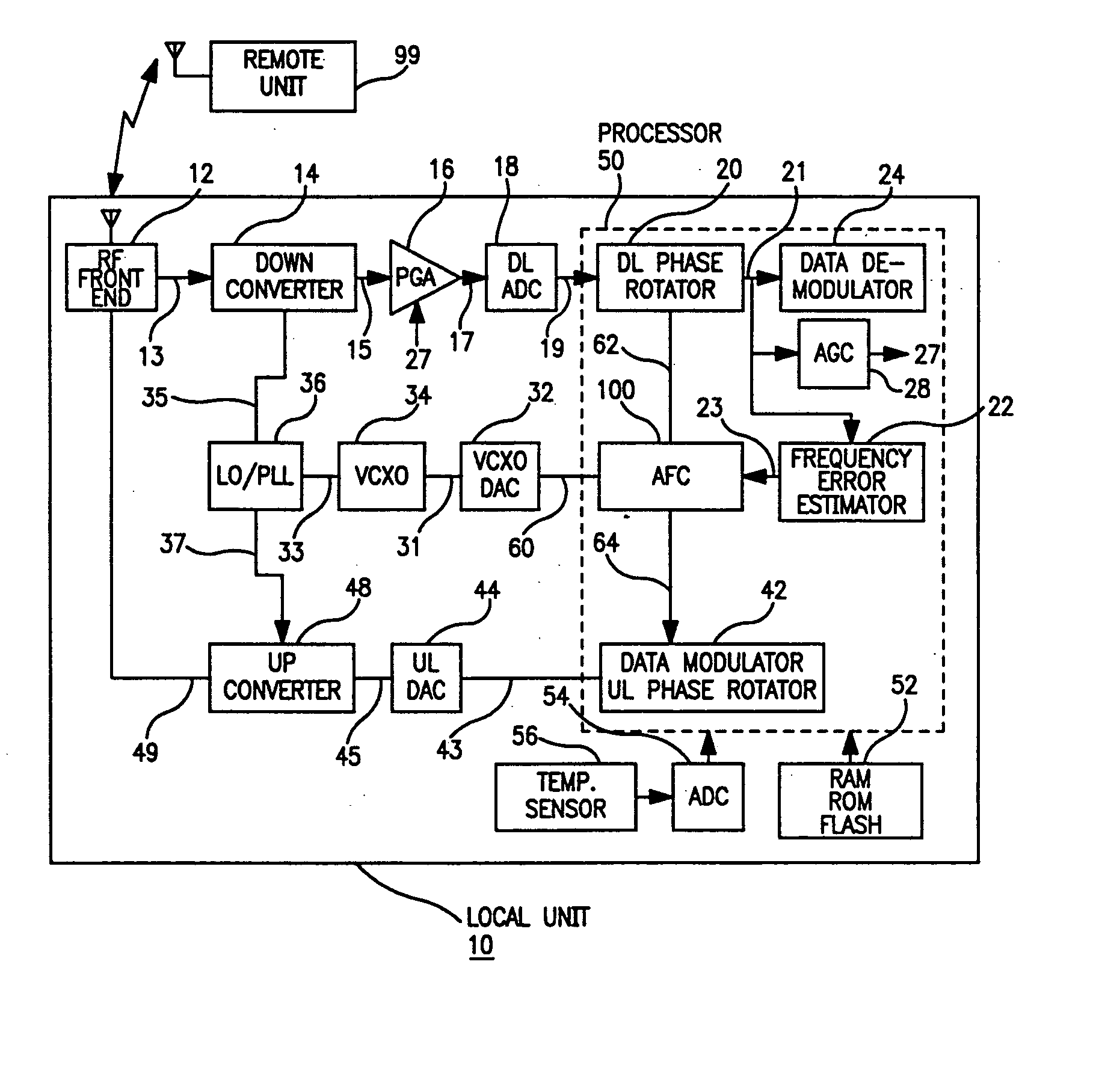
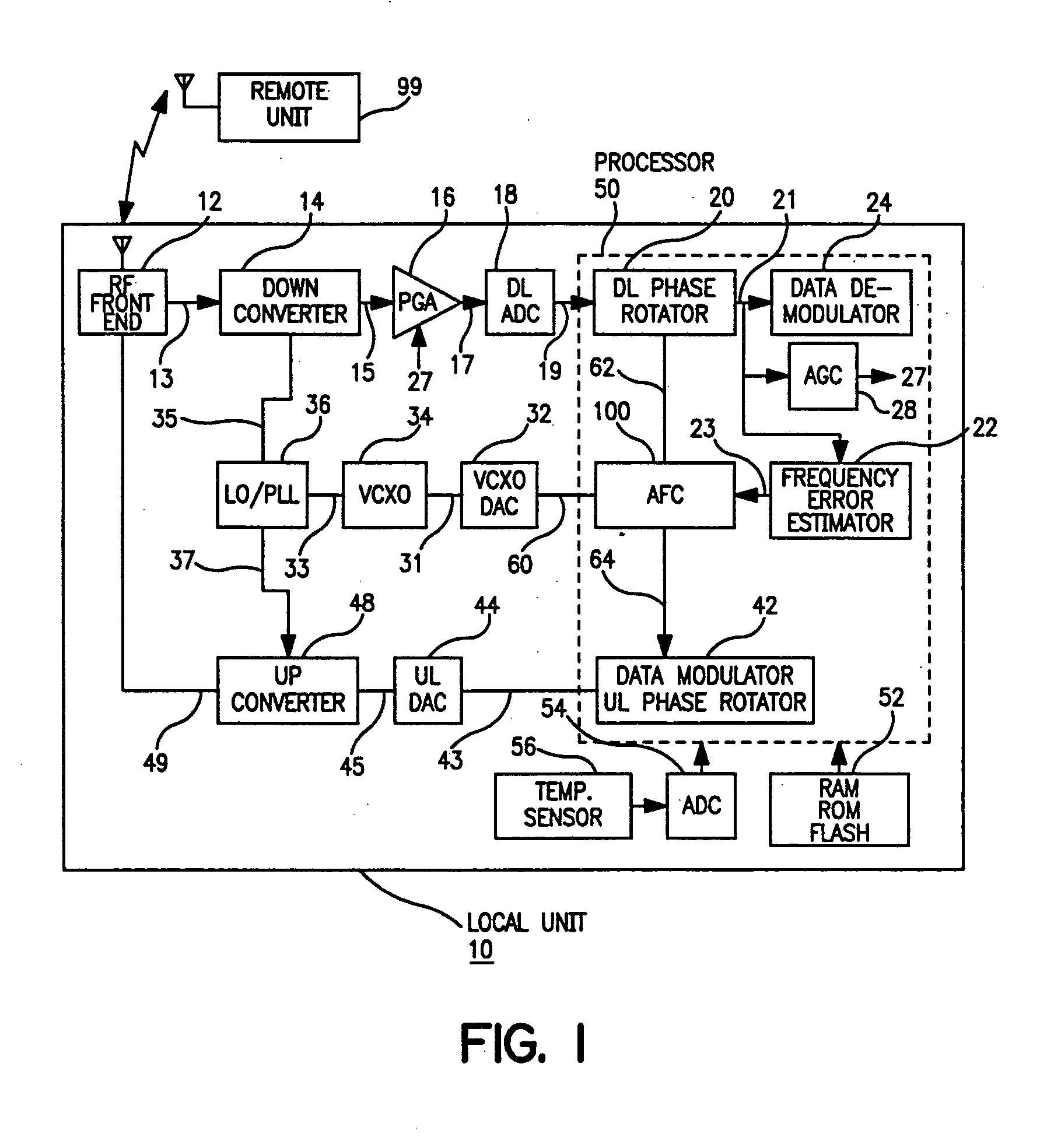
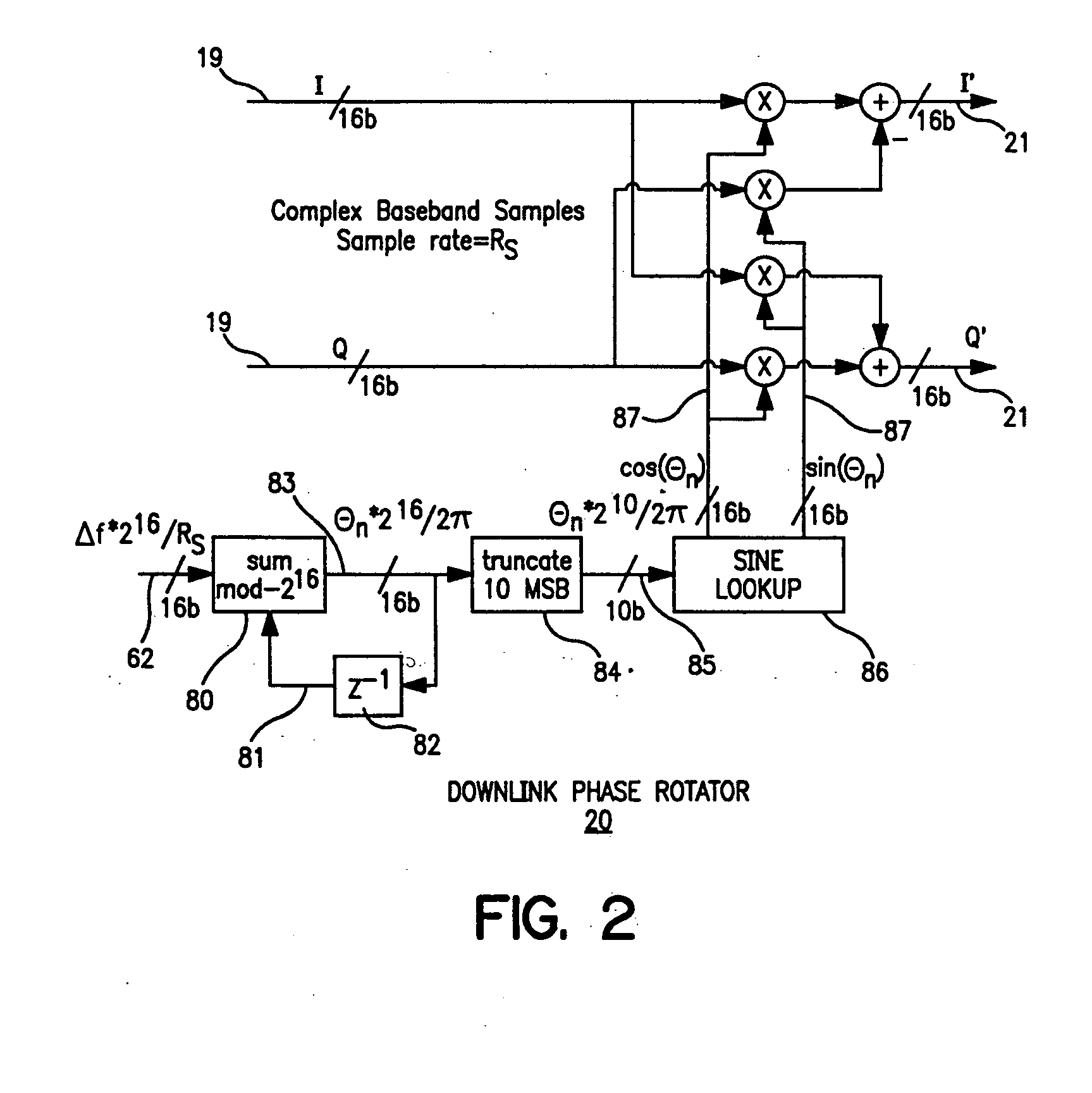
InactiveUS20050078743A1Low costHigh resolutionModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionDigital dataLocal oscillator signal
The present invention provides for a system and method for improvement of radio transmitter and receiver frequency accuracy for a local radio communication unit that communicates digital data with a remote communication unit. In the local unit the received radio signal is down-converted, and converted to complex baseband digital samples by an analog-to-digital converter. A downlink digital phase rotator applies a fine frequency shift to the samples in accordance with a receiver frequency offset command. The resultant baseband signal is used by the data demodulator and by a receiver frequency error estimator to obtain receiver frequency errors. A data modulator generates baseband complex samples which are shifted in carrier frequency by an integrated uplink digital phase rotator in accordance with a transmitter frequency offset command. The modulated samples are then converted by a digital-to-analog converter and upconverted in frequency for radio transmission to the remote unit. The local oscillator signals for both upconverter and downconverter are phase locked to a reference frequency generated by a VCXO. An automatic frequency control (AFC) function nulls the transmitter and receiver frequency error by the frequency adjustment commands to the uplink and downlink phase rotators or to the VCXO digital-to-analog converter (VCXO DAC) by feedback control principals based on measured receiver frequency error. During frequency track mode when communications between local and remote units are possible, the AFC only adjusts radio frequency via phase rotator commands and the VCXO command remains fixed, thereby avoiding communications performance degradation by VCXO frequency quantization error due to the VCXO DAC. The AFC adjusts VCXO frequency only during a preliminary acquisition mode prior to data communications, or to back out excessively large frequency offsets accumulated in the downlink and uplink phase rotators during track mode. When a VCXO adjustment is made in track mode, phase rotator adjustments are simultaneously applied to cancel the errors in transmitter and receiver radio frequencies caused by the step change due to VCXO frequency quantization thereby mitigating VCXO frequency quantization noise.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
High-efficiency linear power amplifier
ActiveUS7042283B2Achieve linearityHigh-efficiency power amplificationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersDigital analog converterAudio power amplifier
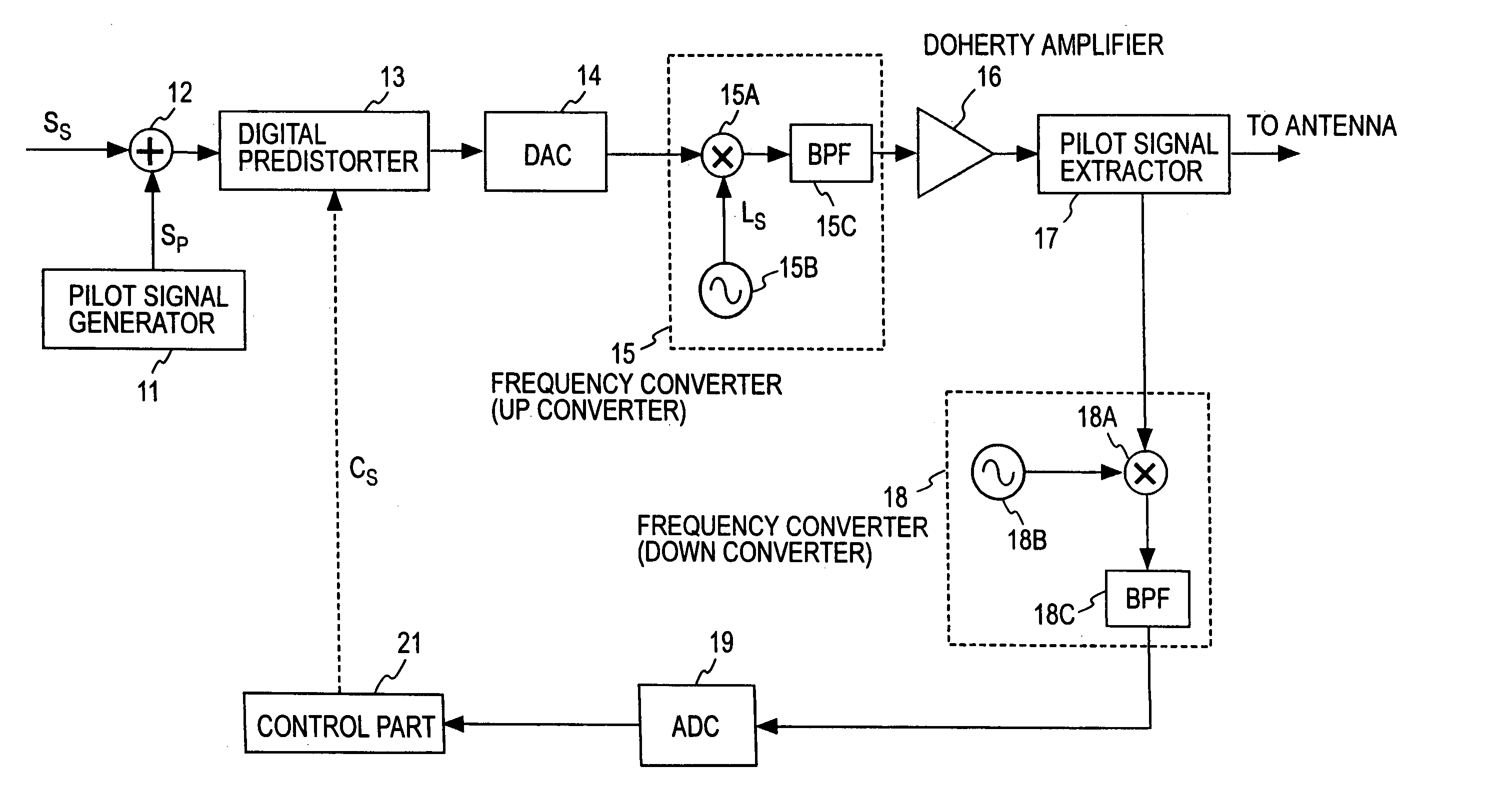
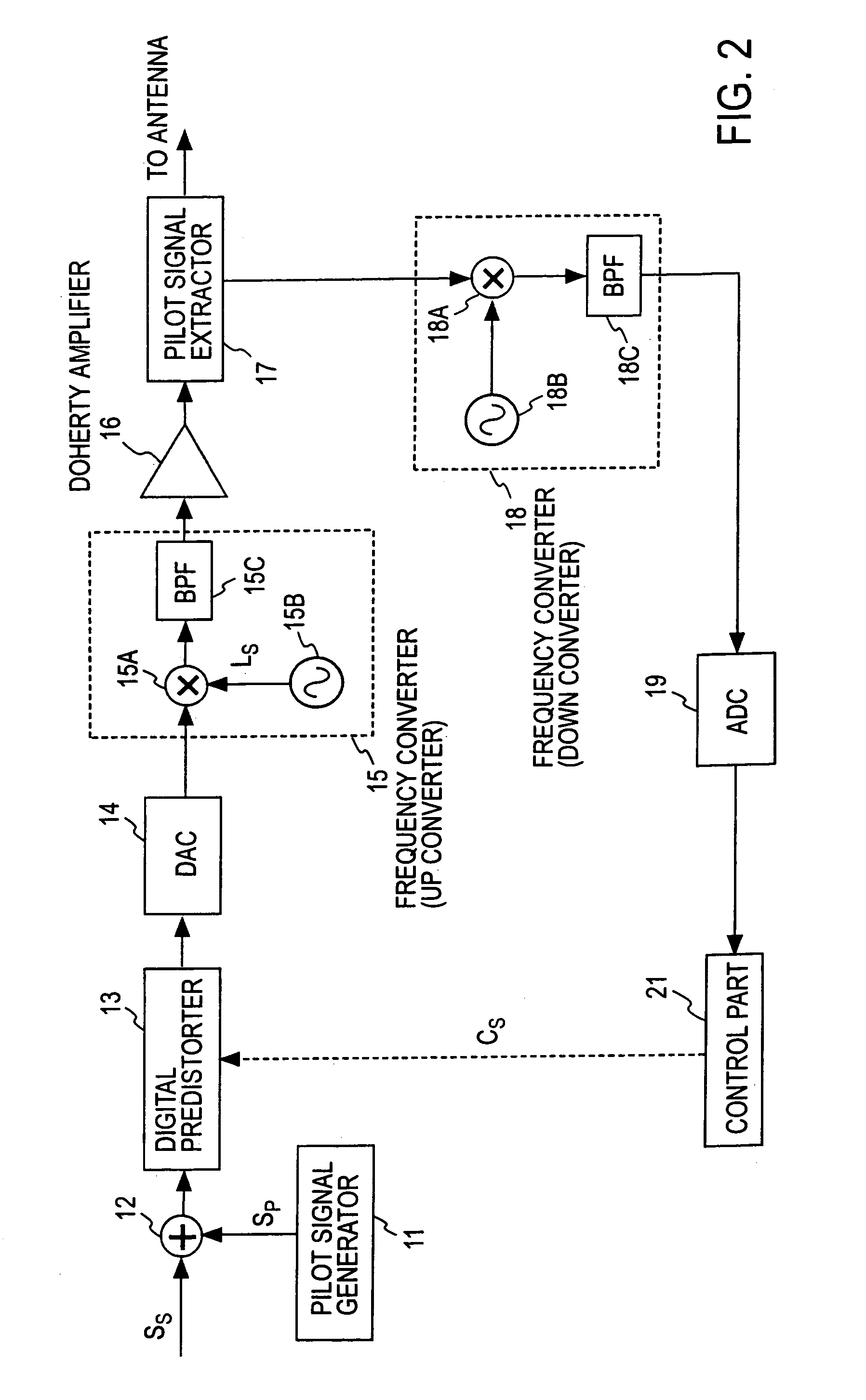
A transmission signal and a pilot signal are predistorted by a digital predistorter 13 by use of a power-series model, and the predistorted output is converted by a digital-analog converter 14 to an analog signal. The analog signal is up converted by a frequency converter 15 to an RF-band signal, which is transmitted after being power-amplified by a Doherty amplifier 16. The pilot signal is extracted by a pilot signal extractor 17 from the output from the Doherty amplifier, and the extracted pilot signal is down converted by a frequency converter 18 to a baseband signal. The baseband pilot signal is converted by an analog-digital converter 19 to a digital pilot signal. A control part 21 detects an odd-order distortion component from the digital pilot signal, and based on the detected result, controls parameters of the digital predistorter.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
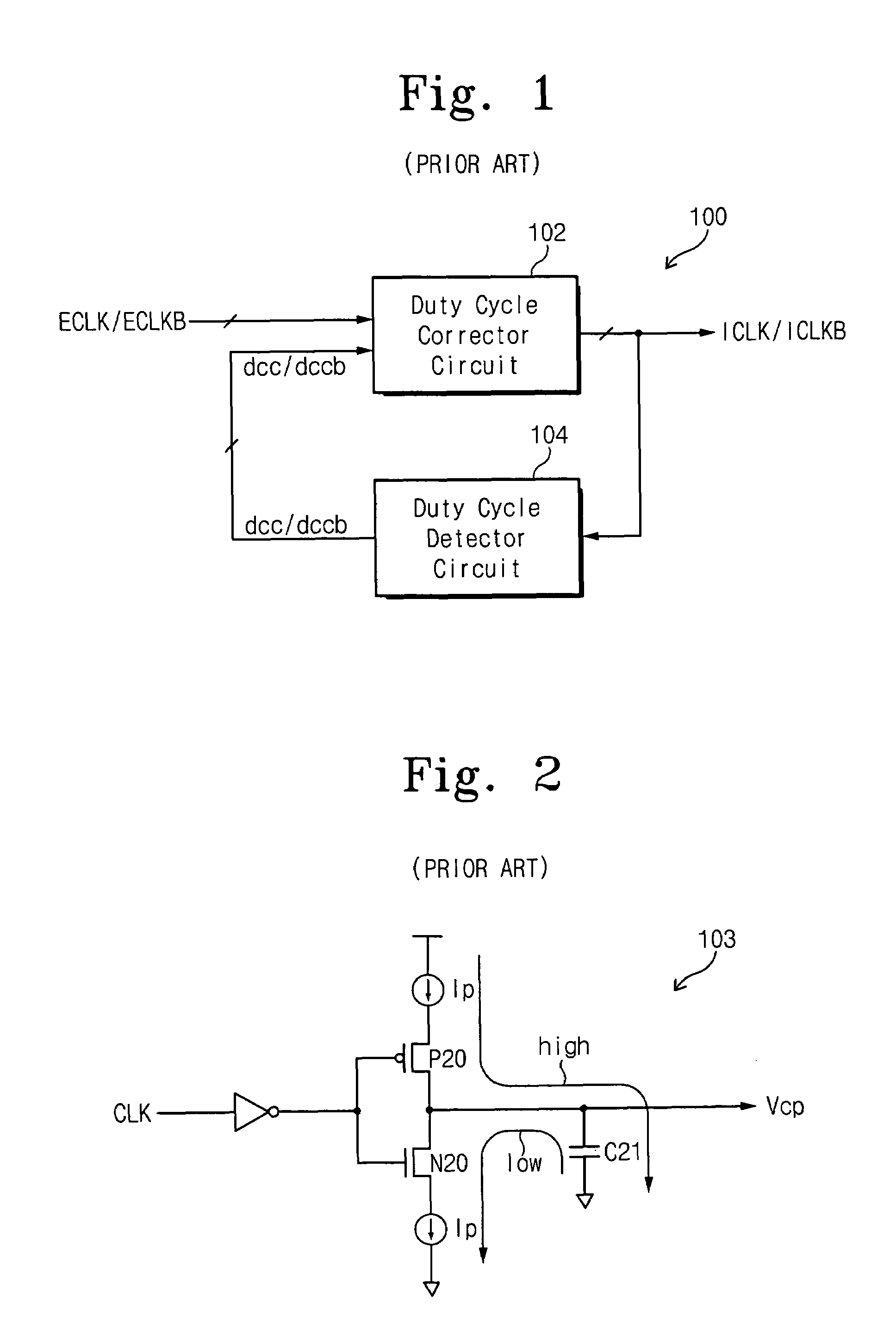
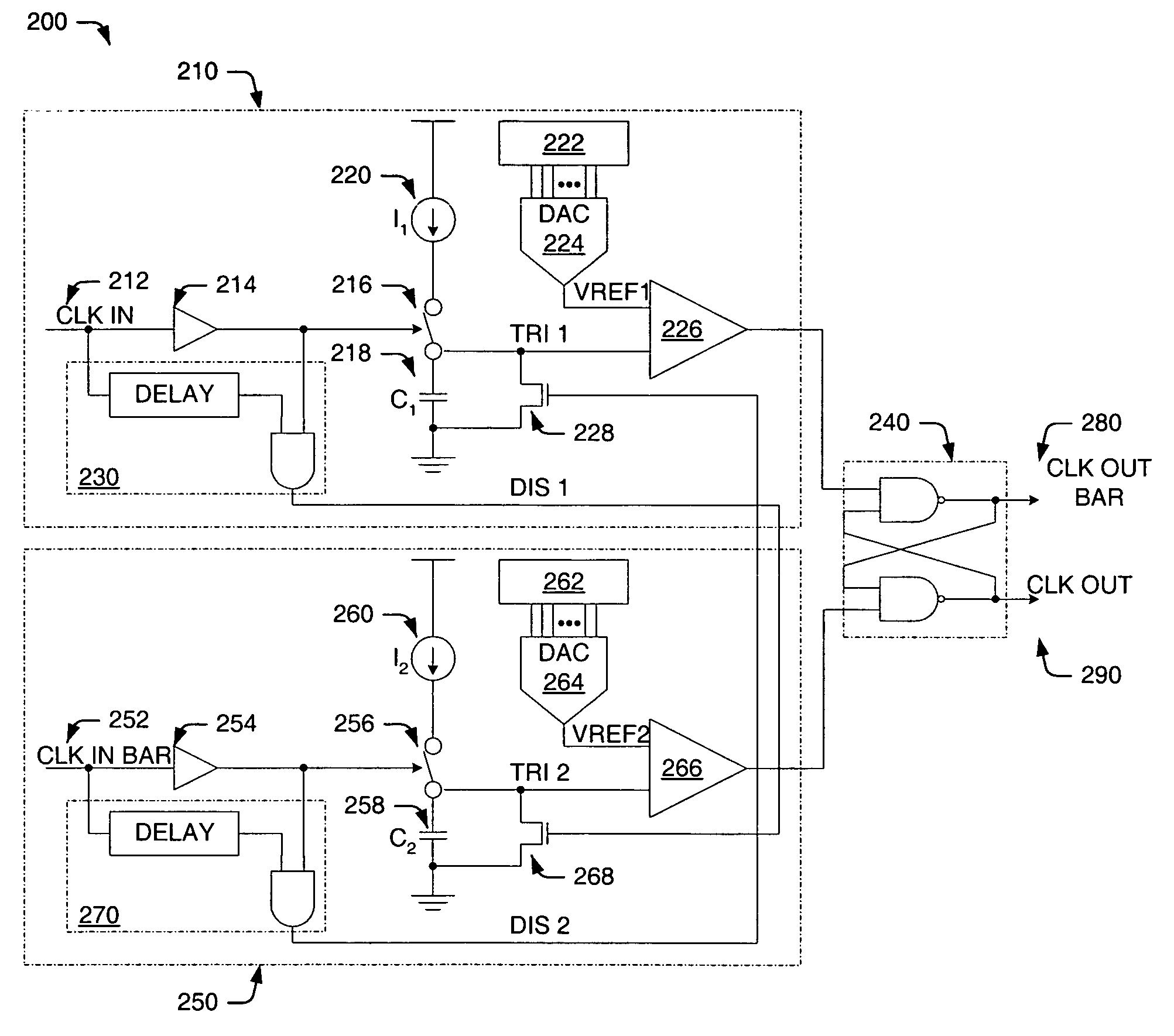
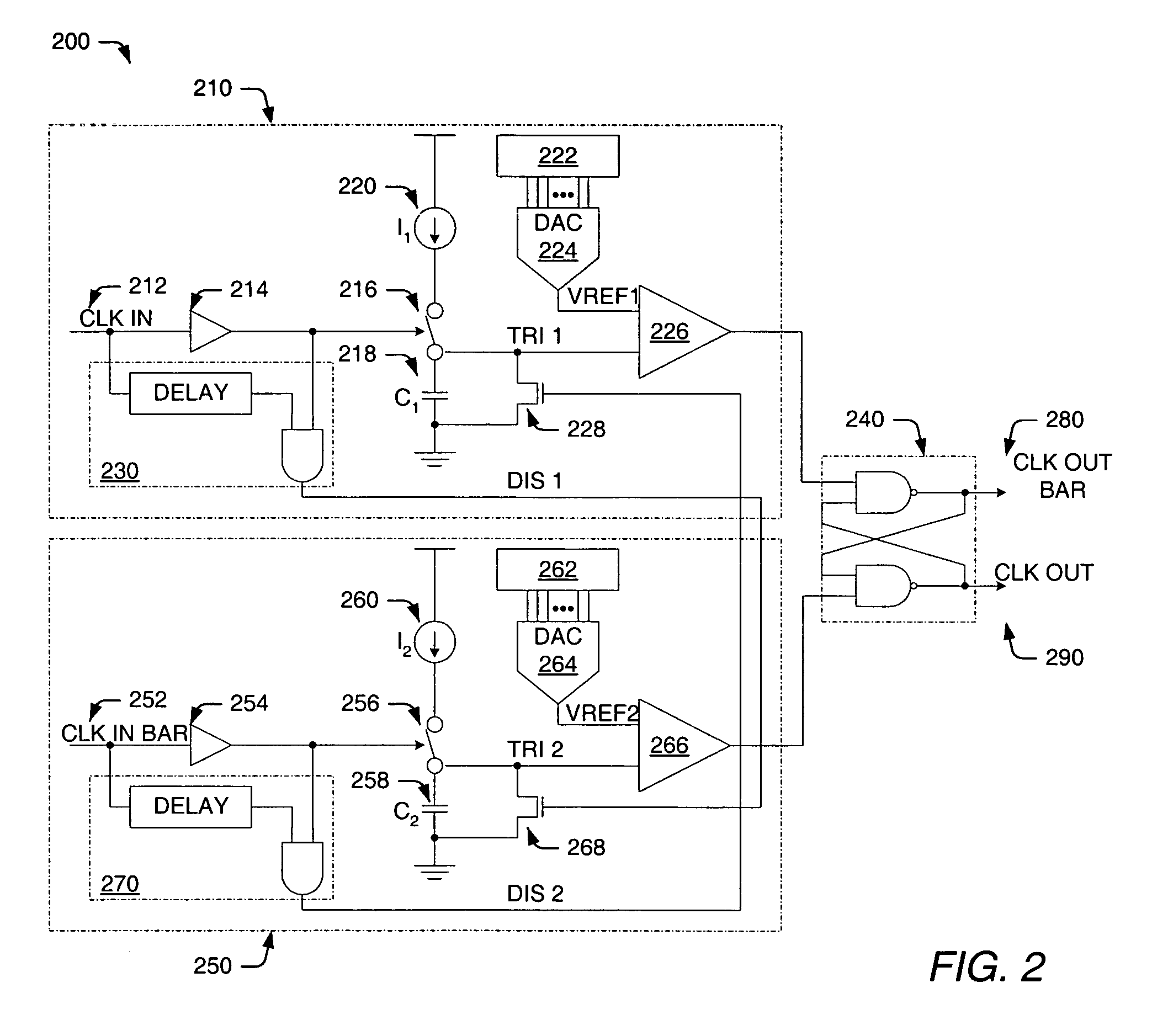
Integrated circuit devices having duty cycle correction circuits that receive control signals over first and second separate paths and methods of operating the same
InactiveUS7015739B2Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationDigital analog converterDetector circuits
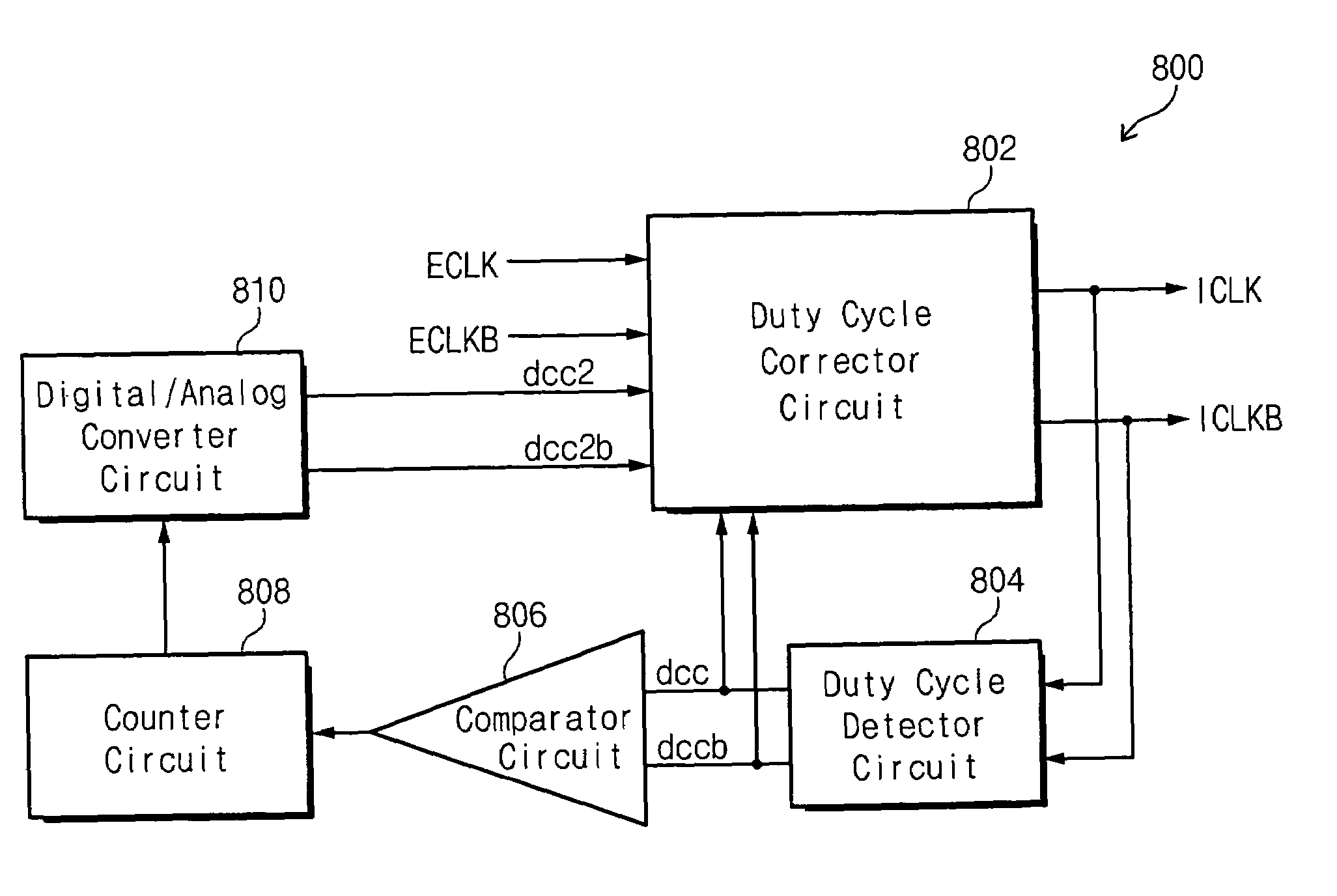
Digital duty cycle correction circuits are provided including a duty cycle detector circuit configured to generate first and second control values associated with a first internal clock signal and a second internal clock signal, respectively. A comparator circuit is also provided and is configured to compare the first control value to the second control value and provide a comparison result. A counter circuit is configured to perform an addition and / or a subtraction operation responsive to the comparison result to provide a digital code. A digital to analog converter is configured to generate third and fourth control values responsive to the digital code. Finally, a duty cycle corrector circuit is configured to receive first and second external clock signals and the first through fourth control values and generate the first and second internal clock signals having a corrected duty cycle. The first and second control values are received over a first path and the third and fourth control values are received over a second path, different from the first path. Related methods of operating duty cycle correction circuits are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Programmable phase shift and duty cycle correction circuit and method
ActiveUS7138841B1Manipulation where pulse delivered at different timesElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitPhase shifted
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
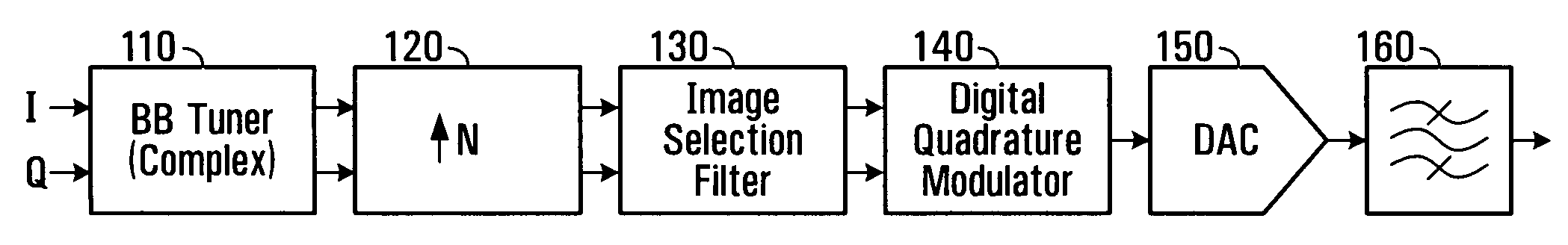
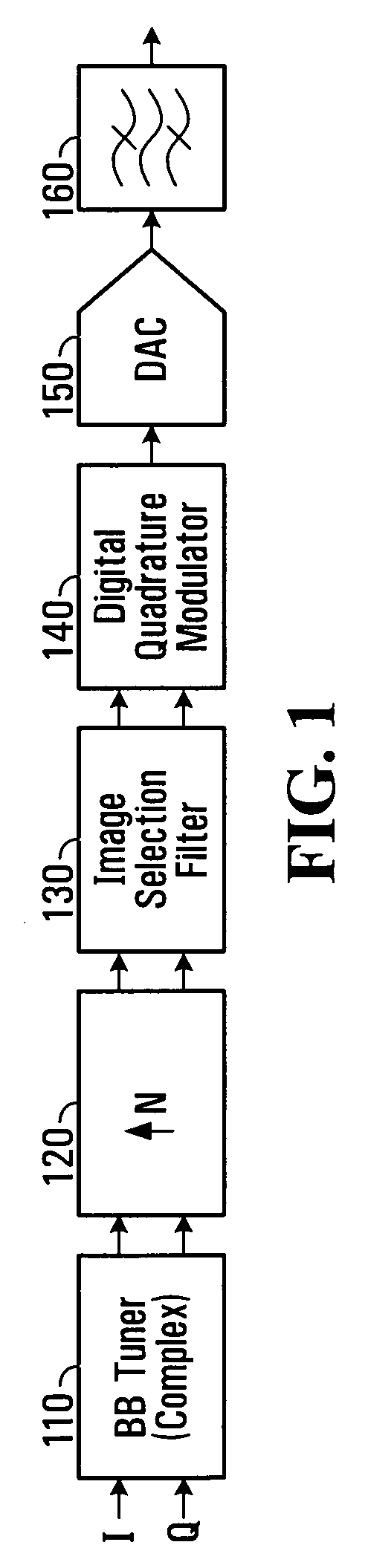
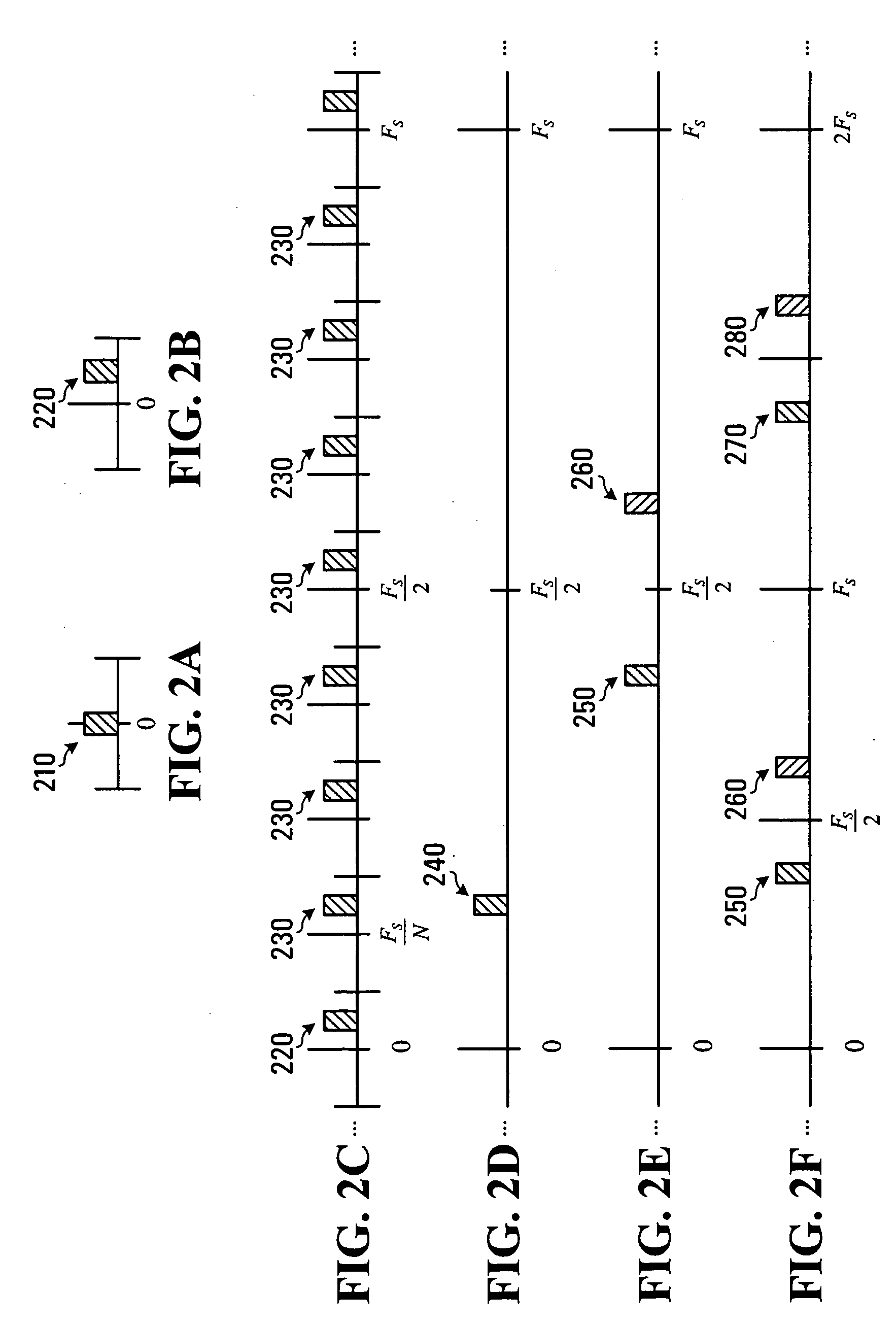
Methods and systems for programmable digital up-conversion
InactiveUS20100098191A1Reduce complexityModulation transferenceDigital technique networkDigital analog converterEngineering
Methods and apparatus are described herein that make use of complex tuning, the inherently repetitive nature of sampled signals, and programmable digital filtering to create a flexible digital up-conversion system that utilizes a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) with a fixed effective sample rate while still being adapted for tunability over a wide frequency range. With a knowledge of the fixed effective sample rate of the DAC and a desired frequency of up-conversion and combining complex tuning at baseband and up-sampling by a factor of N with a programmable passband filter configured to select one of a plurality of signal images resulting from the up-sampling, it is possible to translate a baseband input signal to a wide range of frequencies above or below Fs, without changing the sampling rate of the fixed rate DAC used in the up-conversion process.
Owner:APPLE INC
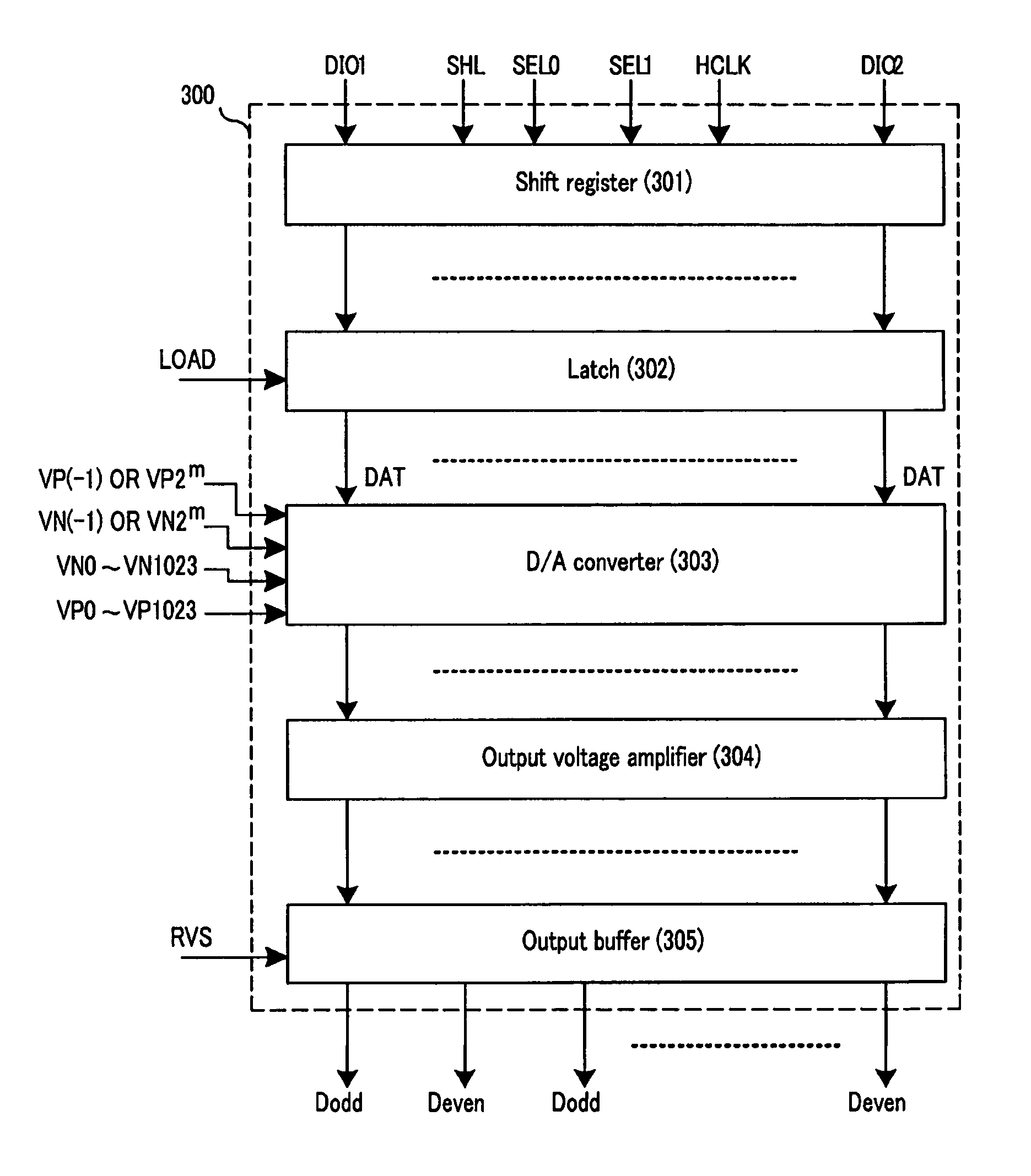
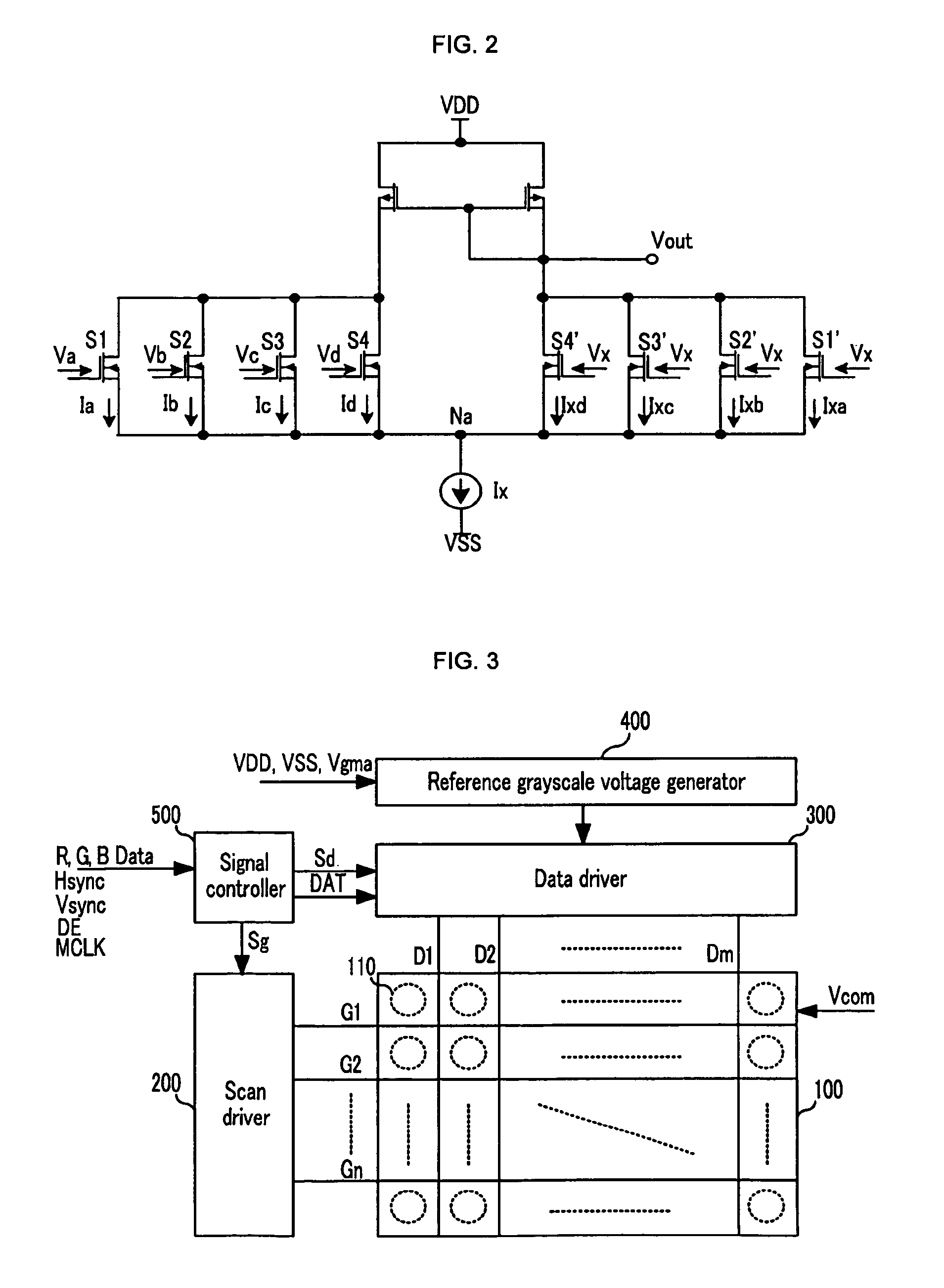
Liquid crystal display, driving apparatus, digital-analog converter and output voltage amplifier thereof
InactiveUS8294657B2Reduce areaLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsDifferential amplifiersVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a liquid crystal display, a driving device thereof, a digital to analog converter, and an output voltage amplifying circuit. The present invention provides a liquid crystal display driving device including a reference gray voltage generator for generating a plurality of reference gray voltages, and a data driver for generating a plurality of gray voltages based on the plurality of reference gray voltages and applying a data signal that is generated by selecting a gray voltage corresponding to m-bit video signals applied from the outside from among the plurality of gray voltages to the pixel The data driver includes: a voltage generator for selecting a first gray voltage and a second gray voltage corresponding to bit values of (m−k) bits from among the video signal from among the plurality of gray voltages, and outputting the first and second gray voltages; an output voltage generator for outputting 2k voltages determined as one of the first and second gray voltages corresponding to bit values of k bits from among the video signal; and an output voltage amplifier for generating the data signal by combining the 2k voltages, and applying the data signal to a plurality of pixels. According to the present invention, a liquid crystal display having a small cost and area can be realized.
Owner:MC TECH CO LTD
Multiplexer and Modulation Arrangements for Multi-Carrier Optical Modems
ActiveUS20120251119A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSuper-channelModem device
Consistent with the present disclosure, data, in digital form, is received by a transmit node of an optical communication, and converted to analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to drive a modulator. The modulator, in turn, modulates light at one of a plurality of wavelengths in accordance with the received data forming a plurality of corresponding carriers. The plurality of carriers are then optically combined with a fixed spacing combiner to form a superchannel of a fixed capacity. Accordingly, the number of carriers are selected according to a modulation format and symbol rate to realize the fixed capacity, for example. The superchannel is then transmitted over an optical communication path to a receive node. At the receive node, the superchannel is optically demultiplexed from a plurality of other superchannels. The plurality of carriers are then supplied to a photodetector circuit, which receives additional light at one of the optical signal carrier wavelengths from a local oscillator laser. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is provided in the receive node to convert the electrical signals output from the photodetector into digital form. The output from the ADC is then filtered in the electrical domain, such that optical demultiplexing of the carriers is unnecessary.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method and apparatus for sensing flash memory using delta sigma modulation
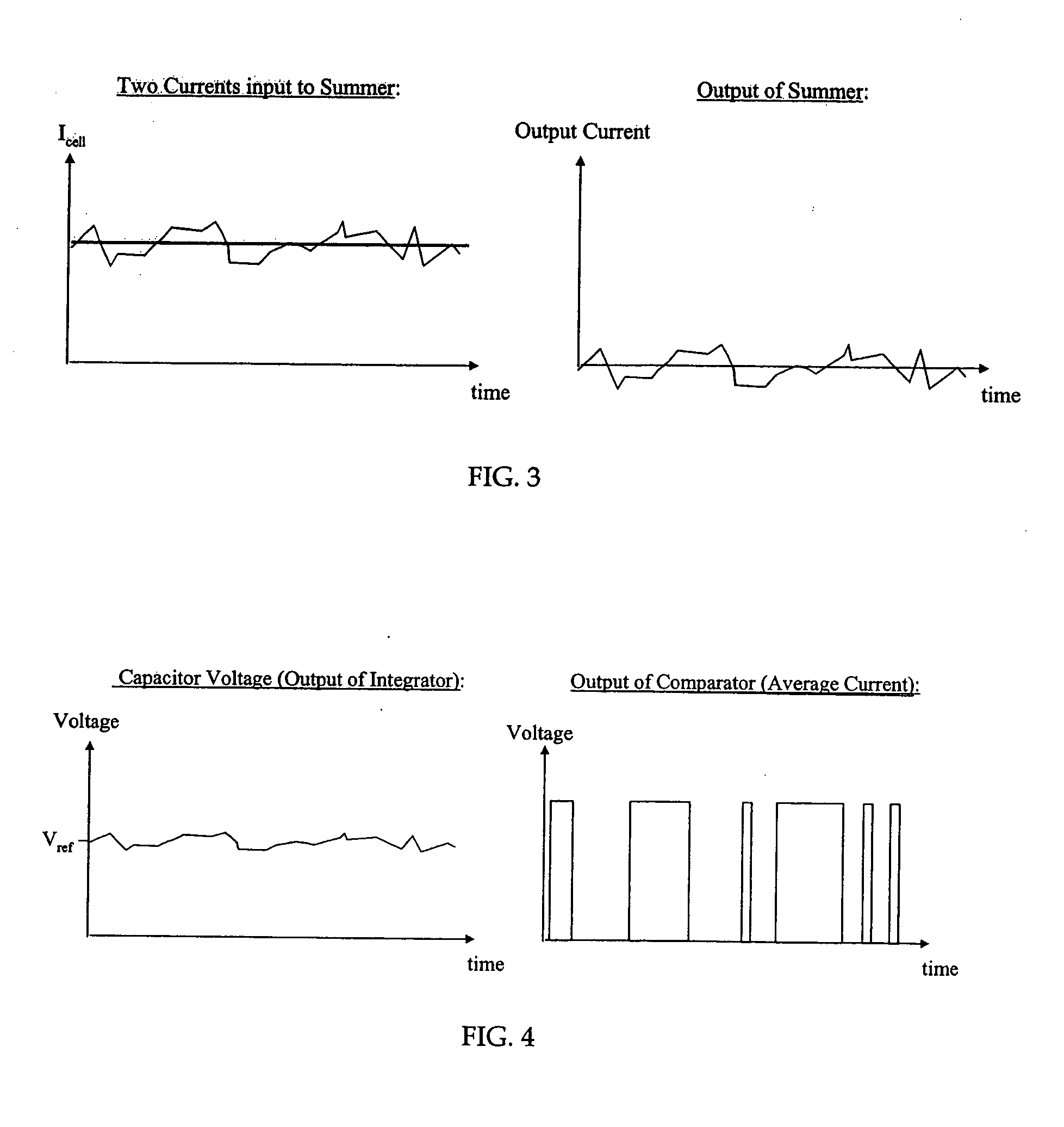
ActiveUS20060250853A1Accurate inductionHigh circuitryRead-only memoriesDigital storageConvertersAverage current
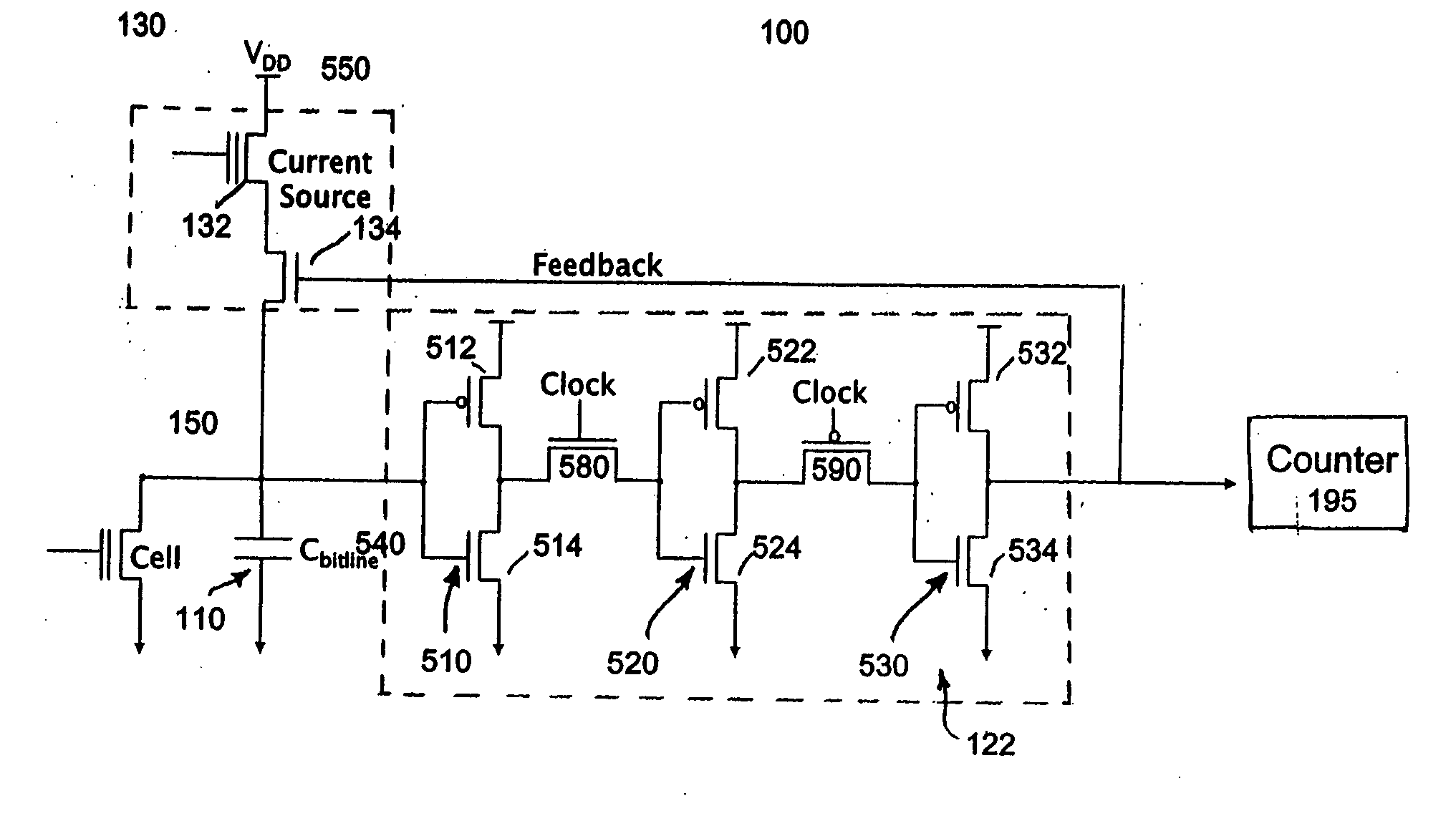
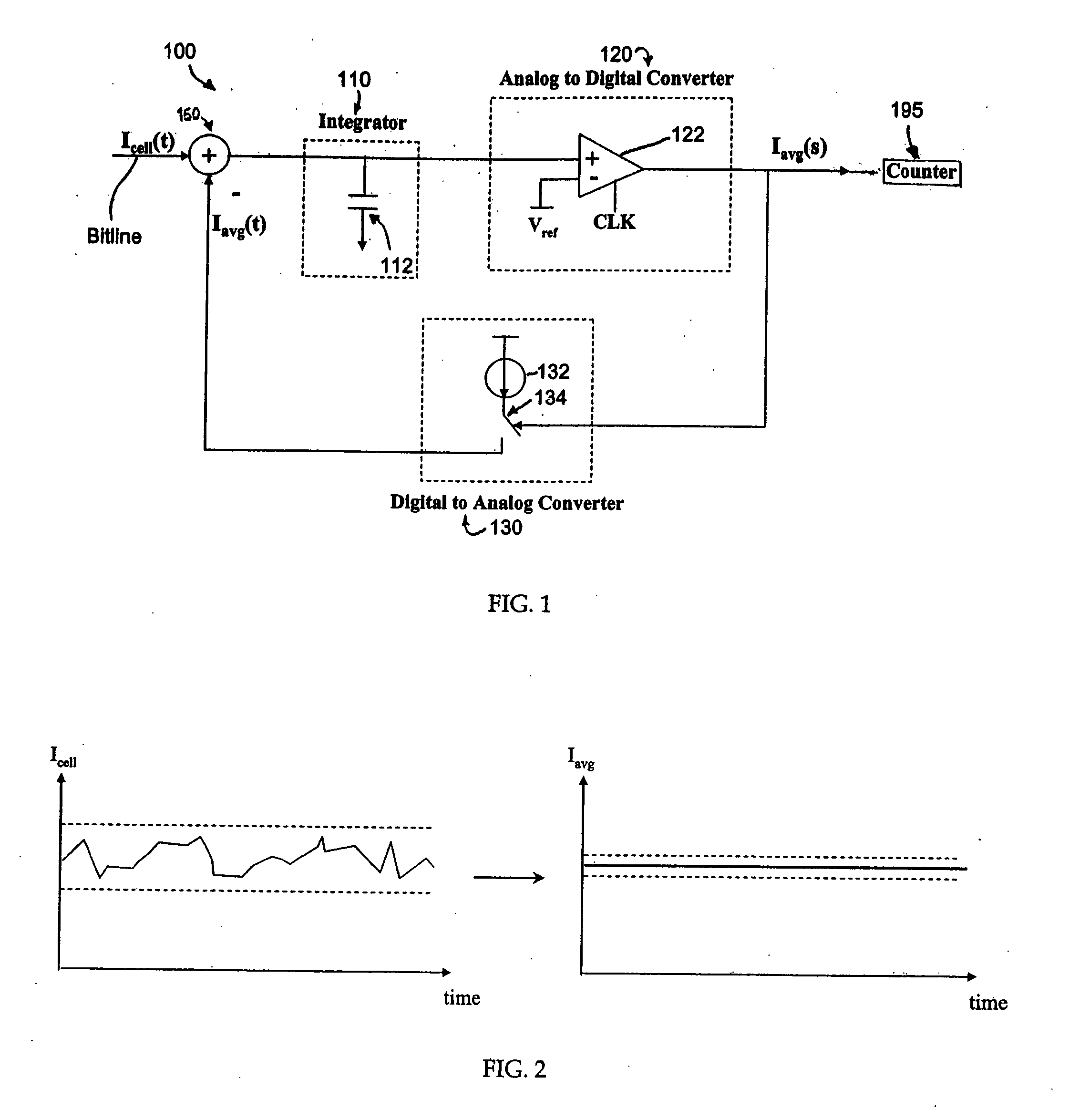
A simple method and device for accurately measuring flash memory cell current. The sensing scheme comprises an integrator, an analog to digital converter, and a digital to analog converter. The method comprises the acts of applying an input current and a feedback output current to a summer, integrating the resulting summer output over time, passing the integrated output to a clocked comparator, outputting a comparator output which controls a feedback circuit that keeps the integrator's voltage at the same level as a reference voltage, and outputting a digital average current to a counter. Delta sigma modulation (averaging) is employed to cancel out noise that would otherwise affect the cell current measurement.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
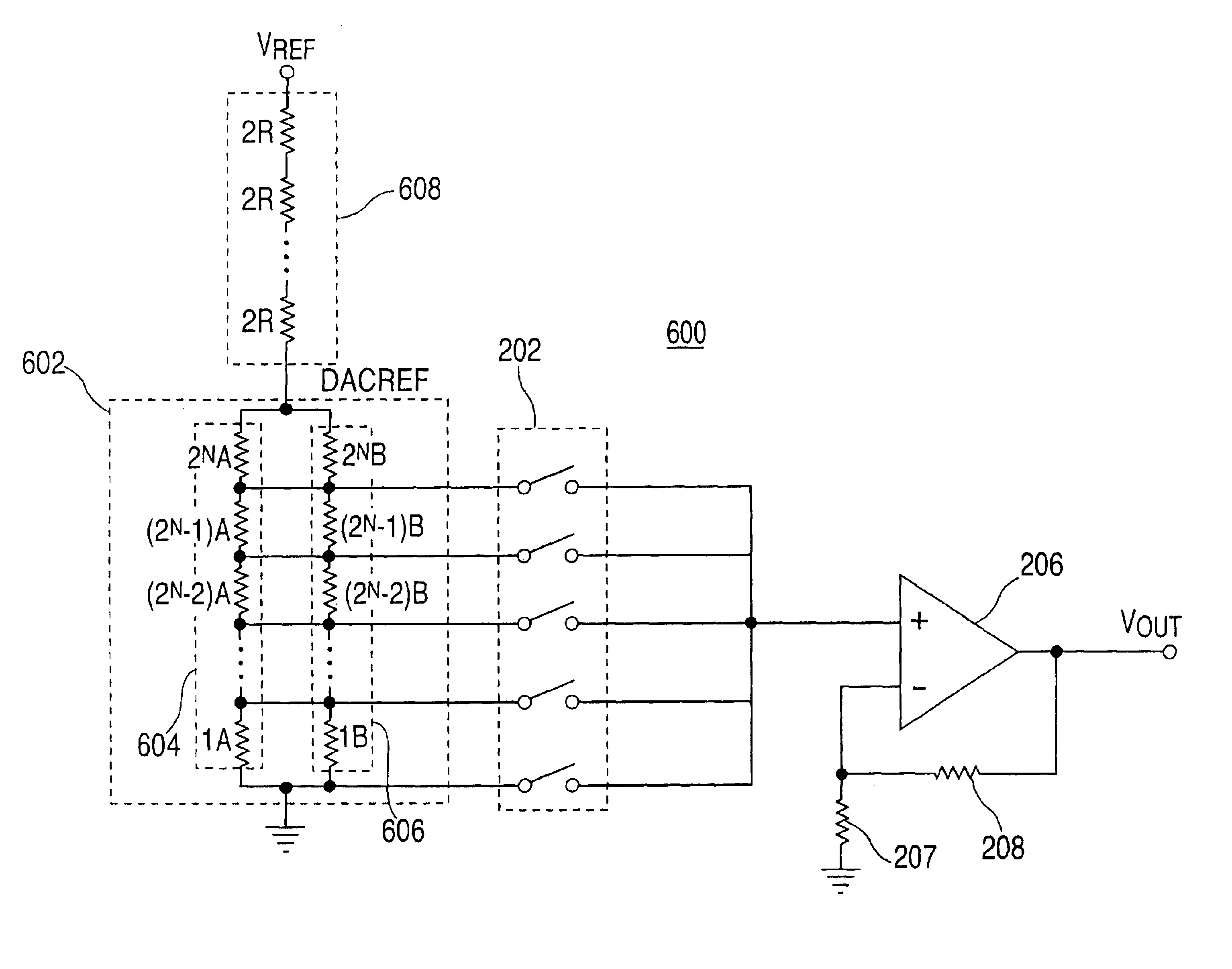
Extended range digital-to-analog conversion
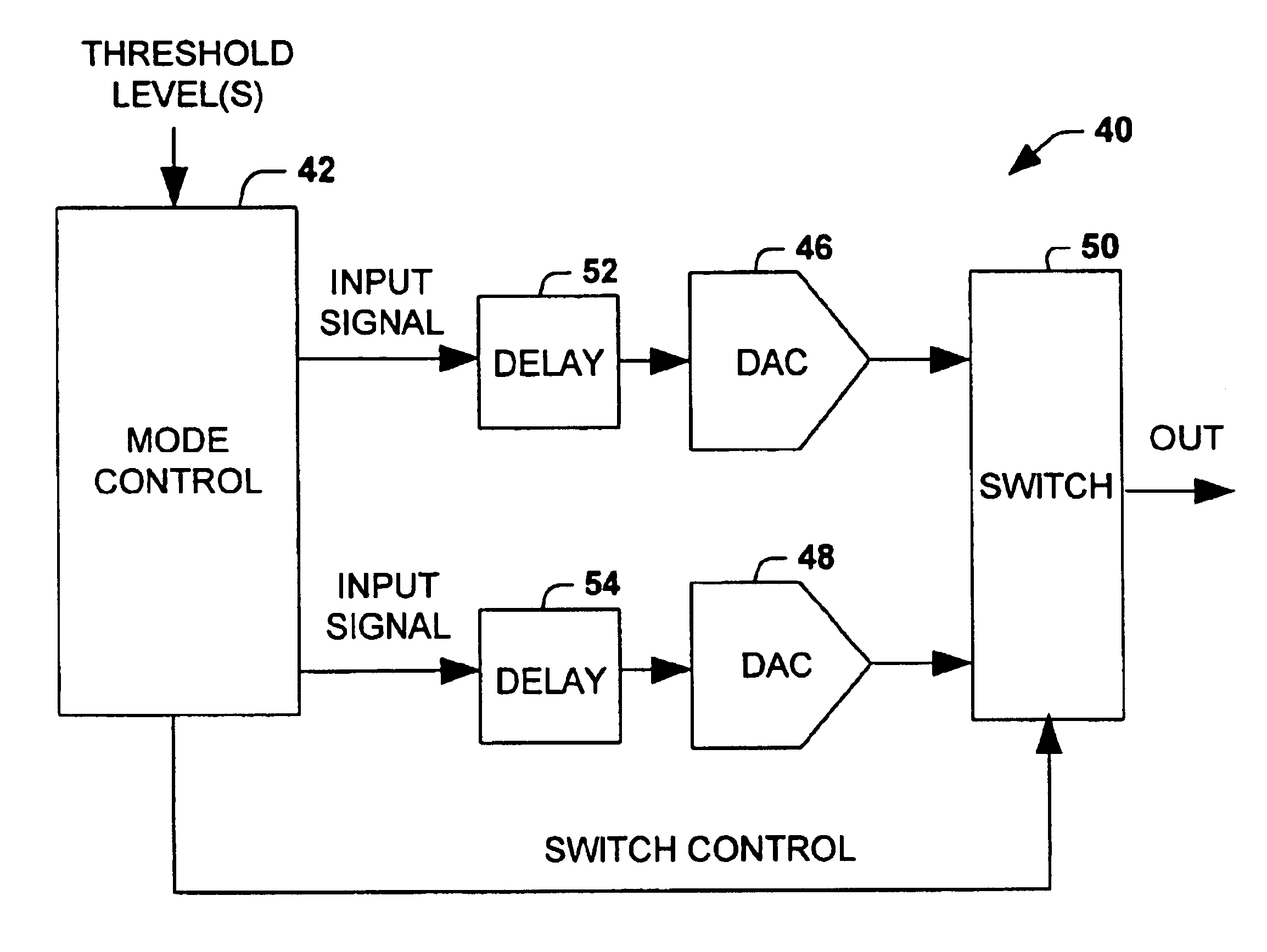
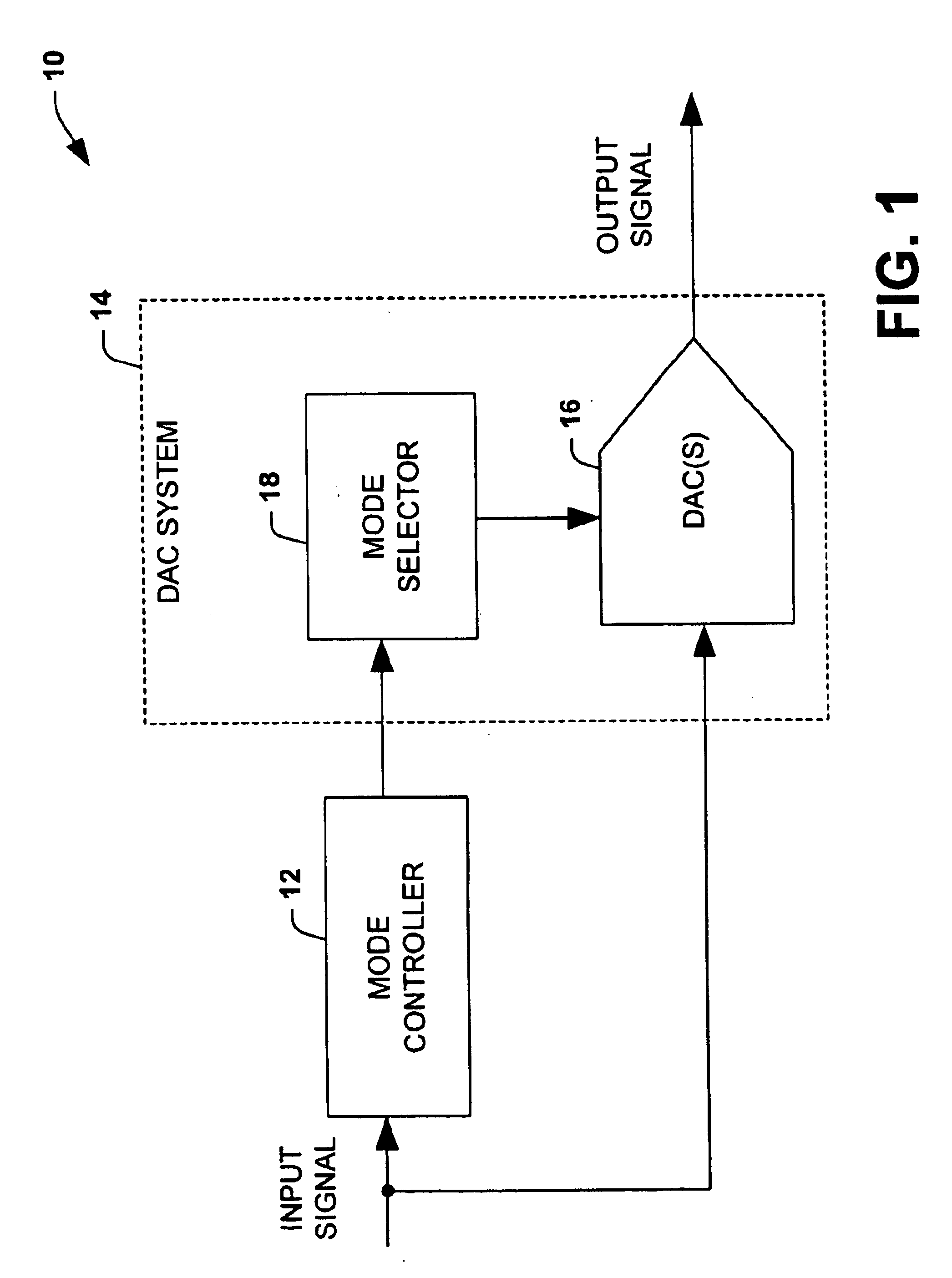
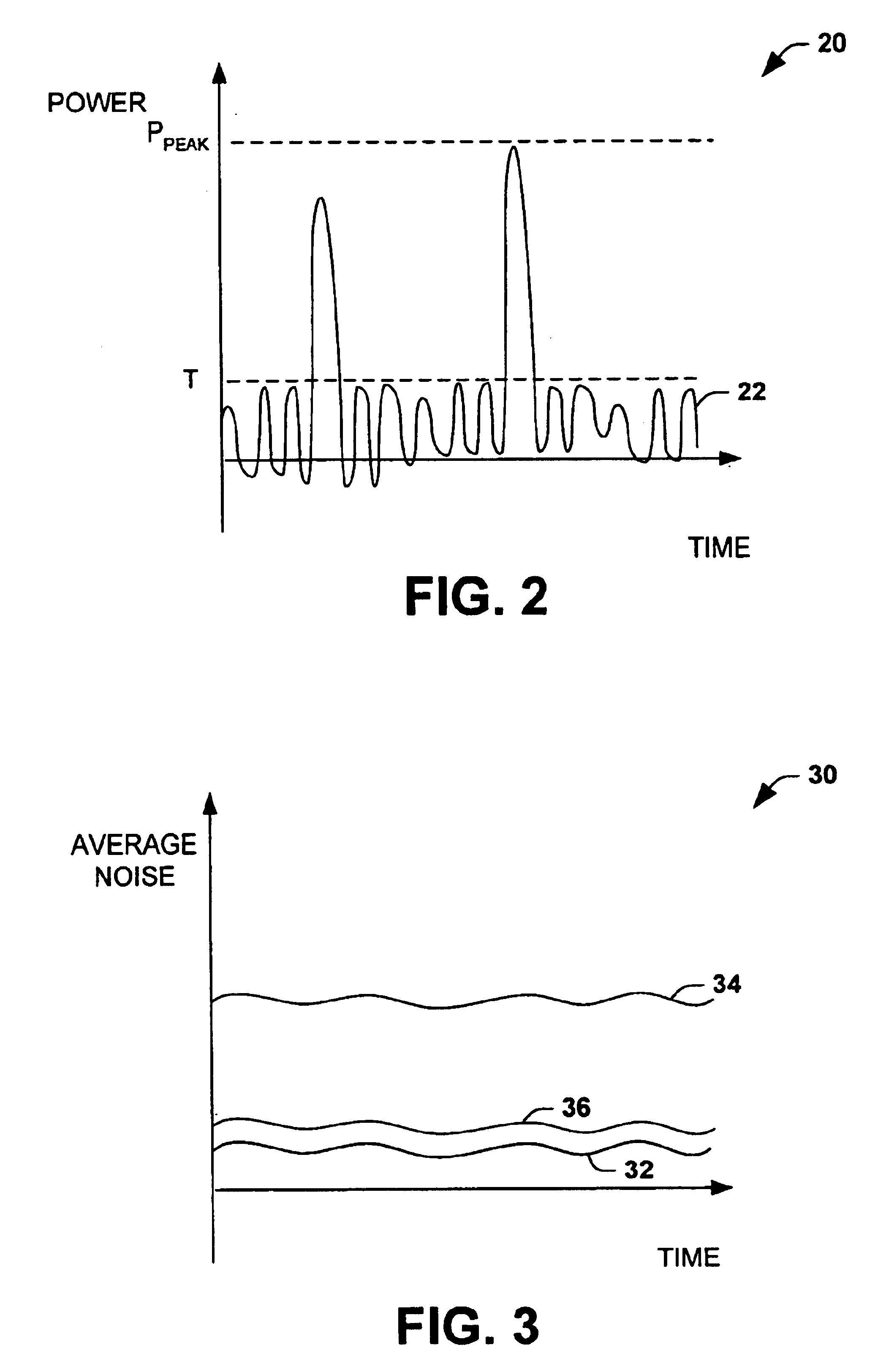
InactiveUS6822595B1Reduce quantization noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterNoise level
A conversion system converts an input signal from a digital signal to an analog signal over an extended dynamic range. The system includes a DAC system and a mode selector. The mode selector selects a mode of operation for the digital-to-analog converter system from a plurality of modes. The mode selector selects a mode according to a characteristic of the input signal. Each of the modes is associated with an instantaneous dynamic range and quantization noise level of the DAC system. The ensemble of modes provides an improvement in total or effective dynamic range compared to any DAC component within the DAC system.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Adaptive rectifier Architecture and method for switching regulators
ActiveUS20080298106A1Improve accuracyImprove power efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDigital analog converterSwitching cycle
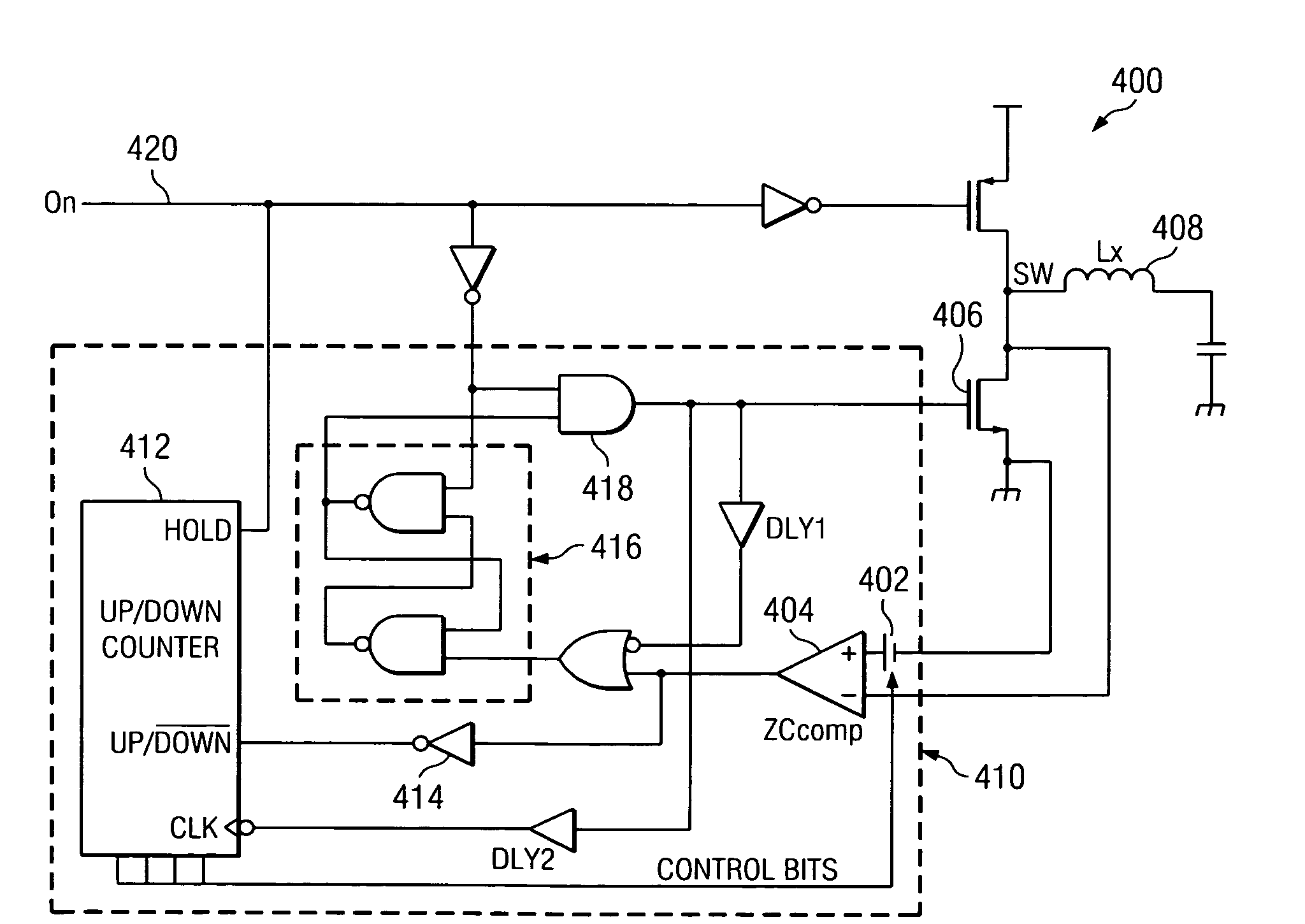
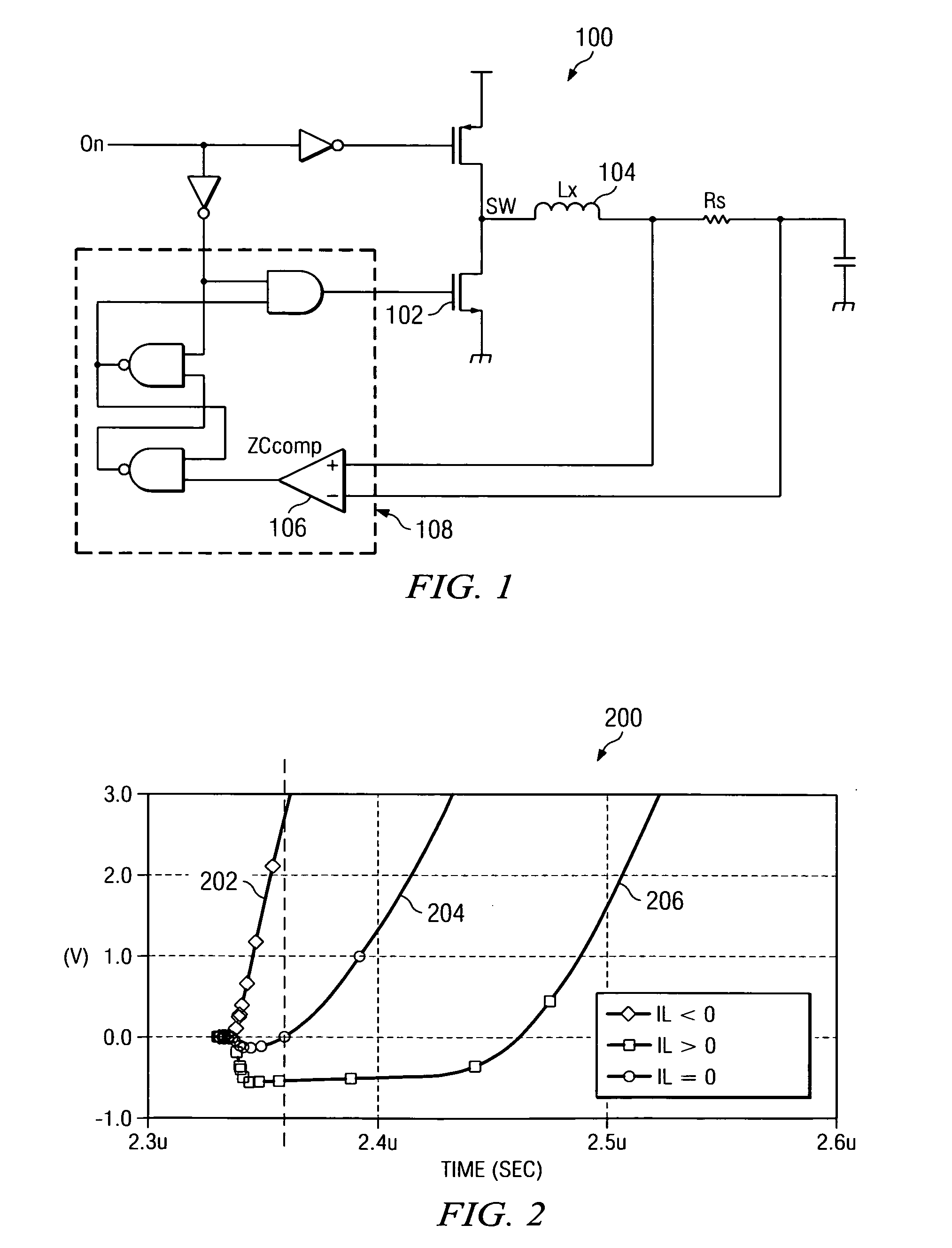
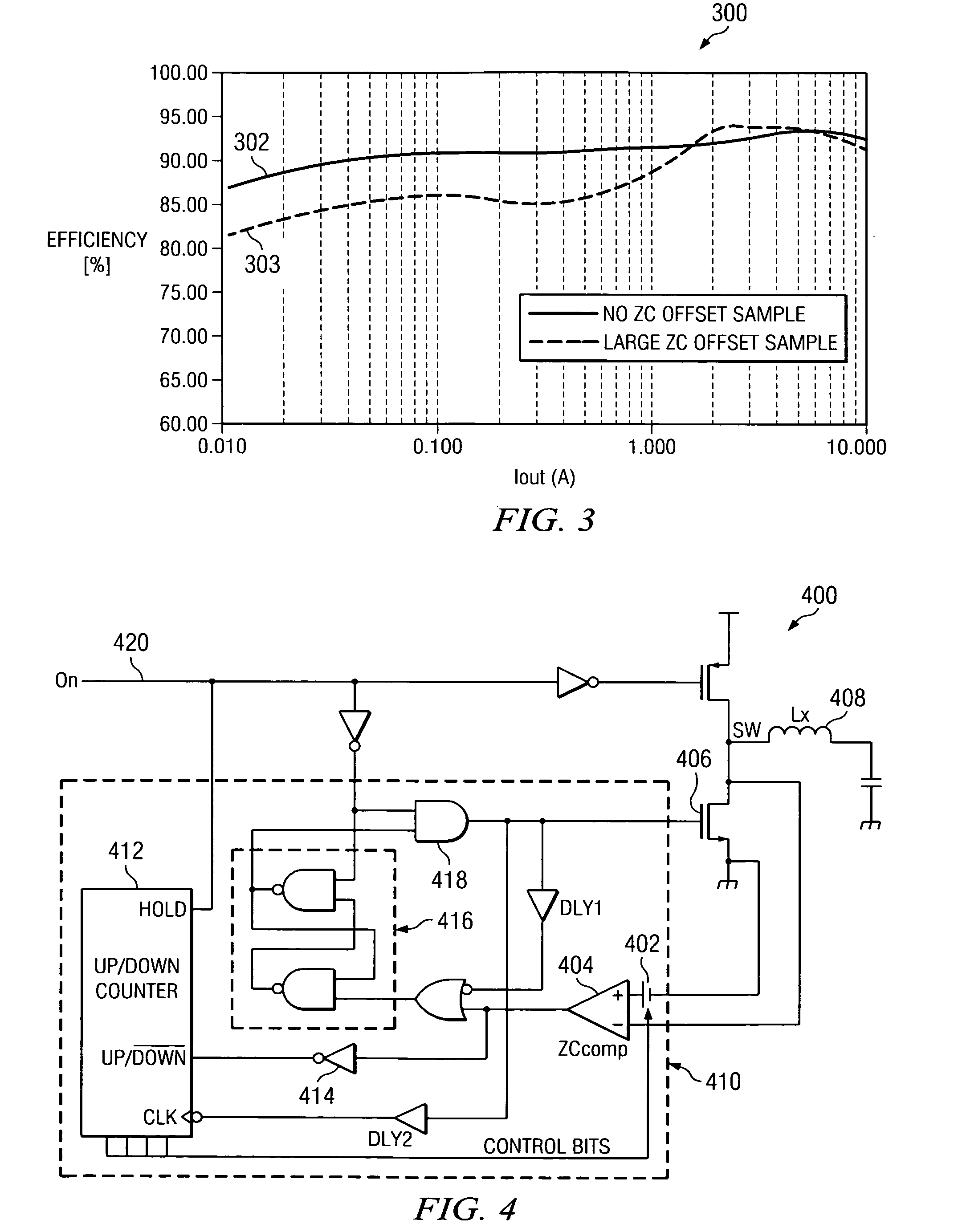
An adjustable compensation offset voltage is applied to a comparator to vary turn-off timing of a synchronous rectifier. A comparator output indicates when current through an inductor coupled to the synchronous rectifier should be approaching zero. If the synchronous rectifier is turned off before the current through the inductor reaches zero, the compensation offset voltage is adjusted to delay the synchronous rectifier turn-off for the next switching cycle. If the synchronous rectifier is turned off after the current through the inductor reaches zero, the compensation offset voltage is adjusted to advance the synchronous rectifier turn-off for the next switching cycle. An up / down counter, in conjunction with a digital to analog converter, may be used to provide the adjustment to the compensation offset voltage. The adjustable compensation offset voltage improves the accuracy of synchronous rectifier turn-off in relation to a zero inductor current, thereby improving power converter efficiency.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
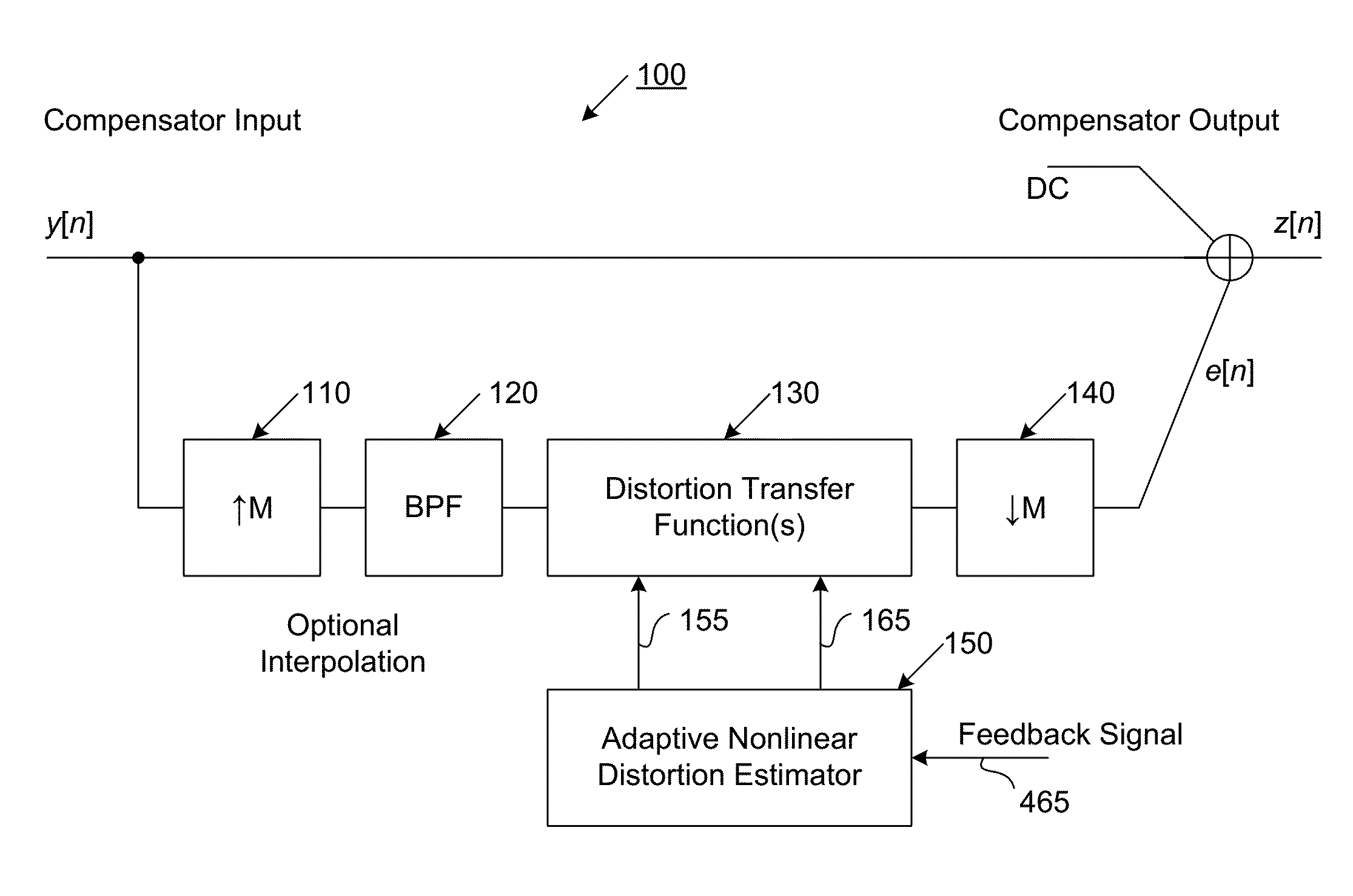
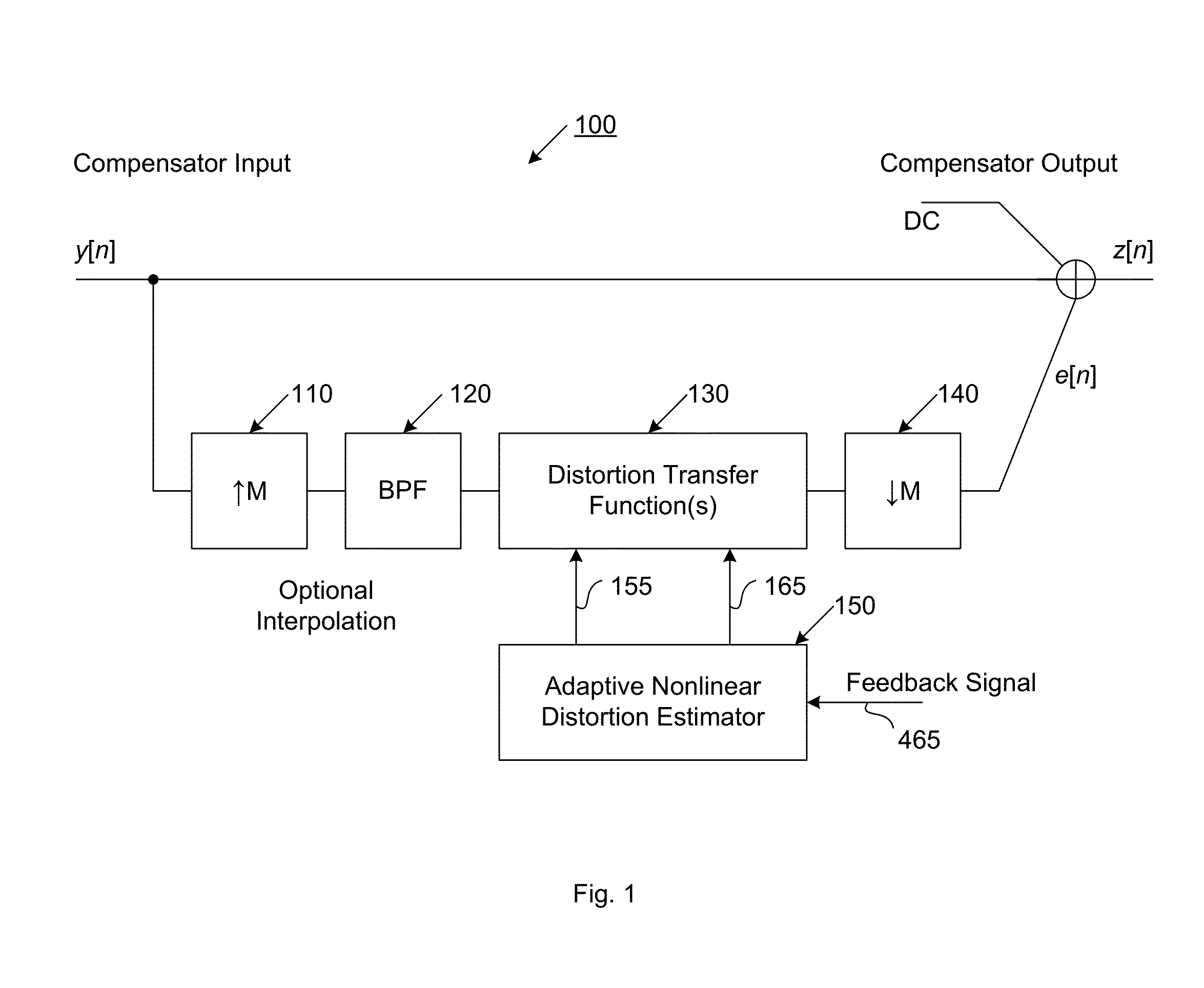
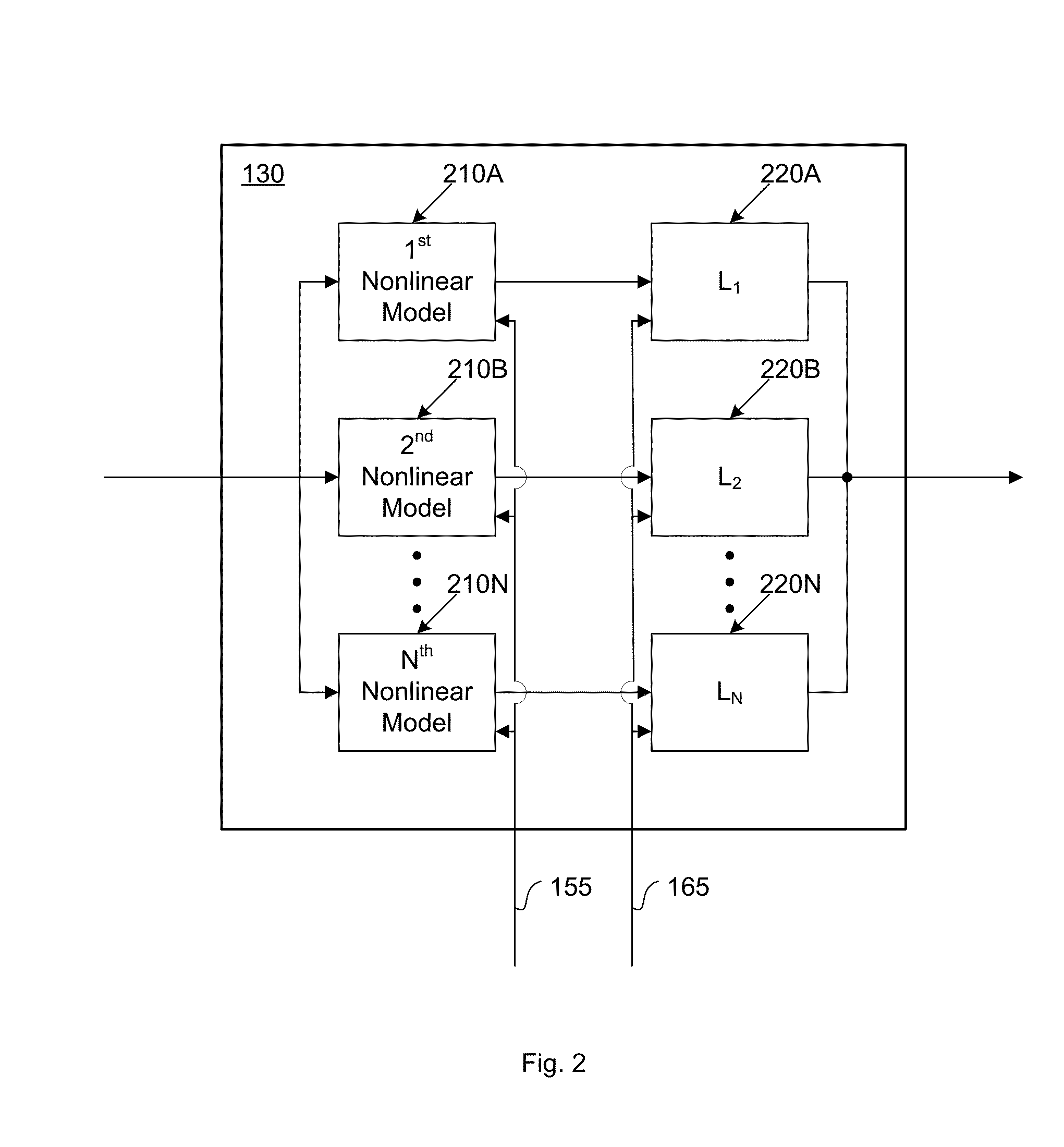
ActiveUS20160191020A1Easy to processReduce complexityChannel dividing arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Class H Drive
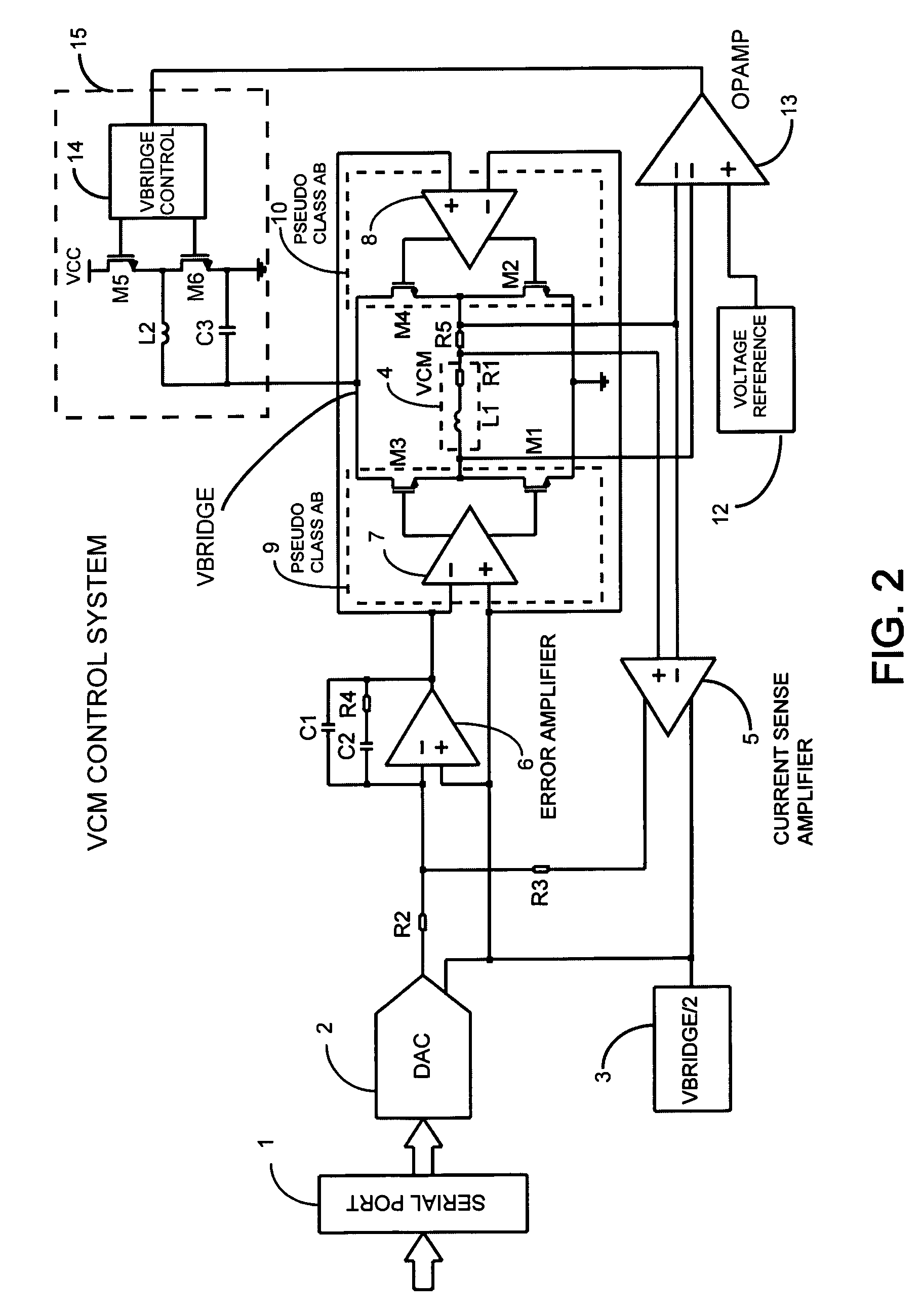
InactiveUS20080310046A1Increase the switching frequencyImprove motor efficiencySynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlAudio power amplifierDigital analog converter
A method for driving a load by using an output stage amplifier in full bridge configuration whose supply is modulated by means of a fast switching power converter, controlled in order to maintain the stage's output common mode at its minimum voltage, is presented. The modulation of the switching power converter output is obtained by a feedback control system regulating directly the voltage of the bridge output stage terminals. This bridge unipolar class H stage allows driving the load with high accuracy and improved efficiency without introducing switching noise and EMI at the load terminals typical of PWM driving. This method can be applied with the same benefits to class AB, pseudo class AB or to class A output stages. When this method is associated with an imposed current driving approach and with a current oversampling digital to analog converter the resulting advantages are very significant for accurate motor control applications.
Owner:MENEGOLI PAOLO +1
Real-time audio processing of ambient sound
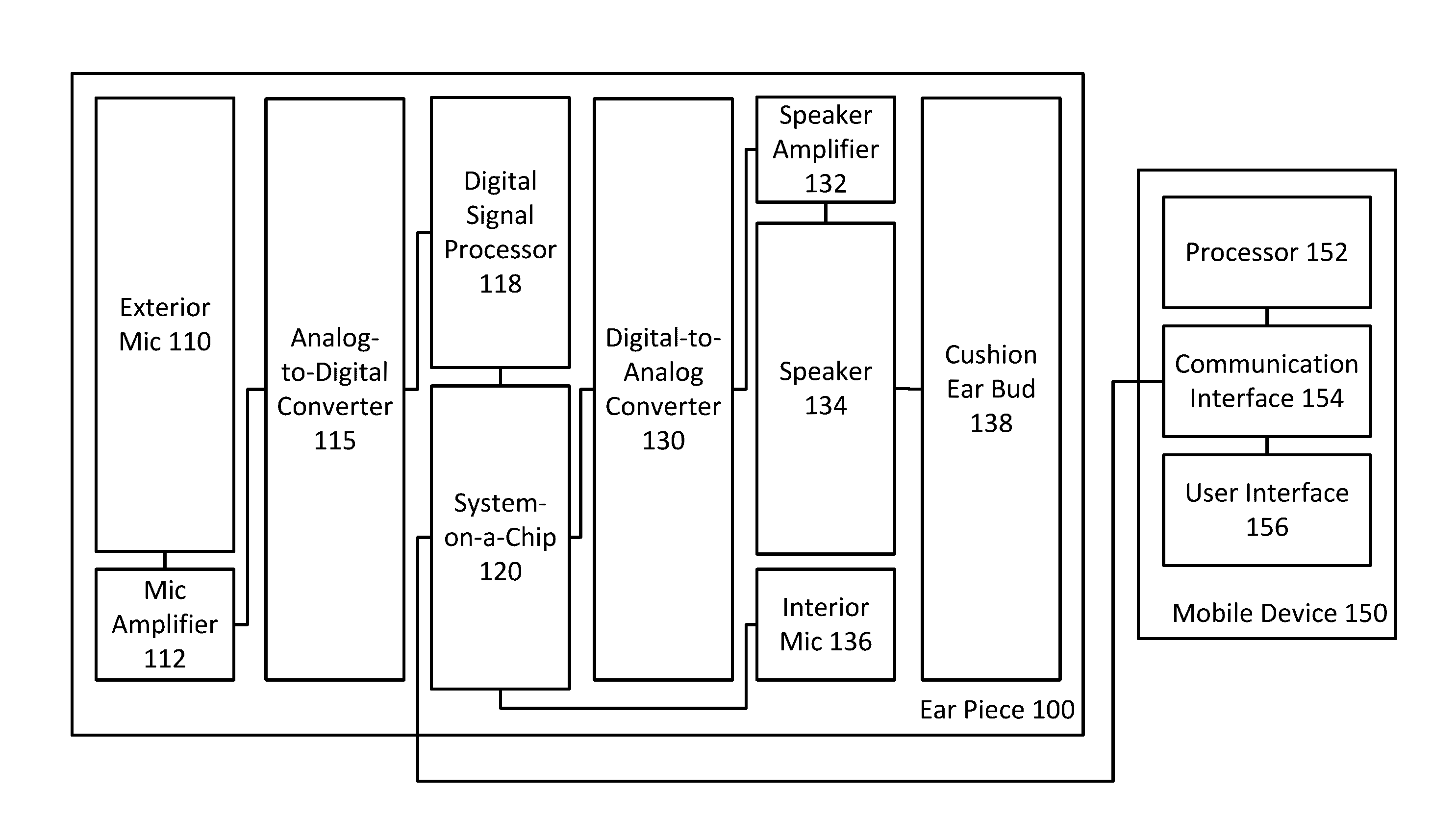
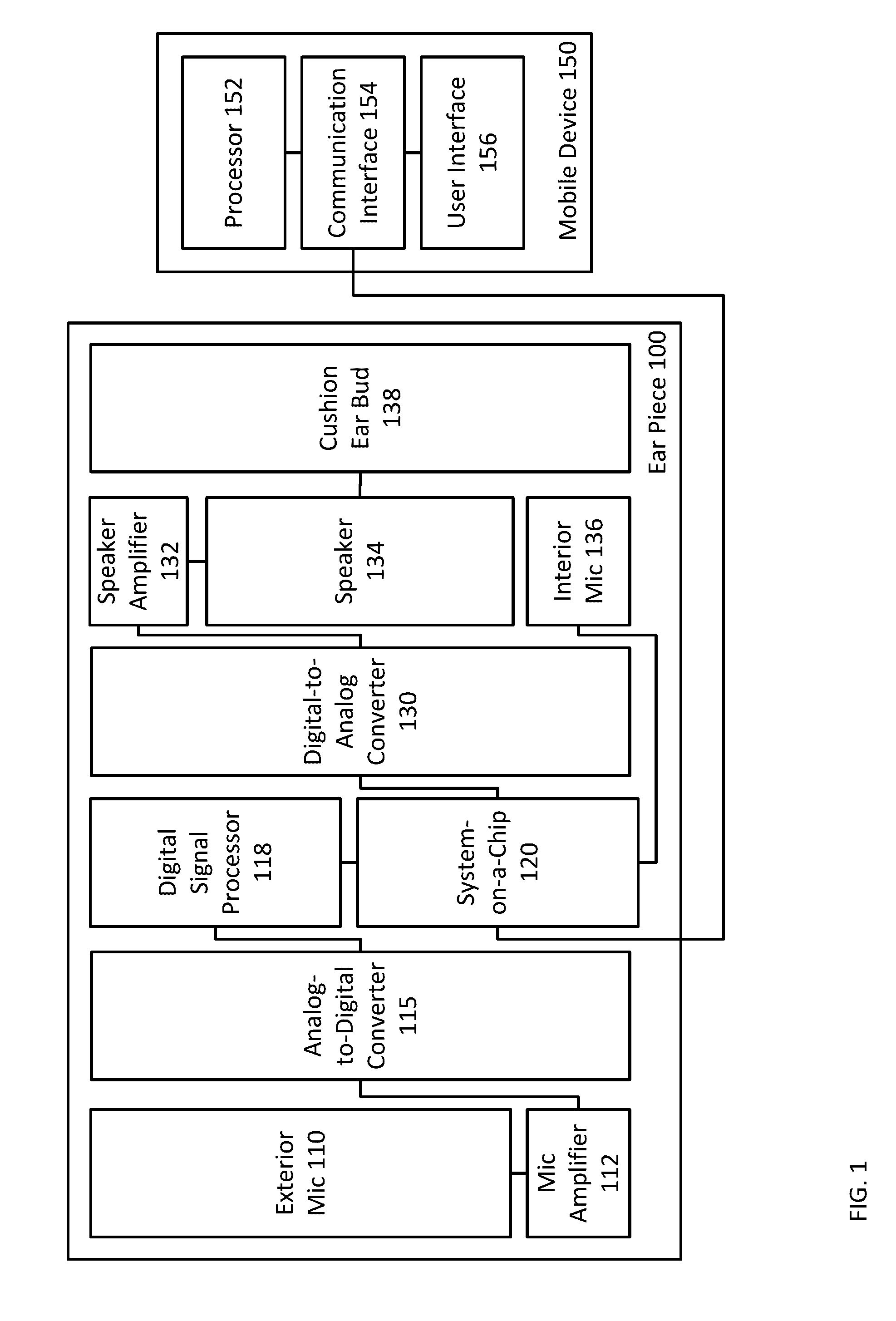
An earpiece for real-time audio processing of ambient sound includes an ear bud that provides passive noise attenuation to the earpiece such that exterior ambient sound is substantially reduced within an ear of a wearer, an exterior microphone that receives ambient sound and converts the received ambient sound into analog electrical signals, and an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog electrical signals into digital signals representative of the ambient sounds. The earpiece further includes a digital signal processor that performs a transformation operation on the digital signals according to instructions received from a mobile device, the transformation operation transforms the digital signals into modified digital signals, a digital-to-analog converter that converts the modified digital signals into modified analog electrical signals, and a speaker that outputs the modified analog electrical signals as audio waves.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Excess delay compensation in a delta sigma modulator analog-to-digital converter
InactiveUS6414615B1Electric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationDigital analog converterAnalog signal
A high-performance delta sigma analog-to-digital converter. The high-performance delta sigma analog-to-digital converter includes a first mechanism for converting an input analog signal to a digital output signal. The first mechanism is characterized by a transfer function that is altered relative to an ideal transfer function. A second mechanism compensates for the alteration in the transfer function via a single additional digital-to-analog converter. In a specific embodiment, the alteration includes an additional pole and an additional zero induced by feedback delays in the first mechanism. The feedback delays include signal dependent jitter delay and feedback digital-to-analog converter cell switching delays. The second mechanism includes an additional latch that compensates for the signal dependent jitter delay. The first mechanism includes a resonator and a quantizer. The second mechanism includes a feedback path from an output of the quantizer to the resonator. The feedback path includes a first latch positioned between an output of the quantizer and the additional digital-to-analog converter. The additional latch is positioned at an output of the first latch and eliminates signal dependent jitter delay in the analog-to-digital converter. The additional feedback digital-to-analog converter is a non-return-to-zero digital-to-analog converter, an output of which is connected to the resonator.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
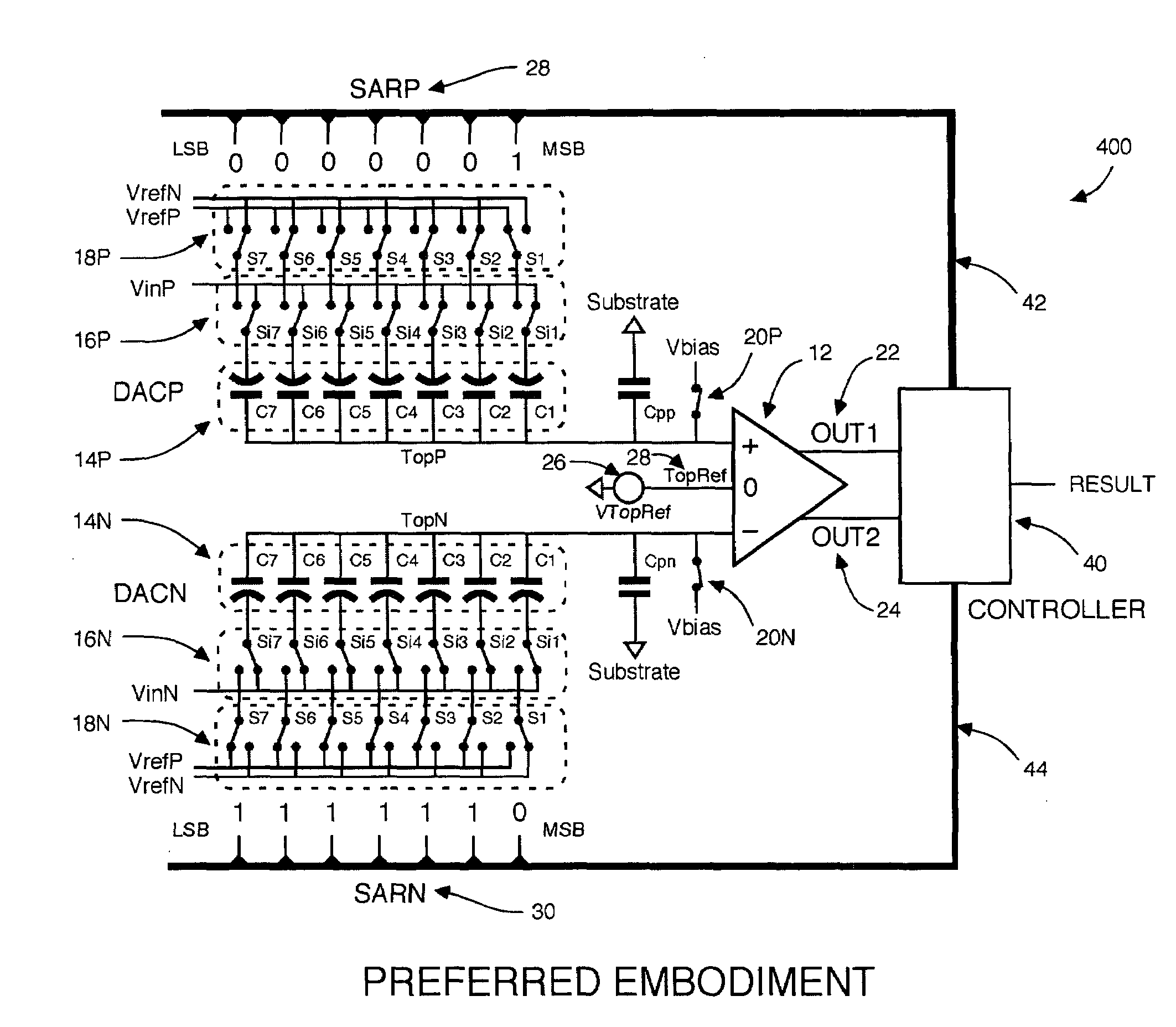
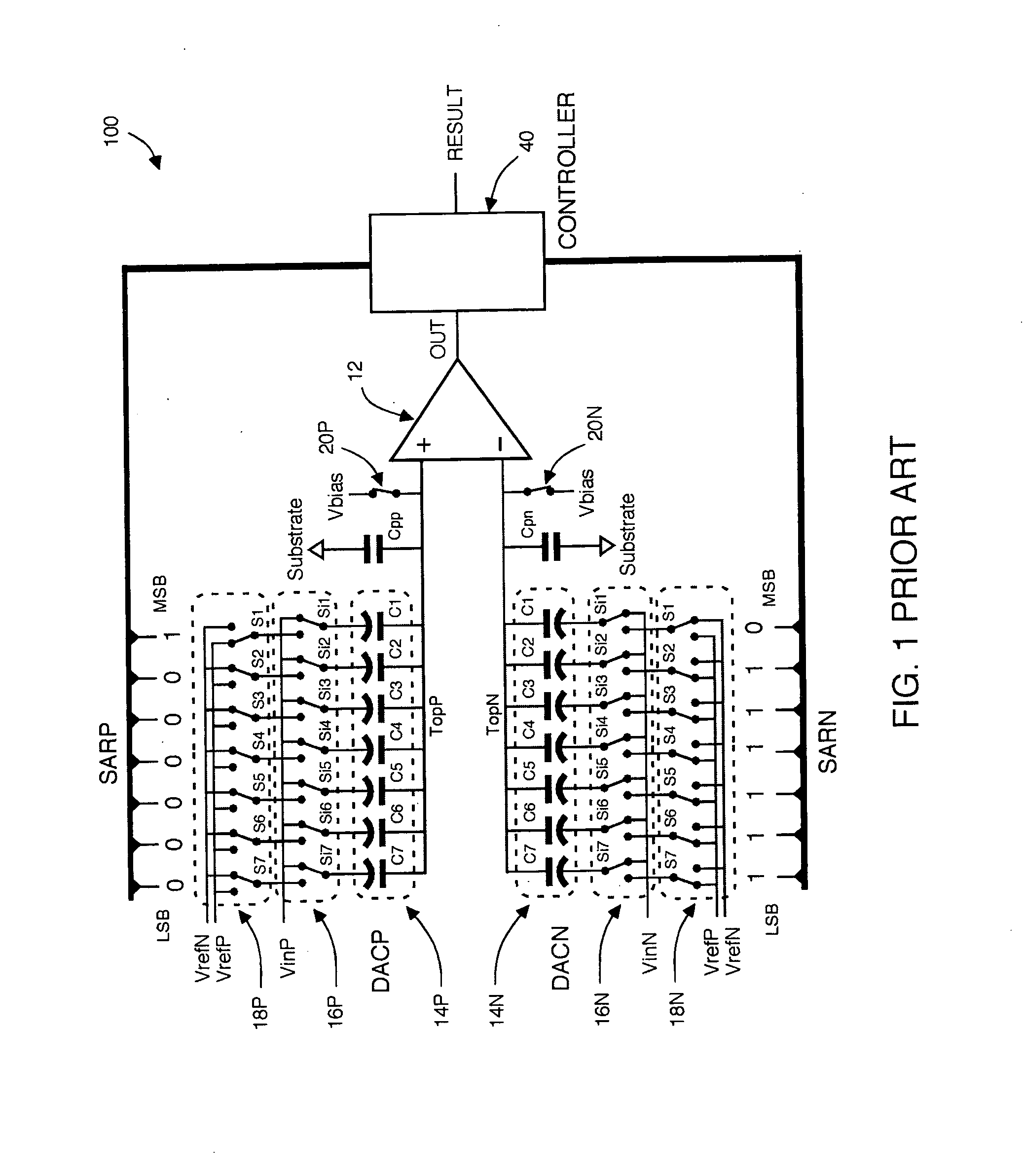
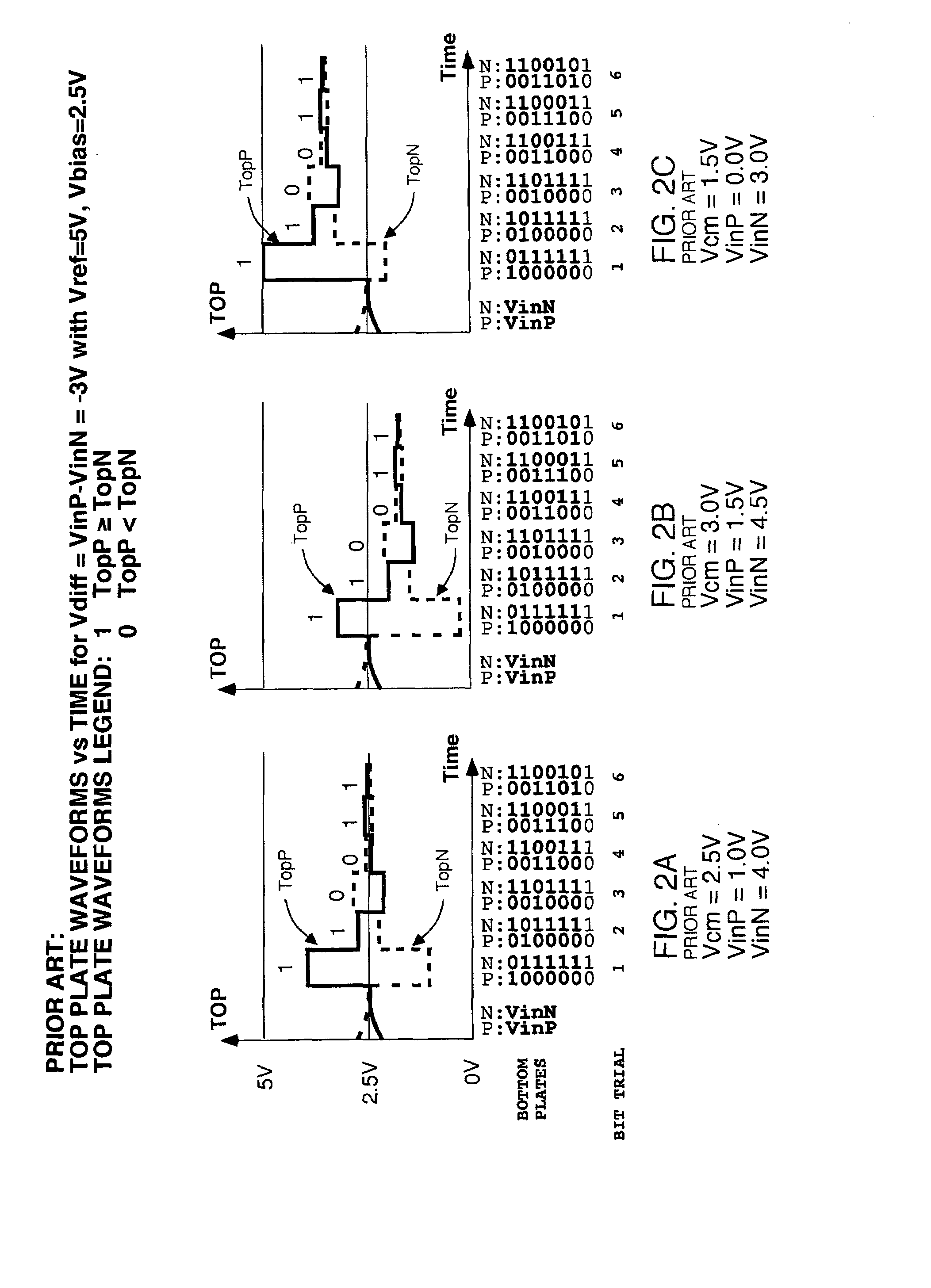
Differential input successive approximation analog to digital converter with common mode rejection
ActiveUS7432844B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsOutput compareVoltage reference
A Successive Approximation Routine converter is provided in which a comparator is responsive to an output of a first Digital to Analog Converter, and an output of a second Digital to Analog Converter and to a DAC common mode output reference voltage, and wherein the comparator provides data to a SAR controller indicating which one of the DAC outputs is greater than the other, and how a common mode voltage on the DAC outputs compares to the reference voltage. On this basis the SAR controller can add or subtract a common mode offset to the trial words being presented at a given bit trial such that both differential and common mode convergence is achieved.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
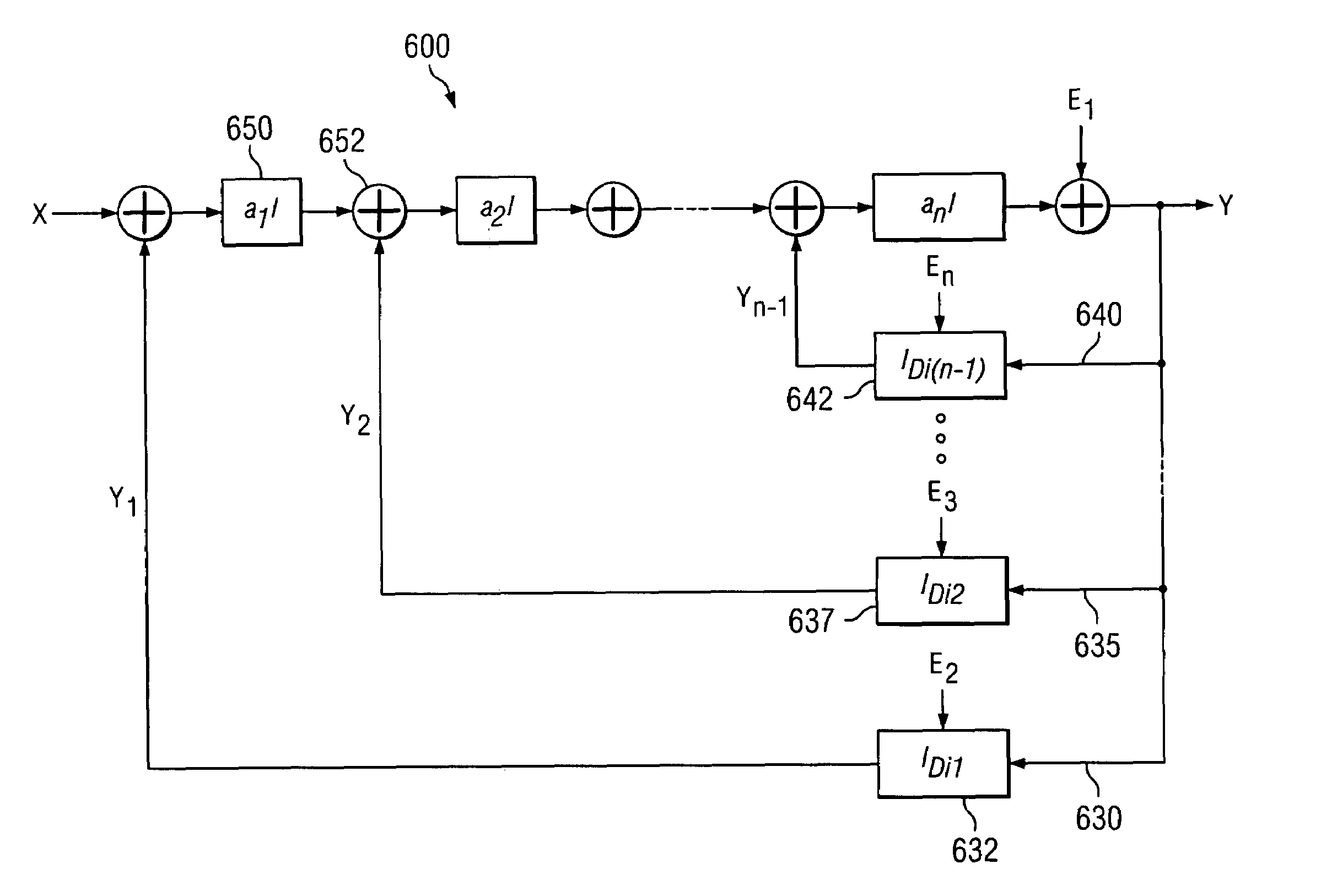
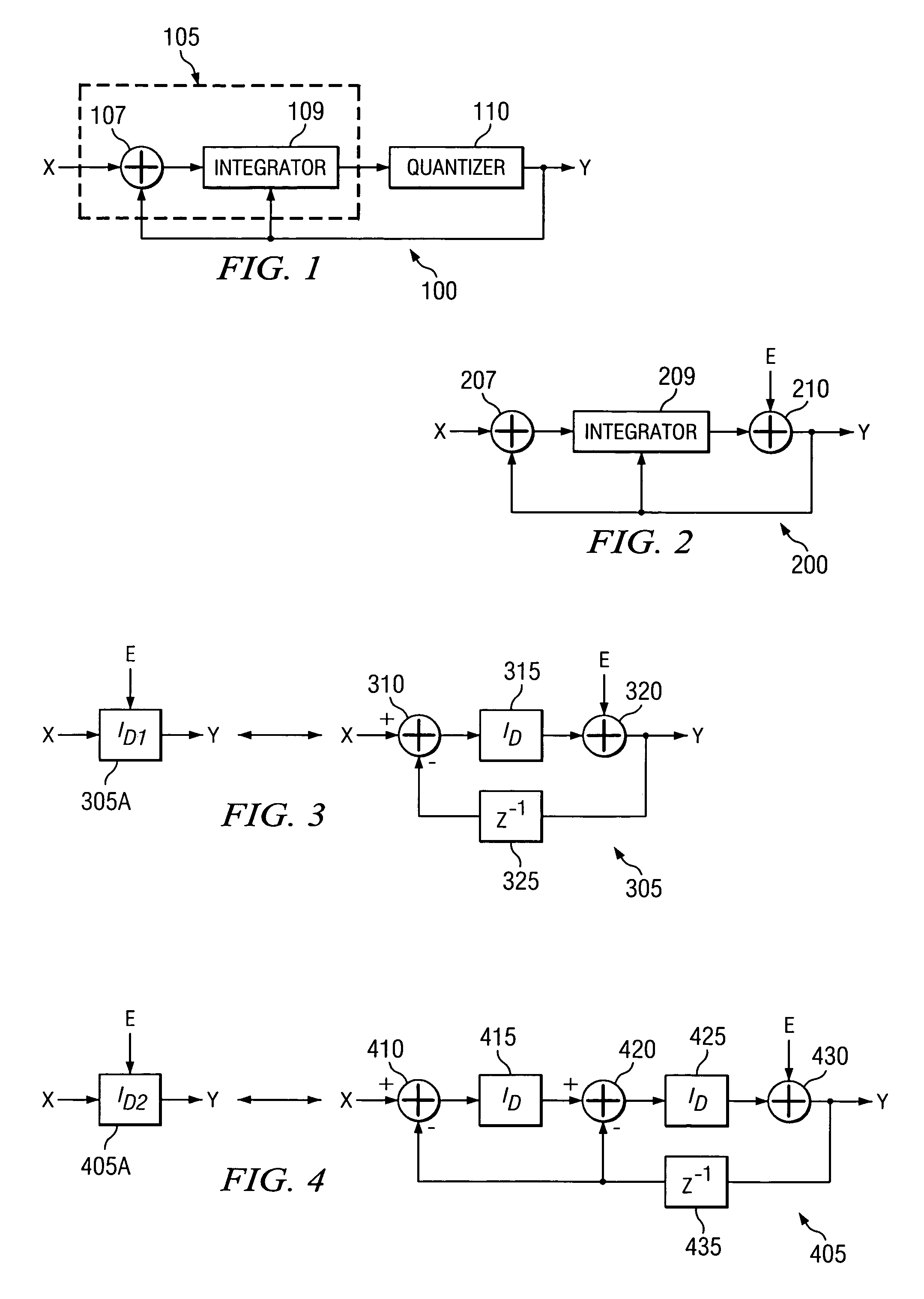
Sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with truncation error cancellation in a multi-bit feedback digital-to-analog converter (DAC)
ActiveUS6967608B1Reduce complexityCancel out truncation errorDifferential modulationDigital analog converterImage resolution
A method for reducing the complexity of a multi-bit DAC in a sigma-delta ADC. The DAC resolution can be made to be less than that of the quantizer by canceling truncation error present in multi-bit DACs. Truncation errors are introduced by differences between the digital output word of the quantizer and the digital input word of the feedback DAC(s). The truncation error(s) can be cancelled and eliminated from the system transfer function. A preferred embodiment comprises expanding all feedback loops in the ADC, adding an adjusted truncation error for each feedback loop to an inner feedback loop, and then calculating a correction term for each adjusted truncation error. The correction term can be calculated by zeroing all signals except for the adjusted truncation error being canceled and then calculating a truncation error transfer function.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
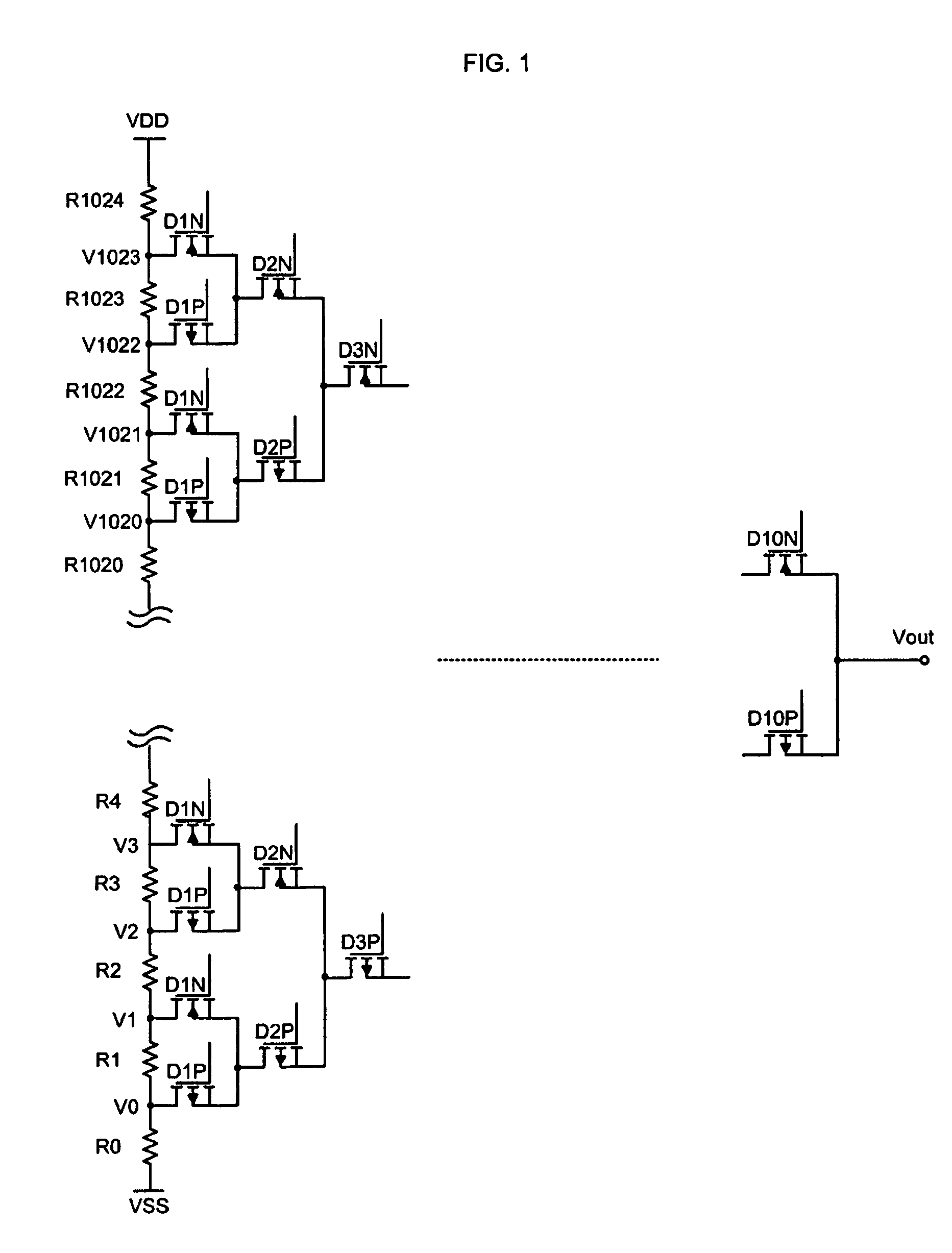
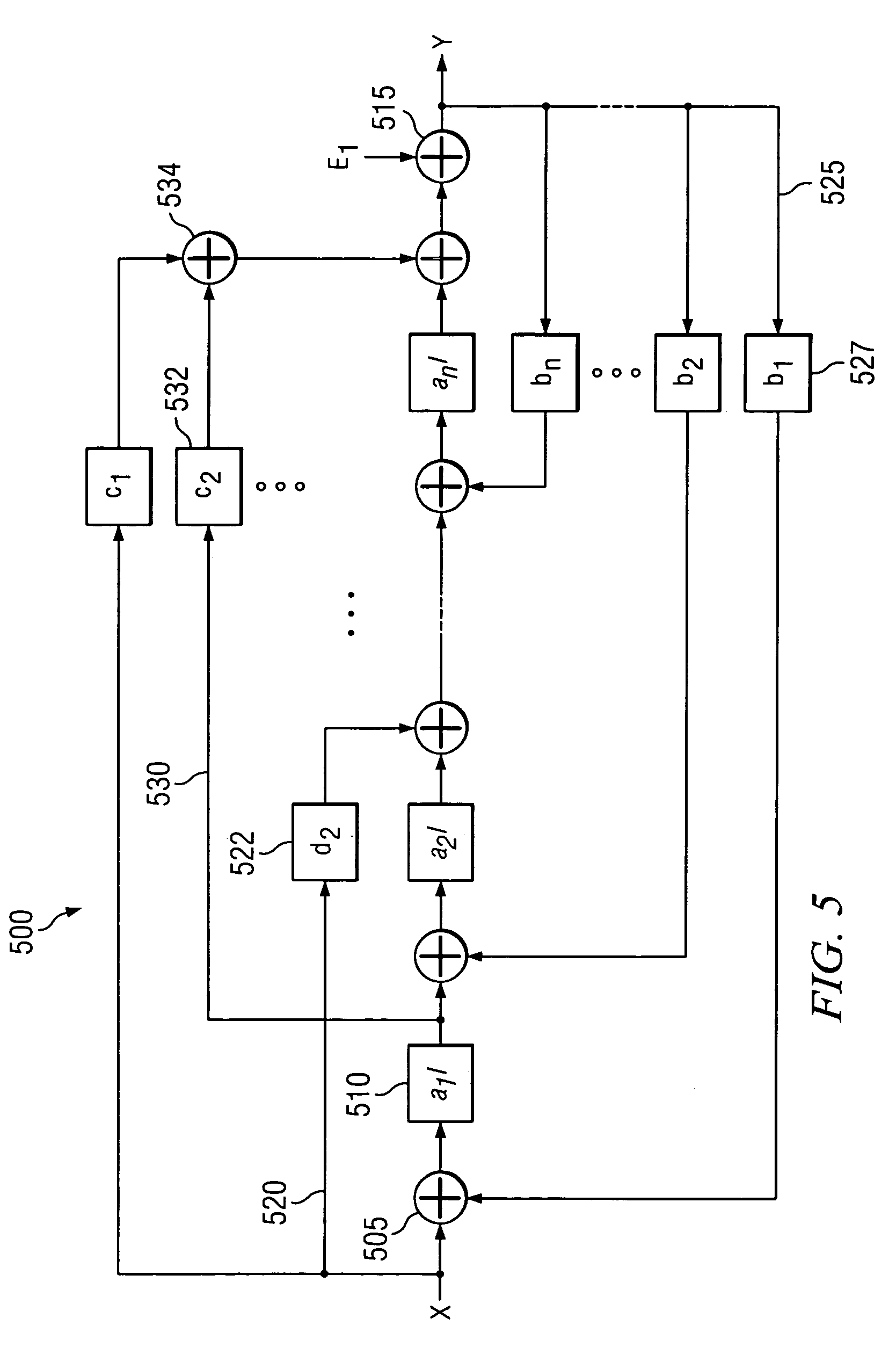
Gradient insensitive split-core digital to analog converter
InactiveUS6937178B1Offsetting effectCancellation effectElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsElectrical resistance and conductanceDigital analog converter
Digital to analog converter circuits and methods are provided for producing an analog output voltage indicative of a digital input signal with at least partial insensitivity to error gradients. Described are split-core resistive elements, which include a plurality of one-dimensional or multi-dimensional resistive strings, that may be used to reduce or substantially eliminate the effects that error gradients have on the linearity of the analog output voltages of a resistive string or interpolating amplifier DACs. The resistor strings that make up the split-core resistive elements are configured in such a manner that combining respective output voltages from each of the resistor strings results in an analog output voltage that is at least partially insensitive to the effects of error gradients.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
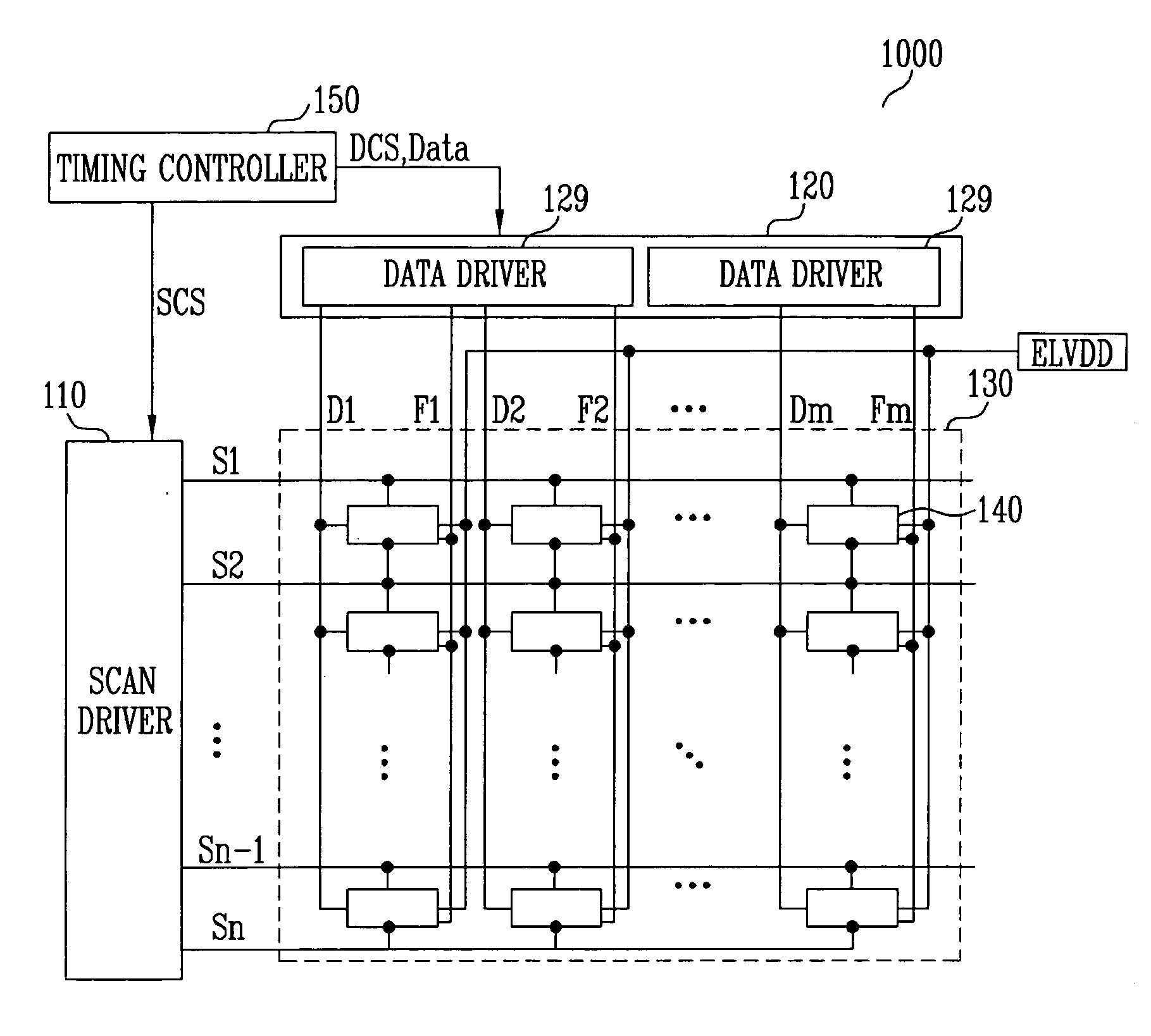
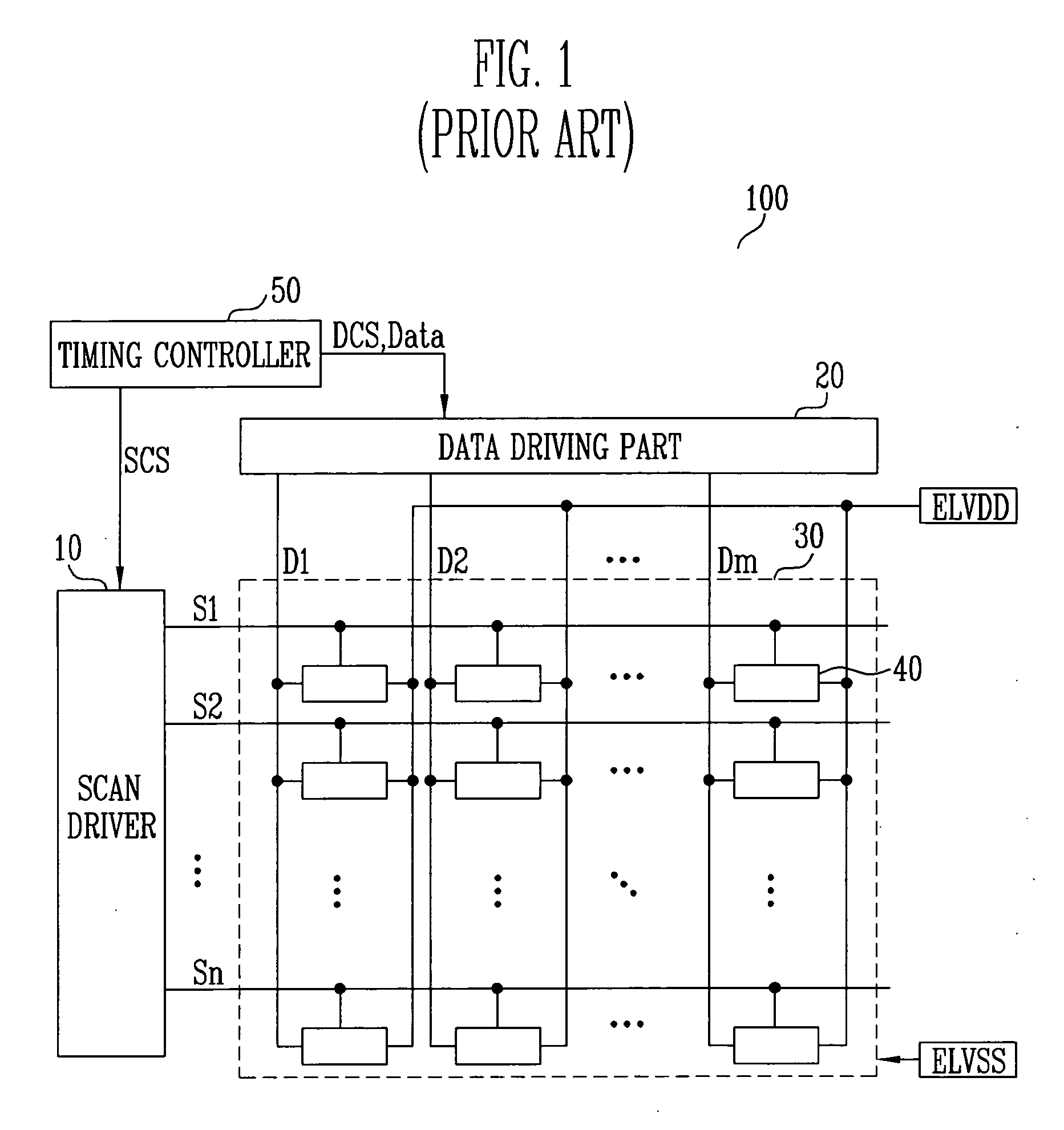
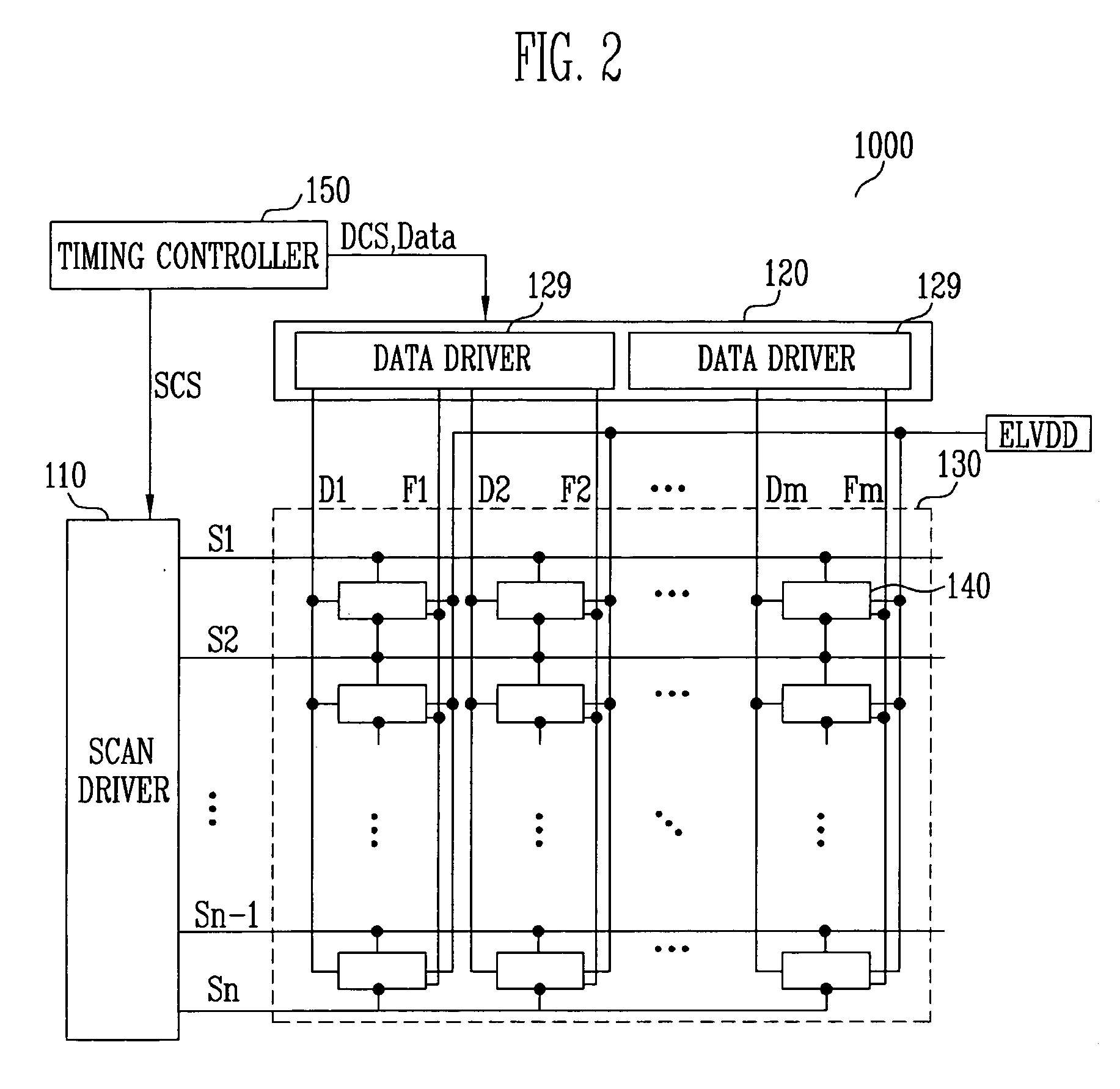
Data driving circuit and organic light emitting display comprising the same
InactiveUS20080122819A1Improve display qualityPrevent display quality degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital-analogue convertorsDigital analog converterReference current
Provided are a data driving circuit of an organic light emitting display and an organic light emitting display comprising the same. The organic light emitting display comprises a reference pixel controller, a data driver, and a display panel. The reference pixel controller comprises a light detector for detecting an amount of light emission of a reference pixel and outputting a first control signal thereof and a reference current controller for outputting a second control signal controlling an amount of a reference current according to the first control signal. The data driver comprises a current source for outputting a current having the same amount as the reference current according to the second control signal and a digital-analog converter for outputting a data current by scaling the current having the same amount as the reference signal to be proportioned to a data signal. The display panel formed of pixels, each of which comprises an organic light emitting device that emits light in accordance with the data current.
Owner:IKAIST CO LTD
Data driver and light emitting diode display device including the same
A data driver and a light emitting diode display device including the circuit that cause a pixel current through the light emitting diode to be independent of the threshold voltage of a transistor driving the light emitting diode. The data driver includes a voltage digital-analog converter for generating a data voltage and a current digital-analog converter for generating a sensing current, both corresponding to input data, and a voltage control block for receiving the pixel current that corresponds to the data voltage and is fed back from the pixel to the voltage control block changing the amount of current charging a capacitor in the voltage control block and controlling the data voltage supplied to the pixel. Controlling and adjusting the data voltage helps uniformity in the display brightness regardless of non-uniformity of transistors in each pixel.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for adaptive DC level control
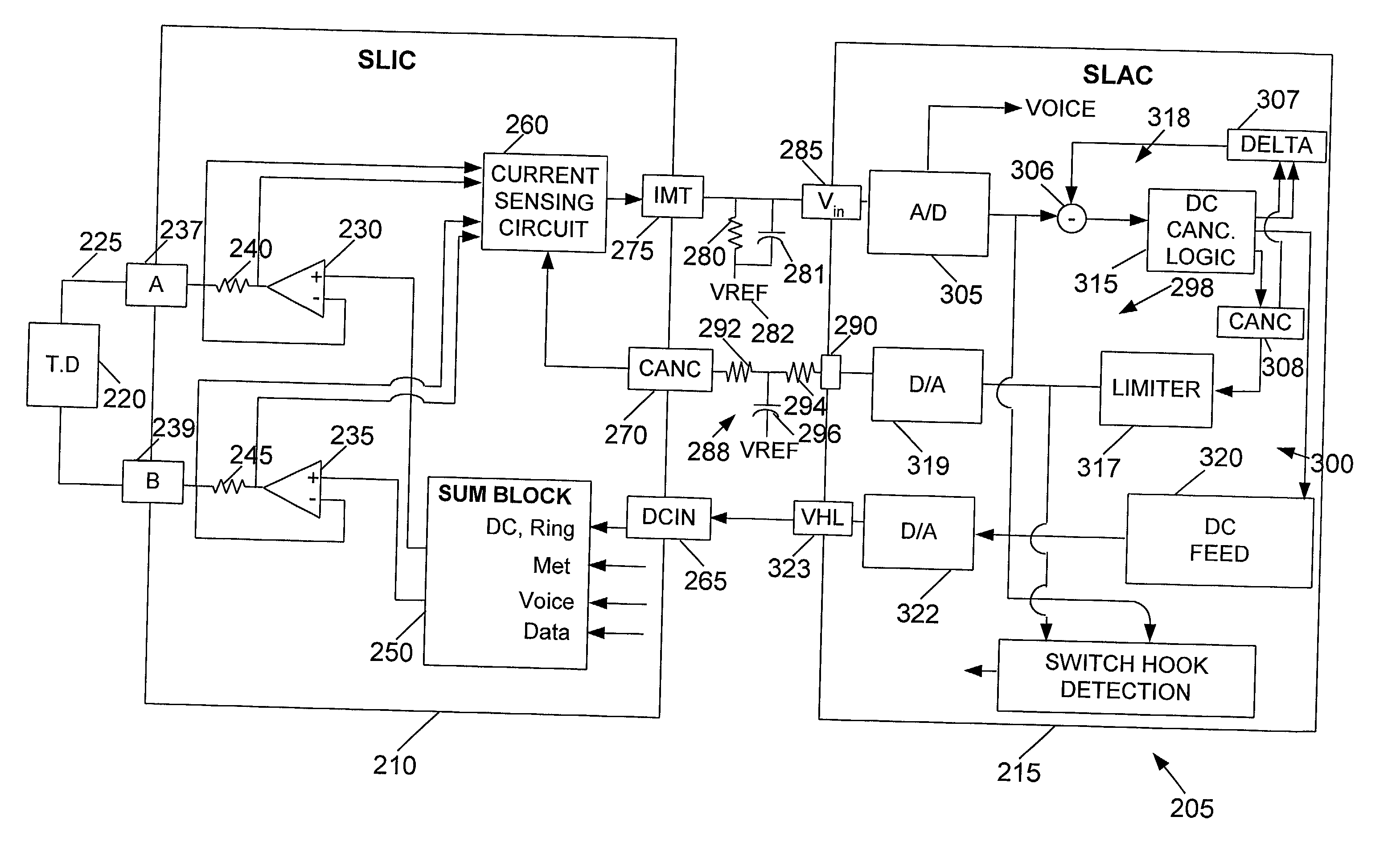
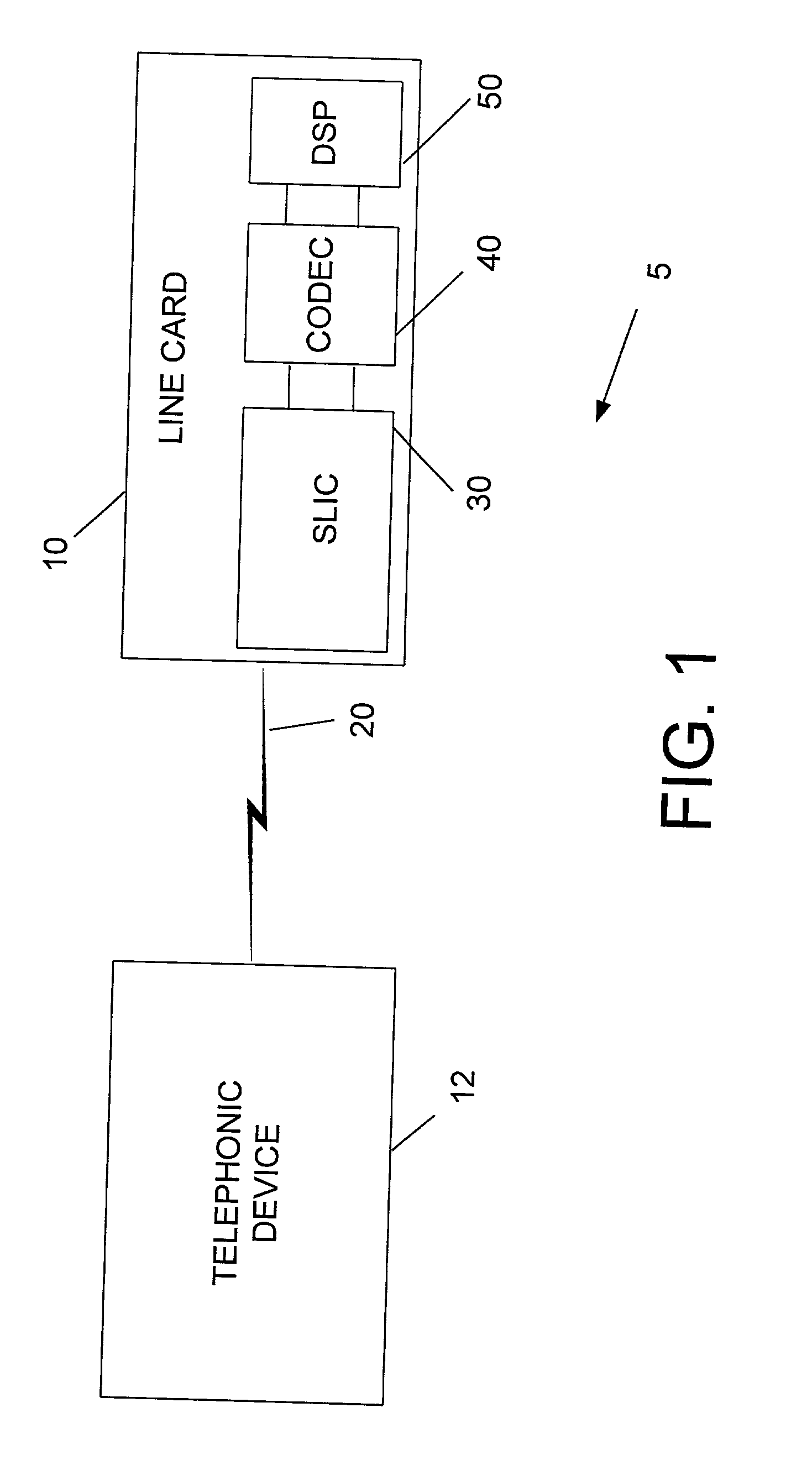
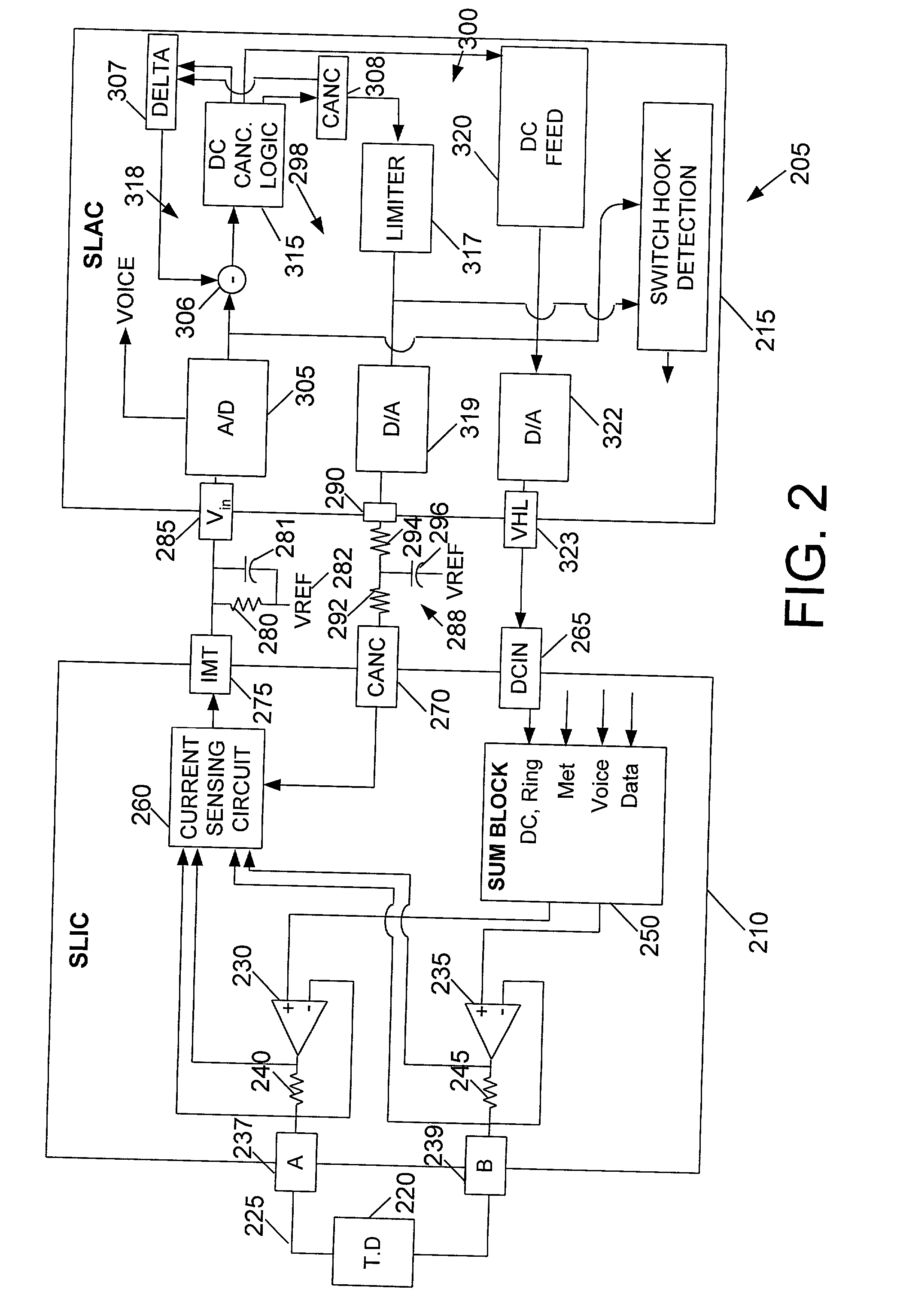
ActiveUS20020084923A1Cordless telephonesElectric signal transmission systemsDigital analog converterDigital input
A method and apparatus is provided for DC level control in a line card. The method includes receiving a digital input signal, determining a first DC component value of the digital input signal at a first preselected time, and determining a second DC component value of the digital input signal at a second preselected time. The method further includes determining a difference between the first DC component value and the second DC component value. The method includes providing the first DC component value to a digital-to-analog converter in response to determining that the difference is less than a first preselected value. The apparatus includes a digital-to-analog converter and logic. The logic is coupled to the digital-to-analog converter, wherein the logic is capable of receiving a digital input signal, determining a first DC component value of the digital input signal at a first preselected time, and determining a second DC component value of the digital input signal at a second preselected time. The logic is farther capable of determining a difference between the first DC component value and the second DC component value, and providing the first DC component value to the digital-to-analog converter in response to determining that the difference is less than a first preselected value.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com