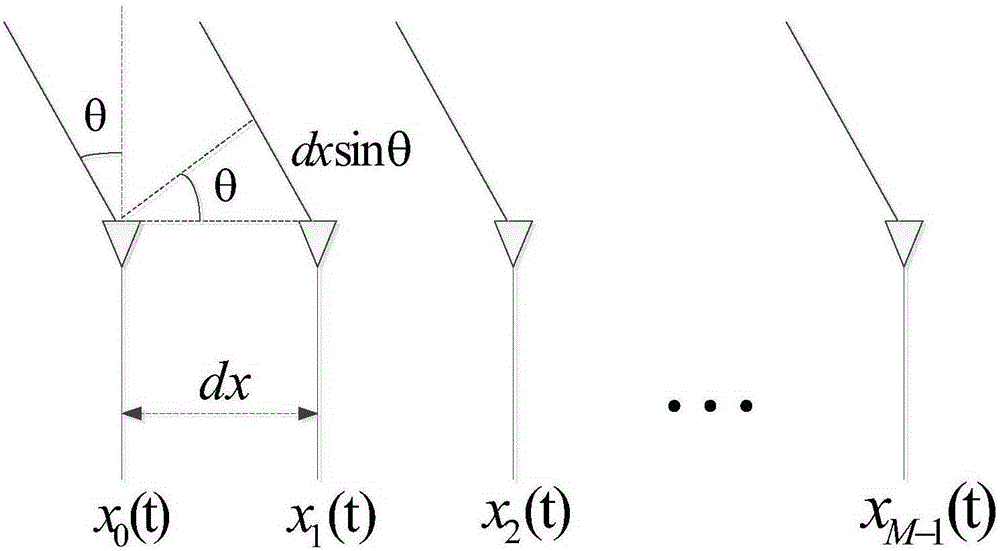
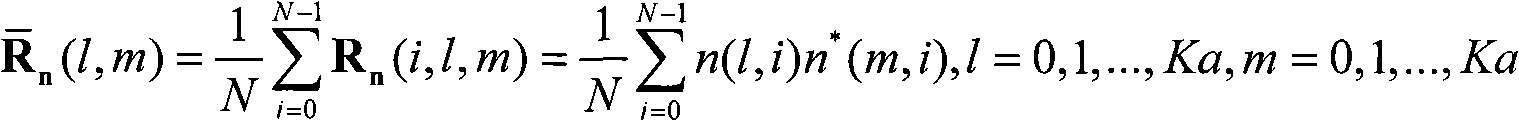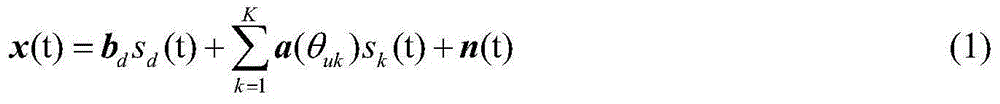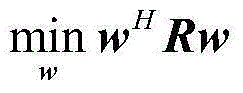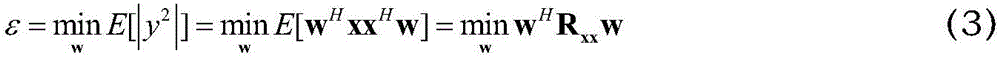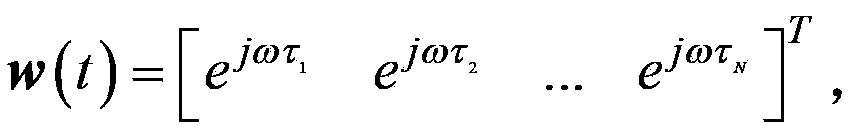Patents
Literature
75 results about "Null steering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zero-forcing precoding. Zero-forcing (or null-steering) precoding is a method of spatial signal processing by which the multiple antenna transmitter can null multiuser interference signals in wireless communications.
Smart radio incorporating Parascan(R) varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end
ActiveUS7107033B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterRF front end
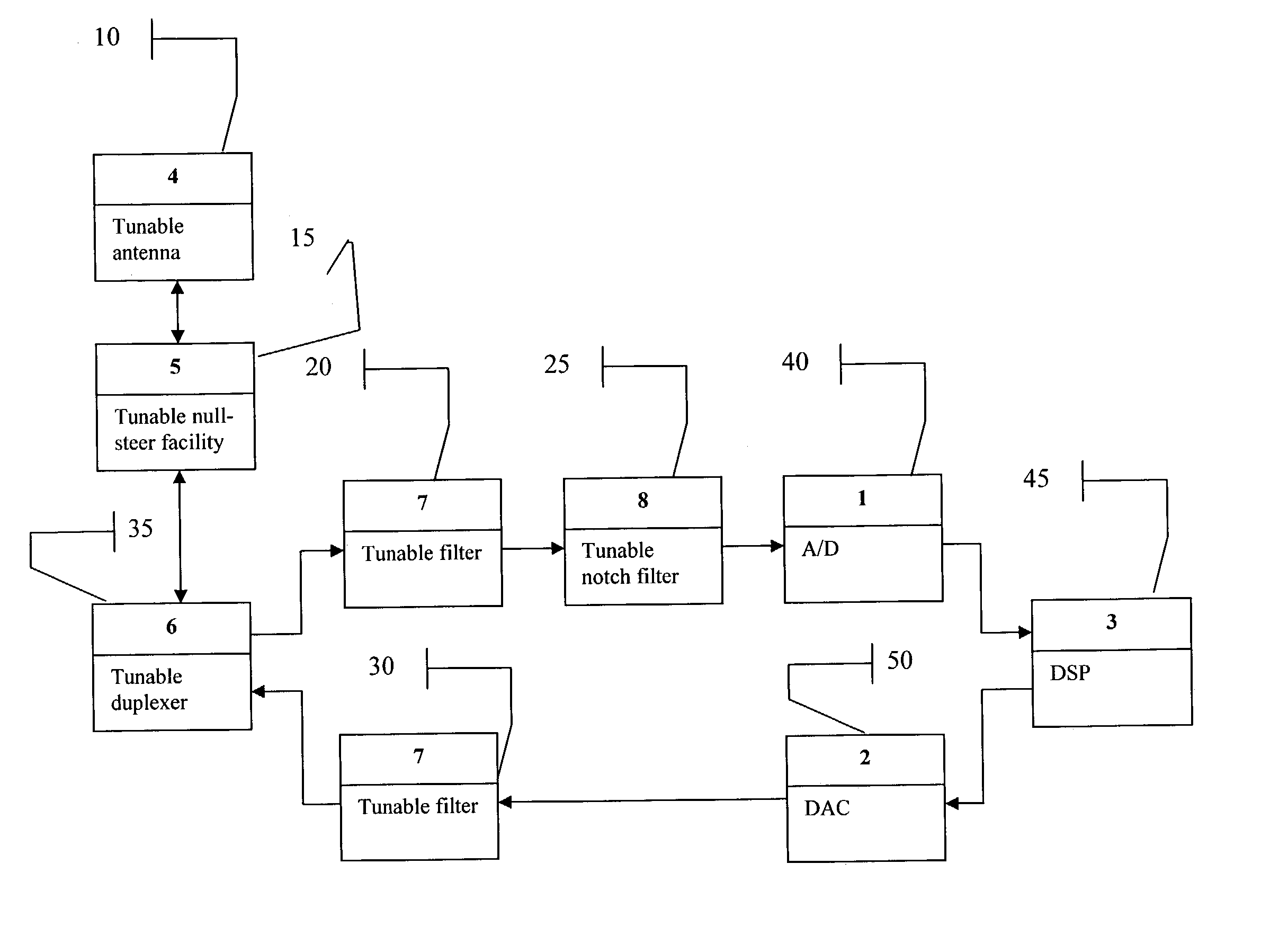
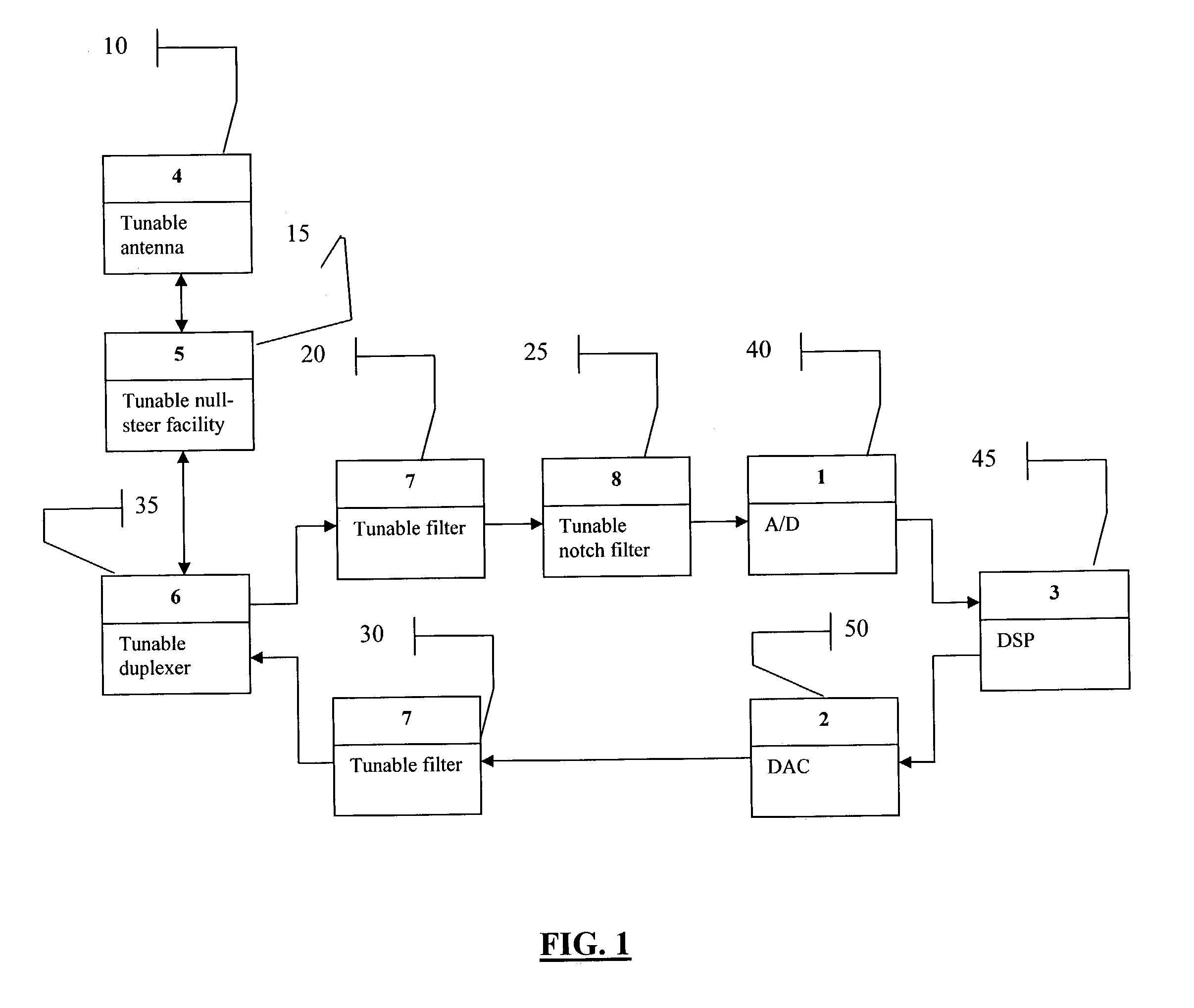
A smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end. More specifically, this is provided for by a smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end that comprises at least one tunable antenna; at least one antenna null steering facility associated with said at least on tunable antenna; at least one tunable duplexer receiving the output from and providing input to said at least one antenna null steering facility; a first tunable RF filter receiving the output from said at least one tunable duplexer and providing the input to an analog to digital converter, said analog to digital converter providing the input to a digital signal processor, the output of which is input for a digital to analog converter; a second tunable RF filter receiving the analog output of said digital to analog converter and providing an input to said at least one tunable duplexer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
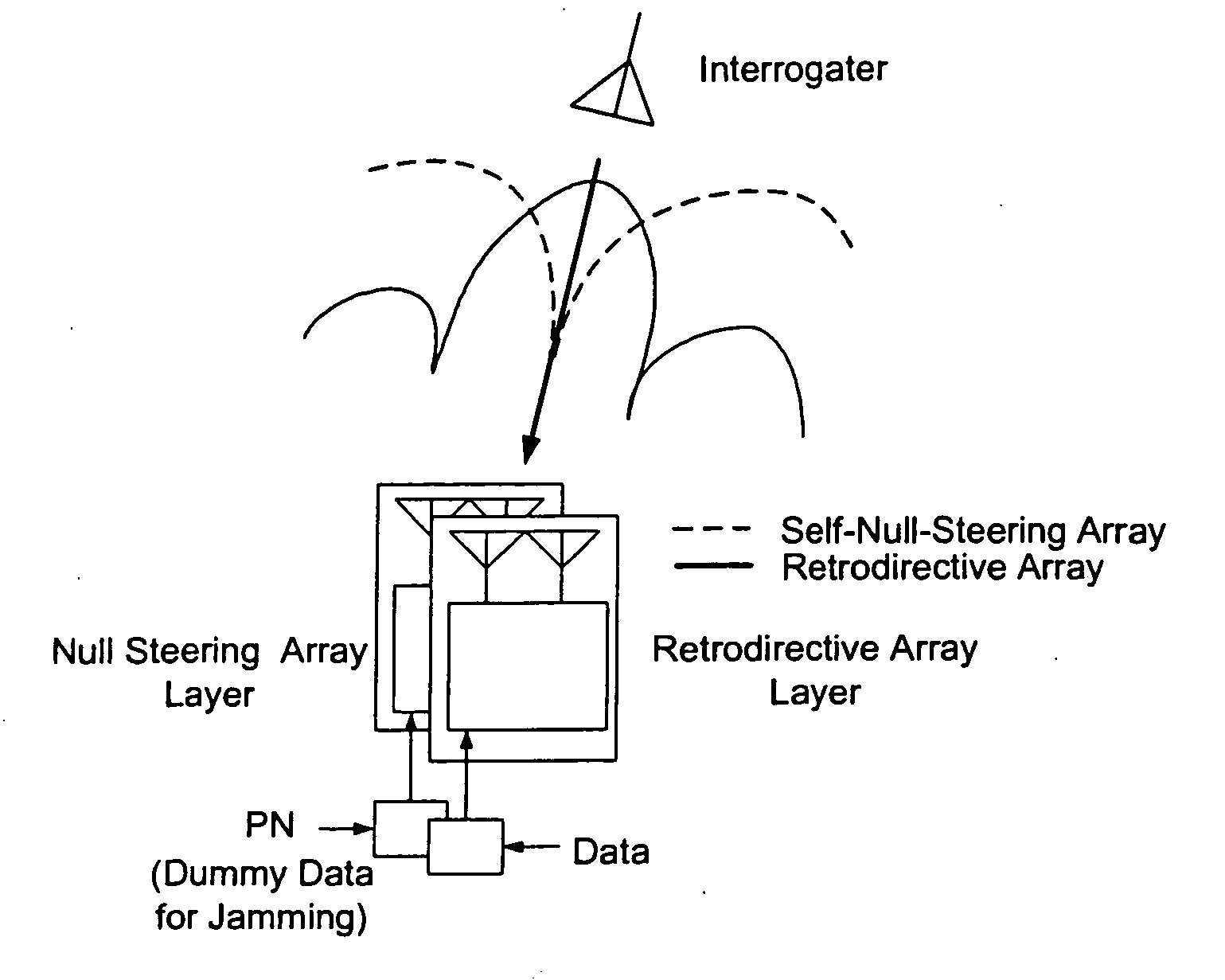
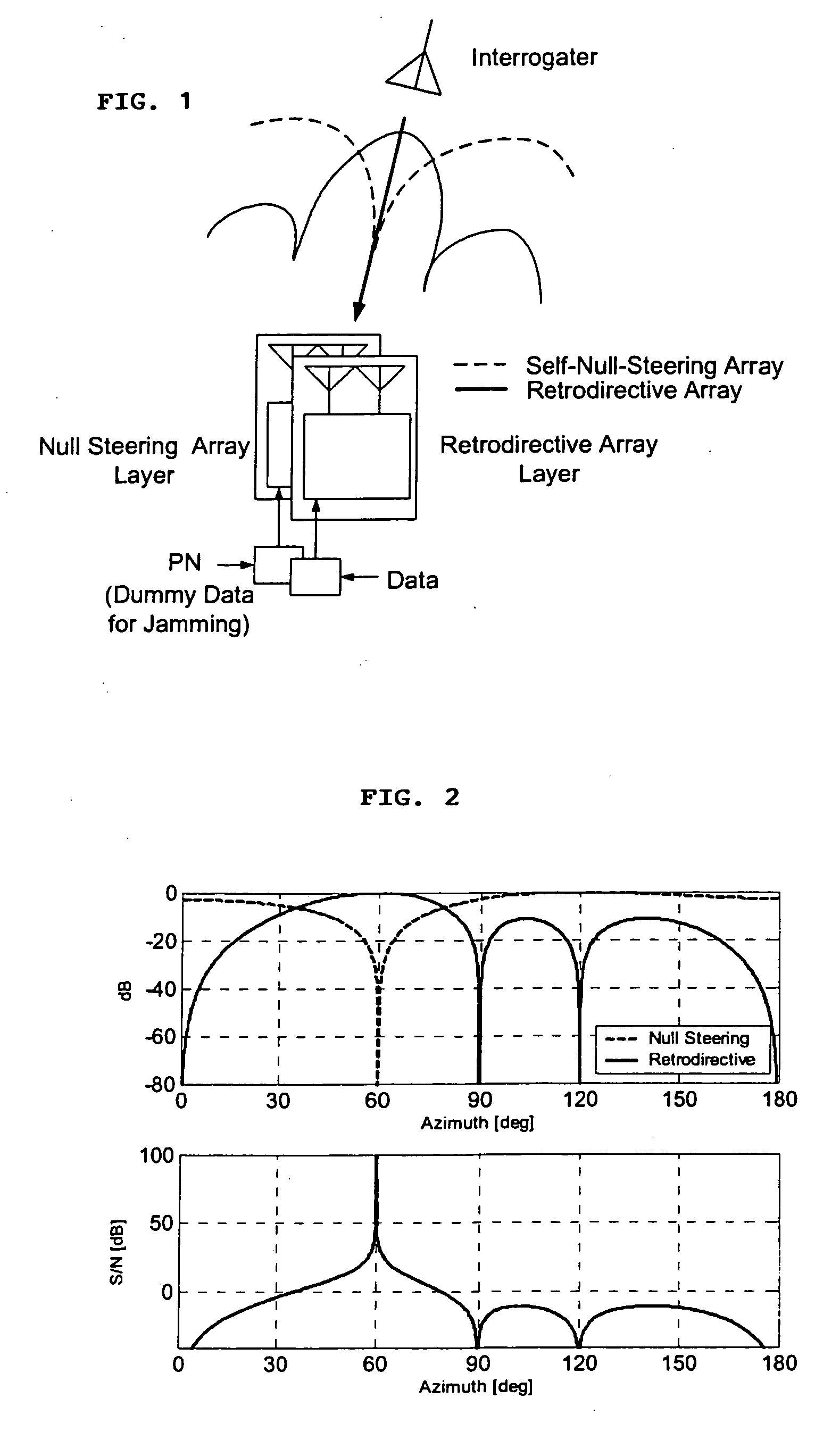
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
ActiveUS7006039B2Increase user capacityImprove directivityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsFrequency spectrum
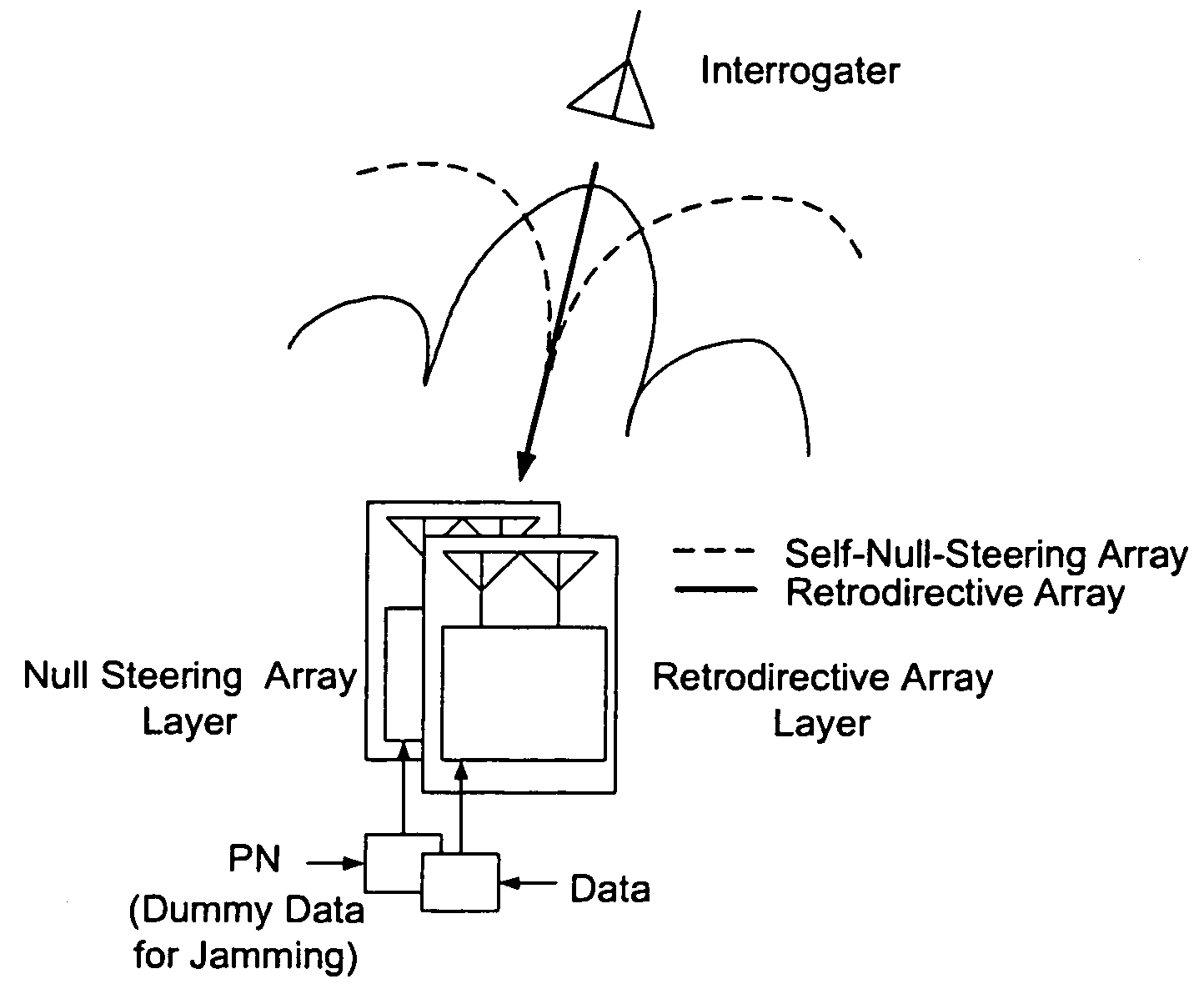
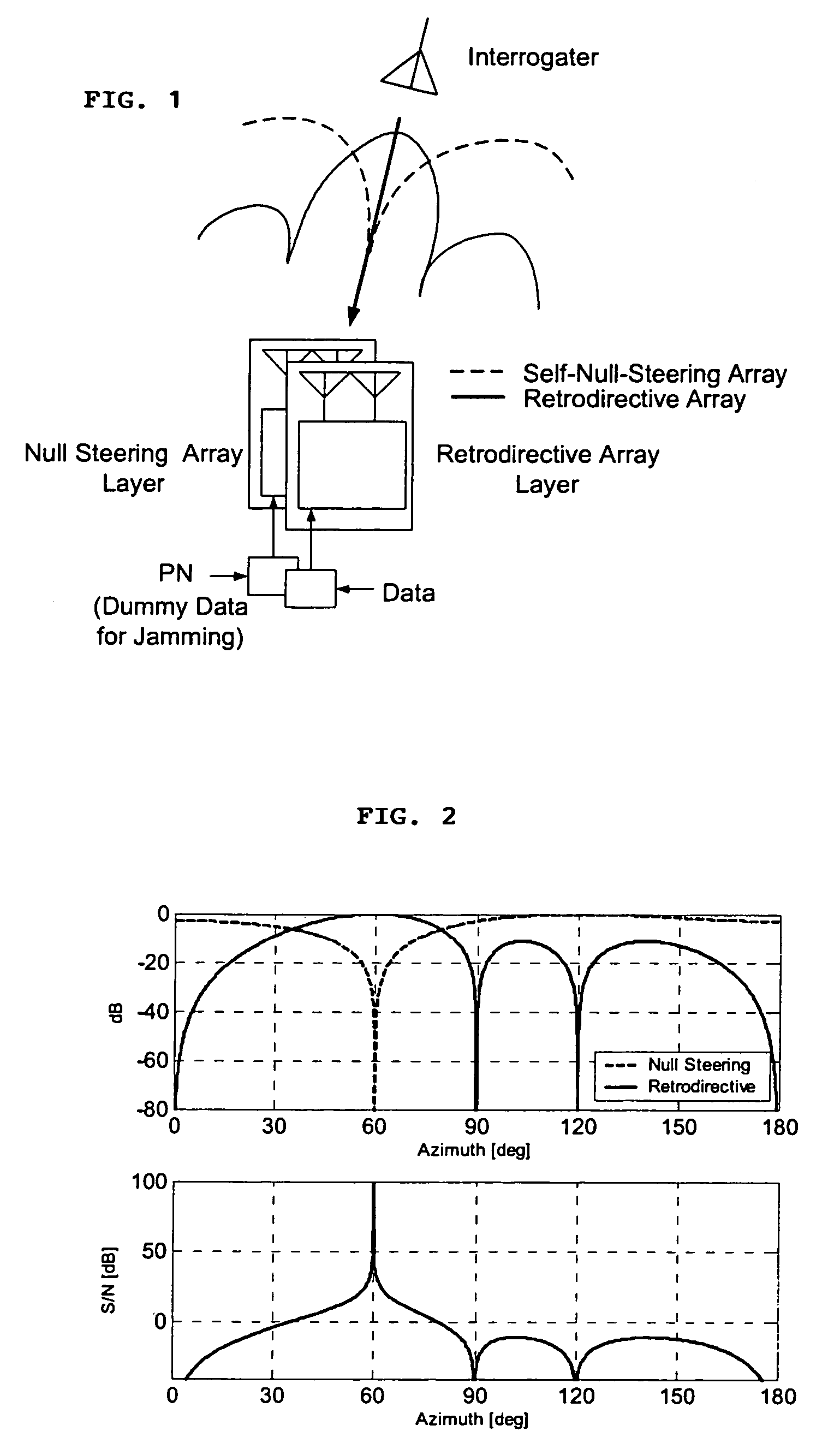
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
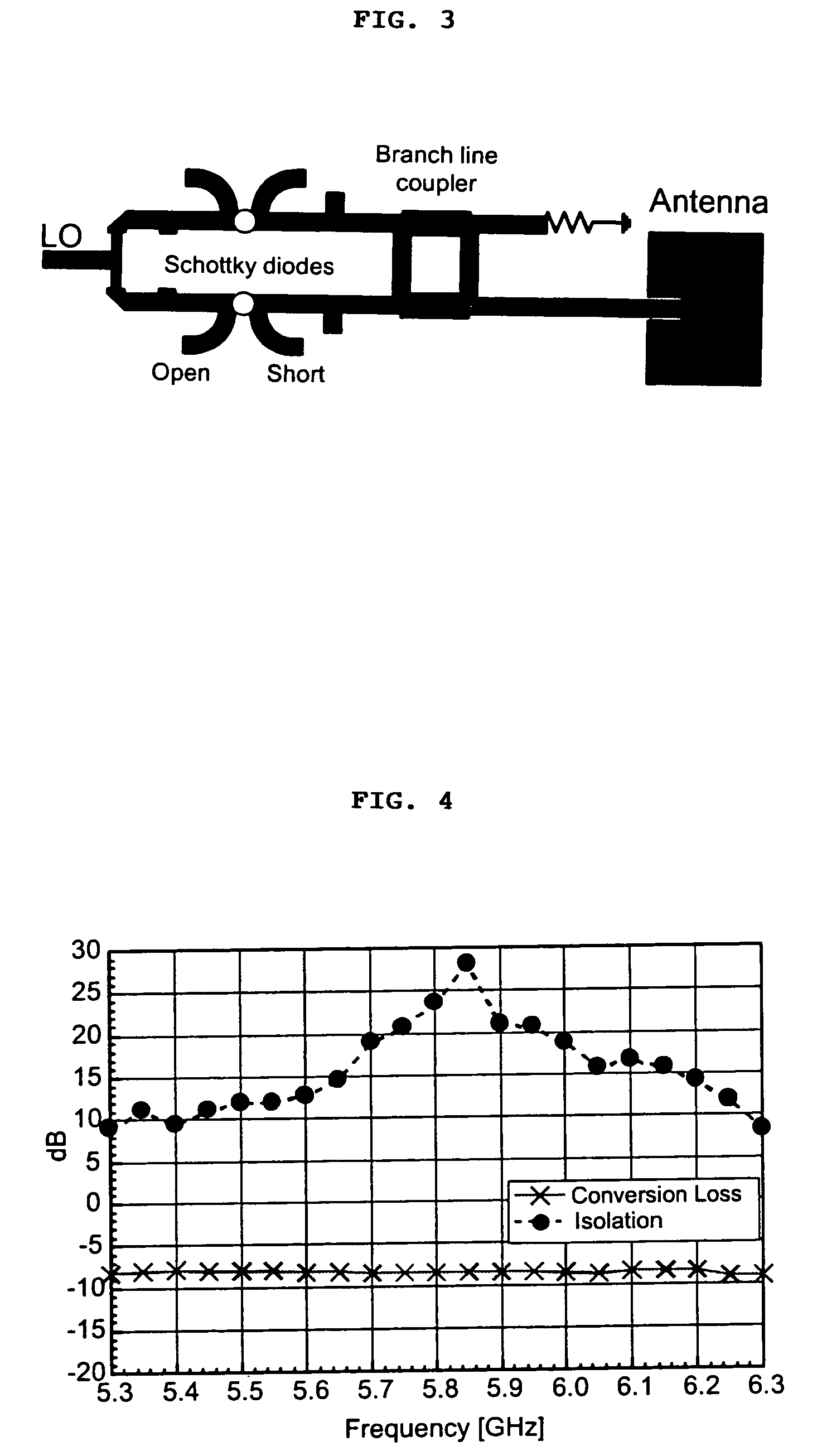
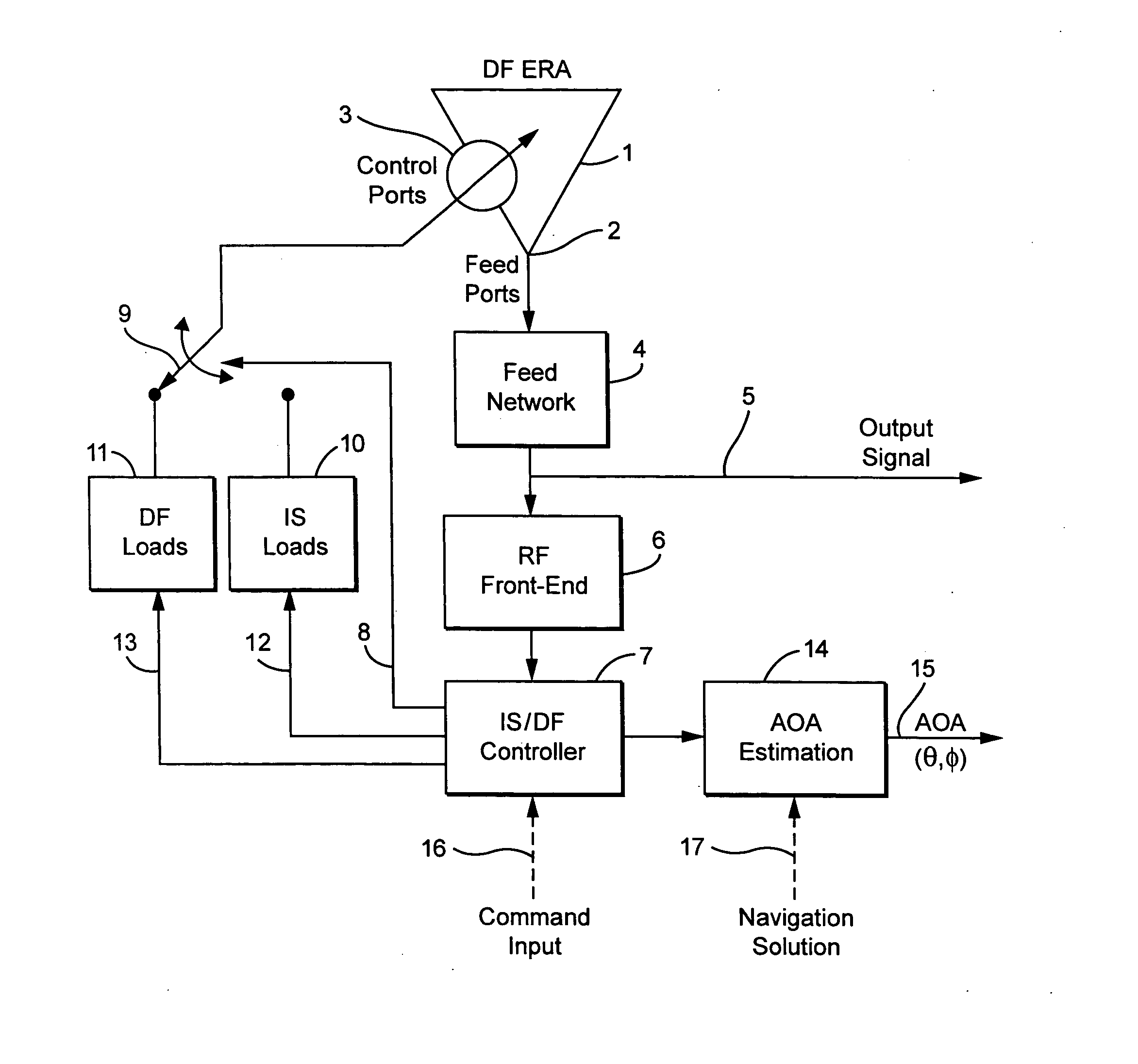
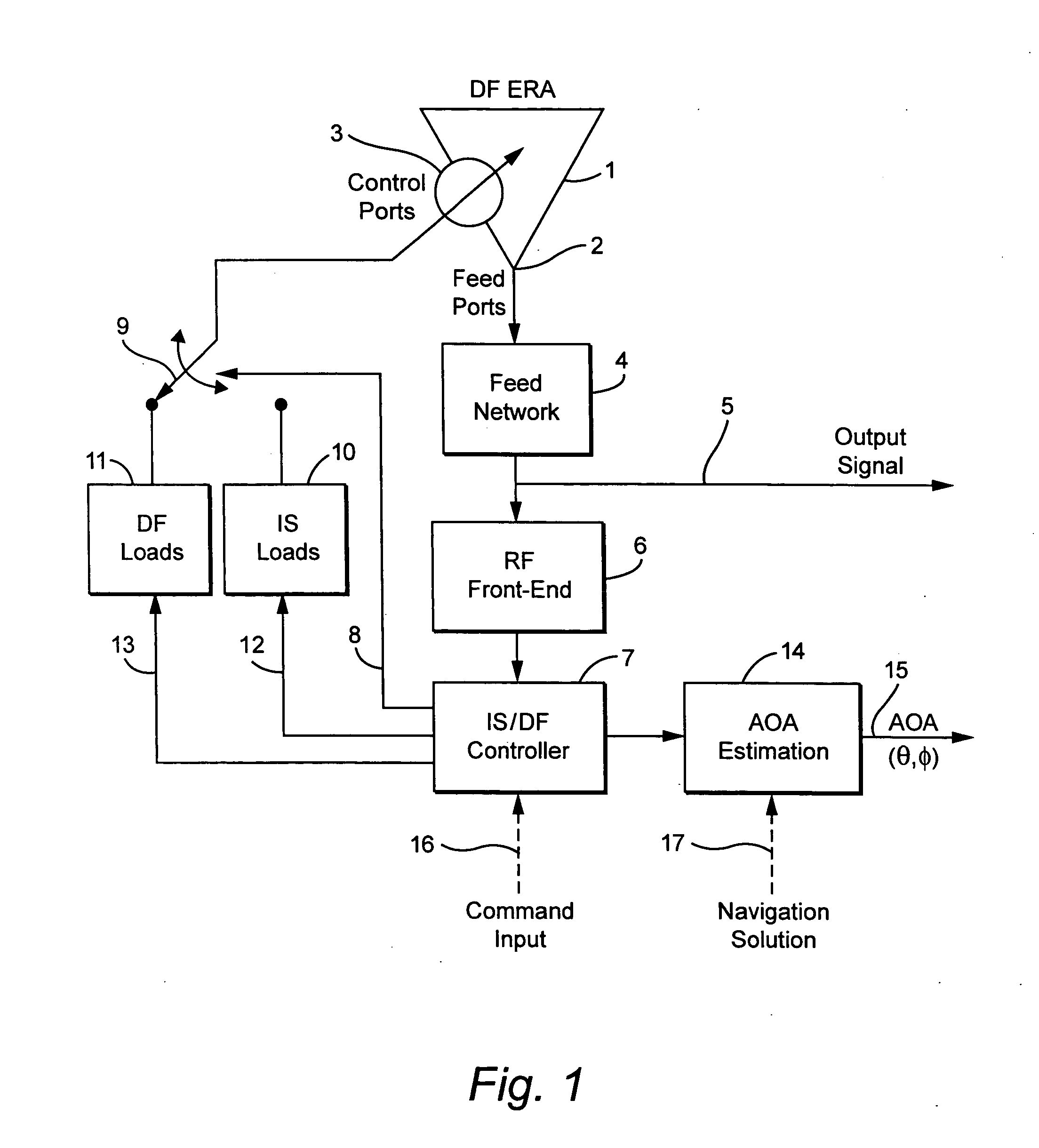
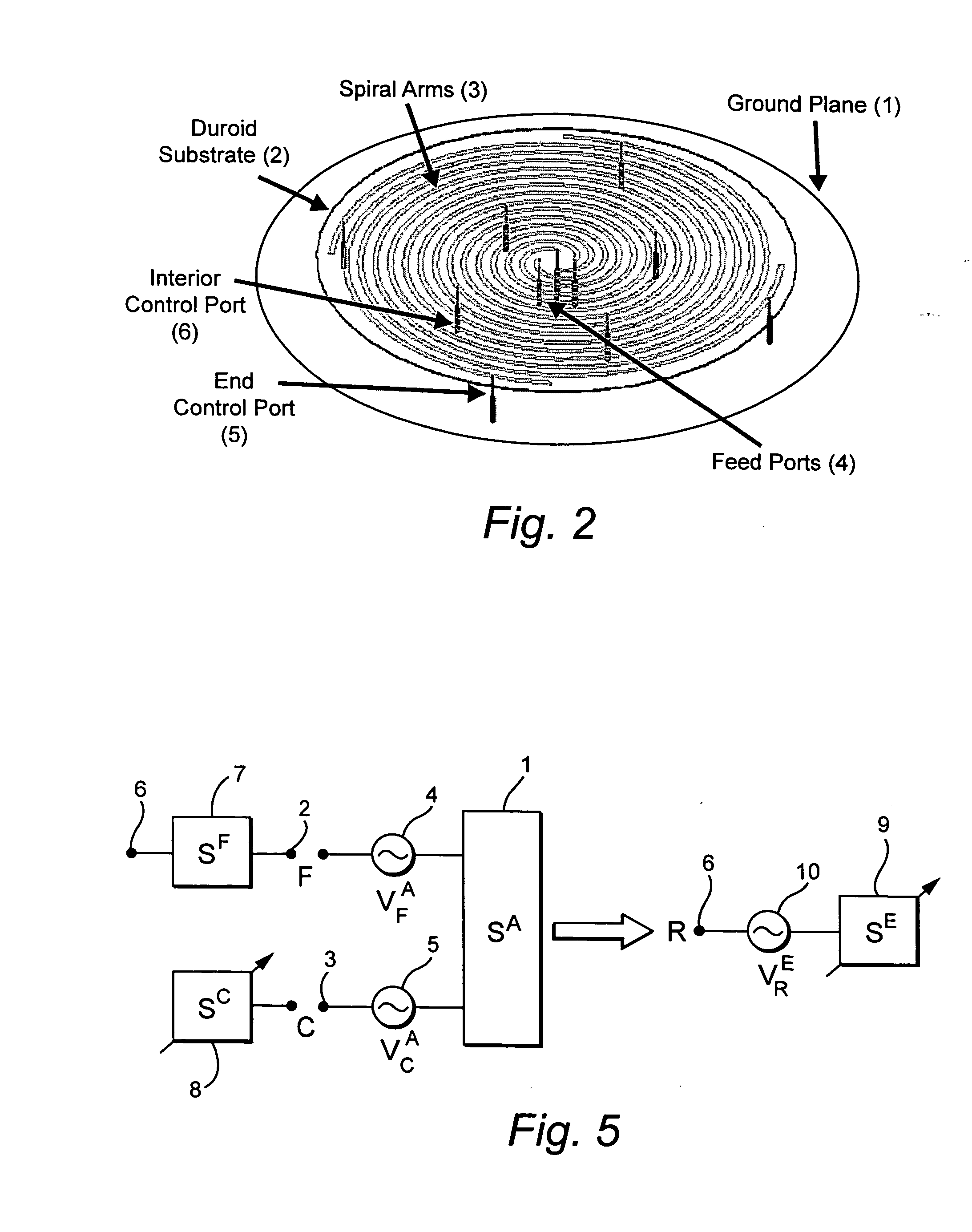
Compact antenna system for polarization sensitive null steering and direction-finding
ActiveUS20070293150A1Reduce adverse effectsEnhance jammer-to-signal (J/S) toleranceSubstation equipmentAntenna feed intermediatesRadio frequencyFeedback control
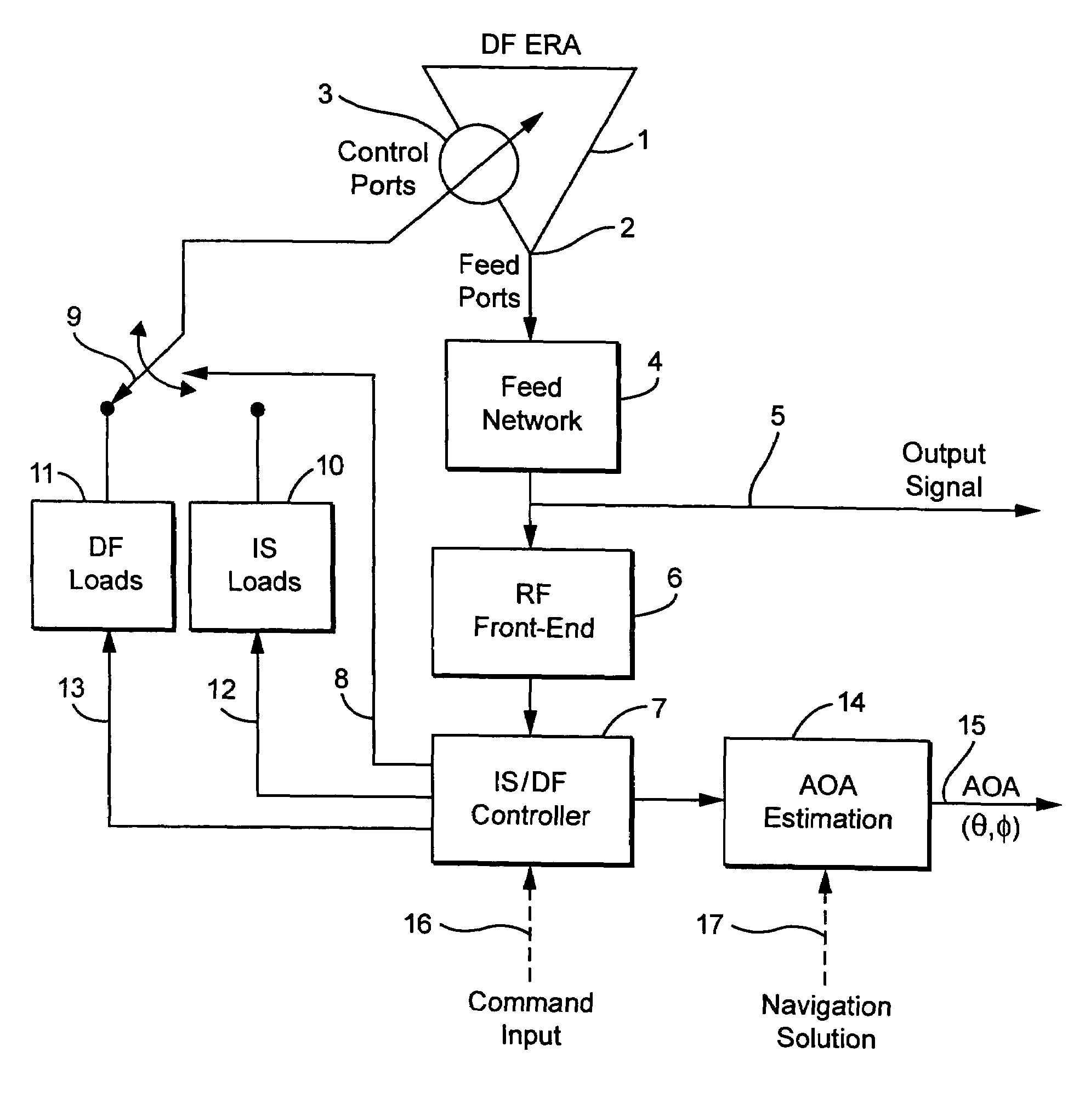
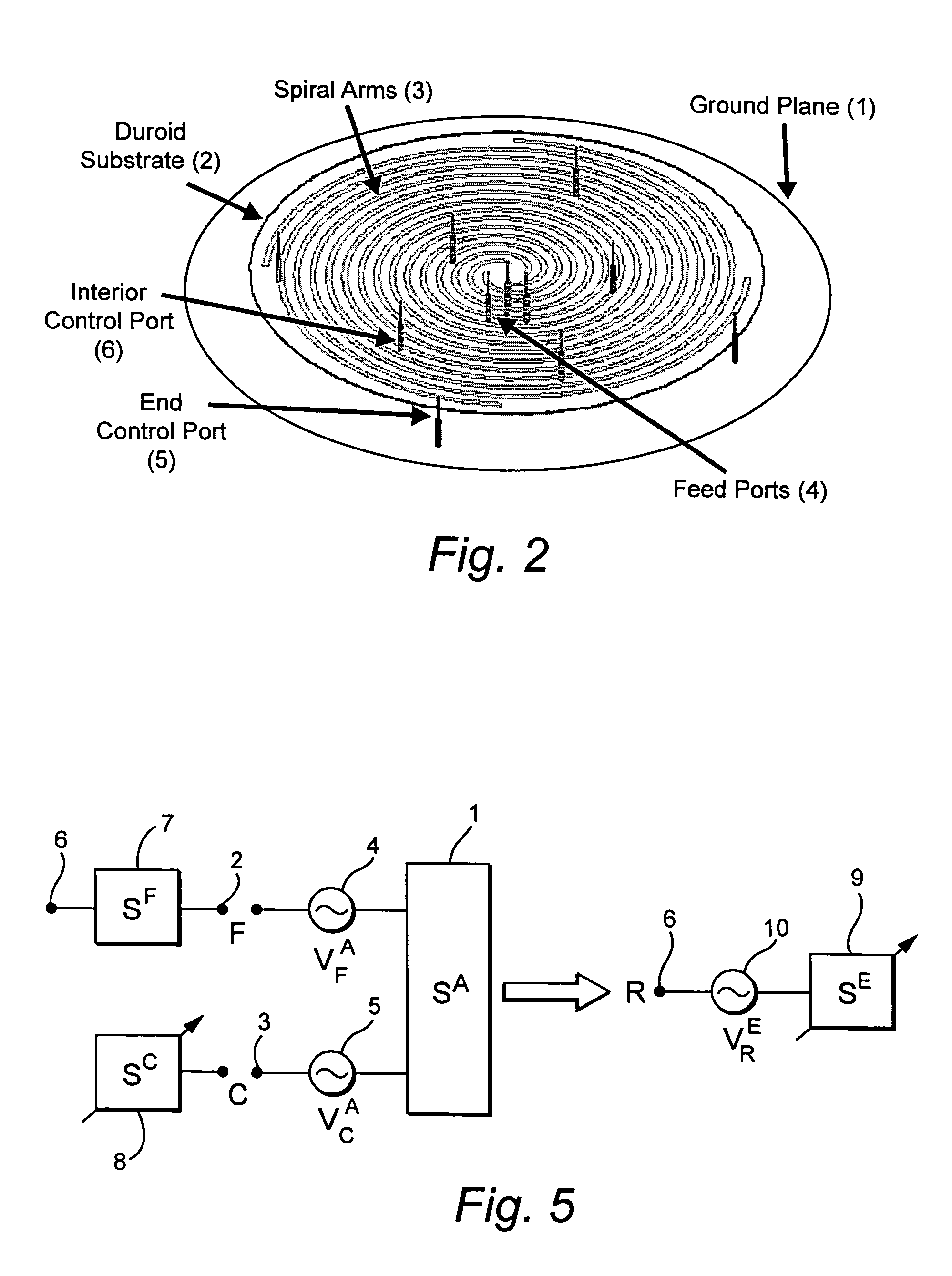
A compact, non-phased-array, electronically reconfigurable antenna (ERA) system with at least two operational modes has a first operational objective that is polarization-sensitive null steering (PSNS) and a second operational objective that is direction-finding (DF). The system can rapidly switch between two operational states. In the first state, the system behaves like a polarization filter (PF) and operates as a controlled reception pattern antenna (CRPA), while in the second state the system behaves as an angle-of-arrival (AOA) sensor and operates as a fixed reception pattern antenna (FRPA). The system may include a spiral-mode antenna with both feed and load ports; a mode-forming network; an electronics package; and feedback control electronics. Radio frequency (RF) interference rejection and RF direction-finding may be performed as well as reduction and / or elimination of multiple jamming signals that are intentionally or unintentionally directed at a Global Positioning System (GPS). The determination of direction and location of the source of jamming signals may also be achieved.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
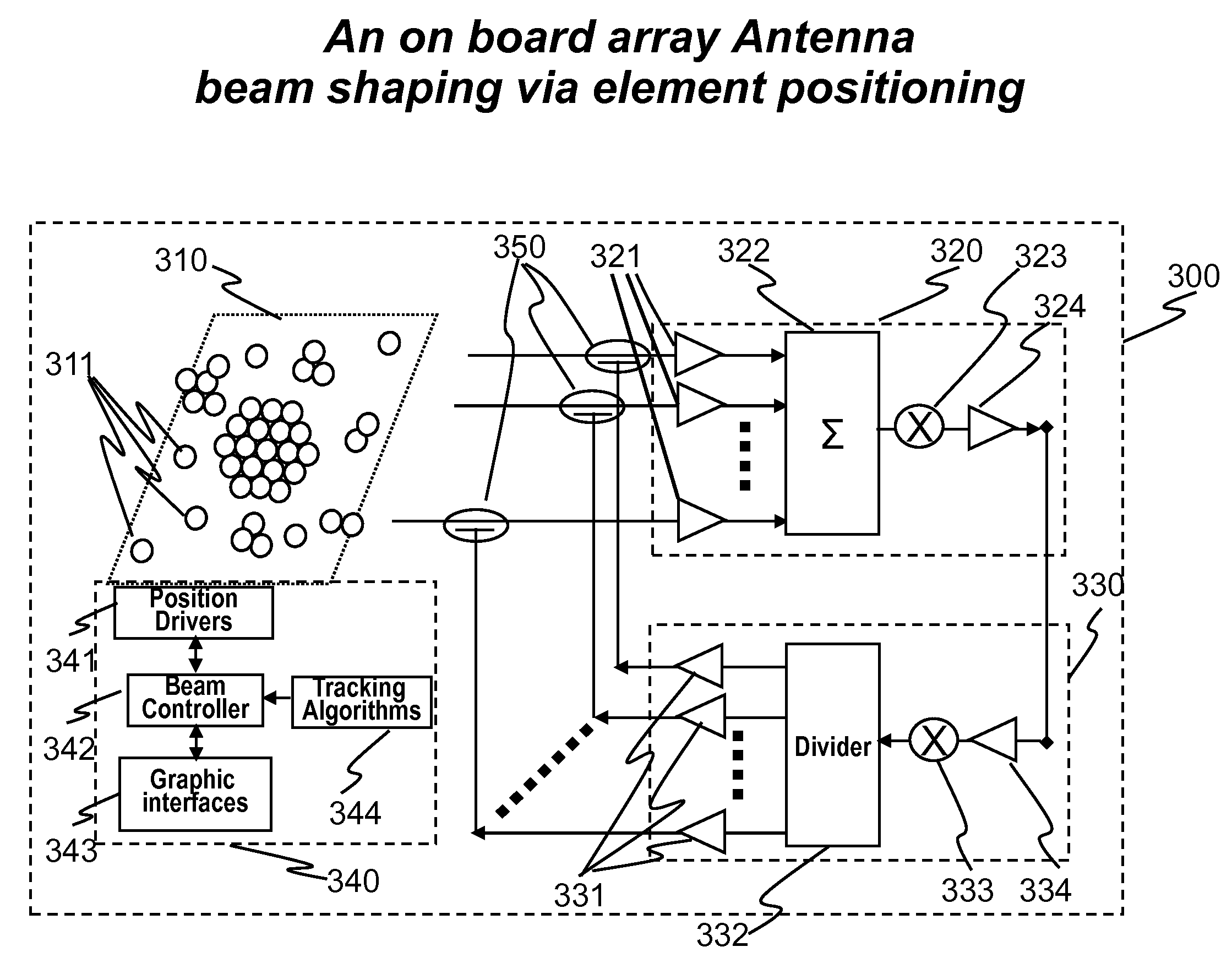
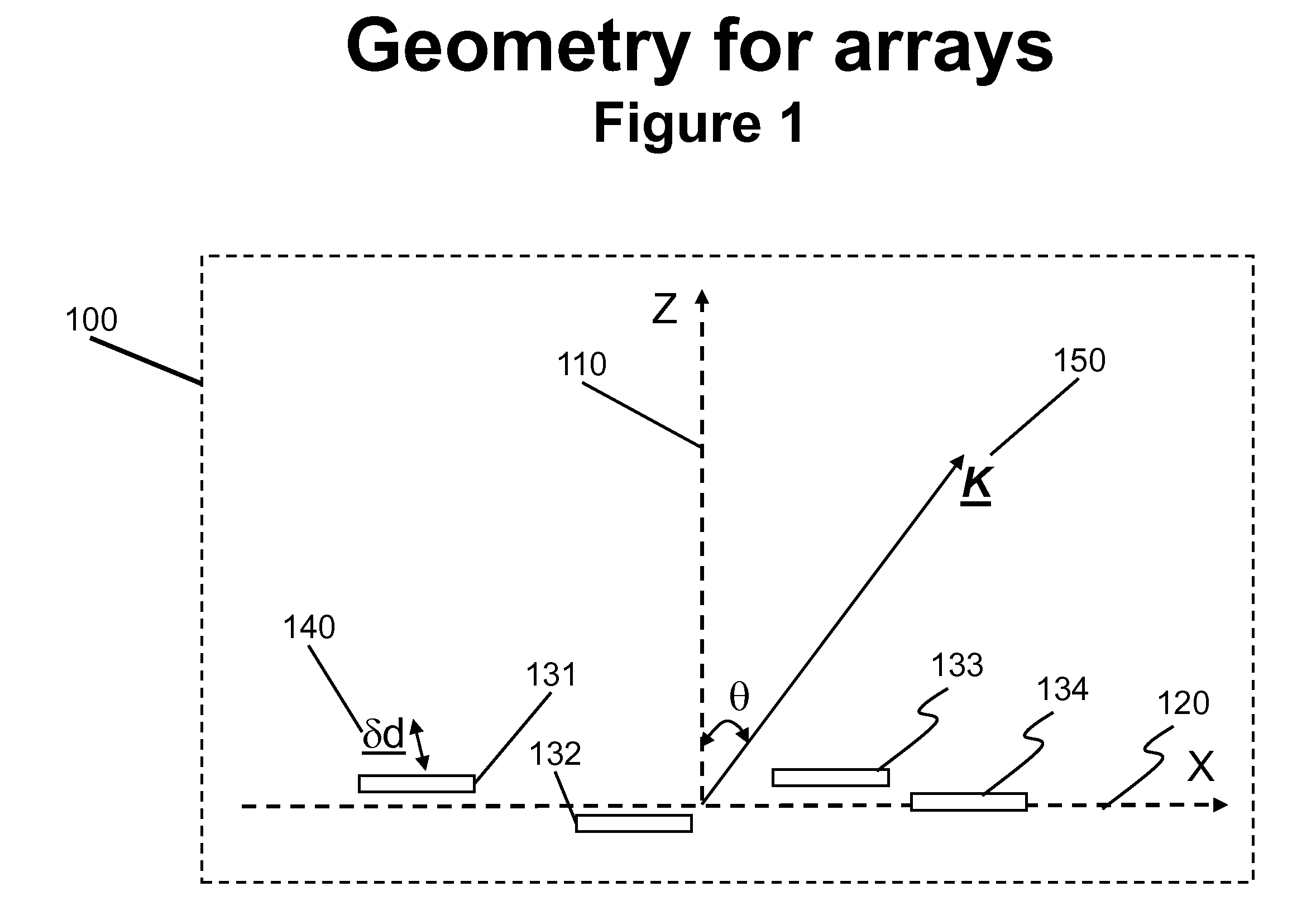
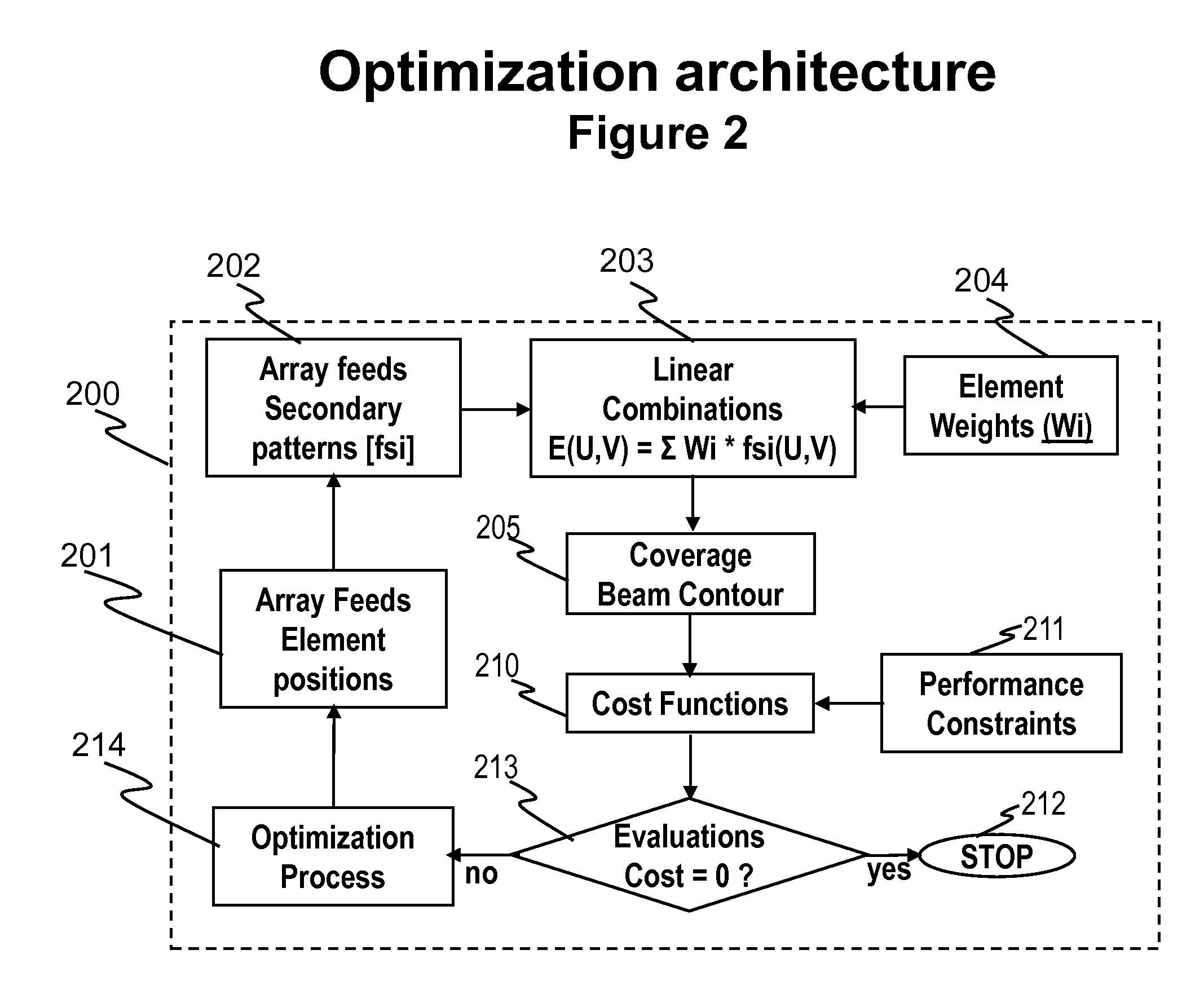
Architectures and Methods for Novel Antenna Radiation Optimization via Feed Repositioning
ActiveUS20110032173A1Complex antenna designCost-effective methodCollapsable antennas meansAntenna designSatellite antennas
The present invention relates to antenna architectures and methods on re-configurable multi-element antennas via feed re-positioning for various optimized radiation contours, including beam forming (or shaping) and / or null steering on contoured beams, spot beams, and orthogonal beams. The feed re-positioning techniques can also be used in radiation pattern optimization processing during antennas designing phases for fixed beams. The techniques are applicable for satellite communications. For satellite antennas, the beam shaping capability via element repositioning can be utilized for (1) optimized geometries on satellite antennas for given desired coverage areas, (2) re-optimizing radiation contours for reconfigurable antenna on board satellites in operation, (3) additional flexibility for satellite antennas using ground based beam forming (GBBF). As to satellite ground terminals, the same techniques are applicable for both fixed and mobile satellite terminals featuring either single beam or multiple beams. For fixed terminals, are applicable for terrestrial based communications; such as retrofitting existing antennas eliminating interference radiations coming from fixed or slow varying directions.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
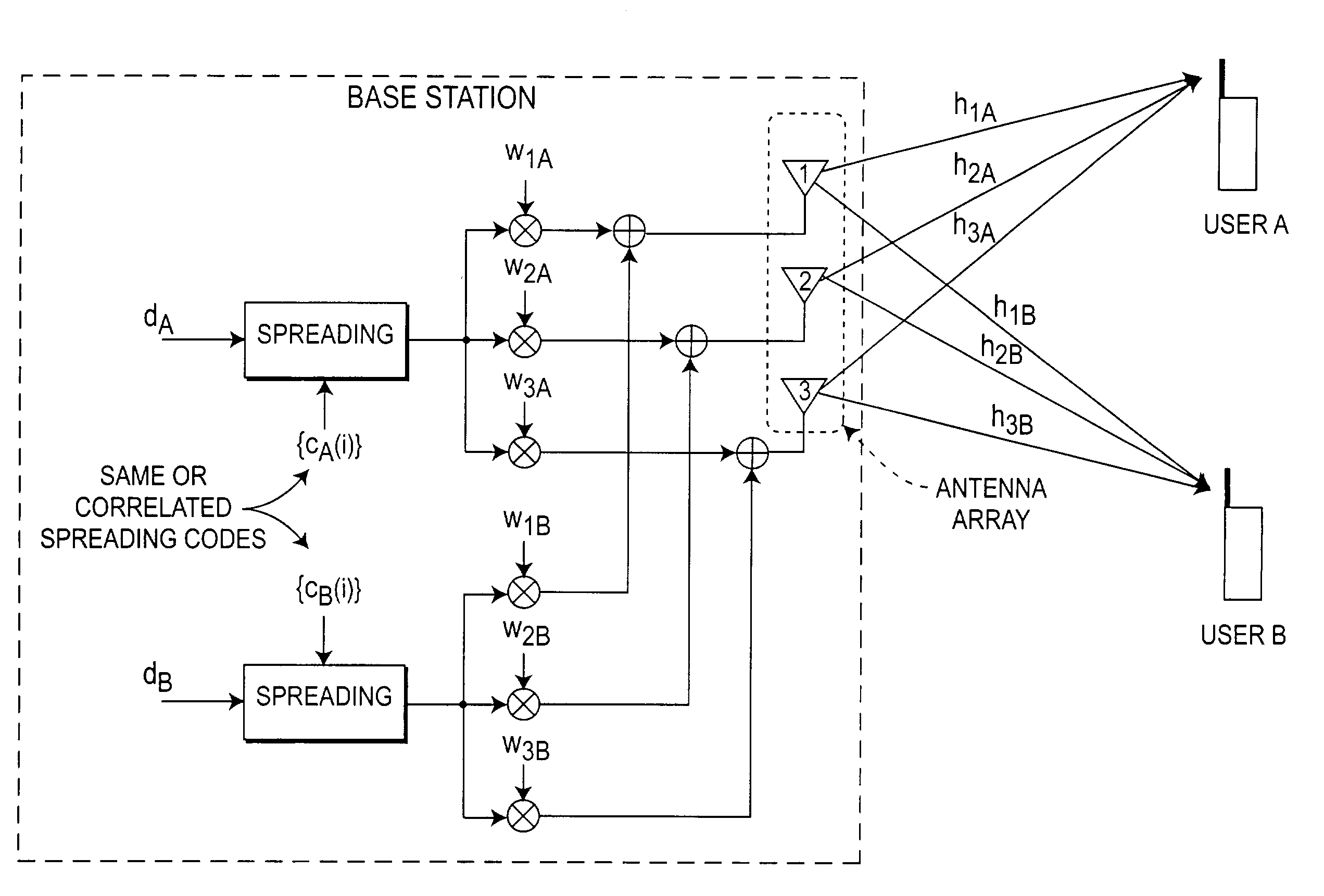
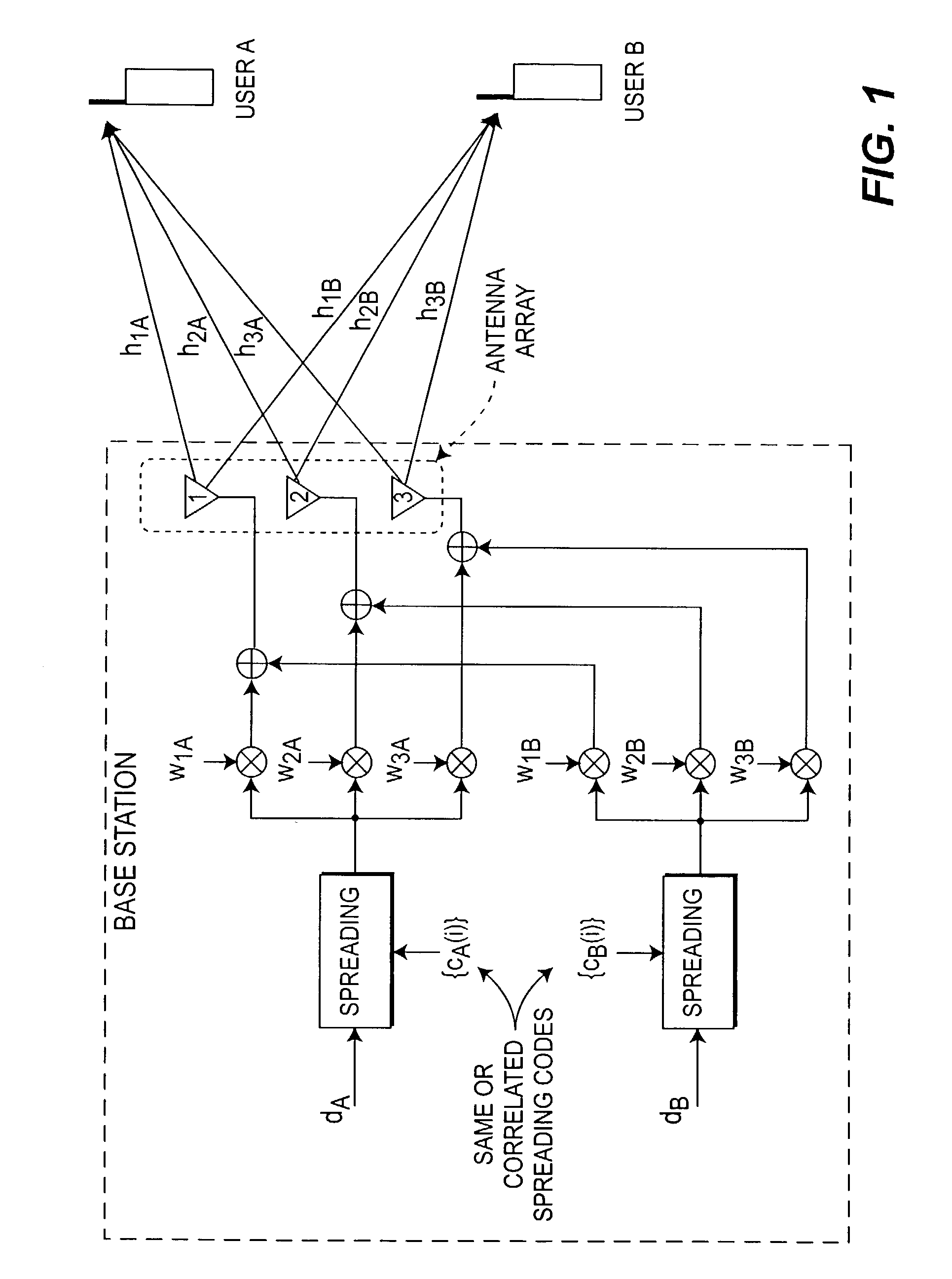
Method and system for code reuse and capacity enhancement using null steering
InactiveUS7218684B2Increase capacityMaintain propertiesSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysData capacityEngineering
The number of users and data capacity of wireless systems are increased by employing apparatus and method for increasing the number of spreading codes available in the system by providing a mechanism to reuse the already allocated spreading code or use the codes that may correlate to those already being used within the same sector / cell. This, in return, provides capacity improvement proportional to the number of added base station (BS) antennas for each cell. An antenna null steering technique for code allocation maintains the cross correlation properties of the codes only for the desired user and to obtain a gain in capacity improvement.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
InactiveUS20060238414A1Increase user capacityImprove directivityDirection finders using radio wavesAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsCommunications security
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Antenna system
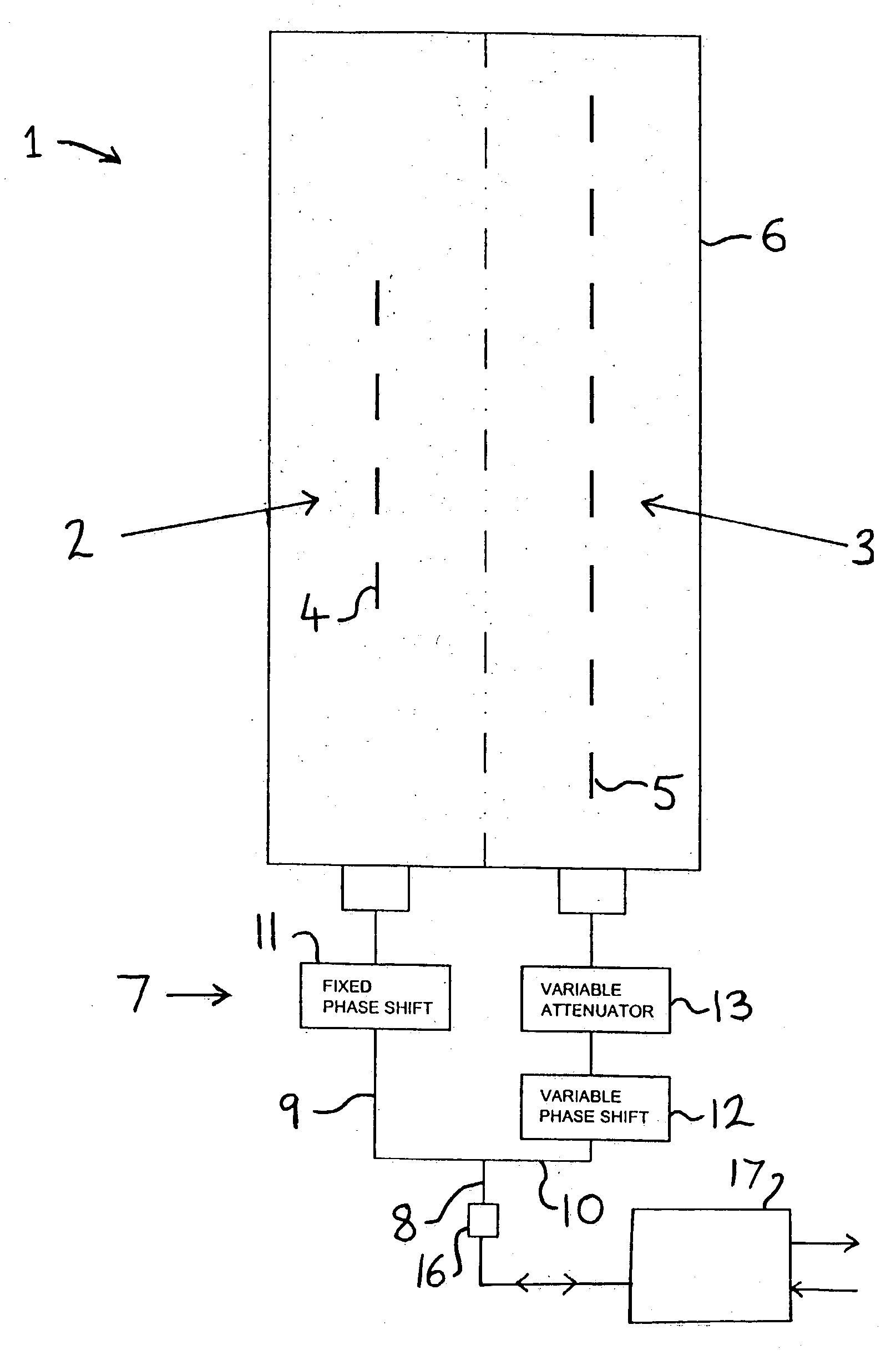
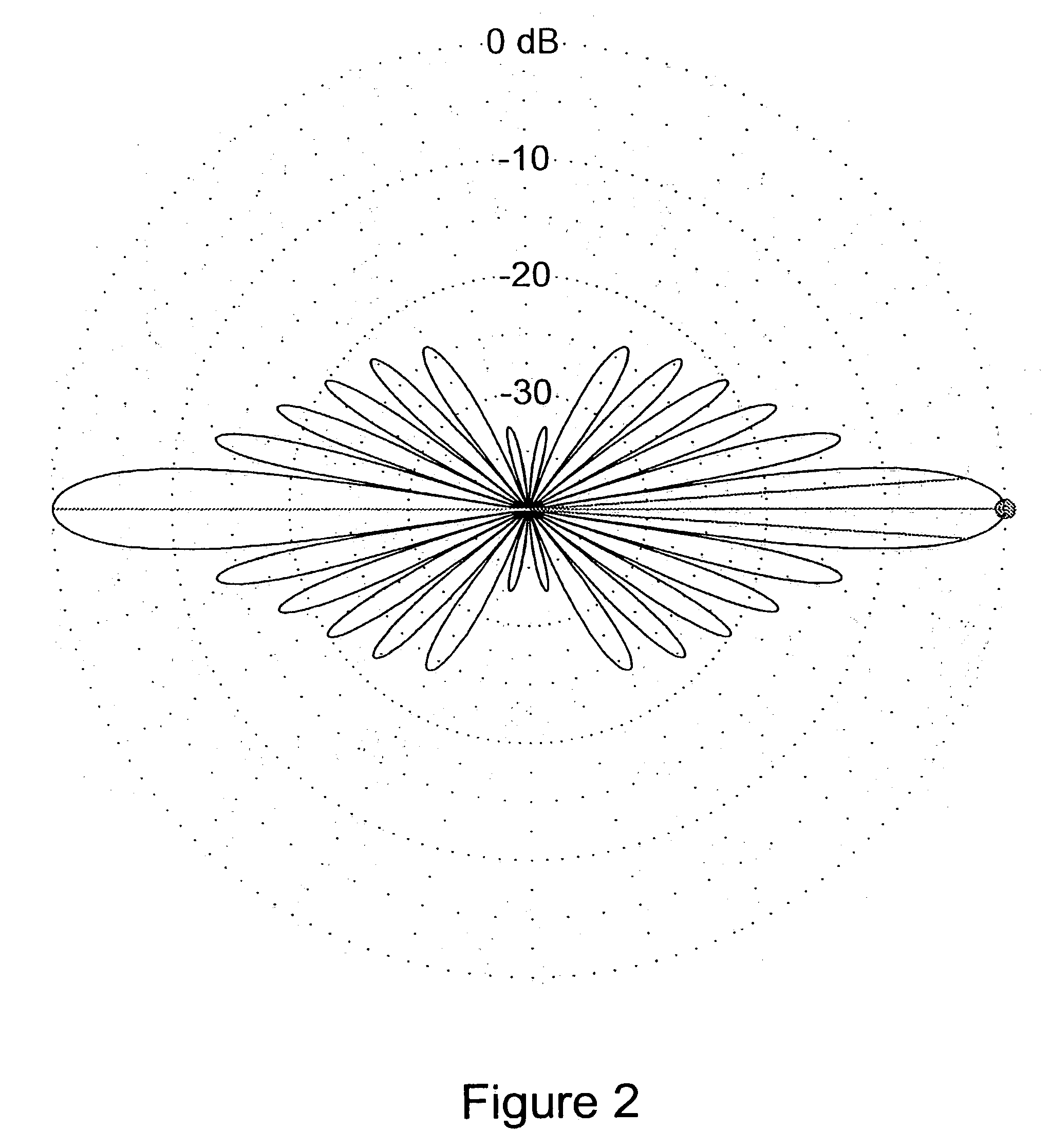
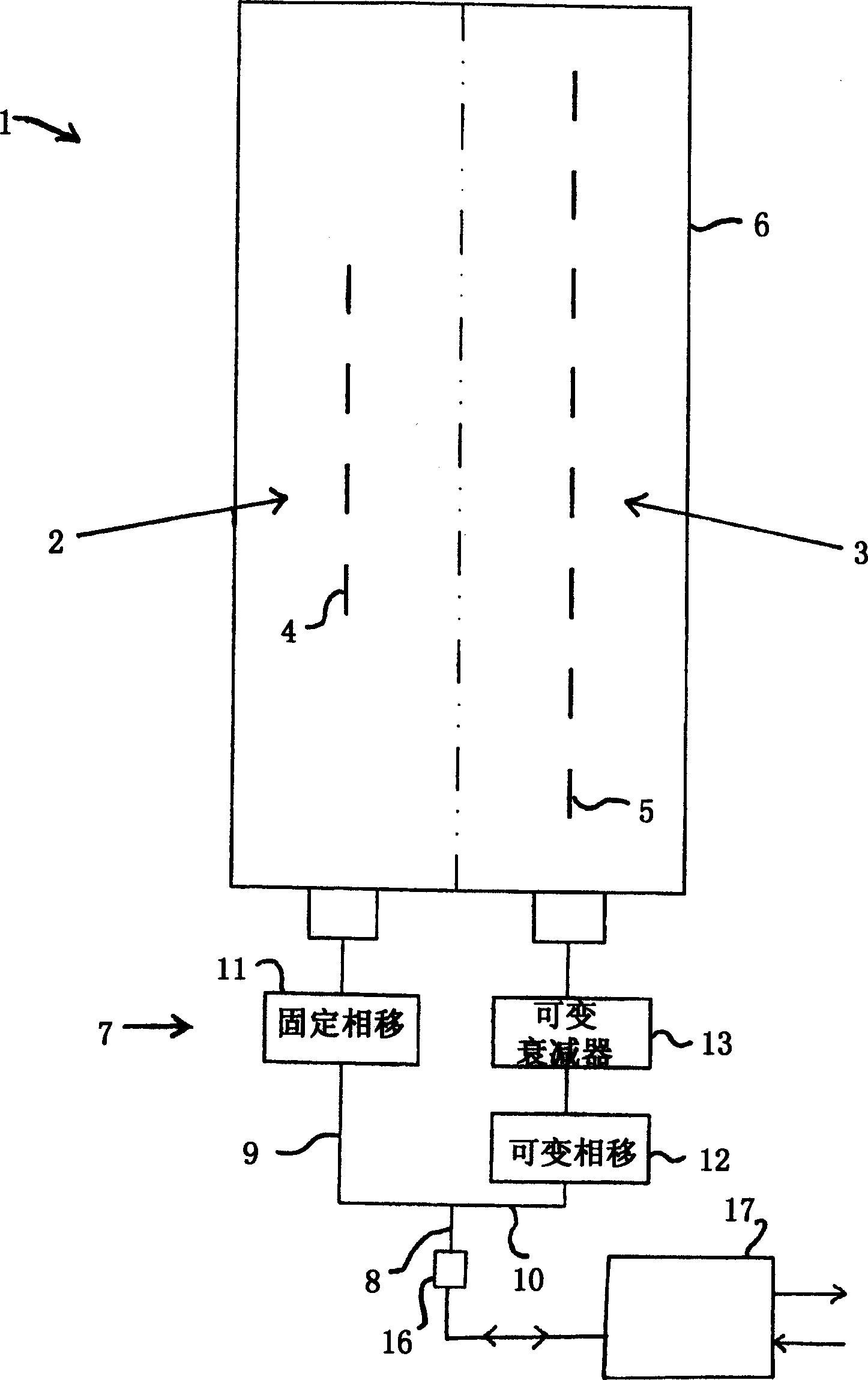
An antenna system including a coverage antenna (2) with a coverage beam pattern; and an auxiliary antenna (3) with an auxiliary beam pattern. The auxiliary beam pattern is arranged to perform sidelobe suppression, null steering, null addition, or null-fill. In the case where the auxiliary antenna is used to perform sidelobe suppression, the auxiliary beam pattern has a mainlobe with: an amplitude lower than an amplitude of a mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a width lower than a width of said mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a phase different to a phase of a sidelobe of said coverage beam pattern; and a direction which is selected so as to at least partially suppress said sidelobe.
Owner:ANDREW CORP
Compact antenna system for polarization sensitive null steering and direction-finding
ActiveUS7577464B2Reduce adverse effectsEnhance jammer-to-signal (J/S) toleranceSubstation equipmentAntenna feed intermediatesEngineeringOperation mode
A compact, non-phased-array, electronically reconfigurable antenna (ERA) system with at least two operational modes has a first operational objective that is polarization-sensitive null steering (PSNS) and a second operational objective that is direction-finding (DF). The system can rapidly switch between two operational states. In the first state, the system behaves like a polarization filter (PF) and operates as a controlled reception pattern antenna (CRPA), while in the second state the system behaves as an angle-of-arrival (AOA) sensor and operates as a fixed reception pattern antenna (FRPA). The system may include a spiral-mode antenna with both feed and load ports; a mode-forming network; an electronics package; and feedback control electronics. Radio frequency (RF) interference rejection and RF direction-finding may be performed as well as reduction and / or elimination of multiple jamming signals that are intentionally or unintentionally directed at a Global Positioning System (GPS). The determination of direction and location of the source of jamming signals may also be achieved.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
Antenna system optimized for siso and MIMO operation
ActiveUS20130109449A1Improve performanceImprove antenna performanceSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentCommunications systemRadiation mode
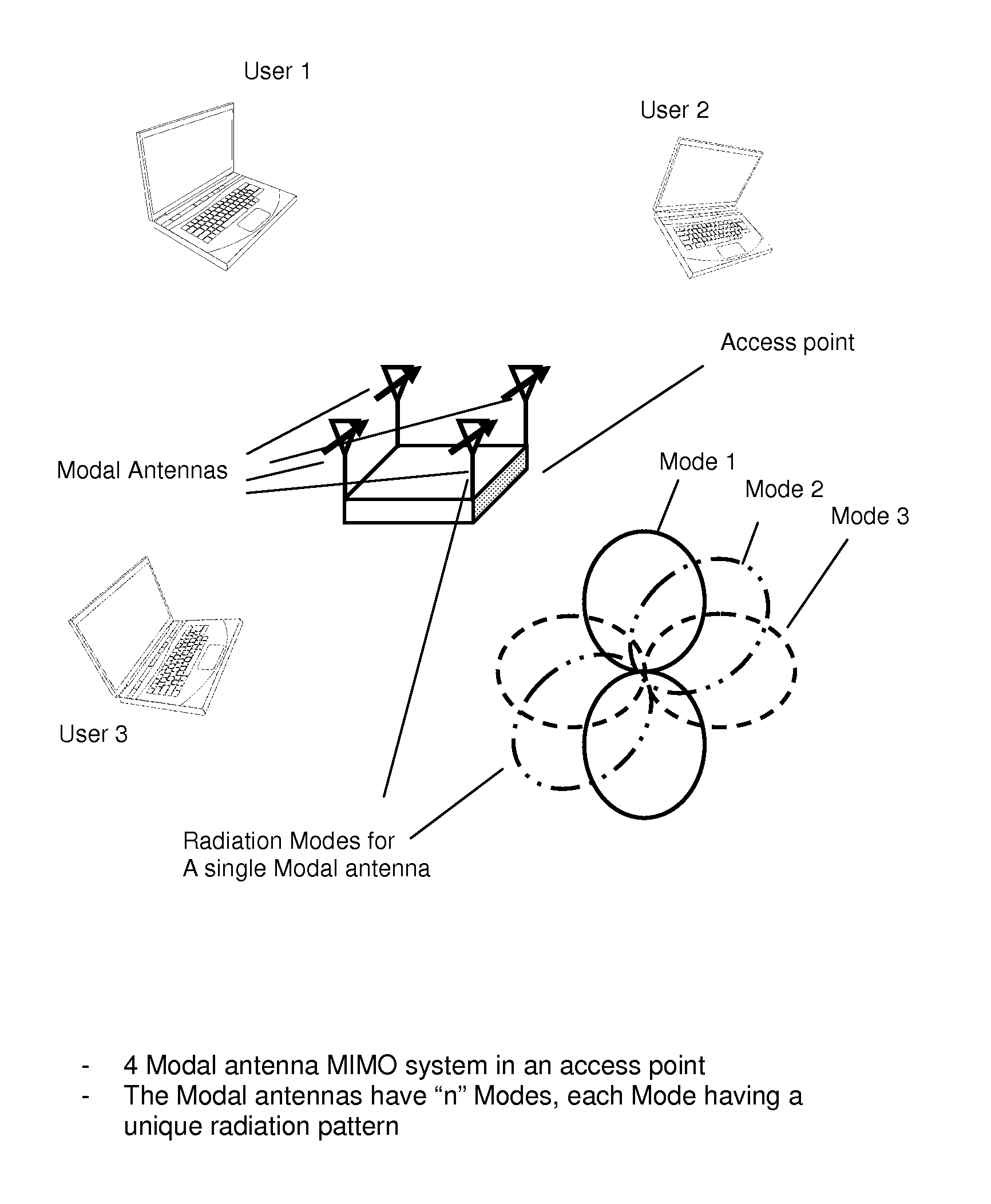
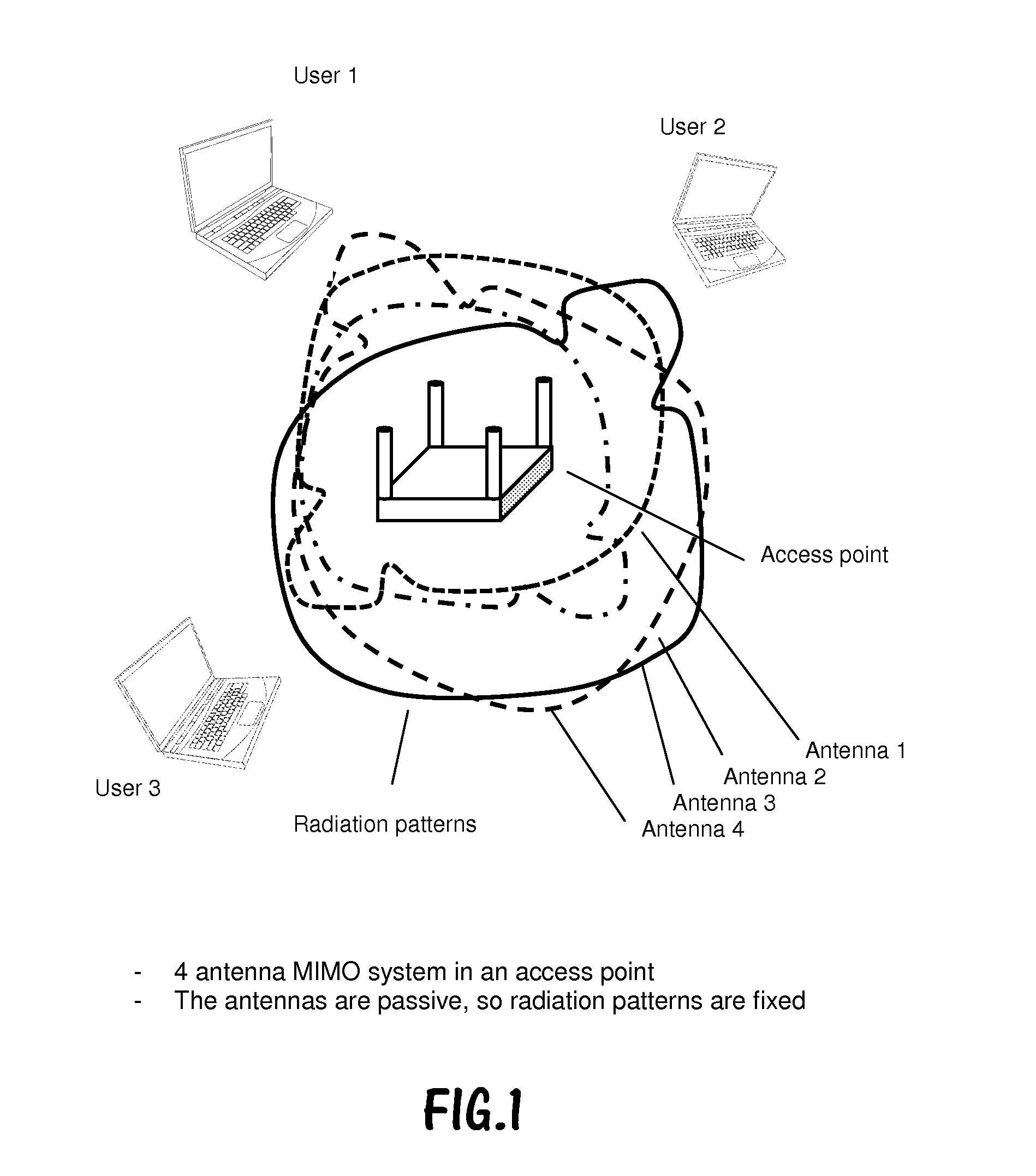
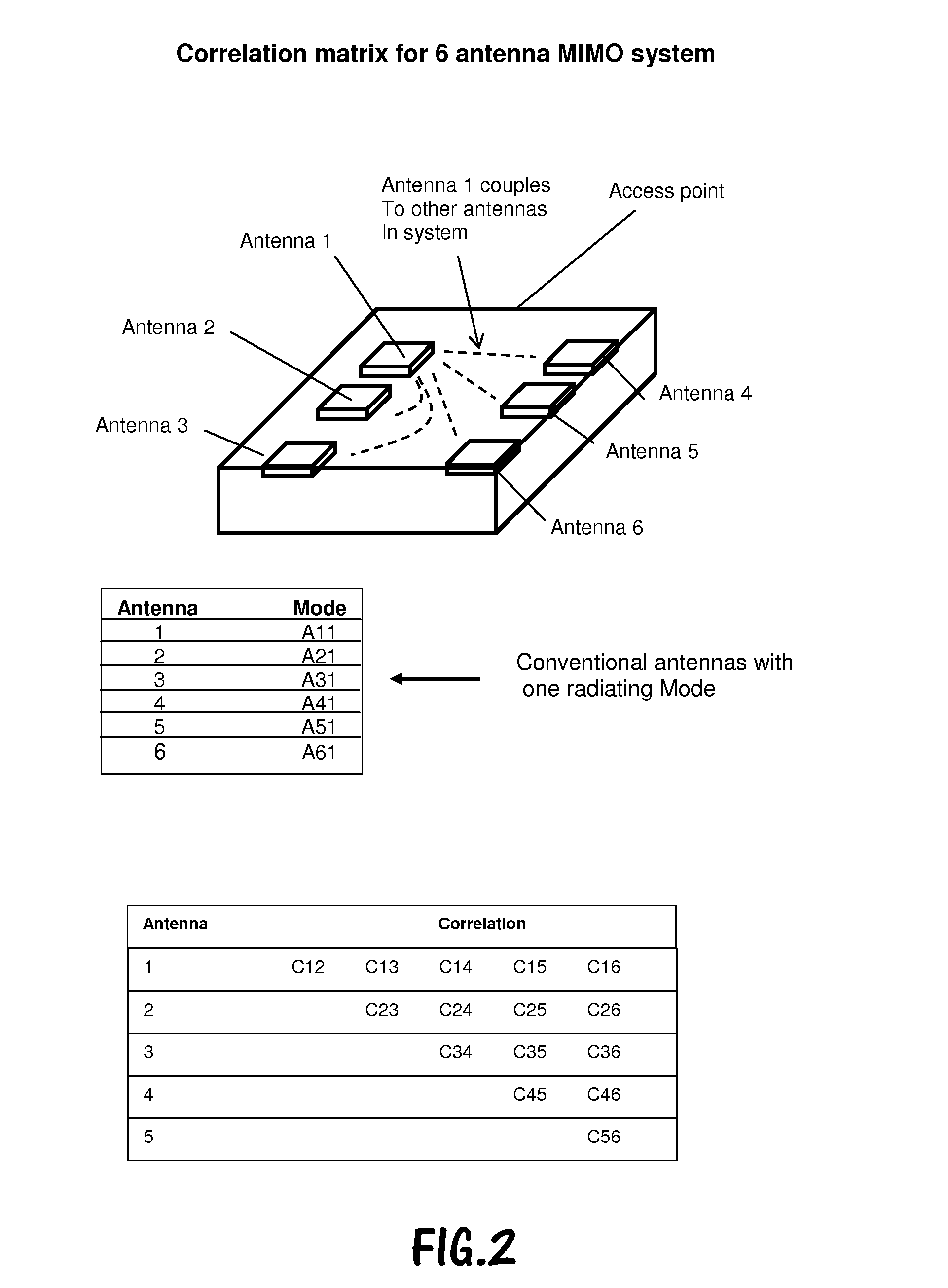
An active antenna system and algorithm is described that provides for improved performance from LTE communication systems operating in Category 1 mode, where one antenna is used. For the LTE SISO case (category 1), a modal antenna capable of generating multiple radiation patterns will provide improved throughput due to improved resistance to fading. Modal (Null Steering) antenna technology is implemented in a multi-antenna system to provide for single and multiple antenna operation wherein one or more antennas have two or more radiation modes. An algorithm has been developed that determines when to switch from SISO to MIMO operation.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Adaptive null streering for frequency hopping networks
A method and apparatus for performing adaptive null steering in a slow frequency hopping environment. Where base stations have smart beamforming antenna capability and are interconnected by a base station controller, thus accommodating cyclic and pseudo-random frequency hopping, each base station forwards information on arrival time, frequency and received power of all subscriber communications and co-channel interferers to the controller for correlation. Periodicity information relating to co-channel interferers is returned to the applicable base station, to enable the generation of a null in the direction of arrival of the interferer. Where few base stations have smart beamforming capability, frequency hopping is cyclic only, and each base station generates its own periodicity information. Base stations may also calculate direction of arrival and time of arrival information, and forward this to the controller, if applicable. The invention enhances network capabilities including a subscriber localizing capability hitherto unavailable to network operators.
Owner:TENXC WIRELESS
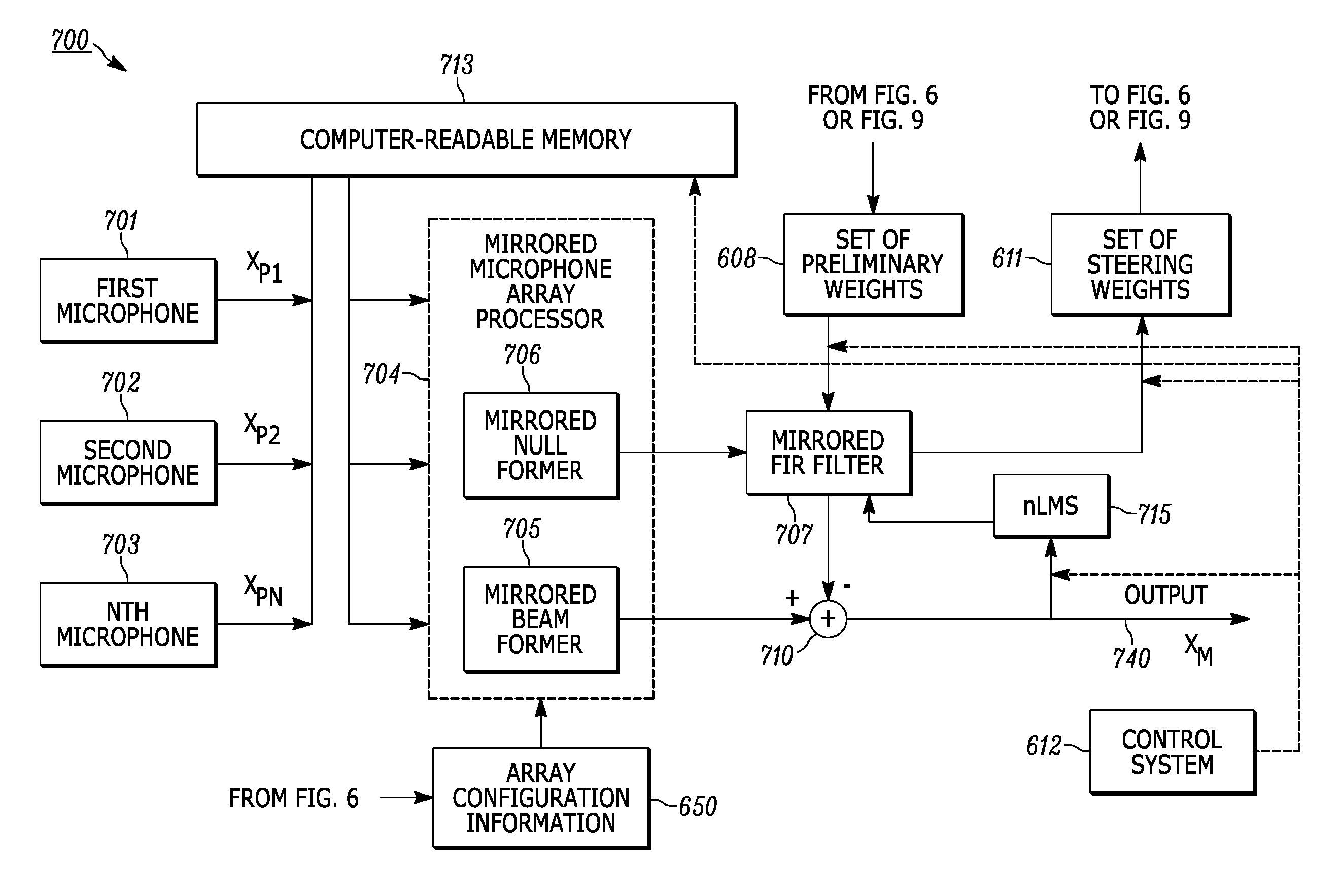
Methods and apparatuses for performing null steering of adaptive microphone array
ActiveUS9479885B1Reduce distractionsMicrophonesSignal processingAmplitude responseAngular orientation
Configuring an adaptive microphone array to gather signals from a main lobe of the array, and configuring the array to reduce side interference gathered from sources that are not situated within the main lobe. A memory stores test signals gathered by the array at a plurality of predetermined angular bearings with reference to the array in an anechoic chamber. Signals gathered in real time are processed to provide a preliminary output and preliminary weights. The test signals are retrieved from memory. The preliminary weights are applied to the test signals to provide null steering weights. The null steering weights and the preliminary output are processed to reduce or minimize the amplitude response of the array at the angular orientation.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
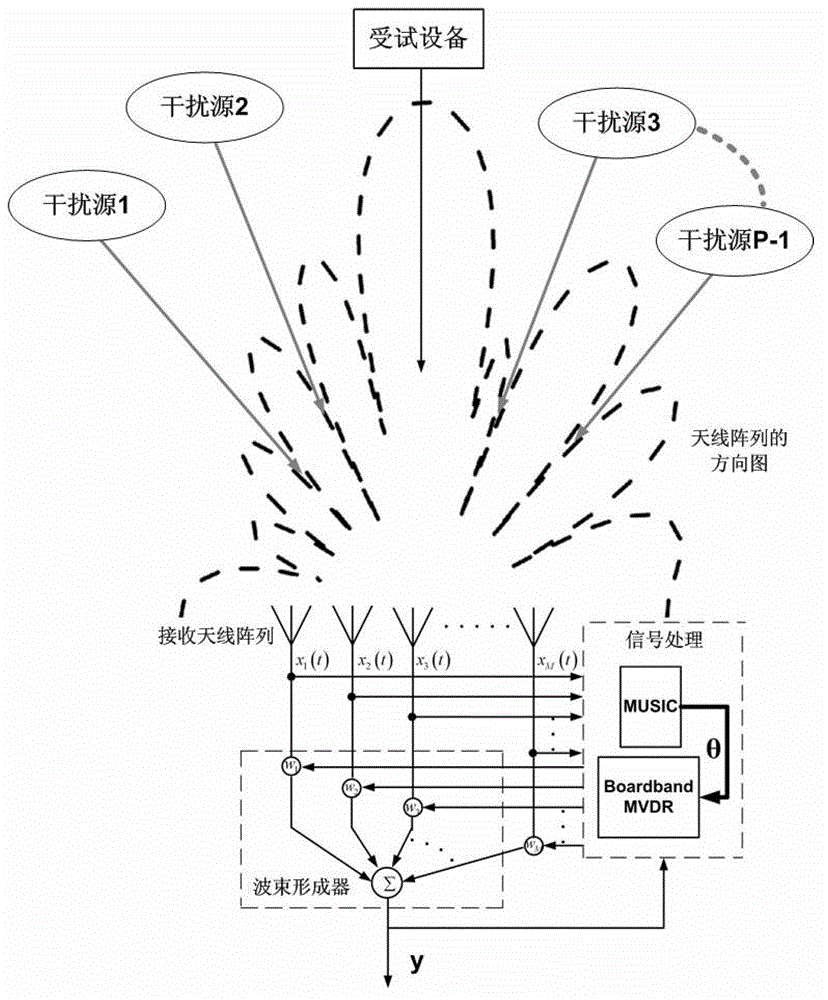
Ambient interference resisting method for testing electromagnetic radiation emission field
InactiveCN102944757ASuppress interferenceAccurately obtain radiated emission characteristicsElectromagentic field characteristicsSignal classificationEstimation methods
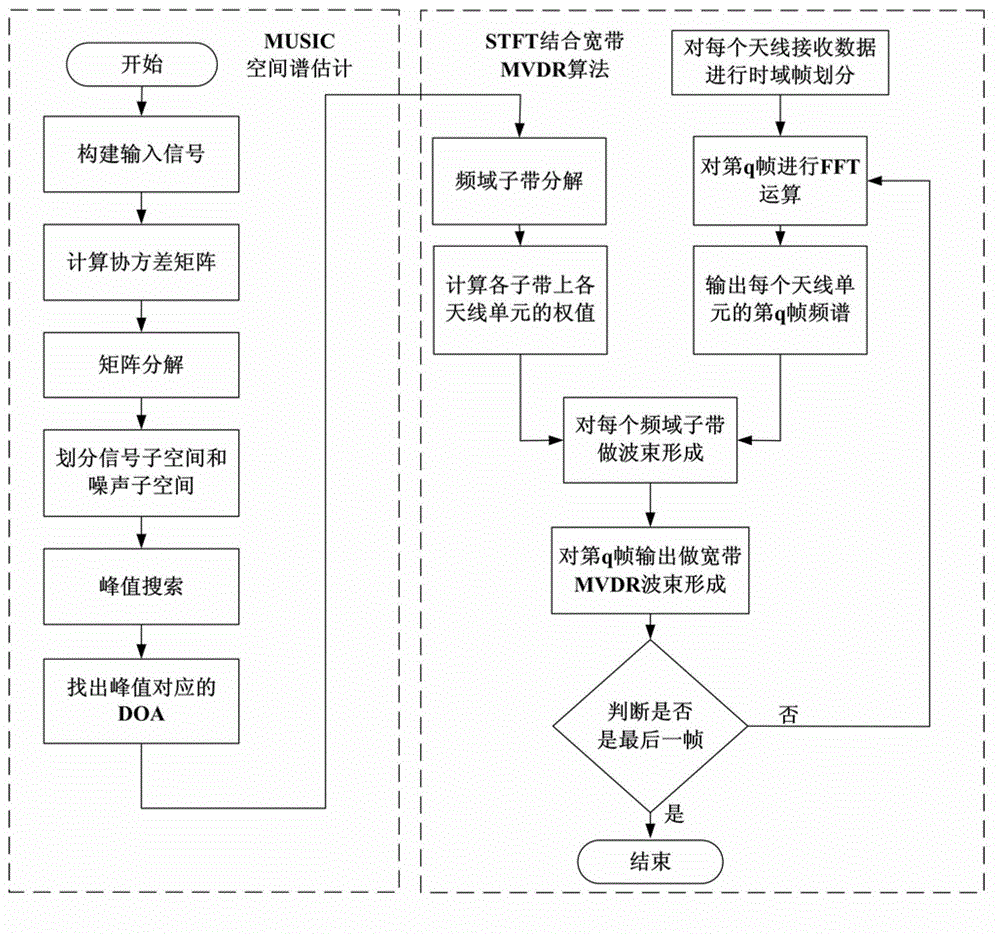
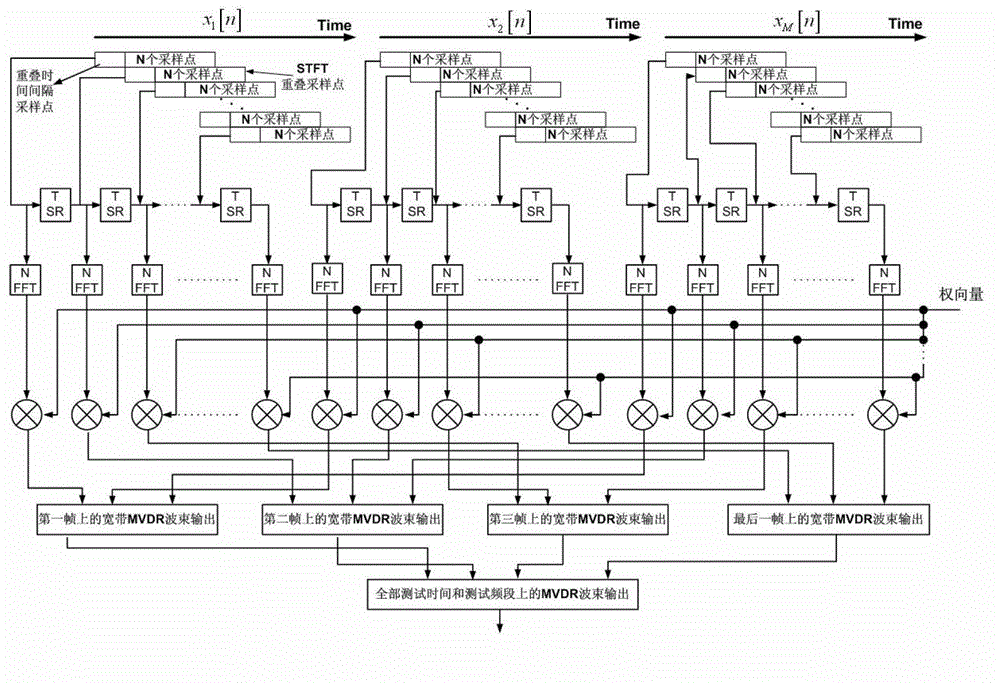
The invention discloses an ambient interference resisting method for testing an electromagnetic radiation emission field. The method specifically includes that a receiving antenna array is arranged in the testing field, each antenna unit can receive mixed signals composed of a tested device radiation signal and an interference signal, and by means of a spatial spectrum estimation method based on a multiple signal classification algorithm (MUSIC), the direction of arrival of each signal is obtained. According to a spatial spectrum estimation result, by means of a minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) beam forming criterion, each antenna array element receiving signal is subjected to optimal weighting, in the premise that the tested device radiation signal is not distorted, array beams form null steering along the coming direction of the interference signal, and spatial filtering of the interference signal is achieved. According to the ambient interference resisting method, the MUSIC spatial spectrum estimation method and the MVDR beam forming technology are introduced into the field of electromagnetic compatibility testing, so that the ambient interference generated during testing of field radiation emission can be effectively inhibited, and radiation emission characteristics of a tested device in actual work environment can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Antenna system
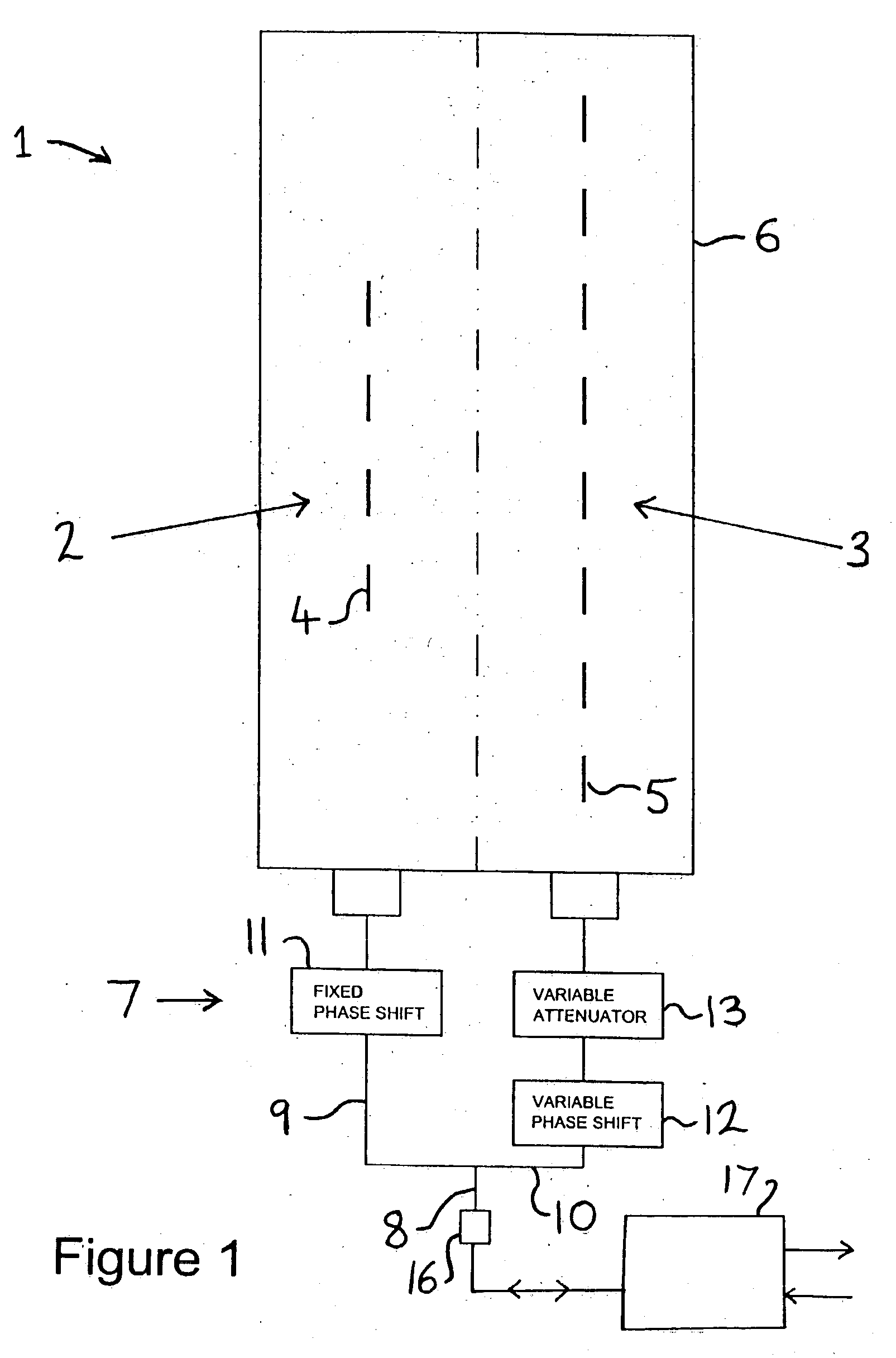
An antenna system including a coverage antenna (2) with a coverage beam pattern; and an auxiliary antenna (3) with an auxiliary beam pattern. The auxiliary beam pattern is arranged to perform sidelobe suppression, null steering, null addition, or null-fill. In the case where the auxiliary antenna is used to perform sidelobe suppression, the auxiliary beam pattern has a mainlobe with: an amplitude lower than an amplitude of a mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a width lower than a width of said mainlobe of said coverage beam pattern; a phase different to a phase of a sidelobe of said coverage beam pattern; and a direction which is selected so as to at least partially suppress said sidelobe.
Owner:ANDREW CORP
Antijam null steering conformal cylindrical antenna system
InactiveUS6388610B1Reduce sensitivityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPolarisation/directional diversityCylindrical arrayAntenna element
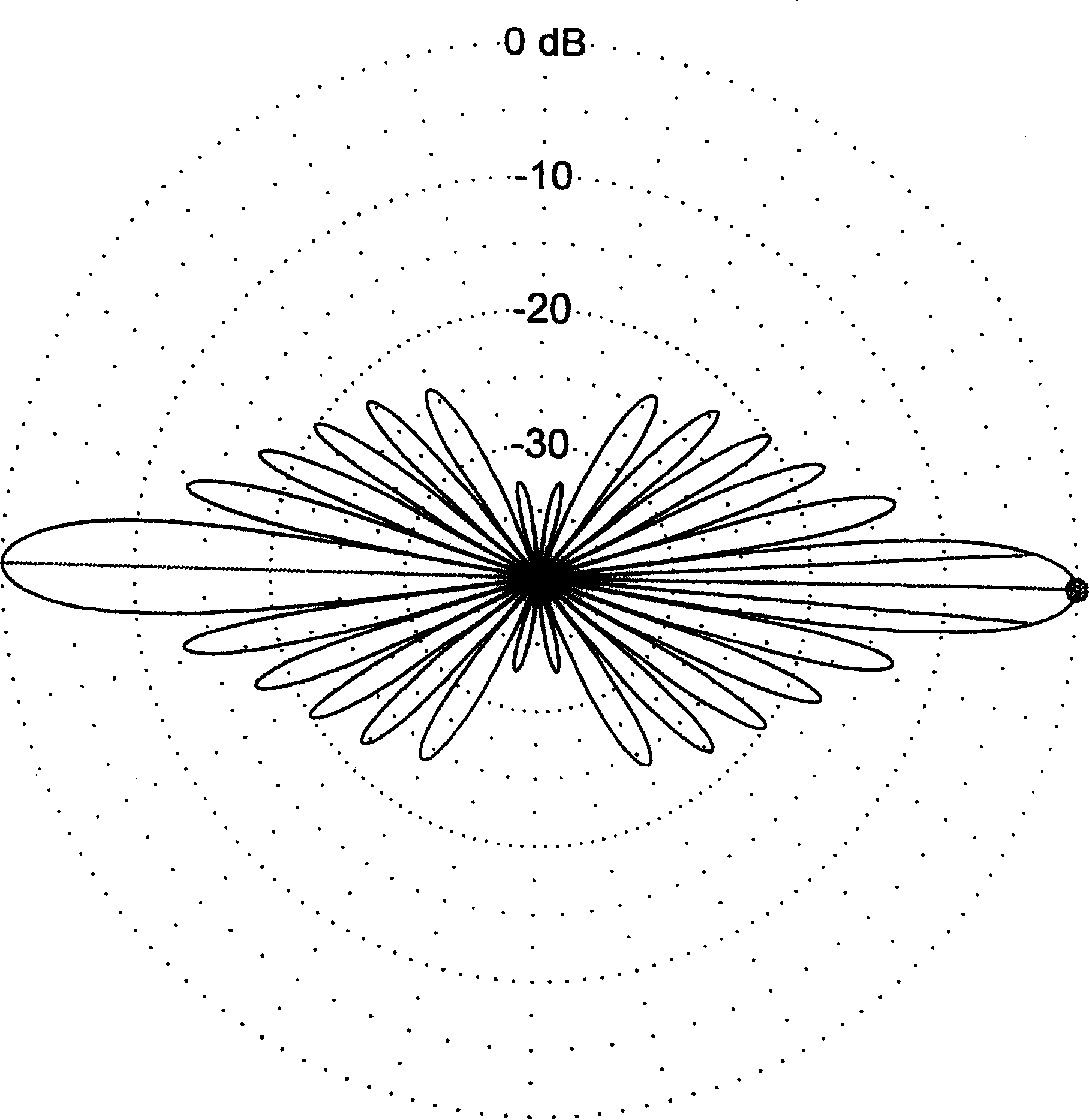
An antijam null steering conformal cylindrical antenna system includes a cylindrical array of linearly polarized individually weighted antenna elements; a plurality of weighting circuits one associated with each of the elements; and means, responsive to the power output of the weighting circuit, for decreasing the sensitivity in the direction of the maximum incident power.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
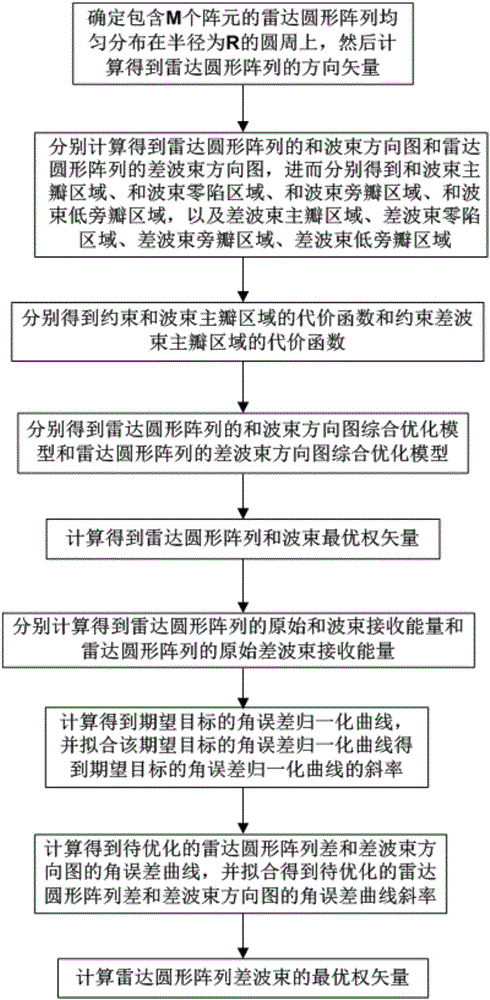
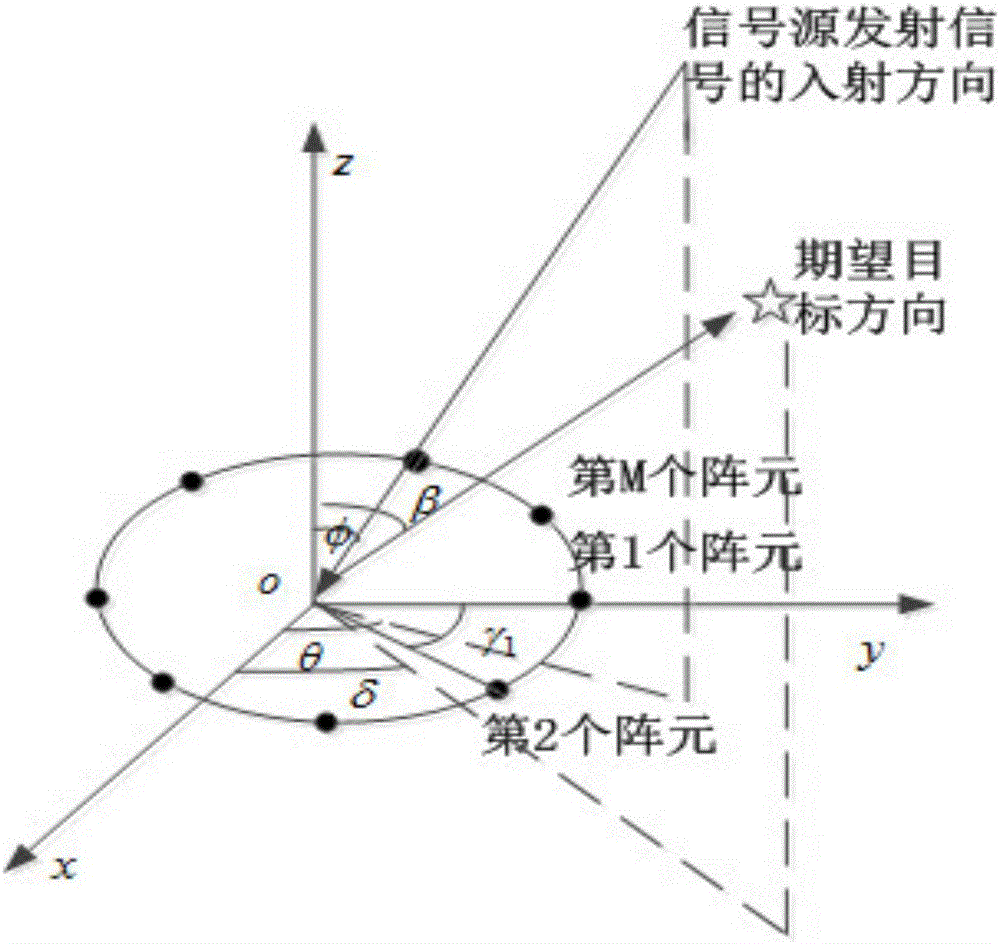
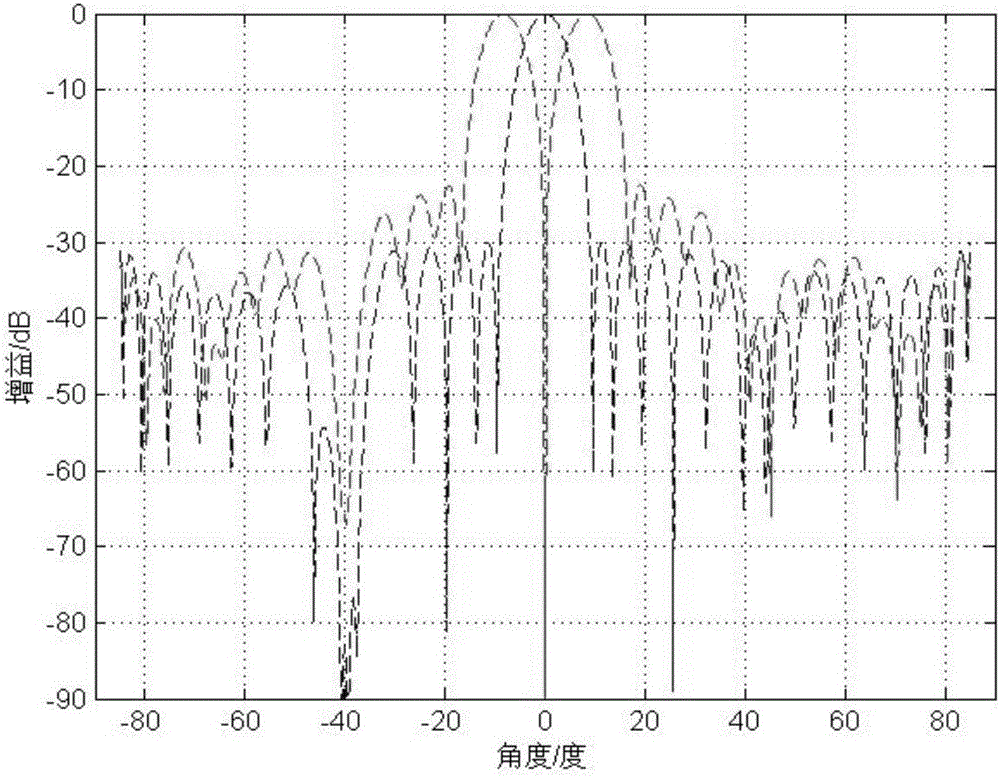
Convex optimization algorithm-based radar array sum-difference beam directional diagram optimization method
ActiveCN106772260AImproved clutter suppression performanceSide lobe lowWave based measurement systemsInternal combustion piston enginesOptimal weightRadar
The invention discloses a convex optimization algorithm-based radar array sum-difference beam directional diagram optimization method. The method comprises the steps of determining that a radar circular array containing M array elements is uniformly distributed on a circumference with the radius being R, and then determining a sum beam main lobe area, a sum beam null steering area, a sum beam side lobe area, a sum beam low side lobe area, a difference beam main lobe area, a difference beam null steering area, a difference beam side lobe area and a difference beam low side lobe area; respectively obtaining a cost function for restraining the sum beam main lobe area and a cost function for restraining the difference beam main lobe area; further obtaining a sum beam directional diagram comprehensive optimization model of the radar circular array and a difference beam directional diagram comprehensive optimization model of the radar circular array, and calculating a radar circular array sum beam optimal weight vector; sequentially obtaining a slope of an angle error normalization curve of an expected target and a curve slope of an angle error curve of a radar circular array sum-difference beam directional diagram to be optimized, and calculating an optimal weight vector of a radar circular array difference beam.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
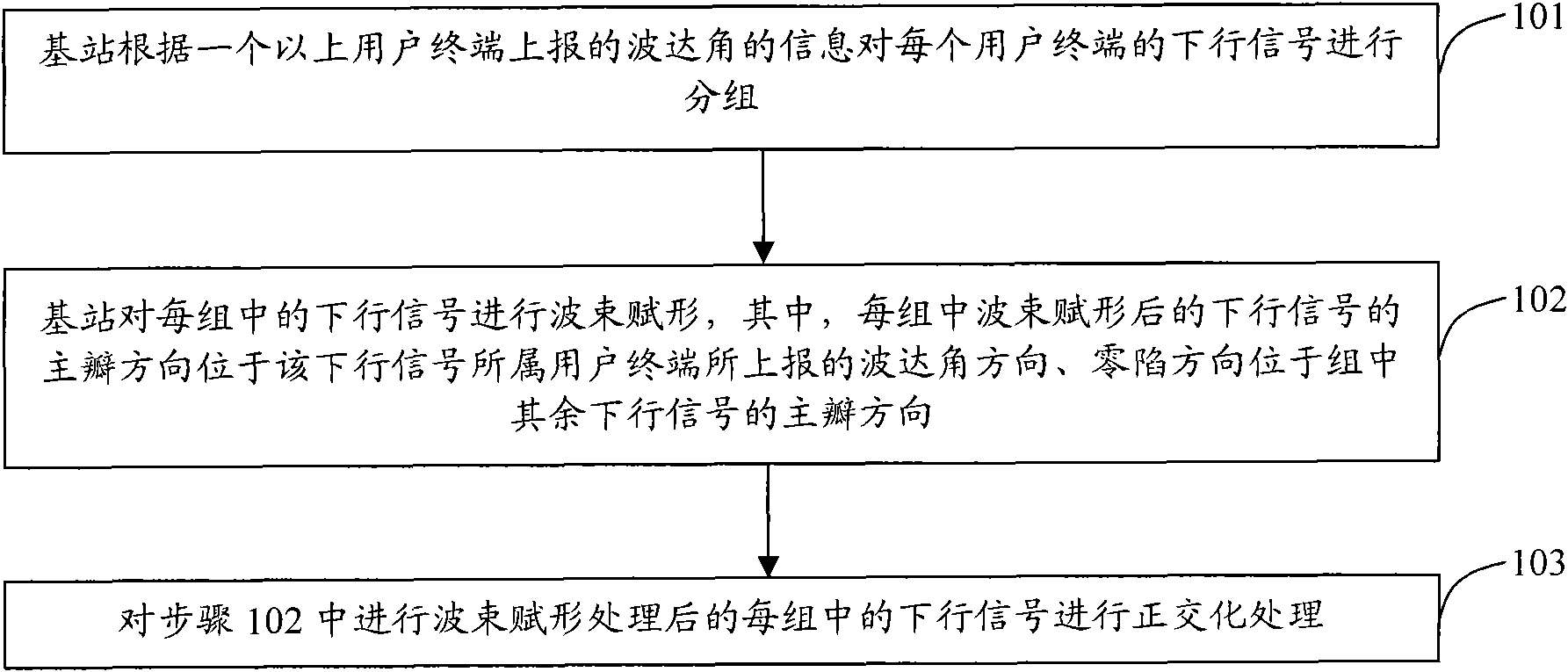
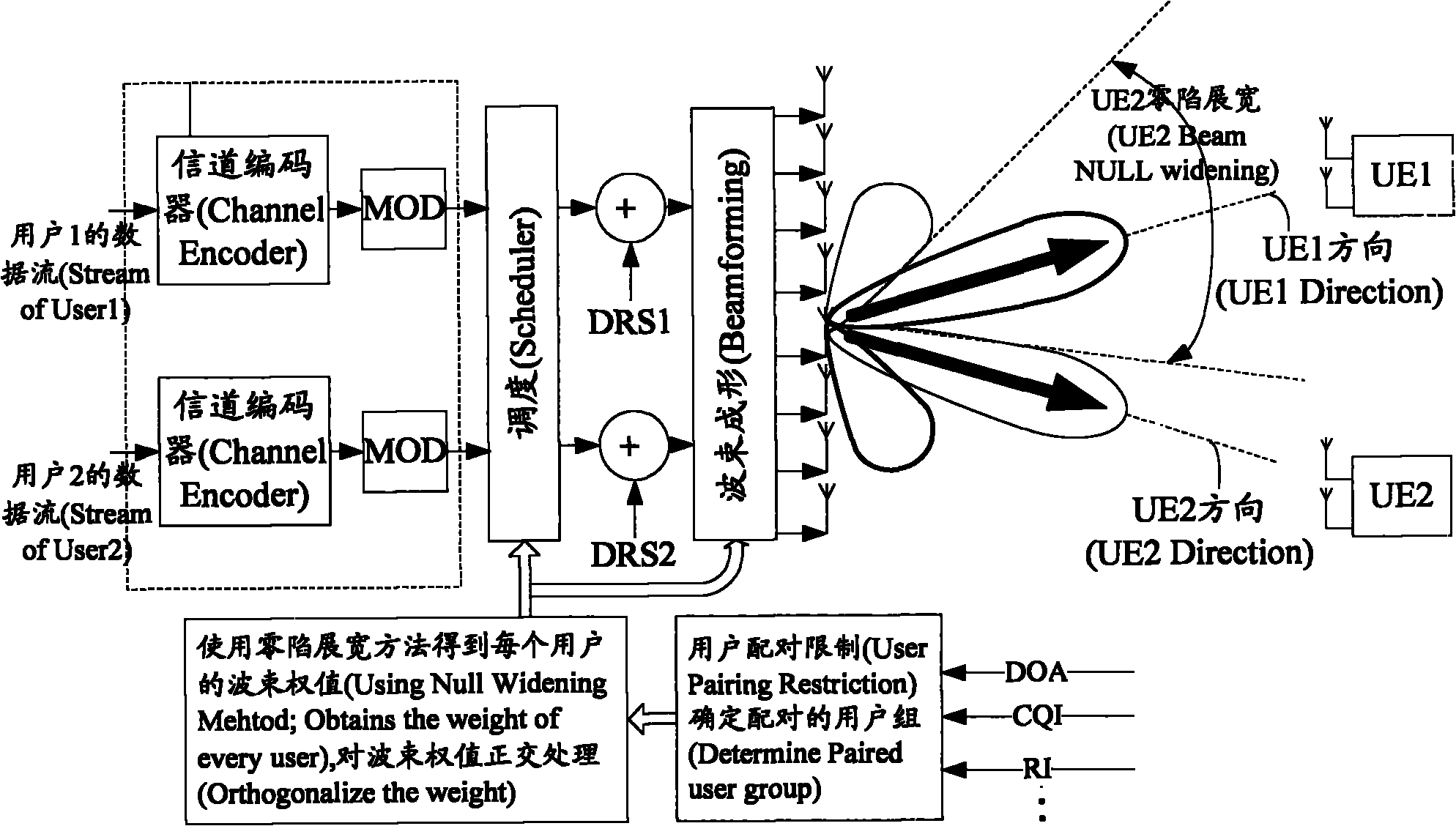
Multi-user beam shaping method and device based on frequency division duplex system
InactiveCN101800581AIncrease capacityReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningEngineeringMain lobe
The invention discloses a multi-user beam shaping method based on a frequency division duplex system. A base station groups for downlink signals of each user terminal based on information of arrival angles reported by more than one user terminal and carries out beam shaping on the downlink signals in each group, wherein the main lobe direction of downlink signals subjected to beam shaping in each group is arranged in the arrival angle direction reported by a user terminal located by the downlink signals, and the null steering direction is arranged in the main lobe direction of the other downlink signals. The invention also discloses a device for realizing the method. The invention ensures that interference between downlink signals of every two user terminals in each group is further lowered and the downlink signals in the same group can use resources of simultaneous frequency, thereby enhancing the volume of the frequency division duplex system while ensuring the quality of communication.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Sequence detecting method and apparatus for multi-antenna system
ActiveCN101291165ASuppress noiseSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsSequence signalWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a sequence detection method for a multi-antenna system. The method comprises the steps of: calculating a space covariance matrix according to a sequence signal received by each antenna of the multi-antenna system; estimating a direction of a coming wave according to the space covariance matrix; determining a weight coefficient corresponding to the direction of the coming wave; performing the forming combination to the sequence signals received by the plurality of antennae according to the weight coefficient; and performing the sequence detection to the combined sequence signals. The invention discloses a sequence detection device for the multi-antenna system. The embodiment of the invention estimates the direction of the coming wave through calculating the space covariance matrix to determine the weight coefficient, and utilizes the weight coefficient to perform the forming combination to the received signals, which ensures that a major lobe of a directional diagram aims at the direction of the coming wave of the sequence signals, the directivity is improved, a null steering is formed at the interference direction of the coming wave, effective inhibit to noise and interference is realized, thereby the sequence detection precision is improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Active MIMO antenna configuration for maximizing throughput in mobile devices
ActiveUS20160020838A1Improve antenna performanceImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringMimo antennaMobile device
An active antenna system and algorithm is proposed that provides for dynamic tuning and optimization of antenna system parameters for a MIMO system that will provide for greater throughput. As one or multiple antennas are loaded or de-tuned due to environmental changes, corrections to correlation and / or isolation are made by tuning the active antenna. A null-steering technique is implemented to alter the near-field and far-field characteristics to aid in modifying correlation and isolation in the multi-antenna system.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method
ActiveCN104701639AOffset grating lobesFast convergenceDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadiation lossEngineering
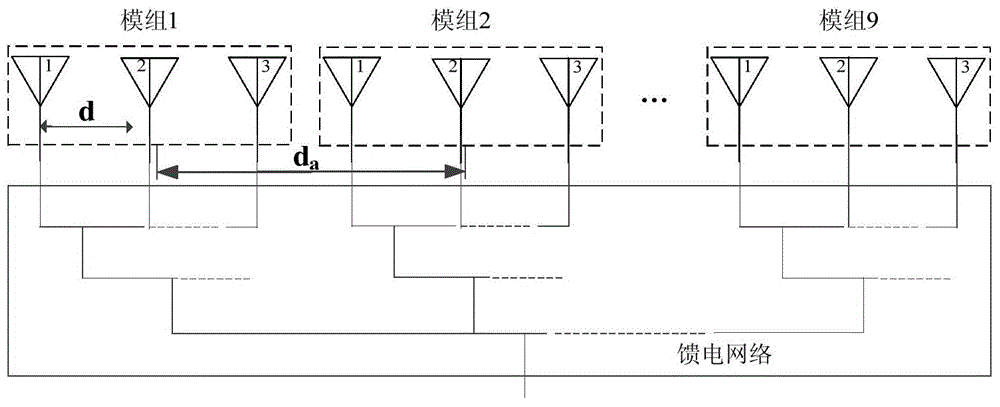
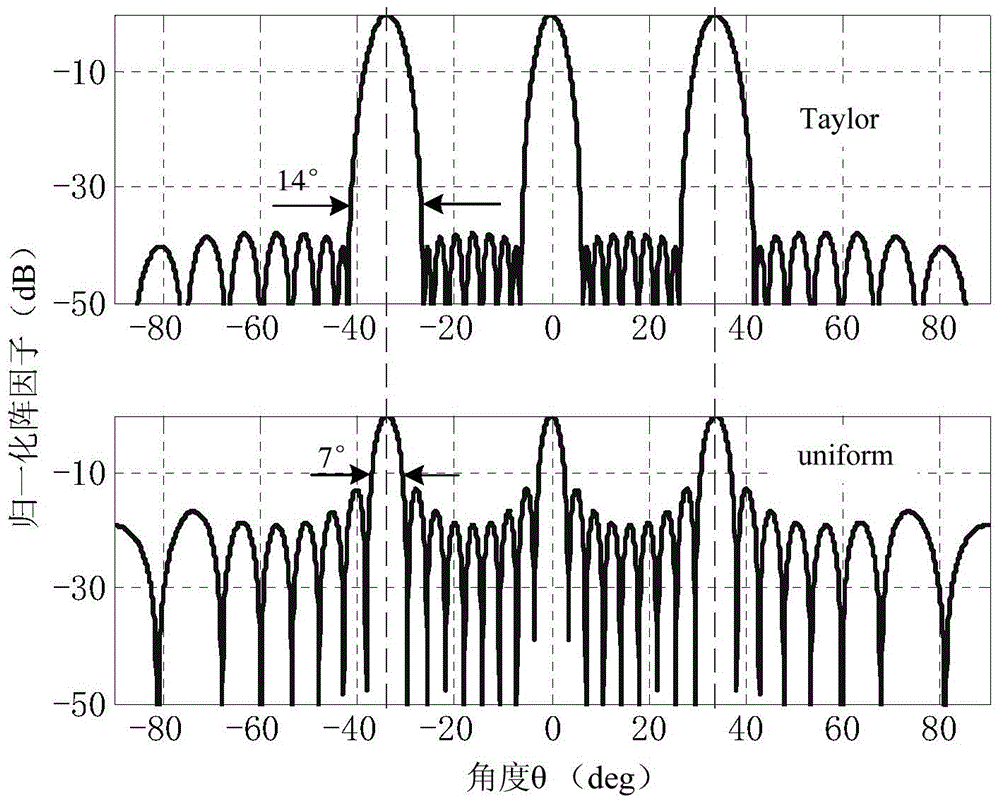
The invention provides an array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method, and relates to a modular array antenna. The method includes the steps that 1, array antenna parameters are selected; 2, the array antenna is divided into at least two modules; 3, a Taylor synthetic method is selected to calculate an array factor directional diagram of the modules; 4, an SPM synthetic method is selected to obtain a directional diagram with null steering, and the null steering angle is made to correspond to the grating lobe angle of the array factor directional diagram; 5, a directional diagram multiplication principle is adopted, the grating lobe of the array factor directional diagram is offset, the low-minor lobe radiation directional diagram is achieved, and the excitation amplitude of all arrays is controlled through the preset null steering angle; 6, if the obtained low-minor lobe radiation directional diagram cannot meet the design requirement, step 2 is executed, and the array antenna is regrouped. According to the array antenna Taylor-Schelkunoff polynomial design method, the excitation amplitude of all the arrays can be controlled through the preset null steering angle, a modular feed network is achieved through an equipower distributor with the phase and impedance being matched, the radiation loss is reduced, and the design and manufacturing cost is lowered.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Base station, communication control method, and processor
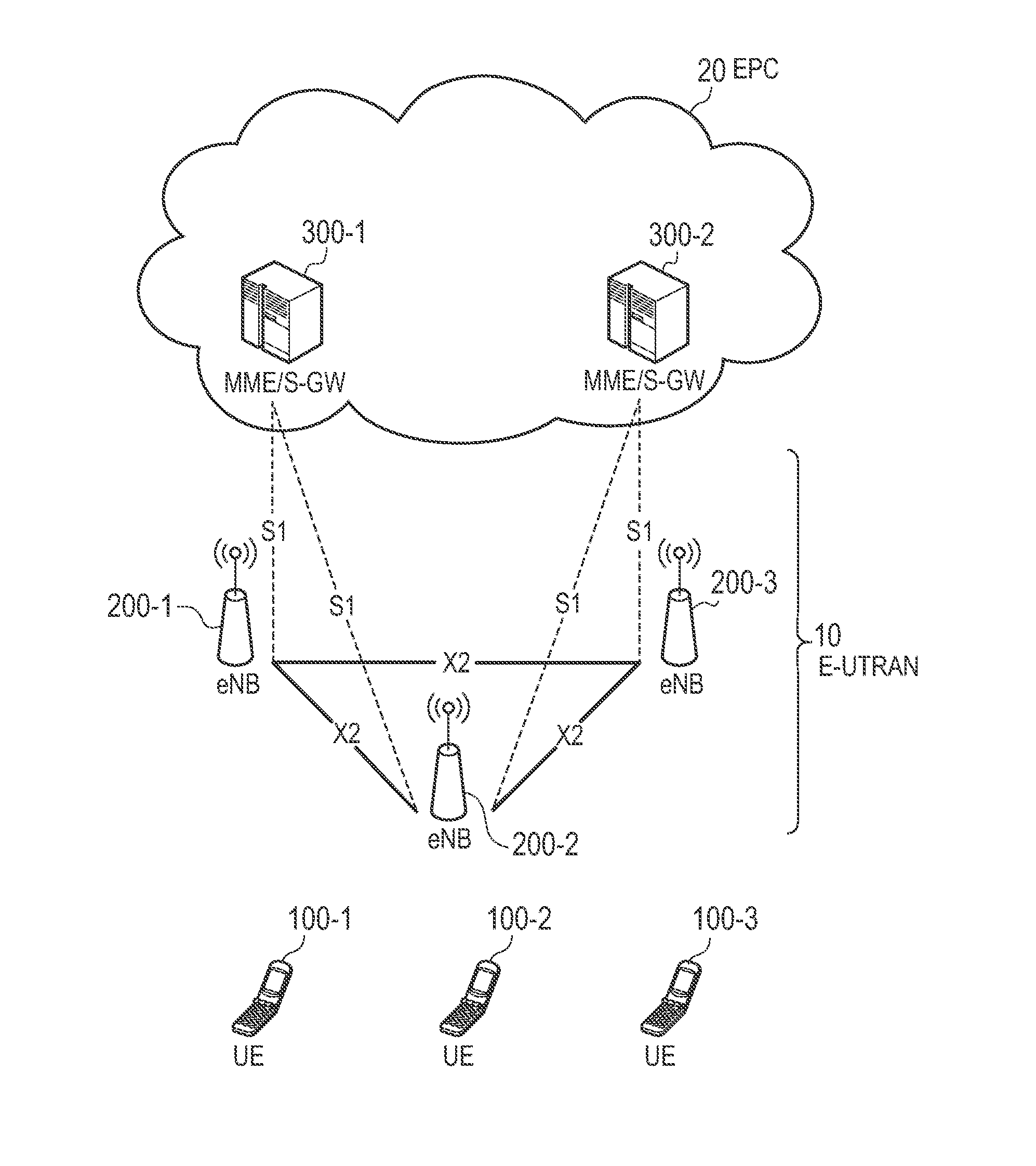
ActiveUS20160127024A1Efficient use ofSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversitySteering controlMobile communication systems
In a mobile communication system that supports downlink multi-antenna transmission, a base station managing a cell receives beamforming control information fed back from each of a plurality of beamforming target terminals connected to the cell, and null steering control information fed back from a null steering target terminal. When there exists no beamforming target terminal that feeds back the beamforming control information that coincides with the null steering control information, the base station selects, as a pair terminal, a beamforming target terminal that feeds back the beamforming control information containing a predefined rank indicator.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
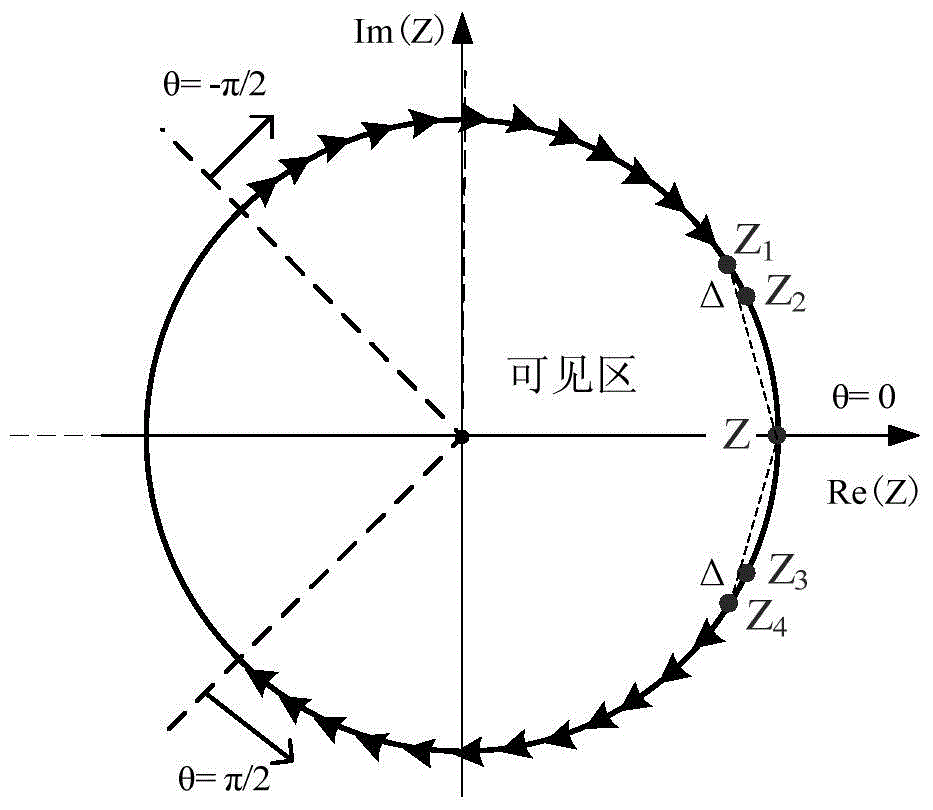
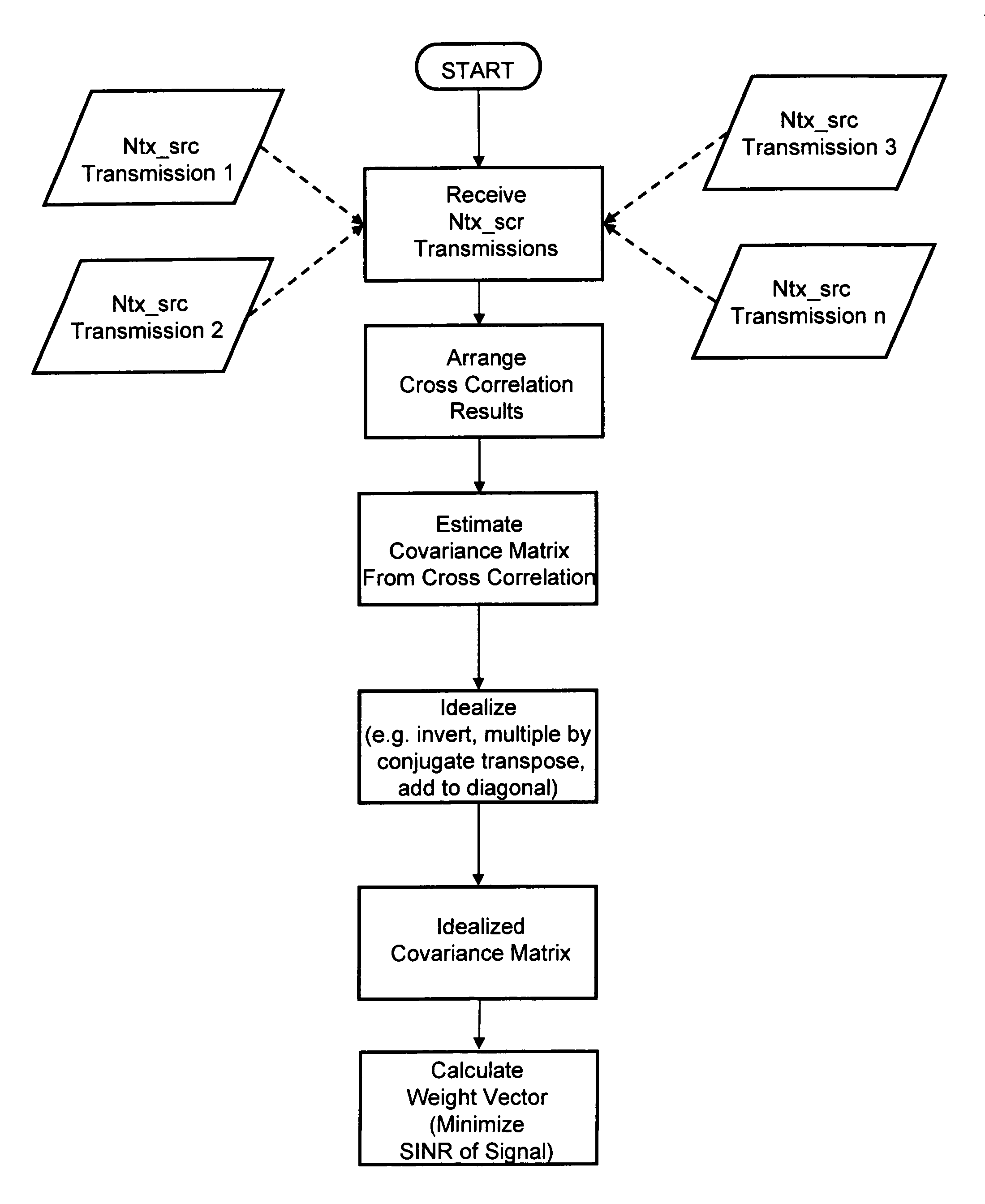
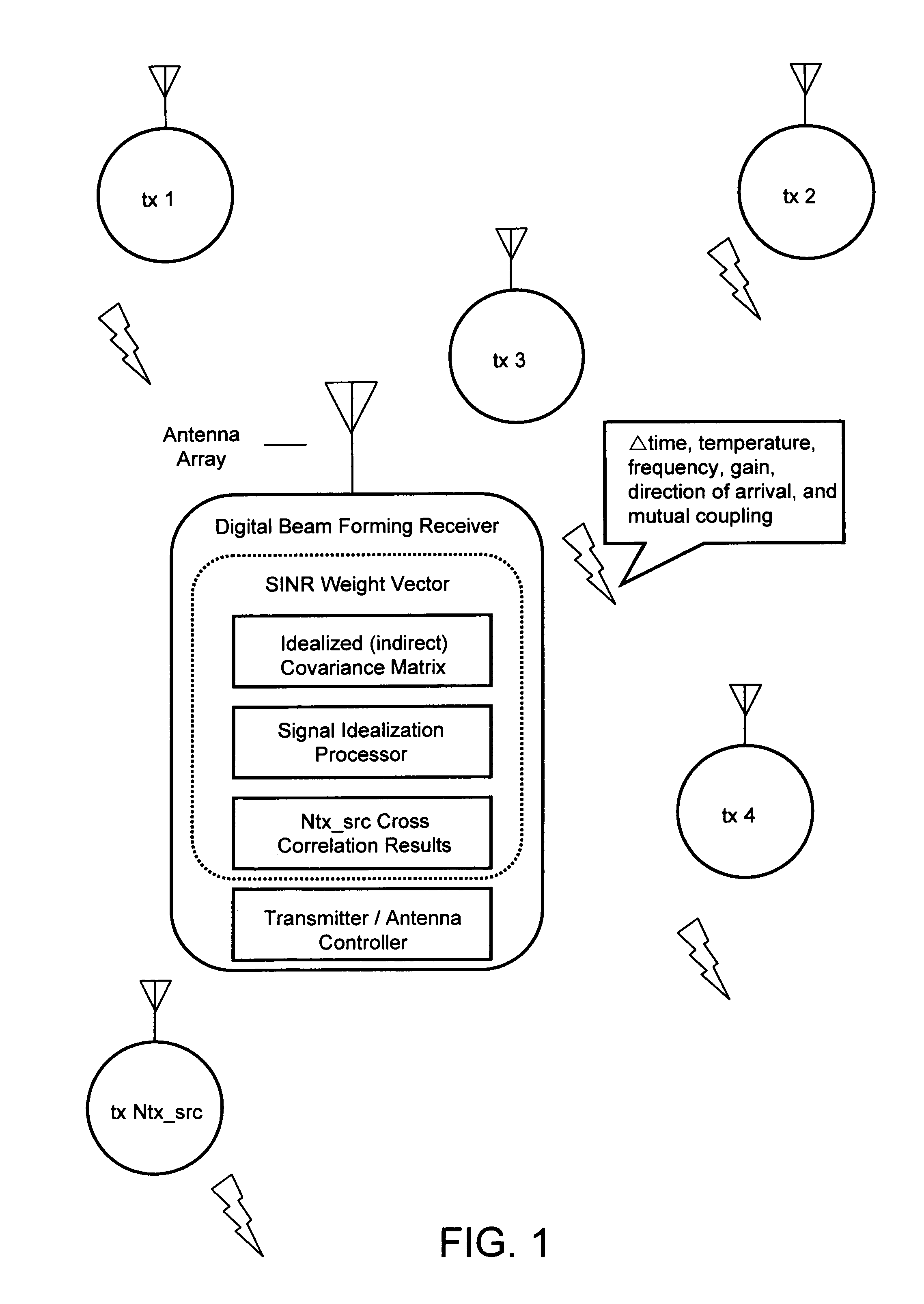
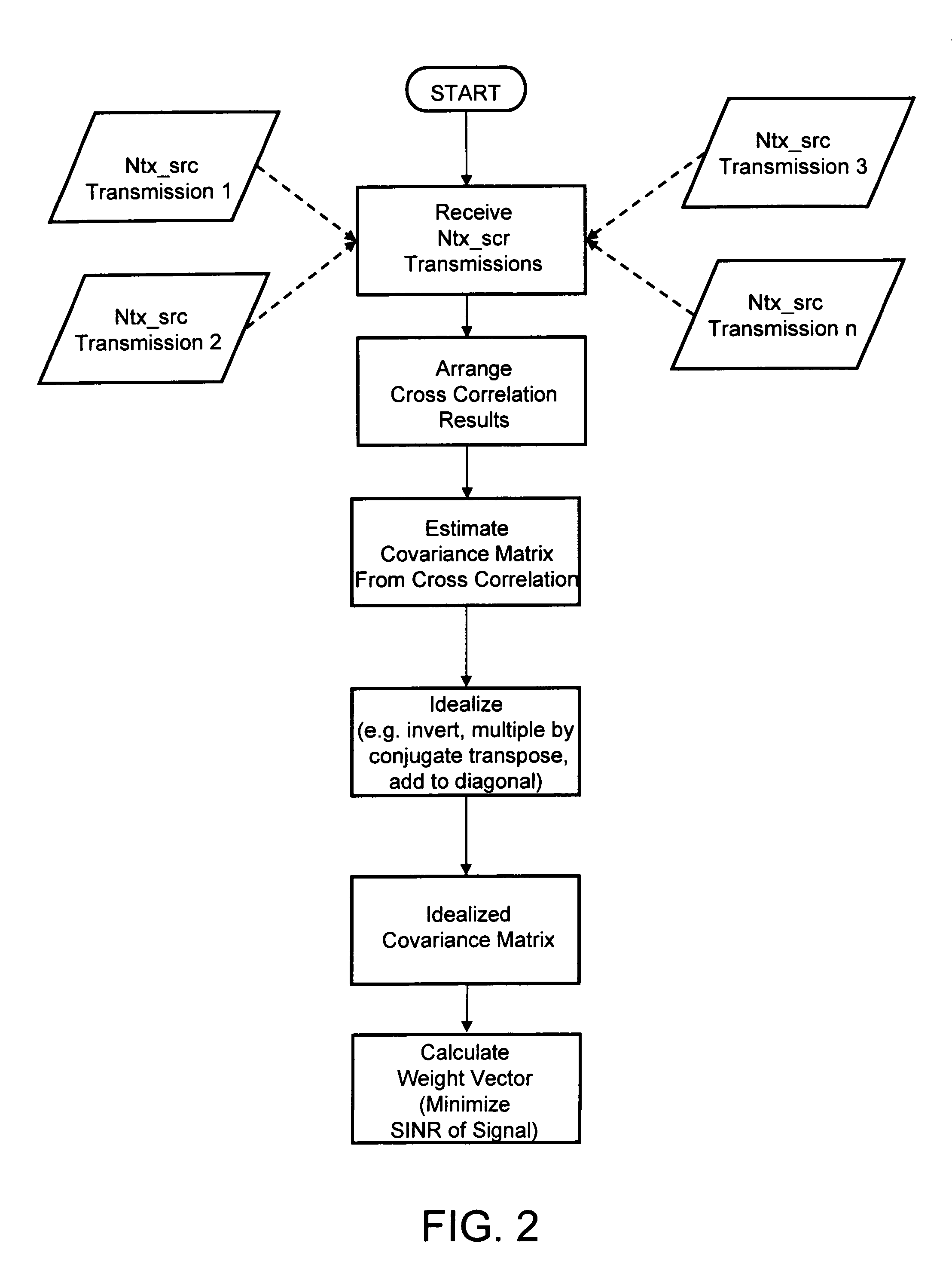
Digital beamforming method and apparatus for pointing and null steering without calibration or calculation of covariance matrix
InactiveUS7570211B1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
The method and system provides an improvement in signal to noise plus interference without utilizing a calculated covariance matrix or calibrated antenna array, and does not require knowledge of the array geometry. The system utilizes the cross correlation of the output of each antenna element to estimate a weight vector for resolving a signal in a multiple simultaneous source environment.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Formation method of MIMO tracking radar emission wave beam based on radio frequency stealth
InactiveCN105044684AGuaranteed multi-target tracking and detection performanceImprove RF Stealth PerformanceWave based measurement systemsWeight coefficientMulti target tracking
The invention provides a formation method of a MIMO tracking radar emission wave beam based on radio frequency stealth and belongs to the communication radar technology field. Through designing a weighting coefficient of an orthogonal transmitting waveform, a directional wave beam is formed at a target azimuth and a zero limit of a width is formed along an interception receiver direction. And a discrete long ball sequence method is used to form a wide wave beam along a target direction so as to simultaneously detect a wide sector. Finally, according to a wave beam gain of each target direction, radar radiation detection is performed on minimum power needed by a target. Through null steering and radiation power, radio frequency stealth performance of a MIMO radar is controlled and increased so that multi-target tracking detection performance of the MIMO radar is guaranteed and simultaneously radio frequency stealth performance is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Active MIMO antenna configuration for maximizing throughput in mobile devices
ActiveUS20130135163A1Improve antenna performanceImprove performanceIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsElectrically short antennasMimo antennaEngineering
An active antenna system and algorithm is proposed that provides for dynamic tuning and optimization of antenna system parameters for a MIMO system that will provide for greater throughput. As one or multiple antennas are loaded or de-tuned due to environmental changes, corrections to correlation and / or isolation are made by tuning the active antenna. A null-steering technique is implemented to alter the near-field and far-field characteristics to aid in modifying correlation and isolation in the multi-antenna system.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Radar main lobe interference suppression method based on neural network
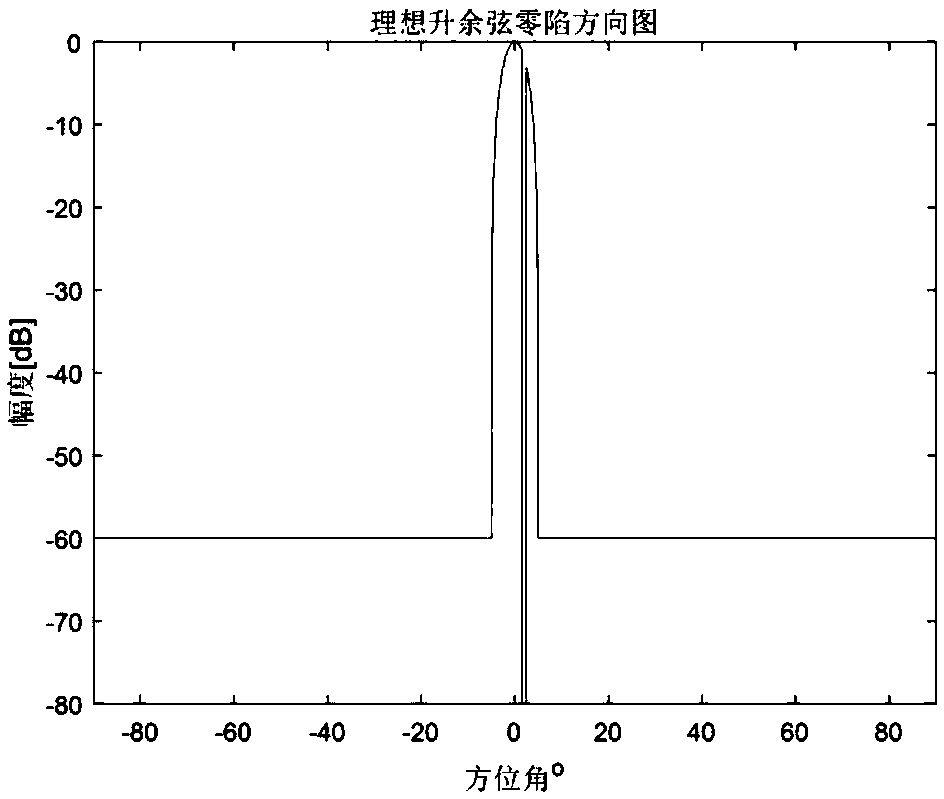
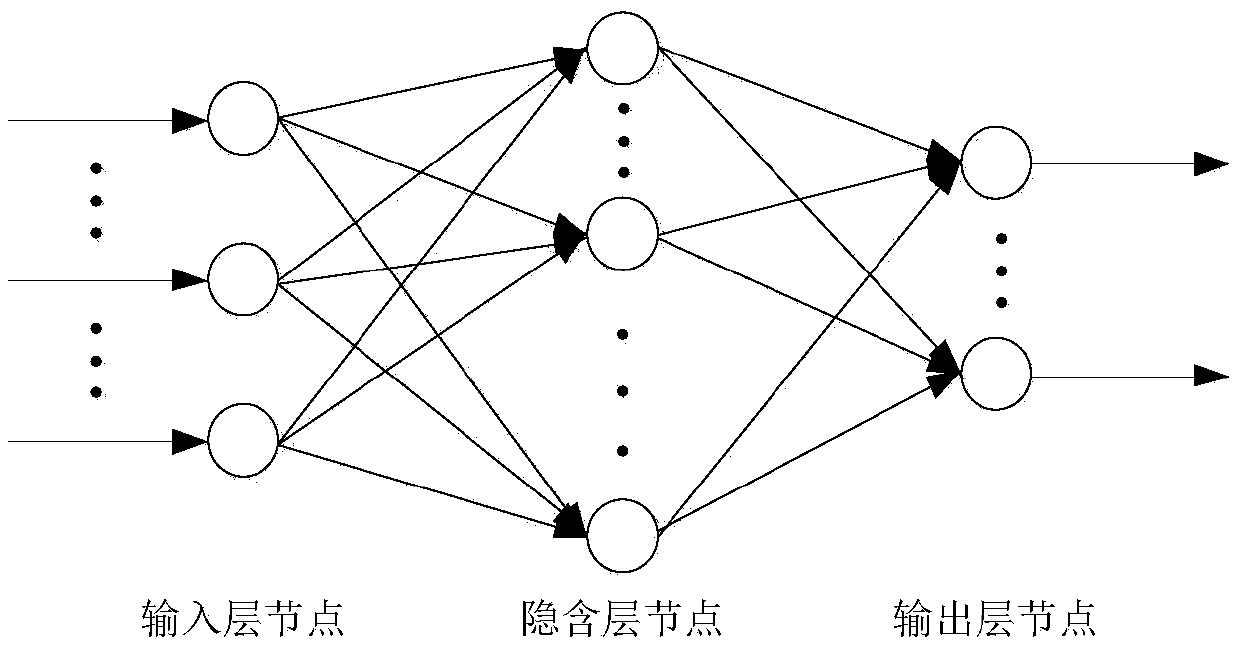
InactiveCN108957406AImprove accuracyReduce energy lossWave based measurement systemsNerve networkRadar
The invention discloses a radar main lobe interference suppression method based on a neural network and belongs to the technical field of radar. The method comprises a step of determining a steering vector of a received signal according to a geometric model of a radar array element arrangement after a main lobe interference direction is known and constructing a received signal model of the targetsignal and an interference signal, a step of constructing an ideal low side lobe null steering directional diagram according to the known main lobe interference direction, a step of creating a training sample through an input signal, taking the ideal low side lobe null steering directional diagram as an expected signal sample, establishing a suitable neural network model on the above basis and training, and a step of applying the trained neural network and verifying the input signal to obtain an output directional diagram. According to the method, the neural network is employed to suppress themain lobe interference, compared with the conventional method, the method of the invention has the advantages that null steering is formed at an interference position, the shape preserving of a mainlobe directional diagram and a low side lobe level are achieved, an ideal directional diagram is obtained, the accuracy of the angle measurement is improved, the energy loss of a target signal is reduced, the stability of a system is improved, the requirements of angle measurement can be satisfied well, and therefore, the system performance is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Main lobe interference suppression method and device
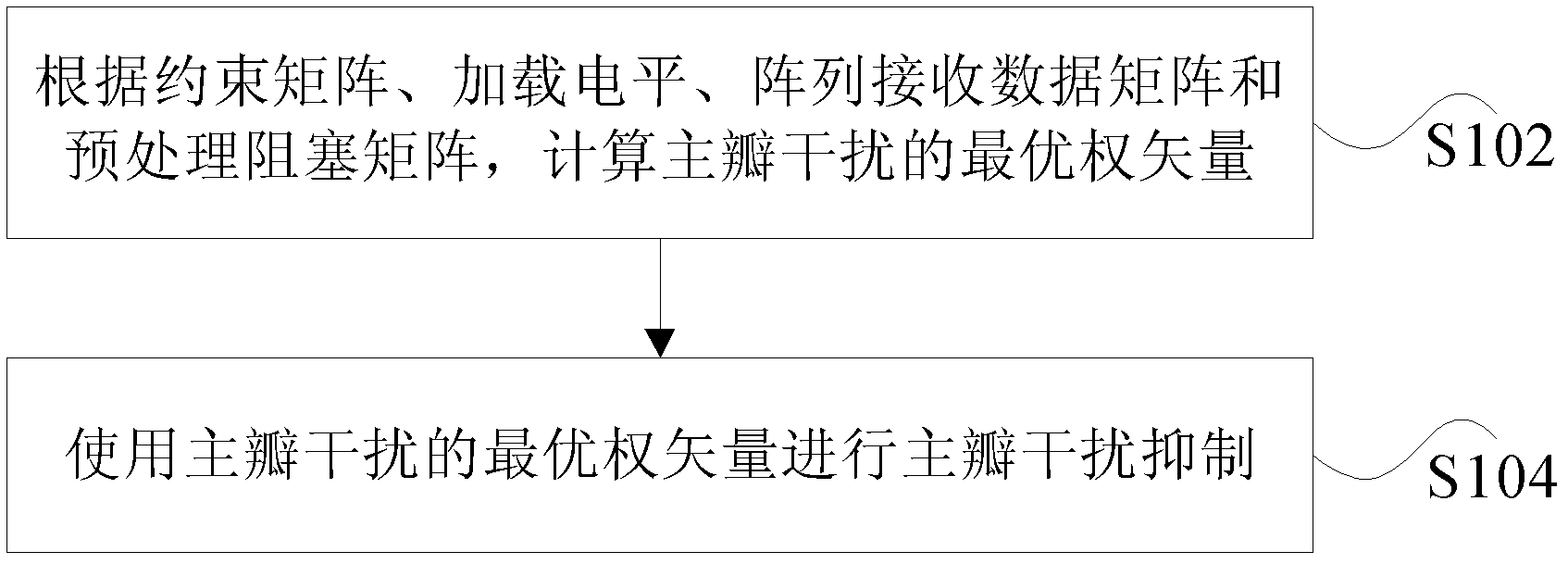
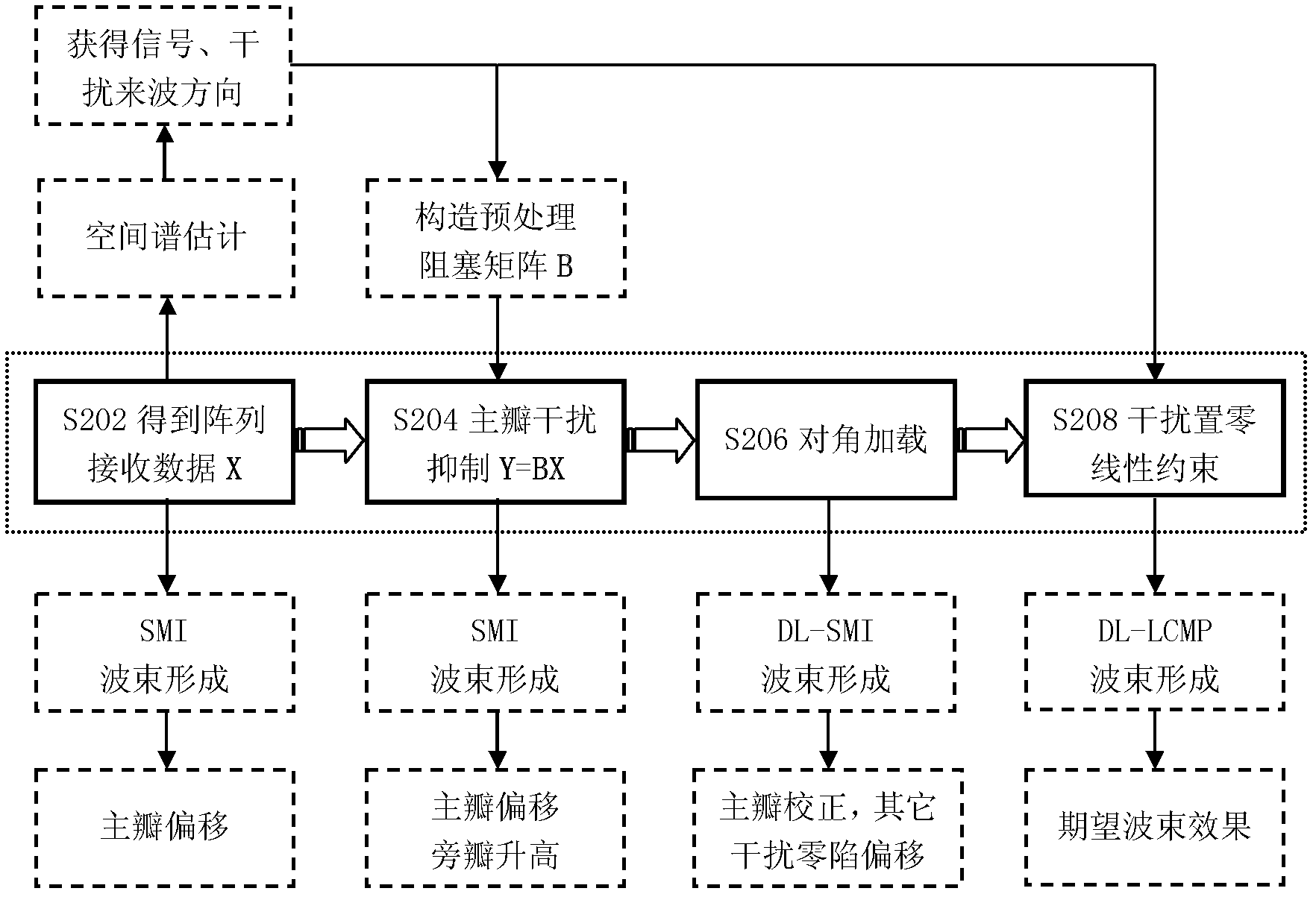
ActiveCN103178881AImproved main beam pointingEnhanced inhibitory effectSpatial transmit diversityOptimal weightEngineering
The invention discloses a main lobe interference suppression method and device. The method includes calculating an optimal weight vector of main lobe interference according to a constraint matrix, a load electrical level, an array receive data matrix and a preprocessing block matrix; and using the optimal weight vector of main lobe interference to perform main lobe interference suppression. By means of the main lobe interference suppression method and device, main beams are enabled to point to an expected target direction, and simultaneously, main lobe interference is inhibited from forming deep null steering in other interference directions.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Matrix reconstruction based adaptive anti-interference multipath multi-beam forming method
InactiveCN105158741AFast convergenceImprove the noise-to-interference ratioWave based measurement systemsDigital signal processingDecomposition
The invention discloses a matrix reconstruction based adaptive anti-interference multipath multi-beam forming method, and belongs to the field of digital signal processing. The method comprises the steps of firstly acquiring an autocorrelation matrix of interference signals through a method of matrix reconstruction, further acquiring an orthogonal complementary space of an interference subspace, then projecting array reception data to the orthogonal complementary space of the interference subspace so as to achieve the purposes of suppressing incoherent interference signals and acquiring data only containing coherent signals, and finally acquiring an array weighted vector of an adaptive anti-interference multipath multi-beam forming device through a method of eigenvalue decomposition. Under the condition of knowing the number of the interference signals and the range of an incident angle of each coherent signal in incident signals, multiple beams are formed in the incident direction of the coherent signals so as to carry out phase-coherent accumulation effectively on the coherent signals, and information of the coherent signals are sufficiently utilized; and null steering is formed at the incident direction of the interference signals so as to achieve the purposes of suppressing interference and improving the signal to interference and noise ratio of array output.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
United anti-interference method based on array antennas and GPS/SINS
ActiveCN103792550AImprove anti-interference abilitySuppression of interfering signalsNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteVIT signals
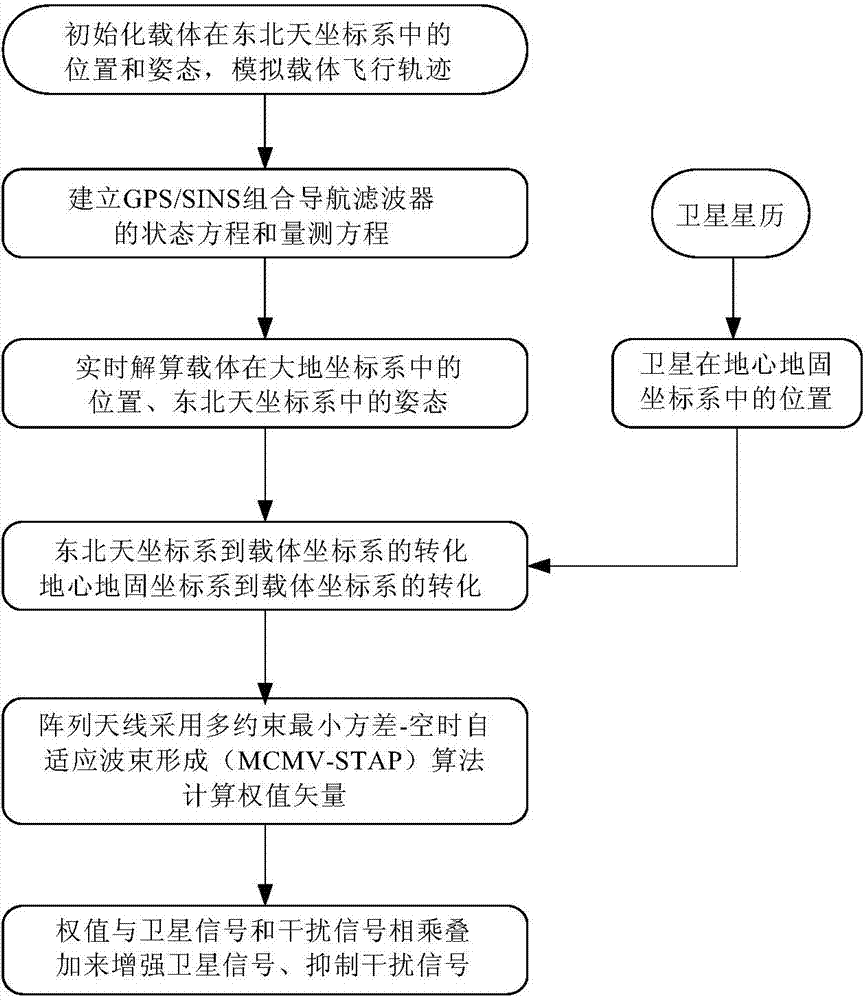
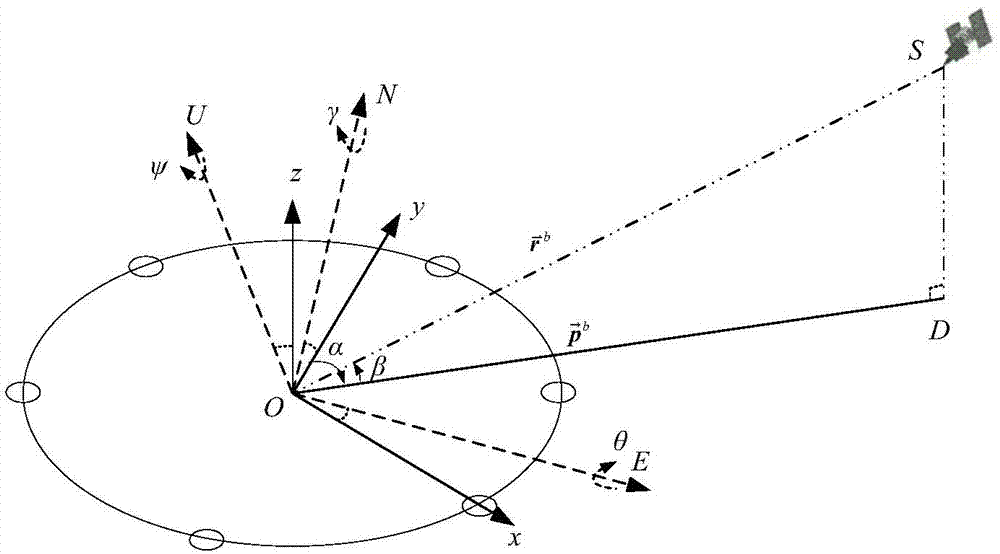
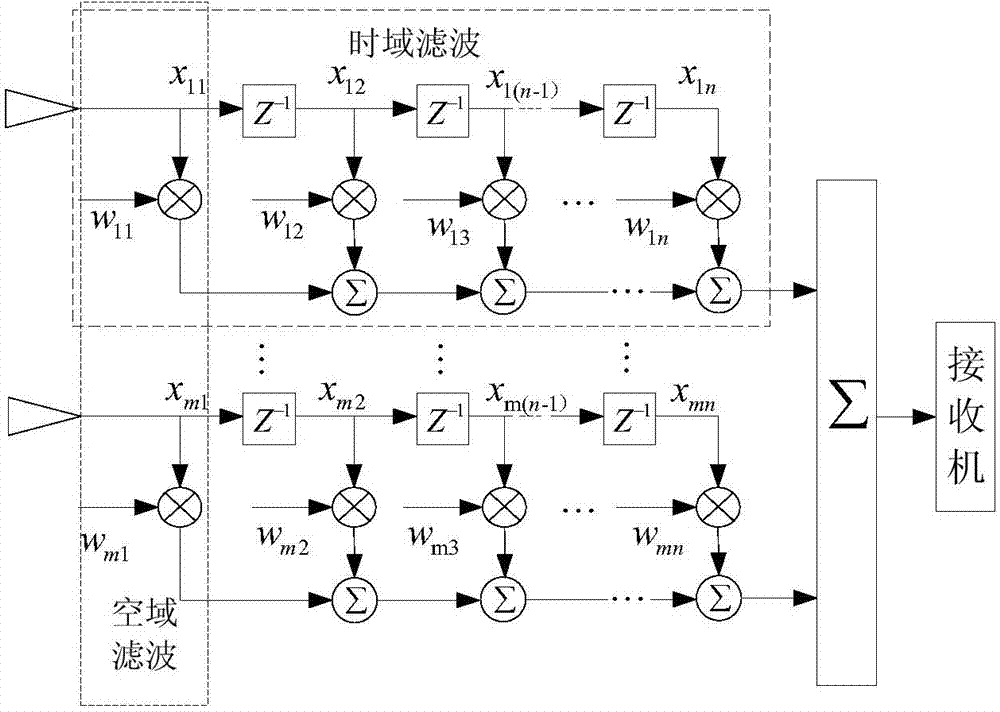
The invention provides a united anti-interference method based on array antennas and a GPS / SINS. The method includes the steps that after the position and the posture of a carrier are initialized, a GPS / SINS integrated navigation state equation and a measurement equation are built; the position and the posture of the carrier are provided in real time through GPS / SINS integrated navigation, and the current position of a satellite is calculated according to satellite ephemeris information to obtain a guiding vector from the satellite to the carrier; the guiding vector serves as prior information of a multi-constraint minimum variance space-time self-adaptive processing algorithm and suppresses broadband interference and narrow-band interference in a space domain and a time domain at the same time. According to the united anti-interference method, wave beams can be formed in the direction of a plurality of visual satellites at the same time, and null steering is formed in the interference direction, so that interference signals are suppressed while satellite signals are enhanced. An antenna array of a round structure is adopted, the position and the posture of the carrier are provided for forming the wave beams of the array antennas through GPS / SINS integrated navigation, the position of satellite is provided by the adoption of a satellite ephemeris, and therefore the prior information is provided for forming the wave beams.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Adaptive anti-interference method for satellite navigation system based on 2-norm multi-target optimization
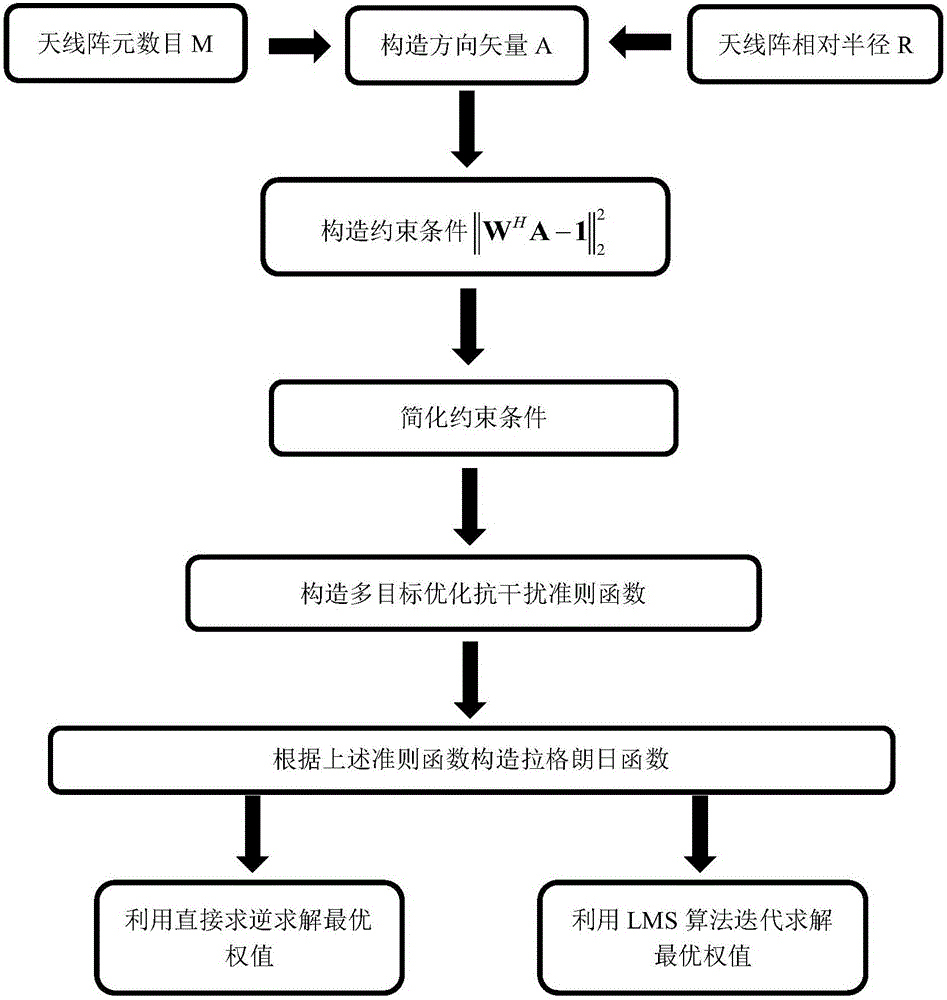
ActiveCN106324625AAddresses issues with gain unevenness in wide and non-interfering directionsTake up less resourcesSatellite radio beaconingAntenna gainMatrix optimization
The invention discloses an adaptive anti-interference method for a satellite navigation system based on 2-norm multi-target optimization, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, constructing a direction vector and a constraint condition; 2, simplifying the constraint condition; 3, constructing a multi-target optimization anti-interference criterion; 4, solving the optimal solution to the multi-target optimization anti-interference criterion. According to the invention, a 2-norm matrix optimization function which enables the antenna gain in all directions to be constant is added to a single optimization function of a conventional blind anti-interference algorithm, thereby enabling an original optimization problem to be converted into multi-target optimization from single-target optimization, enabling the antenna gains in all directions to tend to be constant, and solving the problems that a directional diagram null steering opening is large in width in the blind anti-interference algorithm and the gains in non-interference directions are not flat.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
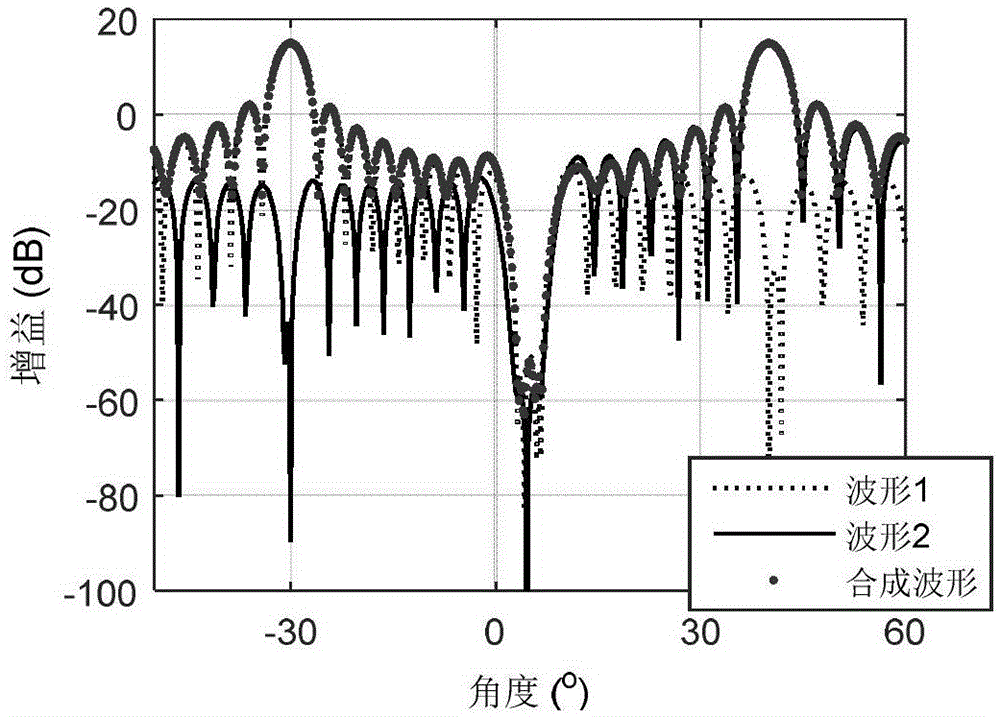
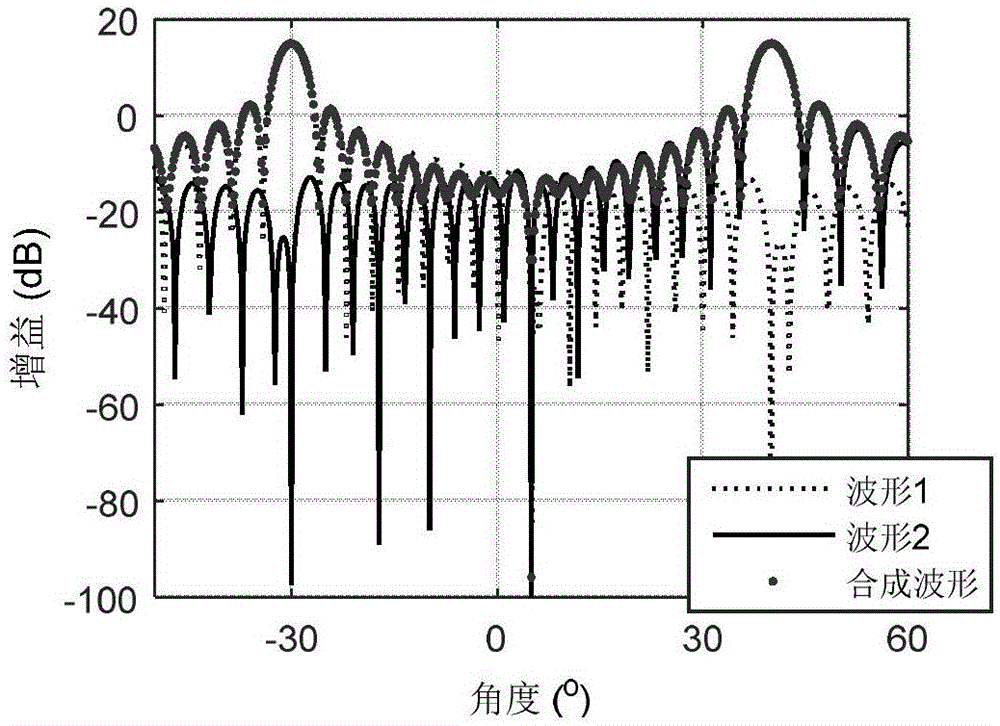
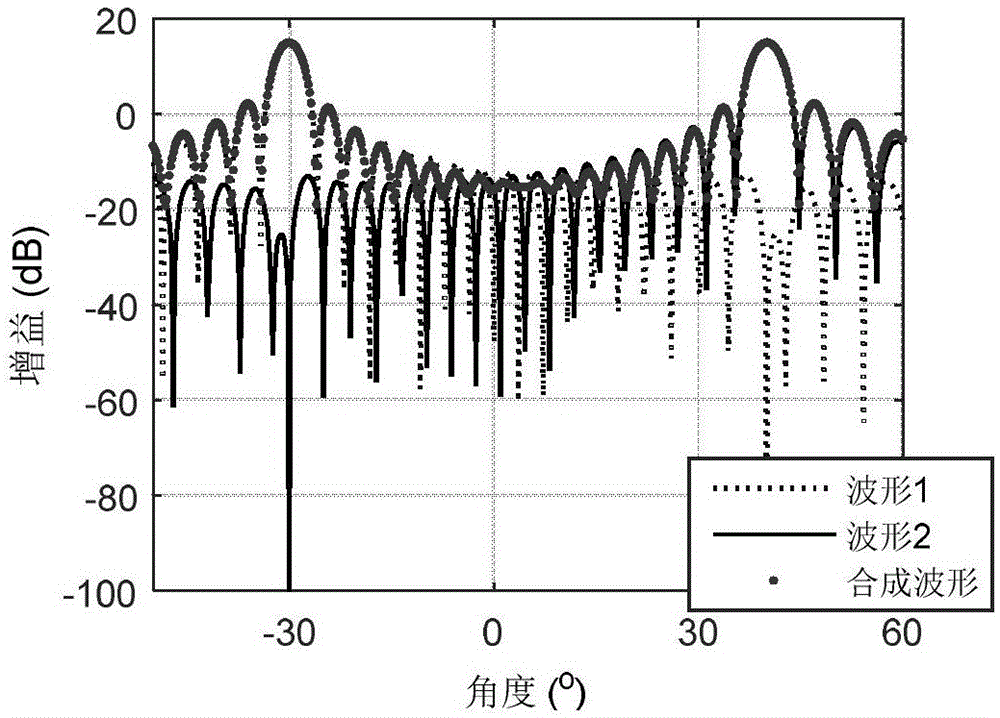
Fixed null-steering beamforming method
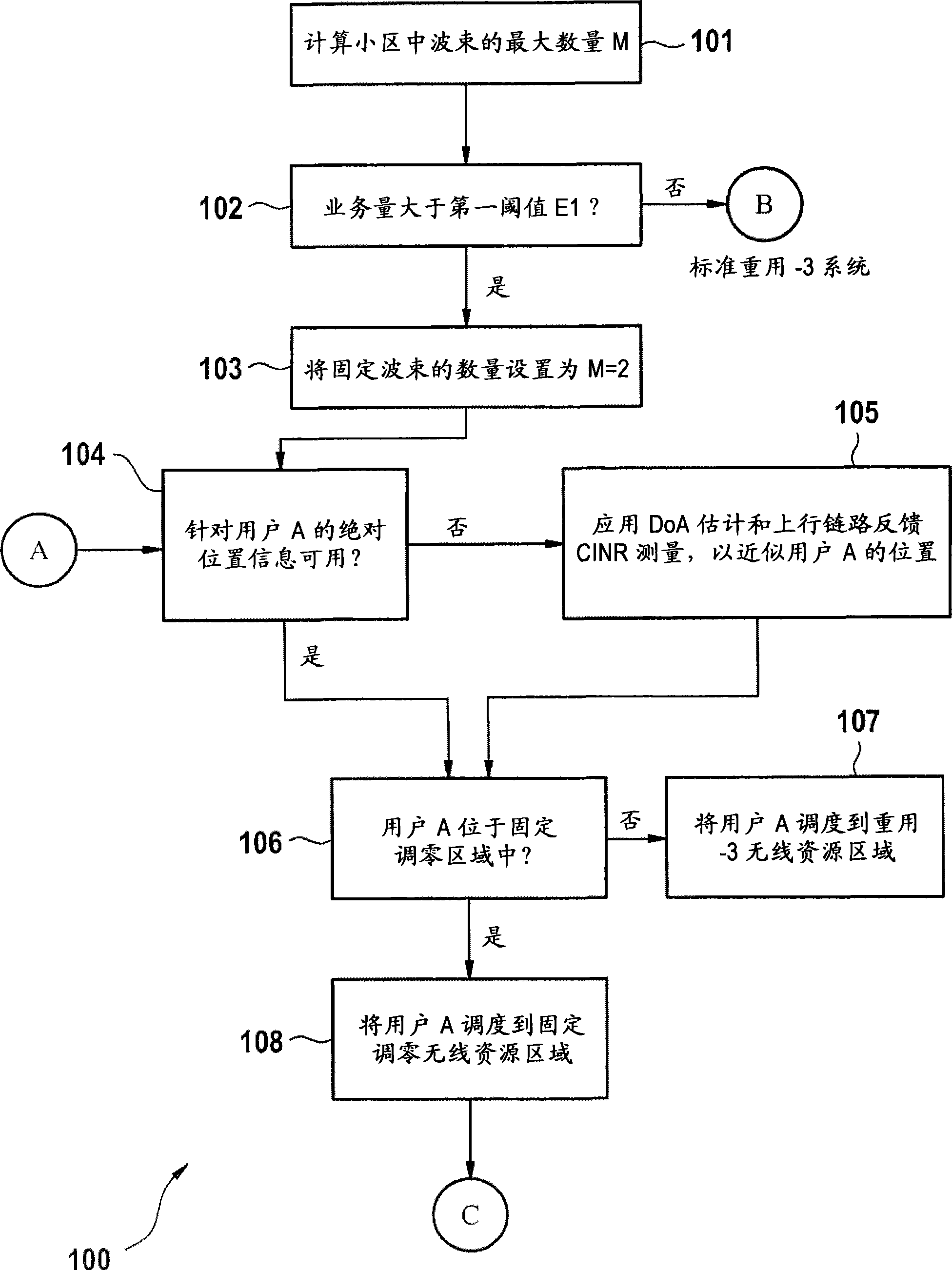
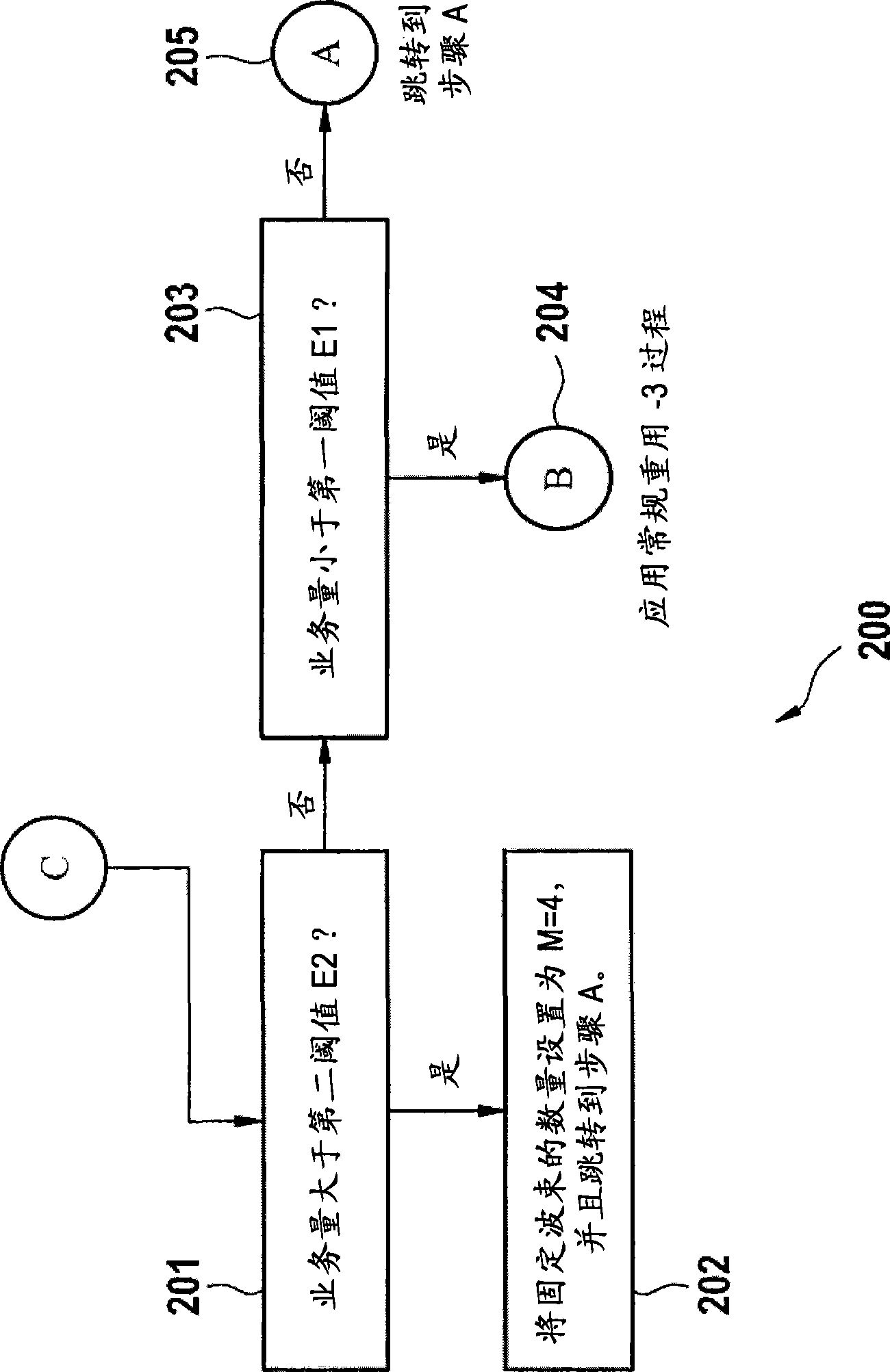
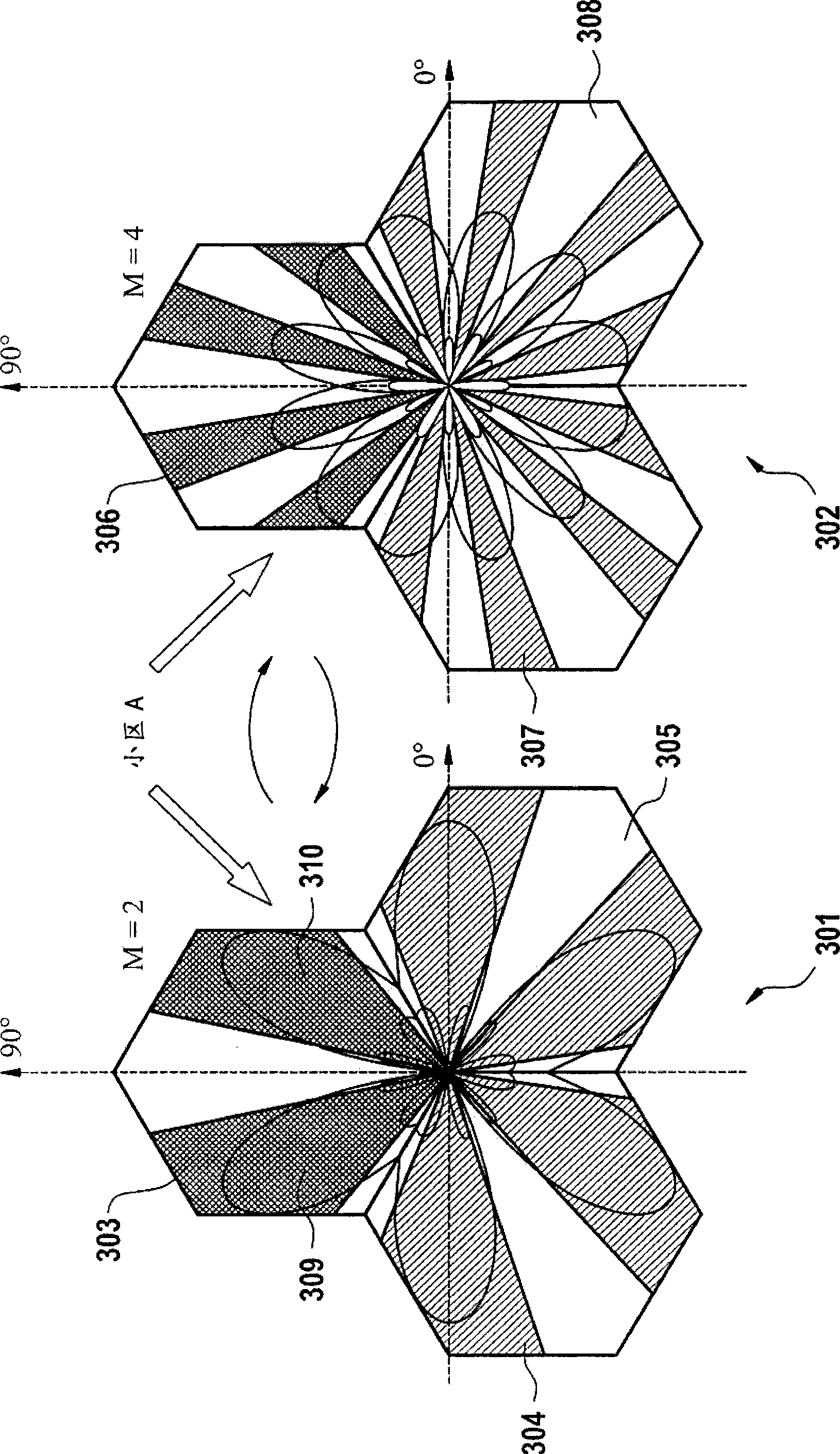
The invention relates to a fixed null-steering beamforming method. Particularly, the invention relates to a frequency reuse method in a base station of a Frequency Division Multiplexing Access wireless communication system, the wireless communication system comprising at least the base station adapted for covering a cell, at least one wireless terminal coupled to the base station, the method comprising the steps of: calculating a maximum number of beams per cell by obtaining a number of antennas of the base station; initiating a fixed null-steering beamforming by setting a number of orthogonal fixed beams to a first constant on a portion of the cell, if a traffic of the base station is bigger than a first threshold; obtaining an absolute or an approximate location of the wireless terminal within the cell; scheduling the wireless terminal to fixed null-steering resources, if the absolute or approximate location of the wireless terminal is within the beam zone of the cell; setting the number of orthogonal fixed beams to a second constant of the fixed null-steering beamforming, if the traffic is bigger than a second threshold.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Feedback decision type large-dynamic self-adaption array antenna beam forming method
ActiveCN103441788ASolve the problem of "self-zero trap"Easy to implementSpatial transmit diversityInterference resistanceSelf adaptive
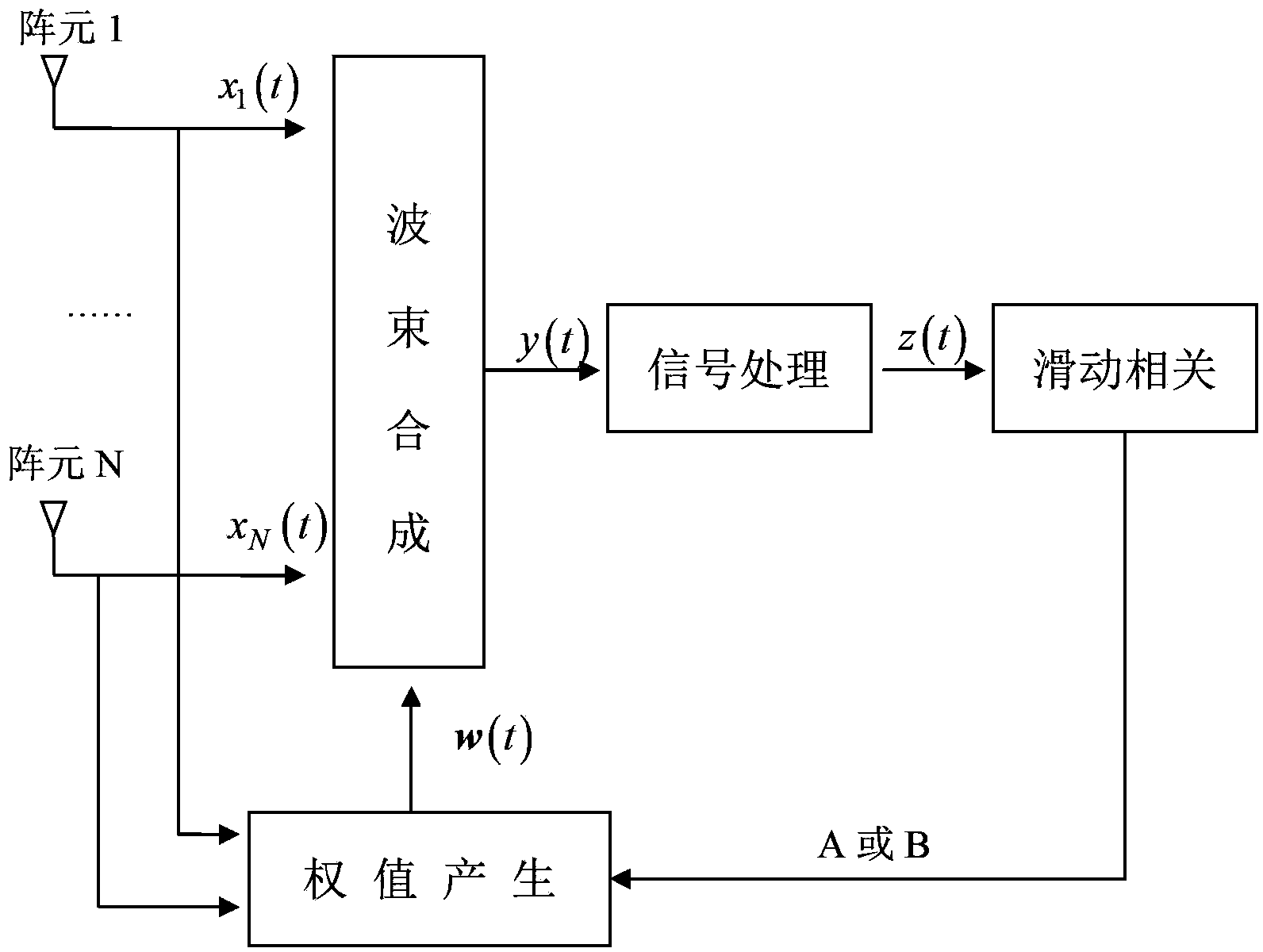
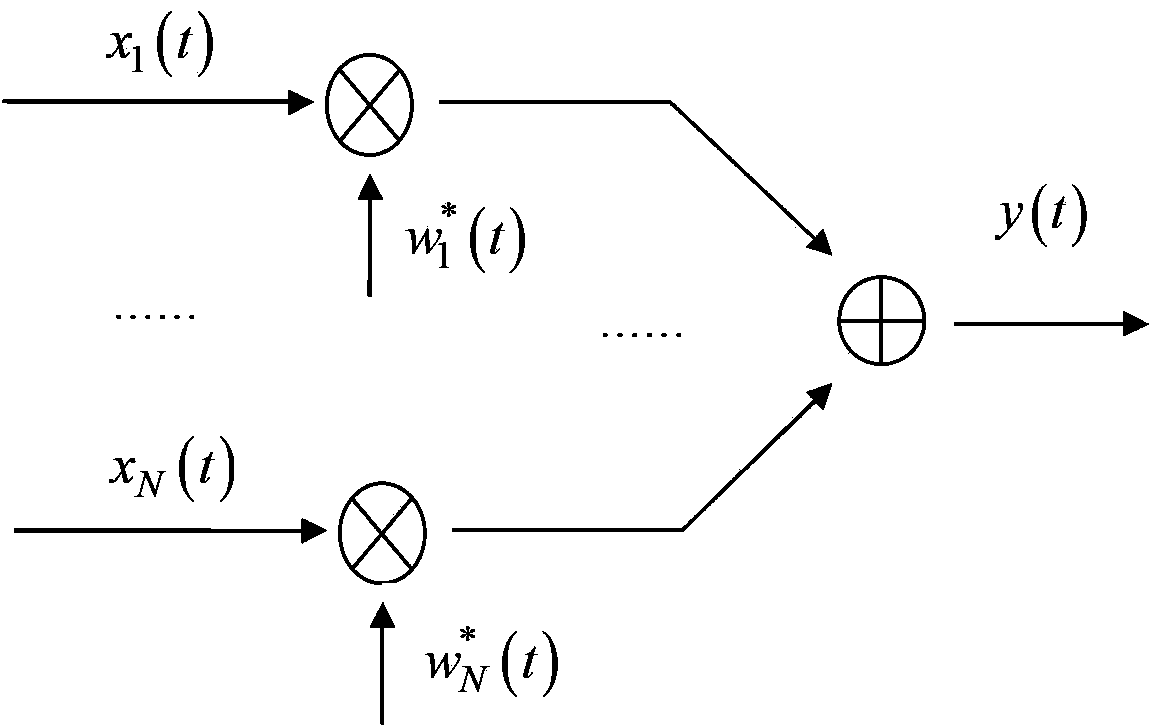
The invention discloses a feedback decision type large-dynamic self-adaption array antenna beam forming method. According to the method, a transmitter transmits sign frames periodically, and a self-adaption array antenna on a receiver selects different weight vector calculating methods according to decision feedback on base band demodulation signals. The array antenna of the receiver comprises an array face, a weight value generating module, a beam forming module, a signal processing module and a sliding correlation module. The signals generated after beams are formed are demodulated by the signal processing module, and then base band signals are output; sliding correlation operation is performed on the base band signals and local pseudo-random codes, the correlation operation result controls a weight vector calculating method in the weight value generating module, working is performed in the phased array mode if the sliding correction module outputs the correlation peak, and working is performed in the anti-interference mode if the sliding correction module does not output the correlation peak. The method overcomes the self null steering problem of self-adaption array antenna expectation signals under large dynamic, is easy to achieve in engineering and can be applied to various anti-interference wireless communication transmit-receive systems.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com