Fixed null-steering beamforming method
A technology of fixed beam and zero adjustment, which is applied in the field of computer program products, can solve the problems of reducing sensitivity and achieve the effect of low channel interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
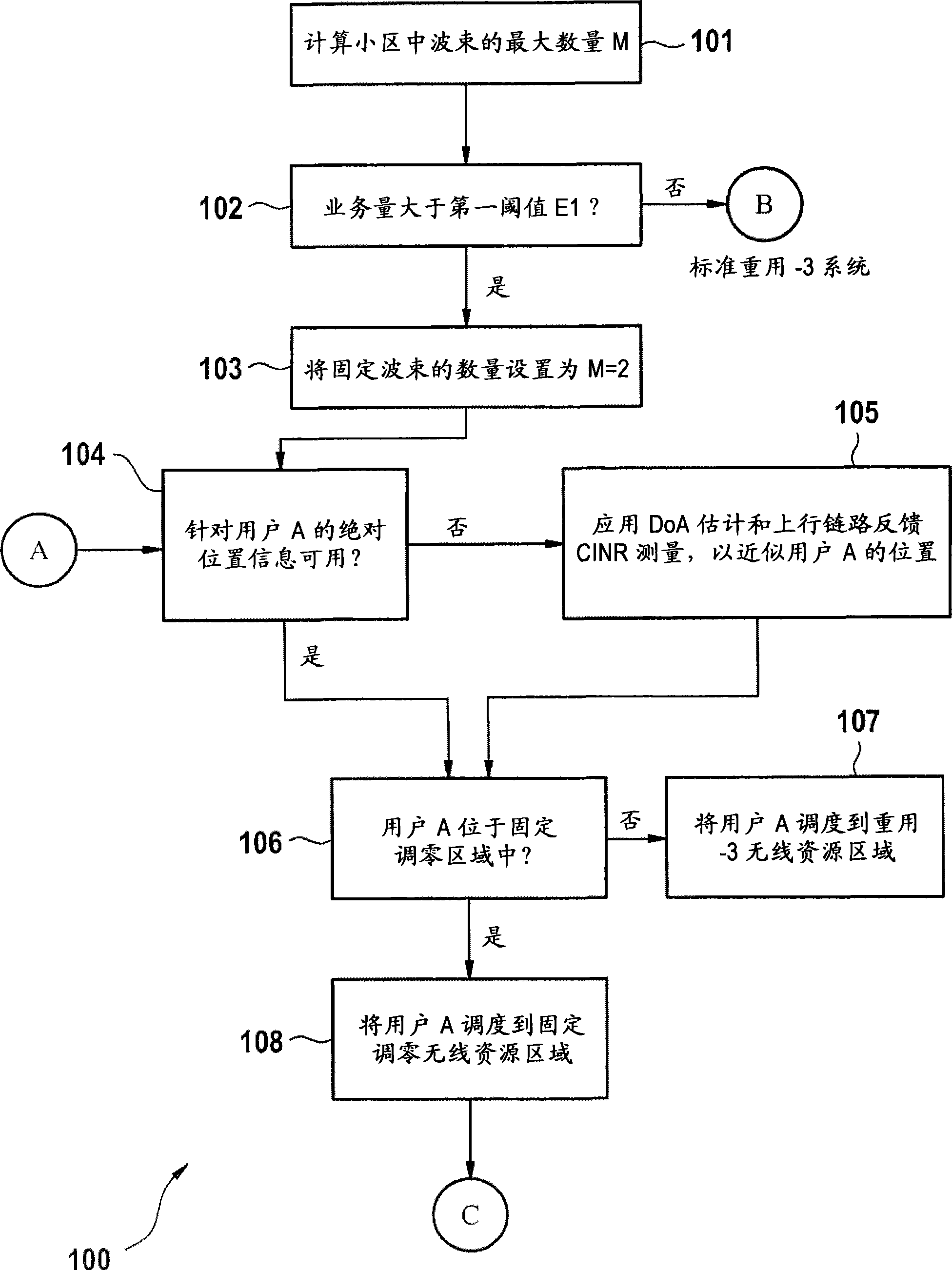
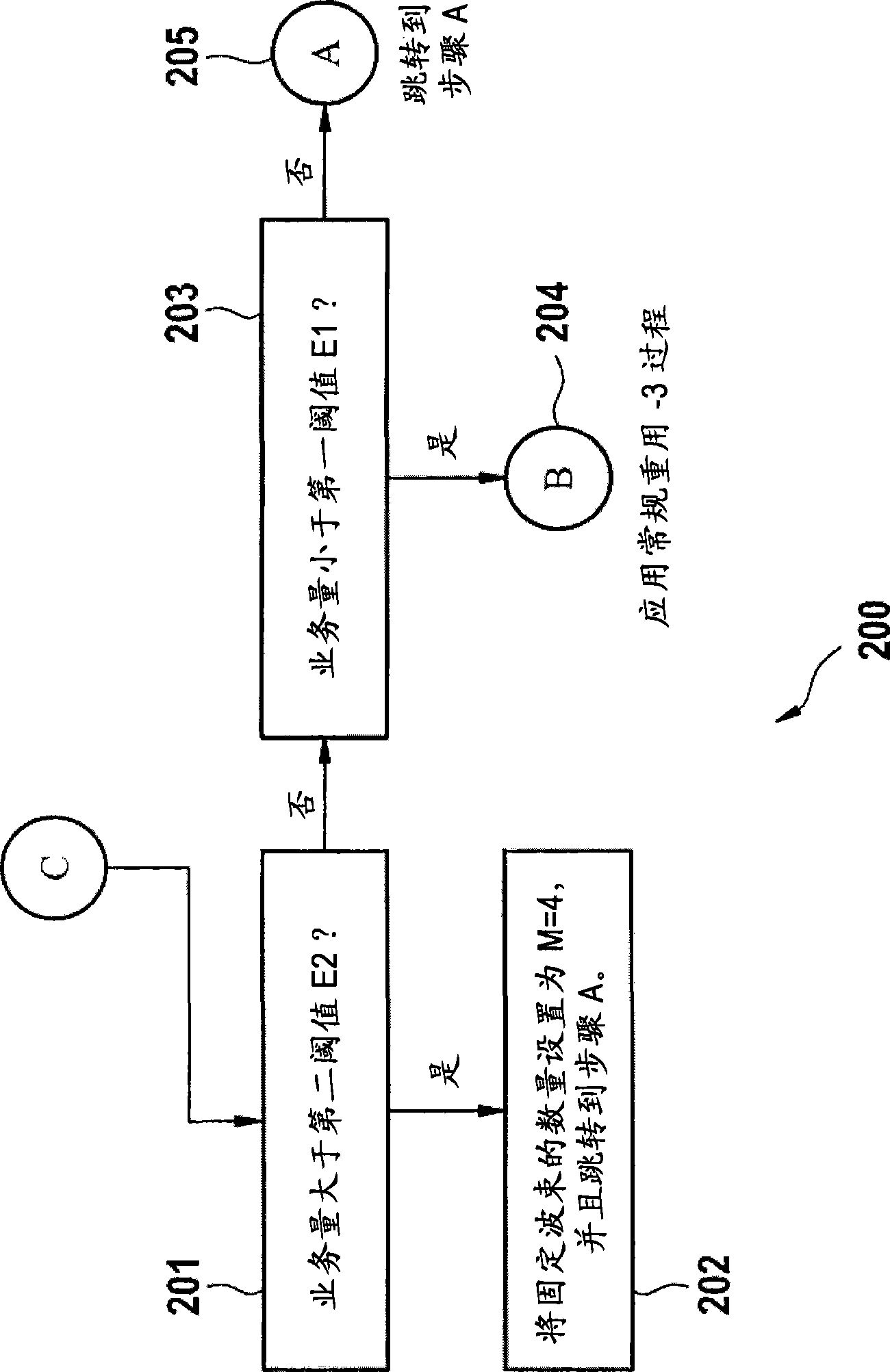
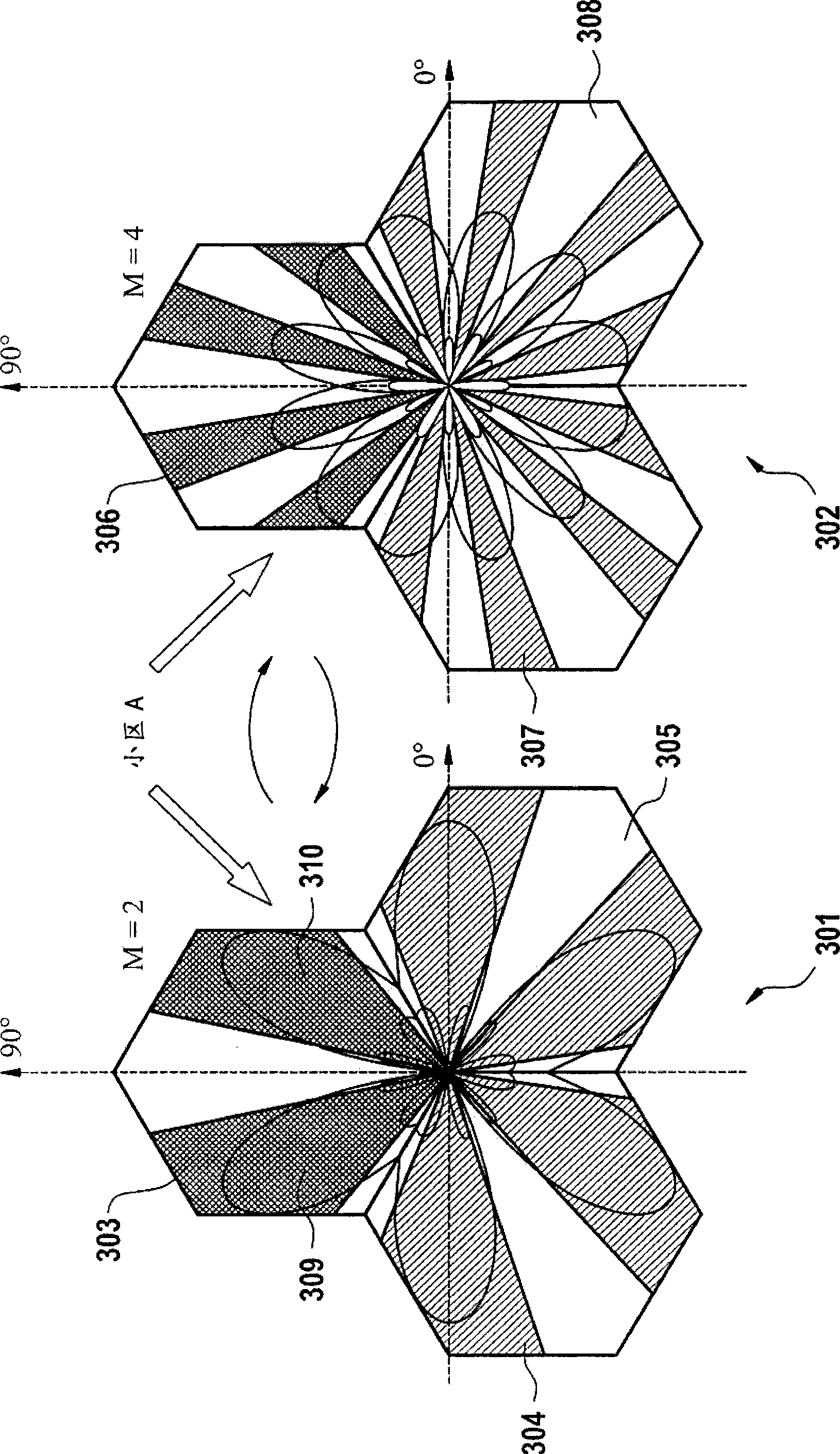
[0027] figure 1 A method 100 of fixedly nulled beamforming in a base station is shown, comprising a first step 101 in which the maximum number M of beams in a cell is calculated max . This calculation is primarily dependent on the number of antennas the base station is using to transmit to wireless terminals within the cell and to the sector angle coverage within the cell. Maximum number of beams M max Indicates an upper bound on the possible beams that can be allocated within a cell. In a second step 102, the traffic volume of the base station is measured and compared with a first threshold E1. The traffic represents all communications between the base station and all wireless terminals within the cell covered by the base station. If the traffic volume is less than the first threshold E1, the standard reuse-3 system is used and no fixed orthogonal beams are formed in the cell. Otherwise, if the traffic volume is greater than the first threshold, then in the third step 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com