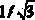Patents
Literature
531 results about "Cell cluster" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
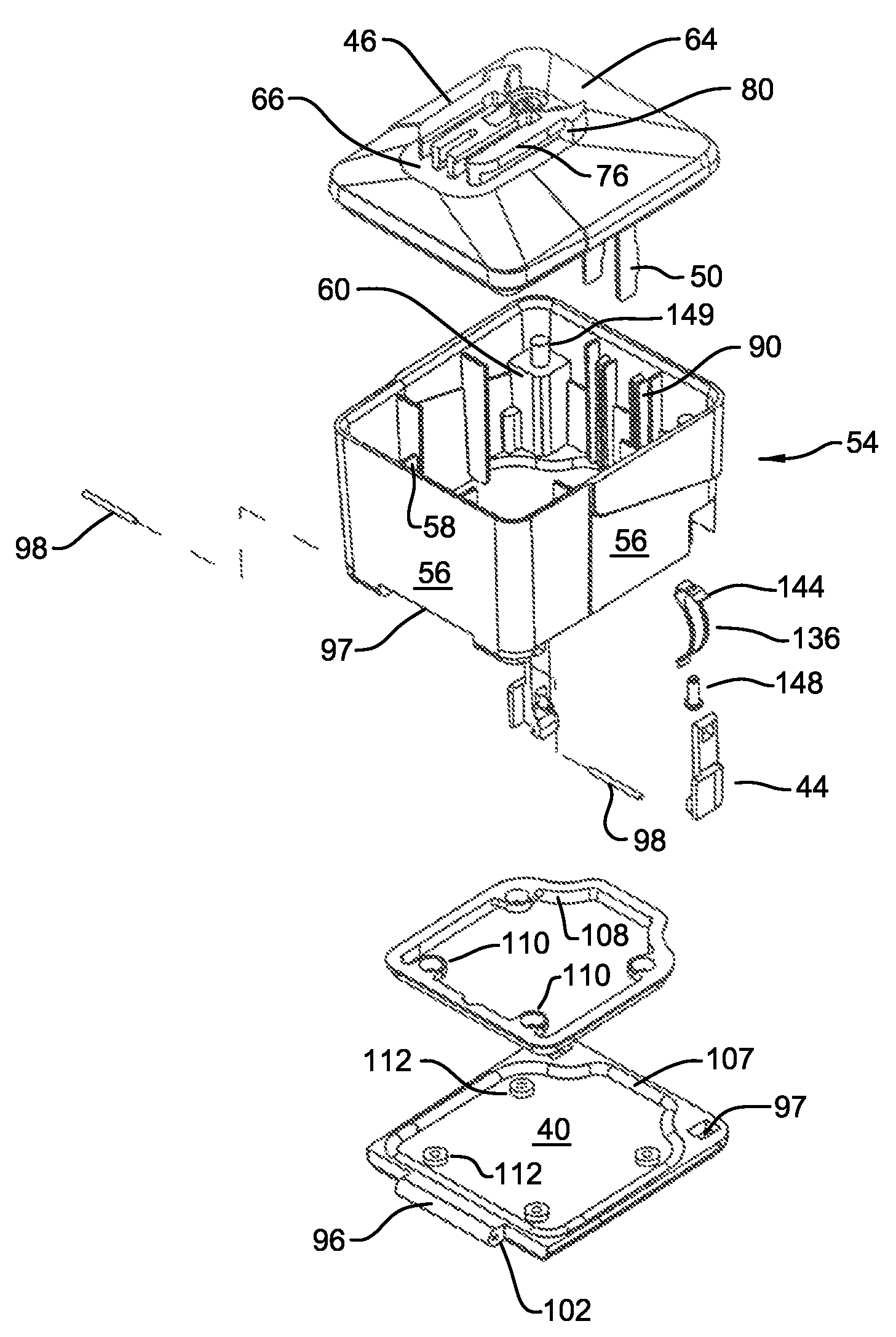
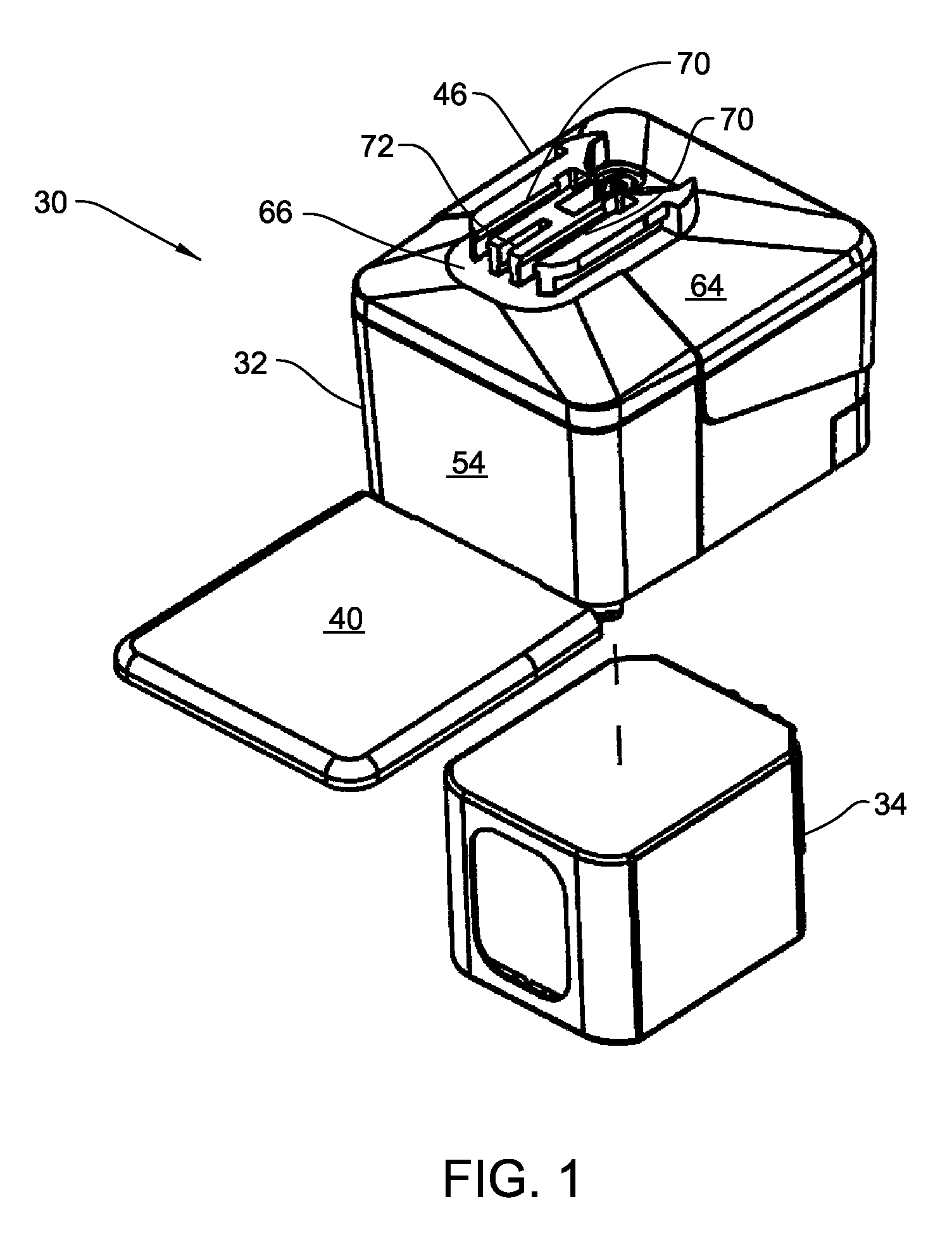
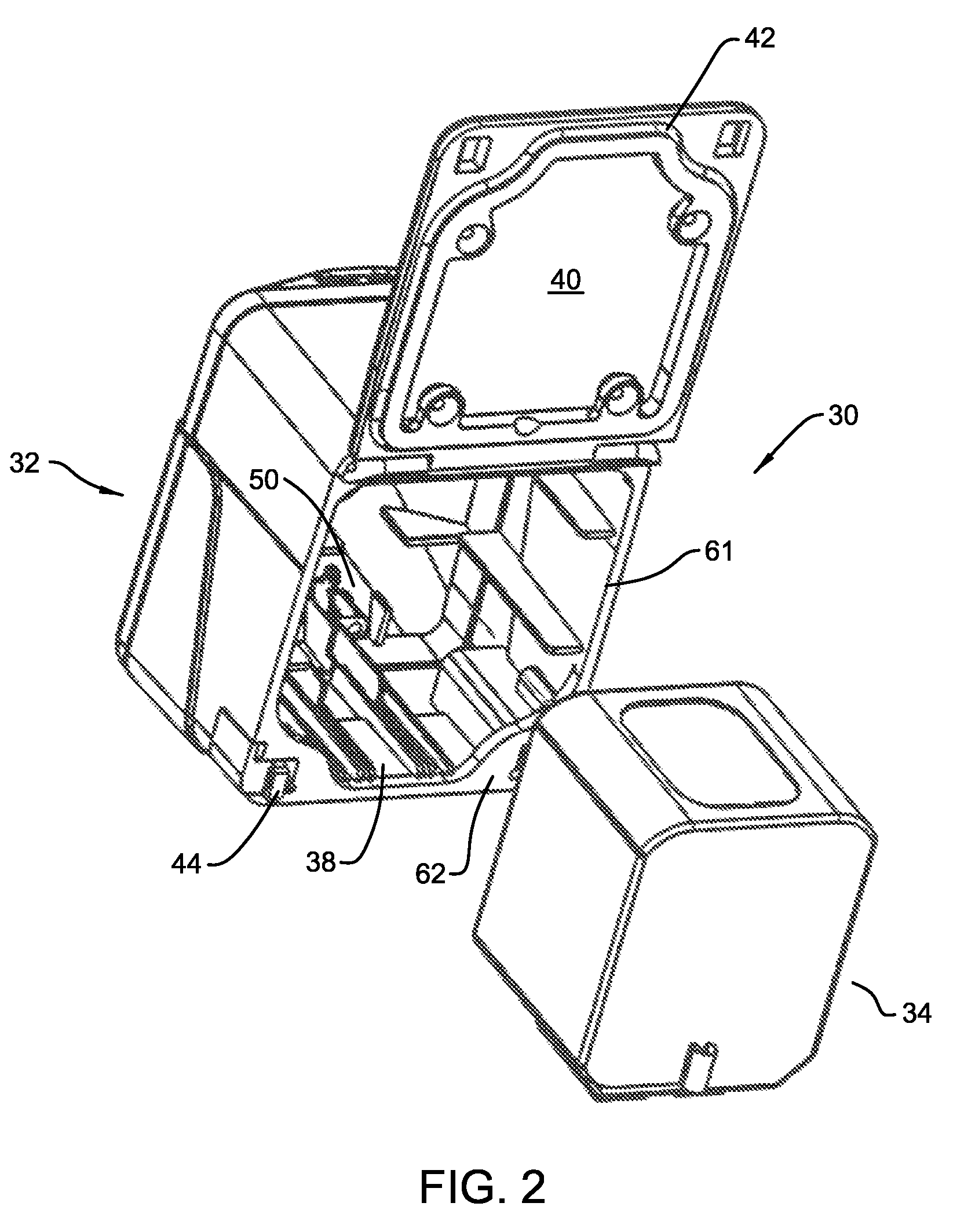
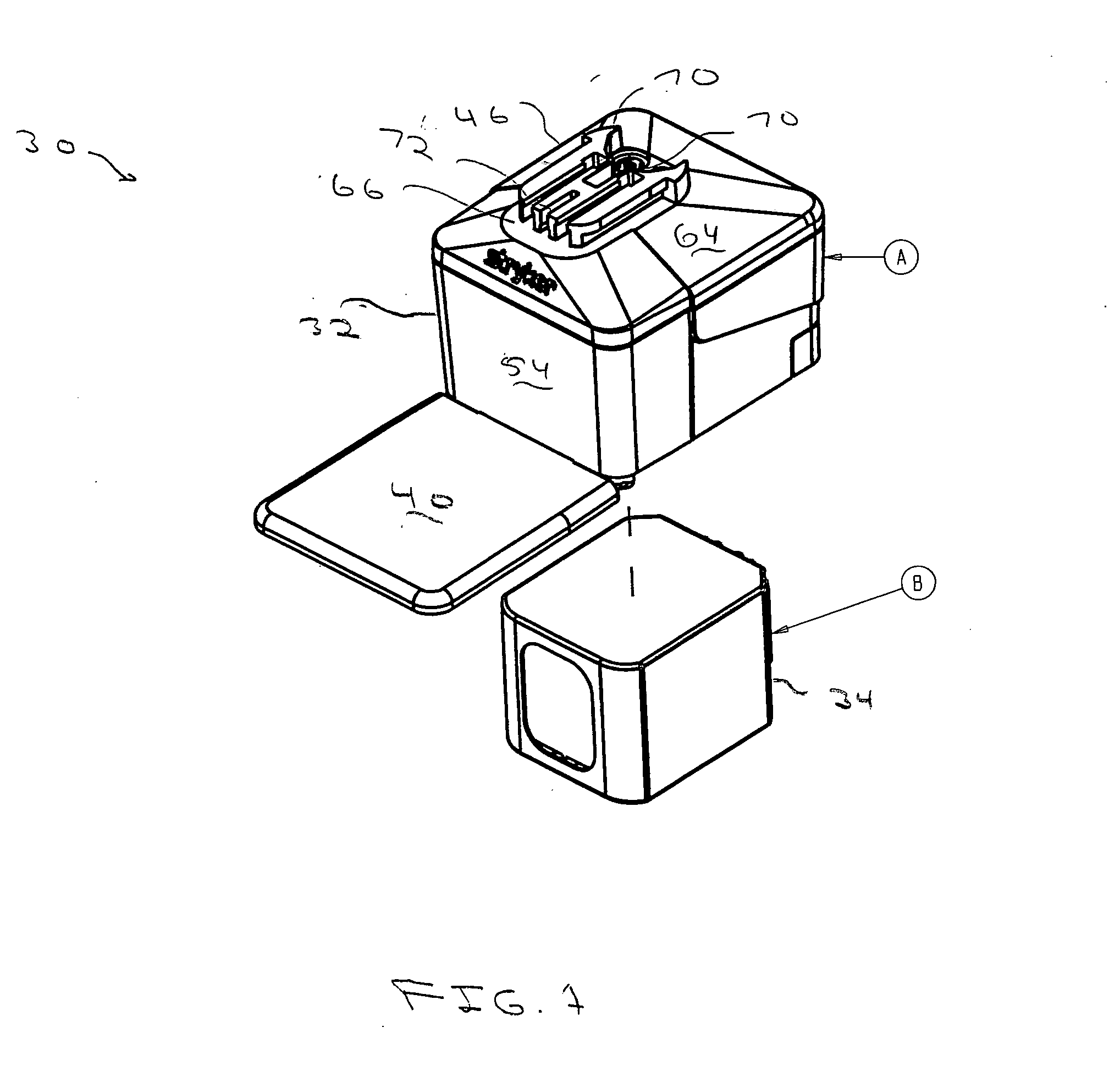
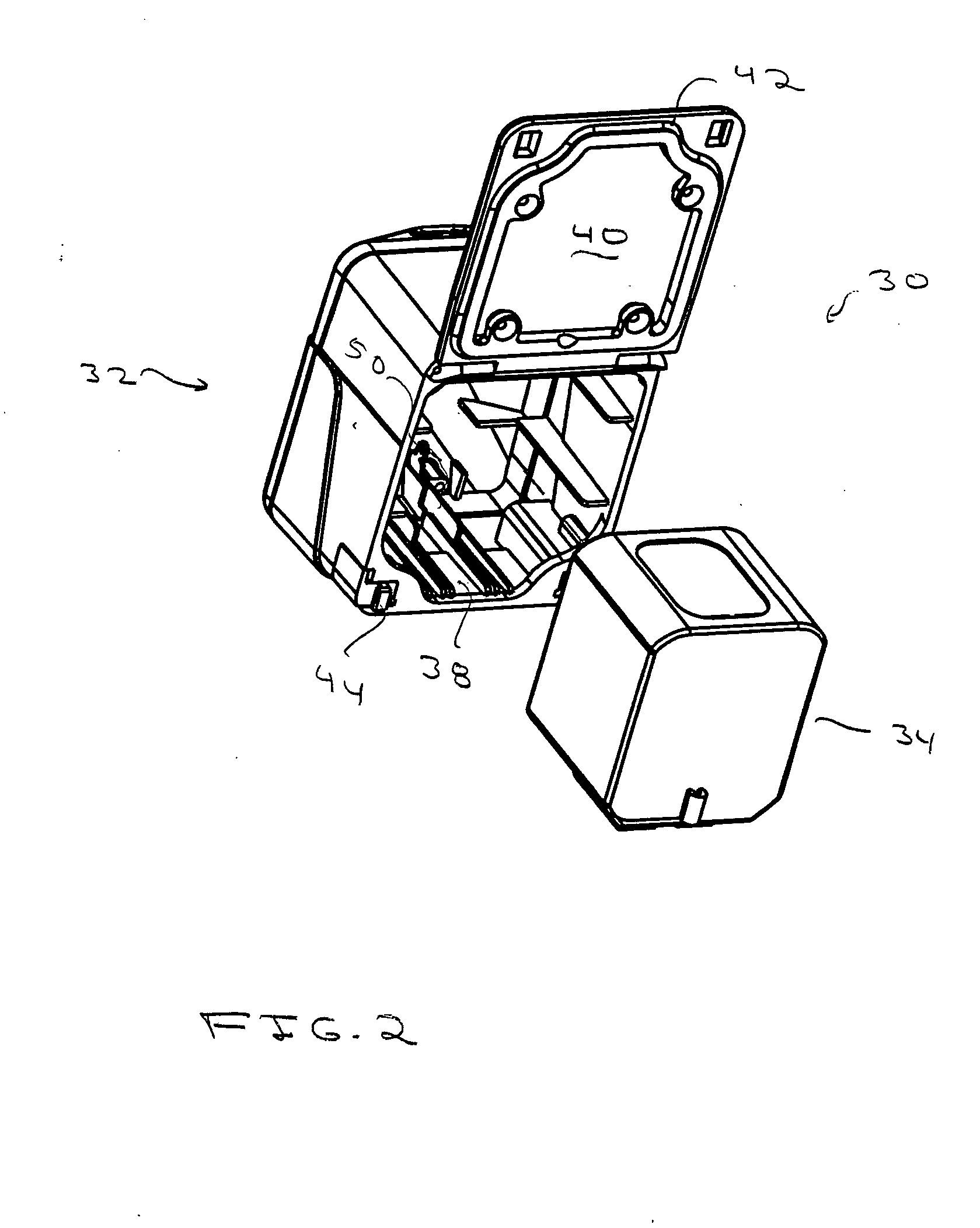
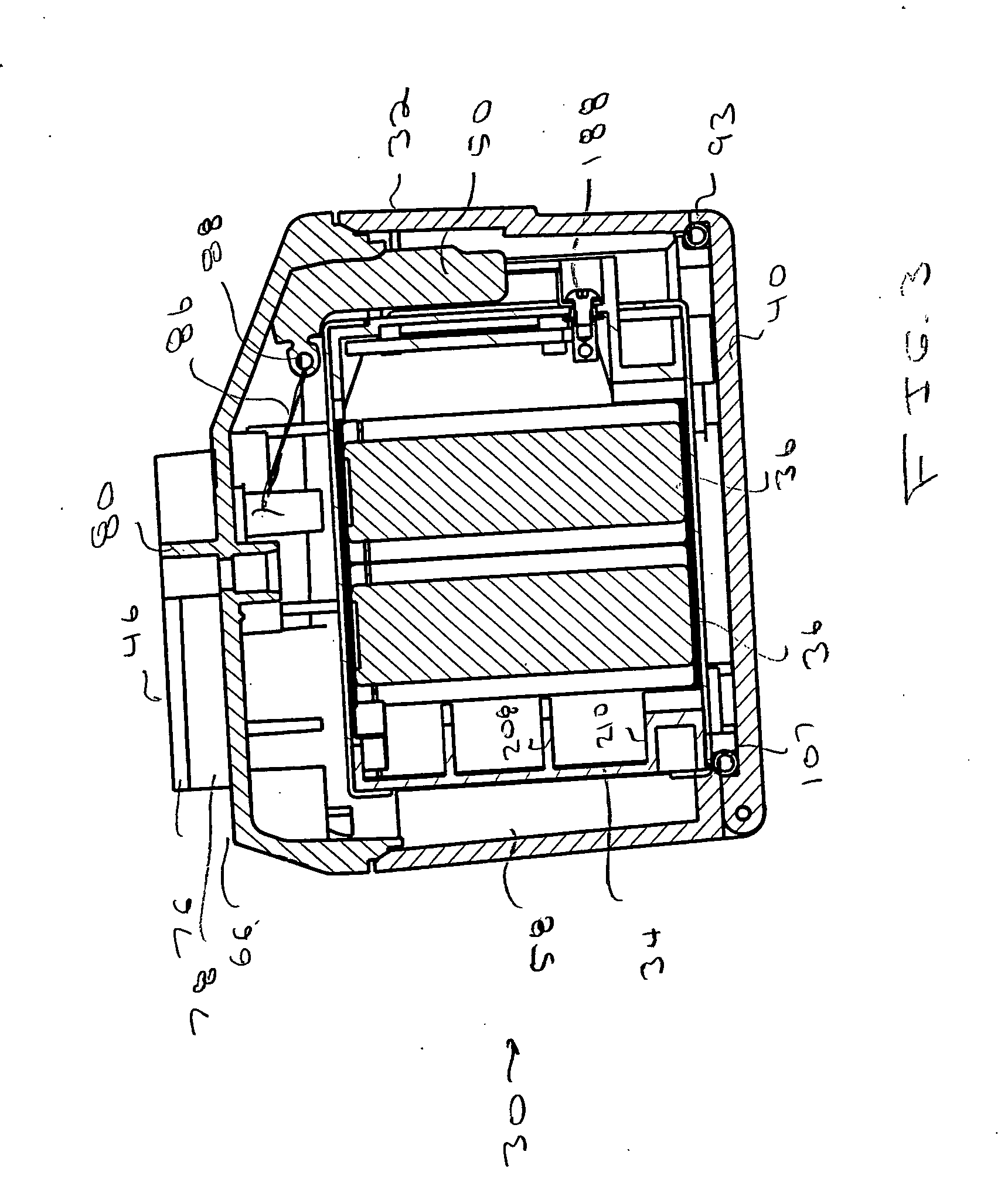
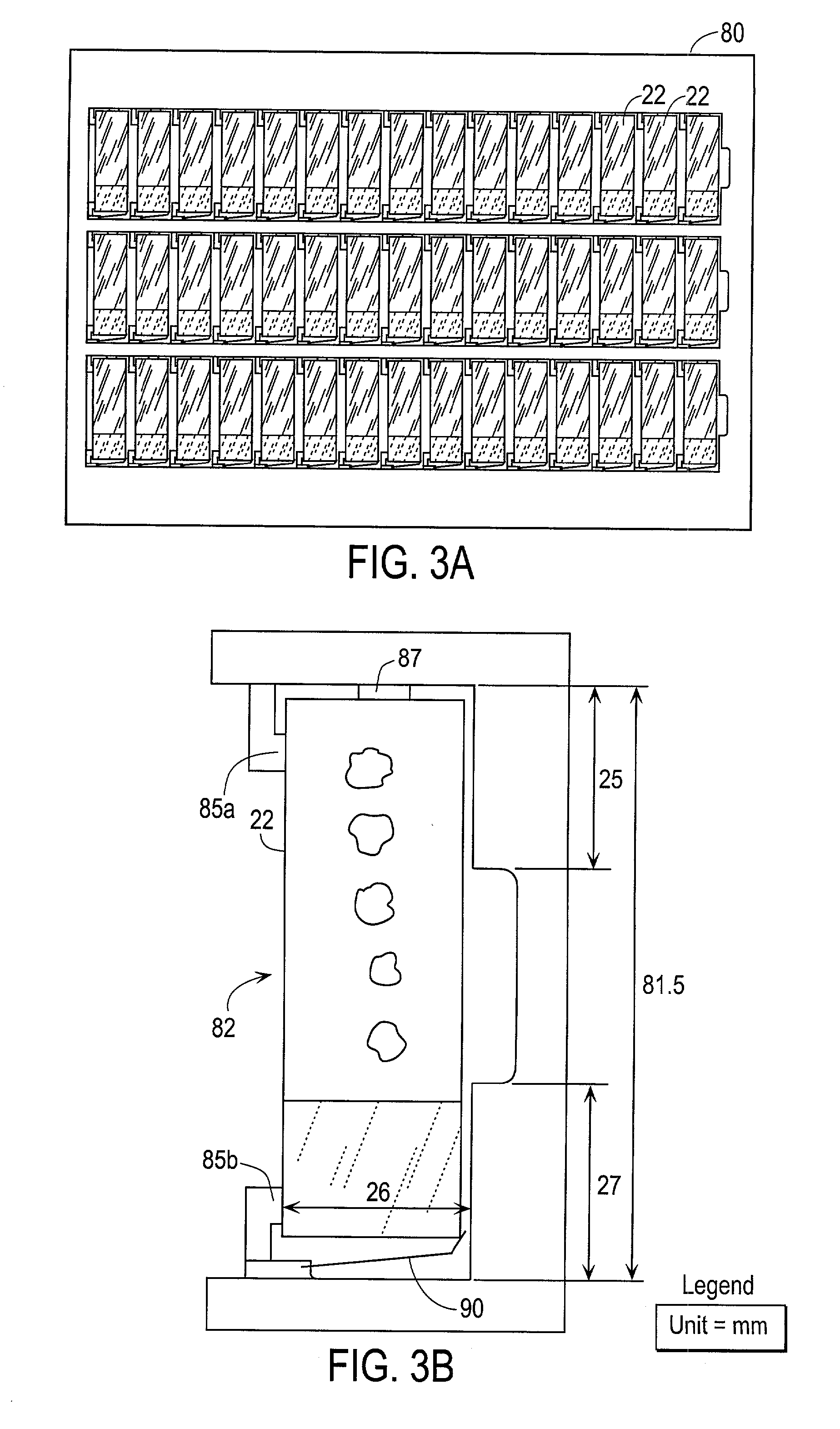
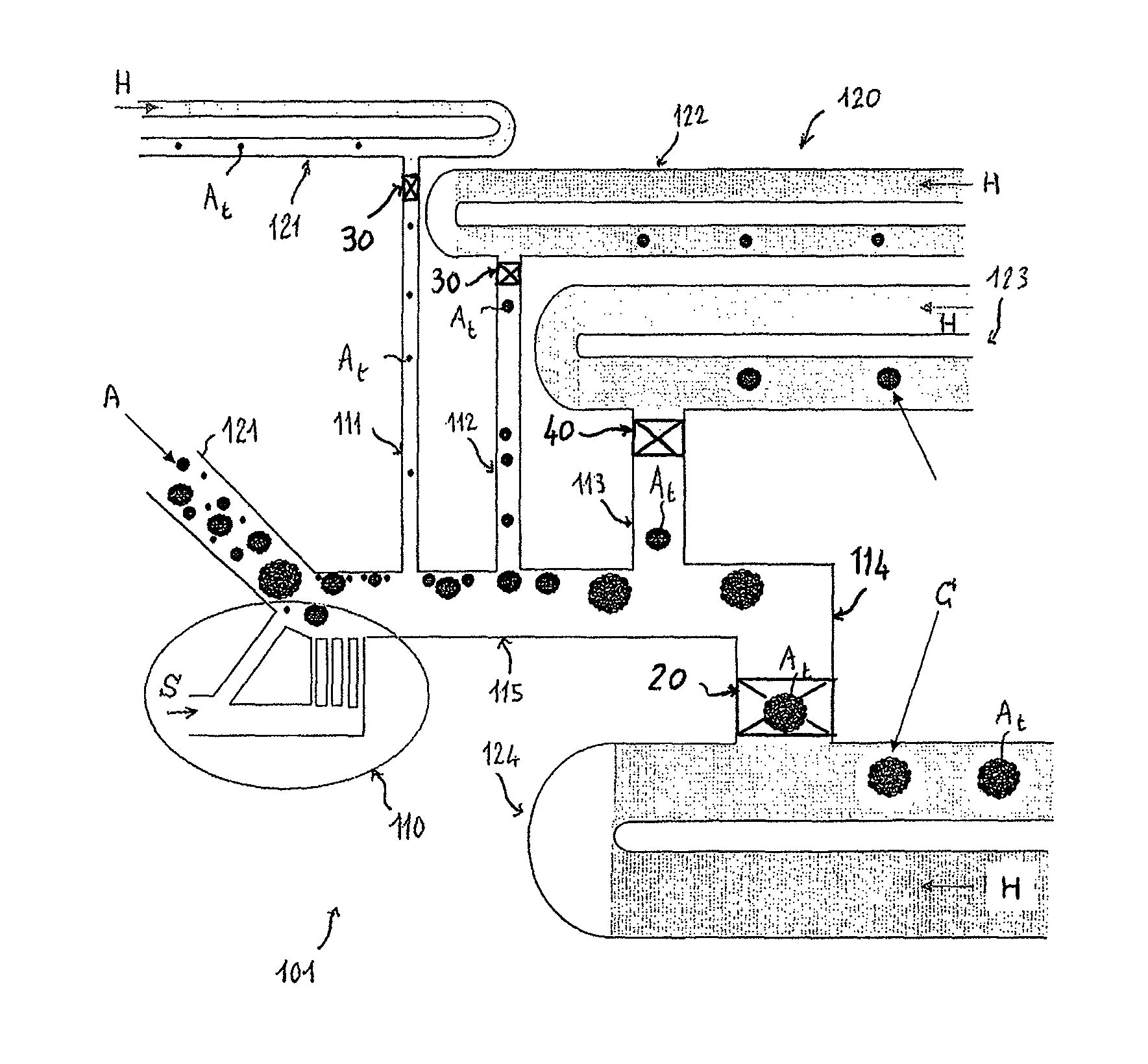
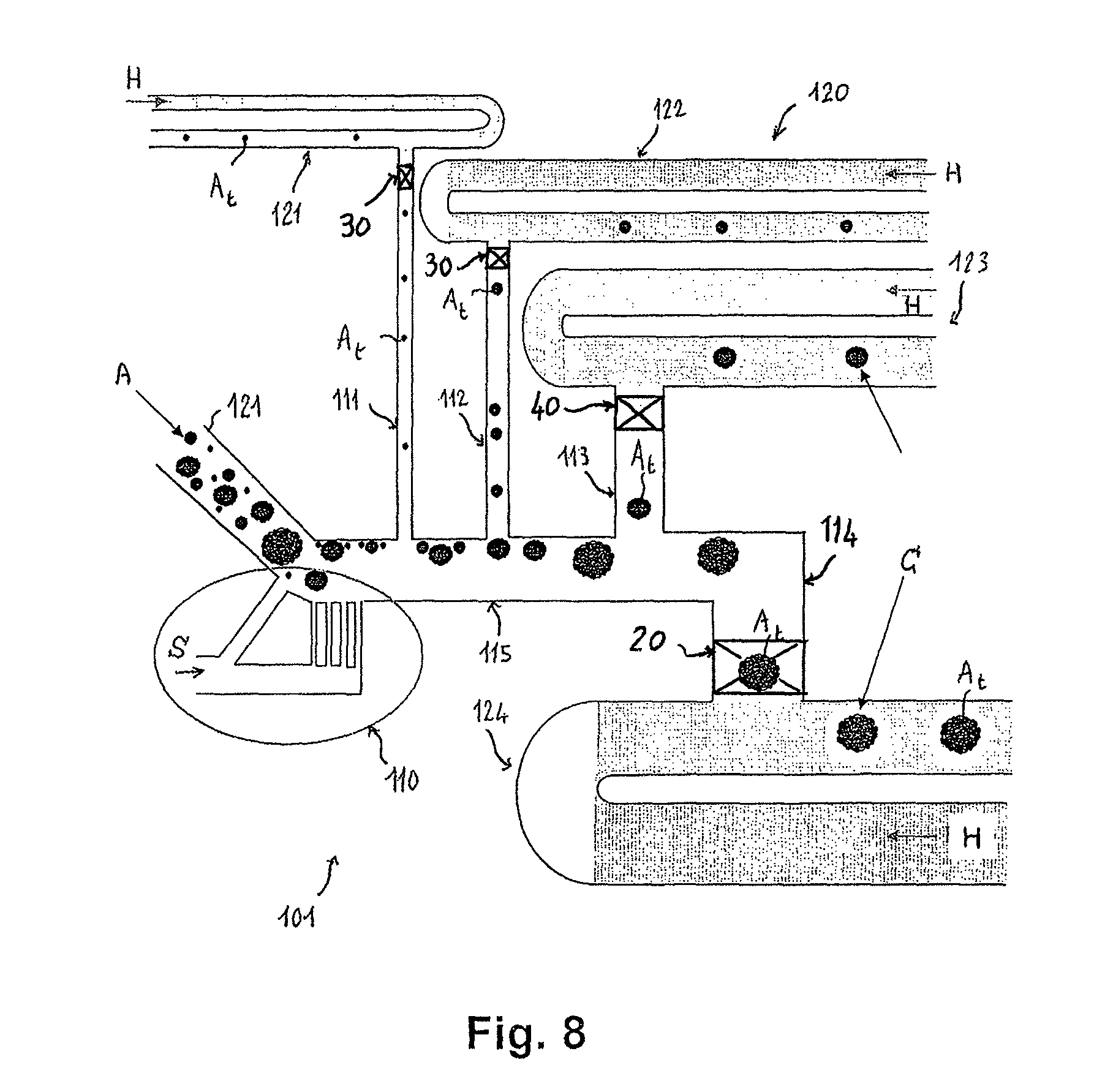
Aseptic battery with a removal cell cluster, the cell cluster configured for charging in a socket that receives a sterilizable battery
A battery assembly with a housing that contains a removable battery pack. The housing, which is sterilizable, has a head designed to couple to a power consuming device. The battery pack, which is not sterilizable, contains at least one rechargeable cell. The battery pack has a head dimensioned to fit the same charger socket that can receive a sterilizable battery. The battery pack has contacts that abut charger contacts. The housing has internal contacts. Collectively, the housing and battery pack are shaped so that, when the battery pack seats in the housing, the battery pack contacts abut the housing internal contacts. The housing internal contacts are connected to the housing external contacts for supply power to the power consuming device. A cover selectively holds the battery pack in the housing chamber.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
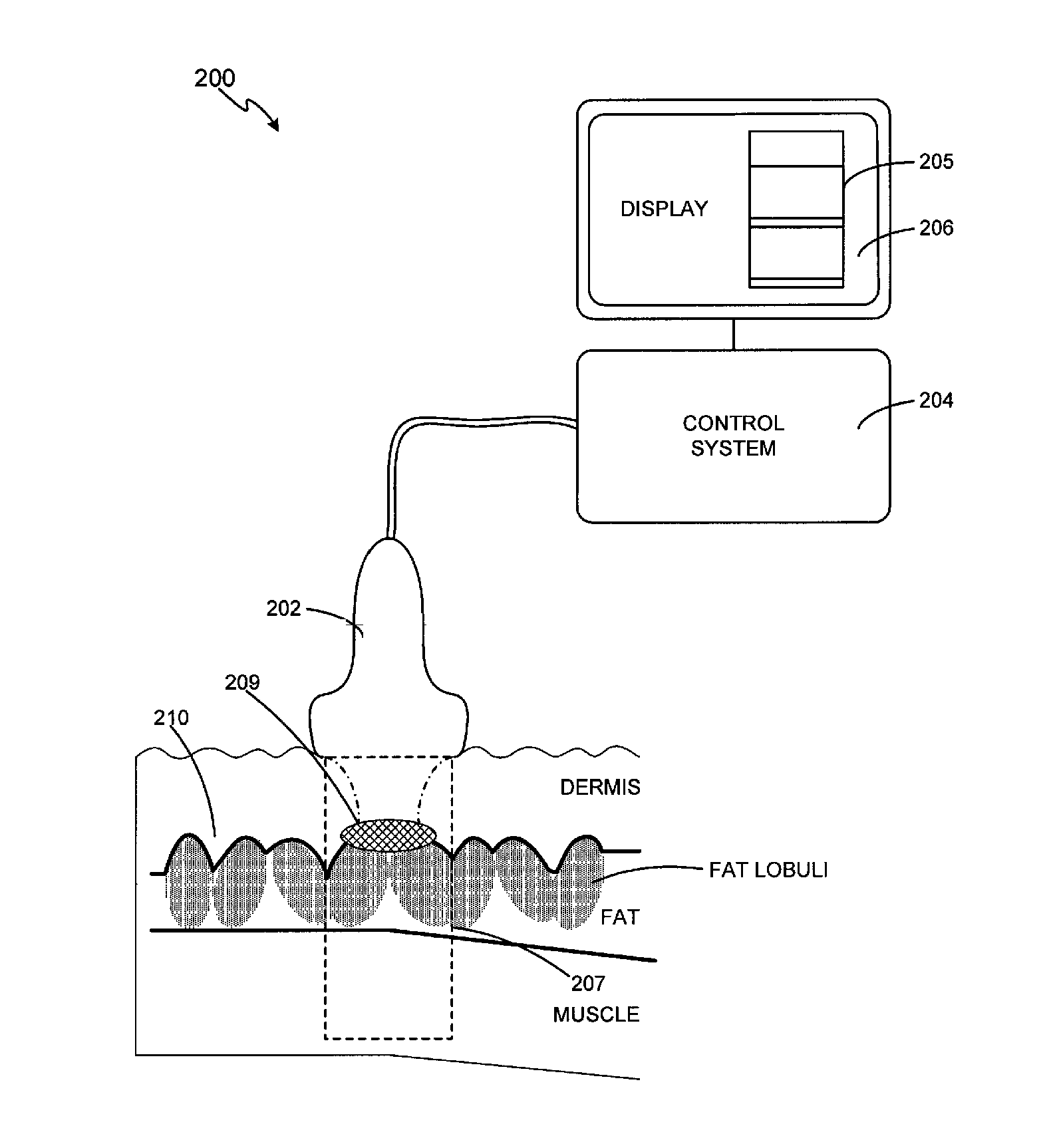
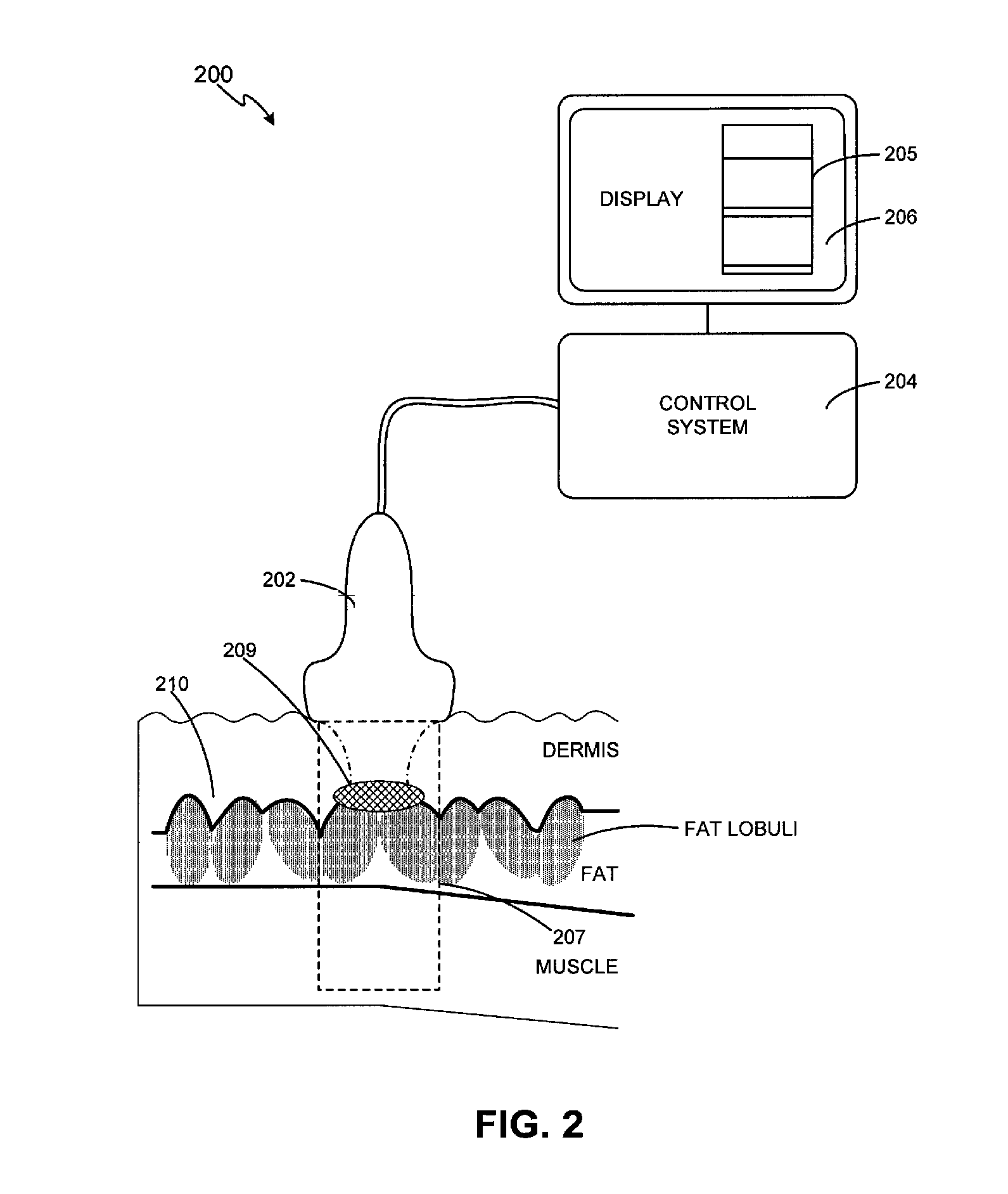
Method and system for treating cellulite
ActiveUS8133180B2Good lookingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyThermal injuryUltrasound imaging
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Method and system for solving cellular communications frequency planning problem
InactiveUS6522885B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningHigh bandwidthFrequency reuse
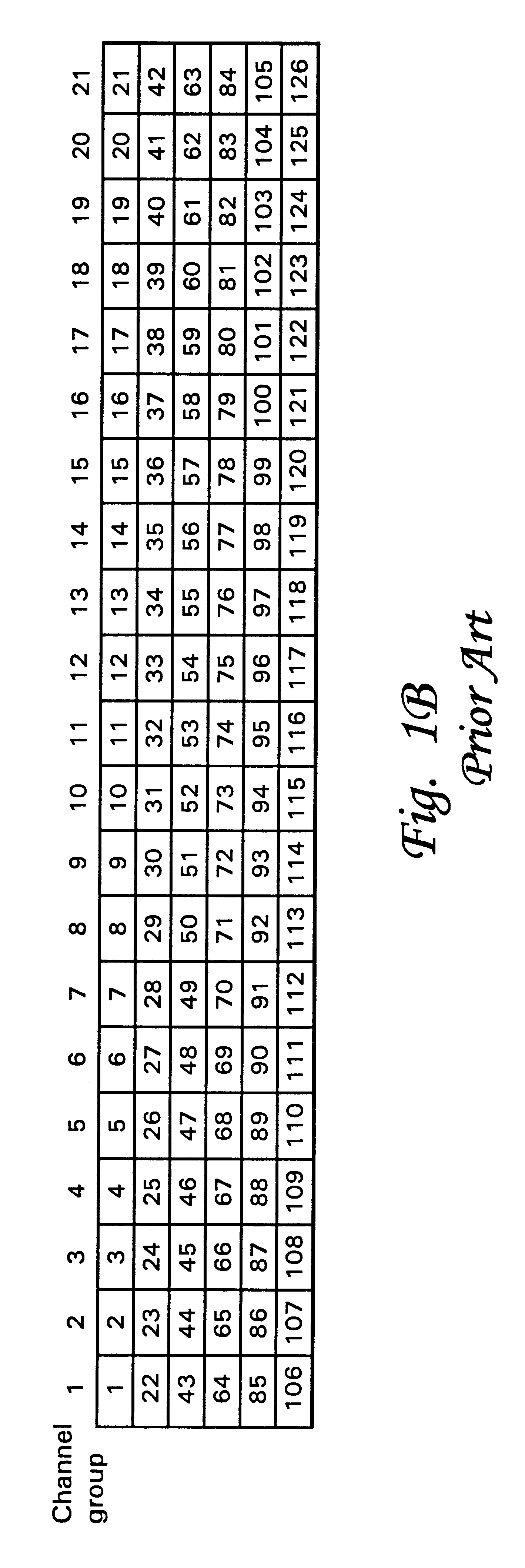
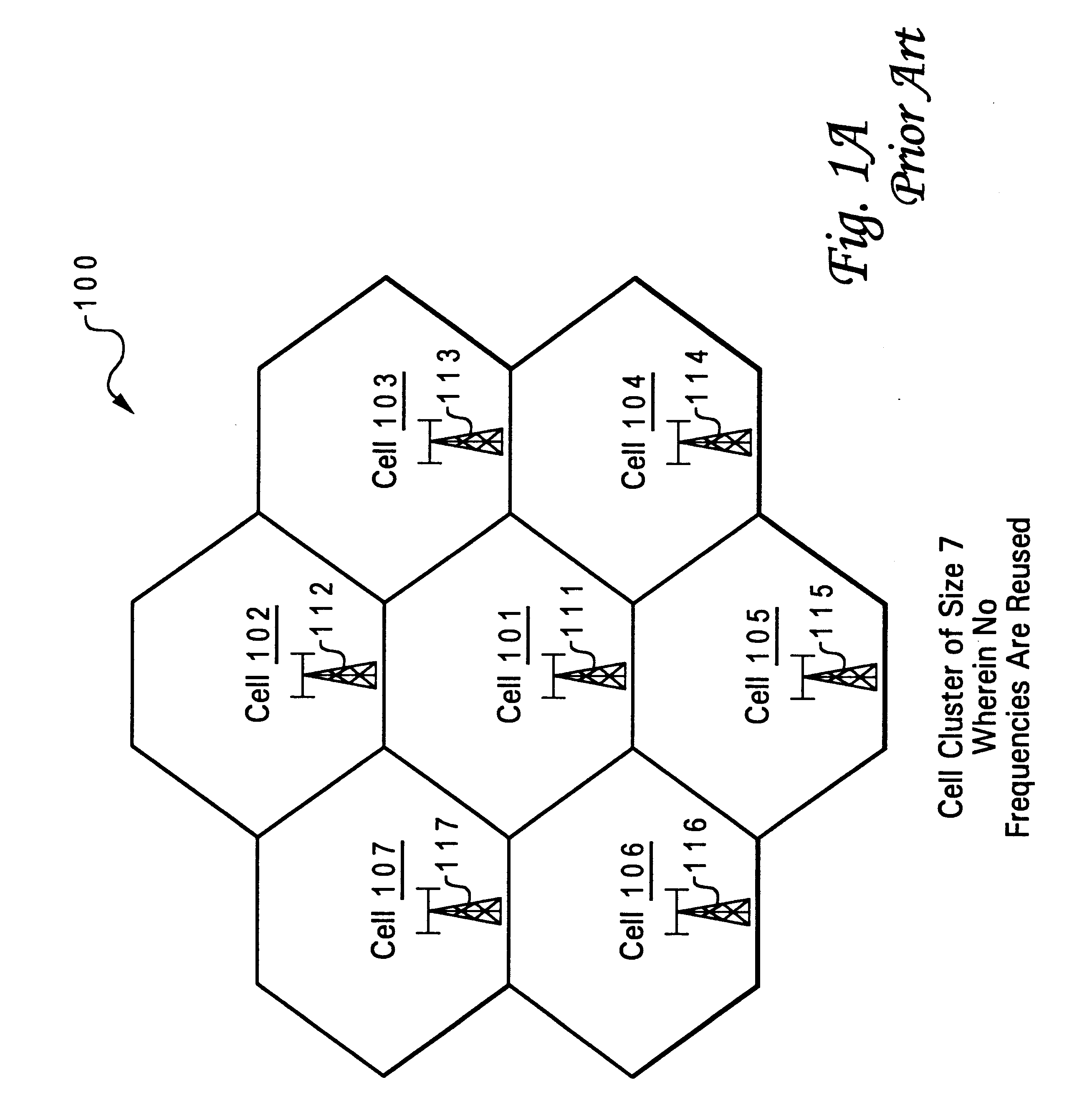
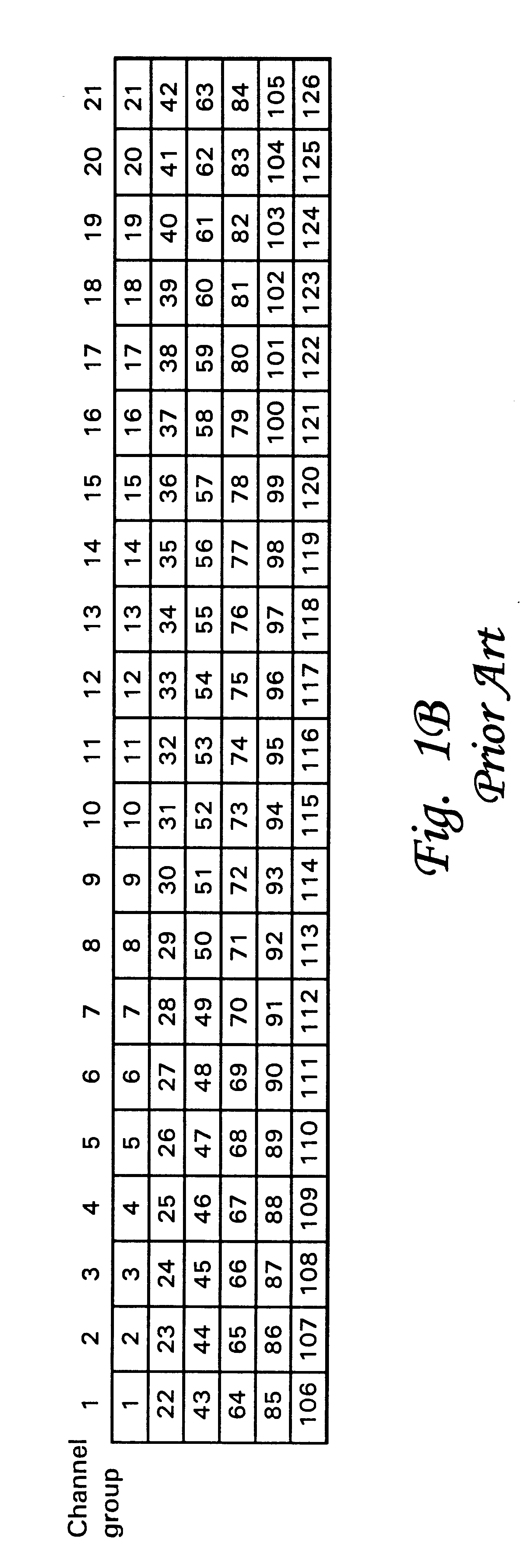
A method and system for use with wireless communications systems having a plurality of groups of channels, and wherein the method and system assign specific groups of channels such that channel interference is minimized. The method and system accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: define a geographic area; map the defined geographic area with at least one high bandwidth cell cluster wherein each cell has at least one sector; and eliminate channel adjacencies by selectively assigning channels, drawn from the plurality of groups of channels, to the at least one high bandwidth cell cluster. The method and system further accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: select a frequency reuse table having a predefined frequency reuse factor; and define a high bandwidth cell cluster over which the frequency reuse table is utilized such that the defined frequency reuse factor is effectively maintained while the communications efficiency of a wireless communications system is enhanced.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and system for solving cellular communications frequency planning problem
InactiveUS6178328B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionHigh bandwidthFrequency reuse
A method and system for use with wireless communications systems having a plurality of groups of channels, and wherein the method and system assign specific groups of channels such that channel interference is minimized. The method and system accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: define a geographic area; map the defined geographic area with at least one high bandwidth cell cluster wherein each cell has at least one sector; and eliminate channel adjacencies by selectively assigning channels, drawn from the plurality of groups of channels, to the at least one high bandwidth cell cluster. The method and system further accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: select a frequency reuse table having a predefined frequency reuse factor; and define a high bandwidth cell cluster over which the frequency reuse table is utilized such that the defined frequency reuse factor is effectively maintained while the communications efficiency of a wireless communications system is enhanced.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
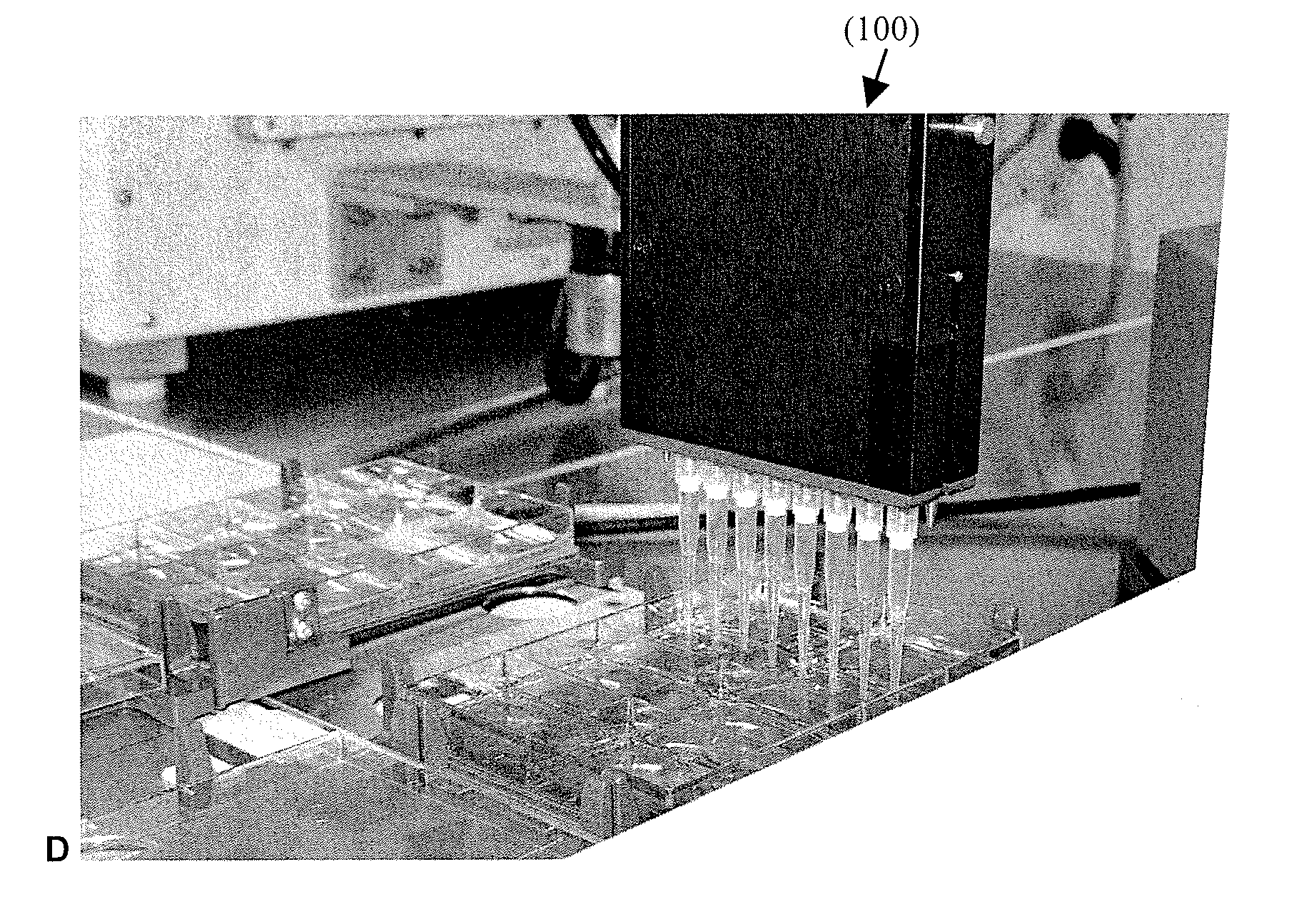
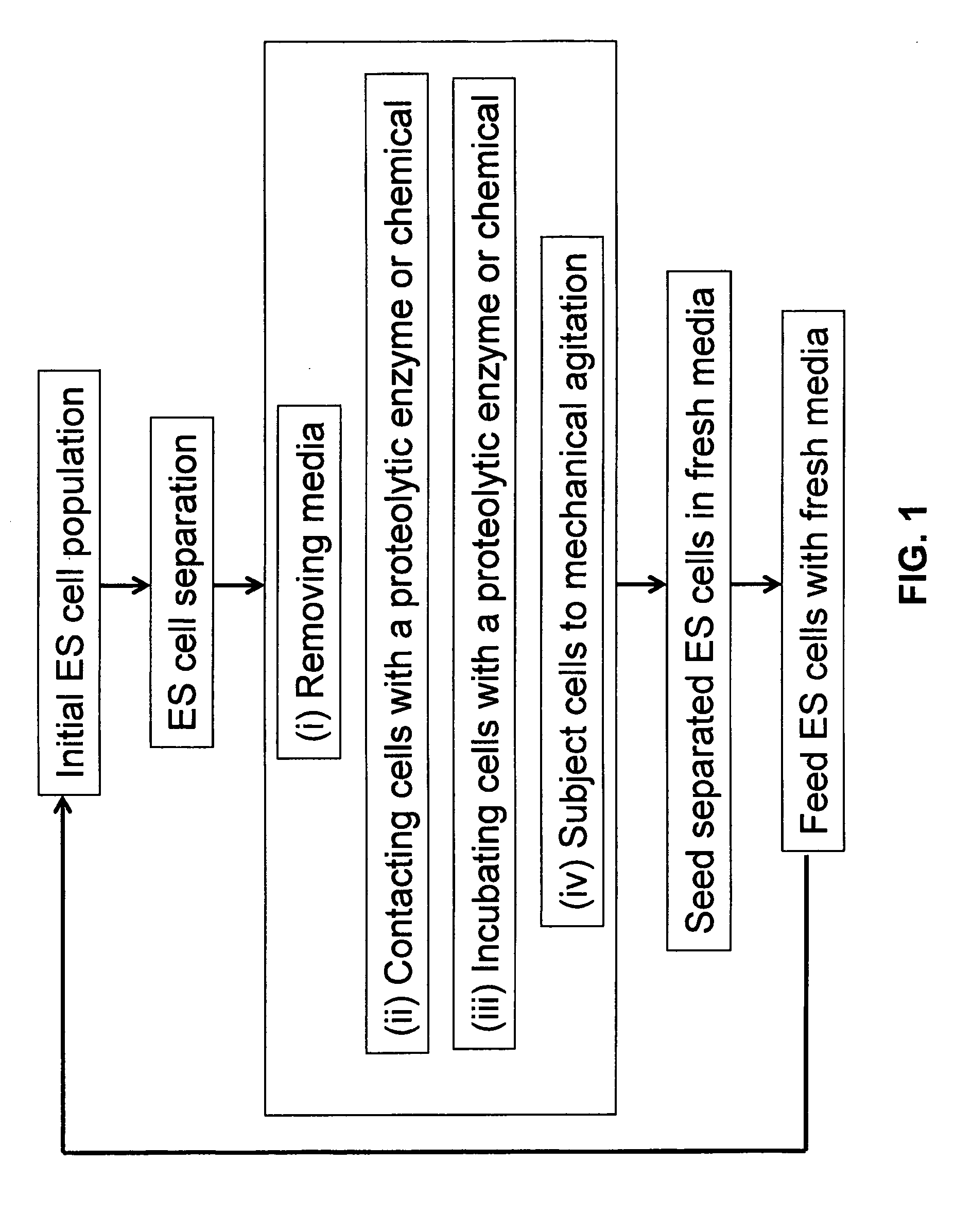
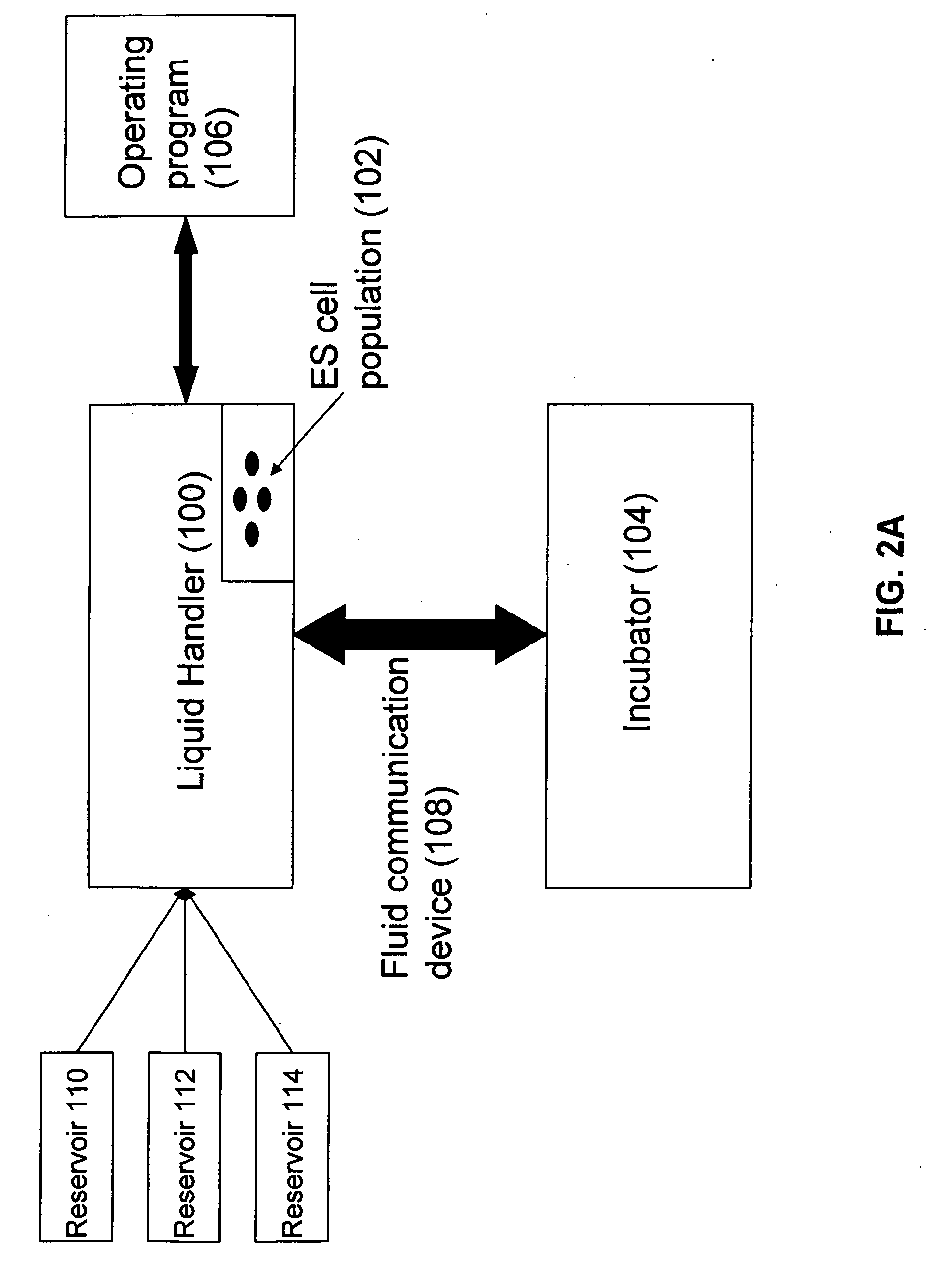
Automated method and apparatus for embryonic stem cell culture
ActiveUS20090029462A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyCell cluster
The invention concerns methods for automated culture of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) such as human ESCs. In some aspects, methods of the invention employ optimized culture media and limited proteolytic treatment of cells to separate cell clusters for expansion. Automated systems for passage and expansion of ESCs are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
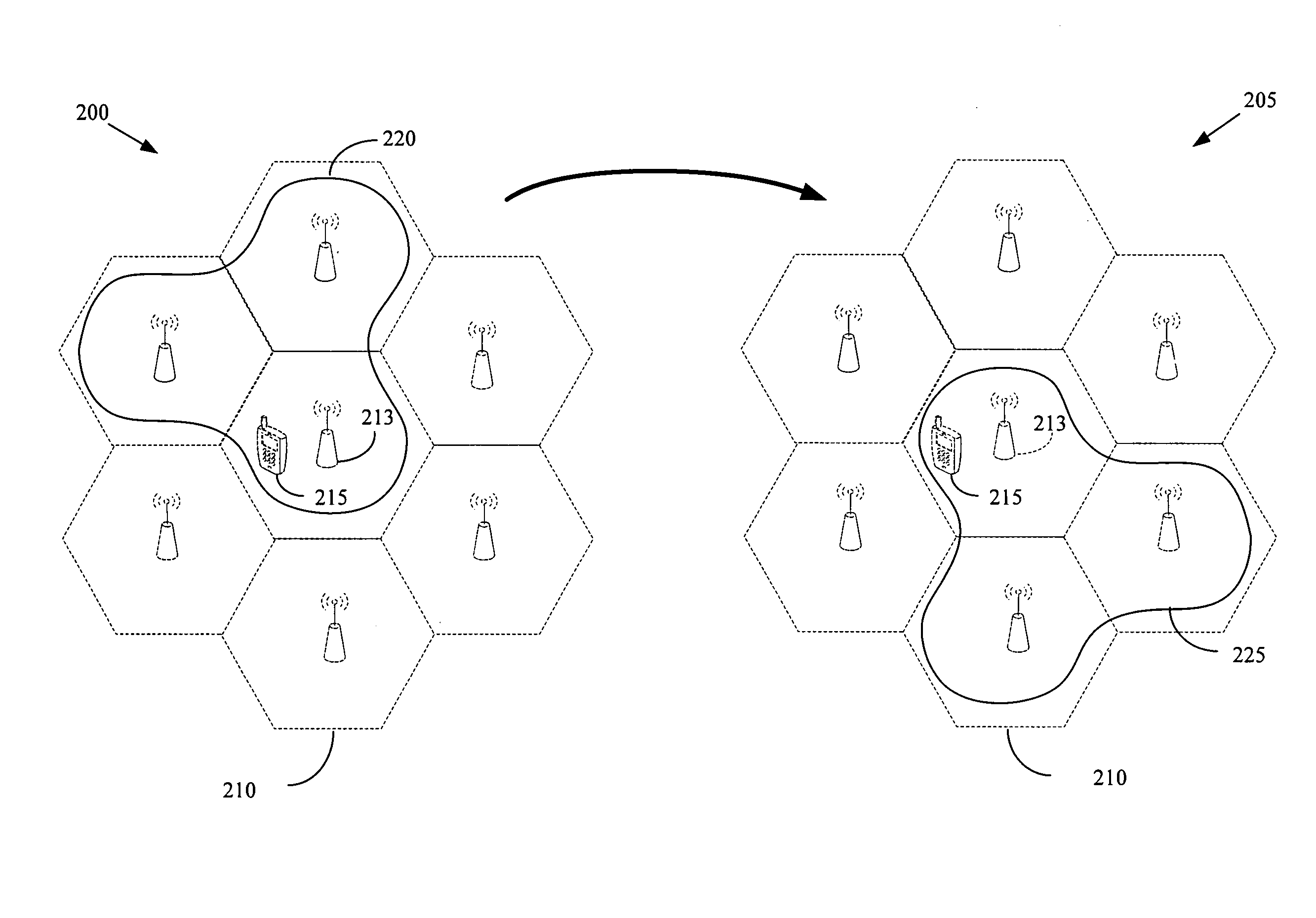
Method for adaptive formation of cell clusters for cellular wireless networks with coordinated transmission and reception
InactiveUS20090312027A1Well formedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningCommunications systemCell cluster
The present invention provides a method of forming clusters of cells in a wireless communication system. The method includes accessing information generated by measuring channel conditions for at least one mobile unit and a plurality of cells in the wireless communication system. The method also includes adding more than one of the plurality of cells to at least one cell cluster based on the accessed information and coordinating communication between the cells in each cell cluster and the mobile unit(s).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Cultured human pancreatic islets, and uses thereof
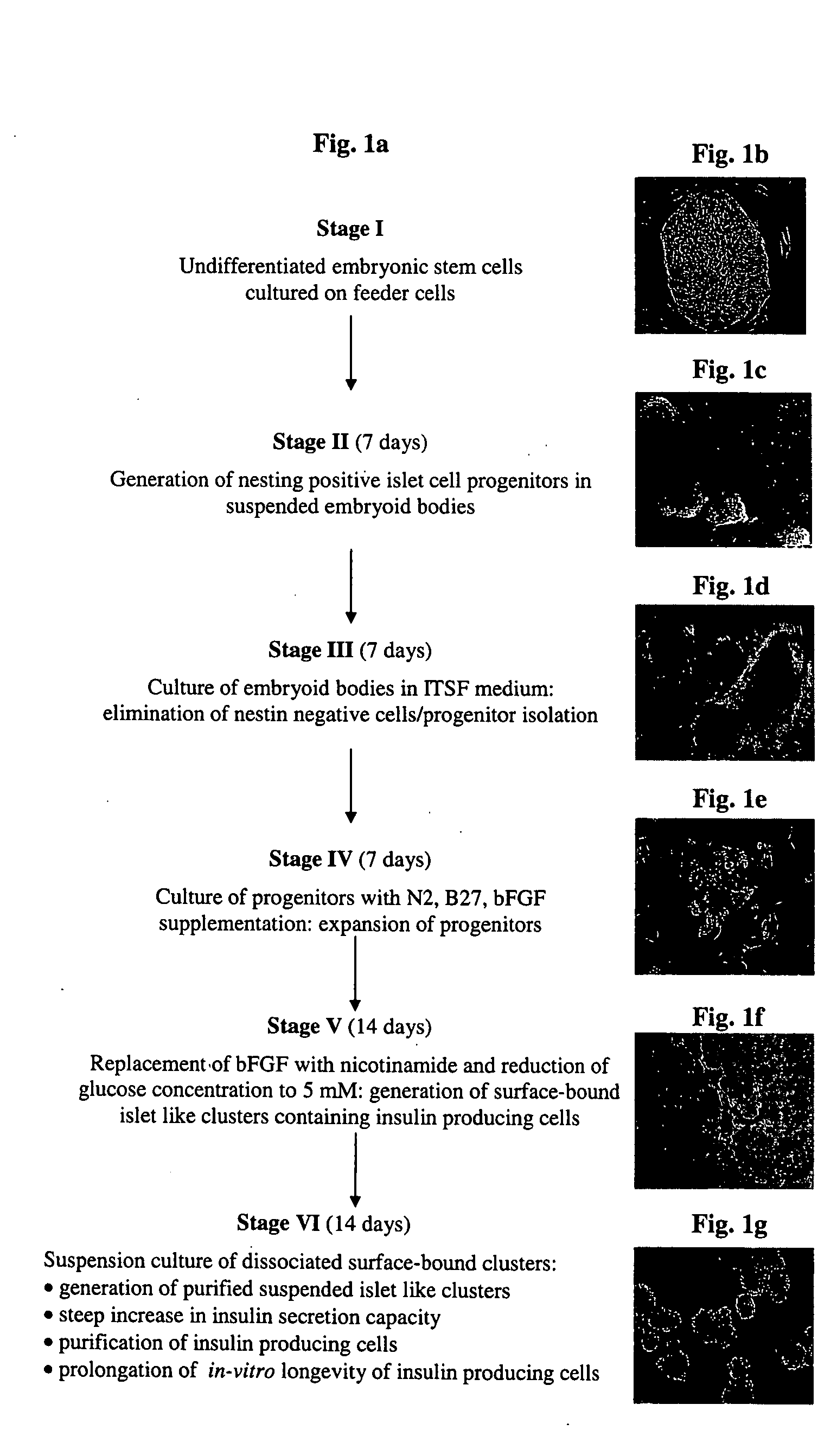
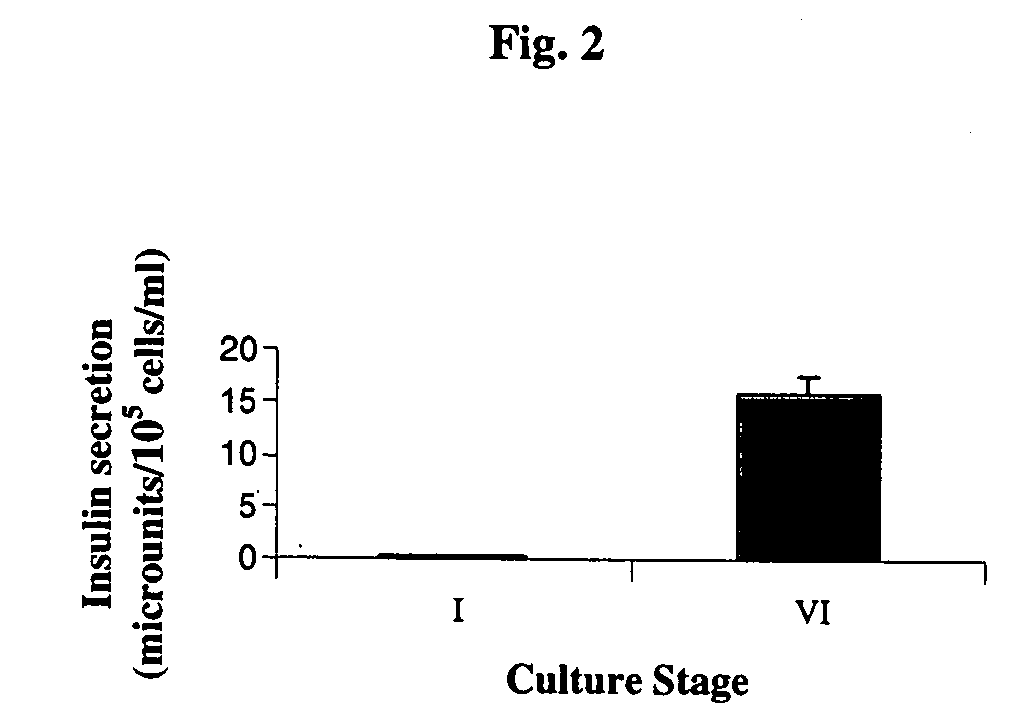
A method of generating cells capable of secreting insulin is disclosed. The method comprises subjecting mammalian embryonic stem cells to set of culturing conditions suitable for differentiation of at least a portion thereof into cells displaying at least one characteristic associated with a pancreatic islet cell progenitor phenotype, and subjecting such differentiated cells to a set of culturing conditions suitable for formation of surface bound cell clusters including insulin producing cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
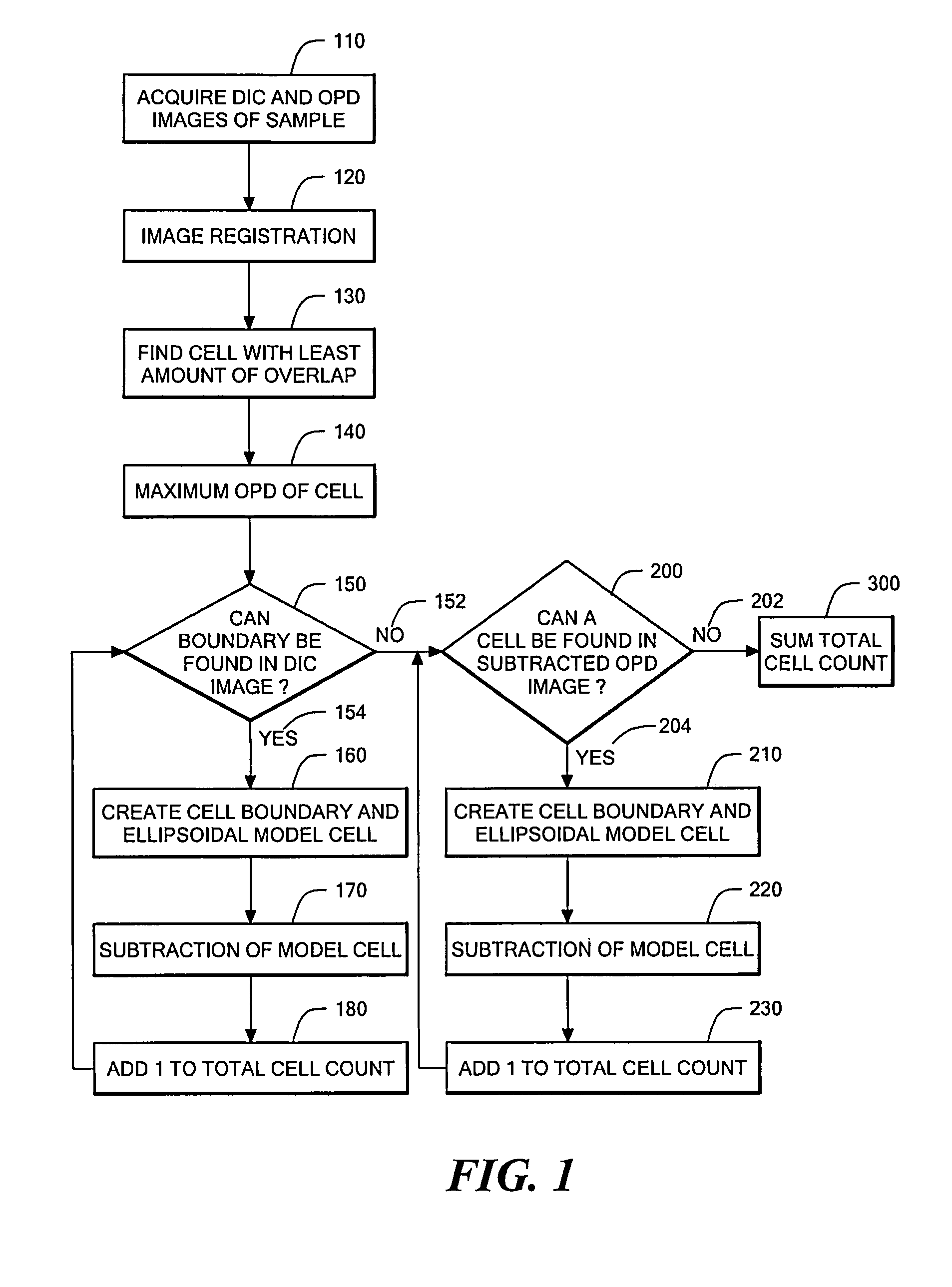
Phase subtraction cell counting method
InactiveUS20080032325A1Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDevelopmental stage
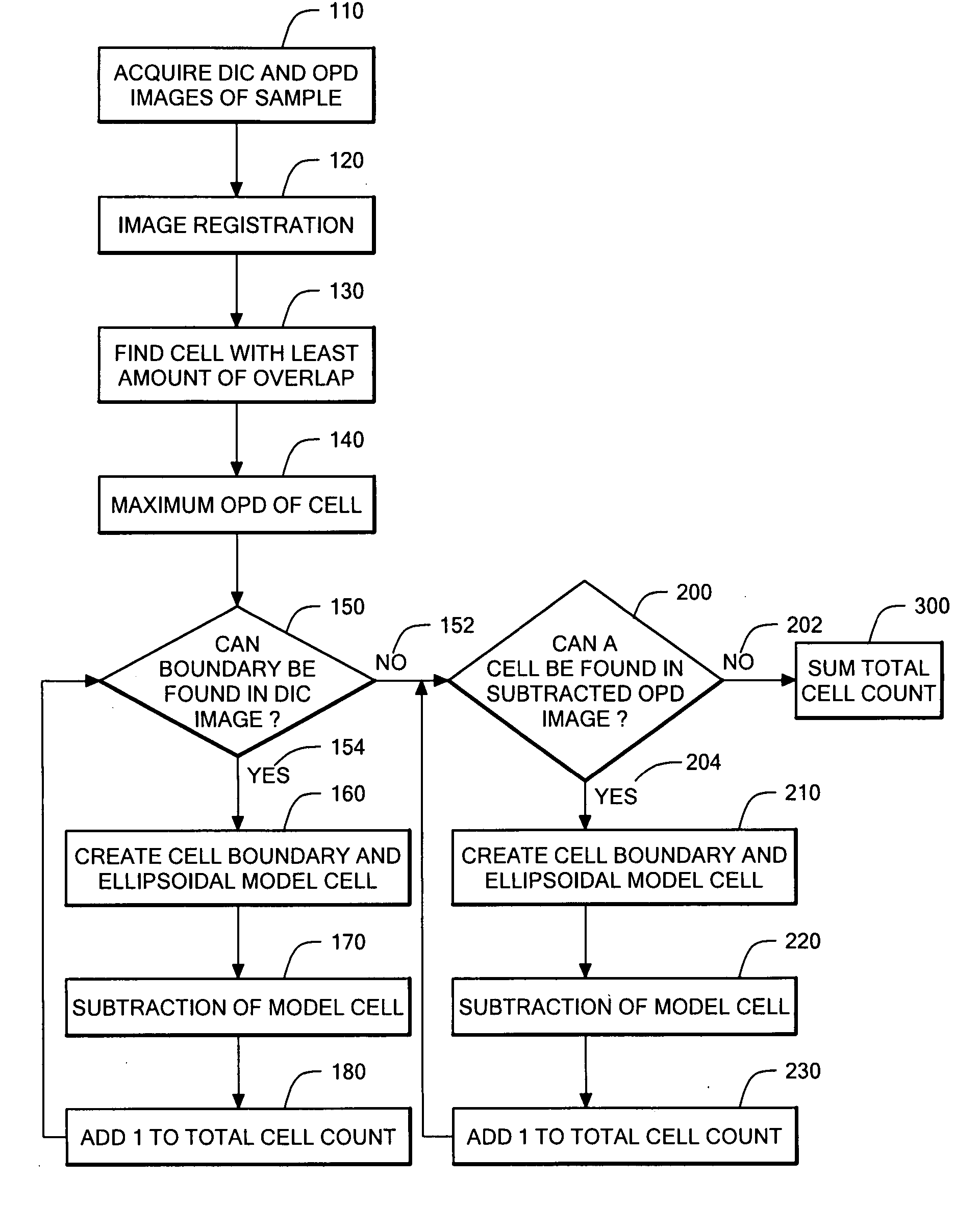
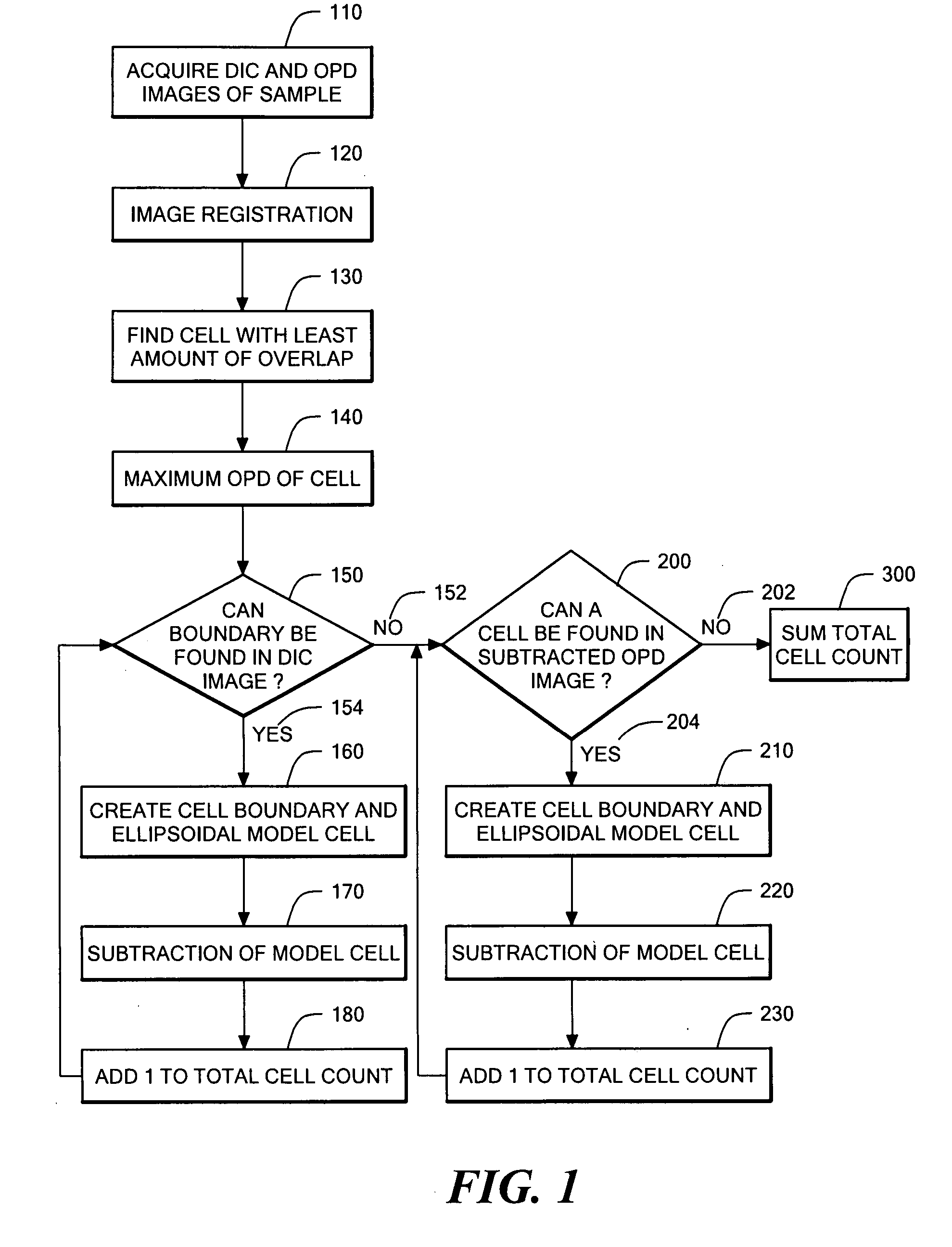
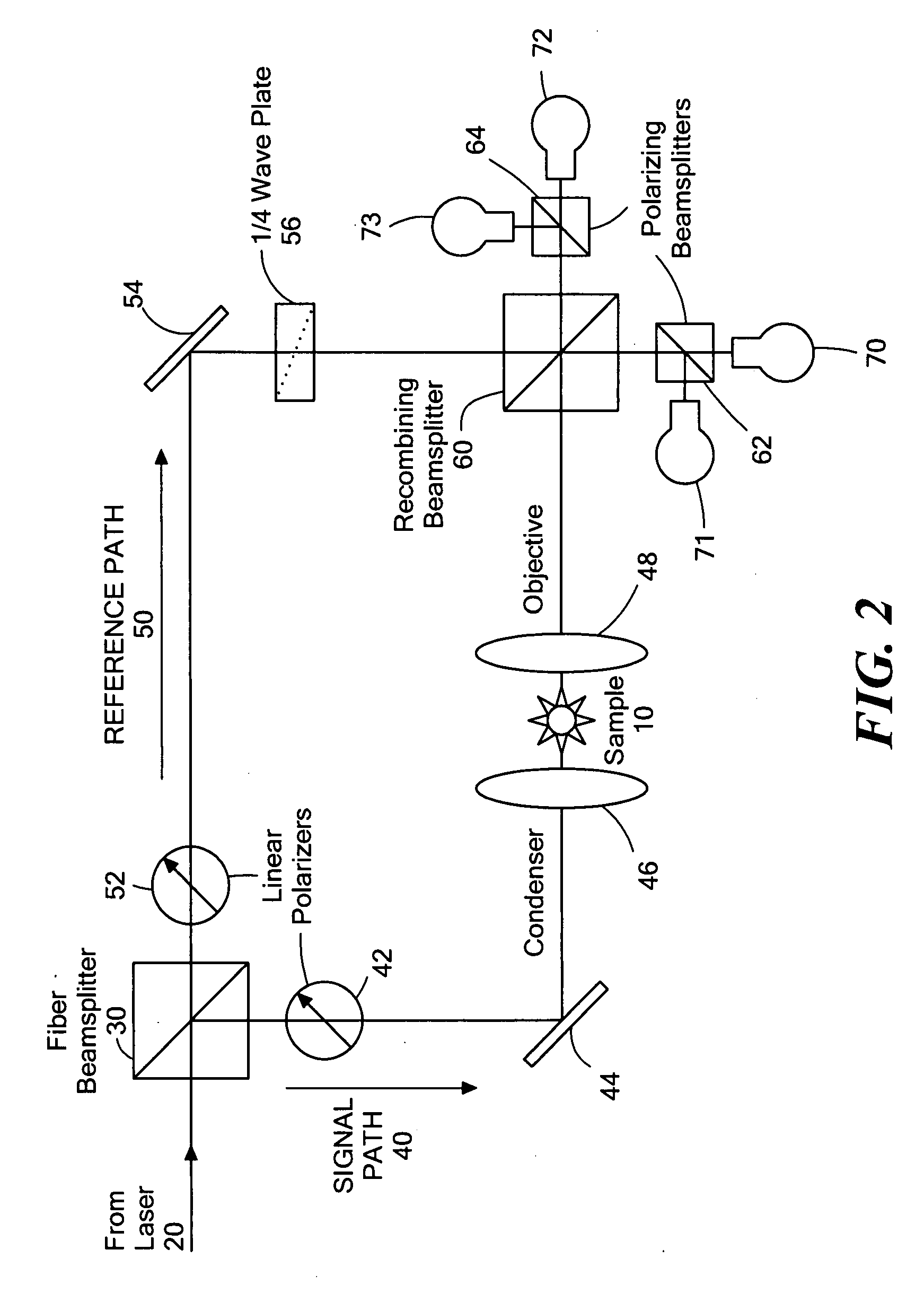
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Aseptic battery assembly with removable cell cluster
ActiveUS20070182369A1Minimized dimensionBatteries circuit arrangementsSurgeryRechargeable cellCell cluster
A battery assembly with a housing that contains a removable battery pack. The housing, which is sterilzable, has a head designed to couple to a power consuming device. The battery pack, which is not sterlizable, contains at least one rechargeable cell. The battery pack has a head dimensioned to fit the same charger socket that can receive a sterlizable battery. The battery pack has contacts that abut charger contacts. The housing has internal contacts. Collectively, the housing and battery pack are shaped so that, when the battery pack seats in the housing, the battery pack contacts abut the housing internal contacts. The housing internal contacts are connected to the housing external contacts for supply power to the power consuming device. A cover selectively holds the battery pack in the housing chamber.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
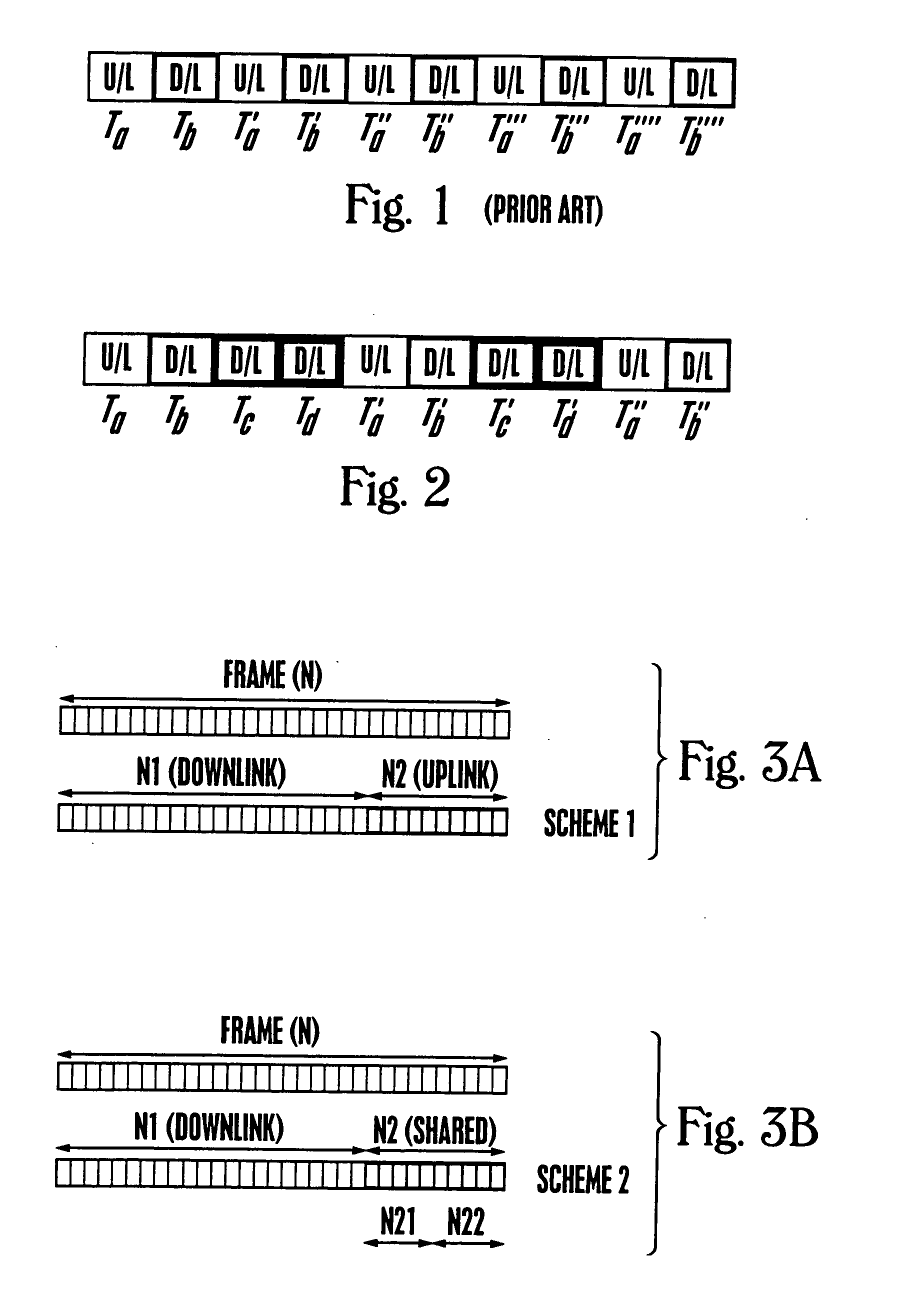
Adaptive time division duplexing method and apparatus for dynamic bandwidth allocation within a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20050243745A1Easy to useSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrame basedUplink transmission
An adaptive time division duplexing (ATDD) method and apparatus for duplexing transmissions on a communication link in wireless communication systems. Communication link efficient is enhanced by dynamically adapting to the uplink and downlink bandwidth requirements of the communication channels. Time slots are flexibly and dynamically allocated for uplink or downlink transmissions depending upon the bandwidth needs of a channel. Communication link bandwidth requirements are continuously monitored using sets of predetermined bandwidth requirement parameters. Communication channels are configured to have either symmetric or asymmetric uplink / downlink bandwidths depending upon the needs of the channel. Channel bandwidth asymmetry can be configured alternatively in favor of the uplink transmissions (i.e., more time slots are allocated for uplink transmissions than for downlink transmissions) or in favor of the downlink transmissions (i.e., more time slots are allocated for downlink transmissions than for uplink transmissions). A myriad of time slot allocation schemes are possible. One simplified time slot allocation scheme uses a “frame-based” approach. A preferred channel bandwidth analysis technique is disclosed which monitors and updates bandwidth requirement parameters associated with communication sessions, base stations and cell cluster controllers. In accordance with this technique, a communication session is preferably assigned both an “initial” and an “actual” set of bandwidth parameters.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
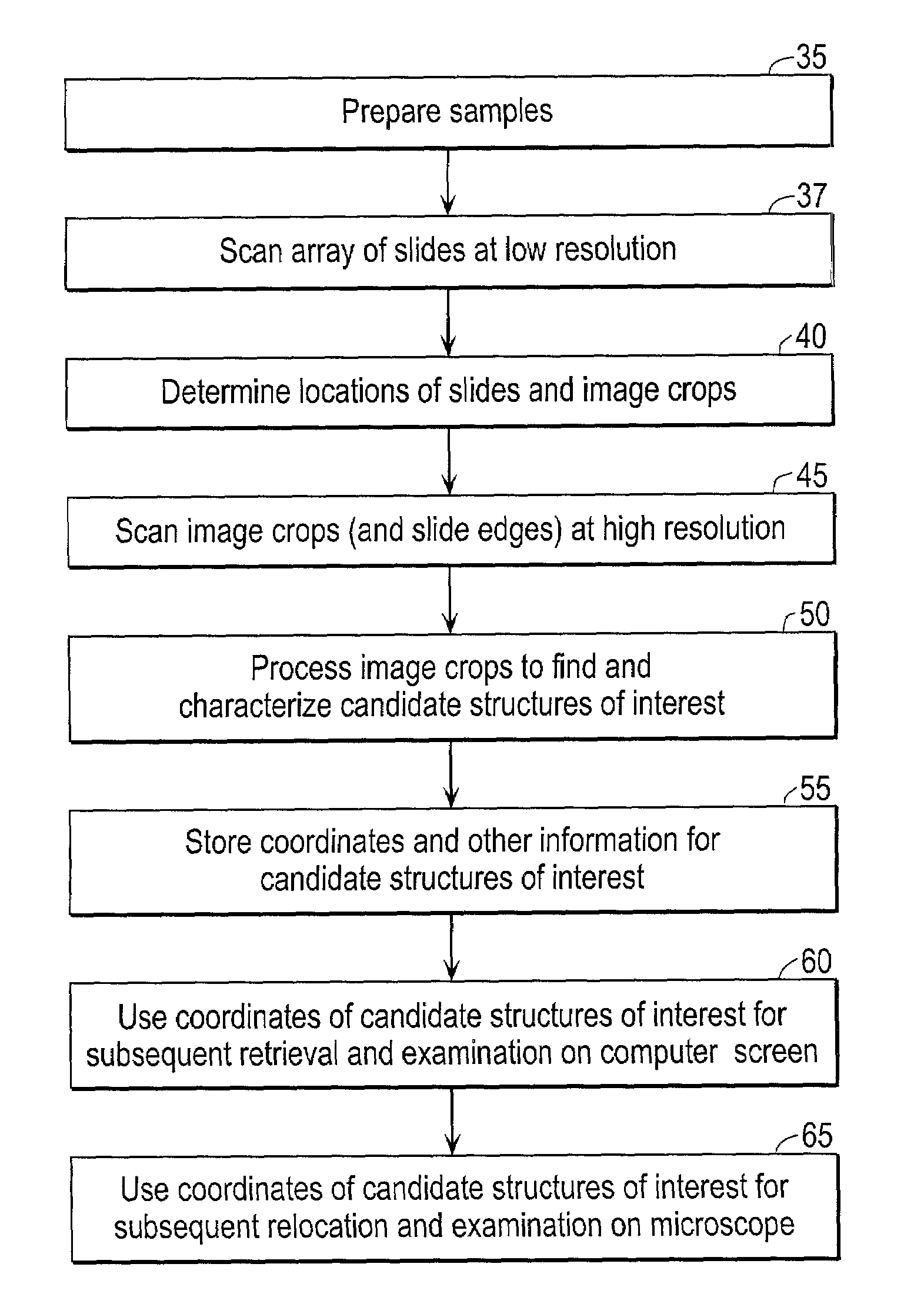
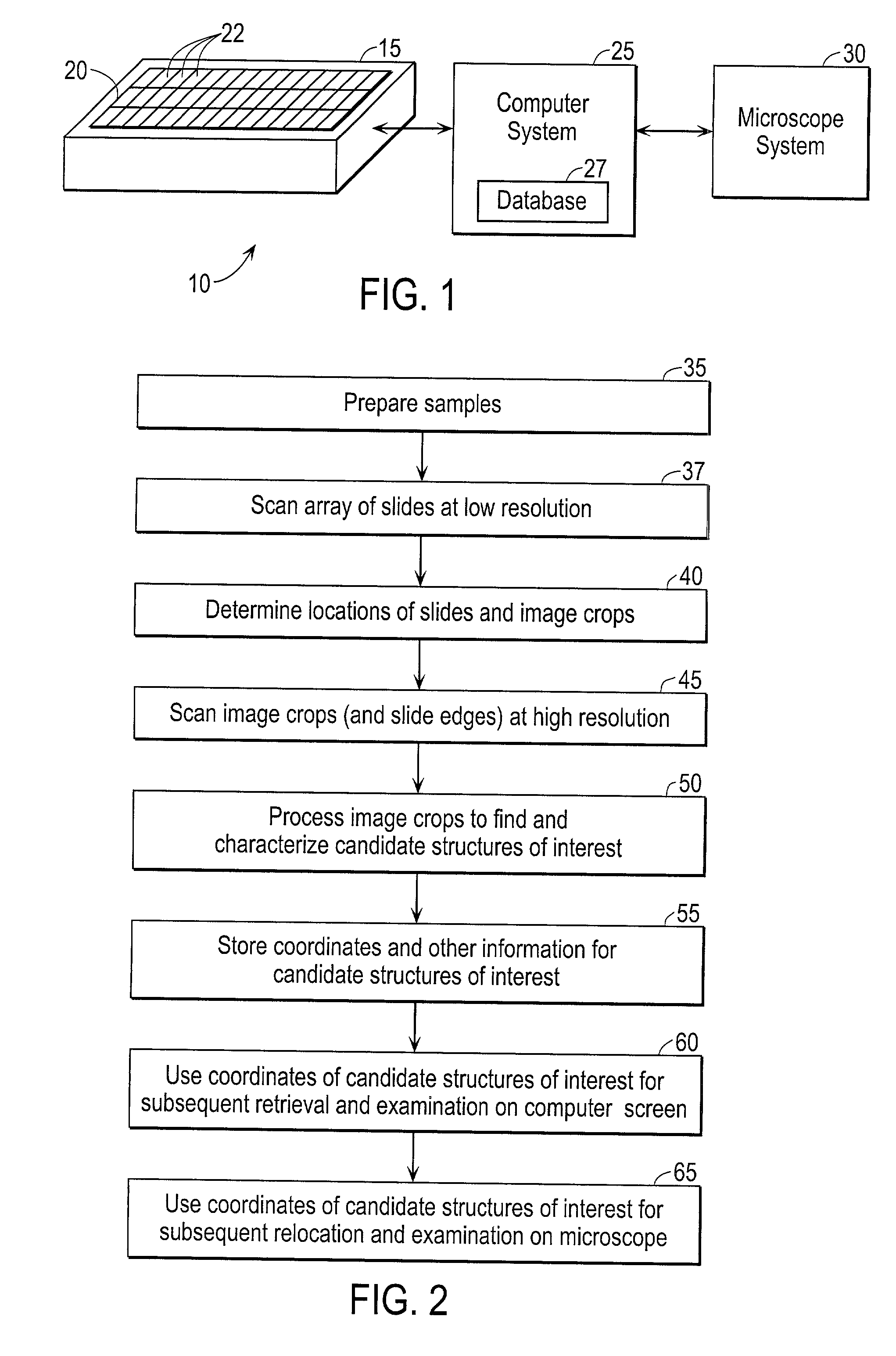
Automated scanning method for pathology samples
Scanning and analysis of cytology and histology samples uses a flatbed scanner to capture images of the structures of interest such as tumor cells in a manner that results in sufficient image resolution to allow for the analysis of such common pathology staining techniques as ICC (immunocytochemistry), IHC (immunohistochemistry) or in situ hybridization. Very large volumes of such material are scanned in order to identify cells or clusters of cells which are positive or warrant more detailed examination, and if analysis at higher resolution is necessary, information regarding these positive events is transferred to a secondary microscope, such as a conventional scanning microscope, to allow further analysis and review of the selected regions of the slide containing the sample.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Methods of using G-CSF mobilized C-Kit+ cells in the production of embryoid body-like cell clusters for tissue repair and in the treatment of cardiac myopathy
InactiveUS20050186182A1Enhance mobilizationInhibition of differentiationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsMyopathyTissue repair
The present invention relates to methods of using granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) polypeptide, alone and in conjunction with stromal cell derived factor (SDF-1) polypeptide, to increase the mobilization of c-Kit+ stem cells in the blood, bone marrow, tissue, heart or other organs for the subsequent production of embryoid body-like cell clusters. These embryoid body-like cell clusters can be used for cell replacement therapy, for the treatment of cardiac myopathy and other diseases and disorders, and for screening agents that drive or inhibit differentiation and proliferation.
Owner:AMGEN INC
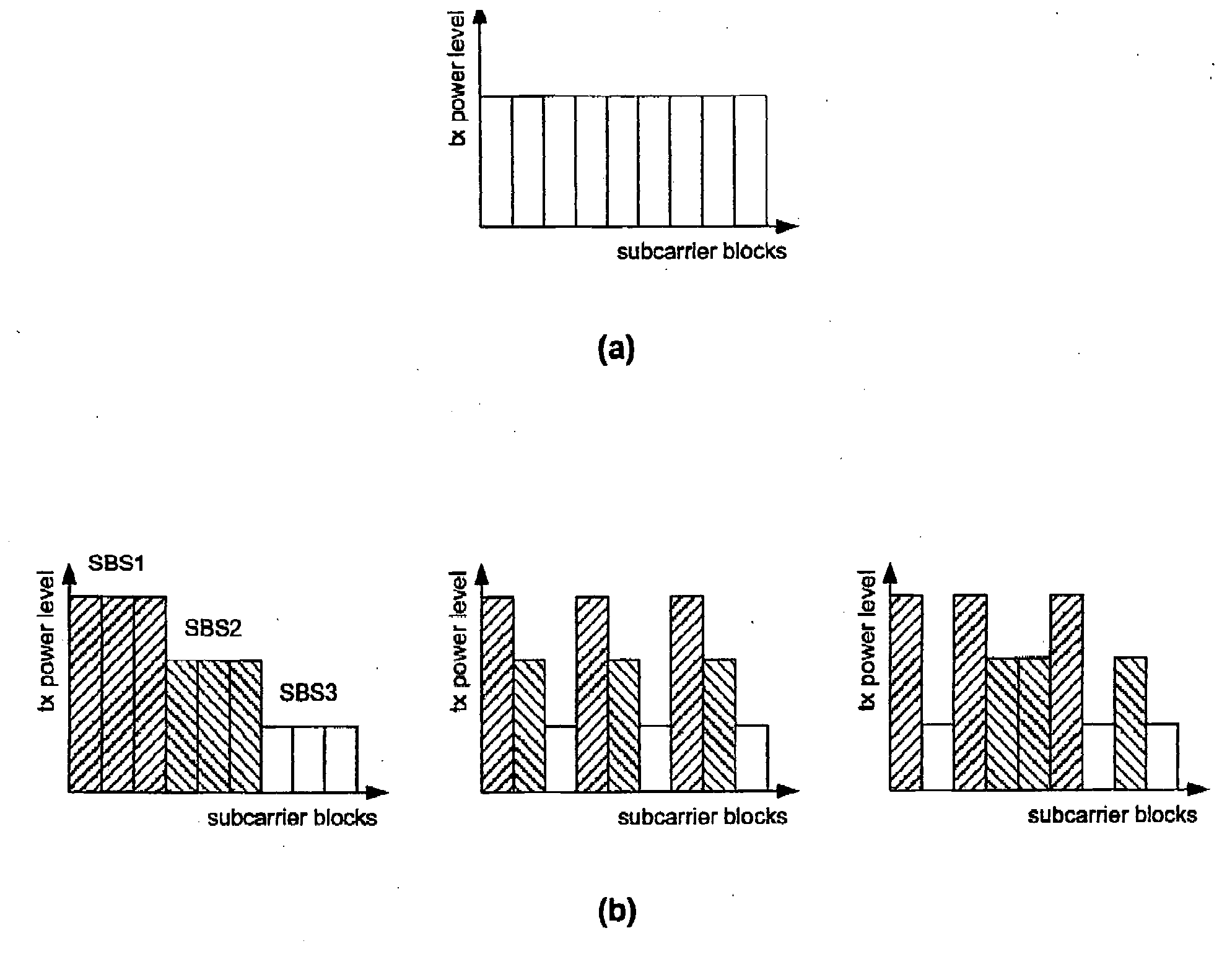
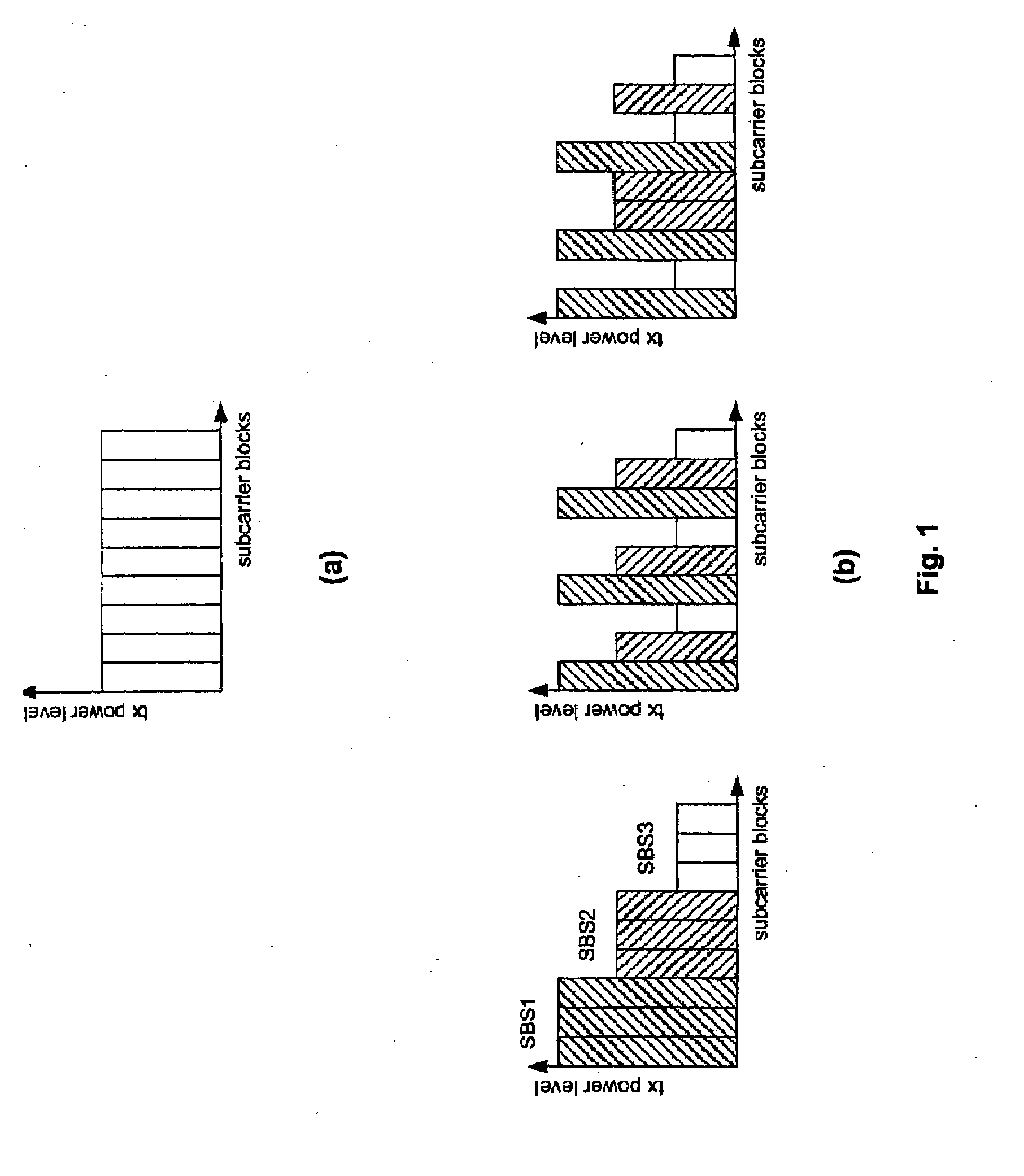
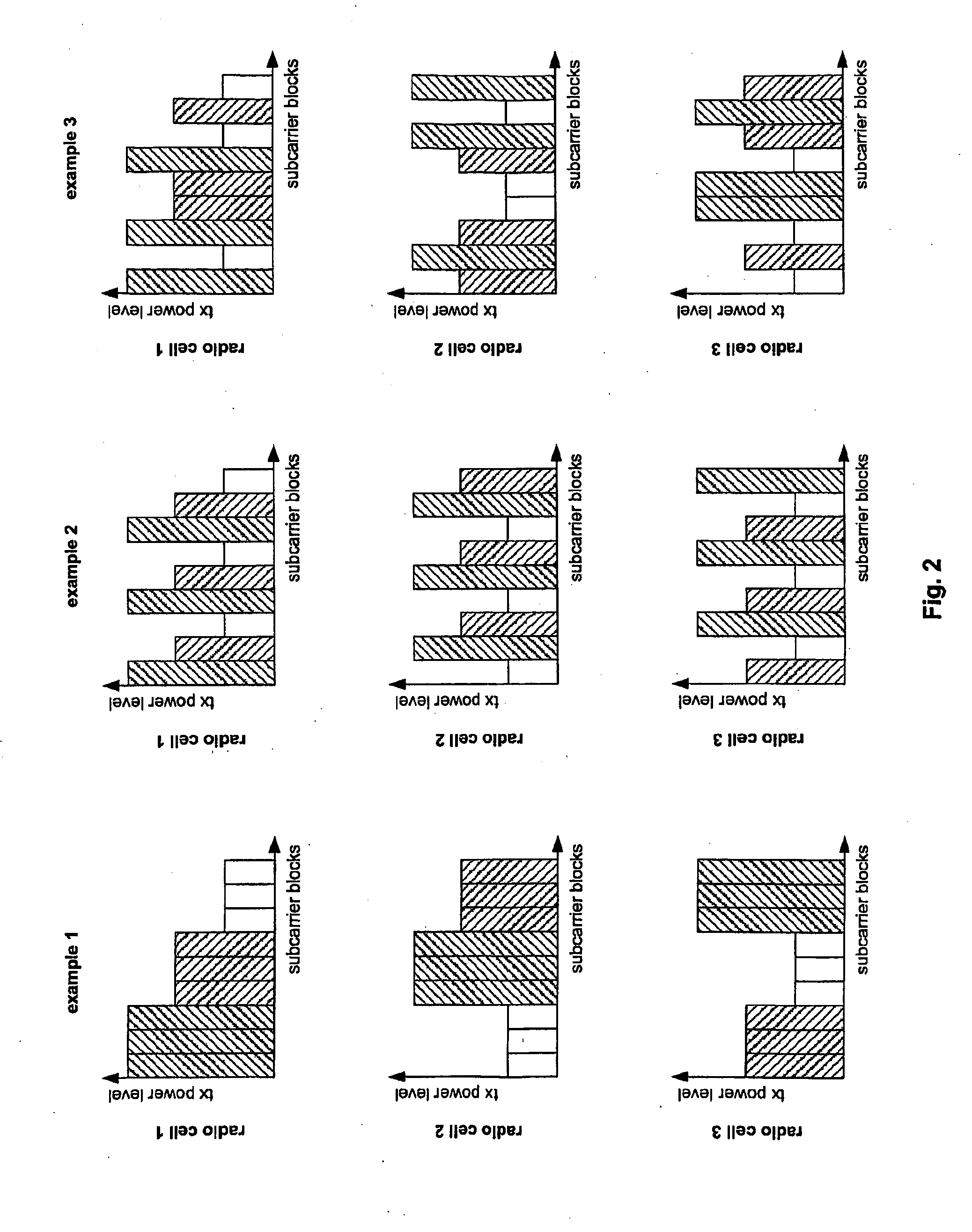
Transmission Power Level Setting During Channel Assignment for Interference Balancing in a Cellular Wireless Communication System
ActiveUS20090221297A1Reduce large average signalSignificant signal interferencePower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemEngineering
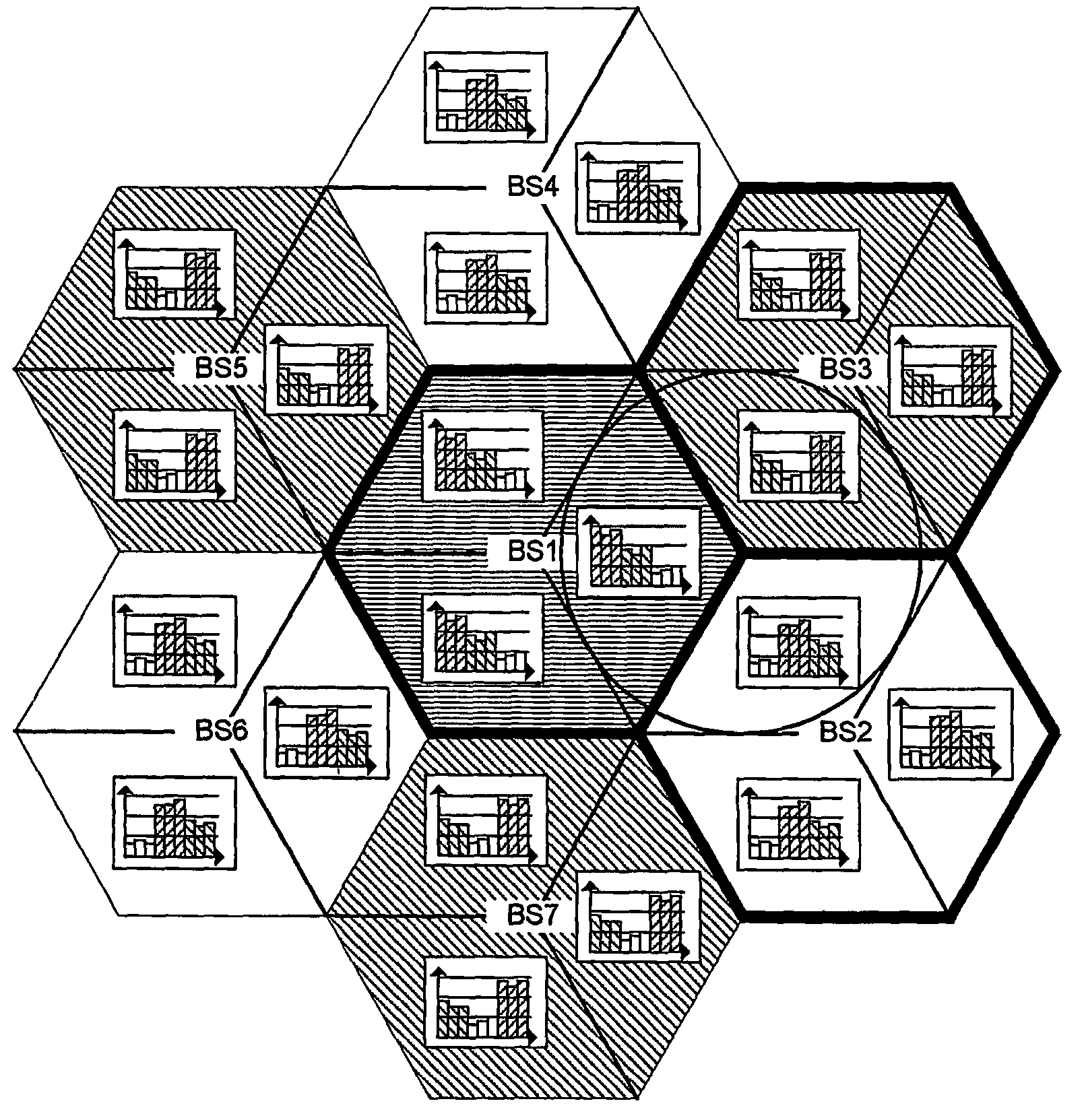
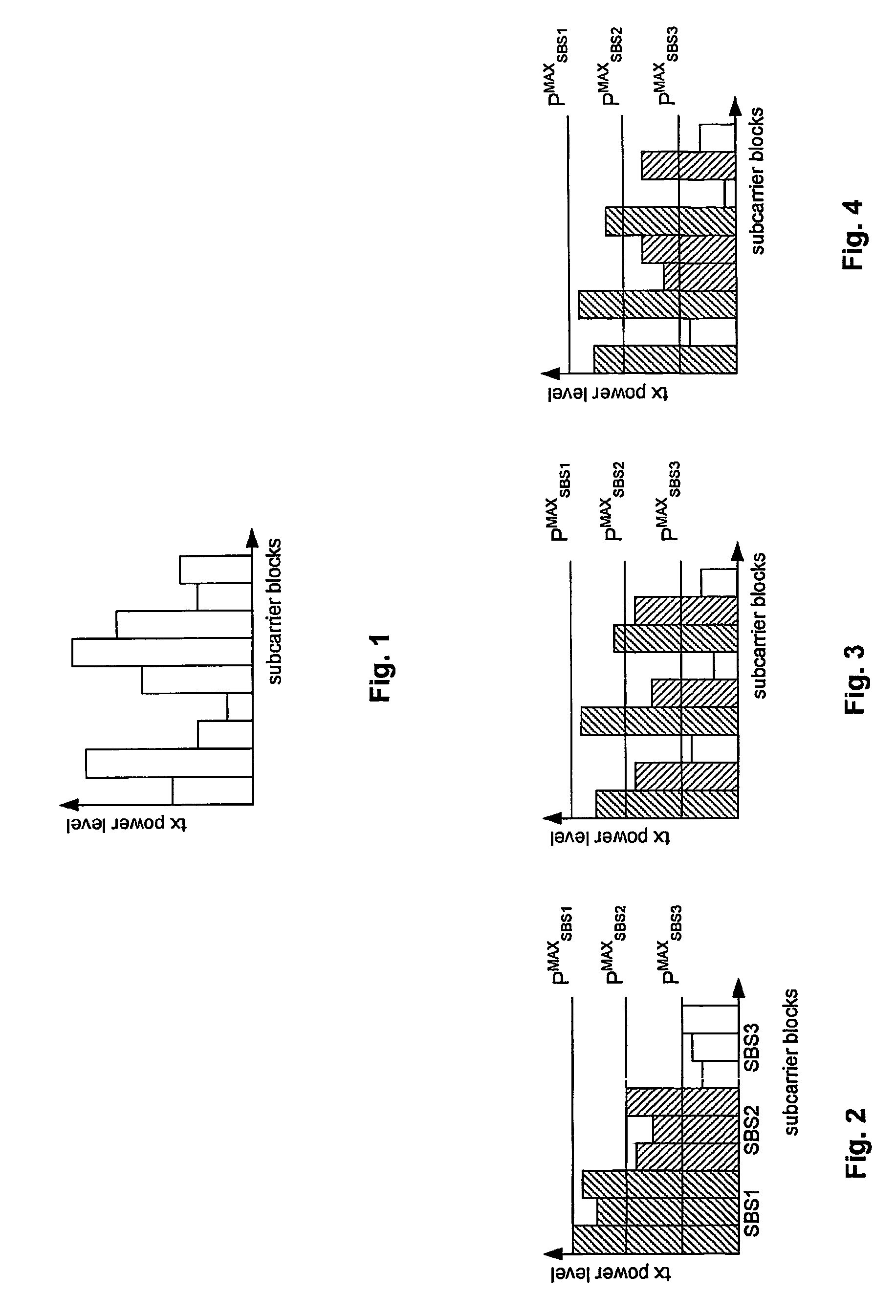
The present invention relates to a method for balancing the distribution of interference between radio cells in a wireless communication system comprising cells in which subcarrier blocks are used for communication. A number of adjacent cells build a cell cluster. Moreover, the present invention relates to a corresponding method adapted for use in a system in which multi beam antennas or multiple antennas are used. Furthermore, the present invention relates to base stations performing the above method as well as a communication system comprising the base stations. To reduce the large average SIR variations without causing additional SIR estimation, measurement and calculation problem as introduced with power control the invention suggests to group subcarrier blocks into a plurality of subcarrier block sets in each cell of a cell cluster, to determine transmission power levels for each of the cells of said cell cluster, and to assign transmission power levels to the subcarrier block sets.
Owner:APPLE INC
Interference suppressing method in wireless communication system
ActiveCN101291515AImprove quality and efficiencyImprove system efficiencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork deploymentCommunications system
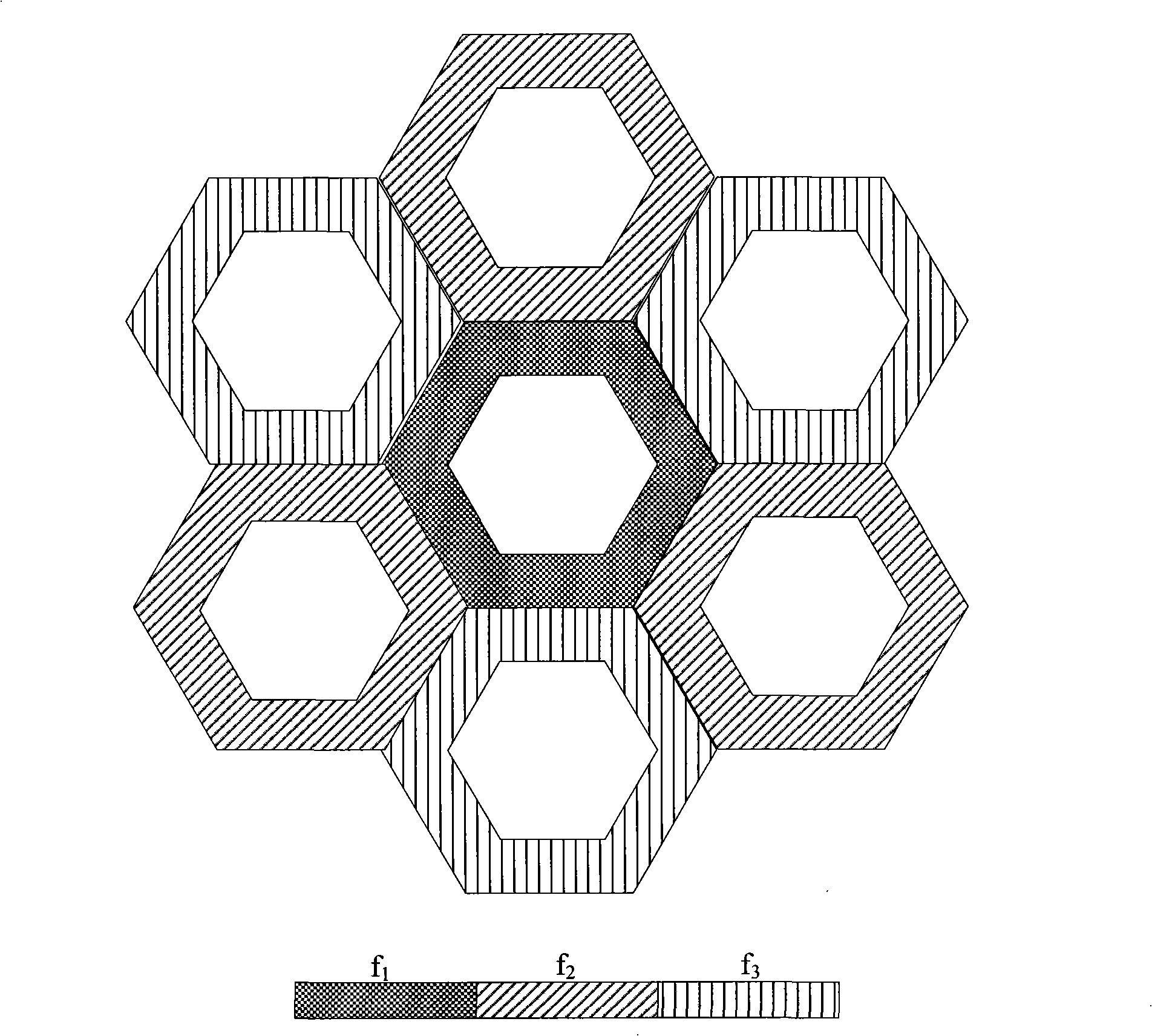
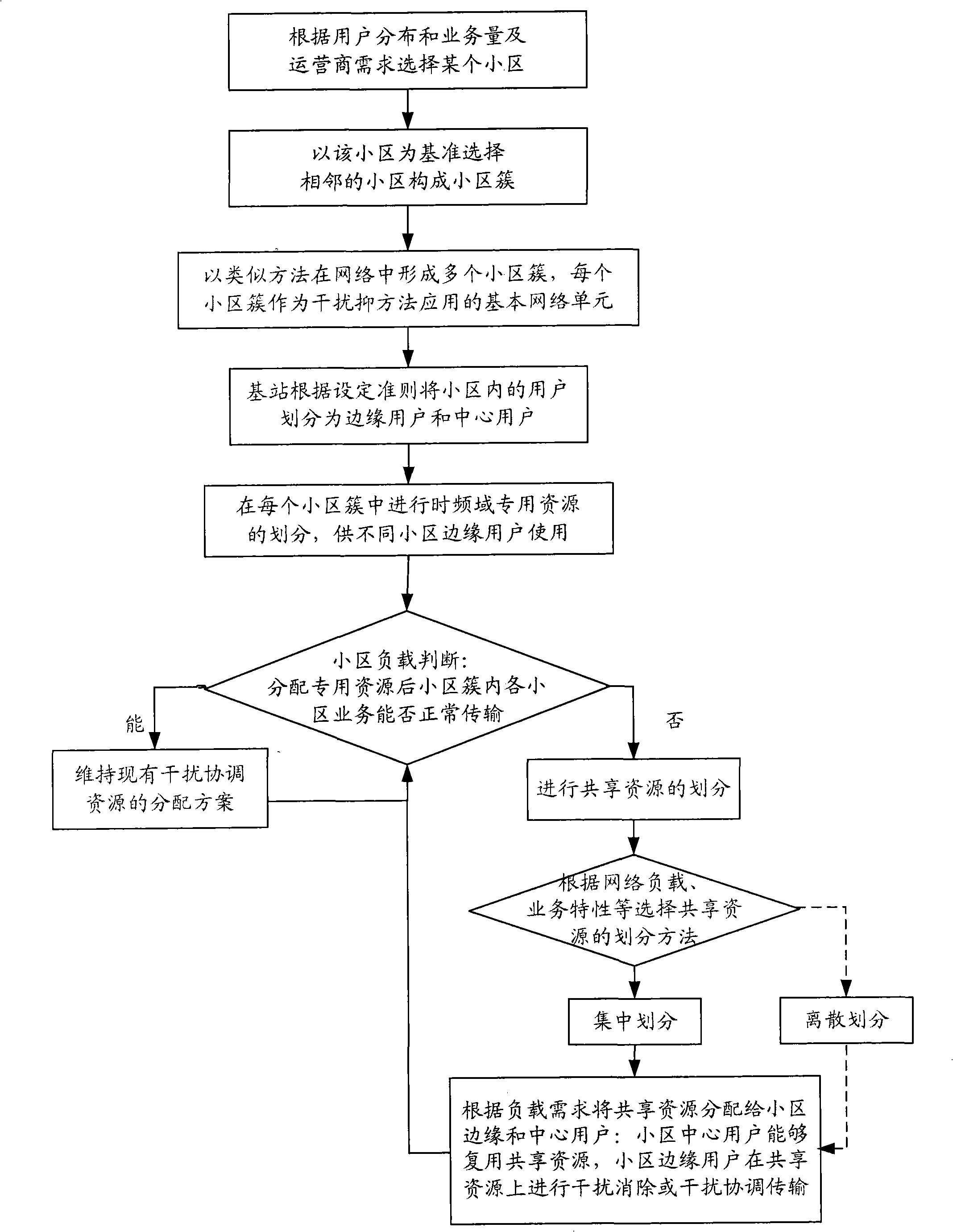
The invention provides a method for restraining the interference in a wireless communication system. According to the business and the user characteristic, a plurality of cells in the system are divided into a plurality of cell clusters; each cell cluster utilizes the same time-frequency resource distributing method, different cell clusters utilize different time-frequency resource distributing methods; and the interference suppression between different cells and different cell clusters is realized by flexibly dividing and adjusting the time-frequency two-dimension resource in order to respond to the change in the load in the cell, thereby effectively avoiding the interference between cells. On the basis of dividing the special resource for coordinating the interference for an edge user of the cell, the method utilizes an intensified or discrete dividing method to divide the shared resource in order to realize the flexible response to the change in the load of the cell and the interference suppression between cells, improves the flexibility of the system to respond to the change in the load of the cell and the system efficiency, saves the network investment and improves the flexibility of the network design.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Transmission power range setting during channel assignment for interference balancing in a cellular wireless communication system
ActiveUS7877108B2Large fluctuationsPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for balancing the distribution of interference between radio cells in a wireless communication system comprising cells in which subcarrier blocks are used for communication. A number of adjacent cells build a cell cluster. Moreover, the present invention relates to a corresponding method adapted for use in a system in which multi beam antennas or multiple antennas are used. Furthermore, the present invention relates to base stations performing the above method as well as a communication system comprising the base stations. To reduce the large average SIR variations without causing additional SIR estimation, measurement and calculation problem as introduced with power control the invention suggests to group subcarrier blocks into a plurality of subcarrier block sets in each cell of a cell cluster, to determine transmission power ranges for each of the cells of said cell cluster, and to assign transmission power ranges to the subcarrier block sets to perform TPC within the ranges.
Owner:APPLE INC
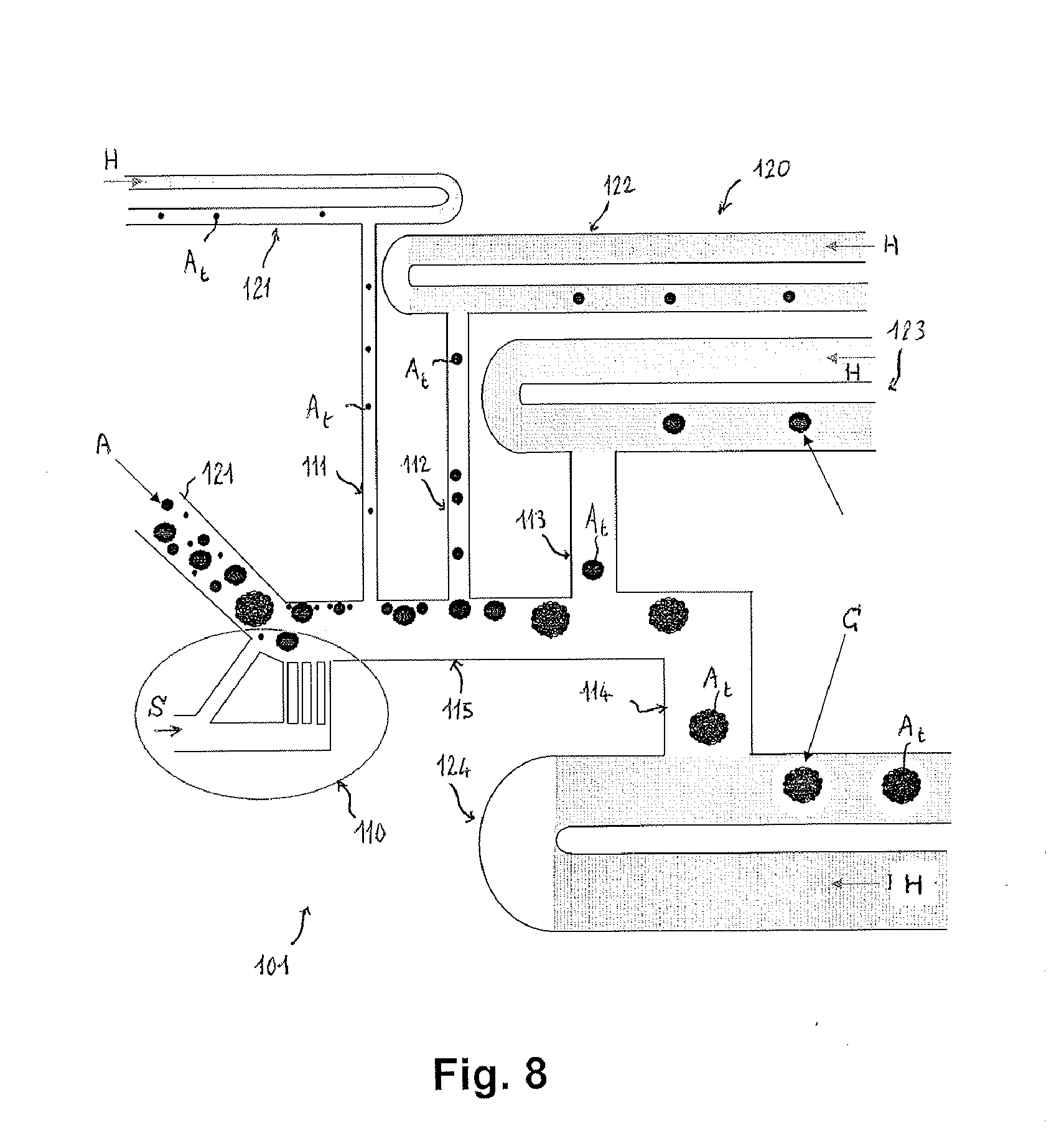
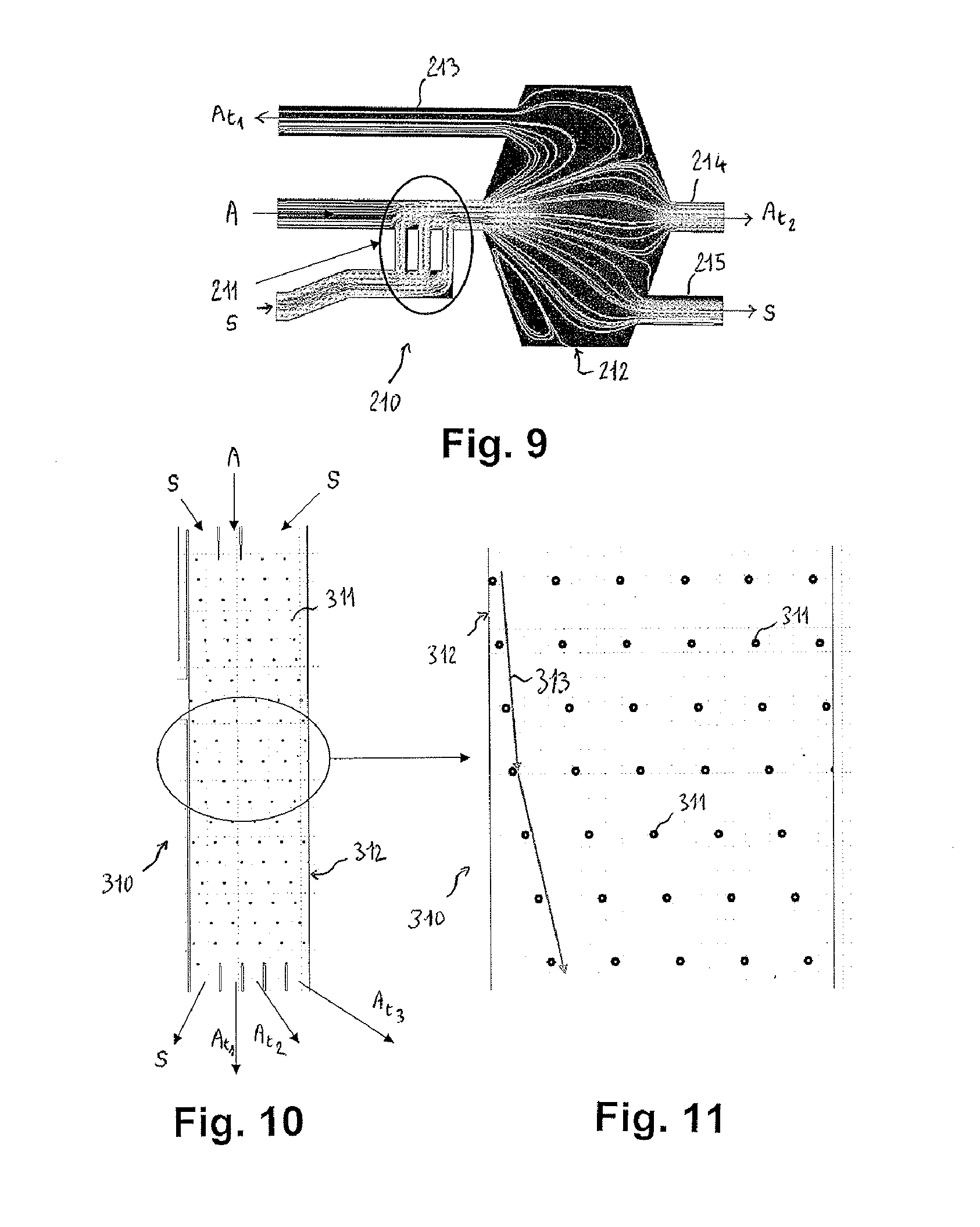
Microfluidic system and method for sorting cell clusters and for the continuous encapsulation thereof following sorting thereof
ActiveUS20090286300A1Minimized pressure lossMaintenance conditionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringCell cluster
A microfluidic system and method for sorting cell clusters, and for the continuous and automated encapsulation of the clusters, once sorted, in capsules of sizes suitable for those of these sorted clusters is provided. The microfluidic system comprises a substrate in which a microchannel array comprising a cell sorting unit is etched and around which a protective cover is bonded, and the sorting unit comprises deflection means capable of separating, during the flow thereof, relatively noncohesive cell clusters, each of size ranging from 20 μm to 500 μm and of 20 to 10 000 cells approximately, such as islets of Langerhans, at least two sorting microchannels arranged in parallel at the outlet of said unit being respectively designed so as to transport as many categories of sorted clusters continuously to a unit for encapsulation of the latter, also formed in said array.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Methods and systems for automated segmentation of dense cell populations
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Method and apparatus for performing coordinated multi-point transmission and reception in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110124345A1Improve system efficiencyAssess restrictionNetwork planningCommunications systemCell ID
A method and an apparatus for performing a Coordinated Multi-Point (CoMP) transmission in a wireless communication system are provided. An operating method of a base station for the CoMP transmission in a wireless communication system includes performing a cell clustering for CoMP transmission of a terminal, receiving a reference signal from the terminal, determining cell IDentifier (ID) information of the terminal, when the terminal uses a cell ID for the CoMP transmission, comparing a Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) value of the reference signal with a threshold, and when the CQI value of the reference signal is greater than or equal to the threshold, participating in the CoMP transmission of the terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
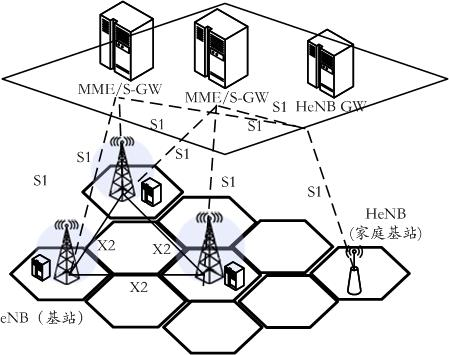
Method, apparatus and base station for balancing load of honeycomb collaboration relay network
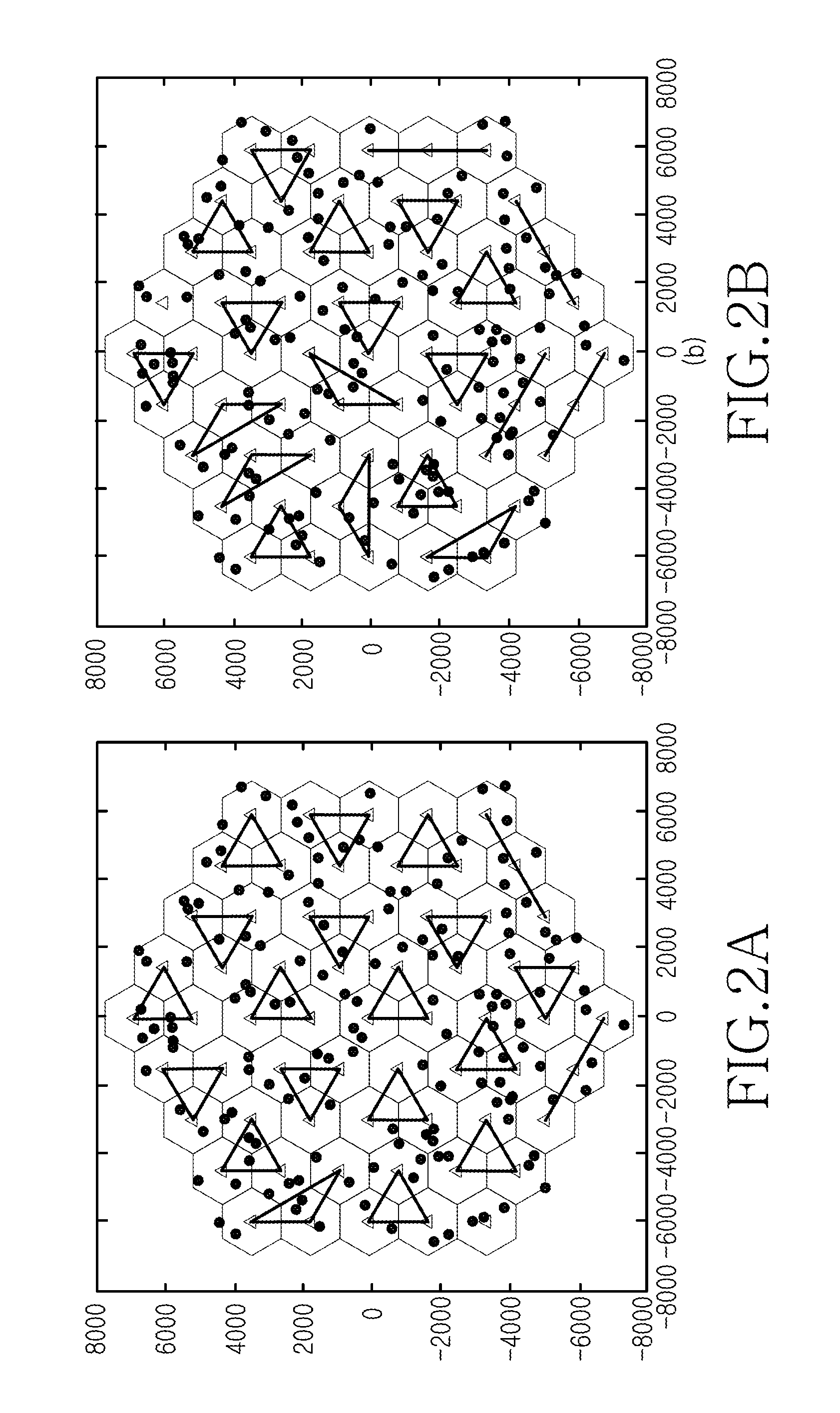
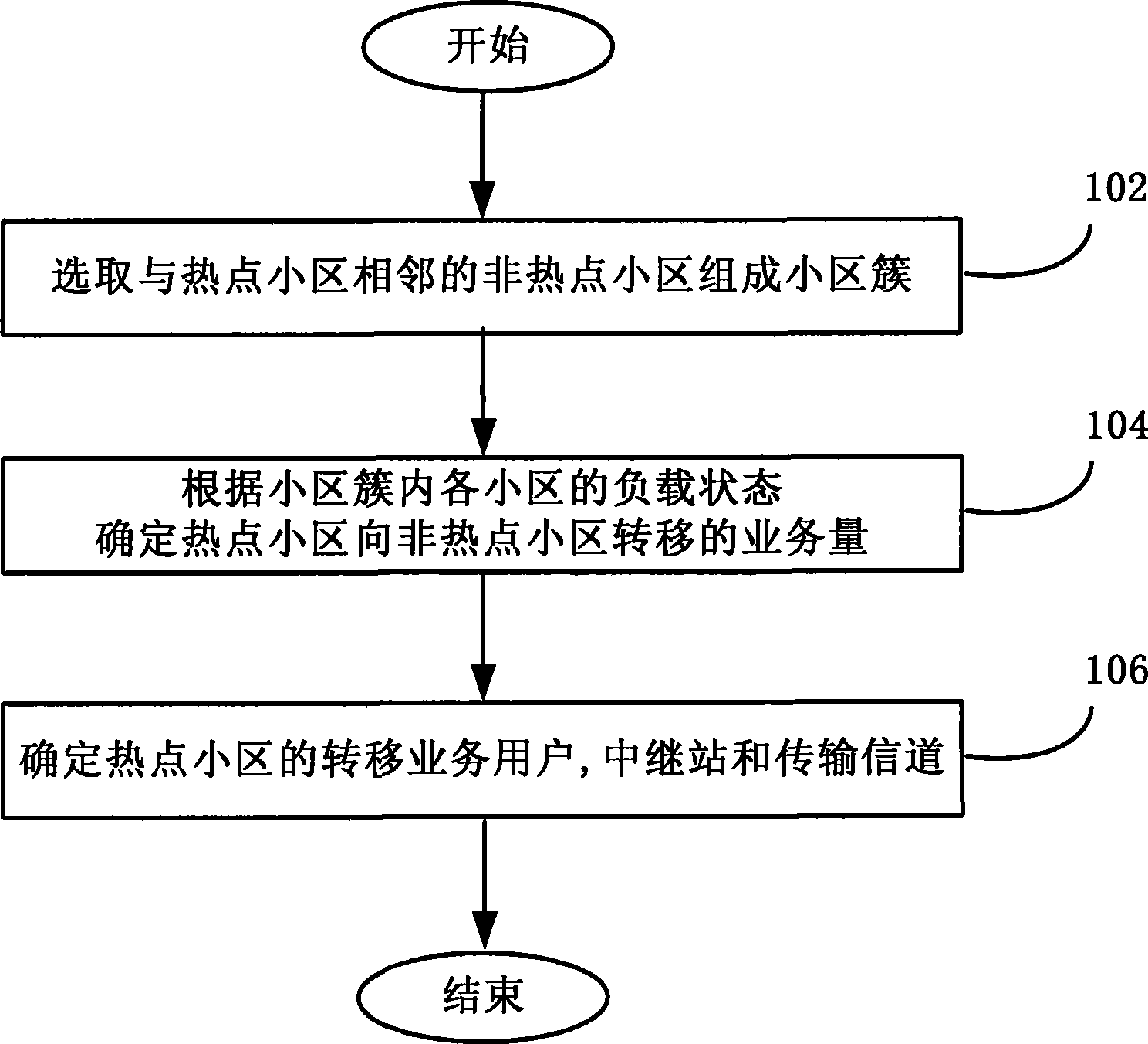
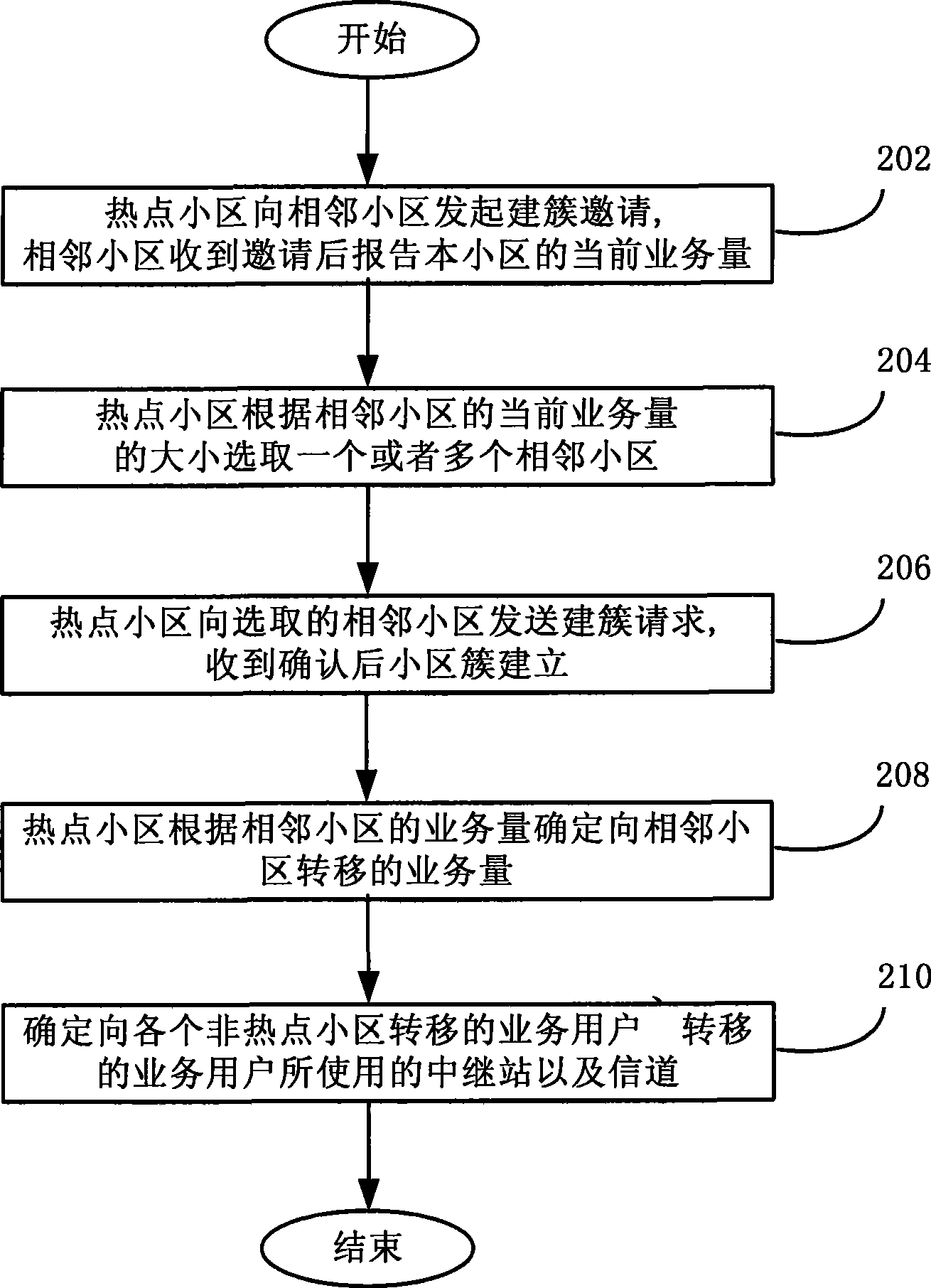
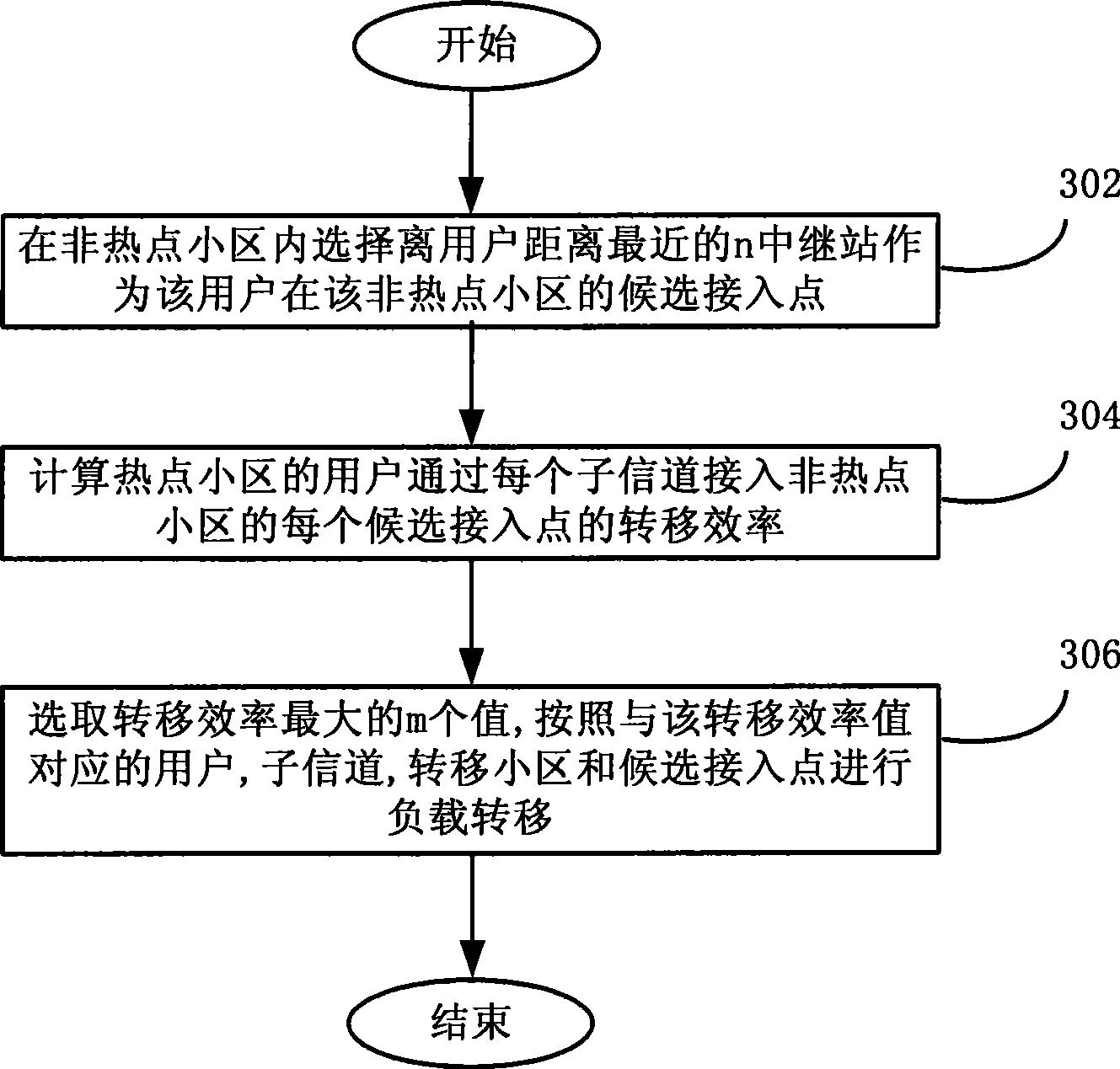
InactiveCN101415207AReduce blocking rateImprove spectral efficiencyPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumCell cluster
The invention discloses a load balancing method used in a cellular cooperative relay network, a device thereof and a base station, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: selecting a cell cluster consisting of non-hotspot cells adjacent to hotspot cells; determining the traffic volume transferred from the hotspot cells to the non-hotspot cells according to load conditions of various cells in the cell cluster; and determining users transferring the traffic in the hotspot cell, relay stations and transmission channels used by the traffic users. By dynamic establishment of the cell cluster, the load balancing method, the device and the base station can timely adapt to the burst and the uneven distribution of the traffic in a network, thus effectively balancing the load; the traffic load balancing ensures real-time traffic QoS in the hotspot cells, and minimizes the blocking rate of the whole cell cluster system; and the resource scheduling based on the transfer efficiency meets the load balancing requirements, and effectively improves the spectral efficiency of cell cluster systems.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
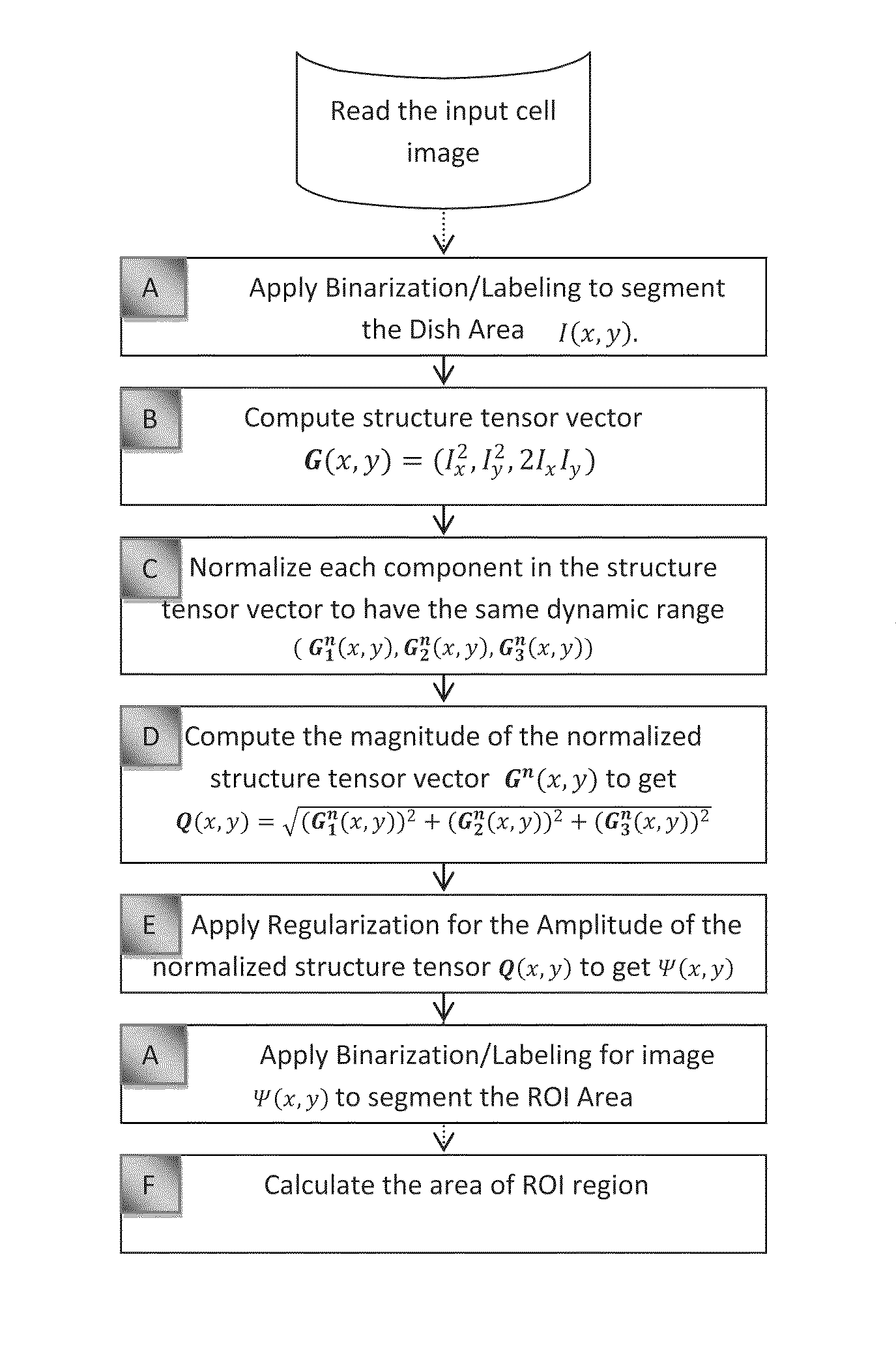
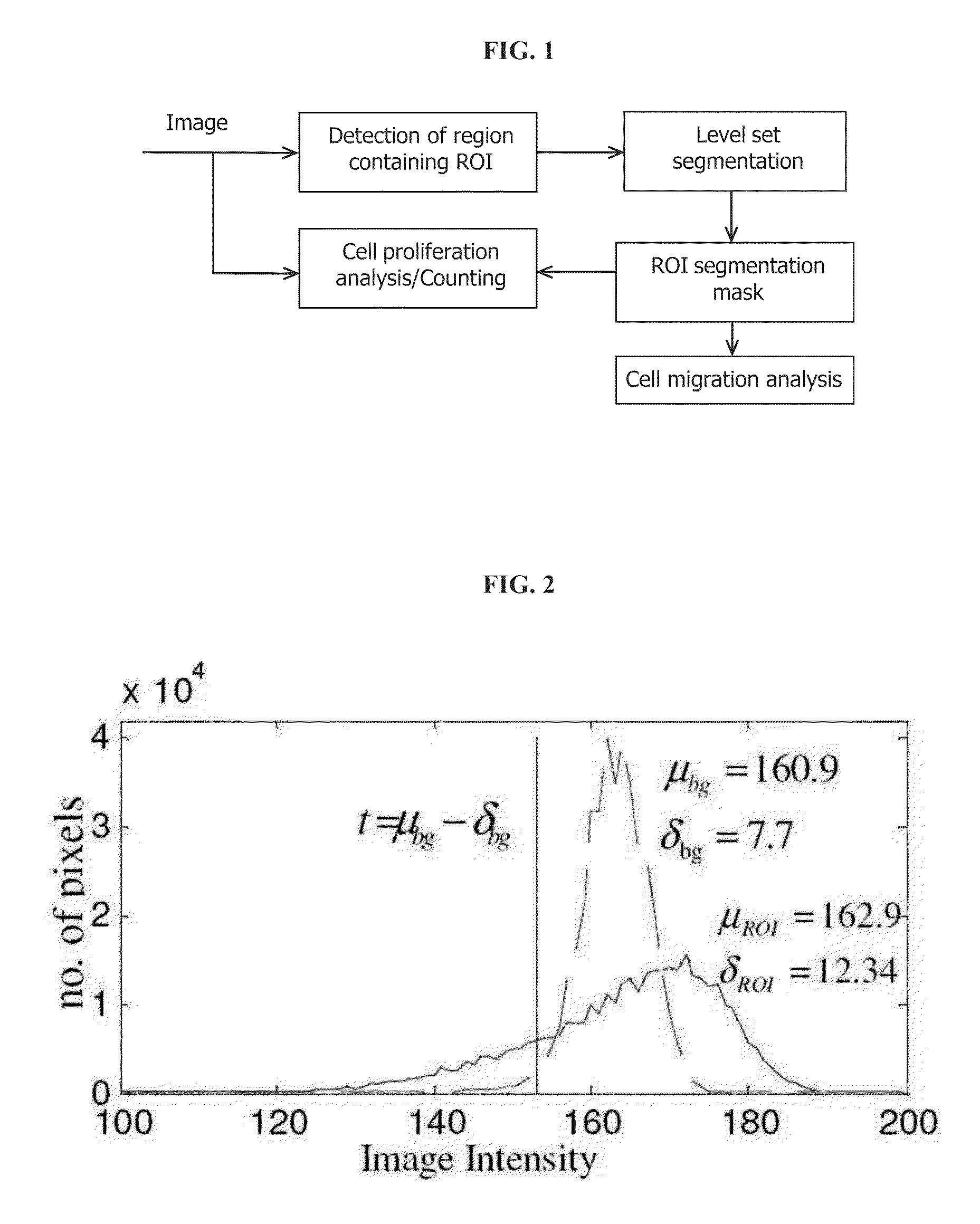
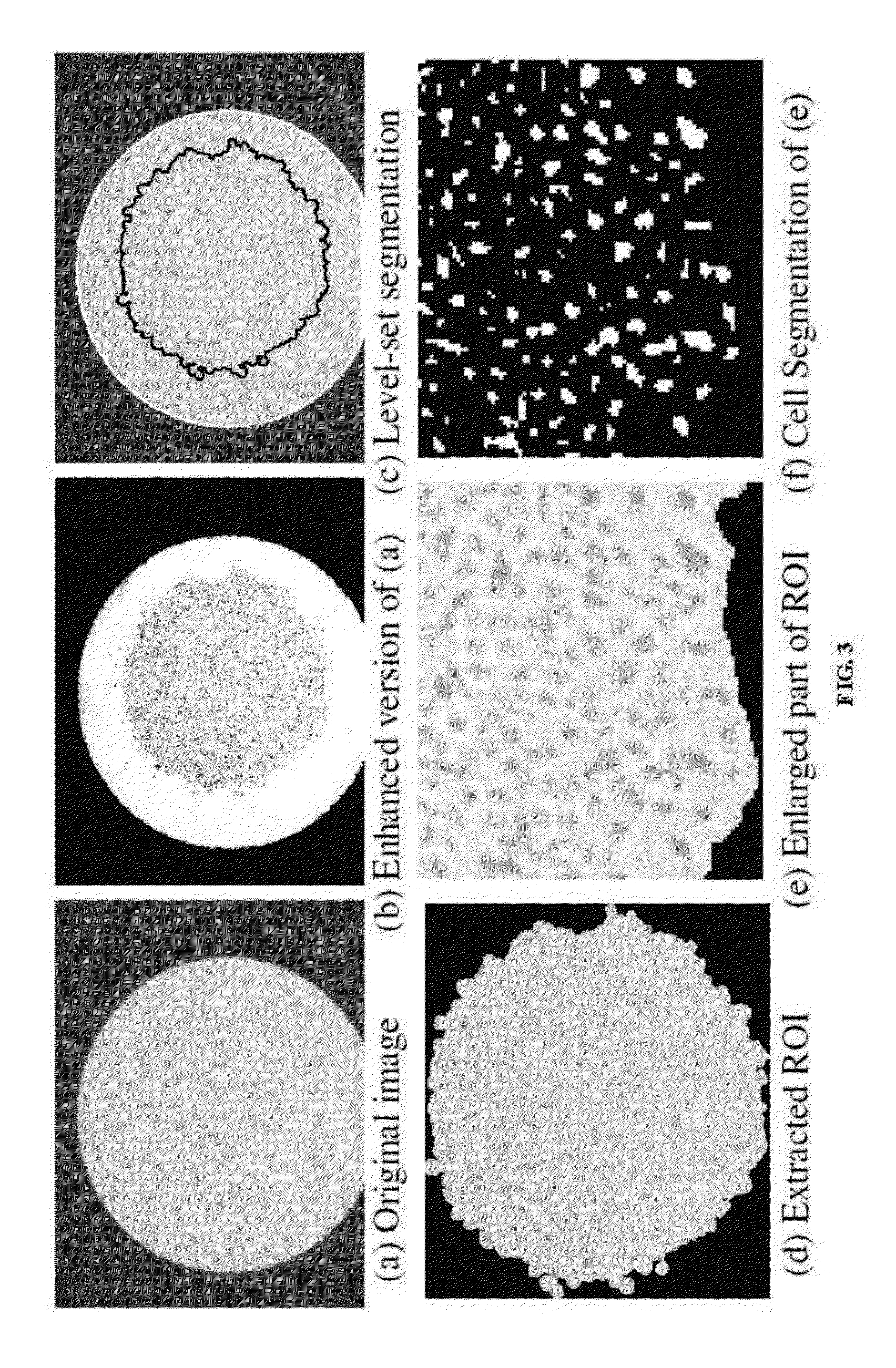
Automatic Cell Migration and Proliferation Analysis
The disclosed methods and apparatus provide for the automatic segmentation and analysis of the overall migration rate and proliferation rate of cells that may be used with any resolution image and without the need to prepare the sample or the image before the image is analyzed. In particular embodiments, the method or apparatus of analyzing a cell image comprise performing a structure tensor analysis and / or regularization and / or a histogram-based analysis and / or a level-set analysis to classify pixels in the image into a region of interest (ROI), corresponding to cell clusters, and a non-significant region. Methods and apparatus for cell migration analysis comprise means for computing the areas of the segmented ROIs for a set of images. Methods and apparatus for cell proliferation analysis comprise means for counting the number of cells within the segmented ROIs for a set of images.
Owner:KARAM LINA JAMIL +1
Phase subtraction cell counting method
InactiveUS8428331B2Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionDevelopmental stageMicroscopic image
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
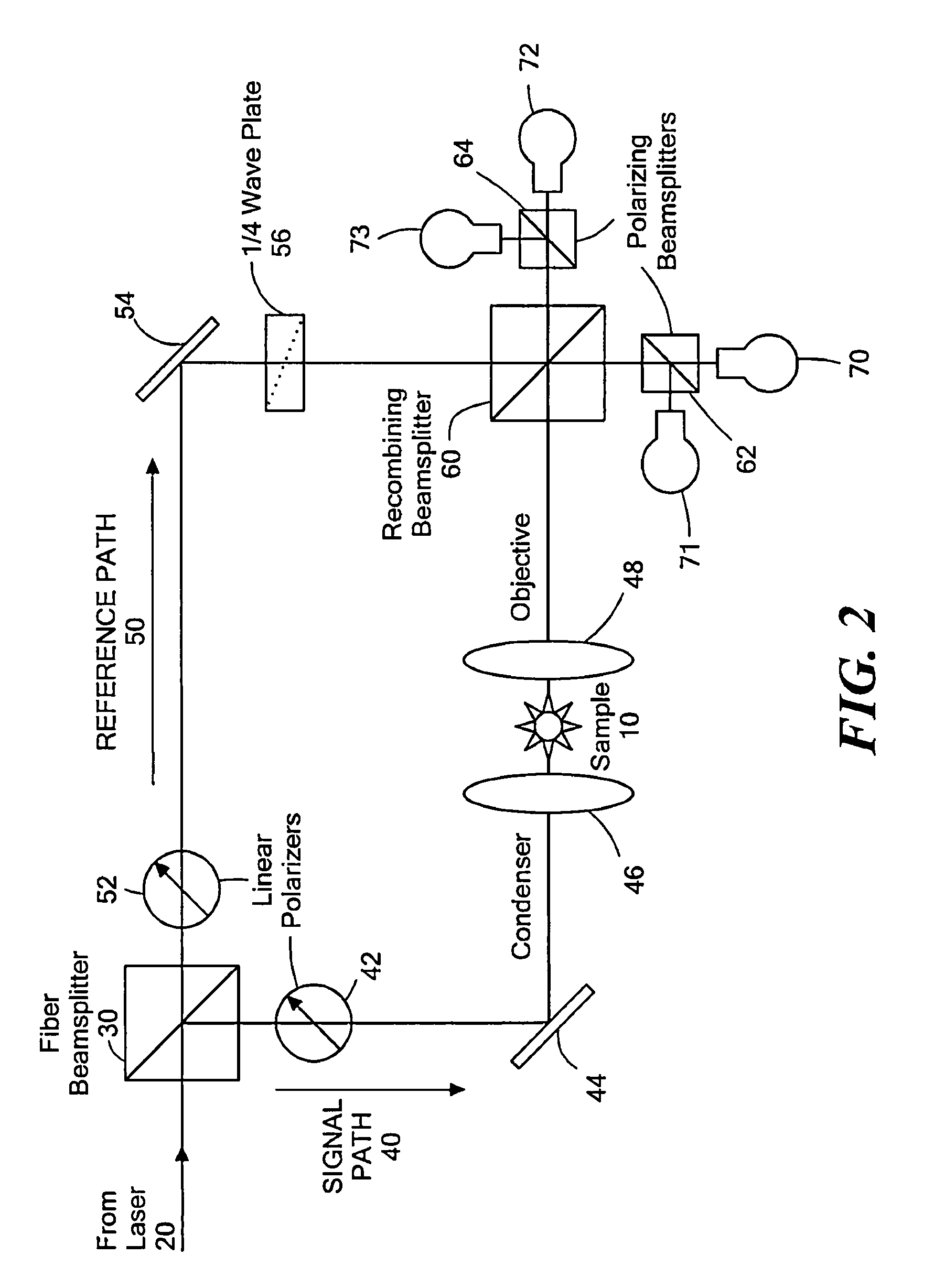
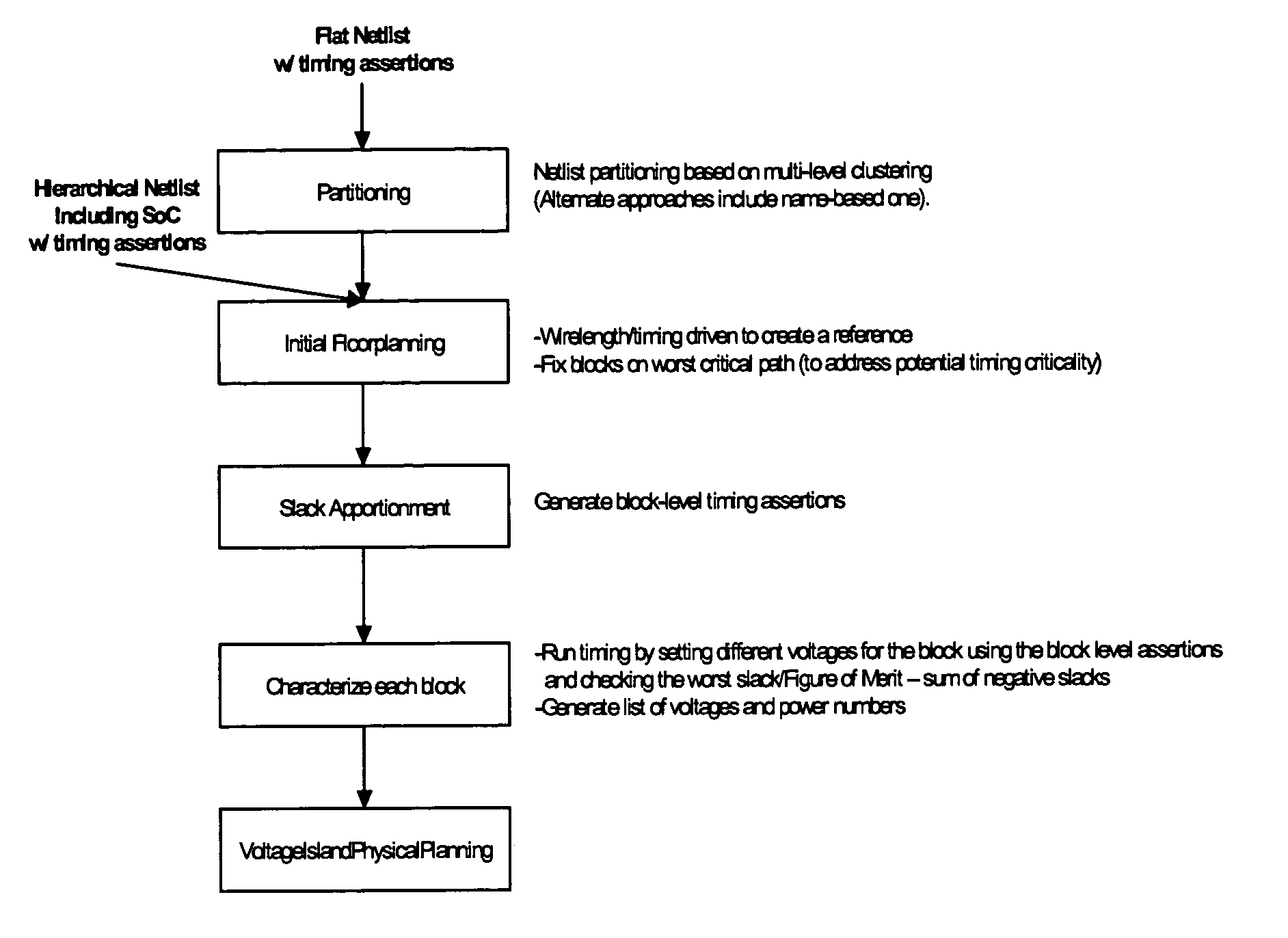
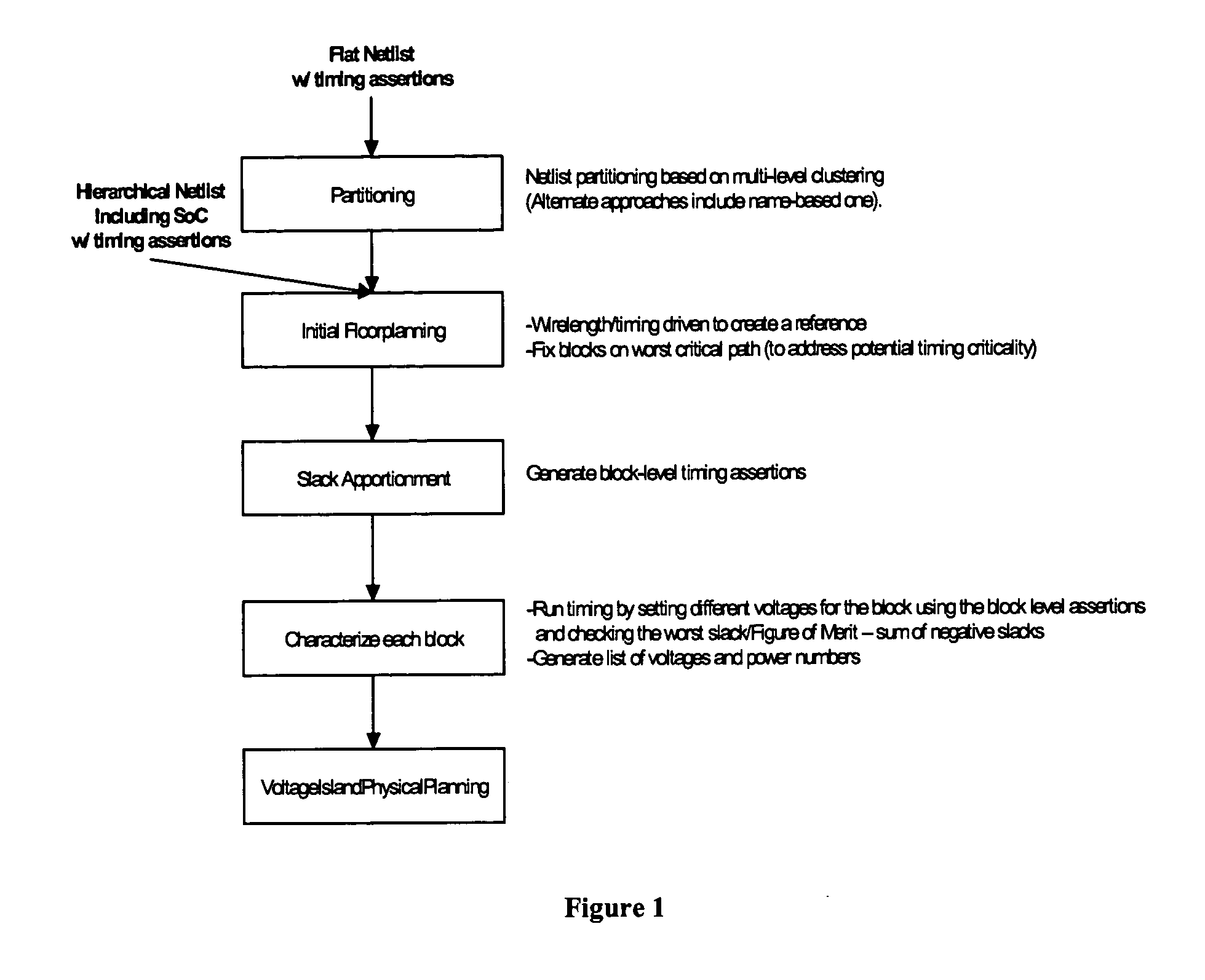
Method of physical planning voltage islands for ASICs and system-on-chip designs
InactiveUS20050278676A1Minimize power consumptionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPhysical planningIslanding
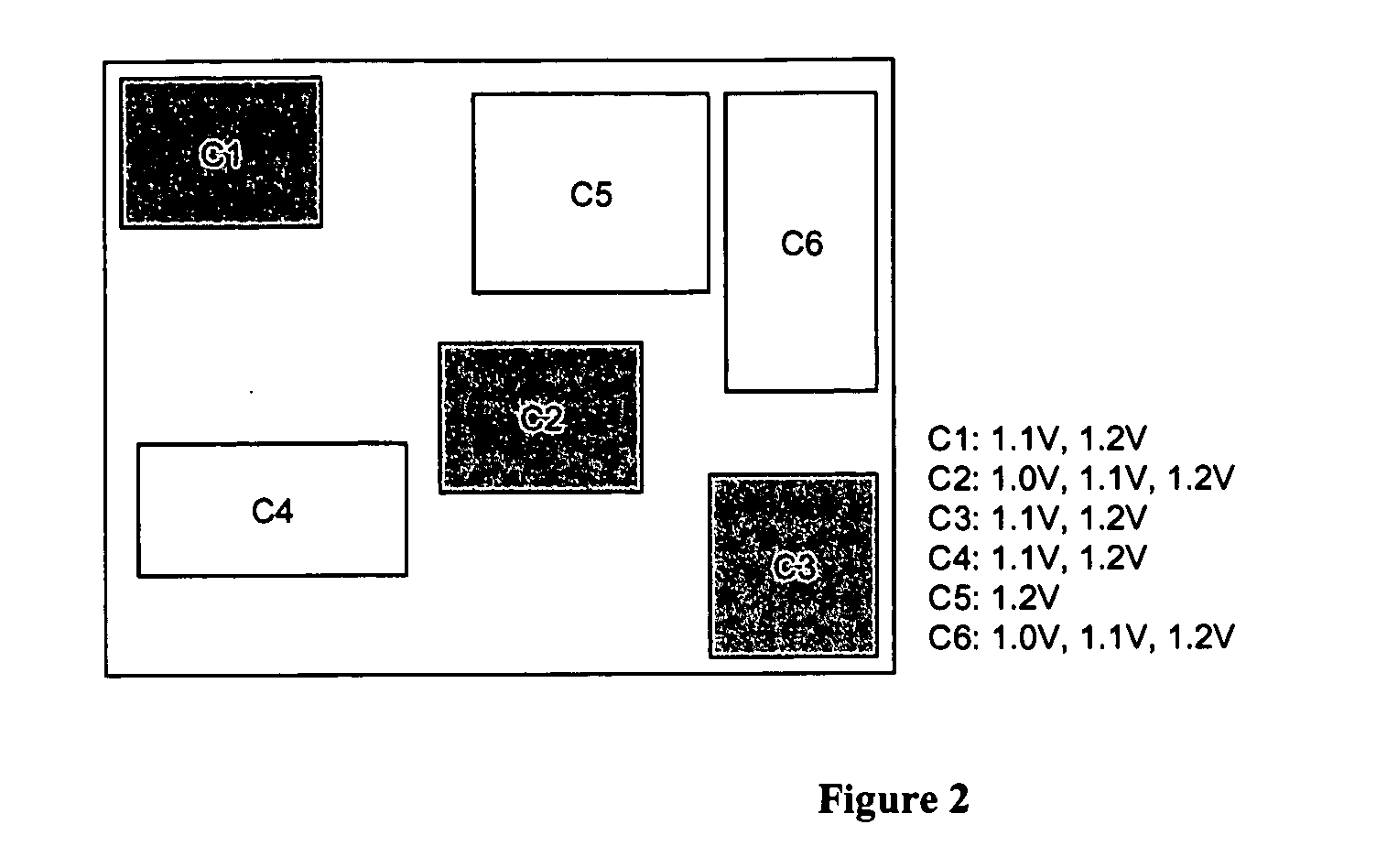
Voltage islands enable a core-level power optimization of ASIC / SoC designs by utilizing a unique supply voltage for each cluster of the design. Creating voltage islands in a chip design for optimizing the overall power consumption consists of generating voltage island partitions, assigning voltage levels and floorplanning. The generation of voltage island partitions and the voltage level assignment are performed simultaneously in a floorplanning context due to the physical constraints involved. This leads to a floorplanning formulation that differs from the conventional floorplanning for ASIC designs. Such a formulation of a physically aware voltage island partitioning and method for performing simultaneous voltage island partitioning, level assignment and floorplanning are described, as are the definition and the solution of floorplanning for voltage island based designs executed under area, power, timing and physical constraints. The physical planning of voltage islands includes: a) characterizing cell clusters in terms of voltages and power consumption values; b) providing a set of cell clusters that belong to a single voltage island Random Logic Macro (RLM); and c) assigning voltages for the voltage island RLMs, all within the context of generating a physically realizable floorplan for the design.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Mobile load balancing method
ActiveCN102098728AIncrease profitReduce overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
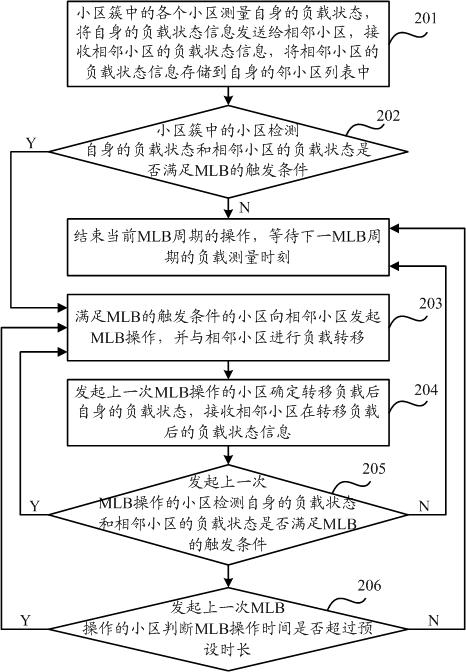
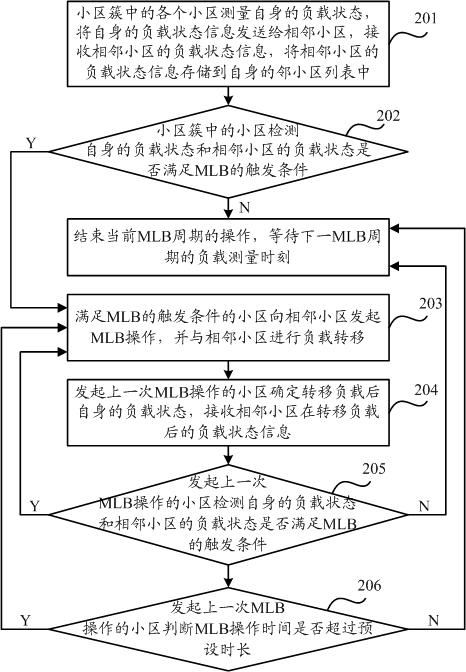
The invention discloses a mobile load balancing (MLB) method which is applied to a wireless cellular mobile communication system and realizes load balance between adjacent cells in a same cell cluster by taking a cell cluster containing a plurality of cells as a base unit. Concretely, each cell in the cell cluster initiates MLB operation to the adjacent cells according to the load state per se and the load states of the adjacent cells and carries out load transfer with the adjacent cells. The MLB operation initiated by each cell comprises active MLB initiated by a light load cell and passive MLB initiated by a serious overload cell. The cells in the cell cluster can periodically initiate MLB operation for many times, thereby realizing load balance gradually and stably between two adjacent cells, solving the problem of overload of the cell subjected to MLB, avoiding the occurrence of a ping-pong effect, and increasing the convergence rate of load balancing. The adjacent cells exchange load state information, thereby saving the network signaling overhead, lowering the load of network interaction, increasing the utilization ratio of wireless resources, and furthermore ensuring the stability of the network.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
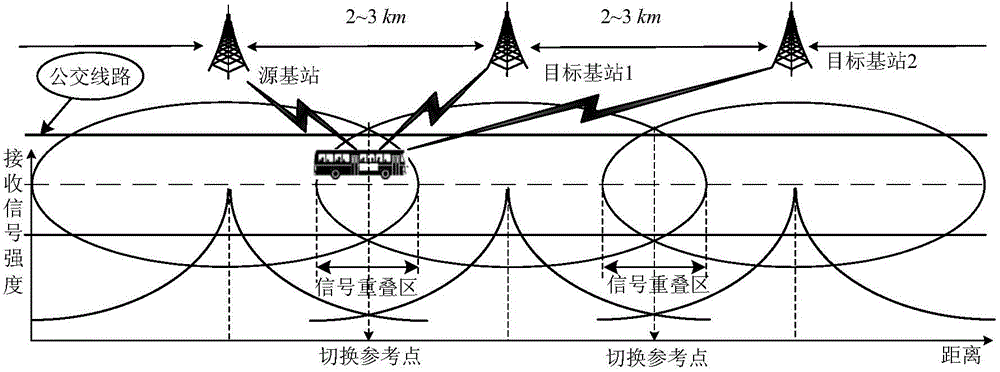
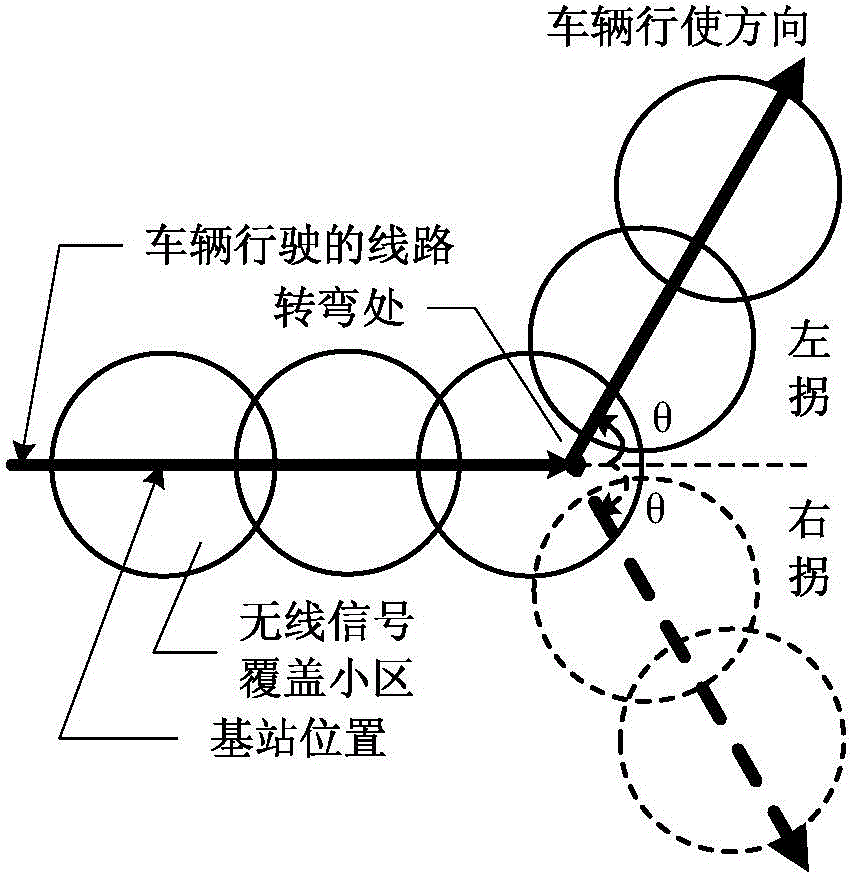
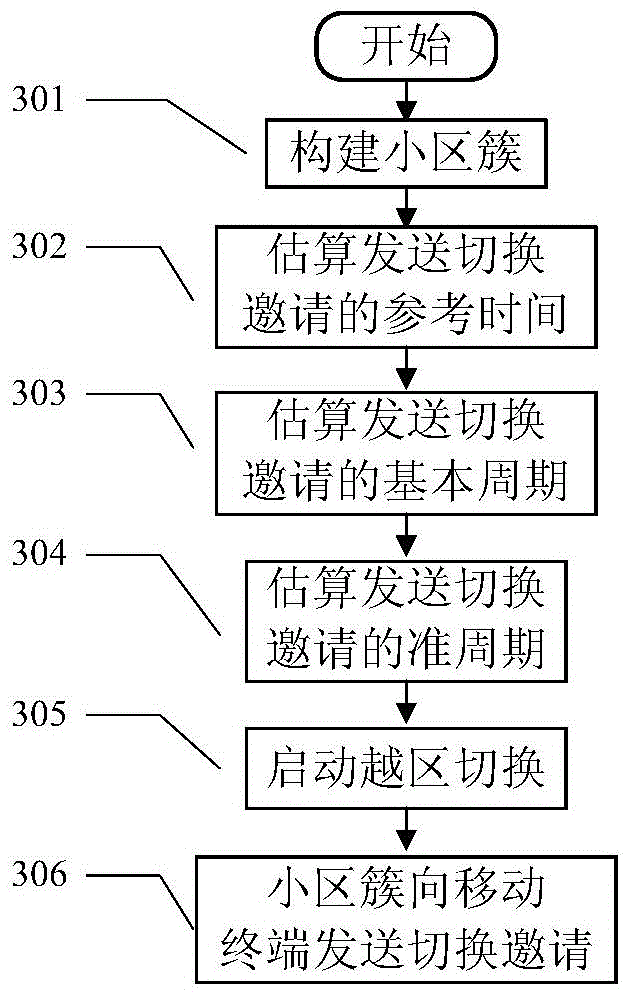
Quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending
The invention discloses a quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending. The quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending comprises, according to the mobile line diagram and the moving speed of a mobile terminal as well as the localization information of the base station of a serving cell and the base station of a neighboring cell to structure a cell cluster and to determine the reference time, the basic period and the quasi-period for transmitting handoff invitation; transmitting the handoff invitation to the mobile terminal periodically through every substation in the cell cluster and accordingly triggering handoff. The quasi-periodic handoff triggering mechanism based on handoff invitation sending overcomes the shortcomings of traditional handoff triggering mechanisms based on signal strength receiving and enables handoff triggering to be timely, accurate and reliable, and meanwhile, shortens the executing time for handoff, improves the handoff speed and efficiency and avoids ping-pong handoff, thereby having a broad application prospect in wireless communication environments with relatively fixed mobile lines and relatively high moving speed such as high-speed railways, highways, urban BRT (bus rapid transit) and the like.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
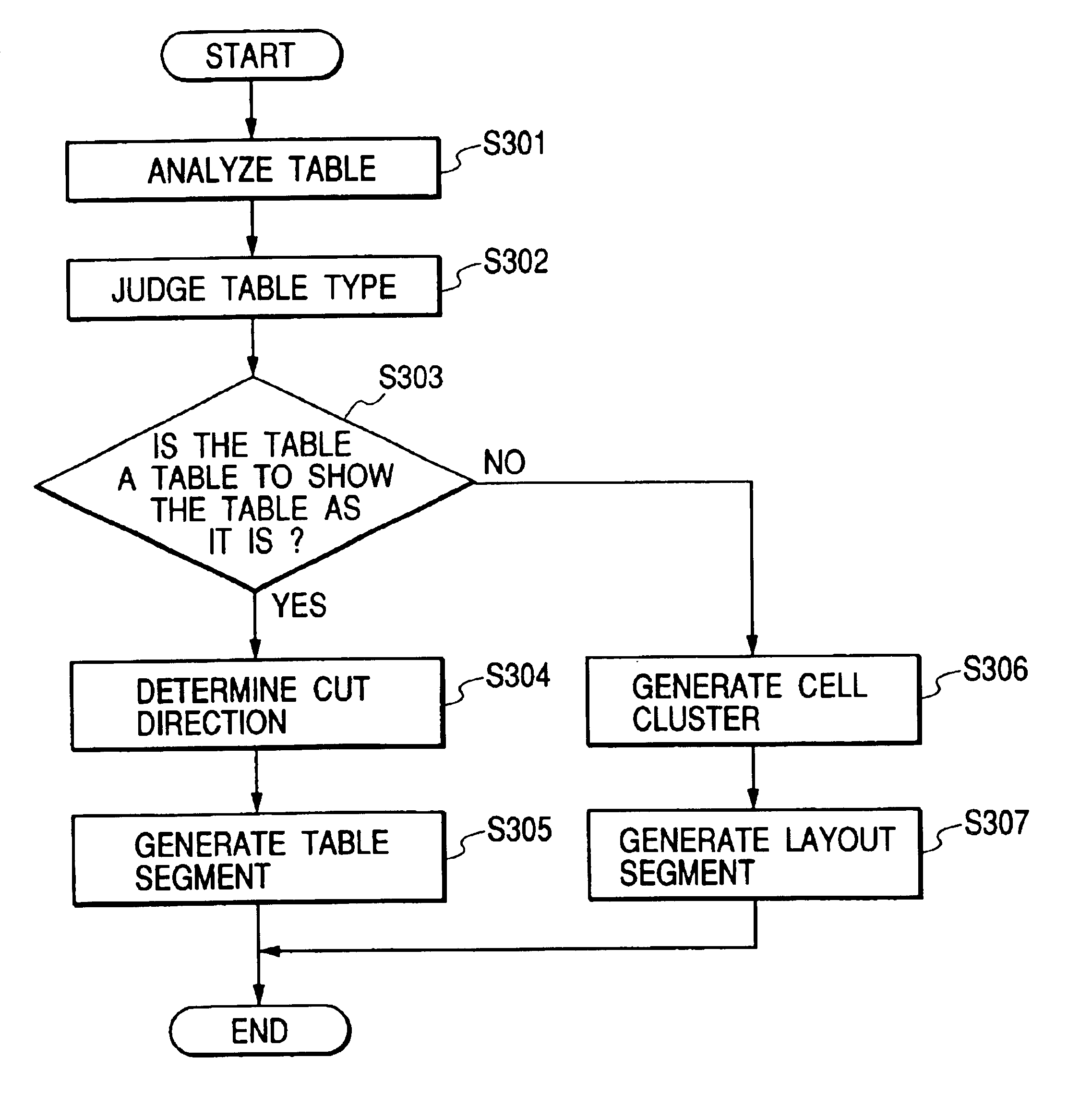
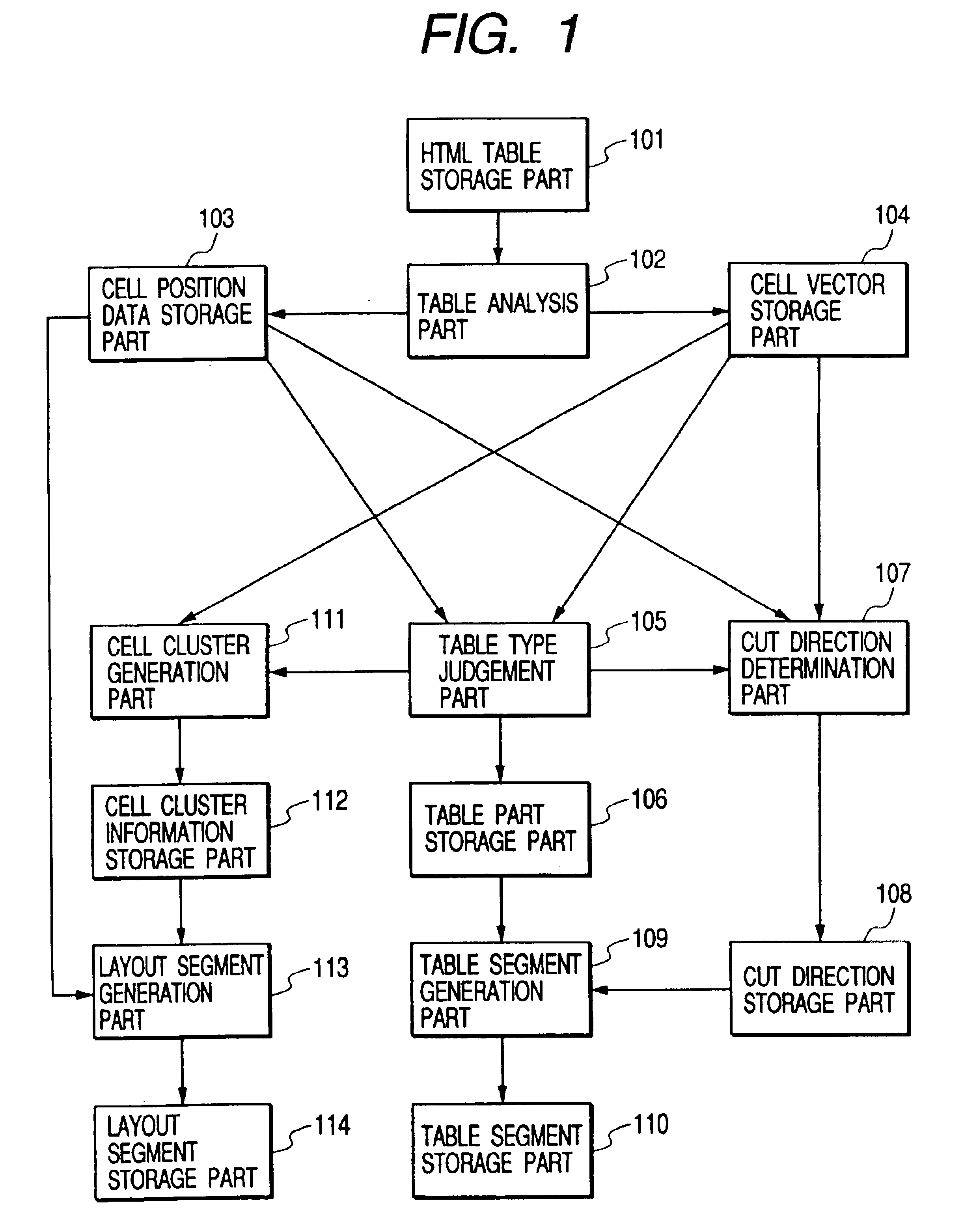
Apparatus and method for dividing document including table
InactiveUS6865720B1Natural language data processingOffice automationTheoretical computer scienceCell cluster
A table in an HTML document is analyzed to generate cell position data indicating a positional relationship between cells and cell vectors representing characteristics of the cells, and a table type is judged with reference to the cell position data and the cell vectors, and, if the table type is a table describing a table, it is judged whether the data is represented in a column or a row with reference to the cell position data and the cell vectors, and a cut direction of the table is determined, and segments are generated with reference to the table type and the cut direction. If the table type is a table for layout, the cells are clustered with reference to the cell vectors, and the segments are generated with reference to the cell position data and cell cluster information.
Owner:CANON KK
Multi-cell coordination large-scale MIMO pilot frequency multiplexing transmission method
InactiveCN103997394AReduce overheadNet Spectral Efficiency ImprovementError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
The invention provides a multi-user large-scale MIMO pilot frequency multiplexing transmission method based on multi-cell coordination. According to the transmission method, all base stations provided with a large-scale antenna array wirelessly communicate with several users on the same time-frequency resource, it is not required that the users in the same cell use complete orthogonal pilot frequency, it is not required either that different cells completely multiplex the same pilot frequency, and the users in the same cell or the different cells can multiplex the same pilot frequency. Multi-cell coordination communication is adopted, and a cell cluster is formed by the multiple cells. The transmission method includes the steps that all the cell base stations obtain statistics channel information of all the users in the cell cluster and send the information to a central control unit which takes charge of coordinating all the cells in the cell cluster; according to the statistics channel information, the central control unit allocates pilot frequency to all the users in the cell cluster and feeds back a result to all the base stations; all the base stations obtain all user channel estimations and statistical characteristics of errors of the user channel estimations by using pilot frequency signals sent by all the users, and the base stations perform uplink robust receiving and downlink robust pre-coding according to all the user channel estimations and the statistical characteristics of the errors of the user channel estimations. The transmission method can reduce the pilot frequency overhead substantially and improve net spectrum efficiency of a system and is high in adaptability to pilot frequency allocation algorithms, and uplink receiving and downlink pre-coding transmission has robustness.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Artificial intelligence auxiliary radiograph reading system for cervix uteri cell sap liquid-based smear
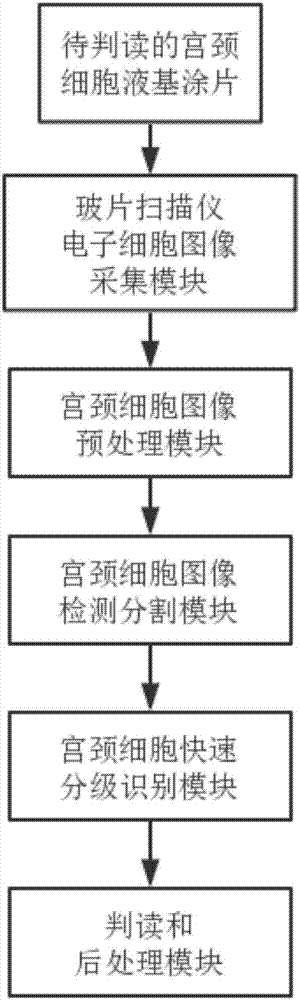
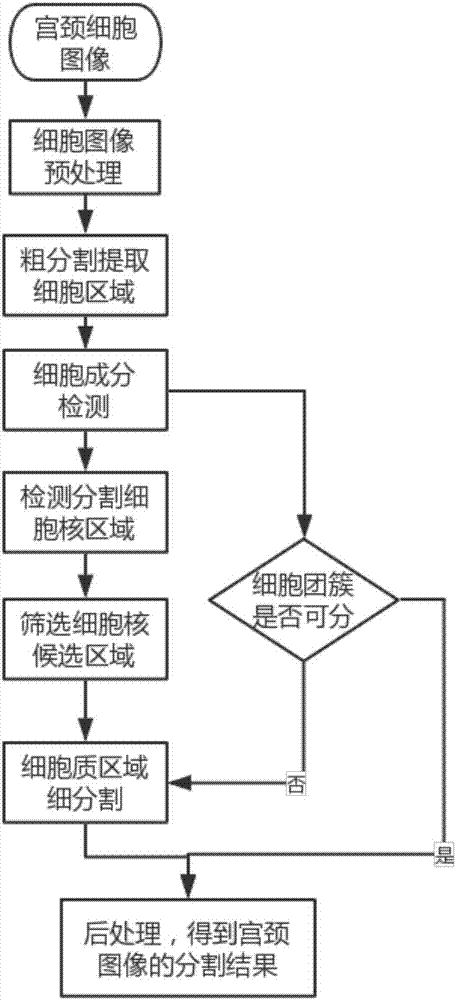
ActiveCN107274386AReduce labor intensityIncreased sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an artificial intelligence auxiliary radiograph reading system for a cervix uteri cell sap liquid-based smear. The system comprises a cell image acquisition module, a cell image preprocessing module, a cell image detection segmentation module, a quick hierarchical recognition module of a cell and an interpretation and postprocessing module, wherein the cell image detection segmentation module is used for automatically detecting different cell ingredients of the image cell, and simultaneously carrying out automatic segmentation on a cell nucleuse, cytoplasm and a background in the same cell ingredient, and a segmentation result is trimmed and optimized; the quick hierarchical recognition module of the cell is used for identifying a segmented image and distinguishing the segmented image into a single cell or a cell cluster; a double-current convolutional neural network of an additional knowledge field and a constructed cell mapping knowledge domain are adopted to carry out hierarchical recognition on single cell to independently obtain two hierarchical results; a double-current convolutional neural network of the cell cluster is adopted to realize the recognition of inseparable cell clusters; and the interpretation and postprocessing module is used for carrying out combined interpretation on two types of hierarchical results of the single cell, and conflict processing is carried out to obtain the hierarchical result of the single cell.
Owner:深思考人工智能机器人科技(北京)有限公司
Microfluidic system and method for sorting cell clusters and for the continuous encapsulation thereof following sorting thereof
ActiveUS8263023B2Improve final performanceMinimize formationSamplingTransportation and packagingEngineeringLangerhans Islets
A microfluidic system and method for sorting cell clusters, and for the continuous and automated encapsulation of the clusters, once sorted, in capsules of sizes suitable for those of these sorted clusters is provided. The microfluidic system comprises a substrate in which a microchannel array comprising a cell sorting unit is etched and around which a protective cover is bonded, and the sorting unit comprises deflection means capable of separating, during the flow thereof, relatively noncohesive cell clusters, each of size ranging from 20 μm to 500 μm and of 20 to 10 000 cells approximately, such as islets of Langerhans, at least two sorting microchannels arranged in parallel at the outlet of said unit being respectively designed so as to transport as many categories of sorted clusters continuously to a unit for encapsulation of the latter, also formed in said array.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
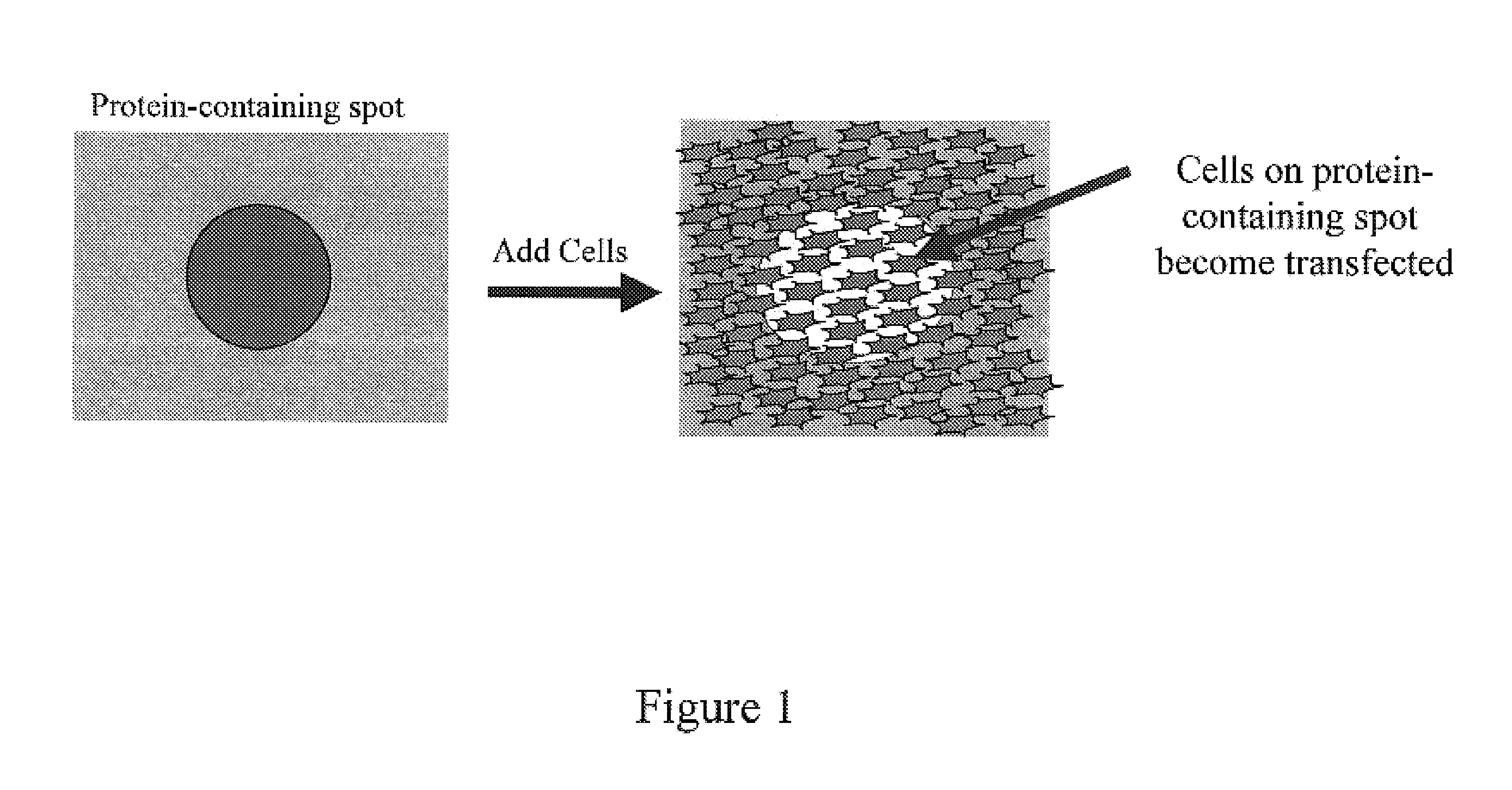
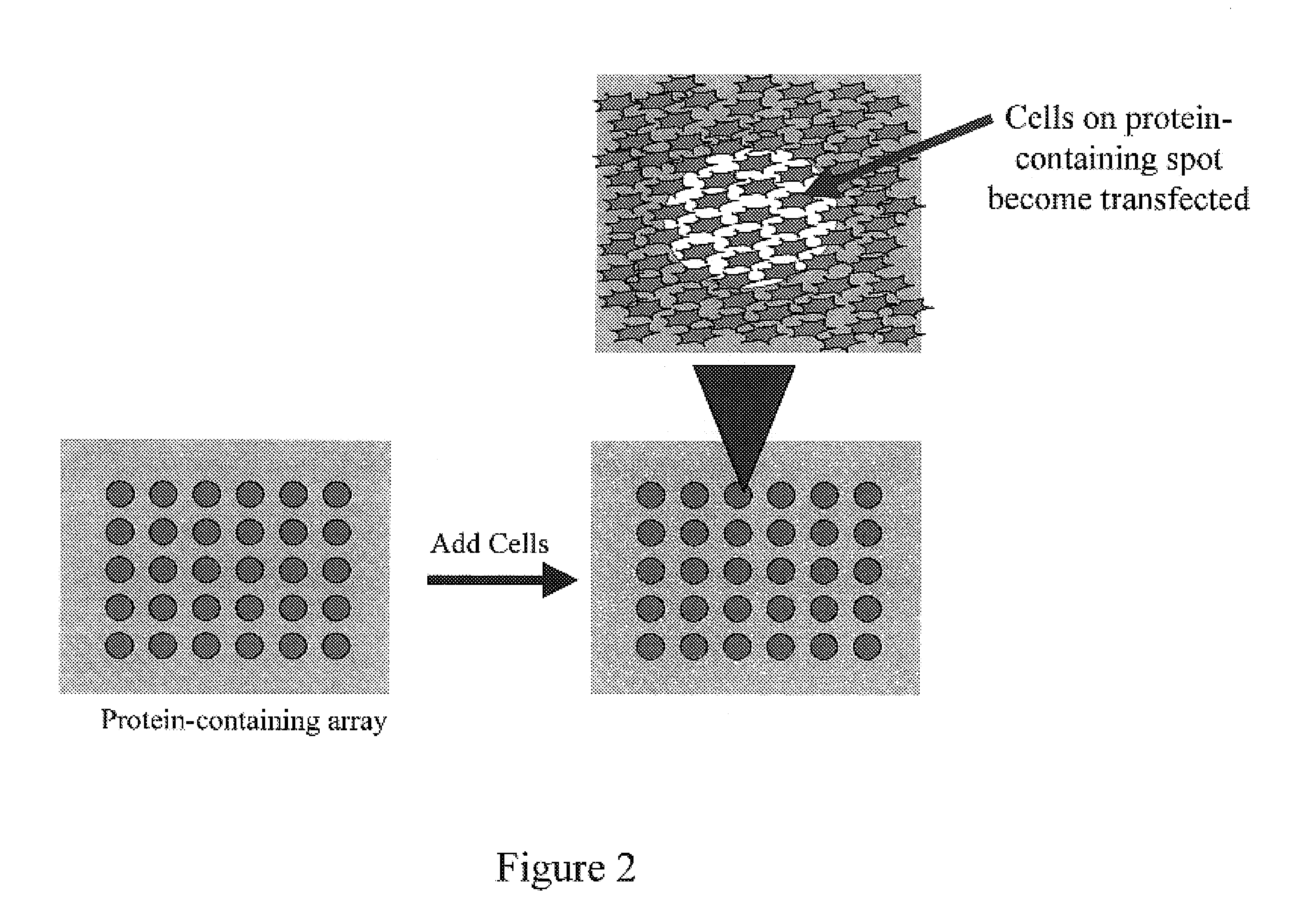
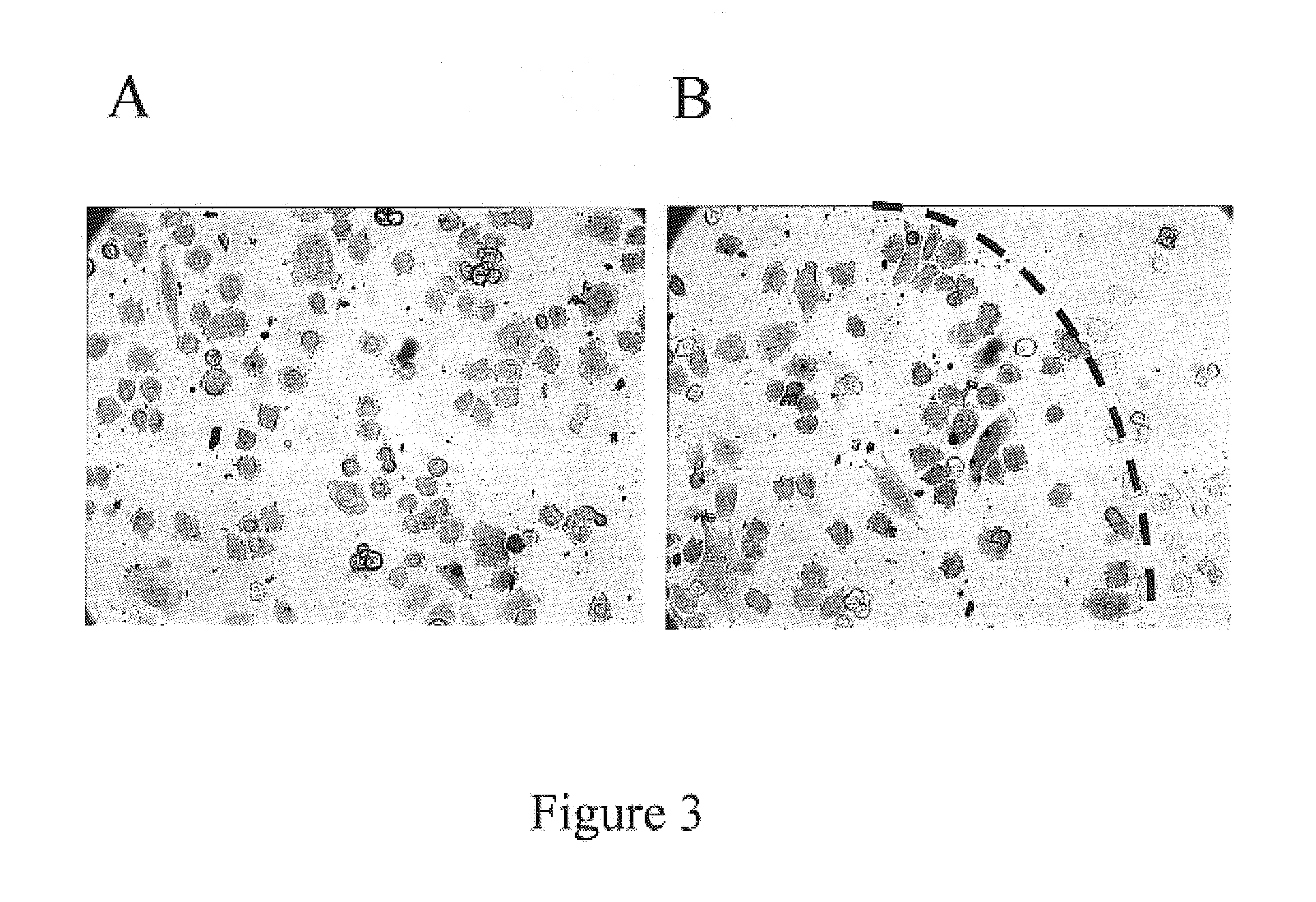
Method and device for protein delivery into cells
InactiveUS7105347B2Reduce deliveryImprove delivery efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVolumetric Mass DensityCell cluster
Owner:CORNING INC
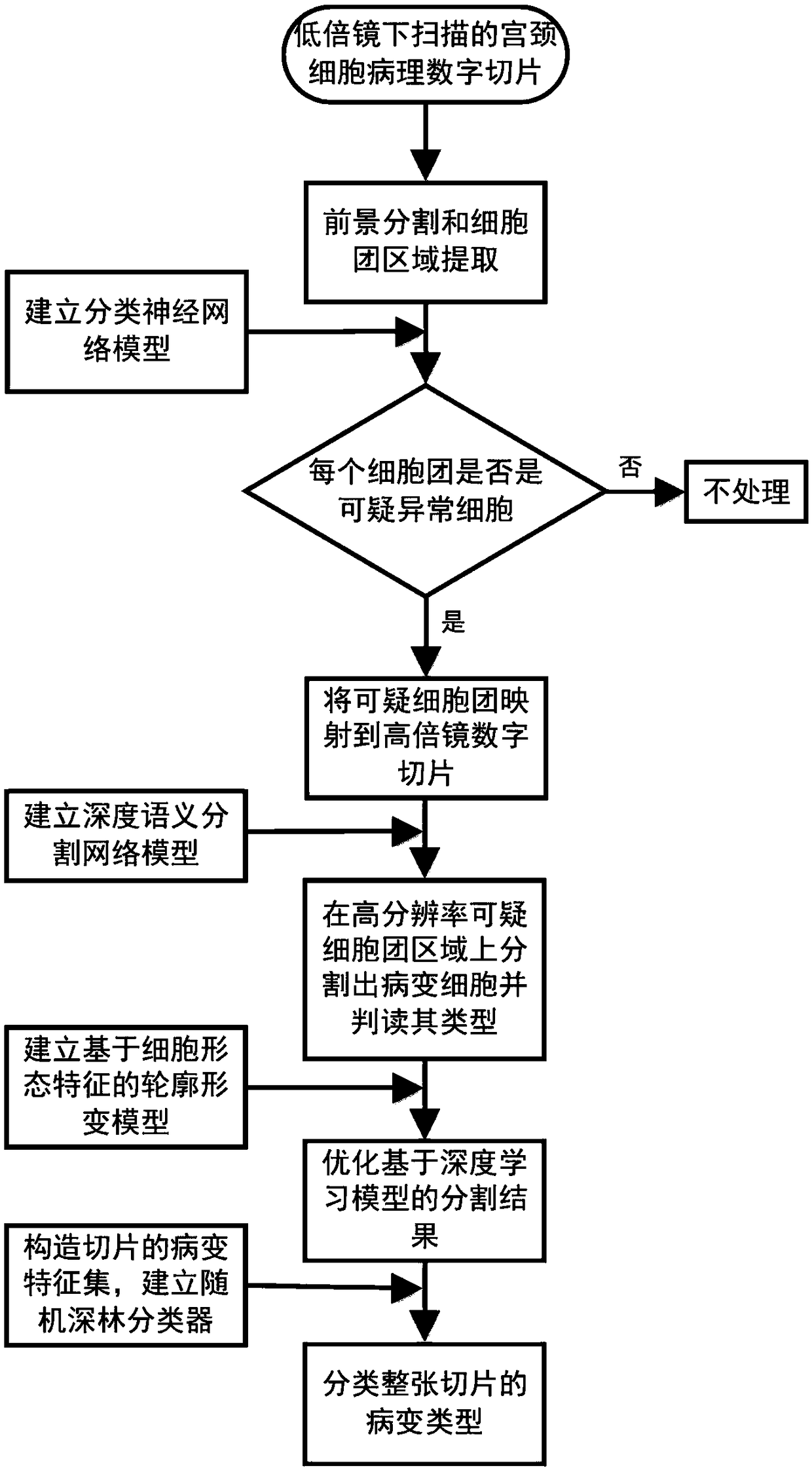
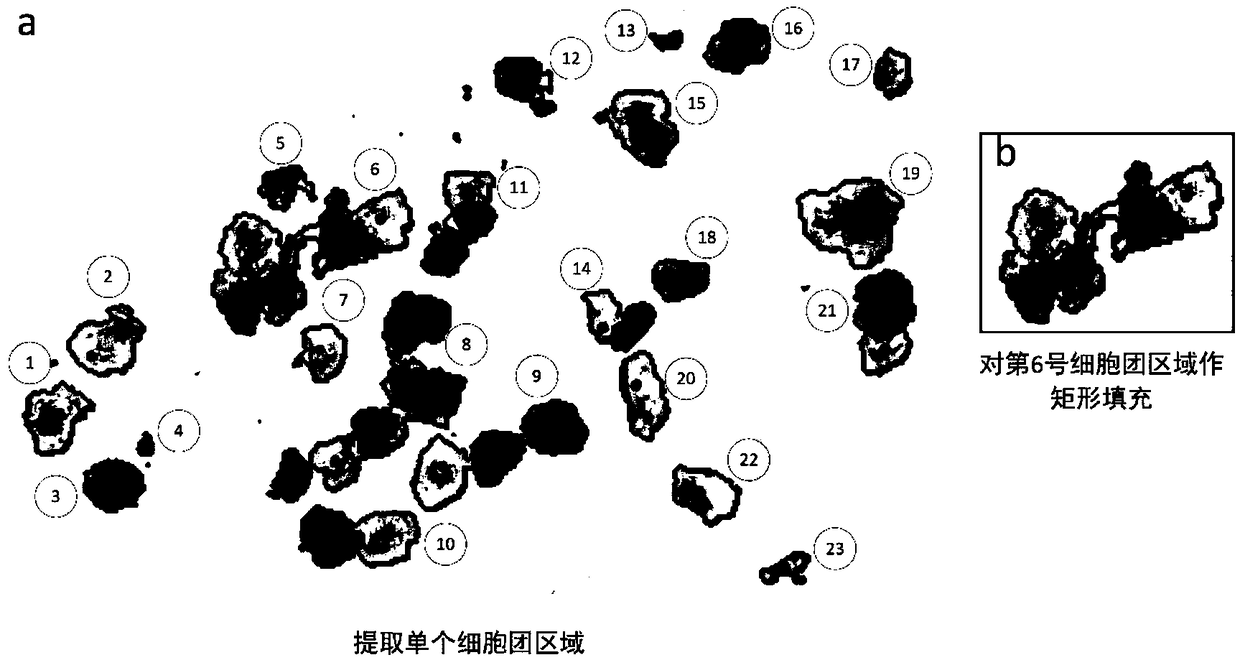
A cervical cell pathological slice classifying method with high and low resolution combination
ActiveCN109034208ASolve the recognition accuracySolve the recognition efficiencyRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsFeature setImage resolution
The invention discloses a cervical cell pathological slice automatic judging method with high and low resolution combination, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: extracting a single cell mass region on a low-resolution cervical pathological slice image; extracting a single cell mass region from the low-resolution cervical pathological slice image; identifying suspicious abnormal cell clusters from low-resolution cell clusters; mapping suspected abnormal cell mass regions into high resolution slice images; semantically segmenting pathological cells from thehigh-resolution region of suspicious cell clusters and interpreting the type; according to the type, quantity and confidence of the segmented lesion cells, establishing the feature set of the slice, and then classifying the lesion type of the whole slice. The invention takes cell cluster as processing and recognition unit, utilizes classification neural network model to quickly identify suspiciousabnormal cell cluster on low-resolution digital slice, then divides out pathological cell on high-resolution suspicious area and judges its type, at the same time, improves recognition accuracy and recognition efficiency.
Owner:怀光智能科技(武汉)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com