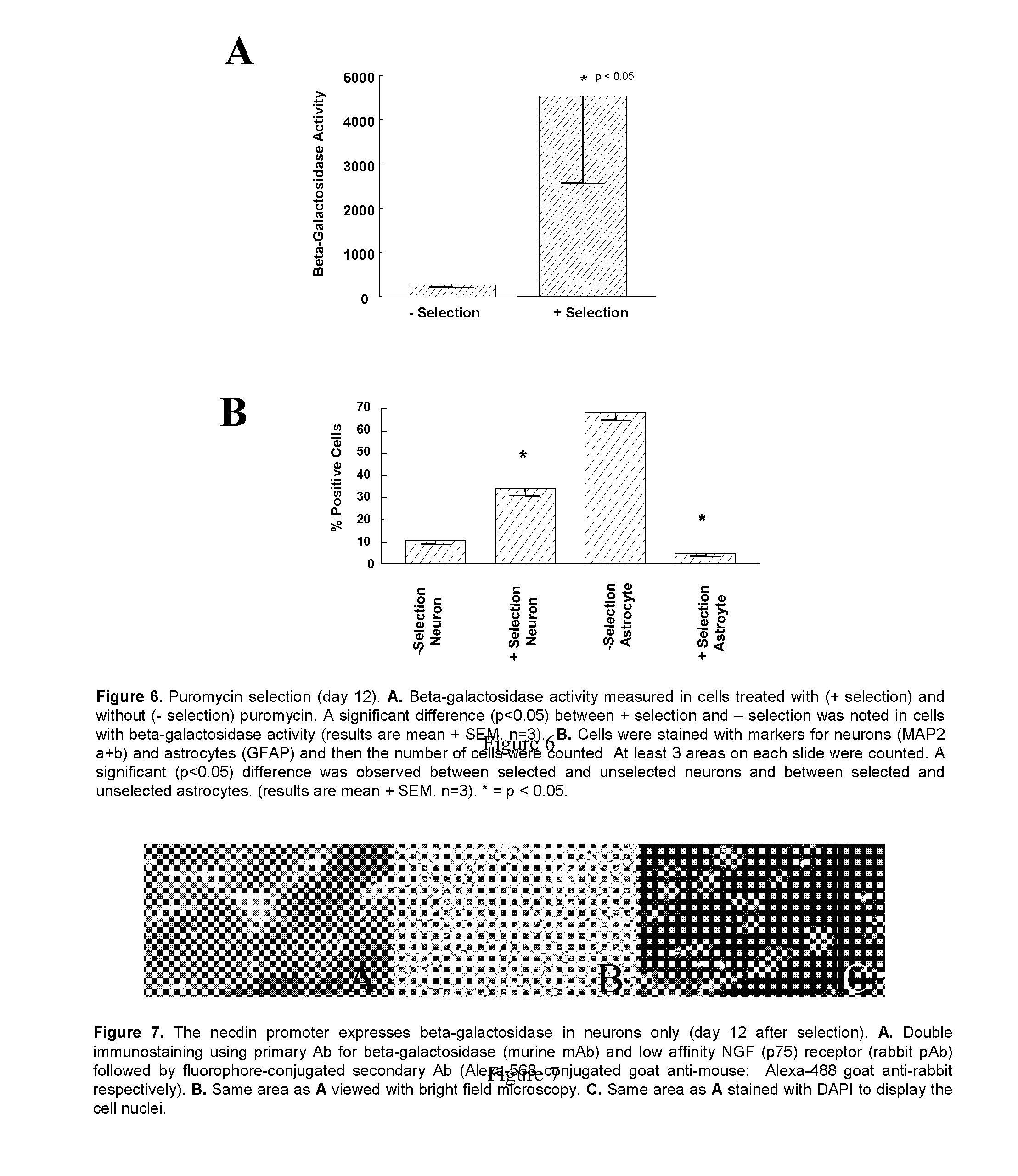
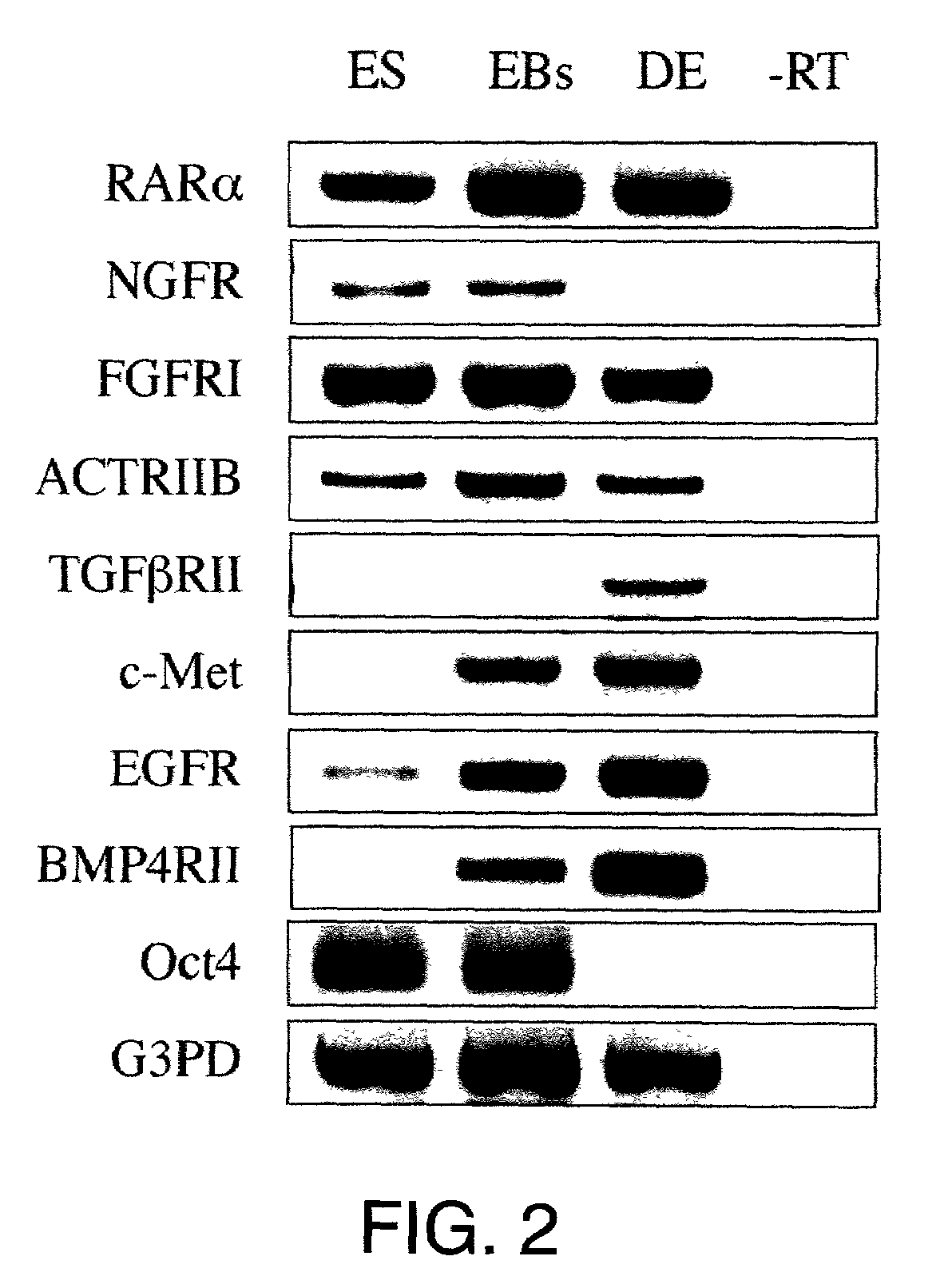
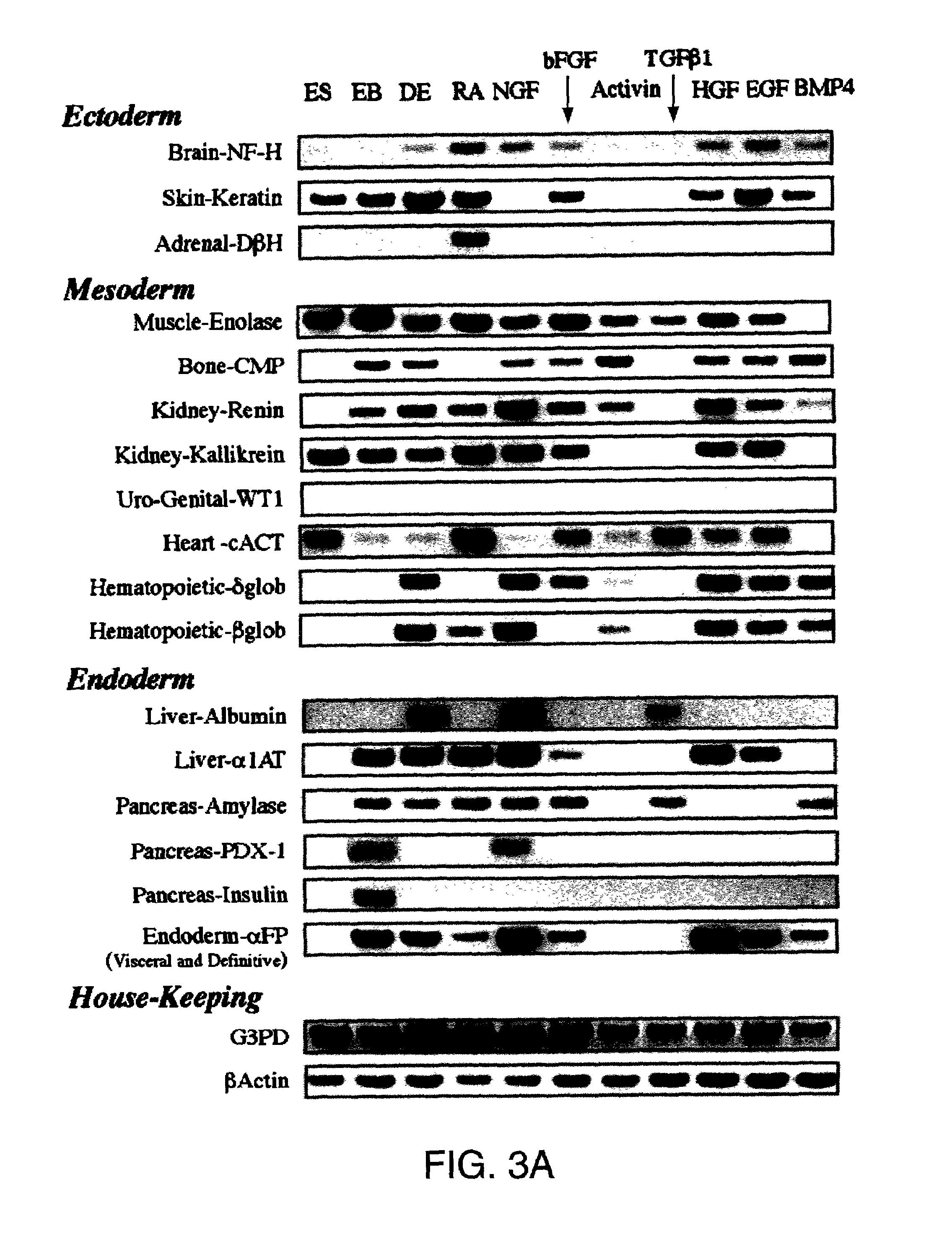
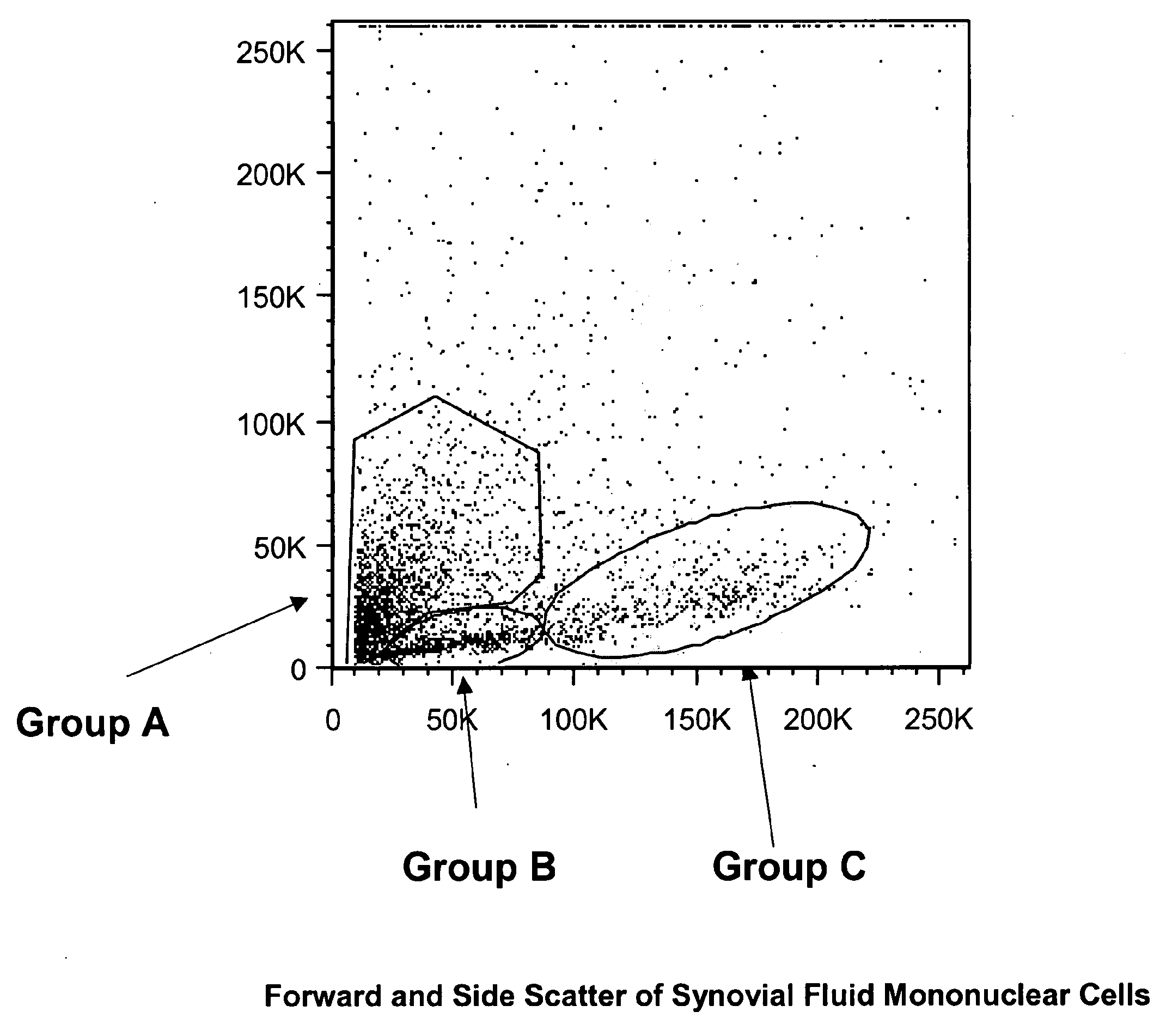
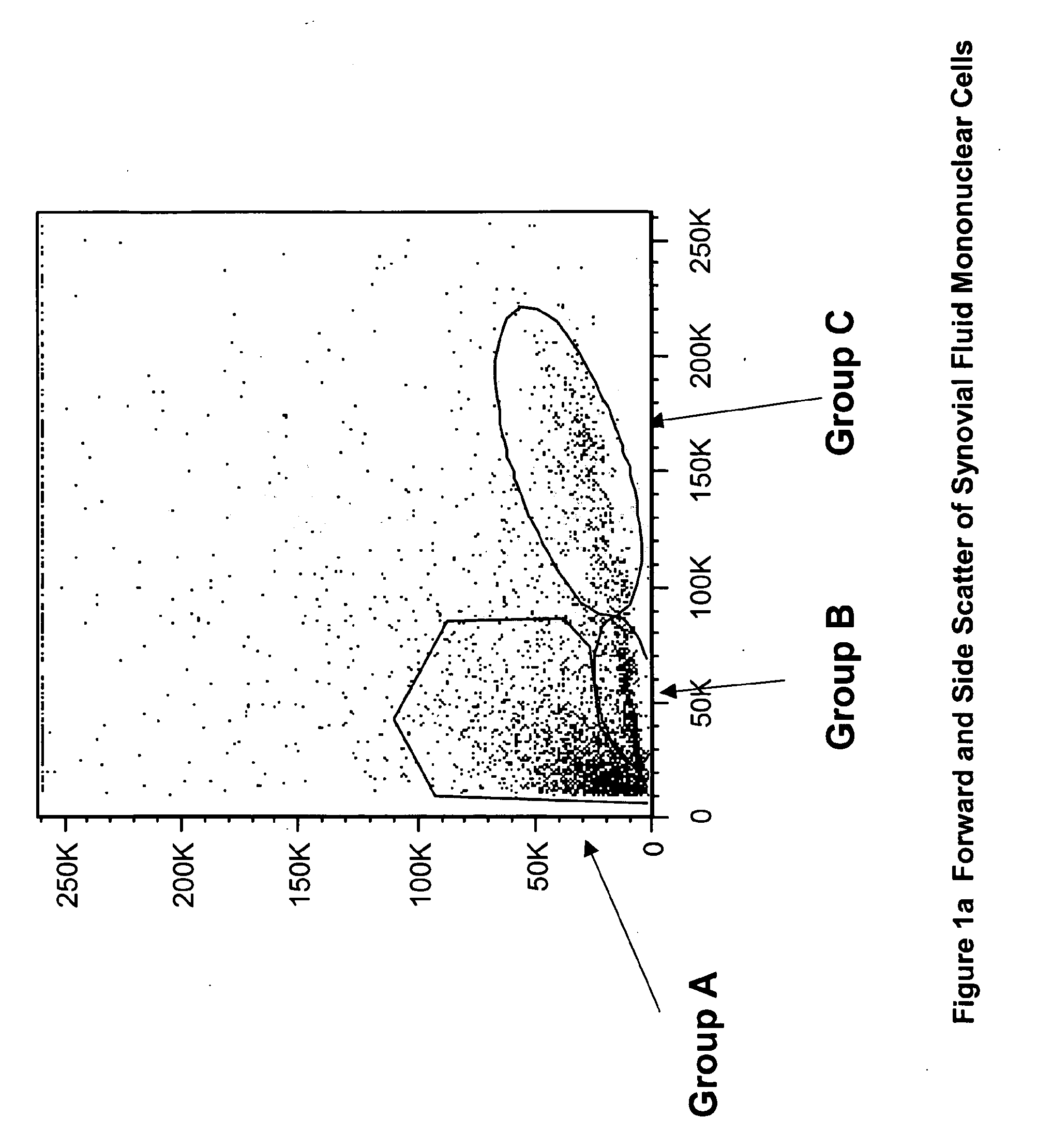
Patents
Literature
441 results about "Embryoid body" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
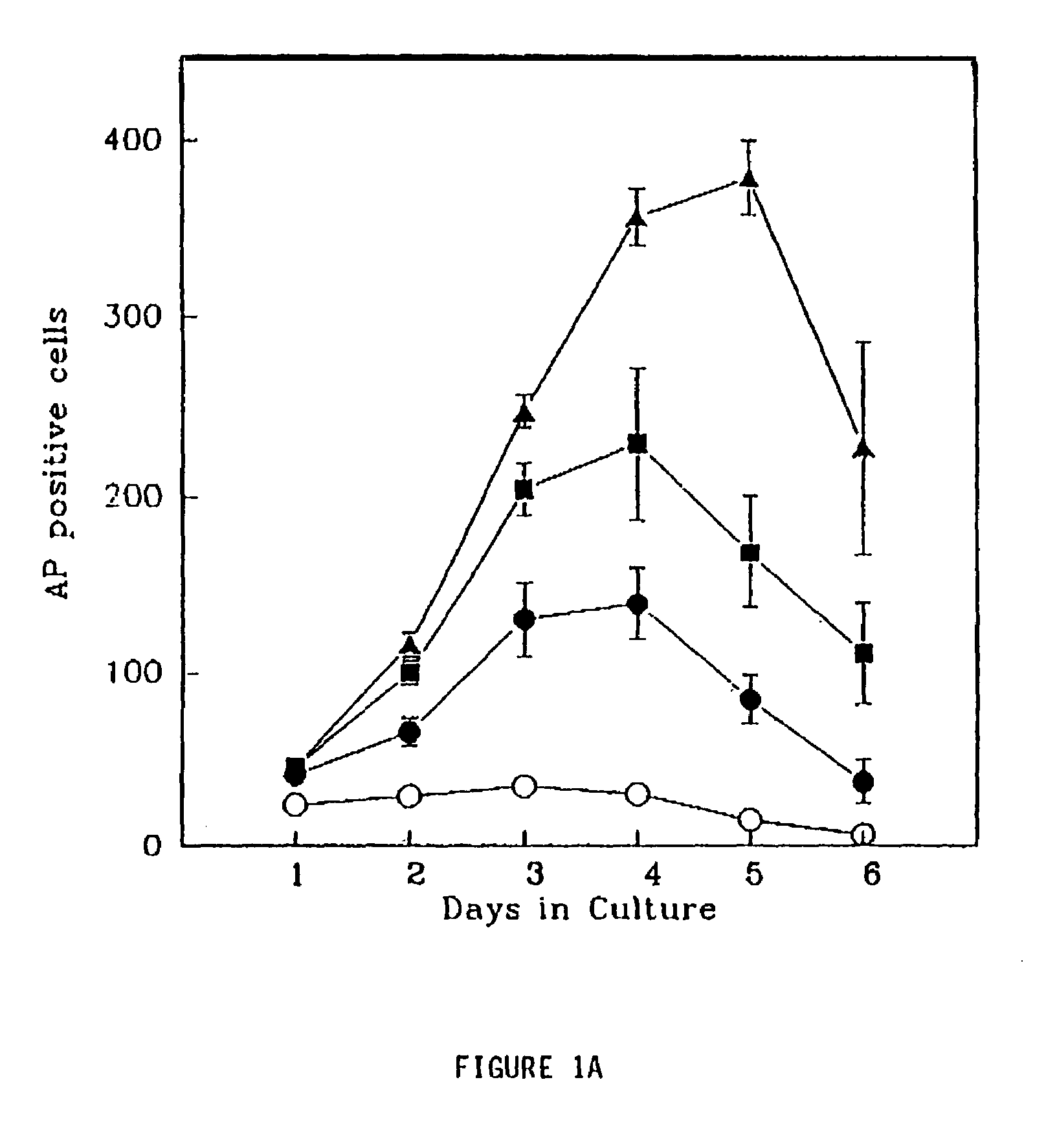
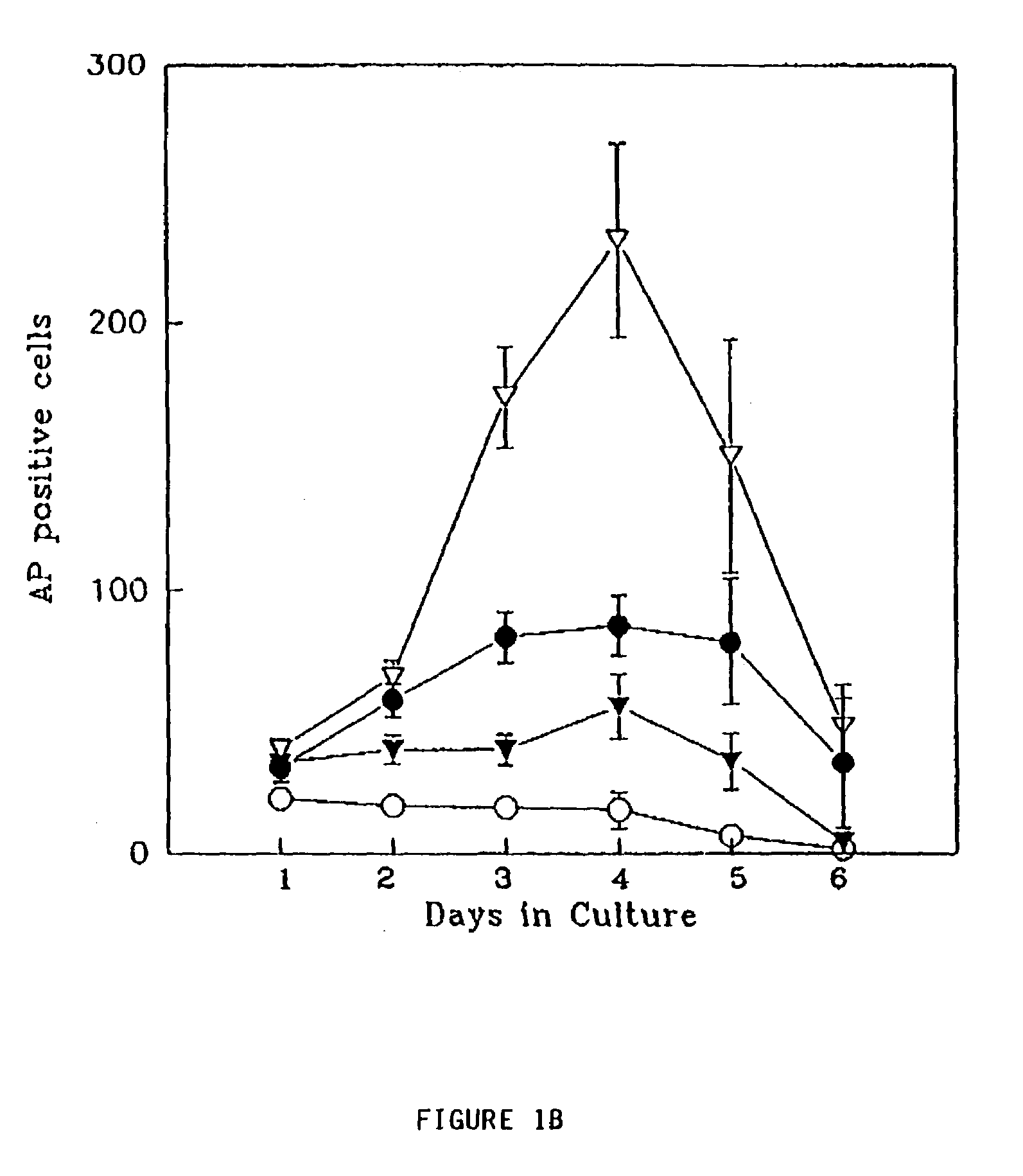
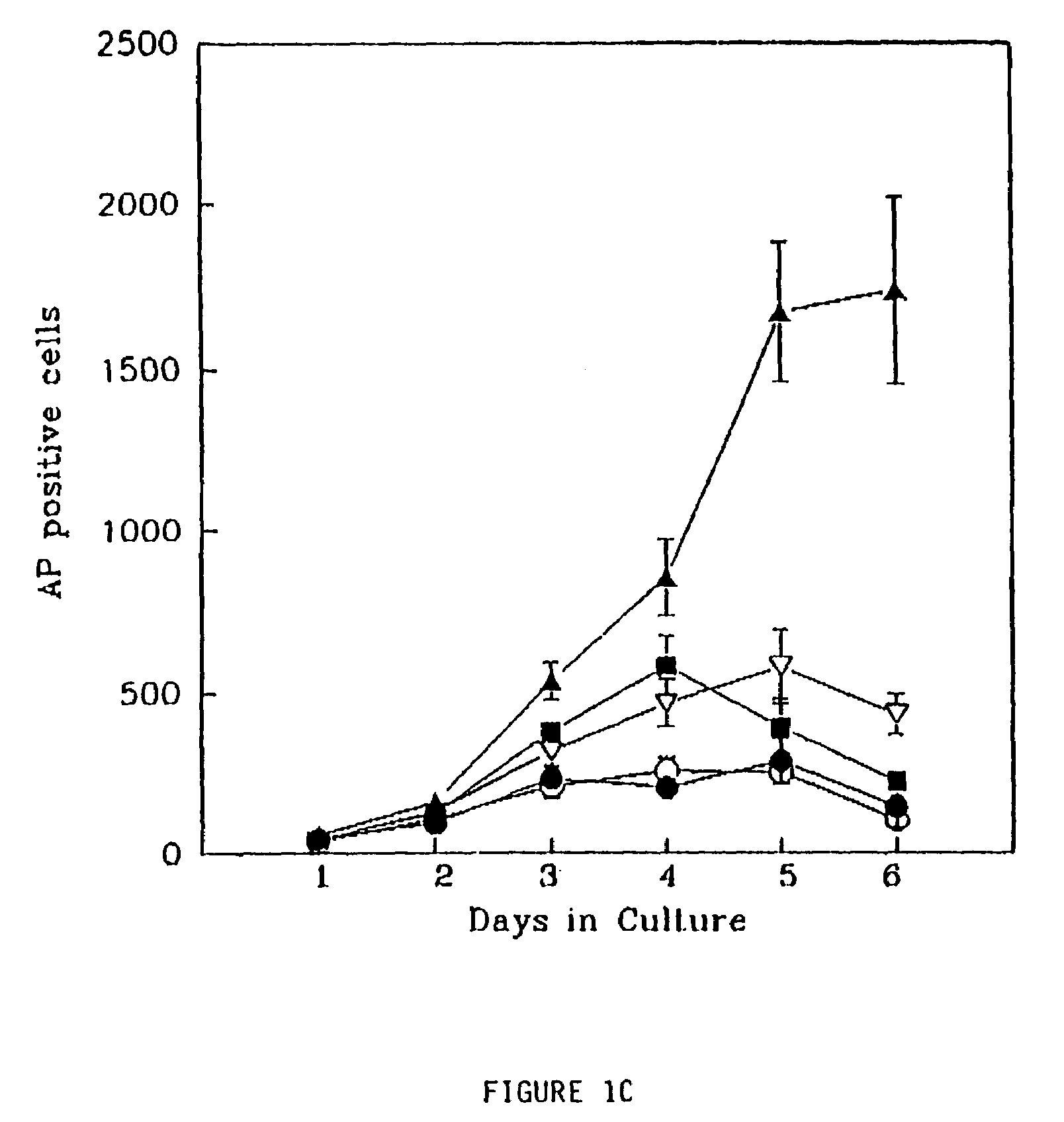
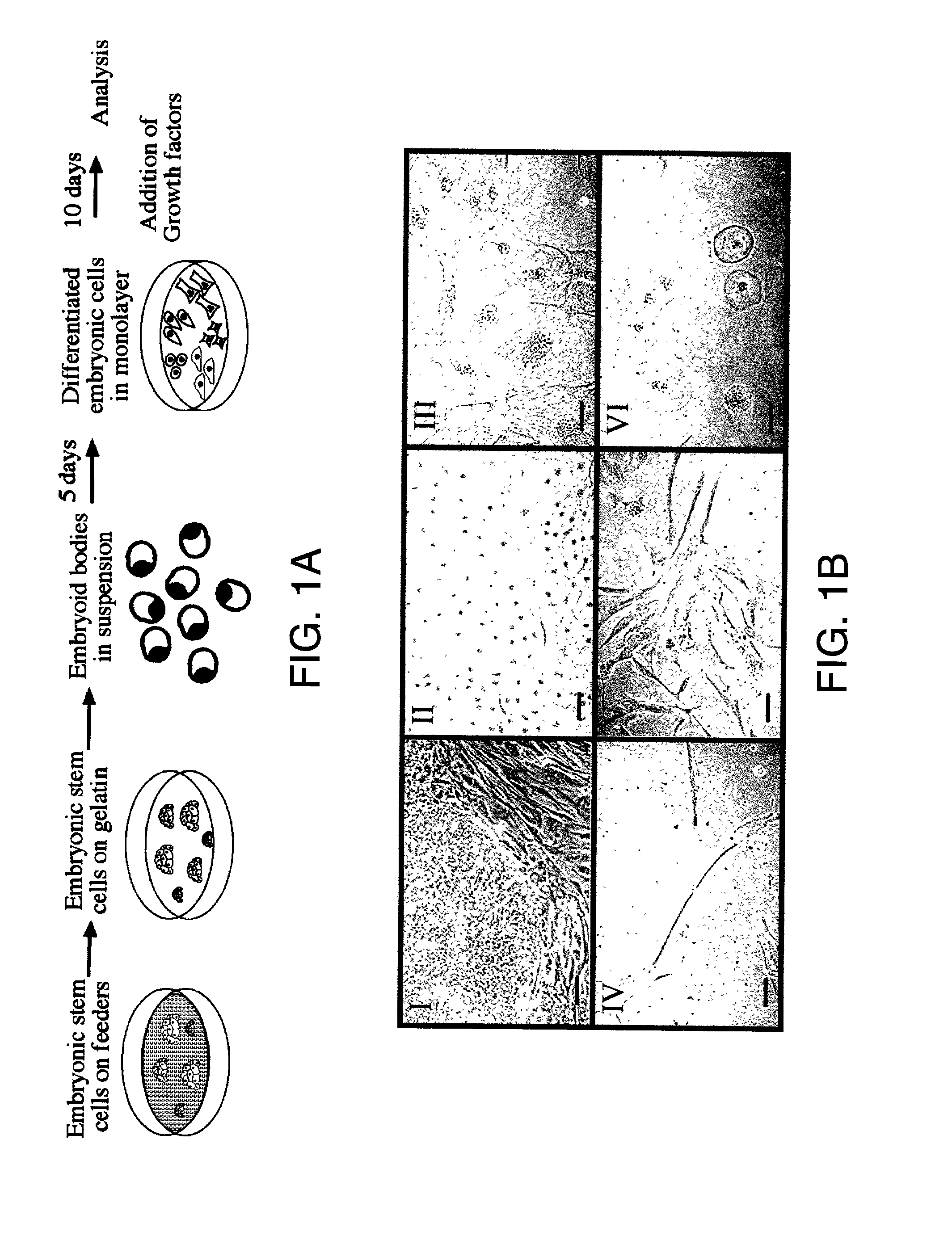
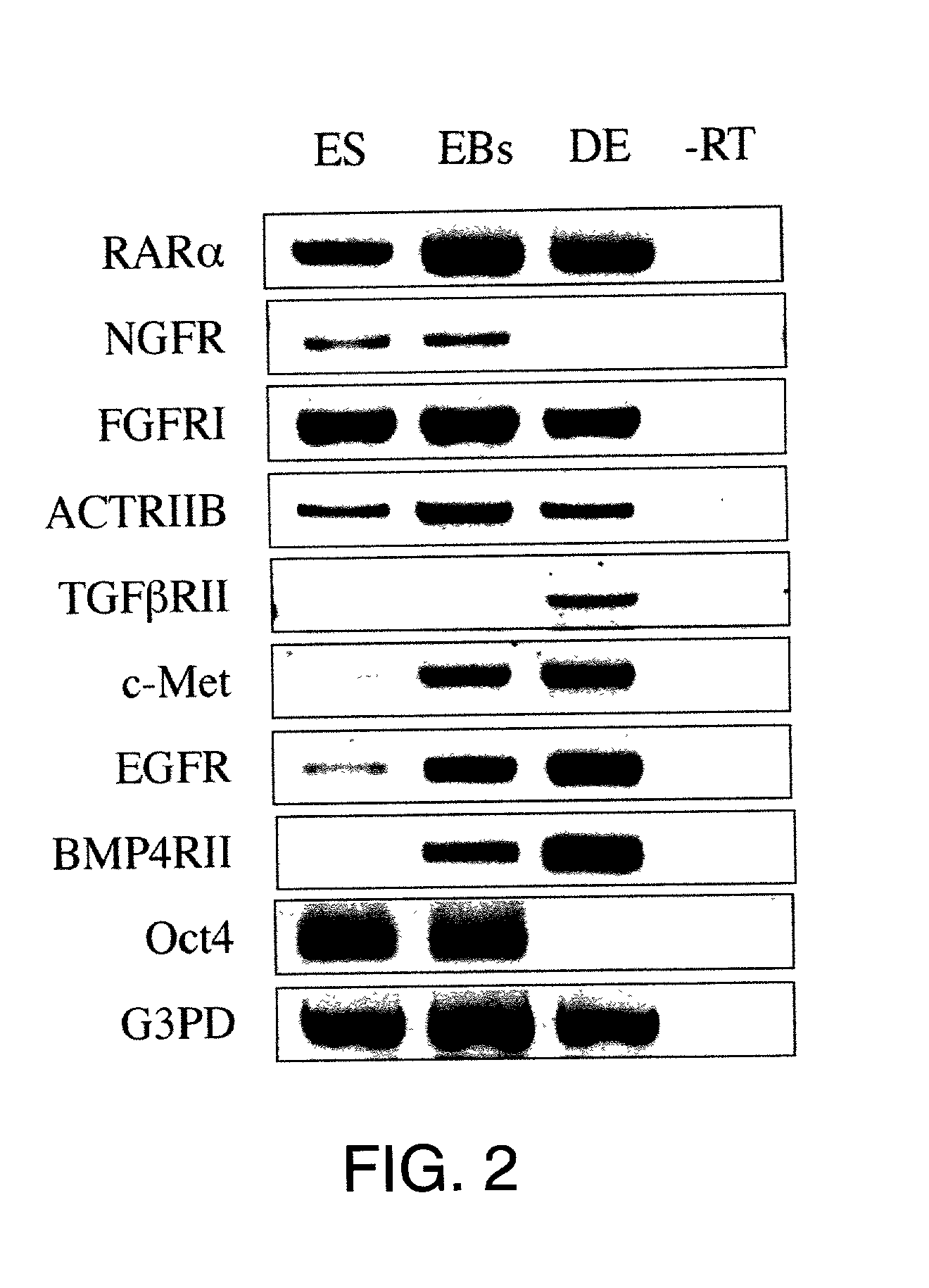
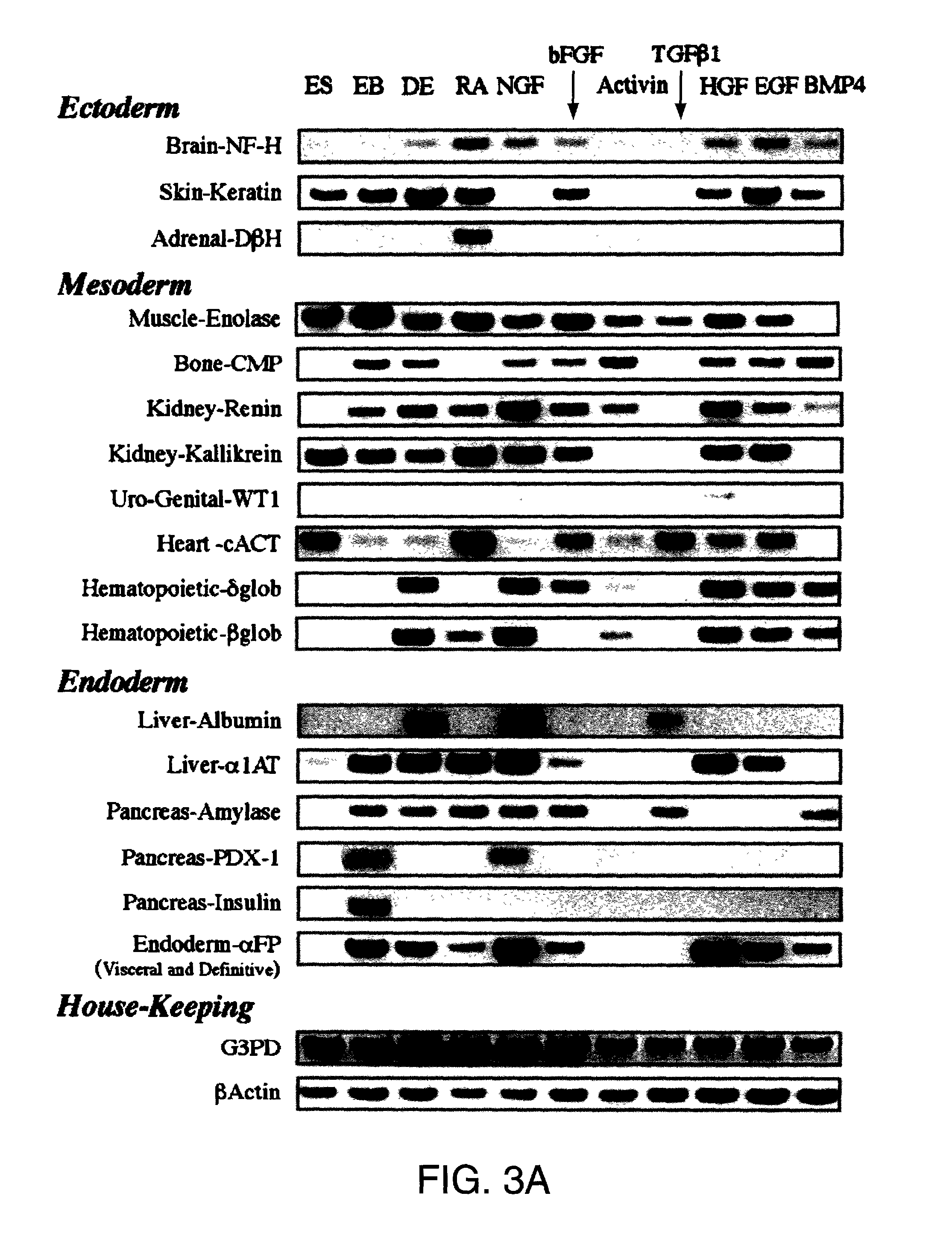
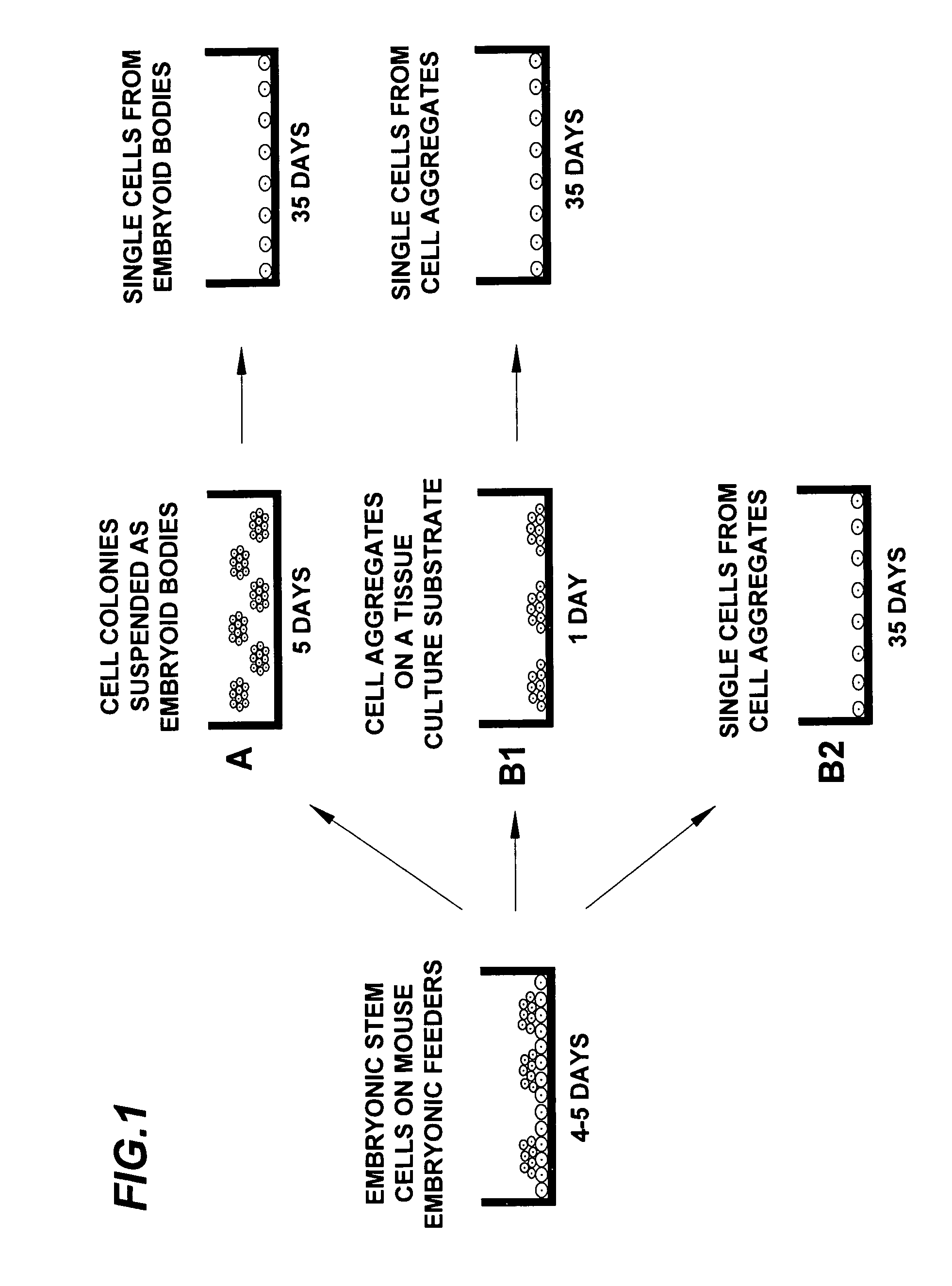
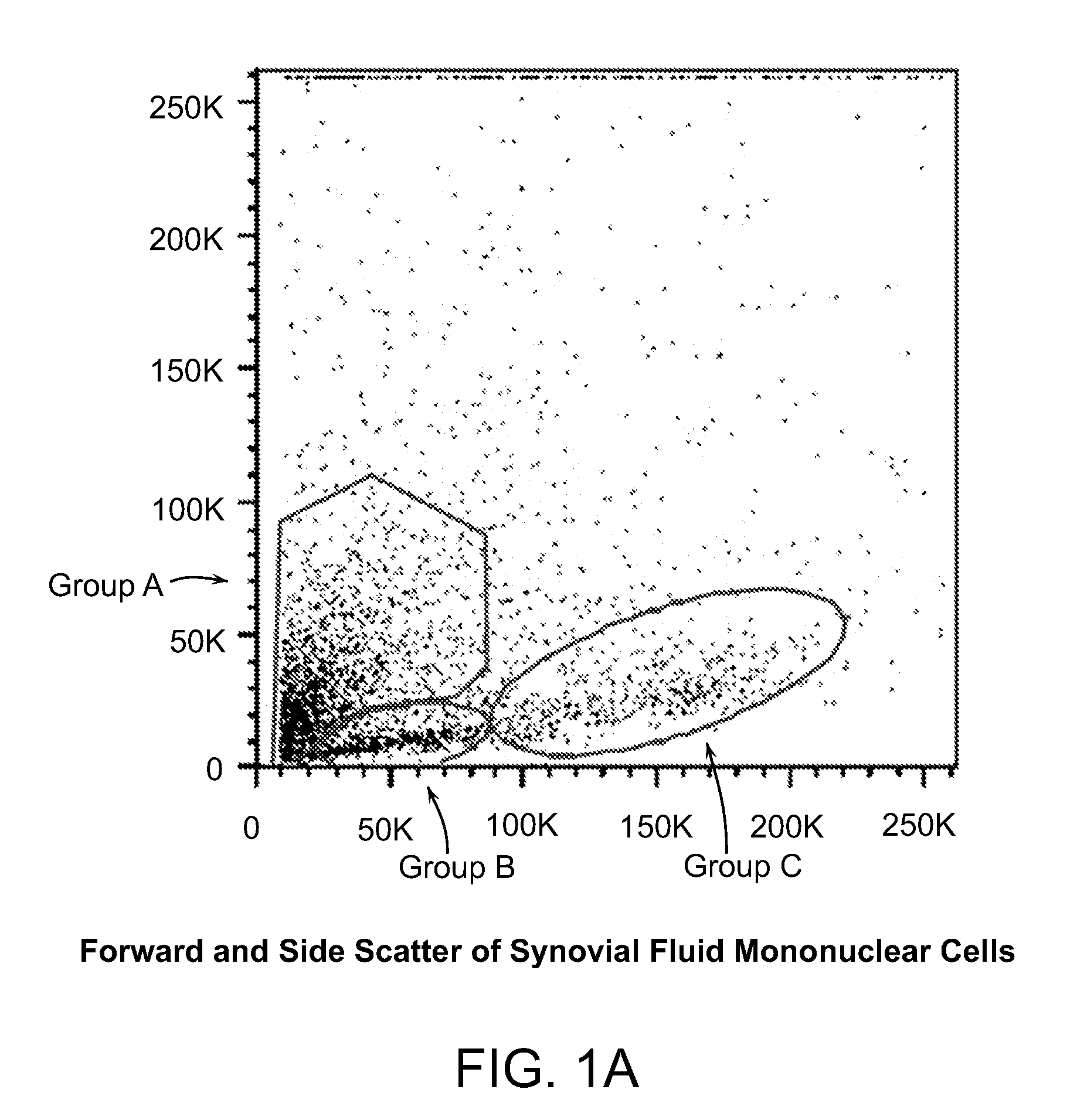
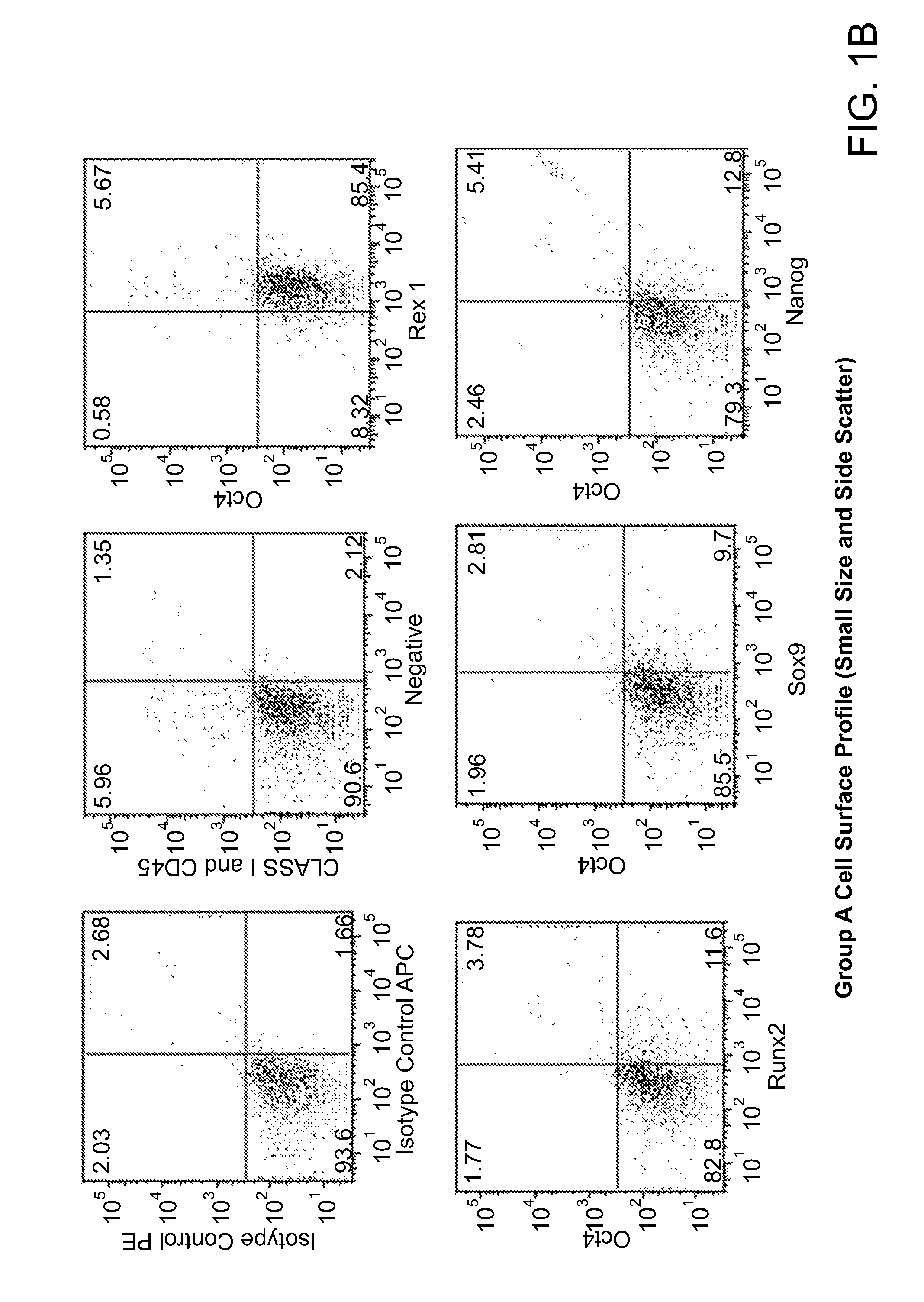
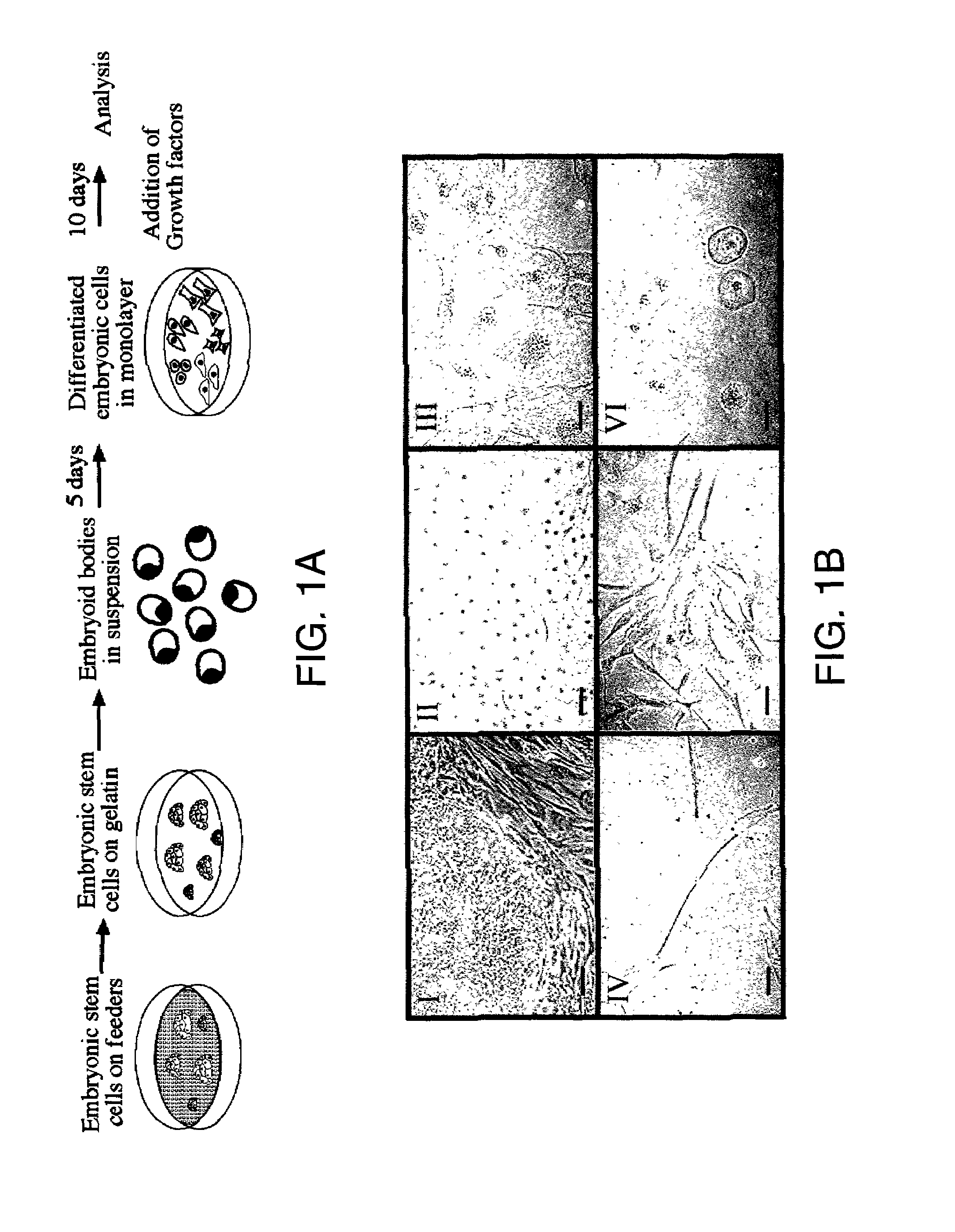
Embryoid bodies (EBs) are three-dimensional aggregates of pluripotent stem cells. The pluripotent cell types that comprise embryoid bodies include embryonic stem cells (ESCs) derived from the blastocyst stage of embryos from mouse (mESC), primate, and human (hESC) sources. Additionally, EBs can be formed from embryonic stem cells derived through alternative techniques, including somatic cell nuclear transfer or the reprogramming of somatic cells to yield induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS). Similar to ESCs cultured in monolayer formats, ESCs within embryoid bodies undergo differentiation and cell specification along the three germ lineages – endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm – which comprise all somatic cell types.
Pluripotential embryonic stem cells and methods of making same
The present invention provides a non-mouse, including human, pluripotential embryonic stem cell which can:(a) be maintained on feeder layers for at least 20 passages; and(b) give rise to embryoid bodies and multiple differentiated cell phenotypes in monolayer culture.The invention further provides a method of making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell comprising culturing germ cells and germ cell progenitors in a composition comprising a growth enhancing amount of basic fibroblast growth factor, leukemia inhibitory factor, membrane associated steel factor, and soluble steel factor to primordial germ cells under cell growth conditions, thereby making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell.Also provided are compositions useful to produce the pluripotent embryonic stem cells and methods of screening associated with the method of making the embryonic stem cell.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Directed differentiation of embryonic cells
Methods are described for mapping a pathway of differentiation of a population of embryonic cells which includes exposing the cells to an exogenous factor and measuring gene expression products that are characteristic of a particular cell type or lineage. Directing differentiation of human embryonic cells relies on dissociated embryoid bodies which are then exposed to one or more exogenous factors to enrich a culture for a particular cell type. The differentiated cells may be used for treating a medical condition in a human. Kits for determining differentiation pathways and screening exogenous factors for their utility in differentiation are provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Bioprocess for the generation of cells from spheroid-forming cells
InactiveUS20030119107A1Inhibit aggregationCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusHigh cellVolumetric Mass Density
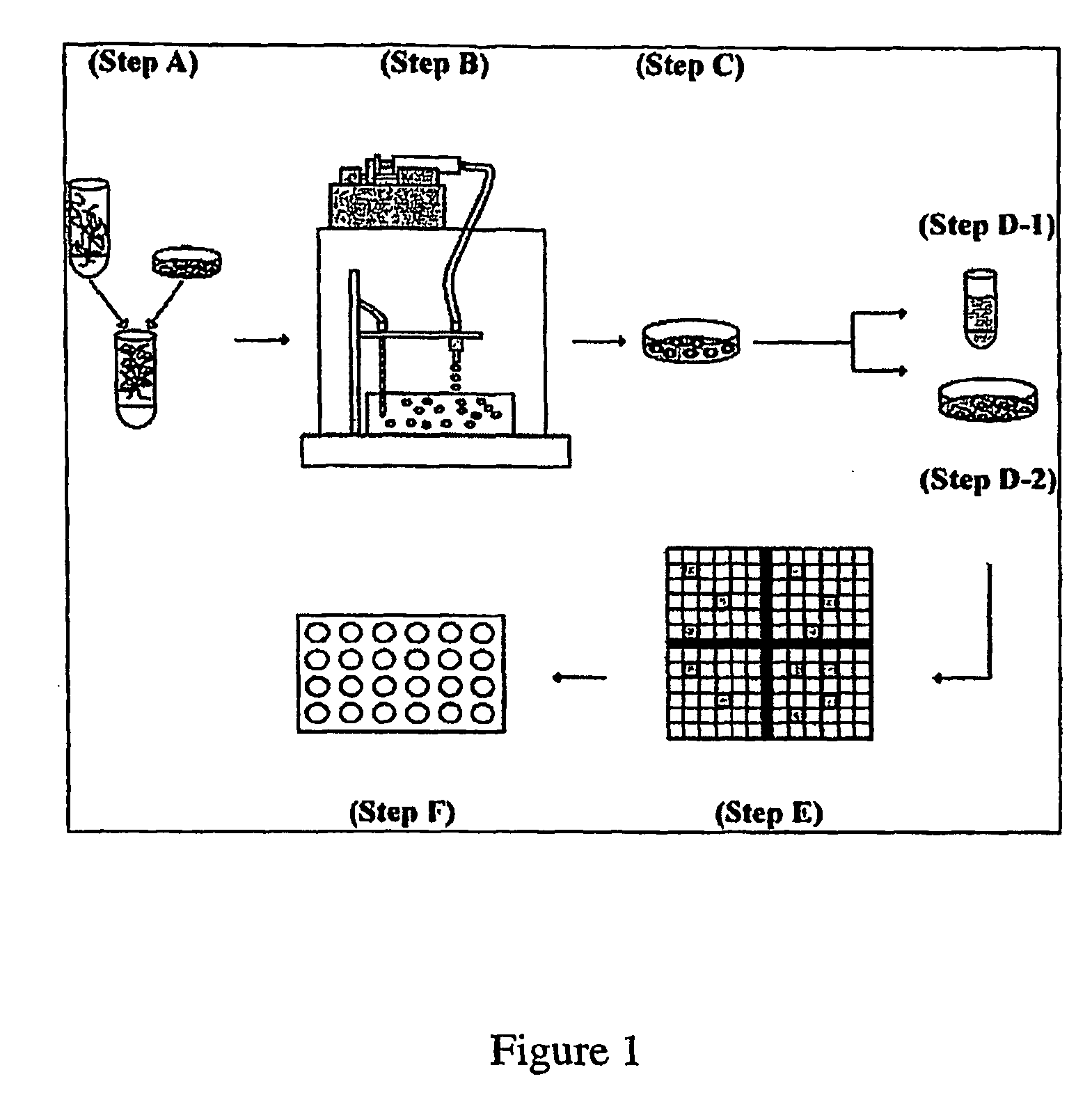
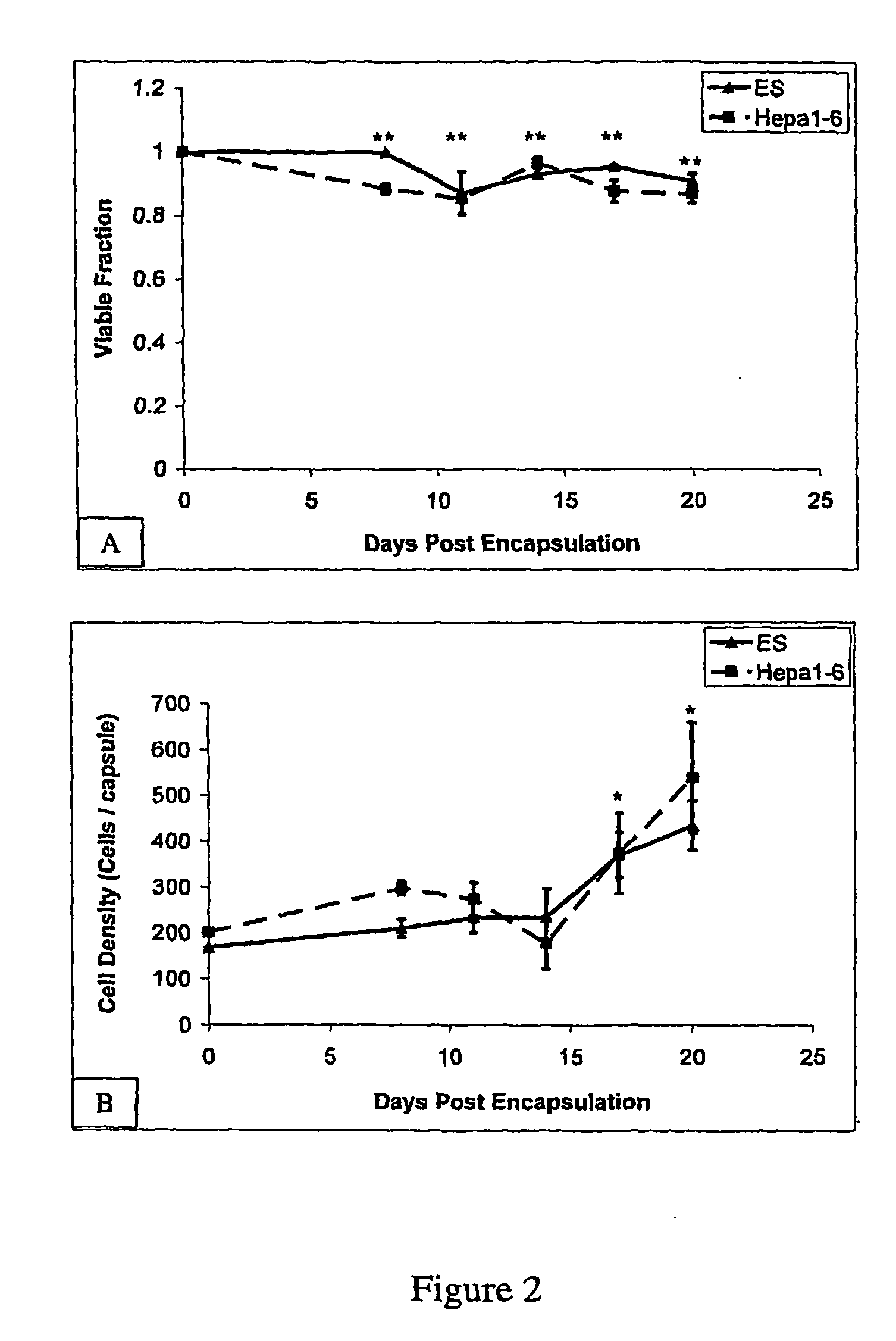
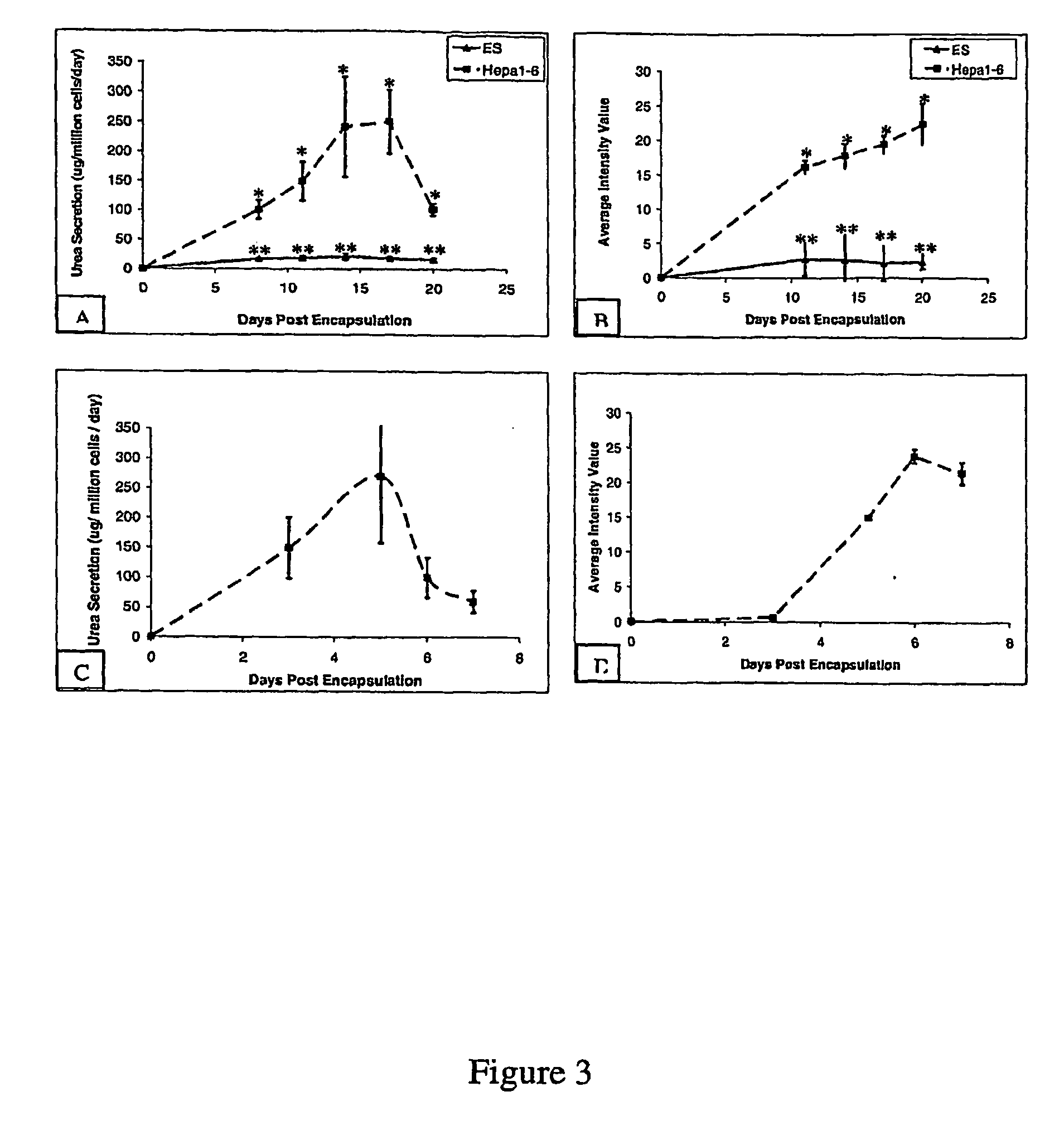
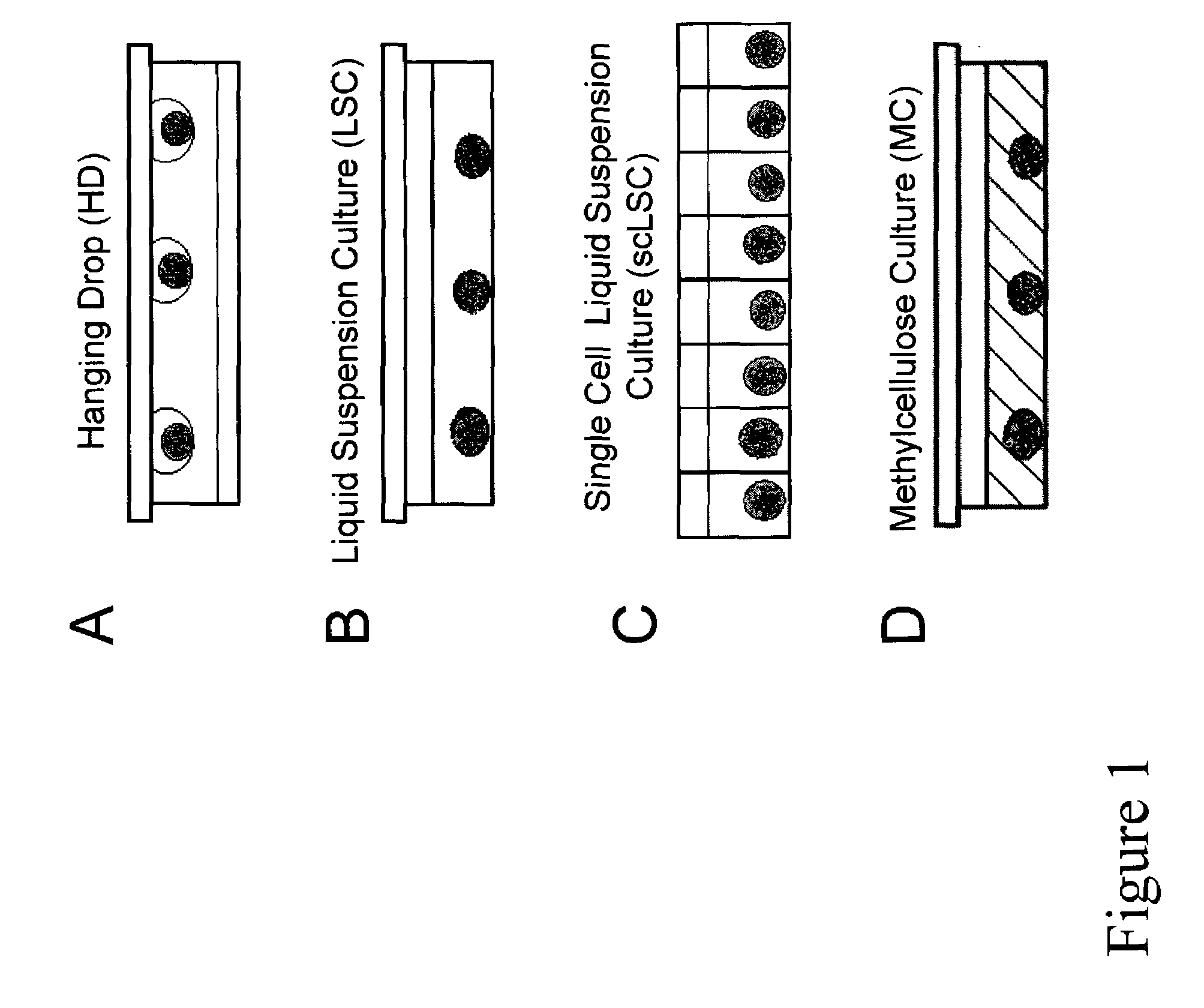
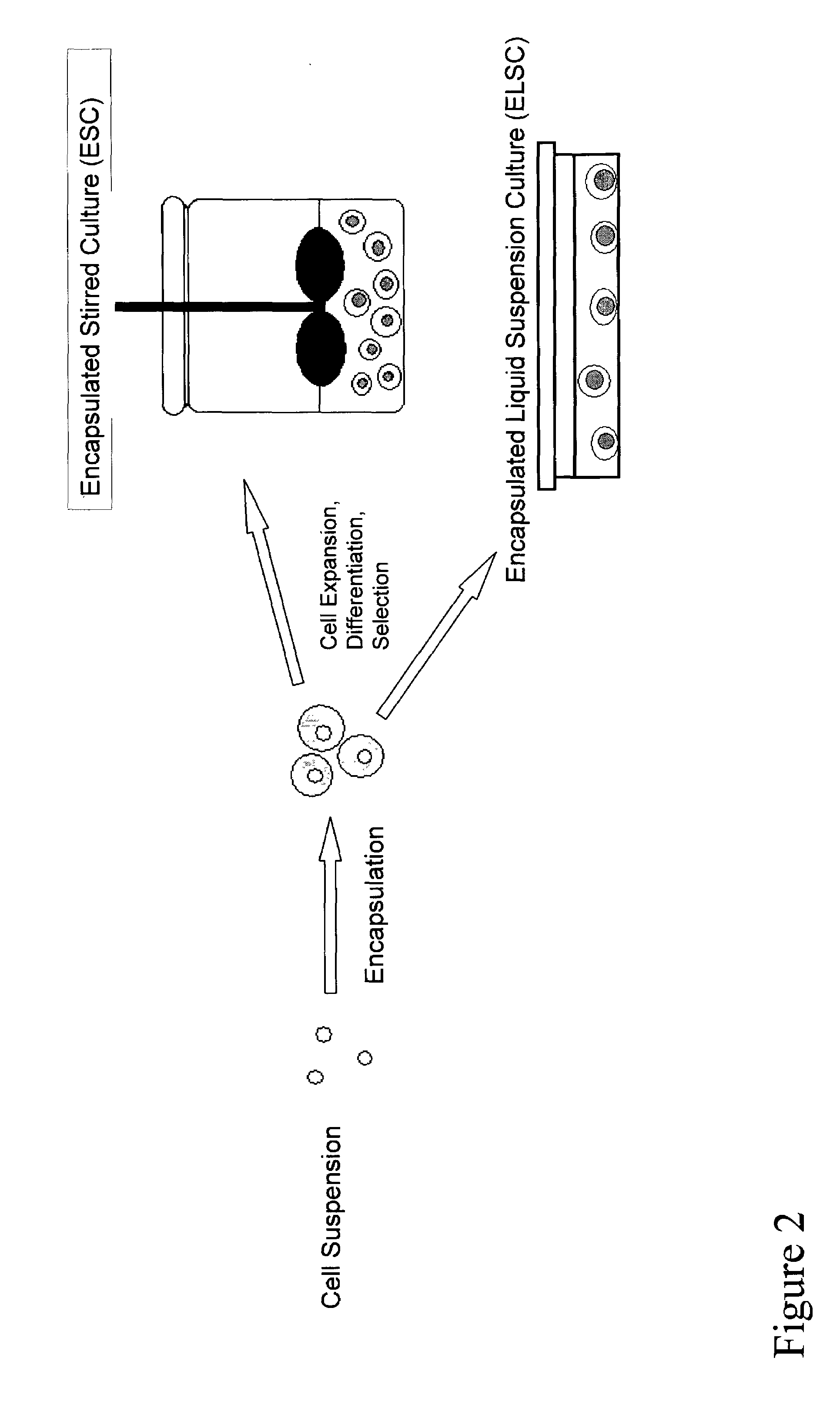
The present inventors identified aggregation of embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies (EBs) as the cause of the difficulty in generating large numbers of the embryonic stem cells (ES) cell-derived tissues. To counter this, the invention provides a novel bioprocess where aggregation of spheroid forming cells, such as embryonic stem cells and spheroids, such as EBs is controlled, such as by encapsulation of within a matrix. As a result, EBs can be generated with high efficiency and cultured in high cell density, well-mixed systems. Well-mixed conditions facilitate measurement and control of the bulk media conditions and allow for the use of scalable bioreactor systems for clinical production of tissue. Therefore, the invention enables generation of ES cell-derived tissue on a clinical scale. The invention is also applicable to any spheroid-forming cells and other types of pluripotent cells.
Owner:CARDION AG
Methods of using G-CSF mobilized C-Kit+ cells in the production of embryoid body-like cell clusters for tissue repair and in the treatment of cardiac myopathy
InactiveUS20050186182A1Enhance mobilizationInhibition of differentiationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsMyopathyTissue repair
The present invention relates to methods of using granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) polypeptide, alone and in conjunction with stromal cell derived factor (SDF-1) polypeptide, to increase the mobilization of c-Kit+ stem cells in the blood, bone marrow, tissue, heart or other organs for the subsequent production of embryoid body-like cell clusters. These embryoid body-like cell clusters can be used for cell replacement therapy, for the treatment of cardiac myopathy and other diseases and disorders, and for screening agents that drive or inhibit differentiation and proliferation.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Methods of generating human cardiac cells and tissues and uses thereof
A method of generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype is disclosed. The method comprises (a) partially dispersing a confluent cultured population of human stem cells, thereby generating a cell population including cell aggregates; (b) subjecting said cell aggregates to culturing conditions suitable for generating embryoid bodies; (c) subjecting said embryoid bodies to culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation in at least a portion of the cells of said embryoid bodies, said culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation including adherence of said embryoid bodies to a surface, and culture, medium supplemented with serum, thereby generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method of making embryoid bodies from primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7220584B2Efficiently formedDead animal preservationArtificial cell constructsCells embryoIndividual animal
Primate embryoid bodies are formed from primate ES cells. The ES cells form clumps. One then removes the clumps, as clumps, and permits incubation under non-adherent conditions. The development of embryoid bodies from primate ES cells is dependent on maintaining the aggregation of cells, as individualized cells will rapidly die.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Submerged plant breeding blanket and application thereof
ActiveCN102668831AOvercoming implantation difficultiesOvercome difficultyLayered productsHorticultureVegetationFiber
The invention relates to a submerged plant breeding blanket and application thereof. The submerged plant breeding blanket disclosed by the invention is respectively composed of a carrier layer, a matrix layer and an adhesive layer from bottom to top, wherein the carrier layer is composed of palm and bamboo plant fiber; the matrix layer is composed of a growing matrix suitable for submerged plants to grow; and the adhesive layer is composed of a plant fiber net. The invention further provides a submerged vegetation transplantation technology which is characterized in that after being subjected to seedling culture, submerged plant seedling breeding embryoid bodies prepared by virtue of the breeding blanket are transplanted to the water bottom of an ecological restoration area for planting and restoring submerged vegetation of the ecological restoration area. Compared with the traditional submerged plant transplantation technology method, the submerged vegetation transplantation technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low transplantation cost, high speed, high survival rate, convenient technology, strong technical maneuverability, high community forming speed after transplantation, high breeding speed, good community stability and the like, and can be used for realizing the quick transplantation and the community construction and configuration of the submerged plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI INVESTIGATION DESIGN & RES INST
Method of Inducing Differentiation of Embryo-Stem Cell Into Hepatocyte and Hepatocyte Induced by the Method
InactiveUS20080206733A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHepatocyte growth factorCultured cell
With respect to a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cells into hepatocytes, in order to obtain safe hepatocytes that are adequately functionable and able to supply in large quantity, a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cell into hepatocyte, wherein the embryo-stem cells are cultured in the presence of deletion type hepatocyte growth factor is provided. Further, a method for differentially inducing embryo-stem cells into hepatocytes comprising (a) a step of forming the embryoid body of the embryo-stem cells and (b) a step of culturing the embryoid body in the presence of deletion type hepatocyte growth factor is provided.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Method for culturing stem cells
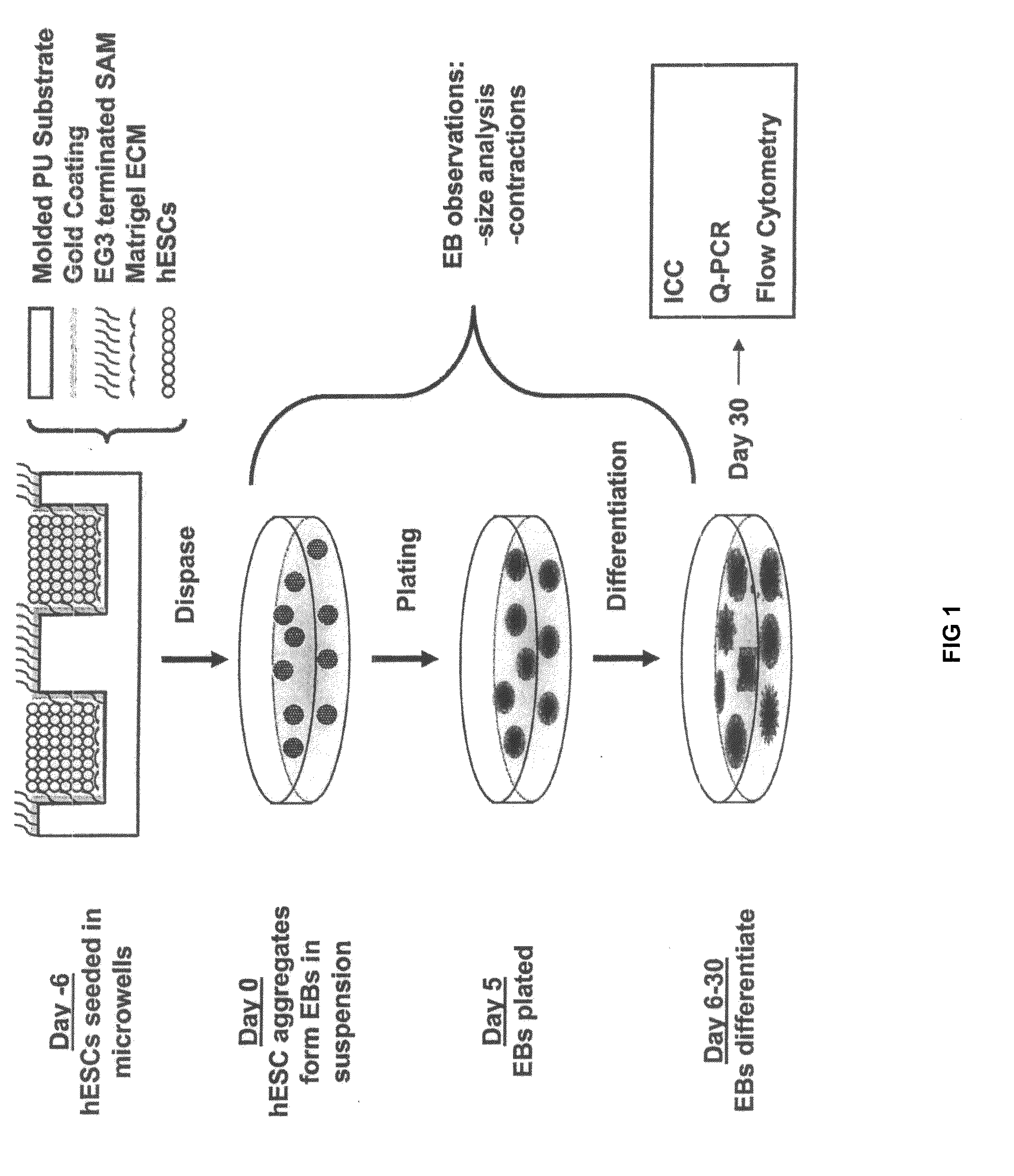
ActiveUS20100197013A1Narrow size distributionUniform sizeMacromolecular librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansGerm layerMatrigel
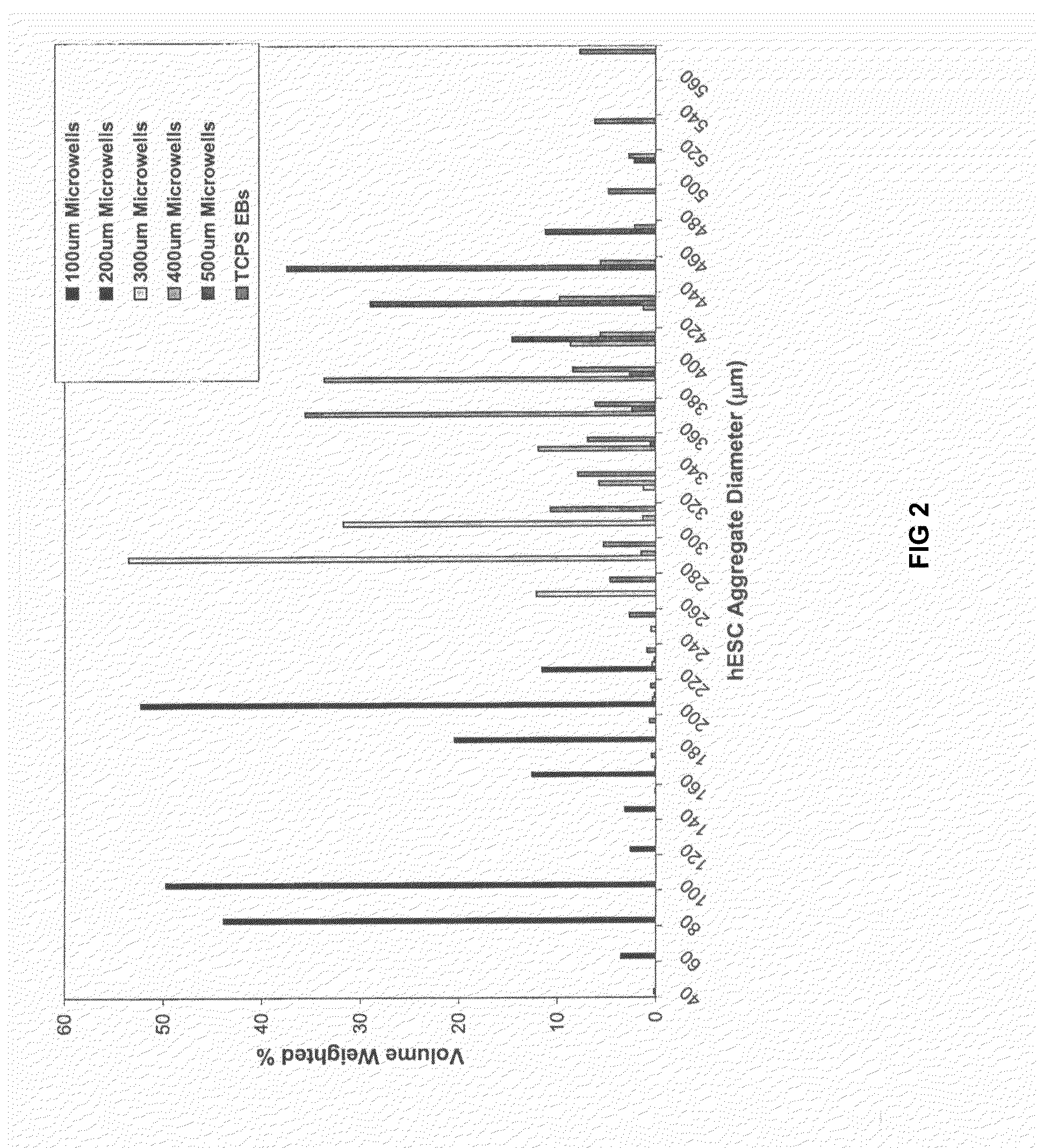
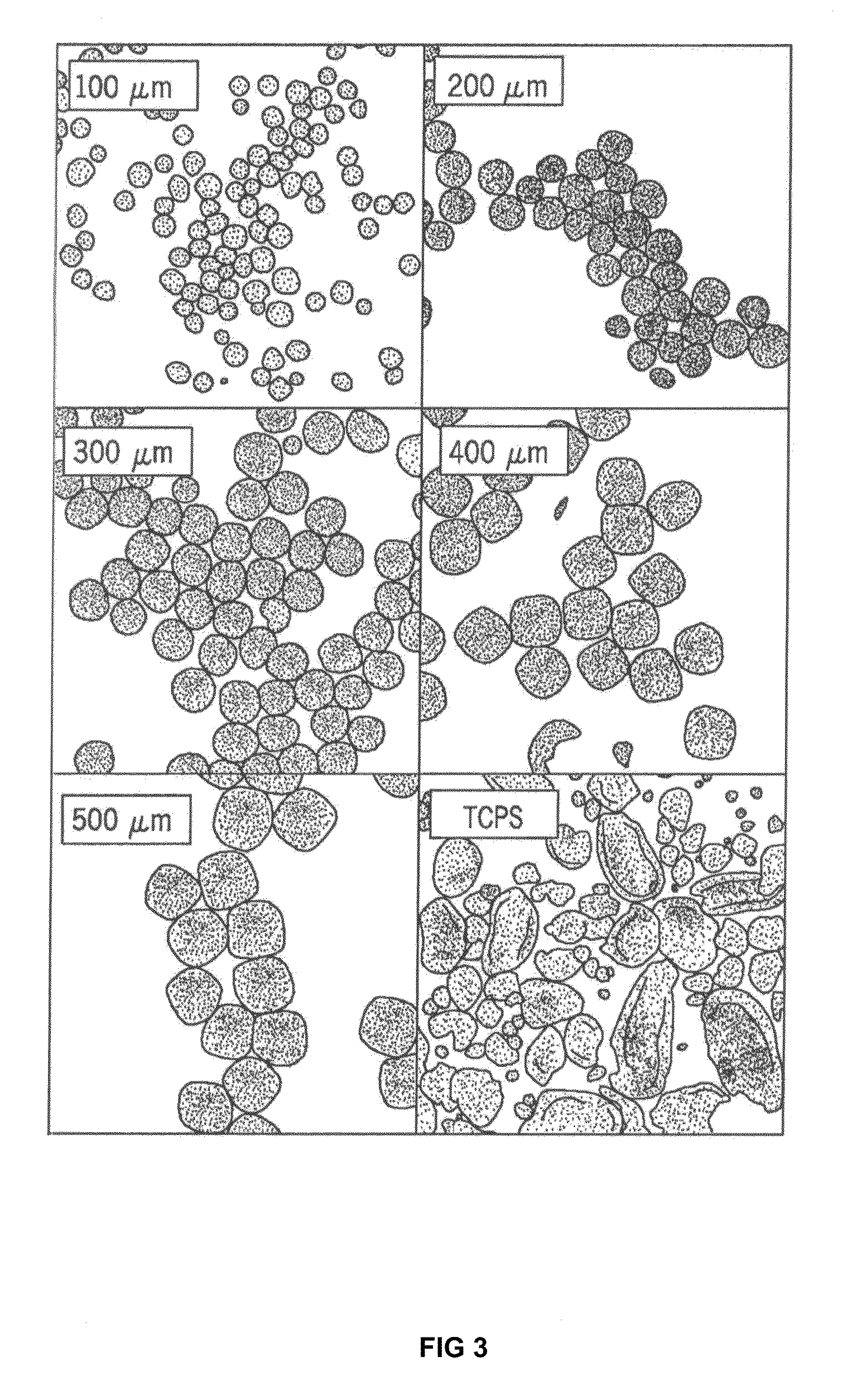
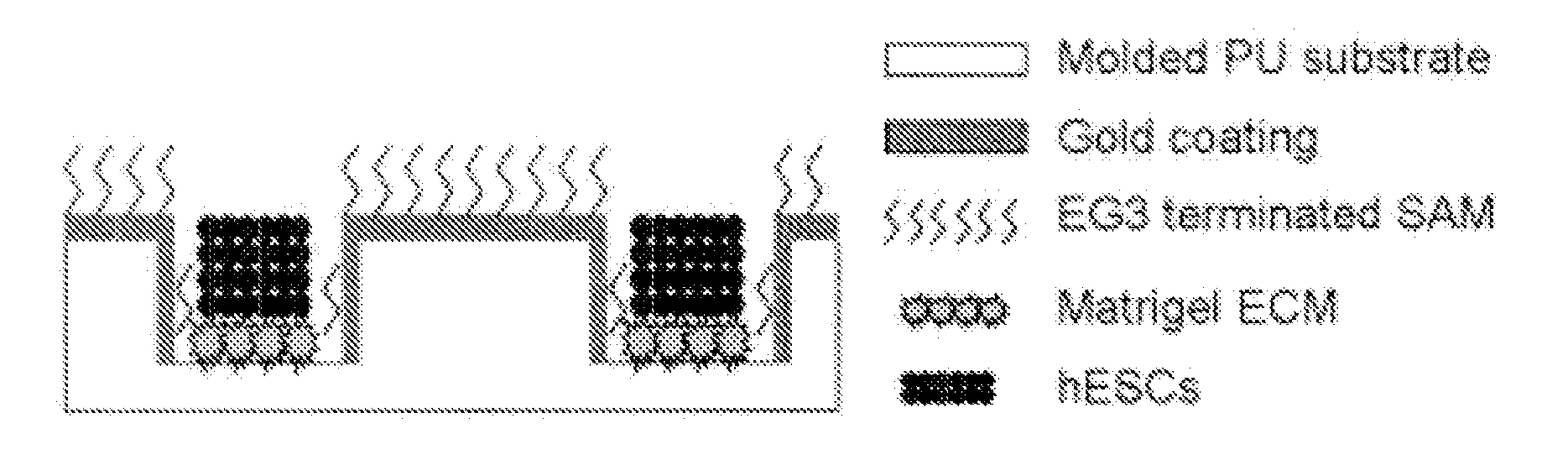
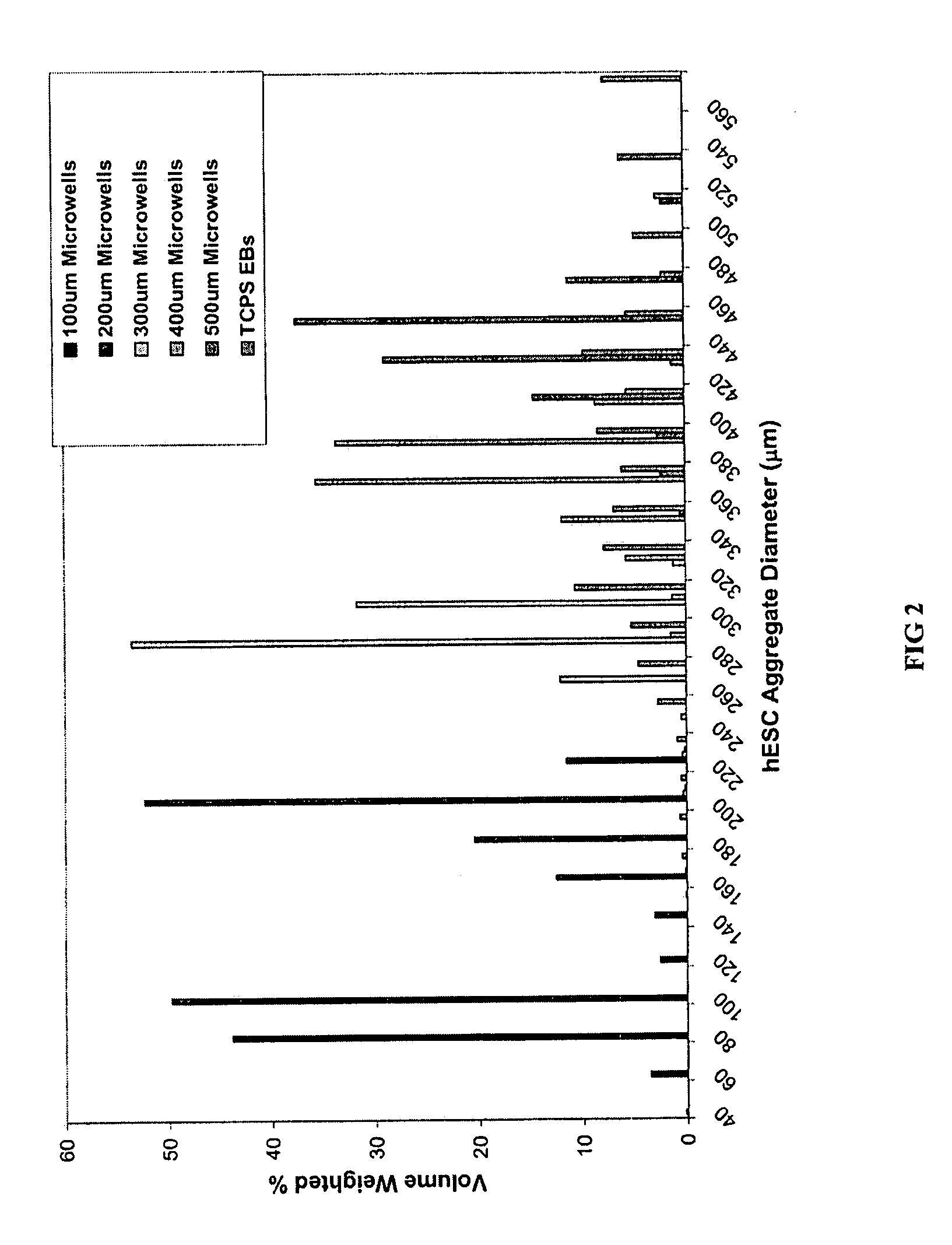
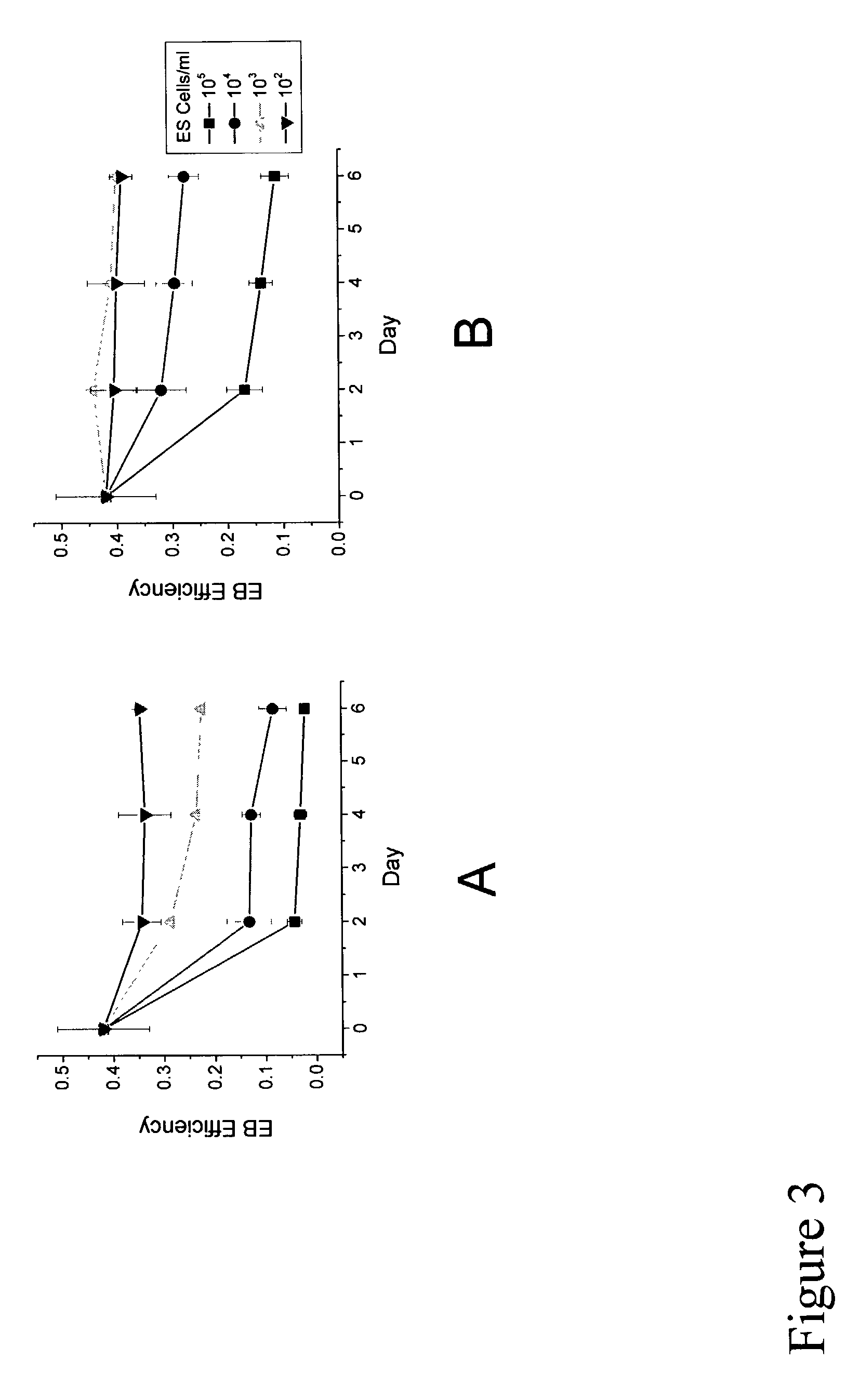
A three-dimensional microwell system that supports long term pluripotent cell culture and formation of homogeneous embryoid bodies (EBs) is described. Microwell-cultured pluripotent cells remain viable and undifferentiated for several weeks in culture and maintain undifferentiated replication when passaged to Matrigel®-coated, tissue culture-treated polystyrene dishes. Microwell-cultured pluripotent cells maintain pluripotency, differentiating to each of the three embryonic germ layers. Pluripotent cell aggregates released from microwells can be passaged for undifferentiated replication or differentiated to monodisperse EBs. The ability to constrain pluripotent cell growth in three dimensions advantageously provides for more efficient, reproducible culture of undifferentiated cells, high-throughput screening, and the ability to direct pluripotent cell differentiation by generating monodisperse EBs of a desired size and shape. Cardiomyocyte-rich EBs are obtained from pluripotent cells cultured in microwells of defined size and shape.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Embryoid Body - Based Screen
InactiveUS20070015210A1Uniform sizeEasy to produceGenetically modified cellsLibrary screeningTest agentConceptus
Disclosed are embryoid bodies having a uniform size of approximately 415 nm and comprising genetically modified embryonic stem cells, and methods of making same. The genetically uniform embryoid bodies can be multiplexed as one embryoid body per well in a multiwell format, and used as a high to medium throughput screen for test agents that affect the development and homeostasis of animals, including humans. The genetic modification of the embryonic stem cells is a promoter-report-selection construct that enables the selection and detection of cells of a particular lineage in the EB, to determine the effects of a test agent.
Owner:GENEPROTECH
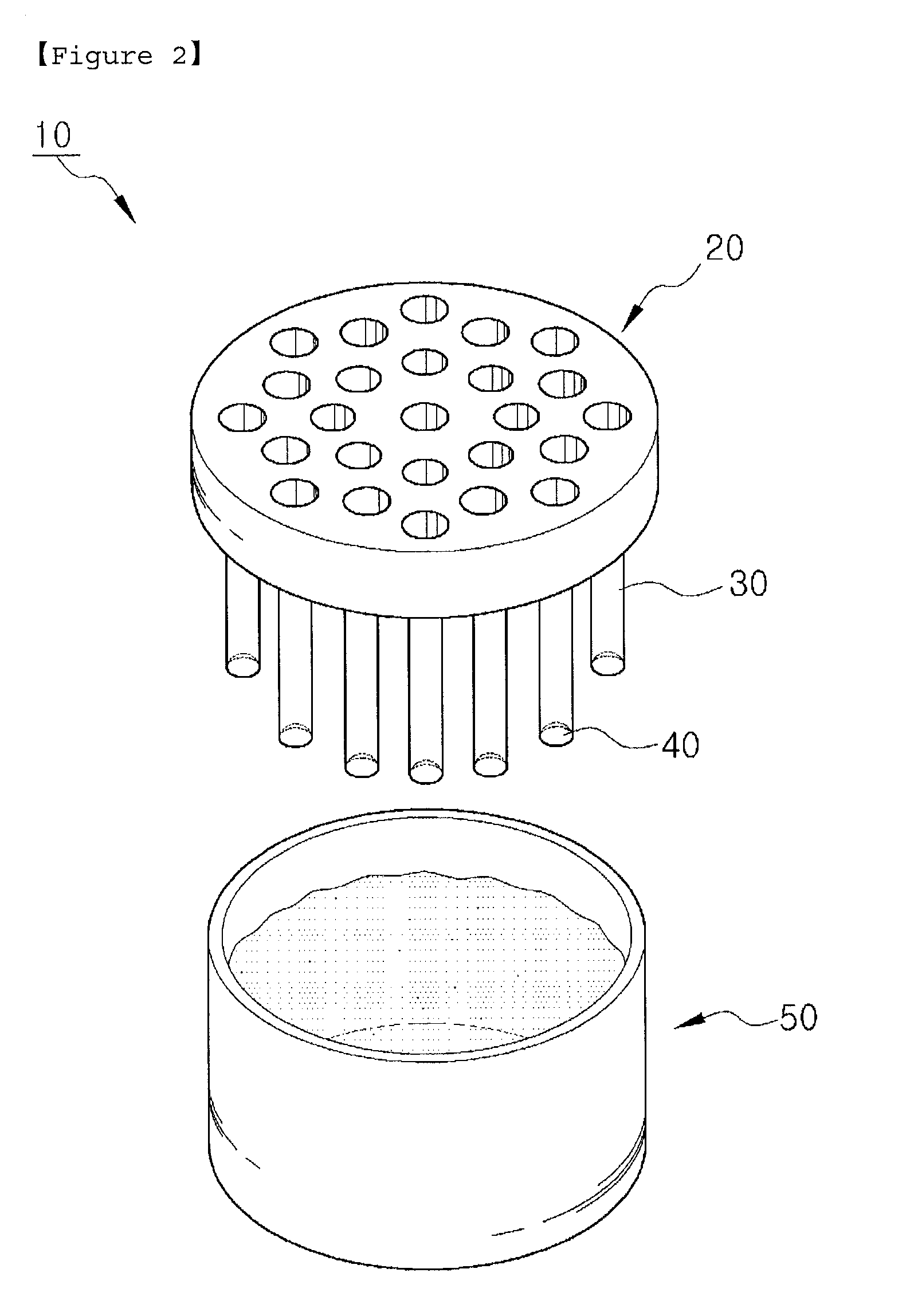
Apparatus and method for culturing stem cells
InactiveUS20120064627A1Simple and rapid and scalable cultureEasy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeat sensitivePolymer chemistry
A method is provided to prepare a plurality of microwells suitable for the formation of embryoid bodies from embryonic stem cells. The method requires applying an image-forming material to a heat sensitive thermoplastic material in a designed pattern and heating the material under conditions that reduce the size of the receptive material by at least about 60% to create a mold. A polymer such as PDMS is then applied to the mold and removed to form the microwells. In an alternative aspect, the plurality of microwells on receptive material are prepared by etching a microwell designed pattern into a heat sensitive thermoplastic material support and then heating the material under conditions that reduce the size of the receptive material by at least about 60%.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
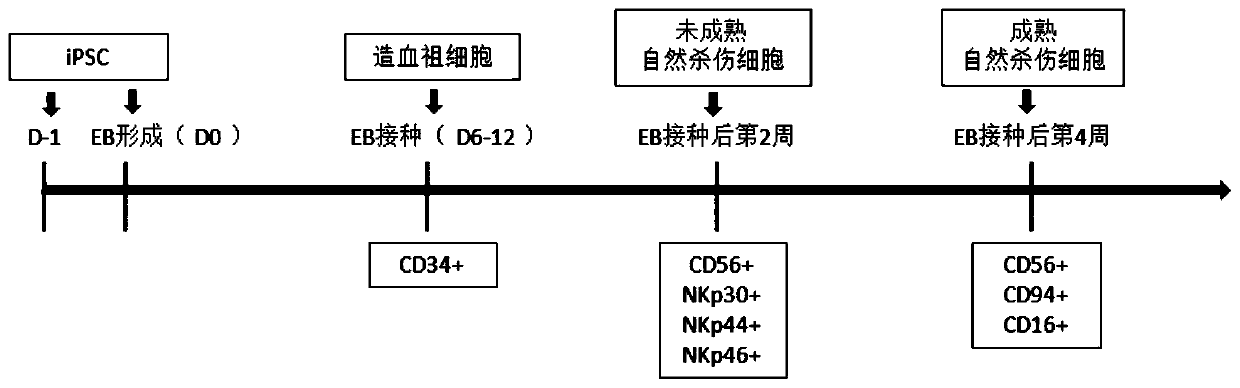
Rat embryonic stem cell
ActiveUS20120142092A1Microbiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationEmbryoNa k atpase activity
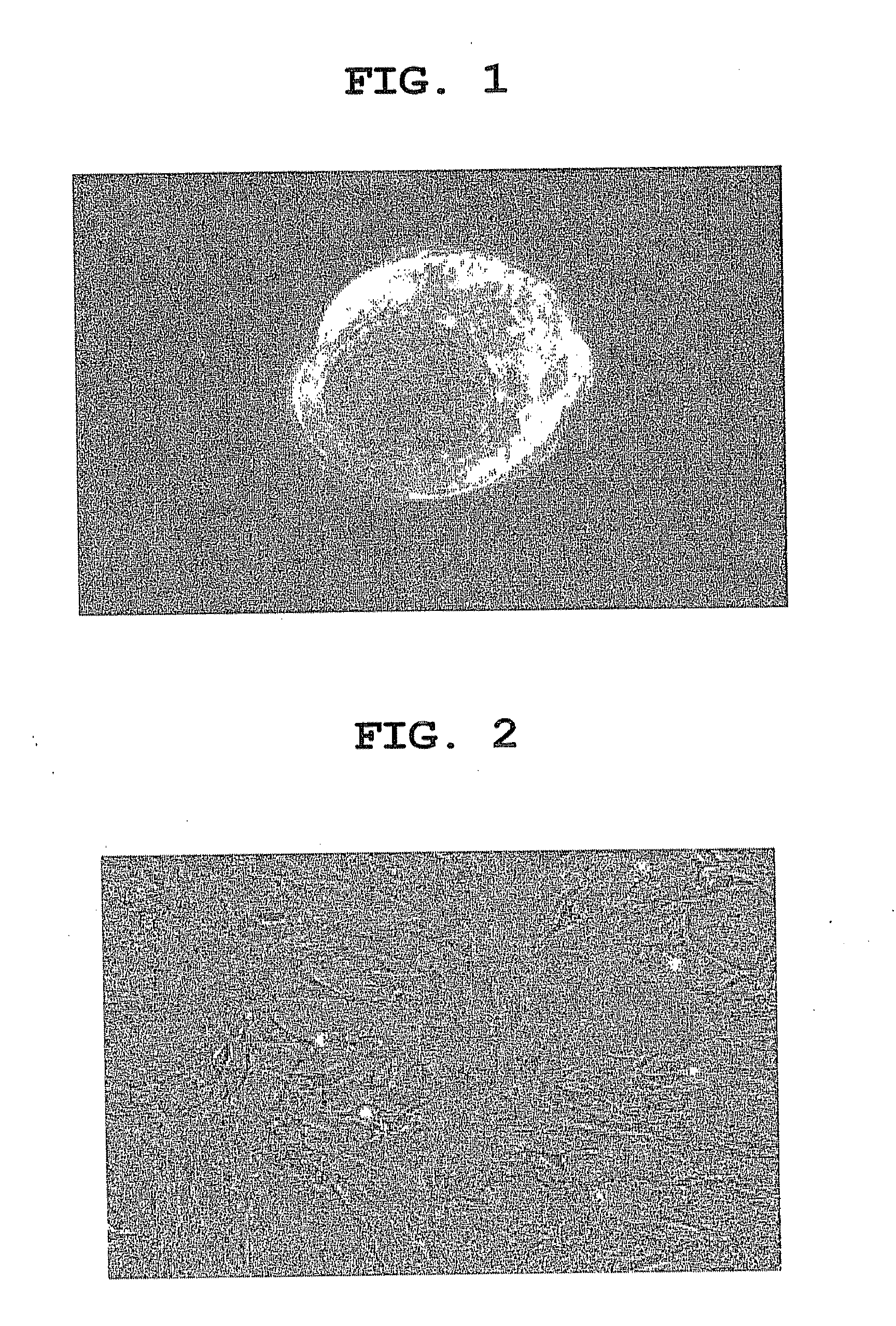
The present invention provides a rat embryonic stem cell characterized by having the following properties of (a) expressing Oct3 / 4 gene and Nanog gene, (b) positive for alkaline phosphatase activity, (c) having an embryoid body forming ability, (d) expressing SSEA (Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen)-1 and SSEA-4, (e) having the same number of chromosomes as does a normal rat cell, (f) capable of being subcultured and holding the undifferentiated state, (g) having in vitro pluripotency, (h) having a potential to differentiate for cells of three embryonic germ lineages, (i) having teratoma formation ability, and (j) having an ability to produce a chimeric rat, a method of establishing the aforementioned rat embryonic stem cell and the like.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into natural killer cells and application
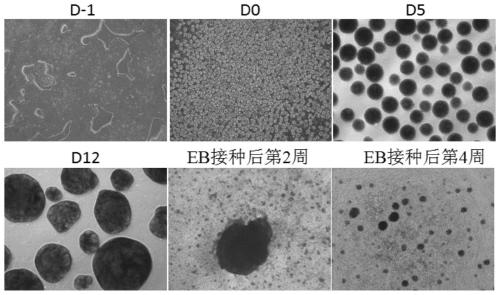
ActiveCN111235105ALow costAvoid expensiveCulture processDead animal preservationHematopoietic progenitor cell differentiationNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, specifically to a method for differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into natural killer cells and an application. The invention disclosesa pluripotent stem cell-derived natural killer cell. The pluripotent stem cell-derived natural killer cell expresses CD56, Nkp30, Nkp44 and Nkp46, and also expresses markers CD16 and CD94 of a maturenatural killer cell. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the natural killer cell. The method comprises the following steps: S1, formation of an embryoid body; S2, differentiation of the embryoid body into hematopoietic progenitor cells; S3, differentiation of the hematopoietic progenitor cells into NK cells; and S4, maturation and expansion of the NK cells. With the differentiation method provided by the invention, the pluripotent stem cells can be rapidly, efficiently, simply and conveniently induced to be differentiated into the natural killer cells with low cost on the basis of a culture medium with definite components and an optimized cell factor combination.
Owner:安徽中盛溯源生物科技有限公司
Methods of generating functional human tissue
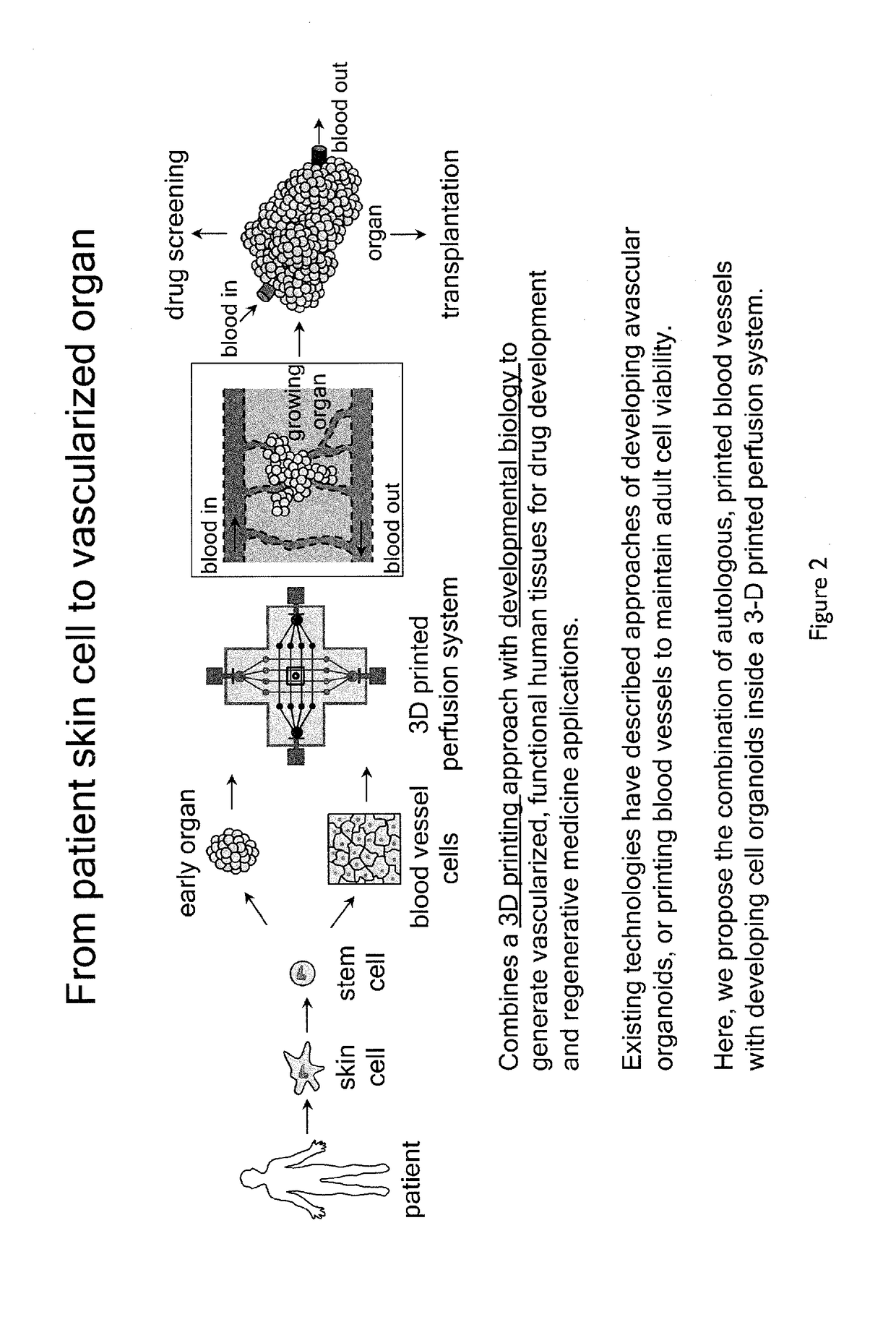
Methods of tissue engineering, and more particularly methods and compositions for generating various vascularized 3D tissues, such as 3D vascularized embryoid bodies and organoids are described. Certain embodiments relate to a method of generating functional human tissue, the method comprising embedding an embryoid body or organoid in a tissue construct comprising a first vascular network and a second vascular network, each vascular network comprising one or more interconnected vascular channels; exposing the embryoid body or organoid to one or more biological agents, a biological agent gradient, a pressure, and / or an oxygen tension gradient, thereby inducing angiogenesis of capillary vessels to and / or from the embryoid body or organoid; and vascularizing the embryoid body or organoid, the capillary vessels connecting the first vascular network to the second vascular network, thereby creating a single vascular network and a perfusable tissue structure.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Amplification of cell populations from embryonic stem cells
Culturing embryonic stem cells without the use of embryoid bodies leads to a increase in the frequency of predetermined cell types.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
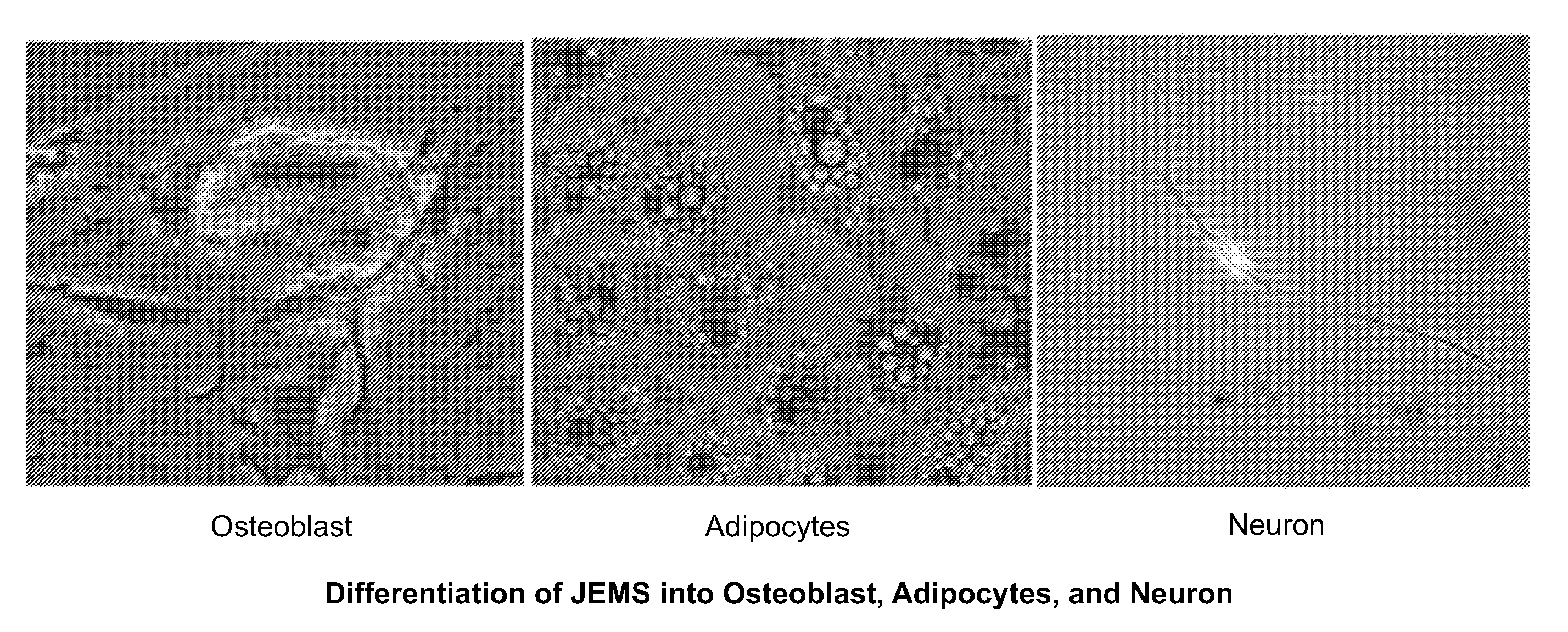
ActiveUS20110070205A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderGerm layerMHC class I
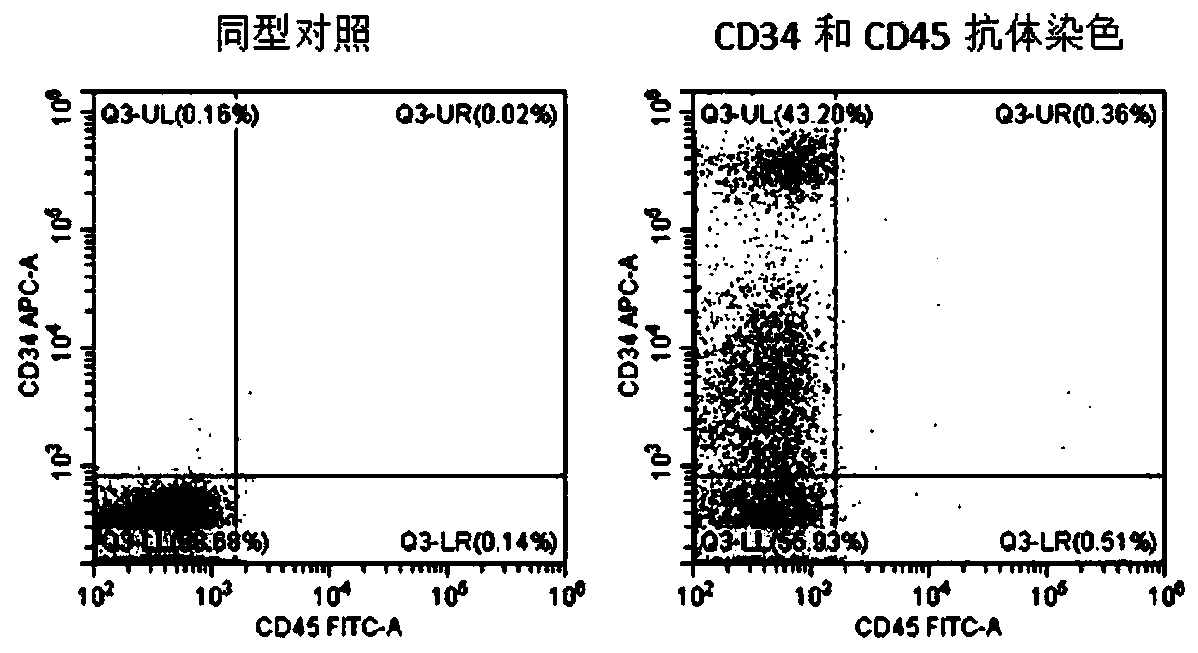
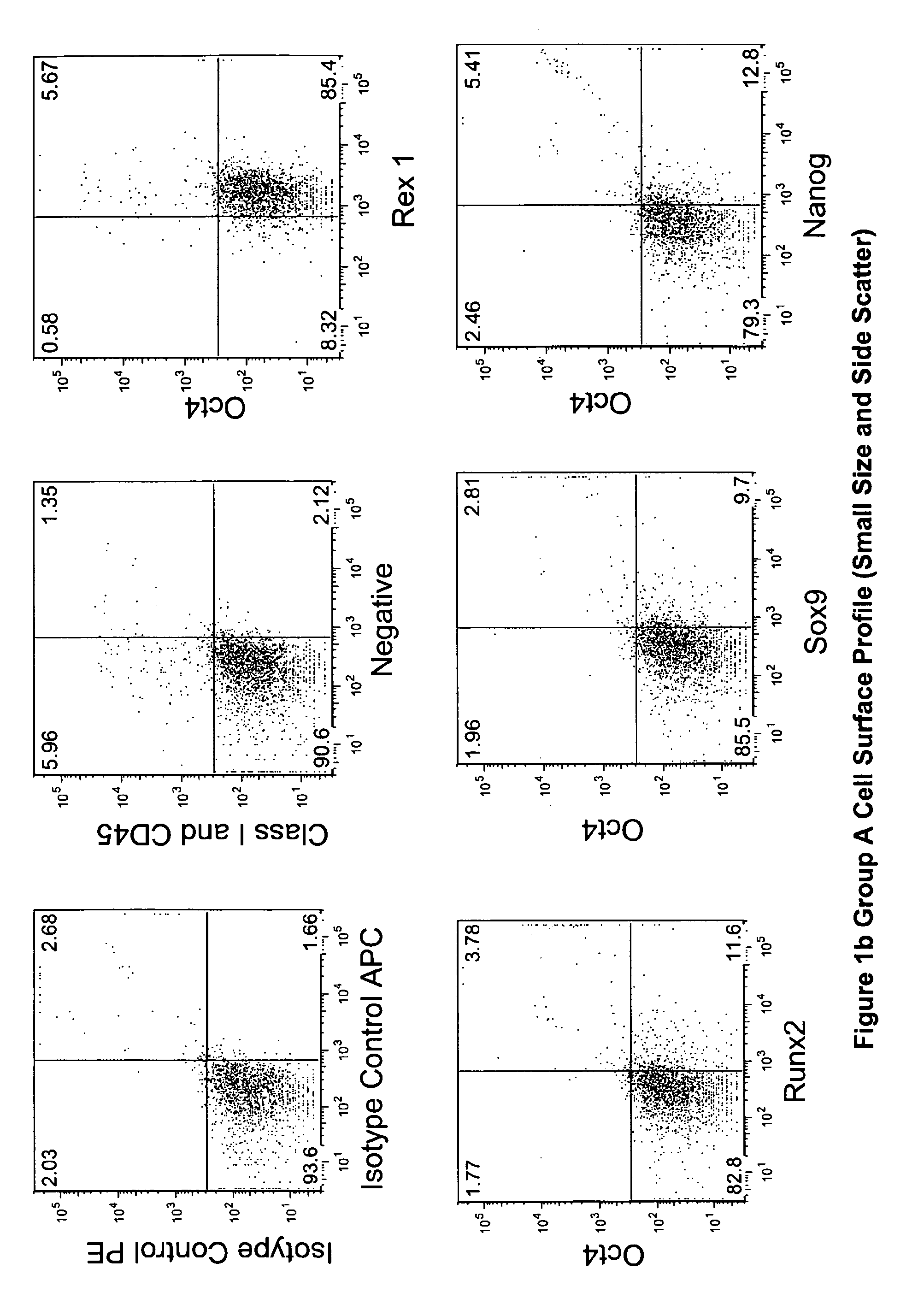
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1, TWIST, KLF-4 and Stella but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105, CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
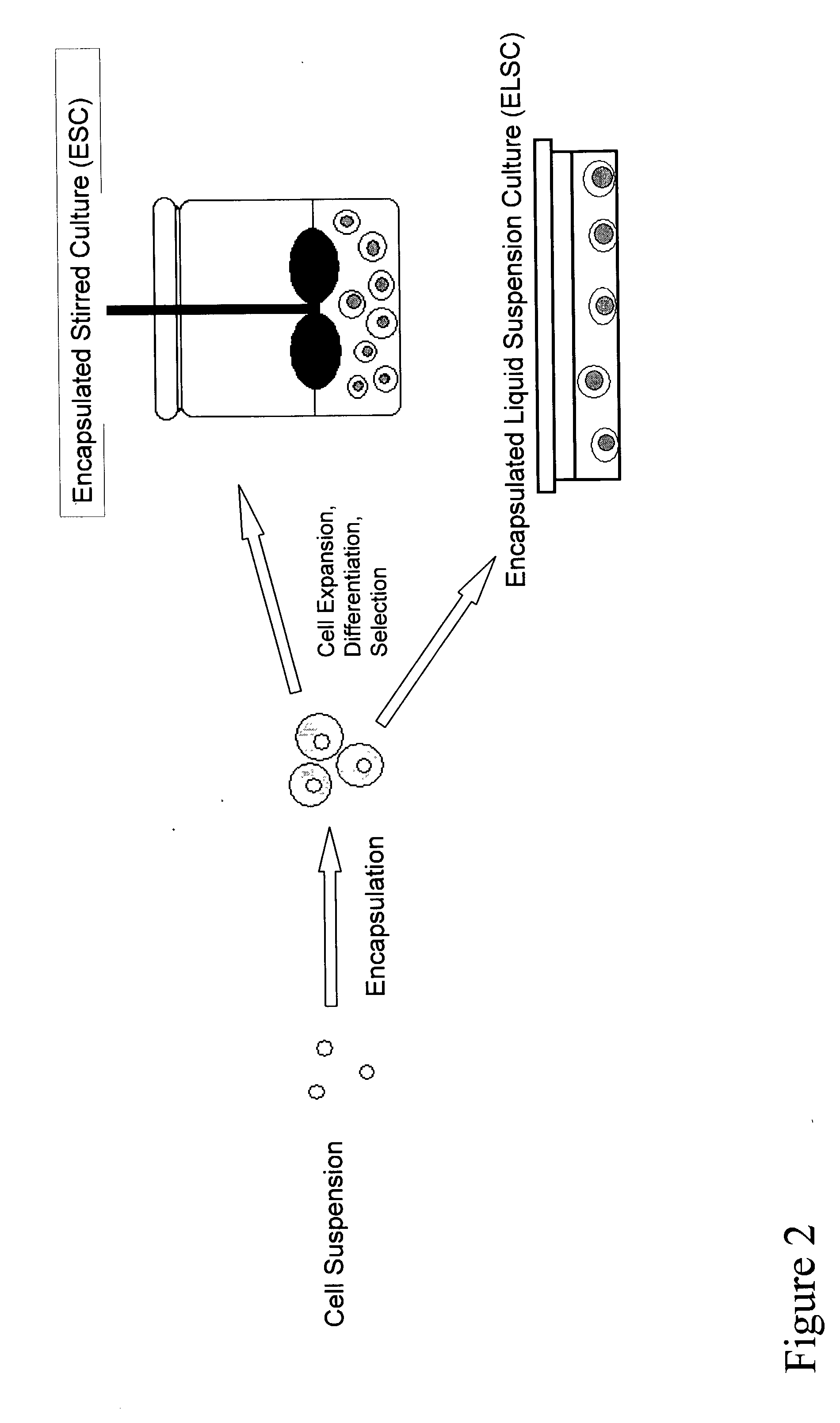
Devices and methods for production of cell aggregates
InactiveUS20110086375A1Efficiently generate tissue-level organizationReduce chaosBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityCell clustering
The present application provides methods and devices for the production and recovery of cell aggregates. In one embodiment, the device is a microwell device with a high density of microwells. The application also provides a device for extracting cell aggregates such as stem cells or embryoid bodies from well plates. Such cell aggregates are used for the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells such as embryonic stem cells, in the fields of developmental biology and regenerative medicine / tissue engineering.
Owner:UNGRIN MARK +1
Method for culturing stem cells
PendingUS20080026460A1AdvantageouslyCell differentiation profile of EBs can be controlledBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGerm layerMatrigel
A three-dimensional microwell system that supports long term embryonic stem cell (ESCs) culture and formation of homogeneous embryoid bodies (EBs) is described. Microwell-cultured ESCs remain viable and undifferentiated for several weeks in culture and maintain undifferentiated replication when passaged to Matrigel®-coated, tissue culture-treated polystyrene dishes. Microwell-cultured ESCs maintain pluripotency, differentiating to each of the three embryonic germ layers. ESC aggregates released from microwells can be passaged for undifferentiated replication or differentiated to monodisperse EBs. The ability to constrain ESC growth in three dimensions advantageously provides for more efficient, reproducible culture of undifferentiated cells, high-throughput screening, and the ability to direct ESC differentiation by generating monodisperse EBs of a desired size and shape.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Directed differentiation of human embryonic cells
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100291042A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocidePancreatic cellsDiseaseMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1 and TWIST but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
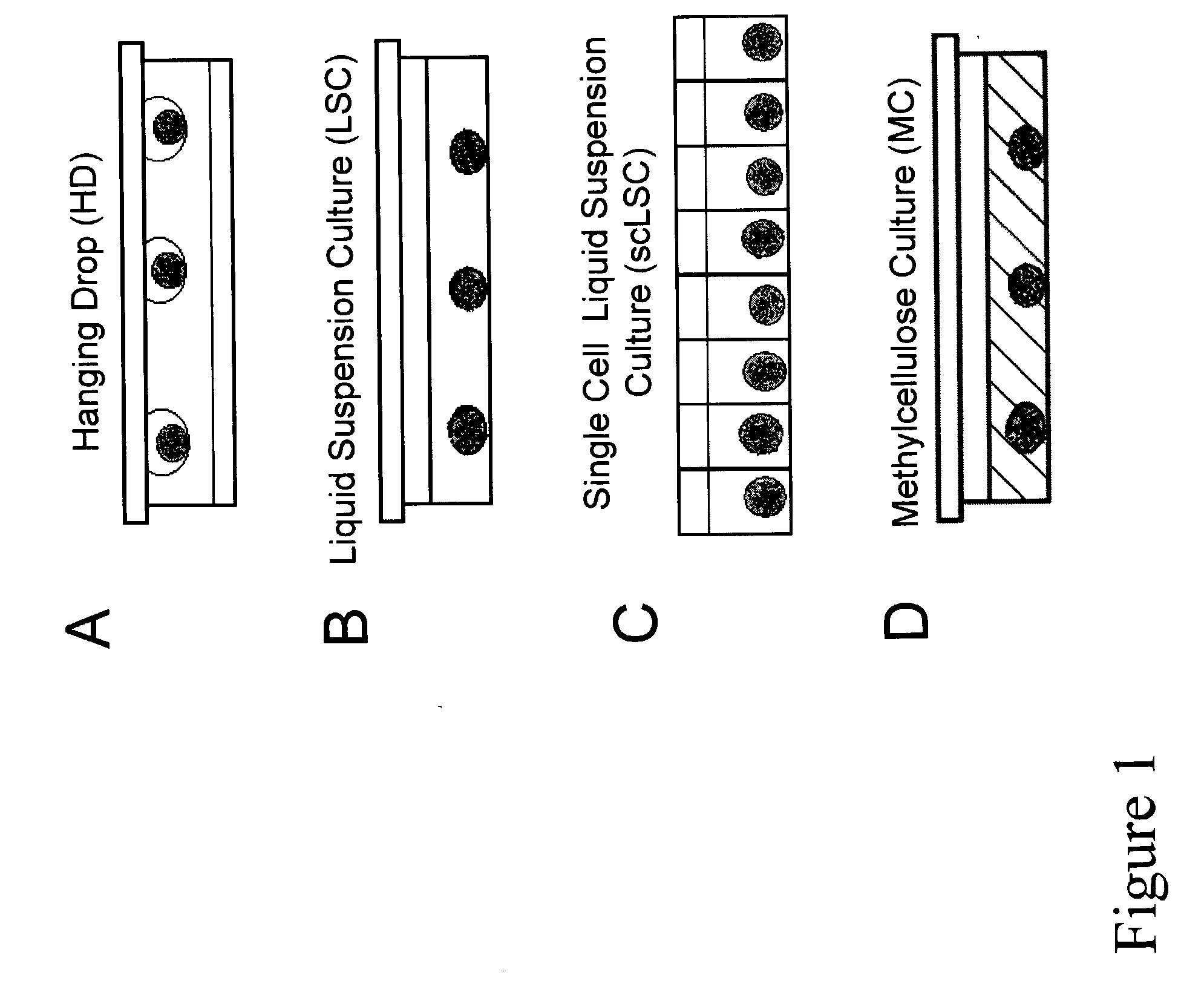
Alginate poly-L-Lysine encapsulation as a technology for controlled differentiation of embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20090311765A1Induce depolymerizationArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsPolyelectrolyteSingle cell suspension
Alginate polyelectrolyte encapsulation is used for the controlled differentiation of embryonic stem cells. An isolated cell population is provided. The cell population includes a single cell suspension of ES cells encapsulated within an alginate polyelectrolyte microenvironment. The encapsulated ES cells are capable of differentiating within said microenvironment into hepatocyte lineage cells in the absence of embryoid body intermediates or growth factor supplementation.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
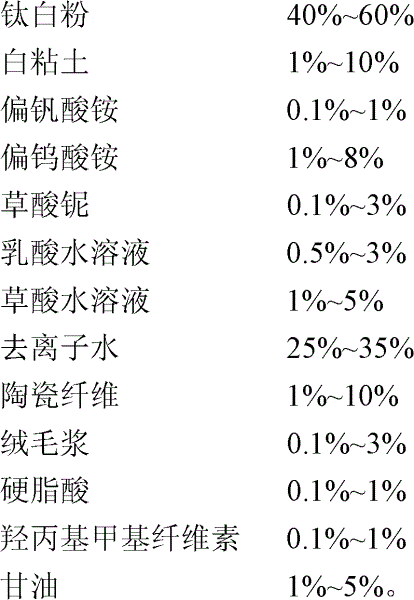
Honeycomb SCR smoke denitration catalyst embryoid body and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102614866AImprove plasticityImprove adhesionDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsTungstateNiobium
The invention discloses a honeycomb SCR (Selective Catalytive Redution) smoke denitration catalyst embryoid body and a preparation method thereof. The honeycomb SCR smoke denitration catalyst body consists of the following raw materials as per percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of titanium dioxide, 1 to 10 percent of white clay, 0.1 to 1 percent of ammonium metavanadate, 1 to 8 percent of ammonium meta-tungstate, 0.1 to 3 percent of niobium oxalate, 0.5 to 3 percent of lactic acid aqueous solution, 1 to 5 percent of oxalic acid aqueous solution, 25 to 35 percent of deionized water, 1 to 10 percent of ceramic fiber, 0.1 to 3 percent of fluff pulp, 0.1 to 1 percent of stearic acid, 0.1 to 1 percent of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and 1 to 5 percent of glycerol. The honeycomb SCR smokedenitration catalyst embryoid body has high plasticity, caking property and mechanical strength. The method is simple and convenient in operation and low in cost. Each component of the prepared catalyst body is dispersed uniformly; the catalyst body is easy in forming and demolding in the extrusion process and has high finished product rate; and the catalyst prepared by the embryoid body has highdenitration efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
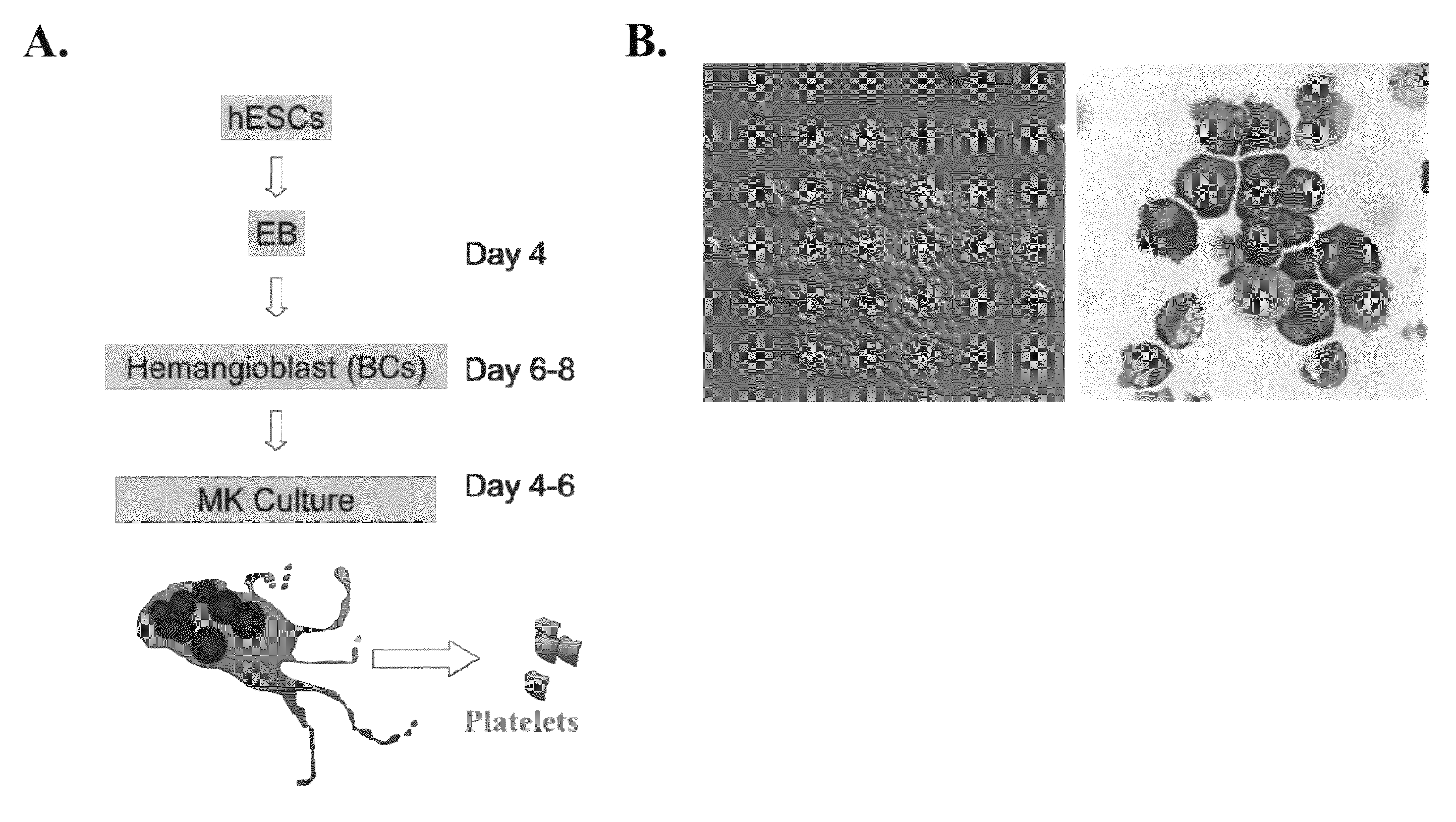
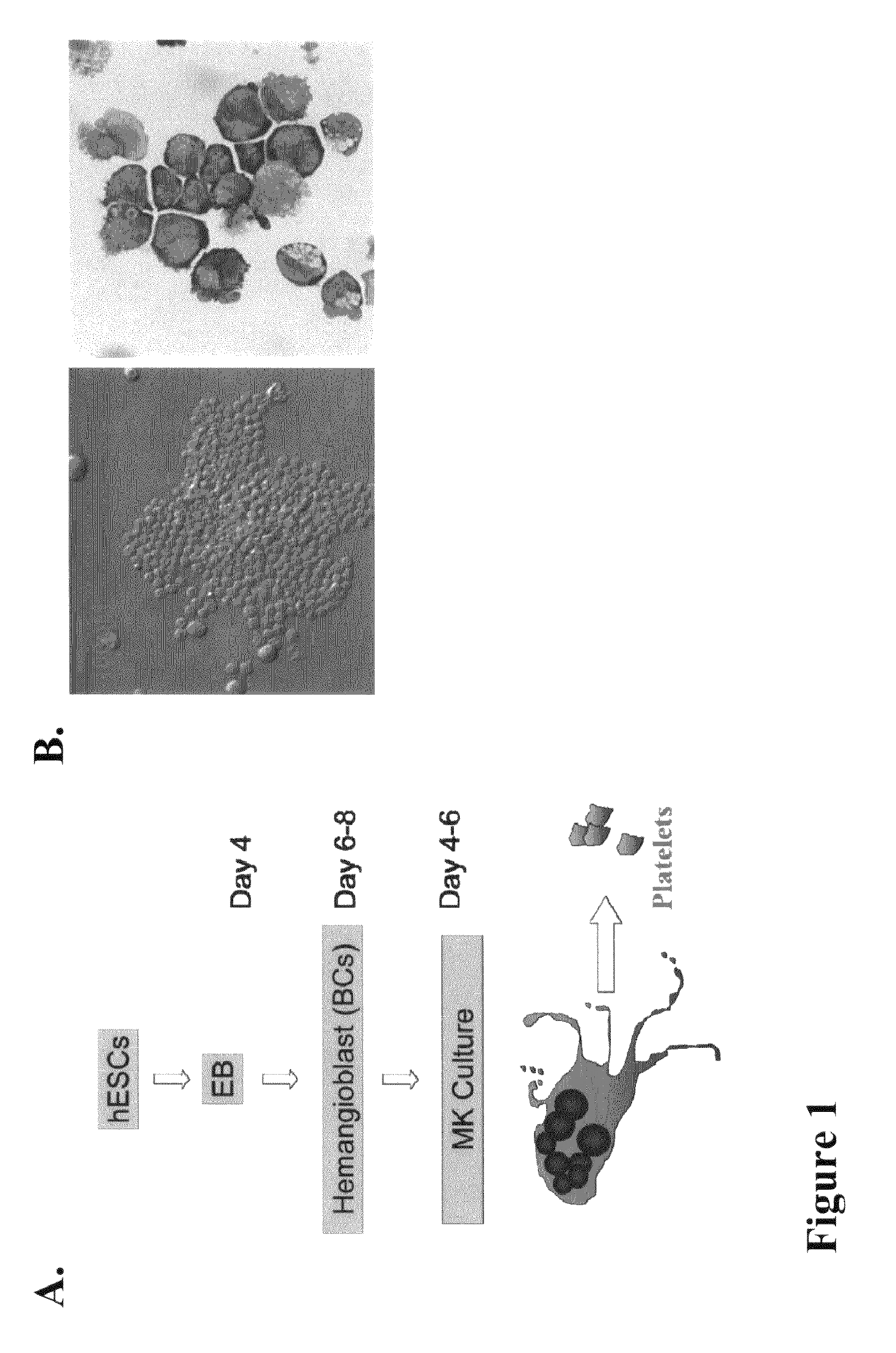
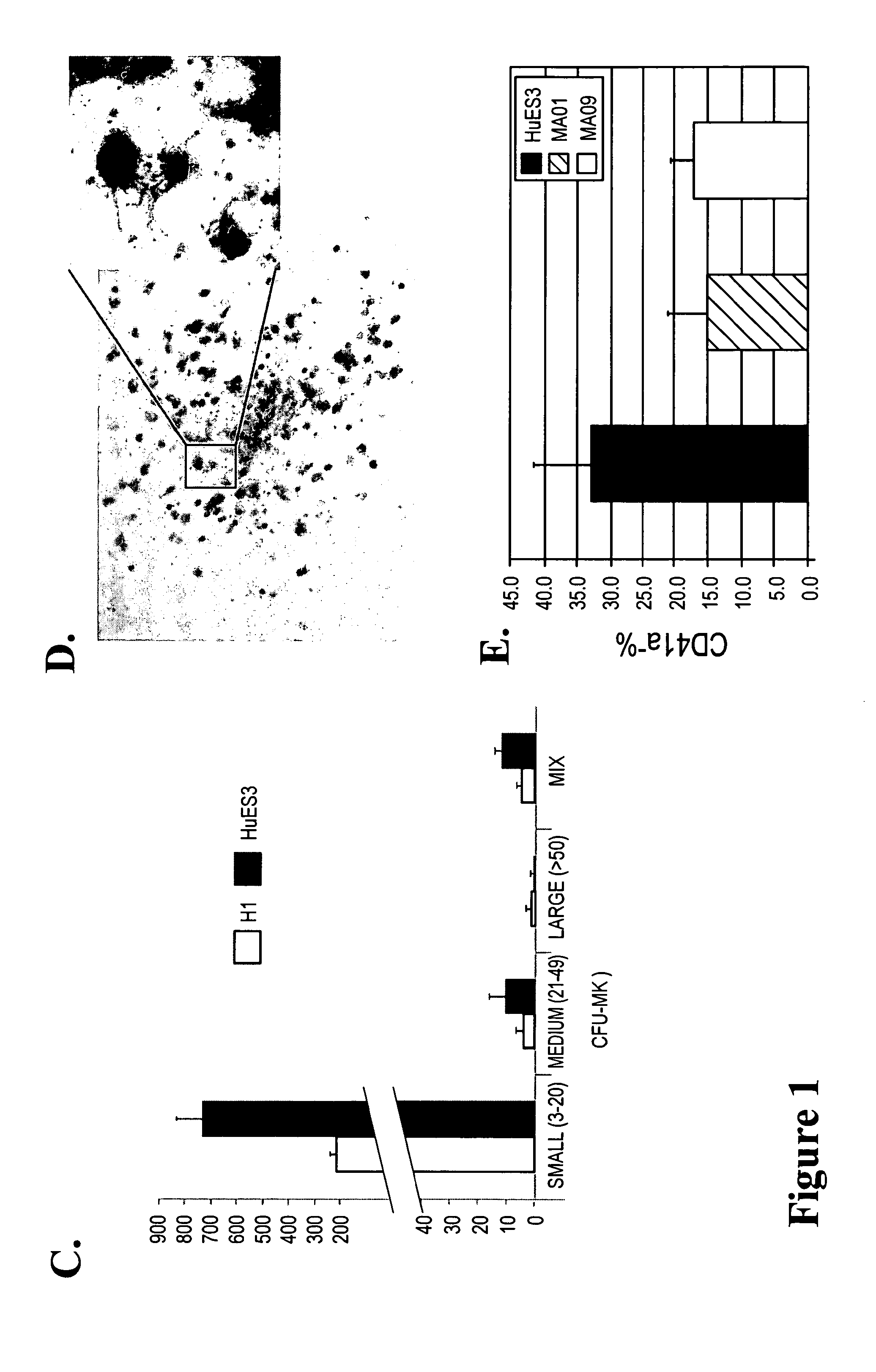
Large scale generation of functional megakaryocytes and platelets from human embryonic stem cells under stromal-free conditions
ActiveUS20120315338A1Transfusion is neededReduce or eliminate an immunity mediated host reactionCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsSerum igeBiology
The present invention provides a method of generating megakaryocytes and platelets. In various embodiments, method involves the use of human embryonic stem cell derived hemangioblasts for differentiation into megakaryocytes and platelets under serum and stromal-free condition. In this system, hESCs are directed towards megakaryocytes through embryoid body formation and hemangioblast differentiation. Further provided is a method of treating a subject in need of platelet transfusion.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
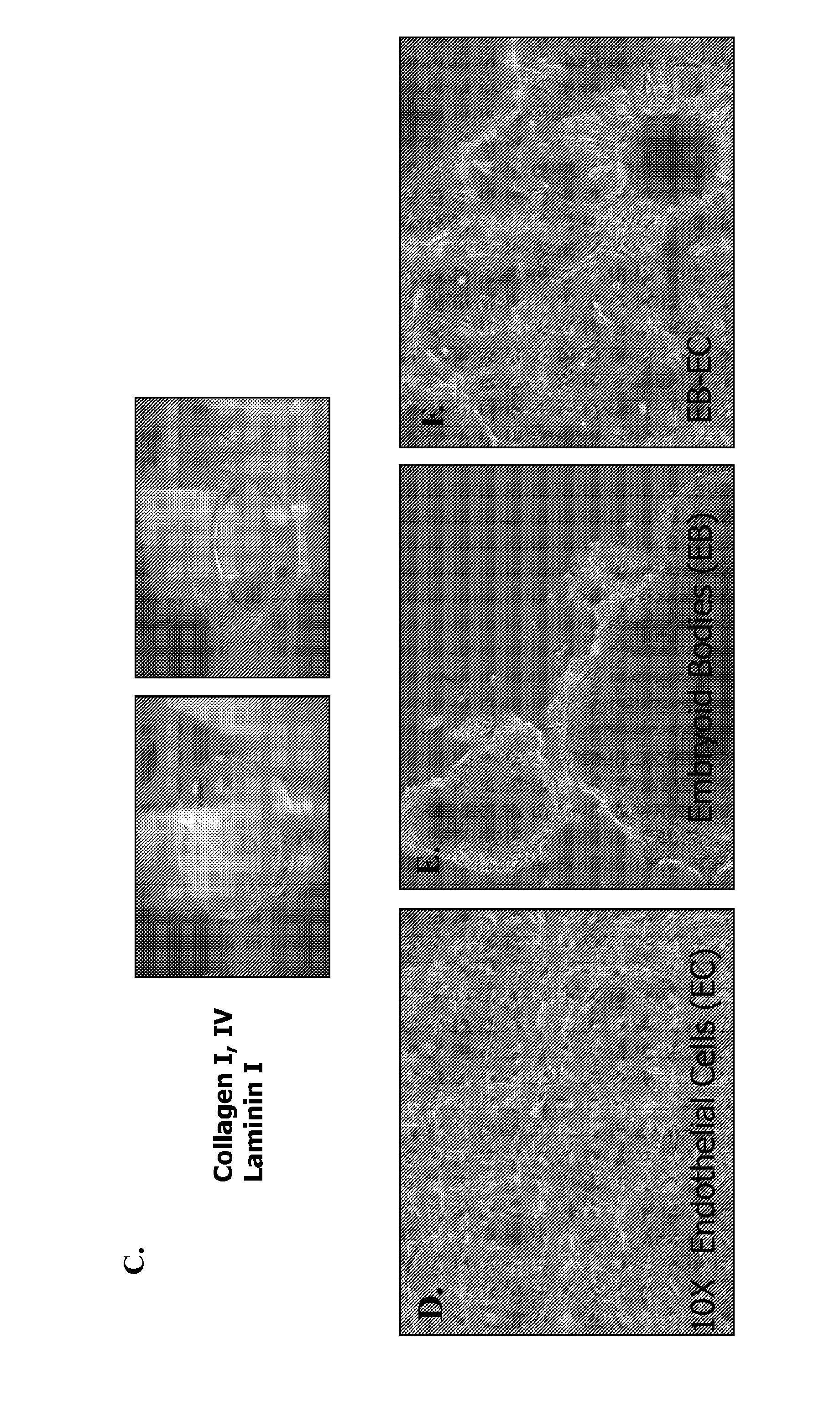
Pancreatic insulin-producing beta-cell lines derived from human pluripotent stem cells
Production of beta-cells from stem cells from pluripotent stem cells have always been significantly lacking in at least one of the following properties: 1) functional properties related to insulin-production and glucose signaling response, 2) mature phenotype such as biochemical markers or cell structures, 3) efficiency in production of differentiated cells. Described herein is multistep differentiation protocol which substantially overcomes all of the existing limitations. Pluripotent stem cells, including induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can be differentiated using an embryoid body (EB) formation step, followed by B maturation via endothelial cells (EC) co-culturing and incubation with a sequential series of bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-related growth factor cocktails. The resulting cells displayed functional properties, including insulin-production and glucose signaling response, and mature phenotype of C-peptide expression.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Cotton leafstalk tissue cultivation and high-differentiation cotton material selective breeding method
InactiveCN1864477AImprove conversion efficiencyHigh differentiation ratePlant phenotype modificationPlant tissue cultureScreening methodPlantlet
The present invention discloses cotton tissue culturing process and its application in screening out high differentiation rate cotton line. The cotton tissue culturing process includes the following steps: 1. adopting sterilized leaf stem as explant and inducing callus in callus inducing culture medium; 2. completing the differentiating culture of the callus in differentiating culture medium; and 3. further culturing of the differentiated embryonic callus in embryoid germinating and seedling forming culture medium to obtain regenerated plant. The process has high differentiation rate, and may be applied in screening out high differentiation rate cotton line. In addition, the screened high differentiation rate cotton can raise the converting efficiency of agrobacterium mediating process and shorten the converting period greatly. The present invention is significant in tissue culture, selective breeding and variety improvement of cotton.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
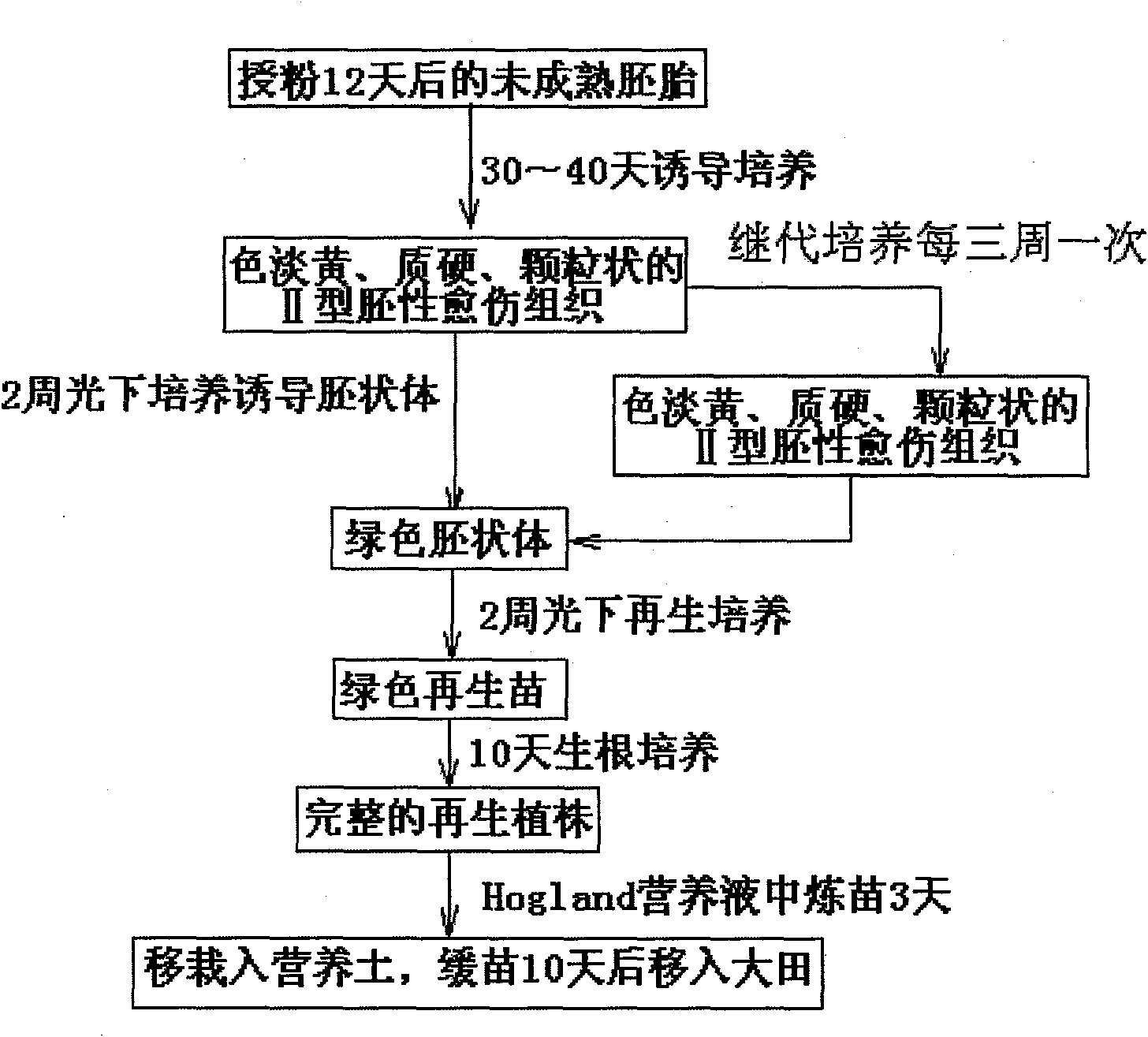
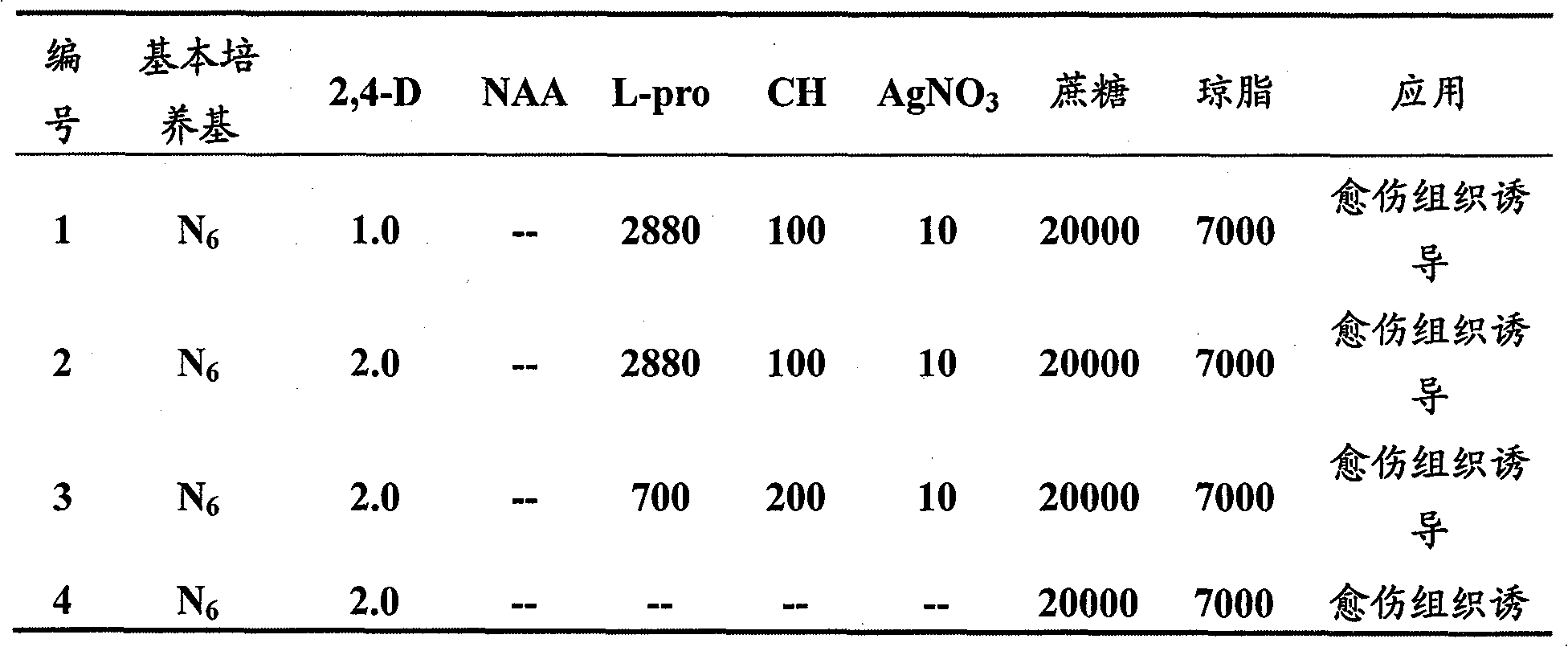
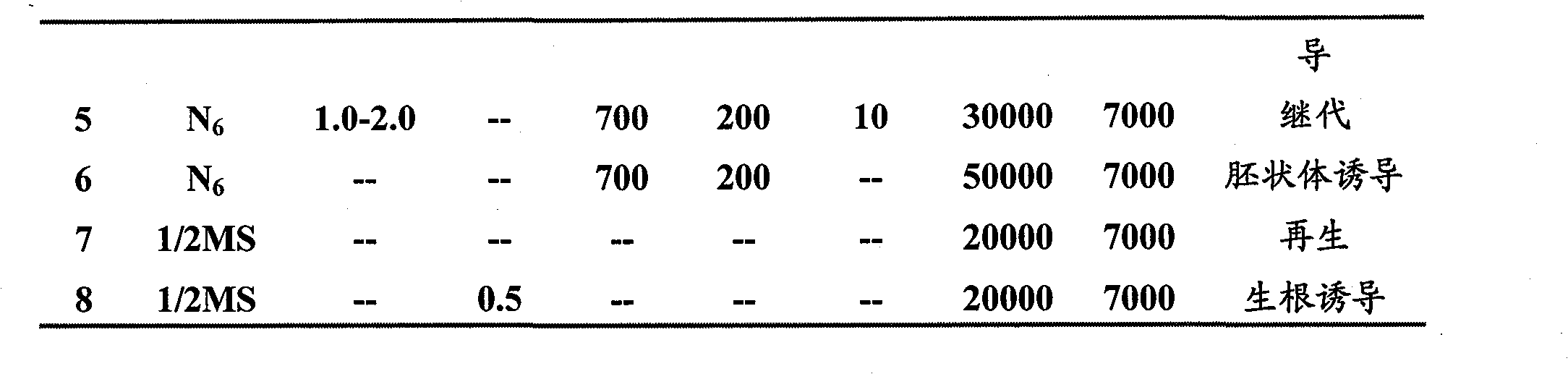
Method for building high-efficiency regeneration system of superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531
InactiveCN101779598AHigh induction ratePromote rapid proliferationCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureField cropNutrient solution
The invention discloses a method for building a high-efficiency regeneration system of superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531, belonging to the field of plant genetic engineering and transgenosis breeding. The invention takes an agriculture line 531 rataria as an explant, induces in a callus induction medium and produces an II-type embryonic callus; the II-type embryonic callus is subjected to embryoid induction under light in an embryoid induction medium to produce a green embryoid; then, the green embryoid is transported to a regeneration medium and is cultured into a regeneration plant under light; root induction is carried out in a rooting medium, and acclimatization is carried out in Hogland nutrient solution to ensure that a new thick root grows on the root of the regeneration plant; the root is transplanted to nutritional soil for rejuvenation culture; and finally, the root is transplanted to a land for growing field crops to normally grow and seed. The regeneration technology is suitable for the superior corn self-bred line agriculture line 531 with high application value, can ensure that the superior quality of agriculture line 531 corn can be inherited in the corn transgenosis breeding process, and has an important meaning for functional genome group research.
Owner:GRAIN RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Bioprocess for producing uniform embryoid bodies from embryonic stem cells in a high density bioreactor
InactiveUS7547547B2Inhibit aggregationCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusHigh cellHigh density
The present inventors identified aggregation of embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies (EBs) as the cause of the difficulty in generating large numbers of the embryonic stem cells (ES) cell-derived tissues. To counter this, the invention provides a novel bioprocess where aggregation of spheroid forming cells, such as embryonic stem cells and spheroids, such as EBs is controlled, such as by encapsulation of within a matrix. As a result, EBs can be generated with high efficiency and cultured in high cell density, well-mixed systems. Well-mixed conditions facilitate measurement and control of the bulk media conditions and allow for the use of scalable bioreactor systems for clinical production of tissue. Therefore, the invention enables generation of ES cell-derived tissue on a clinical scale. The invention is also applicable to any spheroid-forming cells and other types of pluripotent cells.
Owner:CARDION AG
Method for obtaining dihaploid plants of sweet peppers
InactiveCN102047843AImprove cultivation efficiencyIncrease DH Strain RatioPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenotypeCapsicum baccatum
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
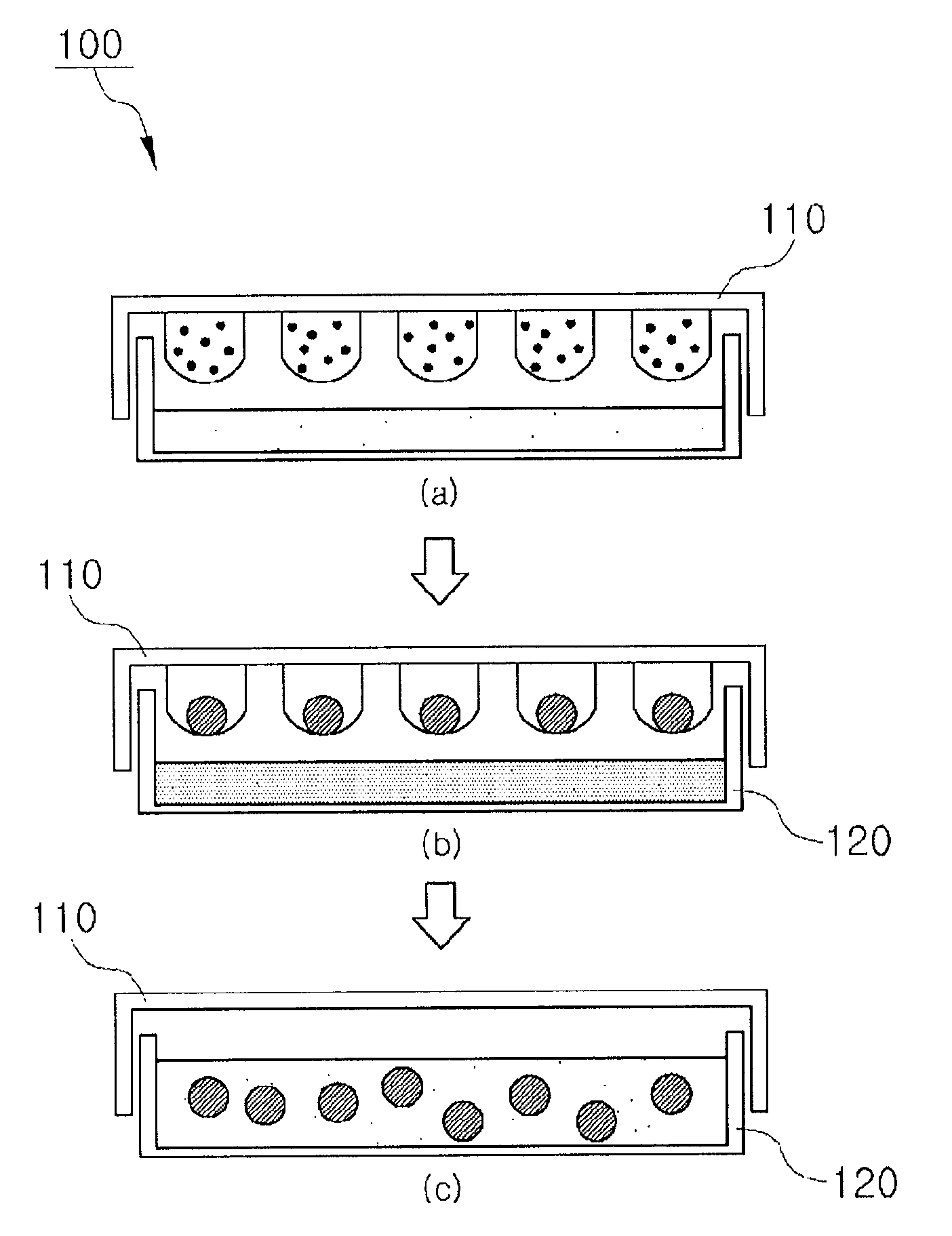
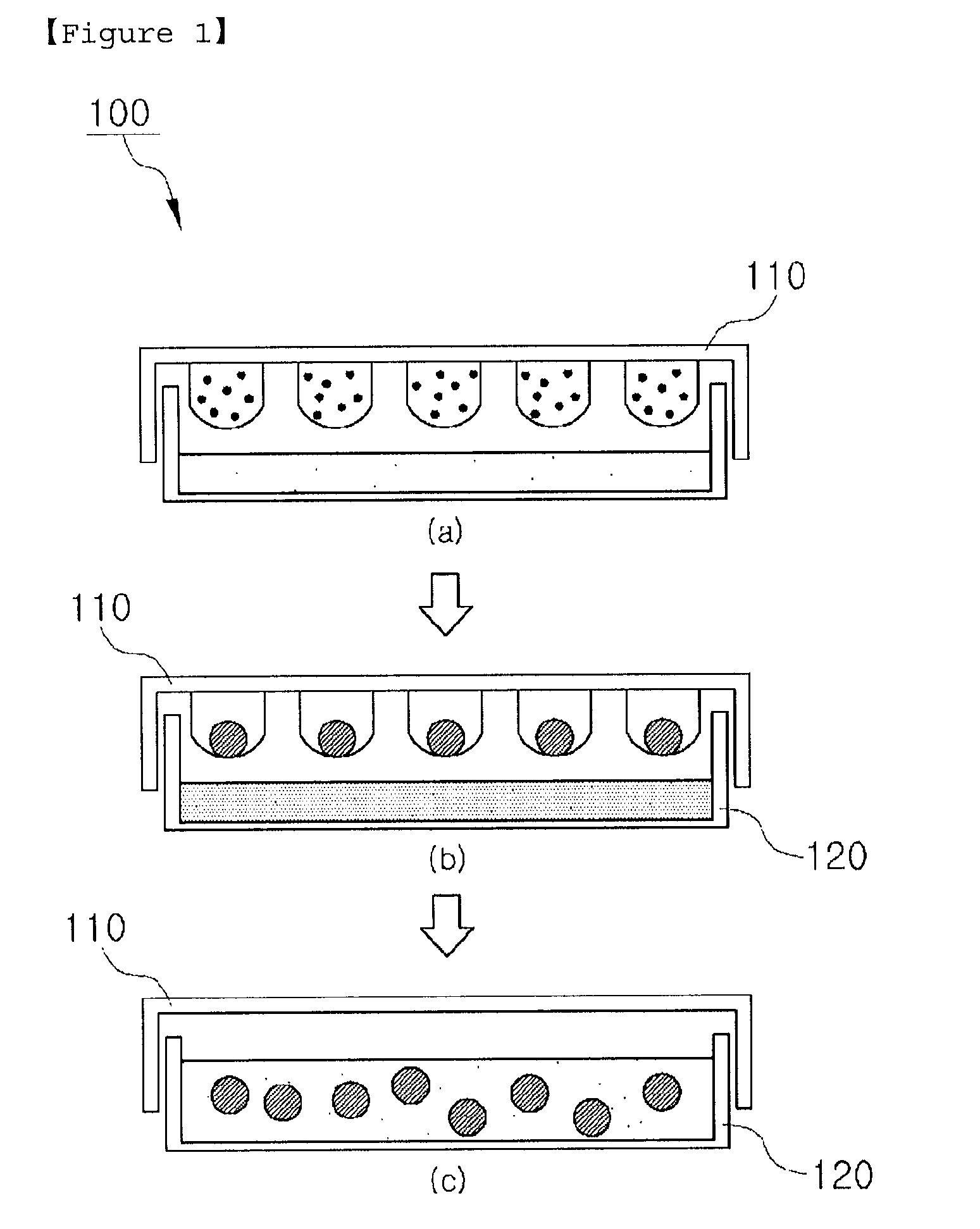
Container for germ layer formation and method of forming germ layer
ActiveUS20060252148A1Formed easily and efficientlyWell formedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGerm layerCulture cell
The invention relates to a vessel for embryoid formation used for forming embryoid bodies from ES cells easily without complicated technique, and to a method for forming embryoid bodies easily and efficiently using the vessel. The method includes the steps of (A) providing a vessel for embryoid formation having a coating layer formed from a compound having a particular PC-like group on a vessel surface defining a region for floating culture of ES cells, and (B) floating culturing ES cells in the vessel to form embryoid bodies.
Owner:NOF CORP
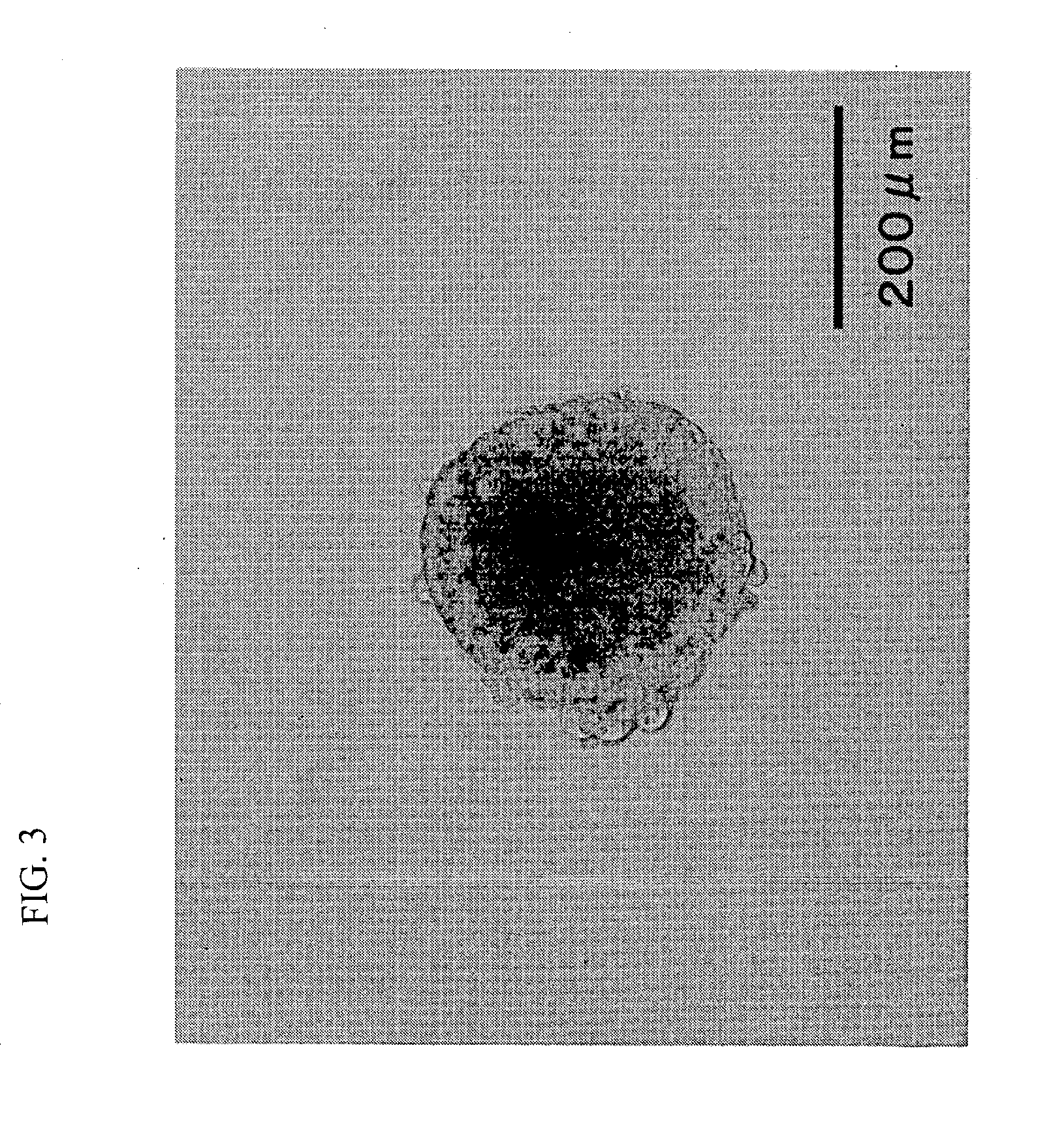
Cell culture dish for the embryoid body formation from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20100112684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCells embryoEmbryonic stem cell
The present invention relates to a cell culture dish for the erabryoid body formation from embryonic stem cells, which facilitates efficient and stable differentiation of embryonic stem cells by forming embryoid body in grooves on the bottom of a support adhered on the back of the lid for the culture dish by hanging drop culture.
Owner:IND FOUND OF CHONNAM NAT UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com