Patents
Literature
721 results about "High cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
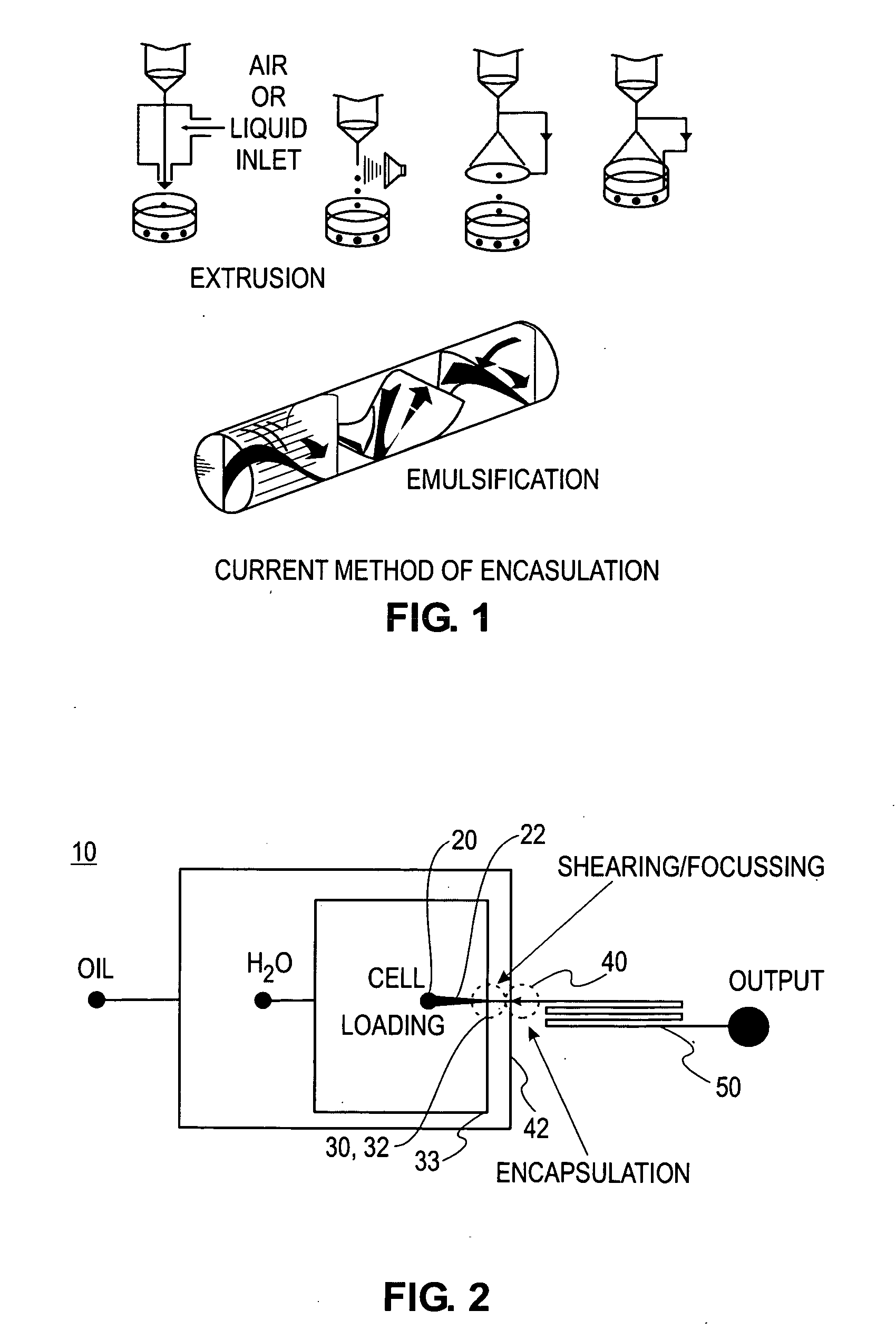
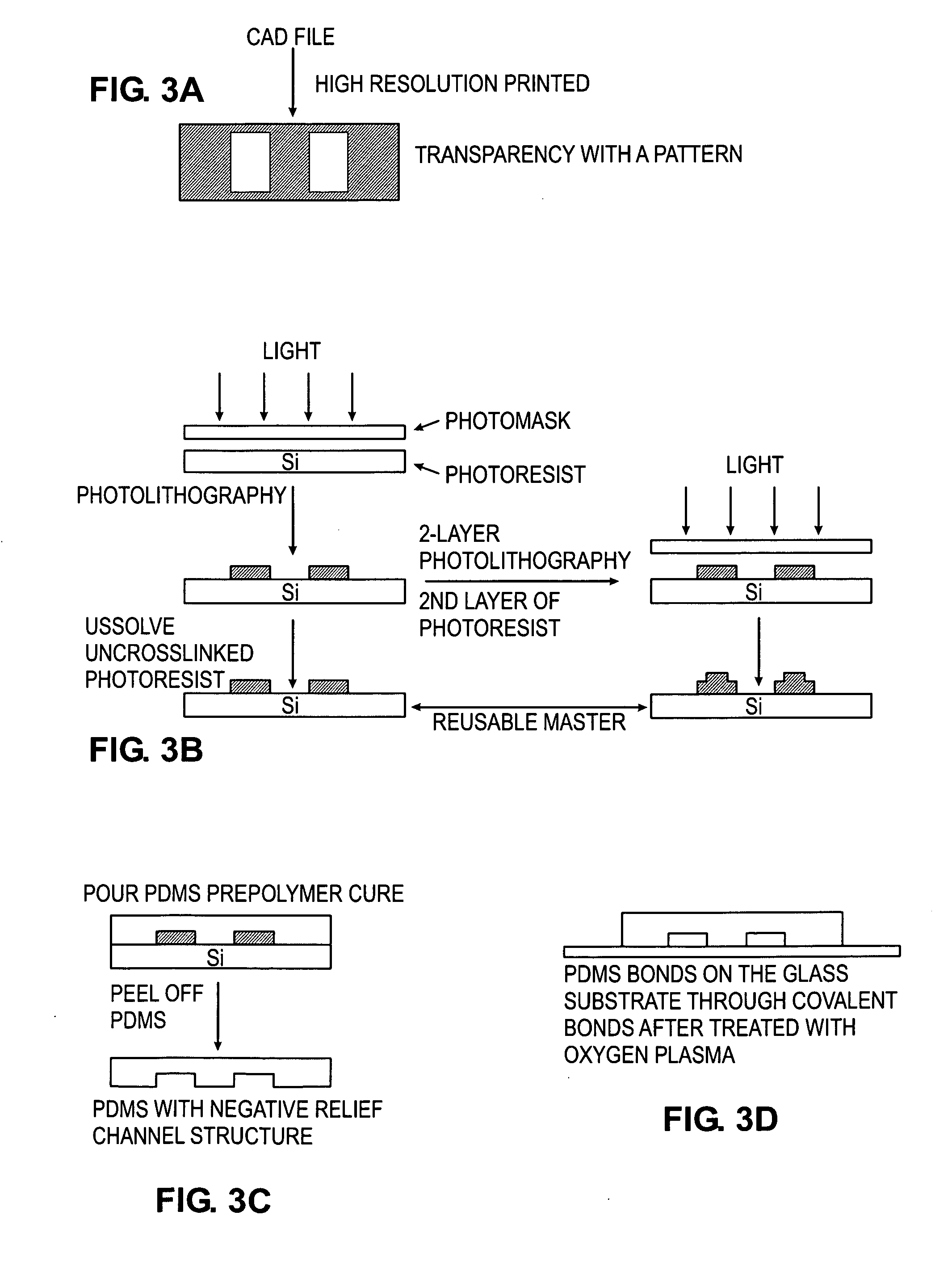
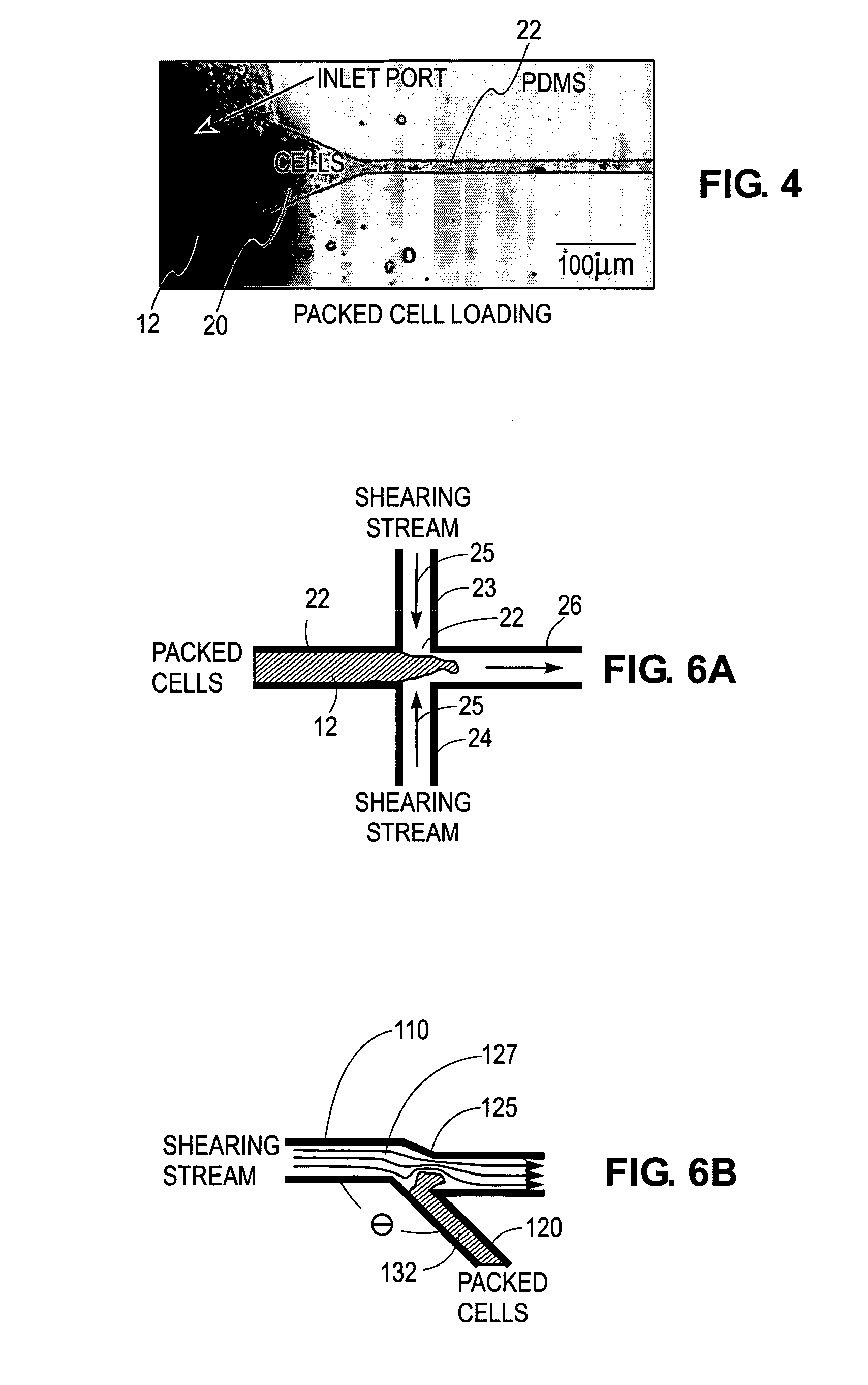
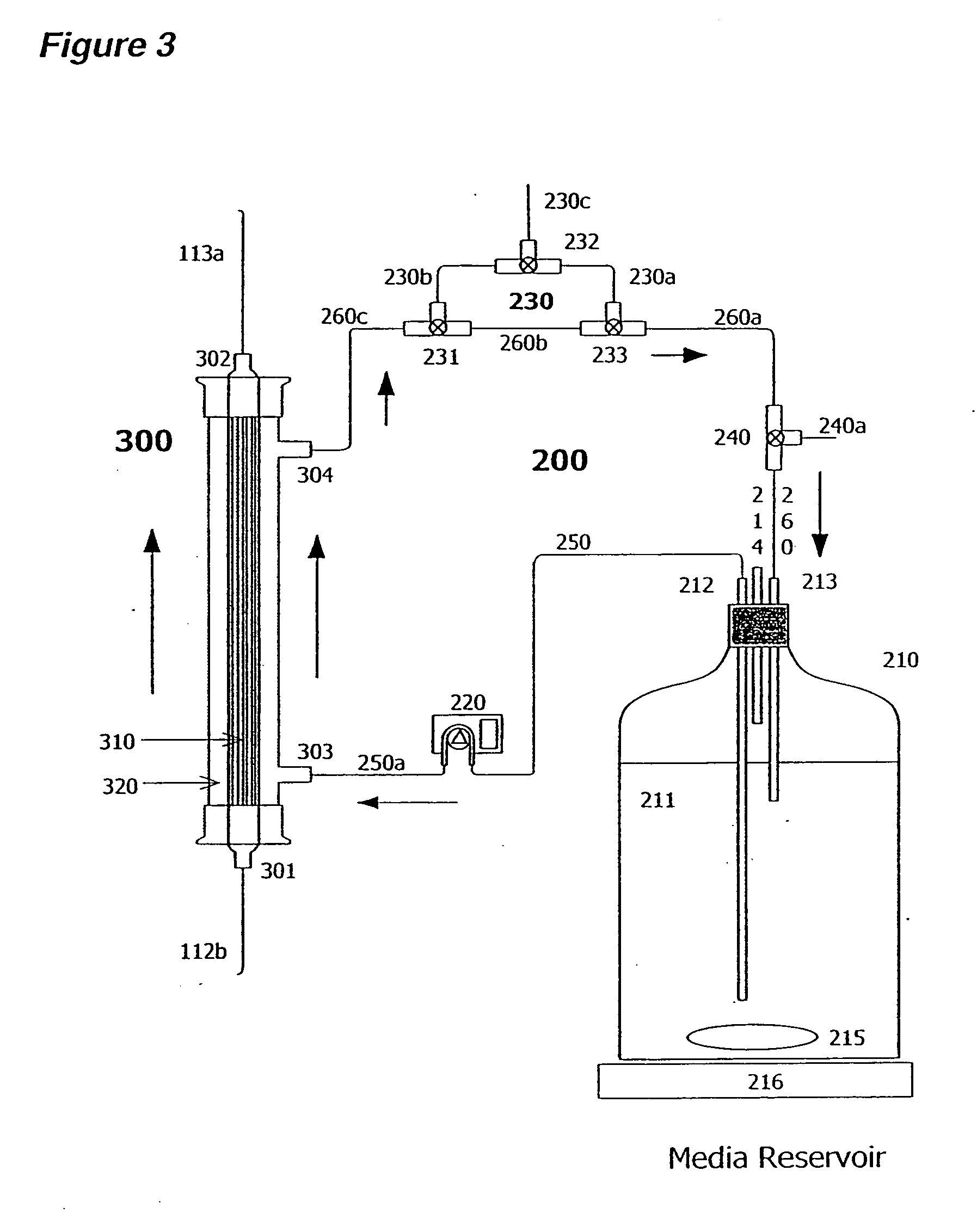
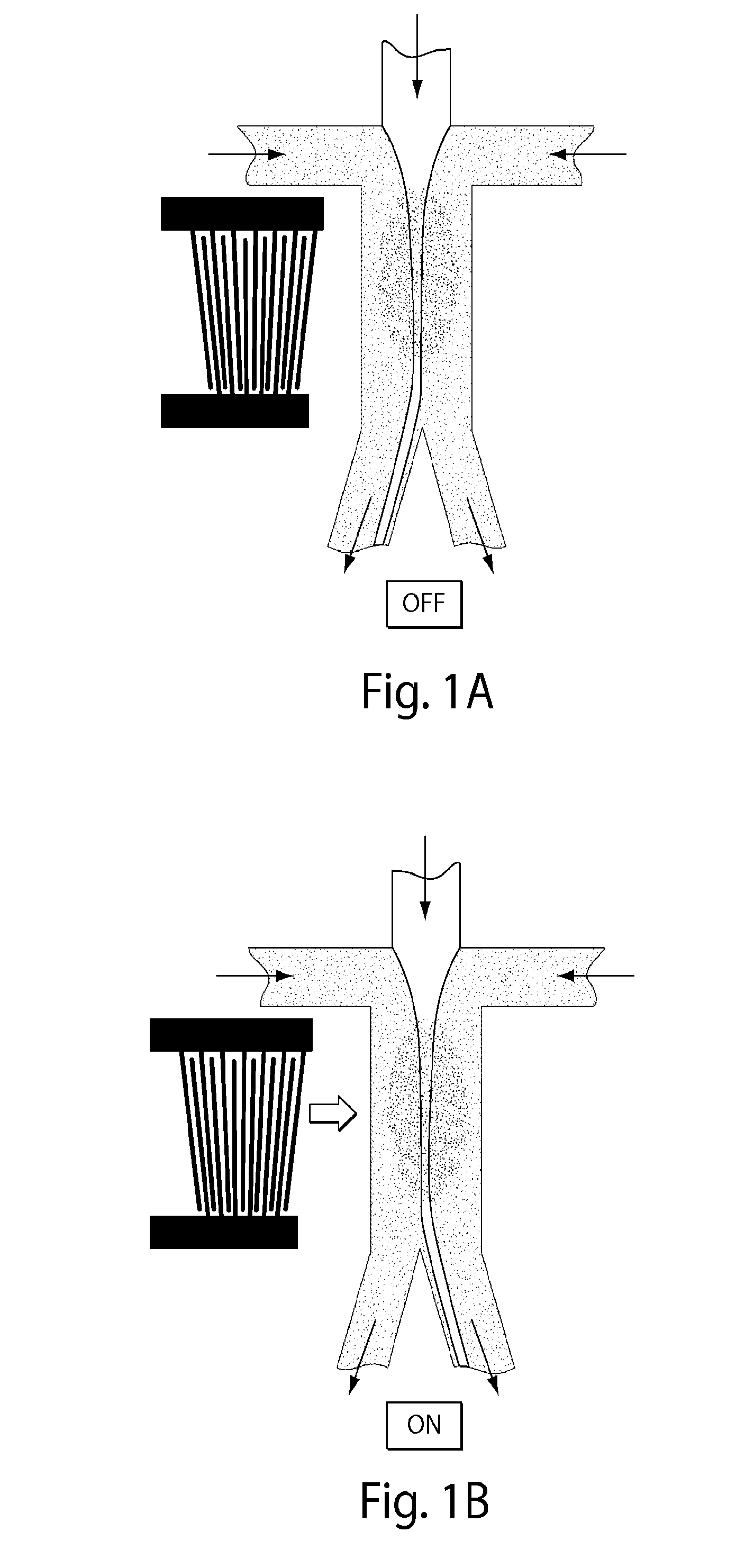
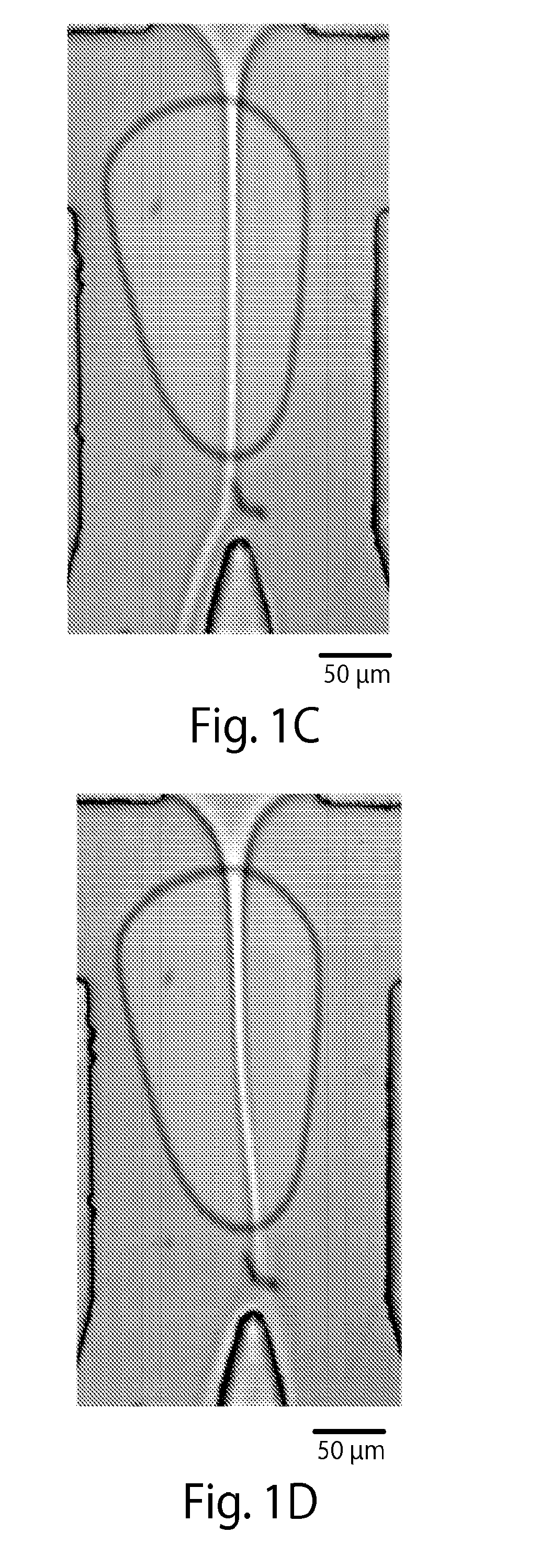
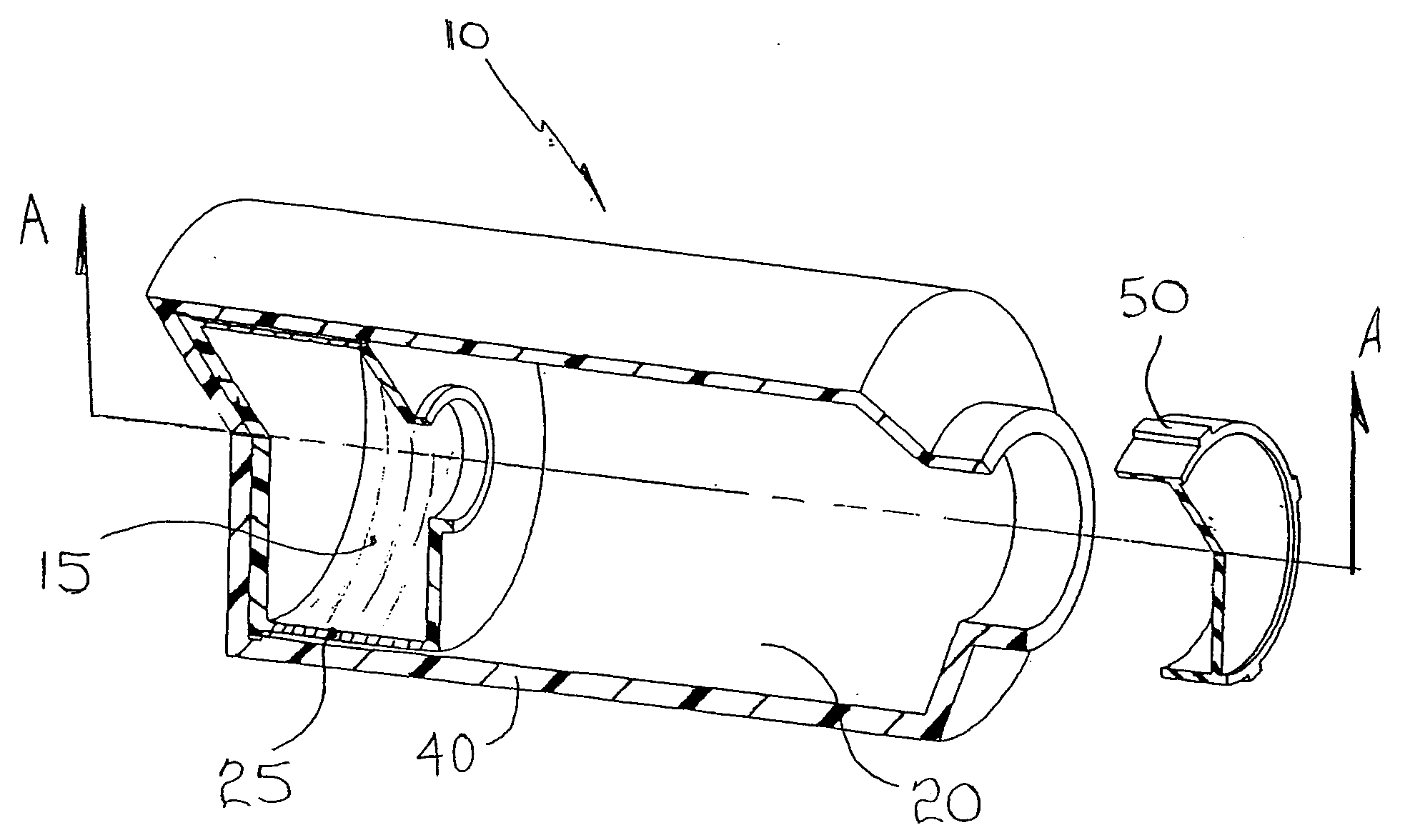
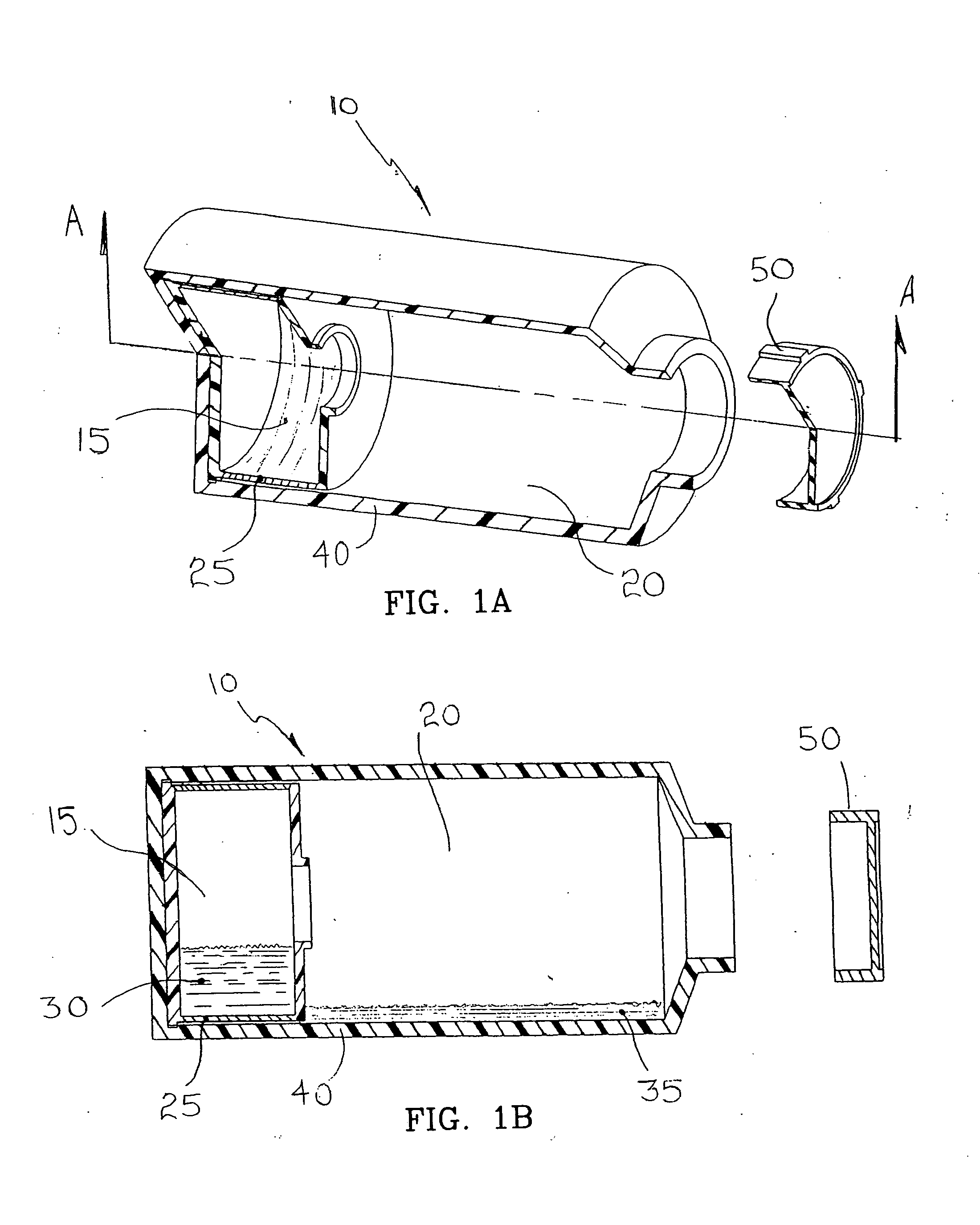
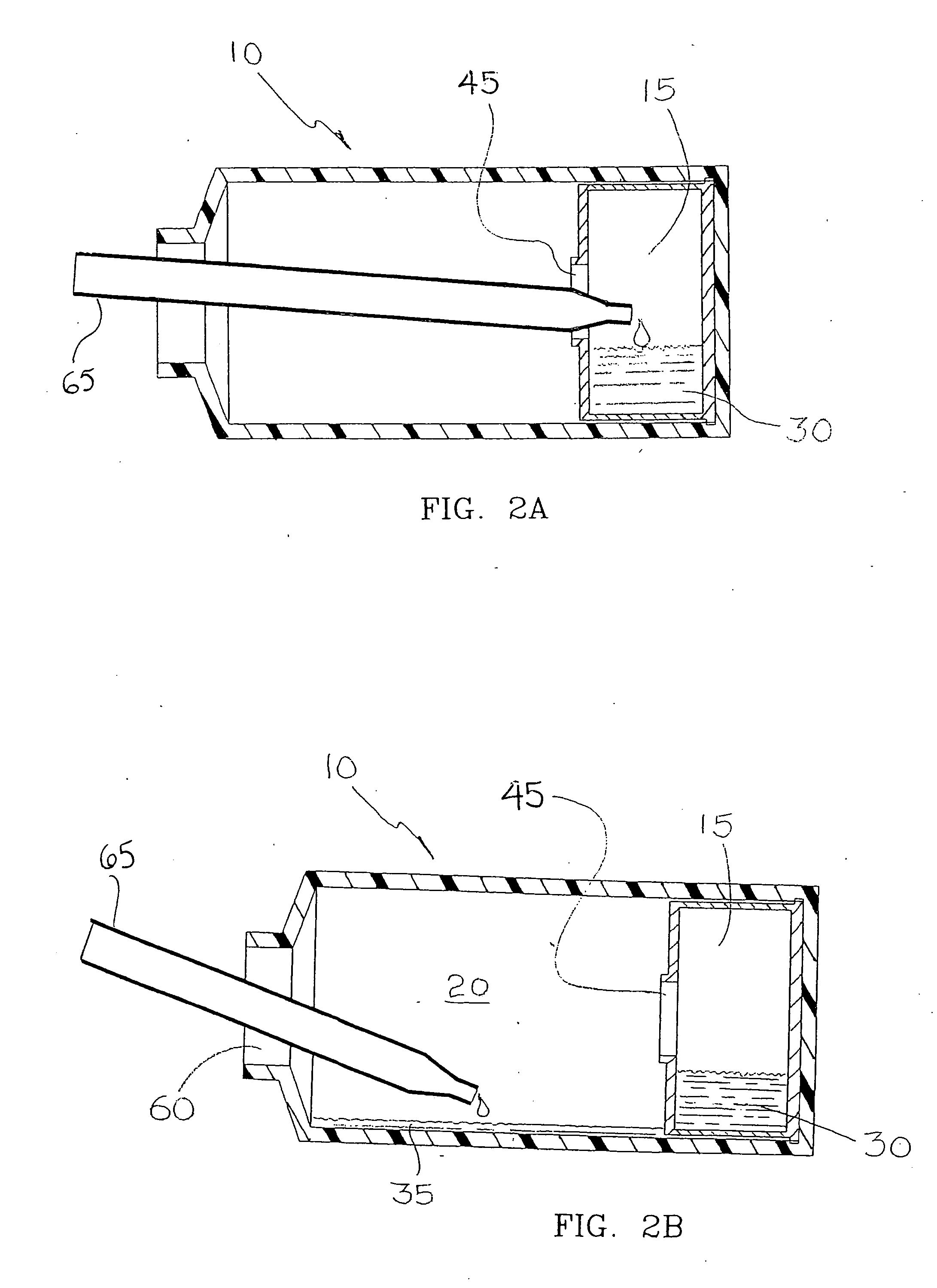
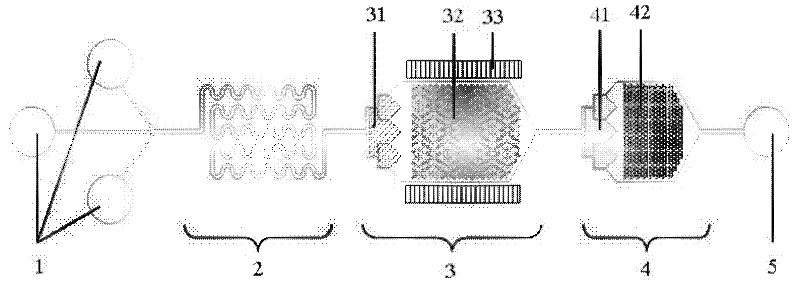
Microfluidic device for the encapsulation of cells with low and high cell densities
ActiveUS20060051329A1Small minimum droplet sizeUniform polymerization timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideHigh cellEngineering
Devices and methods for the encapsulation of cells on microfluidic platforms are disclosed. The microfluidic device generally includes a plurality of functional regions to shear, focus, and encapsulate a desired cell or group of cells into a droplet. The microfluidic device can further comprise a polymerization zone to form a polymer bead around the droplet.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7332303B2Low production costQuality improvementAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHigh cellBiotechnology
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for producing biodiesel using high-cell-density cultivation of microalga Chlorella protothecoides in bioreactor
InactiveUS20090211150A1Reduce acidityAdjust pHFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeHigh cellHigh density
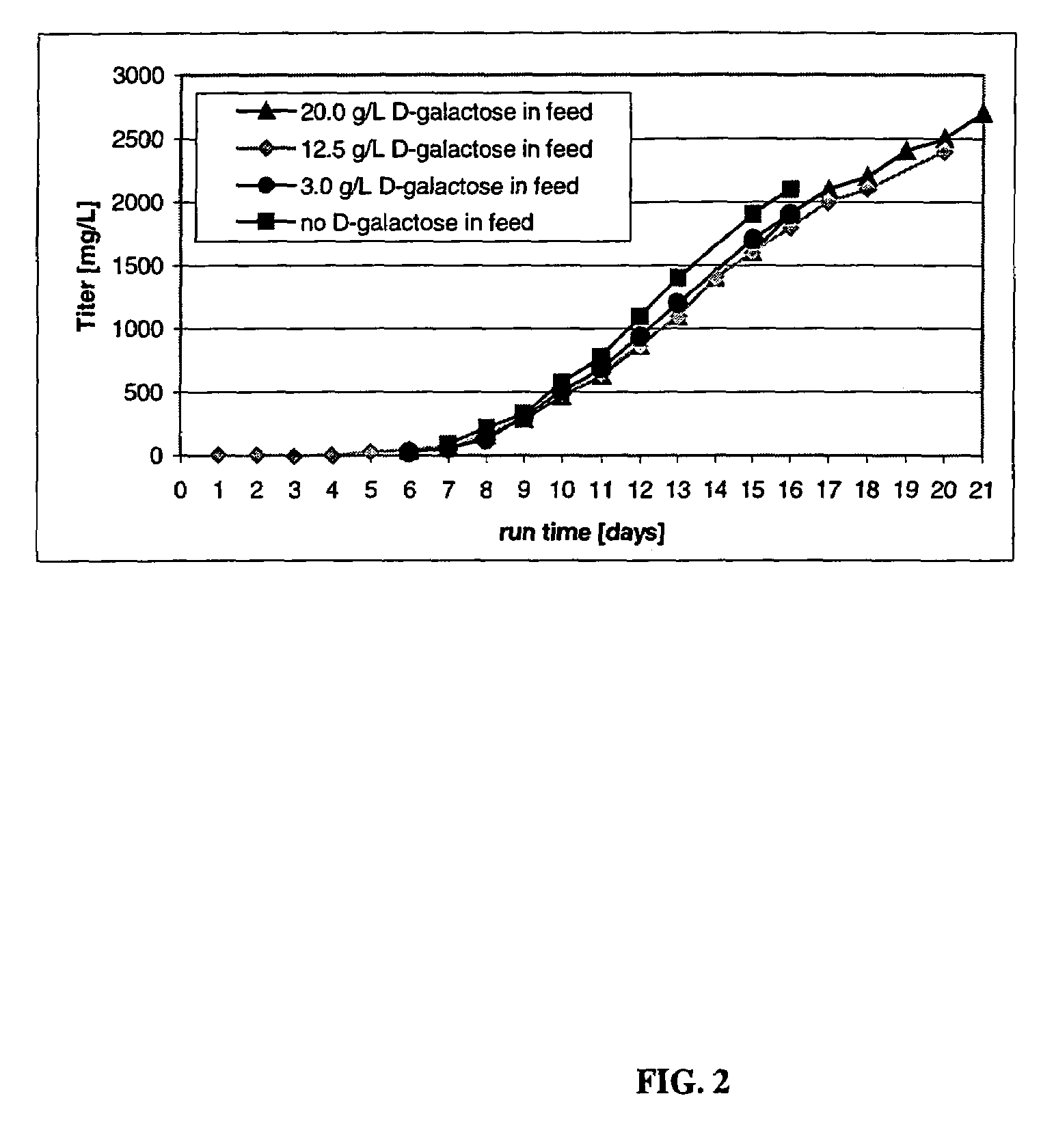
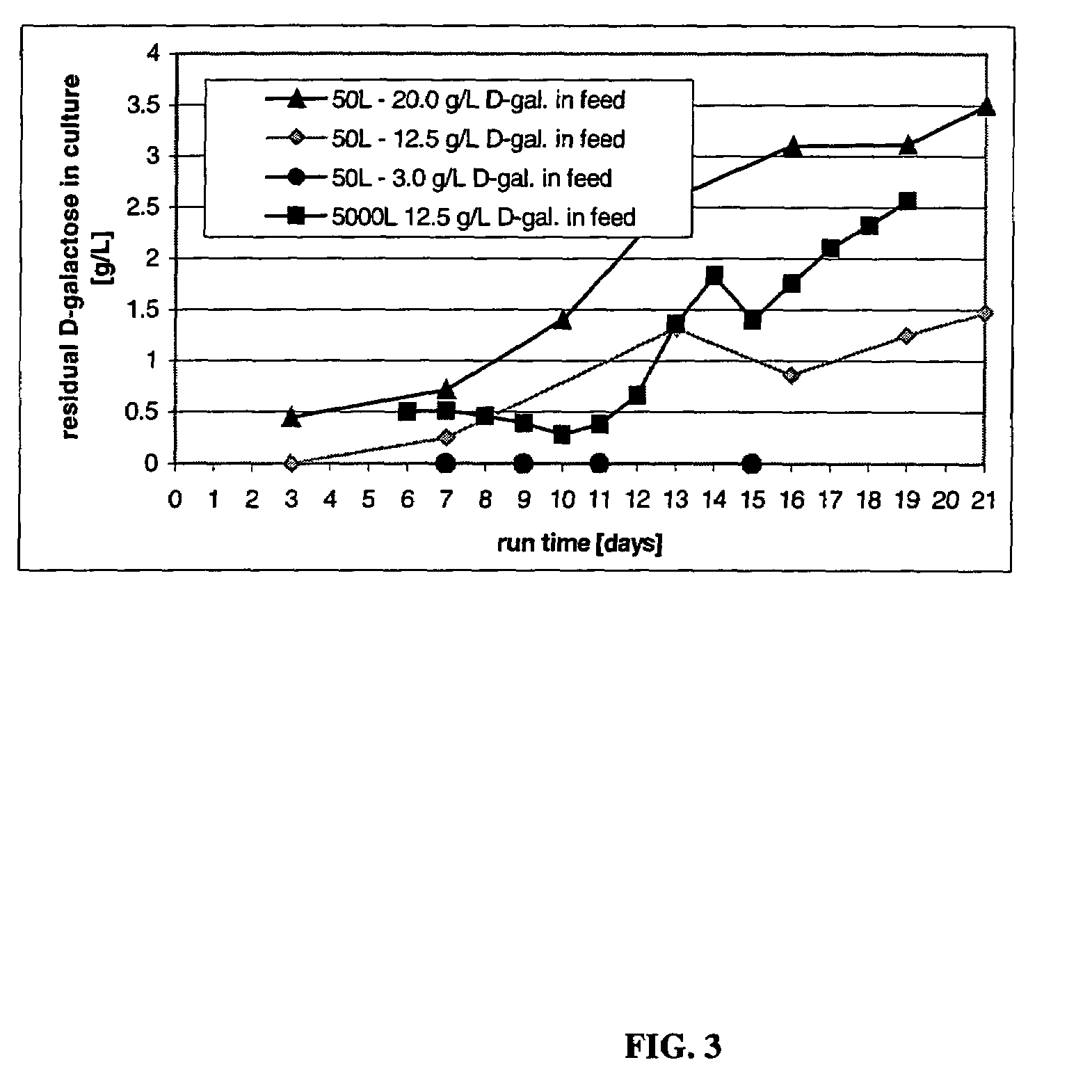
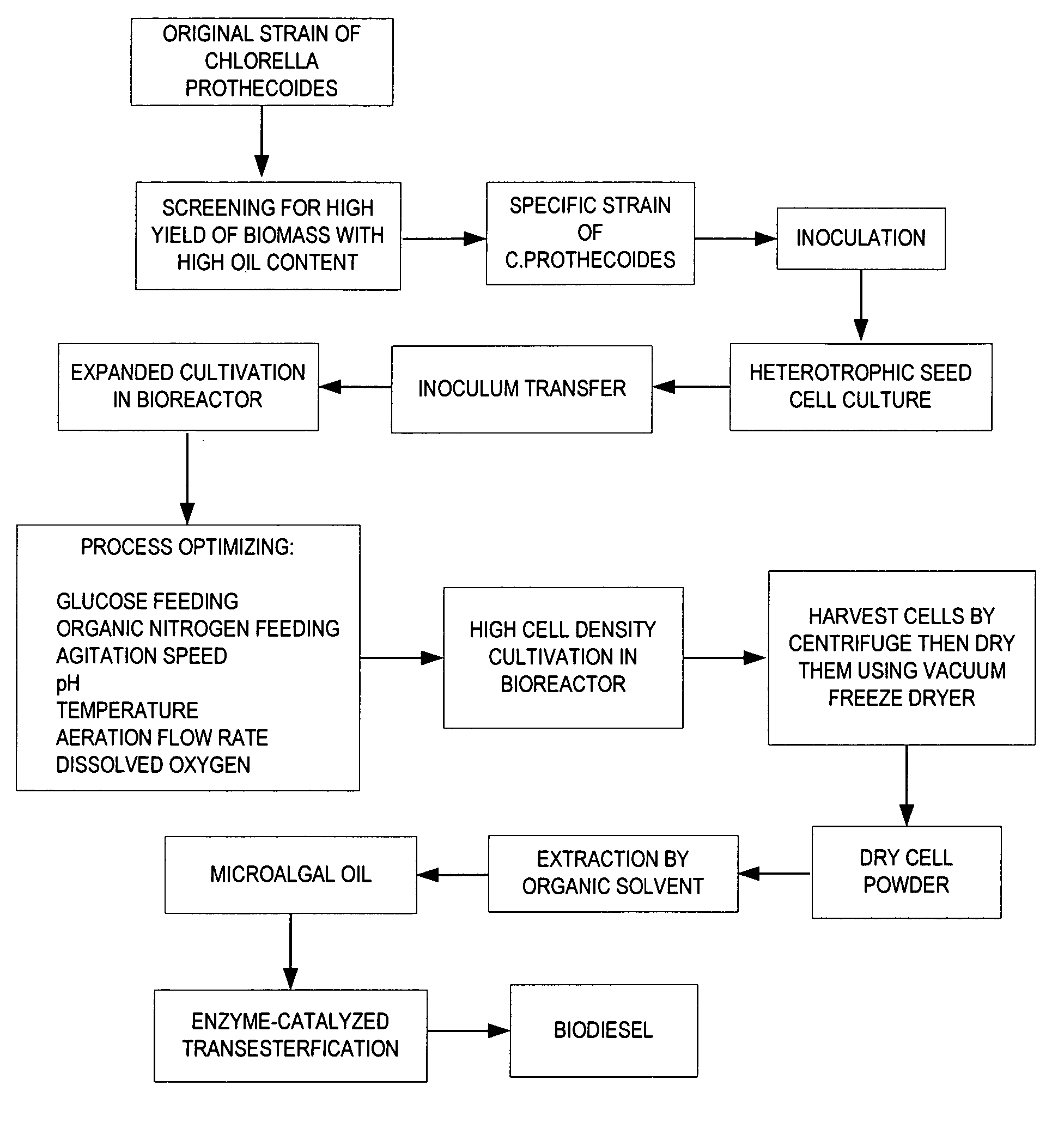
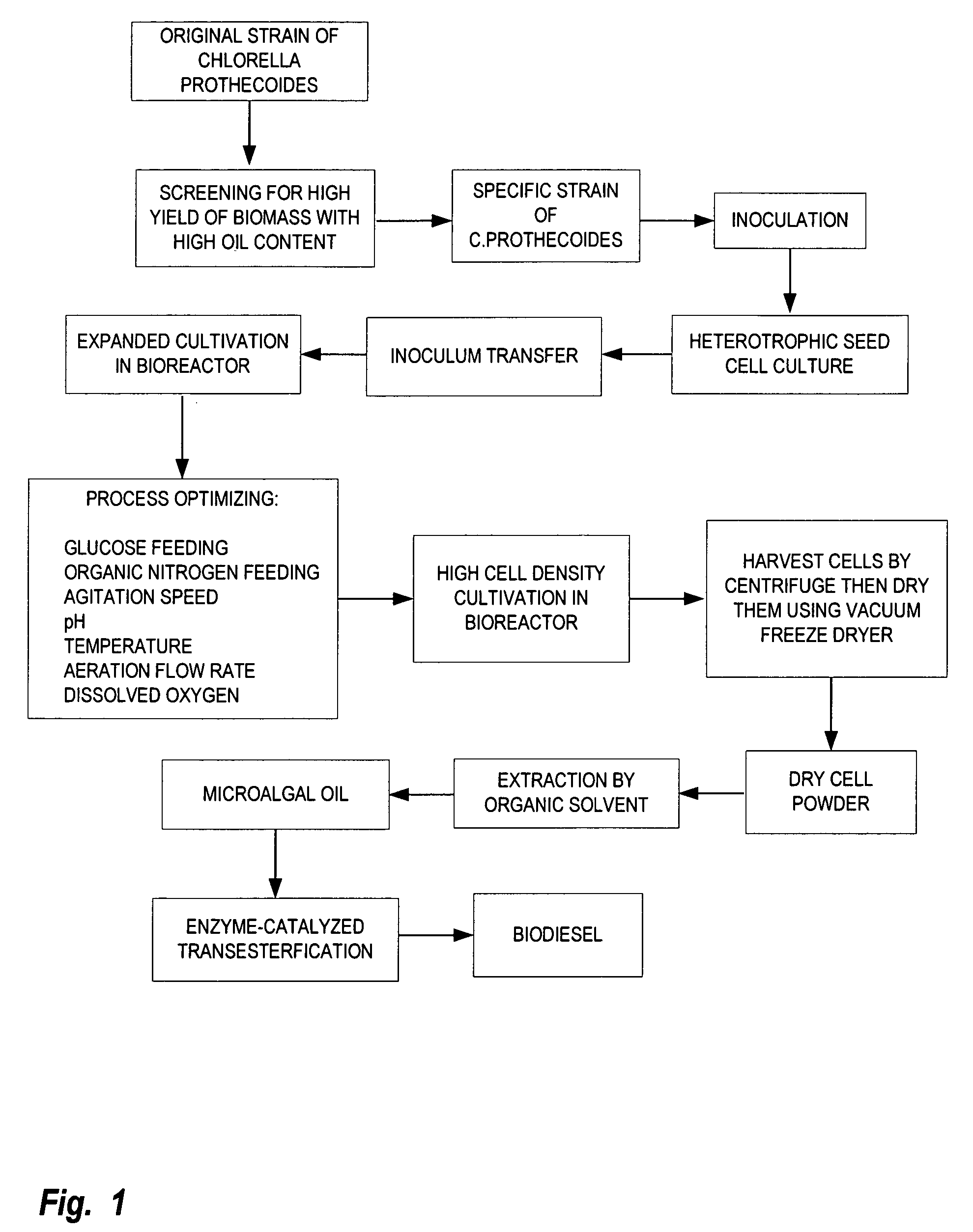
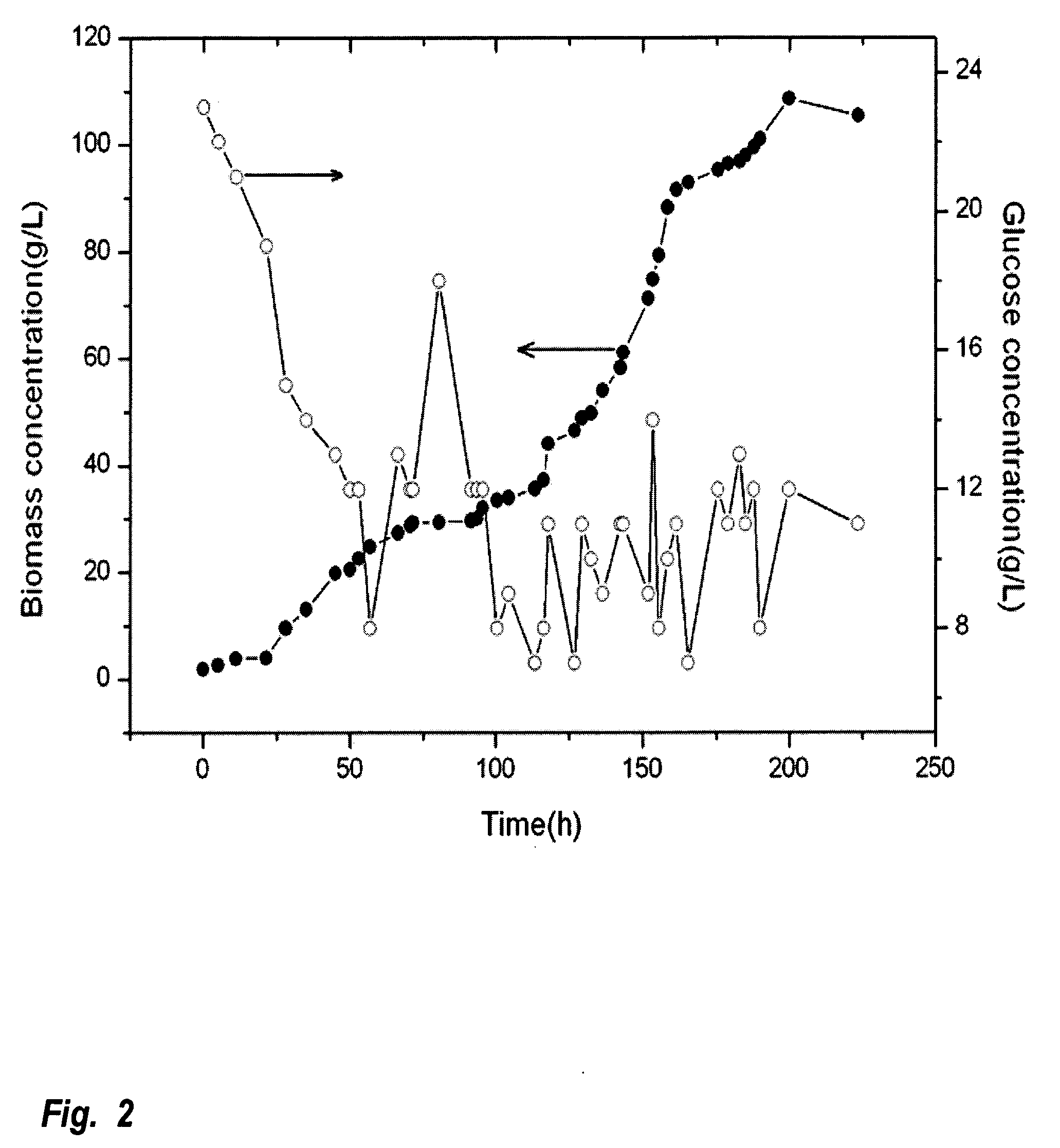
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a strain of microalga chlorella protothecoids, by screening a specific strain with characteristics of high yield of biomass and high oil content, cultivating the screened strain for high-cell-density growth for up to 108 grams of dry cell weight per liter of the suspension in a bioreactor using solutions containing carbohydrates as feed, harvesting and drying the high density cultivated algal cells to extract oil from the dried algal cells, and producing the biodiesel by reaction of catalyzed transesterification using the extracted oil as feedstock.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
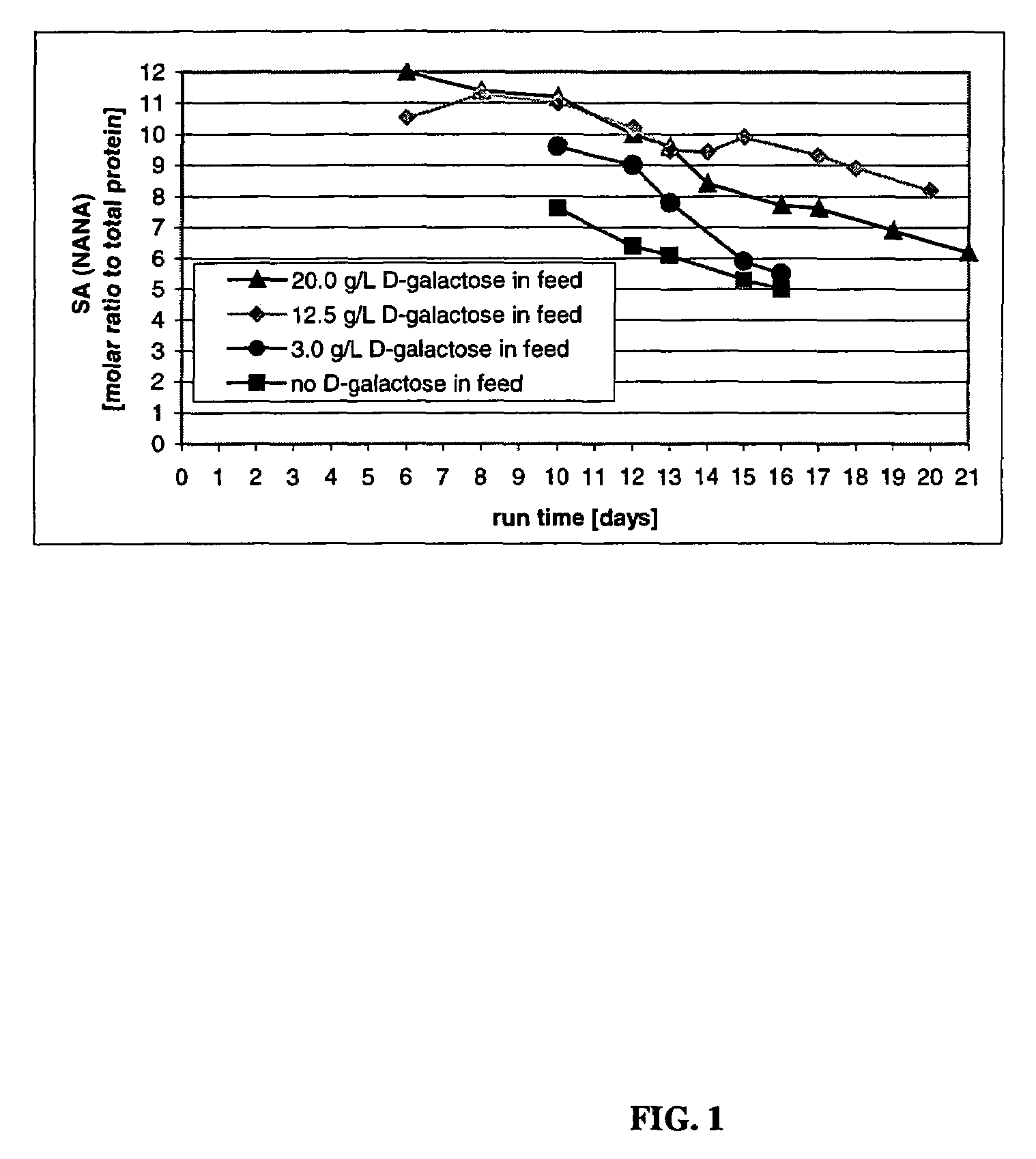
ActiveUS20050084933A1Increased and enhanced sialic acid contentLow production costAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiotechnologyHigh cell
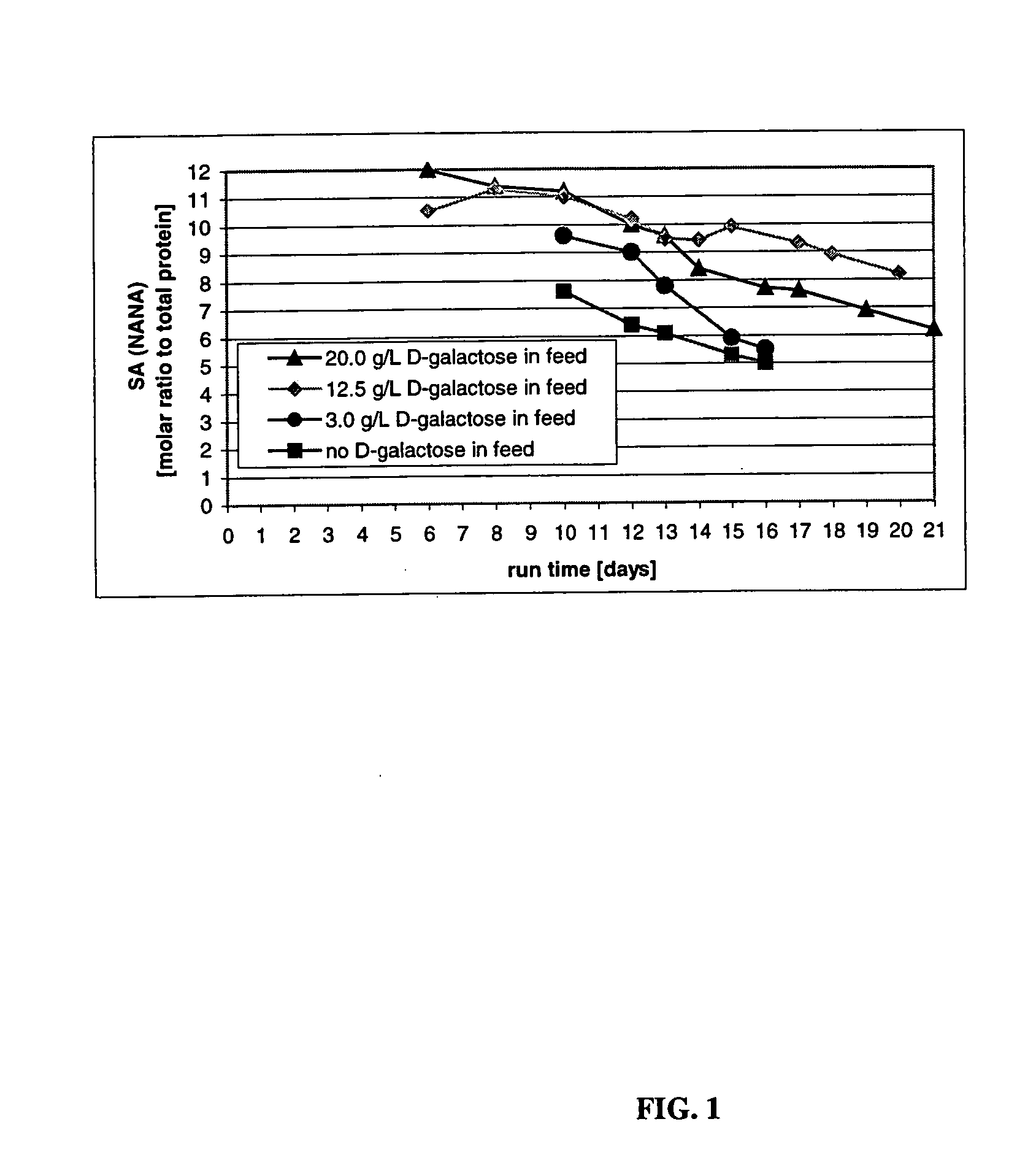
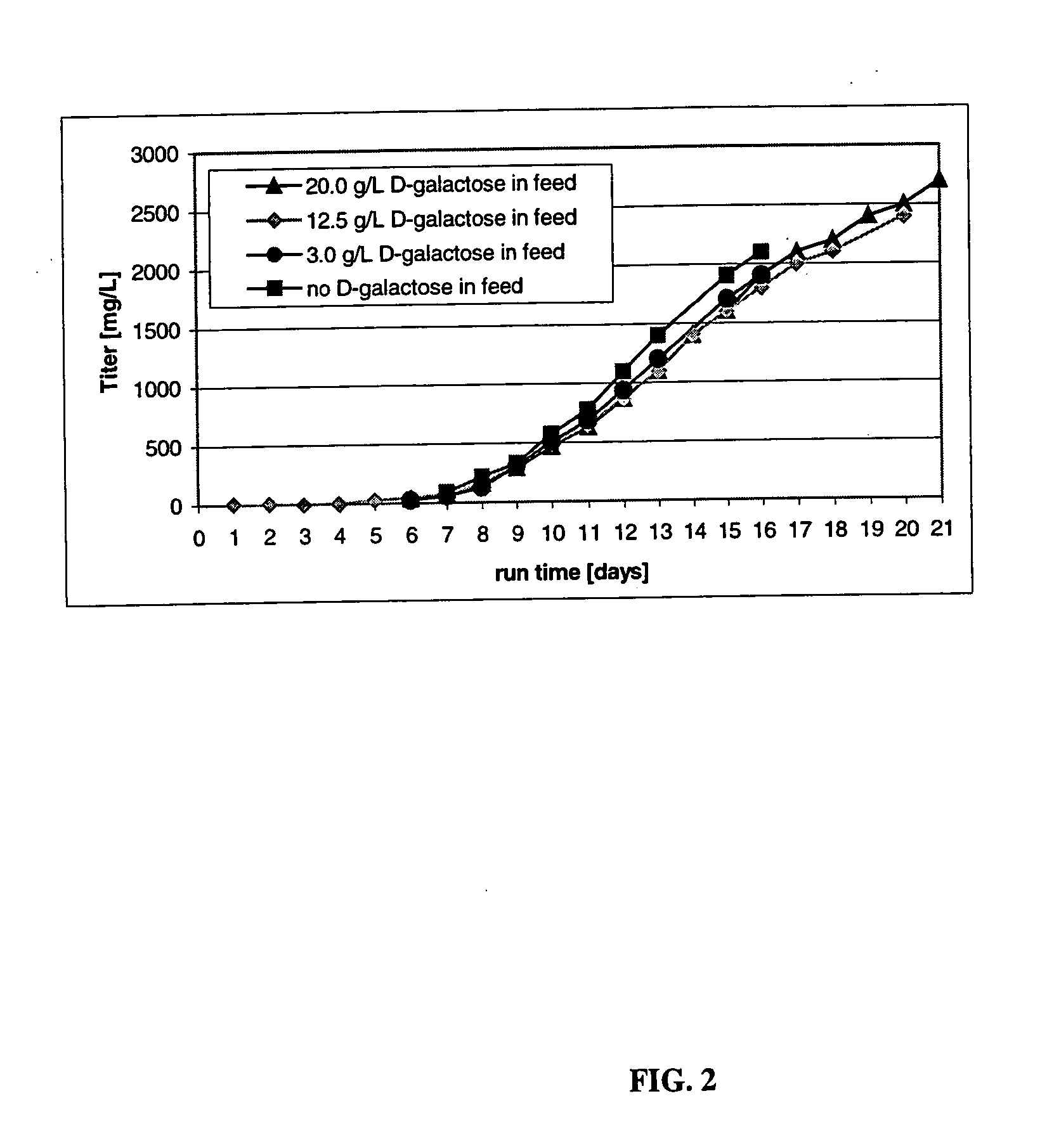
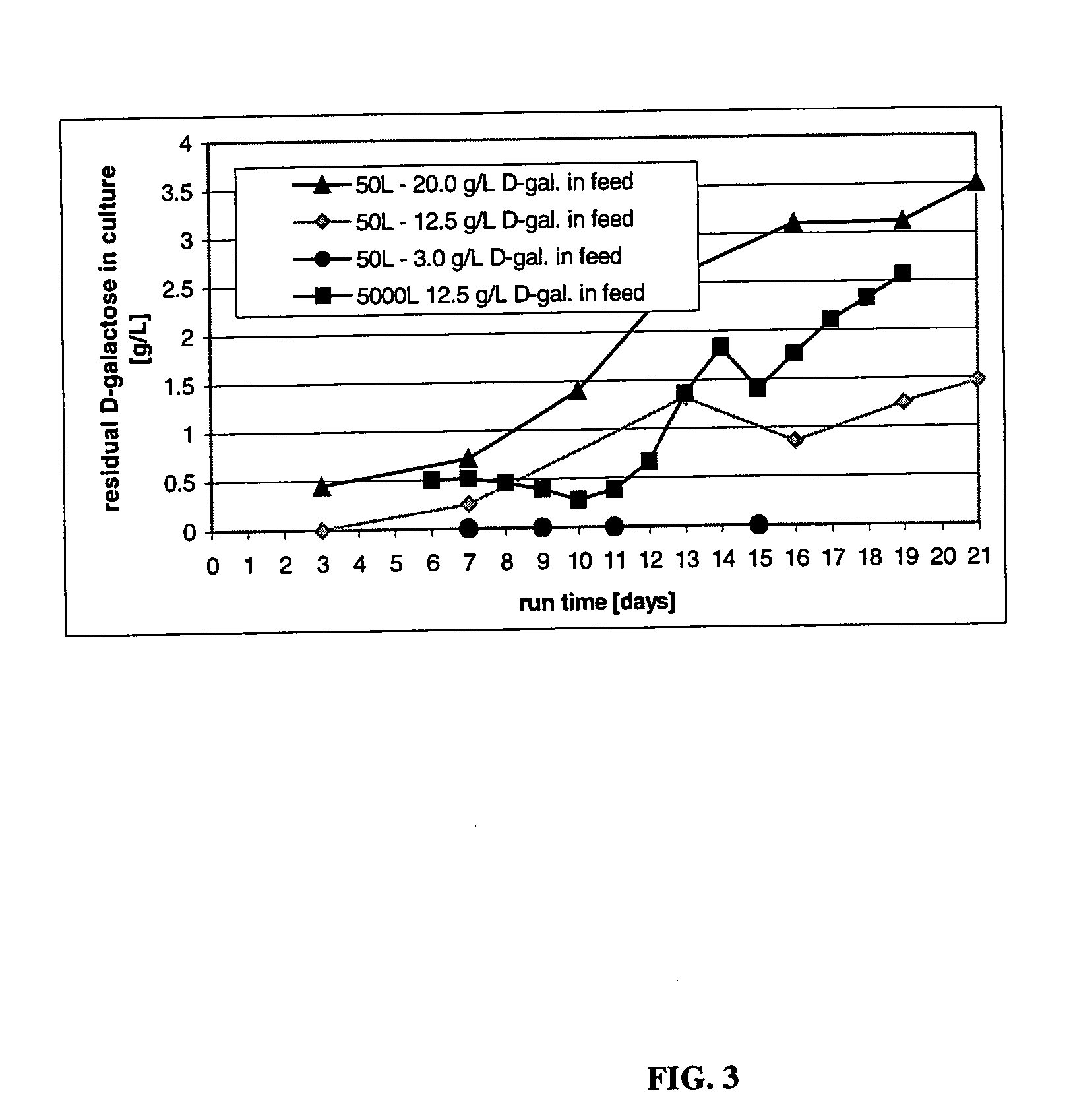
The present invention describes methods and processes for the production of proteins, particularly glycoproteins, by animal cell or mammalian cell culture, illustratively, but not limited to, fed-batch cell cultures. The methods comprise feeding the cells with D-galactose, preferably with feed medium containing D-galactose, preferably daily, to sustain a sialylation effective level of D-galactose in the culture for its duration, thus increasing sialylation of the produced proteins. The methods can also comprise at least two temperature shifts performed during the culturing period, in which the temperature is lower at the end of the culturing period than at the time of initial cell culture. The cell culture processes of the invention involving two or more temperature shifts sustain a high cell viability, and can allow for an extended protein production phase. The methods can also comprise the delayed addition of polyanionic compound at a time after innoculation. Supplementation of the cultures with D-galactose, preferably in a feed medium, to sustain galactose at sialylation effective levels in the cultures until the end of a culture run reverses a decline in sialylation that accompanies culture scale up, and is advantageous for large scale culturing processes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
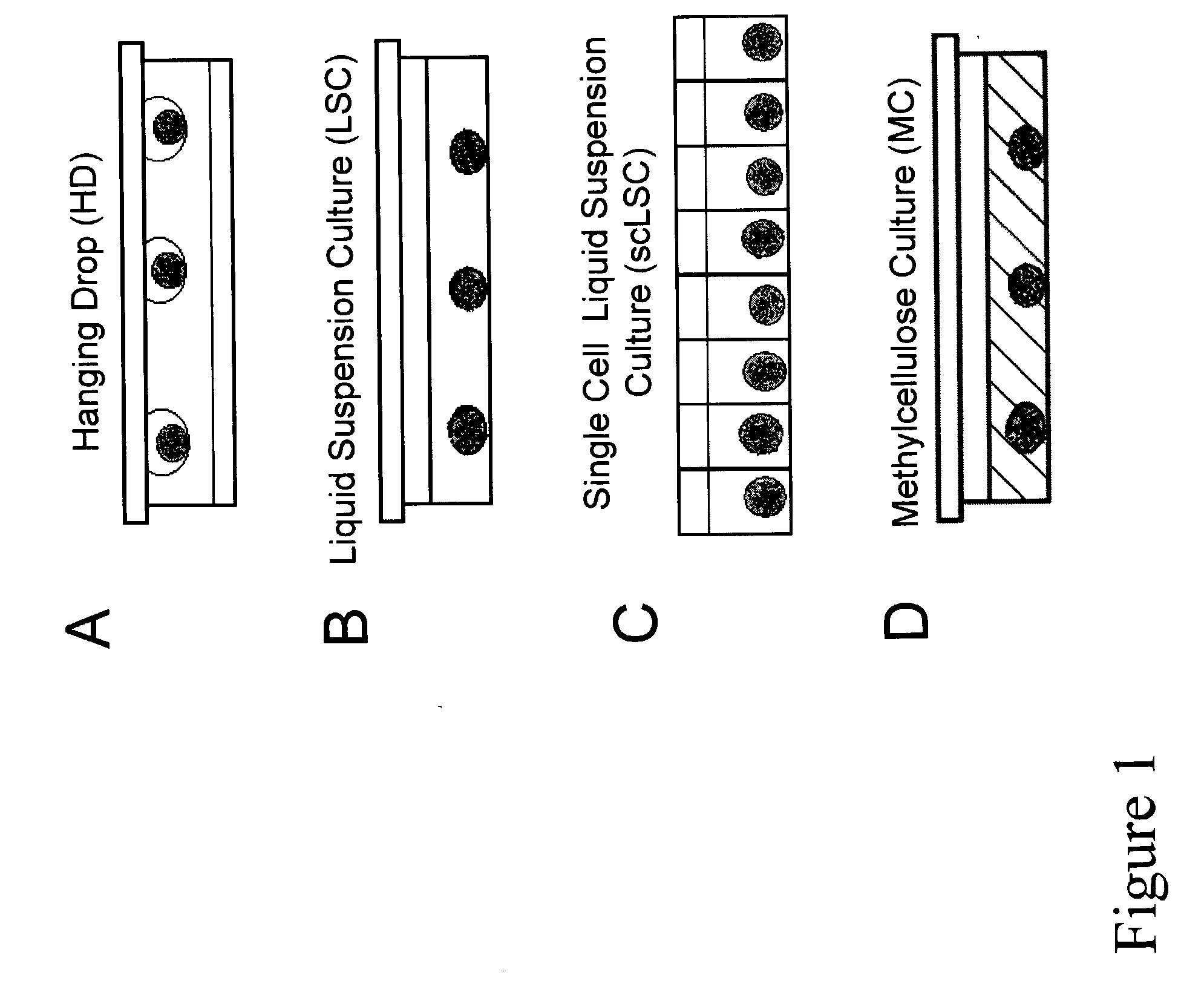
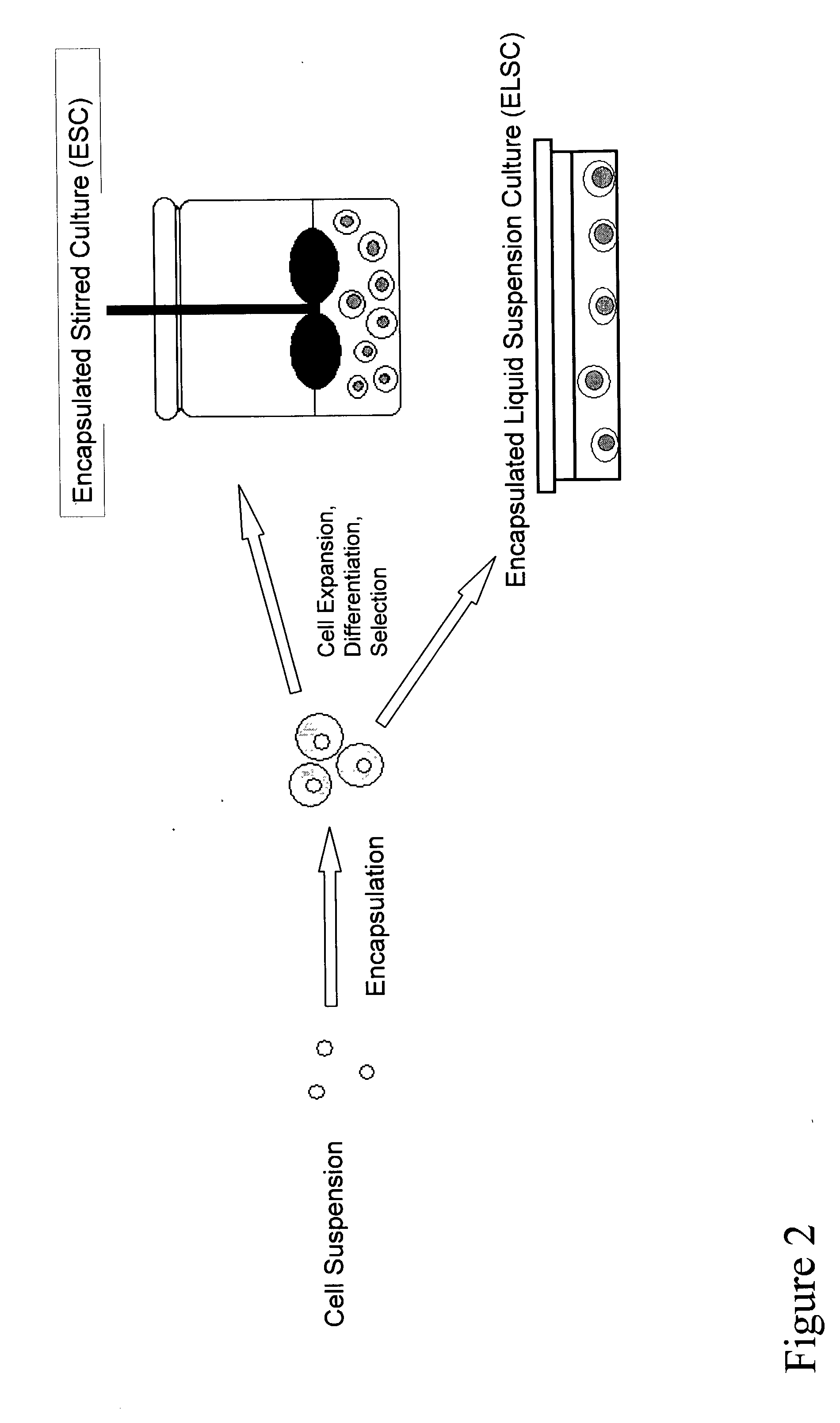
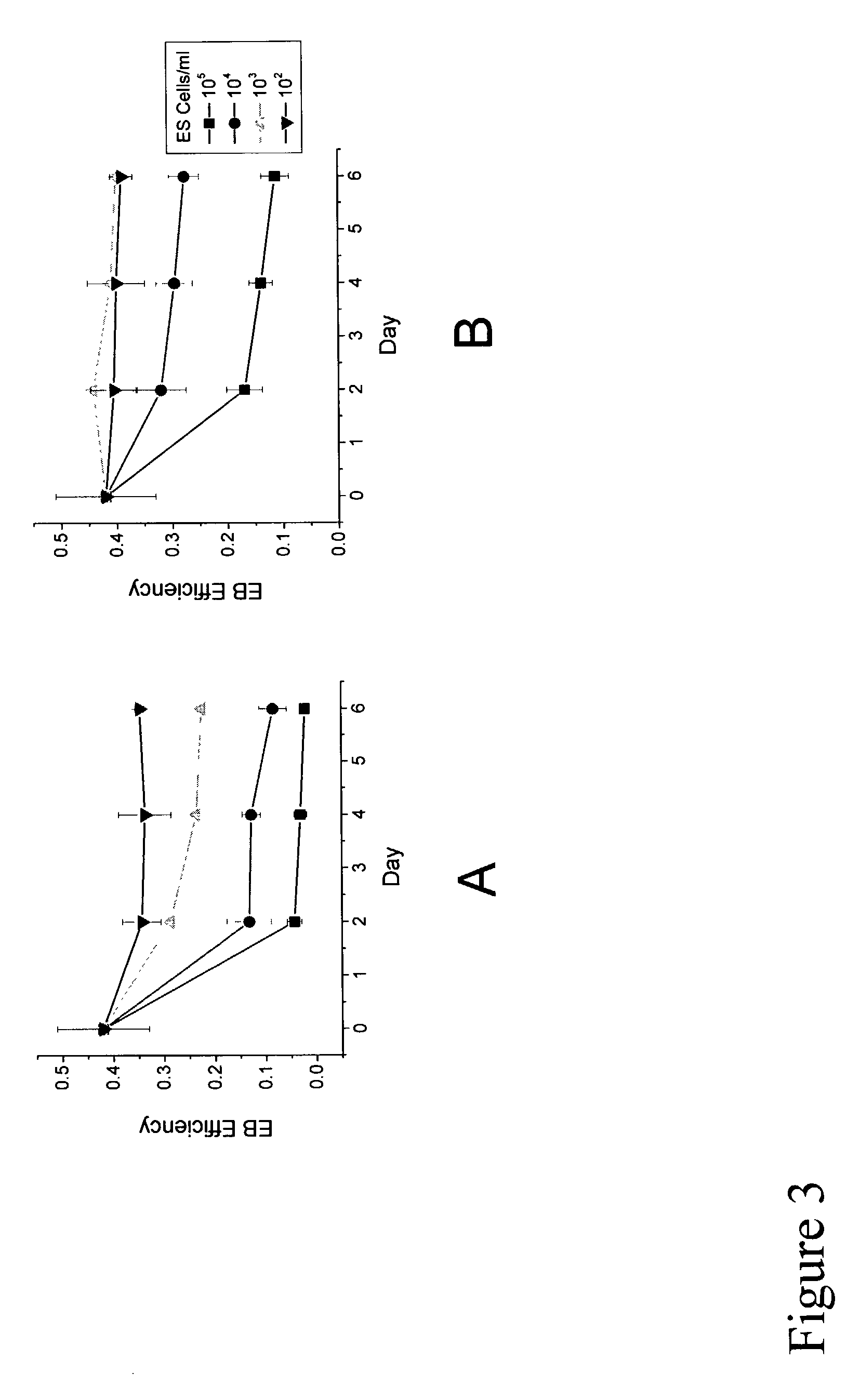
Bioprocess for the generation of cells from spheroid-forming cells
InactiveUS20030119107A1Inhibit aggregationCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusHigh cellVolumetric Mass Density
The present inventors identified aggregation of embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies (EBs) as the cause of the difficulty in generating large numbers of the embryonic stem cells (ES) cell-derived tissues. To counter this, the invention provides a novel bioprocess where aggregation of spheroid forming cells, such as embryonic stem cells and spheroids, such as EBs is controlled, such as by encapsulation of within a matrix. As a result, EBs can be generated with high efficiency and cultured in high cell density, well-mixed systems. Well-mixed conditions facilitate measurement and control of the bulk media conditions and allow for the use of scalable bioreactor systems for clinical production of tissue. Therefore, the invention enables generation of ES cell-derived tissue on a clinical scale. The invention is also applicable to any spheroid-forming cells and other types of pluripotent cells.
Owner:CARDION AG
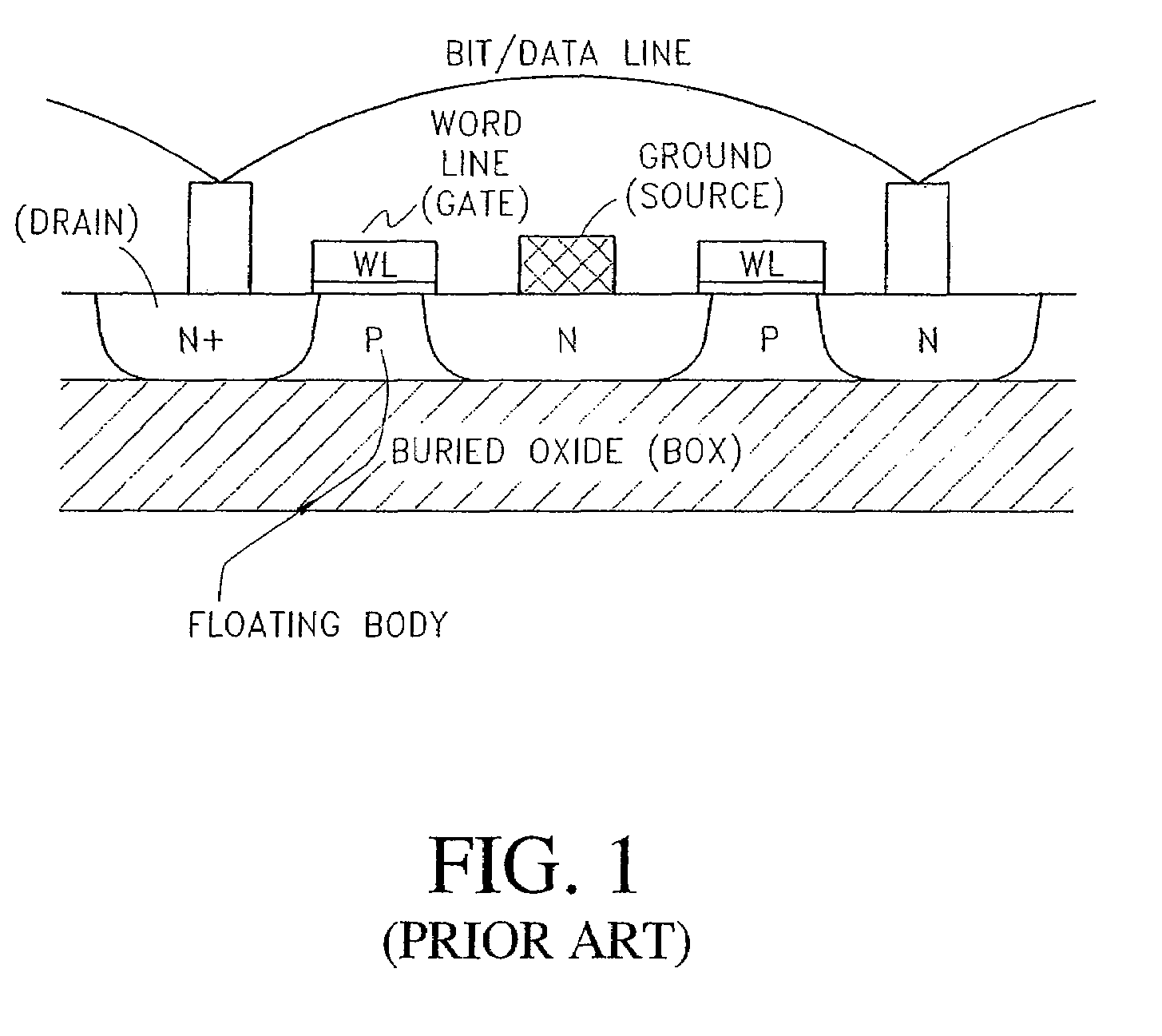
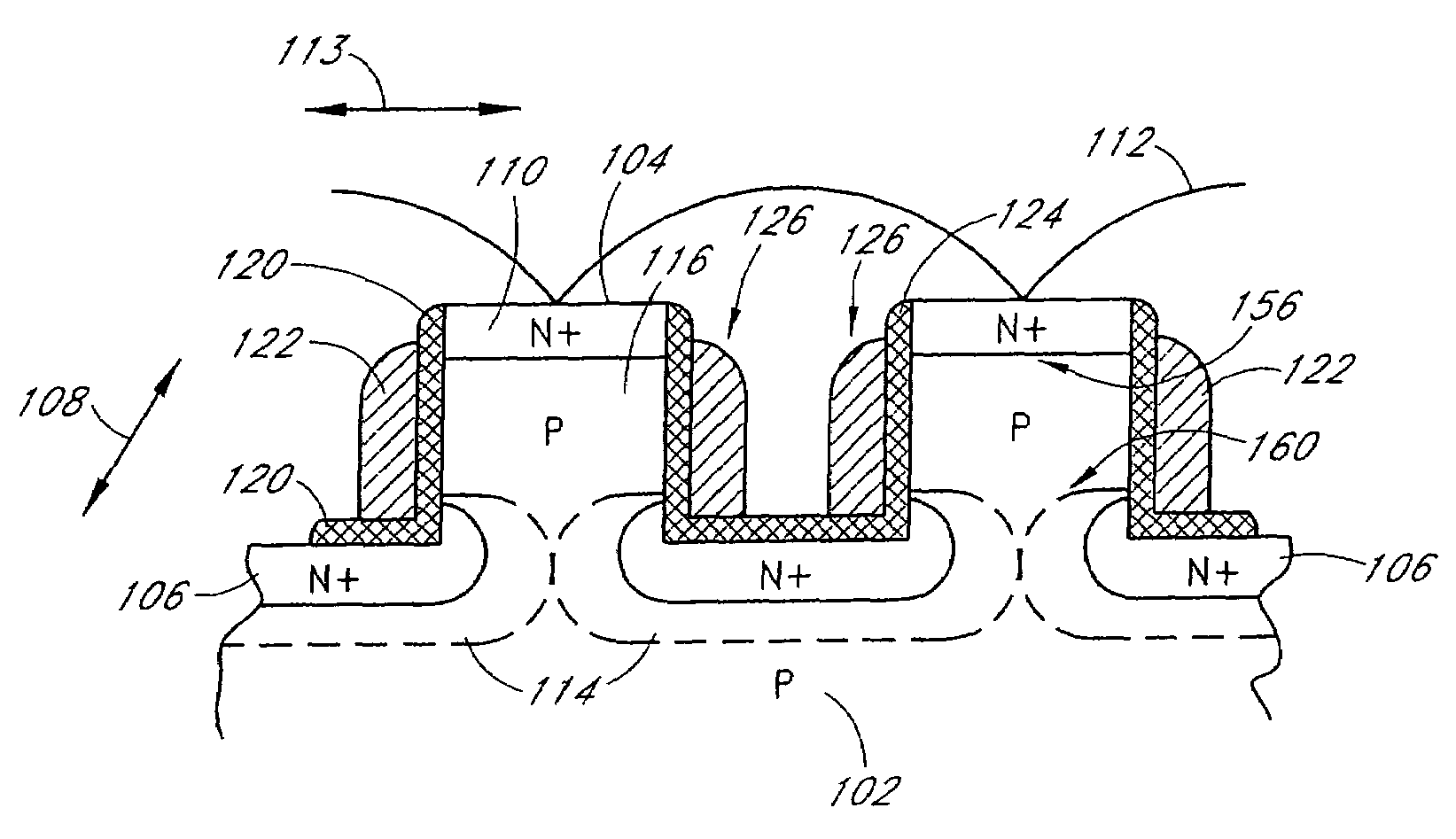
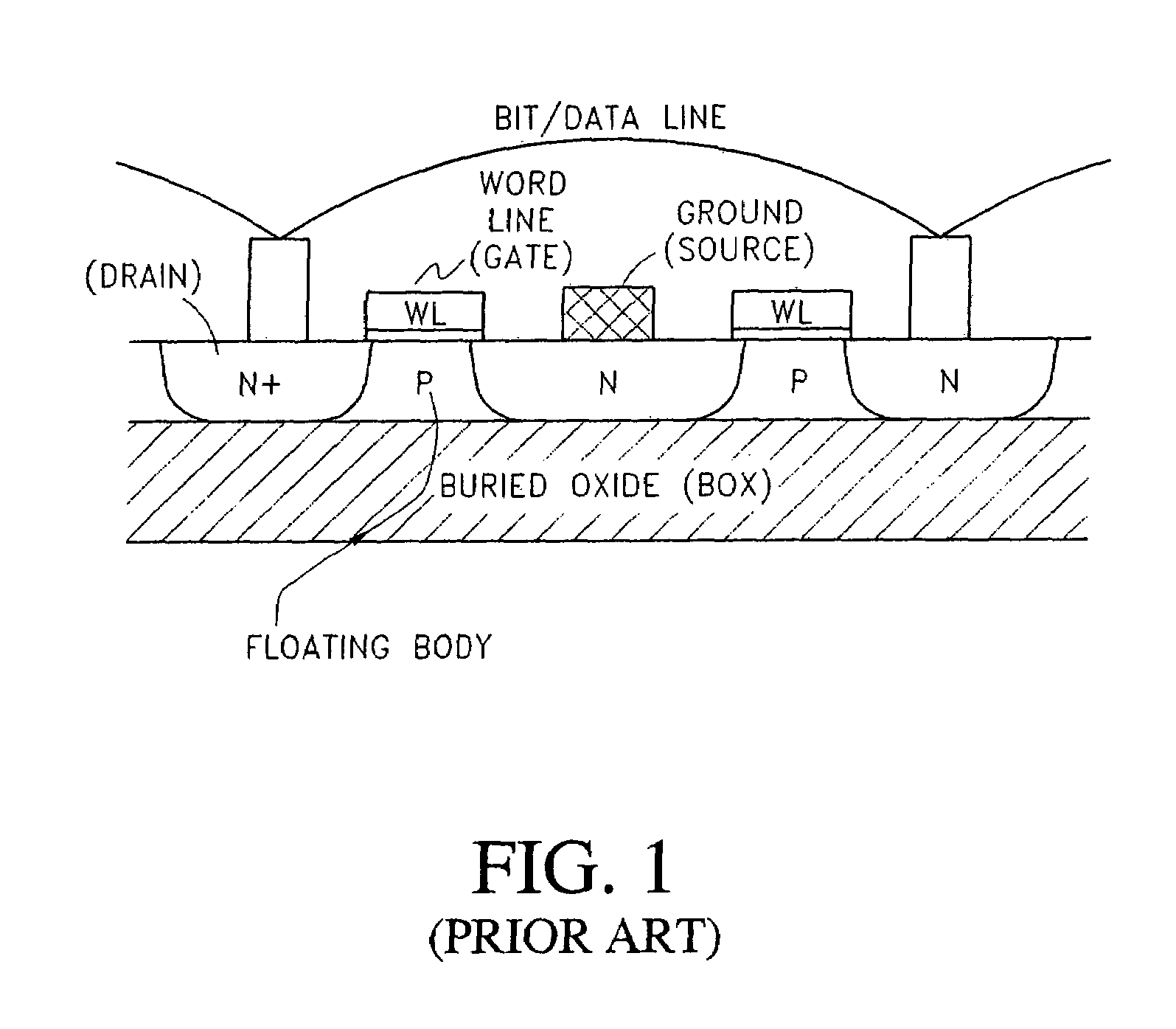
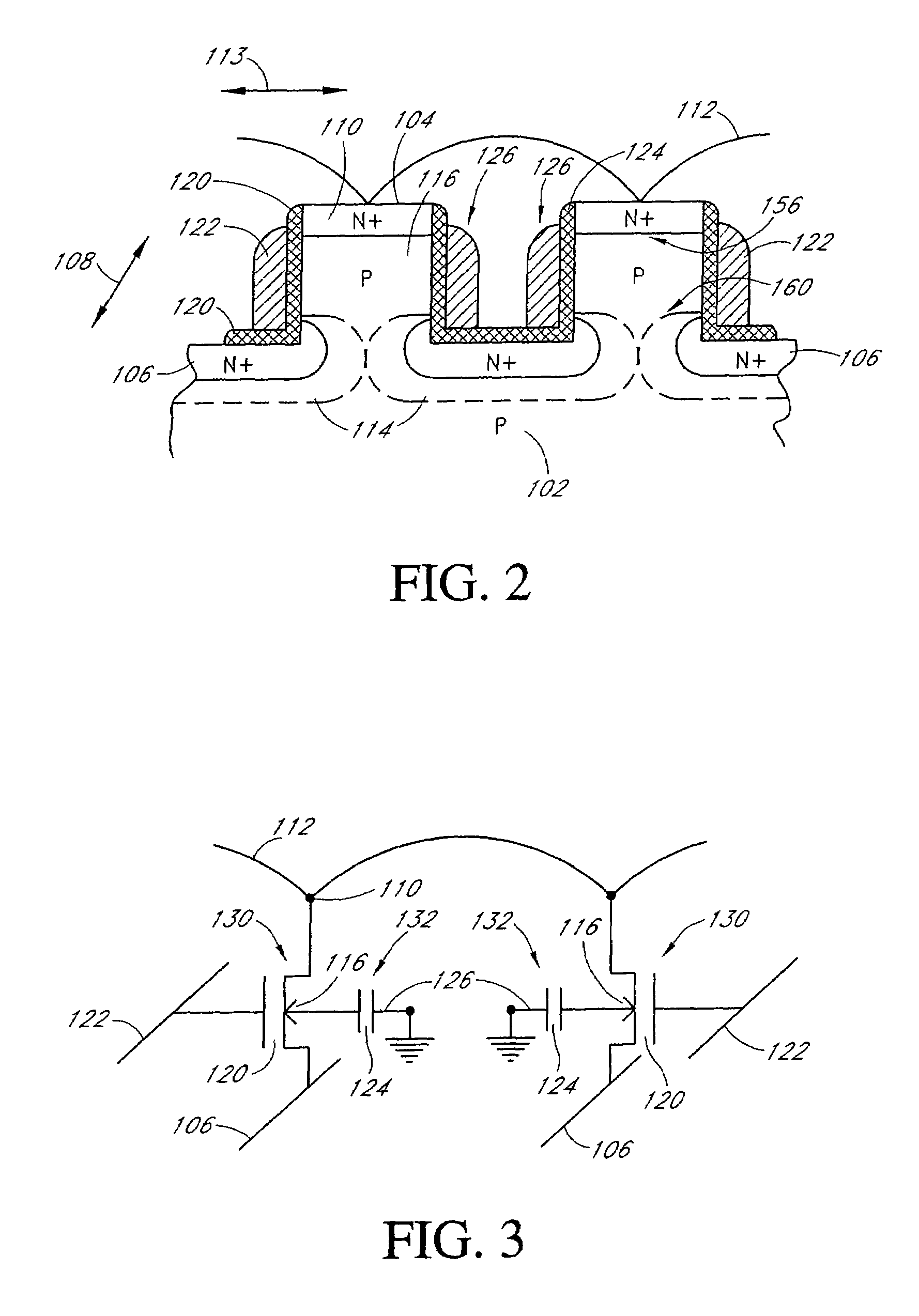
Long retention time single transistor vertical memory gain cell
ActiveUS7271052B1High band gap energyAvoid excessive leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh cellRetention time
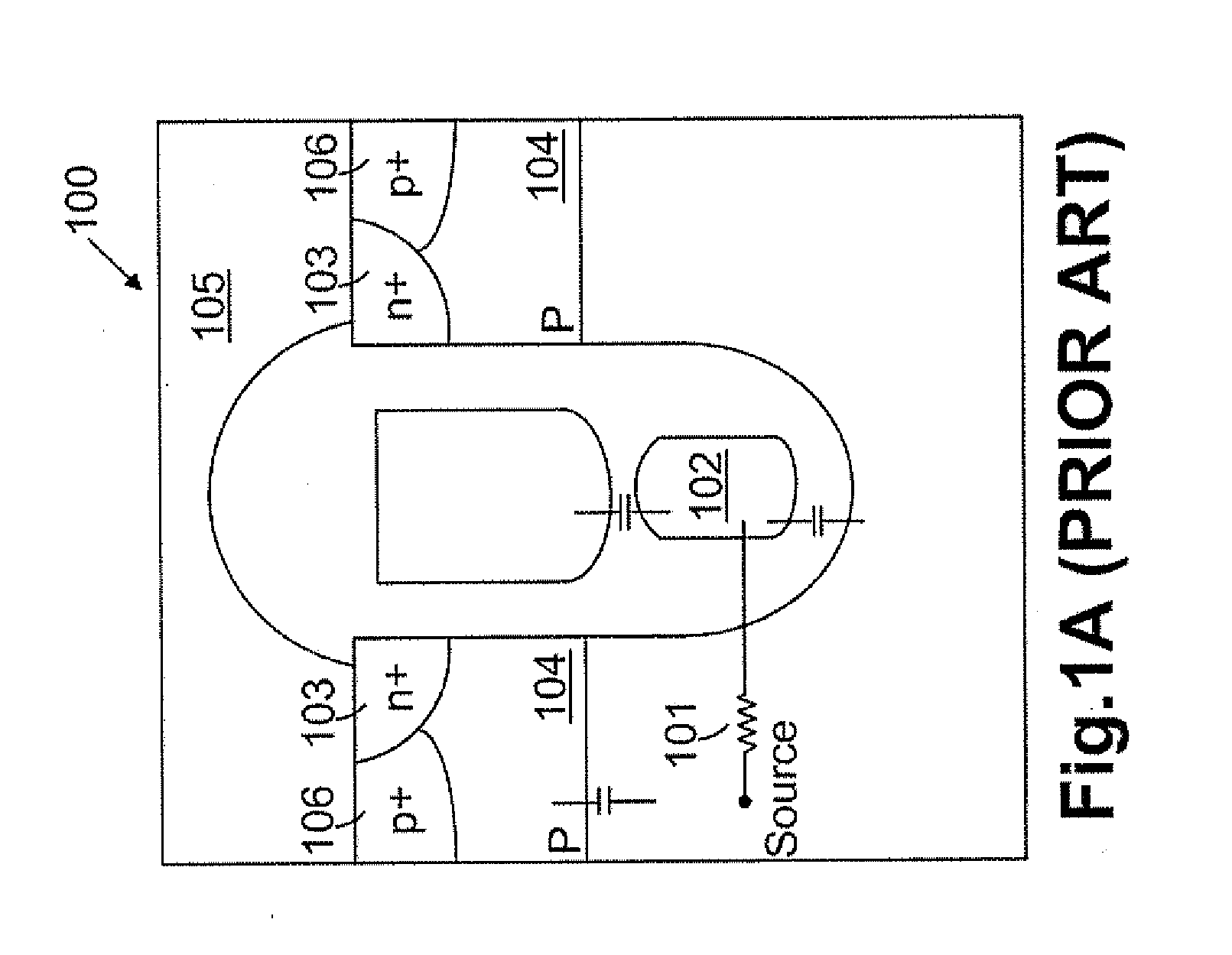
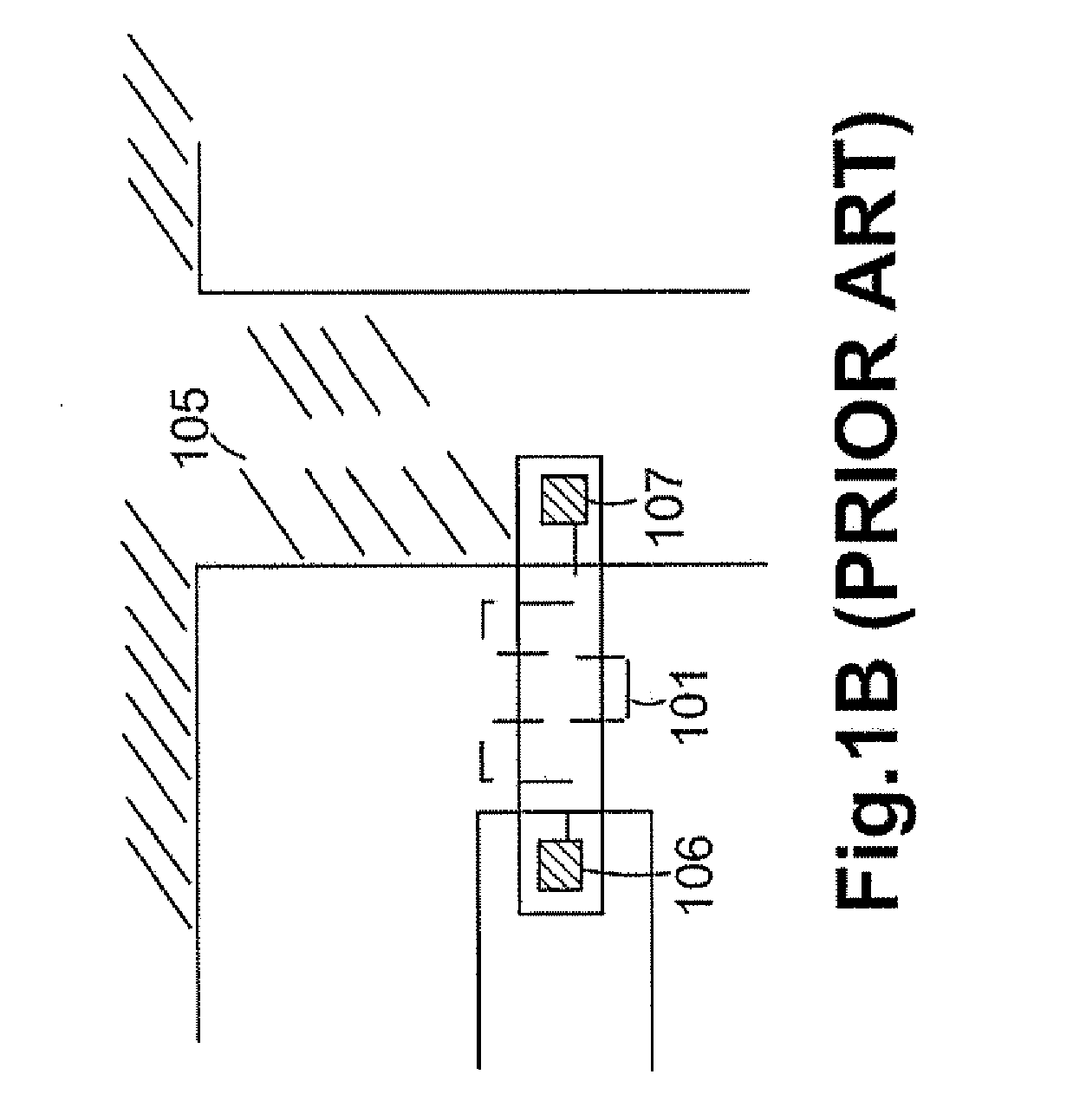
A single transistor vertical memory gain cell with long data retention times. The memory cell is formed from a silicon carbide substrate to take advantage of the higher band gap energy of silicon carbide as compared to silicon. The silicon carbide provides much lower thermally dependent leakage currents which enables significantly longer refresh intervals. In certain applications, the cell is effectively non-volatile provided appropriate gate bias is maintained. N-type source and drain regions are provided along with a pillar vertically extending from a substrate, which are both p-type doped. A floating body region is defined in the pillar which serves as the body of an access transistor as well as a body storage capacitor. The cell provides high volumetric efficiency with corresponding high cell density as well as relatively fast read times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Apparatus and methods for producing and using high-density cells and products therefrom
InactiveUS20060019385A1High densityQuick exchangeAnimal cellsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh cellHigh density
Disclosed and claimed is apparatus and methods for the growth of cells to high density, products therefrom and uses thereof. Also disclosed and claimed is the use of this method for the growth to high-density insect cells, such as the Spodoptera frugiperda Sf900+ cell line (ATCC: CRL 12579). Further disclosed is the infection of Sf900+ cells at high cell density with wild type and recombinant baculoviruses to produce baculovirus and DNA or gene or expression products.
Owner:PROTEIN SCI
Acoustic waves in microfluidics
Various aspects of the present invention relate to the control and manipulation of fluidic species, for example, in microfluidic systems. In one set of embodiments, droplets may be sorted using surface acoustic waves. The droplets may contain cells or other species. In some cases, the surface acoustic waves may be created using a surface acoustic wave generator such as an interdigitated transducer, and / or a material such as a piezoelectric substrate. The piezoelectric substrate may be isolated from the microfluidic substrate except at or proximate the location where the droplets are sorted, e.g., into first or second microfluidic channels. At such locations, the microfluidic substrate may be coupled to the piezoelectric substrate (or other material) by one or more coupling regions. In some cases, relatively high sorting rates may be achieved, e.g., at rates of at least about 1,000 Hz, at least about 10,000 Hz, or at least about 100,000 Hz, and in some embodiments, with high cell viability after sorting.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Compartmentalized device for cell culture, cell processing, and sample dialysis
ActiveUS20050101009A1More efficient dialysis of laboratory samplesImprove concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh cellVolumetric Mass Density
A versatile compartmentalized cell culture device, with a selectively permeable membrane separating the compartments, provides many attributes relative to traditional devices. It can be configured for high-density cell culture, co-culture, and sample dialysis while rolling or standing still. It can also be configured for continuous movement of liquid between compartments. The wide combination of attributes not found in other membrane based cell culture and bioprocessing devices includes more cell capacity, more cell secreted product capacity, higher cell and product density, increased medium capacity, minimized use of exogenous growth factors, compatibility with standard cell culture equipment and protocols, increased scale up efficiency, capacity to function when rolling or standing still, capacity for perfusion without the need for pumps, and more efficient sample dialysis.
Owner:WHEATON INDS
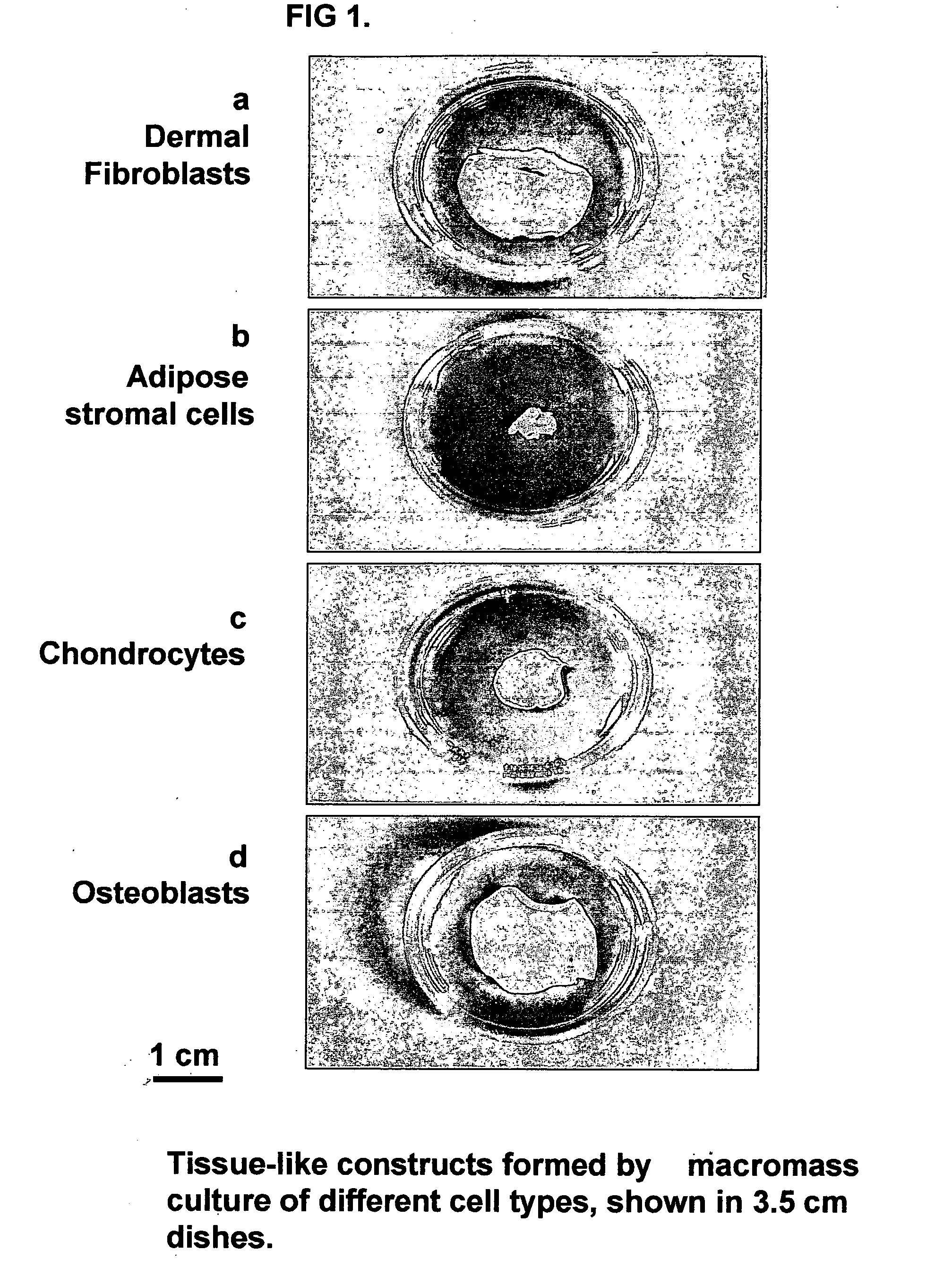
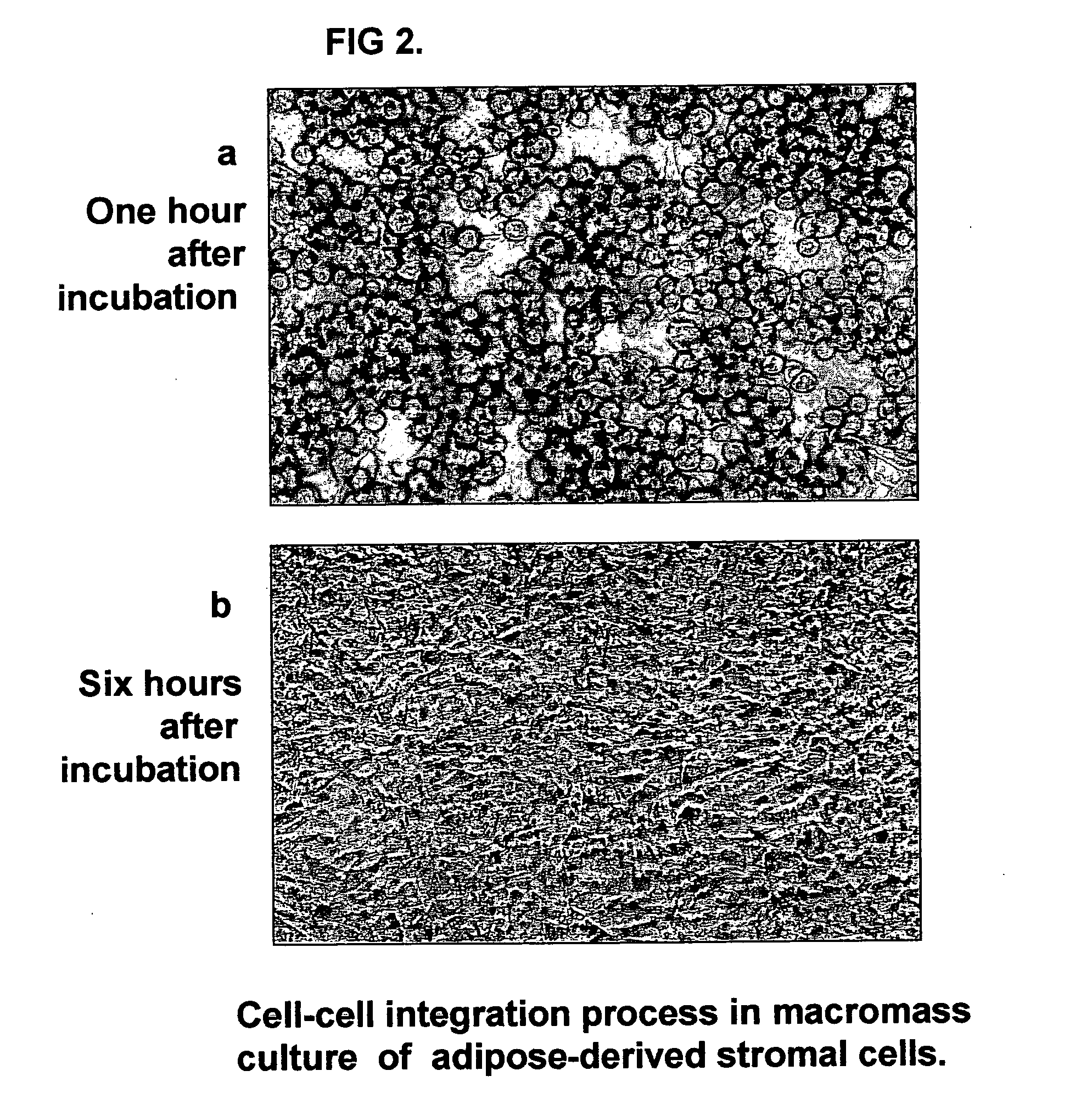
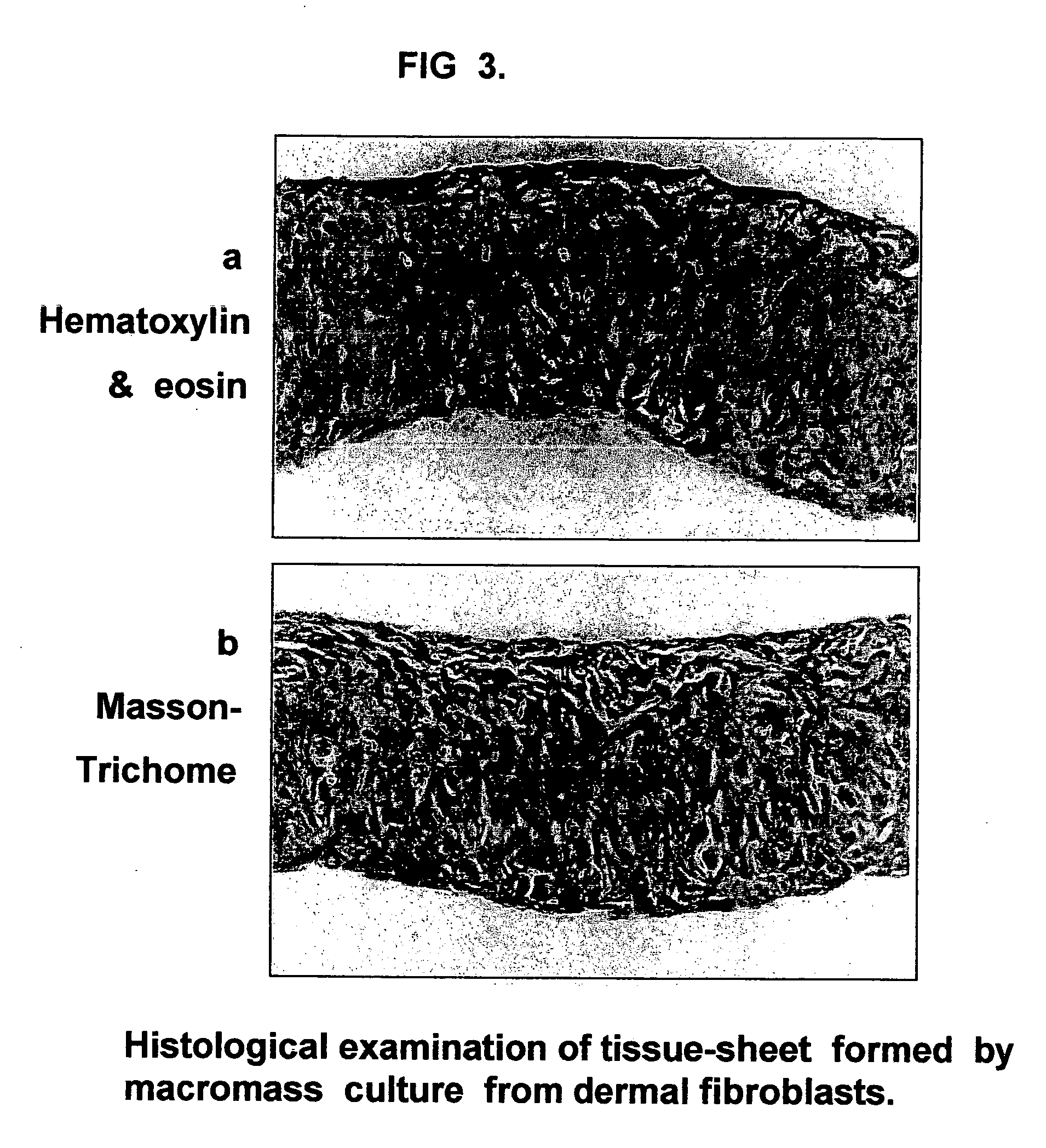
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
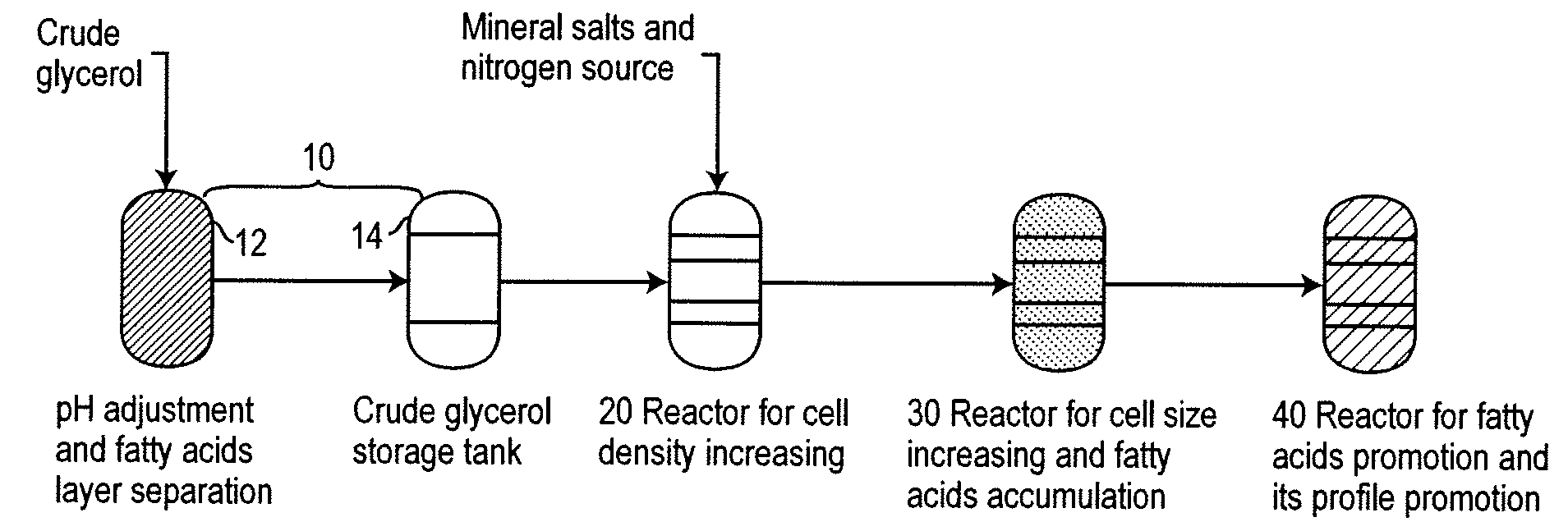
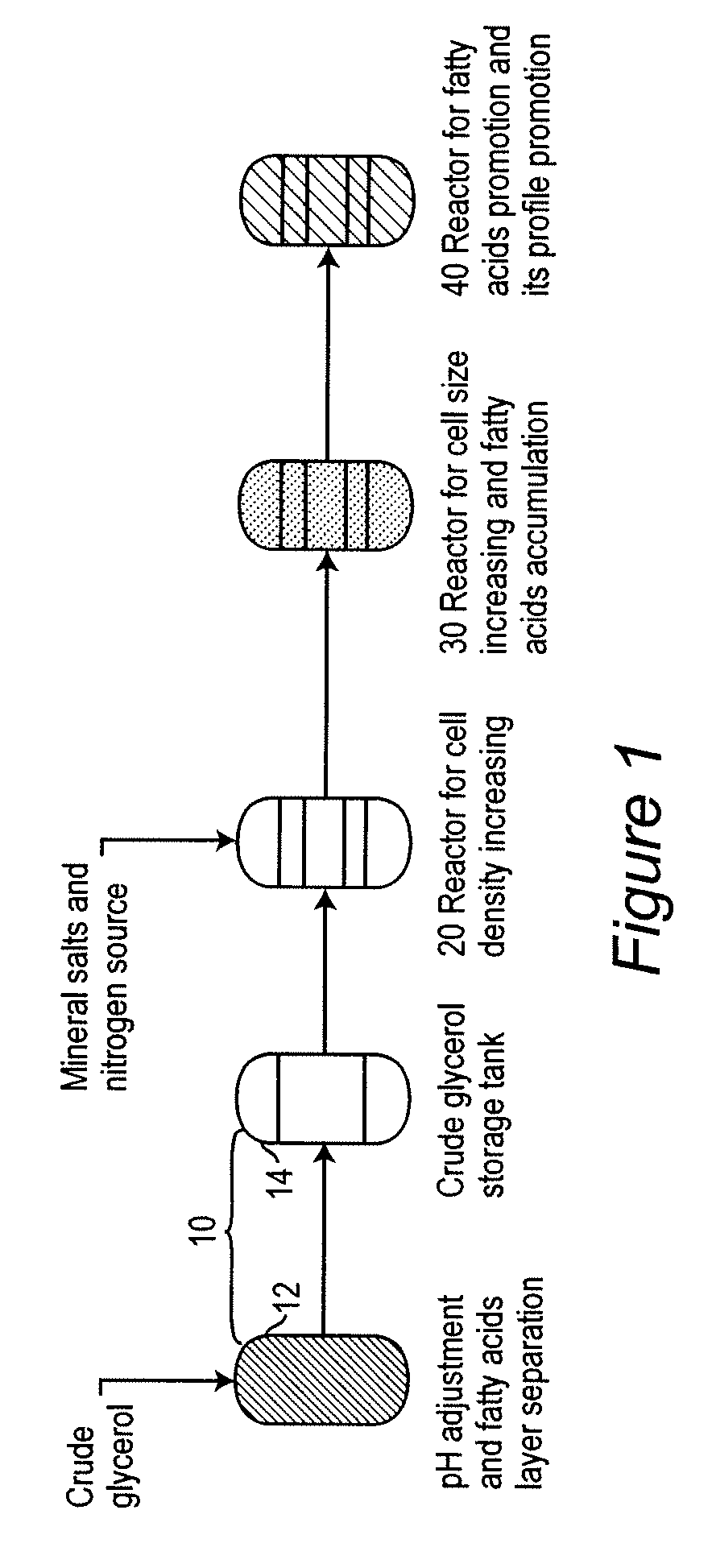
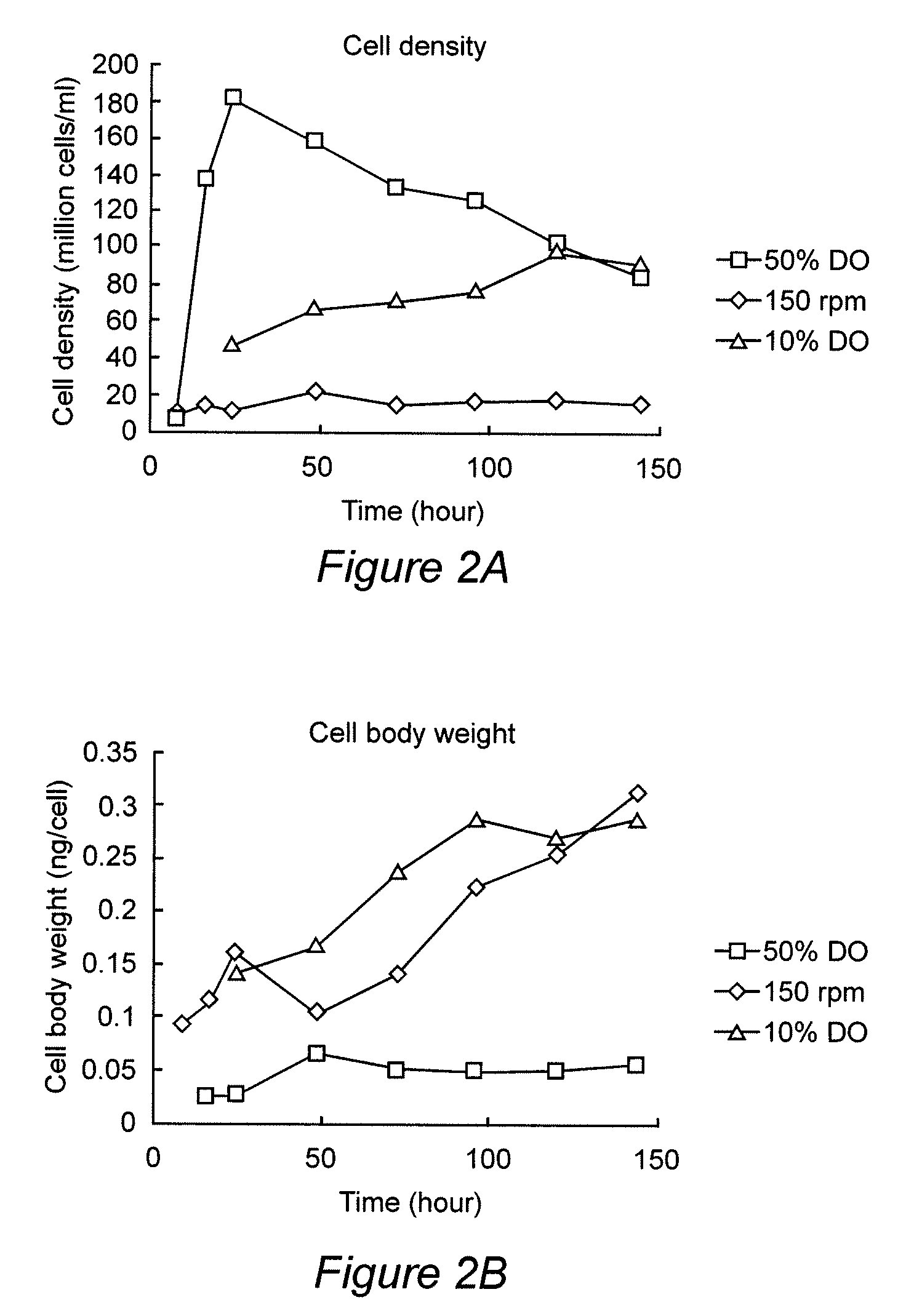
Heterotrophic algal high cell density production method and system
InactiveUS20090209014A1Increase cell densityIncrease biomassUnicellular algaeBiofuelsHigh cellHigh density
A multiphase culturing process for high density heterotrophic microalgal growth uses crude glycerol as the primary carbon source and produces ω-3 fatty acids. The process uses multiphase growth conditions that decouple the phases of increasing cell density and increasing cell size and fatty acid production. The entire process is integrated with biodiesel production.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
High cell density process for growth of Listeria
InactiveUS20060121053A1Increase productionIncrease costAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenHigh cell
The present invention relates to fed batch culture methods for high cell density growth of Listeria which produce cultures having an OD600 greater than about 2.2 or higher. In particular, the invention provides methods for high cell density growth of Listeria comprising growth in a pH controlled bioreactor and, optionally, the gradual addition of a carbon source, e.g., glucose, with or without one or more additional nutrients, e.g., vitamins, when growth in the initial culture is nearly complete or complete. In one embodiment, the methods of the invention are used to produce Listeria-based compositions, e.g., vaccines comprising Listeria that express a tumor-associated antigen, e.g., an EphA2 antigenic peptide, for eliciting an immune response against hyperproliferative cells.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Front gate line electrode silver conductor slurry for environment friendly silicon solar cell
ActiveCN101483207AGood chemical stabilityImprove electrical performanceFinal product manufactureConductive materialHigh cellElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a formula of an environment-friendly Ag conductor slurry for a silicon solar cell front gate line electrode and a processing method thereof. The component and the content (weight percentage) of the Ag slurry are: a metal Ag powder 60-80, a lead-less glasses adhesive 1-10, an Ohm contact additive agent 0. 05-10, and organic resin 2-15and a slurry modifying agent 1-8 The production method of the environment-friendly Ag conductor slurry comprises a preparation of the lead-less glass adhesive, a formula of the Ag slurry and a processing process of the slurry. The developing Ag slurry implements the slurry lead-free by using a Ba-Zn-B glass material and the lead content of the slurry is less than 100 ppm, while the content of other harmful substances such as Hg and Cd or the like is all conformed to the environment protection demand. A good Ohm contact is formed on the silicon surface of the Ag line and the cell by adding the Ohm contact forming agent in the slurry. The Ag slurry has strong adhesive force, superior weldability, good Ohm contact and high cell conversion efficiency after a continuous tunnel furnace fast heat treatment when the Ag slurry is used in the silicon solar cell front gate line electrode.
Owner:河北晶乐光电科技有限公司
Methods for enhanced protein production
ActiveUS20130017577A1Increase cell densityA large amountAnimal cellsMicroorganism separationHigh cellLiquid layer
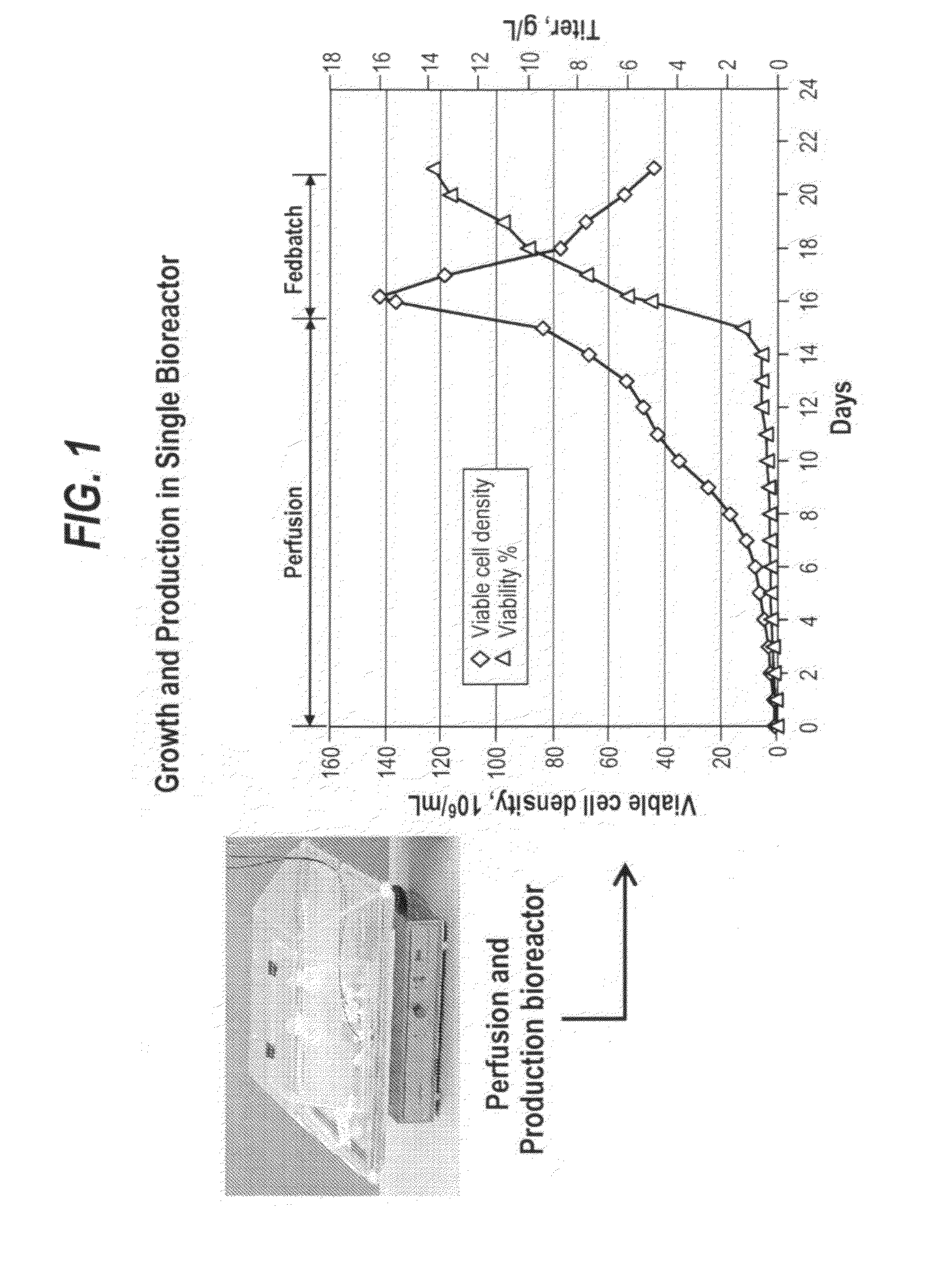
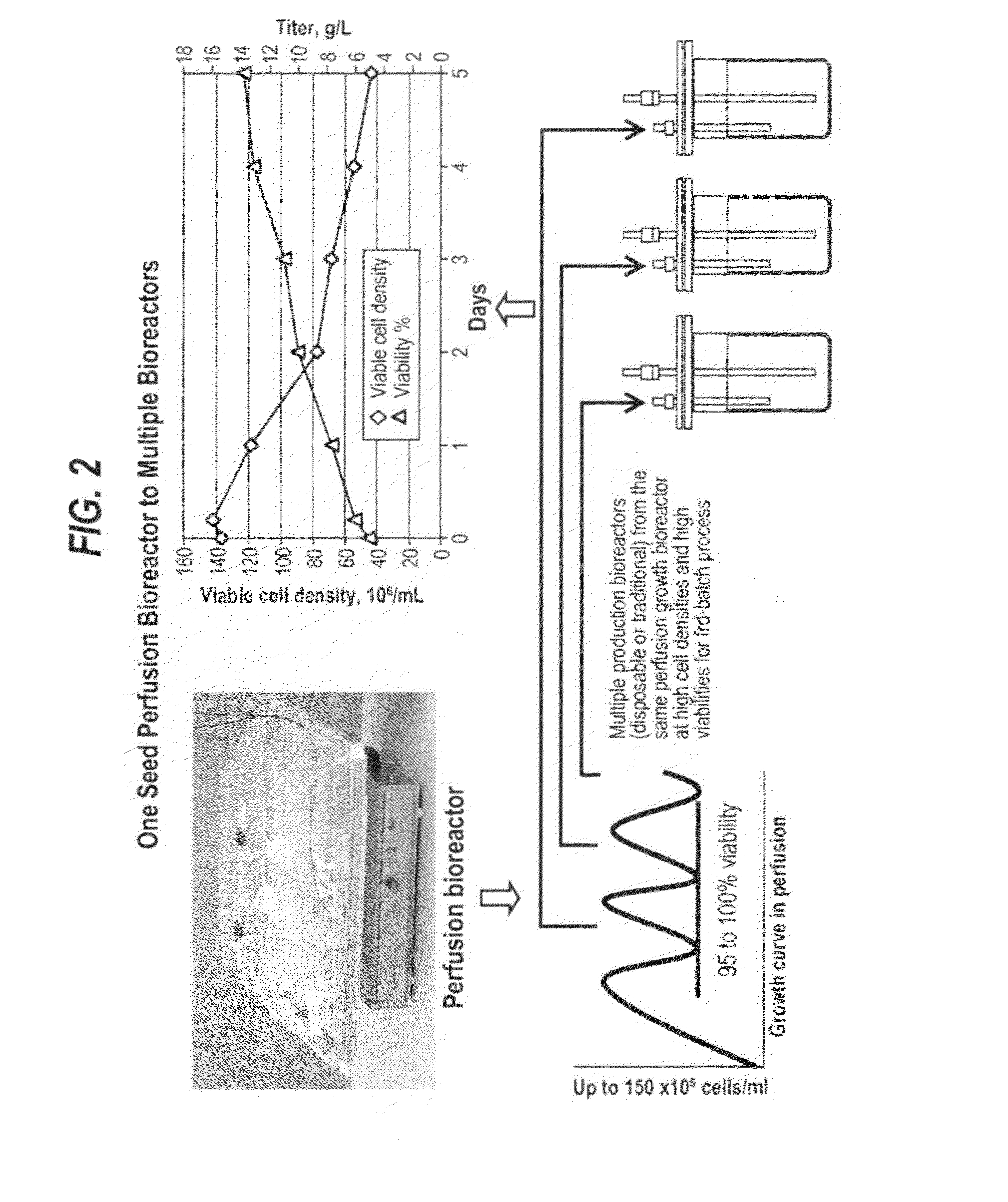
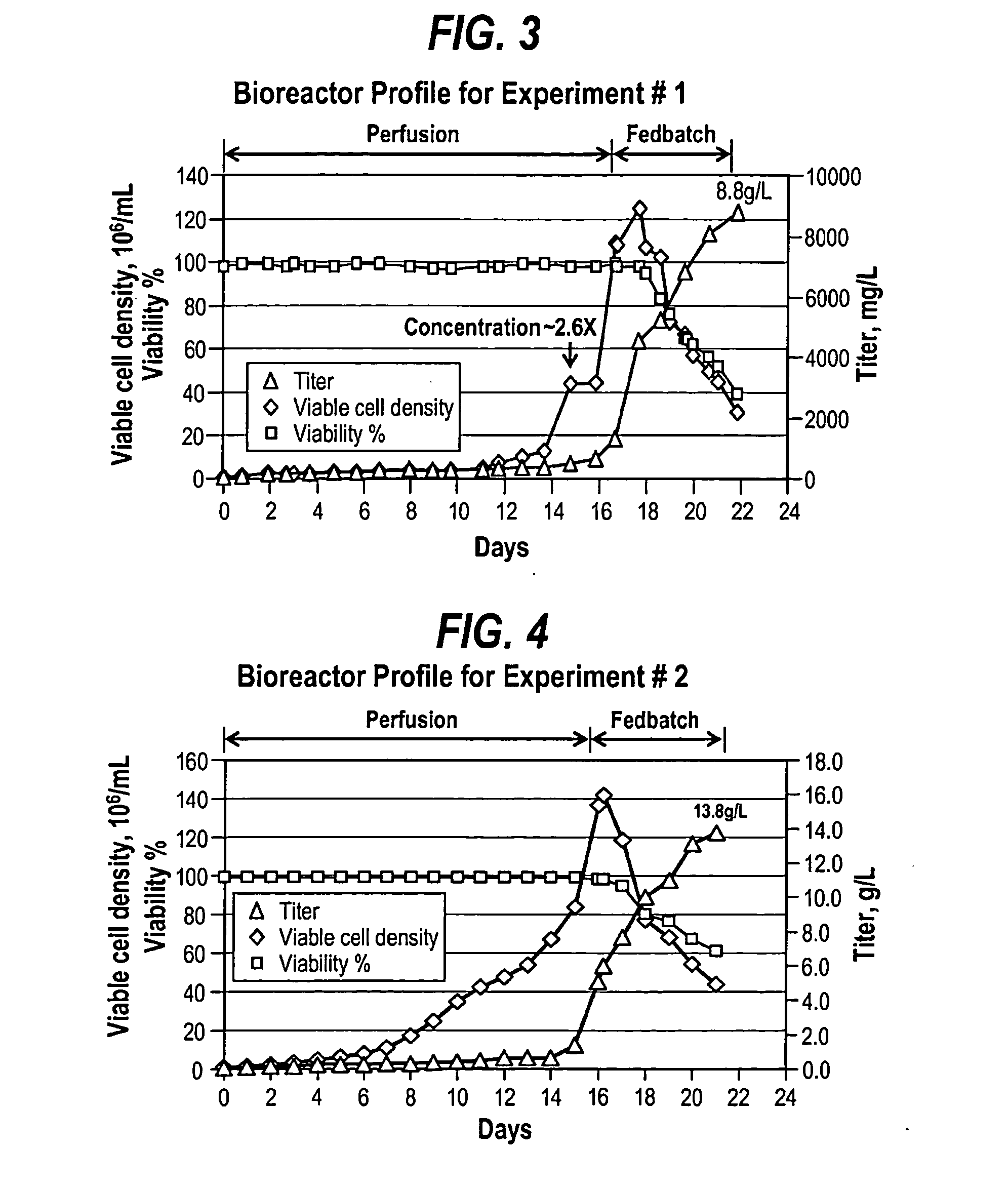
The present invention provides a method of increasing protein production in a cell culture by growing cells that produce the protein (e.g., the growth phase) in a perfusion cell culture to a high cell density (i.e., at least above about 40×106 cells / N mL) and then switching to a protein production phase, wherein the cells are cultured in a fed-batch cell culture. The present invention further provides a method for clarifying a protein from a cell culture by adjusting the pH of the cell culture to below neutral pH (i.e., below a pH of 7) and settling the cell culture, such that the cell culture separates to form a supernatant layer and a cell-bed layer, wherein the protein is in the supernatant layer.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
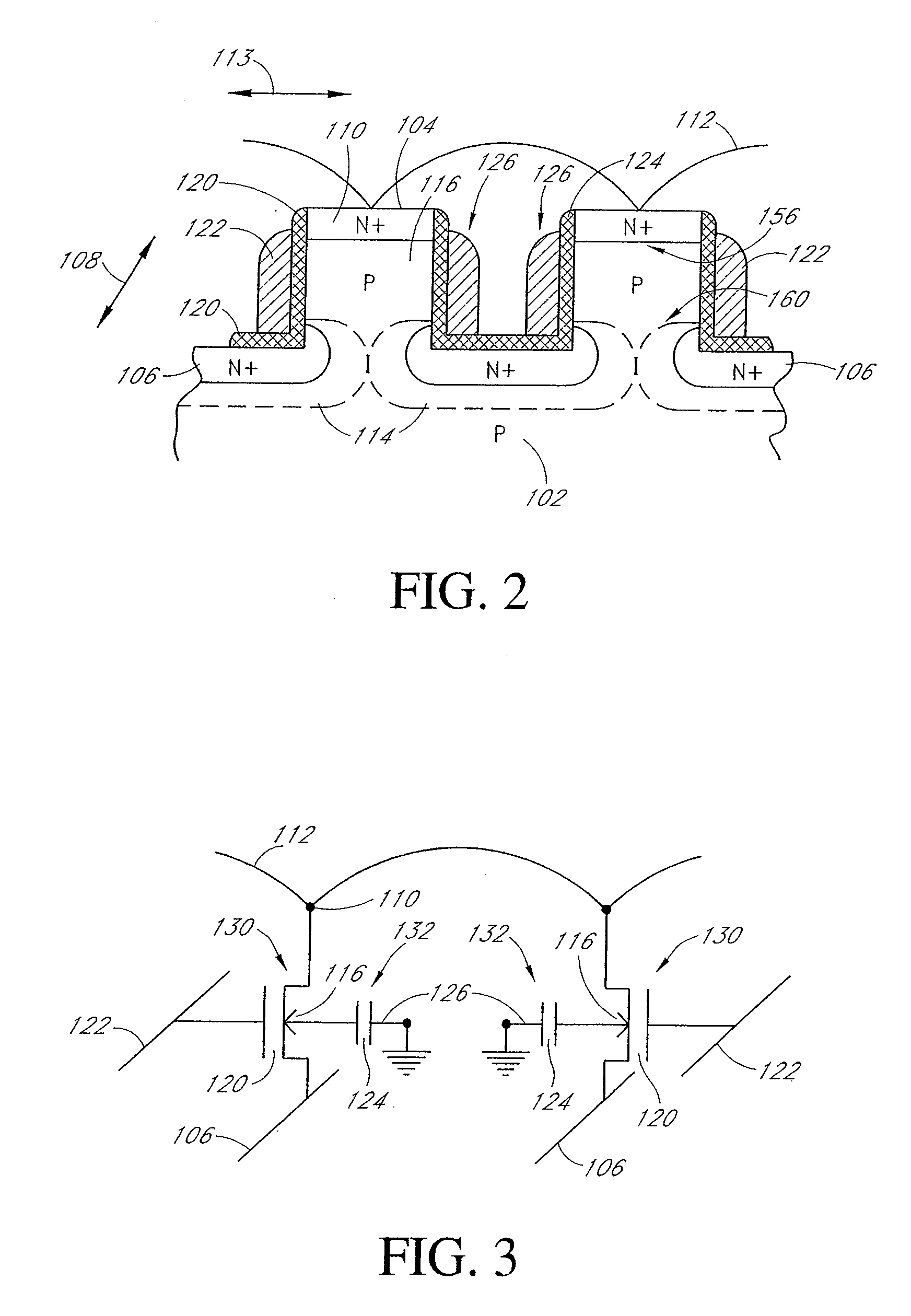
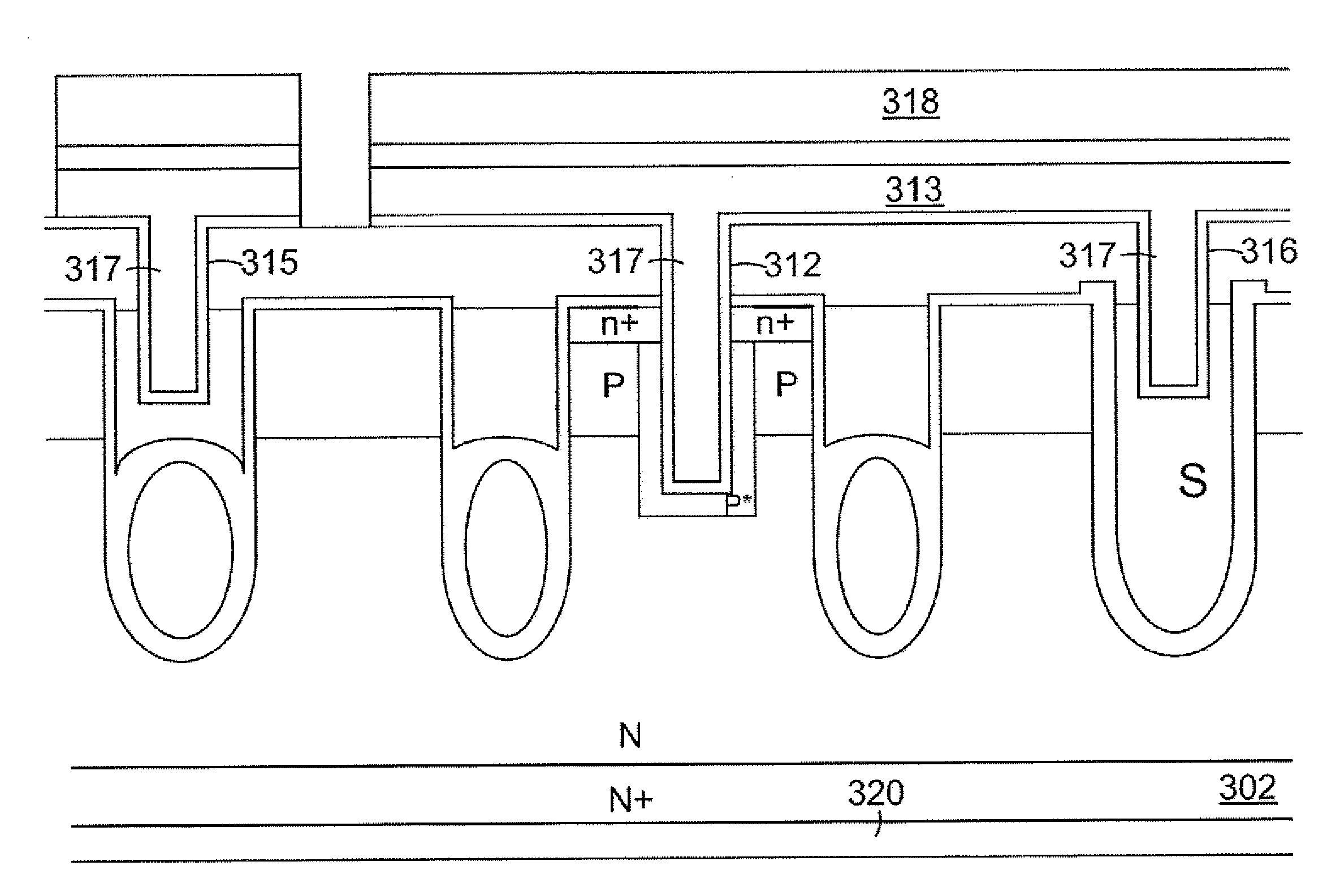
High switching trench mosfet
ActiveUS20120292694A1Improve performanceIncrease costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh cellTrench mosfet
A shielded gate trench metal oxide semiconductor filed effect transistor (MOSFET) having high switching speed is disclosed. The inventive shielded gate trench MOSFET includes a shielded electrode spreading resistance placed between a shielded gate electrode and a source metal to enhance the performance of the shielded gate trench MOSFET by adjusting doping concentration of poly-silicon in gate trenches to a target value. Furthermore, high cell density is achieved by employing the inventive shielded gate trench MOSFET without requirement of additional cost.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
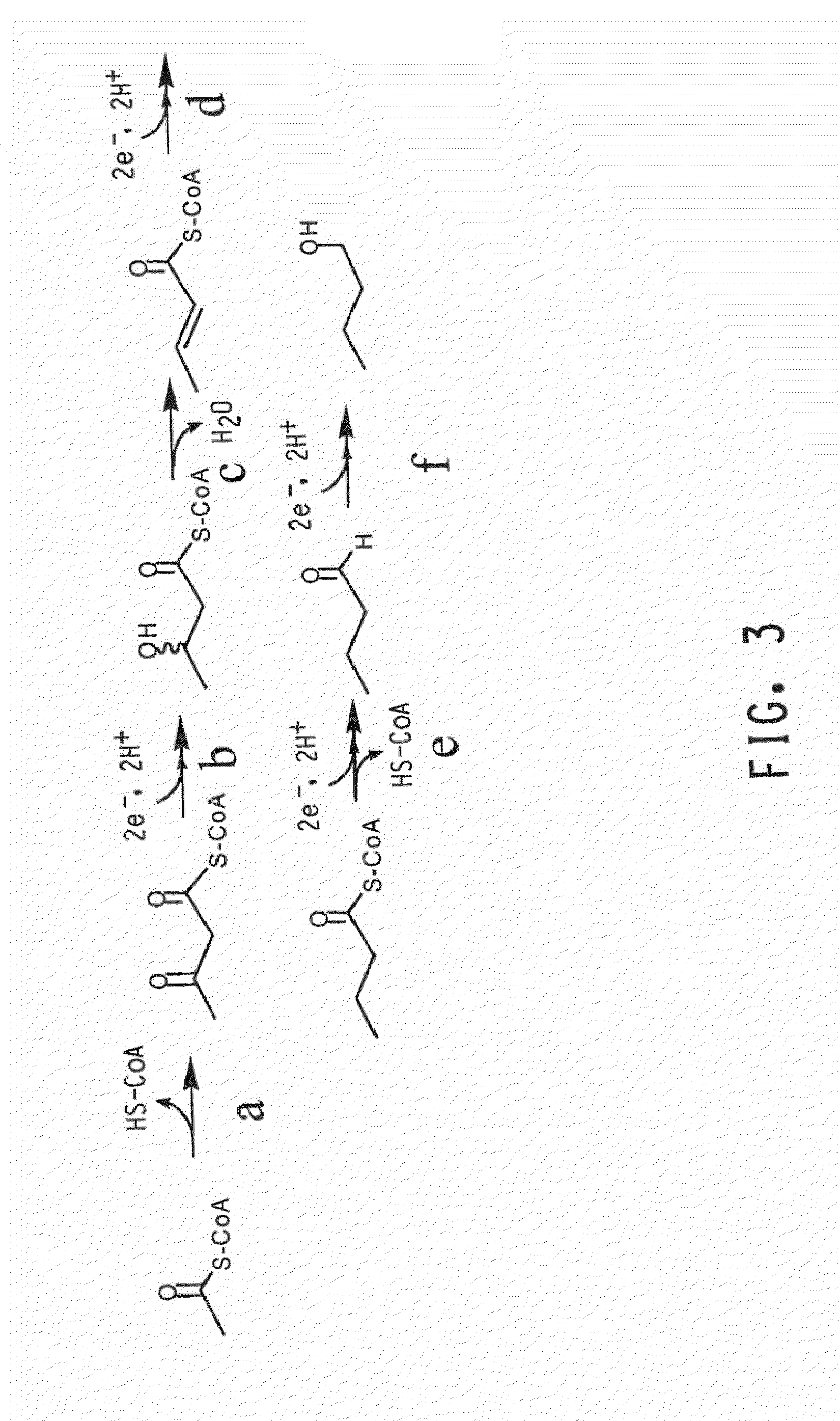
Yeast production culture for the production of butanol
High cell density cultures of yeast were found to have higher tolerance for butanol in the medium. The high cell density yeast cultures had greater survival and higher glucose utilization than cultures with low cell densities. Production of butanol using yeast in high cell density cultures is thus beneficial for improving butanol production.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
Integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood
The invention relates to an integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood. The integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood comprises three inlets, an erythrocyte lysis unit, a leucocyte capture unit, a cancer cell capture unit and an outlet, wherein the three inlets, the erythrocyte lysis unit, the leucocyte capture unit, the cancer cell capture unit and the outlet are connected orderly. The leucocyte capture unit comprises a first diverter, a soft magnetic microcolumn array and permanent magnets. The first diverter is connected with the soft magnetic microcolumn array. The permanent magnets are arranged at two sides of the soft magnetic microcolumn array. The cancer cell capture unit comprises a second diverter and a capture microstructure array, wherein the second diverter and the capture microstructure array are connected orderly. Compared with the prior art, the integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood has the advantages of high integration degree, simple operation, high cell capture efficiency, simple manufacture processes and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
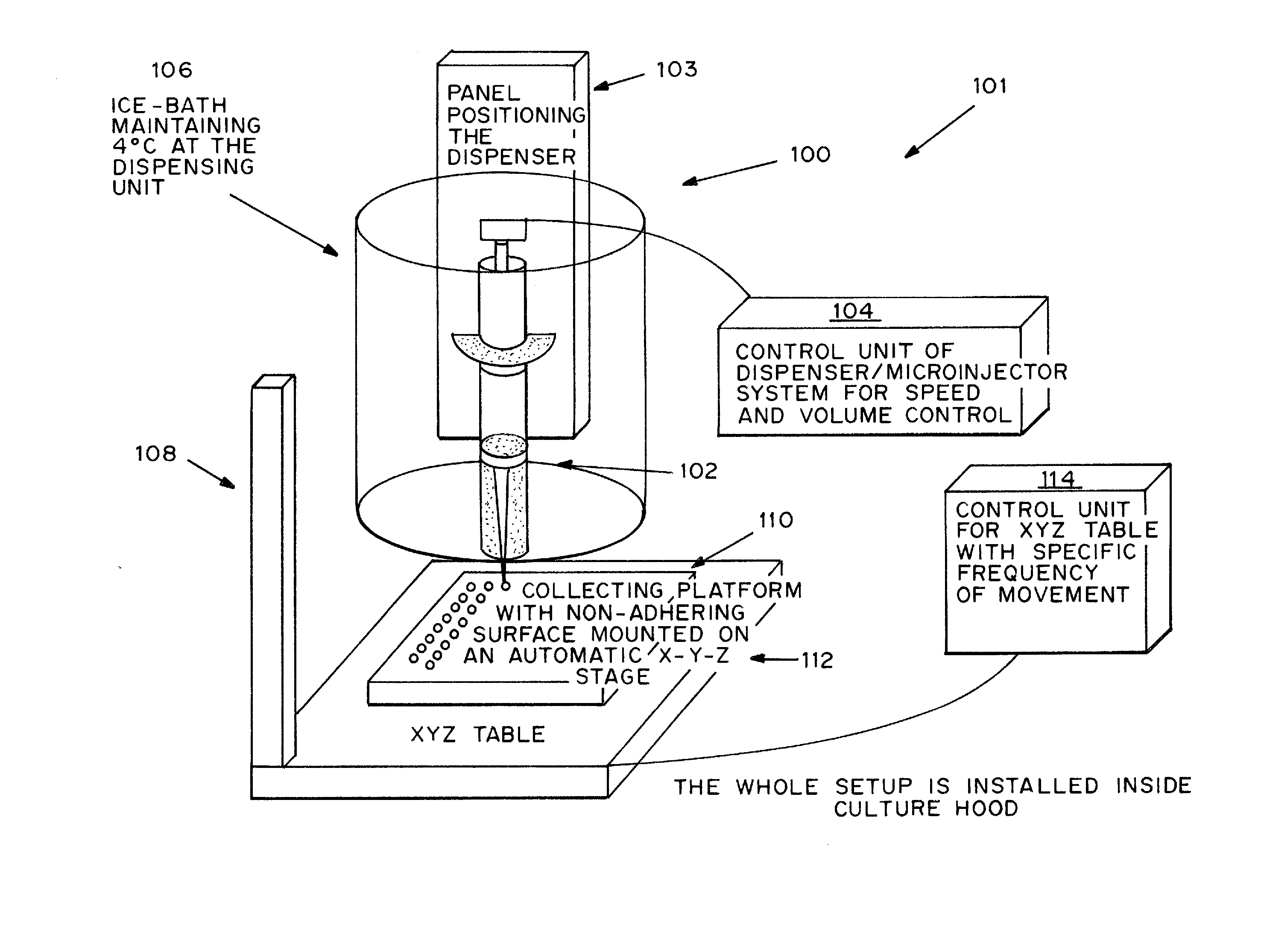
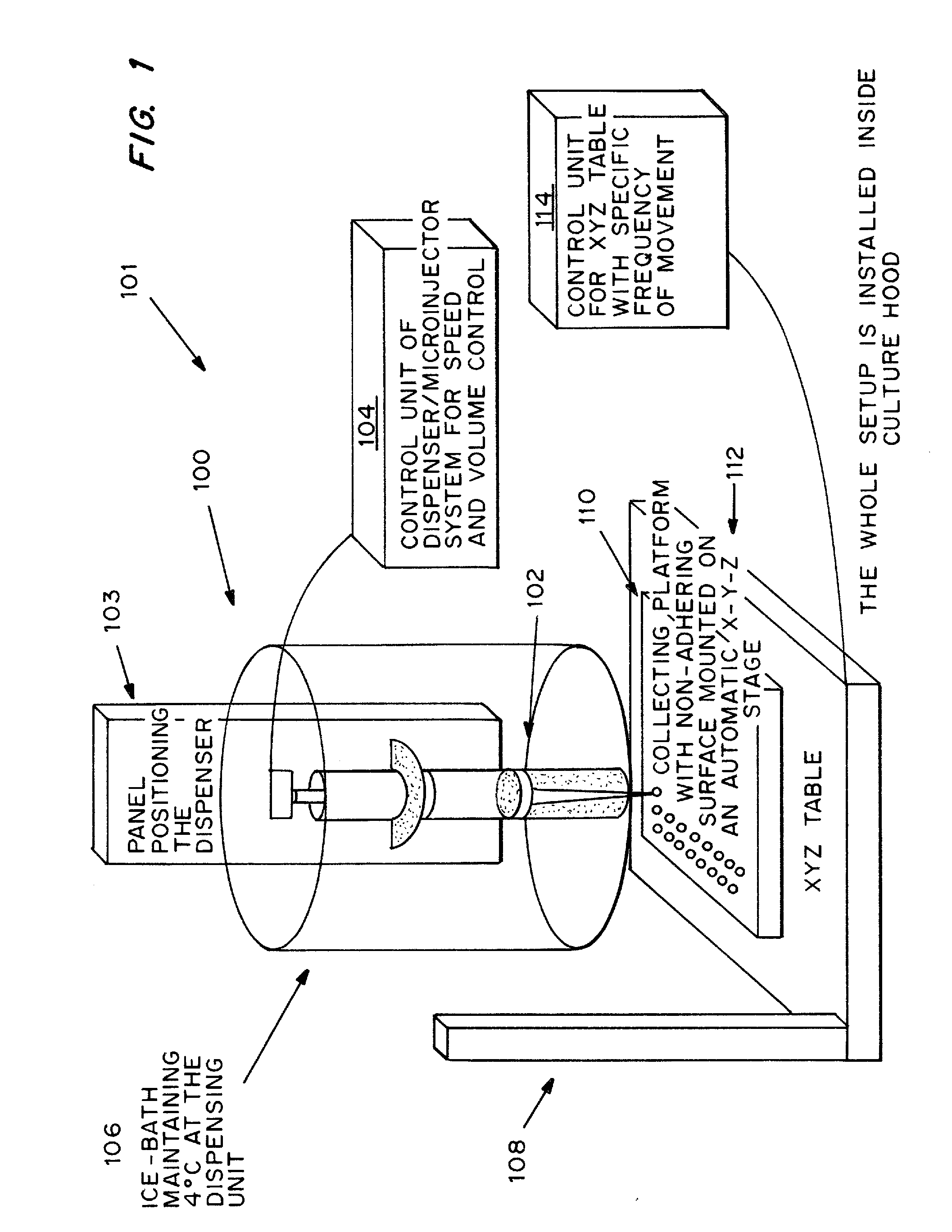
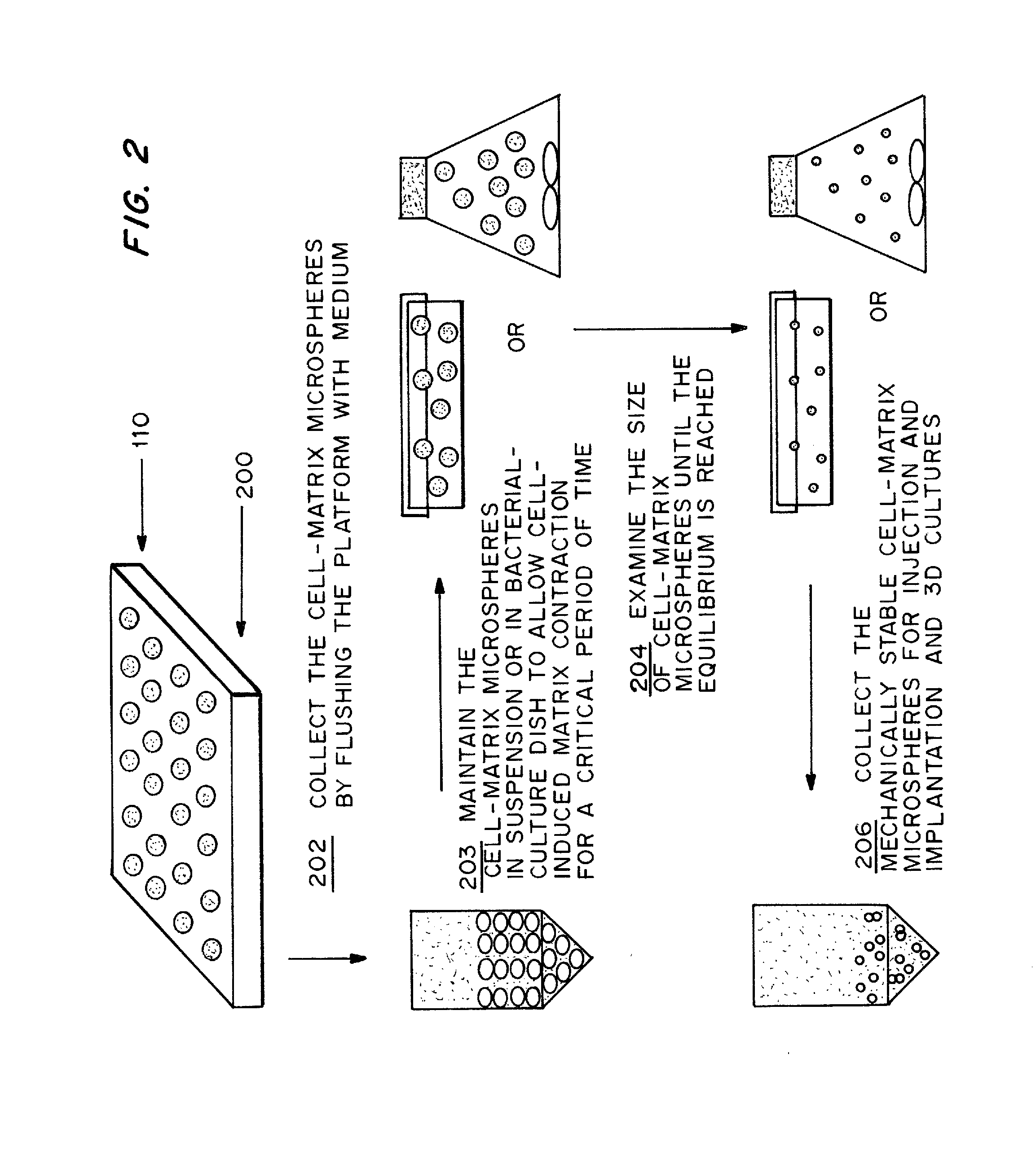
Cell-matrix microspheres, methods for preparation and applications
ActiveUS20080031858A1Increased protein productivityStable cell-matrix microspheresBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzymatic digestionHigh cell
A method has been developed to produce stable cell-matrix microspheres with up to 100% encapsulation efficiency and high cell viability, using matrix or biomaterial systems with poor shape and mechanical stability for applications including cell therapeutics via microinjection or surgical implantation, 3D culture for in vitro expansion without repeated cell splitting using enzymatic digestion or mechanical dissociation and for enhanced production of therapeutic biomolecules, and in vitro modeling for morphogenesis studies. The modified droplet generation method is simple and scalable and enables the production of cell-matrix microspheres when the matrix or biomaterial system used has low concentration, with slow phase transition, with poor shape and mechanical stability.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
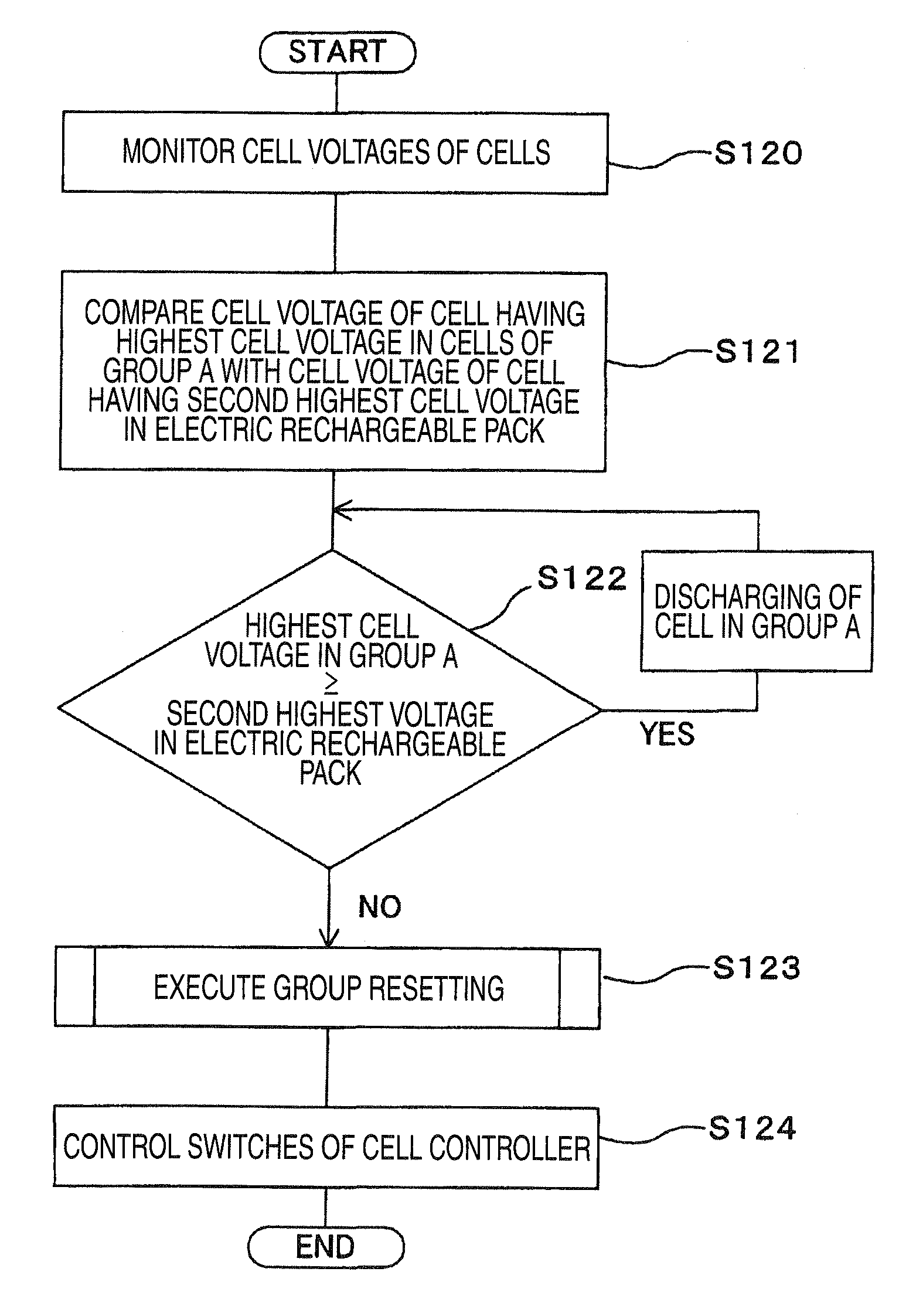
Discharge control system
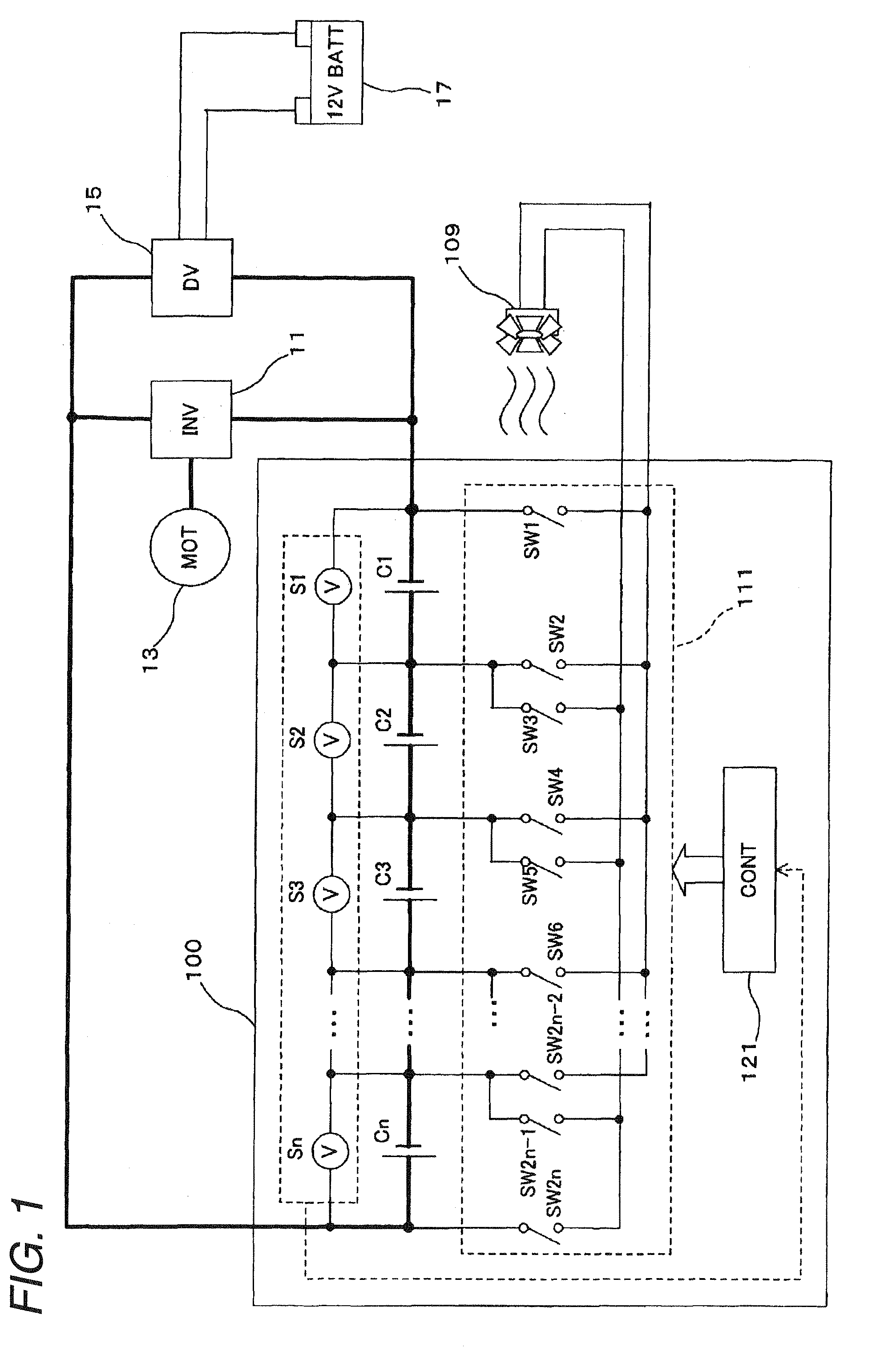
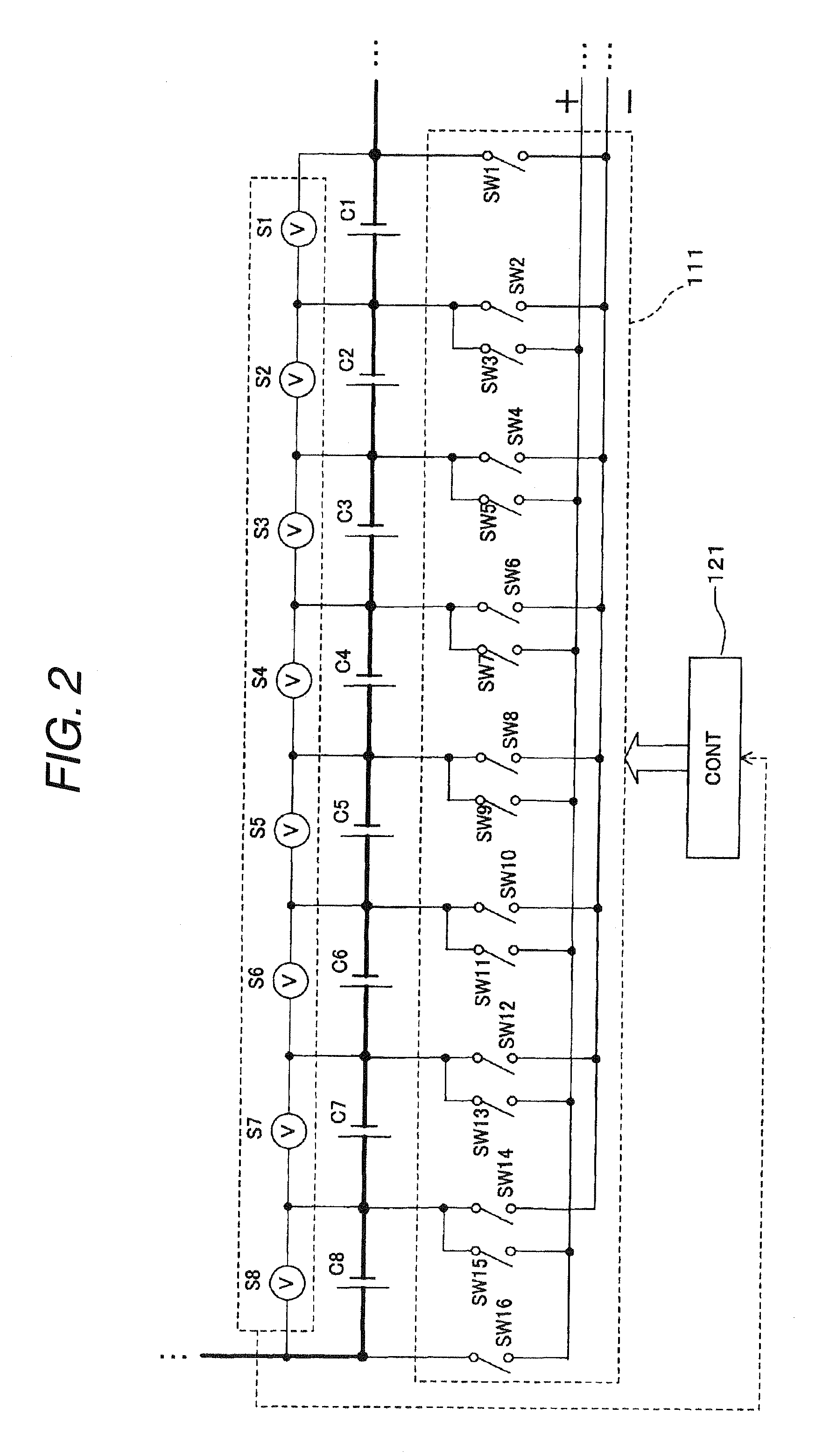
InactiveUS20090115372A1Improve efficiencyEnergy consumptionCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerHigh cellControl system
A discharge control system of a electric storage pack has a plurality of electric rechargeable cells connected in series and a discharge line is connected from a electric rechargeable cell to a load driving feeding circuit. The discharge control system includes cell voltage detection units for detecting respective cell voltages of the plurality of cells, a switch group made up of a plurality of switches connected between the plurality of cells, and a control unit which designates a cell having a highest cell voltage in the plurality of electric rechargeable cells possessed by the electric storage pack in accordance with detection results by the cell voltage detection units and on / off controls the switches of the switch group individually so as to form a discharge line from a electric rechargeable cell of the group to the load driving feeding circuit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method to control cell adhesion and growth on biopolymer surfaces
Methods for treating surfaces of polymeric substrates (as used in medical implants) with inert plasmas to promote the growth of bioentities (such as cells) on these surfaces is disclosed. The treated surfaces are subsequently exposed to an environment to form functionalities associated with enhanced growth of the bioentity on the surface. For example, the substrate may be exposed to the ambient environment. The bioentity may then be deposited on the modified surface. This inert plasma treatment and exposure to a suitable environment does not degrade the implants, and thus improved implants are created. Also, due to the specific functional groups at the modified surface, high cell densities are achieved.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
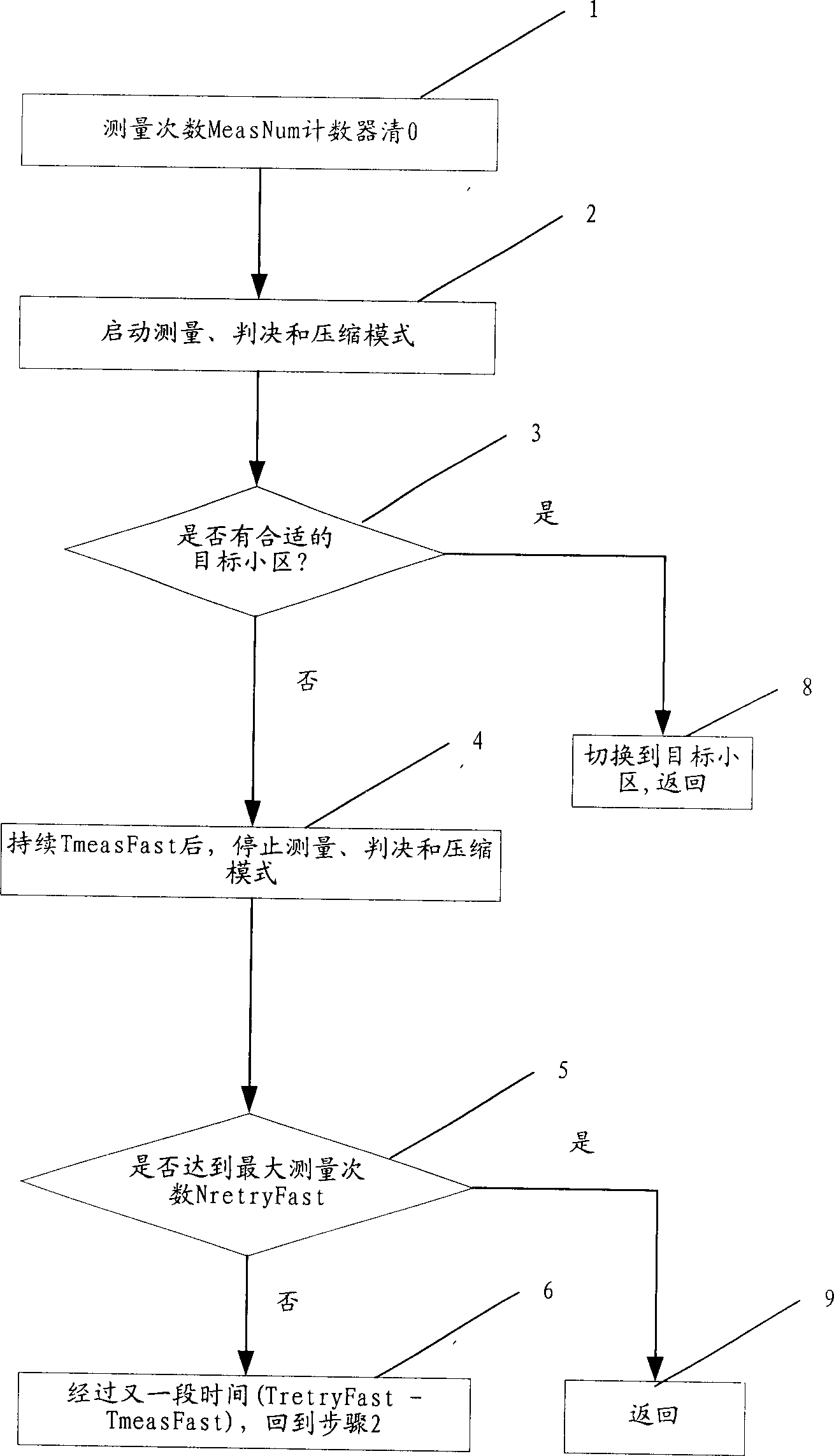
Method of providing or receiving cell load information using at least dual periodicity
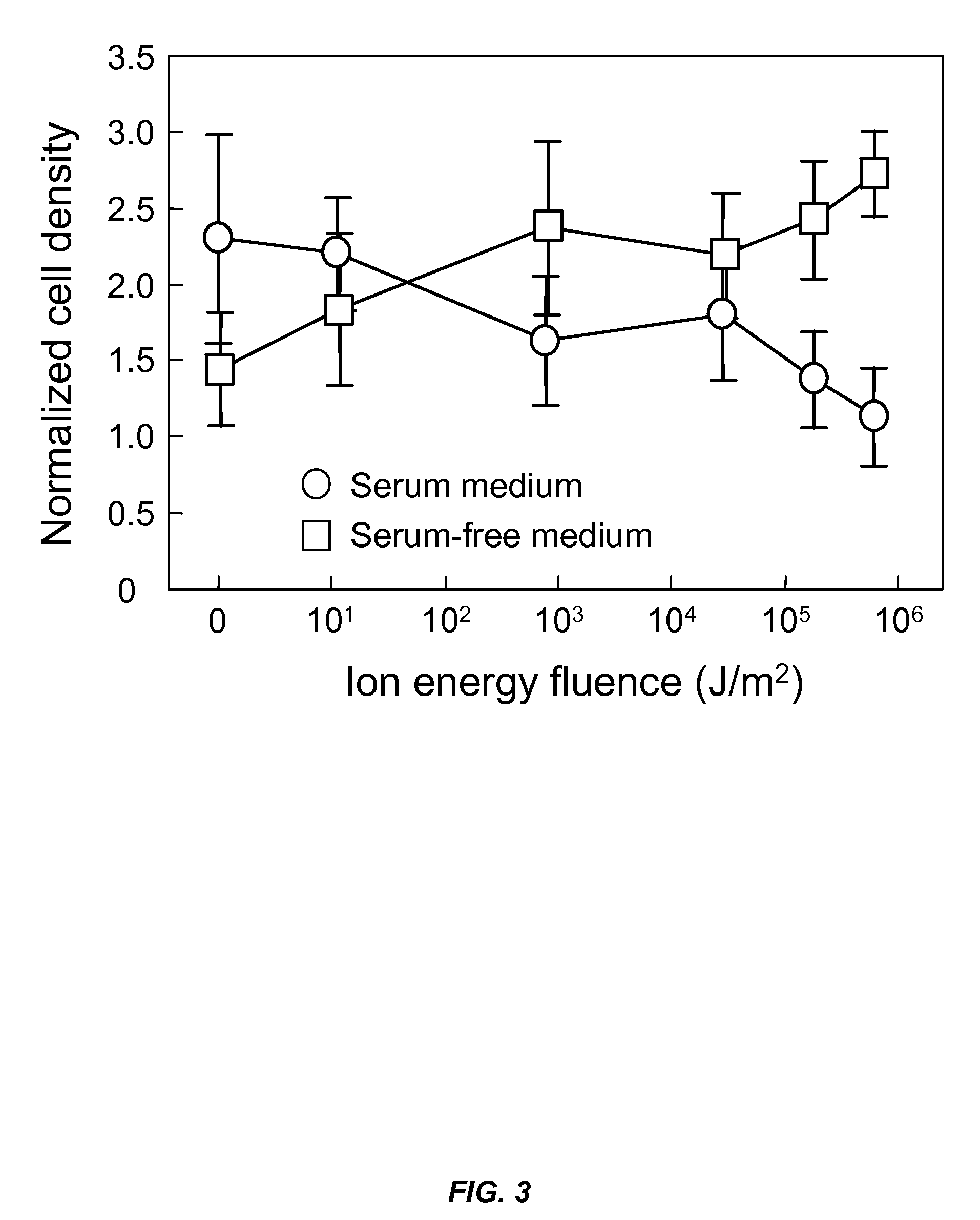
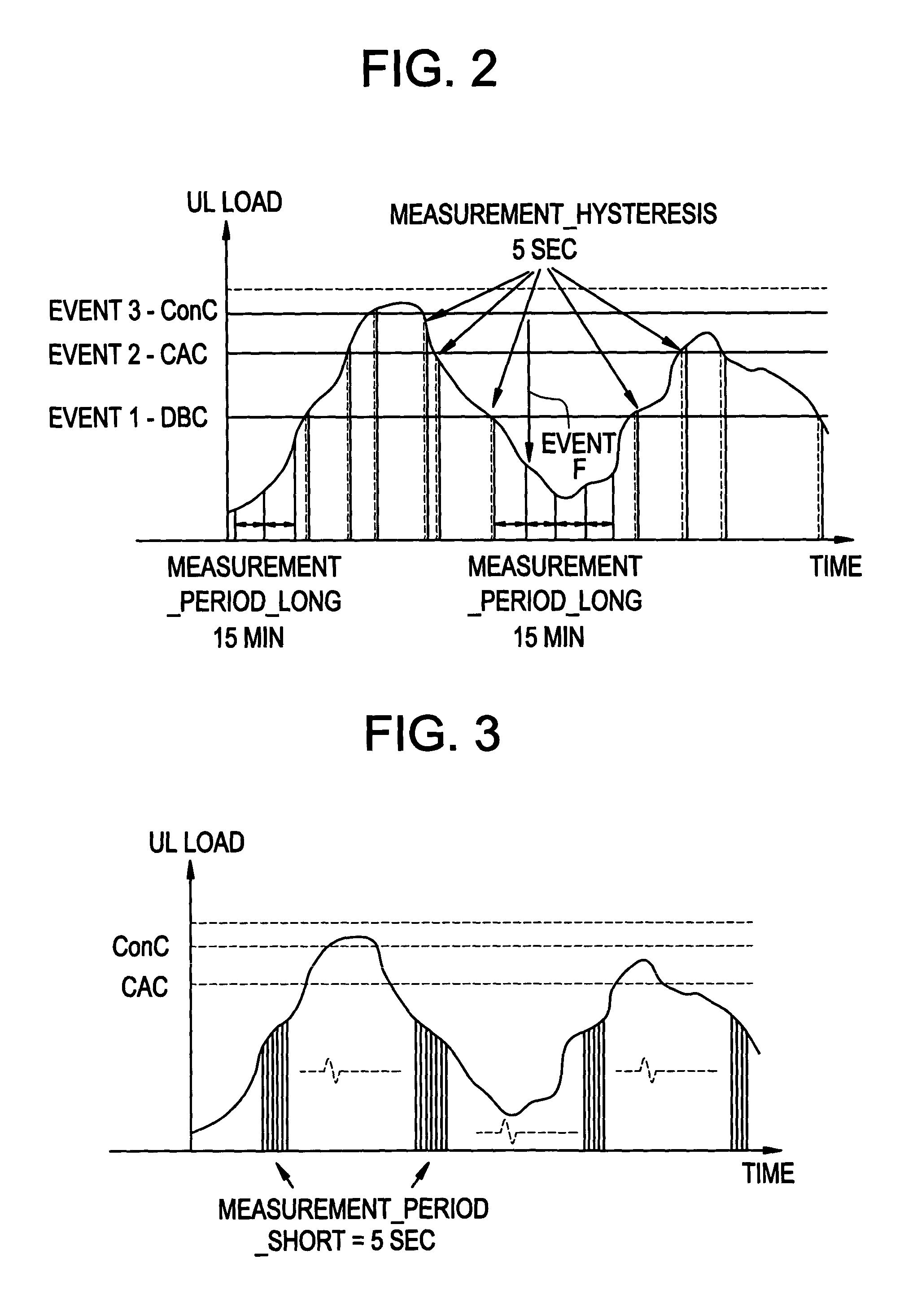
InactiveUS20050043034A1Improve measurement precisionIncrease frequencyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData switching networksHigh cellCommunications system
A method of providing and / or receiving cell load information in a wireless communication system where the cell load information is provided and / or received at a first periodicity when in a period of low cell loading and received at a second periodicity, higher than the first periodicity when in a period of high cell loading. A method of providing and / or receiving cell load information in a wireless communication system where the cell load information is provided and / or received based on periodic events and threshold-driven events.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Manufacturing foams by stress-induced nucleation
InactiveUS6080798AShort induction timeThe implementation process is simpleCoatingsVitrificationStress induced
The invention disclosed provides a method for inducing nucleation in a polymer by subjecting the polymer containing dissolved gas to an external stress generated, for example, by applying hydrostatic or mechanical pressure. The applied stress restricts the bubble growth so that the foamed materials have small cells and high cell density. Such microcellular foams can be produced over a wide low temperature range, i.e. from the temperature at which the polymer is conditioned with the blowing agent up to about the glass transition temperature of the polymer-blowing agent system. Stress induced nucleation can also be conducted at higher temperatures i.e. up to about the Tg of the neat polymer, leading to foams with larger cells. A variety of homogeneous and heterogeneous foams can be produced by this technique.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Aptamer-based microfluidic chip capable of capturing cancer cells and preparation thereof as well as separation method of cancer cells
InactiveCN103087899AFast preparation methodAvidin immobilization method is simpleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh cellAptamer
The invention discloses an aptamer-based microfluidic chip capable of capturing cancer cells, which is formed by reversibly sealing an upper-layer polymer chip and a lower-layer slide carrier, wherein a cell capturing channel is arranged between the upper-layer polymer chip and the lower-layer slide carrier; the bottom surface of the channel is rough; and avidin is fixed on the bottom surface. The preparation of the microfluidic chip comprises the steps of making a chip die by photoetching, and casting to obtain a polymer chip; processing the slide carrier with hydrofluoric acid and bonding with the polymer chip; and fixing avidin in the cell capturing channel to obtain a microfluidic chip. The microfluidic chip disclosed by the invention can be used for separating cancer cells; and the separation comprises the steps of adding biotin-modified aptamer into a sample, and incubating; and leading the mixed solution after the incubation into the microfluidic chip, wherein the target cancer cells in the mixed solution are combined with the avidin through the biotin to realize separation of the target cancer cells. The microfluidic chip disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high cell capturing efficiency, convenience in operation, strong generality, low cost and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Stem cells preparation for repairing wound surface and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102670654AImprove survival rateProlong survival timePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellHydroxyethyl starch
The invention discloses a stem cells preparation for repairing a wound surface and preparation method thereof, wherein the stem cells preparation uses umbilical cords, placentae or mesenchymal stem cells between amniotic membranes as living cells, and is added with high polymer material sodium alginate with excellent biocompatibility, sodium hyaluronate, chitosan and hydroxyethyl starch as cell stabilizer. The stem cells preparation for repairing the wound surface has higher cell viability and is durable in action, and breaks through technical limitations of effectiveness of the mesenchymal stem cells for treating.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH STEM CELL INST CO LTD
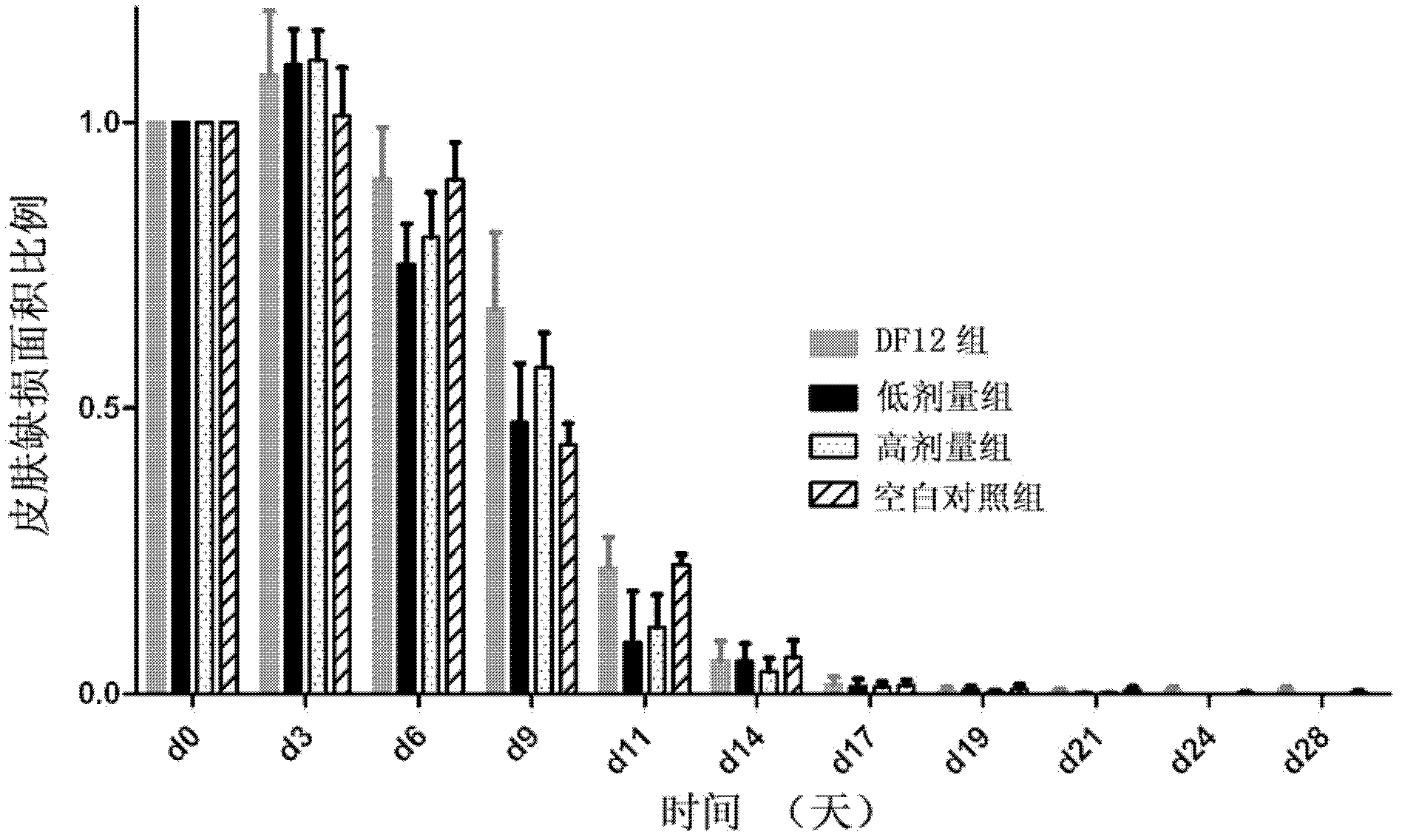
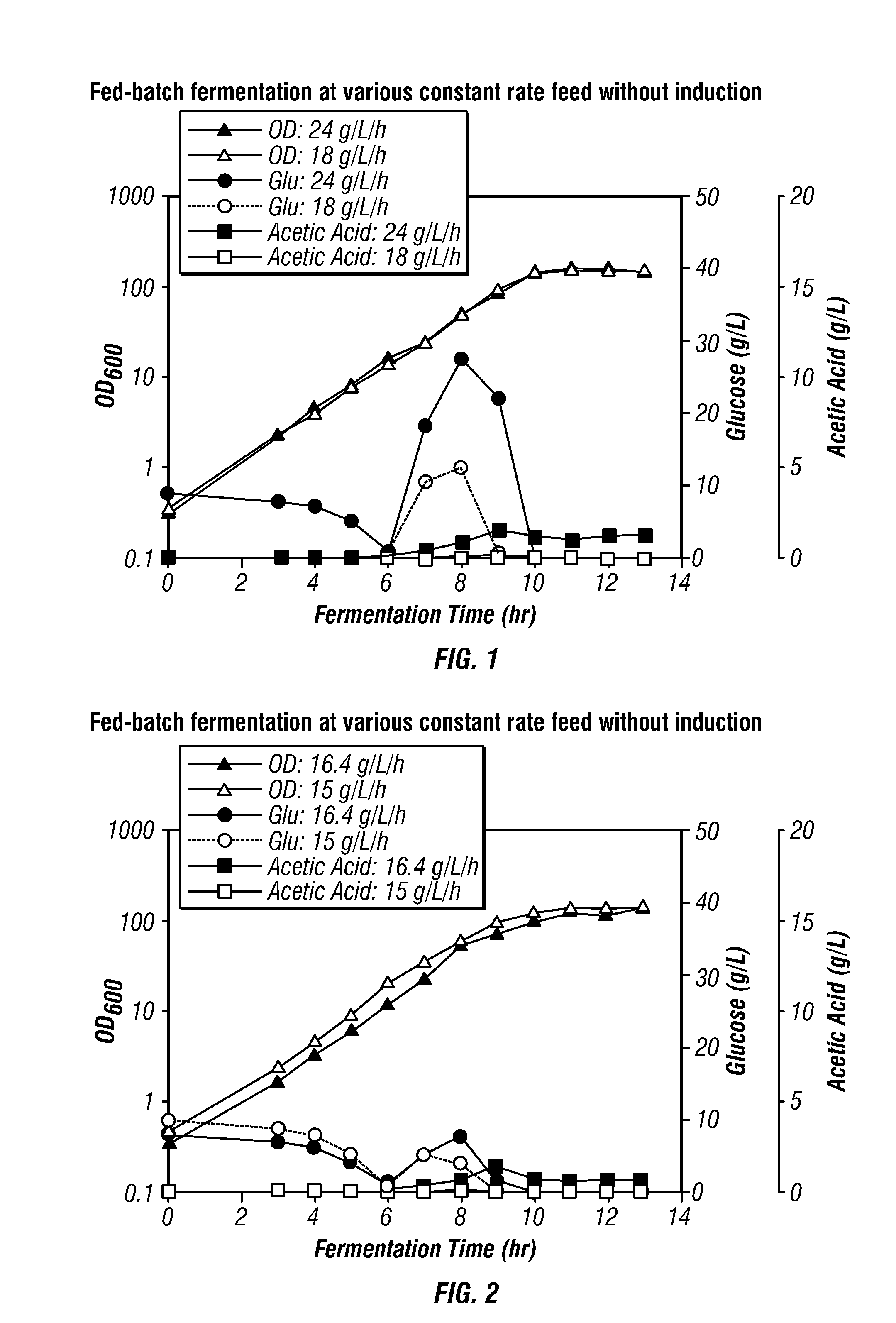
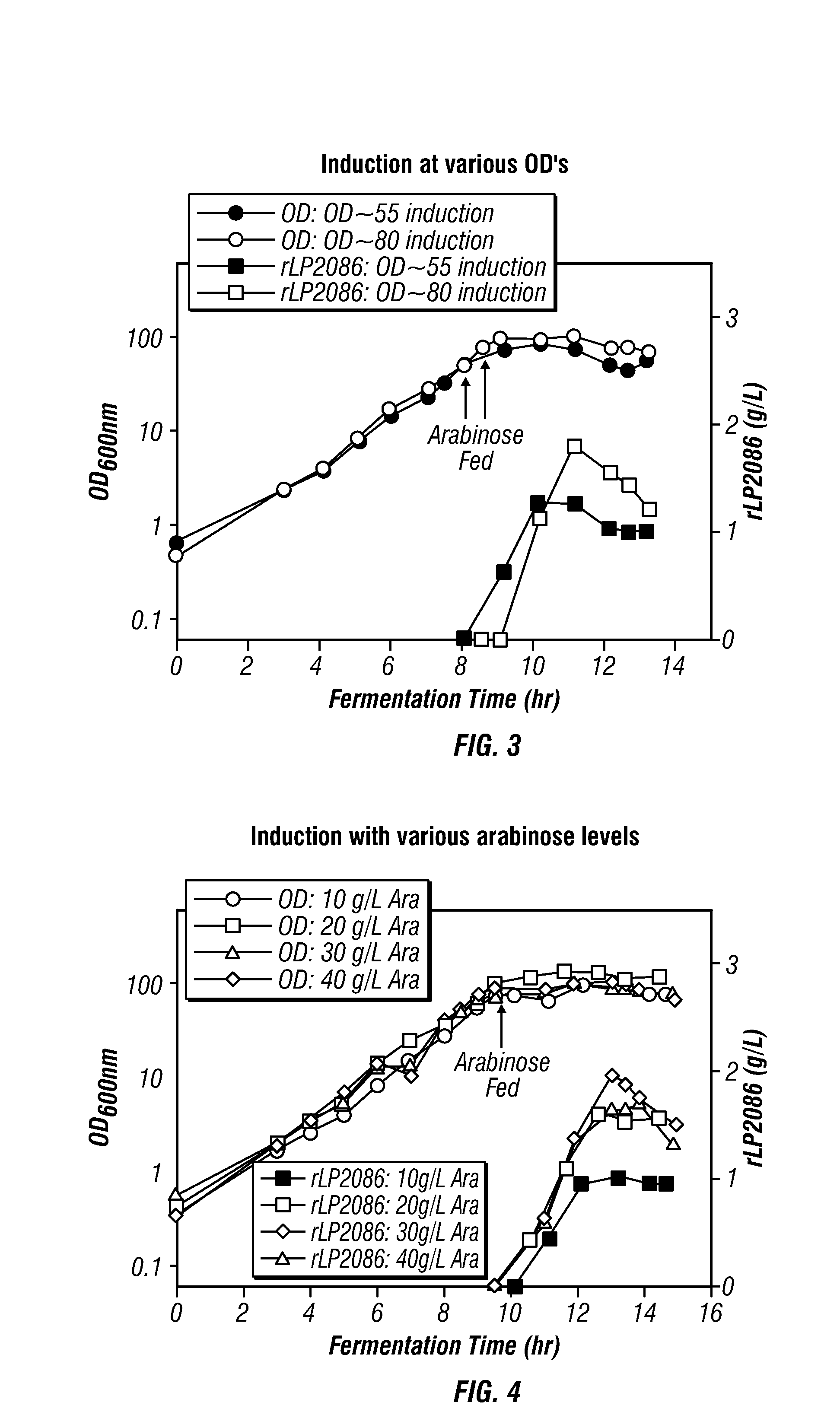
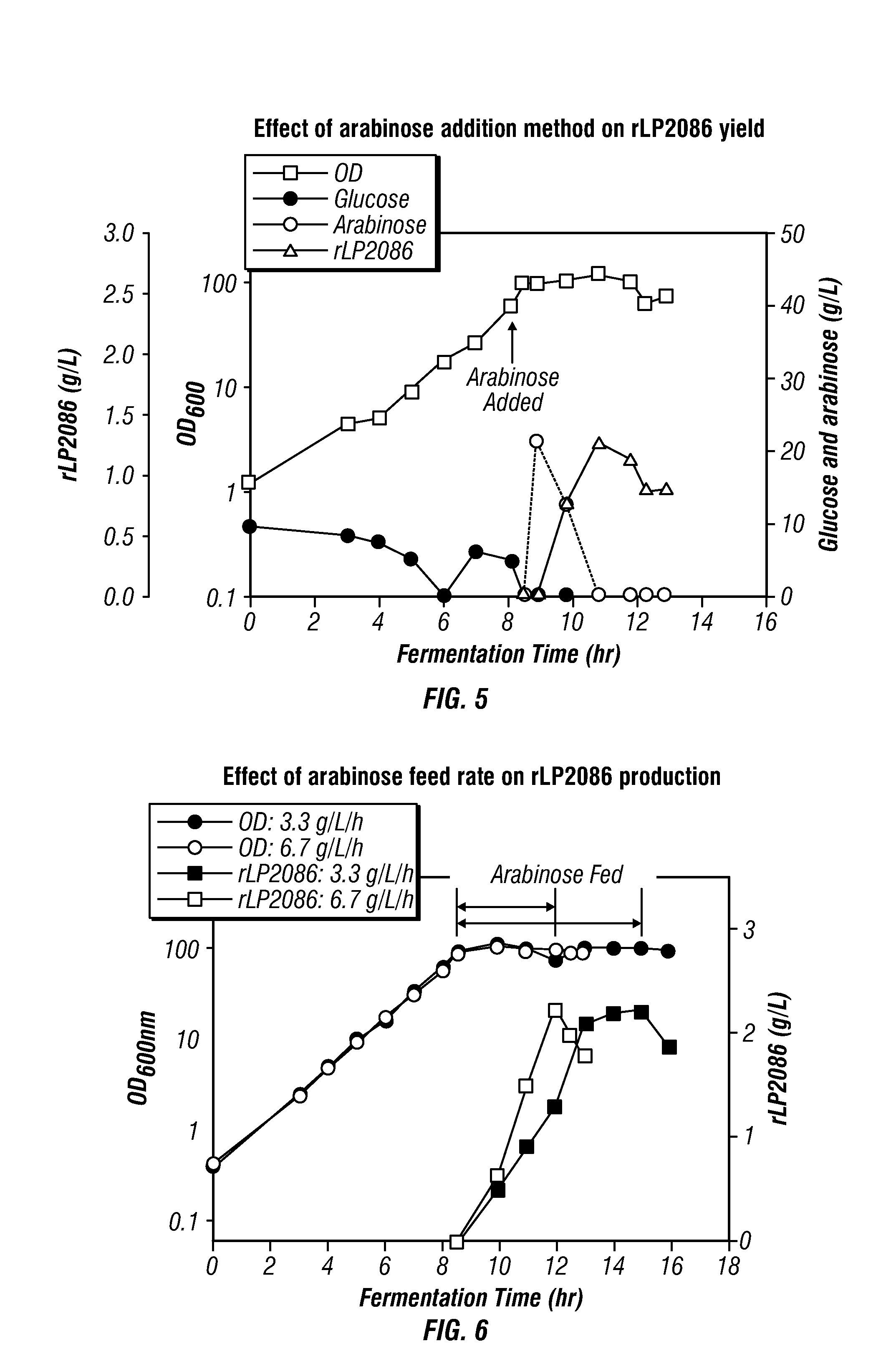
High-cell density fed-batch fermentation process for producing recombinant protein
Methods for producing proteins, for example, recombinant meningococcal 2086 proteins, using fed-batch fermentation with continuous input of an inducer after achieving a threshold parameter, and optionally continuous input of a carbon source, for example, a constant rate input, to improve protein yields, as well as high density protein compositions and compositions for use in the methods of the present invention, are provided.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Long retention time single transistor vertical memory gain cell
ActiveUS7151024B1High band gap energyAvoid excessive leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh cellRetention time
A single transistor vertical memory gain cell with long data retention times. The memory cell is formed from a silicon carbide substrate to take advantage of the higher band gap energy of silicon carbide as compared to silicon. The silicon carbide provides much lower thermally dependent leakage currents which enables significantly longer refresh intervals. In certain applications, the cell is effectively non-volatile provided appropriate gate bias is maintained. N-type source and drain regions are provided along with a pillar vertically extending from a substrate, which are both p-type doped. A floating body region is defined in the pillar which serves as the body of an access transistor as well as a body storage capacitor. The cell provides high volumetric efficiency with corresponding high cell density as well as relatively fast read times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
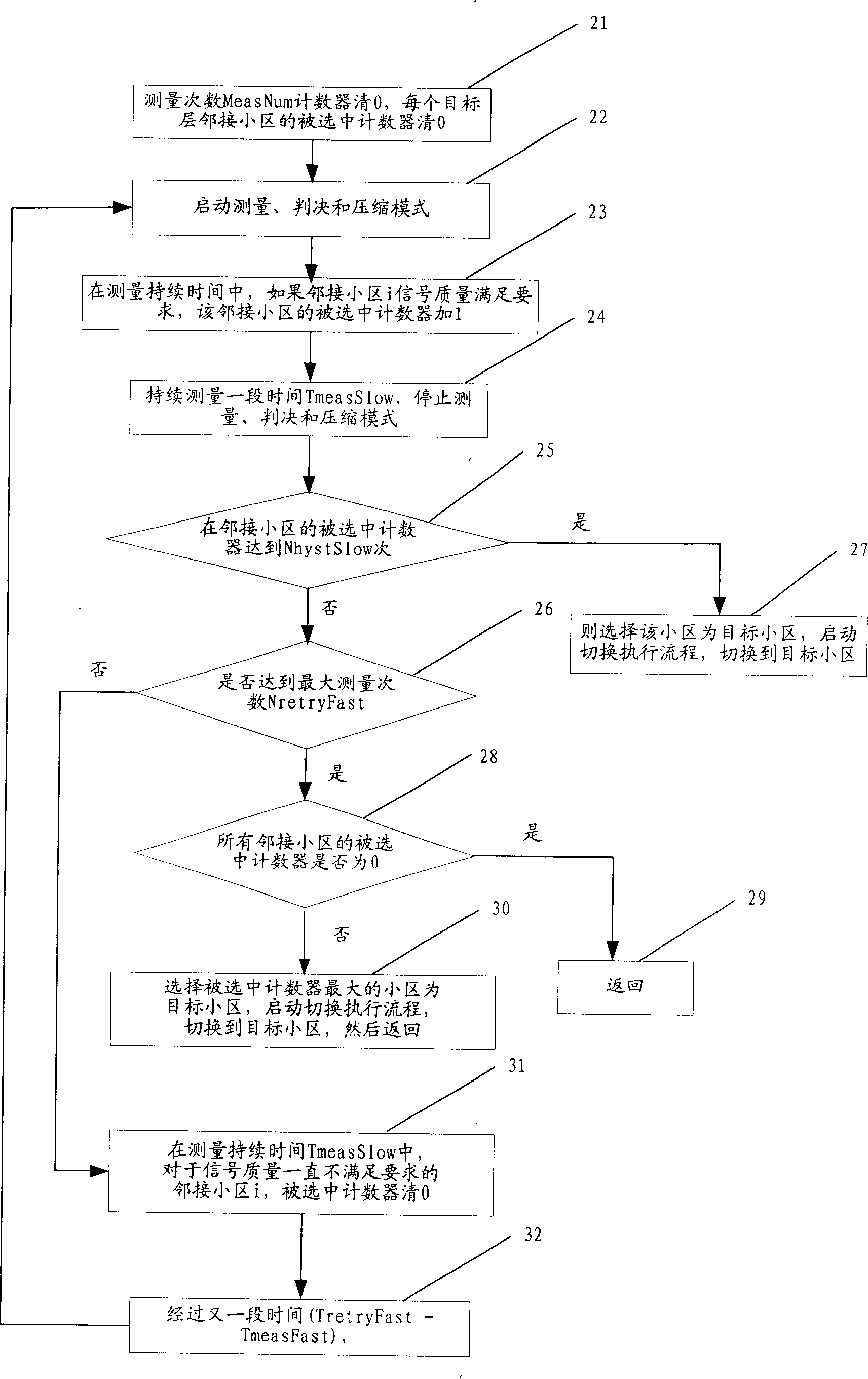
Interlaminar switching method in WCDMA hierarchical network
ActiveCN1802006AAvoid switchingLittle impact on performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationHigh cellMarine engineering
Present invention provides interlayer switch method for WCDMA layering network. It contains measuring traveling platform speed, when traveling platform speed is quickly and existing higher cell, then adopting Intermission measurement mode switching to higher cell, when traveling platform speed is normal, then staying in said layer, when traveling platform speed is slow, and existing lower cell, then adopting Intermission measurement mode switching to lower cell. Said invention reduces influence of start compression mode to system performance, and avoiding ping-pong switching.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
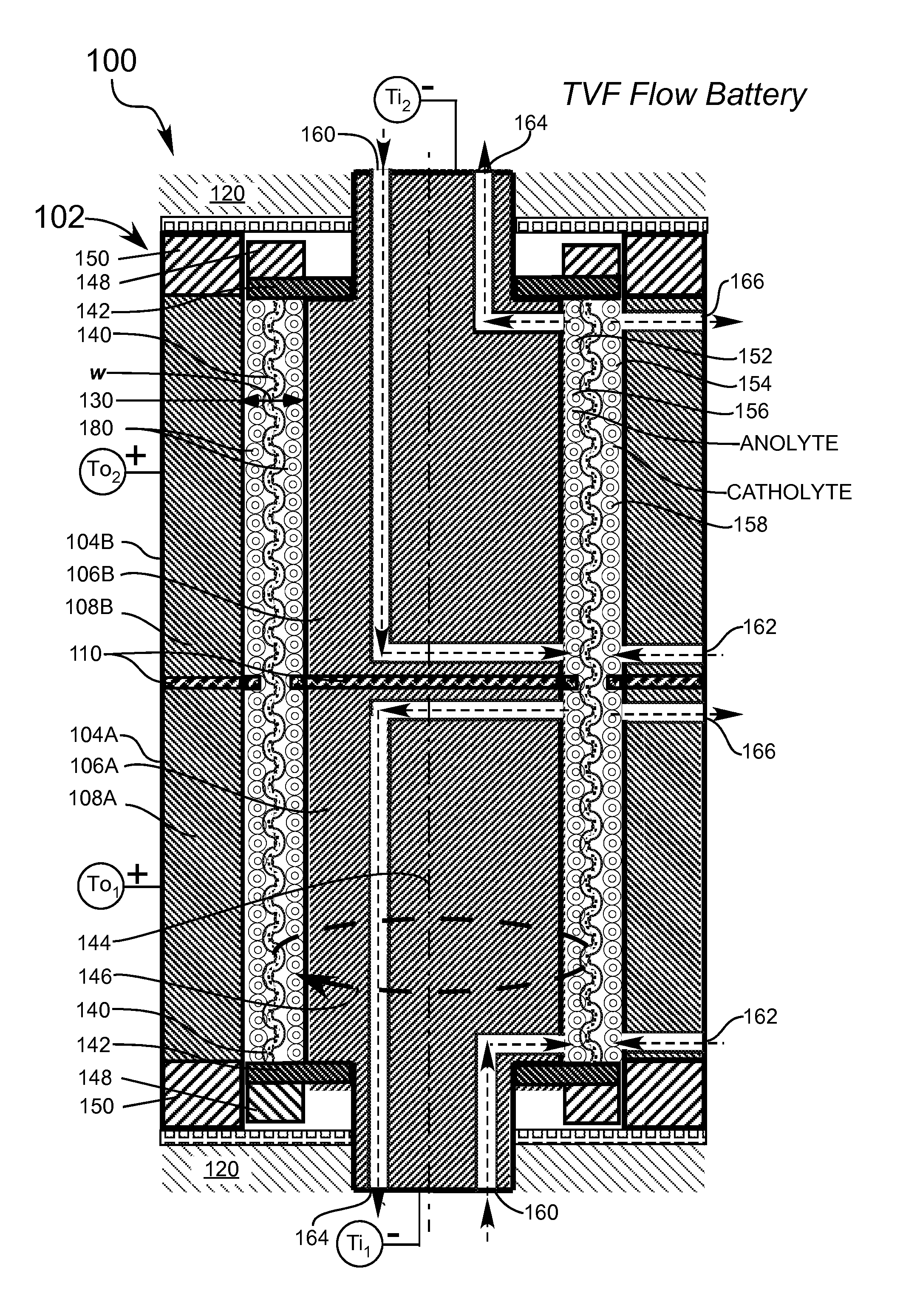
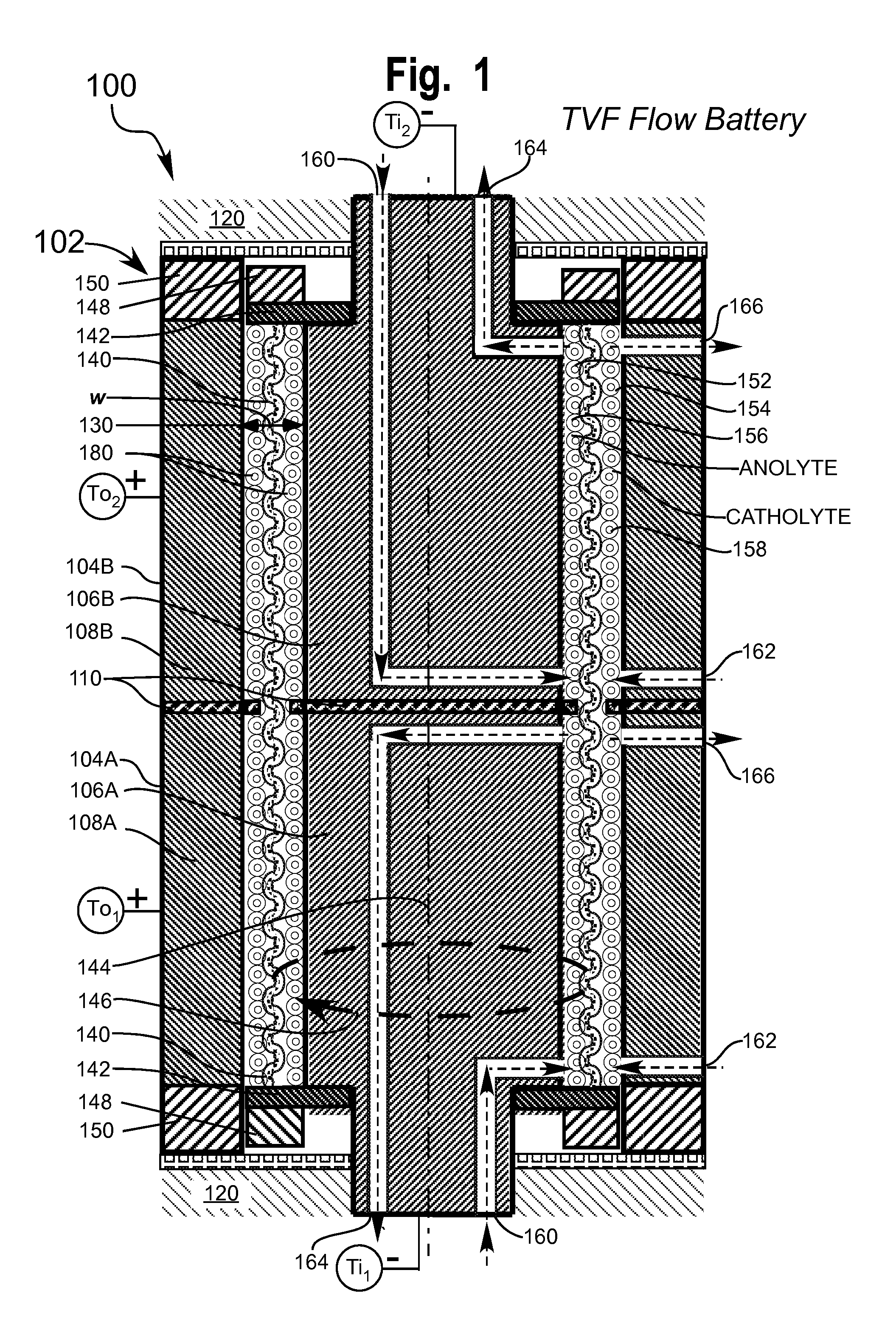
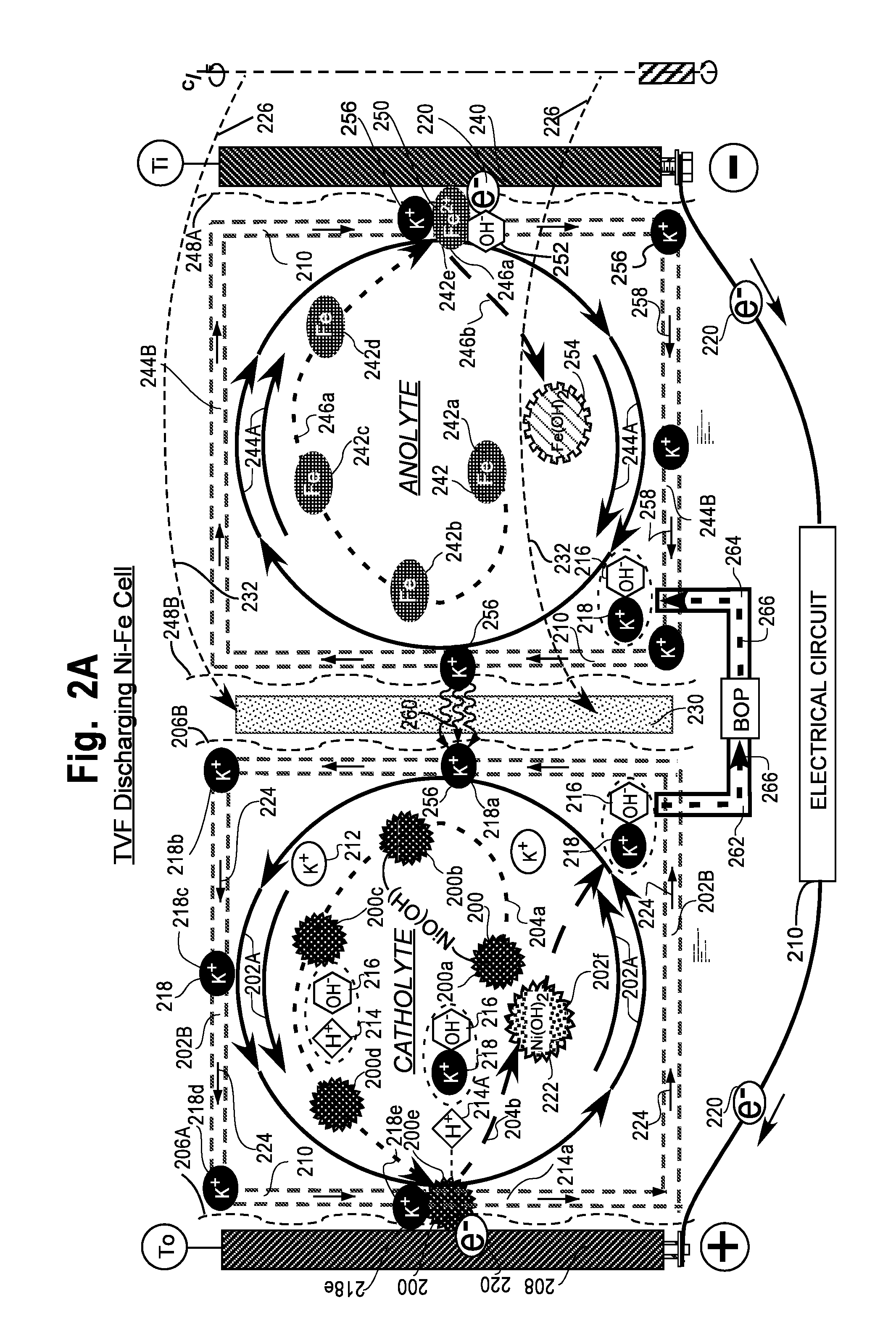
Taylor vortex flow electrochemical cells utilizing particulate electrolyte suspensions
InactiveUS20140255812A1Improve performanceReducing their electropotentialsElectrolyte moving arrangementsWater management in fuel cellsParticulatesHigh cell
Taylor Vortex Flow galvanic electrochemical cells (100, 300, 500) such as batteries, flow cells and fuel cells for converting chemical energy into electrical energy and comprising a cylindrical spinning particulate filter (140, 230) between static cylindrical current collectors (106, 108) for use with electrolytes containing galvanic charge transfer particles (200, 242, 380, 420) functioning as numerous miniature electrodes and means for pumping electrolyte through the filter to produce accelerated reaction electrochemistry for higher cell power density are disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY SCI CALIFORNIA
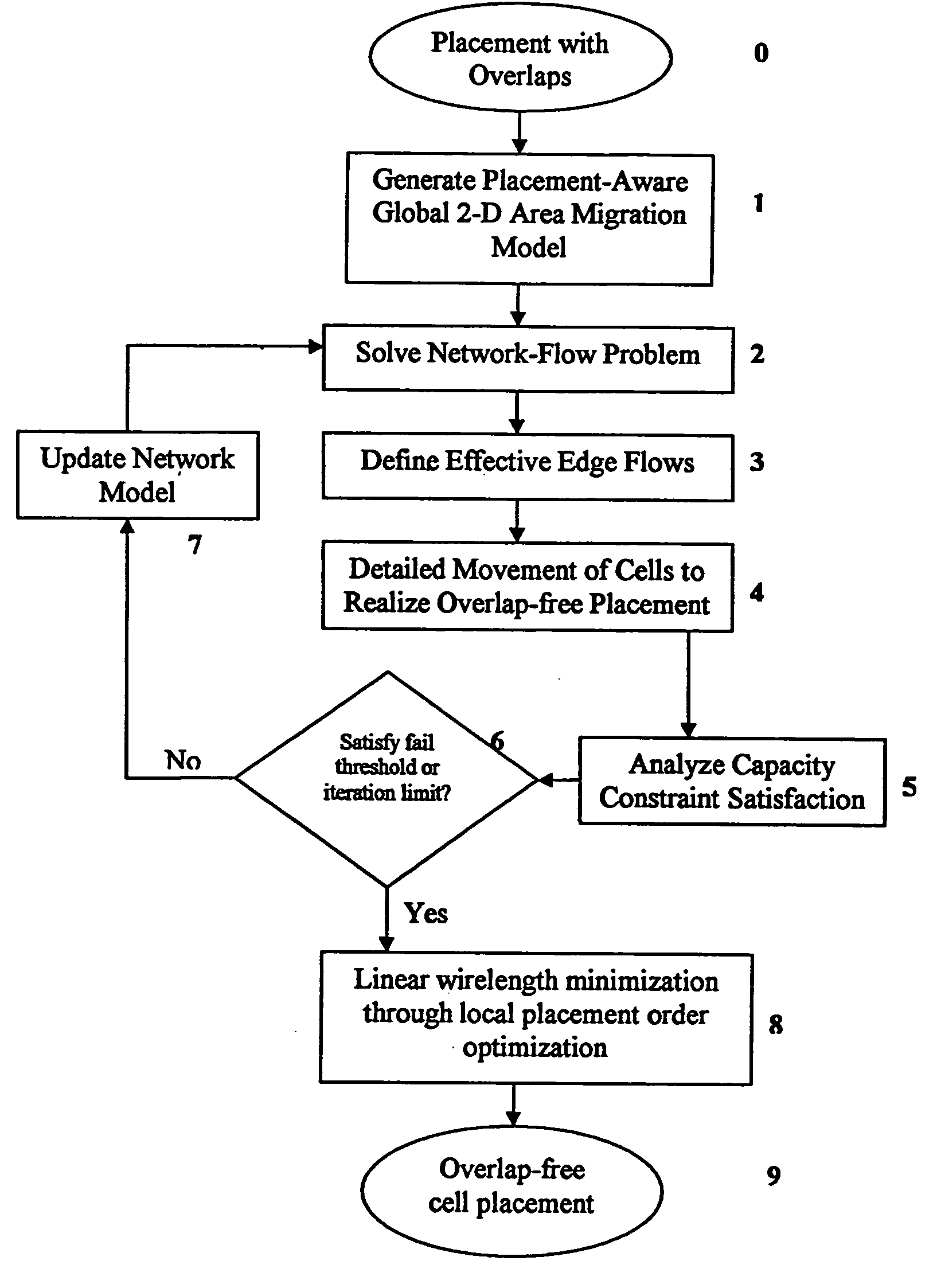
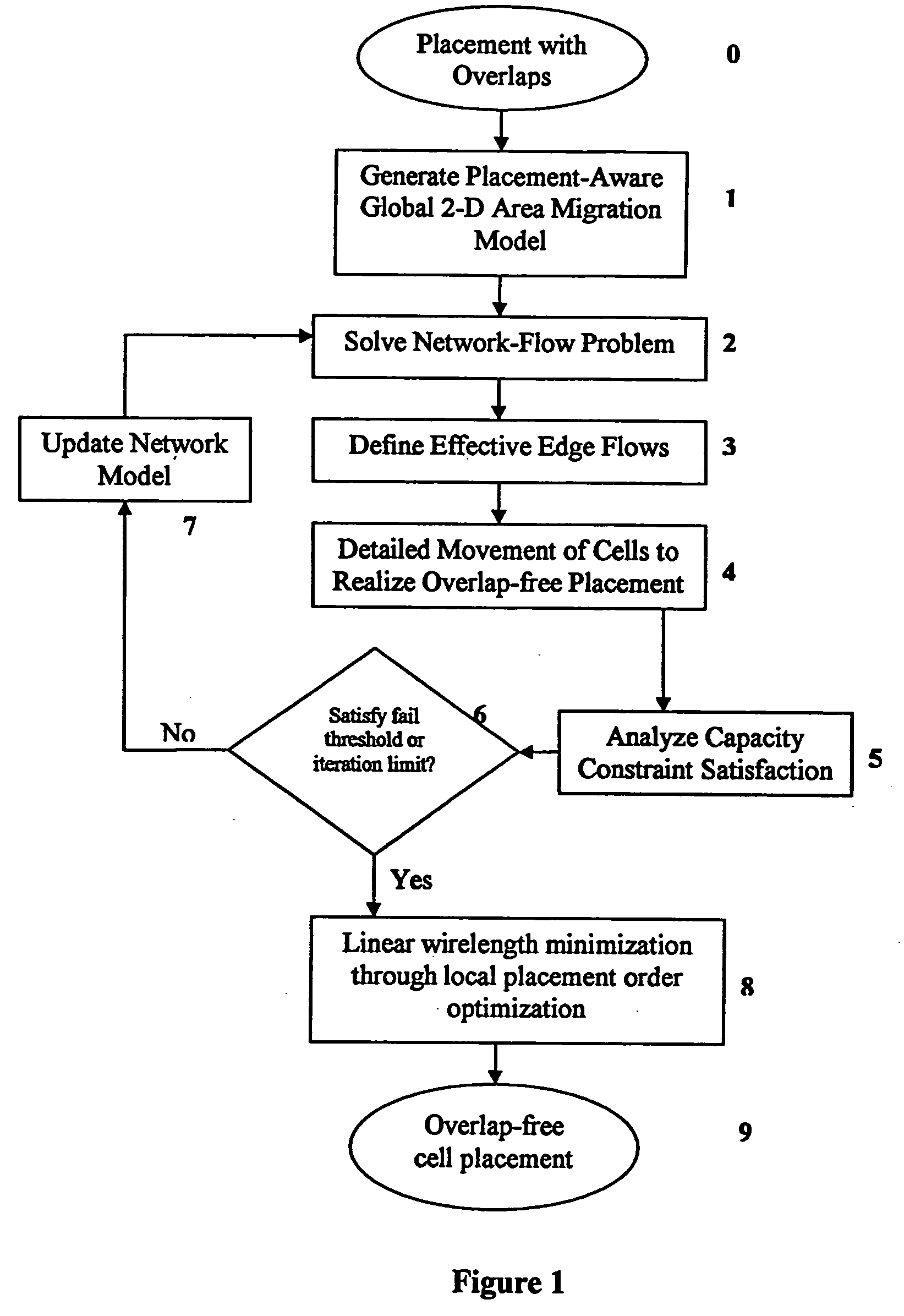
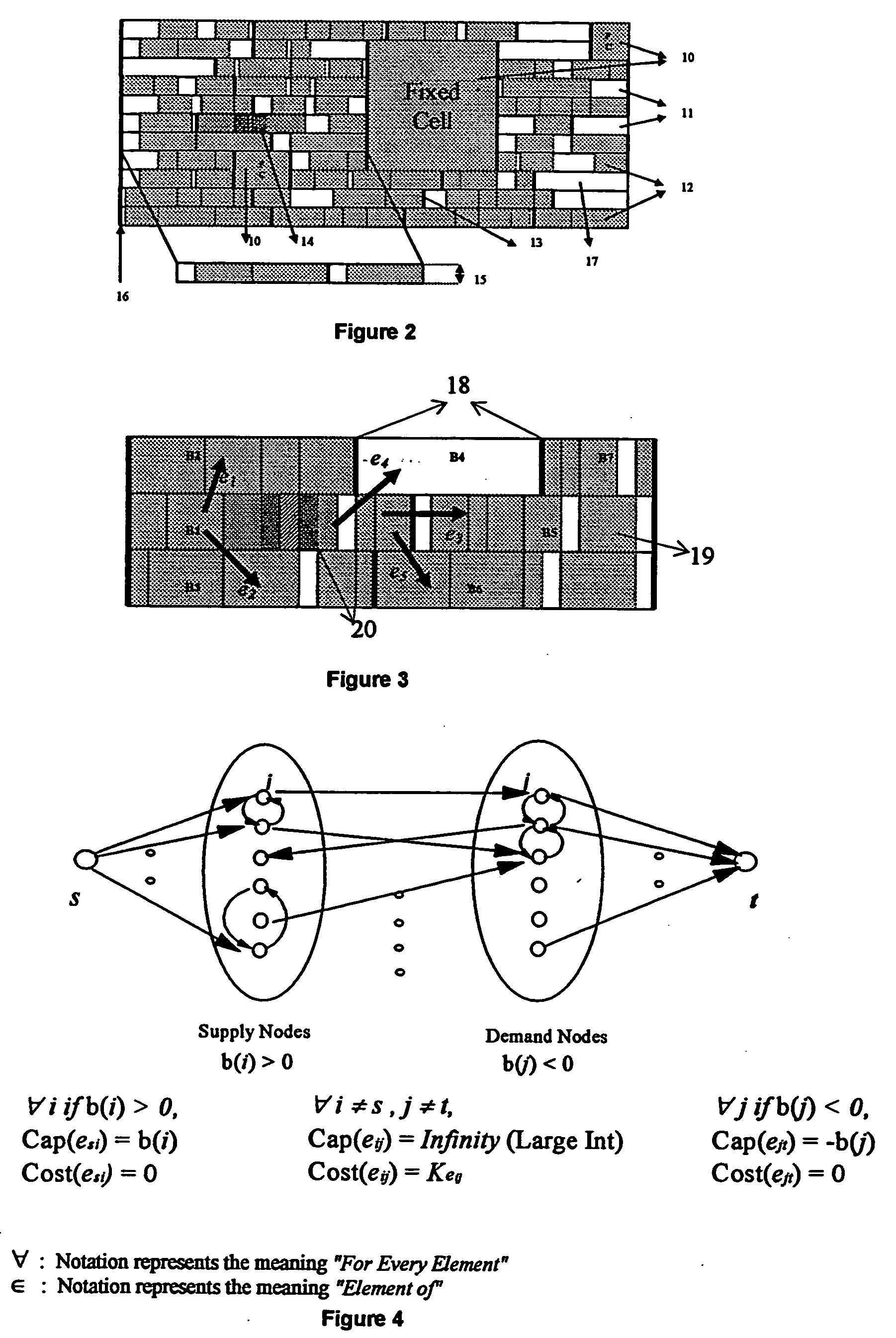
Method for legalizing the placement of cells in an integrated circuit layout
InactiveUS20050166169A1Maintain qualityAutomatically resolve cell overlapsComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationHigh cellIntegrated circuit layout
A method for resolving overlaps in the cell placement (placement legalization) during the physical design phase of an integrated chip design is described. This problem arises in several contexts within the physical design automation area including global and detailed placement, physical synthesis, and ECO (Engineering Change Order) mode for timing / design closure The method involves capturing a view of a given placement, solving a global two-dimensional area migration model and locally perturbing the cells to resolve the overlaps with minimal changes to the given placement. The method first captures a two-dimensional view of the placement including blockage-space, free-space and the given location of cells by defining physical regions. The desired global area migration across the physical regions of the placement image is determined such that it satisfies area capacity-demand constraints. The method also provides moving the cells between physical regions along previously computed directions of migration to minimize the movement cost. Also provided is an approximate method to model the movement of multi-row high cells.
Owner:IBM CORP
High Capacity Structures and Monoliths Via Paste Imprinting
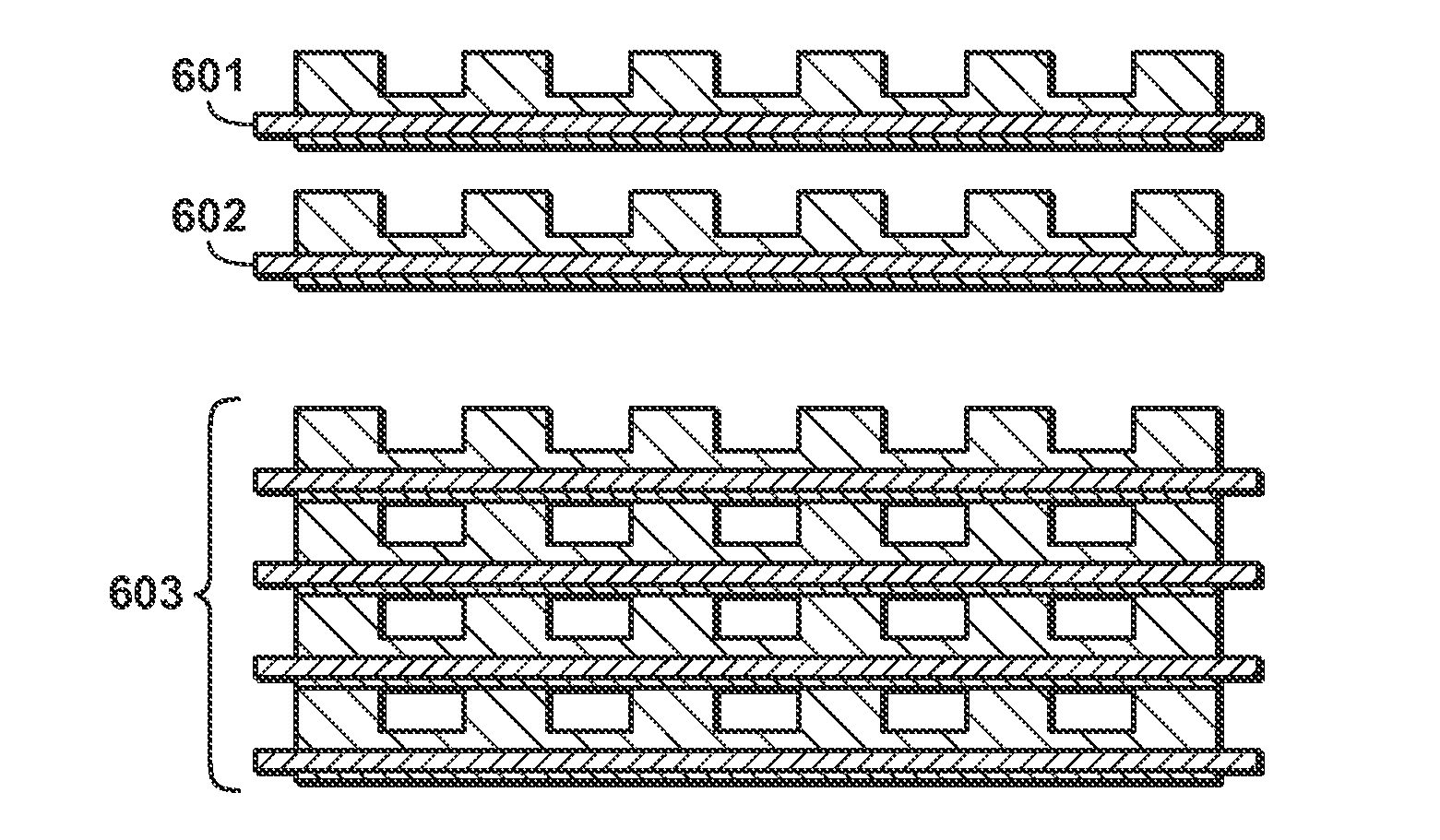
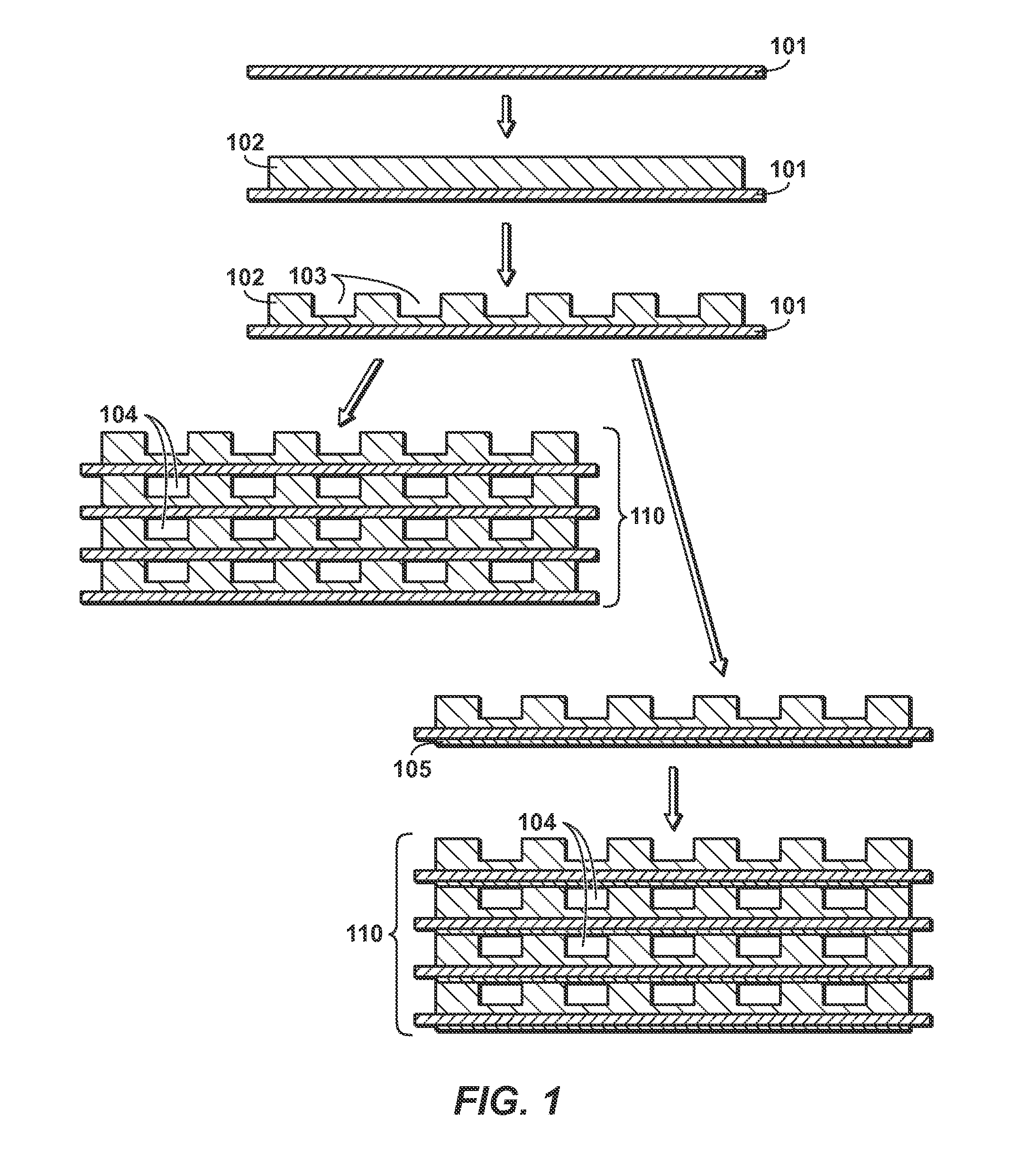
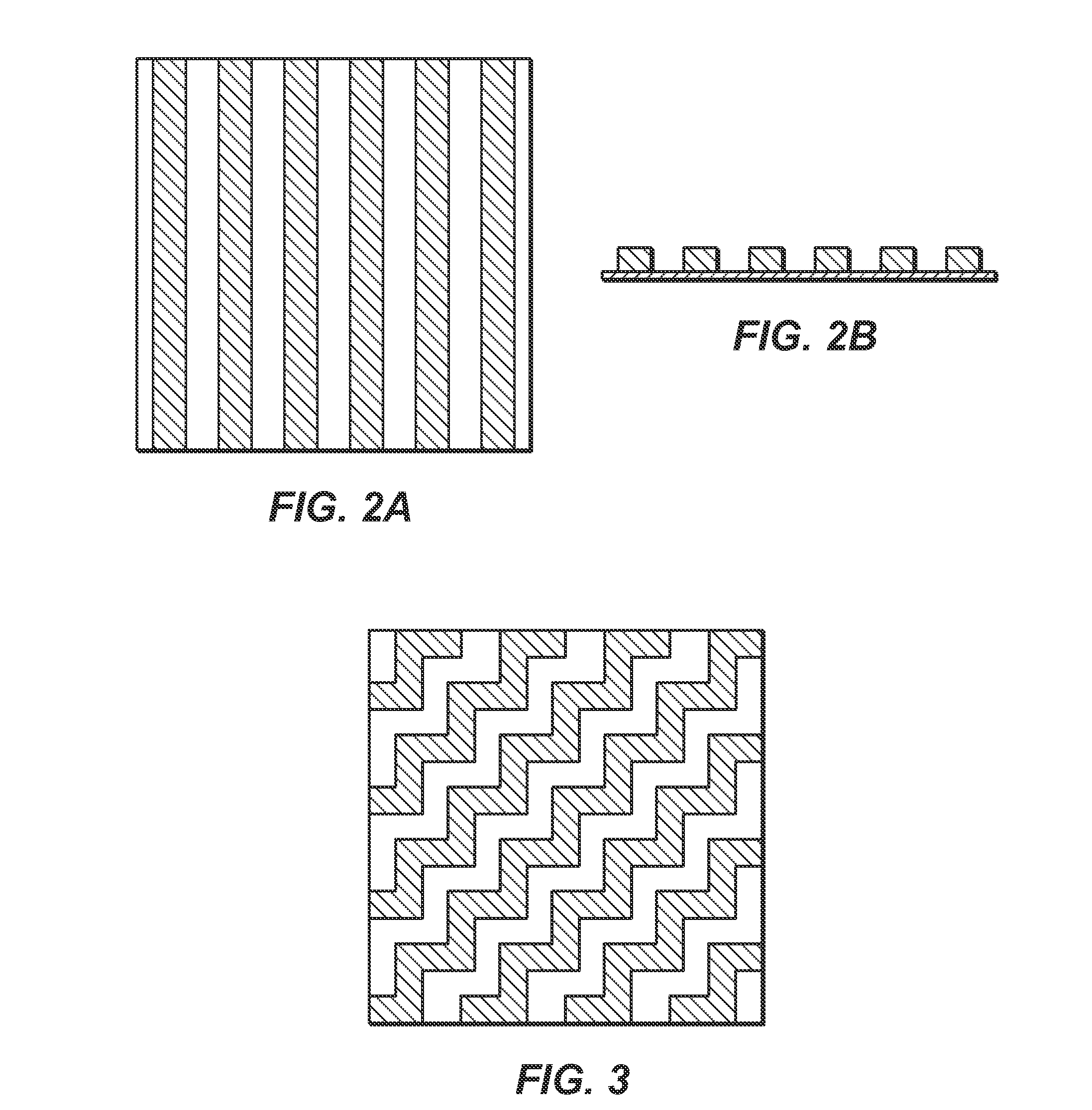
The disclosure relate generally to structures, forms, and monoliths, and methods of preparing the same. This disclosure can produce uniform structured passageways or channels of active material, including adsorbent or catalyst, by imprinting or molding features into a paste on a support that can be subsequently assembled into a gas or liquid treating structure, i.e. a monolith. The paste, which can include an active material, binder, and other potential additives, can be applied to the support or pushed through a support (as in a mesh) as a thin film. The paste can be imprinted, stamped, shaped or otherwise handled to give features of desired height, shape, width, and positioning. When stacked or rolled, the features of one layer contact a subsequent layer, which seal to form passageways. The resulting structure can have high cell-density (>1000 cells per square inch) and a large volume fraction of active material.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com