Aptamer-based microfluidic chip capable of capturing cancer cells and preparation thereof as well as separation method of cancer cells
A microfluidic chip and nucleic acid aptamer technology, applied in the field of cell separation, can solve the problems of not being able to solve the influence of laminar flow well, the capture efficiency is not high, and the probability of cell contact is small, so as to achieve good economy and application promotion Value, simple fixation method, non-immunogenic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
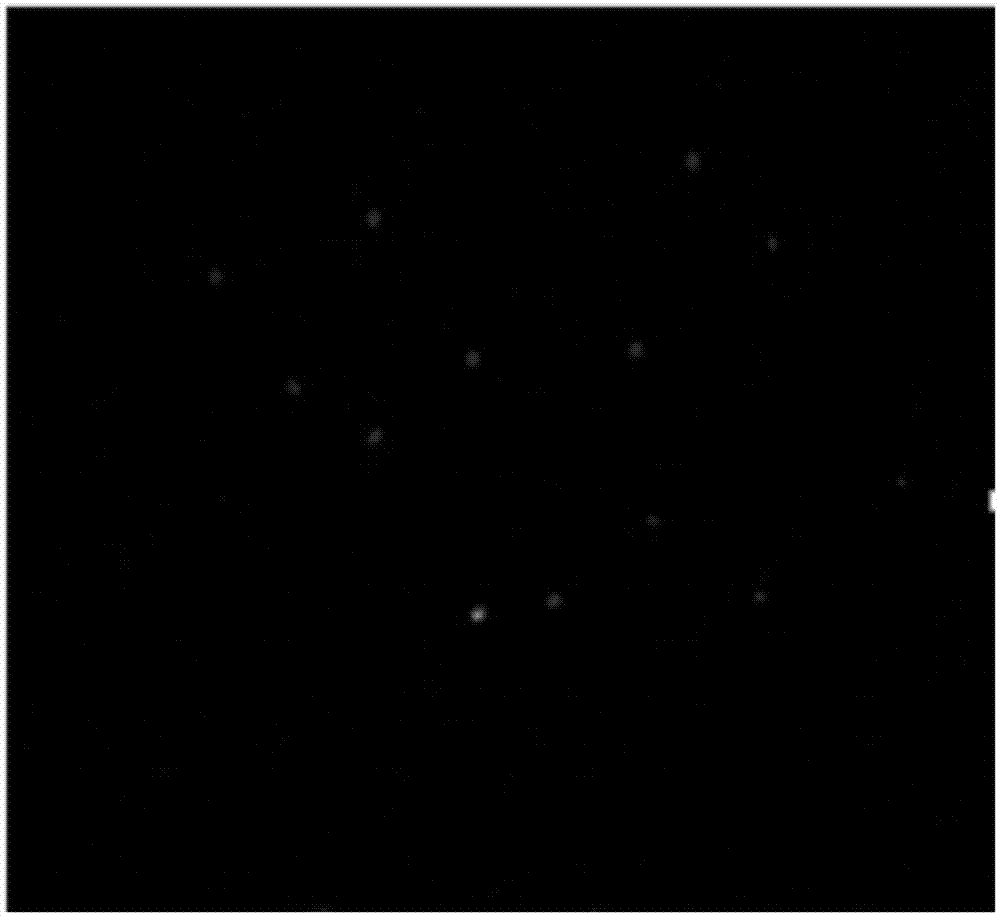
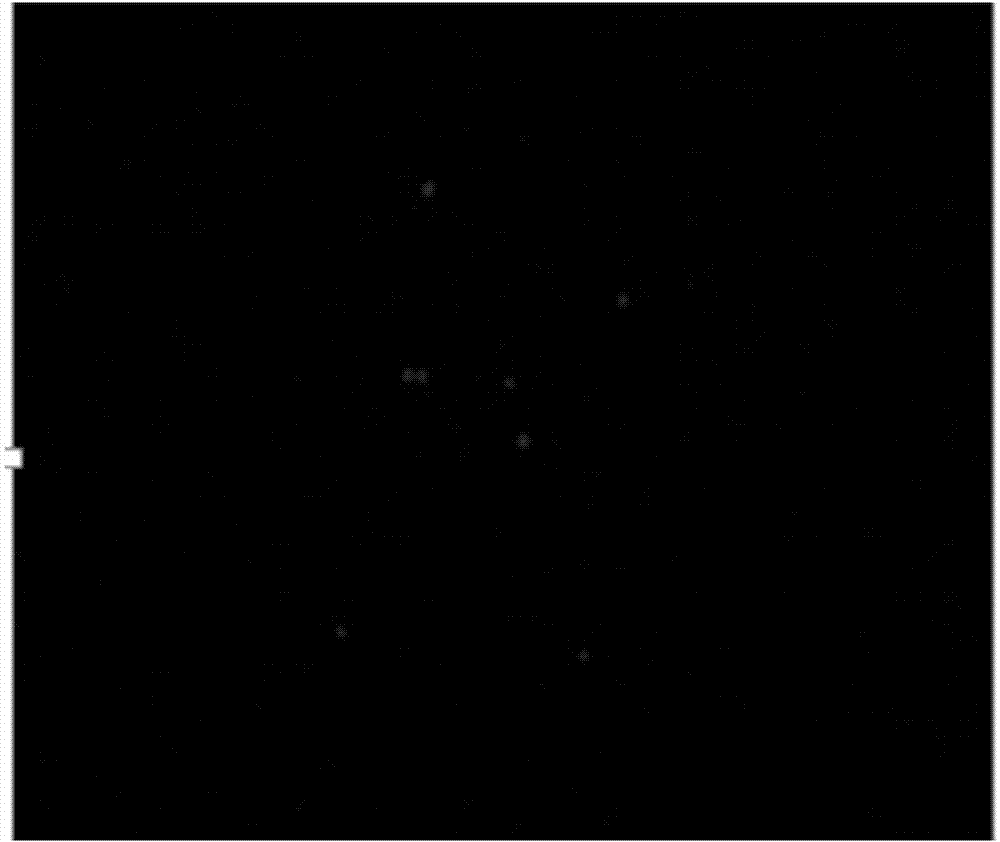
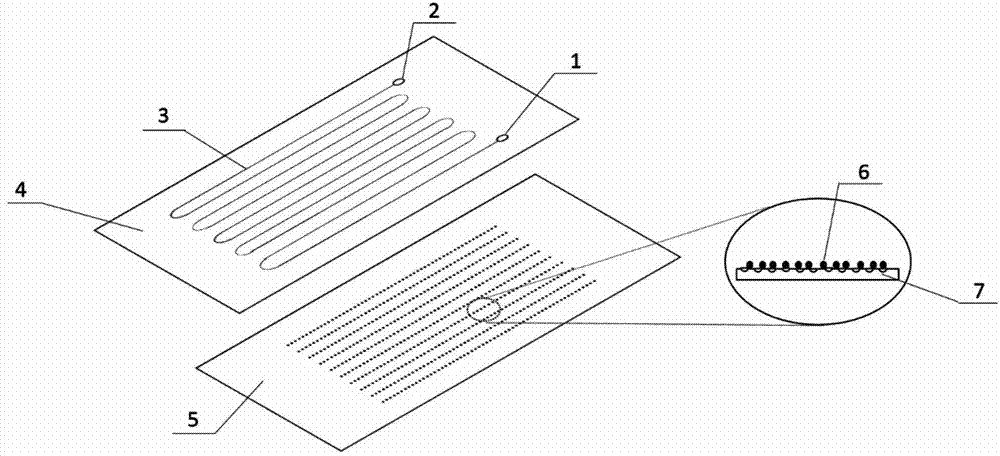
[0033] a kind of like figure 1 The nucleic acid aptamer-based microfluidic chip of the present invention that can capture cancer cells is shown. The microfluidic chip is formed by reversibly sealing an upper layer of light-transmitting and air-permeable PDMS polymer chip 4 and a lower layer of glass carrier 5. The microfluidic chip is provided with a sample inlet 1 and a sample outlet 2, and a snake-shaped cell capture channel 3 is provided between the PDMS polymer chip 4 and the glass slide carrier 5, and the cell capture channel 3 connects the sample inlet 1 and the sample outlet. The sample port 2 is connected, and the upper inner surface of the cell capture channel 3 is provided with a herringbone structure protruding from top to bottom, and the bottom surface 7 of the cell capture channel 3 is an uneven glass slide carrier surface (see figure 1 Partial enlargements in and Figure 4 ); avidin 6 is immobilized on the bottom surface of cell capture channel 3 .
[0034] In ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com